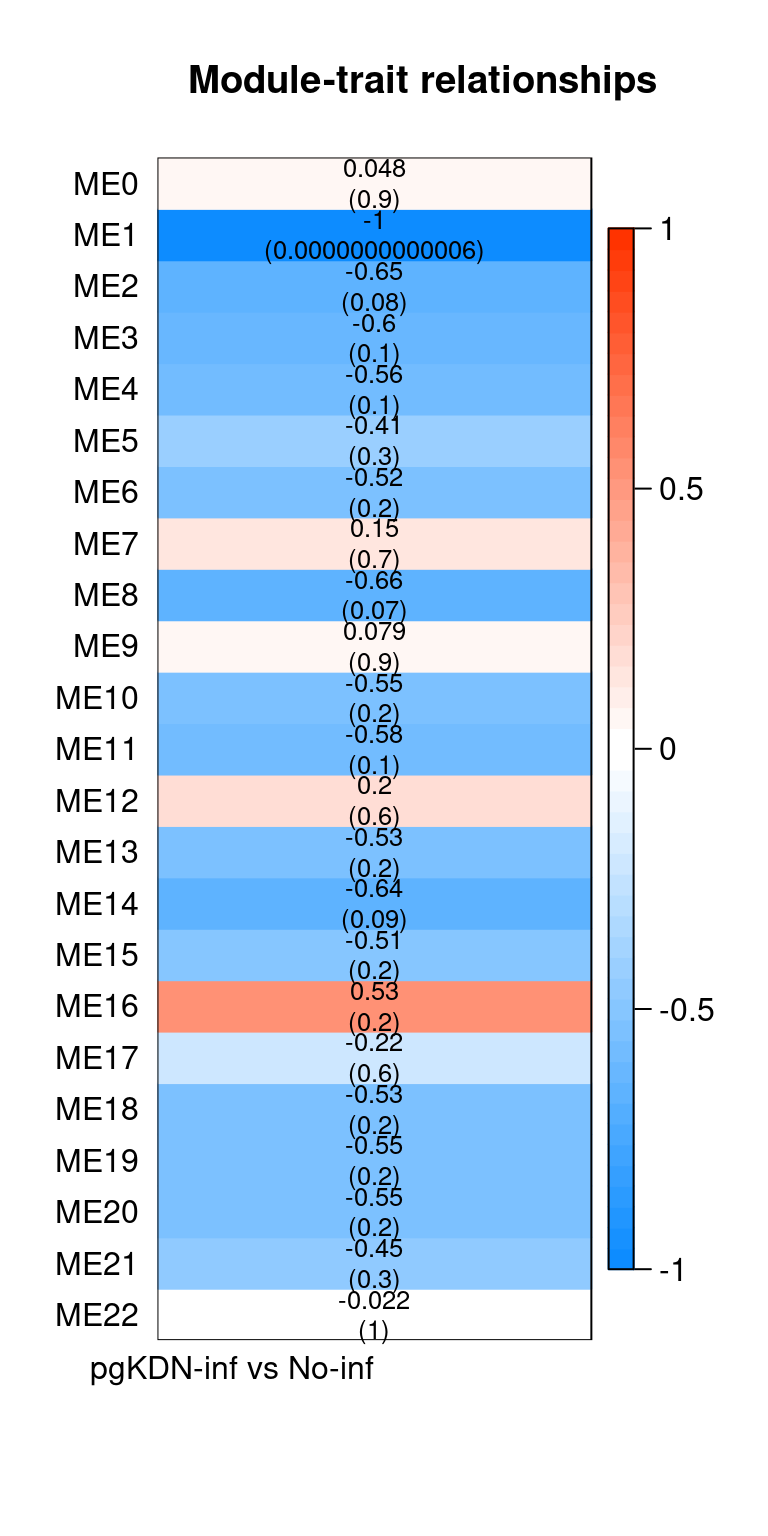
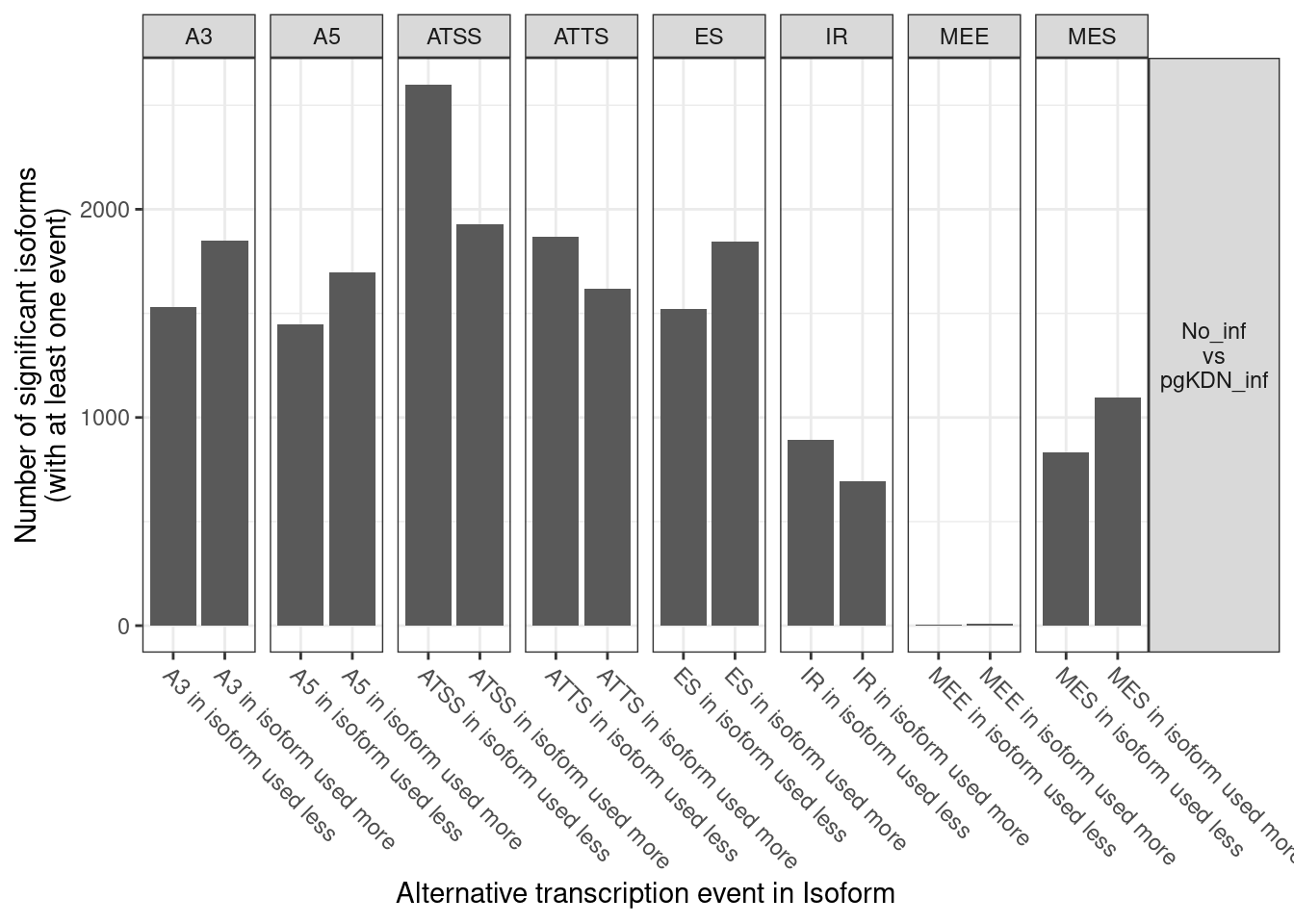
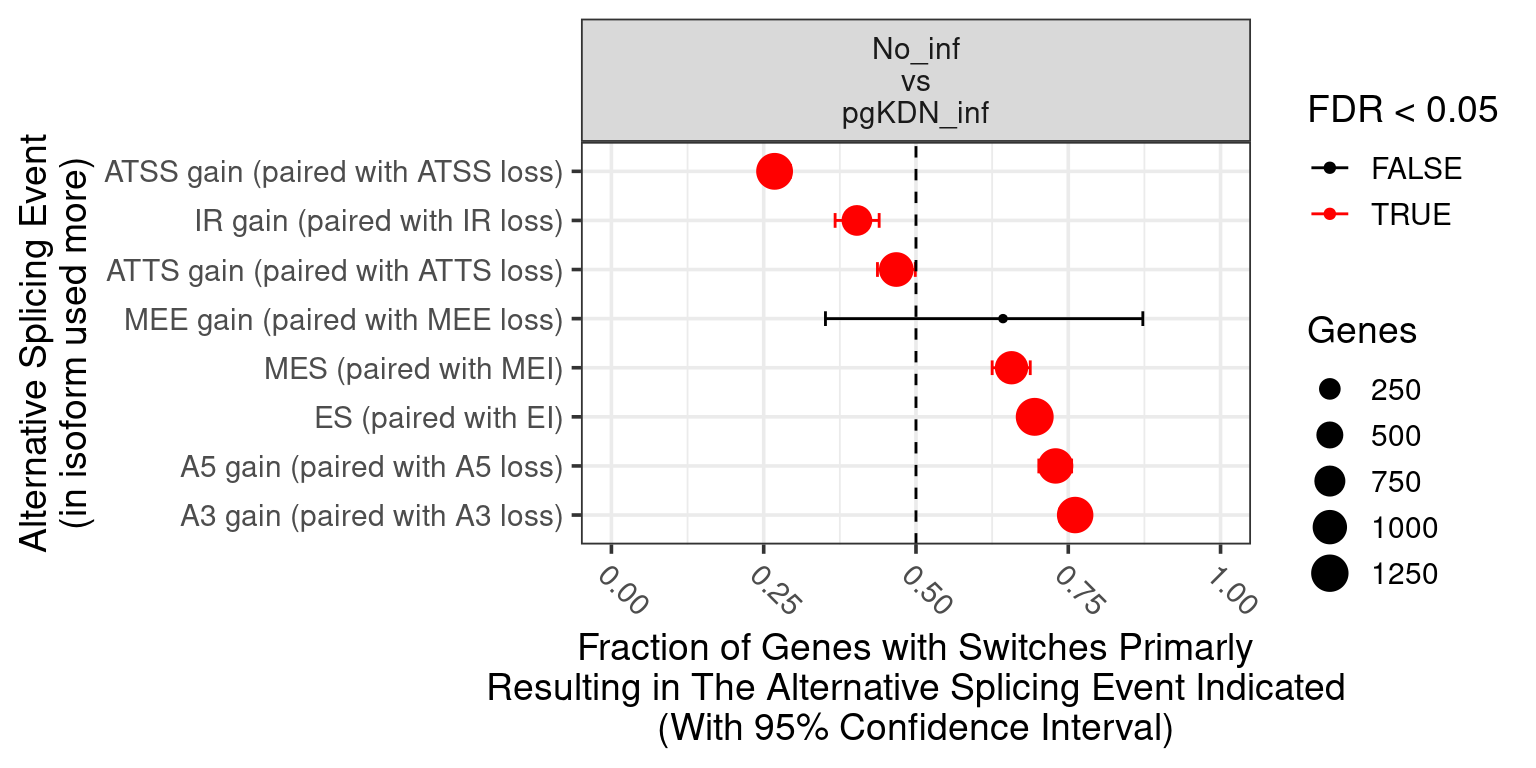
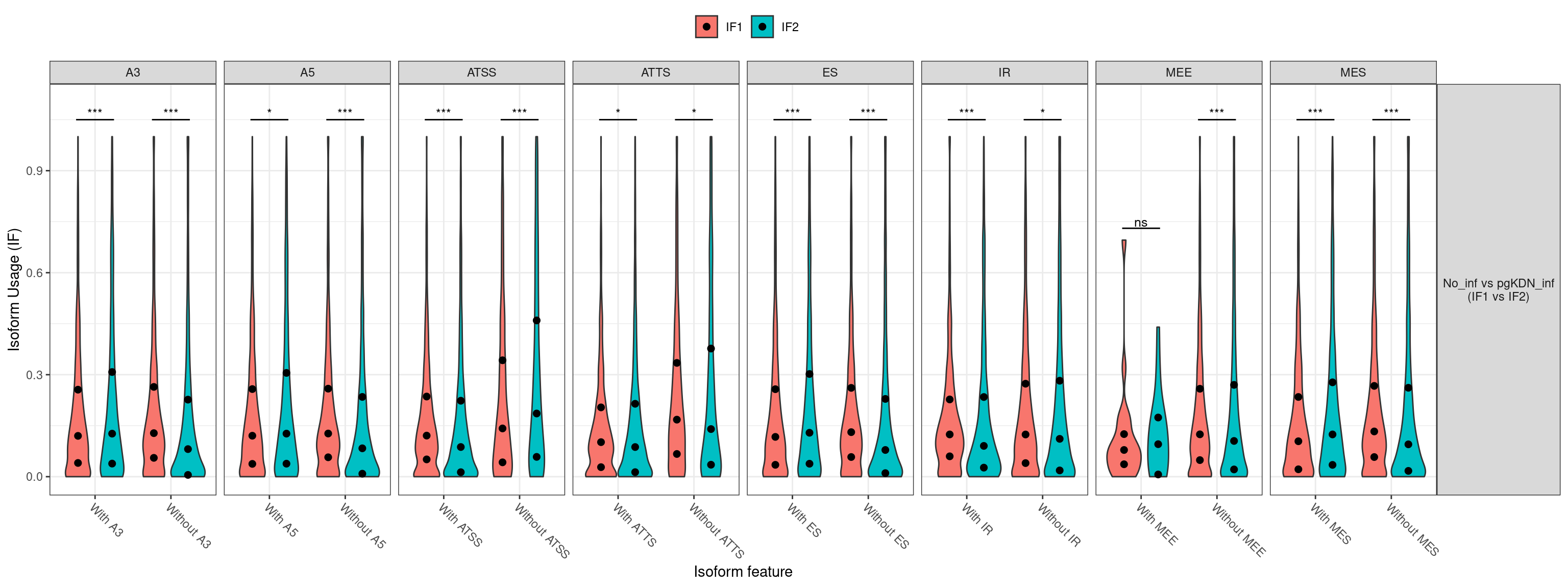
| ENSG00000000003 |
7105 |
TSPAN6 |
protein_coding |
O43657 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. The protein encoded by this gene is a cell surface glycoprotein and is highly similar in sequence to the transmembrane 4 superfamily member 2 protein. It functions as a negative regulator of retinoic acid-inducible gene I-like receptor-mediated immune signaling via its interaction with the mitochondrial antiviral signaling-centered signalosome. This gene uses alternative polyadenylation sites, and multiple transcript variants result from alternative splicing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:7105; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of viral-induced cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0039532]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123] |
22908223_TSPAN6 functions as a negative regulator of the RLR pathway by interacting with MAVS in a ubiquitination-dependent manner. 28279219_Results shows that TSPAN6 is a crucial player in Amyloid Precursor Protein-C-terminal fragment turnover 32468130_Tetraspanin 7 and its closest paralog tetraspanin 6: membrane organizers with key functions in brain development, viral infection, innate immunity, diabetes and cancer. 34521767_Tetraspanin 6 is a regulator of carcinogenesis in colorectal cancer. 35184157_TSPAN6 is a suppressor of Ras-driven cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000067377 |
Tspan6 |
68.794786 |
3.8080914798 |
1.929068 |
0.201659189 |
96.184089 |
0.00000000000000000000010468282714622747749717723160433093827369342942147455027518778477441108165635341720189899206161499023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001022580098397298199736173754357621263985491883811370250628334718778766898594767553731799125671386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.2325161 |
13.4592901 |
28.3122451 |
2.9758821 |
| ENSG00000000938 |
2268 |
FGR |
protein_coding |
P09769 |
FUNCTION: Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that transmits signals from cell surface receptors devoid of kinase activity and contributes to the regulation of immune responses, including neutrophil, monocyte, macrophage and mast cell functions, cytoskeleton remodeling in response to extracellular stimuli, phagocytosis, cell adhesion and migration. Promotes mast cell degranulation, release of inflammatory cytokines and IgE-mediated anaphylaxis. Acts downstream of receptors that bind the Fc region of immunoglobulins, such as MS4A2/FCER1B, FCGR2A and/or FCGR2B. Acts downstream of ITGB1 and ITGB2, and regulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization, cell spreading and adhesion. Depending on the context, activates or inhibits cellular responses. Functions as negative regulator of ITGB2 signaling, phagocytosis and SYK activity in monocytes. Required for normal ITGB1 and ITGB2 signaling, normal cell spreading and adhesion in neutrophils and macrophages. Functions as positive regulator of cell migration and regulates cytoskeleton reorganization via RAC1 activation. Phosphorylates SYK (in vitro) and promotes SYK-dependent activation of AKT1 and MAP kinase signaling. Phosphorylates PLD2 in antigen-stimulated mast cells, leading to PLD2 activation and the production of the signaling molecules lysophosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol. Promotes activation of PIK3R1. Phosphorylates FASLG, and thereby regulates its ubiquitination and subsequent internalization. Phosphorylates ABL1. Promotes phosphorylation of CBL, CTTN, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1, PTK2B/PYK2 and VAV2. Phosphorylates HCLS1 that has already been phosphorylated by SYK, but not unphosphorylated HCLS1. Together with CLNK, it acts as a negative regulator of natural killer cell-activating receptors and inhibits interferon-gamma production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P14234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10739672, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17164290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1737799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7519620}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Immunity;Innate immunity;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). The encoded protein contains N-terminal sites for myristylation and palmitylation, a PTK domain, and SH2 and SH3 domains which are involved in mediating protein-protein interactions with phosphotyrosine-containing and proline-rich motifs, respectively. The protein localizes to plasma membrane ruffles, and functions as a negative regulator of cell migration and adhesion triggered by the beta-2 integrin signal transduction pathway. Infection with Epstein-Barr virus results in the overexpression of this gene. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2268; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; aggresome [GO:0016235]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; Fc-gamma receptor I complex binding [GO:0034988]; immunoglobulin receptor binding [GO:0034987]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002768]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; myoblast proliferation [GO:0051450]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; negative regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032815]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043306]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045088]; regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050764]; regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045859]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11928806_Substitution of two relevant serines with glutamic acid residues in urokinase prevents urokinase activation of p55fgr needed for cell migration and adhesion. 17845055_Recruitment of the coactivator, SRC2, is coupled to cooperative DNA binding by the progesterone receptor. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21300758_Fgr plays a biologically significant role in ovarian cancer growth and might represent an important target 23896410_Data indicate that combined treatment using SFK (LYN, HCK, or FGR) and c-KIT inhibitor dasatinib dasatinib and chemotherapy provides a novel approach to increasing p53 activity and enhancing targeting of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) stem cells. 25972488_we provide evidence for involvement of HCK and FGR in FCRL4-mediated immunoregulation and for the functional importance of posttranslational modifications of the FCRL4 molecule. 27324824_the Src tyrosine kinase Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma viral (v-fgr) oncogene homolog (FGR) is associated with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid resistance. 28585144_Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of gene modules for the prognosis of esophageal cancer yielded PTAFR and FGR as the most important hub genes for predicting patient survival. 29763550_Fgr protein is overexpressed in acute myelogenous leukemia. 30352950_Fgr is a transforming oncoprotein that functions independently of SH3-SH2 domain regulation 31790499_These studies show that Hck and Fgr expression influences inhibitor sensitivity and the pathway to acquired resistance in Flt3-ITD+ AML. 34902430_A Model for the Signal Initiation Complex Between Arrestin-3 and the Src Family Kinase Fgr. |
ENSMUSG00000028874 |
Fgr |
410.653679 |
4.2721542139 |
2.094964 |
0.093533503 |
520.304766 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000036327539987115746524125056802902137237626537798619294922347951372989296476158372806043891164617505036561844434590489052293882156428704298975073042291156392308252584965641141670482836325795008812774362651311245334809 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018176084413892489753541546868470763134473701598821747946228961835992402588756304754289752194819667163795258172434415779782405087993346515342786535436993010192174507780638776378339896658976742441882468641057655334594 |
Yes |
No |
672.6673617 |
42.9384585 |
158.5003983 |
8.2619338 |
| ENSG00000001084 |
2729 |
GCLC |
protein_coding |
P48506 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the ATP-dependent ligation of L-glutamate and L-cysteine and participates in the first and rate-limiting step in glutathione biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9675072}. |
Acetylation;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Glutathione biosynthesis;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Sulfur metabolism; glutathione biosynthesis; glutathione from L-cysteine and L-glutamate: step 1/2. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9675072}. |
Glutamate-cysteine ligase, also known as gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase is the first rate-limiting enzyme of glutathione synthesis. The enzyme consists of two subunits, a heavy catalytic subunit and a light regulatory subunit. This locus encodes the catalytic subunit, while the regulatory subunit is derived from a different gene located on chromosome 1p22-p21. Mutations at this locus have been associated with hemolytic anemia due to deficiency of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and susceptibility to myocardial infarction.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:2729; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamate-cysteine ligase complex [GO:0017109]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glutamate binding [GO:0016595]; glutamate-cysteine ligase activity [GO:0004357]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; aging [GO:0007568]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:0035729]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to thyroxine stimulus [GO:0097069]; cysteine metabolic process [GO:0006534]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; L-ascorbic acid metabolic process [GO:0019852]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation [GO:2000490]; negative regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901029]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051900]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0046685]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; response to human chorionic gonadotropin [GO:0044752]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to nitrosative stress [GO:0051409]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
11820781_Expression of the gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene is inducible by certain nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., indomethacin) in colon cancer cells. 11844594_Genetic determinants of lung cancer short-term survival: the role of glutathione-related genes 11972604_Oxidant stress induces gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthesis in human bronchial epithelial NCI-H292 cells. 12070177_identification of a variant antioxidant response element in the promoter region 12500194_redox-sensitive elements directing expression of the glutamate cysteine ligase in CYP2E1-expressing cells are present in the ARE4 distal portion of the 5'-flanking region, perhaps a reflection of metabolic adaptation to CYP2E1-generated oxidative stress. 12598062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12663448_A new gamma-GCSH mutation from gamma-GCS deficiency, a C>T missense mutation at nucleotide 379, encodes a predicted Arg127Cys amino acid change. The mutated amino acid lies within a cleft on the protein surface of gamma-GCSH, containing Cys249. 14676828_GCS is up-regulated by antiestrogens mediated by estrogen receptor beta. 15451055_Review. The most important element in both Gclc and Gclm expression is the electrophile response element in their promoters. 15485876_data provide the first report of glutamylcysteine ligase (GCLC) expression in the islet and demonstrate that adenoviral overexpression of GCLC increases intracellular glutathione levels and protects the beta cell from adverse effects of IL-1 beta 16322067_Adrenomedullin regulates cellular glutathione content via modulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit expression 16403949_Results suggest that TNF-alpha elevates the expression of lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) and that LEDGF is one of the transactivators of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase heavy subunit gene. 16491484_Drug-resistant cells have the inherent ability to maintain increased gamma-GCS activity. 16599007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16690975_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16690975_This study found an association between variants in GCLC, a novel candidate gene, and cystic fibrosis lung function; this effect was observed only in patients with a mild CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) genotype 16766924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17109620_Activation of insulin signaling through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/Nrf2/ GCLc pathway affords significant cell protection by maintaining cellular redox balance. 17207022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17207022_The genetic polymorphism in GCLC -129C/T is not associated with susceptibility to COPD in a southern Chinese population of Han nationality. 17333241_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17344309_upregulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase as part of the long-term adaptation process to iron accumulation in neurons 17479437_GCLC promoter polymorphisms may influence glutamate decarboxylase 65 autoantibody levels the age at which type 1 diabettes is diagnosed. 17479437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17643973_The -588TT/-23TT genotype was found to be associated with decreased risk of allergic asthma after adjustment for age, gender and smoking status using regression analysis (OR=0.33 95% CI 0.15-0.70, p=0.036) but with increased risk of non-allergic asthma. 17921251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17961430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18035085_GCLC T allele, together with hypertension and male sex, is associated with cardiovascular events in our study population. 18035085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18066575_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18276794_Glutamate cysteine ligase iz induced by hydroxynonenal through the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway in respiratory epithelium. 18420959_GCLC is a novel susceptibility gene for low level of lung function in copd 18420959_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18549827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18549827_decreasing trend of GCL activity was observed in the order of 7/7>7/9>9/9 (P=0.04) 18560528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18926903_results support the functional importance of insulin in Nrf2-dependent transcriptional upregulation of GCLc in GSH recovery during oxidative challenge and suggest a possible role for hypoglycemia in promoting insulin-mediated GCLc upregulation 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19041695_study of consequences of impaired glutathione synthesis, due to GAG trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in catalytic subunit of glutamate cysteine ligase, on regulation of the proteome; findings show altered proteome reaction in response to oxidative stress 19347979_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19515364_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19567187_PD98059 and erythromycin could block AP-1 transduction pathway, but increase the synthesis of gamma-GCS induced by 4-hydroxynonenal in bronchial epithelial cells. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19817962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19817962_Polymorphisms of glutamate-cystein ligase and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein genes may be associated with non-alcoholic liver disease progression. 20180881_Regulation of GCL(cat) by MYCN accounts for the survival of neuroblastoma cells against oxidative damage; GCL should be considered a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20655259_An ethnic-specific polymorphism in the catalytic subunit of glutamate-cysteine ligase impairs the production of glutathione intermediates in vitro. 20655259_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20659789_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673128_high-risk glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit GAG trinucleotide repeat genotypes lead to alterations of plasma thiols levels that reflect a dysregulation of redox control 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20712757_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20732852_Data show that activation of the PPARgamma/PGC-1alpha pathway may protect against COPD progression by upregulating gamma-GCS and relieving oxidative stress. 20970495_Posttranslational modification and regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase by the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. 21105962_SNPs not associted with schizophrenia in Japanese individuals 21156206_These results provide evidence that interaction of the two variations can efficiently impair GCLC expression and thus suggest its involvement in the pathogenesis of diseases related to GSH metabolism. 21277635_SNPs not associated with self-reported depression 21438662_the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) -129C/T (rs17883901) in glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) and SNPs I128T (rs3816873) and Q95H (rs61733139) in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease 21444626_Results suggest that GAG polymorphism affects GCLC expression via translation, and thus may be associated with altered risk for GSH-related diseases and toxicities. 21555518_GCLC is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21657237_The impacts of four clinical missense mutations on GCLC enzymatic function in vivo and in vitro, was evaluated. 21871559_insulin increased GCLc promoter activity, which required a prerequisite increase or decrease in medium glucose 21962117_The functional SNPs CYBA -675 T --> A and GCLC rs17883901, probably associated with cellular redox imbalances, modulate the risk for renal disease in the studied population of type 1 diabetes patients 22249522_Data show for the first time that GCLC may serve a dual role, as a surrogate marker for cellular redox state as well as malignant potential of melanoma cells. 22452920_Data suggest that microRNA/mRNA pairs in hsa-miR-140-3p/RAD51AP1/, hsa-miR-145/E2F3, hsa-miR-139-5p/TOP2A, and hsa-miR-133a/GCLC were correlated with ovarian tumorigenesis. 22610501_A functional trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the 5'-untranslated region of the glutathione biosynthetic gene GCLC is associated with increased risk for lung and aerodigestive tract cancers. 22824134_rs761142 in GCLC was found to be associated with reduced GCLC mRNA expression and with SMX-induced hypersensitivity in HIV/AIDS patients. 23255485_Genistein up-regulated HO-1 and Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase expression through the EKR1/2 and PKC /Nrf2 pathways during oxidative stress. 23443115_The Kaplan-Meier analysis shows that rs3736729 on GCLC presents a significant association with disease-free survival and overall survival. 23448276_These data strongly indicate a discrepancy between the regulation of GCLC and of GGT following the oxidative stress situation due to mitochondrial uncoupling. 23758905_Polymorphisms in GCLC, GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 genes associated with metabolism of glutathione act on cystic fibrosis severity. 23770363_1,25 (OH) vitamin D significantly upregulated expression of GCLC and GR and lowered secretion of IL-8 and MCP-1 in high-glucose exposed U937 monocytes. 24068433_the CYP1A1 (rs2606345, rs4646903, rs1048943), GCLC, AGT, and AGTR1 genes was associated with pleuritis, empyema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, all PC and acute respiratory failure (ARF). 24665821_H2S upregulates GCLC and GSH and inhibits IL-1beta levels, which may be what mediates the beneficial effects of H2S-rich compounds in mitigating the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis 25353619_miR-433 targets both catalytic (GCLc) and regulatory (GCLm) subunits of GCL. 26059756_GCLC and GSS were expressed at higher levels in colon cancer tissue, as compared with normal mucosa. 26087411_Cigarette smoke-induced hypermethylation of the GCLC promoter is related to the initiation and progression of COPD. 26365678_Data suggest expression of hepatocyte GCLC and GCLM can be regulated by dietary component; alpha-lipoic acid, a vitamin B complex nutrient, protects against oxidative stress/cytotoxicity induced by cadmium via restoration of GCLC and GCLM expression. 26520442_Glutaminolysis is activated in ES2 and OVCAR3, though ES2 exclusively synthesizes amino acids and GSH. ES2 cells are more resistant to carboplatin than OVCAR3 and the abrogation of GSH production by BSO sensitizes ES2 to carboplatin. HNF1beta regulates the expression of GCLC, but not GCLM, and consequently GSH production in ES2 26894974_High GCLC expression is associated with chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer. 27069063_GCLC polymorphisms correlated with brain GSH and Glu levels in psychosis. 27117941_(i) melatonin counteracted UVR-induced alterations in the ATP synthesis and reduced free radical formation; (ii) melatonin induced the translocation of Nrf2 transcription factor from the cytosol into the nucleus resulting in, (iii) melatonin enhanced gene expression of phase-2 antioxidative enzymes including gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (gamma-GCS), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), and NADPH: quinone dehydrogenase-1 (NQO1... 28103909_A panel consisting of IGFBP1, KIM1, GCLC and GSTM1 genes could be used in combination for early screening of CKDu, whereas these genes in addition with FN1, IGFBP3 and KLK1 could be used to monitor progression of CKDu. The regulation of these genes has to be studied on larger populations to validate their efficiency for further clinical use. 28185919_Knockdown of CD44 reduced the protein level of xCT, a cystine transporter, and increased oxidative stress. However, an increase in GSH was also observed and was associated with enhanced chemoresistance in CD44-knockdown cells. Increased GSH was mediated by the Nrf2/AP-1-induced upregulation of GCLC, a subunit of the enzyme catalyzing GSH synthesis 28265008_Taken together, our findings provide evidence that G9a protects head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC)cells against chemotherapy by increasing the synthesis of GSH, and imply G9a as a promising target for overcoming cisplatin resistance in HNSCC 28411284_NQO1 and GCLC were both functionally sufficient to autonomously confer a tamoxifen-resistant metabolic phenotype, characterized by i) increased mitochondrial biogenesis, ii) increased ATP production and iii) reduced glutathione levels. 28457937_The findings indicate that expression of the transcription factor NRF2 and its effector GCL are both profoundly deregulated in endometriotic lesions towards increased growth and fibrogenetic processes. 28993271_Glutathione biosynthesis during the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in THP-1 macrophages is tightly and differentially regulated via GCLC and GCLM subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. 29023060_Study found that the frequency of C/T polymorphism genotype of GCLC gene in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis is 36.4%. 29039508_the present study demonstrated that cells transformed by chronic exposure to 3MC exhibited inhibition of GSH biosynthesis by suppression of GCL protein expression and reduction of cysteine availability, which may subsequently render cells vulnerable to oxidative stress. 29474642_High expression of GCLC in tumor tissue may be a potential predictor of treatment failure. 29549912_gamma-GCS has a role in chemo- and radio-resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells 30959073_Results provide evidence that the functional SNPs rs17883901 in GCLC and rs713041 in GPX4 modulate the risk for diabetic retinopathy in the studied population of type 1 diabetes individuals, widening the spectrum of candidate genes for this complication. 32054366_Genetic susceptibility analysis of GCLC rs17883901 polymorphism to preeclampsia in Chinese Han women. 32715377_Genetic variants in glutamate cysteine ligase confer protection against type 2 diabetes. 33357455_Non-canonical Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Activity Protects against Ferroptosis. 34642912_Association of Polymorphisms of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Genes GCLC C-129 T and GCLM C-588 T with Risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Chinese Women. 35386070_Genetic variation at the catalytic subunit of glutamate cysteine ligase contributes to the susceptibility to sporadic colorectal cancer: a pilot study. 36359768_Ferroptosis-Related Gene GCLC Is a Novel Prognostic Molecular and Correlates with Immune Infiltrates in Lung Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000032350 |
Gclc |
233.406373 |
2.4048644483 |
1.265956 |
0.257466463 |
23.614873 |
0.00000117674478194760034141660379886085152634223049972206354141235351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004130500114517617471358076203236109336103254463523626327514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
320.0610522 |
72.7373869 |
133.5979135 |
22.0897197 |
| ENSG00000001630 |
1595 |
CYP51A1 |
protein_coding |
Q16850 |
FUNCTION: A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in sterol biosynthesis. Catalyzes 14-alpha demethylation of lanosterol and 24,25-dihydrolanosterol likely through sequential oxidative conversion of 14-alpha methyl group to hydroxymethyl, then to carboxylaldehyde, followed by the formation of the delta 14,15 double bond in the sterol core and concomitant release of formic acid (PubMed:20149798, PubMed:8619637). Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR; NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase) (PubMed:20149798, PubMed:8619637). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20149798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8619637}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Heme;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microsome;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; zymosterol biosynthesis; zymosterol from lanosterol: step 1/6. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:8619637}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This endoplasmic reticulum protein participates in the synthesis of cholesterol by catalyzing the removal of the 14alpha-methyl group from lanosterol. Homologous genes are found in all three eukaryotic phyla, fungi, plants, and animals, suggesting that this is one of the oldest cytochrome P450 genes. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:1595; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; monooxygenase activity [GO:0004497]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; sterol 14-demethylase activity [GO:0008398]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900222]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694]; sterol metabolic process [GO:0016125] |
12145339_A cAMP-responsive element binding site is essential for sterol regulation of the human lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase gene. 15611056_Plays primary roles in determining strength of interactions with azoles 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676367_the liver X receptor alpha directly silencing the expression of two key cholesterologenic enzymes (lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase (CYP51A1), and squalene synthase (farnesyl diphosphate farnesyl transferase 1)) via novel negative LXR DNA response elements 20149798_The substantial conformational changes in the B' helix and F-G loop regions are induced upon ligand binding, consistent with the membrane nature of the protein and its substrate. 20547249_Studies indicate that CPY51 structures from various eukaryotic organisms are strikingly similar. 22180046_The new CYP51A1 inhibitor 2-((3,4-dichlorophenethyl)(propyl)amino)-1-(pyridin-3-yl)ethanol (LEK-935) on the proteome of primary human hepatocytes were analyzed. 24353279_Data show that forkhead transcription factor 4 (FoxO4) interacts with sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)2 and hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)2alpha to modulate lanosterol 14alpha demethylase (CYP51) promoter activity. 24358204_Our results indicate a new link between a cholesterol synthesis gene CYP51A1 and pregnancy pathologies. 24362992_Low nucleotide variability of CYP51A1 is seen in cholesterol and bile acid synthesis and xenobiotic metabolism pathways. 24502137_The studied azoles selectively interacted with human cytochrome P450 51A1, which showed the highest affinity towards ketoconazole. 24711211_Suggest that GDF9, possibly with FSH, may play significant roles in the regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis and the expression of CYP51A1 in granulosa cells which might be a predictor for unfertilization. 26002733_Acyl-Carbon Bond Cleaving Cytochrome P450 Enzymes: CYP17A1, CYP19A1 and CYP51A1. 27313059_Molecular insights regarding substrate profile, faster catalysis, and weaker susceptibility of human CYP51 to inhibition. 28830911_the regulation of expression of human CYP51A1, the lanosterol 14alpha-demethylase, is reported. 29807244_Analysis of molecular docking data demonstrated the ability of abiraterone and galeterone to bind to the active site of CYP51A1, but abiraterone occupies the position closer to the heme. 31904814_the E3 ubiquitin ligase membrane-associated ring-CH-type finger 6 (MARCH6), known to control earlier rate-limiting steps in cholesterol synthesis, also control levels of LDM and the terminal cholesterol synthesis enzyme, 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase. 32493730_A requirement for an active proton delivery network supports a compound I-mediated C-C bond cleavage in CYP51 catalysis. 33031537_Concerning P450 Evolution: Structural Analyses Support Bacterial Origin of Sterol 14alpha-Demethylases. |
ENSMUSG00000001467 |
Cyp51 |
670.847885 |
4.5359153760 |
2.181394 |
0.067605986 |
1114.767557 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020382611417627891404450953994884207750871110971614453141804197932472428158326877686137 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023321499575518425188711154317953955040309288539033166534364998419313868753707621303855 |
Yes |
No |
1094.6815913 |
62.0370775 |
243.2768774 |
11.0439817 |
| ENSG00000002016 |
5893 |
RAD52 |
protein_coding |
P43351 |
FUNCTION: Involved in double-stranded break repair. Plays a central role in genetic recombination and DNA repair by promoting the annealing of complementary single-stranded DNA and by stimulation of the RAD51 recombinase. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12379650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702565}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene shares similarity with Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad52, a protein important for DNA double-strand break repair and homologous recombination. This gene product was shown to bind single-stranded DNA ends, and mediate the DNA-DNA interaction necessary for the annealing of complementary DNA strands. It was also found to interact with DNA recombination protein RAD51, which suggested its role in RAD51 related DNA recombination and repair. A pseudogene of this gene is present on chromosome 2. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Additional alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:5893; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein-DNA complex [GO:0032993]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; DNA double-strand break processing involved in repair via single-strand annealing [GO:0010792]; DNA recombinase assembly [GO:0000730]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; double-strand break repair via single-strand annealing [GO:0045002]; mitotic recombination [GO:0006312]; regulation of nucleotide-excision repair [GO:2000819] |
11456495_The ring-shaped quaternary structure of RAD52 and the formation of higher ordered complexes of rings appear to contribute to the extreme thermal stability of RAD52. 11691922_reduces double-strand break-induced homologous recombination with overexpression in mammalian cells 11809887_differential effects of Rad52p overexpression on gene targeting and extrachromosomal homologous recombination in a human tumor cell line 12023982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12139939_Analysis of the human replication protein A:Rad52 complex: evidence for crosstalk between RPA32, RPA70, Rad52 and DNA 12191481_Crystal structure of the homologous-pairing domain from the human Rad52 recombinase in the undecameric form. 12370410_crystal structure of the single-strand annealing domain 12372413_RAD52 may play a role in transcription regulation and in targeting DNA damage on transcription active loci to recombinational repair 12376524_women with Ser346ter nonsense polymorphism of RAD52 not at increased risk of breast cancer in case-control study 12750383_coordinated WRN and RAD52 activities are involved in replication fork rescue after DNA damage 12883740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14690434_Rad52 facilitates homologous recognition between single-stranded DNA and duplex-DNA through a process that involves unwinding or transient unpairing of the interacting duplex via a novel three-stranded intermediate that does not lead to strand exchange. 14734547_the ternary complex of hRad52 and XPF/ERCC1 is the active species that processes recombination intermediates generated during the repair of DNA double strand breaks and in homology-dependent gene targeting events 15205482_For both yeast Rad52 and HsRad52, the yield of strand-exchange reactions was proportional to the fractional A.T content of the DNA substrates, but both enzymes catalyzed exchange with substrates that contained up to at least 50% G.C 15205484_formation of a stoichiometric complex between HsRad52 and single-stranded DNA was found to be critical for strand exchange activity 15571718_analysis of residues important for DNA binding in the full-length human Rad52 protein 15670896_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15670896_RAD52 Y415X polymorphism is not associated with epithelial ovarian cancer in Australian women 15766559_purified hRad51 and hRad52 interact with each other as well as with Mini chromosome maintenance (MCM) proteins in HeLa cell extracts 15958648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16018971_Interestingly, presence of hRad52 restores the ability of hRad51 binding to such DNA targets as well. 16367760_DNA-induced disassembly of higher-order forms of Rad51 and Rad52 proteins as steps that precede protein assembly during hRad51 presynapsis on DNA, in vitro. 16638864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16956909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17040915_Rad52 protein functions by binding to single-stranded DNA formed as intermediates of recombination rather than by binding to the unprocessed DNA double-strand break. 18086758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18203022_germline mutations in RAD51, RAD51AP1, RAD51L1, RAD51L3, RAD52 and RAD54L are unlikely to be causal of an inherited predisposition to CLL. 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18313388_Data show that DNA repair synthesis, catalyzed by human DNA polymerase eta (poleta) acting upon the priming strand of a D loop, leads to capture and annealing of the second end of a resected DSB in reactions mediated by RAD52 protein. 18449888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18593704_Rad52 aligns two recombining DNA molecules within the first and second DNA binding sites to stimulate the homology search and strand invasion processes. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18990028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074292_model for hRad52-mediated DNA annealing where ssDNA release and dsDNA zippering are coordinated through successive rearrangement of overlapping nucleoprotein complexes 19092295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19092295_Of the 21 loci screened, RAD52 2259 and RAD52 GLN221GLU may be of importance to disease process and may be associated with papillary thyroid cancer risk in Saudi Arabian population. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19237606_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19506022_Results indicate that RAD52 cooperates with OGG1 to repair oxidative DNA damage and enhances the cellular resistance to oxidative stress. 19530647_These data show that phosphorylated RPA promoted formation of a complex with monomeric Rad52 and caused the transfer of single stranded DNA from RPA to Rad52. 19536092_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19661089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714462_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19799994_This study demonstrated a positive correlation between molecular beacon fluorescence intensity, RAD52 gene expression and both gamma ionising radiation and antineoplastic concentration in human TK6 cells. 19996105_aRPA interacted with both Rad52 and Rad51 and stimulated Rad51 strand exchange. 20081207_hRad52 stably binds and wraps both, protein free and replication protein A-coated ssDNA. 20150366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20190268_the possibility of sumoylation playing an important role in the nuclear transport of RAD52 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20644561_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21148102_Rad52 can respond to DNA double-strand breaks and replication stalling independently of BRCA2 21804533_RAD52(Y104pCMF) specifically targets and wraps ssDNA. Phosphorylation at Y104 enhances ssDNA annealing activity of RAD52 by attenuating dsDNA binding. 22001234_Silencing of the Rad52 gene in fractionated group of A549 cells made the cells radiosensitive. 22860035_The recruitment kinetics of Rad52 is slower than that of Mdc1, but exhibits the same dependence on LET 22964643_RAD52 is an alternative repair pathway of RAD51-mediated homologous recombination, and a target for therapy in cells deficient in the BRCA1-PALB2-BRCA2 repair pathway. 23188672_rs7963551 located at the hsa-let-7 binding site may alter expression of RAD52 and contribute to the development of breast cancer in Chinese women. 23209746_Both RAD52 variants and protein expression can predict platinum resistance, and RAD52 variants appeared to predict prognosis in cervical cancer patients. 23339595_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in RAD52 are associated with myelodysplastic syndromes. 23836560_RAD52 mutation is associated with leukemia. 24047694_Nuclear/chromatin PTEN mediates DNA damage repair through interacting with and modulating the activity of Rad52. 24204313_Our findings reveal a novel RAD52/MUS81-dependent mechanism that promotes cell viability and genome integrity in checkpoint-deficient cells, and disclose the involvement of MUS81 to multiple processes after replication stress 24415301_Our data did not show association between LIG4 and RAD52 SNPs and SLE, its clinical manifestations or ethnicity in the tested population. 24729511_This study found that only the RAD52 rs7963551 single nucleotide polymorphism was significantly associated with hepatitis B virus related - hepatocellular carcinoma risk. 25012956_RAD52 rs7963551 single nucleotide polymorphism was significantly associated with glioma risk. 25365323_We have demonstrated that Rad51 and Rad52 dependent homologous recombination is coupled to HSV-1 DNA replication. 25395584_BRG1-RAD52 complex mediates the replacement of RPA with RAD51 on single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to initiate DNA strand invasion. Loss of BRG1 results in a failure of RAD51 loading onto ssDNA, abnormal homologous recombination repair 25793373_these results implicate increased RAD52 expression in both genetic susceptibility and tumorigenesis of upper aerodigestive tract and lung squamous cell carcinoma tumors. 26013599_Study discovered two cis-expression quantitative trait loci SNPs in the RAD52 gene that are associated with its expression and are also associated with lung squamous cell carcinomas (LUSC) risk. 26735576_RAD52 gene polymorphism is associated with colorectal cancer. 27362509_The C-terminal region of yRad52, but not of hRAD52, is involved in ssDNA annealing. This suggests that the second DNA binding site is required for the efficient ssDNA annealing by yRad52. We propose an updated model of Rad52-mediated ssDNA annealing. 27487923_Structure of the human DNA-repair protein RAD52 containing surface mutations has been reported. 27984745_The mitotic DNA synthesis is RAD52 dependent, and RAD52 is required for the timely recruitment of MUS81 and POLD3 to common fragile sites in early mitosis. 28176781_Rad52 competes with Ku for binding to S-region double-strand DNA breaks (DSB) free ends, where it facilitates a DSB synaptic process, which favours intra-S region recombination. 28329678_DNA-bound RAD52 is efficient at capturing ssDNA in trans. 28549257_Human RAD52-null cells retain a significant level of single-strand annealing (SSA) activity demonstrating perforce that additional SSA-like activities must exist in human cells. Moreover, the SSA activity associated with RAD52 is involved in, but not absolutely required for, most homology-directed repair (HDR) subpathways. Specifically, a deficiency in RAD52 impaired the repair of DNA DSBs. 28551686_Data suggest RAD52 binds tightly to RPA/ssDNA complex in presynaptic complex and inhibits RPA turnover; during presynaptic complex assembly, most of RPA and RAD52 is displaced from ssDNA, but some RAD52/RPA/ssDNA complexes persist as interspersed clusters surrounded by RAD51 filaments. (RAD52 = Rad52 DNA repair/recombination protein; RPA = replication protein A; ssDNA = single-stranded DNA; RAD51 = Rad51 recombinase) 28602639_Rad52 inverse strand exchange plays an important role in RNA-templated double strand break repair in vivo. 29024686_n a cohort of patients with typical symptoms of ischemic heart disease, a common single nucleotide polymorphism of the human RAD52 gene has a role in increased hazard of death, showing that it may influence aging 29145865_The mechanism by which RAD52 depletion causes synthetic lethality in BRCA1 mutant cancer cells depends on the 5' endonuclease EEPD1, which normally functions to cleave stressed replication forks to initiate HR repair. 29245274_our study demonstrated that RAD52 polymorphisms were associated with colorectal cancer in a Chinese Han cohort 29334356_Importantly, p53 defects or depletion unexpectedly allow mutagenic RAD52 and POLtheta; pathways to hijack stalled replication forks, which the authors find reflected in p53 defective breast-cancer patient COSMIC mutational signatures. These data uncover p53 as a keystone regulator of replication homeostasis within a DNA restart network. 29590107_inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) protein by siRNA or inhibitor treatment demonstrated that the acetylation of RAD52 at DSB sites is dependent on the ATM protein kinase activity, through the formation of RAD52, p300/CBP, SIRT2, and SIRT3 foci at DSB sites 29845285_Due to its similarity to RAD52, we hypothesized that RDM1 potentially repairs DNA doublestrand breaks arising through DNA replication. 30590106_RAD52 protein, just as BRCA2, interacts with pCHK1 checkpoint protein and helps maintain the checkpoint control in BRCA2 deficient cells during DNA damage response 30692206_RAD52 and SLX4 mediate distinct postreplicative DNA repair processes that maintain ALT telomere stability and cancer cell viability 30926821_RAD52 limits excessive remodelling of stalled replication forks, thus indirectly assisting RAD51 and BRCA2 in protecting forks from unscheduled degradation and preventing genome instability. 31015609_Study shows that ectopic expression of RAD52 and dn53BP1 improves homology-directed repair during CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing. 31171703_lead to mitotic DNA synthesis (MiDAS) at telomeres mediated by RAD52 through its highly conserved N-terminal domain 31381562_RAD52 and POLQ are both synthetic lethal with loss of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes. Furthermore, RAD52 and POLQ have been implicated in chromosomal break repair events that use flanking repeats to restore the chromosome. Combined disruption of RAD52 and POLQ causes at least additive hypersensitivity to cisplatin and a synthetic reduction in replication fork restart velocity. 31495919_Human RECQL4 represses the RAD52-mediated single-strand annealing pathway after ionizing radiation or cisplatin treatment. 31777915_ROS-induced telomeric R-loops promote repair of telomeric DSBs through CSB-RAD52-POLD3-mediated BIR, a previously unknown pathway protecting telomeres from ROS. ROS-induced telomeric SSBs may not only give rise to DSBs indirectly, but also promote DSB repair by inducing R-loops, revealing an unexpected interplay between distinct ROS-induced DNA lesions. 31799622_Our work introduces for the first time RAD52 as another interacting partner of DSS1 and shows that both proteins are important players in the SSA and BIR pathways of DSB repair. 31832684_We show pronounced suppression of gene-conversion with increasing DNA double-strand breaks load that is not due to RAD51 availability and which is delimited but not defined by 53BP1 and RAD52. 32143539_Aberrant Expression of RAD52, Its Prognostic Impact in Rectal Cancer and Association with Poor Survival of Patients. 32175645_The RAD52 S346X variant reduces risk of developing breast cancer in carriers of pathogenic germline BRCA2 mutations. 32401173_RAD52 variants influence NSCLC risk in the Chinese population in a high altitude area. 32945515_RAD52 aptamer regulates DNA damage repair and STAT3 in BRCA1/BRCA2deficient human acute myeloid leukemia. 33275133_The function of RAD52 N-terminal domain is essential for viability of BRCA-deficient cells. 33440161_RAD52 Adjusts Repair of Single-Strand Breaks via Reducing DNA-Damage-Promoted XRCC1/LIG3alpha Co-localization. 33536619_BRCA1 and RNAi factors promote repair mediated by small RNAs and PALB2-RAD52. 34789290_Nickel nanoparticle-induced cell transformation: involvement of DNA damage and DNA repair defect through HIF-1alpha/miR-210/Rad52 pathway. 35190531_Rad52 mediates class-switch DNA recombination to IgD. 35210412_SF3B4 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating alternative splicing of RAD52. |
ENSMUSG00000030166 |
Rad52 |
42.950949 |
0.3255239509 |
-1.619164 |
0.352362659 |
20.714346 |
0.00000533150718769542975348325539175498022359533933922648429870605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017298976937873059277770218522540801586728775873780250549316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.6797218 |
6.0824421 |
57.9293353 |
13.2297360 |
| ENSG00000002587 |
9957 |
HS3ST1 |
protein_coding |
O14792 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) to catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group to position 3 of glucosamine residues in heparan (PubMed:9346953, PubMed:8900198, PubMed:9988768). Catalyzes the rate limiting step in the biosynthesis of heparan sulfate (HSact) (PubMed:8900198, PubMed:9988768). This modification is a crucial step in the biosynthesis of anticoagulant heparan sulfate as it completes the structure of the antithrombin pentasaccharide binding site (PubMed:8900198, PubMed:9988768). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8900198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9346953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9988768}. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase |
|
Heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzymes are key components in generating a myriad of distinct heparan sulfate fine structures that carry out multiple biologic activities. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzyme family. It possesses both heparan sulfate glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase activity, anticoagulant heparan sulfate conversion activity, and is a rate limiting enzyme for synthesis of anticoagulant heparan. This enzyme is an intraluminal Golgi resident protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9957; |
Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 1 activity [GO:0008467]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0006024]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012] |
15096036_In this paper a conformational change is described that occurs in heparan sulfate 3-O-sulfotransferase-1 upon binding to heparan sulfate. 24247246_Golgi-targeted HS3st1 localizes in the Golgi and results in the formation of a single type of AT-binding site and high anti-factor Xa activity 28126521_Compared with Hs3st1+/+ mice, Hs3st1-/- mice were more susceptible to LPS-induced death due to an increased sensitivity to TNF 35909476_HS3ST1 Promotes Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Targeting the SPOP/FADD/NF-kappaB Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000051022 |
Hs3st1 |
417.055999 |
34.7414385862 |
5.118586 |
0.638889737 |
46.482519 |
0.00000000000924394483951924951071532133861787623382855194620333350030705332756042480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000051370717556966917443589942671917946727389026051469045341946184635162353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
792.3105545 |
282.4877168 |
22.4642039 |
5.9726007 |
| ENSG00000003056 |
4074 |
M6PR |
protein_coding |
P20645 |
FUNCTION: Transport of phosphorylated lysosomal enzymes from the Golgi complex and the cell surface to lysosomes. Lysosomal enzymes bearing phosphomannosyl residues bind specifically to mannose-6-phosphate receptors in the Golgi apparatus and the resulting receptor-ligand complex is transported to an acidic prelyosomal compartment where the low pH mediates the dissociation of the complex. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the P-type lectin family. P-type lectins play a critical role in lysosome function through the specific transport of mannose-6-phosphate-containing acid hydrolases from the Golgi complex to lysosomes. The encoded protein functions as a homodimer and requires divalent cations for ligand binding. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:4074; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endosome [GO:0005768]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; retromer complex binding [GO:1905394]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; lysosomal transport [GO:0007041]; protein targeting to lysosome [GO:0006622]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; secretion of lysosomal enzymes [GO:0033299] |
12697764_sorting of the CD-MPR in late endosomes requires a distinct di-aromatic motif with only limited possibilities for variations 15167696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15620351_All 5 MPRci-deficient lines resisted infection by cell-free, but not cell-associated, VZV, secreted lysosomal enzymes, and released infectious virions when infected by cell-associated VZV 17210618_We conclude that the CI-MPR participates in lysosomal and granular targeting of serglycin and basic proteins such as lysozyme associated with the proteoglycan in hematopoietic cells. 18003638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18088323_sortilin and mannose-6-phosphate receptors recycle to the TGN in SNX1-dependent carriers, which we named endosome-to-TGN transport carriers 18367545_Missorting of cathepsin D in GARP-depleted cells results from accumulation of recycling MPRs in a population of light, small vesicles downstream of endosomes. 19345684_Data demonstrate that Rab31 is required for transport of mannose 6-phosphate receptors from the trans-Golgi network to endosomes and for the Golgi/TGN organization. 20351714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22015004_mediates in vitro human immunodeficiency virus and sperm cell interaction 22163010_Mannose receptor (MR) engagement by mesothelin GPI anchor polarizes tumor-associated macrophages and is blocked by anti-MR human recombinant antibody 22768187_Sortilin is a new alpha-Gal A receptor expressed in renal endothelial cells and that this receptor together with the M6PR is able to internalize circulating alpha-Gal A. 24407285_These data indicate that clathrin is required for the function of AP-1- and GGA-coated carriers at the trans-Golgi network but may be dispensable for outward traffic en route to the plasma membrane. 24788816_Results suggest that Rab protein Rab29 is essential for the integrity of the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and participates in the retrograde trafficking of mannose-6-phosphate receptor (M6PR). 27105913_In light of existing report suggesting critical role of Nef-GCC185 interaction reveals valuable mechanistic insights affecting specific protein transport pathway in docking of late endosome derived Rab9 bearing transport vesicle at TGN elucidating role of Nef during viral pathogenesis. 29275103_Most rotavirus strains require the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor, sortilin-1, and cathepsins to enter cells. 29769659_Mannose-6-phosphate receptor: a novel regulator of T cell immunity. 30086159_Results suggest that, in hormone-responsive breast cancer cells, CD-MPR and cathepsin D are distributed together, and that their expression and distribution are influenced by estradiol. These findings strongly support the involvement of the CD-MPR in the pro-enzyme transport in MCF-7 cells, suggesting the participation of this receptor in the procathepsin D secretion previously reported in breast cancer cells. 31840180_The co-localization of M6PR and of GCC2 with ASOs is influenced by the PS modifications, which have been shown to enhance the affinity of ASOs for proteins, suggesting that localization of these proteins to LEs is mediated by ASO-protein interactions. Reduction of M6PR levels also decreased PS-ASO activity in mouse cells and in livers of mice treated subcutaneously with PS-ASO, indicating a conserved mechanism. 32437666_Monochorionic twins with selective fetal growth restriction: insight from placental whole-transcriptome analysis. 34244781_Golgi-58K can re-localize to late endosomes upon cellular uptake of PS-ASOs and facilitates endosomal release of ASOs. 34688818_Association between genetic variants in oxidative stress-related genes and osteoporotic bone fracture. The Hortega follow-up study. |
ENSMUSG00000007458 |
M6pr |
1518.548280 |
2.4500953762 |
1.292838 |
0.079771164 |
257.651443 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000055776889489476892137220008145729808669906317515912061546289762520261430399589154247982937832532833352846589080292495511136555163172338524421557063442955737286865769419819116592407226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000013836418300246704780741792573742377985125995577486762534265650310278391369083031409098651010870454563143762788605980970200065041227809356060973050572826537063519936054944992065429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2238.5803791 |
104.9405792 |
920.4759847 |
32.2766817 |
| ENSG00000003402 |
8837 |
CFLAR |
protein_coding |
O15519 |
FUNCTION: Apoptosis regulator protein which may function as a crucial link between cell survival and cell death pathways in mammalian cells. Acts as an inhibitor of TNFRSF6 mediated apoptosis. A proteolytic fragment (p43) is likely retained in the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) thereby blocking further recruitment and processing of caspase-8 at the complex. Full length and shorter isoforms have been shown either to induce apoptosis or to reduce TNFRSF-triggered apoptosis. Lacks enzymatic (caspase) activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9880531}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Host-virus interaction;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulator of apoptosis and is structurally similar to caspase-8. However, the encoded protein lacks caspase activity and appears to be itself cleaved into two peptides by caspase-8. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, and partial evidence for several more variants exists. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:8837; |
CD95 death-inducing signaling complex [GO:0031265]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; death-inducing signaling complex [GO:0031264]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; ripoptosome [GO:0097342]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0097153]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097199]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis [GO:0097200]; death receptor binding [GO:0005123]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to nitric oxide [GO:0071732]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:1903845]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902042]; negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process [GO:1903944]; negative regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901740]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903427]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix organization [GO:1903055]; positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072126]; positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation [GO:2000347]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060544]; regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation [GO:0014842]; response to testosterone [GO:0033574]; skeletal muscle atrophy [GO:0014732]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; skeletal muscle tissue regeneration [GO:0043403]; skeletal myofibril assembly [GO:0014866]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11830587_The human herpes virus 8-encoded viral FLICE inhibitory protein physically associates with and persistently activates the Ikappa B kinase complex. 11877293_Higher levels of expression of FLIP were present in TRAIL-resistant multiple myeloma cells, and sensitivity to TRAIL was restored by lowered FLIP protein levels. 11940602_An inducible pathway for degradation of FLIP protein sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 12031968_cFLIP may have an impact on the outcome of death receptor-triggered responses by directing the intracellular signals from beta-cell death to beta-cell survival 12060768_switches Fas-mediated glucose signaling in human pancreatic beta cells from apoptosis to cell replication switches Fas-mediated glucose signaling in human pancreatic beta cells from apoptosis to cell 12115181_FLICE-inhibitory protein expression in synovial fibroblasts and at sites of cartilage and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. 12393527_results demonstrate a definite role for FLIP in the stem cell factor-induced protection of erythroid colony forming cells from IFNgamma-initiated apoptosis 12407100_These results provide new insights into the mechanisms of bile acid cytotoxicity and the proapoptotic effects of cFLIP phosphorylation in TRAIL signaling. 12432255_c-FLIP may play a critical role in regulating Fas-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer cells 12477972_The consequences of FasL overexpression depend on the subcellular compartment and species in which FasL enforced expression is targeted and this is at least partially related to FLIP levels 12496285_c-FLIP expression is regulated by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and modulates Fas-mediated signaling in glioma cells 12496481_In response to doxorubicin, the level of FLIP decreased in all prostatic cell lines tested and correlated with the onset and magnitude of CASP8 and PARP cleavage in PC3 cells. 12496482_The metabolism of FLIP is essential to the death of prostatic cells in culture. 12552004_Adenovirus E1A inhibited TNF-alpha-dependent induction of c-FLIP(S) mRNA and stimulated ubiquitination- and proteasome-dependent degradation of c-FLIP(S) protein in Hela cells 12556488_Our results show that c-FLIP(L) and c-FLIP(S) potently control TRAIL responses, both by distinct regulatory features, and further imply that the differentiation state of malignant cells determines their sensitivity to death receptor signals. 12574377_Constitutive expression of the long form of human FLIP leads to an enhanced and prolonged inflammatory response in the central nervous system during experimental allergic encephalitis in DBA mice. 12592338_Constitutively active Akt1 protects HL60 leukemia cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis through a mechanism involving NF-kappaB activation and up-regulation of this protein 12716387_Expression is increased in stomach cancer 12746452_cFLIP-L exerts its anti-apoptotic activity, in part, by inhibiting p38 MAPK activation, an additional anti-apoptotic effect for this protein. 12820373_cFLIP is an important determinant of susceptibility to death receptor-induced apoptosis in bladder carcinomas. 14562111_FLIP(L) and FLIP(S) are differentially regulated, and that the relative levels of both isoforms play a role in the regulation of apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome 14578361_In T cells, c-FLIP expression led to inhibition of IL-2 production, in contrast to the readily detectable c-FLIP-induced activation in Jurkat cells. 14637155_In this study, we show that c-FLIP(L) but not c-FLIP(S) physically binds to Daxx through interaction between C-terminal domain of c-FLIP(L) and Fas-binding domain of Daxx, an alternative Fas signaling adaptor. 14662022_Akt activity promotes human gastric cancer cell survival against TRAIL-induced apoptosis via upregulation of FLIP(S), and that the cytotoxic effect of TRAIL can be enhanced by modulating the Akt/FLIP(S) pathway in human gastric cancers. 15024054_Results demonstrate that FLIP(p43) processed by caspase 8 specifically interacts with TRAF2 and subsequently induces activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 15078899_the selective down-regulation of c-FLIP by small interfering RNA oligoribonucleotides was sufficient to sensitize Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells to CD95 and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis 15096587_down-regulation of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein through the use of specific small inhibitory RNAs leads to reduced viability of the L428 and L591 HL-derived cell lines 15183989_The frequent expression and coexpression of Fas, FasL, and c-FLIP in urothelial carcinomas implicates c-FLIP as an inhibitor of the Fas-FasL-induced death pathway in these tumors. 15258564_FLIP plays a significant role in the regulation of apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells and their sensitivity to cisplatin. 15273717_Regulation by AMP-activated protein kinase-related kinase 5 15297424_the inhibitory protein c-FLIP(L) is involved in resistance to CD95-mediated apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma cells with wild-type p53 15304499_When fusesd with Tat protein, prevesnts adverse apoptosis nd prolongs survival in tumor cells. 15334061_Malignant mesothelioma cells develop an intrinsic resistance to apoptosis induced by death receptors upregulating the expression of the antiapoptotic protein c-FLIP. 15354734_strong c-FLIP expression in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma was associated with transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; the majority of DLBCL cases tested were strongly c-FLIP-positive. 15459191_cFLIP(L) is not only a central antiapoptotic modulator of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis but also an inhibitor of TRAIL-induced NF-kappaB activation and subsequent proinflammatory target gene expression 15485835_c-FLIPL is recruited to death receptor 5 independent of Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) 15540114_Results indicate that some tumor cells are resistant to death receptor-mediated apoptosis by expressing cellular FLIP, and that histone deacetylase inhibitors sensitize such resistant tumor cells by directly downregulating cellular FLIP mRNA. 15557152_Constitutive overexpression of c-FLIP (long form) in T cells is sufficient to drive Th2 polarization of effector T cell responses and indicates that it might function as a key regulator of T helper (Th) cell differentiation. 15644494_DDB2 regulates TNF signaling-mediated apoptosis via cFLIP and contributes to acquired cross-resistance. 15653751_T cell blasts surviving activation-induced cell deathare memory CD44high cells with increased c-FLIP expression. 15686714_Heart graft rejection biopsies have elevated FLIP mRNA expression levels. 15701649_c-FLIPR, an isoform of c-FLIP, is a new regulator of death receptor-induced apoptosis. 15701651_CLARP inhibits caspase-8 induced, ASC-mediated NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 production 15722350_cFLIP/CFLAR is an essential NF-kappa B-dependent antiapoptotic gene in the tumor necrosis factor alpha-regulated pathway in epidermal keratinocytes 15731171_c-FLIP promoter was shown to contain multiple functional androgen response elements. 15760909_c-FLIP(L) functions primarily as an inhibitor of death receptor-mediated apoptosis through TRAIL and caspase-8 activation 15761846_Established and analyzed a transgenic mouse model that overexpresses human c-FLIPS (CFLAR) in thymocytes and peripheral T cells. Data suggests a specific in vivo function for c-FLIPS in the maintenance of restimulated T cells. 15815586_differential spatial and temporal regulation of cFLIP-alpha and cFLIP-delta expression that may influence the magnitude of cell death 15832422_c-FLIP is specially overexpressed in colon cancers and it might contribute to carcinogenesis of normal colonic mucosa. 15843523_A mechanism by which c-FLIP(long form)(CFLAR) influences effector T cell function in CFLAR transgenic mice is via its activation of caspase-8, which in turn cleaves CFLAR to allow receptor interacting protein (RIP)1 recruitment and NF-kappa B activation. 15864316_Our results suggest for the first time a critical role for FLIP in the regulation of apoptosis triggered by TRAIL in endometrial carcinoma cells. 15886205_The conformation-based predisposition of c-FLIP(S) to ubiquitin-mediated degradation introduces a novel concept to the regulation of the death-inducing signaling complex 15899875_FLIP protected mouse lung endothelial cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation by blocking both caspase 8/Bid and Bax/mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. 15917295_c-FLIP knock-down with a small interfering RNA significantly restores Fas-mediated apoptosis in infected cells 15956881_The majority of Langerhans cell histiocytosis cells express this protein. 16014121_c-FLIP might contribute to the carcinogenesis and aggressiveness of endometrial carcinoma and might be a useful prognostic factor in the tumor 16052233_findings show that E2F1 triggers apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines by a mechanism involving the specific downregulation of the cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein short, leading to caspase-8 activation at the death-inducing signaling complex 16052516_results demonstrate a critical role for PKCdelta/NF-kappaB in the regulation of FLIP in human colon cancer cells 16077198_Cycloheximide sensitizes colorectal tumor cells to TNF-alpha induced apoptosis by reducing FLIP levels. 16211288_the PI 3-K/Akt signaling pathway may, in part, regulate Fas-mediated apoptosis in HL-60 cells through c-FLIP expression 16247474_c-FLIP inhibits apoptosis in response to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer cells 16298825_Expression of FLIP molecules may be, at least in part, an early prognostic indicator in the treatment of elderly acute myeloid leukemia patients. 16304056_overexpression of c-FLIP protects ALK+ ALCL cells from FAS-induced apoptosis and may contribute to ALCL pathogenesis. 16403915_c-FLIP confers Tax-mediated resistance toward CD95-mediated apoptosis. 16436054_Taken together, Tax inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis by up-regulating c-FLIP expression in HTLV-I-infected cells, and NF-kappaB activity plays an essential role in the up-regulation of c-FLIP. 16441226_Review focuses on the role of c-FLIP as a tumour progression factor, with particular emphasis on contribution of c-FLIP to pathogenesis of Hodgkin's lymphoma. 16472594_Inhibition of Flip by antisense oligonucleotide reverted the resistance of CD LPLs to FAS-induced apoptosis. 16611896_results suggested that the TNF-alpha-induced apoptotic pathway is inhibited by a sustained c-FLIP expression associated with the expression of HCV core protein, which may play a role in HCV-mediated pathogenesis 16720717_Results suggest that, in addition to its proapoptotic function, par-4 acts as a novel transcription cofactor for androgen receptors to target c-FLIP gene expression. 16740746_The NFkappaB-mediated overexpression of cFLIP(long)represent alternative mechanisms for deregulating the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in LBCL subtypes defined by gene expression profiling. 16901543_Anti-apoptotic signaling of CD40 involves induction of c-FLIP proteins. 17056549_These data demonstrate specific activation of c-FLIP by HCMV IE2 and indicate a novel role for c-FLIP in the pathogenesis of HCMV retinitis. 17070520_Treatment with sodium arsenite resulted in upregulation of the endogenous TRAIL and downregulation of the cFLIP gene expression followed by cFLIP protein degradation and, finally, by acceleration of TRAIL-induced apoptosis 17106251_Doxorubicin-mediated downregulation of cFLIPS at the post-transcriptional level is sufficient to enhance TRAIL sensitivity in PC3 prostate carcinoma cells. 17272514_Enforced long-form cFLIP (cFLIP(L)) expression reduced release of cathepsin B from lysosomes and attenuated apoptosis. 17376892_induction of the short c-FLIP isoforms inhibits the onset of CD95-induced apoptosis in primary CD40-stimulated ALL cells despite high CD95 expression. 17440816_Downregulation of either FLIP or XIAP but not Bcl-2 restored sensitivity of Colo320 cells to Apo2L/TRAIL. 17441421_There was a negative relationship between the expression of FLIP and PTEN in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 17450141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17513603_c-FLIP plays a pivotal role in modulating drug-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells 17559541_The expression of Fas, FasL and c-FLIP in colorectal carcinoma implicates c-FLIP as an inhibitor of the Fas-FasL-induced death pathway in these tumors. Moreover, c-FLIP conveys independent prognostic information in the presence of classic prognosticators. 17573774_cFLIP-L is prone to aggregate and impairs ubiquitin-proteasome system function, which could be involved in the pathological function of cFLIP-L expressed in certain cancer cells 17581950_FLIP(L) is essential for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/tumor necrosis factor receptor I (TNFRI)-mediated neuroprotection after glucose deprivation in transgenic mice. 17638906_RIP and c-FLIP-mediated assembly of the death-inducing signaling complex in nonrafts is a critical upstream event in TRAIL resistance 17646662_enhanced proliferative nature of human leukemia cells is caused by elevated NF-kappaB and FLIP responses 17659339_bortezomib and TRAIL combination caused further down-regulation of cFLIP protein and increased apoptosis in CHL cells 17697742_VPA significantly increased sensitivity of leukemic cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and led to downregulation of c-FLIP (L) expression. 17726263_Caspase-8 and cFLIP are upregulated during colorectal carcinogenesis. 17762208_The mechanism by which antioxidant status alters FLIP levels following neonatal HI may be related to the ability to detoxify H2O2 produced following neonatal HI. 17912957_Human keratinocytes were transfected with either Flip, Faim, or Lifeguard (LFG). Our results suggest that heterotopic expression of antiapoptotic proteins can induce the resistance of keratinocytes to a major mechanism of rejection. 17922291_Overexpression of cFLIP(L) is a frequent event in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 17932249_reconstitution of ATM kinase activity decreases FLIP protein levels and restores Fas sensitivity in Hodgkin lymphoma-derived cells 17982483_CK2 regulates endometrial carcinoma cell sensitivity to TRAIL and Fas by regulating FLIP levels. 17988665_IFN-alpha causes a transient upregulation of c-FLIP expression, at least through PKCalpha-mediated activation of NF-kappaB 18073330_(c-FLIP), which is dependent on the NF-kappaB pathway in normal muscle cells, is down-regulated in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A biopsies. 18084329_cFLIP represents an attractive therapeutic target for melanoma treatment, especially in combination with TRAIL receptor agonists. 18189268_Sanguinarine-mediated apoptosis is blocked by ectopic expression of Bcl-2 and cFLIPs 18243739_Study indicated that c-FLIP(L) might be a suppressor of Fas-mediated apoptosis in Fas antigen expressing colon carcinoma cells. 18257744_interaction of calmodulin cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein 18264131_Since Gli2 silencing not only downregulates cFlip, but also Bcl-2, Gli2 could be a key target for a novel therapeutic approach in basal cell carcinoma. 18314443_cFLIP was overexpressed in CD4+/CD26- tumor cells with normal or enhanced Fas expression 18339897_TTP plasma-mediated apoptosis appears to involve IFNG-induced acceleration of c-FLIP degradation, sensitizing cells to TRAIL-mediated caspase-8 activation and cell death. 18391984_FOXO3a mediates the androgen-dependent regulation of FLIP and contributes to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of LNCaP cells. 18398344_c-Flip (CASP8 and FADD-like apoptosis regulator) is a key regulator of the cardiac response to ventricular pressure overload. 18414015_c-FLIPL promotes the motility of HeLa cells by activating FAK and ERK, and increasing MMP-9 expression. 18509086_preventing autocrine CD95L signaling by c-FLIP facilitates T-cell effector function and an efficient immune response 18593367_reversion of Fas resistance is mediated through CD40/CD40L ligation rather than IFN-gamma stimulation by inhibiting synthesis of c-FLIP 18603835_cFLIP is an essential pro-survival factor for granulosa cells, and it prevents granulosa cell apoptosis by inhibiting procaspase-8 activation. 18726983_Androgenic protection from TRAIL-induced apoptosis is via enhanced transcription of FLIP in prostate cancer cells. Loss of androgen-sensitivity in androgen-depletion-independent prostate cancer cells. Potential target for therapy of prostate cancer. 18767116_anti-apoptotic functions of cFLIPs may be attributed to inhibit oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis through the sustained XIAP protein level and Akt activation. 18820704_These results suggest that simultaneously targeting both FLIP and XIAP may prove useful in the treatment of cancers, particularly those in which the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway has been compromised. 18823309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18838202_Overexpression of FLIP reduced TRAIL and TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in ML-1 cells. However, while FLIPL completely abrogated apoptosis, FLIPS allowed for BID cleavage and caspase-3 activation. 18840411_an apoptotic inhibitory complex comprised of DR5, FADD, caspase-8, and c-FLIP(L) exists in MCF-7 cells, and the absence of c-FLIP(L) from this complex induces DR5- and FADD-mediated caspase-8 activation in the death inducing signaling complex 19090833_Ubiquitination of cFLIP(L) inhibits the interaction between cFLIP(L) and Itch in T. cruzi-infected cells. 19109151_While dispensable for the development of bone marrow precursor B cells, cFLIP is necessary for B cell maturation in the periphery. 19115040_These data suggest caspase 8, but not cFLIP, activation induced by C5a leads to cell death if protein synthesis of antiapoptotic protein(s) is blocked. 19161534_FLIP expression was strong in most (103/107; 96.3%) of the prostate cancers, and only four cancers (3.7%) showed decreased immunoreactivities compared with the normal cells. 19177145_modulation of the CD95 signaling pathway by cFLIP in basal keratinocytes may explain the spatial localization of spongiosis in suprabasal epidermal layers, and provides new insights into the pathogenesis of spongiosis formation in eczematous dermatitis 19203346_the loss of Bcr-Abl in imatinib-resistant K562 cells led to the down-regulation of c-FLIP and subsequent increase of TRAIL sensitivity 19223508_Increase in FLIP is associated with prostate tumors. 19243385_inhibition of c-FLIP(L) expression might be a potential strategy for lung cancer therapy, especially for those lung cancers resistant to the agonistic antibody against death receptors 19249545_Pig islets expressing human c-FLIP(L) are significantly resistant to human cytotoxic lymphocyte killing and exhibit beneficial effects to prolong xenograft survival. 19282655_Over-expression of c-FLIP confers the resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis on gallbladder carcinoma. 19321593_Overexpression of c-FLIPL is associated with ovarian cancer. 19339247_TNFalpha facilitates the reduction of FLIP(L) protein, which is dependent on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling. 19343040_S193 phosphorylation is mediated by PKC-aplha and PKC-beta and reveal a connection between c-FLIP phosphorylation and ubiquitylation, as S193 mutations differently affect c-FLIP ubiquitylation. 19363595_gp120 plays an important role, via involvement of c-FLIPL, in T-cell apoptotic cell death due to HIV-1 infection. 19372246_c-FLIP expression is induced in the abnormal alveolar epithelium of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/usual interstitial pneumonia 19398149_the short isoform of c-FLIP and bcl-2 are key regulators in TRAIL-Myricetin mediated cell death in malignant glioma. 19409438_In summary, the short isoform of c-FLIP is a key regulator in TRAIL-Embelin-mediated apoptosis in malignant glioma. 19433309_These findings describe a novel function of c-FLIP-L involved in AP-1 activation and cell proliferation. 19439735_production of either c-FLIP(S) or c-FLIP(R) in humans is defined by a single nucleotide polymorphism in a 3' splice site of the c-FLIP gene (rs10190751A/G); increased lymphoma risk associated with the rs10190751 A genotype causing c-FLIP(R) expression. 19476635_Increased c-FLIP is associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical carcinoma. 19543235_FADD-Like Apoptosis Regulating Protein silencing sensitized non-small-cell lung cancer cells but not normal cells to chemotherapy in vitro, and silencing FLIP in vivo retarded non-small-cell lung cancer cells xenograft. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19710364_The interaction between Mib1 and cFLIP decreases the association of caspase-8 with cFLIP, which activates caspase-8 and induces cell death. 19728335_IKKalpha, IKKbeta, RANK, Maspin, c-FLIP, Cip2 and cyclinD1 were found to show significant differences between hepatocellular tumor tissue and its corresponding adjacent tissue. 19734124_CD133-high cells may be resistant to TRAIL due to high expression of FLIP. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19798106_Data suggest that c-FLIP downregulation represents a mechanism by which diverse anticancer regimens can facilitate tumor cell execution by CD95/Fas through the direct pathway of caspase activation. 19802016_Results suggest that Akt confers resistance, in part, by modulating CDDP-induced, p53-dependent FLIP ubiquitination. 19816511_Results identify c-FLIP(L) as a susceptibility factor under the influence of epistatic modifiers for the development of autoimmunity. 19890350_Knockdown of c-FLIP by a enhanced basic apoptosis rates in cutaneous lymphoma cells and diminished the CD30-mediated suppression of apoptosis, thus proving the significance of c-FLIP in this context 19896469_These results indicate that AMPK activators facilitate the activation by TRAIL of an apoptotic cell death program through a mechanism independent of AMPK and dependent on the down-regulation of cFLIP levels. 19906927_our results demonstrate that apoptosis of HSV-1-infected iDCs requires both c-FLIP downregulation and diminished expression of viral LAT. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19949310_CDODO-Me-12 and CDODO-Me-11 downregulated the levels of anti-apoptosis protein c-FLIP in HL-60, U937 and K562 leukemic cell lines. 19956887_eupatolide could augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by down-regulating c-FLIP expression through the inhibition of AKT phosphorylation 20016063_role for nuclear cFLIP-L in the modulation of Wnt signaling 20087343_Egr-1 drives c-FLIP expression and the short splice variant of c-FLIP (c-FLIP(S)) specifically inhibits DR5 activation. 20218968_The role of c-FLIP is critical in the protection of erythroid-differentiated cells from apoptosis or in the determination of their sensitivity to TNF-mediated programmed cell death. 20224598_FLIP expression is transcriptionally regulated by hnRNP K and nucleolin, and may be a potential prognostic and therapeutic marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 20227749_Data demonstrate that c-FLIP(L) exhibits multiple functions in ovarian cancer: first by concomitantly evading the natural immunity mediated by TRAIL-induced cell death, and second by augmenting cell motility and invasion in vivo. 20335528_Although deletion of cFLIP does not alter the primary development of B cells, adoptively transferred cFLIP-deficient follicular B cells do not effectively participate in the germinal center response. 20372864_Disclose a novel regulatory mechanism inHepG2 cells where down-regulation of c-FLIP by miR-512-3p contributed to taxol-induced apoptosis. 20449949_Data suggest that FLIP potentially extends the lifespan of synovial cells and thus contributes to the progression of joint destruction in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561424_mRNA expressions of DLK1, c-FLIPL and c-FLIPS are abnormal in bone marrow mononuclear cells of myelodysplastic syndrome patients. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20595005_PDCD4 plays an important role in mediating the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through FLIP suppression. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20696707_The function of c-FLIP(L) as a pro- or antiapoptotic protein in DR-mediated apoptosis is important for understanding the regulation of CD95-induced apoptosis, where subtle differences in c-FLIP concentrations determine life or death of the cells. 20802294_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20812013_CD30/CD95 crosstalk experiments revealed that CD30 ligation leads to NFkappaB-mediated cFLIP upregulation in cALCL cells, which in turn enhanced resistance to CD95-mediated apoptosis. 20876774_Both the long and the short isoform of the antiapoptotic protein c-FLIP are critical regulators of death receptor-induced apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma cells and are suppressed by chemotherapeutics. 20882347_Triggering of death receptor apoptotic signaling by human papillomavirus 16 E2 protein in cervical cancer cell lines is mediated by interaction with c-FLIP. 20975036_These studies indicate that cFLIP protein is a crucial component of the signaling pathway involved in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21071136_review of molecular mechanisms that control c-FLIP expression and current research into inhibitors of the protein [review] 21107885_Itch/AIP4-independent proteasomal degradation of cFLIP induced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA sensitizes breast tumour cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 21153369_regulation of cell death by c-FLIP phosphorylation 21307400_Reveal unique regulatory networks in acute myeloid leukemia whereby FLIP regulation of HO-1 provides cells with secondary anti-apoptotic protection against TNF induced death signals in these highly death-resistant cells. 21324892_Modeling reveals that dynamic regulation of c-FLIP levels determines cell-to-cell distribution of CD95-mediated apoptosis. 21403465_Silencing FLIP(L) modifies TNF-induced apoptotic protein expression. 21435442_KSR1 is overexpressed in endometrial carcinoma and regulates proliferation and TRAIL-induced apoptosis by modulating FLIP levels 21454681_Cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (cFLIP) isoforms block CD95- and TRAIL death receptor-induced gene induction irrespective of processing of caspase-8 or cFLIP in the death-inducing signaling complex 21480219_BAY 11-7085 rapidly inhibited c-FLIP(L) expression in colon and pancreatic cancer cell lines during adhesion to mesothelial cells. 21525012_Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated tissue transglutaminase overexpression couples acquired tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance and migration through c-FLIP and MMP-9 proteins in lung cancer cells 21562857_increased expression of cFLIP protects cells from both interferon-alpha and death receptor mediated apoptosis 21638304_cFLIP expression showed no significant correlation to DLBCL subtypes (GCB or non-GCB) but was associated with a worse clinical outcome. 21691254_Data suggest that persistent Flice inhibitory protein-S expression is involved in the longevity of neonatal polymorphonuclear leukocytes. 21803845_PMLRARalpha binds to Fas and suppresses Fas-mediated apoptosis through recruiting c-FLIP in vivo. 21856935_our study reveals a novel link between NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt and establishes c-FLIP as an important regulator of FasL-mediated cell death. 21868755_a novel mechanism through which the regulatory effects of c-FLIP on death receptor signaling in neoplastic cells are controlled by glycogen synthase kinase-3 21912376_results demonstrate that the H204 residue is responsible for c-FLIP(L) binding to CaM, which mediates the anti-apoptotic function of c-FLIP(L) 22027693_This study identifies SART1 as a previously unidentified regulator of c-FLIP and drug-induced activation of caspase-8. 22072062_Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensitizes cells to TRAIL through down-regulation of FLIP and Mcl-1 and PERK-dependent up-regulation of TRAIL-R2. 22126763_Kashin-Beck disease patients have significant increased FADD expression in the middle layer but decreased FLIP expression in the upper layer of the cartilage. 22190004_It was diminished expression of the c-FLIP(L) isoform in urothelial carcinoma tissues as well as in established carcinoma cell lines compared with normal urothelial tissues and cells, whereas c-FLIP(S) was unchanged. 22219201_an important role for TRAF7 in the activation of JNK following TNFalpha stimulation and involvement of this protein in regulating the turnover of c-FLIP 22288650_data suggest that Ro52/SSA is involved in death receptor-mediated apoptosis by regulating c-FLIP(L) 22345097_API-1 reduces c-FLIP and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis independent of its Akt-inhibitory activity 22393362_BCL-X(L) and BCL-2 but not FLIP(L) acts in synergy with MYC to drive AML development 22504646_Survival of activated and also of immature dendritic cells is regulated by BAK and shows that tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is protective only in the presence of FLIPL. 22683265_analysis of stoichiometry of the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex and demonstration of how procaspase-8, procaspase-10, and c-FLIP form DED chains at the DISC, enabling the formation of dimers and efficient activation of caspase-8 22753273_CHOP represses cFLIPL expression in Caki cells. 22781394_review of the structural and functional biology of c-FLIP with direct relevance to carcinogenesis [review] 22842544_TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human renal cancer cells by upregulation of DR5 as well as downregulation of c-FLIP and Bcl-2. 22948392_Suppression of HSP70 expression sensitizes NSCLC cell lines to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by upregulating DR4 and DR5 and downregulating c-FLIP-L expressions 23028678_the 'biomarker signature' of FLIP/Sp1/Sp3 combined with Gleason score predicted disease recurrence 23167276_Adult acute myeloid leukemia patients with higher-than-median mRNA expression of the long splice form(but not the short splice form) had significantly lower 3 year overall survival than those with low expression. 23230268_Apoptosis-related genes such as the caspase-8, FLIP, and DR5 genes specifically interfere with interferon-induced apoptosis. 23235765_Data show that alterations of the apoptosis-related protein FLIP is common in granulosa cell tumor (GCT), and suggest that expression of FLIP might play role in the pathogenesis of GCT, possibly by inhibiting apoptosis. 23247197_SIRT1 inhibition increases Ku70 acetylation, and the acetylated Ku70 with a decreased function mediates the induction of DR5 and the down-regulation of c-FLIP by up-regulating c-Myc/ATF4/CHOP pathway,promotes the TRAIL-induced apoptosis 23255321_c-FLIP may play an important role in the metastatic potential of osteosarcoma to the lung 23319802_findings provide the first evidence showing that mTORC2 stabilizes FLIP(S), hence connecting mTORC2 signaling to the regulation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis 23322903_Studies indicate that the anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP is an important regulator of death receptor signaling, including TNFR1, Fas, DR4, and DR5. 23371318_ERK controls epithelial cell death receptor signalling and c-FLIP in ulcerative colitis 23483900_A novel mechanism of HBx-induced NF-kappaB activation in which ternary complex formation is involved among HBx, p22-FLIP and NEMO, is reported. 23518915_An increased expression of c-FLIP may be an important factor in the progression of cervical cancer 23519470_novel ROS-dependent post-translational modifications of the c-FLIP protein that regulate its stability, thus impacting sensitivity of cancer cells to TRAIL. 23615398_CHOP-mediated DR5 upregulation and proteasome-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP. 23696271_cFLIP upregulated the expression of viral re |
ENSMUSG00000026031 |
Cflar |
654.674533 |
2.1070617994 |
1.075233 |
0.150276276 |
50.356118 |
0.00000000000128229722007386733925078009820206504103430600327584443220985122025012969970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007576744182662241739085966480612966116731099575076768815051764249801635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
891.4698234 |
80.6532347 |
425.8871813 |
28.4433023 |
| ENSG00000003989 |
6542 |
SLC7A2 |
protein_coding |
P52569 |
FUNCTION: Functions as permease involved in the transport of the cationic amino acids (arginine, lysine and ornithine); the affinity for its substrates differs between isoforms created by alternative splicing (PubMed:9174363). May play a role in classical or alternative activation of macrophages via its role in arginine transport (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P18581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9174363}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Functions as permease that mediates the transport of the cationic amino acids (arginine, lysine and ornithine), and it has much higher affinity for arginine than isoform 2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9174363}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Functions as low-affinity, high capacity permease involved in the transport of the cationic amino acids (arginine, lysine and ornithine). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9174363}. |
Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cationic amino acid transporter and a member of the APC (amino acid-polyamine-organocation) family of transporters. The encoded membrane protein is responsible for the cellular uptake of arginine, lysine and ornithine. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:6542; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; basic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015174]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; L-arginine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0061459]; L-lysine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015189]; L-ornithine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0000064]; amino acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0089718]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; L-alpha-amino acid transmembrane transport [GO:1902475]; L-amino acid transport [GO:0015807]; L-arginine import across plasma membrane [GO:0097638]; L-arginine transmembrane transport [GO:1903826]; L-ornithine transmembrane transport [GO:1903352]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11665818_analysis of the genomic organization 12787129_Keratinocytes express cationic amino acid transporters 1 and 2. Cationic amino acid transporter mediated L-arginine essential for inducible nitric oxide synthase and arginase enzyme, which modulate proliferation and differentiation of epidermal cells. 15064952_Insulin increased L-arginine transport and the mRNA levels for hCAT-1 and hCAT-2B 18172665_distribution of human cationic amino acid transporters 1 (hCAT1) and 2 (hCAT2) in healthy skin and compared it to psoriatic skin lesions by means of immunohistochemistry 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20430034_Activation of PKCalpha by phorbol esters or thymeleatoxin causes a transient increase of arginine transport through system y(+), referable to the induction of SLC7A2 mRNAs and to the increased expression of CAT2 transporters. 20600019_Addition of spermine or knockdown of CAT2 inhibited L-Arg uptake, NO production, and iNOS protein levels, whereas knockdown of ODC had the opposite effect. CAT2 and ODC were increased in mouse and human H pylori gastritis tissues. 22787143_A chimera carrying the functional domain of the orphan protein SLC7A14 in the backbone of SLC7A2 mediates trans-stimulated arginine transport. 22870827_CAT1, CAT2, and CAT3 localized in adult brains but with uneven distribution. 24019517_Identification of cysteine residues in human cationic amino acid transporter hCAT-2A that are targets for inhibition by N-ethylmaleimide. 28501704_genetic association studies in population in Tennessee: Data suggest that an SNP in SLC7A2 (rs2720574) is associated with response to dietary calcium and magnesium in prevention of colorectal polyps and colorectal ademonas. 28684763_L-homoarginine is a substrate of the cationic amino acid transporters CAT1, CAT2A and CAT2B. 32008093_Human cationic amino acid transporters are not affected by direct nitros(yl)ation. 32647070_SLC7A2 serves as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. 34108444_SLC7A2 deficiency promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by enhancing recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressors cells. |
ENSMUSG00000031596 |
Slc7a2 |
27.483840 |
7.6925027190 |
2.943453 |
0.387357751 |
65.400925 |
0.00000000000000061110216505495216396077020855791925060463738597973937238805319793755188584327697753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004428015687879771152821753316055162121164193861355684589398151729255914688110351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.6043382 |
11.6465881 |
6.4702484 |
1.3712998 |
| ENSG00000004799 |
5166 |
PDK4 |
protein_coding |
Q16654 |
FUNCTION: Kinase that plays a key role in regulation of glucose and fatty acid metabolism and homeostasis via phosphorylation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase subunits PDHA1 and PDHA2. This inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, and thereby regulates metabolite flux through the tricarboxylic acid cycle, down-regulates aerobic respiration and inhibits the formation of acetyl-coenzyme A from pyruvate. Inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase decreases glucose utilization and increases fat metabolism in response to prolonged fasting and starvation. Plays an important role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels under starvation, and is involved in the insulin signaling cascade. Via its regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, plays an important role in maintaining normal blood pH and in preventing the accumulation of ketone bodies under starvation. In the fed state, mediates cellular responses to glucose levels and to a high-fat diet. Regulates both fatty acid oxidation and de novo fatty acid biosynthesis. Plays a role in the generation of reactive oxygen species. Protects detached epithelial cells against anoikis. Plays a role in cell proliferation via its role in regulating carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15955060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18658136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21816445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21852536}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Carbohydrate metabolism;Glucose metabolism;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide |
|
This gene is a member of the PDK/BCKDK protein kinase family and encodes a mitochondrial protein with a histidine kinase domain. This protein is located in the matrix of the mitrochondria and inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by phosphorylating one of its subunits, thereby contributing to the regulation of glucose metabolism. Expression of this gene is regulated by glucocorticoids, retinoic acid and insulin. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5166; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring) kinase activity [GO:0004740]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of acetyl-CoA biosynthetic process from pyruvate [GO:0010510]; regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045124]; regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process [GO:0010565]; regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042304]; regulation of fatty acid oxidation [GO:0046320]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906]; regulation of pH [GO:0006885]; response to starvation [GO:0042594] |
12145475_The expression of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 was downregulated in the failing heart. 12582211_results support the concept that a reduced tissue availability of fatty acids consequent to a massive lipid malabsorption influences glucose metabolism acting through the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 14966024_mRNA levels are increased in skeletal muscle during fasting 15047604_Expression of constitutively active PKB alpha abrogates dexamethasone stimulation of hPDK4 promoter activity. 15581486_Gene expression regulation is affected by retinoic acid and histone acetyation (review). 15721319_activation of FXR may suppress glycolysis and enhance oxidation of fatty acids via inactivation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by increasing PDK4 expression 15776585_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15955060_in human muscle, hormonal and nutritional conditions may control PDK2 and PDK4 mRNA expression via a common signalling mechanism. 16757381_retinoic acids (RA) as well as Trichostatin A (TSA), an inhibitor of histone deacetylase (HDAC), regulate PDK4 gene expression 17652214_Accumulation of im lipids plays a more important role than impaired activation of Akt-mediated pathways in the regulation of muscle PDK4 gene expression in lipid-induced acute insulin-resistant states 17669420_PDK2, PDK3 and PDK4 are primary PPARbeta/delta target genes in humans underlining the importance of the receptor in the control of metabolism 18519799_PDK4 upregulation in adipocytes participates in the hypolipidemic effect of thiazolidinediones through modulation of glyceroneogenesis 18658136_PDK4 with bound ADP exists in equilibrium between the open and the closed conformations 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20715114_PDK4 gene is downregulated in colic adenocarcinoma. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21852536_Data show that overexpression of ErbB2 maintains PDH flux by suppressing PDK4 expression in an Erk-dependent manner. 21883960_mRNA of PGC-1alpha and PDK4 increases markedly in both type I and type II skeletal muscle after either continuous or interval exercise 21904029_The present structures demonstrate the flexible and dynamic aspects of PDK4 in the open conformation and provide a basis for the development of novel inhibitors targeting the nucleotide-binding pocket of PDK4. 22019269_PDK4 polymorphisms may not be associated with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome. 23050013_Data show that the orphan nuclear receptor estrogen related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) plays a critical role in hypoxia-mediated activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) gene expression. 24837562_Methylation increased in PDK4, IL1 B, IL6, and TNF promoters 12 months after gastric bypass. 25164809_PDK4 promotes tumorigenesis through activation of the CREB-RHEB-mTORC1 signaling cascade. 25311062_Fatty acids induce the expression of PDK4 mRNA, which was increased in myotubes cultured from obese and T2DM donors. 25609694_ZBTB2 may increase cell proliferation by reprogramming glucose metabolic pathways to favor glycolysis by upregulating PDK4 expression via repression of RelA/p65 expression 25794976_Swiss PDB Viewer identifies NFkappaB subunit p100/p49 as a potential interacting partner for PDK4. Relationship between PDK4 and apoptosis is suggested. 26506419_High PDK4 expression is associated with hepatocellular cancer. 26560812_upregulation of PDK4 promotes vascular calcification by increasing osteogenic markers with no adverse effect on bone formation, demonstrating that PDK4 is a therapeutic target for vascular calcification. 26728993_FXR may promote the proliferation of tumor cells and the hepatocytes in the process of liver regeneration by activating the PDK4-mediated metabolic reprogramming to generate glycolytic intermediates essential for rapid biomass generation, establishing a mechanistic link between cell proliferation and metabolic switch. 27001465_Inhibition of CK2 increased the expression of metabolic regulators, PDK4 and AMPK along with the key cellular energy sensor CREB. 27181711_Results show that PDK4-specific 5'UTR DNA methylation is positively associated with eicosapentaenoic and arachidonic acid in adult males. 27456128_We found that PDK4 gene and protein expression was significantly elevated in pulmonary arterial hypertension pericytes and correlated with reduced mitochondrial metabolism, higher rates of glycolysis, and hyperproliferation 27456910_Combined speed endurance and endurance exercise amplify the exercise-induced PGC-1alpha and PDK4 mRNA response in trained human muscle. 27641336_Low PDK4 expression is associated with lung tumorigenesis. 28003426_inhibition of PDK4 activity in Hepatocellular carcinoma cells increased cyclin E1, cyclin A2, and E2F1 proteins. 28208156_Increased PDK4 expression is associated with colon cancer. 28594398_it was found that low expression of FAM210B was significantly correlated with decreased survival and enhanced metastasis in vivo and in vitro, and the loss of FAM210B led to an increased mitochondrial respiratory capacity and reduced glycolysis through the downregulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4). 28814762_down-regulation of PDK4 is critical for the metabolic shift from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation during syncytialization, which may be a prerequisite for the proper implementation of syncytiotrophoblast functions 29128353_In conclusion, our data indicated that PDK4 potentially contributes to the hepatic steatosis in NASH via regulating several signaling pathway and PDK4 may be a new therapeutic strategy against NAFLD. 30093112_miR-15b-5p acted as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by directly targeting PDK4 and inhibiting its expression. 30342991_Up-regulation of miR-23a played an important role in colorectal cancer cell proliferation through direct repressing PDK4. 30868666_lncRNA PCAT19 promotes the proliferation of laryngocarcinoma cells via modulation of the miR-182/PDK4 axis. 31099942_Reduction of mitochondria and up regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 of skeletal muscle in patients with chronic kidney disease. 31106493_Reduced ALDH1A1 expression was observed in KIS37-treated pancreatic tumors, suggesting that cancer cell stemness was also suppressed in the orthotopic tumor model. The aforementioned results indicate that KIS37 administration is a novel therapeutic strategy for targeting PDK4 in KRAS-activated intractable human pancreatic cancer 31330194_PDK4 could be regulated by a ceRNA mechanism which mediated by lncRNA ENST00000608794 and miR-15b-5p. ENST00000608794 derepressed expression of PDK4 through competitively binding to miR-15b-5p. 31351920_PDK4 upregulation implies an overarching metabolic shift towards increased utilization of fatty acids as energy fuel, and thus constitutes a sensitive marker of enhanced fatty acid oxidation. 31595421_LINC00243 modulated expression of endogenous miR-507-targeted PDK4. LINC00243 promotes proliferation and glycolysis in NSCLC cells by positively regulating PDK4 through sponging miR-507. 31809757_Mice deficient in pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 are protected against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. 32216839_Association of epigenetics of the PDK4 gene in skeletal muscle and peripheral blood with exercise therapy following artificial knee arthroplasty. 32323921_STAT3-dependent analysis reveals PDK4 as independent predictor of recurrence in prostate cancer. 32390009_Ascites-derived ALDH+CD44+ tumour cell subsets endow stemness, metastasis and metabolic switch via PDK4-mediated STAT3/AKT/NF-kappaB/IL-8 signalling in ovarian cancer. 32444598_N(6)-methyladenosine regulates glycolysis of cancer cells through PDK4. 32856615_Role of PDK4 in insulin signaling pathway in periadrenal adipose tissue of pheochromocytoma patients. 33221963_PDK4 promotes tumorigenesis and cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma via transcriptional regulation of EPAS1. 33257740_microRNA-9-5p regulates the mitochondrial function of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through suppressing PDK4. 33626342_PDK4 dictates metabolic resistance to ferroptosis by suppressing pyruvate oxidation and fatty acid synthesis. 33739370_Identification of differentially expressed genes and the role of PDK4 in CD14+ monocytes of coronary artery disease. 33763657_A single-cell atlas of the healthy breast tissues reveals clinically relevant clusters of breast epithelial cells. 33819358_LINC00662 modulates cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis via sponging miR-103a-3p and upregulating PDK4. 34165388_LncRNA CASC2 Alleviates Sepsis-induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the miR-152-3p/PDK4 Axis. 34252986_Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4-mediated metabolic reprogramming is involved in rituximab resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by affecting the expression of MS4A1/CD20. 34370552_Circular RNA circ-ERBB2 Elevates the Warburg Effect and Facilitates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth by the MicroRNA 136-5p/Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Axis. 34817334_Androgen regulated protein and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 in severe erectile dysfunction: A gene expression analysis, and computational study of protein structure. 35080746_Dual-specificity Tyrosine Phosphorylation-regulated Kinase Inhibitor ID-8 Promotes Human Somatic Cell Reprogramming by Activating PDK4 Expression. |
ENSMUSG00000019577 |
Pdk4 |
42.397812 |
0.0472681050 |
-4.402989 |
0.422092602 |
175.096663 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000057029286085792263759659471229890511717950893228027951128763238117478553265899076980859330225614504364557710847094540440593846142292022705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000009457890591306670891463289372771280654643582549062768797888019003566464458902817238976226123933023276144083091310221789171919226646423339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6577132 |
1.0834623 |
77.9329042 |
8.7449112 |
| ENSG00000005073 |
3207 |
HOXA11 |
protein_coding |
P31270 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. |
Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. This gene is involved in the regulation of uterine development and is required for female fertility. Mutations in this gene can cause radio-ulnar synostosis with amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3207; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein-DNA complex [GO:0032993]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; cartilage development involved in endochondral bone morphogenesis [GO:0060351]; chondrocyte development [GO:0002063]; developmental growth [GO:0048589]; dorsal/ventral pattern formation [GO:0009953]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; embryonic skeletal joint morphogenesis [GO:0060272]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; mesodermal cell fate specification [GO:0007501]; metanephros development [GO:0001656]; organ induction [GO:0001759]; positive regulation of cell development [GO:0010720]; positive regulation of chondrocyte development [GO:1902761]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; prostate gland development [GO:0030850]; proximal/distal pattern formation [GO:0009954]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to testosterone [GO:0033574]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; uterus development [GO:0060065] |
11830496_NUP98 primer and a degenerate primer corresponding to the third helix of the homeodomain of HOXA demonstrated that NUP98 was fused in-frame to HOXA11 in the patient with CML ( chronic myelogenous leukemia) 12060755_expressed in the developing kidney 15167850_HOXA gene expression is up-regulated at the ectopic implantation site in the fallopian tube and it may play a role in ectopic pregnancies. 15467538_study reveals a novel expression pattern for homeo box A11(HOXA11) gene in human endometrium 15674412_The HOXA11 gene cluster is in T-cell malignancies resulting in deregulated HOXA gene expression and is in keeping with a previous report suggesting HOXA deregulation in MLL-rearranged T cell lymphoblastic leukemia. 15731295_HOXA10 and HOXA11 expression increases during the menstrual cycle, increasing drastically in the midluteal phase, at the time of implantation. 18274672_HOXA11 is critical for development and maintenance of uterosacral ligaments and deficient in pelvic prolapse. 19255789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19255789_Our findings do not support the hypothesis that mutations in the HOXA11 coding regions are involved in the pathogenesis of human non-syndromal congenital renal parenchymal malformations. 19372592_Expression of HOXA11 represses the expression of p53 in uterosacral ligaments. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19609949_Methylation of HOXA11 gene is associated with high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions in cervical cancer 19727442_HoxA-11 is required for prolactin expression in decidualized embryonic stem cells and turns into an activator when combined with FOXO1A; HOXA-10 is unable to upregulate PRL expression when co-expressed with FOXO1A 19938081_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20457539_No subject with female genital tract anomalies showed a plausible causative mutation in HOX A10 or HOX A11. 20457539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20695189_Our results suggest that altered HOXA11 gene expression in the endometrium during a menstrual cycle may be a common phenomenon among patients with endometriosis and may cause infertility in this group of patients 21526497_The result suggest that HOXA-11 gene expression in the endometrium during the implantation window may not be altered in patients with idiopathic infertility. 21987111_Endometrial HOXA11 and LIF mRNA expression levels (normalized to beta-actin expression) were significantly decreased in endometrium of infertile patients with endometriosis compared with healthy fertile controls 22233680_reduced HOXA11 expression may contribute to endometriosis-associated infertility 22251480_Data show that up-regulation of the HOXA7, HOXA9, HOXA11, and PBX3 resulting from the down-regulation of miR-181 family members probably contribute to the poor prognosis of patients with nonfavorable cytogenetically abnormal AML (CA-AML). 23624749_Promoter methylation of HOXA11 is associated with glioblastoma. 23979130_Lower expression of HOXA11 is associated with endometriosis-associated infertility. 24259349_Study suggests that HOXA11 hypermethylation may contribute to the progression of NSCLC by promoting cell proliferation or migration. 24306662_Low HOXA11 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 24745830_Mutations in the coding region of HOXA11 are not common in Chinese women with Mullerian duct anomalies. 25590359_Epigenetic silencing of HOXA11 promotes gastric cancer proliferation, migration and invasion through activation of Wnt signaling. 25630974_The overexpression of miR-30d or 181a suppressed HOXA11 mRNA. 26056923_Laparoscopic endometrioma resection increases peri-implantation endometrial HOXA-11 mRNA expression. 26552702_Regulated HOXA10 and HOXA11 expression is necessary for endometrial receptivity; decreased HOXA10 or HOXA11 expression leads to decreased implantation rates. Alternation of HOXA10 and HOXA11 expression has been identified as a mechanism of the decreased implantation associated with endometriosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome, leiomyoma, polyps, adenomyosis, and hydrosalpinx. 27456940_The treatment resistance induced by the underexpression of HOXA11 can contribute to a poor prognosis in GBM. 28038461_Hypermethylation of HOXA11 is an independent prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. Suggest HOXA11 as a potential tumor suppressor. 28261830_These results suggest that mutations in the coding sequence of HOXA11 might not be a common cause of cryptorchidism, while common polymorphisms in the HOXA11 gene might contribute to the risk of developing unilateral cryptorchidism. 28372536_We conclude that the expression patterns of HoxA10, HoxA11, and HoxA13 and their actions in regulating CAP genes in the uterus create regionalized myometrium phenotypes in women that may be important to control regionalized myometrium contractility for maintaining pregnancy. 28380439_Results show that aberrant hypermethylation and the methylation-induced down-regulation of HOXA11 may promote lung adenocarcinoma progression. 28423531_our study demonstrated that HOXA11 function as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma 28558357_HOXA11 silencing suppressed osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion and induced cell arrest. 28701685_High expression of lncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis by affecting EMT. 28749709_demonstrated that HOXA11-antisense(AS) functioned as a molecular sponge for miR-124, and overexpression of miR-124 attenuated the proliferation and invasion-promoting effect of HOXA11-AS 28832185_Bioinformatics prediction forecast that miR-140-5p directly targeted HOXA11-antisense RNA at 3'-UTR, which was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay 29034803_HOXA11-AS functions as a competing endogenous RNA. 29415429_we uncovered a novel potential regulatory mechanism between HOTTIP and one of its physical HOXA clusters, HOXA11. Hence, HOTTIP may mediate, at least partly, HOXA11 expression involved in cell growth, migration, and apoptosis of breast cancer MCF-7 cells. 29914539_HOXA11 high expression might lead to the occurrence and development of lung squamous cancer. 30402857_HOXA11-AS regulates diabetic arteriosclerosis-related inflammation via PI3K/AKT pathway 31144606_Study found that HOXA11 is hypermethylated and significantly downregulated in cisplatin resistant lung adenocarcinoma tumors and cell lines and that the 5-aza-CdR treatment restores HOXA11 expression and reverses the hypermethylation of CpG islands. 31411918_HOXA11-AS induced collagen synthesis via sponging miR-124-3p-mediated Smad5 signaling in keloid cells. 31493246_HOXA11-AS could inhibit miR-124 expression by binding to EZH2 and thus promoted the migration and invasion of HCC cells. 31532317_Abnormal methylation levels of the HOXA10 and HOXA11 promoters were found in the endometrium of women with tubal infertility and repeated implantation failures. 31670914_Correlation of miR-181a and three HOXA genes as useful biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. 31695791_A self-enforcing HOXA11/Stat3 feedback loop promotes stemness properties and peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer cells. 31757938_Study suggested that HOXA11-AS silencing exerts an antitumor effect, suppressing HCC development via Wnt signaling pathway inactivation by decreasing the methylation level of the HOXA11 promoter. 32046414_Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling Improves Endometrial Homeobox Gene Expression in PCOS. 32666543_A homozygous HOXA11 variation as a potential novel cause of autosomal recessive congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. 32901858_Long noncoding RNA HOXA11AS accelerates cell proliferation and epithelialmesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating the miR5063p/Slug axis. 33173982_Molecular mechanism of extracellular matrix disorder in pelvic organ prolapses. 34080665_HOXA11 plays critical roles in disease progression and response to cytarabine in AML. 34844098_Combined expression of HOXA11 and CD10 identifies endometriosis versus normal tissue and tumors. 35106863_The lncRNA HOXA11-AS acts as a tumor promoter in breast cancer through regulation of the miR-125a-5p/TMPRSS4 axis. 35430506_Decreased expression of transcription factor Homeobox A11 and its potential target genes in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000038210 |
Hoxa11 |
89.936749 |
0.2063517106 |
-2.276823 |
0.214241498 |
117.393126 |
0.00000000000000000000000000235451568129417015423255522970287937585543146206761458144040560813092203152480097472221132193226367235183715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000027554730611319303693111113417871964212262696257751592141756074143548078947407731220664572902023792266845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.9767268 |
4.3872472 |
155.7061623 |
12.4094620 |
| ENSG00000005243 |
51226 |
COPZ2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P299 |
FUNCTION: The coatomer is a cytosolic protein complex that binds to dilysine motifs and reversibly associates with Golgi non-clathrin-coated vesicles, which further mediate biosynthetic protein transport from the ER, via the Golgi up to the trans Golgi network. Coatomer complex is required for budding from Golgi membranes, and is essential for the retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport of dilysine-tagged proteins. The zeta subunit may be involved in regulating the coat assembly and, hence, the rate of biosynthetic protein transport due to its association-dissociation properties with the coatomer complex. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P53600}. |
Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;ER-Golgi transport;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the adaptor complexes small subunit family. The encoded protein is a subunit of the coatomer protein complex, a seven-subunit complex that functions in the formation of COPI-type, non-clathrin-coated vesicles. COPI vesicles function in the retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport of dilysine-tagged proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:51226; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; COPI vesicle coat [GO:0030126]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006891]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0006890] |
19167404_The solution structure of a truncated form (residues 1-149; zeta-COP149) of human zeta-COP (total 177 residues), is reported. 21746916_The knockdown of COPZ1, but not of COPZ2 encoding isoform coatomer protein complex zeta2, caused Golgi apparatus collapse, blocked autophagy, and induced apoptosis in both proliferating and nondividing tumor cells. |
ENSMUSG00000018672 |
Copz2 |
28.663143 |
0.3169239769 |
-1.657791 |
0.299122674 |
32.439321 |
0.00000001229728827040523142242269715633876114857514494360657408833503723144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000053119102976640687972877976057856086455899458087515085935592651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2308572 |
2.5611195 |
41.9874436 |
4.7657759 |
| ENSG00000005882 |
5164 |
PDK2 |
protein_coding |
Q15119 |
FUNCTION: Kinase that plays a key role in the regulation of glucose and fatty acid metabolism and homeostasis via phosphorylation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase subunits PDHA1 and PDHA2. This inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, and thereby regulates metabolite flux through the tricarboxylic acid cycle, down-regulates aerobic respiration and inhibits the formation of acetyl-coenzyme A from pyruvate. Inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase decreases glucose utilization and increases fat metabolism. Mediates cellular responses to insulin. Plays an important role in maintaining normal blood glucose levels and in metabolic adaptation to nutrient availability. Via its regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, plays an important role in maintaining normal blood pH and in preventing the accumulation of ketone bodies under starvation. Plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation and in resistance to apoptosis under oxidative stress. Plays a role in p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17222789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19833728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21283817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22123926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7499431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9787110}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Carbohydrate metabolism;Glucose metabolism;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide |
|
This gene encodes a member of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase family. The encoded protein phosphorylates pyruvate dehydrogenase, down-regulating the activity of the mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Overexpression of this gene may play a role in both cancer and diabetes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:5164; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex [GO:0005967]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring) kinase activity [GO:0004740]; cellular response to nutrient [GO:0031670]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of acetyl-CoA biosynthetic process from pyruvate [GO:0010510]; regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050848]; regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process [GO:0010565]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906]; regulation of pH [GO:0006885] |
12816949_study of facilitated interaction between the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 and the dihydrolipoyl acetyltransferase 15169745_The increased PDK activity was independent of changes in intra-mitochondrial effectors, and PDK-2 and PDK-4 protein content, suggesting that it was caused by a change in the specific activity of the existing kinases. 15491150_A mechanism for pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 regulation is supported in which kinase activity is limited by ADP dissociation and pyruvate binding. 15491151_Reductive acetylation stimulates activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 by speeding up ADP dissociation. 15955060_in human muscle, hormonal and nutritional conditions may control PDK2 and PDK4 mRNA expression via a common signalling mechanism. 16401071_Crystallographic studies reveal several PDHK2 structures with C-terminal cross arms that span a large trough region between the N-terminal regulatory (R) domains of the PDHK2 dimers. Three novel ligand binding sites are located in the R domain of PDHK2. 16517984_analysis of ligand induced effects on pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2 16962287_These studies identify ORP9 as a PDK-2 substrate and negative regulator of Akt phosphorylation at the PDK-2 site. 17669420_PDK2, PDK3 and PDK4 are primary PPARbeta/delta target genes in humans underlining the importance of the receptor in the control of metabolism 18220414_Critical role of specific ions for ligand-induced changes regulating pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2. 18220415_Pi is suggested to facilitate transmission within PDHK2 of the stimulatory signal of acetylation from the distal lipoyl-group binding site to the active site. 19147752_mitochondrial ND2 mutation contributes to HIF1alpha accumulation via increased ROS production, up-regulation of PDK2, attenuating PDH activity, thereby increasing pyruvate, resulting in HIF1alpha stabilization 19194729_PKD1 children have more and larger renal cysts, larger kidneys and higher ambulatory BP than do PKD2 children. 19833728_the DW-motif has a pivotal role in mediating communications between the DCA-, the nucleotide-, and the lipoyl domain-binding sites of PDK2 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21115670_PKD2 mutations are associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. 22123926_Results established that wild-type p53 prevents manifestation of the Warburg effect by controlling Pdk2. These findings elucidate a new mechanism by which p53 suppresses tumorigenesis acting at the level of cancer cell metabolism. 22614004_Mitochondrial activation by inhibition of PDKII suppresses HIF1a signaling and angiogenesis in cancer. 22910903_Inactivation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. 23300259_Germline mutations in PKD2 gene is associated with autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. 23376776_we for the first time demonstrated that a low-nutrient condition drives cancer cells to utilize glycolysis to produce ATP, and this increases the Warburg effect through a novel mechanism involving ROS/AMPK-dependent activation of PDK. 24356970_The final compound of this series, 2-[(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)sulfonyl]isoindoline-4,6-diol, designated PS10, inhibits all four PDK isoforms with IC50 = 0.8 muM for PDK2. 25976231_both PDK 1 and 2 isoforms are overexpressed in cutaneous melanoma compared to nevi, this expression being associated with the expression of the mTOR pathway effectors and independent of the BRAF mutational status 26416963_The findings of the present study reveal a novel survival pathway that functionally couples the unique glycolytic phenotype in cancer cells to hypoxia resistance via a PDK2-dependent mechanism that switches Bnip3 from cell death to survival. 26607904_High glycolysis and PDK2 overexpression are closely linked to cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer cells, which can be reversed by PDK2 nhibition. 26909964_The data demonstrate potential roles of PDK2 and ABCG2 polymorphisms in the metabolic phenotypes of Tibetan gout patients. 28178523_PDK2/PARL senses defects in mitochondrial bioenergetics. 29725130_MiR-422a regulates cellular metabolism and malignancy by targeting PDK2 in gastric cancer. 30457021_we identified PDK2 as the most up-regulated kinase encoding gene in Cisplatin resistant lung adenocarcinoma and PDK2-dependent Cisplatin-resistance promotes tumour growth of lung adenocarcinoma mainly through transcriptional regulation of CNNM3 30578412_Overexpression of PDK2 and PDK3 reflects poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. 33236596_[Expression Level of Protein Kinase D in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Diverse Differentiation]. 33783904_Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005397 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating the miR-326/PDK2 axis. 34464482_PDK2 leads to cisplatin resistance through suppression of mitochondrial function in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000038967 |
Pdk2 |
106.598939 |
0.4338881002 |
-1.204605 |
0.210598022 |
32.239655 |
0.00000001362807197819758481575125915862684022883399848069529980421066284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000058473936743661725465573875040042883810542662104126065969467163085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
70.5509722 |
11.0967904 |
164.5447693 |
17.8596171 |
| ENSG00000006025 |
114881 |
OSBPL7 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZF2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) family, a group of intracellular lipid receptors. Like most members, the encoded protein contains an N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain and a highly conserved C-terminal OSBP-like sterol-binding domain. Two transcript variants encoding the same isoform have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:114881; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0097038]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; sterol binding [GO:0032934]; sterol transporter activity [GO:0015248]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901800]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21669198_ORP7 negatively regulates GS28 protein stability via sequestration of GATE-16, and may mediate the effect of 25-OH on GS28 and Golgi function. 21763455_In preliminary results, significantly higher levels of OSBP2 and OSBPL-7 mRNA were seen in blood samples from cholangiocarcinoma patients than in healthy controls. |
ENSMUSG00000038534 |
Osbpl7 |
148.000371 |
0.3116910862 |
-1.681811 |
0.160802044 |
110.394744 |
0.00000000000000000000000008029771938372018575638885945191507628958937760538648494970239235558884249854827430681325495243072509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000885133934356766270204516528224994147522974003909752608925206760967507868542725191218778491020202636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.2760287 |
8.1318287 |
223.3677727 |
17.1483822 |
| ENSG00000006282 |
64847 |
SPATA20 |
protein_coding |
Q8TB22 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in fertility regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Spermatogenesis |
|
Predicted to be involved in carbohydrate metabolic process; cell differentiation; and spermatogenesis. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64847; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
23118872_SSP411 has potential as a biomarker for the diagnosis of Cholangiocarcinoma |
ENSMUSG00000020867 |
Spata20 |
445.382450 |
0.4686617356 |
-1.093381 |
0.079697245 |
189.966762 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000032328547127480282538872154877316916974547659065489118786981072162463246428048638048902758702303595014591937480651073766324543612427078187465667724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000005833366205398643184482746344733288946328288369816408819805762074845419905085244649573613796357485665125411702924829171479359501972794532775878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
283.3284114 |
13.9298778 |
609.0471191 |
19.6456610 |
| ENSG00000006283 |
8913 |
CACNA1G |
protein_coding |
O43497 |
FUNCTION: Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1G gives rise to T-type calcium currents. T-type calcium channels belong to the 'low-voltage activated (LVA)' group and are strongly blocked by mibefradil. A particularity of this type of channel is an opening at quite negative potentials and a voltage-dependent inactivation. T-type channels serve pacemaking functions in both central neurons and cardiac nodal cells and support calcium signaling in secretory cells and vascular smooth muscle. They may also be involved in the modulation of firing patterns of neurons which is important for information processing as well as in cell growth processes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10648811, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10692398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26456284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26715324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29878067}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Spinocerebellar ataxia;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Voltage-sensitive calcium channels mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells, and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division, and cell death. This gene encodes a T-type, low-voltage activated calcium channel. The T-type channels generate currents that are both transient, owing to fast inactivation, and tiny, owing to small conductance. T-type channels are thought to be involved in pacemaker activity, low-threshold calcium spikes, neuronal oscillations and resonance, and rebound burst firing. Many alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:8913; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; voltage-gated sodium channel complex [GO:0001518]; low voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0008332]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential [GO:0086056]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved SA node cell action potential [GO:0086059]; voltage-gated sodium channel activity [GO:0005248]; AV node cell action potential [GO:0086016]; AV node cell to bundle of His cell signaling [GO:0086027]; calcium ion import [GO:0070509]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction [GO:0086002]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; membrane depolarization during action potential [GO:0086010]; membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential [GO:0086045]; membrane depolarization during SA node cell action potential [GO:0086046]; neuronal action potential [GO:0019228]; positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0045956]; regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization [GO:0060371]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; response to nickel cation [GO:0010045]; SA node cell action potential [GO:0086015]; SA node cell to atrial cardiac muscle cell signaling [GO:0086018]; sinoatrial node development [GO:0003163] |
11927664_Specific contribution of human T-type calcium channel isotypes (alpha(1G), alpha(1H) and alpha(1I)) to neuronal excitability. 12676336_Since allele and genotype distributions of CACNA1G polymorphisms in cases studied are not remarkably different from control groups, CACNA1G is not an important susceptibility gene for childhood absence epilepsy in the Han Chinese population. 12752779_The down-regulation of alpha 1G T-type calcium channel mRNA in differentiated Y79 cells is mediated primarily by decreased activity of promoter A, which could occur in conjunction with repression of the activity of promoter B. 15465033_Data describe the construction of a new cell line stably expressing alpha(1G) and Kir2.1 subunits in HEK293 cells. 15774856_T-type voltage-operated Ca2+ channels are required for cell cycle progression and proliferation of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell. 16671074_CACNA1G is a human gene for T-type Ca(v)3.1 calcium channels that is subject to extensive alternative RNA splicing 17397049_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17397049_collective findings flag CACNA1G as a potential susceptibility locus for idiopathic generalized epilepsy subsyndromes 17446221_Primary T-type subunit expressed in some myometrial smooth muscle cells is Cav3.1. 17591929_A panel of markers including at least RUNX3, CACNA1G, IGF2, and MLH1 can serve as a sensitive and specific marker panel for CIMP(Cpg island methylator phenotype)-high. 18591418_The sodium channel toxins tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin interact with the alpha-subunit of T-type Ca 2+ channels. 18663131_This study reports the concentration dependence of currents through Ca(V)3.1 T-type calcium channels stably expressed in HEK 293 cells. 18663132_A study evaluating whether the effect of Ni(2+) on Ca(V)3.1 is affected by permeant ions is reported. 18801335_These results suggest that RanBPM could be a key regulator of Ca(v)3.1 channel-mediated signaling pathways. 19211869_Elevated brain levels of Cacna1g channel identify a key causal component of pure absence epilepsy and a major genetic component of the epileptogenic pathway. 19455149_establishing CACNA1G as a novel candidate gene for autism, these alleles do not contribute a sufficient genetic effect to explain the observed linkage, indicating that there is substantial genetic heterogeneity despite the clear linkage signal 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20435690_Results reveal an intracellular WPb-independent P-selectin pool in pulmonary capillary endothelium, where the regulated P-selectin surface expression is triggered by Ca(2+) transients evoked through activation of the alpha(1G) T-type channel. 21438841_The function of T-type Ca(2+) channels is important for the proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells. 21788606_Data showed expression of L-type (Ca(v) 1.2), P/Q-type (Ca(v) 2.1), and T-type subtype (Ca(v) 3.1 and Ca(v) 3.2) voltage-gated calcium channels (Ca(v)s) in renal artery and dissected intrarenal blood vessels from nephrectomies. 22469755_Cav3.1 channels may contribute to the repression of tumor proliferation and the promotion of apoptosis mediated via Cav3.1-specific calcium signals 22572848_Augmentation of CaV3.1 currents by Ras-ERK activation is associated with enhanced trafficking of channels to the plasma membrane. 22574369_The abnormal mRNA expressions of T-type channel alpha1H and alpha1G may be one of the causes of declined semen quality and infertility in varicocele patients. 22973059_Cd(2) carried sizable inward currents through Ca(v)3.1 channels (210 +/- 20 pA at -60 mV with 2 mM Cd(2)). 22973060_Ca(V)3.1 channels represent a likely pathway for Fe(2) entry into cells. 23488970_Ethanol affects CaV3.2 but not CaV3.1 nor CaV3.3 channel isoforms. 24268883_CaV3.1 downregulation is a major initiating factor for the increased production of the toxic Ab peptide, then the CaV3.1 T-type calcium channel represents a novel target for preventative therapeutics in Alzheimer's disease. 26056284_CaV3.1 channel is required for the generation of a given set of thalamocortical rhythms during unconsciousness. Further, that thalamocortical resonant neuronal activity supported by this channel is important for the control of vigilance states 26456284_A Recurrent Mutation in CACNA1G Alters Cav3.1 T-Type Calcium-Channel Conduction and Causes Autosomal-Dominant Cerebellar Ataxia. 26488564_CaV3.1, CaV3.2 and CaV3.3 channels, are best recognized for their negative voltage of activation and inactivation thresholds that allow them to operate near the resting membrane potential of neurons. 26715324_In 2 families with autosomal dominant SCA, a CACNA1G mutation p.Arg1715His was found at S4 of repeat IV, the voltage sensor of the CaV3.1 which shifted it toward a positive potential. 27134080_Electrophysiological studies showed a significant increase in Cd(2+) and manganese (Mn(2+)) currents through the CaV3.1 mutants as well as a reduction in the inhibitory effect of Cd(2+) on the Ca(2+) current. 28165634_CACNA1G variant is associated with differential antiepileptic drug response in childhood absence epilepsy. 28556246_The results of this study provide support for Cacna1g as a genetic modifier in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome and suggest that Cav3.1 may be a potential molecular target for therapeutic intervention in patients 28655554_Here we show that T-type channels Cav3.1 and Cav3.2 are present in the lung and PASMCs from iPAH patients and control subjects. The blockade of T-type channels by the specific blocker, TTA-A2, prevents cell cycle progression and PASMCs growth 28800734_T-type channel calcium influx invokes a novel dynamic interaction between CaM and Cav3.1 channels to trigger a signaling cascade that leads to alphaCaMKII activation. 28806761_Cacna1g exclusively expressed in serosal PDGFRalpha+ cells is a new pathological marker for gastrointestinal diseases. 28846697_In gastric cancer, expression of all the CACNA (1G, 1H, 1I) genes was associated with overall survival (OS) among stage I-IV patients. By combining the three potential biomarkers, a TTCC signature was developed, which retained a significant association with OS both in stage IV and stage I-III patients. Alterations in CACNA gene expression are linked to tumour prognosis. 28972185_human Cav3.1, Cav3.2, and Cav3.3 T-type channels specifically associate with CaM at helix 2 of the gating brake in the I-II linker of the channels. 29385656_Cav3.1 and LC3-II proteins are highly expressed in BRAFV600E compared with NRAS mutant melanomas, both in cell lines and biopsies. 29509247_CACNA1G-AS1 was identified as an oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer, promoting cell invasion and migration via increasing HNRNPA2B1 expression. 29720258_These findings reveal spectrin (alpha/beta) / ankyrin B cytoskeletal and signaling proteins as key regulators of T-type calcium channels expressed in the nervous system. 29878067_Three subjects share a recurrent c.2881G>A/p.Ala961Thr variant while the fourth patient has the c.4591A>G/p.Met1531Val variant. Both mutations drastically impaired channel inactivation properties with significantly slower kinetics. This study highlights the prevalence of de novo mutations in early-onset cerebellar atrophy and demonstrates that A961T and M1531V are gain of function mutations. 30403912_The S4 segments in domains I-IV of the CaV3.1 channel unequally contribute to channel gating by voltage. 31766050_cryo-electron microscopy structures of human Cav3.1 alone and in complex with a highly Cav3-selective blocker, Z944, at resolutions of 3.3 A and 3.1 A, respectively 31836334_Infantile-Onset Syndromic Cerebellar Ataxia and CACNA1G Mutations. 32428730_CaV3.1 channel pore pseudo-symmetry revealed by selectivity filter mutations in its domains I/II. 32736238_De novo CACNA1G variants in developmental delay and early-onset epileptic encephalopathies. 32795940_Deterministic model of Cav3.1 Ca(2+) channel and a proposed sequence of its conformations. 32878331_Novel Missense CACNA1G Mutations Associated with Infantile-Onset Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy. 33098379_Early-onset severe spinocerebellar ataxia 42 with neurodevelopmental deficits (SCA42ND): Case report, pharmacological trial, and literature review. 33394292_Overexpression of T-type calcium channel Cav3.1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: association with proliferation and anti-apoptotic activity. 34403092_Downregulation of Cav3.1 T-type Calcium Channel Expression in Age-related Hearing Loss Model. 34674590_The T-type Calcium Channel Cav3.1 in Y79 Retinoblastoma Cells is Regulated by the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000020866 |
Cacna1g |
33.739193 |
13.2409835789 |
3.726938 |
0.439683382 |
82.941170 |
0.00000000000000000008453211685302926508999527542914580826155232666197796476299786139207981250365264713764190673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000741791940993288865483338944025519922078858416072890021031316365451857564039528369903564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
61.6330812 |
16.4992003 |
4.6916155 |
1.1496734 |
| ENSG00000006327 |
51330 |
TNFRSF12A |
protein_coding |
Q9NP84 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFSF12/TWEAK. Weak inducer of apoptosis in some cell types. Promotes angiogenesis and the proliferation of endothelial cells. May modulate cellular adhesion to matrix proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11728344}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Apoptosis;Cell adhesion;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway and regulation of wound healing. Predicted to be located in cell surface and ruffle. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51330; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; regulation of wound healing [GO:0061041] |
12445828_These results indicated that TWEAK could induce pro-inflammatory reactions via fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14)on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 12496418_FN14 is the sole mediator of the multiple pathways of TWEAK-induced cell death in all TWEAK-sensitive tumor cell lines. 12651623_up-regulated in migrating glioma cells in vitro and overexpressed in advanced glial tumors 15140220_TWEAK acts on human keratinocytes as an inducer of RANTES via Fn14. 15353286_TWEAK/TWEAK receptor interactions have roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and systemic autoimmune diseases [review] 15611130_Fn14 protein functions, in part, through the NFkappaB signaling pathway to up-regulate BCL-XL and BCL-W expression to foster malignant glioblastoma cell survival. 16503147_Expression of Fn14 in subcutaneous adipose tissue from obese patients. 16526941_the TWEAK-Fn14 interaction is highly dependent on multiple Fn14 residues located in both CRD modules 16809572_TWEAK and Fn14 are expressed in atherosclerotic plaques and could be novel mediators of atherosclerosis. 17018610_The Fn14 promoter has NF-kappaB binding sites mediating positive feedback causing sustained overexpression of Fn14 & enduring glioma cell invasion. The Fn14 cascade operates as a positive feedback mechanism for elevated & sustained Fn14 expression. 17124496_These results indicate that the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway is a novel regulator of skeletal muscle precursor cells and illustrate an important mechanism by which inflammatory cytokines influence tissue regeneration and repair. 17383968_Fn14 receptor is required for the expression of myogenic regulatory factors and differentiation of myoblasts into myotubes. 17594693_Fn14 protein expression increased with disease progression in esophageal adenocarcinoma 18505918_Fn14-mediated NF-kappaB pathway activation has a role in in breast tumor invasion and metastasis 19018248_Taken together, these findings indicate that the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway contributes to inflammation and tissue injury and is, therefore, a potential therapeutic target in MS. 19241374_determination of the solution structure of the Fn14 cysteine-rich domain (CRD)(Glu28-Ala70) by heteronuclear NMR 19349318_Human cardiomyocytes express the TWEAK receptor Fn14. TWEAK/Fn14 may be important in regulating myocardial structural remodeling and function and may play a role in the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19828625_Fn14 (TWEAK receptor) is a novel potential mediator of adipogenesis that is expressed differentially in immature-appearing and mature adipocytes and in benign and malignant adipose tissue-derived tumors. 19895311_Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK)/fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 interaction may have proinflammatory effects in retinal pigment epithelial cells. TWEAK increased the production of IL-8 and MCP-1 via Fn14. 19963275_These data reveal the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway for regulation of microbial-induced inflammation in the female reproductive tract. 20004376_TWEAK/FN-14 might regulate the effects of interleukin 18 adn 15 in the human endometrium. 20189297_Fn14 expression is high in endometrial cancers and promotes apoptosis of these cancer cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20487651_TWEAKR/Fn14 was expressed on the cell membrane and in the cytoplasm of Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes 20557950_The transgenic Fn14/TWEAK receptor pathway in a mouse model is adversely involved in inflammatory and ischemic brain disease associated with the strongest increase of endogenous neuroprotective G-CSF and the G-CSF receptor system. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610643_Oligomerization of soluble TWEAK differentially affects Fn14-mediated activation of the classical and nonclassical NF-kappa B pathway. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20810696_the TWEAK-Fn14 axis can regulate activation of TF and PAI-1 expression in vascular cells 20844036_Regulation of TWEAKR expression by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNA prevents TWEAK-induced apoptosis and inflammatory cytokine expression. 20927042_Fn14 expression was highly upregulated in ischemic renal tissues and tubular epithelial cells of biopsies 21153335_REVIEW: TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in tissue remodeling 21303425_Suggest that the renal TWEAK/Fn14 and IP-10/CXCR3 axis may contribute to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. 21435232_TWEAK/Fn14 signalling is important in the pathogenesis of inflammation and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. 21483105_This is the first study, presenting together the TNFSF members APRIL, BAFF, TWEAK and their receptors in different areas of normal renal tissue and renal cell carcinoma. 21708117_GRP94, FN14, and inhibin have roles in brain and non-brain metastases in ErbB-2+ and ErbB-2- breast neoplasms 21828059_Overexpression of Fn14 promotes androgen-independent prostate cancer progression through MMP-9. 21993017_effect of Fn14 on cell growth was mediated by the NF-kappaB activity and eventually by the transcriptional regulation of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family gene 22055894_The effect of interaction between TWEAK and its receptor fibroblast growth factor-inducible-14 (Fn14) on cytokine expression in RAFLS. 22081603_binding of TWEAK to Fn14 22521346_RAR is able to interact with cytoplasmic AFP and binds to the element of the regulatory region of the Fn14 gene in the neoplastic tissue of human hepatocellular carcinoma patients 22634180_Elevated expression of Fn14 in non-small cell lung cancer correlates with activated EGFR and promotes tumor cell migration and invasion. 22637703_Fn14, the receptor for TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis, is selectively upregulated in patients with Alcoholic Hepatitis. 22672874_This review describes an emerging role of the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, with a particular focus on inflammatory bowel diseases. 22767506_LCN2 and TWEAKR-TWEAK as crucial downstream effectors of NFAT1 that regulate breast cancer cell motility and invasive capacity. 22896023_Glomerular Fn14 and tubulointerstitial TWEAK and IP-10 expression appeared to have consistent changes in relation to the histological class of lupus nephritis and correlated with the histological activity index. 23107828_we show that TWEAK/Fn14 can signal through the JAK-STAT pathway to induce interferon-beta, and that the ability of TWEAK to induce tumor cell apoptosis is mediated by JAK-STAT signaling. 23288170_TWEAK/Fn14 can regulate expression and secretion of HMGB1 in monocytes/macrophages, participating in the inflammatory response associated with atherosclerotic plaque development. 23300011_Fn14 protein may have a role in breast carcinoma progression 23320797_The Fn14/TWEAK pathway contributes to the endothelial steps of neuroinflammation. 23438059_TWEAK binds to hFn14 by surface plasmon resonance (View interaction) xeFn14 binds to TWEAK by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay 23443741_The expression of TWEAK and Fn14 in neuroblastoma suggests that TWEAK functions as an important regulator of primary neuroblastoma growth, invasion and survival. 23469193_TWEAK/Fn14, by activating macrophages, could be ovarian tumor suppressors. 23722548_Induced overexpression of Fn14 levels in MCF7 cells through HER2 (ERBB2) signaling translated to an improved therapeutic index of hSGZ treatment. 23750247_insight into the Fn14 signaling mechanism 23775076_Data indicate that the Src homology 3 domain-containing GEF (SGEF) promotes fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14) proinvasive signaling in glioblastoma via TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2). 23886137_Fn14 overexpression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 23968277_abundantly expressed in the dermal vessel wall of lesional skin in patients with urticarial vasculitis but not controls 23999007_Increased podocyte Fn14 expression is associated with proteinuric kidney disease. 24056367_results validate the TWEAK-Fn14 interaction as a chemically tractable target and provide the foundation for further exploration utilizing chemical biology approaches focusing on validating this system as a therapeutic target in invasive cancers. 24122208_These new findings of the effect of Fn14 on valvular interstitial cell-like differentiation may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for heart valve disease treatment. 24337061_High FN14 expression is associated with resistance to 5-fluorouracil in gastric cancer. 24408972_We found that the TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK)/fibroblast growth factor inducible-14 (Fn14) pathway is involved in the development of pathologic retinal neovascularization. 24467773_TWEAK-Fn14 axis may be involved in the pathogenesis of polymyositis and dermatomyositis 24469836_Results position TWEAK-Fn14 signaling through Mcl-1 as a significant mechanism for NSCLC tumor cell survival 24652288_a model in which constitutive down-regulation of Fn14 facilitates dynamic regulation of Fn14 protein levels and prevents spontaneous or inappropriate receptor signaling. 24710956_Receptor-targeted therapeutics for both MET and FN14 are in clinical development, the use of which may mitigate the metastatic potential of NSCLC. 24970477_results define one upstream mechanism, via FN14 signaling, through which the NFkappaB pathway contributes to prostate cancer metastasis. 25054270_Fn14 modulates cell growth and drug resistance by upregulating Bcl-xl expression through the NF-kappaB pathway. 25375638_TweakR protein was expressed in about half of human breast cancer samples 25392346_Results indicate that oncogenic Src may contribute to Fn14 overexpression in solid tumors, and that Src mediated cell invasion could potentially be inhibited with Fn14- targeted therapeutics. 25539934_The first human data to show a transient activation of the TWEAK-Fn14 axis. 26016896_HPV type 16 infections keratinocytes turns from apoptosis to proliferation cycle under FN14 protein influence. 26224570_TWEAK/Fn14 interaction promotes oxidative stress through NADPH oxidase activation in macrophages. 26264384_TWEAK/Fn14 activation induces keratinocyte proliferation under psoriatic inflammation 26300004_In this review article, we summarize studies indicating that (i) Fn14 gene expression is low in normal brain tissue but is upregulated in advanced brain cancers and, in particular, in GB tumors ; TWEAK: Fn14 engagement as well as Fn14 overexpression can stimulate glioma cell migration, invasion and resistance to chemotherapeutic agents in vitro. 26446946_Evidence that higher tumor Fn14 expression is required for pharmacodynamic response to the anti-TWEAK monoclonal antibody RG7212 in patients with Fn14-positive solid tumors. 26497551_Results indicate that FN14 and GRP94 are prediction/prognosis markers which open up new possibilities for preventing/treating brain metastasis in breast cancer patients. 26592249_Fn14 has multiple roles in tumor metastasis. (Review) 26625141_Activated Fn14 expression increases extracellular matrix synthesis and fibroblast activation. Activation of Fn14 is done by the TGF-beta signaling pathway through the transcription factor SMAD4. 27051016_The results demonstrated that vitreous fluid from patients with PDR had higher levels of TWEAK and Fn14 than that from T2DM patients without PDR, thus suggesting an important regulatory role of TWEAK/Fn14 signaling in the pathogenesis of PDR. 27254081_Data suggest that expression of Fn14 on a tumor can initiate cachexia; an antibody against Fn14 may be an effective antineoplastic agent. [REVIEW] 27350337_EGFR Del 19 may promote Fn14 and JAK1/STAT1 expression in NSCLC. 27441657_The results suggest that TWEAK/Fn14 interaction directly favors inorganic phosphate-induced vascular smooth muscle cells calcification by activation of both canonical and non-canonical NF-kappaB pathways. 28103571_Data show that aurintricarboxylic acid (ATA) targets the TNF-related WEAK inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK)-fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14) signaling axis, which could potentially be developed as a new therapeutic agent for treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) patients. 28138696_TNFRSF12A was knocked down in the SMMC7721 cell line through siRNA. This demonstrated that cells exhibited reduced reproductive and metastatic capacity ex vivo. 28180936_Fn14 is a receptor of mitogen TWEAK (tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis), expressed on the membranes of HPCs and promoting their proliferation. 28411440_TWEAK upregulated the expression of Fn14. 28455246_Fn14.TRAIL can be converted into a highly effective TRAIL oligomer upon binding to TWEAK which induces lymphoblast apoptosis. 28636775_Expression of the TWEAK-Fn14 axis was upregulated in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease and might play a role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid disease. 29143982_TWEAK/Fn14 interaction induces proliferation and migration in human airway smooth muscle cells via activating the NF-kappaB pathway 29190188_PK/PD model suggested a unique bell-shaped relationship between target coverage and antibody affinity for anti-Fn14 monoclonal antibody. 29251323_Results show that Fn14 expression is high compared in non-small cell lung cancer compared to normal lung tissues. In addition, high Fn14 expression is associated with poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. 29257217_TWEAK/Fn14 contributes to endothelial dysfunction through modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and mitochondrial ROS. 29500337_Data demonstrated that the Src/Fn14/NF-kappaB axis plays a critical role in NSCLC metastasis. 29724813_EGFR inhibitors display limited therapeutic efficacy in Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) patients, the EGFRvIII-Stat5-Fn14 signaling pathway represents a node of vulnerability in the invasive GBM cell populations.Implications: Targeting critical effectors in the EGFRvIII-Stat5-Fn14 pathway may limit GBM tumor dispersion, mitigate therapeutic resistance, and increase survival. 29741404_Expression level of Fn14 was significantly associated with overall survival and disease-free survival in low-grade gliomas. Fn14 was an independent predictive biomarker for the progression and prognosis in low-grade gliomas. 29897522_High FN14 expression is associated with recurrent glioblastoma and temozolomide resistance. 30142200_High levels of TNFRSF12A associated with MMP-9 overexpression may be important to explain the progression of breast cancer, and survival could be improved using therapy targeting TNFRSF12A. 30414907_TWEAK/Fn14 signals contribute to the progression of cutaneous SCC, possibly involving the TNF-alpha-independent TNFR2 signal transduction. 30576385_These results demonstrate that TWEAK/Fn14 signaling contributes to Graves' orbitopathy (GO) pathogenesis. Moreover, serum TWEAK level is a potential diagnostic biomarker for inflammatory GO, and modulating TWEAK activity may be an effective therapeutic strategy for suppressing inflammation and tissue remodeling in GO. 31023317_Mechanistic studies demonstrated that overexpression of Fn14 could reduce the formation of a Mdm2-p53-R248Q-Hsp90 complex by downregulating Hsp90 expression, indicating that degradation of p53-R248Q was accelerated via Mdm2-mediated ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway 31181286_Study found increased expression of TWEAK and Fn14 in tissue lesions from Crohn's disease (CD) patients compared with ulcerative colitis and healthy controls. Functional studies showed that TWEAKR mediates experimental CD-like ileitis, by regulation of multiple innate and adaptive cellular pathways. 31500625_Biofluid quantification of TWEAK/Fn14 axis in combination with a selected biomarker panel improves assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness. 32053869_Tumor Necrosis Factor-Like Weak Inducer of Apoptosis (TWEAK)/Fibroblast Growth Factor-Inducible 14 (Fn14) Axis in Cardiovascular Diseases: Progress and Challenges. 32526219_TWEAK/Fn14 axis in respiratory diseases. 32846846_Decreased expression of TNFRSF12A in thyroid gland cancer predicts poor prognosis: A study based on TCGA data. 33991013_Elevated fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 expression transforms proneural-like gliomas into more aggressive and lethal brain cancer. 34155062_TWEAK Signaling Pathway Blockade Slows Cyst Growth and Disease Progression in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. 34353698_ThPOK transcriptionally inactivates TNFRSF12A to increase the proliferation of T cells with the involvement of the NF-kB pathway. 34517088_BMP2-induction of FN14 promotes protumorigenic signaling in gynecologic cancer cells. 34542797_The TWEAK/Fn14/CD163 axis-implications for metabolic disease. 34597335_Activation of fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 in the early phase of childhood IgA nephropathy. |
|
|
126.144494 |
4.9910646376 |
2.319348 |
0.975956546 |
5.042502 |
0.02473274668551352431511425322696595685556530952453613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043427949212250724353445718861621571704745292663574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
175.6884217 |
115.1758081 |
33.8978735 |
15.8501097 |
| ENSG00000006453 |
55971 |
BAIAP2L1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHR4 |
FUNCTION: May function as adapter protein. Involved in the formation of clusters of actin bundles. Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in response to bacterial infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17430976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19366662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22921828}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of the IMD (IRSp53/MIM homology domain) family. Members of this family can be subdivided in two groups, the IRSp53-like and MIM-like, based on the presence or absence of the SH3 (Src homology 3) domain. The protein encoded by this gene contains a conserved IMD, also known as F-actin bundling domain, at the N-terminus, and a canonical SH3 domain near the C-terminus, so it belongs to the IRSp53-like group. This protein is the substrate for insulin receptor tyrosine kinase and binds to the small GTPase Rac. It is involved in signal transduction pathways that link deformation of the plasma membrane and remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. It also promotes actin assembly and membrane protrusions when overexpressed in mammalian cells, and is essential to the formation of a potent actin assembly complex during EHEC (Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli) pedestal formation. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:55971; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046626]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
17430976_Study characterised IRTKS, which has widespread tissue distribution, is a substrate for the insulin receptor and binds Rac, and expression of IRTKS induces clusters of short actin bundles rather than filopodia-like protrusions. 19366662_Screening of the mammalian SH3 proteome for the ability to bind EspF(U) identified the SH3 domain of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate (IRTKS), a factor known to regulate the cytoskeleton. 21098279_Results describe the NMR structure of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate (IRTKS) SH3 domain in complex with a repeat from Escherichia coli-secreted protein F-like protein encoded on prophage U (EspF(U)). 21840312_data suggest Src-stimulated IRTKS phosphorylation is essential for its function in cell motility 21887275_These data suggest that IRTKS is a novel regulator of p53, modulating low level of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination in unstressed cells. 23175443_Identification of a novel oncogenic FGFR3-BAIAP2L1 fusion protein in bladder cancer. 23693078_IRTKS can interact with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), results in the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 25589496_Lacking the Bin-Amphiphysin-Rvs (BAR) dimerization domain of BAIAP2L1. 26222696_Upregulation of BAIAP2L1 is associated with ovarian cancer. 27278019_Rho family GTPases use the I-BAR proteins, IRSp53 (also known as BAIAP2), IRTKS and Pinkbar, as a central mechanism to modulate cell morphology. 27693783_IRTKS promoted serum-induced cell migration along with enhanced phosphorylation of mitogen activated kinases Erk1/2 and p38, and activation of small GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42. In addition, cells overexpressing IRTKS exhibited an increased polarity characterized by elongated cytoplasm and extensive lamellipodia at leading edges. 30197089_IRTKS localizes to the distal tips of actively growing microvilli via a mechanism that requires its N-terminal I-BAR domain. At microvillar tips, IRTKS promotes elongation through a mechanism involving its C-terminal actin-binding WH2 domain. 34811939_BAIAP2L1 enables cancer cell migration and facilitates phospho-Cofilin asymmetry localization in the border cells. 36057038_Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate (IRTKS) promotes the tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000038859 |
Baiap2l1 |
10.837842 |
0.3751680242 |
-1.414391 |
0.515679094 |
7.485427 |
0.00622003143879818441719375954335191636346280574798583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012455252209559246681647159959993587108328938484191894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5339052 |
2.5653272 |
20.0982389 |
4.4158989 |
| ENSG00000006468 |
2115 |
ETV1 |
protein_coding |
P50549 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator that binds to DNA sequences containing the consensus pentanucleotide 5'-CGGA[AT]-3' (PubMed:7651741). Required for olfactory dopaminergic neuron differentiation; may directly activate expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P41164, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7651741}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ETS (E twenty-six) family of transcription factors. The ETS proteins regulate many target genes that modulate biological processes like cell growth, angiogenesis, migration, proliferation and differentiation. All ETS proteins contain an ETS DNA-binding domain that binds to DNA sequences containing the consensus 5'-CGGA[AT]-3'. The protein encoded by this gene contains a conserved short acidic transactivation domain (TAD) in the N-terminal region, in addition to the ETS DNA-binding domain in the C-terminal region. This gene is involved in chromosomal translocations, which result in multiple fusion proteins including EWS-ETV1 in Ewing sarcoma and at least 10 ETV1 partners (see PMID: 19657377, Table 1) in prostate cancer. In addition to chromosomal rearrangement, this gene is overexpressed in prostate cancer, melanoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:2115; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; mechanosensory behavior [GO:0007638]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; peripheral nervous system neuron development [GO:0048935]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
12917345_ER81 is acetylated by two coactivators/acetyltransferases, p300 and p300- and CBP-associated factor (P/CAF) . Whereas p300 acetylates two lysine residues (K33 and K116) within the ER81 N-terminal transactivation domain, P/CAF targets only K116. 12947087_attenuation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling by activating Smad7 transcription may proceed not only through TGF-beta receptor-regulated Smad proteins but also an independent pathway involving transcription factor ER81 and TAK1 protein kinase 14747462_transcription factor ER81 is regulated by oncogenic HER2/Neu and ACTR in mammary tumorigenesis 17032499_demonstrate for the first time that the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion gene can be detected in a proportion of HGPIN lesions and that this molecular rearrangement is an early event that may precede chromosome-level alterations in prostate carcinogenesis 17390040_findings show that the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion is common in prostate cancer and that the related TMPRSS2-ETV1 fusion is very rare 17505060_Expression transitions from androgen-induced to androgen-independent as prostate cancer cells switch from hormone-dependent to hormone-refractory. 17632455_TMPRSS2-ERV1 fusion protein was found in 1/82 prostate neoplasms. 17634427_These results imply that c-Jun plays a pivotal role in the pathway that connects ligand-activated AR to elevated ETV1 expression, leading to enhanced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and prostate cancer cell invasion. 18474293_Detection of ETS fusion gene by RT-PCR is feasible on formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded samples. 18594527_Studies report a novel fusion partner for ETV1 and highlight the considerable heterogeneity of ETV1 gene rearrangements in human prostate cancer. 18628953_Sox-9, ER81 and VE-cadherin have roles in retinoic acid-mediated trans-differentiation of breast cancer cells 18726892_ETV1 and HER2/Neu synergized to upregulate the endogenous Rcl gene. ETV1 also bound to the Rcl promoter. 19223501_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19465903_1% histologic variant of prostate carcinoma or variation morphologies demonstrated ETV! aberrations 19718948_Transcriptional activation of hTERT in breast carcinomas by the Her2-ER81-related pathway. 19789348_Overexpression of ETV1 is associated with tha induction of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. 20104229_ERG/ETV1 gene rearrangements and PTEN gene loss status should now prospectively be incorporated into a predictive model to establish whether predictive performance is improved. 20160028_Melanoma cell lines, including those with ETV1 amplification, exhibited dependency on ETV1 expression for proliferation and anchorage-independent growth. 20927104_the ETS family member ETV1 is highly expressed in the subtypes of interstitial cells of Cajal sensitive to oncogenic KIT mediated transformation, and is required for their development 21298110_in clinical prostate cancer overexpression of full-length ETV1 is due to genomic rearrangements involving different chromosomes 21559405_ERG and ETV1 mediated prostate cancer cell invasion is inhibited by YK-4-279 21622576_The coordinate expression of Etv1 with POMC cell differentiation and its interaction with the highly cell-restricted Tpit factor indicate that Etv1 participates in a combinatorial code for pituitary cell-specific gene expression. 21673681_High ER81 expression is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. 21689625_Pea3 and Erm, but not Er81, play an important role in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 22351694_Data show that MAPKAP kinase 2 overexpression is associated with expression of p38 MAP kinase and ETV1 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). 22425584_Reviews evidence for a role of ETV1, 4 and 5 as oncoproteins and describe modes of their action. 22901226_High ER81 expression is associated with breast cancer. 23076342_High ETV1 expression is associated with prostate cancer. 23284306_Our collective results identify a regulatory pathway involving ETV1, ATR, and TERT that is preferentially important for proliferation of diverse p53- cancer cells 23512661_confirmed the association of an ETV1 expression signature with aggressive disease and poorer outcome in patient data 23522042_Proprioceptive sensory neurons innervating hypaxial and axial muscles depend critically on Etv1 for survival. 23774214_Non-sigma 14-3-3 proteins synergized with ETV1 to activate transcription. 23817021_Expression of ERG and ETV1 correlated with higher AR transcriptional output in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer specimens. 23977394_The gastrointestinal stromal tumor-specific transcription factor ETV1 may have no prognostic potential, whereas its downstream gene KCTD10 is associated with a favorable prognosis. 24100634_ETV1 expression is significantly correlated with Snail expression in human gastric tumor samples. In summary, we present data that ETV1 promotes Snail expression to induce EMT-like metastatic progression in gastric cancer. 24157551_Elevated levels of either wild-type ETV1 or its truncated derivative, dETV1, which mimics the product of an oncogenic rearrangement in certain tumors, results in increased expression of mRNA for p14ARF, a known activator of p53. 24737027_These results point to a new avenue for pharmacologic ETV1 inhibition and may inform a general means to discover small molecule perturbagens of transcription factor oncoproteins. 24970355_Results show that ETV1 was upregulated at a higher rate in Gastrointestinal stromal tumor and was correlated with KIT expression. 25073704_ETV1 expression is a rare event in human melanoma and seems to be rather based on hyperactivation of MAPK signals, by BRAF (V600E) mutation, than on ETV1 gene amplification. 25203299_developed a novel RNA in situ hybridization-based assay for the in situ detection of ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues from prostate needle biopsies, prostatectomy, and metastatic PCa specimens using RNA probes 25479232_YK-4-279 is a potent inhibitor of ETV1 and inhibits both the primary tumor growth and metastasis of fusion positive prostate cancer xenografts. 25595908_ETV1 overexpression is associated with prostate cancer aggressiveness. 25631336_These results illuminate the complex interplay of AR, ETV1, and PTEN pathways in pre-cancerous neoplasia and early tumorigenesis 25736805_mutation of the KIT protein that stabilizes ETV1 is likely to be a key step by which an endogenous brain-cell progenitor may form a germinoma. 25884720_ETV1 and COP1 are a pair of independent predictors of prognosis for triple-negative breast cancer. 26243012_conclude that ETV1 is specifically expressed in the majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumors, even in some KIT-negative cases 26731476_these data reveal a JMJD2A/ETV1/YAP1 axis that promotes prostate cancer initiation and that may be a suitable target for therapeutic inhibition. 27633918_C646 treatment attenuated ETV1 protein expression and inactivated KIT-dependent pathways. Taken together, the present study suggests that CBP/p300 may serve as novel antineoplastic targets and that use of the selective HAT inhibitor C646 is a promising antitumor strategy for Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 27783944_four oncogenic ETS (ERG, ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5), and no other ETS, interact with the Ewing's sarcoma breakpoint protein, EWS. 28161714_Structured and disordered regions cooperatively mediate DNA-binding autoinhibition of ETV1, ETV4 and ETV5. 28408625_the prostate cancer-related oncogenic E26 transformation-specific (ETS) transcription factors, ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5, were required for TAZ gene transcription in PC3 prostate cancer cells 28859074_Our results indicate that assessing AP1 and PEA3 transcription factor status might be a good indicator of OAC status. However, we could not detect any associations with disease stage or patient treatment regime. This suggests that the PEA3-AP1 regulatory module more likely contributes more generally to the cancer phenotype. In keeping with this observation, depletion of ETV1 and/or ETV4 causes an OAC cell growth defect 29126392_Our data indicate that miR-17-5p acts as a tumour suppressor in Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)by targeting ETV1, and a low-abundance of miR-17-5p may be involved in the pathogenesis of TNBC. These findings indicate that miR-17-5p may be a therapeutic target for TNBC 29967479_A cardiomyocyte-autonomous, ETV1-dependent pathway that is responsible for specification of rapid conduction zones in the heart was identified. 30629294_Findings cast light on genes and networks regulated by ETV1 in prostate cancer cells, and open new fronts for studying the role of ETV1 and its target genes in tumorigenesis. 31016435_Strong ETV1 protein expression has a negative impact on prostate cancer outcome 31381204_A novel PTPRZ1-ETV1 fusion in gliomas. 31461652_Dualism of FGF and TGF-beta Signaling in Heterogeneous Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Activation with ETV1 as a Critical Determinant. 31584209_ERG overexpression was observed in 85 of 151 (56%) cases, followed by SPINK1 in 61 of 151 (40%), ETV1 in 9 of 149 (6%), and ETV4 in 4 of 141 (3%). There were 25 of 151 (17%) cases showing both ERG and SPINK1 overexpression within different regions of either the same tumor focus or different foci. 31862871_Biosynthetic CircRNA_001160 induced by PTBP1 regulates the permeability of BTB via the CircRNA_001160/miR-195-5p/ETV1 axis. 32580154_Frequent copy number gains of SLC2A3 and ETV1 in testicular embryonal carcinomas. 32797637_Identification of regulatory mRNA and microRNA for differentiation into cementoblasts and periodontal ligament cells. 32901065_Low ETV1 mRNA expression is associated with recurrence in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 33174020_Cooperation between ETS transcription factor ETV1 and histone demethylase JMJD1A in colorectal cancer. 35860243_ETV1 Positively Correlated With Immune Infiltration and Poor Clinical Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. 36109787_HGF-mediated elevation of ETV1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating PTK2 and c-MET. |
ENSMUSG00000004151 |
Etv1 |
38.300834 |
8.4285120075 |
3.075278 |
0.625460544 |
20.453403 |
0.00000611008295858492322743475005930591237301996443420648574829101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000019673827327380773627484369936446739757229806855320930480957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
64.8076795 |
24.8165332 |
7.6364942 |
2.2552108 |
| ENSG00000006740 |
9912 |
ARHGAP44 |
protein_coding |
Q17R89 |
FUNCTION: GTPase-activating protein (GAP) that stimulates the GTPase activity of Rho-type GTPases. Thereby, controls Rho-type GTPases cycling between their active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. Acts as a GAP at least for CDC42 and RAC1 (PubMed:11431473). In neurons, is involved in dendritic spine formation and synaptic plasticity in a specific RAC1-GAP activity (By similarity). Limits the initiation of exploratory dendritic filopodia. Recruited to actin-patches that seed filopodia, binds specifically to plasma membrane sections that are deformed inward by acto-myosin mediated contractile forces. Acts through GAP activity on RAC1 to reduce actin polymerization necessary for filopodia formation (By similarity). In association with SHANK3, promotes GRIA1 exocytosis from recycling endosomes and spine morphological changes associated to long-term potentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1LQX4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5SSM3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11431473}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Endosome;Exocytosis;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse |
|
Enables phospholipid binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including modification of dendritic spine; negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction; and regulation of plasma membrane bounded cell projection organization. Located in leading edge membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9912; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; leading edge membrane [GO:0031256]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; modification of dendritic spine [GO:0098886]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051490]; negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035021]; neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098887]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061001]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0099152]; regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035020]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11431473_Demonstrates that the RhoGAP domains of RICH-1 and RICH-2 can catalyze GTP hydrolysis of both Rac1 and Cdc42, but not of RhoA. 19273615_Knocking down expression of RICH 2 causes loss of the apical actin network and apical microvilli, an increase in actin bundles at the basal surface, and a reduction in cell height. (RICH 2 protein) 21107268_Besides the already known chromosome 6 associations, the analysis of low-frequency single nucleotide polymorphisms brought up a new association in the RICH2 gene for progression to AIDS. 28069446_RICH2 is implicated in viremic control of HIV-1 in black South African individuals. 28527113_Rho GTPase activating protein 44 (ARHGAP44) expression is lower in lung carcinoma compared with normal tissues. The GTP hydrolysis activity on cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) and the expression level of ARHGAP44 are negatively correlated with cell migration and invasion. 31136984_Rho GTPase-activating protein RICH2 (RICH2) is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 33223223_CD317 mediates immunocytolysis resistance by RICH2/cytoskeleton-dependent membrane protection. |
ENSMUSG00000033389 |
Arhgap44 |
12.312147 |
0.3340451058 |
-1.581885 |
0.433853747 |
14.173373 |
0.00016671307979322056184653955135388514463556930422782897949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000443286805575200063694873975350674299988895654678344726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7308924 |
1.7677741 |
17.2279327 |
3.1760279 |
| ENSG00000006837 |
51265 |
CDKL3 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVW4 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDK) family. CDK family members are highly similar to the gene products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc28, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc2, and are known to be important regulators of cell cycle progression. This gene was identified as a gene absent in leukemic patients with chromosome 5q deletion. This loss may be an important determinant of dysmyelopoiesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51265; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; dendrite extension [GO:0097484]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
12927787_NKIAMRE is a member of a conserved family of kinases with homology to both MAP kinases and cyclin-dependent kinases 17945021_cdkl3 transfected in anchorage-independent (suspension) HeLa cells overexpressed relative to attached cells and lead to elevated proliferation and faster transition G0/G1 phases to S phase relative to controls. Same in two HEK-293 and a CHO cell lines. 18412109_data suggest that the CDKL3 gene is a strong candidate for nonsyndromal autosomal dominant mild mental retardation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32234750_CDKL3 promotes osteosarcoma progression by activating Akt/PKB. 33232736_CircTP53 promotes colorectal cancer by acting as a miR-876-3p sponge to increase cyclin-dependent kinase-like 3 expression. 34097336_Identification of CDKL3 as a critical regulator in development of glioma through regulating RRM2 and the JNK signaling pathway. 34329837_Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-205-5p exerts inhibitory effect on the progression of liver cancer through regulating CDKL3. 34427098_Cyclin-dependent kinase like 3 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression via inhibiting the p53 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000020389 |
Cdkl3 |
36.098897 |
0.0917170397 |
-3.446666 |
0.814486560 |
14.693005 |
0.00012651502938624149124935414079118345398455858230590820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000343229725139162491695521417511827166890725493431091308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3.6937963 |
2.0332761 |
40.3765655 |
15.5563205 |
| ENSG00000007129 |
90273 |
CEACAM21 |
protein_coding |
Q3KPI0 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90273; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
21682944_This study revealed CEACAM21 as novel schizophrenia candidate genes in the Jewish population |
ENSMUSG00000078795+ENSMUSG00000007209 |
Ceacam15+Ceacam9 |
118.326344 |
0.4042933110 |
-1.306526 |
0.163824856 |
64.100415 |
0.00000000000000118236637151411929334432052805215327290097549958747258358471299288794398307800292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000008434861113363170179850274217897934107116583550556310200363441254012286663055419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.7647541 |
7.4625856 |
171.4145854 |
12.2144480 |
| ENSG00000007171 |
4843 |
NOS2 |
protein_coding |
P35228 |
FUNCTION: Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body (PubMed:7531687, PubMed:7544004, PubMed:7682706, PubMed:7504305). In macrophages, NO mediates tumoricidal and bactericidal actions. Also has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such PTGS2/COX2 (By similarity). As component of the iNOS-S100A8/9 transnitrosylase complex involved in the selective inflammatory stimulus-dependent S-nitrosylation of GAPDH on 'Cys-247' implicated in regulation of the GAIT complex activity and probably multiple targets including ANXA5, EZR, MSN and VIM (PubMed:25417112). Involved in inflammation, enhances the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL6 and IL8 (PubMed:19688109). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P29477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19688109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25417112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7504305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7531687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7544004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7682706}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;FAD;Flavoprotein;FMN;Heme;Iron;Metal-binding;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
Nitric oxide is a reactive free radical which acts as a biologic mediator in several processes, including neurotransmission and antimicrobial and antitumoral activities. This gene encodes a nitric oxide synthase which is expressed in liver and is inducible by a combination of lipopolysaccharide and certain cytokines. Three related pseudogenes are located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4843; |
cortical cytoskeleton [GO:0030863]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; arginine binding [GO:0034618]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; FMN binding [GO:0010181]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; NADP binding [GO:0050661]; nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0004517]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; tetrahydrobiopterin binding [GO:0034617]; arginine catabolic process [GO:0006527]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response in mucosa [GO:0002227]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0006809]; nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0007263]; peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation [GO:0018119]; positive regulation of guanylate cyclase activity [GO:0031284]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of killing of cells of another organism [GO:0051712]; positive regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001912]; prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032310]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cellular respiration [GO:0043457]; regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900015]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] |
11294696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11297817_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11397889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11424980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11443559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11525805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11692109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11761338_The specific NOS2 inhibitor, 1400W, sensitizes HepG2 cells to genotoxic, oxidative, xenobiotic, and endoplasmic reticulum stresses 11783017_Inos enzyme overexpressioin is an early event in esophageal carcinogenesis and useful biomarkers for early detection. 11849384_Human renal epithelial cells express iNOS in response to cytokines but not bacteria 11880293_The human alveolar type II epithelium-like cell line A549 expresses nitric oxide synthase type 2 (NOS2) 11907646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11956620_Immunohistochemical expression of iNOS in colorectal carcinoma 11978184_Increased expression of iNOS may be responsible for gastric carcinogenesis and tumor aggressiveness of gastric cancer and correlates significantly with lymph node metastasis in northern China. 11985259_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11985871_demonstrated that the iNOS gene was actively transcribed in cutaneous leishmaniasis lesions 12060397_Inducible nitric oxide synthase is expressed in normal human melanocytes but not in melanoma cells 12080081_epithelial iNOS binds to EPB50 which directs vectorial nitric oxide output 12081717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12081717_allelic polymorphism of the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene associated with retinopathy in an Asian Indian population 12097137_enzyme expressed in septic patients is nitrated on selected tyrosine residues; implications for enzymic activity 12117977_expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in skin lesions of patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis 12119468_Data show that prostacyclin receptor mediated increases in cAMP play a role in enhancing LPS/IFN-gamma-induced iNOS expression in human monocytes/macrophages and may contribute to the increased production of NO during peritonitis. 12125143_expression is increased in malaria, thus producing more nitric oxide 12135432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140750_inducible nitric oxide synthase promoter polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis 12167619_iNOS is induced by HIV-1 tat in astrocytes and may play a role in HIV-associated dementia 12174362_expressions of iNOS and VEGF may serve as indexes for evaluating staging of gastric carcinoma and forecasting its risk of metastasis 12195390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12221289_iNOS is subject to ubiquitination and ubiquitination is required for its degradation. 12223351_EGF protects against oxidative disruption of the intestinal barrier by stabilizing the cytoskeleton in large part through the activation of PKC-zeta and downregulation of iNOS 12237122_These results suggest that IL-15 is a potent regulator of iNOS expression by HGEC and involved in innate immunity in the mucosal epithelium. 12243747_Data demonstrate that the PI3-kinase signaling pathway is involved in basal trophoblast motility and that both mitogen-activated protein kinase and PI3-kinase signaling pathways are important in HGF-stimulated motility and iNOS expression. 12296866_Synovial fluid leucocytes, in particular granulocytes, express iNOS and may thus contribute to intra-articular NO production in arthritis. 12374680_iNOS may not correlate with cancer cell-proliferative activity or apoptosis 12381793_role of NF-kappa B-repressing factor (NRF) in basal repression of the hiNOS gene 12399227_strong upregulation of iNOS might contribute to inflammatory processes in fulminant hepatic failure 12406306_Activation might be associated with malignant potential of epithelial odontogenic tumors 12421162_Association analysis of five polymorphic microsatellite markers in cluster headache (CH) patients reveals that genetic variations in NOS2A do not contribute greatly to CH susceptibility. 12421162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12431203_hepatic inducible nitric oxide synthase staining was significantly more intense in patients with chronic viral hepatitis; these results suggest that inducible nitric oxide synthase may have a critical role in the pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis 12433515_NOS2 promoter -1173 C-->T single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with protection against cerebral malaria and severe malarial anaemia 12433515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445411_Increased intrahepatic iNOS expression and nitrotyrosine accumulation in biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis, related to histological severity of liver disease. 12445599_nitric oxide synthases(inducible, brain and endothelial) were expressed in human pregnant term uterus and did not change in the myometrium during labor 12452003_A positive correlation was found between the positive expression of iNOS mRNA and invasive growth as well as neck lymph node metastatsis of squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. 12459168_Data show that nitric oxide produced by inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) increases the activity of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, and this effect is probably mediated by endocellular cGMP. 12462194_inducible nitric oxide synthase-cyclooxygenase 2 interactions are involved in tumor cell angiogenesis and migration 12482371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12486325_Upregulation of iNOS in myelodysplastic syndromes has no significant correlation with apoptosis. 12489192_Immunolocalization of inducible nitric oxide synthase in gingiva in localized juvenile periodontitis patients. iNOS in gingivitis. Macrophages expressed high levels of iNOS. 12490535_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12508391_Altered genetic control of NOS2 transcription may be a risk factor for SLE among African-American females. 12508391_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12509623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12533668_study demonstrate that expression of the MDA-7 tumor suppressor can negatively regulate iNOS expression in malignant melanoma cell lines 12552317_A single haplotype, uniquely defined by the NOS2A-1659T allele, was associated with cerebral malaria by a transmission disequilibrium . 12578118_upregulation of hepatic iNOS, associated with peroxisomal localization, is an early molecular early molecular response to hemorrhagic shock 12590140_Studies of binding of KLF6 to the human iNOS promoter reveal CACCC binding sites and transactivation of iNOS promoter in diverse pathophysiological conditions: NaCN-induced hypoxia, heat shock, serum starvation, and PMA/ionophore stimulation 12598314_Expression in human colorectal cancer correlates with tumor angiogenesis. 12601489_findings suggest that upregulation of iNOS expression for local NO production in bone marrow may contribute in part to the pathogenesis of aplastic anemia 12607534_results suggest that LTA might activate PC-PLC and PI-PLC to induce PKC activation, which in turn initiates NF-kappaB activation, and finally induces iNOS expression and NO release in RAW 264.7 macrophages 12631094_A significant increase in calcium/calmodulin-independent NOS activity (iNOS) and iNOS mRNA expression was found in the medulla of obstructed kidneys. 12641410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12687343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12690222_Adenoviral-mediated overexpression of human iNOS causes increased superoxide production in carotid arteries from cholesterol- but not chow-fed rabbits. It is associated with reduced endothelium-dependent and independent vessel relaxation in these animals. 12709136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12709136_results do not support any association of iNOS gene polymorphism to the development of coronary artery lesion in a Japanese population 12732844_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12736741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12736741_influence of promoter polymorphism of NOS2A gene on susceptibility and outcome was studied in 140 multiple sclerosis Spanish patients; no association was found between susceptibility, course or outcome of the disease, and NOS2A polymorphisms 12768436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12777376_rate of intramolecular electron transfer between the two flavins in the iNOS flavin domain was faster than that of the nNOS flavin domain. 12788789_a physical interaction between c-Fos and STAT-1 participates in NOS2 gene transcriptional activation in lung epithelium 12799216_evidence of undetectable levels of TNF-alpha and NO in infants with congenital hypothyroidism 12800233_The transition from hyperplastic ACF to dysplastic ACF may be a crucial step in the ACF-adenoma-carcinoma sequence, in which iNOS plays an important role by regulating tumor cell apoptosis, proliferation and angiogenesis. 12816735_Results describe the expression of nitric oxide synthases 1, 2, and 3 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, suggesting their involvement in muscle dysfunction in this disease. 12824008_Immunocytochemical localization in oral mucosa and lymph nodes of patients with paracoccidioidomycosis 12828935_The results suggest that activation and nuclear localization of EGFR may be needed for induction of NOS-2 in response to elevated intraocular pressure in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. 12875991_Data describe the correlation between inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 activities and p53 gene status in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in vivo and in vitro. 12919943_NF-kappaB activation may play a role in protecting gastric epithelial cells from H. pylori-induced apoptosis by upregulating endogenous inducible nitric oxide synthase. 12937869_NO generation from iNOS in the malignant epithelium and from eNOS in tumor stroma play a important role in tumor angiogenesis in bladder cancer 12948935_potential mechanism for reduced NOS2 expression in cystic fibrosis is diminished signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT1) activity, possibly due to an increase in expression of protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 (PIAS1). 12958187_iNOS transcription involves CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Protein-beta binding to a promoter response element in liver cells. 14551604_Haplotypic relationship between SNP and microsatellite markers at the NOS2A locus was studied in two populations. 14551604_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14574328_induction of iNOS splice variants in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells leads to the activation of a caspase-3-dependent apoptotic pathway 14614131_mechanisms of in vivo iNOS dimer formation 14614209_Both eNOS and iNOS mRNA expression in placental tissues in labor were significantly higher than those in the amnion, chorion laeve, decidua vera and myometrium. 14616549_In contrast to unseparated blood cells, NOS II was demonstrable both in isolated blood neutrophils and exudated cells. 14623011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14636285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14638407_Hepatitis C virus core protein transactivates iNOS gene promoter through NF-kappaB activation 14677189_Lymphocytic infiltration and iNOS expression and activity were detected in duodenal and colonic mucosa from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. May indicate inflammatory process in small intestine and colon of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. 14715665_The FMN/FMNH couple is ~100 mV in all 3 isoforms and unlikely to be catalytically competent; the other three flavin couples are around -250 mV. Reduction of the flavins by the pyridine nucleotide couple at -325 mV is thermodynamically favorable. 14740870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14764920_Data suggest that expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in circulating leukocytes and endothelial cells correlates with the severity of coronary arterial wall injury and the progression of lesions in patients with acute Kawasaki disease. 14981908_iNOS is suggested to be a significant molecule for renal cell carcinoma to acquire not only hypoxic adaptation but also the ability to invade into veins and form tumor thrombi. 14985675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14991947_The expression of iNOS is related to the biological behaviors of primary gallbladder carcinoma 15026539_Data show that relaxin potentiates the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by endothelial cells from human umbilical vein 15044505_Healthy human dental pulp tissue failed to exhibit any iNOS; however, acute inflammation enhanced the mRNA and protein levels of iNOS, mainly in the leukocytes. 15107292_autocrine activation of NOS2 is defective in cystic fibrosis cells, but IFN-gamma induction of antiviral host defense is intact. 15112337_Results describe the relationship between the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and inducible nitric oxide synthase in gastric cancer. 15115662_JNK signaling plays an important role in the inhibitory effects of cAMP on IL-1beta+IFNgamma-induced iNOS gene expression in cultured hepatocytes 15174013_This study results provide strong evidence for linkage and association to a new candidate disease gene on chromosome 17q11 in MS and suggest that variation within NOS2A or a nearby locus contributes to disease susceptibility. 15180967_Exercise during head-down-tilt bed rest altered NOS 2/caveolin 3 co-immunostaining patterns of subsarcolemmal focal accumulations in vastus lateralis or soleus myofibers, which suggests reorganization of sarcolemmal microdomains. 15205363_Nitric oxixde generated by iNOS predominantly inhibits the growth of tumor cells in their free form, but enhances the growth of solid tumors. 15222024_iNOS and COX-2 may play a synergistic role in the pathogenesis of gastric MALT lymphoma. 15222037_half of the cases expressed iNOS and COX-2, but these two enzymes do not seem to be the key step in angiogenesis or carcinogenesis of pancreatic adenocarcinomas. 15226517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15242984_Constitutive NOS activities are responsible for E2-induced NO production in neuroblastoma cells. Differential activation of NOS isoforms in these cells occurs in response to different treatments. 15259072_Chronic H pylori infection induces iNOS expression and subsequent DNA damage as well as enhances anti-apoptosis signal transduction. 15271950_activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) is significantly elevated in children with Plasmodium falciparum malarial anemia and inversely associated with hemoglobin levels. 15275951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15284293_The coupled induction of iNOS and p53 upregulation in intrinsic renal cells of IgA nephropathy may be linked with both pro- and anti-apoptotic activities 15349722_fivefold upregulation of interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) gene expression. Inducible, but not constitutive NO-synthase gene expression was upregulated fivefold in samples from rejecting patients suggesting a local induction of NO in response to immune events 15482399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15482484_Ultraviolet beta rays induce iNOS mRNA and enzyme activity in skin endothelial cells 15484300_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15484300_iNOS Ser(608)Leu allele may be a potential determinant of susceptibility to cigarette -alcohol induced gastric cancer 15492785_Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase is negatively associated with human breast cancer progression 15494775_Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism is associated with endothelial dysfunction in healthy young men. 15532709_down-regulation by LPA of cytokine-induced increases in NOS2 activity is likely to involve a Rho-dependent signaling pathway 15583989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15601772_analysis of the cellular posttranslational mechanisms of iNOS 15609395_Inactivation of antioncogene p53 and overexpression of iNOS might play a synergetic role in the process of carcinogenesis of human gastric carcinoma. 15617837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15631944_The inducible nitric oxide synthase Expression is generally accompanied by a parallel upregulation in l-arginine transport which is dependent, at least in part, on the synthesis of new carrier proteins. 15631946_The inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and activity were found in almost 50% of bladder cancer patients, in both BT and in NT. 15642965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15654505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15683721_activation of AP-1 is involved only during the low level of iNOS induction by IL-1beta but not during the high level of induction by IL-IF. Activation of NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta was involved in the induction of iNOS by IL-1beta as well as by IL-IF. 15695237_important role in the early stage of colorectal carcinogenesis 15754329_Higher expression of iNOS is associated with neoplasm invasiveness of retinoblastoma 15784171_The relationship of NOS gene variants to Fabry disease, hypertension and coronary disease was studied. 15838334_Suggest that HIF-1alpha induces VEGF/ET-1/iNOS during gastric ulcer healing. 15849807_NO produced by iNOS may play a stronger role in promoting gastric adenocarcinoma growth than in suppressing its growth 15856071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15856945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15922861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15940772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15940772_Significant differences in the NOS2A promoter polymorphism allele and genotype frequency between Henoch-Schonlein Purppura(HSP)patients and controls suggest a potential role for this gene in the susceptibility to HSP and in the development of nephritis 16020977_over expression of iNOS might be associated with tumor progression by stimulating angiogenesis and suppressing immune responses in gastric carcinoma 16105645_A mutational analysis was performed on 30 samples to detect polymorphisms in the NOS2 promoter region that contains important NF-kappaB sites and three point mutations were identified in this region 16136006_The lack of stimulating signals may be a reason for negative iNOS detection and negligible apoptotic rate in parathryoid adenoma 16191398_TIAR seems to be involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of human iNOS expression 16195370_IL-1Ra, Bcl-2, and iNOS are upregulated and counter the proinflammatory and proapoptotic effects of ischemia-reperfusion 16211247_The effect of a soluble Abeta peptide, Abeta(1-40), on the expression of NOS-2 in astrocytes was determined. 16229182_No correlation was detected between the HIF-1alpha and iNOS in nasal polyps. 16243805_The expression of iNOS was related with tumor angiogenesis. 16260491_iNOS seems to be a major instigator of beta-amyloid deposition and disease progression in mice with Alzheimer's-like disease resulting from transgenic expression of mutant human beta-amyloid precursor protein and presenilin-1. 16265698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16265698_potential implication for NOS2A TAAA gene polymorphism in giant cell arteritis susceptibility 16282997_acute alcohol intoxication is accompanied by changes in iNOS enzyme expression in certain brain structures 16288199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16290060_These results suggest that iNOS-mediated nitrative stress contributes to development of oral carcinogenesis from leukoplakia through DNA damage as well as oxidative stress. 16311916_iNOS has a role in L. tropica especially during the early stages of the infection 16326029_e-NOS and i-NOS are weakly expressed in the MCF-7 cell line, but are stimulated differently.The MCF-7 cell may contain both a constitutive NOS and an inducible NOS. 16335796_Reishi inhibits NOS2 expression in macrophages. 16352737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16442500_iNOS and cyclooxygenase-2 play an important role in the apoptosis induction in trophoblasts of human fetal membrane tissues 16456243_The observed decrease in pulmonary expression of iNOS in patients with CDH suggests a potential role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension in newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. 16464859_evidence presented that PARP-1 is a novel trans-activator of the iNOS promotor in mesengial cells and that its binding to a specific cis-element of the iNOS promotor appears to be regulated by the end product NO in a feedback inhibition circuit 16543247_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16557582_ability of iNOS to predict outcomes for these patients may be independent of other known prognostic factors, providing a new molecular marker with significant potential for clinical uti 16569659_palmitoylation of inducible NOS at position 3 exquisitely determines its transit along the secretory pathway following a route that cannot be mimicked by a surrogate myristoylation or by a palmitate at position 2. 16573167_Expression of iNOS and Ki-67 protein in hemangioma is significantly higher than that in vascular malformation. 16574921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16634870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16681724_Expression of iNOS in serous and low-grade carcinomas was significantly higher than that in nonserous and high-grade carcinomas 16684839_mifepristone stimulates the release of NO and the expression of iNOS in cervical cells of women in early pregnancy 16703578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16771679_Data suggest that human-specific release of nanomolar levels of nitrite may result from differences between human and mouse NOS2 genes, which may program different degrees of nitric oxide responses to inflammatory signals in humans than in mice. 16780147_nNOS and iNOS might be involved in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. 16813666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16813666_Polymorphisms in NOS2 gene are associated with transcriptional activity of NOS2 gene and with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary hypertension. 16820946_Results suggest that P. aeruginosa type III secretion system not only accounts for higher expression of Fas and release of FasL but also leads to overproduction of NO and to a NO/iNOS-dependent up-regulation of Fas-FasL proteins. 16823855_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16823855_This study support NOS2A as a genetic risk factor in PD, potentially by influencing AAO and by modifying the inverse association between PD and smoking. 16848803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16865710_NOS overexpression stimulates the transcription and translation of a range of extracellular matrix genes important to the structure of connective tissues such as tendons 16889995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16919057_These findings substantiate the hypothesis of transitory delayed inflammation, as suggested by the animal model, and suggest the possibility of using therapeutic approaches to target NF-kappaB transcription in the treatment of migraine. 16924421_This study reveals the capacity of B-cell neoplasms to express iNOS in situ. In conclusion, our study revealed that there is a positive relation between iNOS expression and apoptosis (p = 0.032 spearman correlation). 16937436_Over-expression of iNOS and HIF-1alpha in colorectal carcinoma is correlated with the biological character microvessel density. 16950790_PTB is involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of INOS. 16950998_current findings provide evidence for expression of all 3 of the NOS isoforms at all of the airway levels studied in the developing lung and in all of the levels studied of the developing vascular tree from 22 weeks to term 17062130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17062169_These results suggest that iNOS plays a pivotal role in the endogenous production of NO under the basal condition, which is involved in the activity of the inwardly rectifying K(+) channel in cultured human proximal tubule cells. 17065568_Astrocytes are a source of iNOS and may play a role in the evolution of pediatric brain injury days after the initial insult. 17070441_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17070441_Our study did not demonstrate an association between iNOS gene polymorphisms and diabetic nephropathy. 17070777_TNF-induced activation of pro-inflammatory signaling in EC leading to enhanced expression of iNOS and NO production was dependent on Syk. 17072962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17072962_The iNOS C150T polymorphism is associated with the risk of H pylori-related gastric cancer in a Japanese population, and it may play an important role in increasing the risk of gastric cancer in Asian countires with the highest rates of gastric cancer. 17149600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17159127_NOS2A is not a major susceptibility locus in a relatively young sample population of 340 German patients with Parkinson disease. 17159127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17160951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17174475_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17177683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17189532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17223386_A mutation of iNOS Ser608Leu is associated with protection against silicosis and against severity of silicosis in Chinese iron miners exposed to silica dust. 17223386_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17233833_an oxidative DNA lesion, occurred to a much greater extent in Malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH) tissue specimens from deceased patients than in live patients. iNOS, NF-kappaB and COX-2 were colocalized with 8-nitroguanine in MFH tissues 17240318_negative correlation between blood pressure and iNOS mRNA with intermittant, but not chronic hypoxia, may suggest differential modulation of the hemodynamic response to the 2 exposure patterns 17267840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17272999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17296902_Extracellular SOD, endothelial NOS, and inducible NOS gene polymorphisms do not constitute a risk factor for developing BD (Behcet disease) in Japan. 17296902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17320454_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17322004_The results suggest that JNK regulates human iNOS expression by stabilizing iNOS mRNA possibly by a tristetraprolin -dependent mechanism. 17328085_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17404026_No association of NOS-2 and cyclooxygenase -2 polymorphisms with cervical cancer is found in Korean women. 17404026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17408468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17456572_Differences in eNOS and iNOS mRNA expression at the adipose tissue level may have a limited effect on lipolysis and tissue perfusion. 17475563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17475563_Results suggest that a polymorphism in the NOS2A gene influences the susceptibility to tuberculosis and suggests a role for NOS2A in the pathogenesis of mycobacterial infection. 17482959_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17482959_findings suggest that the polymorphic (CCTTT)n repeat in the iNOS promoter region might be involved in the development of urothelial carcinoma, especially in those who have ever smoked 17492134_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/gamma ligands can down-regulate iNOS DNA methylation 17492662_iNOS protein was detectable in peripheral-blood eEPCs, but not in cord-blood eEPCs and HUVECs; iNOS mRNA was more concentrated in peripheral-blood eEPCs than in cord-blood eEPCs and HUVECs 17507652_The mechanisms by which the C-terminal four amino acids of inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) interact with proteins that contain PDZ (PSD-95/DLG/ZO-1) domains resulting in the translocation of NOS2 to the cellular apical domain, is analyzed. 17553719_all liver samples from patients with chronic hepatitis B and Hepatitis C had marked iNOS expression and a correlation between iNOS and severity of disease was detected 17600738_Nitric oxide synthase induction has a role in cytotoxic nitrogen-related oxidant formation in conjunctival epithelium of dry eye 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17650819_The HIF-1alpha and iNOS expression index of cholesteatoma epithelium was significantly higher than that of external ear canal normal skin. 17657783_iNOS protein seems to be associated with extracapsular spread and invasion in head and neck cancer. 17674321_The levels of intralesional expression of mRNA of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon, interleukin-10, RANTES, and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in Mediterranean spotted fever are reported; levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase are also reported. 17675371_increased expression of NOS2 in bronchial tissue & smooth muscle cells in COPD patients; upregulation of NOS2 in COPD is involved in airway tone regulation & functional airflow limitation; increased arginase activity is involved in airway sensitivity 17687170_iNOS staining was not demonstrated in normal oral epithelium. In oral epithelial dysplasia, staining was seen in all cases (100%) in the basal layers of the epithelium and in 30% of cases it extended into the parabasal compartments as well. 17693978_COX-2 and iNOS was significantly higher in chronic fatigue syndrome patients than in normal controls. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17709521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17720813_NOS2 regulates cytokine-induced S-nitrosylation of p65, resulting in decreased NF-kappaB binding to the NOS2 promoter, thereby inhibiting further NOS2 expression. 17761309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804409_Study shows iNOS activity is acutely up-regulated by activation of the B1-kinin receptor in human endothelial cells or transfected HEK293 cells to generate 2.5-5-fold higher NO than that stimulated by Arg alone. 17849424_Endogenous p53 mutations at CpG dinucleotides provide further evidence for a molecular link between chronic inflammation and esophageal malignancy. 17854833_In conclusion, we found that the NOS2A (CCTTT)(14) allele was detected more frequently in the control group than in the RRMS patients, thus confirming the scientific interest on this marker. 17854833_Observational study of gene-disease assoc |
ENSMUSG00000020826 |
Nos2 |
24.480498 |
2.0618909676 |
1.043968 |
0.327997601 |
10.169423 |
0.00142788951159199457331683280614242903538979589939117431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003245903155875225990639743045562681800220161676406860351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.9275002 |
14.9668417 |
9.8452912 |
5.2092049 |
| ENSG00000007237 |
8522 |
GAS7 |
protein_coding |
O60861 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in promoting maturation and morphological differentiation of cerebellar neurons. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Growth arrest-specific 7 is expressed primarily in terminally differentiated brain cells and predominantly in mature cerebellar Purkinje neurons. GAS7 plays a putative role in neuronal development. Several transcript variants encoding proteins which vary in the N-terminus have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8522; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812] |
15948147_This work reports the identification of two human Gas7 cDNA: hGas7-a with 2,427 nucleotides, which encodes 330 amino acids, and hGas7-b with 2,610 nucleotides, which encodes 412 amino acids according to predicted open-reading-frames. 19801671_hGas7b has a role in microtubular maintenance and is possibly implicated in Alzheimer disease 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20890993_Knockdown of Gas7 by shRNA preferentially suppressed the Gas7b protein isoform in human preneuronal cells and to reduce apoptosis induced either by serum starvation or by the antineoplastic agents in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. 21452305_regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts by enhancing Runx2-dependent gene expression 22496485_The results suggest that regulation to maintain an appropriate concentration of hGas7b is required for healthy neurotransmission. 22570627_Intraocular pressure (IOP)was significantly associated with rs11656696, located in GAS7 at 17p13.1 and with rs7555523, located in TMCO1 at 1q24.1.These data suggest that we have identified two clinically relevant genes involved in IOP regulation. 22662195_These findings indicate that Gas7 is involved in motor neuron function associated with muscle strength maintenance. 24151073_We conclude that lower neuronal Gas7b levels may impact Alzheimer disease progression. 26506240_Low GAS7C increases cancer cell motility by promoting N-WASP/FAK/F-actin cytoskeleton dynamics. It also enhances beta-catenin stability via hnRNP U/beta-TrCP complex formation. 27189492_These results demonstrate GAS7 as a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. 29022762_Polymorphism rs11656696 is not associated with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) nor any of its endophenotypic traits such as intraocular pressure and cup/disk ratio and is thus not a risk factor for POAG in this Saudi cohort 29261660_Among 8 SNPs in 3 loci that showed at least nominal association (P |
ENSMUSG00000033066 |
Gas7 |
612.615076 |
2.1262126849 |
1.088286 |
0.075731819 |
206.464068 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008115894891711936792459139073444722736702650387998556761360532944215505662464085593386823467556443453733064751948357703689729270024599827593192458152770996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001597208114688909020738114817778233023841640386305320557355079087195351019597808212010303092618980645055908622854880414554390455350585398264229297637939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
835.4503360 |
38.0501457 |
395.6709513 |
13.8566242 |
| ENSG00000007350 |
8277 |
TKTL1 |
protein_coding |
P51854 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of a two-carbon ketol group from a ketose donor to an aldose acceptor, via a covalent intermediate with the cofactor thiamine pyrophosphate. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Thiamine pyrophosphate;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transketolase that acts as a homodimer and catalyzes the conversion of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to D-ribose 5-phosphate and D-xylulose 5-phosphate. This reaction links the pentose phosphate pathway with the glycolytic pathway. Variations in this gene may be the cause of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:8277; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; thiamine pyrophosphate binding [GO:0030976]; transketolase activity [GO:0004802]; glucose catabolic process [GO:0006007]; thiamine metabolic process [GO:0006772] |
15991799_demonstrate the presence of a second transketolase enzyme (TKTL1) in humans. This protein and its mutations and clinical implications are characterized. 16465194_Findings strongly indicate that overexpression of TKTL1 is responsible for observed tumor-specific effects of transketolase enzyme reactions 16969476_TKTL1 upregulation is a common phenomenon in gastric cancer and cancer of the gastroesophageal junction leading to an enhanced, oxygen-independent glucose usage which might contribute to a more aggressive tumor growth 17321041_RNAi-mediated suppression of TKTL1 in hepatoma cells significantly reduces total transketolase activity and inhibits proliferation. Findings suggest that TKTL1 plays an important role in glycometabolism and cell cycle progression in tumors. 17321041_These results indicate that TKTL1 gene influences total transketolase activity and cell proliferation in human hepatoma cells. 18302154_Transketolase, but not G6PD activity, was more elevated in metastasizing tumors and TKTL1 protein was significantly overexpressed in progressing tumors (p = 0.03). 18394773_expression of transketolase-like enzyme 1 was found in 81% of granulosa cell tumors of the ovary 18550470_Compared with grades II and III astrocytic gliomas, glioblastoma multiformes showed higher expression of TKTL1, more positive tumors, and a higher percentage of positive tumor cells. 18615628_findings suggest that tktl1 overexpression in thyroid carcinoma is a factor which facilitates tumor growth and progression 18686341_results suggest that both Transketolase-like enzyme 1 (TKTL1) and p-Akt protein play an important role in the progression of cervical neoplasia 19065656_TKTL1 overexpression may be considered not only as a new tumor marker but also as a good target for anticancer therapy. 19331662_TKTL1 plays an important role in total transketolase activity and cells proliferation in uterine cervix cancer 19655166_Expression of pAkt, GLUT1 and TKTL1 were higher in breast cancer and DCIS than in normal tissue. 20103683_TKTL1 is a novel candidate oncogene that is epigenetically activated by aberrant hypomethlation and contributes to a malignant phenotype through altered glycolytic metabolism and HIF1alpha accumulation. 20200485_Overexpression of TKTL1 is associated with gastric cancer. 20385008_LDH5 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and could serve as a marker for malignancy. LDH5 correlates positively with the prognostic marker transketolase like 1 protein. 20592357_transketolase-like 1 protein (TKTL1) is expressed in human endometrial cancer 20596653_TKTL1 does not regulate glucose metabolism in malignant cells. 20826743_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in TKTL1 is associated with diabetic nephropathy. 20884117_Transketolase-like protein 1 confers resistance to serum withdrawal in vitro. 21854597_Investigated the expression of VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2 and TKTL1 in patients with LARC treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and cetuximab. High TKTL1 expression significantly correlated with disease free survival. 21980427_correlation of TKTL expression with tumor stage, probability of tumor recurrence and survival in colorectal cancer 22027741_TKTL1 overexpression is a new and independent predictor of survival for patients with non-small cell lung cancer 22445516_TKTL1 could be a target protein for improved therapeutic strategies in some cases of lung cancer. 22658715_TKTL1 is dysregulated in malignant tumors of the ocular adnexa, and enhanced expression seems to predict clinical outcome, especially the tumor recurrence rate. 22803947_TKLT1 is devoid of two critical histidine residues that are conserved in other TK. 23118983_No transketolase activity of TKTDelta38 can be detected for conversion of physiological sugar substrates thus arguing against an intrinsically encoded enzymatic function of TKTL1 in tumor cell metabolism 23130932_EDIM-TKTL1 blood test revealed good concordance with FDG-PET/CT results in patients with malignancies demonstrating its efficacy to detect upregulation of glucose metabolism in primary tumors or metastases. 23261987_Data indicate that transketolase (hTKT). shares 61% sequence identity with transketolase-like protein (TKTL1). 24193262_In 50% of colorectal cancer patients, TKTL1 protein expression was upregulated in tumor compared to non-tumor tissue. TKTL1 expression correlated with HIF-1alpha protein expression and was induced upon hypoxic conditions. 24304513_DNASEX and TKTL1 detection in patient blood is associated with poor disease-free survival rate in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24390277_TKTL1 expression levels appear to decline in the course of CML with lowest levels during blast crisis. A potential reason is a shift of TKTL1-high-expressing mature granulocytes towards TKTL1-low-expressing immature cells and blasts. 25572961_the cytoplasmatic expression of TKTL1 is specific for MIBC tissue compared with histopathologically benign urothelium. 26032094_our results suggest that TKTL1 as a key prognostic factor may be a novel target for therapy of the patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 26187043_Data revealed exceptional occurrence of TKTL1 in a panel of malignant human cell lines in vitro suggesting that its presence was unrelated to either the rate of glucose consumption/lactic acid production or resistance against chemo- and radiotherapy. 26349965_TKTL1 is associated with a more aggressive behavior in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells 26406948_Both TKTL1 and p63 are independent prognostic factors of the poor outcome of gastric cancer patients 26650256_We show that high TKTL1 in tumor tissue can lead to poor survival in colorectal cancer. TKTL1 thus can serve as a candidate marker for identifying patients at risk of recurrent disease 26907172_Data provide evidence for an important role of TKTL1 in aerobic glycolysis and tumor promotion in melanoma that may result from defective promoter methylation. 27916418_Knockdown of TKTL1 additively complements cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting the levels of NADPH and ribose-5-phosphate, indicating that TKTL1 may be a promising target to improve the therapeutic effect combining with cisplatin for the patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 29885837_Inhibition of TKTL1 expression reverses paclitaxel resistance in human ovarian cancer cells and reduces cell proliferation. 30044385_The research provides evidence that TKTL1 renders tumor cells more resistant to radiation therapy and to hypoxic conditions. 30119993_The results obtained in this study suggest that pentose phosphate pathway and its key enzyme TKTL1 is altered throughout the prostate cancer tumorigenesis 30646877_Homology modelling of TKTL1 and TKTL2 using transketolase (TKT) as template, revealed that both could assume a folded structure like TKT. TKTL1/2 presented a cleft of suitable dimensions between the homodimer surfaces that could accommodate the co-factor-substrate. An appropriate cavity and a hydrophobic nodule were also present in TKTL1/2 and implicated in aminopyrimidine and thiazole ring binding in TKT, respectively. 31771043_For the first time we analyzed Apo10 and TKLT1 in patients with cholangiocellular (CCC), pancreatic (PC), and colorectal carcinoma (CRC). 32434192_Transketolase-Like Protein 1 and Glucose Transporter 1 in Gastric Cancer. 32795237_High TKTL1 expression as a sign of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer with synchronous rather than metachronous liver metastases. 33109565_Use of AKR1C1 and TKTL1 in the Diagnosis of Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions from Mexican Women. 33326930_CircDUSP16 Contributes to Cell Development in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating miR-497-5p/TKTL1 Axis. 35408935_TKTL1 Knockdown Impairs Hypoxia-Induced Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase and Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase Overexpression. 36074851_Human TKTL1 implies greater neurogenesis in frontal neocortex of modern humans than Neanderthals. |
ENSMUSG00000031397 |
Tktl1 |
253.677990 |
0.4593050857 |
-1.122475 |
0.100570291 |
126.608535 |
0.00000000000000000000000000002262818049450365227112574307922607525619389515340150185876980928168628061077170127157742740564572159200906753540039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000285219422800063103696057316138587668719122686766208229506981041932985593951276059865307388463406823575496673583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
164.0705084 |
11.3613428 |
360.0940869 |
16.3708964 |
| ENSG00000007384 |
64285 |
RHBDF1 |
protein_coding |
Q96CC6 |
FUNCTION: Regulates ADAM17 protease, a sheddase of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor ligands and TNF, thereby plays a role in sleep, cell survival, proliferation, migration and inflammation. Does not exhibit any protease activity on its own. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15965977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18524845, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18832597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21439629}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Growth factor binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable growth factor binding activity and serine-type endopeptidase activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of protein secretion; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; and regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process. Located in Golgi membrane and endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64285; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042058]; regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0061136]; regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050708] |
15965977_RHBDF1 is a seven-transmembrane protein with a long N-terminal cytoplasmic extension that comprises half of the polypeptide sequence, and is found in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, but not on the cell surface 18524845_RHBDF1 has a pivotal role in sustaining growth signals in epithelial cancer cells and thus may serve as a therapeutic target for treating epithelial cancers. 18832597_RHBDF1 is critically involved in a G protein-coupled receptors ligand-stimulated process leading to the activation of latent epidermal growth factor receptor ligands 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20970119_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 24648344_RHBDF1 is a critical component of a molecular switch that regulates HIF1alpha stability in cancer cells in hypoxia. 26109405_The expression of iRhom1 was increased by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stressors, such as thapsigargin and tunicamycin, leading to the enhancement of proteasome activity, especially in ER-containing microsomes. 26535007_results explain how loss of the amino terminus in iRhom1 and iRhom2 impairs TNF signaling, despite enhancing ADAM17 activity 29654741_that the regulatory effects of RHBDF1 on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and on cell proliferation are partially attributable to the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway 29727209_findings indicate that perturbations of apicobasal polarity by high levels of RHBDF1 is a significant attribute in the development of breast neoplasia. 30279141_RHBDF1 is an indispensable component of the protein trafficking machinery involved in GPCR-mediated EGFR transactivation, and is an attractive therapeutic target for cancer. 31661139_Results revealed that cervical cancer (CC) tissues had higher levels of iRhom1 than adjacent normal tissues. Its increased expression was significantly associated with tumor stage, size, and parametrium invasion as well as poor outcomes. Knockdown of iRhom1 in HeLa cells inhibited cell growth, disrupted the cell cycle, and promoted apoptosis. 34276048_RHBDF1 promotes AP-1-activated endothelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor fibrotic stroma formation. 35585977_Attenuation of Excess TNF-alpha Release in Crohn's Disease by Silencing of iRHOMs 1/2 and the Restoration of TGF-beta Mediated Immunosuppression Through Modulation of TACE Trafficking. 35595096_Alternative splicing of the human rhomboid family-1 gene RHBDF1 inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor activation. |
ENSMUSG00000020282 |
Rhbdf1 |
244.712141 |
0.4847795641 |
-1.044599 |
0.161057730 |
41.538430 |
0.00000000011557646507859926859026191471059834964263401957396126817911863327026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000595015216100497075900845257739229035576222770487220259383320808410644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
165.6814327 |
16.3629822 |
344.5542714 |
23.6149139 |
| ENSG00000007516 |
8938 |
BAIAP3 |
protein_coding |
O94812 |
FUNCTION: Functions in endosome to Golgi retrograde transport. In response to calcium influx, may interact with SNARE fusion receptors and membrane phospholipids to mediate endosome fusion with the trans-Golgi network. By promoting the recycling of secretory vesicle transmembrane proteins, it indirectly controls dense-core secretory vesicle biogenesis, maturation and their ability to mediate the constitutive and regulated secretion of neurotransmitters and hormones. May regulate behavior and food intake by controlling calcium-stimulated exocytosis of neurotransmitters including NPY and serotonin and hormones like insulin (PubMed:28626000). Proposed to play a role in hypothalamic neuronal firing by modulating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic inhibitory neurotransmission (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80TT2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28626000}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Exocytosis;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport |
|
This p53-target gene encodes a brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor. The protein is a seven-span transmembrane protein and a member of the secretin receptor family. It interacts with the cytoplasmic region of brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1. This protein also contains two C2 domains, which are often found in proteins involved in signal transduction or membrane trafficking. Its expression pattern and similarity to other proteins suggest that it may be involved in synaptic functions. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:8938; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; secretory vesicle [GO:0099503]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; dense core granule maturation [GO:1990502]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0035774]; positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0001956]; regulation of dense core granule exocytosis [GO:1905413]; regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0032228]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] |
23698091_Baiap3 is gender specifically associated with anxiety and benzodiazepine use disorder. 28626000_BAIAP3 functions indirectly in dense-core vesicle exocytosis by affecting DCV maturation through its role in DCV protein recycling. 33561007_Integrated analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression profiling identifies BAIAP3 as a novel target of dysregulated hsa-miR-1972 in age-related white matter lesions. |
ENSMUSG00000047507 |
Baiap3 |
20.230236 |
0.1413056459 |
-2.823109 |
0.590099098 |
22.188085 |
0.00000247203182849004800137183816832742166980096953921020030975341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008359035461285935160501495144735883968678535893559455871582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1893675 |
1.8584828 |
29.6206654 |
8.4566849 |
| ENSG00000008086 |
6792 |
CDKL5 |
protein_coding |
O76039 |
FUNCTION: Mediates phosphorylation of MECP2 (PubMed:15917271, PubMed:16935860). May regulate ciliogenesis (PubMed:29420175). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15917271, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16935860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29420175}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene is a member of Ser/Thr protein kinase family and encodes a phosphorylated protein with protein kinase activity. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked infantile spasm syndrome (ISSX), also known as X-linked West syndrome, and Rett syndrome (RTT). Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6792; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; dendritic growth cone [GO:0044294]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cilium assembly [GO:1902017]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175] |
15492925_CDKL5 mutations are associated with epilepsy, X-linked mental retardation and a clinical phenotype that overlaps Rett syndrome. 15635068_A proportion of Rett syndrome atypical cases may result from mutations in CDKL5. (review) 15917271_demonstrate that MeCP2 and CDKL5 interact both in vivo and in vitro and that CDKL5 is indeed a kinase, which is able to phosphorylate itself and to mediate MeCP2 phosphorylation 16015284_novel pathogenic CDKL5 mutations were identified in three girls, two of whom had initially been diagnosed with the early onset seizure variant of Rett Syndrome (RTT) and the other with early onset seizures and some features of RTT 16326141_Patients with the CDKL5 mutation have an early onset, epileptic encephalopathy in infancy that evolves into myoclonic seizures in childhood with a unique EEG pattern. 16611748_CDKL5 mutations are a significant cause of infantile spasms and early epileptic seizures in female patients, and of a later intractable seizure disorder, irrespective of whether they have suspected Rett syndrome. 16611748_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16935860_CDKL5 phosphorylation is required for its entrance into the nucleus whereas a portion of the COOH-terminal domain is responsible for a stable residency in this cellular compartment probably through protein-protein interactions 17049193_The observation of this study and review of the literature suggest that a broader polymorphic electroclinical pattern with both generalized and focal seizures may occur in patients with CDKL5 mutations. 17089071_CDKL5 mutations may a rare cause of Rett syndrome. 17089071_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17993579_screened entire coding region of CDKL5 in 151 affected girls with a heterogeneous phenotype ranging from encephalopathy with epilepsy to atypical Rett syndrome, and identified 3 novel missense mutations in catalytic domain Ala40Val, Arg65Gln, Leu220Pro 18063413_clinical features & electroencephalographic findings of 2 patients affected by a previously unreported CDKL5 mutation; both manifest Hanefeld variant Rett syndrome & had early-onset seizures, hand stereotypies, congenital psychomotor delay & hypotonia 18266744_Epileptic phenotype in CDKL5 mutations, and a potential relationship between the phenotype and the genotype. 18701457_CDKL5 expression is modulated during neuronal development and its subcellular distribution is tightly regulated by the C-terminal tail 18790821_18 different mutations (7 novel ones) were identified in 20 unrelated girls. These mutations were identified in eight patients with encephalopathy with RTT-like features, five with infantile spasms and seven with encephalopathy with refractory epilepsy. 18809835_CDKL5 gene mutations may represent a cause of severe or profound mental retardation and early-onset intractable seizures, also in boys. 19241098_Results describe the correlation of genotype and phenotype in CDKL5 mutated female carriers. 19428276_a novel p.Arg970X mutation in the last exon of the CDKL5 gene resulting in late onset seizure disorder. 19471977_Data demonstrate the first instance of genomic deletion as the molecular basis of CDKL5 deficiency in females. 19552836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19564592_We report CDKL5 mutations in boys with severe encephalopathy and early-onset intractable epilepsy. 19734009_CDKL5 mutations are not responsible for early onset severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy 19740913_CDKL5 is involved in pre-mRNA processing, by controlling splicing factor dynamics. 19780792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19780792_We found CDKL5 mutations in 8.2% (4 of 49) of patients and genomic deletions in 8.2% (4 of 49). Overall, abnormalities of the CDKL5 gene accounted for 16.3% (8 of 49) of patients. 19793311_The CDKL5 mutation rate is high (28%) in women with early-onset seizures and infantile spasms. 20397747_seven polymorphic variations and four de novo mutations of the CDKL5 gene were identified, and in all instances of the latter the clinical phenotype was that of an epileptic encephalopathy. 20493745_Two patients (one female, one male) with CDKL5 mutations have epileptic spasms after tonic seizures but never present infantile spasms as the main seizure type or hypsarrhythmia in electroencephalography. 20513142_Data indicate that MEF2C missense de novo mutations in severe mental retardation showed diminished MECP2 and CDKL5 expression. 20602487_CDKL5 mutation is associated with epileptic encephalopathy. 20728410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21107515_CDKL5 deficit may induce changes in synaptic plasticity in the patient's brain. 21124335_CDKL5 exon 16b should now be considered in the genetic screening of patients presenting with a CDKL5-related disease profile. 21293276_We report the first case of an exonic deletion of CDKL5 in a male and emphasize the importance of underappreciated mosaic exonic copy number variation in patients with early-onset seizures and RTT-like features of both genders. 21309761_Infants with CDKL5-related early epileptic encephalopathy can present in the first year of life with an unusual. 21318334_A novel CDKL5 exon and pathogenic mutations in patients with severe mental retardation, early-onset seizures and Rett-like features. 21502606_the distinctive hypermotor-tonic-spasms sequence is a feature of CDKL5 epileptic encephalopathy. 21750574_female CDKL5-mutated iPSCs maintain X-chromosome inactivation and clones express either the mutant CDKL5 allele or the wild-type allele that serve as an ideal experimental control. 21765152_This study present clinical phenotype of 5 girls having a mutation in the CDKL5 gene 21770923_mutations in early onset epileptic encephalopathy 21775177_A novel CDKL5 mutation is identified in an ambulatory girl who had severe mental retardation and multiple types of seizures without Rett-like features. 22264704_sought to determine the historic, clinical, and prognostic features of epilepsy secondary to CDKL5 mutations. all children developed infantile spasms. All children demonstrated developmental delay and visual impairment. 22430159_The patients with clinical features of Rett syndrome, with epileptic encephalopathy before 6 months of age, regardless the presence of genetic abnormalities (mutations in MeCP2 or CDKL5 or both) or even in their absence. 22678952_Recurrent mutations in the CDKL5 gene in patients with epileptic encephalopathies can be associated with either a milder or a more severe phenotype. 22779007_This review surveys the current state of CDKL5 research with emphasis on the clinical symptoms associated with mutations in CDKL5, the different mechanisms regulating its functions, and the connected molecular pathways. 22832775_CDKL5 mutations cause severe epilepsy in infancy with subsequent epileptic encephalopathy. 22867051_The importance of CDKL5 mutations as etiological factors in neurodevelopmental disorders was shown. The CDKL5 gene sequence and its rearrangements should be thoroughly analyzed in females with Rett syndrome, severe encephalopathy and epilepsy. 22921766_a functional axis between MYCN and CDKL5 governing both neuron proliferation rate and differentiation. 22922712_CDKL5 is localized at excitatory synapses and contributes to correct dendritic spine structure and synapse activity. 23064044_Identification of eleven novel sequence variations including four pathogenic mutations in the CDKL5 gene. 23151060_study examines the presence of breathing and sleep abnormalities in a small series of patients with CDKL5 mutations 23242510_3 known & 3 new (V966Im A1911V, H589H)mutations in the C-terminal domain of CDKL5 were found in Indian patients with Rett syndrome negative for MECP2. 23583054_aberrations of CDKL5 and ARX combined are an important consideration in the genetic forms of early-onset epilepsy in boys 23756444_CDKL5 gene is not useful in practical molecular diagnosis of atypical Rett syndrome. 23828526_study described the clinical condition and characterization of two first Brazilian patients with CDKL5 mutations, including the first Brazilian case of atypical Rett related to abnormalities in this gene 24564546_Mutations in the CDKL5 gene associtaed with Hanefield variants of Rett syndrome and early-onset epileptic encephalopathies. 24738188_Its mutation causes Rett syndrome.(review) 25266480_CDKL5 gene mutations accounted for 5.4% of boys with early onset epileptic encephalopathy 25315662_Data suggest that the increased dosage of cyclin dependent kinase like 5 protein(CDKL5) might have affected interactions of this kinase with its substrates, leading to perturbation of neurodevelopmental and neurobehavioral abnormalities. 25762588_study presents the genotype of 2 sisters, a CDKL5 mutation c. 283-3_290del, but different phenotype 25864828_It was indicated that CDKL5 controls excitatory synaptic transmission and the conditions associated with CDKL5 deviation in man indicates synaptic abnormalities. 26239053_Rett syndrome with early epilepsy and the congenital variant are mainly due to variations in the CDKL5 and FOXG1 genes, respectively 26701947_Mutations in exon 8 of cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 gene were determined to be disease-causing in epileptic encephalopathy. 27062609_In the asymptomatic mother, the mutated copy of the CDKL5 gene was inactivated in 90% of blood cells. We also identified a premature stop codon (p.Arg926*) in IQSEC2 in a patient with a Rett-like phenotype. Finally, exome sequencing enabled us to characterize a heterozygous de novo missense (p.Val408Ala) in KCNA2 in a girl with infantile-onset seizures variant of Rett syndrome (RTT) 27171548_The genetic etiology of Rett syndrome (RTT) without MECP2, CDKL5, and FOXG1 mutations is heterogeneous, overlaps with other NDDs, and complicated by a high mutation burden. Dysregulation of chromatin structure and abnormal excitatory synaptic signaling may form two common pathological bases of RTT. 27265524_The results suggested the mutant CDKL5 was responsible for the Rett syndrome disease. 27315173_We have characterised the predominant brain isoform of CDKL5, a 9.7 kb transcript comprised of 18 exons with a large 6.6 kb 3'-untranslated region (UTR), which we name hCDKL5_1. In addition we describe new exonic regions and a range of novel splice and UTR isoforms 27528505_Although abilities were markedly impaired for the majority with the CDKL5 disorder, some females and a few males had better functional abilities. This variability may be related to underlying gene variants, with females with a late truncating variant having better levels of ability than those with no functional protein. 28780406_mutations in the CDKL5 gene in complex genotypes associated with West syndrome with variable phenotype 29444904_The implication that mutations in an alternative exon of CDKL5 can be clinically important should be considered when selecting appropriate genetic tests for patients suspected of having a CDKL5-related disorder. 29510241_CDKL5 truncation was identified in a case of encephalopathy manifesting transient methylmalonic acidemia. 29618004_a dramatic reduction of expression of the GluA2 subunit occurs concomitantly with its hyper-phosphorylation on Serine 880 and increased ubiquitination. Consequently, Cdkl5 silencing skews the composition of membrane-inserted AMPA-Rs towards the GluA2-lacking calcium-permeable form 30266825_These data reveal the first cellular substrates of CDKL5, which may represent important biomarkers in the diagnosis and treatment of CDKL5 disorder, and illuminate the functions of this poorly characterized kinase. 30377159_new consensus for evaluating CDKL5/STK9-dependent signalling mechanisms. 30378547_diaper changing-induced reflex seizures as one of the presenting features in a case of CDKL5-related epilepsy 30561084_Twenty-five parents of individuals registered in the International CDKL5 Disorder Database participated in semi-structured telephone interviews to explore areas that supported or challenged their child's QOL 30928302_Pathogenic variants include deletions, truncations, splice variants, and missense variants. Pathogenic missense variants occur exclusively within the kinase domain or affect splice sites. The CDKL5 protein is widely expressed in the brain, predominantly in neurons, with roles in cell proliferation, neuronal migration, axonal outgrowth, dendritic morphogenesis, and synapse development. Review. 30929312_CDKL5 is a gene identified as causative genes in atypical forms of Rett syndrome. 31108505_we showed that selective cortical deletion of CDKL5 from excitatory cells is sufficient to produce abnormalities of visual cortical responses, demonstrating that the normal function of cortical circuits is dependent on CDKL5. 31225800_that CDKL5 mutations likely play a direct role in psychomotor development, whereas epilepsy is one of the clinical features associated with this complex disorder 31717404_the evolution and molecular features of MeCP2, CDKL5, and FOXG1 and their binding partners, were analyzed. 31858726_CDKL5 promotes proliferation, migration, and chemotherapeutic drug resistance of glioma cells via activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 31925439_Targeting of CDKL5 promoter causes significant reactivation of the inactive allele affected by X chromosome inactivation; this change is associated with removal of methyl groups from CpG dinucleotides. 31942678_Progressive EEG Changes in CDKL-5 Related Epileptic Encephalopathy. 32002787_Increased DNA Damage and Apoptosis in CDKL5-Deficient Neurons. 32034940_Expanding the phenotype of the CDKL5 deficiency disorder: Are seizures mandatory? 32105570_Rett Syndrome, a Neurodevelopmental Disorder, Whole-Transcriptome, and Mitochondrial Genome Multiomics Analyses Identify Novel Variations and Disease Pathways. 32111237_Novel CDKL5 mutations were found in patients in China: retrospective investigation in cases of CDKL5-related disorders. 32125365_study provides the first evidence that gene therapy mediated by Adenovirus vectors can be used for treating CDKL5 disorder. 32445745_Unusual double mutation in MECP2 and CDKL5 genes in Rett-like syndrome: Correlation with phenotype and genes expression. 32588892_Dopaminergic loss of cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 recapitulates methylphenidate-remediable hyperlocomotion in mouse model of CDKL5 deficiency disorder. 32641489_Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 is required for pain signaling in human sensory neurons and mouse models. 33044867_Involvement of the CDKL5-SOX9 signaling axis in rhabdomyolysis-associated acute kidney injury. 33047306_Exploring genotype-phenotype relationships in the CDKL5 deficiency disorder using an international dataset. 33106377_Phenotypes in adult patients with Rett syndrome: results of a 13-year experience and insights into healthcare transition. 33341033_Exploring quality of life in individuals with a severe developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder. 33989939_CDKL5 deficiency disorder in males: Five new variants and review of the literature. 34229227_Clinical manifestation of CDKL5 deficiency disorder and identified mutations in a cohort of Slovak patients. 35483386_CDKL5 deficiency disorder: clinical features, diagnosis, and management. 36202289_Neuronal hyperexcitability and ion channel dysfunction in CDKL5-deficiency patient iPSC-derived cortical organoids. 36417806_CDKL5 deficiency causes epileptic seizures independent of cellular mosaicism. |
ENSMUSG00000031292 |
Cdkl5 |
27.910162 |
0.3488362436 |
-1.519378 |
0.454290570 |
10.891055 |
0.00096629750437998403536643543532136391149833798408508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002253523647440127015972866075799174723215401172637939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.1191315 |
3.9382253 |
40.5757106 |
7.8209157 |
| ENSG00000008226 |
9940 |
DLEC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y238 |
FUNCTION: Essential for spermatogenesis and male fertility (By similarity). May play an important role in sperm head and tail formation (By similarity). May act as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BLA1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10213508}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Tumor suppressor |
|
The cytogenetic location of this gene is 3p21.3, and it is located in a region that is commonly deleted in a variety of malignancies. Down-regulation of this gene has been observed in several human cancers including lung, esophageal, renal tumors, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. In some cases, reduced expression of this gene in tumor cells is a result of aberrant promoter methylation. Several alternatively spliced transcripts have been observed that contain disrupted coding regions and likely encode nonfunctional proteins.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:9940; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; beta-tubulin binding [GO:0048487]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; defense response to tumor cell [GO:0002357]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
16756719_DLEC1 suppresses the growth of ovarian cancer cells and its downregulation is closely associated with promoter hypermethylation and histone hypoacetylation 17099870_Silencing of DLEC1 expression by promoter hypermethylation and histone deacetylation may be important in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis. 18191269_DLEC1 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene that plays an important role in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. 18594535_DLEC1 methylation was an independent marker of poor survival in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma. 19156137_DLEC1 underwent promoter methylation-associated silencing in colon and gastric tumour cell lines and primary tumours. 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20530412_DLEC1 expression levels were significantly lower in samples from patients who developed metastasis, local recurrence, or died of breast cancer when compared to those who were disease free for >10 years. 20630829_Frequent epigenetic inactivation of deleted in lung and esophageal cancer 1 gene by promoter methylation is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer. 20639048_DLEC1 is often down-regulated by CpG methylation and shows tumor inhibitory function in renal cell carcinoma cells, indicating its role as a tumor suppressor 20952247_results demonstrate that down-expression and promoter methylation of DLEC1 increased from normal tissues to premalignancies and then to malignancies. 21443130_Epigenetic inactivation of DLEC1 was crucial in gastric and colorectal carcinogenesis. DLEC1 methylation in serum may be a promise biomarker for GAC and CRAC early diagnosis. 22569009_Repression of DLEC1 in squamous cell carcinoma tissues is associated with promoter hypermethylation. DLEC1 is downregulated in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma and inverted papilloma and has a distinct mechanism. 23050586_methylation-mediated silencing of DLEC1 plays an important role in multiple lymphomagenesis, and may serve as a non-invasive tumor marker for lymphoma diagnosis 25574068_DLEC1 methylation was not associated with the clinicopathological variables of gastric cancer. 25648635_DLEC1 mediates tumor-suppressive activities through NF-kappaB signaling. 25746324_DLEC1 is down-regulated in head and neck squamous cell tumors and it's promoter methylation is not associated with the clinicopathological parameters. 27287342_the expression levels of DLEC1 and ITGA9 were prominently decreased in lung tumor samples 28674222_We found no correlation between the DLEC1, TUSC4 and MLH1 gene expression and NSCLC patient characteristics (gender, age and smoking) or cancer histopathology. No significant differences in the gene expression among NSCLC subtypes indicate the weakness of DLEC1, TUSC4 and MLH1 expression analysis as potential differentiating markers of NSCLC subtypes in the Polish population. 30610381_DLEC1 methylation can be utilized to identify a subset with a better prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas of the small duct type. 31176573_that the KLF4 and DLEC1 genes can be considered potential methylation biomarkers for uterine leiomyomas 32144534_Compared with negative methylation (Nm), DLEC1-positive methylation (Pm) was associated with increased GC risk in PS (OR 2.083, 95% CI 1.220-3.558, P = 0.007), but PBX3 Pm was not associated with GC risk. 33144677_Dlec1 is required for spermatogenesis and male fertility in mice. 33153431_PM2.5 exposure and DLEC1 promoter methylation in Taiwan Biobank participants. |
ENSMUSG00000038060 |
Dlec1 |
10.594867 |
0.3323802800 |
-1.589093 |
0.627995122 |
6.082235 |
0.01365478911113728738291328568266180809587240219116210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025418676665454199847804517276017577387392520904541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6064571 |
2.2586184 |
17.5700404 |
4.3545915 |
| ENSG00000008256 |
9265 |
CYTH3 |
protein_coding |
O43739 |
FUNCTION: Promotes guanine-nucleotide exchange on ARF1 and ARF6. Promotes the activation of ARF factors through replacement of GDP with GTP. Plays a role in the epithelial polarization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23940353, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9707577}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Reference proteome;Tight junction |
|
This gene encodes a member of the PSCD (pleckstrin homology, Sec7 and coiled-coil domains) family. PSCD family members have identical structural organization that consists of an N-terminal coiled-coil motif, a central Sec7 domain, and a C-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. The coiled-coil motif is involved in homodimerization, the Sec7 domain contains guanine-nucleotide exchange protein (GEP) activity, and the PH domain interacts with phospholipids and is responsible for association of PSCDs with membranes. Members of this family appear to mediate the regulation of protein sorting and membrane trafficking. This encoded protein is involved in the control of Golgi structure and function, and it may have a physiological role in regulating ADP-ribosylation factor protein 6 (ARF) functions, in addition to acting on ARF1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9265; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; establishment of epithelial cell polarity [GO:0090162]; Golgi vesicle transport [GO:0048193]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; regulation of ARF protein signal transduction [GO:0032012] |
15878955_GRP1 is a new corepressor for thyroid hormone receptors, which modulates both positive and negative regulation by T3 by decreasing TR-complex formation on thyroid response elements 21932773_incorporation of the E345K charge reversal mutation into the GRP1 PH domain enhances PI(4,5)P(2) affinity 8-fold and yields constitutive plasma membrane targeting in cells 22454518_The PH domains of cytohesin 2/ARNO and cytohesin 3/GRP1 are responsible for the differential effects of these proteins on cell adhesion to fibronectin. 24966920_Cytohesin-3 was upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues, correlating with overall survival/relapse-free survival and tumor size/vascular invasion. |
ENSMUSG00000018001 |
Cyth3 |
284.118734 |
0.4491656913 |
-1.154680 |
0.211322044 |
29.126126 |
0.00000006781626377404046969477882048776828938230210042092949151992797851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000271338588589004430245857444475854336474185402039438486099243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
177.0662934 |
23.9740407 |
396.8163448 |
38.0380683 |
| ENSG00000008441 |
4784 |
NFIX |
protein_coding |
Q14938 |
FUNCTION: Recognizes and binds the palindromic sequence 5'-TTGGCNNNNNGCCAA-3' present in viral and cellular promoters and in the origin of replication of adenovirus type 2. These proteins are individually capable of activating transcription and replication. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA replication;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor that binds the palindromic sequence 5'-TTGGCNNNNNGCCAA-3 in viral and cellular promoters. The encoded protein can also stimulate adenovirus replication in vitro. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:4784; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
16565071_NFI-X cooperates with (activator protein 1)AP-1 by an unknown mechanism in astrocytes, which results in the expression of a subset of astrocyte-specific genes. 16928756_temporal and dose-dependent interference by an AP-1 family member, c-Jun, upon NF-1 proteins binding an NF-1 consensus site derived from JC virus promoter sequence 18754024_First report of structural alterations of the NFIA gene in hematopoietic diseases (polycythemia vera and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, type 1). 19418463_an expression program of NFIs is executed during the differentiation of astrocytes, with NFI-X and -C controlling the expression of astrocytic markers at late stages of differentiation. 20150379_Nuclear factor IA may play a role in astrocytoma biology. 20673863_These findings demonstrate that allelic NFIX mutations trigger distinct phenotypes, depending specifically on their impact on nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. 21189253_NFI-X3 activates GFAP expression, in part, by inducing alterations in the nucleosome architecture that lead to the increased recruitment of RNA polymerase II 21953450_NFI-X3 and STAT3 control the migration of differentiating astrocytes as well as migration and invasion of glioma cells via regulating YKL-40 expression. 22301465_missense mutations in NFIX were able to cause Sotos-like features. 22422452_DNA methylation shows genome-wide association of NFIX, RAPGEF2 and MSRB3 with gestational age at birth. 24924640_Deletions in the 3' part of the NFIX gene including a recurrent Alu-mediated deletion of exon 6 and 7 account for previously unexplained cases of Marshall-Smith syndrome. 25118028_NFIX analysis should be considered in patients presenting with overgrowth, macrocephaly and developmental delay including those in whom Sotos syndrome has been considered clinically but are negative for pathogenic NSD1 variants. 25220407_TGF-beta-mediated suppression of ANT2 through NF1/Smad4 complexes contributes to oxidative stress and DNA damage during induction of cellular senescence. 26200704_Report novel mutations of NFIX gene causing Marshall-Smith syndrome or Sotos-like syndrome. 26653554_miR-1290 functions as a tumor oncogene in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting NFIX 26695693_Plasma miR-1914* and -1915 interact with NFIX RNA. 28076901_Studies indicate the role of nuclear factor one (NFIs) as epigenetic regulators in cancer. 28442439_A novel de novo pathogenic variant in the NFIX gene identified in a case of Marshall-Smith syndrome with precocious puberty and aortic root dilatation. 28800311_Compared to noncancerous esophageal mucosa, miR-1290 expression was upregulated, while NFIX mRNA expression was downregulated in ESCC tissues. Data suggest that the dysregulation of miR-1290-NFIX axis may play crucial roles in esophageal carcinogenesis and progression. 29184170_Microduplications encompassing NFIX cause intellectual disability, short stature and small head circumference. 29897170_Malan syndrome is caused by deletions or point mutations of NFIX clustered mostly in exon 2. There is no genotype-phenotype correlation except for an increased risk for epilepsy with 19p13.2 microdeletions. Variants arose de novo, except in one family in which mother was mosaic. Variants causing Malan and Marshall-Smith syndrome can be discerned by differences in the site of stop codon formation 29899543_Data show that miR-744-5p expression directly downregulated mRNA and protein expression of nuclear factor I X (NFIX) and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC). 30264502_We identified recurrent targeting of NFIX by HPV16 insertion in anal carcinomas, supporting a role for this gene in oncogenesis 30287093_It showing the contribution of NFIX to muscle development and muscular dystrophies, hematopoiesis, cancer, and neural stem cell biology, highlighting the importance of this knowledge in the development of therapeutic targets. 30418046_NFIX downregulation might independently predict poor prognosis in LUAD. DNA hypermethylation might be an important cause of the downregulation 31045890_Secretory carcinoma of the skin associated with the presence of novel NFIX-PKN1 translocation. 31369202_Malan syndrome due to shared NFIX variants was diagnosed in the brothers using exome sequencing. 31888753_Knockdown of circNFIX inhibits progression of glioma in vitro and in vivo by increasing miR-378e and decreasing RPN2, providing a novel mechanism for understanding the pathogenesis of glioma. 32277047_Excess of de novo variants in genes involved in chromatin remodelling in patients with marfanoid habitus and intellectual disability. 32701632_A de-novo NFIX mutation causes a case of neonatal lethal Marshall-Smith syndrome. 32945093_Pathogenic variant in NFIX gene affecting three sisters due to paternal mosaicism. 34132359_Long noncoding RNA SNHG3 promotes the development of nonsmall cell lung cancer via the miR13433p/NFIX pathway. 34492536_A novel miRNA-762/NFIX pathway modulates LPS-induced acute lung injury. 35791460_CircNFIX regulates chondrogenesis and cartilage homeostasis by targeting the miR758-3p/KDM6A axis. 36060149_Long Intergenic Nonprotein Coding RNA 00174 Aggravates Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via MicroRNA-185-5p/Nuclear Factor IX axis. |
ENSMUSG00000001911 |
Nfix |
25.655455 |
0.3887987829 |
-1.362904 |
0.319156968 |
18.814869 |
0.00001440398095526436588495293456002599441490019671618938446044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000044356928625016069501867110869142152296262793242931365966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.3335694 |
3.0443212 |
37.1280828 |
4.9271307 |
| ENSG00000008516 |
64386 |
MMP25 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPA2 |
FUNCTION: May activate progelatinase A. |
Calcium;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. However, the protein encoded by this gene is a member of the membrane-type MMP (MT-MMP) subfamily, attached to the plasma membrane via a glycosylphosphatidyl inositol anchor. In response to bacterial infection or inflammation, the encoded protein is thought to inactivate alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor, a major tissue protectant against proteolytic enzymes released by activated neutrophils, facilitating the transendothelial migration of neutrophils to inflammatory sites. The encoded protein may also play a role in tumor invasion and metastasis through activation of MMP2. The gene has previously been referred to as MMP20 but has been renamed MMP25. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:64386; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; hard palate development [GO:0060022]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12860995_MMP25 is regulated by clusterin in vivo 17513868_MT6-MMP may play a role in colon cancer and exhibit unique biochemical and structural properties that may regulate proteolytic function at the cell surface. 18936094_the stem region of MT6-MMP is the dimerization interface, an event whose outcome imparts protease stability to the protein 19726693_MMP-25 plays an important role in multiple sclerosis pathology 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20308072_Biochemical characterization of the cellular glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked membrane type-6 matrix metalloproteinase. 20337648_individuals with history of chronic airways inflammation (asthma and COPD) serum leukolysin may be a metabolic marker associated with chronic atopy-associated respiratory inflammation. 20501611_MT6-MMP is present in the membrane, granules and nuclear/endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi fractions of PMNs where it is displayed as a disulfide-linked homodimer of 120 kDa 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22367194_MT6-MMP regulates neutrophil and monocyte chemotaxis and by generating 'eat-me' signals upon vimentin cleavage potentially increases phagocytic removal of neutrophils to resolve inflammation. 23851692_IL-2-upregulated MT6 cell-surface expression correlates with CD16 downmodulation. MT6, sequestered in intracellular compartments in unstimulated NK cells, translocates to the effector-target cell interface of CD16-mediated immunological synapses. 24669030_In absolute mRNA levels, significant differences were found in expression of MMP2, MMP24, and MMP25 in gastric carcinoma compared with superficial gastritis. |
ENSMUSG00000023903 |
Mmp25 |
19.381267 |
0.4692766074 |
-1.091490 |
0.393458879 |
7.615616 |
0.00578650007906867432788677874100358167197555303573608398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011663080863997490888017694032896542921662330627441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.9915220 |
4.3393068 |
30.0297655 |
6.3301368 |
| ENSG00000008853 |
23221 |
RHOBTB2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYZ6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a small Rho GTPase and a candidate tumor suppressor. The encoded protein interacts with the cullin-3 protein, a ubiquitin E3 ligase necessary for mitotic cell division. This protein inhibits the growth and spread of some types of breast cancer. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:23221; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cortical cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030865]; engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:0043652]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
12370419_A previously uncharacterized gene, DBC2 (deleted in breast cancer), was cloned from a homozygously deleted region at human chromosome 8p21. 15663929_two networks were found to react substantially to DBC2 expression--one of the networks regulates cell growth through cell-cycle control and apoptosis; the other network is related to cytoskeleton and membrane trafficking 17023000_DBC2 plays an essential role in microtubule-mediated VSVG transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. 17517369_Our results indicate that the down-regulation of CCND1 is an essential step for DBC2's growth suppression of cancer cells. 17617377_These findings indicate that the resistant T-47D cells survive DBC2 induction by rapid destruction of DBC2 through 26S proteasome-mediated protein degradation. 17653899_The researchers isolated three novel mutations in the DBC2 gene in breast cancer families in Iran. 17906984_Mutations & allelic loss in the DBC2 gene are uncommon in gastric cancers in Korean patients, so it is unlikely to play a major role. 3 new polymorphisms in the coding region were found. 18039672_RhoBTB2 up-regulated during drug-induced apoptosis, with this being primarily dependent on E2F1. 18640857_aberrant methylation in DBC2 promoter may be responsible for the expression loss of DBC2 expression in bladder cancer and this hypermethylation event could play a crucial role in the early stage of bladder tumorigenesis. 18762809_CXCL14 is a gene target of RhoBTB2 and supports downregulation of CXCL14 as a functional outcome of RhoBTB2 loss in cancer. 19173804_The expression of Fas, CTLA-4 and RhoBTB2 at the mRNA level is involved in genesis and progression of breast cancer. 19714462_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937980_Frequent loss of RhoBTB2 expression is associated with sporadic breast cancer. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20930524_Ectopic expression of RhoBTB2 results in decreased phosphorylation of ezrin and Akt2 in both MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 cells. 20980811_RhoBTB2 is establishing itself as a tumor suppressor with increasing relevance towards malignancies. 21801820_Overexpression of RhoBTB2 in breast tumor cells significantly inhibited the proliferation and colony formation of tumor cells. In addition, RhoBTB2 also elevated the apoptotic ratio and caused typical changes of apoptotic morphology. 22901165_Loss of DBC2 expression is an early and progressive event in the development of lung adenocarcinoma. 23546941_Thus loss of DBC2 expression is caused by abnormal methylation of DBC2 and might have a role in breast cancer development. 24356943_). The results demonstrated that aberrant methylation of RhoBTB2 may be responsible for the suppression of RhoBTB2 mRNA expression in breast cancer, a significant event during the genesis of breast cancer that correlated with progesterone receptor status 24485767_Mutation in the promoter and exon 7 of DBC2 gene is not common in the Chinese population and may not contribute to the susceptibility for breast cancer in China 24608665_data suggest a new paradigm for Hsp90-modulated assembly of a Cul3/DBC2 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that may extend to other E3 ligase complexes. 27941885_these findings provide evidence that DBC2 suppresses tumorigenesis in breast cancer by ubiquitinating MSI2. 29276004_missense variants in the BTB-domain-encoding region of RHOBTB2 as causative for a developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. 33504645_RHOBTB2 Mutations Expand the Phenotypic Spectrum of Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood. 34074803_Identification of RHOBTB2 aberration as an independent prognostic indicator in acute myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000022075 |
Rhobtb2 |
354.949712 |
0.4923460993 |
-1.022255 |
0.182038581 |
30.684134 |
0.00000003036376862800164742548365533550414063768130290554836392402648925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000126138256388771251461619659142709970467421953799203038215637207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
239.0505867 |
29.0551646 |
490.3120585 |
42.4255505 |
| ENSG00000009724 |
10747 |
MASP2 |
protein_coding |
O00187 |
FUNCTION: Serum protease that plays an important role in the activation of the complement system via mannose-binding lectin. After activation by auto-catalytic cleavage it cleaves C2 and C4, leading to their activation and to the formation of C3 convertase. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10946292}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Autocatalytic cleavage;Calcium;Complement pathway;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Hydrolase;Hydroxylation;Immunity;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Sushi |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase S1 family of serine proteases. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate A and B chains that heterodimerize to form the mature protease. This protease cleaves complement components C2 and C4 in order to generate C3 convertase in the lectin pathway of the complement system. The encoded protease also plays a role in the coagulation cascade through cleavage of prothrombin to form thrombin. Myocardial infarction and acute stroke patients exhibit reduced serum concentrations of the encoded protein. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:10747; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; serine-type endopeptidase complex [GO:1905370]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; complement component C4b binding [GO:0001855]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; cell surface pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002752]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; complement activation, lectin pathway [GO:0001867]; positive regulation of opsonization [GO:1903028]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12421953_The interaction of recombinant MASP2, its N-terminal complement modules, and MBL-associated protein 19 with L-ficolin/p35 has been characterized by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. 15117939_Results describe the x-ray structure of human mannan-binding lectin-associated protein 19 (MAp19), and identify the residues involved in the interaction of MAp19 with mannan-binding lectin and L-ficolin. 15746044_MASP-2 concentration in serum proved to be an independent prognostic marker with high MASP-2 levels predicting recurrence and poor survival. 16029433_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16040602_Structural insights are presented into MASP2 autoactivation. 16112196_The mRNA distribution of masp1 and masp2 were found very similar to that of mbl2, while masp3 mRNA seemed ubiquitous present at quite high levels when compared to liver 16395704_MASP-2 expression in ESCCs was associated with late clinical stage (p = 0.009, O.R. = 3.430) and nodal metastasis (p = 0.001, O.R. = 4.520). 17045845_Concentrations and genotypes of MASP-2 and mannan-binding lectin in 109 cystic fibrosis patients were correlated to lung function and chronic infections 17096357_The data indicate a strong genetic influence for the serum levels of MBL and for MASP-2 activity with a significant genetic correlation between the two traits. 17252003_MASP-2 present in individuals homozygous for p.377A or p.99Q had a normal enzyme activity whereas MASP-2 in individuals homozygous for p.126L was non-functional 17303612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17303612_variations in MASP2 appear to be of limited importance in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease 17565323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17614162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17709141_MASP-2 is a major physiological target of C1-inhibitor. 17971300_We conclude that Stat3 binding is important for MASP2 promoter activity. 17984804_In this study, MASP-2 deficiency was associated with an increased risk of fever and neutropenia in children treated with chemotherapy for cancer. 18177377_Data show that interaction of calreticulin with recombinant MBL was fully inhibited by recombinant MASP-2, but not by the MASP-2 D105G variants characterized by defective MBL binding ability. 18221301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18221301_Our data do not seem to suggest a role for MBL2 and MASP2 polymorphisms in HCC susceptibility either for HBV-HCV infection-dependent HCC or for HCC raised as a consequence of exposure to different risk factors. 18295674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18295674_Results suggest that the D105G mutation in the MASP2 gene does not play a major role in the pathogenesis of rheumatic fever. 18400978_No association with aortic regurgitation of rheumatic etiology was detected with the variant of the MASP2 gene. 18582923_MASP2 alleles and genotypes did not associate with any measurment of severity or outcome of community-acquired pneumonia 18582923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18596574_Infants later developing necrotising enterocolitis had significantly higher MASP-2 cord blood levels compared with controls. 18638656_High postoperative levels of MASP-2 are associated with poor prognosis in patients curatively resected for colorectal cancer 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18849076_Poly(ethylene glycol)s generate complement activation products in human serum through increased alternative pathway turnover and a MASP-2-dependent process 19050632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19234189_Naturally occurring variant forms of MASP-2 differ in mannan-binding lectin activity and enzymatic activity and may have implications for susceptibility to infections of individuals with various genotypes. 19234189_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19275590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19307021_Serum MASP-2 concentrations correlated with gestational age and birthweight and were significantly lower in premature babies and other pre-term babies compared with term babies. 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19405982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19405982_There is no association between MASP2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to SARS coronavirus infection. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19737459_SARS-CoV N interacts with MAP19 and increased the expression of MAP19 in cells. 19775369_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20002787_The MASP2-mediated release of FPA and FPB may play a role in early immune activation. Additionally, MASP-catalysed deposition and polymerization of fibrin on the surface of micro-organisms may be protective by limiting the dissemination of infection. 20042521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20042521_the outcome of intensive care unit (ICU) patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) regarding the existence of functionally relevant MBL2 and MASP2 gene polymorphisms was studied 20150204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20593422_Donor and recipient gene polymorphisms in the lectin complement pathway (MBL2, FCN2, MASP2) are major determinants of the risk of clinically significant bacterial infection and mortality after orthotopic liver transplantation. 20593422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20817870_MASP-1 has a crucial role in the initiation steps of lectin pathway activation most probably by activating MASP-2 21198752_In contrast to what has been demonstrated for serum levels of mannan-binding lectin (MBL) and MBL-associated serine protease 2, the genotypes do not predict disease course of the colorectal cancer patients 21203938_binding of Mannan Binding Lectin to hepatitis C virus glycoproteins was able to activate the complement system via MBL-associated serine protease 2 21489885_MASP2*CD genotypes, most of them generating low MASP-2 levels, are associated with high risk of chagasic cardiomyopathy 21843573_MASP2 gene polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to hepatitis C virus infection. 21871896_Data show that both MAp19 and MASP-2 were mainly expressed in hepatocytes. 21926545_Results suggest that MBL and MASP-2 play only a minor role in the inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. 21974696_It is postulated that the elevation of concentration of the two components of the leptin pathway, L-ficolin and MASP-2, may compensate for the insufficient activity of the LP in mannose-binding lectin deficiency. 22071314_Interactions required for the cleavage of C4 by MASP-2 are likely to be facilitated by the initial binding of C4 to an exosite on the protease. 22173059_Data show no association of donor and recipient MBL2 and MASP2 genotype with allograft outcome, and analysis of SNPs and haplotypes in the FCN2 gene of the donor and recipient did not reveal an association with transplant outcome. 22178059_MASP-2 levels in the peripheral circulation are significantly reduced in myocardial infarction (MI) patients compared with those of healthy individuals or of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients without acute MI. 22236007_In patients with haematological malignancy undergoing chemotherapy, those with low M-ficolin levels were more likely to develop severe infections. 22380611_A common MASP2 mutation (R439H, rs12085877), was protective against placental malaria and occurred in 33% of non-affected women. 22511776_Monospecific inhibitors show that both mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease-1 (MASP-1) and -2 Are essential for lectin pathway activation and reveal structural plasticity of MASP-2. 22691502_MASP-1 activates MASP-2 and, moreover, inhibition of MASP-1 prevents autoactivation of MASP-2 22966085_A crucial role of MASP-1 is demonstrated in the activation of MASP-2, as well as of MASP-3, based on a patient harboring a nonsense mutation in the common part of the MASP1 gene. 23142462_Data indicate that the median concentration of MASP-2/ficolin-3 complexes was 119.7 AU/ml (range: 2.9-615.5 AU/ml). 23220946_collectin-11 associates with all the known MBL-associated serine proteases (MASP-1, MASP-2 and MASP-3) as well as the lectin complement pathway regulator MAP-1. 23402018_MASP-2 is a key enzyme that cleaves C4 and C2 to assemble a C3 convertase--{review} 23785123_In this study, we demonstrate that, although MASPs do not directly form heterodimers, the addition of mannan-binding lectin or ficolins allows the formation of MASP-1-MASP-2 co-complexes. 23861212_The present study describes an association between a polymorphism in the MASP2 gene and susceptibility to HTLV-1 infection, and provides further evidence of an association between the MBL2 gene and HTLV-1 infection. 23911397_Studies indicate that initiation of lectin compleme pathway leads to activation of the serine proteases MASP-1 and MASP-2 resulting in deposition of C4 on the activator and assembly of the C3 convertase. 23935922_low MASP-2 levels increase the susceptibility to leprosy in general and to lepromatous leprosy in particular. MASP2 genotypes and MASP-2 levels might thus be of prognostic value for leprosy progression. 24227370_results show that SNPS in MASP2 are significantly more susceptible to infectious complications, SIRS and septic shock. 24424083_Data indicate that MASP-1 and MASP-2 can readily form heterodimers after dissociation and re-association, however, in the presence of Ca(2+) exchange of subunits is slow between the homodimers. 24632598_Study found the first evidence that MASP-2 deficiency might play an important role in the development of RA and articular symptoms among relatives of RA patients. 24856568_Bipolar disorder is associated with the MBL2 LXPA haplotype and lower MASP-2 levels. 25038892_expression of MBL and MASP-2 is altered in ovarian cancer, possibly indicating involvement of the lectin pathway of complement activation in the disease 25042985_Both ficolin-3 and MASP-2 levels correlated inversely with the time from the onset of the attack of hereditary angioedema until blood sampling 25312983_polymorphism of MASP-2 (rs6695096) gene was associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis. 25318078_MASP2 gene polymorphisms and protein levels seem to play an important role in the development of rheumatic fever and establishment of rheumatic heart disease. 25359215_TFPI inhibits lectin pathway of complement activation by direct interaction with MASP-2. 25533914_Because MASP-1 and MASP-2 have been shown to interact directly with blood coagulation, elevated levels of these proteins may play a role in the enhanced thrombotic environment and consequent vascular complications in diabetes. 25862418_Polymorphisms in MASP1 and MASP2 genes are associated with the susceptibility or protection to infectious diseases. (Review) 25887173_Polymorphisms of mannose-binding lectin (rs7096206) and MASP-2 (rs2273346 and rs6695096) were associated with the susceptibility of tuberculosis, and there were gene-gene interactions among them. 26382056_MBL2 and MASP2 deficiencies protect against the development of systemic inflammatory response after pediatric cardiac surgery. 26614707_MASP-1 and MASP-2 are activated during blood clotting. This activation is triggered by activated platelets and by the generation of fibrin during thrombotic reactions in vitro and in vivo, and may represent a novel activation/amplification mechanism in thromboinflammation. 26728378_Data show that the vector expressing mannose-binding lectin associated protein 19 (MAp19) has been prepared successfully, and can express the target protein (MAp19) in the eukaryotic cells (HeLa cells). 26924055_genotype not associated with acute cellular rejection after kidney transplantation 27055907_MASP-2 was not associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in diabetics. 27312152_The ficolin-3/MASP-2 complex was significantly lower in the cardiac syndrome X patients compared to controls. 27585546_This study suggests that hMASP-2 can induce a protective efficacy in BCG-infected rabbit skin models, which affects both the progress of lesions and the survival of the mycobacteria within them. 27588826_Genetically determined MASP-2 levels seem to have a two-edge effect in HIV and probably HCV/HBV coinfection, whereas low levels increase the susceptibility to infection, but on the other side protects against AIDS. 27725284_This is the first comprehensive meta-analysis indicates that the MASP-2 functional gene (rs72550870) polymorphism is not associated with the infection diseases, and the key functional gene polymorphism of rs72550870 did not increase susceptibility to the infection diseases. 28086930_The results of this study show that MASP-2 contributes to severity and outcome in pneumococcal meningitis. In patients with pneumococcal meningitis, MASP-2 concentration was elevated in the CSF and high levels were associated with poor functional outcome. 28132614_Comparative analysis of C4 alone, C4-Tryp, and C4-MASP2 revealed the impact of Tryp on C4 was similar as MASP2. 28303635_High MAp19 concentration is associated with microalbuminuria in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. 28720568_The complement lectin pathway serine proteases, MASP-1 and MASP-2, can be associated with ischaemic stroke development risk and may participate in pathological events leading to post-ischaemic brain damage. Moreover rs3203210 and rs147270785 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the MASP1 and MASP2 genes, respectively, are strongly associated with ischaemic stroke. 29807983_MASP2, but not MBL in very low birth weight infants may indicate increased risk for late-onset infection 30952698_Novel MASP-2 inhibitors developed via directed evolution of human TFPI1 are potent lectin pathway inhibitors. 30995222_The allele rs7567833G, the genotypes rs7567833AG and rs7567833GG, and the COLEC11*GGC haplotype were related to T. cruzi infection and clinical progression towards symptomatic Chagas Disease (CD). COLEC11 and MASP2*CD risk genotypes were associated with cardiomyopathy, suggesting that both loci act synergistically in immune modulation of the disease. 31549610_Sporotrichosis patients had decreased levels of MBL and MASP-2 in their serum samples compared with controls. Our findings linked, for the first time, MASP-2 deficiencies with susceptibility to Sporothrix sp. 31828694_Should MASP-2 Deficiency Be Considered a Primary Immunodeficiency? Relevance of the Lectin Pathway. 31869396_that MASP-2 deficiency can increase susceptibility to adult Herpes simplex virus encephalitis 32677764_Association of MASP2 levels and MASP2 gene polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus. 32681658_MASP2 levels are elevated in thrombotic microangiopathies: association with microvascular endothelial cell injury and suppression by anti-MASP2 antibody narsoplimab. 33180422_The Clinical Significance of Serum MASP-2 and IDH1 in the Early Diagnosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 33433161_The Role of Mannose-binding Lectin in Infectious Complications of Pediatric Hemato-Oncologic Diseases. 33753877_Impact of MASP2 gene polymorphism and gene-tea drinking interaction on susceptibility to tuberculosis. 35483450_Synergy of protease-binding sites within the ecotin homodimer is crucial for inhibition of MASP enzymes and for blocking lectin pathway activation. 35861070_High Levels of Complement Activating Enzyme MASP-2 Are Associated With the Risk of Future Incident Venous Thromboembolism. 35924689_Mannose binding lectin-associated serine protease 2 (MASP2) gene polymorphism and susceptibility to human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infection in blood donors from Mashhad, Iran. 36149051_Significance of Mannan Binding Lectin-Associated Serine Protease 2 in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles in IgA Nephropathy. 36153401_Mannan-binding lectin serine protease-2 (MASP-2) in human kidney and its relevance for proteolytic activation of the epithelial sodium channel. |
ENSMUSG00000028979 |
Masp2 |
18.124129 |
0.3168941944 |
-1.657927 |
0.414886157 |
15.991500 |
0.00006362750352176909892417538960884826337860431522130966186523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000180569496631669272786180346912487948429770767688751220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.5602847 |
2.1976573 |
27.5794495 |
4.2760719 |
| ENSG00000009950 |
51085 |
MLXIPL |
protein_coding |
Q9NP71 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor. Binds to the canonical and non-canonical E box sequences 5'-CACGTG-3' (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Williams-Beuren syndrome |
|
This gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factor of the Myc/Max/Mad superfamily. This protein forms a heterodimeric complex and binds and activates, in a glucose-dependent manner, carbohydrate response element (ChoRE) motifs in the promoters of triglyceride synthesis genes. The gene is deleted in Williams-Beuren syndrome, a multisystem developmental disorder caused by the deletion of contiguous genes at chromosome 7q11.23. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:51085; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; carbohydrate response element binding [GO:0035538]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; fatty acid homeostasis [GO:0055089]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; glucose mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010255]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0090324]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045723]; positive regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045821]; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0046889]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; triglyceride homeostasis [GO:0070328] |
16644671_This evolutionally conserved mechanism may play an essential role in glucose-responsive gene regulation. 18193043_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193044_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193046_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193046_Genome-wide scan identifies variation in MLXIPL associated with plasma triglycerides. 18591247_Glucose activates ChREBP by increasing its rate of nuclear entry and relieving repression of its transcriptional activity.( 18606808_Phosphorylation of ChREBP was essential for its interaction with CRM1 for export to the cytosol, whereas nuclear import of ChREBP requires dephosphorylated ChREBP to interact with importin alpha. 18946681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18946681_tested the hypothesis that the MLXIPL rs3812316 variant predicts plasma triglyceride (TG) levels. We found no difference between individuals with high TG and controls, and no association between the variant and plasma TG levels among the controls 18950580_The transcription factor ChRepsilonBP is a major mediator of glucose action on lipogenic genes & a key determinant of lipid synthesis in vitro. Review. 19148283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19252981_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19252981_we were not able to find any statistically significant association between the single nucleotide polymorphisms in the FAS, ChREBP and SREPB-1 genes and an increased risk of breast cancer 19487539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19571538_G771C polymorphism significantly related to coronary artery disease in Chinese patients 19680233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19995986_suppression of ChREBP led to a p53-dependent reduction in tumor growth. These results demonstrate that ChREBP plays a key role both in redirecting glucose metabolism to anabolic pathways and suppressing p53 activity 20025850_a new nuclear export signal site ('NES1') of ChREBP was reported. 20158509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20570916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20580033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20679960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20965718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20972250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21036147_These results suggest that the O-linked glycosylation of ChREBP itself or other proteins that regulate ChREBP is essential for the production of functional ChREBP. 21145868_in immortalized hepatocytes and in HepG2 hepatoma cells, only SREBP1c was able to induce adiponutrin/PNPLA3 expression, whereas ChREBP was unable to modulate its expression 21282101_ChREBP is a critical and direct mediator of glucose repression of PPARalpha gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells 21665952_an important mechanism by which importin-alpha and 14-3-3 control movement of ChREBP in and out of the nucleus in response to changes in glucose levels in liver 21726544_The rs3812316 and the haplotypes in ChREBP gene appeared to be related to high susceptibility to CAD 21811631_ChREBP may function as a transcriptional repressor as well as an activator. 21835137_Our study reports that PP2A activity is dispensable for ChREBP activation in response to glucose and that dephosphorylation on Ser-196 is not sufficient to promote ChREBP nuclear translocation in the absence of a rise in glucose metabolism. 21840420_The dramatic increase of ChREBP mRNA and protein levels during preadipocyte differentiation suggests a role in adipogenesis. 21938000_Multiple linear regression models based on 2373 individuals of Asian origin showed that the H allele of the MLXIPL gene was significantly associated with decreased concentrations of plasma triglycerides. 22338092_sorcin retains ChREBP in the cytosol at low glucose concentrations and may act as a Ca(2+) sensor for glucose-induced nuclear translocation and the activation of ChREBP-dependent genes. 22466288_ChREBP-beta expression in human adipose tissue predicts insulin sensitivity, indicating that it may be an effective target for treating diabetes. 22546860_ChREBP overexpression induced expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (Scd1), the enzyme responsible for the conversion of saturated fatty acids (SFAs) into MUFAs 23209190_Data from obese adolescents with prediabetes/early type 2 diabetes suggest that expression of ChREBP-alpha/beta in abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue is inversely related to hyperglycemia severity and positively correlated to insulin resistance. 23443556_de novo lipogenesis predicts metabolic health in humans in a tissue-specific manner and is likely regulated by glucose-dependent carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein activation. 23530060_Farnesoid X receptor inhibits the transcriptional activity of carbohydrate response element binding protein in human hepatocytes. 23597489_Data suggest that CHREBP is a central regulator of glycolysis/lipogenesis in liver and apoptosis/proliferation in specific cell types. [REVIEW] 23604004_Data suggest that the activity of CHREBP is regulated via various mechanisms and that CHREBP is involved in the modulation of glucose and lipid metabolism in liver, pancreatic beta-cells, and adipose tissue. [REVIEW] 23803610_FOXO1 inhibits beta cell TXNIP transcription and suggest that FOXO1 confers this inhibition by interfering with ChREBP DNA binding at target gene promoters. 24055811_FLII is a component of the ChREBP transcriptional complex and negatively regulates ChREBP function in cancer cells. 24366300_The ChREBP expression may be reflective of an aerobic metabolic phenotype that may conflict with hypoxia-induced signalling but provide a mechanism for growth at the oxygenated edge of the tumours. 24448738_The MLXIPL-rs3812316 was associated with lower baseline triglycerides and lower hypertriglyceridemia. 24449882_ChREBP plays a key role in reprogramming glucose and lipid metabolism in human cytomegalovirus infection. 24616092_The ChREBP mutant, W130A, did not exhibit HG-induced lipid accumulation and fibrotic proteins, suggesting that the Trp-130 residue in the MCR3 domain is important in the development of glomerulosclerosis. 24664750_High glucose-induced, ChREBP-mediated, and normoxic HIF-1alpha activation that may be partially responsible for neovascularization in both diabetic and age-related retinopathy. 24845031_demonstrates that Chrebp interacts with AR and regulates its transcriptional activity 24989072_Significant linkage disequilibria were noted among ZNF259, BUD13 and MLXIPL SNPs and serum lipid levels. 25111846_results demonstrate that AGEs-RAGE signaling enhances cancer cell proliferation in which AGEs-mediated ChREBP induction plays an important role. 25288136_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms alleles near MLXIPL that were associated with higher coffee consumption. 25573592_Polymorphisms in lipid level modifier MLXIPL, GCKR, GALNT2, CILP2, ANGPTL3 and TRIB1 genes are highly associated with plasma lipid level changes. 26124292_A major function of Mio in mitosis is to regulate the activation/deactivation of Plk1 and Aurora A. 26147751_Metformin down-regulates high-glucose-induced TXNIP transcription by inactivating ChREBP and FOXO1 in endothelial cells, partially through AMP-activated protein kinase activation 26177557_the single nucleotide polymorphism of MLXIPL is significantly associated with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. 26384380_Data suggest that expression of ChREBPbeta isoform is up-regulated in pancreatic beta-cells in response to elevated levels of glucose (i.e., hyperglycemic conditions). 26526060_Diet-induced obesity increases basal expression of ChREBPbeta, which may increase the risk of developing hepatic steatosis, and fructose-induced activation is independent of gluconeogenesis. 26910886_Evaluation of the conservation of ChREBP and MondoA sequences demonstrate that MondoA is better conserved and potentially mediates more ancient function in glucose metabolism. 27029511_The results revealed the novel mechanism by which HNF-4alpha promoted ChREBP transcription in response to glucose, and also demonstrated that ChREBP-alpha and HNF-4alpha synergistically increased ChREBP-beta transcription. 27033449_High glucose-mediated induction of PDGF-C via ChREBP in mesangial cells contributes to the development of glomerular mesangial expansion in diabetes. 27281235_results indicated that the age and total cholesterol concentrations were independent influential factors of ChREBP methylation and DNMT1 variants could probably influence LDL-C to further modify ChREBP DNA methylation 27599772_p = 6.69 x 10(-9) ] on chr7 at the carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein-encoding (MLXIPL) gene locus displayed significant protective characteristics, while another variant rs6982502 [0.76 (0.68-0.84); p = 5.31 x 10(-7) ] on chr8 showed similar but weaker properties. 27669460_these findings support a carbohydrate-mediated, ChREBP-driven mechanism that contributes to hepatic insulin resistance. 27854512_This cross-sectional study suggests that MLXIPL rs3812316 genotypes may be associated with Triglyceride levels. there were significantly different genotype distributions in two TG categories: (1) subjects with normal TG values had a significantly higher G allele frequency than those with elevated TG levels 27919710_ChREBP regulates gene transcription related to glucose and lipid metabolism. Findings from knockout mice and human subjects suggest that ChREBP helps to induce hepatic steatosis, dyslipidemia, and glucose intolerance. [review] 28027934_ChREBP role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.The involvement of ChREBP in FASN promoter histone modification. 28123933_ChREBP and FGF21 constitute a signaling axis likely conserved in humans that mediates an essential adaptive response to fructose ingestion that may participate in the pathogenesis of NAFLD and liver fibrosis. 28606928_A nutrient-sensitive mTOR/ChREBP regulated transcriptional network could be a novel target to improve beta cell survival and glucose homeostasis in diabetes. 28768172_ChREBP was initially studied as a master regulator of lipogenesis in liver and fat tissue, it is now clear that ChREBP functions as a central metabolic coordinator in a variety of cell types in response to environmental and hormonal signals, with wide implications in health and disease. 29153407_AKT2 drives de novo lipogenesis in adipocytes by stimulating ChREBPbeta transcriptional activity and that cold induces the AKT2-ChREBP pathway in brown adipose tissue to optimize fuel storage and thermogenesis. 29764859_Data (including data from studies using tissues/cells from transgenic mice) suggest that ChREBPalpha up-regulates expression and activity of NRF2, initiating mitochondrial biogenesis in beta-cells; induction of NRF2 is required for ChREBPalpha-mediated effects and for glucose-stimulated beta-cell proliferation. [NRF2 = nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 protein] 29858861_The results of this population-based study provide evidence for a relationship between lipid regulatory gene polymorphisms including GCKR (rs780094), GCKR (rs1260333), FADS (rs174547), and MLXIPL (rs3812316) with dyslipidemia in an Iranian population. 30079502_we provide evidence that the rs1051943 A allele creates a functional miR-1322 binding site in ChREBP 3'-UTR and post-transcriptionally down-regulates its expression, possibly associated with levels of plasma lipids and glucose. 30420491_The expression levels of ChREBP and several cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6) were up-regulated in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. 31227231_The HCF-1:ChREBP complex resides at lipogenic gene promoters, where HCF-1 regulates H3K4 trimethylation to prime recruitment of the Jumonji C domain-containing histone demethylase PHF2 for epigenetic activation of these promoters.. these findings define HCF-1's interaction with ChREBP as a previously unappreciated mechanism whereby glucose signals are both relayed to ChREBP and transmitted for epigenetic regulation 31407220_Expressions of Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein and Glucose Transporters in Liver Cancer and Clinical Significance. 31409643_our results indicate that SMURF2 reduces aerobic glycolysis and cell proliferation by promoting ChREBP ubiquitination and degradation via the proteasome pathway in colorectal cancer cells. We conclude that the SMURF2-ChREBP interaction might represent a potential target for managing colorectal cancer 31413120_Two cases were hemizygous for the rare T allele at rs12539160 in MLXIPL, previously associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder. 31782782_TXNIP induced by MondoA, rather than ChREBP, suppresses cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 32583421_Carbohydrate response element-binding protein regulates lipid metabolism via mTOR complex1 in diabetic nephropathy. 32776146_The structure of importin alpha and the nuclear localization peptide of ChREBP, and small compound inhibitors of ChREBP-importin alpha interactions. 33320482_Transcription factor ChREBP - the coordinator of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism', trans 'Czynnik transkrypcyjny ChREBP - koordynator metabolizmu weglowodanow i lipidow. 34270325_Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption May Modify Associations Between Genetic Variants in the CHREBP (Carbohydrate Responsive Element Binding Protein) Locus and HDL-C (High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol) and Triglyceride Concentrations. 34461288_High glucose mediates the ChREBP/p300 transcriptional complex to activate proapoptotic genes Puma and BAX and contributes to intervertebral disc degeneration. 34600826_ChREBP deficiency alleviates apoptosis by inhibiting TXNIP/oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy. 34769488_The Roles of Carbohydrate Response Element Binding Protein in the Relationship between Carbohydrate Intake and Diseases. 34784250_Thyroid hormone signaling promotes hepatic lipogenesis through the transcription factor ChREBP. 34948094_Transcription Factor ChREBP Mediates High Glucose-Evoked Increase in HIF-1alpha Content in Epithelial Cells of Renal Proximal Tubules. |
ENSMUSG00000005373 |
Mlxipl |
31.071949 |
0.3465438622 |
-1.528890 |
0.308031058 |
25.219511 |
0.00000051161997665099007368276658180850091639513266272842884063720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001875685756425388515521591320522887258448463398963212966918945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0089007 |
3.4926044 |
46.5841505 |
6.2800100 |
| ENSG00000010256 |
7384 |
UQCRC1 |
protein_coding |
P31930 |
FUNCTION: Component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase, a multisubunit transmembrane complex that is part of the mitochondrial electron transport chain which drives oxidative phosphorylation. The respiratory chain contains 3 multisubunit complexes succinate dehydrogenase (complex II, CII), ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase (cytochrome b-c1 complex, complex III, CIII) and cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV, CIV), that cooperate to transfer electrons derived from NADH and succinate to molecular oxygen, creating an electrochemical gradient over the inner membrane that drives transmembrane transport and the ATP synthase. The cytochrome b-c1 complex catalyzes electron transfer from ubiquinol to cytochrome c, linking this redox reaction to translocation of protons across the mitochondrial inner membrane, with protons being carried across the membrane as hydrogens on the quinol. In the process called Q cycle, 2 protons are consumed from the matrix, 4 protons are released into the intermembrane space and 2 electrons are passed to cytochrome c (By similarity). The 2 core subunits UQCRC1/QCR1 and UQCRC2/QCR2 are homologous to the 2 mitochondrial-processing peptidase (MPP) subunits beta-MPP and alpha-MPP respectively, and they seem to have preserved their MPP processing properties (By similarity). May be involved in the in situ processing of UQCRFS1 into the mature Rieske protein and its mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS)/subunit 9 when incorporated into complex III (Probable). Seems to play an important role in the maintenance of proper mitochondrial function in nigral dopaminergic neurons (PubMed:33141179). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07256, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33141179, ECO:0000305|PubMed:29243944}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Electron transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Neuropathy;Parkinsonism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Transit peptide;Transport |
|
Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within mitochondrial electron transport, ubiquinol to cytochrome c. Located in mitochondrion. Implicated in Alzheimer's disease. Biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7384; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial respirasome [GO:0005746]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III [GO:0005750]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase activity [GO:0008121]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; cellular respiration [GO:0045333]; mitochondrial electron transport, ubiquinol to cytochrome c [GO:0006122]; oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0006119]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to alkaloid [GO:0043279] |
16775426_UQCRC1 was highly expressed in breast and ovarian tumors 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26943237_Gene expression level of UQCRC1 is significantly higher in AD patients when compared to normal controls. 27845902_dysregulated UQCRC1 and UQCRFS1 are involved in impaired mitochondrial electron transport chain function. 31276465_High miR-214-3p expression may promote osteosarcoma cell proliferation by targeting UQCRC1. 32666668_The lack of association between ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein I (UQCRC1) variants and Parkinson's disease in an eastern Chinese population. 33141179_Mitochondrial UQCRC1 mutations cause autosomal dominant parkinsonism with polyneuropathy. 33248804_Lack of evidence for association of UQCRC1 with Parkinson's disease in Europeans. |
ENSMUSG00000025651 |
Uqcrc1 |
765.889227 |
2.0363286326 |
1.025970 |
0.094123117 |
117.665166 |
0.00000000000000000000000000205274168126329245369133873561874146558446371391720701512829589113564329565242427833027250017039477825164794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000024084632126745785387102922215499682291656756333353827608853861964353731094090615982850067666731774806976318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1017.7889613 |
63.2647347 |
502.9817712 |
23.3771975 |
| ENSG00000010318 |
51533 |
PHF7 |
protein_coding |
Q9BWX1 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in spermatogenesis. |
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Spermatogenesis is a complex process regulated by extracellular and intracellular factors as well as cellular interactions among interstitial cells of the testis, Sertoli cells, and germ cells. This gene is expressed in the testis in Sertoli cells but not germ cells. The protein encoded by this gene contains plant homeodomain (PHD) finger domains, also known as leukemia associated protein (LAP) domains, believed to be involved in transcriptional regulation. The protein, which localizes to the nucleus of transfected cells, has been implicated in the transcriptional regulation of spermatogenesis. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:51533; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
22894908_PHF7 promoter binds H4K12ac in mature spermatozoa. |
ENSMUSG00000021902 |
Phf7 |
43.426719 |
0.4235520587 |
-1.239389 |
0.267493062 |
21.643510 |
0.00000328318919565238101534163962791357249670909368433058261871337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010919304310011073653454913290339334253076231107115745544433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.8394411 |
4.3293841 |
59.0764025 |
6.7532137 |
| ENSG00000010319 |
56920 |
SEMA3G |
protein_coding |
Q9NS98 |
FUNCTION: Has chemorepulsive activities for sympathetic axons. Ligand of NRP2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The transcription of this gene is activated by PPAR-gamma, and the resulting protein product plays a role in endothelial cell migration. Expression of this gene also inhibits tumor cell migration and invasion. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:56920; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526] |
18781179_In gliomas, SEMA3B, SEMA3G and NRP2 expressions were related to prolonged survival 18818766_Sema3G inhibits tumor progression from MDA-MB-435 but not from MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. It inhibits tumor angiogenesis in MDA-MB-231 cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20947821_Identify Sema3G as a primarily endothelial cell-expressed class 3 semaphorin that controls endothelial and smooth muscle cell functions in autocrine and paracrine manners. 22562223_overexpressed SEMA3G inhibited the migratory and invasive behavior of U251MG cancer cells 25335934_Results identify Sema3g as one of the downstream effectors of PPAR-gamma, which is centrally involved in regulating endothelial cell migration. 27180624_Results indicate that Sema3G protein is secreted by podocytes and protects them from inflammatory kidney diseases and diabetic nephropathy. 32452055_Identification of a four immune-related genes signature based on an immunogenomic landscape analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 33586674_Endothelium-derived semaphorin 3G attenuates ischemic retinopathy by coordinating beta-catenin-dependent vascular remodeling. |
ENSMUSG00000021904 |
Sema3g |
11.409636 |
0.2945696599 |
-1.763319 |
0.459505198 |
15.779960 |
0.00007115218680423473184004645730738047859631478786468505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000200268168808257954584609028536590358271496370434761047363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0566151 |
1.5811532 |
17.2492260 |
3.1338407 |
| ENSG00000010361 |
80199 |
FUZ |
protein_coding |
Q9BT04 |
FUNCTION: Probable planar cell polarity effector involved in cilium biogenesis. May regulate protein and membrane transport to the cilium. Proposed to function as core component of the CPLANE (ciliogenesis and planar polarity effectors) complex involved in the recruitment of peripheral IFT-A proteins to basal bodies. May regulate the morphogenesis of hair follicles which depends on functional primary cilia (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UYI6}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a planar cell polarity protein that is involved in ciliogenesis and directional cell movement. Knockout studies in mice exhibit neural tube defects and defective cilia, and mutations in this gene are associated with neural tube defects in humans. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:80199; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; embryonic body morphogenesis [GO:0010172]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; establishment of planar polarity [GO:0001736]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway involved in neural plate anterior/posterior pattern formation [GO:2000314]; negative regulation of neural crest formation [GO:0090301]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neural tube development [GO:0021915]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; positive regulation of cilium assembly [GO:0045724]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of cilium assembly [GO:1902017]; regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0008589]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
21840926_Data propose that mutations in Fuzzy may account for a subset of neural tube defects in humans. 29421438_results in vitro show that FUZ is responsible for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression and metastasis, suggesting that FUZ can be a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC. 30026307_this study unveils a generic Fuz-mediated apoptotic cell death pathway in neurodegenerative disorders. 33658400_Pan-cancer investigation reveals mechanistic insights of planar cell polarity gene Fuz in carcinogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000011658 |
Fuz |
15.148562 |
0.1997359255 |
-2.323834 |
0.656391371 |
11.730827 |
0.00061473257678198425704024776550227215921040624380111694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001486720110323134060384409060873167618410661816596984863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4828744 |
2.4309617 |
27.7741468 |
7.9101008 |
| ENSG00000010404 |
3423 |
IDS |
protein_coding |
P22304 |
FUNCTION: Lysosomal enzyme involved in the degradation pathway of dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10838181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11731225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28593992}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Metal-binding;Mucopolysaccharidosis;Reference proteome;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sulfatase family of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate two polypeptide chains. This enzyme is involved in the lysosomal degradation of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Mutations in this gene are associated with the X-linked lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis type II, also known as Hunter syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:3423; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; iduronate-2-sulfatase activity [GO:0004423]; sulfuric ester hydrolase activity [GO:0008484]; dermatan sulfate catabolic process [GO:0030209]; glycosaminoglycan catabolic process [GO:0006027]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan catabolic process [GO:0030200] |
11462244_novel mutations in Italian patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II 15146464_patterns of cytosine methylation in the entire IDS gene 15500445_Mucopolysaccharidosis type II patients with sever CNS involvement and age of onset by 3 years of age had four IDS amino acid substitutions S333L,C53X,E341K, and P480R. 15614569_a total of 17 identified missense, small deletion, and nonsense mutations were further characterized by transient expression studies. 15909065_large deletion correlated with the severe phenotype of this Hunter syndrome patient. 16133661_The IDS gene was analyzed in Japanese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis II. 16480701_IDS activity in female carriers was less than a half of the normal level 16617305_These findings suggest methylation patterns in the beginning of IDS genomic region are polymorphic in humans and that hypermethylation in this region in some individuals predisposes them to CpG mutations resulting in Hunter syndrome. 16699754_The balance between constitutive and cryptic splice sites in the IDS gene is very sensitive. 16735228_A new point mutation (T1140C) in exon 8 of the IDS gene was found in Hunter syndrome. 17063374_the IDS gene is prone to splicing mutations in Portuguese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II 17091340_analysis of iduronate-2-sulfatase enzymatic activity, protein processing and structure 17284421_Two novel mutations were identified in the human iduronate-2-sulfatase (IDS) gene in two patients from unrelated families with mucopolysaccharidosis type II(MPS II). 17616540_Identification of a novel nonsense mutation (p.Y54X) in the IDS gene of severely affected MPS II patients of African origin. 17655837_The molecular characterization of one novel missense mutation (p.S305P) and 1 splice site mutation (c.1006 +5G > C) associated with mucopolysaccharidosis type II was presented. 17657858_frame-shift deletion mutation (1062 del 16) was identified in exon 7 of the patient's IDS gene 18500569_Hunter syndrome in Thailand is caused by a diverse set of defects affecting both IDS protein production and activity. 18546295_A new mutation, an A>T change at nucleotide 595, substitutes a premature stop codon for a lysine at amino acid 199 of the IDS enzyme. 19602578_IDS has a role in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion via a mechanism that involves the activation of exocytosis through phosphorylation of PKCalpha and MARCKS. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933090_The results illustrated that the deletion and frame-shift mutation of c.876-877 del TC detected in IDS gene was a novel pathologic mutation,, which was the underlying cause of MPS II of this patient. 20104590_The in vivo correction of heritable gene lesions at the RNA level operating via a correction mechanism akin to RNA-editing, was observed for IDS mutant transcript. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21062272_Family members with 3 generations of X-inactivation with Hunter syndrome have 1568A>G missence mutation in the IDS gene 21108396_study describes a woman with mild manifestations of Hunter syndrome who gave birth to a daughter; both the mother and daughter carried the p.R443X mutation in exon 9 of the ID2S gene 21593745_LCR-initiated rearrangements at the IDS locus, completed with Alu-mediated recombination or non-homologous end joining 22286622_Two new mutations were discovered: p.K236N (c.708G>C) and p.Q80K (c.238C>A) which resulted in a severe phenotype and early death of Muccopolysaccharridosis Type II patients from Bulgaria and Macedonia. 22492741_genetically analyze patients with severe Hunter syndrome that showed a total deletion of the iduronate-2-sulphatase (IDS) gene 22622771_A report of a novel IDS nonsense mutation resulting in mucopolysaccharidosis type II in several patients from a Chinese family. 22990955_a novel (p.R468P) and five known (p.R88C, p.D148V, p.G224A, p.Y348X, and p.R468Q) IDS mutations were shown to result in proteins with little or no IDS activity and altered protein processing, when expressed in COS7 cells 23867855_Identification of a splice site mutation in the IDS gene associated with mucopolysaccharidosis type II. 24125893_30 novel iduronate sulfatase mutations have been identified in mucopolysaccharidosis type II Latin American patients. 24780617_p.Ser142Phe and p.Ile360Tyrfs*31 mutations caused the severe disease manifestation 25038527_This study evaluated a novel mutation in the IDS gene among 8 male Hunter syndrome patients; there was a quantitative deficiency of NK and B cell with normal responses in other immune parameters. 26762690_Extensive iduronate 2-sulfatase (Hunter syndrome) (IDS) gene deletions were identified in four mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPSII) patients. 27146977_Functional characterization of all the novel sequence variants identified in the study would be helpful to confirm the clinical significance and to determine the effect of these variations on the function of respective proteins (IDUA and IDS) 27246110_Study identified 16 novel mutations in the IDS gene and revealed that the severe type of mucopolysaccharidosis type II is strongly associated with large structural alteration of the gene. 28186595_A splicing mutation, c.709-1G>A, was detected in the proband, for which his mother was heterozygous. 28543354_Study analyzed the genotype-phenotype relationship for 17 patients with mucopolysaccharidosis II and performed expression studies for 12 variants, nine of which have not been reported previously; speculated that very low or cell-type-specific IDS residual activity is sufficient to prevent the neuronal phenotype. 28593992_IDS structure revealed by X-ray crystallography provides essential insight into multiple mechanisms by which pathogenic mutations interfere with enzyme function, and a compelling explanation for severe Hunter syndrome phenotypes. 30639582_Genetic analysis of 63 Chinese patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type II: Functional characterization of seven novel IDS variants 31029429_Mucopolysaccharidosis type II R468Q IDS mutant could not be refolded in the calnexin cycle.Calnexin accelerates the folding of the mucopolysaccharidosis type II mutant IDS in the endoplasmic reticulum. 32070051_Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II: One Hundred Years of Research, Diagnosis, and Treatment. 33290290_Diverse clinical outcome of Hunter syndrome in patients with chromosomal aberration encompassing entire and partial IDS deletions: what is important for early diagnosis and counseling? 34670126_Identification and structure characterization of novel IDS variants causing mucopolysaccharidosis type II: A retrospective analysis of 30 Chinese children. 34830113_Loss of Function of Mutant IDS Due to Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Degradation: New Therapeutic Opportunities for Mucopolysaccharidosis Type II. 35916809_Mutational spectrum of the iduronate-2-sulfatase gene in Mexican patients with Hunter syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000035847 |
Ids |
1741.438655 |
2.5004798126 |
1.322205 |
0.071656830 |
333.229107 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001903240747359962213641795118407489386207312602675748332966739849000522109688858942741675858135577656835556930438545394577744661004479554673250534604236982227977204934096982569865369461226123348751571029424667358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000600252851090449601891213427863623612688189044282558095756353780071563301231769758866237075123385887866828596314356935475150326614124153406625366078740463023920137018109130752391462693129398076052893884479999542236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2528.3291611 |
113.7491092 |
1018.9408507 |
34.2710466 |
| ENSG00000010626 |
10233 |
LRRC23 |
protein_coding |
Q53EV4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Leucine-rich repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10233; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829] |
Mouse_homologues 17971504_Lrrc23 is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. 34585727_LRRC23 is a conserved component of the radial spoke that is necessary for sperm motility and male fertility in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000030125 |
Lrrc23 |
11.881636 |
0.3595936703 |
-1.475560 |
0.540944202 |
7.270046 |
0.00701140137338692945312423887571640079841017723083496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013892909688708696136494324946397682651877403259277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9445788 |
2.1165036 |
16.5253153 |
3.7715740 |
| ENSG00000011021 |
1185 |
CLCN6 |
protein_coding |
P51797 |
FUNCTION: Voltage-gated channel mediating the exchange of chloride ions against protons. Functions as antiporter and contributes to the acidification of the late endosome lumen. The CLC channel family contains both chloride channels and proton-coupled anion transporters that exchange chloride or another anion for protons. The presence of conserved gating glutamate residues is typical for family members that function as antiporters. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20466723}. |
Alternative splicing;Antiport;ATP-binding;CBS domain;Chloride;Disease variant;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the voltage-dependent chloride channel protein family. Members of this family can function as either chloride channels or antiporters. This protein is primarily localized to late endosomes and functions as a chloride/proton antiporter. Alternate splicing results in both coding and non-coding variants. Additional alternately spliced variants have been described but their full-length structure is unknown. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:1185; |
endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; antiporter activity [GO:0015297]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; chloride transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015108]; voltage-gated chloride channel activity [GO:0005247]; cell volume homeostasis [GO:0006884]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
17534424_differential sorting of endogenous (late endosomal) versus overexpressed (early and recycling endosomal) ClC-6 is reminiscent of that of other late endosomal/lysosomal membrane proteins 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20466723_late endosomal ClC-6 mediates proton/chloride countertransport in heterologous plasma membrane expression 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21060006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25794116_A non-synonymous single nucleotide variation (SNV) was identified in the voltage-sensitive chloride channel 6 gene. 26658788_These findings implicate the effect of rare coding variants in CLCN6 in Blood Pressure variation and offer new insights into Blood Pressure regulation. 33217309_A Recurrent Gain-of-Function Mutation in CLCN6, Encoding the ClC-6 Cl(-)/H(+)-Exchanger, Causes Early-Onset Neurodegeneration. 33737586_Exploring dementia and neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis genes in 100 FTD-like patients from 6 towns and rural villages on the Adriatic Sea cost of Apulia. |
ENSMUSG00000029016 |
Clcn6 |
323.309590 |
0.4899901155 |
-1.029175 |
0.174551266 |
34.034604 |
0.00000000541406134064478934450723342231004409086381201632320880889892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000024215619814520329620326230340120188255781386033049784600734710693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
230.1676858 |
39.0831613 |
474.6901484 |
58.3045974 |
| ENSG00000011028 |
9902 |
MRC2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBG0 |
FUNCTION: May play a role as endocytotic lectin receptor displaying calcium-dependent lectin activity. Internalizes glycosylated ligands from the extracellular space for release in an endosomal compartment via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. May be involved in plasminogen activation system controlling the extracellular level of PLAUR/PLAU, and thus may regulate protease activity at the cell surface. May contribute to cellular uptake, remodeling and degradation of extracellular collagen matrices. May play a role during cancer progression as well as in other chronic tissue destructive diseases acting on collagen turnover. May participate in remodeling of extracellular matrix cooperating with the matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10683150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12972549}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the mannose receptor family of proteins that contain a fibronectin type II domain and multiple C-type lectin-like domains. The encoded protein plays a role in extracellular matrix remodeling by mediating the internalization and lysosomal degradation of collagen ligands. Expression of this gene may play a role in the tumorigenesis and metastasis of several malignancies including breast cancer, gliomas and metastatic bone disease. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:9902; |
focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649] |
11903048_Investigation of the role of Endo180/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor-associated protein as a collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) receptor 12068012_Endo180 was found to be distinct within the mannose receptor family in that the tyrosine-based motif is not required for efficient delivery to and recycling from early endosomes 12244146_Mannose receptor activity is up-regulated by surfactant protein A on monocyte-derived macrophages. 12399458_characterization of the monosaccharide binding sites 12645947_Approximately 60% of the initial association of HIV with macrophages that lack expression of DC-SIGN (a dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor/HIV-1-binding protein) is mediated by the macrophage mannose receptor. 12668656_By using cell isolates from uPARAP deficient mice, it is demonstrated that uPARAP is a collagen receptor. Thus uPARAP deficient fibroblasts can not internalize collagen and show a reduced adhesion/migration on collagen surfaces 12952933_Results suggest that Endo180 is a crucial link between urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor and setting of the internal cellular compass. 12972549_Endo180 plays a physiological role in mediating collagen matrix remodelling during tissue development and homeostasis 17189524_Data suggest that uPARAP/Endo180 participates in the connective tissue destruction during head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by mediating cellular uptake and lysosomal degradation of collagen. 17974964_To investigate the consequence of Endo180 up-regulation, MCF7 cells transfected with Endo180 were inoculated into immunocompromised mice; expression of wild-type Endo180, but not an internalization-defective Endo180 mutant, showed enhanced tumor growth. 19584075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861500_Endo180 is a novel regulator of membrane-bound matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) activity, MT1-MMP-dependent MMP-2 activation and urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) activity. 20339555_fibrillar collagen deposition and the collagen internalization receptor endo180 have roles in glioma invasion 20845060_Our present study suggests that uPARAP may be involved in glioma cell invasiveness through actin cytoskeletal rearrangement 21768090_A novel functional role of collagen glycosylation: interaction with the endocytic collagen receptor uparap/ENDO180. 22072289_TGFbeta1-Endo180-dependent collagen deposition is dysregulated at the tumour-stromal interface in bone metastasis. 23433549_Our findings correlate for the first time impaired collagen uptake via Endo180 with the pericellular accumulation of collagen fragments during photoaging. 24161566_MRC2 is downregulated by UVA irradiation and reduces collagen internalization; this can be recovered by all-trans retinoic acid 25381222_Study identifies the interaction between lectin domain in Endo180 and CD147 as an Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition suppressor and indicates that stabilization of this molecular complex improves prostate cancer survival rates. 25408555_AGE-dependent modification of the basal lamina induces invasive behaviour in non-transformed prostate epithelial cells via Endo180 pathway linked to cancer progression. 26284904_The positive correlation between suPLAUR expression and body mass index, suggests that leukocyte recruitment in obese tissue may be regulated, at least in part, through the splicing of the PLAUR transcript. 26466547_Our findings identify sarcoma cell-resident uPARAP/Endo180 as a central player in the bone degeneration of advanced osteosarcoma 26527274_A model of the ligand-binding region of uPARAP was obtained by molecular replacement. 27247422_results provide a molecular mechanism to support the structural flexibility of uPARAP, and shed light on the structural flexibility of other members of the MR family 29061505_Endo180 knockdown in pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs) attenuated the invasive abilities of PSCs and co-cultured pancreatic cancer cells, and decreased the expression level of phosphorylated myosin light chain 2 (MLC2). 30366943_In lung tissue from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients, a strong up-regulation of uPARAP was observed in fibroblasts adjacent to regions with SP-D secretion. 31376337_These results indicate that a substance secreted from UVB-exposed keratinocytes regulates Endo180 expression and that IL-1alpha may play an important role in the maintenance of Endo180. 32072971_Mathematical modelling of the role of Endo180 network in the development of metastatic bone disease in prostate cancer. 34012764_MRC2 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Diabetic Nephropathy. 34768883_The Collagen Receptor uPARAP in Malignant Mesothelioma: A Potential Diagnostic Marker and Therapeutic Target. |
ENSMUSG00000020695 |
Mrc2 |
2485.168461 |
0.3382481566 |
-1.563846 |
0.035607819 |
1957.150641 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1273.3519608 |
33.2046016 |
3792.1454479 |
65.9275457 |
| ENSG00000011052 |
654364 |
NME1-NME2 |
protein_coding |
P22392 |
FUNCTION: Major role in the synthesis of nucleoside triphosphates other than ATP. The ATP gamma phosphate is transferred to the NDP beta phosphate via a ping-pong mechanism, using a phosphorylated active-site intermediate (By similarity). Negatively regulates Rho activity by interacting with AKAP13/LBC (PubMed:15249197). Acts as a transcriptional activator of the MYC gene; binds DNA non-specifically (PubMed:8392752, PubMed:19435876). Binds to both single-stranded guanine- and cytosine-rich strands within the nuclease hypersensitive element (NHE) III(1) region of the MYC gene promoter. Does not bind to duplex NHE III(1) (PubMed:19435876). Has G-quadruplex (G4) DNA-binding activity, which is independent of its nucleotide-binding and kinase activity. Binds both folded and unfolded G4 with similar low nanomolar affinities. Stabilizes folded G4s regardless of whether they are prefolded or not (PubMed:25679041). Exhibits histidine protein kinase activity (PubMed:20946858). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P36010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15249197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19435876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20946858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25679041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8392752}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide metabolism;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring NME1 and NME2 genes. The significance of this read-through transcription and the function of the resulting protein product have not yet been determined. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:4831;hsa:654364; |
cell periphery [GO:0071944]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; G-quadruplex DNA binding [GO:0051880]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity [GO:0004550]; protein histidine kinase activity [GO:0004673]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; CTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006241]; GTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006183]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; nucleoside diphosphate phosphorylation [GO:0006165]; nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0009142]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045618]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of epidermis development [GO:0045682]; UTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006228] |
20101217_Plakoglobin has a role in regulating the metastasis suppressor activity of Nm23. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
232.445289 |
3.6827775132 |
1.880794 |
0.134188912 |
198.641515 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000413322186782870623826924602132186409865047738997296801608596647054671884383973678572283844499592646157398192173493267631556591368280351161956787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000077913607623437677036624790849420402121611504367415030381789316128953957197220816869992604743966364396195904489742650733674622642865870147943496704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
374.7402587 |
31.7320810 |
102.5358104 |
6.9861986 |
| ENSG00000011376 |
23395 |
LARS2 |
protein_coding |
Q15031 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the attachment of leucine to its cognate tRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26537577}. |
Acetylation;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Deafness;Disease variant;Ligase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
This gene encodes a class 1 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Each of the twenty aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyzes the aminoacylation of a specific tRNA or tRNA isoaccepting family with the cognate amino acid. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23395; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; aminoacyl-tRNA editing activity [GO:0002161]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; leucine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004823]; leucyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006429]; mitochondrial translation [GO:0032543]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418] |
15737668_Upregulation of LARS2 is a hallmark of 324A>G mutation. The accumulation of 3243A>G mutation in the brain may have a pathophysiologic role in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. 15919814_In this study, we provide evidence that the LARS2 gene may represent a novel type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene. 15919814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18796578_There was investigated whether overexpression of human mitochondrial LeuRS suppressed translation and respiratory chain defects associated with the pathogenic A3243G mutation in human cells. 19129950_data indicate that inactivation of LARS2 by both genetic and epigenetic mechanisms may be a common and important event in the carcinogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 19847392_No evidence to support previous data indicating a role in type 2 diabetes susceptibility in humans with LARS2 single nucleotide polymorphisms 19847392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20194621_The alteration of aminoacylation tRNA(Leu(UUR)) caused by the A3243G mutation led to mitochondrial translational defects and thereby reduced the aminoacylated efficiencies of tRNA(Leu(UUR)) as well as tRNA(Ala) and tRNA(Met). 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23541342_Mutations in LARS2, encoding mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase, lead to premature ovarian failure and hearing loss in Perrault syndrome. 24413189_Leucyl tRNA synthetase is able to partially rescue defects caused by mutations in non-cognate itochondrial-tRNAs. 26272616_analysis of the CP1 domain in human mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetase 26657938_This represents the first independent replication of the involvement of LARS2 mutations in Perrault syndrome, contributing valuable information for the further understanding of this disease 26970254_ere we present eight families affected by Perrault syndrome. In five families we identified novel or previously reported variants in HSD17B4, LARS2, CLPP and C10orf2 29071539_IARS2 knockdown inhibits proliferation, suppresses colony formation, and causes cell cycle arrest in AGS cells. 29205794_We concluded that Perrault syndrome patients with LARS2 mutations are at risk for neurologic problems, despite previous notions otherwise. 29762635_We report novel associations between methylation at MSI2 and LARS2 and obesity-related traits. These results provide further insight into mechanisms underlying obesity-related traits, which can enable identification of new biomarkers in obesity-related chronic diseases. 30737337_This study adds LARS2 and KARS pathogenic variants as gene defects that may underlie deafness, ovarian failure, and leukodystrophy with mitochondrial signature. 32442335_The expanding LARS2 phenotypic spectrum: HLASA, Perrault syndrome with leukodystrophy, and mitochondrial myopathy. 35585880_LARS2 Regulates Apoptosis via ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Ovarian Granulosa Cells. 35659337_Leucine-tRNA-synthase-2-expressing B cells contribute to colorectal cancer immunoevasion. |
ENSMUSG00000035202 |
Lars2 |
171.185931 |
2.5751616310 |
1.364663 |
0.211756837 |
39.980169 |
0.00000000025655432171836584497244328883093066745457733190960425417870283126831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001286257401006480965197812297944306852981455335793725680559873580932617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
239.9025617 |
32.6797677 |
93.7881864 |
9.3803939 |
| ENSG00000011422 |
5329 |
PLAUR |
protein_coding |
Q03405 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Plays a role in localizing and promoting plasmin formation. Mediates the proteolysis-independent signal transduction activation effects of U-PA. It is subject to negative-feedback regulation by U-PA which cleaves it into an inactive form. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes the receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator and, given its role in localizing and promoting plasmin formation, likely influences many normal and pathological processes related to cell-surface plasminogen activation and localized degradation of the extracellular matrix. It binds both the proprotein and mature forms of urokinase plasminogen activator and permits the activation of the receptor-bound pro-enzyme by plasmin. The protein lacks transmembrane or cytoplasmic domains and may be anchored to the plasma membrane by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) moiety following cleavage of the nascent polypeptide near its carboxy-terminus. However, a soluble protein is also produced in some cell types. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. The proprotein experiences several post-translational cleavage reactions that have not yet been fully defined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5329; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein complex involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098637]; serine-type endopeptidase complex [GO:1905370]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; urokinase plasminogen activator receptor activity [GO:0030377]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001268]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034112]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of fibrinolysis [GO:0051917]; regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010755]; regulation of proteolysis [GO:0030162]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; urokinase plasminogen activator signaling pathway [GO:0038195] |
11728456_uPA regulates uPAR expression at a post-transcriptional level, by promoting the binding of uPAR mRNA to a stabilizing factor. 11756447_uPA-dependent VSMC adhesion is a function of selective Vn phosphorylation by the ectoprotein kinase CK2 11814408_oxidative stress in AD and microglial activation establish a possible involvement of uPAR in AD pathogenesis. 11903048_Investigation of the role of Endo180/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor-associated protein as a collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) receptor 11928806_Amino acid substitutions at serine residues in UPA prevent signaling through UPAR, and prevents physical association of UPAR with alphavbeta5 vitronectin receptor, which is required for MCF-7 urokinase-dependent cell migration. 11928807_UPA receptor is weakly upregulated by bFGF in normal muscle satellite cells, while it is strongly up-regulated by TGFbeta, mainly in dystrophic myoblasts. 11928816_Coculture of monocytes and vascular smooth muscle results in increased expression of cell surface-associated uPAR in VSMC and up-regulation of UPA in monocytes, resulting in VSMC migration. 11928822_REVIEW: The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and cell motility. 11959893_Targeting urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor on human glioblastoma tumors with diphtheria toxin fusion protein DTAT. 12017319_uPA receptor is expressed in benign and malignant thyroid tumors. 12023845_essential role in acute inflammation as well as in chronic degenerative vascular processes such as atherosclerosis 12023847_Structural analysis of the interaction between urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor: a potential target for anti-invasive cancer therapy. Review. 12070711_Interferon-alpha (Intron A) upregulates urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor gene expression 12084931_interaction with urokinase mediates inhibitory signal for HIV-1 replication 12115506_expression of uPA and uPAR is associated with the clinical behaviour of bladder neoplasms 12124797_Human breast adenocarcinoma cell lines promote angiogenesis by providing cells with uPA-PAI-1 and by enhancing their expression. 12130664_prognostic biomarker for endometrial cancer 12138365_MCP-1, MCP-2 & MCP-3 increased uPAR mRNA levels in time-dependent & dose-dependent manners. Up-regulation of uPAR in target cells might be an important and common feature of chemoattractants. 12174885_circulating UPA is not up-regulated by the circulating P105 fraction of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene: in vivo evidence from patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer 12180971_Bikunin downregulates constitutive & PMA-stimulated uPAR mRNA & protein Through suppression of upstream ERK cascade targets, whether cells were treated with exogenous bikunin or transfected with bikunin gene. 12244126_Mutation of NFKB1 protein's promoter binding site (-45 bp) impaired the ability of ITGB3BP to downregulate this protein. 12297505_uPA-mediated uPAR cleavage and D1 removal, occurring on the cell surface of several cell types, can play a fundamental role in the regulation of multiple uPAR functions 12376466_seprase and the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), co-localize in the plasma membrane of LOX malignant melanoma cells 12393547_recognition of uPA by alpha(M)beta(2) allows for formation of a multicontact trimolecular complex, in which a single uPA ligand may bind to both uPAR and alpha(M)beta(2); interaction of uPA with each receptor influences cell adhesion and migration 12393744_Urokinase receptor surface expression regulates monocyte adhesion in acute myocardial infarction 12405290_correlates with cox2 expression levels and is responsible for poor prognosis of colorectal cancer 12479856_The diphtheria toxin/urokinase fusion protein (DTAT) is selectively toxic to CD87 expressing leukemic cells, showing that specific CD87 binding is one factor important in the sensitivity of patient's leukemic blasts to DTAT 12665127_uPAR up-regulated the Mac-1 adhesion to fibrinogen, and focal adhesion kinase and MAPK were involved in this regulation 12665524_the interaction between uPAR and Man-6-P/IGF2R is a low percentage binding event and that suPAR and full-length uPAR bind the Man-6-P/IGF2R by different mechanisms. 12704669_uPAR expression in lung cancer is regulated at a posttranscriptional level by uPA 12708473_The expression of uPAR was significantly correlated with gastric tumor size, depth, lymph node involvement, differentiation & vascular invasion. 12736046_Plasma uPAR levels are greater in those with bladder cancer than in healthy subjects (P /=7) & more than 90% lymph node metastases but not in normal prostate, benign prostate hyperplasia or prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia 17001307_A novel intragenic enhancer in the u-PAR gene required for constitutive and inducible expression was defined. 17028265_uPAR expression of lung airway epithelial cells is regulated at the level of mRNA stability by inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase-mediated dephosphorylation of uPAR mRNA binding proteins and demonstrate that the process involves SHP2. 17079488_Expression of HER-2 and uPAR in primary tumors predicted gene status in 100 and 92% of patients, respectively 17101149_Pro188, Asn190, Gly191, and Arg192 residues of uPAR are the key residues for the antibody recognition, while Pro189 and Arg192 render specificity of ATN615 for human uPAR 17145753_Urokinase receptor (uPAR) is required for maximal alpha5beta1 integrin-dependent responses to fibronectin that promote tumor cell invasion. 17237151_Proteolytic regulation of uPAR by airway trypsin-like kinase is likely to modulate cell adherence and motility, as well as tissue remodeling during the inflammatory response in the airways. 17264329_Elevation of plasma uPA and uPAR levels in CaP patients are partly caused by local release from the prostate. Plasma levels of uPA and uPAR are associated with biologically aggressive CaP, disease progression after radical prostatectomy, and metastasis 17297470_These data suggest Pdcd4 as a new negative regulator of intravasation, and qas the invasion-related gene u-PAR. It is the first study to implicate Pdcd4 regulation of gene expression via Sp1/Sp3. 17319000_uPAR of cancerous cells was more often observed in lobular carcinomas. 17327908_uPA and uPAR are involved in generation of drug-resistant small-cell lung cancer cell phenotype. uPAR-positive cells may define a functionally important population of cancer cells in SCLC. 17330942_uPAR behaves as a lynchpin in promoting tumorigenesis by forming functionally active multiprotein complexes. 17344041_PLAUR and the somatomedin B region of VTN direct the localization of UPA to focal adhesions in microvessel endothelial cells. 17427199_ERK cascade regulates motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via uPAR production and p70S6K phosphorylation. 17487556_forced expression of urokinase receptor coupled with exogenous addition of urokinase restored migration of CTR-knock-down spheroids. 17507651_These data support a novel hypothesis that maintaining full-length uPAR on the cell surface regulates the fibroblast to myofibroblast transition and that down-regulation of uPAR is necessary for myofibroblast differentiation. 17510314_These data suggest that Src-induced u-PAR gene expression and invasion/intravasation in vivo is also mediated via AP-1 region -190/-171, especially bound with c-Jun phosphorylated at Ser(73/63). 17517866_LasB is able to cleave uPAR both within the sequence linking D1 to D2 and at the carboxy terminus of D3. 17523079_Altered expression of UPAR was observed in high-risk soft tissue sarcomas. 17548471_These observations demonstrate a novel regulatory role for p53 as a uPAR mRNA binding protein that down-regulates uPAR expression, destabilizes uPAR mRNA, and thereby contributes to the viability of human airway epithelial or lung carcinoma cells. 17548516_A direct uPAR-vitronectin interaction is both required and sufficient to initiate downstream changes in cell morphology, migration, and signal transduction. 17549401_Simultaneous down-regulation of uPAR and uPA induced caspase-8 mediated apoptosis. 17664334_Results suggest that in hypoxia, uPAR activates diverse cell signaling pathways that cooperatively induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and may promote cancer metastasis. 17706320_High tumour cell C4.4A expression is associated with shorter survival for non-small cell lung cancer patients. 17880283_review of uPA - uPAR interactions with membrane proteins to modify signal transduction pathways and their role in oral squamous cell carcinoma 17952591_uPAR-del4/5 and rab31 mRNA represent independent prognostic markers in breast cancer and may be components of different, but possibly associated, tumor-relevant signaling pathways. 17963689_The role of the ligand uPA on uPAR localization and on the composition of the lipid membrane microdomains, is studied. 18021410_Plasma suPAR levels, as measured by the suPARnostic(R) assay, were strongly predictive of survival in ART-naive HIV-1 infected patients. Furthermore, plasma suPAR levels were not influenced by uPAR promoter polymorphisms. 18029284_elevated in polycystic ovary syndrome 18048089_The carotid atherosclerosis is independently related to uPA/its soluble receptor system in dialysis patients 18056417_The data demonstrate that cell surface protein assemblies are important in regulating the dynamics and localization of uPAR at the cell membrane and the exchange of monomers and dimers. 18084301_uPAR is required to activate alphavbeta3 integrin in podocytes, promoting cell motility and activation of the small GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1 18095109_The expression of constitutively activated RelA/NF-kappaB is associated with malignancy potential in astrocytic tumors and may play a critical role in the regulation of u-PA expression and invasiveness in gliomas. 18097558_suPAR, a soluble form of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor, inhibits human prostate cancer cell growth and invasion. 18247343_the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is upregulated by lysophosphatidic acid in human gastric cancer cells 18257282_The plasma uPAR and uPA levels in nosebleed patients before treatment is higher than that in normal group. 18315930_The change of plasma suPAR level in multiple myeloma contributes to predict the development and prognosis of the disease. 18328568_suPAR associated to important glucose metabolic aberrations in HIV-infected patients on HAART; suPAR was stable after a glucose challenge 18362146_A composite role of vitronectin and urokinase in the modulation of cell morphology upon expression of the urokinase receptor. 18376415_reports the crystal structures of uPAR in complex with both urokinase (uPA) and vitronectin and reveal that uPA occupies the central cavity of the receptor, whereas vitronectin binds at the outer side of the receptor 18487955_UPAR mediates anticancer activity of PEDF. 18508598_The structural biology of uPAR is reviewed with special emphasis on its multidomain composition and the interaction with its natural protein ligands 18508599_Role of the serine protease urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its high affinity receptor uPAR/CD87 in chronic kidney disease [REVIEW]. 18511987_distribution of genotypes and frequencies of alleles of the (CA)(n) repeat polymorphism in intron 3 of the uPAR gene, uPAR antigen levels and microvessel density in tumour and distant mucosa samples from 52 patients with colorectal cancer 18599586_Report increased expression of uPAR by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial cells. 18644795_analysis of conformational changes in the alpha(M)beta(2) headpiece and reorientation of its transmembrane domains when alpha(M)beta(2) interacts with uPAR 18673553_urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor has a role in oral squamous cell carcinoma 18691743_the plasma levels of uPA and uPAR are closely related to the degree and period of inflammation in patients with acute or chronic hepatitis B, and that uPA and uPAR might be important indicators for disease progression 18718938_Interaction of SRPX2 with uPAR involved in the functioning, the development and disorders of the speech cortex. 18725541_uPAR cooperates with integrin complexes containing beta(3) integrin to drive formation of the p130Cas-CrkII signaling complex and activation of Rac, resulting in a Rac-driven elongated-mesenchymal morphology, cell motility, and invasion. 18762175_Free fatty acids modify the expression for uPAR in the PMA-differentiated human monocyte/macrophage-like cell line U937. 18788551_uPA and uPAR in the synovial fluid may play a role in the pathogenesis of temporomandibular disorders. 18808175_Differential proteome expression is associated with UPAR suppression in malignant epithelial cancer. 18813792_the simultaneous downregulation of uPAR and MMP-9 induces apoptosome-mediated apoptosis through FADD-associated protein RIP and caspase 9 18813852_The aim of this study was to investigate whether UPAR co-localises with macrophages in symptomatic carotid plaques, and whether UPAR expression is associated with plaque rupture. 18819934_Enhanced expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is associated with the invasion of glioblastoma. 18830568_Data suggest that production of the active form of suPAR by neutrophils may contribute to the recruitment of monocytes and other cells to the sites of acute inflammation where neutrophil accumulation and activation occur. 18940913_uPAR and beta1-integrin interactions are essential to signals induced by integrin matrix ligands or uPA in lung cancer cells. 18941116_either uPA/uPAR interaction, Mac-1 activation, or prevention of its association with uPAR triggers a signaling pathway leading to the inefficient release of HIV from monocytic cells 18949356_uPA/uPAR downregulation inhibits radiation-induced migration, invasion and angiogenesis in IOMM-Lee meningioma cells and decreases tumor growth in vivo. 18953252_Expression of kallikrein 7 diminishes pancreatic cancer cell adhesion to vitronectin and enhances urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor shedding. 18954937_suPAR, prevents the interaction of urokinase with membrane-anchored uPAR on residual normal cells. 18957516_Caveolin-1 plays a dual role in the fibronectin assembly regulated by uPAR signaling. 19008962_These results indicate that, in addition to the ligand-induced endocytosis of uPAR, efficient surface expression and membrane trafficking might also be driven by an uncommon macropinocytic mechanism coupled with rapid recycling to the cell surface. 19017363_NYD-SP8 has a role in regulating ECM degradation, providing a novel mechanism that modulates urokinase signalling in the suppression of cancer progression 19020743_EGF induces uPAR expression via ERK-1/2, AP-1, and NF-kappaB signaling pathways and, in turn, stimulates cell invasiveness in human gastric cancer AGS cells 19037107_M6P/IGF2R controls cell invasion by regulating alphaV integrin expression and by accelerating uPAR cleavage, leading to the loss of the urokinase/vitronectin/integrin-binding site on uPAR. 19050704_study evaluated the expression level of uPAR mRNA and the presence of isolated tumour cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood in gastric cancer patients and clarified its clinical significance 19088796_Data show the effects of nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide on the expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA), urokinase-PA, u-PA receptor, and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 19115132_The higher expression of uPAR/uPA in most of the opportunistic cerebral lesions supports their role in these diseases, suggesting their contribution to tissue injury. 19117638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19123477_analysis of urokinase, urokinase receptor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in colon cancer liver metastases 19157142_The positive expression of uPA and uPAR in hypopharyngeal carcinoma were significantly higher than in normal tissue. 19176991_Urokinase & its receptor UPAR exert a regulatory effect on physiologic cell migration as well as tumor growth and metastasis. Review. 19177204_uPAR is under transcriptional control of HIF and that this is important for hypoxia-induced metastasis 19298527_survivin is an essential mediator of arthritogenic properties of uPA regulating its synthesis in synovial fibroblasts and uPAR expression in leucocytes 19383607_role of uPAR in the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells 19403319_the 20-26 amino acid residues of uPA are important for the binding between uPA and uPAR, and that the electrostatic interactions between the charged amino acid residues existing in both uPA and uPAR have large contribution to the binding 19404710_the expression levels of u-PAR in peripheral blood and bone marrow evaluated preoperatively indicate the potential of breast cancer to relapse or metastasize after surgery. 19411312_u-PAR may interact with multiple integrins in normal human lung fibroblasts thereby promoting attachment, spreading, and migration. 19433314_siRNA to uPAR significantly inhibited cell proliferation and migration and stimulated apoptosis, to a greater extent than uPA siRNA. 19435784_uPAR gene amplifications identify a subgroup of particularly aggressive tumors 19436306_LPS promotes tumour cell ECM adhesion and invasion through activation of the u-PA system in a TLR-4- and NF-kappaB-dependent manner. 19443020_This study represents the first report to identify PLAUR as a potential asthma susceptibility gene and determine PLAUR regions underlying this association, including a role in influencing plasma PLAUR levels 19443353_study demonstrated that uPA and PAI-1 are useful predictors of distant metastases in a subset of early stage, node-negative breast cancer patients 19461880_study shows that uPAR is upregulated upon exposure to B. burgdorferi; uPAR plays an important role in phagocytosis of B. burgdorferi by leukocytes 19472211_Plasminogen activator inhibitors regulate cell adhesion through a uPAR-dependent mechanism. 19475533_Tumor stroma is the predominant UPAR-expressing tissue in human breast cancer: prognostic impact is reported. 19480010_High u-PAR-gene expression is associated with thyroid neoplasms. 19497996_uPAR may promote cancer metastasis independent of uPA. 19546228_These results demonstrate that uPAR-initiated cell signaling may be targeted to reverse EMT in cancer. 19609941_Data show that uPAR expressed in macrophages and neutrophils in all cases. 19616049_Soluble urokinase receptor conjugated to carrier red blood cells binds latent pro-urokinase and alters its functional profile. 19635932_Link overexpression of uPAR to the pathogenesis of malignant pleural mesothelioma, and demonstrate that this receptor contributes to accelerated tumor growth in part through interactions with uPA. 19638192_Protein analysis confirmed expression of multiple different forms of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (UPAR) in the same cells as well as expression of soluble uPAR in cell supernatants 19642359_Abnormally high levels of Annexin II and u-PAR expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells may contribute to the increased production of plasmin, leading to primary hyperfibrinolysis. 19691446_uPAR-mediated VSMC differentiation employs lipid rafts. 19717562_ECRG2 is involved in the regulation of cell migration/invasion through uPA/uPAR/beta1 integrin pathway. 19740518_uPA, but not uPAR, is an independent prognostic factor and that this negative effect on survival is relevant specifically for mismatch repair-proficient colorectal cancers. 19756998_Neutrophils contribute to or are responsible for the generation of increased suPAR levels during the inflammatory response and, release the chemotactically active form of suPAR that might be involved in lymphocyte recruitment into the inflamed tissues. 19782465_lithocholic acid induces uPAR expression via Erk-1/2 and AP-1 pathway and, in turn, stimulate invasiveness of human |
ENSMUSG00000046223 |
Plaur |
5109.132593 |
2.9407769417 |
1.556197 |
0.024185448 |
4222.465107 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7652.8605265 |
121.3611621 |
2620.7120127 |
33.2195125 |
| ENSG00000012171 |
7869 |
SEMA3B |
protein_coding |
Q13214 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits axonal extension by providing local signals to specify territories inaccessible for growing axons. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the class-3 semaphorin/collapsin family, whose members function in growth cone guidance during neuronal development. This family member inhibits axonal extension and has been shown to act as a tumor suppressor by inducing apoptosis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:7869; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; chemorepulsion of axon [GO:0061643]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526] |
11809707_Human Semaphorin 3B (SEMA3B) located at chromosome 3p21.3 suppresses tumor formation in an adenocarcinoma cell line. 11922394_Identification of semaphorin 3B as a direct target of p53. 12810670_SEMA3B gene alterations may play a important role in the malignant transformation of NSCLC via a two-hit mechanism, including epigenetic changes and allelic loss, for tumor suppressor gene inactivation. 15273288_VEGF165, produced by tumor cells, acts as an autocrine survival factor and that SEMA3B mediates its tumor-suppressing effects, at least in part, by blocking this VEGF autocrine activity. 15831529_Heterozygous or homozygous variant genotype confers a >40% reduced relative risk of lung cancer in Latino Americans controlling for other lung cancer risk factors. 15831529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17452250_Higher level of SEMA3B expression was found in differentiated tumors with favorable histopathology (n = 19) than in tumors with unfavorable histology. 18356290_A putative role for SEMA3B as an osteoblast protein that regulates bone mass and skeletal homeostasis. 18458115_SEMA3B exerts unexpected functions in cancer progression by fostering a prometastatic environment through elevated IL-8 secretion. 18757406_Repulsion of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells by sema3B-m was mediated primarily by the neuropilin-1 receptor but sema3B-m was also able to transduce signals via neuropilin-2 18922901_SEMA3B is a potential tumor suppressor that induces apoptosis in SEMA3B-inactivated tumor cells through the Np-1 receptor by inactivating the Akt signaling pathway. 18985860_IGFBP-6 is the effector of tumor suppressor activity of SEMA3B. 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19548530_SEMA3B plays role in inhibiting of growth of renal, ovarian and colorectal cancer cells. 19683737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19683737_These data indicate that polymorphisms in SEMA3B are associated with prostate cancer risk and poor prognosis in Hispanic and nonHispanic white men 20088387_that methylation of promoter CpG-island contributed into inactivation of SEMA3B gene-suppressor in RCC. 20124444_semaphorin-3B and semaphorin-3F have roles in ovarian cancer 23292452_Three candidate tumor-suppressor genes, SEMA3B, AXUD1 and GNAT1 may be involved in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23906303_Loss of Sema3B expression is associated with biochemical recurrence of patients with low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer. 24280143_The transcriptional activity of RHOA, SEMA3B, and CKAP2 genes was assessed in blood samples of leukaemia patients and healthy donors. 24402303_CpG methylation of SEMA3B epigenetically regulates SEMA3B expression during development of gastric cancer. 25335892_although plexin-A4 overexpression restored Sema3A signaling in plexin-A1-silenced cells, it failed to restore Sema3B signaling in plexin-A2-silenced cells. 25454475_SEMA3B mRNA and protein is not altered in severe early onset preeclamptic placentas. 25961819_Aberrant expression and methylation of SEMA3B could be suggested as markers of lung and renal cancer progression. 26828533_Maternal SEMA 3B level increased in preeclampsia before the onset of manifestations, indicating that SEMA 3B plays a role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia 27050958_As the clinical pathological glioma grade increased, SEMA3B expression decreased. 27349960_By upregulating p53 and p21 expression and inhibiting Akt (Ser473) phosphorylation, SEMA3B could induce cell cycle arrest at G1/S phase. 28581515_data provide new insights into the role of SEMA3B in mammary gland and provides a new branch of GATA3 signaling that is pivotal for inhibition of breast cancer progression and metastasis 29763494_Advanced peri-implantitis lesions showed higher levels of gene expression for Sem3A and Sem4D and lower levels of Sem4A in comparison to tissues obtained from a healthy dental implant. 30656427_Low SEMA3B expression is associated with gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. 30868892_miR-374b promotes glioma process in vitro through suppressing SEMA3B via targeting GATA3 30915595_the findings suggest that SEMA3B and SEMA3B-AS1 may act as tumor suppressors and may serve as potential targets for antitumor therapy. 30972979_our research revealed the regulation of EFEMP1 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in HCC. EFEMP1 may suppress the growth of HCC cells by promoting SEMA3B. 31217417_Analysis of the SEMA3B expression profile shows the complexity of neoplastic transformation, which confirms the different expression of SEMA3B in endometrial cancer cells and endothelial cells. 32534052_Semaphorin 3B-associated membranous nephropathy is a distinct type of disease predominantly present in pediatric patients. 35001548_Central Role of Semaphorin 3B in a Serum-Induced Arthritis Model and Reduced Levels in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000057969 |
Sema3b |
12.081708 |
0.1805135533 |
-2.469821 |
0.531323954 |
23.608648 |
0.00000118055742867044427803972610202531967615868779830634593963623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004141912918273296616007532466863239051235723309218883514404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4846450 |
1.3094743 |
19.6984794 |
4.2248943 |
| ENSG00000012174 |
51360 |
MBTPS2 |
protein_coding |
O43462 |
FUNCTION: Zinc metalloprotease that mediates intramembrane proteolysis of proteins such as ATF6, ATF6B, SREBF1/SREBP1 and SREBF2/SREBP2 (PubMed:11163209, PubMed:10805775). Catalyzes the second step in the proteolytic activation of the sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) SREBF1/SREBP1 and SREBF2/SREBP2: cleaves SREBPs within the first transmembrane segment, thereby releasing the N-terminal segment with a portion of the transmembrane segment attached (PubMed:10805775, PubMed:27380894, PubMed:9659902). Mature N-terminal SREBP fragments shuttle to the nucleus and activate gene transcription (PubMed:10805775, PubMed:27380894, PubMed:9659902). Also mediates the second step in the proteolytic activation of the cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-6 (ATF6 and ATF6B) (PubMed:11163209). Involved in intramembrane proteolysis during bone formation (PubMed:27380894). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10805775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11163209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27380894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9659902}. |
Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Ichthyosis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Palmoplantar keratoderma;Protease;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a intramembrane zinc metalloprotease, which is essential in development. This protease functions in the signal protein activation involved in sterol control of transcription and the ER stress response. Mutations in this gene have been associated with ichthyosis follicularis with atrichia and photophobia (IFAP syndrome); IFAP syndrome has been quantitatively linked to a reduction in cholesterol homeostasis and ER stress response.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:51360; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; ATF6-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:0036500]; bone maturation [GO:0070977]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis [GO:0031293]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1990440]; regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0045540]; regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1905897]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
11850408_S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage is involved in regulating XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. 15299016_S2P cleavage is blocked by the bulky ATF6 luminal domain, which is reduced in size by S1P 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19361614_assign the IFAP syndrome locus to the 5.4 Mb region between DXS989 and DXS8019 on Xp22.11-p22.13 and provide evidence that missense mutations of membrane-bound transcription factor protease, site 2 (MBTPS2) are associated with this phenotype 19689518_study presents the largest kindred of ichthyosis follicularis, alopecia and photophobia (IFAP) reported to date clearly demonstrating X-linked inheritance; missense mutations of the gene, MBTPS2 are associated with the IFAP phenotype in this kindred 20672378_Missense mutations in the MBTPS2 gene have been identified as the cause of Follicularis Spinulosa Decalvans (KFSD). 20854407_Chinese family with a mild IFAP phenotype and a novel mutation in the MBTPS2 gene 21315478_We confirm that MBTPS2 mutations cause ichthyosis follicularis atricia and photophobia syndrome in patients of Chinese origin 21426410_Both intronic MBTPS2 c.671-9T>G and c.225-6T>A point mutations are ichthyosis follicularis, alopecia and photophobia syndrome causing mutations. 22816986_We report a fourth pedigree affected with Keratosis Follicularis Spinulosa Decalvans resulting from a recurrent missense mutation in the MBTPS2 gene. 22931912_We demonstrate a novel association between an MBTPS2 mutation and an X-linked form of Olmsted syndrome. 23316014_In male patients, a genotype-phenotype correlation has begun to emerge, linking the site of the mutation in MBTPS2 with the clinical outcome described as IFAP syndrome. 23571157_S2P is essential owing to its activation of the sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs); in the absence of exogenous lipid, cells lacking S2P cannot survive. (Review) 27380894_MBTPS2 mutations cause defective regulated intramembrane proteolysis in X-linked osteogenesis imperfecta. 28717930_This study identified a direct regulatory effect of MBTPS2 on TRPV3 which can partially contribute to the overlapping clinical features of IFAP and Olmsted syndromes under a common signaling pathway. 29951998_Study reports a novel missense mutation c.638C>T (p.Ser213Leu) in MBTPS2 in a large Chinese family with keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans. 30294811_Study reports a three-generation Chinese pedigree with a mild phenotype of ichthyosis follicularis with atrichia and photophobia syndrome caused by a novel hemizygous missense mutation c.1494G>T (p.Leu498Phe) in exon 11 of MBTPS2. 30589367_MBTPS2 mutation is associated with Retinal venous tortuosity. 33743732_MBTPS2, a membrane bound protease, underlying several distinct skin and bone disorders. |
ENSMUSG00000046873 |
Mbtps2 |
201.668079 |
2.0547905589 |
1.038991 |
0.124225741 |
70.292123 |
0.00000000000000005114151050214838914718086493047574634087331881720020487769318151549668982625007629394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000392741256509734739275727908616480262330743406830324548906219206401146948337554931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
271.8240109 |
20.1023228 |
133.2316678 |
7.6660545 |
| ENSG00000012660 |
60481 |
ELOVL5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NYP7 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first and rate-limiting reaction of the four reactions that constitute the long-chain fatty acids elongation cycle. This endoplasmic reticulum-bound enzymatic process allows the addition of 2 carbons to the chain of long- and very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) per cycle. Condensing enzyme that acts specifically toward polyunsaturated acyl-CoA with the higher activity toward C18:3(n-6) acyl-CoA. May participate in the production of monounsaturated and of polyunsaturated VLCFAs of different chain lengths that are involved in multiple biological processes as precursors of membrane lipids and lipid mediators (By similarity) (PubMed:10970790, PubMed:20937905). In conditions where the essential linoleic and alpha linoleic fatty acids are lacking it is also involved in the synthesis of Mead acid from oleic acid (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHI7, ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10970790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937905}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spinocerebellar ataxia;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937905}. |
This gene belongs to the ELO family. It is highly expressed in the adrenal gland and testis, and encodes a multi-pass membrane protein that is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum. This protein is involved in the elongation of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Mutations in this gene have been associated with spinocerebellar ataxia-38 (SCA38). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:60481; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic tree [GO:0097447]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; fatty acid elongase activity [GO:0009922]; very-long-chain 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase activity [GO:0102756]; alpha-linolenic acid metabolic process [GO:0036109]; fatty acid elongation, monounsaturated fatty acid [GO:0034625]; fatty acid elongation, polyunsaturated fatty acid [GO:0034626]; fatty acid elongation, saturated fatty acid [GO:0019367]; linoleic acid metabolic process [GO:0043651]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0035338]; positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045723]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; unsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006636]; very long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042761] |
18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363506_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363506_Our genome-wide association study identified SRBD1 and ELOVL5 as new susceptibility genes for (normal tension glaucoma) NTG. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21383846_Not being breastfed resulted in a disadvantage in cognition (5 to 8 points) among children CC homozygote for rs2397142 (low ELOVL5 activity), but not among those carrying the G allele. 21508110_Typical POAG associated with ELOVL5 gene polymorphism may have a late rather than an early onset. 22293571_minor allele copies at rs2294867 associated with an increase in total and LDL cholesterol...number of minor allele copies at rs761179 associated with increase in total cholesterol... However, associations not replicated in independent populations. 23099444_a novel link between Elovl5-mediated synthesis of 18:1,n-7 and GNG through the control of the mTORC2-Akt-FoxO1 pathway 24167612_Changes in the mRNA-expression levels of FADS1 and 2 directly affect blood DGLA levels and D6D activity. This study suggests that lower mRNA-expressions of FADS2 and ELOVL5 are associated with higher risk of atopic eczema in young children. 25065913_In transfection experiments, subcellular localization of altered ELOVL5 showed a perinuclear distribution with a signal increase in the Golgi compartment, whereas the wild-type showed a widespread signal in the endoplasmic reticulum. 26321664_performed a detailed promoter/enhancer analysis of ELOVL5 gene, and identified two new SREBP binding sites, one in the 10 kb upstream region and one in the exon 1 26433464_SCA38 subtype is very rare in Mainland China; no disease-related gene mutations in ELOVL5. 28245901_common variations associated with polyunsaturated fatty acid levels in breast milk 28931069_Low ELOVL5 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 30291282_The ELOVL5 gene was significantly differentially expressed in adipose tissues from unrelated type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients and in human pancreatic islets. The results demonstrate that blood-derived DNA methylation is associated with T2D risk as a proxy for cumulative epigenetic status in human adipose and pancreatic tissues. 30914501_The that maternal genetic variants in ELOVL2 and ELOVL5 were associated with PUFA levels in breast milk and that the combination of SNP haplotypes and higher DHA intake increased PUFA concentrations. 33547161_ELOVL5 Is a Critical and Targetable Fatty Acid Elongase in Prostate Cancer. 35670054_ELOVL5-mediated fatty acid elongation promotes cellular proliferation and invasion in renal cell carcinoma. 36056008_Downregulation of Elovl5 promotes breast cancer metastasis through a lipid-droplet accumulation-mediated induction of TGF-beta receptors. |
ENSMUSG00000032349 |
Elovl5 |
1696.170474 |
2.7232713016 |
1.445341 |
0.040100381 |
1329.408127 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000459703743605920126435717481672311441236 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000628261782928090760190182559202264361461 |
Yes |
No |
2512.8392963 |
59.2591863 |
929.4987971 |
17.9484848 |
| ENSG00000012779 |
240 |
ALOX5 |
protein_coding |
P09917 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxygenation of arachidonate ((5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate) to 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoate (5-HPETE) followed by the dehydration to 5,6- epoxyeicosatetraenoate (Leukotriene A4/LTA4), the first two steps in the biosynthesis of leukotrienes, which are potent mediators of inflammation (PubMed:8631361, PubMed:21233389, PubMed:22516296, PubMed:24282679, PubMed:19022417, PubMed:23246375, PubMed:8615788, PubMed:24893149, PubMed:31664810). Also catalyzes the oxygenation of arachidonate into 8-hydroperoxyicosatetraenoate (8-HPETE) and 12-hydroperoxyicosatetraenoate (12-HPETE) (PubMed:23246375). Displays lipoxin synthase activity being able to convert (15S)-HETE into a conjugate tetraene (PubMed:31664810). Although arachidonate is the preferred substrate, this enzyme can also metabolize oxidized fatty acids derived from arachidonate such as (15S)-HETE, eicosapentaenoate (EPA) such as (18R)- and (18S)-HEPE or docosahexaenoate (DHA) which lead to the formation of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPM) lipoxin and resolvins E and D respectively, therefore it participates in anti-inflammatory responses (PubMed:21206090, PubMed:31664810, PubMed:8615788, PubMed:17114001, PubMed:32404334). Oxidation of DHA directly inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and sprouting angiogenesis via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) (By similarity). It does not catalyze the oxygenation of linoleic acid and does not convert (5S)-HETE to lipoxin isomers (PubMed:31664810). In addition to inflammatory processes, it participates in dendritic cell migration, wound healing through an antioxidant mechanism based on heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) regulation expression, monocyte adhesion to the endothelium via ITGAM expression on monocytes (By similarity). Moreover, it helps establish an adaptive humoral immunity by regulating primary resting B cells and follicular helper T cells and participates in the CD40-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) after CD40 ligation in B cells through interaction with PIK3R1 that bridges ALOX5 with CD40 (PubMed:21200133). May also play a role in glucose homeostasis, regulation of insulin secretion and palmitic acid-induced insulin resistance via AMPK (By similarity). Can regulate bone mineralization and fat cell differentiation increases in induced pluripotent stem cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P48999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17114001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19022417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21200133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21206090, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21233389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22516296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23246375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24282679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24893149, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31664810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32404334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8615788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8631361}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Direct protein sequencing;Hydrolase;Iron;Leukotriene biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; leukotriene A4 biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8631361}. |
This gene encodes a member of the lipoxygenase gene family and plays a dual role in the synthesis of leukotrienes from arachidonic acid. The encoded protein, which is expressed specifically in bone marrow-derived cells, catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid to 5(S)-hydroperoxy-6-trans-8,11,14-cis-eicosatetraenoic acid, and further to the allylic epoxide 5(S)-trans-7,9-trans-11,14-cis-eicosatetrenoic acid (leukotriene A4). Leukotrienes are important mediators of a number of inflammatory and allergic conditions. Mutations in the promoter region of this gene lead to a diminished response to antileukotriene drugs used in the treatment of asthma and may also be associated with atherosclerosis and several cancers. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:240; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear envelope lumen [GO:0005641]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; arachidonate 12(S)-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0004052]; arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0004051]; arachidonate 8(S)-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0036403]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on single donors with incorporation of molecular oxygen, incorporation of two atoms of oxygen [GO:0016702]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; dendritic cell migration [GO:0036336]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; hepoxilin biosynthetic process [GO:0051122]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; leukocyte chemotaxis involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002232]; leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002523]; leukotriene A4 biosynthetic process [GO:1901753]; leukotriene biosynthetic process [GO:0019370]; leukotriene metabolic process [GO:0006691]; leukotriene production involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002540]; linoleic acid metabolic process [GO:0043651]; lipid oxidation [GO:0034440]; lipoxin biosynthetic process [GO:2001301]; lipoxygenase pathway [GO:0019372]; long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042759]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1903573]; negative regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903671]; negative regulation of vascular wound healing [GO:0061044]; negative regulation of wound healing [GO:0061045]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to arterial endothelial cell [GO:1904999]; regulation of cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:1900407]; regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900015]; regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045598]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of inflammatory response to wounding [GO:0106014]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903426] |
11471199_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11796736_molecular basis of the specific subcellular localization of the C2-like domain 11844797_promotion of phosphorylation at Ser-271 by MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 and arachidonic acid 12107604_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12111389_Theoretical model of the tertiary structure of the 5-lipoxygenase catalytic domain, using the resolved structure of rabbit 15-lipoxygenase as a template. 12140292_Data show that the previously identified bipartite-motif region within 5-lipoxygenase is not a functional import sequence, whereas the newly identified basic region constitutes a true nuclear import sequence. 12163367_marked expression of 5-LOX in human pancreatic cancer tissues 12234060_there is no evidence of increased expression of 5-LO mRNA in either quiescent or active stages of inflammatory bowel disease 12525578_results demonstrating mechanisms for activation of 5-LO differ considerably between cell types 12629151_LOX5 and FLAP pathway in monocytes and microglia yields products toxic toward neurons (neuroblastoma cell line) 12664574_examines the binding of calcium to this enzyme (REVIEW) 12730086_CON6 mouse point mutations (I645V and V646I) as well as the double mutant (I645V+V646I) introduced by site-directed mutagenesis into human 5-LO exhibited reduced catalytic activities but retained their positional specificity & substrate affinity. 12751728_LTC4 production by eosinophils in asthmatic subjects with alternative forms of ALOX-5 core promoter 12751768_upregulated in colon cancer; affecting cell survival 12751769_upregulation in glioblastoma multiforme 12859962_Data show that inhibition of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase induces rapid activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in human prostate cancer cells which is prevented by the 5-lipoxygenase metabolite, 5(S)-HETE. 12893830_5-lipoxygenase can be activated by calcium and low levels of hydroperoxides 12907138_human breast tumours aberrantly express significantly higher levels of 5-lipoxygenase; levels of 5-lipoxygenases were also particularly high in tumours from patients who died of breast cancer. 12911785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14532840_Lipoxygenase is induced in bladder cancer. Results suggest that lipoxygenase inhibitors may mediate potent antiproliferative effects against bladder cancer cells. 14749922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14749922_possible involvement of 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5) gene polymorphism in ASA-intolerant asthma (AIA) in a Korean population 14767568_increased expressions of 5-LOX and 12-LOX were detected in testicular cancer tissues 15010818_Up-regulation of 5-Lipoxygenase is associated with prostate cancer 15219851_determination of binding sites for calcium and magnesium 15280375_PKA phosphorylates 5-LO on Ser-523, which inhibits the catalytic activity of 5-LO and reduces cellular LT generation 15301234_Expression of 5-lipoxygenase mRNA was observed in muscle tissues from patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies suggesting a role in pathogenesis of this disease. 15308583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308583_polymorphisms in arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is associated with colon cancer risk 15616590_Data show that 5-lipoxygenase activity increases during senescence-like growth arrest via a p53/p21-dependent pathway in both human and mouse embryo fibroblasts. 15661803_Increased 5-lipoxygenase expression is associated with esophageal cancer 15848143_Mutagenesis of 5LO C-terminal mutants showed that hidrogen bonds are required for a stabilizing C-terminal loop. 15923196_In the absence of Ca2+ (chelated using EDTA), OAG strongly and concentration-dependently stimulated 5-LO enzyme from polymorphonuclear leukocytes 15933245_The expression of 5-LO is elevated in symptomatic compared with asymptomatic plaques and is associated with acute ischemic syndromes 16135563_results suggest that splitting of BL41-E95-A cells induces de novo synthesis of a protein involved in the activation of casp-6 and casp-8, which cleaves 5-LO. 16165096_Nuclear export of 5-LO depends on the stress-induced activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. 16275640_Arachidonic acid regulates the translocation of 5-LO in human neutophild unraveling a novel mechanism of the cAMP-mediated inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis 16293801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16361798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16361798_the polymorphism of ALOX5 at positions of -1708 G > A showed significant difference in genotype frequency between aspirin-intolerant urticaria and aspirin-intolerant asthma 16364163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16402861_mizolastine down-regulated 5-LOX mRNA expression and inhibited 5-LOX translocation from nucleus to cytoplasm in fibroblasts 16413224_the GC-rich part of the 5-lipoxygenase gene promoter, including a novel Sp1 site, appear important for basal (rather than upregulated) transcription of 5-lipoxygenase gene in monocytic cells 16495221_a critical regulatory role of arachidonate reacylation that limits leukotriene biosynthesis in concert with 5-lipoxygenase and cytosolic phospholipase A(2)alpha activation 16531984_Administration of omega-3 reduced significantly ALOX5 activity, with no effect on ALOX5 protein expression. 16537708_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16672272_The binding between human 5-lipoxygenase with its inhibitors can be investigated by SPR technology and molecular docking simulation. 16698924_5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene A4 hydrolase expression in atherosclerotic lesions correlates with symptoms of plaque instability 16733792_The stratified squamous epithelial cells from inflamed or hyperplastic tissues of palatine and pharyngeal tonsils (nasopharyngeal-associated lymphoid tissue) express 5-lipoxygenase protein. 16750418_analysis of vitamin D receptor (VDR) binding to putative vitamin D response elements within the 5-LO promoter and analysis its function 16899822_human 5-lipoxygenase is inhibited by dihydroxydocosahexaenoic acids of the neuroprotectin D family 16919603_Sequence analysis and deletion studies indicate the existence of up to four Smad binding elements and at least one TGFbeta responsive element far downstream of the transcriptional start site of the 5-lipoxygenase gene. 16924104_Coactosin-like protein (CLP) up-regulates Ca(2+)-induced 5-lipoxygenase (5LO) activity, and increases the amount of Leukotriene A(4) formed by 5LO. 17018618_ANXA7 and p53 can distinctly regulate LOX transcription that is potentially relevant to the arachidonic acid -mediated cell growth control in tumor suppression. 17072961_results suggest that 5-lipoxygenases is up-regulated in colorectal cancer and that inhibition of its expression might be valuable in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer 17080223_platelet-stimulated proliferation of fibroblasts is mediated by an increased 5-LO activity 17115186_Multiple ALOX5 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) independently predict severe carotid artery disease. 17115186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17236225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17236225_no significant associations of the 2 5-LOX polymorphisms with the risk of colorectal adenoma 17373700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373938_The data did not support a significant effect of ALOX5-promoter polymorphism on MI risk. 17434678_Suppression of 5-lipoxygenase gene is involved in triptolide-induced apoptosis in pancreatic tumor cell lines. 17460547_CYSLTR2 and ALOX5 polymorphisms may predispose a minority of individuals to excessive cysteinyl-leukotriene concentrations, yielding a distinct asthma phenotype most likely to respond to leukotriene modifier pharmacotherapy. 17460547_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17467166_involved in tumor progression of several cell types and may also participate in lymphomagenesis, especially Epstein Barr virus-mediated. 17500032_In silico screening of the whole 5-LO gene area (84 kb, including 10 kb promoter region) was performed and 22 putative vitamin D response elements were identified. 17521309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17616938_5-Lipooxygenase up-regulation is an important step in renal cancer progression. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17825794_These results suggest that overexpression of 5-LO and LTB(4) in atherosclerotic plaques possibly promote MMP-induced plaque rupture in diabetes. 17894944_TsA increases 5-LO promoter activity by the enhanced recruitment of Sp1 and Sp3 to the 5-LO promoter 17909879_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17909879_data do not provide consistent evidence of association between genomic variation in ALOX5 and clinical variability in aBMD in healthy 17924829_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18174194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18174194_The observation of an association of ALOX5 variants with susceptibility to tuberculosis contributes evidence of the importance of 5-LO products to the regulation of immune responses to M. tuberculosis. 18179798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18179798_variant 5-lipoxygenase promoter genotypes do not have a major role in myocardial infarction 18180307_CMV infection induces 5-lipoxygenase expression and leukotriene B4 production in vascular smooth muscle cells 18204779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204779_These results suggest that E254K in the 5-LO might be associated with bronchial asthma. 18218859_Tertiary-butanolcauses moderate suppression of 5-LO and hardly inhibits 5-LO translocation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. 18280718_Results describe the cyclooxygenase (COX) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) selectivity of COX inhibitors. 18295198_Describe an ex vivo human whole blood assay to evaluate the efficacy and selectivity of 5-LOX inhibitors. 18339529_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18366797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18369664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18369664_findings do not support a link between common allelic variation in or near ALOX5 or ALOX5AP and the risk of coronary artery disease 18398223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18421027_5-LOX was expressed in 6% of ovarian neoplasms. 18421434_Role of ALOX5 in pancreatic function in human islets is assessed through short interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown experiments. 18525291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571838_Report the long-term effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on COX-1/2, 5-LOX and leukotriene receptors in patients with a risk gastritis phenotype--a link to gastric carcinogenesis. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18678882_5-lipoxygenase is upregulated in the Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. 18842779_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18842779_The 3 and 4 variants lead to higher 5-LO expression and provide additional evidence that these alleles are associated with greater risks of atherosclerosis and MI in the context of a high-AA diet. 18843019_No significant effect of ALOX5 genotype on breast cnacer risk. 18927292_5-LOX is overexpressed in adenomatous polyps and cancer. 18976020_There is a relationship between 5-LO expression and the neoangiogenesis process as reflected by intratumoral microvessel density in human sporadic colorectal adenocarcinomas. 18978352_nuclear import, which is regulated by phosphorylation on Ser-523, to determine the subcellular distribution of 5-LO, which in turn regulates leukotriene biosynthesis. 18991687_The pro-inflammatory alleles of COX-2 and 5-LO were overrepresented in MI and under-represented in centenarians whereas age-related controls displayed intermediate values 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18996667_The development of methodology for clinical measurement of ALOX5 intermediates from peripheral blood mononuclear cells is reported. 19022417_Results suggest that the formation of miRNAs may be regulated by 5LO in leukocytes and cancer cells expressing this lipoxygenase. 19053751_microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 and 5-lipoxygenase can be inhibited by pirinixic acid derivatives 19075240_identify multiprotein complexes for leukotriene synthesis on the outer and inner nuclear membranes of mast cells and neutrophils, centered on the 5-Lipoxygenase-Activating Protein and 5-Lipoxygenase 19083497_Grape seed and red wine polyphenol extracts inhibit this enzyme in seveal tumor cell lines. 19130089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131661_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19134178_a role of the 5-LO pathway in B cells before the cells finally differentiate to plasma cells 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19214143_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19224689_5-LOX protein expression in human bronchial epithelial cells can be regulated by benzidine. 19233132_LTC(4)S interacts in vitro with both FLAP and 5-LO and that these interactions involve distinct parts of LTC(4)S. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19390118_5-LO was the enzyme responsible for the generation of the HepsilondGuo DNA-adduct in CESS cells. 19423540_Nine SNPs distributed across eight genetic regions (ALOX5, IRAK3, ITGB2, NCF2, NFKB1, SELP, SOD1, and STAT1) were associated with risk of glioma with P value of A in intron 6 to rs2229136A>G in exon 13.five-repeat genotype was the most frequent Sp1/Egr1 promoter tandem repeat variant 19450127_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19473080_Genotyping the GGGCGG tandem repeat promoter polymorphism in ALOX5 by pyrosequencing assay is reported. 19473080_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19497113_5-LO is expressed in synovial tissue, mainly in macrophage-like cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis; 5-LO enzyme, however, is not detected in T- or B-lymphocytes from these synovial biopsies. 19524426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19717473_The shorter repeat alleles of the 5-LO promoter lead to higher gene expression. 19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19807693_Results of the present study support a role for CLP as a chaperoning scaffold factor, influencing both the stability and the activity of 5-LO. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19919819_The 5-lipoxygenase-leukotriene A4 pathway might play roles in the proliferation of human glioma cells. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20110601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20126469_HBxDelta127 promotes cell growth through a positive feedback loop involving 5-LOX and fatty acid synthase 20128419_no association between gene polymorphism and bronchial asthma in a Spanish population 20173757_A natural mutant of hepatitis B virus X gene (HBx) with a deletion from 382 to 401 base pairs (termed HBxDelta127), promotes hepatoma cell growth through activating SREBP-1c involving 5-LOX. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20372792_Cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase pathways have roles in diosgenin-induced apoptosis in HT-29 and HCT-116 colon cancer cells 20382140_The mRNA levels of ALOX5 implicated pathways differed significantly in gliomas according to the histological type. 20388081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20549218_The results support the role of 5-LOX in early stages of colon carcinogenesis. 20592751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21098726_alternative 5-LO isoforms may represent a new mechanism for the regulation of the 5-LO pathway and lipid mediator biosynthesis 21200133_alternative ROS production pathway that is triggered by CD40 ligation, involves 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), and results in activation of p38 MAPK 21224059_these results illustrate the novel role of Alox5 in adaptive humoral immunity by managing primary B cells and Tfh cells in vivo. 21233389_identified a 5-LOX-specific destabilizing sequence involved in orienting the carboxyl terminus, which binds the catalytic iron; report the crystal structure at 2.4 angstrom resolution of 5-LOX stabilized by replacement of this sequence 21296957_ALOX5 gene variants affect eicosanoid production and response to fish oil supplementation. 21314617_The interaction between ceruloplasmin of human plasma, and 5-lipoxygenase, the key enzyme of leukotriene synthesis, is shown for the first time 21403093_The upregulation of the LT pathway in human aortic valve stenosis taken together with the potentially detrimental LT-induced effects on valvular myofibroblasts, suggests one possible role of inflammation in the development of aortic stenosis 21482803_Biosynthesis of hemiketal eicosanoids by cross-over of the 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 pathways. 21540635_genetic polymorphism is associated with white blood cell counts in workers exposed to benzene 21605700_the expression and activity of both cyclooxygenase-2 and lipoxygenase-5 was markedly increased in two different cell culture models of cystic fibrosis 21723968_arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase can be considered for validation as a potential marker for diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis. 21729626_The SNPs of ALOX(5)AP and LTC(4)S are associated with asthma. 21883892_Only class I histone deacetylase inhibitors induce 5-LO promoter activity. Induction of 5-LO mRNA expression correlated with histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation. 22050225_The bioinformatic analysis of the 5-LO surface for putative protein-protein interaction domains and molecular modeling of the dimer interface suggests a head to tail orientation of the dimer which also explains the localization of previously reported ATP binding sites. 22253131_study suggests that ALOX5 can enhance invasion in PTC through a 5-HETE dependent induction of MMP-9, and demonstrates a relationship ALOX5 can enhance invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma through a 5(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid dependent induction of MMP-9, and demonstrates a relationship between ALOX5 and tumor invasion not been previously described 22282663_inherited variation in IL1A and ALOX5 seems to affect ovarian cancer risk 22293202_the lipid metabolism enzyme 5-LOX and its metabolite LTB4 are capable of activating transcription factor NF-kappaB in hepatoma cells. 22363630_The coupling of alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay is involved in the regulation of 5-LO gene expression. 22433003_Licofelone inhibits IL-18-induced 5-lipoxygenase enzyme activity in human mesangial cells. 22516296_phosphorylation of 5-LOX at S663 not only down-regulates leukotriene synthesis but also stimulates lipoxin production in inflammatory cells that do not express 15-LOX, redirecting lipid mediator biosynthesis to the production of mediators of inflammation. 22616993_evidence for epigenetic modifications of valvular interstitial cells in valvular heart disease 22690932_The aim of this study was to evaluate the immunohistochemical expression of 5-LOX pathway proteins in oesophageal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesion, Barrett's metaplasia 22739369_These findings indicate that the efficacy of fish oil supplements vary by ALOX5 genotype. 22808264_The functional interaction between Acyl-CoA synthetase 4, 5-lipooxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 controls tumor growth. 22825379_increased 15-LOX-1 and decreased 5- and 12-LOX levels at the onset of kidney cancer reversing with the progressing stage of the disease or the grade of tumor 23067353_The Sp1 promoter repeat variants of ALOX5 were found to be associated with coronary artery disease. 23079278_genetic association studies in population of Han Chinese in Eastern China: Using a recessive genetic model, an SNP in ALOX5 (rs2029253) is associated with reduced risk of ischemic stroke. 23079635_5-lipoxygenase is involved in the maintenance of normal dopamine function in the striatum. 23179791_Data indicate that focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation and cell migration require Src, Gi/Go, COX-2 and LOXs activities. 23332172_A novel functional role for neuronal 5-lipoxygenase shows modulation of tau phosphorylation. 23351835_Adipose tissue arachidonic acid content is associated with the expression of 5-lipoxygenase in atherosclerotic plaques. 23448388_Our study is the first to show that ALOX5 is associated with susceptibility to pediatric TB in a subset of children in northern China. The rs2115819 T allele of ALOX5 presents a risk factor for childhood TB disease. 23485709_The inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase blocks the release of organic osmolytes and the concomitant cell volume restoration following hypoosmotic swelling of A549 cells. 23572152_The changes of LTB4 concentration in serum and the mRNA expression level of 5-LO in decidua may play an important role in the success and maintenance of a healthy pregnancy. 23600541_ALOX5 polymorphism associates with increased leukotriene production and reduced lung function and asthma control in children with poorly controlled asthma. 23642263_UPF1 is a critical gene expression regulator of 5-lipoxygenase and other proteins in the monocytes. 23720274_LPS-induced Mac-1 expression on monocytes was significantly inhibited by pre-treatment with U-75302, a BLT1-receptor antagonist, suggesting a pivotal role of 5-LO-derived leukotrienes 23727898_A significant increase was found in 5-lipoxygenase gene expression in Alzheimer's disease patients compared to controls. 23746795_The results indicated that the individuals bearing AA genotype of ALOX5AP1 SG13S114T/A polymorphism are more prone to stroke and bad outcome as well as with aspirin resistance than TA and TT genotypes. 23752617_Studies indicate that suppression of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) activity reduces the cell proliferation activity and induces intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. 23828562_The results of our study failed to confirm whether the selected variants in ALOX5 gene within the LT metabolism pathway contribute to platelet reactivity in a diabetic population treated with ASA. 24005813_Polymorphisms within FLT3, EGFR, NEIL3, and ALOX5 may contribute to the occurrence of GBM. 24036216_Jurkat T cells overexpressing 5-LO failed to activate PPARgamma in macrophages, while their 5-LO overexpressing apoptotic counterparts did. 24130502_we demonstrate that the upregulation of Alox5 by RUNX1-ETO9a occurs via the CH zinc finger transcription factor KLF6, a protein required for early hematopoiesis and yolk sac development 24226420_5-LO disruption improves wound healing and alters fibroblast function by an antioxidant mechanism based on HO-1 induction. 24335295_Inhibition of the 5-lipoxygenase/LTB4 pathway could potentially be used in treatment to control Kaposi's sarcoma and primary effusion lymphoma. 24350867_The 5-LOX/LTC4 /CysLT1 signaling pathway regulates EGF-induced cell migration by increasing Tiam1 expression. 24480307_Mutation of Arg101 to Asp in intact 5-LOX leads to increased activity. 24662827_Increased metabolites of 5-lipoxygenase from hypoxic ovarian cancer cells promote tumor-associated macrophage infiltration. 24746852_Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) induced up-regulation of 5-lipoxygenase in both ex vivo HCMV-infected placental explants and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) 25001243_Data suggest that the co-carcinogens benzidine and hydrogen peroxide induce expression of ALOX5 mRNA and protein in tracheobronchial epithelial cells; the co-carcinogens decrease cell proliferation but enhance apoptosis, actions inhibited by knockdown of ALOX5 by RNA interference. Benzidine appears to undergo metabolic activation to benzidine diimine by ALOX5. 25193960_Low leukotriene B4 receptor 1 leads to ALOX5 downregulation at diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia. 25218842_Study identified a novel splice variant of 5-LO consisting of 139 amino acids due to premature stop. It was found to be expressed in HepG2 cells only, raising the possibility for putative role in liver cancer development. 25229347_involvement of lipoxygenase pathways in TNF-alpha-induced production of cytokines and chemokines 25309925_5-LOX inhibition reduced apoptotic death, restored the initial IL-2/INF-gamma ratio, and more importantly reverted micro-calpain activation induced by simulated microgravity. 25359714_Two of the most potent/selective inhibitors (HIR-303 and HIR-309) were reductive inhibitors and were potent against 5-LOX in human whole blood, indicating that isoflavans can be potent and selective inhibitors against human leukocyte 5-LOX 25454978_contributes to inflammatory microenvironment of precancerous pancreatic lesions 25483364_Results suggest that the level of 5-LOX expression was increased in pancreatic cancer tissues and may be related to lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. 25540201_These findings indicate that the oncogenic function of c-Myc in prostate cancer cells is regulated by 5-Lox activity, revealing a novel mechanism of 5-Lox action 25721704_Report no association between ALOX5 SNPs and atherosclerotic plaque phenotypes. 26070487_Genotoxic stress induces the ALOX5 mRNA and protein expression in a p53-dependent manner. 26076991_GSAP cleavage via caspase-3 is regulated and depend upon the availability of 5-Lipoxygenase in Alzheimer's disease. 26173130_investigated potential mechanisms by which 5-LO13 interferes with 5-LO product biosynthesis in transfected HEK293 cells 26210919_The study shows that 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) in B cells is phosphorylated on Ser523 and demonstrates for the first time a chemical difference between 5-LO in myeloid cells and B cells. 26327594_THE 5-LOX interface involving the four cysteines 159, 300, 416 and 418 is important for the translocation to the nuclear membrane and the colocalization with FLAP. 26329759_AF4 and AF4-MLL mediate transcriptional elongation of 5-lipoxygenase mRNA by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. 26334317_These results suggest that COX-2 and 5-LO play roles in tumorigenesis and the progression of primary glioblastoma and that the co-expression pattern of COX-2/5-LO may be used as an independent prognostic factor in this disease. 26378572_Increased PUFA Content and 5-lipoxygenase pathway expression are associated with subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammation in obese women with type 2 diabetes. 26427761_The study explores the substrate access portal of 5-Lipoxygenase. 26505400_we identified differences in the frequency distribution in the Tibetan population located in the ALOX5 , VKORC1 and PTGS2 genes 26707712_our data suggest that the inhibition of both COX-2/5-LOX may be an effective therapeutic approach for colon cancer management, particularly for those patients with high expression of COX-2/5-LOX 26842853_The observation that the coexpression of FLAP with a subset of the 5-LOX mutants restores 5-LOX-wild-type (wt)-like levels of products formed in intact cells suggests a physical protein-protein interaction, beyond colocalization, of 5-LOX and FLAP. 26852002_the Alox-5 gene might play a role in the differentiation of multiple drug resistant and non-resistant erythroleukemic cell lines 26944113_This study identified a SNP (rs10507391) in ALOX5 gene as a novel genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's disease and body mass index. 26959713_Copy number variation in ALOX5 is associated with NSAIDs-induced urticaria and/or angioedema. 27016075_The anticancer effects by 13'-COOHs appeared to be partially independent of inhibition of COX-2/5-LOX. Using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, we found that 13'-COOHs increased intracellular dihydrosphingosine and dihydroceramides after short-time incubation in HCT-116 cells, and enhanced ceramides while decreased sphingomyelins during prolonged treatment 27025886_ALOX5 gene variants do not appear to be related to clinical CHD events or subclinical atherosclerosis regardless of bioavailable enzyme substrate levels in multiethnic cohort. 27060751_Dimethyl ester of bilirubin exhibits anti-inflammatory activity through inhibition of secretory phospholipase A2, lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase. 27411387_ROS production induced by the 5-LO pathway mediates the anti-cancer effects of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide and N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. 27635633_Oxidative stress decreased the levels of PNPLA2 transcripts with no effect on ALOX5 expression. Exogenous additions of P1 peptide or overexpression of the PNPLA2 gene decreased both LTB4 levels and death of RPE cells undergoing oxidative stress. 27784744_our results define Alox5 as a key genetic effector of JAK2V617F in driving polycythemia vera 27855198_a novel putative protein isoform of human 5-LO that lacks exon 4, termed 5-LODelta4, was identified. 27893808_Polymorphisms in the 5-Lipoxygenase is associated with Incident Myocardial Infarction. 28096231_Specific inhibitors of COX-2 and 5-LOX decreased formation of HKD2 and HKE2 Platelets did not form HKs from exogenous 5S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, implying that COX-1 is not involved 28257804_coexpression of the isoforms inhibited or stimulated 5-LO-WT expression in transiently and stably transfected HEK293T cells suggesting that the isoforms have other functions than canonical leukotriene biosynthesis 28500307_our work shows that ALOX5 plays a moderate anti-tumor role and functions as a drug sensitizer, with a therapeutic potential, in MLL-rearranged AML. 28566527_Adipose tissue eicosapentaenoic acid and arachidonic acid and the ALOX-5 tandem repeat polymorphism did not significantly interact to affect the risk of myocardial infarction. 28786533_Study shows that higher COX-2 and ALOX5 expression in colorectal cancer (CRC) t |
ENSMUSG00000025701 |
Alox5 |
48.317540 |
2.3713871155 |
1.245731 |
0.333518604 |
13.525945 |
0.00023528791473643068414209333916176092316163703799247741699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000609164992371464121372059974390822389977984130382537841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.8511554 |
14.5487118 |
28.4245008 |
4.6718968 |
| ENSG00000012817 |
8284 |
KDM5D |
protein_coding |
Q9BY66 |
FUNCTION: Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Does not demethylate histone H3 'Lys-9', H3 'Lys-27', H3 'Lys-36', H3 'Lys-79' or H4 'Lys-20'. Demethylates trimethylated and dimethylated but not monomethylated H3 'Lys-4'. May play a role in spermatogenesis. Involved in transcriptional repression of diverse metastasis-associated genes; in this function seems to cooperate with ZMYND8. Suppresses prostate cancer cell invasion. Regulates androgen receptor (AR) transcriptional activity by demethylating H3K4me3 active transcription marks. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17320160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17320162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17351630, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26747897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27185910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27427228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27477906}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Dioxygenase;Iron;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing zinc finger domains. A short peptide derived from this protein is a minor histocompatibility antigen which can lead to graft rejection of male donor cells in a female recipient. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:8284; |
fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone demethylase activity [GO:0032452]; histone H3K4 demethylase activity [GO:0032453]; histone H3K4me/H3K4me2/H3K4me3 demethylase activity [GO:0034647]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nuclear androgen receptor binding [GO:0050681]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; histone H3-K4 demethylation [GO:0034720]; regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060765]; T cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002457] |
15613541_The presence of H-Y antibodies correlated with chronic graft-versus-host disease 16988213_HY-specific CD8+ T cells also could be detected directly in the peripheral blood of women with a history of at least two pregnancies that produced males. 17320162_Study shows that JARID1d and MBLR occupy human Engrailed 2 gene and regulate its expression and histone H3 lysine 4 methylation levels. 18459961_Results suggest that SMCY may have a male-specific function as a histone H3K4 demethylase by recruiting a meiosis-regulatory protein to condensed DNA. 19223392_HY-restricting HLA class II alleles is associated with pregnancy outcome in patients with recurrent miscarriage subsequent to firstborn boys. 19541808_compared with other recipient-donor gender combinations, female recipients of male donor kidney transplants in the United States have an increased short-term risk but not long-term risk for adverse outcomes 26215926_Of 820 proteins present in all four replicates of two treatments, the abundance of 209 proteins changed significantly in response to KDM5D suppression 26728332_The expression profiles of KDM5D isoforms were investigated in prostate cancer cell lines along with their gene regulatory network. 26747897_study identifies JARID1D as an anti-invasiveness histone methylation modifier that acts against prostate cancer cell metastasis by repressing metastatic gene programs; results also highlight a preclinical rationale for using JARID1D as a prognostic marker in advanced prostate cancer 27185910_Loss of KDM5D expression leads to docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer. 29863497_loss of the male-specific histone demethylase lysine-specific demethylase 5D (KDM5D) encoded on the Y chromosome epigenetically modifies histone methylation marks and alters gene expression, resulting in aggressive prostate cancer 30826357_KDM5D exhibited pronounced overexpression in blood vessels with cardiovascular disease. 30864186_KDM5D inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer through demethylation in the promoter of Cul4A in male. 31560558_Down-Regulation of a Male-Specific H3K4 Demethylase, KDM5D, Impairs Cardiomyocyte Differentiation. 32196595_ETV4 promotes the progression of gastric cancer through regulating KDM5D. 32732223_X- and Y-Linked Chromatin-Modifying Genes as Regulators of Sex-Specific Cancer Incidence and Prognosis. 33040644_Increased Expression of Y-Encoded Demethylases During Differentiation of Human Male Neural Stem Cells. 34127738_Y disruption, autosomal hypomethylation and poor male lung cancer survival. 34688635_KDM5D inhibits the transcriptional activation of FKBP4 by suppressing the expression of E2F1 in colorectal cancer in males. |
ENSMUSG00000056673 |
Kdm5d |
538.590606 |
0.4687508279 |
-1.093107 |
0.090664059 |
144.624046 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000259510253851685593217504001565361363993774821359237582259333742361790336411267209046414665418733846991017344407737255096435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000036830493719719991082885231045129522807591340660381646824980191309678309236849238811513373992312381233205087482929229736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
367.5786629 |
33.7535550 |
791.1553710 |
51.8621627 |
| ENSG00000012822 |
57658 |
CALCOCO1 |
protein_coding |
Q9P1Z2 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a coactivator for aryl hydrocarbon and nuclear receptors (NR). Recruited to promoters through its contact with the N-terminal basic helix-loop-helix-Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain of transcription factors or coactivators, such as NCOA2. During ER-activation acts synergistically in combination with other NCOA2-binding proteins, such as EP300, CREBBP and CARM1. Involved in the transcriptional activation of target genes in the Wnt/CTNNB1 pathway. Functions as a secondary coactivator in LEF1-mediated transcriptional activation via its interaction with CTNNB1. Coactivator function for nuclear receptors and LEF1/CTNNB1 involves differential utilization of two different activation regions (By similarity). In association with CCAR1 enhances GATA1- and MED1-mediated transcriptional activation from the gamma-globin promoter during erythroid differentiation of K562 erythroleukemia cells (PubMed:24245781). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CGU1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24245781}.; FUNCTION: Seems to enhance inorganic pyrophosphatase thus activating phosphogluomutase (PMG). Probably functions as component of the calphoglin complex, which is involved in linking cellular metabolism (phosphate and glucose metabolism) with other core functions including protein synthesis and degradation, calcium signaling and cell growth. {ECO:0000269|Ref.1}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Wnt signaling pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables several functions, including armadillo repeat domain binding activity; beta-catenin binding activity; and nuclear receptor coactivator activity. Involved in positive regulation of gene expression and positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in cytosol and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57658; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; armadillo repeat domain binding [GO:0070016]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030518]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
15522220_Results report a novel human protein, calphoglin, which activates inorganic pyrophosphatase (IPP) and enhances phosphoglucomutase activity through the activated IPP. 16344550_CoCoA uses different combinations of functional domains in its synergistic coactivator function with beta-catenin or GRIP1 16931570_The N terminus of CoCoA contains another activation domain , which is necessary and sufficient for synergistic activation of LEF1-mediated transcription by CoCoA and beta-catenin. 19165232_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19183483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31953347_A HOTAIR regulatory element modulates glioma cell sensitivity to temozolomide through long-range regulation of multiple target genes. 32525583_CALCOCO1 acts with VAMP-associated proteins to mediate ER-phagy. |
ENSMUSG00000023055 |
Calcoco1 |
403.330465 |
0.2800419515 |
-1.836285 |
0.105474337 |
305.049192 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002616690923518704899790372506391878198154914244147921323116900449449709164561582953616171413149579451647595657559141149149703862553937776495471579998035429327584262614676477443076407780608860775828361511230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000769369681895141052432216461284717981014149584690266999306575809886449002292216399873469895722768479003185512896776026760108394443463414471619565218092674394154991237074203702661634451942518353462219238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
180.8024092 |
13.6328863 |
649.3751159 |
31.8626677 |
| ENSG00000013375 |
5238 |
PGM3 |
protein_coding |
O95394 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of GlcNAc-6-P into GlcNAc-1-P during the synthesis of uridine diphosphate/UDP-GlcNAc, a sugar nucleotide critical to multiple glycosylation pathways including protein N- and O-glycosylation. {ECO:0000303|PubMed:24589341, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24698316, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24931394}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Carbohydrate metabolism;Disease variant;Isomerase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Nucleotide-sugar biosynthesis; UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine biosynthesis; N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate from alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate (route I): step 2/2. {ECO:0000303|PubMed:24589341, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24698316, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24931394}. |
This gene encodes a member of the phosphohexose mutase family. The encoded protein mediates both glycogen formation and utilization by catalyzing the interconversion of glucose-1-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate. A non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism in this gene may play a role in resistance to diabetic nephropathy and neuropathy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:5238; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphoacetylglucosamine mutase activity [GO:0004610]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; glucosamine metabolic process [GO:0006041]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006048] |
12174217_PGM(3) is identical to AGM(1). 20221814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20221814_Polymorphic analysis of the human phosphoglucomutase-3 gene. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24589341_Autosomal recessive hypomorphic PGM3 mutations underlie a disorder of severe atopy, immune deficiency, autoimmunity, intellectual disability, and hypomyelination. 24698316_Impairment of PGM3 function leads to a novel primary (inborn) error of development and immunity because biallelic hypomorphic mutations are associated with impaired glycosylation and a hyper-IgE-like phenotype. 24931394_define PGM3-CDG as a treatable immunodeficiency, document the power of whole-exome sequencing in gene discoveries for rare disorders, and illustrate the utility of genomic analyses in studying combined and variable phenotypes 26482871_Data indicate the effect of the phosphoglucomutase 3 (PGM3) mutation for four immunodeficient siblings in a Swedish family. 26687240_PGM3 mutation identified in a patient with hyper IgE syndrome results in lack of glycosylation at Asn264 and altered glycosylation profile. 28543917_Novel PGM3 Mutation Is Associated With a Severe Phenotype of Bone Marrow Failure, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, Skeletal Dysplasia, and Congenital Malformations. 28704707_study reports the first founder mutation in PGM3 gene (p.Glu340del) in twelve Tunisian PGM3 deficient patients belonging to three consanguineous families originating from a rural district in west central Tunisia 30578875_our findings demonstrate that defective glycosylation in PGM3-deficient patients results in reduced expression of unglycosylated gp130 protein and consequently, impaired gp130-dependent STAT3 phosphorylation. 31231132_Deficiency of phosphoglucomutase 3 (PGM3) is an autosomal recessive disorder of N- and O-glycosylation. 31707513_Compound Heterozygous PGM3 Mutations in a Thai Patient with a Specific Antibody Deficiency Requiring Monthly IVIG Infusions. 35011738_Targeting PGM3 as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy in KRAS/LKB1 Co-Mutant Lung Cancer. 35723049_PGM3 regulates beta-catenin activity to promote colorectal cancer cell progression. |
ENSMUSG00000056131 |
Pgm3 |
246.694526 |
3.8698773763 |
1.952288 |
0.354370760 |
28.478250 |
0.00000009475698614136352051083887282692530540373354597249999642372131347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000374160812050969933732319202060456753144990216242149472236633300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
317.1923895 |
160.0609754 |
81.3318057 |
29.2876055 |
| ENSG00000014257 |
55 |
ACP3 |
protein_coding |
P15309 |
FUNCTION: A non-specific tyrosine phosphatase that dephosphorylates a diverse number of substrates under acidic conditions (pH 4-6) including alkyl, aryl, and acyl orthophosphate monoesters and phosphorylated proteins (PubMed:10506173, PubMed:15280042, PubMed:20498373, PubMed:9584846). Has lipid phosphatase activity and inactivates lysophosphatidic acid in seminal plasma (PubMed:10506173, PubMed:15280042). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10506173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15280042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20498373, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9584846}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Tyrosine phosphatase that acts as a tumor suppressor of prostate cancer through dephosphorylation of ERBB2 and deactivation of MAPK-mediated signaling (PubMed:20498373). In addition to its tyrosine phosphatase activity has ecto-5'-nucleotidase activity in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Generates adenosine from AMP which acts as a pain suppressor (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CE08, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20498373}.; FUNCTION: [PAPf39]: (Microbial infection) Forms amyloid beta-sheet fibrils in semen. These fibrils, termed SEVI (semen-derived enhancer of viral infection) capture HIV virions, attach them to target cells and enhance infection (PubMed:18083097, PubMed:19451623, PubMed:19897482). SEVI amyloid fibrils are degraded by polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a constituent of green tea (PubMed:19451623). Target cell attachment and enhancement of HIV infection is inhibited by surfen (PubMed:19897482). Also similarly boosts XMRV (xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus) infection (PubMed:19403677). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18083097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19403677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19451623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19897482}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amyloid;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Lysosome;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of orthophosphoric monoester to alcohol and orthophosphate. It is synthesized under androgen regulation and is secreted by the epithelial cells of the prostate gland. An alternatively spliced transcript variant encoding a longer isoform has been found for this gene. This isoform contains a transmembrane domain and is localized in the plasma membrane-endosomal-lysosomal pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:55; |
acid phosphatase complex [GO:1904097]; azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate phosphatase complex [GO:1904144]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; 5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0008253]; acid phosphatase activity [GO:0003993]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lysophosphatidic acid phosphatase activity [GO:0052642]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; thiamine phosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0042131]; XMP 5'-nucleosidase activity [GO:0106411]; adenosine metabolic process [GO:0046085]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; nucleotide metabolic process [GO:0009117]; positive regulation of adenosine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060168]; purine nucleobase metabolic process [GO:0006144]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; thiamine metabolic process [GO:0006772] |
11833784_Effect of tartaric acid on conformation and stability of human prostatic phosphatase: an infrared spectroscopic and calorimetric study. 12032838_Identification and characterization of regulatory elements of the human prostatic acid phosphatase promoter. 12362977_analysis of mRNA levels in hyperplastic prostate stimulated with steroid hormones and growth factors 12719131_equilibrium unfolding of dimeric human prostatic acid phosphatase involves an inactive monomeric intermediate 12962324_In dilute solutions, several active prostatic acid phosphatase species exist, which are involved in concentration-dependent dissociation/association equilibria 14623260_Human prostatic acid phosphatase's regulatory regions were analyzed in transgenic mice and cell line transfections, in order to clarify the mechanisms of tissue-specific gene expression 14690244_protein binding with Con A in seminal plasma 15240830_Transcriptional activation of the prostatic acid phosphatase gene by NF-kappaB in human prostate cancer cells. 15280042_Prostatic acid phosphatase inactivates lysophosphatidic acid in seminal plasma. 15578709_analysis of prostatic acid phosphatase binding 15985366_the GAAAATATGATA-like elements are involved in the transcriptional regulation of hPAP promoter constructs in prostatic cells. 16004602_JFC1 differentially regulates the secretion of PSAP and PSA, and Rab27a and PI3K play a central role in the exocytosis of prostate-specific markers. 16076555_1,25D-mediated decreases in prostate cancer cells and C81 LN cell growth are in part due to decreases in tyrosine kinase signaling that result from up-regulation of cellular prostatic acid phosphatase. 17455230_PAP (133-152) and PAP (173-192) were immunogenic and processed from whole PAP in HLA-DRB1*1501 tg mice. These peptides were capable of stimulating CD4 T lymphocytes from HLA-DRB1*1501-positive patients with granulomatous prostatitis and normal donors. 17638863_Prostatic acid phosphatase is not a prostate specific target 18940592_Suppresses pain by functioning as an ecto-5'-nucleotidase, activating A1-adenosine receptors in the dorsal spinal cord. 19108401_presence of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in breast cyst fluid may suggest its possible role in the development of breast cancer from cystic breast diseases 19301031_PSAP might be predictive of tumor stage in incidental prostate cancer and represent a valuable adjunct for clinical decisions in terms of individual therapeutic management. 19403677_Prostatic acid phosphatase boosts the infectivity of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus. 19636017_Report safety and immunological efficacy of a DNA vaccine encoding prostatic acid phosphatase in patients with stage D0 prostate cancer. 19759923_The obtained N-terminal amino-acid sequence of boar PTAP showed 92% identity with the N-terminal amino-acid sequence of human PAP. The determined sequence of a 354 bp nucleotide fragment showed 90% identity with the corresponding sequence of human PAP. 19902966_molecular details of PAPf39 peptide fibril formation may aid in elucidating the mechanism of how PAPf39 fibrils are involved in HIV etiology 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20392611_Data show that prostatic acid phosphatase(PAP) as a sensitive tumor marker for prostate cancer. 20498373_prostatic acid phosphatase, an authentic tyrosine phosphatase, dephosphorylates ErbB-2 and regulates prostate cancer cell growth 20645695_Most of the features of PAP including gene regulation, gene/protein structure, functions, its role in tumor progression and evolutionary features are discussed. Review. 21487525_Our studies confirmed that, while prostatic acid phosphatase expression is not restricted to prostate tissues, its expression in other human tissues is approximately 1-2 orders of magnitude less than that observed in the prostate. 22082367_PAP is strongly expressed in prostate cancer bone metastases in 7/7 patients, while prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is only weakly expressed. 22090109_Peptide fragments derived from N-proximal and C-proximal of the PAP form fibrillar structures and increase virion attachment to cells. 22354963_in the in vivo environment, PAP(248-286) is likely to form fibrils efficiently, thus providing an explanation for the presence of semen-derived enhancer of viral infection in human semen. 23314347_PAPf39 is a 39 residue peptide fragment from human prostatic acidic phosphatase. Recombinant PAPf39 showed amyloid fibril formation. 23698773_Studies suggest that understanding of prostatic acid phosphatase function and regulation of expression will have a significant impact on understanding prostate cancer (PCa) progression and therapy. 23897810_Soluble ecto-5'-nucleotidase (5'-NT), alkaline phosphatase, and adenosine deaminase (ADA1) activities in neonatal blood favor elevated extracellular adenosine. 24338683_Data indicate that prostate acid phosphatase-based peptide vaccine PAP-114-128 peptide appears to be a relevant for the treatment of prostate cancer. 24434023_Data indicate that hypoxia regulates prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) through hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha (HIF2alpha) and from stimulated A2B adenosine receptors. 24829029_ACPP increases significantly in epithelial cells of ovarian carcinoma, which indicates that it may be a candidate biomarker for diagnosis of epithelia-derived ovarian cancer in women. 24854630_GCNT1 is over-expressed in prostate cancer and is associated with higher levels of core 2 O-sLe(x) in PSA, PAP and MUC1 proteins. 25740984_Certain factors identified within semen, termed semen-derived enhancers of virus infection (SEVI), fragments of prostatic acid phosphatase, have been shown to significantly enhance HIV-1 infectivity. 26419820_Prostatic acid phosphatase delays prostate cancer cell growth in G1 phase of the cell cycle. 27357282_Thirteen single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) in acid phosphatase prostate (ACPP) were suggested as candidate causal alleles that underlie ACPP regulation and expression. 27393931_we have measured the intramolecular diffusion of the full length and 8-residue deletion peptides at two different pHs and found a correlation with fibrillization lag time. These results can be explained by a simple kinetic model of the early stages of aggregation in which oligomerization is controlled by the rate of peptide reconfiguration. 28060825_Enhanced TDPase and TMPase activities may contribute to the reduction of TDP level in AD patients. The results imply that an imbalance of phosphorylation-dephosphorylation related to thiamine and glucose metabolism may be a potential target for AD prevention and therapy. 34677582_Multifunctionality of prostatic acid phosphatase in prostate cancer pathogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000032561 |
Acpp |
353.373071 |
0.2460823588 |
-2.022787 |
0.162472683 |
149.982198 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000017492454694551303088979863659842967193917729176767459005774257876330126759950171688856308642445736012405177461914718151092529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000002569041107378877879822110161484197641944742891930238063706434164302797222526055260648399081180315306482953019440174102783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
138.5637490 |
14.2950773 |
567.5753996 |
39.3405145 |
| ENSG00000015153 |
10138 |
YAF2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IY57 |
FUNCTION: Binds to MYC and inhibits MYC-mediated transactivation. Also binds to MYCN and enhances MYCN-dependent transcriptional activation. Increases calpain 2-mediated proteolysis of YY1 in vitro. Component of the E2F6.com-1 complex, a repressive complex that methylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3, suggesting that it is involved in chromatin-remodeling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11593398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12706874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9016636}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a zinc finger containing protein that functions in the regulation of transcription. This protein was identified as an interacting partner of transcriptional repressor protein Yy1, and also interacts with other transcriptional regulators, including Myc and Polycomb. This protein can promote proteolysis of Yy1. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:10138; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
11953439_YEAF1/RYBP and YAF-2 are functionally distinct members of a cofactor family for the YY1 and E4TF1/hGABP transcription factors. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25603536_These findings uncovered an apoptotic signaling cascade linking YAF2, PDCD5, and TP53 during genotoxic stress responses. 30672021_LINC00341 interacts with miR-141 to suppress its functional binding to the 3'-untranslated region of YAF2 messenger RNA whereby supporting chondrocyte survival and preventing osteoarthritis progression. 30915747_miR-34b inhibits the migration/invasion and promotes apoptosis of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by YAF2. 33784512_YAF2 exerts anti-apoptotic effect in human tumor cells in a FANK1- and phosphorylation-dependent manner. |
ENSMUSG00000022634 |
Yaf2 |
90.062943 |
0.4144372062 |
-1.270775 |
0.365940844 |
11.565361 |
0.00067191844984521530408788647648066216788720339536666870117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001615230670963416822333291733571059012319892644882202148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.6598518 |
17.5742186 |
130.4498852 |
30.0453913 |
| ENSG00000015171 |
10771 |
ZMYND11 |
protein_coding |
Q15326 |
FUNCTION: Chromatin reader that specifically recognizes and binds histone H3.3 trimethylated at 'Lys-36' (H3.3K36me3) and regulates RNA polymerase II elongation. Does not bind other histone H3 subtypes (H3.1 or H3.2) (By similarity). Colocalizes with highly expressed genes and functions as a transcription corepressor by modulating RNA polymerase II at the elongation stage. Binds non-specifically to dsDNA (PubMed:24675531). Acts as a tumor-suppressor by repressing a transcriptional program essential for tumor cell growth. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R5C8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10734313, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16565076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24675531}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Inhibits Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2-mediated transcriptional activation and host cell proliferation, through direct interaction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26845565}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Cell cycle;Chromatin regulator;Chromosomal rearrangement;Chromosome;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene was first identified by its ability to bind the adenovirus E1A protein. The protein localizes to the nucleus. It functions as a transcriptional repressor, and expression of E1A inhibits this repression. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10771; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0034243] |
10734313_The adenovirus E1A binding protein BS69 is a corepressor of transcription through recruitment of N-CoR. 11733528_the C-terminal Mynd domain of BS69 (amino acids 516-561) or Mynd domains of the Caenorhabditis elegans proteins Bra-1 and Bra-2 bind not only to E1A but also to the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 oncoprotein and the Myc-related cellular protein MGA 16300738_BS69 controls E1A stability via inhibition of ubiquitination. 16382137_The recruitment and aggregation of BS69 is a prerequisite for JNK activation by LMP1. 16565076_BS69 has roles in gene repression and chromatin remodeling 17721438_Data indicate that BS69 is involved in cellular senescence mainly through the p53-p21Cip1 pathway. 19766626_BS69 forms oligomers. The PHD and MYND domains are important for the cellular localization of BS69. PIAS1 and Ubc9 interact with BS69 and promote the sumoylation of BS69. BS69 plays inhibitory roles in both muscle and neuron differentiation. 19795416_Knockdown of BS69 resulted in a decrease of IFN-beta induction, suggesting that BS69 is a positive regulator for the TLR3-TICAM-1 pathway and negative regulatory properties in NF-kappaB activation. 20138174_Data found that BS69 directly interacted with TRAF3, a negative regulator of NF-kappaB activation. Results revealed that TRAF3 was involved in the BS69-mediated suppression of LMP1/CTAR1-induced NF-kappaB activation. 20425112_Data show significant association between the copy number variations of BS69 and some hematological malignancies. 20732415_BRAM1 acts as a negative signal regulator located at the very proximal end of lymphotoxin beta receptor complex assembly. 24590075_identification of ZMYND11 as an H3.3-specific reader of H3K36me3 that links the histone-variant-mediated transcription elongation control to tumor suppression 24675531_We propose that BS69 specifically associates with H3K36me3-enriched chromatin through the PWWP domain, which facilitates the recruitment of MYND-bound transcription and chromatin remodeling factors 24795016_ZMYND11 represses gene expression by binding H3.3K36me3 and preventing transcription elongation. 25263594_this study identifies an H3.3K36me3-specific reader and a regulator of intron retention and reveals that BS69 connects histone H3.3K36me3 to regulated RNA splicing, providing significant, important insights into chromatin regulation of pre-mRNA processing. 26608508_In this study, we show that this translocation results in an in-frame translocation fusing exon 12 of the tumor suppressor gene ZMYND11 to exon 3 of the chromatin protein MBTD1, encoding a protein of 1,054 amino acids 28119415_Interaction with ZMYND11 mediates opposing roles of Ras-responsive ETS1 and ETS2. 28933030_The ZMYND11 gene has important functions in epigenetic regulation. 29066350_Taken together, ZMYND11 was demonstrated to be a potential and extremely promising suppressor of GBM, while miRNA-196a-5p was quite an important target of treatment of GBM. 30469473_the E1A proteins from HAdV-C5 and -A12 bind the cellular repressor protein BS69. This occurs via a SLiM containing a conserved PXLXP motif, which is present in CR2 of E1A. This SLiM confers interaction with the MYND domain of BS69. 31283782_Our data indicate that increased association with BS69 restricts the function of type 2 EBNA2 as a transcriptional activator and driver of B cell growth and may contribute to reduced B-cell transformation by type 2 EBV. 32097528_ZMYND11-related syndromic intellectual disability: 16 patients delineating and expanding the phenotypic spectrum. 32512976_MicroRNA-196b promotes cell growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer by targeting ZMYND11. 33594072_ZMYND11-MBTD1 induces leukemogenesis through hijacking NuA4/TIP60 acetyltransferase complex and a PWWP-mediated chromatin association mechanism. 34216016_ZMYND11 variants are a novel cause of centrotemporal and generalised epilepsies with neurodevelopmental disorder. 34969361_microRNA-10a-5p from gastric cancer cell-derived exosomes enhances viability and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by targeting zinc finger MYND-type containing 11. 35705031_Oncogenic ZMYND11-MBTD1 fusion protein anchors the NuA4/TIP60 histone acetyltransferase complex to the coding region of active genes. |
ENSMUSG00000021156 |
Zmynd11 |
118.044413 |
0.4748288172 |
-1.074521 |
0.152123011 |
50.529255 |
0.00000000000117401640606457949398404461191029306841096535585222682129824534058570861816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006962025774814461082737999053278736463074016782570652139838784933090209960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
77.7140465 |
7.7542959 |
164.8932318 |
10.7114996 |
| ENSG00000015413 |
1800 |
DPEP1 |
protein_coding |
P16444 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes a wide range of dipeptides including the conversion of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4 (PubMed:2303490, PubMed:6334084, PubMed:31442408, PubMed:32325220). Hydrolyzes cystinyl-bis-glycine (cys-bis-gly) formed during glutathione degradation (PubMed:32325220). Possesses also beta lactamase activity and can hydrolyze the beta-lactam antibiotic imipenem (PubMed:6334084, PubMed:32325220). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2303490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31442408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32325220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6334084}.; FUNCTION: Independently of its dipeptidase activity, acts as an adhesion receptor for neutrophil recruitment from bloodstream into inflamed lungs and liver. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31428}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Dipeptidase;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a kidney membrane enzyme involved in the metabolism of glutathione and other similar proteins by dipeptide hydrolysis. The encoded protein is known to regulate leukotriene activity by catalyzing the conversion of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. This protein uses zinc as a cofactor and acts as a disulfide-linked homodimer. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2020]. |
hsa:1800; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; beta-lactamase activity [GO:0008800]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043027]; dipeptidase activity [GO:0016805]; GPI anchor binding [GO:0034235]; metallodipeptidase activity [GO:0070573]; metalloexopeptidase activity [GO:0008235]; modified amino acid binding [GO:0072341]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; antibiotic metabolic process [GO:0016999]; cellular lactam catabolic process [GO:0072340]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to nitric oxide [GO:0071732]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; glutathione catabolic process [GO:0006751]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; homocysteine metabolic process [GO:0050667]; leukotriene D4 catabolic process [GO:1901749]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12144777_Crystal structure of human renal dipeptidase involved in beta-lactam hydrolysis 15145522_DPEP1 has a role in colorectal carcinoma 20031578_CPS1, MUT, NOX4, and DPEP1 is associated with plasma homocysteine in healthy Women. 20031578_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20824289_DPEP1 is expressed in the early stages of colon carcinogenesis and affects cancer cell invasiveness. 21076463_we identified a novel immunohistochemical marker, dipeptidase 1, to distinguish primary mucinous ovarian cancers from ovarian metastasis of colorectal cancers. 22363658_DPEP1 plays a role in pancreatic cancer aggressiveness. 23839495_Dipeptidase 1 has been identified as an excellent marker of high-grade IEN and CRC, and may thus be applied for screening of early neoplastic lesions and for prognostic stratification. 26392408_In this study, we present an analysis of Neanderthal introgression at the dipeptidase 1 gene, DPEP1. 26824987_The results suggest that DPEP1 promotes cancer metastasis by regulating E-cadherin plasticity and that it might be a potential therapeutic target for preventing the progression of colon cancer. 31541079_DPEP1 is a direct target of miR-193a-5p and promotes hepatoblastoma progression by PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. 32068254_DPEP1 expression promotes proliferation and survival of leukaemia cells and correlates with relapse in adults with common B cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. 34291562_The relationship between common variants in the DPEP1 gene and the susceptibility and clinical severity of osteoarthritis. 34426578_A single genetic locus controls both expression of DPEP1/CHMP1A and kidney disease development via ferroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000019278 |
Dpep1 |
209.001171 |
0.0198682527 |
-5.653391 |
0.291314703 |
629.480377 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064838753370114187823352047063174941142583611234406568214878291527753645667053393673802155172262483546431318174522455930461907718290895780815523441123106463508632207789004911020776284336480159 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000037826877460193100221437392167854103726429786900707430441312511588131089933874206991879786515491079643702818712588522468317235292736322018621033180744735103691230631380622664095653822734371356 |
Yes |
No |
7.2921540 |
1.5289612 |
369.1009782 |
30.9642807 |
| ENSG00000015475 |
637 |
BID |
protein_coding |
P55957 |
FUNCTION: Induces caspases and apoptosis (PubMed:14583606). Counters the protective effect of BCL2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70444, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583606}.; FUNCTION: [BH3-interacting domain death agonist p15]: Induces caspase activation and apoptosis (PubMed:15661737, PubMed:32029622). Allows the release of cytochrome c (PubMed:32029622). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15661737, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32029622}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Induces ICE-like proteases and apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583606}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Induces ICE-like proteases and apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583606}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Does not induce apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583606}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Induces ICE-like proteases and apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583606}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a death agonist that heterodimerizes with either agonist BAX or antagonist BCL2, and thus regulate apoptosis. The encoded protein is a member of the BCL-2 family of cell death regulators. It is a mediator of mitochondrial damage induced by caspase-8 (CASP8); CASP8 cleaves this encoded protein, and the COOH-terminal part translocates to mitochondria where it triggers cytochrome c release. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:637; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; death receptor binding [GO:0005123]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; establishment of protein localization to membrane [GO:0090150]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; hepatocyte apoptotic process [GO:0097284]; mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport [GO:0042775]; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization [GO:0097345]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:1902230]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; positive regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process [GO:2000271]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010918]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:0006626]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050678]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042129]; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0001836]; signal transduction in response to DNA damage [GO:0042770]; supramolecular fiber organization [GO:0097435] |
11741882_tBid-induced permeabilization of the outer membrane permits release of cytochrome c and Smac/DIABLO from all domains of intermembrane space. tBid-induced loss of DeltaPsi(m) occurs after cytochrome c release and reflects impairment of oxidative metabolism 11790791_Cytochrome c release upon Fas receptor activation on translocation of full-length bid 11805084_tBID Homooligomerizes in the mitochondrial membrane to induce apoptosis 11940658_calpain-mediated Bid cleavage and calpain-independent Bak modulation: two separate pathways in cisplatin-induced apoptosis 11971973_These data strongly suggest that in TNF-induced apoptosis, Hsp72 specifically interferes with the Bid-dependent apoptotic pathway via inhibition of JNK. 12061801_Cleavage of Bid is required for tyrosine and phenylalanine deficiency-induced apoptosis of human A375 melanoma cells 12193163_Bax oligomerization in mitochondrial membranes requires tBid (caspase-8-cleaved Bid) and a mitochondrial protein 12419244_Bid, Bax, and lipids cooperate to form supramolecular openings in the outer mitochondrial membrane 12598529_one or more distinct cellular mechanisms regulate Bid cleavage by caspases 8 and 3 in situ. 12754217_identified for the first time a predominant role for the caspase-8/Bid pathway in signaling associated with hyperoxic lung injury and cell death in vivo and in vitro 12766488_The helix H6 of tBid controls mitochondrial binding. A 33 amino acid long domain, which encompassed H6 and H7, behaved as the minimum domain in tBid that was sufficient for mitochondrial binding. 12804595_BID cleavage requires caspase 8 in the course of p53-dependent apoptosis triggered by fast neutrons in lymphoid cells 12808108_Bid-mediated apoptosis requires Bax and Bak 12934063_Bid cleavage by granzyme B is prevented during blockage of CD8T cell lysis by herpes simplex virus-1 Us3 protein kinase 14581476_BID has a role in mediating apoptosis induced by lysosomal disruption 14583606_three novel endogenously expressed isoforms of Bid are distinct in their expression, their cellular localization, and their effects upon cellular apoptosis 14716828_H pylori may enhance Bid, Bax and Bcl-2 mRNA levels and cause deregulation of these apoptosis-associated genes expressions, which may play a role during development of gastric adenocarcinoma induced by H pylori. 14769944_BID is a target of PLZF repression and a candidate gene to mediate the PLZF-induced resistance to apoptosis 15024076_Data show that oxygen deprivation cancer cells provoked decreased mRNA and protein levels of proapoptotic Bid and Bad, and that hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) was dispensable for the down-regulation of Bad but required for that of Bid. 15117953_Bid, cleaved by an undefined aspartate-specific protease, can be a key mediator of the apoptotic response to DNA-damaging anticancer regimens 15123718_Data report the characterization and conformation of tBid protein in lipid membrane environments. 15173176_BID cleavage requires caspase 2 15323553_The amphipathic helix alpha 7 of Bid inserts in membranes as part of the alpha 6-alpha 7 hairpins in a model chimeric system, showing direct potentiality for this Bid fragment to acquire a membrane inserted state. 15501827_a more detailed model for the reorganization of the structure of BID on membranes 15574335_a specific interaction between Bax Halpha1 and their BH3 domains allows Bid and PUMA to function as 'death agonists' of Bax 15615731_Bid mediates apoptotic synergy between TRAIL and DNA damage 15637055_removal of N-terminal domains of Bid by caspase-8 and Mcl-1 by caspase-3 enables the maximal mitochondrial perturbation that potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis 15809076_phosphatidylethanolamine could not induce dissociation of caspase-8 cleavage product, tBid, from the amino terminal fragment, nBid 16077201_Cathepsin B substrate, BID, serves as molecular switch between apotosis and autophagy in camptothecin treated breast cancer cells. 16172118_proteolytic activation of Bid and the subsequent induction of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway through Bax/Bak is essential for apoptosis triggered by caspase-2 16380381_Data demonstrate a novel regulation of tBid by Mcl-1 through protein-protein interaction in apoptotic signaling from death receptors to mitochondria. 16475813_Peptide = to BH3 region of proapoptotic protein BID, bound in cleft of antiapoptotic protein BCL-w. Binding induced major conformational rearrangements in both peptide & protein components & led to displacement & unfolding of BCL-w C-terminal alpha-helix. 16485030_MAPK pathway inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells by prohibiting anchoring of tBid to the mitochondrial membrane. 16908521_Acyl coenzyme A-binding protein has a role in augmenting bid-induced mitochondrial damage and cell death by activating mu-calpain 16964285_Bid was cleaved upon ASC activation, and suppression of endogenous Bid expression using small-interfering RNAs in type-II cells reduced the ASC-mediated apoptosis 16987815_tBID engages BAX to trigger its pro-apoptotic activity 17052454_membrane targeting of stapled BID BH3 optimizes its ability to activate BAX, supporting a model in which BID directly engages BAX to trigger mitochondrial apoptosis 17200714_Activator BH3-only occupation of BCL2 may prime cancer cells for death, offering a potential explanation for the marked chemosensitivity of certain cancers. 17226776_These findings indicate that phosphorylation of PLS3 by PKC-delta induces PLS3 activation to facilitate mitochondrial targeting of tBid and apoptosis. 17289999_results indicate that BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis at least primarily by engaging the multiple pro-survival relatives guarding Bax and Bak 17308307_GzmK-induced caspase-independent death occurs through Bid-dependent mitochondrial damage that is different from GzmA 17431792_Bid cleavage occurs prior to the activation of caspase-8 during TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in U2OS cells 17534194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17549073_Existence of Bid activation pathways in eosinophils other than those mediated by the classic initiator caspases. 17635912_mitochondrial TOM complex is required for tBid/Bax-induced cytochrome c release 17666167_Impaifred kinetics of Bax-GFP and Smac/DIABLO-GFP in caspase 8 and bid-silenced and Bcl-2-overexpressed breast cancer cells exposed to camptothecin. 17762183_sondition (pH=8.0) induces cell apoptosis by activating caspase-8, which cleaves Bid to tBid, tBid translocation to mitochondria, and then activating the caspase-3 in the human lung adenocarcinoma cells 17765974_GzmH directly processes Bid to produce the active form tBid leading to cytochrome c release. 17855051_Bax translocation by UV irradiation is a Bid-independent event and inhibited by overexpression of Bcl-x(L). 18089817_BH3 profiling reveals that mitochondrial BCL-2 is primed by death signals after egf receptor inhibition in lung cancer cells. 18165867_In the absence of serum, the suppression of either Bad, Bim or Bid expression delayed cell death under several stress conditions 18166654_We conclude that unconventional ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent degradation of tBid-N is required to unleash the proapoptotic activity of tBid-C. 18173728_activation of Bid is required for inducing apoptosis in this experimental model 18195012_BIM and tBID follow different strategies to trigger BAX-driven mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization with strong potency 18297401_A downstream substrate for caspase-8, Bid, is also cleaved in vinorelbine-treated cells, but the Bid truncation is also observed in caspase-8-deficient Jurkat cells. 18317451_PKC epsilon mediates TRAIL resistance by Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Hdm2 resulting in suppression of p53 expression and downregulation of Bid in breast cancer cells 18373075_Bid both exhibits S phase checkpoint activation and plays a pro-apoptotic role in response to different degrees of etoposide-induced DNA damage in HCC cells. 18469004_degradation of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members by lysosomal cathepsins synergizes with cathepsin-mediated activation of Bid to trigger a mitochondrial pathway to apoptosis 18593990_Bad and Bid proteins have roles in survival for patients with stage II and III colon cancers 18648372_In high HIF-1alpha nuclear-positive cell subpopulations, there was a significant reduction in Bid expression 18665919_thrombin induces activation and mitochondrial translocation of Bid, Bax and Bak, and evokes mitochondrial membrane depolarization 18838202_Overexpression of FLIP reduced TRAIL and TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in ML-1 cells. However, while FLIPL completely abrogated apoptosis, FLIPS allowed for BID cleavage and caspase-3 activation. 18925930_In early severe sepsis a gene expression pattern with induction of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bim and Bid is observed in peripheral blood. 19029793_tBID and other BCL-2 proteins have a role in osteosarcoma [commentary] 19046991_gene silencing protects primary CD8+ lymphocytes and HeLa cells from apoptosis 19052714_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19219602_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19233849_tBid plays an important regulatory role in the execution of DNA damage-induced cytochrome c release and apoptosis 19246452_genetic deletion of the lysosomal serine protease CLN2 and the subsequent loss of its catalytic function confer resistance to TNF in non-neuronal somatic cells in a Bid-dependent manner, indicating that CLN2 plays a role in TNF-induced cell death 19381674_Bid provides a connection between the death receptor and the mitochondrial pathway of gal-1 induced apoptosis in human Jurkat T lymphocytes. 19423537_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423537_Our data provide persuasive evidence against an overall association between invasive breast cancer risk and ERCC4 rs744154, TNF rs361525, CASP10 rs13010627, PGR rs1042838, and BID rs8190315 genotypes among women of European descent. 19454696_Granulysin can target lysosomes to induce partial release of lysosomal contents into the cytosol; relocalized lysosomal cathepsin B can process Bid to active tBid to cause cytochrome c and apoptosis-activating factor release from mitochondria. 19640637_Bid may serve as a critical integrating factor of the death receptor and mitochondrial pathway in alpha-tocopheryl succinate-mediated apoptosis. 19641510_Protease-cleaved Bid goes to mitochondria & permeabilizes the outer membrane. It is a sentinel for protease-mediated death signals. Bid is a BH3-only protein structurally & functionally related to multi-BH region Bcl-2-family proteins. Review. 19670908_Characterization of binding thermodynamics reveals that the interaction of BID with BCL-XL is driven by enthalpy but disfavored by the entropy associated with the conformational order induced in BID upon binding BCL-XL. 19711428_Calpains activated by HCV proteins degrade Bid and thus dampen apoptotic signaling. These results suggest that inhibiting calpains could lead to an improved efficiency of immune-mediated elimination of HCV-infected cells. 19820711_Data indicate that tBID-BCL(XL) interactions in solution and lipid membranes are distinct, and they support a model in which BCL(XL) inhibition of tBID takes place predominantly at the membrane. 19890662_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19918914_Data revealed that the level of tBid expression in breast cancer cells were nearly 11 times more than normal cells because of the cancer specific promoters. 19929986_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140092_Results indicate that the central helices of BAX, BCL-xL and BID have different abilities to interact with and destabilize membranes in vitro, suggesting proteins have been shaped to perform slightly different functions in apoptosis regulation. 20187936_In rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast like synovial cells phosphorylation of Akt protects against Fas-induced apoptosis through inhibition of Bid cleavage. 20356928_The interface between apoptosis initiation and execution by determining caspase-8 activation, Bid cleavage and mitochondrial engagement (onset of mitochondrial depolarisation) in individual HeLa, was analysed. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20802294_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041309_BH3 peptides other than Bim and Bid exhibited various degrees of direct activation of the effector Bax or Bak 21060336_show that due to the high affinity of BAX for BCL-2, BCL-w and A1, and of BAK for BCL-X(L), MCL-1 and A1, only a subset of BH3-only proteins, including BID, could be expected to free BAX or BAK from the antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins to elicit apoptosis 21072056_Cells stabilize active caspase-8 on the mitochondria in order to specifically target mitochondria-associated BID. 21113148_a direct role for the BH3 interacting domain death agonist acting at the level of the DNA damage sensor complex to amplify the Atr-directed cellular response to replicative damage 21148306_The BH3 alpha-helical mimic BH3-M6 disrupts Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2, and MCL-1 protein-protein interactions with Bax, Bak, Bad, or Bim and induces apoptosis in a Bax- and Bim-dependent manner. 21178828_Data show that the expression of apoptosis proteins caspase-3,-8,-9, and Bid in the RNP of the disc and the SNP was different in each patient. 21223573_When tBid was introduced into the HIV-1 LTR-based, Tat- and Rev-dependent transgene expression vector pLRed(INS)2R, very efficient induction of apoptosis was observed within 24 hours,but only in the presence of both HIV-1 regulatory proteins Tat and Rev. 21367852_BH3-only activator proteins Bid and Bim are dispensable for Bax activation and mitochondrial apoptosis induced by Bcl-xL deficiency 21642428_Permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane by Bax/truncated Bid (tBid) proteins as sensitized by cardiolipin hydroperoxide translocation: mechanistic implications for the intrinsic pathway of oxidative apoptosis. 21751259_Data show that G-Rh2 and Bet A cooperated to induce Bax traslocation to mitochondria and cytochrome c release, and enhanced cleavage of caspase-8 and Bid. 21856753_chronic ethanol increases CYP2E1 activity in adipose, leading to Bid-mediated apoptosis and activation of complement via C1q 21859891_propose a model in which BID associates with RPA and stimulates the recruitment and/or stabilization of ATR-ATRIP to the DNA damage sensor complex 22052011_The results suggested that BID and BAX proteins act as signal-transducing factors in mitochondrion-dependent type II apoptosis in granulosa cells. 22115752_14-3-3 theta/tau and tBID have roles as predictive biomarkers of neoadjuvant chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer 22130162_critical for controlling cell viability regulated by IFN-alpha in ovarian adenocarcinoma cells 22189507_Results suggest that truncated BID specifically interacts with phosphatidylserine/cardiolipin and decreases membrane integrity without the aid of other pro-apoptotic proteins. 22213163_adenosine downregulates Bcl-X(L and upregulates Bid, disrupting mitochondrial membrane potentials to allow cytochrome c efflux, and then causing activation of caspase-9 and the effector caspase-3, as mediated via A(2a) adenosine receptors 22246181_The key differential events in apoptotic cells are p53-dependent activation of the DR4 death receptor pathway, caspase 8-mediated cleavage of BID, and BID-dependent activation of poised BAX at the mitochondria. 22339673_Decreased apoptosis and expression of Bid, increased level of Bcl-Xl may play some important roles in human jejunal stromal tumors, and Bcl-Xl/Bid ratio may be as a new potentially associated index. 22354970_p14(ARF)-induced apoptosis in p53 protein-deficient cells is mediated by BH3-only protein-independent derepression of Bak protein through down-regulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL proteins 22393005_Bid engages a ROS-dependent, local intermitochondrial potentiation mechanism that amplifies the apoptotic signal as a wave 22416135_Molecular basis of the interaction between proapoptotic truncated BID (tBID) protein and mitochondrial carrier homologue 2 (MTCH2) protein 22464442_mechanism of proapoptotic BH3 proteins Bad and Bid binding to Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 in breast cancer cells 22860893_Data indicate that recombinant (r)IL-24 stimulated the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway genes Bax, Bid, Casp8, COX6C, COX7B after 36 h. 22964611_Three cathepsin D-specific cleavage sites in Bid, Phe24, Trp48, and Phe183, were identified. 23019260_Patients with Parkinson disease have an activated Bid-mediated destructive signal pathway via tumor necrosis factor death receptor I (TNFRI) in the temporal cortex. 23109891_EG also activated the death receptor-dependent pathway of apoptosis by enhancing the expression of caspases-8, -9, and -3 and the Bcl-2 interacting domain (Bid). 23192964_Diva binds peptides derived from the BH3 domain of several other proapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, including mouse Harakiri, Bid, Bak and Bmf. 23352961_GrH induced cell death via a Bcl-2-sensitive mitochondrial pathway without direct processing of Bid. 23418437_Caspase-8 binding to cardiolipin in giant unilamellar vesicles provides a functional docking platform for bid 23604079_BAK activation follows a 'hit-and-run' mechanism whereby BID dissociates from the trigger site, which allows BAK oligomerization at an overlapping interface. 23744079_Data indicate that Mtch2 accelerated conformational change in membrane-bound tBid (Bid) enables it to activate Bax. 23851982_FTY720 induces apoptosis of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells via dual activation of BIM and BID and overcomes various types of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 24038028_Using gene reporter assays, we show that promoter variations in 11 intrinsic apoptosis genes, including ADPRT, APAF1, BCL2, BAD, BID, MCL1, BIRC4, BCL2L1, ENDOG, YWHAB, and YWHAQ, influence promoter activity in an allele-specific manner. 24074954_Therefore, BID and BIM have nonoverlapping roles in the induction of apoptosis via BAK and BAX, affecting chemotherapy response. 24158446_structural details on the membrane-associated state of tBid and the functional implications of its membrane-associated BH3 domain 24398548_BID is associated with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament , and both the G allele of a missense SNP (rs8190315, Ser10Gly) and C allele of a synonymous SNP (rs2072392, Asp60Asp) are risk factors for the development of ossification 24621205_Association of BID gene polymorphisms with proteinuria of immunoglobulin A nephropathy 24645842_Reduced Bid expression is associated with endometrial cancer. 24741635_BID expression was found in 53.6% of gastric cancer patients. 24767991_Bid is phosphorylated during mitosis within its regulatory loop and sensitizes mitochondria for mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization if mitotic exit is delayed. 24901048_Binding to membranes is regulated by cleavage of Bid to truncated Bid (tBid), by conformation changes in tBid and Bax, and by interactions with other proteins. 25077544_JNK1/2 regulate Bid by direct phosphorylation at Thr59. 25208882_Inhibition of NANOGP8 or NANOG enhances the cytotoxicity of BH3 mimetics. 25253693_Gli1 has a role in regulating the S-phase checkpoint in tumor cells via Bid protein, and its inhibition sensitizes to DNA topoisomerase 1 inhibitors 25368155_The extrinsic apoptotic pathway and BID are activated in adenomas from NSAID-treated patients. NSAIDS only activate BID in cells with APC deficiency and ensuing c-Myc activation. 25404359_this study emphasizes that the coordinated action of hGzmB-activated p53 and GzmB-cleaved Bid is important for GzmB-induced cell death and for cytotoxic lymphocyte/Natural Killer Cell-mediated killing of target cells. 25522269_Tax confers apoptosis resistance to HTLV-1-infected T cells by suppressing the expression of Bim and Bid. 26417093_Motifs of VDAC2 required for mitochondrial Bak import and tBid-induced apoptosis. 26699404_Data suggest, in models of spatial propagation of mitochondrial permeabilization during apoptosis, there appears to be requirement for cooperative signaling involving truncated-BID and ROS (reactive oxygen species) for efficient/ robust propagation. 26758067_The results indicate that BID-independent pathways are responsible for FAS-dependent human islet cell death in Type 1 diabetes. 26827940_The BID-MTCH2 axis regulates the differentiation/apoptosis of stem cells and mitochondrial metabolism. (Review) 27053107_the results establish that cleavage by caspase 8 and the subsequent association with the outer mitochondrial membrane are two critical events that activate Bid during death receptor-mediated apoptosis. 27461583_Combined therapy with Seliciclib((R)) and Belinostat((R)) results in eradication of non-small cell lung cancer via apoptosis induction and BID activation. 27763642_an oligomeric arrangement of Bid, Bax, and possibly other members of the Bcl-2 family of proteins that form a self-propagating network that permeabilizes the outer-mitochondrial membrane. 27878291_The adenovirus-mediated truncated Bid overexpression induced by the Cre/LoxP system can effectively eliminate CD133+ ovarian cancer stem cells, representing a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of ovarian cancer. 28004114_MiR-20a-directed regulation of BID in colorectal cancer. 28187446_administration of SMAC or BH3 mimetics following short-term paclitaxel treatment could be an effective therapeutic strategy for TNBC, while only BH3-mimetics could effectively overcome long-term paclitaxel resistance 28416970_Results from genome-wide DNA methylation, functional network analysis and pyrosequencing, show selective CpG sites (NOS1AP, BID, and GABRB1) differentially methylated in smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients compared to nonsmokers. 28888620_The caspase-8/Bid/cytochrome c axis links signals from death receptors to mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. 29182622_caspase-10 was dispensable for enhancement of cisplatin/LA-12 and TRAIL combination-induced cell death and stimulation of Bid cleavage 29440708_Differential roles for FL_BID and t-BID in Burkitt's lymphoma during apoptosis. There is a functional cooperation between BAK and BAX during VT-1-induced apoptosis and, unexpectedly, that activation of caspase-8 and production of t-BID were not mandatory for initiation of the cell death process. 29969781_results suggest that histone modifications in the promoter region of miR-500a may be responsible for the increased expression of miR-500a in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which promotes cancer progression by targeting BID, indicating that miR-500a may be a potential prognostic predictor and therapeutic target for HCC patients. 30281024_These results identify a role for Bid in homeostatic mitochondrial cristae reorganization, that we link to human cardiac disease. 30652348_The findings suggest that the cleaved Bid protein acts as an amplifier of apoptotic signaling through mitochondria, thus enhancing the activity of cysteine cathepsins following stefin B degradation. 31767857_BID and the alpha-bisabolol-triggered cell death program: converging on mitochondria and lysosomes. 34389447_Influence of thyroid hormone in the expression of the marker pro-apoptosis BID, in spite of the predominance of anti-apoptosis activation in intratiroidal lymphocytic infiltration in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 34931711_BCL-2-family protein tBID can act as a BAX-like effector of apoptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000004446 |
Bid |
829.191181 |
2.0697090576 |
1.049428 |
0.095874050 |
118.547117 |
0.00000000000000000000000000131590943571948290197410082339946145327825100361077561782623800823156757708320974131765979109331965446472167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000015613201986510907343379165634461888883502804227612838484014656330651116440677572683171092648990452289581298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1090.2954728 |
64.4428477 |
530.4523820 |
23.2404916 |
| ENSG00000015568 |
84220 |
RGPD5 |
protein_coding |
Q99666 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
RAN is a small GTP-binding protein of the RAS superfamily that is associated with the nuclear membrane and is thought to control a variety of cellular functions through its interactions with other proteins. This gene shares a high degree of sequence identity with RANBP2, a large RAN-binding protein localized at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex. It is believed that this RANBP2 gene family member arose from a duplication event 3 Mb distal to RANBP2. Alternative splicing has been observed for this locus and two variants are described. Additional splicing is suggested but complete sequence for further transcripts has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:729540;hsa:84220; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus [GO:0006607]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790] |
|
|
|
285.604286 |
0.0763882278 |
-3.710506 |
1.360736143 |
5.834748 |
0.01571265722398344777399614713431219570338726043701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028831280535305283535540965544896607752889394760131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8969501 |
4.9962621 |
65.3454534 |
44.1240429 |
| ENSG00000017260 |
27032 |
ATP2C1 |
protein_coding |
P98194 |
FUNCTION: ATP-driven pump that supplies the Golgi apparatus with Ca(2+) and Mn(2+) ions, both essential cofactors for processing and trafficking of newly synthesized proteins in the secretory pathway (PubMed:16192278, PubMed:30923126, PubMed:21187401, PubMed:12707275, PubMed:20439740). Within a catalytic cycle, acquires Ca(2+) or Mn(2+) ions on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and delivers them to the lumenal side. The transfer of ions across the membrane is coupled to ATP hydrolysis and is associated with a transient phosphorylation that shifts the pump conformation from inward-facing to outward-facing state (PubMed:16192278, PubMed:16332677, PubMed:30923126). Plays a primary role in the maintenance of Ca(2+) homeostasis in the trans-Golgi compartment with a functional impact on Golgi and post-Golgi protein sorting as well as a structural impact on cisternae morphology (PubMed:20439740, PubMed:14632183). Responsible for loading the Golgi stores with Ca(2+) ions in keratinocytes, contributing to keratinocyte differentiation and epidermis integrity (PubMed:14632183, PubMed:10615129, PubMed:20439740). Participates in Ca(2+) and Mn(2+) ions uptake into the Golgi store of hippocampal neurons and regulates protein trafficking required for neural polarity (By similarity). May also play a role in the maintenance of Ca(2+) and Mn(2+) homeostasis and signaling in the cytosol while preventing cytotoxicity (PubMed:21187401). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80XR2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10615129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12707275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14632183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16192278, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16332677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20439740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21187401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30923126}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Calcium transport;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Ion transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases. This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium ions. Defects in this gene cause Hailey-Hailey disease, an autosomal dominant disorder. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:27032; |
cis-Golgi network membrane [GO:0033106]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; P-type calcium transporter activity [GO:0005388]; P-type ion transporter activity [GO:0015662]; P-type manganese transporter activity [GO:0140613]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular manganese ion homeostasis [GO:0030026]; epidermis development [GO:0008544]; Golgi calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0032468]; Golgi calcium ion transport [GO:0032472]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; manganese ion transport [GO:0006828]; positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0042998]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; trans-Golgi network membrane organization [GO:0098629] |
11841554_failed to yield any clear correlation between the nature of the mutation and clinical features of Hailey-Hailey disease. 11966689_Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD) is caused by mutations in the ATP2C1 gene. 12707275_the crucial role of Asp-742 in the architecture of the SPCA1 ion-binding site and a role of Gly-309 in Mn2+ transport selectivity. 12804581_SPCA1 Ca2+ pump has a role in the Ca2+ accumulation in the Golgi apparatus of HeLa cells 14632183_the abnormal Ca2+ signaling seen in Hailey-Hailey disease keratinocytes correlates with decreased protein levels of ATP2C1. 14747290_ATP2C1 (PMR1) plays an important role, which is at least partially nonoverlapping with that of sarco(endo-)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPases, in the control of beta-cell Ca(2+) homeostasis and insulin secretion. 15191544_Functional analyses of Hailey Hailey disease-mutant A528P demonstrated a low level of protein expression, despite normal levels of mRNA and correct targeting to the Golgi, suggesting instability or abnormal folding of the mutated hSPCA1 polypeptides 15336968_A review of the role of SPCA1 in ion homeostasis in the golgi apparatus and in Hailey-Hailey disease. 15545997_Two copies of mutated ATP2C1 were found in an index case diagnosed with type 2 segmental Hailey-Hailey disease. 15623514_important contributions of the Golgi-localized ATP2C1 protein in homeostatic maintenance throughout the secretory pathway. 15811949_Intracellular Ca(2+) stores and store-dependent [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations in human spermatozoa rely primarily on a thapsigargin/cyclopiazonic acid-insensitive Ca(2+) pump, SPCA1. 15955096_Sp1 and YY1 transactivate human ATP2C1 promoter via cis-enhancing elements and that incomplete upregulation of ATP2C1 transcription contributes to keratinocyte-specific pathogenesis of Hailey-Hailey disease. 16192278_Relative to SERCA1a, the active SPCA1a, SPCA1b, and SPCA1d enzymes displayed extremely high apparent affinities for cytosolic Ca(2+) in activation of the overall ATPase and phosphorylation activities. 16297192_The high allelic heterogeneity of the ATP2C1 gene was confirmed, which supports the notion that Hailey-Hailey disease is a genetically homogeneous disorder. 16332677_analysis of SPCA1 and SPCA2 isoenzymes by steady-state and transient kinetic analyses 16484827_a spectrum of ATP2C1 gene mutations is present in Japanese HHD patients. 16540292_mutations in the ATP2C1 gene may have a role in Hailey-Hailey disease (case report) 16621454_ATP2C1 plays a role in basal keratinocytes to stay in the undifferentiated state, and its reduction causes differentiation and up-localization to suprabasal layers most likely via manganese starvation in the Golgi apparatus of keratinocytes. 16644186_Mutated with a trinucleotide deletion in a case of Hailey-Hailey disease with affective disorder. 17503064_identifies novel nonsense and missense mutations in ATP2C1 gene in Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease 17911984_Eight mutations were found in 8 unrelated families and 1 sporadic case, and these new findings have further improved our understanding of the role of ATP2C1 in HHD. 18205868_Three novel ATP2C1 mutations in Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. To date, at least 98 ATP2C1 mutations ha ve been reported worldwide in patients with HHD. 18211433_There is a novel deletion mutation of the ATP2C1 gene in Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. 18247307_Three mutations in ATP2C1 gene were found that could affect the transcription and translation, and further the function of protein encoded by ATP2C1 gene. 18259764_The ATP2C1 gene plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of Hailey-Hailey disease. 18266684_findings suggest that the novel mutation site identified in the ATP2C1 gene and local factors encountered (e.g. friction and heat) may both play important roles in the pathogenesis of Hailey-Hailey disease 18372165_seven different heterozygous mutations in seven of eight Hailey-Hailey disease patients 18709316_Two heterozygous mutations, a novel mutation p.AlaVal and a known mutation p. ARG799x, were identified. One case showed typical phenptype and the other, atypical features of keratotic papules without erosion. 19126050_results indicate that the novel c.2251delGT (p.V751fs) mutation in the ATP2C1 gene is responsible for Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD) in this Chinese family; this study expands the spectrum of ATP2C1 mutations associated with HHD 19144698_Data show that the calcium dependencies of intracellular Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA and SPCA) activity are the same in human Alzheimer disease and normal brain but that of plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) is different. 19426624_Subsequent genetic testing revealed a deletion in the ATP2C1 gene that led us to conclude that this case of ADCF is probably a variant of familial benign chronic pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease). 19775426_The PMR1 mediated decrease in PTH mRNA levels involves the PTH mRNA 3' Untranslated Regions, KSRP and the exosome. 20055875_two specific novel mutations of the ATP2CL gene were identified two typical Chinese pedigrees with Hailey-Hailey disease 20226632_Six novel ATP2C1 mutations are identified in Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. 20236194_Heterogeneous mutations of the ATP2C1 gene cause Hailey-Hailey disease in Hong Kong Chinese. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363212_SPCA1 is associated with cholesterol-rich domains of HT29 cells, and the cholesterol-rich environment is essential for the functioning of the pump 20403116_The detection of an ATP2C1 gene mutation in this infant confirmed the diagnosis of Hailey Hailey disease 20604898_Correct SPCA1 functioning is crucial to intra-Golgi transport and maintenance of the Golgi ribbon. 20837466_SPCA1 inhibites the processing of IGF1R in MDA-MB-231 cells. 21187401_analysis of a gain-of-function mutation in a Golgi P-type ATPase that enhances Mn2+ efflux and protects against toxicity 21571222_The SPCA1 knockdown, like ADF/cofilin1 knockdown, inhibited Ca(2+) uptake into the TGN and caused missorting of secretory cargo. 21883398_we report five novel mutations and four recurrent mutations of the ATP2C1 gene in Chinese patients. This further expands the mutation spectrum in Hailey-Hailey Disease. 22124882_genetic polymorphism is associated with Hailey-Hailey disease in Chinese patients 22543864_Human PMR1 bound to c-Src, was tyrosine phosphorylated, sedimented on polysomes, and catalyzed the selective decay of a PMR1 substrate mRNA. Human PMR1 expression stimulated cell motility. 22607350_we report four novel mutations of the ATP2C1 gene involved in HHD, expanding the repertoire of ATP2C1 mutations underlying HHD. 22639968_SPCA1 regulates the levels of claudins 1 and 4, but does not affect desmosomal protein levels in keratinocytes. 23344038_Data suggest that calcium ATPase ATP2C1 gene expression is influenced by an overlapping protein asteroid homolog 1 ASTE1 gene. 23442470_A novel mutation is identified in ATP2C1 linked to Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. 23474827_Case Report: haploinsufficiency of ATP2C1 mutations is the causative mechanism of Hailey-Hailey disease. 24352221_We report sibling cases of Hailey-Hailey disease with novel mutations in the ATP2C1 gene that showed unique and atypical clinical phenotypes mimicking seborrheic dermatitis, pemphigus vulgaris, or pemphigus foliaceus 24981372_we identified two causative genetic mutations responsible for Hailey-Hailey disease. 25179631_The CFL-1-dependent recruitment of actin to SPCA1 following calcium influx is critical for secretory cargo sorting. 25256005_We speculate that a novel pathogenic mechanism involving SPCA1, p63, and IRF6 may play a role in the skin lesions occurring in HHD. 25658765_This is the first genetic report of HHD from Lebanon in which we identified three novel mutations in ATP2C1 and shed light on the molecular mechanisms and pathogenesis of HHD by linking stress signals like heat shock to the observed phenotypes 25837627_Besides the level of functional ATP2C1 protein, levels of other ATPase proteins may influence expressivity of the disease and may also contribute to atypical presentations in three male members of the Hailey Hailey disease family. 26242806_A heterozygous deletion mutation, c. 2445_2454del 10bp, p.Cys814Leu fs*7, was detected in all three Hailey-Hailey disease subjects. This mutation has not yet been described. 26782588_Two novel ATP2C1 mutations have been found in two unrelated Chinese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease pedigree. 27095120_In this study, direct DNA sequencing was used to identify ATP2C1 gene mutations in four Chinese families and two sporadic cases with Hailey-Hailey disease. 27277681_review of the literature about the mutations occurring on the ATP2C1 gene and summarize how they are distributed along the gene and how missense mutations affect protein expression 27528123_results indicate that an ATP2C1/NOTCH1 axis might be critical for keratinocyte function and cutaneous homeostasis, suggesting a plausible model for the pathological features of Hailey-Hailey disease 28035777_Studies indicate that Darier disease (DD) is caused by mutations in the ATP2A2 gene, whereas the ATP2C1 gene is associated with Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD). 28264934_SPCA1a is highly sensitive to the lipid environment and that several SERCA inhibitors, including thapsigargin (Tg), also block SPCA1a activity, although at higher concentrations only. There were differences in the relative contribution of Tg side chains in the inhibition of SERCA1a versus SPCA1a. 28551824_This article aims to critically discuss the clinical and pathological features of Hailey-Hailey disease, differential diagnoses, and genetic and functional studies of the ATP2C1 gene in Hailey-Hailey disease. [review] 28618103_The Secretory Pathway Ca(2+) -ATPases SPCA1 and SPCA2 are strongly induced under osteogenic conditions that elicit microcalcifications. SPCA gene expression is significantly elevated in breast cancer subtypes that are associated with microcalcifications. 28692648_xpressing either wild-type or mutant forms of SLC30A10 was sufficient to inhibit the effect of ATP2C1 in response to Mn challenge in both zebrafish embryos and HeLa cells. These findings suggest that either activating ATP2C1 or restoring the Mn-induced trafficking of ATP2C1 can reduce Mn accumulation, providing a possible target for treating HMDPC. 29024641_The calcium pump SPCA1 regulates proteases within the trans-Golgi network that require calcium for their activity and are critical for virus glycoprotein maturation. 29104283_We examined 2 familial and 2 sporadic cases of Hailey-Hailey Disease. Genomic DNA polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing of the ATP2C1 were performed from HHD patients, unaffected family members, and 200 healthy individuals.We detected 3 heterozygous mutations, including 2 novel frameshift mutations (c.819insA (273LfsX) and c.1264insTAGATGG (421LfsX)) and 1 recurrent nonsense mutation (c.115C>T (R39X)). 29555205_the functional coupling between SPCA1 and Orai1 increases cytosolic and intraluminal Ca(2+) levels, representing a novel mechanism of store-independent Ca(2+) entry that may be affected in Hailey-Hailey disease. 30385858_y Western blot we observed the conversion of HMBS protein from a 47 kDA to 40 kDa product by E. coli K12, O18:K1 and by purified lipopolysaccharide. While ATP2C1 protein was released from platelets, E. coli either reduced the secretion or broke down the released protein making it undetectable by antibodies. 30393074_SPCA1 activity is controlled by the sphingomyelin content of the trans-Golgi network membrane 30923126_A biochemical analysis indicated that Ca(2+) binding to the N-terminal EF-hand-like motif promotes the activity of SPCA1a by facilitating autophosphorylation. 31435946_Our findings update the spectrum of mutations in ATP2C1 in Hailey-Hailey disease. 31455819_Characterization of Hailey-Hailey Disease-mutants in presence and absence of wild type SPCA1 using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as model organism. 31652305_TMEM165 was constitutively degraded in lysosomes in the absence of SPCA1. 31983024_Novel and recurrent variants of ATP2C1 identified in patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. 32335229_SPCA1 governs the stability of TMEM165 in Hailey-Hailey disease. 32817219_The Golgi Calcium ATPase Pump Plays an Essential Role in Adeno-associated Virus Trafficking and Transduction. 33229570_The SERCA residue Glu340 mediates interdomain communication that guides Ca(2+) transport. 33345454_Generalized Hailey-Hailey disease: Novel splice-site mutations of ATP2C1 gene in Chinese population and a literature review. 33801794_Crosstalk among Calcium ATPases: PMCA, SERCA and SPCA in Mental Diseases. 33926923_Genome-wide association study identifies RNF123 locus as associated with chronic widespread musculoskeletal pain. 35274376_Two novel mutations in the ATP2C1 gene found in Japanese patients with Hailey-Hailey disease. 35787370_Calcium and the Ca-ATPase SPCA1 modulate plasma membrane abundance of ZIP8 and ZIP14 to regulate Mn(II) uptake in brain microvascular endothelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000032570 |
Atp2c1 |
1038.295025 |
2.7799846262 |
1.475077 |
0.121192309 |
143.128946 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000550855355400899120162747063962962632206225945890975081145389548142458569010048453478420663054215822285186732187867164611816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000077508341713224702698000161782627273857437340475460825177365770662333955166760151526267330623909401765558868646621704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1548.1362905 |
138.2806306 |
562.4969303 |
37.0634119 |
| ENSG00000018408 |
25937 |
WWTR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZV5 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional coactivator which acts as a downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis (PubMed:11118213, PubMed:18227151). The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ (PubMed:18227151). WWTR1 enhances PAX8 and NKX2-1/TTF1-dependent gene activation (PubMed:19010321). In conjunction with YAP1, involved in the regulation of TGFB1-dependent SMAD2 and SMAD3 nuclear accumulation (PubMed:18568018). Plays a key role in coupling SMADs to the transcriptional machinery such as the mediator complex (PubMed:18568018). Regulates embryonic stem-cell self-renewal, promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (PubMed:18227151, PubMed:18568018). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11118213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18227151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18568018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19010321}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables transcription coactivator activity. Involved in several processes, including hippo signaling; positive regulation of cell differentiation; and regulation of signal transduction. Located in cytosol and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25937; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; glomerulus development [GO:0032835]; heart process [GO:0003015]; hippo signaling [GO:0035329]; kidney morphogenesis [GO:0060993]; mesenchymal cell differentiation [GO:0048762]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of metanephric nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0072307]; regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060390]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146]; stem cell division [GO:0017145]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894] |
16099986_coactivates Runx2-dependent gene transcription while repressing PPARgamma-dependent gene transcription; results indicate that TAZ functions as a molecular rheostat that modulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation 17927494_Decreased osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells of myeloma patients was in part due to TNF-alpha suppressed TAZ expression. 18374411_Seven placental transcripts characterize HELLP-syndrome. 18413727_TAZ plays a role in the migration, invasion, and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells and thus presents a novel target for the detection and treatment of breast cancer. 18568018_Data demonstrate that in response to TGFbeta stimulation the transcriptional regulator TAZ binds heteromeric Smad2/3-4 complexes and is recruited to TGFbeta response elements. 19324876_These results reveal a novel mechanism for TEADs to regulate nuclear retention and thus the transforming ability of TAZ. 19324877_Disruption of TEAD-TAZ binding or silencing of TEAD expression blocked the function of TAZ to promote cell proliferation and to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition, demonstrating TEAD as a key downstream effector of TAZ. 19538860_CD138(+) myeloma cells inhibited mRNA expression of TAZ in mesenchymal stem cells, which could be partially reversed by blocking TNF-alpha. 19542741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19542741_TAZ mutations are not a cause of thyroid dysgenesis in the series of patients studied. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20049872_data indicate that TNF-alpha enhances osteogenic differentiation of adipocyte mesenchymal stem cells via the activation of NF-kappaB and a subsequent increase of TAZ expression 20164440_The present study was aimed at investigating the role of TAZ in uterine physiology by examining its presence in the human uterine endometrium and its involvement in in vitro decidualization of human stromal fibroblasts. 20850437_the first PDZ domain of zona occludens-1 (ZO-1) and 2 (ZO-2) interacts with the carboxy-terminal PDZ binding motif of TAZ 20858893_Hippo pathway negatively regulates TAZ function by both limiting its nuclear accumulation and promoting its degradation. 20972459_Data show that direct interaction of Wbp2 with TAZ depends on the WW domain of TAZ. 21131195_the activated effectors of the RAS/RAF/MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase)/ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase) signalling pathway are involved in the expression of TAZ, supporting the idea that this may also occur in thyroid papillary carcinoma 21189257_PP1A and ASPP2 play a critical role in promoting TAZ function by antagonizing the LATS kinase through TAZ dephosphorylation. 21224387_novel mechanism to restrict the activity of TAZ and YAP through physical interaction with Amot and AmotL1 21349946_Findings define the TAZ-TEAD-Cyr61/CTGF signaling pathway as an important modifier of the Taxol response in breast cancer cells. 21584898_the presence of a WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion in all EHE tested from bone, soft tissue, and visceral location 21654799_findings identify YAP/TAZ as sensors and mediators of mechanical cues instructed by the cellular microenvironment 22045023_TAZ promotes breast cell growth partially through protecting KLF5 from WWP1-mediated degradation and enhancing KLF5's activities. 22078877_Study shows that the activity of TAZ, a transducer of the Hippo pathway, is required to sustain self-renewal and tumor-initiation capacities in breast cancer stem cells. 22108137_Results demonstrate that kaempferol fortifies TAZ activity, which enhances RUNX2-mediated osteoblast differentiation and suppresses PPARgamma-stimulated adipocyte differentiation. 22190458_TAZ expression was lower in proneural glioblastomas and lower-grade gliomas, which correlated with CpG island hypermethylation of the TAZ promoter compared with mesenchymal glioblastomas 22234184_The authors show that YAP and TAZ, the transcriptional co-activators in the Hippo pathway, suppress Wnt signalling without suppressing the stability of beta-catenin but through preventing its nuclear translocation. 22429593_Using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and subsequent sequencing, we confirmed an identical WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion transcript product from different nodules in each patient. 22470139_WWTR1 is an oncogene and has an important role in the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and in tumor growth in vivo. 22481233_High TAZ expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 22692215_a novel mechanism of TAZ regulation and role of TAZ in modulating tissue growth and tumor development in response to PI3K signaling. 22717556_The aim of the present paper was to evaluate Wwox and TAZ, nuclear effectors of Hippo-related pathways, were involved in E-cadherin expression in bone metastases specimens from breast cancer. 22825057_TAZ-dependent secretion of AREG indicates that activation of the EGFR signaling is an important non-cell-autonomous effector of the Hippo pathway, and TAZ as well as its targets may play significant roles in breast tumorigenesis and metastasis. 22895435_Studies indicate that the transcriptional co-activators YAP and TAZ recently emerged as key mediators of the biological effects that are observed in response to extracellular matrix (ECM) elasticity and cell shape. 23026745_NPHP9 promotes signalling through the transcriptional co-activator TAZ. 23245942_TAZ activation is a general feature of Wnt signaling and is functionally relevant to mediate Wnt biological effects. 23258147_Stiffer substrates resulted in upregulation of canonical Wnt modulators, TAZ and sFRP-1, and thus may influence the progression of glaucoma. 23372686_TAZ regulates AXL, and plays an important role in clonogenicity and non-adherent growth in vitro and tumor formation in vivo. 23566416_Considering bone-metastasis specimens, nuclear HIF-1alpha-TAZ co-localisation occurred in neoplastic and supportive cells, such as fibroblasts and endotheliocytes. 23673366_TAZ protein and TEAD transcription factors interaction is functionally important for TAZ-induced cell migration. 23695671_Expression of miR-135b, LZTS1, LATS2 and nuclear TAZ predicts poor outcomes of non-small-cell lung cancer. 23727052_In conclusion, substratum stiffness alters YAP/TAZ expression and YAP localization in trabecularmeshwork cells which then may modulate the expression of extracellular matrix proteins important in glaucoma. 23762387_Overexpression of TAZ is associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer. 23780915_convergent optimization of the YAP/TAZ TEAD binding site suggests that the similarity in the affinities of binding of YAP to TEAD and of TAZ to TEAD is important for Hippo pathway functionality. 23897276_Both YAP and TAZ contribute to the invasive and metastatic capacity of melanoma cells. 23954413_Study reports that physical and architectural features of a multicellular sheet inform cells about their proliferative capacity through mechanical regulation of YAP and TAZ, known mediators of Hippo signaling and organ growth. YAP/TAZ activity is confined to cells exposed to mechanical stresses. 23959471_WWTR1 promotes malignant cell growth and inhibits apoptosis by cyclin A and CTGF regulation. 24324261_post-transcriptional regulation of Dicer is controlled by the cell density-mediated localization of the Hippo pathway effectors TAZ (transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif) and YAP (Yes-associated protein) (TAZ/YAP). 24510127_these results show that TAZ mediates Wnt3a-stimulated osteogenic differentiation through PP1A, suggesting that the Wnt signal regulates the Hippo pathway. 24515112_ECG stimulates osteoblast differentiation through the activation of TAZ and RUNX2, revealing a novel mechanism for green tea-stimulated osteoblast differentiation 24531710_this study designates TAZ as a novel biomarker and a possible therapeutic target for breast cancer 24613358_TAZ interacts with components of the SWI/SNF complex to modulate lineage-specific gene expression. 24648515_Nuclear TAZ/YAP also cooperate with TGFbeta signaling to promote phenotypic and transcriptional changes in nontumorigenic cells to overcome TGFbeta-repressive effects. 24707483_TAZ is highly expressed in SRCC. 24747426_knowledge of how YAP and TAZ function as mechanosensors and mechanotransducers 24860833_There was no significant correlation between the expression of TAZ and AREG in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 24951773_Our findings emphasize the tumorigenic role of TAZ and may serve as the basis for new treatment strategies. 25029906_Over expression of TAZ was associated with abnormal expression of beta-catenin, which is correlated with poor prognosis of patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction 25078107_TAZ and YAP are differentially regulated by hypoxia in cancer cells 25290150_YAP, TAZ and HSP90 take part in contact guidance and intercellular junction formation in corneal epithelial cells. 25353289_Report CAMTA1-WWTR1 gene fusion in thoracic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma but not epithelioid angiosarcoma. 25354978_Overexpression of TAZ upregulates connective tissue growth factor (CTGF)expression and Taz induces CTGF expression via modulating the activation of TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling pathway. 25361000_we demonstrate that the oncogenic activity of TAZ is essential for propagation of the malignant phenotype in triple-negative breast cancer 25425573_Conversely, increased expression of betaPIX in breast cancer cell lines re-couples the Hippo kinase cassette to Yap/Taz, promoting localization of Yap/Taz to the cytoplasm and inhibiting cell migration and proliferation. 25495189_TAZ is associated with the proliferation and invasiveness of HCC cells. 25502501_Immortalized fibroblasts conditionally expressing active YAP or TAZ mutant proteins overcome soft matrix limitations on growth and promote fibrosis 25542152_miR-125a-5p is an important regulator of TAZ in glioma cells 25561492_TAZ regulates the transcription of the alpha5 subunit of LM511 and the formation of a LM511 matrix 25587023_Human breast cancer database analysis revealed that increased expression (greater than the median) of both TAZ and HIF-1 target genes, but neither one alone, is associated with significantly increased patient mortality. 25592648_this article summarizes the current understanding of the biological functions of YAP and TAZ, and how the regulation of these two proteins can be disrupted in cancer.[Review][ 25633292_miR-141 is a potent tumor suppressor in the stomach, and its growth inhibitory effects are, in part, mediated through its downstream target gene, TAZ. 25650113_Results revealed that TAZ is a differentially expressed molecule in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) suggesting it as an important regulator, TAZ might be as a new diagnostic biomarker in HCC. 25652178_Data shows that YAP and Taz play important roles in organ size control and normal tissue regeneration and there expression is upregulated in many human cancer. [review] 25704916_findings have revealed critical links between TAZ, EMT and CSCs in OSCC initiation and progression, and also established TAZ as a novel cancer biomarker and viable druggable target for OSCC therapeutics. 25760078_HDAC9 promotes tumor formation of glioblastoma via TAZ-mediated EGFR pathway activation. 25794680_The study defines a YAP/TAZ-regulated transcriptional program in oral squamous cell carcinoma and reveals novel roles for nuclear YAP/TAZ activity in the onset and progression of this cancer. 25817592_we demonstrate additional structural complexity in WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion transcripts in epithelioid haemangioendothelioma 25843714_Our demonstration of the transcriptional co-repressor activity of YAP/TAZ opens a new avenue for understanding the Hippo signaling pathway. 25849865_Cytoplasmic retention of YAP/TAZ correlates with active ciliogenesis. knockdown of YAP/TAZ is sufficient to induce ciliogenesis, whereas YAP/TAZ hyperactivation suppresses serum starvation-mediated ciliogenesis. 25870251_Patients with strong TAZ expression showed poorer clinical outcomes with respect to both recurrence and overall survival. 25895125_In ovarian cancer cells, miR-129-5p, directly represses TAZ expression, leading to the inactivation of TEA domain transcription, and the downregulation of Hippo downstream genes, connective tissue growth factor and Cyclin A. 25940705_Overexpression of TAZ in neuroblastoma BE(2)-C cells increases cell proliferation, self renewal and colony formation. TAZ knockdown reverses this. TAZ promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity by up-regulating CTGF and PDGF-beta genes. 25961935_Our findings elucidate the mechanistic basis of the oncogenic properties of TAZ-CAMTA1 fusion 25979969_Data suggest that activation of TAZ (tafazzin) inhibits adipogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells; interaction of TAZ and protein phosphatases (PP1A, PP2A) up-regulates dephosphorylation and transport of TAZ to cell nucleus. 25995450_TAZ negatively regulate transcription of DeltaNp63 through TEAD1,2,3 and 4 transcription factors. 26043698_TAZ inhibits temozolomide induced apoptosis via upregulation of MCL-1 (myeloid cell leukemia 1) and high expression of TAZ predicts a poor prognosis for GBM patients 26059435_Taken together, these results complement our previous findings and establish bidirectional crosstalk between HIF-1alpha and TAZ that increases their transcriptional activities in hypoxic cells. 26104008_FAT1 protein acts upstream of Hippo signalling through TAZ protein to regulate neuronal differentiation. 26116754_PARD3 promotes interaction between PP1A and LATS1 to induce LATS1 dephosphorylation and inactivation,leading to dephosphorylation and activation of TAZ 26125451_MicroRNA-9-3p was identified as the tumour-suppressor miR targetting TAZ expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 26136233_Compelling preclinical evidence showed that TAZ/YAP are often aberrantly engaged in breast cancer, where their hyperactivation culminates into a variety of tumor-promoting functions. (Review) 26315112_preS2 upregulates TAZ expression by repressing miRNA-338-3p. TAZ is necessary for preS2-promoted HCC proliferation and migration. 26320173_factor:TAZ transcriptional co-activator and activation of sE-Cadherin/proto-oncogene protein HER-2 signaling could be potential oncogenic pathways for breast cancer (BC) metastasis. 26381823_these data reveal a previously unknown role for TAZ and the Hippo pathway in the progression of aggressive subtypes of endometrial cancer. 26416426_Results show TAZ functioned as an oncogene and promoted pancreatic cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression. 26420216_these studies demonstrate that TAZ and YAP exhibit different functional roles in hepatocellular carcinoma progression, including chemoresistance and tumorigenicity 26432639_This study identifies a novel mechanism of TAZ regulation by YAP, which has significant implications for our understanding of Hippo pathway regulation, YAP-isoform specific signaling, and the role of these proteins in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis 26439301_YAP/TAZ regulate transcriptional elongation from the enhancer elements by recruiting the Mediator complex and promoting phenotypes of overgrowth and tumorigenesis. 26464030_Suggest that high expression of TAZ plays a significant role in retinoblastoma's aggressiveness, and predicts poor prognosis for patients with retinoblastoma. 26491017_activation of the Nherf1-PP1alpha-TAZ pathway in osteoblasts is targeted by histone deacetylase inhibitors 26567630_TAZ may be involved in pancreatic tissue regeneration, and that deregulation of these proteins may play a role in neoplastic transformation and stellate cell functions in both PDAC and pancreatitis. 26611634_The TAZ play an essential role in amino acid-induced mTORC1 activation, particularly under nutrient-limiting conditions. 26667495_A YAP/TAZ-miR-130/301 molecular circuit exerts systems-level control of fibrosis in a network of human diseases and physiologic conditions 26668268_Actin remodeling confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through YAP/TAZ activation 26678338_MYC-driven change in mitochondrial dynamics limits YAP/TAZ function in mammary epithelial cells and breast neoplasms. 26750334_The activity of the YAP/TAZ transcriptional coactivators, was found to be regulated by metabolic pathways, such as aerobic glycolysis and mevalonate synthesis, and by the nutrient-sensing LKB1-AMPK and TSC-mTOR pathways. (Review) 26758663_Various studies show that in human cancers, the Hippo pathway is frequently deregulated allowing YAP1 and TAZ to escape the inhibition by the Hippo pathway. The upregulation of YAP1 and TAZ induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increases drug resistance in cancer cells. TAZ is implicated in cancer stemness.[review] 26838548_ABL kinases promote breast cancer osteolytic metastasis by modulating tumor-bone interactions through TAZ and STAT5 signaling. 26885614_High TAZ expression is associated with breast cancer. 26989177_the transcription regulators YAP and TAZ localise to the nucleus in the basal layer of skin and are elevated upon wound healing. 27094723_miR-125a-5p functions as an important tumor suppressor that suppresses the EGFR pathway by targeting TAZ to inhibit tumor progression in retinoblastoma. 27129148_Study showed that TAZ and YAP are commonly activated oncoproteins in sarcomas. 27155083_Nuclear localization of YAP and TAZ was reduced in DMOG-treated primary tubular epithelial cells. 27167112_Data show that TAZ, a WW-domain-containing transcriptional co-activator, could promote the acceleration of cell cycle and cell proliferation through EGFR pathway. 27179930_PDE/cGMP/PKG signaling targets Hippo/TAZ pathway to maintain stemness of prostate cancer stem cells. 27184927_TAZ is significantly associated with poor survival in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Constitutively active TAZ S89A significantly increased proliferation of C2C12 myoblasts and, importantly, colony formation on soft agar, suggesting transformation. However, TAZ then switches to enhance myogenic differentiation in C2C12 myoblasts. 27237790_SnoN interacts with multiple components of the Hippo pathway to inhibit the binding of Lats2 to TAZ and the subsequent phosphorylation of TAZ, leading to TAZ stabilization. 27248471_Data suggested that the co-expression of the Hippo transducers TAZ/YAP and CTGF may be an adverse prognostic factor in male breast cancer. 27291091_Results show that YAP and TAZ transcription are regulated by Cbx7 inhibiting glioblasoma cell migration. 27300434_Studies indicates that YAP/TAZ are essential for cancer initiation or growth of most solid tumors. Their activation induces cancer stem cell attributes, proliferation, chemoresistance, and metastasis. YAP/TAZ are sensors of the structural and mechanical features of the cell microenvironment. [review] 27373987_Paralog of TAZ (YAP) expression can be upregulated by TAZ inhibition which leads to EGFRI resistance. 27382053_thromboxane A2 signaling activates YAP/TAZ to promote Vascular Smooth Muscle migration and proliferation, indicating YAP/TAZ as potential therapeutic targets for cardiovascular diseases. 27412635_Besides its role in normal tissue development, TAZ plays critical roles in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and stemness in multiple human cancers. 27422606_Thus, it could be concluded that EPO and IGF1 possessed a potent synergism in promoting osteogenic differentiation, and the synergism was mainly attributed to co-regulation of different osteogenic regulators PPARgamma and TAZ, which were targeted genes of EPO and IGF1 respectively. 27429252_Together, these data illustrate that YAP/TAZ signaling is responsive to hydrogel stiffness and degradability, but the outcome is dependent on the dimensionality of cell-biomaterial interactions. 27479603_results demonstrate that skeletal stem/stromal cell mobilize Snail/Slug-YAP/TAZ complexes to control stem cell function 27527859_YAP/ TAZ pathways contribute to the proliferation/quiescence switch during colon cancer 5FU treatment according to the concerted regulation of Cyclin E1 and CREB 27548520_extracellular matrix stiffening sustains vascular cell growth and migration through YAP/TAZ-dependent glutaminolysis and anaplerosis 27554639_TAZ regulates cell proliferation and sensitivity to vitamin D3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by regulating tp53/CYP24A1 pathway. 27578003_Wnt signaling upregulated WBP2 by disrupting ITCH-WBP2 interactions via EGFR-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of WBP2 and TAZ/YAP competitive binding. 27583562_results highlight both CYR61 and TAZ genes as potential predictive biomarkers for stratification of the risk for development of adenocarcinoma and suggest a potential mechanistic route for Barrett's esophagus neoplastic progression 27608849_this study indicates that TAZ proteins are linked to prognosis and therefore could be therapeutic targets in conventional osteosarcomas 27627196_SCLC cell lines of the YAP/TAZ subgroup had higher sensitivity to the widely used anticancer agent for SCLC, topotecan. 27671657_These results demonstrate a critical role of the activation of YAP/TAZ by disturbed flow in promoting atheroprone phenotypes and atherosclerotic lesion development. 27717711_Collectively, our study identified an unexpected transcriptional repression function of the BET bromodomain and a novel mechanism for TAZ upregulation. 27721022_CytoD modified MKL1, a coactivator of serum response factor (SRF) regulating CTGF induction, and promoted its nuclear localization. 27764783_TAZ is overexpressed in glioma and translocated more into nucleus in high grade glioma. TAZ is involved in gliomagenesis by promoting glioma growth and may benefit to epithelial mesenchymal transformation. 27797825_High TAZ expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 27826640_Growing evidence suggests that transcriptional effectors of the Hippo pathway, YAP and TAZ, promote resistance to various anti-cancer therapies, including cytotoxic chemotherapy, molecular targeted therapy, and radiation therapy. [review] 27851961_WIP controls tumor growth by boosting signals that stabilize the YAP/TAZ complex via a mechanism mediated by the endocytic/endosomal system. 27852064_FZD7 may promote glioma cell proliferation via upregulation of TAZ. 27881410_These findings demonstrate sufficiency of TAZ activation for driving fibroblast proliferation, contraction, and soluble profibrotic factor expression, and mechanical context-dependent crosstalk of TAZ with other pathways in regulating Col1a1 expression. 27973704_A group of miRNAs have been demonstrated to directly target components of the Hippo signaling pathway, such as YAP, TAZ and LATS1/2 in oncogenesis. (Review) 27987320_AXL/TAZ/YAP expression is associated with poor prognosis in male breast cancer patients. 27999199_Rottlerin exerted its tumor suppressive function via inactivation of TAZ in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. 28055015_mechanistic study revealed that miR-224 functions by inhibiting the tumor suppressor, SMAD4, to support the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma (OS) cells. Our findings indicate that targeting TAZ and miR-224 could be a promising approach for the treatment of OS. 28068223_TAZ represents a previously unrecognized factor that contributes to the critical process of steatosis-to-Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis progression. 28078823_Our goal is to describe the physiological roles of Hippo signaling in several normal organ systems, as well as to emphasize how disruption of the Hippo pathway, and particularly hyperactivation of YAP1/TAZ, can be oncogenic (review) 28115535_These results suggest that vinculin promotes the nuclear localization of transcription factor TAZ to inhibit the adipocyte differentiation on rigid extracellular matrix. 28128737_These results indicate that TAZ is an independent prognostic factor and plays an important role in Non-Small Cell lung cancer (NSCLC)progression and may serve as a novel therapeutic target of NSCLC. 28154141_Data indicate the role of tyrosine kinase c-Src (Src) in rescuing Taz (transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif) from E3 ligase SCF(beta-TrCP)-mediated degradation. 28166194_establish a new cancer stem cell signalling pathway downstream of mtp53 in which AKT2 regulates WIP and controls YAP/TAZ stability. 28202507_YAP and TAZ, which are inhibited by the HIPPO tumor suppressor pathway, modify PI3K/AKT pathway signaling in endometrial cancer. 28249901_ETAR stimulation acted via downstream G-protein Galphaq/11 and Rho GTPase to suppress the Hippo pathway, thus leading to YAP/TAZ activation, which was required for ETAR-induced tumorigenesis. Overall, these results indicate a critical role of the YAP/TAZ axis in ETAR signaling 28346439_YAP/TAZ act as natural inhibitors of TBK1 and are vital for antiviral physiology. 28381547_eIF5A-PEAK1 signaling controls YAP1/TAZ expression, which is associated with increased pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumorigenicity 28400537_Data indicate that injury reduced YAP and TAZ activity in cultured podocyte cell line grown on stiff substrates. 28408625_the prostate cancer-related oncogenic E26 transformation-specific (ETS) transcription factors, ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5, were required for TAZ gene transcription in PC3 prostate cancer cells 28415606_this study identified TAZ as a novel inducer of lung cancer stem cells and the first transcriptional activator of the stem cell marker ALDH1A1 28416184_In colorectal carcinoma TIAM1 suppresses tumor progression by regulating YAP/TAZ activity. 28416659_Mechanistically, YOD1 deubiquitinates ITCH, an E3 ligase of LATS, and enhances the stability of ITCH, which leads to reduced levels of LATS and a subsequent increase in the YAP/TAZ level. 28430338_Author found a significant direct correlation between TAZ expression and VIII CN schwannoma volumes on latest preoperative ceMRI (p/=2.1 cm3 than in those with a volume |
ENSMUSG00000027803 |
Wwtr1 |
77.065472 |
0.2251660216 |
-2.150939 |
0.232946693 |
88.126457 |
0.00000000000000000000614008422768659294504437508490205758196256155692388109740894458488114082683750893920660018920898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000056220622332911985611894307956061259613936134235964530141832495857556750706862658262252807617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.1026570 |
5.8984015 |
107.8937877 |
17.9651857 |
| ENSG00000019102 |
23584 |
VSIG2 |
protein_coding |
Q96IQ7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23584; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] |
20659327_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000001943 |
Vsig2 |
93.194513 |
0.1121151351 |
-3.156947 |
0.229866232 |
213.074512 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000293168328009985305482640986332040502996513139252682892203448151991965967741030579968114371013841633538626856100152865487913633746330788198974914848804473876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000059933026612567635525186035807082156916850352580868949696897006510345230843124177594882801471294881676088253809727763492601337880216760822804644703865051269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5010141 |
2.9980032 |
166.4432882 |
14.7955868 |
| ENSG00000019169 |
8685 |
MARCO |
protein_coding |
Q9UEW3 |
FUNCTION: Pattern recognition receptor (PRR) which binds Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (PubMed:9468508). Also plays a role in binding of unopsonized particles by alveolar macrophages (By similarity). Binds to the secretoglobin SCGB3A2 (PubMed:12847263). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUB9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12847263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9468508}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Collagen;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the class A scavenger receptor family and is part of the innate antimicrobial immune system. The protein may bind both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria via an extracellular, C-terminal, scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain. In addition to short cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains, there is an extracellular spacer domain and a long, extracellular collagenous domain. The protein may form a trimeric molecule by the association of the collagenous domains of three identical polypeptide chains. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8685; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; amyloid-beta clearance [GO:0097242]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898] |
11820786_An arginine-rich segment in domain V of MARCO and particularly its RXR motifs play a critical role in high-affinity bacterial binding. 12097327_characterization of a MARCO protein domain involved in binding to bacteria 12847263_Northern blot and in situ hybridization experiments indicate that MARCO is expressed by alveolar macrophages in the lung; retroviral vector-mediated expression cloning determines that MARCO is a receptor for UGRP1. 16237101_a dominant role for MARCO in the human AM defense against inhaled particles and pathogens. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19403625_Expansion of small sputum macrophages in cystic fibrosis shows a failure to express MARCO and CD206. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20810988_MARCO is an important phagocytic receptor used by human and mouse macrophages to clear C. sordellii from the infected uterus 21299846_Data suggest that bacteria induce glial cell activation and rCRAMP expression via FPRL1 and MARCO, and these receptors contribute to the host defence against infection. 21886847_genetic variants in MARCO gene were associated with pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility in Chinese Han population 21986627_These results demonstrate that the S. mutans lipoprotein PpiA contributes to suppression of MARCO-mediated phagocytosis of this bacterium by macrophages. 22470185_In this review, we showed that SR-A and MARCO trigger intracellular signaling, modulating pro-inflammatory and microbicidal activities of macrophages. 22470186_This review demonstrated that class A SR and MARCO are major pattern recognition receptors mediating opsonin-independent phagocytosis. 23154236_We identified 9 non-synonymous variants in the MARCO gene and showed that these variants are not major risk factors for COPD or lung infection. H101Q heterozygotes had increased sepsis risk. 23249958_Significant associations of four SNPs and haplotypes with antibody response to cholera vaccine in three genes, MARCO, TNFAIP3 and CXCL12. 23617307_Polymorphisms within the human class A scavenger receptor MARCO correlate with susceptibility/resistance to tuberculosis in a Gambian population. 23739639_herpes simplex virus type 1 binds to MARCO to enhance its capacity for disease. 25089661_Vaccinia virus bound directly to MARCO, and overexpression of MARCO increased susceptibility to vaccinia infection. 25186548_None of the nonsynonymous variants discovered by resequencing of the structurally similar MARCO were associated with lung function or risk of COPD. 26886650_identified as a disease-associated molecule in IgG4-related disease by DNA microarray 26888252_These data suggest the SRCR domain of MARCO is the key domain in modulating ligand binding, enhancing downstream pro-inflammatory signaling and MARCO-mediated cellular adhesion. 26892079_Identifying N-linked glycan moiety and motifs in the cysteine-rich domain critical for N-glycosylation and intracellular trafficking of SR-AI and MARCO. 27554839_this translational investigation identified gene candidates, including Marco, for host susceptibility to multiple phenotypes of RSV disease in mice that closely mimic human disease, and a polymorphism in human MARCO associated with increased risk of RSV disease severity in infants. 27706807_this paper shows that key gene of intermediate proinflammatory monocytes, such as MARCO, is expressed three- to fourfold more in juvenile idiopathic arthritis-enthesitis-related arthritis 27806438_Expression of MARCO declined progressively as hepatocellular carcinoma condition is aggravated. 27853145_results suggest that MARCO polymorphisms may regulate phagocytosis of M. tuberculosis and susceptibility and severity of pulmonary tuberculosis 28298522_this study shows that MARCO modulates inflammatory responses against Cryptococcus neoformans infection 28408365_Increasing MARCO expression by targeting Nrf2 signaling or the Akt-TFEB-MARCO pathway are promising strategies to improve bacterial clearance and survival in postinfluenza bacterial pneumonia. 28693442_MARCO single nucleotide polymorphisms rs12998782 increases risk to pulmonary tuberculosis in a Chinese Han population. 28866086_CD36 and MARCO are associated with the susceptibility of Chinese Han females to carotid atherosclerosis. Menopausal status may affect the association between gene polymorphisms and carotid atherosclerosis in the female Chinese Han population. 29165618_Q452 and F282 are important for ligand association and phagocytosis of bacteria. Q452 and F282 are examples of positively selected mutations in MARCO, and both enhance the intrinsic function of the receptor. 29522575_High surface expression of SR-A6 facilitates HAdV-C5 infection. 29769337_the absence of MARCO does not interfere with the efficiency of HSV-1 entry and that the inhibitory effect on viral adsorption by poly(I), a ligand of MARCO, is independent of MARCO. 31381879_MARCO is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)progression and it can be defined as a novel probable biomarker as well as treatment target for HCC. 32740454_Genetic Susceptibility to Life-threatening Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Previously Healthy Infants. 33293426_Targeting MARCO and IL37R on Immunosuppressive Macrophages in Lung Cancer Blocks Regulatory T Cells and Supports Cytotoxic Lymphocyte Function. 33311558_Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to cellular internalization of exosomes by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. 33363539_Binding of Macrophage Receptor MARCO, LDL, and LDLR to Disease-Associated Crystalline Structures. 34011400_Single-cell characterization of macrophages in glioblastoma reveals MARCO as a mesenchymal pro-tumor marker. 34398403_TLR2 Potentiates SR-Marco-Mediated Neuroinflammation by Interacting with the SRCR Domain. 34626585_Scavenger receptor MARCO contributes to macrophage phagocytosis and clearance of tumor cells. 35364781_Association of the MARCO polymorphism rs6761637 with hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility and clinical characteristics. |
ENSMUSG00000026390 |
Marco |
28.542635 |
26.8935729197 |
4.749190 |
0.572054766 |
89.452131 |
0.00000000000000000000314148454754064551142207387764987429308890871608694834109893820328629487903526751324534416198730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000029144130686172174114073288482929433786535375868064650685396177465236178250052034854888916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.3833412 |
19.3725441 |
1.9446966 |
0.6778511 |
| ENSG00000020181 |
25960 |
ADGRA2 |
protein_coding |
Q96PE1 |
FUNCTION: Endothelial receptor which functions together with RECK to enable brain endothelial cells to selectively respond to Wnt7 signals (WNT7A or WNT7B) (PubMed:28289266, PubMed:30026314). Plays a key role in Wnt7-specific responses, such as endothelial cell sprouting and migration in the forebrain and neural tube, and establishment of the blood-brain barrier (By similarity). Acts as a Wnt7-specific coactivator of canonical Wnt signaling: required to deliver RECK-bound Wnt7 to frizzled by assembling a higher-order RECK-ADGRA2-Fzd-LRP5-LRP6 complex (PubMed:30026314). ADGRA2-tethering function does not rely on its G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) structure but instead on its combined capacity to interact with RECK extracellularly and recruit the Dishevelled scaffolding protein intracellularly (PubMed:30026314). Binds to the glycosaminoglycans heparin, heparin sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate (PubMed:16982628). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91ZV8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16982628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28289266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30026314}. |
Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
Predicted to enable G protein-coupled receptor activity. Involved in positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Part of Wnt signalosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25960; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900747]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050920]; regulation of establishment of blood-brain barrier [GO:0090210]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
16982628_Proteolytically processed soluble tumor endothelial marker TEM5 mediates endothelial cell survival during angiogenesis by linking integrin alpha(v)beta3 to glycosaminoglycans 19853600_TEM5 expression during capillary morphogenesis is induced by the small GTPase Rac and mediates contact inhibition of proliferation in endothelial cells. 22013897_Thrombin-induced shedding of tumour endothelial marker 5 and exposure of its RGD motif are regulated by cell-surface protein disulfide-isomerase. 24582749_Observed an inverse correlation between the expression of miR-138-5p and GPR124 in lung adenocarcinoma specimens. Knockdown of GPR124 mimicked the effects of miR-138-5p on the sensitivity to gefitinib. 28600358_Data suggest that GPR124 promotes cell adhesion via interaction with Elmo1-Dock180 and intersectin 1/2; this constitutes a previously unrecognized heteromeric complex that is putatively involved in GPR124-dependent adhesive/angiogenic responses in vascular endothelial cells. (GPR124 = G-protein coupled receptor 124; Elmo1 = ELMO domain-containing protein 1; Dock180 = dedicator of cytokinesis protein 1 180 kDa) 31058365_Increases and decreases in GPR124 expression in glioblastoma cells reduce cell proliferation by differentially altering the duration mitotic progression. GPR124 interacts with ch-TOG, a known regulator of both microtubule (MT)-plus-end assembly and mitotic progression. Changes in GPR124 expression and ch-TOG similarly affect MT assembly. 31352222_Serum TEM5 and TEM7 concentrations correlate with clinicopathologic features and poor prognosis of colorectal cancer patients 32991049_Variants of WNT7A and GPR124 are associated with hemorrhagic transformation following intravenous thrombolysis in ischemic stroke. 35649360_An integrated model for Gpr124 function in Wnt7a/b signaling among vertebrates. |
ENSMUSG00000031486 |
Adgra2 |
213.905029 |
0.0961001559 |
-3.379317 |
0.167871485 |
454.112711 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009185119513894724968218721539297331373766776671121703739655116707076019486379271985336841010311739455048050734084174298473668294204036397659377918526498955636123656007572294923725741753621101423088342574742262490148468996421408142 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003941057093752503883345914622802684191833326712598523345578149703902457451883052778847776973461567258065189038908622253520611130478055993986893921061783776929685249071794744164705337354842609128308994274851184268539083349434998801 |
Yes |
No |
37.9080419 |
4.2525042 |
397.2240442 |
23.5549844 |
| ENSG00000020426 |
4331 |
MNAT1 |
protein_coding |
P51948 |
FUNCTION: Stabilizes the cyclin H-CDK7 complex to form a functional CDK-activating kinase (CAK) enzymatic complex. CAK activates the cyclin-associated kinases CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 by threonine phosphorylation. CAK complexed to the core-TFIIH basal transcription factor activates RNA polymerase II by serine phosphorylation of the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of its large subunit (POLR2A), allowing its escape from the promoter and elongation of the transcripts. Involved in cell cycle control and in RNA transcription by RNA polymerase II. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10024882}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Direct protein sequencing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene, along with cyclin H and CDK7, forms the CDK-activating kinase (CAK) enzymatic complex. This complex activates several cyclin-associated kinases and can also associate with TFIIH to activate transcription by RNA polymerase II. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:4331; |
CAK-ERCC2 complex [GO:0070516]; cyclin-dependent protein kinase activating kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0019907]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; transcription factor TFIIH core complex [GO:0000439]; transcription factor TFIIH holo complex [GO:0005675]; transcription factor TFIIK complex [GO:0070985]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0061575]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; adult heart development [GO:0007512]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA helicase activity [GO:1905775]; nucleotide-excision repair [GO:0006289]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591] |
12140753_The cyclin H/cdk7/Mat1 kinase activity is regulated by CK2 phosphorylation of cyclin H. 12213824_Retinoid-induced G1 arrest and differentiation activation are associated with a switch to enzyme hypophosphorylation of retinoic acid receptor alpha. 12527756_interaction with MTA1 and role in regulating estrogen receptor transactivation functions 16935935_In response to ATRA, PML/RARalpha is dissociated from CAK, leading to MAT1 degradation, G1 arrest, and decreased CAK phosphorylation of PML/RARalpha 17628022_Retinoic-acid-induced RAR-CAK signaling events appear to proceed intrinsically during granulocytic development of normal primitive hematopoietic cells. ALDH-governed RA availability may mediate this process by initiating RAR-CAK signaling. 17707548_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17707548_These results suggested that genetic variants in CAK genes, Cdk7, cyclin H, MAT1, might modulate the risk of lung cancer in a gene-gene interaction mode, which consist to the biochemical interaction of corresponding proteins. 19584075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23765726_The intrinsically programmed MAT1 expression and fragmentation regulate granulopoiesis. 27301701_Expressions of components of the CAK complex, CDK7, MAT1, and Cyclin H are elevated in breast cancer. 31421084_MAT1 serves as a promoter in the lung metastasis of osteosarcoma through increasing AKT1 expression. 32245994_Study presents the high-resolution crystal structure of the Arch domain of XPD with its interaction partner MAT1, a central component of the CDK activating kinase complex. The analysis of the interface led to the identification of amino acid residues that are crucial for the MAT1-XPD interaction. 32453410_The regulatory effect of has-circ-0001146/miR-26a-5p/MNAT1 network on the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma. 32663249_Potentially functional variants in nucleotide excision repair pathway genes predict platinum treatment response of Chinese ovarian cancer patients. |
ENSMUSG00000021103 |
Mnat1 |
50.844504 |
2.5104082081 |
1.327922 |
0.570334888 |
5.203919 |
0.02253602770190650181336700086376367835327982902526855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.039903043291763432010021972473623463883996009826660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.4026709 |
35.6035226 |
28.5803719 |
10.1596363 |
| ENSG00000020577 |
23034 |
SAMD4A |
protein_coding |
Q9UPU9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a translational repressor of SRE-containing messengers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16221671}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Synapse;Synaptosome;Translation regulation |
|
Sterile alpha motifs (SAMs) in proteins such as SAMD4A are part of an RNA-binding domain that functions as a posttranscriptional regulator by binding to an RNA sequence motif known as the Smaug recognition element, which was named after the Drosophila Smaug protein (Baez and Boccaccio, 2005 [PubMed 16221671]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:23034; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; P-body [GO:0000932]; synapse [GO:0045202]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation repressor activity [GO:0030371]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening [GO:0000289]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727] |
16221671_Smaug 1 has a role in RNA granule formation and translation regulation in neurons 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22201125_The Smaug1 is expressed during synaptogenesis, and Smaug1 knockdown affected the number and size of synapses, and also provoked an impaired response to repetitive depolarizing stimuli, as indicated by a reduced induction of Arc/Arg3.1. 32292524_Circular RNA SAMD4A controls adipogenesis in obesity through the miR-138-5p/EZH2 axis. 34080649_circSAMD4A participates in the apoptosis and autophagy of dopaminergic neurons via the miR29c3pmediated AMPK/mTOR pathway in Parkinson's disease. 34219323_RNA-binding protein SAMD4A inhibits breast tumor angiogenesis by modulating the balance of angiogenesis program. |
ENSMUSG00000021838 |
Samd4 |
195.200113 |
0.4112422720 |
-1.281940 |
0.237828263 |
28.367534 |
0.00000010033389740182798382673993488334307500053910189308226108551025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000395335911812861979077929732231955206600559904472902417182922363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.0117441 |
18.3942101 |
259.8619731 |
31.8961989 |
| ENSG00000020633 |
864 |
RUNX3 |
protein_coding |
Q13761 |
FUNCTION: Forms the heterodimeric complex core-binding factor (CBF) with CBFB. RUNX members modulate the transcription of their target genes through recognizing the core consensus binding sequence 5'-TGTGGT-3', or very rarely, 5'-TGCGGT-3', within their regulatory regions via their runt domain, while CBFB is a non-DNA-binding regulatory subunit that allosterically enhances the sequence-specific DNA-binding capacity of RUNX. The heterodimers bind to the core site of a number of enhancers and promoters, including murine leukemia virus, polyomavirus enhancer, T-cell receptor enhancers, LCK, IL3 and GM-CSF promoters (By similarity). May be involved in the control of cellular proliferation and/or differentiation. In association with ZFHX3, up-regulates CDKN1A promoter activity following TGF-beta stimulation (PubMed:20599712). CBF complexes repress ZBTB7B transcription factor during cytotoxic (CD8+) T cell development. They bind to RUNX-binding sequence within the ZBTB7B locus acting as transcriptional silencer and allowing for cytotoxic T cell differentiation. CBF complexes binding to the transcriptional silencer is essential for recruitment of nuclear protein complexes that catalyze epigenetic modifications to establish epigenetic ZBTB7B silencing (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20599712}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the runt domain-containing family of transcription factors. A heterodimer of this protein and a beta subunit forms a complex that binds to the core DNA sequence 5'-PYGPYGGT-3' found in a number of enhancers and promoters, and can either activate or suppress transcription. It also interacts with other transcription factors. It functions as a tumor suppressor, and the gene is frequently deleted or transcriptionally silenced in cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:864; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; core-binding factor complex [GO:0016513]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation [GO:0043371]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; ossification [GO:0001503]; peripheral nervous system neuron development [GO:0048935]; positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation [GO:0043378]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to transforming growth factor beta [GO:0071559] |
12824905_RUNX3 methylation is associated with gastric cancers 12855590_RUNX3/AML-2 binding to the CD11a promoter correlates with increased RUNX3/AML-2 protein levels and enhanced CD11a/CD18 cell surface expression 12875960_These results strongly suggest that RUNX3 is one of the tumor suppressors involved in the pathogenesis of testicular yolk sac tumors in infants. 14715269_results suggest that loss of RUNX3 expression by DNA hypermethylation is frequently associated with the evolution of lung cancer 14760761_Inactivation of RUNX3 gene through allelic loss and promoter hypermethylation might be one of the major mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. 15051926_Our results overall suggest that transcriptional inactivation of RUNX3 by promoter hypermethylation may participate in the stomach carcinogenesis. 15138260_Data show that RUNX3 is a target of the acetyltransferase activity of p300 acetyltransferase. 15273736_Transcriptional repression of RUNX3 is caused by promoter hypermethylation of the RUNX3 CpG island in colorectal cancer cell lines. 15386419_Expression of RUNX3 is down regulated in a significant portion of gastric cancer cases; may be involved in gastric carcinogenesis 15688019_RUNX3 regulates RUNX1 expression in human B lymphoid cell lines. 15728469_The percentage of CD4-8+ cells increases and the percentage of CD4+8+ and CD4+8- cells simultaneously decreases in the Runx3-transgenic thymus. Thus, Runx3 can drive thymocytes to select the CD4-8+ lineage. 15778373_an inhibitory element was identified in the KIR2DL4 promoter and an activating element was found in the KIR3DL3 promoter; AML-2 acts as a repressor of expression of both KIR2DL4 and KIR3DL3 in mature NK cells 15780064_Hypermethylation of RUNX3 may play an important role in early events of hepatocarcinogenesis. 15819721_The expression of RUNX3 protein in lung AC might play a pivotal role in tumor progression and patients' survival 15824739_Hypermethylation of p16, RUNX3, and HPP1 in Barreett exophagus may represent independent risk factors for the progression of Barrett esophagus to esophageal cancer. 16080503_RUNX3 aberrant methylation might play an important role in colorectal cancers, especially in poorly-differentiated colorectal cancers. 16091737_findings refute a role for RUNX3 as a tumor-suppressor gene in early-onset gastric carcinogenesis 16135801_RUNX3 is required for the TGF-beta-dependent induction of p21 expression in stomach epithelial cells. 16140942_RUNX3 was found to be inactive in 82% of gastric cancers through either gene silencing or protein mislocalization to the cytoplasm. 16142337_RUNX3 is downregulated by hemizygous deletion at 1p36 in human lung cancer cell lines 16155404_Promoter hypermethylation of RUNX3 gene may occur as an early event in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and that methylation may be a major mechanism for inactivation of RUNX3 gene in HCC. 16328045_RUNX3 gene plays an important role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer, and aberrant methylation is an important mechanism of inactivation of the RUNX3 gene in lung AdC. 16367921_detection of hypermethylation at multiple regions within the RUNX3 CpG island may be useful in the diagnosis and risk assessment of gastric cancer 16373335_RUNX3 cooperates with FoxO3a/FKHRL1 to participate in the induction of apoptosis by activating Bim 16442267_KAP5 gene expression in human hair follicles is regulated by Runx1 16582583_The expression of RUNX3 was studied in esophageal mucosa and squamous cell carcinoma as well as in comparison with clinicopathological profiles. 16627973_analysis of how the RUNX3 gene induces apoptosis in gastric cancer 16684349_results suggest that mammalian RUNX family transcription factors are novel binding partners and substrates for the Pim-1 kinase, which may be able to regulate their activities during normal hematopoiesis as well as in leukemogenesis 16767156_results indicate that although the deregulation of Wnt signalling could contribute to the pathogenesis of a subset of basal cell carcinomas (BCC), RUNX3 appears to be a universal downstream mediator of a constitutively active Shh pathway in BCC 16818622_In breast tumors, hypermethylation of RUNX3 was observed in 23 of 44 cases. Mislocalization of the protein, with or without methylation, seems to account for RUNX3 inactivation in the vast majority of the tumors. 16887969_Runx3 impairs the activity of the proximal regulatory region of the CD36 gene in myeloid cells through in vitro recognition of two functional RUNX-binding elements. 16984612_Methylation rates (MR) in four of the cancer cell lines that lost RUNX3 mRNA ranged from 99.0% to 99.7% (mean, 99.4%), whereas MR in the remaining cell line that expressed RUNX3 mRNA was 0.6%. 17195845_transcription factor Runx3 is induced in T helper type 1 cells in a T-bet-dependent manner, and that both transcription factors T-bet and Runx3 are required for maximal production of interferon-gamma and silencing of the gene encoding IL-4 in Th1 cells 17380460_RUNX3 protein expression in tumor tissues was significantly higher than that in non-tumor tissues, and was correlated with tumor differentiation. 17384682_RUNX3 silencing promotes radioresistance in esophageal cancers 17470130_RUNX3 is involved in TGF-beta-induced expression of p21 and the resulting induction of TGF-beta-dependent G(1) arrest. 17471240_The present data suggest that TGF-beta, LMO1, possibly RUNX3, and GSDM form a regulatory pathway for directing the pit cells to apoptosis. 17584746_Runx3 determines TrkC positive sensory neuron identities through the transcriptional repression of TrkB when Trk-BTrkC double positive neurons differentiate into TrkC single positive neurons. 17591800_Important target of DNA methylation in the evolution of microsatellite instability in gastric cancer. 17591929_A panel of markers including at least RUNX3, CACNA1G, IGF2, and MLH1 can serve as a sensitive and specific marker panel for CIMP(Cpg island methylator phenotype)-high. 17606310_the hypermethylation of RUNX3 gene is a useful biomarker to predict the prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer 17914577_Promoter hypermethylation of RUNX3 is associated with neoplasms 17923751_Eighty-five percent of breast cancer tissues showed downregulated RUNX3 gene expression, whereas it was downregulated in only 25% of normal breast tissues. 17956589_RUNX3 expression suppressed cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis via the death-receptor mitochondria-mediated pathway in human gastric carcinoma MKN-1 cells. 18058463_Results suggest that epigenetic silencing of RUNX3 gene expression by promoter hypermethylation may play an important role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development. 18097595_H. pylori infection contributes to Runx3 methylation in gastric cancer tissues...subsequent loss of Runx3 expression may therefore affect gastric carcinogenesis. 18256927_RUNX3 inactivation by promoter hypermethylation and protein mislocalization constitute an early event in breast cancer progression. 18259121_RUNX3 inhibits growth of HCC cells and HCC xenografts in mice in combination with adriamycin 18288406_RUNX3 mRNA expression levels were lower in invasive esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 18349282_RUNX was found to be methylated significantly more frequently in NSCLC tissues than noncancerous tissues. 18426645_Methylation of runx3 gene promoter probably plays a role in the pathogenesis of acute leukemia. 18430739_RUNX3 is a target for repression by EZH2 in gastric cancer cells 18475302_Hypermethylation and LOH appear to be common mechanisms for inactivation of RUNX3 in pancreatic cancer. Therefore, RUNX3 may be an important tumour suppressor gene related to pancreatic cancer. 18494051_shRNAs targeted to gene promoter regions of RUNX3 induced transcriptional repression with chromatin changes characteristic of inaction promoters, which was independent of DNA methylation. 18500170_Downregulation of RUNX3 may play a role in disease progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 18572225_Findings indicate that RUNX3 inactivation may play an important role in carcinogenesis of the endometrium, especially in high-grade endometrial carcinoma. 18580070_With the increased progression of breast cancer, the expression of RUNX3 protein tends to decrease. The expression of RUNX3 protein has a definite value in judging prognosis in breast cancer. 18636364_Promoter hypermethylation is a main mechanism of reduced or loss expression of Runx3 gene in gastric cancer. 18639281_RUNX3 methylation carries a 100-fold increase in the risk of bladder tumor. The rate of RUNX3 hypermethylation in primary bladder tumors is 71.2%. This suggests that patterns of promoter methylation are causally associated with bladder tumorigenesis. 18663147_RUNX3 is found to be commonly repressed by the t(8;21) and inv(16) fusion proteins and might have an important role in core-binding factor AML 18668679_Increased Runx3 is associated with ulcerative colitis. 18676844_prevalence of methylation at RUNX3, a polycomb target gene, increased as a function of age at bladder tumor diagnosis and a history of smoking 18684727_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18684727_genetic variants in RUNX3 may modulate the risk of bladder cancer. 18717361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18717361_There is a strong correlation between the RH120480 fragment of RUNX3 gene mutation and keloid. 18772112_Data demonstrate that RUNX3 functions as a tumor suppressor by attenuating Wnt signaling. 18850007_Hypoxia upregulates G9a histone methyltransferase & HDAC1. Overexpression of G9a & HDAC1 attenuated RUNX3 expression. The overexpression of G9a & HDAC1, but not their mutants, inhibited the nuclear localization & expression of RUNX3. 18937968_Results suggest that RUNX3 has a role in cell proliferation and viability in ovarian cancer. 18949360_Clinical and experimental data support the notion that RUNX3 is a tumor suppressor in human colon cancer. 18953836_The promoter hypermethylation may be one of the predominant inactivation mechanisms of the Runx3 gene, and may be associated with carcinogenesis of human gastric cancer. 19012242_RUNX3 could be considered to play an important role in maintaining the chief cell phenotype. 19015875_Protein mislocalization of RUNX3 occurs frequently in mouth squamous cell carcinoma and may be a useful diagnostic markers and potential therapeutic target. 19159630_Results describe thet role of P53/P21 and RUNX 3 in the effects of 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine on human cancer cells. 19174785_data suggest RUNX3 inactivation due to promoter hypermethylation in colorectal polyps represents an early event in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. 19223906_A role for RUNX3 as a tumour suppressor in colorectal cancer. 19290488_loss of RUNX3 expression is highly associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. The re-expression of RUNX3 may induce apoptosis and inhibit the growth as well as invasion/migration of cancer cells. 19336521_RUNX3 is down-regulated during melanoma progression. 19403666_RUNX3 specifically binds to the RUNX1 promoter in EBV-infected cells and downregulates RUNX1. 19470943_Methylation in RUNX3 was associated with prostate cancer mortality only in one of the two cohorts studied 19521519_RUNX3 has an oncogenic role in head and neck cancer 19552756_Genetic variants in the Runt-related transcription factor 3 gene contribute to gastric cancer. 19552756_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19571605_RUNX3 is involved in TGF-beta-dependent and -independent cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction pathways in colon cancer cell line HT-29 19596937_Quantification of epigenetic changes in serum RUNX3 methylation using RTQ-MSP is useful for the detection and monitoring of gastric cancer 19603429_REVIEW: RUNX3-mediated repression of RUNX1 in B cells 19645591_RUNX3 gene methylation in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and ovarian cancer cell lines is reported. 19695681_promoter hypermethylation of the p16, Runx3, MGMT, and DAPK genes may play an important role in the pathogenesis of gastric precancerous lesions and early gastric adenocarcinoma 19706291_The tight junction protein claudin-1 has gastric tumor suppressive activity and is a direct transcriptional target of RUNX3 19727221_There was a significantly negative correlation between RUNX3 expression and severity of H. pylori-associated gastric lesions. 19728008_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19728008_association between RUNX3 rs760805 polymorphism and the risk of gastric atrophy 19800882_RUNX3 suppresses Notch signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC7721 cells by its interaction with ICN1 (intracellular domain of Notch1) and thus recruitment to the RBP-J recognition motif of downstream genes of Notch signaling. 19827872_DNA copy-number loss on 1p36.1 harboring RUNX3 with promoter hypermethylation and associated loss of RUNX3 expression in liver fluke-associated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 19886737_Thymoma neoplastic epithelial cells can induce Th-POK expression in T-cell subsets similarly to the normal thymic epithelial cells. In addition, there was no significant difference in Runx3 expression in T-cell subsets between normal thymi and thymomas. 19917773_Transcription factors RUNX1 and RUNX3 in the induction and suppressive function of Foxp3+ inducible regulatory T cells. 19933870_Transgenic expression of Runx3 in mice accelerated CD4-positive cells to a T helper type (Th)1 cell-biased population or down-modulated Th2 cell responses, in part by neutralizing transcription factor GATA3. 20100835_tyrosine phosphorylation of RUNX3 by activated Src is associated with the cytoplasmic localization of RUNX3 in gastric and breast cancers 20160714_Methylation of RUNX3 was significantly more prevalent in UC-CRC cases compared with controls. 20190752_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20228843_Runx3 is essential for lung epithelial cell differentiation, and that downregulation of Runx3 is causally linked to the preneoplastic stage of lung adenocarcinoma. 20300977_Aberrant promoter methylation of Runx3 and CHFR genes may be involved in the carcinogenesis and development of gastric cancer 20306685_Studies show that FISH technic for the detection of CBF chromosomal aberrations was significantly higher than conventional cytogenetics. 20353948_RUNX3 acts as a novel co-activator for p53 through regulating its DNA damage-induced phosphorylation at Ser-15 20392673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20392673_RUNX3 might be involved in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis by regulating the expression of genes related with immune response 20442291_Loss of RUNX3 is associated with colorectal cancer. 20492341_Hypermethylation downregulates Runx3 gene expression and its restoration suppresses gastric epithelial cell growth by inducing p27 and caspase3 in human gastric cancer. 20599712_ATBF1 associates with RUNX3 and translocates to the nucleus in response to TGF-beta signal transduction and might function in the nucleus as tumor suppressor and transcriptional regulator. 20615577_p33 isoform is induced upon monocyte-derived dendritic cell maturation and downregulates IL-8 expression 20631058_Loss of RUNX3 through EZH2 and DNA methylation is associated with colorectal cancer. 20676134_studies identify RUNX3 as a novel cellular target of H. pylori CagA and also reveal a mechanism by which CagA functions as an oncoprotein by blocking the activity of gastric tumor suppressor RUNX3. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682997_RTQ-MSP-based quantification of serum RUNX3 methylation is useful for the detection and monitoring of colorectal cancer. 20801098_cyclin D1 provides a transcriptional switch that allows the tumor suppressor activity of RUNX3 to be repressed in cancer cells. 20887385_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20887385_Significant haplotype associations between CASP9 and inflammatory bowel disease were identified, while no association of RUNX3 haplotypes with either ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease was found 20955380_RUNX3 inactivation occurs specifically in Ductal carcinoma in situ and ductal carcinoma cells 21088106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21105967_low expression or deletion of RUNX3 in salivary gland tumors might play a pivotal role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression 21109941_The present study suggests that RUNX3 might play an important role in the development of UC-Ca. 21128246_These findings provide evidence for RUNX3-mediated suppression of gastric cancer invasion and metastasis and define a novel molecular mechanism that for the metastasis-inhibiting activity of RUNX3 21135153_RUNX3 methylation and expression associated with advanced precancerous gastric lesions. 21205092_Loss of RUNX3 expression by histone deacetylation is associated with biliary tract carcinogenesis. 21205319_Data show that a negative or weak signal was detected for RUNX3 expression in HCC tissue. 21223798_The pattern of Runx3 gene methylation is related to the tumorigenesis of salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. 21223819_The methylation of RUNX3 plays an important role in the silencing of RUNX3 expression in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma cell lines. 21254652_Hypermethylation of the Runx3 promoter occurs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, and the decreasing of Runx3 mRNA expression may be related to lymph node metastasis. 21288908_induction of RUNX3 may be a mechanism to maintain Notch-transformed mesenchymal cells during heart development. 21302620_Frequency of Runx3 methylation was significantly associated with tumor size in gastric cancer. 21354923_RUNX3 protein expression is lowered in hepatic cell carcinoma as compared with that in the surrounding normal tissue. 21523770_Several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in RUNX3 were significantly associated with susceptibility to intestinal-type gastric cancer 21567090_RUNX3 methylation may occur as a common event in the development of ACC and that methylation may be a major mechanism for inactivation of RUNX3 in ACC. 21567391_RUNX3 deregulation is associated with Helicobacter pylori-induced pathogenesis and development of intestinal metaplasia. 21612813_RUNX3 is frequently expressed in the nuclei of ovarian cancer cell lines and plays an oncogenic role in ovarian cancer. 21637926_RUNX3 restoration downregulated cancer stem cells by suppressing JAG1-mediated Notch signaling 21640801_A role for RUNX3 as a tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma. 21656750_RUNX3 plays an important role in melanoma pathogenesis and may serve as a promising prognostic marker for melanoma. 21658745_The spreading pattern of the runt-related transcription factor-3 methylation may play an a role in the progression of adenoid cystic carcinoma. 21678419_This study showed that show that RUNX3 is a principal and evolutionarily conserved component of the MST pathway. 21706051_Consistent with its ability to regulate the levels of ERalpha, expression of RUNX3 inversely correlates with the expression of ERalpha in breast cancer cell lines, human breast cancer tissues and Runx3(+/-) mouse mammary tumors 21756810_A lower expression of Runx3 gene may play an important role in the carcinogenesis and progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 21781566_Promoter methylation might be one of the important factors of RUNX3 inactivation, and might play an important role in carcinogenesis and progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 21803306_there was a significant correlation between Runx3 protein and TGF-beta(1) in patients with irritable bowel syndrome(P |
ENSMUSG00000070691 |
Runx3 |
1322.540475 |
7.5639386313 |
2.919138 |
0.057141341 |
2896.300380 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2352.6106944 |
83.8159592 |
313.2408074 |
9.8432535 |
| ENSG00000021762 |
114879 |
OSBPL5 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0X9 |
FUNCTION: Lipid transporter involved in lipid countertransport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the plasma membrane: specifically exchanges phosphatidylserine with phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P), delivering phosphatidylserine to the plasma membrane in exchange for PI4P, which is degraded by the SAC1/SACM1L phosphatase in the endoplasmic reticulum. Binds phosphatidylserine and PI4P in a mutually exclusive manner (PubMed:23934110, PubMed:26206935). May cooperate with NPC1 to mediate the exit of cholesterol from endosomes/lysosomes (PubMed:21220512). Binds 25-hydroxycholesterol and cholesterol (PubMed:17428193). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17428193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21220512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23934110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26206935}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) family, a group of intracellular lipid receptors that play a key role in the maintenance of cholesterol balance in the body. Most members contain an N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain and a highly conserved C-terminal OSBP-like sterol-binding domain. This gene has been shown to be imprinted, with preferential expression from the maternal allele only in placenta. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:114879; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact site [GO:0140268]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; oxysterol binding [GO:0008142]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; phosphatidylserine transfer activity [GO:0140343]; phospholipid transporter activity [GO:0005548]; sterol binding [GO:0032934]; sterol transporter activity [GO:0015248]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; cholesterol transport [GO:0030301]; Golgi to plasma membrane transport [GO:0006893]; phosphatidylserine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036150]; phospholipid transport [GO:0015914] |
12504849_OBPH1/Obph1 gene is imprinted, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in human and mouse. 19032366_OSBPL5 is relatd to invasion and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. 20201924_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20644730_Telomeric NAP1L4 and OSBPL5 of the KCNQ1 cluster, and the DECORIN gene are not imprinted in human trophoblast stem cells. 21220512_ORP5 may cooperate with NPC1 to mediate the exit of cholesterol from endosomes/lysosomes. 25963840_Results show that OSBPL5 and CALU were expressed at higher levels in the lung tissues of metastasis-positive cases than that in the metastasis-negative cases suggesting they can promote invasiveness of lung cancer cells. 26206935_ORP5 and ORP8 could mediate PI4P/phosphatidylserine (PS) countertransport between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the plasma membrane (PM), thus delivering PI4P to the ER-localized PI4P phosphatase Sac1 for degradation and PS from the ER to the PM. 27113756_mammalian ORP5 and ORP8 proteins localize to ER-mitochondrial MCS, in addition to ER-PM contact sites. 28970484_ORP5/8 are endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane proteins implicated in lipid trafficking that localize to ER-plasma membrane (PM) contacts and maintain membrane homeostasis. Here the authors show that PtdIns(4,5)P 2 plays a critical role in the targeting and function of ORP5/8 at the PM. 29358326_Data suggest that ORP5/OSBPL5 promotes cell proliferation, cell motility, and invasiveness of neoplasm cells; this effect of ORP5/OSBPL5 depends on functional OSBP-related domain (ORD). ORP5/OSBPL5 is needed for activation of mTORC1 signaling and for transport of mTOR to lysosomes. (mTORC1 = mechanistic target of rapamycin complex-1; mTOR = mechanistic target of rapamycin) 29472386_ORP5/8 recruitment to the plasma membrane occurs through interactions with the N-terminal Pleckstrin homology domains and adjacent basic residues of ORP5/8 with both phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. 29748134_ORP5/8 regulate Ca(2+) signaling at specific membrane contact sites foci. 32570981_ORP5 and ORP8: Sterol Sensors and Phospholipid Transfer Proteins at Membrane Contact Sites? |
ENSMUSG00000037606 |
Osbpl5 |
172.642738 |
0.2576414826 |
-1.956563 |
0.209053993 |
84.796912 |
0.00000000000000000003306404129182886579792251920371034330647225678707021854271091987342856555187609046697616577148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000295593730749481553617051055239600937154507954075070039028083623833254023338668048381805419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
65.9161206 |
12.3731242 |
256.9266781 |
33.9009180 |
| ENSG00000022267 |
2273 |
FHL1 |
protein_coding |
Q13642 |
FUNCTION: May have an involvement in muscle development or hypertrophy. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy;Isopeptide bond;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the four-and-a-half-LIM-only protein family. Family members contain two highly conserved, tandemly arranged, zinc finger domains with four highly conserved cysteines binding a zinc atom in each zinc finger. Expression of these family members occurs in a cell- and tissue-specific mode and these proteins are involved in many cellular processes. Mutations in this gene have been found in patients with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Multiple alternately spliced transcript variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:2273; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0010972]; positive regulation of potassium ion transport [GO:0043268]; regulation of membrane depolarization [GO:0003254]; regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901016] |
12917103_SLIM1 may play an important role during the early stages of skeletal muscle differentiation, specifically in alpha5beta1-integrin-mediated signaling pathways 16407297_FHL1 is a novel regulator of myosin-binding protein C activity that may have a role in sarcomere assembly 17589823_Fasting insulin and insulin sensitivity index responses to exercise training were associated with DNA sequence variation in FHL1 in white men. 17589823_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18073142_These results characterize TLX1 as a dual function regulator whose activity in respect to FHL1 is critically dependent upon its cellular concentration, as well as cell type and promoter context. 18179888_Study characterized a new disorder, X-linked myopathy with postural muscle atrophy (XMPMA), and identified FHL1 as the causative gene. 18179901_In a large Italian-American pedigree with dominant Scapuloperoneal syndrome all of the affected individuals have a missense change (c.365G-->C) in the FHL1 gene encoding FHL1. 18244901_The results shows that HOXD13 gene mutation was not involved in outbreak in idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus, but changes of HOXD13 and FHL1 gene expression related to the development of talipes equinovarus malformation. 18274675_a novel laser microdissection/proteomics approach has helped identify both inherited and de novo mutations in FHL1, thereby defining a new X-linked protein aggregation disorder of muscle. 18281375_Results support a role of FHL1 as a key molecular component in the I(Kur) complex in human atrium, where it likely regulates functional expression of KCNA5. 18465173_Fhl1 gene was underexpressed in clinical gastric cancer. 18725486_upregulated in various forms of PH, including idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension 18758158_Hoxd13 and Fhl1 were expressed in the interdigital tissues of E12.5 rat embryo. Luciferase assay and EMSA identified a novel promoter region of Fhl1 that directly interacts with Hoxd13 19075112_FHL1 appears to modulate muscle mass and strength enhancement. 19139564_Human four-and-a-half LIM family members suppress tumor cell growth through a TGF-beta-like signaling pathway. 19171836_Four novel mutations are identified in FHL1: heterozygous missense mutations in patients 1 and 2 (fatal infantile form), in-frame deletion in patient 3, and hemizygous mutation in patient 4. All mutations are located in the second LIM domain of FHL1. 19181672_The mutations detected were exclusive to the second LIM domain of FHL1 and were found in both sporadic as well as familial cases of reducing body myopathy. 19401155_The results presented here suggested the cooperative transcriptional regulation of estrogen signaling by FHL1 and RIP140. 19687455_As a consequence of C terminal FHL1 gene mutations, the X-linked myopathy characterized by postural muscle atrophy (XMPMA) phenotype and morphotype with cytoplasmic bodies are found. 19716112_FHL1 should be considered as a gene associated with the X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy phenotype, as well as with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 19850343_The pH-regulated antigen 1 (Pra1) protein was identified as a novel Factor H and FHL-1 binding protein. 20186852_Our finding expands the phenotypic spectrum of the recently identified FHL1-associated myopathies and widens the differential diagnosis of Emery-Dreifuss-like syndromes. 20571991_This study reported a novel LIM2 domain mutation in FHL1 in a family with Reducing body myopathy with cytoplasmic bodies and spinal rigidity. 20596604_Expression levels of FHL1 mRNA increased in all cell lines tested, as shown by RT-PCR. The methylation index of FHL1 in our samples was significantly higher in 70 BC specimens than in 10 normal bladder epithelium specimens. 20633900_A novel missense mutation in the LIM2 domain of FHL1 co-segregated with X-linked scapuloperoneal myopathy in the family 20969868_FHL1B/PP2A(Cbeta) interaction may illustrate a novel cell-cycle regulatory pathway. 21126853_FHL1 protein expression is downregulated in thoracic aortic dissection. 21219870_These results indicate that USP15 is involved in the regulation of hypertrophic responses in cardiac muscle through transcriptional and post-translational modulation of SLIM1. 21310615_This review will profile each of the FHL1, with a comprehensive analysis of mutations, a comparison of the clinical and histopathological features and will present several hypotheses for the possible disease mechanism(s)--{REVIEW} 21629301_We report on three British families with a heterogeneous myopathy clinical presentation segregating a single FHL1 gene mutation and haplotype, suggesting that this represents a founder mutation. 21702045_reduced expression of FHL1 may play an important role in the development and progression of lung cancer. 22053194_In order to substantiate a possible relation between K(v1.5) and FHL1C, a pull-down assay was performed. 22094188_FHL-1 may regulate estrogen receptor signaling function through regulation of AKT activation besides the physical and functional interaction with Estrogen receptor alpha. 22094483_FHL1 dystrophies are associated with myofibrillar myopathies pathology; mutations in the LIM2 domain are associated with reducing bodies composed of distinct tubulofilaments. 22143536_The decrease in or loss of FHL1 expression may be related to the incidence, progression, invasiveness, and metastatic potential of gastric cancer. 22219185_FHL1-3 inhibit HIF-1 transcriptional activity and HIF-1alpha transactivation domain function by oxygen-independent mechanisms. 22523091_FHL1 is a novel disease gene for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 22541254_A mother, daughter, and son suffering from FHL1 myopathy have a mutation in the second LIM domain of fhl1 with musculoskeletal involvement. 22689052_FHL1 is a methylation-silenced tumor-suppressor gene on chromosome X in gastrointestinal cancers, and that its silencing contributes to the formation of an epigenetic field for cancerization. 22778266_A novel mechanism involving four-and-a-half LIM domain protein-1 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-2 regulates titin phosphorylation and mechanics. 22923418_C224W mutation of FHLi protein had slightly elevated pulmonary artery pressure 23123766_FHL1 downregulation is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23169582_performed a clinical, muscle MRI, and histopathological characterization and immunoblot and genetic analysis of the FHL1 protein in a family with 4 individuals affected by reducing body myopathy. Identified a novel missense mutation in FHL1 23456229_mutation of FHL1 confers a complex phenotype through both gain- and loss-of-function mechanisms 23965743_This study demonistrated that the expand the morphologic features of reducing body myopathy , clearly demonstrate the localization of FHL1 in skeletal muscles. 23975679_Data show that loss of FHL1 function leads to myopathy in vivo and suggest that loss of function of FHL1 may be one of the mechanisms underlying muscle dystrophy in patients with FHL1 mutations. 24114807_Data indicate that four-and-a-half LIM domain 1 gene FHL1 mutation causing isolated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with X-chromosomal inheritance. 24516350_These data suggested that up-regulated FHL1 in smooth muscle in HSCR might be associated with intestinal wall remodeling in HSCR and might be one of the risk factors for gastrointestinal motor dysfunction 24634512_This is the first study to show that FHL1 mutations identified in several clinically distinct myopathies lead to similar protein aggregation and impair myotube formation. 24952875_The study has revealed that FHL1C overexpression induces Jurkat cell apoptosis. 25272045_Our results suggest that miR-410 may function as an oncomiR and are consistent with its key function in regulating FHL1 in certain digestive system cancers. 25305316_FHL-1 is the predominant complement regulator in Bruch's membrane having direct implications for age-related macular degeneration. 25695429_FRG1 mice overexpressing FHL1 showed an improvement in the dystrophic phenotype 25724586_In healthy individuals, FHL1A is the predominant splice variant and is mainly found in skeletal and cardiac muscle. In two individuals with an Emery-Dreifuss plus phenotype with pulmonary artery hypoplasia and facial dysmorphology, there was demonstrated loss of isoform A and B, and an almost 200-fold overexpression of isoform C. 26017856_Knockdown of FHL1 with FHL1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) promoted tumor growth and Cyclin D and cyclin E were markedly elevated at both the protein and mRNA level. 26146054_FHL1 shRNA could significantly accelerate tumor cell growth via inhibiting the expression of FHL1 26551678_results indicate that anti-FHL1 autoantibodies in peripheral blood have promising potential as a biomarker to identify a subset of severe IIM. 26857240_Mutations in FHL1 cause unclassifiable cardiomyopathy with coexisting Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. 26908444_Low FHL1 expression is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 26933038_a novel FHL1 splice site variant results in the absence of FHL1A and the abundance of FHL1C, which may contribute to the complex and severe phenotype of Uruguay syndrome. 27765816_results provide evidence that FHL1A interacts with PLEKHG2 and regulates cell morphological change through the activity of PLEKHG2. 27911330_Altogether, the specific localization of FHL1B and its modulation in disease-patient's myoblasts confirmed FHL1-related Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy as a nuclear envelope disease. 28094252_FHL1 increase inhibitory CDC25 phosphorylation by forming a complex with CHK2 and CDC25, and sequester CDC25 in the cytoplasm by forming another complex with 14-3-3 and CDC25, resulting in increased radioresistance in cancer cells. 28444561_We have uncovered FHL1 as a novel potential regulator of calcium homeostasis in both fish and humans and have implicated it in isolated hypoparathyroidism. 28489964_results suggest that FHL1A specifically interacts with PLEKHG2 to regulate a function of PLEKHG2 that is modified by the interaction of Gbetagamma and Galphas. 29434030_FHL1 can either suppress or promote tumor cell growth depending on the status of the sites for phosphorylation by Src. 30073757_This study revealed that miR-483-3p derived from IGF2 was associated with Hirschsprung's disease by targeting FHL1 and may provide a new pathway to understand the aetiology of Hirschsprung's disease. 30249901_FHL1 promote paclitaxel resistance in hepatocellular carcinomas cells through regulating apoptosis induced by paclitaxel, suggesting that FHL1 may be a promising molecular target for Hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. 30379883_Based on bioinformatic analysis, MMP1 and FHL1 are potentially functional proteins associated with differences of highly-metastatic prostate cancer PC-3M-1E8 cell line and poorly-metastatic PC-3M-2B4 cell line. 31273321_FHL1-related clinical, muscle MRI and genetic features in six Chinese patients with reducing body myopathy. 31554973_study shows that FHL1 is a key factor expressed by the host that enables chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infection and identifies the interaction between nsP3 and FHL1 as a promising target for the development of anti-CHIKV therapies 33053208_FHL1 promotes glioblastoma aggressiveness through regulating EGFR expression. 33055253_Structural and Functional Characterization of Host FHL1 Protein Interaction with Hypervariable Domain of Chikungunya Virus nsP3 Protein. 33515430_A Dominant C150Y Mutation in FHL1 Induces Structural Alterations in LIM2 Domain Causing Protein Aggregation In Human and Drosophila Indirect Flight Muscles. 35249471_Upregulation of FHL1, SPNS3, and MPZL2 predicts poor prognosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients with FLT3-ITD mutation. 35607917_Three novel FHL1 variants cause a mild phenotype of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. 35916339_Targeting FHL1 impairs cell proliferation and differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells. 36017148_MiR-96-5p Facilitates Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Phenotypes by Inhibiting FHL1. |
ENSMUSG00000050035 |
Fhl4 |
244.835957 |
0.3755357566 |
-1.412978 |
0.111981434 |
162.092494 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000039489502620306521256801721479309522841672396391489171618238997788453052876815393641854221815643347093249815316085005179047584533691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000006135421670270781273779218004265388336015924717186601658937324484954952741348009801988262756911041151397512294352054595947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
137.0913229 |
9.9814502 |
367.6661685 |
17.2543274 |
| ENSG00000022976 |
55778 |
ZNF839 |
protein_coding |
A8K0R7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55778; |
metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
28138309_ZNF839 single nucleotide polymorphism association with colorectal cancer patients survival |
ENSMUSG00000021271 |
Zfp839 |
101.567071 |
0.4219941192 |
-1.244705 |
0.162616980 |
59.580094 |
0.00000000000001174168190355259640676028561189526494695236323584364157568415976129472255706787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000078526155367664842787595197828845789661902400402571089443881646730005741119384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.0428440 |
5.8155200 |
131.6377970 |
9.0938543 |
| ENSG00000023171 |
57476 |
GRAMD1B |
protein_coding |
Q3KR37 |
FUNCTION: Cholesterol transporter that mediates non-vesicular transport of cholesterol from the plasma membrane (PM) to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (By similarity). Contains unique domains for binding cholesterol and the PM, thereby serving as a molecular bridge for the transfer of cholesterol from the PM to the ER (By similarity). Plays a crucial role in cholesterol homeostasis in the adrenal gland and has the unique ability to localize to the PM based on the level of membrane cholesterol (By similarity). In lipid-poor conditions localizes to the ER membrane and in response to excess cholesterol in the PM is recruited to the endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites (EPCS) which is mediated by the GRAM domain (By similarity). At the EPCS, the sterol-binding VASt/ASTER domain binds to the cholesterol in the PM and facilitates its transfer from the PM to ER (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80TI0}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable cholesterol binding activity; cholesterol transfer activity; and phospholipid binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cellular response to cholesterol and cholesterol homeostasis. Located in endoplasmic reticulum membrane; endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact site; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57476; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact site [GO:0140268]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cholesterol transfer activity [GO:0120020]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; sterol binding [GO:0032934]; sterol transfer activity [GO:0120015]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; intracellular sterol transport [GO:0032366] |
20332261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20731705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29934528_GRAMD1B regulates cell migration in breast cancer cells through JAK/STAT and Akt signaling 31719211_Circular RNA circGRAMD1B inhibits gastric cancer progression by sponging miR-130a-3p and regulating PTEN and p21 expression. 32738348_Aster-B coordinates with Arf1 to regulate mitochondrial cholesterol transport. 33604931_Molecular basis of accessible plasma membrane cholesterol recognition by the GRAM domain of GRAMD1b. 35394870_Aster proteins mediate carotenoid transport in mammalian cells. |
ENSMUSG00000040111 |
Gramd1b |
202.519015 |
0.2259721702 |
-2.145783 |
0.175108230 |
147.281166 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000068118865148053794987152462262533270733338927159146892977757922946378094644739162777553886929382542803068645298480987548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000009828293739836500039804673121715038063879452268980802725255403599264521954458696172086604181394875467958627268671989440917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.4754062 |
12.4983921 |
325.9653496 |
38.1802274 |
| ENSG00000023445 |
330 |
BIRC3 |
protein_coding |
Q13489 |
FUNCTION: Multi-functional protein which regulates not only caspases and apoptosis, but also modulates inflammatory signaling and immunity, mitogenic kinase signaling and cell proliferation, as well as cell invasion and metastasis. Acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase regulating NF-kappa-B signaling and regulates both canonical and non-canonical NF-kappa-B signaling by acting in opposite directions: acts as a positive regulator of the canonical pathway and suppresses constitutive activation of non-canonical NF-kappa-B signaling. The target proteins for its E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity include: RIPK1, RIPK2, RIPK3, RIPK4, CASP3, CASP7, CASP8, IKBKE, TRAF1, and BCL10. Acts as an important regulator of innate immune signaling via regulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), Nodlike receptors (NLRs) and RIG-I like receptors (RLRs), collectively referred to as pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Protects cells from spontaneous formation of the ripoptosome, a large multi-protein complex that has the capability to kill cancer cells in a caspase-dependent and caspase-independent manner. Suppresses ripoptosome formation by ubiquitinating RIPK1 and CASP8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21931591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23453969}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the IAP family of proteins that inhibit apoptosis by binding to tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors TRAF1 and TRAF2, probably by interfering with activation of ICE-like proteases. The encoded protein inhibits apoptosis induced by serum deprivation but does not affect apoptosis resulting from exposure to menadione, a potent inducer of free radicals. It contains 3 baculovirus IAP repeats and a ring finger domain. Transcript variants encoding the same isoform have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:330; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043027]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060546]; NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0038061]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:2000116]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045088]; regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060544]; regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing signaling pathway [GO:0070424]; regulation of RIG-I signaling pathway [GO:0039535]; regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034121]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
11960389_REVIEW: Genetic alterations involving API2 underlying the pathogenesis of MALT lymphoma 12082024_promotes tumor cell survival in mesothelioma 12161039_Interferon-beta therapy exerts a regulatory effect on peripheral T lymphocytes through an anti-apoptosis mechanism that involves the downregulation of cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein expression. 12243753_These results indicate that IAPs alone are not the main factor responsible for the resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cells to treatment. 12393423_pathway and antiapoptotic effect of up-regulation of cIAP2 by G-CSF in neutrophils, and overexpression of cIAP2 in chronic neutrophilic leukemia 12525502_Cellular inhibitors of apoptosis 1 and 2 are ubiquitin ligases for the apoptosis inducer Smac/DIABLO. 12651604_Fuses with MALT1 and defines a distinctive clinicopathologic subtype in pulmonary extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. 12651874_cIAP1 and cIAP2 are potential oncogenes and are overexpressed in multiple lung cancers with or without higher copy numbers 12815069_these results indicate that unlike Smac/DIABLO, Omi/HtrA2's catalytic cleavage of IAPs is a key mechanism for it to irreversibly inactivate IAPs and promote apoptosis. 12926068_cIAP-2 is an important regulator of apoptosis in bladder cancer and its overexpression may make tumours less susceptible to therapy involving apoptosis. 14527959_overexpression of PKC delta induced cIAP-2 promoter activity and increased NF-kappa B transactivation, suggesting regulation of cIAP-2 expression by a PKC delta/NF-kappa B pathway 14562112_copy numbers of API2-MALT1 do not reflect tumor cell proportions, and that the number of copies of API2-MALT1 in a tumor cell is different for each clinical sample. 14708638_Relative risk of death was lower for cytoplasmic c-IAP1, cytoplasmic c-IAP2, and nuclear c-IAP2 expression. It was higher for nuclear c-IAP1 expression. 14960576_levels of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 are regulated by Smac/DIABLO through the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway 15023888_PR39 causes an increase in gene expression from a transfected human cDNA IAP-2 promoter in BAEC cells. PR39-induced increase in the level of IAP-2 mRNA in BAECs is due to an increase in transcription rate and mRNA stability. 15037009_decreased cIAP2 may play a role in increased apoptosis in aged humans 15078890_cAMP can induce c-IAP2 expression in colon cancer cells through CREB phosphorylation and CRE-dependent transcription in a manner that involves activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK 15183896_X-linked XIAP is present in Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and is up-regulated in conditions where apoptosis is prevented. 15363040_Detection of API2-MALT1 fusion transcripts is useful for evaluating the prognosis and clinical behavior of the MALT lymphoma. 15598810_NF-kappa B signaling, once activated in a CD40-dependent immune response, is maintained and enhanced through deregulation of MALT1 or formation of an API2-MALT1 fusion 15696476_API2-MALT1 transcript was confirmed to be associated with the levels of apoptosis and API2 of MALT lymphoma. 15845643_cIAP2 expression is up-regulated by IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma through the JAK2-STAT3 pathway, and increased expression of the cIAP2 protein may contribute to an IFN-alpha- and IFN-gamma-mediated antiapoptotic effect on human neutrophils. 15856013_Upregulation of c-IAP2 by E6 and E7 may confer resistance to apoptosis that is necessary for sustained growth of some HPV16- and HPV18-positive cancer cells. 15982633_Taken together, our results strongly indicated that API2-MALT1 possesses a novel mechanism of self-activation by up-regulating its own expression in t(11;18)(q21;q21)-carrying MALT lymphomas. 16142363_IAP-2, XIAP, and survivin may make an important contribution to the resistance to the apoptotic effect of cisplatin in prostate cancer 16339151_cIAP1 and cIAP2 bind but do not inhibit caspases 16356540_demonstrates, for the first time, that BIRC3 (anti-apoptotic protein), COL3A1 (matrix protein synthesis), and CXCL3 (chemokine) were up-regulated in the thrombin-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells 16395399_Common translocation in MALT lymphoma results in a fusion of the cIAP2 region on chromosome 11q21 with the MALT1 gene on chromosome 18q21. 16395405_cIAP2 is an inhibitor of antigenic signaling and implicate its dysfunction in MALT lymphomas. 16467195_Tax-mediated HIAP-1 overexpression is required to suppress endogenous apoptosis and, therefore, is essential for the survival of HTLV-1-transformed lymphocytes 16761316_Eosinophils of hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) patients (but not normal eosinophils) express high levels of cellular IAP-2 (cIAP-2) and inhibit the caspase cascade in HES eosinophils. 16775419_results reveal a physiological function of cIAP2, identify Bcl10 upregulation as a unifying molecular mechanism for MALT lymphomas, and define the mechanism and effects of this upregulation in t(11;18)-positive mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas 16799641_Detachment-induced upregulation of XIAP and cIAP2 delays anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. 16813569_Cell cycle-dependent G2/M-phase-specific cIAP2 expression is enhanced by NF-kappaB activation, and selective down-regulation of cIAP2 causes cells blocked in mitosis with nocodazole to become susceptible to apoptosis. 16891304_the t(11, 18)(q21;q21) translocation creating the c-IAP2.MALT1 fusion protein activates NF-kappaB independently of TRAF1 AND TRAF2 and contributes to human malignancy in the absence of signaling adaptors that might otherwise regulate its activity 16983704_Differential expression of IAPs in B-cell lymphomas suggests differences in pathogenesis that may have implications for novel treatment strategies targeting IAPs. 16984419_Persistent infection of epithelial cell line with Chlamydophila pneumoniae resulted in the upregulation of the NF-kappaB regulated inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 but not inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 and apoptosis resistance. 17069460_In particular, the stability of cIAP-2 is modulated by the presence of X-linked IAP and their interaction is stabilized in infected cells. 17133355_TNF-alpha induced expression of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 via MAP kinases, but not via NF-kappaB, and that MAP kinases participated in the inhibition of apoptosis by induction of c-IAPs in TNF-alpha-stimulated endothelial cells 17179183_Trp323 of BIR3 plays a pivotal role both in maintaining necessary conformation for caspase-9 interaction and to a lesser extent, recognition of Smac-type peptide. 17626072_Bortezomib inhibited expression of cIAP-1, cIAP-2, and XIAP, which are regulated by NF-kappaB and function as inhibitors of apoptosis. 17927572_Levels of IAP-2 and Bax were decreased in A375 cells and HIF-1alpha was increased during hypoxia. 17972100_Inflammation during active ulcerative colitis causes an upregulation of cIAP2 in regenerating epithelium, rendering the cells less susceptible to Fas ligation. 17993464_Data show that Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein protects cells against death by elevating cIAP2 proteins. 18195037_cIAP2 mRNA mediates translation only via ribosome bypassing 62 uAUGs. Shunting efficiency was altered by stress & was facilitated by a conserved RNA folding domain (1,470 to 1,877 nucleotides upstream) in a region not scanned by shunting ribosomes. 18216531_The sequencing analysis of RT-PCR prducts confirmed the presence of the characteristic API2-MALT1 fusion transcript in patients with MALT lymphoma. 18508827_haem oxygenase-1 plays a central role in NNK-mediated cell proliferation by promoting the expression of p21(Cip1/Waf1/Cid1), inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 and B-cell lymphoma-2 but inhibiting the activity of Bad 18566024_XIAP and HIAP-1 in myelin lesions were co-localized with microglia and T cells in multiple sclerosis 18570872_cIAP1 and cIAP2 promote cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ubiquitin ligases that maintain constitutive ubiquitination of the RIP1 adaptor protein. 18621737_c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 are required for TNFalpha-stimulated RIP1 ubiquitination and NF-kappaB activation. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18768389_IL-3 up-regulates the expression of the antiapoptotic proteins cIAP2, Mcl-1, and Bcl-X(L) and induces a rapid and sustained de novo expression of the serine/threonine kinase Pim1 that closely correlates with cytokine-enhanced survival. 18931663_The ubiquitin-associated domain is required for XIAP and CIAP2-MALT1 to activate NF-kappaB. 18953427_c-IAP2 is consistently overexpressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells; study reports that c-IAP2 plays a major role in the resistance of NPC cells to apoptosis induced by TLR3 stimulation 19029953_PERK activity inhibits the ER stress-induced apoptotic program through the induction of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis (cIAP1 and cIAP2) proteins 19060847_Methylation and API2/MALT1 fusion in colorectal extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19223549_cIAP1, cIAP2, and XIAP act cooperatively via nonredundant pathways to regulate genotoxic stress-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation. 19234489_TRAF2 interaction is critical for c-IAP2/MALT1-mediated increases in the NF-kappaB activity, increased expression of endogenous NF-kappaB target genes and resistance to apoptosis. 19243308_c-IAP1 can be targeted for degradation by two distinct processes,through degradation of the TRAF2-c-IAP1 heterodimer or through induced autoubiquitination of c-IAP1 by IAP antagonists 19302291_cIAP2 may therefore play an important role as a target therapy in colorectal cancer 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19358671_Rickettsia rickettsii-induced expression of cIAP2 in host endothelial cells is likely not a major contributor to protection against staurosporine-induced cell death. 19416853_ARIA knockdown significantly increased inhibitor of apoptosis cIAP-1 and cIAP-2 protein expression 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19763917_Arsenic trioxide suppresses transcription of cIAP2 mRNA in NB-4 cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923725_Results provide the first structures of BIR domains from human NAIP and cIAP2. 20063052_Adenosine downregulated the expression of mRNAs and proteins for Bcl-X(L) and inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 (IAP2) to directly inhibit caspase-3, -7, and -9, but upregulated the expression of mRNA and protein for DIABLO, an inhibitor of IAPs. 20078866_IAPs could be involved in prostate disorder (BPH, PIN and PC) development since might be provoke inhibition of apoptosis and subsequently cell proliferation 20079017_API2-MALT1 fusion gene is a distinctive genetic aberration in MALT lymphomas, and is not present in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 20097753_virus-triggered ubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6 by cIAP1 and cIAP2 is essential for type I IFN induction and cellular antiviral response 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385093_crystal structures of the TRAF2: cIAP2 and the TRAF1: TRAF2: cIAP2 complexes; biochemical, structural, and cell biological studies on the interaction between TRAF2 and cIAP2 and on the ability of TRAF1 to modulate this interaction 20447407_Results describe the complex between baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) 1 of cIAP1/2 and the coiled-coil region of TRAF2. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20547836_cancer cell lines evade Smac mimetic-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of cIAP2, which although initially degraded, rebounds. cIAP2 is induced by TNFalpha via NF-kappaB and modulation of the NF-kappaB signal renders cells sensitive to Smac mimetics 20576118_Poly(I:C) induces intense expression of c-IAP2 and cooperates with an IAP inhibitor in induction of apoptosis in cancer cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20691152_TTP can bind to the 2nd AU-rich elements of cIAP2 mRNA 3'UTR and destabilize cIAP2 mRNA by forming complexes with Dcp2 and Xrn1. 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20863547_These results support a role for Tax-dependent cIAP-2 expression in preventing the death of naturally infected CD8(+) cells and thereby in their clonal expansion in vivo. 20959404_cIAP2 upregulated by E6 via EGFR/PI3K/AKT cascades may contribute to cisplatin resistance, revealing that the EGFR or PI3K inhibitor combined with cisplatin may improve the chemotherapeutic efficacy in HPV-infected lung cancer. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21152357_we confirm that mRNA and protein levels for cIAP2 are highly up-regulated in breast cancer cells by E2 and cytokines 21229359_TRAF2 and cIAP2 are involved in TWEAK-induced MMP-9 production in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. 21273489_study shows API2-MALT1 fusion oncoprotein induces proteolytic cleavage of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK); resulting deregulated NIK activity is associated with constitutive noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling, enhanced B cell adhesion and apoptosis resistance 21331077_Data show that inhibitor-induced rapid degradation of cIAPs requires binding to TRAF2, and reveal an unexpected difference between cIAP1 and cIAP2. 21795072_Data show that inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (cIAP1) and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein (cIAP2) expression was significantly increased in bladder cancer compared with normal bladder urothelium. 21817100_cIAP1/2 are important regulators of inflammatory processes in endothelial cells. 21849505_The USP19 deubiquitinase regulates the stability of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2. 21865390_These data reveal a novel mechanism for the inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by cIAP2 via acceleration of the ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated decay of polymerase. 21881048_BIRC3 disruption is a common mechanism across marginal zone B-cell lymphomagenesis. 21931591_cIAP1 and cIAP2 are direct E3 ubiquitin ligases for all four RIP proteins 21963223_cIAP2 may play an important role in Helicobacter pylori -induced gastric carcinogenesis 22068233_our results suggest that CpG-induced protection may be mediated by c-IAP-2 through the calcium-activated JNK pathway 22083956_NF-kappaappaB, acting through two response elements, is required for estrogen receptor recruitment to an adjacent estrogen response element in the BIRC3 promoter. 22403404_resistance to Vpr-induced apoptosis is specifically mediated by cIAP1/2 genes independent of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1, which play a key role in maintaining cell viability. 22434933_c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 were required for canonical activation of NF-B and MAPK by members of the TNFR family. 22820591_The expression of C-IAP2 in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with tumor recurrence and metastasis. 23032264_A novel role for cIAP2 in maintaining wild-type p53 levels by preventing both an NFkappaB-mediated increase and IKKalpha/-beta-dependent transcriptional and post-translational modifications of MDM2. 23052480_we present cIAP-2 as a novel inducer of platinum resistance in ovarian carcinoma cells, and suggest an axis beginning with an encounter between cisplatin and these cells, mediated sequentially by IL-6 and cIAP-2, resulting in cisplatin resistance 23243274_Clonal evolution from lower to higher risk implicated the emergence of NOTCH1, SF3B1, and BIRC3 abnormalities in addition to TP53 and 11q22-q23 lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 23250032_BIRC2 and BIRC3 act as a molecular brake to rein in activation of the JNK signalling pathway and to fine-tune NF-kappaB and JNK signalling to ensure transcriptional responses are appropriately matched to extracellular inputs. 23558524_BIRC3 gene mutation is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 23770847_our study implicates RIP1 ubiquitination as a critical component of API2-MALT1-dependent lymphomagenesis 23852810_Cytoplasmic expression of HuR is associated with cIAP2 expression in OSCCs 24008361_palmitate did not decrease cIAP-1 and cIAP-2 mRNA expression in the cells 24194568_we note that the compounds that sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL are the most efficacious in binding to X-linked IAP, and in inducing cellular-IAP (cIAP)-1 and cIAP-2 degradation 24266799_increased expression with progression of chronic myeloid leukaemia 24349465_a number of genes not previously known to be affected by RUNX2 expression, in particular BIRC3, genes encoded on the mitochondrial genome, and several genes involved in bone and tooth formation. 24371121_Data indicate that silencing of IAPs, IAP1 IAP2 and XIAP, reduced the TRAP-evoked RhoA activation. 24425875_cisplatin significantly triggered the proteasomal degradation of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 and 2 (c-IAP1 and c-IAP2), and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) in a ROS-dependent manner 24552816_Distinctive role of c-IAP2 as stabilizer of XIAP, which is likely involved in regulation of NFkappaB activation and apoptosis in GBM cells was determined. 24577083_Selenite caused CYLD upregulation via LEF1 and cIAP downregulation, both of which contribute to the degradation of ubiquitin chains on RIP1 and subsequent caspase-8 activation and colorectal tumor cell apoptosis. 24584352_in 11q-deleted patients treated with first-line chemotherapy, ATM mutation rather than BIRC3 deletion and/or mutation identifies a subgroup with a poorer outcome. 24595242_Data indicate that tumor necrosis factor inducible protein A20-mediated inhibitor of apoptosis protein-2 (cIAP-2) is important in endothelial cell resistance to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)-induced apoptosis. 24633224_cIAPs constitutively downregulate PACS-2 by polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, thereby restraining TRAIL-induced killing of liver cancer cells 24841289_XIAP, cIAP1, and cIAP2, members of inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins, are critical regulators of cell death and survival and are attractive targets for new cancer therapy 25046208_CIAP1 and cIAP2 represent novel therapeutic targets for the prevention of spontaneous preterm birth. 25113061_cIAP1 and cIAP2 expression is increased in placenta from women with pre-existing maternal obesity and in response to treatment with pro-inflammatory cytokines 25246529_Identification and function of the NIK IAP binding motif, which promotes c-IAP1-dependent ubiquitylation of NIK. 25273171_these findings suggest that GDC-0152 results in human leukemia apoptosis through caspase-dependent mechanisms involving down-regulation of IAPs and inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling. 25394657_cIAP2 is in conclusion a regulator of human intestinal wound healing through enhanced migration along with activation of Rac1 25513960_TNF-alpha induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via accelerated degradation of the inhibitor of apoptosis family members, CIAP2, XIAP, and survivin. 25549803_Data indicate that Smac/DIABLO showed an inverse correlation with inhibitor of apoptosis proteins XIAP, cIAP-1 and cIAP-2. 25569716_API2-MALT1 induces paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the tumour suppressor protein LIMA1. 25692408_LapR cells possessed increased levels of 2 of the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs), survivin and c-IAP-2, which are reported to block caspase activation downstream of cytosolic cytochrome C release. 25911380_Data suggest that the seventh zinc finger motif of DNA-binding protein A20 plays important role in NFkappaB-mediated apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha; A20 appears to bind and thus down-regulate inhibitor of apoptosis proteins cIAP1/2. 26077759_these results indicate that N. gonorrhoeae stimulation of human endocervical epithelial cells induces the release of cIAP2, an essential regulator of cell death and immune signaling. 26291056_this study candidates BIRC3 as one of the potentially useful predictive marker for discriminating patients with oesophageal and oesophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma who will most likely benefit from preoperative chemoradiotherapy. 26513451_cIAP2 is upregulated in regenerative epithelial cells both in ulcerative colitis and in experimental intestinal wounds. Inhibition of cIAP2 decreases wound healing in vitro possibly through inhibition of migration. [review] 26815504_High BIRC3 expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 26819056_The clinical impact of small subclones harboring NOTCH1, SF3B1, or BIRC3 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients appears to be less pronounced than that of small TP53 mutated subclones. 26888114_Study demonstrate that BIRC3 expression increases secondary to acquisition of temozolomide TMZ and irradiation resistance in glioblastoma. 27070702_cIAP1 and cIAP2 mediate BCL10 ubiquitination essential for BCR-dependent NF-kB activity in the ABC subtype of DLBCL. cIAP1/2 attach K63-linked polyubiquitin chains on themselves and on BCL10, recruiting IKK and LUBAC essential for IKK activation. 27074575_We show that BIRC3 has a unique role in facilitating glioma progression from low- to high-grade 27248820_Results indicate that Pellino-1 contributes to lung oncogenesis through the overexpression of inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 (cIAP2) and promotion of cell survival and chemoresistance. 27282269_The expression of cIAP2 mRNA was significantly higher in the groups with Helicobacter pylori(+), atrophic gastritis/intestinal metaplasia(+), and Helicobacter pylori-positive early gastric cancer than in the control, Helicobacter pylori(+), and atrophic gastritis/intestinal metaplasia(-) groups. 27304223_Polymorphisms in the BIRC3 gene are associated with a protective effect with regards to asthma susceptibility, and a reduced load of inflammatory cells. 27420950_Network analysis identified BIRC3 as pathogenic gene in childhood asthma. 27534557_destabilization of TRAF2 by miR-17 reduced the ability of TRAF2 to associate with cIAP2, resulting in the downregulation of TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaBp65, c-Jun, and STAT3 nuclear translocation and the production of IL-6, IL-8, MMP-1, and MMP-13 in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. 28295868_CIAP2 expression was elevated in human GBC tissues. 28635396_we indicated that miR-34a can inhibit tumor invasion and metastasis in osteosarcoma, and its mechanism may be partly related to downregulating the expression of C-IAP2 and Bcl-2 protein directly or indirectly. 28839258_we have uncovered a novel role for BIRC3 as a targetable biomarker and mediator of hypoxia-driven habitats in GBM. 29286141_High BIRC3 expression is associated with Oral squamous cell carcinoma. 29518103_NAIP expression is most abundant in M2 macrophages, while cIAP1 and cIAP2 show an inverse pattern of expression in polarized cells, cIAP2 is preferentially expressed in M1-macrophages and cIAP1 in M2-macrophages. IAP antagonist treatment of resting M0 macrophages preceding polarization stimulation, induced upregulation of NAIP in M2 and downregulation of cIAP1 in M1 and M2 but an induction of cIAP2 in M1 macrophages. 30368883_BIRC3 induces tumor proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. BIRC3 may serve as a novel therapeutic target for liver cancer. 30385739_Sensitization and reversal of glioblastoma cells resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by IAP- and Bcl-2 antagonism has been reported. 30431128_Experimental results demonstrated that cIAP2 regulated the expression of p53 and thus was likely to be a potential mechanism for evironmental pollutant perfluorodecanoic acidinduced inhibition of gastric cell senescence resulted in growth promotion revealing possible role for cIAP2 in gastric carcinogenesis. 30487125_Study shows the impact of BIRC3 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia disease progression in the absence of BIRC3 mutations and shows altered canonical NF-kappaB target gene activation with therapeutic implications. 30670910_HuR mediated overexpression of IAP1 significantly correlates with poor outcomes and early progression of pancreatic cancer. 30948266_We investigated the function of the long BIRC3 3' UTR, which is upregulated in leukemia. The 3' UTR does not regulate BIRC3 protein localization or abundance but is required for CXCR4-mediated B cell migration. We established an experimental pipeline to study the mechanism of regulation and used mass spectrometry to identify BIRC3 protein interactors. 31215169_Results found that BIRC3 was upregulated in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines and specimens. HCP5 competitive sponging of miR-219, BIRC3 target, leads to activation of BIRC3 in apoptosis signaling pathway to promote TNBC progression. 31371416_Biological and clinical implications of BIRC3 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 31540997_The findings identify ZFAND2A/AIRAP as a novel stress-regulated survival factor implicated in the stabilization of the antiapoptotic protein cIAP2 and as a new potential therapeutic target in melanoma 32015491_Clinical significance of TP53, BIRC3, ATM and MAPK-ERK genes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: data from the randomised UK LRF CLL4 trial. 32026660_SURF4 maintains stem-like properties via BIRC3 in ovarian cancer cells. 32028675_A20 Promotes Ripoptosome Formation and TNF-Induced Apoptosis via cIAPs Regulation and NIK Stabilization in Keratinocytes. 32053868_Future Therapeutic Directions for Smac-Mimetics. 32322338_Increased Expression of BIRC2, BIRC3, and BIRC5 from the IAP Family in Mesenchymal Stem Cells of the Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly (WJSC) in Younger Women Giving Birth Naturally. 32382056_WTAP and BIRC3 are involved in the posttranscriptional mechanisms that impact on the expression and activity of the human lactonase PON2. 33310033_cIAP2 via NF-kappaB signalling affects cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33435582_Regulation of Anti-Apoptotic SOD2 and BIRC3 in Periodontal Cells and Tissues. 33599891_cIAP2 expression and clinical significance in pigmented villonodular synovitis. 33737574_Death agonist antibody against TRAILR2/DR5/TNFRSF10B enhances birinapant anti-tumor activity in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. 34244476_Biological significance of monoallelic and biallelic BIRC3 loss in del(11q) chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression. 34389694_Clinical Positioning of the IAP Antagonist Tolinapant (ASTX660) in Colorectal Cancer. 34914932_Targeting cIAPs attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis by increasing MMP9 expression derived from neutrophils. 34971648_Multiomics analysis identifies BIRC3 as a novel glucocorticoid response-associated gene. 34997070_BIRC2-BIRC3 amplification: a potentially druggable feature of a subset of head and neck cancers in patients with Fanconi anemia. 35008722_A Novel Role of BIRC3 in Stemness Reprogramming of Glioblastoma. 35039877_Proteomic analysis of inhibitor of apoptosis proteinlike protein2 on breast cancer cell proliferation. 35287655_Exploration of induced sputum BIRC3 levels and clinical implications in asthma. 35968588_[The correlation of CD49d expression pattern with molecular genetics and hotspot gene mutants in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia]. 35985688_Prognostic Significance of the BIRC2-BIRC3 Gene Signature in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000032000 |
Birc3 |
71.240925 |
3.7993976690 |
1.925771 |
0.223761640 |
75.827831 |
0.00000000000000000309507770259544835373572154750963311737531477147681181066873890017632220406085252761840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000025309333457234802272428076716779635594516929686793697829028104706594604067504405975341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
114.5788529 |
15.1190562 |
30.4021599 |
3.3376336 |
| ENSG00000023909 |
2730 |
GCLM |
protein_coding |
P48507 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Glutathione biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Sulfur metabolism; glutathione biosynthesis; glutathione from L-cysteine and L-glutamate: step 1/2. |
Glutamate-cysteine ligase, also known as gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase, is the first rate limiting enzyme of glutathione synthesis. The enzyme consists of two subunits, a heavy catalytic subunit and a light regulatory subunit. Gamma glutamylcysteine synthetase deficiency has been implicated in some forms of hemolytic anemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:2730; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamate-cysteine ligase complex [GO:0017109]; enzyme regulator activity [GO:0030234]; glutamate-cysteine ligase activity [GO:0004357]; glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit binding [GO:0035226]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; aging [GO:0007568]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:0035729]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cellular response to thyroxine stimulus [GO:0097069]; cysteine metabolic process [GO:0006534]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; hepatic stellate cell activation [GO:0035733]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; positive regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase activity [GO:0035229]; regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051900]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to human chorionic gonadotropin [GO:0044752]; response to nitrosative stress [GO:0051409]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
12081989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12081989_Polymorphism in the 5'-flanking region is associated with myocardial infarction 12975258_A -588T polymorphism of the GCLM gene causes a decrease in endothelial NO bioactivity, causing impairment of endothelium-dependent vasomotor function in large and resistance coronary arteries. The GCL-GSH-NO axis may defend against coronary artery disease 12975258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14532974_GCLM has a role in cisplatin (CDDP)-resistance in lung cancer 15451055_Review. The most important element in both Gclc and Gclm expression is the electrophile response element in their promoters. 15946948_Reduction-oxidation regulation of gamma-GCSh expression is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. 16081425_in most tissues, glutanmate-cysteine ligase modifier submit (GCLM) is limiting, suggesting an increase in GCLM alone would increase gamma-GC synthesis; in kidney, gamma-GC synthesis may be controlled post-translationally 16599007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16677451_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16677451_The polymorphism of GCLM -588C/T and -23G/T sites were associated with susceptibility to COPD. 16766924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16909399_The gene of the key GSH-synthesizing enzyme, glutamate cysteine ligase modifier (GCLM) subunit, is strongly associated with schizophrenia in two case-control studies and in one family study. 17333241_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17344309_upregulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase as part of the long-term adaptation process to iron accumulation in neurons 17548779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17643973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17924854_the present data strongly indicates that, in spite of its functional impact, the GCLM C-588T polymorphism is - at least in a German cohort - not an independent risk indicator of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction 17961430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18066575_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18449862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18560528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18614560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18991850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18991850_Results suggest that a common genetic variation in the GCLM gene might not contribute to the risk of methamphetamine-use disorder and schizophrenia in the Japanese population. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126404_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19153097_Overexpression of GCL in granulosa cells can augment glutathione synthesis and ameliorate various sequelae associated with exposure to oxidative stress and irradiation. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19455074_It is unlikely that functional mutations in the GCLM gene could play a major role in genetic predisposition to schizophrenia. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19584774_association study in the Chinese population yielded no supportive evidence for GCLM as a susceptible gene in schizophrenia 19808663_Data show that induction of HO-1, GCLM, and NQO1 by OA-NO2 Is Nrf2-dependent. 19896490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20061124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20061124_To further investigate the role of the GCLM locus in schizophrenia susceptibility, we studied three SNPs and haplotypes in the region of GCLM using Han Chinese case-control samples. 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20598694_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20712757_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20970495_Posttranslational modification and regulation of glutamate-cysteine ligase by the alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. 21105962_SNPs not associted with schizophrenia in Japanese individuals 21277635_SNPs not associated with self-reported depression 21504558_When eicosapentaenoic+docosahexaenoic acid or erythrocyte-mercury were divided into tertiles, GCLM-588 TT genotype individuals showed a lower risk than CC genotype; however, there were few TT carriers and the results were not statistically significant. 21555518_GCLM is a functional target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq and knockdown analysis in HEK 293 cells. 23743623_TP is expressed at high levels in human GBM tumors and shRNA knockdown of TP in U87 GBM cells results in a significant increase in cellular GCL enzymatic activity 24535845_Ten of the 17 maternal SNPs and 2 of the 17 fetal SNPs were found within the GCLM gene conotruncal heart defect cases. 24557597_Upregulation of both GCLC and GLCM mRNA levels in response to cysteine deprivation was dependent on new protein synthesis. 24786516_miR-320a has a role in modulating the induction of HO-1, GCLM and OKL38 by oxidized phospholipids in endothelial cells 25353619_miR-433 targets both catalytic (GCLc) and regulatory (GCLm) subunits of GCL. 25789740_Knockdown of glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit by siRNA causes the gold nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells. 26220190_This study demonstrated that Tuberous sclerosis complex neuropathology requires glutamate-cysteine ligase. 26365678_Data suggest expression of hepatocyte GCLC and GCLM can be regulated by dietary component; alpha-lipoic acid, a vitamin B complex nutrient, protects against oxidative stress/cytotoxicity induced by cadmium via restoration of GCLC and GCLM expression. 26507778_Data suggest gene expression in vascular endothelium is altered by dietary factors; aged garlic extract induces expression of HMOX1 (heme oxygenase-1) and GCLM via activation of NRF2-ARE (nuclear factor erythroid 2-antioxidant response element) signaling. 26520442_Glutaminolysis is activated in ES2 and OVCAR3, though ES2 exclusively synthesizes amino acids and GSH. ES2 cells are more resistant to carboplatin than OVCAR3 and the abrogation of GSH production by BSO sensitizes ES2 to carboplatin. HNF1beta regulates the expression of GCLC, but not GCLM, and consequently GSH production in ES2 26894974_High GCLM expression is associated with chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer. 28757675_Two promoter polymorphisms of GCLM (-588C/T) and GCLC (-128T/C) are associated with an increased risk of ischemic heart disease in Kazakhstan population. 28993271_Glutathione biosynthesis during the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in THP-1 macrophages is tightly and differentially regulated via GCLC and GCLM subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. 32715377_Genetic variants in glutamate cysteine ligase confer protection against type 2 diabetes. 33421846_Association of glutamate cystein ligase (GCL) activity Peroxiredoxin 4 (prxR4) and apelin levels in women with preeclampsia. 34642912_Association of Polymorphisms of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Genes GCLC C-129 T and GCLM C-588 T with Risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Chinese Women. |
ENSMUSG00000028124 |
Gclm |
232.787082 |
3.7151404664 |
1.893417 |
0.134572125 |
198.981941 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000348335732748352824855015277450412659789810805234921318691719384487420515435250453309836317664667697763874718334346086701103217819763813167810440063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000066085288115240202142954546501505609242612023658376282464162843430420340993599148567820592274957049329776199704609279672595789634215179830789566040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
368.5402940 |
28.0586261 |
100.0322452 |
6.1931041 |
| ENSG00000025434 |
10062 |
NR1H3 |
protein_coding |
Q13133 |
FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that exhibits a ligand-dependent transcriptional activation activity (PubMed:19481530, PubMed:25661920). Interaction with retinoic acid receptor (RXR) shifts RXR from its role as a silent DNA-binding partner to an active ligand-binding subunit in mediating retinoid responses through target genes defined by LXRES (By similarity). LXRES are DR4-type response elements characterized by direct repeats of two similar hexanuclotide half-sites spaced by four nucleotides (By similarity). Plays an important role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis, regulating cholesterol uptake through MYLIP-dependent ubiquitination of LDLR, VLDLR and LRP8 (PubMed:19481530). Interplays functionally with RORA for the regulation of genes involved in liver metabolism (By similarity). Induces LPCAT3-dependent phospholipid remodeling in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes of hepatocytes, driving SREBF1 processing and lipogenesis (By similarity). Via LPCAT3, triggers the incorporation of arachidonate into phosphatidylcholines of ER membranes, increasing membrane dynamics and enabling triacylglycerols transfer to nascent very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles. Via LPCAT3 also counteracts lipid-induced ER stress response and inflammation, likely by modulating SRC kinase membrane compartmentalization and limiting the synthesis of lipid inflammatory mediators (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0Y9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19481530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25661920}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the NR1 subfamily of the nuclear receptor superfamily. The NR1 family members are key regulators of macrophage function, controlling transcriptional programs involved in lipid homeostasis and inflammation. This protein is highly expressed in visceral organs, including liver, kidney and intestine. It forms a heterodimer with retinoid X receptor (RXR), and regulates expression of target genes containing retinoid response elements. Studies in mice lacking this gene suggest that it may play an important role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:10062; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sterol response element binding [GO:0032810]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of lipid transport [GO:0032369]; negative regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043031]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; negative regulation of pancreatic juice secretion [GO:0090188]; negative regulation of pinocytosis [GO:0048550]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; negative regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1903573]; negative regulation of secretion of lysosomal enzymes [GO:0090341]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060336]; phosphatidylcholine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036151]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of cholesterol transport [GO:0032376]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045723]; positive regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0051006]; positive regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051247]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034145]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transporter activity [GO:0032411]; positive regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0010867]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; sterol homeostasis [GO:0055092]; triglyceride homeostasis [GO:0070328] |
11875109_data suggest a model in which LXR ligands trigger an autoregulatory loop leading to selective induction of hLXRalpha gene expression 12032151_studies demonstrate that activated LXR induces the expression of the apoE/C-I/C-IV/C-II gene cluster in both human and murine macrophages 12054659_Different regulation of the LXRalpha promoter activity by isoforms of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins 12117567_interaction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha with liver X receptor alpha antagonizes the stimulatory effect of their respective ligands on the murine cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene promoter 12161442_LXRa is regulated by fatty acids in human cells 12198243_SHP is able to interact with LXR and to modulate its transcriptional activity. 12470296_PGC-1 alpha serves as a co-activator for the liver X receptor (LXR) alpha 12932788_These data enable the identification of the amino acids that coordinate the interaction of both steroidal and non-steroidal ligands in the ligand-binding pocket of liver X receptor alpha. 12957674_hLXRalpha and hLXRgeta transactivated a reporter gene bearing a truncated FPPS promoter containing a putative direct repeat 4 (DR4) LXR response element, and direct interaction was demonstrated 14699103_LXRalpha and LXRbeta regulate transcription of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in macrophages 15319359_unliganded TRbeta1 suppresses promoter activity driven by LXRalpha and its ligand, whereas transactivation by T3-bound TRbeta1 is not affected by LXRalpha in the presence or absence of oxysterols 15353176_LXRalpha plays an important role in the cAMP-mediated regulation of human renin gene transcription by binding to cAMP responsive element in the promoter. 15539633_LXRs are expressed and functional in primary human coronary artery smooth muscle cells; their ligands inhibit cell proliferation and neointima formation 15548517_activation of the liver X receptors (LXR) dramatically promoted lipid accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells 15625283_In the human body, the LXRalpha protein is highly expressed in macrophage lineage cells and foam cells in atherosclerotic lesions 16054077_The beneficial effect of hepatic LXRalpha was abrogated by a synthetic LXR agonist, which activated SREBP-1c and its target genes. 16106051_liver X receptor-alpha in mouse kidney and HK-2 proximal tubular cells is downregulated by LPS and cytokines 16170053_expression of alternative LXRalpha transcripts in certain biological contexts may impact LXR signaling and lipid metabolism 16249184_LXRalpha is a negative modulator of Abcd2, acting through a novel regulatory mechanism involving overlapping SREBP and LXRalpha binding sites 16354658_competitive binding of coactivators and corepressors can explain the tissue-specific behavior of partial liver X receptor alpha and beta agonists 16482468_LXR agonists may lead to increased utilisation of lipids and glucose in muscle cells without affecting the mechanism of action of insulin. 16567856_Data demonstrate that LXR-alpha activation altered all of the cellular cholesterol fluxes. 16758300_LXR-alpha gene plays a crucial role in the regulation of innate immunity at the genomic level. 16904112_Results provide evidence that liver X receptors alpha and beta are phosphorylated proteins. 16920108_Data show that liver X receptor alpha regulates the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene, which mediates the endocytic uptake of LDL cholesterol in the liver. 16941683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16941683_in the investigated German sample, no evidence of association of ABCB11 and LXRA to gallstone susceptibility was detected. The gallstone trait is not allelic to progressive familial cholestasis at the ABCB11 locus. 16956579_myeloperoxidase is regulated by LXR and PPARalpha ligands 16973760_LXR-alpha and LXR-beta independently interfere with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation at the level of the pituitary and the adrenal gland 17108812_One LXRA single nucleotide polymorphism, rs2279238, and one common haplotype, CAAGCC, as well as two LXRB single nucleotide polymorphisms, LB44732G>A and rs2695121, were associated with obesity phenotypes. 17110595_novel mechanism of inflammatory gene regulation (C-reactive protein) by LXR ligands 17135302_ROS and NF-kappaB, but not LXR, mediate the IL-1beta-induced downregulation of ABCA1 via a novel transcriptional mechanism, which might play an important role of proinflammation in the alteration of lipid metabolism. 17217555_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17218271_These studies define parallel but functionally distinct pathways that are utilized by PPARgamma and LXRs to differentially regulate complex programs of gene expression that control immunity and homeostasis. 17255360_LXR is a potent modulator of dendritic cells maturation and function mediated in part by blocking the expression of fascin. 17272748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17296605_LXRalpha is regulated not only by oxysterol derivatives but also by PKA-mediated phosphorylation, which suggests that nutritional regulation of SREBP-1c and lipogenesis could be regulated at least partially through modulation of LXR 17391100_Results suggest that co-repression of LXR activity by RIP140 involves an atypical binding mode of RIP140 and a repression element in the RIP140 C-terminus. 17396233_These data indicate for the first time that human macrophage aP2 promoter is a direct target for the regulation by LXR/RXR heterodimers. 17405904_We show here that primary hASM cells express liver X receptor (LXR; alpha and beta subtypes), an oxysterol-activated nuclear receptor that controls expression of genes involved in lipid and cholesterol homeostasis, and inflammation. 17416342_The LXR agonist T0901317, therefore, acts as an antiandrogen in human prostate cancer cells. 17452725_Haplotype 2 associated with reduced mortality from infectious disease. Haplotype 2 also associated with higher levels of plasma apolipoprotein E, a target gene of the LXRalpha (p =.018), and higher levels of triglycerides (p =.041). 17628006_This novel insight that thyroid hormone regulates LXR-alpha mRNA levels and promoter activity should shed light on a cross talk between LXR-alpha and TR-beta1 as a new therapeutic target against dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. 17644777_atorvastatin reduces LPL and EL expression by reducing the activation of LXRalpha and NF-kappaB, respectively 17724434_It was proposed that LXR is a key regulator of cytokine release in LPS-challenged human monocytes, possibly by interfering with translational events. 17766241_In summary, this study is the first to demonstrate anti-inflammatory actions of LXRs in the lung. 17845217_LXRalpha and LXRbeta are expresed in the majority of the cell types in human skin. 17960176_important roles of LXRalpha in differentiation and inflammatory signaling in sebaceous glands 18007013_Upregulation of ABCG5/ABCG8 in gallstone patients, possibly mediated by increased liver X receptor (LXR) alpha, may contribute to the cholesterol supersaturation of bile, a prerequisite for gallstone formation. 18024509_May modulate the bile acid biosynthetic pathway at a unique site downstream of cholesterol 7-alpha- ydroxylase (CYP7A1) and 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C4) and may also modulate the metabolism of steroid hormones and certain xenobiotics. 18096827_Laminar flow increases LXR function via a PPARgamma-CYP27 dependent mechanism, which reveals an atheroprotective role for laminar flow exerting on endothelium. 18182682_review of role of activation of PPARalpha, -beta/delta, or -gamma or LXRs in skin physiology and cytology and disease 18209740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18209740_results suggest that NR1H3 plays an important role in the HDL-cholesterol metabolism and in the genetic susceptibility to metabolic syndrome. 18250151_reveal a previously unrecognized role for phosphorylation in restricting the repertoire of LXRalpha-responsive genes 18276933_LXR (as a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor) is able to bind the ENG promoter on an LXR response element and mediates the activation of ENG gene expression by LXRalpha in JAR cells. 18327405_CRP modulates the expression of genes that contribute to both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in human monocytes. Among these novel anti-inflammatory effects, we show clearly that CRP activates the LXRalpha pathway. 18372238_Protein kinase C alpha modulates liver X receptor alpha transactivation. 18511497_These data identify Rev-erbalpha as a new LXR target gene, inhibiting LXR-induction of TLR-4 in a negative transcriptional feedback loop, but not cholesterol homeostasis gene expression. 18562803_FXRalpha down-regulates CETP gene expression via binding to the DR4RE sequence within the CETP 5' promoter and this FXRalpha binding is essential for FXRalpha inhibition of LXRalpha-induced CETP expression. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18669643_Data show that, at sufficiently high concentration, the NR corepressor (NCoR) influences the activity of the liver X receptor (LXR) even in the presence of a potent full agonist that destabilizes NCoR binding. 18789440_IFN-gamma down-regulates ABCA1 expression by inhibiting LXRalpha in a JAK/STAT signaling pathway-dependent manner 18854425_25-Hydroxycholesterol-3-sulfate regulates macrophage lipid metabolism via the LXR/SREBP-1 signaling pathway. 19060910_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19105208_mediates HBV-associated hepatic steatosis 19119143_Suppression of 2,3-oxidosqualene cyclase by high fat diet contributes to liver X receptor-alpha-mediated improvement of hepatic lipid profile. 19164445_Data suggest that LXR ligands prevent LXRalpha from ubiquitination and degradation by detaching BARD1/BRCA1, which may be critical for early transactivation of ligand-stimulated LXRalpha through binding of LXRalpha to the promoters of target genes. 19201410_PPARg, PPARd and LXRa are involved in the regulation of ABCA1 expression and HDL biogenesis in a cooperative signal transduction pathway 19211025_The present study was directed to explore the functional genomics of LXR-alpha gene within blood mononuclear cells of subjects suffering from coronary heart disease (CHD). 19261092_the inhibitory activity of liver X receptor alpha, ATP-binding cassette transporter and macrophage scavenger receptor A by LPS may be related to the transformation of human macrophages into foam cells. 19292929_Common genetic variation in LXRA is unlikely to affect the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or quantitative phenotypes related to glucose homeostasis 19292929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19360318_Cholesterol synthesis was activated in NAFLD liver, meaning that cholesterol metabolism is dysregulated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 19366697_A mechanism for LXRalpha in controlling the gene expression of LGK that involves activation through SREBP-1c and PPARgamma and inhibition through SHP, is proposed. 19380774_Liver X receptors alpha and beta are constitutively expressed and functional in human B cells. 19426978_LXR-activating oxysterols induce the expression of inflammatory markers in endothelial cells through LXR-independent mechanisms. 19481530_Data describe the requirement of GPS2 for ABCG1 gene transcription and cholesterol efflux from macrophages, and implicate GPS2 in facilitating LXRalpha/beta recruitment to an ABCG1-specific promoter/enhancer unit upon ligand activation. 19645823_The expression of LXR-alpha at both mRNA and protein level was significantly higher in perilesional skin as compared to the normal skin of vitiligo patients. 19697157_LXRbeta protein expression was unaltered in photoaged skin (p = 0.75). Our data therefore suggest that, while not playing a major role in skin aging, robust cutaneous expression implies a fundamental role for LXRbeta in epidermal biology. 19796621_Deletion of liver X receptors (Lxralpha and beta) reduced cell cycle progression and ventral midbrain neurogenesis, resulting in decreased dopaminergic neurons at birth. 19798078_LXR-alpha gene knockdown within normal human keratinocytes simulated the genomic profile observed in psoriatic skin lesions. 19837721_LXRalpha and LXRbeta control cholesterol homeostasis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933273_O-GlcNAcylation of LXR is a novel mechanism by which LXR acts as a glucose sensor affecting LXR-dependent gene expression, substantiating the crucial role of LXR as a nutritional sensor in lipid and glucose metabolism. 20005944_sauchinone has the capability to inhibit LXRalpha-mediated SREBP-1c induction and SREBP-1c-dependent hepatic steatosis 20037595_production in tumors inhibits functional expression of CCR7 in dendritic cells and dampens antitumor responses 20057170_results provide evidence that TGF-beta1 up-regulates expressions of ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI through the LXR alpha pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells 20080977_DAX-1 acts as a novel corepressor of liver X receptor alpha and inhibits hepatic lipogenesis 20118482_activation of LXRalpha stimulates renin expression and induces mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into renin-secreting, juxtaglomerular-like cells 20139031_Data clarified the PAR-2 expression of human macrophages and suggested that tryptase might promote lipid accumulation in macrophages and foam cell formation by suppressing LXRalpha activation via PAR-2/LXRalpha/LXRalpha target genes signaling pathway. 20190811_Liver X Receptor activation downregulates AKT survival signaling in lipid rafts and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. 20219900_Results suggest that liver X receptors play a regulatory role in fatty acid metabolism by direct regulation of ACSL3 in human placental trophoblast cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364260_LXR activation inhibits chemokine-induced migration of CD4-positive lymphocytes by reducing PI-3 kinase activity and activation of Rac-1 with subsequent inhibition of MLC phosphorylation, f-actin formation and ICAM3 translocation. 20410489_Activation of LXR alpha represents a novel lipid-signaling paradigm that alters the inflammatory response of human dendritic cells. 20494359_Indicate that LXRalpha has an essential role in the regulation of CETP expression and maintaining reverse cholesterol transport. 20506155_Data suggest that berberine abrogates the formation of foam cells by macrophages by enhancing LXRalpha-ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20655109_Gene expression of LXRalpha was significantly decreased in placental tissues, while increased expression was observed for LXRalpha in adipose tissue, from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. 20836841_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20837115_Results establish for the first time that LPCAT3 is specifically regulated by LXRalpha. 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20868688_Data suggest the ability of FoxO1 to inhibit LXRalpha binding with the LXRE in the SREBP-1c promoter. 20945144_Data suggest LXRalpha has a role in regulation of lipid synthesis in keratinocytes; activation of LXRalpha via a ligand leads to accumulation of lipid droplets and increases expression of SREBP-1c, FAS, PPARalpha, PPARbeta, and PPARgamma. 21042792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21125317_the Liver X Receptor-alpha gene activated in cancerous cells of diverse origin results in the regulation of genes forcing these cells to enter into the state of apoptosis 21136146_elevated expression of LXRalpha may be involved in the progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy, and demethylation of LXRalpha is likely to be responsible for its increased expression in myocardial tissues. 21187453_an important role of LXRs in the coordinated regulation of lipid metabolic and inflammatory gene programs in macrophages 21245992_PXR and LXR polymorphisms, but not NF-kB or PPARgamma, may contribute to risk of IBD, especially among never smokers 21266776_This study reports a novel signaling pathway underlying liver X receptor-mediated regulation of Th17 cell differentiation and autoimmunity. 21310851_the expression of hsa-miR-613 can be transcriptionally activated by LXR-alpha 21315073_CIDEA binds to liver X receptors and regulates their activity in vitro. 21316679_Genetic polymorphisms in NR1H3 and its target genes ABCA1, APOE, CETP and LPL contribute to the genetic variance for HDL-cholesterol concentrations in adolescence. 21349840_Liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor (LXR-RXR) heterodimer cistrome reveals coordination of LXR and AP1 signaling in keratinocytes 21350215_Different regulatory activities of the liver X receptoralpha (and PPARgamma) pathways identified a distinct macrophage subpopulation with a low susceptibility to become foam cells. 21356276_we concluded that LXR-alpha/beta gene expression ratio is a critical factor to activate POMC gene expression in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas. 21440016_This increase in hepatitis B virus transcription and replication was directed by nuclear receptor LXRalpha induction in the presence of oxysterols. 21562465_LXRA genotypes were associated with variable risk for cardiovascular outcomes and pharmacogenetic effect. 21625070_decreased expression in atherosclerotic artery macrophages infected with Chlamydia pneumoniae 21775116_The mRNA levels of LXRalpha and SREBP-1c, transcription factors that regulate SCD-1, were decreased by 10,12 conjugated linoleic acid in human adipocytes. 21889884_FGF21 gene expression was negatively regulated by LXR in HepG2 cells and mouse primary hepatocytes. 21903943_Functional genetic variation in liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha) predicts risk of ischemic vascular disease in the general population. 21937108_RXRalpha and LXR activate two promoters in placenta- and tumor-specific expression of PLAC1. 21951066_LXR alpha/beta play a role in the regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase and alpha-synuclein expression; the extent to which the oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol utilizes these pathways to modulate expression levels of these two proteins is characterized. 22027013_Te results of this study suggested taht genetic variations in MMEL1, ECE1, ECE2, AGER, PLG, PLAT, NR1H3, MMP3, LRP1, TTR, NR1H2, and MMP9 genes do not play major role among the Finnish AD patient cohort. 22137263_Data suggest that expression of LXRalpha in androgen-independent prostate neoplasm cells can be regulated by dietary factors (here, the carotenoid lycopene). 22257474_LXR are involved in the metabolism and inflammation in human diseases; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is classically associated with lipid metabolic disorders and inflammatory responses. 22311022_Two genetic variants in LXRalpha independently influence the susceptibility to metabolic risk factors of polycystic ovary syndrome patients. 22367754_liver x receptors are activated by phospholipase A2 modified low density lipoproteins in human macrophages 22399489_Regulation of LXRalpha pre-mRNA splicing may be involved in the pathogenesis of LXRalpha-related diseases 22503545_PAPP-A may first down-regulate expression of LXRalpha through the IGF-1/PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway and then decrease expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, SR-B1 and cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 22547570_Lxralpha regulates the androgen response in prostate epithelium 22569763_serum LXRa ligand oxysterol levels could be surrogate markers of insulin resistance, and high oxysterol levels in the circulation may play an important role in the development of hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance followed by NAFLD 22610535_Activation of LXR-alpha and LXR-beta Suppresses Proliferation of Human Colon Cancer Cells. 22634718_Liver X receptor regulates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness, matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation, interleukin-6 and CXCL10. 22641099_Studied the effect of HCV NS5A protein, core protein, and viral replication on the intracellular lipid accumulation and the LXRalpha-regulated expression of lipogenic genes. 22707265_Data suggest that taurine, a dietary component, is a direct ligand of LXR-alpha and appears to control gene expression of LXR-alpha and it's responsive genes (e.g., ATP-binding cassette transporters) in enterocytes, macrophages, and hepatocytes. 22723445_Pharmacological activation of endothelial LXRs reduces angiogenesis by restraining cholesterol-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 compartmentation and signaling. 22749359_The induction of ABCG1 and its mediated 7-ketocholesterol efflux from endothelial cells by cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucoside resulted from liver X receptor alpha activation. 22766509_Discussion of the role of LXR in orchestrating lipid homeostasis and neuroinflammation in the brain. The ability of LXR to attenuate Alzheimer disease pathology makes them potential therapeutic targets for this neurodegenerative disease. [Review Article] 22916038_An allele-specific regulatory polymorphism within NR1H3 (coding for LXR-a), rs7120118, coincides with causal SNPs for HDL-C levels associated with cardiovascular disease in Caucasian patients. 22984430_The regulation of SREBP-1c gene expression by SIRT1 may require the deacetylation of LXR transcription factors. 22990668_Activation of LXRalpha during inflammatory response may constitute an endogenous protective mechanism in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 23018104_Activation of LXR reduced the binding of the transcriptional factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB to the ET-1 gene promoter region, thereby regulating gene expression. 23041609_LXRalpha transactivates the expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 through common two cis-elements 23099324_activation of the LXR could have a beneficial, therapeutic effect in the prevention of bacterial-induced bone erosion 23163651_Higher expression of LXR-alpha in perilesional melanocytes decreases adhesion, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinases, and increases apoptosis leading to vitiligo lesions. 23185273_Three new cell surface markers that could be useful to monitor LXR activation, were identified. 23313547_LXRalpha levels appear as a limiting factor for macrophage cholesterol efflux in humans. 23393188_The study identified highly integrated LXRalpha ligand-dependent transcriptional networks, including the APOE/C1/C4/C2-gene cluster, which contribute to the reversal of cholesterol efflux and the dampening of inflammation processes in foam cells to prevent atherogenesis. 23416078_TR-beta and LXR-alpha competitively up-regulate the human Seladin-1 promoter, sharing the same response element, site A. 23451202_STX4 is a new LXRalpha-ligand to study transcriptional regulation of anti-atherogenic processes in cell or ex vivo models, and provides a promising lead structure for pharmaceutical development 23496987_MiR-613 suppresses lipogenesis by directly targeting LXRalpha in HepG2 cells. 23564066_LXRalpha plays a central role in neopterin-induced downregulation of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 23680128_PGC-1b, a coactivator of both LXR-alpha and SREBP-1, was markedly down-regulated by OEPAs compared with EPA. 23686114_Treatment of human THP-1 macrophages with endogenous or synthetic LXR ligands stimulates both transcriptional and posttranscriptional pathways that result in the selective recruitment of the LXRalpha subtype to LXR-regulated promoters. 23732298_Liver x receptor alpha positively regulates the basal expression of CYP3A4 in hepatocytes. 23733886_evidence for the existence of an LXR-IDOL-mediated internalization pathway for the LDLR that is distinct from that used for lipoprotein uptake 23812424_LXRalpha-mediated downregulation of FOXM1 suppresses the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 23838803_Data indicate that LXR-beta genotypes (rs35463555) and (rs2695121) were associated with risk of gallbladder cancer (GBC) as compared to healthy controls whereas LXR-alpha (rs7120118) was not associated with GBC risk. 23867395_LXRalpha activates FoxO1 transcription through a direct binding on its promoter region. 24036496_Liver X receptor activation stimulates iron export in human alternative macrophages. 24100084_Variants in LXRalpha and LXRbeta genes are not potential contributors to the risk of metabolic syndrome and related traits in an Iranian population. 24118845_The liver X receptor activation has anti-inflammatory effects on CXC10, CCL5 and IL-10 production from alveolar macrophages. 24180251_There was no significant association between two NR1H3 single nucleotide polymorphisms and obesity, even after adjustment for age and sex. The odds ratios for obesity were: 1.32 (0.85-2.74) for rs11039155 and 0.77 (0.30-1.99) for rs2279238. 24265317_Results indicate that Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) activates SMILE gene expression, which leads to repression of liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha)-mediated hepatic lipogenic enzyme gene expression. 24278306_genetic variation in NR1H3 modulates the expression of LXRalpha and the levels of soluble Abeta42. 24289152_Data suggest PAF (platelet activating factor)/PAF receptor signaling exerts proinflammatory effect on neutrophil via downregulation of LXRa/target genes (ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1, ABC G1, sterol response element binding protein 1c). 24533572_The rsl2221497 polymorphism in LXRalpha gene is associated with susceptibility of coronary heart disease in Han population. 24618263_Activation of LXRs interfered with the release of interleukin-6 from macrophages and, thus, inhibited fibroblast activation and collagen release. 24713062_PPARalpha and LXRalpha interact with high affinity, resulting in altered protein conformations, the affinity of this interaction and the resulting conformational changes could be altered by endogenous PPARalpha ligands, namely long chain fatty acids. 24751522_PPARgamma negatively regulates the expression of miR-613 at transcriptional level, and miR-613 suppressed LXRalpha and ABCA1 by targeting the 3'-UTR of their mRNAs. 24832115_Studies indicate that no liver X receptor (LXR) modulator has successfully progressed beyond phase I clinical trials. 24842676_Report significant reduction in LXR-alpha transcript in testes of men with azoospermia. 24886807_Data indicata that -1830 T>C polymorphism within liver X receptors alpha gene (NR1H3) promoter region may be involved in regulation of NR1H3 expression. 24996838_LXRalpha rather than LXRbeta plays a predominant role in mediating cholesterol efflux in human macrophages. 25005769_SREBP-2 rs2228314 G to C change and variant C genotype as well as LXRalpha rs11039155 G to A change and variant A may contribute to PCOS in Chinese Han population 25028566_The expression of liver X receptor alpha is a potential predictor for the expression of hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase 2a1 in human liver. 25035925_study suggests that the anti-atherogenic properties of IL-10 may include enhancing effects on cholesterol efflux mechanism that involves cross-talk with LXRalpha activation 25073010_NR1H3 accelerates hepatic differentiation through an HNF4alpha-dependent reciprocal network. 25102981_This research suggests that LXR is an attractive target for treatment and regulation of hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. 25187371_PRMT3 translocation by palmitic acid is coupled to the binding of LXRalpha, which is responsible for the onset of fatty liver. 25255963_ligands selectively regulate placenta gene targets and functional pathways 25264165_The data indicate a direct inhibitory interaction of polyunsaturated fatty acids with LXRalpha, a consequent reduction of SREBP-1 and of its binding to SCD1 promoter. 25283515_An increase of 55% in LXR-alpha gene expression at RNA level was observed in Atorvastatin + 22-R hydroxycholestrol compared to 24% in Ascorbic acid + 22-ROH cholesterol. 25332231_FHL2 is a transcriptional coactivator of LXRs and may be an important determinant of cholesterol metabolism in SMCs 25437875_TRAP80 is a selective regulator of hepatic lipogenesis and is required for LXR-dependent SREBP-1c activation. 25450400_data suggest that ASXL3 is another corepressor of LXRalpha, promoting to the regulation of lipid homeostasis 25600616_Propofol up-regulates expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-B1 through the PPARgamma/LXRalpha pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 25659329_LXRb is the dominant isoform in the rat myocardium and the expression of both LXR isoforms (LXRa and LXRb) did not change after administration of T0901317 25661920_These results clearly indicate a novel mechanism in which CCAR2 may regulate the transcriptional activation function of LXRalpha due to its specific inhibition of SIRT1 and serve to regulate cellular proliferation. 25729942_the rsl2221497 polymorphism in the LXRalphagene was associated with the susceptibility to stroke in a Chinese population. 25779847_treatment with Ang-(1-7) promoted cholesterol efflux in Ang II-treated THP-1 macrophages, partly through inactivation of p38 and JNK signaling and by inducing the expression of PPARg and LXRa. 25867319_The rs12221497 polymorphism in the LXRalpha gene was associated with the susceptibility to stroke in a Han Chinese population. 25962847_Data show that menin, encoded by the MEN1 gene, inhibits the transcriptional activity of nuclear receptor liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha). 25980575_This study provides the first evidence to show LXR activation reduces cadmium-induced apoptotic cell death of human renal proximal tubular cells by inhibition of reactive oxygen species production and JNK activation. 26160456_These results identify LXRalpha as a key cardiac transcriptional regulator that helps orchestrate an adaptive metabolic response to chronic cardiac stress. 26261553_Lipoxin A4 increases ABCA1 expression and promotes cholesterol efflux through LXRalpha pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 26379423_Suggest that blocking cholesterol deposition and inhibiting the LXRalpha pathway-induced inflammatory response might be one of the main mechanisms by which anthocyanins exert their protective effects in diabetic nephropathy. 26595172_Studied the role of LXRalpha with Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenesis of MSCs. 26602218_Intestinal activation of LXR reduces the production of chylomicrons by a mechanism dependent on the apical localization of SR-B1. 26635040_The anti-inflammatory effects of platelet-derived microparticles in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells involve liver X receptor activation. 26669941_LXR-alpha might downregulate S1PR2 expression via miR-130a-3p in quiescent HUVECs. Stimulation of TNF-alpha attenuates the activity of LXR-alpha and results in enhanced S1PR2 expression. 26692490_In conclusion, our data indicate that HNF-4alpha may have a wider role in cell and plasma cholesterol homeostasis by controlling the expression of LXRalpha in hepatic cells. 26756785_PPARalpha and LXRalpha may be mediators by which omega3PUFA attenuate bile acid-induced hepatocellular injury 26814197_these data identify a new mechanism of LXR regulation that involves TIPARP, ADP-ribosylation and MACROD1. 26964694_these data show that YXS is effective in mitigating MI/R injury by suppressing mitochondrial mediated apoptosis and oxidative stress and by upregulating LXRalpha, thereby providing a rationale for future clinical trials and clinical applications 26991262_RXRalpha negatively regulates the transcription and expression by directly binding to the RARE in the promoter of Cx43 27016616_combined PPARgamma C1431T, PGC-1alpha G482S, and LXRalpha -115G/A polymorphisms increase the risk of coronary artery disease and predicted the severity of coronary atherosclerosis in Thais 27253448_mutant NR1H3 (LXRA) alters gene expression profiles, suggesting a disruption in transcriptional regulation as one of the mechanisms underlying Multiple Sclerosis pathogenesis. 27343431_AMPK activates LXRalpha and ABCA1 expression in human macrophages 27351826_this study shows that show that H2O2 exerts a du |
ENSMUSG00000002108 |
Nr1h3 |
108.080517 |
0.4180573236 |
-1.258227 |
0.246643284 |
25.672920 |
0.00000040446291418988651515615878259679583095476118614897131919860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001496959030452037191989450755358337374900656868703663349151611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.7541302 |
9.1275249 |
146.4003775 |
15.1887403 |
| ENSG00000026025 |
7431 |
VIM |
protein_coding |
P08670 |
FUNCTION: Vimentins are class-III intermediate filaments found in various non-epithelial cells, especially mesenchymal cells. Vimentin is attached to the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria, either laterally or terminally. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31000}.; FUNCTION: Involved with LARP6 in the stabilization of type I collagen mRNAs for CO1A1 and CO1A2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21746880}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cataract;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Intermediate filament;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a type III intermediate filament protein. Intermediate filaments, along with microtubules and actin microfilaments, make up the cytoskeleton. The encoded protein is responsible for maintaining cell shape and integrity of the cytoplasm, and stabilizing cytoskeletal interactions. This protein is involved in neuritogenesis and cholesterol transport and functions as an organizer of a number of other critical proteins involved in cell attachment, migration, and signaling. Bacterial and viral pathogens have been shown to attach to this protein on the host cell surface. Mutations in this gene are associated with congenital cataracts in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:7431; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; polysome [GO:0005844]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; keratin filament binding [GO:1990254]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural constituent of eye lens [GO:0005212]; astrocyte development [GO:0014002]; Bergmann glial cell differentiation [GO:0060020]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to muramyl dipeptide [GO:0071225]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; lens fiber cell development [GO:0070307]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; regulation of mRNA stability [GO:0043488]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395] |
11744725_These findings suggest that platelet vimentin may regulate fibrinolysis in plasma and thrombi by binding platelet-derived Vn.PAI-1 complexes. 11827972_association with MICAL, a novel CasL interacting molecule 12084347_Vimentin expression correlates with the cytoplasmic localization of wild-type p53 in human primary glioblastoma. 12169273_Menin's interaction with glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin suggests a role for the intermediate filament network in regulating menin activity. 12194205_Results describe the asymmetric distribution of vimentin in the human sperm head. 12210485_expression correlated with motility of prostate carcinoma cells, poor cell differentiation, and presence of bone metastasis 12366696_specific interaction of the periplakin linker domain with keratin 8 and vimentin 12466525_The 3' untranslated region of human vimentin mRNA binds protein complexes containing eEF-1gamma and HAX-1. 12483219_It is secreted by activated monocyte-derived macrophages 12727854_vimentin expression contributes to the invasive phenotype in androgen-independent prostate cancer but cannot confer it alone. 12750294_The vimentin promoter is a target of the beta-catenin/TCF pathway and strongly suggest an implication of this regulation in epithelial cell migration/invasion in breast cancer. 12761892_role of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase-2 phosphorylation in retaining assembly capacity 12829607_vimentin, in conjunction with low molecular weight heparan sulfate proteoglycans, contributes to the enhanced binding of human group IIA PLA2 to apoptotic T cells 12906105_High MW vimentin was formed after the digestion of vimentin by caspase-3 but not caspase-8. It acted as an autoantigen to form anti-vimentin autoantibody in vivo. 14595690_findings implicate reduced vimentin in the conversion of these tumorigenic prostate epithelial cells into slow growing, less aggressive cells 15231822_study of human vimentin rod 1 structure and the sequencing of assembly steps in intermediate filament formation 15255035_It is unlikely that ependymal vimentin is directly involved in the pathogenesis of Chiari II malformation, but may reflect a secondary upregulation due to defective expression of another gene. 15456890_Data suggest that the PAL-E antibody defines secretion of vimentin as a molecular distinction among endothelial cells and exposes a novel, extracellular role for vimentin in the blood vasculature. 15556930_examination of mutation the LNDR to LNDS motif in vimentin to examine role in epidermolysis bullosa simplex 15777792_Interacts with alpha2beta1-enriched focal adhesions and this association is lost after prolonged adhesion of endothelial cells to collagen. 16270034_Results indicate that protein kinase C epsilon-mediated phosphorylation of vimentin is a key process in integrin traffic through the cell. 16298568_Kidney recipients from non-heart-beating donors showed higher levels of anti-vimentin antibodies than heart-beating donors. 16365157_Apoptotic neutrophils express vimentin on their surface; these cells may participate in the development of autoantibodies directed against cytoskeletal proteins, a condition frequently reported in several inflammatory diseases. 16487365_All polyps were immunohistochemically positive for vimentin. 16568083_regulation of vimentin is controlled by SIP1 in breast neoplasms 16703512_isolated & identified vimentin as the major skeletal-muscle group A streptococcus (GAS)-binding protein; vimentin expression was up-regulated on injured skeletal-muscle cells in vitro and was expressed in muscle tissues from a patient with GAS myonecrosis 16901892_actin and vimentin filaments can interact directly through the tail domain of vimentin 16912072_Data show that the architecture of the vimentin cytoskeleton is modified by perturbation of the GTPase ARF1. 17031402_Increased vimentin expression was found in pseudomyxoma peritonei. 17050693_unit-length filaments appears to be a dynamic and a relatively loosely packed structure with a roughly even mass distribution over its cross-section 17056548_Vimentin is involved in binding of NKp46 to M. tuberculosis H37Ra-infected mononuclear phagocytes. 17083913_The regulatory protease factor Xa is able to cleave IbeA between R297 and K298 residues, and this cleavage abolishes the IbeA-vimentin interaction. 17289402_Vimentin filaments in cross-section exhibit predominantly a four-stranded protofibrilar organization with a right-handed supertwist with a helical pitch of about 96 nm. 17403663_a kinetic model for the in vitro assembly of intermediate filaments from tetrameric vimentin 17476115_Vimentin is a major arterial substrate for transglutaminases.Transglutaminase-mediated vimentin dimerization produces a novel unifying pathway by which vasodilatory and remodeling responses may be regulated. 17585878_In conclusion, ablation of vimentin expression inhibits migration and invasion of colon and breast cancer cell lines. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17652163_The nestin(-) vimentin(+) fibroblasts may represent a novel type of multipotent adult stem cells in human dermis. 17663720_ZBP-89 functions as a repressor by recruiting HDAC1 to the vimentin promoter. 17703067_study of vimentin protein filament structure and assembly by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of site-directed spin labels. Review. 17719575_The suppression of vimentin expression by ras, and the relief of this suppression by TGFbeta, occurs in a promoter-independent fashion, possibly through sequences in the first or second intron. 17960581_Rults indicate that cysteine 328 in vimention is the main site for prostaglandin PGA(1) addition. 18046501_The vimentin expression patterns in human malignant glioma cells strongly depend on cellular density, algorithms of drug delivery and chemo/radio treatment. 18155753_The interstitial vimentin immunopositivity correlated with sclerotic/fibrotic lesions (interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophies, vascular hyalinosis/fibrosis, chronicity index), and negatively with glomerular filtration rate. 18176708_Immunohistochemical identification of the combination of calponin and vimentin is suggested for the identification of myoepithelial cells in salivary gland tumors. 18184460_The protein level of vimentin was higher in PC-3M-1E8 cells with high metastatic potential than in PC-3M-2B4 cells with low metastatic potential. 18219106_Primary colorectal carcinomas display aberrant expression of vimentin, and have activated Notch and TGFbeta signaling pathways. 18241054_Vimentin isoforms are differentially expressed in normal and transformed astrocytes. 18407667_ability of Surfactant protein A to interact with desmin and vimentin, and to prevent polymerization of desmin monomers, shed light on unexpected and wider biological roles of this collectin 18464297_Affects prostate cancer cells motility and invasiveness. 18632620_coordination of vimentin and detyrosinated microtubules provides structural support for the extensive microtentacles observed in detached tumor cells and a possible mechanism to promote successful metastatic spread 18653473_the O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes associate with kinases and phosphatases at M phase to regulate the posttranslational status of vimentin 18681838_Endosomal lipid accumulation in Niemann-Pick type C1 disease leads to inhibition of protein kinase C, hypophosphorylation of vimentin and Rab9 entrapment. 18695932_vimentin is required for dengue virus serotype 2 infection. 18790770_The role of vimentin in proliferation and motility, was studied. 18947333_Our results argue for the involvement of galectin-1 in the PKCepsilon/vimentin-controlled trafficking of integrin-beta1 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18985821_Solitary fibrous tumor of the liver expressing CD34 and vimentin: a case report. 19013628_These findings suggest that the turnover rate of hepatitis C virus core protein is regulated by cellular vimentin content. 19117942_Head and rod 1 interactions in vimentin: identification of contact sites, structure, and changes with phosphorylation using site-directed spin labeling and electron paramagnetic resonance. 19126778_These results reveal for the first time an important functional role for vimentin in the maintenance of lens integrity. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19168853_Characteristic giant axonal neuropathy (GAN) mutant-induced ovoid aggregates of vimentin are not produced in normal fibroblasts after disrupting microtubule assembly, either by TBCE overexpression or depolymerizing drugs. 19252475_immunohistochemistry, using a panel composed of desmin, smoothelin, and vimentin, may be potentially useful for staging of bladder carcinoma. 19331162_Vimentin was frequently methylated in advanced colorectal carcinoma. 19366731_Data show that intermediate filament recruitment to focal adhesions in endothelial cells requires beta3 integrin, plectin and the microtubule cytoskeleton, and is dependent on microtubule motors. 19386766_The upregulation of vimentin expression during epithelial to mesenchymal transitions may stabilize Scrib to promote directed cell migration. 19403668_An intact vimentin network is required for cytomegalovirus infection onset. 19404921_Loss of cytokeratin and gain of vimentin expression are indicators of biologically aggressive breast carcinoma. 19422834_The low propensity of the wild-type coil 1A to form a stable two-stranded coiled coil is most likely a prerequisite for the end-to-end annealing of unit-length filaments into filaments. 19447876_Results show there was high risk of biochemical recurrence associated with tumors that displayed high levels of expression of TGF-beta1, vimentin, and NF-kappaB and low level of cytokeratin 18. 19476621_The three markers (ER, Vim and CEA) and their respective panel expressions showed statistically significant (p |
ENSMUSG00000026728 |
Vim |
2923.661012 |
4.1409103689 |
2.049948 |
0.039831280 |
2658.485206 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4756.6528625 |
103.8290001 |
1157.3421887 |
20.9339695 |
| ENSG00000026297 |
8635 |
RNASET2 |
protein_coding |
O00584 |
FUNCTION: Ribonuclease that plays an essential role in innate immune response by recognizing and degrading RNAs from microbial pathogens that are subsequently sensed by TLR8 (PubMed:31778653). Cleaves preferentially single-stranded RNA molecules between purine and uridine residues, which critically contributes to the supply of catabolic uridine and the generation of purine-2',3'-cyclophosphate-terminated oligoribonucleotides (PubMed:31778653). In turn, RNase T2 degradation products promote the RNA-dependent activation of TLR8 (PubMed:31778653). Also plays a key role in degradation of mitochondrial RNA and processing of non-coding RNA imported from the cytosol into mitochondria (PubMed:28730546, PubMed:30184494). Participates as well in degradation of mitochondrion-associated cytosolic rRNAs (PubMed:30385512). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16620762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19525954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22735700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28730546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30184494, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30385512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31778653}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endonuclease;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lyase;Lysosome;Mitochondrion;Nuclease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This ribonuclease gene is a novel member of the Rh/T2/S-glycoprotein class of extracellular ribonucleases. It is a single copy gene that maps to 6q27, a region associated with human malignancies and chromosomal rearrangement. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8635; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; endoribonuclease activity [GO:0004521]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; ribonuclease T2 activity [GO:0033897]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401] |
15809705_RNASET2 found to significantly decrease the metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cell line in vivo; tumor suppression by RNASET2 is suggested to not be mediated by its ribonuclease activity 16620762_The results presented herein represent a further advancement toward the molecular understanding of the tumour suppressive properties of the human RNASET2 protein. 18543608_Loss of RNASET2 is associated with melanoma 19382914_RNaseT2 is a cell growth regulator and it does not induce senescence in SV40 immortalized cell lines. 19525954_Study shows that loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding the RNASET2 glycoprotein lead to cystic leukoencephalopathy, an autosomal recessive disorder with an indistinguishable clinical and neuroradiological phenotype. 20526339_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20601676_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21199949_Familial cystic leukoencephalopathy arising in RNASET2-deficient humans is a manifestation of an lysosomal storage disorders in which rRNA is the best candidate for the noxious storage material. 21446958_The expression of the human tumor suppressor protein RNASET2 was studied in baculovirus-insect cell and Pichia pastoris heterologous systems. 21646684_Molecular signature induced by RNASET2, a tumor antagonizing gene, in ovarian cancer cells. 21994792_Tax represses expression of RNase T2. 22188480_a possible involvement of RNASET2 in P-body formation in mammalian cells. 22732457_RNASET2--an autoantigen in anaplastic large cell lymphoma identified by protein array analysis. 22735700_The catalytic features of RNase T2 in presence of bivalent cations were analyzed and the structural consequences of known clinical mutations were investigated. 23258633_Higher expression of RNASET2 in the semen of asthenozoospermia individuals may contribute to sperm motility impairment. 23630276_Ribonuclease T2, an ancient and phylogenetically conserved RNase, has a role in development of ovarian neoplasms 24327149_Genotypes of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in RNASET2 gene were determined. 24457966_RNASET2 contributes to vitiligo pathogenesis by inhibiting TRAF2 expression. 24842157_Results show that downregulation of RNASET2 and GGNBP2 in drug-resistant ovarian cancer tissues/cells contributes to the regulation of drug resistance in ovarian cancer. 25426551_RNASET2 has antitumorigenic and antiangiogenic activities; a truncated version of human RNASET2, starting at E50 (trT2-50) and devoid of ribonuclease activity, has actin binding and anticancer-related biological activities 25663099_describe a multi-step strategy that allows production of highly pure, catalytically competent recombinant RNASET2 in both wild-type and mutant forms 25797262_Biological features allow to put forward the hypothesis that the RNASET2 protein can act as a molecular barrier for limiting the damages and tissue remodeling events occurring during the earlier step of cell transformation. 25928629_RNASET2 tag SNP but not CCR6 polymorphisms is associated with autoimmune thyroid diseases in the Chinese Han population 26067323_RNASET2 may contribute to the development of vitiligo by inhibiting TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 expression and lead directly to apoptosis of melanocytes 26293343_inhibits melanocyte outgrowth through interacting with shootin1; this effect may be associated with vitiligo pathogenesis 28400196_RNASET2, an IBD susceptibility gene, is a component of TL1A-mediated pathways regulating cytokine production. 28568286_Studied association of and RNASET2, GPR174, and PTPN22 gene polymorphisms and liver damage(LD) due to Graves' disease (GD) hyperthyroidism. Found GPR174 rs3827440, PTPN22 rs3789604, and RNASET2 rs9355610 were significantly associated with altered GD-derived LD risk. 28730546_RNASET2 is the enzyme that degrades the RNAs 29581387_High RNASET2 expression is associated with reduced sperm motility. 29763721_In poorly differentiated lung neuroendocrine carcinomas, RNASET2 expression may be upregulated as a consequence of the activation of the hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha pathway, thus behaving as an alarmin-like molecule. 30218741_The human RNASET2 protein affects the polarization pattern of human macrophages in vitro. 30385512_Regulation of mitochondrion-associated cytosolic ribosomes by mammalian mitochondrial ribonuclease T2 31778653_the lysosomal endoribonuclease RNase T2 is a non-redundant upstream component of TLR8-dependent RNA recognition. 32294405_Immune Sensing of Synthetic, Bacterial, and Protozoan RNA by Toll-like Receptor 8 Requires Coordinated Processing by RNase T2 and RNase 2. 32295832_Zebrafish disease model of human RNASET2-deficient cystic leukoencephalopathy displays abnormalities in early microglia. 33767133_FBXO6-mediated RNASET2 ubiquitination and degradation governs the development of ovarian cancer. 34299186_Hypoxia Enhances the Expression of RNASET2 in Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells: Role of PI3K/AKT Pathway. 36012339_Human RNASET2: A Highly Pleiotropic and Evolutionary Conserved Tumor Suppressor Gene Involved in the Control of Ovarian Cancer Pathogenesis. 36054934_Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-associated disease is associated with BANK1, RNASET2 and TNIP1 polymorphisms. 36466822_Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of RNASET2 in Crohn's disease: Disease-risk polymorphism modulates allelic-imbalance in expression and circulating protein levels and recombinant-RNASET2 attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion. |
ENSMUSG00000094724+ENSMUSG00000095687 |
Rnaset2b+Rnaset2a |
1391.542020 |
0.3717312845 |
-1.427668 |
0.042407767 |
1174.016313 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002706018311538202868872263906758127594315847784263642363518194728417233641 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003273838547401956990822847027192852073186173140685042645749495561925752460 |
Yes |
No |
767.3370016 |
22.5401150 |
2079.4512626 |
38.5157266 |
| ENSG00000026508 |
960 |
CD44 |
protein_coding |
P16070 |
FUNCTION: Cell-surface receptor that plays a role in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration, helping them to sense and respond to changes in the tissue microenvironment (PubMed:16541107, PubMed:19703720, PubMed:22726066). Participates thereby in a wide variety of cellular functions including the activation, recirculation and homing of T-lymphocytes, hematopoiesis, inflammation and response to bacterial infection (PubMed:7528188). Engages, through its ectodomain, extracellular matrix components such as hyaluronan/HA, collagen, growth factors, cytokines or proteases and serves as a platform for signal transduction by assembling, via its cytoplasmic domain, protein complexes containing receptor kinases and membrane proteases (PubMed:18757307, PubMed:23589287). Such effectors include PKN2, the RhoGTPases RAC1 and RHOA, Rho-kinases and phospholipase C that coordinate signaling pathways promoting calcium mobilization and actin-mediated cytoskeleton reorganization essential for cell migration and adhesion (PubMed:15123640). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15123640, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16541107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18757307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19703720, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22726066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23589287, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7528188}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood group antigen;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. Transcripts for this gene undergo complex alternative splicing that results in many functionally distinct isoforms, however, the full length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing is the basis for the structural and functional diversity of this protein, and may be related to tumor metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:960; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; macrophage migration inhibitory factor receptor complex [GO:0035692]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; hyaluronic acid binding [GO:0005540]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; hyaluronan catabolic process [GO:0030214]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; monocyte aggregation [GO:0070487]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043518]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:1902166]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034116]; positive regulation of monocyte aggregation [GO:1900625]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis [GO:2000392]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; wound healing, spreading of cells [GO:0044319] |
11466334_Interaction of CD44 when cross-linked on rheumatoid synovial cells with hyaluronan fragments present in the surrounding extracellular matrix augments Fas expression and Fas-mediated apoptosis of synovial cells. 11716065_Hyaluronate receptors mediate glioma cell migration and proliferation. The expression of the HA-receptors, CD44, and RHAMM, is virtually ubiquitous amongst glioma cell lines, and glioma tumor specimens. 11727257_Expression in uterine smooth muscle tumors 11740562_cd44 dependent group A Streptococcus binding to keratinocytes induce cytoskeletal rearrangements 11759056_results suggest that CD44S and CD44v5 are differentially expressed in early and advanced ovarian serous carcinomas and support previous studies that suggest a role for CD44 and stromal hyaluronic acid in the dissemination of ovarian epithelial cancer 11792412_sCD44 levels could be a useful prognostic marker for aggressive lymphoma 11825898_Three SIBLINGs (small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins) enhance factor H's cofactor activity enabling MCP-like cellular evasion of complement-mediated attack. 11839564_wide prevalence of CD44 cleavage suggests that it plays an important role in the pathogenesis of human tumors 11840273_variant isoforms involved in plasma cell adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells and in the multiple myeloma disease process 11935029_In mice, CD44 plays a role in resolving the inflammatory response following lung injury by clearance of inflammatory hyaluronan fragments, clearance of apoptotic PMNs, and generation of active TGFbeta 1. 12032545_A novel PKC-regulated mechanism controls CD44 ezrin association and directional cell motility. 12090473_TNFalpha and IL-8 regulate the expression and function of CD44 variant proteins in human colon carcinoma cells. 12145196_CD44 directs membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase to lamellipodia by associating with its hemopexin-like domain. 12145287_CD44 interaction with the TGF-betaRI kinase promotes activation of multiple signaling pathways required for ankyrin-membrane interaction, tumor cell migration, and oncogenic events during HA and TGF-beta-mediated metastatic breast tumor progression 12168806_CD44 has a functional role in inflammatory processes and tumor susceptibility 12183053_a signal transduction cascade or cross-talk emanating from CD44 to c-Met 12198147_Initial steps of Shigella binding and cell entry depend on the cholesterol/sphingolipid raft-mediated CD44-IpaB interaction. 12223485_Data suggest that intramembranous processing of CD44 occurs by a presenilin-1-dependent gamma-secretase activity at two distinct sites. 12226094_CD44 spontaneously released from normal bronchial epithelial cells can accumulate as an integral component of the matrix, where it may play a role in the organization of matrices and in anchoring growth factors and chemokines to the matrix 12235127_Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction inhibits migration of osteoclast-like cells by down-regulating MMP-9. 12297287_Engagement of CD44 either by its natural ligand hyaluronan or a specific antibody on a cell line induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of focal adhesion kinase. 12371152_reduction in the expression of CD44 may confer growth advantage and malignant properties to tumour cells 12393872_Autocrine/paracrine prostaglandin E2 production by non-small cell lung cancer cells regulates antigen in cox-2-dependent invasion 12407110_exon v10-encoded B[X(7)]B motif is solely responsible for the enhanced adhesive activity of exon v10-containing CD44 isoforms 12411303_results show that genes such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1alpha, and beta(2)-adrenergic receptor (beta(2)-AR) were specifically up-regulated by CD44 ligation, suggesting a novel role for CD44 in immunoregulation and inflammation 12421945_CD44 induction in THP-1 monocytic cells is the result of the distinct involvement of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling and may require JNK-dependent activation of Egr-1. 12439723_Butyrate significantly inhibited transcription of the CD44 gene and abolished epidermal growth factor-mediated up-regulation of the reporter gene luciferase subcloned upstream to the CD44 promoter (-1.1 kb) and transfected to HM7 cells 12452061_studied CD44v6 expression in intraductal papilloma, and its malignant transformation, intraductal breast carcinoma 12479099_Increase of CD44s, MMP-9, and Ki-67 were involved in the growth and local invasion of osteosarcoma. 12485845_Antagonistic signaling pathways regulate alternative splicing in T cells. 12506143_Crystal retention in human kidney may depend on expression of CD44 antigen-, osteopontin-, and hyaluronic acid-rich cell coats by damaged distal tubular epithelium. 12508241_CD44 silencing is controlled in part by a complex and tumor cell-specific process involving hypermethylation of the CD44 gene promoter and exon 1 regions. 12511569_regulation of interaction with hyaluronan by E-cadherin and role in mediating tumor invasion and branching morphogenesis 12574156_CD44 interaction with the alpha 1(IV)1263-1277 region from basement membrane collagen is modulated by ligand glycosylation 12629514_Our present findings suggest important implications for understanding CD44-dependent signal transduction and a potential role of PS/gamma-secretase activity in the functional regulation of adhesion molecules. 12635659_expressed by cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage in vitro and by oligodendrogliomas in vivo; could play a role in migration of tumor cells in oligodendrocytic tumors 12650924_Crosslinking of CD44 on osteoblastic cells with specific antibodies augmented the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1 12702150_role of CD44 variant isoform v10 in adhesion of lymphocytes to melanoma cells 12711360_Review. CD44 and ezrin and their respective complex have properties suggesting that they may be important in the process of tumour-endothelium interactions, cell migrations, cell adhesion, tumour progression and metastasis. 12727228_Data demonstrate that blockade of the ERK pathway suppressed the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 3, 9, and 14, and CD44, and markedly inhibited the invasiveness of tumor cells. 12730955_that Src contributes in part to malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor cell invasion by increasing CD44 levels. 12748184_CD44 interaction with p115RhoGEF and ROK plays a pivotal role in promoting Gab-1 phosphorylation leading to Gab-1.PI 3-kinase membrane localization, AKT signaling, and cytokine (M-CSF) production during HA-mediated breast cancer progression 12767055_The presence of Abeta 1-40 fragment, alone or in combination with IL1beta, induced an increase in the percentage of cells expressing CD44 12779084_Higher relative expression of SR55 protein was associated with an altered pattern of CD44 variants incorporating exon v7 as determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Southern blot analysis. 12801931_hydrolysis by hyaluronan oligosaccharides 12820426_Expressions of CD44s and CD44v6 play an important role in tumor progression. 12826680_CD44 alternative v9 exon contains a splicing enhancer responsive to the SR proteins 9G8, ASF/SF2, and SRp20 12842543_CD44v5 expression is independently positively correlated with the agressiveness of thymic epithelial tumors. 12883358_Post-translational modification of CD44s represents the principal regulatory mechanism of CD44s-mediated functions in melanoma. 12893366_CD44 expression correlates with T stage in renal cell carcinoma, although this correlation does not reach statistical significance; no association of CD44 expression with survival is found in renal cell carcinoma patients who underwent nephrectomy. 12908752_The expression of CD44 standard in 30 oligodendrogliomas was studied in order to verify its possible prognostic role. CD44H could have prognostic value regarding the occurrence of relapses. 12909589_CD44 is important for bronchial epithelial cell binding to hyaluronic acid and that cytokines known to be expressed in inflammation can increase binding independently of the level of CD44 expression. 12911725_We conclude that the cell adhesion molecule CD44 is expressed infrequently in papillary serous endometrial carcinoma. 12928429_analysis of the hyaluronan recognition mode of CD44 12949055_CD44v6 expression and cell adhesion in HepG2 cells depends on osteopontin 14504094_CD44-hyaluronic acid interactions may contribute to lymphocytotropism to skin in acute GVHD. 14534711_CD44 v6 has a role in metastatic potential of carcinoma cells increasing the migration capacity and participating in invasion via changes in adhesion to the extracellular ligands, but is not necessary to modify the clinical history of the metastases 14534719_CD44v6 is upregulated in transformated colon cancer cells 14614016_high CD44 expression is associated with mucinous epithelial ovarian cancer 14623895_cleavage of CD44 catalyzed by ADAM10 is augmented by the intracellular signaling elicited by engagement of CD44, through Rac1-mediated cytoskeletal rearrangement, and suggest that CD44 cleavage contributes to the migration and invasion of tumor cells 14644158_RhoA induced clustering of MMP-9 was observed in advancing lamellipodia at the forefront of endothelial cells, where this proteinase colocalized with RhoA and CD44 14669354_Detection of PCNA and CD44mRNA expression in colorectal cancer may be useful for evaluating liver metastasis of cancer cells. 14981907_CD44 variant isoforms on 55 transitional cell carcinoma tissue specimens were examined and expression of CD44v5 was inversely related to tumor grade 15009704_dermatan sulfate-CD44H proteoglycan is essential for fibroblast migration into fibrin clots and that platelet-derived growth factor, the stimulus for migration, induces the production of chondroitin-sulfate- and dermatan-sulfate-glycanated CD44H. 15013310_CD44 expression in renal allografts correlates with renal function. 15017146_NMR analysis of the hyaluronan-binding domain of CD44 15023889_Maximal CD44 expression on isolated monocytes is decreased in patients with a poor collateralization compared with patients with a good collateralization. 15040016_Heparanase, CD44v6 and nm23 may play important roles in the invasive infiltration and lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinomas 15048167_CD44 was mainly expressed by the endothelial cells of high endothelial venules, fibroblasts in stromal compartments and large mononuclear cells.Its expression suggest that it participates in trafficking of leukocytes,especially lymphocytes to the omentum. 15060082_The ability of TSG-6 to modulate the interaction of hyaluronan with CD44 has important implications for CD44-mediated cell activity at sites of inflammation, where TSG-6 is expressed. 15123640_Data suggest that hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with Rac1-protein kinase N gamma plays a pivotal role in phospholipase C gamma1-regulated calcium signaling and cortactin-cytoskeleton function required for keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion and differentiation. 15239258_CD44 expression in primary lesions is related to higher frequency of extrahepatic metastasis. This may be clinicopathologically useful parameter in predicting occurrence of distant metastasis. 15292257_alpha2beta1 integrin and CD44/CSPG receptor binding on human melanoma cell activation has been evaluated herein using triple-helical peptide ligands incorporating collagen peptides. 15313120_role in tumor induced angiogenesis 15361838_Recombinant CD44-hyaluronic acid binding domain represents a novel class of angiogenesis inhibitors based on a cell-surface receptor. 15509527_CD44 variants have roles in a feedback loop in endothelial cells in human atheroma and abdominal aortic aneurysm 15516973_Osteopontin protein-binding activity was inhibited by the CD44 blocking antibody. 15531362_CD44 expression identifies astrocyte-restricted precursor cells. 15558018_The conserved binding ability of the Hemopexin domains suggests that CD44 may act as a core molecule assembling multiple Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinases on the cell surface. 15578568_modulating role of CD44 in osteoclast formation appears to depend on the microenvironment 15638368_CD44 variant 4 may influence the progression of colorectal cancer. 15638386_CD44v10 takes part in local cancer progression. (CD44v10) 15641486_High CD44 expression is associated with colorectal carcinomas 15645378_statistical relationship found between HPV16 infection and the expression of CD44v6 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 15652352_CD44-mediated hyaluronan binding in myeloid cells is regulated by phosphorylated ERM and the actin cytoskeleton. 15728517_Engagement of CD44 mediates deactivation of human monocytes in the presence of tumor cells, an effect apparently involved in IL-1 receptor associated kinase-M (IRAK-M) up-regulation. 15736104_data obtained with human arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro support a role of CD44 in the smooth muscle cell response to the metabolic and hormonal disorders of diabetes 15783086_We conclude that CD44v6 expression correlates with a higher proliferative activity and with a stem cell-like phenotype in both cell lines and with cellular atypia in HT1197 cells. 15809746_CD44 and membranous E-cadherin expression were correlated with the depth of primary tumour invasion. 15816636_CD44v6 expression is associated with deep stromal invasion in cervical carcinoma 15867228_CD44 expression may be a favorable prognostic factor in patients with node-negative invasive breast carcinoma. 15923644_TNF-alpha-induced CD44 expression was regulated by AP-1 through the activation of the CaMK-II pathway, whereas LPS-induced CD44 transcription was regulated specifically by Egr-1 through JNK activation. 15943035_after the 10-year follow-up, expression of CD44v7-v8 was associated with poor prognosis for breast cancer patients 15962382_measurement of CD44v6 expression in peripheral blood by RT-PCR is not suitable for detection of circulating tumor cells. 15990174_CD44 and CD49d are putative activity markers and CD44 a potential novel therapeutic target in multiple sclerosis. 16002044_Serine 180 is the site for chondroitin sulfate addition in CD44H and that this negatively regulates hyaluronan binding. 16085055_Function of tumor-derived soluble CD44, like the transmembrane form of the receptor, can be regulated. 16166750_Patients who later developed renal allograft rejection had statistically significantly increased soluble CD44 levels, but not soluble ICAM-1, IL-2R or CRP in plasma prior to transplantation. 16177123_CD44 is part of the putative cell surface vitamin D binding protein binding site complex and functions to mediate the chemotactic cofactor effect. 16208414_CD44 ligation by MAb induces activation of both initiator caspase-8 and -9 and effector caspase-3 and -7; but only inhibition of caspase-3/7 and caspase-8 reduces CD44 ligation-induced apoptosis 16219515_human cervical CD44 mRNA expression is induced by interleukin-1beta so hyaluronic acid in the cervical tissue is increased because of the expression of CD44 16229685_The cleavage of the ectodomains of L1 and CD44 is initiated in an endosomal compartment that is subsequently released in the form of exosomes. 16234326_Directional migration of breast cancer cells towards hyaluronan is dependent on CD44 16248506_There was a significant positive correlation between the expression of CD44v6 and MMP-9 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 16311123_results suggest an established Wnt signaling pathway in most gastric cancers, a close correlation of beta-catenin/TCF4-mediated signaling with tumor dissemination, and the unlikelihood of a direct effect of activated Wnt signaling on CD44 expression 16325770_Taken together, engagement of CD44 (e.g., hyaluronan) and glycated albumin induced the differentiation of resting monocytes into foam macrophages through the induction of MSRs. 16352650_variant isoforms of CD44 on LS174T colon carcinoma cells possess selectin binding activity, in contrast to the standard isoform of CD44 on hematopoietic-progenitor cells. 16354706_SRm160, a splicing coactivator, regulates CD44 alternative splicing in a Ras-dependent manner. 16390331_EGF induces ADAM10-mediated CD44 cleavage through Rac1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and thereby promotes tumour cell migration and invasion. 16407205_These results are consistent with the concept that tumor cells generate hyaluronan oligosaccharides that bind to tumor cell CD44 through the expression of their own constitutive hyaluronidases. 16415175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16419149_Data suggest that CD44 expression level is linked to the cell cycle in gastrointestinal tumor cells, which in turn leads to cell cycle dependent alterations of their adhesion behaviour to endothelium. 16478744_CD44 was methylated in the prostatic tumor epithelium from four of the five patients but not in the tumor stroma. 16494036_CD44v6 functions in the carcinogenesis process of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 16504370_results suggest that CD44 splicing variants might play a role in the invasion of trophoblast into maternal tissue in early pregnancy 16530165_There is a cryptic splice site, in intron 6 of the human CD44 gene, used during mRNA processing. 16533775_Increased CD44 antigen is associated with relapses in non-small cell lung cancers 16554035_We conclude that cell matrix factors act cooperatively with cytokines to induce the expression of the components of the NADPH-oxidase in monocytic progenitor cells. 16565089_CD44 interaction with LARG and EGFR plays a pivotal role in Rho/Ras co-activation, PLC epsilon-Ca2+ signaling, and Raf/ERK up-regulation required for CaMKII-mediated cytoskeleton function and in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression 16565092_expression of HCELL confers robust and predominant tumor cell binding to E- and L-selectin 16620830_An IL-6-CD44 feedback loop in macrophages may aggravate atherosclerosis development. 16636662_CD44 ligation triggers a novel caspase-independent cell death pathway via calpain-dependent AIF release in erythroleukemia cells. 16652145_functional experiments, tet-regulated induction of CD44s potentiated the migration and invasion of MCF7F cells through HA-supplemented Matrigel 16702221_CD44-hyaluronan (HA) interaction is involved inand leukocyte adhesion. 16713680_Hyaluronidase and CD44 hyaluronan receptor are expressed in squamous cell laryngeal carcinoma 16809345_Results suggest that hyaluronan suppresses PDGF beta-receptor activation by recruiting a CD44-associated tyrosine phosphatase to the receptor. 16848180_The expressions of CD44 and nm23-H1 in the metastatic lymph node tumor had no difference compared with that in primary tumor of supraglottic or hypopharyngeal cancer. 16868940_Overexpression of CD44v6 is associated with early-onset gastric carcinomas 16969488_up-regulated CD44s expression in metastases is associated with a shorter disease-free survival of colorectal neoplasms 16998483_BCR-ABL-expressing leukemic stem cells depend to a greater extent on CD44 for homing and engraftment than do normal hematopoietic stem cells 16998484_CD44 is a key regulator of acute myeloid leukemic stem cells 17085435_The order-to-disorder transition of the carboxyl-terminal region by hyaluronan binding may be involved in CD44-mediated cell migration. 17092940_N-WASP plays a pivotal role in regulating hyaluronan-mediated CD44-ErbB2 interaction, beta-catenin signaling, and actin cytoskeleton functions that are required for tumor-specific behaviors and ovarian cancer progression 17135256_CD44 variant isoform (CD44v) is a functional P-selectin ligand on colon carcinoma, providing a novel perspective on the enhanced metastatic potential associated with tumor CD44v overexpression and the role of selectins in metastasis. 17136494_interaction between membrane-bound hyaluronan and the cell surface CD44 was involved in the up-regulation of FasL expression on T cells and subsequent activation-induced cell death 17237445_increased CD44, ezrin, radixin, and moesin phosphorylation represents a key molecular abnormality that guides T cell adhesion and migration in SLE patients. 17265493_Chondrocytes with low chondrogenic capacity expressed higher levels of IGF-1, MMP-2, aggrecanase 2, while chondrocytes with high chondrogenic capacity expressed higher levels of CD44, CD151, and CD49c. 17332338_OPN-CD44(V) interaction promotes ECM-derived survival signal mediated through integrin activation, which may play an important role in the pathogenic development and progression of gastric cancer. 17343740_CD44 surface expression is an important event in the activation of MMP-9 and migration of prostate cancer cells. 17383158_study describes disease-specific CD44 variant expressed on synovial fluid cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients 17392272_an effect of CD44 on tumor cell motility may depend in part on its ability to partner with additional proteins, such as cell surface Rhamm. 17464868_Cell adhesion protein CD44 (especially CD44v6 isoform) expression was up-regulated in cervical carcinoma associated with humanpapillomavirus (HPV) infection 17479111_novel mechanism of apoptosis induction in Crohn disease mediated by CD44v7 ligation 17482182_In endometrium, l-selectin is found in greater abundance in interstitial space than in epithelium. 17516109_Loss of CD44 expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors was associated with disease progression. 17540049_CD44+ breast cancer cells are successful in overcoming an engraftment incompatibility that exists when injecting human cells into mouse adipose tissue 17579117_claudin-7-associated EpCAM is recruited into (tetraspanin-enriched membrane microdomains) and forms a complex with CO-029 and CD44v6 that facilitates metastasis formation 17581168_Two novel CD44 antigens of high incidence have been identified: IN3 (INFI) and IN4 (INJA) in the IN (Indian) blood group system. Lack of IN3 and IN4 results from homozygosity for mutations encoding H85Q and T163R in CD44, respectively. 17589956_TNM staging, preoperative CEA and CD44v6 were independent prognostic factors for rectal cancer patients with total mesorectal excision. 17599831_CD44-induced cell migration is dependent on its complex formation with Lyn and its consequent regulation of AKT phosphorylation in colon cancer cells. 17611661_Low expression of CD44s is related to tumour cell invasiveness and may be of clinical relevance as a prognostic factor. 17611662_Data indicate a positive association of CD44 expression with the malignant activities of CNE-2L2 cells and suggest a possible therapeutic effect of direct introduction of siRNA to CD44 into tumors in some solid tumors with high expression of CD44 gene. 17627000_SolCD44 is elevated in the majority of head and neck cancer 17638891_CD44+alpha2beta1+ cell population is enriched in tumor-initiatin prostate cancer cells 17657222_AML1-ETO and its splice variant AML1-ETO9a regulate the expression of the CD44 gene, linking the 8;21 translocation to the regulation of a cell adhesion molecule that is involved in the growth and maintenance of the acute myeloid leukemia blast/stem cells 17679465_CD44 may have an important role in the development of malignancy and in the determination of biological features of keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. 17702746_CD44 is an important regulator of HGF/c-Met-mediated in vitro and in vivo barrier enhancement, a process with essential involvement of Tiam1, Rac1, dynamin 2, and cortactin. 17708612_Fuzheng Yiliu granules enhance the immune adhesion function of RBCs and reduce the number of CD44(+)-cells in esophageal carcinoma patients. 17726647_Signals from the extracellular association CD44-ezrin-actin are an important modulator of Fas-mediated apoptosis. 17846873_our findings provided additional evidence that the pathological stress, such as chronic inflammation, altered the expression of CD44 isoforms in oral epithelia and saliva of oral lichen planus patients 17849363_Pesence of many CD44 isoforms, which cannot be distinguished with commercially used antibodies, but may play a different role in pathogenesis and spread of neuroblastoma. 17911438_CD44 targeting by antibody, passively injected into DBA/1 mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) and NOD mice with type I diabetes or actively generated by CD44 cDNA vaccination of SJL/j mice with autoimmune encephalomyelitis[review] 17914409_gene expression profiling study of contribution of GM-CSF and IL-8 to the CD44-induced differentiation of acute monoblastic leukemia 17919613_The concentration of the soluble form of CD44, a competitive inhibitor for CD44 and hyaluronic acid binding, is higher in the peritoneal fluid of patients with endometriosis than in the peritoneal fluid of patients without endometriosis. 17940137_Multisite v3 splicing enhancer is functional irrespective of flanking intron length and spatial organization within v3. 17945212_Results indicate that siRNA targeting a discrete sequence of human CD44 may provide a potential therapeutic option for colon cancer. 17945213_These findings indicate that the secretion of soluble CD44 contributes to colon cancer growth in vitro, possibly as a decoy receptor. 17975002_CD44v6-positive sorted lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells showed loss of heterozygosity at the TSC2 locus; binding of CD44v6 antibody resulted in loss of cell viability. 17987038_Finding identify OPN and CD44v6 as predictive markers of recurrence or aggressiveness in laryngeal intraepithelial neoplasia, and overall, point out an important signalling complex in the evolution of laryngeal dysplasia. 18005092_Expression defines phenotypic stages in B cell precursor develoment. 18048043_higher levels found in the placentas of pre-eclamptic compared with normotensive women 18077444_cell migration involving CD44-mediated signaling through ERK1/2 is modulated by hyaluronan 18092951_Significance of CD44 expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder and explanaion for results on the relationship between CD44 expression and the biological behaviour of urothelial cells. 18094716_The CD44 gene is silenced in NB4 acute promyelocytic leukemia cells by DNA methylation of a CpG island & underacetylation of histone H3 at the promoter. Brahma protein & phosphorylated RNA Pol II interact with the promoter region of CD44. 18155656_These are the first data to suggest a role for osteocytes and OPN in the recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to aid in fracture repair. 18160820_Various adhesion proteins, including CD44, are involved in the contact of human hematopoietic progenitor cells and human mesenchymal stromal cells. 18162778_staining for TCL1, CD38, and CD44 are useful ancillary tests to identify B-cell tumors 18193058_These findings establish that the HCELL glycoform of CD44 confers tropism to bone and unveil a readily translatable roadmap for programming cellular trafficking by chemical engineering of glycans on a distinct membrane glycoprotein. 18199543_Hyaluronic acid synthase-1 expression regulates bladder cancer growth, invasion, and angiogenesis through CD44. 18214619_We believe that CD44s-mediated adhesion of malignant cells to other cells or to the extracellular matrix is responsible for the invasive features of biliary tract neoplasms, its aggressive progression, and its resistance to treatment. 18227732_study demonstrates decreased expression of CD44s accompanied by increased expression of CD44v6 and increased stromal hyaluronan in breast cancer 18234849_The apparent metastatic potential associated with CD44 overexpression on colon carcinoma cells and the critical roles of P-selectin and fibrin(ogen) in metastatic spread are reported. 18246799_The expression of CD44-v6 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma had a close relation to tumor differentiation and lymph node metastasis. 18265895_Crucial participants in tumour invasion and metastases are matrix metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase inhibitors and cellular adhesion molecules. They play roles in tumour invasion and metastasis in non-small-cell lung carcinomas. 18276068_Here we show that epidermal growth factor (EGF) and heregulin induce CD44 shedding in JIMT-1, an ErbB2-overexpressing cell line resistant to trastuzumab, accompanied by internalization and intramembrane proteolysis of CD44 and enhanced cellular motility. 18279620_E-cad, CD44v6 and PCNA play important roles in invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 18326820_B-CLL cells attached to and bound proMMP-9 and active MMP-9, and this was inhibited by blocking the expression or function of alpha4beta1 or CD44. 18350162_demonstrated, for the first time, that breast cancer cell CD44v4 is a major E-selectin ligand in facilitating tumor cell migration across endothelial monolayers 18372518_diminished or lack of CD44 may be an accompaniment of enhanced metastatic potential 18375392_CEA and CD44v cooperate to mediate colon carcinoma cell adhesion to E- and L-selectin at elevated shear stresses. 18387829_HSP72 was associated with CD44v6 precursor fragments in human colonic carcinoma cells. The interaction between HSP72 and CD44v6 in human colonic carcinoma cells may contribute to study the pathogenesis and immunotherapy of colonic carcinoma. 18396641_No apparent correlation is observed between CD44v6 expression in gastric carcinoma and that of sCD44v6 in the blood. 18414895_Immunohistochemical assessment of both Survivin and CD44v6 status in negative surgical margin may be a valuable approach for predicting recurrence and survival after curative surgery for laryngeal cancer. 18415803_analysis of variant CD44 expression by human fibroblasts 18438684_Clinical significance of the positive correlation of elevated CD44 blood levels and lymph node metastases of breast cancers. 18441325_HA binding to tumor cells promotes Nanog protein association with CD44 followed by Nanog activation and the expression of pluripotent stem cell regulators, and forms a complex with Stat-3 in the nucleus leading to Stat-3 and MDR1 activation 18450428_In vitro reconstructed normal human epidermis expresses differentiation-related proteoglycans (CD44, syndecan-1, desmosealin, and 7C1). 18450824_CD44 has a pivotal role in the trans-endothelial migration of NPCs across brain endothelial cells 18476625_the pathogenesis, development and prognosis of laryngeal carcinoma maybe closely related to the high expression of PD4 and CD44v6, CD44v9 proteins. 18476632_CD44 and nm23-H1 proteins play an important coordinated regulation role in the carcinogenesis, development and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma. 18495204_In breast tissue, CD44(+)/CD24(-/low) tumor cells seem to be associated with lack of lymph node metastasis and a tendency toward an increase of the relapse-free survival of the patients. 18502033_TIMP1 functions as a differentiating and survival factor of GC B cells by modulating CD44 and SHP1 in the late centrocyte/post-GC stage, regardless of EBV infection. 18502153_Report expression of tenascin-c and CD44 receptors in cardiac myxomas. 18513329_High molecular weight hyaluronan-CD44 signaling from the apical surface-membrane regulates orientation of mitotic spindle axis to align the parallel to the basal extracellular matrix. 18516325_E-cadherine and CD44 immunoexpression in oral squamous cell carcinoma as prognosis factors. 18559090_analysis of CD44 and CD24 expression in breast tumors 18577517_Hyaluronic acid promotes CD44-EGFR interaction, which in turn activates PKC signaling, involving Akt, Rac1, Phox, and the production of ROS, FAK, and MMP-2, to enhance melanoma cell motility. 18608209_Bladder cancer stem (initiating) cells might be among EMA(-) CD44v6(+) subset. 18612220_CD44-positive neuroblastomas produced multicellular metastases predominantly located in the intra- and periarterial space of the lung. 18614011_In the absence of p53 function, the resulting derepressed CD44 expression is essential for the growth and tumor-initiating ability of highly tumorigenic mammary epithelial cells. 18632604_CD44 but not CD24 may be involved in the breast cancer pathway and is a target for oncolytic virotherapy 18644869_This study demonstrates an important role of the dynamic raft reorganization induced by CD44 clustering in eliciting the matrix-derived survival signal through the CD44-SRC-integrin beta1 axis . 18651220_Some cases of chronic pancreatitis and autoimmune pancreatitis expressed CD44 in centroaci |
ENSMUSG00000005087 |
Cd44 |
2245.970947 |
2.5517621590 |
1.351494 |
0.069609154 |
367.535923 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064373146662466432153714463635293122156844662908227467791766309072240952699138556489910159722016282428040505417174404155782589840434084413844935936515175718021676420107368436707892489213861141725725630025056744898392935283482074737548828125000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022096456854372196176556876279734029897821863247315183406417610893819616335392211834014927224859721858881528234736564409120177491943410555499856539182221095268140019000444691390978930395413846787854364461800571461935760453343391418457031250000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3252.5239125 |
137.5193500 |
1284.2618027 |
40.5732731 |
| ENSG00000026751 |
57823 |
SLAMF7 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ25 |
FUNCTION: Self-ligand receptor of the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family. SLAM receptors triggered by homo- or heterotypic cell-cell interactions are modulating the activation and differentiation of a wide variety of immune cells and thus are involved in the regulation and interconnection of both innate and adaptive immune response. Activities are controlled by presence or absence of small cytoplasmic adapter proteins, SH2D1A/SAP and/or SH2D1B/EAT-2. Isoform 1 mediates NK cell activation through a SH2D1A-independent extracellular signal-regulated ERK-mediated pathway (PubMed:11698418). Positively regulates NK cell functions by a mechanism dependent on phosphorylated SH2D1B. Downstream signaling implicates PLCG1, PLCG2 and PI3K (PubMed:16339536). In addition to heterotypic NK cells-target cells interactions also homotypic interactions between NK cells may contribute to activation. However, in the absence of SH2D1B, inhibits NK cell function. Acts also inhibitory in T-cells (By similarity). May play a role in lymphocyte adhesion (PubMed:11802771). In LPS-activated monocytes negatively regulates production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (PubMed:23695528). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHK6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11698418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11802771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16339536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23695528, ECO:0000269|Ref.4}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 3 does not mediate any NK cell activation. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in adaptive immune response. Predicted to act upstream of or within regulation of natural killer cell activation. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57823; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101]; natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042267]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
15368295_CS1-L and CS1-S may differentially regulate human NK cell functions 16410313_blocking the engagement of 2B4, NTB-A and CRACC has no effect on the proliferation or development of the cytotoxic potential of NK cells but triggering by their physiological ligands on MHC class I-negative target cells induces potent NK cell cytotoxicity 17878365_CS1 may play a role in the regulation of B lymphocyte proliferation during immune responses 17906076_CS1 was expressed at adhesion-promoting uropod membranes of polarized Multiple Myeloma cells, andis required for MM cell adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells 17981603_2B4, NTB-A and CRACC have roles in the regulation of Natural Killer cell function [review] 18216865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18451245_HuLuc63 eliminates myeloma cells, at least in part, via NK-mediated ADCC and shows the therapeutic potential of targeting CS1 with HuLuc63 for the treatment of multiple myeloma. 19904767_Data show that pair-wise ligations of 2B4 with DNAM-1 and/or NKG2D lead to increased effector functions of primary CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells to suboptimal levels of anti-CD3 stimulation. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20345977_altered expression of splice variants of CS1 and 2B4 that mediate differential signalling in PBMC from patients with SLE. 23250953_These data suggest an involvement of CRACC-mediated NK cell activation in periodontal tissue destruction and point to a plausible distinction in the pathobiology of aggressive and chronic periodontitis. 23695528_SLAMF7 plays an inhibitory role in human monocytes to control proinflammatory immune responses. 23956418_These results suggest a role for CD319 and CD229 in the systemic lupus erythematosus disease process. 24299175_Our data highlight the therapeutic potential of targeting CD319 in rheumatoid arthritis 25312647_SLAMF7-triggered inhibition is mediated by a mechanism involving Src kinases, CD45, and SHIP-1 that is defective in MM cells 26310579_Blimp-1 regulates the transcription of CS1 gene in NK and B cell lines from multiple myeloma and diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. 27116021_Cohort statistics revealed a significant increase of circulating sSLAMF7 in multiple myeloma patients versus normal controls 28076903_Memory CD8+ T cells from SLE patients displayed decreased amounts of SLAMF7, a surface receptor that characterizes effector CD8+ T cells. Ligation of SLAMF7 increased CD8+ T cell degranulation capacity and the percentage of IFNgamma-producing cells in response to antigen challenge in SLE patients and healthy controls. SLAMF7 engagement promoted cytotoxic lysis of target cells in response to stimulation with viral antig... 28424516_phagocytosis of haematopoietic tumour cells during SIRPalpha-CD47 blockade was strictly dependent on SLAM family receptors in vitro and in vivo; in both mouse and human cells, this function required a single SLAM family member, SLAMF7 (also known as CRACC, CS1, CD319), expressed on macrophages and tumour cell targets 29785767_The data show that the great majority of primary patient plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) cases from a variety of subtypes express SLAMF7. From a diagnostic histopathology perspective, SLAMF7 may be a useful addition to a panel of markers for the diagnosis and characterization of PBL 29905534_These data provide emerging evidence that SLAMF7 could be a target of potential therapeutic intervention in carotid atherosclerosis. 30530590_this study shows that SLAMF7 is a critical negative regulator of IFN-alpha-mediated CXCL10 production in chronic HIV infection 30710089_cancer cell expression of SLAMF7 is not required for phagocytosis and, in contrast to CD47 expression, should not be used as selection criterion for CD47-targeted therapy. 30918427_Down-regulation of SLAMF7 and up-regulation of TREM1 occur in primary and metastatic stage IV colorectal cancer tissues. 31115879_immune receptor CD48 is overexpressed on MM cells together with SLAMF7, and that CD48 may be considered as an alternative target for treatment of MM in cases showing weak expression of SLAMF7. 31164030_Strong expression of SLAMF7 in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and large granular lymphocyte leukemia - a prominent biomarker and potential target for anti-SLAMF7 antibody therapy. 31566043_Advanced systemic mastocytosis with strong expression of signaling lymphocyte activation marker family member 7 (SLAMF7) responsive to therapy with elotuzumab and lenalidomide. 32487061_Association of circulating SLAMF7(+)Tfh1 cells with IgG4 levels in patients with IgG4-related disease. 33017079_CD319 (SLAMF7) an alternative marker for detecting plasma cells in the presence of daratumumab or elotuzumab. 33288545_SLAMF7 Signaling Reprograms T Cells toward Exhaustion in the Tumor Microenvironment. 33311473_SLAMF7 and IL-6R define distinct cytotoxic versus helper memory CD8(+) T cells. 33420283_Combinatorial targeting of multiple myeloma by complementing T cell engaging antibody fragments. 34693521_SLAMF7 selectively favors degranulation to promote cytotoxicity in human NK cells. 34732412_SLAMF7 and TREM1 Mediate Immunogenic Cell Death in Colorectal Cancer Cells: Focus on Microsatellite Stability. 35148199_SLAMF7 engagement superactivates macrophages in acute and chronic inflammation. 36199066_SLAMF7 modulates B cells and adaptive immunity to regulate susceptibility to CNS autoimmunity. |
ENSMUSG00000038179 |
Slamf7 |
577.801048 |
3.8675588544 |
1.951423 |
0.093479309 |
433.460520 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000286888458618137795605567926429124769586252555927088135120829102618462844402876682429157153167509752532938029003031488950758220268118698880908715759913681414323971137920662715919668580589789907555916480440369754884845837517087709534619 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000115696001344363769588140811319468726691274509809070329245744069766977475571982399492092207142767138506391785490138504423440045962933003460350562116265532838844975683996410909668425583446794821397153295557371854759033433841389969199895 |
Yes |
No |
913.6370288 |
50.5897960 |
237.9039389 |
10.5582467 |
| ENSG00000028137 |
7133 |
TNFRSF1B |
protein_coding |
P20333 |
FUNCTION: Receptor with high affinity for TNFSF2/TNF-alpha and approximately 5-fold lower affinity for homotrimeric TNFSF1/lymphotoxin-alpha. The TRAF1/TRAF2 complex recruits the apoptotic suppressors BIRC2 and BIRC3 to TNFRSF1B/TNFR2. This receptor mediates most of the metabolic effects of TNF-alpha. Isoform 2 blocks TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis, which suggests that it regulates TNF-alpha function by antagonizing its biological activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12370298}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Pharmaceutical;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This protein and TNF-receptor 1 form a heterocomplex that mediates the recruitment of two anti-apoptotic proteins, c-IAP1 and c-IAP2, which possess E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. The function of IAPs in TNF-receptor signalling is unknown, however, c-IAP1 is thought to potentiate TNF-induced apoptosis by the ubiquitination and degradation of TNF-receptor-associated factor 2, which mediates anti-apoptotic signals. Knockout studies in mice also suggest a role of this protein in protecting neurons from apoptosis by stimulating antioxidative pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7133; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily complex [GO:0002947]; varicosity [GO:0043196]; tumor necrosis factor binding [GO:0043120]; tumor necrosis factor receptor activity [GO:0005031]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; aging [GO:0007568]; aortic valve development [GO:0003176]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; glial cell-neuron signaling [GO:0150098]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010614]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0003332]; negative regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150079]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; positive regulation of apoptotic process involved in morphogenesis [GO:1902339]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of myelination [GO:0031643]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; pulmonary valve development [GO:0003177]; regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002718]; regulation of myelination [GO:0031641]; regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150077]; regulation of RNA biosynthetic process [GO:2001141]; regulation of T cell cytokine production [GO:0002724]; regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042129]; RNA destabilization [GO:0050779]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
11126399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11144293_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11163081_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11169260_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11212177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11285131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11315843_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11357933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11371414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11600223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737221_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11762942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11861282_induced marked apoptosis in T cells from HIV-infected persons; associated with both alteration of Bcl-2 expression and activation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 11882518_insulin resistance and blood pressure are linked to altered shedding of TNF-alpha receptors in type 2 diabetes mellitus 11904678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11904678_Polymorphisms of the TNF gene and the TNF receptor superfamily member 1B gene are associated with susceptibility to ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, respectively. 11907583_mediates ubiquitination and degradation of TRAF2 11961180_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11961180_TNFRII exon 6 SNP does not seem to be associated with susceptibility to juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 11979305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11979305_polymorphism is associated with the incidence of graft-versus-host disease and relapse rate in unrelated bone marrow transplantation (uBMT) 12011375_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12049175_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12122509_a possible marker for the early diagnosis of rejection and for prognosis after renal transplantation 12144133_The high level of TNF alpha expression was noted both for typical and sought TNF R2/R7 isoforms and 3) A considerable number of samples displayed higher levels of TNF R2 isoforms than TNF R2/R7 mRNA expression in differentiated thyroid carcinomas 12161545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12161545_methionine 196 arginine polymorphism in exon 6 of the TNF receptor 2 gene (TNFRSF1B) is associated with the polycystic ovary syndrome and hyperandrogenism. 12209506_A TNFR2 recessive factor, in linkage disequilibrium with the 196R allele, plays a major role in a subset of families with multiple cases of rheumatoid arthritis. 12209507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12217957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12220546_Review. Blockade of the p75TNFR may be helpful in treating systemic autoimmunity since its function may be essential for systemic tissue damage. 12233877_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12233877_in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, preliminary study results showed a trend towards a higher prevalence of the GG genotype for the exon 6 TNFRII polymorphism in the less responsive patients with more aggressive disease 12296856_Thalidomide and its analogues have distinct and opposing effects on TNF-alpha and TNFR2 during co-stimulation of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells, suggesting a possible role for TNF-mediated events during co-stimulation. 12351485_Increased levels of this receptor are found in lean nondiabetic offspring of type 2 diabetic subjects. 12353079_Both adipose tissue and blood PAI-1 levels were positively associated with TNFRSF1A and TNFRSF1B in obesity. 12364441_plasma IL-8 was related to body mass index, percentage of body fat, fat mass and soluble TNF-alpha receptor 2 12370298_TNFR2 binds to Etk but is not involved in Etk activation in human cells 12371624_Review: role in signaling in chronic inflammatory disorders 12500222_Elevated serum levels of soluble TNF-alpha receptor type II are strongly associated with the development of acute renal failure in patients with septic shock. 12530121_serum levels elevated in asthmatic patients during acute attack 12559634_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12601524_No association with narcolepsy in German patients, in contrast with Japanese. 12601524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12610052_Plasma sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 were inversely related to insulin sensitivity and might contribute to the development of insulin resistance in glucose-intolerant subjects. 12610797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12610797_TNFR2ms 18 may have a protective effect on the development of rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwanese, while TNFR2ms 15 tends to have a precipitating effect. 12651071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12661999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12730509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12739039_An ethnic difference in the TNFR2 promoter variable number of tandem repeats has been found that may be associated with clinical phenotypes in systemic lupus erythematosus. 12739039_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12770792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12786601_TNFR2 activates cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) by causing its translocation to plasma membrane and perinuclear subcellular regions and by causing an increase in intracellular calcium that may contribute to the translocation and activation of cPLA2. 12858434_Neither the +36 TNFRSF1A SNP nor the +196 TNFRSF1B SNP is associated with RA severity in a population of Caucasian patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 12858434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12858454_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12880679_levels of sTNFR concentrations were either similar (in sera) or significantly lower (in CM) in the patients with acute HPV infection compared with the controls 12882979_TL1A-induced NF-kappaB activation and c-IAP2 production prevent DR3-mediated apoptosis 12918703_Serum levels and Adamantiades-Behcet's disease activity 12960285_TNF-RII plays a unique role among the T cell costimulatory molecules, as TNF-RII ligation can have positive and negative effects on TCR-dependent signaling. 14506926_Deficient expression of TNF-RII mRNA in the endometrium of women at the earliest stages of endometriosis may play a significant role in the pathophysiology of this disease. 14532286_cells pre-stimulated through TNFR-2 prior to subsequent activation of TNFR-1, showed enhanced cell death and recruitment of RIP to the TNFR-1 complex; TNFR-2 signaling may play a role in controlling viral infection 14565595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14651520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14651520_There is a significant association between exon 10 nt 1668*T-->G tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 gene polymorphism of and susceptibility to MS. 14688526_Association between recipient and donor TNFRII 196R allele status and acute or extensive chronic GVHD incidence, respectively, may reflect reduced circulating sTNFRII. 14688526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14728878_The level of the sTNF-R2 was elevated in myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS) patients. 14872483_Distribution of the TNFR2 196 R/R and TNFR1 +36 A/A genotypes in familial rheumatoid arthritis could suggest an interaction between TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the genetic susceptibility for rheumatoid arthritis. 14872483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15000697_significantly up-regulated in plasma of HIV seropositive patients who used opiates compared to those who did not. 15018649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15022314_Association between the TNFRII 196 M/R gene polymorphism and the functional severity of early rheumatoid arthritis. 15022314_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15041705_Expression of TNF-receptor 2 (TNF-R2) but not TNF-receptor 1 (TNF-R1) was detected in myeloma cell lines. 15071724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15091317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15091317_The TNFRII 196R G allele does not appear to be associated with Alzheimer's disease susceptibility in a Japanese population. 15142217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15146559_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15212671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15212671_TNFR2 polymorphism is not associated with susceptibility to endometriosis. 15252214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15274667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15355698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15457442_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15459750_The TNFR2 expression was increased in human leukaemic TF-1 cells by granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-3 (IL-3), with TNFR1 expression unaffected. 15526005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15555301_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15572357_The mutated form TNFR2(196ARG) shows a reduction of inducible TRAF2 recruitment upon TNF-alpha stimulation 15585313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15603867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15603867_polymorphism and plasma levels in rheumatoid arthritis 15657078_The data confirm the capacity of TNFR2 to generate an apoptotic cell death signal independent of TNFR1. 15674653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15674653_the polymorphism of the TNFRII, might not participate in the pathogenesis of SLE in Vietnamese. 15743036_TNFR2 and TNFR2/R7 are dysregulated and have roles in colorectal cancer 15784704_Infliximab reduces solble levels in Crohn disease. 15787661_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15805680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15842589_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15851552_Genetic variations in these proinflammatory mediators and their receptors appear to influence the susceptibility and severity of the inflammatory response within the eyes of patients during the development of IAU(idiopathic acute anterior uveitis). 15851552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15863392_Genetic variation in TNFRII may predict the late onset of breast carcinoma, relapse and death for patients with breast carcinoma 15863392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15886863_polymorphism of the TNFR2 gene is associated with peak bone density in Chinese nuclear families. 15920055_Increased levels of sTNF-RII were strongly associated with risk of coronary disease among diabetic women, independent of hyperglycemia. 15943902_TNFR2 and TNFR1 signal transduction mechanisms involved in activation of NFkappaB and CMV promoter-enhancer were compared with respect to their susceptibility towards inhibitors of intracellular signaling. 16003175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16003175_There is no association with hypertension of TNFRSF1B polymorphism at a hypertension locus on chromosome 1p36. 16142859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142859_Polymorphism of TNFRSF1B gene are associated with iron deficient anemia in patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. 16195372_TNFR1 and TNFR2 have roles in cell type-specific renal injury 16277675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16282562_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16502120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16502120_TNFR2 polymorphism is not associated with bone mineral density in two independent Caucasian populations 16580225_tumor necrosis factor alpha and TNFR1 and TNFR2 have roles in cellular differentiation 16645020_DS-TNFR2 might play a role as a counterpart of the proinflammatory environment associated with insulin resistance. 16731080_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16732050_Independently associated with brachial-ankle pulse-wave velocity in nonobese Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. 16732051_May have a protective effect in protecting vasodilation in glucose intolerance. 16871413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16871413_There is an association of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 M196R polymorphism with knee osteoarthritis, but not rheumatoid arthritis. 16979382_In summary, the circulating concentration of DS-TNFR2 seems to be inversely linked to metabolic disorders, hinting at a possible anti-inflammatory role. 16980123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17028114_196R allele of the functional M196R polymorphism of TNF-RII is a risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus, especially in the Asian population (Review) 17028114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17207711_A genetic difference in TNFR2 promoter variable number of tandem repeats may play a major role in susceptibility to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis 17207711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17220297_TNFR2 signaling induces selective c-IAP1-dependent ASK1 ubiquitination and terminates mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling 17258924_Positively associated with vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 in type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance 17267158_TNF-RI and -RII promoter gene polymorphisms and variations in protein and gene expression of these receptors are unlikely to play a major role in the development of Alzheimer's disease 17331078_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17346438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17530646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17634906_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17763205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17785864_Transmembrane tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF receptor (TNFR)1/2 are interaction partners contributing to TNF-alpha production in monocytes. 17825894_TNF-RII-supported TCR costimulation is defective in common variable immunodeficiency. 17852784_Transplantation of TNFRSF1B-transfected mesenchymal stem cells improved left ventricular function following myocardial infarction. 17998218_study failed to demonstrate an association of TNFR2 T676G polymorphism with primary Sjogren's syndrome 18038243_Genetic variation in TNFRSF1B plays a role in the determination of bone structure in Caucasian postmenopausal women, possibly through effects on osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. 18038243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18068948_Data show that Type D personality is associated with substantially increased TNFR2 and TNF-alpha activity. 18080762_TNFalphaRII levels were assessed in chronic liver diseases as possible marker to assess severity of disease/response to treatment. 18083240_The increase of plasma TNF-alpha in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients in the presence of a slight increase of sTNFR-1 & -2 supports a functionally significant activation of the TNF system in ALS. 18088549_noticed the largest number of mRNA copies for TNFalpha and TNF R2/R7 in healthy cells at stage III of the disease 18173921_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18206417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18206417_TNF-alpha-308 G/A may be related to susceptibility, whereas -609 TT TNFR1 and 1690 C/T TNFR2 SNPs may be protective to tobacco-related oral squamous cell carcinoma. 18248655_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18248655_These results suggest that tumour necrosis factor receptor genotypes may be involved in the different responses to infliximab in Japanese patients with Crohn's disease. 18309487_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18337349_The circulating levels of sTNF-R2 were approximately 60% higher in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected than in non-infected neonates (1,635 +/- 101 and 1,027 +/- 100 pg/mL, respectively) and remained higher at 1 year of age. 18385279_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18415772_sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 were found at increased plasma concentrations in active Behcet's disease (BD), with the highest concentration in active BD with arthritis. 18417150_Engineered chimeric receptor from TNFRSF1B and Fas protein which could be used to screen for TNFR2-related therapeutic molecules. 18510047_Higher percentage of peritoneal fluid macrophages expressing TNFR1 and TNFR2 proteins in endometriosis suggests dependence of these cells on TNF-alpha stimulation. 18535030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18538149_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18544535_oxidative stress promotes TNFR receptor (TNFR1- and TNFR2) self-interaction and ligand-independent and enhanced ligand-dependent TNF signaling 18565259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18565259_statistically significant association between the TNFRSF1B-M196R single nucleotide polymorphism and response to infliximab in a French cohort 18571427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571427_TNFRII was implicated in Graves disease development in the Tunisian population 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18671942_These results suggest an important role for Smurf2 binding to TRAF2 in determining specific signalling outputs of TNF-R2. 18679053_Serum levels of sTNFR1 and sTNFR2 were increased in schizophrenic patients when compared with controls (all p |
ENSMUSG00000028599 |
Tnfrsf1b |
1861.308281 |
2.0639493206 |
1.045408 |
0.095438814 |
118.115251 |
0.00000000000000000000000000163600275244260880505567314114471515255408055112112761162719957993424914517721635576208427664823830127716064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000019302478518027900486724278650654126124229240136349401303459308630196115431909564819079605513252317905426025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2504.2512624 |
170.0907228 |
1222.1405193 |
60.7788335 |
| ENSG00000028277 |
5452 |
POU2F2 |
protein_coding |
P09086 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that specifically binds to the octamer motif (5'-ATTTGCAT-3') (PubMed:2904654, PubMed:7859290). Regulates IL6 expression in B cells with POU2AF1 (By similarity). Regulates transcription in a number of tissues in addition to activating immunoglobulin gene expression (PubMed:2901913, PubMed:2904654). Modulates transcription transactivation by NR3C1, AR and PGR (PubMed:10480874). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q00196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10480874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2328728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2901913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2904654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7859290}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Activates the U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) promoter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1739980}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a homeobox-containing transcription factor of the POU domain family. The encoded protein binds the octamer sequence 5'-ATTTGCAT-3', a common transcription factor binding site in immunoglobulin gene promoters. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:5452; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
14662861_The function of human Oct-2 in immunoglobulin(Ig)-secreting cells requires plasmacytoma-specific coativator OCA-B working synergistically to sustain the gene expression profile of the Ig-secreting cell. 14707079_DNase I-hypersensitive site 4 (hs4) enhancer activity in mature Burkitt's lymphoma B cells is regulated by synergistic involvement of both Oct-2 and NF-kappa B family members; Oct-2 is required for hs4 enhancer activity. 15796964_Alteration of the OCT2 locus does not correlate with its suppressed expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. 15831936_physical binding to the family of repeats in Epstein-Barr virus oriP by the cellular transcription factors Oct-1 and Oct-2 was demonstrated by using an electrophoretic mobility-shift assay 16186795_Oct-2, therefore, acts as a cell survival factor in t(14;18) lymphoma cells by directly activating the antiapoptotic gene bcl-2. 17442950_The transcription factors Oct-1 and -2 inhibit and enhance, respectively, the expression of exon 1-containing transcripts and CCR5 surface levels. 18695675_Oct-2 and its cofactor Bob-1 have an important function in mediating the IgH enhancer-bcl-2 promoter region interactions 19270158_Oct-2, was studied in detail and found to be a bifunctional regulator: It can either repress or induce neuronal differentiation, depending on the particular isoform 19271143_Data suggest that OCT2 and/or OCT3 might be involved in the initial component of histamine uptake, whereas the later component of histamine uptake is likely to be mediated by another, as yet undefined uptake system(s). 19536068_Renal OCT2 expression is no important in the renal excretion of metformin 19625999_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20141429_OCT-2 may act as a cell survival factor in acute myeloid leukemia by mediating expression of downstream targets, such as BCL-2. 20363215_Gefitinib may exert an inhibitory effect on the intracellular accumulation of drugs transported by hOCT1 and hOCT2. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21424034_Twenty-two cases of nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma were studied for the immunohistochemical expression of Pax-5, Oct-2, BOB.1, Bcl-6 protein and MUM1/IRF-4. 22158496_Half of the cases displayed Oct-2 expression (15/30 cases) of systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma measured by tissue microarray immunohistochemistry. 22346751_B-cell specific transcription factor, Oct-2, inhibits the function of the viral immediate-early protein, BZLF1, and prevents lytic viral reactivation. Oct-2 potentiates establishment of EBV latency in B cells. 24367622_a differential control exerted by both Oct-1 and Oct-2 in the transcriptional regulation of the HMGA1 gene 24435047_Mutations in linker histone genes HIST1H1 B, C, D, and E; OCT2 (POU2F2); IRF8; and ARID1A underlying the pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma. 26019213_POU2F2 regulated ROBO1 transcription, thus functionally contributing to Gastric cancer metastasis. 27009953_findings show that cellular factors OCT2 and HCF1 bind OriP in association with Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 to maintain elevated histone H3K4me3 and transcriptional enhancer function 28750683_Identification of novel prostate cancer drivers, ERF, CREB3L1, and POU2F2, using RegNetDriver, a framework for integration of genetic and epigenetic alterations with tissue-specific regulatory network. 33512466_OBF1 and Oct factors control the germinal center transcriptional program. 33832481_POU2F2 promotes the proliferation and motility of lung cancer cells by activating AGO1. 33931589_POU2F2 regulates glycolytic reprogramming and glioblastoma progression via PDPK1-dependent activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. 33965958_Long Non-Coding RNA ARAP1-AS1 Facilitates the Progression of Cervical Cancer by Regulating miR-149-3p and POU2F2. 35526483_CBX7 represses the POU2F2 to inhibit the PD-L1 expression and regulate the immune response in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000008496 |
Pou2f2 |
2073.920147 |
3.2678193709 |
1.708328 |
0.050098552 |
1152.837558 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000108438898871431493335733179830166233212404268360730879292709511615944558844830 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000128044651787386301515895633296529228803938307959747013892025520987371128711950 |
Yes |
No |
3179.2315787 |
109.9632044 |
979.8719817 |
26.2349826 |
| ENSG00000029534 |
286 |
ANK1 |
protein_coding |
P16157 |
FUNCTION: Attaches integral membrane proteins to cytoskeletal elements; binds to the erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.2, to Na-K ATPase, to the lymphocyte membrane protein GP85, and to the cytoskeletal proteins fodrin, tubulin, vimentin and desmin. Erythrocyte ankyrins also link spectrin (beta chain) to the cytoplasmic domain of the erythrocytes anion exchange protein; they retain most or all of these binding functions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12456646}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform Mu17]: Together with obscurin in skeletal muscle may provide a molecular link between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12527750}. |
3D-structure;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Elliptocytosis;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Hydroxylation;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
Ankyrins are a family of proteins that link the integral membrane proteins to the underlying spectrin-actin cytoskeleton and play key roles in activities such as cell motility, activation, proliferation, contact and the maintenance of specialized membrane domains. Multiple isoforms of ankyrin with different affinities for various target proteins are expressed in a tissue-specific, developmentally regulated manner. Most ankyrins are typically composed of three structural domains: an amino-terminal domain containing multiple ankyrin repeats; a central region with a highly conserved spectrin binding domain; and a carboxy-terminal regulatory domain which is the least conserved and subject to variation. Ankyrin 1, the prototype of this family, was first discovered in the erythrocytes, but since has also been found in brain and muscles. Mutations in erythrocytic ankyrin 1 have been associated in approximately half of all patients with hereditary spherocytosis. Complex patterns of alternative splicing in the regulatory domain, giving rise to different isoforms of ankyrin 1 have been described. Truncated muscle-specific isoforms of ankyrin 1 resulting from usage of an alternate promoter have also been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:286; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; M band [GO:0031430]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; spectrin-associated cytoskeleton [GO:0014731]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; cytoskeletal anchor activity [GO:0008093]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045199]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12130521_ankyrin and protein 4.1 are cleaved by native and recombinant falcipain-2 near their C-termini 12444090_interaction of hydrophilic domain with two N-terminal immunoglobulin domains of titin 12527750_A small muscle-specific isoform of the ANK1 gene, ank1.5, interacts with obscurin. Since ank1.5 is localised on the sarcoplasmic reticulum and obscurin on the myofibrils, these two proteins may provide a molecular link between these subcellular regions. 15040428_identification of ankyrin as a target of spectrin's E2/E3 activity 16718373_The interactions of three protein 4.2-derived recombinant proteins with CDB3 and ankyrin were investigated by using Far-Western blot and pull-down assay. 16762928_off rates of the band 3-ankyrin interaction are sufficiently slow to allow sustained erythrocyte deformation without loss of elasticity 17128827_Allelic and genotypic frequencies were similar in both studied groups for the G199A and Memphis I polymorphismsin Hereditary Spherocytosis among the Mexican population. 17128827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17520478_It was shown that the region within beta-spectrin involved in interactions with ankyrin includes a lipid-binding site and binding is inhibited by ankyrin. Our results shows: the ankyrin-sens. lipid-bind. site of beta-spectrin exhibits a helical conform. 17716929_Our results therefore indicate the importance of N-terminal region for lipid-binding activity of the beta-spectrin ankyrin-binding domain and its substantial role in maintaining the spectrin-based skeleton distribution. 17720975_Structural and mutational studies of the binding region on small Ank1 for obscurin suggest that it consists of two ankyrin repeats with very similar structures. 18768923_Ankyrin facilitates intracellular trafficking of alpha1-Na+-K+-ATPase in polarized cells. 18987618_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20479128_Generated a library of more than 16,000 ANK-1 promoters with degenerate sequence around the dinucleotide deletion mutation and cloned the functional promoter sequences. Identified the wild type and three additional sequences, and derived a consensus. 20858683_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21071415_The Hereditary Spherocytosis mutation in the human Ankyrin-1 promoter disrupted the binding of the transcription factor TFIID, the major component of the pre-initiation complex. 21099109_a region upstream of the promoter is a barrier insulator. The region exhibited functional and structural characteristics of a barrier, including prevention of gene silencing, appropriate chromatin configuration and occupancy by barrier-associated proteins 21177872_cytoskeletal ankyrin family are substrates for FIH-catalyzed hydroxylations 21493712_Determination of structural models of the complex between the cytoplasmic domain of erythrocyte band 3 and ankyrin-R repeats 13-24. 22456796_results indicate that the ANK1 locus is a new, common susceptibility locus for type 2 diabetes across different ethnic groups 22573887_The interaction of KCTD6 with ankyrin-1 may have implications beyond muscle for hereditary spherocytosis, as KCTD6 is also present in erythrocytes, and erythrocyte ankyrin isoforms contain its mapped minimal binding site. 22968456_A tissue-specific chromatin loop brings NF-E2 and ANK1E into close proximity preventing gene silencing and mutagenesis leading to hereditary spherocytosis. 23013433_The ankyrin-binding site on band 3 is located near the deoxygenated hemoglobin-binding site, therefore following deoxygenation ankyrin is displaced from band 3. 23457408_ANK1 rs516946 confers impaired insulin release. 24758720_The study reports the refinement for a protein heterodimer complex using limited EPR spectroscopic data and a rigid-body docking algorithm: a three-dimensional model for an ankyrin 1-BND3 complex. 24903897_A novel L1340P mutation in the ANK1 gene is associated with hereditary spherocytosis. 25129075_Our analyses suggest that these DNA methylation changes may have a role in the onset of Alzheimer disease given that we observed them in presymptomatic subjects and that six of the validated genes connect to a known susceptibility gene network. 25129077_We identified a differentially methylated region in the ankyrin 1 (ANK1) gene that was associated with neuropathology in the entorhinal cortex, a primary site of Alzheimer disease manifestation. 26107955_analysis of a novel p.Q1772X ANK1 mutation in a Korean family with hereditary spherocytosis [case report of two family members] 26611832_rs515071 in ANK1 is a novel genetic risk for late-onset Alzheimer's disease susceptibility in Han Chinese. 26830532_Mutational characteristics of ANK1 and SPTB genes in Korean hereditary spherocytosis have been described. 27054339_Ankyrin-1 is induced to a greater extent than the embedded miRNA following DNA damage. 27121283_ANK1 rs508419-C type 2 diabetes (T2D)-risk allele alters DNA-protein complex binding leading to increased promoter activity and sAnk1 expression; thus, increased sAnk1 expression in skeletal muscle might contribute to T2D susceptibility. 27144336_The present study demonstrates that ANK1 is aberrantly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinomas in association with promoter hypomethylation 27989623_Study shows that Ankyrin-1 forms a high-affinity interaction with AE1 tetramers but does not associate with AE1 dimers in erythrocyte membranes. 28487373_These results suggest that sAnk1 interacts with SLN both directly and in complex with SERCA1 and reduces SLN's inhibitory effect on SERCA1 activity. 28694211_Two novel mutations in ANK1 (Y216X and E142X) are responsible for hereditary spherocytosis. 28700589_ANK1 is up-regulated 4-fold in Alzheimer disease microglia, but not in neurons or astrocytes from the same individuals. 28965852_Aberrant ANK1 methylation is highly prevalent in lung cancer, discriminate tumors by histology and patients' smoking history, and contributes to miR-486-5p repression. 29099659_Our finding suggested that a de novo nonsense mutation in ANK1 may be causative to HS which plays an important role in supplementing the mutational spectrum of the ANK1 and explaining the mechanism of HS. 29149168_Transient Receptor Potential Vanniloid-1 channel (TRPV-1) has a role in the cough reflex and airway expression is increased in patients with chronic cough. The Ankyrin-1 receptor (TRPA-1) is often co-expressed 30439595_ANK1 is characterized by region and disease-specific differential DNA methylation in multiple neurodegenerative diseases. 30836122_The current meta-analysis suggests that ANKK1 Taq1A and DRD2 C957T polymorphisms have limited if any effect on the performance on executive function tasks in healthy adults. 31014431_High-throughput sequencing revealed ANK1 gene mutations in patients 1 to 3, namely c.3398(exon29)delA, c.4306C>T and c.957(exon9)_c.961(exon9)delAATCT, among which c.3398(exon29)delA had not been reported before 31016877_ANK1 loss-of-function mutations are associated with hereditary spherocytosis. 31125575_The conserved aspartic acid residue at the C-terminus of the MEC motif for MESA binding to erythrocyte ANK1. 31598945_The c.247delG mutation in ANK1 caused hereditary spherocytosis type I in this family 31669644_By SDS-PAGE and sequenced the ANK1 gene. 32133777_A clinical and experimental study of adult hereditary spherocytosis in the Chinese population. 33187473_Novel nonsense mutation p. Gln264Ter in the ANK1 confirms causative role for hereditary spherocytosis: a case report. 33410423_Human ankyrins and their contribution to disease biology: An update. 33620149_Clinical manifestation and phenotypic analysis of novel gene mutation in 28 Chinese children with hereditary spherocytosis. 35560067_Acquired spherocytosis due to somatic ANK1 mutations as a manifestation of clonal hematopoiesis in elderly patients. 35631165_The SNP rs516946 Interacted in the Association of MetS with Dietary Iron among Chinese Males but Not Females. 36336297_A novel splicing mutation of ANK1 is associated with phenotypic heterogeneity of hereditary spherocytosis in a Chinese family. |
ENSMUSG00000031543 |
Ank1 |
12.133179 |
0.1025134976 |
-3.286114 |
0.652196779 |
31.730992 |
0.00000001770738390387128066205869479296519664046627440256997942924499511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000075276781803323763511817450985730282297936355462297797203063964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.7352326 |
0.8067702 |
17.2375023 |
3.7574707 |
| ENSG00000030582 |
2896 |
GRN |
protein_coding |
P28799 |
FUNCTION: Secreted protein that acts as a key regulator of lysosomal function and as a growth factor involved in inflammation, wound healing and cell proliferation (PubMed:28541286, PubMed:28073925, PubMed:18378771, PubMed:28453791, PubMed:12526812). Regulates protein trafficking to lysosomes and, also the activity of lysosomal enzymes (PubMed:28453791, PubMed:28541286). Facilitates also the acidification of lysosomes, causing degradation of mature CTSD by CTSB (PubMed:28073925). In addition, functions as wound-related growth factor that acts directly on dermal fibroblasts and endothelial cells to promote division, migration and the formation of capillary-like tubule structures (By similarity). Also promotes epithelial cell proliferation by blocking TNF-mediated neutrophil activation preventing release of oxidants and proteases (PubMed:12526812). Moreover, modulates inflammation in neurons by preserving neurons survival, axonal outgrowth and neuronal integrity (PubMed:18378771). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18378771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28453791, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28541286}.; FUNCTION: [Granulin-4]: Promotes proliferation of the epithelial cell line A431 in culture.; FUNCTION: [Granulin-3]: Inhibits epithelial cell proliferation and induces epithelial cells to secrete IL-8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526812}.; FUNCTION: [Granulin-7]: Stabilizes CTSD through interaction with CTSD leading to maintain its aspartic-type peptidase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28453791}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Granulins are a family of secreted, glycosylated peptides that are cleaved from a single precursor protein with 7.5 repeats of a highly conserved 12-cysteine granulin/epithelin motif. The 88 kDa precursor protein, progranulin, is also called proepithelin and PC cell-derived growth factor. Cleavage of the signal peptide produces mature granulin which can be further cleaved into a variety of active, 6 kDa peptides. These smaller cleavage products are named granulin A, granulin B, granulin C, etc. Epithelins 1 and 2 are synonymous with granulins A and B, respectively. Both the peptides and intact granulin protein regulate cell growth. However, different members of the granulin protein family may act as inhibitors, stimulators, or have dual actions on cell growth. Granulin family members are important in normal development, wound healing, and tumorigenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2896; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; astrocyte activation involved in immune response [GO:0002265]; lysosomal lumen acidification [GO:0007042]; lysosomal transport [GO:0007041]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; microglial cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002282]; negative regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903979]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of neutrophil activation [GO:1902564]; negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response [GO:0060266]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of aspartic-type peptidase activity [GO:1905247]; positive regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048680]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of defense response to bacterium [GO:1900426]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of inflammatory response to wounding [GO:0106016]; positive regulation of lysosome organization [GO:1905673]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of protein folding [GO:1903334]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12031912_downregulated significantly in acute myeloid leukemia patients whose white blood cell count was higher than 100 x 10(9)/L cells 12526812_PEPI has a role in wound healing and innate immunity 12538450_PCDGF has a role as a new autocrine growth factor in epithelial ovarian cancer 12588988_granulin is a cellular protein that interacts with cyclin T1 to inhibit transcription 12914763_PC-cell-derived growth factor has a critical role in breast cancer tumorigenesis. 12931033_identified two proteins that interacted with the Tat protein of the caprine arthritis encephalitis virus: the EGF-like repeats 1-6 of the extracellular domain of the human Notch2 receptor and the epithelin/granulin growth factor precursor 14652816_an important role of PCDGF in breast cancer pathogenesis and a potential novel target for the treatment of breast cancer 14977833_PCDGF has a role in the development of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia 15569995_the Granulin-epithelin precursor has a role in hepatocellular carcinoma growth, invasion, and metastasis 15653695_Data show that the granulin/epithelin precursor and some of its constituent granulin repeats can inhibit HIV-1 transcription via Tat without directly binding to cyclin T1. 16533762_Overexpression of acrogranin is associated with uterine leiomyosarcoma 16857791_PC cell-derived growth factor stimulates proliferation and confers Trastuzumab resistance to Her-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells 16862115_PGRN haploinsufficiency leads to neurodegeneration because of reduced PGRN-mediated neuronal survival; and involvement of PGRN in frontotemporal dementia pathogenesis 16862116_results identify mutations in PGRN as a cause of neurodegenerative disease and indicate the importance of PGRN function for neuronal survival 16950801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16950801_Patients with PGRN mutations revealed variable onset ages with language dysfunction as a common presenting symptom, neuropathological examination showed dementia with ubiquitin-positive inclusions in all PGRN mutation carriers. 16983677_This study discovered a new PGRN mutation (R493X) resulting in a stop codon in two frontotemporal dementia patients. 16983685_familial frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive, tau-negative inclusions caused by a missense mutation in the signal peptide of progranulin.(ALA-9 ASP). 17157414_This study identified a novel 4 bp deletion mutation in exon 7 of PGRN gene (Leu271LeufsX10) associated with a variable clinical presentation ranging from FTDP-17 to corticobasal syndrome. 17202431_Mutations in progranulin (PGRN), predicted to cause premature truncation of the PGRN coding sequence, are found in patients with inherited FTLD with immunoreactive ubiquitin (ub-ir) inclusions (FTDL-U) and ub-ir neuronal intranuclear inclusions. 17210807_primary progressive aphasia has Progranulin mutations. 17228326_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17228326_Two novel frameshift mutations and three possible pathogenic missense mutations are reported. 17261172_PCDGF plays an important role in stimulating proliferation and promoting invasion in ovarian cancer. 17266030_Granulin-epithelin precursor overexpression was associated with CDDP chemoresistance. Finally, GEP overexpression increased tumor formation and protected cells from tumor regression in response to CDDP treatment in vivo 17278999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17291356_Increased PGRN expression by microglia may play a pivotal role in the response to brain injury, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. 17345602_the mutation spectrum in PGRN leading to loss of functional PGRN as the basis for frontotemporal dementia 17353379_Findings from this study suggest that PGRN mutations may be associated with a specific and severe pattern of cerebral atrophy in subjects with ubiquitin-positive inclusions. 17371905_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17371905_PGRN mutations are not a common cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis phenotypes 17383054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17383054_The results revealed that the common variations in IFT74 and GRN neither constitute strong ALS risk factors nor modify the age-at-onset. 17417739_We describe a new mutation in the PGRN gene (A303AfsX57) associated with late-onset frontotemporal dementia and with 'cat's eye' shaped intranuclear and cytoplasmatic ubiquitin immunoreactive inclusions in the neuropathological exam. 17436289_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17436289_Progranulin null mutations in both sporadic and familial frontotemporal dementia. 17439980_A single GRN mutation in the two families studied was associated with variable clinical presentations consistent with the frontotemporal dementia syndrome 17458552_Marked variation of the clinical phenotype makes it difficult to predict which cases of familial frontotemporal dementia will turn out to have a progranulin mutation. 17522386_PGRN mutations at 17q21 may occur in apparently sporadic frontotemporal lobar dementia with ubiquitinated inclusions cases and in cases presenting with either primary progressive aphasia or the behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia. 17572900_Progranulin mutations cause haploinsufficiency leading to TDP-43 accumulation in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 17620546_The current results imply further genetic heterogeneity of frontotemporal dementia, as we detected only one GRN-linked family (about 1%). The value of discovering large kindred includes the possibility of a longitudinal study of GRN mutation carriers. 17698705_Patients with a GRN mutation differ clinically from those with the same pathologic diagnosis but no GRN mutation. 17826340_Clinical heterogeneity is associated with GRN haploinsufficiency, and genetic variability on the wild-type GRN allele might have a role in the age-related disease penetrance of GRN mutations. 17826340_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17949857_Age of onset, clinical phenotypes and MRI findings associated with most PGRN mutations varied significantly both within and among kindreds. Some kindreds with PGRN mutations exhibited lateralized topography of degeneration across all affected individuals. 17950702_Progranulopathies are a major cause of the main phenotypes included in the FTLD complex. 17984093_A progranulin mutation located within the signal sequence (PGRN A9D) results in cytoplasmic missorting with extremely low expression. 18157829_reduced PGRN in absence of mutant protein is sufficient to cause neurodegeneration and that previously reported PGRN mutation frequencies are underestimated. 18166610_MAPT and PGRN are responsible for the largest number of familial cases. Each of these genes differs by disease mechanism. Moreover mutations in both genes are associated with significant interfamilial and intrafamilial phenotypic variation. 18183624_2 pathogenic progranulin gene mutations in 4 frontotemporal dementia families were discovered: a single-base substitution within the 3' splice acceptor site of intron 6/exon 7 (g.5913A>G [IVS6-2A>G]) & a missense mutation in exon 1 (g.4068C>A) 18184915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184915_PGRN acts as a modifier of the course of disease in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, through earlier onset and shorter survival. 18192287_sequencing of PGRN in 223 consecutive patients with FTLD revealed the presence of 13 mutations, or 14 mutations if a single affected sibling of two other affected siblings with proven PGRN mutation is included. 18223198_Findings demonstrate a distinct molecular phenotype for GRN in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitinated inclusions, not readily apparent on clinical or histopathological examination. 18234697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18234697_patients with GRN mutations: have a shorter disease duration (with the exception of FTD-MND); present bvFTLD, language output impairment or with CBS; have parietal lobe dysfunction; and have evidence of asymmetrical brain atrophy on MR imaging. 18245784_the clinical diagnosis at onset was fvFTD in 63% (20/32) of the mutation carriers, PPA in 16% (5/32), Alzheimer's disease in 9% (3/32), CBDS and LBD each in 6% (2/32) of the mutation carriers. 18314228_This study identified two novel heterozygous mutations in two unrelated patients, Cys139Arg in the PGRN gene and Val412Ile in the PSEN1 gene. 18322394_An asymmetric degenerative process is associated with mutations in the progranulin (PGRN) gene and is seen in 3 PGRN cases presenting with either corticobasal syndrome or frontotemporal dementia and language deterioration. 18359860_High-resolution NMR showed that only the three GEMs, hGrnA, hGrnC, and hGrnF, contain relatively well-defined three-dimensional structures in solution, while others are mainly mixtures of poorly structured disulfide isomers. 18378771_Study reports that PGRN levels are reduced in the cerebrospinal fluid from frontotemporal lobe dementia patients with a PGRN mutation; PGRN and its proteolytic fragments promote neuronal survival and enhance neurite outgrowth in cultured neurons. 18392865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18392865_one PGRN pathogenetic mutation was found, consisting of a four-base pair deletion in the coding sequence of exon 8 (delCACT) in frontotemporal lobar degeneration 18413467_Features in patients with FTDP linked to mutations in MAPT and PGRN, highlighting the many similarities but also a few important differences. 18413474_Describe the clinical, neuropsychologic, and radiologic features of a family with a C31LfsX35 mutation in the progranulin gene CCDS11483.1 18442119_This study further expands the clinical and pathological spectrum of PGRN mutations, and suggests the diagnosis could be missed in some individuals with atypical presentations. 18464284_Two mutations were found: a novel pathogenic insertion (p.Gln300GlnfsX61) and a previously described point variant (p.T182M) of unclear pathogenicity in one of patients. 18479928_PGRN mutations exert their pathogenic effect through haploinsufficiency and underlines the diversity of clinical presentations associated with these PGRN alterations. 18543312_Although the complete phenotypic spectrum associated with GRN mutations is not yet fully characterized, it was shown that it is highlyheterogeneous, suggesting the influence of modifying factors. 18551524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18551524_We report the following findings: (1) confirmation of high progranulin expression levels in peripheral blood; (2) two subjects with reduced progranulin levels and mutations in the PGRN gene confirmed by direct sequencing. 18565828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18565828_Our data support a role for PGRN in patients with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer disease (AD). Further, we hypothesize that at least some PGRN missense mutations might lead to loss of functional protein. 18593276_Brain magnetic resonance imaging structural changes in a pedigree of asymptomatic progranulin mutation carriers. 18706200_Results show that PCDGF have higher expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, which indicate that they have a close relationship with angiogenesis. 18723384_There were no mutations in GRN inperry syndrome. 18723524_Genetic variability in a miR-659 binding-site of GNR increased the risk for TDP-43 positive frontotemporal dementia. 18723524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18752597_In a patient with late-onset Alzheimer's disease, a novel allelic variant in exon 1 (g100169G > A) leads to p.Gly35Arg. 18752597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18768919_Data demonstrate that progranulin protein is strongly reduced in plasma and CSF of affected and unaffected subjects carrying mutations in progranulin gene (PGRN Leu271LeufsX10 and Q341X). 18768919_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18771956_Mutations in the gene that encodes progranulin (GRN) on chromosome 17q21-22 have been identified in patients with hereditary FTD who have tau-negative, ubiquitin-positive inclusions. 18838661_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18838661_Our results do not support a major role for PGRN in the genetic etiology of Parkinson disease 18848708_This study found increased staining for PGRN in motor tracts with vacuolar degeneration and glial cells in ALS sample spinal cord and brainstem sections compared to controls. 18855025_Data suggest that the progranulin Gly35fs mutation causes frontotemporal dementia with variable clinical presentation in a large Swedish family, most likely through nonsense-mediated decay of mutant PGRN mRNA and resulting haploinsufficiency. 18955727_Data show progranulin immunoreactivity throughout the medial temporal lobe in all dementia with Lewy bodies. 19012866_findings add further support to the significance of GRN in frontotemporal dementia etiology and the presence of modifying genes 19016491_Genetic variability in the GRN gene may also increase the risk for developing Alzheimer disease in a gender-specific manner. 19016491_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020205_We identified a novel Cys521Tyr progranulin gene variant in a progressive nonfluent aphasia family. Cys521Tyr may be associated with early brain impairment not limited to language areas and compensated by recruitment of bilateral auxiliary cortical areas. 19049508_Mutations in progranulin are rare among Finnish patients with frontotemporal lobar dementia (FTLD) and FTLD-motor neuron disease. Single nucleotide polymorphisms are frequent and suggest high genetic variability of the progranulin gene. 19049508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19056610_Progranulin is a novel marker of chronic inflammation in obesity and type 2 diabetes that closely reflects omental adipose tissue macrophage infiltration. 19091059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19101631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19101631_study estimated the contribution of the PGRN Leu271LeufsX10 mutation to frontotemporal lobar degeneration and related disorders in the Brescia cohort 19133655_This study demenostreated that a new progranulin gene mutation (Arg547Cys) in a Parkinsonism and impulse control disorder. 19158106_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19179604_Proepithelin may play a critical role as an autocrine growth factor in the establishment and initial progression of prostate cancer. 19237611_Proepithelin may prove a novel biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of bladder neoplasms. 19255408_Patterns of atrophy identified on head magnetic resonance imaging show no regions of greater gray matter loss in subjects with mutations in PGRN, compared to gray matter loss in subjects with mutations of microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) gene. 19321167_The expression of PGRN mainly reduces inflammation and its degradation into GRNs enhances inflammation in atherosclerotic plaque and may contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis. 19446372_These data argue that homozygosity of the single nucleotide polymorphism rs5848 on the 3'UTR of progranulin is not a risk factor for frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 19473366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473366_This finding shows that GRN rs5848 does not affect the risk of Parkinson's disease in the US and Polish populations 19487464_Findings demonstrate that ADAMTS-7, a direct target of PTHrP signaling, negatively regulates endochondral bone formation by associating with and inactivating GEP chondrogenic growth factor. 19618231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625741_Grn protein mutation influence mRNA levels in brain and peripheral mononuclear cells in patients with Alzheimer's disease. 19625741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632744_This study suggested that No major progranulin genetic variability contribution to disease etiopathogenesis in an ALS in Italy. 19649643_GRN mutation carriers have increased levels of mRNA transcript from the normal allele in brain, and proliferation of microglia likely increases progranulin levels in affected regions of the frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inclusions brain 19649643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19730170_both PGRN and MAPT genes seem not to be the major genetic cause of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in Northern Italy 19730171_our finding further supports the idea that progranulin mutations might indeed represent a novel, significant genetic determinant of Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration in Northern Italy. 19795409_PGRN has roles in diseases ranging from cancer to dementia [review] 19847305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19847305_variation of GRN at rs5848 does not contribute to the etiology of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in the Dutch population 19858458_Frontotemporoparietal dementia patients carrying the c.709-1G>A single pathogenic splicing mutation in the PGRN gene showed heterogeneous clinical and neuropsychological features and commonly developed corticobasal syndrome as the disease progressed. 19863344_Progranulin activated the MAPK-signaling pathway in NIH-OVCAR-3 cells. Progranulin expression may be potentially involved in the pathogenesis and malignant progression of ovarian cancer 19864668_study describes the presence of a novel 1048_1049insG GRN mutation in family DRC219 in which the proband has a corticobasal syndrome associated with behavioural symptoms 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19938685_Recent studies have identified 44 different mutations in more than 100 families with FTDP-17 (MAPT), and 66 different mutations in more than 100 families with FTDP-17 (PGRN). 19940479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940479_alterations in gene copy number of PGRN and MAPT are not a cause of disease in a collection of frontotemporal lobar degeneration patients 19963041_According to these data, progranulin does not likely play a major role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis 20020531_Sixteen different non-synonymous changes, eleven of which are novel variants, were identified in GRN AND MAPT. 20028451_mutations affect the function of full-length PGRN as well as elastase cleavage of PGRN into GRNs, leading to neurodegeneration 20045477_the effects of GRN and MAPT mutations are expressed in partly overlapping but distinct anatomical networks that link specific molecular dysfunction with clinical phenotype. 20054825_Suggest that intracellular GEP is a promoter-specific transcriptional repressor that modulates the function of cellular and viral transcription factors. 20061636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20061636_The progranulin genotype represents a susceptibility factor for development of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in individuals who do not carry GRN causal mutations. 20087814_Data suggest that there may be an association between schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and granulin mutations in Latino populations that should be investigated further. 20142524_Pathogenic mutations were found only in frontotemporal dementia-spectrum cases and not in other related neurodegenerative diseases. Haploinsufficiency of GRN is the predominant mechanism leading to frontotemporal dementia. 20142525_Alzheimer disease-like phenotype associated with the c.154delA mutation in progranulin. 20154673_TMEM106B variants also contribute to genetic risk for frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 inclusions in individuals with mutations in GRN. 20171924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197700_The results of this study suggested that a genetic variant in GRN may be a risk factor for hippocampal sclerosis in the elderly. 20215705_the anti-inflammatory effects of HDL/APOAI on macrophages might be due to suppression of the conversion of progranulin into proinflammatory granulins by forming a complex. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20387302_evidence for a role of circulating GRN as a biochemical biomarker in neurodegeneration is reviewed, with a specific focus on its relevance in Alzheimer's disease 20463744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463744_Progranulin gene haplotypes influence the risk of developing primary progressive multiple sclerosis in males. 20479936_These findings identify miR-29b as a novel posttranscriptional regulator of PGRN expression, raising the possibility that miR-29b or other miRNAs might be targeted therapeutically to increase hPGRN levels in some frontotemporal dementia patients. 20489155_These findings indicate that miR-107 contributes to granulin expression regulation with implications for brain disorders. 20570546_study reports an Italian family with rapidly progressing frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism associated with the GRN c.C1021T mutation 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20682318_Expression of GEP and ABCB5 in liver cancer stem cells is associated with chemoresistance and reduced survival times of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 20711061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20798611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20858962_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20858962_Prospective serum screening is a surrogate diagnostic marker for progranulin mutations. 20884628_Findings indicate that the mitogen and growth factor GRN is dysregulated via the miR-15/107 gene group in multiple human cancers, which may provide a potential common therapeutic target. 20930269_The novel PGRN mutation is a disease-causing mutation and is associated with substantial intra-familial clinical heterogeneity in frontotemporal dementia. 20930271_the novel frame-shift mutation T278SfsX7 in progranulin of patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration 20933034_PGRN can exert a protective role against hypoxic stress in the brain, a principal risk factor involved in the pathogenesis of frontotemporal dementia. 20947212_frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) patients with homogeneous genetic background well may be used in the search of disease modulators to elucidate genotype-phenotype correlations of progranulopathies(Progranulin Thr272fs mutation). 20975516_we identified a novel exon 6 splice donor site deletion (IVS6+5_8delGTGA) in in the progranulin gene in 2 unrelated patients with Frontotemporal lobar degeneration 21047645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21047645_the T allele of the rs5848 polymorphism is associated with a lower serum PGRN levels in populations beyond FTLD-TDP and may thereby increase the risk of other neurodegenerative conditions. 21085476_Data show that comparing to T2D the IFG subjects had higher serum chemerin, progranulin, fetuin-A and RBP4 levels which was not detectable in the comparison of the T2D and IGT group. 21087763_identified significant association of a locus on chromosome 1p13.3 with plasma GRN levels through an unbiased genome-wide screening approach and implicated SORT1 as an important regulator of GRN levels 21107132_Upregulation of progranulin is a marker of the microglial response that occurs with progression in motor neuron diseases. 21123963_Progranulin expression in the human placenta differs between the first and third trimester. 21178100_TMEM106B SNPs significantly reduced the disease penetrance in patients with GRN mutations, potentially by modulating GRN levels. 21204008_PGRN plays an important role in neurite outgrowth 21212639_The homozygous TT genotype of the progranulin allele rs5848 may play a role in the genetic risk of Alzheimer disease development 21224065_These data demonstrate that progranulin acts as a chemoattractant in the brain to recruit or activate microglia and can increase endocytosis of extracellular peptides such as amyloid beta. 21232819_Here we show that progranulin deficit increased cell cycle activity in immortalized lymphocytes. 21258152_the clinical heterogeneity of frontotemporal dementia associated with the GRN Asp22fs mutation in a large Italian family 21263192_Urinary proepithelin may be considered as a non-invasive, sensitive, and specific urine-based test for bladder cancer diagnosis and/or prognosis. 21289198_Elevation of GRN levels occurs via a translational mechanism independent of lysosomal degradation, autophagy, or endocytosis. 21393509_study reports PGRN bound directly to tumor necrosis factor receptors and disturbed the TNFalpha-TNFR interaction. 21454553_Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (vorinostat) up-regulates progranulin transcription 21482928_Patients with the c.26C>A progranuliln mutation appear to have a younger age at onset of frontotemporal lobar degeneration and at death and more parkinsonian features than those with other progranulin mutations. 21645364_Data suggest that circulating IL-6 is increased in progranulin (PGRN)-mutated frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) patients, as compared to both PGRN non-mutated FTLD patients and controls. 21677378_Our data extend the phenotypic spectrum and the complexity of neurodegenerative diseases linked to GRN mutations 21707777_These findings suggest that the upregulation of PGRN via the p38MAPK and MEK1/2 signaling pathway in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells may contribute to the carcinogenic process. 21753165_Subjects with FTD with GRN mutations have a faster rate of whole brain atrophy than subjects with FTD with MAPT mutations, with similar rates of hippocampal atrophy. 21800185_Occurrence of GRN mutations in Tuscany, Central Italy, confirming that genetic variations in this gene could be a considerable genetic cause of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 21802097_Changes of progranulin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) skin are related to the disease process and metabolic alteration of progranulin may take place in the skin of patients with ALS. 21813674_This study demonistrated that PGRN knockdown severely alters neuronal connectivity in vitro and that the synaptic vesicle phenotype observed in culture is consistent with that observed in the hippocampus of FTD patients 21891865_This study suggested that GRN mutation carriers have normal or borderline CSF biomarkers regardless of the clinical presentation and the speci fi ctype of mutation. 21891869_This study suggested that GRN mutation possible cause of the Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 21892962_Data show that plasma progranulin levels were reduced in a subgroup of patients with autism. 22032330_The miRNA family of ncRNAs showed distinct expression patterns in post-mortem brain tissue of FTLD-TDP patients carrying loss-of function mutations in PGRN compared to FTLD-TDP patients without known mutations. 22045426_Compared with controls, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients have higher serum progranulin concentrations, which are closely associated with lipid values and the extent of hepatic fibrosis 22068162_Progranulin expression is upregulated in cholangiocarcinoma and progranulin exerts growth-promoting effects on cholangiocarcinoma. 22088468_Progranulin proteins were overexpressed in breast cancer. Progranulin may be a valuable marker for assessing the metastasis and prognosis of breast cancer, and could provide the basis for new combination regimens with antiangiogenic activity 22127750_study denomistrated that Genetic screening identified patients bearing PGRN mutaton but still the majority of FTLD cases with an inherited familial trait are negative to genetic analyses. 22130207_these findings suggest that compensatory mechanisms of brain plasticity are present in GRN-related frontotemporal lobar degeneration, but with different patterns at a preclinical and symptomatic disease stage. 22176685_Lysophosphatidic acid activation of PGRN involving the ERK pathway is critical to promote MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell invasion. 22194816_Protein expression of GEP in fetal and adult livers was examined in human and mouse models by immunohistochemical staining and flow cytometry. 22204653_Receiver operating characteristic curves analysis confirmed that serum GRN can provide diagnostic discriminations for gastric cancer patients. 22280948_Current cases show that intrafamilial phenotypic heterogeneity may be encountered with the GRN p.Glu498fs mutation, which leads to progranulin haploinsufficiency. 22316048_The survival factor GP88 is a novel prognostic biomarker, predictive of recurrence risk and increased mortality for non-metastatic estrogen receptor positive invasive ductal carcinoma patients. 22338605_The aim of this review is to highlight what is known regarding PGRN biology--{REVIEW} 22348647_The Mutation of PGRN is involved in patients with Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22366795_Patterns of atrophy therefore differed across subjects with C9ORF72, tau and progranulin mutations and sporadic frontotemporal dementia 22397762_A significantly higher expression level of progranulin in pN(-) TNBC suggests that progranulin is a promising new target for pN(-) TNBC treatment. 22491866_monozygotic twins demonstrated strong clinical, neuroimaging, and serum progranulin level similarities, demonstrating the importance of shared genetic profiles beyond environmental influences in the symptomatic expression of the disease. 22505994_GRN variability decreases the risk to develop BPD and schizophrenia, and progranulin plasma levels are significantly lower in BPD patients than in controls. 22509390_Our results establish microglia as a significant source of progranulin(PGRN), and MMP-12 and SLPI as modulators of PGRN proteolysis 22608501_analysis of different clinicopathological phenotypes determined by progranulin-mutation dosage 22623979_Inactivation of CDK/pRb pathway normalizes survival pattern of lymphoblasts expressing the FTLD-progranulin mutation c.709-1G>A. 22647257_GRN null mutations are detected in Spanish patients with severely reduced serum PGRN levels, but not in patients with slightly reduced PGRN levels. 22665040_PKC signaling is involved in the regulation of progranulin protein expression in 2 different ovarian cancer cell lines. 22761921_Serum PGRN levels were clinically significant for predicting recurrence in patients with HR-positive breast cancer during adjuvant tamoxifen therapy 22787763_Progress in clinical genetics concerning PGRN, one of the putative genes for FTLD, was reviewed and physiological functions and neuro-degeerative mechanism of the gene were discussed. 22792281_TPM3 is an interacting partner of granulin-epithelin precursor and may play an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis. 22797721_The degree of methylation of the GRN promoter is increased in patients with FTLD as compared with controls, likely leading to a decreased expression of GRN. 22802426_PGRN concentrations are markedly lower after pregnancy regardless of the gestational glucose tolerance state. PGRN levels per se do not discriminate between mild gestational diabetes and normal glucose tolerance in pregnant women. 22819134_This study reveled that the unusually high prevalence and the clinical phenotype associated with different GRN mutations. 22859297_Progranulin: a proteolytically processed protein at the crossroads of inflammation and neurodegeneration. 22890097_The A allele of rs5848 is functionally relevant by reducing the expression of granulin in the inferior temporal cortex of neuropathologically confirmed Alzheimer's disease patients. 22890101_Estimation of the progranulin p.Leu271LeufsX10 mutation has been traced back to a single founder in the Middle Ages who had frontotemporal lobe dementia and lived in Italy. 22945272_Increased expression of progranulin protein in villous trophoblast cells in cases of preeclampsia |
ENSMUSG00000034708 |
Grn |
5133.195911 |
0.3904919764 |
-1.356635 |
0.030802863 |
1929.549406 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2926.2496539 |
52.5865265 |
7548.0861624 |
89.8647860 |
| ENSG00000033011 |
56052 |
ALG1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BT22 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the addition of the first of nine mannose moieties to form a dolichol-lipid linked oligosaccharide intermediate required for proper N-linked glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10704531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14973778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26931382}. |
Alternative splicing;Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycosyltransferase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14973778}. |
The enzyme encoded by this gene catalyzes the first mannosylation step in the biosynthesis of lipid-linked oligosaccharides. This gene is mutated in congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ik. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:56052; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; chitobiosyldiphosphodolichol beta-mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0004578]; mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0000030]; dolichol-linked oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0006488]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20679665_DNA sequencing of ALG1 revealed nine different mutations, seven of which have not been previously reported. Clinical presentations of deficiency are severe, with dysmorphias, CNS involvement and ocular disturbances 22966035_Family study defining the phenotype of deficiency of beta-1,4 mannosyltransferase (MT-1) congenital disorder of glycosylation (CDG), due to ALG1 gene mutations. Four novel ALG1 mutations were identified. 24157261_Was detected in the patient's ALG1-coding sequence. 26931382_Study presents molecular, clinical and biochemical findings in the largest collection of ALG1-CDG cases ever reported at a single time with 39 cases, bringing the total number to 57. This ranks it the third most common CDG type behind PMM2-CDG and ALG6-CDG. In addition, highly lethal genotype were identified and confirm the presence of a unique xeno-tetrasaccharide in ALG1-CDG patients. 29309433_evaluated the genetic association of WDR3 and ALG1 in schizophrenia. We examined 21 single nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs; W1 (rs1812607)-W16 (rs6656360), A1 (rs8053916)-A10 (rs9673733)] from these genes using the Japanese case-control sample (1,808 schizophrenics and 2,170 matched controls). No significant genetic associations of these SNPs were identified. However, we detected a significant association of W4 (rs319471) |
ENSMUSG00000039427 |
Alg1 |
128.504418 |
2.2296756603 |
1.156834 |
0.229245618 |
24.933660 |
0.00000059337302139072028336728862121796090889347397023811936378479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002154005360483775250541801926651430676429299637675285339355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
159.0666287 |
23.7600762 |
71.6834375 |
7.9048960 |
| ENSG00000033050 |
10061 |
ABCF2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UG63 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. ATP-binding cassette proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intracellular membranes. Alterations in this gene may be involved in cancer progression. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 3 and 7. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2019]. |
hsa:10061;hsa:114483834; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524] |
16203778_ABCF2 may have a role in progression of clear cell ovarian adenocarcinomas 16996567_Data suggest that ABCF2 protein may be a candidate marker for clear cell adenocarcinomas of the ovary and the uterine corpus and may be important for the pathogenesis of these diseases. 19002184_Among cervical cancer cases, 149 (55.8%) expressed ABCF2. The overall survival was longer in ABCF2-negative than ABCF2-positive cases 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22252987_Overexpression of ABCF2 suppressed RVD. 28112439_The NRF2-overexpressing cell line, containing high levels of ABCF2, was more resistant to cisplatin-induced apoptosis compared to its control ovarian cancer cell line; whereas the NRF2 knockdown cell line with low levels of ABCF2, was more sensitive to cisplatin treatment than its control cell line. 31758671_Circ-TCF4.85 silencing inhibits cancer progression through microRNA-486-5p-targeted inhibition of ABCF2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35412955_Circular RNA Eps15-homology domain-containing protein 2 induce resistance of renal cell carcinoma to sunitinib via microRNA-4731-5p/ABCF2 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000028953 |
Abcf2 |
290.926193 |
2.1065684120 |
1.074895 |
0.152261241 |
49.210478 |
0.00000000000229919278779851002958954898122351982953440185930560346605489030480384826660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000013387015995229195180108815608245327165998217466835740196984261274337768554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
394.0658608 |
44.2573666 |
187.8663411 |
15.6282087 |
| ENSG00000033170 |
2530 |
FUT8 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYC5 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the addition of fucose in alpha 1-6 linkage to the first GlcNAc residue, next to the peptide chains in N-glycans. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17172260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29304374, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9133635}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;SH3-binding;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
This gene encodes an enzyme belonging to the family of fucosyltransferases. The product of this gene catalyzes the transfer of fucose from GDP-fucose to N-linked type complex glycopeptides. This enzyme is distinct from other fucosyltransferases which catalyze alpha1-2, alpha1-3, and alpha1-4 fucose addition. The expression of this gene may contribute to the malignancy of cancer cells and to their invasive and metastatic capabilities. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:2530; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; alpha-(1->6)-fucosyltransferase activity [GO:0046921]; glycoprotein 6-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase activity [GO:0008424]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; GDP-L-fucose metabolic process [GO:0046368]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; L-fucose catabolic process [GO:0042355]; N-glycan fucosylation [GO:0036071]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491]; oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0009312]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; protein N-linked glycosylation via asparagine [GO:0018279]; receptor metabolic process [GO:0043112]; regulation of cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:1900407]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system [GO:0007585]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
14514715_Expression of FUT8 is regulated by three different promoters, starting transcription in exons A, B, or C. 14568171_These results suggest that FUT8 expression may be a key factor in the progression of thyroid papillary carcinomas, but not follicular carcinomas, and decreases in FUT8 expression might be linked to anaplastic transformation. 17488527_We investigated mRNA levels of glycosyltransferases, namely N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase a (GnT)-IVb, and found that (GnT)-IVb expression was increased in HLE-cells resistant to Epirubicin 19179362_Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) expression was significantly suppressed in Fut8(-/-) mice, suggesting that Fut8 was required for VEGFR-2 expression. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21652057_in colorectal carcinoma patients with moderate or strong alpha(1,6)fucosyltransferase expression, a significant decrease in the overall (P = .04) and disease-free (P = .03) survival rates was observed 22011814_The FUT8 gene Thr267Lys polymorphism is associated with human pulmonary emphysema (PE). 23352314_alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase 8 expression might be a good indicator of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. High alpha 1,6-fucosyltransferase 8 expression may play an important role in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression 23609441_findings define FUT8 as a novel factor for hemoglobin production and demonstrate that core fucosylation plays an important role in erythroid differentiation 24130780_miR-122 and miR-34a are able to target FUT8 3'UTR 24232099_Results suggest that FUT4-, FUT6- or FUT8-mediated MDR in human HCC is associated with the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and the expression of MRP1. 24906821_Our results suggest that FUT8 may be associated with aggressive PCa and thus is potentially useful for its prognosis. 25174450_MiR-198 was shown to target the 3'UTR of FUT8 directly to downregulate FUT8 expression. 25572677_High expression of FUT8 is associated with an unfavorable clinical outcome in patients with potentially curatively resected NSCLCs, suggesting that FUT8 can be a prognostic factor. 26596733_Expression of FUT8 can stratify breast cancer tissue and may be considered a prognostic marker for breast cancer patients 27008861_The production of the homogeneous core-fucosylated Man5GlcNAc2 glycoform of EPO in the FUT8-overexpressed HEK293S GnT I(-/-) cell line represents the first example of production of fully core-fucosylated high-mannose glycoforms. 27533464_FUT8 is regulated by microRNAs and has a role in hepatocellular carcinoma progression 27773385_This study demonstrated that the alteration of FTU8 expression in the superior temporal gyrus of elderly patients with schizophrenia. 27967290_We observed a strong correlation between EVI1 and alpha1, 6-fucosyltransferase (FUT8) in the chronic phase of the disease and both of them were found to be up-regulated with the progression of the disease. 28440416_the possibility that the higher fucose levels on cell surface glycans of aggressive anaplastic thyroid cancer samples (ATCs), compared to those of less aggressive papillary thyroid cancer samples(PTC), may be at least in part responsible for the more aggressive and metastatic phenotype of ATCs compared to PTCs, as the expression levels of FUCA1 and FUT8 were inversely related in these two types of cancers. 28609658_FUT8 is a driver of melanoma metastasis which, when silenced, suppresses invasion and tumor dissemination. 28678517_This study thus provides insights into the interplay among FUT8, N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase , and GnT-V in N-linked glycosylation during the assembly of glycoproteins. 28729420_results suggest that an appropriate polypeptide context or other adequate structural elements in the acceptor substrate could facilitate the core fucosylation by FUT8 28982386_Our results reveal a positive feedback mechanism of FUT8-mediated receptor core fucosylation that promotes TGF-b signaling and EMT, thus stimulating breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis. 29304374_loss of function mutations in FUT8 cause a congenital disorder of glycosylation (FUT8-CDG) characterized by defective core fucosylation. 29339807_we also demonstrated that overexpression of FUT8 might be responsible for the decreased PSA expression in prostate cancer specimens. To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the functional role of fucosylated enzyme in the development of castration-resistant prostate cancer. 29975776_expression in relation to p53 is a prognostic biomarker for patients with stage II and III colorectal cancer 30712666_critical role in maintaining the normal functions of trophoblastic cells 31022917_HCV-induced FUT8 promotes proliferation and 5-FU resistance of Huh7.5.1 cells. 31381176_MicroRNA-198-5p inhibits the migration and invasion of non-small lung cancer cells by targeting fucosyltransferase 8. 32049367_Expanding the molecular and clinical phenotypes of FUT8-CDG. 32080177_Report the crystal structure of FUT8 complexed with GDP and a biantennary complex N-glycan (G0), which provides insight into both substrate recognition and catalysis. FUT8 follows an SN2 mechanism and deploys a series of loops and an alpha-helix which all contribute in forming the binding site. 32147455_Involvement of the alpha-helical and Src homology 3 domains in the molecular assembly and enzymatic activity of human alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase, FUT8. 32220931_Structural basis of substrate recognition and catalysis by fucosyltransferase 8. 32350116_The SH3 domain in the fucosyltransferase FUT8 controls FUT8 activity and localization and is essential for core fucosylation. 32378902_Impact of Increased FUT8 Expression on the Extracellular Vesicle Proteome in Prostate Cancer Cells. 32474852_A lectin-based glycomic approach identifies FUT8 as a driver of radioresistance in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32888953_FUT8 Remodeling of EGFR Regulates Epidermal Keratinocyte Proliferation during Psoriasis Development. 33004438_Characterizing human alpha-1,6-fucosyltransferase (FUT8) substrate specificity and structural similarities with related fucosyltransferases. 33323540_Role of FUT8 expression in clinicopathology and patient survival for various malignant tumor types: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 33500381_cFUT8 promotes liver cancer progression by miR-548c/FUT8 axis. 33571582_alpha1,6-Fucosyltransferase contributes to cell migration and proliferation as well as to cancer stemness features in pancreatic carcinoma. 33608773_Up-regulation of FUT8 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells during liver fibrogenesis. 33734311_Appropriate aglycone modification significantly expands the glycan substrate acceptability of alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (FUT8). 33976130_FUT8-mediated aberrant N-glycosylation of B7H3 suppresses the immune response in triple-negative breast cancer. 34021424_LncRNA LEF1-AS1/LEF1/FUT8 Axis Mediates Colorectal Cancer Progression by Regulating alpha1, 6-Fucosylationvia Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. 34036684_Fucosyltransferase 8 regulation and breast cancer suppression by transcription factor activator protein 2gamma. 35237113_Fucosyltransferase 8 is Overexpressed and Influences Clinical Outcomes in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. 36252012_The ulcerative colitis-associated gene FUT8 regulates the quantity and quality of secreted mucins. |
ENSMUSG00000021065 |
Fut8 |
549.054955 |
2.5242880324 |
1.335877 |
0.105870409 |
156.802983 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000565198523233907816508991525897125913111235511731720698387507414338724088070777502111642756404616405596641470765462145209312438964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000085562361055717739448050775076779617982839993783432567473601511430396494038230002796321363358472700255674681102391332387924194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
781.0842646 |
58.7235207 |
312.1327200 |
17.6426148 |
| ENSG00000033178 |
55236 |
UBA6 |
protein_coding |
A0AVT1 |
FUNCTION: Activates ubiquitin by first adenylating its C-terminal glycine residue with ATP, and thereafter linking this residue to the side chain of a cysteine residue in E1, yielding a ubiquitin-E1 thioester and free AMP. Specific for ubiquitin, does not activate ubiquitin-like peptides. Differs from UBE1 in its specificity for substrate E2 charging. Does not charge cell cycle E2s, such as CDC34. Essential for embryonic development. Required for UBD/FAT10 conjugation. Isoform 2 may play a key role in ubiquitin system and may influence spermatogenesis and male fertility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15202508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17597759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17889673}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P22314}. |
Modification of proteins with ubiquitin (UBB; MIM 191339) or ubiquitin-like proteins controls many signaling networks and requires a ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), a ubiquitin conjugating enzyme (E2), and a ubiquitin protein ligase (E3). UBE1L2 is an E1 enzyme that initiates the activation and conjugation of ubiquitin-like proteins (Jin et al., 2007 [PubMed 17597759]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:55236; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; FAT10 activating enzyme activity [GO:0019780]; ubiquitin activating enzyme activity [GO:0004839]; amygdala development [GO:0021764]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; dendritic spine development [GO:0060996]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; learning [GO:0007612]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; protein modification by small protein conjugation [GO:0032446]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
17580310_UBE1L2 is a novel E1 enzyme specific for ubiquitin 17597759_Human Uba6 and Ube1 have distinct preferences for E2 charging in vitro, and their specificity depends in part on their C-terminal ubiquitin-fold domains, which recruit E2s 17889673_The identification of an E1-like protein, termed E1-L2, that activates both ubiquitin and another ubiquitin-like protein, FAT10, is reported. 18353650_Ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 6 activates not only ubiquitin, but also the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10[review] 22427669_Data indicate the potential role of cytokine-induced FAT10 expression in regulating Uba6 pathways. 22999844_Diminished ubiquitylation phenotype observed in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infected cells corresponds to a strong reduction in the abundance of both Ube1 and Uba6. 26284580_Interstitial microdeletions including the chromosome band 4q13.2 and the UBA6 gene as possible causes of intellectual disability and behavior disorder. 27569286_this study revealed a novel function of LMO2 involving in the regulatory hierarchy of UBA6-USE1-FAT10ylation pathway by targeting the E1 enzyme UBA6. 28134249_Polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of ezrin and CUGBP1 require Uba6, but not Uba1, and that Uba6 is involved in the control of ezrin localization and epithelial morphogenesis. These data suggest that distinctive substrate pools exist for Uba1 and Uba6 that reflect non-redundant biological roles for Uba6. 31692446_These findings demonstrate that UBA6 and BIRC6 negatively regulate autophagy by limiting the availability of LC3B. 32315024_Ubiquitination-activating enzymes UBE1 and UBA6 regulate ubiquitination and expression of cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5. 32497710_Down-regulation of UBA6 exacerbates brain injury by inhibiting the activation of Notch signaling pathway to promote cerebral cell apoptosis in rat acute cerebral infarction model. 34320783_UBA6 and NDFIP1 regulate the degradation of ferroportin. 34951345_Long noncoding RNA UBA6-AS1 inhibits the malignancy of ovarian cancer cells via suppressing the decay of UBA6 mRNA. |
ENSMUSG00000035898 |
Uba6 |
459.193573 |
2.2240638842 |
1.153198 |
0.179913255 |
40.185587 |
0.00000000023094583502329340049259424452922232276486091961942292982712388038635253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001163399496567853496700709944454855265805193198502820450812578201293945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
565.4438281 |
71.1067140 |
255.5095000 |
23.4999972 |
| ENSG00000033867 |
9497 |
SLC4A7 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6M7 |
FUNCTION: Electroneutral sodium- and bicarbonate-dependent cotransporter with a Na(+):HCO3(-) 1:1 stoichiometry (PubMed:10347222, PubMed:12403779, PubMed:14736710, PubMed:14578046). Mediates the sodium-dependent bicarbonate transport important for pH recovery after acid load as well as for regulation of steady-state pH in the duodenum and vascular smooth muscle cells (By similarity). Plays a key role in macrophage acidification, mediating bicarbonate import into the cytoplasm which is crucial for net acid extrusion and maintenance of cytoplasmic pH during phagocytosis (PubMed:29779931). Provides cellular bicarbonate for de novo purine and pyrimidine synthesis and is a key mediator of de novo nucleotide synthesis downstream of mTORC1 signaling in proliferating cells (PubMed:35772404). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BTY2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10347222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14578046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14736710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29779931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35772404}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 6]: Plays a key role in macrophage acidification, mediating bicarbonate import into the cytoplasm which is crucial for net acid extrusion and maintenance of cytoplasmic pH during phagocytosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29779931}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This locus encodes a sodium bicarbonate cotransporter. The encoded transmembrane protein appears to transport sodium and bicarbonate ions in a 1:1 ratio, and is thus considered an electroneutral cotransporter. The encoded protein likely plays a critical role in regulation of intracellular pH involved in visual and auditory sensory transmission. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:9497; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; sodium:bicarbonate symporter activity [GO:0008510]; solute:inorganic anion antiporter activity [GO:0005452]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; auditory receptor cell development [GO:0060117]; bicarbonate transport [GO:0015701]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; ion homeostasis [GO:0050801]; phagosome acidification [GO:0090383]; purine nucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0006164]; pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0006221]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
12403779_The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator interacts with and regulates the activity of the bicarbonate salvage trransporter isoform 3 14578046_structural and functional study 14736710_NBC3 and CAII interact to maximize the HCO(3)(-) transport rate. Although PKA decreased NBC3 transport activity, it did so independently of the NBC3/CAII interaction and did not involve phosphorylation of NBC3Ct. 17624982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17624982_Results suggest that SLC4A7 allelic variants might alter dispositions and/or excretion of drugs and neurotransmitters in brain and periphery in ways that could contribute to differential vulnerabilities to addictions. 19330027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20095854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20145138_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20542029_NBCn1 inhibition attenuated cathepsin release and had no net effect on viability of MCF7 cells. 21224233_The present study generated a series of chimeras of human NBCe1-A and human NBCn1-A (SLC4A7). Replacing the fourth extracellular loop (EL4) of human NBCe1-A with EL4 of NBCn1-A creates an electroneutral NBC. 22120673_Data show that DeltaNErbB2 expression elicited Na(+), HCO(3)(-) cotransporter NBCn1 upregulation, Ser(703)-phosphorylation of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1. 22383045_Simultaneous switching of the putative transmembrane segment (TM6) and TM12 of NBCe1 for those from NBCn1 severely impairs the expression of the transporter at the plasma membrane. 22907202_Na(+),HCO(3)(-)-cotransport is a major determinant of pH(i) in breast cancer. 23117855_The SLC4A7 variant rs4973768 is associated with breast cancer risk. 24788003_Upregulation of NBCn1 during human breast carcinogenesis contributes to the characteristic acid distribution within human breast carcinomas. 25241983_We demonstrate, for the first time, that 3 different pHi regulators responsible for acid extruding, i.e. NHE and NBC, and MCT, are functionally co-existed in cultured radial artery smooth muscle cells. 25249183_A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of blood pressure and hypertension in Chinese identified three new loci (CACNA1D, CYP21A2, and MED13L) and a newly discovered variant near SLC4A7. 27609814_this is the first work to demonstrate 3'UTR-mediated NBCn1 regulation, shows that p95HER2 regulates NBCn1 expression at multiple levels, and substantiates the central position of p95HER2-NBCn1 signaling in breast cancer. 27784683_the disease-associated T allele of a new hypertension risk variant rs820430 linked increased hypertension risk through higher SLC4A7 expression, and rs820430 functioned as an enhancer of SLC4A7 transcription by allele distinctively increased c-Fos transcription factor binding. 28087731_The finding of a genotypic influence on SLC4A7 expression and pHi regulation in vascular smooth muscle cells provides an insight into the molecular mechanism underlying the association of variation at the SLC4A7 locus with blood pressure 28087757_rs3278 and rs3755652 stimulate an alternative transcription of the SLC4A7 gene, increasing the production of a defective transporter. 29779931_SLC4A7 and bicarbonate-driven cytoplasmic pH homeostasis as an important element of phagocytosis and the associated microbicidal functions in macrophages. 32620847_Increased Alcohol Consumption in Mice Lacking Sodium Bicarbonate Transporter NBCn1. 35772404_The mTORC1-SLC4A7 axis stimulates bicarbonate import to enhance de novo nucleotide synthesis. |
ENSMUSG00000021733 |
Slc4a7 |
1147.162154 |
4.7164655208 |
2.237706 |
0.064821527 |
1201.461035 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002936132407526243642394052928367685034406531935311696986854865516973 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003581596226040277104393176569191084794224517461608966870446892573098 |
Yes |
No |
1901.4325431 |
66.2219520 |
405.8511015 |
11.9623314 |
| ENSG00000034152 |
5606 |
MAP2K3 |
protein_coding |
P46734 |
FUNCTION: Dual specificity kinase. Is activated by cytokines and environmental stress in vivo. Catalyzes the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in the MAP kinase p38. Part of a signaling cascade that begins with the activation of the adrenergic receptor ADRA1B and leads to the activation of MAPK14. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21224381, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8622669}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the MAP kinase kinase family. This kinase is activated by mitogenic and environmental stress, and participates in the MAP kinase-mediated signaling cascade. It phosphorylates and thus activates MAPK14/p38-MAPK. This kinase can be activated by insulin, and is necessary for the expression of glucose transporter. Expression of RAS oncogene is found to result in the accumulation of the active form of this kinase, which thus leads to the constitutive activation of MAPK14, and confers oncogenic transformation of primary cells. The inhibition of this kinase is involved in the pathogenesis of Yersina pseudotuberculosis. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode distinct isoforms have been reported for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5606; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; MAP kinase kinase activity [GO:0004708]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060048]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to sorbitol [GO:0072709]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; heart development [GO:0007507]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035331]; p38MAPK cascade [GO:0038066]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11971971_Results show that oncogenic ras provokes premature senescence by sequentially activating the MEK-ERK and MKK3/6-p38 pathways in normal, primary cells. 11980910_role in activating Mirk protein kinase 12054652_interacts with phospholipase c-beta 2 12377770_role in pathway that promotes urokinase plasminogen activator mRNA stability in invasive breast cancer cells 12589052_TAK1- and MKK3-mediated activation of p38 are facilitated by Smad7 13679851_MKK3 is selectively activated by the new subfamily of Ste20-like kinases. 15375157_a specific requirement for p150(Glued)/dynein/functional microtubules in activation of MKK3/6 and p38 MAPKs in vivo. 15516490_MAP kinase kinase3- and 6-dependent activation of the alpha-isoform of p38 MAP kinase is required for the cytoskeletal changes induced by neutrophil adherence and influences subsequent neutrophil migration toward endothelial cell junctions 15677464_H-Ras-specific activation of Rac-MKK3/6-p38 pathway has a role in invasion and migration of breast epithelial cells 15778394_MKK3 and MKK6 make individual contributions to p38 activation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes after cytokine stimulation 15797859_p38 mediates EGF receptor activation after oxidant injury; Src activates MMK3, which, in turn, activates p38; and the EGF receptor signaling pathway plays a critical role in renal epithelial cell dedifferentiation 16709574_Bax is phosphorylated by stress-activated JNK and/or p38 kinase and phosphorylation of Bax leads to mitochondrial translocation prior to apoptosis 17406030_Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase 3 (MKK3) is a key activator of p38 MAPK in glioma; MKK3 activation is strongly correlated with p38 activation in vitro and in vivo. 17438131_Cytokine activation of MAPK14 and apoptosis is opposed by ACTN4 targeting of protein phosphatase 2A for site-specific dephosphorylation of MEK3. 19047046_as a mediator of SF- and Src-stimulated NF-kappaB activity. Finally, the Src/Rac1/MKK3/6/p38 and Src/TAK1/NF-kappaB-inducing kinase pathways exhibited cross-talk at the level of MKK3. 19672773_Data provide evidence that p38 Map kinase (MAPK) pathway is activated leading to increased upregulation of mixed lineage kinase 3, MKK3/6, MSK1, and Mapkapk2, upon treatment of BCR/ABL expressing cells with dasatinib. 20805296_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21137025_MAP2K3 is identified as a protein to promote senescence in human breast epithelial cells. 21206905_LFA-1-induced stabilization of ARE-containing mRNAs in T cells is dependent on HuR, and occurs through the Vav-1, Rac1/2, MKK3 and p38MAPK signaling cascade 21368234_The p38 MAPK pathway transgene is dispensable for the development of natural killer (NK)T cells; however, NKT cell cytokine production and NKT-mediated liver damage are highly dependent on activation of this pathway. 22154358_Data suggest aberrant MAP2K protein (MKK3, MKK4, MKK6, and MKK7) expression indicates that altered cellular signal transduction mediated via JNK and p38 may be common in bladder cancer. 22164285_the balance between MKK6 and MKK3 mediates p38 MAPK associated resistance to cisplatin in NSCLC 22696064_miR-20a acts in a feedback loop to repress the expression of MKK3 and to negatively regulate the p38 pathway-mediated VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis 23825110_study concludes MAP2K3 is a reproducible obesity locus that may affect body weight via complex mechanisms involving appetite regulation and hypothalamic inflammation 24112539_MicroRNA-21 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell proliferation through repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase 3. 24480516_Our results suggest that asthma is associated with MKK3 over-expression in CD8+ cells; we have also demonstrated that MKK3 may be critical for airway neutrophilia 24487387_study detected higher MKK3 activation in isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from septic patients compared with nonseptic controls 26149640_miR-21 targets MKK3 in vivo and in vitro, inhibiting the downstream factors IL-6 and TNF-alpha, in ischemia pretreatment protection from ischemia-reperfusion induced kidney injury. 26573508_MKK3 overexpression upregulated the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p16 INK4A and p15 INK4B in hepatocellular carcinoma cells was Bim1, was downregulated following MKK3 overexpression. 27181679_MEK2 was essential for the phosphorylation of MKK3/MKK6 and p38 MAPK that directly impacted on cyclin D1 expression. 27418173_The results revealed upregulation of MEK3, as well as phosphorylated MEK3 and phosphorylated p38 MAPK, in CMM patients. These results provide a 'fingerprint' for mechanistic studies of CMM in the future and highlight the importance of MEK3-p38 MAPK activation in CMM. 27717867_The study identifies MKK3 as a negative regulator of mitochondrial function and inflammatory responses to cigarette smoke and suggests that MKK3 could be a therapeutic target. 28628118_High MKK3 expression is associated with lung cancer. 30305582_Advanced glycation end products significantly activated ASK1, MKK3, and MKK6, which led to activation of p38 MAPK, resulting in upregulated fibrotic response in human coronary smooth muscle cells. 30770795_Expression of human MKK3 in Drosophila is able to initiate JNK-mediated cell migration, cooperates with oncogenic Ras to trigger tumor invasion, and rescue loss-of-lic induced thorax closure defect. 31257538_it was demonstrated that upregulated miR21 expression and downregulated MKK3 expression suppressed cell proliferation and colony formation, promoted apoptosis, delayed the cell cycle, and inhibited cell migration and invasion. The present findings suggested that miR21 could inhibit the cell growth and metastasis of melanoma by negatively regulating MKK3. 31634561_MiR-214 represses the expression of MKK3 via directly binding its 3'UTR in cervical cancer cells.MKK3 role in the malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells. 31695024_MKK3 sustains cell proliferation and survival through p38DELTA MAPK activation in colorectal cancer. 32429593_The MKK-Dependent Phosphorylation of p38alpha Is Augmented by Arginine Methylation on Arg49/Arg149 during Erythroid Differentiation. 32747557_Genome-wide RNA interference screening reveals a COPI-MAP2K3 pathway required for YAP regulation. 32843639_TIPE-mediated up-regulation of MMP-9 promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis through MKK-3/p38/NF-kappaB pro-oncogenic signaling pathway. 33660414_The miR-19b-3p-MAP2K3-STAT3 feedback loop regulates cell proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33774214_Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals Novel Variations in Patients with Familial Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome. 34830095_Quadruple and Truncated MEK3 Mutants Identified from Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Promote Degradation and Enhance Proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000018932 |
Map2k3 |
196.763560 |
2.2466593269 |
1.167781 |
0.145990898 |
63.830300 |
0.00000000000000135611684604418521465436832880593342711169734925852337070750763814430683851242065429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000009641755610603167692749531196958055292333322414122243060319306096062064170837402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
282.8988157 |
23.9635913 |
126.9630596 |
8.2962873 |
| ENSG00000036530 |
10858 |
CYP46A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6A2 |
FUNCTION: P450 monooxygenase that plays a major role in cholesterol homeostasis in the brain. Primarily catalyzes the hydroxylation (with S stereochemistry) at C-24 of cholesterol side chain, triggering cholesterol diffusion out of neurons and its further degradation (PubMed:10377398, PubMed:14640697, PubMed:25017465, PubMed:18621681). By promoting constant cholesterol elimination in neurons, may activate the mevalonate pathway and coordinate the synthesis of new cholesterol and nonsterol isoprenoids involved in synaptic activity and learning (By similarity). Further hydroxylates cholesterol derivatives and hormone steroids on both the ring and side chain of these molecules, converting them into active oxysterols involved in lipid signaling and biosynthesis (PubMed:12077124, PubMed:14640697, PubMed:28190002). Acts as an epoxidase converting cholesta-5,24-dien-3beta-ol/desmosterol into (24S),25-epoxycholesterol, an abundant lipid ligand of nuclear NR1H2 and NR1H3 receptors shown to promote neurogenesis in developing brain (PubMed:25017465). May also catalyze the oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics, such as clotrimazole (PubMed:20667828). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WVK8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10377398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12077124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14640697, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18621681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20667828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25017465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28190002}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cholesterol metabolism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Heme;Iron;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microsome;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism; cholesterol degradation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:14640697}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; C21-steroid hormone metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:14640697}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This endoplasmic reticulum protein is expressed in the brain, where it converts cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol. While cholesterol cannot pass the blood-brain barrier, 24S-hydroxycholesterol can be secreted in the brain into the circulation to be returned to the liver for catabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10858; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; cholesterol 24-hydroxylase activity [GO:0033781]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; steroid hydroxylase activity [GO:0008395]; testosterone 16-beta-hydroxylase activity [GO:0062184]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699]; cholesterol catabolic process [GO:0006707]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; progesterone metabolic process [GO:0042448]; protein localization to membrane raft [GO:1903044]; regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900271]; sterol metabolic process [GO:0016125]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
12123847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12232784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12533085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14640697_In addition to its involvement in cholesterol homeostasis in the brain, CYP46A1 has a broad substrate specificity and is able to metabolize neurosteroids and drugs that can cross the blood-brain barrier and are targeted to the central nervous system. 15034781_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15106838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15106838_Polymorphisms in the CYP46 gene are found not to be risk factors for Alzheimer's disease nor are they associated with parenchymal or vascular accumulation of amyloid-beta protein. 15165699_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15165699_The distribution of CYP46 genotypes was significantly different in AD compared to controls and the CYP46 and ApoE polymorphisms synergically increase the risk for AD development. 15172102_In contrast to two previous reports but in accordance with one other, we were unable to detect an association between an intron 2 polymorphism of CYP46 and Alzheimer disease. 15172102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15286456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15331159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15450677_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15450677_the polymorphism of CYP46 intron 2 is implicated in the susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease and a strong synergistic interaction between CYP46 TT homozoygots 15936520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15936520_The GG genotype of the known rs754203 polymorphic site might be a risk factor for AD, especially in APOE varepsilon4 carriers. Interestingly, in AD patients the rs754203 G allele was more frequent in males than in females. 15975088_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16013913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16055229_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16157450_Based on the results of genome-wide screens, along with biological studies, we selected three genes as candidates for AD risk factors: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H) and cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CH24H). 16157450_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16258842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16734927_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16734927_Polymorphism was associated with the risk of Alzheimer disease(AD) but subjects homozygous for the C alleles were protected from AD with an adjusted odds ratio. 16960449_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335784_here was no significant difference in the genotype or allele frequencies for CYP46 gene between AD patients and controls. 17550732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17854420_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18511756_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18621681_substantial substrate-induced conformational changes in CYP46A1 suggest that structurally distinct compounds could bind in the enzyme active site 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19059217_The expression of CYP46A1, as well as other cytochrome P450s involved in cholesterol homeostasis, are potently regulated by histone acetylation status. 19161969_the substrate, cholesterol, enters CYP46A1 from the membrane 19212968_Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CYP46A1) polymorphisms are associated with faster cognitive deterioration in Chinese older persons 19212968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19286353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19363267_From the logistic regression ananlsis of this stidy showed that the highest risk for was found for Alzheimer's disease individuals who co-inherited APOE epsilon4 allele, PRNP codon 129 homozygosity, PRND codon 174 Thr allele, and CYP46 rs754203 g allele. 19363267_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19553612_The rs754203 SNP in CYP46A1 was associated with a risk for POAG. This polymorphism was not associated with changes in plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol. 19647891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19647891_The data of this study suggested that CYP46 T/C SNP modulates parahippocampal and hippocampal morphology in young subjects. 20193040_These results suggest that a disturbance of cholesterol metabolism may contribute to loss of EAAT2 in AD. 20535486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20667828_Structural basis of drug binding to CYP46A1, an enzyme that controls cholesterol turnover in the brain. 20682755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20693622_Study of two independent Chinese data sets indicates individuals with CYP46A1 promoter bearing the CG haplotype are genetically more susceptible to Alzheimer's disease than those with TA haplotype. 21049985_The average P450 concentrations/mg of total tissue protein were 345 fmol of CYP46A1 and 110 fmol of CYP27A1 in the temporal lobe, and 60 fmol of CYP46A1 and 490 fmol of CYP27A1 in the retina. 21386929_The rs754203 polymorphism itself is unlikely a genetic risk factor for primary open angle glaucoma in Caucasian individuals. 21729100_There was no association between the CYP46 genotype and measures of cognitive event-related potentials. 22185844_Differentiated Ntera2/clone D1 (NT2) cells express the key genes involved in brain cholesterol homeostasis including CYP46A1. 22528464_The intronic polymorphism in CYP46A1 is associated with Alzheimer disease in a Chinese Han population, and the CYP46A1 T allele might be a risk factor. 22977134_The rs754203 C allele in the CYP46A1 gene may confer a higher risk for exudative age-related macular degeneration in patients who carry no risk alleles in the CFH and LOC387715 genes. 23070465_An meta-analysis has successfully proved that CC genotype of the CYP46A1 T/C polymorphism could increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease. 23167762_A meta-analysis indicates that the CYP46 gene SNP rs754203 is not significantly associated with sporadic Alzheimer's disease susceptibility in Chinese Han populations. 23288837_analysis of binding of the cyano- and fluoro-containing drug bicalutamide to cytochrome P450 46A1 23604141_To identify the determinants of tight azole binding to CYP46A1. 23792195_results of meta-analysis suggested that CYP46A1 rs754203 is a minor risk factor for Alzheimer's disease 24924840_While there were no differences in cognitive performance between participants with and those without metabolic syndrome, ApoE and CYP46 genotypes did correlate with mental manipulation scores. 25017465_Human CYP46A1 oxidizes 7-dehydrocholesterol to 24-hydroxy-7-dehydrocholesterol and 25-hydroxy-7-dehydrocholesterol. 25084760_under conditions of membrane cholesterol reduction by increased CYP46A1 expression, neurons increase isoprenoid synthesis and sGTPase prenylation. This leads to a reduction in liver X receptor activity 26358780_hippocampal CYP46A1 protein and 24S-hydroxycholesterol levels were reduced in a mouse model of Alzheimer's Disease-like Tau neuropathology 27026489_CYP46A1 rs4900442 genetic polymorphism was associated with increased risk of Alzheimer disease in the Chinese population, but no evidences were detected in Caucasian population. 27162448_Findings of this study suggest that CYP46A1 gene and PPARgamma2 gene polymorphisms can be a predictive marker for early identification of population at risk of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG). 28206854_Polymorphism within the CYP46A1 gene is a positive risk factor for type 2 diabetes mellitus. 28642370_Data suggest that CYP46A1, the enzyme responsible for the majority of cholesterol elimination from the brain, exhibits activation by neurotransmitters, L-glutamate, L-aspartate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and acetylcholine; L-glutamate-induced CYP46A1 activation may be of physiological relevance. 29516283_the APOEepsilon4 alleles were significantly higher in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and there was a potential synergistic interaction between the CYP46A1 C allele and APOEepsilon4 allele in AD. 31777202_Therapeutic implications of altered cholesterol homeostasis mediated by loss of CYP46A1 in human glioblastoma. 32816363_Identification of CYP46A1 as a new regulator of lipid metabolism through CRISPR-based whole-genome screening. 34546511_Association of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) promoter polymorphism (rs3808607) and cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase (CYP46A1) intron 2 polymorphism (rs754203) with serum lipids, vitamin D levels, and multiple sclerosis risk in the Turkish population. |
ENSMUSG00000021259 |
Cyp46a1 |
12.271856 |
0.1520533273 |
-2.717351 |
0.647882323 |
16.663741 |
0.00004462587448863486022090571458953434103023028001189231872558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000129482584519805487242860575491931740543805062770843505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4118089 |
1.5125663 |
22.3748548 |
6.2377595 |
| ENSG00000037042 |
27175 |
TUBG2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRH3 |
FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. The gamma chain is found at microtubule organizing centers (MTOC) such as the spindle poles or the centrosome. Pericentriolar matrix component that regulates alpha/beta chain minus-end nucleation, centrosome duplication and spindle formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;GTP-binding;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity. Predicted to be a structural constituent of cytoskeleton. Predicted to be involved in microtubule cytoskeleton organization and mitotic sister chromatid segregation. Located in microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:27175; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; gamma-tubulin complex [GO:0000930]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; pericentriolar material [GO:0000242]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle microtubule [GO:0005876]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; meiotic spindle organization [GO:0000212]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; microtubule nucleation [GO:0007020]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; mitotic sister chromatid segregation [GO:0000070]; mitotic spindle organization [GO:0007052] |
20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22235350_gamma-tubulin 2 is able to nucleate microtubules and substitute for gamma-tubulin 1 22806905_Our results reveal for the first time an increased expression of TUBG1 and TUBG2 in lung cancer 27015882_expression of gamma-tubulin2 along with gamma-tubulin1 and a novel TUBG2 splice variant are identified. 28119396_that in the face of predominant gamma-tubulin-1 expression, the accumulation of gamma-tubulin-2 in mature neurons and neuroblastoma cells during oxidative stress may denote a prosurvival role of gamma-tubulin-2 in neurons |
ENSMUSG00000045007 |
Tubg2 |
109.833382 |
0.2788423636 |
-1.842478 |
0.174779673 |
114.796983 |
0.00000000000000000000000000871811321394877807966919410252994045631180586877878877798017716377256425969166642175878223497420549392700195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000099674168116099130356257082132156263867702358635836589937835887278300139868747464788611978292465209960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.4135562 |
5.5732637 |
171.2591496 |
12.5168036 |
| ENSG00000037897 |
4234 |
METTL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBP6 |
FUNCTION: Methyltransferase that mediates the formation of N(7)-methylguanine in a subset of RNA species, such as tRNAs, mRNAs and microRNAs (miRNAs) (PubMed:12403464, PubMed:31031084, PubMed:31031083). Catalyzes the formation of N(7)-methylguanine at position 46 (m7G46) in tRNA (PubMed:12403464, PubMed:31031084). Also acts as a methyltransferase for a subset of internal N(7)-methylguanine in mRNAs (PubMed:31031084). Internal N(7)-methylguanine methylation of mRNAs regulates translation (PubMed:31031084). Also methylates a specific subset of miRNAs, such as let-7 (PubMed:31031083). N(7)-methylguanine methylation of let-7 miRNA promotes let-7 miRNA processing by disrupting an inhibitory secondary structure within the primary miRNA transcript (pri-miRNA) (PubMed:31031083). Acts as a regulator of embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31031083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31031084}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;tRNA processing;tRNA-binding |
PATHWAY: tRNA modification; N(7)-methylguanine-tRNA biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31031084}. |
This gene is similar in sequence to the S. cerevisiae YDL201w gene. The gene product contains a conserved S-adenosylmethionine-binding motif and is inactivated by phosphorylation. Alternative splice variants encoding different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4234; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; tRNA methyltransferase complex [GO:0043527]; tRNA (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008176]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; RNA (guanine-N7)-methylation [GO:0036265]; tRNA methylation [GO:0030488]; tRNA modification [GO:0006400] |
19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20394945_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 25233213_tRNA modifying enzymes, NSUN2 and METTL1, determine sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in HeLa cells 31031083_The results identify METTL1-dependent N7-methylation of guanosine as a new RNA modification pathway that regulates miRNA structure, biogenesis, and cell migration. 31031084_METTL1 acts as a methyltransferase for a subset of internal N(7)-methylguanosine sites in mRNA. 31463732_METTL1 promotes cell proliferation and migration in HCC. METTL1 exerts oncogenic activities via suppression of PTEN signaling. 32430183_METTL1 limits differentiation and functioning of EPCs derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells through a MAPK/ERK pathway. 32698871_METTL1-mediated m(7)G methylation maintains pluripotency in human stem cells and limits mesoderm differentiation and vascular development. 34352206_N(7)-Methylguanosine tRNA modification enhances oncogenic mRNA translation and promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression. 34352207_METTL1-mediated m(7)G modification of Arg-TCT tRNA drives oncogenic transformation. 34371184_METTL1/WDR4-mediated m(7)G tRNA modifications and m(7)G codon usage promote mRNA translation and lung cancer progression. 34898034_METTL1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis via m(7) G tRNA modification-dependent translation control. |
ENSMUSG00000006732 |
Mettl1 |
66.060904 |
2.8272871262 |
1.499418 |
0.330167132 |
20.032812 |
0.00000761246642079183701370698883481580310217395890504121780395507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024220738170055512218127591328453718233504332602024078369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
94.2131171 |
19.4088308 |
33.4687282 |
5.2125909 |
| ENSG00000038382 |
7204 |
TRIO |
protein_coding |
O75962 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RHOA and RAC1 GTPases (PubMed:8643598, PubMed:22155786, PubMed:27418539). Involved in coordinating actin remodeling, which is necessary for cell migration and growth (PubMed:10341202, PubMed:22155786). Plays a key role in the regulation of neurite outgrowth and lamellipodia formation (PubMed:32109419). In developing hippocampal neurons, limits dendrite formation, without affecting the establishment of axon polarity. Once dendrites are formed, involved in the control of synaptic function by regulating the endocytosis of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors (AMPARs) at CA1 excitatory synapses (By similarity). May act as a regulator of adipogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1M0Z1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10341202, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22155786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27418539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32109419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8643598}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Immunoglobulin domain;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;SH3 domain;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a large protein that functions as a GDP to GTP exchange factor. This protein promotes the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, thereby playing a role in cell migration and growth. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:7204; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099170]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase signaling pathway [GO:0007185] |
15199069_present the x-ray structure refined to 1.7-A resolution and effect on signaling pathway by PI 3-kinase 15215162_TRIO amplification is associated with invasive tumor growth and rapid tumor cell proliferation in bladder neoplasms. 15308664_Expression of Tgat in NIH3T3 resulted in the loss of contact inhibition, increase of saturation density, anchorage-independent growth, tumorigenicity in nude mice, and increased invasiveness. 16033331_We have identified neuronal specific isoforms of Trio which could be essential for Trio function in neuronal morphology. 16752383_TRIO represents a candidate target of 5p amplifications in soft tissue sarcomas and might play a crucial role during the progression of this disease. 17391702_Results support a general role for DH-associated PH domains of TRIO in engaging Rho GTPases directly for efficient guanine nucleotide exchange. 17606614_Galphaq directly activates p63RhoGEF and Trio via a conserved extension of the Dbl homology-associated pleckstrin homology domain 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19008376_Data show that Trio, Ect2, and Vav3 are expressed at higher levels in glioblastoma versus low-grade glioma, and are involved in tumor cell migration and invasion. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083228_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22238672_GEF Trio is responsible for lamellipodia formation through its N-terminal DH-PH domain in a Rac1-dependent manner during fibronectin-mediated spreading and migration. 22696684_We conclude that Trio promotes leukocyte transendothelial migration by inducing endothelial docking structure formation in a filamin-dependent manner through the activation of Rac1 and RhoG. 23177739_Trio, is essential for activating Rho- and Rac-regulated signaling pathways acting on JNK and p38. 24859002_Describe here an invadopodia disassembly model, where a signalling axis involving TrioGEF, Rac1, Pak1, and phosphorylation of cortactin, causes invadopodia dissolution. 25065758_TRIO is an EB1 dependent MT plus end tracking protein, and forms a complex with NAV1 at growing MT ends, which regulates TRIO-mediated Rac1 activation and neurite outgrowth. 25065758_The +TIP Navigator 1 (NAV1) is important for neurite outgrowth and interacts and colocalizes with TRIO, a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor that enables neurite outgrowth by activating the Rho GTPases Rac1 and RhoG. 25355950_TRIO controls Rac1 activation in dividing cells which counteracts MgcRacGAP function in cytokinesis. 25851347_Aberrant expression of TRIO might play an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through promoting cell proliferation and invasion, and TRIO may be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of HCC 26116572_our data show the importance of spatio-temporal regulation of the actin cytoskeleton through Trio and Rac1 at VE-cadherin-based cell-cell junctions in the maintenance of the endothelial barrier. 26235986_Strong statistical evidence for a causal role of TRIO in neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. 26721934_TRIO loss of function is associated with mild intellectual disability and affects dendritic branching and synapse function. 27528700_A recurrent rearrangement involving TRIO with various partners was identified in 5.1% of non-translocation-related sarcoma cases. TRIO translocations are either intrachromosomal with TERT or interchromosomal with LINC01504 or ZNF558. All translocations led to a truncated TRIO protein either directly or indirectly by alternative splicing. TRIO rearrangement is associated with a modified transcriptomic program. 27907191_The findings provide a mechanism for the presynaptic targeting of Trio and support a model in which Piccolo and Bassoon play a role in regulating neurotransmission through interactions with proteins, including Trio, that modulate the dynamic assembly of F-actin during cycles of synaptic vesicle exo- and endocytosis. 28224356_study found TRIO somatic frameshift mutations in gastric cancers (GCs) and colorectal cancers (CRCs) with MSI-H, but not in CRCs and GCs with MSS (p |
ENSMUSG00000022263 |
Trio |
90.253512 |
3.1252245230 |
1.643960 |
0.306299689 |
27.753792 |
0.00000013777790700094127671804418184403617786415452428627759218215942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000536004719908775191245919183868906543466437142342329025268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
132.3269966 |
35.5554603 |
43.1481885 |
8.5672461 |
| ENSG00000038427 |
1462 |
VCAN |
protein_coding |
P13611 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in intercellular signaling and in connecting cells with the extracellular matrix. May take part in the regulation of cell motility, growth and differentiation. Binds hyaluronic acid. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cataract;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hyaluronic acid;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Sushi |
|
This gene is a member of the aggrecan/versican proteoglycan family. The protein encoded is a large chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan and is a major component of the extracellular matrix. This protein is involved in cell adhesion, proliferation, proliferation, migration and angiogenesis and plays a central role in tissue morphogenesis and maintenance. Mutations in this gene are the cause of Wagner syndrome type 1. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:1462; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; interphotoreceptor matrix [GO:0033165]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; membrane [GO:0016020]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring compression resistance [GO:0030021]; glycosaminoglycan binding [GO:0005539]; hyaluronic acid binding [GO:0005540]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell recognition [GO:0008037]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; glial cell migration [GO:0008347]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] |
11566024_PDGF stimulates the formation of versican-hyaluronan aggregates and pericellular matrix expansion in arterial smooth muscle cells 11805102_beta 1-Integrin-mediated glioma cell adhesion and free radical-induced apoptosis are regulated by binding to a C-terminal domain of PG-M/versican 11839575_involved in the progression of melanomas and may be a reliable marker for clinical diagnosis 11932252_Cleavage of the carboxyl tail from the G3 domain of aggrecan but not versican and identification of the amino acids involved in the degradation 12221092_independent of the degree of vascularization, human adult tissues show a limited expression of versican isoforms V0, V2, and V3 12438652_CSPG2 contains a bona fide p53 binding site in its first intron and its expression highly correlates with TP53 dosage. Using in vitro and in vivo assays, we showed CSPG2 to be directly transactivated by p53. 12553048_Synthesis and expression of mRNA encoding for different versican splice variants is related to the aggregation of human epithelial mesothelioma cells. 12888576_versican/PG-M binds to hyaluronan 12972299_All melanoma cell lines with an early or intermediate degree of differentiation expressed V0 and V1 versican isoforms, whereas V2 and V3 expression was shown only by undifferentiated cell lines. 14558097_humoral immunity to versican as well as immunity to aggrecan may be of importance in the development of the spinal pathology characteristic of spondylarthropathies. 14724283_the interaction between versican and hyaluronan in many tissues is stabilized by Link protein 15073129_versican and tenascin have roles in preventing relapse of node-negative breast cancer 15142969_Versican is 1 of the main genes upregulated after vascular injury. It is a main component in stented & nonstented restenotic lesions. It influences the assembly of ECM & elastic fiber fibrillogenesis of basic importance in vascular disease ECM remodeling. 15336555_Malignant cells can actively influence the composition of the extracellular matrix through TGFbeta1 and other soluble factors. 15522894_PG-M/versican binds to P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 and has a role in mediating leukocyte aggregation 15590670_Cartilage link protein and versican did not bind directly to each other in solution yet formed ternary complexes with hyaluronan 15599946_negative effect of TGFbeta1 on ADAMTS-1, -5, -9, and -15 coupled with increases in their inhibitor, TIMP-3 may aid the accumulation of versican in the stromal compartment of the prostate in BPH and prostate cancer 15712181_versican is related to higher tumor recurrence rate and more advanced disease 15748997_versican plays an important role in reducing oxidant injury through an enhancement of cell-matrix interaction 15871917_Specific expression of versican in the anagen hair follicles suggests its importance to maintain the normal growing phase of humans. 16043844_Results of RT-PCR analysis indicated that the c.4004-2 A-->G mutation activates a cryptic splice site, located 39 bp downstream from the authentic 3' splice acceptor site. 16110303_This is the first report about the presence of various forms of versican in the anterior segment of the eye and the alterations in the mRNA patterns of these forms when cells are placed in culture 16311904_We suggest that upregulation of versican in the infarcted myocardium may have a role in the inflammatory reaction, which mediates subsequent chemotaxis in the infarcted heart. 16431924_Versican G3 domain promotes blood coagulation through suppressing the activity of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-1 16493581_although the exact interaction between tenascin-C and PG-M/versican remains not entirely clear, these two molecules appear to play significant roles in the 16636652_The splice site mutation described here may lead to a complete lack of exon 8 in CSPG2 transcripts, which shortens the predicted protein by 1754 amino acids and leads to severe reduction of glycosaminoglycan attachment sites. 16648628_the versican G3 domain regulates neuronal attachment, neurite outgrowth, and synaptic function of hippocampal neurons via EGFR-dependent and -independent signaling pathways 16877430_Wagner disease and ERVR (erosive vitreoretinopathy) may belong to a largely overlooked group of diseases that are caused by mRNA isoform balance shifts, representing a novel disease mechanism. 16917090_(Single nucleotide polymorphisms)SNPs in strong linkage disequilibrium and haplotypes constituting these SNPs in versican gene are associated with intracranial aneurysms(IAs). Variation in or near versican gene may play role in susceptibility to IAs. 16917090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065588_Epithelial versican expression was significantly higher in patients with lymph node metastasis of endometrial cancer 17097211_versican in the umbilical cord vein wall is elevated in pre-eclampsia in comparison to the corresponding control vessels 17363913_Loss of the hyaluronan (HA)-binding ability of versican followed by HA exclusion may be responsible for the pathological and phenotypical changes observed in solar elastosis. 17453002_TGF-beta2 triggers the malignant phenotype of high-grade gliomas by induction of migration, and that this effect is, at least in part, mediated by versican V0/V1. 17728259_Using transient transfection assays in prostate cancer LNCaP and HeLa cells engineered to express the AR, study shows that synthetic androgen R1881 and dihydrotestosterone stimulate expression of a versican promoter-driven luciferase reporter vector. 18484070_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18621549_Excess decorin, biglycan, and versican may be associated with the remodeling of other matrix components in myxomatous mitral valves. 18704747_Report deregulation of versican and elastin binding protein in solar elastosis. 18819099_High steady state levels of versican variants V0, V1, and V3 mRNA transcript and gene product are detected in the nodular tissues than in the non-nodular parenchyma of benign prostatic hyperplasia. 19073385_superficial spreading melanoma is associated with a significant overexpression of peritumoral versican suggesting a role for versican in the pathogenesis of melanoma 19160015_versican plays a role in cancer invasion and metastasis [review] 19269971_AP-1 and TCF-4 binding sites are the main regulatory regions directing versican production provide new insights into versican promoter regulation during melanoma progression. 19506372_Examine association between versican SNPs and intracranial aneurysms in Japanese cohort. 19506372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19655167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19655167_The intestinal-type gastric cancer susceptibility is associated with two amino acid changes of versican in the GAG-beta domain, which is critical for enhancement of cell proliferation and activation of EGFR signal pathway by versican 19662655_All known isoforms were significantly overexpressed in breast cancer lesions, both at the mRNA and at the protein levels. A new alternatively spliced versican isoform, referred to as V4, was found and cloned. It was also upregulated in breast cancer. 19669783_The versican was only expressed in the developing intervertebral disc interspace. 19700613_Aberrant production of excessive and disorganized extracellular matrix in uterine leiomyoma involves the activation of the TGF-beta3 signaling pathway and excessive production of GAG-rich versican variants. 19717812_versican has an important role in the hyaluronan-dependent binding of monocytes to the ECM of lung fibroblasts stimulated with polyinosine-polycytidylic acid 19901218_Mutation screening of CSPG2 in autosomal dominant vitreoretinopathy families is important for accurate diagnosis. 20053631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20053631_in contrast to IA, HSPG2 and CSPG2 do not associate with AAA. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20204274_Syndecan-1 and versican expression status can serve as an indicator of prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20489207_miR-143 specifically binds to the 3'-untranslated region of versican mRNA. 20619446_Stromal VCAN expression was associated with poorer overall and progression-free survival, platinum resistance, and increased MVDin ovarian neoplasms. 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20729814_versican expression in the stromal compartment of cervical cancers results in reduced numbers of intraepithelial CD8-positive T cells and enhanced local invasion. 21078678_V3 isoform of versican interferes with CD44 and the CD44-EGFR/ErbB2 interaction, altering the signaling pathways, such as ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK, that regulate cell proliferation and migration 21136024_both versican and CD44 play an important role regulating the behavior of malignant melanoma cells 21185131_Suggest that versican expression in in situ breast lesions may define different subtypes of intraductal carcinomas. 21185747_Versican demonstrated distinctive localization relative to nodules within calcified aortic valves. 21244575_High versican is associated with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 21505857_the G1 and G3 domains of versican were upregulated and LTBP-4 was downregulated in breast cancer stroma 21546273_Versican is a key component of the provisional wound repair ECM that is expressed following injury to valvular interstitial cells. 21596823_Versican appears to be a central component of the outflow resistance, where it may organize GAGs and other ECM components to facilitate and control open flow channels in the trabecular meshwork. 21738396_A new VCAN/versican splice acceptor site mutation in a French Wagner family associated with vascular and inflammatory ocular features. 21791066_Data show that elevated levels of versican were correlated with higher tumor grade and invasiveness in carcinomas with MD and MAMCs, whereas increased amounts of decorin were associated with in situ carcinomas in MAMCs. 21828051_a physiological function of ADAMTS5 in dermal fibroblasts is to maintain optimal versican content and PCM volume by continually trimming versican in hyaluronan-versican aggregates. 22096483_Versican G3 domain enhanced tumor cell resistance to apoptosis when cultured in serum free medium, Doxorubicin, or Epirubicin by up-regulating pERK and GSK-3beta (S9P). 22155153_Hyaluronan and versican play a role in T-cell trafficking and function in inflamed tissues. 22318369_Tissue microarray analysis revealed that epithelial expression of versican had significant relations to lymph node metastasis and pathological stages of breast cancer 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22393310_The major isoforms expressed by gastric carcinoma & gastric cell lines were V0 & V1. V1 was higher in gastric carcinoma. Abnormally expressed versican & its isoforms participate in the progress of gastric carcinoma triggered by IL-11. 22406535_RhoGDI2 suppresses lung metastasis in mouse models by reducing the expression of isoforms V1 and V3 of the proteoglycan versican, which is require for lung metastasis. High versican levels portended poor prognosis in patients with bladder cancer. 22493503_E(2) treatment increases the amount of dermal HA and versican V2 via paracrine release of EGF, which may be implicated in the pro-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects of E(2) during photoaging. 22711178_Lack of versican expression is associated with recurrence in colon cancer. 22739342_altered balance of VCAN splice variants in combination with reduction in glycosaminoglycan protein modifications as pathogenic mechanisms in Wagner syndrome 22951719_Mesenchymal cells derived from keloid lesion (KL) cells exhibit above-normal versican production. 23002209_Studies indicate that E-cadherin and versican are involved in cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and metastasis. 23024773_renal versican expression was significantly upregulated as compared to corresponding controls. These data show for the first time an association of renal versican isoform V0 and V1 expression with progressive renal disease. 23099107_Wnt/beta-catenin signal transducting system regulates dermal papilla cell aggregative growth through modifying versican expression by means of acting on the versican gene upstream promoter. 23180826_these results demonstrate that versican V0 and V1 isoforms play important roles in HCC development and that versican mRNAs compete with endogenous RNAs in regulating miRNA functions. 23201264_the glioblastoma cell line U87 stably transfected with versican isoform V2 formed tumors containing extensive vasculature 23424670_versican V1 enhances hCAP18/LL-37 expression in macrophages through activation of TLR2 and subsequent vitamin D-dependent mechanisms which promote ovarian tumor progression in vitro 23568740_No association has been found between polymorphisms of rs251124 and rs3767137 loci of CSPG2 and HSPG2 genes and intracranial aneurysm in the selected population. 23571384_Letter/Case Report: disease causing versican mutation in Wagner syndrome. 23845159_Circulating monocytes may contribute to the fibrotic process in a subset of systemic sclerosis patients by amplifying a positive feedback loop consisting of versican, CCL2, and the influx of monocytes 23963449_Cleaved versican G1 domain-containing fragments (VG1F) can be recaptured by microfibrils through VG1F homotypical interactions to enhance hyaluronan recruitment to microfibrils. 24005989_FoxQ1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by transactivating ZEB2 and VersicanV1 expression. 24174867_A novel c.4004-6T>A nucleotide substitution at the acceptor splice site of intron 7 of the VCAN gene that segregated with the Wagner disease phenotype, was identified. 24180670_CD26 expression on T-anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) line Karpas 299 is associated with increased expression of versican and MT1-MMP and enhanced adhesion. 24240681_Arylsulfatase B regulates versican expression by galectin-3 and AP-1 mediated transcriptional effects. 24927163_Study demonstrated that versican, TGFbeta1, Col7A1 and ITGbeta3 are up-regulated in isolated Cancer stem cells. 24999371_these data suggest that versican regulates the development of peritoneal metastasis originating from cells and spheroids. 25064688_Versican isoform V1 is associated with high-grade gliomas. 25122765_The ADAMTS5 ancillary domain and specific chondroitin sulfate chains of versican are required for proteolysis. 25275064_Versican expression in tumor epithelial cells predicts a good prognosis for gastric cancer patients. 25320080_Versican regulates the growth of leiomyosarcoma tumors. 25562163_Our results suggest that TGF-beta1 up-regulates versican expression by suppressing miR-143, and this pathway is important for osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion. 25623955_Significant elevation of VCAN and its associated molecules imply their role in multiple myeloma 25915825_Versican upregulation in Sezary cells alters growth, motility and resistance to chemotherapy. 26057378_versican mRNA is up-regulated much more highly (>600 fold) by long term hypoxia (5 days) than by 1 day of hypoxia. 26176948_Versican V1 overexpression induces a myofibroblast-like phenotype in cultured fibroblasts. 26395512_Versican localizes to the nucleus in proliferating mesenchymal cells and suggest role in mitotic spindle organization during cell division. 26723257_Results highlight an important role for versican in regulating the expression and assembly of elastin and the phenotype of leiomyosarcoma cells. 26752747_Versican is a novel modulator of hepatic fibrosis. 26873137_VCAN and VEGF were associated with survival in CRC patients with PM after CRS and HIPEC 27126822_the G1 domain of versican can regulate the organization of pericellular hyaluronan and affect phenotype of cultured human dermal fibroblasts 27259980_human myeloma tumors displaying CD8(+) infiltration/aggregates underwent VCAN proteolysis at a site predicted to generate a glycosaminoglycan-bereft N-terminal fragment. 27599582_Gene expression levels of three randomly selected DEGs, VCAN, COL5A1 and KCNJ16, were examined using RT-PCR in 10 ATC samples.. angiogenesis was activated by the high expression of CTHRC1, VCAN and POSTN, providing necessary nutrition for tumor cells 27697422_versican decreases in follicular dermal papilla as an aging-associated change of human hair follicles 27908842_Data indicate that serum versican levels were significantly decreased in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients, and that serum ADAMTS-1 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif-1) and versican levels were significantly and positively correlated with each other. 28035060_Interleukin-17A promotes tongue squamous cell carcinoma metastasis by activating miR-23b/versican pathway in the tumor microenvironment. 28138236_Removal or knockdown of versican may be a possible therapeutic strategy for increasing deposition of insoluble elastin and stimulating repair of elastic fibers in COPD lung. 28242813_This study highlights the oncogenic role of VCAN in renal cell carcinogenesis and suggests that this gene has therapeutic and/or biomarker potential for renal cell cancer. 28320945_VCAN expression in colorectal cancer and its role in cetuximab resistance 28323982_Versican V0 and V1 isoforms were upregulated in the uterine leiomyomas of symptomatic versus asymptomatic women. Abundant cleaved versican was detected in leiomyoma and myometrium, as well as in myometrial and leiomyoma cell lines. VCAN siRNA did not effect cell proliferation, apoptosis, or smooth muscle markers, but reduced ESR1 and PR-A expression. 28481899_Lumican and versican protein expression are associated with colorectal adenoma-to-carcinoma progression 28869452_miR-135a-5p can suppress cell progress including cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in thyroid carcinoma by targeting VCAN 3 '-UTR. 29071374_The macular dysfunction on mfERG was profound and of early onset. A heterozygous mutation in intron 7 of the VCAN gene (c.4004-1G > A) was found. 29515038_Study of complete proteoglycanomes in the ascending aortas of normal and thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection (TAAD) patients and in a mouse model of severe Marfan syndrome identified that massive aggrecan and versican accumulation in ascending TAAD occurs via increased synthesis and/or reduced proteolytic turnover predisposing to type-A dissections. 29748371_Low FOXA2/high VCAN levels mediate the tumor-promoting effects of miR-590-3p. 29861382_Plasma Versican correlated with poor response to induction of chemotherapy in AML cases. 29955124_Depletion of VCAN dampens the cell migration activity induced by Snail or PAPSS2 in MCF 10A cells. 30265729_Examined the production and distribution of versican and hyaluronan in intact vein rings cultured ex vivo, veins perfused ex vivo, and cultured venous adventitial and smooth muscle cells. Immunohistochemistry revealed higher levels of versican in the intima/media compared to the adventitia, and no differences in hyaluronan. In the vasa vasorum, versican and hyaluronan associated with CD34+ progenitor cells. 30657523_The intronic VCAN mutation removes an MMP cleavage site, which alters versican structure and results in abnormal vitreous modeling. Disruption of a versican protein network may underlie clinicopathologic disease features and point to targeted therapies. 30944246_Level of versican V1 was increased in tubular cells of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) patients. Urine C3a and suPAR were increased and bound to the tubular cells in FSGS patients. C3a and suPAR drive versican V1 expression in tubular cells by promoting transcription and splicing, respectively, and the increases in tubular cell-derived versican V1 induce interstitial fibrosis by activating fibroblasts in FSGS. 31605014_VersicanV1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the activation of EGFR-PI3K-AKT pathway. 31771905_The expression of versican and its role in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 31939331_High expression of VCAN is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in gastric cancer. 32001344_The synthesis and secretion of versican isoform V3 by mammalian cells: A role for N-linked glycosylation. 32265939_Versican-A Critical Extracellular Matrix Regulator of Immunity and Inflammation. 32610121_Adipocyte-Derived Versican and Macrophage-Derived Biglycan Control Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. 32623942_Versican and Versican-matrikines in Cancer Progression, Inflammation, and Immunity. 32623950_Clinical and genetic study on two Chinese families with Wagner vitreoretinopathy. 32798403_[Expression of Versican and Its Related Molecules in Patient with Multiple Myeloma and Its Clinical Significance]. 32845502_Versican in the Tumor Microenvironment. 32854301_Identification of Novel Copy Number Variations of VCAN Gene in Three Chinese Families with Wagner Disease. 32970631_Serum amyloid A-containing HDL binds adipocyte-derived versican and macrophage-derived biglycan, reducing its antiinflammatory properties. 33131383_Versican: A Dynamic Regulator of the Extracellular Matrix. 33187989_Loss of versican and production of hyaluronan in lung epithelial cells are associated with airway inflammation during RSV infection. 33631054_Bioinformatics analysis of the prognosis and biological significance of VCAN in gastric cancer. 33649986_Proteoglycan Remodeling Is Accelerated in Females with Angina Pectoris and Diffuse Myocardial Fibrosis: the iPOWER Study. 34130530_INHBA promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells through the upregulation of VCAN. 34162438_Regulatory VCAN polymorphism is associated with shoulder pain and disability in breast cancer survivors. 34293593_miR-543 impairs cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in breast cancer by suppressing VCAN. 34358918_Overexpressed versican promoted cell multiplication, migration and invasion in gastric cancer. 34450332_Identification of novel ADAMTS1, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 cleavage sites in versican using a label-free quantitative proteomics approach. 35403677_Activin A promotes hyaluronan production and upregulates versican expression in human granulosa cellsdagger. 35697329_Versican secreted by the ovary links ovulation and migration in fallopian tube derived serous cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000021614 |
Vcan |
424.613174 |
0.3004216896 |
-1.734939 |
0.143411661 |
141.782483 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000001085032781983117331325386621950217029655414762778861057203552212277732996262600809634236292966491532752115745097398757934570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000151514511467084309536997209056105889022868534855582272422727447634010191673462872351610397636534344201209023594856262207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
187.9906215 |
21.2503059 |
630.3976961 |
50.4272551 |
| ENSG00000039319 |
9765 |
ZFYVE16 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z3T8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in regulating membrane trafficking in the endosomal pathway. Overexpression induces endosome aggregation. Required to target TOM1 to endosomes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11546807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14613930}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes an endosomal protein that belongs to the FYVE zinc finger family of proteins. The encoded protein is thought to regulate membrane trafficking in the endosome. This protein functions as a scaffold protein in the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway and is involved in positive and negative feedback regulation of the bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:9765; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; 1-phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0005545]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; protein targeting to lysosome [GO:0006622]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050] |
14613930_marked recruitment of TOM1 to endosomes was observed in cells overexpressing endofin or its carboxyl-terminal fragment 16775010_The key mode of action of Trx-SARA was to reduce the level of Smad2 and Smad3 in complex with Smad4 after TGF-beta1 stimulation. 17272273_Facilitates TGF-beta signaling as a scaffold protein to promote the R-Smad-Smad4 complex formation by bringing Smad4 to the proximity of the receptor complex. 17570516_our study is the first to identify and validate Endofin, DCBLD2, and KIAA0582 as part of a complex EGF phosphotyrosine signaling network 19887107_Disruption of proper localization to the endosomes and the Y515 phosphorylation of Endofin enhanced MAPK activation suggesting that Endofin negatively modulates EGFR signaling following receptor endocytosis. 26944198_Two SNPs located near the ZFYVE16 gene on chromosome 5 may have played a role in the early, multicompartment sacrocolpopexy failure. |
|
|
428.540087 |
2.0203689789 |
1.014619 |
0.322742133 |
9.697652 |
0.00184503658550166102850220717357387911761179566383361816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004103788427065177199515311201594158774241805076599121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
573.0897146 |
115.5013737 |
285.8442777 |
41.8387611 |
| ENSG00000040933 |
3631 |
INPP4A |
protein_coding |
Q96PE3 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of the 4-position phosphate of phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4)P2) (PubMed:20463662, PubMed:15716355). Catalyzes also inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate and inositol 1,4-bisphosphate (By similarity). Antagonizes the PI3K-AKT/PKB signaling pathway by dephosphorylating phosphoinositides and thereby modulating cell cycle progression and cell survival (PubMed:30071275) (By similarity). May protect neurons from excitotoxic cell death by regulating the synaptic localization of cell surface N-methyl-D-aspartate-type glutamate receptors (NMDARs) and NMDAR-mediated excitatory postsynaptic current (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62784, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EPW0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15716355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20463662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30071275}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Displays no 4-phosphatase activity for PtdIns(3,4)P2, Ins(3,4)P2, or Ins(1,3,4)P3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9295334}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse |
PATHWAY: Signal transduction; phosphatidylinositol signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15716355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20463662}. |
This gene encodes an Mg++ independent enzyme that hydrolyzes the 4-position phosphate from the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate, inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate, and inositol 3,4-bisphosphate. Multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:3631; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; inositol-1,3,4-trisphosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0017161]; inositol-3,4-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0052828]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0016316]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0034597]; inositol phosphate metabolic process [GO:0043647]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15716355_in quiescent cells, the 4-phosphatase colocalized with early and recycling endosomes 18187694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18187694_The +110832A/G (Thr/Ala) variant of INPP4A was significantly associated with asthma in an Indian population. 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463662_INPP4A represents the first signalling protein with a function in neurons to suppress excitotoxic cell death 25338135_Data adds a new etiology to the spectrum of hindbrain malformations in human, and when presented with myoclonic epilepsy may lead to the clinical suspicion of INPP4A defect. 26463840_INPP4A could possibly serve as a candidate gene for alterations associated with asbestos exposure. 27733216_Our findings indicate that upregulation of miR-935 may promote pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration and inhibit cell apoptosis by targeting INPP4A. 30335467_INPP4A is secreted by airway epithelial cells and extracellular INPP4A critically inhibits airway inflammation and remodeling. 31524145_Low INPP4A expression is associated with cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in colorectal cancer. 31978615_Whole exome sequencing identified a novel nonsense INPP4A mutation in a family with intellectual disability. 33109548_miR-935 Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Targets Inositol Polyphosphate-4-phosphatase Type IA (INPP4A). |
ENSMUSG00000026113 |
Inpp4a |
638.861024 |
0.1704700712 |
-2.552410 |
0.837797663 |
7.716583 |
0.00547158637064006775352353884045442100614309310913085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011091967426266639493159793516952049685642123222351074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
200.4304985 |
99.3420884 |
1196.4310102 |
422.7282326 |
| ENSG00000041880 |
10039 |
PARP3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6F1 |
FUNCTION: Mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates mono-ADP-ribosylation of target proteins and plays a key role in the response to DNA damage (PubMed:16924674, PubMed:20064938, PubMed:21211721, PubMed:21270334, PubMed:25043379, PubMed:24598253, PubMed:28447610, PubMed:19354255, PubMed:23742272). Mediates mono-ADP-ribosylation of glutamate, aspartate or lysine residues on target proteins (PubMed:20064938, PubMed:25043379). In contrast to PARP1 and PARP2, it is not able to mediate poly-ADP-ribosylation (PubMed:25043379). Involved in DNA repair by mediating mono-ADP-ribosylation of a limited number of acceptor proteins involved in chromatin architecture and in DNA metabolism, such as histone H2B, XRCC5 and XRCC6 (PubMed:16924674, PubMed:24598253). ADP-ribosylation follows DNA damage and appears as an obligatory step in a detection/signaling pathway leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks (PubMed:16924674, PubMed:21211721, PubMed:21270334). Involved in single-strand break repair by catalyzing mono-ADP-ribosylation of histone H2B on 'Glu-2' (H2BE2ADPr) of nucleosomes containing nicked DNA (PubMed:27530147). Cooperates with the XRCC5-XRCC6 (Ku80-Ku70) heterodimer to limit end-resection thereby promoting accurate NHEJ (PubMed:24598253). Suppresses G-quadruplex (G4) structures in response to DNA damage (PubMed:28447610). Associates with a number of DNA repair factors and is involved in the response to exogenous and endogenous DNA strand breaks (PubMed:16924674, PubMed:21211721, PubMed:21270334). Together with APLF, promotes the retention of the LIG4-XRCC4 complex on chromatin and accelerate DNA ligation during non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) (PubMed:21211721). May link the DNA damage surveillance network to the mitotic fidelity checkpoint (PubMed:16924674). Acts as a negative regulator of immunoglobulin class switch recombination, probably by controlling the level of AICDA /AID on the chromatin (By similarity). In addition to proteins, also able to ADP-ribosylate DNA: mediates DNA mono-ADP-ribosylation of DNA strand break termini via covalent addition of a single ADP-ribose moiety to a 5'- or 3'-terminal phosphate residues in DNA containing multiple strand breaks (PubMed:29361132, PubMed:29520010). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3ULW8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16924674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19354255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20064938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21211721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21270334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23742272, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24598253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25043379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27530147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28447610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29361132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29520010}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA damage;DNA repair;Glycosyltransferase;NAD;Nucleotidyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the PARP family. These enzymes modify nuclear proteins by poly-ADP-ribosylation, which is required for DNA repair, regulation of apoptosis, and maintenance of genomic stability. This gene encodes the poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase 3, which is preferentially localized to the daughter centriole throughout the cell cycle. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10039; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; NAD DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0140294]; NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0003950]; NAD+- protein-aspartate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0140806]; NAD+- protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0140804]; NAD+-protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:1990404]; NAD+-protein-glutamate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0140807]; nucleotidyltransferase activity [GO:0016779]; DNA ADP-ribosylation [GO:0030592]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; negative regulation of isotype switching [GO:0045829]; negative regulation of telomerase RNA reverse transcriptase activity [GO:1905662]; positive regulation of DNA ligation [GO:0051106]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:2001034]; protein auto-ADP-ribosylation [GO:0070213]; protein localization to site of double-strand break [GO:1990166]; protein poly-ADP-ribosylation [GO:0070212]; regulation of mitotic spindle organization [GO:0060236]; telomere maintenance [GO:0000723] |
16924674_PARP-3 is a nuclear protein involved in transcriptional silencing and in the cellular response to DNA damage 17203305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20064938_the interaction between PARP-1 and PARP-3 is unrelated to DNA single-strand break repair 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21211721_PARP-3 has a role in chromosomal DNA double-strand break repair. 21264220_PARP3 gene occupancy in the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-SH occurs preferentially with developmental genes regulating cell fate specification, tissue patterning, craniofacial development and neurogenesis. 21270334_PARP3 is a critical player in the stabilization of the mitotic spindle and in telomere integrity by associating and regulating the mitotic components NuMA and tankyrase 1. 24528514_In some cancer cells, repression of PARP3 could be responsible for an increased telomerase activity. 24598253_PARP3 likely facilitates the recruitment of Ku80 to double strand breaks to antagonize DNA end resection but facilitate Ku-mediated accurate classical non-homologous end-joining. 25255219_MiR-630 reduced apoptosis by downregulating several apoptotic modulators, PARP3, DDIT4, and EP300. 25800440_Identification of ADP-ribosylation sites in PARP3 and the determination of the extent ofpoly(ADP-ribosyl)ated residues in this protein was performed. 26040766_we found that PARP3 interacted with FoxM1 to enhance its transcriptional activity and conferred glioblastoma cell radioresistance. Thus, our data suggest that PARP3 could be a therapeutic target to overcome radioresistance in glioblastoma 27530147_These data identify PARP3 as a molecular sensor of nicked nucleosomes. 27579892_PARP3 controls of TGFbeta-induced epithelial mesenchymal transformation and acquisition of stem-like cell features by stimulation transglutaminase 2/SNAI1 signaling. 27716488_In a process of single-strand DNA repair, PARP3 mono-ADP-ribosylates nucleosomal histone H2B. 29054115_Data indicate that PARP3, a DNA damage-activated ADP-ribosyltransferase, can mono-ADP-ribosylate double-stranded DNA ends. 29361132_PARP3 can PARylate and mono(ADP-ribosyl)ate (MARylate), respectively, 5'- and 3'-terminal phosphate residues at double- and single-strand break termini of a DNA molecule containing multiple strand breaks. 29520010_gapped DNA that was ADP-ribosylated by PARP3 could be ligated to double-stranded DNA by DNA ligases. Moreover, this ADP-ribosylated DNA could serve as a primed DNA substrate for PAR chain elongation by the purified proteins PARP1 and PARP2 as well as by cell-free extracts. 29676938_The integral roles of PARP3 in DNA damage repair. 30039287_Our results indicated this approach with PARP3 inhibitors and vinorelbine is unique and promising for breast cancer patients with metastases. This combination could significantly increase the survival of breast cancer patients with metastases 32785980_Progress and outlook in studying the substrate specificities of PARPs and related enzymes. 34066057_PARP Power: A Structural Perspective on PARP1, PARP2, and PARP3 in DNA Damage Repair and Nucleosome Remodelling. |
ENSMUSG00000023249 |
Parp3 |
57.057082 |
0.3700000833 |
-1.434402 |
0.230055866 |
39.267286 |
0.00000000036958190921269968645964167887547121432723074008208641316741704940795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001831161121174705179605693415882585600718002183384669478982686996459960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.3197681 |
6.5125257 |
82.2275745 |
12.1403605 |
| ENSG00000042062 |
140876 |
RIPOR3 |
protein_coding |
Q96MK2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:140876; |
|
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 35277469_Downregulated Expression of RIPOR3 Correlated with Immune Infiltrates Predicts Poor Prognosis in Oral Tongue Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000074577 |
Ripor3 |
32.850755 |
0.0656409066 |
-3.929261 |
0.524783264 |
61.022256 |
0.00000000000000564332150910948183160444292426519571984891085469904226101789390668272972106933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000038438128968369152218202727608945818476497528759505684092800947837531566619873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6897019 |
1.5173084 |
54.9107824 |
12.5912204 |
| ENSG00000042088 |
55775 |
TDP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NUW8 |
FUNCTION: DNA repair enzyme that can remove a variety of covalent adducts from DNA through hydrolysis of a 3'-phosphodiester bond, giving rise to DNA with a free 3' phosphate. Catalyzes the hydrolysis of dead-end complexes between DNA and the topoisomerase I active site tyrosine residue. Hydrolyzes 3'-phosphoglycolates on protruding 3' ends on DNA double-strand breaks due to DNA damage by radiation and free radicals. Acts on blunt-ended double-strand DNA breaks and on single-stranded DNA. Has low 3'exonuclease activity and can remove a single nucleoside from the 3'end of DNA and RNA molecules with 3'hydroxyl groups. Has no exonuclease activity towards DNA or RNA with a 3'phosphate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12023295, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15111055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15811850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16141202, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22822062}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA repair;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Neurodegeneration;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in repairing stalled topoisomerase I-DNA complexes by catalyzing the hydrolysis of the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of topoisomerase I and the 3-prime phosphate of DNA. This protein may also remove glycolate from single-stranded DNA containing 3-prime phosphoglycolate, suggesting a role in repair of free-radical mediated DNA double-strand breaks. This gene is a member of the phospholipase D family and contains two PLD phosphodiesterase domains. Mutations in this gene are associated with the disease spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy (SCAN1). [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:55775; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 3'-tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0017005]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; exonuclease activity [GO:0004527]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; single strand break repair [GO:0000012] |
10521354_Sequences nearly identical to FLJ11090 are highly homologous to the yeast TDP1 gene. Tdp1 protein cleaves the linkage between a phosphotyrosyl group and the 3'-end of DNA, and has been shown to be involved in the repair of TOP1-induced DNA damage. 11572945_Protein assay of expressed FLJ11090 shows that it encodes human tyrosyl-DNA phodphodiesterase (TDP1). 11839309_1.69 A crystal structure of human tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 12023295_a role for hTdp1 in repair of free radical-mediated DNA double strand breaks bearing terminally blocked 3' overhangs. 12244316_loss-of-function mutations in TDP1 may cause spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy either by interfering with DNA transcription or by inducing apoptosis in postmitotic neurons 12470949_We report the three-dimensional structures of human Tdp1 bound to the phosphate transition state analogs vanadate and tungstate 15248776_conserved sequences and amino acids important for catalytic activity and enzyme specificity were identified 15494395_TDP1 is required for the repair of topoisomerase I-mediated DNA damage and may have a role in the repair of DNA damage mediated by topoisomerase II 15647511_The role of TDP1 in 3'-phosphoglycolate processing during in vitro end joining of DNA double-strand breaks. 15811850_Tdp1 only acts upon double strand breaks in vivo 15920477_inhibitors of Tdp1 could act synergistically with camptothecin in anticancer therapy 16141202_Tdp1 may function to remove a variety of 3' adducts from DNA during DNA repair 16775218_TDP1 has a role in DNA single-strand break repair and neurodegeneration [review] 16935573_it is proposed that Tdp1 is involved in the repair of Top1 cleavage complexes associated with transcription damage in hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy (SCAN1) cells 17600775_TDP1 is also required for the repair of single stranded breaks induced by ionizing radiation (IR), though not measurably for IR-induced DNA double-strand breaks 17707402_Data show that mutation of a conserved active site residue converts tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I into a DNA topoisomerase I-dependent poison. 17948061_This study provides a direct demonstration that Tdp1 repairs Topo I covalent lesions in vivo and suggests that spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy (SCAN1) arises from the recessive neomorphic mutation H493R. 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18347181_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19505854_TDP1 can gain access to and can process blocked 3' termini of double-strand breaks before ends are fully sequestered by DNA-PK, as well as at a later stage after DNA-PK autophosphorylation. 19604089_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19851285_TDP1 phosphorylation at serine residue 81 promotes cell survival and DNA repair in response to carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase-induced DNA double-strand breaks. 20009512_The interaction with Lig3alpha is promoted by serine 81 that is located within a putative S/TQ site in the N-terminus domain of TDP1. 20097655_results suggest human Tdp1 may act using a scanning mechanism, in which Tdp1 bind non-specifically upstream of a 3'-blocking lesion and is preferentially stabilized at 3'-DNA ends corresponding to its site of action. 21041670_These findings provide evidence for TDP1 as a novel mitochondrial enzyme. 21276450_Study investigates substrate specificity of Tdp1; data suggest a role for Tdp1 in a new APE-independent base excision repair pathway. 21628532_topoisomerase 1, tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1, and single-strand break repair modulate transcription-dependent CAG repeat contractions 22155078_Analysis of the active-site mechanism of tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I. 22375014_Our findings reveal a broad involvement of Tdp1 in DNA repair and clarify the role of human TDP1 in the repair of Top2-induced DNA damage. 22415824_study identifies TDP1 as a target for modification by the small ubiquitin-like modifier SUMO and provides evidence implicating SUMOylation in facilitating TDP1 cellular function during single-strand break repair 23536040_These studies suggest that one role of cytoplasmic Tdp1 is the repair of mitochondrial DNA lesions arising from oxidative stress. 23852793_A polymorphism at position rs28365054 in the TDP1 gene had a significant difference (P |
ENSMUSG00000021177 |
Tdp1 |
126.018464 |
2.1435040210 |
1.099971 |
0.179713012 |
37.224095 |
0.00000000105304574536354894625619038844941549593059448852727655321359634399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005029850962779355491498407609504694981694683519890531897544860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
148.5099923 |
16.2614054 |
69.7544110 |
5.8267754 |
| ENSG00000042493 |
822 |
CAPG |
protein_coding |
P40121 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-sensitive protein which reversibly blocks the barbed ends of actin filaments but does not sever preformed actin filaments. May play an important role in macrophage function. May play a role in regulating cytoplasmic and/or nuclear structures through potential interactions with actin. May bind DNA. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin capping;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the gelsolin/villin family of actin-regulatory proteins. The encoded protein reversibly blocks the barbed ends of F-actin filaments in a Ca2+ and phosphoinositide-regulated manner, but does not sever preformed actin filaments. By capping the barbed ends of actin filaments, the encoded protein contributes to the control of actin-based motility in non-muscle cells. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:822; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; centriole [GO:0005814]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; F-actin capping protein complex [GO:0008290]; Flemming body [GO:0090543]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; actin filament severing [GO:0051014]; actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008154]; barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:0051016]; cell projection assembly [GO:0030031]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003] |
12637565_CapG lacks a nuclear export sequence present in structurally related proteins 15454578_importin-beta-dependent nuclear import of the actin modulating protein CapG promotes cell invasion 16767159_CapG is a new tumor suppressor gene involved in the tumorigenic progression of certain cancers 18059028_Comprehension of the mobility and compartmentalization of the CapG protein in normal and in cancer cells in vivo could constitute a new basis to characterize the invasiveness and metastasizing potential of breast cancer. 18237446_Dysregulated expression of gelsolin-like actin capping protein(CapG) was found in premalignant and malignant oral carcinogenesis. 18266911_Results report that NTF2 and Ran control nuclear import of the filamentous actin capping protein CapG. 18461482_CapG mobility in cell nuclei of live breast cancer cells 18709641_the 4 biomarkers CLU, ITGB3, PRAME and CAPG may be used as prognostic factors for patients with stage III serous ovarian adenocarcinomas. 18938132_These results suggest that filamentous actin in the nucleolus might be regulated by actin binding proteins such as CapG. 19011242_several genes that are known to be regulated by DNA methylation were up-regulated dramatically by integrin alpha6beta4 expression, including S100A4, FST, PDLIM4, CAPG, and Nkx2.2. 19166812_A role for the actin-binding protein CapG as a mediator of cross-talk between the actin cytoskeleton and microtubule-based organelles that regulate cell division was proposed. 19188659_Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha up-regulated CapG protein expression under normoxia. Knockdown of HIF-1alpha expression in hPASMCs also inhibited hypoxia-induced CapG up-regulation. 19242827_CapG was upregulated in the stroma cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) compared with normal nasopharyngeal epithelial tissues. CapG possibly plays a role in the complex interaction between NPC cells and the surrounding host tissue. 19439302_Proteomic study of macrophages exposed to oxLDL identifies a CAPG polymorphism associated with carotid atherosclerosis. 21768101_strong down-regulation of MCK activity contributes to F-actin instability and induces post-translational modification of alphaB-crystallin and desmin 21908955_These results suggest that overexpression of CapG may be associated with progression of lung adenocarcinoma. 22155129_CapG was identified as a novel candidate biomarker to predict response to gemcitabine treatment and survival in cholangiocarcinoma. 22190510_Expression of CapG, gelsolin, and P-gp was found to be associated with an increased risk of death from non-small cell lung cancer. 23085225_CapG is involved in the process of metastasis by promoting the invasiveness of tumor cells. 23782053_CapG was up-regulated in the tumor tissues of patients with lymph node metastasis (LNM), whereas it showed an equivalent expression level between non-tumor and tumor tissues of patients without LNM. 24804218_A single nucleotide polymorphism rs6886 inside the CapG gene was identified, affecting a CapG phosphorylation site and thus potentially modifying CapG function. 26466680_On the basis of these results, we propose a model in which dynamic vimentin filaments target CARMIL2 to critical membrane-associated locations, where CARMIL2 regulates CP, and thus actin assembly, to create cell protrusions 26663173_Overexpression of CAPG is associated with glioma. 26757732_The composite biomarker, CAPG and GIPC1 in primary breast tumors, predicted disease outcomes and benefit from zoledronate and may facilitate patient selection for adjuvant bisphosphonate treatment. 28790116_The combination of CTNB1, XPO2, and CAPG achieved 95% sensitivity and 96% specificity for the discrimination of these subtypes. We developed two uterine aspirate-based signatures to diagnose Endometrial cancer and classify tumors in the most prevalent histologic subtypes. This will improve diagnosis and assist in the prediction of the optimal surgical treatment 29399702_Results revealed that CapG is a novel independent prognostic predictor for glioma patients and highlight a key role of CapG in proliferation and metastasis of glioma. 29721098_CAPG competes with the transcriptional repressor arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) for binding to the STC-1 promoter. 29970516_it is demonstrated that CapG is expressed in the cytoplasm and could be used as a prognostic or diagnostic biomarker for mHCC in clinical specimens 30155403_Study suggested that CapG could be used as a biomarker for metastatic CRC in the clinical specimens. Moreover, our in vitro study demonstrated that CapG might contribute on tumor metastasis in human CRCs. 31660072_CapG promotes resistance to paclitaxel in breast cancer through transactivation of PIK3R1/P50. 32309867_The Association Between Gelsolin-like Actin-capping Protein (CapG) Overexpression and Bladder Cancer Prognosis. 32619075_The role of CAPG in molecular communication between the embryo and the uterine endometrium: Is its function conserved in species with different implantation strategies? 33236143_Oncogenic potential of macrophagecapping protein in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 33711419_The migration behavior of human glioblastoma cells is influenced by the redox-sensitive human macrophage capping protein CAPG. 35186171_Overexpression of CAPG Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Immunosuppressive Cell Infiltration in Ovarian Cancer. 36244872_CAPG facilitates diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell progression through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000056737 |
Capg |
1225.178823 |
2.1936457904 |
1.133331 |
0.050432420 |
508.081093 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016584994830267840399481953466374725784779289473184939162342003382412219952136309338055754783315827782474999163954347419013816259461468851792896462357671119419023554367052726167191910775537808610621651185537301033091147 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008052451437327412309624100942946420431527432616638447838341417936351917506361171765345162005383674551467161704060933375826459591905077074239677428470557084475832026693491228595358595996904414685451741616713919094443446 |
Yes |
No |
1695.2672960 |
48.1243598 |
778.1504035 |
17.4458694 |
| ENSG00000043143 |
23338 |
JADE2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQC1 |
FUNCTION: Scaffold subunit of some HBO1 complexes, which have a histone H4 acetyltransferase activity (PubMed:16387653). Acts as a E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase mediating the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target protein histone demethylase KDM1A (PubMed:25018020). Also acts as a ubiquitin ligase E3 toward itself. Positive regulator of neurogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6ZQF7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16387653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25018020}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:25018020}. |
Predicted to enable ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Involved in histone acetylation. Located in nucleoplasm. Part of histone acetyltransferase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23338; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; histone acetyltransferase complex [GO:0000123]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; histone H4K12 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0043997]; histone H4K5 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0043995]; histone H4K8 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0043996]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; histone H3 acetylation [GO:0043966]; histone H4-K12 acetylation [GO:0043983]; histone H4-K5 acetylation [GO:0043981]; histone H4-K8 acetylation [GO:0043982]; histone modification [GO:0016570]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000278]; regulation of DNA replication [GO:0006275]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
Mouse_homologues 25018020_Results show that Jade-2 is a major LSD1 negative regulator during neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo in both mouse developing cerebral cortices and zebra fish embryos. 36008159_JADE2 Is Essential for Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Functions in Mice. |
ENSMUSG00000020387 |
Jade2 |
77.788274 |
0.3576206178 |
-1.483498 |
0.269004174 |
29.950045 |
0.00000004433216859631990025577313505565635320948558728559873998165130615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000180608006757295544087834541883974548426294859382323920726776123046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.8734374 |
6.1256245 |
109.8775196 |
11.4862314 |
| ENSG00000043355 |
7546 |
ZIC2 |
protein_coding |
O95409 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional activator or repressor. Plays important roles in the early stage of organogenesis of the CNS. Activates the transcription of the serotonin transporter SERT in uncrossed ipsilateral retinal ganglion cells (iRGCs) to refine eye-specific projections in primary visual targets. Its transcriptional activity is repressed by MDFIC. Involved in the formation of the ipsilateral retinal projection at the optic chiasm midline. Drives the expression of EPHB1 on ipsilaterally projecting growth cones. Binds to the minimal GLI-consensus sequence 5'-TGGGTGGTC-3'. Associates to the basal SERT promoter region from ventrotemporal retinal segments of retinal embryos. |
Activator;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Holoprosencephaly;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ZIC family of C2H2-type zinc finger proteins. This protein functions as a transcriptional repressor and may regulate tissue specific expression of dopamine receptor D1. Expansion of an alanine repeat in the C-terminus of the encoded protein and other mutations in this gene cause holoprosencephaly type 5. Holoprosencephaly is the most common structural anomaly of the human brain. A polyhistidine tract polymorphism in this gene may be associated with increased risk of neural tube defects. This gene is closely linked to a gene encoding zinc finger protein of the cerebellum 5, a related family member on chromosome 13. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:7546; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11857562_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11857562_Sample was too small to reach definitive conclusions, but the evidence is sufficiently intriguing to encourage further research. 11910512_Holoprosencephaly in monosomy 13q may be related to ZIC2 gene loss of function. 12522805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13678579_Zic2 is an evolutionarily conserved determinant of retinal ganglion cells that project ipsilaterally 14679585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15221788_Four novel ZIC2 mutations found in a cohort of Holoprosencephaly patinets. 15590697_The C-terminal alanine-tract of ZIC2 influences the strength of DNA binding and alters transcriptional activity in a promoter-specific manner 17251188_Forms two different complexes with DNA-dependent protein kinase, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, and RNA helicase A; all the components interacted directly with Zic2 protein 18417618_This transcription factor regulates the expression of EphB1 in RGCs and also suggest the existence of an additional EphB1-independent pathway controlled by Zic2 that contributes to retinal axon divergence at the midline. 19022413_ZIC2, SPRY2, and GPC5 genes are candidate genes suspected to explain the malformations associated with cerebral anomalies in the hypothesis of a contiguous gene syndrome in 13q deletion syndrome 19177455_Loss-of-function as the likely pathogenetic mechanism common to most, if not all, of ZIC2 mutations in holoprosencephaly. 19784848_ZIC2 expression was associated with the histopathologic types of oral squamous cell carcinoma 19955556_Holoprosencephaly due to ZIC2 mutations is distinct from that due to mutations in other genes. 20199689_ZIC1, ZIC2, and ZIC5 may have roles in meningiomas 20531442_screened four known HPE genes in a Dutch cohort of 86 non-syndromic HPE index cases, including 53 family members. We detected 21 mutations (24.4%), 3 in SHH, 9 in ZIC2 and 9 in SIX3 20683983_the smallest 13q deletion associated to DWM allows further narrowing of the previously established critical region for this brain malformation to 13q32.2-32.3. Among the few genes of the deleted region, ZIC2 and ZIC5 seem the most plausible candidates. 21638761_mutation of ZIC2 is a rare cause of, or contributor to, RES associated with HPE. 21661123_Our findings suggest that Zic2 is a positive modulator increasing Gli1 transcriptional and oncogenic activity by retaining Gli1 in the nucleus of cervical cancer cells. 21908606_role for ZIC2 as a transcriptional regulator of the beta-catenin.TCF4 complex. 21940735_Brain malformations, including neuronal migration defects, predominated in individuals with ZIC2 mutations. 22310223_Mutations in ZIC2 is associated with holoprosencephaly. 22733541_ZIC2, a transcription factor related to the sonic hedgehog pathway, is a strong discriminant between MAL and LMP tumors: it may be a major determinant of outcome of EOTs. 22847929_The c.1401_1406dup (p.Ala469_470dup) or alanine tract expansion to 17 residues) in the ZIC2 gene are likely to be medically significant for holoprosencephaly in a Brazilian cohort. 22859937_A high level of sequence variation in the 3'UTR of ZIC2 may be associated with holoprosencephaly. 24150758_ZIC2 and RASGRF1 are susceptibility genes, not only for common myopia, but also for high myopia. 24677696_Mutational screening for HPE genes revealed the occurrence of a frameshift mutation in the ZIC2 gene. 26318045_Data show that Zinc finger protein ZIC 2 (ZIC2) is indispensable in the regulation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell apoptosis. 26426078_ZIC2 acts upstream of OCT4 and recruits the nuclear remodeling factor complex to the OCT4 promoter, initiating OCT4 activation. ZIC2 levels positively correlated to the clinicopathological stages of HCC patients. 27466203_Together SMAD3 and ZIC2 regulate FOXA2 transcription in cultured cells and Zic2 also controls the foxA2 expression during Xenopus development. These findings reveal a new mechanism of NODAL signal transduction in the mammalian node and provide the first molecular explanation of how ZIC2 loss-of-function precipitates Holoprosencephaly (HPE 28577975_miR-1271/Zic2/PAK4 axis plays an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 29442327_the studies confirm the extent of ZIC2 allelic heterogeneity and that pathogenic variants of ZIC2 are associated with both classic and middle interhemispheric variant (MIHV) HPE which arise from defective ventral and dorsal forebrain patterning, respectively. 29588366_High Zic2 expression is associated with liver tumor. 29992973_ZIC2 regulates laterality of cardiovascular system. A subset of holoprosencephaly cases with ZIC2 mutation also exhibit heterotaxy. Mouse mutant shows right isomerism indicating lack of left-sided Nodal signalling in the embryo. Mechanistic studies in vitro indicate that ZIC2 is required for Nodal expression at the embryonic node and binds to the Nodal HBE enhancer in epiblast. 30075825_miR-1284 suppressed the proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells via targeting ZIC2. 30483794_MiR12715p inhibited the progression of AML by targeting ZIC2. 31640781_Results identified loss of ZIC2 expression following DNA hypomethylation as a promising prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. 31884576_MicroRNA-129-5p suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by targeting ZIC2. 32064600_ZIC2 is downregulated and represses tumor growth via the regulation of STAT3 in breast cancer. 32555352_The tumor-suppressive role of microRNA-873 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma correlates with downregulation of ZIC2 and inhibition of AKT signaling pathway. 33439969_Correlation of zinc finger protein 2, a prognostic biomarker, with immune infiltrates in liver cancer. 33557041_De Novo PORCN and ZIC2 Mutations in a Highly Consanguineous Family. 34099631_Multilevel regulation of Wnt signaling by Zic2 in colon cancer due to mutation of beta-catenin. 34232917_Downregulation of LINC00665 suppresses the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via regulating miR-181c-5p/ZIC2 axis. 34278490_ZIC2 upregulates lncRNA SNHG12 expression to promote endometrial cancer cell proliferation and migration by activating the Notch signaling pathway. 35390314_ZIC2 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis through the TGF-beta signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000061524 |
Zic2 |
153.388304 |
0.3426685141 |
-1.545114 |
0.211752000 |
52.255470 |
0.00000000000048730002459074731084284974653894991674166203843299172149272635579109191894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002963555155731120847104886178294256052732913442326889708056114614009857177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83.1778599 |
13.6884456 |
243.8884504 |
27.9964691 |
| ENSG00000043591 |
153 |
ADRB1 |
protein_coding |
P08588 |
FUNCTION: Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. This receptor binds epinephrine and norepinephrine with approximately equal affinity. Mediates Ras activation through G(s)-alpha- and cAMP-mediated signaling. Involved in the regulation of sleep/wake behaviors (PubMed:31473062). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12391161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31473062}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The adrenergic receptors (subtypes alpha 1, alpha 2, beta 1, and beta 2) are a prototypic family of guanine nucleotide binding regulatory protein-coupled receptors that mediate the physiological effects of the hormone epinephrine and the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. Beta-1 adrenoceptors are predominately located in the heart. Specific polymorphisms in this gene have been shown to affect the resting heart rate and can be involved in heart failure. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2019]. |
hsa:153; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; neuronal dense core vesicle [GO:0098992]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; alpha-2A adrenergic receptor binding [GO:0031694]; beta-adrenergic receptor activity [GO:0004939]; beta1-adrenergic receptor activity [GO:0004940]; G protein-coupled neurotransmitter receptor activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:0099579]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway [GO:0071880]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; diet induced thermogenesis [GO:0002024]; fear response [GO:0042596]; heat generation [GO:0031649]; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040015]; norepinephrine-epinephrine-mediated vasodilation involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0002025]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine-norepinephrine [GO:0001996]; positive regulation of the force of heart contraction by epinephrine-norepinephrine [GO:0001997]; regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep [GO:0045187]; response to cold [GO:0009409] |
11052857_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11337934_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11447084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11753577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11854867_A polymorphism in the beta1 adrenergic receptor is associated with resting heart rate 11854867_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11942593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12023679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12029453_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12032746_Gly389Arg ADRB1 variant is associated with greater body weight and BMI in Caucasian women due to a greater fat mass 12032746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12069593_The agonist-specific component of beta1AR downregulation requires internalization correlating more closely with receptor degradation, while the cAMP-specific component does not require internalization and is associated with downregulation of beta1AR mRNA. 12090746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12106601_beta1-adrenoceptor and beta2-adrenoceptor couple to Gs-proteins to activate adenylyl cyclase 12140284_role of heterodimerization with beta 2-adrenergic receptor regulates beta 2-adrenergic receptor internalization and ERK signaling efficacy 12197595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12197595_Suppressive effect of the Gly389 allele of the beta1-adrenergic receptor gene on the occurrence of ventricular tachycardia in dilated cardiomyopathy. 12244098_Results indicate that the proportion of homo- and heterodimers between the closely related beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic receptors is determined by their relative levels of expression. 12270132_Glycosylation regulates receptor surface expression and dimerization 12374873_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12391161_These results suggest a model whereby the physical interaction between the beta1-AR and CNrasGEF facilitates the transduction of Gsalpha-induced cAMP signal into the activation of Ras. 12422153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12455717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12519093_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12529373_An interaction between beta(1)AR and alpha(2A)AR is regulated by glycosylation and may play a key role in cross-talk and mutual regulation between these receptors. 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12643891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12709726_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12815745_An association was not found between B1AR polymorphism and major depression, but there was a tendency for a relation between CC homozygosity and a better and even faster response to antidepressant treatment in patients with major depression. 12815745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12844134_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12847069_The partial agonist activity of bucindolol is dependent on the activation state of the human beta-1 adrenergic receptor 12851615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12921807_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14502278_Data show that the beta(1)-adrenergic receptor Arg389 variant predisposes to heart failure through hyperactive signaling programs, depressed receptor coupling and ventricular dysfunction, and influences the therapeutic response to beta-receptor blockade. 14534524_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14553962_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14734649_internalization of beta(1)AR is both arrestin- and dynamin-dependent and follows the same clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway as beta(2)AR 14990580_PKA-mediated phosphorylation of G protein-coupled receptors might result in motif-dependent desensitization or resensitization. 15055253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15055253_The ADRB1/R389G polymorphism tended to be associated with hypertensive status in male subjects (p=0.0117, p(c)=0.0702). 15079793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15212591_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15212839_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15212839_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the beta1-adrenergic receptor (ADRB1) allelic frequencies were analyzed in Alzheimer's disease. The combination of G protein beta3 subunit and ADRB1 polymorphisms produces AD susceptibility. 15237695_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15312808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15312808_The Ser49Gly functional polymorphism in the beta(1) adrenergic receptor might explain some of the population variance in extraversion and related personality traits. 15331590_the lack of agonist-mediated ubiquitination of beta1AR may prevent its extensive trafficking to lysosomes 15342173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15388645_Substitution of the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of the beta2-adrenergic receptor on the beta1-adrenergic receptor enabled the chimeric G protein-coupled receptor to be functionally and spatially regulated by insulin. 15464701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15479221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15542284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15564877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15685248_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15719258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15735607_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15824464_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15833937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15833937_evidence for an interaction between the beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors was observed in men for longitudinal change in body mass index and women showed suggestive evidence for an interaction between the beta1- and beta3-adrenergic receptors 15861037_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15861037_beta1AR or the beta2AR polymorphisms do not affect patient response to beta-blockade treatment for stable congestive heart failure 15864115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15864115_the Arg389Arg and Ser49Gly polymorphisms may have roles in left ventricular remodeling changes in response to beta-blocker therapy 15917856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15932670_Beta(1)-adrenergic receptor mRNA expressions in myocardium were significantly lower in patients with heart failure than those in control subjects. 16122377_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16153393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16187973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16189366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16210433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16227135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16287427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16315032_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16325708_In this small pilot series, a single nucleotide polymorphism at codon 389 in the beta1-AR seems to correlate with a response to betaxolol therapy in normal, nonglaucomatous volunteers. 16325708_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16402084_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16421173_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16485781_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16487965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16500896_the amphipathic character of helix 8 and side chain projections of Asp382 and Arg384 within the hydrophilic interface might serve as a tethering site for the G protein 16534528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16648137_Val-120, Ile-185, Asp-212, and Lys-253 are critically involved in conformational changes occurring during receptor activation 16728691_Homozygousbeta1AR Arg389Gly predicts cardiac troponin release in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Combining homozygous B1AR Arg389Gly & homozygous deletion of B2AR increases the odds of reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. 16728691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16760361_These findings indicate that Lys324 lies in a groove between helices 3 and 6, and its mutagenesis generates a mutant receptor with very low binding affinity for the GDP-bound isoform of G(s). 16765375_beta1-adrenergic receptors are upregulated and troponin I is dephosphorylated in end-stage heart failure patients supported by ventricular assist devices 16785856_Certain polymorphisms of the ADRB1 and ADRB2 genes influence the pathophysiology of open-angle glaucoma in Japanese patients. 16785856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16815314_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16844790_beta(1)AR-389 variation alters signaling in multiple models and affects the beta-blocker therapeutic response in heart failure 16907703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16914520_These results suggest that the dynamic association of 14-3-3 proteins to both beta(1)AR and Kv11.1 channels is involved in the adrenergic modulation of this critical regulator of cardiac repolarization and refractoriness. 16940053_AKAP79 provides cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase to phosphorylate the beta1-adrenergic receptor and thereby dictate the recycling and resensitization itineraries of the beta1-adrenergic receptor 16946993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16997396_Our results suggest that CRM 1-dependent NES-mediated mechanisms influence the degradation and agonist-mediated down-regulation of the beta1-AR mRNAs. 17023080_In this relatively small study, double homozygosity for Arg389 and Ser49 of the human beta1-adrenergic receptor associated with the risk of symptoms in LQT1. 17023080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17118120_Golgin-160 interacts with beta1AR 17217681_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17223428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17270896_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17329986_Genetic polymorphisms in the B1AR gene have the potential to explain some of the observed ethnic variability in drug response and to improve clinical practice (Review) 17334644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335470_results suggest that the Arg389Gly polymorphism does not have any clinically important impact on the pathogenesis of obesity in Danish white subjects; this variant is most likely not to be a major contributor to the development of hypertension 17339538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17345787_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17345787_Pulse wave velocity and nitroglycerin-induced hyperemia were both closely associated with the Ser49Gly polymorphism. 17383306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463065_An association of positive tilt table testing to a single nucleotide polymorphism with a Gly to Arg switch at position 389 of the beta(1)AR was found. 17463065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17496726_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17512307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17541557_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17585213_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17591269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17635183_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17644825_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17667029_ADRB1/2 genotype is independently associated with the dilated cardiomyopathy phenotype, suggesting their role in favouring susceptibility to the disease. 17680533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17680533_The 389A/G polymorphism in the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor is associated with acute myocardial infarction and is an independent risk factor of AMI. 17845930_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17845930_heart transplant patients with the beta1-AR Gly49 variants had a lower heart rate, and better stress endurance and diastolic function compared with patients homozygous for Ser49; they also showed a trend toward better chronotropic reserve 17893006_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17919552_Milrinone potentiated contractile response to beta 1 and beta 2 adrenergic receptor agonists. 17998459_human betaARs undergo a process of intracellular sequestration that is dynamically reversed after LVAD support. Importantly, mechanical unloading leads to complete reversal in PI3Kgamma and betaARK1-associated PI3K activation. 18059082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18059082_Polymorphisms in ADRB1 and UCP3 may contribute to insulin resistance rather than obesity among Swedish women. 18075464_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18075464_Polymorphosm in beta1-adrenergic receptors determine improvement in left ventricular systolic function in nonischemic cardiomyopathy patients with heart failure after chronic treatment with carvedilol 18155231_Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays an important role in cell death and cardiac dysfunction in beta(1)-extracellular loop (EC)(II) IgG cardiomyopathy, and the effects of beta(1)-EC(II) IgG are mediated via the beta(1)-adrenergic receptor. 18158268_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18193079_In cardiomyocytes derived from embryonic stem cells, beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenoceptors contributed to contractile responses. 18209576_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18209576_the beta1AR gene is highly polymorphic and is commonly found in six haplotypic forms in the population; receptor expression varies by haplotype 18219297_Genetic variants in the beta1-AR gene may determine whether to use beta-blockers in hypertension for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. 18219297_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18239290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18253135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18298953_Arg389Gly polymorphism of the ADRB1 gene confers higher risk of left ventricular hypertrophy in human essential hypertension. 18298953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18308161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18311486_These results confirm the presence of beta1-, beta2-, and beta3-adrenoceptors in human urinary bladder urothelium; they suggest that urothelial beta-adrenoceptors induce the release of a urothelium-derived factor muscle 18323523_The action of certain adrenergic beta 1 receptor blockers in the brain could contribute to their beneficial effect on the failing heart. 18331634_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18346809_Genetic variations of ADRB1 in relationship to morbid obesity and suggests mutations in the BAR-1 coding sequence is not likely a major cause of morbid obesity at least in Japanese. 18346809_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18403719_Conformational rearrangements and signaling cascades involved in ligand-biased mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling through ADRB1. 18413308_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18413560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18413560_The relationship between hemodynamic response to mental stress and mental stress-induced myocardial ischemia (MSIMI) and 5 common functional polymorphisms of beta1-adrenergic receptors (ADRB1) and beta2-adrenergic receptors (ADRB2) was investigated. 18429752_No significant differences were revealed in dynamics of systolic and diastolic BP both at rest and at effort between patients with different genotypes of polymorphic marker Gly389Arg of ADRB1 gene. 18429752_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18452871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18479335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18534365_No association found between single nucleotide polymorphisms in the beta 1 adrenergic receptor and the risk of sudden cardiac death. 18534365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18540901_Beta1Gly49 homozygosity may increase the risk of developing transient tachypnea in the newborn. 18540901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18596718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18596718_significant association of the ADRB1 arg389gly polymorphism with blood pressure and HDL cholesterol 18615004_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18622236_Men with job strain and the Arg389Arg polymorphism were more often on antihypertensive treatment than other men 18622236_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18625943_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18679149_Among patients admitted to the PICU with a meningococcal infection, those with the variant allele of the beta-adrenergic receptor gene-1 at locus 389 were more likely to have a high pediatric risk of mortality score on admission 18679149_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18702937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18702968_Genotype and haplotype of ADRB1 did not significantly affect survival of metoprolol-treated or carvedilol-treated heart failure patients. 18754404_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18754404_results suggest that vasovagal syncope has a genetic component associated with the Arg389Gly polymorphism of the adrenergic receptor. 18772317_catecholamines and isoproterenol stabilize distinct conformations in the beta(1)AR and beta(2)AR 18773997_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18773997_The impact of beta1-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms on HF susceptibility, arrhythmogenesis, and prognosis. Polymorphisms had no influence on HF susceptibility. Gly389 allele was associated with lower prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias 18776959_Beta1- and alpha2c-adrenoreceptor variants as predictors of clinical aspects of dilated cardiomyopathy in people of African ancestry. 18776959_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18794726_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18797399_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18937294_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18947427_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18947427_Three polymorphisms in ADRA2C and five polymorphisms in ADRB1 were involved in eight cross-validated epistatic interactions identifying several two-locus genotype classes with significant relative risks of death/transplant in heart failure patients 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19010176_significant correlation between beta1-AR and G-protein-coupled receptor kinases expression in heart failure heart transplantation patients. 19033826_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19036891_The effects of aerobic fitness and beta1-adrenergic receptor blockade on cardiac work during dynamic exercise. 19037712_Beta1AR-mediated ERK activity involves the Galphas subunit, but not EGFR or Src tyrosine kinase. 19056576_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19073901_Normotensive sodium loading in normal man: regulation of renin secretion during beta1-receptor blockade. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19094446_Knowledge of the combination of CYP2D6 and beta(1) adrenoreceptor polymorphisms may be used to guide antihypertensive therapy using beta(1) adrenoreceptor antagonists. 19094446_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19167638_Genotype polymorphism frequencies for B1 receptor (amino acid positions 389 and 49) and alpha 2c receptor (deletion 322-325) are not significantly different in SC patients compared to female controls. 19301767_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19378229_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19378229_There was no significant difference in relation to genotype distribution and allele frequencies of any analysed b1-AR and b2-AR polymorphisms between IDCM patients and controls. 19477404_The alpha(2C) Del322-325 polymorphism exclusively or in combination with the beta(1)Arg389 allele is not associated with an increased risk of adverse events in HF. 19509284_Beta-arrestin is required for the maintenance of a beta1-Adrenergic receptor -epidermal growth factor receptor interaction that can direct cytosolic targeting of extracellular regulated kinase in response to catecholamine stimulation. 19515093_Results indicate that homodimerization of the alpha1-adrenoceptor occurs early during biosynthesis and that chaperones can promote dimerization and cell surface targeting, most likely by stabilizing conformations compatible with the two processes. 19538012_Collectively, the promoting action of chloroform-extract from cigarette smoke on esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma cell proliferation is beta-adrenoceptor- and COX-2-dependent. 19542315_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19553224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19576569_Study addressed the recent evolutionary history of ADRB genes in human populations and found that ADRB1 is neutrally evolving. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19621046_sorbents on the basis of the conformational antigens (ADRB1) were more effective in comparison with those containing linear peptide precursors. 19623647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19623647_The Arg389 allele of the ADRB1 gene was associated with an elevated risk of myocardial infarction. 19628119_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19673943_Marked interethnic difference exist in beta(1)-adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms. 19673943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19743955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19743955_The polymorphisms of the ADRB1 gene were associated with essential hypertension. 19745105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19779464_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19842931_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19845516_Heterozygous variant of Ser49gly of beta-adrenoreceptor gene was significantly more often met in patients with SSNS and their healthy relatives than in subjects of control group. 19883298_Addition of 6 thermostabilizing mutations into both hbeta(2)AR and hbeta(2)AR increased their apparent T(m)s by 17 degrees C and 11 degrees C, respectively; the mutations affected the global conformation to the predominantly antagonist bound form 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20023040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20023040_The prevalence of polymorphisms of b1AR, b2AR, and GNAS were similar between patients and controls. 20044737_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20079238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20079238_The Gly389Arg CC genotype of beta(1)-adrenoceptor genes may be involved in cardiovascular complication in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. 20116105_These results demonstrate a unique synergistic pro-inflammatory response mediated through a beta(1)-AR cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism in lipopolysaccharide-challenged monocytic cells. 20123316_In a Chinese cohort, carriers of a genetic variant of beta-1 adrenergic receptor are found to be more susceptible to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 20129829_No association of the polmorphisms Arg492Cys (ADRA1A gene), Ser49Gly and Arg389Gly (ADRB1), Arg16Gly and Gln27Glu (ADRB2), 825C/T (GNB3), -1021C/T (DBH) and S/L (SLC6A4) with both tilt test outcomes and new syncopal episodes was found 20144152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20144152_increase of LV myocardial mass turned out age of patients, level of systolic arterial pressure, presence of excessive body mass and carriage of Arg/Arg genotype of polymorphic marker Gly389Arg of ADRB1 gene. 20185488_Genetic polymorphisms of the adrenergic system (the combination of beta(1)-Gly389Arg and GNB3 C825T) may help to identify heart failure patients who are more likely to receive appropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillators therapies. 20185488_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20203292_ADRB1 was overexpressed in bronchi of cystic fibrosis patients. 20235788_In 1112 never-treated essential hypertension patients and 203 normotensive controls, tightly linked SNPs of beta-adrenergic receptors ADRB1, ADRB2 and the G-protein beta3-subunit GNB3 were genotyped. 20235788_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20300048_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20300048_genetic variation of beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptor has a role in response to four classes of antihypertensive treatment 20352314_Beta1-AR Arg389Gly and beta2-AR Arg16Gly SNPs are not related to the response to carvedilol therapy. The beta2-AR Gln27Glu SNP is a determinant of the left ventricular ejection fraction response to this agent in patients with chronic heart failure. 20352314_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20374546_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20384459_Heterozygous genotype (Ser49Gly) of ADRB1 gene can be considered as one of the genetic predictors for development of primary or secondary atrial fibrillation. 20384459_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414837_[review] functionally active autoantibodies directed against the cardiac beta1-adrenergic receptor have been assigned a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of immune cardiomyopathy 20426789_Increased ADRB1 expression may account for some of the functional changes of hormone-sensitive lipase in patients with cancer cachexia. 20443839_The role of beta-receptor selectivity for the interaction between the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) insertion/deletion polymorphism and beta-blocker therapy was investigated in 479 subjects with left ventricular dysfunction. 20459474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20470286_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20470286_The beta1AR Arg389Gly polymorphism is not an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in subjects with overt diabetic nephropathy. 20537417_Development of late hypertension after aortic coarctation repair could not be related to the investigated genomic polymorphism: the correlation of the ACE I/D and the ADRB1 c.1165C>G 20537417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20581797_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20581797_Report a significant interaction between ADRB1 Arg389Gly variant status and 'beta-blocking' effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on heart rate and blood pressure. 20587416_N-terminal cleavage represents a novel regulatory mechanism of cell surface beta(1)ARs. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20625396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20643254_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-en |
ENSMUSG00000035283 |
Adrb1 |
191.225612 |
0.3336279488 |
-1.583688 |
0.119191344 |
183.120962 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000001009297447482346674451344323705851336995756092771877247277502427190358396874903514540086539219655590982993413617929689962693373672664165496826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000176716848455983826117864685103591273580218452624010614806116308624088558575641204951801652057691256270458013410973308054963126778602600097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
97.3821203 |
7.4429790 |
293.8350749 |
13.6432430 |
| ENSG00000044446 |
5256 |
PHKA2 |
protein_coding |
P46019 |
FUNCTION: Phosphorylase b kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of serine in certain substrates, including troponin I. The alpha chain may bind calmodulin. |
Calmodulin-binding;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycogen metabolism;Glycogen storage disease;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Glycan biosynthesis; glycogen metabolism. |
Phosphorylase kinase is a polymer of 16 subunits, four each of alpha, beta, gamma and delta. The alpha subunit includes the skeletal muscle and hepatic isoforms, and the hepatic isoform is encoded by this gene. The beta subunit is the same in both the muscle and hepatic isoforms, and encoded by one gene. The gamma subunit also includes the skeletal muscle and hepatic isoforms, which are encoded by two different genes. The delta subunit is a calmodulin and can be encoded by three different genes. The gamma subunits contain the active site of the enzyme, whereas the alpha and beta subunits have regulatory functions controlled by phosphorylation. The delta subunit mediates the dependence of the enzyme on calcium concentration. Mutations in this gene cause glycogen storage disease type 9A, also known as X-linked liver glycogenosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been reported, but the full-length nature of these variants has not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:5256; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; phosphorylase kinase complex [GO:0005964]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; phosphorylase kinase activity [GO:0004689]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; generation of precursor metabolites and energy [GO:0006091]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; protein modification process [GO:0036211] |
12862311_Gene analysis was confirmed to represent a useful procedure for diagnosing x-linked liver glycogenosis, for which liver biopsy had previously been required to detect hepatic phosphorylase kinase deficiency 12876330_alpha- and beta-subunits possess amino-terminal glucoamylase-like domains and suggests that they might possess a previously overlooked amylase activity 17581768_Alu-mediated, large deletion-spanning introns 19-26 in PHKA2 is associated with X-linked liver glycogenosis 18950708_Results show that phosphorylase kinase (PhK) alpha subunit missense mutations or small in-frame deletions/insertions may have a direct impact on the PhK alpha functions. 21131218_two novel mutations found in two GSD type IX patients with different residual enzyme activities 21857251_The present case also represents the first known reported case of liver PhK deficiency with an PHKA2 mutation and liver cirrhosis. 21911307_We found that the missense mutation p.Pro1205Leu in the PHKA2 gene is a common cause of hepatic phosphorylase-kinase deficiency in Dutch patients, suggesting a founder-effect 27103379_In this study we summarized the PHKA2 mutation spectrum in Korean glycogen storage disease type IX patients and found that the most common mutation type was gross deletion. 28627441_Clinical data and analyzed the PHKA2 gene of 17 Chinese male patients suspected of having Glycogen storage disease (GSD) type IXa; study detected 14 mutations in 17 patients, including 8 novel mutations; exons 2 and 4 were hot spots. 30925902_Study identified a novel mutation in PHKA2 (c.2972C > G, p.G991A) in patients with relatively rare phenotype of GSD IXa, including hypoglycaemia and delayed motor development. 32387637_A novel frameshift PHKA2 mutation in a family with glycogen storage disease type IXa: A first report in Vietnam and review of literature. 33317799_Benign or not benign? Deep phenotyping of liver Glycogen Storage Disease IX. 34117828_PHKA2 variants expand the phenotype of phosphorylase B kinase deficiency to include patients with ketotic hypoglycemia only. |
ENSMUSG00000031295 |
Phka2 |
99.236127 |
0.4153766467 |
-1.267508 |
0.198539601 |
40.542882 |
0.00000000019234797566178596621782702132677977599484187010148161789402365684509277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000974615901396485008704378257481885233781682131848356220871210098266601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.1552936 |
11.3530651 |
137.9680416 |
19.5134774 |
| ENSG00000047346 |
56204 |
FAM214A |
protein_coding |
Q32MH5 |
FUNCTION: Transcription regulator that syncronizes transcriptional and translational programs to promote macrophage invasion of tissues. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q69ZK7}. |
Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:56204; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000034858 |
Fam214a |
160.558266 |
0.3412076092 |
-1.551278 |
0.291947069 |
27.207620 |
0.00000018273699379417979021258348210077215867386257741600275039672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000701299539366119067804921163866715971835219534114003181457519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83.7562684 |
21.3306510 |
245.3682424 |
44.5370837 |
| ENSG00000047597 |
7504 |
XK |
protein_coding |
P51811 |
FUNCTION: Recruits the lipid transfer protein VPS13A from lipid droplets to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32845802}. |
Amino-acid transport;Blood group antigen;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This locus controls the synthesis of the Kell blood group 'precursor substance' (Kx). Mutations in this gene have been associated with McLeod syndrome, an X-linked, recessive disorder characterized by abnormalities in the neuromuscular and hematopoietic systems. The encoded protein has structural characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic membrane transport proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7504; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular magnesium ion homeostasis [GO:0010961]; myelination [GO:0042552]; regulation of axon diameter [GO:0031133]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741] |
17379193_In human cortex, the results show expression of XK in cortical neurons with an apparent cytoplasmic localization. 17469188_Sequence analysis demonstrated a 5 bp deletion in exon 2 of the XK gene in McLeod syndrome. 21145924_This study identified one non-synonymous and one intron variant in mood disorder and schizophrenia subjects, respectively, in XK. 21463873_Novel XK protein mutations are reported in two patients who exhibit typical clinical characteristics of McLeod syndrome. 24635891_study reports the clinical findings and a novel nonsense hemizygous mutation, c.154C>T (p.Gln52X) at exon 1 of XK gene in a Taiwanese family with McLeod syndrome 24816235_The XK gene was not linked to hypermutability in red cells from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. 26308465_the expression of KX is critical to normal morphology, and null mutations are associated with the McLeod neuroacanthocytosis syndrome. 32845802_XK is a partner for VPS13A: a molecular link between Chorea-Acanthocytosis and McLeod Syndrome. 35994651_A partnership between the lipid scramblase XK and the lipid transfer protein VPS13A at the plasma membrane. |
ENSMUSG00000015342 |
Xk |
263.208151 |
0.4243010974 |
-1.236840 |
0.106029813 |
137.834415 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000007921413200343104682892172728139800214346999296812737846717858389858726414667077799208055877144829537428449839353561401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000001076611959825637363087475144858215731262262881357888435438819870457492141378014974956167648656446544919162988662719726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
157.8260187 |
10.9648409 |
374.9077099 |
17.0146715 |
| ENSG00000047644 |
55841 |
WWC3 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULE0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WWC family of proteins, which also includes the WWC1 (KIBRA) gene product and the WWC2 gene product. The protein encoded by this gene includes a C2 domain, which is known to mediate homodimerization in the related WWC1 gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:55841; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; negative regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035331]; negative regulation of organ growth [GO:0046621]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035330] |
29115863_WWC3 interacted with T cell factor 4 (TCF4). 33837178_WBP2 negatively regulates the Hippo pathway by competitively binding to WWC3 with LATS1 to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression. |
|
|
210.292343 |
0.1916899274 |
-2.383154 |
0.849023294 |
7.083474 |
0.00777980576511599387912188063864959985949099063873291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015253710559658883658129546745385596295818686485290527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
72.4967665 |
36.2801778 |
379.6296854 |
135.0678747 |
| ENSG00000047648 |
395 |
ARHGAP6 |
protein_coding |
O43182 |
FUNCTION: GTPase activator for the Rho-type GTPases by converting them to an inactive GDP-bound state. Could regulate the interactions of signaling molecules with the actin cytoskeleton. Promotes continuous elongation of cytoplasmic processes during cell motility and simultaneous retraction of the cell body changing the cell morphology. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10699171}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3-binding |
|
This gene encodes a member of the rhoGAP family of proteins which play a role in the regulation of actin polymerization at the plasma membrane during several cellular processes. This protein is thought to have two independent functions, one as a GTPase-activating protein with specificity for RhoA, and another as a cytoskeletal protein that promotes actin remodeling. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:395; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; actin filament [GO:0005884]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; phospholipase activator activity [GO:0016004]; phospholipase binding [GO:0043274]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; focal adhesion assembly [GO:0048041]; negative regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051895]; negative regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051497]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of phospholipase activity [GO:0010518]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
18434237_Human ARHGAP6 protein possessing GTPase stimulating activity for RhoA on the catalytic properties of PLC-delta1, was studied. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19960375_the RhoGAP6 isoform 1 variant might serve as a biomarker for the development and progression of colorectal cancer 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23251683_Failed ARHGAP6 expression did not appreciably alter the severity of enamel defects when AMELX was absent. 30816546_ARHGAP6 was found to have low expression in tumor tissues from patients with lung cancer, accompanied by high expression of MMP9 and VEGF. In A549 and H1299 cells, upregulation of ARHGAP6 inhibited tumor growth and metastasis and reduced the levels of MMP9, VEGF and pSTAT3, while the levels STAT3 were unchanged. 34338998_MiR-96-5p is an oncogene in lung adenocarcinoma and facilitates tumor progression through ARHGAP6 downregulation. |
ENSMUSG00000031355 |
Arhgap6 |
46.494840 |
0.4951968377 |
-1.013926 |
0.224217481 |
20.767815 |
0.00000518470188268761747137948481256586319432244636118412017822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000016855991142834631863400493556603976230690022930502891540527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.3259061 |
4.8081718 |
67.9489486 |
6.3337683 |
| ENSG00000048162 |
51491 |
NOP16 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3C1 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is localized to the nucleolus. Expression of this gene is induced by estrogens and Myc protein and is a marker of poor patient survival in breast cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:51491; |
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273] |
18373870_HSPC111 is an estrogen and c-Myc target gene that is over-expressed in breast cancer and is associated with an adverse patient outcome. 24425784_RNA 3'-phosphate cyclase (RTCD1/RTCA) interacted with HSPC111, and RTCD1 was involved in the HSPC111 multiprotein complex in regulating rRNA production and ribosomal biogenesis. 35027547_Cancer-derived exosomal HSPC111 promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by reprogramming lipid metabolism in cancer-associated fibroblasts. |
ENSMUSG00000025869 |
Nop16 |
116.878014 |
2.6460278104 |
1.403828 |
0.151085104 |
88.167562 |
0.00000000000000000000601380710769164874878450802725853535438828955147429509509385270327186390204587951302528381347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000055132790627036486332321660237810504610363777202704319837719970642808675620472058653831481933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
168.2639660 |
15.3985394 |
64.0937234 |
4.7518012 |
| ENSG00000048342 |
57545 |
CC2D2A |
protein_coding |
Q9P2K1 |
FUNCTION: Component of the tectonic-like complex, a complex localized at the transition zone of primary cilia and acting as a barrier that prevents diffusion of transmembrane proteins between the cilia and plasma membranes. Required for ciliogenesis and sonic hedgehog/SHH signaling (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18513680}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Joubert syndrome;Meckel syndrome;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa |
|
This gene encodes a coiled-coil and calcium binding domain protein that appears to play a critical role in cilia formation. Mutations in this gene cause Meckel syndrome type 6, as well as Joubert syndrome type 9. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:57545; |
ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; MKS complex [GO:0036038]; axoneme assembly [GO:0035082]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; embryonic brain development [GO:1990403]; heart development [GO:0007507]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; motile cilium assembly [GO:0044458]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; protein localization to ciliary transition zone [GO:1904491]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
18387594_A homozygous splice-site mutation segregating in the family with autosomal-recessive mental retardation, within a coiled-coil and C2 domain-containing gene, CC2D2A was identified. 18513680_CC2D2A appears to have at least two cilia-related functions: the molecule seems to be a part of the basal body complex where the cilium is assembled from and also seems to act as a sensor for the intracellular calcium. 18950740_CC2D2A is mutated in Joubert syndrome and interacts with the ciliopathy-associated basal body protein CEP290. 19068953_CC2D2A causes autosomal-recessive mental retardation with retinitis pigmentosa. 19574260_Mutations in MKS3 are responsible for the majority of COACH syndrome, with minor contributions from CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L. 19777577_Mutations within the CC2D2A gene are associated with Meckel and Joubert syndromes. 21068128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22023432_Results suggest the involvement of CC2D1A and CC2D2A in mental retardation in the Han Chinese population, and some specific haplotypes may be susceptible or protective. 22241855_CC2D2A testing should be prioritised in patients with JS and ventriculomegaly and/or seizures. Patients with CC2D2A-related JS should be monitored for hydrocephalus and seizures. 26485645_these data support a model where CC2D2A associates with NINL to provide a docking point for cilia-directed cargo vesicles, suggesting a mechanism by which transition zone proteins can control the protein content of the ciliary compartment. 26862157_Mutations in CC2D2A were the most common cause of an antenatal cystic kidney disease and a suspected ciliopathy in Saudi Arabian cohort. 28374938_Using a dedicated bioinformatics algorithm for TE detection, we identified an exonic retrotransposon insertion of L1 to the CC2D2A locus in a patient with Meckel-Gruber syndrome, the most severe form of the ciliopathy phenotypes. 30267408_Our study identifies for the first time CC2D2A mutations in isolated RCD and underlines the power of WES to decipher complex phenotypes. 31577543_Atypical, milder presentation in a child with CC2D2A and KIDINS220 variants. 32747192_Primary cilia biogenesis and associated retinal ciliopathies. 32989887_Whole exome sequencing identified a novel missense alteration in CC2D2A causing Joubert syndrome 9 in a Pakhtun family. 33486889_Update of genetic variants in CEP120 and CC2D2A-With an emphasis on genotype-phenotype correlations, tissue specific transcripts and exploring mutation specific exon skipping therapies. |
ENSMUSG00000039765 |
Cc2d2a |
17.559554 |
0.0795016103 |
-3.652872 |
0.539207128 |
51.211938 |
0.00000000000082912865117910976429753038895053592191239366648858322150772437453269958496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004958646228283492958615705043608543447011816063252354069845750927925109863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.2662098 |
0.8090956 |
29.4554490 |
5.4253231 |
| ENSG00000049089 |
1298 |
COL9A2 |
protein_coding |
Q14055 |
FUNCTION: Structural component of hyaline cartilage and vitreous of the eye. |
3D-structure;Collagen;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Stickler syndrome |
|
This gene encodes one of the three alpha chains of type IX collagen, the major collagen component of hyaline cartilage. Type IX collagen, a heterotrimeric molecule, is usually found in tissues containing type II collagen, a fibrillar collagen. This chain is unusual in that, unlike the other two type IX alpha chains, it contains a covalently attached glycosaminoglycan side chain. Mutations in this gene are associated with multiple epiphyseal dysplasia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1298; |
collagen type IX trimer [GO:0005594]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] |
11308397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11805640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12244547_mutations leading to skipping of exon 3 within the COL3 domain of the alpha2-chain of collagen type IX may be relatively common in patients with a special subtype of multiple epiphyseal dysplasia 12782139_Both Trp2 and Trp3 allelic products are incorporated into cross-linked fibrillar network of developing human cartilage apparently normally. Any pathological consequences are likely to be long-term and indirect rather than from overt misassembly of matrix. 15167667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15523498_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15625128_The collagen IX is cartilage specific, and expressed in hypertrophic chondrocytes and bone. 15922184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16133074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16249825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16371896_A population study using magnetic resonance imaging to define degenerative disc disease demonstrates that the TRP2 allele (Gln326Trp)of COL9A2 is a significant risk factor for development and severity of degeneration. 16371896_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16440132_A Japanese family with an autosomal dominant multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED EDM2) was studied; genomic analysis for COL9A2 identified an Ex3-1A>G heterozygous mutation, which has been proved to result in skipping of exon 3. 16586133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17024315_Association of a COL9A2 specific haplotype with lumbar disc disease in the Japanese population. 17024315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17471097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18080148_Homozygosity for the Arg allele of Col9A2 seems to be more frequent in the patient group with early recurrence although the differences in the allele frequencies were statistically not significant. 18080148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18246003_COL9A2 polymorphisms were associated with intervertebral disc mechanics, relating genetic variations and debilitating mechanical alterations that may ultimately result in intervertebral disc degeneration. 18246003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18469698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20358595_This study extends the range of gene-mutations that can cause multiple epiphyseal dysplasia-related myopathy. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21159828_Data show that the associating G allele in COL9A2 changes a glutamine to arginine or to tryptophan and may predispose to both hip osteoarthritis and lumbar disc degeneration, making it a candidate for degenerative connective tissue diseases. 21228751_Data indicate that no causal SNPs in COL9A2 were significantly associated with LSS, but Haplotype Analysis showed that the 'GCAGCG' haplotype (HAP2) was overrepresented in LSS patients. 21311409_Studies indicate that two SNPs that introduce tryptophan polymorphisms in COL9A2 and COL9A3 are independently linked to an increased risk of lumbar disc disease. 21671392_loss of function mutation in the COL9A2 gene causes autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome 23132862_The NC2 domain of type IX collagen determines the chain composition but also the chain register of the triple helix. 24636772_The allelic variants in the collagen IX genes - COL9A2 and COL9A3 have been identified as genetic risk factors for intervertebral disc disease--{review} 24711017_Two novel mutations, c.143G>C in exon 2 and c.884G>A in exon 17 of the COL9A2 gene, may contribute to the development of pathological myopia. 24983932_Meta-analysis. Our results suggest that the COL9A2 rs12077871, rs12722877, and rs7533552 polymorphisms may not be associated with lumbar disc disease. 28002589_Study provides evidence that the COL9A2 Gln326Arg polymorphism contributes to the development of intervertebral disc disease in the Chinese population. 29506578_rs12077871, rs12722877, and rs7533552 variants in COL9A2 were not significantly associated with a predisposition to lumbar disc degeneration. 30288688_No significant association was found between COL9A2 polymorphism rs7533552 and the risk of lumbar disc degeneration. 31090205_Homozygous type IX collagen variants, COL9A1, COL9A2, and COL9A3, causing recessive Stickler syndrome, expand the disease phenotype. 32419506_Lack of association between COL1A1 and COL9A2 single nucleotide polymorphisms and intervertebral disc degeneration. 33356723_Autosomal recessive Stickler syndrome associated with homozygous mutations in the COL9A2 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000028626 |
Col9a2 |
1315.237742 |
0.3501641948 |
-1.513897 |
0.050692968 |
905.245487 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000071042541143702810971411889556068168016988484015566534011611059334788305523221457494898414329606721084751252416791125972145148569631 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064330546458960340008821851144543351287679979673752382306115238009465226654356416583559893805096904483589967554620872140448020031502 |
Yes |
No |
690.5058346 |
22.0441241 |
1987.1035634 |
40.2739945 |
| ENSG00000049192 |
11174 |
ADAMTS6 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKP5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. Members of the family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature enzyme. Expression of this gene may be regulated by the cytokine TNF-alpha. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:11174; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; cardiac septum development [GO:0003279]; coronary vasculature development [GO:0060976]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
16129570_Study shows that the ADAMTS6 transcript contains unusually large untranslated regions (UTRs) at both the 5' and 3'end, and the 5'UTR contains 11 AUG codons upstream of the predicted ADAMTS6 start codon. 18579725_The gain of function studies indicated that ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 6 activate NR5A1 gene expression. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26686553_Novel inguinal hernia susceptibility genes are identified as EFEMP1, WT1, EBF2 and ADAMTS6. 27542224_ADAMTS6 inhibits breast tumor development by regulating the ERK pathway via binding of miR-221-3p 27779234_Using siRNA, over-expression and mutagenesis, it was found ADAMTS6 inhibits and ADAMTS10 is required for focal adhesions, epithelial cell-cell junction formation, and microfibril deposition. 29475036_High ADAMTS-6 expression is a marker of poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 30012220_Exome-chip meta-analysis identifies novel loci associated with cardiac conduction, including ADAMTS6. 33851708_Identified a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 6 serve as a novel gastric cancer prognostic biomarker by bioinformatics analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000046169 |
Adamts6 |
17.064740 |
0.1576761017 |
-2.664964 |
0.598717828 |
20.686436 |
0.00000540978692171837939459870872593860724464320810511708259582519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017533696742328345314059639958870207010477315634489059448242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1180603 |
2.1157396 |
32.4789641 |
8.0263139 |
| ENSG00000049249 |
3604 |
TNFRSF9 |
protein_coding |
Q07011 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFSF9/4-1BBL. Possibly active during T cell activation. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor contributes to the clonal expansion, survival, and development of T cells. It can also induce proliferation in peripheral monocytes, enhance T cell apoptosis induced by TCR/CD3 triggered activation, and regulate CD28 co-stimulation to promote Th1 cell responses. The expression of this receptor is induced by lymphocyte activation. TRAF adaptor proteins have been shown to bind to this receptor and transduce the signals leading to activation of NF-kappaB. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3604; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033084] |
12009595_intragraft gene expression is not a risk factor for acute cardiac allograft rejection 12356681_4-1BB enhanced expansion, survival and effector functions of newly primed CD8(+) T cells. 12384425_4-1BB plays a role in the differentiation of CD28(-)CD8(+) effector memory CTLs in cord blood. 12516549_relative importance of CD134 (OX40) and CD137 (4-1BB) in the costimulation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells under comparable conditions of antigenic stimulation 12645943_4-1 BB ligand can costimulate human CD28- T cells, resulting in cell division, inflammatory cytokine production, increased perforin levels, enhancement of cytolytic effector function, as well as the up-regulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-X(L). 13130507_First evidence of expression and synthesis of CD137 and its ligand by human brain cells. 14716821_4-1BB mRNA, which was not detectable in normal liver, was found in 19 liver tissues adjacent to tumor edge ( |
ENSMUSG00000028965 |
Tnfrsf9 |
161.907507 |
6.4809465284 |
2.696205 |
0.165736930 |
284.880085 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064889310029078796309119630264107669777440944284334371432157309937404328176269552710902291828832995287053648172101783902501434872466542242883258766865349205336943594346621466684155166149139404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000017703626913663640835178373516536353914726561178813281285109781508794668492701437065746929645720765777249185695964418530958296466151407942834443849261267123901264497476404358167201280593872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
283.0808412 |
30.3710909 |
43.8929217 |
4.0804727 |
| ENSG00000049449 |
5954 |
RCN1 |
protein_coding |
Q15293 |
FUNCTION: May regulate calcium-dependent activities in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen or post-ER compartment. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
Reticulocalbin 1 is a calcium-binding protein located in the lumen of the ER. The protein contains six conserved regions with similarity to a high affinity Ca(+2)-binding motif, the EF-hand. High conservation of amino acid residues outside of these motifs, in comparison to mouse reticulocalbin, is consistent with a possible biochemical function besides that of calcium binding. In human endothelial and prostate cancer cell lines this protein localizes to the plasma membrane.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:5954; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701] |
18561328_RCN1 also is expressed on the cell surface of several endothelial cell lines, including human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMVECs), bone marrow endothelial cells (BMEC), and transformed human bone marrow endothelial cells (TrHBMEC). 18688696_Data show that calumenin in the presence of calcium binds specifically to thrombospondin-1, but closely-related reticulocalbin does not form a similar complex. 19474196_deletion of Rcn1 directly or indirectly contributes to the eye phenotype in Pax6 contiguous gene deletions 20724591_Increased RCN1 is associated with systemic sclerosis and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. 21272564_reticulocalbin-1 may be an important molecule in understanding lymphatic endothelial cells in tumors function and control of lymphatic metastasis. 23916412_a promising role of RCN1 as a possible marker in Renal cell carcinoma 24451493_Ca(2+) binding caused an increase in the alpha-helix content of human RCN1. On the other hand, RCN1 did not change the structure with Mg. 25242635_reticulocalbin-1 plays a key role in the development of doxorubicin-associated resistance 27468573_RCN1 expression was not statistically significantly different to healthy controls but was associated with disease activity score and could be used as a stratification biomarker for systemic sclerosis patients. 27790916_irradiated tumor cells were observed to significantly up-regulate the expression of calcium-binding proteins CALM1, CALU, and RCN1, suggesting important roles for these mediators in promoting tumor cell survival during hypoxia 29453900_RCN1 may promote cell survival and serve as a useful target for cancer therapy. 30172915_Our data indicate that RCN1 expression may have an vital role at promoting the occurrence of non-small cell lung cancer 32436770_Reticulocalbin-1 knockdown increases the sensitivity of cells to Adriamycin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell apoptosis. 32871760_Salivary NUS1 and RCN1 Levels as Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis. |
ENSMUSG00000005973 |
Rcn1 |
876.788846 |
2.5426004469 |
1.346305 |
0.085275716 |
245.563810 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000024077038870184354926534012785355224956626963716111789399833615954868483711626042108458928778234677642690529386712862836033175381890234368741782189360378652054350823163986206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005686033499582737029943141885605291683605904442936765295046636058263422836555814333808315201850834884139110301467587614796624076647126033723367299899109639227390289306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1274.9324138 |
65.8648173 |
505.2234124 |
19.8185463 |
| ENSG00000049759 |
23327 |
NEDD4L |
protein_coding |
Q96PU5 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates the polyubiquitination of lysine and cysteine residues on target proteins and is thereby implicated in the regulation of various signaling pathways including autophagy, innate immunity or DNA repair (PubMed:31959741, PubMed:33608556, PubMed:20064473). Inhibits TGF-beta signaling by triggering SMAD2 and TGFBR1 ubiquitination and proteasome-dependent degradation (PubMed:15496141). Downregulates autophagy and cell growth by ubiquitinating and reducing cellular ULK1 or ASCT2 levels (PubMed:28820317, PubMed:31959741). Promotes ubiquitination and internalization of various plasma membrane channels such as ENaC, SCN2A/Nav1.2, SCN3A/Nav1.3, SCN5A/Nav1.5, SCN9A/Nav1.7, SCN10A/Nav1.8, KCNA3/Kv1.3, KCNH2, EAAT1, KCNQ2/Kv7.2, KCNQ3/Kv7.3 or CLC5 (PubMed:26363003, PubMed:27445338). Promotes ubiquitination and degradation of SGK1 and TNK2. Ubiquitinates BRAT1 and this ubiquitination is enhanced in the presence of NDFIP1 (PubMed:25631046). Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). Involved in the regulation of TOR signaling (PubMed:27694961). Ubiquitinates and regulates protein levels of NTRK1 once this one is activated by NGF (PubMed:27445338). Plays a role in antiviral innate immunity by catalyzing 'Lys-29'-linked cysteine ubiquitination of TRAF3, resulting in enhanced 'Lys-48' and 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of TRAF3 (PubMed:33608556). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CFI0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12911626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15040001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15217910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15489223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15496141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15576372, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19144635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25631046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26363003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27445338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27694961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33608556}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a member of the Nedd4 family of HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases transfer ubiquitin from E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes to protein substrates, thus targeting specific proteins for lysosomal degradation. The encoded protein mediates the ubiquitination of multiple target substrates and plays a critical role in epithelial sodium transport by regulating the cell surface expression of the epithelial sodium channel, ENaC. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with essential hypertension. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:23327; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; potassium channel inhibitor activity [GO:0019870]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; sodium channel inhibitor activity [GO:0019871]; sodium channel regulator activity [GO:0017080]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901380]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901017]; negative regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000009]; negative regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1902306]; negative regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:2000650]; positive regulation of caveolin-mediated endocytosis [GO:2001288]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; regulation of membrane depolarization [GO:0003254]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; regulation of membrane repolarization [GO:0060306]; regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901016]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1902305]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086005] |
11840194_Candidate gene for autosomal dominant orthostatic hypotensive disorder. 12139396_This ubiquitin-protein ligase is expressed in mouse mandibular salivary duct cells and regulates the amiloride-sensitive Na+ conductance in these cells. 12522688_The ubiquitin ligase NEDD4L is a candidate gene for essential hypertension on both functional and genetic grounds 12876068_Alternate transcripts of Nedd4-2 may interact with ENaC differently. hNedd4-2 has role in regulation of ENaC. Protein domains are important for Nedd4-2 function. 12876068_Identification of multiple splice forms and 5' variants of Nedd4l. 5' variants inhibit ENaC-mediated Na+ transport when reconstituted in FRT epithelia. Other splice forms encode Nedd4L isoforms with 2 to 4 WW domains having varying affinity for ENaC. 14615060_Results describe the isolation of three new NEDD4L transcripts designated NEDD4Lf, NEDD4Lg and NEDD4Lh, which encode different forms of the NEDD4L protein. 15044175_SGK1 stimulates the NaPi IIb, at least in part, by phosphorylating and thereby inhibiting Nedd4-2 binding to its target. 15140763_The differential phosphorylation status between wild-type and mutant Nedd4-2 provides an explanation for the different potential to inhibit ENaC activity. 15328345_cAMP regulates ENaC in part by phosphorylation and inhibition of Nedd4-2. Moreover, Nedd4-2 is a central convergence point for kinase regulation of Na(+) transport. 15576372_Nedd4-2 phosphorylation induces SGK ubiquitination and degradation 16103266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16103266_Significant association between several SNPs and hypertension in US whites, Greek whites, and African-Americans. Genetic variation in NEDD4L may play role in development or progression of some forms of hypertension. 16716084_14-3-3 inhibits the interaction between the WW domains of hNedd4-2 and the PY motif of the epithelial Na(+) channel, ENaC 16788695_genetic NEDD4L variation affecting cross-sectional and longitudinal blood pressure is possibly as a consequence of altered NEDD4L interaction with ENaC 17331106_Study identified three NEDD4-2 missense changes in highly conserved residues (S233L, E271A and H515P) in families with photosensitive generalized epilepsy. 17487281_Genetic NEDD4L variation seems to affect salt sensitivity and P-renin in normotensive subjects, suggesting that genotyping of NEDD4L may be clinically useful to identify subjects who benefit from dietary salt restriction in the prevention of hypertension 17487281_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17502380_Nedd4-2 binds to and ubiquitinates ENaC at the cell surface, which targets surface ENaC for degradation, and thus, reduces epithelial Na(+) transport. 17544362_G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 interacts not only with epithelial Na(+) channels, but also with both Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 17652939_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18268134_The human Nedd4L gene, especially the evolutionarily new isoform I, is a candidate gene for hypertension. 18293164_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18293164_Our results support rs3865418 but not rs4149601 polymorphism of NEDD4L gene implicated in the prevalence of hypertension in Chinese Hans. 18321968_These observations suggest that NEDD4L and possibly other NEDD4-like proteins can ubiquitylate and activate ESCRT-I to function in virus budding. 18321969_budding of various HIV-1 L-domain mutants is dramatically enhanced by ectopic Nedd4-2s, a native isoform with a truncated C2 domain. 18322022_Nedd4-2 reduces the half-life of epithelial sodium channel subunits and enhances the ubiquitination of alpha, beta, and gamma epithelial sodium channels 18498246_WW domains of Nedd4-2 bind (weakly) to a PY motif (LPXY) located within its own HECT domain and inhibit auto-ubiquitination. HECT PY-motif mutation does not affect ubiquitination or down-regulation of a known Nedd4-2 substrate, ENaC. 18577513_Nedd4-2 differentially interacts with and regulates TTYH1-3 18591455_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18591455_Physiological interaction between the ADD1 and WNK1-NEDD4L pathways influences the effects of variants in these genes on sodium-related BP regulation. 19144635_the interplay between Nedd4-2-related E3 ligases that regulate ACK1 levels and Cbl that modifies EGF receptor impinges on cell receptor dynamics. 19364400_Whereas the C2 domain-containing NEDD4L isoform is capable of shuttling between the plasma membrane and intracellular compartments in response to calcium stimulus the C2-lacking isoform can not. 19381069_The protein-protein interaction between the WW domain of Fe65 and the putative binding motif of Nedd4-2 down-regulates Fe65 protein stability and subcellular localization through its ubiquitylation, to contribute to cell apoptosis. 19615332_the loss of NEDD4 association on IL-2Rgamma(c) is accompanied by a dramatic increase of the half-life of the receptor subunit. 19617352_the SGK1/Nedd4-2 signaling pathway regulates both CFTR and ENaC trafficking in CF epithelial cells 19635985_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19635985_The A allele of NEDD4L may be a useful marker for predicting hypertension, orthostatic hypotension, and antihypertensive response to hydrochlorothiazide. 19664597_NPC2 binds C2 domain of human Nedd4L. 19690890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706893_Nedd4-2 is an E3 ligase recruited by Ndfip1 for the ubiquitination of DMT1 within human neurons. 19917253_Results identify Nedd4L as the ubiquitin ligase in TGF-beta induced phosphorylation of the transcription factors Smad2 and Smad3. 19953087_Although several substrates were recognized by both Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2, others were specific to only one, with several Tyr kinases preferred by Nedd4-1 and some ion channels by Nedd4- 20003179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20003179_two common SNPs of NEDD4L (296921-296923delTTG and rs2288775), were found to be associated with essential hypertension in Kazakh females 20051513_role of WW3 and WW4 domains of Nedd4-2 in dopamine transporter ubiquitination was demonstrated; siRNA analysis demonstrated that this polyubiquitination is mediated by Nedd4-2 cooperation with UBE2D and UBE2L3 E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes 20064473_Results describe the crystal structure of a complex between the HECT domain of NEDD4L and the E2 UbcH5B bearing a covalently linked Ub at its active site (UbcH5B approximately Ub). 20090362_the role of NEDD4L-mediated ubiquitination in the pathogenesis of hypertension is disscussed 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20466724_analysis of phosphorylatable residues that activate Nedd4-2 and may work together with residues targeted by inhibitory kinases (SGK1 and protein kinase A) to govern Nedd4-2 regulation of epithelial ion transport 20504882_Nedd4-2 interacts with occludin to inhibit tight junction assembly and the regulation of paracellular conductance in the collecting duct. 20675381_Nedd4-2 induces binding of ENaC to Hrs, which mediates the sorting decision between ENaC degradation and recycling. 21039987_Over-expression of Nedd4L might lead to gallbladder cancer invasion by regulating the transcription of the MMP-1 and MMP-13 genes. 21052022_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21052022_NEDD4L rs4149601 polymorphism influences the efficacy of beta-blocker and/or diuretic-based antihypertensive treatment both in terms of blood pressure reduction and cardiovascular disease protection. 21088674_Combining gene expression profiling and linkage analysis identified NEDD4L as a candidate gene involved in regulating sodium lithium countertransport activity. 21154329_genetic variations of the NEDD4L gene may be associated with obesity in Xinjiang Kazakh general population 21176637_D-C-G-G haplotype of NEDD4L but not rs4149601 polymorphism was linked with hypertension in Kazakh. 21478478_the data support the conclusion that Usp2-45 action on epithelial Na(+) channel is promoted by various interactions, including through binding to Nedd4-2 21852580_stimulated NCC ubiquitylation at the surface of transfected HEK293 cells 21900244_Neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 4-2 (Nedd4-2) regulation by 14-3-3 protein binding at canonical serum and glucocorticoid kinase 1 (SGK1) phosphorylation sites. 21909941_Our results suggest for the first time that negative Nedd4L expression is strongly related to the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer 22217575_expression of Nedd4L is down-regulated in human gliomas. 22361880_Nedd4-2 mediated ubiquitination regulates the cell surface expression of CHT1 in HEK293 cells. 22385262_Three members of Nedd4 (neural-precursor-cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated)-like ubiquitin E3 ligases, Nedd4, Nedd4-2 and Itch were identified, as the ubiquitin E3 ligases for the long isoform of AMOT, AMOT/p130. 22505712_GLT-1 endocytosis is independent of its phosphorylation and that Nedd4-2 mediates PKC-dependent down-regulation of the transporter. 22879586_hERG expression in the plasma membrane is regulated by Cav3 via Nedd4-2 22904170_Nedd4-2 does not ubiquitinate and thereby regulate wt-CFTR in human airway epithelial cells. 22957059_CNP12587 region, overlapping NEDD4L, may have a role in underlying height variation in Chinese females 23262292_Understanding of the contribution of Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 in regulating key functions in the brain is shedding new light on the ubiquitination signal not only in orchestrating degradation events but also in protein trafficking 23353631_NEDD4L rs4149601, rs292449 and rs75982813 may be predictors for blood pressure response to hydrochlorothiazide in whites, and NEDD4L rs4149601 may be a predictor for adverse cardiovascular outcomes in whites not treated with hydrochlorothiazide 23396981_NEDD4L is a negative feedback regulator of Wnt signaling. 23549273_These results suggested that the functional variant of NEDD4L, rs4149601, may be associated with obesity and related phenotypes, and further genetic and functional studies are required to understand its role in the manifestation of obesity. 23589291_SGK1,3 enhances the expression level of mature hERG channels by inhibiting Nedd4-2 as well as by promoting Rab11-mediated hERG recycling. 23594824_WNK4 inhibits ENaC channel activity independently of Nedd4-2-mediated ENaC ubiquitination. 23792956_Data indicate that Rab4 regulates ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) channel density via neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 4-2 (Nedd4-2). 23812770_Low NEDD4L expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 24047422_Genetic variation in NEDD4L may have sex-dependent effects in the development of essential hypertension in Han Chinese 24214981_PI3K-SGK1 pathway stabilizes Kv7.1 surface expression by inhibiting Nedd4-2-dependent endocytosis and thereby demonstrates that Nedd4-2 is a key regulator of Kv7.1 localization and turnover in epithelial cells. 24284497_The NEDD4L salt sensitivity-associated genotype was associated with higher blood pressure, which may translate into increased risk for CVD morbidity and mortality. 24312311_NEDD4L may play a tumor suppressive role in colorectal cancer 24373531_NEDD4L-rs12606138 and rs8094327 are risk factors for dyslexia in a German cohort. 24446284_rs2288775 was significantly associated with metabolic syndrome x in female Kazakh in China. 24451387_Nedd4-2 plays an important role in the regulation of HCN1 trafficking and may compete with TRIP8b(1a-4) in this process 24456330_Nedd4L expression may be increased to facilitate tumour growth in many melanomas. 24657276_glucocorticoid stimulation therefore appears to allow cAMP-dependent control of Na(+) absorption by facilitating the effects of PKA upon the Nedd4-2 24831004_Human NHE3, but not non-primates NHE3s, is ubiquitinated by Nedd4-2. 25295397_The mechanisms of activation and degradation of the NEDD4L:the transition from the closed to the active form is regulated by a competition of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and Ca2+. 25542253_Our results suggest that three screened NEDD4-2 variants do not play a leading role in the pathogenesis of photosensitive epilepsy in the Turkish population. 25785312_Proteomics analysis of EV71-infected cells reveals the involvement of host protein NEDD4L in EV71 replication. 26130719_DDB2 can bind to the promoter region of NEDD4L and recruit enhancer of zeste homolog 2 histone methyltransferase to repress NEDD4L transcription by enhancing histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation at the NEDD4L promoter. 26363003_Data show that membrane protein Ndfip1 recruits E3 ubiquitin (Ub) ligase Nedd4-2 to the Golgi to target ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) channel for degradation while membrane protein Ndfip2 also mediates Nedd4-2 interaction with hERG in the Golgi. 26554540_the regulation of Nedd4L protein expression may play a role in the development of ovarian cancers. 26581907_overexpression of miR-93 in lung cancer cells promoted TGF-b-induced EMT through downregulation of NEDD4L. The analysis of publicly available gene expression array datasets indicates that low NEDD4L expression correlates with poor outcomes among patients with lung cancer, further supporting the oncogenic role of miR-93 in lung tumorigenesis and metastasis. 26608079_Propose regulation of placental SNAT2/LAT1 ubiquitination by mTORC1 and Nedd4-2. 26740304_Overexpression of Nedd4-2 enhanced hOAT4 ubiquitination, and inhibited hOAT4 transport activity. 26823285_both Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2 are important regulators for hOAT1 ubiquitination, expression, and function 27022162_These findings provide evidence that Nedd4-2 is up-regulated in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress by the spliced form of X-box binding protein 1 and that this is important in the induction of an appropriate autophagic response. 27146988_This study demonstrated that it is possible to downregulate Kv1.3 channel density through activation of an E3 ubiquitin ligase and that inhibition of the protease pathway or mutation of the Nedd4-2 catalytic site prevents Kv1.3 modulation. 27339899_NEDD4L negatively regulates PIK3CA protein levels via ubiquitination and is required for the maintenance of PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. 27445338_USP36 actions extend beyond TrkA because the presence of USP36 interferes with Nedd4-2-dependent Kv7.2/3 channel regulation. 27694961_evidence implicating E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4L in the pathogeny of periventricular nodular heterotopia 28017963_study demonstrated significant genetic interaction on Na intake with child obesity by salt-sensitive genes variations, NEDD4L and CYP11beta2 28572241_WW3 and WW4 domains of Nedd4-2 are critical for its association with and modulation of the transporter. 28608480_Sgk1 stimulated OAT3 transport activity by interfering with the inhibitory effect of Nedd4-2 on the transporter. This study provides important insights into how OAT3-mediated drug elimination is regulated in vivo. 28820317_ULK1 phosphorylation at 3 different sites on the same ULK1 target region for NEDD4L is preparatory for its ubiquitylation and subsequent degradation. 29175326_Collectively, Nedd4L plays a tumor suppressive role in HCC, possibly through triggering MAPK/ERK-mediated apoptosis, and Nedd4L downregulation may be a potential prognostic biomarker as well as a therapeutic target for HCC. 29662198_A critical role for the miR106b-25/NEDD4L/NOTCH1 axis in the disease. 30232011_NEDD4-2 Y485 is critical for GPCR inflammatory signaling. 30287686_a conserved catalytic ensemble comprising Glu-646 and Arg-604 that supports HECT-ubiquitin thioester exchange and isopeptide bond formation was identified at the active-site Cys-922 of NEDD4-2. 30967264_Downregulation of NEDD4L is found in non-small cell lung cancer samples compared with normal samples. NEDD4L low expression could be an independent prognostic factor. NEDD4L suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. 31357244_that the C2-lacking Nedd4-2 represses excitatory synaptic strength most likely through GluA1 ubiquitination-independent mechanisms 31618441_Novel genetic variants in KIF16B and NEDD4L in the endosome-related genes are associated with nonsmall cell lung cancer survival. 31673244_We observed that the NEDD4L mRNA and protein levels decreased significantly (P C (p.Leu706Pro) of the NEDD4L gene probably underlies the periventricular nodular heterotopia 7 disorders in the patient. 31959741_NEDD4L downregulates autophagy and cell growth by modulating ULK1 and a glutamine transporter. 31993646_A Variant in the NEDD4L Gene Associates With Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease in the Southeastern Han Chinese Population. 32332792_Study shows that NEDD4-2 protein levels are reduced in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and identifies extra- and intracellular disease mechanisms that link Nedd4-2 deficiency to impaired muco-ciliary clearance and dysregulation of TGFbeta signaling, two abnormalities that have been implicated in the pathogenesis of IPF. 32811647_NEDD4L-mediated LTF protein degradation limits ferroptosis. 33045005_Novel loci for childhood body mass index and shared heritability with adult cardiometabolic traits. 33058421_NEDD4L-mediated Merlin ubiquitination facilitates Hippo pathway activation. 33106424_USP7 regulates ALS-associated proteotoxicity and quality control through the NEDD4L-SMAD pathway. 34284061_Interactions between AMOT PPxY motifs and NEDD4L WW domains function in HIV-1 release. 34319380_Association Between NEDD4L Variation and the Genetic Risk of Acute Appendicitis: A Multi-institutional Genome-Wide Association Study. 34475212_Tril dampens Nodal signaling through Pellino2- and Traf6-mediated activation of Nedd4l. 35090513_Downregulation of NEDD4L by EGFR signaling promotes the development of lung adenocarcinoma. 35145234_CircKDM4B suppresses breast cancer progression via the miR-675/NEDD4L axis. 35353342_NEDD4L suppresses PD-L1 expression and enhances anti-tumor immune response in A549 cells. 35593463_NEDD4L inhibits cell viability, cell cycle progression, and glutamine metabolism in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via ubiquitination of c-Myc. 35964538_CircRNA circUSP36 impairs the stability of NEDD4L mRNA through recruiting PTBP1 to enhance ULK1-mediated autophagic granulosa cell death. |
ENSMUSG00000024589 |
Nedd4l |
81.113911 |
3.6198999667 |
1.855950 |
0.532572830 |
11.417939 |
0.00072738322161213430847026550907230557641014456748962402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001735840962165740089528931378026754828169941902160644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
115.8448711 |
38.2547479 |
31.9787719 |
7.7773303 |
| ENSG00000050393 |
63933 |
MCUR1 |
protein_coding |
Q96AQ8 |
FUNCTION: Key regulator of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) required for calcium entry into mitochondrion (PubMed:23178883, PubMed:26445506, PubMed:27184846, PubMed:26976564). Plays a direct role in uniporter-mediated calcium uptake via a direct interaction with MCU (PubMed:23178883). Probably involved in the assembly of the membrane components of the uniporter complex (uniplex) (PubMed:27184846). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23178883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26445506, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26976564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27184846}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium transport;Coiled coil;Ion transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Involved in calcium import into the mitochondrion and positive regulation of mitochondrial calcium ion concentration. Is integral component of mitochondrial inner membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:63933; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; calcium import into the mitochondrion [GO:0036444]; calcium ion import [GO:0070509]; mitochondrial calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0006851]; positive regulation of mitochondrial calcium ion concentration [GO:0051561] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25565209_CCDC90A is not directly implicated in MCU function, and that the Ca2+ uptake defect associated with loss of CCDC90A function is likely secondary to the respiratory chain deficiency. 26976564_MCUR1 regulates the calcium threshold for the mitochondrial permeability transition. 27001609_Data suggest that MCU regulator (EMRE) might be a structural factor for opening of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU)-forming pore. 28938844_The survival advantage conferred by MCUR1-mediated mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake was majorly caused by elevated production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and subsequent AKT/MDM2- induced P53 degradation. 30909929_Results found MCUR1 expression significantly higher in HCC with metastasis and associated with tumor progression. The essential role of MCUR1 in promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration was found through the activation of ROS/Nrf2/Notch signaling by inducing mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake. 32978391_Yeast homologs of human MCUR1 regulate mitochondrial proline metabolism. 34459387_MCUR1 is a prognostic biomarker for ovarian cancer patients. |
ENSMUSG00000021371 |
Mcur1 |
107.700152 |
2.3240644593 |
1.216650 |
0.324022831 |
13.707250 |
0.00021362821321787206409886783475826632638927549123764038085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000556405933844325269535535660736513818847015500068664550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
152.5024682 |
31.2109258 |
65.8073573 |
9.8461252 |
| ENSG00000050405 |
51474 |
LIMA1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHB6 |
FUNCTION: Actin-binding protein involved in actin cytoskeleton regulation and dynamics. Increases the number and size of actin stress fibers and inhibits membrane ruffling. Inhibits actin filament depolymerization. Bundles actin filaments, delays filament nucleation and reduces formation of branched filaments (PubMed:12566430). Plays a role in cholesterol homeostasis. Influences plasma cholesterol levels through regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption. May act as a scaffold protein by regulating NPC1L1 transportation, an essential protein for cholesterol absorption, to the plasma membrane by recruiting MYO5B to NPC1L1, and thus facilitates cholesterol uptake (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ERG0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12566430}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;LIM domain;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a cytoskeleton-associated protein that inhibits actin filament depolymerization and cross-links filaments in bundles. It is downregulated in some cancer cell lines. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene, and expression of some of the variants maybe independently regulated. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:51474; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin monomer binding [GO:0003785]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; intestinal cholesterol absorption [GO:0030299]; negative regulation of actin filament depolymerization [GO:0030835]; ruffle organization [GO:0031529] |
18093941_EPLIN functions to link the cadherin-catenin complex to F-actin and simultaneously stabilizes this population of actin fibers, resulting in the establishment of the adhesion 18796137_expression of EPLIN-alpha in breast cancer is down-regulated in breast cancer cells . 19221476_EPLIN protein may function during cytokinesis to maintain local accumulation of key cytokinesis proteins at the furrow. 20848180_EPLINalpha over-expression can regulate HECV cell motility, matrix adhesion and tubule formation in vitro and slow in vivo tumour formation, suggesting an anti-angiogenic role for EPLINalpha. 21625216_EPLIN downregulation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells and correlates with clinical lymph node metastasis. 22194609_EPLIN clutch is necessary for stabilization of capillary structures in an angiogenesis model. 22493360_Together with the findings that EPLIN-alpha inhibits cellular growth and invasion, we conclude that EPLIN-alpha is a tumour suppressor of oesophageal cancer 23188829_EGF promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and induces degradation of EPLIN, a putative suppressor of prostate cancer metastasis. 24135282_a major activity of DNp73 is to establish initiation of the invasion-metastasis cascade via EPLIN-dependent IGF1R regulation 26350886_EPLIN is functionally linked to molecules like actin and paxillin and has been implicated in a number of potential pathways to enhance metastatic potential 27035883_Data provide evidence that downregulation of EPLIN-alpha may be associated with poor prognosis for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), and that this molecule appears to play a tumour suppressor role by inhibition of EOC growth and migration. 28465438_Reduction in the levels of hCDC14A and eplin mRNA is frequently associated with colorectal carcinoma and is correlated with poor prognosis. Authors therefore propose that eplin dephosphorylation by hCDC14A reduces actin dynamics to restrict tumor malignancy. 29880681_this study identifies LIMA1 as a key protein regulating intestinal cholesterol absorption. 30098000_Study proposes a role for EPLIN's ability to regulate the aggressive characteristics of prostate cancer cells partially through regulating FAK/Src signaling. 31644899_EPLIN-alpha and -beta Isoforms Modulate Endothelial Cell Dynamics through a Spatiotemporally Differentiated Interaction with Actin. 32496561_LUZP1 and the tumor suppressor EPLIN modulate actin stability to restrict primary cilia formation. 33999101_Rab40-Cullin5 complex regulates EPLIN and actin cytoskeleton dynamics during cell migration. 34356662_Epithelial Protein Lost in Neoplasm, EPLIN, the Cellular and Molecular Prospects in Cancers. |
ENSMUSG00000023022 |
Lima1 |
306.030753 |
5.1544829196 |
2.365828 |
0.135199102 |
304.018282 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004388762605112065743966201380005191824752434668839196267413748211949465053022621469968639145484044573080641574590097306615814343395134924028672234003498549142015909010038077209259199662483297288417816162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001280200317222412847388398053379428629117083631186827874216710155440306563594430947131975601224583194100236714239618217590579788732991804182507327261596483353682908792881001147634378867223858833312988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
516.8624322 |
38.4292122 |
101.0243914 |
6.2554669 |
| ENSG00000050820 |
9564 |
BCAR1 |
protein_coding |
P56945 |
FUNCTION: Docking protein which plays a central coordinating role for tyrosine kinase-based signaling related to cell adhesion (PubMed:12832404, PubMed:12432078). Implicated in induction of cell migration and cell branching (PubMed:12432078, PubMed:12832404, PubMed:17038317). Involved in the BCAR3-mediated inhibition of TGFB signaling (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61140, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12432078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12832404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17038317}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Diabetes mellitus;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;SH3-binding |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Crk-associated substrate (CAS) family of scaffold proteins, characterized by the presence of multiple protein-protein interaction domains and many serine and tyrosine phosphorylation sites. The encoded protein contains a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain, a proline-rich domain, a substrate domain which contains 15 repeat of the YxxP consensus phosphorylation motif for Src family kinases, a serine-rich domain, and a bipartite Src-binding domain, which can bind both SH2 and SH3 domains. This adaptor protein functions in multiple cellular pathways, including in cell motility, apoptosis and cell cycle control. Dysregulation of this gene can have a wide range of effects, affecting different pathways, including cardiac development, vascular smooth muscle cells, liver and kidney function, endothelial migration, and cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2017]. |
hsa:9564; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; actin filament reorganization [GO:0090527]; antigen receptor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0050851]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:0035729]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048012]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048011]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010] |
11779709_Tyrosine phosphorylation of p130CAS regulates localization and downstream signaling with profound affects on cell movement. 11820787_Binding of the adapter protein p130Cas to the C-terminal of Pyk2 in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells is phosphorylation-independent and is not affected by acute exposure to thrombin. 12135674_The association of Cas with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein is associated with cell migration in stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha-stimulated Jurkat cells 12397603_phosphorylation of p130(Cas) can prevent cells from anoikis and contribute to tumor cell anchorage independence and metastasis 12529399_R-Ras promotes focal adhesion formation by signaling to FAK and p130(Cas) through a novel mechanism that differs from but synergizes with the alpha2beta1 integrin. 12738793_Requirement of the p130CAS-Crk coupling for metastasis suppressor KAI1/CD82-mediated inhibition of cell migration in a metastatic prostate cancer cell line. 15121874_endogenous Sin influences T-lymphocyte signaling by sequestering signaling substrates and regulating their availability 15448007_BCAR1 has a role in progression of primary breast cancer 15784259_crystal structure of p130cas SH3 domain 15923424_Our studies suggested that pRb2/p130-complexes bind to the ER-alpha promoter and could be involved in the transcriptional regulation of the ER-alpha gene by altering chromatin structure and DNA methylation pattern. 16040804_p130Cas and paxillin function as effectors of GD3-mediated signaling, leading to such malignant properties as rapid cell growth and invasion in melanoma cells 16440329_LOX regulates cell motility/migration through changes in actin filament polymerization, which involve the regulation of the p130(Cas)/Crk/DOCK180 16597701_Fibronectin rigidity response involves force-dependent Fyn phosphorylation of p130Cas with rigidity-dependent displacement. 16644720_PTP1B mediates of RhoA-dependent phosphorylation of p130Cas. 17038317_The interaction between Ack1 and p130(Cas) occurred through their respective SH3 domains, while the substrate domain of p130(Cas) was the major site of Ack1-dependent phosphorylation. 17129785_Cas acts as a primary force sensor, transducing force into mechanical extension and thereby priming phosphorylation and activation of downstream signaling. 17251438_p130CAS is an important component in the netrin signaling pathway acting between tyrosine kinases and small GTPase Rac1 and is essential for commissural axon guidance in vivo. 17616674_the spatial and temporal regulation of BCAR3/p130(Cas) interactions within the cell is important for controlling breast cancer cell motility 17982677_Activation of the FAK-src molecular scaffolds and p130Cas-JNK signaling cascades by alpha1-integrins during colon cancer cell invasion. 18078823_Focal adhesion kinase as well as p130Cas and paxillin should be a crucial molecule undergoing stronger tyrosine phosphorylation in GD3-expressing melanoma cells. 18095869_focal adhesion kinase positively regulates Caco-2 spreading on collagen IV via p130(Cas) phosphorylation 18164686_The interaction of MT1-MMP with p130Cas at the cell periphery suggests the existence of a close interplay between pericellular proteolysis and signaling pathways involved in endothelial cell migration. 18321991_p130Cas-mediated control of TGF-beta/Smad signaling may provide an additional clue to the mechanism underlying resistance to TGF-beta-induced growth inhibition. 18725541_uPAR cooperates with integrin complexes containing beta(3) integrin to drive formation of the p130Cas-CrkII signaling complex and activation of Rac, resulting in a Rac-driven elongated-mesenchymal morphology, cell motility, and invasion. 18842495_In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), there is a negative correlation between the positive expression of p130Cas and the normal expression of E-cadherin/beta-catenin. p130Cas plays important roles in the invasion, metastasis and prognosis of HCC. 19029090_The lysyl oxidase pro-peptide attenuates fibronectin-mediated activation of focal adhesion kinase and p130Cas in breast cancer cells. 19086031_Data suggest that endothelin-1 stimulates the GTPase Rap1 by a mechanism involving Pyk2 activation and recruitment of the p130Cas/BCAR3 complex in human glomerular mesangial cells. 19329671_Evidence for the role of CAS in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle contractility, cell migration, hypertrophy, and growth is presented 19330798_targeting the product of the BCAR1 gene by a peptide which mimics the phosphorylated substrate domain may provide a new molecular avenue for treatment of antiestrogen resistant breast cancers. 19331827_BCAR1 is essential for the rapid estrogen effect on osteoclast differentiation, through estrogen receptor alpha and possibly Traf6. 19357231_Propofol inhibits pressure-stimulated macrophage phagocytosis via the GABAA receptor and dysregulation of p130cas phosphorylation. 19412734_The crucial interactions required for anti-estrogen resistance occur within the substrate domain of BCAR1 19822523_p130Cas is required for mammary tumor growth and transforming growth factor-beta-mediated metastasis through regulation of Smad2/3 activity 19844255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940159_the c-Src/Cas/BCAR3 signaling axis is a prominent regulator of c-Src activity, which in turn controls cell behaviors that lead to aggressive and invasive breast tumor phenotypes 20688056_CAS plays a role in regulating the extension of cell protrusions and promotes the migration of cancer cells. 20961652_Analyses indicate that p130Cas expression in ErbB2 positive human breast cancers significantly correlates with higher risk to develop distant metastasis, thus underlying the value of the p130Cas/ErbB2 synergism in regulating breast cancer invasion. 21047529_BCAR-1 is a physiological substrate of Syk. 21245381_Knockdown of NRP1 or P130Cas or expression of either NRP1DeltaC or a non-tyrosine-phosphorylatable substrate domain mutant protein (p130(Cas15F)) was sufficient to inhibit growth factor-mediated migration of glioma and endothelial cells. 21291860_p130Cas, Src and talin function in both oral carcinoma invasion and resistance to cisplatin. 21306301_These results indicate a role for NRP1 and NRP1 glycosylation in mediating PDGF-induced VSMC migration, possibly by acting as a co-receptor for PDGFRalpha and via selective mobilization of a novel p130Cas tyrosine phosphorylation pathway. 21630091_Immunohistochemical analysis of microarrayed human oral squamous cell carcinoma revealed a significant correlation between uPAR and p130cas expression. 21765937_Cas proteins do not affect E-cadherin transcription, but rather, BCAR1 and NEDD9 signal through SRC to promote E-cadherin removal from the cell membrane and lysosomal degradation. 21937722_These findings reveal an important role of CAS Y12 phosphorylation in the regulation of focal adhesion assembly, cell migration, and invasiveness of Src-transformed cells. 21957230_Increased p130cas expression is associated with poor clinical outcome in human ovarian carcinoma, and p130cas gene silencing decreases tumor growth through stimulation of apoptotic and autophagic cell death. 22081014_The structure of the NSP3-p130Cas complex reveals that this closed conformation is instrumental for interaction of NSP proteins with a focal adhesion-targeting domain present in Cas proteins. 22084245_a novel function for PTK6 at the plasma membrane 22106368_Data show that phosphorylation of Src family kinases and the adaptor protein p130CAS, resulting in actin recruitment and CD36 clustering by 50-60% of adherent beads. 22144090_CrkI and p130(Cas) complex regulates the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells. 22241677_BCAR1 is an independent predictor of recurrence following radical prostatectomy for 'low risk' prostate cancer. 22395610_Zyxin phenotype is mediated by partners alpha-actinin and p130Cas and ensures that motile cells in a three-dimensional matrix explore the largest space possible in minimum time. 22431919_p130Cas signaling induces the expression of EGR1 and NAB2 22476538_Ezrin and BCAR1/p130Cas mediate breast cancer growth as 3-D spheroids 22558353_Overexpression of BCAR1 is a predictor of poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer and plays important carcinogenic roles in carcinogenesis. 22711540_BCAR3 expression may regulate Src signaling in a BCAR3-p130(cas) complex-dependent fashion by altering the ability of the Src SH3 domain to bind the p130(cas) SBD 22892392_Study shows that BCAR4 expression identifies a subgroup of ER-positive breast cancer patients without overexpression of ERBB2 who have a poor outcome and might benefit from combined ERBB2-targeted and antioestrogen therapy. 23042269_The aim of this study is to evaluate the role of p130cas, E-cadherin, and beta-catenin expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 23098208_these data identify a new p130Cas/Cyclooxygenase-2 axis as a crucial element in the control of breast tumor plasticity. 23152477_This study identified rs4888378 in the BCAR1-CFDP1-TMEM170A locus as a novel genetic determinant of carotid intima-media thickness and coronary artery disease risk. 23239970_These results suggest that alteration of morphogenetic pathways due to p130Cas over-expression might prime mammary epithelium to tumorigenesis 23287717_p130Cas acts as survival factor by limiting PMA-mediated cell cluster disruption and resulting cell death in HL-60 cells. 23345605_Disruption of p130Cas attenuates both invasion and migration of the metastatic variant 23457408_BCAR1 rs7202877 may mediate its diabetogenic impact through impaired beta-cell function. 23740246_Data indicate that Abi1 is activated by the c-Abl-Crk-associated substrate (CAS) pathway, and Abi1 reciprocally controls the activation of its upstream regulator c-Abl. 23839042_P130Cas overexpression synergizes with ErbB2 in mammary cell transformation and promotes ErbB2-dependent invasion. 23872147_Our results suggest that elevated expression and tyrosine phosphorylation of p130Cas contributes to the resistance to TGF-beta-induced growth inhibition. 23904007_Increased BCAR1 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 24284072_Our results show that endogenous Cul5 suppresses epithelial cell transformation by several pathways, including inhibition of Src-Cas-induced ruffling through SOCS6 24494199_Data introduce hitherto unappreciated paradigms whereby reactive oxygen species can reciprocally regulate the cellular localization of pro- and anti-migratory signaling molecules, p130cas and PTEN, respectively. 24584939_BCAR1 and BCAR3 scaffolding proteins have roles in cell signaling and antiestrogen resistance 24928898_Cas promotes cell migration by linking actomyosin contractions to the adhesion complexes through interaction with Src and the actin cytoskeleton. 25253349_Collectively, these studies demonstrate that p130Cas acts as a bridging molecule between the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced entry signal complex and the downstream trafficking signalosome in endothelial cells. 25727852_BCAR1 has a pivotal role in the regulation of tissue homeostasis in pathological conditions such as cancer. (Review) 25805500_p130(Cas) exon 1 variants display altered functional properties; shorter 1B isoform exhibited diminished FAK binding activity + reduced cell migration + invasion; longest variant 1B1 exhibited the most efficient FAK binding + greatly enhanced migration 26276885_expression quantitative trait loci studies implicate BCAR1 as the causal gene of coronary artery disease Carotid intima-media thickness 26716506_Elevated levels of p130Cas is associated with trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. 26867768_Full-length and truncated p130Cas phosphorylated substrate domain molecules were expressed in breast cancer cells. Breast cancer cells expressing the full-length SD and the functional smaller SD fragment (spanning SD motifs 6-10) were injected into the mammary fat pads of mice. Both the complete and truncated SD significantly increased the occurrence of metastases to multiple organs. 27068854_blockade of GD3-mediated growth signaling pathways by siRNAs might be a novel and promising therapeutic strategy against malignant melanomas, provided signaling molecules such as p130Cas and paxillin are significantly expressed in individual cases. 27293031_Silencing of p130Cas and inhibition of FAK activity both strongly reduced imatinib and nilotinib stimulated invasion. 27400161_Tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and p130 Crk-associated substrate (CAS) was found to be correlated with pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness. 28223315_the p130Cas FAT domain uniquely confers a mechanosensing function. 28337997_These results suggest that miR-24-3p functions as a tumor suppressor and the miR-24-3p/p130Cas axis is a novel factor of cancer progression by regulating cell migration and invasion. 28442738_The authors herein prove, for the first time, that the transcriptional repressor Blimp1 is a novel mediator of p130Cas/ErbB2-mediated invasiveness. Indeed, high Blimp1 expression levels are detected in invasive p130Cas/ErbB2 cells and correlate with metastatic status in human breast cancer patients. 29304771_the results of our study identify BCAR1 as a prognostic biomarker with potential clinical value for risk stratification of ERG-negative prostate cancer. 30188962_study showed that RBMS1 gene rs7593730 and BCAR1 gene rs7202877 were significantly associated with type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population 30422386_a novel interaction of p130Cas with Ser/Thr kinase PKN3, is reported. 30531837_a feedforward autocrine loop to promote invasion through a FAK>p130Cas>c-Jun>MMP-9 signaling axis. 30639111_p130Cas (BCAR1) is recruited to filopodia tips via its C-terminal Cas family homology domain (CCHD) and acts as a mechanosensitive regulator of filopodia stability. 33001583_BCAR1 promotes proliferation and cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma via upregulation of POLR2A. 33042270_CSRP2 suppresses colorectal cancer progression via p130Cas/Rac1 axis-meditated ERK, PAK, and HIPPO signaling pathways. 33144694_Mutant TP53 interacts with BCAR1 to contribute to cancer cell invasion. 33334252_High Expression of BCAR1 by Circulating Tumor Cells and Tumor Tissues Is Predictive of a Poor Prognosis of Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma Potentially Due to Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. 34169835_A Cas-BCAR3 co-regulatory circuit controls lamellipodia dynamics. 34192548_Targeting p130Cas- and microtubule-dependent MYC regulation sensitizes pancreatic cancer to ERK MAPK inhibition. 34326687_BCAR1 plays critical roles in the formation and immunoevasion of invasive circulating tumor cells in lung adenocarcinoma. 34830244_p130Cas Is Correlated with EREG Expression and a Prognostic Factor Depending on Colorectal Cancer Stage and Localization Reducing FOLFIRI Efficacy. 34922945_Docking Protein p130Cas Regulates Acinar to Ductal Metaplasia During Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Development and Pancreatitis. 35031902_Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of RET, BCAR1, and BCAR3 expression in patients with Luminal A and B breast cancer subtypes. |
ENSMUSG00000031955 |
Bcar1 |
317.528065 |
14.5486279329 |
3.862811 |
0.191305337 |
395.093177 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064432444084116925742664405771757354570471213907030687399142809203668608757086854989659983410453613085375130190861986430650514403481842940538410590975479326290895778162413426897351278889659072356699969276288059356373738584267130136140622198582 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023955236138074703045670779853365959538546940621980948998006925400597445326097268209429243324621427282502670264722496529644587480024987958672141592176429115302103302344844599316203629604733880638974966017579670482517961715984711190685629844666 |
Yes |
Yes |
601.2832354 |
61.4470970 |
40.8191021 |
3.7014471 |
| ENSG00000051009 |
84067 |
FHIP1B |
protein_coding |
Q8N612 |
FUNCTION: Component of the FTS/Hook/FHIP complex (FHF complex). The FHF complex may function to promote vesicle trafficking and/or fusion via the homotypic vesicular protein sorting complex (the HOPS complex). FHF complex promotes the distribution of AP-4 complex to the perinuclear area of the cell (PubMed:32073997). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32073997}. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is part of the FTS/Hook/FHIP (FHF) complex, which can interact with members of the homotypic vesicular protein sorting (HOPS) complex. This interaction suggests that the encoded protein is involved in vesicle trafficking. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:84067; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; FHF complex [GO:0070695]; early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:0045022]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:1905719]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
|
ENSMUSG00000044465 |
Fhip1b |
899.365505 |
0.3611602977 |
-1.469289 |
0.106107148 |
185.256888 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000344919147309349129205539585937976730069954136058574658284132992760613378381531269416134304541339011980754375441549086644954513758420944213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000060824451783584138854877192911988678573605577634468123537605569633182808241940057487963866553502727136108936545344505475441110320389270782470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
470.8883163 |
47.2439757 |
1312.8809093 |
93.9104962 |
| ENSG00000052802 |
6307 |
MSMO1 |
protein_coding |
Q15800 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the three-step monooxygenation required for the demethylation of 4,4-dimethyl and 4alpha-methylsterols, which can be subsequently metabolized to cholesterol (PubMed:21285510, PubMed:28673550, PubMed:23583456, PubMed:26114596). Also involved in drug metabolism, as it can metabolize eldecalcitol (ED-71 or 1alpha,25-dihydroxy-2beta-(3-hydroxypropoxy)-cholecalciferol), a second-generation vitamin D analog, into 1alpha,2beta,25-trihydroxy vitamin D3; this reaction occurs via enzymatic hydroxylation and spontaneous O-dehydroxypropylation (PubMed:26038696). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21285510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26038696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28673550, ECO:0000305|PubMed:23583456, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26114596}. |
Alternative splicing;Cataract;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; zymosterol biosynthesis; zymosterol from lanosterol: step 3/6. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:23583456, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26114596}.; PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; cholesterol biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:21285510, ECO:0000305|PubMed:23583456, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26114596, ECO:0000305|PubMed:28673550}. |
Sterol-C4-mehtyl oxidase-like protein was isolated based on its similarity to the yeast ERG25 protein. It contains a set of putative metal binding motifs with similarity to that seen in a family of membrane desaturases-hydroxylases. The protein is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane and is believed to function in cholesterol biosynthesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6307; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-4 methylsterol oxidase activity [GO:0000254]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126] |
18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21285510_human SC4MOL encodes a methyl sterol oxidase that may have a role in psoriasiform dermatitis, microcephaly, and developmental delay 22791750_variants in/near SC4MOL, were associated with FI and IR in this cohort of African Amer 24144731_SC4MOL is situated within the psoriasis susceptibility locus PSORS9, and may be a genetic risk factor for common skin conditions. [review] 33161406_New Homozygous Missense MSMO1 Mutation in Two Siblings with SC4MOL Deficiency Presenting with Psoriasiform Dermatitis. |
ENSMUSG00000031604 |
Msmo1 |
825.644495 |
4.3344789060 |
2.115859 |
0.061128313 |
1274.397014 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000414144767322152977179411230847270215918515503172795 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000531545805710867685899388229938829869986414149578057 |
Yes |
No |
1361.9532548 |
53.0263475 |
316.5860394 |
10.4243653 |
| ENSG00000053372 |
51154 |
MRTO4 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKD2 |
FUNCTION: Component of the ribosome assembly machinery. Nuclear paralog of the ribosomal protein P0, it binds pre-60S subunits at an early stage of assembly in the nucleolus, and is replaced by P0 in cytoplasmic pre-60S subunits and mature 80S ribosomes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20083226}. |
Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis |
|
This gene encodes a protein sharing a low level of sequence similarity with ribosomal protein P0. While the precise function of the encoded protein is currently unknown, it appears to be involved in mRNA turnover and ribosome assembly. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51154; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; preribosome, large subunit precursor [GO:0030687]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process [GO:0000956]; ribosomal large subunit assembly [GO:0000027]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] |
20083226_characterization of Mrt4; findings show Mrt4 is a trans-acting factor involved in ribosome maturation, with nucleus-cytoplasm shuttling capacity 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26494001_Human Mrt4 undergoes phosphorylation in vivo and serines S229, S233, and S235 are phosphorylated by CK2 kinase in vitro. |
ENSMUSG00000028741 |
Mrto4 |
309.694194 |
2.5095476010 |
1.327427 |
0.099104183 |
181.302084 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000002518420131733008749746199669498706443929659989595183635295480048427912086628793078983476048632802651091201068256353323704388458281755447387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000435267929091091416683217823153274679620806296899221693570850410180922874163848477417450605443827334455758615305853709287475794553756713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
446.3544029 |
25.3494837 |
179.1827030 |
8.1420561 |
| ENSG00000053918 |
3784 |
KCNQ1 |
protein_coding |
P51787 |
FUNCTION: Potassium channel that plays an important role in a number of tissues, including heart, inner ear, stomach and colon (PubMed:10646604, PubMed:25441029). Associates with KCNE beta subunits that modulates current kinetics (PubMed:9312006, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:19687231). Induces a voltage-dependent current by rapidly activating and slowly deactivating potassium-selective outward current (PubMed:9312006, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:25441029). Promotes also a delayed voltage activated potassium current showing outward rectification characteristic (By similarity). During beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation participates in cardiac repolarization by associating with KCNE1 to form the I(Ks) cardiac potassium current that increases the amplitude and slows down the activation kinetics of outward potassium current I(Ks) (By similarity) (PubMed:9312006, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505). Muscarinic agonist oxotremorine-M strongly suppresses KCNQ1/KCNE1 current (PubMed:10713961). When associated with KCNE3, forms the potassium channel that is important for cyclic AMP-stimulated intestinal secretion of chloride ions (PubMed:10646604). This interaction with KCNE3 is reduced by 17beta-estradiol, resulting in the reduction of currents (By similarity). During conditions of increased substrate load, maintains the driving force for proximal tubular and intestinal sodium ions absorption, gastric acid secretion, and cAMP-induced jejunal chloride ions secretion (By similarity). Allows the provision of potassium ions to the luminal membrane of the secretory canaliculus in the resting state as well as during stimulated acid secretion (By similarity). When associated with KCNE2, forms a heterooligomer complex leading to currents with an apparently instantaneous activation, a rapid deactivation process and a linear current-voltage relationship and decreases the amplitude of the outward current (PubMed:11101505). When associated with KCNE4, inhibits voltage-gated potassium channel activity (PubMed:19687231). When associated with KCNE5, this complex only conducts current upon strong and continued depolarization (PubMed:12324418). Also forms a heterotetramer with KCNQ5; has a voltage-gated potassium channel activity (PubMed:24855057). Binds with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PubMed:25037568). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97414, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0N7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10646604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10713961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11101505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12324418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19687231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24855057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25037568, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8900283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9108097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9312006}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Non-functional alone but modulatory when coexpressed with the full-length isoform 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9305853}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Atrial fibrillation;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Deafness;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Long QT syndrome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Short QT syndrome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel required for repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. This protein can form heteromultimers with two other potassium channel proteins, KCNE1 and KCNE3. Mutations in this gene are associated with hereditary long QT syndrome 1 (also known as Romano-Ward syndrome), Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, and familial atrial fibrillation. This gene exhibits tissue-specific imprinting, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in some tissues, and biallelic expression in others. This gene is located in a region of chromosome 11 amongst other imprinted genes that are associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), and itself has been shown to be disrupted by chromosomal rearrangements in patients with BWS. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:3784; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral part of cell [GO:1990794]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; ion channel complex [GO:0034702]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005251]; outward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0015271]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding [GO:0034236]; protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding [GO:0034237]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization [GO:0086089]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization [GO:0086008]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization [GO:1902282]; adrenergic receptor signaling pathway [GO:0071875]; atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086014]; auditory receptor cell development [GO:0060117]; cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060048]; cellular chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0030644]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to epinephrine stimulus [GO:0071872]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; corticosterone secretion [GO:0035934]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound [GO:0050910]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion [GO:0001698]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; heart development [GO:0007507]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; intestinal absorption [GO:0050892]; iodide transport [GO:0015705]; membrane repolarization during action potential [GO:0086011]; membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098914]; membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086013]; membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098915]; negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:1902260]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:1903817]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060452]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901381]; potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0097623]; potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0055075]; potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1990573]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization [GO:0060372]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of gastric acid secretion [GO:0060453]; regulation of gene expression by genomic imprinting [GO:0006349]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of membrane repolarization [GO:0060306]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization [GO:0060307]; regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel activity [GO:1905150]; renal absorption [GO:0070293]; renal sodium ion absorption [GO:0070294]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; rhythmic behavior [GO:0007622]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; stomach development [GO:0062094]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086005] |
9020845_KCNQ1 gene is imprinted in a tissue-specific manner, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in some tissues, excluding cardiac muscle. 11136691_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11289718_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11743032_Observational study of gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 11761407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11761407_common polymorphisms of LQTS-associated genes might modify arrhythmia susceptibility in potential gene carriers. 11799244_regulation by PKA-dependent phosphorylation requires a macromolecular complex that includes PKA, PP1, and the targeting protein yotiao 11877438_Kcnq1 locus that regulates long range repression on the paternally derived p57Kip2 and Kcnq1 alleles in an imprinting domain that includes Igf2 and H19. This ICR appears to possess a unidirectional chromatin insulator function in somatic cells. 11997281_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12051962_evidence that not only homozygous but also compound heterozygous mutations in KvLQT1 may cause Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome in nonconsanguineous families 12080180_the analysed region of the KVLQT1 gene is not commonly involved in pathogenesis of the long QT syndrome 12402336_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12442276_Four novel KCNQ1 missense mutations were identified in long QT syndrome in China. 12482884_External acidification acts on homomeric and heteromeric KCNQ1 channels via multiple mechanisms to affect gating and maximum conductance. 12511562_Kcnq1 analysis shows that methylation occurs as a consequence of silencing 12522251_the S140G mutation in KCNQ1 is likely to initiate and maintain atrial fibrillation by reducing action potential duration and effective refractory period in atrial myocytes 12524525_A cytoplasmic carboxy-terminal subunit interaction domain (sid) suffices to transfer assembly properties between KCNQ3 and KCNQ1. 12612194_Co-activation of hKvLQT1 improves CaCC-mediated Cl- secretion in native CF airway epithelia, and may have a therapeutic effect in the treatment of CF lung disease. 12670483_expressed strongly in heart, skeletal muscle, and kidney, less in placenta, lung, and liver, and weakly in brain and blood cells. Electrophysiological study showed that KCNE4 modulates the activation of the KCNQ1 channel. 12690509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12820704_missense mutations in KCNQ1 and SCN5A in a case of congenital Long QT Syndrome 12849668_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14510661_Novel compound heterozygous nonsense mutations in C-terminus of KCNQ1 can cause Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS). 14576198_We characterize molecular determinants of R-L3 interaction with KCNQ1 channels, use computer modeling to propose a mechanism for drug-induced changes in channel gating, & determine its effect on several long-QT syndrome-associated mutant KCNQ1 channels 14661677_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14678125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14731347_Two novel deletion mutations and one novel polymorphism of KCNQ1 gene were identified among 6 Chinese families with congenital long QT syndrome(LQTS). 14756674_Long-term follow-up of a LQT1 family with two KCNQ1amino acid alterations in cis (V254M-V417M); the V254M mutation introduced into Xenopus oocytes reduced the IKs current, while the effect of the V417M variant was negligible 14760488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14761891_ER quality control prevents minK-L51H/KvLQT1 complexes from trafficking to the plasma membrane, resulting in decreased I(Ks). 14998624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15028050_Beta-blockers are widely used to prevent the lethal cardiac events associated with the long QT syndrome (LQTS), especially in KCNQ1-related LQTS (LQT1) patients. 15051636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15176425_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15226366_despite the high degree of homology of the pore region among the various K(+) channels, KCNQ1 channels display significant structural and functional uniqueness. 15234419_LQT1 patients with transmembrane mutations are at higher risk of congenital LQTS-related cardiac events and have greater sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation, as compared with patients with C-terminal mutations. 15242738_a P448R polymorphism in KCNQ1 may have a role in long QT syndrome in Chinese patients 15340049_The unmethylated Kcnq1 imprinting control region harbors bidirectional silencer activity and drives expression of an antisense RNA. 15367556_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15389592_Expression of KCNQ1 and KCNE1 associated with early stages of spermatogenesis and with presence of undifferentiated healthy or neoplastic germ cells. KCNQ1/KCNE1 may be involved in K+ transport, probably during germ-cell development. 15459184_NF-Y transcription factor as a crucial regulator of antisense promoter-mediated bidirectional silencing and the parent of origin-specific epigenetic marks at the Kcnq1 imprinting control region 15511625_mutational analysis in a family with Romano-Ward syndrome 15534720_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15649981_These findings indicate the importance of a putative pore helix-S5-S6 interaction for normal KCNQ1 channel deactivation and confirm its role in KCNQ1 inactivation. 15696484_A missense mutation G940A(G314S) in the KCNQ1 gene was identified, which was the 'hot spot' of long QT syndrome mutation. 15707997_Based upon previous studies and the present results, it is concluded that both hKCNE4 and mKCNE4 have a drastic inhibitory impact on both hKCNQ1 and mKCNQ1 currents. 15746444_A variant in intron 1 of the KCNQ1 gene (rs757092, +1.7 ms/allele) is associated with QT interval length. 15746444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15840476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15851119_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15904893_hydrophobic or aromatic residues involved in S6 transmembrane domain and the base of the pore helix of KCNQ1 15924777_The single heterozygous mutation in KCNQ1 may also cause Jervell-Lange-Nielsen syndrome. 16129795_can function as a repolarization reserve when IKr, the rapid delayed rectifier, is reduced by disease or drug and can prevent excessive action potential prolongation and development of arrhythmogenic early afterdepolarizations 16132053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16132053_This suggests that genetic determinants located in KCNQ1, KCNE1, KCNH2 and SCN5A influence QTc length in healthy individuals and may represent risk factors for arrhythmias or cardiac sudden death in patients with cardiovascular diseases. 16155735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246960_KCNQ1-A341V single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with greater risk than that reported for large databases of long QT syndrome. 16253915_A variant in intron 1 of the KCNQ1 gene (rs757092, +1.7 ms/allele) is associated with QT interval length. 16308347_interaction of MiRP2-72 with KCNQ1-338; and MinK-59,58 with KCNQ1-339, 340 16414944_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16487223_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16487842_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16540748_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16556865_Calmodulin binding to KCNQ1 is essential for correct channel folding and assembly and for conferring Ca(2+)-sensitive IKS-current stimulation, which prevents risk of ventricular arrhythmias. 16556866_Calmodulin is a constitutive component of KCNQ1 K+ channels, the most commonly mutated long-QT syndrome (LQTS) locus. 16563243_None of the SNPs of KCNQ1 were associated with atrial fibrillation phenotype. 16563243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16610241_supports the involvement of voltage-gated K+ channel in cell proliferation 16631607_These results suggest that KCNE2 can functionally couple to KCNQ1 even in the presence of KCNE1. 16723781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16818214_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16818214_patients who reportedly are genotype negative may benefit from re-examination of those regions susceptible to allelic dropout due to primer-disrupting SNPs, particularly exon 15 in KCNQ1. 16823764_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16823764_Polymorphisms within the KCNQ1 gene are associated with susceptibility Noise-induced hearing loss. 16880338_Long QT syndrome patients with mutations on the HERG gene have greater QT interval prolongation than patients with mutations of the KCNQ1 gene. 16987820_The identification and characterization of mutations in KCNQ1 specific to Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome in a single family are reported. 17010804_Women affected by the common KCNQ1-A341V mutation are at low risk for cardiac events during pregnancy and without excess risk of miscarriage; their infants delivered by C-section because of fetal distress are extremely likely to also be mutation carriers 17016049_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17016049_no association between atrial fibrillation and single nucleotide polymorphisms 17130521_identification of secondary structure within the KCNE1 C-terminal domain provides structural scaffold to map protein-protein interactions with the pore-forming KCNQ1 subunit as well as the cytoplasmic regulatory proteins anchored to KCNQ1-KCNE complexes. 17161064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17161064_Six novel mutations--4 in ANK2, 1 in KCNQ1, and 1 in SCN5A--were found in the patients with torsades de pointes. 17210839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17210839_We demonstrated that 9.5% of cases diagnosed as SIDS carry functionally significant genetic variants in LQTS genes (KCNQ1, KCNH2, SCN5A, KCNE1, KCNE2, KCNJ2, CAV3). 17227916_The unique S4 charge paucity of KCNQ1 facilitates its unique conversion to a leak channel by ancillary subunits such as MiRP2. 17292394_provide a mechanistic basis for the pathogenesis of long QT syndrome caused by a splicing mutation in KCNQ1 17310097_External pH can modify current amplitude and biophysical properties of KCNQ1. KCNE subunits work as molecular switches by modulating the pH sensitivity of human KCNQ1. 17384445_In chronic heart failure (CHF), the relative abundance of KCNE1 compared to KCNQ1 genes might contribute to the prolongation of QT interval through reducing the net outward current during the plateau of the action potential. 17467630_Human KCNQ1 S140G is likely to be a causative mutation responsible for atrioventricular blocks. 17470695_In type-1 long-QT syndrome, mutations located in the transmembrane portion of the ion channel protein and the degree of ion channel dysfunction caused by the mutations are important independent risk factors influencing its clinical course. 17470695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17482572_LQT1 mutation M520R leads to ER-retention and dysfunctional trafficking of the mutant channel resulting in haploinsufficiency. 17534376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17544529_In Australians A) causes incomplete transcriptional aberration of the KCNQ1 gene, leaving 10% of the normal allele transcript intact, which restores the hearing function 19029186_Specific KCNE4 domains responsible for the inhibitory effects on heterologously expressed KCNQ1 were identified. The KCNE4 C-terminus is critical for KCNQ1 modulation and physically interacts with KCNQ1. 19056345_Changes of amino acid residue at the pore center of KCNQ1 may alter the channel function but this depends on the electrical charge or the size of amino acid residue. 19077539_KCNE variants reveal a critical role of the beta subunit carboxyl terminus in PKA-dependent regulation of the IKs potassium channel, KCNQ1. 19114714_Derlin-1 did not modify KCNQ1 expression level, and no interaction between endogenous KCNQ1 and Derlin-1 could be detected. 19131515_the extracellular flank of the transmembrane helix of E1 is located between S1 and S6 on different subunits of Q1 (Q1 TM helics). 19139916_We conclude that tyrphostin A25 inhibits KCNQ1/KCNE1 current by lowering tyrosine phosphorylation on unidentified nonchannel protein(s) that directly or indirectly regulate the open probability of the KCNQ1 pore in a PIP(2)-independent manner. 19149796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19149796_Within KCNQ1 there was weak evidence for association between the minor allele of IVS12 +14T>C and increased QTc (P = 0.02) in myocardial sodium and potassium channel genes and QT interval duration in diabetics. 19156197_phenylboronic acid (PBA) activates KCNQ1/KCNE1 complexes 19160088_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19167356_These results indicate that the F275S KCNQ1 mutation leads to impaired polypeptide trafficking that in turn leads to reduction of channel ion currents and altered gating kinetics. 19198868_We performed mutation analysis for genes implicated in long QT syndrome (KCNQ1, KCNH2, and SCN5A) in 17 sudden unexplained death autopsy cases. 19202166_MinK is an endocytic chaperone for KCNQ1. 19218243_PDE4D3, like protein kinase A and protein phosphatase 1, is recruited to the I(Ks) channel via AKAP-9 and contributes to its critical regulation by cAMP 19247372_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19252135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19252135_The increased risk for type 2 diabetes associated with KCNQ1 genetic variration is likely to be caused by a reduction in insulin secretion. 19261104_Syncope did not occur in patients with the C-terminal domain mutations up to the age of 6-9 years, but family members of patients with the C-terminal domain mutations had a history of syncope in their elementary school days. 19289549_Cell membrane stretch and cell volume sensitivity are independently regulated by KCNMB1 (BK) and KCNQ1 channels, respectively. 19305408_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19305409_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19308350_KCNQ1 was associated with type 2 diabetes susceptibility in a Chinese population, possibly through its effect on beta cell function 19308350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19322600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19340287_results support several roles for KCNE1 C-terminus interaction with KCNQ1: regulation of channel assembly, open-state destabilization, and kinetics of channel deactivation 19348785_the effects of the G314S mutation on KCNQ1 were studied. 19366866_Common genetic variation in KCNQ1 is associated with insulin secretion upon oral glucose load in a German population at increased risk of type 2 diabetes. 19366866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19372218_although KCNE1 relies on KCNQ1 coassembly for more efficient cell surface expression, KCNE2 can independently traffic to the cell surface, thus becoming available for substituting KCNE1 in the IKs channel complex 19401414_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19448982_We confirmed the association of KCNQ1 with type 2 diabetes in the population of mainland China 19490272_Mutations in highly conserved amino acid residues in the KCNQ1 gene are asssociated with significant risk of cardiac events. 19490272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19502414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19516902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19516902_the KCNQ1 rs2237895 minor allele associates with reduced insulin release following an oral glucose load 19521339_this study reveals the specific interaction between the KCNE1 C-terminus and the Kv7.1 dimeric coiled-coil helix C, thereby providing a simple means to guide assembly of the IKS channel complex. 19523148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19540844_A novel missense mutation in the KCNQ1 gene, KCNQ1 P320H, was identified in the hereditary long QT syndrome patient presenting with recurrent syncope and aborted sudden death triggered by physical stress and swimming. 19551538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19556355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19556355_effect of KCNQ1 variants on type 2 diabetes is mainly mediated through impaired B-cell function. 19575309_These data implicate rs2237892 in KCNQ1 as a protective gene variant against premature coronary artery disease and any association of the 4 single nucleotide polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus could not be replicated. 19584308_A common variant in the KCNQ1 gene is associated with increased risk of future type 2 diabetes in Scandinavians, because of its effect on insulin secretion. 19584308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19590188_All KCNQ1 protein mutants shifted the voltage dependence of activation to the right and reduced the voltage dependence of deactivation kinetics. 19632626_The researchers identified a family with lone atrial fibrillation caused by a mutation in the highly conserved S3 channel region of KCNQ1. 19646991_Data found striking functional similarities due to mutations in KCNQ1 and NPPA genes which led to I(Ks) 'gain-of-function', atrial AP shortening, and consequently altered calcium current as a common mechanism between diverse familial AF syndromes. 19714318_Study demonstrates a colse link beween single nucleotide polymorphisms in KCNQ1 and gestational diagetes mellitus. 19716085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19716085_The researchers found evidence of KCNQ1 mutations in many individuals in a cohort of patients with long QT syndrome. 19741467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19798621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19798621_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in KCNQ1 is associated with type 2 diabetes. 19808498_7 of the missense mutations have profound pathological dominant-negative loss-of-function properties, confirming their likely disease-causing nature 19817925_Genetic testing in this long-QT Syndrome population suggests a common KCNQ1 Leu266Pro founder effect 19825999_Results describe the functional alterations caused by KCNQ1 mutations which were identified in compound heterozygous state in two patients with autosomal-recessive LQTS not accompanied by hearing loss. 19841300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19843919_When reconstituted in Chinese hamster ovary cells, long-Qt syndrome KCNQ1 mutant channels showed complex gating defects without dominant negative effects or a relatively mild decreased current density. 19850681_KCNQ1 polymorphisms shown to be associated with increased risk for T2DM in the recent GWA study might also represent genetic factors contributing to the development of gestational gestational diabetes in Koreans. 19850681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19880070_26 South African LQTS families all segregating the same KCNQ1 mutation (A341V) caused by a founder effect. The disease allele in all of these families descends from a common ancestor 19892838_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19907016_Report KCNQ1 mutations which alter slow potassium current, protein trafficking and interactions with KCNE1 resulting in long QT syndrome type 5. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913547_the rate-dependent biophysical properties of the LQT1 H258R mutant are counteracted by a dominant negative effect on channel trafficking [review] 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934648_Stimulation by PKA and PKC can partially rescue LQT1 mutant KCNQ1 channels with weakened response to PIP(2) by strengthening channel interactions with PIP(2). 19940153_Data suggest that KCNQ1-KCNE1 complexes interact intermittently with the actin cytoskeleton via the C-terminal region and this interaction may have a functional role. 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19959132_The researchers found an association between LQTS mutation KCNQ1-T587M and the potential for malignant phenotype in long Qt syndrome patients. 20031635_The dominant-negative Y111C-KCNQ1 mutation, associated with a severe phenotype, presents with a low incidence of sudden cardiac death. 20040519_2 of the 8 MiRP2 extracellular domain acidic residues (D54 and D55) are important for KCNQ1-MiRP2 constitutive activation. 20044973_The structural and functional changes related to the glycine to serine amino acid substitution in the S5 segment may also influence the activity of the whole KvLQT1 channel. 20056949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056949_The results suggest that KCNQ1 is a new candidate gene for conferring susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. 20071715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085748_These results provide the novel information that epidermal growth factor receptor kinase, but not Src-family kinases, regulates the recombinant cardiac I(Ks) stably expressed in HEK 293 cells via phosphorylating KCNQ1 protein of the channel. 20108749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20138589_first report of both Romano Ward and Jervell Lange Nielsen syndromes in siblings with the same KCNQ1 gene mutation 20139709_While assembly of KCNE1 with KCNQ1 does not require co-translation, functional KCNQ1-KCNE1 channels assemble early in the secretory pathway and reach the plasma membrane via vesicular trafficking. 20174558_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20186784_Mutations at KCNQ1 and an unknown locus cause long QT syndrome in a large Australian family: implications for genetic testing. 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20226272_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20368164_That long QT syndrome mutations in KCNQ1 cause epilepsy reveals the dual arrhythmogenic potential of an ion channelopathy coexpressed in heart and brain and motivates a search for genetic diagnostic strategies 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20386770_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400777_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400777_Two common intronic variants in KCNQ1 and SCN5A were associated with sudden cardiac death in individuals of European ancestry. 20421371_S3 mutants of KCNQ1 cause LQTS predominantly through biophysical effects on the gating of I(Ks), but some mutants also show protein stability/trafficking defects, which explains why the kinetic gain-of-function mutation S209F causes LQT1. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20470906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20479109_Generate a closed-state model of the KCNQ1-KCNE1 cytoplasmic region where these protein-protein interactions are poised to slow activation gate opening. 20490451_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20509872_Observati |
ENSMUSG00000009545 |
Kcnq1 |
425.644878 |
0.4004511898 |
-1.320302 |
0.078805378 |
286.426504 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000029867926445076993933180221778633642272394673911733967929110152611584018730268139816124694807944747758901758358115101188889373550682672936210111946147571657323230298608507382596144452691078186035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008224824521069709577769532850690440690455954116274780259054402528810169475825702702759332629339246436320405518426794216645370621546674701538192130964439172970126268324975171708501875400543212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
241.2354081 |
18.0889830 |
605.2419759 |
31.2552153 |
| ENSG00000054277 |
23596 |
OPN3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H1Y3 |
FUNCTION: G-protein coupled receptor which selectively activates G proteins via ultraviolet A (UVA) light-mediated activation in the skin (PubMed:28842328, PubMed:31380578, PubMed:31097585). Binds both 11-cis retinal and all-trans retinal (PubMed:31097585). Regulates melanogenesis in melanocytes via inhibition of alpha-MSH-induced MC1R-mediated cAMP signaling, modulation of calcium flux, regulation of CAMK2 phosphorylation, and subsequently phosphorylation of CREB, p38, ERK and MITF in response to blue light (PubMed:28842328, PubMed:31097585). Plays a role in melanocyte survival through regulation of intracellular calcium levels and subsequent BCL2/RAF1 signaling (PubMed:31730232). Additionally regulates apoptosis via cytochrome c release and subsequent activation of the caspase cascade (PubMed:31730232). Required for TYR and DCT blue light-induced complex formation in melanocytes (PubMed:28842328). Involved in keratinocyte differentiation in response to blue-light (PubMed:30168605). Required for the UVA-mediated induction of calcium and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling resulting in the expression of MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP9 and TIMP1 in dermal fibroblasts (PubMed:31380578). Plays a role in light-mediated glucose uptake, mitochondrial respiration and fatty acid metabolism in brown adipocyte tissues (By similarity). May be involved in photorelaxation of airway smooth muscle cells, via blue-light dependent GPCR signaling pathways (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUK7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28842328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30168605, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31097585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31380578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31730232}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Chromophore;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Photoreceptor protein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Retinal protein;Sensory transduction;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Opsins are members of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptor superfamily. In addition to the visual opsins, mammals possess several photoreceptive non-visual opsins that are expressed in extraocular tissues. This gene, opsin 3, is strongly expressed in brain and testis and weakly expressed in liver, placenta, heart, lung, skeletal muscle, kidney, and pancreas. The gene may also be expressed in the retina. The protein has the canonical features of a photoreceptive opsin protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23596; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 11-cis retinal binding [GO:0005502]; all-trans retinal binding [GO:0005503]; G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity [GO:0008020]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; photoreceptor activity [GO:0009881]; cellular response to light stimulus [GO:0071482]; cellular response to UV-A [GO:0071492]; detection of light stimulus [GO:0009583]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of melanin biosynthetic process [GO:0048022]; phototransduction [GO:0007602]; positive regulation of cellular respiration [GO:1901857]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; positive regulation of melanin biosynthetic process [GO:0048023]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; response to blue light [GO:0009637] |
12063405_Assignment of panopsin (OPN3) to human chromosome band 1q43 12242008_Human OPN3 gene consists of six exons and expresses various splice variants. 14623461_Related persons with heterozygous germline deletions of 1q42.3, which includes EXO1, RGS7, KMO, CHML, and OPN3, showed no phenotypic abnormalities other than multiple leiomyomatosis. 18344558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18344558_Polymorphisms in the OPN3 and CHML genes are associated with asthma and atopic asthma. 19626040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22313545_Decreased OPN3 levels in Bel7402(5-FU) cells activated the anti-apoptotic pathway through increasing phospho-Akt and the Bcl2/Bax ratio, while overexpression of OPN3 inactivated this pathway. 28842328_OPN3 and the multimeric tyrosinase/tyrosinase-related protein complex induced after its activation appear as new potential targets for regulating melanogenesis but also to protect dark skins against blue light in physiological conditions and in pigmentary disorders. 30284927_This is the first demonstration of photorelaxation in airway smooth muscle via an OPN receptor-mediated pathway. 31097585_OPN3 and MC1R colocalize at both the plasma membrane. 31653550_Illuminating insights into opsin 3 function in the skin. 31730232_Opsin3 Downregulation Induces Apoptosis of Human Epidermal Melanocytes via Mitochondrial Pathway. 31802643_Expression of OPN3 in lung adenocarcinoma promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis. 32166706_Activation of an Endogenous Opsin 3 Light Receptor Mediates Photo-Relaxation of Pre-Contracting Late Gestation Human Uterine Smooth Muscle Ex Vivo. 33611338_Identification of OPN3 as associated with non-syndromic oligodontia in a Japanese population. 33955704_Expression of OPN3 in acral lentiginous melanoma and its associated with clinicohistopathologic features and prognosis. 34029574_TGFbeta2 Upregulates Tyrosinase Activity through Opsin-3 in Human Skin Melanocytes In Vitro. 35577105_OPN3 Regulates Melanogenesis in Human Congenital Melanocytic Nevus Cells through Functional Interaction with BRAF(V600E). 36017595_The effects of missense OPN3 mutations in melanocytic lesions on protein structure and light-sensitive function. |
ENSMUSG00000026525 |
Opn3 |
102.177166 |
3.0957817007 |
1.630304 |
0.220147668 |
54.094905 |
0.00000000000019103593220474859517957508078210449939805630481526321773344534449279308319091796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001190244980726926637682527418675945040044475420337732884945580735802650451660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
149.8431279 |
21.8209867 |
48.5414962 |
5.4497395 |
| ENSG00000054598 |
2296 |
FOXC1 |
protein_coding |
Q12948 |
FUNCTION: DNA-binding transcriptional factor that plays a role in a broad range of cellular and developmental processes such as eye, bones, cardiovascular, kidney and skin development (PubMed:11782474, PubMed:15299087, PubMed:15684392, PubMed:16492674, PubMed:27907090, PubMed:14506133, PubMed:14578375, PubMed:15277473, PubMed:16449236, PubMed:17210863, PubMed:19793056, PubMed:19279310, PubMed:25786029, PubMed:27804176). Acts either as a transcriptional activator or repressor (PubMed:11782474). Binds to the consensus binding site 5'-[G/C][A/T]AAA[T/C]AA[A/C]-3' in promoter of target genes (PubMed:7957066, PubMed:11782474, PubMed:12533514, PubMed:14506133, PubMed:19793056, PubMed:27804176). Upon DNA-binding, promotes DNA bending (PubMed:7957066, PubMed:14506133). Acts as a transcriptional coactivator (PubMed:26565916). Stimulates Indian hedgehog (Ihh)-induced target gene expression mediated by the transcription factor GLI2, and hence regulates endochondral ossification (By similarity). Acts also as a transcriptional coregulator by increasing DNA-binding capacity of GLI2 in breast cancer cells (PubMed:26565916). Regulates FOXO1 through binding to a conserved element, 5'-GTAAACAAA-3' in its promoter region, implicating FOXC1 as an important regulator of cell viability and resistance to oxidative stress in the eye (PubMed:17993506). Cooperates with transcription factor FOXC2 in regulating expression of genes that maintain podocyte integrity (By similarity). Promotes cell growth inhibition by stopping the cell cycle in the G1 phase through TGFB1-mediated signals (PubMed:12408963). Involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction by increasing cell proliferation, migration and invasion (PubMed:20406990, PubMed:22991501). Involved in chemokine CXCL12-induced endothelial cell migration through the control of CXCR4 expression (By similarity). Plays a role in the gene regulatory network essential for epidermal keratinocyte terminal differentiation (PubMed:27907090). Essential developmental transcriptional factor required for mesoderm-derived tissues, such as the somites, skin, bone and cartilage. Positively regulates CXCL12 and stem cell factor expression in bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells, and hence plays a role in the development and maintenance of mesenchymal niches for haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC). Plays a role in corneal transparency by preventing both blood vessel and lymphatic vessel growth during embryonic development in a VEGF-dependent manner. Involved in chemokine CXCL12-induced endothelial cell migration through the control of CXCR4 expression (By similarity). May function as a tumor suppressor (PubMed:12408963). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11782474, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12533514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14506133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14578375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15277473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15299087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15684392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16449236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16492674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17210863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17993506, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19279310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19793056, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20406990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22991501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25786029, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26565916, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27804176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27907090, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7957066}. |
Activator;Angiogenesis;Deafness;Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Peters anomaly;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene belongs to the forkhead family of transcription factors which is characterized by a distinct DNA-binding forkhead domain. The specific function of this gene has not yet been determined; however, it has been shown to play a role in the regulation of embryonic and ocular development. Mutations in this gene cause various glaucoma phenotypes including primary congenital glaucoma, autosomal dominant iridogoniodysgenesis anomaly, and Axenfeld-Rieger anomaly. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2296; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA binding, bending [GO:0008301]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic process involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003275]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; eye development [GO:0001654]; germ cell migration [GO:0008354]; glomerular epithelium development [GO:0072010]; glycosaminoglycan metabolic process [GO:0030203]; heart development [GO:0007507]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lacrimal gland development [GO:0032808]; lymph vessel development [GO:0001945]; maintenance of lens transparency [GO:0036438]; mesenchymal cell development [GO:0014031]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of apoptotic process involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:1902257]; negative regulation of lymphangiogenesis [GO:1901491]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045930]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neural crest cell development [GO:0014032]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; paraxial mesoderm formation [GO:0048341]; positive regulation of core promoter binding [GO:1904798]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:1901534]; positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation [GO:1902038]; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045618]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of organ growth [GO:0046620]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084]; ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055010] |
11740218_Four different FOXC1 mutations were found in four of six Japanese pedigrees with Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome. 11782474_FOXC1 is under complex regulatory control with multiple functional domains modulating FOXC1 transcriptional regulation. 11821690_none of the families had a detectable FOXC1 mutation. 12408963_FOXC1 functions as a tumor suppressor through TGF-beta1 mediated signals. 12454026_Novel mutation in FOXC1 wing region causing Axenfeld-Rieger anomaly. 12592227_Significant genetic heterogeneity of FOXC1 was observed in a multi-ethnic population studied in this region of India resulting in variable ARA phenotypes. 12614756_This report confirms that Rieger syndrome (with dental and facial abnormalities) can be caused by a mutation in FOXC1. It is also the first report of Peters anomaly being caused by a FOXC1 mutation. 14506133_Structural and functional analyses of disease-causing missense mutations in the forkhead domain of FOXC1 were performed. 14578375_A novel mutation in helix 1 of the FOXC1 forkhead domain has been identified and the importance of position 86 in FOXC1 activity demonstrated. 15299087_Determination of amino acids within the forkhead domain of FOXC1 that are important for FOXC1 function. 15477465_in Axenfeld-Rieger anomaly, a T-->C transition, is predicted to result in a change of isoleucine to threonine (Ile9lThr) in a highly conserved location within the first helix of the forkhead domain. 16449236_Functional interaction between FOXC1 and PITX2A underlies the sensitivity to FOXC1 gene dosage in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome and related anterior segment dysgeneses. 16492674_FOXC1 protein levels and activity are tightly regulated by post-translational modifications 16638984_The frequency of mutations in the FOXC1, GJA1, PITX2, and CYP1B1 genes in this study were 25%, 12.5%, 0% and 0%, respectively. 16936096_The findings in the present study clearly demonstrate that FOXC1 and PITX2 mutations are responsible for a significant proportion of Axenfeld-Rieger malformations in Germany. 16952980_these data implicate specific members of the FOX family of TFs (FOXC1, C2, P1, P4, and O1A) not previously suggested in heart failure pathogenesis. 17000708_This study reveals an important role for FOXC1 in the direct regulation of the FGF19-FGFR4-MAPK pathway to promote both the development and maintenance of anterior segment structures within the eye. 17157569_A patient is described with a 6pter deletion detected by SNP genotyping and DNA probes involving the FOXC1 gene. 17197537_Patients with FOXC1 mutations have the mildest prognosis for glaucoma development, whereas patients with PITX2 defects and patients with FOXC1 duplication have a more severe prognosis for glaucoma development than do patients with FOXC1 mutations. 17486624_PITX2, BARX1, and FOXC1 mutations were absent in De Hauwere syndrome and suggest that De Hauwere syndrome is caused by a different gene. 17558846_In addition, no pathogenic sequence variations were found in DCN, DSPG3, LUM, PITX2 and FOXC1, which have also been implicated in corneal and anterior segment dysgenesis. 17653043_Novel mutation in Helix1 and novel deletion in Wing1 and Beta2 of forkhead domain of FOXC1 gene have been identified in two families with Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome. 17993506_FOXC1 regulates the expression of FOXO1A and binds to a conserved element in the FOXO1A promoter 18484311_Heterozygous FOXC1 mutation is associated with congenital glaucoma and aniridia 18498376_the role of FOXC1 mutations in the spectrum of anterior segment dysgenesis . 18564921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18616618_The exclusion of these genes as likely candidates supports the hypothesis that the ocular phenotype associated with peters' anomaly segregating in this family is a distinct, new, autosomal dominant entity in the anterior segment dysgenesis spectrum. 18676636_Failure of p32 to interact with FOXC1 containing the disease-causing F112S mutation indicates that impaired protein interaction may be a disease mechanism for AR malformations. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18708620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18708620_The present study indicates a limited role of FOXC1 in primary congenital glaucoma pathogenesis. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19279310_Severe molecular consequences, including the inability of the W152G protein aggregates to form protective aggresomes, may underlie the aniridia phenotype that results from the FOXC1 W152G mutation. 19513095_A brief review of the clinical features and the relevant diagnostic approaches, together with a detailed review of published PITX2 and FOXC1 mutations in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome, is given. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19626132_A potential susceptibility role for FOXC1 in generating severe eye pathologies, is demonstrated. 19626132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19668217_FOXC1 is required for normal cerebellar development and is a major contributior to chromosome 6p25.3 Dandy-Walker syndrome. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19793056_first FOXC1 missense mutation, P297S, that occurs outside of the forkhead domain is reported and functionally examined; 889C > T transition, resulting in P297S, was identified in two unrelated individuals with anterior segment dysgenesis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056007_Quantitative methylation analysis identified ABCB1, FOXC1, PPP2R2B and PTEN as novel genes to be methylated in ductal carcinoma in situ. 20338046_We investigated methylation patterns in the promoter regions of ABCB1, ATM, BRCA1, CDH3, CDKN2A, CXCR4, ESR1, FBXW7, FOXC1, GSTP1, IGF2, HMLH1, PPP2R2B, and PTEN75 in well-described pre-treatment samples from locally advanced breast cancer 20406990_Overexpression of the transcription factor FOXC1 is associated with basal-like breast cancer. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20881294_FOXC1 and PITX2 genetic defects explain 40% of our large anterior segment malformations. 20881294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21031026_MYOC and FOXC1 mutations are not involved in pathogenesis of primary congenital glaucoma patients. 21031026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21278591_No mutations were found by direct sequencing of PITX2 and FOXC1 genes, in the twin sisters. 21353197_This high frequency of causal submicroscopic chromosomal aberrations in patients with congenital ocular malformation warrants implementation of array comparative genomic hybridization in the diagnostic work-up of these patients. 21400511_Our results present dysfunctional miRNAs in endometrial cancer and identify a crucial role for miR-204-FOXC1 interaction in endometrial cancer progression 21424368_Elevated FOXC1 expression was associated with Basal-like breast cancer. 21465172_When FOXC1 was stably transfected into MDA-MB-231 cells, the migration and invasion of the cells were repressed. 21837767_FOXC1 and PITX2 can independently regulate their own and each other's target gene promoters and do not show synergistic action in vitro. 22120723_the BRCA1-GATA3 interaction is important for the repression of genes associated with triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer (BLBCs) including FOXC1 22249250_FOXC1 regulates the functions of human basal-like breast cancer cells by activating NF-kappaB signaling. 22493429_findings demonstrate that SC motifs mediate the inhibitory function of this region by serving as sites for SUMOylation and reveal a novel mechanism for acute and reversible regulation of FOXC1/C2 function 22569110_FOXC1 deletions were observed in four cases of anterior segment dysgenesis and related conditions. 22645147_Findings identify MMP7 as a novel mechanism through which FOXC1 may regulate the basal-like breast cancer invasive phenotype and the propensity of these cancers to metastasize. 22736943_No significant associations were identified between FOXC1, TGFbeta2, and BMP4 alleles and haplotypes and primary open-angle glaucoma. 22903608_Our data confirm that FOXC1 haploinsufficiency plays a major role in the phenotype of patients with 6p25 deletions. 22911555_overexpression of FoxC1 in hepatpcellular carcinoma is a strong indicator of more-aggressive tumors and poor clinical outcome. 22991501_FOXC1 contributes to microvascular invasion in primary hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 23242609_High FOXC1 expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 23264086_High expression of FOXC1 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer patients. 23444221_Data indicate that among 31 thymus development-related genes, PBX1 copy number gain and FOXC1 copy number loss were presented in 43.0% and 39.5% of the tumors, respectively. 23541832_The data suggest existence of a complex regulatory pathway in the trabecular meshwork part of which includes interactions between FOXC1, miR-204, MEIS2, and ITGbeta1. 23687430_A novel c.317delA mutation in FOXC1 in a Korean family with Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome, is reported. 24556684_Dysfunction of the stress-responsive FOXC1 transcription factor contributes to trabecular meshwork cell death and the earlier-onset glaucoma observed in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome patients. 24889262_Report lncRNA FOXC1 upstream transcript (FOXCUT) overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24914578_We report a novel FOXC1 mutation (p. R127L) in a three-generation family with three ARS and heart defect patients. 25031703_we showed that a novel long non-coding RNA FOXCUT and its neighboring gene FOXC1 may function as a lncRNA-mRNA gene pair, which may represent a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients 25124473_We demonstrate that FOXC1 is required for epidermal growth factor-elicited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. 25130698_suggest that reduced expression of miR-639 underscores the mechanism of TGFbeta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tongue squamous cell carcinoma by targeting FOXC1 and may serve as therapeutic targets in the process of metastasis 25250569_Genome-wide association analysis linked the FOXC1-interacting transcription factor PITX2 to cerebral small-vessel disease. 25786029_The results support that moderate and variable FOXC1 transactivation changes are associated with moderate goniodysgenesis, dominant glaucoma and remarkable phenotypic variability. 25809640_This study shows that hsa-miR548-l regulates FOXC1 translation, contributing to better understand the fine regulation of the biological function of this transcription factor. 25875420_Our data indicate that miR-138-5p may play an important role in regulating pancreatic cancer cell growth, possibly through targeting FOXC1 26041837_FOXC1 assay (IHC & qRT-PCR) accurately identified basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) in FFPE samples. FOXC1 expression also predicted the development of brain metastasis. 26049754_Foxc1 is essential for progenitor cell development and maintenance of bone marrow niches for these cells upregulating CXCL12 and SCF expression and inhibiting of adipogenic processes in cell progenitors. (Review) 26065367_In HCC cell lines, IL8 activates expression of FOXC1 via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling to AKT and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. FOXC1 expression leads to transactivation of CXCR1 and CCL2, promoting inflammation and invasivion/metastasis. 26198045_miR-495 acts as a tumour suppressor gene by targeting FOXC1 at the post-transcriptional level in endometrial cancer 26220699_data reveal the presence of translation regulatory sequences in the UTRs of FOXC1 and provide evidence for a possible role of rare FOXC1 variants as modifying factors of goniodysgenesis in primary congenital glaucoma. 26240509_ARS is an autosomal dominant disorder with high penetration. It is primarily caused by a mutation of the pituitary homeobox 2 (PITX2) or forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) gene. Mutations in PITX2 on chromosome 4q25, or in FOXC1 at 6p25, have been identified in approximately 40% to 70% of patients with ARS 26382291_Disruptions of enhancers near FOXC1 and GMDS may influence brain development. 26565916_FOXC1 directly binds Gli2 and potentiates Gli2 DNA-binding activity. 26585487_These findings suggest that miR-4792 functions as a tumor suppressor in NPC development and progression by targeting FOXC1. 26643481_These data suggest that deregulation of FOXC1 or its downstream genes play a major role in the pathogenesis of coarctation of the aorta in humans. 26752265_A meta-analysis of the top SNPs identified three new associated loci in primary open angle glaucoma--TXNRD2, ATXN2, and FOXC1 27041579_Here, we demonstrate a novel FOXC1-driven mechanism that suppresses ERa expression in breast cancer. We find that FOXC1 competes with GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) for the same binding regions in the cis-regulatory elements upstream of the ERa gene and thereby downregulates ERa expression and consequently its transcriptional activity 27214551_FOXC1 and FOXC2 are essential regulators of lymphangiogenesis and may have roles in lymphatic-associated diseases 27242366_This report presents the clinical characteristics of a Belgian family with a 3.4 Mb deletion of chromosome 6p25, including the FOXC1 gene. 27463523_A novel heterozygous FOXC1 variant segregated with the disease in a family with Axenfeld Rieger Syndrome. A novel homozygous variant in the FOXC1 gene segregated in a family with ARS and congenital glaucoma. 27533251_Forkhead box C1 protein (FOXC1) promotes melanoma cell function by regulating macrophage stimulating 1 receptor (MST1R) and activating MST1R/PI3K/AKT pathway. 27685901_Elevated expression of FOXC1 enhanced the invasion ability of BLCB cells in vitro. 27708239_expression of FOXC1 in BRCA1 mutant cell lines correlates with sensitivity to olaparib. Whether this is due to rates of proliferation or another mechanism is yet to be explored, but this, and the specificity of FOXC1 in BRCA1-mutant tumors, suggests a possible role for FOXC1 as a marker for targeted therapy. 27907090_this study defines FOXC1 as a regulator specific for KC terminal differentiation and establishes its potential position in the genetic regulatory network. 28028927_Results showed a significant higher FOXC1 expression in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer than that in estrogen receptor-positive. Its overexpression reduced expression of ERalpha and cellular responses to tamoxifen suggesting that FOXC1 regulated expression of ERalpha and affected sensitivity of tamoxifen treatment in breast cancer 28111183_this report describes an Italian family in which four subjects share brachydactyly type E and a 3 Mb microduplication in region 6p25. The duplication involves the gene FOXC1, expressed during the osteoblast differentiation, which appears a potential candidate gene for brachydactyly. 28288141_This review will summarize current knowledge on the function and regulation of FOXC1 in tumor development and progression with a focus on basal-like breast cancer, as well as the implications of these new findings in cancer diagnosis and treatment. [review] 28435457_Taken together, these data indicate that FOXC1 is a novel hypoxia-induced transcription factor and plays a critical role in tumor microenvironment-promoted lung cancer progression. 28493031_FOXC1 is correlated with chemosensitivity to anthracycline and could be used as an indicator of chemosensitivity in sporadic triple-negative breast cancer 28513611_Glaucoma prevalence and phenotype are characterized in a cohort of glaucoma patients and their family members with FOXC1 variants. 28575017_present work reveals that FOXC1 is an important regulator of exocytosis and establishes a new link between FOXC1 and MYOC-associated glaucoma 28629477_novel EGFR-NF-kappaB-FOXC1 signaling axis that is critical for BLBC cell function 28635400_Our findings suggested that FOXCUT expression contributed to the development and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting FOXC1 and that FOXCUT might be useful as a potential nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarker and therapeutic target. 28657660_Genomic analysis of blood and excised valve tissue showed down-regulation of FOXC1 but also FOXC2 expression in the diseased aortic valve. This allows us to speculate on the potential role of FOXC1 in aortic valve anomalies. 28684636_Results provide evidence that FOXC1 is not required for initiation of EMT events but rather participates in the specification of mesenchymal cell phenotype through regulation of FGF receptor switching from FGFR2-IIIb to FGFR1-IIIc in response to TGFb1-induced EMT. 28810526_In regulating cervical cancers metastasis by targeting FOXC1. 29249801_FOXC1 can bind directly to the WNT5A promoter region to activate its expression. WNT5A activates NF-kappaB signaling to induce MMP7 expression. Collectively, this demonstrates a FOXC1-elicited non-canonical WNT5A signaling mechanism comprising NF-kappaB and MMP7 that is essential for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell invasiveness, thereby providing implications toward developing an effective therapy for TNBC. 29328384_Knockdown of FOXC1 markedly suppressed cell migration and invasion in vitro, and resulted in downregulation of phosphorylatedRACalpha serine/threonineprotein kinase, protooncogene cMyc and Bcell lymphoma 2. 29660031_Low FOXC1 expression is associated with Meningioma. 29803789_Study determined that the expression of a novel circRNA, circIRAK3, was increased in metastatic breast cancer (BC) cells and predictive of BC recurrence and identified miR-3607 as a circIRAK3-associated miRNA. FOXC1 the target of miR-3607, was downregulated in circIRAK3-silenced cells and mediated circIRAK3-induced BC cell migration. FOXC1 in turn could bind to the IRAK3 promoter, triggering a positive-feedback loop. 29847662_We show the abrogation of latanoprost signalling when FOXC1 is knocked down via siRNA in a trabecular meshwork cell line. We propose that the lower levels of active FOXC1 in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome patients with glaucoma account for the lack of response to prostaglandin-based medications. 29884889_we identified forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) as a novel regulator of colorectal cancer metastases. FOXC1 directly binds its target genes integrin alpha7 (ITGA7) and fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) and activates their expression 29939776_Truncations may be the primary mutation type in PITX2. Glaucoma onset may be earlier in patients with mutations in PITX2 than in those without mutations in PITX2 and FOXC1. A block of the anterior chamber angle by the end of the iris might represent the main factor influencing the development of glaucoma in ARS patients with an asymmetric aniridia phenotype. 29959321_Targeting EZH2 reactivates a breast cancer subtype-specific anti-metastatic transcriptional program driven by FOXC1. 29978194_This patient was diagnosed with Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome caused by FOXC1 mutation conferring an increased risk for glaucoma and associated cerebellar dysgenesis. 30003742_High FOXC1 enhanced the proliferation, migratory ability and EMT of BLBC cells. 30060822_Foxc1 promoted cell proliferation by upregulation PI3K/AKT signaling, which was inflammation-dependent. 30171256_FOXC1 expression was higher in colorectal cancer specimens than in benign tissue and correlated with poorer survival. Silencing FOXC1 expression in CRC cells inhibited proliferation and colony formation and decreased their glucose consumption and lactate production. Overexpression did the opposite and downregulated FBP1 by binding its promoter. The FOXC1/FBP1 axis induces CRC cell proliferation and reprograms metabolism. 30189871_This study demonstrates that FOXC1 induces cancer stem cells (CSCs)-like properties in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by promoting beta-catenin expression. The findings indicate that FOXC1 is a potential molecular target for anti-CSC-based therapies in NSCLC 30290049_Study discovered that overexpression of FOXC1 significantly enhanced, whereas its knockdown significantly reduced, the capabilities of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell invasion and motility in vitro and metastasis to the lung in vivo. Also, FOXC1 enhanced the expression of CXCR4, probably through its transcriptional up-regulation in TNBC cells. 30431099_High FOXC1 expression is associated with epithelialtomesenchymal transition of glioma cells. 30457409_Heterozygous pathogenic variants in the PITX2 and FOXC1 genes accounted for 66% (6/9) of the ARS/ASD cases. The absence of PAX6 or CYP1B1 abnormalities could reflect our small sample size, although their analysis could be justified in ARS/ASD patients that present with congenital glaucoma or aniridia. 30464116_The present study has successfully demonstrated that FOXC1 protein plays a crucial part in regulating VIC osteogenic differentiation. At the same time, we also proved that FOXC1 is a direct target gene of miR- 138 using dual-luciferase reporter assay. Our study also confirmed the function of FOXC1 in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human aortic valvular Interstitial Cells. 30514661_Study in Lebanese family reports the first documented human case with a mutation in FOXC1 regulating multi-organ developmental pathways that reflect a conserved mechanism in cell differentiation and proliferation. 30722065_our structural analysis and accompanying biochemical assays provide a molecular basis for understanding disease-causing mutations in FOXC1 and FOXC2 30889612_Both patients exhibited commonly reported phenotypes associated with the 6p25.3 deletion of the FOXC1 gene. They also exhibited vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia and kissing carotid arteries, which have not been previously reported in association with this deletion. 31372939_FOXC1 protein expression indicated poor survival outcome in various carcinomas, especially in patients with breast cancer, suggesting it as a possible biomarker for the prognosis in multiple carcinomas. [review] 31512996_C/EBPalpha Regulates FOXC1 to Modulate Tumor Growth by Interacting with PPARgamma in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 31588228_Role of FOXC1 in regulating APSCs self-renewal via STI-1/PrP(C) signaling. 31597217_FOXC1 in the mediation of NSCLC metastasis through interaction with the lysyl oxidase (LOX) promoter and further revealed that targeted inhibition of LOX protein activity could prevent lung metastasis in murine xenograft models. 31650548_FOXC1 is strongly suggested as a pro-metastatic gene in colorectal cancer by transcriptionally activating MMP10, SOX4 and SOX13. 31836490_Childhood glaucoma genes and phenotypes: Focus on FOXC1 mutations causing anterior segment dysgenesis and hearing loss. 31837247_Forkhead box C1 promotes the pathology of osteoarthritis by upregulating beta-catenin in synovial fibroblasts. 31892566_COUP-TFII knock-down promoted proliferation and invasion via activation of Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin and up-regulation of FOXC1. 31916318_FOXC1 negatively regulates BMP-SMAD activity and Id1 expression during osteoblast differentiation. 32046874_TRIP6 promotes tumorigenic capability through regulating FOXC1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32107877_MIR-138-5P inhibits the progression of prostate cancer by targeting FOXC1. 32295643_The diagnosis and phacoemulsification in combination with intraocular lens implantation for an Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome patient with small cornea: a case report. 32445751_HOXB2 and FOXC1 synergistically drive the progression of Wilms tumor. 32475988_Phenotype expansion of heterozygous FOXC1 pathogenic variants toward involvement of congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract (CAKUT). 32631953_Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome-associated mutants of the transcription factor FOXC1 abnormally regulate NKX2-5 in model zebrafish embryos. 32632082_Forkhead Box C1 (FOXC1) Expression in Stromal Cells within the Microenvironment of T and NK Cell Lymphomas: Association with Tumor Dormancy and Activation. 32690597_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating miR-204-5p/FOXC1. 32733009_Cross-talk between GLI transcription factors and FOXC1 promotes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia dissemination. 32832252_Exome Sequencing in a Swiss Childhood Glaucoma Cohort Reveals CYP1B1 and FOXC1 Variants as Most Frequent Causes. 32878637_FOXC1-mediated LINC00301 facilitates tumor progression and triggers an immune-suppressing microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the HIF1alpha pathway. 32905845_FOXC1 variant in a family with anterior segment dysgenesis and normal-tension glaucoma. 33057161_EZH2 regulates expression of FOXC1 by mediating H3K27me3 in breast cancers. 33231930_Gene-specific facial dysmorphism in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome caused by FOXC1 and PITX2 variants. 33414365_Loss of FOXC1 contributes to the corneal epithelial fate switch and pathogenesis. 33522955_FOXC1 promotes HCC proliferation and metastasis by Upregulating DNMT3B to induce DNA Hypermethylation of CTH promoter. 33568052_ELAVL1 is transcriptionally activated by FOXC1 and promotes ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy. 33727172_Tumor-specific overexpression of histone gene, H3C14 in gastric cancer is mediated through EGFR-FOXC1 axis. 33771836_Super-Enhancer-Associated Transcription Factors Maintain Transcriptional Regulation in Mature Podocytes. 33965401_Transcription factor FOXC1 positively regulates SFRP1 expression in androgenetic alopecia. 34041718_Knockdown of HCG18 Inhibits Cell Viability, Migration and Invasion in Pediatric Osteosarcoma by Targeting miR-188-5p/FOXC1 Axis. 34082653_MicroRNA miR-106a-5p targets forkhead box transcription factor FOXC1 to suppress the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of ectopic endometrial stromal cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. 34106567_USP28 promotes aerobic glycolysis of colorectal cancer by increasing stability of FOXC1. 34298004_MicroRNA-495/TGF-beta/FOXC1 axis regulates multidrug resistance in metaplastic breast cancer cells. 34334155_[FOXC1 Knockdown Reverses Gefitinib Resistance in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer]. 34432784_[
|
ENSMUSG00000050295 |
Foxc1 |
8.857560 |
0.3562506883 |
-1.489035 |
0.515354735 |
8.743915 |
0.00310636822054594389716508651133608509553596377372741699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006627637313567236003464255844619401614181697368621826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6221334 |
1.5944371 |
13.0557874 |
2.7100888 |
| ENSG00000055163 |
26999 |
CYFIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q96F07 |
FUNCTION: Involved in T-cell adhesion and p53/TP53-dependent induction of apoptosis. Does not bind RNA. As component of the WAVE1 complex, required for BDNF-NTRK2 endocytic trafficking and signaling from early endosomes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5SQX6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15048733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17245118}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell adhesion;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA editing;Synapse;Synaptosome |
|
Predicted to enable small GTPase binding activity. Involved in activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity; apoptotic process; and cell-cell adhesion. Located in perinuclear region of cytoplasm and synapse. Part of SCAR complex. Implicated in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 65. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26999; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; SCAR complex [GO:0031209]; synapse [GO:0045202]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097202]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; dendrite extension [GO:0097484]; positive regulation of neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0051388]; positive regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045862]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833] |
17245118_The CYFIP2 promoter contains a p53-responsive element that confers p53 binding as well as transcriptional activation of a heterologous reporter. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19910030_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20228810_Protein complexes containing CYFIP/Sra/PIR121 coordinate Arf1 and Rac1 signalling during clathrin-AP-1-coated carrier biogenesis at the trans-golgi network. 21252116_Studies identify a novel proapoptotic gene target, CYFIP2, which is downregulated by IMP-1, and mediates the regulation of cell survival and K-Ras expression in colon cancer cells. 22268788_Increased expression of the cytoplasmic FMR1-interacting protein 2 (CYFIP2), a known FMRP interactor, is detected in fragile X syndrome. 22430187_blood samples of lateral sclerosis patients were found to have significantly different levels of expression of CyFIP2 and RbBP9 compared to the levels of expression in control subjects. 28692454_Study characterized the functional roles of the two brain-specific phosphorylation sites (S582 and T1067) of CYFIP2 in cultured hippocampal neurons; found that overexpression of the phospho-blocking T1067A mutant significantly decreased the density of stubby spines, but not other types of spines. Study found that T1067 phosphorylation of CYFIP2 could potentially weaken the interaction between CYFIP2 and Nap1. 29534297_This study identified de novo CYFIP2 variants at the Arg87 residue in cause early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. 29752658_The current study provides further supports for contribution of CYFIP1/2 in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and potentiates it as a peripheral marker for ASD diagnosis. 30021865_The importance of the ATRX/DAXX pathway was confirmed by the first-ever pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pNEN)-specific protein-damaging hotspot mutation in DAXX. In this study, both novel genes, including the pro-apoptotic CYFIP2 gene and hedgehog signaling PTCH2, and novel pathways, such as the MAPK-ERK pathway, were implicated in pNEN. 30664714_This study evidenced a variety of de novo variants in CYFIP2 as a novel cause of mostly severe intellectual disability with seizures and muscular hypotonia. 33149277_New insights into the clinical and molecular spectrum of the novel CYFIP2-related neurodevelopmental disorder and impairment of the WRC-mediated actin dynamics. 34327661_Cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein (CYFIP) family members and their function in neural development and disorders. 34558636_NUAK2 silencing inhibits the proliferation, migration and epithelialtomesenchymal transition of cervical cancer cells via upregulating CYFIP2. 35955843_Molecular Dynamics of CYFIP2 Protein and Its R87C Variant Related to Early Infantile Epileptic Encephalopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000020340 |
Cyfip2 |
149.361477 |
4.8169915636 |
2.268132 |
0.415699596 |
26.874676 |
0.00000021708477195949542191823840222436592384269715694244951009750366210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000826030222769309684084876408555198068484060058835893869400024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
209.4996134 |
56.0246465 |
44.1399069 |
8.7549122 |
| ENSG00000055732 |
55283 |
MCOLN3 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDD5 |
FUNCTION: Nonselective ligand-gated cation channel probably playing a role in the regulation of membrane trafficking events. Acts as Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel with inwardly rectifying activity (PubMed:18369318, PubMed:19497048, PubMed:19522758, PubMed:19885840, PubMed:29106414). Mediates release of Ca(2+) from endosomes to the cytoplasm, contributes to endosomal acidification and is involved in the regulation of membrane trafficking and fusion in the endosomal pathway (PubMed:21245134). Does not seem to act as mechanosensory transduction channel in inner ear sensory hair cells. Proposed to play a critical role at the cochlear stereocilia ankle-link region during hair-bundle growth (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of autophagy (PubMed:19522758). Through association with GABARAPL2 may be involved in autophagosome formation possibly providing Ca(2+) for the fusion process (By similarity). Through a possible and probably tissue-specific heteromerization with MCOLN1 may be at least in part involved in many lysosome-dependent cellular events (PubMed:19885840). Possible heteromeric ion channel assemblies with TRPV5 show pharmacological similarity with TRPML3 (PubMed:23469151). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R4F0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18369318, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19497048, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19522758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19885840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20378547, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21245134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23469151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29106414, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Lipid-binding;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes one of members of the mucolipin cation channel proteins. Mutation studies of the highly similar protein in mice have shown that the protein is found in cochlea hair cells, and mutant mice show early-onset hearing loss and balance problems. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:55283; |
autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; NAADP-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0072345]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626] |
16606612_there is a hierarchy controlling the subcellular distributions of the TRPMLs such that TRPML1 and TRPML2 dictate the localization of TRPML3 and not vice versa 17962195_The A419P mutation affects TRPLMe channel glycosylation and causes massive cell death 18162548_TRPML3(A419P) and (I362T+A419P) at physiological potentials may have a role in hair cell degeneration and deafness 18369318_First characterization of wild-type TRPML3 calcium-permeable channel properties and its regulation by extracytosolic (luminal)hydrogen ion (H+). 19299509_The deaf-waddler isoform of PMCA2, operating at 30% efficacy, showed a significantly decreased ability to rescue the Ca(2+) loading of cells expressing TRPML3(A419P). 19497048_Results show that mucolipin 3 is a novel calcium channel that plays a crucial role in the regulation of cargo trafficking along the endosomal pathway. 19522758_These findings reveal a prominent role for TRPML3 in regulating endocytosis, membrane trafficking and autophagy, perhaps by controlling the Ca(2+) in the vicinity of cellular organelles that is necessary to regulate these cellular events. 19885840_Data show that TRPMLs form distinct functional channel complexes. 20378547_analysis of the TRPML3 channel pore and its stable expansion by the Varitint-Waddler-causing mutation 20736310_TRPML 1, 2 and 3 assemblies regulated cell viability and starvation-induced autophagy. 22753890_Negatively charged amino acids in the extracellular loops of TRPML3 may interfere with the observed sodium inhibition. 23469151_TRPML3 and TRPV5 heteromers could have a biological function 24269818_these results suggest that TRPML3 plays a role in autophagosome maturation through the interaction with GATE16, by providing Ca(2+) in the fusion process. 29577631_The work elucidates the molecular architecture and provides insights into how multiple ligands regulate TRPML1 and TRPML3. (Review) 30215288_palmitoylation is a prerequisite for the function of MCOLN3/TRPML3 as a Ca(2+) channel in autophagosome formation. |
ENSMUSG00000036853 |
Mcoln3 |
39.417494 |
0.2531773227 |
-1.981780 |
0.278648908 |
53.677266 |
0.00000000000023628165947612427136713880473922783532082086965786515975196380168199539184570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001467192803478163342944742577542550330009160641786536416475428268313407897949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0919585 |
2.9284261 |
64.0699025 |
6.7584257 |
| ENSG00000055955 |
3700 |
ITIH4 |
protein_coding |
Q14624 |
FUNCTION: Type II acute-phase protein (APP) involved in inflammatory responses to trauma. May also play a role in liver development or regeneration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19263524}. |
Acute phase;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is secreted into the blood, where it is cleaved by plasma kallikrein into two smaller forms. Expression of this gene has been detected only in liver, and it seems to be upregulated during surgical trauma. This gene is part of a cluster of similar genes on chromosome 3. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:3700; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; hyaluronan metabolic process [GO:0030212]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097] |
14661079_Genetic variation at ITIH4 locus is one of the likely candidate determinants for plasma cholesterol metabolisms 14661079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16271702_ITIH4 and MTJ1 co-immunoprecipitate from total liver protein extracts and SANT domain of HTJ1 protects the ITIH4(588-930) recombinant fragment 18455532_The inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 (ITIH4) protein was significantly present more in interstial cystitis than controls 19263524_ITIH4 is an anti-inflammatory protein, and suggests that further investigation into its potential use in the diagnosis and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke is warranted. 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21331437_Findings suggest that ITI-H4 expression may be used as a biomarker, which could facilitate the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic tools. 23417432_A truncated fragment of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 was the sole protein found to be significantly enhanced in the prostate cancer patients compared to the controls. 23436019_Expression of the 85 kDa ITIH4 was substantial in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis compared with controls or patients with muscular dystrophy, Alzheimer diseases, or Parkinson diseases 24461634_A novel association between suicide attempt and the ITIH3/4-region in a combined group of patients with bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and related psychosis spectrum disorders. 24836184_Worse survival among HCC patients with low ITIH4. 24861553_Four novel body mass index-associated loci near the KCNQ1(rs2237892), ALDH2/MYL2 (rs671, rs12229654), ITIH4 (rs2535633) and NT5C2 (rs11191580) genes are identified in East Asian-ancestry populations. 24884609_Isoform-specific ITIH4 glycosylation and utilization of O-glycosylation sites on ITIH4 differs between cell lines and serum. 25977605_Serum ITIH4 may be a PM10-specific biomarker in COPD and may be related to inflammation. 26206863_confirmed the association of schizophrenia with ITIH3/4 in a Han Chinese population 26408095_ITIH4 peptide isoform as a preterm birth biomarker and its associated SNP implications 26991396_this report has further supported for associations of genetic variants in the ITIH4 and CALN1 genes with schizophrenia and provided the first evidence that the variants regulate ITIH4 AND CALN1 expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex 28828637_Low ITIH4 expression is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 29992445_ITIH4 SNPs rs3821831 and rs2239547 were studied in pregnant depressed Japanese women. Compared with the TT genotype of ITIH4 SNP rs2239547, the CC genotype was significantly related to a reduced risk of depressive symptoms during pregnancy. SNP rs3821831 was not related to these symptoms.The GCCT haplotype of rs2535629, rs736408, rs3821831, and rs2239547 was significantly positively associated with depressive symptoms. 30348621_The ITI-H4 (N(688)) might be a crucial inflammatory factor which contributes to the pathogenesis of recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL). Moreover, it is expected that this study would give some insights into potential functional mechanisms underlying RPL. 31955064_sgp120 or ITIH4 is cleaved when the contact system is activated and this cleavage could be used as a biomarker in patients with hereditary angioedema with normal C1 inhibitor 33238047_Citrullinated inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 in arthritic joints and its potential effect in the neutrophil migration. 33348064_ITIH4, as an inflammation biomarker, mainly increases in bacterial bloodstream infection. 34247200_Associations between KCNQ1 and ITIH4 gene polymorphisms and infant weight gain in early life. 34687700_ITIH4 is a novel serum biomarker for early gastric cancer diagnosis. |
ENSMUSG00000021922 |
Itih4 |
46.700006 |
0.1108416958 |
-3.173427 |
0.641051084 |
21.549769 |
0.00000344764170825805359209617617644028086942853406071662902832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011425054246495031822546811772767227921576704829931259155273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4268808 |
2.7911870 |
58.6516811 |
17.4221914 |
| ENSG00000056291 |
10886 |
NPFFR2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5X5 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for NPAF (A-18-F-amide) and NPFF (F-8-F-amide) neuropeptides, also known as morphine-modulating peptides. Can also be activated by a variety of naturally occurring or synthetic FMRF-amide like ligands. This receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of a subfamily of G-protein-coupled neuropeptide receptors. This protein is activated by the neuropeptides A-18-amide (NPAF) and F-8-amide (NPFF) and may function in pain modulation and regulation of the opioid system. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:10886; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; neuropeptide receptor activity [GO:0008188]; opioid receptor binding [GO:0031628]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; detection of abiotic stimulus [GO:0009582]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; regulation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0045761]; regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:2000479]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408] |
12609745_Evidence does not support the hypothesis that NPGPR is involved in feeding regulation. 15127947_The BIBP3226 and PFR(Tic)amide, on Human neuropeptide FF receptor subtype 2 (hNPFF2) were investigated. 15608144_neuropeptide FF analogs show that NPFF2 receptors couple to the four subunits assayed. 16336216_expression of hNPFF2 receptor mRNA was up-regulated by neuropeptide FF 17157836_NPFF system may also have species-specific features since the NPFF2 receptor mRNA expression differs from that reported for rat 17503329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17503329_findings suggest that a common haplotype in the GPR74 gene protects against obesity, which, in part, is caused by a relief of inhibition of lipid mobilization from adipose tissue 18565622_we identified hFF2 positive neurons in the forebrain and medulla oblongata of individuals who died suddenly. 19944730_species-related differences in the binding properties of NPFF(2) receptors 20600636_Besides regulation of reproduction, kisspeptins have a potential to mediate physiological effects on autonomic regulation and nociception in humans via the NPFF2R pathways. 21818152_Four genetic loci were strongly and independently associated with obesity, NPY2R, NPFFR2, MC4R, and FTO. 22375000_These data show that NPFF-induced heterologous desensitization of MOP receptor signaling is mediated by GRK2 and could involve transphosphorylation within the heteromeric receptor complex. 25326382_The NPFF2 neuropeptide FF receptor phosphorylation sites have been mapped and their role identified in receptor regulation. 26211894_Effects of systematic N-terminus deletions and benzoylations of endogenous RF-amide peptides on NPFF1R, NPFF2R, GPR10, GPR54 and GPR103. 33058233_Genome-wide association analysis of psoriasis patients treated with anti-TNF drugs. |
ENSMUSG00000035528 |
Npffr2 |
11.565215 |
27.0768552928 |
4.758988 |
0.909389584 |
51.580778 |
0.00000000000068711031029020765905072886506833651281897501483797441323986276984214782714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004134426489964722945473489209934273144395056043265412881737574934959411621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.2755062 |
14.2688931 |
0.8289290 |
0.5155171 |
| ENSG00000056558 |
7185 |
TRAF1 |
protein_coding |
Q13077 |
FUNCTION: Adapter molecule that regulates the activation of NF-kappa-B and JNK. Plays a role in the regulation of cell survival and apoptosis. The heterotrimer formed by TRAF1 and TRAF2 is part of a E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex that promotes ubiquitination of target proteins, such as MAP3K14. The TRAF1/TRAF2 complex recruits the antiapoptotic E3 protein-ubiquitin ligases BIRC2 and BIRC3 to TNFRSF1B/TNFR2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10692572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16323247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18429822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19287455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19698991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385093}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor (TNFR) associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins associate with, and mediate the signal transduction from various receptors of the TNFR superfamily. This protein and TRAF2 form a heterodimeric complex, which is required for TNF-alpha-mediated activation of MAPK8/JNK and NF-kappaB. The protein complex formed by this protein and TRAF2 also interacts with inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins (IAPs), and thus mediates the anti-apoptotic signals from TNF receptors. The expression of this protein can be induced by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). EBV infection membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is found to interact with this and other TRAF proteins; this interaction is thought to link LMP1-mediated B lymphocyte transformation to the signal transduction from TNFR family receptors. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:7185; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; thioesterase binding [GO:0031996]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070534]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001236]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
12411322_Study of regulation of TRAF1, which was overexpressed in B-CLL lymphocytes, shows NF-kappaB/Rel activity in B-CLL nuclear extracts bind to TRAF1 promoter elements and regulation is IKK-independent. 12709429_results suggest that tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1(TRAF1) exerts regulatory effects on receptor-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation by targeting inhibitor of kappab kinase complex 14557256_stoichiometry of TRAF1-TRAF2 heteromeric complexes ((TRAF2)2-TRAF1 versus TRAF2-(TRAF1)2) determines their capability to mediate CD40 signaling but has no major effect on TNF signaling 14981539_Actinomycin D blocked PMA-mediated TRAF1 expression in colon cancer cells, suggesting induction at the transcriptional level. 16304992_A constitutive expression of TRAF1, TRAF2, and TANK/I-TRAF in human gliomas was documented 16891304_the t(11, 18)(q21;q21) translocation creating the c-IAP2.MALT1 fusion protein activates NF-kappaB independently of TRAF1 AND TRAF2 and contributes to human malignancy in the absence of signaling adaptors that might otherwise regulate its activity 17235653_The expression of TRAF1 (TNF receptor associated factor 1) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was significantly decreased in SLE patients. 17405906_Lymphocytes and lymphoma cells from lymphoma-associated NF-kappaB2 mutant transgenic mice express high levels of TRAF1. 17804836_A common genetic variant at the TRAF1-C5 locus on chromosome 9 is associated with an increased risk of anti-CCP-positive rheumatoid arthritis. 17804836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17827388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17880261_A polymorphism in the TRAF1/C5 region increases the susceptibility to and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. 17880261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18429822_Study identifies TRAF1 as a substrate of PKN1 kinase activity in vitro and in vivo, and show that this phosphorylation event is required for attenuating downstream kinase activities. 18432273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18432273_STAT4 but not TRAF1/C5 variants influence the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus in Colombians. 18434327_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18434327_STAT4 and the TRAF1/C5 loci are associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. 18576341_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18576341_TRAF1-C5 locus genetic variant SNP rs3761847 is associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis 18593758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18625278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18625278_study concludes that mutant alleles or genotypes of both TRAF1 and STAT4 polymorphisms are associated with the development of Rheumatoid arthritis in our population. 18759306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18794853_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023125_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116907_The risk of death in rheumatoid arthritis is increased in TRAF1/C5 rs3761847 GG homozygotes 19180477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287455_TRAF1 shifts the quality of integrated TNFR1-TNFR2 signaling from apoptosis induction to proinflammatory NFkappaB signaling. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336421_Association of TRAF1-C5 locus with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility was detected in the Japanese populations with modest magnitude, while no significant association was observed for systemic lupus erythematosus. 19336421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401279_Genetic markers in the 6q23 region and TRAF1-C5 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis, in particular with positive anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide and rheumatoid factor profile. 19401279_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19416238_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19433411_A significant association was found for the TRAF1-C5 locus in systemic lupus erythematosis, implying that this region lies in a pathway relevant to multiple autoimmune diseases. 19433411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19540595_Data show that TRAF1 is an important molecule mediating both the CD30 signaling-dependent and independent NF-kappaB activation, which prevents the lymphoma cells from spontaneous and induced apoptosis. 19565500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19617629_adiponectin augmented the expression of A20, suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 3, B-cell CLL/lymphoma (BCL) 3, TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 1, and TNFAIP3-interacting protein (TNIP) 3. 19674979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19698991_a role for TRAF1 as a positive regulator of the NF-kappaB alternative pathway. 19714643_TRAF1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with rheumatoid arthritis in both Asians and Caucasians and are possibly correlated with causative variations. 19741008_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19902201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19918040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19918040_Results showed no influence of rs10818488 and rs2900180 TRAF1/C5 gene polymorphisms in susceptibility to and clinical expression of giant cell arteritis. 20030635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20030635_results point to the involvement of the TRAF1/C5 locus in the aetiology of familial and severe alopecia areata (AA), and provide further support for a shared aetiology between AA and other autoimmune disorders. 20049410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20205706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20233754_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385093_crystal structures of the TRAF2: cIAP2 and the TRAF1: TRAF2: cIAP2 complexes; biochemical, structural, and cell biological studies on the interaction between TRAF2 and cIAP2 and on the ability of TRAF1 to modulate this interaction 20413583_the human TRAF1 mRNA has an unusually long 5'-UTR that contains internal ribosome entry segment regulating its translation. 20439292_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20479942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20797713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20822712_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20822712_Our results do not show that the PTPN22, STAT4 and TRAF1/C5 gene polymorphisms may confer a direct risk of cardiovascular disease disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 20856938_Interaction of TRAF1 with I-kappa B kinase-2 and TRAF2 is important for regulation of NF-kappa B activity. 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21153322_4-1BBL and TRAF1 in the CD8 T cell response to influenza virus and HIV 21492465_Significant differences in SNPs rs3761847 and rs7021206 at TRAF1/C5 were observed between the case and control groups, the allelic p-value was 0.0018 with an odds ratio of 1.28 for rs3761847 and 0.005 with an odds ratio of 1.27 for rs7021206. 21724995_Death domain SXXE/D motifs of TNFR1-death domain are phosphorylated, as is required for stable TNFR1-TRADD complex formation and subsequent activation of NF-kappaB in inflamed mucosa. 21968398_A genetic association of the TRAF1/C5, C1q, and eNOS gene polymorphism, but not of STAT4 and PTPN22, was found to confer a degree of risk for systemic lupus erythematosus in the Turkish population. 22184633_These findings identify TRAF1 as a potential biomarker of HIV-specific CD8 T cell fitness during the chronic phase of disease and a target for therapy. 22196377_TRAF1 polymorphisms contribute to rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility, activity, and severity in an Egyption population. 22284611_We confirmed the positive association of rs10818488 A allele with rheimatoid arthritis in Tunisia. 22586175_the present data do not support the initial findings that single-nucleotide polymorphisms of TRAF1-C5 and TNFAIP3-OLIG3 rare associated with the severity of joint destruction in RA. 22820624_An association was found between the rs10818488 polymorphism of TRAF1-C5 and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythemaosis in Europeans [Meta-analysis] 23125866_The frequency of TRAF1 rs3761847 and rs2900180 polymorphisms did not differ between patients and controls. 23242182_This represents the second independent study correlating rs2900180 at the TRAF1 locus with radiological severity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. 23321589_TRAF1 polymorphism is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in North Africa group and rheumatoid arthritis in European population. 23414308_activation of TRAF-2 may be early events in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease 23543740_TRAF1.NIK is a central complex linking canonical and non-canonical pathways by disrupting the TRAF2-cIAP2 ubiquitin ligase complex 23710202_The association between rs2900180 and rs3761847 polymorphisms and quality of life variables indicates that TRAF1 is involved in the induction of impaired quality of life in primary biliary cirrhosis. 24144456_genetic polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Europeans Read More: http://informahealthcare.com/doi/full/10.3109/08820139.2013.837917 24234752_Genetic polymorphism rs10818488 in TRAF1/C5 gene might be associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. [Meta-analysis] 24321457_Single nucleotide polymorphism of TRAF1 predicts the clinical response to anti-TNF treatment in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 24338224_These findings suggest that the rs0818488 in TRAF1/C5 region is not associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Iranian population. 24952347_DNMT3L can address DNMT3A/B to specific sites by directly interacting with TFs that do not directly interact with DNMT3A/B 25158810_The increased serum TRAF-1 may be a useful non-invasive indicator of Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) development. 25500258_TRAF1/C5 rs10818488 polymorphism is not a genetic risk factor for acquired aplastic anemia in a Chinese population. 25533804_TRAF1-ALK translocation contributes to neoplastic phenotype in anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. 25566937_Rs2900180 in C5-TRAF1 and linked variants in a 66Kb region were associated with radiographic progression in ACPA-negative RA 25834819_This study did not replicate the association between PTPRC and the response to anti-TNF treatment in our Southern European population. We found that TRAF1/C5 risk RA variants potentially influence anti-TNF treatment response. 25996949_Data suggest that, during B-cell transformation by Epstein-Barr virus, LMP1 (EBV latent membrane protein 1) induces signaling that stimulates Lys63-polyubiquitin chain attachment to TRAF1 (TNF receptor-associated factor 1) in the B-lymphocytes. 26615960_Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in angiotensin II receptor, type 1 (AGTR1), transcription factor AP-2 beta (TFAP2B), and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 1 (TRAF1) have been reported to be associated with the incidence of PDA in preterm infants. 26860405_TRAF1 functions as a positive regulator of insulin resistance, inflammation, and hepatic steatosis dependent on the activation of ASK1-P38/JNK axis. 27060717_Helicobacter pylori infection induces the overexpression of TRAF1 in gastric epithelial cells. The upregulation of TRAF1 plays an antiapoptotic role in Helicobacte pylori -infected gastric cells and may contribute to the gastric carcinogenesis. 27151821_The structure reveals both similarities and differences with other TRAF family members, which may be functionally relevant to TRAFs. The authors also found that the TRAF-N coiled-coil domain of TRAF1 is critical for the trimer formation and stability of the protein. 27592369_TRAF1 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of autoantibodies and may serve as a serologic inflammatory marker of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 27827325_Alleles of rs2416804 in TRAF1 were identified as being linked and associated with carotid intima-media thickness. 27893701_this study reveals an unexpected role for TRAF1 in negatively regulating Toll-like receptor signaling, providing a mechanistic explanation for the increased inflammation seen with a rheumatoid arthritis-associated single-nucleotide polymorphism in the TRAF1 gene 28082808_H. pylori infection significantly inhibits the cleavage of TRAF1 via a CagA-dependent mechanism, which would increase the relative amounts of full-length TRAF1 and exert an antiapoptotic effect on H. pylori-infected cells. 28155233_Molecular basis for TANK recognition by TRAF1 revealed by the crystal structure of TRAF1/TANK complex has been reported. 28470428_TRAF1, CTGF, and CX3CL1 genes are hypomethylated in osteoarthritis 28926524_Authors demonstrated that TRAF1 expression had no significant prognostic value for GBM. 29528567_Results showed that TRAF1 was frequently upregulated in NSCLC tissues compared with adjacent non-cancerous lung tissues. TRAF1 expression was positively associated with NSCLC lymphatic metastasis and histological grade and was negatively associated with overall patient survival. 29875129_The authors found that tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), as well as TRAF1 and 3, directly binds to the active caspase-2 dimer. 30173777_The data suggest that miR-483 is a colorectal cancer suppressor which could inhibit cell proliferation and migration, possibly via targeting TRAF1. 30619326_Study review the role of TRAF1 as a positive and negative regulator in different signaling pathways and the role of TRAF1 in human disease. 31570557_Association of TRAF1/C5 Locus Polymorphisms with the risk of developing severe neurocysticercosis in the Mexican population. 32093731_TRAF1 suppresses antifungal immunity through CXCL1-mediated neutrophil recruitment during Candida albicans intradermal infection. 32671611_TRAF4, a new substrate of SIAH1, participates in chemotherapy resistance of breast cancer cell by counteracting SIAH1-mediated downregulation of beta-catenin. 32959187_Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identifies RHOH and TRAF1 as key candidate genes for psoriatic arthritis. 34363926_A genetic variant in the TRAF1/C5 gene lead susceptibility to active pulmonary tuberculosis by decreased TNF-alpha levels. 35194031_FXR1 can bind with the CFIm25/CFIm68 complex and promote the progression of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder by stabilizing TRAF1 mRNA. 35538475_N(6)-methyladenosine-modified TRAF1 promotes sunitinib resistance by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis in a METTL14-dependent manner in renal cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000026875 |
Traf1 |
534.567798 |
2.1595209367 |
1.110711 |
0.100737806 |
120.352689 |
0.00000000000000000000000000052956739656078228621273116682045538924966843780551956735295706091728697639461898027946062939008697867393493652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000006323960172521962572414555835257449606954461817921592535878034013744659761271926790016095765167847275733947753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
699.2498048 |
41.8909307 |
325.8495763 |
14.4264754 |
| ENSG00000057252 |
6646 |
SOAT1 |
protein_coding |
P35610 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the formation of fatty acid-cholesterol esters, which are less soluble in membranes than cholesterol (PubMed:16154994, PubMed:16647063, PubMed:9020103, PubMed:32433614, PubMed:32433613, PubMed:32944968). Plays a role in lipoprotein assembly and dietary cholesterol absorption (PubMed:16154994, PubMed:9020103). Utilizes oleoyl-CoA ((9Z)-octadecenoyl-CoA) preferentially as susbstrate: shows a higher activity towards an acyl-CoA substrate with a double bond at the delta-9 position (9Z) than towards saturated acyl-CoA or an unsaturated acyl-CoA with a double bond at the delta-7 (7Z) or delta-11 (11Z) positions (PubMed:11294643, PubMed:32433614). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11294643, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16154994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16647063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32433613, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32433614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32944968, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9020103}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the acyltransferase family. It is located in the endoplasmic reticulum, and catalyzes the formation of fatty acid-cholesterol esters. This gene has been implicated in the formation of beta-amyloid and atherosclerotic plaques by controlling the equilibrium between free cholesterol and cytoplasmic cholesteryl esters. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:6646; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cholesterol O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0034736]; fatty-acyl-CoA binding [GO:0000062]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0008374]; sterol O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0004772]; cholesterol efflux [GO:0033344]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; cholesterol storage [GO:0010878]; low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034383]; macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010742]; positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process [GO:0042986]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034379] |
12533546_allosteric activation by cholesterol 12851640_polymorphism of the gene encoding acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (SOAT1) is involved in the regulation of beta-amyloid peptide generation, is associated with low brain amyloid load and with low cerebrospinal fluid levels of cholesterol 14729857_ACAT-1 transcripts predominate in human liver and ACAT-2 transcripts predominate in human duodenum and support the notion that ACAT-2 has an important regulatory role in liver and intestine. 15158756_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15219857_expression in monocytes infiltrating from the circulation to vascular walls may be enhanced by pre-existing transforming growth factor-beta1 15253151_A stable upstream stem-loop structure enhances selection of the first 5'-ORF-AUG as a main start codon for translation initiation of ACAT1 mRNA. 15308631_increasing DGAT1, ACAT1, or ACAT2 expression stimulates the assembly and secretion of VLDL from liver cells 15353128_a glucocorticoid response element (GRE) located within human ACAT1 gene P1 promoter to response to the elevation of human ACAT1 gene expression by dexamethasone could be functionally bound with glucocorticoid receptor (GR) proteins. 15768051_The results of a comprehensive genetic assessment of SOAT1 variants in the NIMH AD Genetics Initiative study sample are presented. 15850387_Disulfide linkage map shows that cysteine(C)92 is located on the cytoplasmic side of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and the disulfide is located in the ER lumen, while all other free Cs are located within the hydrophobic region(s) of the enzyme. 15992359_The structural features of various sterols as substrates and/or activators of ACAT1 and ACAT2 in vitro are reported. 16013913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043284_Our results indicate that the polymorphism rs1044925 in the 3'UTR of SOAT1 gene does not affect the risk of SAD in the northern Han-Chinese. 16154994_results led us to construct a revised, nine-transmembrane domain model, with the active site His-460 located within a hitherto undisclosed transmembrane domain, between Arg-443 and Tyr-462 16230498_Serum-induced depletion of cellular cholesterol available for esterification by ACAT was a strong, independent predictor of major adverse cardiovascular events and death. 16474185_The new ACAT inhibitor VULM1457 in concentration 0.03 and 0.1 micromol/l significantly down-regulated specific AM receptors on HepG2 cells, reduced AM secretion of HepG2 cells exposed to hypoxia. 16647063_histidine residues located at the active site are very crucial both for the catalytic activity of the enzyme and for distinguishing ACAT1 from ACAT2 with respect to enzyme catalysis and substrate specificity 16763159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17412327_These data show that even a modest decrease in ACAT activity can have robust suppressive effects on Abeta generation. 17593314_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17593314_Our study confirmed cognitive decline and highly frequent delirium after bypass heart surgery and excluded the possible role of SOAT-1 genotype polymorphisms in their genesis 17622762_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17622762_SOAT1 gene may possibly be only a minor risk factor in Alzheimer's disease 17691824_Several residues in one subunit closely interact with the same residues in the other subunit; mutating these res. to Cys does not lead to loss in enzyme activity. Mutating residues F453, A457, or H460 to Cys causes large loss in enzyme activity. 18000807_increase in the in vitro ACAT1 activity in PC-3 prostate cancer cells treated with androgen 18269457_In clear cell type renal cell carcinoma upregulation of ACAT-1 leads to high ACAT enzymatic activity, which accelerates the accumulation of cholesterol ester. 18393248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18393248_The results suggest that rs1044925 polymorphism in ACAT1 gene is not only associated with serum LDL-C and nHDLC levels in healthy Chinese subjects in Chengdu area, but also with HDL-C level in subjects with endogenous hypertriglyceridemia. 18542101_RNA secondary structures located in the vicinity of the GGC(1274-1276) codon are required for production of the 56-kDa isoform. 18779653_ACAT inhibition may stimulate cholesterol-catabolic (cytochrome P450) pathway in lesion-macrophages. 18971559_Angiotensin II enhances foam cell formation by upregulating ACAT1 expression predominantly through the actions of AT(1) receptor via the G protein/c-Src/PKC/MAPK pathway in human monocyte-macrophages 19217763_Docosahexaenoic acid can act as a substrate for ACAT1. In the manner of a poor substrate, docosahexaenoic acid also inhibited the activity of ACAT1. 19269342_Results suggest that the ERK, p38MAPK and JNK signaling pathways may be involved in insulin-mediated regulation of ACAT1, but no PI3K and PLC-gamma signaling pathways were involved in the present study. 19502590_Results show that signaling through ACAT/cholesterol esterification is a novel pathway for the CCK2R that contributes to tumor cell proliferation and invasion. 19625677_Leptin accelerates cholesteryl ester accumulation in human monocyte-derived macrophages by increasing ACAT-1 expression. 19851860_High ACAT1 expression is associated with estrogen receptor negative basal-like breast cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460577_Macrophages cope with cholesterol loading by using a novel mechanism: they produce more ER-derived vesicles with elevated ACAT1 enzyme activity without having to produce more ACAT1 protein. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20843517_the plaque-modulating effects of K-604 can be explained by stimulation of procollagen production independent of ACAT inhibition in addition to potent inhibition of macrophage ACAT-1 20945045_Visfatin may down-regulate the ABCA1 expression and up-regulate the ACAT1 expression via PPARgamma signal transduction pathway, which decreases the outflow of free cholesterol, increases the content of cholesterol esters, and then induces foam cell formation. 21143839_the polymorphism of rs1044925 in the ACAT-1 gene is mainly associated with female serum total cholesterol, LDL-C and ApoB levels in the Bai Ku Yao population 21177161_In THP-1-derived macrophages and foam cells, the expression level of ACAT-1 and cellular cholesterol content increased significantly in response to asymmetric dimethylarginine treatment in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. 21239516_SF-1-dependent up-regulation of SOAT1 may be important for maintaining readily-releasable cholesterol reserves needed for active steroidogenesis and during episodes of recurrent stress. 21266192_These findings suggest the potential involvement of MAPK and STAT pathways in norcantharidin-induced apoptogenesis. 21803834_These studies demonstrate that both SIAE and SOAT activities seem to be responsible for the enhanced level of Neu5,9Ac(2) in lymphoblasts, which is a hallmark in acute lymphoblastic leukemia 22243772_The present study shows that the C allele carriers of ACAT-1 rs1044925 SNP in male hyperlipidemic subjects had higher serum total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and ApoAI levels than the C allele noncarriers. 22275303_Essential oil of Pinus koraiensis leaves significantly inhibited hACAT1 levels in HepG2 cells. 23109900_Several lipid-related gene polymorphisms interact with overweight/obesity to modulate blood pressure levels. 23305686_ABCA1 and ACAT1 DNA methylation induced by homocysteine may play a potential role in ABCA1 and ACAT1 expression and the accumulation of cholesterol in monocyte-derived foam cells 23564383_The molecular mechanism of insulin action is mediated via interaction of the functional IRE upstream of the ACAT1 P1 promoter with C/EBPalpha and is MAPK-dependent. 23835473_The exo-endo trans-splicing is dependent on the interchromosomal region of the 4.3-kb human ACAT1 chimeric mRNA, and that the chimeric mRNA is necessary for the production of the ACAT1 56-kDa isoform. 23994608_PLA/AT-1 is at least partly responsible for the generation of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine in mammalian cells. 24407243_Induction of apoptosis and necroptosis by 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol is dependent on activity ACAT1. 24517390_the enzyme activity of ACAT1 with Gln526 is less active than that of ACAT1 with Arg526 by 40%; Pro347 located near transmembrane domain 5 plays an important role in modulating enzyme catalysis 24577316_Data show that the C allele of acyl-CoA acyltransferase-1 (ACAT-1) rs1044925 was associated with a decreased risk of coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke patients. 25339759_Acat1 gene knock-out increases phagocytic uptake of amyloid beta-protein (1-42). 25617738_Suggest retinal pigment epithelium metabolism of 7-ketocholesterol occurs by esterification to fatty acids via cPLA2alpha and SOAT1 followed by selective efflux to HDL. 26252415_ACAT1 regulates glioblastoma-cell proliferation via modification of the Akt and/or the ERK1/2 pathway. 26305886_Data indicate that mitotane confers adrenal-specific cytotoxicity and down-regulates steroidogenesis by inhibition of sterol-O-acyl-transferase 1 (SOAT1) leading to lipid-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. 26474739_ACAT1 has a role in regulating the dynamics of free cholesterols in plasma membrane which leads to the APP-alpha-processing alteration 27177773_TLR4 siRNA inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by suppressing ACAT1 expression, suggesting that TLR4 may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of colorectal cancer 27281560_Intracranial GBM xenografts were used to determine the effects of genetically silencing SOAT1 and SREBP-1 on tumor growth. 27346255_Our results demonstrated the contrasting effects of STC1 and STC2-derived peptides on human macrophage foam cell formation associated with ACAT1 expression and on HASMC migration. 27647838_these results illustrate that ACAT1-catalyzed esterification of 24S-OHC with long-chain unsaturated fatty acid followed by formation of atypical LD-like structures at the ER membrane is a critical requirement for 24S-OHC-induced cell death. 28595267_Higher Gleason grade was associated with lower LDLR expression, lower SOAT1 and higher SQLE expression. Besides high SQLE expression, cancers that became lethal despite primary treatment were characterized by low LDLR expression (odds ratio for highest versus lowest quintile, 0.37; 95% CI 0.18-0.76) and by low SOAT1 expression (odds ratio, 0.41; 95% CI 0.21-0.83). 29567472_Soat-1 role in atherosclerosis 29593722_the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 was activated by TB-PE, and its chemical inhibition prevented the accumulation of lipid bodies and ACAT expression in macrophages. In terms of the host immune response, TB-PE-treated macrophages displayed immunosuppressive properties and bore higher bacillary loads. 31236660_There was a significant difference and a higher frequency of AA and AC genotypes (p = 0.047 and p = 0.016, respectively) of the SOAT1 (ACAT-1) gene in asymptomatic chagasic individuals. 31978092_the expression and contribution of ACAT-1 (SOAT1) in ovarian cancer progression, was examined. 32101051_Association Between LOX-1, LAL, and ACAT1 Gene Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Carotid Plaque in a Northern Chinese Population. 32433613_cryo-electron microscopy structure of human ACAT1 (SOAT1) in complex with nevanimibe, an inhibitor that is in clinical trials for the treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia 32433614_cryo-electron microscopy structure of human ACAT1(SOAT1) as a dimer of dimers; structural and biochemical characterization helps to rationalize the preference of ACAT1 for unsaturated acyl chains, and provides insight into the catalytic mechanism of enzymes within the MBOAT family 32633781_SOAT1 promotes mevalonate pathway dependency in pancreatic cancer. 32646003_A Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Inhibits Foam Cell Formation of Macrophages in Type 1 Diabetes via Suppression of CD36 and ACAT-1 Expression. 33057949_Relationship Between Genetic Variants of ACAT1 and APOE with the Susceptibility to Dementia (SADEM Study). 34039309_Impacts of the SOAT1 genetic variants and protein expression on HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 34326474_High expression of Sterol-O-Acyl transferase 1 (SOAT1), an enzyme involved in cholesterol metabolism, is associated with earlier biochemical recurrence in high risk prostate cancer. 34460058_SOAT1 is a new prognostic factor of colorectal cancer. 34670102_SOAT1 enhances lung cancer invasiveness by stimulating AKT-mediated mitochondrial fragmentation. 35354120_piRNA-6426 increases DNMT3B-mediated SOAT1 methylation and improves heart failure. 35409086_SOAT1: A Suitable Target for Therapy in High-Grade Astrocytic Glioma? 35941608_High-affinity SOAT1 ligands remodeled cholesterol metabolism program to inhibit tumor growth. |
ENSMUSG00000026600 |
Soat1 |
476.922989 |
2.3848782139 |
1.253916 |
0.087037140 |
206.475754 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008068387441994432837771905505396050150955803500350704589006191250637840412805555431326123157972135110608601150858625473266672045724590134341269731521606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001589978620077941535797123277575986654751787363359460397966905411647249009060568250668144351777664640538462223525307918936544382404463249258697032928466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
629.7806506 |
36.1717595 |
265.7460916 |
11.4211803 |
| ENSG00000058262 |
29927 |
SEC61A1 |
protein_coding |
P61619 |
FUNCTION: Component of SEC61 channel-forming translocon complex that mediates transport of signal peptide-containing precursor polypeptides across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (PubMed:12475939, PubMed:22375059, PubMed:29719251, PubMed:32814900, PubMed:28782633). Forms a ribosome receptor and a gated pore in the ER membrane, both functions required for cotranslational translocation of nascent polypeptides (PubMed:22375059, PubMed:29719251, PubMed:28782633). May cooperate with auxiliary protein SEC62, SEC63 and HSPA5/BiP to enable post-translational transport of small presecretory proteins (PubMed:22375059, PubMed:29719251). Component of a ribosome-associated ER translocon complex involved in multi-pass membrane protein transport into the ER membrane and biogenesis (PubMed:32820719). The SEC61 channel cooperates with the translocating protein TRAM1 to import nascent proteins into the ER (PubMed:8616892). Controls the passive efflux of calcium ions from the ER lumen to the cytosol through SEC61 channel, contributing to the maintenance of cellular calcium homeostasis (PubMed:28782633). Plays a critical role in nephrogenesis, specifically at pronephros stage (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P61620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12475939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22375059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28782633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29719251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32814900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32820719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8616892}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Translocation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SECY/SEC61- alpha family. It appears to play a crucial role in the insertion of secretory and membrane polypeptides into the endoplasmic reticulum. This protein found to be tightly associated with membrane-bound ribosomes, either directly or through adaptor proteins. This gene encodes an alpha subunit of the heteromeric SEC61 complex, which also contains beta and gamma subunits. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:29927; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; Sec61 translocon complex [GO:0005784]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; protein transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008320]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; signal sequence binding [GO:0005048]; cotranslational protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006613]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0006620]; post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation [GO:0031204]; pronephric nephron development [GO:0039019]; protein insertion into ER membrane [GO:0045048]; protein targeting to ER [GO:0045047]; SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006614]; SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation [GO:0006616] |
18480044_analysis of translocation through the Sec61 translocon by the nascent polypeptide structure within the ribosome 21102557_At the cellular level, two different calmodulin antagonists stimulated calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum through SEC61 channels. 21406962_Silencing the SEC61A1 gene using two different siRNAs in HeLa cells for 96 hours had little effect on cell growth and viability. However, calcium leakage from the ER was greatly decreased in the SEC61A1-silenced cells. 21987770_The present study indicates that Sec61alpha is a host protein involved in Ebola virus (EBOV) replication, specifically in EBOV genome transcription and replication. 22375059_The human SEC61A1 gene is essential for cell growth and viability. 22505607_Short secretory proteins appear to be ubiquitously transported across the ER membrane through the Sec61 translocon. 22796945_BiP limits ER Ca(2+) leakage through the Sec61 complex by binding to the ER lumenal loop 7 of Sec61alpha in the vicinity of tyrosine 344. 24497544_Cotransin, a substrate-selective Sec61 inhibitor, traps nascent transmembrane domains in the cytosolic vestibule, permitting detailed interrogation of an early pre-integration intermediate. 24699819_Unpicking the central dogma of molecular biology step-by-step identifies the Sec61 translocon as the target of anti-inflammatory activity of mycolactone, explaining why production of Sec61-dependent proteins (secretory, ER resident and membrane bound) is lost even though transcription and translation are unaffected. 24934166_Sec61 complex is calcium permeable, the Sec61 complex is tightly regulated in its equilibrium between the closed and open conformations, or 'gated', by ligands, such as signal peptides of the transport substrates 26085089_BiP facilitates Sec61 channel closure (i.e. limits ER Ca(2+) leakage) via the Sec61 channel with the help of ERj3 and ERj6 26356418_Nuclear envelope associated endosome-mediated transfer depends on the nuclear envelope proteins SUN1 and SUN2, as well as the Sec61 translocon complex. 27282568_EPO (7q22) and SEC-61(7p11) emerged as new candidate genes susceptible to genetic losses with 57.7% deletions identified in regions on chromosome 7. 27373685_Tomography densities at subnanometer resolution revealed an intricate network of interactions between the ribosome, Sec61 and accessory translocon components that assist in protein transport, membrane insertion and maturation 27392076_findings provide a mechanism by which mutations in SEC61A1 lead to an autosomal-dominant syndromic form of progressive chronic kidney disease; we highlight protein translocation defects across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, the principal role of the SEC61 complex, as a contributory pathogenic mechanism for autosomal-dominant tubulo-interstitial kidney disease 27821549_data provide definitive genetic evidence that Sec61 is the host receptor mediating the diverse immunomodulatory effects of mycolactone and identify Sec61 as a novel regulator of immune cell functions. 27932072_The discovery of export-specific sec61 mutants and of mammalian ER-associated degradation (ERAD) substrates whose export is dependent on the 19S regulatory particle suggest that dismissal of a role of Sec61 in export may have been premature. 28219954_the effect of mycolactone on transmembrane protein biogenesis depends on how the nascent chain initially engages the Sec61 complex. 28504640_The authors propose that the Sec61-IRE1alpha complex defines the extent of IRE1alpha activity and may determine cell fate decisions during endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions. 28679634_The direct contribution of Sec61 to antigen cross-presentation, endosome-to-cytosol export, and endoplasmic reticulum-to-cytosol export. 28782633_SEC61A1-V85D triggered the terminal unfolded protein response in multiple myeloma cell lines. 29540678_Shows that inhibition of Sec61 by mycolactone drives rapid and broad translational reprogramming of a subset of genes involved in stress responses that is initially protective but ultimately leads to cell death 29915147_Sec61 blockade induces proteostatic stress in the cytosol and the endoplasmic reticulum. 30213864_An mH segment in a nascent chain was cross-linked to the Sec61alpha pore-interior positions at TM5 and TM10, as well as the lateral gate. 31197453_Sec61alpha measurement has not an additional prognostic benefit for esophageal cancer patients. 32325141_Defective Sec61alpha1 underlies a novel cause of autosomal dominant severe congenital neutropenia. 32692975_Structure of the Inhibited State of the Sec Translocon. 34211117_An alternative pathway for membrane protein biogenesis at the endoplasmic reticulum. 35064074_Phenylbutyrate rescues the transport defect of the Sec61alpha mutations V67G and T185A for renin. |
ENSMUSG00000030082 |
Sec61a1 |
3148.201320 |
2.1308345345 |
1.091419 |
0.035758771 |
930.015243 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000293079314131050375544406540313931802171747711418660806722650984457689613470207467539722170227116824293393046104261205558709222 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000275531890227662634793998474114129156572895180527620490247180479734845980039803733695527264997103399541018000100728543667472357 |
Yes |
Yes |
4313.0699597 |
85.0962504 |
2038.4409909 |
31.2241154 |
| ENSG00000058335 |
5923 |
RASGRF1 |
protein_coding |
Q13972 |
FUNCTION: Promotes the exchange of Ras-bound GDP by GTP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11389730}. |
Alternative splicing;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) similar to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC25 gene product. Functional analysis has demonstrated that this protein stimulates the dissociation of GDP from RAS protein. The studies of the similar gene in mouse suggested that the Ras-GEF activity of this protein in brain can be activated by Ca2+ influx, muscarinic receptors, and G protein beta-gamma subunit. Mouse studies also indicated that the Ras-GEF signaling pathway mediated by this protein may be important for long-term memory. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:5923; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035254]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; long-term memory [GO:0007616]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048168]; regulation of NMDA receptor activity [GO:2000310]; regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035020]; regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046578]; regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035023]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0044342] |
14749369_RasGRF family exchange factors, both endogenous and ectopically expressed, are present in the endoplasmic reticulum but not in the Golgi complex 16855028_Taken together our results demonstrate that U2AF35a is essential for HeLa cell division and suggest a novel role for both U2AF35 protein isoforms as regulators of alternative splicing of a specific subset of genes. 16969075_Vitamin K3 inhibitor H32 differentially inhibited growth of normal and liver tumor cells by preferentially inhibiting the actions of Cdc25 phosphatases 17030618_Rasgrf1 transgenic repeats serve at least two functions: first, to establish Rasgrf1 DNA methylation in the male germ line, and second, to resist global demethylation in the preimplantation embryo. 17611684_zoledronate induces DNA damage and S phase arrest, accompanied by activation of the ATM/Chk1/cdc25 pathway in a human osteosarcoma cell line 19678938_Enhanced expression and post-translational modification of RasGRF1 contributes to MMP-3 production in RA 19692568_Farnesylated or geranylgeranylated TC21 can be activated by RasGRF1 due to its pleckstrin homology 1 domain, by a mechanism independent of localization & of its ability to associate to membranes. 20835236_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20835236_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in RASGRF1 is associated with refractive errors and myopia. 21685891_Demonstrate a role for RasGRF1/2 as negative regulators of Cdc42 activation, suppressing tumor cell movement, cytoskeletal dynamics and cell transformation. 22752028_RasGRF1 plays an important role in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma pathogenesis 22961779_Aberrant methylation of RASGRF1 is associated with an epigenetic field defect and increased risk of gastric cancer. 23200899_Decreased expression of Ras-GRF1 could be involved in the pathogenesis of human temporal lobe epilepsy. 23834555_In this study, there was no association of the analyzed SNPs located in RASGRF1. GJD2, and ACTC1 with pathological myopia. 24150758_ZIC2 and RASGRF1 are susceptibility genes, not only for common myopia, but also for high myopia. 24597981_Rasgrf-1 is a novel GEF protein that has a role in BCR signaling and its overexpression further activates the Ras/Erk/MAPK pathway in CLL specimens. 25267792_CARD9 regulates H-Ras activation by linking Ras-GRF1 to H-Ras, which mediates Dectin-1-induced extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) activation and proinflammatory responses when stimulated by their ligands. 26440052_Data show that microRNA miR-137 directly recognized the 3'-UTR (3'-untranslated region) of the RASGRF1 (Ras protein-specific guanine nucleotide-releasing factor 1) transcript and regulated RASGRF1 expression. 26521038_Impaired RASGRF1/ERK-mediated GM-CSF response characterizes CARD9 deficiency in French-Canadians. 26644762_Carriers of the rs8027411 G allele in the RASGRF1 gene may be at a lower risk of high myopia in Chinese and Japanese populations. (Meta-analysis) 27856453_Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers a localized signaling module on the ER surface involving Nox4-dependent calcium mobilization, which directs local Ras activation through ER-associated, calcium-responsive RasGRF. 29044055_genetic variants in BICC1 and RASGRF1 are closely associated with high myopia, which appears to be a potential candidate for high myopia in Chinese Han population. 29530990_Low RASGRF1 expression due to hypermethylation is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 29793445_Our studies have shown that the heritability of myopia makes 66.4% in Lithuania. We detected significant associations between the combinations of GJD2 CC and RASGRF1 GT and odds ratio of developing myopia. 31943943_Benzothiazole amphiphiles promote RasGRF1-associated dendritic spine formation in human stem cell-derived neurons. 34799483_RASGRF1-rearranged Cutaneous Melanocytic Neoplasms With Spitzoid Cytomorphology: A Clinicopathologic and Genetic Study of 3 Cases. |
ENSMUSG00000032356 |
Rasgrf1 |
293.472060 |
3.2234215988 |
1.688593 |
0.114286419 |
219.955622 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009248333118732380710387330341104189530732522305577208939852635694013809028482497715527809414910413454603007740886945787519256290121205665855086408555507659912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001961284437248418746476494502763533276123557133592053517004327916792128187321191681015793215739783479784725559710137262605864072462225067283725365996360778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
432.6469152 |
30.3874108 |
135.2526129 |
7.6075688 |
| ENSG00000058404 |
816 |
CAMK2B |
protein_coding |
Q13554 |
FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that functions autonomously after Ca(2+)/calmodulin-binding and autophosphorylation, and is involved in dendritic spine and synapse formation, neuronal plasticity and regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) transport in skeletal muscle (PubMed:16690701). In neurons, plays an essential structural role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton during plasticity by binding and bundling actin filaments in a kinase-independent manner. This structural function is required for correct targeting of CaMK2A, which acts downstream of NMDAR to promote dendritic spine and synapse formation and maintain synaptic plasticity which enables long-term potentiation (LTP) and hippocampus-dependent learning. In developing hippocampal neurons, promotes arborization of the dendritic tree and in mature neurons, promotes dendritic remodeling. Also regulates the migration of developing neurons (PubMed:29100089). Participates in the modulation of skeletal muscle function in response to exercise (PubMed:16690701). In slow-twitch muscles, is involved in regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) transport and in fast-twitch muscle participates in the control of Ca(2+) release from the SR through phosphorylation of triadin, a ryanodine receptor-coupling factor, and phospholamban (PLN/PLB), an endogenous inhibitor of SERCA2A/ATP2A2. In response to interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) stimulation, catalyzes phosphorylation of STAT1, stimulating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway (By similarity). Phosphorylates reticulophagy regulator RETREG1 at 'Ser-151' under endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions which enhances RETREG1 oligomerization and its membrane scission and reticulophagy activity (PubMed:31930741). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08413, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16690701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29100089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31930741}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Synapse;Transferase |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family and to the Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase subfamily. Calcium signaling is crucial for several aspects of plasticity at glutamatergic synapses. In mammalian cells, the enzyme is composed of four different chains: alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. The product of this gene is a beta chain. It is possible that distinct isoforms of this chain have different cellular localizations and interact differently with calmodulin. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:816; |
calcium- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase complex [GO:0005954]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; synapse [GO:0045202]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0009931]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0004683]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061003]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of synapse maturation [GO:0090129]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060998]; regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048169]; regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001222]; regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation [GO:0014733]; regulation of synapse structural plasticity [GO:0051823]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11042361_mRNA levels are elevated in the frontal cortex in schizophrenia. 11710563_Four distinct isoforms of CAMKII were isolated. Two of them were characterized as CaMKII alpha and beta subunits.expression is developmentally regulated in both human fetal and adult brain to different degrees 11889801_role in cell communication 12496285_CaMK II regulates c-FLIP expression and phosphorylation, thus modulating Fas-mediated signaling in glioma cells 14565989_exercise increases the activity of CaMKII in skeletal muscle, suggesting that it may have a role in regulating skeletal muscle function and metabolism during exercise in humans 14722083_measured differences in CaMKII binding affinities for CaM play a minor role in the autophosphorylation of the enzyme, largely dictated by autophosphorylation rate for alpha, beta, gamma and delta isoforms 15665723_the function of CaMK II is essential for PAF-induced macrophage priming, while CaMK IV is not specific for priming by PAF and appears to have a direct link in TLR4-mediated events 15792370_presence of a CaMKIIbeta isoform that can target the SR presumably via its membrane anchor alphaKAP defines a previously unrecognized Ca2+/CaM regulatory system in myocardium 16126727_thrombomodulin induces Ca2+ signals and nitric oxide synthesis through EGFR and calmodulin kinase II 16247765_The expression of CaMKII beta was significantly elevated in schizophrenia and in depression. 16247765_expression significantly elevated in frontal cortex in schizophrenia & depression; because CaMKIIbeta influences expression of neuroreceptors & neural outgrowth & pruning, altered expression in schizophrenia or depression may contribute to these diseases 17419996_regulated degradation of liprinalpha1 is important for proper LAR receptor distribution, and could provide a mechanism for localized control of dendrite and synapse morphogenesis by activity and CaMKII. 18302935_These FLIM versions of Camui could be useful for elucidating the function of CaMKII both in vitro and in vivo. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21479273_The novel cGMP/PKG/ROS/calmodulin/CaMKII signaling pathway may regulate cardiomyocyte excitability by opening K(ATP) channels and contribute to cardiac protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. 21610080_Characterization of a central Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIalpha/beta binding domain in densin that selectively modulates glutamate receptor subunit phosphorylation. 21871176_Promoter methylations of CAMK2B and ARFGEF1 are novel epigenetic markers identified in breast cancer cell lines. 21884935_Study presents the crystal structure of an autoinhibited full-length human CaMKII holoenzyme, revealing an unexpected compact arrangement of kinase domains docked against a central hub, with the calmodulin-binding sites completely inaccessible. 22750393_beta-carotene reverses the IL-1beta-mediated reduction in paraoxonase-1 expression via induction of the CaMKKII pathway in human endothelial cells 25045698_Due to similarity of structure variations, we suggest that these compounds may have an effect on beta-CaMKII and that sengesterone may have a similar efficacy as the control. 28130256_TGFbeta elevated the expression of CamK IIbeta and CamK IIdelta, while siRNA silencing of those two subtypes significantly reduced TGFbeta-mediated expression of collagen A1 and fibronectin 1. 29100089_The importance of CAMK2A and CAMK2B and their auto-phosphorylation in human brain function. 29410121_CaMKII regulates KCNQ1 at S484 during sustained beta-AR stimulation to inhibit IKs. The ability of CaMKII to inhibit IKs may contribute to arrhythmogenicity during HF. 32149607_Flexible linkers in CaMKII control the balance between activating and inhibitory autophosphorylation. 33019657_CaMKIIbeta in Neuronal Development and Plasticity: An Emerging Candidate in Brain Diseases. |
ENSMUSG00000057897 |
Camk2b |
10.970105 |
0.3092011279 |
-1.693383 |
0.588711218 |
8.188833 |
0.00421490278632365936856141175326229131314903497695922851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008751155595180363372387333242841123137623071670532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9132616 |
2.1343083 |
16.0258757 |
4.6617532 |
| ENSG00000058453 |
9696 |
CROCC |
protein_coding |
Q5TZA2 |
FUNCTION: Major structural component of the ciliary rootlet, a cytoskeletal-like structure in ciliated cells which originates from the basal body at the proximal end of a cilium and extends proximally toward the cell nucleus (By similarity). Furthermore, is required for the correct positioning of the cilium basal body relative to the cell nucleus, to allow for ciliogenesis (PubMed:27623382). Contributes to centrosome cohesion before mitosis (PubMed:16203858). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CJ40, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16203858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27623382}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell projection;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable kinesin binding activity and structural molecule activity. Involved in several processes, including centriole-centriole cohesion; positive regulation of cilium assembly; and positive regulation of protein localization to cilium. Located in cytoskeleton; cytosol; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9696; |
9+2 motile cilium [GO:0097729]; actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary rootlet [GO:0035253]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; subapical part of cell [GO:0120219]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; centriole-centriole cohesion [GO:0010457]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; ciliary basal body organization [GO:0032053]; epithelial structure maintenance [GO:0010669]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; establishment of organelle localization [GO:0051656]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; positive regulation of cilium assembly [GO:0045724]; positive regulation of protein localization to cilium [GO:1903566]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein localization to organelle [GO:0033365] |
16767081_Our findings suggest that the HTLV-I Tax oncoprotein targets TAX1BP2 causing genomic instability and aneuploidy. 22610972_we demonstrated that TAX1BP2 was frequently underexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and that loss of TAX1BP2 promoted the growth of HCC cells by suppressing activation of the p38/p53/p21 pathway. 23070519_C-NAP1 and rootletin restrain DNA damage-induced centriole splitting and facilitate ciliogenesis. 24240686_Data show that serine-922 of TAX1BP2 protein is the phosphorylation site of ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase. 28089774_It has been proposed that the archetypal linker protein Rootletin maintains centrosome cohesion in part through inhibition of VHL-mediated Cep68 degradation. 29463719_CEP68 is important in forming rootletin filaments that branch off centrioles and to modulate the thickness of rootletin fibers. 29649211_Rootletin forms large, diffusionally stable bifurcating fibers, which amass slowly on mature centrioles over many hours from anaphase. Nascent centrioles (procentrioles), in contrast, do not form roots and must be licensed to do so through PLK1 activity. 31799620_Up-regulated microRNA-33b inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gallbladder cancer through down-regulating CROCC. 32325071_Identification of a Structurally Dynamic Domain for Oligomer Formation in Rootletin. |
ENSMUSG00000040860 |
Crocc |
129.522747 |
0.1829483345 |
-2.450492 |
0.405236767 |
33.282237 |
0.00000000797073958215335535721835142665414597473727553733624517917633056640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000035035174577898609313678145258524887495354960265103727579116821289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
36.1521298 |
12.8311434 |
196.9683634 |
49.4986686 |
| ENSG00000058866 |
1608 |
DGKG |
protein_coding |
P49619 |
FUNCTION: Diacylglycerol kinase that converts diacylglycerol/DAG into phosphatidic acid/phosphatidate/PA and regulates the respective levels of these two bioactive lipids (PubMed:8034597). Thereby, acts as a central switch between the signaling pathways activated by these second messengers with different cellular targets and opposite effects in numerous biological processes (By similarity). Has no apparent specificity with regard to the acyl compositions of diacylglycerol (PubMed:8034597). Specifically expressed in the cerebellum where it controls the level of diacylglycerol which in turn regulates the activity of protein kinase C gamma. Through protein kinase C gamma, indirectly regulates the dendritic development of Purkinje cells, cerebellar long term depression and ultimately cerebellar motor coordination (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91WG7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8034597}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; glycerolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:8034597}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme that is a member of the type I subfamily of diacylglycerol kinases, which are involved in lipid metabolism. These enzymes generate phosphatidic acid by catalyzing the phosphorylation of diacylglycerol, a fundamental lipid second messenger that activates numerous proteins, including protein kinase C isoforms, Ras guanyl nucleotide-releasing proteins and some transient receptor potential channels. Diacylglycerol kinase gamma has been implicated in cell cycle regulation and in the negative regulation of macrophage differentiation in leukemia cells. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1608; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; diacylglycerol kinase activity [GO:0004143]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; diacylglycerol metabolic process [GO:0046339]; glycerolipid metabolic process [GO:0046486]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lipid phosphorylation [GO:0046834]; negative regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090038]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773] |
12732202_diacylglycerol kinase gamma regulates macrophage differentiation. 17803461_the interaction of diacylglycerol kinase gamma with the Src homology 2 and C1 domains of beta2-chimaerin is induced synergistically by Phorbol ester and hydrogen peroxide 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20215397_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24486543_these results indicate that DGKG is an anionic phospholipid binding protein that preferably interacts with a small highly charged head group that is very close to the glycerol or sphingosine backbone. 28218473_Epigenetic silencing of DGKG expression is associated with skin cancer. 30399372_Decreased expression of DGKgamma in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues was an independent risk factor for a poor prognosis. 31722116_Characterization of alpha-synuclein N-terminal domain as a novel cellular phosphatidic acid sensor. |
ENSMUSG00000022861 |
Dgkg |
54.962244 |
0.0950713755 |
-3.394845 |
0.326519551 |
111.296709 |
0.00000000000000000000000005094570121281415557361485890681837885012131121061834569268756687227916839233454737723150174133479595184326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000564109939910830341011862268349898371425607573845847800607799500487420790717507657063833903521299362182617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.3695752 |
2.6403027 |
120.9824423 |
16.6407611 |
| ENSG00000059573 |
5832 |
ALDH18A1 |
protein_coding |
P54886 |
FUNCTION: Bifunctional enzyme that converts glutamate to glutamate 5-semialdehyde, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10037775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11092761, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26297558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26320891}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Multifunctional enzyme;NADP;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Oxidoreductase;Proline biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-proline biosynthesis; L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde from L-glutamate: step 1/2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26297558}.; PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-proline biosynthesis; L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde from L-glutamate: step 2/2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26297558}. |
This gene is a member of the aldehyde dehydrogenase family and encodes a bifunctional ATP- and NADPH-dependent mitochondrial enzyme with both gamma-glutamyl kinase and gamma-glutamyl phosphate reductase activities. The encoded protein catalyzes the reduction of glutamate to delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, a critical step in the de novo biosynthesis of proline, ornithine and arginine. Mutations in this gene lead to hyperammonemia, hypoornithinemia, hypocitrullinemia, hypoargininemia and hypoprolinemia and may be associated with neurodegeneration, cataracts and connective tissue diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5832; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glutamate 5-kinase activity [GO:0004349]; glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004350]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; citrulline biosynthetic process [GO:0019240]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536]; L-proline biosynthetic process [GO:0055129]; ornithine biosynthetic process [GO:0006592]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; proline biosynthetic process [GO:0006561] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18401542_analysis of function and regulation of Delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase 18478038_These data suggest that P5CS may possess additional uncharacterised functions that affect connective tissue and central nervous system function. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20946940_ALDH18A1 genetic variants are associated with Down syndrome in subjects with dementia of Alzheimer's disease. 20946940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21739576_expansion of the phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations in ALDH18A1 24913064_A frameshift deletion of one nucleotide and a microdeletion affecting the ALDH18A1 gene, respectively, in a homozygous state in both patients, was identified. 26026163_autosomal recessive transmission of ALDH18A1 mutations, and predominant complex hereditary spastic paraplegia with marked cognitive impairment 26320891_Recurrent De Novo Mutations Affecting Residue Arg138 of Pyrroline-5-Carboxylate Synthase Cause a Progeroid Form of Autosomal-Dominant Cutis Laxa. 27989597_ALDH18A1 gene during vertebrate and invertebrate evolution and a proposal for generating the bifunctional vertebrate and invertebrate ALDH18A1 gene from a bacterial operon (proBA) encoding glutamyl kinase and glutamyl phosphate reductase. 28228640_This is the first report of an individual with ALDH18A1-ADCL due to a substitution at a residue other than p.Arg138. Knowledge of the complete spectrum of dominant-acting mutations that cause this rare syndrome will have implications for molecular diagnosis and genetic counselling of these families. 29915212_Novel mutations in the ALDH18A1 gene in complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia with cerebellar ataxia and cognitive impairment. 32017139_Delta(1) -Pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase deficiency: An emergent multifaceted urea cycle-related disorder. 32075946_Inhibition of the ALDH18A1-MYCN positive feedback loop attenuates MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma growth. 33573605_SPG9A with the new occurrence of an ALDH18A1 mutation in a CMT1A family with PMP22 duplication: case report. |
ENSMUSG00000025007 |
Aldh18a1 |
143.561842 |
2.1464319359 |
1.101940 |
0.176952865 |
38.627783 |
0.00000000051283691073558116124222250577983743535792626744296285323798656463623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002511437558877630113598350492854806292886138407993712462484836578369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
192.6012822 |
23.1054166 |
90.3944766 |
8.1897098 |
| ENSG00000059728 |
4084 |
MXD1 |
protein_coding |
Q05195 |
FUNCTION: Component of a transcriptional repressor complex together with MAX (PubMed:8425218). In complex with MAX binds to the core DNA sequence 5'-CAC[GA]TG-3' (PubMed:8425218). Antagonizes MYC transcriptional activity by competing with MYC for MAX binding (PubMed:8425218). Binds to the TERT promoter and represses telomerase expression, possibly by interfering with MYC binding (PubMed:12837246). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12837246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8425218}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the MYC/MAX/MAD network of basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factors. The MYC/MAX/MAD transcription factors mediate cellular proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. The encoded protein antagonizes MYC-mediated transcriptional activation of target genes by competing for the binding partner MAX and recruiting repressor complexes containing histone deacetylases. Mutations in this gene may play a role in acute leukemia, and the encoded protein is a potential tumor suppressor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:4084; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Mad-Max complex [GO:0070443]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12366697_Mad1 gene transfer inhibits the proliferation of human melanoma cells 12538578_examination of functionality of basic domains compared with Myc 12553908_X-ray structures of Myc-Max and Mad-Max recognizing DNA. Molecular bases of regulation by proto-oncogenic transcription factors. 12824180_Mad expression and Id2 down-regulation are important events during the TGF-beta cytostatic program in epithelial cells. 15235594_HBP1 and Mad1 repressors bind the Sin3 corepressor PAH2 domain with opposite helical orientations 15282543_MAD1 and Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-myc reciprocally regulate ribosomal DNA transcription, providing a mechanism for coordination of ribosome biogenesis and cell growth 15645079_c-myc and mad1 can regulate the hTERT transcript in a different manner in hTERT positive cells, but not in normal cells 17082780_Max as a novel co-activator of C/EBPalpha functions, thereby suggesting a possible link between C/EBPalpha and Myc-Max-Mad network. 17577784_Mad1, Mxi1 and Rox genes were expressed and displayed mutations in haematological malignancies. 17998413_The PTEN tumor suppressor gene is a target of MAD1. 18155722_Mxd1 D112a and Max N78a and H81d, which are located in the leucine zippers of the proteins, can dictate the specificity of heterodimerization and whether or not the Mxd1/Max/DNA complex forms. 18203738_Results suggest STAT3 functions as a C/EBPbeta cofactor in the regulation of the MAD1 gene. 18451027_This study provides a direct link between the growth factor signaling pathways regulated by PI3 kinase/Akt and MAP kinases with Myc-mediated transcription. 18457265_Missense mutations in Mad1, Mxi1 and Rox were found in acute leukemia patients. 19526459_results suggest that phosphorylation of MAD1 by AKT inhibits MAD1-mediated transcription suppression and subsequently activates the transcription of MAD1 target genes 19766114_TGF-beta can override Myc activity despite a stabilizing cancer mutation and induce senescence in myeloid tumor cells, at least in part by induction of Mad1 24675462_miR-17-92 cluster members miR-19a/b facilitated gastric cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis through targeting the antagonist of c-Myc -- MXD1. 24954085_This study suggests that genetic variants of MXD1 may modulate the effect of smoking on carotid plaque burden. 25611699_down regulation of miR-202 increased the expression of its target Mxd1, followed by Mxd1 recruitment to the Sin3A repressor complex and through its dimerization with Max, and increased repression of Myc-Max target proteins. 26698869_TCP10L stabilizes MAD1 protein level through direct interaction, and they cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression. 27520398_the miR-382-5p/MXD1 axis plays a critical role in myelopoiesis by affecting the lineage choice of CD34(+) hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. 27588501_Results suggest a role for MAX dimerization protein 1 (MXD1) in the control of ribosome biogenesis. 28543796_Study revealed that HIF-1alpha-induced Mxd1 contributes to cisplatin-resistance in hypoxic osteosarcoma cells by directly repressing PTEN, which leads to the activation of PI3K/AKT antiapoptotic and survival pathway. 30419548_these data show that MXD1 functions as a negative regulator of BCR-ABL1 expression and subsequently inhibits proliferation and sensitizes chronic myeloid leukemia cells to imatinib treatment 31635836_Compared with noncancerous breast tissues, miRNA-382-5p expression was upregulated but MXD1 mRNA expression was downregulated in breast cancer tissues. The dysregulation of miRNA-382-5p-MXD1 axis may be involved in the development and aggressive progression of breast cancer. miRNA-382-5p may target MXD1, leading to cell invasion and proliferation in breast cancer cells in vitro. 32794336_MXD1 regulates the H9N2 and H1N1 influenza A virus-induced chemokine expression and their replications in human macrophage. 33537096_Targeting miR-21 with NL101 blocks c-Myc/Mxd1 loop and inhibits the growth of B cell lymphoma. 34761715_MXD1 is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated With Specific Molecular Change and Tumor Microenvironment Feature in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000001156 |
Mxd1 |
144.030080 |
2.4325518879 |
1.282471 |
0.184213549 |
47.913376 |
0.00000000000445472023689207835226746947092463734495237925870014805695973336696624755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000025347598572292627293725072994557811351112874831414956133812665939331054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
202.8519721 |
36.5000621 |
84.0549877 |
11.2013838 |
| ENSG00000059804 |
6515 |
SLC2A3 |
protein_coding |
P11169 |
FUNCTION: Facilitative glucose transporter that can also mediate the uptake of various other monosaccharides across the cell membrane (PubMed:9477959, PubMed:26176916). Mediates the uptake of glucose, 2-deoxyglucose, galactose, mannose, xylose and fucose, and probably also dehydroascorbate (PubMed:9477959, PubMed:26176916). Does not mediate fructose transport (PubMed:9477959, PubMed:26176916). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26176916, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8457197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9477959}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables dehydroascorbic acid transmembrane transporter activity; glucose binding activity; and glucose transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in glucose import across plasma membrane and transport across blood-brain barrier. Is integral component of plasma membrane. Biomarker of Alzheimer's disease; acanthosis nigricans; diabetes mellitus; and type 2 diabetes mellitus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:6515; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0055056]; dehydroascorbic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0033300]; galactose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005354]; glucose binding [GO:0005536]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; hexose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015149]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; dehydroascorbic acid transport [GO:0070837]; galactose transmembrane transport [GO:0015757]; glucose import [GO:0046323]; glucose import across plasma membrane [GO:0098708]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659]; L-ascorbic acid metabolic process [GO:0019852]; monosaccharide transmembrane transport [GO:0015749]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11991658_GLUT3 is expressed by normal articular chondrocytes. 12064911_observed differential response of individual isoforms GLUT1, GLUT3, & GLUT4 in neutrophils and granulocytes to hypoglycemia may represent a mechanism to protect the cells from the stress of glucose deprivation 12112827_glucose transporter 1 and 3 in the placenta 12397394_Restricted to regenerating muscle fibres and nerves in adult human muscle. GLUT3 may be important for glucose supply in fetal muscle fibres and regenerating adult muscle fibres. 12583599_Embedded in microvillous (maternal-facing) and basal (fetal-facing) membranes of syncytiotrophoblast, main placental barrier layer. (review) 14757434_Differentiation of THP-1 monocytes into macrophages was associated with marked induction of GLUT 3 and GLUT 5 protein expression, and high levels of GLUT 1, GLUT 3, and GLUT 5 were maintained after transformation to foam cells. 16049004_in platelets glucose transport through GLUT3 is regulated by changes in surface expression and affinity modulation, which are both under control of PKB 16125330_We present an alternative hypothesis centring on presumed deficits in membrane bound glucose transporter proteins GLUT 1 and GLUT 3, either in absolute numbers or functional capacity. 16136514_This review presents a model incorporating hypoxia responsive facilitative GLUT1 and GLUT3 as putative components of the glucose sensing apparatus in chondrocytes 17442736_During trophoblast hypoxia glucose transporters (GLUT1/3) are upregulated via HIF-1 alpha pathway. 17559076_Regulation of GLUT3 and glucose uptake by the cAMP signallling pathway in the breast cancer cell line ZR-75 is reported. 17611657_Findings suggest that characteristic differences in the patterns of glucose uptake can exist according to the histological type and that GLUT1, GLUT3 and GLUT4 could be related to tumor angiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. 17920708_IGF-1 plays a role in maintaining muscle GLUT3 expression and basal glucose uptake via the transcriptional factor Sp1. 18172662_GLUT3 expression was studied in normal and degenerate intervertebral discs. 18299470_In hyperthyroidism: 1) basal abundance of GLUT3 and GLUT4 on the plasma membrane is increased and 2) the sensitivity of the recruitment of GLUT3 and GLUT4 transporters on the plasma membrane in response to IGF-I is increased 18401196_GLUT-3 gene expression level was high in head and neck carcinoma (HNCs), and its expression was associated with an increased incidence of lymph node metastasis of HNCs. 18764953_differential expression of Glut-3 by benign and malignant melanocytic lesions 18802725_Sertoli cells express GLUT1 and GLUT3 throughout pubertal development. 19261894_the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and its regulation of cell surface GLUT3 expression is critical in mediating neuronal tolerance to excitotoxicity 19536037_study to evaluate the expression of glucose transporters (Gluts) 1 and 3 in Hodgkin and nonHodgkin lymphoma and to assess the association between their expression and the tumor intensity on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography 19554504_The expression pattern of GLUT3 is reported in newly diagnosed esophageal adenocarcinoma by means of immunohistochemistry. 19659459_The neuronal glucose transporter 3 was decreased to a bigger extent in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus brain than in Alzheimer's disease brain. 19681047_At physiological glucose, GLUT1 and GLUT3 are the predominant active isoforms in HeLa cells and rat hepatocarcinoma AS-30D tumor cells, respectively. 19782666_expression of HIF-1alpha and GLUT-3 in glioma was correlated significantly with tumors' pathological grade, which can be taken as a pair of useful markers for predicting the biological behavior of glioma 19786962_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19786962_Results suggest a possible transregulation effect on SLC2A3, which might lead to glucose deficits in dyslexic children and could explain their attenuated mismatch negativity in passive listening tasks. 20308990_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428049_GLUT1 and GLUT3 protein expression are indicators of poor prognosis outcome in oral squamous cell carcinoma, probably due to the enhanced glycolytic metabolism of more aggressive neoplastic cells. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20599725_In pluripotent stem cells and in human cancer disease, podocalyxin may function in part to regulate and maintain the cell surface expression of the glucose-3-transporter. 20870738_DNA-damaging agents reduce GLUT3 expression in cancer cells through activation of the MEK-ERK pathway independently of p53, leading to cell death or apoptosis 21920790_SLC2A1 and SLC2A3 predominate in both human islets and beta-cells their expression level was 2.8 and 2.7 fold higher than SLC2A2 respectively and GLUT2 is therefore unlikely to be the principal glucose transporter in human beta-cells 22000473_GLUT3 is present in the syncytial microvillous membrane early in gestation and decreases thereafter, supporting the idea that GLUT3 is of greater importance for glucose uptake early in gestation. 22069254_human islets from T1D predominantly express GLUT1 and, to a much lesser extent, GLUT3 on their surface instead of GLUT2. 22113212_Human glucose transporter type 3 (GLUT3)in the brain exhibits water channel properties 22234467_in placenta, CRH produced locally regulates GLUT1 and GLUT3 expression, CRHR1 and CRHR2-mediated differential regulation of GLUT1 and GLUT3 expression 22265971_miR-195-5p is a novel and also the first identified miRNA that targets GLUT3, and the aberrant decreased expression of miR-195-5p and consequent GLUT3 up-regulation may contribute to bladder carcinogenesis. 22270867_High GLUT3 is associated with endometrial and breast cancers. 22645302_We clarified that early hypoxia-responsive genes are functionally associated with glycolysis, including SLC2A3. 22663547_assessed how triiodothyronine (T(3)) acutely affects glucose transport and the content of GLUT4, GLUT1, and GLUT3 at the surface of muscle cells, and possible interactions between T(3) and insulin action. 22706202_Data show that elevated CAV1 upregulates glucose uptake and ATP production through HMGA1-mediated GLUT3 transcription, suggesting that CAV1 may render tumor cells growth advantages by enhancing aerobic glycolysis. 22876317_hypoxia-induced increases in glucose uptake through GLUT3 are important for lipid synthesis in macrophages, and may contribute to foam cell formation in hypoxic regions of atherosclerotic lesions. 22901689_GLUT3 shows increasing promoter methylation across gestation. 22901702_FDG uptake in malignant melanoma is determined by GLUT-1 and GLUT-3, whereas HK-2 and Ki-67 play no role in FDG uptake of malignant melanoma 23341039_The level of GLUT3 is correlated with the level of full-length CREB in Alzheimer brain samples. 23343953_sensitive and specific marker for embryonal carcinomas and yolk sac tumors 23720776_Data indicate that GLUT1 and GLUT3 oligomeric states and transport activities are determined by transmembrane helix 9 sequence. 23995067_Nutrient restriction contributes to tumor progression by enriching for brain tumor initiating cells (BTICs); BTICs outcompete for glucose uptake by co-opting the high affinity neuronal glucose transporter, type 3 (Glut3, SLC2A3). 24011442_Data suggest that expression of GLUT3/SLC2A3 (but not GLUT1 or GLUT4) is up-regulated in placenta in pregnancies complicated by intrauterine growth restriction (with expression of GLUT3 in cytotrophoblasts greater than in syncytiotrophoblasts). 24124917_Decreased miR-106a in GBM tissues and conferred a poor survival of GBM patients. SLC2A3 was identified as a core target of miR-106a in GBM cells. 24178905_study presents discovery and characterization of a large copy-number variant (CNV) within the chr12p13.31 interval; genotyping of this CNV in multiple population samples produced evidence that a deletion spanning the SLC2A3 gene confers substantial protection against rheumatoid arthritis 24452335_Data from human genetic analysis, molecular biology and a Drosophila Huntington's disease (HD) model strongly support the hypothesis that increased dosage of SLC2A3 ameliorates HD phenotypes. 24463787_Patients after coronary artery bypass graft surgery, who have low GLUT3 levels are at increased risk for new-onset postoperative atrial fibrillation. 24813597_deletions and single-nucleotide variations involving the GLUT3 gene that may be associated with increased susceptibility to myelomeningocele (MM). 25306890_Leptin at concentrations used in the study does not change glucose transport into lymphocytes and seems to have no influence on the expression of GLUT1, GLUT3, GLUT4 and and leptin receptors 25412955_Positive expression of SLC2A1, SLC2A3, and HIF-1alpha genes was noted in 83.9, 82.1, and 71.7% of SCC specimens and in 34.4, 59.4, and 62.5% of laryngeal cancer samples. Higher levels of mRNA/protein for GLUT1 and HIF-1alpha were noted in SCC compared to NCM 25578782_Glut3 is a downstream target of mTORC1, and it is critical for oncogenic mTORC1-mediated aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenesis. 25728965_We observed a strong relationship between characteristics of adaptive change to hypoxia, GLUT3 expression among birth weight-discordant twin 25892112_The SLC2A3 duplication was the most frequent CNV detected and the only significant finding in our combined analysis , indicating that the SLC2A3 duplication might serve as a genetic modifier of congenital heart defect 26176916_Using lipidic cubic phase crystallization and microfocus X-ray diffraction, we determined the structure of human GLUT3 in complex with D-glucose at 1.5 A resolution in an outward-occluded conformation 26513490_Both Glut1 and GLUT3 are strongly expressed by papillary thyroid carcinomas, and their expressions were significantly associated with the presence of the BRAF V600E mutation. 26639784_GLUT3 and OCT4 expression were correlated suggesting that Human embryonic stem cells self-renewal is regulated by the rate of glucose uptake. 26643879_High Glut3 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 27302065_effects of physiologically relevant phospholipids on glucose transport in liposomes containing purified GLUT4 and GLUT3. The anionic phospholipids, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylglycerol, and phosphatidylinositol, were found to be essential for transporter function by activating it and stabilizing its structure. 28086215_Studies suggest that a combination of glucose transporter s (GLUTs) 1 and 3 might help predict malignancy of cancers and direct effective cancer therapy. 28138554_GLUT3 was upregulated in bevacizumab-resistant glioblastoma versus sensitive xenografts and patient specimens. 28224622_Both common and rare SLC2A3 variation impacting regulation of neuronal glucose utilization and energy homeostasis may result in neurocognitive deficits known to contribute to ADHD risk. 28631569_We found that insulin increases the cytotoxic effect of 5-fluorouracil and cyclophosphamide in vitro up to two-fold. The effect was linked to enhancement of apoptosis, activation of apoptotic and autophagic pathways, and overexpression of glucose transporters 1 and 3 as well as inhibition of cell proliferation and motility 28663252_GLUT3-mediated glucose utilization and glycogenolysis in platelets promotes alpha-granule release, platelet activation, and postactivation functions. 28852964_PPAR-gamma and Akt regulate GLUT1 and GLUT3 surface localization during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection 28951307_N-methyl-D aspartate (NMDA) receptor activity increases GLUT3 expression. 29198914_identify a subset of tumors within the 'proneural' and 'classical' subtypes that are addicted to aberrant signaling from integrin alphavbeta3, which activates a PAK4-YAP/TAZ signaling axis to enhance Glut3 expression 29614685_1) that decrease of GLUT3 is associated with the reduction of protein O-GlcNAcylation in Alzheimer's disease (AD)brain, 2) that GLUT3 level is negatively correlated with calpain I activation in human brain, 3) that calpain I proteolyzes GLUT3 at the N-terminus in vitro, and 4) that activation of calpain I is negatively correlated with protein O-GlcNAcylation in AD brain. 29664658_GLUT3 plays a fundamental role in the survival and resistance of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells to vincristine. 29715514_miR-29c was down-regulated in Prostate cancer samples. SLC2A3, a regulator of glycolysis, was validated as a direct target of miR-29c. Moreover, functional studies showed miR-29c could inhibit cell growth, induce apoptosis and deceased the rate of glucose metabolism. 30049187_means of immunolabeled cells for GLUT-3 varied approximately from 19% to 73% 30305725_We also showed that IL-8 stimulation of colon and lung cancer cells-induced glucose uptake and expressions of glucose transporter 3 (GLUT3) and glucosamine fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase (GFAT), a regulator of glucose flux to the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway, resulting in enhancement of protein O-GlcNAcylation 30943948_Results show that upregulation of the SLC2A3 gene is associated with decreased overall survival and disease-free survival in colorectal cancer patients. SLC2A3 gene expression analysis may be useful for predicting prognosis and survival of CRC patients. 30954677_Study provides evidence that rs7309332 genetic variant in GLUT3 may be useful in predicting survival of patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer. 31131051_Activation of the Glut3-YAP signaling pathway acts as a master activator to reprogram cancer metabolism and thereby promotes metastasis. 31182397_low neonatal white blood cell GLUT3 concentrations make discerning differences between degrees of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy as well as assessing effectiveness of therapeutic hypothermia difficult 31534543_CAV1 - GLUT3 signaling is important for cellular energy and can be targeted by Atorvastatin in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 31617996_Key Factors in Conformation Transformation of an Important Neuronic Protein Glucose Transport 3 Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. 31690629_Hypoxia drives glucose transporter 3 expression through hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF)-mediated induction of the long noncoding RNA NICI. 31832727_Hypoxia-induced modulation of glucose transporter expression impacts (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET-CT imaging in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31916238_A Key Role of DNA Damage-Inducible Transcript 4 (DDIT4) Connects Autophagy and GLUT3-Mediated Stemness To Desensitize Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastomas. 32012400_this work suggests that tumor cell-derived ANGPTL2 accelerates activities associated with glycolytic metabolism in lung cancer cells by activating TGF-beta-ZEB1-GLUT3 signaling. 32203209_Decreased vitamin C uptake mediated by SLC2A3 promotes leukaemia progression and impedes TET2 restoration. 32580154_Frequent copy number gains of SLC2A3 and ETV1 in testicular embryonal carcinomas. 32627711_SLC2A3 rs12842 polymorphism and risk for Alzheimer's disease. 32873793_GLUT3 induced by AMPK/CREB1 axis is key for withstanding energy stress and augments the efficacy of current colorectal cancer therapies. 32908869_Expression of GLUT3 and HIF-1alpha in Meningiomas of Various Grades Correlated with Peritumoral Brain Edema. 32989212_HMGA1 Promotes Hepatic Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Inducing Expression of Glucose Transporter 3 (GLUT3). 33402433_Orthosteric-allosteric dual inhibitors of PfHT1 as selective antimalarial agents. 33421130_Overexpression of GLUT3 promotes metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by modulating the inflammatory tumor microenvironment. 33586490_High NOV/CCN3 expression during high-fat diet pregnancy in mice affects GLUT3 expression and the mTOR pathway. 33773574_Placental glucose transporter 1 and 3 gene expression in Monochorionic twin pregnancies with selective fetal growth restriction. 34031595_Single-cell metabolic imaging reveals a SLC2A3-dependent glycolytic burst in motile endothelial cells. 34781282_Peritoneal Expression of SGLT-2, GLUT1, and GLUT3 in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. 34791627_Epithelial mesenchymal transition regulator TWIST1 transcription factor stimulates glucose uptake through upregulation of GLUT1, GLUT3, and GLUT12 in vitro. 34831313_GLUT1, GLUT3 Expression and 18FDG-PET/CT in Human Malignant Melanoma: What Relationship Exists? New Insights and Perspectives. 35260183_miR-3189-targeted GLUT3 repression by HDAC2 knockdown inhibits glioblastoma tumorigenesis through regulating glucose metabolism and proliferation. 35316657_The glucose transporter GLUT3 controls T helper 17 cell responses through glycolytic-epigenetic reprogramming. 35466476_SLC2A3 variants in familial and sporadic congenital heart diseases in a Chinese Yunnan population. 35484435_Evolutionary balance between foldability and functionality of a glucose transporter. 35501580_RIP140 inhibits glycolysis-dependent proliferation of breast cancer cells by regulating GLUT3 expression through transcriptional crosstalk between hypoxia induced factor and p53. |
|
|
233.810045 |
2.3039260312 |
1.204094 |
0.168825053 |
50.301354 |
0.00000000000131858506789843504758412957834468292846533121753793693642364814877510070800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007781813515466175110717573834579884484857759119336151343304663896560668945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
329.8977584 |
33.9528763 |
144.0281694 |
11.2921344 |
| ENSG00000060558 |
2769 |
GNA15 |
protein_coding |
P30679 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. |
ADP-ribosylation;GTP-binding;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
Enables G protein-coupled receptor binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be part of heterotrimeric G-protein complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2769; |
heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding [GO:0031683]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; action potential [GO:0001508]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060158]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007207]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482] |
11686331_Megakaryocytopoiesis was accompanied by down-regulation of the 43 kDa and 46 kDa variants of G16alpha, constant expression of Gsalpha, and up-regulation of Gqalpha and Gialpha1/2. 12095632_role of intracellular loops of cannabinoid CB1 receptor in functional interaction with Galpha16. 12670499_G protein-coupled receptors activate STAT3 via G alpha(16), a G alpha subunit which is primarily expressed in hematopoietic cells. 14551213_Galpha16 stimulates STAT3 via a c-Src/JAK- and ERK-dependent mechanism 16218966_Results suggest that the G(q) class proteins are degraded through the proteasome pathway and that cellular localization and/or other protein interactions determine their stability. 18755267_Co-stimulation of G(s) and G(q) can result in the fine-tuning of STAT3 activation status, and this may provide the basis for cell type-specific responses following activation of hIP. 19275934_The paper describes G alpha 15 resistance to arrestin-desensitization making it differ from other heterotrimeric G proteins (Gq, Gs, Gi, G12/13 class) 19687291_The ability of CCR1 to signal through Galpha(14/16) thus provides a linkage for chemokines to regulate NF-kappaB-dependent responses. 20150327_This review summarizes the specific features that distinguish Galpha15/GNA15 (G15 alpha subunit) from all other alpha subunits of the Gq class. G15 is a heterotrimeric G protein complex that is named after its alpha subunit. 21486497_beta3 region of Galpha16 is essential for interaction with TPR1 and the subsequent activation of Ras 22227248_This paper shows how G alpha 15 and other Gq class members phosphorylate PKD in differing patterns 23200847_G15 ectopic presence could functionally contribute to the transformation process since siRNA-induced depletion of Galpha15 in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines dramatically inhibited anchorage-independent growth and resistance to the lack of nutrients. 24204697_Data indicate the importance of Galpha16 as a downstream effector of the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway and as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of non small cell lung cancer. 25701539_GNA15 was not expressed in normal neuroendocrine cells but was overexpressed in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasia cell lines. |
ENSMUSG00000034792 |
Gna15 |
540.001961 |
3.2427282893 |
1.697208 |
0.076067015 |
509.547569 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007955193580903256630251923240005249984688863990096382582104295256694289207836588613399355479209729800456864701273022648086240965499740421504478877667994932597576747571446746666601731787262866341580922980917071308256688 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003900952068243589967140538267278983777549119897332270057388324208920576985167319117003498134324962073069299169218943619720299162852098129978617964508865661904006823107114049130621545732908111597270218230693433266486808 |
Yes |
No |
835.5427249 |
35.5010575 |
259.5661827 |
9.2130387 |
| ENSG00000060718 |
1301 |
COL11A1 |
protein_coding |
P12107 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in fibrillogenesis by controlling lateral growth of collagen II fibrils. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cataract;Collagen;Deafness;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Ectodermal dysplasia;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Metal-binding;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Stickler syndrome |
|
This gene encodes one of the two alpha chains of type XI collagen, a minor fibrillar collagen. Type XI collagen is a heterotrimer but the third alpha chain is a post-translationally modified alpha 1 type II chain. Mutations in this gene are associated with type II Stickler syndrome and with Marshall syndrome. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in this gene is also associated with susceptibility to lumbar disc herniation. Multiple transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:1301; |
collagen type XI trimer [GO:0005592]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; heparan sulfate binding [GO:1904399]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; cartilage condensation [GO:0001502]; chondrocyte development [GO:0002063]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound [GO:0050910]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; ossification [GO:0001503]; proteoglycan metabolic process [GO:0006029]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; tendon development [GO:0035989]; ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055010]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11707154_A statistically significant difference has been found in COL11A1 expression between normal tissue and adenomas from a familial adenomatous polyposis patient, and all adenomas give evidence of an active adenomatous polyposis coli/beta-catenin pathway. 12673280_sequence variations in these genes can play a role in the etiology of Robin sequence, cleft palate and micrognathia but are not common causes of these phenotypes. 12805369_CBF/NF-Y proteins regulate the transcription of COL11A1 by directly binding to the ATTGG sequence in the proximal promoter region 15286167_Six pedigrees with type 2 Stickler syndrome with mutations in COL11A1. 15922184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17236192_Heterozygous COL11A1 mutations were found in 10 individuals with Stickler or Marshall syndromes. 17999364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17999364_Type XI collagen is critical for intervertbral dis metabolism and its decrease is related to lumbar disc herniation. 18040076_This study is the first to show that collagen XI is present in the Golgi apparatus of normal human colon goblet cells and localizes collagen XI in both normal and malignant tissue. 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19306436_The data above suggest that focal adhesion pathway may have a role in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer, and the expression profile of collagen genes may be a potential biomarker to distinguish malignant from premalignant lesions in stomach 19337631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083228_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20513134_Study identified 57 novel mutations including missense changes in both COL2A1 and COL11A1. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21035103_These findings identify COL11A1 as a locus for fibrochondrogenesis and indicate that there might be phenotypic manifestations among carriers. 21527992_Common polymorphisms in four candidate genes (COL11A1, COL18A1, FBN1 and PLOD1) were unlikely to play important roles in the genetic susceptibility to high myopia. 21668896_our data shall improve the overall understanding of fibrochondrogenesis especially in surviving homozygous patients and, at least partly, explain the phenotypic variability associated with COL11A1 gene mutations. 22189268_variants detected in COL11A1 in patients with Stickler syndrome 22322826_Characterize mouse monoclonal antibody specific for human procollagen 11A1 and report its use for immunohistochemistry in human breast tumor tissue. 22499343_study reports the first evidence that adds COL11A1 defect as a cause of Marshall syndrome with a recessive mode of inheritance 22510797_a TT genotype of COL11A1 polymorphism may be a significant risk factor for limbus vertebra in Japanese collegiate gymnasts. 23497244_COL11A1 allelic imbalance is common in osteoarthritis but is not a risk factor for osteoarthritis. 23505305_Axial length, anterior chamber depth and keratometry were not associated with rs3753841 or rs11024102 genotypes including after adjusting for age and sex. 23922384_The study demonstrates that some mutations in COL11A1 are recessive, modified by alternative splicing and result in type 2 Stickler syndrome rather than fibrochondrogenesis. 23934190_COL11A1 may promote tumor aggressiveness via the TGF-beta1-MMP3 axis and COL11A1 expression can predict clinical outcome in ovarian cancer patients. 24194920_proCOL11A1 is a specific marker for pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts, and thus, anti-proCOL11A1 is a powerful new tool for cancer research and clinical diagnostics. 24474268_The three genetic susceptibility loci for primary angle-closure glaucoma did not underlie any major phenotypic diversity in terms of disease severity or progression. 24636772_Some studies have shown the association between gene COL11A1 polymorphism c.4603C>T and intervertebral disc disease--{review} 24804215_Extracellular matrix proteins expression profiling in chemoresistant variants of the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line. 24854855_Our study suggests that rs1676486 and rs12138977 in COL11A1 as well as rs216489 and rs11024102 in PLEKHA7 are associated with an increased risk of PAC/PACG in the Han Chinese population 25091507_These cases highlight both a novel dominant COL11A1 mutation causing a significant skeletal dysplasia. 25175819_COL11A1 expression is a promising marker of invasive breast lesions, and may be included in immunohistochemical panels aiming at identifying infiltration in problematic breast lesions. 25240749_Expanded spectrum of mutations in the COL11A1 and COL11A2 genes in Stickler syndrome. 25417197_The immunodetection of procollagen 11A1 in cancer-associated stromal cells could be a useful biomarker for human colon adenocarcinoma characterisation. 25511741_Studies indicate that collagen type XI alpha 1 (colXIalpha1) is overexpressed at mRNA and protein levels in many cancer types. 25732101_This meta-analysis suggests that PLEKHA7 rs11024102 is associated with PACG (primary angle closure glaucoma) in Asian population and COL11A1 rs3753841 has a genetic association with the development of PACG both in Caucasian and Asian populations. 25761876_COL11A1/(pro)collagen 11A1 expression is a remarkable biomarker of human carcinoma-associated stromal cells and carcinoma progression. 26087191_Analysis of 104 epithelial ovarian carcinoma patients showed that high COL11A1 mRNA levels are significantly associated with poor chemoresponse and clinical outcome. 26448946_These data suggest that pro-COL11A1 expression is a highly sensitive biomarker to predict malignant relapse of intraductal papilloma. 26497787_Familial linkage studies for primary angle-closure glaucoma have been performed and identified MYOC causative primary angle-open-glaucoma disease 26504042_High Col11A1 mRNA expression is associated with Adenocarcinoma of the Papilla of Vater and Pancreas Carcinoma. 27021528_COL11A1 antibody can assist in distinguishing the cancer-associated desmoplastic stroma from that associated with misplaced adenomatous mucosa. It is particularly helpful when electrocautery artifacts or mucin pools interfere with the diagnosis of invasive carcinoma. However, COL11A1 has limited value in diagnosing superfically invasive carcinomas with very little desmoplastic stroma. 27336854_Chondrogenic potential was higher and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling was more potently activated by a GSK-3beta inhibitor in the posterior than in the anterior part of the human infant sclera. 27373316_COL11A1 may sever as a biomarker for metastatic NSCLC. 27389768_Study found one gene significantly associated when looking for associations between multiple common and rare variants with pneumococcal meningitis susceptibility, namely the COL11A1 gene. 27390512_In this study, three novel and two known mutations in the COL2A1 gene were identified in six of 16 Chinese patients with Stickler syndrome. This is the first study in a cohort of Chinese patients with Stickler syndrome, and the results expand the mutation spectrum of the COL2A1 gene. 27455018_No significant association of PLEKHA7 rs11024102, COL11A1 rs3753841 and PCMTD1-ST18 rs1015213 with primary angle closure glaucoma was found among ethnic Han Chinese from Sichuan 27614704_genetic variants of COL11A1 contribute to adult height in Chinese Han population but not to children height 27936936_Investigated genetic variants in COL11A1 predisposing to primary hip OA in Han Chinese individuals.Two SNPs (rs1241164 and rs4907986) were found to be significantly associated with hip OA risk (adjusted p = 0.000731 and 0.000477). An increased risk of OA was associated with possession of the C allele of rs1241164 and the T allele of rs4907986. 28004111_COL11A1 is overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues and regulates cell proliferation and migration. 28393072_the racial differences of COL11A1 were consistent across multiple molecular levels, with higher mutation frequency, higher methylation, and lower expression in White patients. This indicated that COL11A1 might play important roles in ESCC, especially in White population. Additional studies are needed to further explore their functions in esophageal cancer 28583914_The SNPs rs1337185 in COL11A1 and rs162509 in ADAMTS5 are associated with susceptibility to lumbar disc degeneration. The C allele of rs1337185 is risky for patients who are affected by lumbar pathologies such as disc herniation, stenosis and spondylolisthesis. The G allele of rs16250 represents a risk factor for the development of disc herniation. 28815582_we demonstrate how COL11A1 regulates twist family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1-related protein 1 (TWIST1) to induce chemoresistance and inhibit apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells 28944648_COL11A1 4603C/T gene polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of cervical disc degeneration, but not lumbar disc degeneration, in Japanese collegiate wrestlers. 29025374_proCOL11A1, fibroblast-activated protein, secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine, and periostin expression was significantly increased in the intratumoral stroma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas compared to paired non-neoplastic pancreata 29321344_We confirmed that the rs1676486 of COL11A may be functionally associated with lumbar disc herniation (LDH) in the Chinese population. Extracellular matrix related proteins may play an important role in the pathogenesis of LDH. Our findings shed light on a better understanding of the pathogenesis of LDH, which could be a promising target for a novel treatment modality of LDH. 29769618_COL11A1 confers cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. 29773097_These results showed that the frequency distribution of genotypes of the rs2229783 polymorphism in COL11A1 was significantly different between the Kashin-Beck Disease (KBD) and control groups; the expression level of COL11A in cartilage was significantly lower in the KBD group, but no association was found between the rs2229783 and the severity of KBD. 29781737_results suggested that common polymorphisms in these two candidate genes were unlikely to play major roles in the genetic susceptibility to HM. Nevertheless, to avoid filtering real myopia genes, the role of COL11A1 and COL18A1 in the pathogenesis of myopia requires more refinement in both animal models and human genetic epidemiological studies 30181686_In summary, it is not easy to differentiate stickler syndrome (STL) from early-onset high myopia with routine ocular examination in outpatient clinics. Awareness of atypical phenotypes and newly recognized signs may be of help in identifying atypical STL, especially in children at eye clinics. 30227835_Plasma samples from lung cancer patients and healthy heavy-smokers controls were tested for levels of COL11A1 and COL10A1 (n = 57 each) and SPARC (n = 90 each). Higher plasma levels of COL10A1 were detected in patients (p = 0.001), a difference that was driven specifically by females (p A) of the COL11A1 gene has been identified in a pedigree affected with congenital high myopia 31545476_we revealed that COL11A1 and TWIST1 were significantly upregulated at the mRNA and protein levels within rightsided colon cancer compared with in leftsided colon cancer samples (P |
ENSMUSG00000027966 |
Col11a1 |
239.308510 |
0.2186221283 |
-2.193489 |
0.139192006 |
249.471789 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003385281734132149055616827504423878277736590461575802585780161455637784271433124298353362201268931703319605219087546014374229172041372790678045306966836847095692064613103866577148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000809834009656248319928140354872418633252507602693922943249409858386710019698835285293167135754281396146178509734513173663885040649105541941954466977904303348623216152191162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.3922617 |
19.3083663 |
396.3171843 |
62.7759582 |
| ENSG00000060982 |
586 |
BCAT1 |
protein_coding |
P54687 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first reaction in the catabolism of the essential branched chain amino acids leucine, isoleucine, and valine. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Aminotransferase;Branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis;Cytoplasm;Lipid metabolism;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes the cytosolic form of the enzyme branched-chain amino acid transaminase. This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transamination of branched-chain alpha-keto acids to branched-chain L-amino acids essential for cell growth. Two different clinical disorders have been attributed to a defect of branched-chain amino acid transamination: hypervalinemia and hyperleucine-isoleucinemia. As there is also a gene encoding a mitochondrial form of this enzyme, mutations in either gene may contribute to these disorders. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:586; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; branched-chain-amino-acid transaminase activity [GO:0004084]; L-isoleucine transaminase activity [GO:0052656]; L-leucine transaminase activity [GO:0052654]; L-leucine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity [GO:0050048]; L-valine transaminase activity [GO:0052655]; branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic process [GO:0009082]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; leucine biosynthetic process [GO:0009098]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; valine biosynthetic process [GO:0009099] |
17007058_Our results suggest that ECA39 is a dominant predictive factor for distant metastasis in patients with advanced colorectal cancer (CRC). 17846126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18074675_The BCAT1 identified in the amplified 12p11-p12 region may play a certain role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma development. 18419134_hBCATc has redox mediated associations with several neuronal proteins involved in G-protein cell signaling, indicating a novel role for hBCATc in cellular redox control 19119849_The effect of nitric oxide modification on the functionality of human mitochondrial and cytosolic branched-chain aminotransferases (hBCATm and hBCATc, respectively) was investigated. 19260141_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20639392_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22107788_BCATc (cytosolic) has an overall redox potential that is 30 mV lower than BCATm (mitochondrial). Furthermore, the CXXC motif of BCATc was estimated to be 80 mV lower, suggesting that BCATm is more oxidizing in nature. 23043456_The mitochondrial isoform human brain BCAT 2 is largely confined to vascular endothelial cells, whereas the cytosolic human brain BCAT 1 is restricted to neurons. 23758864_Over-expression of BCAT1, a c-Myc target gene, induces cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 23793099_A central role for BCAT1 in glioma pathogenesis, making BCAT1 and branched-chain amino acids metabolism attractive targets for the development of targeted therapeutic approaches to treat patients with glioblastoma. 24463277_levels of branched-chain aminotransferase-1 (BCAT1) transcripts are significantly decreased on the polysomes of both RPS19 and RPL11 cells and that translation of BCAT1 protein is especially impaired in cells with small RP gene mutations 25261097_Focal deletions of the BCAT1 were associated with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 26173071_BCAT1 overexpression is associated with advanced tumour status, and implies adverse clinical outcomes of urothelial carcinoma 26372729_BCAT1 is strongly overexpressed in ovarian cancer. 26783998_Mechanistic investigation revealed that BCAT1 might be an important regulator responsible for DOT1L-mediated sphere formation and cell migration in breast cancer cells 27246112_BCAT1 plays a pathogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by causing cell proliferation and chemoresistance. The MYC transcription factor is involved in regulating the transcriptional activity of BCAT1. BCAT1 expression has prognostic significance for the survival of patients with HCC. 28005267_BCAT1 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28052414_The tumor suppressive role of miR-218 was mediated by negatively regulating branched-chain amino acid transaminase 1 (BCAT1) protein expression. Importantly, overexpression of BCAT1 decreased the chemosensitivity to cis-diaminedichloroplatinum treatment of PC3 and DU145 cells. 28235484_It has been demonstrated that branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) catabolism is activated in human breast cancer, and abolishment of BCAA catabolism by knocking down BCAT1 inhibits breast cancer cell growth by repressing mTOR-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and function. 28319069_Phenotypic analyses using a lentiviral-mediated BCAT1 short hairpin RNA knockdown revealed that BCAT1 sustains proliferation in addition to migration and invasion and that its overexpression enhanced the capacity of antiestrogen-sensitive cells to grow in the presence of antiestrogens. 28699638_regulatory role in macrophage function 29144447_by limiting intracellular alphaKG, BCAT1 links branched-chain amino acid catabolism to HIF1alpha stability and regulation of the epigenomic landscape, mimicking the effects of IDH mutations; results suggest the BCAA-BCAT1-alphaKG pathway as a therapeutic target to compromise leukaemia stem-cell function in patients with IDH(WT)TET2(WT) AML 29211698_Data suggest that both oncogenic mutations and cancer tissue-of-origin influence BCAA (branched-chain amino acid) metabolism in neoplastic tissue and neoplastic expression of cytosolic BCAT1 and mitochondrial BCAT2. (BCAT = branched-chain-amino-acid transaminase) [REVIEW] 29447920_up-regulation of BCAT1 indicated a poor survival rate of gastric cancer and may serve as a useful marker for predicting the outcome of patients with gastric cancer 29796114_Study has shown that BCAT1 and IKZF1 methylation are common events in colorectal cancer (CRC) with almost all cancer tissues showing significant levels of methylation in the two genes. The presence of ctDNA in blood is stage-related and show rapid reversion to negative following surgical resection. Monitoring methylated BCAT1 and IKZF1 levels could therefore inform adequacy of surgical resection. 29915159_BCAT1 overexpression may induce circulating tumor cells (CTC) release by triggering EMT and may be an important biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) metastasis. In liver cancer, CTC examination may represent an important 'liquid biopsy' tool to detect both early disease and recurrent or metastatic disease, providing cues for early intervention or adjuvant therapy 30113684_Positive BCAT1 stain could be used to exclude diffuse gliomas with IDH1 codon 132 and IDH2 codon 172 mutations 30265706_Branched chain amino acid transaminase 1 (BCAT1) is overexpressed and hypomethylated in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease who experience adverse clinical events 30310175_Our study identifies BCAT1 as a novel methylome signature distinguishing spindle/desmoplastic melanoma from cutaneous malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. 30378334_The high expression of c-myc may promote the invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer, and the high expression of bcat1 may promote the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer, which may have a synergistic effect in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer. 31982508_BCAT-induced autophagy regulates Abeta load through an interdependence of redox state and PKC phosphorylation-implications in Alzheimer's disease. 32571264_Prognostic significance of branched-chain amino acid transferase 1 and CD133 in triple-negative breast cancer. 32694827_Tumour-reprogrammed stromal BCAT1 fuels branched-chain ketoacid dependency in stromal-rich PDAC tumours. 32958500_Evaluation of Circulating Tumor DNA for Methylated BCAT1 and IKZF1 to Detect Recurrence of Stage II/Stage III Colorectal Cancer (CRC). 33148611_BCAT1 affects mitochondrial metabolism independently of leucine transamination in activated human macrophages. 33367952_Differential expression of the BCAT isoforms between breast cancer subtypes. 33493139_Enrichment of branched chain amino acid transaminase 1 correlates with multiple biological processes and contributes to poor survival of IDH1 wild-type gliomas. 33500319_Variables Associated with Detection of Methylated BCAT1 or IKZF1 in Blood from Patients Without Colonoscopically Evident Colorectal Cancer. 33760210_BCAT1 overexpression regulates proliferation and cMyc/GLUT1 signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 34646394_Proteomic analysis of lung cancer cells reveals a critical role of BCAT1 in cancer cell metastasis. 34932898_A single nucleotide polymorphism in BCAT1 gene is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 34984849_BCAT1: A risk factor in multiple cancers based on a pan-cancer analysis. 35290664_Detection of recurrent colorectal cancer with high specificity using a reporting threshold for circulating tumor DNA methylated in BCAT1 and IKZF1. 36111572_BCAT1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression through enhanced mitochondrial function and NF-kappaB pathway activation. 36123616_Translation of a tissue epigenetic signature to circulating free DNA suggests BCAT1 as a potential noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for lung cancer. 36260995_BCAT1 redox function maintains mitotic fidelity. |
ENSMUSG00000030268 |
Bcat1 |
1227.738127 |
4.2671727223 |
2.093281 |
0.074105813 |
777.465039 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000428207808010308171477154257757042772820694978583620542850716488705842603186986210374875607144735316307365867247467043399041062214282282958878312536962081298297 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000325791095166605597330096512341817829215525577472126219792035110212767694138955955600155423040203442463342461728416091592487548940189203344116066092216346228336 |
Yes |
No |
1954.0437813 |
93.2585194 |
461.3962628 |
17.1138933 |
| ENSG00000061938 |
10188 |
TNK2 |
protein_coding |
Q07912 |
FUNCTION: Non-receptor tyrosine-protein and serine/threonine-protein kinase that is implicated in cell spreading and migration, cell survival, cell growth and proliferation. Transduces extracellular signals to cytosolic and nuclear effectors. Phosphorylates AKT1, AR, MCF2, WASL and WWOX. Implicated in trafficking and clathrin-mediated endocytosis through binding to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and clathrin. Binds to both poly- and mono-ubiquitin and regulates ligand-induced degradation of EGFR, thereby contributing to the accumulation of EGFR at the limiting membrane of early endosomes. Downstream effector of CDC42 which mediates CDC42-dependent cell migration via phosphorylation of BCAR1. May be involved both in adult synaptic function and plasticity and in brain development. Activates AKT1 by phosphorylating it on 'Tyr-176'. Phosphorylates AR on 'Tyr-267' and 'Tyr-363' thereby promoting its recruitment to androgen-responsive enhancers (AREs). Phosphorylates WWOX on 'Tyr-287'. Phosphorylates MCF2, thereby enhancing its activity as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) toward Rho family proteins. Contributes to the control of AXL receptor levels. Confers metastatic properties on cancer cells and promotes tumor growth by negatively regulating tumor suppressor such as WWOX and positively regulating pro-survival factors such as AKT1 and AR. Phosphorylates WASP (PubMed:20110370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10652228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11278436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16247015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16257963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16472662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17038317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18262180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18435854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20110370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20333297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20383201}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Coated pit;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endocytosis;Endosome;Kinase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a tyrosine kinase that binds Cdc42Hs in its GTP-bound form and inhibits both the intrinsic and GTPase-activating protein (GAP)-stimulated GTPase activity of Cdc42Hs. This binding is mediated by a unique sequence of 47 amino acids C-terminal to an SH3 domain. The protein may be involved in a regulatory mechanism that sustains the GTP-bound active form of Cdc42Hs and which is directly linked to a tyrosine phosphorylation signal transduction pathway. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified from this gene, but the full-length nature of only two transcript variants has been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10188; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cytoophidium [GO:0097268]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; Grb2-EGFR complex [GO:0070436]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; GTPase inhibitor activity [GO:0005095]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004712]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; WW domain binding [GO:0050699]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:2000369]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
14733946_ACK-1 and ACK-2 have roles in transducing Cdc42 signals directly to the nucleus 15123659_binding specificity to activated Cdc42-associated kinase is conferred by a specific region in Cdc42 15308621_crystal structures of the human ACK1 kinase domain in both the unphosphorylated and phosphorylated states 16137687_Data show that in the presence of SNX9, synaptojanin-1 is able to colocalize with distinct ACK1 containing vesicles. 16247015_overexpression of Ack1 in cancer cell lines can increase the invasive phenotype of these cells; Ack1 is involved in extracellular matrix-induced integrin signaling, ultimately activating signaling processes like the activation of the small GTPase Rac 16288044_Ack1 promotes prostate tumorigenesis by tyrosine phosphorylation of tumor suppressor Wwox at Tyr-287. It results in polyubiquitination and degradation of Wwox. 16288044_Molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90beta (Hsp90beta)-bound Ack1 and treatment of prostate cells with geldanamycin, a Hsp90 inhibitor, inhibited Ack1 kinase activity and suppressed prostate tumorigenesis. 16316319_Dimerization in response to EGF and activated Cdc42-associated tyrosine kinase 2 (ACK2), which is mediated by the BAR domain, is essential for the intracellular function of SH3PX1. 16777958_These experiments suggest a functional role for Ack as an early transducer of multiple extracellular stimuli. 17038317_The interaction between Ack1 and p130(Cas) occurred through their respective SH3 domains, while the substrate domain of p130(Cas) was the major site of Ack1-dependent phosphorylation. 17109515_The results were confirmed at the level of mRNA and protein, and suggested that four genes (OPCML, RNASE1, YES1 and ACK1) could play a key role in the tumorigenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer. 17494760_Ack1 activated by surface signals or oncogenic mechanisms may directly enhance AR transcriptional function and promote androgen-independent progression of prostate cancer. 17494760_Ack1 promotes prostate cancer progression to androgen-independence via androgen receptor tyrosine phosphorylation at Tyr-267 and Tyr-363, both sites located within the transactivation domain. 18262180_These data suggest that Ack1 is involved in an early step of EGFR desensitization. 18435854_TNK2 enhanced migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by preserving EGFR expression, inspite of its previously reported signalling via BCAR1, explaining its oncogenic behaviour in vitro and correlation with metastatic human breast cancer in vivo. 18477472_These data define Ack1 as a novel interaction partner of nephrocystin-1 and implicate cell-cell junctions and the renal collecting duct in the pathology of nephronophthisis. 19144635_the interplay between Nedd4-2-related E3 ligases that regulate ACK1 levels and Cbl that modifies EGF receptor impinges on cell receptor dynamics. 19815557_Results identify several receptor tyrosine kinases, including Axl, that can bind to the ACK1/MIG6 homology region. 20086093_These findings suggest an essential role of Nedd4-1 in regulation of EGFR degradation through interaction with and ubiquitination of ACK. 20110370_Cancer-associated mutations activate the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Ack1. 20333297_Ack1 mediated AKT/PKB tyrosine 176 phosphorylation regulates its activation 20359967_Data show that the ACK1 S985 N mutant is unable to bind ubiquitin, which contributes to ACK1 protein stability and stabilizes EGFR after EGF stimulation, thereby prolonging mitogenic signaling in cancer cells. 20432460_Recent advances in understanding the physiological functions of Ack1 signaling in normal cells and the consequences of its hyperactivation in various cancers, are discussed. 21129804_SNP rs2278034 in ACK1 is associated with IFN therapy outcome in patients with HCV. ACK1 may play a role in innate and IFN-induced antiviral action against HCV. 21309750_ACK1 is not autoinhibited but requires Src for activation. 21418896_The up-regulated expressions of ACK1 protein and mRNA are correlated with the progression and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22322295_Ack1 activates AKT directly in pancreatic and other cancer cell lines by phosphorylating AKT at Tyr176 to promote cell survival. 22566699_Ack1-mediated androgen receptor phosphorylation modulates radiation resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer 22952966_ACK1 directly binds and phosphorylates the Arp2/3 regulatory protein cortactin, potentially providing a direct link to Arp2/3-based actin dynamics during EGFR degradation. 23208506_the molecular mechanisms modulating ACK1 23598414_Ack1 interacts with Trk receptors and becomes tyrosine phosphorylated and its kinase activity is increased in response to neurotrophins. 23686771_describes a family with severe autosomal recessive infantile onset epilepsy. identified a homozygous missense variant in TNK2. 24085293_Ack1 acts in a kinase-independent manner to promote TRAIL-R1/2 accumulation in lipid rafts. These findings identify Ack1 as an essential player in the spatial regulation of TRAIL-R1/2. 24178904_TNK2 amplification is an independent predictor of a poor prognosis in patients with GC and leads to an increase in the malignant potential of GC cells. 24413169_A novel role for Ack1 in diverting activated EGFR into a non-canonical degradative pathway. 24461128_we describe the role of ACK1, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase in abrogating migration and invasion in KRAS mutant lung adenocarcinoma 25148682_ACK1 interacts with KDM3A to regulate the mammary tumor oncogene HOXA1. 25257795_Increased ACK1 tyrosine phosphorylation correlated with upregulated PDGFR-beta activity and AKT activation. 25347744_Studies indicate that activated CDC42 kinase 1 (ACK1) interacts with the estrogen receptor (ER) and regulates the activity of androgen receptor (AR) to promote the growth of breast cancer and prostate cancer. 25427824_We uncovered ten new mutations in TNK2 and DDR1 within serous and endometrioid ECs, thus providing novel insights into the mutation spectrum of each gene in EC. 25445114_expression of Ack1 plays an important role as predictor of recurrence and poor outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. 25678401_ACK1 promotes EMT, migration, and invasion by activating AKT-POU2F1-ECD signalling in Gastric cancer cells. ACK1 may be employed as a new prognostic factor and therapeutic target for gastric cancer. 25738261_Our results indicate that ACK1 is an independent prognostic marker and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression 25945695_Results found that the expression of ACK1 was significantly up-regulated in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) samples and demonstrate that ACK1 played an oncogenic role in the progression of NSCLC. 26498357_we demonstrate that amplification of ACK1 promotes gastric tumorigenesis by inducing an ECD-dependent ubiquitination degradation of p53 26536663_Ack1 overexpression promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 26595808_TNK2 (and TNR) harbored rare, genetic variants in individuals with familial Parkinson's Disease. 26621748_that the cdc42-activated, nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, Ack1, is a DAT endocytic brake that stabilizes DAT at the plasma membrane. 26677978_Authors identified tyrosine kinase nonreceptor 2 (TNK2) point mutations that exhibited oncogenic capacity. 27926694_ACK1 protein is increased extensively in colitis and colorectal dysplasia. ACK1 overexpression may play a role in colorectal inflammation and neoplasms. 28188290_findings identify ACK1 as a novel SLP-76-associated protein-tyrosine kinase that modulates early activation events in T cells. 28189676_miR-24 represses metastasis of human osteosarcoma cells by targeting Ack1 via AKT-MMP2-MMP9 pathway. 28539360_These findings suggest that ACK adopts a dock and coalesce binding mechanism with Cdc42. In contrast to other CRIB-family effectors and indeed other intrinsically disordered proteins, hydrophobic residues likely drive Cdc42-ACK binding. 28739485_HSP90 is an upstream regulator of the ACK1-dependent phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3. 28921811_ACK1 activated AKT and Src enhanced nuclear factor-small ka, CyrillicB (NF-small ka, CyrillicB) activity, suggesting a correlation between NF-small ka, CyrillicB signaling and TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis in Caco-2 cells. Results demonstrate that ACK1 plays an important role in modulating TNF-alpha-induced aberrant cell proliferation and apoptosis, mediated in part by ACK1 activation. 29386546_blockade of ACK1/TNK2 could be a new therapeutic modality to target recalcitrant Prostate cancer stem-like cells. 30282494_Knockdown of activated Cdc42-associated kinase inhibits human extravillous trophoblast migration and invasion and decreases protein expression of pho-Akt and matrix metalloproteinase. 31769754_Together, these data support a model wherein TNK2, WASL, and NCK1 comprise a pathway important for the entry of multiple picornaviruses. 31772931_in this review, we will be summarizing the structural characteristics, activation, and regulation of ACK1 in breast cancer, aiming to deeply understand the functional and mechanistic role of ACK1 and provide novel therapeutic strategies for breast cancer treatment. 31819114_Interaction between androgen receptor and coregulator SLIRP is regulated by Ack1 tyrosine kinase and androgen. 32162707_Targeted inhibition of ACK1 can inhibit the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. 33159968_Loss of ACK1 Upregulates EGFR and Mediates Resistance to BRAF Inhibition. 33484472_TNK2 promoted esophageal cancer progression via activating egfr-akt signaling. 33495411_Identification of downstream signaling cascades of ACK1 and prognostic classifiers in non-small cell lung cancer. 35429500_Assembly of nuclear dimers of PI3K regulatory subunits is regulated by the Cdc42-activated tyrosine kinase ACK. 36178070_Activity of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Ack1 is regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation of its Mig6 homology region. |
ENSMUSG00000022791 |
Tnk2 |
386.406863 |
0.4742874685 |
-1.076166 |
0.113544148 |
89.115291 |
0.00000000000000000000372460912281319667747563247402757492654622544023512664636190588884900876109895762056112289428710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000034445633241054375864896986200998839698127657453815064834794223980196647971752099692821502685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
265.1117687 |
17.9300019 |
562.8873895 |
25.9477362 |
| ENSG00000063015 |
124925 |
SEZ6 |
protein_coding |
Q53EL9 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in cell-cell recognition and in neuronal membrane signaling. Seems to be important for the achievement of the necessary balance between dendrite elongation and branching during the elaboration of a complex dendritic arbor. Involved in the development of appropriate excitatory synaptic connectivity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Sushi;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is thought to contain five cysteine-rich motifs that are similar to sushi domains, as well as two domains similar to the amino terminal half of the CUB (for complement C1r/C1s, Uegf, Bmp1) domain. Mutations in this gene have been associated with febrile seizures. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:124925; |
apical dendrite [GO:0097440]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; cerebellar Purkinje cell layer development [GO:0021680]; excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060079]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090036]; synapse maturation [GO:0060074] |
17086543_The human SEZ-6 gene is related to the occurrence and development of FS and may be a novel candidate gene for epilepsy. Screening for mutations in SEZ-6 may be valuable in predicting FS recurrence or the development of epilepsy. 30309378_Study describes a targeted exome sequencing analysis of a large Italian kindred with Alzheimer disease, negative for PSEN and APP variants, that indicated the SEZ6 heterozygous mutation R615H is associated with the pathology. 34135477_ADAMTS1, MPDZ, MVD, and SEZ6: candidate genes for autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. |
ENSMUSG00000000632 |
Sez6 |
28.699479 |
0.1542145177 |
-2.696990 |
0.433922500 |
38.376067 |
0.00000000058343530880583305471965264608555368219811043672962114214897155761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002841143239186438846068525807507521019346086177392862737178802490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4924075 |
2.2531120 |
48.9644071 |
9.3114950 |
| ENSG00000064195 |
1747 |
DLX3 |
protein_coding |
O60479 |
FUNCTION: Likely to play a regulatory role in the development of the ventral forebrain. May play a role in craniofacial patterning and morphogenesis. |
3D-structure;Amelogenesis imperfecta;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Many vertebrate homeo box-containing genes have been identified on the basis of their sequence similarity with Drosophila developmental genes. Members of the Dlx gene family contain a homeobox that is related to that of Distal-less (Dll), a gene expressed in the head and limbs of the developing fruit fly. The Distal-less (Dlx) family of genes comprises at least 6 different members, DLX1-DLX6. Trichodentoosseous syndrome (TDO), an autosomal dominant condition, has been correlated with DLX3 gene mutation. This gene is located in a tail-to-tail configuration with another member of the gene family on the long arm of chromosome 17. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the autosomal dominant conditions trichodentoosseous syndrome and amelogenesis imperfecta with taurodontism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1747; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; hair cell differentiation [GO:0035315]; hair follicle cell proliferation [GO:0071335]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; odontoblast differentiation [GO:0071895]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11343707_results suggest that a serine residue in the homeodomain of the mouse Dlx3 protein can be directly phosphorylated by a protein kinase C-dependent pathway, which affects the DNA binding activity of Dlx3. 11773066_AP-2 gamma and Dlx 3, together with an additional transcription factor(s) that are conserved between humans and mice, are required for trophoblast-specific expression of 3 beta-HSD VI. 11792834_Genomic structure and functional control of the Dlx3-7 bigene cluster 14670999_Overexpression of C/EBP beta was sufficient to increase basal expression of a Dlx3 reporter gene in a dose-dependent manner. 15454107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15454107_results suggest that DLX3 gene is important in bone formation and/or homeostasis of the appendicular skeleton 15666299_This is the first report of a mutation within the homeodomain of DLX3. 16187309_p63 and Dlx play central roles in embryonic patterning and regulation of different developmental processes, and their mutations have been associated with ectodermal dysplasias [review] 16247549_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16301156_mutation has positive effects on bone density throughout life 16467978_DLX-3 gene expression was increased in dental follicle cells during osteogenic differentiation. 16687405_Smad6 appears to functionally interact with Dlx3, altering the ability of Dlx3 to bind target gene promoters. 17559453_gene defect of trichodentoosseous syndrome has been localized only in the DLX3 gene 17611665_Results show that differential DLX3 methylation could be a new epigenetic marker for genotypic B-cell leukemia subgroup with high-risk features. 18203197_Carboxy-terminus of the DLX3 protein is critical in determining its function during development in hair, tooth, and bone. 18362318_The identified mutation was c.561_562delCT mutation in the DLX3 gene. This study clearly showed that the c.561_562delCT mutation had not only enamel defects, but also other clinical phenotypes resembling those of TDO syndrome. 18492670_DLX3(TDO) has a dominant negative effect on DLX3(WT) transcriptional activity 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19282665_Dlx3 triggers p63 protein degradation by a proteasome-dependent pathway. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19608154_Enamel hardness with 2-bp del in DLX3 was about 53% normal enamel hardness. Mutant enamel thickness was about 50% normal thickness. Calcium level in enamel with 2-bp del was slightly decreased; magnesium level was slightly increased, compared to normal. 20151948_A genetic investigation revealed a de-novo mutation in the DLX3 gene on chromosome 17q21. 20542333_Nuclear expression for DLX3 was observed in villous cytotrophoblasts, syncytiotrophoblast and extravillous cytotrophoblast in the proximal regions of the cytotrophoblast cell columns in first trimester placental tissues. 21252474_DLX3 homeodomain mutations cause tricho-dento-osseous syndrome with novel phenotypes 21268066_SUMOylation of DLX3 by SUMO1 promotes its transcriptional activity. 21520071_In cells expressing equal amounts of mutant and wild-type DLX3, deltaNp63alpha protein level was efficiently regulated, implying that heterozygosity at the DLX3 locus protects tricho-dento-osseous patients from severe p63-associated skin defects. 21802725_DLX3 acts upstream of syncytin, 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, and the human gonadotropin beta-subunit to play a regulatory role in villous cytotrophoblast differentiation. 22107079_DLX3 stimulates osteogenic differentiation via BMP2 dependent pathway. 22113468_Increased DLX3 expression in idiopathic fetal growth restricion (FGR) may contribute to trophoblast dysfunction observed in FGR. 23831639_DLX3 orchestrates the expression of multiple regulators of trophoblast differentiation and that expression of these regulatory genes is abnormal in fetal growth restriction. 24321094_In conclusion, results of our study suggest that the NOTCH-signaling pathway, which is activated during the osteogenic differentiation of DFCs. 24924519_Results suggest that Dlx3 is a novel target of PKA, and that PKA mediates BMP signaling during osteoblast differentiation, at least in part, by phosphorylating Dlx3 and modulating its stability and function. 25247779_rs2278163 SNP of DLX3 might be associated with dental caries susceptibility in Japanese children. T and C alleles of rs2278163 SNP may potentially be involved in caries susceptibility and caries protection respectively. 26104267_genetic analysis revealed a novel de novo missense mutation c.533A>G (p.Q178R) in the conserved homeodomain of the DLX3 gene. This DLX3 mutation is the sixth causative mutation for TDO to be identified so far. 26522723_Data establish the DLX3-p53 interplay as a major regulatory axis in epidermal differentiation and suggest that DLX3 is a modulator of skin carcinogenesis. 26674964_ER-alpha regulates the osteoblast differentiation through modulation of Dlx3 expression and/or interaction with Dlx3. 26762616_we identified a recurrent 2-bp deletion in the DLX3 gene in a new family and described their mild clinical phenotype related to the DLX3 mutation. 27368119_We showed that the supplementation of the osteogenic differentiation medium with PTHrP inhibited the alkaline phosphatase activity and the expression of the transcription factor DLX3, but the depletion of PTHrP did not support the differentiation of DFCs.We showed that SUFU (Suppressor Of Fused Homolog) was not regulated during the osteogenic differentiation in DFCs 27924851_Our research of DLX3 mutation protecting aging-related bone loss opens the possibility of its therapeutic potential in bone regeneration and bone loss disease. 27996093_Identify a novel cis-acting sequence (-369 to -320) at the placental growth factor promoter, which was critical for mediating the basal and DLX3/GCM1-dependent PGF promoter activities. 28135572_Novel de novo mutation of DLX3 significantly decreases the proliferation rate and inhibits the odontogenic differentiation and mineralization of hDPCs, suggesting that this novel mutation of DLX3 can influence the dentinogenesis in TDO syndrome. 28186503_DLX3 expression specifically modulates regulatory networks such as Wnt signaling, phosphatase activity and cell adhesion. 28515447_our studies demonstrate that DLX3 physically interacts with GCM1 and inhibits its transactivation activity, suggesting that DLX3 and GCM1 may form a complex to functionally regulate placental cell function through modulation of target gene expression. 28963438_DLX3 regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell proliferation through H19/miR-675 axis. 29059672_Variability in the BMP2 and DLX3 genes was not associated with dental caries in primary and permanent dentition in Czech children 29604248_miR-675 regulates the odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp cells by epigenetic regulating DLX3. 30095208_new DLX3 variants found in families with melogenesis imperfecta with attenuated tricho-dento-osseous syndrome 31029881_suggest that MU-DLX3 significantly inhibits hDPCs differentiation via H19/miR-675 axis and provides a new mechanism insight into how MU-DLX3 epigenetically alters H19 methylation status and expression contributes to dentin hypoplasia in Tricho-Dento-Osseous syndrome 31202458_The data implied that DLX3 regulated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway through histone modification of DKK4 during the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. 31331058_our results support a putative CD271-DLX3 connection in keratinocytes and foment further studies to identify the signaling events that orchestrate their mutual regulation in the epidermis. DLX3 and CD271 are required for fine tuning the regulation of the epidermal differentiation process. 33655330_Effects of DLX3 on the osteogenic differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cellderived mesenchymal stem cells. 33947961_Loss of DLX3 tumor suppressive function promotes progression of SCC through EGFR-ERBB2 pathway. 34925225_The miR-4739/DLX3 Axis Modulates Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (BMSC) Osteogenesis Affecting Osteoporosis Progression. 35096127_The Imbalance Expression of DLX3 May Perform Critical Function in the Occurrence and Progression of Preeclampsia. 35714441_Novel DLX3 variant identified in a family with tricho-dento-osseous syndrome. 36012753_Salt Dependence of DNA Binding Activity of Human Transcription Factor Dlx3. |
ENSMUSG00000001510 |
Dlx3 |
192.585958 |
0.2741179973 |
-1.867131 |
0.123104358 |
242.512044 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000111424201602539445336086627376030592575548717371276592330246936653537808544607706995141329357691159186683620822432159174225419299947514818402427572152646462200209498405456542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000025940397723241046640509300495532683940440964988871252059626441028498428517355374745989548373866681202049833619061922517629509410256628820778956878712051548063755035400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.5098382 |
6.8530827 |
310.5932356 |
14.9449654 |
| ENSG00000064201 |
10077 |
TSPAN32 |
protein_coding |
Q96QS1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene, which is a member of the tetraspanin superfamily, is one of several tumor-suppressing subtransferable fragments located in the imprinted gene domain of chromosome 11p15.5, an important tumor-suppressor gene region. Alterations in this region have been associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, adrenocortical carcinoma, and lung, ovarian and breast cancers. This gene is located among several imprinted genes; however, this gene, as well as the tumor-suppressing subchromosomal transferable fragment 4, escapes imprinting. This gene may play a role in malignancies and diseases that involve this region, and it is also involved in hematopoietic cell function. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10077; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; integrin alphaIIb-beta3 complex [GO:0070442]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; negative regulation of myeloid dendritic cell activation [GO:0030886]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein maturation [GO:0051604]; regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050688]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098] |
20709950_In the absence of both CD37 and Tssc6, immune function is further altered when compared with CD37- or Tssc6-deficient transgenic mice, demonstrating a complementary role for these two molecules in cellular immunity. 31487788_TSPAN32 mRNA level is significantly reduced in CD4 T cells of multiple sclerosis patients. 34207245_Altered Expression of TSPAN32 during B Cell Activation and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. |
ENSMUSG00000000244 |
Tspan32 |
194.979742 |
0.4713911216 |
-1.085004 |
0.191684822 |
31.691855 |
0.00000001806783925343400980911468434349231859670226185698993504047393798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000076720744355778481569318159611486906968025323294568806886672973632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
130.8170287 |
15.8579340 |
279.8048162 |
23.2809241 |
| ENSG00000064547 |
9170 |
LPAR2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBW0 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a mediator of diverse cellular activities. Seems to be coupled to the G(i)/G(o), G(12)/G(13), and G(q) families of heteromeric G proteins. Plays a key role in phospholipase C-beta (PLC-beta) signaling pathway. Stimulates phospholipase C (PLC) activity in a manner that is independent of RALA activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15143197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19306925}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of family I of the G protein-coupled receptors, as well as the EDG family of proteins. This protein functions as a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor and contributes to Ca2+ mobilization, a critical cellular response to LPA in cells, through association with Gi and Gq proteins. An alternative splice variant has been described but its full length sequence has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:53978; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; lysophosphatidic acid receptor activity [GO:0070915]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222] |
12123830_demonstrate that two biological fluids, blood plasma and seminal plasma, differentially activate LPA receptors 12668280_results suggested that LPA(2) and LPA(3) may be involved in VEGF expression mediated by LPA signals in human ovarian oncogenesis 12759391_LPA may directly increase the level of cyclin D1 in ovarian cancer cells, increasing their proliferation. 15535846_Upregulation of LPA2 may play a role in carcinogenesis, particularly in postmenopausal breast cancer. 15728708_LPA2 is the major LPA receptor in colon cancer cells and cellular signals by LPA2 are largely mediated through its ability to interact with NHERF2. 15755723_formation of the LPA receptor/PDZ domain-containing RhoGEF complex plays a pivotal role in LPA-induced RhoA activation 16904289_These results demonstrate that MAGI-3 interacts directly with LPA(2) and regulates the ability of LPA(2) to activate Erk and RhoA. 17496233_EDG4 and EDG2 cooperate to promote LPA-stimulated chemotaxis in breast tumor cell lines. 17765657_data suggest that LPA receptor-dependent expression of CTGF and CYR61 represents a common host response after interaction with bacteria. 17965021_lysophosphatidic acid 2 receptor mediates down-regulation of Siva-1 to promote cell survival 18703779_A role for the transgenic lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)2 receptor is identified in regulating smooth muscle cell migratory responses in the context of vascular injury. 18754873_LPA and LPA receptors, LPA(2) as well as LPA(1), represent potential therapeutic targets for patients with MPM 19001604_Expression of LPA2 during ovarian carcinogenesis contributes to ovarian cancer aggressiveness, suggesting that the targeting of LPA production and action may have potential for the treatment of ovarian cancer. 19025891_Switching of LPA receptor expression from LPA3 to LPA1, may be involved in prostate cancer progression and/or androgen independence 19081821_LPA(1) receptor, LPA(2) and LPA(3) receptors-induced VASP phosphorylation is a critical mediator of tumor cell migration initiation 19116446_LPA2 and Gi/Src pathways are significant for LPA-induced COX-2 expression and cell migration that could be a promising drug target for ovarian cancer cell metastasis. 19860625_Data show that CLL cells express LPA receptors LPA(1-5) and VEGF receptors, and the plasma levels of VEGF are elevated in CLL patients. 19899077_show that human microglia express LPA receptor subtypes LPA(1), LPA(2), and LPA(3) on mRNA and protein level. LPA activation of C13NJ cells induced Rho and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and enhanced cellular ATP production. 20890765_LPA2 gene mutation may play some role in the pathogenesis of colon cancer. 21134377_MAGI-3 competes with NHERF-2 to negatively regulate LPA2 receptor signaling in colon cancer cells. 21234797_This work shows for the first time that key components of the LPA pathway are modulated following traumatic brain injuries in humans. 21964883_found that LPA receptor 2/3-mediated IL-8 expression occurs through Gi/PI3K/AKT, Gi/PKC and IkappaB/NF-kappaB signaling 23084965_LPA2 and LPA6 receptor subtypes are predominant in both HPAECs and HMVECs 23569130_Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) increased hepatocellular carcinoma cells cell invasion, which was LPA-receptor dependent. 24061591_LPA1 and LPA2 are major LPA receptor subtypes compared with low-expressed LPA3 in PANC-1 tumor cells. 24613836_Crystal structure of NHERF2 PDZ1 domain complex with C-terminal LPA2 sequence. The PDZ1-LPA2 binding specificity is achieved by hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts with the last four LPA2 residues contributing to specific interactions. 24950964_the RhoA-regulated formin Dia1 is involved in entosis downstream of LPAR2 25463482_Suggest that LPA2 and LPA3 may function as a molecular switch and play opposing roles during megakaryopoiesis of K562 cells. 26327335_Data show high expression levels of LPAR2 and LPAR1 in endometrial cancer tissue with positive correlations with FIGO stage suggesting them as potential biomarkers for endometrial cancer progression. 26937138_LPAR2 mRNA is up-regulation in colorectal cancer. 27124742_epithelial dysplasia was observed in founder mouse intestine, correlating LPA2 overexpression with epithelial dysplasia. The current study demonstrates that overexpression of LPA2 alone can lead to intestinal dysplasia. 27244685_The results indicate that LPA2 and LPA3 receptors play opposing roles during red blood cells differentiation. 27583415_LPA2 mRNA levels were associated with poorer differentiation, and higher LPA6 levels were associated with microvascular invasion in HCC; both became a risk factor for recurrence after surgical treatment when combined with increased serum ATX levels 27805252_LPA2 expression was associated with HIF-1alpha expression and that a high level of LPA2 was associated with shorter overall survival and was an independent prognostic predictor for breast cancer in Chinese women. 28205098_These results suggest that LPA signaling via LPA2 may play an important role in the regulation of cellular functions in HT1080 cells treated with cisplatin. 29621954_Study shows that due to the high LPAR2 and LPAR4 transcript and protein expression in endometriotic ovarian cysts and positive correlations of both these receptors with the PR-B and ERbeta, respectively, those receptors seem to be the most promising predictors of the endometriotic cysts. 29859140_Investigated the roles of LPA receptors in the regulation of cellular functions during tumor progression in osteosarcoma cell lines. MG63-R7-C cell activities were inhibited by LPA2 knockdown, suggesting that LPA signaling via LPA2 plays an important role in the acquisition of malignant properties during tumor progression in MG-63 cells. 30093116_LPAR2 and LPAR5 regulate cellular functions during tumor progression in fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. 31115486_It was revealed that LPA may stimulate the expression of Notch1 and Hes family bHLH transcription factor 1, and the phosphorylation of protein kinase B which belongs to the Notch pathway. 31235682_The positive expression rate of LPA2 and KLF5 were statistical different in gastric adenocarcinoma, GIN, and normal gastric tissue (P |
ENSMUSG00000031861 |
Lpar2 |
259.938569 |
0.2792305094 |
-1.840472 |
0.335178298 |
28.462753 |
0.00000009551852462124095311665696213243581524920955416746437549591064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000377066976038918533270440525823063993016148742754012346267700195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
104.2783116 |
22.5392950 |
377.4254404 |
58.2469600 |
| ENSG00000064687 |
10347 |
ABCA7 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZY2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the translocation of specific phospholipids from the cytoplasmic to the extracellular/lumenal leaflet of membrane coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP (PubMed:24097981). Transports preferentially phosphatidylserine over phosphatidylcholine (PubMed:24097981). Plays a role in lipid homeostasis and macrophage-mediated phagocytosis (PubMed:14592415, PubMed:12917409, PubMed:12925201, PubMed:14570867). Binds APOA1 and may function in apolipoprotein-mediated phospholipid efflux from cells (PubMed:12917409, PubMed:14570867, PubMed:14592415). May also mediate cholesterol efflux (PubMed:14570867). May regulate cellular ceramide homeostasis during keratinocyte differentiation (PubMed:12925201). Involved in lipid raft organization and CD1D localization on thymocytes and antigen-presenting cells, which plays an important role in natural killer T-cell development and activation (By similarity). Plays a role in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages (By similarity). Macrophage phagocytosis is stimulated by APOA1 or APOA2, probably by stabilization of ABCA7 (By similarity). Also involved in phagocytic clearance of amyloid-beta by microglia cells and macrophages (By similarity). Further limits amyloid-beta production by playing a role in the regulation of amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein (APP) endocytosis and/or processing (PubMed:26260791). Amyloid-beta is the main component of amyloid plaques found in the brains of Alzheimer patients (PubMed:26260791). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91V24, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12917409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14570867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14592415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24097981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26260791}. |
Alternative splicing;Alzheimer disease;Amyloidosis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Lipid transport;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Phagocytosis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the ABC1 subfamily. Members of the ABC1 subfamily comprise the only major ABC subfamily found exclusively in multicellular eukaryotes. This full transporter has been detected predominantly in myelo-lymphatic tissues with the highest expression in peripheral leukocytes, thymus, spleen, and bone marrow. The function of this protein is not yet known; however, the expression pattern suggests a role in lipid homeostasis in cells of the immune system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10347; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; glial cell projection [GO:0097386]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; apolipoprotein A-I receptor activity [GO:0034188]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; floppase activity [GO:0140328]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; phosphatidylcholine floppase activity [GO:0090554]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; phospholipid transporter activity [GO:0005548]; amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process [GO:0150094]; amyloid-beta formation [GO:0034205]; apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038027]; cholesterol efflux [GO:0033344]; high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034380]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process [GO:0042985]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; negative regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045806]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903898]; peptide cross-linking [GO:0018149]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; phospholipid efflux [GO:0033700]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; plasma membrane raft organization [GO:0044857]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900223]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:1901076]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of phospholipid efflux [GO:1902995]; positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000010]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504]; regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902991]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
12917409_ABCA7 has the ability to bind apolipoproteins and promote efflux of cellular phospholipids without cholesterol, and has a possible role of ABCA7 in cellular phospholipid metabolism in peripheral tissues 12925201_Overexpression of ABCA7 in HeLa cells resulted in increased expression of intracellular and cell surface ceramide and elevated intracellular phosphatidylserine levels. 14570867_ABCA7 compensates the function of ABCA1 for release of cell cholesterol in a certain condition(s). 14592415_Alternative splicing could be involved in the post-transcriptional regulation of the expression and function of human ABCA7 15593299_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15930518_the ABCA7-mediated reaction generated mostly small cholesterol-poor particles; ABCA7 produces this HDL subfraction only as a very minor component. 16908670_These studies reveal a major role of ABCA7 and not -A1 in the clearance of apoptotic cells and therefore suggest that ABCA7 is an authentic orthologue of CED-7. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19721717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21173549_[REVIEW]ABCA7 seems to be one of the key molecules linking sterol homeostasis and the host defense system 21460840_ABCA7 and the MS4A6A/MS4A4E gene cluster are new Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci. 23324282_The ABCA7 gene is regulated by sterol in a direction opposite to that of ABCA1. 23669301_Interactions between two cholesterol metabolizing genes, ABCA7 and APOE epsilon4, are associated with memory and Alzheimer's disease. 24064683_The minor G allele frequency of the rs1788799 polymorphisms in NPC1 might be a protective factor while the rs3764650 polymorphisms of ABCA7 might not be related to sporadic Alzheimer's disease in the Han Chinese population. 24097981_These studies provide the first direct evidence for ABCA1 and ABCA7 functioning as phospholipid transporters and suggest that this activity is an essential step in the loading of apoA-1 with phospholipids for HDL formation. 24113560_ABCA7 (rs3,764,650) was associated with sporadic Alzheimer disease in the Chinese population, with both ApoEepsilon4-carrier and aging being factors enhancing its risk. 24141082_the rs3764650T allele that decreases AD risk is associated with increased ABCA7 expression 24530172_In Alzheimer's disease patients with cognitive impairments, an association was linked to SNPs of ABCA7. 24643655_Collectively, our analysis further supports previous findings that the ABCA7 rs3764650 polymorphism is associated with Alzheimer disease susceptibility. 24743338_Of those 394 variants, 34 showed strong evidence of regulatory function (RegulomeDB score |
ENSMUSG00000035722 |
Abca7 |
323.660577 |
0.2424170427 |
-2.044437 |
0.188421319 |
111.806961 |
0.00000000000000000000000003938505800608097512380029214825940383430531215285482013151072592469512448354329592348221922293305397033691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000437085305390793411554517254687252937761093430874278031006746561440510362439582081606204155832529067993164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
119.3673810 |
15.7295449 |
494.0151865 |
45.1868711 |
| ENSG00000064763 |
55711 |
FAR2 |
protein_coding |
Q96K12 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reduction of saturated but not unsaturated C16 or C18 fatty acyl-CoA to fatty alcohols. A lower activity can be observed with shorter fatty acyl-CoA substrates (PubMed:15220348). It may play a role in the production of ether lipids/plasmalogens and wax monoesters which synthesis requires fatty alcohols as substrates (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8WVX9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15220348}. |
Alternative splicing;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the short chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily. It encodes a reductase enzyme involved in the first step of wax biosynthesis wherein fatty acids are converted to fatty alcohols. The encoded peroxisomal protein utilizes saturated fatty acids of 16 or 18 carbons as preferred substrates. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 2, 14 and 22. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:55711; |
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; alcohol-forming fatty acyl-CoA reductase activity [GO:0102965]; fatty-acyl-CoA reductase (alcohol-forming) activity [GO:0080019]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0035336]; wax biosynthetic process [GO:0010025] |
15220348_fatty alcohol synthesis in mammals is accomplished by two fatty acyl-CoA reductase isozymes that are expressed at high levels in tissues known to synthesize wax monoesters and ether lipids 15220349_wax monoester synthesis in mammals involves a two step biosynthetic pathway catalyzed by fatty acyl-CoA reductase and wax synthase enzymes 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29652635_Results indicate fatty acyl CoA reductase 2 FAR2's role in the development of mesangial matrix expansion and chronic kidney disease. |
ENSMUSG00000030303 |
Far2 |
502.812559 |
0.3688213443 |
-1.439006 |
0.081769486 |
313.401407 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000039651888452976166542387579564997120877613493084890838318420795313913774357110175940260278618177593751458906064463513584993595645048816976851387453520075042022894787828549449312798280686820362461730837821960449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011847406347488426232737607392307884091337947155475079220229013548241956129297871185172625013959969243810016864353357961225420451956415389019295520608664620926841544473100478751526054566056700423359870910644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
264.4351876 |
17.9130008 |
720.6729562 |
33.0271593 |
| ENSG00000065029 |
7629 |
ZNF76 |
protein_coding |
P36508 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7629; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006359] |
15280358_ZNF76 functions as a transcriptional repressor through its interaction with TBP and sumoylation modulates its transcriptional repression activity 16337145_Our study shows that ZNF76, a TBP-interacting transcriptional modulator, is regulated by both lysine modifications and alternative splicing. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33664275_The ZNF76 rs10947540 polymorphism associated with systemic lupus erythematosus risk in Chinese populations. 34793589_ZNF76 predicts prognosis and response to platinum chemotherapy in human ovarian cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024220 |
Zfp523 |
295.263179 |
0.4231128895 |
-1.240885 |
0.304253736 |
16.144770 |
0.00005868037601381937893012946672044449769600760191679000854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000167431345440551709348453446324356264085508882999420166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
189.7605656 |
35.9640605 |
451.0890694 |
61.5335205 |
| ENSG00000065054 |
9351 |
SLC9A3R2 |
protein_coding |
Q15599 |
FUNCTION: Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin family and thereby helps to link them to the actin cytoskeleton and to regulate their surface expression. Necessary for cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of SLC9A3 (PubMed:18829453). May also act as scaffold protein in the nucleus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10455146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18829453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9096337}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the NHERF family of PDZ scaffolding proteins. These proteins mediate many cellular processes by binding to and regulating the membrane expression and protein-protein interactions of membrane receptors and transport proteins. The encoded protein plays a role in intestinal sodium absorption by regulating the activity of the sodium/hydrogen exchanger 3, and may also regulate the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) ion channel. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:9351; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein-membrane adaptor activity [GO:0043495]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; type 2 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031799]; type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031800]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003] |
11786550_Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 2b interacts preferentially with Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 2 in apical plasma membranes 11893083_E3KARP has a restricted tissue distribution with the highest expression being found in lung. It is largely colocalized with moesin and radixin, especially in the alveoli of the lung, as well as being highly enriched in the renal corpuscle. 12075354_Na(+)/H(+ ) exchanger regulatory factor 2 directs parathyroid hormone 1 receptor signalling. 12080047_A2BR binds to E3KARP upon agonist stimulation. 12369822_When the second PDZ domain of E3KARP is bound to down regulated in adenoma (dra) gene product, a structural link is built between the functionally coupled Na+/H+ and Cl-/HCO3- exchangers in the proximal colon. 12444200_NHERF2 and SGK1 interact to enhance ROMK1 activity by enhancing abundance of channel protein in cell membrane, allowing integration of genomic regulation and activation of SGK1 and NHERF2 in control of ROMK1 activity and renal K(+) excretion. 14623317_NHERF2, with ROMK1 and SGK1 has a role in regulating protein abundance in the plasma membrane and K(+) current 15665527_demonstration of the significance of SGK1 and NHERF2 as TRPV5 modulators which are likely to participate in the regulation of calcium homeostasis by 1,25(OH)2D3 15728708_LPA2 is the major LPA receptor in colon cancer cells and cellular signals by LPA2 are largely mediated through its ability to interact with NHERF2. 16166090_the function of SIP-1/NHERF2 as an SRY cofactor during testis determination is conserved between human and mouse 16615918_analysis of NHERF recognition by ERM proteins 17229887_N-cadherin and beta-catenin play role in cell migration via PDGF-Rbeta-mediated signaling through the scaffolding molecule NHERF2 19091402_While the presence of forskolin results in an increase in OCTN2 protein expression, the increase in uptake capacity may be compensated by the decreased expression of PDZK1, NHERF1 or NHERF2. 20430067_The results of this study revealed that NHERF-2 can interact with GLAST in astrocytes to enhance GLAST stability and activity. 20562104_NHERF1 and NHERF2 exhibit isotype-specific effects on G protein activation. 20618342_The authors generated a HeLa cell line stably expressing HA-tagged NHERF2 and found that Map, EspI and NleH1 colocalize and interact with intracellular NHERF2 via their C-terminal PDZ-binding motif. 20663896_Apical scaffolding protein NHERF2 modulates the localization of alternatively spliced plasma membrane Ca2+ pump 2B variants in polarized epithelial cells. 21134377_MAGI-3 competes with NHERF-2 to negatively regulate LPA2 receptor signaling in colon cancer cells. 21187068_WNK4 and NHERF2 synergistically regulate TRPV5 by enhancing its forward trafficking and increasing its stability at plasma membrane, respectively. 21191106_Data show that both NHERF2 and NHERF1 are involved in setting NHE3 activity. 22343917_NHERF-2 is a negative regulator of endothelial proliferation and may have important roles in endothelial homeostasis and vascular modeling. 22371496_CaMKII inhibition of NHE3 reguires NHEF2. 22587461_AnxA2 and NHERF2 form a scaffold complex that links adjacent Tir molecules at the plasma membrane forming a lattice that could be involved in retention and dissemination of other effectors at the bacterial attachment site. 23284683_functional regulation of C3aR by NHERFs in human mast cells 23612977_NHERF2 domain was functionally significant in NHE3 regulation, being necessary for stimulation by lysophosphatidic acid of activity and increased mobility of NHE3 23985317_Data indicate that the tails promote different microvillar localizations for EBP50 and E3KARP, which localized along the full length and to the base of microvilli, respectively. 24613836_Crystal structure of NHERF2 PDZ1 domain complex with C-terminal LPA2 sequence. The PDZ1-LPA2 binding specificity is achieved by hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts with the last four LPA2 residues contributing to specific interactions. 24760985_Lysophosphatidic acid stimulation of NHE3 exocytosis in polarized epithelial cells occurs with release from NHERF2 via ERK-PLC-PKCdelta signaling. 26310448_Moreover, the S303D mutation enhances the in vivo dynamics of the E3KARP tail alone, whereas in vitro the interaction of E3KARP with active ezrin is unaffected by S303D 28392297_Studies support a role for NHERF-1 and NHERF-2 (Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factors 1 and 2) in regulating the distribution of Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluRs) in the murine brain, while conversely the effects of the mGluR2/3 PDZ-binding motifs on receptor signaling are likely mediated by interactions with other PDZ scaffold proteins beyond the NHERF proteins. 31597772_PDZ domain-containing protein NHERF-2 is a novel target of HPV-16 and HPV-18 E proteins. |
ENSMUSG00000002504 |
Slc9a3r2 |
113.187962 |
0.1524244472 |
-2.713834 |
0.198137787 |
201.758770 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000086305210496280785516620204195828792813519111039979900050766726288888825155983939482402666395635314241665579199454987405215611317998991580680012702941894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016608408173730175119789650412705424497194363529419181917896153008154174714094458511007175187647790797057780758810320576035479689380736090242862701416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.6013246 |
4.0941760 |
189.1553169 |
16.0700643 |
| ENSG00000065057 |
4913 |
NTHL1 |
protein_coding |
P78549 |
FUNCTION: Bifunctional DNA N-glycosylase with associated apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) lyase function that catalyzes the first step in base excision repair (BER), the primary repair pathway for the repair of oxidative DNA damage (PubMed:9927729). The DNA N-glycosylase activity releases the damaged DNA base from DNA by cleaving the N-glycosidic bond, leaving an AP site. The AP-lyase activity cleaves the phosphodiester bond 3' to the AP site by a beta-elimination. Primarily recognizes and repairs oxidative base damage of pyrimidines. Has also 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoG) DNA glycosylase activity. Acts preferentially on DNA damage opposite guanine residues in DNA. Is able to process lesions in nucleosomes without requiring or inducing nucleosome disruption. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10882850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11328882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11380260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11695910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12140329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12144783, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12519758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14734554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15533839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17923696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20005182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20110254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21930793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8990169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9045706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705289, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9890904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9927729}. |
3D-structure;4Fe-4S;Alternative initiation;Direct protein sequencing;DNA damage;DNA repair;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Lyase;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA N-glycosylase of the endonuclease III family. Like a similar protein in E. coli, the encoded protein has DNA glycosylase activity on DNA substrates containing oxidized pyrimidine residues and has apurinic/apyrimidinic lyase activity. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:4913; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051539]; class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity [GO:0140078]; damaged DNA binding [GO:0003684]; DNA N-glycosylase activity [GO:0019104]; DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity [GO:0003906]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxidized purine nucleobase lesion DNA N-glycosylase activity [GO:0008534]; oxidized pyrimidine nucleobase lesion DNA N-glycosylase activity [GO:0000703]; base-excision repair, AP site formation [GO:0006285]; depyrimidination [GO:0045008]; nucleotide-excision repair [GO:0006289]; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision, 5'-to lesion [GO:0006296] |
11328882_NTH1 is involved in removal of 8-oxoguanine from 8-oxoguanine/guanine mispairs in DNA 12144783_recombinant hNTH1 lacking 55, 72 or 80 residues from the N terminus had four- to fivefold higher activities than the full-length enzyme 12519758_substrate selectivity of mammalian NTH1 and the concomitant selective stimulation of activity by APE1 are indicative of selective repair of oxidative damage in different regions of the genome 14522981_dimerization of hNTH1 involving the N-terminal tail masks the inhibitory effect of this tail and plays a critical role in its catalytic turnover in the cell 14734554_hNTH1 and hNEIL1 but not hNEIL2 excised the two stereoisomers of thymine glycol (5R-Tg and 5S-Tg), but their isomer specificity was markedly different 15358233_search for the factors interacting with NTH1 shows GST-NTH1 fusion protein precipitates proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and p53 as well as XPG from human cell-free extracts 15533839_NTH1 is a DNA glycosylase that excise 5-formyluracil, 5-hydroxymethyluracil and Thymine glycol in human cells. 16111924_hNTH1 plays two roles in the processing of radiation damages: repair of potentially lethal single lesions and generation of lethal double strand breaks at clustered damage sites. 16446124_Nth1 released 5R,6S 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diastereoisomer (Tg2) much more rapidly than cis 5S,6R-deoxyribonucleoside diastereoisomer (Tg1) regardless of the opposing purine. Neil1 released Thymine glycol non-stereoselectively. 17150535_The damage specificity of human homologues of Endo III (hNTHl) and Endo VIII (hNEIL1 and hNEIL2) is compared to elucidate the repair role in cells. 17923696_These observations suggest that access to sterically occluded lesions entails the partial, reversible unwrapping of DNA from the histone octamer, allowing hNTH1 to capture its DNA substrate when it is in an unwound state. 18307537_YB-1 binds specifically to the auto-inhibitory domain of hNTH1, providing a mechanism by which YB-1 stimulates hNTH1 activity. 18515411_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19414504_Downregulation of NTH1 is associated with gastric cancer. 19414504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20226869_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574454_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22465744_we demonstrated that hNEIL1 and hNTH1 cleave Oz sites as efficiently as 5-hydroxyuracil sites. Thus, hNEIL1 and hNTH1 can repair Oz lesions 25938944_A homozygous loss-of-function germline mutation in the NTHL1 gene predisposes to a new subtype of BER-associated adenomatous polyposis and colorectal cancer. 26400813_NTH1 polymorphisms may be associated with non-small cell lung cancer pathogenesis. 26559593_This study extends the description of biallelic mutations in NTHL1 beyond the single c.268C-->T,p.Q90* mutation that was observed previously. 27713038_We therefore found published evidence to support the association between variants in NTHL1 and RPS20 with CRC. 27839712_Both Ntg1 and its human homologue, NTHL1, can be SUMO-modified in response to oxidative stress. 28292631_WT NTHL1 (human) and Nth (E. coli) are remarkably alike with respect to specificity of glycosylase reaction, and although NTHL1 is a much slower enzyme than Nth, the tighter binding of NTHL1 compensates, resulting in similar kcat/Kd values for both enzymes with each of the substrates tested. For NTHL1 Gln287Ala, specificity for substrates positioned opposite G is lost, but not that of substrates positioned opposite A. 28575236_Data indicate that DNA glycosylases MYH, UNG2, MPG, NTH1, NEIL1, 2 and 3 on nascent DNA. 28709015_NTHL1 in these extracts was able to excise thymine glycol from both naked DNA and sites in nucleosomes that earlier studies had shown to be sterically accessible. However, the same extracts were able to excise lesions from sterically-occluded sites in nucleosomes only after the addition of Mg2+/ATP. 29610152_This paper demonstrates that cellular NTH1 protein is induced in response to oxidative stress following hydrogen peroxide treatment of cells and that accumulation of NTH1 on chromatin is exacerbated in the absence of TRIM26. 30207305_The processing of the lesions was evaluated by purified enzyme cocktails of hNTH1 and hOGG1 as well as with a HeLa cell extract. Interestingly, the yield of double-strand breaks (DSBs) resulting from the processing of the bistranded lesions are appreciably lower when the DNA is treated with the HeLa cell extract compared with the relevant purified enzyme cocktail in both models 30552997_The results suggest that the NTHL1 variants Q90X, Y130X, R153X, and Q287X, but not R19Q, V179I, V217F, or G286S, were defective in 5OHU repair and the alleles encoding them were considered to be pathogenic for NTHL1-associated polyposis. 30649547_he lyase activity of hNTHL1, and the 3' diesterase activity of APE1, which had been seen as relatively dispensable, may have been preserved during evolution to enhance base excision repair (BER) in chromatin 30753826_NTHL1 is a multi-tumor predisposition gene with a high lifetime risk for extracolonic cancers and a typical mutational signature observed across tumor types, which can assist in the recognition of this syndrome. 31227763_NTHL1 biallelic mutations seldom cause colorectal cancer, serrated polyposis or a multi-tumor phenotype, in absence of colorectal adenomas. 32109332_An Excimer Clamp for Measuring Damaged-Base Excision by the DNA Repair Enzyme NTH1. 32860789_Monoallelic NTHL1 Loss-of-Function Variants and Risk of Polyposis and Colorectal Cancer. 32949222_Evaluating the role of NTHL1 p.Q90* allele in inherited breast cancer predisposition. 33087284_NTHL1 in genomic integrity, aging and cancer. 33454955_Further delineation of the NTHL1 associated syndrome: A report from the French Oncogenetic Consortium. 34250384_Prevalence and Characterization of Biallelic and Monoallelic NTHL1 and MSH3 Variant Carriers From a Pan-Cancer Patient Population. 34871433_Caught in motion: human NTHL1 undergoes interdomain rearrangement necessary for catalysis. 36279116_Human endonuclease III/NTH1: focusing on the [4Fe-4S] cluster and the N-terminal domain. |
ENSMUSG00000041429 |
Nthl1 |
66.809288 |
0.3267301058 |
-1.613829 |
0.204398517 |
64.321906 |
0.00000000000000105664383407967783879312908561010999116440086959683997136494326696265488862991333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000007559894809023773374428624751999418965393222162585384893418449792079627513885498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
33.1601300 |
4.3140922 |
102.6102618 |
8.1554071 |
| ENSG00000065183 |
10885 |
WDR3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UNX4 |
|
3D-structure;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear protein containing 10 WD repeats. WD repeats are approximately 30- to 40-amino acid domains containing several conserved residues, which usually include a trp-asp at the C-terminal end. Proteins belonging to the WD repeat family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10885; |
nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; Pwp2p-containing subcomplex of 90S preribosome [GO:0034388]; small-subunit processome [GO:0032040]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; snoRNA binding [GO:0030515]; maturation of SSU-rRNA [GO:0030490] |
20392698_WDR3 has an essential function in 40 S ribosomal subunit synthesis and in ribosomal stress signaling to p53-mediated regulation of cell cycle progression in cancer cells 20578902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20578902_results indicate for the first time that WDR3 is a risk factor to thyroid cancer, suggesting its implication in the etiology of thyroid cancer 23049746_WDR3 can modulate genome stability in thyroid cancer patients. 29309433_evaluated the genetic association of WDR3 and ALG1 in schizophrenia. We examined 21 single nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs; W1 (rs1812607)-W16 (rs6656360), A1 (rs8053916)-A10 (rs9673733)] from these genes using the Japanese case-control sample (1,808 schizophrenics and 2,170 matched controls). No significant genetic associations of these SNPs were identified. However, we detected a significant association of W4 (rs319471) 33648545_Overexpressed WDR3 induces the activation of Hippo pathway by interacting with GATA4 in pancreatic cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000033285 |
Wdr3 |
481.600321 |
5.6935390864 |
2.509326 |
0.120321881 |
416.860069 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001177322173189571140786263185649710181851616435709606408097664036542161869006822750994669731190916322036643754765322340623628382809501562952214417937281864933514375471484822146779381147476948327774270962981993039273379494133280054324330877 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000457296717796791343323424598266310862074488910485171732850411259582413481199804356681866733666438704883094628604586108655596501767809249458988467219928768869359235343788803032841155173564395546216627041078882861902504656809870242639703974 |
Yes |
No |
756.2043664 |
67.1016620 |
134.0044838 |
9.0514981 |
| ENSG00000065308 |
9697 |
TRAM2 |
protein_coding |
Q15035 |
FUNCTION: Necessary for collagen type I synthesis. May couple the activity of the ER Ca(2+) pump SERCA2B with the activity of the translocon. This coupling may increase the local Ca(2+) concentration at the site of collagen synthesis, and a high Ca(2+) concentration may be necessary for the function of molecular chaperones involved in collagen folding. Required for proper insertion of the first transmembrane helix N-terminus of TM4SF20 into the ER lumen, may act as a ceramide sensor for regulated alternative translocation (RAT) (PubMed:27499293). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14749390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27499293}. |
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Translocation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
TRAM2 is a component of the translocon, a gated macromolecular channel that controls the posttranslational processing of nascent secretory and membrane proteins at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane.[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2004]. |
hsa:9697; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032964]; protein insertion into ER membrane [GO:0045048]; SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation [GO:0006616] |
14749390_TRAM2, as a part of the translocon, is required for the biosynthesis of type I collagen by coupling the activity of SERCA2b with the activity of the translocon 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25957402_results support a role of DAP12 in stabilizing TREM2-CTF, thereby protecting against excessive pro-inflammatory responses. 33514403_A comprehensive enhancer screen identifies TRAM2 as a key and novel mediator of YAP oncogenesis. 34793833_Identification of TRAMs as sphingolipid-binding proteins using a photoactivatable and clickable short-chain ceramide analog. 34826698_TRAM2 promotes the malignant progression of glioma through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000041779 |
Tram2 |
819.637515 |
0.4553146049 |
-1.135064 |
0.059517257 |
367.948964 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000052332516182446132314883046796575072063962872853197814247289243298401674140872358095089776103763682525882664620814154233572612638783465164560565774914198545219455208183916037672585065337628517492454946133384474649119511013850569725036621093750000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018047381748899647317665678082439225247322008792238239070818936651543560869149484861572169533007302241453595044113028620842581077109502645511282493473709923546326914595189315352259770448531257894817306230983433579240227118134498596191406250000000000 |
Yes |
No |
519.0300383 |
22.4456514 |
1147.1993441 |
33.3504633 |
| ENSG00000065320 |
9423 |
NTN1 |
protein_coding |
O95631 |
FUNCTION: Netrins control guidance of CNS commissural axons and peripheral motor axons. Its association with either DCC or some UNC5 receptors will lead to axon attraction or repulsion, respectively. Binding to UNC5C might cause dissociation of UNC5C from polymerized TUBB3 in microtubules and thereby lead to increased microtubule dynamics and axon repulsion (PubMed:28483977). Involved in dorsal root ganglion axon projection towards the spinal cord (PubMed:28483977). It also serves as a survival factor via its association with its receptors which prevent the initiation of apoptosis. Involved in tumorigenesis by regulating apoptosis (PubMed:15343335). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15343335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28483977}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Laminin EGF-like domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Netrin is included in a family of laminin-related secreted proteins. The function of this gene has not yet been defined; however, netrin is thought to be involved in axon guidance and cell migration during development. Mutations and loss of expression of netrin suggest that variation in netrin may be involved in cancer development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9423; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; basement membrane [GO:0005604]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; anterior/posterior axon guidance [GO:0033564]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; Cdc42 protein signal transduction [GO:0032488]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; chemorepulsion of axon [GO:0061643]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060603]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; motor neuron migration [GO:0097475]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; nuclear migration [GO:0007097]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of glial cell migration [GO:1903975]; regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051963]; substrate-dependent cell migration, cell extension [GO:0006930]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
12810718_Netrin binds discrete subdomains of DCC and UNC5 and mediates interactions between DCC and heparin 14602071_Data demonstrate that alpha6beta4 integrin mediates pancreatic epithelial cell adhesion to Netrin-1, whereas recruitment of alpha6beta4 and alpha3beta1 regulate the migration of putative pancreatic progenitors on Netrin-1. 15491747_DCC/netrin-1 signaling may commit cells to the transition of endometrial gland architecture or function from a proliferating to a secretory phase. 15573119_Binding of netrin-1 to its receptors inhibits tumour suppressor p53-dependent apoptosis (review) 15574733_Netrin binds through multiple domains to both DCC and Unc5c. 15811950_Raft localization of DCC is required for netrin-1-induced DCC-dependent ERK activation, and netrin-1-mediated axon outgrowth requires lipid raft integrity. 16158190_Review suggests possible roles of netrin-1 in nervous system development, neovascularisation, adhesion and tumorigenesis. 16181408_Ligand-mediated down-regulation of deleted in colorectal cancer might participate in loss of netrin-responsiveness in developing nervous system. 16203981_Endothelial expression of netrin-1 may inhibit basal cell migration into tissues and its down-regulation with the onset of sepsis/inflammation may facilitate leukocyte recruitment. 18253061_Both deleted in colorectal cancer (DCC) and neogenin become tyrosine phosphorylated in cortical neurons in response to netrin-1. 18353983_Netrin-1 expression observed in a large fraction of human metastatic breast tumors confers a selective advantage for tumor cell survival. 18400890_Although cAMP can alter response of axons to netrin-1, we conclude that netrin-1 does not alter cAMP levels in axons attracted by this cue and that soluble adenyl cyclase is not required for axon attraction to netrin-1. 18439993_Data show that Netrin-1 expressing cells inhibited angiogenic sprouting of unc5b expressing blood vessels, but had no pro-angiogenic activity at any stage of development examined. 18455953_In adults, decreased expression within the spinal cord injury lesion; likely an inhibitor of regenerating neural progenitors 18469807_PIKE-L acts as a downstream survival effector for netrin-1 through UNC5B in the nervous system 18653556_Netrin 1, through its receptor DCC, inhibits RhoA in embryonic spinal commissural neurons. 18692059_NF-kappaB activation that occurs in response to inflammation confers a selective advantage for tumor development through NF-kappaB-mediated netrin-1 up-regulation 18796601_netrin-1 is not only an attractive cue for developing commissural axons but also promotes their survival 18922894_the transcriptionally active TAp73alpha tumor suppressor is implicated in the apoptosis induced by netrin-1 in a p53-independent and DCC/ubiquitin-proteasome dependent manner. 19122655_HIF-1alpha-dependent induction of netrin-1 attenuates hypoxia-elicited inflammation at mucosal surfaces 19211441_High levels of netrin-1 found in 43 of the 92 NSCLC tumor samples. Interference with netrin-1 in human lung cancer cell lines was associated with UNC5H-mediated cell death in vitro and with tumor growth inhibition and/or regression in xenografted mice. 19349462_Netrin-1 up-regulation is a potential marker for poor prognosis in stage 4 neueroblastoma in infants. 19822088_Netrin-1 inhibited migration of synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthitis. 19826074_Netrin-1 protein functions might vary with its localization in the placenta and probably with time of gestation. 19940358_Study suggests that Netrin-1 promotes melanoma cell invasion and migration and therefore has an important role in the progression of malignant melanoma. 20007677_Netrin-1 is an early, predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiopulmnoary bypass. 20029409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20036673_Netrin-1 has a role in cardioprotection 20075388_Pulmonary netrin-1 levels are repressed during acute lung injury. 20080097_Netrin-1 might be an important regulator of pancreatic tumor growth that functions in tumor and endothelial cells. 20305387_Data propose that induction of netrin-1 expression via NFkappaB in inflammatory bowel diseases patients could affect colorectal tumor promotion and progression 20609112_our findings might indicate also an important role for DCC and netrin-1 in human foetal central nervous system development 20620466_Urinary netrin-1 levels are increased in patients with various forms of acute kidney injury, and may therefore serve as a biomarker. 21193949_Netrin-1 may regulate the development of placental vessels and plays a key role in the pathogenesis of fetal growth restriction. 21303223_Plasma netrin-1 can be used as diagnostic biomarker of many human cancers. 21505994_Netrin-1 enhanced the viability, migration and tube formation of human placental microvascular endothelial cells. 21733374_Gene silencing of netrin-1 could inhibit viability, proliferation, migration, and tubal formation of HUVECs, and placental angiogenesis. 21740336_Properties and perspectives of uNGAL and Netrin-1 for their appropriate clinical utilization. 21789787_overexpression is predictive of ovarian malignancies 21980448_an autocrine function for netrin-1 and netrin-3 in U87 and U373 cells that slows migration 22231519_It was shown that netrin-1 was secreted by macrophages in human and mouse atheroma, where it inactivated macrophage migration out of atherosclerotic plaques. 22252496_Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 controls the expression of the uncoordinated-5-B receptor, but not of netrin-1, in first trimester human placenta 22332546_netrin-1 protein expression may be related to tumorigenesis and tumor progression of gastric cancer. 22588384_Netrin-1 and DCC are increased in diseased lumbar intervertebral discs and may play a role in the process of neurovascular growth. 22685302_knockdown of DSCAM inhibits netrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of UNC5C and Fyn as well as the interaction of UNC5C with Fyn. The double knockdown of both receptors abolishes the induction of Fyn tyrosine phosphorylation by netrin-1 22779713_Netrin 1 gene mutation found in patients diagnosed with superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome. 22871610_Data indicate that DeltaN-netrin-1 stimulated cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. 22889408_There was no relationship between the basal netrin-1 and decline in netrin-1 concentrations and the progression-free survival and overall survival in gastric cancer. 23195957_Netrin-1 promotes glioblastoma cell invasiveness and angiogenesis by multiple pathways including activation of RhoA, cathepsin B, and cAMP-response element-binding protein 23512105_In addition, eight genes classified as 'second tier' hits in the original study (PAX7, THADA, COL8A1/FILIP1L, DCAF4L2, GADD45G, NTN1, RBFOX3 and FOXE1) showed evidence of linkage and association in this replication sample. 23526078_Netrin-1 was upregulated in kidney carcinoma. 23538444_Netrin-1 protects hypoxia-induced mitochondrial apoptosis through HSP27 expression via DCC- and integrin alpha6beta4-dependent Akt, GSK-3beta, and HSF-1 in mesenchymal stem cells. 23549787_netrin-1 forms a complex with both Notch2 and Jagged1. 23666553_Higher netrin-1 and lower UNC5B expression in all prostate carcinoma cell lines indicated that netrin-1 and UNC5B could be used to predict metastasis. 24092381_Tubular atrophy and low netrin-1 gene expression are associated with delayed kidney allograft function. 24122613_Data indicate that dysregulation of expression of netrin-1 NTN1 in smooth muscle cell (SMC) and its chemorepulsive receptor UNC5B in macrophages are involved in the development of atherosclerosis and unstable plaques. 24174661_Netrin-1 increases the frequency and amplitude of excitatory postsynaptic p otentials (EPSPs) recorded from cortical pyramidal neurons. 24262644_promotes angiogenesis and accelerates atherosclerosis, protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury, and reduces the infarct size. 24293316_The netrin-1 upregulation which appears to be p53-dependent is a survival mechanism as netrin-1 silencing by siRNA is associated with a potentiation of cancer cell death upon Doxorubicin treatment. 24338005_Studies indicate that elevating netrin-1 expression increased migration and invasion in colorectal cancer cells. 24442237_These results suggest that in hypoxic HCC cells, netrin-1 activates downstream signaling pathways to induce EMT activation with subsequent production of multiple inflammatory mediators which in turn promotes cancer invasion. 24528886_In bladder cancer cells, netrin-1 expression is increased compared to control cells. 24584118_Netrin-1 is highly expressed in obese but not lean adipose tissue, where it directs the retention of macrophages, promoting inflammation. NTN1 also promotes insulin resistance. 24647424_Data indicate both total and nuclear netrin-1 expression as prognostic factors in brain metastases patients in contrast to other prognostic markers in oncology such as patient age, number of brain metastases or Ki67 proliferation index. 24716747_Increased maternal netrin-4 levels in IUGR neonates may reflect in utero hypoxia, while the negative correlations between fetal netrin-1 and -4 levels may exert the dynamic balance between their angio- and anti-angiogenic properties. 24738865_Ntn-1 induces MMP-12-dependent E-cad degradation via the distinct activation of PKCalpha and FAK/Fyn, which is necessary to govern the activation of ERK, JNK, and NF-KB in promoting motility of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 24778312_novel model for the spatial regulation of axon branching by Netrin-1, in which localized plasma membrane expansion occurs via TRIM9-dependent regulation of SNARE-mediated vesicle fusion. 24812271_Netrin-1 promotes medulloblastoma cell invasiveness and angiogenesis, and demonstrates elevated expression in tumor tissue and urine of patients with pediatric medulloblastoma. 24827071_Netrin-1 ameliorates myocardial infarction-induced myocardial injury. 25001177_netrin-1 promoted pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by upregulation of murine double minute 2 (Mdm2). 25022751_results of another in vitro assay, in which endothelial cells were co-cultured with human fibroblasts, however, showed that Mel2a-netrin1 CM inhibited tube formation through blocking elongation and coalescence of human umbilical vein endothelial cells 25154466_early urinary biomarker in the diagnosis of septic acute kidney injury 25289643_These studies demonstrate that semaphorin 3A and netrin-1 can be useful early diagnostic biomarkers of AKI after liver transplantation. 25353184_Careful phenotyping of patients combined with molecular and functional studies in zebrafish identifed netrin-1 as a potential shared genetic factor for cardiac and thyroid congenital defects. 25483983_These results identify Netrin-1 as a key regulator of osteoclast differentiation that may be a new target for bone therapies. 25569157_Investigation of the mechanisms that trigger local translation revealed a role for calcium-dependent retrograde netrin-1/DCC receptor signaling. 25903786_results demonstrate that netrin 1 is an important regulator of blood-brain barrier maintenance that protects the central nervous system against inflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis. 25950802_NTN1-DCC pathway contains targets of FDA-approved drugs and may offer promise for guiding applied clinical research on preventive and therapeutic interventions for AMD 26039999_Netrin-1 stimulates phosphatase 1A to dephosphorylate YAP, which leads to decreased ubiquitination and degradation, enhancing YAP accumulation and signaling 26393880_MUC4 has a role in promoting neural invasion mediated by the axon guidance factor Netrin-1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 26573873_Akt-FoxO1 signaling pathway plays an essential role during liver regeneration 26749424_Enhanced detection of netrin-1-expressing CD14(low) cells in patients with systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease was observed, and antibody-mediated netrin-1 neutralization attenuated detection of fibrocytes in all settings. 26859457_identify the V-2 domain of netrin-1 to be important for its interaction with the Ig1/Ig2 domains of UNC5H2 26944719_High Plasma netrin-1 levels are associated with peripheral artery disease in smokers. 27031829_Netrin-1 enhanced infectivity of hepatitis C virus particles and promoted viral entry by increasing the activation and decreasing the recycling of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a protein that is dysregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. 27060954_Netrin-1 reduced the Abeta1- 40-induced Abeta1-42 increase, increased sAbetaPPalpha, and reversed the Abeta-induced sAbetaPPalpha decrease in vitro 27067437_Data show that netrin-1 concentrations elevated in advanced non-small cell lung cancer compared to a healthy control group, and netrin-1 concentrations decreased with chemotherapy. 27087488_Data suggest that urinary netrin-1 may be a new biomarker for determining early tubular injury in obese children. 27400127_netrin-1 degradation products are capable of modulating vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy 27422368_NETRIN1 signaling pathway is identified as a candidate pathway for major depressive disorder and should be explored in further large population studies. 27651158_cell proliferation and survival were decreased following targeted deletion of Netrin-1. Cell invasion was dramatically diminished in Netrin-1 knockdown Glioblastoma stem cells. Moreover, Netrin-1 knockdown Glioblastoma stem cells exhibited less proangiogenic activity. 27727089_Our study has shown an increase in netrin-1 expression that could be linked with macrophage infiltration and polarization in the epicardial adipose tissue of patients with coronary artery disease 27793362_upregulation of netrin-1 expression in different forms of cancer, and the increased expression of netrin-1 has been linked to its functions as a survival and invasion promoting factor. 27815019_that netrin-1 may function as a positive regulator of hypoxia-triggered malignant behavior in prostate cancer by activating the Yes-associated protein signaling 28069038_Results demonstrate that NTN1 is an important regulator of stemness and motility of glioblastoma cells. Furthermore, it deciphers a novel mechanism where NTN1 activates Notch signaling and subsequent stemness in invasive glioblastoma cells. 28241866_Netrin-1 acts as a non-canonical angiogenic factor produced by human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells. 28250059_Netrin-1 restores cell injury and impaired angiogenesis in vascular endothelial cells upon high glucose via PI3K/AKT-eNOS signaling. 28443497_we review the Netrin-1 mediated regulation of cancer, its potential use as a biomarker, and the targeting of the Netrin-1 pathway to treat cancers 28475012_Our observations revealed that SOX6 is a tumor suppressor in ovarian cancer cells, and SOX6 exerts an inhibitory effect on the proliferation, invasion, and tumor cell-induced angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells, whereas nerin-1 plays an opposite role and its expression is inversely correlated with SOX6. 28489749_NTN1 rs9788972 is identified as a risk locus for nonsyndromic orofacial clefts susceptibility in a northern Chinese population; SNPs in PAX7 were not associated with any increased risk 28677863_Netrin-1 decreased in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and in multiple sclerosis patients, mainly during relapse, suggesting an anti-inflammatory role of netrin-1 28704853_Conclusion RBP4 may be used as a predictive factor of diabetic nephropathy patients complicated with silent cerebral infarction (SCI) and is positively correlated with cognitive dysfunction. RBP4/Lp-PLA2/Netrin-1 pathway activation may be one of the occurrence mechanisms in diabetic nephropathy complicated with SCI. 28945198_Three mutations in exon 7 of NTN1 in 2 unrelated families and 1 sporadic case with isolated congenital mirror movements (CMM), a disorder characterized by involuntary movements of one hand that mirror intentional movements of the opposite hand. 29199452_increased concentrations of urinary SEMA-3A and urinary Netrin-1 are found in urine from children with severe hydronephrosis and that their concentrations are related to the degree of obstruction. 29202173_This study implicates DCC and NTN1 mutations in the pathophysiology of CHH consistent with the role of these two genes in the ontogeny of GnRH neurons in mice. 29234153_the current data suggest that netrin-1 can act as a pro-metastatic factor in NSCLC by enhancing cell invasion, migration, and VM via PI3K/AKT and ERK-mediated EMT process, thereby implicating netrin-1 as a novel promising therapeutic target against aggressive non-small cell lung cancer. 29277614_Such data indicate that cooperation between the UPR and UNC5A depletion as previously observed by ourselves in HCC patients samples may foster liver cancer development and growth. 29297981_Four genes-ACT1, PIN1, DNMT1 and NTN1-emerged as having roles in pathways that may influence Primary Biliary Cholangitis pathogenesis in British Columbia First Nations people. 29305865_Collectively, our results defined netrin-1 as a positive regulator of malignant tumor metastasis in GC by activating the YAP signaling, with potential implications for new approaches to GC therapy. 29328435_miR214 reduces chemoresistance by targeting netrin1 in bladder cancer cell lines. 30106432_High NTN1 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 30197049_Findings indicate that variation in the NETRIN1 signaling pathway may confer risk for major depressive disorder through effects on a number of white matter tracts. 30402937_The GxE interaction analysis revealed a significant interaction between maternal environmental contact with agrotoxics and rs16969816 (OR: 0.25, 95% CI: 0.08-0.74, p = .01), and pairwise interaction test with NTN1 rs1880646 yielded significant p values in the 1,000 permutation test for rs16969681, rs16969816, and rs16969862. 30479344_netrin-1 as a major signal that mediates the dynamic crosstalk between inflammation and chronic erosion of the extracellular matrix in Abdominal aortic aneurysm, is reported. 30506619_Our study suggested allele G at rs4791774 in NTN1 gene is risk of NSCLO, which could greatly increase the risk to have a baby with cleft. 30578605_rs4791774 exhibited a nominal association with missing of maxillary canine and premolar. 30719925_We found a significantly higher netrin-1 level in patients with CO poisoning. However, we were unable to find any significant difference in the patients with neurological involvement with respect to netrin-1 level, netrin-1 may present subclinically neurological effects. Therefore, we believe that netrin-1 cannot be used as a marker of CO poisoning severity. 30852966_Elevated serum netrin-1 levels were associated with improved prognosis at 3 months after ischemic stroke, suggesting that serum netrin-1 may be a potential prognostic biomarker for ischemic stroke. 30968155_Netrin1 mediated epithelialmesenchymal transition of A549 and PC9 cells in vitro, which may be associated with the PI3K/AKT pathway. This effect was not observed under normoxic conditions. Serum concentration of netrin1 was found to be significantly higher in nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients compared with healthy donors. Findings highlight a novel role for netrin1 in NSCLC development under hypoxia. 31047878_Serum netrin-1 might represent a potential biomarker for reflecting severity, inflammation and prognosis of human aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. 31088838_Netrin-1, a navigation cue during embryonic development, is upregulated in cancer-associated fibroblasts and regulates cancer cell stemness. 31162046_We further provide a combination of protein localisation and phenotypic evidence in chick, humans, mice and zebrafish that Netrin-1 has an evolutionarily conserved and essential requirement for f optic fissure closure (OFC), and is likely to have an important role in palate fusion. 31219796_High netrin-1 levels are associated with early diabetic kidney injury in type 1 diabetes. 31226147_Human TUBB3 mutations specifically perturb netrin-1/UNC5C-mediated repulsion. 31407237_The authors suggest that Netrin-1 enhances N-cadherin junctions to promote liver cancer cell collective migration in 3D cell culture and may subsequently increase liver cancer metastasis. 31769036_Netrin-1 and its receptor Unc5b may have essential roles in periodontal inflammation 31780810_The functional variant of NTN1 contributes to the risk of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 31806640_Netrin-1 and Its Receptor DCC Are Causally Implicated in Melanoma Progression. 31953174_Macrophage-derived netrin-1 is critical for neuroangiogenesis in endometriosis. 32151395_The identification and function of a Netrin-1 mutation in a pedigree with premature atherosclerosis. 32228196_Serum netrin-1 levels at presentation and delayed neurological sequelae in unintentional carbon monoxide poisoning. 32231305_Netrin-1 promotes naive pluripotency through Neo1 and Unc5b co-regulation of Wnt and MAPK signaling. 32267322_High Serum Netrin-1 and IL-1beta in Elderly Females with ACS: Worse Prognosis in 2-years Follow-up.', trans 'Niveis Elevados de Netrina-1 e IL-1beta em Mulheres Idosas com SCA: Pior Prognostico no Acompanhamento de Dois Anos. 32319367_is abnormal expression of Netrin-1 in serum of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia 32417215_Serum netrin-1 concentrations are associated with clinical outcome in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. 32474463_Serum netrin-1 as a biomarker for colorectal cancer detection. 32912541_Decreased Serum Netrin-1 as a Predictor for Post-Stroke Depression in Chinese Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. 32917498_Decreased serum netrin-1 is associated with ischemic stroke: A case-control study. 32926844_IGF2BP1 silencing inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of high glucose-induced non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating Netrin-1. 33095273_Growth cone repulsion to Netrin-1 depends on lipid raft microdomains enriched in UNC5 receptors. 33351190_Netrin-1 and its receptor DCC modulate survival and death of dopamine neurons and Parkinson's disease features. 33546947_Association between serum netrin-1 and prognosis of ischemic stroke: The role of lipid component levels. 33741358_Serum netrin-1 as a potential biomarker for functional outcome of traumatic brain injury. 34470826_Delta40p53 isoform up-regulates netrin-1/UNC5B expression and potentiates netrin-1 pro-oncogenic activity. 34569430_Serum Netrin-1 and Urinary KIM-1 levels as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of early preeclampsia. 34585999_Netrin-1 expression and targeting in multiple myeloma. 35063900_The role of serum netrin-1 level in the detection of early-onset preeclampsia. 35188847_Two Useful Umbilical Biomarkers for Therapeutic Hypothermia Decision in Patients with Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy with Perinatal Asphyxia: Netrin-1 and Neuron Specific Enolase. 35236266_Netrin-1 in Post-stroke Neuroprotection: Beyond Axon Guidance Cue. 35485895_[Netrin-1, a novel antitumoral target].', trans 'La netrine-1, une nouvelle cible antitumorale. 35489200_Inactivation of axon guidance molecule netrin-1 in human colorectal cancer by an epigenetic mechanism. 35493300_Netrin-1: A Serum Marker Predicting Cognitive Impairment after Spinal Cord Injury. 35779428_Rs9891446 in NTN1 is associated with right-side cleft lip in Han Chinese population. 35974411_Netrin-1 induces the anti-apoptotic and pro-survival effects of B-ALL cells through the Unc5b-MAPK axis. 35981361_[Effect of Netrin-1 on VEGFA Expression in T-ALL Cells and Its Related Mechanism]. 36093435_Exosomal lncRNA PCAT1 Promotes Tumor Circulating Cell-Mediated Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis by Regulating the Activity of the miR-329-3p/Netrin-1-CD146 Complex. 36297056_Netrin-1 Promotes Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity and Is Associated with Insulin Resistance. 36361539_Netrin-1 Stimulates Migration of Neogenin Expressing Aggressive Melanoma Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000020902 |
Ntn1 |
13.438712 |
5.9206997778 |
2.565768 |
0.513446034 |
27.617266 |
0.00000014785310228225413536850792791538244941307311819400638341903686523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000573537921073868911147535052524881749036467226687818765640258789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.5219783 |
8.0293953 |
3.9996297 |
1.1721187 |
| ENSG00000065357 |
1606 |
DGKA |
protein_coding |
P23743 |
FUNCTION: Diacylglycerol kinase that converts diacylglycerol/DAG into phosphatidic acid/phosphatidate/PA and regulates the respective levels of these two bioactive lipids (PubMed:2175712, PubMed:15544348). Thereby, acts as a central switch between the signaling pathways activated by these second messengers with different cellular targets and opposite effects in numerous biological processes (PubMed:2175712, PubMed:15544348). Also plays an important role in the biosynthesis of complex lipids (Probable). Can also phosphorylate 1-alkyl-2-acylglycerol in vitro as efficiently as diacylglycerol provided it contains an arachidonoyl group (PubMed:15544348). Also involved in the production of alkyl-lysophosphatidic acid, another bioactive lipid, through the phosphorylation of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl glycerol (PubMed:22627129). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15544348, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2175712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22627129, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; glycerolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:15544348, ECO:0000305|PubMed:2175712, ECO:0000305|PubMed:22627129}. |
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the eukaryotic diacylglycerol kinase family. It acts as a modulator that competes with protein kinase C for the second messenger diacylglycerol in intracellular signaling pathways. It also plays an important role in the resynthesis of phosphatidylinositols and phosphorylating diacylglycerol to phosphatidic acid. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2017]. |
hsa:1606; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; diacylglycerol kinase activity [GO:0004143]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; diacylglycerol metabolic process [GO:0046339]; glycerolipid metabolic process [GO:0046486]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lipid phosphorylation [GO:0046834]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205] |
14734770_Defects in both polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) transendothelial migration and PMN diacylglycerol kinase alpha signaling are implicated as disordered functions in subjects with localized aggressive periodontitis. 15117825_PPARgamma agonists upregulate DGKalpha production.This suppresses the diacylglycerol/protein-kinase-C signaling pathway. 15870081_DGKalpha is crucial for the control of cell activation and also for the regulation of the secretion of lethal exosomes, which in turn controls cell death. 15928040_ALK-mediated alphaDGK activation is dependent on p60src tyrosine kinase, with which alphaDGK forms a complex; alphaDGK activation is involved in the control of ALK-mediated mitogenic properties. 17276726_These results strongly suggest that DGKalpha is a novel positive regulator of NF-kappaB, which suppresses TNF-alpha-induced melanoma cell apoptosis. 17911109_diacylglycerol kinase alpha-conserved domains have a role in membrane targeting in intact T cells 18004883_2,3-dioleoylglycerol binds to a site on the alpha and zeta isoforms of diacylglycerol kinase that is exposed as a consequence of the substrate binding to the active site. 18424699_Lck-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of diacylglycerol kinase alpha regulates its membrane association in T cells.( 19751727_These results strongly suggest that DGKalpha positively regulates TNF-alpha-dependent NF-kappaB activation via the PKCzeta-mediated Ser311 phosphorylation of p65/RelA. 21252909_Diacylglycerol kinase alpha is a key regulator of the polarised secretion of exosomes. 21493725_findings further suggest that DGL-alpha and -beta may regulate neurite outgrowth by engaging temporally and spatially distinct molecular pathways 22048771_SAP-mediated inhibition of DGKalpha sustains diacylglycerol signaling, thereby regulating T cell activation 22271650_Antigen-specific CD8-positive T cells from DGKalpha-deficient transgenic mice show enhanced expansion and increased cytokine production after lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, yet DGK-deficient memory CD8+ T cells exhibit impaired expansion. 22425622_DGKalpha is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activation of the MAPK pathway. 22573804_DGK-alpha was more highly expressed in CD8-tumor-infiltrating T cellscompared with that in CD8non-tumor kidney-infiltrating lymphocytes. 24158111_High diacylglycerol kinase alpha expression is associated with glioblastoma. 24887021_These data indicates the existence of a SDF-1alpha induced DGKalpha - atypical PKC - beta1 integrin signaling pathway, which is essential for matrix invasion of carcinoma cells. 25248744_DGKalpha generates phosphatidic acid to drive its own recruitment to tubular recycling endosomes via its interaction with MICAL-L1 25921290_Redundant and specialized roles for diacylglycerol kinases alpha and zeta in the control of T cell functions. 26420856_An abandoned compound that also inhibits serotonin receptors may have more translational potential as a DGKa inhibitor, but more potent and specific DGKa inhibitors are sorely needed 26964756_Decreased DNA methylation at this enhancer enables recruitment of the profibrotic transcription factor early growth response 1 (EGR1) and facilitates radiation-induced DGKA transcription in cells from patients later developing fibrosis. 27498782_LIPFDGKA might serve as a potential possible biomarkers for diagnosis of gastric cancer, and their downregulation may bring new perspective into the investigation of gastric cancer prognosis 27697466_Diacylglycerol kinases alpha and zeta are up-regulated in cancer in cancer, and contribute towards tumor immune evasion and T cells clonal anergy. (Review) 27731506_DGKalpha isoform is highly expressed in the nuclei of human erythroleukemia cell line K562, and its nuclear activity drives K562 cells through the G1/S transition during cell cycle progression. 29967261_This novel study demonstrates efficient ablation of diacylglycerol kinase in human CAR-T cells that leads to improved antitumor immunity and may have significant impact in human cancer immunotherapy 30653270_This study presents the first crystal structure of EF-hand domains of diacylglycerol kinase alpha in its Ca(2+) bound form and characterize Ca(2+) -induced conformational changes, which likely regulates intra-molecular interactions. 31766109_Upon neutrophil stimulation, DGK-alpha activation is necessary for migration and a productive response. This paper focuses on the role of DGK-alpha in obstructive respiratory diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but also rare genetic diseases such as alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. [review] 32341033_DGKA Provides Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer Through Activation of c-JUN-WEE1 Signaling. 32345612_Diacylglycerol kinases regulate TRPV1 channel activity. 33608256_DGKA Mediates Resistance to PD-1 Blockade. 34293268_Diacylglycerol Kinase Inhibition Reduces Airway Contraction by Negative Feedback Regulation of Gq-Signaling. 35131384_DGKA interacts with SRC/FAK to promote the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000025357 |
Dgka |
53.016066 |
0.4122103073 |
-1.278548 |
0.338353812 |
13.990535 |
0.00018373317661624696123245925605260708834975957870483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000484700927051975893368462866561685586930252611637115478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.0908169 |
7.5306366 |
83.4795930 |
12.7133764 |
| ENSG00000065665 |
55176 |
SEC61A2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H9S3 |
FUNCTION: Appears to play a crucial role in the insertion of secretory and membrane polypeptides into the ER. It is required for assembly of membrane and secretory proteins. Found to be tightly associated with membrane-bound ribosomes, either directly or through adaptor proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Translocation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has similarity to a mouse protein which suggests a role in the insertion of secretory and membrane polypeptides into the endoplasmic reticulum. It may also be required for the assembly of membrane and secretory proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:55176; |
Sec61 translocon complex [GO:0005784]; protein transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008320]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; signal sequence binding [GO:0005048]; post-translational protein targeting to membrane, translocation [GO:0031204]; SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation [GO:0006616] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000025816 |
Sec61a2 |
65.868471 |
0.4369195517 |
-1.194560 |
0.245801902 |
23.455501 |
0.00000127836660104382631522612363134117074991991103161126375198364257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004470194511112740177864212365310692121056490577757358551025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.9671290 |
6.5780500 |
94.6822924 |
10.5127557 |
| ENSG00000065802 |
51665 |
ASB1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y576 |
FUNCTION: Probable substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin-Cullin-SOCS-box protein) E3 ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:16325183). Mediates Notch-induced ubiquitination and degradation of TCF3/E2A and JAK2 (PubMed:21119685). May play a role in testis development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WV74, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16325183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21119685}. |
ANK repeat;Developmental protein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
The protein encoded by this gene contains an ankyrin repeat sequence and SOCS box domain. The SOCS box serves to couple suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS) proteins and their binding partners with the elongin B and C complex, targeting them for ubiquitination and degradation. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:51665; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28540928_Epigenetic regulation of the stress-responsive Asb1 gene in anxiety-related phenotypes. |
ENSMUSG00000026311 |
Asb1 |
345.851214 |
3.1830950329 |
1.670430 |
0.178604075 |
84.187363 |
0.00000000000000000004500380625180494948262860554111079729566145486473947813152451935536646487889811396598815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000400395527592911976664040340253557299177900819839897770223424711133475284441374242305755615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
479.1694396 |
52.6541429 |
151.5052630 |
12.4270567 |
| ENSG00000065833 |
4199 |
ME1 |
protein_coding |
P48163 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of (S)-malate in the presence of NADP(+) and divalent metal ions, and decarboxylation of oxaloacetate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7622060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7757881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8187880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8804575}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a cytosolic, NADP-dependent enzyme that generates NADPH for fatty acid biosynthesis. The activity of this enzyme, the reversible oxidative decarboxylation of malate, links the glycolytic and citric acid cycles. The regulation of expression for this gene is complex. Increased expression can result from elevated levels of thyroid hormones or by higher proportions of carbohydrates in the diet. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4199; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NAD+) activity [GO:0004471]; malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NADP+) activity [GO:0004473]; malic enzyme activity [GO:0004470]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; NAD binding [GO:0051287]; NADP binding [GO:0050661]; oxaloacetate decarboxylase activity [GO:0008948]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; malate metabolic process [GO:0006108]; NADH metabolic process [GO:0006734]; NADP metabolic process [GO:0006739]; nucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0009165]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; pyruvate metabolic process [GO:0006090]; regulation of NADP metabolic process [GO:1902031]; response to carbohydrate [GO:0009743]; response to hormone [GO:0009725] |
11352855_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16757477_that the single mutation of Gln362 to Lys in human m-NAD-ME changes it to an NADP+-dependent enzyme, which is characteristic because it is non-allosteric, non-cooperative, and NADP+-specific 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19293334_although ME1 overexpression augments anaplerosis and glucose stimulated insulin secretion in INS-1 832/13 cells, it is not likely involved in methyl succinate and glucose stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic islets 19416979_human c-NADP-ME exists mainly as a tetramer, whereas human m-NAD(P)-ME exists as a mixture of dimers and tetramers 19464998_A series of R98/D102 mutants examined the possible interactions between Arg98 and Asp102 using double-mutant cycle analysis. Kinetic analysis revealed that the catalytic efficiency of was severely affected by mutating both Arg98 and Asp102 residues. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21555518_ME1 is a functional target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq and knockdown analysis in HEK 293 cells. 22456781_cytosolic malic enzyme 1 gene polymorphism is associated with the degree of suppression of parathyroid hormone after long-term calcium supplementation; the effect is probably mediated through an increase in intestinal calcium absorption 23114090_essential role for ME1 in the production of cytosolic NADPH and maintenance of migratory and invasive abilities of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells 23284632_the differential protein stability between dimer and tetramer interface interactions of human c-NADP-ME 23334421_p53 represses the expression of the tricarboxylic-acid-cycle-associated malic enzymes ME1 and ME2 in human and mouse cells 25753478_ME1 overexpression associates with unfavorable prognoses in patients with HCC, suggesting that ME1 is a poor prognostic predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma. 26173780_ME1 expression was found to be mutant-KRAS-associated in NSCLC cancer cell lines. Patients with elevated ME1 had worse outcomes after radiotherapy. Transamination generating cytosolic NADPH via ME1 may contribute to radioresistance. 26381116_ME1/ME2 expression phenotype may have a potential to be a valuable marker for sebaceous differentiation in sebaceous lesions. 28475173_The critical roles of miR-30a and ME1 in the development of KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer indicate therapy potentials for this subtype of cancer. 28848047_these findings uncover a direct cross-talk mechanism between ME1 and PPP, may reveal an alternative model for signaling transduction via protein conformational simulation, and pave the way for better understanding how metabolic pathways are coordinated in cancer. 29601126_Findings indicate that malic enzyme 1 (ME1) is a valid target for molecular therapy in oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCCs). 29620192_Bioinformatics analysis identified that miR612 targeted ME1, which expression was high and inversely associated with miR612 expression in bladder cancer tissues. 29654155_results shed light on crucial roles of ME1-mediated production of NADPH in gastric cancer growth and metastasis 30250042_A small molecule inhibitor of ME1 suppressed growth of human CRC cells in vitro, but had little effect on normal rat intestinal epithelial cells. Targeting of ME1 may add to the armentarium of therapies for cancers of the gastrointestinal tract. 30425310_ME1 promotes basal-like breast cancer progression and associates with poor prognosis 31735643_In which ME1 transcripts are upregulated. 32998265_Malic Enzyme 1 Is Associated with Tumor Budding in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas. 33619771_Adaptive and Constitutive Activations of Malic Enzymes Confer Liver Cancer Multilayered Protection Against Reactive Oxygen Species. 33751897_miR-885-5p Inhibits Invasion and Metastasis in Gastric Cancer by Targeting Malic Enzyme 1. 35727698_Targeting Ferroptosis Vulnerability in Synovial Sarcoma: Is It All About ME1? |
ENSMUSG00000032418 |
Me1 |
222.171230 |
6.0573767489 |
2.598693 |
0.128281711 |
450.727547 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000050093517513614350396335923454211333804859621532666229585327605822650054188421961178989762622961785587707170739014368611432405966495199401558950987879836098935137279073662106334300702570808389558762355174858571676409119203495306494 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000021185682478537187037405763789103428797847348321437475282534707188731122361934974821104877845607079926846508873528966464713469723552627638473231388968378664502729263827535150545611186255138303870913418942388827243909276520970698512 |
Yes |
No |
384.5705640 |
29.4693265 |
63.9635405 |
4.3460156 |
| ENSG00000065911 |
10797 |
MTHFD2 |
protein_coding |
P13995 |
FUNCTION: Although its dehydrogenase activity is NAD-specific, it can also utilize NADP at a reduced efficiency. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16100107}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Magnesium;Mitochondrion;Multifunctional enzyme;NAD;NADP;One-carbon metabolism;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial bifunctional enzyme with methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase and methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activities. The enzyme functions as a homodimer and is unique in its absolute requirement for magnesium and inorganic phosphate. Formation of the enzyme-magnesium complex allows binding of NAD. Alternative splicing results in two different transcripts, one protein-coding and the other not protein-coding. This gene has a pseudogene on chromosome 7. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:10797; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activity [GO:0004477]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004487]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0004488]; phosphate ion binding [GO:0042301]; folic acid metabolic process [GO:0046655]; tetrahydrofolate interconversion [GO:0035999]; tetrahydrofolate metabolic process [GO:0046653] |
18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18830263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19493349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23295955_Data indicate that the reduced vimentin expression in response to EPHB4, WIPF2 and MTHFD2 silencing was observed at mRNA and protein levels. 24451681_The highest scoring pathway is mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism and is centred on MTHFD2. 24870594_Data indicate that methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP + -dependent) 2 (MTHFD2)was differentially expressed in breast cancer tissue, suggesting as a prognostic factor and a potential therapeutic target for future breast cancer treatments. 26461067_These findings suggest a previously unknown role for MTHFD2 in cancer cell proliferation, adding to its known function in mitochondrial folate metabolism. 27257051_siRNA-mediated silencing of MTHFD2 inhibited migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines, but no obvious effects on cell proliferation, apoptosis or cell cycle distribution were detected. MTHFD2 is overexpressed in HCC, and is associated with poor prognosis and cellular features connected to metastatic disease. 27315223_metabolic alterations in MCF7 cells observed as a consequence of MTHFD2 suppression 27325891_Mechanistically, MYC regulates the expression of MTHFD2, and MTHFD2 knockdown suppresses the TCA cycle. 27899380_crystal structure of MTHFD2 in complex with a substrate-based inhibitor and the enzyme cofactors NAD(+) and inorganic phosphate. 28059050_miR-92a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by directly regulating MTHFD2 expression in AML. 29895827_endothelial cells undergo MTHFD2-mediated reprogramming toward serine-glycine and mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism to compensate for the loss of ATP in response to oxidized phospholipids during atherosclerosis 30466107_Knocking down MTHFD2 expression in renal cell carcinoma cells, decreased cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were observed and accompanied by the reduced expression of vimentin. 30532069_Therapies targeting MTHFD2 may eradicate tumors and prevent recurrence. 31209892_MicroRNA-33a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer cell growth by inhibiting MTHFD2. 31289360_MTHFD2 links RNA methylation status to the metabolic state of tumor cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma. 31377316_Cancer cells retain expression of both MTHFD isozymes, but only MTHFD2 displays prominent upregulation in cancer. 31624245_Combinatorial targeting of MTHFD2 and PAICS in purine synthesis as a novel therapeutic strategy. 31778025_Down-regulation of MTHFD2 inhibits NSCLC progression by suppressing cycle-related genes. 32088725_High Expression of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase 2 (MTHFD2) in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and its Clinical Prognostic Significance. 32880830_Detection and characterisation of novel alternative splicing variants of the mitochondrial folate enzyme MTHFD2. 32925794_Identification of MTHFD2 as a novel prognosis biomarker in esophageal carcinoma patients based on transcriptomic data and methylation profiling. 33015789_Clinical significance of circ-MTHFD2 in diagnosis, pathological staging and prognosis of NSCLC. 33468252_Glioma cells require one-carbon metabolism to survive glutamine starvation. 33782411_The folate cycle enzyme MTHFD2 induces cancer immune evasion through PD-L1 up-regulation. 34121323_MTHFD2 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma by regulating AKT/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signalling. 34231329_MTHFD2 promotes ovarian cancer growth and metastasis via activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. 34244426_p53 deficiency induces MTHFD2 transcription to promote cell proliferation and restrain DNA damage. 34632667_Non-metabolic function of MTHFD2 activates CDK2 in bladder cancer. 35135596_Up-regulation of MTHFD2 is associated with clinicopathological characteristics and poor survival in ovarian cancer, possibly by regulating MOB1A signaling. 35228749_Pharmacological targeting of MTHFD2 suppresses acute myeloid leukemia by inducing thymidine depletion and replication stress. 35349697_Deacetylation of MTHFD2 by SIRT4 senses stress signal to inhibit cancer cell growth by remodeling folate metabolism. 35894196_[Association of maternal MTHFD1 and MTHFD2 gene polymorphisms with congenital heart disease in offspring].', trans 'MTHFD1MTHFD2. 36051358_ATF4/MYC Regulates MTHFD2 to Promote NSCLC Progression by Mediating Redox Homeostasis. 36089117_Folate enzyme MTHFD2 links one-carbon metabolism to unfolded protein response in glioblastoma. 36131208_Metabolic collateral lethal target identification reveals MTHFD2 paralogue dependency in ovarian cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000005667 |
Mthfd2 |
694.005568 |
4.3131230156 |
2.108733 |
0.098281636 |
447.437806 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000260449446659939135131724127256592184404508424957616077634850644217274588777162470510244974050502804729763248115480867399049910819267279190875710603401533531816478502969879475706775740567871380226524234358730358460379775773187533415 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000109211188428997199491138097526695251792482975417271361198625408024683511447283990145799502365806358976750421621212597555462910143918808174618548076351299897341838979830882370703698133662138526513135298390762344676288705154964008797 |
Yes |
No |
1118.8619135 |
64.7157042 |
261.0098184 |
11.8154312 |
| ENSG00000066032 |
1496 |
CTNNA2 |
protein_coding |
P26232 |
FUNCTION: May function as a linker between cadherin adhesion receptors and the cytoskeleton to regulate cell-cell adhesion and differentiation in the nervous system (By similarity). Required for proper regulation of cortical neuronal migration and neurite growth (PubMed:30013181). It acts as negative regulator of Arp2/3 complex activity and Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization (PubMed:30013181). It thereby suppresses excessive actin branching which would impair neurite growth and stability (PubMed:30013181). Regulates morphological plasticity of synapses and cerebellar and hippocampal lamination during development. Functions in the control of startle modulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30013181}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Lissencephaly;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables actin filament binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin nucleation; regulation of neuron migration; and regulation of neuron projection development. Located in cytoplasm. Implicated in complex cortical dysplasia with other brain malformations. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1496; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; adherens junction [GO:0005912]; axon [GO:0030424]; catenin complex [GO:0016342]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; brain morphogenesis [GO:0048854]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; negative regulation of Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin nucleation [GO:0034316]; prepulse inhibition [GO:0060134]; radial glia guided migration of Purkinje cell [GO:0021942]; regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001222]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975]; regulation of synapse structural plasticity [GO:0051823] |
18163523_CTNNA2 is differentially regulated by smoking in schizophrenic patients. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18839057_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22833195_Common variants in CTNNA2 are associated with excitement-seeking and risk-taking. 24100690_CTNNA2 and CTNNA3 are tumor suppressor genes frequently mutated in laryngeal carcinomas. 25041903_CTNNA2 gene increases the risk of alcohol addiction in White women. 25824743_Single nucleotide polymorphism in CTNNA2 is associated with breast cancer susceptibility. 27167163_SNP 50-kb upstream from CTNNA2 was associated with impulsivity in Native American sample. 27497070_One association in the CTNNA2 gene on chromosome 2p12 [rs1567532, hazard ratio (HR) = 1.75, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.19-2.58, P = 0.005 for homozygotes for the minor allele] and one in the last intron of the RUNX2 gene on chromosome 6p21 (rs12209785, HR = 0.88, 95% CI 0.80-0.98, P = 0.014 for heterozygotes) are of particular relevance. These loci do not coincide with those that showed the strongest associations in t 28746715_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in CTNNA2 show associations in Schizophrenia and general cognitive function. 30526004_Novel-miR-4885 can bind to 3' untranslated region of CTNNA2 to reduce cell adhesion. |
ENSMUSG00000063063 |
Ctnna2 |
7.138147 |
0.2054853742 |
-2.282892 |
0.838429220 |
6.463279 |
0.01101262451749166100534171874869571183808147907257080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020949392689544647783161934739837306551635265350341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0266897 |
1.3133293 |
10.5482721 |
4.0080826 |
| ENSG00000066056 |
7075 |
TIE1 |
protein_coding |
P35590 |
FUNCTION: Transmembrane tyrosine-protein kinase that may modulate TEK/TIE2 activity and contribute to the regulation of angiogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20227369}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the tyrosine protein kinase family. The encoded protein plays a critical role in angiogenesis and blood vessel stability by inhibiting angiopoietin 1 signaling through the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Ectodomain cleavage of the encoded protein relieves inhibition of Tie2 and is mediated by multiple factors including vascular endothelial growth factor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:7075; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; branching involved in lymph vessel morphogenesis [GO:0060854]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; lymphatic endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060836]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; plasma membrane fusion [GO:0045026]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001936]; regulation of extracellular matrix assembly [GO:1901201]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; tissue remodeling [GO:0048771]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
11866538_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates the Tie-2:Tie-1 receptor complex 11920509_high expression independently associated with shorter survival in patients with early chronic phase CML 17724803_Results describe the expression of angiopoietin-1, 2 and 4 and Tie-1 and 2 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors, leiomyomas and schwannomas. 17728252_Activation of Tie1 ectodomain cleavage increases cartilage oligomeric protein angiopoietin 1 activation of Tie2. 17786322_Overexpression and activation of Tie1 is associated with breast and colonic neopalsms 18675456_the trophoblastic shell of the very early human placenta, as well as endothelial cells and ACC exhibited strong staining intensity for Tie-1 19236867_Tie-1 has an inflammatory function in endothelial cells. 19880500_A natural antisense transcript was identified for tyrosine kinase containing immunoglobulin and epidermal growth factor homology domain-1 (tie-1), tie-1AS long noncoding RNA in zebrafish, mouse, and humans. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164029_The Tie-1 immunoreactivity was dominantly observed in the heamangiogenic cells and cells cords, whereas the matured villi showed immunoreactivity only in other components. 20227369_Provide evidence for Tie1-Tie2 complex formation on the cell surface and identify molecular surface areas essential for recognition. The Tie1-Tie2 interactions are dynamic, inhibitory, and differentially modulated by angiopoietin-1 and -2. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22235284_the effects of factors activating ectodomain cleavage on both Tie1 and Tie2 within the same population of cells, and their impact on angiopoietin signalling 22342979_these results suggest that the expression level of Tie1 and its physical interaction with Tie2 defines whether Ang2 functions as a Tie2 agonist or antagonist, thereby determining the context-dependent differential endothelial sensitivity to Ang2. 22421998_Data propose that EndMT associated with Tie1 downregulation participates in the pathological development of stroma observed in tumours. 22987233_The decreasing expression of Tie1 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of primary lower extremity varicose veins. 26436659_T794A-expressing human umbilical vein endothelial cells formed significantly shorter tubes with fewer branches in three-dimensional Matrigel cultures, but did not alter Tie1 or Tie2 tyrosine phosphorylation or downstream signaling. 26489611_The inhibition of Tie-2 exerted by Tie-1can be relieved by Tie-1 ectodomain cleavage mediated by tumor- and inflammatory-related factors, which causes destabilization of vessels and initiates vessel remodeling in cancer. (Review) 27548530_Tie1 directly interacts with Tie2 to promote ANG-induced vascular responses under noninflammatory conditions, whereas in inflammation, Tie1 cleavage contributes to loss of ANG2 agonist activity and vascular stability 27695111_In vitro binding assays with purified components reveal that Tie-integrin recognition is direct, and further demonstrate that the receptor binding domain of the Tie2 ligand Ang-1, but not the receptor binding domain of Ang-2, can independently associate with a5b1 or aVb3. cooperative Tie/integrin interactions selectively stimulate ERK/MAPK signaling in the presence of both Ang-1 and fibronectin 27941161_Ang,Tie1 and Tie2 play roles in vascular development and pathogenesis of vascular diseases.[review] 28464467_We identified colorectal cancer as a novel Tie1-expressing tumor, with Tie1-positive cells hardly detectable in the normal intestine. Tie1 expression did not influence cancer cell proliferation in regular in vitro cultures, but significantly affected malignant growth of transplanted tumors in vivo. 29355844_Tie1 has regulatory functions in angiogenesis and vascular abnormalization as well as metastasis 30806032_Results found deregulated expression of TIE1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues to be associated with poor clinical outcome. 31340773_Study in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with a taxane-bevacizumab combination chemotherapy revealed that overall and progression-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a high baseline Tie1 level demonstrating the prognostic value of baseline Tie1 plasma concentration in patients with metastatic breast cancer. 32947856_TIE1 as a Candidate Gene for Lymphatic Malformations with or without Lymphedema. 33812182_Involvement of small extracellular vesicle-derived TIE-1 in the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells. 34942230_A novel cis-regulatory variant modulating TIE1 expression associated with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in Han Chinese children. |
ENSMUSG00000033191 |
Tie1 |
52.614044 |
0.2021477062 |
-2.306518 |
0.321874982 |
50.237558 |
0.00000000000136215637389518846442464639928791411585366766257010340268607251346111297607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000008013323267713424044930171797953828531635434018198793637566268444061279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8309551 |
3.2112025 |
69.1200142 |
10.7527859 |
| ENSG00000066185 |
84217 |
ZMYND12 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0C1 |
|
Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84217; |
metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
|
ENSMUSG00000070806 |
Zmynd12 |
26.257430 |
0.4430664146 |
-1.174405 |
0.357257004 |
10.894262 |
0.00096462605997647322703808514532397566654253751039505004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002249981138630332763717056820951256668195128440856933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0898563 |
4.0605673 |
36.6476048 |
6.2005932 |
| ENSG00000066230 |
6550 |
SLC9A3 |
protein_coding |
P48764 |
FUNCTION: Involved in pH regulation to eliminate acids generated by active metabolism or to counter adverse environmental conditions. Major proton extruding system driven by the inward sodium ion chemical gradient (PubMed:26358773). Plays an important role in signal transduction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26358773}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiport;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an epithelial brush border Na/H exchanger that uses an inward sodium ion gradient to expel acids from the cell. Defects in this gene are a cause of congenital secretory sodium diarrhea. Pseudogenes of this gene exist on chromosomes 10 and 22. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:6550; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; brush border [GO:0005903]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; potassium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015386]; sodium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015385]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; sodium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098719] |
11841999_studies suggest that the NHE3 expression is regulated by a combination of cis elements and their cognate transcription factors that include the AP-2 and Sp1 family members 12167607_NHE3 is important for cAMP sensitivity of receptor-mediated, clathrin-dependent endocytosis 12397398_Functional NHE3 activity is required to allow optimal absorption of dipeptides across the human intestinal epithelium. 12799307_Albumin-induced increases in expression and activity of NHE3 in proximal tubule cells suggest a possible mechanism for Na+ retention in response to proteinuria. 15070904_binding of the KOR to NHERF-1/EBP50 facilitates oligomerization of NHERF-1/EBP50, leading to stimulation of NHE3. 15197272_Ezrin is necessary for NHE3 recruitment to the apical membrane and NHE3-dependent pH(i) increases triggered by Na(+)-glucose cotransport. 15201541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201541_high degree of structural conservation of the NHE3 gene 15531580_Akt2-dependent ezrin phosphorylation leads to NHE3 translocation and activation 15754324_Amino acid uptake via hPAT1 is inhibited by activators of the cAMP pathway indirectly through inhibition of NHE3 activity. 15911629_PLG has the potential to simultaneously regulate calcium signaling pathways and regulate pHi via an association with NHE3 linked to DPP IV, necessary for tumor cell proliferation and invasiveness 16421216_Co-expression of NHE3 with SLC26A3 supports its function and may have an impact on pathophysiology of male subfertility both in congenital chloride diarrhoea and in cystic fibrosis, as well as spermatoceles. 16464174_Transcriptional stimulation of the human NHE3 promoter activity by PMA: PKC independence and involvement of the transcription factor EGR-1. 16760259_These data indicate that IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha may repress the NHE3 promoter activity in C2BBe1 cells by PKA-mediated phosphorylation of Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors. 16971495_Acute effect of glucocorticoids on NHE3 is mediated by a glucocorticoid receptor dependent mechanism that activates SGK1 in a nongenomic manner. 17276988_NHE3 expression is required for dome formation in confluent polarized epithelial cells. 17307723_Syt I plays a pivotal role in mediating cAMP- and Ca(2+)-induced endocytosis of NHE3 (but not in inhibition of activity) through cargo recognition of NHE3 and subsequent recruitment of AP2-clathrin assembly required for membrane endocytosis 17540780_Our data suggest that the differential regulation of NHE3 gene expression by NaB and IFN-gamma/TNF-alpha is mediated through alternative pathways that converge on Sp1/Sp3. 17881426_No mutation was found in the coding regions and intron-exon boundaries of the genes for CA II, CA IV, CA XIV, kNCB1, NHE3, NHE8, NHRF1, NHRF2 and SLC26A6 amplified from genomic DNA of family members with pRTA. 18085326_Level of NHE3 expression in brainstem tissue may contribute to the vulnerability of infants for sudden infant death syndrome. 18433466_Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli EspF was found to be responsible for decreased NHE3 activity; however, neither EspF-induced apoptosis nor the interaction of EspF with sorting nexin-9, an endocytic protein, were involved. 18614797_CK2 binds to the NHE3 C terminus and stimulates basal NHE3 activity by phosphorylating a separate single site on the NHE3 C terminus 18801914_The role of aldosterone in sodium absorption by intestinal cells via multiple changes in cellular processes, including SGK1 NHE3 and sodium pump activity is reported. 19056765_Functional coupling of the downregulated in adenoma Cl-/base exchanger DRA and the apical Na+/H+ exchangers NHE2 and NHE3 in intestinal epithelial cells. 19303862_These data indicate that 5-HT suppresses the transcriptional activity of the NHE3 promoter and this effect may be mediated by PKCalpha and modulation of DNA-binding affinities of Sp1 and Sp3. 19338654_AII increases, in an aldosterone independent fashion, activity and expression of the apical sodium/hydrogen exchanger NHE3 in cultured Caco2BBE cells. 19389806_Report morphological adaptation with preserved proliferation/NHE3 content in the colon of patients with short bowel syndrome. 19473983_The PLC-gamma-binding site in NHE3 was identified (amino acids 586-605) and shown to be a critical regulatory domain for protein complex formation. 19479940_The functional and molecular expression of NHEs in cultured human endolymphatic sac (ES) epithelial cells was determined and the effect of IFN-gamma on NHE function, was examined. 19535329_NHERF3 colocalizes and directly binds NHE3 at the plasma membrane under basal conditions. 19772970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19772970_Our findings suggest the involvement of polymorphisms in the NHE3 gene and promoter in cases of SIDS, which may result in an overexpression of NHE3 in the medulla oblongata. 19854014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19926819_intestinal epithelial Syt 1 plays an important role in cAMP-stimulated endocytosis of apical NHE3 through cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of S605 that is required for NHE3 and Syt 1 association 20080968_betaPix up-regulates NHE3 membrane expression and activity by Shank2-mediated protein-protein interaction and by activating Rho GTPases in the apical regions of epithelial cells 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20691413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20691413_single-nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes in SLC9A3 in whites are significantly associated with preeclampsia. 20967843_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20967843_the potential role of SLC9A3 as a modifier of CF lung disease severity was examined. 21832242_It was shown that lysophosphatidic acid 5 receptor transactivated the epidermal growth factor receptor and that inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor blocked lysophosphatidic acid 5 receptor-dependent activation of NHE3. 22447429_SLC9A3 is downregulated in patients with ulcerative colitis. 22466613_Single nucleotide polymorphism in SLC9A3 gene is associated with cystic fibrosis. 23086913_In conclusion, LA-induced increase in NHE3 expression may contribute to the upregulation of intestinal electrolyte absorption and might underlie the potential antidiarrheal effects of probiotics. 23324582_High urine NHE3 is associated with ischemic acute tubular necrosis than other causes of acute kidney injury. 23370527_Data suggest that EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) activation mediates PPARG- (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-) induced sodium and water reabsorption via upregulation of NHE3 and AQP1 (aquaporin 1) in proximal tubules. 23612977_NHERF2 domain was functionally significant in NHE3 regulation, being necessary for stimulation by lysophosphatidic acid of activity and increased mobility of NHE3 23769829_IRBIT plays an important role in intracellular pH regulation, mediated by NHE3, and further regulated by SPAK. 23784542_Carbachol stimulated enterocyte MUC17 endocytosis is concomitant with NHE3 internalization and CFTR membrane recruitment. 23810111_Data suggest that NHE3 expression is significantly decreased in term placenta of patients with pre-eclampsia as compared to normotensive patients; NHE3 is almost undetectable in cytosol of preeclamptic syncytiotrophoblasts. 24398676_1) NHE3 basal activity is regulated by a signaling complex that is controlled by sequential effects of two kinases, Akt and GSK-3, which act on a Ser cluster in the same NHE3 C-terminal domain that binds ezrin 24590378_the three NHE3 SNPs are unlikely to play a major role in the pathogenesis of SIDS in Caucasian infants;further genetic investigations in different ethnicities are required to determine whether variations in NHE3 are associated with an increased SIDS risk 24657527_NHE3 can act as a direction sensor for cells and that NHE3 phosphorylation in persistent directional cell migration does not involve PI3K/Akt during electrotaxis. 24713550_CCH-mediated inhibition of NHE3 activity is not dependent on clathrin and involves lipid rafts and requires Cdc42. 24788043_PKC-eta associates with NHE3 and gamma tubulin to promote the cell polarity during migration. 24831004_Human NHE3, but not non-primates NHE3s, is ubiquitinated by Nedd4-2. 24928903_Myosin VI mediates the movement of NHE3 to the microvillus in intestinal epithelial cells. 25271043_Inflammation-induced loss of PDZK1 expression may contribute to the NHE3 dysfunction observed in the inflamed intestine. 25552580_C. difficile inhibits NHE3 in vivo, which creates an altered environment favored by C. difficile. 25674247_NHE3 may play a role in the pathogenesis of human cholesterol gallstone disease 25715704_Results demonstrate decreased transport activity in three SNPs of NHE3 and provide mechanistic insight into how these SNPs impact NHE3 function. 25855080_Study identifies RSK2 as a new kinase that regulates NHE3 activity by direct phosphorylation. 26258413_these findings indicate the importance of NHE3 in diabetic diarrhea and suggest LPA administration as a potential therapeutic strategy for management of diabetic diarrhea. 26358773_Recessive mutations in NHE3, a downstream target of GC-C, caused congenital sodium diarrhea and implied primary basal NHE3 malfunction as a predisposition for inflammatory bowel disease in a subset of patients. 26377793_Data demonstrate a role for Per1 in the transcriptional regulation of NHE3 and SGLT1 in the kidney. 27109987_Expression of NHE3 and DRA was reduced with high tacrolimus levels and impaired renal function after intestinal transplantation. 27733387_This review focuses on novel findings of NHE3 in the intestine and the kidney as well as novel drug developments targeting NHE3. [review] 28283572_NHE3 binds to NHERF proteins via both an internal Class II PBM and C-terminal Class I PBM, which interact. The former determines NHE3 stability in the PM, and the latter determines total expression and percent PM expression. 28495802_We demonstrate that NHE3-799C is a common variant of NHE3 that is enriched in Asian populations; however its presence seems to have limited clinical significance in humans and is not associated with compromised function or abnormal transport regulation. 28882825_Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha directly regulates NHE3 promoter activity and its basal expression in the intestine. 29126251_Low NHE3 expression is associated with hypophosphatemia in calcium stone formers. 29167115_Intestinal NHE3 gene expression is regulated by changes in its DNA methylation. 30797621_Most of Taiwanese congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens (CBAVD) have at least one variant of SLC9A3 deletion and CFTR IVS8-5T, which co-contribute to Taiwanese CBAVD. [review] 30956978_an association between congenital bilateral absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD) and loss of SLC9A3 and propose that specific defects in the reproductive duct due to SLC9A3 variants drive CBAVD development. 31276831_The knowledge of this genetic form of non-syndromic CSD means that it can be detected early during the third trimester of pregnancy by the combined use of US signs, MRI and amniotic fluid digestive enzymes. Its main differential diagnosis is CCD due to mutation of the SLC26A3 gene. 32557227_Altered absorptive function in the gall bladder during cholesterol gallstone formation is associated with abnormal NHE3 complex formation. 33095475_Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 7 (USP7) and USP10 mediate deubiquitination of human NHE3 regulating its expression and activity. 34823064_Nedd4-2-dependent Ubiquitination Potentiates the Inhibition of Human NHE3 by Cholera Toxin and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. 35719363_Intestine-Specific NHE3 Deletion in Adulthood Causes Microbial Dysbiosis. 36189974_Downregulation of NHE-3 (SLC9A3) expression by MicroRNAs in intestinal epithelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000036123 |
Slc9a3 |
78.601067 |
0.3201727566 |
-1.643078 |
0.189050366 |
76.856578 |
0.00000000000000000183834877370470836915071560691161885526875927161988884955823309041988977696746587753295898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000015175630816488532397190437852092267547271104137941027945046812419604975730180740356445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.0008336 |
4.3339998 |
113.3661688 |
8.8095381 |
| ENSG00000066294 |
8832 |
CD84 |
protein_coding |
Q9UIB8 |
FUNCTION: Self-ligand receptor of the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family. SLAM receptors triggered by homo- or heterotypic cell-cell interactions are modulating the activation and differentiation of a wide variety of immune cells and thus are involved in the regulation and interconnection of both innate and adaptive immune response. Activities are controlled by presence or absence of small cytoplasmic adapter proteins, SH2D1A/SAP and/or SH2D1B/EAT-2. Can mediate natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity dependent on SH2D1A and SH2D1B (By similarity). Increases proliferative responses of activated T-cells and SH2D1A/SAP does not seem be required for this process. Homophilic interactions enhance interferon gamma/IFNG secretion in lymphocytes and induce platelet stimulation via a SH2D1A-dependent pathway. May serve as a marker for hematopoietic progenitor cells (PubMed:11564780, PubMed:12115647. PubMed:12928397, PubMed:12962726, PubMed:16037392) Required for a prolonged T-cell:B-cell contact, optimal T follicular helper function, and germinal center formation. In germinal centers involved in maintaining B-cell tolerance and in preventing autoimmunity (By similarity). In mast cells negatively regulates high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor signaling; independent of SH2D1A and SH2D1B but implicating FES and PTPN6/SHP-1 (PubMed:22068234). In macrophages enhances LPS-induced MAPK phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation and modulates LPS-induced cytokine secretion; involving ITSM 2 (By similarity). Positively regulates macroautophagy in primary dendritic cells via stabilization of IRF8; inhibits TRIM21-mediated proteasomal degradation of IRF8 (PubMed:29434592). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q18PI6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12115647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12928397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12962726, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16037392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22068234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29434592, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Autophagy;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a membrane glycoprotein that is a member of the signaling lymphocyte activation molecule (SLAM) family. This family forms a subset of the larger CD2 cell-surface receptor Ig superfamily. The encoded protein is a homophilic adhesion molecule that is expressed in numerous immune cells types and is involved in regulating receptor-mediated signaling in those cells. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:8832; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; defense response [GO:0006952]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032685]; negative regulation of interleukin-18 production [GO:0032701]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of mast cell activation [GO:0033004]; negative regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043305]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production [GO:0071639]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043030]; regulation of store-operated calcium entry [GO:2001256]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
12928397_CD84 enhances proliferation of human activated T cells by a Src homology 2 domain-containing cytoplasmic adaptor protein SLAM-associated protein (SAP)-independent mechanism. 17563375_The structure of CD84 provides insight into SLAM family function. Point mutations were studied. 18243321_These data suggest that CD84 may play a role in modulating Fc epsilon RI-mediated signaling in mast cells. 22068234_CD84 is highly expressed in mast cells and that it contributes to the regulation of FcepsilonRI signaling 23435417_data show that overexpression of CD84 in CLL is an important survival mechanism that appears to be an early event in the pathogenesis of the disease 23555300_These findings support a model in which CD84 genotypes and/or expression may serve as a useful biomarker for response to etanercept treatment in RA patients of European ancestry 24635044_up-regulated in Kawasaki disease arteriopathy 27452524_Results show that CD84 expressed on CLL cells interact with CD84 expressed on cells in their microenvironment, inducing cell survival in both sides. 29434592_our experiments identified SLAMF5 as a novel cell surface receptor modulator of autophagy and revealed an unexpected link between the SLAMF and IRF8 signaling pathways, both implicated in multiple human pathologies. 30514120_Among 29 immune and inflammatory proteins, CXCL1, CD84 and TNFRSF10A were associated with early post-acute coronary syndrome (ACS) after initial ACS-admission 31772329_Bone marrow dendritic cells support the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in a CD84 dependent manner. 33465053_CD84 is a regulator of the immunosuppressive microenvironment in multiple myeloma. |
ENSMUSG00000038147 |
Cd84 |
29.316178 |
2.2497073775 |
1.169737 |
0.299154857 |
15.526582 |
0.00008135316201871992450572051991386501867964398115873336791992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000226518142123430688428947776813515702087897807359695434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.8920014 |
8.8841741 |
18.7677799 |
3.0596006 |
| ENSG00000066336 |
6688 |
SPI1 |
protein_coding |
P17947 |
FUNCTION: Pioneer transcription factor, which controls hematopoietic cell fate by decompacting stem cell heterochromatin and allowing other transcription factors to enter otherwise inaccessible genomic sites. Once in open chromatin, can directly control gene expression by binding genetic regulatory elements and can also more broadly influence transcription by recruiting transcription factors, such as interferon regulatory factors (IRFs), to otherwise inaccessible genomic regions (PubMed:23658224, PubMed:33951726). Transcriptionally activates genes important for myeloid and lymphoid lineages, such as CSF1R (By similarity). Transcriptional activation from certain promoters, possibly containing low affinity binding sites, is achieved cooperatively with other transcription factors. FCER1A transactivation is achieved in cooperation with GATA1 (By similarity). May be particularly important for the pro- to pre-B cell transition (PubMed:33951726). Binds (via the ETS domain) onto the purine-rich DNA core sequence 5'-GAGGAA-3', also known as the PU-box (PubMed:33951726). In vitro can bind RNA and interfere with pre-mRNA splicing (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17433, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6BDS1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23658224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33951726}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes an ETS-domain transcription factor that activates gene expression during myeloid and B-lymphoid cell development. The nuclear protein binds to a purine-rich sequence known as the PU-box found near the promoters of target genes, and regulates their expression in coordination with other transcription factors and cofactors. The protein can also regulate alternative splicing of target genes. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6688; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity [GO:0001216]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity [GO:0001217]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; NFAT protein binding [GO:0051525]; protein sequestering activity [GO:0140311]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; STAT family protein binding [GO:0097677]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; anatomical structure regression [GO:0060033]; apoptotic process involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:1902262]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; defense response to tumor cell [GO:0002357]; endothelial to hematopoietic transition [GO:0098508]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; follicular B cell differentiation [GO:0002316]; germinal center B cell differentiation [GO:0002314]; granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030851]; immature B cell differentiation [GO:0002327]; interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070102]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0043011]; myeloid leukocyte differentiation [GO:0002573]; negative regulation of adipose tissue development [GO:1904178]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process [GO:0045347]; negative regulation of neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043314]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin [GO:0120186]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; oncogene-induced cell senescence [GO:0090402]; pericyte cell differentiation [GO:1904238]; positive regulation of antifungal innate immune response [GO:1905036]; positive regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045579]; positive regulation of microglial cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:1904151]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000529]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; pro-T cell differentiation [GO:0002572]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045646]; regulation of histone H3-K27 acetylation [GO:1901674]; regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation [GO:1905453]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; TRAIL-activated apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0036462]; transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling [GO:0045815]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
11926990_PU.1 trans activation of gp91(phox) promoter 11929801_Loss of PU.1 expression is associated with defective immunoglobulin transcription in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin disease. 12036891_Multiple PU.1 sites cooperate in the regulation of p40(phox) transcription during granulocytic differentiation of myeloid cells. 12091339_C/EBPalpha and PU.1 interact physically and colocalize in myeloid cells, and C/EBPalpha blocks the function of PU.1. 12130514_Heterozygous PU.1 mutations are associated with acute myeloid leukemia, causing disruption of PU.1 function, contributing to the block in cell differentiation found in AML patients. 12130529_Distinct functions for STAT1 and PU.1 in transcriptional activation of Fc gamma receptor I promoter. 12202480_Interacts with other transcription factors to regulate transcription of the gene encoding eosinophil granule major basic protein 12393465_PU.1 transcriptional activity is down-regulated by AML1-ETO in t(8;21) myeloid leukemia by physical binding. 12778491_Transactivation & DNA-binding domains of PU.1 were required for induction of Stat6-mediated transcription. The co-operation of PU.1 & Stat6 in Igepsilon gene transactivation fine-tunes cell-type-restricted expression of IL-4-induced gene responses. 12832449_PU.1 directly regulated the expression of only the glutathione peroxidase gene through binding sites in the promoter and a 3' regulatory region. 12896880_PU.1 is critical in the terminal differentiation of human alveolar macrophages. 14623259_In conclusion, we provide evidence for AML-1, PU.1, and Sp3 cooperatively and directly mediating BPI-expression during myeloid differentiation. 14647463_MeCP2 acts as a corepressor of PU.1 probably due to facilitating complex formation with mSin3A and HDACs. 14706103_downregulated by Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection in monocytes 15242870_in B cells, E47 and PU.1/IRF-4 interact with the E-box motifs and the EICE, respectively, and act synergistically in the activation of CIITA-PIII 15304486_RANKL-induced cathepsin K gene expression is cooperatively regulated by the combination of the transcription factors and p38 MAP kinase in a gradual manner. 15339679_Antibodies to LSP1 and PU.1 may represent useful reagents for the differential diagnosis between T-cell-rich B-cell lymphoma and lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's disease. 15598817_high PU.1 activity favors dendritic cells at the expense of macrophage fate by inhibiting expression and activity of the macrophage factor MafB. 15625130_The expression of PU.1 is a critical event for osteoclastogenesis. 15632149_nuclear import of the transcription factor PU.1 occurs via RanGTP-stimulated binding to Nup153 15796964_Alteration of the PU.1 locus does not correlate with its suppressed expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. 16051608_PU.1 regulates the tissue-specific expression of dendritic cell-specific (ICAM)-3-grabbing nonintegrin. 16083856_PU.1 regulates RANK gene transcription; this may represent one of the key roles of PU.1 in osteoclast differentiation 16149049_Our results indicate that the NMTS region of Runx1 is required for functional interactions with PU.1. 16223775_PU.1 and Id2 modulate lineage options of langerhans cell precursors, downstream of TGF-beta1. 16263717_c-Myb and c-Ets family members (Ets-1/2, PU.1, and Spi-B) control hGR 1A promoter regulation in T- and B-lymphoblast cells 16298389_PU.1, in addition to its positive role in TAL-1 expression in early hematopoietic progenitors, may also act as a mediator of TAL-1 silencing in some hematopoietic lineages 16320347_The c.-292 T allele in the ALOX15 promoter generates a novel binding site for the transcription factor SPI1 that results in higher transcription of the gene in macrophages. 16352814_PU.1 is suppressed in acute promyelocytic leukemia, and that all-trans retinoic acid restores PU.1 expression in cells harboring t(15;17). 16642264_hydroquinone induces a dysregulation in the external signals modulating PU.1 protein phosphorylation and this dysregulation may be an early event in the generation of benzene-induced AML 16698794_Spi-1 affects splicing decisions in a promoter binding-dependent manner 16861236_PU.1-Ets domain and the GATA-1 C-terminal zinc finger (CF) form a low affinity interaction in which specific regions of each protein are implicated. 16973891_The mechanism of action of VIP on monocyte differentiation may be via inhibition of the transcription factor PU.1. 17200120_IRF8 cooperates with PU.1 and IRF-2 to activate a composite ets/IRF-cis element in the NF1 promoter. The conserved IRF domain tyrosine in ICSBP/IRF8 is required for interaction with the DNA-bound PU.1-IRF2 heterodimer. 17218319_findings provide an insight into the structure of the hematopoietic cell-specific P2 promoter of the SHP-1 gene and identify PU.1 as the transcriptional activator of the P2 promoter 17386941_IRF8 is involved in a cooperative interaction with transcription factors Spi-1/PU.1 and non-tyrosine phosphorylated Stat1 in the formation of a pre-associated, poised complex for interleukin 1-beta gene induction. 17410194_data strongly indicate that germline mutations in SPI1 and MADD genes do not confer a high risk of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and do not make a major contribution to the familial risk of the disease 17545613_PU.1 was down-regulated in the majority of human myeloma cell lines and a subset of freshly isolated myeloma cells, in contrast to relatively high expression of PU.1 in normal plasma cells. 17562868_The type IV isoform of PML interacted with PU.1, promoted its association with p300, and then enhanced PU.1-induced transcription and granulocytic differentiation and PU.1 directly activates the transcription of the C/EBPepsilon gene. 17621263_Ski-mediated repression of PU.1 is due to Ski's ability to recruit histone deacetylase 3 to PU.1 bound to DNA. 17623651_Transcription factor PU.1 controls transcription start site positioning and alternative TLR4 promoter usage. 17671233_C/EBPalpha binds and activates the PU.1 distal enhancer to induce monocyte lineage. 17694175_identify a single nucleotide polymorphism within this element in humans that is more frequent in acute myeloid leukemia with a complex karyotype, leads to decreased enhancer activity, and reduces PU.1 expression in myeloid progenitors 18056638_PU.1 activates the transcription of miR-424, and this up-regulation is involved in stimulating monocyte differentiation through miR-424-dependent translational repression of NFI-A 18288635_These data provide evidence that NFATc1, in concert with PU.1, are involved in regulation of beta(3) integrin expression during osteoclast differentiation. 18308386_Low PU.1 levels were observed in monoblastic leukemias 18316480_Arginine-methylated RUNX1 regulates PU.1 gene expression. 18635311_PU.1 is severely impaired in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia but is restored upon treatment. 18657865_PU.1 is involved in the regulation of human innate epithelial defences 18676813_PU.1 expression is modulated by the balance of functional sense and antisense RNAs regulated by a shared cis-regulatory element. 19076642_suggest that PU.1-binding motifs are essential for PARG promoter activity and that PU.1 modulates PARG gene expression during differentiation of HL-60 cells. 19111020_LSECtin is expressed by liver myeloid cells, and its expression is dependent on the PU.1 transcription factor. 19118563_These data provide critical insights into the transcriptional regulation of the IP gene in human megakaryocytic and endothelial cells, identifying Sp1, PU.1 and Oct-1 as the critical factors involved in its basal regulation in humans. 19158090_PU.1 directs Mi2beta to erase an established DNase I-hypersensitive site, in an ATP-dependent reaction subsequent to PU.1 binding to chromatin, whereas ACF will not support erasure 19208846_EVI1 point mutant, unable to bind PU.1, restores the activation of PU.1-regulated genes and allows a normal differentiation of bone marrow progenitors in vitro. 19281794_PU.1 protein is cleaved into two fragments of 24 kDa and 16 kDa during apoptosis progression in leukemic cell lines and primary leukemic cells by caspase-3. 19382896_This review focuses on important protein-protein interactions of PU.1 that play a crucial role in regulation of normal as well as malignant haematopoiesis. 19428102_we revealed the mRNA expression of annexin 1 was negatively correlated with PU.1 mRNA expression in 43 primary AML specimens 19502584_Reduced expression of mast cell-related molecules and transcription factors GATA-1/2 and up-regulation of C/EBPalpha in PU.1 transfectants indicate that enforced PU.1 suppresses mast cell-specific gene expression through these transcription factors. 19542915_PU.1 is a valuable immunohistochemical marker for identifying cutaneous histiocyte- and dendritic cell-derived lesions 19564417_The recruitment of BCL6 to promoter regions by PU.1 represents a new regulatory mechanism that expands the number of genes regulated by this important transcriptional repressor. 19632992_Data show that PU.1 participates in the regulation of MD-2 in nonmyeloid cells cooperatively with C/EBPbeta. 19747912_ATRA-induced increase of Vav1 expression and phosphorylation may be involved in recruiting PU.1 to the CD11b promoter and in regulating CD11b expression during the late stages of neutrophil differentiation of APL-derived promyelocytes. 19749795_PU.1 is capable of inducing apoptosis in certain myeloma cells by direct transactivation of TRAIL. 19825991_Collectively, we show that either activation of PU.1 or inhibition of GATA-1 efficiently reverses the transcriptional block imposed by GATA-1 and leads to the activation of a myeloid transcriptional program directed by PU.1. 19828640_PU.1 is shown to be required for B cell receptor (BCR)-induced expression of positive regulatory domain I-binding factor 1 (PRDM1) in lymphoma cells and in PU.1-positive myeloma cells. 19890096_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19966852_Here, we identified nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) to activate PU.1 expression through a novel site within the upstream enhancer element. 20471086_ZNF300 was activated by PU.1 and suggested that the regulation may be involved in the progression of leukemia development and hematopoietic differentiation. 20660370_Spi-1 increases the speed of replication by acting specifically on elongation rather than enhancing origin firing. 20947507_increased NF-kappaB activity leads to increased miR-155, which results in decreased PU.1, and consequently reduced CD10 mRNA and protein. 21094529_CLEC5A expression in monocyte/macrophage and granulocytes is regulated by PU.1. 21176776_ATRA up-regulates the expression of PU.1; and PU.1 preferentially binds to one of the two putative binding sites on the RIG-G promoter 21216962_Positive regulatory domain I (PRDM1) and IRF8/PU.1 counter-regulate MHC class II transactivator (CIITA) expression during dendritic cell maturation. 21239694_PU.1 regulates its expression in B cells and macrophages by differentially associating with cell type-specific transcription factors at one of its cis-regulatory elements 21360505_A SNP in the 3'-untranslated region of SPI1 is associated with elevated SPI1 mRNA level and with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. 21402070_PU.1 is a major transcriptional activator of LIMD1 21402921_Data show that two transcription factors, PU.1 and C/EBPalpha, appear to synergistically mediate enhancer creation and affect NF-kappaB target selection in THP-1 cells. 21421043_PU.1 expression levels were increased in the monocytes of major depressive disorder patients, but not in those of schizophrenic or bipolar patients. PU.1 bound to both the TREM-1 & DAP12 promoters. 21474105_regulation of adult hematopoiesis through TIF1gamma-mediated transcriptional repression of TAL1 and PU.1 target genes. 21518930_RUNX1 deficiency is associated with persistent corepressor interaction with PU.1. 21725055_IFN-gamma induces expression of PU.1 in human erythroid precursors. 21732487_PKCdelta regulated PU.1 activity by affecting its transactivation activity, whereas its DNA binding activity remained unaffected 21789226_Expression of PU.1 downstream of activated JAK2 may explain why JAK2 mutations are frequently observed in myeloproliferative neoplasms patients. 21897363_Upon macrophage differentiation PU.1 represses the miR-17-92 cluster promoter by an Egr-2/Jarid1b-mediated H3K4 demethylation mechanism whose deregulation may contribute to leukaemic states. 22012064_Studies identified a physical and functional interaction between RUNX1 (AML1) and MLL and show that both are required to maintain the histone lysine 4 trimethyl mark (H3K4me3) at 2 critical regulatory regions of the AML1 target gene PU.1. 22075620_the down-regulation of PU.1 expression suppresses the expression of SIRPalpha1. 22083997_Two signals are required for the self-renewal of Friend virus leukemia stem cells, proviral insertional activation of Spi1 and Hedgehog-dependent signaling. 22096565_Data show that IRF8 binds a large number of genes by targeting two distinct motifs, half of which are also targeted by PU.1. 22145969_Transcriptional regulation of MIR29B by PU.1 (SPI1) and MYC during neutrophil differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia cells. 22231443_results thus shed light on how PU.1 and Ikaros can act as lineage competency factors to facilitate both myeloid and lymphoid developmental programs 22446486_Age- and differentiation-status-related epigenetic modifications of PU.1 is a unique regulator of Th9 memory acquisition and Th9 immunity. 22498738_HK3 is: (1) directly activated by PU.1, (2) repressed by PML-RARA, and (3) functionally involved in neutrophil differentiation and cell viability of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. 22569057_Low PU.1 expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia patients is required for disease initiation and progression. 22674382_These data suggest that aberrant methylation of PU.1 may play a role in CML pathogenesis, and may therefore serve as a useful biomarker and potential target for demethylating drugs. 22780968_Epigenetic modification of PU.1 in chronic myeloid leukemia patients and K562 cell line might be responsible for the reduced expression of PU.1. 22824976_PU.1 positively regulates the ST2 promoter as a transcription factor that directly transactivates the ST2 promoter via Ets-family-related cis-element in mast cells and basophils. 23118933_PU.1 sites may have served as anchor loci for the formation of new and functionally relevant PPARG binding sites throughout evolution. 23212521_Data suggest that PU.1 is a potent tumor suppressor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) and that induction of PU.1 with demethylation agents and/or histone deacetylase inhibitors is a possible therapeutic option for patients with cHL. 23252456_PU.1 and CEBPA are direct transcriptional regulators of CORO1A in acute promyelocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia. 23395001_PU.1 mediates chromosome looping and functions as a master regulator of HSC proliferation. 23483680_These results show that PU.1 controls human microglial viability and function and suggest PU.1 as a molecular target for manipulation of human microglial phenotype. 23501100_MT-1A is epigenetically regulated by PU.1 during monocytic differentiation. 23534406_TLR2 down-regulates FcepsilonRI and its transcription factor PU.1 in human Langerhans cells. 23770850_PML/RARalpha suppresses PU.1-dependent activation of the proteasome immunosubunits in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 24028770_PU.1- targeted genes undergo Tet2-coupled demethylation and DNMT3b-mediated methylation in monocyte-to-osteoclast differentiation. 24038216_The tumor suppressor gene DAPK2 is induced by the myeloid transcription factors PU.1 and C/EBPalpha during granulocytic differentiation but repressed by PML-RARalpha in APL. 24086757_the expression control of Tal2 in hematopoietic cells 24379003_Given the importance of C/EBPs and PU.1 in myeloid development, these results, thus, suggest that restoration of the normal function of the myeloid cell transcriptional machinery is a major molecular mechanism underlying the differentiation induction 24445817_our findings demonstrate that PU.1 contributes to the development of MLL leukemia, partially via crosstalk with the MEIS/HOX pathway. 24498324_Data show that CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) together with ISWI ATPase SMARCA5 and members of the Cohesin complex associate with the SPI1 protein is disrupted in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts. 24504023_HSF1 appears as a fine-tuning regulator of SPI1/PU.1 expression at the transcriptional and post-translational levels during macrophage differentiation of monocytes. 24639354_we have demonstrated that PU.1, GATA1, and GATA2 are involved in the expression of FcepsilonRI in a human mast cell line and primary human mast cells using siRNA with high transfection efficiency, and by ChIP assay. 24695740_Data indicate that transcription factors RUNX1 and PU.1 cooperated to exchange corepressors for coactivators, and deficiency of RUNX1, frequent in leukemia, caused aberrant recruitment of specific corepressors instead of coactivators to PU.1. 24908389_Mice with PU.1 deficiency in T cells were protected from colitis, whereas treatment with antibody to IL-9 suppressed colitis 24952944_DNA complex may be relevant to an emerging role of PU.1, but not Ets-1, as a pioneer transcription factor in vivo 24996056_IL-32theta; reduces PKCdelta-mediated phosphorylation of PU.1, resulting in attenuation of IL-1beta production 25005557_hnRNP K and PU.1 act synergistically during granulocytic differentiation, hnRNP K seems to have a negative effect on PU.1 activity during monocytic maturation 25043887_The PU.1-regulated MAP1S gene is implicated in neutrophil differentiation and autophagy control. 25072246_PU.1 suppressive target gene, metallothionein 1G, inhibits retinoic acid-induced NB4 cell differentiation. 25092144_A novel network has been described in acute myeloid leukemia in which FLT3-ITD signaling induces oncogenic miR-155 by p65 and STAT5 thereby targeting transcription factor PU.1. 25184385_The increased CITED2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia results in better hematopoietic stem cell survival, lower PU.1 levels, and perturbed myeloid differentiation program that contributes to leukemia persistence. 25185713_Runx-dependent PU.1 chromatin interaction and transcription of PU.1 are essential for both normal and leukemia stem cells. 25205721_This review summarizes current knowledge and ideas of molecular mechanisms by which PU.1 controls hematopoiesis and suppresses leukemia. [review] 25987019_Loss of PU.1 expression is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 26126967_PU.1 recruitment coupled with increased histone acetylation induces gene expression and activates a monocyte/macrophage transcriptional programme. 26149389_This study demonstrated positive regulation of monocyte/macrophage differentiation by lnc-MC and uncovered an elaborate regulation mechanism composed of PU.1, lnc-MC, miR-199a-5p, and ACVR1B. 26261072_PU.1 downregulation was noted in B-CLL/SLL samples positive for the adverse prognostic markers CD38 and ZAP-70. 26429314_This study showed that HCV infection might abrogate NK cytotoxic potential through altering PU.1, NKG2D receptor and perforin molecules. 26657848_Collectively, IMiDs exert demethylation activity through inhibiting DNMT1, 3a, and 3b, and up-regulating PU.1 expression, which may be one of the mechanisms of the anti-myeloma activity of IMiDs. 26851695_SPI1-GFI1B transcriptional network is an important regulatory axis in acute myeloid leukemia as well as in the development of erythroid versus myelomonocytic cell fate 26942192_Our data suggest that E2A antagonism of PU.1 activity contributes to its ability to commit multipotential hematopoietic progenitors to the lymphoid lineages. 27010793_The GATA-1-mediated inhibition of PU.1 gene transcription in human AML-erythroleukemias mediated through the URE represents important mechanism that contributes to PU.1 downregulation and leukemogenesis that is sensitive to DNA demethylation therapy 27105023_we conclude that PU.1 transactivates the pIII through direct binding to Ets-motifs in the promoter in pDCs 27146823_PU.1 directly activates the expression of HOTAIRM1 through binding to the regulatory region of HOTAIRM1 during granulocytic differentiation. 27306059_This study demonstrated the novel role of PU.1 in the immune response to A. fumigatus through upregulation of Dectin-1 expression and its translocation to the nucleus in A. fumigatus-stimulated THP-1 cells. 27480083_Our results suggest the existence of a Vav1/PU.1/miR-142-3p network that supports all-trans retinoic acid -induced differentiation in acute promyelocytic leukemia -derived cells 27617961_we demonstrated that miR-22 promoted monocyte/macrophage differentiation, and MECOM (EVI1) mRNA is a direct target of miR-22 and MECOM (EVI1) functions as a negative regulator in the differentiation.The miR-22-mediated MECOM degradation increased c-Jun but decreased GATA2 expression, which results in increased interaction between c-Jun and PU.1 27671860_Inhibition of endogenous miR-155 in B cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients restores PU.1 and reduces production of antibodies. 27708417_PU.1 binds to OX40L promoter in dendritic cells. 28216155_Forced FOG1 protein expression in K562 erythroleukemia cells induced the expression of SLC4A1 protein, but repressed that of transcription factor PU.1. 28229452_PU.1 and IL-9 may play a role in AD pathogenesis and relate to disease severity and clinical eruption types. 28232093_PU.1 is an important modulator of VDR signaling in monocytes. 28325862_expression of an essential mediator of neutrophil terminal differentiation, the ets transcription factor PU.1, was significantly decreased in Hbb(th3/+) neutrophils in beta-thalassemia 28347818_Moreover, the expression of a cell proliferation marker Ki67 was significantly decreased in tumors from the mice not taking doxycycline, compared with that of tumors from the mice continuously taking doxycycline. The present data strongly suggest that PU.1 functions as a tumor suppressor of myeloma cells in vivo. 28362429_PU.1 supports TRAIL-induced cell death by inhibiting RelA-mediated cell survival and inducing DR5 expression. 28368411_PU.1-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells is associated with IRF4 downregulation and subsequent IRF7 upregulation. 28376714_RUNX1 overexpression induced partial DNA demethylation at SPI1 proximal promoter. 28415748_Data show that protein phosphatase-1 alpha (PP1alpha) is required to maintain checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1) in a dephosphorylated state and for the accelerated replication fork progression in Spi1/PU.1 transcription factor-overexpressing cells. 28440496_the results indicate that PU.1 may be a critical factor for the innate defense against A. fumigatus, and may therefore be a potential target for the prophylaxis and treatment of IPA. 28481873_PU.1 has a role in tumor suppression in PEL and its down-regulation is associated with PEL development. 28586009_In contrast, expression of Spi1/PU.1 in a Fli1 producing erythroleukemia cell line in which fli1 is activated, resulted in increased proliferation through activation of growth promoting proteins MAPK, AKT, cMYC and JAK2 28628103_Alzheimer's disease heritability was enriched within the PU.1 cistrome, implicating a myeloid PU.1 target gene network in AD. 28671687_findings highlight a unique role of SPI1 fusions in high-risk pediatric T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 28805986_Most cases of histiocytic sarcoma expressed histiocytic markers CD68 (6 of 7 cases), CD163 (5 of 5 cases), and PU.1 (3 of 4 cases). 28912174_These results bring indirect evidence that leukemia develops from cells which have bypassed Spi1-induced senescence. Overall, our results reveal senescence as a Spi1-induced anti-proliferative mechanism that may be a safeguard against the development of acute myeloid leukemia. 29083320_study provides proof of concept that PU.1 inhibition has potential as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of AML and for the development of small-molecule inhibitors of PU.1. 29472524_miR-142-3p inhibits autophagy during sorafenib treatment and is upregulated by PU.1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 29511345_Data showed that the Ets transcription factor PU.1 regulated the elevated expression of PFKFB3 in tyrosine kinase inhibitor -resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 29532991_Nuclear PU.1/Vav1 association accompanies the transcription of miR-29b but, at variance with the APL-derived NB4 cells, in which the protein is required for the association of PU.1 with both miRNA promoters, Vav1 is part of molecular complexes to the PU.1 consensus site in Kasumi-1. 29693176_PU.1 3'UTR attenuates TNFalphainduced proliferation and cytokine release of RAFLS by acting as a ceRNA for FOXO3 to regulate miR155 activity. 29801457_at 3 months after cardiopulmonary bypass, monocytes continued to express a new macrophage-like milieu that was associated with the persistent activation of the PU.1/M-CSF pathway. 30124174_these results suggest that attenuating PU.1 may be a valid therapeutic approach to limit microglial-mediated inflammatory responses in Alzheimer's disease 30355733_As evaluated by ChIP, cultured lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated THP-1 cells incubated with l-arginine had significantly decreased IL1B transcription and reduced C/EBP-beta association with Spi1 on the IL1B promoter. 30387140_PU.1, the myeloid transcription factor (which has also been identified in lung epithelial cells), co-operates with the vitamin D receptor and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (CEBPalpha). 30550771_CEBPA supports vitamin D signaling concerning actions of the innate immune system, but uses the antagonism with PU.1 for suppressing possible overreactions of adaptive immunity. 30555023_FIS1, SPI1, PDCD7 and Ang2 were significantly overexpressed in CN-AML patients 30700907_identification of the transcription factor PU.1 as an essential regulator of the pro-fibrotic gene expression program 30718772_A transcription factor PU.1 is critical for Ccl22 gene expression in dendritic cells and macrophages. 30721335_PU.1 was downregulated in myelodysplastic syndrome. Its expression was inversely related to disease aggressiveness and AML transformation. PU.1 and JDP2 expression correlate and are concurrently reduced with the extent of differentiation arrest and aggression/prognosis in MDS/AML. It was upregulated upon azacytidine treatment. 30986495_These findings illustrate that combined PU.1/CITED2 deregulation induces a transcriptional program that promotes HSPC maintenance, which might be a prerequisite for malignant transformation. 31414895_A new functional Cd4 lymphocyte subgroup, Th9 cells, express transcription factor PU.1 and cytokine interleukin-9 characteristically. (Review) 31431533_The importance of down-regulation of Runx1 and Pu.1 in erythropoiesis is further supported by genome-wide analyses showing that their DNA-binding motifs are highly overrepresented in regions that lose chromatin accessibility during early erythroid development. 31764996_PU.1 subcellular localization in acute myeloid leukaemia with mutated NPM1. 31785408_Additional functional PU.1 site may increase TLR4 expression. 32128405_Intrinsic disorder controls two functionally distinct dimers of the master transcription factor PU.1. 32128906_Long noncoding RNA LINC00324 exerts protumorigenic effects on liver cancer stem cells by upregulating fas ligand via PU box binding protein. 32379601_Abnormal expression of colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) and transcription factor PU.1 (SPI1) in the spleen from patients with major psychiatric disorders: A role of brain-spleen axis. 32532019_Folate Receptor beta (FRbeta) Expression in Tissue-Resident and Tumor-Associated Macrophages Associates with and Depends on the Expression of PU.1. 32590190_SPI1-induced upregulation of lncRNA SNHG6 promotes non-small cell lung cancer via miR-485-3p/VPS45 axis. 33446637_PU.1 drives specification of pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells to LSEC-like cells. 33653779_Upregulation of Metallothionein-1G Accelerates G1/S Transition in the Growth Phase of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia NB4 Cells. 33713236_Expression of Transcription Factor PU.1 in Stromal Cells as a Prognostic Marker in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 33741901_CircSPI1 acts as an oncogene in acute myeloid leukemia through antagonizing SPI1 and interacting with microRNAs. 33863903_Genetic perturbation of PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophil enhancers associates with autoimmune disease. 33897697_PU.1 and IRF8 Modulate Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome via Regulating Its Expression in Human Macrophages. 33951726_Constrained chromatin accessibility in PU.1-mutated agammaglobulinemia patients. 33966135_Expression profile of PU.1 in CD4(+)T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 34010414_Core-binding factor leukemia hijacks the T-cell-prone PU.1 antisense promoter. 34099591_S100A8 and S100A9, both transcriptionally regulated by PU.1, promote epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and invasive growth of dermal keratinocytes during scar formation post burn. 34230493_Oncogenic cooperation between TCF7-SPI1 and NRAS(G12D) requires beta-catenin activity to drive T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 34378358_Chromatin Remodeling of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis is Mediated by an HGF-PU.1-DPP4 Axis. 34738863_Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 plays a carcinogenic role in gastric cancer by recruiting transcriptional factor SPI1 to upregulate ST8SIA1 expression. 35058453_Expression of the transcription factor PU.1 induces the generation of microglia-like cells in human cortical organoids. 35065610_STAT3 and SPI1, may lead to the immune system dysregulation and heterotopic ossification in ankylosing spondylitis. 35078433_The role of SPI1-TYROBP-FCER1G network in oncogenesis and prognosis of osteosarcoma, and its association with immune infiltration. 35253752_Association of SPI1 Haplotypes with Altered SPI1 Gene Expression and Alzheimer's Disease Risk. 35285058_Cytokine responses to LPS in reprogrammed monocytes are associated with the transcription factor PU.1. 36118415_LINC01094/SPI1/CCL7 Axis Promotes Macrophage Accumulation in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Tumor Cell Dissemination. 36198346_SPI1 mediates transcriptional activation of TPX2 and RNF2 to regulate the radiosensitivity of lung squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000002111 |
Spi1 |
1351.134475 |
2.3631399126 |
1.240705 |
0.043903630 |
811.100511 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020827198239223809680077446462911912281350673269224090380268404877398378399985980678441829640200795471365758370247875130948655439702107904953829103944058 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016439007808071843654335241081650206938159945431047788383729120472883402773134366461772799346179369677174827523613408447102382835341416673867907207986302 |
Yes |
No |
1915.8497206 |
48.6039074 |
816.4739202 |
16.7071966 |
| ENSG00000066697 |
91283 |
MSANTD3 |
protein_coding |
Q96H12 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
|
hsa:91283; |
|
28212443_MSANTD3 rearrangement as a recurrent event in salivary gland AcCC 30520817_we find the HTN3-MSANTD3 gene fusion to be a recurrent event in acinic cell carcinoma with prominent serous differentiation and an indolent clinical course |
ENSMUSG00000039693 |
Msantd3 |
155.588972 |
3.4411660039 |
1.782897 |
0.158216787 |
128.147262 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001042163355515000882900237180059088822388999911396612342604806625472682189199489719011459953890152974054217338562011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000132950139389813433595438434973473472297507686435644421033067188853181447654415447967579666510573588311672210693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
244.1330638 |
22.0033033 |
71.3680171 |
5.2589902 |
| ENSG00000066739 |
55102 |
ATG2B |
protein_coding |
Q96BY7 |
FUNCTION: Lipid transfer protein required for both autophagosome formation and regulation of lipid droplet morphology and dispersion (PubMed:22219374, PubMed:31721365). Tethers the edge of the isolation membrane (IM) to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mediates direct lipid transfer from ER to IM for IM expansion (PubMed:22219374, PubMed:31721365). Binds to the ER exit site (ERES), which is the membrane source for autophagosome formation, and extracts phospholipids from the membrane source and transfers them to ATG9 (ATG9A or ATG9B) to the IM for membrane expansion (By similarity). Lipid transfer activity is enhanced by WDR45/WIPI4, which promotes ATG2B-association with phosphatidylinositol 3-monophosphate (PI3P)-containing membranes (PubMed:31721365). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q2TAZ0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22219374, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31721365}. |
Autophagy;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid droplet;Lipid transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein required for autophagy. The encoded protein is involved in autophagosome formation. A germline duplication of a region that includes this gene is associated with predisposition to myeloid malignancies. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:55102; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; phagophore assembly site [GO:0000407]; phagophore assembly site membrane [GO:0034045]; lipid transfer activity [GO:0120013]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:0000422]; late nucleophagy [GO:0044805]; piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus [GO:0034727]; reticulophagy [GO:0061709] |
19197948_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22219374_Depletion of both Atg2A and Atg2B causes clustering of enlarged lipid droplets in an autophagy-independent manner. These data suggest that mammalian Atg2 proteins function both in autophagosome formation and regulation of lipid droplet morphology and dispersion. 22350415_miR-130a inhibited autophagy by reducing autophagosome formation, an effect mediated by downregulation of the genes ATG2B and DICER1. 25322940_miR-143 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting autophagy-related 2B in non-small cell lung cancer H1299 cells. 26280900_demonstrate that overexpression of ATG2B and GSKIP enhances hematopoietic progenitor differentiation, including of megakaryocytes, by increasing progenitor sensitivity to thrombopoietin 27265029_This study highlights the transcriptional inactivation mechanisms of ATG2B, ATG4D, ATG9A and ATG9B promoter methylation status and the possible origin of autophagy signal pathway repression in invasive ductal carcinomas. 27960588_Our results suggest that these three genes that are critical components of the autophagy pathway (ATG16L, ATG2B, ATG5) are not significant risk factors among Spanish patients with either pseudoexfoliation syndrome or pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. 28800131_Authors demonstrate that inhibition of autophagosome completion by Atg2A/B deletion accumulates immature autophagosomal membranes that promote non-canonical caspase-8 activation in response to nutrient starvation via an intracellular death-inducing signaling complex (iDISC). 29562274_miR-143 may induce bowel inflammation by regulating ATG2B and autophagy, suggesting that miR-143 might play a critical role in the development of Crohn's Disease 32009292_A conserved ATG2-GABARAP family interaction is critical for phagophore formation. 32335541_MicroRNA-375 exacerbates knee osteoarthritis through repressing chondrocyte autophagy by targeting ATG2B. 32407879_miR-1278 sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to cisplatin and suppresses autophagy via targeting ATG2B. 32726125_miR-375 targeting autophagy-related 2B (ATG2B) suppresses autophagy and tumorigenesis in cisplatin-resistant osteosarcoma cells. 33130456_MiR-143-3p targets ATG2B to inhibit autophagy and promote endothelial progenitor cells tube formation in deep vein thrombosis. 33250346_Polymorphism in autophagy gene ATG2B is not associated with bladder cancer recurrence after intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) immunotherapy in Asian patients. 33554699_ATG2B/GSKIP in de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML): high prevalence of germline predisposition in French West Indies. 33760149_miR1433p inhibits endometriotic stromal cell proliferation and invasion by inactivating autophagy in endometriosis. 33824300_LncRNA-HOTAIR activates autophagy and promotes the imatinib resistance of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells through a mechanism involving the miR-130a/ATG2B pathway. 34172895_Germline ATG2B/GSKIP-containing 14q32 duplication predisposes to early clonal hematopoiesis leading to myeloid neoplasms. 34320900_Crocin exerts anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects on cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma via miR-320a/ATG2B. 34695177_Downregulation of LINC01296 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer via targeting miR-143-3p/ATG2B. 34748402_Loss of Atg2b and Gskip Impairs the Maintenance of the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Pool Size. 35902797_The prognostic value of autophagy related genes with potential protective function in Ewing sarcoma. |
ENSMUSG00000041341 |
Atg2b |
237.596503 |
0.3290916529 |
-1.603439 |
0.354457143 |
19.588531 |
0.00000960440237082214184828783676284302828207728452980518341064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000030110658239875706914789182944147682974289637058973312377929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
131.9811495 |
34.4054948 |
403.8813792 |
75.7400305 |
| ENSG00000066923 |
10734 |
STAG3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UJ98 |
FUNCTION: Meiosis specific component of cohesin complex. The cohesin complex is required for the cohesion of sister chromatids after DNA replication. The cohesin complex apparently forms a large proteinaceous ring within which sister chromatids can be trapped. At anaphase, the complex is cleaved and dissociates from chromatin, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. The meiosis-specific cohesin complex probably replaces mitosis specific cohesin complex when it dissociates from chromatin during prophase I. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31682730}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Centromere;Chromosome;Chromosome partition;Disease variant;Meiosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Premature ovarian failure;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is expressed in the nucleus and is a subunit of the cohesin complex which regulates the cohesion of sister chromatids during cell division. A mutation in this gene is associated with premature ovarian failure. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:10734; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000775]; cohesin complex [GO:0008278]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; meiotic cohesin complex [GO:0030893]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; synaptonemal complex [GO:0000795]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; establishment of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0034089]; sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0007062]; synaptonemal complex assembly [GO:0007130] |
18299561_identified as one of five genes containing 11 somatic mutations in a panel that included 132 colorectal cancers, then demonstrated that down-regulation of such homologs resulted in chromosomal instability and chromatid cohesion defects in human cells 18788457_plays a role in regulation of transcription due to genetic imprinting, sister chromatid exchange, chromosome segregation and as an insulator element. (review) 19270026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635389_we show evidence for the involvement of a common allele of STAG3 in the development of epithelial ovarian cancer 24597867_We identified a homozygous 1-bp deletion inducing a frameshift mutation in STAG3 on chromosome 7. Female mice devoid of Stag3 are sterile. 26059840_STAG3 truncating variant as the cause of primary ovarian insufficiency has been found in two sisters in a consanguineous Lebanese family. 27500726_Loss of STAG2 or STAG3, which encode subunits of the cohesin complex, in melanoma cells results in resistance to BRAF inhibitors (BRAFi). Loss-of-function mutations in STAG2, as well as decreased expression of STAG2 or STAG3 proteins were found in several tumor samples from patients with acquired resistance to BRAFi and in BRAFi-resistant melanoma cell lines. 28393351_RT-PCR revealed that the mutation causes loss of wild-type donor splice-site which leads to aberrant splicing of STAG3 mRNA and consecutive formation of STAG3 alternative transcript (p.Leu490Thrfs*10) . This is the first report of splice-site mutation of STAG3 gene causes POI in 2 Han Chinese patients. 28802712_c.677C > G associated with primary ovarian insufficiency 29724914_Rec8-Stag3 cohesin is shown to be susceptible to Wapl-dependent ring opening and sororin-mediated protection. 31115363_The association of stromal antigen 3 (STAG3) sequence variations with spermatogenic impairment in the male Korean population. 31125047_For the first time, study reports biallelic variants in STAG3, in one sporadic patient, and a homozygous RNF212 variant, in the two brothers, as the genetic cause of non-obstructive azoospermia. Meiotic studies allowed the detection of the functional consequences of the mutations and provided information on the role of STAG3 and RNF212 in human male meiosis. 31363903_This is the first report of STAG3 mutations in a Caucasian family with primary ovarian insufficiency. 31682730_Mutations in the stromal antigen 3 (STAG3) gene cause male infertility due to meiotic arrest. 32634216_STAG3 homozygous missense variant causes primary ovarian insufficiency and male non-obstructive azoospermia. 33039558_The meiosis-specific cohesin component stromal antigen 3 promotes cell migration and chemotherapeutic resistance in colorectal cancer. 33980954_Analysis of STAG3 variants in Chinese non-obstructive azoospermia patients with germ cell maturation arrest. 34497033_Biallelic loss of function variants in STAG3 result in primary ovarian insufficiency. 34828315_A Long Contiguous Stretch of Homozygosity Disclosed a Novel STAG3 Biallelic Pathogenic Variant Causing Primary Ovarian Insufficiency: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. 35503298_New STAG3 gene variant as a cause of premature ovarian insufficiency', trans 'Nueva variante del gen STAG3 causante de insuficiencia ovarica prematura 35941537_The upregulation of stromal antigen 3 expression suppresses the phenotypic hallmarks of hepatocellular carcinoma through the Smad3-CDK4/CDK6-cyclin D1 and CXCR4/RhoA pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000036928 |
Stag3 |
33.210396 |
0.1264177352 |
-2.983729 |
0.395830365 |
62.887374 |
0.00000000000000218870772318336499528075689959545692339908540963167027371127915102988481521606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000015339660965900507883315944384873192675759149411485182668002380523830652236938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7167578 |
1.9455655 |
61.4409493 |
7.6647808 |
| ENSG00000067064 |
3422 |
IDI1 |
protein_coding |
Q13907 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the 1,3-allylic rearrangement of the homoallylic substrate isopentenyl (IPP) to its highly electrophilic allylic isomer, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8806705}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Isomerase;Isoprene biosynthesis;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Peroxisome;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism |
PATHWAY: Isoprenoid biosynthesis; dimethylallyl diphosphate biosynthesis; dimethylallyl diphosphate from isopentenyl diphosphate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8806705}. |
IDI1 encodes a peroxisomally-localized enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) to its highly electrophilic isomer, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), which are the substrates for the successive reaction that results in the synthesis of farnesyl diphosphate and, ultimately, cholesterol. It has been shown in peroxisomal deficiency diseases such as Zellweger syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy that there is reduction in IPP isomerase activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3422; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; isopentenyl-diphosphate delta-isomerase activity [GO:0004452]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; dimethylallyl diphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0050992]; isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0009240]; isoprenoid biosynthetic process [GO:0008299] |
14629038_only one of the two isoforms (IDI1) is highly conserved, ubiquitously expressed and most likely responsible for housekeeping isomerase activity 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20955688_Within the 40-kb region on 10p15.3 subtelomere, which harbours two genes encoding isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase 1 (IDI1) and IDI2, there was found a segmental copy-number gain in a large proportion of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. 25950736_The present findings suggest that IDI1 and IDI2 may be associated with the production of cholesterol metabolites in neurons, leading to alpha-synuclein aggregation during the process of Lewy body formation. 30567295_Canonical pathway analysis, using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software, revealed that the only genes in the 'superpathway of cholesterol biosynthesis' were Idi1 (upregulated) and Hmgcs2 (downregulated). The Idi1 and Hmgcs2 genes have regulatory roles in atrial lipotoxic myopathy associated with atrial enlargement |
ENSMUSG00000058258 |
Idi1 |
290.738074 |
2.6764664447 |
1.420330 |
0.131830064 |
114.859552 |
0.00000000000000000000000000844733232423802423575480550930969824478747380613539105622106773817392650141600007884790102252736687660217285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000096653197756397867640755917957408603352939398000857584631758385121803444500754309842704969923943281173706054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
415.9163146 |
31.3151861 |
156.4257684 |
9.1741316 |
| ENSG00000067113 |
8611 |
PLPP1 |
protein_coding |
O14494 |
FUNCTION: Magnesium-independent phospholipid phosphatase of the plasma membrane that catalyzes the dephosphorylation of a variety of glycerolipid and sphingolipid phosphate esters including phosphatidate/PA, lysophosphatidate/LPA, diacylglycerol pyrophosphate/DGPP, sphingosine 1-phosphate/S1P and ceramide 1-phosphate/C1P (PubMed:9305923, PubMed:9705349, PubMed:9607309, PubMed:10962286, PubMed:17379599). Also acts on N-oleoyl ethanolamine phosphate/N-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-ethanolamine phosphate, a potential physiological compound (PubMed:9607309). Through its extracellular phosphatase activity allows both the hydrolysis and the cellular uptake of these bioactive lipid mediators from the milieu, regulating signal transduction in different cellular processes (PubMed:10962286, PubMed:12909631, PubMed:15461590, PubMed:17379599). It is for instance essential for the extracellular hydrolysis of S1P and subsequent conversion into intracellular S1P (PubMed:17379599). Involved in the regulation of inflammation, platelets activation, cell proliferation and migration among other processes (PubMed:12909631, PubMed:15461590). May also have an intracellular activity to regulate phospholipid-mediated signaling pathways (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10962286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12909631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15461590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17379599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9305923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9607309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705349}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; phospholipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10962286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9305923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9607309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705349}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the phosphatidic acid phosphatase (PAP) family. PAPs convert phosphatidic acid to diacylglycerol, and function in synthesis of glycerolipids and in phospholipase D-mediated signal transduction. This enzyme is an integral membrane glycoprotein that plays a role in the hydrolysis and uptake of lipids from extracellular space. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:8611; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; caveola [GO:0005901]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ceramide-1-phosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0106235]; diacylglycerol diphosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0000810]; lipid phosphatase activity [GO:0042577]; phosphatidate phosphatase activity [GO:0008195]; sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0042392]; androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030521]; ceramide metabolic process [GO:0006672]; intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030518]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; phospholipid dephosphorylation [GO:0046839]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingosine metabolic process [GO:0006670] |
12426308_this enzyme regulates interleukin-4-mediated STAT6 signaling. 12444089_This protein and phosphoprotein SET regulate androgen production by P450c17. 14506139_lipid phosphate phosphatase-1 has a role in regulating accumulation of lysophosphatidic acid in ovarian cancer 16950767_Lipopolysaccharide-induced up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 depends on the activity of the Mg(+2)-dependent phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase 1 (PAP-1) 17005594_LPP1 and LPP3 are distributed in distinct lipid rafts that may provide unique microenvironments defining their non-redundant physiological functions. 17169329_These results suggest that the expression of PAP2a is directly regulated by p73. 18755152_These results suggest that LPP1a is important for the determination of plasma FTY720-P levels. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23426360_Phosphorylation of lipin 1 and charge on the phosphatidic acid head group control its phosphatidic acid phosphatase activity and membrane association 23936490_the first of the two transmembrane regions in human SAC1 (TM1) functions in Golgi localization |
ENSMUSG00000021759 |
Plpp1 |
45.132121 |
3.0840644828 |
1.624833 |
0.274133522 |
35.483462 |
0.00000000257225240741440159918936428416844780509009638080897275358438491821289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011860807726784306139083233926946603364882548703462816774845123291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.1281873 |
10.5922227 |
22.2982906 |
2.8189783 |
| ENSG00000067191 |
782 |
CACNB1 |
protein_coding |
Q02641 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of L-type calcium channels (PubMed:1309651, PubMed:8107964, PubMed:15615847). Regulates the activity of L-type calcium channels that contain CACNA1A as pore-forming subunit (By similarity). Regulates the activity of L-type calcium channels that contain CACNA1C as pore-forming subunit and increases the presence of the channel complex at the cell membrane (PubMed:15615847). Required for functional expression L-type calcium channels that contain CACNA1D as pore-forming subunit (PubMed:1309651). Regulates the activity of L-type calcium channels that contain CACNA1B as pore-forming subunit (PubMed:8107964). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P19517, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1309651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15615847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8107964}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell membrane;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the calcium channel beta subunit family. It plays an important role in the calcium channel by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three transcript variants encoding three distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:782; |
L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:1990454]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0008331]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0005245]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; positive regulation of muscle contraction [GO:0045933]; regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel [GO:1902514]; regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901385] |
19821165_Data show that the length-dependent mechanism of modulating inactivation kinetics of beta(2) calcium channel subunits can be confirmed and extended to the beta(1) calcium channel subunit. 21098446_CACNB1, encoding cardiac L-type calcium channel beta 1 subunit, is a potential target for microRNA-328 in transgenic mice. 27129199_These results provide new insights into the role of muscle-specific proteins on the structural arrangement of alpha1S intracellular loops and point to a new conformational effect of the beta1a subunit in supporting skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling. 29212769_Data show that mutant variant V156A results in instability of protein subdomains of beta1a subunit leading to a phenotype of Ca(2+) dysregulation that partly resembles that of other malignant hypertension-linked mutations of DHPR alpha1S subunit. |
ENSMUSG00000020882 |
Cacnb1 |
45.364712 |
0.2729013231 |
-1.873549 |
0.472788831 |
14.790656 |
0.00012012925641662373444154554569252013607183471322059631347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000327081317968892543342207535062016177107580006122589111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.1744934 |
7.1540731 |
73.9638252 |
17.9867253 |
| ENSG00000067225 |
5315 |
PKM |
protein_coding |
P14618 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the final rate-limiting step of glycolysis by mediating the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to ADP, generating ATP (PubMed:20847263, PubMed:15996096, PubMed:1854723). The ratio between the highly active tetrameric form and nearly inactive dimeric form determines whether glucose carbons are channeled to biosynthetic processes or used for glycolytic ATP production (PubMed:20847263, PubMed:15996096, PubMed:1854723). The transition between the 2 forms contributes to the control of glycolysis and is important for tumor cell proliferation and survival (PubMed:20847263, PubMed:15996096, PubMed:1854723). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15996096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1854723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20847263}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform M2]: Isoform specifically expressed during embryogenesis that has low pyruvate kinase activity by itself and requires allosteric activation by D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) for pyruvate kinase activity (PubMed:18337823, PubMed:20847263). In addition to its pyruvate kinase activity in the cytoplasm, also acts as a regulator of transcription in the nucleus by acting as a protein kinase (PubMed:18191611, PubMed:21620138, PubMed:22056988, PubMed:22306293, PubMed:22901803, PubMed:24120661). Translocates into the nucleus in response to various signals, such as EGF receptor activation, and homodimerizes, leading to its conversion into a protein threonine- and tyrosine-protein kinase (PubMed:22056988, PubMed:22306293, PubMed:22901803, PubMed:24120661, PubMed:26787900). Catalyzes phosphorylation of STAT3 at 'Tyr-705' and histone H3 at 'Thr-11' (H3T11ph), leading to activate transcription (PubMed:22306293, PubMed:22901803, PubMed:24120661). Its ability to activate transcription plays a role in cancer cells by promoting cell proliferation and promote tumorigenesis (PubMed:18337823, PubMed:22901803, PubMed:26787900). Promotes the expression of the immune checkpoint protein CD274 in BMAL1-deficient macrophages (By similarity). May also act as a translation regulator for a subset of mRNAs, independently of its pyruvate kinase activity: associates with subpools of endoplasmic reticulum-associated ribosomes, binds directly to the mRNAs translated at the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes translation of these endoplasmic reticulum-destined mRNAs (By similarity). Plays a role in caspase independent cell death of tumor cells (PubMed:17308100). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52480, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17308100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18191611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20847263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21620138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22056988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22306293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22901803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24120661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26787900}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform M1]: Pyruvate kinase isoform expressed in adult tissues, which replaces isoform M2 after birth (PubMed:18337823). In contrast to isoform M2, has high pyruvate kinase activity by itself and does not require allosteric activation by D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) for activity (PubMed:20847263). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20847263}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycolysis;Hydroxylation;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Pyruvate;Reference proteome;Transferase;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; pyruvate from D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate: step 5/5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15996096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1854723}. |
This gene encodes a protein involved in glycolysis. The encoded protein is a pyruvate kinase that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, generating ATP and pyruvate. This protein has been shown to interact with thyroid hormone and may mediate cellular metabolic effects induced by thyroid hormones. This protein has been found to bind Opa protein, a bacterial outer membrane protein involved in gonococcal adherence to and invasion of human cells, suggesting a role of this protein in bacterial pathogenesis. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding a few distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:5315; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; histone H3T11 kinase activity [GO:0035402]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; potassium ion binding [GO:0030955]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; pyruvate kinase activity [GO:0004743]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; canonical glycolysis [GO:0061621]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; positive regulation of cytoplasmic translation [GO:2000767]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; programmed cell death [GO:0012501] |
12820312_measurement of fecal Tumor M2-PK concentrations might provide an interesting screening tool for colorectal cancer 12820320_With the fuzzy logic method and a tumor marker panel (including the new marker Tumor M2-PK), a useful diagnostic tool for the detection of progression in lung cancer patients is available 12820337_phosphorylated at tyrosine residues in breast cancer patients; did not find any evidence that this phosphorylation is initiated by the oncoprotein HER-2/neu 15996096_The X-ray structure of tumor specific PKM2 complexed with Mg2+, K+, inhibitor oxalate, and allosteric activator fructose 1,6-bisphosphate has been determined, and its unique structural characteristics relative to other known isoforms have been analyzed. 16132722_PanK4 interacts with Pkm2 and thereby may modulate the glucose metabolism through regulating the activity of Pkm2. 17011640_PK can function as an autoimmune target and that this immunoreactivity may be associated with Tourette syndrome, obsessive compulsive disorder, and associated disorders 17406361_A sensitive and specific tumor marker for colorectal cancer, seen in older adults. 17414054_An elevated level in this enzyme on admission in suspected periampullary cancer is a predictor of adverse prognosis in periampullary cancer. 18298799_PKM2 exists in either an active tetrameric form which has high affinity for its substrate phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) or a less active dimeric form which has low affinity for its substrate. 18337815_results indicate that expression of this phosphotyrosine-binding form of pyruvate kinase is critical for rapid growth in cancer cells 18394773_expression of pyruvate kinase M2 isoenzyme was found in 53% 0f granulosa cell tumors of the ovary 18464261_aberrant reduction of miR-133a and miR-133b was associated with the dysregulation of M2-type pyruvate kinase (PKM2) in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the tongue. 18519040_NS5B interacted with M2 type pyruvate kinase but not L type pyruvate kinase. 18789002_Data confirmed the cancer-associated expression of the PKM2 variant with primary colon cancer and colon cancer cell lines, with PKM2 expressed at high levels in colon cancer and in colon cancer cell lines. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19097497_fecal pyruvate kinase M2 is an inferior biological marker of inflammatory bowel disease when compared with fecal calprotectin 19265196_Differential behavior of missense mutations in the intersubunit contact domain of the human pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme. 19401544_The gene ratio test with the PKM2 gene for survival of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma has robust predictive value. 19734428_Pyruvate kinase M2 and prednisolone resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19754967_Complete lack of M2-PK expression was observed in benign pancreatic ducts, premalignant lesions and cancer. 19820423_Tumor-M2-PK may have a role in diagnosing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 19920249_Studies suggest that regulation of PKM2 seems to be pivotal for regulating glycolysis in proliferating cells. regulation of PKM2 seems to be pivotal for regulating glycolysis in proliferating cells. 19920251_Data show that oncogenic forms of fibroblast growth factor receptor type 1 inhibit the pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) isoform by direct phosphorylation of PKM2 tyrosine residue 105 (Y(105)). 20010808_human gliomas overexpress c-Myc, PTB, hnRNPA1 and hnRNPA2 in a manner that correlates with PKM2 expression 20082317_the association of PKM2 and HSPD1, two differentially expressed proteins, with MDR were analyzed, and the results showed that they could contribute considerably to the cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cell 20133837_splicing repressors hnRNP A1 and A2, as well as the polypyrimidine-tract-binding protein PTB, contribute to control of pyruvate kinase isoform M1 and M2 expression 20304929_human pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme dominant mutations promote cellular growth and polyploidy 20332442_Increased M2 pyruvate kinase is associated with cervical cancer progression. 20592362_M2PK has a role in preventing, and pAkt has a role in enhancing progression of breast cancer 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20667897_human glioblastoma cells with high levels of PKM2 expressed lower levels of miR-326, suggestive of endogenous regulation of PKM2 by miR-326. 20721957_Overexpression of PKM2 is associated with recurrences in chordomas. 20847263_histidine-phosphorylated PGAM1 correlated with expression of PKM2 in cancer cell lines; decreased pyruvate kinase activity in PKM2-expressing cells allows PEP-dependent histidine phosphorylation of PGAM1 and may provide an alternate glycolytic pathway 20857498_This review aims to provide an overview of the involvement of human PKM2 in various physiological pathways with possible functional implications. 20962042_inhibition of PKM2 by PRL contributes to the PRL-stimulated cell 20977946_A study on the relationship between prothymosin alpha kinase(ProTalphaK) activity and pyruvate kinase isoforms confirmed that the M2 isoform is the enzyme responsible for ProTalphaK activity in proliferating cells. 21325052_Components of the mTOR/HIF1alpha/Myc-hnRNPs/PKM2 glycolysis signaling network could be targeted for the treatment of cancer caused by an aberrant RTK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway 21620138_Interaction of PKM2 with prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3) enhances PKM2 binding to HIF-1alpha and PKM2 coactivator function; PKM2 participates in a positive feedback loop that promotes HIF-1 transactivation and reprograms glucose metabolism in cancer cells. 21725354_Data show that pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) was a binding partner of death-associated protein kinase (DAPk). 22044881_Exons are the key determinants of PK-M splicing isoform ratios. 22052977_findings show, in lung cancer cells, increases in intracellular ROS caused inhibition of PKM2 through oxidation of Cys(358);regulatory properties of PKM2 may confer an additional advantage to cancer cells by allowing them to withstand oxidative stress 22056988_epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation induces translocation of PKM2, but not PKM1, into the nucleus, where K433 of PKM2 binds to c-Src-phosphorylated Y333 of beta-catenin 22140559_These findings indicate that the MUC1-C subunit regulates glycolysis and that this response is conferred in part by PKM2. 22231432_These findings suggest that plasmatic Tu M2-PK levels of more than 20 U/mL may be a predictor of death risk. 22236875_PKM2 did not lead to lactate accumulation in breast cancer cells. 22271574_Pyruvate kinase M2-specific siRNA induces apoptosis and tumor regression. 22306293_PKM2 upregulates mek5 Transcription by promoting stat3 DNA interaction and phosphorylation of stat3. 22334075_PPARgamma contributes to PKM2 and HK2 expression in fatty liver 22465421_In patients with age-related macular degeneration, anti-PKM2 IgG serves as a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis. 22509023_PKM2-expressing cells can maintain mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activity and proliferate in serine-depleted medium, but PKM1-expressing cells cannot. 22627140_PKM2 may function as an upstream molecule that regulates p65 function and thus enhances the growth of tumor cells. 22736014_Fecal M2-PK is increased in children with active Crohn's disease. 22807066_the expression of PKM2 plays a critical role in development of colorectal cancer, and it may provide a growth advantage for colon cancer cells. 22824010_review of role of PKM2 in cancer cells, cell proliferation, and neoplastic cell transformation: PKM2 expression is increased and facilitates lactate production/oxidative stress in cancer cells. [REVIEW] 22864959_Bile M2-PK is a novel tumor marker for biliary tract cancer and correlates with tumor aggressiveness and poor outcome. 22889453_PKM2 and HSPA5 may play an important role in the progression of endometrioid carcinoma. These two proteins are potential biomarkers to better predict high-risk endometrioid carcinoma and thereby guide clinical therapy. 22901803_These findings highlight the role of PKM2 as a protein kinase in its nonmetabolic functions of histone modification, which is essential for its epigenetic regulation of gene expression and tumorigenesis. 23064226_serine can bind to and activate human PKM2, and that PKM2 activity in cells is reduced in response to serine deprivation 23071357_PKM2 is induced translocation into the nucleus, where it activates transcription of various genes by interacting with and phosphorylating specific nuclear proteins, endowing cancer cells with a survival and growth advantage. 23086999_Upon glucose starvation, cellular SAICAR concentration increased in an oscillatory manner and stimulated PKM2 activity in cancer cells. 23123196_Report metabolic cooperation between the EGFR/PKC-epsilon/NF-kappaB pathway in PKM2 upregulation and tumorigenesis. 23130662_Glycolytic enzymes PGK1 and PKM2 are novel transcriptional targets of PPARgamma in breast cancer. 23155487_Manipulation of PK-M mutually exclusive alternative splicing by antisense oligonucleotides. 23178880_Findings highlight the importance of nuclear functions of PKM2 in the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis. 23212076_summarizes the biological characteristics of PKM2 and discusses the dual role in cancer metabolism as well as the potential therapeutic applications 23267074_M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase is dispensable for tumor maintenance and growth. 23317289_pkm2 expression was higher in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma than in normal tissue, and was related to neoplasm differentiation. 23423437_findings add additional complexity to how PKM2 is regulated in cells and support the notion that modulating PKM2 activity enables cells to adapt their metabolic state to specific physiological contexts. 23451252_Showed a 3-5 fold further increase in PKM2 RNA and protein expression. 23515579_Findings collectively support the utility of PKM2 as a therapeutic target for high lactate-producing glycolytic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 23530218_X-ray structures and biophysical binding data of M2PYK complexes explain how fluctuations in concentrations of amino acids, thyroid hormone, and glucose metabolites switch M2PYK to provide the cell with nutrient sensing and growth signaling mechanism 23576436_the conversion between the pyruvate kinase and protein kinase activities of PKM2 may be an important mechanism mediating the effects of growth signals in promoting cell proliferation. 23640882_PKM2 is a novel substrate of PTP1B tyrosine phosphorylation. 23752568_PKM2 is secreted in metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines; differences between secretomes of the two metastatic human cell lines are also explored. 23793810_PKM2 overexpression is a marker of metastasis, invasion and poor prognosis of Gallbladder cancer. 23794342_Serum M2-pyruvate kinase levels may be useful in distinguishing malignant and benign lesions of the colon and may provide insight in terms of survival. 23814019_NPM-ALK-mediated phosphorylation of PKM2 and metabolic reprogramming has a role in anaplastic large cell lymphoma 23840737_Cytoplasmic PKM2 expression were correlated with each other. 23846818_overexpression of PKM2 provides a selective growth advantage for papillary thyroid cancer cells through activation of glycolysis. Aberrant PKM2 overexpression may serve as a novel biomarker and a potential treatment target for papillary thyroid cancer. 23880164_Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients with high PKM2 expression in the nucleus had significantly shorter survival times. 24077665_Suggest that isoform switch of PKM1 to PKM2 in cancers is tissue-specific and targeting PKM2 activity in tumors remains a promising approach for clinical intervention of multiple cancer types. 24100037_PKM2 activity in beta-cells is oscillatory and are consistent with pulsatile PFK1 being the mediator of slow glycolytic oscillations. 24120138_These data suggest that regulation of pyruvate kinase M2 isoform activity supports the different metabolic requirements of proliferating and nonproliferating tumor cells. 24120661_K433 acetylation links cell proliferation and transformation to the switch of PKM2 from a cytoplasmic metabolite kinase to a nuclear protein kinase 24142698_PIM2 could directly phosphorylate PKM2 on the Thr-454 residue, resulting in an increase of PKM2 protein levels. Compared with wild type, PKM2 with the phosphorylation-defective mutation displayed a reduced effect on glycolysis. 24316223_These findings highlight the role of PKM2 as a protein kinase controlling the fidelity of chromosome segregation, cell-cycle progression, and tumorigenesis. 24344305_JMJD5 has a role in regulating PKM2 nuclear translocation and reprogramming HIF-1alpha-mediated glucose metabolism 24466275_High PKM2 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 24471565_PKM2 acts as a transcriptional coactivator for ERalpha and small-molecule PKM2 activators inhibit ERalpha transcriptional activity and reduce E2-induced cell proliferation. 24481450_PKM2-Oct4 interaction controls glioma cell death and differentiation. 24492614_This study demonstrates for the first time the possible predisposition of Bloom syndrome patients with impaired PKM2 activity to cancer. 24508027_this study discusses the current understanding of PKM2 in regulating cancer metabolism. 24606918_ligand-induced protein kinase activity from PKM2 is a mechanism that directly couples cell proliferation with intracellular metabolic status 24619225_Data indicate that pyruvate kinase PKM1 regulates miR-124 expression via hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF4alpha). 24626155_increased PKM2 is the culprit of enhanced aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells 24649481_FC reflects pediatric IBD severity and activity better than M2-PK. This difference is particularly pronounced when identifying patients with mild UC and UC in remission. 24658033_HSP40 interacts with pyruvate kinase M2 and regulates glycolysis and cell proliferation in tumor cells. 24686087_The overexpression of PKM2, particularly its dimer form, induces CRC cell migration and cell-matrix adhesion by driving STAT3 transcription, which is required for the PKM2-induced activation of beta1-integrin-FAK signalling, Snail-2 signalling. 24699725_The addition of M2-PK in a biennial bowel screening programme is acceptable to patients, feasible and detects additional adenomas, potentially at an earlier stage. 24716919_study revealed that nuclear translocation of PKM2, regulated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC cells) EMT and migration in vitro; These discoveries provided novel role of PKM2 in the progression of HCC 24747424_PKM2 regulation and the benefits it confers to cancer cells 24759699_The two markers pyruvate kinase isoform M2 and calprotectin did not prove their clinical utility in differential diagnosis of infectious acute diarrhea in those children demanding hospitalization. 24762230_Overexpression of PKM2 and LDH5 associates with key clinicopathological features and unfavourable prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 24795025_Findings suggest that the altered metabolism observed in most cancer cells may facilitate a SAICAR-dependent PKM2 functional switch that sustains cell proliferation. 24817408_Up-regulation of PKM2 might protect intestinal epithelial cells against apoptosis possibly through Bcl-xl in Crohn's disease. 24859886_Data indicate that zinc finger protein SNAIL modulates ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (RPS6KB1)/HIF-1alpha/protein kinase 2 (PKM2) signaling pathway through miR-128. 24884829_upregulation and specific modification to PKM2 associate with prostate cancer progression. 24898807_overexpression of miR-122 in 5-FU-resistant cells resensitizes 5-FU resistance through the inhibition of PKM2 24982407_PKM2 and PKM1 have no value as predictive markers of NSCLC regardless of the histological type and grade of malignancy. 25041845_PKM2 depletion could provoke glutamine metabolism by enhancing the beta-catenin signaling pathway and consequently promoting its downstream c-Myc-mediated glutamine metabolism in colon cancer cells. 25070887_Only the dimeric PKM2 possess the activity in promoting tumor angiogenesis, which is consistent with the observations that PKM2 in circulation of cancer patients is a dimer form. 25233397_High PKM2 levels were associated with low platinum sensitivity in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. 25260566_expression increased in pre-eclamptic placenta at delivery 25263439_TRIM35 regulates the Warburg effect and tumorigenicity through interaction with PKM2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25313085_This previously unidentified finding of the molecular interaction of PKM2 in the nucleus sheds light on the significance of PKM2 expression in cancer cells. 25344422_median bile M2-PK levels were significantly elevated in patients with malignant biliary strictures 25411978_PKM2 gene regulates the behavior of pancreatic cancer cells via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways 25412762_PKM2-regulated MLC2 phosphorylation, which is greatly enhanced by EGF stimulation or EGFRvIII, K-Ras G12V and B-Raf V600E mutant expression, plays a pivotal role in cytokinesis, cell proliferation and brain tumour development. 25444918_High Pyruvate Kinase, M2-Type expression is associated with low radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer. 25514599_Data suggest that targeted therapy aimed at pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) may represent an effective treatment approach for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 25541689_Results show that PKM2 over-expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma was associated with down-regulation of its regulator mir-122 resulting in an aggressive clinicopathological features and poor prognosis. 25576919_Data suggest that pyruvate kinase isoform M2 (PKM2)/tripartite motif-containing 35 (TRIM35) expression could be a biomarker for the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and target for cancer therapy. 25644089_AIC-47, acting through the PPARgamma/beta-catenin pathway, induced down-regulation of c-Myc, leading to the disruption of the bcr-abl/mTOR/hnRNP signaling pathway, and switching of the expression of PKM2 to PKM1 in acute myeloid leukemia. 25645022_K422R, a patient-derived mutation of PKM2, favors a stable, inactive T-state tetramer because of strong intermolecular interactions. 25649613_PKM2 knockdown leaded to increased radiosensitivity of radioresistant cell lines. Significant inhibition in tumor size under regular radiotherapy was found in Balb/c-nude mice bearing radioresistant NSCLC tumors with PKM2 knockdown. 25661370_PKM2 is an active protein kinase, and promotes liver cancer cell proliferation by up-regulating HIF-1alpha and Bcl-xL expression. 25703326_Disruption of PKM2/NF-kappaB/miR-148a/152 feedback loop can regulate cancer cell growth. 25708858_we investigated the inter-action between PKM2 and USP20. Our results suggest a new molecular pathway in cancer metabolism through the regulation of PKM2. 25732087_PKM2 could be secreted from colon cancer cells, and purified PKM2 protein mimicing the secreted PKM2 was able to promote colon cancer cell migration. 25735978_observed a shift in the enzyme pyruvate kinase from the adult M1 (PKM1) isoform to the fetal M2 (PKM2) isoform, a hallmark of the Warburg Effect, in sunitinib-treated patients developing cardiac failure 25738776_isoform switch of PKM1 does indeed occur, but it switches to other isoforms rather than PKM2 25768091_3 SNPs (rs2856929, rs8192381 and rs8192431) of PKM2 could generate an alternative transcript by influencing splicing factor binding. 25773278_The regulation of PKM2 oligomerization may be a general mechanism to modulate PKM2 activity. 25788265_PKM2 serves as a promising biomarker for poor prognosis of patients with HCC and its knockdown induces HCC apoptosis by stabilizing Bim. 25808097_High PKM2 expression significantly correlated with poor response to chemotherapy in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 25818238_Suggest that miR-124 acts as a tumor-suppressor and a modulator of energy metabolism through a PTB1/PKM1/PKM2 feedback cascade in human colorectal tumor cells. 25880801_Our data shows that overexpression and increased phosphorylation of PKM2 and LHDA is a common finding in thyroid malignancies. 25893434_Low expression of PKM2 was associated with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 25912843_Glucose transporter 1 expression exhibits a strong correlation with 18F-FDG uptake in cholangiocellular carcinoma tissue, while pyruvate kinase type M2 expression was not associated with fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake. 25936600_Overexpression of PKM2 contributes to radiation resistance and acts a poor prognosis indicator in patients with locally advanced cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 25955657_oxaliplatin and PKM2 silencing altered cell death gene expression patterns. 25964202_Data show that cosilencing of pyruvate kinase M2 and multidrug resistance gene-1 (PKM-2 and MDR-1) improves the efficacy of paclitaxel against multidrug resistance (MDR) ovarian cancer in a murine model. 25970228_PKM2 is critically involved in OSCC initiation and progression probably by promoting cell proliferation and migration as well as reducing apoptosis. 26059508_The maintenance of high glycolysis levels by Pkm2 (and Hk2) overexpression preserves the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. 26082202_The downregulation of PKM2 induced apoptosis and autophagy in A549 cells and this autophagy protected the cells from apoptotic cell death. 26092770_findings provide a molecular mechanism for how HIF-1 dysregulation fuels both angiogenesis and tumor metabolism in KS and support further investigations on therapeutic approaches targeting HIF-1 and PKM2 for KS treatment. 26140362_purine biosynthetic pathway enzymes PPAT and PAICS, as well as pyruvate kinase activity are increased in lung cancer 26158845_Data show that the M2 pyruvate kinase (M2-PK)Quick, rapid, point-of-care test is a highly accurate test in the detection of colorectal cancer (CRC). 26172294_Data show that pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme (PKM2 )was positively regulated by NF-kappa B (NF-kappaB)/transcription factor RelA (RelA) at the transcriptional level. 26183399_pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), an established effector of Warburg-like glycolytic behavior, has a role in oxidative phosphorylation metabolism induced by cancer associated fibroblasts 26234680_findings point to PKM2 and PTBP1 as new potential therapeutic targets to improve response of PDAC to chemotherapy 26252254_Data show that miR-122 has a low expression in Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, and correlates with poor prognosis. It plays an important role in the invasion and metastasis of HCC by targeting PKM2. 26252736_These results suggested roles of O-GlcNAcylation in modulating serine phosphorylation, as well as in regulating PKM2 activity and expression. 26258887_The PARP14-JNK1-PKM2 regulatory axis is an important determinant for the Warburg effect in tumour cells and provides a mechanistic link between apoptosis and metabolism. 26290635_PKM2 can regulate cell motility through the EGF/EGFR and TGFbeta/TGFR signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 26300261_Using [(32)P]-phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) we examine the direct substrates of PKM2 using recombinant enzyme and in vitro systems where PKM2 is genetically deleted. The findings argue against a role for PKM2 as a protein kinase. 26339369_PKM2 expression was correlated with VEGF-C expression, and combination of PKM2 and VEGF-C levels had the better prognostic significance in predicting the poor outcome of patients with breast cancer. 26385349_Loss of PKM2 expression was associated with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. 26404132_PKM2 was involved in progression of ESCC. 26405201_PKM2 sensitizes AhR-mediated detoxification in actively proliferating cells such as cancer and fetal cells. PKM2 and p300 constitute a complex with AhR on chromatin. 26410533_PKM2 interacts with DDB2 and reduces cell survival upon UV irradiation. 26453405_PKM2 expression was positively correlated with cell proliferation and knockdown of PKM2 contributed to the increased cell adhesion rate in multiple myeloma. 26464675_Our results suggest that overexpression of PKM2 and HK1, especially the latter, significantly associates with lymphatic metastasis, advanced clinical staging and unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer. 26493215_laforin/malin complex is able to interact with and ubiquitinate both PKM1 and PKM2 26493994_Critical roles of PKM2 in the stemness of breast cancer cells which may elevate the therapeutic effect on breast cancer patients. 26500058_Data show that pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) directly interacted with mutant growth factor receptor (EGFR) and heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90), and thus stabilized EGFR by maintaining its binding with HSP90 and co-chaperones. 26500118_PKM2 exhibits a tumor-suppressive role through altered Warburg effect in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 26506517_High PKM2 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 26542452_The activation of STAT3 by nuclear PKM2 was associated with gefitinib resistance. 26576639_PKM2 regulates neural invasion of HC cells at least in part via regulation of SDC2. 26607846_Overexpression of PKM2 is associated with high risks of recurrent metastasis in primary breast carcinoma. 26617865_our studies reveal the prognostic value of PKM2 in colorectal cancer 26639784_GLUT3 and OCT4 expression were correlated suggesting that Human embryonic stem cells self-renewal is regulated by the rate of glucose uptake. 26702927_PKM2/TG2 interplay plays an important role in the regulation of autophagy in particular under cellular stressful conditions such as those displayed by cancer cells. 26715276_Increased PKM2 expression is associated with triple-negative breast cancer. 26739387_in hypoxic pancreatic tumors PKM2 interferes both with NF-kappaB/p65 and HIF-1alpha activation that ultimately triggers VEGF-A secretion and subsequent blood vessel formation. 26780311_Mammalian photoreceptors contain dimeric and tetrameric PKM2 and LDH-A. This is consistent with the ability to switch between energy production and biosynthesis like a proliferating tissue, possibly due to demands of opsin synthesis. 26787900_demonstrate that PKM2 deacetylation is integral to SIRT6-mediated tumor suppression and inhibition of metastasis. Additionally, reduced SIRT6 levels correlate with elevated nuclear acetylated PKM2 levels in increasing grades of hepatocellular carcinoma 26874904_These results define a novel mechanism by which PKM2 regulates glioma cell growth, and also define a novel set of potential therapeutic targets along the PKM2-HuR-p27 pathway 26876154_Our results provided the first phosphorylome of PKM2 and revealed a constitutive mTORC1 activating mechanism in cancer cells. 26926077_PKM2 interacts with Tristetraprolin directly, regulates Tristetraprolin transcriptional modification, destabilizes Tristetraprolin, and then impairs cell proliferation in breast cancer. Collectively, the results offer evidence of a role for PKM2 in Tristetraprolin regulation in cancer cells which may be a potential therapy target in breast cancer. 26926996_PKM2 serves a previously unidentified role as a molecular integrator of metabolic dysfunction, oxidative stress and tissue inflammation and represents a novel therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. 26959741_we demonstrated that SHP-1 dephosphorylates PKM2Y105 to inhibit the Warburg effect and nucleus-dependent cell proliferation, and the dephosphorylation of PKM2Y105 by SHP-1 determines the efficacy of targeted drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment 26975375_Ubiquitylation of PKM2 by parkin does not affect its stability but decreases its enzymatic activity. 26981025_Data indicate that combined use of immunochemical test for hemoglobin (FIT) and fecal M2-type pyruvate kinase (M2-PK) permitted the identification of 18 more neoplasm (25%). 26989901_Multivariable analysis showed that combined expression of pyruvate kinase type M2 and lactate dehydrogenase A was an independent poor prognostic marker for survival. 26992222_High PKM2 expression is associated urothelial tumorigenesis. 27012213_PKM1 has a role in resistance to anti-cancer drugs 27014756_Faecal tumor M2-pyruvate kinase ELISA may have utility as an adjunct to faecal occult blood test in a screening context, but do not support its use in symptomatic patients. 27040384_the anticancer activity of tanshinone A was targeted at metabolic regulation of miR-122/PKM2 in human esophagus cancer cells. 27163637_These findings suggest that 3,3',5-triiodothyroxine (T3) can inhibit apoptosis and oxidative stress in an oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion model AC16 and HCM-a cells by regulating the PKM2/PKM1 ratio. 27167190_In this study, we indicate that P53 (N340Q/L344R) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through upregulation of PKM2 27197174_Acetylation of PKM2 is associated with breast Cancer. 27199445_Jmjd8 is upregulated during endothelial differentiation and regulates endothelial sprouting and metabolism by interacting with pyruvate kinase M2. 27249540_PKM2 is a transcriptional co-activator of HIV-1 long terminal repeat. 27283076_Elevated expression of PKM2 is a prognostic factor for poor gallbladder cancer (GBC) clinical outcomes, implied involving of PKM2 in GBC progression. 27340866_Authors report that AKT directly interacts with PKM2 and phosphorylates it at Ser-202, which is essential for the nuclear translocation of PKM2 protein under stimulation of IGF-1. In the nucleus, PKM2 binds to STAT5A and induces IGF-1-stimulated cyclin D1 expression, suggesting that PKM2 acts as an important factor inducing STAT5A activation under IGF-1 signaling. 27385486_We further hypothesize that mTOR/PKM2 pathway stimulation serves to sustain the oncogenic activity of mutant p53 through both the enhancement of chemoresistance and of aerobic glycolysis of cancer cells 27413251_In CRC, sensitivity of M2PK, iFOBT, and Hb/Hp complex proved to be high. Combined use of M2PK, iFOBT, and FC may be valuable in the detection of large adenomas. 27431728_High PKM2 expression is associated with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. 27485204_EGFR activation results in c-Src-mediated Cdc25A phosphorylation at Y59, which interacts with nuclear pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). 27573352_Results show that PKM2 physically associates with TSC22D2 reducing its nuclear localization and contributing to tumor suppressor function of TSC22D2 in colorectal cancer. 27602585_Data show that cytomegalovirus encoded chemokine receptor US28 (US28) signaling in activation of the HIF-1alpha/PKM2 feedforward loop in fibroblasts and glioblastoma cells. 27644251_PKM2 expression was elevated in the cancerous tissues and it was more abundant than the adjacent normal tissues. the overall survival for patients with high PKM2 expression was significantly lower than those with low PKM2 expression. 27683215_PKM2 activity is higher in patients with NSCLC than in healthy subjects. The level of PKM2 activity is associated with advanced stage of cancer. 27801666_PKM2 knockdown resulted in increased p53 expression and prolonged half-life of p53. PKM2 could directly bind with both p53 and MDM2 and promote MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination. The dimeric PKM2 significantly suppressed p53 expression compared with the other PKM2 mutants. 27810895_PKM2 interferes with phosphorylation of P53 at serine 15, known to stimulate P53 activity by the ATM serine/threonine kinase. 27821480_RBM4 is induced and is involved in the PKM splicing switch and neuronal gene expression during hypoxia-induced neuronal differentiation. 27894667_Nuclear PKM2 expression as an independent risk factor for early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. 27911861_over-expression of PKM2 is associated with poor prognosis in most solid cancers and it might be a potentially useful biomarker for predicting cancer prognosis in future clinical applications. 27989750_UCP2 stimulates hnRNPA2/B1, GLUT1 and PKM2 expression and sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to glycolysis inhibition. 28025580_study aims to look for gene expression-based prognostic markers in multiple myeloma, and investigate the relationship between CD147 and key glycolytic enzymes (LDHA, PDK1 and PKM2) that are the regulators of Warburg effect 28035139_These findings uncover a novel mechanism through which mitochondrial PKM2 phosphorylates Bcl2 and inhibits apoptosis directly. 28036303_Report that PKM2 is succ |
ENSMUSG00000032294 |
Pkm |
8968.932370 |
2.9808103958 |
1.575705 |
0.017507956 |
8317.186031 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13613.1224527 |
173.4931286 |
4601.0847226 |
46.3927795 |
| ENSG00000067533 |
51018 |
RRP15 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3B9 |
|
Acetylation;Citrullination;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that co-purifies with human nucleoli. A similar protein in budding yeast is a component of pre-60S ribosomal particles, and is required for the early maturation steps of the 60S subunit. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51018; |
preribosome, large subunit precursor [GO:0030687]; maturation of 5.8S rRNA [GO:0000460]; maturation of LSU-rRNA [GO:0000470] |
15769876_The budding yeast homolog of human RRP15 is required for maturation of 60S ribosomal particles 28099941_Data suggest that ribosomal RNA-processing protein 15 (RRP15) might be a potential target for cancer therapy. 34343634_Inhibition of ribosomal RNA processing 15 Homolog (RRP15), which is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses tumour growth via induction of senescence and apoptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000001305 |
Rrp15 |
237.098627 |
2.0381773241 |
1.027280 |
0.249265421 |
16.221030 |
0.00005636491016700362512289665395393001290358370169997215270996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000160949134081055062828538582131443490652600303292274475097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
296.4151600 |
47.3081208 |
147.4232827 |
17.2310600 |
| ENSG00000067606 |
5590 |
PRKCZ |
protein_coding |
Q05513 |
FUNCTION: Calcium- and diacylglycerol-independent serine/threonine-protein kinase that functions in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade, and is involved in NF-kappa-B activation, mitogenic signaling, cell proliferation, cell polarity, inflammatory response and maintenance of long-term potentiation (LTP). Upon lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment in macrophages, or following mitogenic stimuli, functions downstream of PI3K to activate MAP2K1/MEK1-MAPK1/ERK2 signaling cascade independently of RAF1 activation. Required for insulin-dependent activation of AKT3, but may function as an adapter rather than a direct activator. Upon insulin treatment may act as a downstream effector of PI3K and contribute to the activation of translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 and subsequent glucose transport in adipocytes. In EGF-induced cells, binds and activates MAP2K5/MEK5-MAPK7/ERK5 independently of its kinase activity and can activate JUN promoter through MEF2C. Through binding with SQSTM1/p62, functions in interleukin-1 signaling and activation of NF-kappa-B with the specific adapters RIPK1 and TRAF6. Participates in TNF-dependent transactivation of NF-kappa-B by phosphorylating and activating IKBKB kinase, which in turn leads to the degradation of NF-kappa-B inhibitors. In migrating astrocytes, forms a cytoplasmic complex with PARD6A and is recruited by CDC42 to function in the establishment of cell polarity along with the microtubule motor and dynein. In association with FEZ1, stimulates neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. In the inflammatory response, is required for the T-helper 2 (Th2) differentiation process, including interleukin production, efficient activation of JAK1 and the subsequent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT6. May be involved in development of allergic airway inflammation (asthma), a process dependent on Th2 immune response. In the NF-kappa-B-mediated inflammatory response, can relieve SETD6-dependent repression of NF-kappa-B target genes by phosphorylating the RELA subunit at 'Ser-311'. Phosphorylates VAMP2 in vitro (PubMed:17313651). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11035106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12162751, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15084291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15324659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17313651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9447975}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Involved in late synaptic long term potention phase in CA1 hippocampal cells and long term memory maintenance. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02956}. |
Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Inflammatory response;Kinase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Protein kinase C (PKC) zeta is a member of the PKC family of serine/threonine kinases which are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation and secretion. Unlike the classical PKC isoenzymes which are calcium-dependent, PKC zeta exhibits a kinase activity which is independent of calcium and diacylglycerol but not of phosphatidylserine. Furthermore, it is insensitive to typical PKC inhibitors and cannot be activated by phorbol ester. Unlike the classical PKC isoenzymes, it has only a single zinc finger module. These structural and biochemical properties indicate that the zeta subspecies is related to, but distinct from other isoenzymes of PKC. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5590; |
apical cortex [GO:0045179]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; axon hillock [GO:0043203]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; myelin sheath abaxonal region [GO:0035748]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; PAR polarity complex [GO:0120157]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; tight junction [GO:0070160]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity [GO:0004698]; insulin receptor substrate binding [GO:0043560]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phospholipase binding [GO:0043274]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein kinase C activity [GO:0004697]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; activation of phospholipase D activity [GO:0031584]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045197]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; long-term memory [GO:0007616]; long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:0060291]; membrane depolarization [GO:0051899]; membrane hyperpolarization [GO:0060081]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of hydrolase activity [GO:0051346]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050732]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; neuron projection extension [GO:1990138]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046628]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-13 production [GO:0032736]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of interleukin-5 production [GO:0032754]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein transport [GO:0051222]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production [GO:2000553]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation [GO:0045630]; protein kinase C signaling [GO:0070528]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0098696]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle transport along microtubule [GO:0047496] |
11740573_Isoforms of protein kinase C and their distribution in human adrenal cortex and tumors 11765038_Investigation of the inhibitory effects of chelerythrine chloride on the translocation of the protein kinase C betaI, betaII, zeta in human neutrophils 11960776_PKC-zeta is required in EGF protection of microtubules and intestinal barrier integrity against oxidant injury. 12021260_role of PKCzeta in T cells through the control of NFAT function by modulating the activity of its transactivation domain 12056906_PKC zeta expressed in human neutrophils can phosphorylate p47phox and induce both its translocation and NADPH oxidase activation as well as the binding of p47phox to the cytosolic fragment of p22phox. 12093536_REVIEW:Interaction of protein kinase C isozymes with membranes containing anionic phospholipids utilizing fluorescent phorbol esters to probe the properties of the C1 domains 12105221_shows for the first time that topoisomerase II beta is a substrate for PKC zeta, and that PKC zeta may significantly influence topoisomerase II inhibitor-induced cytotoxicity by altering topoisomerase II beta activity through its kinase function 12223351_EGF protects against oxidative disruption of the intestinal barrier by stabilizing the cytoskeleton in large part through the activation of PKC-zeta and downregulation of iNOS 12242277_The adapter protein ZIP binds Grb14 and regulates its inhibitory action on insulin signaling by recruiting protein kinase Czeta. 12244101_catalytic domain of PKC zeta is intrinsically inactive and dependent on the transphosphorylation of the activation lo 12435813_the role of PKCzeta in the negative regulation of drug-induced SM-CER pathway. 12493764_Protein kinase C zeta-GATA-2 signaling regulates VCAM1 stimulation by thrombin in endothelial cells 12671055_hypoxia decreases Na,K-ATPase activity in alveolar epithelial cells by triggering its endocytosis through mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and PKC-zeta-mediated phosphorylation of the Na,K-ATPase alpha(1) subunit 12748064_PKC zeta has a role in the actin organization in ET-1-stimulated cells may play a role in myometrial contraction in pregnant women. 12783114_The novel varepsilon and eta and atypical zeta, but not the conventional alpha and beta and the novel delta PKCs, may be involved in the signaling pathways involved in thrombin-induced human platelet P-selectin expression 12791393_PKCzeta has a role in regulating cell survival in tumor cells 12882907_Defective aPKC activation contributes to skeletal muscle insulin resistance in glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes 12900386_enteropathogenic E coli infection of intestinal epithelial cells activates several signaling pathways including PKC zeta and ERK that lead to NF-kappa B activation, thus ensuring the proinflammatory response. 12905622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12905768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12920244_disregulation of the function of atypical zeta PKC might be involved in the acquisition of an invasive and metastatic phenotype in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. 12970910_PRKCZ gene may be associated with type 2 diabetes in Han population in North China. The haplotypes at five SNP sites in this gene may be responsible for this association. 14570876_protein kinase C iota/lambda binds to Rab 2, which inhibits aPKCiota/lambda-dependent GADPH phosphorylation [Protein kinase C lambda] 14744756_PKCzeta is responsible for the activation of HIF-alpha by inhibiting the mRNA expression of FIH-1 thus promoting the transcription of hypoxia-inducible genes. 15069075_phosphorylation of Ser(318) by PKC-zeta might contribute to the inhibitory effect of prolonged hyperinsulinemia on IRS-1 function. 15081397_identification of neuronal protein KIBRA as a novel substrate 15159477_There was expression of protein kinase C zeta in abnormal muscle fibers. Protein kinase C isoforms may play a role in the pathogenesis of myofibrillar myopathy. 15172966_involvement of PKC zeta in thrombin-induced permeability changes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells 15210811_GTPase RhoA and atypical protein kinase Czeta are required for TLR2-mediated gene transcription. 15254234_PKCzeta activity is regulated by nucleotide exchange factor ECT2 15285019_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in protein kinase Cz (PKCZ) gene probably play a role in the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes by affecting the expression level of the relevant genes. 15313379_PKC-zeta, is critical to regulation of LPS-induced TLR4 lipid raft mobilization within macrophages. 15358551_PKCzeta could act as a modulator of nucleotide excision repair activity by regulating the expression of XPC/hHR23B heterodimer 15362041_The differential regulation of protein kinase C-zeta by enteropathogenic E. coli and enterohemorrhagic E. coli may in part explain the less profound effect of the latter on the barrier function of tight junctions. 15499829_We analyzed the dependence of the expression of some selected protein kinase C isoenzymes on the availability and/or action of androgens. 15544481_Disruption of the cellular environment through genetic mutation, disease, injury, or exposure to pro-oxidants, alcohol, or other insults can induce pathological PKC activation. 15604116_A role for PKCzeta in relaxin-mediated stimulation of cAMP was demonstrated. 15630457_stromal cell-derived factor 1 triggered PKC-zeta phosphorylation, translocation to the plasma membrane, and kinase activity 15808853_Results indicate that protein kinase C (PKC) zeta modulates hMutS alpha (MSH2, MSH6)stability and protein levels, and suggest a role for PKC zeta in genome stability by regulating mismatch repair activity. 15870274_Ajuba is a new cytosolic component of the IL-1 signaling pathway modulating IL-1-induced NF-kappaB activation by influencing the assembly and activity of the aPKC/p62/TRAF6 multiprotein signaling complex 15887250_PKCZ mediates opposing effects on Na(+)-K(+)-Exchanging ATPase activity in a breast neoplasm cell line. 15935276_data support the notion that PKCzeta is essential for LPS-induced NF-kB p65 subunit nuclear translocation in human myometrial cells 15956717_described a novel bifurcated pathway by which relaxin stimulates Gs alpha and 1-Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase /PKCzeta leading to increased cyclic AMP production 16011831_In this process p62-dependent Akt phosphorylation occurred via the release of Akt from PKCzeta by association of p62 and PKCzeta, which is known as a negative regulator of Akt activation. 16287866_phosphorylation and inhibition of caspase 9 by PKCzeta restrain the intrinsic apoptotic pathway during hyperosmotic stress 16407220_PKC zeta-dependent AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation may play an important role in regulating not only cellular energy metabolism but also signaling pathways that control cell growth, differentiation, and survival. 16611744_Myosin II-B resides in a complex with p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) and atypical protein kinase C (PKC) zeta (aPKCzeta) and the interaction between these proteins is EGF-dependent. 16644736_atypical PKCs are required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport in myocytes and adipocytes 16798739_PKCzeta is a necessary component of the IL-1 and TNF signaling pathways in chondrocytes that result in catabolic destruction of extracellular matrix proteins in osteoarthritic cartilage 16931574_Protein kinase Czeta/mammalian target of rapamycin/S6 kinase pathway plays an important role for the transition of androgen-dependent to androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. 16940160_Studies indicate that PKC-zeta inhibits colon cancer cell growth and enhances differentiation and apoptosis, while inhibiting the transformed phenotype of these cells. 16943418_These studies have revealed a novel mechanism of Trichostatin A action through derecruitment of a repressor from the Luteinizing hormone receptor gene promoter in a PI3K/PKCzeta-induced Sp1 phosphorylation-dependent manner. 17024099_the primary signaling pathway for LPC-dependent dendrite formation in human melanocytes involves the activation of PKCzeta and PKCzeta phosphorylation is Rac dependent 17313651_activated form phosphorylates VAMP2 in vitro 17346701_We propose that increased water influx through AQP9 is critically involved in the formation of membrane protrusions, and that AQP9-induced actin polymerization is augmented by activation of Cdc42 and PKC(zeta). 17369850_aPKCzeta cortical loading is associated with Lgl cytoplasmic release and tumor growth in Drosophila and human epithelia 17389234_In tumor cells, protein kinase C (PKC) zeta was activated to phosphorylate RhoGDI-1, which liberated RhoGTPases, leading to their activation. 17398070_MAP3K8 and PRKCZ cooperate in the regulation of the transcriptional activity of NFATC2 through the phosphorylation of its amino-terminal domain. 17525161_PKCzeta may function as a physiological Bax kinase to directly phosphorylate and interact with Bax, which leads to sequestration of Bax in cytoplasm and abrogation of the proapoptotic function of Bax 17541951_In osteoblasts of rheumatoid arthritis & osteoarthritis patients, PKC-zeta decreased when compared with normal cells. Treatment with IL-1beta & TNF-alpha significantly decreased PKC-zeta expression in post-traumatic osteoblasts. 17544492_first study to show that allergic disease is associated with altered expression of T-cell PKC isozymes in the neonatal period 17682059_Data show that in renal cell carcinoma, the Cut-like homeodomain protein is involved in FIH-1 transcriptional regulation and is controlled by a specific signaling event involving protein kinase C zeta. 17786270_Hemoglobin promptly and markedly modified the levels of expression of both calcium-dependent PKCalpha and calcium-independent PKCzeta. 17850789_These data suggest that PKCzeta activation plays a predominant role in regulation of PGE(2)-dependent melanocyte dendricity. 17850925_In peripheral T-cells from severe cases of Alzheimer's patients, Abeta(1-42) treatment stimulates two distinct PKC-delta- and PKC-zeta-producing T-cell subpopulations which are not noticeable in healthy adult and elderly subjects. 18050214_PKCzeta is involved in regulation of IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB signaling in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes, which regulates downstream expression of ADAMTS-4 and NOS2 via NF-kappaB. 18067888_Data suggest that foreign body giant cell formation is supported by PKCbeta, PKCdelta, and PKCzeta in combined diacylglycerol-dependent (PKCbeta and PKCdelta) and -independent (PKCzeta) signaling pathways. 18094075_PKCzeta is the predominant isoform mediating stretch-induced COX-2 expression 18166155_PKC zeta, but not PKCalpha, positively regulates Casp-2S mRNA assembly triggered by topoisomerase inhibitors 18296444_Protein kinase C-epsilon regulates sphingosine 1-phosphate-mediated migration of human lung endothelial cells through activation of phospholipase D2, protein kinase C-zeta, and Rac1 18313384_Results show that protein kinase C zeta phosphorylates and specifically stabilizes SRC-3 in a selective ER-dependent manner. 18319301_Data identify PKCzeta as regulators of EC lumenogenesis in 3D collagen matrices. 18343365_Spisulosine inhibits the growth of the prostate tumor cells through intracellular ceramide accumulation and PKCzeta activation. 18354190_modulation of PKC may have therapeutic potential in the prevention of smoke-related lung injury 18385757_PKCzeta is an important transduction molecule downstream of TNF-alpha signaling and is associated with increased expression of CD1d that may enhance CD1d-natural killer T cell interactions in psoriasis lesions. 18571841_Atypical protein kinase C (PKC-iota/-zeta) phosphorylates IKKalphabeta in transformed non-malignant and malignant prostate cell survival. 18615853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18615853_PRKCZ gene variants associated with the development of type 2 diabetes in this study needs to be investigated in a larger population to reveal any potential effects on metabolism. 18668687_FIC1 signals to FXR via PKC zeta. FIC1-related liver disease is likely related to downstream effects of FXR on bile acid homeostasis. 18760839_These results show a new function of HIV-1 Tat, its ability to regulate CXCR4 expression via PKCzeta. 18989463_role for host PKCsigma (PKCzeta) on the invasion of hepatocytes by sporozoites 19033536_PKC-zeta dependent stimulation of the human MCT1 promoter involves transcription factor AP2. 19061073_These results indicate that insulin induces dynamic associations between PKCzeta, 80K-H, and munc18c and that 80K-H may act as a key signaling link between PKCzeta and munc18c in live cells. 19086264_the role of protein kinase C zeta (PKCzeta) in interleukin (IL)-8-mediated activation of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) in human neutrophils 19164129_crucial implication of PKC-delta, PKC-zeta, ERK-1/2, and p38 in human blood eosinophil migration through extracellular matrix components 19187446_Protein kinase C zeta controls glioblastoma cell migration and invasion by regulating the cytoskeleton rearrangement. 19201988_PKCzeta is required for CSF-1-induced chemotaxis of macrophages. 19304661_There is a novel ceramide binding domain (C20zeta) in the carboxyl terminus of aPKC. 19339512_Enhancement of calcium transport in Caco-2 monolayer through PKCzeta-dependent Cav1.3-mediated transcellular and rectifying paracellular pathways by prolactin. 19380829_Atypical protein kinase C isozyme PKCzeta associates functionally with small GTPase RhoA and acts as a signaling component downstream of RhoA. 19460843_Serine proteases decrease intestinal epithelial ion permeability by activation of protein kinase Czeta. 19502590_Data show that cholesteryl ester formation was dependent on protein kinase zeta/ extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (PKCzeta/ERK1/2) activation. 19751727_These results strongly suggest that DGKalpha positively regulates TNF-alpha-dependent NF-kappaB activation via the PKCzeta-mediated Ser311 phosphorylation of p65/RelA. 19809379_Findings support the hypothesis that hepatocyte FIC1 enhances FXR signaling via a PKCzeta-dependent signaling pathway. 19812540_Patients who had an elevated anti-PKCzeta titer developed kidney allograft rejection, which was significantly more likely to result in graft loss. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20236250_These results suggest that beta-catenin play an inhibitory role for dendrite formation through the modulation of PKCzeta and PKCdelta. 20236512_RHOA and PRKCZ, and their downstream effectors, can represent important pharmacological targets that could potentially control the highly metastatic attitude of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 20407013_Protein kinase C(PKC)zeta is a novel mitogenic downstream mediator of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor, and a therapeutic target as well, in some carcinomas. 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20417648_Inhibition of PKCzeta may be a novel drug target for thrombin-induced inflammatory hyperpermeability. 20463008_These data identify atypical PKC isozymes as STAT and ERK activators that mediate c-fos and collagenase expression. 20501645_PKC zeta is differentially expressed in ovarian carcinomas and is phosphorylated in response to apoptotic stimuli in primary ovarian carcinoma cells. 20538799_Results show that PKCzeta binds and phosphorylates ERK5, thereby decreasing eNOS protein stability and contributing to early events of atherosclerosis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20679531_PKC zeta function in T helper cells is required for directional secretion of CD40 ligand (CD40L) and interferon (IFN)-gamma toward dendritic cells. 20844151_low levels of expression are associated with poorly differentiated tumours and a poor outcome in breast cancer patients 20941506_aPKC-zeta had moderate sensitivity as a marker of gastric dysplasia and additional studies are needed to establish its role in the diagnosis of dysplasia. 20949042_found that protein kinase C (PKC) zeta binds and phosphorylates LRRK2 both in vitro and in vivo 21081127_Results show that both PKC epsilon and PKC zeta isoforms are involved in the formation of ROS by C2-ceramide and the opening of the mPTP. 21390241_The prognostic impact of TGF-beta1, NF-kappaB p105, PKC-zeta, Par-6alpha, E-cadherin and vimentin in non-gastrointestinal stromal tumor soft tissue sarcomas, was investigated. 21454526_that upon DAMGO treatment, MOR activates PKCzeta through a PDK1-dependent signaling pathway to induce CCR5 phosphorylation and desensitization. 21549621_Data indicate that both tumor focality and Par3/Par6/atypical protein kinase C (APKC) expression were significantly associated with tumor recurrence. 21619587_Results indicate that phosphorylation of human DNMT1 by protein kinase C is isoform-specific and provides the first evidence of cooperation between PKCzeta and DNMT1 in the control of the DNA methylation patterns of the genome. 21624955_The PKCzeta activation by d-flow induces endothelial cell (EC) apoptosis by regulating p53. 21645497_human platelets express PKCzeta, and it may be constitutively phosphorylated at the activation loop threonine 410 and the turn motif threonine 560 under basal resting conditions, which are differentially dephosphorylated by outside-in signaling 21667320_Changes in PKC iota, PKC zeta, and non-muscle MyoIIA expression are likely to participate in pathogenesis of epithelial barrier function in response to local pro-inflammatory signals. 21780947_two key (hub) PPARgamma direct target genes, PRKCZ and PGK1, were experimentally validated to be repressed upon PPARgamma activation by its natural ligand, 15d-PGJ2 in three prostrate cancer cell lines 21849550_Inhibition of protein kinase M zeta results in a reduction of synaptic PSD-95 accumulation in developing visual cortex 21871968_The LNO(2) mediated signaling in lung type II epithelial cells occurs via a unique pathway involving PKCzeta. 21895402_High levels of protein kinase C zeta expression were associated with lymphatic metastasis in squamous cervical cancer. 22231931_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in protein kinase C zeta are associated with bipolar affective disorder. 22242160_HGF induced functional CXCR4 receptor expression in breast cancer cells. The effect of HGF was specifically mediated by PKCzeta activity. 22324796_Report role of PKC-zeta induction in bronchial inflammation and airyway hyperresponsiveness. 22390153_Western Blot data showed decreased expression (p |
ENSMUSG00000029053 |
Prkcz |
57.644171 |
0.4359410094 |
-1.197795 |
0.235711676 |
25.928579 |
0.00000035428495445497812701816540623123152897733234567567706108093261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001317854316470634373211845771778349956093734363093972206115722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.0832731 |
6.3060967 |
85.6039748 |
9.5137684 |
| ENSG00000067840 |
57595 |
PDZD4 |
protein_coding |
Q76G19 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be located in cell cortex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57595; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
15077175_Might play an important role in the proliferation of SS cells and might be a suitable target for SS drugs. 15138636_PDZRN4L showed 49.9% total-amino-acid identity with PDZRN4 short isoform (PDZRN4S). PDZ, PR34H1 and PR34H2 domains were conserved between PDZRN4L and PDZRN4S. |
ENSMUSG00000002006 |
Pdzd4 |
18.033349 |
5.4049993527 |
2.434294 |
0.429054195 |
35.421581 |
0.00000000265528479583708932046954053548138557916402646696951705962419509887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012220768190382112546204089486602539782467147233546711504459381103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.8324189 |
8.2901528 |
5.3568832 |
1.3186530 |
| ENSG00000067842 |
492 |
ATP2B3 |
protein_coding |
Q16720 |
FUNCTION: ATP-driven Ca(2+) ion pump involved in the maintenance of basal intracellular Ca(2+) levels at the presynaptic terminals (PubMed:25953895, PubMed:27035656, PubMed:22912398, PubMed:18029012). Uses ATP as an energy source to transport cytosolic Ca(2+) ions across the plasma membrane to the extracellular compartment (PubMed:25953895, PubMed:27035656). May counter-transport protons, but the mechanism and the stoichiometry of this Ca(2+)/H(+) exchange remains to be established (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64568, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18029012, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22912398, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25953895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27035656}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Calcium transport;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disease variant;Ion transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type primary ion transport ATPases characterized by the formation of an aspartyl phosphate intermediate during the reaction cycle. These enzymes remove bivalent calcium ions from eukaryotic cells against very large concentration gradients and play a critical role in intracellular calcium homeostasis. The mammalian plasma membrane calcium ATPase isoforms are encoded by at least four separate genes and the diversity of these enzymes is further increased by alternative splicing of transcripts. The expression of different isoforms and splice variants is regulated in a developmental, tissue- and cell type-specific manner, suggesting that these pumps are functionally adapted to the physiological needs of particular cells and tissues. This gene encodes the plasma membrane calcium ATPase isoform 3. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:492; |
extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; parallel fiber [GO:1990032]; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0098688]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019829]; calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015085]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; P-type calcium transporter activity [GO:0005388]; P-type calcium transporter activity involved in regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:1905056]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; calcium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1990034]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; regulation of cardiac conduction [GO:1903779]; regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051480] |
12784250_role in the intracellular Ca(2+) extrusion of syncytiotrophoblast-like structure originating from the differentiation of cultured trophoblast cells isolated from human term placenta 17336174_Expression of the placental calcium transporter PMCA3 mRNA predicts neonatal whole body bone mineral content 19733838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22912398_Mutation of plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 3 in a family with X-linked congenital cerebellar ataxia impairs Ca2+ homeostasis. 23416519_Somatic mutations in ATP2B3 gene leads to aldosterone-producing adenomas and secondary hypertension. 24082052_ATP2B3 mutations are present in aldosterone-producineg adenomas that result in an increase in CYP11B2 gene expression and may account for the dysregulated aldosterone production in a subset of patients with sporadic primary aldosteronism. 24179102_Somatic mutations found in KCNJ5, ATP1A1, and ATP2B3 appear to be the driving forces for a higher aldosterone production and proliferations of glomerulosa cells. 25953895_Novel PMCA3 missense mutation co-occurring with a heterozygous mutation in LAMA1 impaired cellular Ca2+ homeostasis in patients with Cerebellar Ataxia. 26285814_Mutations in ATP2B3 gene is associated with aldosterone-producing adenomas. 26351028_Different mutations (KCNJ5, ATP1A1, ATP2B3, and CACNA1D) are found in different aldosterone-producing nodules from the same adrenal, suggesting that somatic mutations are independent events triggered by mechanisms that remain to be identified. 27035656_In summary, the APA-associated ATP2B3(Leu425_Val426del) mutant promotes aldosterone production by at least 2 different mechanisms: 1) a reduced Ca(2+) export due to the loss of the physiological pump function; and 2) an increased Ca(2+) influx due to opening of depolarization-activated Ca(2+) channels as well as a possible Ca(2+) leak through the mutated pump. 27632770_The ataxia related G1107D mutation of the PMCA 3 impairs its calcium pumping function. The mutation affects the interplay of calmodulin with its binding domain on the pump, decreasing its stimulation. 28807751_Authors report a novel PMCA3 mutation (G733R substitution) in the catalytic P-domain of the pump in a patient affected by non-progressive ataxia, muscular hypotonia, dysmetria and nystagmus. 36207321_The ataxia-linked E1081Q mutation affects the sub-plasma membrane Ca(2+)-microdomains by tuning PMCA3 activity. |
ENSMUSG00000031376 |
Atp2b3 |
19.152205 |
0.1016184046 |
-3.298766 |
0.488217274 |
56.765074 |
0.00000000000004911117874583024775757732564774470670440923922295262116222147597000002861022949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000317234572555122314754303721843919221278548098430505319811345543712377548217773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5255590 |
1.1808140 |
34.9142917 |
5.5496371 |
| ENSG00000068366 |
2182 |
ACSL4 |
protein_coding |
O60488 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of long-chain fatty acids to their active form acyl-CoA for both synthesis of cellular lipids, and degradation via beta-oxidation (PubMed:24269233, PubMed:22633490, PubMed:21242590). Preferentially activates arachidonate and eicosapentaenoate as substrates (PubMed:21242590). Preferentially activates 8,9-EET > 14,15-EET > 5,6-EET > 11,12-EET. Modulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by regulating the levels of unesterified EETs (By similarity). Modulates prostaglandin E2 secretion (PubMed:21242590). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35547, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21242590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22633490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269233}. |
Alport syndrome;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Elliptocytosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Intellectual disability;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Membrane;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of the long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme preferentially utilizes arachidonate as substrate. The absence of this enzyme may contribute to the cognitive disability or Alport syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene generates multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:2182; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0044233]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; palmitoyl-CoA ligase activity [GO:0090433]; very long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031957]; embryonic process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060136]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008610]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0035338]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0035336]; negative regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032307]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024] |
11731423_Fatty acid CoA ligase 4 is up-regulated in colon adenocarcinoma. 11889465_FACL4, encoding fatty acid-CoA ligase 4, is mutated in nonspecific X-linked mental retardation 12525535_FACL4 is highly expressed in hippocampal and cerebellar neurons and may have a role in X linked mental retardation. 12824887_Overexpression of Fatty acid-CoA ligase 4 is associated with human hepatocellular carcinoma 15108178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15849811_FACL4 is involved in the hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and both cAMP and p38 MAPK pathways are associated with the regulation of FACL4 16276108_Disruption of DMD and the absence of ACSL4 in a patient are responsible for neuromuscular disease and cognitive impairment. 17934335_FACL4 affects HCC cell growth and suggest that modulation of FACL4 expression/activity is an approach for treatment of HCC. 18059177_FACL4 might play a role in the growth of hepatic cancer cells. 18614287_No association between polymorphisms in the FACL4 (fatty acid-CoA ligase 4) gene and nonspecific mental retardation in Qin-Ba mountain region of China. 18614287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19346733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19346733_The common SNP (C to T substitution) in the first intron of the FACL4 gene is associated with altered Fatty Acid composition of plasma phosphatidylcholines in patients with metabolic syndrome . 19617635_ACSL4 can substitute the functions of dAcsl(l(2)44DEa in organismal viability, lipid storage and the neural wiring in visual center. 20351714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452052_This study found no significant relationship between FACL4 and cognitive function. 21085606_Data suggest that the development of combinatory therapies that profit from the ACSL4, lipooxygenase and COX-2 synergistic action may allow for lower medication doses and avoidance of side effects. 21242590_CSL4 modulates PGE release from human erial smooth muscle cells. 21384559_A total of six novel and 11 known single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified. Further studies are warranted to analyze the candidate genes at Xq11.1-q21.33. 21903867_the involvement of SHP2 activity in the regulation of the expression of the fatty acid-metabolizing enzyme ACSL4 22808264_The functional interaction between Acyl-CoA synthetase 4, 5-lipooxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 controls tumor growth. 24155918_ACSL4 can serve as both a biomarker for, and mediator of, an aggressive breast cancer phenotype. 24201376_conclude that in our model system exogenous fatty acids are channeled preferentially towards phosphatidylinositol by ACSL4 overexpression 24576478_MiR-205 down-regulates ACSL4 through targeting its 3'UTR in hepatoma cells. 24879802_studies have identified a novel substrate-induced posttranslational regulatory mechanism by which AA downregulates ACSL4 protein expression in hepatic cells. 25500141_Upregulation of ACSL4 is responsible for the increase in triacylglycerol species containing long polyunsaturated fatty acids during activation of hepatic stellate cells. 25645621_Report PPARdelta-mediated regulatory mechanism for ACSL4 expression in liver tissue and cultured hepatic cells. 26282205_In vitro analysis showed that a recombinant COX-2 enzyme more effectively metabolized 5(S)-HETE to 5-11-diHETE compared to COX-1 enzyme. 26536660_we demonstrate that ACSL4 can be considered a novel activator of the mTOR pathway 26636648_Suggest role for ACSL4 expression in development of castration-resistant prostate cancer. 26949059_ACSL4 plays a tumor-suppressive role in gastric cancer. 27565726_ACSL4 is not only a sensitive monitor of ferroptosis, but also an important contributor of ferroptosis. 27928700_Data show that ELOVL7, SOCS3, ACSL4 and CLU were upregulated while PRKAR1A and ABCG1 were downregulated in the phlegm-dampness group. 28193492_ACLS4 and ACLS3 have roles in insulin secretion 28334272_Silencing of ACSL4 eliminated the 17beta-estradiol-induced increase in AA and EPA uptake. 28498416_These results suggest that ACSL1, ACSL4 and ACSL5 expression is regulated by ER signaling pathways and ACSL5 is a potential novel biomarker for predicting prognosis of breast cancer patients. 28887439_Study demonstrated that ACSL4 was overexpressed in HCC. 29450800_ACSL3 distribution closely overlapped with proteins involved in trafficking from the trans-Golgi network and endosomes. In contrast, the ACSL4 localisation pattern more closely followed that of calnexin which is an endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone. 30264402_The regulatory network among peroxisomal ABCD2:ACSL4:VLCFA serves as a novel regulator of cartilage homeostasis, and these data may provide novel insights into the role of peroxisomal fatty acid metabolism in pathogenesis of human osteoarthritis (OA). 30414939_ACSL4 role in the drug resistance in breast cancer cell lines. 31160087_the A20-ACSL4 axis plays important roles in erastin-induced endothelial ferroptosis. 31311992_Regulatory mechanisms leading to differential Acyl-CoA synthetase 4 expression in breast cancer cells. 31672604_LncRNA NEAT1 promotes docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer by regulating ACSL4 via sponging miR-34a-5p and miR-204-5p. 31789401_Study shows that the expression of ACSL4 is downregulated in human glioma tissues and cells and demonstrates that ACSL4 protects glioma cells and exerts antiproliferative effects by activating a ferroptosis pathway. These results also highlight the pivotal role of ferroptosis regulation by ACSL4 in its protective effects on glioma. 32286604_Immunohistochemical staining reveals differential expression of ACSL3 and ACSL4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic gastrointestinal metastases. 33038905_Tumor suppressor miR-424-5p abrogates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer through targeting ACSL4. 33068124_New inhibitor targeting Acyl-CoA synthetase 4 reduces breast and prostate tumor growth, therapeutic resistance and steroidogenesis. 33340617_ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway. 33539003_Cytochrome P450 reductase (POR) as a ferroptosis fuel. 34288826_Long non-coding RNA H19 protects against intracerebral hemorrhage injuries via regulating microRNA-106b-5p/acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 axis. 34358518_Acyl-CoA synthetase-4 mediates radioresistance of breast cancer cells by regulating FOXM1. 34482070_Predictive and prognostic impact of ferroptosis-related genes ACSL4 and GPX4 on breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 35197442_Thrombin induces ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. 35567995_ACSL4 promotes colorectal cancer and is a potential therapeutic target of emodin. 35603967_CRISPR/Cas9 Screens Reveal that Hexokinase 2 Enhances Cancer Stemness and Tumorigenicity by Activating the ACSL4-Fatty Acid beta-Oxidation Pathway. 35868067_ACSL4 is overexpressed in psoriasis and enhances inflammatory responses by activating ferroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000031278 |
Acsl4 |
1988.766658 |
3.3384539760 |
1.739180 |
0.050718172 |
1165.690486 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000174503343274528353853722167159628137952038813091643643720105072342996284545 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000209404011929434024624466600591553765542446575709972372464126086811595541454 |
Yes |
Yes |
2950.4705612 |
414.7246955 |
893.0843472 |
91.4194301 |
| ENSG00000068383 |
3632 |
INPP5A |
protein_coding |
Q14642 |
FUNCTION: Phosphatase that specifically hydrolyzes the 5-phosphate of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol 1,4-bisphosphate, and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrasphosphate to inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate (PubMed:8013665, PubMed:8769125, PubMed:8626616). Plays a crucial role in the survival of cerebellar Purkinje cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TNC9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8013665, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8769125}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane-associated type I inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) 5-phosphatase. InsP3 5-phosphatases hydrolyze Ins(1,4,5)P3, which mobilizes intracellular calcium and acts as a second messenger mediating cell responses to various stimulation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3632; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; inositol-1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0052659]; inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0052658]; inositol-polyphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0004445]; PH domain binding [GO:0042731]; inositol phosphate dephosphorylation [GO:0046855]; inositol phosphate metabolic process [GO:0043647]; inositol phosphate-mediated signaling [GO:0048016]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856] |
20876729_NPP5Amay play a role in development and progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma tumors 26051944_The ataxic phenotype and characteristics neurodegeneration of the Inpp5a Gt(OST50073)Lex mouse indicate a crucial role for Inpp5a in purkinje cells survival. 28653606_the overexpression of miR-181a-5p enhanced cell proliferation and invasion and inhibited apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by negatively targeting INPP5A |
ENSMUSG00000025477 |
Inpp5a |
56.395520 |
0.4304432209 |
-1.216105 |
0.380857497 |
9.888289 |
0.00166333948320227767610213209792391353403218090534210205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003733564997012727565417478103881876450031995773315429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.6342543 |
7.9103568 |
66.7319274 |
12.9516360 |
| ENSG00000068489 |
55771 |
PRR11 |
protein_coding |
Q96HE9 |
FUNCTION: Plays a critical role in cell cycle progression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23246489}. |
Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Involved in regulation of cell cycle. Located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55771; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] |
17672918_the apparent occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 10 is discussed 23246489_our results strongly demonstrated that this newly identified gene, PRR11, had a critical role in both cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis, and might serve as a novel potential target in the diagnosis and/or treatment of human lung cancer. 25666944_Overexpression of PRR11 inhibits cell proliferation and induces premature chromatin condensation. 25971332_Microarray analysis revealed that several genes involved in cell proliferation, cell adhesion, and cell migration were altered in PRR11-knockout cells. 25973065_Targeted depletion of PRR11 caused a dramatic cell cycle arrest followed by massive apoptotic cell death, and eventually resulted in a significant decrease in growth and viability in lung cancer cell lines. 26162986_PRR11-SKA2 bidirectional transcription unit, which is a novel direct target of NF-Y, is essential for the accelerated proliferation and motility of lung cancer cells 26252227_PRR11 may be widely activated in human gastric cancer. 28257042_p53 negatively regulates the expression of the PRR11-SKA2 bidirectional transcription unit through NF-Y, suggesting that the inability to repress the PRR11-SKA2 bidirectional transcription unit after loss of p53 might contribute to tumorigenesis. 28574724_these findings indicated that miR-144-3p induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer by targeting PRR11. 29393495_these findings further illustrate the suppressive role of miR-195 in prostate cancer (PCa), and indicate a novel role of PRR11 in PCa. Importantly, the newly identified miR-195/PRR11 axis may aid with identifying potential therapeutic targets in PCa. 30007956_PRR11 regulated self-renewal and tumorigenicity of gastric cancer stem cells through MAPK signaling, and could be used as a therapeutic target for gastric cancer. 30165366_PRR11 positively regulated cell proliferation-related proteins, including c-myc and cyclin D1, and increased and decreased the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 and PRR11 expression was mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 30248355_PRR11 plays an oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression, through activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, and may represent a valuable prognostic marker and therapeutic target for HCC. 30551440_Knockdown of DLX6-AS1 inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion and promoted apoptosis by downregulating PRR11 expression and upregulating miR-144 in NSCLC. 31075210_MicroRNA-211-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits the migration of osteosarcoma cells by targeting proline-rich protein PRR11. 32169900_Proline-rich 11 (PRR11) drives F-actin assembly by recruiting the actin-related protein 2/3 complex in human non-small cell lung carcinoma. 33127913_Proline rich 11 (PRR11) overexpression amplifies PI3K signaling and promotes antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer. 33477943_HEDGEHOG/GLI Modulates the PRR11-SKA2 Bidirectional Transcription Unit in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinomas. 34379360_PRR11 unveiled as a top candidate biomarker within the RBM3-regulated transcriptome in pancreatic cancer. 34488538_MicroRNA-26b-5p suppresses the proliferation of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting proline rich 11 (PRR11). 34499617_PRR11 promotes ccRCC tumorigenesis by regulating E2F1 stability. 35126622_miR-204-5p Hampers Breast Cancer Malignancy and Affects the Cell Cycle by Targeting PRR11. 35181621_PRR11 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Colorectal Cancer through Activating the EGFR/ERK/AKT Pathway via Increasing CTHRC1. |
ENSMUSG00000020493 |
Prr11 |
610.166638 |
2.0991191286 |
1.069784 |
0.155621375 |
46.494961 |
0.00000000000918543748717718413245429761317627486566506078702332160901278257369995117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000051084045708641761600465034276230850626698831717931170715019106864929199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
762.9477120 |
124.0186827 |
365.2673134 |
43.2159585 |
| ENSG00000068615 |
65055 |
REEP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H902 |
FUNCTION: Required for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) network formation, shaping and remodeling; it links ER tubules to the cytoskeleton. May also enhance the cell surface expression of odorant receptors (PubMed:20200447). May play a role in long-term axonal maintenance (PubMed:24478229). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20200447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24478229}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a mitochondrial protein that functions to enhance the cell surface expression of odorant receptors. Mutations in this gene cause spastic paraplegia autosomal dominant type 31, a neurodegenerative disorder. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:65055; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network [GO:0071782]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; olfactory receptor binding [GO:0031849]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization [GO:0071786]; protein insertion into membrane [GO:0051205] |
16720576_RTP and REEP gene expression in human circumvallate papillae and testis, both of which are sites of taste receptor gene expression. 16826527_REEP1 is widely expressed and localizes to mitochondria, which underlines the importance of mitochondrial function in neurodegenerative disease. 18321925_Mutations in the receptor expression enhancing protein 1 (REEP1) have recently been reported to cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia type SPG31. We identified 13 novel and 2 known REEP1 mutations in 16 familial and sporadic patients. 18644145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18644145_Our results confirm the previously observed mutation range of 3% to 6.5%, respectively, and they widen the spectrum of REEP1 mutations 19034539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19034539_Results identify the frequency of REEP1 mutations in both autosomal dominant HSP (ADHSP) and sporadic spastic paraparesis (SSP) and analyse the genotype/phenotype correlation of mutations so far described in REEP1. 19072839_A novel splice-site mutation (REEP1 c417+1g>a) was identified in chiease family of ADHSP. 19781397_Receptor expression-enhancing protein 1 gene (SPG31) mutations are rare in Chinese Han patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia. 20200447_Hereditary spastic paraplegias(HSP) proteins atlastin-1, spastin, and REEP1 interact within the tubularER membrane in corticospinal neurons to coordinate ER shaping and microtubule dynamics. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20718791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20718791_previously unreported autosomal dominant mutations in the REEP1 gene in hereditary spastic paraplegia 21618648_Identification of 12 different heterozygous REEP1 mutations, including two exon deletions, associated with either a pure or a complex phenotype. 22703882_Whole-exome sequencing of two affected individuals revealed a single candidate variant within the linking regions, i.e., a splice-site alteration in REEP1 23108492_A novel REEP1 mutation is identified in a cohort of patients with upper motor neuron syndrome. 24051375_REEP1 is a neuron-specific, membrane-binding, and membrane curvature-inducing protein that resides in the endoplasmic reticulum. 24355597_Expression of the REEP1/REEP2 subfamily appears to be restricted to neuronal and neuronal-like exocytotic tissues, consistent with neuronally restricted symptoms of REEP1 genetic disorders. 24478229_Functional mutation analysis reveal that distinct pathomechanisms are associated with REEP1 mutations and shed new light on its probable functions. 24986827_Nonsense variants in REEP1 causing haploinsufficiency/loss of function are responsible for autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP)-type SPG31. 26201691_we show that REEP1 facilitates endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria interactions, a function diminished by disease-associated mutations. 26671083_This study demonstrated that REEP1 gene mutation associated with hereditary spastic paraplegias in group of Polish patients 29107646_Pathology of spastic paraplegia type 31 may contain dosage effect of REEP1 transcripts. 29124833_Study identified a heterozygous nonstop variant in REEP1. Mutations in this gene have classically been associated with the upper motor neuron disorder hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP). 29908077_The REEP1 c.606 + 43G>T caused Spastic Paraplegia and primary progressive multiple sclerosis. 30637453_REEP1 variants cause polyneuropathy in SPG31. 31055810_deletional variation of the REEP1 gene probably underlies the disease in this pedigree |
ENSMUSG00000052852 |
Reep1 |
21.030641 |
0.4909745311 |
-1.026280 |
0.337125549 |
9.465279 |
0.00209397637046554669151832150930658826837316155433654785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004604065429475862926411711129048853763379156589508056640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.4820583 |
2.7377247 |
23.5632455 |
3.6422592 |
| ENSG00000068697 |
9741 |
LAPTM4A |
protein_coding |
Q15012 |
FUNCTION: May function in the transport of nucleosides and/or nucleoside derivatives between the cytosol and the lumen of an intracellular membrane-bound compartment. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein that has four predicted transmembrane domains. The function of this gene has not yet been determined; however, studies in the mouse homolog suggest a role in the transport of small molecules across endosomal and lysosomal membranes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9741; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765] |
21553234_hOCT2 interacts with LAPTM4A in lysosomes and late endosomes and regulates endocytotic recruitment. 33836347_LAPTM4alpha is targeted from the Golgi to late endosomes/lysosomes in a manner dependent on the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-1 and ESCRT proteins. |
ENSMUSG00000020585 |
Laptm4a |
1150.729667 |
2.8163485378 |
1.493826 |
0.047209982 |
1031.366842 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000027311732878194677112929380228449182654371868089011135898273389757610500306594899626809613159806302932304 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000029211679513199526759401673719541614399377435760183597006783980059236605526012086430879993998550298269671 |
Yes |
No |
1709.5635507 |
51.5673990 |
611.5727912 |
14.9966163 |
| ENSG00000068831 |
10235 |
RASGRP2 |
protein_coding |
Q7LDG7 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a calcium- and DAG-regulated nucleotide exchange factor specifically activating Rap through the exchange of bound GDP for GTP. May also activate other GTPases such as RRAS, RRAS2, NRAS, KRAS but not HRAS. Functions in aggregation of platelets and adhesion of T-lymphocytes and neutrophils probably through inside-out integrin activation. May function in the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1/CHRM1 signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10918068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14702343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17576779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17702895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24958846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27235135}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Synaptosome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a brain-enriched nucleotide exchanged factor that contains an N-terminal GEF domain, 2 tandem repeats of EF-hand calcium-binding motifs, and a C-terminal diacylglycerol/phorbol ester-binding domain. This protein can activate small GTPases, including RAS and RAP1/RAS3. The nucleotide exchange activity of this protein can be stimulated by calcium and diacylglycerol. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:10235; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; synapse [GO:0045202]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12239348_CalDAG-GEFI plays a role in inside-out signaling to alphaIIbbeta3 20606303_analyzed the 5'-flanking region of rasgrp2 gene by a luciferase assay, which revealed that not only a promoter but also silencer regions were present upstream of D1E, suggesting rasgrp2 expression is controlled by a combination of promotion and repression 23530823_NIH3T3 cells were found nonpermissive to mtHSV but they became permissive following transformation with the Rasgrp2 gene. This effect was linked to the activation of the Ras-PKR signaling pathway. 23563504_RasGRP2 increases cell viability and cell-matrix adhesion through increased Ras expression and Rap1 activation, respectively, in endothelial cells. 23611601_phosphorylation of CalDAG-GEFI is a critical mechanism by which PKA controls Rap1b-dependent platelet aggregation 24958846_Human CalDAG-GEFI gene (RASGRP2) mutation affects platelet function and causes severe bleeding. 27022025_RasGRP2 is exceptional in that its C1 domain has very weak binding affinity (Kd = 2890 +/- 240 nm for [(3)H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate. We have identified four amino acid residues responsible for this lack of sensitivity. Replacing Asn(7), Ser(8), Ala(19), and Ile(21) with the corresponding residues from RasGRP1/3 (Thr(7), Tyr(8), Gly(19), and Leu(21), respectively) conferred potent binding affinity (Kd = 1.47 +/- 0.03 nm). 27107697_These studies identify RasGRP2 as a novel substrate of ERK1/2 and define a negative-feedback loop that regulates the BRaf-MEK-ERK signaling cascade. This negative-feedback loop determines the amplitude and duration of active ERK1/2. 27235135_These patients are the first cases of a CalDAG-GEFI deficiency due to homozygous RASGRP2 mutations that are linked to defects in both leukocyte and platelet integrin activation. 28637664_Eleven cases with unexplained bleeding or platelet disorders harbored 11 different, previously unreported RASGRP2 variants that were biallelic and likely pathogenic. 28726538_we here describe a novel mutation in RASGRP2 that affects both expression and function of CalDAG-GEFI and that causes impaired platelet adhesive function and significant bleeding in humans. 29970392_results indicate that CD38 promotes RasGRP2/Rap1-mediated CLL cell adhesion and migration by increasing intracellular Ca2+ levels. 30076153_RASGRP2 was identified to be involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by promoting adhesion, migration and IL-6 production from fibroblast-like synoviocytes 31724816_RASGRP2 mutation is associated with bleeding disorders. 32041177_RasGRP2 Structure, Function and Genetic Variants in Platelet Pathophysiology. 32609603_A novel missense variant in the RASGRP2 gene in patients with moderate to severe bleeding disorder. 33536515_RasGRP2 inhibits glyceraldehyde-derived toxic advanced glycation end-products from inducing permeability in vascular endothelial cells. 33711653_Mutations in RASGRP2 gene identified in patients misdiagnosed as Glanzmann thrombasthenia patients. 34681791_The Role of RASGRP2 in Vascular Endothelial Cells-A Mini Review. 34830306_CalDAG-GEFI Deficiency in a Family with Symptomatic Heterozygous and Homozygous Carriers of a Likely Pathogenic Variant in RASGRP2. 35122233_Novel RASGRP2 variants in platelet function defects: Indian study. |
ENSMUSG00000032946 |
Rasgrp2 |
53.359683 |
0.0973345497 |
-3.360904 |
0.340775779 |
102.994927 |
0.00000000000000000000000336007602072783210973318625771696625645881836952669793000815739829334471977517750929109752178192138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000035074060867003394109822951058917806829066633408568863365310883540432174143575139169115573167800903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.4337963 |
3.2405186 |
96.1974527 |
21.5537293 |
| ENSG00000069020 |
375449 |
MAST4 |
protein_coding |
O15021 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the microtubule-associated serine/threonine protein kinases. The proteins in this family contain a domain that gives the kinase the ability to determine its own scaffold to control the effects of their kinase activities. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014] |
hsa:375449; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
17086981_high expression level of MAST4 in most normal human tissues, with an exception of in testis, small intestine, colon and peripheral blood leukocyte. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 29948376_Molecular studies incriminated different genes, mainly CACNA1H and MAST4. Since at least 2 susceptibility genes were likely shared by different populations, genetic factors involved in the majority of Tunisian Genetic generalized epilepsies families remain to be discovered. 33219327_Mast4 knockout shows the regulation of spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal via the FGF2/ERM pathway. 35064934_Estrogen-Responsive Gene MAST4 Regulates Myeloma Bone Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000034751 |
Mast4 |
78.707854 |
2.3438094596 |
1.228855 |
0.300617786 |
16.431689 |
0.00005043500634403623867881363840304231871414231136441230773925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000145082965043456406156394122852759664965560659766197204589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
113.0064961 |
20.2324039 |
48.5109899 |
6.5778699 |
| ENSG00000069329 |
55737 |
VPS35 |
protein_coding |
Q96QK1 |
FUNCTION: Acts as component of the retromer cargo-selective complex (CSC). The CSC is believed to be the core functional component of retromer or respective retromer complex variants acting to prevent missorting of selected transmembrane cargo proteins into the lysosomal degradation pathway. The recruitment of the CSC to the endosomal membrane involves RAB7A and SNX3. The CSC seems to associate with the cytoplasmic domain of cargo proteins predominantly via VPS35; however, these interactions seem to be of low affinity and retromer SNX proteins may also contribute to cargo selectivity thus questioning the classical function of the CSC. The SNX-BAR retromer mediates retrograde transport of cargo proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and is involved in endosome-to-plasma membrane transport for cargo protein recycling. The SNX3-retromer mediates the retrograde endosome-to-TGN transport of WLS distinct from the SNX-BAR retromer pathway (PubMed:30213940). The SNX27-retromer is believed to be involved in endosome-to-plasma membrane trafficking and recycling of a broad spectrum of cargo proteins. The CSC seems to act as recruitment hub for other proteins, such as the WASH complex and TBC1D5 (Probable). Required for retrograde transport of lysosomal enzyme receptor IGF2R and SLC11A2. Required to regulate transcytosis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR-pIgA) (PubMed:15078903, PubMed:15247922, PubMed:20164305). Required for endosomal localization of WASHC2C (PubMed:22070227, PubMed:28892079). Mediates the association of the CSC with the WASH complex via WASHC2 (PubMed:22070227, PubMed:24980502, PubMed:24819384). Required for the endosomal localization of TBC1D5 (PubMed:20923837). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15078903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15247922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20164305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20923837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22070227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23395371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24819384, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24980502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28892079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30213940, ECO:0000303|PubMed:21725319, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22070227, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22513087, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23563491}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) The heterotrimeric retromer cargo-selective complex (CSC) mediates the exit of human papillomavirus from the early endosome and the delivery to the Golgi apparatus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25693203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30122350}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Parkinson disease;Parkinsonism;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene belongs to a group of vacuolar protein sorting (VPS) genes. The encoded protein is a component of a large multimeric complex, termed the retromer complex, involved in retrograde transport of proteins from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. The close structural similarity between the yeast and human proteins that make up this complex suggests a similarity in function. Expression studies in yeast and mammalian cells indicate that this protein interacts directly with VPS35, which serves as the core of the retromer complex. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55737; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dopaminergic synapse [GO:0098691]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; mitochondrion-derived vesicle [GO:0099073]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; retromer complex [GO:0030904]; retromer, cargo-selective complex [GO:0030906]; tubular endosome [GO:0097422]; D1 dopamine receptor binding [GO:0031748]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; mitochondrial fragmentation involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043653]; mitochondrion to lysosome transport [GO:0099074]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of late endosome to lysosome transport [GO:1902823]; negative regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process [GO:1905166]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; negative regulation of protein homooligomerization [GO:0032463]; negative regulation of protein localization [GO:1903828]; neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to plasma membrane [GO:0099639]; neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098887]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of dopamine biosynthetic process [GO:1903181]; positive regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060161]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior [GO:0090326]; positive regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090141]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of Wnt protein secretion [GO:0061357]; protein destabilization [GO:0031648]; protein localization to endosome [GO:0036010]; regulation of cellular protein metabolic process [GO:0032268]; regulation of dendritic spine maintenance [GO:1902950]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010821]; regulation of postsynapse assembly [GO:0150052]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of synapse maturation [GO:0090128]; regulation of terminal button organization [GO:2000331]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147]; transcytosis [GO:0045056]; vesicle-mediated transport in synapse [GO:0099003]; voluntary musculoskeletal movement [GO:0050882]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
17101778_These observations indicate that the mammalian retromer complex assembles by sequential association of SNX1/2 and Vps26-Vps29-Vps35 subcomplexes on endosomal membranes and that SNX1 and SNX2 play interchangeable but essential roles. 17891154_crystal structure of a VPS29-VPS35 subcomplex showing how the metallophosphoesterase-fold subunit VPS29 acts as a scaffold for the carboxy-terminal half of VPS35 19531583_Membrane recruitment of the cargo-selective retromer subcomplex VPS35/29/26 is catalysed by the small GTPase Rab7 and inhibited by the Rab-GAP TBC1D5. 20164305_Depletion of the retromer by siRNA against Vps35 leads to mis-sorting of DMT1-II to LAMP2-positive structures, and expression of siRNA-resistant Vps35 can rescue this effect. 20619655_Vps35 mediates vesicle transport between the mitochondria and peroxisomes. 21515373_Knockdown of retromer protein VPS35 activity produces no change in the quantity or cellular distribution of total cellular amyloid precursor protein (APP) and has no affect on internalization of cell-surface APP. 21733561_Frameshift mutations of VPS genes and losses of expression of Vps13A and Vps35 proteins are common in gastric cancers and colorectal cancers with high microsatellite instability. 21763482_Disruption of VPS35 and retromer-mediated trans-membrane protein sorting, rescue, and recycling in the neurodegenerative process led to Parkinson disease. 21763483_Only a single heterozygous variant in the VPS35 gene caused late-onset Parkinson disease in this family. 21849449_The amino-terminal conserved, glutamate-rich sequence of herpesvirus saimiri Tip specifically interacts with the human retromer subunit Vps35 and inhibits retromer activity. 22154191_The results of this study concluded that VPS35 c.1858G>A mutation is an uncommon cause of familial Parkinson's disease. 22278960_Failed to find any case of VPS35 pAsp620Asn mutation in a cohort of Italian patients with familial Parkinson disease. 22336192_Hence, our data do not support a major role for VPS35 variations in the genetic etiology of Lewy body disorders in the Flanders-Belgian population. 22410496_This study suggested that VPS35 Asp620Asn may be not associated with PD in Chinese population. 22513087_Data show that a component of the WASH regulatory complex (SHRC), FAM21, directly interacts with the retromer CSC protein VPS35. 22517097_We have extended the number of autosomal dominant PD families with VPS35 mutations to 13 families, worldwide; D620N is the most frequent. 22673036_VPS35 variants are not associated with Parkinson's disease in the mainland Chinese population. 22801713_VPS35 mutations are a rare cause of PD in different populations. 22891780_result suggests that mutation in the VPS35 coding region probably does not represent a major cause of late-onset Parkinson Disease in the Chinese Han population. 22991136_This study reported that VPS35 mutation in Japanese patients with typical Parkinson's disease. 23125461_Our study apart from identifying the p.Asp620Asn variant in familial cases also identified it in idiopathic Parkinson disease cases, and thus provides genetic evidence for a role of p.Asp620Asn in Parkinson disease in different populations worldwide. 23261770_Mutations in VPS35 were found to not play a role in Parkinson disease patients from Southwest China. 23408866_There is no evidence for an overall contribution of genetic variability in VPS35 (or EIF4G1) to Parkinson disease development in this large family. 23411763_Pathogenic mutation in VPS35 impairs its protection against MPP(+) cytotoxicity in dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease. 23536430_Pathogenic VPS35 mutations provide important insights into novel molecular targets for parkinson disease. 23726718_Its mutation causes Parkinson's disease in Indian population. 24152121_Dominant expression of Vps35 D620N mutation results in endosomal trafficking alterations that may underpin its role in PD. 24262182_In 2011 two groups reported the identification of the same missense mutation (p.Asp620Asn) in the vacuolar protein sorting 35 (VPS35) gene, as a novel cause of autosomal dominant parkinson disease. 24740878_dominant VPS35 mutations lead to neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. 24819384_D620N mutation in VPS35 restricts WASH complex recruitment to endosomes, inhibiting autophagy. The autophagy defects can be explained, at least in part, by abnormal trafficking of the autophagy protein ATG9A. 24854799_Its mutation is not a common cause of familial Parkinson's disease. 24980502_the major defect of the D620N mutation in the retromer component VPS35 lies in the association to the actin-nucleating Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and SCAR homolog (WASH) complex. 25367362_provides molecular insights into the essential role of Vps26 and Vps35 in Rab7-mediated recruitment of the core retromer complex 25393110_Mutagenesis studies coupled with coimmunoprecipitations revealed that retromer-mediated trafficking requires the Env cytoplasmic tail that we show binds directly to retromer components Vps35 and Vps26. 25416282_VPS35 p.D620N is loss-of-function mutation with respect to VPS35 regulating synaptic transmission and AMPA-type glutamate receptors recycling in mouse cortical neurons and dopamine neuron-like cells produced from stem cells of human p.D620N carriers. 25475142_This study demonstrated that Genetic variability of VPS35 in parkinsonism. 25937119_Data indicate that vesicular transport proteins VPS35 and VPS29 influence the levels of the other subunit of retromer. 26251041_findings provide evidence that the VPS35 D620N mutation likely confers pathogenicity through a partial loss of function mechanism and that this may be linked to other known pathogenic mechanisms such as mitochondrial dysfunction 26300542_VPS35 D620N and EIF4G1 R1205H mutations are not a common cause of Parkinson disease in the Greek population. 26547032_neither the R120W nor the N370S variant of the GBA gene nor D620N mutation of the VPS35 gene were detected among the Parkinson disease cases or the controls. 26618722_VPS35 mutations cause mitochondrial fragmentation and cell death in cultured neurons in vitro, in mouse substantia nigra neurons in vivo and in human fibroblasts from an individual with PD who has the VPS35(D620N) mutation. 26947123_VPS35 has been associated with autosomal dominant forms of Parkinson's disease with a high but incomplete penetrance . 26965691_The retromer complex is a highly conserved membrane trafficking assembly composed of three proteins - Vps26, Vps29 and Vps35, which are impaired in neurodegenerative diseases. (Review) 27262440_deletion of VPS35 in yeast (vps35Delta) leads to a dose-dependent growth defect towards copper. This increased sensitivity could be rescued by transformation with yeast wild-type VPS35 but not by the expression of a construct harboring the yeast equivalent (i.e. D686N) of the most commonly identified VPS35-associated Parkinson disease mutation, p.D620N 27385586_the Vps35 R524W-containing retromer has a decreased endosomal association, which can be partially rescued by R55, a small molecule previously shown to stabilize the retromer complex, supporting the potential for future targeting of the retromer complex in the treatment of Parkinson disease. 27460146_It could interact with DRD1 and regulate DRD1 cell surface recycling, as well as DRD1- mediated dopamine signaling. 27502489_Silencing VPS35 increased N-Ras's association with cytoplasmic vesicles, diminished GTP loading of Ras, and inhibited mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and growth of N-Ras-dependent melanoma cells. 27777137_The absence of mutations in VPS35 genes reveals that they are uncommon causes of Parkinson disease in Brazil 27889239_X-ray crystallographic analysis of a 4-component complex comprising the VPS26 & VPS35 subunits of retromer, sorting nexin SNX3, & recycling signal from the divalent cation transporter DMT1-II; analysis identifies a binding site for canonical recycling signals at the interface between VPS26 & SNX3; shows cooperative interactions among the VPS subunits, SNX3 & cargo that couple signal-recognition to membrane recruitment. 27917878_These experimental data establish the retromer complex as a key spatiotemporal regulator of IFNAR endosomal sorting and a new factor in type-I IFN-induced JAK/STAT signalling and gene transcription. 28040727_results lend further support to the notion that VPS35-DLP1 interaction is key to the retromer-dependent recycling of mitochondrial DLP1 complex during mitochondrial fission and provide a novel therapeutic target to control excessive fission and associated mitochondrial deficits. 28129035_a novel regulator of N-Ras trafficking and signaling 28222538_Present data support a role for perturbed VPS35 and retromer function in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. 28383562_These findings provide new mechanistic insights into the role of VPS35 in the regulation of AIMP2 levels and cell death. 28765075_these results suggest that VPS35 D620N mutation-induced excessive mitochondrial fission leads to the defects in the assembled complex I and supercomplex and causes bioenergetics deficits. 29743203_LRRK2-mediated Rab10 phosphorylation is increased in neutrophils as well as monocytes isolated from three Parkinson's patients with a heterozygous VPS35[D620N] mutation. 32071398_DNA and RNA sequencing identified a novel oncogene VPS35 in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. 32540366_Enhanced Hyaluronan Signaling and Autophagy Dysfunction by VPS35 D620N. 32737286_Retromer stabilization results in neuroprotection in a model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. 33032646_Endosomal dysfunction in iPSC-derived neural cells from Parkinson's disease patients with VPS35 D620N. 33142012_Mitochondrial and Clearance Impairment in p.D620N VPS35 Patient-Derived Neurons. 33347683_Formation of retromer transport carriers is disrupted by the Parkinson disease-linked Vps35 D620N variant. 33611076_Clinical manifestations of Parkinson's disease harboring VPS35 retromer complex component p.D620N with long-term follow-up. 33636388_Impaired neurogenesis in the hippocampus of an adult VPS35 mutant mouse model of Parkinson's disease through interaction with APP. 33800686_Parkinson's Disease Causative Mutation in Vps35 Disturbs Tetherin Trafficking to Cell Surfaces and Facilitates Virus Spread. 34127073_Parkinson's disease-associated VPS35 mutant reduces mitochondrial membrane potential and impairs PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. 34530877_Endosomal traffic and glutamate synapse activity are increased in VPS35 D620N mutant knock-in mouse neurons, and resistant to LRRK2 kinase inhibition. 34602481_VPS35 Downregulation Alters Degradation Pathways in Neuronal Cells. 35690672_ITRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveals that VPS35 promotes the expression of MCM2-7 genes in HeLa cells. 35766879_Mutant VPS35-D620N induces motor dysfunction and impairs DAT-mediated dopamine recycling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000031696 |
Vps35 |
761.372648 |
2.6605484441 |
1.411724 |
0.157489114 |
77.931899 |
0.00000000000000000106654997386940132589124881292101610026354878052364796511830569158973958110436797142028808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000008910690389158254978686545088686961502803032153963592315593089665526349563151597976684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
985.3607409 |
96.1585369 |
372.8606493 |
26.7062487 |
| ENSG00000069482 |
51083 |
GAL |
protein_coding |
P22466 |
FUNCTION: Endocrine hormone of the central and peripheral nervous systems that binds and activates the G protein-coupled receptors GALR1, GALR2, and GALR3. This small neuropeptide may regulate diverse physiologic functions including contraction of smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tract, growth hormone and insulin release and adrenal secretion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1370155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1722333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25691535}. |
3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Hormone;Neuropeptide;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a neuroendocrine peptide that is widely expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and also the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, adrenal gland and urogenital tract. The encoded protein is a precursor that is proteolytically processed to generate two mature peptides: galanin and galanin message-associated peptide (GMAP). Galanin has diverse physiological functions including nociception, feeding and energy homeostasis, osmotic regulation and water balance. GMAP has been demonstrated to possess antifungal activity and hypothesized to be part of the innate immune system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:51083; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; galanin receptor activity [GO:0004966]; galanin receptor binding [GO:0031763]; neuropeptide hormone activity [GO:0005184]; type 1 galanin receptor binding [GO:0031764]; type 2 galanin receptor binding [GO:0031765]; type 3 galanin receptor binding [GO:0031766]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; feeding behavior [GO:0007631]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; negative regulation of lymphocyte proliferation [GO:0050672]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cortisol secretion [GO:0051464]; positive regulation of large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity [GO:1902608]; positive regulation of timing of catagen [GO:0051795]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010737]; regulation of glucocorticoid metabolic process [GO:0031943]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to immobilization stress [GO:0035902]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
11712539_galanin is expressed developmentally in the DRG 12471460_an involvement of GAL in various physiological functions of the gastrointestinal tract 12647269_data suggest a role for endogenous galanin in the adaptive responses to acute orthostatic stress preventing syncope in susceptible individuals 12654333_Galanin is present in human DRGs together with CGRP and substance P, mostly in small neurons. Galanin may mediate processing of sensory information, especially pain, in human DRGs and dorsal horn. 12769595_The involvement of galanin is reviewed in the modulation of such functions as neurotransmitter release, memory, pain, depression, anxiety, obesity, gut motility, neuroendocrine regulation, development and neuroregeneration. 14700749_corticotroph, but not GH adenomas, express high levels of galanin, in addition to ACTH, and in some tumors both polypeptides are synthesised in the same cell population; galanin levels in plasma were not influenced by the tumor galanin content 14706552_human galanin expresses amphipathic properties in the presence of phospholipids which in turn amplifies its vasoactive effects in the intact peripheral microcirculation. 15283968_These galanin-LHRH and LHRH-galanin contacts may be functional synapses, and they may be the morphological substrate of the galanin-controlled gonadal functions in humans. 15648541_Serum galanin concentration in post-menopausal women is related to severity of climacteric syndrome; presence of nervousness in post-menopausal women is related to lower serum galanin level. 15735230_Blood levels correlate with type 2 diabetes and not with obesity or hormonal status in postmenopause. 15893372_mechanistic relationship between amyloidosis and GAL over expression in Alzheimer disease 15927790_We suggest that expression of galanin in the medial and lateral components of the mamillary bodies may be of transient occurrence and may serve a significant role in the synaptogenesis. 15930442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15930442_The analyzed single nucleotide polymorphisms in GAL and GALR1 do not play major role in early onset obesity or dietary fat intake in obese children and adolescents. 15944034_The co-expression of galanin and its receptors supports a role for galanin in tumor cell pathology via autocrine/paracrine mechanisms 16314872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16314872_There is a haplotype association with alcoholism in both the Finnish (P=0.001) and Plains Indian (P=0.004) men. 16787232_This review presents considerable evidence that has accumulated implicating both galanin and GALP as playing important roles in regulating food and water intake behavior and related neuroendocrine functions. 17083333_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17573119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17573119_polymorphisms in the galanin gene are associated with symptom severity in female patients suffering from panic disorder. 18196269_Developmentally regulated expression of galanin and somatostatin may play a role in liver morphogenesis. 18272487_point to GalR2 as a possible target for therapeuthic interventions in pheochromocytoma 18322398_Galanin fiber hyperinnervation of cholinergic forebrain nucleus basalis neurons upregulates the expression of choline acetyltransferase. 18518925_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18973137_GAL, coding for the neuropeptide galanin, and GALR1, a galanin receptor, were identified as candidate genes of oncogenesis in squamous cell carcinoma using a survey of parallel chromosomal alterations and gene expression studies in 10 SCC cell lines. 18988886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18988886_The common allele of rs2187331, residing in the promoter region of GAL, is significantly associated with hypertriglyceridemia . 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19749437_provides substantive evidence that GAL sustains the expression of genes subserving multiple neuroprotective mechanisms in hyperinnervated cholinergic NB neurons compared to nonhyperinnervated neu-ron 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237460_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20237460_The reported associations in independent samples of Alzheimer Disease and Major Depressive Disorder support an estrogen-dependent function of GAL in pathophysiology of anxiety and depression, affecting response to antidepressant treatment. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21042317_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21042317_This study suggested that the adenylate GAL related to major depressive disorder. 21199668_acute alcohol withdrawal was associated with decreased galanin serum levels 21352816_Chronic constriction injury results in galanin upregulation in dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve, although less in transgenic mice with nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition. 21707521_Study revealed that plasmin was present in tumor tissue, and that it was responsible for processing progalanin to galanin(1-20) in the extracellular environment. 21716262_Analysis in neuroblastoma cells demonstrates that GAL5.1 acts as an enhancer of promoter activity after protein kinase C activation. 22078238_Cerebrospinal fluid levels of total but not free IgG autoantibodies against galanin are increased in patients with Alzheimer's disease, resulting in increased percentage of galanin autoantibodies present as immune complexes. 22162474_Circulating galanin levels at birth are not affected by GDM and IUGR, providing no evidence for alternations in hypothalamic galanin expression and secretion in humans, as they were previously documented in experimental models. 22226150_The results indicate the continuous presence of GAL-ergic innervation in the immediate vicinity of the cancer invasion, which may be attributed to increased contraction of the affected part of intestine. 22859720_Moreover, we have identified a novel role for the GalR1/galanin receptor-ligand axis in chemoresistance, providing evidence to support its further evaluation as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker in colorectal cancer . 23261456_These results suggest that the activation of progalanin by plasmin in the extracellular compartment was involved in MMP-9 and MMP-2 activation and in angiogenesis in tumor tissue. 23278944_Galanin has a role in regulating eccrine sweat gland secretion 23341594_localization of the transcripts for galanin and its receptors (GalR1-R3), tryptophan hydroxylase 2, tyrosine hydroxylase, nitric oxide synthase and the three vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUT 1-3) in the locus coeruleus and the dorsal raphe nucleus 23741354_The SNPs of rs694066 in the GAL gene showed a positive correlation with the major depressive disorder in the Chinese Han population. 24106965_Galanin plays a crucial role in inhibiting insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells to prevent hyperinsulinemia, which is a characteristic of type 2 diabetes mellitus. [review] 24397394_Data suggest that plasma levels of galanin and interleukin-6 are up-regulated in second trimester in women with gestational diabetes (glucose intolerant/insulin resistant) as compared to normal pregnant women (with normal glucose/insulin tolerance). 24503374_The plasma galanin levels are higher in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus than in normal pregnancy. 24706871_Variants in genes for galanin (GAL) and its receptors (GALR1, GALR2, GALR3), despite their disparate genomic loci, conferred increased risk of depression and anxiety in people who experienced childhood adversity or recent negative life events. 25228436_found no association of the galanin enhancer genotype with any of the other pathophysiological parameters measured 25504183_Data shows that high expression of GAL is associated with poor prognosis of stage II colorectal cancer patients (CRC) and GAL expression may be related to the aggressive behavior of CRC. 25545502_Galanin can be regarded as an immunomodulatory peptide as it can sensitize polymorphonuclear neutrophils towards pro-inflammatory cytokines in humans and mice. 25691535_Mutations in the human GAL gene cause temporal lobe epilepsy. 25779965_Galangin-induced down-regulation of BACE1 by epigenetic mechanisms 25917569_Galanin released by cancer induces neuritogenesis, facilitating perineural invasion. 26122049_This is the first report of the various galanin receptors in the human eye. 26253934_Elevated galanin may predict the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus for development of Alzheimer's disease. 26572146_GAL and its receptors, GALR1 and GALR2, play a role in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis 26621352_This study demonstrated that Galanin upregulation within the basal forebrain cholinergic system in LBD 27474259_results indicated that obese individuals have higher plasma GAL and GALP concentrations and both peptide concentrations were positively correlative to triglyceride concentrations in obese human 27538957_Low levels of plasma galanin is associated with obese subjects with hypertension. 27550417_Serum galanin (GAL) levels are significantly higher in the obese group compared with lean subjects during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). 27685843_Study provides evidence that GAL and GALR1/2 genes were identified as aberrantly methylated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 27837916_Galanin per se did not affect the dynamic mass redistribution of natural killer (NK) cells, but significantly enhanced the response of NK cells to IL-18 27870457_The analyses revealed that the presence of the galanin gene minor allele (G) increased susceptibility to multiple sclerosis in men (OR = 2.49, P = 0.008) but not in women. 27914762_majority of intrinsic choroidal neurons were GAL-positive 27940914_GAL and its receptor GALR3 are differentially methylated and expressed in brains of major depressive disorder subjects in a region- and sex-specific manner. 27943416_ultraviolet irradiation upregulated galanin mRNA and protein expression in keratinocytes in vitro and in human skin in vivo 28336906_Our results identified FGL2, GAL, SEMA4D, SEMA7A, and IDO1 as new candidate genes that could be involved in MSCs-mediated immunomodulation. FGL2, GAL, SEMA4D, SEMA7A, and IDO1 genes appeared to be differentially transcribed in the different MSC populations. Moreover, these genes were not similarly modulated following MSCs-exposure to inflammatory signals 28416367_Higher serum galanin levels were determined in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. 28720509_Study found dramatic reduction in von Willebrand factor extrusion and multimer expression by the neuropeptide galanin in cultured endocardial endothelial cells from heart failure patients. Results suggest that a combination of beta-blockers and galanin therapy may be one therapeutic option for improving endocardial endothelial anticoagulant function. 28987550_SNP rs948854 in the GAL gene seems to be involved in the modulation of depressive state, especially in individuals with GG genotype. 29331040_results suggested that four differentially expressed genes, Jun, Gal, Cd74, and C1qb, had the potential to serve as prognostic or predictive markers for neuropathic pain, suggesting a potential application in the improvement of prognostic tools and treatments. 29654647_GAL, GAP43 and NRSN1 single nucleotide polymorphisms and related gene-gene interaction networks might be involved in the altered susceptibility to Hirschsprung disease in the Han Chinese population. 30019295_elevated high expression of CASP3 or CASP8 in the neurons from MPs was accompanied by a decreased expression of GAL. To our knowledge, this is the first report describing the decomposition of myenteric plexuses (MPs) within cancer-affected human stomach wall and the possible role of apoptosis in this process. 30373200_Notable changes in the dense network of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript- (CART-) and galanin -containing nerve fibers (an increase) were observed in the longitudinal (LML) and lamina muscularis mucosae (LMM) within carcinoma-affected areas of the human stomach. 30616468_Low Galanin expression is associated with gastric cancer. 31881033_Study revealed two statistically significant associations between anxiety and the galanin rs948854_C-rs4432027_C haplotype and the rs1042577_T single-locus allele, respectively. 32757697_Further evidence for the association of GAL, GALR1 and NPY1R variants with opioid dependence. 33534034_Serum Galanin in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. 33552060_Review: Occurrence and Distribution of Galanin in the Physiological and Inflammatory States in the Mammalian Gastrointestinal Tract. 34925648_Increased Serum Neuropeptide Galanin Level Is a Predictor of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Hip Fracture. 35913979_Structure of the human galanin receptor 2 bound to galanin and Gq reveals the basis of ligand specificity and how binding affects the G-protein interface. |
ENSMUSG00000024907 |
Gal |
27.472423 |
3.2754741547 |
1.711704 |
0.326143547 |
28.536706 |
0.00000009193891828058509728447236005605125441775271610822528600692749023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000364007090617338014109093417489115829255297285271808505058288574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.4234777 |
8.5774861 |
13.3864994 |
2.1794771 |
| ENSG00000069849 |
483 |
ATP1B3 |
protein_coding |
P54709 |
FUNCTION: This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-3 subunit is not known. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Sodium;Sodium transport;Sodium/potassium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of Na+/K+ and H+/K+ ATPases beta chain proteins, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane. The glycoprotein subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes a beta 3 subunit. This gene encodes a beta 3 subunit. A pseudogene exists for this gene, and it is located on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:483; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sodium:potassium-exchanging ATPase complex [GO:0005890]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATPase activator activity [GO:0001671]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; cellular potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0030007]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; membrane repolarization [GO:0086009]; positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032781]; positive regulation of potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1903288]; positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901018]; positive regulation of sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1903278]; potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1990573]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0036376]; sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0035725] |
12456588_role in T and B lymphocyte activation 17176442_These results evidenced that the beta3 subunit of Na, K ATPase is expressed on RBC membrane but the epitope recognized by mAb P-3E10 is hidden in normal RBCs. we showed the association of beta3 subunit and alpha subunit of Na, K ATPase. 17446412_Elevated Na+ -K+ -ATPase activity postexercise may contribute to reduced fatigue after training. 24236063_B7H3 and ATP1B3 are overexpressed in tumor endothelial cells, favoring an angiogenic phenotype. 26694617_Data suggest that ATP1B3 is binding partner of BST-2 and regulates stability of BST-2; ATP1B3 is co-factor that accelerates BST-2 degradation and reduces BST-2-mediated restriction of HIV-1 replication/tropism and NFkappaB activation. 27240146_Our study demonstrated that ATP1B3 inhibit EV71 replication by enhancing the production of type-I interferons, which could act as a potential therapeutic target in EV71 infection. 29940031_ligation of the Na, K ATPase beta3 subunit on monocytes by mAb P-3E10 arbitrated T cell hypofunction. This mAb might be a promising novel immunotherapeutic antibody for the treatment of hyperresponsive T cell associated diseases. 30792309_These results demonstrate that CASPR1 binds with ATP1B3 and thereby contributes to the regulation of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase maturation and trafficking to the plasma membrane in brain microvascular endothelial cells. 33534085_ATP1B3 Restricts Hepatitis B Virus Replication Via Reducing the Expression of the Envelope Proteins. 33868261_Integrative Transcriptomic, Proteomic and Functional Analysis Reveals ATP1B3 as a Diagnostic and Potential Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 35790431_[Screening and identification of key genes ATP1B3 and ENAH in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma: based on data mining and clinical validation]. |
ENSMUSG00000032412 |
Atp1b3 |
769.374731 |
2.7436841753 |
1.456114 |
0.068633400 |
452.546217 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020136858948097743397055027003587360934381983146310910751112853321542947910968858700435830689854064879592869257324651327456275350953434740926321612381920220053200671510101121316413133338387320341350654083985932636275713939855702420 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008590174510807013800451242397854937913961286250753956564046623525950268884542623413607369823539847287615014762873485688549217583518074745590041274010153854158994642288575110521547584902930534443870929634632458923649167000711043717 |
Yes |
No |
1133.3169978 |
47.1203041 |
416.0246145 |
13.6933367 |
| ENSG00000070018 |
4040 |
LRP6 |
protein_coding |
O75581 |
FUNCTION: Component of the Wnt-Fzd-LRP5-LRP6 complex that triggers beta-catenin signaling through inducing aggregation of receptor-ligand complexes into ribosome-sized signalsomes. Cell-surface coreceptor of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, which plays a pivotal role in bone formation. The Wnt-induced Fzd/LRP6 coreceptor complex recruits DVL1 polymers to the plasma membrane which, in turn, recruits the AXIN1/GSK3B-complex to the cell surface promoting the formation of signalsomes and inhibiting AXIN1/GSK3-mediated phosphorylation and destruction of beta-catenin. Required for posterior patterning of the epiblast during gastrulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11357136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15778503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16341017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16513652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17326769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17400545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19107203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19293931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19801552}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Endocytosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene family. LDL receptors are transmembrane cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of lipoprotein and protein ligands. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a receptor or, with Frizzled, a co-receptor for Wnt and thereby transmits the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling cascade. Through its interaction with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling cascade this gene plays a role in the regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, and migration and the development of many cancer types. This protein undergoes gamma-secretase dependent RIP- (regulated intramembrane proteolysis) processing but the precise locations of the cleavage sites have not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. |
hsa:4040; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; Wnt-Frizzled-LRP5/6 complex [GO:1990851]; coreceptor activity involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:1904928]; coreceptor activity involved in Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0071936]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0019210]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0005041]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; toxin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019534]; Wnt receptor activity [GO:0042813]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in neural crest cell differentiation [GO:0044335]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in regulation of cell proliferation [GO:0044340]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904948]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071901]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0034392]; neural crest cell differentiation [GO:0014033]; neural crest formation [GO:0014029]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:0090118]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904953]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in somitogenesis [GO:0090244] |
12897152_Wnt canonical signaling through LRP6 establishes a novel mechanism for receptor activation which is opposite to the general paradigm of ligand-induced receptor oligomerization 15271658_role for an LDL receptor-related protein in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and survival through the evolutionary conserved Wnt signaling cascade. 15516984_LRP6 may function as a potential oncogenic protein by modulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling 15908424_SOST antagonizes Wnt signaling by binding to the extracellular domain of the Wnt coreceptors LRP5 and LRP6 and disrupting Wnt-induced Frizzled-LRP complex formation. 16263759_Together our results show that in addition to serving as a folding chaperone, Mesd can function as a receptor antagonist by inhibiting ligand binding to mature LRP6. 16355283_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16365045_a direct interaction between LRP6 and GSK3 results in an attenuation of GSK3 activity 16384981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16384981_These data suggest that LRP6, VEGF, and VLDLR may play a role in the risk of developing (age-related macular degeneration)AMD. 16513652_active CKIepsilon generation may induce a negative feedback loop by phosphorylation of sites on LRP5/6 that modulate axin binding and hence beta-catenin degradation 16564009_LRP6 is required for anthrax toxin lethality; LRP6 enables toxin internalization by interacting at the cell surface with PA receptors 16989816_Mesd and LRP6 modulate Wnt signaling. 17326769_These findings suggest a novel mechanism for LRP6 in Wnt signaling: induction of ectodomain shedding of LRP6, followed by the gamma-secretase involved proteolytic releasing its intracellular domain. 17332414_results link a mutation in LRP6 which encodes a co-receptor in the Wnt signaling pathway to coronary artery disease and multiple cardiovascular risk factors 17376403_The finding that GRB10 interferes with the binding of Axin to LRP6 indicated a possible molecular mechanism by which the overexpression of GRB10 suppresses Wnt signaling. 17517621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17517621_report the association between common LRP6 variants and late-onset Alzheimer's disease in a multicenter case-control series as well as in a large family-based series ascertained 17569865_it is proposed that Wnts induce coclustering of receptors and Dvl in LRP6-signalosomes, which in turn triggers LRP6 phosphorylation to promote Axin recruitment and beta-catenin stabilization 17698587_Results identify a novel feedback mechanism by which Wnt, including Wnt3a, negatively regulates LRP6 at the mRNA level. 17765217_While secreted Wise either synergizes or inhibits the Wnt signals depending on the partner ligand, ER-retained Wise consistently blocks the Wnt pathway. ER-retained Wise reduces LRP6 on the cell surface, making cells less susceptible to the Wnt signal. 17804805_RSPO1 regulates Wnt signaling by inhibiting internalization of LRP6. 18077588_Both Fz and Dvl functions are critical for Wnt-induced Lrp6 phosphorylation through Fz-Lrp6 interaction. Axin, a key scaffolding protein in the Wnt pathway, is required for Lrp6 phosphorylation via its ability to recruit Gsk3. 18083125_each LRP6 PPPS/TP motif contributes in a combinatorial fashion to activate the canonical Wnt-beta-catenin pathway 18350154_data argue against a human-specific role for LRP6 in anthrax toxin entry and suggest instead that involvement of this protein may be restricted to certain cell types independently of their species of origin 18362152_PPPSP motifs represents a built-in amplifier for Wnt signaling by the LRP6 family of receptors. 18378904_propose that palmitoylation serves to tilt the long, 23-residue transmembrane domain of LRP6 with respect to the plane of membrane to prevent a hydrophobic mismatch and subsequent recognition by the ER quality control 18406176_No association was seen between FRZB, LRP5 and LRP6 variants with radiographic osteoarthritic outcomes in two population-based cohorts 18406176_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493104_We found no evidence for a substantial effect of LRP5 or LRP6 SNPs on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes or clinical characteristics of diabetic subjects in Japanese population. 18502762_Kremen may not be essential for Dkk1-mediated Wnt antagonism and Kremen may only play a role when cells express a high level of LRP5/6 18505732_DKK1 inhibition of LRP6 is independent of LRP6 internalization and degradation 18524778_analysis of the structural basis of the interaction between Dkk and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 18606139_WNT3 and DKK1 regulate distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta catenin signaling. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18717822_The authors show that LRP6 can indeed form a complex with anthrax toxin receptors, and that this interaction plays a role both in Wnt signalling and in anthrax toxin endocytosis. 18772438_Wnt3a stimulates formation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate through frizzled & dishevelled; in turn PtdIns (4,5)P2 regulated phosphorylation of LRP6 at Thr1479 & Ser1490; study reveals signaling mechanism for Wnt to regulate LRP6 phosphorylation 18838381_BAMBI interacts with Wnt receptor Frizzled5, coreceptor LRP6, and Dishevelled2 and increases the interaction between Frizzled5 and Dishevelled2 18981475_PTH treatment led to phosphorylation of LRP6 and an increase in amount of beta-catenin in osteoblasts with a concurrent increase in bone formation in rat. Thus, LRP6 coreceptor is a key element of the PTH signaling that regulates osteoblast activity. 19015224_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19107203_Phosphorylated LRP6/5 both recruits and directly inhibits GSK3beta using two distinct portions of its cytoplasmic sequence. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19293931_propose a working model that Axin recruitment to the phosphorylated LRP6 places GSK3 in the vicinity of multiple phosphorylated PPPSPXS motifs 19339249_These studies reveal unique properties of the LRP6 beta-propeller domains and provide novel tools to understand LRP6 function in ligand binding and Wnt signaling. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19477926_Results identify the first propeller domain as a novel regulatory domain for DKK1 binding to LRP6. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667113_A common variant in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 gene (LRP6) is associated with LDL-cholesterol. 19667113_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19711366_PPP(S/T)P motif phosphorylation of the free LRP6 intracellular domain is not required to activate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and attenuate GSK3beta activity 19801552_Results identify GRK5/6 as novel kinases for the single transmembrane receptor LRP6 during Wnt signaling. 19833493_LRP6 variants with impaired Wnt/beta-catenin signaling appear to be involved in early coronary and carotid artery atherosclerosis, at least in hypertensive patients. 19833493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19881541_found that mammary glands from mouse mammary tumor virus-LRP6 mice exhibit significant Wnt activation evidenced by the translocation of beta-catenin from membrane to cytoplasmic/nuclear fractions. 19898734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898734_results suggest that SNP in LRP6, is not associated with bone mineral density in the Slovenian population 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20053636_Results suggest that Dkk1 induces the internalization of LRP6 to suppress its phosphorylation in the lipid raft and allows subsequent recycling of LRP6 so that it can be reused for signaling. 20057906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20093360_analysis of the frizzled8.Wnt3a.LRP6 signaling complex reveals multiple Wnt and Dkk1 binding sites on LRP6 20137080_The canonical Wnt-signaling proteins LRP6 and Dvl2 and Dvl3 are involved in the regulation of beta-catenin. 20194742_Expression of the Wnt signaling coreceptor LRP6 is up-regulated in a subpopulation of human breast cancers. 20351274_SERPINA3K is a high-affinity, endogenous antagonist of LRP6 20388731_Dishevelled signals through LRP5/6 in human cells and Drosophila embryos. 20390408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460648_Gbetagamma activates GSK3 to promote LRP6-mediated beta-catenin transcriptional activity 20543981_results reveal a novel role for Dkk1 in preventing Wnt ligand-induced LRP6 down-regulation and contribute significantly to our understanding of Dkk1 function in Wnt/LRP6 signaling 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20676368_Results suggest that LRP6-ICD can differentially modulate Wnt pathway transcriptional activity depending upon its subcellular localization and differential protein-protein interactions. 20846389_The mRNA expression levels of DKK-1 binding receptor LRP5/6 and Krm1/2 in SCs from patients with MM were significantly higher than those in myeloma cells and in SCs from healthy donors. 20926594_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926594_We found common polymorphisms of LRP5 associated with osteoporotic fractures, and polymorphisms of the LRP6 gene associated with BMD, thus suggesting them as likely candidates to contribute to the explaination of the hereditary influence on osteoporosis. 20974802_direct phosphorylation of LRP6 by MAPKs provides a unique point for convergence between WNT/beta-catenin signaling and mitogenic pathways 21245321_findings implicate LRP6 as a critical modulator of PDGF-dependent regulation of cell cycle in smooth muscle and indicate that loss of this function contributes to development of early atherosclerosis in humans 21397183_Two structural and functional domains of MESD required for proper folding and trafficking of LRP5/LRP6. 21536646_these results identified TMEM198 as a membrane scaffold protein that promotes LRP6 phosphorylation and Wnt signaling activation. 21887268_These studies uncover a new and important molecular tuning mechanism for differential regulation of LRP5 and LRP6 phosphorylation and signaling activity. 21944579_The consensus E1 binding sequence motif is important for DKK1 and SOST binding to LRP6 and for inhibitory function. 21984209_Results provide key insights for understanding LRP5/6 structure and the interaction of LRP5/6 with DKK1, as well as for drug discovery. 22000855_The LDL-receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6), alongside Frizzled receptors, transduces Wnt signaling across the plasma membrane. 22000856_The Wnts bound to either portion of the LRP6 ectodomain likely bear a similar spatial relationship to Frizzled coreceptors. 22128165_LRP6 protein regulates low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-mediated LDL uptake. 22372892_The conformation of the LRP6 intracellular domain is elongated before activation; this is based on the intrusion of the Frizzled complex into the ensemble space of the proline rich region of LRP6, which alters the shape of its available ensemble space. 22393312_LRP6 as a new candidate gene in ileal Crohn's Disease; an association of a non-synonymous SNP (rs2302685; Ile1062Val) with early onset ileal Crohn's Disease 22490400_The C allele of the rs11054731 within the LRP6 gene was associated with increased risk and extent of CAD in Chinese. 22570728_overexpression of LRP6 contributes to the hyperactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human HCCs and suggest it may play a role in hepatocarcinogenesis. 22589387_Crystal structures of the LRP6 ectodomain in complex with DKK1, along with mutagenesis studies, provide considerable insights into the molecular basis for DKK-mediated inhibition and Wnt signaling through LRP5/6 22606268_sLRP6E1E2, by inhibiting interaction between Wnt and its receptor, suppressed Wnt-induced cell proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 22696217_peptide derived from the loop 2 region of sclerostin blocked the interaction of sclerostin with LRP5/6 and also inhibited Wnt1 but not Wnt3A or Wnt9B signaling. This suggests that these Wnts interact with LRP6 in different ways 22871567_These results demonstrate LRP6 as the predominant Wnt3a LRP-receptor in human mesenchymal stem cells, which cannot be substituted by LRP5. 22907437_Arf modulates LRP6 phosphorylation for the transduction of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 23077088_Data indicate that LRP6, BCL2L14, DUSP16, CREBL2, and CDKN1B were involed in centromeric (12p11.21-12p13.2) deletion in ETV6-RUNX1 B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). 23218566_The LRP6delta3 isoform is a novel splice variant which shows diminished wnt signaling activity and is associated with Alzheimer's disease. 23302227_results show that Cav-1 interacts with LRP6 to generate an integrated signaling module that leads to the activation of IGF-IR/IR and results in stimulation of Akt-mTORC1 signaling and aerobic glycolysis in prostate cancer 23306204_SOX9 regulates low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) and T-cell factor 4 (TCF4) expression and Wnt/beta-catenin activation in breast cancer. 23395167_the LRP6(R611C) mutation diminishes TCF7L2-dependent transcription of the IR while it increases the stability of IGFR and enhances mTORC1 activity. 23638027_Wnt3a-induced transcriptional responses and induction of alkaline phosphatase activity, an early marker of osteoblast differentiation, require the Wnt co-receptors LRP5 and LRP6 23666756_A novel role of kallistatin in preventing breast tumor growth and mobility by direct interaction with LRP6. 23703864_Americans with early onset familial coronary artery disease and metabolic syndrome and healthy Northern European controls were screened for nonconservative mutations in LRP6; 3 novel mutations were identified which cosegregated with the metabolic traits in the kindreds of affected subjects and none in controls 23754096_Pantoprazole treatment caused a decrease in phospho-LRP6, but not in LRP6. 23773994_Results indicate that Lrp6 mediates not only canonical Wnt signaling, but can also modulate non-canonical pathways involving RhoA-dependent mechanisms to impact neurulation, possibly through intracellular complexes with DAAM1. 23811937_Data indicate that upregulated miR-126 upon coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) infection targets SPRED1, LRP6, and WRCH1 genes, mediating cross-talk between ERK1/2 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways, and thus promoting viral replication. 23987510_Lypd6 appears to control Lrp6 activation specifically in membrane rafts, which is essential for downstream signaling. 24203697_This study demonstrates the association of rare and novel missense mutations in LRP6 that is an inhibitor rather than an activator of the non-canonical planar cell polarity pathway with human neural tube defects. 24265322_Data show that beta-arrestins regulate Wnt3a-induced low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (Lrp6) phosphorylation by the regulation of the membrane dynamics of Amer1. 24392029_Syndecan-1 modulates the cancer stem cell phenotype via regulation of the Wnt and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathways 24412065_GSK3 is sequestered into multivesicular bodies through and interaction between p120-catenin/cadherin and LRP5/6. 24427284_results demonstrated that the novel loss-of-function variants identified in this study might contribute to disease liability in a subset of coronary artery disease (CAD) and defects in Wnt signal activation might be important contributing factors for the onset of CAD 24457908_LRP6 may influence glucose metabolism in type II fibers of human skeletal muscles. 24607787_Rottlerin is a novel LRP6 inhibitor, promoting protein degradation. 24704686_Data indicate that miR-202 suppresses the expression of LRP6 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6) by binding to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of its mRNA. 24743782_The results suggested that the lack of affinity between human DKK3 and human LRP5/6 results from: i) insertion of the 7 amino acids, and ii) P258 in human DKK3. 24843317_The LRP6 rs10845498 SNP is associated with a reduced risk of lung SCC, while tobacco smoke increases the risk 24906453_Data provides the first evidence that LRP6 rs2302685 polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of MI in Chinese subjects, and the association is more evident among younger individuals, which probably due to the elevated LDL-C levels. 25143377_The LRP6 tyrosine mutant increased in signaling activation in response to Wnt3a/beta-catenin stimulation. 25240815_the metastasis and angiogenesis functions of miR-126-3p were mediated by LRP6 and PIK3R2. 25242217_LRP6 (and Wnt signaling) are significantly downregulated in Alzheimer's disease brains. 25301448_High LRP6 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 25358452_Particularly for TNBC associated with Skp2/LRP6 overexpression. 25425204_The interaction between Wnt isoforms and their LRP6 cognate receptor depends on the jutting loop present in Wnt3a but absent in Wnt5b. 25500543_LRP6 phosphorylation by ERK1/2 may provide a unique point of convergence between KRAS/MAPK and Wnt/beta-catenin signalings during oncogenesis 25546815_LRP6 variants outside of YWTD repeats could potentially predispose embryos to neural tube defectss, whereas Lrp6 modulation of Wnt/planar cell polarity signaling would be more essential than its canonical pathway role in neural tube closure. 25783012_No mutations in LRP5 and LRP6 could be identified 25902418_Lrp6 binds to Frizzled, preventing Frz-regulated non-canonical Wnt pathway activation and further non-canonical pathway-mediated tumour metastasis. 25959626_findings suggest that rescuing LRP5/6-mediated Wnt signaling improves neuronal cell survival and reduces tau phosphorylation, which support the hypothesis that Wnt signaling might be an attractive therapeutic strategy for managing AD 26031789_LRP6 variants may be associated with risk of ischaemic stroke. 26063413_miR513c functions as a tumor suppressor miRNA, mediated predominantly through the direct suppression of the expression of LRP6. 26120271_LRP6 and VEGF levels in the vitreous body from patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy were increased and correlated mutually. 26387593_Loss-of-Function Mutations in the WNT Co-receptor LRP6 Cause Autosomal-Dominant Oligodontia. 26797284_Accordingly, we propose that the anti-fibrotic activity of adiponectin may be mediated through AdipoR1/R2 receptors 26963285_We identified a frameshift (c.4594delG, p.Cys1532fs) and a canonical splice-site mutation (c.3398-2A>C, p.?) in LRP6, respectively, in the patient with tooth agenesis (TA) and orofacial clefting (OFC) and in the patient with severe TA only. Mutations in LRP6 cause TA in humans 27089893_results suggest that miR-29b inhibits expression of LRP6 and HuR post-transcriptionally, thus playing a role in the regulation of IEC proliferation and intestinal epithelial homoeostasis. 27285107_sustained activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling due to abrogation of Merlin-mediated inhibition of LRP6 phosphorylation may be a cause of Neurofibromatosis type II disease. 27455246_Mutant LRP6 Impairs Endothelial Cell Functions Associated with Familial Normolipidemic Coronary Artery Disease. 27524201_Structure of the dual-mode Wnt regulator Kremen1 and insight into ternary complex formation with LRP6 and DKK1 have been presented. 27751231_The authors show that folding of the Wnt signaling coreceptor LRP6 is promoted by ubiquitination of a specific lysine, retaining it in the ER while avoiding degradation. 27821587_findings revealed an unrecognized role of Caprin-2 in facilitating LRP5/6 constitutive phosphorylation at G2/M through forming a quaternary complex with CDK14, Cyclin Y, and LRP5/6. 28042322_Taken together, this study reveals evidence demonstrating a mechanism by which the LPR6/ GSK3beta/E2F1 axis-upregulated LSH promoted gliomas. 28052259_LRP6 ectodomain becomes highly compact upon complexation with the Wnt antagonist Dkk1, suggesting a potential role for the ectodomain conformational change in the regulation of receptor oligomerization and signaling. 28187755_LncRNA PTCSC3 inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioma cells and suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by targeting LRP6 28247948_data suggest that LRP6 promotes negative breast cancer cell migration and invasion by regulating the expression and function of S100A4 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway 28387660_Increased LRP6 gene expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 28418856_High Expressions of LRP6 is associated with cancer. 28425175_VAP1 cleaved the extracellular region of LRP6 at Glu1196-Leu1197, the C-terminus of the 4th propeller domain. This cleavage removes four inhibitory beta-propeller structures, resulting in activation of LRP5/6. 28696417_we focus on the role of LRP6 genetic polymorphisms and Wnt signaling in complex diseases, and the mechanisms from mouse models and cell lines. It is also highly anticipated that LRP6 variants will be applied clinically in the future 28821575_LRP6 endocytosis proceeds by two routes, depending on the presence of LDL, and that LRP6 controls the intracellular destination of NPC1L1 in hepatocytes. 28870205_CCN2 plays a promoting role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)progression through activating LRP6 in a HSPGs-dependent manner. Heparin in combination with chemotherapy has a synergic effect and could be a treatment choice for HCCs with a high CCN2 expression. 28880263_LRP6 expression was found to be upregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissues, and correlated with a cluster of clinicopathologic parameters, including smoking, drinking, tumor differentiation status, lymph node metastasis and survival time. 28960852_Three rare missense mutations (c.1514A>G, p.Y505C); c.2984A>G, p.D995G; and c.4280C>A, p.P1427Q) of the LRP6 gene were identified in Chinese NTD patients. The Y505C mutation is a loss-of-function mutation on both WNT/beta-catenin and PCP signaling. The D995G mutation partially lost inhibition on PCP signaling without affecting WNT/beta-catenin signaling. The P1427Q mutation dramatically increased WNT/beta-catenin signa... 29017031_identify ANGPTL4 as a Wnt signaling antagonist that binds to syndecans and forms a ternary complex with the Wnt co-receptor Lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 29402412_Therefore, our study demonstrates that miR-183 is a tumor suppressor microRNA that plays a major role in OS. 29439617_Study shows that low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 Is essential for trophoblast survival and invasion. 29500247_We identified rare damaging variants in four genes known to be mutated in syndromic lip and/or cleft palate (syCL/P) : TP63 (one family), TBX1 (one family), LRP6 (one family) and GRHL3 (two families), and clinical reassessment confirmed the isolated nature of their lip and/or cleft palate (CL/P). 29864925_knockdown of LRP6 inhibited the cell viability by activation of Drp1 in glucose deprived-cardiomyocytes. 30039844_LRP6 rs2302685 (V1062I) variant carriers are associated with an increased risk of hyperlipidemia in Iranian children and adolescents. 30069874_Results indicate the key role in the interaction of LY6/PLAUR domain containing 6 (LYPD6) with LDL receptor related protein 6 (LRP6). 30070011_LRP6 regulates alternative pre-mRNA splicing. 30361437_oligomerizations of FZDs and LRP5/6 can integrate the cytoplasmic protein Dishevelled into the LRP5/6 signalosome, resulting in a robust activation of ligand-independent beta-catenin signaling 30474181_association of LRP5 intronic rs4988319 and rs3736228 (Ala1330Val) with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (cADHD) was observed among girls, whereas in boys association between LRP6 rs2302685 (Val1062Ile) and cADHD was present (OR = 1.66, CI = 1.20-2.31, p = .0024). In the PGC-ADHD dataset tendency of associations were observed only among females for LRP5 rs3736228 and for LRP6 rs2302685. 30583072_High LRP6 expression is associated with hepatocarcinogenesis. 30605688_Authors show that AAK1 promotes clearance of LRP6 from the plasma membrane to suppress the WNT pathway. 30684559_low-expressed LRP6 may be responsible of lower migration and invasion of extravillous trophoblasts and subsequent preeclampsia. 30711569_MEG3 functions as a potential hepatocyte lipid degeneration suppressor. MEG3 helps to alleviate lipid over-deposition, probably by binding to miR-21 to regulate the expression of LRP6. 30976847_We found that the rs2302685 mutation, which impaired the function of LRP6, was present in higher frequency among alcoholics with alcoholic liver disease than those without alcoholic liver disease 31085352_New explanation for autosomal dominant high bone mass: Mutation of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. 31332306_the results together with previous data such as the development of Split-hand/foot malformation (SHFM) in Lrp6 knockout mice, the presence of SHFM in two subjects with 19q13 deletions involving UBA2, and strong mouse Uba2 expression in the developing limb buds, imply that LRP6 and UBA2 represent plausible candidate genes for SHFM. 31544984_LRP6 regulates Rab7-mediated autophagy through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to modulate trophoblast cell migration and invasion. 31588233_VSTM2A suppresses colorectal cancer and antagonizes Wnt signaling receptor LRP6. 31744930_Dynamic palmitoylation controls the microdomain localization of the DKK1 receptors CKAP4 and LRP6. 31811407_Cardiac-specific LRP6 knockout induces lipid accumulation through Drp1/CPT1b pathway in adult mice. 32076828_Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6-mediated signaling pathways and associated cardiovascular diseases: diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities. 32319541_LRP6 is involved in the proliferation, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells via miR346. 32573887_The rs2302685 polymorphism in the LRP6 gene is associated with bone mineral density and body composition in Iranian children. 32844563_A novel missense mutation of LRP6 identified by whole-exome sequencing in a Chinese family with non-syndromic tooth agenesis. 32945478_MicroRNA590 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelialtomesenchymal transition of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting lowdensity lipoprotein receptorrelated protein 6. 33065966_TRAP1 Regulates Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway through LRP5/6 Receptors Expression Modulation. 33097721_Sclerostin inhibits Wnt signaling through tandem interaction with two LRP6 ectodomains. 33118644_Clinical Phenotype and Relevance of LRP5 and LRP6 Variants in Patients With Early-Onset Osteoporosis (EOOP). 33136328_PAR1&2 driven placenta EVT invasion act via LRP5/6 as coreceptors. 33164649_Lrp6 Dynamic Expression in Tooth Development and Mutations in Oligodontia. 33391525_ERK1/2 inhibition reduces vascular calcification by activating miR-126-3p-DKK1/LRP6 pathway. 33391533_Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 regulates cardiomyocyte-derived paracrine signaling to ameliorate cardiac fibrosis. 33400244_MiR-30a suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by targeting LRP6. 33501755_Circ-LRP6 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinomas. 33545636_Distinct roles of LRP5 and LRP6 in Wnt signaling regulation in the retina. 33676964_Hsa_circ_0099198 facilitates the progression of retinoblastoma by regulating miR-1287/LRP6 axis. 34042263_The complex role of Wnt ligands in type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications. 34180138_Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 Cell Surface Availability Regulates Fuel Metabolism in Astrocytes. 34359960_Unveiling the Roles of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 in Intestinal Homeostasis, Regeneration and Oncogenesis. 34615853_Transmembrane protein 97 exhibits oncogenic properties via enhancing LRP6-mediated Wnt signaling in breast cancer. 34671210_Lrp6 Genotype affects Individual Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Silibinin Therapeutic Response via Wnt/beta-catenin-Cyp2e1 Signaling. 34734756_PUM1 modulates trophoblast cell proliferation and migration through LRP6. 34896607_Variants in the Wnt co-receptor LRP6 are associated with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 34930169_MicroRNA-513c-5p is involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia by regulating of low-density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein 6. 35211755_circLRP6 contributes to osteosarcoma progression by regulating the miR1413p/HDAC4/HMGB1 axis. 35277657_SIK2 maintains breast cancer stemness by phosphorylating LRP6 and activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 35840698_An LRP6 mutation (Arg360His) associated with low bone mineral density but not cardiovascular events in a Caucasian family. 35961235_Mutations in LRP6 highlight the role of WNT signaling in oral exostoses and dental anomalies. |
ENSMUSG00000030201 |
Lrp6 |
66.236765 |
2.1665516732 |
1.115401 |
0.373587026 |
8.704312 |
0.00317458213681968883651540735968410444911569356918334960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006756572795884442303449013422778079984709620475769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
97.3529076 |
22.3539159 |
45.5581755 |
7.6235571 |
| ENSG00000070367 |
10640 |
EXOC5 |
protein_coding |
O00471 |
FUNCTION: Component of the exocyst complex involved in the docking of exocytic vesicles with fusion sites on the plasma membrane. |
Acetylation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the exocyst complex, a multiple protein complex essential for targeting exocytic vesicles to specific docking sites on the plasma membrane. Though best characterized in yeast, the component proteins and functions of exocyst complex have been demonstrated to be highly conserved in higher eukaryotes. At least eight components of the exocyst complex, including this protein, are found to interact with the actin cytoskeletal remodeling and vesicle transport machinery. The complex is also essential for the biogenesis of epithelial cell surface polarity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10640; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocyst [GO:0000145]; midbody [GO:0030496]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; epithelial cell apoptotic process [GO:1904019]; establishment of planar polarity [GO:0001736]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; Golgi to plasma membrane transport [GO:0006893]; membrane fission [GO:0090148]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; post-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006892]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904]; vesicle tethering involved in exocytosis [GO:0090522] |
14662749_Data show that GTP-bound ARF6 interacts with Sec10, a subunit of the exocyst complex involved in docking of vesicles with the plasma membrane. 15880602_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19297529_The exocyst protein Sec10 regulates primary ciliogenesis. 20053792_Exocyst Sec10 overexpression reduces damage to tubular epithelial barriers caused by hydrogen peroxide and speeds the recovery of normal epithelial barrier function after such an injury. 23037926_These data confirm that the exocyst is preferentially involved in basolateral protein translation and translocation, and may well act through the phosphorylation of Sec61beta. 25298525_Suggest that the exocyst sec10, acting through EGFR, endocytosis, and the MAPK pathway is a candidate therapeutic target for acute kidney injury. 30824539_show that EXOC5 mRNA almost completely rescues the ciliary phenotypes in exoc5-mutant zebrafish, unlike the EXOC5CTS-m mRNA, which could not efficiently rescue the phenotypes 31694916_The EXOC5 knockdown increases ARF6 levels and decreases EPS8L2 levels, and that EXOC5 overexpression increases EPS8L2. |
ENSMUSG00000061244 |
Exoc5 |
562.538265 |
2.0647325248 |
1.045955 |
0.137357972 |
57.197135 |
0.00000000000003942450543833155975274737964597810138884289438143682104964682366698980331420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000256685355213839339488796662053759243887155611085759687739482615143060684204101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
764.5092494 |
61.3207013 |
372.7628124 |
22.0814086 |
| ENSG00000070371 |
8218 |
CLTCL1 |
protein_coding |
P53675 |
FUNCTION: Clathrin is the major protein of the polyhedral coat of coated pits and vesicles. Two different adapter protein complexes link the clathrin lattice either to the plasma membrane or to the trans-Golgi network (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene is a member of the clathrin heavy chain family and encodes a major protein of the polyhedral coat of coated pits and vesicles. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with meningioma, DiGeorge syndrome, and velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:8218; |
clathrin coat of trans-Golgi network vesicle [GO:0030130]; clathrin complex [GO:0071439]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle [GO:0045334]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; coated vesicle [GO:0030135]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; membrane [GO:0016020]; sorting endosome [GO:0097443]; spindle [GO:0005819]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; clathrin light chain binding [GO:0032051]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] |
15133132_Clathrin isoform CHC22 binds to sorting nexin 5 through a coiled-coil domain. 19478182_role for CHC22 in formation of insulin-responsive GLUT4 compartments in muscle & adipocytes; CHC22 associated with expanded GLUT4 compartments in muscle in type 2 diabetes 20065094_CHC22 was required for retrograde trafficking of certain cargo molecules from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22891263_Depletion of clathrin heavy chain (CHC)17, but not the CHC22 clathrin isoform, by ribonucleic acid interference (RNAi) induces centrosome amplification and multipolar spindles. 26068709_CLTCL1 is significantly upregulated in the developing human brain 29097553_Provide biochemical evidence for separate regulation and distinct functional niches for CHC17 and CHC22 in HeLa cells. Furthermore, the greater stability of the CHC22 coat relative to the CHC17 coat may be relevant to its excessive accumulation with GLUT4 during insulin resistance. 29402896_Clathrin heavy chain 22 contributes to the control of neuropeptide degradation and secretion during neuronal development. Study suggests This suggests that a reduction in CHC22 expression in sensory neural precursors may license a step in neuron precursor neurodevelopment; and that this step is mediated through control of a novel neuropeptide processing pathway. 31159924_These analyses suggest that ancestral human dietary change influenced selection of allotypes that affect CHC22's role in metabolism and have potential to differentially influence the human insulin response. 32620516_Building GLUT4 Vesicles: CHC22 Clathrin's Human Touch. |
|
|
28.234868 |
0.4141140403 |
-1.271900 |
0.417881746 |
8.916203 |
0.00282651494907057909342085189052795612951740622520446777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006085087609142611660140165241728027467615902423858642578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.4824456 |
8.5144315 |
32.6007691 |
15.4133208 |
| ENSG00000070785 |
8891 |
EIF2B3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR50 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the exchange of eukaryotic initiation factor 2-bound GDP for GTP. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Initiation factor;Leukodystrophy;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is one of the subunits of initiation factor eIF2B, which catalyzes the exchange of eukaryotic initiation factor 2-bound GDP for GTP. It has also been found to function as a cofactor of hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. Mutations in this gene have been associated with leukodystrophy with vanishing white matter. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:8891; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B complex [GO:0005851]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor complex [GO:0032045]; nucleotidyltransferase activity [GO:0016779]; translation initiation factor activity [GO:0003743]; cytoplasmic translational initiation [GO:0002183]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852]; translational initiation [GO:0006413] |
18263758_Study reports 9 novel mutations in EIF2B genes in 8 patients, increasing number of known mutations to more than 120. Using homology modeling, analyzed the impact of novel mutations on the 5 subunits of eIF2B protein (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon) 18632786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25761052_Results show significant higher incidence of Chinese patients with EIF2B3 mutations compared with Caucasian patients. The c.1037T>C in EIF2B3 was confirmed to be a founder mutation in Chinese explaining the genotypic differences between ethnicities. 26625702_To determine the tolerance differences to ERS, cell viability and apoptosis rates were detected in oligodendrocyte cell lines transfected with EIF2B3-c.1037T>C or the wild type. We confirmed that oligodendrocytes with mutant EIF2B3 was less tolerant to ERS than the wild type, with decreased cell viability and increased apoptosis rates. 33517449_Eif2b3 mutants recapitulate phenotypes of vanishing white matter disease and validate novel disease alleles in zebrafish. |
ENSMUSG00000028683 |
Eif2b3 |
148.691034 |
2.3048447923 |
1.204670 |
0.145015357 |
69.457677 |
0.00000000000000007807190664615304769109248612368224513028602324542573609456042049714596942067146301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000593073258928059214480038706765360122007719881950110751844817968958523124456405639648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
204.4474143 |
19.2864228 |
89.2206470 |
6.5493761 |
| ENSG00000070882 |
26031 |
OSBPL3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H4L5 |
FUNCTION: Phosphoinositide-binding protein which associates with both cell and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membranes (PubMed:16143324). Can bind to the ER membrane protein VAPA and recruit VAPA to plasma membrane sites, thus linking these intracellular compartments (PubMed:25447204). The ORP3-VAPA complex stimulates RRAS signaling which in turn attenuates integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) activation at the cell surface (PubMed:18270267, PubMed:25447204). With VAPA, may regulate ER morphology (PubMed:16143324). Has a role in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, cell polarity and cell adhesion (PubMed:18270267). Binds to phosphoinositides with preference for PI(3,4)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3 (PubMed:16143324). Also binds 25-hydroxycholesterol and cholesterol (PubMed:17428193). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16143324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17428193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18270267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25447204}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) family, a group of intracellular lipid receptors. Most members contain an N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain and a highly conserved C-terminal OSBP-like sterol-binding domain. The encoded protein is involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and organization of the actin cytoskeleton. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:26031; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; filopodium tip [GO:0032433]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0097038]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; sterol binding [GO:0032934]; sterol transporter activity [GO:0015248]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699] |
16143324_The intracellular targeting determinants of oxysterol binding protein (OSBP)-related protein 3 (ORP3) were studied using a series of truncated and point mutated constructs. 18270267_The present findings demonstrate a new function of ORP3 as part of the machinery that controls the actin cytoskeleton, cell polarity and cell adhesion. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25447204_phosphorylation of ORP3 controls its association with VAPA. Furthermore, ORP3-VAPA complexes stimulate R-Ras signaling. 26812496_It indicates that VAPB along with ORP3 plays a central role in maintenance of the intracellular PtdIns4P gradient. 30018135_The silencing of VAP-A or ORP3 abrogated the association of Rab7-positive late endosomes with nuclear envelope invaginations and, hence, the transport of endocytosed EV-derived components to the nucleoplasm of recipient cells. 31659255_Aneuploidy-inducing gene knockdowns overlap with cancer mutations and identify Orp3 as a B-cell lymphoma suppressor. 32234213_Calcium-stimulated disassembly of focal adhesions mediated by an ORP3/IQSec1 complex. 32819557_The crystal structure of ORP3 reveals the conservative PI4P binding pattern. 32824360_Downregulation of ORP3 Correlates with Reduced Survival of Colon Cancer Patients with Advanced Nodal Metastasis and of Female Patients with Grade 3 Colon Cancer. 33857182_Structure of human ORP3 ORD reveals conservation of a key function and ligand specificity in OSBP-related proteins. 34584127_Oxysterol binding protein-like 3 (OSBPL3) is a novel driver gene that promotes tumor growth in part through R-Ras/Akt signaling in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000029822 |
Osbpl3 |
1699.129433 |
0.3139823277 |
-1.671245 |
0.153505067 |
111.941945 |
0.00000000000000000000000003679278041400708690662498077388347976948595189247913080515100112802598895933581246708854450844228267669677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000408624107532539190996134661711236950478850237537880340605941072385171378145152232264081249013543128967285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
836.2305229 |
88.9457836 |
2682.2202134 |
205.0316599 |
| ENSG00000070961 |
490 |
ATP2B1 |
protein_coding |
P20020 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium from the cytoplasm to the extracellular space thereby maintaining intracellular calcium homeostasis. Plays a role in blood pressure regulation through regulation of intracellular calcium concentration and nitric oxide production leading to regulation of vascular smooth muscle cells vasoconstriction. Positively regulates bone mineralization through absorption of calcium from the intestine. Plays dual roles in osteoclast differentiation and survival by regulating RANKL-induced calcium oscillations in preosteoclasts and mediating calcium extrusion in mature osteoclasts (By similarity). Regulates insulin sensitivity through calcium/calmodulin signaling pathway by regulating AKT1 activation and NOS3 activation in endothelial cells (PubMed:29104511). May play a role in synaptic transmission by modulating calcium and proton dynamics at the synaptic vesicles. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:G5E829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29104511}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Calcium transport;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Ion transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type primary ion transport ATPases characterized by the formation of an aspartyl phosphate intermediate during the reaction cycle. These enzymes remove bivalent calcium ions from eukaryotic cells against very large concentration gradients and play a critical role in intracellular calcium homeostasis. The mammalian plasma membrane calcium ATPase isoforms are encoded by at least four separate genes and the diversity of these enzymes is further increased by alternative splicing of transcripts. The expression of different isoforms and splice variants is regulated in a developmental, tissue- and cell type-specific manner, suggesting that these pumps are functionally adapted to the physiological needs of particular cells and tissues. This gene encodes the plasma membrane calcium ATPase isoform 1. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:490; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; dendritic spine membrane [GO:0032591]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body membrane [GO:0032809]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; photoreceptor ribbon synapse [GO:0098684]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019829]; calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015085]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; P-type calcium transporter activity [GO:0005388]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; aging [GO:0007568]; brain development [GO:0007420]; calcium ion export [GO:1901660]; calcium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1990034]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to corticosterone stimulus [GO:0071386]; cellular response to vitamin D [GO:0071305]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051481]; neural retina development [GO:0003407]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of cardiac conduction [GO:1903779]; regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:1900076]; regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051480]; regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction [GO:0003056]; response to cold [GO:0009409] |
11786550_Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 2b interacts preferentially with Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 2 in apical plasma membranes 12784250_role in the intracellular Ca(2+) extrusion of syncytiotrophoblast-like structure originating from the differentiation of cultured trophoblast cells isolated from human term placenta 12851406_PMCA1 has a high sensitivity to degradation by calpain 15911623_modulation of PMCA has important effects in regulating the proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells, involving changes in cell cycle kinetics but not cell cycle arrest 16328033_Inactivation of the PMCA1 gene is a frequent and early event during oral carcinogenesis, and gene expression may be regulated by an epigenetic mechanism. 16412504_PMCA activity is influenced by membrane lipid composition and structure. The naturally high degree of lipid order in plasma membranes such as those found in human lens may serve to support PMCA activity. 16488415_Alterations in the region of the alternative splicing site A change the sensitivity to Ca(2+) of the human isoform 4 of the PMCA. 16669348_This phenomenon correlates with the greater increase in [Ca2+]c induced by higher concentrations of thrombin, which further confirms that SERCA and PMCA activities are regulated by [Ca2+]c 16933204_Despite similar total calcium contents, lower SERCA and PMCA activities were found in sacs associated with hydrocele compared to those associated with undescended testis suggest a difference among the levels of cytosolic calcium. 18657858_PMCA1 is shown to be present in the human syncytiotrophoblast homogenate. 18929409_PMCA is the main mechanism involved in Ca(2+) efflux in ECV 304 cells. 19017653_Muscarinic-induced recruitment of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase involves PSD-95/Dlg/Zo-1-mediated interactions. 19070897_These results indicate that in intact cells the Ca(2+) pump is protected from glycation-induced inactivation. 19144698_Data show that the calcium dependencies of intracellular Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA and SPCA) activity are the same in human Alzheimer disease and normal brain but that of plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) is different. 19396169_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19430479_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19840794_Data show that in the presence of plasma membrane Ca(2+) ATPase inhibitors, locally-released Ca(2+) propagates from one cell to another, indicating that Ca(2+) was self-amplified to mediate intercellular Ca(2+) waves. 19892708_The transmembrane domain of the PMCA undergoes major rearrangements resulting in altered lipid accessibility upon Ca(2+) binding and activation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19960030_Consistent genetic factors for ATP2B1, CSK, ARSG and CSMD1 were present, which have been shown to be associated with high blood pressure and hypertension in two Korean cohorts. 19960030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20479155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20700443_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20852445_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20921432_this study confirmed common genetic variation in ATP2B1 to be associated with blood pressure levels and risk of hypertension 21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21126504_Cloned the C-terminal domain of the human PMCA isoform 1b, and characterized its properties in solution. The expressed protein maintains its tendency to oligomerize in aqueous solutions, but it is dissociated by amphipathic molecules. 21400627_Immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of TRPV6 and PMCA1 in the uterus revealed that both proteins are abundantly expressed in the cytoplasm of endometrial and glandular epithelial cells during menstrual phases. 22229515_Polymorphism near the ATP2B1 gene is associated with hypertension risk in East Asians. 22246182_The authors provide data revealing both functional and physical links between the activation of stromal interacting molecule 1 (STIM1) and PMCA-mediated Ca(2+) clearance. 23079715_Association of the ATP2B1 gene and susceptibility to hypertension, blood pressure traits and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocities in a Chinese population. 23759979_The present study confirmed the significant association of ATP2B1 rs17249754 with risk of hypertension among Chinese children. 23817774_The downregulation of PMCA1 and the disruption of calcium homeostasis may play important roles in UVB-induced HLE B-3 cell apoptosis. 24584935_analysis of how human plasma membrane Ca2+ pump PMCA h4xb is hyperactivated by mutation of Glu99 to Lys 24642721_Report that ATP2B1 rs2681472 is associated with early-onset preeclampsia in Northern Han Chinese women. 25385345_ATP2B1 rs12817819 A allele is associated with increased risk for drug resistant hypertension. 25605721_An increase of phosphatidylcholine/detergent molar ratio leads to a biphasic behavior of the PMCA Ca2+-ATPase activity, whose maximum depends on phosphatidylcholine characteristics. 25618516_rs11105378 near ATP2B1 was associated with increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure in a Chinese population. 26116539_While PMCA1b has a housekeeping function in colon cancer cells, PMCA4b participates in the reorganization of the calcium signaling machinery during cell differentiation. 26307527_Data show that plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) was associated with tubulin in normotensive and hypertensive erythrocytes. 26933664_Crossover analysis and stratified analysis indicated that BMI has a major effect on the development of hypertension, while ATP2B1 variants have a minor effect 27149052_Excessive sodium intake significantly modified the risk of developing Hypertension associated with ATP2B1 rs17249754 genetic trait. Homozygote carriers may be at higher risk of hypertension, when they consume excessive sodium intake. 28934190_people with the major allele of ATP2B1 rs17249754 are susceptible to hypertension especially in low intake of Ca and high ratio of Na and K 29416109_enhanced eNOS activity induced by ATP2B1 gene silencing may be mediated via higher levels of intracellular Ca(2+), and the effect was confirmed to be dependent on the eNOS-calmodulin interaction 29902063_rs17249754-A (OR = 0.43, p = 0.0002) and rs1401982-G (OR = 0.47, p = 0.0007) were associated with decreased susceptibility of concurrent extra and intracranial stenosis even after Bonferroni correction. These two minor alleles were also significantly associated with less stenotic arteries and moderate-to-severe stenosis. 29982197_No significant association was found between ATP2B1 gene polymorphism and the odds of high blood pressure. 30190470_Cryoelectron microscopy reveals the PMCA1 structure in complex with neuroplastin. 31242870_ATP2B1 rs17249754 is positively associated with the risk of developing essential hypertension in patients from Burkina Faso, West Africa. 31858526_Association of ATP2B1 gene polymorphism with incidence of eclampsia. 33760199_Serum from patients with hypertension promotes endothelial dysfunction to induce trophoblast invasion through the miR27b3p/ATPase plasma membrane Ca(2+) transporting 1 axis. 33781822_Plasma membrane calcium ATPase 1 regulates human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis and viability. 33801794_Crosstalk among Calcium ATPases: PMCA, SERCA and SPCA in Mental Diseases. 34205207_Sorcin Activates the Brain PMCA and Blocks the Inhibitory Effects of Molecular Markers of Alzheimer's Disease on the Pump Activity. 34486947_ATP2B1 genotypes rs2070759 and rs2681472 polymorphisms and risk of hypertension in Saudi population. 35031021_Re-wiring and gene expression changes of AC025034.1 and ATP2B1 play complex roles in early-to-late breast cancer progression. 35253182_ATP2B1 gene rs71454161, rs73196661 and rs73196675 polymorphisms in eclampsia. 35358416_De novo variants in ATP2B1 lead to neurodevelopmental delay. |
ENSMUSG00000019943 |
Atp2b1 |
3317.183808 |
9.9133620174 |
3.309374 |
0.101372645 |
923.562531 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007407686368054418413123319543990148793171282500675782284074459074156182106721056422789546339397692516634488484863628331622969267 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006876569232231649350350571511871169038270440637837237293827897127900787688424726763548925970757323385881257081798016697191026331 |
Yes |
Yes |
5933.8842077 |
371.3518898 |
602.7538220 |
28.4804872 |
| ENSG00000071051 |
8440 |
NCK2 |
protein_coding |
O43639 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein which associates with tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors or their cellular substrates. Maintains low levels of EIF2S1 phosphorylation by promoting its dephosphorylation by PP1. Plays a role in ELK1-dependent transcriptional activation in response to activated Ras signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10026169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16835242}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Translation regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the NCK family of adaptor proteins. The protein contains three SH3 domains and one SH2 domain. The protein has no known catalytic function but has been shown to bind and recruit various proteins involved in the regulation of receptor protein tyrosine kinases. It is through these regulatory activities that this protein is believed to be involved in cytoskeletal reorganization. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8440; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; cytoskeletal anchor activity [GO:0008093]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling adaptor activity [GO:0035591]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; dendritic spine development [GO:0060996]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; immunological synapse formation [GO:0001771]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced eIF2 alpha phosphorylation [GO:1903912]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903898]; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1990441]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902237]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of translation in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0036493]; regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0007176]; signal complex assembly [GO:0007172]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
11950595_Nck-2 interacts with focal adhesion kinase and modulates cell motility. Using a mutational strategy, the formation of the Nck-2-FAK complex is mediated by interactions involving multiple SH2 and SH3 domains of Nck-2. 12110186_Recruitment of Nck by CD3 epsilon reveals a ligand-induced conformational change essential for T cell receptor signaling and synapse formation. 15764601_analysis of binding between the Tyr-phosphorylated human ephrinB2 and Nck2 SH2 domain 16604428_Molecular model of the first SRC homology 3 domain of Nck2. 16636066_Nck1 (Nckalpha) and Nck2 (Nckbeta and Grb4): binding specificities of both SH2 domains are essentially indistinguishable 16752908_determined the NMR structures and dynamic properties of the hNck2 SH3 domains and to define their ligand binding preferences with nine proline-rich peptides derived from Wire, CAP-1, CAP-2, Prk, Wrch1, Wrch2, and Nogo 16835242_Data show that Nck (isoforms 1 and 2) as a component of the CReP/PP1c holophosphatase complex contributes to maintain eIF2alpha in a hypophosphorylated state, and modulates translation and eIF2alpha signaling in response to ER stress. 17803907_Demonstrate connection between septins/SOCS7/NCK signaling and the DNA damage response. 17906149_the adaptors Nck and ShcA influenced adherence of S. Typhimurium to non-phagocytic cells. 18555270_Data show that Nck forms a complex with an atypical PxxDY motif of the CD3epsilon tail, which encompasses Tyr166 within the activation motif and a T-cell receptor endocytosis signal. 18723748_Results point to NCK2 as a disease candidate gene and further supports the GLC1B locus as an important genomic region that is associated with the genetic predisposition to glaucoma. 19242519_independent roles and mechanisms of action of Nckalpha and Nckbeta in dermal fibroblast migration, which is critical for wound healing. 19956763_biophysical analysis of Nck2 SH3 domain 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21880263_Nck2 is an adaptor protein composed of 3N-SH3 domains followed by a unique Cterminal SH2 domain. It interacts with PINCH in integrin signal transduction, cell migratio and survival. Review. 21949127_p21-Activated kinase 3 (PAK3) protein regulates synaptic transmission through its interaction with the Nck2/Grb4 protein adaptor. 21992144_Nck2 effectively influences human melanoma phenotype progression. 23349798_Data show that both HK2 and NCK2 are expressed in the retinal ganglion cell layer. 23524290_The hNck2 SH3 domain also exhibited pH dependent monomer-dimer transition. 23533358_NCK2 is involved in the susceptibility to opiates addiction. 24287595_Proteasomal degradation of Nck1 but not Nck2 regulates RhoA activation and actin dynamics. 25482634_Tir-Intimin interaction recruits the Nck adaptor to a Tir tyrosine phosphorylated residue where it activates neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP). 26004008_Data suggest that PINCH1 and Nck2 critically participate in the regulation of cellular radiosensitivity and EGFR function and downstream signaling in a cellular model of human squamous cell carcinoma. 27033705_Nck1 and Nck2 Interact with WTIP. Nck1/2 integrates nephrin with the Hippo kinase cascade through association with the adaptor protein WTIP. 29218693_This study provides evidence of a possible role of NCK2 as biomarker of ovarian cancer progression. 29911835_There was no difference in the Nck2 mRNA expression between the SLE patients and the healthy subjects. 31512042_The minor allele frequency (MAF) of rs678350 was significantly higher in NTG patients (MAF = 0.32) than in controls (MAF = 0.23) (OR, 1.586; 95% CI, 1.058 to 2.375; P = 0.028). This trend was more significant in the dominant model (OR, 1.908; 95% CI, 1.144 to 3.180; P = 0.015). 31638742_Nck adapter proteins promote podosome biogenesis facilitating extracellular matrix degradation and cancer invasion. 33917227_Cooperative Interaction of Nck and Lck Orchestrates Optimal TCR Signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000066877 |
Nck2 |
1045.570033 |
0.4050415000 |
-1.303858 |
0.053935639 |
590.637248 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018209528405681819083949610008171936861751572942324795310583830786548614827347862887982885731081530608895180968797082397098466843764556565975465667230485474023601292253229439308964509103036073360770133 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009917809567079839670136369135527419665910637450758774882552162096483977912746251725880959520162459775940949325804066119388843261998764156066182903610934235224156942193960167587571684779950420614568639 |
Yes |
Yes |
614.8824051 |
20.8941876 |
1529.0570645 |
33.8444527 |
| ENSG00000071073 |
11320 |
MGAT4A |
protein_coding |
Q9UM21 |
FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase that catalyze the transfer of GlcNAc from UDP-GlcNAc to the GlcNAcbeta1-2Manalpha1-3 arm of the core structure of N-linked glycans through a beta1-4 linkage and participates in the production of tri- and tetra-antennary N-linked sugar chains (PubMed:17006639). Involved in glucose transport by mediating SLC2A2/GLUT2 glycosylation, thereby controlling cell-surface expression of SLC2A2 in pancreatic beta cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q812G0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17006639}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17006639}. |
This gene encodes a key glycosyltransferase that regulates the formation of tri- and multiantennary branching structures in the Golgi apparatus. The encoded protein, in addition to the related isoenzyme B, catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) from UDP-GlcNAc in a beta-1,4 linkage to the Man-alpha-1,3-Man-beta-1,4-GlcNAc arm of R-Man-alpha-1,6(GlcNAc-beta-1,2-Man-alpha-1,3)Man-beta-1, 4-GlcNAc-beta-1,4-GlcNAc-beta-1-Asn. The encoded protein may play a role in regulating the availability of serum glycoproteins, oncogenesis, and differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11320; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi stack [GO:0005795]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; alanine-glyoxylate transaminase activity [GO:0008453]; alpha-1,3-mannosylglycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008454]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; glyoxylate metabolic process [GO:0046487]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
15688387_upregulation of mannosyl (alpha-1,3-)-glycoprotein beta-1,4-N-acetyl-glucosaminyl-transferase is associated with metastatic colorectal carcinoma 16434023_analysis of expression of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-IVa and IVb (GnT-IVa and b) in pancreatic cancer 17006639_GnT-IVa is more active than GnT-IVb under physiological conditions and it primarily contributes to the biosynthesis of N-glycans. 17488527_We investigated mRNA levels of glycosyltransferases, namely, N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase a (GnT)-IVa, and found that (GnT)-IVa expression was decreased in HLE-cells Epirubicin resistant. 17953760_The results of this work suggest that in T2D subjects, high levels of glucose and triglycerides are accompanied by an increase on MGAT4A mRNA levels and WBC count; condition that suggests a pro-inflammatory state due to a chronic metabolic stress. 19751437_GNT-IV genetic variation is not associated with gastric cancer. 23169300_Findings suggest that GnT-IVa is involved in regulating invasion of choriocarcinoma through modifications of the oligosaccharide chains of beta1 integrin. 26589799_Data suggest microRNA-424 regulates expression of MGAT4A (mannoside beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase A), OGT (O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase), and GALNT13 (polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 13) in mammary epithelium. 28534963_GnT-IVa may contribute to the malignancy of choriocarcinoma by promoting cell adhesion, migration and invasion through glycosylation of integrin beta1 and LAMP-2. |
ENSMUSG00000026110 |
Mgat4a |
387.162898 |
0.4590544519 |
-1.123263 |
0.098779557 |
128.980088 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000685021568287601235181625721651032188332998859503157755708046763214151770446575830109114946253612288273870944976806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000087616276845103939828028509834088136948612416115850775376310147331026534909311637155937546594941522926092147827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
255.1411439 |
22.9831687 |
561.0981195 |
35.5067303 |
| ENSG00000071242 |
6196 |
RPS6KA2 |
protein_coding |
Q15349 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of ERK (MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1) signaling and mediates mitogenic and stress-induced activation of transcription factors, regulates translation, and mediates cellular proliferation, survival, and differentiation. May function as tumor suppressor in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16878154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7623830}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene encodes a member of the RSK (ribosomal S6 kinase) family of serine/threonine kinases. This kinase contains two non-identical kinase catalytic domains and phosphorylates various substrates, including members of the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway. The activity of this protein has been implicated in controlling cell growth and differentiation. Alternative splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:6196; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; meiotic spindle [GO:0072687]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; synapse [GO:0045202]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004712]; ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity [GO:0004711]; brain renin-angiotensin system [GO:0002035]; cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010659]; cellular response to carbohydrate stimulus [GO:0071322]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; heart contraction [GO:0060047]; heart development [GO:0007507]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045835]; oocyte maturation [GO:0001556]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of protein processing [GO:0070613]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12016217_Characterization of the terminal domain as a protein kinase 14646589_chronic activation CREB and p90RSK in the epileptic hippocampus may be closely associated with the histopathological changes of Ammon's horn sclerosis 15112576_overexpressed in breast tumors 15995633_The accumulation of S6K2 in the nuclei of cancer cells and the correlation with the expression of PCNA and Ki-67 suggest the involvement of S6K2 in the regulation of malignant growth 16621805_p90Rsk-mediated modulation of Hdm2 nuclear is linked to cytoplasmic shuttling with the diminished ability of p53 to regulate cell cycle checkpoints that ultimately leads to transformation 16626623_The large C-terminal domain of ERK5 is not required for binding or activation of RSK by ERK5. 16878154_The above results suggest that RPS6KA2 is a putative tumour suppressor gene to explain allele loss at 6q27. 16895915_there is a functional link between S6K1 II and CK2 signaling, which involves the regulation of S6K1 II nuclear export by CK2-mediated phosphorylation of Ser-17 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21035469_Data show that genetic variation in RPS6KA1, RPS6KA2, and PRS6KB2 were associated with risk of developing colon cancer while only genetic variation in RPS6KA2 was associated with altering risk of rectal cancer. 21035469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21527514_p90RSK2 is dispensable for BCR-ABL-induced myeloid leukemia, but may be required for pathogenesis and lineage determination in FLT3-internal tandem duplication-induced hematopoietic transformation. 23564320_Data indicate that S6 kinase 2 (S6K2) can phosphorylate histone H3 at position Thr45, which may play a role during cell proliferation and/or differentiation. 23635776_Overexpression of RSK3 or RSK4 supports tumor cell proliferation upon PI3K inhibition both in vitro and in vivo therby contributing to drug resistance. 23727904_genetic association study in Han population in China: Data suggest that SNPs in RSK3 (rs2229712) and in MEK1 (rs28730804) demonstrate gene-gene interaction that affects antidepressant drug outcome in female patients with major depressive disorder. 24403857_Kinome screening revealed RPS6KA2 expression, in human pancreatic cancer cells, protects against erlotinib induced apoptosis. 26977024_RSK1 and 3 but not RSK2 are down-regulated in breast tumour and are associated with disease progression. RSK may be a key component in the progression and metastasis of breast cancer. 29144123_Data suggest that millisecond dynamic changes in PDZ1 domain conformation are responsible for higher affinity of scribble PDZ1 for phosphorylated ligands; oligopeptide fragments of RPS6KA2 and MCC were used as ligands in these nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shift experiments. (RPS6KA2 = ribosomal protein S6 kinase 2; MCC = mutated in colorectal cancer protein) 31937753_Elevated ribosomal protein S6 kinase A2 (RSK3) expression is responsible for BET bromodomain inhibitors (BETi) resistance. Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-jun (JunD)-dependent RSK3 transcription mediates BETi resistance. JunD/RSK3 signalling correlates to BET inhibition sensitivity. Loss of BRD4/FOXD3/miR-548d-3p axis enhances JunD/RSK3 signalling and determines BET inhibition resistance. 32869517_Genome-wide association study of cafe-au-lait macule number in neurofibromatosis type 1. 34550011_Multiomics analysis identifies key genes and pathways related to N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in ovarian cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000023809 |
Rps6ka2 |
860.778842 |
3.0384281308 |
1.603325 |
0.056673195 |
826.235530 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010668376568755167918302004098970032236539860420859727072236607654022260791498800648121616050667272817541436491846742667067864043241465167057476614445 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008846361694091363841978074918233401524750068057890521280791505047280641418018858602913024032489408778775899024999330020069375112131079234950301557234 |
Yes |
No |
1280.5555619 |
75.2412864 |
423.5730489 |
18.9805788 |
| ENSG00000072071 |
22859 |
ADGRL1 |
protein_coding |
O94910 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-independent receptor of high affinity for alpha-latrotoxin, an excitatory neurotoxin present in black widow spider venom which triggers massive exocytosis from neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Receptor for TENM2 that mediates heterophilic synaptic cell-cell contact and postsynaptic specialization. Receptor probably implicated in the regulation of exocytosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Autocatalytic cleavage;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the latrophilin subfamily of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR). Latrophilins may function in both cell adhesion and signal transduction. In experiments with non-human species, endogenous proteolytic cleavage within a cysteine-rich GPS (G-protein-coupled-receptor proteolysis site) domain resulted in two subunits (a large extracellular N-terminal cell adhesion subunit and a subunit with substantial similarity to the secretin/calcitonin family of GPCRs) being non-covalently bound at the cell membrane. Latrophilin-1 has been shown to recruit the neurotoxin from black widow spider venom, alpha-latrotoxin, to the synapse plasma membrane. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:22859; |
axon [GO:0030424]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; synapse [GO:0045202]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; latrotoxin receptor activity [GO:0016524]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; positive regulation of synapse maturation [GO:0090129] |
20971062_In this article they evaluated the amount of p120-p85 complex still presented on the cellular membrane and confirmed that on cell surface major amount of mature CIRL-1 presented as a p120-p85 subunit complex. 26485751_Data suggest teneurin-1/TENM1 (and possibly TENM3) undergoes proteolysis to TCAPs (teneurin C-terminal associated peptides) that form intercellular adhesive units with latrophilin; signaling via TENM1 TCAPs appears to regulate reproduction. [REVIEW] 27322212_Our findings demonstrate that latrophilin-1 could be considered as a novel biomarker of human acute myeloid leukaemia 27325752_A single SNP in LPHN1 (rs3810256) was identified, with the minor allele increasing the risk of asthma. 29907881_Cortisol facilitates the immune escape of human acute myeloid leukemia cells by inducing latrophilin 1 expression. 29938681_alterations in latrophilin expression occur in AML cells expressing P-gp 30457553_These findings reveal a novel mechanism of axonal pathfinding, whereby latrophilin-1 and Lasso mediate both short-range interaction that supports synaptogenesis, and long-range signaling that induces axonal attraction. 31339586_results suggest that SSB splicing selectively affects the duality of LPHN1 signaling toward opposing cAMP pathways 35907405_ADGRL1 haploinsufficiency causes a variable spectrum of neurodevelopmental disorders in humans and alters synaptic activity and behavior in a mouse model. |
ENSMUSG00000013033 |
Adgrl1 |
76.918817 |
0.3972794185 |
-1.331774 |
0.207471237 |
42.377092 |
0.00000000007526648186664840453892608101470261365573133360840074601583182811737060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000391863588131121886668521627373334981214725303289014846086502075195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.9697148 |
9.8721549 |
100.9183851 |
17.1497966 |
| ENSG00000072134 |
22905 |
EPN2 |
protein_coding |
O95208 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the formation of clathrin-coated invaginations and endocytosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10567358}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endocytosis;Lipid-binding;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein which interacts with clathrin and adaptor-related protein complex 2, alpha 1 subunit. The protein is found in a brain-derived clathrin-coated vesicle fraction and localizes to the peri-Golgi region and the cell periphery. The protein is thought to be involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Alternate splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:22905; |
clathrin coat of endocytic vesicle [GO:0030128]; clathrin vesicle coat [GO:0030125]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; negative regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903671]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030948]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25871009_Epsins are required for Dishevelled stability and Wnt signalling activation in colon cancer development. 28717225_EPN2 mRNA is a direct target of miR-1224. |
ENSMUSG00000001036 |
Epn2 |
25.685139 |
0.2912036299 |
-1.779900 |
0.388820369 |
20.565616 |
0.00000576218181373757644869650768049140765469928737729787826538085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000018594185301872897663356259956302096725266892462968826293945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.6404140 |
4.1041612 |
40.6157490 |
9.9631042 |
| ENSG00000072135 |
26469 |
PTPN18 |
protein_coding |
Q99952 |
FUNCTION: Differentially dephosphorylate autophosphorylated tyrosine kinases which are known to be overexpressed in tumor tissues. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, the mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains a PEST motif, which often serves as a protein-protein interaction domain, and may be related to protein intracellular half-live. This protein can differentially dephosphorylate autophosphorylated tyrosine kinases that are overexpressed in tumor tissues, and it appears to regulate HER2, a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:26469; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004726]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; blastocyst formation [GO:0001825]; negative regulation of ERBB signaling pathway [GO:1901185]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
14660651_BDP1 has a role in negative regulation of HER2 signaling 16303740_novel isoform of PTPN18 based on analysis of expressed sequence tags was discovered; deletion of 4 exons in the catalytic domain of the isoform may alter enzymatic activity; 2 of the novel isoform predictions were experimentally validated through RT-PCR 25081058_PTPN18 regulates HER2-mediated cellular functions through defining both its phosphorylation and ubiquitination barcodes. 29742497_PTPN12, PTPRN and PTPN18 were independent prognostic factors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 31034093_Downregulation of PTPN18 can inhibit proliferation and metastasis and promote apoptosis of endometrial cancer 32027948_Phospho-PTM proteomic discovery of novel EPO- modulated kinases and phosphatases, including PTPN18 as a positive regulator of EPOR/JAK2 Signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000026126 |
Ptpn18 |
215.708388 |
0.4197437556 |
-1.252419 |
0.108090426 |
136.869163 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000012879797832399092489956373471793652551870325090842117519036397219030447988313145481382993029484396174666471779346466064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000001740895750972624408846121042819910730775263125699487714764594004710497911847337775687050154260759882163256406784057617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
122.4936334 |
8.6572712 |
294.0090687 |
13.4309720 |
| ENSG00000072201 |
84708 |
LNX1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TBB1 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of NUMB. E3 ubiquitin ligases accept ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Mediates ubiquitination of isoform p66 and isoform p72 of NUMB, but not that of isoform p71 or isoform p65. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70263}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 provides an endocytic scaffold for IGSF5/JAM4. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70263}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a membrane-bound protein that is involved in signal transduction and protein interactions. The encoded product is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, which mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of proteins containing phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domains. This protein may play an important role in tumorogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. A pseudogene, which is located on chromosome 17, has been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:84708; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
9535908_The tyrosine phosphorylation of the LDNPAY sequence motif in mouse LNX could generate a binding site for the phosphorylation-dependent binding of other PTB domain-containing proteins. 15367597_identifed ligand of Numb protein X as an Np9-interacting partner; findings point to the possibility that Np9 affects tumorigenesis through the LNX/Numb/Notch pathway 16002321_The presence of multiple protein binding domains involved in signal transduction and interaction with Numb and SKIP suggested an important role for LNX in tumorogenesis. 16122940_A direct interaction between ErbB2 and mouse LNX1 was identified, suggesting that LNX1 may be involved in neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling in perisynaptic Schwann cells. 16324299_LNX was closely related to human gliomas and suggested it plays an important role in gliomas by notch signaling. 17504929_Describes various glioblastoma multiforms containing the amplicon on chromosomal segment 4q12, including the LNX1 gene. 17936276_The interaction of c-Src with LNX1 depends on the C-terminal PDZ ligand of c-Src. 18940473_Both gene sequence alterations and amplifications of LNX1 and Numbl are present in a subset of human gliomas. 18940473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19132087_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19701800_LNX and RhoC might be part of a larger protein complex that would have important functions in signaling transduction about regulating the transcriptional activities of AP-1. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21104141_Down-regulation of LNX could result in cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase through inhibition of beta-catenin, MAPK, NFkappaB, c-Myc-dependent pathway and activation of p53, TGF-beta-dependent pathway. 22045731_LNX1 and LNX2 interact with CD8alpha and promote its ubiquitylation and endocytosis 22066909_The authors found a high level of LNX1 and LNX2 mRNAs in endocarditis, the principal manifestation of chronic Q fever, but not in acute Q fever. 22087225_identify and confirm six novel LNX1 binding partners: KCNA4, PAK6, PLEKHG5, PKC-alpha1, TYK2 and PBK, and suggest that LNX1 functions as a signalling scaffold. 22889411_LNX1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of PBK inhibited cell proliferation and enhanced sensitivity to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. 29190716_study provided the evidences that LNX1 signaling plays important roles in regulating the stemness of colon cancer cells 29496391_Study reveals how the LNX1 RING domain is structurally and mechanistically dependent on other motifs for its E3 ligase activity, and describes how dimeric LNX1 recruits ubiquitin (Ub)-loaded Ubc13 for Ub transfer via E3 ligase-mediated catalysis. |
ENSMUSG00000029228 |
Lnx1 |
31.904756 |
28.0188721820 |
4.808327 |
0.586434552 |
79.604141 |
0.00000000000000000045746580925115446203642709179167728799894484711106076163522615729561948683112859725952148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000003885037597552957661603125324441237706231792728358035923785784859774139476940035820007324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.8425212 |
21.0464701 |
2.0550816 |
0.7017567 |
| ENSG00000072274 |
7037 |
TFRC |
protein_coding |
P02786 |
FUNCTION: Cellular uptake of iron occurs via receptor-mediated endocytosis of ligand-occupied transferrin receptor into specialized endosomes (PubMed:26214738). Endosomal acidification leads to iron release. The apotransferrin-receptor complex is then recycled to the cell surface with a return to neutral pH and the concomitant loss of affinity of apotransferrin for its receptor. Transferrin receptor is necessary for development of erythrocytes and the nervous system (By similarity). A second ligand, the heditary hemochromatosis protein HFE, competes for binding with transferrin for an overlapping C-terminal binding site. Positively regulates T and B cell proliferation through iron uptake (PubMed:26642240). Acts as a lipid sensor that regulates mitochondrial fusion by regulating activation of the JNK pathway (PubMed:26214738). When dietary levels of stearate (C18:0) are low, promotes activation of the JNK pathway, resulting in HUWE1-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the mitofusin MFN2 and inhibition of mitochondrial fusion (PubMed:26214738). When dietary levels of stearate (C18:0) are high, TFRC stearoylation inhibits activation of the JNK pathway and thus degradation of the mitofusin MFN2 (PubMed:26214738). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26214738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26642240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3568132}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for new-world arenaviruses: Guanarito, Junin and Machupo virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17287727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18268337}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a cell surface receptor necessary for cellular iron uptake by the process of receptor-mediated endocytosis. This receptor is required for erythropoiesis and neurologic development. Multiple alternatively spliced variants have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:7037; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; HFE-transferrin receptor complex [GO:1990712]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; Hsp70 protein binding [GO:0030544]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; transferrin receptor activity [GO:0004998]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; aging [GO:0007568]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of mitochondrial fusion [GO:0010637]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of isotype switching [GO:0045830]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; response to copper ion [GO:0046688]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to iron ion [GO:0010039]; response to manganese ion [GO:0010042]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; transferrin transport [GO:0033572]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11096344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11783942_gene coding and flanking regions were sequenced and examined for mutations that might modulate the iron burden of individuals harboring the common mutant hemochromatosis HFE genotype or cause hemochromatosis independent of mutations in the HFE gene 11800564_mutational analysis of the transferrin receptor reveals overlapping HFE and transferrin binding sites 11891802_location was observed on or near the cell surface suggesting it might participate in surface membrane transport of iron 11929045_Analysis of TFRC1 genotypes and HFE gene mutations in French porphyria cutanea tarda (sPCT)patients revealed that, independently from HFE gene mutations, an association was found between the IVS4+198 T allele in the TFRC1 gene and sPCT patients. 11929045_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12032198_a biological marker of erythropoiesis: blood levels in chronic hemodialysis patients 12071581_Circulating levels are affectd by endurance training along with other indicators of iron status in female athletes. 12163483_Results suggest that transferrin receptor shedding is constitutively mediated by a member of the metalloprotease family known as ADAM (for a disintegrin and metalloprotease) that is inhibited by tumor necrosis factor alpha protease inhibitor-2 (TAPI-2). 12200453_Multiple, conserved iron-responsive elements in the 3'-untranslated region of transferrin receptor mRNA enhance binding of iron regulatory protein 2 12222675_membrane-associated forms of neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G may be involved in alternative transferrin receptor shedding in U937 cells 12372835_determination of transferrin recycling pathway requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity 12406888_TfR and TfR2 have similar cellular localizations in K562 cells and coimmunoprecipitate to only a very limited extent. Western analysis of the receptors under nonreducing conditions reveals that they can form heterodimers. 12445428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445428_TfR1 polymorphisms bore no detectable relation to disease severity or response to therapy. 12473103_human transferrin receptor recognizes a complex of Yb3+-transferrin which is a possible pathway for Yb3+ accumulation in cells 12538733_Association between IgA deposits and CD71 expression and their co-localization in mesangium provide strong evidence that CD71 is major IgA receptor on mesangial cells. 12707725_presence in blood serves as a diagnostic indicator of hemolytic anemia 12767055_The concomitant presence of Abeta 1-40 fragment and of IL1beta or TNFalpha caused an increase in the percentage of CD71 positive cells 12904899_in beta-thalassemic patients, significant reduction of CD49d, CD29 and CD71 antigen expression was found in peripheral blood nucleated red cells 14691533_analysis of ligand recognition by the human transferrin receptor 14705946_Reductive release of iron from transferrin, which binds Fe2+ very weakly, is physiologically feasible, a further indication that the transferrin receptor is more than a passive conveyor of transferrin and its iron. 14727087_Increased expression of CD71 antigen is associated with melanoma 14752097_MPP(+)-dependent aconitase inactivation, Tf-iron uptake, and oxidant generation result in the depletion of intracellular tetrahydrobiopterin, leading to the uncoupling of nNOS activity 14769051_Study proposes mechanism of interaction of transferrin with its receptor based on at least two different TFR species: the TFR species found in the neutral media of biological fluids, and the acidic species found in the mildly acidic media of the endosome. 14980223_analysis of the structure of TfR-Tf complex explains differences in the iron-release properties of free and receptor bound Tf 15313461_Transferrin receptor 1 is a gatekeeper for regulating iron [review]. 15349772_Toxoplasma gondii infection resulted in increased activity in the iron response protein IRP1, which, in this state, stabilizes transferrin receptor mRNA from degradation. 15371488_monocyte-derived dendritic cells express another IgA receptor (IgA-R), the transferrin receptor (TfR) 15623846_utility of sesrum TfR outcomes for the detection of iron deficiency during early lactation. 15668490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15775751_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15880641_Transferrin receptor (TfR) and hemochromatosis factor, as well as TfR and DMT1 interact in placental trophoblast cells 15894659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15924420_The effects of mutating the liganding residues in the two lobes of transferrin and the subtle indications of cooperativity between lobes point to the importance of the transferrin receptor in effecting iron release from the C-lobe. 15941956_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15987753_functional cooperation between pIgA1 and TfR for IgA1 deposition and mesangial cell proliferation and activation 16085060_Aluminum interference with transferrin receptor-mediated iron incorporation might trigger the upregulation of non-transferrin bound iron uptake. 16092918_TfR1 expression is attenuated in a cell-density-dependent manner in human lung cancer H1299 cells and in murine B6 fibroblasts as the result of a marked decrease in mRNA content. 16271988_Soluble transferrin receptor is an additional parameter to ferritin for the diagnosis of iron-deficiency anemia 16326028_hypothesis that one molecular mechanism by which 11q23 deletions confer a poor prognosis in CLL is via increased TfR expression secondary to ATM loss, resulting in the increased cellular iron import, and hence increased capacity for malignant growth 16332734_Iron binding C- and N-lobes of Tf sequester iron as a function of complex formation; these structural changes promote tighter binding of the metal ion and facilitate efficient ion transport during endocytosis. 16354665_soluble transferrin receptor release is directly regulated by binding of its ligand ferritransferrin 16508012_These findings provide a molecular basis for increased TFRC1 expression in human tumors, illuminate the role of TFRC1 in the c-Myc target gene network 16564538_mechanism of iron release from the N-lobe and C-lobe of serum transferrin in interaction with intact transferrin receptor 1 at 4.35 times normal) was associated with a complex and severe history of disease requiring splenectomy, occasional red blood cells transfusions, and early start and continuous iron chelation therapy 28714470_TFR1 was increased in myelodysplastic syndrome patients and expression was upregulated in CD34+ cells from patients with refractory anaemia with ringed sideroblasts (RARS). 28837569_TfR1 was highly expressed in glioblastomas and associated with shorter survival in the whole cohort, but not in the individual malignancy grades 28980921_Cell viability and surface expression of transferrin receptor (CD71) and glycophorin A (GPA) were analyzed before and after re-culture by flow cytometry. These studies show differential sensitivities of these surface proteins on K562 cells to proteases, and suggest molecular mechanisms of transmembrane protein transport and cycling. 29286585_Our data provide evidence that blocking TfR could significantly inhibit lung adenocarcinoma (LAC) proliferation by targeting the oncogene KRAS; therefore, TfR may be a therapeutic target for LAC. In addition, our results suggest a new method for blocking the signal from the oncogene KRAS by targeting TfR in LAC. 29295890_The results suggest a role of microRNAs in the TfR1 regulation in the iron-regulatory protein-iron-responsive element system. 29302006_These data show that TfR1-PvRBP2b invasion pathway is critical for the recognition of reticulocytes during P. vivax invasion. 29388418_In agreement with previous studies with truncated forms of these receptors, holo-Tf binds to the TfR1 homologue significantly stronger than to TfR2. 29395073_palmitoylation is reported as a hitherto unreported level of post-translational TfR1 regulation. 29488316_These results strongly support that protozoan proteins RON2 and RN4 and host protein CD71 participate in Plasmodium vivax's complex invasion process, thus providing new pertinent targets for blocking P. vivax merozoites' specific entry to their target cells. 29875008_Transferrin receptor -1 (CD71) expression in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia is an adverse prognostic factor. 29969719_Transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) mediates cellular uptake of holo-Tf and H-ferritin; New World arenaviruses and Plasmodium vivax use TfR1 for entry into host cells. In hepatocytes, TfR2 forms a complex with HFE and serves as an iron sensor. In erythroblasts, TfR2 forms a complex with EPO receptor and regulates erythropoiesis. 30050123_Aberrant CD71-positive and mitochondria-CD71 negative reticulocytes is associated with aberrant erythroid terminal maturation and mitochondrial degeneration in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndromes. 30056091_High TFR1 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 30391537_the role of transferrin receptor in H. pylori attachment into the gastric mucosa 30552136_Ferritin is up-regulated by inflammation and exhibits cytokine-like activity in periodontal ligament cells inducing a signaling cascade through transferrin receptor via ERK/P38 MAPK. 30593316_The associations between polymorphisms of TMPRSS6 and the levels of serum ferritin and soluble transferrin receptor are observed in pregnant women. 30728365_miR-148a regulates expression of the transferrin receptor 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30782157_Circular TFRC could directly bind to miR-107 and relieve suppression for targeted TFRC expression urinary bladder carcinoma. 30811632_The mRNA expression levels of TFR-1 were significantly increased in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues compared with adjacent non-cancerous tissues (P = 0.0013), but there were no differences in other genes. 30850661_The data account for transferrin-independent binding of ferritin to CD71 and suggest that select pathogens may have adapted to enter cells by mimicking the ferritin access gate. 30854239_Low expression of placental TfR1 is associated with |
ENSMUSG00000022797 |
Tfrc |
2287.322649 |
3.9273277696 |
1.973548 |
0.044447356 |
1987.987890 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3761.6652879 |
92.9351593 |
964.7138992 |
19.7892507 |
| ENSG00000072422 |
9886 |
RHOBTB1 |
protein_coding |
O94844 |
|
GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Rho family of the small GTPase superfamily. It contains a GTPase domain, a proline-rich region, a tandem of 2 BTB (broad complex, tramtrack, and bric-a-brac) domains, and a conserved C-terminal region. The protein plays a role in small GTPase-mediated signal transduction and the organization of the actin filament system. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:9886; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cortical cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030865]; engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:0043652]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
16170569_Frequent allelic loss and decreased expression of RHOBTB1 suggested that this gene has a role in tumorigenesis of a subset of HNSCC (Head-Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma). 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23258531_we found that miR-31 acts as an oncogene in colon cancer and identified RhoBTB1 as a new target of miR-31 further study demonstrated that miR-31 contributed to the development of colon cancer at least partly by targeting RhoBTB1. 28219369_RhoBTB1 regulates the integrity of the Golgi complex through METTL7B. RhoBTB1 is required for expression of METTL7B and silencing of either protein leads to fragmentation of the Golgi. Loss of RhoBTB1 expression is linked to Golgi fragmentation in breast cancer cells. Restoration of normal RhoBTB1 expression rescues Golgi morphology and dramatically inhibits breast cancer cell invasion. 31431478_RhoBTB1 associates with ROCK1 and ROCK2 and its association with ROCK1 is via its Rho domain. 32354068_RNA Interference Screening Identifies Novel Roles for RhoBTB1 and RhoBTB3 in Membrane Trafficking Events in Mammalian Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000019944 |
Rhobtb1 |
47.227923 |
0.1183481926 |
-3.078890 |
0.516122382 |
32.599189 |
0.00000001132619908583317766275327514178053456284089861583197489380836486816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000049111251030228467897832895019960552929205732652917504310607910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.8720418 |
3.2985713 |
59.8904045 |
19.6802391 |
| ENSG00000072657 |
29953 |
TRHDE |
protein_coding |
Q9UKU6 |
FUNCTION: Specific inactivation of TRH after its release. |
Aminopeptidase;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M1 family. The encoded protein is an extracellular peptidase that specifically cleaves and inactivates the neuropeptide thyrotropin-releasing hormone.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:29953; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; aminopeptidase activity [GO:0004177]; metalloaminopeptidase activity [GO:0070006]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; pyroglutamyl-peptidase activity [GO:0016920]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; peptide catabolic process [GO:0043171]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000050663 |
Trhde |
102.590082 |
0.3669173318 |
-1.446473 |
0.269623637 |
28.100643 |
0.00000011516761665538455575182296688682703766914983134483918547630310058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000451733728895422834063950795133179916263088671257719397544860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.8869474 |
10.0610472 |
164.0025461 |
19.5019083 |
| ENSG00000072778 |
37 |
ACADVL |
protein_coding |
P49748 |
FUNCTION: Very long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is one of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases that catalyze the first step of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation, an aerobic process breaking down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA and allowing the production of energy from fats (PubMed:7668252, PubMed:9461620, PubMed:18227065, PubMed:9839948, PubMed:9599005). The first step of fatty acid beta-oxidation consists in the removal of one hydrogen from C-2 and C-3 of the straight-chain fatty acyl-CoA thioester, resulting in the formation of trans-2-enoyl-CoA (PubMed:7668252, PubMed:9461620, PubMed:18227065, PubMed:9839948). Among the different mitochondrial acyl-CoA dehydrogenases, very long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase acts specifically on acyl-CoAs with saturated 12 to 24 carbons long primary chains (PubMed:21237683, PubMed:9839948). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18227065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21237683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9461620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9599005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9839948}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;FAD;Fatty acid metabolism;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7668252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9599005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9839948}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is targeted to the inner mitochondrial membrane where it catalyzes the first step of the mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway. This acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase is specific to long-chain and very-long-chain fatty acids. A deficiency in this gene product reduces myocardial fatty acid beta-oxidation and is associated with cardiomyopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:37; |
extrinsic component of mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0031314]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003995]; fatty-acyl-CoA binding [GO:0000062]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; long-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004466]; very-long-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0017099]; energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds [GO:0015980]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA dehydrogenase [GO:0033539]; negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045717]; negative regulation of fatty acid oxidation [GO:0046322]; regulation of cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0090181]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; temperature homeostasis [GO:0001659] |
16464760_A new a unique mutation (IVS13+25G>A) is reported in a compound heterozygote carrying the 1748 C>T mutation in exon 18. 17374501_the bacterial expression system developed here will significantly advance our understanding of both the clinical aspects of VLCAD deficiency and the basic biochemistry of the enzyme 17457695_In asymptomatic mild VLCADdeficiency, a fat-reduced diet may not be necessary, whereas in later infancy and adolescence, strenuous physical exercise may require additional energy from medium-chain fat. 17514507_Report the course of disease in a pair of monozygotic twin sisters. 17999356_Bezafibrate, a widely prescribed hypolipidemic drug, cn be used for the correction of VLCAD deficiency and exemplifies the integration of molecular information in a therapeutic strategy 18156936_Loss of heterozygosity on 17p13 and down-regulation of ACADVL can be used to discriminate adrenal cortex neoplasms from adrenocortical adenoma. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19327992_This study confirms that VLCAD deficiency, although being less frequent than CPT II deficiency, should be systematically considered in the differential diagnosis of exercise-induced rhabdomyolysis. 19889959_Results suggest a novel regulatory mechanism for homeostatic VLCAD activity, whose dysregulation might be involved in the production of oxidative stress and in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 20060901_Missense mutations in Very-Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase is associated with inborn errors of lipid metabolism. 20099975_Down regulation of ACADVL is associated with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 20107901_Case Report: missense mutation within the ACADVL gene responsible for very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency and sudden infant death. 20952238_Analyzed potential rhabdomyolysis-susceptibility genes (RYR 1, CPT II, VLCAD and CYP 2D6) from autopsy samples of methamphetamine abusers; no obvious relationship between the genetic mutations observed in this study and rhabdomyolysis was seen. 21932095_Identification of 2 VLCAD mutations leads to precautions in the management of the children with VLCAD deficiency. 22093928_The expressions of LCHAD gene and protein are remarkably reduced in early onset severe preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome. 23169530_These findings support the importance of considering that mutations may be present in the ACADVL gene when a significant partial deficiency is found in CPTII activity, but no mutations in the CPT2 gene can be identified. 23480858_These results emphasize the importance of functional investigation of abnormal NBS or clinical testing suggestive but not diagnostic of very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase . 24801231_11 mutations in ACADVL gene in 7 patients, 7 reported (p.S22X, p.W427X, p.A213T, p.G222R, p.R450H, c.296-297delCA, c.1605+1G>T), 4 novel (p.S72F, p.Q100X, p.M437T, p.D466Y). p.R450H and p.D466Y (14.28%, 2/14 alleles) mutations identified in 2 alleles. 26385305_following variants should be considered likely pathogenic c.1273G > A (p.A425T), c.1001T > G (p.M334R), c.538G > A (p.A180T), c.640T > G (p.F214V), c.1076C > T (p.A359V), c.1019G > T (p.G340V), c.889_891delGAG (p.E297del), and c.1103A > C (p.Q368P); patients homozygous for the most common pathogenic variant, c.848T > C (p.V283A) can be expected to have a more benign clinical course 27209629_We retrospectively analyzed early outcomes for individuals who were diagnosed with VLCAD deficiency by NBS and describe initial presentations, diagnosis, clinical outcomes and treatment in a cohort of 52 individuals ages 1-18year. 27246109_There are currently no biochemical markers for prediction of disease severity and for the need for treatment in VLCAD deficiency. Mutation analysis may offer predictive value but this may not be robust enough for a large proportion of those mutations that have not been previously reported in clinically affected patients. 27871288_LCHAD and MCAD are differentially expressed in maternal and fetal tissues during normal late pregnancy, which may represent a metabolic adaptation in response to physiological maternal dyslipidemia during late pregnancy. 29459657_The authors provide novel insights into the cellular energy household of cells from HADHA/ACADVL patients and demonstrate for the first time a connection between fatty acid metabolism, mitochondrial morphology and reactive oxygen species in patients with these rare genetic disorders. 30194637_Sequencing of the ACADVL gene revealed that all individuals with activities below 24% were true Very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (VLCADD) patients, individuals with residual activities between 24 and 27% carried either one or two mutations. Twenty new mutations could be identified and functionally classified based on their effect on enzyme function. 30840296_homozygous mutation in ACADVL associated with pediatric familial dilated cardiomyopathy 30950014_VLCADD is relatively rare in southern China, for which late-onset form is common 31794763_One potential hotspot ACADVL mutation in Chinese patients with very-long-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. 32804429_Mitochondrial energetic impairment in a patient with late-onset glutaric acidemia Type 2. 33150772_Novel ACADVL variants resulting in mitochondrial defects in long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. 34704412_Screening and follow-up results of fatty acid oxidative metabolism disorders in 608 818 newborns in Jining, Shandong province. 35001339_VLCAD inhibits the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular cancer cells through regulating PI3K/AKT axis. 35218577_Characterization of exonic variants of uncertain significance in very long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase identified through newborn screening. 35760926_Structural basis for defective membrane targeting of mutant enzyme in human VLCAD deficiency. 36078043_Treatment of VLCAD-Deficient Patient Fibroblasts with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor delta Agonist Improves Cellular Bioenergetics. |
ENSMUSG00000018574 |
Acadvl |
777.644591 |
0.3789395381 |
-1.399960 |
0.140542779 |
96.396254 |
0.00000000000000000000009404491583835331540889931186978817186805972814267843861137856180387739613024677964858710765838623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000920492677569028469404410488526736997710611746837073536694432546179100995686894748359918594360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
432.7694553 |
39.1759337 |
1150.4910700 |
74.1745184 |
| ENSG00000072818 |
9744 |
ACAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q15027 |
FUNCTION: GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for ADP ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) required for clathrin-dependent export of proteins from recycling endosomes to trans-Golgi network and cell surface. Required for regulated export of ITGB1 from recycling endosomes to the cell surface and ITGB1-dependent cell migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11062263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16256741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17398097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17664335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22645133}. |
3D-structure;ANK repeat;Endosome;GTPase activation;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nitration;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity and metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in protein transport and regulation of catalytic activity. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9744; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
11050434_Centaurin beta1/KIAA0050, is a member of the centaurin family of ADP-ribosylation factor directed GTPase-activating proteins. Binding of phosphoinositides to a pleckstrin homology domain may regulate subcellular localisation and activity. 11062263_Centaurin beta1/KIAA0050, or ACAP1, is a phospholipid dependent, ARF6 preferring GTPase-activating protein. It can regulate cytoskeletal and membrane trafficking events in the cell periphery and may be regulated via a phosphoinositide-binding PH domain. 15525538_ACAP1 promotes endocytic recycling by recognizing recycling sorting signals. 17005562_CENTB1 selectively down-regulates NF-kappaB activation via NODs pathways, creating a 'feedback' loop and suggesting a novel role of CENTB1 in innate immune responses to bacteria and inflammatory responses 17010122_Results suggest that two ARF6 downstream molecules, PIP5K and ACAP1, function together in endosomal tubulation and that phosphoinositide levels may regulate endosomal dynamics. 17664335_Results suggest that ACAP1, a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) 6, is part of a novel clathrin coat complex that is regulated by ARF6 for endocytic recycling in two key physiological settings. 18003747_ACAP1 has robust, constitutive Arf6 GAP activity in vivo, with little activity toward Arf1. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22188517_the oncogenic potential of USP6 is linked to its ability to integrate cell migration and cytokinesis by regulating Arf6/ACAP1. 22645133_phosphorylation of ACAP1 relieves a localized mechanism of autoinhibition in regulating cargo binding 23317930_CENTB1 was up-regulated in patients with active UC as compared to UC remission and healthy control groups suggesting that it is involved in the inflammatory process. 25225293_ACAP1 and ARAP2 each colocalize with Arf6 but they did not colocalize with each other and have opposing effects on focal adhesions. 25502766_The serum lever of Alzheimer's disease were decrease and the expression of ACAP1 strongly correlated with the Mini-Mental State Examination scores of the AD patients 31291238_As ACAP1 is an unconventional BAR protein, our findings broaden the understanding of the mechanistic spectrum by which proteins assemble into higher-ordered structures to achieve membrane deformation 32456571_Expression of ACAP1 Is Associated with Tumor Immune Infiltration and Clinical Outcome of Ovarian Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000001588 |
Acap1 |
22.107110 |
0.3705903877 |
-1.432103 |
0.519953224 |
7.047301 |
0.00793847705132164939423322636002922081388533115386962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015540042609749010402153679422099230578169226646423339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8191540 |
5.3453684 |
32.2168767 |
9.8843746 |
| ENSG00000073008 |
5817 |
PVR |
protein_coding |
P15151 |
FUNCTION: Mediates NK cell adhesion and triggers NK cell effector functions. Binds two different NK cell receptors: CD96 and CD226. These interactions accumulates at the cell-cell contact site, leading to the formation of a mature immunological synapse between NK cell and target cell. This may trigger adhesion and secretion of lytic granules and IFN-gamma and activate cytotoxicity of activated NK cells. May also promote NK cell-target cell modular exchange, and PVR transfer to the NK cell. This transfer is more important in some tumor cells expressing a lot of PVR, and may trigger fratricide NK cell activation, providing tumors with a mechanism of immunoevasion. Plays a role in mediating tumor cell invasion and migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15471548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15607800}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for poliovirus. May play a role in axonal transport of poliovirus, by targeting virion-PVR-containing endocytic vesicles to the microtubular network through interaction with DYNLT1. This interaction would drive the virus-containing vesicle to the axonal retrograde transport. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2538245}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Pseudorabies virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9616127}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Is prevented to reach cell surface upon infection by Human cytomegalovirus /HHV-5, presumably to escape immune recognition of infected cell by NK cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15640804}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The external domain mediates cell attachment to the extracellular matrix molecule vitronectin, while its intracellular domain interacts with the dynein light chain Tctex-1/DYNLT1. The gene is specific to the primate lineage, and serves as a cellular receptor for poliovirus in the first step of poliovirus replication. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:5817; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045954]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002860]; susceptibility to natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042271]; susceptibility to T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0060370] |
11751937_We propose that the cytoplasmic domain may target CD155-containing endocytic vesicles to the microtubular network 11983699_activation of expression of sonic hedgehog protein 12913096_Data show that both PVR and Nectin-2 represent specific ligands for the DNAM-1 triggering receptor. 12943679_CD155 may have an important role in cellular function 14652024_These data indicate that Tage4 represents the functional orthologue of CD155 in mouse. 15076773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15136589_that DNAM-1 regulates monocyte extravasation via its interaction with CD226 expressed at endothelial junctions on normal cells. 15194502_These results suggest that CD155alpha plays a role in the regulation of cell adhesion and cell motility. 15194795_cytoplasmic domain of PVR directly interacts with Tctex-1 and plays an important role in retrograde transport of poliovirus-containing vesicles along microtubules in vivo 15279713_Upregulation of the molecular target CD155 renders explant cultures of high-grade malignant gliomas highly susceptible to a prototype oncolytic poliovirus recombinant. 15536144_Analysis of the ligands for triggering NK receptors revealed the consistent expression of cd155 and cd112 in myeloid leukemias, and less frequent expression in lymphoblastic leukemias 15640804_Evasion of NK cell killing was mediated by human cytomegalovirus UL141 blocking surface expression of CD155 17446174_Necl-5 has a critical role in integrin alphavbeta3 clustering and focal complex formation 17507470_Results describe the establishment of a poliovirus oral infection system in human poliovirus receptor-expressing transgenic mice that are deficient in alpha/beta interferon receptor. 17534374_no statistically significant association between this marker allele and non-syndromic clefting 17893876_CD155, at least in part, enhances the proliferation of ras-mutated cells 19011098_crystal structure of C155 D1D2 has been determined to 3.5-A resolution and fitted into approximately 8.5-A resolution cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of the virus-receptor complexes for the 3 PV serotypes 19056733_CD96-driven adhesion to CD155 may be crucial in developmental processes 19319949_The Ala67Thr mutation in the poliovirus receptor is a possible risk factor for the development of vaccine-associated or paralytic poliomyelitis associated with wild-type virus. 19801517_evidence provided for the contribution of DNAM-1/CD155 interactions to the reduction of DNAM-1 expression, suggesting that chronic receptor-ligand interactions in the tumor environment may induce loss of DNAM-1 on tumor-associated NK cells. 19815499_TIGIT is expressed by all NK cells, it binds PVR and PVRL2 but not PVRL3, and it inhibits NK cytotoxicity 20331633_Necl-5 plays a role in mediating tumor cell invasion and that the overexpression of Necl-5 in cancer cells has clinical significance for prognostic evaluation of patients with primary pulmonary adenocarcinoma. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21330602_CD155 is an IFNgamma-inducible immune regulatory protein on the surface of human endothelial cells that attenuates the acquisition of effector functions in CD8 T cells. 21383766_Data show that a high expression of CD112 and CD155 (DNAM-1 ligands) on leukemic blasts. 21998457_The host TICAM-1 pathway, particularly in macrophages, serves as a source of type I interferon induction that protects poliovirus (PV) receptor-bearing transgenic mice from PV infection and paralytic death. 22169283_Expression of PVR in B-ALL cells is modulated by epigenetic mechanisms. 22301152_the PVR downmodulation by Nef and Vpu is a strategy evolved by HIV-1 to prevent NK cell-mediated lysis of infected cells. 22363471_This investigation has enhanced understanding of cell invasion and confirmed CD44 to play a more significant role in this biological process than CD155. 22692919_we demonstrated the expression of both CD155 mRNA and protein in bone and soft tissue sarcoma cell lines 22929570_The concordant computational and experimental data of the present study indicate that the extent of NECL-5 expression correlates with melanoma progression. 23276719_findings suggest Necl-5 expression in lung cancer cells is crucial for their invasiveness in the cancer-stromal interaction 23333754_PVR resides in the recently identified lateral border recycling compartment, similar to PECAM and CD99. 23980210_The CD226/CD155 interaction regulates the proinflammatory (Th1/Th17)/anti-inflammatory (Th2) balance in humans. 24045107_Vpr upregulates PVR during Hiv-1 infection by activating ATR kinase that triggers the DNA damage rsponse pathway and G2 arrest. 24598754_UL141 can inhibit cell-surface expression of both natural killer (NK) cell-activating ligand CD155 as well as TRAIL death receptors (TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2). 24817116_TIGIT/PVR ligation signaling mediates suppression of IFN-gamma production via the NF-kappaB pathway. 24828608_In granulosa cells, there are significant changes in expression during follicular maturation. 25113908_Ala residues 10, 14 and 18 in the TM domain of Vpu are required for CD155 downregulation. 25209846_UPR decreases CD226 ligand CD155 expression and sensitivity to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in hepatoma cells. 25320021_Our findings suggest that loss of CD155 expression may play an important role in the immune escape of HCC cells and thus CD155 may serve as a prognostic marker as well as a potential therapeutic target for HCC. 25609078_The present study provides evidence that regulation of the PVR/CD155 DNAM-1 ligand expression by nitric oxide may represent an additional immune-mediated mechanism and supports the anti-myeloma activity of nitric oxide donors. 25631086_The cell-surface receptor (Pvr) catalyzes a large structural change in the poliovirus that exposes membrane-binding protein chains. 25862891_CD155 may play a critical role through both immunological and non-immuno logical mechanisms in pancreatic cancer and may be a therapeutic target for this intractable malignancy. 25972481_CD155 (PVR/Necl5) mediates a costimulatory signal in CD4+ T cells and regulates allergic inflammation. 26842126_implying that TIGIT exerts immunosuppressive effects by competing with DNAM-1 for the same ligand, CD155 27049654_sCD155 levels were significantly decreased after surgical resection of cancers. Thus, sCD155 level in serum may be potentially useful as a biomarker for cancer development and progression 27296670_The authors demonstrate that HIV and specifically Nef and/or Vpu do not modulate CD155 on infected primary T cells and both CD155 and NKG2D ligands synergize as a natural killer cell receptor to trigger natural killer cell lysis of the infected cell. 27733551_data reveal that MICA and PVR are directly regulated by human cytomegalovirus immediate early proteins, and this may be crucial for the onset of an early host antiviral response 27834324_The SNP detection assay was successfully developed for identification of Ala67Thr polymorphism in human PVR/CD155 gene. The SNP assay will be useful for large scale screening of DNA samples. 28084312_These findings highlight the importance of the TIGIT/CD226/PVR axis as an immune checkpoint barrier that could hinder future 'cure' strategies requiring potent HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells 28395975_soluble CD226 elevated in sera of CTCL patients would be important for tumor immunity by interacting with CD155 on tumor cells. 28730595_Studies showed that CD155 was frequently overexpressed in human malignant tumors. Its overexpression promotes tumor cell invasion and migration, and is associated with tumor progression. [review] 28816021_CD155 is one of key molecules promoting the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 28883004_Data show that gastric cancer cells inhibit T-cell metabolism through CD155/TIGIT signaling. 29381645_Studied association of poliovirus receptor (PVR/CD155) mutation and cleft lip and cleft palate. Validated previous findings that PVR/CD155 markers are associated with cleft lip and palate. 29431243_Study investigated the more detailed mechanism for this cis-interaction of Necl-5 with the PDGF receptor beta. Necl-5 contains three Ig-like domains and the PDGF receptor beta contains five Ig-like domains at their extracellular regions; showed that the third Ig-like domain of Necl-5 cis-interacted with the fifth Ig-like domain of the PDGF receptor beta. 29878245_CD155 was found to be expressed in pediatric brain tumors and in medulloblastoma and pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma tumor cell lines. 30039180_Our results also suggest that CD155 upregulation may be a mechanism underlying Adr resistance by breast cancer cells. 30528596_Results show the structural binding of CD155 ectodomain with the first immunoglobulin domain (D1) of CD96. 30591568_The hybrid complex structure of CD226-ecto binding to the first domain of CD155 (hCD155-D1) reveals a conserved binding interface with the first domain of CD226 (D1), whereas the second domain of CD226 (D2) both provides structural supports for the unique architecture of CD226 and forms direct interactions with CD155. 30880756_The results of real-time PCR indicated that poliovirus receptor (CD155) was significantly overexpressed in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell lines in comparison with the human normal cell line. 31035013_These results suggest an interaction between CD155 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer (BC), and they also suggest that CD155 could be an effective prognostic biomarker for BC. 31036057_The increased MIF secretion by the A549R and H460R cells could be suppressed by a multiple kinase inhibitor, dasatinib, which resulted in the decreased of oncogenic network of Src, CD155 and MIF expression 31253644_The DNAM-1/Necl-5 interaction was underpinned by conserved lock-and-key motifs located within their respective D1 domains, but also included a distinct interface derived from DNAM-1 D2. Mutation of the signature DNAM-1 'key' motif within the D1 domain attenuated Necl-5 binding and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. 31372841_High expression of soluble CD155 in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. 31377744_Large-scale analysis reveals the specific clinical and immune features of CD155 in glioma. 31383549_Poliovirus receptor CD155 is up-regulated in muscle-invasive bladder cancer and predicts poor prognosis. 31387897_Blockade of TIGIT/CD155 Signaling Reverses T-cell Exhaustion and Enhances Antitumor Capability in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 31485637_Expression of TIGIT/CD155 in cancerous tissue is significantly elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 31830330_Study identified for the first time that CD155 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), is associated with poor prognosis and contributes to the aggressive phenotype. Mechanistically, IL-6/Stat3 and TGF-beta/Smad3 pathways may be involved in CD155-associated TNBC epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. CD155 knockdown suppressed TNBC cell in vitro motility and in vivo metastasis. 31883911_Tumor intrinsic and extrinsic immune functions of CD155. 31954274_Combined evaluation of the expression status of CD155 and TIGIT plays an important role in the prognosis of LUAD (lung adenocarcinoma). 32040157_Tumor-derived soluble CD155 inhibits DNAM-1-mediated antitumor activity of natural killer cells. 32321756_Structure of MHC-Independent TCRs and Their Recognition of Native Antigen CD155. 32345648_Tumor CD155 Expression Is Associated with Resistance to Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy in Metastatic Melanoma. 32411795_Overexpression of an Immune Checkpoint (CD155) in Breast Cancer Associated with Prognostic Significance and Exhausted Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes: A Cohort Study. 32446718_The immune suppressive factors CD155 and PD-L1 show contrasting expression patterns and immune correlates in ovarian and other cancers. 32554931_Combination of PD-L1 and PVR determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade. 32727790_Mutant KRAS Promotes NKG2D(+) T Cell Infiltration and CD155 Dependent Immune Evasion. 32804915_TIGIT Can Exert Immunosuppressive Effects on CD8+ T Cells by the CD155/TIGIT Signaling Pathway for Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro. 32902876_The risk of unintentional propagation of poliovirus can be minimized by using human cell lines lacking the functional CD155 gene. 32917981_Direct interaction between CD155 and CD96 promotes immunosuppression in lung adenocarcinoma. 33053330_CD155 on Tumor Cells Drives Resistance to Immunotherapy by Inducing the Degradation of the Activating Receptor CD226 in CD8(+) T Cells. 33185939_Aberrant expression of junctional adhesion molecule-A contributes to the malignancy of cervical adenocarcinoma by interaction with poliovirus receptor/CD155. 33399495_Targeting CD155 by rediocide-A overcomes tumour immuno-resistance to natural killer cells. 33504618_Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Controls CD155 Expression on Macrophages and Mediates Tumor Immunosuppression. 33576304_CD155-Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Implications Based on Multiple Analyses of Databases Across 33 Human Cancers. 33616718_Overexpression of poliovirus receptor is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. 33855917_TIGIT and CD155 as Immune-Modulator Receptor and Ligand on CD4(+) T cells in Preeclampsia Patients. 33879814_Overexpression of PVR and PD-L1 and its association with prognosis in surgically resected squamous cell lung carcinoma. 34030043_The N-linked glycosylations of TIGIT Asn(32) and Asn(101) facilitate PVR/TIGIT interaction. 34115802_Immunohistochemical analysis of CD155 expression in triple-negative breast cancer patients. 34353426_Acetate decreases PVR/CD155 expression via PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer cells. 34504191_DNAM-1/CD226 is functionally expressed on acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and is associated with favorable prognosis. 34514998_CD155: A Key Receptor Playing Diversified Roles. 34608548_Immune checkpoint CD155 promoter methylation profiling reveals cancer-associated behaviors within breast neoplasia. 35262683_CD155 expression impairs anti-PD1 therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. 35324958_Prognostic value of CD155/TIGIT expression in patients with colorectal cancer. 35384345_CD155/SRC complex promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inhibiting the p38 MAPK signalling pathway and correlates with poor prognosis. 35729552_Blocking TIGIT/CD155 signalling reverses CD8(+) T cell exhaustion and enhances the antitumor activity in cervical cancer. 35858240_CD155/TIGIT signalling plays a vital role in the regulation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-induced natural killer-cell exhaustion in multiple myeloma. 35870689_CD155 in tumor progression and targeted therapy. 35947095_CD155 mutation (Ala67Thr) increases the binding affinity for and the signaling via an inhibitory immunoreceptor TIGIT. |
ENSMUSG00000040511 |
Pvr |
312.666808 |
2.6039740217 |
1.380715 |
0.102950511 |
181.650609 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000002113655828662239827420435563220474398852814706396872799768834285586797330942993984440627793209773748294550387016865755640537827275693416595458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000367030118012407737663697789645537026203146540245880238286592973213514351653448644678462164994617882203282316355696934806474018841981887817382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
482.2578428 |
30.4958438 |
186.1925369 |
9.3995262 |
| ENSG00000073350 |
3993 |
LLGL2 |
protein_coding |
Q6P1M3 |
FUNCTION: Part of a complex with GPSM2/LGN, PRKCI/aPKC and PARD6B/Par-6, which may ensure the correct organization and orientation of bipolar spindles for normal cell division. This complex plays roles in the initial phase of the establishment of epithelial cell polarity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632202}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
The lethal (2) giant larvae protein of Drosophila plays a role in asymmetric cell division, epithelial cell polarity, and cell migration. This human gene encodes a protein similar to lethal (2) giant larvae of Drosophila. In fly, the protein's ability to localize cell fate determinants is regulated by the atypical protein kinase C (aPKC). In human, this protein interacts with aPKC-containing complexes and is cortically localized in mitotic cells. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3993; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; myosin II binding [GO:0045159]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; establishment of spindle orientation [GO:0051294]; establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045197]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; leucine transport [GO:0015820]; regulation of establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0032878]; regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0008593]; regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050708] |
15632202_binding between Lgl2 and LGN play a role in mitotic spindle organization through regulating formation of the LGN.NuMA complex; Lgl2 forms a Lgl2.Par-6.aPKC.LGN complex, which responds to mitotic signaling to establish normal cell division 18155665_The identification and functional characterization of the promoter region ( approximately 1.2kb) of the Hugl-2 gene are reported. 18199550_Retention of Lgl2 expression is critical for the epithelial phenotype;its loss might be involved in metastasis. 19403135_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407852_We propose that Lgl2 may be a potential marker to rule out gastric epithelial dysplasia and adenocarcinoma in diagnostic specimens. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20233622_Lgl2 differentiates pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia-3 and ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas from lower-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias. 20941506_There is a role of Lgl2 immunohistochemistry as an adjunct in the diagnosis of foveolar-type gastric dysplasia. 22580609_Hugl-2 induces MET and suppresses Snail tumorigenesis. 23110097_Hugl1 and Hugl2 play an essential role in the maintenance of breast epithelial polarity and differentiated cell morphology, as well as growth control. 23332925_Loss or aberrant Lgl2 staining was useful in identifying Barrett gastric foveolar dysplasia 24318287_It is correlated with lymphatic invasion and lymph node metastasis. 24513855_The crystal structures of the Dlg4 GK domain in complex with two phosphor-Lgl2 peptides reveal the molecular mechanism underlying the specific and phosphorylation-dependent Dlg/Lgl complex formation. 30996345_LLGL2 functions as a promoter of tumour growth and not as a tumour suppressor in ER(+) breast cancer; beyond breast cancer, adaptation to nutrient stress is critically important, and findings identify an unexpected role for LLGL2 in this process 31088962_The crystal structures of human lethal giant larvae homolog 2 (Lgl2) in both its unphosphorylated and atypical protein kinase C(aPKC) phosphorylated states are presented and investigated in this article. 31088964_Study and determination of the crystal structure of lethal giant larvae homolog 2 (Lgl2). 32385218_A human cell polarity protein Lgl2 regulates influenza A virus nucleoprotein exportation from nucleus in MDCK cells. 36192404_Co-expression effect of LLGL2 and SLC7A5 to predict prognosis in ERalpha-positive breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000020782 |
Llgl2 |
108.874150 |
0.4991716456 |
-1.002392 |
0.171962932 |
33.909392 |
0.00000000577392972673340789758282860116324342047988693593651987612247467041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000025786143045865387527854889330482246467823870261781848967075347900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.5755341 |
9.6546243 |
139.9472849 |
13.4750101 |
| ENSG00000073417 |
5151 |
PDE8A |
protein_coding |
O60658 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes (PubMed:18983167). May be involved in maintaining basal levels of the cyclic nucleotide and/or in the cAMP regulation of germ cell development (PubMed:18983167). Binding to RAF1 reduces RAF1 'Ser-259' inhibitory-phosphorylation and stimulates RAF1-dependent EGF-activated ERK-signaling (PubMed:23509299). Protects against cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide and staurosporine (PubMed:23509299). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18983167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23509299}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;cAMP;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; 3',5'-cyclic AMP degradation; AMP from 3',5'-cyclic AMP: step 1/1. |
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) family, and PDE8 subfamily. This PDE hydrolyzes the second messenger, cAMP, which is a regulator and mediator of a number of cellular responses to extracellular signals. Thus, by regulating the cellular concentration of cAMP, this protein plays a key role in many important physiological processes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:5151; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0047555]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cAMP catabolic process [GO:0006198]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death [GO:1903206]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12681444_Comparison of enzymatic characterization and gene organization of PDE8B and PDE8A. 15596729_in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that the association with IkappaB greatly enhanced the enzyme activity of PDE8A1 18983167_kinetic properties of the highly active PDE8A1 catalytic domain prepared from refolding and its crystal structures in the unliganded and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX) bound forms at 1.9 and 2.1 A resolutions 19482904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19482904_The findings exclude a significant role for PDE8A as a PCOS candidate gene, and as a Las major determinant of androgen levels in women. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21920574_Polymorphism in PDE8A affects HIV-1 replication in primary macrophages. 22673573_PDE8 activity can be modulated by a kinase 23509299_PDE8A can bind tightly to Raf-1, regulate Raf-1 phosphorylation on S259, and, in so doing, regulate the cross-talk node whereby cAMP exerts an inhibitory effect on Raf-1 signaling, retarding subsequent ERK phosphorylation and activation. 25229150_a novel and critical role for phosphodiesterases in moderating local concentrations of cAMP in microdomains and signal resetting 25295610_PDE8A supports HIV-1 replication in macrophages 27560698_SNPs within genes SCHIP1 and PDE8A were associated with measures of facial size in both the GWAS and replication cohorts and passed a stringent genomewide significance threshold adjusted for multiple testing of 34 correlated traits. For both SCHIP1 and PDE8A, we demonstrated clear expression in the developing mouse face by both whole-mount in situ hybridization and RNA-seq 29262264_PDE8 is expressed in lipid rafts of human airway smooth muscle cells(HASM), where it specifically regulates beta2-adrenergic receptor/ AC6 signaling to modulate HASM responsiveness and airway remodeling in asthma. 30770787_Editing of PDE8A mRNA displayed clear regional difference when comparing dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA9) and anterior cingulate cortex (BA24). There were significant intra-regional differences between non-psychiatric control individuals and depressed suicide decedents. 33931591_Phosphodiesterase 8A to discriminate in blood samples depressed patients and suicide attempters from healthy controls based on A-to-I RNA editing modifications. 34936285_Phosphodiesterase 8A Regulates CFTR Activity in Airway Epithelial Cells. 36277728_cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase 8A and 8B isoforms are differentially expressed in human testis and Leydig cell tumor. |
ENSMUSG00000025584 |
Pde8a |
145.065816 |
2.5549217646 |
1.353279 |
0.400831547 |
11.005794 |
0.00090827512675308572955013008964897380792535841464996337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002131352567820845884255520630290448025334626436233520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
196.2390194 |
48.9702116 |
77.6237152 |
14.1507169 |
| ENSG00000073605 |
55876 |
GSDMB |
protein_coding |
Q8TAX9 |
FUNCTION: [Gasdermin-B]: Precursor of a pore-forming protein that acts as a downstream mediator of granzyme-mediated cell death (PubMed:32299851). This form constitutes the precursor of the pore-forming protein: upon cleavage, the released N-terminal moiety (Gasdermin-B, N-terminal) binds to membranes and forms pores, triggering pyroptosis (PubMed:32299851). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32299851}.; FUNCTION: [Gasdermin-B, N-terminal]: Pore-forming protein produced by cleavage by granzyme A (GZMA), which causes membrane permeabilization and pyroptosis in target cells of cytotoxic T and natural killer (NK) cells (PubMed:27281216, PubMed:32299851). Key downstream mediator of granzyme-mediated cell death: (1) granzyme A (GZMA), delivered to target cells from cytotoxic T- and NK-cells, (2) specifically cleaves Gasdermin-B to generate this form (PubMed:32299851). After cleavage, moves to the plasma membrane, homooligomerizes within the membrane and forms pores of 10-15 nanometers (nm) of inner diameter, triggering pyroptosis (PubMed:32299851). Binds to membrane inner leaflet lipids, such as phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, bisphosphorylated phosphatidylinositols, such as phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate, and more weakly to phosphatidic acid (PubMed:28154144). Also binds sufatide, a component of the apical membrane of epithelial cells (PubMed:28154144). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28154144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32299851}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytolysis;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Necrosis;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane beta strand |
|
This gene encodes a member of the gasdermin-domain containing protein family. Other gasdermin-family genes are implicated in the regulation of apoptosis in epithelial cells, and are linked to cancer. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants. Additional variants have been described, but they are candidates for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and are unlikely to be protein-coding. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2016]. |
hsa:55876; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; wide pore channel activity [GO:0022829]; cytolysis [GO:0019835]; cytotoxic T cell pyroptotic process [GO:1902483]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; granzyme-mediated programmed cell death signaling pathway [GO:0140507]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269] |
15010812_Evolutionary recombination hotspot around the GSDML-GSDM locus is closely linked to oncogenomic recombination hotspot around the PPP1R1B-STARD3-TCAP-PNMT-PERLD1-ERBB2-C17orf37-GRB7 amplicon at human chromosome 17q12. 18038310_GSDML may be a secretory or metabolic product involved in a secretory pathway, and changes in the regulation of GSDML splicing variant transcription and translation may be seen in the development and/or progression of gastrointestinal and hepatic cancers. 19029000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19051310_Study investigated the expression pattern of the GSDM family genes in the upper gastrointestinal epithelium and cancers 19068216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19133921_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19133921_polymorphisms in ORMDL3 and the adjacent GSDML may contribute to childhood asthma. 19732864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19732864_The disease-linked haplotype and putative causal DNA variants of ZPBP2/GSDMB/ORMDL3 locus via a combination of genetic and functional analyses, were identified. 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378605_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20601676_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20860503_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21337730_The GSDMA (rs7212938) and GSDMB (rs7216389) polymorphisms are associated with asthma susceptibility and intermediate asthma phenotypes. 22295569_Five markers on chromosome 17q12-21 showed statistically significant association with bronchial asthma .SNP rs7216389 with the strongest evidence for association is located within the first intron of the GSDMB gene. 22370936_Significant associations between two SNPs, rs2305480 and rs8067378 in the GSDML gene, and asthma were found in this study. 22732088_GSDMB/ORMDL3 variants contribute to asthma susceptibility and eosinophil-mediated bronchial hyperresponsiveness. 24044605_rs11078928 is associated with the production of a novel GSDMB transcript lacking an internal segment 24066901_GSDMB SNP rs2305480 (Ser311Pro) was associated with asthma diagnosis (p = 8.9x10-4), bronchial hyperresponsiveness to methacholine (p = 8.2x10-4) and severity (p = 1.5x10-4) with supporting evidence from a second GSDMB SNP rs11078927 (intronic). 24315451_3 SNPs associated with the fraction of exhaled nitric oxide in childhood asthma are rs3751972 in LYRM9; rs944722 in NOS2; and rs8069176 near GSDMB; all at 17q12-q21. 24675552_Gasdermin-B promotes invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells 24848122_No association between GSDMB polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis was observed. 25256354_Results confirmed the genetic association between GSDMB/ ORMDL3 and childhood asthma and show significant differences in the DNA methylation levels of ORMDL3 promoter of asthmatic children. 26016667_The GSDMB-driven HSVtk expression vector had a therapeutic effect on the occult peritoneal dissemination model mice. 26270739_GSDMB variants have been shown to be associated with Asthma in children with Rhinovirus infections -induced wheezing illnesses. 26484354_Based on our results and published findings on GSDMA, GSDMB, LRRC3C, and related proteins, we propose that this locus in part affects IBD susceptibility via effects on apoptosis and cell proliferation 26534891_childhood asthma is associated with gene polymorphism; meta-analysis 26886240_we investigated the association between GSDMA and GSDMB variants and the incidence of adult and childhood asthma among Jordanians.An association between the GSDMB T/C single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotype and the incidence of childhood asthma was found 27462779_Data identifies the ERBB2 co-amplified and co-expressed gene GSDMB as a critical determinant of poor prognosis and therapeutic response in HER2-positive breast cancer. 27799535_These studies demonstrate that GSDMB, a gene highly linked to asthma but whose function in asthma is previously unknown, regulates AHR and airway remodeling without airway inflammation through a previously unrecognized pathway in which GSDMB induces 5-LO to induce TGF-beta1 in bronchial epithelium. 28052796_We found strong associations among GSDMB polymorphisms and the presence of AERD and FEV1 in Korean patients with asthma. Our findings indicated that genetic variations of GSDMB may be associated with the development of AERD and aspirin-induced bronchospasm. 28120299_The rs8067378 SNP variants may increase the expression of GSDMB and the risk of the development and progression of cervical SCC. 28154144_Full-length GSDMB and its N-terminal domain bind to phosphoinositides or sulfatide, but not cardiolipin. The GSDMB N-terminal domain binds liposomes containing sulfatide, suggesting a role in sulfatide transport. A loop with SNP AAs from controls (Gly299:Pro306) shows high conformational flexibility, but one with AAs (Arg299:Ser306) from people at risk for IBD and asthma is less so and has higher positive surface charge. 28272342_GSDMB levels are significantly modulated by NMD. Importantly, both AS isoforms and the identified ecircRNA were significantly dysregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of relapsing-remitting MS patients compared to controls. 28588209_These results showed that the PBC susceptibility allele of rs12946510 disrupted the enhancer region for ORMDL3 and GSDMB gene expression (Fig. 6). Chromatin interaction between the sequence that contains rs12946510 and the upstream sequence of ORMDL3 and GSDMB also supported this enhancer model 28826527_Chromosome 17q21 genes ORMDL3 and GSDMB are linked to asthma and other immune diseases. (Review) 29330013_Our study identified a functional asthma variant in the GSDMB gene of the 17q21 locus and implicates GSDMB-mediated epithelial cell pyroptosis in pathogenesis. 29374573_we show that local CpG methylation mediates a proportion, but not all, of the functional effects of cis-acting asthma-susceptibility regulatory variants on GSDMB and ORMDL3 gene expression 30321352_GSDMB promotes caspase-4 activity, which is required for the cleavage of GSDMD in non-canonical pyroptosis, by directly binding to the CARD domain of caspase-4. 32299851_this study demonstrated that GZMA from cytotoxic lymphocytes cleaves and activates GSDMB to induce target cell pyroptosis. 32496997_Association between Gasdermin A, Gasdermin B Polymorphisms and Allergic Rhinitis Amongst Jordanians. 32795586_Genetic analyses identify GSDMB associated with asthma severity, exacerbations, and antiviral pathways. 33810791_Household mold exposure interacts with inflammation-related genetic variants on childhood asthma: a case-control study. 33941434_ORMDL3/GSDMB genotype is associated with distinct phenotypes of adult asthma. 33963941_Association of Gasdermin B Gene GSDMB Polymorphisms with Risk of Allergic Diseases. 34022140_Pathogenic ubiquitination of GSDMB inhibits NK cell bactericidal functions. 34076350_The GSDMB rs7216389 SNP is associated with chronic rhinosinusitis in a multi-institutional cohort. 34326684_USP24-GSDMB complex promotes bladder cancer proliferation via activation of the STAT3 pathway. 34957313_Upregulated GSDMB in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Is Associated with Immune Infiltrates and Poor Prognosis. 35021065_GSDMB is increased in IBD and regulates epithelial restitution/repair independent of pyroptosis. 35381269_Genome-wide study of early and severe childhood asthma identifies interaction between CDHR3 and GSDMB. 36201519_GSDM gene polymorphisms regulate the IgE level in asthmatic patients. |
|
|
41.362495 |
0.0973823979 |
-3.360195 |
0.404073429 |
70.328602 |
0.00000000000000005020448882241425116559126746775241618325440190592420797166539614408975467085838317871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000385746098396061599176759334887844044085924044996255277695240692992229014635086059570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6187682 |
1.9566232 |
78.8559597 |
11.5939910 |
| ENSG00000073670 |
4185 |
ADAM11 |
protein_coding |
O75078 |
FUNCTION: Probable ligand for integrin in the brain. This is a non catalytic metalloprotease-like protein. Required for localization of the potassium channel subunit proteins KCNA1/KV1.1 and KCNA2/KV1.2 at cerebellar cortex basket cell distal terminals, is thereby involved in ephaptic inhibitory synchronization of Purkinje cell firing and response to stress (By similarity). Plays a role in spatial learning and motor coordination (By similarity). Involved in the nociceptive pain response to chemical-derived stimulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R1V4}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease) protein family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins, and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This gene represents a candidate tumor suppressor gene for human breast cancer based on its location within a minimal region of chromosome 17q21 previously defined by tumor deletion mapping. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4185; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; behavioral response to acetic acid induced pain [GO:0061367]; behavioral response to formalin induced pain [GO:0061368]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; multicellular organismal response to stress [GO:0033555]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
11545539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000020926 |
Adam11 |
42.508177 |
0.0652511002 |
-3.937854 |
0.408678174 |
116.315832 |
0.00000000000000000000000000405323610127089615503518880873953750260670974114534668886601543623380053925353561083966269507072865962982177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000046885395654199395425325176785458298582914267423130101575585897435668233240724234178742335643619298934936523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2547626 |
1.4852709 |
81.2218745 |
10.7845944 |
| ENSG00000073737 |
10170 |
DHRS9 |
protein_coding |
Q9BPW9 |
FUNCTION: 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase that converts 3-alpha-tetrahydroprogesterone (allopregnanolone) to dihydroxyprogesterone and 3-alpha-androstanediol to dihydroxyprogesterone (PubMed:11294878, PubMed:29541409). Also plays a role in the biosynthesis of retinoic acid from retinaldehyde (PubMed:11304534, PubMed:12618084). Can utilize both NADH and NADPH. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VD48, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11294878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11304534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12618084, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29541409}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Microsome;NAD;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Signal;Steroid metabolism |
|
This gene encodes a member of the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. This protein demonstrates oxidoreductase activity toward hydroxysteroids and is able to convert 3-alpha-tetrahydroprogesterone to dihydroxyprogesterone and 3-alpha-androstanediol to dihydroxyprogesterone in the cytoplasm, and may additionally function as a transcriptional repressor in the nucleus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:10170; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004022]; androstan-3-alpha,17-beta-diol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047044]; androsterone dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047023]; NAD-retinol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004745]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; racemase and epimerase activity [GO:0016854]; steroid dehydrogenase activity [GO:0016229]; testosterone dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0047035]; 9-cis-retinoic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042904]; androgen metabolic process [GO:0008209]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; progesterone metabolic process [GO:0042448]; retinol metabolic process [GO:0042572]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202] |
15190067_expression of retinol dehydrogenase L is regulated by APC and CDX2 16691198_Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 9 is a moonlighting protein that functions as both a metabolic enzyme and as a transcriptional repressor. 17244623_retinoic acid-responsive genes are induced by Epstein-Barr virus lytic infection through induction of a retinol-metabolizing enzyme, DHRS9 26254099_decreased expression of DHRS9 correlates with tumor progression and may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer 27239845_Even at early stages of malignant transformation, a significant decrease in ADH1B, ADH3, RDHL, and RALDH1 mRNA levels was observed in 82, 79, 73, and 64% of tumor specimens, respectively 28594751_DHRS9 is a specific and stable marker of human regulatory macrophages. 30149992_The study findings suggest that DHRS9 might be a useful diagnostic and prognostic marker for oral squamous cell carcinoma 32752300_Are Mutations in the DHRS9 Gene Causally Linked to Epilepsy? A Case Report. 36340269_Transcription Factor FXR Activates DHRS9 to Inhibit the Cell Oxidative Phosphorylation and Suppress Colon Cancer Progression. |
ENSMUSG00000027068 |
Dhrs9 |
48.060727 |
0.0466360779 |
-4.422410 |
0.420693237 |
165.213991 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000008214180489417923287181968673965220527017894070665050574259502271307837116765004925213777973701527630734364748832376790232956409454345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001302269645798158404510008338749142876035656780104364548505349685975586286019213513889546128315857081991779864438285585492849349975585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3589183 |
1.2834492 |
94.1393815 |
11.1779908 |
| ENSG00000073792 |
10644 |
IGF2BP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6M1 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding factor that recruits target transcripts to cytoplasmic protein-RNA complexes (mRNPs). This transcript 'caging' into mRNPs allows mRNA transport and transient storage. It also modulates the rate and location at which target transcripts encounter the translational apparatus and shields them from endonuclease attacks or microRNA-mediated degradation (By similarity). Preferentially binds to N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-containing mRNAs and increases their stability (PubMed:29476152). Binds to the 5'-UTR of the insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) mRNAs (PubMed:9891060). Binding is isoform-specific. Binds to beta-actin/ACTB and MYC transcripts. Increases MYC mRNA stability by binding to the coding region instability determinant (CRD) and binding is enhanced by m6A-modification of the CRD (PubMed:29476152). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23640942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29476152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9891060}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;mRNA transport;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Translation regulation;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein that binds the 5' UTR of insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) mRNA and regulates its translation. It plays an important role in metabolism and variation in this gene is associated with susceptibility to diabetes. Alternative splicing and promoter usage results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes are found on several chromosomes. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:10644; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; mRNA 5'-UTR binding [GO:0048027]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; N6-methyladenosine-containing RNA binding [GO:1990247]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation regulator activity [GO:0045182]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; CRD-mediated mRNA stabilization [GO:0070934]; mRNA transport [GO:0051028]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of RNA metabolic process [GO:0051252] |
15225648_HMGA2 differentially regulates expression of IMP family members during mouse embryogenesis. 15618018_Study suggests that there is a significant association between expression of IMP-2 and the growth of tumor cells, in which IMP-2 is associated with apoptosis induced by tretinoin. 17296566_VICKZ exhibits differential expression in lymphoma subtypes and thus may be a marker of potential value in the diagnosis and study of hematopoietic neoplasia. 17426251_we provide evidence that there is a strong and statistically significant correlation between HMGA2 and IMP2 gene expression in human liposarcomas. 17463246_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463248_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463249_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17827400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17928989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162508_The association of 6 loci with type 2 diabetes risk in Japanese patients is reported. 18259684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426861_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18430866_Novel evidence for a rare variant in the 3' downstream region of IGF2BP2 in type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. 18430866_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18443202_Little evidence of association was observed between SNPs in IGF2BP2 and type 2 diabetes in African Americans. 18469204_Data confirmed the associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms in IGF2BP2 with risk for type 2 diabetes in Asians. 18469204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18477659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18516622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18544707_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18591388_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18597214_Gene variants of CDKAL1, PPARG, IGF2BP2, HHEX, TCF7L2, and FTO predispose to type 2 diabetes in the German KORA 500 K study population. 18597214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18598350_IGF2BP2 SNPs revealed a significant association with type 2 diabetes 18598350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18618095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18618095_Variants of CDKAL1 and IGF2BP2 attenuate the first phase of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion but show no effect on the second phase of insulin secretion in hyperglycmia and type 2 diabetes. 18633108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18633108_The results indicate that in Chinese Hans, common variants in IGF2BP2 loci independently or additively contribute to type 2 diabetes risk, likely mediated through beta-cell dysfunction. 18694974_Study show that polymorphisms in IGF2BP2 were associated with type 2 diabetes risk in the studied population. 18719881_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18853134_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18984664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18991055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19002430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19008344_Data show that SNPs in IGF2BP2 did not confer a significant risk for type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 19008344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19018773_IGF2BP2 stimulation increases radiosensitivity of a pancreatic cancer cell line through endoplasmic reticulum stress under hypoxic comditions. 19020323_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19020324_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19033397_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19033397_Type 2 diabetes susceptibility of IGF2BP2 was confirmed in Japanese. 19082521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19139842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19148120_IGF2BP2 single-nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with body fat and this effect on body fat influences insulin resistance which may contribute to type 2 diabetes mellitus risk. 19148120_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19225753_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19228808_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19247372_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258404_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258437_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258437_The IGF2BP2 variant shows a nominal interaction with exposure to famine in wartime in utero and predisposition to type 2 diabetes. 19279076_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19401414_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19502414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19592620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19602701_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720844_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741166_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19794065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19808892_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19862325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19892838_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20043145_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20075150_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20142250_prostate cancer was inversely associated with the IGF2BP2 rs4402960 T allele 20161779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20215779_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20384434_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20490451_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20509872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20523342_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20523342_findings show that IGF2BP2 rs1470579 and rs4402960 polymorphisms may be associated with the development of type 2 diabetes and these polymorphisms may affect the therapeutic efficacy of repaglinide in Chinese T2DM patientsmellitus 20550665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20580033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20616309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627640_non-replications of IGF2BP2 associations with type 2 diabetes 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20879858_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20929593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20956565_Data reveal how the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression by IMP-2 contributes to the control of adhesion structures and stable microtubules and demonstrate an important function for IMP-2 in cellular motility. 21145819_The induction of a steatotic phenotype implies that p62 plays a role in hepatic pathophysiology 21422097_IGF2 is emerging as an important gene for ovarian cancer. 21576258_Double phosphorylation promotes IMP2 binding to the IGF2 leader 3 mRNA 5' untranslated region, and the translational initiation of this mRNA 21771882_involved in the selective autophagic clearance of non-ubiquitylated aggregation-prone substrates 21839790_meta-analysis suggested that IGF2BP2 rs4402960 polymorphism conferred elevated risk of T2DM, especially in European, East Asian and South Asian populations 22015911_rs4402960 and rs1470579 lymorphisms of the IFG2BP2po is a risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. 22032244_IGF2BP2 genetic variation is associated with type 2 diabetes. 22096510_Six SNP(rs7754840 in CDKAL1, rs391300 in SRR, rs2383208 in CDKN2A/2B, rs4402960 in IGF2BP2, rs10830963 in MTNR1B, rs4607517 in GCK)risk alleles of type 2 diabetes were associated with GDM in pregnant Chinese women. 22245690_Data validate that IGF2BP2 susceptibility variants rs4402960 and rs1470579 associate with T2DM in Lebanese Arabs. 22427968_Two isoforms of the mRNA binding protein IGF2BP2 are generated by alternative translational initiation. 22770937_genetic association studies: Data suggest that an SNP in IGF2BP2 (rs4402960) is associated with type 2 diabetes; IGF2BP2 may have genetic interactions with insulin-like growth factor II with a protective effect in male patients with type 1 diabetes. 22899010_oncofetal insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IMP2, IGF2BP2) regulates oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in primary glioblastoma (GBM) sphere cultures (gliomaspheres) 22923468_Association to type 2 diabetes was found for rs13266634 (SLC30A8), rs7923837 (HHEX), rs10811661 (CDKN2A/2B), rs4402960 (IGF2BP2), rs12779790 (CDC123/CAMK1D), and rs2237892 (KCNQ1). 23029108_IGF2BP2 alternative variants were associated with GADA negative diabetes. The IGF2BP2 haplotypes and diplotypes increased the risk of diabetes in Malaysian subject. 23144361_In African Americans, seven of the 29 SNPs examined were found to be associated with T2D risk at P = 0.05, including rs6769511 (IGF2BP2). 23257922_p62 exerts IGF2-independent antiapoptotic action, which is facilitated via phosphorylation of ERK1/2. 23364967_Polymorphisms in PPARgamma(2) and IGF2BP2 were shown to be highly correlated with GDM occurrence, whereas no correlation was found for KCNQ1 polymorphisms. 23403707_IGF2BP2 genetic variants contribute to insulin resistance in Russian NIDDM patients. 23418049_Our results revealed two novel genes (IGF2BP2 and TNFRSF13B), whose function could account for the biologic pathways influencing MetS phenotypes. 23421499_there is a strong immune response of anti-p62 in sera from patients with colon cancer compared with normal human sera (NHS). 23536553_findings implicate the HMGA2-IGFBP2-NRAS signaling pathway as a critical oncogenic driver in embryonic rhabdomyosarcoma 23656854_IGF2BP2 may play a role in susceptibility to schizophrenia in Han Chinese, supporting the hypothesis that the co-occurrence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and schizophrenia may be explained by shared genetic risk variants. 23670970_TCF7L2 was replicated in this study (P = 0.004; combined analysis P = 3.8 x 10(-6)), and type 2 diabetes SNPs at or near CDKAL1, CDKN2A/B, and IGF2BP2 were associated with CFRD 24229666_IGF2BP2 was strongly associated with the risk of T2DM in Chinese Han population. 24636221_rs4402960 of IGF2BP2 gene is a strong candidate for Type 2 diabetes susceptibility and overweight/obesity risk. 24814803_VICKZ1 and VICKZ2 are overexpressed in ovarian carcinoma effusions suggesting a biological role at this anatomical site, and appear to have a role in proteolysis and invasion. VICKZ2 may be a prognostic marker in ovarian serous carcinoma effusions. 24898818_The case-control study and meta-analysis revealed a significant association between the IGF2BP2 rs4402960 variant and type 2 diabetes in Moroccan and Arab populations.[meta-analysis] 25062844_The present study provided data suggesting that the wild C allele of IGF2BP2 (rs4402960) had a protective effect against T2DM in obese subjects of Chinese Han population. 25247335_The IGF2BP2 gene rs1470579 and rs4402960 polymorphisms were associated with type 2 diabetes patients and therapeutic efficacy of pioglitazone in this Chinese population 25661373_The IGF2BP2 gene rs4402960 polymorphism increases the breast cancer risk of Chinese females with Han nationality, and is a breast cancer predisposing gene. 25719943_Imp2 regulates the activity of IGF2, which further activates PI3K/Akt signaling. 25721883_Data suggest that autoantibody against IGF2 mRNA-Binding Protein 2 (IMP2/p62) may be a useful serum biomarker for early-stage breast cancer screening and diagnosis. 26107517_HPV16 Down-Regulates the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 to Promote Epithelial Invasion 26115082_Our results suggest IGF2BP2 and KCNQ1 polymorphisms might be independent predictors of chemotherapeutic response 26160756_Data show that insulin-like growth factor-2-mRNA-binding proteins IGF2BP1, IGF2BP2, and IGF2BP3 are direct targets of microRNA-1275 (miR-1275). 26416451_p62/IMP2 stimulates cell migration and reduces cell adhesion, contributing to breast cancer progression. 26889980_IMP2 expression is higher in ovarian and endometrial high-grade serous carcinomas (HGSC) than in ovarian or endometrial endometrioid carcinoma. Knockdown in ovarian HGSC cell line decreased cell proliferation. 27153315_IGF2BP2 as a post-transcriptional regulatory mRNA-binding factor that contributes to Colorectal carcinogenesis. 27184842_insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IMP2) binds to let-7 miRNA recognition elements (MREs) and prevents let-7 target gene silencing. 27294943_Our data suggests that IGF2BP2 polymorphisms are associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Asian populations. 27391348_IGF2BP2/IMP2 expression is linked to short survival and metastasis in esophageal adenocarcinoma 27625022_Study conclude that integration of genomic and transcriptomic data implicate circulating IGF2BP2 mRNA levels associated with glucose and insulin homeostasis 27733218_miR-1193 suppressed proliferation and invasion of human breast cancer cells via translational suppression of IGF2BP2. 28753127_IGF2BP2 protein is a tumor promoter that drives cancer proliferation through its client mRNAs IGF2 and HMGA1. 29217458_Data show that insulin-like growth factor-II mRNA-binding protein 2 and 3 (IMP2/3)-miR-200a-progesterone receptor axis represents a double-negative feedback loop and serves as a new potential therapeutic target for the treatment of Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). 29339719_miR-181a-5p suppresses the invasion and migration of cytotrophoblasts, and its inhibitory effects were at least partially mediated by the suppression of IGF2BP2 expression 29410390_rs4402960 (IGF2BP2) and rs2736098 (TERT) are identified as independent risk factors for type 2 diabetes. The simultaneous presence of both risk alleles confers a three-fold increased risk of developing the disease. 29476152_The direct binding of IGF2BPs to RNA N(6)-methyladenosine through their KH domains enhances mRNA stability and translation. 29510198_The miR-485-5p/IGF2BP2 axis orchestrates the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. 30220054_IGF2BP2 and HMGA2 are significantly upregulated in metaplastic carcinoma compared to other breast cancer subtypes. 30242153_RNA interference-mediated knockdown of the Drosophila ortholog of IGF2BP2 in insulin-producing cells, a model for mammalian beta cells, conferred increased insulin output. 30247605_HMGA2 and IGF2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IMP2) were highly expressed in the granulosa cells (GCs) of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and the HMGA2/IMP2 pathway promoted GC proliferation. Cyclin D2 and SERPINE1 mRNA binding protein 1 were regulated by IMP2 and were highly expressed in women with PCOS. 30335898_This study suggests that IGF2BP2 rs1470579 A > C and IGFBP3 rs6953668 G > A polymorphisms may decrease genetic susceptibility to Esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma in eastern Chinese Han population. 30371117_neither rs4402960 nor rs11705701 associated with gestational diabetes; rs4402960 and/or rs11705701 may affect length of gestation and Apgar score of newborn 30513526_The results showed that IGF2BP2 was overexpressed in Acute Myelocytic Leukemia patients. 31064983_Study generated a high-resolution, genome-wide map of chromatin architecture in pancreatic islets and used this map to annotate candidate target genes of islet enhancers. At the IGF2BP2 locus, type 2 diabetes risk alleles reduce islet chromatin accessibility and expression of target gene IGF2BP2 and that conditional knockout of IGF2BP2 homolog Imp2 in mouse islets impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. 31089713_Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) enhances aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells through stabilizing glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) mRNA. 31230592_Study showed that the expression of IGF2BP2 was significantly increased in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) tumor tissues. Also, IGF2BP2 enhanced SOX2 mRNA stability via an m6A-dependent manner. 31692433_RHPN1-AS1 Drives the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Regulating miR-596/IGF2BP2 Axis. 31791342_the in vivo experiments further identified the antitumor effects of inhibiting LINRIS in CRC, and the analysis of LINRIS/IGF2BP2 expression in the tissues from patients indicated their unique role in the development of CRC. 31804607_IGF2BP2 regulates DANCR by serving as an N6-methyladenosine reader. 31852504_We comprehensively reveal the oncogenic role of IGF2BP2 in pancreatic cancer carcinogenesis and confirm that genomic amplification and the silencing of miR-141 contribute to its activation. Our findings highlight that IGF2BP2 may be a promising molecular target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. 31938912_rs11927381 Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Contribution of Smoking to the Realization of Susceptibility to the Disease. 32329795_Influence of IGF2BP2, HMG20A, and HNF1B genetic polymorphisms on the susceptibility to Type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han population. 32662505_Lack of association between IGF2BP2 rs4402960 polymorphism and gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. 32668274_Initiation of stress granule assembly by rapid clustering of IGF2BP proteins upon osmotic shock. 32713259_IGF2BP2 stabilized FBXL19-AS1 regulates the blood-tumour barrier permeability by negatively regulating ZNF765 by STAU1-mediated mRNA decay. 32767321_Functional characterization of the long noncoding RNA MIR22HG as a tumour suppressor in cervical cancer by targeting IGF2BP2. 32784624_IGF2BP2 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Clinical Characteristics and Development of Oral Cancer. 33390804_Evidence of association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms in lipid metabolism-related genes and type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Chinese population. 33452460_Overexpression of Hmga2 activates Igf2bp2 and remodels transcriptional program of Tet2-deficient stem cells in myeloid transformation. 33526059_LINC00460/DHX9/IGF2BP2 complex promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by mediating HMGA1 mRNA stability depending on m6A modification. 33561557_Identification of proteins related with pemetrexed resistance by iTRAQ and PRM-based comparative proteomic analysis and exploration of IGF2BP2 and FOLR1 functions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 33705986_RNA m6A reader IMP2/IGF2BP2 promotes pancreatic beta-cell proliferation and insulin secretion by enhancing PDX1 expression. 33754909_Identification of Prognostic RBPs in Osteosarcoma. 33758932_microRNA-320b suppresses HNF4G and IGF2BP2 expression to inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth of lung cancer. 33824282_ZEB1-induced LINC01559 expedites cell proliferation, migration and EMT process in gastric cancer through recruiting IGF2BP2 to stabilize ZEB1 expression. 34185427_m(6) A modification of lncRNA PCAT6 promotes bone metastasis in prostate cancer through IGF2BP2-mediated IGF1R mRNA stabilization. 34309973_IGF2BP2 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer through a YAP-dependent mechanism. 34340128_IGF2BP2 knockdown suppresses thyroid cancer progression by reducing the expression of long non-coding RNA HAGLR. 34345216_SUMOylation of IGF2BP2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry of glioma via regulating OIP5-AS1/miR-495-3p axis. 34380038_Actinin BioID reveals sarcomere crosstalk with oxidative metabolism through interactions with IGF2BP2. 34518440_lncRNA HCG11 suppresses human osteosarcoma growth through upregulating p27 Kip1. 34608837_Targeting PD-L1 (Programmed death-ligand 1) and inhibiting the expression of IGF2BP2 (Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2) affect the proliferation and apoptosis of hypopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 34624573_LncRNA HCG11 mediated by METTL14 inhibits the growth of lung adenocarcinoma via IGF2BP2/LATS1. 34696797_CircCD44 plays oncogenic roles in triple-negative breast cancer by modulating the miR-502-5p/KRAS and IGF2BP2/Myc axes. 34705667_Identification of the function and mechanism of m6A reader IGF2BP2 in Alzheimer's disease. 34709120_N6-methyladenosine reader YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 3 or insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 knockdown protects human bronchial epithelial cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inactivating p38 MAPK, AKT, ERK1/2, and NF-kappaB pathways. 34743750_N6-methyladenosine reader IMP2 stabilizes the ZFAS1/OLA1 axis and activates the Warburg effect: implication in colorectal cancer. 34750570_Loss of Hilnc prevents diet-induced hepatic steatosis through binding of IGF2BP2. 34753397_Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 regulates proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of keratinocytes by modulating heparanase stability. 35011587_WT1-AS/IGF2BP2 Axis Is a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma According to ceRNA Network Comprehensive Analysis Combined with Experiments. 35014946_Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2-stabilized long non-coding RNA Taurine up-regulated gene 1 (TUG1) promotes cisplatin-resistance of colorectal cancer via modulating autophagy. 35089636_Insulin-like growth factor II-producing colonic carcinoma presenting with non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia: An autopsy report revealing neuroendocrine differentiation in the metastatic foci and literature review. 35092501_The analysis of N6-methyladenosine regulators impacting the immune infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35129592_IGF2BP2 maybe a novel prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 35163144_Deep Resequencing of 9 Candidate Genes Identifies a Role for ARAP1 and IGF2BP2 in Modulating Insulin Secretion Adjusted for Insulin Resistance in Obese Southern Europeans. 35173309_LINC01021 maintains tumorigenicity by enhancing N6-methyladenosine reader IMP2 dependent stabilization of MSX1 and JARID2: implication in colorectal cancer. 35318440_m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 promotes tumor cell proliferation by destabilizing IGF2BPs target genes and worsens the prognosis of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. 35446451_The ''m6A writer'' METTL3 and the ''m6A reader'' IGF2BP2 regulate cutaneous T-cell lymphomas progression via CDKN2A. 35502827_N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) reader IGF2BP2 promotes gastric cancer progression via targeting SIRT1. 35526050_LncRNA-PACERR induces pro-tumour macrophages via interacting with miR-671-3p and m6A-reader IGF2BP2 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 35561648_Circ_0000775 promotes the migration, invasion and EMT of hepatic carcinoma cells by recruiting IGF2BP2 to stabilize CDC27. 35706003_The role of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding proteins in female reproductive pathophysiology. 35707044_lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 Facilitates Tumorigenesis and Ferroptosis Resistance through SLC7A11 by IGF2BP2 Pathway in Melanoma. 35763110_N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) reader IGF2BP2 stabilizes HK2 stability to accelerate the Warburg effect of oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. 35894142_Decreased RNAbinding protein IGF2BP2 downregulates NT5DC2, which suppresses cell proliferation, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in diffuse large Bcell lymphoma cells by regulating the p53 signaling pathway. 35907138_Circular RNA circPBX3 promotes cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells via interacting with IGF2BP2 to stabilize ATP7A mRNA expression. 35919812_Cytoplasmic IGF2BP2 Protein Expression in Human Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Prognostic and Clinical Implications. 36281789_IGF2BP2 serves as a core m6A regulator in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 36416324_Construction and clinical evaluation of N6-methyladenosine risk signature of YTHDC2, IGF2BP2, and HNRNPC in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000033581 |
Igf2bp2 |
516.297585 |
0.3350290669 |
-1.577642 |
0.095282222 |
271.448769 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000054847833293958450611004290966602633303788370801066985396510010503397043710068450530884451640107007069550557044262742317993956365086126569179817854361247767003284536713181296363472938537597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014277848666998706997283401302132168253674112232165438149619461848042107107144565438511207874358260218014641202345321198828944413811809395016903638259836428758831061713863164186477661132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
260.1465223 |
17.4115593 |
781.5529762 |
36.1542210 |
| ENSG00000074219 |
8463 |
TEAD2 |
protein_coding |
Q15562 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor which plays a key role in the Hippo signaling pathway, a pathway involved in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein MST1/MST2, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Acts by mediating gene expression of YAP1 and WWTR1/TAZ, thereby regulating cell proliferation, migration and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction. Binds to the SPH and GT-IIC 'enhansons' (5'-GTGGAATGT-3'). May be involved in the gene regulation of neural development. Binds to the M-CAT motif. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18579750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19324877}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables several functions, including DNA-binding transcription factor activity; disordered domain specific binding activity; and transcription coactivator binding activity. Involved in hippo signaling; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; and protein-containing complex assembly. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. Part of TEAD-YAP complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8463; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; TEAD-YAP complex [GO:0140552]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; disordered domain specific binding [GO:0097718]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; embryonic heart tube morphogenesis [GO:0003143]; embryonic organ development [GO:0048568]; hippo signaling [GO:0035329]; lateral mesoderm development [GO:0048368]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; notochord development [GO:0030903]; paraxial mesoderm development [GO:0048339]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000736]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368466_structural and functional analysis of the YAP-binding domain of human TEAD2 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 25995450_TAZ negatively regulate transcription of DeltaNp63 through TEAD1,2,3 and 4 transcription factors. 31485614_the increased cisplatin sensitivity induced by miR608 overexpression was reversed by transfection of TEAD2 in nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. The present data suggested that miR608 may represent a novel candidate biomarker for the evaluation of cisplatin sensitivity in patients with NSCLC. 32087359_Multiple-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) is an inborn disorder of fatty acid and amino acid metabolism caused by mutations in the genes encoding for human electron transfer flavoprotein (ETF) and its partner electron transfer flavoprotein:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETF:QO). Conformational analysis of the riboflavin-responsive ETF:QO-p.Pro456Leu variant associated with mild multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. 32323824_TEAD2 as a novel prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000030796 |
Tead2 |
11.256168 |
0.2083508991 |
-2.262913 |
0.650649189 |
12.109757 |
0.00050158660337489241291819563883791488478891551494598388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001231235367672278702144694761955179274082183837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6847157 |
1.5899446 |
18.1865661 |
4.1165457 |
| ENSG00000074416 |
11343 |
MGLL |
protein_coding |
Q99685 |
FUNCTION: Converts monoacylglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol (PubMed:19029917, PubMed:20079333, PubMed:21049984, PubMed:22969151, PubMed:24368842). Hydrolyzes the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol, and thereby contributes to the regulation of endocannabinoid signaling, nociperception and perception of pain (PubMed:19029917, PubMed:20079333, PubMed:21049984, PubMed:22969151, PubMed:24368842). Regulates the levels of fatty acids that serve as signaling molecules and promote cancer cell migration, invasion and tumor growth (PubMed:20079333). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19029917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20079333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21049984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22969151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24368842}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Hydrolase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Nitration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine esterase |
PATHWAY: Glycerolipid metabolism; triacylglycerol degradation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35678}. |
This gene encodes a serine hydrolase of the AB hydrolase superfamily that catalyzes the conversion of monoacylglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol. The encoded protein plays a critical role in several physiological processes including pain and nociperception through hydrolysis of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Expression of this gene may play a role in cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:11343; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; acylglycerol lipase activity [GO:0047372]; lipase activity [GO:0016298]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; acylglycerol catabolic process [GO:0046464]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006633]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; monoacylglycerol catabolic process [GO:0052651]; regulation of endocannabinoid signaling pathway [GO:2000124]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; triglyceride catabolic process [GO:0019433] |
17621164_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17621164_not associated with susceptibility to alcoholism in a Japanese population. 18452279_full proteomic characterization of hMGL was carried out, which showed (1) an absence of intramolecular disulfide bridges in the functional, recombinant enzyme and (2) the post-translational removal of the enzyme's N-terminal methionine 18721756_Identification of amino acids critical to the catalytic activity 19014633_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19233690_Gene Ontology analysis indicated a significant alteration of oxygen transport (increased hemoglobin gene expression) and lipid metabolism [including monoglyceride lipase and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) gene]. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19957260_An apolar helix covering the active site also gives structural insight into the amphitropic character of MAGL, and likely explains how MAGL interacts with membranes to recruit its substrate. 19962385_MGL shares the classic fold of the alpha/beta hydrolase family but depicts an unusually large hydrophobic occluded tunnel with a highly flexible lid at its entry and the catalytic triad buried at its end. 20079333_Study shows that monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) is highly expressed in aggressive cancer cells and primary tumors; it regulates a fatty acid network enriched in oncogenic signaling lipids that promotes migration, invasion, survival, and tumor growth. 20464001_Identification of an active site hydrogen bond network in human monoacylglycerol lipase. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20855465_Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is the most abundant endocannabinoid in the brain and is believed to be hydrolyzed primarily by serine hydrolase monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) in a transgenic mouse model with targeted disruption of MAGL. 20976246_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21118518_One interval in the FAAH promoter and three intervals in the MGLL gene were associated with high BMI. 21308848_Data present a high-resolution structure of a ligand-bound, soluble form of human monoglyceride lipase. 21543155_High MAGL is associated with colorectal cancer. 21802006_MAGL is elevated in androgen-independent versus androgen-dependent human prostate cancer cell lines, and pharmacological or RNA-interference disruption of this enzyme impairs prostate cancer aggressiveness. 22349814_results suggest that MGL plays a negative regulatory role in phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt signaling and tumor cell growth 22664939_No association was found between our inflammatory bowel disease cohort and the candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms for MGL (CD/HC: P=0.37 and UC/HC: P=0.25). 22827915_MGL expression declines after peaking in infancy. 23455058_Data indicate that N,N-dimethyl-5-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-2H-tetrazole-2-carboxamide inhibited monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) with IC50 0.028 muM. 23553709_MGL interaction with a phospholipid membrane bilayer induces regional changes in the enzyme's conformation that favor its recruiting lipophilic substrate from membrane stores to the active site resulting in enhanced MGL catalytic activity. 24368842_Mutation of Cys242 was also found to impair inhibition of monoacylglycerol lipase. 24593280_In obese humans, FAAH or MGL activity in adipocytes is not affected by diabetes, dyslipidaemia or other markers of metabolic dysfunction. 24616451_In subcutaneous adipose tissue, DAGL-a mRNA was upregulated and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) mRNAs were down-regulated in obese subjects, but the diets had no influence. 24633487_role of monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) in the cancer progress 25078047_Molecular dynamics and nudged elastic band simulations were used to explore the conformational transition pathway of the helix alpha4 of human monoacylglycerol lipase. 25120746_Our findings establish that MAGL promotes metastases in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 25636199_The study identified monoacylglycerol lipase as a YAP transcriptional target and an inhibitor of anchorage-dependent cell growth. 26000748_Monoacylglycerol lipase sulfenylation might act as an intrinsic neuroprotective mechanism by potentiating 2-AG signaling at CB1 receptors. 26555264_The data highlight specific inter-residue interactions within hMGL 26595473_there was evidence that MGLL rs604300 genotype interacts with early life adversity to predict threat-related basolateral amygdala habituation, a neural phenotype linked to the endocannabinoid system and addiction 26948343_the presence and differential distribution of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoglyceride lipase (MGLL) in relation to CB1 during the maturation of human oocytes, was investigated. 26997225_This study unravels a novel mechanism of SND1 function and identifies MGLL as a unique tumor suppressor for HCC. MGLL might function as a homeostatic regulator of Akt restraining its activation. 27366945_MGLL may have a role in progression of gastrointestinal stromal tumors 27767105_RNA interference, specific pharmacological inhibitor JZL-184 and gene knock-in of MAGL were utilized to investigate the effects of MAGL on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. MAGL played important roles in both proliferation and invasion of HCC cells. 27884159_the upregulation of MAGL in hepatocellular carcinoma cells promoted cell growth and invasiveness abilities, and mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition 28088576_we clarify the key role of Phe159 and Ile179, two conserved residues within the lid domain, in regulating substrate specificity in MAGL. We conclude by proposing that other structurally related lipases may share this lid-domain-mediated mechanism for substrate specificity. 28213089_This review summarizes the basics of monoglyceride metabolism and provides an overview on the therapeutic potential of MGL. [Review] 29379013_Using a multimethod approach, the authors show that the dynamically relevant Trp-289 and Leu-232 residues serve as communication hubs within an allosteric protein network that controls signal propagation to the active site, and thus, regulates active-inactive interconversion of human MGL. 29968710_Study utilizing colorectal cancer patients tissue samples, mouse tumor cell lines and xenograft models identify MGLL as a switch for CB2/TLR4-dependent macrophage activation and provide potential targets for cancer therapy. 30978461_Low mRNA expression and activity of monoacylglycerol lipase in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells 31357777_overexpression of MAGL inhibits the proliferation of MHCC97H hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vivo, and its mechanism may be associated to the release of inflammatory factors from tumor-associated macrophages 31695165_Brain structural changes in cannabis dependence: association with MAGL. 31734989_The expression level of MAGL has positive correlation with the malignant degree in hepatocellular carcinoma patients, and negative correlation with prognosis 32483456_Dysregulated expression of monoacylglycerol lipase is a marker for anti-diabetic drug metformin-targeted therapy to correct impaired neurogenesis and spatial memory in Alzheimer's disease. 32532977_ARS2/MAGL signaling in glioblastoma stem cells promotes self-renewal and M2-like polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. 33116203_Conformational gating, dynamics and allostery in human monoacylglycerol lipase. 33973101_Research progress on FASN and MGLL in the regulation of abnormal lipid metabolism and the relationship between tumor invasion and metastasis. 34657876_Decreased serum levels of glycerol-3- phosphate dehydrogenase 1 and monoacylglycerol lipase act as diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000033174 |
Mgll |
193.432428 |
6.3369363946 |
2.663786 |
0.212839053 |
149.014337 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000028471260722825952600612064248257353152451797106912477996371915235260667588643655721383795599577215540421093464829027652740478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000004169006034413799795972244902338231355390327283629795840987390383481481378122607922250605211322849186217354144901037216186523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
285.9530789 |
84.1757283 |
46.2224505 |
10.0294825 |
| ENSG00000074590 |
9891 |
NUAK1 |
protein_coding |
O60285 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in various processes such as cell adhesion, regulation of cell ploidy and senescence, cell proliferation and tumor progression. Phosphorylates ATM, CASP6, LATS1, PPP1R12A and p53/TP53. Acts as a regulator of cellular senescence and cellular ploidy by mediating phosphorylation of 'Ser-464' of LATS1, thereby controlling its stability. Controls cell adhesion by regulating activity of the myosin protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) complex. Acts by mediating phosphorylation of PPP1R12A subunit of myosin PP1: phosphorylated PPP1R12A then interacts with 14-3-3, leading to reduced dephosphorylation of myosin MLC2 by myosin PP1. May be involved in DNA damage response: phosphorylates p53/TP53 at 'Ser-15' and 'Ser-392' and is recruited to the CDKN1A/WAF1 promoter to participate in transcription activation by p53/TP53. May also act as a tumor malignancy-associated factor by promoting tumor invasion and metastasis under regulation and phosphorylation by AKT1. Suppresses Fas-induced apoptosis by mediating phosphorylation of CASP6, thereby suppressing the activation of the caspase and the subsequent cleavage of CFLAR. Regulates UV radiation-induced DNA damage response mediated by CDKN1A. In association with STK11, phosphorylates CDKN1A in response to UV radiation and contributes to its degradation which is necessary for optimal DNA repair (PubMed:25329316). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12409306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15273717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19927127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20354225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21317932, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25329316}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables p53 binding activity and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including protein phosphorylation; regulation of cellular senescence; and regulation of myosin-light-chain-phosphatase activity. Located in cytoplasm; microtubule cytoskeleton; and nuclear lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9891; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000772]; regulation of myosin-light-chain-phosphatase activity [GO:0035507]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796] |
12409306_Data suggest that a novel AMPK family member, ARK5, is the tumor cell survival factor activated by Akt and acts as an ATM kinase under the conditions of nutrient starvation. 13679856_ARK5 suppresses the apoptosis induced by nutrient starvation and death receptors via inhibition of caspase 8 activation. 15060171_Results report that a novel AMPK catalytic subunit family member, ARK5, plays a key role in tumor malignancy downstream of Akt. 15273717_ARK5 negatively regulates procaspase-6 by phosphorylation at Ser257, leading to resistance to the FasL/Fas system. 15354411_overexpression of ARK5 is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis 16044163_ARK5 is a transcriptional target of the Large-MAF family through MARE sequence and that ARK5 may in part mediate the aggressive phenotype associated with c-MAF- and MAFB-expressing myelomas 16488889_NDR2 is an upstream kinase of ARK5 that plays an essential role in tumor progression through ARK5 18254724_NUAK1 and MARK4 are substrates of USP9X 19927127_Cells that constitutively express NUAK1 suffer gross aneuploidies and show diminished expression of the genomic stability regulator LATS1, whereas depletion of NUAK1 with shRNA exerts opposite effects. 20354225_the LKB1-NUAK pathway has roles in controlling myosin phosphatase complexes and cell adhesion 20602751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20978832_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21317932_A novel role for NUAK1 in LKB1-related signaling pathways; NUAK1 can regulate cell proliferation and exert tumor suppression through direct interaction with p53. 21750233_NUAK1 and PPP1CC are identified as positional candidate loci for skeletal muscle strength phenotypes. 22105900_ARK5 enhanced the invasive and metastatic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells under regulation by Akt. 22460906_in human and murine cell lines, oncogenic levels of MYC establish a dependence on AMPK-related kinase 5 for maintaining metabolic homeostasis and for cell survival; ARK5 is an upstream regulator of AMPK and limits protein synthesis via inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin 1 (mTORC1) signalling pathway 23063350_ARK5 can promote glioma cell invasion by regulating cytoskeleton rearrangement and matrix metalloproteinase activation. 23215946_High NUAK1 expression correlates with poor prognosis and involved in human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells migration and invasion. 23516026_Overexpression of ARK5 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 23934065_We demonstrate that miR-211 contributes to melanoma adhesion by directly targeting a gene, NUAK1. 24785407_Expression of NUAK1 is controlled by cyclin-dependent kinase, PLK1, and the SCFbetaTrCP (Skp, Cullin and F-boxbetaTrCP) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. 24943992_Overexpression of NUAK1 is associated with disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. 25242509_Data indicate that miR-96 suppresses the expression of (nua) kinase family 1 (NUAK1) by targeting its 3' untranslated region (3' UTR). 25412236_Results indicate that NUAK1 is excessively expressed in NSCLC and plays important roles in NSCLC invasion. 26151663_ARK5 was upregulated in ovarian cancer tissues, promoted epithelialmesenchymal transition and inhibited miR-1181 expression in ovarian cancer cells 26255969_MiR-145 functions as a tumor suppressor targeting NUAK1 in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 26882562_High NUAK1 expression are correlated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition induction in head and neck cancer. 27126361_ARK5 confers doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 27720485_Nuak1 downregulation decreases tau levels in a human cell line. 28662499_The elevated ARK5 expression was closely associated with cancer metastasis and patient survival, and it seemed to function in Gastric Cancer cells migration and invasion via epithelial-mesenchymal transition alteration, together with the alteration of the mTOR/p70S6k signals, Slug and SIP1. 29106388_High NUAK1 expression is associated with cancer. 29500295_This work identifies NUAK1 as a key facilitator of the adaptive antioxidant response that is associated with aggressive disease and worse outcome in human colorectal cancer. Our data suggest that transient NUAK1 inhibition may provide a safe and effective means for treatment of human colorectal cancer via disruption of intrinsic antioxidant defenses 29566768_Confirmation studies (step 4) provided additional evidence that NUAK1 and STK11 have PTEN-SSL patterns of activity. Consistent with PTEN-SSL status, inhibition of the NUAK1 protein kinase by the small molecule drug HTH-01-015 selectively impaired viability in multiple PTEN-deficient breast cancer cell lines, while mutations affecting STK11 and PTEN were largely mutually exclusive across large pan-cancer data sets. 29575772_the impaired cell migration and invasion by SNHG1 siRNA could be rescued by cotransfection of miR-145-5p in CNE and HNE-1 cells. LncRNA SNHG1 promoted the expression of NUAK1 by down-regulating miR-145-5p and thus promoted the aggressiveness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through AKT signalling pathway and induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). 30121842_NUAK1 is excessively expressed in NPC and may serve as a potential predictor of prognosis for NPC. 30720082_The current study demonstrated that ARK5 is a critical factor involved in SKOV3 cell invasion and ARK5 increases invasive potential by promoting EMT and activating the AktmTORMMPs pathway. 31090959_Identification of a nuclear localization signal and importin beta members mediating NUAK1 nuclear import inhibited by oxidative stress. 32418991_miR-622 is a novel potential biomarker of breast carcinoma and impairs motility of breast cancer cells through targeting NUAK1 kinase. 33000197_AMPactivated protein kinase family member 5 is an independent prognostic indicator of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas. 34097192_LINC00922 promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT process of liver cancer cells by regulating miR-424-5p/ARK5. 35194062_Loss of LKB1-NUAK1 signalling enhances NF-kappaB activity in a spheroid model of high-grade serous ovarian cancer. 36255069_Circ_0003998 upregulates ARK5 expression to elevate 5-Fluorouracil resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through binding to miR-513a-5p. |
ENSMUSG00000020032 |
Nuak1 |
28.476484 |
3.1374982087 |
1.649615 |
0.323985041 |
26.559071 |
0.00000025560174405632553290451431000918081082318167318589985370635986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000965334007391238700743901768319688017072621732950210571289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.3488680 |
8.6769493 |
13.9013259 |
2.2720644 |
| ENSG00000074660 |
8578 |
SCARF1 |
protein_coding |
Q14162 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the binding and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein (Ac-LDL). Mediates heterophilic interactions, suggesting a function as adhesion protein. Plays a role in the regulation of neurite-like outgrowth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a scavenger receptor that is expressed in endothelial cells. It regulates the uptake of chemically modified low density lipoproteins, including acetylated low density lipoprotein (Ac-LDL), and it may be involved in atherogenesis. This gene is regulated by the transcription factors ZNF444/EZF-2 and SP1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013]. |
hsa:8578; |
endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; low-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0030169]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cholesterol catabolic process [GO:0006707]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; neuron remodeling [GO:0016322]; positive regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048680]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898] |
11978792_Characterization of the gene and its regulation by a novel transcription factor, endothelial zinc protein-2 12154095_SRECI binds to SRECII and has a similar tissue distribution pattern 21190681_GP2 is a binding partner of the scavenger receptor expressed on endothelial cells I (SREC-I) but not of SR-AI and SR-BI. Dendritic cells express SREC-I and also bind and internalize GP2. 24788600_In several assay systems this type F-scavenger receptor, termed SREC-I, bound to cell wall techoic acid in a charge dependent manner and mediated adhesion to nasal epithelial cells in vitro. 25155057_These studies in addition to our earlier findings showed SREC-I to play a primary role in chaperone-associated antigen uptake both through cross priming of MHC class I molecules and entry into the class II pathway. 25641411_Scavenger receptor SREC-I promotes double stranded RNA-mediated TLR3 activation in human monocytes 29242513_SCARF-1 promotes adhesion of CD4(+) T cells to human hepatic sinusoidal endothelium under conditions of shear stress 32296440_Molecular and Cellular Interactions of Scavenger Receptor SR-F1 With Complement C1q Provide Insights Into Its Role in the Clearance of Apoptotic Cells. 34236384_The Role of SREC- in Innate Immunity to Aspergillus fumigatus Keratitis. 35082161_SCARF1-Induced Efferocytosis Plays an Immunomodulatory Role in Humans, and Autoantibodies Targeting SCARF1 Are Produced in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. |
ENSMUSG00000038188 |
Scarf1 |
42.190582 |
0.4576795999 |
-1.127590 |
0.296059890 |
14.376851 |
0.00014963051885574733660712321015040515703731216490268707275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000400436616034375799950267849069973635778296738862991333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.9826964 |
8.0081483 |
53.8897017 |
12.7274092 |
| ENSG00000074800 |
2023 |
ENO1 |
protein_coding |
P06733 |
FUNCTION: Glycolytic enzyme the catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate (PubMed:29775581, PubMed:1369209). In addition to glycolysis, involved in various processes such as growth control, hypoxia tolerance and allergic responses (PubMed:2005901, PubMed:10802057, PubMed:12666133, PubMed:29775581). May also function in the intravascular and pericellular fibrinolytic system due to its ability to serve as a receptor and activator of plasminogen on the cell surface of several cell-types such as leukocytes and neurons (PubMed:12666133). Stimulates immunoglobulin production (PubMed:1369209). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10802057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12666133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1369209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2005901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29775581}.; FUNCTION: MBP1 binds to the myc promoter and acts as a transcriptional repressor. May be a tumor suppressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10082554}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Glycolysis;Hydroxylation;Isopeptide bond;Lyase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Plasminogen activation;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; pyruvate from D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate: step 4/5. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:1369209}. |
This gene encodes alpha-enolase, one of three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. Each isoenzyme is a homodimer composed of 2 alpha, 2 gamma, or 2 beta subunits, and functions as a glycolytic enzyme. Alpha-enolase in addition, functions as a structural lens protein (tau-crystallin) in the monomeric form. Alternative splicing of this gene results in a shorter isoform that has been shown to bind to the c-myc promoter and function as a tumor suppressor. Several pseudogenes have been identified, including one on the long arm of chromosome 1. Alpha-enolase has also been identified as an autoantigen in Hashimoto encephalopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:2023; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; M band [GO:0031430]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear outer membrane [GO:0005640]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phosphopyruvate hydratase complex [GO:0000015]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphopyruvate hydratase activity [GO:0004634]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; canonical glycolysis [GO:0061621]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1903298]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001171]; positive regulation of muscle contraction [GO:0045933]; positive regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010756]; response to virus [GO:0009615] |
12297304_Proteomic analysis of human brain identifies alpha-enolase as a novel autoantigen in Hashimoto's encephalopathy. 12787059_A target of excess protein nitration in Alzheimer disease (AD) brain, providing evidence of the importance of oxidative stress in AD progression 12847697_The alpha-enolase protein is the target protein of serum anti-endothelial antibody in Behcet's disease patients. 15324934_antibodies against human alpha-enolase target antigens in retinal ganglion cells and inner nuclear layer cells and induce the apoptotic death of sensitive cells in rat retinal explants 15805119_Results suggest a novel role of c-myc promoter-binding protein 1 for suppression of prostate cancer cell growth by regulating the MEK5-mediated signaling pathway. 16359544_ENO1 has tumour suppressor activity and high level of ENO1 expression has growth inhibitory effects 16762917_Depletion of MBP-1 in prostate cancer cells perturbs cell proliferation by inhibiting cyclin A and cyclin B1 expression. 17284257_Our results indicate that differential subcellular localization of ENO1 products may be closely related to carcinogenesis of the oral epithelium 17387692_alpha-crystallin B, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and alpha-enolase identified as significantly S-glutathionylated in Alzheimer's disease infeior parietal lobule 17996313_These findings further support the distinct roles of alpha-enolase and its MBP-1 variant in maintaining cell homeostasis. Moreover, these data suggest a novel function for NS1-BP in the control of cell proliferation. 17996313_alpha-enolase and MBP-1 associate with the kelch protein NS1-BP. c-Myc gene transcriptional repression exerted by MBP-1 is enhanced by NS1-BP. 18033204_Enolase on the surface of cells may be a receptor for plasminogen. The enolase/plasminogen (plasmin) system is one of the mechanisms facilitating the invasiveness of pathogens and it plays a role in myogenesis and in the development of tumor tissues. 18070418_TGF-beta1-induced growth arrest was associated with notable downregulation of the myc-binding protein-1 (MBP-1). 18490439_These results indicate that the activated Notch1 receptor and alpha-enolase or MBP-1 cooperate in controlling c-myc expression through binding the YY1 response element of the c-myc promoter to regulate tumorigenesis. 18560153_Crystal structure of ENO1 is presented at 2.2 A resolution. Despite its high sequence similarity to other enolases, the ENO1 structure exhibits distinct surface properties, explaining its various activities, including plasmin(ogen) and DNA binding. 18668562_Alpha-enolase was citrullinated in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. 18682748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18691435_demonstration that IL8, DES and ENO1 act as the central elements in colon cancer susceptibility, and protein biosynthesis and the ribosome-associated function categories largely account for the colon cancer tumuorigenesis 18813785_HIF-1alpha-regulated glycolysis module is closely related to the aggressive phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma, and ENO1, a glycolysis module gene, might have a role in preventing metastasis 19182206_An important mechanism of inflammatory cell invasion mediated by increased cell-surface expression of ENO-1. 19255486_Crystals of alpha-Enolase from human liver were obtained by the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method and diffracted to 2.5 A resolution. 19339807_fatty acid-binding protein-5, squamous cell carcinoma antigens 2, alpha-enolase, annexin II, apolipoprotein A-I and albumin were detected at a high level in Atopic dermatitis skin lesions, but scarcely in the normal controls 19425054_Results indicate that alpha-enolase elicits a PDAC-specific, integrated humoral and cellular response (proliferative response by T-cells). 19433310_Isozymes alpha- and gamma-enolases were identified as targets for cathepsin X. 19655245_Inhibition of ENO-1 expression significantly augmented 4-OHT cytotoxicity in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. 19795461_Association of upregulated ACLY and ENO1 expression by chi square for all probe sets (reporters) combined and correlation for numbers of probe sets indicating shared upregulation of these genes. 19846662_These results suggest that MBP-1-suppressed COX-2 expression plays an important role in the inhibition of growth and progression of gastric cancer. 20181627_melanoma antigen expressed in G361, a representative melanoma cell line/ reacted with autoantibodies in patient sera 20435467_a prognostic role of ENO1 overexpression was demonstrated in head and neck cancer and ENO1-mediated promotion of cell transformation and invasion partly via induced CCL20 expression. 20498720_SEDLIN is present in the nucleus, forms homodimers and that SEDT-associated mutations cause a loss of interaction with the transcription factors MBP1, PITX1 and SF1. 20721957_Overexpression of ENO1 is associated with recurrences in chordomas. 20849415_novel transcript was alternatively transcribed from intron III of the ENO1 gene and was feasible for MBP-1 production 20864512_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20886042_Loss of nuclear MBP-1 expression is associated with the progression of invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 21159241_The elevated levels of ENO1 protein in the tumor tissues and the plasma samples from NSCLC patients indicate ENO1 may be a candidate biomarker of lung cancer. 21360494_These results extend, confirm, and generalize the evidence supporting the specificity of the anti-CEP-1 antibody-positive subgroup of patients with rheumatoid arthritis among anti-CCP antibody-positive patients with RA. 21640210_glomerular alpha-enolase is a target antigen of autoimmunity in human MGN. Circulating anti alpha-enolase auto-antibodies can be detected in sera of a significant quota of membranous glomerulonephritis patients. 21751384_Silencing of ENO1 resulted in growth inhibition and cell cycle arrest of gastric cancer cells. 21839816_Data show six differentially expressed proteins were identified as HSP70, PPIA and alpha-Enolase (up-regulated) S100-A9, PIMT and beta-5 tubulin (down-regulated), most of which had been shown to play a potential role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 21950004_ENO1 over expression may play a important role in cell proliferation and progression of nasopharyngeal cancer. 22272336_Data show that ENOA, PARK7 and Beta-actin are proper reference standards in obesity studies based on omental fat. 22551201_Increased citrullination of Arg9 in ENO1 is associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Alzheimer's disease. 22577163_results indicate that C-peptide has the capacity to activate alpha-enolase through a specific interaction between E27 of the peptide and K434 of the enzyme 22623332_ENO1-positive monocytes and macrophages are found in the inflamed synovium from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 22895339_ENO1 is a passenger locus homozygously deleted as part of the 1p36 locus in glioblastoma and inhibition of ENO2 is selectively lethal to ENO1 deleted tumor cells, but not normal non-cancerous cells. 23113677_plasma levels are significantly higher in renal cell carcinoma patients than in controls 23131860_results indicate that Streptococcus sanguinis infection and the sera of Behcet's disease patients with active disease are inflammatory stimuli that can induce membranous alpha-enolase expression in endothelial cells 23381546_The reduction in enolase-1 expression significantly decreases the response to hypoxia and enhances the sensitivity of the cells to radiation therapy. 23676977_ENO1 overexpression can inhibit EMT in vitro by suppressing ERK1/2 phosphorylation 23894455_surface alpha-enolase promotes extracellular matrix degradation and invasion of cancer cells and that targeting surface alpha-enolase is a promising approach to suppress tumor metastasis. 24099319_Citrullination of ENO1 is associated with neoplasms. 24628430_the differential association of ENO-1 with caveolar proteins regulates ENO-1 subcellular localization and, consequently, ENO-1-dependent cell migration and invasion. 24650096_Overexpression of ENO1 is associated with glioma progression. 24790181_These data show a multiantibody composition in lupus nephritis, where IgG2 autoantibodies against alpha-enolase and annexin AI predominate in the glomerulus and can be detected in serum. 24841372_Our data suggest that ENO1 was upregulated by CagA protein thereby providing a novel mechanism underlying H. pylori-mediated gastric diseases. 24984566_Using shotgun proteomics together with western blotting and ELISA, we identify sputum ENO1 as a biomarker candidate for lung cancer 24998431_the results indicated that the combination of ENO1 and CYPA can serve as a potential molecular marker for the early detection of NPC. 25068682_Isotypes of anti-citrullinated fibrinogen and alpha-enolase can be found in the serum of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis of all onset types. 25171719_alpha-enolase binds plasminogen and modulates its activation, it is plausible to speculate the association of the increase in alpha-enolase secretion by infected hepatic cells with the haemostatic dysfunction observed in dengue patients 25805497_STIM1/ORAI1-mediated Ca2+ influx regulates enolase-1 exteriorization in cancer cells. 25860938_High ENO1 expression is associated with invasiveness of pancreatic cancer. 25887760_This study showed that ENO1 is responsible for non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and metastasis 25910678_The association of ENO1 and GPI with postthaw sperm viability and motility was confirmed using Pearson's linear correlation. ENO1 and GPI can be used as markers of human sperm freezability before starting the cryopreservation procedure. 25918939_tRK1 forms a complex with human enolases and interacts with tRK1 and human pre-lysyl-tRNA synthetase (preKARS2) 25944790_alpha-Enolase increases after injury and may activate pulmonary endothelial cells and prime PMNs through plasmin activity and PAR-2 activation 25951350_In this study, ENO1 silencing significantly reduced cell glycolysis, proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro, as well as tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo by modulating p85 suppression. 25978602_Systems biology approach reveals possible evolutionarily conserved moonlighting functions for enolase 26024773_ENO1 is an independent prognostic factor, significantly correlated with overall survival of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma patients. 26037892_Low ENO1 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 26097998_ENO1 induces gene expression, lactate production, cell proliferation and migration and can be negatively regulated by FBXW7 at the posttranslational level. 26144282_Data suggest that endoplasmic reticulum stress up-regulates ENO1/MBP1 expression through the AKT/PERK/eIF2a signaling axis in both breast cancer cells and non-tumor cells. 26432922_An immune-modulatory role has been proposed for surface alpha-enolase and our findings of decreased expression suggest that deficits in surface alpha-enolase merit investigation in the context of immune dysfunction during ageing and vascular disease 26734996_High ENO1 expression is associated with cancer. 26856295_Our findings showed that both S100beta and NSE levels similarly increased during CPB and immediately after CPB during sevoflurane and propofol based anesthesia. 26882120_ENO1 was demonstrated to be up-regulated by HIF-1alpha in retinal pigment epithelial cells in response to hypoxia, without influencing VEGF secretion. 27025255_ENO1 is able to activate in vitro the CD14-dependent TLR4 pathway on monocytes involving a dual mechanism firstly pro-inflammatory and secondly anti-inflammatory. 27210467_comparing the T cell receptor repertoire of ENO1-specific peripheral and infiltrating tumor T cells from the same patient suggests that ENO1-specific T cells, despite having a different functional profile, can recirculate from the tumor to the periphery. 27996156_ENO1 is a potent promoter of colorectal cancer genesis and metastasis at least in part though regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway. 28086938_ENO1 promotes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) cells cell survival, migration, and metastasis through cooperation with integrins and uPAR 28415822_The study provides solid evidence that there is the interaction between GRN A and ENO1 and the interaction is responsible for the effects of GRN A on glucose uptake as well as cancer cell migration and invasion. 28456790_ENO1 can elicit humoral immune response in NSCLC and its autoantibody has association with the tumorigenesis of NSCLC. Furthermore, these intriguing results suggest the possibility of autoantibody against ENO1 serving as a potential diagnostic biomarker in NSCLC and have implications for defining novel histological determinants of NSCLC. 28548950_ENO1 is a novel biomarker to predict drug resistance and overall prognosis in gastric cancer. 28728510_serum anti-alpha-enolase antibody levels positively correlated with serum whole IgG and 24-hour urine protein and negatively correlated with serum D-dimer level in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 28763860_ENO1 may promote the development of HCC[hepatocellular carcinoma ], possibly by participating in the regulation of the Notch signaling pathway. 28770703_The levels of alpha enolase IgG antibodies correlated with the number of oral ulcers, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and CRP levels. 28824297_Our results suggested that alpha-enolase level was significantly elevated in pancreatic cancer tissues, which was closely associated with pancreatic cancer progression 29080231_The authors found that ENO1 expression was upregulated in the hepatitis B virus-infected liver tissues and cells. Silencing of ENO1 resulted in a significant reduction in hepatitis B virus replication, and this siRNA-mediated reaction also caused the upregulation of expression of type I interferon and downstream interferon-stimulated genes. 29090499_ENO1 is a crucial factor promoting neoplastic transformation exclusively in terminal respiratory unit (TRU) subtype lung adenocarcinomas (ADCs). 29404888_Together these findings suggest a possible mechanism of host invasion by HIV-1 through the CAWLEAQ motif of Nef-mediated regulation of ENO1 and identify a potential therapeutic target for HIV-1 entry at mucosal barriers. 29430682_We propose that ENO1 is a useful indicator of parakeratosis and might have a potential role in cellular TJ barrier function in the epidermis 29465373_Alpha-enolase is a target autoantigen in Behcet's disease, particularly associated with disease activity, mucocutaneous and articular involvement. 29497031_Oncogenic role of WBP2 in glioma was through modulating ENO1 and glycolysis activity via the ENO1-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 29501774_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) was identified to be responsible for Eno-1 methylation. Overexpression of PRMT5 and caveolin-1 enhanced levels of membrane-bound extracellular Eno-1 and, conversely, pharmacological inhibition of PRMT5 attenuated Eno-1 cell-surface localization. 29913409_Elevated ENO1 could promote the proliferation of retinoblastoma cells. 29924389_Evidence for B7-H3 mediating tumor glycolysis, via interacting with ENO1. 29986635_Our data provide strong evidence that alpha-enolase short hairpin RNA interference vector can effectively suppress the proliferation and increase chemosensitivity of MKN45 cells, which may provide a novel gene therapy for gastric cancer. 30242159_regulates the metabolic reprogramming and malignant phenotype of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells in pulmonary arterial hypertension 30518748_A novel lncRNA, TCONS_00006195, represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting enzymatic activity of ENO1. 30541900_Targetting an LncRNA P5848-ENO1 axis inhibits tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30582908_ENO1 enhances gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through the protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway. 30602955_Serum enolase can be considered as a more sensitive and specific marker and used as a sensitive diagnostic or prognostic marker for ischemic related diseases. 30683669_Although several studies have shown that tumors can outcompete T cells for glucose, thus limiting T cell metabolic activity, we report that a down-regulation in the activity of ENOLASE 1, a critical enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, represses glycolytic activity in CD8(+) TILs. 30779465_Reference interval for serum neuron-specific enolase in a large healthy Chinese adult cohort. 30943007_our data revealed that ENO1 plays a novel and protective role in cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury 31138830_Neutrophil Extracellular Traps protein composition is specific for patients with Lupus nephritis and includes methyl-oxidized alphaenolase (methionine sulfoxide 93). 31218757_Enolase1 overexpression regulates the growth of gastric cancer cells and predicts poor survival. 31329371_E6AP and Enolase1 interacted and colocalized more in the cytoplasmic periphery in breast cancer cells and further demonstrated that E6AP also targeted ENO1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation in these cells. 31357775_Serum ENO1 was statistically significant in hepatocellular carcinoma tumor size, tumor metastasis, TNM stage, and Edmondson grade, and the elevated levels of ENO1 had significantly reduced the survival time 31431517_Up-regulated ENO1 promotes the bladder cancer cell growth and proliferation via regulating beta-catenin. 31957179_FGFRL1 affects chemoresistance of small-cell lung cancer by modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway via ENO1. 31957838_Inhibition of alpha-enolase affects the biological activity of breast cancer cells by attenuating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 32238431_An arrestin-1 surface opposite of its interface with photoactivated rhodopsin engages with enolase-1. 32521855_Silencing of ENO1 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells. 32707136_Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 46 promotes tumor metastasis through stabilizing ENO1 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32841760_Experimental validation of influenza A virus matrix protein (M1) interaction with host cellular alpha enolase and pyruvate kinase. 32917235_Alpha-enolase in viral target cells suppresses the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integration. 33067426_Enolase 1 regulates stem cell-like properties in gastric cancer cells by stimulating glycolysis. 33176280_Circular RNA circSEMA5A promotes bladder cancer progression by upregulating ENO1 and SEMA5A expression. 33184263_Exosome-derived ENO1 regulates integrin alpha6beta4 expression and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. 33318144_F. nucleatum targets lncRNA ENO1-IT1 to promote glycolysis and oncogenesis in colorectal cancer. 33628097_Impact of Tissue Enolase 1 Protein Overexpression in Esophageal Cancer Progression. 34035230_Colorectal cancer cell intrinsic fibroblast activation protein alpha binds to Enolase1 and activates NF-kappaB pathway to promote metastasis. 34099892_ENO1 promotes antitumor immunity by destabilizing PD-L1 in NSCLC. 34119259_Significance of serum neuron-specific enolase in transient global amnesia. 34312368_C5aR1-positive neutrophils promote breast cancer glycolysis through WTAP-dependent m6A methylation of ENO1. 34335983_CCDC65 as a new potential tumor suppressor induced by metformin inhibits activation of AKT1 via ubiquitination of ENO1 in gastric cancer. 34547627_Upregulation of alpha enolase (ENO1) crotonylation in colorectal cancer and its promoting effect on cancer cell metastasis. 34863626_Identification of alpha-enolase as a potential immunogenic molecule during allogeneic transplantation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. 35121990_ENO1 suppresses cancer cell ferroptosis by degrading the mRNA of iron regulatory protein 1. 35489746_Expression of ENO1 Is Up-regulated in Low-grade Glioma and Positively Correlated With Meningioma Grade. 35796020_HIF1alpha and MBP1 are associated with the progression of breast cancer cells by repressing betacatenin transcription. 35925486_alpha-Enolase inhibits apoptosis and promotes cell invasion and proliferation of skin cutaneous melanoma. 35945200_Circular RNA circNFKB1 promotes osteoarthritis progression through interacting with ENO1 and sustaining NF-kappaB signaling. 36361568_ENO1 Binds to ApoC3 and Impairs the Proliferation of T Cells via IL-8/STAT3 Pathway in OSCC. |
ENSMUSG00000063524+ENSMUSG00000059040 |
Eno1+Eno1b |
4900.816795 |
2.3717946053 |
1.245979 |
0.025117349 |
2479.757494 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6962.6457849 |
106.0585808 |
2956.8889441 |
35.5320425 |
| ENSG00000074855 |
57719 |
ANO8 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCE9 |
FUNCTION: Does not exhibit calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) activity. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables intracellular calcium activated chloride channel activity. Involved in chloride transport. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57719; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; intracellular calcium activated chloride channel activity [GO:0005229]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
15647853_Human TMEM16H gene, consisting of 18 exons, is located at human chromosome 19p13.11. 31061173_Anoctamin 8 (ANO8) as a key tether in the formation of the Endoplasmic reticulum/Plasma membrane (ER/PM) junctions that is essential for STIM1-STIM1 interaction and STIM1-Orai1 interaction and channel activation at a ER/PM PI(4,5)P2-rich compartment. Ano8 assembles all core Calcium signaling proteins. 32942997_Whole-exome sequencing reveals ANO8 as a genetic risk factor for intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. |
ENSMUSG00000034863 |
Ano8 |
310.504651 |
2.5598536810 |
1.356061 |
0.130974023 |
106.464320 |
0.00000000000000000000000058333352819151943833208499026450506947772785231356129783527924361234348604732247167703462764620780944824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000006248187863647915182950102738446862084429825933175827512369512211666544576615933692664839327335357666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
462.3847069 |
31.8053114 |
181.2971660 |
9.9152893 |
| ENSG00000074964 |
55160 |
ARHGEF10L |
protein_coding |
Q9HCE6 |
FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RHOA, RHOB and RHOC. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16112081}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene belongs to the RhoGEF subfamily of RhoGTPases. Members of this subfamily are activated by specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and are involved in signal transduction. The encoded protein shows cytosolic distribution. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:55160; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; SREBP signaling pathway [GO:0032933] |
16112081_In intact cells, GrinchGEF induced specifically Rho activation and enhanced RhoA-C-specific downstream effects. 18849993_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29979793_Inherited variants in ARHGEF10L and AKAP6, with potential transcriptional regulatory function and association with Epithelial ovarian cancer risk, warrant investigation in independent Epithelial ovarian cancer study populations. 30444969_increased expression of ARHGEF10L stimulates hepatocellular tumorigenesis by activating the RhoA-ROCK1- phospho Ezrin/Radixin/Moesin pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32154766_ARHGEF10L expression regulates cell proliferation and migration in gastric tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000040964 |
Arhgef10l |
101.709390 |
0.4465647028 |
-1.163059 |
0.270009912 |
18.247577 |
0.00001939725637693393166705209396116771358720143325626850128173828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000058849641135363791797068672151382884294434916228055953979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.5246572 |
10.9852304 |
136.4009471 |
17.4489129 |
| ENSG00000075213 |
10371 |
SEMA3A |
protein_coding |
Q14563 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the development of the olfactory system and in neuronal control of puberty. Induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Could serve as a ligand that guides specific growth cones by a motility-inhibiting mechanism. Binds to the complex neuropilin-1/plexin-1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22416012}. |
Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism;Immunoglobulin domain;Kallmann syndrome;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is a member of the semaphorin family and encodes a protein with an Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain, a PSI domain and a Sema domain. This secreted protein can function as either a chemorepulsive agent, inhibiting axonal outgrowth, or as a chemoattractive agent, stimulating the growth of apical dendrites. In both cases, the protein is vital for normal neuronal pattern development. Increased expression of this protein is associated with schizophrenia and is seen in a variety of human tumor cell lines. Also, aberrant release of this protein is associated with the progression of Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10371; |
axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; neuropilin binding [GO:0038191]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; basal dendrite arborization [GO:0150020]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; nerve development [GO:0021675]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; neural crest cell migration involved in autonomic nervous system development [GO:1901166]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; olfactory bulb development [GO:0021772]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001224]; regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048841]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in neuron projection guidance [GO:1902285]; sensory system development [GO:0048880]; sympathetic ganglion development [GO:0061549]; sympathetic nervous system development [GO:0048485]; sympathetic neuron projection extension [GO:0097490]; sympathetic neuron projection guidance [GO:0097491] |
12610647_sema3A is elevated in schizophrenia, and is associated with downregulation of genes involved in synaptic formation and maintenance. 12730958_human glioma cells express class 3 semaphorins and receptors for soluble and membrane-bound semaphorins, suggesting a possible role of the semaphorin/neuropilin system in the interactions of human malignant glioma with the nervous and immune systems. 12879061_during vascular development and experimental angiogenesis, endothelial cells generate autocrine chemorepulsive signals of class 3 semaphorins (SEMA3 proteins) that localize at nascent adhesive sites in spreading endothelial cells 14500350_Breast carcinoma cells support an autocrine pathway involving SEMA3A, plexin-A1, and NP1 that impedes their ability to chemotax. 14656993_new role of Sema-3A in VEGF function mediated by p38 MAPK and suggest that the abrogation of regulated Sema-3A expression is responsible for VEGF-driven growth of tumor cells 15517571_the chemorepulsive signals mediated by Sema 3A play an important role in preventing nerve fibers growth in the umbilical cord and in gestational uterine tissues. 15831706_extensive inhibition of platelet function by Sema3A appears to be mediated, at least in part, through impairment of agonist-induced Rac1-dependent actin rearrangement 16330548_Down-regulation of NRP1 by NRSF overexpression reduced Sema3A activity. It was concluded that NRSF is a transcription factor that silences NRP1 expression and thereby diminishes the Sema3A mediated inhibition of HaCaT keratinocyte migration 16684957_Vascular endothelial growth factor165 (VEGF165) and semaphorin3A (SEMA3A) elicit pro- and antiangiogenic signals respectively in endothelial cells (ECs) by binding to their receptors VEGFR-2, neuropilin-1 and plexin-a. 16791896_In the regulation of the immune response Sema-3A plays a novel role as a modulator of cross-talk between activated dendritic cells and T cells. 17369353_NP-1/Sema-3A-mediated interactions participate in the control of human thymocyte development 17390026_sema3A and sema3C have opposite roles in neoplasm invasiveness and adhesion 17569671_combinations of sema3A and sema3F may be able to inhibit tumor angiogenesis more effectively than single semaphorins. 17607942_This review highlights the effect of Sema3A on axonal growth cones, the intracellular signaling pathways that lead to the cellular effects, and the evidence for collapsin-response-mediator proteins (CRMPs) as a component of the Sema3A signaling cascade. 17631638_Overexpression of SEMA3A may favor malignant activities of tumor cells. Negative clinicopathol correlations suggest that SEMA3A might represent a novel intervention target for pancreatic cancer patients. 17684500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17989695_structural analysis of semaphorin and VEGF binding 18056484_Semaphorin3A (Sema3A) triggers a proapoptotic program that sensitizes leukemic T cells to Fas (CD95)-mediated apoptosis. 18160633_Human neuroma contains increased levels of semaphorin 3A, which surrounds nerve fibers and reduces neurite extension in vitro. 18272814_The sulfated polysaccharides dextran sulfate and fucoidan, but not others, reduce endothelial cell-surface levels of NRP1, NRP2, and to a lesser extent VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, and block the binding and in vitro function of semaphorin3A and VEGF(165). 18625544_The role of semaphorins and their receptors in the progression of lung cancer was studied. 18787945_SEMA3A suppression of tumor cell migration is dependent on alpha2beta1, the expression of which is stimulated in breast tumor cells by an autocrine SEMA3A pathway. 18818766_Sema3A inhibits tumor development from MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cancer cells, but not from MDA-MB-435 or MDA-MB-468. It inhibits tumor angiogenesis in all of the formed tumors. The inhibition is correlated with the expression of NRP-1 of the tumors cells. 18831963_These findings indicate that EGF released from corneal epithelial cells up-regulates the expression of Sema3A in corneal fibroblasts. 19296128_Our findings suggest a role for SEMA3A as an antiangiogenic factor in meningiomas with its decrease being associated with the development of recurrences. 19480842_Data show that consistent with increased NRP-1 expression, cell surface binding of Sema3A increased during M2 differentiation. 19684614_Sema3A as an autocrine signal for neuropilin-1 to promote glioblastoma (GBM) dispersal by modulating substrate adhesion and suggest that targeting Sema3A-neuropilin-1 signaling may limit GBM infiltration. 19817889_Dysregulation of the Sema3A pathway plays a key role in prostatic cancer progression. 19855168_NRP2 is necessary to trigger Sema3A-induced glioma cell repulsion and attraction. 19886821_Results demonstrate the critical role of Galectin-1 and Sema-3A in mesenchymal stem cell functions and may open new perspectives in the understanding and treatment of various immune and neoplastic disorders. 19957197_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19957197_neither Sema3A nor Sema4D likely influence the susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease 20051117_In degenerate intervertebral disc samples, sema3A expression decreased significantly 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20382125_these findings indicate that semaphorin 3A released from corneal fibroblasts may play an important role in the regulation of intercellular communication between corneal epithelial cells as well as in the maintenance of corneal structure and function. 20655307_incubation of breast tumor cells with recombinant Sema3A rapidly increased eIF4E activity, RhoA protein levels, and RhoA activity; Sema3A impedes breast tumor cell migration in part by stimulating RhoA 21205984_Both systemic and tumor-targeted delivery of SEMA3A inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth in multiple mouse models; moreover, SEMA3A inhibits the metastatic spreading from primary tumors. 21656899_SEMA3A expression was upregulated in the aganglionic smooth muscle layer of the colon in some patients with HSCR and our data suggest that increased SEMA3A expression may be a risk factor for HSCR pathology 21784300_We found no genome-wide statistically significant associations but identified several plausible candidate genes among findings at p |
ENSMUSG00000028883 |
Sema3a |
29.238055 |
2.3006876104 |
1.202065 |
0.339258429 |
12.593085 |
0.00038717647783202718174758172331451078207464888691902160644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000970406658651846000876450837324682652251794934272766113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.4423128 |
7.6091427 |
16.9066540 |
2.5970341 |
| ENSG00000075340 |
119 |
ADD2 |
protein_coding |
P35612 |
FUNCTION: Membrane-cytoskeleton-associated protein that promotes the assembly of the spectrin-actin network. Binds to the erythrocyte membrane receptor SLC2A1/GLUT1 and may therefore provide a link between the spectrin cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. Binds to calmodulin. Calmodulin binds preferentially to the beta subunit. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18347014}. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Adducins are heteromeric proteins composed of different subunits referred to as adducin alpha, beta and gamma. The three subunits are encoded by distinct genes and belong to a family of membrane skeletal proteins involved in the assembly of spectrin-actin network in erythrocytes and at sites of cell-cell contact in epithelial tissues. While adducins alpha and gamma are ubiquitously expressed, the expression of adducin beta is restricted to brain and hematopoietic tissues. Adducin, originally purified from human erythrocytes, was found to be a heterodimer of adducins alpha and beta. Polymorphisms resulting in amino acid substitutions in these two subunits have been associated with the regulation of blood pressure in an animal model of hypertension. Heterodimers consisting of alpha and gamma subunits have also been described. Structurally, each subunit is comprised of two distinct domains. The amino-terminal region is protease resistant and globular in shape, while the carboxy-terminal region is protease sensitive. The latter contains multiple phosphorylation sites for protein kinase C, the binding site for calmodulin, and is required for association with spectrin and actin. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:119; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; F-actin capping protein complex [GO:0008290]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane raft [GO:0044853]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:0051016]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:0050901]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] |
12427140_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12653680_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14517477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14553963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14553963_there was significant heterogeneity between Slavic and Italian subjects in the phenotype-genotype relationships with beta-adducin 15528469_Expression of the hypertensive rat or human variant of adducin into normal renal epithelial cells recreates the hypertensive phenotype with higher Na+,K+-ATPase activity, mu2-subunit hyperphosphorylation, and impaired Na+,K+-ATPase endocytosis. 15716695_Polymorphisms in the ADD2 and ADD3 genes taken alone were not associated with blood pressure and renin activity 15834281_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15963851_The very high levels of expression of ADD2 suggest that its promoter may be useful for directing erythroid-specific gene expression. 16105548_beta-adducin is a downstream target of and regulated by the PTN/RPTPbeta/zeta signaling pathway 16497648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301826_Changes in intra-erythrocyte cations in ADD2 1797CC homozygous men might lead to osmotic fragility of erythrocytes, but to what extent they reflect systemic changes or are possibly involved in blood pressure regulation remains unknown. 17301826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17854487_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17854487_hypertension candidate gene variation may influence BP responses to specific antihypertensive drug therapies and measurement of genetic variation may assist in identifying subgroups of hypertensive patients benefiting from antihypertensive drug therapies 18003638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18667944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18787518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18959617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19838659_ALPHA AND BETA ADDUCIN POLYMORPHISMS AFFECT DECLINE OF RENAL FUNCTION IN HUMAN IGA NEPHROPATHY. 19838659_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21606488_phosphorylation of beta-adducin by GSK3 promotes efficient neurite outgrowth in neurons. 24129186_chorein interacts with beta-adducin and beta-actin. 25425738_Taken together, these results show that beta-adducin is a pivotal lipid raft-associated protein in PSGL-1-mediated neutrophil rolling on P-selectin. 26045217_ADD2 and NCX1 variants influence the risk and the clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. 26723519_Study evaluated effects of ADD genetic variability on cognitive functions in a sample of patients with schizophrenia, known to show a wide and heterogeneous neuropsychological deficit and found that ADD2 C1797T polymorphism showed diffuse effects on almost every cognitive domain. 27493446_Aberrant DNA methylation of ADD2 could be potential screening markers of colorectal cancer. 29901076_betaadducin was demonstrated to have a critical role in neutrophil migration. |
ENSMUSG00000030000 |
Add2 |
43.717870 |
2.6581513929 |
1.410423 |
0.259521075 |
30.040607 |
0.00000004230930193049167119497799816572880526877042939304374158382415771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000172605112353249596900416117442600416609366220654919743537902832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.6775093 |
9.1937470 |
23.2599654 |
2.8515425 |
| ENSG00000075399 |
9605 |
VPS9D1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2B5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in ATP synthesis coupled proton transport. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9605; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis [GO:0015986]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
|
ENSMUSG00000001062 |
Vps9d1 |
102.868446 |
0.2713665915 |
-1.881685 |
0.170553938 |
128.820523 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000742366203627232520468232522898318299515740564643205252118125861782669428639864356300748227113217581063508987426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000094868616151843739695660482687341633736045980400153551686675017401207304955715327032805816998006775975227355957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.2780892 |
5.7739430 |
156.2436150 |
13.5918916 |
| ENSG00000075651 |
5337 |
PLD1 |
protein_coding |
Q13393 |
FUNCTION: Function as phospholipase selective for phosphatidylcholine (PubMed:8530346, PubMed:9582313). Implicated as a critical step in numerous cellular pathways, including signal transduction, membrane trafficking, and the regulation of mitosis. May be involved in the regulation of perinuclear intravesicular membrane traffic (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8530346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9582313}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase which catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine in order to yield phosphatidic acid and choline. The enzyme may play a role in signal transduction and subcellular trafficking. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants with both catalytic and regulatory properties. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:5337; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cholinergic synapse [GO:0098981]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D activity [GO:0070290]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phospholipase D activity [GO:0004630]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; inositol lipid-mediated signaling [GO:0048017]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; phospholipid catabolic process [GO:0009395]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of microvillus assembly [GO:0032534]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693]; regulation of vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0060627]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
11821392_alpha-Synuclein interacts with phospholipase D isozymes and inhibits pervanadate-induced phospholipase D activation in human embryonic kidney-293 cells 11830497_regulation of polymorphonuclear leukocyte degranulation and oxidant production 11950840_Detecting protein-phospholipid interactions. Epidermal growth factor-induced activation of phospholipase D1b in situ 12011045_binding of the Rho family member Cdc42 to PLD1 and the subsequent stimulation of its enzymatic activity are distinct events 12014986_PLD1 is threonine-phosphorylated in human-airway epithelial cells by a PKCdelta and src dependent mechanism 12149127_activation of phospholipases D1 and D2 by S1P regulates the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and IL-8 secretion in Beas-2B cells 12388543_activity regulated by actin in a polymerization-dependent, isoform-specific manner 12593858_activated by ADP-ribosylated RhoA 12615079_elevated PLD activity generates survival signals allowing cells to overcome default apoptosis programs 12782287_PLD isozymes stimulate cell growth by repressing expression of p21 gene 12813467_Phospholipase D confers rapamycin resistance in human breast cancer cells. Elevated PLD activity in MCF-7 cells also caused rapamycin resistance for S6 kinase phosphorylation and serum-induced Myc expression. 12839565_protein kinase C alpha associates with phospholipase D1 and enhances basal phospholipase D activity in a protein phosphorylation-independent manner in melanoma cells, which contributes to the cell's high invasive potential. 14596936_results indicate that PKCdelta inhibits TPA-induced PLD1 activation mediated by PKCalpha through the association with PLD1 14646617_isoenzyme PLD1 is stimulated by phorbol ester and requires ADP-ribosylation factor, protein kinase C and Rho proteins for full activity 15067001_phospholipase D causes translocation of protein kinase C (PKC)betaII but not PKCbetaI to a juxtanuclear subset of recycling endosomes 15210717_phospholipase D isozymes mediate EGCG-induced COX-2 expression through PKC and p38 in immortalized astroglial line and normal astrocyte cells 15339843_PLD1 activity by regulating phosphatidic acid formation controls the early signals initiated by FcepsilonRI aggregation that lead to mast cell degranulation.PH 15668389_importance of phospholipase D in the oncogenic ability of Ras 16109716_phospholipase D suppresses protein phosphatase 2A and is involved in the mTOR survival pathway in the transformation of human cells 16339545_PLD1 is activated by exclusion from lipid rafts and that this activation conveys antiproliferative signals in lymphoid cells 16341931_These results suggest that intact phosphorylation sites within the MARCKS ED are required for PLD activation and influence both membrane-cytoskeletal organization and cell viability. 16449386_overexpression of PLD1 decreases, and down-presenilin 1, through its loop region, binds to phospholipase D1 (PLD1), thereby recruiting it to the Golgi/trans-Golgi network 16517737_adhesion stimulates PLD activity, and that PLD1 regulates the initial stages of phagocyte adhesion 16608858_endogenous PLD1 is a critical factor in the organization of the actin-based cytoskeleton, with regard to cell adhesion and migration 16622417_PLD functions as a GTPase activating protein (GAP) through its phox homology domain (PX), which directly activates the GTPase domain of dynamin and increased epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) endocytosis at physiological EGF concentrations. 16873675_demonstration of the involvement of PLD1 and PLD2 and its enzymatic activity toward chemokines in the key physiologic process of leukocyte migration 16919239_PLD1 may play a crucial role in collagen type I production through mTOR signaling in human dermal fibroblast. 16978840_We show that human PLD1b (hPLD1b) is an actin-binding protein and the N-terminus is predominantly involved in this interaction. 17065600_PLD1 regulates 8-Br-cAMP-induced decidualization through PLA2G1B, and PLD1 upregulation is essential for decidualization of endometrial stromal cells. 17069807_TNFalpha/CHX-induced cell death was significantly lowered in cells overexpressing PLD1 17071135_isoform selective Arf/PLD interaction and not Arf/PtdIns4P5K will be the critical trigger in the formation of distinct, optimal triples of Arf/PLDs/PtdIns4P5Ks 17130901_Our results indicate a possible role for novel PKC isoforms in the regulation of P2X(7)-mediated PLD activity. 17433303_VDR and retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRalpha) binds to the VDRE and increases PLD1 gene expression in HaCaT cells. 17627030_Plays a major role in promoting HIV-1 long terminal repeat transactivation and virus replication. 17640750_These results demonstrate for the first time that PLD1 and PLD2 isozymes enhance cobalt chlorde-induced COX-2 expression through differential signaling pathways in astroglioma cells. 17724165_PLD control over expression of the Mac-1 activation epitope is critical for neutrophil migration to fMLP but not C5a. 17726467_PLD1 and phospho-mTOR are coexpressed in a subset of phospho-Akt-negative breast carcinomas. 17853892_phospho-cofilin by its stimulatory effect on PLD1 may control a large variety of cellular functions. 17986621_These findings indicate the involvement of phospholipase D activation in hBD-2 up-regulation in gingival epithelial cells. 18067864_These results suggest that elevated expression and activity of PLD attenuate phorbol myristate acetate-induced Egr-1 expression via PI3K pathway. 18344600_Depletion of phospholipase D1 by RNA interference reduced the velocity of the migration,of NBT-II cells. 18432522_we present evidence for the presence of both PLD1 and PLD2 in platelets and indicate a role in platelet activation. 18480413_Phospholipase D activity regulates integrin-mediated cell spreading and migration by inducing GTP-Rac translocation to the plasma membrane 18550814_PLD1 is required for Rheb activation of the mTOR pathway. 18569866_a role for PKA in the regulation of thrombin-induced PLD1 activity and translocation in platelets. 18573349_These data have identified a novel regulatory domain in PLD1. 18636075_Cleavage of PLD1 by caspases promotes apoptosis via modulation of the p53-dependent cell death pathway. 18694819_Phospholipase D1 is cleaved at one internal site and is significantly decreased during apoptosis. 18945966_different mechanisms appear to control the agonist-induced secretion of von Willebrand factor and tissue-type plasminogen activator, with only the former requiring PLD1 19366706_These results demonstrate a role of PLD in hyperoxia-mediated IQGAP1 activation through Rac1 in tyrosine phosphorylation of Src and cortactin, as well as in p47(phox) translocation and reactive oxygen species formation in human lung endothelial cells. 19487697_PLD1 acts as an important regulator in house dust mite allergen Der f 2-induced expression and production of IL-13 through activation of activating transcription factor-2 activation in human bronchial epithelial cells. 19707939_Inhibited PLD1&2 by siRNA and determined the activity of formyl peptide receptors. Depletion of PLD1&2 resulted in a marked reduction of formyl peptide receptor activity due to inhibited ERK1/2 phosphorylation and cAMP level reduction. 19763255_temporal regulation of EGFR endocytosis is achieved by auto-regulatory PLD1 which senses the receptor activation and triggers the translocation of AP2 near to the activated receptor 19896495_Data show that there is a functional relationship between phospholipases D1/2 and MAP kinases in the human HeLa carcinoma cell line. 19994725_Mutated ras induced PLD1 gene expression through increased Sp1 transcription factor. 20158570_Results indicate PLD activation is required in PMA-stimulated respiratory burst. 20188462_Platelet-derived growth factor-induced PLD1 expression via NFkappaB may enhance invasiveness of breast cancer cells. 20189990_a novel regulatory mechanism in PLD1 functioning, particularly in the context of subcellular trafficking between different membrane compartments. 20231899_AMPK-mediated PLD1 activation is required for (14)C-glucose uptake through ERK stimulation 20442281_Upregulated phospholipase D1 is associated with a positive feedback loop to reinforce the Wnt/beta-catenin/TCF signaling in neoplasms 20693286_Data show that formylpeptides induce sequential activation of AKT, ERK1/2, and PLD, which represents a novel signaling pathway. 20711340_PLD isozyme acts as a novel transcriptional target and positive feedback regulator of Wnt signaling, and then promotes Wnt-driven anchorage-independent growth of colorectal cancer cells. 21113078_Nuclear localization of phospholipase D1 mediates the activation of nuclear protein kinase C(alpha) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. 21228924_The PLD1/PA-mTORC2 signal pathway is overactivated in endometrial carcinomas. 21326806_The activation with overexpression of components of the mTORC2-PLD1 pathway in ULMS and to a lesser degree in STUMP provides insight into their tumorigenic mechanisms. 21536681_cPLA(2)-dependent AA release is required for VEGF-induced Src-PLD1-PKCgamma-mediated pathological retinal angiogenesis 21620893_Activation of PLD1 contributes to IL-15-mediated osteoclastogenesis via the MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. 21760893_Host cell PLD1 and PLD2 accompanied A. fumigatus conidia during internalization. 22024166_amino acids stimulate PLD1 translocation to the lysosomal region where mTORC1 activation occurs in an hVps34-dependent manner, and this translocation is necessary for mTORC1 activation 22457329_Studies indicate that phospholipase D (PLD) as a mediator of nutrients to mTORC1. 22504301_PLD acts as an important regulator in Bcl-2 expression by activating STAT3 involving the phosphorylation of Ser727 through the PLA(2)/G(i)/ERK1/2, RhoA/ROCK/p38 MAPK, and Rac1/p38 MAPK pathways. 22609963_Diacylglycerol stimulates acrosomal exocytosis by feeding into a PKC- and PLD1-dependent positive loop that continuously supplies phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 22718838_Stx1B and Stx2B induce acute VWF secretion in a PLD1-dependent manner but do so by differentially modulating PKCalpha, RhoA, and ADP-ribosylation factor 6. 22824913_The hydrophobic amino acids involved in the interdomain association of PLD1 are required for vesicular localization and disturbance of its nuclear localization. 23131846_PLD1 in the tumor environment promotes tumor growth and metastasis 23178798_These results indicate that PKD is downstream of PLD and suggest that PKD is one of the mechanisms through which PLD promotes aldosterone production in response to AngII in adrenal glomerulosa cells. 23314176_The direct association of PLD1 with the 5-HT2A receptor's carboxy-terminal tail domain displays selective disruption of its PLD signalling pathway. 23698760_The impact of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) supplementation on phospholipase D (PLD) trafficking and activity in mast cells was investigated. 23723068_Data indicate that after P2Y6 receptor stimulation both phospholipase D (PLD) and DGKzeta enzymes are responsible for producing phosphatidic acid (PA). 23793974_This data indicates that CAY10593 impairs human P2X7 independently of PLD1 stimulation and highlights the importance of ensuring that compounds used in signalling studies downstream of P2X7 activation do not affect the receptor itself. 23804711_chemokine unresponsiveness in chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes results from failure of Arf1/phospholipase D1-mediated translocation of Rap1 to the plasma membrane for GTP loading and may be a specific feature of anergy induced by DNA Ags. 23912460_Suppression of PLD1 activity prevents FAM83B-mediated transformation. 24103483_PlD1 and PLD2 play roles in cell migration, invasion and metastasis. [review] 24556997_Downregulation of Chk-alpha with siRNA increased PLD1 expression, and downregulation of PLD1 increased Chk-alpha expression. 24618697_Phospholipase D is involved in the formation of Golgi associated clathrin coated vesicles in human parotid duct cells. 24632948_Insufficient PLD1 activity, and the associated changes in phospholipid compositions within membranes, may be a factor in impaired autophagic process and protein accumulation in Lewy body diseases. 24802400_The present study indicates that PLD1 plays a role in regulating type I collagen accumulation through induction of autophagy. 24990946_Cellular and physiological roles for phospholipase D1 in cancer. 25172550_Results indicate distinctive roles of phospholipase D PLD1 and PLD2 isoforms in pathological conditions in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). 25197077_PLCdelta1 has tumor-suppressive functions in colorectal cancer through E-cadherin induction. 25361009_These observations define a novel function of PLD1 as a previously unrecognized HIF-1alpha regulator. 25489735_PED/PEA-15 overexpression is sufficient to block hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in Ins-1E cells through a PLD-1 mediated mechanism 25523098_Ectopic expression of PLD1 or PLD2 in human glioma U87 cells increased the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein. 26250158_MicroRNA-638 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting phospholipase D1 in human gastric carcinoma 26335962_Our data extend the knowledge for a variety of possible roles of PLD1 in allergic disorders including asthma pathogenesis 26680696_These findings reveal a novel role of the PLD1-pleckstrin homology domain as a positive regulator of endocytosis and provide a link between PLD1 and HIF-1alpha in the EGFR endocytosis pathway. 27713167_Simultaneous high expression of PLD1 and Sp1 predicts a poor prognosis for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. 27793751_protein kinase C-epsilon regulation, phospholipase D1 protects retinal pigment epithelium cells from lipopolysaccharide-induced damage 27799408_In hearts of PLD1 knockout mice, we detected marked tricuspid regurgitation, right atrial enlargement, and increased flow velocity, narrowing and thickened leaflets of the pulmonic valve. CONCLUSIONS: The findings support a role for PLD1 in normal heart valvulogenesis. 27809301_These findings reveal a novel role of PLD1 in sustaining cancer cell survival during metabolic stress. 28087476_Suggest PLD expression in high grade serous ovarian carcinoma may have a role in mediating progression to effusions and chemoresistance. 28229303_The results of this study shown that significant PLD1 down-regulation has been observed in total MS patients compared with controls. 28423060_Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C inhibition down- regulates CXCR4 expression and interferes with proliferation, invasion and glycolysis in glioma cells. 28939743_Low PLD1 expression and high ICAT expression were significantly associated with increased survival in colorectal cancer patients. 28986032_studies implicate PLD1 in neurotransmission, although its precise role is of some debate. Altogether, the production of phosphatidic acid by these enzymes offer an interesting and novel pathway for the regulation of the synaptic vesicle cycle. 29571767_findings reveal an unforeseen role for alpha-syn in PLD regulation: PLD1 downregulation may constitute an early mechanism in the initial stages of WT alpha-syn-triggered neurodegeneration. 30369483_Here, expressed were human PLD1 and human PLD2 in Drosophila and the study found that while reconstitution of human PLD1 is able to completely rescue retinal degeneration in a loss of function dPLD mutant, human PLD2 was less effective in its ability to mediate a rescue. 30511626_PLD signaling pathway is directly involved in stroma-cancer interactions in the colon. 31379206_MiR-638 may be a tumour suppressor in OSCC by targeting PLD1/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway 32067228_Promotion of cell autophagy and apoptosis in cervical cancer by inhibition of long noncoding RNA LINC00511 via transcription factor RXRA-regulated PLD1. 32067682_Clinical activity of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) blockade in never, light, and heavy smokers with non-small-cell lung cancer and PD-L1 expression >/=50. 32578172_Roles for Phospholipase D1 in the Tumor Microenvironment 32661773_Increased phospholipase D activity contributes to tumorigenesis in prostate cancer cell models. 32725633_Phospholipase D1 inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma to temozolomide and suppresses its tumorigenicity. 32869317_Phospholipase D1 is upregulated by vorinostat and confers resistance to vorinostat in glioblastoma. 33191863_Blockade of PLD1 potentiates the antitumor effects of bortezomib in multiple myeloma cells by inhibiting the mTOR/NF-kappaB signal pathway. 33495125_Structure and regulation of human phospholipase D. 33645542_Biallelic loss-of-function variants in PLD1 cause congenital right-sided cardiac valve defects and neonatal cardiomyopathy. 33784016_Hypoxia-induced cofilin 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating the PLD1/AKT pathway. 34320341_RalA and PLD1 promote lipid droplet growth in response to nutrient withdrawal. 34431424_PLD1 knockdown reduces metastasis and inflammation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by modulating NF-kappaB and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways. 34810254_Click chemistry-enabled CRISPR screening reveals GSK3 as a regulator of PLD signaling. 34876384_Phospholipase D1-generated phosphatidic acid modulates secretory granule trafficking from biogenesis to compensatory endocytosis in neuroendocrine cells. 35775110_Phospholipase D1 promotes cervical cancer progression by activating the RAS pathway. 36362078_Exosome Secretion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Ovarian Cancer Are Regulated by Phospholipase D. |
ENSMUSG00000027695 |
Pld1 |
44.222758 |
0.4426244444 |
-1.175845 |
0.452725539 |
6.174726 |
0.01295879797487451377813183484022374614141881465911865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024285406057535274121361723587142478208988904953002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
27.9178946 |
8.3899054 |
62.8008250 |
12.9662534 |
| ENSG00000075826 |
25956 |
SEC31B |
protein_coding |
Q9NQW1 |
FUNCTION: As a component of the coat protein complex II (COPII), may function in vesicle budding and cargo export from the endoplasmic reticulum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16495487}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein of unknown function. The protein has moderate similarity to rat VAP1 protein which is an endosomal membrane-associated protein, containing a putative Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II phosphorylation site. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:25956; |
COPII vesicle coat [GO:0030127]; endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070971]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; vesicle coat [GO:0030120]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; COPII-coated vesicle cargo loading [GO:0090110]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16495487_The SEC31B protein is an orthologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sec31p, a component of the COPII vesicle coat that mediates vesicular traffic from the endoplasmic reticulum. |
ENSMUSG00000051984 |
Sec31b |
40.577181 |
0.3569963361 |
-1.486019 |
0.567104664 |
6.645733 |
0.00993936044549118165314371964313977514393627643585205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019062494825292337213840099252593063283711671829223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.6641026 |
9.4901956 |
66.7696239 |
18.6535135 |
| ENSG00000075826_ENSG00000166136 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
119.391730 |
0.1701317821 |
-2.555275 |
1.088402856 |
4.936616 |
0.02629346523670630583757734655137028312310576438903808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.045819545087814057826580693699725088663399219512939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.5048167 |
16.1766357 |
198.5938296 |
67.5025195 |
| ENSG00000076067 |
5939 |
RBMS2 |
protein_coding |
Q15434 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a small family of proteins which bind single stranded DNA/RNA. These proteins are characterized by the presence of two sets of ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence (RNP-CS) that contain conserved motifs, RNP1 and RNP2, originally described in RNA binding proteins, and required for DNA binding. The RBMS proteins have been implicated in such diverse functions as DNA replication, gene transcription, cell cycle progression and apoptosis. This protein was isolated by phenotypic complementation of cdc2 and cdc13 mutants of yeast and is thought to suppress cdc2 and cdc13 mutants through the induction of translation of cdc2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5939; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; poly(A) binding [GO:0008143]; poly(U) RNA binding [GO:0008266]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA processing [GO:0006396] |
30514345_RBMS2 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer and positively regulated the expression of P21 by stabilizing its mRNA. |
ENSMUSG00000040043 |
Rbms2 |
36.630952 |
0.4276806092 |
-1.225394 |
0.382605573 |
10.090063 |
0.00149071002082964499182993201031877106288447976112365722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003379339564958617949524954937601251003798097372055053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.9317820 |
14.0327136 |
43.2055989 |
23.4623789 |
| ENSG00000076554 |
7163 |
TPD52 |
protein_coding |
P55327 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables calcium ion binding activity and protein homodimerization activity. Involved in B cell differentiation. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and perinuclear region of cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7163; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; secretion [GO:0046903] |
15576473_TPD52 bound to annexin VI in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner suggesting that these molecules may act in concert to regulate secretory processes in plasma cells 15986428_tumor protein D52 represents a novel molecular marker in ovarian cancer, which is broadly expressed across the different histologic subtypes 16620967_While D52 transcript was detected in T-ALL and pre-B ALL at comparable frequencies, D52 was less frequently detected in ALL bone marrow with hyperdiploid karyotypes, compared with samples with normal karyotypes. 16631610_Additionally, the expression profile shows that hD55 is testis-specific, indicating a potential role for hD55 in testis development and spermatogenesis. 17418805_Thus, our studies not only provide molecular basis of PC-1 transcription regulation, but also define a new regulatory sequence that may be used to restrict expression of therapeutic genes to prostate cancer in the prostate cancer gene therapy. 17947466_PrLZ as a marker for prostate cancer progression and metastasis, and its pattern of expression is suggestive of a proto-oncogene 18698023_Tumor protein D52 was overexpressed in breast cancer tissue 18710659_CLIC1 and TPD52 were significantly (P |
ENSMUSG00000027506 |
Tpd52 |
125.401893 |
0.4875764398 |
-1.036300 |
0.355036332 |
8.251060 |
0.00407282092767467622518307024392925086431205272674560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008478820436174643038196307998077827505767345428466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.9676949 |
19.4620000 |
154.6966993 |
29.2088211 |
| ENSG00000076555 |
32 |
ACACB |
protein_coding |
O00763 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA and plays a central role in fatty acid metabolism (PubMed:16854592, PubMed:19236960, PubMed:20457939, PubMed:20952656, PubMed:19900410, PubMed:26976583). Catalyzes a 2 steps reaction starting with the ATP-dependent carboxylation of the biotin carried by the biotin carboxyl carrier (BCC) domain followed by the transfer of the carboxyl group from carboxylated biotin to acetyl-CoA (PubMed:19236960, PubMed:20457939, PubMed:20952656, PubMed:26976583). Through the production of malonyl-CoA that allosterically inhibits carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 at the mitochondria, negatively regulates fatty acid oxidation (By similarity). Together with its cytosolic isozyme ACACA, which is involved in de novo fatty acid biosynthesis, promotes lipid storage (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q4Z2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16854592, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19236960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19900410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20457939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20952656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26976583}. |
3D-structure;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biotin;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Ligase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; malonyl-CoA biosynthesis; malonyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19900410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26976583}. |
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a complex multifunctional enzyme system. ACC is a biotin-containing enzyme which catalyzes the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA, the rate-limiting step in fatty acid synthesis. ACC-beta is thought to control fatty acid oxidation by means of the ability of malonyl-CoA to inhibit carnitine-palmitoyl-CoA transferase I, the rate-limiting step in fatty acid uptake and oxidation by mitochondria. ACC-beta may be involved in the regulation of fatty acid oxidation, rather than fatty acid biosynthesis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2022]. |
hsa:32; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity [GO:0003989]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; biotin binding [GO:0009374]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; acetyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0006084]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006633]; malonyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:2001295]; negative regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043086]; negative regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0031999]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of heart growth [GO:0060421]; positive regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010884]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
12086953_The effect of a 3-month low-intensity endurance training program on fat oxidation and expression 12413941_elevation of AMPK via phosphorylation is not sufficient to maintain elevated ACCbeta Ser(221) phosphorylation during exercise 14627750_down-regulation of acetyl coa carboxylase 2 (ACC2) mRNA, induced by the lowering of plasma insulin concentration, is related to improvement of insulin sensitivity 15590647_differential regulation of ACCbeta gene expression between tissues 17223360_The expression, purification, and characterization of ACC2 were investigated. 17521700_observations provide complete information about the pattern and levels of LKB1 and p-ACC immunostaining in normal tissues and in lung tumors 18031993_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18455495_Differential activation of recombinant ACC1 and ACC2 by citrate is reported. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19034549_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19190759_Human adipose tissue, unlike rodent adipose, expresses more ACC2 mRNA relative to the oxidative tissues muscle and heart. 19390150_The human ACC2 CT-domain C-terminus is comprised of three intertwined alpha-helices that extend outwards from the enzyme on the opposite side to the ligand-binding site. 19618481_results point towards major differences in ACC tissue distribution between humans and rats 19846279_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19900410_the crystal structures of the biotin carboxylase domain of human ACC2 phosphorylated by AMP-activated protein kinase was reported. 20139635_data suggest that insulin and glucocorticoid have positive effects on both acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha(ACC1) and beta(ACC2) gene transcription 20168990_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20168990_These results suggest that ACACB is a strong candidate for conferring susceptibility for proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20514549_ACACB overexpression in renal proximal tubular epithelial cell increased proinflammatory cytokine expression, such as IL-6, at least partly by increasing mRNA stability through a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. 20519229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20519229_The acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase beta (ACACB) gene is associated with nephropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. 20599696_This study demonstrates that NRF-1 is a novel transcriptional inhibitor of the human ACCbeta gene promoter in the mammalian heart. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20799892_The -368 C/T single-nucleotide polymorphism in ACACB P-II binds HepG2 nuclear proteins that affect promoter activity in an allele-specific fashion. 20855566_Acetyl-CoA carboxylase beta (ACC2) plays a key role in fatty acid synthesis and oxidation pathways. 20855566_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20965718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21553357_A gene polymorphism in acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase beta may be associated with the C-reactive protein level in a prediabetic and diabetic population. 21887335_Common variants within the ACACB locus appear to regulate adipose gene expression 21908218_In conclusion, common polymorphisms of ACACB gene are associated with obesity and, independently, with type 2 diabetes in postmenopausal women 21953464_Structure-guided inhibitor design for human acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase by interspecies active site conversion. 23081748_TT genotypes of ACACB gene (rs2268388) and CC genotype of AGTR1 gene (rs5186) confers the risk of diabetic nephropathy in Asian Indian patients with T2DM. 23156397_Its involvement in the development of diabetic nephropathy is explained by the promotion of the so-called micro-inflammation associated with the diabetic state. 23460794_These data support a role for ACACB in obesity and potential roles for altered lipid metabolism in susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. 25262148_Our meta-analysis supports that the apolipoprotein E epsilon2 allele and acetyl-CoA carboxylase beta rs2268388 C>T might act as promotion factors of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes. 26022126_The knockdown of ACC2 reduced palmitic acid -induced autophagy and thus protects the cells from palmitic acid - induced lipotoxicity with attenuated lipid accumulation and rescued cell viability. 26030797_A significant association exists of ACACB gene polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy among Caucasian patients with diabetes. 27635760_PHD3 loss in cancer enables metabolic reliance on fatty acid oxidation via deactivation of ACC2. 27693630_Cetuximab-mediated activation of AMPK and subsequent phosphorylation and inhibition of ACC is followed by a compensatory increase in total ACC, which rewires cancer metabolism from glycolysis-dependent to lipogenesis-dependent. 28081256_Inhibition of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1 (ACC1) and 2 (ACC2) Reduces Proliferation and De Novo Lipogenesis of EGFRvIII Human Glioblastoma Cells 28290443_ACC2 gene (ACACB) expression was decreased by 25% in HCC tissue compared to non-cancerous liver tissue. 28768177_of ACCs decreased polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) concentrations in liver due to reduced malonyl-CoA, which is required for elongation of essential fatty acids. 29107296_Targeted analysis of DNA methylation array revealed the mesenchymal stem cells in infants born to obese mothers had hypermethylation in genes regulating Fatty Acid Oxidation (PRKAG2, ACC2, CPT1A, SDHC) and corresponding lower mRNA content of these genes. Moreover, mesenchymal stem cells methylation was positively correlated with infant adiposity. 29772612_Results identified ACC2 amino acid mutations affecting specific inhibition of the isozyme by compound CD-017-0191. They form two clusters separated by 60-90 A: one located in the vicinity of the BC active site and the other one in the vicinity of the ACC1 phosphorylation sites in the central domain, suggesting a contribution of the interface of two ACC dimers in the polymer to the inhibitor binding site. 33957017_Faster lipid beta-oxidation rate by acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 inhibition alleviates high-glucose-induced insulin resistance via SIRT1/PGC-1alpha in human podocytes. 34085602_Identification of core gene in obese type 2 diabetes patients using bioinformatics analysis. 34939260_Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase beta gene polymorphism does not predict cardiovascular risk susceptibility in Chinese type 2 diabetic individuals. |
ENSMUSG00000042010 |
Acacb |
34.782693 |
0.2935365545 |
-1.768388 |
0.451161356 |
14.010485 |
0.00018179405251161272162249704642533743026433512568473815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000480100235296368558352009259238002414349466562271118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4148364 |
4.2775616 |
45.3002520 |
9.9543557 |
| ENSG00000076662 |
3385 |
ICAM3 |
protein_coding |
P32942 |
FUNCTION: ICAM proteins are ligands for the leukocyte adhesion protein LFA-1 (integrin alpha-L/beta-2) (PubMed:1448173). ICAM3 is also a ligand for integrin alpha-D/beta-2. In association with integrin alpha-L/beta-2, contributes to apoptotic neutrophil phagocytosis by macrophages (PubMed:23775590). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1448173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23775590}. |
3D-structure;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phagocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family. All ICAM proteins are type I transmembrane glycoproteins, contain 2-9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains, and bind to the leukocyte adhesion LFA-1 protein. This protein is constitutively and abundantly expressed by all leucocytes and may be the most important ligand for LFA-1 in the initiation of the immune response. It functions not only as an adhesion molecule, but also as a potent signalling molecule. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:3385; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909] |
11784723_A novel serine-rich motif in the intercellular adhesion molecule 3 is critical for its ezrin/radixin/moesin-directed subcellular targeting 11799126_identification of DC-SIGN binding sites 12021323_interactions with DC-SIGN does not promote DC-SIGN mediated HIV-1 transmission 12571844_Expression of DC-SIGN and its ligand, ICAM-3, is found in substantial amounts only in RA synovium, suggesting that their interaction is implicated in the additional activation of synovial macrophages that leads to the production of EMMPRIN and MMP-1. 12600815_the expression of ICAM-1 might involve both p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB activities, whereas the regulation of CD11b, CD18, and ICAM-3 expressions might be mediated through p38 MAPK but not NF-kappaB. 12743567_ICAM-3 is highly expressed on the surface of human eosinophils and has a role in the downregulation of GM-CSF production. 14704632_Relationship of intercellular adhesion molecule-3 and hepatocyte growth factor with amyloidosis A in chronic renal-failure patients. There was a higher density of intercellular adhesion molecule-3-positive cells in the patients with amyloidosis A. 14726630_ICAM-3 is expressed on human bone marrow endothelial cells and controls endothelial integrity via reactive oxygen species-dependent signaling. 14970226_soluble DC-SIGN bound to gp120-Fc more than 100- and 50-fold better than ICAM-2-Fc and ICAM-3-Fc, respectively. Binding sites are described. 15163761_acts as a costimulating molecule to increase HIV-1 transcription and viral replication, a process allowing productive infection of quiescent CD4+ T lymphocytes. 15880373_Expression of ICAM-3 can be used as a valuable biomarker to predict the radiation resistance in cervical cancer that occurs during radiotherapy. 15958383_the hybrid domain of integrin alphaL beta2 has different requirements of affinity states for ICAM-1 and ICAM-3 binding 17145745_The results suggest that ICAM-3 assists in the interaction of granulocytes with DC-SIGN of dendritic cells. 17570115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17570115_Patients with SARS homozygous for ICAM3 Gly143 showed significant association with higher lactate dehydrogenase levels and lower total white blood cell counts. 17591777_talin induced an intermediate affinity alphaLbeta2 that adhered constitutively to its ligand intercellular adhesion molecule ICAM-1 but not ICAM-3. 17913807_Here we demonstrate that leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), and ICAM-3 are enriched at the VS and that inhibition of these interactions influences conjugate formation and reduces VS assembly. 18261116_This is the first case of CD20 positive mycosis fungoides involving a lymph node to be reported in the literature. 18354203_extended alpha(L)beta(2) with an open headpiece is required for ICAM-3 adhesion 19225705_Lower expression of ICAM-3 and higher expression of ICAM-1 suggest that AMs may be involved in the pathogenesis of scleroderma. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19801714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19801714_no significant risk association was found for SARS infection for the ICAM-3 Asp143Gly SNP. 19898481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956847_ICAM-3 enhances the migratory and invasive potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inducing MMP-2 and MMP-9 via Akt and CREB 20086017_CCR1 antagonist, BX471, did not significantly alter ICAM-3 expression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21239057_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in ICAM3 gene is associated with lymphoma. 21381019_induction of morphological polarization in primary T lymphocytes and Jurkat cells enhances Kidins220/ARMS colocalization with ICAM-3 21712539_the cross-talk between neutrophils and NK cells is mediated by ICAM-3 and CD11d/CD18, respectively. 22117198_ICAM-3 may be an important adhesion molecule involved in chemotaxis to apoptotic human leukocytes. 22205703_the molecular basis of allergen-induced Th2 cell polarization 22396536_analysis of activated apoptotic cells induce dendritic cell maturation via engagement of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM-3)-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN), and beta2 integrins 22479382_Results indicate that the ICAM-3 gene promoter is negatively regulated by RUNX3. 23144795_Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-3 mRNA is upregulated in non-adherent endothelial forming cells. 23775590_ICAM3 acts as recognition receptors in the phagocytosis portals of macrophages for engulfment of apoptotic neutrophils. 24177012_this data clearly indicate that ICAM-3 promotes drug resistance via inhibition of apoptosis. 24474251_with larger patient groups and preferably detailed histopathological and clinical evaluations, are needed to explain the severity of ICAM-1, ICAM-2, and ICAM-3 molecules in Barrett's esophagus 27552332_Increased expression of PECAM-1, ICAM-3, and VCAM-1 in colonic biopsies from patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in clinical remission is associated with subsequent flares; this suggests that increases in the expression of these proteins may be early events that lead to flares in patients with IBD 29477378_we identify a potential CSC regulator and suggest a novel mechanism by which ICAM3 governs cancer cell stemness and inflammation. 29671117_Lewis-antigen-containing ICAM-2/3 on Jurkat leukemia cells interact with DC-SIGN to regulate DC functions. 29729315_exploration of the underlying mechanism demonstrated that ICAM3 not only binds to LFA-1 with its extracellular domain and structure protein ERM but also to lamellipodia with its intracellular domain which causes a tension that pulls cells apart (metastasis). 32013031_Changes in the Surface Expression of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 3, the Induction of Apoptosis, and the Inhibition of Cell-Cycle Progression of Human Multidrug-Resistant Jurkat/A4 Cells Exposed to a Random Positioning Machine. 32371447_Vascular injury biomarkers and stroke risk: A population-based study. 33999358_Association of Circulating ICAM3 Concentrations with Severity and Short-term Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke. 35849332_Functional evaluation of various ICAM3 transcript variants in diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. |
|
|
160.906748 |
0.4213759629 |
-1.246820 |
0.121196697 |
107.469763 |
0.00000000000000000000000035122334215354415381208428148284175499025346756021915519270539516628881759885416613542474806308746337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000003797843611858103865485656577612026832891993699589856489336460953175345078847158220014534890651702880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.7337310 |
12.3880621 |
239.3455280 |
20.7842688 |
| ENSG00000076826 |
57662 |
CAMSAP3 |
protein_coding |
Q9P1Y5 |
FUNCTION: Key microtubule-organizing protein that specifically binds the minus-end of non-centrosomal microtubules and regulates their dynamics and organization (PubMed:19041755, PubMed:23169647). Specifically recognizes growing microtubule minus-ends and autonomously decorates and stabilizes microtubule lattice formed by microtubule minus-end polymerization (PubMed:24486153). Acts on free microtubule minus-ends that are not capped by microtubule-nucleating proteins or other factors and protects microtubule minus-ends from depolymerization (PubMed:24486153). In addition, it also reduces the velocity of microtubule polymerization (PubMed:24486153). Required for the biogenesis and the maintenance of zonula adherens by anchoring the minus-end of microtubules to zonula adherens and by recruiting the kinesin KIFC3 to those junctional sites (PubMed:19041755). Required for orienting the apical-to-basal polarity of microtubules in epithelial cells: acts by tethering non-centrosomal microtubules to the apical cortex, leading to their longitudinal orientation (PubMed:27802168, PubMed:26715742). Plays a key role in early embryos, which lack centrosomes: accumulates at the microtubule bridges that connect pairs of cells and enables the formation of a non-centrosomal microtubule-organizing center that directs intracellular transport in the early embryo (By similarity). Couples non-centrosomal microtubules with actin: interaction with MACF1 at the minus ends of non-centrosomal microtubules, tethers the microtubules to actin filaments, regulating focal adhesion size and cell migration (PubMed:27693509). Plays a key role in the generation of non-centrosomal microtubules by accumulating in the pericentrosomal region and cooperating with KATNA1 to release non-centrosomal microtubules from the centrosome (PubMed:28386021). Through the microtubule cytoskeleton, also regulates the organization of cellular organelles including the Golgi and the early endosomes (PubMed:28089391). Through interaction with AKAP9, involved in translocation of Golgi vesicles in epithelial cells, where microtubules are mainly non-centrosomal (PubMed:28089391). Plays an important role in motile cilia function by facilitatating proper orientation of basal bodies and formation of central microtubule pairs in motile cilia (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80VC9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19041755, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23169647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24486153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26715742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27693509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27802168, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28089391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28386021}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables actin filament binding activity and microtubule minus-end binding activity. Involved in several processes, including microtubule cytoskeleton organization; regulation of organelle organization; and zonula adherens maintenance. Located in cytoplasm; nucleoplasm; and zonula adherens. Colocalizes with centrosome and microtubule minus-end. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57662; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule minus-end [GO:0036449]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; zonula adherens [GO:0005915]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; microtubule minus-end binding [GO:0051011]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; epithelial cell-cell adhesion [GO:0090136]; establishment of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045198]; establishment or maintenance of microtubule cytoskeleton polarity [GO:0030951]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; microtubule anchoring [GO:0034453]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; protein transport along microtubule [GO:0098840]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051893]; regulation of Golgi organization [GO:1903358]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507]; regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031113]; regulation of organelle organization [GO:0033043]; zonula adherens maintenance [GO:0045218] |
19041755_KIAA1543 is a non-centrosomal minus end binding protein. It is termed Nezha(a character in Chinese mythic novel (Journey to the West)). 19508979_The CKK domain binds microtubules and represents a domain that evolved with the metazoa. 26715742_These findings demonstrate that apically localized CAMSAP3 determines the proper orientation of microtubules, and in turn that of organelles, in mature mammalian epithelial cells. 27349180_data suggest that CDH23-C is a CAMSAP3/Marshalin-binding protein that can modify MT networks indirectly through its interaction with CAMSAP3/Marshalin. 27693509_ACF7, a member of the spectraplakin family of cytoskeletal crosslinking proteins, interacts with Nezha (also called CAMSAP3) at the minus ends of noncentrosomal microtubules and anchors them to actin filaments. 27802168_in mammalian intestinal epithelial cells, the spectraplakin ACF7 (also known as MACF1) specifically binds to CAMSAP3 and is required for the apical localization of CAMSAP3-decorated microtubule minus ends. 28089391_CAMSAP3-dependent Golgi vesicle clustering and graded microtubule dynamics 30282632_Findings suggest that CAMSAP3 functions to protect lung carcinoma cells against EMT by suppressing Akt activity via microtubule regulation and that CAMSAP3 loss promotes EMT in these cells. 33566684_Rab14/MACF2 complex regulates endosomal targeting during cytokinesis. |
ENSMUSG00000044433 |
Camsap3 |
22.366229 |
0.3207523252 |
-1.640468 |
0.417229803 |
15.406290 |
0.00008669920288915128488670125417314693549997173249721527099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000240451002375774685725778878619962597440462559461593627929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5275103 |
3.9969060 |
23.8237347 |
8.8195432 |
| ENSG00000076928 |
9138 |
ARHGEF1 |
protein_coding |
Q92888 |
FUNCTION: Seems to play a role in the regulation of RhoA GTPase by guanine nucleotide-binding alpha-12 (GNA12) and alpha-13 (GNA13) subunits (PubMed:9641915, PubMed:9641916). Acts as GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for GNA12 and GNA13, and as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RhoA GTPase (PubMed:9641915, PubMed:9641916, PubMed:8810315, PubMed:30521495). Activated G alpha 13/GNA13 stimulates the RhoGEF activity through interaction with the RGS-like domain (PubMed:9641916). This GEF activity is inhibited by binding to activated GNA12 (PubMed:9641916). Mediates angiotensin-2-induced RhoA activation (PubMed:20098430). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20098430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30521495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8810315, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9641915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9641916}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Rho GTPases play a fundamental role in numerous cellular processes that are initiated by extracellular stimuli that work through G protein coupled receptors. The encoded protein may form complex with G proteins and stimulate Rho-dependent signals. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been defined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9138; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
12372594_coexpression of a dominant negative PDZ-RhoGEF abrogated the ability of plexin-B1 to cause stress fiber formation 12525488_rgRGS domain may serve a structural or allosteric role in the regulation of the nucleotide exchange activity of p115RhoGEF on Rho by Galpha(13) 12748184_CD44 interaction with p115RhoGEF and ROK plays a pivotal role in promoting Gab-1 phosphorylation leading to Gab-1.PI 3-kinase membrane localization, AKT signaling, and cytokine (M-CSF) production during HA-mediated breast cancer progression 12754211_data demonstrate a pathway of Rho activation involving protein kinase c alpha-dependent phosphorylation of p115Rho guanine exchange factor 15143072_Data show that different rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (rhoGEFs; p115rhoGEF, LARG and PDZrhoGEF) mediate downstream rho signaling by the thrombin and lysophosphatidic acid receptors. 15735747_Several features of a typical alpha/RGS interaction are preserved in the alpha(13)/p115RhoGEF interaction. 17493936_analysis of a novel cross-talk exerted from the LPA/Galpha(13)/p115RhoGEF/RhoA pathway to the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor/Galpha(s)/adenylyl cyclase pathway 18320579_A pronounced and rapid translocation of p115-RhoGEF from the cytosol to the plasma membrane was observed upon activation of several G(12/13)-coupled receptors in a cell type-independent fashion. 19720875_Data show that microtubules in neighboring cells reorient and target p115 RhoGEF to sites where dying cells are squeezed out of the epithelial sheet. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20619149_ARHGEF1 is involed in hypertension by controlling its molecular mechanisms. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21064165_The linker region connecting the N-terminal RGS-homology domain and the Dbl homology domain inhibits the intrinsic guanine nucleotide exchange activity of p115. 21454492_Mechanistic insights into specificity, activity, and regulatory elements of the regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS)-containing Rho-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) p115, PDZ-RhoGEF (PRG), and leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG). 22086927_Thromboxane receptor signaling is required for fibronectin-induced matrix metalloproteinase 9 production by human and murine macrophages and is attenuated by the Arhgef1 molecule. 22500016_Upon beta(2)AR activation, both betaArrestin2 and p115RhoGEF translocate to the plasma membrane, with concomitant activation of RhoA and formation of focal adhesions and stress fibers. 22661716_Activation of p115-RhoGEF requires direct association of Galpha13 and the Dbl homology domain. 23070684_High GEF1 expression is associated with metastasis of pancreatic cancer. 23718289_The action of DOCK7 in vivo may involve the coordinated integration of Cdc42/Rac1 signaling in the context of the membrane recruitment of a DOCK7 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) complex. 23816534_Modification of p115RhoGEF at Serine(330) regulates its RhoGEF activity. 24465552_The novel role for p115RhoGEF in regulation of epithelial plasticity is dependent on Rho-DRF signaling module. 24855647_Regulated localization is sufficient for hormonal control of regulator of G protein signaling homology Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (RH-RhoGEFs). 25916117_contactin-1 displayed the ability to phosphorylate the RhoA activator p115 RhoGEF 26911374_We have reported here for the first time a reduced activity of both Rac1 and Cdc42 in human pheochromocytoma resection as well as tumor-associated expression changes of FARP1, ARHGEF1, and ARHGAP36 28179147_Data indicate that the crystal structure of PDZ-RhoGEF PDZ domain in complex with the CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2) C-terminal PDZ binding motif. 28655771_Data suggest that MCP1/CCL2 induces activation/tyrosine phosphorylation of ARHGEF1/p115-RhoGEF and up-regulates RAC1 signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs); ARHGEF1 inhibition suppresses MCP1-induced VSMC migration and proliferation. (ARHGEF1 = Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1; RAC1 = Rac family small GTPase 1; CCL2 = C-C motif chemokine ligand 2) 29071730_High ARHGEF1 expression is associated with asthmatic airway hyper-responsiveness. 32808262_Identification of Rho GEF and RhoA Activation by Pull-Down Assays. 35037717_Integrative multiomics and in silico analysis revealed the role of ARHGEF1 and its screened antagonist in mild and severe COVID-19 patients. |
ENSMUSG00000040940 |
Arhgef1 |
1832.555448 |
0.3216749487 |
-1.636325 |
0.204398797 |
61.091298 |
0.00000000000000544884513998163006024986110030576660955350942749930709396721795201301574707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000037130634471896979749219616050582586383530924595275379829217854421585798263549804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
933.5172791 |
93.8939601 |
2923.9058000 |
211.9626900 |
| ENSG00000077044 |
8527 |
DGKD |
protein_coding |
Q16760 |
FUNCTION: Diacylglycerol kinase that converts diacylglycerol/DAG into phosphatidic acid/phosphatidate/PA and regulates the respective levels of these two bioactive lipids (PubMed:12200442, PubMed:23949095). Thereby, acts as a central switch between the signaling pathways activated by these second messengers with different cellular targets and opposite effects in numerous biological processes (Probable). By controlling the levels of diacylglycerol, regulates for instance the PKC and EGF receptor signaling pathways and plays a crucial role during development (By similarity). May also regulate clathrin-dependent endocytosis (PubMed:17880279). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9PUQ8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12200442, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17880279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23949095, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Coated pit;Cytoplasm;Endocytosis;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Transport;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; glycerolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12200442}. |
This gene encodes a cytoplasmic enzyme that phosphorylates diacylglycerol to produce phosphatidic acid. Diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid are two lipids that act as second messengers in signaling cascades. Their cellular concentrations are regulated by the encoded protein, and so it is thought to play an important role in cellular signal transduction. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8527; |
clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; diacylglycerol kinase activity [GO:0004143]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; diacylglycerol metabolic process [GO:0046339]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lipid phosphorylation [GO:0046834]; negative regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090038]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:2000370]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12200442_Alternative splicing of the gene generates two isoforms differing in their expression patterns and in regulatory functions 15228384_Phosphorylation is involved in the control of subcellular localization of DGKdelta1. 17357084_Disruption of diacylglycerol kinase delta (DGKD) is associated with seizures in humans and mice. 18267070_Study identified reduced diacylglycerol kinase delta (DGKdelta) expression and DGK activity in skeletal muscle from type 2 diabetic patients. 18334213_Polymerization of DGK delta regulates the activity of the enzyme by sequestering DGK delta in an inactive cellular location. 20064931_Data indicate a novel mechanism where diacylglycerol kinase delta and protein kinase Calpha modulate the levels of ubiquitinated epidermal growth factor receptors through Akt and ubiquitin-specific protease 8. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20857926_Zinc site mutations impair DGKdelta localization to cytoplasmic puncta and enhance localization the plasma membrane. 22406787_This study demonistrated that the lack of association of DGKD SNPs with PD in the Han Chinese population. 23184957_Diacylglycerol signaling limits Akt activation through diacylglycerol kinase delta and PHLPP2. 28199087_purification and characterization of DGKepsilon's enzymatic and conformational properties 31980461_Diacylglycerol kinase delta and sphingomyelin synthase-related protein functionally interact via their sterile alpha motif domains. |
ENSMUSG00000070738 |
Dgkd |
593.119080 |
0.4981466269 |
-1.005358 |
0.114928387 |
75.763535 |
0.00000000000000000319751822995318479687185634724717426795980447000130632295711308188401744700968265533447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000026118079177702824951157186419949144996988655274307300491187788793467916548252105712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
416.1826167 |
29.4251408 |
841.2315814 |
42.5878534 |
| ENSG00000077147 |
56889 |
TM9SF3 |
protein_coding |
Q9HD45 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in protein localization to membrane. Predicted to be located in exocytic vesicle. Predicted to be active in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56889; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; protein localization to membrane [GO:0072657] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24642718_TM9SF3 participates in tumor invasion and serves as a prognostic factor. 28390114_Authors confirmed that TM9SF3 was a target gene of miR-1193 by luciferase reporter gene assay. Gene overexpression and knockdown experiments in Jurkat cells revealed that TM9SF3 positively regulated cell proliferation and invasion. |
ENSMUSG00000025016 |
Tm9sf3 |
1164.833447 |
2.3241505167 |
1.216704 |
0.104529292 |
132.404535 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000122036264031169471009912144946707825096700774209923000708365675510111017839910653101642701301443594275042414665222167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000015912148914311496567528463490246316936172894670841926697200460851812334572125649800877766892881481908261775970458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1556.3160453 |
133.7201050 |
675.2303907 |
42.3838328 |
| ENSG00000077232 |
54431 |
DNAJC10 |
protein_coding |
Q8IXB1 |
FUNCTION: Endoplasmic reticulum disulfide reductase involved both in the correct folding of proteins and degradation of misfolded proteins. Required for efficient folding of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum by catalyzing the removal of non-native disulfide bonds formed during the folding of proteins, such as LDLR. Also involved in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) by reducing incorrect disulfide bonds in misfolded glycoproteins recognized by EDEM1. Interaction with HSPA5 is required its activity, not for the disulfide reductase activity, but to facilitate the release of DNAJC10 from its substrate. Promotes apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12411443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18400946, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19122239, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23769672}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Oxidoreductase;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an endoplasmic reticulum co-chaperone which is part of the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation complex involved in recognizing and degrading misfolded proteins. The encoded protein reduces incorrect disulfide bonds in misfolded glycoproteins. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]. |
hsa:54431; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum chaperone complex [GO:0034663]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ATPase activator activity [GO:0001671]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; disulfide oxidoreductase activity [GO:0015036]; Hsp70 protein binding [GO:0030544]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on a sulfur group of donors, disulfide as acceptor [GO:0016671]; protein-disulfide reductase activity [GO:0015035]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:0036498]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032781]; protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0034975]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
12411443_ERdj5 is a ubiquitous protein localized in the ER and is particularly abundant in secretory cells. Its transcription is induced during ER stress, suggesting potential roles for ERdj5 in protein folding and translocation across the ER membrane. 12446677_JPDI may have roles in folding of some proteins in the ER, chaperoning by BiP and formation of proper disulfide bonds 14587667_The organization of the functional motifs of hMTHr suggests that the protein might be a member of a molecular chaperone family. 18400946_ERdj4 and ERdj5 promote turnover of misfolded SP-C and this activity is dependent on their ability to stimulate BiP ATPase activity. 18653895_study found that an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein ERdj5 had a reductase activity, cleaved the disulfide bonds of misfolded proteins & accelerated ER-associated degradation through its physical and functional associations with EDEM & BiP 19122239_ERdj5 decreases neuroblastoma cell survival by down-regulating the UPR, raising the possibility that this protein could be a target for anti-tumor approaches. 23363602_ERdj5, by binding to Sel1L, triggers BiP-Cholera toxin interaction proximal to the Hrd1 complex; postulate this scenario enables the Hrd1-associated retrotranslocation machinery to capture the toxin efficiently once the toxin is released from BiP 23769672_ERdj5 acts as the endoplasmic reticulum reductase, both preparing misfolded proteins for degradation and catalyzing the folding of proteins that form obligatory non-native disulfides. 25055872_ERdj5 is a member of the proteostasis network that regulates rod opsin biogenesis and supports a role for disulfide bond formation/reduction in rod opsin biogenesis and disease. 28479060_Role of ERdj5 conformational dynamics in endoplasmic reticulum associated degradation 30967862_Ablation of the Chaperone Protein ERdj5 Results in a Sjogren's Syndrome-Like Phenotype in Mice, Consistent With an Upregulated Unfolded Protein Response in Human Patients. 31902119_Downregulation of DNAJC10 (ERDJ5) is associated with poor survival in breast cancer. 32196553_AAV-mediated ERdj5 overexpression protects against P23H rhodopsin toxicity. 34988580_DNAJC10 correlates with tumor immune characteristics and predicts the prognosis of glioma patients. |
ENSMUSG00000027006 |
Dnajc10 |
1021.630055 |
2.0753396154 |
1.053347 |
0.211112941 |
24.404264 |
0.00000078095640772345683820607675426628269121920311590656638145446777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002794335182618749110241814295751971997106011258438229560852050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1357.2119283 |
183.9089801 |
658.1485513 |
64.8419500 |
| ENSG00000077348 |
56915 |
EXOSC5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQT4 |
FUNCTION: Non-catalytic component of the RNA exosome complex which has 3'->5' exoribonuclease activity and participates in a multitude of cellular RNA processing and degradation events. In the nucleus, the RNA exosome complex is involved in proper maturation of stable RNA species such as rRNA, snRNA and snoRNA, in the elimination of RNA processing by-products and non-coding 'pervasive' transcripts, such as antisense RNA species and promoter-upstream transcripts (PROMPTs), and of mRNAs with processing defects, thereby limiting or excluding their export to the cytoplasm. The RNA exosome may be involved in Ig class switch recombination (CSR) and/or Ig variable region somatic hypermutation (SHM) by targeting AICDA deamination activity to transcribed dsDNA substrates. In the cytoplasm, the RNA exosome complex is involved in general mRNA turnover and specifically degrades inherently unstable mRNAs containing AU-rich elements (AREs) within their 3' untranslated regions, and in RNA surveillance pathways, preventing translation of aberrant mRNAs. It seems to be involved in degradation of histone mRNA. The catalytic inactive RNA exosome core complex of 9 subunits (Exo-9) is proposed to play a pivotal role in the binding and presentation of RNA for ribonucleolysis, and to serve as a scaffold for the association with catalytic subunits and accessory proteins or complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11782436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21255825}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Exosome;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;rRNA processing |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Involved in DNA deamination and exonucleolytic catabolism of deadenylated mRNA. Acts upstream of or within defense response to virus. Located in nucleolus; nucleoplasm; and transcriptionally active chromatin. Part of exosome (RNase complex). [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56915; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000177]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; euchromatin [GO:0000791]; exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000178]; nuclear exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000176]; nucleolar exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0101019]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA deamination [GO:0045006]; exonucleolytic catabolism of deadenylated mRNA [GO:0043928]; nuclear mRNA surveillance [GO:0071028]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, exonucleolytic, 3'-5' [GO:0034427]; polyadenylation-dependent snoRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0071051]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; rRNA catabolic process [GO:0016075]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; U4 snRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0034475] |
11812149_association of hCsl4p with the exosome is mediated by protein-protein interactions with hRrp42p and hRrp46p 12419256_Protein-protein interactions between human exosome components support the assembly of RNase PH-type subunits into a six-membered PNPase-like ring. 16815301_These results in our study indicates gene silencing of SOCS1 remarkably enhanced the cytotoxicity efficiency of CML28 DNA vaccine in DCs. 18157497_rAAV/CML28-transduced DCs vaccine may serve as a feasible approach for the treatment of CML28-associated cancers. 20660080_Results suggest that Rrp46 forms a homodimer separately from exosome complexes and, depending on species, is a structural component of the machinery that cleaves DNA during apoptosis. 23392705_Further, subcellular co-localization assay showed that the two proteins could co-localize in the cytoplasm of K562 cells, but WT1/CML28 complexes were not detected by using immunoprecipitation. 30567989_The roles of Prdx1 and Exosc5 in host defense mechanisms in HBV infection. 32504085_Biallelic variants in the RNA exosome gene EXOSC5 are associated with developmental delays, short stature, cerebellar hypoplasia and motor weakness. 34089229_Risk of sudden cardiac death in EXOSC5-related disease. |
ENSMUSG00000061286 |
Exosc5 |
100.097095 |
2.0271142023 |
1.019427 |
0.189464421 |
28.708053 |
0.00000008415307673254197567840365849095585204509006871376186609268188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000334527178177301253055709153241825681845966755645349621772766113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
138.7301638 |
15.3426874 |
68.6992962 |
5.8022390 |
| ENSG00000077585 |
7107 |
GPR137B |
protein_coding |
O60478 |
FUNCTION: Lysosomal integral membrane protein that regulates the localization and activity of mTORC1, a signaling complex promoting cell growth in response to growth factors, energy levels, and amino acids (PubMed:31036939). Interacts with Rag GTPases and increases the lysosomial localization and activity of Rag GTPases and thereby regulates mTORC1 translocation and activity in lysosome (PubMed:31036939). Involved in the regulation of lysosomal morphology and autophagy (PubMed:31036939). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31036939}.; FUNCTION: Acts also as a negative regulator of osteoclast activity (By similarity). Involved in interleukin-4-induced M2 macrophage polarization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BNQ3}. |
Autophagy;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of TORC1 signaling; positive regulation of protein localization to lysosome; and regulation of GTPase activity. Located in lysosomal membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7107; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; negative regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045779]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; positive regulation of protein localization to lysosome [GO:0150032]; positive regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904263]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043030] |
31036939_PR137B-knockout cells exhibited defective autophagy and an expanded lysosome compartment, similar to Rag-knockout cells. Like zebrafish RagA mutants, GPR137B-mutant zebrafish had upregulated TFEB target gene expression and an expanded lysosome compartment in microglia. |
ENSMUSG00000021306 |
Gpr137b |
269.733132 |
2.8712656157 |
1.521687 |
0.122988930 |
152.574189 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000004746068983079238409366957909363163412052569432618744021185356897298046386201723040153553677747422234745044988812878727912902832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000702627664897187149216227668136257259898202016172638390623361660244779493392257096280248407360602413973538205027580261230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
406.8377747 |
28.6729015 |
142.5704817 |
7.9909299 |
| ENSG00000077935 |
27127 |
SMC1B |
protein_coding |
Q8NDV3 |
FUNCTION: Meiosis-specific component of cohesin complex. Required for the maintenance of meiotic cohesion, but not, or only to a minor extent, for its establishment. Contributes to axial element (AE) formation and the organization of chromatin loops along the AE. Plays a key role in synapsis, recombination and chromosome movements. The cohesin complex is required for the cohesion of sister chromatids after DNA replication. The cohesin complex apparently forms a large proteinaceous ring within which sister chromatids can be trapped. At anaphase, the complex is cleaved and dissociates from chromatin, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. The meiosis-specific cohesin complex probably replaces mitosis specific cohesin complex when it dissociates from chromatin during prophase I (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Centromere;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Meiosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
SMC1L2 belongs to a family of proteins required for chromatid cohesion and DNA recombination during meiosis and mitosis (3:Revenkova et al., 2001 [PubMed 11564881]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:27127; |
chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000775]; cohesin complex [GO:0008278]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lateral element [GO:0000800]; meiotic cohesin complex [GO:0030893]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0007062] |
20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25216700_High SMC1B expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 26673124_Data show that structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 1B (SMC1B) is expressed in primary fibroblasts. 28364521_Through the translational regulation of novel RNA targets SMC1B and TEX11, DAZL may have a key role in regulating chromosome cohesion and DNA recombination; two processes fundamental in determining oocyte quality and whose establishment in foetal life may support lifelong fertility. |
ENSMUSG00000022432 |
Smc1b |
62.895572 |
0.1619018266 |
-2.626809 |
1.016833518 |
5.721612 |
0.01675733874568180806208239630450407275930047035217285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.030592247357608348679036680550780147314071655273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.9800504 |
10.3671448 |
114.1450196 |
43.9415466 |
| ENSG00000077984 |
8530 |
CST7 |
protein_coding |
O76096 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits papain and cathepsin L but with affinities lower than other cystatins. May play a role in immune regulation through inhibition of a unique target in the hematopoietic system. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Thiol protease inhibitor |
|
The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and the kininogens. The type 2 cystatin proteins are a class of cysteine proteinase inhibitors found in a variety of human fluids and secretions. This gene encodes a glycosylated cysteine protease inhibitor with a putative role in immune regulation through inhibition of a unique target in the hematopoietic system. Expression of the protein has been observed in various human cancer cell lines established from malignant tumors. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8530; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004869]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inhibition of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097340]; negative regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903979]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; positive regulation of myelination [GO:0031643] |
12423348_cystatin F is an intracellular cysteine peptidase inhibitor with readily regulated expression 15212960_CST7 is secreted, but artificial modification of its C-terminus can induce its endocytic targeting. 15752368_Cystatin F was not colocalized with cystatin C shich suggests distinct functions for these two cysteine protease inhibitors in U937 cells. 16601115_analysis of reduction-dependent activation of human cystatin F 18256700_A latent protease inhibitor which is itself regulated by proteolysis in the endocytic pathway. 19192250_Data demonstrate the addition of N-linked sugars to an Asn-X-Cys motif in cystatin F and suggest that the mannose 6-phosphate sorting machinery is used to divert cystatin F from the secretory pathway and to mediate its uptake from extracellular pools. 21344476_Transgenic cystatin F is expressed in model mice only during demyelination; in chronic demyelination, remyelinating ability is lost. 22365146_Regulation of cathepsins S and L by cystatin F during maturation of dendritic cells. 30033148_during monocyte to macrophage differentiation, the endosomal/lysosomal proteolytic activity can be regulated by cystatin F whose expression is under the control of transcriptional factor C/EBP alpha. 31059105_Cystatin F was identified as the key subunit of family 2 cystatins in survival analysis. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients who harbored a higher expression level of CST7 had a lower risk in overall survival. The prognostic nomogram indicated that the CST7 expression model effectively predicted the outcomes of patients with earlystage PDAC. 32947653_Exploring the factors underlying remyelination arrest by studying the post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of cystatin F gene. 33868254_Transcriptomic Profiling Identifies Neutrophil-Specific Upregulation of Cystatin F as a Marker of Acute Inflammation in Humans. 34189679_Cystatin F acts as a mediator of immune suppression in glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000068129 |
Cst7 |
8.867862 |
10.9804255518 |
3.456862 |
0.736384209 |
27.460878 |
0.00000016030468892780308246752245249222568190816673450171947479248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000618911119166720764369813388705576784332151873968541622161865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.7904922 |
7.9327211 |
1.5421712 |
0.6749300 |
| ENSG00000078081 |
27074 |
LAMP3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UQV4 |
FUNCTION: Lysosomal membrane glycoprotein which plays a role in the unfolded protein response (UPR) that contributes to protein degradation and cell survival during proteasomal dysfunction (PubMed:25681212). Plays a role in the process of fusion of the lysosome with the autophagosome, thereby modulating the autophagic process (PubMed:24434718). Promotes hepatocellular lipogenesis through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway (PubMed:29056532). May also play a role in dendritic cell function and in adaptive immunity (PubMed:9768752). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24434718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25681212, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29056532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9768752}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays a positive role in post-entry steps of influenza A virus replication, either virus uncoating, cytosolic transport, or nuclear import of viral components, and promotes nuclear accumulation of influenza nucleoprotein/NP at early stages of viral infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21810281}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Supports the FURIN-mediated cleavage of mumps virus fusion protein F by interacting with both FURIN and the unprocessed form but not the processed form of the viral protein F. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32295904}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Promotes the intracellular proliferation of Salmonella typhimuium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27329040}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Dendritic cells (DCs) are the most potent antigen-presenting cells. Immature DCs efficiently capture antigens and differentiate into interdigitating dendritic cells (IDCs) in lymphoid tissues that induce primary T-cell responses (summary by de Saint-Vis et al., 1998 [PubMed 9768752]).[supplied by OMIM, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:27074; |
alveolar lamellar body membrane [GO:0097233]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; establishment of protein localization to organelle [GO:0072594]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901799]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of viral life cycle [GO:1903900]; response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035455] |
16204031_Findings indicate that LAMP3 overexpression is associated with an enhanced metastatic potential and may be a prognostic factor for cervical cancer. 16887987_LAMP-1 and DC-LAMP antigen chimeras follow different trafficking pathways, induce distinct modulatory immune responses, and are able to present cryptic epitopes. 17056097_DC-LAMP staining was lost in solid type adenocarcinomas but persisted in well-differentiated areas and there was no prognostic difference in tumors that reacted with DC-LAMP. 17606713_DC-LAMP has a role in preventing the progression of micrometastatic melanoma in lymph nodes 18292234_In rheumatoid arthritis patients, the number of CD304(+) plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) exceeded that of CD1c(+) myeloid DCs (mDCs), with the majority of infiltrating DCs being CD83(-) or DC-LAMP(-). 19308021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19335688_Because a defect of the granular layer in psoriatic lesions has been recognized, increased expression of lysosome-related CD208 in the basal and suprabasal keratinocytes of psoriatic lesions might represent aberrant epidermal differentiation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20863830_Data show that the ABCA3 N-terminus is proteolytically removed inside acidic LAMP3-positive vesicles MVB/LB. 21319150_In the current breast cancer cohorts, LAMP3 had independent prognostic value. 21596034_Both DC-LAMP and DC-SIGN proteins may be involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. 21810281_LAMP3 is an influenza A virus inducible gene, and plays an important role in viral post-entry steps. 22809326_The crystal structure of the conserved domain of human DC-LAMP was solved. 23294542_the PERK/ATF4/LAMP3-arm of the UPR is an additional pathway mediating hypoxia-induced breast cancer cell migration 23569139_DC-LAMP and DC-SIGN may be involved in the pathogenesis of condyloma acuminatum. 23651994_LAMP3 is a driver of interferon related genes as demonstrated by siRNA experiments and by gene expression in cervical carcer samples. 23876802_These results suggest that Treg-DC interactions may promote chronic H. pylori infection by rendering gastric DCs tolerogenic. 24045183_the association between hypoxia, metastasis, and poor prognosis is due, in part, to hypoxic activation of the unfolded protein response and expression of LAMP3. 24081865_Increase in CD208+ dendritic cells in tonsils is associated with immunoglobulin A nephropathy 24434718_LAMP3 knockdown in MCF7 breast cancer cells increases tamoxifen sensitivity. 24631562_the MCCC1/LAMP3 gene can decrease the risk of Parkinson disease in Chinese population. 24634103_LAMP3 gene expression is relevant for prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. 25362357_LAMP3 and TP53 protein expression was significantly higher in cancerous gastrointestinal tissues compared to normal and benign tissues; only LAMP3 expression correlated with poor overall survival 25681212_LAMP3 regulation as part of the unfolded protein response contributes to protein degradation and cell survival during proteasomal dysfunction. 26191259_In laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, high LAMP3 and high TP53 protein expression was significantly associated with tumor stage and size and patients with high expression of these proteins had poor overall survival. 26263981_our results suggest that epithelial LAMP3 expression is an independent prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . 27329040_study indicates that LAMP-3 is induced by Salmonella infection and recruited to the Salmonella pathogen for intracellular proliferation. 27697285_this study shows that the vitamin D3 reduce the LAMP3 expression during the dendritic cells differentiation and maturation, via NFkappaB pathways 27759212_LAMP3 variants found to be associated with Bipolar disorder or Schizophrenia in other populations are also associated with Bipolar disorder risk in Latinos. 28349821_Immunohistochemical results showed that high lysosome-associated membrane protein 3 cytoplasmic expression was significantly related to tumor grade ( p = 0.038), lymph node metastasis ( p = 0.049), metastasis ( p |
|
|
108.150918 |
23.5782387749 |
4.559384 |
0.290112569 |
351.629812 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000187166175184988773580655615493450526401145785791352917298045140749275374772783721877009561471755561939071475817471463351126528300504124460035932889506161536903079001632814921808787670748502342775443363365184268332086503505706787109375000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000061527232644330384731933560704580383554645211209515541335449120150269609115242574296653482155397949668932481756241880503470982543676977828204763596895009525197248656628937926701567112672069080614445368837550631724298000335693359375000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
211.6120430 |
40.2804407 |
9.0347088 |
1.6197983 |
| ENSG00000078237 |
57103 |
TIGAR |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ88 |
FUNCTION: Fructose-bisphosphatase hydrolyzing fructose-2,6-bisphosphate as well as fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (PubMed:19015259). Acts as a negative regulator of glycolysis by lowering intracellular levels of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate in a p53/TP53-dependent manner, resulting in the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) activation and NADPH production (PubMed:16839880, PubMed:22887998). Contributes to the generation of reduced glutathione to cause a decrease in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) content, correlating with its ability to protect cells from oxidative or metabolic stress-induced cell death (PubMed:16839880, PubMed:19713938, PubMed:23726973, PubMed:22887998, PubMed:23817040). Plays a role in promoting protection against cell death during hypoxia by decreasing mitochondria ROS levels in a HK2-dependent manner through a mechanism that is independent of its fructose-bisphosphatase activity (PubMed:23185017). In response to cardiac damage stress, mediates p53-induced inhibition of myocyte mitophagy through ROS levels reduction and the subsequent inactivation of BNIP3. Reduced mitophagy results in an enhanced apoptotic myocyte cell death, and exacerbates cardiac damage (By similarity). Plays a role in adult intestinal regeneration; contributes to the growth, proliferation and survival of intestinal crypts following tissue ablation (PubMed:23726973). Plays a neuroprotective role against ischemic brain damage by enhancing PPP flux and preserving mitochondria functions (By similarity). Protects glioma cells from hypoxia- and ROS-induced cell death by inhibiting glycolysis and activating mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxygen consumption in a TKTL1-dependent and p53/TP53-independent manner (PubMed:22887998). Plays a role in cancer cell survival by promoting DNA repair through activating PPP flux in a CDK5-ATM-dependent signaling pathway during hypoxia and/or genome stress-induced DNA damage responses (PubMed:25928429). Involved in intestinal tumor progression (PubMed:23726973). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BZA9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16839880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19015259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19713938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22887998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23185017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23726973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23817040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25928429}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Apoptosis;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is regulated as part of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and encodes a protein with sequence similarity to the bisphosphate domain of the glycolytic enzyme that degrades fructose-2,6-bisphosphate. The protein functions by blocking glycolysis and directing the pathway into the pentose phosphate shunt. Expression of this protein also protects cells from DNA damaging reactive oxygen species and provides some protection from DNA damage-induced apoptosis. The 12p13.32 region that includes this gene is paralogous to the 11q13.3 region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57103; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; bisphosphoglycerate 2-phosphatase activity [GO:0004083]; fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 2-phosphatase activity [GO:0004331]; cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010659]; cellular response to cobalt ion [GO:0071279]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; fructose 1,6-bisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0030388]; fructose 2,6-bisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0006003]; glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate [GO:0019661]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; intestinal epithelial cell development [GO:0060576]; mitophagy [GO:0000423]; negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate [GO:1904024]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of mitophagy [GO:1901525]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; negative regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043069]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010666]; positive regulation of DNA repair [GO:0045739]; positive regulation of hexokinase activity [GO:1903301]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt [GO:0043456]; regulation of response to DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:1902153]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
16839880_The decrease of intracellular ROS levels in response to TIGAR may also play a role in the ability of p53 to protect from the accumulation of genomic damage. 18945750_correlation between the recently described p53-inducible apoptosis gene TIGAR and both sensitivity to fludarabine and hENT2 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. 19713938_TIGAR can modulate reactive oxygen species in response to nutrient starvation or metabolic stress, and functions to inhibit autophagy. 21057531_Inhibition of TIGAR by c-Met results in reduction of cellular NADPH and cell death. 21761199_SP1 can interact with the SP1-binding site within TIGAR promoter in vitro and in vivo. Conclusively, SPl is indispensable for basal activity of TIGAR promoter. 21820150_These results suggest that p53 can modulate the metabolic pathways via the proteins SCO2 and TIGAR in human breast cancer. 21864926_TIGAR abrogation provides a novel adjunctive therapeutic strategy against glial tumors by increasing radiation-induced cell impairment, thus allowing the use of lower radiotherapeutic doses. 22782351_TIGAR regulates the expression of genes involved in cell-cycle progression. 22887998_Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) protects glioma cells from starvation-induced cell death by up-regulating respiration and improving cellular redox homeostasis 23185017_The ability of TIGAR to function as a Fru-2,6-BPase was independent of hexokinase 2 binding and mitochondrial localization, although activities can contribute to the activity of TIGAR in limiting mitochondrial ROS levels and protecting from cell death. 23612020_oroxylin A could increase protein and mRNA expression of TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) and synthesis of cytochrome c oxidase 2 (SCO2), which are the key metabolic modulators regulated by p53. 23640457_TIGAR regulates akt and erk phosphorylation but hase no effect on NF-kappa B activation in neocazinostatin-treated cells. 23726973_TIGAR has roles in efficient intestinal regeneration and tumorigenesis 23817040_data provide the first evidence that targeted silencing of TIGAR induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death in HepG2 cells 23832602_TIGAR gene expression is down regulated by oxidative stress through the mediation of reactive oxygen species 24036271_CREB regulates TIGAR expression via a CRE-binding site at the TIGAR promoter. 24363807_TIGAR is correlated with maximal standardized uptake value on FDG-PET and survival in non-small cell lung cancer. 24423178_The kinetic properties and the structural similarity of the best substrates of TIGAR make it unlikely that TIGAR modulates cellular fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels directly. 24632713_Data show targeting MUC1-C is synergistic with bortezomib (BTZ) in suppressing p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis (TIGAR)-mediated regulation of reactive oxygen species levels for combining GO-203 with BTZ in BTZ resistance. 25085248_Results revealed that TIGAR inhibits both apoptosis and autophagy. 25660220_miR-144 targeted TIGAR, inhibited proliferation, enhanced apoptosis, and increased autophagy in A549 and H460 cells 25928429_The Cdk5-AMT signal pathway involved in regulation of DDR by TIGAR. 26191173_TIGAR over-expression could diminish the radiosensitivity of Hs 917.T cells, and the autophagy level induced by ionizing radiation (IR) was also decreased by TIGAR transfection. 26675982_TIGAR expression may be used as a bio-marker for detection of colorectal cancer and can be used as a target for developing therapeutics for the treatment of colorectal cancer. 26691054_TIGAR knockdown reduced tumor growth rate. 26700591_Geranylgeranoic acid induced upregulation of the TIGAR gene, which might inhibit the glycolysis in HuH-7 cells with p53 mutation. 27491040_we investigate the crosstalk between PFKFB3 and TIGAR (TP53-Induced Glycolysis and Apoptosis Regulator), a protein known to protect cells from oxidative stress. Our results show consistent TIGAR induction in HeLa cells in response to PFKFB3 knockdown 27499152_This study demonstrated that a high p53 expression could be associated with the promotion of glycolysis in gastric cancer via the modulation of TIGAR expression. 27705786_simultaneous mutations at all four acetylation sites completely abolish its ability to regulate metabolic targets, such as TIGAR and SLC7A11. Moreover, p53(4KR) is still capable of inducing the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop, but p53-dependent ferroptotic responses are markedly abrogated 27803158_TIGAR expression in breast carcinoma cells promotes metabolic compartmentalization and tumor growth with a mitochondrial metabolic phenotype with lactate and glutamine catabolism. 27884166_High TIGAR expression was an independent predictor of poor survival and high incidence of relapse in adult patients with CN-AML. TIGAR also showed high expression in multiple human leukemia cell lines and knockdown of TIGAR activated glycolysis through PFKFB3 upregulation in human leukemia cells. 28138701_the upregulation of hsamiR101 in ccRCC was induced by hypoxia. Its expression deceased the protein expression of TIGAR and promoted glycolysis. This regulatory pathway may represent a novel mechanism of carcinogenesis and requires further investigation. 28338004_Knockdown of TP53 induced glycolysis and apoptosis(TIGAR) was able to radiosensitize thioredoxin reductase-1-overexpressing gliomas by inhibiting irradiation -induced thioredoxin-1 nuclear transport. 28384067_The study showed that miR-101 inhibited viability, induced apoptosis, pushed glucose metabolism flux from the pentose phosphate pathway into glycolysis in prostate cancer PC3 cell line by decreasing NADPH levels by throughly directly binding to 3'-UTR of TIGAR mRNA and repressing TIGAR expression. 29753331_Study found that downregulation of TIGAR reduced the invasion and metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells in vitro and in vivo. TIGAR and Met protein expression was positively correlated with late stages of lung cancer. Patients with high co-expression of TIGAR and Met presented a significantly worse survival. In addition, Met signaling pathway is involved in TIGAR-induced invasion and metastasis. 29777913_findings demonstrate that the HTLV-1 latency-maintenance factor p30(II) induces the TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) and counters the oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and cytotoxicity caused by the viral oncoproteins Tax and HBZ 30267647_TIGAR protein, is present in SN Lewy bodies of both sporadic PD and DLB. The absence of TIGAR protein in the pathological inclusions of MND or MSA suggests disease specificity and further raises the possibility that TIGAR may be involved in PD pathogenesis. 30814486_TIGAR promotes metabolic reprogramming and regulates NSC differentiation through an epigenetic mechanism. 30823646_TIGAR knockdown enhanced glioma cell sensitivity to cell hypoxia, irradiation and temozolomide. 31062473_Down-regulation of TFAM increases the sensitivity of tumour cells to radiation via p53/TIGAR signalling pathway. 31119791_The miR-885-5p and its precursor both can interact mechanically with TIGAR promoter binding site and alter local chromatin structure, and subsequently upregulate TIGAR expression and participate in liver tumorigenesis. 31317559_TIGAR impedes compression-induced intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and autophagy. 31983610_TIGAR expression is modulated during pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development 32206103_Metabolic remodeling by TIGAR overexpression is a therapeutic target in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. 34082063_Targeting neuroinflammation to treat cerebral ischemia - The role of TIGAR/NADPH axis. 34369624_TCF19 and p53 regulate transcription of TIGAR and SCO2 in HCC for mitochondrial energy metabolism and stress adaptation. 35163828_The Expression of TP53-Induced Glycolysis and Apoptosis Regulator (TIGAR) Can Be Controlled by the Antioxidant Orchestrator NRF2 in Human Carcinoma Cells. 35271998_TIGAR drives colorectal cancer ferroptosis resistance through ROS/AMPK/SCD1 pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000038028 |
Tigar |
66.400820 |
2.3858041828 |
1.254476 |
0.259442383 |
22.948532 |
0.00000166397199234544493388020507812496973087945661973208189010620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005739711756723246017391788093009452609294385183602571487426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.8805945 |
15.6703945 |
39.8147409 |
4.9662484 |
| ENSG00000078246 |
7289 |
TULP3 |
protein_coding |
O75386 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of the Shh signaling transduction pathway: recruited to primary cilia via association with the IFT complex A (IFT-A) and is required for recruitment of G protein-coupled receptor GPR161 to cilia, a promoter of PKA-dependent basal repression machinery in Shh signaling. Binds to phosphorylated inositide (phosphoinositide) lipids. Both IFT-A- and phosphoinositide-binding properties are required to regulate ciliary G protein-coupled receptor trafficking. Not involved in ciliogenesis. During adipogenesis, regulates ciliary trafficking of FFAR4 in preadipocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11375483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20889716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31761534}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Secreted |
|
This gene encodes a member of the tubby gene family of bipartite transcription factors. Members of this family have been identified in plants, vertebrates, and invertebrates, and they share a conserved N-terminal transcription activation region and a conserved C-terminal DNA and phosphatidylinositol-phosphate binding region. The encoded protein binds to phosphoinositides in the plasma membrane via its C-terminal region and probably functions as a membrane-bound transcription regulator that translocates to the nucleus in response to phosphoinositide hydrolysis, for instance, induced by G-protein-coupled-receptor signaling. It plays an important role in neuronal development and function. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2009]. |
hsa:7289; |
9+0 non-motile cilium [GO:0097731]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; cilium [GO:0005929]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; intraciliary transport particle A binding [GO:0120160]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; bone development [GO:0060348]; brain development [GO:0007420]; bronchus morphogenesis [GO:0060434]; central nervous system neuron differentiation [GO:0021953]; embryonic camera-type eye development [GO:0031076]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic neurocranium morphogenesis [GO:0048702]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; ganglion development [GO:0061548]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning [GO:1901621]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway involved in ventral spinal cord patterning [GO:0021914]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning [GO:0060831] |
20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24668219_Data demonstrated that pancreatic cancer patients exhibiting high transcriptional levels of TULP3 showed a poor overall survival rate. 30583862_Formation of primary cilia is downregulated in TULP3-knockout (KO) RPE1 cells. ARL13B and INPP5E fail to localize to primary cilia in TULP3-KO cells. 30640939_TULP3 expression levels were increased in colorectal cancer when compared to the adjacent non-tumoral tissue. In addition, higher TULP3 gene expression was associated to lymphatic and vascular invasion in colon adenocarcinoma and rectum adenocarcinoma, respectively. 34874810_MicroRNA-506 has a suppressive effect on the tumorigenesis of nonsmall-cell lung cancer by regulating tubby-like protein 3. 35344762_TULP3 silencing suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer via the PTEN/Akt/Snail pathway. 35397207_Progressive liver, kidney, and heart degeneration in children and adults affected by TULP3 mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000001521 |
Tulp3 |
29.330061 |
2.3638182959 |
1.241119 |
0.327558183 |
14.310721 |
0.00015497967363966411885080332044850592865259386599063873291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000413952222750894373044100449376969663717318326234817504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.7652255 |
8.0270247 |
18.3172995 |
2.6567586 |
| ENSG00000078269 |
8871 |
SYNJ2 |
protein_coding |
O15056 |
FUNCTION: Inositol 5-phosphatase which may be involved in distinct membrane trafficking and signal transduction pathways. May mediate the inhibitory effect of Rac1 on endocytosis. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Synapse |
|
The gene is a member of the inositol-polyphosphate 5-phosphatase family. The encoded protein interacts with the ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1, which causes translocation of the encoded protein to the plasma membrane where it inhibits clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:8871; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0034596]; phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase activity [GO:0052629]; phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0043813]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphatase activity [GO:0004438]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0004439]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; brain development [GO:0007420]; inositol phosphate dephosphorylation [GO:0046855]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856]; synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0048488] |
14562116_Since Syn 2 is a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphatase involved in cell growth and rearrangement of actin filaments, the increased Syn 2 expression may correlate with the hairy cell leukemia etiology or the characteristic morphologic alterations. 15548694_contributes to the role of Rac1 in cell invasion and migration by regulating the formation of invadopodia and lamellipodia 16102578_Identification of inactivating mutations in the JAK1, SYNJ2, and CLPTM1 genes in prostate cancer cells 21555518_SYNJ2 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 22045296_SYNJ2 is a novel gene in which variation is potentially associated with cognitive abilities. 22213687_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in SYNJ2 are associated with personality disorders. 23076136_Src-mediated phosphorylation of SYNJ2 contributes to invadopodia formation. 24077433_The genetic interactions associated with ILVatrophy rate in this study may be mapping variants inSYNJ2andPI4KAthat interact to decrease synthesisof PIP. 25605973_Synaptojanin 2 is a druggable mediator of metastasis and the gene is overexpressed and amplified in breast cancer. 26616230_Results, combined with previous studies, suggest that rs9365723, located on SYNJ2, is associated with the risk of CRC in a Chinese population. 33641617_Identifying the Prognostic Risk Factors of Synaptojanin 2 and Its Underlying Perturbations Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 35581615_SYNJ2 is a novel and potential biomarker for the prediction and treatment of cancers: from lung squamous cell carcinoma to pan-cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000023805 |
Synj2 |
548.020127 |
3.3071380757 |
1.725583 |
0.083307793 |
428.933050 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002774024087756035049901673704259984126040485018251276702464293383707144482129485549054832056660997326993124466405872232875942605602629807905905357396656802078030775306209802409712715497450348815860460131621733364326427251139466127966351 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001106610690142677761177542847960709262270584503968700599144729135463405743747325587102404391581845000265916046560183784205614115501395209353517113345306309683636768021316862726735393709043824220074313133312708034792546874740921340057875 |
Yes |
Yes |
823.3496240 |
39.1704307 |
250.7830829 |
9.5053629 |
| ENSG00000078399 |
3205 |
HOXA9 |
protein_coding |
P31269 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. Required for induction of E-selectin and VCAM-1, on the endothelial cells surface at sites of inflammation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22269951}. |
Chromosomal rearrangement;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Methylation;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. This gene is highly similar to the abdominal-B (Abd-B) gene of Drosophila. A specific translocation event which causes a fusion between this gene and the NUP98 gene has been associated with myeloid leukemogenesis. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the upstream homeobox A10 (HOXA10) gene.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:3205; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; definitive hemopoiesis [GO:0060216]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; endothelial cell activation [GO:0042118]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045638]; prostate gland development [GO:0030850]; proximal/distal pattern formation [GO:0009954]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to testosterone [GO:0033574]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; uterus development [GO:0060065] |
9058712_demonstrates a physiological role of the mouse protein in blood cell differentiation, with the greatest apparent influence at the level of the commited progenitor 11830496_the fusion gene NUP98-HOXA9 is an important gene in myeloid leukemogenesis. 12082612_Nup98-HoxA9 immortalizes myeloid progenitors, enforces expression of Hoxa9, Hoxa7 and Meis1, and alters cytokine-specific responses in a manner similar to that induced by retroviral co-expression of Hoxa9 and Meis1. 12112533_The HOXA9 cluster gene is frequently expressed in cell lines from acute myeloid leukemia cases with 11p15 translocations; in some cases HOX9 is not fused to NUP98. 12138901_The NUP98/HOXA9 FUSION transcript was detected by PC at exon A and not exon B of NUP98. 12923056_HOXA9 complexed with Pbx1 and DNA, so that the posterior Hox hexapeptide adopts an altered conformation. 14561764_Nup98-HOXA9 has a role in inducing gene transcription in myeloid cells 14562113_B-lineage development can proceed in t(4;11) leukemic blasts in the absence of HOX-A gene expression. 14701735_Hoxa9 and Hoxa7 as well as the Hox coregulators Meis1 and Pbx3 among the targets upregulated by MLL-ENL-ERtm in conditionally transformed cells 14738146_Lower expression of HOXA9 is associated with acute myeloid leukemia-M2 14764452_HoxA9 binds to the EphB4 promoter & stimulates its expression resulting in an increase of endothelial cell migration and tube forming activity. Thus, modulation of EphB4 expression may contribute to the proangiogenic effect of HoxA9 in endothelial cells. 15160920_suggest that MLL aberrations may regulate MEIS1 and HOXA9 gene expression in ALL-derived cell lines, while AML-derived cell lines express these genes independently of the MLL status 15254242_HOXA9 nuclear transport is induced by thrombopoietin in immature hematopoietic cells 15454493_Dnalc4, Fcgr2b, Fcrl, and Con1 genes cooperated with NUP98-HOXA9 in transforming NIH 3T3 cells 15479723_advantage to Meis1-HoxA9 coexpressing cells in vivo, leading to leukemogenesis. 15657436_HOXA9, is a positive regulator of eIF4E. HOXA9 stimulates eIF4E-dependent export of cyclin D1 and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) mRNAs in the nucleus, as well as increases the translation efficiency of ODC mRNA in the cytoplasm. 15681849_CYBB is a common target gene repressed by HoxA10 and activated by HoxA9, and Meis1 and Nup98-hoxA9 have roles in repressing myeloid-specific gene transcription 15960975_The HOXA9 protein expression was significantly downregulated in the MOF knockdown cells compared to control siRNA-treated cells. 16105979_90% of meningioma 1-ets variant gene 6 +/HOXA9+ mice developed AML much more rapidly than control HOXA9+ mice 16630659_The relative HOXA9 expression was higher in patients in the accelerated phase of the disease (pA polymorphism increases congenital talipes equinovarus risk in a Chinese population. 31670914_Correlation of miR-181a and three HOXA genes as useful biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. 31683603_Loss of HOXA9 in cSCC significantly upregulates RELA expression and thus enhances NF-kappaB pathway. RELA transcriptionally promotes not only anti-apoptotic factor BCL-XL but also autophagic genes including ATG1, ATG3, and ATG12. 31740654_The direct regulation of HOXA9 by miR-652 was experimentally validated in uveal melanoma cells by dual luciferase assay and Western blotting. Authors also observed that miR-652 promoted HIF-1alpha signaling via repression of HOXA9 in uveal melanoma cells. 31768018_MicroRNA-708 is a novel regulator of the Hoxa9 program in myeloid cells. 31865042_Longitudinal monitoring of HOXA9 meth-ctDNA is clinically feasible and is strongly correlated to clinical outcomes (PFS, OS). 31875764_MiR-210 inhibited the expression of HOXA9 to activate the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and mediated the occurrence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of pancreatic cancer cells induced by HIF-1a under hypoxia. 31881106_miR-647 inhibits glioma cell proliferation, colony formation and invasion by regulating HOXA9. 31906958_MiR-182-5p and its target HOXA9 in non-small cell lung cancer: a clinical and in-silico exploration with the combination of RT-qPCR, miRNA-seq and miRNA-chip. 31923345_A novel molecular link between HOXA9 and WNT6 in glioblastoma identifies a subgroup of patients with particular poor prognosis. 31986484_Generation and characterization of a human iPSC line derived from congenital clubfoot amniotic fluid cells. 32191343_Detection of aberrant methylation of HOXA9 and HIC1 through multiplex MethyLight assay in serum DNA for the early detection of epithelial ovarian cancer. 32430478_Detection of Promoter DNA Methylation in Urine and Plasma Aids the Detection of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 32730594_Trib1 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression by modulating the transcriptional programs of Hoxa9. 32820015_Entospletinib in Combination with Induction Chemotherapy in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Response and Predictive Significance of HOXA9 and MEIS1 Expression. 33001025_Functional interrogation of HOXA9 regulome in MLLr leukemia via reporter-based CRISPR/Cas9 screen. 33057942_Disruption of CTCF Boundary at HOXA Locus Promote BET Inhibitors' Therapeutic Sensitivity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 33069783_HOXA9/IRX1 expression pattern defines two subgroups of infant MLL-AF4-driven acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 33202249_Gene- and Species-Specific Hox mRNA Translation by Ribosome Expansion Segments. 33461426_Homeobox A5 and A9 expression and beta-thalassemia. 33924850_Nuclear FGFR2 Interacts with the MLL-AF4 Oncogenic Chimera and Positively Regulates HOXA9 Gene Expression in t(4;11) Leukemia Cells. 34163069_Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancer development. 34416888_MicroRNA-638 inhibits the progression of breast cancer through targeting HOXA9 and suppressing Wnt/beta-cadherin pathway. 34514844_HOXA9-methylated DNA as a diagnostic biomarker of ovarian malignancy. 34831074_The Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor Is Required for the NUP98-HOXA9-Induced Aberrant Nuclear Envelope Phenotype. 34850551_ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 triggers the development of LSCC via upregulation of HOXA9. 34913472_Circular RNA circFADS2 inhibits the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-766-3p/HOXA9 axis. 35372588_Comprehensive Landscape of HOXA2, HOXA9, and HOXA10 as Potential Biomarkers for Predicting Progression and Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. 35743243_HOXA9 Overexpression Contributes to Stem Cell Overpopulation That Drives Development and Growth of Colorectal Cancer. 35830966_Downregulation of hsa-miR-548d-3p and overexpression of HOXA9 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients and the risk of R-CHOP chemotherapy resistance and disease progression. 36065412_circ_0052184 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via Targeting miR-604/HOXA9 Axis. 36192425_HOXA9 has the hallmarks of a biological switch with implications in blood cancers. |
ENSMUSG00000038227 |
Hoxa9 |
216.565690 |
0.3650243266 |
-1.453935 |
0.161776852 |
80.119541 |
0.00000000000000000035242971277550303201338912120150852561139969440582447868237636612320784479379653930664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000003005119907895104183623446800363048453583772339929363823229913066370500018820166587829589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
115.7868425 |
13.3521068 |
319.3041381 |
25.0634829 |
| ENSG00000078487 |
55063 |
ZCWPW1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0M4 |
FUNCTION: Dual histone methylation reader specific for PRDM9-catalyzed histone marks (H3K4me3 and H3K36me3) (PubMed:32744506, PubMed:20826339). Facilitates the repair of PRDM9-induced meiotic double-strand breaks (DSBs) (By similarity). Essential for male fertility and spermatogenesis (By similarity). Required for meiosis prophase I progression in male but not in female germ cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6IR42, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20826339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32744506}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Differentiation;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables methyl-CpG binding activity and methylated histone binding activity. Predicted to be involved in meiosis I; positive regulation of DNA metabolic process; and spermatogenesis. Predicted to act upstream of or within homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis. Predicted to be located in XY body. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55063; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis [GO:0007129]; meiosis I [GO:0007127]; positive regulation of DNA recombination [GO:0045911]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000781]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
24743338_Of those 394 variants, 34 showed strong evidence of regulatory function (RegulomeDB score |
ENSMUSG00000037108 |
Zcwpw1 |
74.566118 |
0.2528796801 |
-1.983477 |
0.599026329 |
10.044939 |
0.00152767066315682140988096993083900088095106184482574462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003455696396658189221973156435296914423815906047821044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.0619457 |
12.5115003 |
85.8212304 |
34.3475331 |
| ENSG00000078589 |
27334 |
P2RY10 |
protein_coding |
O00398 |
FUNCTION: Putative receptor for purines coupled to G-proteins. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of G-protein coupled receptors that are preferentially activated by adenosine and uridine nucleotides. There is a pseudogene for this gene nearby on chromosome X. Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:27334; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled purinergic nucleotide receptor activity [GO:0045028]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025] |
18466763_The P2Y(10) receptor is the first receptor identified as a dual lysophospholipid receptor. 29700886_Our data show that the LysoPS-induced eosinophil degranulation most likely occurs through P2Y10. These findings suggest that LysoPS plays a specific role in eosinophils and introduces the possibility of LysoPS/P2Y10-based therapeutics in the treatment of eosinophilic diseases. 34815397_G-protein-coupled receptor P2Y10 facilitates chemokine-induced CD4 T cell migration through autocrine/paracrine mediators. |
ENSMUSG00000050921 |
P2ry10 |
11.553184 |
10.5314893016 |
3.396638 |
0.647710267 |
33.685862 |
0.00000000647697058574539213665940596176447130449815858810325153172016143798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000028725987333414059636891294729002521712857287639053538441658020019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6620206 |
8.8969254 |
2.0771231 |
0.7878693 |
| ENSG00000078596 |
9452 |
ITM2A |
protein_coding |
O43736 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a type II membrane protein that belongs to the ITM2 family. Studies in mouse suggest that it may be involved in osteo- and chondrogenic differentiation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:9452; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process [GO:0042985]; plasma cell differentiation [GO:0002317] |
19541402_Enhanced ITM2A expression inhibits chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. 24516404_our results show one of the first links between phenotypic variation in a population sample and an XCI-escaping locus and pinpoint ITM2A as a potential contributor to the sexual dimorphism in height 25951193_ITM2A expression is positively regulated by PKA-CREB signaling and ITM2A expression interferes with autophagic flux by interacting with vacuolar ATPase. 26125709_The upregulated gene with the largest effect size in ankylosing spondylitis was ITM2A, which plays a role in activation of T cells. (Meta-analysis) 26691219_ITM2A is a new biomarker of poor prognosis in ovarian cancer and a novel tumor suppressor that induces cell cycle arrest, acts as a chemosensitizer, and has therapeutic potential for ovarian cancer. 27809695_ITM2A might be a susceptibility gene for Graves disease in the Xq21.1 locus, and environmental factors, such as viral and bacterial infections, probably contribute to GD pathogenesis by interacting with the risk SNP rs3827440 mediating the regulation of ITM2A expression. 31438969_The ITM2A is a novel positive regulator of autophagy through an mTOR-dependent manner. 32727090_GPR174 and ITM2A Gene Polymorphisms rs3827440 and rs5912838 on the X chromosome in Korean Children with Autoimmune Thyroid Disease. 34161951_Downregulation of ITM2A Gene Expression in Macrophages of Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. 34440772_Integral Membrane Protein 2A Is a Negative Regulator of Canonical and Non-Canonical Hedgehog Signalling. |
ENSMUSG00000031239 |
Itm2a |
45.512033 |
3.8963997847 |
1.962142 |
0.249521365 |
65.682242 |
0.00000000000000052981095759257948305491306646951873586235841123368017768768822861602529883384704589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000003852221543875109421009762287315002153097567069023332564370321051683276891708374023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.9960262 |
12.7229310 |
19.1490232 |
2.7079322 |
| ENSG00000078674 |
5108 |
PCM1 |
protein_coding |
Q15154 |
FUNCTION: Required for centrosome assembly and function (PubMed:12403812, PubMed:15659651, PubMed:16943179). Essential for the correct localization of several centrosomal proteins including CEP250, CETN3, PCNT and NEK2 (PubMed:12403812, PubMed:15659651). Required to anchor microtubules to the centrosome (PubMed:12403812, PubMed:15659651). Also involved in cilium biogenesis by recruiting the BBSome, a ciliary protein complex involved in cilium biogenesis, to the centriolar satellites (PubMed:20551181, PubMed:24121310, PubMed:27979967). Recruits the tubulin polyglutamylase complex (TPGC) to centriolar satellites (PubMed:34782749). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15659651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16943179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20551181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24121310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27979967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34782749}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of centriolar satellites, which are electron dense granules scattered around centrosomes. Inhibition studies show that this protein is essential for the correct localization of several centrosomal proteins, and for anchoring microtubules to the centrosome. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with papillary thyroid carcinomas and a variety of hematological malignancies, including atypical chronic myeloid leukemia and T-cell lymphoma. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. |
hsa:5108; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; pericentriolar material [GO:0000242]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; interkinetic nuclear migration [GO:0022027]; intraciliary transport involved in cilium assembly [GO:0035735]; microtubule anchoring [GO:0034453]; microtubule anchoring at centrosome [GO:0034454]; negative regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050768]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; positive regulation of intracellular protein transport [GO:0090316]; protein localization to centrosome [GO:0071539]; social behavior [GO:0035176] |
15659651_multiple processes involved in regulating the abundance of NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related kinase 2 kinase at the centrosome including microtubule binding, the centriolar satellite component PCM-1, and localized protein degradation 16034466_To study the rearrangement created by the t(8;9)(p22;p24)used dual-colour FISH on metaphases from patient cells using labelled-BAC clones centred on PCM1. 16091753_A genetic translocation in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia yields a new PCM1-JAK2 fusion gene. 16894060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16894060_The PCM1 gene is implicated in susceptibility to schizophrenia and is associated with orbitofrontal gray matter volumetric deficits. 18594780_cytogenetic change of t(8;9)(p22;p24) may induce HLA-DR immunophenotypic switch and a coordination of the two evolutional changes may play a role in leukemic cell progression 18762586_PCM1 gene is implicated in schizophrenia. 18772192_CEP290 binds to PCM-1 and localizes to centriolar satellites in a PCM-1- and microtubule-dependent manner. 19048012_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19455170_decreased colocalization of DISC1 and its binding partner PCM1 after Phe607 DISC1 transfection 20152126_Hook3- and PCM1-mediated dynamic assembly of pericentriolar material is essential for interkinetic nuclear migration. 20360304_DISC1 coding variants modulate centrosomal PCM1 localization, highlight a role for DISC1 in glial function and provide a possible cellular mechanism contributing to the association of these DISC1 variants with psychiatric phenotypes. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20468070_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468070_These data provide further evidence that PCM1-though certainly not a major risk factor in the Northern Swedish population-cannot be ruled out as a contributor to schizophrenia risk and/or protection. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21481569_The data failed to find a significant association between SNPs or haplotypes of the PCM1 gene and schizophrenia in the Japanese population (P>0.28). 21985783_WT HTT regulates ciliogenesis by interacting through huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) with pericentriolar material 1 protein (PCM1). 21998199_PCM1 interacts with Hook2 in a complex that regulates a limiting step required for further initiation of ciliogenesis after centriole maturation. 22100915_NEK7 is essential for PCM accumulation in a cell cycle stage-specific manner. 23110211_CEP90 physically interacts with PCM-1 at centriolar satellites, and this interaction is essential for centrosomal accumulation of the centriolar satellites and eventually for primary cilia formation. 23345402_these data suggest a mechanism whereby the recruitment of Plk1 to pericentriolar matrix by PCM1 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of primary cilia disassembly before mitotic entry. 23372669_Chromosomal translocation [t(8;9)(p22;p24)]/PCM1-JAK2 fusion protein activates SOCS2 and SOCS3 via STAT5 in a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cell line. 24576429_no association between the PCM1 gene and schizophrenia in a Japanese population 24909162_a novel variant in the PCM1 3'UTR is significantly associated with ovarian cancer 24913195_Haematological neoplasms associated with t(8;9)(p22;p24); PCM1-JAK2 have features in common and we suggest that they should be recognized as a specific entity in the WHO classification 27146717_In the absence of PCM1, Mib1 destabilizes Talpid3 through poly-ubiquitylation and suppresses cilium assembly. 28620049_Data suggest that USP9X as an integral component of centrosome where it functions to stabilize PCM1 and CEP55 and to promote centrosome biogenesis; N-terminal domain of USP9X appears to be responsible for physical association of USP9X with PCM1 and CEP55. (USP9X = ubiquitin-specific protease 9X; PCM1 = pericentriolar material 1 protein; CEP55 = 55kDa centrosomal protein) 29567772_detecting PDGFRA, PDGFRB, FGFR1 and PCM1-JAK2 rearrangements is a prerequisite for up-to-date WHO classification, and an essential step in the differential diagnosis of neoplasms with eosinophilia. 30584065_study reveals that USP9X is a constituent of centriolar satellites and functions to maintain centriolar satellite integrity by stabilizing PCM1. 31671755_SNX17 Recruits USP9X to Antagonize MIB1-Mediated Ubiquitination and Degradation of PCM1 during Serum-Starvation-Induced Ciliogenesis. 33214552_PCM1 is necessary for focal ciliary integrity and is a candidate for severe schizophrenia. 34382410_LncRNA-ENST00000421645 promotes T cells to secrete IFN-gamma by sponging PCM1 in neurosyphilis. |
ENSMUSG00000031592 |
Pcm1 |
2148.559583 |
0.4964562734 |
-1.010261 |
0.118586734 |
71.279142 |
0.00000000000000003100966474660554751780088237994061258643313928710927296350519100087694823741912841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000240642824216560379298978810259832172874339915056088323730421052459860220551490783691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1458.3560752 |
139.6759053 |
2954.3543501 |
204.6410049 |
| ENSG00000078687 |
57690 |
TNRC6C |
protein_coding |
Q9HCJ0 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in RNA-mediated gene silencing by micro-RNAs (miRNAs). Required for miRNA-dependent translational repression of complementary mRNAs by argonaute family proteins. As scaffoldng protein associates with argonaute proteins bound to partially complementary mRNAs and simultaneously can recruit CCR4-NOT and PAN deadenylase complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19304925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21981923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21984184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21984185}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;RNA-mediated gene silencing;Translation regulation |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Involved in gene silencing by miRNA; positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay; and positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in P-body and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57690; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; P-body [GO:0000932]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; miRNA-mediated gene silencing [GO:0035195]; miRNA-mediated gene silencing by inhibition of translation [GO:0035278]; positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay [GO:1900153]; positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening [GO:0060213] |
19304925_Through deletion and mutagenesis, study identified the C-terminal part of TNRC6C encompassing the RRM RNA-binding motif as a key effector domain mediating protein synthesis repression by TNRC6C. 19383768_Our findings indicate that TNRC6C, is recruited to miRNA targets through an interaction between their N-terminal domain and an Argonaute protein 20098421_The authors show that a conserved motif in the human GW182 paralog TNRC6C interacts with the C-terminal domain of polyadenylate binding protein 1 (PABC) and present the crystal structure of the complex. 21063388_These findings reveal that despite species-specific differences in the relative strength of the PABPC1-binding sites, the interaction between GW182 proteins and PABPC1 is critical for miRNA-mediated silencing in animal cells. 30938030_confirmed the anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic and pro-autophagy capabilities of TNRC6C-AS1 through STK4 methylation via the Hippo signalling pathway in thyroid carcinoma 30997501_The TNRC6 proteins bind to the 5'end of HCV RNA in a miR-122-dependent fashion and contribute functionally to replication of the viral genome by spatially regulating binding of miR-122/Ago2 to the 5'UTR. 31670606_Expression of TNRC6 (GW182) Proteins Is Not Necessary for Gene Silencing by Fully Complementary RNA Duplexes. 34108231_Impact of scaffolding protein TNRC6 paralogs on gene expression and splicing. 35051175_Massively parallel reporter assays discover de novo exonic splicing mutants in paralogs of Autism genes. |
ENSMUSG00000025571 |
Tnrc6c |
117.684054 |
0.3374707532 |
-1.567166 |
0.289885094 |
28.144705 |
0.00000011257526313087313004896692107334454924227884475840255618095397949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000441800288171147915152945067490675157273471995722502470016479492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.0417907 |
12.3319959 |
168.7914137 |
25.7217048 |
| ENSG00000078900 |
7161 |
TP73 |
protein_coding |
O15350 |
FUNCTION: Participates in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Isoforms containing the transactivation domain are pro-apoptotic, isoforms lacking the domain are anti-apoptotic and block the function of p53 and transactivating p73 isoforms. May be a tumor suppressor protein. Is an activator of FOXJ1 expression (By similarity). It is an essential factor for the positive regulation of lung ciliated cell differentiation (PubMed:34077761). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JJP2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10203277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11753569, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18174154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34077761}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell cycle;Ciliopathy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Lissencephaly;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Primary ciliary dyskinesia;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the p53 family of transcription factors involved in cellular responses to stress and development. It maps to a region on chromosome 1p36 that is frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other tumors, and thought to contain multiple tumor suppressor genes. The demonstration that this gene is monoallelically expressed (likely from the maternal allele), supports the notion that it is a candidate gene for neuroblastoma. Many transcript variants resulting from alternative splicing and/or use of alternate promoters have been found for this gene, but the biological validity and the full-length nature of some variants have not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:7161; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding [GO:0097371]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; mismatch repair [GO:0006298]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060044]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of lung ciliated cell differentiation [GO:1901248]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein tetramerization [GO:0051262]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
9288759_TP73 gene is imprinted, with monoallelic expression likely from the maternal allele. 11675903_expression of p73 in colorectal carcinoma 11720435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11788901_Frequent allelic losses on the short arm of chromosome 1 and decreased expression of the p73 gene at 1p36.3 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity 11804596_DNA damage-induced acetylation potentiates the apoptotic function of p73 by enhancing the ability of p73 to selectively activate the transcription of proapoptotic target genes 11839584_data establish a relationship between p73 gene expression and neuroblastic tumor differentiation and point out a role for the p73 gene in sympathetic neuronal differentiation 11840343_regulated by c-Abl through p38 MAP kinase pathway 11844794_interaction with c-myc and MM1 11844800_Transactivation-deficient Delta TA-p73 inhibits p53 by direct competition for DNA binding: implications for tumorigenesis. 11859407_data seem to indicate that DeltaNp73 is a crucial gene in neuroblastoma pathogenesis 11870517_overexpression in malignant and premalignant lesions suggests role in oncogenic process in cervical epithelium 11891335_Induction of p57(KIP2) expression by p73beta 11909952_Autoinhibitory regulation of p73 by Delta Np73 to modulate cell survival and death through a p73-specific target element within the Delta Np73 promoter. 11920588_loss of reduced TP73 transcript expression through promoter hypermethylation may contribute to the tumorigenesis of oligodendroglial tumors 11925430_Identification and characterization of HIPK2 interacting with this protein and modulating functions of the p53 family in vivo 11957139_p63 and p73 expression may represent an early event in head and neck squamous carcinoma tumorigenesis and may function as oncogenes in the development of these tumors. 11988839_p73 expression is primarily mediated through binding of E2F1 12023887_upregulation by ascorbic acid 12032848_DN-p73 is activated after DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner to regulate p53-induced cell cycle arrest. 12034725_HCMV-mediated inhibition of apoptosis only occurs in p73-expressing cells 12080043_data suggest that p73 stimulates the transcription of the YB-1 promoter by enhancing recruitment of the c-Myc-Max complex to the E-box 12082536_Mouse DDA3 gene is a direct transcriptional target of p73 in transfection assays 12095638_Overexpression of p73beta led to the apoptosis of Hela cells and enhancement of naphthoquinone analog induced cell death. 12097319_is regulated by protein kinase C delta 12133444_p73 gene inactivation might play an important role in the pathogenesis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia . The main mechanism of the loss expression would be the hypermethylation of p73 gene. 12150978_role in expression of DAN during cisplatin-induced cell death and osteoblast differentiation 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12213815_identification of direct target genes combining DNA microarray and chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses 12353228_deletion or methylation of p73 is associated with B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas 12388104_Overexpression of p73 in vascular smooth muscle cells results in decreased cell cycle transit accompanied by apoptosis. 12427762_p73 has roles as a specific dominant negative transcriptional repressor of the cell cycle inhibitor gene p21 blocking p53-mediated apoptosis 12430182_No associations of p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 at exon 2 and p53 Arg72Pro polymorphisms with the risk of digestive tract cancers in Japanese. 12430182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12519788_p53 DNA-binding domain plays a role in p73 interaction. 12534345_This protein and p53 interact with CTF2 and regulate HMG1 gene expression. 12584188_p73 isoforms affect the retinoblastoma protein (RB) tumor suppressor pathway independent of p53 12601175_p73 has a role in apoptosis that requires PMS2 protein 12639967_transcriptional activation function of p73 is specifically targeted by E1A through a mechanism involving p300/CBP proteins during the process of transformation and that p73 may have a role to play as a tumor suppressor 12642871_modulation of level by cyclin G via a negative feedback reglation 12676926_p73 is phosphorylated in a cell cycle-dependent manner and negatively regulated by cyclin-dependent kinases 12750388_p53 and p73alpha have roles in cell migration 12766778_TP73 is an important E2F1 apoptotic target gene in DNA damage response. Acetylation is required for E2F1 recruitment on the P1p73 promoter and for its transcriptional activation. 12782576_Adenovirus-mediated p73 overexpression results in a strong induction of apoptosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 12789260_Analysis of gene expression level profiles showed that parental cell line undergoes apoptosis through an E2F1/p73-dependent pathway while its drug resistant variant evades it. 12810679_The NH(2)-terminal truncated (Delta N) isoforms of p73, which are antiapoptotic, are phosphorylated & stabilized by c-Abl, suggesting a possibility that c-Abl contributes to either pro- or antiapoptotic process depending on the expression of p73 isoforms. 12824179_p73 nuclear matrix association is selectively regulated by c-Abl tyrosine kinase 12841870_p21 is highly correlated with p73 expression irrespective of the p53 mutation status in human esophageal cancers 12853970_p73 protein has its own unique determinants for transactivation and growth suppression. 12875622_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12901798_Three naturally occurring p73 mutants are found in lung cancer cell lines 12920125_M phase-specific phosphorylation of p73 by p34cdc2-cyclin B is associated with negative regulation of its transcriptional activating function 12934108_p73beta, in the presence of mutant p53, retains the ability to transactivate p21 and suppresses cell growth. 12954612_studies unambiguously indicate that SAMp73 binds to lipids. The binding involves protein surface attachment and partial membrane penetration, accompanied by changes in SAMp73 structure. 12969350_Our results indicate that both p73 and p63 may be involved in the development of human buccal squamous-cell carcinoma, perhaps in concert with p53. 14511408_p73 might have a role in LKB1-induced apoptosis in pancreatic neoplasms 14522906_The functional impairment of p73 could be involved in the development of thyroid malignancies. 14614455_transactivation is stimulated by PCAF 14618632_Our data suggest a potential function of DeltaTA-p73 splice isoforms in melanoma progression. 14634023_findings demonstrate that p73 protein elicits apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway using p53 up regulated modulator of apoptosis(PUMA) and Bax protein as mediators 14654522_Loss of expresion is associatd with tumor progression. 14654547_p73 plays a tumor suppressor role in bladder cancer, and its inactivation occurs through an epigenetic mechanism, most probably involving protein degradation. 14678968_p73 regulates transcription of IL-4Ralpha through the unique p73-binding site. 14701724_alternatively spliced isoforms with activity in transactivation and suppression of cell growth 14719122_p73 might play some role in tumor progression of HCC even though p73 should not be considered a candidate gene on chromosome 1p of hepatocellular carcinoma and does not function as a tumor suppressor gene like p53 14732927_The intronic deletion preceding exon 2 of TP73 is an allelic variant common in breast and colorectal cancinomas. 14757278_The level of p73 protein was elevated in white and hard hypertrophic scars 14760085_the first promoter region of TP73 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma 15033688_While p53 can be rightly defined as the guardian of the genome, p73 may be the 'assistant' guardian of the genome! (REVIEW) 15066318_TP73 genetic alterations may contribute to the genesis and/or progression of cervical carcinoma in an HPV-infected transformation zone under prolonged exposure to events related to pregnancy. 15070730_functional cross-talk between p73 and Wwox tumor suppressor protein 15077164_Using siRNA targeted against p53, E2F-1 transcription factors still trigger apoptosis by inducing the E2F-responsive proapoptotic alpha- and beta-isoforms of p73. 15081420_role in regulating HSF-1 responsive gene expression 15138575_up-regulation of TAp73 is associated with high-grade glial tumors 15161684_p73 expression is related to the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells and may play an important role in the regulation of cellular radiosensitivity 15175114_There is a reproducible allelic expression bias in mRNA expression from the TP73 gene in some brains, and inter-individual variation in regulatory sequences of the TP73 locus may affect susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease. 15175157_The ability of c-Abl and p300 to increase p73 stability and transcriptional activity requires Pin1. Pin1 is essential for activation of the apoptotic response by endogenous p73. 15180941_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15180941_p73 exon polymorphism is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 15184504_PML plays a crucial role in modulating p73 function. 15291355_analyses of statistical interactions between polymorphisms (p73 G4A, p53 Arg72Pro and p21 Ser31Arg polymorphisms) revealed the marginally significant risk of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma for interaction between p53 Arg72Pro and p73 G4A polymorphisms 15302867_p73 function is regulated by c-Jun 15359011_Emerging evidence in this review discusses a key survival/death checkpoint in both peripheral and central neurons that involves the p53 tumor suppressor and its newly discovered family members, p73 and p63. 15360002_Overexpression of the p73 is associated with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia 15390192_The aim of this study was to investigate the p73 expression for human buccal epithelial dysplasia (ED) and squamous cell carcinoma 15450420_overexpression of p16INK4a and p73 may be involved in breast cancer and associated with poor tumor characteristics 15466174_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15466174_p73 polymorphism plays a role in the etiology of lung cancer. 15475076_report heterozygous deletions of the p73 locus in 25% of FL and 27% of DLBCL cases; four out of five cases with p73 deletions also exhibited increased Ki67 expression, indicating higher proliferation rates of the tumor cells 15492805_Deregulation of p73 isoform is associated with benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer 15492852_MDM2-p73-P14ARF pathway is involved in the progression of bladder cancer to a more malignant and aggressive form. 15558019_Expression of RanBPM regulates stability of p73 protein. 15572378_E1A increased expression of endogenous TP73 mRNA and protein; E1A activation of p73 and the p53 apoptotic target Noxa can occur in the absence of a functional p53 15572666_PIAS1 is a checkpoint regulator which affects exit from G1 and G2 by sumoylation of p73. 15578704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15598310_p73 protein is likely to play important roles in skin differentiation rather than proliferation or carcinogenesis of the skin. 15609309_p21WAF expression is induced by 5-Aza-CdR by demethylation of p73 leading to p53-independent apoptosis in myeloid leukemia 15650240_p73 has a role in contributing to the oncogenic potential of neuroblastoma cells (review) 15678106_Upon DNA damage Itch itself is downregulated, allowing p73 protein levels to rise and thus interfere with p73 function 15723718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15723830_there is a PKA-Cbeta-mediated inhibitory mechanism of p73 function 15734740_p73, through HDM2, can oppose p53 tumor suppressor function and possibly contribute to tumorigenesis 15737644_This suggests that p73 mediates transcriptional repression through the Sp1 transcription factor. 15741235_DeltaNp73alpha not only acts as an inhibitor of p53/TAp73 functions in neuroblastoma tumors, but also cooperates with wt-p53 in playing a physiological role through the activation of BTG2TIS21/PC3 gene expression 15769743_C terminus inhibits the transcriptional activity of p73 15813917_Inacativaton of this cell cycle regulatory genes by DNA methylation could be associated with tumorigenesis in NK cell disorders. 15844599_No statistical significances of p73 or c-fos expressions were observed between involutional hemangioma and normal skin. 15849742_p73 activation in various breast cancer (BC) cell lines after Adriamycin (ADR) treatment, an agent considered as mandatory in breast cancer chemotherapy. 15865923_Here, we discuss the possibility that the compartmentalization of p73, and the cooperation with the corresponding binding partners, might decide about its apoptosis-inducing activity[review] 15865927_TAp73 induces ER stress by transactivation of Scotin, induces mitochondrial pathway by directly transactivating both Bax & the BH3 only protein PUMA promoters. TAp73 also may activate the death receptor pathway[review] 15877106_the overexpression of the DNp73alpha does not induce a more aggressive cancer phenotype and does not seem to be associated with a reduced response of the cells to treatment with anticancer agents 15919663_p73 turnover is tightly regulated in a transactivation-dependent and -independent manner, resulting in the controlled expression of the various p73 forms. 15921610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15975558_different p73 isoforms can be degraded by calpains, i.e., both N-terminal isoforms (TAp73 and DeltaNp73) as well as the C-terminal isoforms (alpha, beta, gamma, delta) 15978938_The P73 was methylated in 4 (20%) pediatric patients , compared to 14 (26%)respectively in adult patients. 15985436_identification of a novel p73-Kip2/p57 pathway that coordinates mitotic exit and transition to G1 16044147_TP53INP1s are functionally associated with p73 to regulate cell cycle progression and apoptosis. 16087177_Data demonstrate that DNA methylation contributes to increased levels of p73 in Fanconi anemia cells by hampering the binding of the transcriptional repressor ZEB to an intronic regulatory region of the p73 gene. 16087678_reported overexpression of p73alpha in certain tumor types, and this study's findings that p73alpha exerts anti-apoptotic functions, indicate a potential oncogenic activity for p73 16110322_Deregulated expression of human DeltaNp73alpha causes early embryonic lethality when transfected into mice. 16135803_Association of p73 with Tat prevent the acetylation of Tat on lysine 28 by PCAF. 16181796_the IGF-IR gene is a novel downstream target for p63/p73 action 16195739_Delta Np73 is an important gene in hepatocarcinogenesis and a relevant prognostic factor. 16203738_Transient co-transfection of p53 family members showed that p53 and transactivating (TA)-p73, but not TA-p63, repress endogenous AFP transcription additively or independently. 16205639_the p73 gene functions as an important regulator of TERT activity 16235026_The interplay between Tat and p73 may affect Tat contribution to apoptotic events in the brain, limiting its involvement in the neuropathology often observed in the brains of HIV-1 patients. 16290057_TAp73 mRNA expression is impaired in thyroid tumours and implicated in differentiated thyroid tumorogenesis. 16343436_It is thus likely that both RE1 and RE2 are necessary in rendering p63/p73-specific activation of the WNT4 promoter. 16397624_Results illustrate a novel mechanism of the alteration of p53 function that is mediated by a cutaneous HPV type and support the role of HPV38 and deltaNp73 in human carcinogenesis. 16413471_DeltaNp63alpha promotes survival in squamous epithelial malignancy by repressing a p73-dependent proapoptotic transcriptional program. 16430884_Taken together, these results demonstrate that TAD-truncated p73alpha can activate NFkappaB. 16434604_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16449968_S100A2 gene, whose transcript and protein are induced during keratinocyte differentiation, is a direct transcriptional target of p73beta and DeltaNp63alpha 16512489_p73 protein positive expression may play a part in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression and function as an oncogene in the development of LSCC. 16580132_Tau and TAp73alpha were spatially separated within the cell; tau being located in the cytoskeletal compartment whilst TAp73alpha was found in the nucleus. 16636659_Can bind to and activate the gastrin promoter, which leads to transcriptional upregulation of gastrin mRNA. 16645632_There is a signaling loop between Ras-dependent MAPK cascade activation and p73 function. 16721041_The overall data argue against an oncogenic role for isoform DeltaNp73. 16738062_Review. An alternative splice form of c-H-ras, called p19ras, is a positive regulator of p73beta via Mdm2. Implications for this previously unidentified means of regulation are discussed in light of tumor suppression and are extended to p53 and p63. 16741250_CD154 can sensitize leukemia cells to apoptosis via the c-Abl-dependent activation of p73 and mitigate the resistance of p53-deficient CLL cells to anticancer drug therapy. 16750013_Observational study of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16814250_Taken together, our present results strongly suggest that p73-dependent induction of 14-3-3sigma plays an important role in the regulation of chemo-sensitivity of breast cancers bearing p53 mutation. 16815295_Collectively, our results suggest that a loss of the cisplatin sensitivity is at least in part due to a lack of cisplatin-induced p53 phosphorylation, and p73 might cooperate with MDM2 to be involved in this process. 16818688_The expressions of the two p73 main isoforms (deltaNp73 and TAp73alpha) might be potential markers for predicting the prognosis and sensitivity to radiotherapy in patients with cervical cervical squamous cell carcinomas(SCC). 16831876_Data show that the GLX2 gene, which encodes glyoxalase II enzyme, is up-regulated by p63 and p73. 16869745_whereas exogenous p73 exhibits similar transcriptional activity to p53 in H1299 cells, the endogenous p73 that accumulates upon DNA damage in HCT116 cells is unable to compensate for p53 function 16950799_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16953234_results imply that NF-kappaB-mediated degradation of proapoptotic p73 is a novel inhibitory mechanism of p73 that regulates cell survival and death 16980297_Mdm2-mediated NEDD8 modification of TAp73 regulates its transactivation function and may contribute to tumorigenesis 17013834_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17013834_When the p73 and MDM2 polymorphisms were combined, the risk of lung cancer increased in a dose-dependent manner as the number of variant alleles increased 17018588_Squamous cell cancer cells are uniquely dependent on DeltaNp63alpha for survival, unlike normal p63-expressing epithelial cells, and that dependence is mediated through tumor-specific up-regulation of the related protein p73. 17047653_Data show that Tp73 DeltaEx2-3 isoform expression in low-grade tumours anticipates clinical and imaging progression to higher grades, and correlates to the patients' survival. 17058198_p73 gene promoter methylation is associated with Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma 17094900_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17136456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17150106_The differential ability of p53 and p73 to inhibit glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity is due, in part, to differences in their N-terminal and C-terminal sequences. 17169329_These results suggest that the expression of PAP2a is directly regulated by p73. 17297437_interplay of ZNF143, p73 and ZNF143 target genes is involved in DNA repair gene expression and cisplatin resistance 17304243_Studies represent not only the first report that p73 modulates autophagy but also highlight important differences in the mechanism by which starvation, p53 and p73 regulate autophagy and how this contributes to programmed cell death. 17336302_p53, rather than its homologues p63 and p73, may contribute to control of the first metaphase/anaphase transition of mammalian meiosis by downregulation of Cks2 expression 17346710_STAT1 and TA-p73 can interact directly, and p73-mediated Bax promoter activity was observed to be reduced by STAT1 expression in a p53-independent manner for which STAT1 Tyrosine-701 and Serine-727 are key residues. 17347683_First strategy to activate p73 therapeutically may lead to the development of broadly applicable agents for the treatment of malignant disease. 17385050_Results suggest that p53 family members have different functions in extrahepatic bile duct (EBD) carcinomas, and that interactions between p63 and p73 play an important role in tumorigenesis of EBD carcinoma. 17428654_p73 plays a role in tumor prevention and in the cellular response to anticancer treatments. 17446929_Functions in the sensitivity of breast neoplasms to cisplatin. 17452332_nuclear IKK-alpha-mediated accumulation of p73alpha is one of the novel molecular mechanisms to induce apoptotic cell death in response to CDDP, which may be particularly important in killing tumor cells with p53 mutation 17496887_Collectively, our data demonstrates a novel and unexpected role of p73 in augmenting AP-1 transcriptional activity through which it supports cellular growth. 17611664_In vivo co-immunoprecipitation assays showed that p73gamma interacted preferentially with PCAF. 17617876_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17626635_primary medulloblastomas express significant levels of TP73 isoforms, and suggest that they can modulate the survival and genotoxic responsiveness of medulloblastomas cells. 17690711_findings show that deltaN-p73 is a transcriptional target of the PML/RARalpha oncogene; this results in the transcriptional repression of deltaN-p73 17693405_TAp73 is a stress-response gene and a downstream effector in the p53 pathway 17695396_genetic alterations in the methylation status of p73 or RASSF1A along with 1p LOH may result in the malignant transformation of a meningioma. 17716971_VDR is regulated by p63 and p73 and the induction of VDR expression upon DNA damage is p73-dependent 17761206_These data implicate a role for p73 in squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus and suggest a complex interaction between p53, p73 and HPV in the aetiology of the disease. 17825253_Taken together, our data suggest that p73alpha is sequestered in the cytoplasm by filamin A, thereby inhibiting its transcriptional activity. 17889669_These results describe an MST2-dependent effector pathway for RASSF1A proapoptotic signaling and indicate that silencing of RASSF1A in tumors removes a proapoptotic signal emanating from p73. 17912537_Our results indicate the involvement of p73 protein in MB tumorigenesis and define TP73 as a potential prognostic and therapeutic target for medulloblastoma. 17952118_Upregulation of MDR1 by DeltaNp73alpha is mediated by interaction with p53 at the MDR1 promoter. 17982488_p53 and p73 repress a number of growth-related genes and that in many instances this repression may be through the induction of p21. 18022156_Results show that methylation of the p73 gene could be an important mechanism in silencing expression of this gene in human non-small cell lung cancers. 18049450_TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism, but not p73 G4C14>A4TA4 and p21 Ser31Arg, contribute to risk of cutaneous melanoma 18174154_Plk1-mediated dysfunction of p73 is one of the novel molecular mechanisms to inhibit the p53-independent apoptosis 18234963_These results indicate that in thyroid cancer cells, TAp73alpha is able to increase p53 protein level and function by interfering with Mdm2-mediated p53 degradation. 18239687_p73 can function as a tumour suppressor independent of its family member p53 and the its TAp73 isoform is a barrier to anchorage-independent growth 18259191_Data show that following apoptotic stimuli, HtrA2 accumulates in the nucleus and cleaves p73alpha in the C-terminal portion, enabling the protein to increase its transactivation activity on Bax but not on the cell-cycle regulator gene p21. 18260640_The DNA binding domains of p73 exhibited enhanced thermodynamic stability relative to the p53 DBD, and the p73 surface is less complementary for DNA binding, which may account for the differences in affinity and specificity for p53 REs. 18342333_The p73-isoform-related interaction with Sp1 is the underlying mechanism of the diverse outcome on HBV core expression, suggesting a new mechanism by which oncogenic DeltaTAp73 could enhance the carcinogenic process in liver cells. 18343378_p73 in H pylori-induced apoptosis and more generally suggest that the p53 family may play a role in the epithelial cell response to H pylori infection. 18350258_Results show that the C-terminal spliced isoforms of the p73 protein differ in their DNA-binding capacity, but this is not an accurate predictor of transcriptional activity. 18362891_P73 and caspase-cleaved p73 fragments localize to mitochondria and augment TRAIL-induced apoptosis 18418051_TAp73-mediated activation of the p21(cip/waf), 14-3-3sigma and Bax gene promoters is abrogated by expressed PLK1 for which post-translational modification of TAp73 Thr-27 appears to be a key step in MCF7 cells. 18421303_results suggest that co-factors binding to p73 C terminus facilitate activation on Bax but not p21 CIP1/Waf1 promoter and that Brn-3a modulates this interaction 18469517_the deregulation of both the p53 and the p73 pathways plays an important role in inducing head and neck cancers 18477895_a potential function of p73 deletion transcripts in uveal melanoma progression. 18480060_MMR-dependent intrinsic apoptosis is p53-independent, but stimulated by hMLH1/c-Abl/p73alpha/GADD45alpha retrograde signaling 18499675_contribute to a functional linkage between TIP60 and p73beta through MDM2 in the transcriptional regulation of cellular apoptosis 18546269_p73 Isoforms affect VEGF, VEGF165b and PEDF expression in human colorectal tumors. 18555006_p19(ras) interaction with p73beta amplifies p73beta-induced apoptotic signaling responses including Bax mitochondrial translocation, cytochrome c release, increased production of reactive oxygen species and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential. 18565851_Kpm/Lats2 is involved in the fate of p73 through the phosphorylation of YAP2 by Kpm/Lats2 and the induction of p73 target genes that underlie chemosensitivity of leukemic cells. 18579560_transcription factors Sp1 and p73 mediate p53-independent induction of PUMA following serum starvation to trigger apoptosis in human cancer cells. 18593586_These findings reveal a novel role of TAp73alpha in the induction of apoptosis by TGF-beta in cancer cells. 18678646_Study identified a new link between mTOR, p73, and p73-regulated genes associated with autophagy and metabolic pathways. 18701437_findings suggest that the combined variants of p53 and p73 significantly increase the risk of HPV16-associated oral cancer, especially among never-smokers 18701449_The modified Yap1 does not co-activate Runx in supporting Itch transcription. The subsequent reduction in the Itch level gives rise to p73 accumulation. 18719392_Tat contributes to neuronal degeneration through activation of a pathway involving p53 and p73. 18922894_the transcriptionally active TAp73alpha tumor suppressor is implicated in the apoptosis induced by netrin-1 in a p53-independent and DCC/ubiquitin-proteasome dependent manner. 18950845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18988287_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18988287_The p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism may modulate the risk of HPV-16-associated SCCOP, and the p73 variant genotypes may be markers of genetic susceptibility to HPV-16-associated SCCOP, particularly in never smokers and never drinkers. 19008096_data suggest that DeltaNp73beta-induced aberrant mitosis evades the control of the mitotic spindle assay checkpoint, leading to tetraploidy and cell death through mitotic catastrophe rather than apoptosis. 19008105_DeltaNp73 has a role in tangle formation and neuron death, and causes a mouse model of Alzheimer's Disease [review] 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19016816_Compared with paracancerous tissue, p73 mRNA and p73 protein expression in cancerous tissue was increased 19020940_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19020940_Polymorphisms in the P73 gene is associated with significantly poorer response to treatment in pancreatic cancer patients. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19096009_Ectopic expression of miR106b in CLL cells demonstrated that Itch was a direct target of miR106b such that miR106b-induced decreases in Itch resulted in an accumulation of p73. 19106635_Important role of p73 in the anti-tumor effects of NSC176327,and suggest that a close analogue of ellipticine may act by a non-genotoxic mechanism targeting the p53/p73 pathway. 19109226_Detection of epigenetic alterations allows the identification of patients with ALL with standard risk but with poor prognosis. 19111660_The existence of a proapoptotic autoregulatory feedback loop between p73, YAP, and the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) tumor suppressor gene, is shown. 19119599_p73 was not be associated with tumorgenesis of nasal and paranasal sinus carcinoma. 19139399_TAp73 regulates the spindle assembly checkpoint by modulating BubR1 activity. 19148480_Protein isoforms contribute to p73 overpression in non-small cell lung cancer and may contribute to lung cancer development. 19158275_We identified a second transactivation domain (TAD) in p73, located within amino acid residues 381-399. This TAD preferentially regulates genes involved in cell cycle progression and its activity is modified by PKC-dependent phosphorylation at Ser388. 19158275_p73 is able to induce cell cycle arrest independently of its amino-terminal transactivation domain, whereas this domain is crucial for p73 proapoptotic functions. 19173293_a novel p73 regulated mechanism for PTEN expression in thyroid cancer cells. 19182530_Results suggest a novel molecular mechanism leading to aneuploidy involving interference of TAp73alpha with Bub1 and Bub3 resulting in an altered mitotic checkpoint. 19188449_The release of PCAF from hSirT1 repression favors the assembly of transcriptionally active PCAF/E2F1 complexes onto the P1p73 promoter and p53-independent apoptosis. 19197996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19197996_The p73 polymorphism was associated with HPV-16 status in SCCHN 19204927_Analysis of pair wise genotype combinations revealed increase in risk for specific p73-MDM2 and p73-p53 genotype combinations. 19204927_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19293798_BAG-1 inhibits the transactivating functions of p73 and provide new insight into the mechanisms that control the expression of p73. 19360352_Nutlin-3 treatment upregulated TAp73 and E2F1 protein levels. 19386249_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19386249_Study shows that the p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism may be a risk factor for gastric cancer. 19390575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423161_No patient was found to be methylated for the promoter of TP73 while CDKN2A promoter was found to be methylated in 12/45 MM patients (26.6%) at diagnosis and in 1/4 WM patients 19426493_Increased risk of head and neck cancer among individuals with combined p73 exon 2 G4A and p53 intron 3 variant alleles and a protective effect for those carrying the p53 exon 4- |
ENSMUSG00000029026 |
Trp73 |
191.226187 |
0.0413001544 |
-4.597709 |
0.899452776 |
19.536417 |
0.00000987000124803351690727041406470121387428662274032831192016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000030923629467411315927503900891082366797490976750850677490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
23.2582176 |
12.4788259 |
565.4887692 |
214.6618264 |
| ENSG00000079150 |
51661 |
FKBP7 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y680 |
FUNCTION: PPIases accelerate the folding of proteins during protein synthesis. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Isomerase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Rotamase;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) family. Members of this family exhibit PPIase activity and function as molecular chaperones. A similar protein in mouse is located in the endoplasmic reticulum and binds calcium. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51661; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; FK506 binding [GO:0005528]; peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity [GO:0003755]; peptidyl-proline modification [GO:0018208] |
23899896_RUNX1 and FKBP7, involved in erythropoesis and muscle protein synthesis, respectively, are related to change in cardiorespiratory fitness in response to exercise. 28385890_observed changes in activity of six rER-resident PPIases, cyclophilin B (encoded by the PPIB gene), FKBP13 (FKBP2), FKBP19 (FKBP11), FKBP22 (FKBP14), FKBP23 (FKBP7), and FKBP65 (FKBP10), due to posttranslational modifications of proline residues in the substrate. 35444168_Hippocampal volume, FKBP5 genetic risk alleles, and childhood trauma interact to increase vulnerability to chronic multisite musculoskeletal pain. |
ENSMUSG00000002732 |
Fkbp7 |
38.087694 |
2.1217705251 |
1.085269 |
0.312346357 |
11.933009 |
0.00055148041161767855262987314546307970886118710041046142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001342744761050917697356443802902958850609138607978820800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.5174911 |
10.2331906 |
22.5219603 |
3.6166073 |
| ENSG00000079215 |
6507 |
SLC1A3 |
protein_coding |
P43003 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent, high-affinity amino acid transporter that mediates the uptake of L-glutamate and also L-aspartate and D-aspartate (PubMed:7521911, PubMed:8123008, PubMed:20477940, PubMed:26690923, PubMed:28032905, PubMed:28424515). Functions as a symporter that transports one amino acid molecule together with two or three Na(+) ions and one proton, in parallel with the counter-transport of one K(+) ion (PubMed:20477940). Mediates Cl(-) flux that is not coupled to amino acid transport; this avoids the accumulation of negative charges due to aspartate and Na(+) symport (PubMed:20477940). Plays a redundant role in the rapid removal of released glutamate from the synaptic cleft, which is essential for terminating the postsynaptic action of glutamate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P56564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20477940, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26690923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28032905, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28424515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7521911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8123008}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Chloride;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Reference proteome;Sodium;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of a member of a high affinity glutamate transporter family. This gene functions in the termination of excitatory neurotransmission in central nervous system. Mutations are associated with episodic ataxia, Type 6. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:6507; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane protein complex [GO:0098796]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; glutamate binding [GO:0016595]; glutamate:sodium symporter activity [GO:0015501]; high-affinity L-glutamate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005314]; L-glutamate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005313]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015175]; auditory behavior [GO:0031223]; cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation [GO:0048667]; cellular response to cocaine [GO:0071314]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; chloride transmembrane transport [GO:1902476]; cranial nerve development [GO:0021545]; D-aspartate import across plasma membrane [GO:0070779]; gamma-aminobutyric acid biosynthetic process [GO:0009449]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; L-aspartate import across plasma membrane [GO:0140009]; L-glutamate import [GO:0051938]; L-glutamate import across plasma membrane [GO:0098712]; L-glutamate transmembrane transport [GO:0015813]; neuromuscular process controlling balance [GO:0050885]; neurotransmitter transport [GO:0006836]; neurotransmitter uptake [GO:0001504]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050806]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677]; response to light stimulus [GO:0009416]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; transepithelial transport [GO:0070633]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11792462_Dose-dependent modulation of EAAT1-mediated aspartate transport by benzodiazepines suggests a role of glial as well as neuronal transporters in drug action. 11826152_EAAT1 was strongly expressed in a subset of cortical pyramidal neurons in dementia cases showing Alzheimer-type pathology. In addition, tau (which is a marker of neurofibrillary pathology) colocalized to those same pyramidal cells that expressed EAAT1 12769187_Data show that excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)-1 was expressed by activated macrophages/microglia in all HIV-infected cases but not in HIV-negative controls. 12911626_To test whether Nedd4-2, SGK1, SGK3 and protein kinase B regulate EAAT1, cRNA encoding EAAT1 was injected into Xenopus oocytes with or without injection of Nedd4-2, constitutively active[CA] S422DSGK1, inactive K127NSGK1, SGK3 and/or CA T308D,S473DPKB 14713304_Transcriptional regulation of human excitatory amino acid transporter 1 (EAAT1): cloning of the EAAT1 promoter and characterization of its basal and inducible activity in human astrocytes. 14749132_We observed decreased glutamate uptake V(max), without modification of transporter affinity, in aging, which could be linked to the selective decrease of EAAT1 expression and mRNA. Moreover, in AD patients we found a further EAAT1 reduction. 15135231_data show specific localization of glutamate transporters EAAT1, EAAT2 and EAAT3 in the human placenta during development 15535133_Only activated macrophages/microglia (AMM) expressed EAAT-1. Proportion of AMM expressing EAAT-1 did not correlate with severity of neuronal apoptosis, spongiosis, astrocytosis, microgliosis, or PrP deposition, but only with disease duration. 15718040_EAAT1 parameters were mutually correlated (pG (p.Met128Arg) in SLC1A3, in an episodic ataxia patient by whole-exome sequencing. 29654220_To probe the structural role of the TM4b-4c loop of EAAT1 (Rattus norvegicus), each of the 57 amino acid residues was mutated to cysteine. 29891059_Episodic ataxias 6 is caused by heterozygous mutations in SLC1A3, which encodes a subunit of a glial excitatory amino acid transporter, EAAT1. 29999457_within SLC1A3 is associated with accelerated epileptogenesis and clinical post-traumatic seizure development after severe traumatic brain injury 30073554_EAAT1 rs2731880 SNP is associated with amygdala functional connectivity in bipolar disorder. 30122553_p53 promotes the expression of SLC1A3, an aspartate/glutamate transporter that allows the utilization of aspartate to support cells in the absence of extracellular glutamine. Tumor cells with high levels of SLC1A3 expression are resistant to glutamine starvation, and SLC1A3 depletion retards the growth of these cells in vitro and in vivo, suggesting a therapeutic potential for SLC1A3 inhibition. 30334738_Structural analyses of EAAT1 and the consensus designs using hydrogen-deuterium exchange linked to mass spectrometry show that small and highly cooperative unfolding events at the inter-subunit interface rate-limit their thermal denaturation, while the transport domain unfolds at a later stage in the unfolding pathway. 30348896_The TM4b-4c loop and beta-bridge region in TM7 were drawn into close proximity to each other in the inward- and outward-facing conformation of EAAT1. 30418668_GLAST has a novel role in GBM. 30771902_The transcriptional level of glutamate aspartate transporter SLC1A3 was high in CD133+ thyroid cancer cells. Activation of NF-kappaB signaling by CD133 was responsible for SLC1A3 high transcription level in CD133+ thyroid cancer cells. 30817938_An increased expression of GLAST was found in alcoholic brain tissue compared to controls. 30851309_This comprehensive review will discuss the regulatory mechanisms of GLAST/GLT-1, their association with neurological disorders, and the pharmacological agents which mediate their expression and function-{REVIEW} 31523835_SLC1A3 expression promoted tumor development and metastasis while negating the suppressive effects of ASNase by fueling aspartate, glutamate, and glutamine metabolisms despite of asparagine shortage 32065951_Excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)1 and EAAT2 mRNA levels are altered in the prefrontal cortex of subjects with schizophrenia. 32171272_SLC1A3 C3590T is a predisposition factor for stress and depression in an eastern Indian population, whereas SLC1A3 G869C and BDNF G196A were not found to be a risk factor. 32741053_Functional consequences of SLC1A3 mutations associated with episodic ataxia 6. 32819603_EAAT1 variants associated with glaucoma. 33145952_SLC1A3 promotes gastric cancer progression via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. 33183473_Research on the Relationship Between Schizophrenia and Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 1 Gene Based on Nanogold Amplification Technology. 34359875_Deficiency in MT5-MMP Supports Branching of Human iPSCs-Derived Neurons and Reduces Expression of GLAST/S100 in iPSCs-Derived Astrocytes. 35167492_Ataxia-linked SLC1A3 mutations alter EAAT1 chloride channel activity and glial regulation of CNS function. 35192345_Microscopic Characterization of the Chloride Permeation Pathway in the Human Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 1 (EAAT1). |
ENSMUSG00000005360 |
Slc1a3 |
498.918085 |
3.6149263725 |
1.853966 |
0.090213255 |
426.190774 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010964132702970865986389613176216012417543448100843014207101928797306924561415152546232472770804937039706759606947809992057832505465559689302537881875260973815361982220314766754166743385224806505556008940851400502488456392705809603997646 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004338621948950401518694525202969981774668881580426946421158044048141418481836130348632608156488058463551964057605145852614752772859494453111668055516633030020878254315210638448488326270292578763557940598045092039802143397730959176183951 |
Yes |
Yes |
801.4648447 |
41.6601308 |
223.0539873 |
9.5035619 |
| ENSG00000079337 |
10411 |
RAPGEF3 |
protein_coding |
O95398 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RAP1A and RAP2A small GTPases that is activated by binding cAMP. Through simultaneous binding of PDE3B to RAPGEF3 and PIK3R6 is assembled in a signaling complex in which it activates the PI3K gamma complex and which is involved in angiogenesis. Plays a role in the modulation of the cAMP-induced dynamic control of endothelial barrier function through a pathway that is independent on Rho-mediated signaling. Required for the actin rearrangement at cell-cell junctions, such as stress fibers and junctional actin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10777494, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21840392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9853756}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;cAMP;cAMP-binding;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and protein domain specific binding activity. Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of protein modification process; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization; and regulation of syncytium formation by plasma membrane fusion. Located in filopodium; lamellipodium; and microvillus. Colocalizes with cortical actin cytoskeleton and plasma membrane. Biomarker of congestive heart failure. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10411; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cAMP binding [GO:0030552]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; negative regulation of syncytium formation by plasma membrane fusion [GO:0034242]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein acetylation [GO:1901985]; positive regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046827]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of syncytium formation by plasma membrane fusion [GO:0060143]; Rap protein signal transduction [GO:0032486]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11801596_role in regulating protein kinase B activity 12000763_the subcellular localization of Epac is cell cycle-dependent, it disassociates from the nuclear membrane and localizes to the mitotic spindle and centrosomes in metaphase so may play an important role in mitosis 12707263_the LID region plays a pivotal role in the communication between the regulatory and catalytic part of Epac 12783872_Epac signals to the JNK cascade through a new mechanism that does not involve its canonical catalytic action 14615375_results demonstrate that B-CLL cells uniquely activate Rap1 in response to PDE4 inhibitors and suggest that physiologic stimuli that activate EPAC may transmit an antiapoptotic signal 15166221_Epac-Rap signaling promotes cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesions 15202935_a novel protein-binding partner for EPAC1 and EPAC2, light chain 2 of MAP1A (microtubule-associated protein 1A) 15274052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15302884_cAMP-Epac-Rap1 pathway regulates cell spreading and cell adhesion to laminin-5 through the alpha3beta1 integrin but not the alpha6beta4 integrin 15319437_Epac- and Ca2+ control activation of Ras and extracellular signal-regulated kinases by Gs-coupled receptors 15374886_Activation of Epac results in markedly enhanced basal endothelial barrier function by increasing cortical actin and subsequent redistribution of adherens and tight junctional molecules to cell-cell contacts 15545605_intracellular cAMP dynamics and Epac activation 15591041_MAP1A LC2 is a biological enhancer of EPAC1 activity toward Rap1 and associated downstream signaling mechanisms 15601837_cAMP-Epac-Rap1 signaling promotes decreased cell permeability by enhancing VE-cadherin-mediated adhesion lined by the rearranged cortical actin 16115630_Results suggest that in human umbilical vein endothelial cells Epac1 controls VE-cadherin-mediated cell junction formation and induces reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. 16728394_Epac1 and cAMP-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme have similar cAMP affinity, but different cAMP domains 16751380_The Epac1-Rap1 pathway is present in both monocytes and macrophages, but only regulates specific immune effector functions in macrophages. 16754664_GPCRs rapidly activate R-Ras; R-Ras activation by the GPCRs is apparently directly induced by cyclic AMP-regulated Epac proteins; and activated R-Ras specifically controls GPCR-mediated phospholipase D stimulation 16880999_These results demonstrate that Epac plays an important role in connecting the microtubule cytoskeleton network and intracellular cAMP-signalling. 16914720_These data argue for the existence of a novel cAMP/Epac/Rap1/SOCS-3 pathway for limiting IL-6 receptor signaling in Endothelial Cells and illuminate a new mechanism by which cAMP may mediate its potent anti-inflammatory effects. 16940330_activation of Epac1, stimulation of cells with serotonin to induce cAMP production resulted in Rap1 activation, increased cell adhesion and polarization, and enhanced chemotaxis. 17068197_Rap1 mediates cyclic AMP-stimulated neurotensin secretion downstream of both Epac and protein kinase A signaling pathways 17203972_Epac1 inhibits TGFbeta-dependent regulation of cell migration and adhesion through TbetaRI 17284589_Epac1 and Epac2 induce a potent activation of the Ca2+-sensitive big K+ channel, slight membrane hyperpolarization, and increased after-hyperpolarization in cultured cerebellar granule cells. These effects involve activation of Rap and p38 MAPK. 17565009_Epac1 activation in HUVEC results in ERK1/2 activation, and this protein, at least in part, mediates response to the physiologically relevant event of A(2B)AR stimulation 17599964_Epac increased ryanodine receptor phosphorylation at the CaMKII site. Reveal a new signalling pathway by which cAMP governs Ca(2+) release and signalling in cardiac myocytes. 17884339_Cells can contain several non-overlapping PKA- and EPAC-based signaling complexes that allow PDE4D/PDE3B coordination of cell adhesion. 17895245_Protein kinase A, not Epac, suppresses hedgehog activity and regulates glucocorticoid sensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells 17993585_Evidence for involvement of EPAC or an EPAC-like cAMP effector protein in inhibition of human airwway smooth muscle proliferation. 18032709_These data demonstrate that activation of Epac1 increases integrin activity and integrin-dependent homing functions of progenitor cells. 18064650_These results suggest a novel mechanism of ANP protective effects against agonist-induced pulmonary endothelial cell barrier dysfunction via inhibition of Rho signaling by Epac/Rap1-Rac and PKA signaling cascades. 18172027_Epac1 was shown to be responsible for these actin changes and to colocalize with microtubules in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 18202100_There exists in human beta-cells and rat INS-1 cells a novel form of ion channel modulation in which the ATP sensitivity of K(ATP) channels is regulated by Epac. 18323524_Epac1 is mainly expressed in human heart as compared with Epac2 isoform and is increased in heart failure 18421013_The selective use of PKA and Epac-1 pathways to inhibit distinct aspects of fibroblast activation illustrate the pleiotropic ability of PGE(2) to inhibit diverse fibroblast functions. 18434542_The regulation of Epac expression and activation thus appear to be critical for the integration of pro- and anti-fibrotic signals and for the regulation of fibroblast function. 18495799_Epac1 and Epac2 were expressed at the brush border of proximal tubules cells and in the thick ascending limbs of Henle's loop. 18580452_Suggest a role for cAMP/Epac1/Rap1 pathway in regulating proliferation of pancreatic carcinoma cells. 18648773_Epac1 rather than the classic cAMP effector PKA is a crucial element in the signal transduction pathway mediating anti-proliferative effects 18728186_The distribution of DNA-PK between nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments can thus potentially be influenced by relative inputs of cAMP signaling through the EPAC and PKA pathways. 19022848_the AC/cAMP/Epac signaling pathway in ovary may mediate the up-regulation of EGFR by gonadotropins via ERK1/2 and Akt activation 19273589_Results suggest that the regulation of Epac1-Rap signaling by cAMP includes both the release of Epac1 from autoinhibition and its recruitment to the plasma membrane. 19307216_Bacillus anthracis edema toxin altered the protein levels and activity of protein kinase A and exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac), a recently identified cAMP-binding molecule. 19403523_cGMP is recognized by EPAC in an anti conformation and generates several short and long range perturbations. 19464664_prostaglandin E2 activates Rap1 via EP2/EP4 receptors and cAMP-signaling: involvement of Epac1 and PKA 19475578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19475578_Subjects with haplotypes G-C-C and A-C-T had significantly higher and lower GFS-USA scores, respectively. Both samples showed an association between Epac-1 gene variants and anxiety and depression, but for different variants or in opposite directions 19546222_Epac activates the small G proteins Rap1 and Rab3A to achieve exocytosis. 19564576_Epac activation inhibits leukocyte apoptosis significantly. 19582788_Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts via the EP2 receptor and Epac 19657062_Epac regulates melanoma cell migration/metastasis mostly via syndecan-2 translocation and heparan sulfate production. 19710505_These results identify Epac and Rap1 as inhibitory regulators of the angiogenic process 19725049_EPAC-mediated cellular effects require activation of the B-Raf/ERK and mTOR signaling cascades 19920825_Epac inhibits migration and proliferation of human prostate carcinoma cells. 20032304_Data show that actin bundle formation and subsequent linkage between actin bundles and VE-cadherin through alpha- and beta-catenins are important for the stabilization of VE-cadherin at the cell-cell contacts in cAMP-Epac-Rap1 signal-activated cells. 20038525_These results led us to conclude that the Epac-Rap-PLC-[Ca2+]i signaling pathway is involved in cAMP-stimulated Cl- secretion, which is carried by a novel, previously undescribed Cl- channel. 20054824_Conclude that beta-NAD regulates the pulmonary endothelial cell barrier integrity via small GTPase Rac1- and MLCP- dependent signaling pathways. 20547757_Ran-GTP and Epac1 interact with each other in vivo and in vitro. This binding requires a previously uncharacterized Ras association domain in Epac1. 20663796_Epac1 & Epac2 signaling pathways may be associated with cAMP-mediated functional differentiation and syncytialization of trophoblasts. Expression of Epac1 & Epac 2 in placenta at different stages was investigated. 20729327_Activation of protein kinase A (PKA)stimulates dendritic cell maturation, while Epac signaling does not affect maturation. Epac suppresses the effects of PKA when both pathways are activated simultaneously. 20732872_PDE4D tethers EPAC1 in a vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cad)-based signaling complex and controls cAMP-mediated vascular permeability 20855527_Data suggest that ezrin-radixin-moesin proteins are involved in the spatial regulation of Epac1 and cooperate with cAMP- and Rap-mediated signaling to regulate adhesion to the extracellular matrix. 20952690_-induced activation of GpIb-V-IX triggers platelet procoagulant activity and anchorage of a star-like fibrin network. 21047789_the identification of radixin as a scaffolding unit for both cAMP effectors, Epac and PKA 21109603_Adenosine A(B) receptors mediate an early induction of NR4A1 and a decrease in cell proliferation via the cAMP/Epac pathway in coronary artery smooth muscle cells. 21166931_results support the hypothesis that cAMP not localized to a specific signaling pathway can activate EPACs which inhibit ATP release via activation of PKC and suggest a novel role for EPACs in erythrocytes 21393242_PDE3B and EPAC1 bind directly through protein-protein interactions 21454546_cAMP-responsive Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Epac, induces smooth muscle relaxation by down-regulation of RhoA activity 21539721_Epac1 plays a critical role in melanoma metastasis presumably because of modification of heparan sulfate. 21670213_Data show that Epac1 directly interacts with the zinc fingers of RanBP2, tethering Epac1 to the nuclear pore complex, revealing a novel mechanism of Epac1 regulation and an unexpected link between the NPC and cAMP signaling. 21679469_Gbetagamma inhibits Epac-induced Ca 2+ elevation in melanoma cells. Cross talk of Ca 2+ signaling between Gbetagamma & Epac plays a major role in melanoma cell migration. 21750123_Epac1 is expressed in human neutrophils and is involved in cAMP-dependent regulation of Rap1. However, the loading of GTP on Rap1 per se is not sufficient to promote activation of beta2 integrins. 21840392_activation of Epac1 increases the formation of cortical actin bundles at the cell-cell junctions, inhibits junction motility and restores barrier function of PDZ-GEFs depleted, but not Rap1 depleted cells 22082266_Epac1 regulated cell adhesion, leukocyte chemotaxis, phagocytosis and bacterial killing. [review] 22110680_acidosis/GPR4 signaling regulates endothelial cell adhesion mainly through the G(s)/cAMP/Epac pathway 22167199_Induction of intracellular calcium concentration by environmental benzo(a)pyrene involves a beta2-adrenergic receptor/adenylyl cyclase/Epac-1/inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate pathway in endothelial cells 22173835_during Epac1-induced activation of mTORC1 and mTORC2, Epac1 may have an additional function as a scaffold protein 22343288_cAMP induces a conformational change in Epac1 that enables DEP domain-mediated binding to phosphatidic acid, resulting in the tethering of Epac1 at the plasma membrane and subsequent activation of Rap 22363678_Cigarette smoke extract decreased Epac1 expression, but did not affect Epac2 and PKA expression. 22474076_HIF-1alpha binding to the Epac1 promoter recruits hematopoietic stem cells to the ischemic brain following stroke 22479536_Activation of protein kinase A and exchange protein directly activated by cAMP promotes adipocyte differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells 22511766_Data uncover a new Epac-Rap1-dependent pathway by which endothelial cells can regulate WPB exocytosis in response to agonists that signal through cAMP. 22575451_cAMP signaling system inhibits the repair of gamma-ray-induced DNA damage by promoting the ubiquitin-proteasome dependent degradation of XRCC1 in an Epac1-dependent pathway in lung cancer cells. 22759971_cAMP increases adhesion of microvascular smooth muscle cells to fibronectin via an Epac mediated mechanism 23220153_Taken together the results collected indicate that Epac may have an important role in the cardiac response to stress. 23266473_Epac1 competes with PDE4D5 to interact with beta-arrestin2 under beta2AR activation 23352189_These data provide evidence for the involvement of the Epac/Rap1 signaling pathway in cAMP-mediated decidualization of human endometrial stromal cells. 23523631_cAMP signalling decreases the level of the p300 protein by promoting its ubiquitin-proteasome dependent degradation, which is mediated by Epac and p38 MAPK 23646189_Epac1, a downstream effector of cAMP, functions as a pro-inflammatory modulator in prostate cancer cells. 23720748_Data indicate that Epac1-Rap1A-RhoA-ROCK signaling affects Cl- secretion via effects on the apical expression of KCNN4c channels. 23797058_the inhibitory effect of cAMP on migration, ruffling, focal adhesion dynamics and paxillin localisation is mediated by PKA, whilst EPAC potentiates migration. 23804752_data show the expression of EPAC is blunted in HPRT-deficient neuron-like cell lines and fibroblast cells from Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (LNS) patients; propose that the alterations in EPAC/RAP1 signaling and cell migration in HPRT deficiency are crucial for neuro-developmental events that may contribute to neurological dysfunctions in LNS 23968295_cAMP binding to EPAC1 may involve, in addition to the waters from within the first coordination sphere, also some waters from the second coordination sphere of the protein and cAMP. 24316969_Loss of epithelial integrity in tumorigenesis involves activation of RAP1 via exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC). 24453361_Authors have shown that Epac-specific inhibitor treatment or silencing Epac-1 gene expression rendered cells resistant to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. 24631457_AP1 activation and SOCS3 induction by EPAC1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells occur independently of c-Jun phosphorylation on Ser63. 24725364_These data suggested that Epac1 in melanoma cells regulates melanoma progression via the HS-FGF2-mediated cell-cell communication. 24733293_These results demonstrate that glucagon increases hepatic FGF21 secretion via a posttranscriptional mechanism and provide evidence that both the PKA branch and EPAC branch of the cAMP pathway play a role in mediating this effect. 24994109_Our data may suggest that the downregulation of pulmonary Epac1 expression in COPD patients is related to the upregulation of miRNA-7 25122553_EPAC1 and EPAC2 are critical signaling intermediates in osteoclast differentiation that permit RANKL-stimulated NFkB nuclear translocation and actin rearrangements 25159528_Sequestration of sperm Rab27 prevents subsequent cAMP/Epac-dependent calcium mobilization from the acrosome. 25372777_Thyroid carcinoma cell lines showed no or very weak EPAC1 expression and exhibited no growth-promoting effect after EPAC stimulation. 25406016_prostacyclin regulates bone growth via the Epac/Rap1 pathway 25683912_Identified a conserved nuclear pore localisation signal (NPLS; amino acids 764-838 of EPAC1) in the catalytic domains of the cAMP-sensors, EPAC1 and EPAC2A. EPAC1 and EPAC2, display distinct subcellular distributions. 25913012_association of ezrin with the actin cytoskeleton and phosphorylation on Thr567 are required, but not sufficient, for PKA and EPAC1 to synergistically promote cell spreading following elevations in intracellular cAMP. 25955407_Impaired microtubule dynamics, due to reduced EPAC1 signaling, links CFTR function to cystic fibrosis cellular events. 26119090_findings, coupled with the development of EPAC specific small molecule modulators, validate EPAC1 as a promising target for therapeutic interventions 26388312_EPAC activation consistently reverses clinical and experimental impairment of neutrophil phagocytosis. EPAC signals through Rap-1 and bypasses RhoA. EPAC activation represents a novel potential means by which to reverse impaired neutrophil phagocytosis. 26589262_The cAMP exerted divergent effects on proliferation and promoted cell adhesion of different neuroendocrine cell types, these effects being mediated by both Epac and PKA and involving the same effector GTPase Rap1. 26727165_These findings suggested Epac is connected to the SDF-1 signaling cascades. In conclusion, our study revealed that Epac plays a role in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs)homing by promoting adhesion and migration. Appropriate manipulation of Epac may enhance the homing of hMSCs and facilitate their future clinical applications. 26979996_EPAC activity is increased in arterial endothelial cells exposed to laminar-fluid shear stress, activation of EPAC1, and its activation of Rap1, plays a role in promoting alignment and elongation of these cells in the direction of flow. 27117782_We show that hematopoietic cell generation requires cAMP signaling through the Exchange proteins activated by cAMP (cAMP-Epac) axis..in hematopoietic progenitor and stem-like cells, cAMP induction mitigated oxidative stress, created a redox-state balance, and enhanced C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) expression, benefiting the maintenance of these primitive cells 27206858_This interaction is promoted by EPAC1 activation, triggering its translocation to the plasma membrane and binding to NHERF1. Our findings identify a new CFTR-interacting protein and demonstrate that cAMP activates CFTR through two different but complementary pathways - the well-known PKA-dependent channel gating pathway and a new mechanism regulating endocytosis that involves EPAC1. 27277757_our data provide new insight into the essential role of Epac1 in regulating growth of ovarian cancer cells and suggest that Epac1 might represent an attractive therapeutic target for treatment of ovarian cancer. 27344171_This study indicates a novel role for Epac1 in PGE2-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and subsequent activation of beta-catenin 27549789_This review focus is on the function of Epac in the heart. Accumulating evidence has revealed that both Epac1 and Epac2 play important roles in the structure and function of the heart under physiological and pathological conditions. [review] 27558159_The contribution of EGFR, EPAC, and Ca(2+) in CDCA-induced activation of CFTR-dependent Cl(-) secretion. 27598965_No significant association was observed between RAPGEF3 SNPs and the risk of Alzheimer's disease or neuropsychiatric inventory scores. 27602951_Data show that the Epac-Rap1 signaling axis is involved in triapine resistance. 27605450_Microtubule stabilization was further suggested by the finding that ascorbate increased the amount of Epac1 bound to alpha-tubulin. 27808165_Results show that Epac1 binds to importin beta1 which prevents its accumulation in plasma membrane and, uncover a cAMP-independent function of Epac1 at the plasma membrane in the regulation of neurite outgrowth. 28210903_study suggests for the first time the mechanistic insights of mode of action of a primary cAMP-dependent sensor, Exchange protein activated by cAMP 1 (EPAC1), via its interaction with A-kinase anchoring protein 9 (AKAP9). 28260059_The overexpression of EPAC1 can be used as a marker to predict the outcome of patients with GC, and EPAC1 represents a potential therapeutic modality for treating gastric cancer 28489680_Authors show that blockade of cAMP signaling using MDL12330A led to an increase in PUMA transcript levels, but not p21 in melanoma cells. Results suggest that transcriptional repression is one of the functions of the cAMP-Epac signaling pathway. 28851815_These data reveal a MAPK pathway-independent switch in response to cAMP signaling during melanoma progression.Implications: The prosurvival mechanism involving the cAMP-EPAC-RAP1 signaling pathway suggest the potential for new targeted therapies in melanoma. 29111327_EPAC1 and EPAC2 expression levels were significantly lower in bladder cancer tissue than in normal bladder tissue. In addition, bladder cancer cell lines showed reduced EPAC1 mRNA expression. Furthermore, EPAC1 overexpression in bladder cancer cell lines induced morphologic changes and markedly suppressed cell migration without affecting cell viability. 29217666_EPAC1inhibits AnxA2 surface translocation and plasminogen activation via PLCepsilon-PKC pathway. 29388865_Multiple Rap1 effectors control Epac1-mediated tightening of endothelial junctions. 29417338_Cyclic AMP (cAMP), a secondary messenger responsible for various physiological processes regulates cell metabolism by activating Protein kinase A (PKA) and by targeting exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC). EPAC is present in two isoforms EPAC1 and EPAC2, which exhibit different tissue distribution and is involved in GDP/GTP exchange along with activating Rap1- and Rap2-mediated signaling pathways. 29661848_The enhancing effect of mt-cAMP on Ca(2+) uptake was independent from both the mitochondrial membrane potential and Ca(2+) efflux, but was reduced by Epac1 blockade both in intact and in permeabilized cells. 29982410_EPAC1 supports triple negative breast cancer-induced angiogenesis, tumor cell migration and invasiveness as well as pro-metastatic phenotypes in endothelial cells induced through the tumor secretome 30116147_Epac1 can restore normal insulin signaling in the retinal vasculature through reductions in inflammatory cytokines 30185593_Through isoform-specific gene knockdown, the authors found that EPAC2, but not EPAC1, plays a dominant role in controlling RSV replication and virus-induced host responses. 30763357_Coxiella burnetii is a Gram negative bacterium that survives and grows in a large Coxiella replicative vacuole (CRV), which displays lysosomal and autophagic features. This report presents evidence that both, EPAC and its downstream effector Rap2b, were recruited to the CRV. 30809467_PDE4 and Epac1 expression levels are increased in rectal carcinoma tissues, suggesting that the two proteins may be involved in the development of this malignancy. Meanwhile, correlations between PDE4 and Epac1, PDE4 and Cx43, PDE4 and cyclin E1, and Epac1 and Cx43 suggested synergistic effects of these proteins in promoting rectal carcinoma. 31316160_Dysfunctional EAT thickness may promote maladaptive heart remodeling in CVD patients through the ST2-IL33 system, directly related to EPAC protein expression. 31877746_Conformational States of Exchange Protein Directly Activated by cAMP (EPAC1) Revealed by Ensemble Modeling and Integrative Structural Biology. 32333821_MRP4/ABCC4 expression is regulated by histamine in acute myeloid leukemia cells, determining cAMP efflux. 32890866_Downregulation of Epac Reduces Fibrosis and Induces Apoptosis Through Akt Signaling in Human Keloid Fibroblasts. 33298248_Epac: new emerging cAMP-binding protein. 33362237_LSM12-EPAC1 defines a neuroprotective pathway that sustains the nucleocytoplasmic RAN gradient. 33466800_GRKs and Epac1 Interaction in Cardiac Remodeling and Heart Failure. 34571955_Identification and Characterization of an Affimer Affinity Reagent for the Detection of the cAMP Sensor, EPAC1. 34685730_Origin and Isoform Specific Functions of Exchange Proteins Directly Activated by cAMP: A Phylogenetic Analysis. 35834616_EPAC Regulates Melanoma Growth by Stimulating mTORC1 Signaling and Loss of EPAC Signaling Dependence Correlates with Melanoma Progression. 35892592_Absence of EPAC1 Signaling to Stabilize CFTR in Intestinal Organoids. |
ENSMUSG00000022469 |
Rapgef3 |
19.243236 |
0.3920311094 |
-1.350960 |
0.453410446 |
8.857121 |
0.00291947689366643323150007915955939097329974174499511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006266939928812761961829380652488907799124717712402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.0129203 |
3.5388075 |
25.6947872 |
6.0502911 |
| ENSG00000079385 |
634 |
CEACAM1 |
protein_coding |
P13688 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Cell adhesion protein that mediates homophilic cell adhesion in a calcium-independent manner (By similarity). Plays a role as coinhibitory receptor in immune response, insulin action and functions also as an activator during angiogenesis (PubMed:18424730, PubMed:23696226, PubMed:25363763). Its coinhibitory receptor function is phosphorylation- and PTPN6 -dependent, which in turn, suppress signal transduction of associated receptors by dephosphorylation of their downstream effectors. Plays a role in immune response, of T cells, natural killer (NK) and neutrophils (PubMed:18424730, PubMed:23696226). Upon TCR/CD3 complex stimulation, inhibits TCR-mediated cytotoxicity by blocking granule exocytosis by mediating homophilic binding to adjacent cells, allowing interaction with and phosphorylation by LCK and interaction with the TCR/CD3 complex which recruits PTPN6 resulting in dephosphorylation of CD247 and ZAP70 (PubMed:18424730). Also inhibits T cell proliferation and cytokine production through inhibition of JNK cascade and plays a crucial role in regulating autoimmunity and anti-tumor immunity by inhibiting T cell through its interaction with HAVCR2 (PubMed:25363763). Upon natural killer (NK) cells activation, inhibit KLRK1-mediated cytolysis of CEACAM1-bearing tumor cells by trans-homophilic interactions with CEACAM1 on the target cell and lead to cis-interaction between CEACAM1 and KLRK1, allowing PTPN6 recruitment and then VAV1 dephosphorylation (PubMed:23696226). Upon neutrophils activation negatively regulates IL1B production by recruiting PTPN6 to a SYK-TLR4-CEACAM1 complex, that dephosphorylates SYK, reducing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lysosome disruption, which in turn, reduces the activity of the inflammasome. Down-regulates neutrophil production by acting as a coinhibitory receptor for CSF3R by down-regulating the CSF3R-STAT3 pathway through recruitment of PTPN6 that dephosphorylates CSF3R (By similarity). Also regulates insulin action by promoting INS clearance and regulating lipogenesis in liver through regulating insulin signaling (By similarity). Upon INS stimulation, undergoes phosphorylation by INSR leading to INS clearance by increasing receptor-mediated insulin endocytosis. This inernalization promotes interaction with FASN leading to receptor-mediated insulin degradation and to reduction of FASN activity leading to negative regulation of fatty acid synthesis. INSR-mediated phosphorylation also provokes a down-regulation of cell proliferation through SHC1 interaction resulting in decrease coupling of SHC1 to the MAPK3/ERK1-MAPK1/ERK2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways (By similarity). Functions as activator in angiogenesis by promoting blood vessel remodeling through endothelial cell differentiation and migration and in arteriogenesis by increasing the number of collateral arteries and collateral vessel calibers after ischemia. Also regulates vascular permeability through the VEGFR2 signaling pathway resulting in control of nitric oxide production (By similarity). Down-regulates cell growth in response to EGF through its interaction with SHC1 that mediates interaction with EGFR resulting in decrease coupling of SHC1 to the MAPK3/ERK1-MAPK1/ERK2 pathway (By similarity). Negatively regulates platelet aggregation by decreasing platelet adhesion on type I collagen through the GPVI-FcRgamma complex (By similarity). Inhibits cell migration and cell scattering through interaction with FLNA; interfers with the interaction of FLNA with RALA (PubMed:16291724). Mediates bile acid transport activity in a phosphorylation dependent manner (By similarity). Negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P16573, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31809, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16291724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18424730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23696226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25363763}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 8]: Cell adhesion protein that mediates homophilic cell adhesion in a calcium-independent manner (By similarity). Promotes populations of T cells regulating IgA production and secretion associated with control of the commensal microbiota and resistance to enteropathogens (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P16573, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31809}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family, which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Two subgroups of the CEA family, the CEA cell adhesion molecules and the pregnancy-specific glycoproteins, are located within a 1.2 Mb cluster on the long arm of chromosome 19. Eleven pseudogenes of the CEA cell adhesion molecule subgroup are also found in the cluster. The encoded protein was originally described in bile ducts of liver as biliary glycoprotein. Subsequently, it was found to be a cell-cell adhesion molecule detected on leukocytes, epithelia, and endothelia. The encoded protein mediates cell adhesion via homophilic as well as heterophilic binding to other proteins of the subgroup. Multiple cellular activities have been attributed to the encoded protein, including roles in the differentiation and arrangement of tissue three-dimensional structure, angiogenesis, apoptosis, tumor suppression, metastasis, and the modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been reported, but the full-length nature of all variants has not been defined. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:634; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; bile acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015125]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; filamin binding [GO:0031005]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; bile acid and bile salt transport [GO:0015721]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation [GO:0035726]; granulocyte colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:0038158]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; insulin catabolic process [GO:1901143]; insulin receptor internalization [GO:0038016]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; negative regulation of cytotoxic T cell degranulation [GO:0043318]; negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045717]; negative regulation of granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030853]; negative regulation of hepatocyte proliferation [GO:2000346]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 production [GO:0032692]; negative regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0051055]; negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002859]; negative regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:0090331]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001915]; negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050860]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; positive regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001214]; regulation of blood vessel remodeling [GO:0060312]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045601]; regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010594]; regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042058]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of homophilic cell adhesion [GO:1903385]; regulation of immune system process [GO:0002682]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014066]; regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903670]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; wound healing, spreading of cells [GO:0044319] |
10955775_The expression ratio of the long-form and the short-form generated from CEACAM1 (C-CAM1) mRNA by alternative splicing differs significantly in primary NSCLC tissues. 11751883_ability of N. gonorrhoeae to up-regulate its epithelial receptor CEACAM1 through NF-kappaB suggests an important mechanism allowing efficient bacterial colonization during the initial infection process. 11884449_The expression of CD66a observed on NK cells from patients with malignant melanoma suggest the existence of a class I MHC-independent inhibitory mechanism of defense used by these cells to evade attack by CD66a-positive NK cells. 11912215_Quaternary structure of coronavirus spikes in complex with carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule cellular receptors 11994468_Only the long cytoplasmic domain isoform of CEACAM1 is expressed in human granulocytes, B cells, and T cells, since GPI-linked CEA-related proteins have functionally replaced the short cytoplasmic domains in the human. 12011132_High CEACAM 1 expression is associated with development of metastasis in primary cutaneous malignant melanoma patients 12122002_inhibition of prostate tumor angiogenesis by the tumor suppressor CEACAM1 12370272_Role of CEACAM1 protein in the inhibition of activated decidual lymphocyte functions. 12522268_CEACAM1-4S mediates apoptosis and reverts mammary carcinoma cells to a normal morphogenic phenotype in a 3D culture. 12571236_CEACAM1 has a role in internalizing bacteria to epithelial cells 14522961_CEACAM1, a cell-cell adhesion molecule, directly associates with annexin II 14990688_cholesterol is an essential membrane fusion cofactor that can act with or without CEACAMs to promote murine hepatitis virus entry 15004154_The long and short cytoplasmic tails of CEACAM1 serve as inhibitory and costimulatory receptors, respectively, in T cell regulation. 15004155_CEACAM1-4L (long), but not the -4S (short)isoform inhibits IL-2 production in transfected Jurkat cells, while CEACAM1-4S, but not the -4L isoform inhibits proliferation in transfected Kit-225 cells. 15184366_the N-domain of CEACAM1 does not show evidence of recombination 15317738_The sequential digestions clearly identified several different Lewis x glycan epitopes, which may modulate the cell adhesive functions of CEACAM1 15356119_The amino-terminal end of CEACAM1 interacts with CEACAM5, but not with CEACAM6. Both CEACAM1 and CEACAM5 contain the Arg and Gln residues in positions 43 and 44, respectively, whereas CEACAM6 contains 43-Ser and 44-Leu. 15509546_CEACAM1 and alpha(v)beta(3) integrin are functionally interconnected with respect to the invasive growth of melanomas 15536067_constitutive expression of CEACAM1 in microvascular endothelial cells switches them to an angiogenic phenotype, whereas CEACAM1 silencing apparently abrogates the VEGF-induced morphogenetic effects during capillary formation 15568039_failure of the maturing colon cell to express CEACAM1 is likely to contribute to the development of hyperplastic lesions 15602572_role in developing of hyperplastic polyps leading to colon cancer 15604255_CEACAM1 is up-regulated in endothelial cells of angiogenic blood vessels. This in turn is involved in the switch from noninvasive and nonvascularized to invasive and vascularized bladder cancer. 15687237_transmembrane CEACAM1-L expressed on endothelial cells is implicated in the activation phase of angiogenesis by affecting the cytoskeleton architecture and integrin-mediated signaling 15905509_Heterophilic interactions of carcinoembryonic antigen and CEACAM1 inhibit killing by natural killer (NK) cells. The N-terminal domain of CEACAM1 is crucial but not sufficient for both CEACAM1-CEACAM1 homophilic and CEACAM1-CEA heterophilic interactions. 15917161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956076_OPN and CEACAM1 may act as a functional complex involved in the regulation of placental invasiveness. 16115956_Data show that variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that bind to human carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs) 1 and 6 failed to induce detachment and, instead, promoted enhanced host cell adhesion to the ECM. 16246332_Binding of DC-SIGN to both CEACAM1 and Mac-1 is required to establish cellular interactions with neutrophils. 16282604_findings suggest that CEACAM1 participates in immune regulation in physiological conditions and in pathological conditions, such as inflammation, autoimmune disease, and cancer 16291724_The expression of CEACAM1-L led to an increased phosphorylation of focal adhesions and to altered cytoskeletal rearrangements during monolayer wound healing assays. 16332726_first report demonstrating that activators of PKC are able to specifically induce the expression of CEACAM1 in human carcinoma cells 16568082_data show that disappearance of epithelial CEACAM1 in PIN is accompanied by its upregulation in adjacent vasculature which apparently correlates with vascular destabilization and increased vascularization of prostate cancer 16633066_study shows the expression pattern of osteopontin in cellular populations of normal endometrium and in endometrial carcinoma and its correlation with the expression of CEACAM1 16724098_This Review considers the evidence for CEACAM1 involvement in immunity, with emphasis on its functions as a regulatory co-receptor for both lymphoid and myeloid cell types. 16924126_CEACAM1 may be an interesting progression marker in squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer, in particular due to reported immunoregulatory properties. 16929097_the N-terminal domain of human CEACAM1 contains the binding target of the opacity proteins during invasion of Neisseria meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae 16953805_studies imply that distinct polymorphisms in human epithelial CEACAMs have the potential to decrease or increase the risk of infection by the receptor-targeting pathogens 17071610_CEACAM1 functions as a key regulator of contact-dependent control of cell survival, differentiation, and growth by controlling both ERK/MEK and PI3K/Akt pathways 17143599_High expression of CD66a was significantly correlated with tumor invasion, stage, and pre-operation serum carcinoembryonic antigen level. 17471435_In conclusion, M. catarrhalis induced apoptosis in pulmonary epithelial cells--a process that was triggered by interaction between CEACAM1 and UspA1. 17546042_Phosphorylation mimic mutants at either Thr457 or Ser459 (or both), but not null mutants in CEACAM1-4S were able to restore glandular lumen formation. 17605118_Epithelial downregulation of CEACAM1 in superficial bladder tumors and in PIN of the prostate. Concurrently, CEACAM1 is upregulated in endothelial cells of tumor blood vessels. 17612570_data reveal the dual role of CEACAM1 on hepatocarcinogenesis; CEACAM1 acts as tumor suppressor in HepG2 cells in anchorage-depend. growth conditions; in anchorage-independent growth cond it augments cell proliferation by potentiating cell-cell attachment. 17620353_Meningococcal outer membrane vesicle (OMV)preparations bind the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif-containing coinhibitory receptor CEACAM1 and inhibit T-cell activation and proliferation. 17623671_PDIP38 can shuttle between the cytoplasmic and the nuclear compartments and that its subcellular localization is regulated by CEACAM1 17761831_interaction of CEACAM1 with Prox1 and VEGFR-3 plays a crucial role in tumor lymphangiogenesis and reprogramming of vascular endothelial cells to lymphatic endothelial cells 17764466_The studies demonstrate the importance of CEACAMs as mediators of increased cellular invasion under conditions of inflammation and bring to light the potential role of NFkappaB pathway in Opa-mediated invasion by meningococci. 17960155_Haplotypic diversity in CEACAM genes: effects on susceptibility to meningococcal disease. 17960155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17979980_It is reported here that hCEACAM1-4L has a key function in downregulating the protein tyrosine Src kinase associated with hDAF signalling. 18081725_These data argue for a functional role of lipid rafts in CEACAM1-mediated endocytosis that is promoted by the transmembrane domain of the receptor and that might be relevant for CEACAM1 function in physiologic settings. 18215438_high CEACAM-1 expression is associated with an increased angiogenic activity in non-small-cell lung cancer and that the prognostic influence of CEACAM-1 might be derived from this association 18278069_CEACAM1-dependent cell death pathway involves dual cleavage of CEACAM1 and caspase activation and can be activated by CEA. 18424730_CEACAM1 orchestrate an inhibitory program that abrogates extremely proximal events downstream of the TCR/CD3 complex by focusing on the activation of ZAP-70. 18445773_There is a functional role for the long cytoplasmic domain of CEACAM1 in regulation of beta-catenin activity. 18453603_bacteria effectively harness the coinhibitory function of CEACAM1 to suppress the adaptive immune response at its earliest step. 18497748_This explains how UspA1 can engage CEACAM1 at a site far distant from its head group, permitting closer proximity of the respective cell surfaces during infection. 18507857_network of regulatory elements control the alternative splicing of CEACAM1 18705345_Micrometastases of gastric cancer can be detected in circulating peripheral blood using quantitative real-time RT-PCR. CK19 is a better marker than CK18, CK20 and CEA 18794798_CEACAM1 is a direct target of SOX9 in the colon epithelium 18836450_This finding is of particular interest, as it identifies a strategy by which bacteria 'use' CEACAM1 to colonize the pulmonary epithelium. 18843289_cytokine-induced cell-surface expression of CEACAM1 by keratinocytes in the context of a psoriatic environment might contribute to the persistence of neutrophils and thus to ongoing inflammation 19020551_Carcinoembryogenic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule (CEACAM)-1 and the urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)/uPA-receptor (uPAR) pathway were identified as possible mediators in HGF-induced keratinocyte migration. 19077207_Data show that desensitization of neutrophils to any two CEACAMs, 1, 3, 6, or 8, results in selective desensitization to those two CEACAMs, while the cells remain responsive to the other two neutrophil CEACAMs. 19146852_findings suggest that both Thr-457 and Ser-461 are key residues involved in lumen formation of CEACAM1-4L 19243897_Report different expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) and possible roles in gastric carcinomas. 19349857_PETs showing CEACAM1 positivity have a statistically significant correlation with several of the pathologic parameters of aggressive behavior and its overexpression is seen in those cases with increased invasiveness. 19361387_CEACAM1 is an important regulator of lipid metabolism, of tumor progression as a regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway, of normal and tumor neo-angiogenesis and of immunity. 19407471_Repression of CEACAM1 could contribute to cancer progression and may indicate a poor prognosis for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma 19442569_Membranous CEACAM1 inhibits angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, but cytoplasmic CEACAM1 promotes angiogenesis, and even promotes lymphangiogenesis by mediating the transformation of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) into lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) 19454653_Similar to its function in T cells, CEACAM1 may act as an inhibitory B cell coreceptor, most likely through recruitment of SHP-1 and inhibition of a PI3K-promoted activation pathway. 19461083_expression of CEACAM1 in melanomas and primary superficial spreading melanoma was significantly increased. 19487071_Urinary CEACAM1 levels discriminate bladder urothelial carcinoma patients from control subjects. Moreover, urinary levels of CEACAM1 increased with advancing stage and grade. 19545674_Up-regulated expression of CEACAM1 in tubular and/or glomerular cells is an indicator of acute inflammatory processes in biopsy specimens from patients with acute renal allograft rejections. 19633846_this study is about the systemic involvement of CEACAM1 in melanoma patients, including serum CEACAM1 concentrations as well as CEACAM1 expression on circulating lymphocytes. 19720754_while Opa proteins of N. meningitidis can bind to T-cell-expressed CEACAM1, this is not sufficient to overcome the T-cell recognition of bacterial factors 19948502_CEACAM1 transmembrane signaling is initiated by adhesion-regulated changes of cis-interactions that are transmitted to the inner phase of the plasma membrane. 20034698_The Le(x) residues of both, CEACAM1 and CEA, interact with the human Le(x)-binding glycan receptors DC-SIGN and SRCL. 20090913_data suggest that post-confluent contact inhibition is established and maintained by CEACAM1-4L, but disturbances of CEACAM1 signalling by CEACAM1-4S and other CEACAMs lead to undifferentiated cell growth and malignant transformation 20305326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406467_These results establish the selective interaction of several human-restricted bacterial pathogens with human CEACAM1. 20524097_genetic alteration and loss of expression of the CEACAM1 may contribute to the development of colorectal cancers, as an early event. 20682994_CEACAM1 is not present in the majority of adenomatoid tumor blood vessels, which might be related to the lower angiogenic activity and benign behaviour of this tumor. 20737948_CEACAM-1 and CXCL-14 are involved in the occurrence and development of infantile hemangioma. 21050451_Data suggest that transcription activators USF1 and IRF1 interact to modulate CEACAM1 expression and that the chromatin structure of the promoter is likely maintained in a poised state that can promote rapid induction under appropriate conditions. 21106423_from benign to premalignant and malignant lesions, CEACAM1 expression patterns are transformed 21298042_a mechanistically distinct Opa protein-independent interaction between Neisseria meningitidis and human CEACAM1. 21398516_Mechanistic control of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM1) splice isoforms by the heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear proteins hnRNP L, hnRNP A1, and hnRNP M. 21413011_CEACAM1-L dominance is important for colorectal cancer cells invasion and migration. 21487066_Data suggest that plasma markers: CEACAM, ICAM-1, osteopontin, MIA, TIMP-1 and S100B particularly when assessed in combination, can be used to monitor patients for disease recurrenc. 21569294_These data supports that a decreased CEACAM1 expression is related to obesity and a fatty liver. 21671129_upregulated expression plays role in the immunopathogenesis of oral lichen planusr 21695697_High Carcinoembryonic Antigen expression is associated with recurrence in gastric cancer. 22064717_The authors show that the expression of CEACAM1 and CEACAM6 potentiate CEACAM3-dependent responses of neutrophils, exposing a cooperative role for this family of proteins during neisserial infection of neutrophils. 22088515_SCC, CEA, Cyfra 21-1 and NSE are valuable in the early diagnosis of lung cancer among suspicious nodules in the lung, especially when they were assayed together for one patient. 22135912_The prognosis of the patients with low CEACAM1 expression and high tumor pathological grade were poorer than those patients with high expression and low pathological grade, P |
ENSMUSG00000054169+ENSMUSG00000074272+ENSMUSG00000054385 |
Ceacam10+Ceacam1+Ceacam2 |
10.663703 |
0.2144559869 |
-2.221247 |
0.555745734 |
17.412782 |
0.00003007964671173106365603677758713274670299142599105834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000089151723988986045395244151023916856502182781696319580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7958341 |
1.5265033 |
18.0045911 |
4.0761464 |
| ENSG00000079931 |
26002 |
MOXD1 |
protein_coding |
Q6UVY6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Copper;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable copper ion binding activity and dopamine beta-monooxygenase activity. Predicted to be involved in dopamine catabolic process; norepinephrine biosynthetic process; and octopamine biosynthetic process. Part of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26002; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; dopamine beta-monooxygenase activity [GO:0004500]; dopamine catabolic process [GO:0042420]; norepinephrine biosynthetic process [GO:0042421]; octopamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006589] |
15337741_Based on its sequence and localization, MOX (monooxygenase X) is predicted to hydroxylate a hydrophobic substrate in the endoplasmic reticulum. |
ENSMUSG00000020000 |
Moxd1 |
14.772161 |
0.2581369749 |
-1.953791 |
0.550206370 |
12.207561 |
0.00047596216941922758324884368263951728295069187879562377929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001172625875584676867491307206137207685969769954681396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6132936 |
2.3605371 |
25.8198149 |
5.4002394 |
| ENSG00000080298 |
5991 |
RFX3 |
protein_coding |
P48380 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor required for ciliogenesis and islet cell differentiation during endocrine pancreas development. Essential for the differentiation of nodal monocilia and left-right asymmetry specification during embryogenesis. Required for the biogenesis of motile cilia by governing growth and beating efficiency of motile cells. Also required for ciliated ependymal cell differentiation. Regulates the expression of genes involved in ciliary assembly (DYNC2LI1, FOXJ1 and BBS4) and genes involved in ciliary motility (DNAH11, DNAH9 and DNAH5) (By similarity). Together with RFX6, participates in the differentiation of 4 of the 5 islet cell types during endocrine pancreas development, with the exception of pancreatic PP (polypeptide-producing) cells. Regulates transcription by forming a heterodimer with another RFX protein and binding to the X-box in the promoter of target genes (PubMed:20148032). Represses transcription of MAP1A in non-neuronal cells but not in neuronal cells (PubMed:12411430). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P48381, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12411430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20148032}. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene is a member of the regulatory factor X gene family, which encodes transcription factors that contain a highly-conserved winged helix DNA binding domain. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally related to regulatory factors X1, X2, X4, and X5. It is a transcriptional activator that can bind DNA as a monomer or as a heterodimer with other RFX family members. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:5991; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; endocrine pancreas development [GO:0031018]; epithelial cilium movement involved in determination of left/right asymmetry [GO:0060287]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell development [GO:2000078]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; type B pancreatic cell maturation [GO:0072560] |
12411430_Data show that two regulatory factor for X box (RFX1 and 3) binding sites in exon1 of both the mouse and human microtubule-associated protein (MAP1A) gene are important for effective transcriptional repression in non-neuronal cells. 15024578_novel role for the RFX family of transcription factors as modulators of Ras signalling in epithelial cells. 19671664_RFX3 controls the expression of genes involved in primary ciliary dyskinesia. 22415835_Taken together, this study suggests ciliogenic RFX transcription factors regulate FGF-1B promoter activity and the maintenance of F1BGFP(+) NSPCs and GBM-SCs. 23822649_FOXJ1 is an important regulator of cilia gene expression during ciliated cell differentiation, with RFX3 as a transcriptional co-activator to FOXJ1. 29317724_RFX3 interacts with the D sequence of adeno-associated virus inverted terminal repeat and regulates AAV transduction. 30127002_findings reveal a regulation of RFX3 transcription factor and link fatty acid metabolism and protein lipidation to the regulation of ciliogenesis. 35416616_CircRFX3 Up-regulates Its Host Gene RFX3 to Facilitate Tumorigenesis and Progression of Glioma. |
ENSMUSG00000040929 |
Rfx3 |
317.840056 |
7.3633863740 |
2.880369 |
1.047353179 |
6.378500 |
0.01155110187377008865161620576600398635491728782653808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021863845044478906476381752099769073538482189178466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
347.3608899 |
307.5597433 |
46.1368706 |
28.2874480 |
| ENSG00000080493 |
8671 |
SLC4A4 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6R1 |
FUNCTION: Electrogenic sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter with a Na(+):HCO3(-) stoichiometry varying from 1:2 to 1:3. May regulate bicarbonate influx/efflux at the basolateral membrane of cells and regulate intracellular pH. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10069984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11744745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12411514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12730338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12907161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14567693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15218065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15713912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15817634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15930088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16636648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16769890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17661077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23324180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23636456, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29500354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9235899, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9651366}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (NBC) involved in the regulation of bicarbonate secretion and absorption and intracellular pH. Mutations in this gene are associated with proximal renal tubular acidosis. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:8671; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; sodium:bicarbonate symporter activity [GO:0008510]; solute:inorganic anion antiporter activity [GO:0005452]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; bicarbonate transport [GO:0015701]; ion homeostasis [GO:0050801]; positive regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045821]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0036376]; sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0035725]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
12534288_An in vitro transcription/translation analysis in the presence of canine pancreatic microsomal membranes shows that pNBC1 contains 10 transmembrane domains with cytoplasmic localization of the N- and C-termini. 12730338_phosphorylation of Ser1026 mediates the cAMP-dependent shift in the stoichiometry of pNBC1, whereas Thr49 plays an essential role in the cAMP-induced increase in basolateral membrane conductance 14559244_expression of kNBC-1 but not of pNBC-1 was detected in both normal human kidney and renal cell carcinoma tissues 14567693_carbonic anhydrase IV binds EC4 of NBC1, and this interaction is essential for full NBC1 activity 15123668_the electrogenic NBCe1 renders the cell membrane potential an effective regulator of intracellular H(+) buffering and acid/base-coupled metabolite transport 15218065_First direct evidence that a complex of an electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (human kNBC1) with carbonic anhydrase II functions as a transport metabolon. 15273250_a carboxyl-terminal motif with the sequence QQPFLS, which spans amino acid residues 1010-1015, and specifically the amino acid residue Phe (position 1013) are essential for the exclusive targeting of NBC1 to the basolateral membrane 15366422_Early activation of NBC1 activity by 10% CO2 was mediated by NBC1 phosphorylation. 15713912_The expression of two missense mutations of NBC1 in MDCK cells and X. laevis oocytes to determine the distribution of the mutant proteins in polarized cells is reported. 15817634_asymmetry of distribution of kNBC1 charged amino acids involved in ion recognition in putative outward-facing and inward-facing conformations 15930088_NBC1 may have a role in proximal renal tubular acidosis and ocular abnormalities 16159892_PMA inhibition of hkNBCe1 is mediated by Ca-dependent PKC and PMA does not induce downregulation of cotransporter surface expression. ANG II inhibition of hkNBCe1 is mediated by both PKCepsilon and downregulation of cotransporter surface expression. 16622177_NBC1 targets to the basolateral membrane of OK cells by a default mechanism and the COOH terminus plays a role on NBC1 stability in the basolateral membrane. 16687407_CA II does not enhance NBCe1-A activity 16707554_Pathophysiology of proximal renal tubular acidosis(pRTA0 caused by R881C mutation is likely due to deficit of NBCe1-A at proximal tubule basolateral membrane, rather than defect in transport activity of individual molecules. 16857349_Existence of an electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter in the basolateral membrane of respiratory epithelial cells that mediates bicarbonate entry from the interstitium. 17182531_We propose that the phenylalanine-leucine motif in the COOH-terminal tail of NBC1 is essential for the targeting of NBC1 to the basolateral membrane but is distinct from the membrane-targeting di-leucine motif identified in other membrane proteins. 17661077_Of the NBC1 mutations, G486R, like T485S, is a partial loss of function mutation without major trafficking abnormalities, while L522P causes the clinical phenotypes mainly through its inability to reach the plasma membranes. 17881426_No mutation was found in the coding regions and intron-exon boundaries of the genes for CA II, CA IV, CA XIV, kNCB1, NHE3, NHE8, NHRF1, NHRF2 and SLC26A6 amplified from genomic DNA of family members with pRTA. 18223262_Autosomal recessive pRTA with ocular abnormalities' is, for instance, attributable to homozygous mutations in the gene for kNBC-1 18441326_analysis of the SLC4A4 human mutation and structural model 18614622_NBCe1-A-Q29X mutation that causes proximal renal tubular acidosis treated in a targeted and specific manner 19102757_NBC1 expressed in Hek293 is inhibited by cAMP but not by cholinergic stimulation, as opposed to the findings in native intestinal tissue. 19158093_NBCe1-A Transmembrane Segment 1 Lines the Ion Translocation Pathway. 19294449_it is proposed that specific orientation & precise location of the FL motif in the primary sequence of NBC1 are strict requirements for the alpha-helical structure of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain & for targeting of NBC1 to the basolateral membrane 19336397_Amino acid subsitution in this protein produces an increase in chloride transport. 19662435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197274_the pRTA residues in NBCe1-A are buried in the protein complex/lipid bilayer where they perform important structural roles. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20837482_C-terminal transmembrane region of NBCe1-A is tightly folded with unique structural and functional features. 21224233_NBCe1 (SLC4A4) is electrogenic because it has an apparent Na+:HCO stoichiometry of 1:2 or 1:3, whereas NBCn1 (SLC4A7) is electroneutral because it has an apparent stoichiometry of 1:1. 21228764_Identify a novel homozygous nonsense mutation (W516X) in the kidney-type electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter 1 in a patient with isolated proximal renal tubular acidosis. 21234596_among four SNPs, only the K558R variant, which is predicted to lie in transmembrane segment 5, significantly reduces the NBCe1A activity without changing the trafficking behavior or the apparent extracellular Na(+) affinity. 21317537_IRBIT opposes the effects of WNKs and SPAK by recruiting PP1 to the complex to dephosphorylate CFTR and NBCe1-B, restoring their cell surface expression, in addition to stimulating their activities 21621518_the present results suggested that PTH stimulated intestinal HCO(3)(-) secretion, particularly in the ileum, by inducing the basolateral HCO(3)(-) uptake via NBCe1. 21976511_Slc4a4/NBCe1 is a key element in a feedforward mechanism linking excitatory synaptic transmission to fast modulation of glycolysis in astrocytes. 22012331_study finds that NBCe1-B is equally stimulated by autoinhibitory domain removal and coexpression of IRBIT with full-length NBCe1-B. 22383045_Simultaneous switching of the putative transmembrane segment (TM6) and TM12 of NBCe1 for those from NBCn1 severely impairs the expression of the transporter at the plasma membrane. 22415075_the regulation of anion fluxes in insulin-producing cells may involve both SLC4A4 and TMEM16A 22479346_Data identified IGF1, SLC4A4, WWOX, and SFMBT1 as hypertension susceptibility genes by gene based association scan and gene expression analysis. 23303189_novel role of STCH in the regulation of pHi through site-specific interactions with NBCe1-B and NHE1 and subsequent modulation of membrane transporter expression. 23324180_features of NBCe1-like activity in renal preparations are influenced by yet-to-be-identified renal factors 23362273_analysis of NBCe1 protein transmembrane segment 1 and structural effect of proximal renal tubular acidosis (pRTA) S427L mutation 23636456_Suggest NBce1-A missense mutation as new pathogenic mechanism for generating human proximal tubular acidosis. 23917030_a clear understanding of the structure-functional properties of NBCe1 is a prerequisite for elucidating the mechanisms of defective transepithelial bicarbonate transport--{REVIEW} 24121512_A substrate access tunnel in the cytosolic domain is not an essential feature of the solute carrier 4 (SLC4) family of bicarbonate transporters. 24453308_Our results demonstrate a surprisingly high apparent bicarbonate sensitivity mediated by NBCe1 in cortical astrocytes 24489756_The cell membrane gene SLC4A4 and the trafficking regulator gene COPA, which also plays an important role in early endosome maturation, were identified for the cellular entry of poly-arginine peptide. 25568315_Data indicate that a domain-like structure formed by extracellular loop 3 (EL-3) is present at the SLC4 Na+-coupled transporter NBCe1-A dimeric interface. 25612232_our results indicate that SLC4A4 contributes to the HCO3(-) transport and tumor cell phenotype 25743102_The R298S is a temperature-sensitive mutation in NBCe1-A that results in instability of the colloidal system leading to abnormal aggregation. 25866180_These results revealed that insulin can stimulate PT sodium transport even in type 2 diabetes with overt nephropathy. 26055330_miR-224 was significantly downregulated as ameloblasts differentiated, in parallel with upregulation of SLC4A4 and CFTR. 26582410_Common variants in the SLC4A4 gene might contribute to the variation of blood pressure responses to dietary sodium intake in Han Chinese population. 27338124_R510H and Q913R identified in a patient with proximal renal tubular acidosis. Mutant proteins exhibit substantial intracellular retention when expressed in mammalian renal cell lines. Q913R is associated with an unusual HCO3- independent anion-leak in Xenopus oocytes. 28754144_A novel mechanism for variable phenotypic expressivity in band-shaped corneal dystrophy mediated by an AU-rich element (ARE)-creating mutation in SLC4A4 in three unrelated consanguineous families has been described. 29500354_the structure of the membrane domain dimer of human NBCe1 at 3.9 A resolution by cryo electron microscopy, was determined. 29671668_In this retrospective case series, we highlight our experience with children referred to a pediatric ophthalmologist who were found to harbor underlying biallelic SLC4A4 mutations. 29914390_The SLC4A4 transcript was almost undetectable in the proband. 30526387_the sodium bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1-B is expressed in rat and human thyroid 30668544_SLC4A4 expression correlated negatively with miR-223-3p expression in patient samples. Given that miR-223-3p suppressed the SLC4A4/KRAS axis, miR-223-3p gene therapy could be an effective treatment for renal cancer. 32878470_hsa_circRNA_001587 upregulates SLC4A4 expression to inhibit migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer cells via binding to microRNA-223. 32949121_Prognostic Value of SLC4A4 and its Correlation with Immune Infiltration in Colon Adenocarcinoma. 34013380_Sodium bicarbonate transporter NBCe1 regulates proliferation and viability of human prostate cancer cells LNCaP and PC3. 34170291_Extracellular vesicles derived from cancer-associated fibroblast carries miR-224-5p targeting SLC4A4 to promote the proliferation, invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells. 34623331_Electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransporter NBCe1 regulates pancreatic beta cell function in type 2 diabetes. 34719949_A novel I551F variant of the Na(+)/HCO3(-) cotransporter NBCe1-A shows reduced cell surface expression, resulting in diminished transport activity. 35260236_Distal renal tubular acidosis, autoimmune thyroiditis, enamel hypomaturation, and tooth agenesis caused by homozygosity of a novel double-nucleotide substitution in SLC4A4. |
ENSMUSG00000060961 |
Slc4a4 |
128.945479 |
6.7854586247 |
2.762446 |
0.173065069 |
284.893009 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064469899821316864467021774385891532643708490562299551563771092272327439193836388773708358583091757352687922270052280451507208283916718309301722857537905801402280947520750942203449085354804992675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000017621772617826609171185506087641361350407827899507733098472412906713177909664057193532794931335337740385349614632611523383465371241941358865642844246197028755529512267230529687367379665374755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
226.7547605 |
24.8243154 |
33.6458412 |
3.2440944 |
| ENSG00000080573 |
50509 |
COL5A3 |
protein_coding |
P25940 |
FUNCTION: Type V collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen). It is a minor connective tissue component of nearly ubiquitous distribution. Type V collagen binds to DNA, heparan sulfate, thrombospondin, heparin, and insulin. |
Collagen;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an alpha chain for one of the low abundance fibrillar collagens. Fibrillar collagen molecules are trimers that can be composed of one or more types of alpha chains. Type V collagen is found in tissues containing type I collagen and appears to regulate the assembly of heterotypic fibers composed of both type I and type V collagen. This gene product is closely related to type XI collagen and it is possible that the collagen chains of types V and XI constitute a single collagen type with tissue-specific chain combinations. Mutations in this gene are thought to be responsible for the symptoms of a subset of patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type III. Messages of several sizes can be detected in northern blots but sequence information cannot confirm the identity of the shorter messages. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:50509; |
collagen type V trimer [GO:0005588]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; proteoglycan binding [GO:0043394]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; skin development [GO:0043588] |
15136578_analysis of processing of the Pro-alpha1(V)Pro-alpha2(V)Pro-alpha3(V) procollagen heterotrimer 15316020_CBF/NF-Y and two repressors regulate the core promoter of the human pro-alpha3(V) collagen gene 19012342_Absence of obvious disease-causing mutations and null alleles in a cohort of 13 patients with h-EDS is consistent with exclusion of COL5A3 as a candidate gene for this disease. 29168291_This study identified significant interaction between two new genes, COL5A3 and MMP9, which may be accounted for by a degradation of COL5A3 by MMP9 influencing eczema susceptibility |
ENSMUSG00000004098 |
Col5a3 |
12.817512 |
11.2837493202 |
3.496175 |
0.646756682 |
34.075064 |
0.00000000530264542394320425984905497990458400625612966905464418232440948486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000023738867593995055045014001306180606576390346162952482700347900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.7105546 |
9.0071244 |
1.7320307 |
0.6933879 |
| ENSG00000080608 |
9933 |
PUM3 |
protein_coding |
Q15397 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation activity of PARP1 and the degradation of PARP1 by CASP3 following genotoxic stress (PubMed:21266351). Binds to double-stranded RNA or DNA without sequence specificity (PubMed:25512524). Involved in development of the eye and of primordial germ cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:X1WGX5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21266351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25512524}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Chromosome;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in regulation of protein ADP-ribosylation. Located in chromosome; endoplasmic reticulum; and nuclear lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9933; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; regulation of protein ADP-ribosylation [GO:0010835]; regulation of translation [GO:0006417] |
17558408_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18093280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353833_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23480177_Results indicate that mismatches in minor H antigens HA-8 (KIAA0020) and ACC-1 (BCL2A1) predisposed to chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD). 34407138_Phosphorylation of PUF-A/PUM3 on Y259 modulates PUF-A stability and cell proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000041360 |
Pum3 |
358.759104 |
2.5723108681 |
1.363065 |
0.123382086 |
120.431746 |
0.00000000000000000000000000050887850441047334589297327419896162155015957785362338162998839715517161328903195105510803841752931475639343261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000006096628835307294633600252309948731160680195278647003564907728040037733149847376523666753200814127922058105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
507.4051192 |
41.2259995 |
198.3363660 |
12.3426955 |
| ENSG00000081014 |
23431 |
AP4E1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPM8 |
FUNCTION: Component of the adaptor protein complex 4 (AP-4). Adaptor protein complexes are vesicle coat components involved both in vesicle formation and cargo selection. They control the vesicular transport of proteins in different trafficking pathways (PubMed:10066790, PubMed:10436028). AP-4 forms a non clathrin-associated coat on vesicles departing the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and may be involved in the targeting of proteins from the trans-Golgi network (TGN) to the endosomal-lysosomal system. It is also involved in protein sorting to the basolateral membrane in epithelial cells and the proper asymmetric localization of somatodendritic proteins in neurons. AP-4 is involved in the recognition and binding of tyrosine-based sorting signals found in the cytoplasmic part of cargos, but may also recognize other types of sorting signal (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10066790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10436028, ECO:0000305|PubMed:10066790, ECO:0000305|PubMed:10436028}. |
Alternative splicing;Golgi apparatus;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the adaptor complexes large subunit protein family. These proteins are components of the heterotetrameric adaptor protein complexes, which play important roles in the secretory and endocytic pathways by mediating vesicle formation and sorting of integral membrane proteins. The encoded protein is a large subunit of adaptor protein complex-4, which is associated with both clathrin- and nonclathrin-coated vesicles. Disruption of this gene may be associated with cerebral palsy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:23431; |
AP-4 adaptor complex [GO:0030124]; endosome lumen [GO:0031904]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; cargo adaptor activity [GO:0140312]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
20972249_An autosomal recessive form of spastic tetraplegic cerebral palsy with profound intellectual disability, microcephaly, epilepsy and white matter loss in a consanguineous family resulting from a homozygous deletion involving AP4E1. 26542808_The bivalency of the interactions contributes to a higher avidity of tepsin for AP-4. 26544806_Rare Variants in AP4E1 is associated with deficits in intracellular trafficking, and Persistent Stuttering. 31003007_We evaluated 51 stuttering individuals with a mutation in either the GNPTAB, GNPTG, NAGPA, or AP4E1 gene. Mutation carriers achieved significantly less resolution in PSI following therapy, with PSI scores showing significantly less improvement in individuals who carry a mutation (p = 0.0157, RR = 1.75, OR = 2.92) while the group difference in DWS between carriers and non-carriers was statistically not significant. 32895917_Comprehensive genotype-phenotype correlation in AP-4 deficiency syndrome; Adding data from a large cohort of Iranian patients. 32979048_Defining the clinical, molecular and imaging spectrum of adaptor protein complex 4-associated hereditary spastic paraplegia. |
ENSMUSG00000001998 |
Ap4e1 |
237.723846 |
2.2211634008 |
1.151316 |
0.106069818 |
119.620227 |
0.00000000000000000000000000076608637431686657672793863462850125341070525324038031420445329335991094124938549647652052954072132706642150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000009104214883185950694770483717906020434600364263306830031247978264355934750751142559010986587963998317718505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
335.7282528 |
22.3568613 |
152.3528371 |
8.0765093 |
| ENSG00000081041 |
2920 |
CXCL2 |
protein_coding |
P19875 |
FUNCTION: Produced by activated monocytes and neutrophils and expressed at sites of inflammation. Hematoregulatory chemokine, which, in vitro, suppresses hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation. GRO-beta(5-73) shows a highly enhanced hematopoietic activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10725737}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This antimicrobial gene is part of a chemokine superfamily that encodes secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CXC subfamily, is expressed at sites of inflammation and may suppress hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:2920; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; response to molecule of bacterial origin [GO:0002237] |
12892904_modulation of the GRO beta concentration in the endometrium by inflammatory mediators may contribute to the normal and pathological processes of human reproduction by regulating the trafficking of neutrophils into the endometrium 12949249_CXCL2 has antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 15614130_Neutrophil elastase, MIP-2, and TLR-4 have roles in progression of human sepsis and murine peritonitis 16421598_CXCL2 tandem repeat promoter polymorphism is associated with susceptibiltiy to severe sepsis in the Spanish population. 16421598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16697212_CXC chemokine CXCL10 and CC chemokine CCL2 serum levels increase with normal aging 17466952_Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation decreased expression of Grob. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17944017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17944017_data suggest that a tandem repeat polymorphism (AC)n at position -665 in the CXCL2 gene may be an independent predictor of mortality for severe sepsis 17999991_Decrease of CXCL1 and -2 mediated by Curcumin is involved in the inhibition of metastasis in breast cancer cells. 18191274_Peripheral neutrophilia and increased serum chemokines (IL-8 and MIP-2) may indicate hepatic injuries in glycogen storage disease type Ia. 18322244_Resident tissue macrophages are the major source of MIP-2 and KC chemokines; these chemokines are newly synthesized products of signaling through Toll-like receptors. 18835392_In colon epithelial cells, induction of MIP-2 alpha expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha was accompanied by a concomitant reduction in miR-192 expression and miR-192 was observed to regulate the expression of MIP-2 alpha. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19369450_Report gonadotropin-releasing hormone-regulated CXCL2 expression in human placentation. 19435811_Results indicate that EGR-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB mediate GRO/CXCR2 proliferative signaling in esophageal cancer and may represent potential target molecules for therapeutic intervention. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20162422_A significantly increased expression of GRO-2, GRO-3, and IL-8 in colon carcinoma as compared to normal tissue, is reported. 20185584_G-CSF stimulates the expression of the MIP-2 receptor via STAT3-dependent transcriptional activation of Il8rb 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21220697_It can be hypothesized that for some targets, such as CXCL1 and CXCL2, additional signaling may be necessary to fully activate the 3'untranslated region-dependent human antigen R (HuR) function in airway epithelium 21630055_CXCL12 and CXCR4 are related to formation of gastric tumors and lymph node metastasis 21677836_Data suggest that GRObeta may function as an oncogene product and contribute to tumorigenesis and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22056994_Anti-human ANXA1 antibodies and, to a lesser extent, anti-human ANXA4 antibodies increased MIP-2 or IL-8 production. 22615136_Suppression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 by siRNA or by progesterone and calcitriol inhibits endometrial and ovarian tumor cell invasiveness. 22770218_Study uncovered a paracrine network, with the chemokines CXCL1 and 2 at its core, that mediates lung metastasis and chemoresistance in breast cancer. 22771802_This is the first report showing the role of CXCL2 in cancer-associated bone destruction. 23021568_Ubiquinol decreases monocytic expression and DNA methylation of the pro-inflammatory CXCL2 gene in humans. 23225384_This study demonistrated that CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL8, and CXCL11, absent from normal muscle fibers, were induced in DMD myofibers. 23372021_CXCL2, a WAT-produced chemokine being up-regulated in obesity, stimulates neutrophil adhesion to vis WAT endothelial cells. Activated neutrophils in obesity may influence vis WAT-ECs functions and contribute to WAT inflammation. 23554905_Neutrophil priming led to the rapid expression of a common set of transcripts for cytokines, chemokines and cell surface receptors (CXCL1, CXCL2, IL1A, IL1B, IL1RA, ICAM1). 23904157_our results demonstrate the diverse mechanisms by which CXCL2 and CXCL3 mediate normal and asthmatic airway smooth muscle cell migration 24098805_Simultaneous targeting of hCAP-G2 and MIP-2A is a promising strategy for the development of antitumor drugs as a treatment for intractable tumours. 25085744_In this review, a genetic variant in CXCL12 is described that is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. 25682075_Our results demonstrated that resistance to anti-proliferative effects of CXCR2 may also arise from feedback increases in MIP-2 secretion. 25708728_autophagy is required for Hepatitis B virus-induced NF-kappaB activation and release of IL-6, IL-8, and CXCL2 in Hepatocytes 25801245_We have demonstrated that GRObeta, as an oncogene product, contributed to tumorigenesis and metastasis of HCC 25802102_The results link CXCL1 and CXCL2 chemokines with bone marrow adiposity and implicate CXCR2 signaling in promoting effects of marrow fat on progression of skeletal tumors in bone. 26063953_high GRO-beta expression correlates with poor prognosis and contributes to ovarian cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis. 26345899_Polymorphisms in the promoter regions of the CXCL1 and CXCL2 genes contribute to increased risk of alopecia areata in the Korean population 26888013_Reduced rate of sickle-related complications in Brazilian patients carrying HbF-promoting alleles at the BCL11A and HMIP-2 loci 27117207_Functional effects data suggested that recombinant human CXCL2 significantly enhanced the migration, invasion ability of SMMC7721 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, and weakened adhesion ability. 27580404_Chronic inflammation contributes to the change of CXCL12 DNA methylation in buccal cells and that DNA methylation profile of CXCL12 promoter plays important role in development and progression of periodontal disease. 27721403_Results identify the CXCL2/MIF-CXCR2 axis as an important mediator in MDSC recruitment and as predictors in bladder cancer. 28765918_Taken together, the data of the present study demonstrated that TcpC can induce MIP2 production, which may contribute to the characteristic histological change associated with pyelonephritis. 28928065_The studies revealed that, although overall structural and oligomerization features of CXCL3 and CXCL2 are similar, prominent differences were observed in their surface characteristics, thus implicating a functional divergence. 29520695_These results show that AKIP1 is crucial in cervical cancer angiogenesis and growth by elevating the levels of the NF-kappaB-dependent chemokines CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL8. 30259595_Results show that the expression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrated CD11b+ myeloid cells is critically involved in the promotion of the generation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (mo-MDSC) from bone marrow cells. CXCL1 and CXCL2 were found to specifically promote the expansion of mo-MDSC rather than granulocytic MDSC (G-MDSC). 30293547_Overexpressing CXCL2 by lentivirus also apparently inhibited the size and weight of subcutaneous tumours in nude mice and CXCL2 induced HCC cell apoptosis via both nuclear and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. 30564899_We identified CXCL2, an immune-related chemokine, decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma and the regulation mechanism may be controlled by methylation 31292171_These results show that CXCL2 attenuates osteoblast differentiation through inhibition of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 31617252_A-kinase interacting protein 1 might serve as a novel biomarker for worse prognosis through the interaction of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1/chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 in acute myeloid leukemia. 32267022_Association between the rs9131 and rs3806792 polymorphisms of the CXCL2 gene and the risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a Guangxi population. 32439934_Omental adipocytes promote peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer through the CXCL2-VEGFA axis. 32452055_Identification of a four immune-related genes signature based on an immunogenomic landscape analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 32643867_MicroRNA-532-5p is a prognostic marker and inhibits the aggressive phenotypes of osteosarcoma through targeting CXCL2. 32988253_Identification of genes and miRNAs in paclitaxel treatment for breast cancer. 33010041_Increased expression of CXCL2 in ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis and its role in osteoclastogenesis. 33571109_Regulation of tumor immune suppression and cancer cell survival by CXCL1/2 elevation in glioblastoma multiforme. 33793061_CXCL2 benefits acute myeloid leukemia cells in hypoxia. 33807899_The CXCL2/IL8/CXCR2 Pathway Is Relevant for Brain Tumor Malignancy and Endothelial Cell Function. 34085699_CXCL2/10/12/14 are prognostic biomarkers and correlated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34115261_CXCL2-CXCR2 axis mediates alphaV integrin-dependent peritoneal metastasis of colon cancer cells. 34474677_CXCL2-mediated ATR/CHK1 signaling pathway and platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. 34607953_Cis-acting lnc-Cxcl2 restrains neutrophil-mediated lung inflammation by inhibiting epithelial cell CXCL2 expression in virus infection. 35541899_SNAIL Induces EMT and Lung Metastasis of Tumours Secreting CXCL2 to Promote the Invasion of M2-Type Immunosuppressed Macrophages in Colorectal Cancer. 36073801_ARG1 and CXCL2 are potential biomarkers target for psoriasis patients. 36281171_CXCL2 acts as a prognostic biomarker and associated with immune infiltrates in stomach adenocarcinoma. |
|
|
19.387151 |
12.6600365073 |
3.662210 |
0.593600177 |
46.152049 |
0.00000000001094225164670645507495982778571524192574859757343119781580753624439239501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000060467103820811412732133914227296463128613623894125339575111865997314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.9012862 |
14.4180876 |
3.1555406 |
1.0736831 |
| ENSG00000081237 |
5788 |
PTPRC |
protein_coding |
P08575 |
FUNCTION: Protein tyrosine-protein phosphatase required for T-cell activation through the antigen receptor. Acts as a positive regulator of T-cell coactivation upon binding to DPP4. The first PTPase domain has enzymatic activity, while the second one seems to affect the substrate specificity of the first one. Upon T-cell activation, recruits and dephosphorylates SKAP1 and FYN. Dephosphorylates LYN, and thereby modulates LYN activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11909961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2845400}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human cytomegalovirus protein UL11 and mediates binding of UL11 to T-cells, leading to reduced induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple signaling proteins upon T-cell receptor stimulation and impaired T-cell proliferation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22174689}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Repeat;SCID;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitosis, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane segment and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains, and thus is classified as a receptor type PTP. This PTP has been shown to be an essential regulator of T- and B-cell antigen receptor signaling. It functions through either direct interaction with components of the antigen receptor complexes, or by activating various Src family kinases required for the antigen receptor signaling. This PTP also suppresses JAK kinases, and thus functions as a regulator of cytokine receptor signaling. Alternatively spliced transcripts variants of this gene, which encode distinct isoforms, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:5788; |
bleb [GO:0032059]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane microdomain [GO:0098857]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:0043395]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0005001]; alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046633]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; bone marrow development [GO:0048539]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; cell cycle phase transition [GO:0044770]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; DN2 thymocyte differentiation [GO:1904155]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; gamma-delta T cell differentiation [GO:0042492]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; natural killer cell differentiation [GO:0001779]; negative regulation of cell adhesion involved in substrate-bound cell migration [GO:0006933]; negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001960]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032703]; negative regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903979]; negative regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031953]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061099]; negative regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001915]; negative thymic T cell selection [GO:0045060]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; plasma membrane raft distribution [GO:0044855]; positive regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046641]; positive regulation of antigen receptor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0050857]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; positive regulation of Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:1905451]; positive regulation of gamma-delta T cell differentiation [GO:0045588]; positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell migration [GO:2000473]; positive regulation of humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin [GO:0002925]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002639]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes [GO:0048304]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:1903615]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive thymic T cell selection [GO:0045059]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032677]; regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050764]; regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061097]; regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046425]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; stem cell development [GO:0048864]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
11528386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11548742_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11778694_role of CD45RO in the persistent HTLV-1 infection in vivo 11841494_CD45 variant (C77G, exon 4) does not confer susceptibility to either IDDM or Graves' disease 11841494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11862398_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11862398_we examined the frequency of the C77G allele in African and Asian populations from countries with high or low prevalence of HIV infection; Here we report that the variant CD45 C77G allele is absent in African populations 11877294_Requirements of src family kinase activity associated with CD45 for myeloma cell proliferation by interleukin-6 11909961_SKAP55 coupled with CD45 positively regulates T-cell receptor-mediated gene transcription. 11975983_analysis of CD45 isoform expression during T-cell development and selection in the human thymus 11994288_CD45 controls interleukin-4-mediated IgE class switch recombination in human B cells 12008046_Receptor tyrosine phosphatase, CD45 binds galectin-1 but does not mediate its apoptotic signal in Jurkat cells 12022705_Role of high and low molecular weight isoforms of CD45 in the function of naive and memory T lymphocytes. Review. 12028593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12073144_a mutation in PTPRC interferes with splicing and alters the structure of the CD45 molecule 12100025_Biological functions of membrane expressed CD45 isoforms on PMNs were studied. Cross-linking of CD45 isoforms by specific MAbs stimulated different PMN activities by differential suppression on protein tyrosine phosphorylation and p56lck. 12147336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12147336_Role of the C-->G mutation in position 77 of exon 4 of the protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor-type C (PTPRC) gene, coding for the CD45 molecule, for the development of multiple sclerosis (MS) in Italy. 12354383_The spectrin-ankyrin skeleton controls CD45 surface display and interleukin-2 production. 12376545_interactions between RPTP-domain1s and RPTP-domain 2s are a common but specific mechanism that is likely to be regulated- domain2s and the wedge structures are crucial determinants of binding specificity, thus regulating cross-talk between RPTPs 12386161_reaches the cell surface via Golgi-dependent and -independent pathways 12393728_CD45 may play a pivotal role in erythropoiesis. CD45 tyrosine phosphatase inhibits erythroid differentiation of umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells associated with selective inactivation of Lyn. 12430875_difference in sensitivity to stress stimuli and IL6-induced cell growth between CD45+ and CD45- multiple myeloma cells 12499376_CD45 is regulated by ST6Gal I sialyltransferase in a process that leads to T cell death 12519755_CD45 differentially regulates CXCR4-mediated chemotactic activity and MAPK activation by modulating the activities of focal adhesion components 12556471_CD45 mediates its T cell inhibitory activity, causing PP14 to elevate TCR activation thresholds and thereby down-regulate T cell activation 12574355_CD45 via its Janus kinase phosphatase activity is able to suppress IL-4-dependent activation-induced expression of cytidine deaminase in primary B cells. 12595907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12595907_data identify CD45 as a gene associated with autoimmune hepatitis, and further substantiates the hypothesis that CD45 represents a modifier gene of human autoimmunity 12618866_Association of a PTPRC exon A mutation in systemic sclerosis. 12618866_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12626536_CD45 is excluded from the inhibitory, i.e., noncytolytic, but not the activating, NK cell immune synapse, where its redistribution away from intercellular contact may favor inhibitory effector functions. 12633939_The loss of CD45 activity in lymphocytes from the elderly may underlie poor T cell function associated with ageing. 12716971_a polymorphism in exon 6 (A138G) of the gene encoding CD45 that interferes with alternative splicing 12820694_prevalence of a functional mutation in the CD45 gene and distribution of memory and naive T cells in myasthenia gravis 12864992_None of four newly identified nucleotide substitutions in the CD45 gene, namely C77T (Pro59Pro) in exon 4, G69C (Asp121His) in exon 5, T127A (Ile187Asn) and A138G (Thr191Ala) in exon 6, is significantly associated with multiple sclerosis. 12864992_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12880639_identification of CD45RO+ T-cells in the fetus 14525771_strong physical linkage of CD26 with CD45RA outside lipid rafts may be responsible for the attenuation of T-cell activation signaling through CD26 14565647_Review. Myeloma cells expressing CD45 antigens which contain the activation of src family protein-tyrosine kinases independent of IL-6 stimulation proliferate in response to IL-6, but the proliferation of CD45- cells lacking src family PTKs is not. 14625311_CD45-D2 has a role in binding substrate and binds the SD10 region in Lck, which is a novel site involved in substrate recognition 14631169_concluded that CD4+ T lymphocytes from neonates with fetal distress show a transient decrease in the CD45RA expression without an increase in the CD45RO expression 14636588_Results describe a sequence element that is both the primary determinant of CD45 variable exon exclusion following T cell stimulation by PMA and is sufficient to confer activation-induced skipping of a heterologous exon. 14641523_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14726805_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 14979481_IL-6-dependent multiple myeloma cells require CD45 to initiate IL-6 signaling and to maintain Lyn kinase activity, both of which are essential for cell proliferation and cell adhesion. 14983037_Antiretroviral therapy with the anti-CD45RO immunotoxin might reduce the HIV latent reservoir without seriously compromising CD8+ T cell memory responses. 15018649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15057492_CD45 splicing abnormalities might be associated with HIV infection 15214936_Coexpression of CD45RA and CD45RO molecules indicates activation of maternal CD4(+) and CD8(+) lymphocytes 15240561_masking of the alpha2-6-linked sialic acid binding site of CD22 may be mediated by secondary interactions with Sias on CD45 and sIgM 15314282_CD45 plays a significant role in nuclear apoptosis by the regulation of the chloride channels responsible for ionic homeostasis of the cell. 15333587_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15333587_The A138G polymorphism is the cause of altered CD45 isoform expression, promoting splicing towards low molecular weight CD45 isoforms. 15548260_C to G transversion at pos. 77 does not seem to be associated with susceptibility for Type 1 diabetes. 15548260_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15584483_the 77C-->G PTPRC polymorphism is present and preferentially transmitted in a small subgroup (G transversion in susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease 18719244_These data establish that hnRNP LL plays a critical and unique role in the signal-induced regulation of CD45 and demonstrate the utility of cell-based screens for the identification of novel splicing regulatory factors. 18840711_activated CD45RB translocates to lipid rafts and interferes with lipid raft localization 18992193_Aberrant transformation from CD45R0(+)T to CD45RA(+)T has been found in the development of thymocytes of the patients with myasthenia gravis. 19059880_RB(+) germinal center (GC) B cells showed increased signs of terminal differentiation toward CD27(+) post-GC early plasmablast (increased CD38 and RO) or early memory (decreased CD38 and RO) B cells 19111528_Data show that the C77G and C772T variations within the human protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C gene is associated with multiple sclerosis in an Australian population. 19111528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19246294_CD45 is overexpressed in patients with Crohn's disease. 19332764_high CD45 expression of T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas (T-NHLs) allows reliable tumor targeting and disease control supporting anti-CD45 radioimmunotherapy for T-NHL patients 19454697_fodrin degradation occurs during galectin-1 T cell death and CD45 is essential for fodrin degradation to occur 19481264_CD45 recruits adaptor DOK-1 to the proximal plasma membrane to serve as a downstream effector, resulting in negative regulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. 19546439_Data show that CD45, CD11b, CD15, and CD56 were diagnostic parameters with flow cytometry. 19585516_Alloimmune-induced APOBEC3G was found to be significantly increased in CD45RA(-), CCR5(+) and CD45RA(-)CCR7(-) subsets of effector memory T cells. 19635795_Data show that galectin-1 binding to surface CD43 and CD45 on MDDCs induced an unusual unipolar co-clustering of these receptors. 19879912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879912_Our data did not reveal any association between CD45 77C>G transversion and susceptibility to Hashimoto's thyroiditis in a German population 19898481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20093141_Expression of protein isoforms correlates with differential proliferative responses of peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells 20119835_cardiac atrium contains a small C-kit+ CD45- population expressing markers commonly found on endothelial progenitor cells 20164196_CD45 lateral mobility is regulated by the spectrin-ankyrin cytoskeleton of T cells 20191119_CD45O immunoexpression in early rheumatoid arthritis synovium. 20231690_CD45RA-positive and CD45RO-positive regulatory T cells have very distinct gene expression patterns and may not be simply the same cells at different stages of differentiation. 20309874_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20309874_Statistically significant associations were observed between the response to anti-TNF therapy and an rheumatoid arthrits risk allele at the PTPRC gene locus. 20505149_Shift to high molecular weight CD45 isoforms in RNA-binding protein heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L (Hnrpll) transgenic thymocytes does not demonstrably affect T cell signaling and selection in vivo. 20932480_GSK3/TRAP150, complex regulates CD45 alternative splicing and demonstrate a paradigm for signal transduction from the cell surface to the RNA processing machinery through the multifunctional protein PSF. 21054833_the density of CD45RO+ TILs is an independent prognostic factor in non-metastasized (stage I-IIA) Barrett's cancer patients and indicates an important role for the adaptive immunologic microenvironment 21067564_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21106704_The number of CD45-positive cells and mast cells gradually increased with age. 21179414_atRA and TGF-beta, but not IL-2, enable CD4+CD25+CD45RA+ cells to express a phenotype and trafficking receptors similar to natural Tregs 21278234_O-linked glycosylation of CD45RB can be used to follow B cell differentiation and that this regulation may be involved in fine-tuning antigen signaling in the cell. 21507955_A disease-associated polymorphism alters splicing of the human CD45 phosphatase gene by disrupting combinatorial repression by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). 21599592_Data show that CD45+CD19- MCL-ICs play a role in the drug resistance of MCL, and this drug resistance was largely due to quiescent properties with enriched ABC transporters. 21768350_Data show that Pic, a class 2 SPATE protein produced by Shigella flexneri 2a targets a broad range of human leukocyte glycoproteins including CD43, CD44, CD45, CD93, CD162 and the surface-attached chemokine fractalkine. 21818290_The aim was to determine if SPARC, FOXP3, CD8 and CD45RO expression levels are associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) stage, disease outcome and long-term cancer-specific survival. 21952740_Presence of the rs10919563 rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility variant at the PTPRC gene locus predicts improved response to anti-TNF biologic therapy. 22171268_O-glycosylated CD43 and CD45 molecules on T cells regulates cell adhesion and favors the transmission of HTLV-1 from cell to cell. 22174689_pUL11 has immunosuppressive properties, and that disruption of T cell function via inhibition of CD45 is a previously unknown immunomodulatory strategy of CMV 22386990_The study demonstrates the involvement of CD45-mediated signaling in RBL-induced PBMC proliferation and Th1/Th2 cytokine secretion through activation of p38MAPK and STAT-5. 22438252_A tumor suppressor role for CD45 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 22458809_Studies indicate that CD45, nonreceptor SH2 domain-containing PTP-1 (SHP-1) and PEST domain-enriched tyrosine phosphatase (PEP) are expressed at elevated levels in immune cells and play essential roles in T cell homeostasis. 22524693_There is no genetic association between PTPRC exon A 77C>G transversion and liver transplant rejection in a Caucasian population. 22689986_Patient SNP array analysis revealed no change in copy number but loss of heterozygosity for entire length of chromosome 1, indicating that disease was caused by uniparental disomy with isodisomy of the entire maternal Chr1 bearing the mutant CD45 allele 22783574_We found increased expression levels of CD40 and CD45 levels in healthy older versus younger individuals. 22821963_Continuous culture of CD8+CCR7+ cells results in a population that is homogenously positive for CCR7 and CD45RA. 23065155_Data indicate a role for cell-surface gal-3 and CD45 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) survival and suggest therapeutic targets to sensitize DLBCL cells to death. 23171577_[review] Circulating CD34+/KDR+/CD45dim endothelial progenitor cells have great potential as biomarkers of vasculogenesis and endothelial repair wjen research protocols of in vitro culture and flow cytometry are included. 23206327_This study analysis revealed up-regulation of CD14, CD18, CD45, TLR2, TLR4, CD74, C1q, C3, CCL2, and down-regulation of CD36, CX3CR1, CX3CL1 and CD200 in postmenopausal women. 23394998_hnRNP L represses CD45 exon 4 by recruiting hnRNP A1 to a sequence upstream of the 5' splice site 23396948_The E613R allele of CD45 does not function as a hyper- or hypomorphic allele but rather alters the substrate specificity of CD45 for Lyn. 23733486_Very low levels of surface CD45 reflect chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell fragility, are inversely correlated with trisomy 12, and are associated with increased treatment-free survival. 23747721_The CCR7+CD45RA-CD27+CD28+ central memory subset is significantly decreased in the peripheral blood CD4+ T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 23840798_Heterogeneity within the Lin(-)CD45(-) cell fraction is the likely explanation for differences in the hUCB cell populations. 23911702_high CD45 surface expression is associated with a poor prognosis in BCP-ALL as well as in T-ALL. 23953137_the regulation of alternative splicing in CD45 by IkappaBL was independent from the kinase activity of CLK1. 23997015_PTPRC/CD45 is down-regulated in leukemogenic tyrosine kinase expressing cells. 24211716_A glycosylation-dependent CD45RB epitope defines previously unacknowledged CD27-(IgM high) B cell subpopulations enriched in young children and after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 24211831_Galectin-3-induced apoptosis of Jurkat cells is regulated by both O-glycans and N-glycans on CD45. 24231767_spatial regulation of Lck by CD45 and GM1 ganglioside determines the outcome of apoptotic response to Gal-1 and this local regulation may occur only upon intimate effector (Gal-1 expressing) cell-T-cell attachment. 24364909_The rare sub-population of CD45(-)/Lin(-)/SSEA-4(+) VSEL stem cells survived after Hespan sedimentation. 24396288_Hematopoietic cell marker CD45 is expressed in hepatic progenitor cells. 24589677_Results show that CD45 PTP activity is inhibited by galectin-1 in anaplastic large cell lymphoma cell line H-ALCL. 24761979_CD45RA-Foxp3high Tregs increase in the peripheral circulation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. 24852660_Expressing CD45 promoters containing these regions and tethered to green fluorescent protein (GFP) in a primary B-cell differentiation assay and a transplantation model resulted in high levels of GFP in lymphoid, myeloid, and nucleated erythroid cells 25043745_CD45+ cells were abundant in the stroma of physiologically immature placental villi and decreased as pregnancy progressed. 25128530_Phosphatase CD45 both positively and negatively regulates T cell receptor phosphorylation in reconstituted membrane protein clusters, depending on LCK activity. 25312647_SLAMF7-triggered inhibition is mediated by a mechanism involving Src kinases, CD45, and SHIP-1 that is defective in MM cells 25345593_This study demonstrated that the copy number variations of PTPRC relate to opioid dependence. 25381328_long noncoding RNA encoded by the natural antisense gene of CD45 contributes to the expressional regulation of the CD45RO splicing variant via recruitment of DNA methyltransferase and histone modification modulators specific to the sense gene CD45 25421756_Low expression of CD39(+) /CD45RA(+) on regulatory T cells (Treg ) cells in type 1 diabetic children in contrast to high expression of CD101(+) /CD129(+) on Treg cells in children with coeliac disease. 25531767_Late-outgrowth CD45 negative endothelial progenitor cells express markers associated with pluripotency and can directly express an osteogenic phenotype under bone differentiation conditions. 25539460_CD4+CD45RO+CD25-/lowCD127+: CD4+CD45RO+CD25hiCD127-/low ratio in peripheral blood indicates heart transplant recipients at risk for cardiac allograft vasculopathy. 25658353_In T-cells, cholesterol-dependent domains function in the regulation of the Src family kinase Lck (p56lck) by sequestering Lck from its activator CD45. (Review) 25739938_a CD45+/CD19 - cell population in bone marrow aspirates correlated with the clinical outcome of patients with mantle cell lymphoma. 25758468_Our results show that the kinetic strategy used in this study may be a simple and easy approach to assess by RT-FCM the reaction between NO and superoxide ion in whole blood monocytes..The no-wash, no-lyse staining protocol with CD45-KO and CD14-PB allows to differentiate clearly and to gate in the monocyte population in near-physiological conditions 25804232_Patients with the presence of CD8- and CD45RO-positive T cells in bone marrow demonstrated better survival of gastric cancer patients than those with the absence of these cells in bone marrow. 25834819_This study did not replicate the association between PTPRC and the response to anti-TNF treatment in our Southern European population. We found that TRAF1/C5 risk RA variants potentially influence anti-TNF treatment response. 25896535_PTPRC has become the most replicated genetic biomarker of response to TNF inhibitors 25914252_Our results demonstrate that the expression of CD163 and CD206 in monocytes is modulated by LPS in vitro; LPS induces CD163 expression and downregulates the spontaneously increased expression of CD206 26355564_C77G T(reg) showed diminished upregulation of activation markers, lower phosphorylation of p56(lck)(Y505) and a reduced proliferative potential when stimulated with anti-TcR or anti-TcR plus CD28 mAb suggesting decreased responsiveness to activating stimuli. Data suggest that the changes in CD45 isoform combination resulting from the C77G mutation alter the responsiveness 26389592_Findings indicate that CD45 antigen(+) and c-Kit protein(+) hematopoietic cells were more abundant in muscle than in bone marrow between embryonic 14.5 and 17.5 days. 26415521_As CD45 expression vs. SSc is routinely measured in the diagnostics of acute leukemias. 26468019_Data suggest that CD41 and CD45 expression marked the onset of haemangioblastoma (HB) neovascularisation and the stepwise development of the angioformative period, and also the underlying therapeutic targets of anti-vascular treatment. 26667768_CD45RO+ memory T-cells produce IL-17 in patients with atherosclerosis. 26678911_CD45RO in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was found to be a positive prognostic factor in squamous non-small cell lung cancer. 26994849_High CD45 expression is associated with multiple myeloma. 26998761_Data show the structural basis for, and the potent signaling effects of, local CD45 antigen and kinase segregation. 27056269_Our findings suggest that CD45 is a key regulator of BCR-signaling thresholds mediated by T-cell help 27074847_Review/Meta-analysis: Rheumatoid arthritis patients with PTPRC rs10919563 A allele show a poor response to anti-TNF therapy. 27601670_regulatory effect of the mannose receptor (MR) was mediated by a direct interaction with CD45 on the T cell, inhibiting its phosphatase activity, which resulted in up-regulation of CTLA-4 and the induction of T-cell tolerance. Inhibition of CD45 prevented expression of B-cell lymphoma 6 (Bcl-6), a transcriptional inhibitor that directly bound the CTLA-4 promoter and regulated its activity 27718235_we demonstrate for the first time the physiological existence of ct-CD45 in human plasma and show that it may be an extrinsic factor contributing to the maintenance of human T-cell quiescence. 27748273_Our findings suggest that if w/h ratio on SSC versus CD45 plot is less than 1.6, AML may be considered, and if it is more than 1.6, ALL may be diagnosed. Using morphometric analysis of the blast cluster on SSC versus CD45, it was possible to distinguish between ALL and AML, and their subtypes. 28025077_Use of the common leukocyte marker CD45 increases the sensitivity of the diagnosis of lymphocytic myocarditis. 28628650_pUL11 induces IL-10 producing T cells as a result of pUL11 binding to the CD45 phosphatase on T cells. 28655861_CD45 is a regulator of IL-2 synergy in the NKG2D-mediated activation of immature human NK cells 28735895_A phosphosite within the SH2 Domain of Lck regulates its activation by CD45. A negative feedback loop that responds to signaling events tunes active Lck amounts and TCR sensitivity. 28759630_C77G is not associated with ovarian cancer in the Norwegian population. However, it is possibly associated with a less aggressive cancer type. 28982901_Expression of IL10R subunits within the leukocyte population (CD45(+) cells) was significantly higher in primary brain tumors than in metastases. 29133794_Overall, this study reveals the heterogeneity of CD4 effector memory T cells expressing CD45RA and provides insights into T-cell responses against dengue virus and other viral pathogens. 29177949_Five-year disease-free survival for patients with a high transcriptional expression of CD45 (n = 107) was 62.4% and for patients with a low expression (n = 53) it was 36.2% (P = 0.003). Patients with a high expression of CD45 had a better local recurrence-free survival and disease-specific survival. 29366662_CD45 antigen (CD45) plays a significant role in autoimmune diseases and cancer as well as in infectious diseases [Review]. 29467364_TCR phosphorylation negatively correlates with TCR-CD45 separation. 29549706_The results suggest that CD45RO modulates HIV-1 gp120-induced apoptosis by regulating the activity of Lymphocyte Specific Protein Tyrosine Kinase p56(lck) (Lck). 29736038_Data identifies CD45 as a receptor for LukF-PV. The human-specific interaction between LukF-PV and CD45 provides a molecular explanation for resistance of hC5aR1KI mouse neutrophils to PVL and probably contributes to the lack of a PVL-mediated phenotype during infection in these mice. 30248063_these results suggest that PTPRC expression may be useful for distinguishing Parkinson disease from progressive supranuclear palsy patients as part of a biosignature. 30347598_The percentage of CD45high cases in CR patients was 16.4%, which was lower compared to non-CR patients (35.2%, P= 0.017), while no difference in percentage of CD45high cases was found between allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) patients and non-allo-HSCT patients (16.7% vs. 25.7%, P= 0.492). 30825183_Data that CD45RO+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) serve as prognostic factors for predicting overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS) of breast cancer patients. 30842149_The density of CD45-positive cells in the liver parenchyma is an easily measured prognostic biomarker that can identify patient subgroups with a better prognosis. In addition, the density of CD45-positive cells in the liver may assist as a criterion for selecting patients with a high potential for response to adjuvant immunotherapy. 31641081_CD45 functions as a signaling gatekeeper in T cells. 31648475_CD45 expression is a risk prognostic factor of multiple myeloma patients 31760539_JAK2 and PTPRC mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 31855448_The Potential Role of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, Receptor Type C (CD45) in the Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. 32023448_CD45RB Status of CD8(+) T Cell Memory Defines T Cell Receptor Affinity and Persistence. 32170460_Estradiol regulates the expression of CD45 splicing isoforms in lymphocytes. 32446033_Engagement of CD45 alters early signaling events in human T cells co-stimulated through TCR + CD28. 32525407_A N |
ENSMUSG00000026395 |
Ptprc |
2678.630999 |
2.0984958040 |
1.069356 |
0.043181271 |
610.745230 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000770300629253077878593915710730594899748465556267436429940059013190334623107389951422981623604790444282499127383823203889439842714165003705265605037177564087833900713920290727733971742601051751494 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000435618286887947443107052523150261854453600035219613951196228579646571990313163046724771832721479437946444397001707828107887775944940216209688783376633329010423750431438775538865203942249485657108 |
Yes |
Yes |
3731.7022890 |
93.3437972 |
1790.8611575 |
34.4533484 |
| ENSG00000081913 |
23239 |
PHLPP1 |
protein_coding |
O60346 |
FUNCTION: Protein phosphatase involved in regulation of Akt and PKC signaling. Mediates dephosphorylation in the C-terminal domain hydrophobic motif of members of the AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family; specifically acts on 'Ser-473' of AKT2 and AKT3, 'Ser-660' of PRKCB and 'Ser-657' of PRKCA (PubMed:15808505, PubMed:17386267, PubMed:18162466). Isoform 2 seems to have a major role in regulating Akt signaling in hippocampal neurons (By similarity). Akt regulates the balance between cell survival and apoptosis through a cascade that primarily alters the function of transcription factors that regulate pro- and antiapoptotic genes. Dephosphorylation of 'Ser-473' of Akt triggers apoptosis and suppression of tumor growth. Dephosphorylation of PRKCA and PRKCB leads to their destabilization and degradation (PubMed:18162466). Dephosphorylates STK4 on 'Thr-387' leading to STK4 activation and apoptosis (PubMed:20513427). Dephosphorylates RPS6KB1 and is involved in regulation of cap-dependent translation (PubMed:21986499). Inhibits cancer cell proliferation and may act as a tumor suppressor (PubMed:19079341). Dephosphorylates RAF1 inhibiting its kinase activity (PubMed:24530606). May act as a negative regulator of K-Ras signaling in membrane rafts (By similarity). Involved in the hippocampus-dependent long-term memory formation (By similarity). Involved in circadian control by regulating the consolidation of circadian periodicity after resetting (By similarity). Involved in development and function of regulatory T-cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CHE4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTR8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15808505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17386267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18162466, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19079341, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21986499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24530606}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Leucine-rich repeat;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serine/threonine phosphatase family. The encoded protein promotes apoptosis by dephosphorylating and inactivating the serine/threonine kinase Akt, and functions as a tumor suppressor in multiple types of cancer. Increased expression of this gene may also play a role in obesity and type 2 diabetes by interfering with Akt-mediated insulin signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:23239; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004722]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; entrainment of circadian clock [GO:0009649]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046328]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900744]; regulation of T cell anergy [GO:0002667]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
17386267_Mechanism to selectively terminate Akt-signaling pathways through the differential inactivation of specific Akt isoforms by specific PHLPP isoforms. 18162466_PHLPP controls the cellular levels of PKC by specifically dephosphorylating the hydrophobic motif, thus destabilizing the enzyme and promoting its degradation. 18511290_Study focuses on the function of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 in modulating signaling by Akt and PKC. 19079341_Loss of PHLPP expression is associated with colon cancer. 19261608_Bcr-Abl represses the expression of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 and continuously activates Akt1, -2, and -3 via phosphorylation on Ser-473, resulting in the proliferation of CML cells 19690890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19745829_In the striatum, reduced levels of PHLPP1 can contribute to maintain high levels of activated Akt that may delay cell death and allow the recovery of neuronal viability after mutant huntingtin silencing 19797085_demonstrate a key role for beta-TrCP in controlling the level of PHLPP1, and activation of Akt negatively regulates this degradation process. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20513427_The PHLPP1 dephosphorylate Mst1 on the T387 inhibitory site, which activate Mst1 and its downstream effectors p38 and JNK to induce apoptosis. 20574456_Aberrantly expressed UCH-L1 boosts signaling through the Akt pathway by downregulating the antagonistic phosphatase PHLPP1, an event that requires its de-ubiquitinase activity 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20861921_Reduced expression of the tumor suppressor PHLPP1 enhances the antiapoptotic B-cell receptor signal in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells. 21177869_a compensatory feedback regulation in which the activation of Akt is inhibited by up-regulation of PHLPP through mTOR, and this mTOR-dependent expression of PHLPP subsequently determines the rapamycin sensitivity of cancer cells. 21454620_the cellular localization of beta-TrCP1 is altered in glioblastoma, resulting in dysregulation of PHLPP1 and other substrates such as beta-catenin. 21461637_Increased abundance of PHLPP-1, production of which is regulated by insulin, may represent a new molecular defect in insulin-resistant states such as obesity. 21701506_Knockdown of Scribble (Scrib) results in redistribution of PHLPP1 from the membrane to the cytoplasm and an increase in Akt phosphorylation. 21804599_show for the first time a significant disruption of all three members of the PTEN-NHERF1-PHLPP1 tumor suppressor network in high-grade tumors, correlating with Akt activation and patient's abysmal survival 21840483_codeletion of PTEN and PHLPP1 in patient samples is highly restricted to metastatic disease and tightly correlated to deletion of TP53 and PHLPP2 21986499_Knockdown of PHLPP1 or PHLPP2 resulted in an increase in S6K1 phosphorylation. 22044669_PHLPP1 has tumor suppressive activity and might represent a therapeutic or diagnostic tool for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 22144674_PHLPP as a novel tumor suppressor. 22183406_PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 have an effect on retinal rod CNG channel sensitivity. 22237780_Loss of PHLPP1 is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 22340730_Studies suggest that the effects of PHLPP1 deletion on prostate carcinogenesis may be explained by the strong dependence of prostate cancer on phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signalling. 22391563_USP46-mediated stabilization of PHLPP and the subsequent inhibition of Akt. 22426999_a novel USP1-PHLPP1-Akt signaling axis, and decreased USP1 level in lung cancer cells may play an important role in lung cancer progress. 22931649_AG490 time-dependently down-regulated the protein expression of PHLPP and induced apoptosis of K562 cells 23440515_we found that SGT1 was able to regulate the stability of PHLPP1, which is the direct phosphatase for Akt ser473 phosphorylation 23512990_Data indicate that binding affinities for the PH domains of Akt and PHLPP1 were greater than for other PH domain-containing proteins, which may underlie the preferential recruitment of these proteins to membranes containing tocopherols. 23846336_This study reveals functional and mechanistic links between miRNA-224 and the tumor suppressors PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer 24037758_The overall survival time and relapse-free survival time in PHLPP1-positive gastric cancer patients were significantly longer than in PHLPP1-negative patients. 24061475_A hypoxia-induced decrease of PHLPP expression is attenuated by knocking down HIF1alpha but not HIF2alpha. 24121273_Suppression of PHLPP1 by DNA methylation contributes to melanoma development and progression. 24145035_our results reveal WDR48 and USP12 as novel PHLPP1 regulators and potential suppressors of tumor cell survival. 24393845_PHLPP1 is a binding protein for Mst1 and it modulates the Hippo pathway by dephosphorylating Mst1 at the inhibitory Thr(387) of Mst1. 24892992_biochemical characterization of phosphatase domain of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2;PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 have similar in vitro activities and respond comparably to the presence of metallic ions; metallic ions affect structural stability of the domain;identified 3 residues likely involved in metal coordination and 2 that may be important for structural integrity 24945731_miR-141 and its targets PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 play critical roles in NSCLC tumorigenesis 25776496_PHLPP1, along with miR-522, promoted tumor cell growth in glioblastoma cells. 25793736_Aberrant expression of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 correlates with poor prognosis in patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma 26245343_Results showed that PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 gene expression are down-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Their promotor is a target for mir-224. 26427440_Data show that both serine/threonine phosphatases PHLPP and dephosphorylated the physiological substrates of Akt1 and Akt3 with similar efficiencies. 26463718_high levels of PHLPP might reflect a less aggressive lung adenocarcinoma phenotype and predict better survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. 26760962_Increased PHLPP expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 26823799_our results suggest that PHLPP1 plays a crucial role in sacral chordoma 26971226_this study shows that PHLPP1 played a suppression role in inflammatory response of glioma 27248326_Data suggest a tumor suppressor role of Xist in inhibiting AKT activation via regulation of non-X-chromosome gene PHLPP1 expression. 27760826_results identify a novel role of PHLPP in regulating aPKC and cell polarity. 27913677_Studies indicate that two PHLPP isozymes, PHLPP1 and PHLPP2, were identified in a search for phosphatases that dephosphorylate Akt, and thus suppress growth factor signaling. 28139510_Abnormal PHLPP, FoxO3a, and RAD51 protein expressions may be involved in the development of high- and low-grade ovarian serous adenocarcinomas, suggesting common molecular pathways. 28212545_Low PHLPP expression is associated with gallbladder cancer. 28263966_nickel exposure results in DNMT3b induction and MEG3 promoter hypermethylation and expression inhibition, further reduces its binding to c-Jun and in turn increasing c-Jun inhibition of PHLPP1 transcription, leading to the Akt/p70S6K/S6 axis activation, and HIF-1alpha protein translation, as well as malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. 28322791_During LPS induced macrophage inflammatory response, PHLPP levels in macrophages are depleted through the inhibition of SP1 dependent transcriptional regulation. 28696259_Data suggest that PHLPP1 plays an important role in assembly of kinetochores by counteracting RNF41-mediated SGT1 degradation. (PHLPP1 = PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 1; RNF41 = ring finger protein 41; SGT1 = suppressor of G2 allele of SKP1) 29391600_PHLPP1 functions as a metastasis suppressor through its phosphatase activity, and PHLPP1 represents a novel diagnostic and therapeutic marker for metastatic melanoma. 30092222_miR-190 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting PHLPP1. 30904392_PHLPP1 provides a proofreading step that maintains the fidelity of PKC autoinhibition and reveals a prominent loss-of-function mechanism in cancer by suppressing the steady-state levels of PKC. 31582730_Phlpp1 is associated with human intervertebral disc degeneration and its deficiency promotes healing after needle puncture injury in mice. 32294598_PTEN and PHLPP crosstalk in cancer cells and in TGFbeta-activated stem cells. 32480039_Distinct intra-mitochondrial localizations of pro-survival kinases and regulation of their functions by DUSP5 and PHLPP-1. 32587773_Heat shock protein 47 promotes tumor survival and therapy resistance by modulating AKT signaling via PHLPP1 in colorectal cancer. 33029497_USP46 Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Lung Cancer through PHLPP1/AKT Pathway. 33441223_[Down-regulation of PHLPP1 expression ameliorates high glucose-induced autophagy inhibition and apoptosis promotion of podocytes by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway]. 34348155_Inhibition of PHLPP1/2 phosphatases rescues pancreatic beta-cells in diabetes. 34663797_Downregulation of PHLPP induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes eIF2alpha phosphorylation and chemoresistance in colon cancer. 36376971_PHLPP isoforms differentially regulate Akt isoforms and AS160 affecting neuronal insulin signaling and insulin resistance via Scribble. |
ENSMUSG00000044340 |
Phlpp1 |
286.224385 |
0.3631660114 |
-1.461299 |
0.098786145 |
224.414787 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000985027461066022904292403476943363030860033035718889143741149615937639415261282335328242768350373810489378823285216793004044242513389528781431181414518505334854125976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000215074043274178953118289303524345690578423722763348794005211218776958672189466125405462102678160567041500792050713930422247907592314675184752559289336204528808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
154.6112630 |
10.0621967 |
428.7706720 |
17.6528218 |
| ENSG00000081923 |
5205 |
ATP8B1 |
protein_coding |
O43520 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of phospholipids, in particular phosphatidylcholines (PC), from the outer to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane (PubMed:25315773, PubMed:17948906). May participate in the establishment of the canalicular membrane integrity by ensuring asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the canicular membrane (By similarity). Thus may have a role in the regulation of bile acids transport into the canaliculus, uptake of bile acids from intestinal contents into intestinal mucosa or both and protect hepatocytes from bile salts (By similarity). Involved in the microvillus formation in polarized epithelial cells; the function seems to be independent from its flippase activity (PubMed:20512993). Participates in correct apical membrane localization of CDC42, CFTR and SLC10A2 (PubMed:25239307, PubMed:27301931). Enables CDC42 clustering at the apical membrane during enterocyte polarization through the interaction between CDC42 polybasic region and negatively charged membrane lipids provided by ATP8B1 (By similarity). Together with TMEM30A is involved in uptake of the synthetic drug alkylphospholipid perifosine (PubMed:20510206). Required for the preservation of cochlear hair cells in the inner ear (By similarity). May act as cardiolipin transporter during inflammatory injury (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q148W0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17948906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20510206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20512993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25239307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27301931}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Hearing;Intrahepatic cholestasis;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the P-type cation transport ATPase family, which belongs to the subfamily of aminophospholipid-transporting ATPases. The aminophospholipid translocases transport phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from one side of a bilayer to another. Mutations in this gene may result in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1 and in benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5205; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; cardiolipin binding [GO:1901612]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylcholine flippase activity [GO:0140345]; phosphatidylcholine floppase activity [GO:0090554]; phosphatidylserine flippase activity [GO:0140346]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; apical protein localization [GO:0045176]; bile acid and bile salt transport [GO:0015721]; bile acid metabolic process [GO:0008206]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; inner ear receptor cell development [GO:0060119]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; regulation of chloride transport [GO:2001225]; regulation of microvillus assembly [GO:0032534]; regulation of plasma membrane organization [GO:1903729]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; vestibulocochlear nerve formation [GO:0021650]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855] |
12880872_three homologues found and two sequenced and two RNA transcript sizes analysed by northern blot: APT8B2, APT8B3, APT8B4 14988830_Loss of familial intrahepatic cholestasis-1 leads to diminished nuclear translocation of farnesoid X receptor(FXR), with subsequent potential for pathologic alterations in intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporter expression 15239083_54 distinct disease mutations: 10 mutations predicted to disrupt splicing, 6 nonsense mutations, 11 small insertion or deletion mutations predicted to induce frameshifts, 1 large genomic deletion, 2 small inframe deletions, and 24 missense mutations. 15888793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15946126_Loss of familial intrahepatic cholestasis-1 leads to diminished nuclear translocation of farnesoid X receptor(FXR), with subsequent potential for pathologic alterations in intestinal and hepatic bile acid transporter expression 17948906_Coexpression with CDC50 proteins resulted in relocalization of ATP8B1 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. In the plasma membrane, ATP8B1 functions as a flippase for phosphatidylserine. 18668687_FIC1 signals to FXR via PKC zeta. FIC1-related liver disease is likely related to downstream effects of FXR on bile acid homeostasis. 19027009_ATP8B1 deficiency predisposes to cholestasis by favoring bile acid-induced injury in the canalicular membrane but does not directly affect FXR expression 19228886_Knockdown of ATP8B1 expression leads to specific downregulation of the bile acid sensor FXR in HepG2 cells: effect of the FXR agonist GW4064. 19381753_These results suggest that the PFIC1 mutants have a lower stimulatory effect on FXR activity and cannot interact with CDC50A, which may lead to the development of the features of PFIC1. 19478059_show that ATP8B1/Atp8b1 deficiency, both in patients and in Atp8b1(G308V/G308V) mutant mice, causes hearing loss, associated with progressive degeneration of cochlear hair cells 19479804_Post-liver transplantation steatosis may be due to a malfunction of the ATP8B1 product. 19731236_PFIC1 mutations lead to the complete absence of canalicular expression, whereas in BRIC1/ICP residual protein is expressed in the canalicular membrane. 19809379_Findings support the hypothesis that hepatocyte FIC1 enhances FXR signaling via a PKCzeta-dependent signaling pathway. 19918981_A surprisingly large proportion of ATP8B1 mutations resulted in aberrant folding and decreased expression at the plasma membrane. These effects were partially restored by treatment with 4-phenylbutyrate. 20038848_ATP8B1 gene mutations play an important role in Chinese patients with progressive intrahepatic cholestasis and low gamma-glutamyltransferase. The linked mutation P209T and IVS6+5G>T is a hot mutation in the Chinese population. 20216097_We now report evidence that heterozygous genetically determined alteration of ATP8B1 (encoding FIC1) may also represent a risk factor for transient neonatal cholestasis. 20232290_Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis types 1 & 2 differ clinically, biochemically, and histologically at presentation and/or during the disease course. A small proportion of normal-GGT PFIC is likely not due to ATP8B1 or ABCB11 mutations. 20414253_Data identified three novel mutations in BSEP, one novel mutation in MDR3, and one heterozygous mutation in ATP8B1 in PFIC patients. 20447715_facilitating diagnosis and elucidating the differing consequences of ATP8B1 and ABCB11 mutations in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 20512993_critical role in apical membrane organization that is unrelated to its presumed aminophospholipid translocase activity 20683201_Sequence analysis of the genes identified 27% cholestasis subjects with missense, nonsense, deletion, and splice site variants associated with disease phenotypes based on the type of mutation in the JAG1, ATP8B1, ABCB11, or ABCB4 genes. 20852622_results unveil a new paradigm whereby Atp8b1 is a cardiolipin importer whose capacity to remove cardiolipin from lung fluid is exceeded during inflammation or when Atp8b1 is defective 23033845_Novel splice-site mutation in ATP8B1 results in atypical progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. 23060447_Biochemical analysis of P4-ATPase mutations identified in patients with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis 23197899_Case Report: missense ATP8B1 mutation in adult male with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 1. 23213138_FIC1 signals to FXR via a signaling pathway including PLD2 and PKCzeta 23251605_The basal expression of ATP8B1 is driven by a housekeeping-like promoter located 71 kb upstream of the first protein coding exon, and is independent of bile acids and farnesoid X receptor. 23750872_Case Report: suggest contribution of ATP8B1 mutations to drug-induced liver injury from anabolic androgenic steroids marketed as dietary supplements. 24260417_We did not find an association between heterozygous ATP8B1 variants and chronic pancreatitis in our cohort of patients with hereditary and idiopathic chronic pancreatitis. 25239307_Data indicate that the lipid flippase (ATP8B1)-transmembrane protein 30A (CDC50A) heterodimer is essential for the apical localization of sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (SLC10A2/ASBT) in Caco-2 cells. 25421123_We systematically characterized the molecular consequences of 14 ATP8B1 mutations at exon-intron boundaries associated with ATP8B1 deficiency and found that the majority resulted in total exon skipping 26050466_insufficient activity of Atp8b1/FIC1 increases susceptibility to bacterial pneumonia. 26240149_the predominant P4 ATPases in pure pancreatic beta cells and human and rat pancreatic islets were ATP8B1, ATP8B2, and ATP9A. ATP8B1 and CDC50A were highly concentrated in ISG 26382629_As hypothyroidism can be another extrahepatic feature of ATP8B1 deficiency, thyroid function should be monitored in these patients. 27050426_GGT levels in patients with ATP8B1 or ABCB11 deficiency varied with age. The peak GGT value was |
ENSMUSG00000039529 |
Atp8b1 |
209.808576 |
0.1972928936 |
-2.341589 |
0.725375360 |
8.156649 |
0.00429035707072615048185415531634134822525084018707275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008896553858375663703661473391548497602343559265136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.6194703 |
21.7767578 |
162.6963984 |
89.3293595 |
| ENSG00000081985 |
3595 |
IL12RB2 |
protein_coding |
Q99665 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for interleukin-12. This subunit is the signaling component coupling to the JAK2/STAT4 pathway. Promotes the proliferation of T-cells as well as NK cells. Induces the promotion of T-cells towards the Th1 phenotype by strongly enhancing IFN-gamma production. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a type I transmembrane protein identified as a subunit of the interleukin 12 receptor complex. The coexpression of this and IL12RB1 proteins was shown to lead to the formation of high-affinity IL12 binding sites and reconstitution of IL12 dependent signaling. The expression of this gene is up-regulated by interferon gamma in Th1 cells, and plays a role in Th1 cell differentiation. The up-regulation of this gene is found to be associated with a number of infectious diseases, such as Crohn's disease and leprosy, which is thought to contribute to the inflammatory response and host defense. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms and non-protein coding transcripts have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:3595; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; interleukin-12 receptor complex [GO:0042022]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; immune response [GO:0006955]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation [GO:0032819]; positive regulation of NK T cell proliferation [GO:0051142]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496] |
11306945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11441083_In the generation of cell-mediated immunity against intracellular infection, the expression and function of the IL-12 receptor beta 2 chain correlate with the response of Th1-type cells to Mycobacterium leprae antigen. 11940489_STATE OF ART REVIEW. IL-12Rb2 gene is not expressed in EBV-transformed normal B-lymphocytes and in Burkitt's lymphoma B-cell lines. 12719941_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12743658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12768436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12804004_upregulated in Il-12 augmented T cell activation of mononclear leukocytes from HIV seropositive individuals 15004750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15140029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15140029_promoter activity is increased in case of the -465G allele, disrupting the intact GATA site 15901746_Study showed recombinant human interleukin-12 (rhIL-12) safe/well tolerated in healthy subjects given single doses (1 up to 8 ug) subcutaneously. Interferon-gamma and, signal transducer and activator of transcription may be useful biomarkers of rhIL-12. 15976343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17152005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17236132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17602269_Epigenetic silencing of IL-12Rbeta2 is a frequent event in lung cancers. Aberrant methylation of this gene seems to be a useful predictor of long-term outcome for adenocarcinoma of the lung. 17622942_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18353079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18353079_frequencies of variant alleles were significantly higher in aggressive periodontitis patients as compared with healthy controls or chronic periodontitis patients 18474725_IL-12R beta 2 directly restrains multiple myeloma cell growth 18715339_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18771340_These results suggest that these SNPs in IL12RB2 have differential effects on cellular activation of T cells and NK cells. 18927311_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18927311_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in interleukin 12 receptor beta 2 is associated with susceptibility to radiation dermatitis in breast cancer. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19458352_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19458352_Our data show significant associations between primary biliary cirrhosis and common genetic variants at the HLA class II, IL12A, and IL12RB2 loci 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19720917_Studies established the concept that the IL-12Rbeta2 gene is a gatekeeper from cancer. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20060272_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20060272_significant interaction between the IL-12RB1 and IL-12RB2 genes contributes to a 4-fold increased risk for developing extrinsic atopic dermatitis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20350312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20525402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20622878_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20622879_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21285166_Our results support a potential influence of the rs3790567 IL12RB2 polymorphism in the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis. 22076442_data clearly support the IL12RB2 genetic association with systemic sclerosis (SSc), and suggest a relevant role of the interleukin 12 signaling pathway in SSc pathogenesis. 22378604_Variants in IL10 and IL23R-IL12RB2 are associated with Behcet's disease in Iranian patients. 22509293_the -237 polymorphic site in the 5' promoter region of the IL-12Rbeta2 (SNP ID: rs11810249) gene associated with the AP-4 transcription motif GAGCTG 22715389_a differential regulation pattern for genes solely expressed in Th17 cells (IL17A and CCL20) compared to genes expressed in both Th17 and Th1 cells (IL23R and IL12RB2), where high levels of promoter methylation are correlated to near zero 23009887_Data indicate that SNP (rs452204) in the IL1RN gene was significantly associated with higher levels of IL-2 secretion, and IL12RB2 SNP rs3790567 was associated with a decrease in IL-1beta secretion. 23152861_Association of IL12RB2 rs6679356 polymorphism with the age of type 1 diabetes mellitus onset suggests that this gene plays a role in defining the time of disease onset. 23677568_ERbeta2 and IL-12Rbeta5 had longer OS. 23911393_Data indicate that four of the IL-12Rbeta2 variants, N271Y, R313G, A604V and L808R showed reduced IL-12 responses compared to the wild type variant. 24434271_results suggest the rs924080 risk A allele does not affect baseline expression of IL-12RB2, IL-23R, IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha but enhances IL-23R and TNF-alpha expression capacity in response to LPS stimulation; the A allele appears to enhance baseline IL-6 production 24486579_Polymorphisms present in the promoter region of IL12RB2 may not be associated with susceptibility to leprosy or its clinical forms. 24859272_Genetic variations of IL-12B, IL-12Rbeta1, IL-12Rbeta2 in Behcet's disease and VKH syndrome. 25695486_Estrogen receptor beta 2 regulates IL12RB2 expression via p38 MAPK signaling and inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation and invasion. 25720506_IL12RB2 polymorphism is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in the Chinese population. 26547104_IL12RB2 polymorphisms correlate with risk of lung adenocarcinoma. 26552659_The effects of rs3762315 and rs3762316 single nucleotide polymorphisms in 5' flanking region on IL12RB2 transcription 26916345_In ankylosing spondylitis, conditional analysis identified rs11209032 as the probable causal single-nucleotide polymorphism within a 1.14 kb putative enhancer between IL23R and IL12RB2. The rs11209032 single-nucleotide polymorphism downstream of IL23R forms part of an enhancer, allelic variation of which may influence Th1-cell numbers. 26987707_The results of this case-control study suggest that IL-12A, IL-12B, IL12RB1, IL12RB2 and IL23R make no genetic contribution to the susceptibility of Takayasu arteritis in Chinese populations 27464962_this study identified susceptibility single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL12RB2 with Behcet's disease in Han Chinese 27660093_this study shows that single nucleotide polymorphisms of the IL23R-IL12RB2 region are associated with Behcet's disease in a Northern Chinese Han population 28299343_study confirmed the relationship of IL12RB2 polymorphisms with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) susceptibility; provided evidence that IL12RB2 polymorphisms are associated with liver cirrhosis and an increased concentration of disease-specific anti-mitochondrial antibodies in sera of PBC patients 28947543_inhibition of the H3K27 demethylase JMJD3 in naive CD4 T cells demonstrates how critically important molecules required for T cell differentiation, such as JAK2 and IL12RB2, are regulated by H3K27me3. 29103744_Tumor cell differentiation is associated with TILs' expression of IL-12Rbeta2, and an IL-12Rbeta2(+) TIL ratio >/=35%) indicates favorable prognosis in LC 29576322_we analyzed common variants located in genes of the IL12/STAT4 and IL10/STAT3 signaling pathways in patients with myasthenia gravis. 29956791_The Cox proportional hazard models revealed that IL12Rb2 and p38MAPK predicted a long OS. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to reveal a close association between IL12Rb2 and p38MAPK, and their possible function in nonsmall cell lung cancer progression 31158284_Mutation analysis showed three previously reported mutations, two novel mutations in IL-12 R (beta1/beta2), and one previously reported mutation in IL-12 Mendelian Susceptibility to Mycobacterial Disease patients. 33287915_Expressions of IL-12 and its receptors in patients with lumbar disc herniation and their relationship with clinical efficacy. 35923356_Role of Genetic Polymorphisms in IL12Rbeta2 in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000018341 |
Il12rb2 |
228.519719 |
0.3537545006 |
-1.499180 |
0.224729785 |
43.024354 |
0.00000000005406267647160499227277271387740722671799709075912687694653868675231933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000284479538224916109348166517325844603047979575194403878413140773773193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
110.4068511 |
20.1492091 |
314.2837971 |
40.6427951 |
| ENSG00000082074 |
2533 |
FYB1 |
protein_coding |
O15117 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an adapter protein of the FYN and LCP2 signaling cascades in T-cells (By similarity). May play a role in linking T-cell signaling to remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton (PubMed:10747096, PubMed:16980616). Modulates the expression of IL2 (By similarity). Involved in platelet activation (By similarity). Prevents the degradation of SKAP1 and SKAP2 (PubMed:15849195). May be involved in high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor signaling in mast cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZIE4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35601, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10747096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15849195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16980616}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an adapter for the FYN protein and LCP2 signaling cascades in T-cells. The encoded protein is involved in platelet activation and controls the expression of interleukin-2. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:2533; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; immune response [GO:0006955]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
15843031_ADAP lipid interaction defines the helically extended SH3 scaffold as a novel member of membrane interaction domains 15849195_show in an ADAP-deficient Jurkat T cell line that the co-dependence of ADAP and SKAP55 extends beyond their functional and physical interactions and show that SKAP55 protein is unstable in the absence of ADAP 16831444_Lipid binding of ADAP at the immunological synapse most likely contributes to the function of ADAP as a regulator of T cell migration and adhesion. 17511475_An eight-membered ring formed upon oxidation of two neighboring cysteines leads to significant changes in the variable arginine-threonine (RT) loop of the hSH3N domain of this protein. 17785790_ADAP-deficient T-cell-receptor transgenic T cells demonstrate that ADAP is a positive regulator of antigen-dependent, LFA-1 integrin-mediated T cell conjugate formation with antigen presenting cells. 18802088_Naive transgenic ADAP-deficient T cells show impaired adhesion to ovalbumin fragment-bearing antigen-presenting cells that is restored following reconstitution with wild-type ADAP. 19798671_Mass spectrometric identification of ADAP associated with EVL, an actin-binding protein of the ENA/VASP family, DOCK2 and GEF-H1 suggests a direct link between ADAP and the cytoskeleton. 20164171_the ADAP CARMA1 binding site is required for IKK gamma ubiquitination; both TAK1 and CARMA1 binding sites are required for IkappaB alpha phosphorylation and degradation and NF-kappaB nuclear translocation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21536650_a functional cooperation between Nck and ADAP in stabilizing the recruitment of WASp to SLP76 regulates actin rearrangement. 21881001_TM4SF10, possibly through ADAP, may regulate Fyn activity 23628395_our findings indicate an association between polymorphisms located in FYB gene and SLE, suggesting their possible involvement in disease susceptibility and clinical manifestations. 23979596_Multipoint binding of SLP-76 to ADAP facilitates the assembly of SLP-76 microclusters. 24047317_These findings indicate that ADAP regulates two steps of HIV-1 infection cooperatively with two distinct receptors, and as such, serves as a new potential target in the blockade of HIV-1 infection. 24523237_ADAP interacts with talin and kindlin-3 to promote platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation and stable fibrinogen binding. 24769494_ADAP and Nck adapter proteins cooperatively facilitate T cell adhesion to the LFA-1 ligand ICAM-1. 25516138_The autosomal recessive bleeding phenotype seen in several members of this highly consanguineous family included petechial rash, mild epistaxis and thrombocytopenia with some decrease in platelet volume. These clinical findings, together with the results of exome sequencing pointed to only one strong candidate gene, the FYB gene. 25729932_The aim of this study was to perform an association study between seven Fyn-binding protein gene (FYB)-tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and type I diabetes mellitus (T1DM), as well as with disease age of onset. 25876182_FYB nonsense mutations in humans causing small-platelet thrombocytopenia and a significant bleeding tendency. 25909459_Data (including data from studies in knockout/transgenic mice) suggest that ADAP regulates positive feedback loop of TGFbeta1 production and TGFbeta1-induced CD103 expression in CD8+ T-lymphocytes and protects against influenza H5N1 virus infection. 26202465_Data strongly suggest that chemokine-stimulated associations between Vav1, SLP-76, and ADAP facilitate Rac1 activation and alpha4beta1-mediated adhesion, whereas Pyk2 opposes this adhesion by limiting Rac1 activation. 26246585_A distinct set of proteins interaction partners required for chemokine-directed T cell migration is attracted by phosphotyrosine 571 of ADAP, including ZAP70. 27258783_Current knowledge of the functions of the adapter protein ADAP in T cell signaling with a focus on the role of individual phosphotyrosine (pY) motifs for SH2 domain mediated interactions is presented. 27335501_results of this study indicate that a novel T cell adaptor protein, activation-dependent, raft-recruited ADAP-like phosphoprotein (ARAP), plays a unique role in T cells as a part of both the proximal activation signaling and inside-out signaling pathways that result in integrin activation and T cell adhesion 29127148_Ubc9 is an essential regulator of ADAP where it is required for TCR-induced membrane recruitment of the small GTPase Rap1 and its effector protein RapL and for activation of the small GTPase Rac1 in T cell adhesion. 30305305_Findings reveal that ADAP acts upstream of SLP-76 to convert labile, Ca(2+)-competent microclusters into stable adhesive junctions with enhanced signaling potential. 34295339_The Multiple Roles of the Cytosolic Adapter Proteins ADAP, SKAP1 and SKAP2 for TCR/CD3 -Mediated Signaling Events. 34882057_FYB methylation in peripheral blood as a potential marker for the early-stage lung cancer: a case-control study in Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000022148 |
Fyb |
353.057690 |
0.4461420680 |
-1.164425 |
0.141528337 |
66.786449 |
0.00000000000000030257093939958941808613229229794073198117176481253265407644903461914509534835815429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002225185383925231662105893087748193288215087150966331464019276609178632497787475585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
222.7756035 |
22.1351679 |
502.1866256 |
35.2098315 |
| ENSG00000082153 |
9689 |
BZW1 |
protein_coding |
Q7L1Q6 |
FUNCTION: Translation initiation regulator which represses repeat-associated non-AUG (RAN) initiated translation probably by acting as a competitive inhibitor of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 (EIF5) function (PubMed:29470543, PubMed:34260931). Enhances histone H4 gene transcription but does not seem to bind DNA directly (PubMed:11524015). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11524015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29470543, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34260931}. |
Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity and cadherin binding activity. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9689; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; regulation of translational initiation [GO:0006446] |
11524015_Stimulates cell cycle regulation of histone H4 gene transcription. 19446954_BZW1 is a novel factor, promoting the growth of MEC cells 21734401_Data indicate taht candidate genes ACTB, BZW, OCM, MACC1, NXPH1, PRPS1L1, RAC1 and RPA3, which lie within the DFNB90 region, were sequenced and no potentially causal variants were identified. 29470543_results reveal a surprising role for BZW1 and BZW2 in maintaining homeostatic stringency of start codon selection, and taking into account recent biochemical, genetic and structural insights into eukaryotic initiation, suggest a model for BZW1 and BZW2 function 31601833_Overexpression of BZW1 is an independent poor prognosis marker and its down-regulation suppresses lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. 32945505_Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 modifies cell proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via the miR4500/BZW1 axis in ovarian cancer. 33393590_LncRNA NEAT1 promotes glioma cancer progression via regulation of miR-98-5p/BZW1. 33886419_BZW1 promotes cell proliferation in prostate cancer by regulating TGF-beta1/Smad pathway. 34951995_BZW1 Facilitates Glycolysis and Promotes Tumor Growth in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Through Potentiating eIF2alpha Phosphorylation. |
ENSMUSG00000051223 |
Bzw1 |
1782.036602 |
2.1160838837 |
1.081397 |
0.078022109 |
189.338287 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000044337369468810623332573834572775538567110264675056847367477098038724838852991505115569693490805076133311332306496943544971145456656813621520996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000007971005765647317711029581343457437667171890785170160510244230473558614519775438207448240736060503723147806914850477255640726070851087570190429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2245.6551303 |
190.8360477 |
1069.0418937 |
66.1566297 |
| ENSG00000082397 |
23136 |
EPB41L3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2J2 |
FUNCTION: Tumor suppressor that inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Modulates the activity of protein arginine N-methyltransferases, including PRMT3 and PRMT5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15334060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15737618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16420693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9892180}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor |
|
Predicted to enable cytoskeletal protein-membrane anchor activity. Predicted to be a structural constituent of cytoskeleton. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including nervous system development; paranodal junction maintenance; and protein localization to paranode region of axon. Located in cell-cell junction and plasma membrane. Biomarker of meningioma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23136; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; juxtaparanode region of axon [GO:0044224]; paranode region of axon [GO:0033270]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cytoskeletal protein-membrane anchor activity [GO:0106006]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actomyosin structure organization [GO:0031032]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; cortical cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030865]; myelin maintenance [GO:0043217]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; paranodal junction assembly [GO:0030913]; protein localization to juxtaparanode region of axon [GO:0071205]; protein localization to paranode region of axon [GO:0002175]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
11996670_Results show that three 14-3-3 isoforms, beta, gamma and eta, are DAL-1/Protein 4.1B-binding proteins. 12115567_DAL-1 protein functions at the interface between cell adhesion and apoptosis in suppressing breast cancer cell growth 12234973_TSLC1 and DAL-1, two distinct tumor suppressor proteins, directly associate in lung cancer. 12478663_DAL-1 has a role in the development of multiple meningioma and does not function as a tumor suppressor 15138999_Mechanisms such as genetic imprinting and monoallelic expression in combination with los os heterozygosity may be responsible for loss of EPB41L3 protein in early breast tumors. 15334060_DAL-1/4.1B protein significantly inhibits PRMT3 methylation of cellular substrates, which may affect mechanism through which DAL-1/4.1B affects tumor cell growth. 15517334_protein 4.1B in mouse small intestine & DAL-1 in human colon showed similar distributions in normal intestinal epithelial cells; expression reduced in intestinal carcinoma; may function in preventing malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells 15688033_U2 domain, when properly targeted to the plasma membrane, contains all the residues necessary for mediating Protein 4.1B growth suppression. 15731777_4.1B gene deletion was statistically more common in ependymomas. 15837747_DAL-1 methylation is involved in the development and progression of non-small cell lung cancers and provides an indicator for poor prognosis. 16142420_The low mutational frequency in the study discounts sequence variations in DAL-1/4.1B as the main mechanism underlying participation of this gene in the neoplastic transformation of meningiomas. 16152585_promoter methylation of the 4.1B is one of the most frequent epigenetic alterations in RCCC and could predict the metastatic recurrence of the surgically resected RCCC 16205641_methylation of DAL-1 leading to loss of the expression, is an important event in the pathogenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer 16213361_These studies implicate the DAL-1/4.1B locus in sporadic meningiomas less commonly than reported previously, and suggest that it is a progression rather than an initiation locus. 16420693_These results suggest that protein methylation cooperates with DAL-1/4.1B-associated caspase 8-specific activation to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells. 17260099_TSLC1 and DAL-1 are involved in the pathogenesis of breast cancer and are frequently inactivated by methylation 17640904_suggest a more general role for Protein 4.1B as a negative regulator of cancer progression to metastatic disease 18554153_A growing body of evidence supports a role for loss of EPB41L3 in tumor progression, including in prostate cancer [review] 19115211_Our results demonstrate a frequent, predominant epigenetic silencing of CADM1 and DAL-1 in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma (NL), which likely play a synergic role in NL pathogenesis. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19299464_Identify Golgi-specific protein 4.1 that appears to have an essential role in maintaining the structure of the Golgi and in assembly of a subset of membrane proteins. 19796685_Results identify erythrocyte protein band 4.1-like 3 (protein 4.1B) as an intracellular effector molecule of Synaptic Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (SynCAM1) that is sufficient to recruit NMDA-type receptors (NMDARs) to SynCAM1 adhesion sites in COS7 cells. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20651987_An inducible model of EPB41L3 expression in three-dimensional spheroids confirmed that reexpression of EPB41L3 induces extensive apoptotic cell death in ovarian cancers. 21081044_The expressions of TSLC1 and 4.1B in non-small cell lung cancer tissues were significantly lower than that in adjacent lung tissues. 21131357_Structural basis of tumor suppressor in lung cancer 1 (TSLC1) binding to differentially expressed in adenocarcinoma of the lung (DAL-1/4.1B). 21526423_aberrant CADM1 and 4.1B expression is involved in progression of breast cancer, especially in invasion into the stroma and metastasis 21628394_miR-223, induced by the transcription factor Twist, posttranscriptionally downregulates EPB41L3 expression by directly targeting its 3'-untranslated regions. 21796628_Data suggest that the four-gene methylation panel might provide an alternative triage test after primary high-risk papillomavirus (hr-HPV) testing. 22782504_Loss of expression of the differentially expressed in adenocarcinoma of the lung protein is associated with metastasis of non-small cell lung carcinoma. 24828608_In granulosa cells, there are significant changes in expression during follicular maturation. 25183197_Studies indicate that tumor suppressor protein 4.1B/DAL-1 plays a crucial regulatory role in cell growth and differentiation. 25609022_The results suggest that tumor suppressor DAL-1 could also attenuate epithelial-to mesenchymal transition and be important for tumor metastasis in the early transformation process in lung cancer. 25621889_We conclude that EPB41L3, RASSF2 and TSP-1 genes are involved in the pathogenesis of diffuse gliomas 25780926_a central role of CADM1 in stabilizing the complex with 4.1B and MPP3 25881295_Our study demonstrates for the first time that platelet-secreted miR-223 via P-MVs can promote lung cancer cell invasion via targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. 26300315_Downregulation of DAL-1/4.1B expression effectively suppresses DAL-1/4.1B protein expression in lung cancer cells. 26916087_findings reveal that EPB41L3 suppresses tumour cell invasion and inhibits MMP2 and MMP9 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells 26923709_aberrant expression of DAL-1 by hypermethylation in the promoter region results in tumor suppressor gene behavior that plays important roles in the malignancy of gastric cancers 27312663_4.1B gene deletion was sufficient to transform SV40T antigen-immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblasts (iMEFs), as reflected by the ability of 4.1B(-/-) iMEFs to growth in the environments that were growth restrictive for 4.1B(+/+) iMEFs and to form tumors in nude mice, whereas 4.1B(+/+) iMEFs were unable to form tumors in vivo. 29048640_We revealed that DAL-1 was downregulated while HSPA5 was upregulated in NSCLC and found the protein of DAL-1 and HSPA5 co-localized in the cytoplasm and nucleus. We demonstrated that DAL-1 can suppress the expression of HSPA5 on mRNA and protein levels, and decrease EMT, migration, invasion and proliferation abilities by down-regulating HSPA5 30005021_Methylation of EPB41L3 DNA is elevated among WLHIV with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2+) and independently associated with lower CD4 count and antiretroviral agent use. 30962003_The downregulation of DAL-1 and TOB1 expression is associated with shorter survival of gastric cancer patients and may be considered potential novel markers for predicting the outcomes of patients with gastric cancer 31304592_EPB41L3 and HPV 16 L1, L2 and E2 methylation were significantly higher among cases than controls, regardless of early vs. late disease. When HPV 16 genes and EPB41L3 methylation status were combined in a logistic regression analysis, a sensitivity of 70.3% and a specificity of 90.9% were observed for the detection of oropharyngeal cancer from an oral gargle. 31492173_4.1B suppresses cancer cell proliferation by binding to EGFR P13 region of intracellular juxtamembrane segment 31734055_miR-452 promotes the development of gastric cancer via targeting EPB41L3. 31828581_Mutation and Expression of a Candidate Tumor Suppressor Gene EPB41L3 in Gastric and Colorectal Cancers. 32048621_Quantitative methylation results indicated that the level of methylation was significantly higher (hypermethylated) for FLT3 and EPB41L3 and significantly lower (hypomethylated) for SFN in tumour tissues as compared to the adjacent paired normal tissue. 32576279_DNA methylation for cervical cancer screening: a training set in China. 33323539_Erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 3 inhibits osteosarcoma cell invasion through regulation of Snai1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 34579655_The rs9953490 polymorphism of DAL-1 gene is associated with gastric cancer risk in the Han population in Northeast China. 34657240_DAL-1/4.1B promotes the uptake of exosomes in lung cancer cells via Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2). 35569139_Over-expression of EPB41L3 promotes apoptosis of human cervical carcinoma cells through PI3K/AKT signaling. 35619332_Methylation of HPV16 and EPB41L3 in oral gargles and the detection of early and late oropharyngeal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024044 |
Epb41l3 |
82.857431 |
2.6904244533 |
1.427834 |
0.174059170 |
68.968955 |
0.00000000000000010002564106448919288605832916429843637446708804698142225575452357588801532983779907226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000754794714781114787460070915213626138339114994470907538115511670184787362813949584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
124.0238925 |
13.9887822 |
46.3906870 |
4.1945430 |
| ENSG00000082458 |
1741 |
DLG3 |
protein_coding |
Q92796 |
FUNCTION: Required for learning most likely through its role in synaptic plasticity following NMDA receptor signaling. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase protein family. The encoded protein may play a role in clustering of NMDA receptors at excitatory synapses. It may also negatively regulate cell proliferation through interaction with the C-terminal region of the adenomatosis polyposis coli tumor suppressor protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with X-linked cognitive disability. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:1741; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; AMPA glutamate receptor complex [GO:0032281]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; establishment of planar polarity [GO:0001736]; establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045197]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061098]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; receptor localization to synapse [GO:0097120]; regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels [GO:0099072] |
15185169_Loss may lead to altered synaptic plasticity and may explain the intellectual impairment observed in individuals with DLG3 mutations 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19167192_The results of this study suggested a putative role for DLG3/SAP102 in cortical hyperexcitability and epileptogenicity of malformations of cortical development. 19795139_Results identified a novel splice site mutation in the disc-large homolog 3 (DLG3) gene, encoding the synapse-associated protein 102 (SAP102) in one out of 300 families with moderate to severe non-syndromic mental retardation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21252287_DLG3 was identified by genome-wide gene expression analyses as correlated with cellular sensitivity to cisplatin and carboplatin. DLG3 was also found to correlate with cellular sensitivity to platinating agents in NCI-60 cancer cell lines. 21369957_DLG3 did not associate with non-syndromic mental retardation in Chinese Han population; however, further studies are needed. 21384559_A total of six novel and 11 known single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified. Further studies are warranted to analyze the candidate genes at Xq11.1-q21.33. 22745750_Synapse associated protein 102 (SAP102) binds the C-terminal part of the scaffolding protein neurobeachin. 23103165_The PDZ-independent interaction between SAP102 and GluN2B mediates the synaptic clearance of GluN2B-containing NMDARs.(SAP102 protein) 24381070_The data of this study suggested that DLG3 is down-regulated in this cancer type. 24507884_This study identified DLG3 significantly associated loci with a biologically plausible role in schizophrenia. 24739954_miR-1246 might play a role in neurological pathogenesis of human enterovirus 71 by regulating DLG3 gene in infected cells. 25268382_Trans-homophilic interaction of CADM1 activates PI3K by forming a complex with MAGuK-family proteins MPP3 and Dlg. 25555912_These data shed new light on the role of SAP102 in the regulation of NMDAR trafficking. 27222290_Insertion of a guanine into the DLG3 5' UTR, 7 bp upstream of the start codon, down regulated DLG3 protein levels. This non-coding variant segregates with X-linked intellectual disability in a large family. 27222290_The dupG DLG3 variant segregated with non-syndromic X-linked intellectual disability in a large family and was predicted to disrupt folding of the mRNA. 27466188_Following the critical period NMDA receptor function was unaffected by loss of SAP102 but there was a reduction in the divergence of TC connectivity. These data suggest that changes in synaptic function early in development caused by mutations in SAP102 result in changes in network connectivity later in life. 28777483_This family broadens the mutational and phenotypical spectrum of DLG3-associated non-syndromic X-linked intellectual disability and demonstrates that heterozygous female mutation carriers can be as severely affected as males. 29282697_These data provide evidence for a novel mechanism in regulating SAP102 function and glutamate receptor trafficking. 31271664_High expression of DLG3 is associated with decreased survival from breast cancer. 32593652_Silence of lncRNA MIAT-mediated inhibition of DLG3 promoter methylation suppresses breast cancer progression via the Hippo signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000000881 |
Dlg3 |
138.593286 |
0.3950432852 |
-1.339917 |
0.216478623 |
37.306514 |
0.00000000100946880403212566517789301246722788452103714007535018026828765869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000004828178725701288454728834413729604557730112901481334120035171508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.3928928 |
17.1806362 |
216.8265123 |
30.4140082 |
| ENSG00000082701 |
2932 |
GSK3B |
protein_coding |
P49841 |
FUNCTION: Constitutively active protein kinase that acts as a negative regulator in the hormonal control of glucose homeostasis, Wnt signaling and regulation of transcription factors and microtubules, by phosphorylating and inactivating glycogen synthase (GYS1 or GYS2), EIF2B, CTNNB1/beta-catenin, APC, AXIN1, DPYSL2/CRMP2, JUN, NFATC1/NFATC, MAPT/TAU and MACF1 (PubMed:1846781, PubMed:9072970, PubMed:14690523, PubMed:20937854, PubMed:12554650, PubMed:11430833, PubMed:16484495). Requires primed phosphorylation of the majority of its substrates (PubMed:11430833, PubMed:16484495). In skeletal muscle, contributes to insulin regulation of glycogen synthesis by phosphorylating and inhibiting GYS1 activity and hence glycogen synthesis (PubMed:8397507). May also mediate the development of insulin resistance by regulating activation of transcription factors (PubMed:8397507). Regulates protein synthesis by controlling the activity of initiation factor 2B (EIF2BE/EIF2B5) in the same manner as glycogen synthase (PubMed:8397507). In Wnt signaling, GSK3B forms a multimeric complex with APC, AXIN1 and CTNNB1/beta-catenin and phosphorylates the N-terminus of CTNNB1 leading to its degradation mediated by ubiquitin/proteasomes (PubMed:12554650). Phosphorylates JUN at sites proximal to its DNA-binding domain, thereby reducing its affinity for DNA (PubMed:1846781). Phosphorylates NFATC1/NFATC on conserved serine residues promoting NFATC1/NFATC nuclear export, shutting off NFATC1/NFATC gene regulation, and thereby opposing the action of calcineurin (PubMed:9072970). Phosphorylates MAPT/TAU on 'Thr-548', decreasing significantly MAPT/TAU ability to bind and stabilize microtubules (PubMed:14690523). MAPT/TAU is the principal component of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease (PubMed:14690523). Plays an important role in ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex (PubMed:20937854). Phosphorylates MACF1, inhibiting its binding to microtubules which is critical for its role in bulge stem cell migration and skin wound repair (By similarity). Probably regulates NF-kappa-B (NFKB1) at the transcriptional level and is required for the NF-kappa-B-mediated anti-apoptotic response to TNF-alpha (TNF/TNFA) (By similarity). Negatively regulates replication in pancreatic beta-cells, resulting in apoptosis, loss of beta-cells and diabetes (By similarity). Through phosphorylation of the anti-apoptotic protein MCL1, may control cell apoptosis in response to growth factors deprivation (By similarity). Phosphorylates MUC1 in breast cancer cells, decreasing the interaction of MUC1 with CTNNB1/beta-catenin (PubMed:9819408). Is necessary for the establishment of neuronal polarity and axon outgrowth (PubMed:20067585). Phosphorylates MARK2, leading to inhibition of its activity (By similarity). Phosphorylates SIK1 at 'Thr-182', leading to sustainment of its activity (PubMed:18348280). Phosphorylates ZC3HAV1 which enhances its antiviral activity (PubMed:22514281). Phosphorylates SNAI1, leading to its BTRC-triggered ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (PubMed:15448698, PubMed:15647282). Phosphorylates SFPQ at 'Thr-687' upon T-cell activation (PubMed:20932480). Phosphorylates NR1D1 st 'Ser-55' and 'Ser-59' and stabilizes it by protecting it from proteasomal degradation. Regulates the circadian clock via phosphorylation of the major clock components including BMAL1, CLOCK and PER2 (PubMed:19946213, PubMed:28903391). Phosphorylates CLOCK AT 'Ser-427' and targets it for proteasomal degradation (PubMed:19946213). Phosphorylates BMAL1 at 'Ser-17' and 'Ser-21' and primes it for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation (PubMed:28903391). Phosphorylates OGT at 'Ser-3' or 'Ser-4' which positively regulates its activity. Phosphorylates MYCN in neuroblastoma cells which may promote its degradation (PubMed:24391509). Regulates the circadian rhythmicity of hippocampal long-term potentiation and BMAL1 and PER2 expression (By similarity). Acts as a regulator of autophagy by mediating phosphorylation of KAT5/TIP60 under starvation conditions, activating KAT5/TIP60 acetyltransferase activity and promoting acetylation of key autophagy regulators, such as ULK1 and RUBCNL/Pacer (PubMed:30704899). Negatively regulates extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors. Promotes the formation of an anti-apoptotic complex, made of DDX3X, BRIC2 and GSK3B, at death receptors, including TNFRSF10B. The anti-apoptotic function is most effective with weak apoptotic signals and can be overcome by stronger stimulation (PubMed:18846110). Phosphorylates E2F1, promoting the interaction between E2F1 and USP11, stabilizing E2F1 and promoting its activity (PubMed:17050006, PubMed:28992046). Phosphorylates mTORC2 complex component RICTOR at 'Thr-1695' which facilitates FBXW7-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of RICTOR (PubMed:25897075). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P18266, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WV60, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11430833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12554650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14690523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15448698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15647282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16484495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17050006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18348280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1846781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18846110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19946213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20067585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20932480, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22514281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24391509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25897075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28903391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28992046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30704899, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8397507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9072970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9819408}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Alzheimer disease;ATP-binding;Biological rhythms;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Diabetes mellitus;Differentiation;Glycogen metabolism;Kinase;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Signal transduction inhibitor;Transferase;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a serine-threonine kinase belonging to the glycogen synthase kinase subfamily. It is a negative regulator of glucose homeostasis and is involved in energy metabolism, inflammation, ER-stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptotic pathways. Defects in this gene have been associated with Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:2932; |
axon [GO:0030424]; beta-catenin destruction complex [GO:0030877]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; dynactin binding [GO:0034452]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding [GO:0034236]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; tau-protein kinase activity [GO:0050321]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; beta-catenin destruction complex disassembly [GO:1904886]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to interleukin-3 [GO:0036016]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007212]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; ER overload response [GO:0006983]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060079]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0030011]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in osteoblast differentiation [GO:1905240]; negative regulation of dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904339]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902042]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity [GO:2000466]; negative regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045719]; negative regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [GO:2000740]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; negative regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032515]; negative regulation of protein acetylation [GO:1901984]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900181]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; negative regulation of type B pancreatic cell development [GO:2000077]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; neuron projection organization [GO:0106027]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of cilium assembly [GO:0045724]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901030]; positive regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010822]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046827]; positive regulation of protein localization to centrosome [GO:1904781]; positive regulation of protein localization to cilium [GO:1903566]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of axon extension [GO:0030516]; regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050770]; regulation of cellular response to heat [GO:1900034]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814]; regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900271]; regulation of microtubule anchoring at centrosome [GO:0150101]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507]; regulation of microtubule-based process [GO:0032886]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975]; regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046825]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; superior temporal gyrus development [GO:0071109]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
11495916_The intracellular distribution of GSK-3 beta is dynamically regulated by signaling cascades, and apoptotic stimuli cause increased nuclear levels of GSK-3 beta, which facilitates interactions with nuclear substrates. 11903055_Protein kinase A enhances, whereas glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta inhibits, the activity of the exon 2-encoded transactivator domain of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D in a hierarchical fashion. 11967263_Arg(96) mutant has a dominant-negative effect on GSK-3beta-dependent phosphorylation of beta-catenin and targeting of beta-catenin for degradation requires prior priming through phosphorylation of Ser(45) 11986994_signaling systems determining cell fate appear to be important targets of mood stabilizers, and these may include signaling pathways encompassing GSK3beta, including transcription factors regulated by GSK3beta(REVIEW) 12048243_reacts with p53 protein after dna damage 12054501_Human serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase-like kinase (SGKL) phosphorylates glycogen syntheses kinase 3 beta (GSK-3beta) at serine-9 through direct interaction 12086949_improves insulin action and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle 12130654_GSK3b binds to and phosphorylates serine493 in glutamate E segment of NEFH 12147701_A-kinase anchoring protein AKAP220 binds to this enzyme and mediates protein kinase A-dependent inhibition of GSK-3beta 12167628_GSK3beta functions at the nodal point of converging signaling pathways in endothelial cells to regulate vessel growth through its control of vascular cell migration and survival. 12182887_Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta influenced post-natal maturation and differentiation of neurons in vivo in transgenic mice that overexpress a constitutively active GSK-3beta. 12228224_Data show that endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by thapsigargin not only activated the apoptosis effector caspase-3 but also caused a large and prolonged increase in the activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. 12244165_GSK-3 beta is inhibited by endothelial cell costimulation, allowing nuclear accumulation of NFAT and prolonging IL-2 synthesis in the presence of cyclosporin A. 12364325_inhibition of GSK3beta activity appears to trigger nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 and cell cycle progression 12376533_GSK3b expresion is regulated by reelin 12379450_Fresh lymphocytes from schizophrenic patients showed no difference in GSK-3 alpha and GSK-3beta mRNA levels, GSK-3beta protein levels, or total GSK-3 (alpha+beta) enzyme activity compared with findings in control subjects. 12387894_role in phosphorylating tau protein 12554650_Data report the crystal structure of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) in complex with a minimal GSK3beta-binding segment of axin, at 2.4 A resolution. 12566926_plays a role in Alzheimer disease and other CNS disorders (REVIEW) 12584189_GSK3 beta functions as a natural activator of MEKK1 12603528_Messenger RNA of beta-catenin and Tcf-4, but not GSK-3beta, was found to be overexpressed in HCC(hepatocellular carcinoma). 12663502_role in mouse hepatic carcinogenesis 12761178_first demonstration that glycogen synthase kinase-3beta associates with type 1 protein phosphatase/inhibitor-2 (PP1C/I-2) complex and phosphorylates I-2 at T72 in intact cells 12778079_Cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin modulates radiation-dependent G2 phase arrest and involve this enzyme in vitro. 12796505_GSK-3 regulates its own phosphorylation status 12829841_manipulation of GSK-3beta activity may be a mechanism by which HHV-8 latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) may modify transcriptional activity and contribute to the phenotype of HHV-8 primary effusion lymphoma. 12871932_molecular cross-talk between glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3 beta) and the p105 precursor of the NF-kappa B p50 subunit 12900420_glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is suppressed by Akt in prostate cancer cells which leads to the phosphorylation of cAMP-response element-binding protein 12969793_Overexpression of phospho-GSK-3beta is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 14518171_possible role of GSK-3 beta, a pro-apoptotic factor participating in signal transduction involved in cell survival, is discussed in relation to schizophrenia 14520463_Increased expression of glycogen synthase kinase 3 is associated with ovarian epithelial cell transformation and in tumour progression 14523002_role in binding to and promoting action of p53 14536078_multisite phosphorylation by Cdk2 and GSK3 controls cyclin E degradation 14550568_GSK3beta is a potential regulator of platelet function 14561750_activation of Csk and GSK-3beta by Galphaq may contribute to the physiological and pathological effects of Gq-coupled receptors 14617795_a mechanism involving GSK-3beta activation may be responsible for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance in prostate cancer cells 14660640_TSH/cAMP-stimulated p70S6 kinase activity and cell proliferation is regulated by Rap1GAP in thyroid cells 14691449_CF101 inhibits human colon carcinoma growth in mice via modulation of GSK3B. 14729058_GSK3B regulates the cytoskeleton and translocation of Rac1 in keratinocyte lamellipodia. 14729229_No association was detected between GSK3-beta -50 T/C SNP and the presence of bipolar illness. Homozygotes for the wild variant (T/T) showed an earlier age at onset than carriers of the mutant allele (F=5.53, d.f.=2,182, P=0.0047). 14729229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14744935_ER stress induces GSK-3beta binding to p53 in the nucleus and enhances the cytoplasmic localization of the tumor suppressor. 14985354_glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta phosphorylates the androgen receptor, thereby inhibiting androgen receptor-driven transcription 14988008_Clozapine appears to regulate the phosphorylation of GSK3B through Wnt signal pathways involving Dvl upstream but not through the P13K-Akt pathway in human neuroblastoma cells. 14988390_Most importantly, knocking down GSK-3beta expression via a small interference RNA-mediated gene silencing approach also reduced R1881-stimulated gene expression, demonstrating the specificity of GSK-3beta involvement. 14991743_APC/GSK-3beta, through beta-catenin, may crossregulate NF-kappaB signaling pathway 15020233_Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is tyrosine-phosphorylated by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 in fibroblasts. 15026145_These results suggest that short-term exposure to TNF-alpha augments insulin effects through protein kinase B-alpha and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta, whereas long-term exposure causes insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. 15073173_GSK3beta is connected to tau by 14-3-3 and Ser(9)-phosphorylated GSK3beta phosphorylates tau 15132987_6-OHDA inhibited phosphorylation of GSK3beta at Ser9, & induced hyperphosphorylation of Tyr216 with little effect on expression. GSK3beta is a critical intermediate in pro-apoptotic signaling cascades that are associated with neurodegenerative diseases. 15178691_GSK3 beta may function as a repressor to suppress AR-mediated transactivation and cell growth 15179015_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15252116_GSK-3beta has a role in cAMP-induced degradation of cyclin D3 15254796_the reduction in brain GSK-3beta is reflected in CSF of schizophrenia patients 15351432_A glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta promoter gene single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with age at onset and response to total sleep deprivation in bipolar depression. 15351432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15375789_overexpression of human GSK-3beta in skeletal muscle of male mice resulted in impaired glucose tolerance despite raised insulin levels 15379854_A portion of the p53 that is activated in senescent cells is modulated by its association with GSK3beta in the nucleus. 15456937_Results propose a new mechanism by which lithium indirectly inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3beta via phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-dependent activation of protein kinase C alpha. 15517997_In transgenic mice, GSK3betaS9A resulted in hyperphosphorylation of tau and morphology reminiscent of pretangle-like neurons in cortex and hippocampus. 15522877_FRAT-2 enhances GSK3 beta-mediated phosphorylation of a primed substrate to a greater extent than an unprimed substrate 15555766_Total GSK-3 protein was increased in both Alzheimer's disease and in mild cognitive impairment without a compensatory decrease in activity 15609321_GSK3 and PKB/Akt have roles in the integrin-mediated regulation of PTHrP, IL-6 and IL-8 in pancreatic cancer 15631989_Data show that the activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is necessary for the maintenance of the epithelial architecture, and that GSK-3 inhibition stimulates the transcription of Snail. 15719395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15719395_Results indicate that GSK3B may not play a major role in Japanese schizophrenia. 15752768_In kinase assay, we also showed that CABYR variants act as an ideal substrate for GSK3beta within the extensin-like domain and phosphorylation sites on CABYR were mapped. 15799972_KCl-induced depolarization causes undulating GSK-3beta phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, which is regulated for the most part by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt (phosphorylation) and PP2A and PP2B (dephosphorylation), respectively 15940626_a unique cooperative interaction possible between 2 critical oncogenic pathways in colorectal tumorigenesis, and pivotal role of GSK-3beta suggested 15942663_GSK-3beta reactivation is involved in the process through which LY294002 sensitizes hepatoma cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via death receptor and mitochondria signalling pathways 15963640_These data indicate that 14-3-3zeta may not be directly interacting with GSK3beta and tau in the brain, but may indirectly facilitate the interactions by binding to other proteins. 15981102_No significant genetic alterations were found. 15993040_These findings suggest that glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is involved in hydrogen peroxide-mediated inhibition of Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional activity. 16007092_GSK3 has a role in modulating the inflammatory response and toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production 16043125_Our findings demonstrate an unrecognized role of GSK3beta in tumor cell survival and proliferation other than its predicted role as a tumor suppressor. 16055726_GSK3-dependent phosphorylation of Mdm2 regulates p53 abundance 16076840_GSK-3 interacts with and phosphorylates ESRalpha and is involved in the regulation of receptor activity 16107342_multiple kinases, including CK2 and GSK3beta, participate in PTEN phosphorylation and GSK3beta may provide feedback regulation of PTEN 16174773_GSK3beta modulates synphilin-1 ubiquitylation and cellular inclusion formation by SIAH 16198352_findings suggest the ERK/MAPK and PI3K pathways may regulate VEGF expression in part through regulating the action of these repressor proteins 16210249_These results identify glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and FBW7 as potential cancer therapeutic targets and MYC as a critical substrate in the GSK3beta survival-signaling pathway. 16257959_GSK-3beta directly phosphorylates and activates MARK2/PAR-1 16278684_GSK-3, acting through PKCdelta, is a negative regulator of ERK1/2 16289845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16315267_GSK3B polymorphisms alter transcription and splicing and interact with Tau haplotypes to modify disease risk in Parkinson disease 16315267_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16341242_GSK-3 is a specific in vivo modulator of hematopoietic stem cell activity 16365045_a direct interaction between LRP6 and GSK3 results in an attenuation of GSK3 activity 16371352_inhibition of GSK-3beta stimulates COX-2 expression in gastric cancer cells 16397405_A trend was found towards an association for the C allele in the whole group of schizophrenic patients and for the heterozygous T/C genotype of bipolar patients. 16397405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16420965_Our results demonstrate that the flow cytometry-based method is a convenient tool to analyze the effect of GSK-3beta inhibitors on Tau phosphorylation. This 16421604_GSK3beta is not only a critical regulator of proproliferative signalling but also a promiscuous one as PI3K/Akt pools of GSK3beta are, at least in part, functionally interchangeable with those of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway 16428445_GSK-3 and h-prune cooperatively regulate the disassembly of focal adhesions to promote cell migration and that h-prune is useful as a marker for tumor aggressiveness. 16428884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16462886_Cytokine-dependent GSK-3 phosphorylation in hemopoietic cells proceeds primarily through Protein Kinase B independent pathways. 16528748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16543145_The results demonstrate that the control of MCL-1 stability by GSK-3 is an important mechanism for the regulation of apoptosis by growth factors, PI3K, and AKT. 16551619_GSK3beta inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf2 16571670_protection of beta-catenin from ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation induced by glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta inhibition 16601113_GSK-3beta selectively regulates NFkappaB-mediated inflammatory gene expression of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha by controlling the flow of NFkappaB activity between transcription of inflammatory and survival genes 16611631_GSK3 alters phosphorylation of CRMP-1, -2, and -4 isoforms 16645641_findings show an increase in the immunoreactivities for the nuclear C-terminal fragments of APLP2 and for GSK-3beta in the brains of Alzheimer disease patients 16705181_Multisite glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) phosphorylation and ubiquitination by SCFbetaTrCP are required for Gli3 processing. 16757548_there is tissue specificity for the regulation of GSK-3 in humans; in skeletal muscle GSK-3 plays a role in control of metabolism and insulin action, whereas the function in adipose tissue is less clear 16767496_Hypertonic conditions induced with NaCl and other osmolytes were used to stimulate several tumor cell lines, Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3beta (GSK3beta) was rapidly dephosphorylated at serine 9 and its kinase activity was increased. 16787706_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16788573_Results suggest that glycogen synthase kinase-3beta activity is important for the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells, implicating this kinase as a potential therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. 16861141_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16882987_Cyclic expression of GSK-3beta's active and inactive forms in the endometrium suggests that sex hormones regulate its expression. In vitro experiments demonstrate that progesterone induces phosphorylation of endometrial GSK-3beta. 16893889_substrate recognition involves interactions with GSK-3beta residues: Phe67, Gln89, and Asn95, which confer a common basis for substrate binding and selectivity, yet allow for substrate diversity 16912034_analysis of critical variations in the function and regulation of GSK-3alpha and GSK-3beta 16916907_We demonstrate, for the first time in human skeletal muscle, that the regulation of Akt and its downstream signalling pathways GSK-3beta, mTOR and Foxo1 are associated with both the skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy processes. 16934436_These results suggest i) an essential role of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3alpha/beta signaling for a successful replication of VZV and ii) a key function of VZV kinases pORFs 47 and 66 to activate this pathway. 16942622_GSK3 activity has little influence over cyclin D1 expression levels during any cell cycle phase. 16951223_The GSK-3beta nuclear accumulation as a hallmark of poorly differentiated pancreatic adenocarcinoma, and provide new insight into the mechanism by which GSK-3beta regulates NF-kappaB activity in pancreatic cancer. 16981698_GSKIP is a naturally occurring protein that is homologous with the GSK3beta interaction domain of Axin and is able to negatively regulate GSK3beta of the Wnt signaling pathway. 16982692_this study provides, for the first time, insights into the involvement of MRP2 in neurite outgrowth, which occurs in a GSK3beta-dependent manner. 16984735_NT uses PKC-dependent pathways to modulate GSK-3, which may play a role in the NT regulation of intestinal cell growth 16987250_This study fails to support reduced signaling of the AKT-GSK3beta molecular cascade in schizophrenia. 16987514_These results indicate that the protein phosphatase-1/inhibitor-2 complex differentially regulates GSK3 dephosphorylation induced by KCl and that GSK3 activity regulates SERCA2 levels. 17016438_Hypersensitivity of medulloblastoma cells in anchorage-independence is linked to GSK-3beta activity. 17028556_GSK-3B is the missing link between the amyloid and tau-pathology, and position GSK-3B as prominent player in the pathogenesis in Alheimer disease. 17046823_GSK-3beta but also DYRK1B modulates cyclin D1 subcellular localization by the phosphorylation of Thr(288). These results suggest that DIF-3 induces degradation of cyclin D1 through the GSK-3beta- and DYRK1B-mediated threonine phosphorylation in HeLa cells 17050006_offer a new mechanism of regulation of E2F transcription factor 1 by direct binding of GSK3beta to its transactivation domain 17052453_S6K1 regulates GSK3 under conditions of mTOR-dependent feedback inhibition of Akt 17072303_The identification of a beta-catenin-T-cell factor-regulated Axin2-GSK3beta-Snail1 axis provides new mechanistic insights into cancer-associated epithelial-mesenchymal transition programmes. 17098228_The current data suggest that, following exposure to zinc, the sequential activation of Akt and GSK-3beta plays an important role directing hippocampal neural precursor cell death. 17107957_R-Ras and ILK have roles upstream of GSK-3beta in the regulation of neuronal polarity 17139249_These results imply that GSK-3beta may function in transporting centrosomal proteins to the centrosome by stabilizing the BICD1 and dynein complex, resulting in the regulation of a focused microtubule organization. 17150190_We conclude that hCSCs exhibit mesenchymal features and that Akt/GSK-3beta may be crucial modulators for hCSC maintenance in human heart. 17159916_Of special interest was the rapid decrease in expression of MITF in melanocytes treated with DKK1, which is concurrent with the decreased activities of beta-catenin and of glucose-synthase kinase 3beta 17160944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17233643_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17241872_GSK3beta-dependent protein degradation was switched between Hath1 and beta-catenin by Wnt signaling, leading to the dramatic alteration of cell status between proliferation and differentiation in colon cancer 17270183_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17273789_IL-6, via the PI3-kinase/Akt pathway leads to inhibition of the repressive kinases MAPK/pERK and GSK3beta, and this converts inactive HSF-1 to an intermediate DNA-binding form augmenting transcriptional activation in the presence of a second stressor. 17283049_This is the first demonstration of GSK-3beta as the missing link between UV-induced ATR activation and p21 degradation. 17325032_direct regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha subunit stability by GSK-3 may influence physiological processes or pathophysiological situations such as metabolic diseases or tumors 17357145_GSK3beta may be involved in Bipolar Disorder susceptibility in some individuals. 17357145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17368486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17368486_Our results fail to replicate the association of the GSK-3 beta gene with susceptibility to schizophrenia in the Chinese population. 17387146_Results indicate that the turnover of Mcl-1 by beta-TrCP is an essential mechanism for GSK-3beta-induced apoptosis and contributes to GSK-3beta-mediated tumor suppression and chemosensitization. 17389597_abnormal activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta can reduce neuronal viability and synaptic plasticity via modulating Presenilin 1/N-cadherin/beta-catenin interaction and thus have important implications in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer disease. 17434145_Our results imply that phosphorylation of serine 256 in ataxin-3 by GSK 3beta regulates ataxin-3 aggregation. 17437043_APC protein and GSK3beta may synergistically play an important role in the repair of airway epithelial cells. 17437044_GSK3beta may induce G(1) cell cycle arrest in a cyclin D1-dependent fashion and therefore possibly play a growth-inhibitory role in A549 cells. 17438332_antiapoptotic effect of GSK3beta in tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis is mediated by cytosolic, not nuclear, GSK3beta 17475833_Unrestrained glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta is responsible for growth factor withdrawal induced activated T cell death. 17483602_GSK-3beta was dephosphosphorylated at Ser9 & its enzymatic activity increased in palmitate-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. GSK-3beta inhibitors & transduction with a catalytically inactive GSK-3beta protected the cells from apoptosis. 17486076_cyclin D2 expression in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells is regulated by ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent degradation triggered by Thr280 phosphorylation by GSK3beta or p38, which is induced by inhibition of the PI3K pathway 17522055_3,3'-diindolylmethane -induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction are partly mediated through the regulation of Akt/FOXO3a/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin/AR signaling 17562708_phosphorylation sites in tau from Alzheimer brain show that casein kinase 1delta may have a role, together with glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disea 17565981_GSK3beta facilitates the association of T4 and T4C3, and the presence of caspase-cleaved tau is necessary for the evolution of tau oligomers into Sarkosyl-insoluble inclusions even though it is not extensively phosphorylated 17590240_We demonstrated that treatment with EGCG reduced the A beta levels by enhancing endogenous APP nonamyloidogenic proteolytic processing. 17609434_GSK-3 is required for E2-induced ERalpha phosphorylation at Ser-118 and full transcriptional activity of the receptor upon E2 stimulation. 17621172_Single nucleotide polymorphisms are not asociated with bipolar disorder. 17621269_Ajuba promoted GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation of beta-catenin by reinforcing the association between beta-catenin and GSK-3beta. 17628506_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17671694_pGSK-3beta-ser-9 may confer the cisplatin resistance of ovarian carcinomas through the stabilization of p53 expression 17681942_analysis of phosphorylation and regulation of human CTPS1 in human cells shows that GSK3 is a novel regulator of CTPS activity 17697341_observations indicate a role for GSK-3 in accurate chromosome segregation 17711861_a direct link between GSK-3beta and MLK3 activation in a neuronal cell death pathway and identify MLK3 as a direct downstream target of GSK-3beta. 17717075_GnRH treatment mediates the inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3, a protein serine/threonine kinase that regulates beta-catenin degradation within the Wnt signaling pathway 17908237_This indicates that if the majority of tau is phosphorylated at S396/S404, in combination with increased GSK3beta activity, tau aggregation is favored. T 17912008_glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) was found to regulate NF kappa B activation and the proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells.[review] 17951252_modulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/GSK3beta signaling cascades can be beneficial for protecting or facilitating recovery from cellular LeTx intoxication in cells that depend on basal MEK1 activity for proliferation. 17972518_Phosphorylated-GSK3beta-ser9 and EGFR are involved in the histogenesis of different lung carcinomas. 17976739_Association between GSJ-3beta-50T/C polymorphism and personality and psychotic symptoms in mood disorders. 17976739_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17990294_cAMP/PKA signaling activates the canonical Wnt pathway through the inactivation of GSK-3beta, whereas Wnt signaling might inhibit bone resorption through a negative impact on RANKL expression in osteoblasts. 17991738_GSK3B protects melanoma cells from the apoptotic effects sorafenib, providing a survival signal that minimizes cellular injury. 18055457_GSK3beta interacts with and phosphorylates the spindle-associated protein Astrin, resulting in targeting Astrin to the spindle microtubules and kinetochores. 18083346_HSP105 appears to chaperone the responses to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through its interactions with GRP78 and GSK3, and without HSP105 cell death following ER stress proceeds by a non-caspase-3-dependent process. 18156211_sFRP-1 can interact with Wnt receptors Frizzled 4 and 7 on endothelial cells to transduce downstream to cellular machineries requiring Rac-1 activity in cooperation with GSK-3beta 18167338_Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) phosphorylates Cdc25A to promote its proteolysis in early cell-cycle phases. 18178198_Abnormal GSK3beta regulation is a potential mechanism for the insulin resistance that is seen in some women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 18195729_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18201972_phosphorylation of Ser-468 was indispensable for the physical interaction between RelA/p65 and GSK3beta. 18218855_GSK3beta acts as a negative regulator of platelet function in vitro and in vivo. 18219478_When transfected into mice, beta cells have reduced mass and proliferation. 18221734_GSK3beta expression is upregulated in frontal and temporal cortex in ALS with cognitive impairment. 18223684_GSK-3beta enters the nucleus, forms a complex with beta-catenin and lowers the levels of beta-catenin/TCF-dependent transcription in a mechanism that involves GSK-3beta-Axin binding 18243662_Ionizing radiation-induced GSK-3beta phosphorylation could contribute to the transcriptional transactivation of NF-kappaB in an ATM-independent manner. 18252708_that inhibition of the GSK-3beta/eIF2Bepsilon translational control pathway contributes to airway smooth muscle hypertrophy in vitro and in vivo. 18263590_The formation of an ERK.GSK3beta complex retained pERK1/2 in the cytoplasm. 18316369_GSK-3beta regulates the localization of gamma-tubulin ring complex, including GCP5, to the spindle poles, thereby controlling the formation of proper mitotic spindles 18316598_GSK3 beta is a bona fide PRLr kinase that phosphorylates PRLr on Ser(349) and is required for the recognition of PRLr by beta Trcp, as well as for PRLr ubiquitination and degradation 18391981_GSK-3beta modulates the early mitotic Aurora-A level through binding and phosphorylating AIP. 18391982_the functional regulation of p53 by triptolide was mediated by an intranuclear association of p53 with glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta), which was inactivated by protein kinase C (PKC). 18408738_Results suggest that GSK-3 regulates nuclear p27 Kip1 expression through downregulation of Skp2 expression and regulates p27 Kip1 assembly with CDK2, playing a critical role in the G0/G1 arrest associated with intestinal cell differentiation. 18437054_tetrandrine induces G(1) arrest and apoptosis through PI3K/kip1/AKT/GSK3beta pathway 18450971_Activin A may mediate ovarian oncogenesis by activating Akt and repressing GSK to stimulate cellular proliferation. 18451303_p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) also inactivates GSK3beta by direct phosphorylation at its C terminus, and this inactivation can lead to an accumulation of beta-catenin 18500637_Our results suggest that GSK3beta polymorphisms might be involved in schizophrenia risk 18552505_findings suggest that hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) negatively regulated proliferation of CCL13-HBx-stable cells via the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin cascade 18588978_We conclude that the phosphorylation of tau by GSK-3beta either prior to or following polymerization promotes polymer/polymer interactions that result in stable clusters of tau filaments. 18602000_These results demonstrated that GSK3beta is implicated in the regulation of melanogenesis. 18606491_review of the roles of GSK3beta in tumorigenesis and cancer chemotherapy [review] 18615589_inhibition of GSK-3beta by lithium chloride elicited a stimulatory effect on DeltaNp63 promoter activity 18628988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18632640_GSK-3beta signaling is a key regulator of radiation-induced damage in hippocampal neurons 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18687691_isoflavone-induced inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis are partly mediated through the regulation of the Akt/FOXO3a/GSK-3beta/AR signaling network. 18689794_Tissue kallikrein decreased GSK-3beta activity via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway and enhanced VEGF and VEGFR-2 expression in endothelial cells. 18708403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18768676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18768676_Polymorphisms in two components of the insulin signaling pathway, AKT2 and GSK3B, are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 18769147_Inhibition of PI3-K/Akt induces a 40% decrease of cyclin D1 half-life as a result of accumulation of the dephosphorylated/active form of GSK-3beta within the nucleus, where it can phosphorylate cyclin D1 on Thr286 thereby promoting its nuclear export. 18782353_As the downstream of Akt activation, H. pylori infection inactivated the inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta at Ser 9 by its phosphorylation. 18786229_GSK3B is a novel marker and modulator of inflammatory injury in chronic renal allograft disease. 18787224_33 (52%) of 64 mantle cell lymphoma tumors showed nuclear localization of beta-catenin, which significantly correlated with the expression of the phosphorylated/inactive form of GSK3beta 18801732_Reduced CREB phosphorylation (Ser-129) associated with inactivation of GSK3beta by Ser-9 phosphorylation may be the major mechanism underlying PEPCK-C gene suppression by AMPK-activating agents such as biguanide 18804163_Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta is phosphorylated and inhibited by Thrombopoietin-induced Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-akt, promoting survival and proliferation in megakaryocytic cells through a pathway that does not involve beta-catenin 18806775_pharmacological, physiological and genetic studies that demonstrate an oncogenic requirement for GSK3 in the maintenance of a specific subtype of poor prognosis human leukaemia, genetically defined by mutations of the MLL proto-oncogene 18829575_GSK-3 and IKK as potential therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. 18838540_Results describe a convergence point of the GSK-3beta and the glucocorticoid receptor pathways, and suggest a mechanism by which GSK-3beta activity can dictate how cells will ultimately respond to glucocorticoids. 18852124_The fat-1 gene expression inhibited prostate cancer cell proliferation via reduction of GSK-3beta phosphorylation and subsequent down-regulation of both beta-catenin and cyclin D1. 18852354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18852354_To our knowledge, this is the first evidence that a gene known to be involved in tau phosphorylation, GSK3B, is associated with risk for primary neurodegenerative dementias. 18855532_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18952601_Novel regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) by transformin |
ENSMUSG00000022812 |
Gsk3b |
885.724177 |
7.8654905397 |
2.975537 |
0.752876332 |
13.371303 |
0.00025550373594105762987613306158607429097173735499382019042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000658500985243584864570198789124333416111767292022705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1465.6462717 |
792.6569513 |
189.0027024 |
72.7198078 |
| ENSG00000083067 |
80036 |
TRPM3 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCF6 |
FUNCTION: Calcium channel mediating constitutive calcium ion entry. Its activity is increased by reduction in extracellular osmolarity, by store depletion and muscarinic receptor activation. In addition, forms heteromultimeric ion channels with TRPM1 which are permeable for calcium and zinc ions (PubMed:21278253). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12672799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12672827, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21278253}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the family of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels. TRP channels are cation-selective channels important for cellular calcium signaling and homeostasis. The protein encoded by this gene mediates calcium entry, and this entry is potentiated by calcium store depletion. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:80036; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium activated cation channel activity [GO:0005227]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; cation channel activity [GO:0005261]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; cation transmembrane transport [GO:0098655]; cation transport [GO:0006812]; detection of temperature stimulus [GO:0016048]; protein tetramerization [GO:0051262]; sensory perception of temperature stimulus [GO:0050951] |
12672827_The hTRPM3 gene is comprised of 24 exons and maps to chromosome 9q-21.12 and is composed of 1555 amino acids with the characteristic six-transmembrane domain of TRPs and is expressed in kidney and, at lesser levels, in brain, testis, and spinal cord 15550678_TRPM3 is the first ion channel activated by sphingolipids. 15824111_the divalent cation selectivity of TRPM3 channels is regulated by altenrative splicing 17217062_we give an overview of the identified TRPM3 variants and compare their functional properties--{REVIEW} 17233610_TRPM3 may have diverse cellular functions depending on the expression of a particular variant while TRPV4 plays a central role in epithelial homoeostasis by modulating epithelial barrier function [review] 18224337_TRPM3 did not reveal a otosclerosis-causing mutation 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360246_data suggest functional relevance of TRPM3 in contractile and proliferating phenotypes of vascular smooth muscle cells 20401728_Our data establish that TRPM3 channels constitute a regulated entry pathway for zinc ions in pancreatic beta-cells 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21278253_The inhibition of TRPM1 by zinc ions is primarily due to a short stretch of seven amino acids present only in the pore region of TRPM1 but not of TRPM3. 22000496_Progesterone (0.01-10muM) suppressed TRPM3 activity evoked by pregnenolone sulphate. 22451665_Calmodulin and S100A1 protein interact with N terminus of TRPM3 channel. 22961981_TRPM3-ICF deletion mutation variants are regulatory channel subunits fine-tuning TRPM3 channel activity. 23121507_Data using recombinant proteins expressed in vascular endothelial cells suggest that SigmaR1 (sigma 1-type opioid receptor) is not involved in regulation of calcium signaling via TRPC5/TRPM3 (transient receptor potential cation channels C5/M3). 24895737_Pregnenolone sulfate is a powerful activator of TRPM3-mediated gene transcription, while transcription is completely inhibited by mefenamic acid in cells expressing activated TRPM3 channels. 25090642_Missense mutation in the cation channel, TRPM3, underlies inherited cataract and glaucoma. 25517751_The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (VHL) represses TRPM3 directly through miR-204 and indirectly through another miR-204 target, Caveolin 1. 25576487_TRPM3 channel activation changes the gene expression pattern of the cells by activating transcription of c-Jun-, ATF2-, and TCF-controlled genes. 26123194_The TRPM3 activity is rapidly and reversibly inhibited by activation of phosphatases. 26123195_TRPM3 is a phosphoinositide-dependent ion channel. 26493679_Activation of TRPM3 channels increases the transcriptional activation potential of c-Fos in HEK293 cells. 26517445_Phosphoinositols regulate TRPM3. 26546534_This is the first study to examine the involvement of TRPM channel gene variations on the risk of SSc incidence. Our results suggest roles of TRPM3 and TRPM5 gene variants in the susceptibility to or clinical expression of Systemic sclerosis 26891941_rs10780946 TRPM3 polymorphism is associated with asthma-exacerbated respiratory disease susceptibility. 27727448_this study shows that differential expression of TRPM3 and Ca2+ flux between NK cell subtypes may provide evidence for their role in the pathomechanism involving NK cell cytotoxicity activity in chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis 28982580_Genetic experiments revealed that the basic region leucine zipper proteins c-Jun and ATF2 and the ternary complex factor Elk-1 are essential to couple TRPM3 channel stimulation with the IL-8 gene. 29880196_Mutations of lysine residues in calmodulin binding site 2, strongly reduced calmodulin binding and TRPM3 activity indicating the importance of this domain for TRMP3-mediated calcium signaling. 30099483_In the three-stage genome-wide association study in South Korean population the signal in TRPM3 showed the most robust association with thyroid nodules, and those in MIBP/NKX2-1 also demonstrated a possible association. A rs4745021 variant at TRPM3 reached the genome-wide significance threshold in the meta-analysis. 30134818_TRPM3 activity is impaired in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/ Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME) patients suggesting changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration, which may impact NK cellular functions. This investigation further helps to understand the intracellular-mediated roles in NK cells and confirm the potential role of TRPM3 ion channels in the aetiology and pathomechanism of CFS/ME. 30552902_The fact that TRPM3 channel stimulation activates Elk-1 connects TRPM3 with the biological functions of Elk-1, including the regulation of proliferation, differentiation, survival, transcription, and cell migration. 31014226_Study confirmed a significant reduction in amplitude of TRPM3 currents after pregnenolone sulfate stimulation in isolated NK cells from another cohort of CFS/ME patients compared with healthy controls. 31278393_Our findings suggest that TRPM3 is a locus for ID and epilepsy, and should be included in genetic panels targeting these indications. 31451581_activation of Gs- and Gq-coupled G-protein-coupled receptors in recombinant cells and sensory neurons inhibits TRPM3 via Gbetagamma liberation 31736966_Naltrexone Restores Impaired Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 3 Ion Channel Function in Natural Killer Cells From Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Patients. 31796045_Transient receptor potential melastatin 2 channels are overexpressed in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients. 31985045_Functional expression and pharmacological modulation of TRPM3 in human sensory neurons. 32343227_Disease-associated mutations in the human TRPM3 render the channel overactive via two distinct mechanisms. 32427099_Gain of channel function and modified gating properties in TRPM3 mutants causing intellectual disability and epilepsy. 32575443_Machine-Learned Association of Next-Generation Sequencing-Derived Variants in Thermosensitive Ion Channels Genes with Human Thermal Pain Sensitivity Phenotypes. 33122432_The structural basis for an on-off switch controlling Gbetagamma-mediated inhibition of TRPM3 channels. 33417951_TRPM3 channel activation inhibits contraction of the isolated human ureter via CGRP released from sensory nerves. 34266470_The effect of IL-2 stimulation and treatment of TRPM3 on channel co-localisation with PIP2 and NK cell function in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients. 34386996_A novel candidate gene in autosomal dominant facial pruritus. 35146895_Phenotypic spectrum of the recurrent TRPM3 p.(Val837Met) substitution in seven individuals with global developmental delay and hypotonia. 35240732_TRPM3 in the eye and in the nervous system - from new findings to novel mechanisms. |
ENSMUSG00000052387 |
Trpm3 |
19.524493 |
0.1541033911 |
-2.698029 |
0.586689707 |
20.531275 |
0.00000586648611147423827406844829002174890320020494982600212097167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000018914227829916942116936923179437712860817555338144302368164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6319416 |
2.0211678 |
30.4312619 |
8.2814112 |
| ENSG00000083750 |
10325 |
RRAGB |
protein_coding |
Q5VZM2 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding protein that plays a crucial role in the cellular response to amino acid availability through regulation of the mTORC1 signaling cascade (PubMed:18497260, PubMed:20381137, PubMed:24095279, PubMed:23723238). Forms heterodimeric Rag complexes with RRAGC or RRAGD and cycles between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound form (PubMed:18497260, PubMed:20381137, PubMed:24095279, PubMed:23723238). In its active form participates in the relocalization of mTORC1 to the lysosomes and its subsequent activation by the GTPase RHEB (PubMed:18497260, PubMed:20381137, PubMed:23723238). Involved in the RCC1/Ran-GTPase pathway (PubMed:9394008). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18497260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20381137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23723238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24095279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9394008}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Lysosome;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Ras-homologous GTPases constitute a large family of signal transducers that alternate between an activated, GTP-binding state and an inactivated, GDP-binding state. These proteins represent cellular switches that are operated by GTP-exchange factors and factors that stimulate their intrinsic GTPase activity. All GTPases of the Ras superfamily have in common the presence of six conserved motifs involved in GTP/GDP binding, three of which are phosphate-/magnesium-binding sites (PM1-PM3) and three of which are guanine nucleotide-binding sites (G1-G3). Transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10325; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Gtr1-Gtr2 GTPase complex [GO:1990131]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; guanyl ribonucleotide binding [GO:0032561]; cellular response to amino acid starvation [GO:0034198]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to leucine starvation [GO:1990253]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; positive regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032008]; positive regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904263]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032006] |
22749528_Inhibition of glutaminolysis prevents GTP loading of RagB and lysosomal translocation and subsequent activation of mTORC1. 28808055_Data suggest DNM2/RRAGB- (or DNM2/RRAGC-)dependent endocytosis of extracellular amino acids (AAs) plays critical role in mTORC1 transport/activation; recruitment of mTORC1 from cytoplasm to lysosome is suppressed by DNM2 inhibition; AA deprivation appears to be main cause of mTORC1 inactivation via DNM2 inhibition. (RHEB = Ras homolog enriched in brain; DNM2 = dynamin II; RRAG = Ras-related GTP binding protein) 34320917_Elevated Ras related GTP binding B (RRAGB) expression predicts poor overall survival and constructs a prognostic nomogram for colon adenocarcinoma. 34482023_Rag GTPases suppress PRL-3 degradation and predict poor clinical diagnosis of cancer patients with low PRL-3 mRNA expression. 35739524_circEXOC6B interacting with RRAGB, an mTORC1 activator, inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer by antagonizing the HIF1A-RRAGB-mTORC1 positive feedback loop. |
ENSMUSG00000041658 |
Rragb |
72.971063 |
0.4180659158 |
-1.258198 |
0.368954643 |
10.848270 |
0.00098888104774151911954827021133951348019763827323913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002301101098008012137141609088075711042620241641998291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.7607879 |
10.2904439 |
99.7919774 |
17.4535809 |
| ENSG00000083799 |
1540 |
CYLD |
protein_coding |
Q9NQC7 |
FUNCTION: Deubiquitinase that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'- and linear 'Met-1'-linked polyubiquitin chains and is involved in NF-kappa-B activation and TNF-alpha-induced necroptosis (PubMed:18636086, PubMed:26670046, PubMed:27458237, PubMed:26997266, PubMed:27591049, PubMed:29291351, PubMed:18313383, PubMed:32185393). Negatively regulates NF-kappa-B activation by deubiquitinating upstream signaling factors (PubMed:12917689, PubMed:12917691, PubMed:32185393). Contributes to the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and differentiation via its effects on NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:12917690). Negative regulator of Wnt signaling (PubMed:20227366). Inhibits HDAC6 and thereby promotes acetylation of alpha-tubulin and stabilization of microtubules (PubMed:19893491). Plays a role in the regulation of microtubule dynamics, and thereby contributes to the regulation of cell proliferation, cell polarization, cell migration, and angiogenesis (PubMed:18222923, PubMed:20194890). Required for normal cell cycle progress and normal cytokinesis (PubMed:17495026, PubMed:19893491). Inhibits nuclear translocation of NF-kappa-B (PubMed:18636086). Plays a role in the regulation of inflammation and the innate immune response, via its effects on NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:18636086). Dispensable for the maturation of intrathymic natural killer cells, but required for the continued survival of immature natural killer cells (By similarity). Negatively regulates TNFRSF11A signaling and osteoclastogenesis (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of ciliogenesis, allowing ciliary basal bodies to migrate and dock to the plasma membrane; this process does not depend on NF-kappa-B activation (By similarity). Ability to remove linear ('Met-1'-linked) polyubiquitin chains regulates innate immunity and TNF-alpha-induced necroptosis: recruited to the LUBAC complex via interaction with SPATA2 and restricts linear polyubiquitin formation on target proteins (PubMed:26997266, PubMed:26670046, PubMed:27458237, PubMed:27591049). Regulates innate immunity by restricting linear polyubiquitin formation on RIPK2 in response to NOD2 stimulation (PubMed:26997266). Involved in TNF-alpha-induced necroptosis by removing linear ('Met-1'-linked) polyubiquitin chains from RIPK1, thereby regulating the kinase activity of RIPK1 (By similarity). Negatively regulates intestinal inflammation by removing 'Lys-63' linked polyubiquitin chain of NLRP6, thereby reducing the interaction between NLRP6 and PYCARD/ASC and formation of the NLRP6 inflammasome (By similarity). Removes 'Lys-63' linked polyubiquitin chain of MAP3K7, which inhibits phosphorylation and blocks downstream activation of the JNK-p38 kinase cascades (PubMed:29291351). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80TQ2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12917689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12917690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12917691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17495026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18222923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18313383, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18636086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19893491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20194890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20227366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26670046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26997266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27458237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27591049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29291351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32185393}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;Cell cycle;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Thiol protease;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Wnt signaling pathway;Zinc |
|
This gene is encodes a cytoplasmic protein with three cytoskeletal-associated protein-glycine-conserved (CAP-GLY) domains that functions as a deubiquitinating enzyme. Mutations in this gene have been associated with cylindromatosis, multiple familial trichoepithelioma, and Brooke-Spiegler syndrome. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1540; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; spindle [GO:0005819]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; Lys63-specific deubiquitinase activity [GO:0061578]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of interleukin-18-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000493]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1903753]; negative regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032480]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing signaling pathway [GO:0070423]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; protein K63-linked deubiquitination [GO:0070536]; protein linear deubiquitination [GO:1990108]; regulation of cilium assembly [GO:1902017]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001242]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346]; regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060544]; regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010803]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12917689_CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB by specific tumour-necrosis factor receptors (TNFRs) 12917690_inhibition of cylindromatosis tumour suppressor gene (CYLD) enhances activation of NF-kappaB; inhibition of CYLD increases resistance to apoptosis, suggesting a mechanism through which loss of CYLD contributes to oncogenesis 12917691_CYLD negatively regulates NF-kappaB signalling by deubiquitination; CYLD interacts with NEMO and TRAF2 14632188_novel missense mutation in the CYLD gene, designated E474G in Brooke-Spiegler syndrome resembling trichoepithelioma 14676304_CYLD interacts with TRIP and regulates negatively nuclear factor kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor. 15226292_CYLD is induced by NF-kappaB 15289313_Mutations of the tumor suppressor gene CYLD at 16q12-q13 may give rise to familial trichoepithelioma indistinguishable from the phenotype assigned to 9p21. 15341735_Data show that the third cytoskeleton-associated protein-glycine conserved domain of CYLD specifically interacts with one of the two proline-rich sequences of NEMO/IKKgamma. 15496400_CYLD has a role in negative regulation of JNK signaling 15870263_findings suggest that CYLD serves as a novel target of IKK and that the site-specific phosphorylation of CYLD regulates its signaling function 16135788_The tumor suppressor familial cylindromatosis gene (CYLD) was found to be a direct target of BAF57 as determined by chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis. (CYLD) 16230348_study provided direct evidence for the negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) signaling by the tumor suppressor cylindromatosis (CYLD) 16500080_TRPA1 is a novel substrate for the de-ubiquitinating activity of CYLD, and this de-ubiquitination has the net effect of increasing the cellular pool of TRPA1 proteins. 16627981_The combined delivery of CYLD and TRAIL may be a new useful strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma or other tumor cells with enhanced NF-kappaB activity. 16713561_Mouse Cyld can negatively regulate different NF-kappaB pathways; inactivation of TRAF2 controls survival and inflammation, while inhibition of Bcl-3 controls proliferation and tumor growth. 16774947_Reduced expression of CYLD is associated with colon and hepatocellular carcinomas 17495026_additional function of CYLD could provide an explanation for the benign nature of most cylindroma lesions 17606441_in cell line KM-H2, a 2.35 Mb deletion was found at 16q12.1 putatively defining a small critical region for the recurrent 16q deletion in Hodgkin's lymphoma. This region contains the CYLD gene, a known suppressor gene of the NF-mB pathway. 17608805_identifies CYLD for the first time as a critical negative regulator of host antiviral response 17609426_Gene mapping and expression analysis of 16q loss of heterozygosity identifies WWOX and CYLD as being important in determining clinical outcome in multiple myeloma. 17662085_a heterozygous missense mutation c.1787 G > A (p.Gly596Asp, G596D) in CYLD exons was detected in a patient with multiple familial trichoepithelioma & affected family members; CYLD protein was not detected by staining in the trichoepithelioma tumour tissue 17851586_D681 in CYLD is required for cleavage of K63-linked polyubiquitin chains 17875891_study reports a novel CYLD gene mutation at nucleotide 2687 that carries out 1 amino acid change at glycine 896 in the 4 members of a family affected with trichoepithelioma but not in the proband 17925880_CYLD acts as a negative regulator for NF-kappaB-dependent inflammation in vivo, hence protecting the host against detrimental inflammatory response to NTHi infection 18222923_CYLD enhances tubulin polymerization into microtubules by lowering the critical concentration for microtubule assembly. 18234730_the role of CYLD in the pathogenesis of skin appendage tumours characterised by cylindromas, trichoepitheliomas and/or spiradenomas. 18242958_Report a novel missense mutation of CYLD gene in a Chinese family with multiple familial trichoepithelioma. 18245814_Potential role of CYLD (Cylindromatosis) as a deubiquitinating enzyme in vascular cells. 18313383_Results describe the crystal structure of the CYLD USP domain, revealing a distinctive architecture that provides molecular insights into its specificity toward Lys63-linked polyubiquitin. 18332137_These studies bring new insights into the molecular pathogenesis of S. pneumoniae infections through the NFAT-dependent mechanism and further identify CYLD as a negative regulator for NFAT signaling. 18363762_Loss of the UCH domain in CYLD may contribute to oncogenesis by enhancing the degradation of proteins that suppress cell proliferation or promote apoptosis. 18497946_Loss of CYLD might be associated with development of salivary gland tumors 18636086_Findings show that CYLD is a negative regulator of RIG-I-mediated innate antiviral response. 19076795_The mutation in the present case is novel and is predicted to alter the canonical splice acceptor sequence, thereby preventing proper splicing of the transcript. 19462465_cylindromatosis protein mutations, conformation, and physiologic roles in Brooke-Spiegler syndrome [REVIEW] 19481526_Results suggest that IKKepsilon and CYLD function as an oncogene-tumor suppressor network that participates in tumorigenesis. 19800320_CYLD negatively regulates tubulointertitial inflammatory responses via suppressing activation of JNK in tubular epithelial cells, putatively attenuating the progressive tubulointerstitial lesions in IgA nephropathy. 19807742_Five novel germline function-impairing mutations of CYLD in Italian patients with multiple cylindromas 19893491_CYLD controls cell growth and division at the G(1)/S-phase as well as cytokinesis by associating with alpha-tubulin and microtubules through its CAP-Gly domains. 19911186_A novel missense mutation in a Chinese family with multiple familial trichoepithelioma 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917957_The data we present herein confirm that, even within one family, mutations within the CYLD locus give rise to a wide variation of clinical phenotypes. 19951577_CYLD is expressed in renal tubular epithelial cells and appears to be associated negatively with tubulointerstitial lesions. 20151946_We describe a family, in which we performed a molecular-genetic examination and found a new mutation in exon 19 in the CYLD gene leading to a frameshift. 20227366_Loss of CYLD instigates tumor growth in human cylindromatosis through a mechanism in which hyperubiquitination of polymerized Dvl drives enhancement of Wnt3/beta-catenin responses. 20347313_REVIEW: CYLD activity can be governed by different regulatory mechanisms including phosphorylation, thus providing another layer of control for diverse physiological processes 20414373_Data suggest that the inverse correlation between CYLD and activated NF-kappaB in cholesteatoma may be involved in cholesteatoma epithelial hyperplasia. 20502185_study of 10 patients from 8 families with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome; identified 8 novel germline mutations, all of which consisted of substitutions, deletions, and insertions/duplications and all except one led to premature stop codons 20593489_findings uncover Aurora-B and PP2A as novel binding partners of CYLD and suggest that CYLD negatively regulates Aurora-B activity through acting on the PP2A axis. 20607853_biallelic CYLD mutations are rarely involved in classical Hodgkin lymphoma pathogenesis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20797623_STAT3 is not only a downstream target of IL-6 but, with miR-21, miR-181b-1, PTEN, and CYLD, is part of the positive feedback loop that underlies the epigenetic switch that links inflammation to cancer. 20832754_CYLD expression was found to be significantly suppressed in primary T-ALL. 20838385_The occurrence of mutations in the CYLD gene in tumorigenic epidermal cells (carrying previous mutations) increases the aggressiveness of carcinomas, mainly through enhancement of the expression of angiogenic factors. 20854080_Using DirectDNA sequencing analysis, we detected ATBF1, CYLD, PARK2 and WNT9A mutations in stomach and colorectal cancers 20972631_Large rearrangement in CYLD is a cause of familial cylindromatosis 21389835_Neither CYLD nor PTCH germline mutations were found in the 5 patients with Multiple familial trichoepitheliomas 21408173_These results suggest that optineurin regulates NF-kappaB activation by mediating interaction of CYLD with ubiquitinated RIP thus facilitating deubiquitination of RIP. 21420166_Somatic mutation of CYLD gene is rare in hematologic and solid malignancies. 21478324_Loss of CYLD is associated with skin tumorigenesis and metastasis. 21498625_The study thus provides new insights into a novel role for bacterial infection in enhancing host antiviral response; furthermore, it identifies CYLD for the first time as a critical negative regulator of bacterial LPS-induced response. 21552290_Data indicate that the CYLD mutant tumours showed dysregulated tropomyosin kinase (TRK) signalling, with overexpression of TRKB and TRKC in tumours. 21577203_Our data suggest that GLI1-mediated suppression of CYLD has a significant role in basal cell carcinoma progression. 21605102_A novel frameshift mutation, c.1925delC (p.Val548fsX558) was identified which resulted in a premature stop signal at codon 558, leading to the deletion of UCH2 domain and the Cys-X-X-Cys pairs. 21718647_Recurrent inactivation of CYLD occurs through diverse mechanisms in several forms of cancer, unequivocally confirming its tumor suppressor function. It negatively regulates several signaling pathway,including NF-kappaB. Review. 21900959_CYLD overexpression increases keratinocyte differentiation while CYLD loss of function impairs epidermal differentiation. 21931648_Studies indicate that the cylindromatosis/turban tumor syndrome gene (CYLD) ranked highest, followed by acylaminoacyl-peptidase (APEH), dystroglycan (DAG1), macrophage-stimulating protein (MST1) and ubiquitin-specific peptidase 4 (USP4). 22017589_Increased expression of CYLD in lung cancer cells directly blocks TRAIL-induced NF-kappaB activation, & thus increases TRAIL-induced apoptosis in lung cancer cells. 22037414_Following tumor necrosis factor stimulation, caspase 8 cleaves CYLD to generate a survival signal. 22049921_The c.1178-1179delCA (p.T393fs) mutation was found in CYLD gene in the affected members, but not in the healthy individuals in the family 22077640_Brooke-Spiegler syndrome: report of two cases not associated with a mutation in the CYLD and PTCH tumor-suppressor genes. 22157808_Reduced CYLD is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 22362744_miR-19, CYLD and NF-kappaB form a regulatory feed-forward loop, which provides new clues for sustained activation of NF-kappaB in T-ALL. 22469839_the role of CYLD-induced RAC1 activation in melanoma cell migration. 22491319_CYLD negatively regulates TGFb1 signalling via deubiquitinating Akt. 22689134_Cylindromatosis gene mutation analysis confirmed this unique presentation of Brooke-Spiegler syndrome, and revealed a previously unidentified mutation in the cylindromatosis gene. 22832488_these findings demonstrate that the JNK/activator protein 1 signaling pathway underlies the melanoma growth and metastasis that are associated with CYLD loss of function. 22895009_CEP192 promotes robust mitotic spindle assembly by regulating K63-polyubiquitin-mediated signaling through CYLD. 23002441_Lack of both CYLD and A20 do not exacerbate the developmental defects and hyperresponsive activity of A20-deficient B cells. 23171463_We investigated a Hungarian Brooke Spiegler syndrome pedigree with two affected members, demonstrating a novel missense mutation (c.2613C>G; p.His871Gln) in exon 19 within the ubiquitin-specific protease domain of the encoded protein. 23300340_CYLD is a molecular switch for cycles of ubiquitination and deubiquitination that critically regulate growth factor-mediated activation of Akt signaling. 23404581_These results suggest that PLAG1 and CYLD do not play a role in ACC tumorigenesis. 23567228_We report a novel mutation in the CYLD gene in a family with multiple familial trichoepithelioma. 23575688_studies provide insights into how inflammation is tightly regulated via the inhibition of its negative regulator and may also lead to the development of new anti-inflammatory therapeutics that upregulate CYLD expression 23584127_Report CYLD mutations in Hungarian/English families causing Brooke-Speigler syndrome. 23641715_CYLD gene performed from the peripheral blood identified a novel splice site c.2041+1 G>T mutation 23694822_Case Report: novel CYLD mutation was used as an adjunct to the histopathological diagnosis in multiple trichoepithelioma. 23725390_low CYLD expression identifies a subgroup of patients with CLL with inferior outcome. 23832602_CYLD gene expression is down regulated by oxidative stress through the mediation of reactive oxygen species 23861985_CYLD was the only currently known negative regulator of NF-kappaB to be identified. 23879700_Multiple familial trichoepithelioma was not associated with a mutation in the CYLD gene in a Chinese family. CYLD protein expression was observed in trichoepithelioma tumor tissue 24092863_In summary, we believe that the genetic data together with the functional data we provide here promote the case for the candidacy of CYLD as being-at least one-of the causal genes in the NOD2-CYLD gene region. 24104553_Downregulation of CYLD induces tumor cell proliferation, consequently contributing to the aggressive growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. 24247569_found a novel frameshift mutation (c.2255delT) and 2 recurrent nonsense mutations (c.1112C>A and c.2299A>T) of CYLD, the latter was first reported associated with multiple familial trichoepithelioma 24261740_A nonsense mutation was found in a patient with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome and in her nephew who was diagnosed with trichoepithelioma. 24398777_CYLD downregulation may promote breast cancer metastasis via NF-kappaB activation, including RANKL signaling. 24461064_cylindromatosis (CYLD) and OTULIN/Gumby/Fam105B, directly interact with the N-terminal PUB domain-containing region of HOIP. 24469800_findings uncover CYLD as an important player in the orientation of the mitotic spindle and cell division and have important implications in health and disease 24552808_The data provide mechanistic insights into the actions of CYLD in the regulation of microtubule dynamics and cell migration. 24577083_Selenite caused CYLD upregulation via LEF1 and cIAP downregulation, both of which contribute to the degradation of ubiquitin chains on RIP1 and subsequent caspase-8 activation and colorectal tumor cell apoptosis. 24614225_CaMKII-mediated recruitment and upregulation of CYLD is expected to remove K63-linked polyubiquitins and facilitate proteasomal degradation at the postsynaptic density. 24867235_DC-SIGN directs adaptive T helper cell type-2immunity to fucose-expressing pathogens via an IKKepsilon-CYLD-dependent signalling pathway leading to Bcl3 activation. 24909169_Overexpression of non-SUMOylatable mutant CYLD in neuroblastoma cells reduced retinoic acid-induced NF-kappaB activation and differentiation of cells, but instead promoted cell death. 25117167_we identified a novel mutation of the CYLD gene in a Chinese multiple familial trichoepithelioma family. 25130432_the 35kDa CYLD cleaved factor generated by MALT-1 mediated proteolytic cleavage was conspicuously present in human T- ALL subjects of pediatric age group. 25134987_The deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD controls apical docking of basal bodies in ciliated epithelial cells. 25234269_Report a novel heterozygous frameshift mutation c.1169_1170delCA (p.Thr390Argfs) of the CYLD gene in Chinese family with multiple familial trichoepithelioma. 25329885_Expression of nuclear CYLD is a novel prognostic factor for improved survival in patients with HCC undergoing liver resection or transplantation. 25347032_Identify 2 novel large germline rearrangement mutations including 1 pure deletion and 1 deletion/insertion mutation in a cohort of patients with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome and multiple familial trichoepithelioma. 25389768_CYLD negatively regulates nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced IL-8 expression via MKP-1-dependent inhibition of ERK. 25501176_A heterozygous missense mutation (c.1112C>A) in the 9th exon of the CYLD gene was detected in some mother-daughter patients with multiple trichoepitheliomas. 25565632_Here, we report a novel interaction between CYLD and MIB2 that supports the hypothesis that the CYLD/MIB2 interaction might play a pathogenic role in human cancer. 25641919_CYLD displayed its ability to restrict the cells in G2 phase of cell cycle 25751345_A recurrent R936X nonsense mutation of CYLD was identified in a large Chinese family with multiple familial trichoepithelioma. 25782638_Phenotype-genotype correlations for clinical variants caused by CYLD mutations. [Review] 25824771_Low CYLD expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 25923723_Data suggest OPTN (optineurin) is involved in up-regulation of innate immunity in mitosis; mechanism involves phosphorylation/nuclear translocation of CYLD and phosphorylation/mitochondrial translocation of TBK1 (NF-kB-activating kinase). 25935309_CYLD interrupts the ERK- and p38-/AP-1 and c-Myc pathways to suppress Nrf2-operated antioxidative capacity, thereby enhancing oxidative stress in the heart. 26056944_TRAF-6 mediates S. p-induced PAI-1 expression, and CYLD inhibits PAI-1 expression probably through deubiquitinating TRAF-6 26271973_Data show that inhibiting the expression of cylindromatosis (CYLD) gene can suppress the proliferation and migration of umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). 26329847_Novel CYLD germline mutations c.1821_1826+1delinsCT/L607Ffs*9, c.2666A>T/p.D889V and c.2712delT/p.905Kfs*8 were identified in unrelated Brooke-Spiegler Syndrome patients. 26370355_Clinical management of patients with germline CYLD mutations is challenging and we discuss genetic counselling and surgical interventions 26711782_aberrantly expressed miR-130b may regulate cell apoptosis and proliferation of human gastric cancer cells via CYLD, which appears to be a promising therapeutic target for gastric cancer 26717101_Ultraviolet radiation induced CYLD translocation from the cytoplasm to microtubules, posttranslational modification and degradation in a proteasome-independent manner. 26719415_Deubiquitinase CYLD negatively regulates MyD88-mediated signaling by directly interacting with MyD88 and deubiquitinating nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi)-induced K63-linked polyubiquitination of MyD88 at lysine 231. 26861065_Haplotype analysis was performed for the patients with multiple familial trichoepithelioma type 1, patients with familial cylindromatosis and a patient with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome, all of whom carry the same heterozygous nonsense CYLD mutation. 26982322_Study founds the levels of CYLD and SMAD7 significantly decreased in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSSC) cells and proposes a model that CYLD suppresses OSCC metastases through SMAD7. Downregulation of CYLD appears to directly contribute to the distal metastases of primary OSCC and subsequently poor prognosis. 27189061_STAT3 and miR-181b control each other's expression in a positive feedback loop that regulates SFCs via CYLD pathway. 27307491_The predicted PUB domain in the N-terminus of SPATA2 interacts with the USP domain of CYLD and SPATA2 is required for recruitment of CYLD to the TNF-alpha receptor-associated signaling complexes. 27357419_miR20a directly repressed the expression of CYLD, leading to activation of the NFkappaB pathway and the downstream targets, livin and survivin, which potentially induced GC chemoresistance. 27391066_Through deceasing the expression of Cylindromatosis (CYLD), a K63-specific DUB and endogenous blocker of NF-kappaB signaling, miR-130b can in return sustain the persistent activation of NF-kappaB, which may promote the malignant progression of transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. 27448305_Data show that cylindromatosis (CYLD) overexpression and livin knockdown might improve gemcitabine chemosensitivity by decreasing autophagy and increasing apoptosis in bladder cancer (BCa) cells. 27545878_SPATA2 has been described as a previously unrecognized factor in the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex-dependent signaling pathways that serves as an adaptor between HOIP and CYLD, thereby enabling recruitment of CYLD to signaling complexes. 27570065_These results demonstrate the involvement of histone deacetylases in the down regulation of Cyld expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 27591049_The data reveal SPATA2 as a high-affinity binding partner of CYLD and HOIP, and a regulatory component of linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex-mediated NF-kappaB signaling. 27681433_Thrombin-mediated MALT1 protease activation triggers acute disruption of endothelial barrier integrity via CYLD cleavage. 27738385_CYLD Promotes TNF-alpha-Induced Cell Necrosis Mediated by RIP-1 in Human Lung Cancer Cells 28184924_Low CYLD expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 28295222_The current investigations identified a subset of HPV-positive HNSCCs with mutations in the genes TRAF3 (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3) and CYLD (cylindromatosis lysine 63 deubiquitinase). Defects in TRAF3 and CYLD correlated with the activation of transcriptional factor nuclear factor kappaB, episomal HPV status of tumors, and improved patient survival. 28534976_Low expression of CYLD is associated with glioma. 28566736_A substantial number of CLL patient samples express sCYLD. 28572092_theses data show that CYLD regulates the magnitude of ubiquitination of several major effectors of the EGFR pathway by assisting the recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b to the activated EGFR complex. 28629782_TNF phase III signalling displays ongoing TNFR1/NF-kappa B activation in monocytic cells. High- and low-sensitive genes are induced including differentially regulated A20. A20 strictly controls this signalling in an IKK- and partially RIP-dependent manner. The A20-mediated control mechanisms are supported by ABIN1 and CYLD. 28840581_While previous reports have described CYLD as a regulator of DVL proteins; this data suggests the presence of a more complicated reciprocal regulatory mechanism in CML cell lines. 28901464_Knockdown of CYLD expression reversed the cell proliferation promotion by miR1288in in glioblastoma. 29054757_MiR-767 acted as a role of tumor promoter by targeting CYLD in human melanoma. 29166644_CYLD inhibits post-transcriptional regulation of RIG-I and MDA5 expression following TLR3 activation in MCs. CYLD may be involved in the pathogenesis of CKD 29235674_Downregulation of CYLD promotes invasion with mesenchymal transition via ALK5 stabilization in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 29286108_miR-197-3p-induced downregulation of CYLD promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. 29463883_Our study revealed high incidence and sequential CYLD mutations in both basal cell adenoma and adenocarcinoma supporting a single neoplastic continuum for their evolution 29478249_We detected three CYLD splice site mutations, designated c.2108+1G>A, c.2242-2A>G and c.2109-2A>C. These mutations were associated with distinct phenotypes. 29807073_Catalytic domain mutation in CYLD gene is associated with osteosarcoma. 29808164_Studied the role of maternally expressed 3 (lncRNA-MEG3) as an antitumor lncRNA for malignant melanoma by regulating miR-499-5p/CYLD axis. 29974194_No genotype-phenotype correlation was found in tumor disorders of the skin appendages associated with mutations in the CYLD gene. 30132887_CYLD is downregulated in gastric adenocarcinoma and nfectious agents may influence its expression. 30269739_miR-301b plays an oncogenic role in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) possibly by downregulating CYLD and subsequently activating NF-kappaB p65, and this may provide a novel therapeutic approach for TNBC. 30285829_CYLD suppression enhanced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 30362575_these data indicate a critical role for CYLD in suppressing pancreatic tumorigenesis. 30542706_Study revealed that miR-182 expression was significantly upregulated in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) compared with adjacent normal tissues. Overexpression of miR-182 enhanced GIST-T1 cell growth, with increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis. In addition, cylindromatosis (CYLD) was identified as a direct target of miR-182. 30554661_CYLD in the vasculature may be a novel therapeutic target, especially in the early preventive intervention against the initiation of age-related atherogenesis. 31067453_CYLD marshals the centriolar satellites by deubiquitinating and preventing the E3 ligase Mindbomb 1 (MIB1) from marking PCM1 for proteasomal degradation. 31101826_Study reveals alterations of the CYLD gene in 15/15 cylindromas and 5/17 spiradenomas, yet only 2/24 spiradenocarcinomas. Also, a recurrent missense mutation found in the kinase domain of the ALPK1 gene in spiradenomas and spiradenocarcinomas, which is mutually exclusive from mutation of CYLD and can activate the NF-kappaB pathway in reporter assays. 31366726_Results suggest that MIB2 enhances NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation by promoting the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of CYLD. 31406156_CYLD dysregulation in pathogenesis of sporadic inclusion body myositis. 31624251_In addition to biallelic mutations in deubiquitinating enzyme CYLD (CYLD), data show multiple mutations in epigenetic modifiers DNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) and BCL6 co-repressor protein (BCOR) in CYLD cutaneous syndrome (Brooke-Spiegler syndrome). 31635163_CYLD Down-Regulation Induced Cisplatin Resistance through NF-kappaB Hyperactivation. 31833565_A novel nonsense mutation of the CYLD gene in a Turkish family with multiple familial trichoepithelioma. 31860169_LncRNA GMDS-AS1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma development by regulating miR-96-5p/CYLD signaling. 31885317_The long noncoding RNA CRAL reverses cisplatin resistance via the miR-505/CYLD/AKT axis in human gastric cancer cells. 32185393_show here that increased CYLD activity reduces autophagy function, highlighting the importance of autophagy regulation in the pathogenesis of frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 32418059_Doxorubicin sensitizes cancer cells to Smac mimetic via synergistic activation of the CYLD/RIPK1/FADD/caspase-8-dependent apoptosis. 32441799_Reduced expression of CYLD promotes cell survival and inflammation in gefitinib-treated NSCLC PC-9 cells: Targeting CYLD may be beneficial for acquired resistance to gefitinib therapy. 32461623_CYLD-mutant cylindroma-like basaloid carcinoma of the anus: a genetically and morphologically distinct class of HPV-related anal carcinoma. 32602581_Nonsense-mediated decay factor SMG7 sensitizes cells to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis via CYLD tumor suppressor and the noncoding oncogene Pvt1. 32678957_CYLD-related cutaneous syndrome: variable p.Pro482fs*6 phenotype in five individuals from two unrelated families. 32705175_Stress response in periodontal ligament stem cells may contribute to bisphosphonateassociated osteonecrosis of the jaw: A gene expression array analysis. 32738418_Downregulation of CYLD promotes IFN-gamma mediated PD-L1 expression in thymic epithelial tumors. 32783365_A novel large deletion of the CYLD gene causes CYLD cutaneous syndrome in a Chinese family. 32862616_Research on mechanism of miR-130a in regulating autophagy of bladder cancer cells through CYLD. 32892208_CYLD mutation characterizes a subset of HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinomas with distinctive genomics and frequent cylindroma-like histologic features. 32901872_Downregulation of miR181b inhibits human colon cancer cell proliferation by targeting CYLD and inhibiting the NFkappaB signaling pathway. 33031450_Relationship between clinicopathological characteristics and CYLD expression in patients with cholesteatoma. 33031609_The inhibitory effect of the deubiquitinase cylindromatosis (CYLD) on inflammatory responses in human gingival fibroblasts. 33378022_MiR-587 acts as an oncogene in non-small-cell lung carcinoma via reducing CYLD expression. 33507567_CYLD mediates human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell dysfunction in congenital heart disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. 33545631_Podocyte RNF166 deficiency alleviates diabetic nephropathy by mitigating mitochondria impairment and apoptosis via regulation of CYLD signal. 33629796_MicroRNA-370-3p shuttled by breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles induces fibroblast activation through the CYLD/Nf-kappaB axis to promote breast cancer progression. 33999445_TRAF3 and NBR1 both influence the effect of the disease-causing CYLD(Arg936X) mutation on NF-kappaB activity. 34326699_Downregulation of m(6)A Reader YTHDC2 Promotes the Proliferation and Migration of Malignant Lung Cells via CYLD/NF-kappaB Pathway. 34497368_TRIM15 and CYLD regulate ERK activation via lysine-63-linked polyubiquitination. 34610306_Regulation of CYLD activity and specificity by phosphorylation and ubiquitin-binding CAP-Gly domains. 34742871_CYLD destabilizes NoxO1 protein by promoting ubiquitination and regulates prostate cancer progression. 34927777_SOX4 induces drug resistance of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating CYLD through transcriptional activation of microRNA-17. 35025147_Prevalence of CYLD mutations in Vietnamese patients with polycythemia vera. 35131382_CYLD deficiency enhances metabolic reprogramming and tumor progression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via PFKFB3. 35779906_CYLD expression in endometrial carcinoma and correlation with clinicohistopathological parameters. 36000313_CYLD variants identified in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia patients. |
ENSMUSG00000036712 |
Cyld |
436.431546 |
2.0104199558 |
1.007497 |
0.235914293 |
17.889861 |
0.00002340647297047122502673330290967612654640106484293937683105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000070219418911413668303936330694625667092623189091682434082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
585.1963065 |
86.9098152 |
292.7763826 |
31.5935129 |
| ENSG00000083857 |
2195 |
FAT1 |
protein_coding |
Q14517 |
FUNCTION: [Protocadherin Fat 1]: Plays an essential role for cellular polarization, directed cell migration and modulating cell-cell contact. {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is an ortholog of the Drosophila fat gene, which encodes a tumor suppressor essential for controlling cell proliferation during Drosophila development. The gene product is a member of the cadherin superfamily, a group of integral membrane proteins characterized by the presence of cadherin-type repeats. In addition to containing 34 tandem cadherin-type repeats, the gene product has five epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats and one laminin A-G domain. This gene is expressed at high levels in a number of fetal epithelia. Its product probably functions as an adhesion molecule and/or signaling receptor, and is likely to be important in developmental processes and cell communication. Transcript variants derived from alternative splicing and/or alternative promoter usage exist, but they have not been fully described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2195; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; epithelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0003382]; establishment of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity involved in camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0003412]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; lens development in camera-type eye [GO:0002088] |
15922730_Processing of FAT1 and the translocation of its cytoplasmic domain to the nucleus were studied. 16402135_A cadherin gene, FAT, confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder in four independent cohorts. In mice, Fat was shown to be significantly downregulated and Catnb and Enah were significantly upregulated in response to therapeutic doses of lithium. 16979624_Fat1 exhibit co-localisation with Homer-3 in cellular protrusions and at the plasma membrane of HeLa cells 17325662_results identify mutations in FAT as an important factor in the development of oral cancer and indicate the importance of FATs function in some squamous cell carcinomas 17500054_FAT1(WT) is up-regulated in migration, induces cellular process formation when overexpressed, and is necessary for efficient wound healing 17895925_This study did not support the two FAT polymorphism in the affectve disorder. 17938632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17938632_The results of this study supports an involvement of variation at the FAT gene in the etiology of BPAD. 19126244_Results point to a role of the FAT in astrocytic tumorigenesis and demonstrate the use of RAPD analysis in identifying specific alterations in astrocytic tumors. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19893579_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21617878_FAT1 may be involved in the migration and invasion mechanisms of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells 21680732_In vitro localization studies of FAT1 showed that melanoma cells display high levels of cytosolic FAT1 protein, whereas keratinocytes, despite comparable FAT1 expression levels, exhibited mainly cell-cell junctional staining 22116550_data presented demonstrate that Fat1 expression in preB-ALL has a role in the emergence of relapse and could provide a suitable therapeutic target in high-risk preB-ALL 22194967_Lipid accumulation in myotubes derived from obese type 2 diabetic patients arises from abnormal FAT/CD36 cycling. 22959770_FAT1 suppression in activated hepatic stellate cells caused a downregulation of NFkappaB activity 22986533_this study identifies a novel signaling mechanism mediated by FAT1 in regulating the activity of PDCD4 in gliomas. 23354438_Taken together, these data strongly point to FAT1 as a tumor suppressor gene driving loss of chromosome 4q35, a prevalent region of deletion in cancer 23433465_Fat1 may therefore provide a new marker of MRD for patients with ALL lacking known genomic aberrations or within a multiplex approach to MRD detection. 23785297_Our study identifies FAT1 as a critical determinant of muscle form, misregulation of which associates with facioscapulohumeral dystrophy . 24442637_There is a mechanism to regulate death receptor-mediated apoptosis via an interaction between FAT1 and procaspase-8. 24550227_frequency of FAT1-mutated cases was significantly higher in drug resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia than in unselected chronic lymphocytic leukemia 24560745_This work establishes S1-processing as a clear functional prerequisite for ectodomain shedding of FAT1 with general implications for the shedding of other transmembrane receptors. 24590895_FAT1 expression in HCC is regulated via promotor methylation. 24625754_Fat1 is released from pancreatic cancer cells in its soluble form by ADAM10 mediated ectodomain shedding 24972153_Analysis revealed an aberrant expression of FAT1 predominantly in mature BCP-ALL and thymic T-ALL and a high rate of FAT1 mutations. 25150169_FJX1 does not influence the levels of FAT1 ectodomain phosphorylation. 25615407_our data suggest that defective FAT1 is associated with an FSHD-like phenotype. 26018399_FAT1 is expressed at lower levels in muscles that are affected at early stages of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy progression. 26104008_FAT1 protein acts upstream of Hippo signalling through TAZ protein to regulate neuronal differentiation. 26721716_that loss of FAT1 and beta-catenin are associated with breast cancer progression, aggressive behavior, and poor prognosis 26876381_FAT1 mutational status is a strong independent prognostic factor in patients with HPV-negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; FAT1 mutation was significantly associated with better overall survival 26905694_Recessive mutations in FAT1 cause a distinct renal disease entity in four families with a combination of steroid-resistance nephrotic syndrome, tubular ectasia, haematuria and facultative neurological involvement. 27325650_We identified recurrent mutations in the novel penile cancer tumor suppressor genes CSN1(GPS1) and FAT1 27328312_FAT1 and mAb198.3 may offer new therapeutic opportunities for CRC. 27536856_At the molecular level, under hypoxia the FAT1 depletion-associated reduction in HIF1alpha was due to compromised EGFR-Akt signaling as well as increased VHL-dependent proteasomal degradation of HIF1alpha. 27693639_Loss of function mutations in FAT1 and CASP8 prevent cell adhesion and promote cell migration and proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. 27834469_Low FAT1 expression was associated with poor prognosis in children with medulloblastoma. Furthermore, FAT1 may act on Wnt signaling pathway to exert its antitumor effect 28129444_Data show that the two N-terminal SH3 domains of SH3 domain containing ring finger 1 (SH3RF1) protein interact with FAT1 protein. 28366557_Disruption of MAPK/ERK pathway by FAT1 contributes the epithelial mesenchymal transformation in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 28994107_FAT1 has a novel regulatory effect on EMT/stemness markers both via or independent of HIF-1alpha. The functional relevance of this study was corroborated by significant reduction in the number of soft-agar colonies formed in hypoxic-siFAT1 treated U87MG cells. 29565465_Study showed that FAT1 exhibits a high frequency of mutations and a downregulated expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) leading to cell migration and invasion by affecting the cellular mechanical properties of ESCC cells. 29985391_Fat1 functional loss results in YAP1 activation and is associated with human malignancies. 30102337_The findings of this study reveal that FAT1 suppresses head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Somatic mutations in FAT1 may underlie the downregulation of FAT1 expression. FAT1 mutations and expression determine head and neck squamous cell carcinoma recurrence. 30514309_CircFAT1 contains a binding site for the microRNA-375 (miR-375) and can abundantly sponge miR-375 to upregulate the expression of Yes-associated protein 1. 30514801_Truncated FAT1 isoform with mutant NOTCH1 leads to T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia development. 30657779_Two tagSNPs, rs28647489 in FAT1 gene and rs550675 in COL9A1 gene, were significantly associated with the risk of oral malignancy. 30862798_Study findings establish FAT1 as a gene with pleiotropic effects in human, in that frameshift mutations cause a severe multi-system disorder characterized by colobomatous-microphthalmia, ptosis, nephropathy and syndactyly. 31028364_Whole exome sequencing reveals mutations in FAT1 tumor suppressor gene clinically impacting on peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified. 31076104_FAT1 is required for efficient neuritogenesis. 31123786_The most frequently mutated driver genes in our cohort were TP53 (involved in cell cycle control), FAT1 (Wnt signalling, cell-cell contacts, migration) and KMT2D (chromatin modification). Radiomic features of heterogeneity did not correlate significantly with somatic mutations in TP53 or KMT2D. However, somatic mutations in FAT1 and smaller primary tumour volumes were associated with reduced radiomic intra-tumour heterog 31209189_Whole Exome Sequencing analysis revealed a novel mutation in FAT1 (c.10570C > A; Q3524K) in patients of Nephrotic syndrome. 31992226_NFsmall ka, CyrillicB is a critical transcriptional regulator of atypical cadherin FAT1 in glioma. 33133224_circFAT1(e2) Promotes Papillary Thyroid Cancer Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion via the miRNA-873/ZEB1 Axis. 33179443_CircFAT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via miR-30a-5p/REEP3 pathway. 33328637_Fat1 deletion promotes hybrid EMT state, tumour stemness and metastasis. 33420124_Identification of the atypical cadherin FAT1 as a novel glypican-3 interacting protein in liver cancer cells. 33818788_CircFAT1 facilitates cervical cancer malignant progression by regulating ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathway through miR-409-3p/CDK8 axis. 34167951_The Proteomic Landscape of Growth Factor Signaling Networks Associated with FAT1 Mutations in Head and Neck Cancers. 34202629_Whole Exome Sequencing Is the Minimal Technological Approach in Probands Born to Consanguineous Couples. 34258151_circFAT1 Promotes Cancer Stemness and Immune Evasion by Promoting STAT3 Activation. 34314629_Overexpression of circRNA circFAT1 in Endometrial Cancer Cells Increases Their Stemness by Upregulating miR-21 Through Methylation. 34390292_Fat1 suppresses the tumor-initiating ability of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by promoting Yes-associated protein 1 nuclear-cytoplasmic translocation. 34938350_circFAT1(e2) Inhibits Cell Apoptosis and Facilitates Progression in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through miR-298/MYB Axis. 34939311_Clinical significance of FAT1 gene mutation and mRNA expression in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 35279875_FAT1 and MSH2 Are Predictive Prognostic Markers for Chinese Osteosarcoma Patients Following Chemotherapeutic Treatment. 35606602_FAT1 downregulation enhances stemness and cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35714699_CircFAT1 regulates retinal pigment epithelial cell pyroptosis and autophagy via mediating m6A reader protein YTHDF2 expression in diabetic retinopathy. 35720420_Upregulation of Atypical Cadherin FAT1 Promotes an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment via TGF-beta. 35844799_CircFAT1 Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Progression by Sequestering miR-7 from Repressing IRS2-ERK-mediated CCND1 Expression. |
ENSMUSG00000070047 |
Fat1 |
2732.061992 |
2.3252269760 |
1.217372 |
0.071426749 |
283.915187 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000105300330344102077762777814364778502951609935865157711340555848211065849075855249396443818207992279477683556284537016644836284422841388464214691146936415526739680426082657049846602603793144226074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000028675883318799753844774303253854652646828505582551536638338633270680367641076493676811202413483885969494370493240828769247018005806293995757872162806305371685056115893530659377574920654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3756.9266973 |
160.1396818 |
1627.8547390 |
51.5303580 |
| ENSG00000084073 |
10269 |
ZMPSTE24 |
protein_coding |
O75844 |
FUNCTION: Transmembrane metalloprotease whose catalytic activity is critical for processing lamin A/LMNA on the inner nuclear membrane and clearing clogged translocons on the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:33315887, PubMed:33293369). Proteolytically removes the C-terminal three residues of farnesylated proteins. Plays also an antiviral role independently of its protease activity by restricting enveloped RNA and DNA viruses, including influenza A, Zika, Ebola, Sindbis, vesicular stomatitis, cowpox, and vaccinia (PubMed:28246125, PubMed:28169297). Mechanistically, controls IFITM antiviral pathway to hinder viruses from breaching the endosomal barrier by modulating membrane fluidity (PubMed:35283811). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28169297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28246125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33293369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33315887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35283811}. |
3D-structure;Antiviral protein;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M48A family. The encoded protein is a zinc metalloproteinase involved in the two step post-translational proteolytic cleavage of carboxy terminal residues of farnesylated prelamin A to form mature lamin A. Mutations in this gene have been associated with mandibuloacral dysplasia and restrictive dermopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10269; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear inner membrane [GO:0005637]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metalloexopeptidase activity [GO:0008235]; adult walking behavior [GO:0007628]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; CAAX-box protein processing [GO:0071586]; calcium ion import into sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:1990036]; CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade [GO:0061762]; cardiac conduction [GO:0061337]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; cardiac ventricle development [GO:0003231]; cellular lipid metabolic process [GO:0044255]; cellular response to gamma radiation [GO:0071480]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; determination of adult lifespan [GO:0008340]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; growth plate cartilage development [GO:0003417]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; histone H2B-K5 acetylation [GO:0043979]; hypomethylation of CpG island [GO:0044029]; inflammatory cell apoptotic process [GO:0006925]; kidney morphogenesis [GO:0060993]; liver development [GO:0001889]; maintenance of rDNA [GO:0043007]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of miRNA maturation [GO:1903799]; neuromuscular process [GO:0050905]; nuclear envelope organization [GO:0006998]; prenylated protein catabolic process [GO:0030327]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000772]; regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050688]; regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043516]; regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048145]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906]; regulation of histone H4-K16 acetylation [GO:2000618]; regulation of hormone metabolic process [GO:0032350]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle DNA replication [GO:1903463]; regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040014]; regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:1903025]; regulation of stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade [GO:0070302]; regulation of termination of RNA polymerase I transcription [GO:2000730]; regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032006]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization [GO:0060307]; response to DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0072423]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0003229] |
15317753_A premature termination codon mutation in the gene ZMPSTE24 leads to loss of expression of Lamin A as well as abnormal patterns of nuclear sizes and shapes. 15671064_RNA interference of FACE1 protease results in a halt of cell division and accumulation of prelamin A. 15843403_loss causes autosomal recessive restrictive dermopathy 16297189_Restrictive dermopathy is an autosomal recessive laminopathy caused by inactivating ZMPSTE24 mutations that result in defective processing and nuclear accumulation of prelamin A. 17352743_Accumulation of multiple forms of lamin A with down-regulation of FACE-1 suppresses growth in senescent cells. 18230615_darunavir does not inhibit the biochemical activity of ZMPSTE24, nor does it lead to an accumulation of farnesyl-prelamin A in cells. 18435794_ZMPSTE24 deficiency results in accumulation of farnesylated prelamin A, which may be responsible for cellular toxicity and the MAD phenotype. 19351612_inhibition of the prelamin A endoprotease ZMPSTE24 mostly elicits accumulation of full-length prelamin A in its farnesylated form, while loss of the prelamin A cleavage site causes accumulation of carboxymethylated prelamin A in progeria cells. 19383993_glu231X mutation of ZMPSTE24 found in unrelated families with diagnosis of restrictive dermopathy and perhaps specific to India 19453269_ZMPSTE24 performs a critical endoproteolytic cleavage step that removes the hydrophobic farnesyl-modified tail of prelamin A. we discuss the discovery of mammalian ZMPSTE24 & review the unexpected connection between ZMPSTE24 and premature aging[review] 19645629_results suggest that LMNA, ZMPSTE24, and LBR sequence variations are not major genetic determinants involved in scleroderma pathogenesis 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19841875_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20101687_study reports on two brothers affected with restrictive dermopathy; compound heterozygous frameshifting mutations were identified in exon 1 (c.50delA) and exon 5 (c.584_585delAT) of the ZMPSTE24 gene 20550970_Data show that mandibuloacral dysplasia associated with ZMPSTE24 mutations has a more severe phenotype than that associated with lamin A mutations. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20635340_ZMPSTE24 mutations are associated with dermopathy. 20814950_In patients with mandibuloacral dysplasia due to ZMPSTE24 mutations, the onset of disease manifestations such as thin skin and micrognathia occurs as early as 5 months of age. 21108632_A report of a novel and a previously reported homozygous null mutation in ZMPSTE24 in two newborns with restrictive dermopathy. 21724554_Three of 87 patients with metabolic syndrome carry a heterozygous mutation in LMNA or in ZMPSTE24. 22718200_Characterization of disease causing mutations in the ZMPSTE24 gene, residual proteolytic activity correlates with disease severity. 22936788_These data implicate copper as an important factor in promoting prostate cancer cell invasion and indicate that the selective posttranslational activation of ZMP-mediated protein shedding might play a role in this process. 23539603_Laminopathy-associated mutations predicted to reduce ZMPSTE24 activity map to the zinc metalloprotease peptide-binding site and to the bottom of the chamber. 24101728_miR-141-3p, which is overexpressed during senescence as a result of epigenetic regulation, is able to decrease ZMPSTE24 expression levels, and leads to an upregulation of prelamin A in human mesenchymal stem cells. 24169522_complete loss-of-function of ZMPSTE24 leads to RD, whereas other less severe phenotypes are associated with at least one haploinsufficient allele. 26379196_Here, we report on a familial c.50delA (p.Lys17Serfs*21) mutation of the ZMPSTE24 gene, causing RD in two siblings. 26724531_ZMPSTE24 downregulation is a major contributor in VSMC dysfunctions resulting from LMNA mutations or PI treatments that could translate in early atherosclerosis at the clinical level. 27034136_This case demonstrates that accumulation of prelamin A, independent of the loss of function of ZMPSTE24 metallopeptidase that catalyzes processing of prelamin A, can cause a progeroid disorder and that a cell biology assay could be used in precision medicine to identify a potential therapy. 27129777_results establish that the substrate profile of Ste24p is broader than anticipated, being more similar to that of the M16A protease family than that of the Rce1p CAAX protease with which it has been functionally associated 27729169_the present study suggests that inhibition of ZMPSTE24 by both mutational and expressional pathways might together play a role in tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer and gastric cancer harboring microsatellite instability phenotype. 27774687_used a fluorogenic assay of the activity of purified ZMPSTE24 to demonstrate that HIV protease inhibitors directly inhibit the human enzyme in a manner indicative of a competitive mechanism 28246125_ZMPSTE24 is an important element for innate host defense against a broad spectrum of pathogenic viruses. 28594571_ZMPSTE24 is a downstream effector of IFITM3 and is important for interferon-induced transmembrane antiviral activity. 29794150_ZMPSTE24-dependent cleavage of prelamin A and the eight known disease-associated ZMPSTE24 missense mutations, were examined. 30625386_Together these systems offer powerful methodology to study ZMPSTE24 disease alleles and to dissect the specific residues and features of the lamin A tail that are required for recognition and cleavage by the ZMPSTE24 protease. 31644822_The tripartite architecture of the eukaryotic integral membrane protein zinc metalloprotease Ste24. 32199981_Ste24: An Integral Membrane Protein Zinc Metalloprotease with Provocative Structure and Emergent Biology. 32799420_Protein structural and mechanistic basis of progeroid laminopathies. 32872320_ZMPSTE24 Is Associated with Elevated Inflammation and Progerin mRNA. 33130089_OMA1-An integral membrane protease? 33293369_Site specificity determinants for prelamin A cleavage by the zinc metalloprotease ZMPSTE24. 34003736_ZMPSTE24 Regulates SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-enhanced Expression of Endothelial PAI-1. 34647350_Restrictive dermopathy: Three new patients with ZMPSTE24 mutations and a review of the literature. 35597529_An exceptional biallelic N-terminal frame shift mutation in ZMPSTE24 leads to non-lethal progeria due to possible utilization of a downstream alternative start codon. 36197088_The Integral Membrane Protein ZMPSTE24 Protects Cells from SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Pseudovirus Infection and Syncytia Formation. |
ENSMUSG00000043207 |
Zmpste24 |
6995.861439 |
2.0081083468 |
1.005837 |
0.020089404 |
2523.883351 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
9488.2632176 |
109.6084104 |
4759.5220404 |
43.3122582 |
| ENSG00000084731 |
3797 |
KIF3C |
protein_coding |
O14782 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-based anterograde translocator for membranous organelles. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable microtubule binding activity and microtubule motor activity. Predicted to be involved in microtubule-based movement. Predicted to act upstream of or within organelle transport along microtubule. Predicted to be located in microtubule cytoskeleton; neuronal cell body; and neuronal ribonucleoprotein granule. Predicted to be part of kinesin complex. Predicted to be active in microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:3797; |
ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; cytoskeletal motor activity [GO:0003774]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
17881655_FMRP acts also as a molecular adaptor between RNA granules and the neurospecific kinesin KIF3C. 26272184_Results suggest that high expression of KIF3C in breast cancer may be associated with tumor progression and metastasis. 32020481_KIF3C is associated with favorable prognosis in glioma patients and may be regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. 33150178_KIF3C Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Glioma Cells by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway and Inducing EMT. 34193018_Kinesin family member 3C (KIF3C) is a novel non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) oncogene whose expression is modulated by microRNA-150-5p (miR-150-5p) and microRNA-186-3p (miR-186-3p). |
ENSMUSG00000020668 |
Kif3c |
151.532758 |
0.2557800773 |
-1.967024 |
0.302874592 |
39.630383 |
0.00000000030687182233131031557522428131190832950592195516037463676184415817260742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001533839518323786194792926968540492521642093493028369266539812088012695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.0576440 |
17.0991057 |
236.7683036 |
48.0791285 |
| ENSG00000085117 |
3732 |
CD82 |
protein_coding |
P27701 |
FUNCTION: Associates with CD4 or CD8 and delivers costimulatory signals for the TCR/CD3 pathway. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This metastasis suppressor gene product is a membrane glycoprotein that is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily. Expression of this gene has been shown to be downregulated in tumor progression of human cancers and can be activated by p53 through a consensus binding sequence in the promoter. Its expression and that of p53 are strongly correlated, and the loss of expression of these two proteins is associated with poor survival for prostate cancer patients. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3732; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
11839793_An amplification loop, via Vav and SLP76 phosphorylation and Rho-GTPase activation, is initiated by CD82 association with the cytoskeleton, thus permitting cytoskeletal rearrangement and costimulatory activity in T cells. 11895916_Loss of KAII is associated with primary tumos with lymph node metastasis 11981820_Evidence for distinctive signaling of CD82- and beta1 integrin-mediated costimulation at the transcriptional level of IL-2 gene. 12474542_relationship between expression, mrna levels and p53 in human bladder and prostate cancer cell lines. 12579280_downregulation of CD82 antigen is associated with breast tumor progression 12642901_KAI1 induces homotypic aggregation of human prostatic neoplasm cells through Src-dependent pathway. 12684410_KAI1 expression is down-regulated in advanced endometrial cancer 12738793_Requirement of the p130CAS-Crk coupling for metastasis suppressor KAI1/CD82-mediated inhibition of cell migration in a metastatic prostate cancer cell line. 12747469_KAI1 down-regulation is significantly related to the progression of papillary carcinoma, including lymph node metastasis, and its anaplastic transformation. 12750295_EWI2/PGRL associates with the metastasis suppressor KAI1/CD82 and inhibits the migration of prostate cancer cells. 12753720_The abnormal expression of KAI1 participates in malignant progression of colorectal cancer. 12955496_KAI1 is a tumor metastasis suppressor gene in digestive tract carcinomas and cancer cells. 14576349_CD82 regulates compartmentalisation of the EGF receptor 14706010_Decreased expression of KAI1 was associated with the degree of invasiveness and progression of the cancer and was an independent prognostic factor of recurrence in primary pTa and pT1 urothelial bladder carcinoma. 15237426_Sense and antisense genes had no significant effects on cell growth and cell cycles. Sense KAI1 gene decreased invasive ability and decreased mitochondria. Clone formation and invasive ability increased after transfection with antisense KAI1 gene. 15259074_KAI1 is highly related to the metastasis of colonic carcinoma and may be a useful indicator of metastasis in colonic carcinoma. 15375577_CD82 may serve as a prognostic marker of metastasis in thyroid cancer 15454569_CD82 controls the association of cholesterol-dependent microdomains with the actin cytoskeleton in T lymphocytes 15557282_CD82 attenuates integrin alpha6 signaling during a cellular morphogenic process 15592684_Our investigations revealed significantly reduced mRNA expression of metastases suppressor gene KAI1 in breast cancer brain metastasis. 15677461_urokinase receptor proteolytic function is regulated by the tetraspanin CD82 15996322_The decrease of KAI1 mRNA expression may be related to lymph node metastasis and lew differentiation of larynjeal squamous cell carcinoma. 16325219_findings have shown that HTLV-1 Gag associates with CD82-enriched plasma membrane microdomains in Jurkat T cells 16488391_KAI1/CD82 over-expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells suppresses tumor invasiveness and metastatic potential by inducing matrix metalloproteinase-9 inactivation via up-regulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1). 16494006_The expression of CD82 was closely correlated with lymph node metastasis in laryngeal carcinoma. 16861889_REVIEW. The SUMOylation status of the reptin chromatin-remodeling complex modulates the KAI1 metastasis suppressor gene and the invasive activity of cancer cells with metastatic potential. 17166843_Association of HTLV-1 Gag protein with tetraspanin-enriched microdomains is mediated by the inner loops of CD82 and CD81. 17200188_the expression of KAI1 in decidual cells at the human maternal-fetal interface, where the metastasis suppressor might participate in intercellular communication with trophoblast cells and the control of trophoblast invasion 17215249_glycosphingolipids, particularly GM2, form a complex with CD82, and this complex interacts with Met and thereby inhibits HGF-induced Met tyrosine kinase activity, as well as integrin to Met cross-talk 17283532_The expressions of KAI1, nm23, ETS-1 and VEGF proteins were highly related to microvascular density, cervical lymph node metastasis, and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 17393117_Expression of KAI1 in transitional cell carcinoma bladder is reported. 17520389_Expressions of Kiss-1 and KAI-1 mRNA in gastric cancer tissue were significantly lower than those in pericancerous tissue. 17560548_support a model in which KAI1/CD82 attenuates the maturation of the beta1 integrin precursor and thereby suppresses cell migration 17621632_CD82-c-Met complex inhibits hepatocyte growth factor-induced cancer cell migration by the inactivation of small GTP-binding proteins of the Rho family via c-Met adapter proteins 17672940_KAI1 gene could affect the growth pattern and proliferation of MHCC97-H cells, suppress sICAM-1 secretion and E-cadherin production, and inhibit adhesion of MHCC97-H cells. 17982617_Low levels of an alternatively spliced form of KAI1 mRNA are present in most bladder cancer tumours and tumour cell lines, but are not associated with invasive behaviour. 18028322_KAI1 gene functioned as a metastasis inhibitor by regulating the HCC cell biophysical behaviours including aggregation, adhesion, motility and visco-elastic properties. 18037895_gp78 promotes sarcoma metastasis by targeting KAI1 for degradation 18272501_a previously uncharacterized GM2/GM3 heterodimer complexed with CD82 inhibits cell motility through CD82-cMet or integrin-cMet pathway 18305955_Decreased KAI1/CD82 expression is associated with tumour progression, development of metastases and disease-specific death in penile squamous cell carcinomas. 18415123_KAI-1 and p53 show inverse expression in uterine and endometrial carcinomas and sarcomas. The reduced KAI-1 expression may be the result of dysregulated p53 function and could be a step in endometrial carcinogenesis. 18622748_Ablation of Sprouty2 with RNA interference can block the KAI1/CD82-induced suppression of hepatoma cell migration and downregulation of SphK1 expression 18712725_demonstrate for the first time that KAI1 is a target of ER-mediated gene-repression, and thus, it is downregulated in ER-positive breast cancer 18981120_tetraspanins regulate the activity of ADAM10 toward several substrates 19024519_The expressions of nm23 and KAI1 proteins are negatively correlated with clinical stage, but positively with histopathological grade in gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 19048121_Phorbol ester enhances KAI1 transcription by recruiting Tip60/Pontin complexes 19082457_down-regulation of KAI1/CD82 mRNA expression in human melanoma cell lines is related to LOH or allelic imbalance, but not to methylation of the KAI1/CD82 gene region. 19107873_KAI1/CD82 decreased the metastatic phenotype of H1299 lung carcinoma cells by down-regulating Rac1 expression through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. 19116362_the transmembrane (TM) interactions mediated by the Asn, aGln, and Glu polar residues determine a conformation either in or near the tightly packed TM region and this conformation and/or its change are needed for the intrinsic activity of KAI1/CD82 19148553_A marked reduction of KAI1 transcript was observed in invasive ductal breast tumours as compared to normal tissues 19371633_These data strongly indicate that KAI1 may suppress ovarian cancer progression by inhibiting integrin alphavbeta3/vitronectin-provoked tumor cell motility and proliferation as important hallmarks of the oncogenic process. 19489224_The abnormal expression of CD82 which participates in malignant progression of pancreatic cancer is probably associated with LOH of KAI1 gene. 19497983_these studies demonstrate that lipid-dependent endocytosis drives CD82 trafficking to late endosomes and lysosomes, and CD82 reorganizes TEMs and lipid rafts through redistribution of cholesterol. 19549254_High CD82 expression is associated with primary and metastases from estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. 19559406_Levels of CD82 expressed in A431 cells are much higher than those expressed in KB cells and motility of A431 cells is also much higher than that of KB cells. 19656997_KAI1 plays an important role in cell adhesion, invasion and migration of breast cancer cells, in vitro, and is a potential metastasis suppressor gene in breast cancer. 19666408_When p53 dysfunction and low expression of JunB are simultaneous, they may play an important role in down-regulating the expression of KAI1 by synergism in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19680475_Data have identified CD82 as valuable markers for chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. 19755988_Tetraspanin-induced death of myeloma cell lines is autophagic and involves increased UPR signalling. 19951590_Data suggests that KAI1 has prognostic properties in patients with gallbladder carcinoma,8 and that a lower expression of KAI1 is associated with a poor outcome. 20002769_CD82/KAI1 is an excellent marker for distinguishing chromophobe renal cell carcinomas from other types of renal cell tumours, especially from ROs with overlapping phenotype. 20075392_Silencing of CD82 by RNA interference increases integrin beta1, decreases tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression in decidual stromal cells, and promotes the invasion of the first-trimester human trophoblasts in coculture. 20089858_KAI1 has a role in promotion of cell proliferation and mammary gland hyperplasia by the gp78 ubiquitin ligase 20144992_Results highlight the role of TI-VAMP in the secretory pathway of CD82, and support a model in which CD82 allows EGFR entry in microdomains that control its clathrin-dependent endocytosis and signaling. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20864363_Data show that bladder cancer cell lines lacking KAI1 expression were 2x to 10x more invasive than cell lines that expressed KAI1. 21149584_the CD82 tetraspanin is specifically recruited to pathogen-containing phagosomes prior to fusion with lysosomes. 21168384_KAI1 induces autophagy through phosphorylation of extracellular signal-related kinases rather than that of AKT. 21382346_This result revealed that CD82 negatively regulates the HUVECs cell migration. The induction of CD82 gene expression in endothelial cells provided new insights into a specific function of HIF-2. 21454613_KAI1 gene is engaged in NDRG1 gene-mediated metastasis suppression through the ATF3-NFkappaB complex in human prostate cancer. 21459729_demonstrated a regulatory role for KAI1 in sphingosine kinase activation, which leads to decreased invasive ability in disease progression of human pancreatic cancer 21521534_decreased levels of CD82 protein were strikingly associated with the tumor status and the distant metastasis. 21685244_Study demonstrated that the abnormal lower CD82 expression in ESCs induced by TCDD and estrogen may be an important molecular basis of endometriosis pathogenesis through enhancing the CCL2 secretion and CCR2 expression and the invasion of ESCs. 21691075_Metastasis suppressor KAI1/CD82 attenuates the matrix adhesion of human prostate cancer cells by suppressing fibronectin expression and beta1 integrin activation. 21875585_Dissecting the diverse functions of the metastasis suppressor CD82/KAI1. 21961244_The pathological stage of penile carcinoma, but not lymph node metastasis, was positively correlated with the expression of CD82. 21965773_This study investigated the expression of TS and DPD in cervical lymph node metastases and its relationship with primary oral squamous cell carcinoma, as well as the interaction between these enzymes and Kangai 1(KAI1/CD82). 22123080_analysis of the N-Glycosylation pattern of recombinant human CD82 (KAI1), a tumor-associated membrane protein 22152691_Angiogenesis and the expressions of CD82 and HIF-1alpha are related to differentiation, lymph node metastasis and clinical staging in non-small cell lung cancer. 22320990_Germ line mutations in KISS1 and KAI1 are a less frequent event in head and neck cancer patients. 22320993_KAI1 and KISS1 mRNA expression was markedly reduced in tissues of breast cancer compared to adjacent normal tissue. 22390300_These novel observations may indicate that KAI1 exerts profound metastasis-suppressor activity in the tumor malignancy process via inhibition of CDCP1-mediated Src activation, followed by VHL-induced HIF-1alpha degradation and decreased VEGF expression. 22393164_CD82 expression affects endometrial receptivity of the uterine epithelial cells in vitro 22670173_Cyclosporin A promotes trophoblasts invasiveness by stimulating the secretion of CXCL12, and also limits the invasiveness of trophoblasts by indirectly up-regulating the expression CD82. 22679510_Findings suggest that CD82 is an important negative regulator at maternal-fetal interface during early pregnancy, inhibiting human trophoblast invasion and migration. 22681921_expression of MVD, LVD, Kiss-1 and CEA mRNA is related to the prognosis of NSCLC 22718295_Results suggest that immunohistochemical analysis of CD82 (KAI1) and epithelial-specific antigen (ESA) to distinguish chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (ChRCC) from renal oncocytoma (RO). 23055153_Overexpression of CD82 in CD34+/CD38- cells are associated with acute myelogenous leukemia. 23076981_CD82 inhibits canonical Wnt signalling by controlling the cellular distribution of beta-catenin in carcinoma cells. 23102249_The low expression of CD82/KAI1 and E-cadherin was closely related to the invasion, progression and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. 23251627_KAI1/CD82-induced phenotypes likely resulted from the suppression of multiple signaling pathways. 23349235_role in mutual stimulation of chemotactic migration between trophoblast and endometrial stromal cells 23553196_Positive expression of KAI1 protein was found in ovarian tissue in 72.2% cases in BRCA1 mutation carriers and in 72.2 % in the control group. 23617728_High expression of COX-2 and low expression of KAI-1/CD82 are associated with increased tumor invasiveness in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 23696923_KAI1/CD82 and cyclinD1 may serve as markers for determination of invasiveness, metastasis and prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 23704882_A specific association between alpha4beta1 and CD81, CD82 and CD151 was demonstrated and antibodies to CD81 and CD82 augmented adhesion of proerythroblasts to Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1. 23797738_our data suggest that the CD82/STAT5/IL-10 signaling pathway is involved in the survival of CD34(+)/CD38(-)acute myelogenous leukemia cells 23873015_No statistically significant association was observed in KAI1 exon 9. 23873025_CD82/KAI expression prevents IL-8-mediated endothelial gap formation in late-stage melanomas. 23897813_an important new insight into the modulatory role of CD82 in endocytic trafficking of EGF receptor. 24130172_KAI1 overexpression increases ING4 expression.Decreased KAI1 expression correlated with a worse melanoma patient survival.Increased expression of KAI1 reduces melanoma cell migration. 24553302_clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients with CD82 positive expression show poor prognosis 24613834_Taken together, these data suggest that anti-miR-197 suppresses HCC migration and invasion by targeting CD82. 24623721_CD82 overexpression increases the molecular density of alpha4 within membrane clusters, thereby increasing cellular adhesion. 24758564_Low CD82 expression is associated with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 24901051_this study reveals that DeltaNp63alpha upregulates CD82 to inhibit cell invasion, and suggests that GSK3beta can regulate cell invasion by modulating the DeltaNp63alpha-CD82 axis. 25071074_Expression level of KAI1 was downregulated, while the expression level of VEGF was upregulated in the tissues or serum of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Combined detection of KAI1 and VEGF form a reliable panel of diagnostic markers for HCC. 25119390_Hypermethylation of the CD82 promoter may be an event leading to the development of hepatoma and is likely to be involved in tumor progression. 25199507_Serum-free media and hypoxia protected the MiaPaCa-2 cells from a KAI1-induced apoptosis and proliferation inhibition via autophagy induction. 25435431_KAI1-splice does not only counteract the tumor-suppressive actions of KAI1, but - beyond that - promotes alphavbeta3-mediated biological functions in favor of tumor progression and metastasis. 25652145_These results suggested that microRNA-362-3p or CD82 can be exploited as a new potential target for control of gastric cancers in the future. 25688501_KAI-1, might be important biological marker involved in the carcinogenesis, metastasis, and invasion of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 25912735_CD82 down-regulation could be a critical step involved in the EGFR over-expression and the stronger tumorigenic activity triggered by EGFR mutations 25955299_blockade of CD82 in leukemia cells lowered EZH2 expression via activation of p38 MAPK signaling. 26132195_CD82 enhanced the expression of miR-203 and directly downregulated FZD2 expression, suppressing cancer metastasis/cell migration by inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway. 26199094_KAI1 was able to suppress melanoma angiogenesis by downregulating IL-6 and VEGF expression. 26231404_High KAI1 expression is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer. 26246476_Loss of both KAI1 and p27 defines a subgroup of primary melanoma patients with poor prognosis. 26260387_CD82 regulated BCL2L12 expression via STAT5A and AKT signaling and stimulated proliferation and engrafting of leukemia cells. 26335499_Ubiquitously expressed CD82 restrains cell migration and cell invasion by modulating both cell-matrix and cell-cell adhesiveness and confining outside-in pro-motility signaling. 26408312_The expression of KAI1/CD82, CD44, MMP7 and beta-catenin is related to tumor metastasis and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. 26592446_a mechanism where the membrane organization of CD82, through specific posttranslational modifications, regulates N-cadherin clustering and membrane density, which impacts the in vivo trafficking of AML cells. 26681053_Survivin, Bcl-2, and KAI1 are metastasis-related factors in cervical cancer. Overexpression of survivin and Bcl-2, and low expression of KAI1 promotes cervical cancer progress and metastasis. 26918694_KAI1 and KISS1 are implicated in the pathogenesis and maintenance of endometriosis. 27041584_These findings uncovered a hitherto unappreciated function of CD82 in severing the linkage between U2AF2-mediated CD44 alternative splicing and cancer aggressiveness, with potential prognostic and therapeutic implications in melanoma 27082851_KAI1-induced decreases in VEGFC expression are mediated via Src/STAT3 signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer cells. 27103437_Our present work therefore suggests that CD82 on EC is a potential target for anti-angiogenic therapy in VEGFR2-dependent tumor angiogenesis. 27349208_The simultaneous overexpression of p12CDK2-AP1 and CD82 significantly suppressed the in vivo tumor growth. 27417454_these data propose a mechanism where CD82 membrane organization regulates sustained PKCalpha signaling that results in an aggressive leukemia phenotype. These observations suggest that the CD82 scaffold may be a potential therapeutic target for attenuating aberrant signal transduction in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 27509988_Lack of expression of the KAI1 might indicate a more aggressive form of breast cancer. 27641304_CD82 function may be important for muscle stem cell function in muscular disorders. 27764516_that a loss of KAI1/CD82 and an increase in PDGFR expression in gliomas relate to a progressive tumor growth 27793161_KAI1 underexpression is associated with gastric cancer. 27813113_Methylation of CpG islands within the KAI1 promoter region was observed in the low KAI1-expressing prostate cancer cells. 27926483_the results suggest that CD82 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells adhered to the fibronectin matrix by repressing adhesion signaling through lateral interactions with the associated alpha3beta1 and alpha5beta1 integrins, leading to reduced cell migration and invasive capacities. 28030805_CD82 is a component of the promiscuous TIMP-1 interacting protein complex on cell surface of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. CD82 directly binds to TIMP-1 N-terminal region through its large extracellular loop and co-localizes with TIMP-1. 28252644_Overexpression of LAMC2 and knockdown of CD82 markedly promoted GC cell invasion and activated EGFR/ERK1/2-MMP7 signaling via upregulation of the expression of phosphorylated (p)-EGFR, p-ERK1/2 and MMP7. 28260006_The overexpression of KAI1/CD82 inhibited the proliferation and invasion of OSCC-15 cells. 28368419_a sub-population of DeltaNp63 and CD82-positive cells, whose disruption significantly perturbs the development of prostate metastatic tumor growth. 28534512_Authors showed that miR-K6-5p directly targeted the coding sequence of CD82 molecule (CD82), a metastasis suppressor. 29187211_The positive expression rates of KAI1 and nm23 were significantly lower in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma than normal laryngeal mucosa. 29710538_The inhibition of miR-338-5p suppressed growth and metastasis of A375 cells. CD82 mRNA was identified as a direct target mRNA of miR-338-5p. 29760437_CD82-RUNX1-Rab5/22 axis may be a previously unrecognized virulence mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis. 29936782_Low CD82 expression is associated with Biochemical Failure in Prostate cancer. 30005669_liprin-alpha1 as a novel regulator of CD82 30189244_The authors demonstrate a mechanism of CD82 suppression of the invasive and metastatic potentials of epithelial cancer cells. 30280774_Results found that low expression of CD82/KAI1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) was significantly associated with the pathological stage, distant metastasis and poor prognosis of ESCC patients. CD82/KAI1 may inhibit the malignant progression of ESCC by interacting with TGF-beta1. 30306427_Alternative splicing is an important mechanism underlying KAI1 loss of function in breast cancer, and it is associated with bad prognosis (advanced cancer stage). 30604894_Low CD82 expression is associated with breast cancer. 30862962_CD82 accelerated beta-catenin nuclear location and then stimulated the expression of downstream molecules of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway 30948327_KAI1 reversed EMT-related marker expression and inhibited migration and invasion of PC cells. 31010852_these data demonstrate that CD82 organizes the proper assembly of Dectin-1 signaling machinery in response to Candida albicans 31215741_MicroRNA-362-3p maintains EMT by regulating CD82. 31483122_A variant on CD82 gene (rs2303861 polymorphism) may have a role in the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease 31759355_Down Regulation of KAI1 is associated with Breast Cancer. 32203165_Tetraspanin CD82 drives acute myeloid leukemia chemoresistance by modulating protein kinase C alpha and beta1 integrin activation. 32769329_Diagnostic utility of amylase alpha-1A, MOC 31, and CD 82 in renal oncocytoma versus chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. 32986351_Investigations of a Possible Role of SNPs in KAI1 Gene on Its Down-Regulation in Breast Cancer. 33204367_CD82 Suppresses ADAM17-Dependent E-Cadherin Cleavage and Cell Migration in Prostate Cancer. 33298014_Gene expression analysis of human prostate cell lines with and without tumor metastasis suppressor CD82. 33605572_The Role of CK7, S100A1, and CD82 (KAI1) Expression in the Differential Diagnosis of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Oncocytoma. 33655331_Effects of KAI gene expression on ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. 33862453_Small extracellular ring domain is necessary for CD82/KAI1'anti-metastasis function. 33953224_CD82 is a marker to isolate beta cell precursors from human iPS cells and plays a role for the maturation of beta cells. 34207462_Mechanical Control of Cell Migration by the Metastasis Suppressor Tetraspanin CD82/KAI1. 34280124_A positive COX-2/IL-1beta loop promotes decidualization by upregulating CD82. 34445169_CD82 and Gangliosides Tune CD81 Membrane Behavior. 35728771_Proteomic profiling of plasma exosomes reveals CD82 involvement in the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35942551_Lower expression of KAI1 as a biomarker of poor survival prognosis of melanoma combined with colorectal cancer metastasis. |
ENSMUSG00000027215 |
Cd82 |
630.151880 |
3.2733788395 |
1.710781 |
0.124753187 |
181.602445 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000002165458482971855236268486767364932798624196328454996752411069186171931977053988031646354491396000391489852152093753545614163158461451530456542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000375142807613434080593969329679819791346584306438175806815933728734230006687647973254434928230444280935693135425879063404863700270652770996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
944.8368390 |
65.6042392 |
290.1731065 |
15.3209621 |
| ENSG00000085185 |
63035 |
BCORL1 |
protein_coding |
Q5H9F3 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional corepressor. May specifically inhibit gene expression when recruited to promoter regions by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins such as BCL6. This repression may be mediated at least in part by histone deacetylase activities which can associate with this corepressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17379597}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Autism spectrum disorder;Chromatin regulator;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional corepressor that is found tethered to promoter regions by DNA-binding proteins. The encoded protein can interact with several different class II histone deacetylases to repress transcription. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:63035; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122] |
17697391_Dysregulated BCoR-L1 expression is associated with breast cancer 21989985_BCORL1 by genetic criteria is a novel candidate tumor suppressor gene, joining the growing list of genes recurrently mutated in acute myelogenous leukemia. 23793880_genetic association study in population in Italy: Data suggest BCORL1 mutations/single nucleotide polymorphisms are not associated with leukemic transformation of chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) into acute myeloid leukemia (AML). [LETTER] 24047651_Data indicate that sequencing of BCOR and related BCORL1 genes in a cohort of 354 myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) patients identified 4.2% and 0.8% of mutations respectively. 25596268_study concluded that in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia, BCOR and BCORL1 mutations rarely occur 26648304_BCORL1 knockdown up-regulates E-cadherin expression and subsequently inhibits cell migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. 26879601_Studied the clinical significance of BCORL1 and its role in the metastasis of HCC. 29605720_Either endogenous BCORL1 silencing or ectopic BCORL1(Q1076H) expression mimicked the effects of a CRISPR/Cas9-edited BCORL1(Q1076H) locus. 30941876_We report five individuals from three pedigrees with phenotypes including intellectual disability, behavioral difficulties, and dysmorphic features who were found via whole exome sequencing to have variants in BCORL1. In silico analysis of these variants strongly suggests pathogenicity. We propose that hemizygous pathogenic variants in BCORL1 underlie a newly identified X-linked epigenetic syndrome. 32376790_Human X chromosome exome sequencing identifies BCORL1 as contributor to spermatogenesis. 32594217_patients with acquired Acquired pure red cell aplasia may have clonal gene mutations. The patients with BCOR and BCORL1 mutations may suggest a better response to IST compared with those with other mutations. 32776737_Age-Related Co-Expression of BCOR and BCORL1 mRNA in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 33283733_[Clinical Characteristics and Prognostic Significance of BCOR/BCORL1 Gene Mutation in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes]. 33810051_Shukla-Vernon Syndrome: A Second Family with a Novel Variant in the BCORL1 Gene. 34302054_Clinicopathological and genomic characterization of BCORL1-driven high-grade endometrial stromal sarcomas. 34400773_Major brain malformations: corpus callosum dysgenesis, agenesis of septum pellucidum and polymicrogyria in patients with BCORL1-related disorders. 35015684_BCOR and BCORL1 Mutations Drive Epigenetic Reprogramming and Oncogenic Signaling by Unlinking PRC1.1 from Target Genes. 35499168_Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas With BCOR Internal Tandem Duplication and Variant BCOR/BCORL1 Rearrangements Resemble High-grade Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas With Recurrent CDK4 Pathway Alterations and MDM2 Amplifications. |
ENSMUSG00000036959 |
Bcorl1 |
30.086565 |
0.4917752718 |
-1.023929 |
0.304290782 |
11.430242 |
0.00072258280558527084209974322703828875091858208179473876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001725501085655815718122862989503119024448096752166748046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.4353083 |
3.7707676 |
39.7694702 |
5.1245325 |
| ENSG00000085415 |
81929 |
SEH1L |
protein_coding |
Q96EE3 |
FUNCTION: Component of the Nup107-160 subcomplex of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The Nup107-160 subcomplex is required for the assembly of a functional NPC. The Nup107-160 subcomplex is also required for normal kinetochore microtubule attachment, mitotic progression and chromosome segregation. This subunit plays a role in recruitment of the Nup107-160 subcomplex to the kinetochore. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15146057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17363900}.; FUNCTION: As a component of the GATOR subcomplex GATOR2, functions within the amino acid-sensing branch of the TORC1 signaling pathway. Indirectly activates mTORC1 and the TORC1 signaling pathway through the inhibition of the GATOR1 subcomplex (PubMed:23723238). It is negatively regulated by the upstream amino acid sensors SESN2 and CASTOR1 (PubMed:25457612, PubMed:27487210). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23723238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25457612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27487210}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Centromere;Chromosome;Chromosome partition;Isopeptide bond;Kinetochore;Lysosome;Membrane;Mitosis;mRNA transport;Nuclear pore complex;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocation;Transport;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a nuclear pore complex, Nup107-160. This protein contains WD repeats and shares 34% amino acid identity with yeast Seh1 and 30% identity with yeast Sec13. All constituents of the Nup107-160 complex, including this protein, specifically localize to kinetochores in mitosis. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:81929; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; GATOR2 complex [GO:0061700]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; nuclear pore outer ring [GO:0031080]; Seh1-associated complex [GO:0035859]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore [GO:0051315]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to amino acid starvation [GO:0034198]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; mitotic metaphase plate congression [GO:0007080]; mRNA transport [GO:0051028]; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904262]; nuclear pore organization [GO:0006999]; nucleocytoplasmic transport [GO:0006913]; positive regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032008]; positive regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904263]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; protein-containing complex localization [GO:0031503] |
14517296_Sec13 stably interacts with Nup96 at the NPC during interphase and the shuttling of Sec13 between the nucleus and the cytoplasm may couple and regulate functions between these two compartments 21825076_The assembly of soluble Nup107-160 complexes into higher order structures occurs only at sites on the chromatin surface that are already covered with the nuclear envelope. 29618633_Analysis reveals a role for Seh1 at human centromeres, where it is required for efficient localisation of the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC). |
ENSMUSG00000079614 |
Seh1l |
312.462567 |
2.4153957934 |
1.272260 |
0.108849776 |
136.190057 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000018131757876586896499298787988886321767589782805371340470446377063654110050912717042731481242867630498949438333511352539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000002441831626445461672135743696385096809873053207047133532674134468506274950264230919755314985764016455505043268203735351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
442.3522851 |
29.9746396 |
184.4548780 |
9.6340628 |
| ENSG00000085433 |
22911 |
WDR47 |
protein_coding |
O94967 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22911; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; anterior commissure morphogenesis [GO:0021960]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; cerebral cortex radial glia-guided migration [GO:0021801]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; detection of hot stimulus involved in thermoception [GO:0120168]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; motor behavior [GO:0061744]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:0061351]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150] |
34432492_RUSC2 and WDR47 oppositely regulate kinesin-1-dependent distribution of ATG9A to the cell periphery. |
ENSMUSG00000040389 |
Wdr47 |
208.319408 |
2.1081053510 |
1.075947 |
0.149786435 |
51.087387 |
0.00000000000088344149417529409801645612528549863682551107624263408979459200054407119750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000005270653376728917231871764549430448574054985932946237880969420075416564941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
282.7607970 |
25.2688205 |
135.3111793 |
9.2449175 |
| ENSG00000085514 |
29992 |
PILRA |
protein_coding |
Q9UKJ1 |
FUNCTION: Paired receptors consist of highly related activating and inhibitory receptors and are widely involved in the regulation of the immune system. PILRA is thought to act as a cellular signaling inhibitory receptor by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatases like PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPN11/SHP-2 via their SH2 domains that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. Receptor for PIANP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21241660}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as an entry co-receptor for herpes simplex virus 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18358807}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Cell signaling pathways rely on a dynamic interaction between activating and inhibiting processes. SHP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of protein tyrosine residues is central to the regulation of several cell signaling pathways. Two types of inhibitory receptor superfamily members are immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)-bearing receptors and their non-ITIM-bearing, activating counterparts. Control of cell signaling via SHP-1 is thought to occur through a balance between PILRalpha-mediated inhibition and PILRbeta-mediated activation. These paired immunoglobulin-like receptor genes are located in a tandem head-to-tail orientation on chromosome 7. This particular gene encodes the ITIM-bearing member of the receptor pair, which functions in the inhibitory role. Alternative splicing has been observed at this locus and three variants, each encoding a distinct isoform, are described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:29992; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; MHC class I protein binding [GO:0042288]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
18097101_PILRalpha protein was successfully crystallized at 293 K using the sitting-drop vapour-diffusion method and the crystals diffracted to 1.3 A resolution. 18358807_The results demonstrate that cellular receptors for both gB and gD are required for HSV-1 infection and that PILRalpha plays an important role in HSV-1 infection as a coreceptor that associates with gB. 19244335_viral entry via PILRalpha appears to be conserved but that there is a PILRalpha preference among alphaherpesviruses 19457990_Insertional mutations of gB reduced cell fusion activity when PILRalpha was overexpressed much more than nectin-1. 21241660_These results suggest that PANP is involved in immune regulation as a ligand of the PILRalpha. 22396535_Data show that PILRalpha/ligand interactions require conserved PILRalpha arginine (Arg)-133 (mouse) and Arg-126 (human). 22695228_The authors show that the human ocular and highly neurovirulent HSV-1 strain McKrae enters substantially more efficiently into cells via the gB-specific human paired immunoglobulin-like type-2 receptor-alpha (hPILR-alpha). 23302878_The amino terminus of herpes simplex virus 1 gK is functionally and physically associated with the gB-PILRalpha protein complex and regulates membrane fusion of the viral envelope with cellular membranes during virus entry. 24253495_These results contribute our knowledge of the biological functions of HBVDNAPTP1 and provide novel data to aid in the further analysis of the regulatory mechanism of this protein. 24843130_We demonstrated that three residues (Y2, R95, and W108) presented on the surface of PILRalpha form the sialic acid binding site equivalent to those in siglecs but are arranged in a unique linear mode. 24889612_PILRalpha exhibits large conformational change to recognize simultaneously both the sTn O-glycan and the compact peptide structure constrained by proline residues 27029068_The interaction of NK cells with PILRalpha expressing targets lead to elevated IFNgamma secretion and cytotoxicity. In conclusion, PILRalpha is a novel NK activating ligand which binds and activates an unknown NK receptor expressed on a unique NK cell subset. 29046357_Data suggest that, although PILRA exhibits essentially the same recognition of different glycopeptides, slight modifications of linker sugar cause significant changes in a wide area of the binding interface, resulting in a reduction of binding affinity; analogs/fragments of gpb were used in these studies. (PILRA = paired immunoglobin like type 2 receptor alpha; gpb = envelope glycoprotein B, Herpes simplex virus type 1) 29181857_Exome-wide burden analysis revealed significant burden of variants in PILRA in patients with late-onset Alzheimer's disease 29202958_Transcriptome wide association study results identified two novel genes as statistically significantly associated with nonobstructive azoospermia susceptibility: PILRA and ZNF676. 30388101_We propose that PILRA G78R protects individuals from Alzheimer's disease risk via reduced inhibitory signaling in microglia and reduced microglial infection during HSV-1 recurrence. 31297637_Herpes simplex virus type 1 IgG are increased in Alzheimer's disease patients with the protective R78 PILRA genotype. 34602489_Inhibitory Fcgamma Receptor and Paired Immunoglobulin Type 2 Receptor Alpha Genotypes in Alzheimer's Disease. 35617401_The CD8alpha-PILRalpha interaction maintains CD8(+) T cell quiescence. 35918447_PILRA polymorphism modifies the effect of APOE4 and GM17 on Alzheimer's disease risk. |
|
|
21.963249 |
6.9352311145 |
2.793944 |
0.475541102 |
37.675499 |
0.00000000083547374044029833845785167385105708659498446877478272654116153717041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000004014190237271745759077115124104084831202499117352999746799468994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.5483646 |
11.2805023 |
5.9791945 |
1.4787182 |
| ENSG00000085733 |
2017 |
CTTN |
protein_coding |
Q14247 |
FUNCTION: Contributes to the organization of the actin cytoskeleton and cell shape (PubMed:21296879). Plays a role in the formation of lamellipodia and in cell migration. Plays a role in the regulation of neuron morphology, axon growth and formation of neuronal growth cones (By similarity). Through its interaction with CTTNBP2, involved in the regulation of neuronal spine density (By similarity). Plays a role in focal adhesion assembly and turnover (By similarity). In complex with ABL1 and MYLK regulates cortical actin-based cytoskeletal rearrangement critical to sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)-mediated endothelial cell (EC) barrier enhancement (PubMed:20861316). Plays a role in intracellular protein transport and endocytosis, and in modulating the levels of potassium channels present at the cell membrane (PubMed:17959782). Plays a role in receptor-mediated endocytosis via clathrin-coated pits (By similarity). Required for stabilization of KCNH1 channels at the cell membrane (PubMed:23144454). Plays a role in the invasiveness of cancer cells, and the formation of metastases (PubMed:16636290). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60598, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q66HL2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16636290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17959782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21296879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23144454}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coated pit;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endocytosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;Synapse;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is overexpressed in breast cancer and squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. The encoded protein is localized in the cytoplasm and in areas of the cell-substratum contacts. This gene has two roles: (1) regulating the interactions between components of adherens-type junctions and (2) organizing the cytoskeleton and cell adhesion structures of epithelia and carcinoma cells. During apoptosis, the encoded protein is degraded in a caspase-dependent manner. The aberrant regulation of this gene contributes to tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Three splice variants that encode different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:2017; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cortical cytoskeleton [GO:0030863]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; mitotic spindle midzone [GO:1990023]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; podosome [GO:0002102]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; site of polarized growth [GO:0030427]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; profilin binding [GO:0005522]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; dendritic spine maintenance [GO:0097062]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; focal adhesion assembly [GO:0048041]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; lamellipodium organization [GO:0097581]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045987]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833]; regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:1903146]; regulation of axon extension [GO:0030516]; substrate-dependent cell migration, cell extension [GO:0006930] |
11689006_substrate for caspase cleavage during apoptosis 11988077_Primary arrest of circulating platelets on collagen involves phosphorylation of Syk, cortactin and focal adhesion kinase 12060669_The Src-cortactin pathway is required for clustering of E-selectin and ICAM-1 in endothelial cells 12453877_Cdc42/Rac1-dependent activation of PAK may trigger early platelet shape change, at least in part through the regulation of cortactin binding to PAK. 12672817_cortactin links receptor endocytosis to actin polymerization by binding both CD2AP and the Arp2/3 complex, which may facilitate the trafficking of internalized growth factor receptors 12952985_alternative splicing of the F-actin binding domain of cortactin is a new mechanism by which cortactin influences cell migration 15056655_cortactin and EC myosin light chain kinase have roles in mediating lung vascular barrier augmentation evoked by S1P 15064355_RhoGAP functionally interacts with cortactin and represents a novel determinant in the regulation of cell dynamics. 15123640_Data suggest that hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with Rac1-protein kinase N gamma plays a pivotal role in phospholipase C gamma1-regulated calcium signaling and cortactin-cytoskeleton function required for keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion and differentiation. 15159385_HAX-1 binds bile salt export protein (BSEP), cortactin, MDR1, and MDR2. HAX-1 and cortactin regulate BSEP abundance in the apical membrane of cells. 15169891_Erk phosphorylation liberates the SH3 domain of cortactin from intramolecular interactions with proline-rich regions, causing it to synergize with WASP and N-WASP in activating the Arp2/3 complex 15242766_Suppression of cortactin expression with a cortactin antisense oligo significantly impaired S1P-induced capillary formation, migration of endothelial cells, and actin assembly at the cell periphery. 15263018_a major role for a Crk-cortactin complex in actin polymerization downstream of tyrosine kinase signaling 15464244_Overexpression of cortactin may play a role in the metastasis of HCC by influencing cell motility, and cortactin could be a sensitive marker for HCC with intrahepatic metastasis. 15579908_cortactin can restrict N-WASP localization around EGF-bead-induced protrusions 15618548_The p47phox:actin interaction, through cortactin, plays an important role in Ang II-mediated site-directed assembly of functionally active NAD(P)H oxidase, ROS generation, and activation of redox-sensitive p38MAP kinase and Akt, but not ERK1/2. 15842855_EMS1 amplification parallels with the progress of oral carcinogenesis. 16051170_Cortactin promotes cell motility by enhancing lamellipodial persistence, at least in part through regulation of Arp2/3 complex. 16076899_Cortactin recruitment is dependent on the activation of a phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Rac1-GTPase signalling pathway, which is required for actin polymerization and internalization of N. meningitidis. 16261345_Our results demonstrated the dominant expression of p85 form of cortactin in colorectal cancer for the first time. 16280034_cortactin is the crucial gene within the 11q13 amplicon that mediates the invasive potential of human carcinomas 16385081_Tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin by Src family kinases regulates neutrophil transmigration. 16416022_We describe that S1P-stimulated cortactin translocation to the cell periphery to form lamellipodia is specifically mediated by the endothelial S1P1 G-protein coupled receptor, and is regulated by G(i)-mediated Akt-dependent S1P1 receptor phosphorylation. 16442522_Co-localization of cortactin and phosphotyrosine identifies invadopodial complexes closely associated with the plasma membrane at active sites of focal degradation of the extracellular matrix in breast cancer cells. 16489553_Our findings suggest that cortactin plays a role in Listeria internalization, but not in the formation of actin clouds and tails, or in bacteria intracellular motility. 16527272_Increased levels of cortactin, as found in human carcinomas, promote cell migration and invasion by reducing cell spreading and intercellular adhesive strength. 16611226_Cortactin is a requirement for pedestal formation and suggest a novel function for the predicted alpha-helical region of cortactin in actin assembly induced by EPEC and EHEC. 16636290_Results suggest that the AMAP1/cortactin complex, which is not detected in normal mammary epithelial cells, is an excellent drug target for cancer therapeutics. 16652145_functional importance of cortactin to CD44s-promoted metastasis was demonstrated by selective suppression of cortactin in CD44-expressing MCF7F-B5 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells using RNAi 16815198_EMS1 amplification is uncommon and appears to be late event in the development of ethmoid sinus adenocarcinoma. 16825425_The identification of 17 new sites of phosphorylation in cortactin is reported. 16825658_Results suggest that ATP-mediated barrier protection is associated with cytoskeletal activation and is dependent on both Rac activation and cortactin. 16905744_Plays important role in CXCR4 signaling and trafficking as well as in receptor-mediated cell migration. 16937268_Controls osteoclastic bone resorption by regulating actin organization. 17005439_data suggested potential roles in oral carcinogenesis and that TAOS1 might be involved earlier than EMS1. Both genes might be candidate biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis in OSCC 17056576_Tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin dynamically links ICAM-1 to the actin cytoskeleton, enabling ICAM-1 to form clusters and facilitate leukocyte transmigration. 17178864_CTTN is an oncogene in the 11q13 amplicon and exerts functions on tumor metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 17292556_cortactin-mediated signaling pathways, with emphasis on its contribution to tumor progression and metastasis formation.[REVIEW] 17449030_These results indicate that cortactin is involved in keratinocyte migration promoted by both KGF and FGF10. 17451412_Cortactin binding to EHEC virulence factors, Tir and EspF(u), is dependent upon tyrosine phosphorylation during infection. 17483334_A major role of cortactin in invadopodia is to regulate the secretion of MMPs and point to a novel mechanism coupling dynamic actin assembly to the secretory machinery, producing enhanced ECM degradation and invasiveness. 17510372_Higher intensity of cortactin and fascin-1 staining correlated directly with more-advanced cancer stages (TNM) and inversely with survival rates. 17562703_cortactin and actin have roles in hyperoxia-induced activation of NADPH oxidase and ROS generation in human lung endothelial cells 17576929_Cortactin and p120 are shown to directly interact with each other via the cortactin N-terminal region 17627624_Using a variety of approaches including siRNA, expression of dominant negative derivatives and pharmacological inhibitors, Results demonstrate the crucial role of cortactin in the activation of the Arp2/3 complex during InlA-mediated entry. 17643370_in addition to its role in microtubule-dependent cell motility, HDAC6 influences actin-dependent cell motility by altering the acetylation status of cortactin, which, in turn, changes the F-actin binding activity of cortactin 17702746_CD44 is an important regulator of HGF/c-Met-mediated in vitro and in vivo barrier enhancement, a process with essential involvement of Tiam1, Rac1, dynamin 2, and cortactin. 17959782_cortactin-mediated actin remodeling in excitable cells is not only important for cell structure, but may directly impact membrane excitability 18039661_tyrosine protein phosphorylation regulates large conductance voltage- and calcium-activated potassium channels via cortactin 18334127_EMS1 protein expression is related to the carcinogenesis, lymph node metastasis and clinical stage of gastric carcinoma. 18342393_potential mechanisms by which cortactin may link vesicular trafficking and dynamic branched actin assembly to regulate protease secretion for invadopodia-associatedextracellular matrix degradation 18387954_PTP1B regulates cortactin tyrosine phosphorylation by targeting Tyr446 18403644_These results suggest that cortactin hyperphosphorylation suppresses cell migration possibly through the inhibition of membrane localization and tyrosine phosphorylation of p130Cas. 18406052_many studies have documented a role for cortactin in promoting cell motility and invasion, including a critical role in invadopodia, actin rich-subcellular protrusions associated with degradation of the extracellular matrix by cancer cells. 18521921_CTTN gene variation may contribute to severe asthma 18521921_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18607838_Overexpression of cortactin is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas 18678675_These results imply that cortactin is recruited to the site of EHEC adhesion in vitro and ex vivo by different mechanisms and suggest that cortactin might have a role during EHEC infection of mucosal surfaces. 18776588_Cortactin, fascin-1 and EGFR have roles in progression of ovarian carcinomas 18931703_Overexpression of cortactin is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 18991334_The strong relationship of CTTN amplification/overexpression with prognosis and disease outcome reinforces its role as a driver of 11q13 amplification in HNSCC. 19207554_Higher cortactin scores positively related to tumor differentiation of esophageal SqCC. Significantly worse prognosis in patients with high scores of cortactin, poor differentiation, T4 stage, positive for lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis. 19219613_Higher expression of cortactin and survivin significantly correlated with advanced clinicopathological stage in renal cell carcinomas. 19242064_Higher expression of survivin and cortactin correlates significantly with tumor stages and shorter survival time. Survivin and cortactin may be good biomarkers of aggressiveness of colorectal adenocarcinomas. 19457864_SFK and cortactin constitute an important signaling pathway that functionally links E-cadherin adhesion and the actin cytoskeleton 19589785_HER2 carboxyl-terminal fragments regulate cell migration and cortactin phosphorylation 19666237_Results confirm the importance of alterations in CCND1 and CTTN with respect to areca-associated oral squamous cell carcinoma, and demonstrates that there is an early occurrence of amplification of these genes in the risk population. 19684620_This study not only reveals a role of CRT in motility promotion and anoikis resistance in ESCC cells, but also identifies CRT as an upstream regulator in the CRT-STAT3-CTTN-Akt pathway. 19885549_localization of cortactin in cancer cells and interaction between ZO-1 and cortactin are crucial for cancer progression. 19885550_TocP markedly exerted anti-invasive activities through alteration of cortactin distribution 19898426_Our data support a potential role of aberrant cortactin expression in melanoma tumor progression 19947248_The quantity and percentage of EMS1 protein expression in laryngeal carcinoma tissues was significantly higher than those in para carcinoma and in normal laryngeal mucosa tissues. 20053363_Data provide insights into the molecular basis for vascular barrier-regulatory cytoskeletal responses and quantified the critical interactions between non-muscle MLCK isoenzymes and cortactin during vascular barrier regulation. 20069395_In 70 primary oral squamous cell carcinomas and 10 normal oral mucosal specimens, cortactin expression was evaluated by immunological analyses, and the correlations of the overexpression of cortactin with clinicopathologic factors were evaluated. 20213079_CTTN is consistently co-amplified with CCND1 and expressed at higher levels in breast cancers harbouring 11q13 amplification, suggesting that CTTN may also constitute one of the drivers of this amplicon. 20363754_Protein kinase D controls actin polymerization and cell motility through phosphorylation of cortactin 20805359_novel mechanism for regulation of proliferation in 11q13-amplified HNSCC cells, in which overexpressed cortactin acts via RhoA to decrease expression of Cip/Kip CDKIs, and highlight Skp2 as a downstream effector for RhoA in this process 21079800_Data show that concurrent phosphorylation of cortactin by ERK1/2 and tyrosine kinases enables cells with the ability to regulate actin dynamics. 21257711_Our findings suggest a novel mechanism by which an EGFR-Src-Arg-cortactin pathway mediates functional maturation of invadopodia and breast cancer cell invasion 21258212_Cortactin overexpression has been found in many cancer types, including melanomas, ovarian, gastric, hepatic, colorectal and esophageal. (Review) 21373848_TPM4, PDIA and SRC8 were also localized to the trophoblast cells, further highlighting the importance of these cytoskeletal remodelling proteins in early pregnancy 21395182_EMS1 expression was positively related to DcR3, which might play an important role in the carcinogenesis and development of laryngeal carcinoma. 21418910_Endocytosis in colon cancer cells is dependent on an intact expression of CTTN. 21419472_cases of squamous cell laryngeal carcinoma with absent to weak expression of CTTN in the deep invasive front showed good prognosis parameters, and a second group with moderate to strong expression of CTTN were associated with an unfavorable prognosis 21474972_Actinin-1 and cortactin showed matrix-contact-side localization in adenocarcinoma cells. 21503569_Endogenous mature miR-182 expression may have an important role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer through its interference with the target gene CTTN by epigenetic modification. 21562571_These data suggest that the acetylation status of CTTN modulated by the NACC1-HDAC6 deacetylation system induces acceleration of melanoma cell migration activity via an actin-dependent cellular process 21646305_Cortactin and focal adhesion kinase have roles in cancer risk in patients with laryngeal premalignancy 21669400_Cortactin interacts with and stimulates the kinase activity of focal adhesion kinase upon Helicobacter pylori infection. 21856159_Both motility and lamellipodial defects of cortactin-KD cells were fully rescued by plating on increasing concentrations of exogenous extracellular matrix (ECM). Cortactin-KD cell speed defects were not rescued on ECM produced by cortactin-KD cells. 21858086_Data suggest that GEP100-Arf6-AMAP1-cortactin pathway, activated by VEGFR2, appears to be common in angiogenesis and cancer invasion and metastasis, and provides their new therapeutic targets. 22007770_We demonstrated cortactin and MT1-MMP expression in ameloblastoma. 22050448_Knockdown of cortactin or silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 expression inhibited both migration and invasion of DU145 prostate cancer cells. 22078467_The cortactin acts as a bridging molecule between actin filaments and focal adhesions. 22089141_HDAC6 promotes the migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting the cytoskeletal protein cortactin. 22105349_Cortactin phosphorylation, local pH increase, and cofilin activation regulates the dynamic cycles of invadopodium protrusion and retraction and is essential for cell invasion in 3D. 22117553_These results suggest that the actin binding protein cortactin is required for actin stress fiber formation in muscle cells and that this process is absolutely required for translocation of GLUT4-containing vesicles to the plasma membrane. 22219181_MLCK is essential for the translocation and association of cortactin and p47phox. 22282019_a complex containing cortactin and RCC2/TD60 complex that may play a functional role in cells undergoing mitosis. 22297550_Over-expression of cortactin, contained in the 11q13 amplicon, is involved in osteosarcoma carcinogenesis. 22377015_Strong immunoexpression of cortactin is a predicting factor for increased cancer risk in oral premalignant lesions. 22378044_Dephosphorylation of FAK upon inhibition of beta integrin resulted in dissociation of a FAK/cortactin protein complex. This, in turn, downregulated JNK signaling and induced cell rounding, leading to radiosensitization. 22768099_A cooperative interplay between FAK, Src and cortactin enables endocytosis of N. meningitidis into host cells. 22944623_cortactin seems to be a satisfactory marker to predict tumour progression and survival in cases of prostate cancer. 22991200_Regulation of late endosomal/lysosomal maturation and trafficking by cortactin affects Golgi morphology. 23030700_overexpression of cortactin and fascin-1 implies poorer tumor differentiation, advanced AJCC stage, and shorter survival rate in pancreatic and ampulla of Vater adenocarcinomas 23144454_Cortactin controls surface expression of the voltage-gated potassium channel K(V)10.1. 23161539_results suggest that SKAP2 negatively regulates cell migration and tumor invasion in fibroblasts and glioblastoma cells by suppressing actin assembly induced by the WAVE2-cortactin complex 23518204_Overexpression of cortactin is closely associated with liver embolus and metastasis. 23702379_Suggest that SIRT1 and cortactin may play a role in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer and may cooperate during tumor progression in NSCLC. 23991004_Data indicate that luteolin and quercetin attenuate the phosphorylation of cortactin and Src, disruption of invadopodia generation suppression of matrix metalloproteinase MMP9 secretion, and reduction in metastasis. 24120646_Results suggest that elevated shear stress induces MUC5AC hypersecretion via tyrosine-phosphorylated cortactin-associated actin polymerization in cultured human airway epithelial cells. 24265417_GIT1-cortactin association through GIT1-Spa homology domain is required for cortactin localization to the leading edge and is essential for endothelial cell directional migration and tumor angiogenesis. 24409670_Combining cortactin and CTTN mRNA detection with clinicopathologic features improved the predictive power. High expression of both cortactin and CTTN indicated poor survival time of 12 +/- 3.67 months and low expression indicated longer survival time 24414419_Data indicate the specific contribution of fascin and cortactin during invadopodium formation. 24465712_Data suggest that curcumin is an activator of non-receptor type 1 protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN1) and can reduce cell motility in colon cancer via dephosphorylation of pTyr(421)-cortactin (CTTN). 24469447_Cortactin has a role as a scaffold for Arp2/3 and WAVE2 at the epithelial zonula adherens 24532043_Cortactin, another player in the Lyn signaling pathway, is over-expressed and alternatively spliced in leukemic cells from patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 24549769_The present study demonstrated that bladder cancer cells with cortactin knockdown have a reduced capacity to extravasate into the lung from the circulation, due to the decreased invasive character of invadopodia. 24551190_Overexpression of cortactin (CTTN) was observed in 126/198 (63.6%) of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cases and was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis (P = 0.000), pathologic stage (P = 0.000) and poor survival (P |
ENSMUSG00000031078 |
Cttn |
93.183352 |
5.6885222955 |
2.508054 |
0.978965182 |
5.778364 |
0.01622463390843382341488521092287555802613496780395507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029693192373029541480944359932436782401055097579956054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
180.9842405 |
94.1485581 |
31.8117326 |
11.9057655 |
| ENSG00000085999 |
8438 |
RAD54L |
protein_coding |
Q92698 |
FUNCTION: Plays an essential role in homologous recombination (HR) which is a major pathway for repairing DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) gaps, and stalled or collapsed replication forks (PubMed:9774452, PubMed:24798879, PubMed:32457312, PubMed:11459989, PubMed:12205100, PubMed:27264870). Acts as a molecular motor during the homology search and guides RAD51 ssDNA along a donor dsDNA thereby changing the homology search from the diffusion-based mechanism to a motor-guided mechanism. Also plays an essential role in RAD51-mediated synaptic complex formation which consists of three strands encased in a protein filament formed once homology is recognized. Once DNA strand exchange occured, dissociates RAD51 from nucleoprotein filaments formed on dsDNA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P32863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11459989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12205100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24798879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27264870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32457312, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774452}. |
Acetylation;ATP-binding;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Helicase;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the DEAD-like helicase superfamily, and shares similarity with Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad54, a protein known to be involved in the homologous recombination and repair of DNA. This protein has been shown to play a role in homologous recombination related repair of DNA double-strand breaks. The binding of this protein to double-strand DNA induces a DNA topological change, which is thought to facilitate homologous DNA paring, and stimulate DNA recombination. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:8438; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity [GO:0140658]; ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity [GO:0036310]; DNA translocase activity [GO:0015616]; helicase activity [GO:0004386]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; chromosome organization [GO:0051276]; determination of adult lifespan [GO:0008340]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; double-strand break repair via synthesis-dependent strand annealing [GO:0045003]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; reciprocal meiotic recombination [GO:0007131]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
12614485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12614485_The RAD54L polymorphism (2290C/T) can be used as a genetic marker inside the consensus deletion region at 1p32 in human meningiomas. 15975611_Shortened telomeres in murine scid cells expressing mutant RAD54L coincide wirth reduction in recombination at telomeres. 16520463_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16540687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16862129_hRad54, a Swi2/Snf2 protein, binds HJ-like structures with high specificity and promotes their bidirectional branch migration in an ATPase-dependent manner 17054727_Some immortal cells use the alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) pathway to maintain their telomeres instead of telomerase. This is the first genetic evidence that Rad54 is dispensable for the ALT pathway. 17417655_RAD54 is recruited by RAD51-ssDNA filament to the chromatin of the intact chromosome and it remodels that chromatin to facilitate accessibility for strand exchange 17545145_analysis of human rad54 protein interactions with branched DNA molecules 17660833_Rad54 protein causes dissociation of joint molecules by ATP-dependent branch-migration and therefore plays an important role in double strand DNA break repair. 18203022_germline mutations in RAD51, RAD51AP1, RAD51L1, RAD51L3, RAD52 and RAD54L are unlikely to be causal of an inherited predisposition to CLL. 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18617519_Rad51 protein stimulates the branch migration activity of Rad54 protein.( 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19147782_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20813000_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24798879_Nap1 stimulates homologous recombination by RAD51 and RAD54 in higher-ordered chromatin containing histone H1. 25765654_support a model in which RAD54L and RAD54B counteract genome-destabilizing effects of direct binding of RAD51 to dsDNA in tumor cells 25965574_TAF12 and NFYC are transcription factors that regulate the epigenome, whereas RAD54L plays a central role in DNA repair 29295984_Data show that the RAD54 N-terminal domain (NTD) is responsible for initiation of branch migration (BM) through two coupled, but distinct steps; specific binding to Holliday junctions and RAD54 oligomerization. 32333827_Extended in vitro culture of primary human mesenchymal stem cells downregulates Brca1-related genes and impairs DNA double-strand break recognition. 33261027_E2F1 Promotes Progression of Bladder Cancer by Modulating RAD54L Involved in Homologous Recombination Repair. 34079088_Oct4 confers stemness and radioresistance to head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the homologous recombination factors PSMC3IP and RAD54L. 34169999_Association of MTHFR, MTRR and RAD54L Gene Variations with Meningioma and Correlation with Tumor's Histopathological Characteristics on Turkish Cohort. 36071250_Rad54L promotes bladder cancer progression by regulating cell cycle and cell senescence. |
ENSMUSG00000028702 |
Rad54l |
138.837122 |
0.4025063133 |
-1.312917 |
0.417403927 |
9.576335 |
0.00197101454404021792302104110206073528388515114784240722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004359031266112319003003250372785259969532489776611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
78.3366611 |
25.2164574 |
195.1265865 |
45.2494099 |
| ENSG00000086205 |
2346 |
FOLH1 |
protein_coding |
Q04609 |
FUNCTION: Has both folate hydrolase and N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) activity. Has a preference for tri-alpha-glutamate peptides. In the intestine, required for the uptake of folate. In the brain, modulates excitatory neurotransmission through the hydrolysis of the neuropeptide, N-aceylaspartylglutamate (NAAG), thereby releasing glutamate. Involved in prostate tumor progression.; FUNCTION: Also exhibits a dipeptidyl-peptidase IV type activity. In vitro, cleaves Gly-Pro-AMC. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Carboxypeptidase;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Dipeptidase;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Multifunctional enzyme;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the M28 peptidase family. The protein acts as a glutamate carboxypeptidase on different alternative substrates, including the nutrient folate and the neuropeptide N-acetyl-l-aspartyl-l-glutamate and is expressed in a number of tissues such as prostate, central and peripheral nervous system and kidney. A mutation in this gene may be associated with impaired intestinal absorption of dietary folates, resulting in low blood folate levels and consequent hyperhomocysteinemia. Expression of this protein in the brain may be involved in a number of pathological conditions associated with glutamate excitotoxicity. In the prostate the protein is up-regulated in cancerous cells and is used as an effective diagnostic and prognostic indicator of prostate cancer. This gene likely arose from a duplication event of a nearby chromosomal region. Alternative splicing gives rise to multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:2346; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Ac-Asp-Glu binding [GO:1904492]; carboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004180]; dipeptidase activity [GO:0016805]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metallocarboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004181]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; tetrahydrofolyl-poly(glutamate) polymer binding [GO:1904493]; C-terminal protein deglutamylation [GO:0035609]; folic acid-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006760]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
11092759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12042430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12204797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12474535_expressed in prostate tissue, and especially in prostate cancer tissue 12514270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12707400_GCP2 polymorphism explained nearly 50% of the variance of red blood cell folate in ESRD 12707400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12753319_GCP2 1561C>T is associated with elevated folate levels but not homocysteine levels in kidney transplant patients 12753319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12850144_PSMA expression is regulated by NFATc1 with an AP-3 binding site 12855225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12949938_N-linked carbohydrate structures are important for the folate hydrolase function of the protein. Removal of sugars partially or completely causes PSMA to be enzymatically inactive, improperly folded, resulting in increased rate of degradation. 14528023_PSMA is internalized via a clathrin-dependent endocytic mechanism and that internalization of PSMA is mediated by the five N-terminal amino acids 14632302_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15122597_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15141017_proteins binding PSMA 15152093_Analysis of the predicted N-glycosylation sites also provides evidence that these sites are critical for GCPII carboxypeptidase activity 15206943_amino acid segments at the N- and C-termini of the ectodomain of GCPII are essential for its carboxypeptidase activity and/or proper folding 15321811_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15389976_PSMA gene lacks specificity for detecting prostate epithelial cells 15705868_Knockdown of PSMA expression increased invasiveness of LNCaP cells by 5-fold. 15713827_Transcriptional activity of the PSMA promoter/enhancer is prostate specific. 15837926_Structure and relevance to the development of chemotherapeutics and cancer-imaging agents. 15840561_PSMA may function as a receptor internalizing a putative ligand, an enzyme playing a role in nutrient uptake, and a peptidase involved in signal transduction in prostate epithelial cells. [review] 16221666_acquisition of folding determinants in the Golgi is an essential prerequisite for protein trafficking and sorting of PSMA 16496414_The folate hydrolase activity of PSMA may provide a growth advantage to prostate cancer cells in low folate and physiological folate environments. 16522921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16713605_PSMA binds to caveolin-1 and undergoes internalization via a caveolae-dependent mechanism in microvascular endothelial cells 17032155_In suicide gene therapy, anti-PSMA-liposome complex exerted a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of LNCaP xenograft, in contrast to normal IgG-liposome complex. 17150306_Using pure recombinant GCPII and homologous GCPIII, we conclude that GCPII is responsible for the majority of overall NAAG-hydrolyzing activity in the human brain. 17208363_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17684227_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17684227_Polymorphism is associated with higher plasma folate and lower homocysteine concentrations in women who abstain from alcohol. 17689503_Pattern differences in GCP II gene promoter expression in SVG and LNCaP cells suggest that sequences beyond 240 bp may be important for tissue-specific GCP II expression. 17714508_the residues forming the S1 pocket might be more important for the 'fine-tuning' of GCPII substrate specificity 17935484_the intracellular transport of PSMA occurs through populations of DRMs distinct for each biosynthetic form and cellular compartment 18076021_Tissues such as prostate and testes exhibit different GCPII expression levels among the species studied (human, rats, swine). 18234225_Crystal structures of human GCPII in complex with phosphapeptide analogs show the S1 pocket of GCPII and the data indicate the importance of Asn519, Arg463, Arg534, and Arg536 for recognition of the penultimate (i.e., P1) substrate residues. 18249021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18344976_prostate-specific membrane antigen is expressed in tumor-associated neovasculature of the majority of renal cortical tumors 18349274_PSMA is underexpressed in advanced stage endometrial adenocarcinoma (EAC); loss of PSMA expression can be considered as a prognostic marker in patients with EAC; loss of PSMA expression in a subset of EAC cases could be due to epigenetic silencing 18427977_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18534872_Given our finding of frequent expression of PSMA in Schwannomas, they should be clinically considered in the differential diagnosis of a lesion that is positive on PSMA radioimmunoscintigraphy study performed during a metastatic work-up of PCa patient. 18590621_Observational study and meta-analysis of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18626508_the efficacy of 5-FU-based chemotherapy in prostate cancers can be significantly improved by targeted expression of the suicide gene UPRT under the control of prostate-specific membrane antigen promoter/enhancer 18635682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18639471_The present study describes an efficient RNAi system for gene silencing that is specific to prostate cancer cells using the PSMA promoter/enhancer 18823966_Neonatal methylmalonic acid was predicted by maternal methylmalonic acid and GCPII 18823966_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18839017_prostate-specific membrane antigen is expressed in neovasculature from physiologic regenerative and reparative conditions 18842806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18844933_PSMA was the most useful marker to identify residual prostatic carcinoma after hormone therapy. 18974153_Ectopic PSMA expression on PC-3 cells increased the invasive capacity of cells in in vitro invasion assays, which could be competed out by folic acid. These results suggest PSMA facilitates the development of prostate cancer 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19053759_analysis of interactions between human glutamate carboxypeptidase II and urea-based inhibitors 19060911_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19107881_PSM' protein is likely not generated by alternative splicing of the PSMA gene but by different mechanism, probably via an endoproteolytic cleavage of the full-length PSMA. 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19172696_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19172696_although the RFC1 80G > A and FOLH1 1561C > T polymorphisms may influence folate status, they are not likely to have a major independent role in the development of colorectal cancer 19242540_PSMA-fostered RAS-RAC1-MAPK pathway activation produced a strong induction of NF-kappaB activation associated with an increased expression of IL-6 and CCL5 genes. 19301871_Reaction mechanisms of GCPII revealed by mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, and computational methods. 19343734_PSMA and prostate stem cell antigen are both highly expressed in lymph node and bone metastases of prostate cancer. 19394322_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19403271_These data suggest that Glutamate carboxypeptidase II is disrupted in the AH in schizophrenia and localize the defect to the CA1 and CA3 regions. 19427504_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19706844_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19716160_PSMA represents a promising therapeutic and diagnostic target in colorectal and gastric cancer. 19776634_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19936946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20047525_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20047525_parental C1561T polymorphism associated with increased risk for neural tube defects 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452657_These results suggest that a specific antitumor immune response is enhanced by DNA vaccines expressing PSMA 20458436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20624932_important physiological role for GCPII in Abeta clearance in brain and provide the evidence that dysregulation of GCPII is involved in Alzheimer's disease pathology 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20670952_Data show that the selected virus preferentially infects PSMA-expressing cells through the targeting peptide and infects LNCaP tumors after intravenous injection. 20852008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21189143_PSMA and PSA are regulated differentially and the difference in their expression showed a correlation with malignant transformation 21597034_The FOLH1 1561C>T polymorphism may be associated with the risk of depressive symptoms. 21600799_Data indicate that PSA, PSMA, hK2, PSCA, DD3, and their combinations, combined analysis of PSA and/or hK2 expression in pelvic lymph nodes could predict biochemical recurrence free survival (BRFS) following radical prostatectomy (RP). 21604260_Data show that the full-length PSMA sequence containing all three epitopes was poorly immunogenic, but only those against PSMA(27) or PSMA(663) peptides, and not PSMA(711) , were able to kill tumor cells expressing endogenous PSMA. 21606347_Results establish that relative changes in PSMA expression levels can be quantitatively measured and could serve as a biomarker of AR signaling to noninvasively evaluate AR activity in patients with CRPC. 21640619_Data suggest the radioimmunoscintigraphic detection of radiolabeled prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA antibodies might not be entirely specific for prostatic cells 21725290_The finding of PSMA in the bladder cancer neovasculature suggests that this molecule may promote tumor growth and may represent a potential new vascular target in this disease. 22009216_PSMA could be used as an independent prognostic marker for the osteosarcoma patients 22032578_Prostate-specific membrane antigen is expressed in the vasculature of glioblastoma multiforme vessels, thus rendering a potential novel therapeutic vascular target. 22124883_Glutamate carboxypeptidase II gene combined AG GG rs202676 genotype was significantly associated with anencephaly, but not with spina bifida or encephalocele. Overall, the rs202676 A>G polymorphism is a potential risk factor for anencephaly. 22304713_An overview of GCPII/PSMA in cancer, as well as a discussion of imaging and therapy of prostate cancer using a wide variety of PSMA-targeting agents is provided. [review] 22310383_Statistically significant association was not observed between dietary folate levels and GCPII expression. 22322627_The PSM-E splice variant of PSMA suppression effect on cell proliferation is stronger compared to PSMA and the suppression effect on invasiveness is weaker than that of PSMA. 22460809_High expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in the tumor-associated neo-vasculature is associated with worse prog-nosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. 22568207_The survivin promoter exhibited a higher transcriptional activity than PSMA promoter and enhancer in prostate tumor cell lines. 23041906_androgen-deprivation induced a decrease in AR and PSMA levels in androgen-sensitive LNCaP cells, which may be associated with the development of more aggressive disease-state following androgen deprivation therapy. 23259322_To conclude, GCPII haplotypes influenced susceptibility to stroke by influencing homocysteine levels. 23266799_The D191V variant increases breast cancer risk by affecting plasma folate. V108A and P160S variants reduce breast cancer risk. V108A and G245S varients are associated with prostate cancer risk. 23359458_Canine PSMA reveals similar characteristics to human PSMA rendering this protein useful as a translational model for investigations of prostate cancer as well as a suitable antigen for targeted therapy studies in dogs. 23467813_Folate plus vitamin B12 supplementation can improve negative symptoms of schizophrenia, but treatment response is influenced by FOLH1 genetic variation in folate absorption. 23525278_Data indicate that glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII) is not an amyloid peptide-degrading enzyme. 23525279_Data did not show any amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide degradation activity of glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII). 23775497_PSMA is part of a proteolytic cascade where it acts downstream of MMP-2 to create small pro-angiogenic laminin peptides. 23891752_These data suggest that GCPII has two distinctive binding sites for two different substrates and that ABETA degradation occurs through binding to S1 pocket of GCPII. 23979608_the impact of Glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII) haplotypes on the expression of PSMA, BNIP3, Ec-SOD, GSTP1 and RASSF1 genes were elucidated to understand the epigenetic basis of oxidative stress and prostate cancer risk. 23991415_Taking into account the PC phenotypes according to RKIP among PSA-PSMA profiles may improve distinguishing them from cancers that will become more aggressive. 24063417_Data suggest the importance of an aromatic group and succinimide moiety for high affinity of probes with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) 24063616_The increase in gene expression ratio of PSA:PSMA to about 4.95 strongly correlated with the prostate cancer and with high intratumoral angiogenesis. 24130224_High tumor PSMA expression was not an independent predictor of lethal prostate cancer in the current study. 24292502_High glutamate carboxypeptidase II mRNA expression is associated with pelvic lymph node micrometastasis in prostate cancer. 24304465_Tumor-associated vasculature was PSMA-positive in 74% of primary breast cancers and in 100% of breast cancers metastatic to brain. PSMA was not detected in normal breast tissue. No significant association was seen between PSMA and lymph node involvement. 24424840_our data may suggest a new role for PSMA in prostate cancer progression, and provide opportunities for developing non-invasive approaches for diagnosis or prognosis of prostate cancer 24477651_High glutamate carboxypeptidase II levels are associated with pancreatic cancer. 24762500_PSMA expression may be correlated with nanog's expression as well as with other confounders in a population of prostate CSCs. 24764162_This study demonstrates the feasibility of D2B IgG, F(ab')2 and Fab fragments for targeting PSMA-expressing prostate cancer xenografts. 24788382_we focus on the susceptibilities of these PSA-PSMA prostate clones to factors that promote prostate hyperplastic, neoplastic and metastatic development 24939622_Taken together, this study demonstrated that the increase in GCPII induced by VPA is not due to the classical epigenetic mechanism, but via enhanced acetylation of lysine residues in GCPII. 25916744_First evidence of PSMA expression in differentiated thyroid cancer using [Ga]PSMA-HBED-CC PET/CT. 26028103_The findings suggest that C1561T-GCPII variation may be associated with risk for adenomatous polyp, and vitamin C may modify risk by interacting with the variant gene, its expression product and/or folate substrates. 26079448_This study demonstrated that Overexpression and Nucleolar Localization gcp2 in glioblastoma. 26125931_In vitro immunotherapy is described for anti-prostate cancer effects of cytotoxic T lymphocytes induction by recombinant adenovirus mediated PSMA/4-1BBL dendritic cells. 26212031_evaluated the relaxometric properties of these agents in solution, in prostate cancer cells, and in an in vivo experimental model to demonstrate the feasibility of PSMA-based MR molecular imaging 26438155_Systemic treatment with these radiation-sensitizing agents selectively enhanced the potency of external beam radiation therapy for established PSMA-positive tumors. 26471812_Results from genetic models highlight the importance of GCPII genetic variants as relatively novel risk factors for breast cancer and prostate cancer. 26723876_Ad5/35E1aPSESE4 is effective in marking PSA/PSMA-positive prostate cancer cells in patient blood to improve the efficacy of utilizing CTCs as a biomarker. 26739097_In conclusion, we have successfully developed the specific PSMA-targeting IO nanoparticle, DOTA-IO-GUL, as a dual-modality probe for complementary PET/MR imaging 26771706_prostate-specific membrane antigen is significantly overexpressed in adrenocortical carcinoma neovasculature when compared with normal and benign adrenal tumors 26862945_PSMA is highly and specifically expressed in the neovasculature of ovarian, endometrial, and cervical squamous carcinoma 26977010_MDM2 and PSMA may co-regulate the expression of certain MMPs and, thus, the functionality of cells in metastatic breast cancer. 27070640_The risk of coronary disease and ischemic stroke associated with multiple polymorphisms and haplotypes of MADD and FOLH1 in Han Chinese patients are reported in association with alcohol consumption. 27358992_Data show that the expressed antibody could specifically bind to prostate-specific membrane antigen ( PSMA) positive cells. 27387982_Demonstrate that several laminin-derived peptides containing carboxy-terminal glutamate moieties (LQE, IEE, LNE) are bona fide substrates for PSMA. Subsequently, the peptide products were tested for their effects on angiogenesis in various models. 27609368_GCPII may not be a priority target for molecular imaging of atherosclerotic lesions. 28002805_Results provide evidence that PSMA is expressed in the neovasculature of a subset of soft tissue tumors to a variable extent predominantly occurring in sarcomas. 28051996_Xenografted human tumors expressing different levels of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) was produced to assess the clearance, biodistribution and imaging potential of 123I-scFvD2B. 28351335_We also confirmed the specificity and selectivity of prostate-specific membrane antigen targeting by assessing prostate-specific membrane antigen-null PC3 cell lines under the same conditions ( |
ENSMUSG00000001773 |
Folh1 |
121.478950 |
0.0057520546 |
-7.441707 |
0.677494978 |
359.742951 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003202990650105849175484596654246504939925428311002871472470509318739241658096474340648277066358818574980386165793041337581466260879049663734487882764342753319977629632692159056746917570116851655044089286494823909379192627966403961181640625000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001081833912941929796917011105079347141790050327680245382915556487169368658951154031811702413406234549420079237693516732908008549524870908121715109262367910561356197922086648365863127069696271757501260246669971820665523409843444824218750000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1799683 |
0.5812933 |
206.9061047 |
25.5982084 |
| ENSG00000086300 |
29887 |
SNX10 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5X0 |
FUNCTION: Probable phosphoinositide-binding protein involved in protein sorting and membrane trafficking in endosomes. Plays a role in cilium biogenesis through regulation of the transport and the localization of proteins to the cilium. Required for the localization to the cilium of V-ATPase subunit ATP6V1D and ATP6V0D1, and RAB8A. Involved in osteoclast differentiation and therefore bone resorption. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17012226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21844891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22499339}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Endosome;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Osteopetrosis;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sorting nexin family. Members of this family contain a phox (PX) domain, which is a phosphoinositide binding domain, and are involved in intracellular trafficking. This protein does not contain a coiled coil region, like some family members. This gene may play a role in regulating endosome homeostasis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:29887; |
apical cytoplasm [GO:0090651]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extrinsic component of endosome membrane [GO:0031313]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; 1-phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0005545]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; bone mineralization involved in bone maturation [GO:0035630]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; gastric acid secretion [GO:0001696]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; protein localization to centrosome [GO:0071539]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; ruffle assembly [GO:0097178]; tooth eruption [GO:0044691]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050] |
17012226_SNX10 activity may be involved in the regulation of endosome homeostasis 21844891_SNX10 regulates the ciliary trafficking of Rab8a, which is a critical regulator of ciliary membrane extension. 22174188_Since inhibition of vesicular trafficking is essential for osteoclast formation and activity and SNX10 is involved in vesicular trafficking, these studies may identify a new gene involved in the development of bone diseases including osteoporosis. 22499339_Identification of SNX10 as a new osteopetrosis associated gene in consanguineous families of Palestinian origin. 23280965_results confirm the involvement of the SNX10 gene in human ARO and identify a new subset with a relatively favorable prognosis as compared to TCIRG1-dependent cases 23615901_Structure of sorting nexin 11 (SNX11) reveals a novel extended phox homology (PX) domain critical for inhibition of SNX10-induced vacuolation. 25212774_Data suggest Tyr32 and Arg51 in SNX10 are important for protein stability and play critical roles in vacuolation in osteoclasts; mutation Arg16Leu (seen in autosomal recessive osteopetrosis patients) affects protein-protein interactions of SNX10. 25811986_supplementation with calcium gluconate rescued mice from the rachitic phenotype and extended life span in global Snx10-deficient mice, suggesting that this may be a life-saving component of the clinical approach to Snx10-dependent human osteopetrosis 27187610_In this study, whole exome sequencing (WES) was successfully used in six patients with malignant infantile osteopetrosis (MIOP) and identified mutations in four MIOP-related genes (CLCN7, TCIRG1, SNX10, and TNFRSF11A). 28592808_Sequence analysis of the SNX10 transcript in patients with autosomal recessive osteopetrosis revealed activation of a cryptic splice site in intron 4 resulting in a frame shift and a premature stop (p.S66Nfs * 15). 29355659_Sorting nexin 10 (SNX10) was remarkably down-regulated in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues which showed the increased activity of chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) and decreased expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(Cip1/WAF1). 29867114_this work revealed that SNX10 controls mTOR activation through regulating chaperone-mediated autophagy-dependent amino-acid metabolism. 30487700_Weak expression of SNX10 is linked to poor prognosis, and is a suitable prognostic biomarker of stomach adenocarcinoma. 31208298_SNX10 (sorting nexin 10) inhibits colorectal cancer initiation and progression by controlling autophagic degradation of SRC. 32316875_Sorting Nexin 10 Mediates Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages in Atherosclerosis Through the Lyn-Dependent TFEB Signaling Pathway. 33594863_Does Decreased SNX10 Serve as a Novel Risk Factor in Atrial Fibrillation of the Valvular Heart Disease? - A Case-Control Study. 33678645_SNX10 gene mutation in infantile malignant osteopetrosis: A case report and literature review.', trans 'SNX101. 34116656_SNX10 and PTGDS are associated with the progression and prognosis of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 34747049_SNX10-mediated LPS sensing causes intestinal barrier dysfunction via a caspase-5-dependent signaling cascade. 34906048_Identification of Key Amino Acid Residues Involved in the Localization of Sorting Nexin 10 and Induction of Vacuole Formation. 35981699_Osteopetrosis associated with PLEKHM1 and SNX10 genes, both involved in osteoclast vesicular trafficking. |
ENSMUSG00000038301 |
Snx10 |
287.948708 |
0.1789607118 |
-2.482285 |
0.120275198 |
453.508363 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012433839405922837666302352435465690033718390087623017421848978777523364574526277187384538524705941513378661643074975544866259290393153152341748678132200167685825419052418286620897748374751430273790525279159946274789479443921781900 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005319520858881770010924303559331051319763005478659042736162346288238411703294095646748590147101088334847729425027410546118295089375837186418465167030258753932985873826784287894291188056407049891596683647213221476525160047216541911 |
Yes |
No |
89.1605213 |
6.9683948 |
501.4420455 |
22.3366731 |
| ENSG00000086548 |
4680 |
CEACAM6 |
protein_coding |
P40199 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface glycoprotein that plays a role in cell adhesion and tumor progression (PubMed:2803308, PubMed:2022629, PubMed:1378450, PubMed:8776764, PubMed:11590190, PubMed:10910050, PubMed:14724575, PubMed:16204051). Intercellular adhesion occurs in a calcium- and fibronectin-independent manner (PubMed:2022629, PubMed:16204051). Mediates homophilic and heterophilic cell adhesion with other carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules, such as CEACAM5 and CEACAM8 (PubMed:2803308, PubMed:2022629, PubMed:8776764, PubMed:11590190, PubMed:16204051). Heterophilic interaction with CEACAM8 occurs in activated neutrophils (PubMed:8776764). Plays a role in neutrophil adhesion to cytokine-activated endothelial cells (PubMed:1378450). Plays a role as an oncogene by promoting tumor progression; positively regulates cell migration, cell adhesion to endothelial cells and cell invasion (PubMed:16204051). Also involved in the metastatic cascade process by inducing gain resistance to anoikis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and colorectal carcinoma cells (PubMed:10910050, PubMed:14724575). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10910050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11590190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1378450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14724575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16204051, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2022629, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2803308, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8776764}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family whose members are glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol (GPI) anchored cell surface glycoproteins. Members of this family play a role in cell adhesion and are widely used as tumor markers in serum immunoassay determinations of carcinoma. This gene affects the sensitivity of tumor cells to adenovirus infection. The protein encoded by this gene acts as a receptor for adherent-invasive E. coli adhesion to the surface of ileal epithelial cells in patients with Crohn's disease. This gene is clustered with genes and pseudogenes of the cell adhesion molecules subgroup of the CEA family on chromosome 19. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:4680; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endothelial cell-matrix adhesion via fibronectin [GO:1904906]; positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034116]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11896570_Overexpression of CEACAM6 disrupts tissue architecture and blocks colonocyte differentiation 12571231_CEACAM6 subdomains involved in intercellular adhesion activity and subdomains involved in inhibition of cell differentation are identified and their respective activities are independently blocked. 14512395_the first study to demonstrate the prognostic relevance of CEACAM6 overexpression in human colorectal cancer 14724575_CEACAM6 gene silencing reversed the acquired anoikis resistance of tumor cell lines and inhibited in vivo metastatic ability 15081416_overexpression among human malignancies, immunological targeting of this tumor antigen may have therapeutic applicability 15130118_the results show that recognition of CEA and CEACAM6, but not CEACAM1, is accompanied by tight attachment to bacteria of cell surface microvilli-like extensions 15208677_CEACAM6 is an important determinant of pancreatic adenocarcinoma malignant cellular behavior 15316565_Levels of CEACAM6 expression can modulate pancreatic adenocarcinoma cellular invasiveness in a c-Src-dependent manner 15826304_CD66c is regulated in a manner distinct from other myeloid antigens in childhood lymphoblastic leukemia 16115956_Data show that variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that bind to human carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs) 1 and 6 failed to induce detachment and, instead, promoted enhanced host cell adhesion to the ECM. 16899629_The expression of CEACAM6 in ADH lesions is strongly associated with the development of IBC, therefore, it can be applied as a diagnostic marker either singly or in combination with other marker(s) to predict IBC development in women with ADH lesions. 17167768_CEA and CEACAM6 was shown to lead to an increase in the binding of the integrin alpha5beta1 receptor to its ligand fibronectin, without changing its cell surface levels, resulting in increased adhesion of CEA/CEACAM6-expressing cells to fibronectin. 17201906_For all tumors, the amount of CEACAM6 expressed was greater than that of CEACAM5, and reflected tumor histotype. 17286276_CEA-mediated signaling involves clustering of CEA and co-clustering and activation of the alpha5beta1 and associated specific signaling elements on the internal surfaces of membrane microdomains 17503391_CEACAM6 is a biological tumor marker for epithelial ovarian cancers. 17525800_CEACAM6 acts as a receptor for adherent-invasive E. coli adhesion and is abnormally expressed by ileal epithelial cells in Crohn disease. 17653079_findings suggest that CEA (CEACAM5) and CEACAM6 are major target genes for Smad3-mediated TGF-beta signaling. 17909799_All the leukemic samples showed overexpression of CEACAM6 and 8 when compared with normal granulocytes. 17960155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18223215_data support an important role for CEACAM6 in endocrine resistance in breast cancer, which can serve as a powerful predictor of future recurrence 18331757_CEACAM6 is overexpressed in borderline and invasive mucinous ovarian neoplasms. 19077207_Data show that desensitization of neutrophils to any two CEACAMs, 1, 3, 6, or 8, results in selective desensitization to those two CEACAMs, while the cells remain responsive to the other two neutrophil CEACAMs. 19329538_Because CEACAM6 acts as an antiapoptotic factor and stabilizes surfactant function, in addition to a putative role in innate defense against bacteria, we propose that it is a multifunctional alveolar protein 19411761_CEACAM6-associated signaling pathways could be potential targets for the development of biomarkers to predict the response of patients to adenovirus-based therapies, as well as for the development of more potent adenovirus-based therapeutics 20047061_CEACAM6 and a regulatory element near the 3' end of CEACAM3 are associated with cystic fibrosis disease severity and intrapair discordance 20063526_Positivity for both leukemia-associated antigens CD66c and CD25 in combination can predict the presence of BCR/ABL rearrangement in pre-B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 21470677_The highly elevated gene expression of CEACAM6 and CEACAM8 in primary myelofibrosis can serve as molecular markers of myelofibrotic transformation. 21559399_Despite its important role in bacterial attachment in ileal CD, no role was detected for CEACAM6 variants in IBD susceptibility or regarding an ileal CD phenotype 21618249_High serum CEACAM6 is associated with gastric cancer. 21994005_High CEACAM6 expresssion is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 22037359_CEACAM6 is expressed by alveolar and airway epithelial cells of human lung and is secreted into lung-lining fluid, where fully glycosylated protein binds to surfactant. 22064717_The authors show that the expression of CEACAM1 and CEACAM6 potentiate CEACAM3-dependent responses of neutrophils, exposing a cooperative role for this family of proteins during neisserial infection of neutrophils. 22396546_a novel role for NA in enhancing host cell survival by activating the Src/Akt signaling axis via an interaction with carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6/cluster of differentiation 66c (C6). 22975528_CEACAM6 is significantly upregulated in colon cancer tissues and is closely associated with poor prognosis. 23021083_CEACAM6 is focally overexpressed in a large fraction of human HNSCCs in situ. over-expression of CEACAM6 increases tumour growth and tumour initiating activity by suppressing PI3K/AKT-dependent apoptosis of HNSCC in a xenotransplant model of HNSCC. 23027178_The expression of CD66c was significantly higher in colorectal cancer specimens than in normal colon. 23592399_these findings show that PDEF-CEACAM6 is a highly active oncogenic axis in breast cancer 23603913_CEACAM-6 plays an important role in the regulation of CD8+ T-cell responses against multiple myeloma. 23806607_High carcinoembryonic cell adhesion molecule 6 expression is associated with malignant biliary stenoses. 23857344_our findings identified CEACAM6, which is regulated by miR-29a/b/c, as an important positive regulator of EMT in pancreatic cancer 24014076_CD66c expression appears useful only as a predictor of the Ph in adult patients (not in pediatric cases). 24186057_CEACAM6 expression was expressed in different molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Among different subtypes, the highest expression was found with HER2 positive cancers. 24231528_Data indicate that CD66c is frequently expressed in CRLF2-positive as well as hypodiploid cases. 24492534_results suggested that CEACAM6 functions as an oncoprotein in gastric cancer and may be an important metastatic biomarker and therapeutic target 25299082_CEACAM6 may be a valuable biomarker screening for gastric tumor and novel predictor for patients in advanced stages of gastric cancer 25398131_CEACAM6 increased the levels of phosphorylated AKT, which is involved in the progression of a variety of human tumors. 25409014_Results show that pancreatic cancer patients with CEACAM 1, 5 and 6 expression showed a significantly shortened overall survival and elevated serum values are correlated with distant metastasis suggesting a role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 25703140_Data indicate that carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes angiogenesis in gastric cancer via focal adhesion kinase FAK signaling. 25872647_vaccination with recombinant attenuated Salmonella harboring the CEACAM6 and 4-1BBL gene efficiently increased the number of CD3+CD8+ TIL and NK cells, decreased the number of FOXP3 cells and inhibited the development of DMH-induced colorectal cancer 26271985_Data show that carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) and forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) are associated with the malignant degree of pancreatic cancer. 26374831_CEACAM6 protein and mRNA were increased ~4-fold in lungs from infants with chronic lung disease as compared with controls. 26483485_Data suggest ways in which carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules CEACAM6 and CEACAM8 regulate the biological functions of one another. 26673628_show the upregulation of the tumor-associated antigens CEACAM5/6 by trans-signaling of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 26974538_Biliary CEACAM6 can identify patients with extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with a high degree of sensitivity and should be investigated further as a potential screening tool. 26993598_Data suggest that the expression of these TSPAN8, LGALS4, COL1A2 and CEACAM6 in the whole blood may be useful in the detection of colorectal cancer (CRC). 27172290_western blot analysis results indicated that the 1B5A5 epitope is located within an amino-terminal domain of CEACAM6. These results raised the possibility that our approach could lead to discovery of novel biomarkers for the early stage of cancers in a relatively short period of time. 27328063_Monoclonal Antibody 1B5A5 Against CEACAM6 27579896_a 7-gene signature was identified which correctly predicted the primary prefibrotic myelofibrosis group with a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 89%. The 7 genes included MPO, CEACAM8, CRISP3, MS4A3, CEACAM6, HEMGN, and MMP8 27748756_Helicobacter pylori HopQ binds the amino-terminal IgV-like domain of human CEACAM1, CEACAM3, CEACAM5 or CEACAM6 proteins, thereby enabling translocation of the major pathogenicity factor CagA into host cells. 27748768_Here, the authors identify members of the carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule (CEACAM) family as receptors of Helicobacter pylori and show that HopQ is the surface-exposed adhesin that specifically binds human CEACAM1, CEACAM3, CEACAM5 and CEACAM6. 28275137_expression is increased in severe asthma and primarily associated with airway epithelial cells and tissue neutrophils 28292985_In enterocytic C2BBe1 cells, Candida albicans caused a transient tyrosine phosphorylation of CEACAM1 and induced higher expression of membrane-bound CEACAM1 and soluble CEACAM6. 28766906_CD66c (KOR-SA3544) antigen expression of leukemic blasts in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with TLS/FUS-ERG fusion transcript 28892050_CEACAM6 promoted oral squamous cell carcinoma cell invasion, migration, cytoskeletal rearrangement, and metastasis via interaction with EGFR and enhancing it activation. 29110374_Studies provide evidence that dysregulated overexpression of CEACAM6 plays a role in several of the hallmarks of cancer, including uncontrolled proliferation, anoikis resistance, immune evasion, invasion and metastasis. [review] 31171910_CEACAM 1, CEACAM 5 and CEACAM 6 expression appears to be an early event in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Moreover, expression of CEACAM 1, 5 and 6 may represent a useful biomarker that may aid in the identification of precancerous lesions in the pancreas 31222613_High CEACAM6 expression is associated with metastases in breast carcinoma. 31474761_Therapeutic Effect of pHLIP-mediated CEACAM6 Gene Silencing in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 31797958_Carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDA): An integrative analysis of a novel therapeutic target. 32648688_CEACAM6 promotes cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma and is regulated by microRNA-146a and microRNA-26a. 33674603_Identification of CD318, TSPAN8 and CD66c as target candidates for CAR T cell based immunotherapy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 33767593_CD151 promotes Colorectal Cancer progression by a crosstalk involving CEACAM6, LGR5 and Wnt signaling via TGFbeta1. 33919410_The Immunomodulatory CEA Cell Adhesion Molecule 6 (CEACAM6/CD66c) Is a Protein Receptor for the Influenza a Virus. 34847408_Antibody ligation of CEACAM1, CEACAM3, and CEACAM6, differentially enhance the cytokine release of human neutrophils in responses to Candida albicans. 35141051_T cell-mediated elimination of cancer cells by blocking CEACAM6-CEACAM1 interaction. 35302657_In high-grade ovarian carcinoma, platinum-sensitive tumor recurrence and acquired-resistance derive from quiescent residual cancer cells that overexpress CRYAB, CEACAM6, and SOX2. 35896219_Significance of Intraperitoneal-free KRT20 and CEACAM6 mRNA Expression for Peritoneal Recurrence of Gastric Cancer. 35896264_Chitinase 3-like 1, Carcinoembryonic Antigen-related Cell Adhesion Molecule 6, and Ectopic Claudin-2 in the Carcinogenic Processes of Ulcerative Colitis. |
ENSMUSG00000054169+ENSMUSG00000074272+ENSMUSG00000054385 |
Ceacam10+Ceacam1+Ceacam2 |
80.772806 |
0.1136103212 |
-3.137834 |
0.229681766 |
228.492508 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000127088457592152187800311665201599847939392409093868934100088050613219911261076654739889289379458642436223529393950968440842447238197515657631697649776469916105270385742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000028250386055122985367936609617574693250875365670631280097358292390327468798455764085719478445837875547058380084840178366938437132943606755475229874718934297561645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.8646095 |
2.6167122 |
149.4446326 |
11.1144951 |
| ENSG00000087074 |
23645 |
PPP1R15A |
protein_coding |
O75807 |
FUNCTION: Recruits the serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PPP1CA to prevents excessive phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF-2A/EIF2S1, thereby reversing the shut-off of protein synthesis initiated by stress-inducible kinases and facilitating recovery of cells from stress (PubMed:26742780, PubMed:26095357). Down-regulates the TGF-beta signaling pathway by promoting dephosphorylation of TGFB1 by PP1 (PubMed:14718519). May promote apoptosis by inducing p53/TP53 phosphorylation on 'Ser-15' (PubMed:14635196). Plays an essential role in autophagy by tuning translation during starvation, thus enabling lysosomal biogenesis and a sustained autophagic flux (PubMed:32978159). Acts also a viral restriction factor by attenuating HIV-1 replication (PubMed:31778897). Mechanistically, mediates the inhibition of HIV-1 TAR RNA-mediated translation (PubMed:31778897). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556489, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14635196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14718519, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26095357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31778897, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8139541}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Promotes enterovirus 71 replication by mediating the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) activity of viral 5'-UTR. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34985336}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Stress response;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of a group of genes whose transcript levels are increased following stressful growth arrest conditions and treatment with DNA-damaging agents. The induction of this gene by ionizing radiation occurs in certain cell lines regardless of p53 status, and its protein response is correlated with apoptosis following ionizing radiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23645; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; protein phosphatase type 1 complex [GO:0000164]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; protein phosphatase activator activity [GO:0072542]; protein phosphatase regulator activity [GO:0019888]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; negative regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903898]; negative regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032515]; negative regulation of protein dephosphorylation [GO:0035308]; positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced eIF2 alpha dephosphorylation [GO:1903917]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation [GO:1902310]; positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032516]; positive regulation of translational initiation in response to stress [GO:0032058]; protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0070972]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of translational initiation by eIF2 alpha dephosphorylation [GO:0036496]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
12016208_SNF5/INI1 protein facilitates the function of the growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein and modulated protein phosphatase-1 activity 12168790_GADD 34 may play an important role in melanoma progression 12724406_the GADD34-mediated cellular stress response is suppressed by BAG-1 12813455_Human Gadd34 lacking the viral homology domain does not interfere with normal Gadd34-induced apoptosis in cultured cells. This suggests that viral similarity sequences may be required for Gadd34-mediated functions other than apoptosis. 14635187_These findings suggest that phenethylisothiocyanate creates an oxidative cellular environment that induces DNA damage and GADD153, 34 and 45 gene activation, which in turn helps trigger apoptosis 14718519_GADD34-PP1c recruited by Smad7 inhibits TGFbeta-induced cell cycle arrest. 15541008_the up-regulation of GADD34 in response to global ischaemia in the human brain plus its influence on protein synthesis and DNA repair suggests that this protein may have the potential to influence cell survival 16337513_GADD34 may perform important functions in cardiac tissue in response to ischaemia. 17273797_During conditions of cell stress, GADD34 forms a stable complex with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) 1/2, causes TSC2 dephosphorylation, and inhibits signaling by mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR). 18794359_mechanisms that control GADD34 levels in human cells 19131336_GADD34 translation is regulated by a unique 5'UTR uORF mechanism to ensure proper GADD34 expression during eIF2alpha phosphorylation 19776135_Infectious bronchitis virus has developed a combination of two mechanisms, i.e., blocking PKR activation and inducing GADD34 expression, to maintain de novo protein synthesis in IBV-infected cells and, meanwhile, to enhance viral replication. 19901557_The role of the PP1/GADD34 complex in the molecular cascade is to the translocation of CRT to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane. 20040105_The data suggest that EBNA3C interacts with Gadd34, activating the upstream component of the UPR-unfolded protein response (eIF2alpha phosphorylation) while preventing downstream UPR events (XBP1 activation and ATF6 cleavage). 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21518769_the association of with ER modulates intracellular trafficking and proteasomal degradation of GADD34, and in turn, its ability to modify ER morphology 23412101_Low GADD34 expression is associated with malignant mesothelioma. 23708656_Nuclear export of HTLV-1 basic leucine-zipper factor (HBZ) is essential for its interaction with GADD34 and increased phosphorylation of S6 kinase, which is an established downstream target of the mTOR pathway. 24092754_GADD34 phosphorylation on tyrosine 262 modulates endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling and cell fate. 25204313_GADD34 may play a neuroprotective role against amyloid-beta toxicity. 25659802_GADD34 enhances autophagy and suppresses apoptosis stimulated by LPS combined with amino acid deprivation through regulation of mTOR signaling pathway in macrophages. 26041779_GADD34 promotes cell survival and adaptation to increased extracellular osmolarity by increasing the uptake of small neutral amino acids via the amino acid transporter SNAT2. 26083346_stress pathways lead to the induction of the protein GADD34, which appears to provide protection against the toxic effects of the secreted virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection 26095357_The data highlight independent interactions of PP1 and eIF2alpha with GADD34, demonstrating that GADD34 functions as a scaffold both in vitro and in cells 26100893_Data indicate that protein phosphatase 1 subunit GADD34 directly interacts with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit alpha (eIF2alpha). 26142647_GADD34 was increased in neurons of human Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains. Additionally, this finding was also observed in oligodendrocytes in human AD brains. GADD34 could be a therapeutic target for preventing ER stress in neuronal cells in AD. 26742780_The reactive oxygen species-generating NADPH oxidase-4 (Nox4) is induced downstream of ATF4, binds to a PP1-targeting subunit GADD34 at the endoplasmic reticulum, and inhibits PP1 activity to increase eIF2alpha phosphorylation and ATF4 levels. 26743901_The results suggest that dephosphorylation of eIF2a by GADD34 plays an important role in doxorubicin resistance of MCF-7/ADR cells. 26829377_Data of this study strengthen the evidence of an unfolded protein response during the course of RA and provide an insight of the potential interest in GADD34 as a relevant marker for RA. 27177629_ANXA11 rs1049550 and PPP1R15A rs557806 may improve the identification of mCRC patients sensitive to bevacizumab regimens, and further validation is required in large cohorts 27630304_reduction of GADD34 expression significantly suppressed tumor, and resulted in decreased accumulation of MDSCs and T-cells, and inhibition of GADD34 reduced secretion of vascular epithelial growth factor alpha and transforming growth factor beta by MDSCs 27992581_GADD34 constitutes a mechanistic link between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mTOR inactivation, therefore promotes cell survival during endoplasmic reticulum stress. 28984870_The results highlighted a novel role for the GADD34/PP1alpha complex in coordinating the dephosphorylation and reactivation of eIF2alpha and SIRT1 to determine cell fate following oxidative stress. 29109149_Findings highlight that the phosphatase regulator, GADD34, also functions as a kinase scaffold in response to chronic oxidative stress and recruits CK1 and oxidized TDP-43 to facilitate its phosphorylation, as seen in TDP-43 proteinopathies. 29186961_Compared with normal controls, the wild type TT and allele T of rs611251 of PPP1R15A showed higher frequency in gastric carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinomas and lymphomas. 29227599_Inhibition of IRE1 modifies the hypoxic regulation of GADD34 family gene expression in cultured glioma cells. 29491143_Depletion of HES1 increased cell death in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse and human cells, in a manner that depended on the pro-apoptotic gene growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34. 29632131_Loss of GADD34 cause vanishing white matter disease due to translation defects. 30782845_these findings suggest that GADD34 inhibits TRAIL-induced HCC cell apoptosis through TRAF6- and ERK-mediated stabilization of MCL-1. 32978159_GADD34 plays an essential role in autophagy by tuning translation during starvation, thus enabling lysosomal biogenesis and a sustained autophagic flux. Hence, the TFEB-GADD34 axis integrates the mTORC1 and ISR pathways in response to starvation. 34625748_Higher-order phosphatase-substrate contacts terminate the integrated stress response. 34732748_Sensitization of the UPR by loss of PPP1R15A promotes fibrosis and senescence in IPF. 34847777_Substrate recognition determinants of human eIF2alpha phosphatases. 34985336_Enterovirus 71 Activates GADD34 via Precursor 3CD to Promote IRES-Mediated Viral Translation. |
ENSMUSG00000040435 |
Ppp1r15a |
792.805745 |
2.2927800453 |
1.197098 |
0.059324656 |
412.478509 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010583337946447215252176136393176888109354690134069990717113678961354717741926952044014311853098986687713783569330612287936690546768711385890933662457035889067004539150636032207008639892475373564428619429534131288026648496421872058803614891 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004046892955688106475719277292203907552135389051594751566448050290042277827681266143757238850340096110433043393840297912869537628002113026873343445252188848757872084549471148387642113988721533577317591638358917223315853756854254541508453258 |
Yes |
Yes |
1123.5950931 |
40.5281927 |
493.7140357 |
14.1847645 |
| ENSG00000087076 |
51171 |
HSD17B14 |
protein_coding |
Q9BPX1 |
FUNCTION: Has NAD-dependent 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity. Converts oestradiol to oestrone. The physiological substrate is not known. Acts on oestradiol and 5-androstene-3-beta,17-beta-diol (in vitro). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17067289}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Lipid metabolism;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism |
|
17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, such as HSD17B14, are primarily involved in metabolism of steroids at the C17 position and also of other substrates, such as fatty acids, prostaglandins, and xenobiotics (Lukacik et al., 2007 [PubMed 17067289]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:51171; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0044594]; estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004303]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; testosterone 17-beta-dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0047045]; steroid catabolic process [GO:0006706] |
17067289_crystal structure of the DHRS10 apoenzyme exhibits secondary structure of the SDR (short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase) family 22792371_Results show that tumoural expression levels of 17betaHSD14 can predict the outcome of adjuvant tamoxifen treatment in terms of local recurrence-free survival in patients with lymph node-negative ER+ breast cancer. 30836176_Five new variants of HSD17B14 characterized by crystallography and enzyme kinetics. Tyr253' from the adjacent monomer ties the two monomers together. Disulfide bridge formed by Cys255 and Cys255' is not crucial for dimer stabilization. 34261756_Association of Coding Variants in Hydroxysteroid 17-beta Dehydrogenase 14 (HSD17B14) with Reduced Progression to End Stage Kidney Disease in Type 1 Diabetes. |
ENSMUSG00000030825 |
Hsd17b14 |
5.666012 |
0.1177734675 |
-3.085914 |
0.852638013 |
16.627175 |
0.00004549448975227640088467642720537753575626993551850318908691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000131821489741578275157671273909443243610439822077751159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3352608 |
0.8266141 |
11.3976651 |
3.0710672 |
| ENSG00000087245 |
4313 |
MMP2 |
protein_coding |
P08253 |
FUNCTION: Ubiquitinous metalloproteinase that is involved in diverse functions such as remodeling of the vasculature, angiogenesis, tissue repair, tumor invasion, inflammation, and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. As well as degrading extracellular matrix proteins, can also act on several nonmatrix proteins such as big endothelial 1 and beta-type CGRP promoting vasoconstriction. Also cleaves KISS at a Gly-|-Leu bond. Appears to have a role in myocardial cell death pathways. Contributes to myocardial oxidative stress by regulating the activity of GSK3beta. Cleaves GSK3beta in vitro. Involved in the formation of the fibrovascular tissues in association with MMP14.; FUNCTION: PEX, the C-terminal non-catalytic fragment of MMP2, posseses anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor properties and inhibits cell migration and cell adhesion to FGF2 and vitronectin. Ligand for integrinv/beta3 on the surface of blood vessels.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Mediates the proteolysis of CHUK/IKKA and initiates a primary innate immune response by inducing mitochondrial-nuclear stress signaling with activation of the pro-inflammatory NF-kappaB, NFAT and IRF transcriptional pathways. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Autocatalytic cleavage;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene is a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene family, that are zinc-dependent enzymes capable of cleaving components of the extracellular matrix and molecules involved in signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a gelatinase A, type IV collagenase, that contains three fibronectin type II repeats in its catalytic site that allow binding of denatured type IV and V collagen and elastin. Unlike most MMP family members, activation of this protein can occur on the cell membrane. This enzyme can be activated extracellularly by proteases, or, intracellulary by its S-glutathiolation with no requirement for proteolytical removal of the pro-domain. This protein is thought to be involved in multiple pathways including roles in the nervous system, endometrial menstrual breakdown, regulation of vascularization, and metastasis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Winchester syndrome and Nodulosis-Arthropathy-Osteolysis (NAO) syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:4313; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; aging [GO:0007568]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel maturation [GO:0001955]; bone trabecula formation [GO:0060346]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to fluid shear stress [GO:0071498]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular response to UV-A [GO:0071492]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; heart development [GO:0007507]; intramembranous ossification [GO:0001957]; luteinization [GO:0001553]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045906]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; ovulation from ovarian follicle [GO:0001542]; parturition [GO:0007567]; peripheral nervous system axon regeneration [GO:0014012]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis [GO:0060740]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to hyperoxia [GO:0055093]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; tissue remodeling [GO:0048771] |
11168762_involvement of MMPs in microinvasive carcinomas 11728453_non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs suppress MMP-2 expression via repression of transcription 11748988_Activated matrix metalloproteinase-2--a potential marker of prognosis for epithelial ovarian cancer. 11756567_results indicate that two kinds of pro-form and active-form matrix metalloproteinases, MMP-2 and MMP-9, and their degradation products, are present in human seminal plasma 11762702_17beta-estradiol had no influence on production in MG-63 cells or human osteoblast cultures 11782389_Cancer cell-associated fibronectin induces release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 from normal fibroblasts. 11790786_design, synthesis and characterization of potent slow-binding inhibitors 11792711_repression of expression by ATF3 11833938_in differentiating trophoblasts Nitric Oxide regulates the induction of MMP-2 and MMP-9 required for invasion during embryo implantation 11839588_shed as membrane vesicle associated components by endothelial cells and this may be a mechanism for regulating focalized proteolytic activity vital to invasive and morphogenic events during angiogenesis 11844598_Expression of membrane-type-1-matrix metalloproteinase and metalloproteinase-2 in nonsmall cell lung carcinomas 11854622_in pancreatic cancer, invasion into large veins and destroyed type veins could be a risk factor for liver metastasis and that increased expression MMP-2 and MMP-9 were related to such invasion. 11895494_MMP-2 expression seemed to have an important role to play in the epithelial differentiation of tumour cells in synovial sarcoma. 11918086_SB203580, a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor, reduces MMP-2 expression in melanoma cell line MeWO. 11920503_increasing expression and endometrial carcinoma appear closely related 11928808_A study of the col-1 module of MMP2; structural/functional relatedness between gelatin-binding fibronectin type II modules and lysine-binding kringle domains. 11928813_Levels of MMP2 mRNA were reduced in two neuroblastoma clones treated with 300 nM PAF, which was accompanied by an inhibition of invasiveness through Matrigel and by a promotion of differentiation. 11929863_activation by overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells involves reactive oxygen species 11935310_activation associated with malignant lung cell phenotype; correlation between low hemoglobin level and T/N ratio of MMP-2 may indicate indicate significance of MMP-2 for angiogenesis 11948127_Significantly increased activity of MMP-2 was recognized in tumors showing tenascin-C degradation. 11956628_expression level of MMP-2 mRNA may regulate with invasion ability of cervical cancer 12007723_Increased gelatinase activity in Systemic Sclerosis fibroblasts seems to be regulated at translational and/or post-translational level. 12029498_Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in squamous cell carcinomas of immunosuppressed patients. 12034345_destruction of the surrounding matrix by endometriosis might be caused by various MMPs, which are mainly produced in stromal cells. 12077518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085233_N-Myc and Bcl-2 coexpression induces MMP-2 secretion and activation in human neuroblastoma cells 12087091_MMP2 inhibition by NSAIDs via suppression of the ERK/Sp1-mediated transcription. 12103254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115722_Plasmin activates pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 with a membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent mechanism. 12122099_Coexpression of glucose transporter 1 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human cancers 12147229_role in A549 cell migration on laminin-10/11 12147339_solution structure of a catalytic domain of MMP-2 complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor (SC-74020), determined by three-dimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy 12193399_data indicate the involvement of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and matrix metalloproteinase 9 in the cervical ripening process 12194986_calcium regulates MMP2 activation in a MT1-MMP-dependent manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells 12198653_Apoptosis of human hepatic myofibroblasts promotes activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. 12225805_Human fibronectin and MMP-2 collagen binding domains compete for collagen binding sites and modify cellular activation of MMP-2. 12235151_MMP2 activation is increased by Eph B4 receptor stimulation in human cells 12372458_endometrium from women with endometriosis expressed higher levels of MMP-2 and MT1-MMP and lower levels of TIMP-2 than did endometrium from normal women 12374789_role of acidic residues in TIMP-2 and TIMP-4 in binding hemopexin C domain 12376362_MMP-9 level and TIMP-1 levels increased after birth but are not linked to bronchopulmonary dysplasia outcome; low MMP-2 level at birth is associated with the development of BPD 12393408_MMP2 may play a pivotal role in the formation of capillarylike tubular structures in a collagen-containing fibrin matrix in vitro and may be involved in angiogenesis in a fibrinous exudate in vivo. 12393872_Autocrine/paracrine prostaglandin E2 production by non-small cell lung cancer cells regulates enzyme and cd44 in cox-2-dependent invasion 12431239_strong MMP-2 expression correlated with a favorable prognosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma 12438229_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12439941_correlation between expression of MMP-2, TIMP-2 protein and the ratio of MMP-2/TIMP-2 and clinical-pathological parameters of patients with gallbladder carcinoma 12451991_The in vitro invasive ability of ovarian tumor cells appeared to be positive correlated to high expression of VEGF and MMP-2. 12470034_Changes in plasma MMP-2 and TIMP-2 during cardiopulmonary bypass may play an important role in LV remodeling after cardiac surgery. 12471459_up-regulation of MMP-2 in stromal cells of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and in vasculitic neuropathies 12473650_laminin-5 as a substrate for mTLD, suggesting a role for laminin-5 processing by mTLD in the skin. 12475252_There are two TIMP binding sites on the hemopexin domain of MMP-2: one with high affinity that is involved in proMMP-2 or hydroxamate-inhibited MMP-2; and the other with low affinity involved in formation of the complex of active MMP-2 and TIMP-2. 12479097_The over-expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 may play a key role in invasion and lymph-node metastasis of in squamous carcinoma of the cervix. 12486137_Peptide binding results in perturbation of signals from residues located in the gelatin-binding pocket and flexible parts of the molecule. 12522578_No difference in MMP-2 between RG and SG. Only an increase with time under both conditions. 12559990_data demonstrated a moderate elevation of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and significant upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 in stable cell lines overexpressing gamma-synuclein 12586836_gelatinase A is inhibited by amyloid precursor protein, specifically in the decapeptide region 12587534_matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 and membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase mRNA expression in endometriosis was higher than in normal endometrium whereas E-cadherin, alpha- and beta-catenin mRNA expression was not suppressed in endometriosis 12589095_MMP-2 may contribute to eosinophil and mast cell migrations into nasal polyp tissue. 12601782_Data show that cells grown on oxidized ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)discs decreased the release and activity of metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) but not MMP-9 compared to cells grown on control and non-oxidized UHMWPE discs. 12602913_MMP-2 is associated with tumor size, invasiveness and survival in breast cancer. 12614934_TIMP-2 is significantly increased in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer's and Huntington's disease patients. 12615834_In the recurrent implantation failure group, the MMP score and IL-1beta concentration were significantly higher than those in the control group, whereas concentrations of IFN-gamma and IL-10 were significantly lower. 12632066_MMP2 is regulated by IL-8 in invasive pancreatic cancer 12632084_MMP2 is induced by snail protein in squamous cell carcinoma 12642591_triple-helical peptides are highly selective substrates for and are hydrolyzed by human MMP2 and MMP9 12651627_expression and regulation by intestinal myofibroblasts in inflammatory bowel disease 12657623_Gelatinase A is an estrogen-responsive gene and the loss of function polymorphism within an operational estrogen receptor binding site associated with a decrease in genetic fitness underscores the biologic significance of promoter polymorphism analyses. 12657623_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12684625_Increased expression of MMP-2 in advanced stage and high grade renal cell carcinoma might be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis 12753080_Pathogenic amyloid beta stimulates expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2); the increase in activation is largely due to increased expression of membrane type-1 (MT1)-MMP. MMP-2 inhibitors increased HCSM cell viability 12764090_Exploiting their astrocyte environment, glioma cells activate MMP-2 through the urokinase-type plasminogen activator-plasmin cascade, and this leads to the increased invasiveness of glioma cells in the central nervous system. 12832446_PR-3 is able to degrade matrigel components and denatured collagen and to directly activate secreted but not membrane-bound pro-MMP-2 12845641_Increased in situ mmp-2 activity in renal cell tumor tissues correlates with tumor size, grade and vessel invasion 12861074_plays a critical role in inducing tumor cell infiltration, and this invasive phenotype is caused by activation of MMP-2 12873995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12914776_Ultraviolet A downregulates MMP-2 in keratinocytes. 12939660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12952836_The present results indicate that MMP-2 can be helpful in diagnosing Takayasu arteritis [TA] and that MMP-3 and MMP-9 can be used as activity markers for TA 12967855_Both active gelatinases were detected in tears of severe corneal ulcer or severe ocular burn cases. The active form of gelatinase expression may be related to the severity of ulceration. 12970394_differences in the levels of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the normal ovary and ovarian tumours of different histology, including clear cell carcinoma 12970724_palpable tumours demonstrated significantly more MMP-2 and significantly less MMP-9 expression than nonpalpable tumours 14500349_MMP2 increased VEGF release by SKOV3 and OVCAR3 ovarian carcinoma cells. 14519487_results suggest that matrix metalloproteinase 2 plays an important role in tumor invasion and metastasis 14520690_Increased plasma MMP-2 is associated with colorectal cancer 14580155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14604886_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14614057_MMP-2 immunostaining was positive in 4 of 8 cases of invasive carcinoma and stained stromal area around tumor nest. Matrix metalloproteinases are activated in carcinoma in situ and in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of uterine cervix. 14644155_findings established the existence of a novel alternative/complementary pathway by which furin increases tumor cell invasion through an amplification/activation loop between MMP-2 and TGFbeta 14644777_ANG II, via AT(1)R, modulates the secretion of TNF-alpha and MMP-2 from vascular endothelial cells and TNF-alpha mediates the effects of ANG II on MMP-2 release. 14661256_effect of titanium, zirconia and alumina ceramics on activity and secretion in human osteoblasts 14666611_Laminin-5 gamma 2 chain and MMP-2 may contribute synergistically to the formation of budding colorectal tumor cells. 14679018_Increased MMP-2 expression by malignant prostatic epithelia is an independent predictor of decreased prostate cancer disease-free survival. 14694003_a possible of marker for microangiopathies in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. 14697951_Serum MMP-2 does not relate to the late phase of hepatic ischmeic reperfusion injury after human orthotopic liver transplantation. 14710472_Tissue from lateral and medial rectus muscles had different levels of expression of TIMP-1 and 2, MMP-2, and BMP-4,which may underlie different characteristics of these extraocular muscles and may influence wound healing after strabismus surgery. 14713104_one of the mechanisms by which S100A4 may exert its effect on metastasis of some tumors is by regulating the MMP-2 activity. 14732714_the methionine residue and the Met-turn of MMP2 play an essential role in catalysis or active site structure 14744781_data supports a role for MMP-2 in breast cancer progression, both in the growth of primary tumors and in their spread to distant organs 14766248_Stromal MMP-2 occurs early and may play a role early in ovarian adenocarcinoma invasion. 14871985_matrix metalloproteinase-2 has a role in progression of breast carcinoma 14973177_MMP and TIMP may be involved in the feto-neonatal development and may contribute to the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and/or intraventricular hemorrhage in critically ill preterm neonates 14981939_Various growth factors induce migration of human non-small cell lung cancer cells in the presence of extracellular matrix (ECM) components MMP-2 and MMP-9. 14983226_MMP-2, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 are downregulated in human orthotopic liver transplantation 14990702_downregulated by Cytomegalovirus IL-10 activity in uterine microvascular endothelial cells and differentiating-invading cytotrophoblasts 14990972_Matrix metalloproteinase-2 may play a role in the pathogenesis, invasion, and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. 14996438_Analysis of promoter MMP-2 gene variability could help us to understand individual susceptibility to MMP inhibitor treatment of the coronary artery disease. 14996438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15004438_In control myometrium only 10% of Gelatinase A (MMP-2)exists in an active form, whereas in uterine leiomyomas, especially in large ones, the values reach 30% 15009703_elastin derived peptides following interactions with S-Gal elastin receptor can favor melanoma cells invasion through a three-dimensional type I collagen matrix by upregulating MMP-2 activation. 15015767_MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions are prognostic factors predicting the recurrence of meningioma, independent of proliferative potential. 15051038_matrix metalloproteinase 2(MMP-2) was uterine smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential(STUMP), and in 48% of leiomyosarcoma 15056834_MMP-2 correlated negatively with fractional shortening & positively with LV dimension. Changes in the release & activity of MMP-2 may be associated with the mechanisms responsible for cardiac remodeling in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 15067014_MMP-2 or MMP-9 mediated tumor cell invasion requires integrin cytoplasmic-tail motif EKQKVDLSTDC 15102849_although there is a seemingly high structural similarity between TACE and MMP-2, these enzymes are significantly diverse in the electronic and chemical properties within their active sites 15165255_Helicobacter pylori infection results in substantially increased in the gastric mucosa, probably contributed to in large part by tissue-resident macrophages 15201662_Active involvement of MMP-2 and -9 in end-stage liver disease and orthotopic liver transplantation. 15241180_results suggest that matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 contribute to caspase-mediated brain endothelial cell death after hypoxia-reoxygenation by disrupting cell-matrix interactions and homeostatic integrin signaling 15248212_Activated protein C (APC) and MMP-2 are coordinately up-regulated and tightly bound in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid and colocalized in synovia. APC may modulate MMP-2 activity in RA. 15248826_marked difference in MMPs and their inhibitors in the in vitro fertilized women and normally ovulating women 15250832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15254682_EGFR, c-erbB-2, VEGF and MMP-2 and MMP-9 play an important role in tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 15255544_endothelial cell-associated cathepsins B and L are not involved in the invasive growth of capillaries from existing blood vessels and the presence of collagen is necessary for MMP2 expression in endothelial cells 15265790_a mechanism for ROS function in Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) activation of endothelial cell MMP2 and MMP9 during VCAM-1-dependent lymphocyte migration 15271946_Streptococcus pyogenes SpeB activates proMMP-2 with subsequent release of proapoptotic TNF-alpha and sFasL leading to apoptosis, tissue damage and streptococcal invasion in the host. 15277330_MMP-2 plays a pivotal role in oxLDL-induced activation of the sphingomyelin/ceramide signaling pathway and subsequent smooth muscle cell proliferation. 15280384_matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein and bone morphogenetic protein-2 processing and transport in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells is regulated by serum fetuin 15280448_Identified,in the promoter region of the human MMP-2 gene, a cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) consensus domain that is highly responsive to IL-10-dependent down-regulation or MMP2 expression in a primary human prostate tumor cells. 15317806_biochemical analysis of in-tandem fibronectin type II repeats from human matrix metalloproteinase 2 15317818_Brg-1 plays a role in regulating the recruitment of Sp1, Sp3, AP-2, and polymerase II to the MMP-2 promoter. 15351863_data suggest that the MMP-2/TIMP2 system and an activated extrinsic coagulation pathway could cooperate in conditions of elevated SOX and could influence arterial remodeling resulting in the presence of CVD in haemodialysis patients 15375490_Overexpression of MMP-2 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 15381707_the hemopexin domain of MT1-MMP is not required for the activation of proMMP2 on cell surface but is essential for MT1-MMP-mediated invasion in three-dimensional type I collagen 15449075_Increased gelatinase in culture medium of toxic epidermal necrolysis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome skin maintained in organ culture and in blister fluid indicates that these gelatinases may be responsible for detachment of epidermis in these diseases. 15475447_MMP-2 status in stromal fibroblasts, not in tumor cells, was a significant prognostic factor associated with angiogenesis in NSCLC. 15485653_MMP-2 -1306 C-->T polymorphism may be associated with colorectal cancer development and invasion 15485653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15489233_clearance of pro-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2.tissue inhibitor of MMPs (TIMP-2) complex involves binding to the cell membrane and subsequent low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP)-dependent internalization and degradation 15492291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15522165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15541021_The Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 was expressed of cultured human uveal melanocytes, and analysis revealed the Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 mRNA. 15557756_The expression of MMP-2,MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 was lower in the benign and low malignancy ovarian tumors compared with the malignant ones. 15567754_MMP-2 plays an essential role in tumor invasion and metastasis, while TIMP-2 is shown to strongly inhibit cancer invasion and metastasis. 15569994_Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer seems to be partly related to expression of AP-2 and HER2 15604254_In melanoma cells microtubule-dependent traffic of MMP2/MMP9-containing vesicles and exocytosis are critical steps for invasive behavior. 15609121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15609121_breast cancer phenotype and outcome can be influenced by common functional polymorphisms in MMP genes. 15609318_secreted pro-MMP-2 and pro-MMP-9 are downregulated by farnesyltransferase inhibitors in carcinoma cells 15609323_alphav integrins and MMP2 have roles in migration of human ovarian adenocarcinoma cells through endothelial extracellular matrix 15616792_This study found an up-regulation of TIMP-1, TIMP-2 and MMP-2 RNA in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy muscle. 15621117_The correlation between macrophage infiltration and MMP-II supports the role of macrophages in the development of chronic allograft nephropathy. 15632190_Abeta1-42 may play an important role in the negative regulation of TGF-beta1-induced MMP-2 production via Smad7 expression 15637056_furin can directly cleave the RXXR amino acid sequence in the propeptide domain of proMMP-2 leading to inactivation of the enzyme. 15651999_These findings suggest that epimorphin contributes to repair of pulmonary fibrosis in nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, perhaps partly by inducing expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2, which is an important proteolytic factor in lung remodeling. 15665288_MMP-2 is an important determinant of cancer cell behavior but is not inhibited by the collagen binding segment of fibronectin. 15665394_MMP2 may have a role in cervical cancer recurrence 15672417_Hypoxia increased pro-MMP-2 expression, on collagen type I or type IV further via Erk1/2 and p38 MAP kinase signaling for lung fibroblasts 15691365_Inactivating mutations in MMP-2 cause Winchester syndrome, a multicentric osteolysis syndrome. 15731163_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15743799_up-regulation of Ang2, MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and LN 5 gamma 2 is associated with the invasiveness displayed by human gliomas 15754118_High MMP2 expression is associated with breast cancer 15756447_E1AF positively regulates transcription from MT1-MMP genes, which plays an important role in invasion and metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue by converting pro-MMP-2 into active-MMP-2 15820246_Hypoxia induces an increased invasive capacity via gelatinase up-regulation without loss of cell viability in adenocarcinomas 15831360_Age-related MMP-2 upregulation occurs in the human aorta but not in the internal mammary artery. 15841469_MMP-2 is required for the mitogenic and proinvasive effects of reactive oxygen species on hepatic stellate cells and demonstrate that ERK1/2 and PI3K are the main signals involved MMP-2 expression. 15866216_expression up-regulated in Helicobacter species-infected colon and bile duct epithelial cells and hepatocytes. 15878967_Lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine 1-phoshpate enhanced MMP-2 expression in mRNA, protein levels, and also enzymatic activity of cells of the EAhy926 human endothelial cell line. 15885317_Migration of CD4+ T cells is dependent on MMP2 expression; T-helper type 1 (Th1) cells secrete higher levels of MMP2 and have higher migratory capacity in comparison to Th2 cells. 15904490_expression of CD147 is upregulated during the differentiation of monocyte THP-1 cells to macrophage cells, and CD147 induces the secretion and activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and enhances the invasive ability of THP-1 cells 15911696_furin and PC5 play a role in a MT-MMP-MMP-2 proteolytic cascade, involving provision of macrophage MT1-MMP for the activation of pro-MMP-2; furin and PC5 are expressed in monocytes and colocalize with MT1-MMP in macrophages in the atherosclerotic plaque 15929171_MMP-2 may play an important role in the development of invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15949313_COX-2 and MMP-2 may be involved in the airway inflammatory process and contribute to airway remodeling in COPD. 15955221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15955448_MMP-2 was significantly higher in cell extracts from pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients than in control cells, whereas differences were negligible in the culture media. 15955449_HIV-1 interaction with mannose receptor induces promotion of MMP-2 through mannose receptor-mediated intracellular signaling in astrocytes. 15983226_Leptin induced human oarticc smooth muscle cell proliferation and MMP-2 expression through a PKC-dependent activation of NAD(P)H oxidase 15998676_MMP-9 but not MMP-2 was associated with internal elastic lamina degeneration, intimal hyperplasia, and luminal narrowing in giant cell arteritis 15998788_melanoma cells cross-present, in an alpha v beta3-dependent manner, an antigen derived from secreted matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) to human leukocyte antigen A*0201-restricted T cells 16005367_Plasma MMP-2, TIMP-1 and hs-CRP concentrations were significantly increased in type-2 diabetic patients. 16018746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16018746_polymorphisms in the gene promoter do not contribute significantly to the interindividual periodontitis susceptibility 16023005_hemoglobin stimulates the secretion of uPA, MMP-2 and MMP-9 by synovial tissues; possible role of hemoglobin in joint damage after intra-articular bleeding 16023011_generation and modulation of MMP-2 may be directly involved in the different responses seen in knee ligament injuries 16042227_MMP-2 seems to be associated with the chronic progressive phase of the multiple sclerosise. 16082623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16083752_The most invasive cell line secreted the highest amounts of MMP-2 and MMP-9. 16097959_MMP2 immunoreactivity was present in polymyositis and dermatomyositis 16134528_There was a significant correlation between active MMP-2 and the invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Active MMP-2 is a prognostic indicator in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. 16142392_MMP-2 may play an important role in the invasion and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 16142692_Pro-MMP-2 levels were higher at early stages of the degenerative disc disease 16146757_Smad4, but not Smad2, mediates TGF-beta1-induced MMP-2 expression in invasive extravillous trophoblasts 16158251_The expression of MMP2 is consistently significantly higher in neoplastic brain tissue compared to normal brain tissue, and may be involved in the process of metastasis of breast cancer to the brain. 16168111_monocyte and macrophaage cells in the breast tumor microenvironment play an important role in the modulation of MMP-2. 16188099_AP-1 Decoy inhibits the increase in MMP-2 activity and the up-regulation of TIMP-1 induced by bleomycin-A5 in pulmonary fibroblasts. 16188574_MMP-2 may be a marker of microangiopathy 16213873_Although MMP-1 is not detected in patients with persistent ovarian cysts, MMP-2 is expressed in all of the cysts 16260653_FAK regulates integrin-dependent MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and release by T lymphoid cells through src kinase 16275157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16306050_PAF stimulated the gelatinase activity of MMP-2 by activating transcription and MMP-2 expression 16308106_MMP-2/-9 activity correlated positively with cardiomyocyte apoptosis. MMPs have pivotal roles in acute cardiac dysfunction during early multiple organ failure in combined vasoconstrictor-masked hypovolemic and endotoxemia shock. 16313894_Results suggest that MMP-2 might contribute in the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. 16338908_Obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome have elevated serum concentrations of MMP-2. 16339461_variations in EMMPRIN glycosylation forms are associated with either MMP-2 or MMP-9 activity 16341461_These findings strongly indicate that increased MMP-2 expression in uterosacral ligaments is associated with pelvic organ prolapse. 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16359987_Active MMP-2 levels are constant during the menstrual cycle. 16361361_ATP induced phosphorylation of intracellular JNK, and inhibition of the JNK pathway blocked ATP-stimulated MMP-2 release, indicating signaling via this pathway. 16364202_MMP2 activity in human endothelial cells exposed to high glucose is inhibited by acetylsalicylic acid 16379022_These results suggest the activation of proMMP-2 as an important event in the process of uveal melanoma progression. 16407830_Both MAPKAPK2 and HSP27 are necessary for TGFbeta-mediated increases in MMP-2 and cell invasion in human prostate cancer. 16413616_MMP-9 and MMP-2 are mediators of inflammation in chronic otitis media with effusion 16414983_TGF-beta1 increases in vitro airway wound repair via MMP-2 upregulationin respiratory epithelial wound repair. 16424893_Results of this study provide evidence that MMP-2 immunoreactive protein is prognostic in estimation of the aggressive clinical course of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 16425263_The colocalization of EMMPRIN, MT1-MMP and TIMP-2 in human cervical carcinomas seems to be involved in a specific distribution pattern of tumor cell bound MMP-2, which is related with local proteolytic activity. 16453304_results strongly suggest that Src induces MMP-2 expression via transcription activation and the ERK/Sp1 signaling pathway is involved in this process 16456793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16458924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16458924_variations in the MMP2 gene do not contribute to the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm 16476613_MMP-2 expression was increased in posterior wall of thoracic aortic aneurysms. 16510149_association between oxidative stress and the MMPs/TIMPs system in hemodialysis patients could represent one of the mechanisms involved in the progression of atherosclerosis in this population 16551362_PDK1 mediates mammary epithelial cell growth and invasion in part by MT1-MMP induction, which in turn activates MMP-2 and modulates the ECM proteins decorin and collagen 16575904_p16 attenuates Sp1 binding to the MMP-2 promoter to suppress gene transcription and overexpression of Sp1 may counteract p16-induced downregulation of MMP-2. 16585124_potential role of VEGF-A, MMP-2 and MMP-9, and TNF-alpha in the mechanism of idiopathic excessive uterine bleeding; active form of MMP-2 was reduced in women with menorrhagia 16615109_Higher MMP2 activity is associated with breast cancer 16647062_chitooligosaccharides may play an important role in the prevention and treatment of MMP-2 mediated several health problems such as metastasis and wrinkle formation 16718267_Basal secretion levels of active matrix metalloproteinase-2 respond to various extracellular matrix proteins, cytokines, and growth factors in normal human melanocyte cells and melanoma cell lines from different stages of neoplastic progression. 16718824_MMP-2 expression has significant correlation with tumor invasion, tumor differentiation and lymph node metastases; MMP-2 may participate in the development of lymph node micrometastasis of gastric carcinoma 16722933_Up-regulation of MMP-2 expression was observed in atypical and anaplastic meningiomas. 16728425_an imbalance between the MMP-2 and TIMP-2, caused primarily by an increase in TIMP-2 activity, contributes to the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 16739355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16755991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16772717_Increase in serum levels eight days after IVIG treatment in neuromuscular disease. 16776850_When all three proteases are studied in combination, a tendency was found for tumors with high MMP-2, high MMP-14 and low TIMP-2 expression to predict a poor prognosis but the results did not reach significance 16778129_In artery samples in diabetic patients relative to nondiabetic patients, capillary density was reduced to 30%, VEGF expression was reduced by 48%; the expression and the gelatinolytic activity of MMP-2 and -9 were upregulated. 16803520_MMP-2 could be associated with aggressive behavior, but MMP-9 expression diminishes in high-grade tumors. 16829143_These results indicate a temporal relationship between MMP-2 production by endothelial cells and the onset of angiogenic event. 16840178_plasma levels and activities of MMP-2, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 are increased in hypertensive patients, which may reflect abnormal extracellular matrix metabolism 16884384_overexpression of matri |
ENSMUSG00000031740 |
Mmp2 |
390.017498 |
0.4639060910 |
-1.108095 |
0.086814808 |
164.352336 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000012670461367834794136713761665178736134223122913684209613915651112856973517244176126478651326213824279687258922422188334167003631591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001993774091569739545229754978145152467544945333719088234607951031297042517081446071428580858069835868295882619349868036806583404541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
248.4526154 |
13.2948597 |
539.3874877 |
18.8899763 |
| ENSG00000087263 |
55239 |
OGFOD1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N543 |
FUNCTION: Prolyl 3-hydroxylase that catalyzes 3-hydroxylation of 'Pro-62' of small ribosomal subunit uS12 (RPS23), thereby regulating protein translation termination efficiency. Involved in stress granule formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24550447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24550462}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Iron;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Vitamin C |
|
Enables peptidyl-proline 3-dioxygenase activity. Involved in several processes, including peptidyl-proline hydroxylation; regulation of translational termination; and stress granule assembly. Located in cytoplasmic stress granule; cytosol; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55239; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; L-ascorbic acid binding [GO:0031418]; peptidyl-proline 3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0031544]; peptidyl-proline dioxygenase activity [GO:0031543]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; peptidyl-proline hydroxylation [GO:0019511]; protein hydroxylation [GO:0018126]; regulation of translational termination [GO:0006449]; stress granule assembly [GO:0034063] |
20154146_Data suggest that OGFOD1 plays important proapoptotic roles in the regulation of translation and HRI-mediated phosphorylation of eIF2alpha in cells subjected to arsenite-induced stress. 20579638_OGFOD1 plays an important role in ischemic cell survival and an OGFOD1 iron binding residue is required for ATPAF1 gene expression. 24550447_OGFOD1 catalyzes prolyl hydroxylation of RPS23 and is involved in translation control and stress granule formation. 25909288_Propose that OGFOD1 is required for breast cancer cell proliferation and is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. 31112528_The ribosomal prolyl-hydroxylase OGFOD1 decreases during cardiac differentiation and modulates translation and splicing. 32002629_High OGFOD1 expression is associated with papillomavirus-infected laryngeal papillomas. |
ENSMUSG00000033009 |
Ogfod1 |
226.064551 |
2.2280314279 |
1.155770 |
0.163756941 |
49.203144 |
0.00000000000230780524682617071750363360577299110714191709980980249383719637989997863769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000013431863345092381446247144059395951147875547526666650810511782765388488769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
310.8052471 |
39.4156715 |
140.6319716 |
13.2072958 |
| ENSG00000087495 |
116154 |
PHACTR3 |
protein_coding |
Q96KR7 |
|
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the phosphatase and actin regulator protein family. The encoded protein is associated with the nuclear scaffold in proliferating cells, and binds to actin and the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase-1, suggesting that it functions as a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase-1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:116154; |
nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036] |
12925532_scapinin is a putative regulatory subunit of PP1 and is involved in transformed or immature phenotypes of HL-60 cells 16974080_a highly conserved complex genomic organization with four different leader exons; Alternative splicing of exon 5 was found to be limited to human vs. mouse; expression seems to occur predominantly in the brain 19158953_scapinin enhances cell spreading and motility through direct interaction with actin and PP1 plays a regulatory role in scapinin-induced morphological changes 19473719_E2F4, PHACTR3, PRAME family member and CDH12 most probably play important role in non-small-cell lung cancer geneses 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21487013_Because its expression is highest in relatively plastic regions of the adult brain (cortex, hippocampus), scapinin is a new regulator of neurite outgrowth and neuroplasticity in the brain. 22135045_DNA methylation of phosphatase and actin regulator 3 is associated with colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000027525 |
Phactr3 |
293.465846 |
0.0651047466 |
-3.941093 |
0.157658279 |
759.685648 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003143480265487540465321797391535333695779920464083800955695108536315579600120611654478433729694706333590943829653475537665734275202328866530471728639894039354452692 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002343321652454348407124245592171169880372873395584284123202386589819063179483773571399474192733488840114379888127058737045088495189321602860140054156385039329158692 |
Yes |
No |
36.2606635 |
3.8238583 |
560.8929142 |
28.2029234 |
| ENSG00000088256 |
2767 |
GNA11 |
protein_coding |
P29992 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems (PubMed:31073061). Acts as an activator of phospholipase C (PubMed:31073061). Transduces FFAR4 signaling in response to long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) (PubMed:27852822). Together with GNAQ, required for heart development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21278, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27852822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31073061}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Host-virus interaction;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins), which function as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. G proteins are composed of 3 units: alpha, beta and gamma. This gene encodes one of the alpha subunits (subunit alpha-11). Mutations in this gene have been associated with hypocalciuric hypercalcemia type II (HHC2) and hypocalcemia dominant 2 (HYPOC2). Patients with HHC2 and HYPOC2 exhibit decreased or increased sensitivity, respectively, to changes in extracellular calcium concentrations. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:2767; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding [GO:0031683]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; action potential [GO:0001508]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; cellular response to pH [GO:0071467]; cranial skeletal system development [GO:1904888]; developmental pigmentation [GO:0048066]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; entrainment of circadian clock [GO:0009649]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; heart development [GO:0007507]; multicellular organism aging [GO:0010259]; phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060158]; phototransduction, visible light [GO:0007603]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of melanocyte differentiation [GO:0045634]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] |
12130679_the C-terminal domain participates intimately in the efficacy of B1R and B2R G(q/11) coupling by contributing both positive and negative regulatory epitopes. 12759536_GNA11 is involved in signalling of gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor, which negatively regulates cell growth. Down-regulation is suggested to be involved in human breast cancers. 15632174_a new signaling pathway by which G alpha(q/11)-coupled receptors specifically induce Rho signaling through a direct interaction of activated G alpha(q/11) subunits with p63RhoGEF. 15693018_regulation of the PLC pathway through the PTH1R is significantly increased by elevating expression of G(11)alpha in osteoblastic cells. 15863506_TPO integrates G(i), but not G(q), stimulation, supports integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) activation platelet aggregation independently of phospholipase C but requires PI3-kinase and Rap1B 16297597_These results indicate that the thio-acylation status of the alpha1b-adrenoceptor does not regulate G protein activation whereas thio-acylation of Galpha11 plays a key role in activation by the receptor. 16350855_soluble amyloid precursor protein release enhancement induced by muscarinic receptor stimulation was decreased by a G(q/11) minigene construct 16365309_CB(1) receptors are stabilized in a conformation that enables G(q)11 signaling by the WIN55212-2 cannabinoid agonist, thus shifting the G protein specificity of the receptor 16611642_the ability of MAS to up-regulate AT(1) receptor levels reflects the constitutive capacity of MAS to activate Galpha(q)/Galpha(11) and hence stimulate PKC-dependent phosphorylation of the AT(1) receptor 16723377_G(q/11)-coupled receptors are the principal G protein-coupled receptor subfamily mediating cooperative mitogenic signaling in airway smooth musscle. 17056873_The phosphorylation of Galpha11 protein represents a novel mechanism involved in regulation of receptor signaling. 17535809_two distinct regions of the Cav3.3 channel are necessary and sufficient for complete M1 receptor-mediated channel inhibition 17552882_Solubilization of this class of Galpha proteins was observed after prolonged agonist stimulation, induced by ultra high concentration of hormone and in cells expressing a large number of GPCRs, revealing tight binding of G(11)alpha protein to the membrane 18713748_Protein kinase C-related kinase and ROCK are required for thrombin-induced endothelial cell permeability downstream from Galpha12/13 and Galpha11/q 20531218_[review] Gq transgene activation mediates cardiac hypertrophy in vivo in response to pressure overload; transgenic mice with cardiac-specific deletion of Galphaq family proteins show no ventricular hypertrophy in response to pressure overload 21083380_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21083380_Of the uveal melanomas we analyzed, 83% had somatic mutations in GNAQ or GNA11. 21366456_Benign and malignant blue nevi harbor frequent mutations in the Galphaq class of G-protein alpha subunits, Gnaq and Gna11 proteins. 21464134_Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by the RH domain of G protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK2, and Galphaq/11. 21945171_The DNA obtained is of sufficient quality to carry out genotyping for markers on chromosome 3, 6 and 8, as well as screening for somatic mutations in GNAQ and GNA11 genes. 22240728_The presumed association of TRH-R with G(q/11)alpha proteins in plasma membranes was verified by RNAi experiments 22307269_The results expand the spectrum of GNA11 mutations that may occur in melanocytomas. 22758774_In primary melanocytic tumours, GNA11 and N-RAS mutations represent a mechanism of MAPK pathway activation alternative to the common GNAQ mutations 22977135_The vast majority of primary large uveal melanomas harbor mutually-exclusive mutations in GNAQ or GNA11, but very rarely have the oncogenic mutations that are reported commonly in other cancers. 23572068_Letter/Case Report: role of GNAQ/GNA11 mutational analysis in management of choroidal melanoma metastatic to the contralateral orbit. 23599145_This study identifies HRAS mutations in deep penetrating nevi. The presence of HRAS mutations and absence of GNAQ or GNA11 mutations in deep penetrating nevi suggests classification of these nevi within the Spitz rather than the blue nevus category. 23634288_Mutant alleles of the GNA11 or GNAQ genes, which are highly specific for uveal melanoma, were identified in cell-free DNA of 9 of 22 (41%) patients. 23778528_GNAQ and GNA11 mutations are, in equal matter, not associated with uveal melanoma patient outcome. 23802516_Galpha11 mutants with loss of function cause familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia type 2, and Galpha11 mutants with gain of function cause a clinical disorder designated as autosomal dominant hypocalcemia type 2. 23802536_Genomewide linkage analysis, combined with whole-exome sequencing, revealed two different heterozygous mutations affecting Galpha11 as novel causes of autosomal dominant isolated hypoparathyroidism. 23802749_There is a specific Egr-1 binding site at nt-475/-445. Egr-1 evoked an increased GNA11 transcription. 24141786_Metastatic uveal melanoma with GNAQ or GNA11 mutations is responsive to PKC inhibitors. 24308950_Increasing Galpha11 protein expression in osteoblasts can alter gene expression and result in a dual mechanism of trabecular bone loss. 24497640_the PECAM-1.Galphaq/11 mechanosensitive complex contains an endogenous heparan sulfate proteoglycan with HS chains that is critical for junctional complex assembly and regulating the flow response 24576953_melanopsin is a powerful optogenetic tool for the investigation of spatial and temporal aspects of Gq signalling in cardiovascular research 24823460_Our findings indicate that the germline gain-of-function mutation of GNA11 is a cause of autosomal dominant hypoparathyroidism and implicate a novel role for GNA11 in skeletal growth. 24970262_There was a significant association of GNA11 mutation status with metastatic status in uveal melanoma. 25280020_Oncogenic GNA11 mutation is associated with uveal melanoma. 25304237_review discusses the multiple activated signaling targets downstream of mutant GNAQ and GNA11 in uveal melanoma, including MEK, PI3-kinase/Akt, protein kinase C, and YAP 25695059_Involved in the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and GNAQ/11 pathways. 25934394_Identification of Distinct Conformations of the Angiotensin-II Type 1 Receptor Associated with the Gq/11 Protein Pathway and the beta-Arrestin Pathway Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. 26100877_Data show that N-linked glycosylation of protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR1) at extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) controls G12/13 versus Gq G-proteins coupling specificity in response to thrombin stimulation. 26368812_Distribution of GNAQ and GNA11 Mutation Signatures in Uveal Melanoma Points to a Light Dependent Mutation Mechanism. 26399561_Driver mutations are rare in mutational hotspots of BRAF, NRAS, KIT, and GNAQ/GNA11 in oral mucosal melanoma. 26462151_Mutations in GNA11 gene is associated with malignant uveal melanoma. 26645730_Melanomas associated with blue nevi or mimicking cellular blue nevi commonly have GNA11 mutations. 26729423_studies have identified a third Galpha11 mutation (Thr54Met) causing Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia Type 2 and reveal a critical role for the Galpha11 interdomain interface in CaSR signaling and Ca(2+) o homeostasis. 26778290_extensive dermal melanocytosis and phakomatosis pigmentovascularis are associated with activating mutations in GNA11 and GNAQ, genes that encode Galpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins 26818911_a novel germline gain-of-function Galpha11 mutation, Val340Met, causing Autosomal Dominant Hypocalcemia Type 2 demonstrates the importance of the Galpha11 C-terminal region for G-protein function and CaSR signal transduction. 26994139_These findings demonstrate that CaSR-targeted compounds can rectify signaling disturbances caused by germline and somatic Galpha11 mutations, which respectively lead to calcium disorders and tumorigenesis; and that ADH2-causing Galpha11 mutations induce non-constitutive alterations in MAPK signaling. 27089234_GNAQ/GNA11Q209 mutations characterized a distinct, albeit uncommon subtype of non-uveal melanoma (0.5-1%). These mutations were essentially melanoma-specific, occurred in all subtypes of this disease (including cutaneous, mucosal, uveal, and unknown primary), and were mutually exclusive with other common melanoma mutations. 27334330_The identified GNA11 mutation results in biochemical abnormalities typical for autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. Additional features, including short stature and early intracranial calcifications, cosegregated with the mutation. 27498141_GNAQ and GNA11 mutations occur frequently in mucosal melanoma and may be a prognostic factor for MM. Our data implicate that GNAQ/11 may be potential targets for targeted therapy of mucosal melanoma. 27566546_CGRP family of receptors displays both ligand- and RAMP-dependent signaling bias among the Galphas, Galphai, and Galphaq/11 pathways. 27913609_In 33 CASR-negative patients with suspected FHH, Data found two (~6%) with a mutation in AP2S1 (p.Arg15Leu and p.Arg15His). Family screening confirmed the genotype-phenotype correlations. Data did not identify any pathogenic mutations in GNA11. 28012237_Sporadic melanotic schwannoma with overlapping features of melanocytoma bearing a GNA11 mutation in an adolescent girl. 28083870_Results show that postzygotic mosaicism for GNA11 mutations causes an overlapping phenotypic spectrum of vascular and melanocytic birthmarks. 28120216_GNA11 mutations are associated with extremity capillary malformations causing overgrowth. 28248732_The Role of Mutation Rates of GNAQ or GNA11 in Cases of Uveal Melanoma in Japan. 28444874_There were no significant differences in the prevalence of GNAQ and GNA11 mutations between patients with or without metastatic disease 28700778_we find iris melanomas to be related genetically to choroidal and ciliary body melanomas, frequently harboring GNAQ, GNA11, and EIF1AX mutations. 28982892_Mutations in GNAQ and GNA11 genes in Greek uveal melanoma population present frequencies that qualify them as potential targets for customized therapy. 29059311_Adenocarcinomas or adenomas derived from pigmented ciliary epithelium is distinguished from uveal melanoma by the absence of SOX10 expression and presence of the BRAF V600E mutation. 29107092_the induction of luteal Akr1c18 by Galphaq/11 is mediated by the activation of phospholipase C. 29209985_GNA11 Mutation is associated with Uveal Melanomas. 29570931_Mutation in GNA11 is associated with numerous protumorigenic changes within melanocytes. 30204251_In the current sample, the genes GNAS, GNAQ, and GNA11 were widely altered across cancer types, and these alterations often were accompanied by specific genomic abnormalities in AURKA, CBL, and LYN. 30552676_CXCL2-CXCR2 axis mediates through Galphai-2 and Galphaq/11 to promote tumorigenesis and contributes to cancer stem cell properties of CPT-11-resistant LoVo cells. 30783010_The mutations increase mitogenic signaling through the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (RhoA) axis that may represent cancer drivers operating in a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit, G11 (Galphaq/11)-independent manner. 30890659_FR900359 enabled suppression of malignant traits in cancer cells that are driven by activating mutations at codon 209 in Galphaq/11 proteins, we envision that similar approaches could be taken to blunt the signaling of non-Galphaq/11 G proteins. 31173078_Our results indicate that there is marked variation in MAPK activation in uveal melanoma (UM) with GNAQ/11 mutations. Thus, GNAQ/11 mutational status is not a sufficient biomarker to adequately predict UM patient responses to single-agent selective MEK inhibitor therapy. 31189994_our study demonstrated recurrent GNA14/GNAQ/GNA11 mutations were present in the majority of cherry hemangiomas and established its neoplastic nature 31580399_Intraocular Metastasis in Unilateral Multifocal Uveal Melanoma Without Melanocytosis or Germline BAP1 Mutations. 31614358_Mutations of GNAQ, GNA11, SF3B1, EIF1AX, PLCB4 and CYSLTR in Uveal Melanoma in Chinese Patients. 31707589_Our results implicated GNA11 mutations...as essential drivers in the pathogenesis of anastomosing hemangioma 31726051_Reverse Phenotyping in Patients with Skin Capillary Malformations and Mosaic GNAQ or GNA11 Mutations Defines a Clinical Spectrum with Genotype-Phenotype Correlation. 31838126_GNA11 Mutation as a Cause of Sturge-Weber Syndrome: Expansion of the Phenotypic Spectrum of Galpha/11 Mosaicism and the Associated Clinical Diagnoses. 31887832_The minor allele C of rs11084997 in GNA11 gene promoter was associated with decreased risk of Ns-HypoPT in Chinese population. 31992579_Detecting mosaic variants in patients with somatic overgrowth syndromes using cell-free circulating DNA and deep sequencing. 32064597_GNAQ and GNA11 mutant nonuveal melanoma: a subtype distinct from both cutaneous and uveal melanoma. 32771470_Identification of a Mosaic Activating Mutation in GNA11 in Atypical Sturge-Weber Syndrome. 32958754_GPR101 drives growth hormone hypersecretion and gigantism in mice via constitutive activation of Gs and Gq/11. 33003441_Dissecting Gq/11-Mediated Plasma Membrane Translocation of Sphingosine Kinase-1. 33639168_An experimental strategy to probe Gq contribution to signal transduction in living cells. 34260077_Mixed vascular naevus syndrome: report of three children with somatic GNA11 mutation and new systemic associations. 34385710_Somatic mutations of GNA11 and GNAQ in CTNNB1-mutant aldosterone-producing adenomas presenting in puberty, pregnancy or menopause. 35212356_Genomic Profiling of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma Shows Frequent Coexisting BAP1 or SF3B1 and GNAQ/GNA11 Mutations and Correlation With Prognosis. 35580369_In uveal melanoma Galpha-protein GNA11 mutations convey a shorter disease-specific survival and are more strongly associated with loss of BAP1 and chromosomal alterations than Galpha-protein GNAQ mutations. 35715928_GNA11-mutated Sturge-Weber syndrome has distinct neurological and dermatological features. 36440997_Early-onset hypertension associated with extensive cutaneous capillary malformations harboring postzygotic variants in GNAQ and GNA11. |
ENSMUSG00000034781 |
Gna11 |
139.889865 |
0.4820754022 |
-1.052669 |
0.337502514 |
9.425231 |
0.00214020145748599439558534918148779979674145579338073730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004698701995016105539826334336339641595259308815002441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.6813983 |
20.7454376 |
207.7105197 |
31.0716884 |
| ENSG00000088305 |
1789 |
DNMT3B |
protein_coding |
Q9UBC3 |
FUNCTION: Required for genome-wide de novo methylation and is essential for the establishment of DNA methylation patterns during development. DNA methylation is coordinated with methylation of histones. May preferentially methylates nucleosomal DNA within the nucleosome core region. May function as transcriptional co-repressor by associating with CBX4 and independently of DNA methylation. Seems to be involved in gene silencing (By similarity). In association with DNMT1 and via the recruitment of CTCFL/BORIS, involved in activation of BAG1 gene expression by modulating dimethylation of promoter histone H3 at H3K4 and H3K9. Isoforms 4 and 5 are probably not functional due to the deletion of two conserved methyltransferase motifs. Functions as a transcriptional corepressor by associating with ZHX1. Required for DUX4 silencing in somatic cells (PubMed:27153398). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16357870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17303076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18413740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18567530, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27153398}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Citrullination;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
CpG methylation is an epigenetic modification that is important for embryonic development, imprinting, and X-chromosome inactivation. Studies in mice have demonstrated that DNA methylation is required for mammalian development. This gene encodes a DNA methyltransferase which is thought to function in de novo methylation, rather than maintenance methylation. The protein localizes primarily to the nucleus and its expression is developmentally regulated. Mutations in this gene cause the immunodeficiency-centromeric instability-facial anomalies (ICF) syndrome. Eight alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. The full length sequences of variants 4 and 5 have not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:1789; |
catalytic complex [GO:1902494]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0003886]; DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase activity, acting on CpG substrates [GO:0051718]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-methyltransferase activity [GO:0009008]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; C-5 methylation of cytosine [GO:0090116]; DNA methylation [GO:0006306]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628] |
11932749_DNMT1 and DNMT3b cooperate to silence genes in human cancer cells 12015329_An essential role in cancer cell survival 12110732_Overexpression of a splice variant is associated with DNA hypomethylation on pericentromeric satellite regions during human hepatocarcinogenesis 12145218_the human de novo enzymes hDNMT3a and hDNMT3b form complexes with the major maintenance enzyme hDNMT1. 12208751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12208751_The DNMT3B C46359T polymorphism is associated with promoter activity of a novel DNMT3B transcript, and associated with the risk of lung cancer in non-Hispanic whites. 12359337_cloned and characterized the 5'-end of the mRNA and promoter regions 12601140_a registry of all known ICF-causing mutations, DNMT3Bbase, was constructed. The structural principles of the pathogenic mutations based on the modelled structure and the analysis of chi angle rotation changes of mutated side chains are discussed. 12738984_Over-expressed in squamous cell carcinoma of the mouth. 12879017_DNMT3b plays an important role in neoplastic transformation 12925568_DNMT3B is required for the methylation of L1 CpG islands on the inactive X chromosome. 14555514_Overexpression of DNMT3B is associated with breast tumor 14559786_DNMT1 plays a key role in methylation maintenance, DNMT3b may act as an accessory to support the function in ovarian cancer cells. 15148359_DNMT3B co-purifies and interacts, both in vivo and in vitro, with several components of the condensin complex (hCAP-C, hCAP-E and hCAP-G) and KIF4A 15217506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15375549_The DNMT3B C46359T polymorphism is statistically significantly associated with survival outcome in HNSCC patients. 15467427_Down regulation of DNMT3b is associated with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia 15490234_Overexpression of DNMT3b4 is involved in human hepatocarcinogenesis, even at the precancerous stages, not only by inducing chromosomal instability but also by affecting the expression of specific genes 15528220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528220_The DNMT3B -283T > C polymorphism influences DNMT3B expression, thus contributing to the genetic susceptibility to lung cancer. 15580563_two types of ICF patients that harbor different genetic characteristics; ICF type 1 is characterized by DNMT3B mutations and normal methylation of the alpha satellites; Type 2 lacks DNMT3B mutations and shows hypomethylation of the alpha satellites. 15854647_DNMT3B was shown to have a very pronounced flanking sequence preference for human DNA methylation. 15962389_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15962389_The distribution of DNMT3B SNP in North China is distinct from that in Caucasians, but it cannot be used as a stratification marker to predict susceptibility and lymphatic metastasis of gasstric cardia adenocarcinoma. 16004934_involvement of HPV infection in nonsmoking female lung tumorigenesis may be mediated, at least to a certain extent, through the increase of DNMT3b protein expression to cause p16INK4a promoter hypermethylation 16012746_Data suggest that the DNMT3B TT genotype may be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer. 16012746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16194411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16211278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16328059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16463117_we observed that the increase (10%) of genomic DNA methylation in patients with alcoholism was significantly associated with their lowered DNMT-3b mRNA expression 16481298_Transfection with the antisense DNMT3b gene eukaryotic expression plasmid can significantly reduce the expression level of the DNMT3b gene in the human biliary tract carcinoma cell line QBC-939. 16501171_Dnmt3b plays an essential role at different stages of mouse development, and that Immunodeficiency, Centromeric instability and Facial anomalies missense mutations cause partial loss of function 16501248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16543361_Dnmt3b-Dnmt3L interactions play an important role in the regulation of DNA methylation during mammalian development. 16773201_DeltaDNMT3B is the predominant form of DNMT3B in non-small cell lung cancer. 16920385_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16920385_The relative distribution of three DNMT3B SNPs among a Taiwanese population can not be used as a stratification marker to predict either an individual's susceptibility to HNSCC and/or the likelihood of cervical metastasis of HNSCC. 16951144_Expression of DNMT3B variants is common in nsn-small cell lung carcinoma and may play an important role in the development of promoter methylation. 16951151_RAS oncogene induces RECK gene silencing through DNMT3b-mediated promoter methylation which may be useful in treatment of cancer metastasis 17017004_Expression of DNMT3B was inversely correlated with that of p14ARF and p16INK4a. Results suggest that DNMT3B over-expression may be involved in the suppression or lower expression of p14ARF and p16INK4a observed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 17067458_Correlation between the expression of DNMT3b and the methylation of tumor suppressor genes, tumor grade and stage was not found. 17081533_The genes DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B were over-expressed in the ectopic endometrium as compared with normal control subjects or the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis 17149367_The p16 gene promoter was hypermethylated in pterygia, and this hypermethylation was strongly linked to expression of the positive expression of DNMT3b protein and to the suppression of p16 protein. 17277043_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17303076_results showed for the first the direct linkage between DNMT and zinc-fingers homeoboxes protein, leading to enhanced gene silencing by DNMT3B 17318376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17318376_The DNMT3b 39179GT polymorphism may be a genetic determinant of adenocarcinoma of the colon, especially in younger Korean men. 17353906_Results suggest that truncated DNMT3B proteins could play a role in the abnormal distribution of DNA methylation found in cancer cells. 17369845_tobacco exposure induces the abnormal expression of SNCG in lung cancer cells through downregulation of DNMT3B 17532557_DNMT1 plays a key role in maintenance of methylation, and DNMT3B may act as an accessory DNA methyltransferase to epigenetically silence CXCL12 expression in MCF-7 and AsPC1 cells 17538945_Progressive up-regulation of the gene encoding DNMT3B was found in the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. 17688412_We found clinically relevant levels of Hcy (0-500 microM) induced elevation of SAH, declination of SAM and SAM/SAH ratio and reduced expression of SAHH and MBD2, but increased activity of DNMT3a and DNMT3b affecting DNA methylation 17705213_Early prenatal diagnosis of ICF syndrome by mutation detection. 17890317_Expression of microRNA is inversely correlated with DNMT3B in non-small cell lung cancer. 17991895_reveals novel functions for DNMT1 as a component of the cellular response to DNA damage, which may help optimize patient responses to this agent in the future 17998942_the autocrine hGH-stimulated increases in DNMT3A and DNMT3B expression mediate repression of plakoglobin gene transcription by direct hypermethylation of its promoter and consequent phenotypic conversion of mammary carcinoma cells 18006804_promoter DNA methylation can be differentially regulated and DeltaDNMT3Bs are involved in regulation of such promoter-specific de novo DNA methylation 18023104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18023104_genotype and allelotype distribution in Chinese Han hepatocellular carcinoma patients was not significantly different from that in controls 18029387_DNMT3B mutations in ICF syndrome lead to altered epigenetic modifications and aberrant expression of genes regulating development, neurogenesis and immune function. 18097598_DNMT3B might not play a role in hypermethylation of many tumor suppressor genes during carcinogenesis of NPC 18221536_DNMT3b overexpression is associated with human breast cancer 18253830_DNMT3b was over expressed in gastric neoplasms. 18268116_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18268116_Polymorphisms in DNMT3B may be associated with colorectal adenoma risk in the context of low folate and methionine intake. 18336997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18336997_There is no significant association between the DeltaDNMT3B C>T SNP and early onset CRC in HNPCC patients. 18367714_Whereas overexpression of miR-148 results in decreased DNMT3b1 expression, short-hairpin RNA-mediated miR-148 repression leads to an increase in DNMT3b1 expression. 18407600_DNMT3B 579 G>T promoter polymorphism does not have a role in susceptibility to esophageal carcinoma in Chinese 18407600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18413740_Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of the BAG-1 promoter in DNMT1-overexpressing or DNMT3B-overexpressing colon cells show a permissive chromatin status assoscsiated with DNA binding of BORIS. 18414412_DNMT3b may play an important role in modulating NSCLC patient survival and thus be useful for identifying NSCLC patients who would benefit most from aggressive therapy. 18437543_It has been demonstrated that it may not be used as a stratification marker to predict the susceptibility to idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in Chinese population 18437543_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18455294_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18455294_This large study provides reliable risk estimates for associations between DNMT3B variants and SCCHN risk in non-Hispanic whites 18499700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18499700_The association between sequence variants of DNMT1 and 3B and mutagen sensitivity induced by BPDE supports the involvement of these DNMTs in protecting the cell from DNA damage. 18544619_DNMT3b as a putative mediator of epigenetic control through histone modifications of gene expression in pituitary cells. 18563322_DNMT1 and DNMT3b will increase their biological effects and have a synergistic effect on suppressing the growth of cholangiocarcinoma 18567530_Results show that DNA methyltransferase 3B enhances polycomb protein 2-mediated transcriptional repression of FGFR3, and suggest that DNMT3B is a co-repressor of hPc2 in inducing transcriptional repression independent of DNA methylation. 18639864_DNMT gene transcript expression was altered in several brains regions of suicides, including frontopolar cortex, amygdala, and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Increased mRNA and protein expression was found in the frontopolar cortex. 18662374_the DNMT3B -579G>T polymorphism may contribute to the genetic susceptibility to colorectal cancer. 18683034_Decreased mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura 18762900_S270P mutation affects DNMT3B functions via specific, non-covalent interaction with SUMO-1. 18829110_a negative association of DNMT3a and 3b expression with MDS disease risk 19019622_Down-regulation of CXCR4 expression by tamoxifen is associated with DNA methyltransferase 3B up-regulation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. 19024105_role of deltaDNMT3B4/2 in regulating RASSF1A promoter-specific DNA methylation in non-small cell lung cancer. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19107573_Over-expression of DNMT3B treated with 17 beta-estradiol(E(2)) was confirmed by real-time PCR and western blotting analysis. Furthermore, the up-regulation of DNMT3B expression induced by E(2) was suppressed by the addition of ICI182780. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19211935_Down-regulation of DNMT3B results from direct interaction of miR-29b with its 3' untranslated region. 19246518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19326430_DNMT3B C-149T polymorphism is associated with colorectal cancer. 19326430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19399408_Silencing DNMT3b and DNMT1 could inhibit the cell growth and promote apoptosis of bladder carcinoma cells. 19451595_Results show that folate supplementation enhanced the DNA remethylation through the Sp1/Sp3-mediated transcriptional up-regulation of genes coding for Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b proteins. 19465161_Investigated the DNMT3B 149 TT genotype and found it not significantly ass'd w/inc'd risk of hepatocellular carcinoma; but stratification analysis detected a trend towards a risk in female subset of patients and a lesser risk for HCV-infected patients. 19465937_the role of promoter region DNA hypermethylation as a mediator of gene silencing in glioblastoma multiforme cell line using RNAi directed against DNMT1 and DNMT3b was investigated. 19470733_Data support a possible role of DNMT3B in nonrandom de novo CpG island methylation leading to colorectal cancer. 19482874_DNMT3B interacts with CENP-C to modulate DNA methylation and the histone code at centromere. 19502167_DNMT3b may play an important role in regulation of FHIT expression in hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells, but not through methylation of the FHIT promoter. 19517237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19517237_Results showed that individuals with at least one -579G allele were also at significantly decreased risk of gastric cancer [odds ratio (OR), 0.43; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.26-0.72] compared with those having a -579TT genotype. 19576953_DNMT3B may be a candidate gene for susceptibility to early onset schizophrenia. 19620278_nucleosomes containing methylated SINE and LINE elements and CpG islands are the main sites of DNMT3A/3B binding. 19626461_DNMT3B G39179T single nucleotide polymorphism may be a potential genetic susceptibility factor for adenocarcinoma of the colon, especially in younger Chinese Han non-drinker men. 19626461_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19696477_It is shown that the SNP of DNMT3B 579G>T may not be used on its own as a marker to predict the susceptibility to ITP in a Chinese population and that DNMT3B 579G>T promoter SNP varies from one ethnic population to another. 19696477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19763880_The expression of DNMT1, DNMT2, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients, was investigated. 19777235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19777235_The -283C/T polymorphism of the DNMT3B gene influences the progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.( 19786833_description of direct interaction between Dnmt3a and/or Dnmt3b and transcription factors provides rational molecular explanation to the mechanisms of targeted DNA (hyper)methylation. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19798101_Np95, Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in mediating epigenetic silencing through histone modification followed by DNA methylation 19798569_Our data suggest there is no apparent association of common DNMT-1 and DNMT-3B polymorphisms with the risk of breast cancer in Chinese women. 19825994_DNMT3B3Delta5 may play an important role in stem cell maintenance or differentiation and suggest that sequences encoded by exon 5 influence the functional properties of DNMT3B. 19843671_DNMT3B polymorphisms are associated with colorectal cancer. 19843671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19854132_RASSF1A silencing strongly correlates with overexpression of HOXB3 and DNMT3B. 19896490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19932585_Our results indicate that DNMT1 plays the main role in maintenance of methylation of CXCR4 promoter, while DNMT3B may function as an accessory DNA methyltransferase to modulate CXCR4 expression in AsPC1 cells. 20127025_Elevated DNMT3B variants may influence the progression of gastric cancer and may possibly be a powerful indicator for the disease. 20375073_increased binding of DNMT3b to E-cadherin promoter region by K-Ras cause promoter hypermethylation for reduced expression of E-cadherin, leading to the decreased cell aggregation and increased metastasis of human prostate cancer cells. 20381114_expression of DNA methyltransferase 1, 3a, and 3b showed significantly higher levels in stage IV tumors than in stage I or II tumors 20381446_associated with a decreased risk for CIMP+ colorectal cancer 20398054_DNMT3b overexpression is an independent prognostic factor for predicting shortened survival of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. 20398055_DNMT1 and DNMT3b silencing sensitizes human hepatoma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via up-regulation of TRAIL-R2/DR5 and caspase-8. 20426865_benzo [a]pyrene diol epoxide recruited DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 alpha (DNMT3A), but not beta to methylate the RAR-beta2 gene promoter in esophageal cancer cells 20428781_thymine DNA glycosylase was not up-regulated in DNMT1 nor 3B knockdown cancer cells 20448464_Epigenetic alteration of microRNAs in DNMT3B-mutated patients of ICF syndrome 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20480259_DNMT3B -579 G>T polymorphism may alter susceptibility to carcinoma of gallbladder 20480259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506537_Data demonstrate that PI3K/Akt pathway regulates the expression of DNMT3B at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels, which is particularly important to understand the effects of PI3K/Akt and DNMT3B on hepatocarcinogenesis. 20514408_Nucleotide polymorphism of DNMT3B is not associated with methylation of p16CDKN2A gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 20514408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20593030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20833755_In biochemical assays, nanaomycin A revealed selectivity toward DNMT3B. 20838592_This study offers insights into the manner by which DNA methylation patterns are deposited and reveals a new level of interplay between members of the de novo DNMT family. 20952535_Results reveal a compelling new mechanism of RNA-dependent DNA methylation, suggesting that recruitment of DNMT3b by DNA:RNA triplexes may be a common and generally used pathway in epigenetic regulation. 20960050_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20970125_DNMT3B (DNA-methyltransferase 3 beta) mRNA is expressed temporally in the endometrium across the menstrual cycle. 20980350_Depletion of DNMT3b also reduced DNMT3a mRNA and protein 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21081840_DNMT3B has a significant roles in melanoma progression, and may be useful epigenetic biomarkers for disease outcome. 21106767_Results suggest that multidrug resistance is related to overexpression of BCRP/ABCG2 and the decrease of DNA methyltransferases, especially DNMT3b 21154337_DNMT3B gene is associated with early-onset schizophrenia and rs6119954 may plays an important role in age of onset of schizophrenia. 21211326_A gene-gene interaction between DNMT3B and DRD1 was observed in schizophrenia. 21229291_we report significant overexpression of DNMT1 and DNMT3B in glioma 21304883_these data suggest an inheritance model where DNMT3A/3B remain localized to silent methylated domains by binding to nucleosomes containing methylated DNA, enabling faithful maintenance of methylated states in cooperation with DNMT1. 21482616_Data suggest that the global methylation status of germ cells is not affected by spermatogenic defects in spite of aberrant DNMT3B expression indicating the necessity of proper methylation for full spermatogenesis. 21490393_DNA methyltransferase 3b methylates genes in a similar way in mouse intestine and human colon cancer 21519807_The results showed that the -579G allele of DNMT3B was associated with a significantly decreased risk of colorectal cancer. 21521786_DNMT3B1 and DNMT3B2 overexpression resulted in increased methylation of a substantial subset of CpG sites that showed tumor-specific increased methylation in prostate cancer. 21549127_study reveals a novel level of coupling between substrate binding, oligomerization, and catalysis that is likely conserved within the DNMT3 family of enzymes 21559330_in ICF lymphoblasts and peripheral blood, juxtacentromeric heterochromatic genes undergo dramatic changes in DNA methylation, indicating that they are bona fide targets of the DNMT3B protein 21592522_Data show that the levels of DNMT3B mRNA in MDD were significantly increased in a depressive but not in a remissive state. 21698279_tightly controlled down regulation of DNMT3B exon 10 containing transcripts (and exon 10 encoded peptide) upon spontaneous differentiation of PSCs suggests that this DNMT3B splice isoform is characteristic of the pluripotent state 21712824_It was found that the methylator phenotype of Yolk Sac Tumors (YSTs) was coincident with higher levels of expression of the DNA methyltransferase, DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B, suggesting a mechanism underlying the phenotype. 21757290_Data show that Core inhibited p16 expression by inducing promoter hypermethylation via up-regulation of DNMT1 and DNMT3b. 21854760_These preliminary findings suggest that genetic variance may influence DNMT3B expression in pancreatic cancer. 21887463_Significantly higher levels of CXCR4, DNMT3A, DNMT3B and DNMT1 transcript (p=0.0058, 0.0163, 0.0003 and C polymorphism in DNMT3B is associated with risk of cancer in Asians [0.68 (0.53-0.87) for GT vs. TT] but not in Europeans [0.82 (0.63-1.07) for GT vs. TT]. 22009713_A functional sequence variant in DNMT3B is associated with the development of Secondary primary cancers in head and neck cancers early stage patients treated with radiation. 22048249_The analysis of DNMT3B expression showed peaks of mRNA transcripts in primary spermatocytes and in mature ejaculated spermatozoa 22056872_Estrogen receptor alpha is downregulated by TWIST1 (Twist) recruitment of DNMT3B. 22072770_Elevated expression of DNMT1 or DNMT3B alone is not required to maintain restricted latency. 22207353_Results indicate that DNMT3B mediates large-scale methylation patterns in human embryonic stem cells and that DNMT3B deficiency in the cells alters the timing of their neuronal differentiation and maturation. 22236544_The data shows that the DNMT3B (C46359T) polymorphism is associated with oral lichen planus development. Furthermore, increased expression of the enzyme DNMT3B, an epigenetic-associated protein, is present in oral lichen planus. 22244828_Report aberrant DNMT3B regulation in colon cancer and suggest that its expression is associated with the methylation of constitutively hypermethylated promoters in the healthy colon. 22272627_Analysis of Italian late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) patients and matched controls revealed no difference in allele frequencies. No significant effect on disease age at onset was observed. 22301400_Increased DNMT3B gene expression is associated with carcinogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 22349384_Decreased expression levels of DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b in the ectopic endometrium and eutopic endometrium may play a role in patients with abnormal epigenetics which may lead to endometriosis. 22378288_ICF related mutations in DNMT3B (K770E,D817G)alter DNA replication in ICF cell lines. 22394436_Patients with seminomas showing focal DNMT3B expression are at increased risk of relapse, and should be followed up carefully. 22490141_The -579 G allele is a potential protective factor for the occurrence of colorectal cancer; the polymorphism of DNMT3B-149 gene shows no close correlation with the occurrence and development of CRC among Chinese population. 22520950_data suggest that overexpression of DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b might represent a critical event responsible for the epigenetic inactivation of multiple tumor suppressor genes, leading to the development of aggressive forms of sporadic breast cancer 22547080_Pregnancy and the DNMT3b genotype independently influence the arsenic methylation phenotype 22563479_Results show that DNMT3B is dispensable for the maintenance of aberrant DNA methylation patterns in colon cancer cells. 22572543_finding that DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 3 beta (DNMT3B) correlates with the severity of dysmenorrhea suggests that DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferases may be involved in adenomyosis-caused dysmenorrhea and its severity 22664488_DNMT3b-mediated hypermethylation defect in breast cancer cell lines involves the loss of post-transcriptional regulation of DNMT3b by regulatory miRs. 22768205_The data from this study provided the first evidence for differential expression of DNMTs proteins in ovarian cancer tissues and their associations with clinicopathological and survival data in sporadic ovarian cancer patients. 22810147_Findings provide clues on the role of a DNMT3b SNP in prostate cancer progression. 22815530_Our results indicate that DNMT3B7 modifies the epigenome in neuroblastoma cells to induce changes in gene expression and inhibit tumor growth 22885766_Association between a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the promoter of DNMT3B gene and the risk for ITP was investigated. 22898819_mammalian de novo DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B are also DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine dehydroxymethylases 23000068_DNMT3B -579 TT homotype was significantly higher in immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) patients and conferred almost three fold increased risk of ITP (OR=3.16, 95%CI=1.73-5.79). 23025623_Allelic variability in DNMT3B may be relevant to the underlying diathesis for suicidal acts. 23039890_DNMT3B-579G/T, MTHFR+677C/T and +1298A/C polymorphisms were not correlated with the development or prognosis of AITD. 23049596_No significant differences were found in the genotype distribution of DNMT3B polymorphism between the children with ITP and the control group. 23079992_Two SNPs, rs16999593 in DNMT1 and rs2424908 in DNMT3B, are significantly associated with breast cancer risk. 23081874_Combinations of functional DNMT3B promoter polymorphisms are associated with maternal risk of birth of a child with Down syndrome. 23100393_High DNMT3B expression is associated with multiple myeloma. 23251566_This study represents the first report showing that the overexpression of DNMT3B/3B(NC) is an independent predictor of poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia. 23393137_mammalian DNMT1, DNMT3B, and, to a much less extent, DNMT3A, can also act in vitro as DNA demethylases in a Ca2+ ion- and redox state-dependent manner 23486536_Clinical and genetic data of mutations in DNMT3B and ZBTB24 in patients with ICF syndrome, were compared. 23545144_These results demonstrated that down-regulation of DNMT1 or DNMT3B expression in Huh7.5.1 cells severely impaired cell culture-produced hepatitis C virus infection. 23636939_Inactivation of DNMT3B splice variants might play an important role in cell proliferation correlating with the change of p21. 23677709_The 46359CT polymorphism of DNMT3B is associated with the risk of cervical cancer. 23820632_The decreased expression of DNMT1 and DNMT3B mRNA may play an important role in the pathogenesis of TOF. 23894490_our work contributes new insights into the regulation of de novo DNA methylation by inactive DNMT3B isoforms in human cells. 24001151_Mahanine treatment induces the proteasomal degradation of DNMT1 and DNMT3B via the inactivation of Akt, which facilitates the demethylation of the RASSF1A promoter and restores its expression in prostate cancer cells. 24028770_PU.1- targeted genes undergo Tet2-coupled demethylation and DNMT3b-mediated methylation in monocyte-to-osteoclast differentiation. 24069326_DNMT3B polymorphisms may contribute to the genetic susceptibility to AML; in particular, the G allele of rs1569686 serves as a risk factor for AML, whereas the C allele of rs2424908 represents a potential protective factor. 24094886_DNMT3B7 overexpression might interfere with the normal DNA methylation mechanism required for silencing the MENT proto-oncogene, and may accelerate human lymphomagenesis. 24098518_common variants in the DNMT1 and DNMT3B genes influence inter-individual variation in global DNA methylation and the three loci investigated here. 24127215_Nonrandom template segregation in differentiating embryonic stem cells is dependent on DNA methylation and on Dnmt3A/B. 24178910_In conclusion, no significant association was found between the -149C>T polymorphisms in DNMT3B and colorectal cancer susceptibility. 24201117_Foxp3 downregulation in HIV-infected Treg was related to an increase in the expression of DNA methyltransferase3b (DNMT3b) associated with higher methylation of CpG sites in the FOXP3 locus. 24260492_the DNMT3B-579T allele might contribute to the risk of developing thymoma in MG patients, particularly in homozygous TT subjects. 24316981_Fusion of TTYH1 with the C19MC microRNA cluster drives expression of a brain-specific DNMT3B isoform in the embryonal brain tumor. 24333507_A role of DNMT3B in controlling the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and in the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells. 24343426_High DNMT3B expression was associated with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 24362509_SHMT1 C1420T and DNMT3B C46359T polymorphisms are not associated with HNC development in Brazilian population, however, SHMT1 C1420T polymorphism is less frequent in patients with primary site of tumor in larynx 24457336_Expression of myeloperoxidase in acute myeloid leukemia blasts mirrors the distinct DNA methylation pattern involving the downregulation of DNA methyltransferase DNMT3B. 24459426_Association of self-DNA mediated TLR9-related gene, DNA methyltransferase, and cytokeratin protein expression alterations in HT29-cells to DNA fragment length and methylation status. 24469050_Our results identify a key role for DNMT3b in the earliest stages of initiation and provide a comprehensive catalog of genes targeted for silencing by this methyltransferase in non-small-cell lung cancer. 24577265_DNMT3B may be regulating enteric nervous system development through DNA methylation in the neural crest cells, suggesting that aberrant methylation patterns could have a relevant role in Hirschsprung disease. 24603304_Our finding suggests that DNMT3B acts as an antiapoptotic gene in teratocarcinoma stem cells, and mediates apoptosis and differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells induced by Aza-dC 24625449_Activated IL-6 signaling might be responsible to the induction of DNMT3b overexpression on oral cancer 24859147_DNMT3B rs2424932 genotype (P = 0.023) and allele (P = 0.0063) increased the risk of developing schizophrenia in males but not in females. 24952347_DNMT3L can address DNMT3A/B to specific sites by directly interacting with TFs that do not directly interact with DNMT3A/B 25027325_DNMT3B-deficient induced pluripotent stem cells exhibit global loss of non-CG methylation and select CG hypomethylation at gene promoters and enhancers are associated with the ICF syndrome. 25038421_study found carriers of the DNMT3B TGG haplotype were associated with Alzheimer's disease 25083817_High DNA-methyltransferase 3B expression predicts poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia, especially among patients with co-occurring NPM1 and FL |
ENSMUSG00000027478+ENSMUSG00000082079 |
Dnmt3b+Dnmt3c |
45.641967 |
0.2669649958 |
-1.905278 |
0.265670237 |
51.577699 |
0.00000000000068818869357460234101468529963618823964109638691155623746453784406185150146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004137541799250970170715304797081813431049168716668873457820154726505279541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.8063568 |
4.0054905 |
78.0790732 |
9.9442400 |
| ENSG00000088367 |
2036 |
EPB41L1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H4G0 |
FUNCTION: May function to confer stability and plasticity to neuronal membrane via multiple interactions, including the spectrin-actin-based cytoskeleton, integral membrane channels and membrane-associated guanylate kinases. |
Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 (EPB41) is a multifunctional protein that mediates interactions between the erythrocyte cytoskeleton and the overlying plasma membrane. The encoded protein binds and stabilizes D2 and D3 dopamine receptors at the neuronal plasma membrane. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:2036; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; actomyosin structure organization [GO:0031032]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866] |
12181426_protein 4.1N/dopamine receptor interaction is required for localization or stability of dopamine receptors at the neuronal plasma membrane. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 23400781_Kainate receptor GluK2a post-translational modifications differentially regulate association with 4.1N to control activity-dependent receptor endocytosis 26575790_Data suggest that repression of JNK-c-Jun signaling through pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 (PP1) is one of the key anti-tumor mechanisms of neuronal membrane cytoskeletal protein 4.1 (4.1N). 26648170_the data of the current study identified 4.1N as an inhibitor of hypoxiainduced tumor progression in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. 27448302_Data show that overexpression of 4.1N protein decreased expression of flotillin-1, decreased activation of beta-catenin/Wnt pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. 29428502_4.1N, betaII spectrin and ankyrin G are structural components of the lateral membrane skeleton and this skeleton plays an essential role in the assembly of a fully functional lateral membrane. |
ENSMUSG00000027624 |
Epb41l1 |
204.916667 |
0.1718613654 |
-2.540683 |
0.815066071 |
8.298914 |
0.00396687897437558115859568275141100457403808832168579101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008280460141674949453571841218035842757672071456909179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.4868989 |
33.1017224 |
349.6835839 |
134.5066972 |
| ENSG00000088808 |
23368 |
PPP1R13B |
protein_coding |
Q96KQ4 |
FUNCTION: Regulator that plays a central role in regulation of apoptosis via its interaction with p53/TP53 (PubMed:11684014, PubMed:12524540). Regulates TP53 by enhancing the DNA binding and transactivation function of TP53 on the promoters of proapoptotic genes in vivo. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11684014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12524540}. |
3D-structure;ANK repeat;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ASPP (apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53) family of p53 interacting proteins. The protein contains four ankyrin repeats and an SH3 domain involved in protein-protein interactions. ASPP proteins are required for the induction of apoptosis by p53-family proteins. They promote DNA binding and transactivation of p53-family proteins on the promoters of proapoptotic genes. Expression of this gene is regulated by the E2F transcription factor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23368; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786] |
15731768_target of E2F transcription factor 15757645_ASPP1 CpG island aberrant methylation could be one molecular and genetic alteration in wild-type p53 tumours. 15782125_Mdm2 and mdmx prevent ASPP1 and ASPP2 from stimulating the apoptotic function of p53 by binding and inhibiting the transcriptional activity of p53. 16139958_role of ASPP1, ASPP2, and iASPP as apoptotic specific regulators of p53 [review] 16314841_results demonstrate that decreased expression of ASPP1 in patients with ALL is due to an abnormal methylation of its promoter and is associated with a poor prognosis 20034025_ASPP1 and ASPP2 genes are frequently down-regulated by DNA methylation in HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma, which may play important roles in the development of HCC 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20601096_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041410_Data show that Lats2 and ASPP1 shunt p53 to proapoptotic promoters and promote the death of polyploid cells. 21041411_Data show that ASPP1 enhances nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ and YAP/TAZ-dependent transcriptional regulation. 21102414_Suggest that downregulation of ASPP1 by hypermethylation may be involved in the pathogenesis and progress of gestational trophoblastic disease, probably through its effect on apoptosis. 21479363_overexpression of ASPP1 rendered MCF-7 and MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells more sensitive to resveratrol-mediated apoptosis via the E2F pathway 22068052_The ability of ASPP1 to activate YAP results in the decreased expression of LATS2, which lowers the ability of p53 to induce p21, cell-cycle arrest and senescence. 22169642_ASPP1 promoter methylation may be associated with the malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer, and ASPP1 expression promotes cellular apoptosis. 22552744_the mRNA expression of ASPP1 and ASPP2 was frequently dowregulated in tumor tissues, and this decreased significantly in samples expressing wild-type p53 23088536_When the Px(T)PxR motif is deleted or mutated via insertion of a phosphorylation site mimic (T311D), PP-1c fails to bind to all three ASPP proteins, ASPP1, ASPP2 and iASPP. 23392125_ASPP1 and ASPP2 cooperate with oncogenic RAS to enhance the transcription and apoptotic function of p53. 25660448_ASPP1/2 interacted with centrosome linker protein C-Nap1. Co-depletion of ASPP1 and ASPP2 inhibited re-association of C-Nap1 with centrosome at the end of mitosis. 26595804_ASPP1/2-PP1 complexes are required for chromosome segregation and kinetochore-microtubule attachments. 27177208_Increased expression of p53 and ASPP1 and downregulation of iASPP. 28103919_Results showed that the protein expression levels of ASPP1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues and in paired noncancerous tissues were similar but was significantly associated with histological differentiation and invasive depth which suggest that it might be involved in the progression of ESCC. 28594407_results provide new insights into EGR-1/ASPP1 regulatory loop in sensitizing Quercetin-induced apoptosis. EGR-1/ASPP1, therefore, may be potentially used as therapeutic targets to improve cancer's response to pro-apoptosis treatments. 32269211_ASPP1 deficiency promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. 32987288_Apoptosis stimulating protein of p53 (ASPP) 1 and ASPP2 m-RNA expression in oral cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000021285 |
Ppp1r13b |
170.432955 |
0.2888298462 |
-1.791708 |
0.231874598 |
57.326642 |
0.00000000000003691211410250672724046111101238735090955501647047576341265084920451045036315917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000240646114908568611273414393086943307133260955277265225049632135778665542602539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
84.7138222 |
12.5427262 |
295.6665451 |
30.5482387 |
| ENSG00000088827 |
6614 |
SIGLEC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZZ2 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an endocytic receptor mediating clathrin dependent endocytosis. Macrophage-restricted adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to lymphocytes, including granulocytes, monocytes, natural killer cells, B-cells and CD8 T-cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3-linked sialic acid (By similarity). Binds to SPN/CD43 on T-cells (By similarity). May play a role in hemopoiesis. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The encoded protein is a lectin-like adhesion molecule that binds glycoconjugate ligands on cell surfaces in a sialic acid-dependent manner. It is a type I transmembrane protein expressed only by a subpopulation of macrophages and is involved in mediating cell-cell interactions. The protein plays an important role in multiple human diseases and bacterial and viral infections has been shown to enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2021]. |
hsa:6614; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; virion binding [GO:0046790]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell [GO:0075512]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954] |
16002716_Inhibitory signals delivered from human rhinovirus HRV14-treated dendritic cells to cocultured T cells via sialoadhesin (Sn) are critical for induction of T-cell anergy. 17328080_Increased expression of Siglec-1 in circulating systemic sclerosis (SSc) monocytes and tissue macrophages suggests type I IFN-mediated activation of monocytes occurs in SSc, possibly through toll-like receptor (TLR) activation of interferon secretion. 17330143_Sialoadhesin is induced to high levels on CD14(+) cells early after HIV-1 infection in vivo. 18383365_SIGLEC1, used as a surrogate marker for type I interferon, is a potential biomarker to assess disease acitvity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). SIGLEC1+ resident monocytes could act as antigen presenting cells in SLE. 18383365_Siglec-1 (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 1) expression in resident blood monocytes is a potential biomarker for monitoring disease activity, displaying type I IFN responses, and estimating levels of anti-dsDNA antibodies 18414664_Increased sialoadhesin expression on CD14(+) monocytes occurs in response to HIV-1 infection with maximum expression associated with high viral load 19285973_Siglec-1 may be considered as a potential non-invasive indicator for monitoring disease severity and a biomarker for predicting the relative risk of cardiovascular events. 19950173_Data show that the combinatorial signal delivered by R-DC to T cells via B7-H1 and sialoadhesin is crucial for the induction of IL-35(+) Treg. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20653431_Increased expression in monocytes of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22249367_Monocytes overexpress sialoadhesin nonspecifically during intestinal transplant rejection and systemic or enteritic inflammatory states. 22933622_Based on increased SIGLEC1 expression in circulating monocytes, findings suggest a role for SIGLEC1 in the chronic progressive phases of multiple sclerosis. 23271952_These findings identify Siglec-1 as a key factor for HIV-1 spread via infectious dendritic/T-cell synapses. 23593001_downregulation of CD169 expression or neutralizing CD169 function abrogated dendritic cell-mediated HIV-1 capture and trans infection, while exogenous expression of CD169 in receptor-naive cells rescued glycosphingolipid-dependent capture and trans infection. 23610394_the CD169/Sn endocytic pathway is conserved and capable of presenting lipid antigens to iNKT cells 23734742_CD169(+) macrophages in RLNs promote CD8(+) T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity. 24196391_Siglec-1 may play a proinflammatory role in stimulating lymphocyte proliferation and activation in rheumatoid arthritis. 24947940_GM3-CD169 binding is a gp120-independent signal for sequestration and preservation of HIV-1 infectivity. 25033082_evidence identifying sialyllactose-containing gangliosides in the viral membrane and the cellular lectin Siglec-1 as critical determinants for HIV-1 capture and storage by mature DCs and for DC-mediated trans-infection of T cells 25354152_The most abundant cytokine present in semen (TGF-beta1) is able to enhance specifically the expression of an important molecule (CD169) involved in the capture and transmission of HIV-1 particles from the mucosal lumen to the submucosal compartment. 25760631_Our study suggests that HIV-1 capture by CD169 can provide virus evasion from both innate (phagocytosis) and adaptive immune responses 25947229_Siglec-1 on myeloid cells could fuel novel CD4(+) T-cell infections and contribute to HIV-1 dissemination in vivo. 26667473_These results highlight the importance of sialic acids on the V1V2 region in binding to sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin. 26752092_Siglec-1 and Siglec-2 are potential biomarkers in autoimmune disease. (Review) 27174787_CD169 might act as a co-stimulatory molecule for cytotoxic T-cell activation, and could define a population of tumour-infiltrating macrophages with potential anti-tumour properties in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 27510803_classical HIV-1 infectious routes may compensate for the lack of Siglec-1 in fuelling HIV-1 dissemination within infected individuals 27551071_the antibody-sialidase conjugate desialylated tumor cells in a HER2-dependent manner, reduced binding by natural killer (NK) cell inhibitory sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin (Siglec) receptors, and enhanced binding to the NK-activating receptor natural killer group 2D (NKG2D). 27601677_The results reveal marked differences between afferent and efferent ymphatic endothelial cells and identify molecules on lymphatic vessels. Further characterizations of Siglec-1 (CD169) and macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (MSR1/CD204), show that they are discriminatively expressed on lymphatic endothelium of the subcapsular sinus but not on lymphatic vasculature of the lymphatic sinus 27861544_These findings suggest that CD169+ macrophages in RLNs might be a useful marker for assessing clinical stage, including LN states, in patients with breast cancer. 27993350_this study shows that binding of monoclonal antibodies to Sn results in delayed and reduced phagocytosis of fluorescent beads, and that no effect is observed on Fc-mediated phagocytosis or phagocytosis of bacteria by macrophages 28002629_In colorectal tumor, malignant melanoma, and endometrial tumor, it was shown that a high density of CD169-positive macrophages in the lymph node sinus was a predictive factor for better clinical prognosis. 28129379_These data demonstrate a prominent role for Siglec-1 in the internalization of HIV-1 to the virus-containing compartment in infected monocyte-derived macrophages 28501799_High expression of SIGLEC1 in pregnant women with autoantibodies against Ro/SS-A indicates an enhanced risk for autoimmune congenital heart block development. 28794041_High CD169 expression is associated with HIV-1. 28880401_CD169 expression in regional LNs was not associated with PSA-relapse. 28964857_Our findings evidenced for the first time the novel association between SIGLEC1 rs3859664 SNP and active pulmonary TB. Intriguingly, carriers of the polymorphism produced less IL-1ss than non-carriers, suggesting the possible involvement of Siglec-1 signalling pathway with inflammasome complex. 29037117_SIGLEC1 mRNA levels have potential as a novel predictive biomarker for Graves disease relapse. 29266251_In vitro, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) increased expression of Siglec-1 on healthy newborn and adult monocytes. RSV-induced Siglec-1 on monocytes inhibited Interferon gamma production by adult CD4(+) T cells. In contrast,Interferon gamma production by RSV in newborns was not affected by Siglec-1. 30516869_suggest that high expression of CD169 in lymph node sinus macrophages reflects a high potential for anti-cancer immune responses in esophageal cancer patients 31591213_circulating dendritic cell precursors, but not other blood dendritic cell subsets, are susceptible to infection by HIV-1 in a Siglec-1-dependent manner. This constitutes a unique functional feature that might represent a preferential relationship of this emerging cell type with viruses. 31992280_Decreased expression of a phagocytic receptor Siglec-1 on alveolar macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 32223897_Tuberculosis-associated IFN-I induces Siglec-1 on tunneling nanotubes and favors HIV-1 spread in macrophages. 33081587_SIGLEC1 (CD169) is a sensitive biomarker for the deterioration of the clinical course in childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. 33206973_Monocyte CD169 Expression as a Biomarker in the Early Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019. 33489013_Dissemination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is associated to a SIGLEC1 null variant that limits antigen exchange via trafficking extracellular vesicles. 33491921_CD169 and CD64 could help differentiate bacterial from CoVID-19 or other viral infections in the Emergency Department. 33547747_Monocyte CD169 expression in COVID-19 patients upon intensive care unit admission. 33986412_SIGLEC1 (CD169): a marker of active neuroinflammation in the brain but not in the blood of multiple sclerosis patients. 34160241_CyTOF Profiling of Zika and Dengue Virus-Infected Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Identifies Phenotypic Signatures of Monotype Subsets and Upregulation of the Interferon-Inducible Protein CD169. 34387304_Siglec-1 expression on monocytes is associated with the interferon signature in juvenile dermatomyositis and can predict treatment response. 34607536_Prognostic value of CD169-positive macrophages in various tumors: a meta-analysis. 35177553_SIGLEC1 enables straightforward assessment of type I interferon activity in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. 35695299_The role of activated monocyte IFN/SIGLEC1 signalling in Graves' disease. 36279285_CD169-mediated restrictive SARS-CoV-2 infection of macrophages induces pro-inflammatory responses. |
ENSMUSG00000027322 |
Siglec1 |
32.713353 |
0.2078302882 |
-2.266522 |
0.336497719 |
47.221460 |
0.00000000000634024565032349757723823295972489892668999544866892392747104167938232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000035691085354223806836708594029716800147267186105182190658524632453918457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.0362199 |
2.4321441 |
57.7706675 |
6.4790621 |
| ENSG00000088836 |
83959 |
SLC4A11 |
protein_coding |
Q8NBS3 |
FUNCTION: Multifunctional transporter with an impact in cell morphology and differentiation. In the presence of borate B(OH)4(-), acts as a voltage-dependent electrogenic Na(+)-coupled B(OH)4(-) cotransporter controlling boron homeostasis (PubMed:15525507). At early stages of stem cell differentiation, participates in synergy with ITGA5-ITGB1 and ITGAV-ITGB3 integrins and BMPR1A to promote cell adhesion and contractility that drives differentiation toward osteogenic commitment while inhibiting adipogenesis (By similarity). In the absence of B(OH)4(-), acts as a Na(+)-coupled OH(-) or H(+) permeable channel with implications in cellular redox balance (PubMed:15525507, PubMed:28642546). Regulates the oxidative stress response in corneal endothelium by enhancing antioxidant defenses and protecting cells from reactive oxygen species (PubMed:28642546). In response to hypo-osmotic challenge, also acts as water permeable channel at the basolateral cell membrane of corneal endothelial cells and facilitates transendothelial fluid reabsorption in the aqueous humor (PubMed:31273259, PubMed:25007886, PubMed:23813972). In the presence of ammonia, acts as an electrogenic NH3/H(+) cotransporter and may play a role in ammonia transport and reabsorption in renal Henle's loop epithelium (PubMed:27581649). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2AJN7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15525507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23813972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25007886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27581649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28642546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31273259}. |
Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Anion exchange;Cell membrane;Corneal dystrophy;Deafness;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a voltage-regulated, electrogenic sodium-coupled borate cotransporter that is essential for borate homeostasis, cell growth and cell proliferation. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a number of endothelial corneal dystrophies including recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy 2, corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness, and Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:83959; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; active borate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0046715]; bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015106]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; proton channel activity [GO:0015252]; proton transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015078]; sodium channel activity [GO:0005272]; solute:inorganic anion antiporter activity [GO:0005452]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; water transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005372]; bicarbonate transport [GO:0015701]; borate transport [GO:0046713]; cellular cation homeostasis [GO:0030003]; cellular hypotonic response [GO:0071476]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; fluid transport [GO:0042044]; ion homeostasis [GO:0050801]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [GO:2000739]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
11836359_The corneal dystrophy and perceptive deafness (Harboyan syndrome) gene (CDPD1) maps to chromosome 20p13. 12654361_congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy 1 (CHED1) and CHED2 loci on chromosome 20 and the collagen, type VIII, alpha-2 (COL8A2) gene were excluded by linkage and haplotype analyses. 16767101_describe seven different mutations in the SLC4A11 gene in ten families with autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy 16825429_These results confirm that mutations in the SLC4A11 gene cause autosomal recessive corneal endothelial dystrophy. 17220209_These findings extend the implication of the SLC4A11 borate transporter beyond corneal dystrophy to perceptive deafness. 17262014_Novel indel mutation, c.859_862delGAGAinsCCT (E287fsX21) in exon 8 of SLC4A11 gene. Novel in-frame deletion mutation c.2014_2016delTTC or 2017_2019delTTC which will lead to loss of a phenylalanine residue at position 672 or 673 (F672del or F673del). 17397048_report of seven novel mutations and two previously identified mutations in families from India and the United Kingdom with recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy 17667634_CHED2 (congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy) is associated with mutations in SLC4A11, a member of the SLC4 family of base transporters. 17679935_These data add to the mutational repertoire of SLC4A11 and establish the high degree of mutational heterogeneity in autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy. 18024964_SLC4A11 mutations in Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy are reported. 18363173_A novel SLC4A11 mutation (Thr271Met) is associated with autosomal recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy in a pedigree from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and provides additional support that mutations in this gene cause disease. 18474783_This study increases the number of SLC4A11 gene mutations and confirms the role of this gene in causing congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2). 19369245_In this small cohort, no evidence was found of genetic heterogeneity in congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) and that loss of BTR1 function is the most likely mutational mechanism. 20118786_Corneal endothelial cells are more vulnerable to defects in the functional activity of SLC4A11 than cells of the striae vascularis of the inner ear. 20144242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20848555_sequenced SLC4A11 in 192 sporadic and small nuclear late-onset Fuchs corneal dystrophy families and found seven heterozygous missense novel variations that were absent from ethnically matched controls 21203343_The present study detected one novel and three reported changes, adding to the repertoire of mutations in SLC4A11, and recorded a high degree of genetic heterogeneity in Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy. 21288032_biochemical study of SLC4A11 22072594_The reduction in movement of WT SLC4A11 protein to the cell surface caused by Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy SLC4A11 helps to explain the dominant inheritance of this disorder. 22447871_SLC4A11 is necessary for cell survival and may explain the pathologic corneal endothelial cell loss in endotheliopathies due to SLC4A11 mutations. 23462747_Both substitution c.214+242C > T in IL1RN and novel deletion c.2558+149_2558+203del54 in SLC4A11 were observed significantly more frequently in family members with keratoconus. 23615275_To the best of our knowledge, this is the first Korean case of CHED2, confirmed by the c.1239C>A (p.C413*) mutation in the SLC4A11 gene, which has not been previously reported. 23813972_Data shows that the function of SLCA11 is to facilitate the movement of water across the basolateral corneal epithelium. 23864606_SLC4A11 has significant EIPA-sensitive Na(+)-OH(-)(H(+)) and NH4(+) permeability. 23922488_The purpose of this study was to identify the genetic cause of congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy 2 in six Indian families and catalog all known mutations in the SLC4A11 gene. 24348007_Variation in the COL8A2, SLC4A11, and ZEB1 genes is present in only a small fraction of African American cases and as such does not appear to significantly contribute to the genetic risk of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. 24351571_Our observations suggest that congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy caused by homozygous SLC4A11 mutations progresses to Harboyan syndrome, but the severity of this may vary considerably. 24502824_We report a novel nonsense mutation of the SLC4A11 gene in the patient with CHED2. In addition, one of heterozygous carriers in this family showed features of late onset Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. 25007886_SLC4A11 mutations contribute to 11% (5/45) of sporadic late-onset Late-onset Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) in the cohort studied. 25138764_We have described three affected siblings from a non-consanguineous family with Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy 2. 25394471_Potential therapeutic agents to improve the functional impairment of specific SLC4A11 mutant transporters. 25500497_In contrast to the Slc4a11(-/-) mouse, no abnormalities in daily renal ion excretion or polyuria were observed in the Harboyan syndrome patient. 25811729_We found that cells containing mutant SLC4A11 are more vulnerable to oxidative and mitochondrial damage, less able to overcome oxidative stress through the expression of sufficient levels of antioxidant genes, and are more prone to apoptotic death. 26018076_SLC4A11 is a novel NH3/H+ co-transporter. 26286922_study reports a newly identified mutation (c.2024A>C) in the SLC4A11 gene segregating with the diseased haplotype in two consanguineous Pakistani families 26451371_we review the current knowledge on the role of the SLC4A11 gene, protein, and its mutations in the pathophysiology and clinical presentation of CHED. [review] 26619383_we report posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy resulting from a de novo mutation in ZEB1. Additionally, we present a congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy case with a thin Descemet membrane with a novel compound heterozygous SLC4A11 mutation. 26750805_SLC4A11 rs3810560 polymorphism independently affected the sustained viral response rates in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with PEGIFN2b/ribavirin/combination. 27057589_A missense SLC4A11 mutation (Leu843Pro) is responsible for CHED2 in this family; this is the first report of this mutation in a homozygous state. 27121161_Analysis of SLC4A11, ZEB1, LOXHD1, COL8A2 and TCF4 gene sequences in a multi-generational family with late-onset Fuchs corneal dystrophy found no evidence for found polymorophisms causing the disease in this specific pedigree. 27558157_A role of human SLC4A11 in bicarbonate or borate transport. 27581649_These complex ion transport properties need to be addressed in the context of corneal endothelial disease processes caused by mutations in SLC4A11. 27609159_for the first time, compound heterozygous SLC4A11 mutations impair protein function leading to delayed onset of the disease. 27681179_Slc4a11 is an ideally selective H(+)/OH(-) conductive pathway. 28642546_our data suggests a possible role of SLC4A11 in regulating oxidative stress, and might be responsible for both the etiology and treatment of corneal endothelial dystrophy. 29091960_Based on these findings, we infer that high SLC4A11 expression is an independent predictor for poor OS in grade 3/4 serous ovarian cancer. Both DNA amplification and hypomethylation contribute to its upregulation in ovarian cancer 29327391_To identify SLC4A11 mutants that are targets for folding-correction therapy, 54 SLC4A11 missense mutants, were identified. 30557570_Thus, our data suggest that these SLC4A11 mutants, rather than having impaired protein trafficking, show altered H(+) flux properties. 30856043_The five Corneal Dystrophy and Perceptive Deafness (CDPD) patients were homozygous for the same mutation in the SLC4A11 gene. Haplotype analysis of all the affected, including the case reported from Argentina was in accordance with a founder mutation. 31273259_Human Corneal Expression of SLC4A11, a Gene Mutated in Endothelial Corneal Dystrophies. 31323090_This proof-of-concept study highlights the potential of using CE-like cells to investigate the pathogenic consequences of SLC4A11 disease-associated variants 31420327_Observation of nine previously reported and 10 non-reported SLC4A11 mutations among 20 Iranian CHED probands and identification of an MPDZ mutation as possible cause of CHED and FECD in one family. 31691803_Defective cell adhesion function of solute transporter, SLC4A11, in endothelial corneal dystrophies. 32520610_pH dependence of the Slc4a11-mediated H(+) conductance is influenced by intracellular lysine residues and modified by disease-linked mutations. 32884076_Harboyan syndrome: novel SLC4A11 mutation, clinical manifestations, and outcome of corneal transplantation. 33541055_[Identification of novel mutations of SLC4A11 gene in patients with congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy]. 33879471_Autosomal recessive congenital hereditary corneal dystrophy associated with a novel SLC4A11 mutation in two consanguineous Tunisian families. 34637099_SLC4A11 mutations causative of congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED) progressing to Harboyan syndrome in consanguineous Pakistani families. 35291925_Compound heterozygous mutations in the SLC4A11 gene associated with congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy in a Chinese family. 35993514_Corneal dystrophy mutations R125H and R804H disable SLC4A11 by altering the extracellular pH dependence of the intracellular pK that governs H(+)(OH(-)) transport. 36037197_Mutational analysis in sodium-borate cotransporter SLC4A11 in consanguineous families from Punjab, Pakistan. 36115991_Identification and in silico analysis of a spectrum of SLC4A11 variations in Indian familial and sporadic cases of congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy. |
ENSMUSG00000074796 |
Slc4a11 |
35.326722 |
0.2506190980 |
-1.996432 |
0.470583224 |
16.754376 |
0.00004254403136317894498254210677856690381304360926151275634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000123660870996557937075491229172996554552810266613960266113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7479621 |
6.3977391 |
43.8584708 |
18.2966182 |
| ENSG00000088882 |
56265 |
CPXM1 |
protein_coding |
Q96SM3 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in cell-cell interactions. No carboxypeptidase activity was found yet (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Carboxypeptidase;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc |
|
This gene likely encodes a member of the carboxypeptidase family of proteins. Cloning of a comparable locus in mouse indicates that the encoded protein contains a discoidin domain and a carboxypeptidase domain, but the protein appears to lack residues necessary for carboxypeptidase activity.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:56265; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; metallocarboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004181]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; peptide metabolic process [GO:0006518]; protein processing [GO:0016485] |
10073577_This paper deals with mouse CPXM. 27006448_These findings establish CPX-1 as a positive regulator of adipogenesis situated downstream of FGF-1/BAMBI that may contribute to hyperplastic adipose tissue expansion via affecting extracellular matrix remodeling. |
ENSMUSG00000027408 |
Cpxm1 |
52.186285 |
4.3325453696 |
2.115215 |
0.232160024 |
89.668781 |
0.00000000000000000000281563113440709427005539339367508564562779455376710309227796663611442795627226587384939193725585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000026170475783280043057066971569343488314799241077209207388676315275688466499559581279754638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.0342743 |
11.8255912 |
19.7554186 |
2.3924567 |
| ENSG00000088970 |
55857 |
KIZ |
protein_coding |
Q2M2Z5 |
FUNCTION: Centrosomal protein required for establishing a robust mitotic centrosome architecture that can endure the forces that converge on the centrosomes during spindle formation. Required for stabilizing the expanded pericentriolar material around the centriole. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16980960}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa |
|
The protein encoded by this gene localizes to centrosomes, strengthening and stabilizing the pericentriolar region prior to spindle formation. The encoded protein usually remains with the mother centrosome after centrosomal duplication. Sevral transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2013]. |
hsa:55857; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; spindle organization [GO:0007051] |
24680887_Immunohistology revealed KIZ localization at the basal body of the cilia in human fibroblasts, thus shedding light on another ciliary protein implicated in autosomal-recessive RCD 25558830_Kiz phosphorylation depends on a balance between CDC25B and Plk1 activities. 32052671_Progressive RPE atrophy and photoreceptor death in KIZ-associated autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. 33000253_Long noncoding RNA PLK1S1 was associated with renal cell carcinoma progression by interacting with microRNA653 and altering CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000074749 |
Kiz |
79.140609 |
0.3337743543 |
-1.583055 |
0.183225714 |
77.417566 |
0.00000000000000000138379021026595120063910345151564604575780832408708710332123636987944337306544184684753417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000011493946822467888964927102255668152549142293749055883378407116879316163249313831329345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.4493132 |
4.5798763 |
118.9384885 |
8.2890021 |
| ENSG00000089012 |
55423 |
SIRPG |
protein_coding |
Q9P1W8 |
FUNCTION: Probable immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor. On binding with CD47, mediates cell-cell adhesion. Engagement on T-cells by CD47 on antigen-presenting cells results in enhanced antigen-specific T-cell proliferation and costimulates T-cell activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15383453}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the signal-regulatory protein (SIRP) family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP family members are receptor-type transmembrane glycoproteins known to be involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55423; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022409]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870] |
15294972_a novel member of the signal regulatory protein (SIRP) family- with unique characteristics from both alpha and beta genes- termed SIRPgamma 18524990_CD47 is enriched at endothelial junctions, and its interaction with SIRPgamma is required for human T-cell transendothelial migration 19473566_tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14 (TNFRSF14) and signal regulatory protein, gamma (SIRPG) appear to contribute to gender difference in incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. 23826770_SIRPgamma in complex with FabOX117 forms a dimer in the crystal. Binding to the Fab fixes the position of domain 1 relative to domains 2/3 exposing a surface which favours formation of a homotypic dimer. 24162948_The independent non-obstructive azoospermia risk alleles are driven by variants in the protein-coding sequence of the two genes, SIRPA and SIRPG. 30337675_The SNP rs2281808 TT variant reduced SIRPgamma expression on T-cells. SIRPgamma(low) CD8 T-cells in CT and TT individuals were in a heightened effector state with lower activation threshold and had greater gene expression of molecules associated with migratory and cytotoxic potential. SIRPgamma(low) CD8 T-cells were deficient in transcription factors associated with long-term functional memory formation. 32853219_Altered expression of SIRPgamma on the T-cells of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes patients could potentiate effector responses from T-cells. 34799406_Genetic Control of Splicing at SIRPG Modulates Risk of Type 1 Diabetes. |
ENSMUSG00000095788+ENSMUSG00000095028+ENSMUSG00000074677+ENSMUSG00000037902+ENSMUSG00000078780+ENSMUSG00000078783 |
Sirpb1a+Sirpb1b+Sirpb1c+Sirpa+Gm5150+Gm9733 |
9.798773 |
25.5062280473 |
4.672778 |
0.968795032 |
34.939428 |
0.00000000340123128171735119864557647412651314455800388714123982936143875122070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015475392638146764730948162693685565827195205201860517263412475585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.5497178 |
12.8411402 |
0.7756766 |
0.4866433 |
| ENSG00000089041 |
5027 |
P2RX7 |
protein_coding |
Q99572 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for ATP that acts as a ligand-gated ion channel. Responsible for ATP-dependent lysis of macrophages through the formation of membrane pores permeable to large molecules. Could function in both fast synaptic transmission and the ATP-mediated lysis of antigen-presenting cells. In the absence of its natural ligand, ATP, functions as a scavenger receptor in the recognition and engulfment of apoptotic cells (PubMed:21821797, PubMed:23303206). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21821797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23303206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28326637}. |
ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Ligand-gated ion channel;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the family of purinoceptors for ATP. This receptor functions as a ligand-gated ion channel and is responsible for ATP-dependent lysis of macrophages through the formation of membrane pores permeable to large molecules. Activation of this nuclear receptor by ATP in the cytoplasm may be a mechanism by which cellular activity can be coupled to changes in gene expression. Multiple alternatively spliced variants have been identified, most of which fit nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) criteria. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:5027; |
bleb [GO:0032059]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nuclear inner membrane [GO:0005637]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; extracellularly ATP-gated cation channel activity [GO:0004931]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; purinergic nucleotide receptor activity [GO:0001614]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; bleb assembly [GO:0032060]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; calcium-mediated signaling using extracellular calcium source [GO:0035585]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway involved in cell-cell signaling [GO:1905114]; cellular response to ATP [GO:0071318]; cellular response to dsRNA [GO:0071359]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; collagen metabolic process [GO:0032963]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion [GO:0014051]; glutamate secretion [GO:0014047]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; membrane depolarization [GO:0051899]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051882]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; NAD transport [GO:0043132]; negative regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045779]; negative regulation of cell volume [GO:0045794]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; phagolysosome assembly [GO:0001845]; phospholipid transfer to membrane [GO:0006649]; plasma membrane phospholipid scrambling [GO:0017121]; pore complex assembly [GO:0046931]; positive regulation of bleb assembly [GO:1904172]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol [GO:0010524]; positive regulation of cytoskeleton organization [GO:0051495]; positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion [GO:0014054]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glutamate secretion [GO:0014049]; positive regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045821]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 alpha production [GO:0032730]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034767]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051901]; positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032308]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070234]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032310]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; purinergic nucleotide receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035590]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of killing of cells of another organism [GO:0051709]; regulation of sodium ion transport [GO:0002028]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to fluid shear stress [GO:0034405]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705]; synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:0016079]; T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070231]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001913]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; vesicle budding from membrane [GO:0006900] |
11341329_First description of the expression of functional P2X7 receptors in a subpopulation of osteoblasts, activation of which can result in ATP-mediated apoptosis. 11852049_K193 and K311 are essential residues in ATP binding in the hP2X(7)R. 11943260_loss-of-function polymorphic mutation has anti-apoptotic effect, resulting in increase in B-cell numbers in CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) 12404161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12456589_The data show that monocyte-derived DC express the P2X7 receptor whose activation opens a cation-selective channel, and which leads to rapid and near complete shedding of CD23 12493261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12586825_a loss-of-function polymorphism within the P2X(7) receptor: Ile-568 is critical to the trafficking domain, which is between residues 551 and 581. 12633871_detection of nonfunctional receptors in HEK293 cells and B-lymphocytes 12759456_P2X7R activation signals distinct, novel plasma membrane blebbing events (dependent on RhoA activation and Rho-effector kinase activity) and simultaneously initiates release of IL-1 beta. 12787128_Different purinergic receptors have different functional roles in human epidermis with P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors controlling proliferation, while P2X5 and P2X7 receptors control early differentiation, terminal differentiation and death of keratinocytes. 12874219_The data presented are supportive of a model wherein residues Arg578 and Lys579 within the distal C-terminal lipid interaction domain of P2X7 are required for normal trafficking of the receptor as well as ligand binding and channel gating. 12874700_Blockade of the pore-forming P2X7 receptor inhibits formation of multinucleated human osteoclasts in vitro. 12880424_Non-melanoma skin cancers express functional purinergic receptors and that P2X7 receptor agonists significantly reduce cell numbers in vitro. 12931211_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12931211_the influenceof P2X7 genotype on susceptibility to chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or clinical outcome is small 14510944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14607949_A single nucleotide polymorphism (1513A-->C) in the P2X7 gene allows survival of mycobacteria within infected host cells. 14976257_Activation of P2X(7) ionotropic receptors is necessary and sufficient to increase 2-arabinoylglycerol production in microglial cells. 15004138_ATP-induced release of IL-1 beta is slower in monocytes from subjects homozygous for the Glu496Ala loss-of-function polymorphism in the P2X7 receptor, and this reduced rate of IL-1 beta release is associated with a lower ATP-induced potassium ion efflux. 15089763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15089763_Our data do not support a role of the P2X7 genotype as a prognostic marker in B-cell CLL. 15120006_P2X7 alleles modulate LPS-stimulated cytokine production, and may serve as an amplification loop of innate immunity. 15123679_Arg(307) polymorphism abolishes the binding of ATP to the extracellular domain of P2X7. 15155383_Fibroblasts from type 2 diabetes patients are characterized by a hyperactive purinergic loop based either on a higher level of ATP release or on increased P2X7 reactivity. 15184265_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15304508_the reversible permeabilization of erythrocytes by extracellular ATP is mediated by the P2X7 receptor 15472991_signaling via the P2X7R may modulate the astrocytic response to inflammation in the human central nervous system. 15475073_investigated P2X7 expression in 11 human hematopoietic cell lines, representing different lineages, as well as bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMC) samples from 87 leukemia and 10 myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients 15571247_P2X7/Ca2+ influx is modulated by estrogen in human ectocervical epithelial cells 15728711_A mechanism for P2X(7) receptor action, where activation involves a GRK-3-, beta-arrestin-2-, and dynamin-dependent internalization of the receptor into clathrin domains, followed in part by receptor degradation and recycling into the plasma membrane. 15777864_the P2X(7) receptor, via regulation of mature IL-1beta production, plays a common upstream transductional role in the development of pain of neuropathic and inflammatory origin. 15778408_the ability of P2X(7) polymorphisms to regulate the LPS-induced TNF-alpha to IL-10 ratio 15830104_Inflammatory stimuli drive P2X7 expression. The P2X7 receptor may play a role in the inflammatory responses against bacteria infection. 15862308_A 5' intronic splice site polymorphism leads to a null allele of P2X7. 15862308_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15896293_We report the identification of seven variants of human P2X7 which result from alternative splicing. 15899033_Current mapping suggests that murine P2RX7 receptor gene lies within lupus susceptibility locus SLEB4; P2RX7 receptor gene encodes a product with functional characteristics consistent with a role in systemic lupus erythematosus. 15901833_activation of the P2X7 ATP receptor elevates mitochondrial calcium and potential, increases cellular ATP levels, and promotes serum-independent growth 15923180_novel regulation of P2X7R outward and inward permeability to large molecules by Cl-(o) and Na+(o), respectively 15942904_The effect of polymorphisms in the P2X7 gene on the capacity of macrophages to kill mycobacteria is reported. 15972634_increased ATP-dependent activation of the P2X(7) 489T mutant with respect to the wild type receptor 15991050_findings have shown, for the first time, that functional P2X7 receptors are present in human melanomas and that their activation causes a decrease in cell number by apoptosis 16117789_Human Langerhans cells express functional P2X7 receptors, which play a role in the skin immune system. 16228288_P2X7 has a role in preventing apoptosis of human primary osteoclasts 16263709_P2X7 with a Thr357 to Ser polymorphism has absent or reduced function and impaired ATP-induced mycobacterial killing by macrophages 16321858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424024_neuroblastoma cells seem to have molded P2X(7) function to their advantage in two ways (i.e., by silencing P2X(7) proapoptotic activity and by coupling P2X(7) stimulation to release of locally acting trophic factors) 16514055_a novel role for P2X(7) as a pro-inflammatory receptor involved in rapid MMP-9 release and leukocyte recruitment. 16624800_a novel P2X7 variant has apoptosis-inhibitory actions; the truncated variant has a the ability to antagonize its full-length counterpart through hetero-oligomerization 16673375_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16673375_The strongest association was observed in bipolar families at the non-synonymous SNP P2RX7-E13A, which results from an over-transmission of the mutant G-allele to affected offspring. 16740600_shedding of CD21 and CD62L is mediated via the P2X7R. 16822851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16822851_P2RX7 polymorphism might play a causal role in the development of depression. 17032903_Single amino acid differences between species can account for large changes in agonist effectiveness and differentiate between the two widely used agonists at P2X7 receptors. 17036048_pannexin-1 is required for processing of caspase-1 and release of mature IL-1beta induced by P2X(7) receptor activation. 17040997_There is an association between expression of pro-apoptotic P2X(7) receptor and glomerulonephritis in rodent models, and in one form of human glomerulonephritis, the underlying relationship and its functional significance remain to be explored. 17065062_in polarized epithelial cells under steady-state conditions the P2X7-R is located in the apical membrane, and activation of the receptor induces formation of P2X7-R pores preferentially in the apical membrane 17065105_analysis of expression of a truncated naturally occurring variant of the human purinergic receptor P2X7 (P2X7-R) in human cancer cervical cells 17095747_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17130901_Our results indicate a possible role for novel PKC isoforms in the regulation of P2X(7)-mediated PLD activity. 17142754_a novel mechanism of IL-1beta release from activated microglia (brain macrophages) that occurred independently of P2X(7) ATP receptor activation 17197037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17197037_a prominent association found between severity of panic- and agoraphobia symptoms and an exonic SNP (rs3817190) in the CaMKKb gene and a trend for association with an exonic SNP in P2RX7 (rs1718119) with severity scores in the panic- and agoraphobia scale 17257221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17257221_The analysed intragenetic variants of the P2X(7) receptor may not be a susceptibility factor for CD. 17286963_P2X(7) activation by extracellular ATP can induce phosphatidylserine exposure in erythrocytes. 17314141_monocyte-derived human dendritic cells stimulated with a P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) agonist undergo a large release of microparticles containing the membrane-bound form of tissue factor 17482244_Levels of P2X(7) protein and mRNA were significantly lower in vivo, in tissues of complex hyperplasia with atypia or endometrial adenocarcinoma, than in tissues of normal endometrium, simple hyperplasia or complex hyperplasia tissues. 17483156_Human transfected P2X(7) receptor-induced depolarization and associated pottassium efflux may reduce sodium occupancy of the regulatory sodium binding site. 17488689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17488689_The A1513C polymorphism in the P2X7R gene is related to the occurrence of infections and survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. 17558311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17558311_P2X7 Glu496Ala and the Ile568Asn single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with 10-year fracture risk in postmenopausal women and response to hormone replacement therapy treatment. 17895406_This review discusses the need to reinterpret the assumed 'go-it alone' function of the P2X7 receptor in light of convincing biochemical and electrophysiological evidence for the existence of P2X4/P2X7 heteromeric receptors. 17928361_Our results indicate that ADP-ribosylation of R125 positions this common chemical framework to fit into the nucleotide-binding site of P2X7 and thereby gates the channel. 17947359_An enhanced P2X(7)R function might be a feature of human thyroid cancer. 18040764_A significant up-regulation of P2X(7) receptor expression on mononuclear cells was observed after overnight incubation with ATP without any significant differences between rheumatoid arthritis patients and normals. 18071294_Describe negative modulators of P2X-7 receptor. 18089587_a novel P2X7 purinoceptor inflammatory pathway may be involved in the release of interleukin-1 beta, which may be linked to the onset of labor. 18211888_ROS-mediated activation of the ASK1-p38 MAPK pathway downstream of P2X(7) receptor is required for ATP-induced apoptosis in macrophages. 18268501_Although further research is needed to prove that the Gln460Arg change has an aetiological role, it is so far the most convincing mutation to have been found with a role for increasing susceptibility to bipolar and genetically related unipolar disorders 18268501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18436590_Analysis of the P2X(7) receptor gene in the Russian Slavic population showed that the 1513C allele is a possible risk factor for clinical TB, whereas the -762 P2RX7 polymorphism did not appear to be associated with human susceptibility to TB 18523309_Signaling via NADPH oxidase activity is fundamental for the processing of mature IL-1 beta induced in monocytes by ATP receptor P2X7R and caspase-1 activation. 18543274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18543274_case-control analysis did not reveal significant results, but using a symptom severity scale we could support the association between depressive disorder and the G-allele of the Gln460Arg polymorphism in the P2RX7 gene. 18545980_human RA type B synoviocytes, express the P2X7 receptor which may modulate IL-6 release but not inducing changes in cell membrane permeability. 18596211_Explored the pharmacological action of compounds known to block gap junctions on Panx1 channels activated by the P2X(7)R and the mechanisms involved in the interaction between these two proteins. 18614336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18614336_Variation is observed in the purinergic P2RX(7) receptor gene and schizophrenia. 18617511_the P2X7 carboxyl tail is a regulatory module of P2X7 receptor channel activity 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18678419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18682393_increased expression of miR-186 and miR-150 in cancer epithelial cells decreases P2X7 mRNA by activation of miR-186 and miR-150 instability target sites located at the 3'-UTR-P2X7 18765670_P2X(7) is involved in the proliferative cell response to LL-37 and that the structural/aggregational properties of LL-37 determine its capacity to modulate the activation state of P2X(7). 18801407_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18801407_P2RX7 Gln460Arg polymorphism is associated with depression in Hungarian diabetic patients. 18852390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18852390_There is significant evidence of association between the single nucleotide polymorphism rs591874 in the first intron of the P2X7 gene and blood pressure. 18937793_A loss-of-function SNP at position 1513 (1513 A-->C) of the P2X(7) gene does not appear to be a susceptibility gene locus for the development of sporadic SLE. 18937793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18971257_These data demonstrate that P2X7R palmitoylation plays a critical role in its association with the lipid microdomains of the plasma membrane and in the regulation of its half-life. 18987356_In the absence or inactivation of P2X7 receptor, axons grow more rapidly and form more branches in cultured mouse hippocampal neurons, indicative that ATP exerts a negative influence on axonal growth. 19017759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19017759_Possible role of 1513A>C polymorphism as a novel clinical marker of papillary thyroid carcinoma follicular variant. 19068080_Functional inhibition of rat P2X7 receptors by acidic pH was variably affected by the extracellular His85, Lys110, Lys137, Asp197 and His219 residues, with the Asp197 residue being most critical for this inhibition. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19076224_Analysis of P2X7 showed that the 1513A-->C and -762T-->C polymorphisms did not appear to be associated with the susceptibility of the Chinese Han population to tuberculosis. 19076224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19151591_PIP(2) as a critical regulator of the function of the extracellular ligand-gated P2X receptor/channels and provide a novel way to control ATP-mediated cell death. 19160446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19160446_data do not provide support for rs2230912 or the other polymorphisms studied within the P2RX7 locus, being involved in susceptibility to mood disorders 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19186133_a segment composed of residues from part of the M2 domain and part of the putative TM2 segment of P2X(7)R may be partially folded in a beta-sheet conformation: may play an important role in channel/pore formation associated with P2X7R activation 19201928_P2X7 is a cation channel expressed by leukocytes and airway epithelial cells that is important to pathogen control and concomitant cellular inflammation 19204004_Expression of the P2X7 receptor increases the Ca2+ content of the endoplasmic reticulum, activates NFATc1, and protects from apoptosis 19211924_Results suggest that ATP release and autocrine, positive feedback through P2X(7) receptors is required for the effective activation of T cells. 19225709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225709_The geometric dimensions of the proximal femur in perimenopausalwomen are not associated with P2X7 polymorphisms. 19226284_P2X(4) and P2X(7) receptors are expressed by human osteoblast-like cells. P2X(7) receptor is mainly responsible for pore formation although P2X(4) receptors may also be involved. 19264037_level of expression at the injury site may not be linked to the maintenance of neuropathic pain after lingual nerve injury 19309360_Report mechanism of action of species-selective P2X(7) receptor antagonists. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19330776_No allelic or genotypic association between rs2230912 and bipolar I disorder or unipolar major depression P both in the national samples and in the combined European patient sample, was found. 19330776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19396427_Increase in P2X(7) production is one mechanism that may explain how beta cells compensate by adapting to the higher insulin demand 19430700_Results suggested that P2X7 receptor-mediated cytotoxic effects may occur independent of calcium response. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19494237_Data show that nonmuscle myosin closely interacts with P2X(7) and is dissociated from the complex by extracellular ATP. 19548263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19552691_Data confirmed the presence of functional P2X1, P2X4 and P2X7 receptors in LAD2 cells and HLMCs. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19682070_P2X7 receptor-triggered signalling pathways that regulate neurite formation in neuroblastoma cells. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19700502_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19748989_The key P2 receptor subtype that is responsible for the proinflammatory effect of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in vitro and in vivo is P2X7. 19882109_Retinoic acid treatment of human SH-SY5Y cells leads to decreased P2X(7) nucleotide receptor protein expression thus protecting differentiated cells from extracellular nucleotide-induced neuronal death. 19889958_Shockwaves enhance p38 MAPK activation, IL-2 expression, and T-cell proliferation via the release of cellular ATP and feedback mechanisms that involve P2X7 receptor activation and FAK phosphorylation. 19891999_In this preliminary study, we could nominate but not clearly demonstrate rare P2RX7 loss-of-function variants being associated with total hip arthroplasty failure 19891999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19931869_Human P2RX7 single non-synonymous nucleotide polymorphisms affect ATP-activated ion channel function and pore formation. 20007545_a novel pathway of phagocytosis of nonopsonized particles and bacteria, which operate in vivo and require an intact P2X(7)-nonmuscle myosin IIA membrane complex. 20138022_Results describe the effect of protons on the activation of human P2X7 purinergic receptors. 20164546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164546_Study assesses association of -762 T/C, 1513A/C and 1729T/A P2X7 polymorphisms in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and controls. Revealed an association of -762C allele and 1729T allele receptor polymorphisms with PTB in Asian Indian population. 20185692_Activation of epithelial P2X(7)R is mandatory for neutrophil-induced caspase-1 activation and IL-1beta release by intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. 20188863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20196868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20226536_The single nucleotide polymorphisms FKBP5:rs1360780, BDNF:rs6265 (Val66Met), P2RX7:2230912 (Gln460Arg) and CACNA1C:rs1006737 were genotyped in DNA from 457 depression cases (major depression, dysthymia, and mixed anxiety depression. 20351714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360457_investigated the coinheritance of 12 functionally relevant SNPs in the human P2X(7) gene; the functional effect of each singly and in combination was assessed by measuring ATP-induced currents and ethidium(+) uptake 20378545_C-terminal calmodulin-binding motif differentially controls human and rat P2X7 receptor current facilitation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20446288_In this study, we describe a readily applicable genotyping method for rs1653625 polymorphism of P2RX7 by applying a primer that introduces mismatched nucleotides to create a restriction enzyme cleavage site. 20450227_Mapping human P2X7 glycosylation sites reveals residue asparagine-187 is critical for receptor trafficking and function. 20453110_Data show that P2X7B is widely expressed in several human tissues, modulates P2X7A functions, participates in the control of cell growth, and may help understand the role of the P2X7 receptor in the control of normal and cancer cell proliferation. 20488797_P2X7R-mediated T. gondii killing occurs in parallel with host cell apoptosis 20493226_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20493226_Results suggest a possible involvement of P2X(7) in the pathogenesis of inflammatory autoimmune diseases. 20495003_Release of IL-1beta from monocytes showed selectivity for specific TLR agonists and was accelerated by P2X7 receptor activation. 20508067_P2X7R expression was measured in lung tissue and immune cells of mice or in humans with allergic asthma. 20535134_Evidence for associations between the purinergic receptor P2X(7) (P2RX7) and congenital toxoplasmosis. 20535134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605778_mechanisms behind the P2X7-dependent depletion of nuclear phosphorylated Akt 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20661107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20661107_This is the first study demonstrating that the 1513A-->C polymorphism is associated with extrapulmonary tuberculosis in children. 20668222_P2RX7 activation promotes the rapid and robust release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from primary human monocytes, a previously unrecognized role for P2RX7 in angiogenesis and wound repair. 20813842_transcription factor FosB/activating protein-1 (AP-1) activation is a prominent downstream signal of the extracellular nucleotide receptor P2RX7 in monocytic and osteoblastic cells 20819262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819262_The P2X7 receptors gene +1513C allele is a risk factor for the development of tuberculosis in the North Indian Punjabi population. 20837475_Results suggest that N187D P2X7 might be a positive regulator in the progression of hematopoietic malignancies. 20846359_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20846359_polymorphisms at the 1513 locus had a statistically significant association with P2X7 variants and tuberculosis susceptibility, while the -762 locus allele variants were not significantly associated with P2X7 variants and tuberculosis susceptibility 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21187936_Purinergic receptor P2RX7 functionality is necessary for infection of human hepatocytes by hepatitis delta virus and hepatitis B virus 21205829_Residues 155 and 348 contribute to the determination of P2X7 receptor function via distinct mechanisms revealed by single-nucleotide polymorphisms 21233486_we provide evidence of an absolute requirement for the P2X7 receptor, ATP release, and adenosine signaling in human osteoclast formation. 21262970_P2X7 controls the cytokine release from LPS-primed macrophages 21266468_P2RX7 receptor regulates lung surfactant secretion in a paracrine manner. 21335057_P2RX7 gene polymorphisms Gln460Arg (rs2230912) and His155Tyr (rs208294) are not associated with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder or remission following serotonin reuptake inhibitor or electroconvulsive therapy. 21438144_P2RX7 and its risk alleles predisposed to mood disorders consistently in three independent clinical cohorts 21470339_P2X7 receptor A1531C polymorphism is not associated with susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis[Meta-analysis] 21492831_In type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients, a significant association was observed between the proportion of P2X(7)(+)CD14(+) cells and blood LDL-cholesterol. No changes were observed in the function of P2X(7)(+) cells from T2D patients. 21508263_Data show that SAA can induce the expression of pro-IL-1beta and activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome via P2X(7) receptor and a cathepsin B-sensitive pathway. 21565445_This study demonistrated that the P2X7 splice variant receptor was detected in the spinal cord but not in osteoclasts of the P2X7R KO mouse. 21635566_Collectively, our results suggest that the P2X7 1513A/C loss-of-function polymorphism may contribute to susceptibility to extrapulmonary tuberculosis in Tunisian populations. 21640086_5 functional single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P2RX7 gene have been identified in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock, whereas no significant association has been found in patient suffering from hemophagocytic syndromes 21645266_Polymorphism at position 1068 and 1513 in the P2X7R gene might contribute to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis 21651910_Data suggest that P2X7R and P2Y(2)R could be novel therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease. 21670495_These data suggest that protein disulfide isomerase regulates a critical P2X7 receptor-dependent signaling pathway that generates prothrombotic TF, defining a link between inflammation and thrombosis with potential implications for antithrombotic therapy. 21697458_P2X7 receptor mediates the development of visceral hypersensitivity in a mouse model of postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. 21821797_These data suggest that the P2X(7) receptor in its unactivated state acts like a scavenger receptor 21865551_both P2X(7) and Panx-1 are required for GM-CSF promotion of multinucleated macrophages fusion 21911484_The results indicate that calcium in physiological concentrations acts as a negative allosteric modulator of P2X7R by decreasing the affinity of receptors for orthosteric ligand agonists. 21941410_Results demonstrate that lipopolysaccharide modulates the activity of the P2X7R and suggest that this effect could be of physiological relevance. 21978920_Human adipocytes express functionally active P2X(7)R, which modulate the release of inflammatory cytokines, at least in part via inflammasome activation. Adipocytes from metabolic syndrome patients show an enhanced P2X(7)R expression. 21988719_The many roles involving P2X7 suggest that this receptor is essential to fundamental aspects of the innate immune response (P2X7 receptor) 22017219_This study showed an association between specific symptoms of bipolar disorder and the P2RX7 gene. 22048123_The in vivo findings presented here demonstrate for the first time the therapeutic potential of P2X7R antagonism in the treatment of familiar Alzheimer's disease (FAD). 22134903_observations suggest that P2X7R activation caused not only Ca(2+) overload, but also Ca(2+) release via IP3R, sustained Ca(2+) store depletion, ER stress and eventually apoptotic cell death 22137490_significant association of 762T/C and 1513A/C polymorphisms with TB in the P2X7 gene was found in our study population. A sex bias, with only males showing a significant association with the disease, is the first report of this kind. 22163032_corneal epithelial cells express full-length and truncated forms of P2X(7), which ultimately allows P2X(7) to function as a multifaceted receptor that can mediate cell proliferation and migration or cell death 22183411_P2X7 modulates neuronal signalling in retinal rod and cone pathways. 22234152_Certain polymorphic variants of P2RX7 may identify women at greater risk of developing osteoporosis 22250198_results demonstrate a crosstalk between two metabotropic and one ionotropic purinergic receptor that regulates cAMP levels through adenylate cyclase 5 and modulates axonal elongation triggered by neurotropic factors and the PI3K-Akt-GSK3 pathway 22274585_data support that the P2X7 receptor is important in regulation of bone mass. 22295949_Leukocyte P2RX7 receptors had significantly altered pharmacodynamic responses to a specific antagonist (GSK1370319A), directly related to SNP genotype. 22377955_The present findings suggest that L2.3 cells express P2X7R, and this receptor may be involved in HI injury of radial glia by mediating phosphorylation of GSK-3beta. 22447075_The results of this study suggested that selectively targeting P2X7R pore formation may be a new strategy for individualizing the treatment of chronic pain. 22461619_P2X7 receptor-mediated scavenger activity of mononuclear phagocytes toward non-opsonized particles and apoptotic cells is inhibited by serum glycoproteins but remains active in cerebrospinal fluid. 22476940_P2X7 is one of the scavenger receptors involved in the recognition and removal of apoptotic cells in the absence of extracellular ATP and serum--{REVIEW} 22490780_P2X7R activation is required for the release of PGE2 and other autacoids independent of inflammasome activation 22493010_results support the expression of functional P2X(7) in human lung epithelium, although its role in epithelial pathogen defense is likely independent of IL-1 family cytokine processing 22505653_study shows that expression of P2X7 confers several features of cancer cells: enhanced engraftment ability and in vivo growth rate, increased expression of proliferation markers, reduced apoptosis and enhanced VEGF release and angiogenesis 22547202_This review summarizes the current understanding of the structure and function of P2X receptors and gives an update on recent developments in the search for P2X subtype-selective ligands--{REVIEW} 22613720_Data indicate that melittin induced keratinocyte cell function through activation of purinergic P2 receptor P2X7R, ADAM10 and ADAM17. 22623165_Neuroticism was a mediating factor between P2RX7 rs208294 risk alleles and time ill in patients with Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder. Overall, neuroticism was a strong predictor of time ill. 22662160_A common loss-of-function missense variant in the gene encoding the P2X(7) receptor is associated with reduced risk of IS and with IHD in smokers. 22703695_found no significant association between the SNPs studied and systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis 22707062_Functional polymorphisms in the P2X(7) receptor gene and haplotypes containing three of these polymorphisms are associated with osteoporosis. 22743305_P2X(7) functional capacity is associated with asthma risk or disease severity, and these relationships appear to be age related. 22768094_human P2X7R-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation is regulated by activated CD4+CD45RO+ memory T cells. 22776862_Genetic aberrations of P2X7R function are associated with lower bone mineral density and increased osteoporosis risk. 22806078_These results represent the first evidence indicating that the two death receptors, Fas and P2X7R connect functionally via caspase-8 and pannexin 1 hemichannel-mediated ATP release to promote caspase-9/caspase-3-dependent cell death in lymphoid cells. 22891241_Ezrin/radixin/moesin are required for the purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R)-dependent processing of the amyloid precursor protein. 22898868_P2X7R expression allows better adaptabilit |
ENSMUSG00000029468 |
P2rx7 |
93.515824 |
3.0625521846 |
1.614734 |
0.178744840 |
83.496418 |
0.00000000000000000006383153603911994508591684397197758239546220343980004229347824384888099302770569920539855957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000563826135210897875285088431005749226749418738039170036213665326840782654471695423126220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.2689854 |
15.9769731 |
47.2162102 |
4.2886779 |
| ENSG00000089050 |
10741 |
RBBP9 |
protein_coding |
O75884 |
FUNCTION: Serine hydrolase whose substrates have not been identified yet (PubMed:19329999, PubMed:20080647). May negatively regulate basal or autocrine TGF-beta signaling by suppressing SMAD2-SMAD3 phosphorylation (PubMed:20080647). May play a role in the transformation process due to its capacity to confer resistance to the growth-inhibitory effects of TGF-beta through interaction with RB1 and the subsequent displacement of E2F1 (PubMed:9697699). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19329999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9697699}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a retinoblastoma binding protein that may play a role in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene with identical predicted protein products have been reported, one of which is a nonsense-mediated decay candidate. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10741; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to nematode [GO:0009624]; type II pneumocyte differentiation [GO:0060510] |
12296629_RBBP10 was expressed widely in various human tissues, and the expression level is somewhat higher in tumor tissues than in normal tissues. 19004028_The crystal structure of human RBBP9 has been determined at 1.72 A resolution by the seleno-methionyl single-wavelength anomalous diffraction method. 20080647_identify RBBP9 as a tumor-associated serine hydrolase that displays elevated activity in pancreatic carcinomas. RBBP9 promotes pancreatic carcinogenesis. 21689726_Data identified RBBP4 and RBBP9 as required for maintenance of multiple PS cell types, and both RBBPs were bound to RB in PS cells. 21933118_Structure- function studies of RBBP9 suggest possible routes for novel cancer drug discovery programs. 22430187_blood samples of lateral sclerosis patients were found to have significantly different levels of expression of CyFIP2 and RbBP9 compared to the levels of expression in control subjects. |
ENSMUSG00000027428 |
Rbbp9 |
25.433705 |
2.3006942377 |
1.202069 |
0.299846431 |
16.411911 |
0.00005096397785984991001028213131185395923239411786198616027832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000146433387816115361196658839482154235156485810875892639160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.5920439 |
6.3825205 |
15.1543527 |
2.2555829 |
| ENSG00000089847 |
170961 |
ANKRD24 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF21 |
|
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:170961; |
|
35175278_ANKRD24 organizes TRIOBP to reinforce stereocilia insertion points. |
ENSMUSG00000054708 |
Ankrd24 |
80.901134 |
0.1128908377 |
-3.147000 |
1.033010475 |
7.734851 |
0.00541650388212834479201296389305753109510987997055053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010987850096236170469032877861081942683085799217224121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.6912388 |
13.0355107 |
125.3330464 |
81.6120435 |
| ENSG00000090006 |
8425 |
LTBP4 |
protein_coding |
Q8N2S1 |
FUNCTION: Key regulator of transforming growth factor beta (TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3) that controls TGF-beta activation by maintaining it in a latent state during storage in extracellular space. Associates specifically via disulfide bonds with the Latency-associated peptide (LAP), which is the regulatory chain of TGF-beta, and regulates integrin-dependent activation of TGF-beta. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q14766}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Growth factor binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene binds transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) as it is secreted and targeted to the extracellular matrix. TGFB is biologically latent after secretion and insertion into the extracellular matrix, and sheds TGFB and other proteins upon activation. Defects in this gene may be a cause of cutis laxa and severe pulmonary, gastrointestinal, and urinary abnormalities. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:8425; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; microfibril [GO:0001527]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; glycosaminoglycan binding [GO:0005539]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; transforming growth factor beta binding [GO:0050431]; transforming growth factor beta receptor activity [GO:0005024]; elastic fiber assembly [GO:0048251]; hormone secretion [GO:0046879]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0017015]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
16157329_Extracellular matrix is an important site of deposition for LTBP-3 and LTBP-4. 16456143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18487557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18487557_Our findings suggest that variations in or near the HPN and LTBP4 genes do not play a role in the susceptibility to IA in the Dutch population. 18585707_Novel functions for LTBP-4 as an adhesion molecule. 19836010_Mutations in LTBP4 cause a syndrome of impaired pulmonary, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, musculoskeletal, and dermal development. 19897194_Meta-analysis of abdominal aortic aneurysm size and growth rates demonstrated a significant association with the LTBP4 21011A>T genotype (a 2% decrease in AAA diameter, or a 0.53 mm/year reduction in AAA growth rate, per T allele [p=0.03, p=0.01]). 19897194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19998449_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20175115_These data suggest that LTBP-4 functions are modified by tissue-specific expression of the two N-terminally distinct variants, which in addition exhibit significant differences in cellular processing and targeting. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21468687_The lack of LTBP4-mediated targeting in malignant mammary tumor tissues may lead to a possible modification of TGF-ss1 and BMP bioavailability and function. 21505857_the G1 and G3 domains of versican were upregulated and LTBP-4 was downregulated in breast cancer stroma 22829427_Data indicate mutations of FBLN4, FBLN5, and LTBP4 in 12 probands presenting with type 1 recessive cutis laxa. 23440719_LTBP4 haplotype influences age at loss of ambulation, and should be considered in the management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. 23741501_Latent transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 4 is downregulated in esophageal cancer via promoter methylation. 25338755_In the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the human LTBP4 transgene exacerbated muscular dystrophy symptoms and resulted in weaker muscles with an increased inflammatory infiltrate. 25476005_We show that corticosteroid treatment and the IAAM haplotype of the LTBP4 gene are significantly associated with prolonged ambulation in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy 25641372_In Caucasians with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and LTBP4 genotype there was a protective effect on age at loss of ambulation. 25675815_It recruits elastin to microfibrils via fibulin-5. 25882708_Our results show that LTBP4 interacts with TGFBR2 and stabilizes TGFbeta receptors by preventing their endocytosis and lysosomal degradation in a ligand-dependent and receptor kinase activity-dependent manner. 26918958_The LTBP4 VTTT allele is associated with increased risk of dilated cardiomyopathy in European Americans. LTBP4 protein with the IAAM residues bound more latent TGFbeta compared to the LTBP4 VTTT protein. 27270107_High LTBP4 expression is associated with recurrence in glioblastoma. 28263294_Studied the potential role of LTBP-4 in scleroderma through clinical, in vivo and in vitro studies. Results suggest that LTBP-4 protein level is increased in plasma and skin tissue of scleroderma patients; found LTBP-4 to be a potential biomarker to differentiate systemic scleroderma (SSc) from localized scleroderma (LSc) patients. 29766838_DMD gene mutations involving the hinge 3 region, actin-binding domain, and exons 45-49, as well as the LTBP4 IAAM haplotype, were not associated with age of left ventricular dysfunction onset inDuchenne muscular dystrophy. 30463013_an AMPK-LTBP4 axis in inflammatory macrophages controls the production of TGF-beta1, which is further activated by and acts on fibroblastic cells, leading to fibrosis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 32658840_Serum latent transforming growth factor-beta binding protein 4 as a novel biomarker for idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis. 33302946_Two novel compound heterozygous variants of LTBP4 in a Chinese infant with cutis laxa type IC and a review of the related literature. 34645813_LTBP4 affects renal fibrosis by influencing angiogenesis and altering mitochondrial structure. 34958866_Aberrant interaction between mutated ADAMTSL2 and LTBP4 is associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. 36011296_LTBP4, SPP1, and CD40 Variants: Genetic Modifiers of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Analyzed in Serbian Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000040488 |
Ltbp4 |
141.236504 |
0.4640383187 |
-1.107684 |
0.330205263 |
10.992531 |
0.00091479814829396313355380776499714556848630309104919433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002145284504102144048504063889026838296558707952499389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
96.3444130 |
24.5647362 |
209.2739890 |
38.2789931 |
| ENSG00000090020 |
6548 |
SLC9A1 |
protein_coding |
P19634 |
FUNCTION: Involved in pH regulation to eliminate acids generated by active metabolism or to counter adverse environmental conditions. Major proton extruding system driven by the inward sodium ion chemical gradient. Plays an important role in signal transduction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11350981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15035633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8901634}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiport;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a Na+/H+ antiporter that is a member of the solute carrier family 9. The encoded protein is a plasma membrane transporter that is expressed in the kidney and intestine. This protein plays a central role in regulating pH homeostasis, cell migration and cell volume. This protein may also be involved in tumor growth. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:6548; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cation-transporting ATPase complex [GO:0090533]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; ion binding [GO:0043167]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; potassium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015386]; protein phosphatase 2B binding [GO:0030346]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; sodium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015385]; sodium:proton antiporter activity involved in regulation of cardiac muscle cell membrane potential [GO:0086040]; solute:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015299]; cardiac muscle cell contraction [GO:0086003]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to acidic pH [GO:0071468]; cellular response to antibiotic [GO:0071236]; cellular response to cold [GO:0070417]; cellular response to electrical stimulus [GO:0071257]; cellular response to epinephrine stimulus [GO:0071872]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0030011]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; neuron death [GO:0070997]; positive regulation of action potential [GO:0045760]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070886]; positive regulation of calcium:sodium antiporter activity [GO:1903281]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010613]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability [GO:0035794]; positive regulation of the force of heart contraction [GO:0098735]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell membrane potential [GO:0086036]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling [GO:0010882]; regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051893]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; regulation of pH [GO:0006885]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051492]; regulation of the force of heart contraction by cardiac conduction [GO:0086092]; response to acidic pH [GO:0010447]; response to muscle stretch [GO:0035994]; sodium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0036376]; sodium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098719]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863] |
11852051_Anion exchanger isoform 2 operates in parallel with Na(+)/H(+) exchanger isoform 1 during regulatory cell volume decrease. 12065894_Data indicate for the first time that two acid extruders, Na(+)-H(+) exchanger and Na(+)-HCO(3)(-) symporter, exist functionally and pH(i) dependently in human atrial cardiomyocytes. 12226101_serum-independent activation of NHE1 by bound CHP2 is one of the key mechanisms for the maintenance of high pH(i) and the resistance to serum deprivation-induced cell death in malignantly transformed cells 12479094_MCT1 and NHE1 genes play important regulation roles in proliferation and growth of tumor cells, probably by affecting pHi. 12562776_both Arg(440) in IL5 and Gly residues in the conserved segment of TM11 appear to constitute important elements for proper functioning of the putative 'pH(i) sensor' of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 1. 12682826_Regulation of placental NHE-1 not due to differences in C-terminus structure. Suppression regulated post-transcriptionally. Change in NHE-1 may contribute to adequate provision of electrolytes and nutrients to fetus. 12765964_identification in human reticulocytes and erythrocytes of an alternative splicing of NHE lacking the amiloride binding site 12905871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14680478_Both Pro167 and Pro168 are strictly required for NHE function and may play critical roles in the structure of transmembrane segment IV of the NHE. 15035633_Association of NHE1 with calcineurin B homologous protein (CHP) is crucial for maintenance of the pH(i) sensitivity of NHE1; tightly bound Ca2+ ions may serve as important structural elements in the pHi sensor of NHE1. 15096511_NHE1 promotes cell survival by dual mechanisms: by defending cell volume and pH(i) through Na(+)/H(+) exchange and by functioning as a scaffold for recruitment of a signalplex that includes ERM, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and Akt 15269707_Children with higher baseline Na-Li countertransporter(CT) had greater blood pressure change than children in lower baseline Na-Li CT and were associated with greater risk of high blood pressure compared to lower Na-Li CT. 15465015_Results describe the topogenesis of a hydrophobic lumenal loop segment between transmembrane segments 9 and 10 of human sodium/hydrogen exchanger isoform 1. 15523538_The relative fluorescence density of NHE-1 is significantly higher in isolated liver nuclei of human, when compared with those of rabbit and rat. 15535843_The antagonistic roles of RhoA and Rac1 in cell motility/invasion and cytoskeletal organization in breast cancer may be due to their concerted action on NHE1 activity as a convergence point. 15610042_acidic aa sequence is critical in proper conformation of the cytosolic domain, calmodulin binding, and in activity 15677483_Transmembrane (TM) segment IV of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1) is an unusually structured TM segment exquisitely sensitive to mutagenesis and Phe161 is a pore-lining residue. 15772858_NHE activity in the microvillus of syncytiotrophoblasts is attributable predominantly to NHE1. 15823043_The results suggest that PP1 is an important regulatory phosphatase of NHE1, that it can bind to and dephosphorylate the protein, and that it regulates NHE1 activity in vivo. 15843433_a pseudopodial-located RhoA/ROCK/p38/NHE1 signal module is regulated by Protein Kinase A gating and then regulates invasion in breast cancer cell lines 16002403_Data show that the Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE), NHE1, is functionally active in HEK 293 cells, and resides in lipid rafts or caveolae, which may create cellular microdomains where pH(i) is tightly regulated. 16306134_In conclusion, EGF protects esophageal epithelial cells against acid through NHE activation via Ca(2+)/calmodulin and the PKC pathway. 16475831_carbonic anhydrase II binds to the penultimate group of 13 amino acids of the cytoplasmic tail of NHE1. a novel phosphorylation-regulated CAII binding site exists in distal amino acids of the NHE1 tail. 16511206_crystallographic analysis of the human calcineurin homologous protein CHP2 bound to the cytoplasmic region of the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 16710297_These findings suggest that CHP serves as an obligatory subunit that is required both for supporting the basic activity and regulating the pH-sensing of NHE1 via interactions between distinct parts of these proteins [CHP2]. 16861220_TM VII is a critical transmembrane segment structured as an interrupted helix, with several residues that are essential to both protein function and sensitivity to inhibition. 17050540_helix formation of the cytoplasmic region of NHE1 by calcineurin B homologous protein 1 is a prerequisite for generating the active form of NHE1 17073455_data support the view that dimerization of two active subunits are required for NHE1 to possess the exchange activity in the neutral pH(i) range 17167226_the existence of a positive feedback loop between NHE1 and ERK can pose a barrier against apoptosis. 17209041_Both intact Ser(770) and Ser(771) were required for sustained acidosis-mediated activation of NHE1 17332506_The NHERF1 PDZ2 domain regulates PKA-RhoA-p38-mediated NHE1 activation and invasion in breast tumor cells. 17339567_Review. The role of NHE-1 hyperactivity in cardiac overload, ischemia/reperfusion injury, and myocardial hypertrophy is discussed. 17349711_Vpr-mediated NHE1 dyregulation is in part through GR pathway 17565280_We highlight evidence for the nontransport functions of NHE1 and describe how the structural functions are integrated with ion translocation to regulate a range of cellular processes[review] 17662110_Results support the view that the multiple charged residues identified in this study, along with several basic residues reported previously, participate in the regulation of the intracellular pH sensing of Na+/H+ exchanger 1. 17894388_Epidermal growth factor upregulates NHE1 by post-translational regulation that is important for cervical cancer cell invasiveness. 17913870_These data provide the first evidence that both EGF and S1P stimulate NHE activity in the syncytiotrophoblast; they appear to do so predominantly by activating the NHE1 isoform. 17916606_NHE1 activity generates a proton gradient at the cell surface accompanied by the cells' ability to respond to changes in pH in melanoma 17943310_T84 human colon cells contain three isoforms of the Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE1, NHE2, and NHE4, but not the Cl-dependent NHE 17981808_Model structure of the Na+/H+ exchanger 1 in human and E. coli 17982256_Three MAPKs exhibit unique interrelationships with the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger, NHE1, after osmotic cell shrinkage:ERK1/2, JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK. 18003619_Data support a novel molecular function of Daxx as an upstream regulator of NHE1 in ischemic cell death. 18094063_after the 4-wk sprint training period, the expression of the muscle Na+-K+ pump alpha1-subunit and Na+/H+-exchanger isoform 1 was higher 18094149_These observations suggest that Na(+)/H(+) exchange plays a permissive role in cell motility but is not required for the initiation or development of the migratory response. 18263712_NHE1 regulates Ca(2+) signaling via the modulation of Ca(2+) release from the endoplasmic reticulum, contributing to the regulation of proliferation in brain pericytes. 18264982_Data suggest that localization of NHE-1 in membrane cholesterol- and caveolin-rich microdomains constitutes a novel physiological negative regulator of NHE-1 activity. 18407588_NHE1 has a role in restraining the malignant behavior of human gastric carcinoma cells 18480176_critical for countering renal tubular atrophy and chronic renal disease progression 18508719_Enhanced activity of the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE-1) after myocardial stretch is considered a key step of the signaling pathway leading to cardiac hypertrophy[REVIEW]. 18508767_The structure of a peptide representing amino acids 338-365 of NHE1 determined by using high resolution NMR in dodecylphosphocholine micelles showed two helical regions kinked with a large bend angle around a pivot point at amino acid Ser(351) 18701649_These findings jklconfirm a necessary function for NHE1 during apoptosis and reveal the critical regulatory sites that mediate the alkalinizing activity of NHE1 in the early stages of a cell death response. 18757828_Protein kinase B/Akt phosphorylates and inhibits the cardiac Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1. 18776042_Activation of NHE1 is sufficient to generate Ca2+ signals that induce cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. 18996841_Membrane targeting and coupling of NHE1-integrinalphaIIbbeta3-NCX1 by lipid rafts following integrin-ligand interactions trigger Ca2+ oscillations. 19176522_analysis of transmembrane XI of the NHE1 isoform of the Na+/H+ exchanger 19301149_Inhibition of the Na+-H+ exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1) also inhibited leptin-induced superoxide anion production but at the same time amplified leptin-induced production of other oxidative species 19479940_The functional and molecular expression of NHEs in cultured human endolymphatic sac (ES) epithelial cells was determined and the effect of IFN-gamma on NHE function, was examined. 19622752_Results predict that other functions shared by Akt and NHE1, including cell growth and survival, might be regulated by increased H(+) efflux. 19835836_Structural and functional analysis of extracellular loop 2 of the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger. 19854014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19876777_Over-expression of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 19887620_These data provide evidence for tumor-selective downregulation of NHE1 by activated PPARgamma 19958503_results suggest that both NHE1 and MnSOD have peroxisome proliferator response elements binding motif in their upstream/promoter region and hence are regulated by PPAR upon ligand binding. 20138826_neurotensin /NTR1 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells seems to promote the induction of a metastatic phenotype, in contrast to its varying effects on tumor cell proliferation. 20338684_NHE1 plays a role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) invasion and that NHE1 may be a potential therapeutic target for HCC treatment. 20427472_Results suggest that the association of NHE-1 with Na-K-ATPase is critical for ouabain-mediated regulation of Na-K-ATPase and that these effects may play a role in cardioglycoside-stimulated hypertension. 20542029_NHE1 is a potential target in breast cancer and in spite of their similar transport functions, NHE1 and NBCn1 serve different functions in MCF-7 cells 20547664_data show a concordance among NHE1 localization, the generation of a well-defined acidic extracellular pH in the nanospace surrounding invadopodia, and matrix-degrading activity at invadopodia of human malignant breast carcinoma cells 20561412_The expression of NHE1 is up-regulated during apoptosis of HL-60 cells induced by etoposide. 20609358_The AMP-dependent kinase AMPK is a powerful regulator of NHE1 activity and thus contributes to the regulation of cytosolic pH (pHi) and pHi-dependent metabolic pathways. 20737315_The expression levels of NHE1 mRNA and protein are significantly up-regulated in gastric carcinoma tissue. 20855896_Nedd4-1 and beta-arrestin-1 as key regulators of NHE1 ubiquitylation, endocytosis, and function. 20974853_a structural model of the transmembrane part of hNHE1 21047280_This review focuses on the contribution of NHE-1 in atherogenesis and considers the relationship between NHE-1 and vascular risk factors of certain diseases, including hypertension and inflammation. 21063092_The calmodulin binding site A of hNHE1 protein is responcible for the stimulation with angiotensin II, the calmodulin binding site B is important to maintain its basal activity. 21148407_Intracellular pH gradients established by NHE1 activity exist along the axis of cell movement. 21170089_Na(V)1.5 and NHE1 are functionally coupled and enhance the invasiveness of cancer cells by increasing H(+) efflux. 21185840_NHE1 might participate in HIF-1-induced angiogenesis due, at least in part, to the alteration of calpain activity. 21221801_These findings suggest that NHE-1 in ulcerative colitis is regulated by NFkB induced through TLR-4 and MyD88 signaling mechanism. 21261728_NHE1 was overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and that inhibition of NHE1 could be a potential therapeutic target for HCC. 21345796_B-Raf associates with and stimulates NHE1 activity and that B-Raf(V600E) also increases NHE1 activity that raises intracellular pH. 21349616_This review of role of NHE1 in pathogenesis of lactic acidosis causing kidney dysfunction focuses on the benefits of NHE1 transporter inhibition. 21413028_In mineralizing osteoblasts, slightly basic basal intracellular pH is maintained, and external acid load is dissipated, by high-capacity Na(+) /H(+) exchange via NHE1 and NHE6. 21425832_That normal NHE1 function depends on a protein recognition element within the ID region that may be linked to NHE1 trafficking via an acidic ER export motif. 21454803_Silencing the NHE1 gene significantly inhibited the hypoxia-induced proliferation, hypertrophy, and migration of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via repression of the nuclear transcription factor E2F1. 21669197_The NHE1 mediates MDA-MB-231 cells invasion partly through regulating MT1-MMP in ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways dependent manner. 21729545_inhibition of NHE1 activity can promote hypoxia-induced K562 cell differentiation 21867601_Expression of NHE1 is up-regulated during apoptosis of HL-60 cells. Expression was not up-regulated in K562 cells. 21931166_molecular mechanisms of the phosphorylation-dependent regulation of NHE1 21997166_NHE1 mediates HeLa cell metastasis via regulating the expression and localization of MT1-MMP and provides a theoretical basis for the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting cervical cancer. 22120673_Data show that DeltaNErbB2 expression elicited Na(+), HCO(3)(-) cotransporter NBCn1 upregulation, Ser(703)-phosphorylation of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1. 22138972_results indicate that NHE1 is necessary for IGF-II-induced proliferation response of human gastric myofibroblasts 22216126_Inhibition or shRNA-based depletion of the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE-1, along with intracellular pH monitoring by live-cell imaging, revealed that invadopodia formation is associated with alterations in cellular pH homeostasis 22270364_a novel function for NHE1 and NCX1 in membrane blebbing and permeability, and establish a link between membrane blebbing and integrin signaling. 22301060_Increased apical Na/H exchanger activity correlates with increased apical NHE1 expression in mutant cells, and increased apical localization in collecting ducts of kidney sections from transgenic polycystic kidney disease mice compared with control mice. 22494070_NHE1 plays a critical role in the hypoxia-induced differentiation of K562 cells by regulating C/EBPa gene expression via activation of p38 MAPK signalling pathway. 22688515_NHE1 directly binds to calcineurin A and activates downstream NFAT signaling, leading to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy 22718548_NHE-1 on 1p is silenced in oligodendrogliomas secondary to IDH-associated hypermethylation and 1p allelic loss. 22772156_results suggest that EL4 makes an extension upward from TM VII to make up part of the mouth of the NHE1 protein and is involved in cation selectivity or coordination 22922957_Extracellular acidosis induces Ca(2+) oscillation via NHE1, leading to Ca(2+)/CaMKII-dependent CREB activation in human central nervous system pericytes. 22984264_Loss of both N-myristoylation and calcium binding of CHP3 decreases cell surface stability of NHE1. 23184727_Report that NHE1 generates measurable pH nanodomains right at focal adhesions in melanoma cells. 23220151_Functional insights inferred from NHE1 structure models and analysis. [Review] 23224899_NHE-1 is important for microglial (macrophage) activation and participates in the inflammatory response under pathological conditions including cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury. 23303189_novel role of STCH in the regulation of pHi through site-specific interactions with NBCe1-B and NHE1 and subsequent modulation of membrane transporter expression. 23331996_NHE1 is a new ATP-binding transporter that belongs to a major facilitator superfamily. 23393197_Studies indicate that the activity of Na+/H+ Exchanger (NHE1) is regulated through the phosphorylation of key amino acids in the cytosolic domain as well as by its interaction with other intracellular proteins and lipids. 23429007_The molecular mechanisms underlying NHE1 regulation. [Review] 23429008_NHE1 mediated contributions to myocardial injury may be attenuated by pharmacological inhibition. [Review] 23602949_Phosphorylation of S770/S771 changes the conformation of the NHE1 C-terminal regulatory region in a pH-dependent manner. 23677982_NHE1 appears to be the only significant regulator of intracellular pH in preimplantation mouse embryos. 23678047_acute acidosis activates NHE1 in mammalian kidney cells 23837875_Disruption of the DNM2-dependent retrograde trafficking of NHE1 contributes to cardiomyocyte apoptosis. 23902689_NaV1.5 colocalises with NHE-1 and caveolin-1 at the sites of matrix remodelling in invadopodia. 24088894_NHE1 and calmodulin associate in vivo through endothelin-dependent cytosolic signaling pathways. 24136992_modulation of NHE1 activity by various activators and inhibitors occurs through the direct binding of these molecules to the LID, which alters the association of the LID with the plasma membrane. 24337203_Protease activity suppression increases relative invadopodial NHE1 expression, while NHE1 inhibition increases acid-induced protease secretion. 24378530_The regulation of NHE-1 activity mediated by PKC-beta activation involves NHE-1 phosphorylation, which implies that the phosphorylation of NHE-1 directly affects glutamate-induced neuronal cell death. 24434427_CD44 regulates the metastasis of breast cancer cells through regulating NHE1 expression, which could be used as a novel strategy for breast cancer therapy. 24594116_probucol via inhibition of NHE1 attenuates atherosclerosis lesion growth and promotes plaque stability 24717311_NHE1 upregulation is an important cytoprotective mechanism in human glioma cells. 24840010_NHE1 transmembrane (TM) region VI from V240 to V245 is closely associated with TM region VII and, in agreement with nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structure of VI-VII segments, V242 and F260 are in close association. 24891603_Talin has a role in regulating moesin-NHE-1 recruitment to invadopodia in breast cancer 25043809_CIAPIN1 targeted NHE1 to mediate differentiation of K562 cells via ERK1/2 pathway. 25162926_The results demonstrate that the Ser771Pro human genetic mutation has significant and detrimental physiological effects on the activity of the NHE1 protein, SLC9A1. 25190744_Concurrent speed endurance and resistance training increases skeletal muscle NHE1 activity. 25205112_Mutation of SLC9A1 is associated with ataxia-deafness Lichtenstein-Knorr syndrome. 25241983_We demonstrate, for the first time, that 3 different pHi regulators responsible for acid extruding, i.e. NHE and NBC, and MCT, are functionally co-existed in cultured radial artery smooth muscle cells. 25275700_These results suggest a novel tumor suppressor function of merlin in melanoma cells: the inhibition of the proto-oncogenic NHE1 activity, possibly including its downstream signaling pathways. 25350536_The findings are consistent with a role for R425 in both neutralizing a helix dipole and maintaining NHE1 structure and function. 25372487_PKC-delta activates p38/MAPK, responsible for the inhibition of MMP-2 and -9 secretion, PKC-epsilon activates a pathway made of ERK1/2, mTOR and S6K responsible for the inhibition of NHE1 activity and cell migration. 25514463_Data suggest that Na/H exchanger isoform one (NHE1) is critical in triple-negative breast cancer metastasis. 25620102_The NHE-1 is a ubiquitously expressed cell membrane protein which regulates intracellular pH (pH(i)) and extracellular pH (pH(e)) homeostasis and cell volume. 25677682_This review focuses on the role of NHE1 and OPN in cardiac remodeling and emphasizes the signaling pathways implicating OPN in the NHE1-induced hypertrophic response. 25724898_CIAPIN1 over-expression decreases NHE1 expression and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. 25748234_Importantly, the specific NHE1 inhibitor cariporide reduced both three-dimensional growth and invasion independently of PDAC subtype and synergistically sensitized these behaviors to low doses of erlotinib. 25760855_Functional studies of N266H mutation in SLC9A1 gene showed a minor effect on the level of expression and no effect on targeting of the protein, however there was a complete absence of SLC9A1 activity. 25802333_the results support the anti-apoptotic role of HO-1 induced by NHE1 in the K562R cell line and IM-insensitive CML patients 26234675_the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells expressing JAK2V617F compromises the NHE-1/Bcl-xL deamidation pathway by repressing NHE-1 upregulation in response to DNA damage. hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), FOXO3A is largely localized within the nuclei despite the presence of JAK2V617F mutation, suggesting that JAK2-FOXO signaling has a different effect on progenitors compared with stem cells. 26397063_the present study revealed that miR-27b is upregulated by HPV16 E7 to inhibit PPARg expression and promotes proliferation and invasion in cervical carcinoma cells. 26646587_Data show that both mineralcorticoid receptor (MR) and G-protein estrogen receptor (GPER) contribute to the proliferation and migration of breast and endothelial cancer cells by sodium-hydrogen exchanger 1 protein (NHE-1) upon aldosterone exposure. 26775040_interaction of NHE1, NCX1 and CaM mediates the effects of IL6 on human hepatocellular carcinoma 26821117_In human ovarian cancer cells the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is overexpressed leading to increased formation of nitric oxide (NO). The NO promotes a glycolytic phenotype (Warburg effect) leading to H+ generation, which are removed via the sodium, proton (H+) exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1) reducing the intracellular content of this acid equivalent. 26944480_NHE1 is a plasma membrane transporter that uses the energy of the chemical gradient created by the Na+/K+ ATPase to couple the transport of one extracellular sodium for one intracellular proton. NHE1 functional domains, functional features, protein interactions, role in cell migration, and inhibitors are reviewed. A model of its role in pH control in tumor cells is described. Review. 27049728_NHE1 mutation is associated with metastatic potential and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of triple-negative breast cancer. 27083547_Human NHE1 acts as an ERK2 membrane protein scaffold in vivo that is necessary for ERK2 activation via direct interactions, and loss of scaffolding by NHE1 leads to decreased ERK2 activation. 27176613_Data show for the first time that PRLR activation stimulates breast cancer cell invasiveness via the activation of NHE1. Data propose that PRL-induced NHE1 activation and the resulting NHE1-dependent invasiveness may contribute to the metastatic behavior of human breast cancer cells. 27287871_NHE1 function plays an important role in glioma-microglia interactions, enhancing glioma proliferation and invasion by stimulating microglial release of soluble factors. 27302366_Study shows for the first time that CD95L activates NHE1, which thereby enhances cell migration. Using a combination of inhibitors and site-directed mutagenesis, results subsequently demonstrate that this mechanism occurs through a modification of NHE1 cooperative response to intracellular protons and that it involves both the Akt and RhoA-dependent pathways. 27434882_The transcription factor Zeb1 binds to the Na+/H+ exchanger 1 promoter, suggesting that Zeb1 directly controls Na+/H+ transcription. 27529686_Results indicate that Nav 1.7 promotes GC progression through MACC1-mediated upregulation of NHE1. 27636896_results demonstrate that early stop codon polymorphisms have significant and deleterious effects on the activity of the SLC9A1 protein product. The 735-NHE1 mutant, without the last 80 amino acids, had more minor defects 27650500_These data identify a molecular mechanism for pH-sensitive PI(4,5)P2 binding regulating NHE1 activity and suggest that the evolutionarily conserved cluster of four histidines in the proximal cytoplasmic domain of NHE1 may constitute a proton modifier site. 27751915_These data provides the first insight into the signalling molecules that form the NHE1 interactome in triple-negative breast cancer cells. 27773735_NHE1 regulates intracellular pH in human ovarian tumour cells. NHE1 activity is a pro-proliferative factor in human ovarian tumour cells. 27902974_The suppression of NHE1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) may enhance malignant potential by mediating PI3K-AKT signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Notch signaling, and may be related to a poor prognosis in patients with ESCC. 28055960_Genetic disruption of the intracellular pH-regulating proteins Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (SLC9A1) and carbonic anhydrase 9 reduces the proliferation of colon cancer cells. 28098891_High NHE1 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 28268168_Findings suggest that Na(+)/H(+) exchanger1 (NHE1) could be a target for anti-invasion/metastasis therapy. 28432487_The expression pattern of sNHE suggested that this protein may be involved in the regulation of sperm motility, and aberration of its expression in sperm may contribute to the pathogenesis of asthenozoospermia. 28554535_The disordered distal tail of the Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) is six-times phosphorylated (S693, S723, S726, S771, T779, S785) by the mitogen activated protein kinase 2 (MAPK1, ERK2). Using NMR spectroscopy, this study found that two out of those six phosphorylation sites had a stabilizing effect on transient helices. 28806945_NHE1 and Akt are downregulated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by tumor microenvironment conditions, more potently than by hypoxia alone. This inhibits endothelial cell migration and growth in a manner likely modulated by the cancer cell secretome. 28925083_This study provides the first line of evidence for a causative role of astrocytic NHE1 protein in reactive astrogliosis and ischemic neurovascular damage 30018422_a novel homozygous SLC9A1 truncating mutation, c.862del (p.Ile288Serfs*9), in two affected siblings. The patients showed cerebellar ataxia but neither of them showed sensorineural hearing loss nor a neuromuscular phenotype. 30033048_Intracellular pH dropped and NHE1 activity increased in hepatocytes under NH4Cl treatment. NH4Cl treatment decreased pHi induced by NH4Cl was associated with increased apoptosis, low cell proliferation and ATP depletion, and it stimulated PI3K and Akt phosphorylation.This effect was considerably reduced by NHE1 inhibition. 30044661_ittle, if any, active H(+) transport, supported by ATP, occurred. Major transporters include cariporide-sensitive NHE1 in basolateral membranes and ClC3 and ClC5 in apical osteoblast membranes. The mineralization inhibitor levamisole reduced bone formation and expression of alkaline phosphatase, NHE1, and ClC5. 30071192_intracellular loop 5 of NHE1 is a critical, intracellular loop with a propensity to form an alpha helix, and many residues of this intracellular loop are critical to proton sensing and ion transport 30287853_CHP3 bound with high affinity to CHP-binding domain of NHE1 with an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of 56 nM determined by microscale thermophoresis. 30333031_Data reveal significantly higher SLC9A1 mRNA levels in higher grade glioma and strongly suggest that NHE1 protein emerges as a marker for tumorigenesis and prognosis in glioma. 30834261_The accelerated net acid extrusion from the human colon cancer tissue was sensitive to the Na(+)/H(+)-exchange inhibitor cariporide. We conclude that enhanced net acid extrusion via Na(+)/H(+)-exchange elevates intracellular pH in human colon cancer tissue. 30977986_Differentiated Caco-2BBe cells display particularly high mRNA expression levels of NHE2, which can be functionally identified in the apical membrane. Although at low intracellular pH, NHE2 transport rate was far lower than that of NHE1. NHE2 activity was nevertheless essential for the maintenance of the steady-state pHi of these cells. 31067690_We believe the preclinical work herein discussed provides a persuasive rationale for examining the potential role of NHE-1 inhibitors for cardiac resuscitation in humans. 31093311_NHE1 (Na+/H+ exchanger 1) expression and ERK1/2 phosphorylation decreased along with CIAPIN1 upregulation. 31357694_By measuring the kinetic parameters of the NHE1 activity in the oncogene-transformed cells, it was found that NHE1 was constitutively activated by the oncogene expression via an increased sensitivity of its allosteric proton regulatory sites for the intracellular H+. This (the lowering of the H+-sensitivity threshold of NHE1) was responsible for its constitutive activation and the subsequent extracellular acidification 31375679_Study shows how calcineurin (CN) is recruited to plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger 1 (NHE1) and identify an NHE1 phosphorylation site, T779, that is critical for regulating NHE1 transport activity. CN specifically dephosphorylates pT779 to return NHE1 activity to basal levels. 31561854_Findings imply that Na/H exchanger 1 (NHE1) is a potential target in cytotoxic or differentiation-induction treatment for acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 31723030_NHE1 overexpression specifically induces death of induced pluripotent stem cells via sustained ROCK activation, probably caused by an increase in local pH near NHE1 32469979_our results suggest that dysregulation of NHE1 contributes to breaches in blood brain barrier integrity, drug penetrance, and the behavioral sensitivity to the antimigraine agent, sumatriptan. 32703317_Roles of hsa-miR-12462 and SLC9A1 in acute myeloid leukemia. 32841374_Characterization of intracellular buffering power in human induced pluripotent stem cells and the loss of pluripotency is delayed by acidic stimulation and increase of NHE1 activity. 33201382_Role of Genetic Mutations of the Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger Isoform 1, in Human Disease and Protein Targeting and Activity. 33273619_The intracellular lipid-binding domain of human Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 1 forms a lipid-protein co-structure essential for activity. 33655882_Dynamic Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 1 (NHE1) - calmodulin complexes of varying stoichiometry and structure regulate Ca(2+)-dependent NHE1 activation. 33804289_Screening of 5- and 6-Substituted Amiloride Libraries Identifies Dual-uPA/NHE1 Active and Single Target-Selective Inhibitors. 34000263_Type-1 Na(+)/H(+) exchanger is a prognostic factor and associate with immune infiltration in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. 34038242_Ethyl isopropyl amiloride decreases oxidative phosphorylation and increases mitochondrial fusion in clonal untransformed and cancer cells. 34108458_Structure and mechanism of the human NHE1-CHP1 complex. 34205045_Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors Ameliorate Endothelium Barrier Dysfunction Induced by Cyclic Stretch through Inhibition of Reactive Oxygen Species. 34638919_Inhibition of NHE-1 Increases Smoke-Induced Proliferative Activity of Barrett's Esophageal Cell Line. 34768780_Amino Acids 785, 787 of the Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger Cytoplasmic Tail Modulate Protein Activity and Tail Conformation. 34933181_The positive feedback loop of NHE1-ERK phosphorylation mediated by BRAF(V600E) mutation contributes to tumorigenesis and development of glioblastoma. 34948058_Roles of the Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger Isoform 1 and Urokinase in Prostate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. 34979106_Hypoxia enhances motility and EMT through the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE-1 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. 35084672_Permissive role of Na(+)/H(+) exchanger isoform 1 in migration and invasion of triple-negative basal-like breast cancer cells. 35339998_Requirement of Na+/H+ Exchanger NHE1 for Vasopressin-Induced Osteogenic Signaling and Calcification in Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000028854 |
Slc9a1 |
325.031852 |
2.0882236478 |
1.062276 |
0.177017931 |
35.438836 |
0.00000000263186619362783106667477120606257745549783066962845623493194580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012120544467378092912602353145405664758271768732811324298381805419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
432.0599034 |
47.0616860 |
208.6073527 |
16.7582086 |
| ENSG00000090097 |
57060 |
PCBP4 |
protein_coding |
P57723 |
FUNCTION: Single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein that binds preferentially to oligo dC. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ribonucleoprotein;RNA-binding |
|
This gene encodes a member of the KH-domain protein subfamily. Proteins of this subfamily, also referred to as alpha-CPs, bind to RNA with a specificity for C-rich pyrimidine regions. Alpha-CPs play important roles in post-transcriptional activities and have different cellular distributions. This gene is induced by the p53 tumor suppressor, and the encoded protein can suppress cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in G(2)-M. This gene's protein is found in the cytoplasm, yet it lacks the nuclear localization signals found in other subfamily members. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but the full-length nature for only some has been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57060; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048025]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of mRNA stability [GO:0043488]; regulation of RNA metabolic process [GO:0051252] |
17973258_expression of alpha CP-4 can inhibit proliferation and tumorigenesis of lung cancer cells, both in vivo and in vitro, by delaying the progression of the cell cycle 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26196957_PCBP4 plays important roles in the induction of cisplatin resistance in human maxillary cancers. |
ENSMUSG00000023495 |
Pcbp4 |
225.367290 |
0.3247093559 |
-1.622779 |
0.114808812 |
205.886231 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010849633630815646366280016412133992146317063375576347021828807665386334208732243129477388906934848036984514837687541312372108137651594006456434726715087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002123880535687519073289224697786295882066005252820452989783851729462627652579388955793032891427325175061953616432509385492100051351371803320944309234619140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
112.3441603 |
8.5611932 |
348.2459383 |
16.6681476 |
| ENSG00000090238 |
83719 |
YPEL3 |
protein_coding |
P61236 |
FUNCTION: Involved in proliferation and apoptosis in myeloid precursor cells. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of cellular senescence. Predicted to be located in nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83719; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; positive regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000774] |
20388804_Findings point to YPEL3 being a novel tumor suppressor, which upon induction triggers a permanent growth arrest in human tumor and normal cells. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21196260_In this review we show that transcriptionally active forms of p73 and p63, family members of p53, can transactivate the human YPEL3 gene[review] 21267786_YPEL3 is downregulated in colon tumors. 21671470_YPEL3 expression, which is induced by the removal of estrogen or treatment with tamoxifen triggers cellular senescence in MCF-7 cells while loss of YPEL3 increases the growth rate of MCF-7 cells. 27400785_Data show that YPEL3 is downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cell lines and tissue samples and it suppresses NPC EMT and metastasis by suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 29988027_Expression of the YPEL3 gene was upregulated in human colonic adenocarcinoma tissue. 32544203_yippee like 3 (ypel3) is a novel gene required for myelinating and perineurial glia development. 34675221_Steroid sulfatase deficiency causes cellular senescence and abnormal differentiation by inducing Yippee-like 3 expression in human keratinocytes. |
ENSMUSG00000042675 |
Ypel3 |
289.757108 |
0.3091873987 |
-1.693447 |
0.133176550 |
160.651757 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000081517155980837149627941899339690884309964074155551502257905386248830327998268695257819646830723531172324669569206889718770980834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000012559428207485972413196289325094953390466411170417032789901497769301817347539172176658299581904210118210585278575308620929718017578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
137.1770012 |
14.6146271 |
445.7567232 |
32.3014065 |
| ENSG00000090339 |
3383 |
ICAM1 |
protein_coding |
P05362 |
FUNCTION: ICAM proteins are ligands for the leukocyte adhesion protein LFA-1 (integrin alpha-L/beta-2). During leukocyte trans-endothelial migration, ICAM1 engagement promotes the assembly of endothelial apical cups through ARHGEF26/SGEF and RHOG activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11173916, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17875742}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for major receptor group rhinovirus A-B capsid proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1968231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2538243}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Coxsackievirus A21 capsid proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11160747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16004874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9539703}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Upon Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/HHV-8 infection, is degraded by viral E3 ubiquitin ligase MIR2, presumably to prevent lysis of infected cells by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and NK cell. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11413168}. |
3D-structure;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is typically expressed on endothelial cells and cells of the immune system. It binds to integrins of type CD11a / CD18, or CD11b / CD18 and is also exploited by Rhinovirus as a receptor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3383; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; adhesion of symbiont to host [GO:0044406]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; membrane to membrane docking [GO:0022614]; negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000352]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902042]; positive regulation of cellular extravasation [GO:0002693]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell [GO:0046813]; regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001910]; regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900027]; T cell activation via T cell receptor contact with antigen bound to MHC molecule on antigen presenting cell [GO:0002291]; T cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002457]; T cell extravasation [GO:0072683] |
11072593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11250042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11354638_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11361181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11409120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11469468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11508575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11716965_A defective expression of ICAM-1 (CD54) on secretory endometrial cells is associated with endometriosis. 11726228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11751911_IFN-gamma activates PLC-gamma2 via an upstream tyrosine kinase to induce activation of PKC-alpha and c-Src or Lyn, resulting in activation of STAT1alpha, and GAS in the ICAM-1 promoter, followed by initiation of ICAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion. 11776680_Premature labor is associated with up-regulation of adhesion molecules in the lower uterine segment 11817671_Role of ICAM-1 in the aggregation and adhesion of human alveolar macrophages in response to TNF-alpha and INF-gamma. 11831440_Transient exposure of human bronchial epithelial cells to cytokines IFNG and TNFA, but not IL1B, leads to persistent increased expression of ICAM-1. 11831864_Incubation of endothelial cells with conditioned media derived from stimulated macrophages modulates ICAM1 mRNA expression. Results suggest TNF-alpha and activation of the NF-kB pathway are involved. 11837795_heat shock decreases endothelial cell ICAM-1 expression via inhibition of IKK activity 11838958_Down-regulation of cell adhesion molecules LFA-1 and ICAM-1 after in vitro treatment with the anti-TNF-alpha agent thalidomide. 11847011_significant increase in plasma levels between day 1 and day 5 of G-CSF-induced stem cell mobilization; possible effect on leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions 11877286_oncogenic transformation by BCR-ABL may increase susceptibility of leukemic progenitors to NK cell cytotoxicity by a mechanism involving overexpression of ICAM-1 11881155_ICAM-1 participated in cell attachment to X- and Y-fragments, rather than to intact fibrinogen or late degradation products, fragments D and E. 11893710_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11911111_Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene polymorphisms in isolated polymyalgia rheumatica. 11911111_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11914659_raised sICAM-1 in breast cancer, like the acute phase response, reflects inflammation 11922919_Elevated soluble CD40 ligand is related to the endothelial adhesion molecules in patients with acute coronary syndrome. 11929876_Dynamic regulation of LFA-1 activation and neutrophil arrest on intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in shear flow 11935152_Relation between glycemic control, hyperinsulinaemia and plasma concentration in patients with glucose intolerance or niddm 11936473_colocalization of ICAM-1 and B7.1 molecules was demonstrated in Hashomoto's thyroiditis whereas no B7.1 expression was observed in Graves' disease 11953106_CD54 may play an important role in pathogenic process (in COPD) 11956618_expression of ICAM1 in colorectal cancer 11963839_women with stage III and IV endometriosis had higher serum concentrations of soluble VCAM-1, lower serum concentration of soluble ICAM-1 11983194_Prolonged, low dose alpha-tocopherol therapy counteracts intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 activation 12011765_Blood levels of ICAM1 are low in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients 12020443_X-ray doses of A is associated with an earlier age of GD onset and that the c.1405A-->G polymorphism of the ICAM-1 gene could predispose to Graves' ophthalmopathy 14572449_ICAM-1 protein is selectively expressed in cortical tubers, but is only minimally expressed in control cortex, adjacent nontuberal cortex of the tuberous sclerosis complex. 14572618_TNFalpha stimulates binding of nuclear proteins to the nuclear factor kappa beta (NFkappaB) and the CAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) consensus sites in the ICAM-1 promoter in these cells 14605444_findings indicate that cytochalasin E activates protein kinase C under the depolymerization of actin filament, leading to the induction of interleukin-8 production and the up-regulation of CD54 in HeLa cells 14609725_intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression was enhanced in the macrophage-derived foam cells 14634129_Vascular endothelium generates microfilament-, microtubule-, and calcium-dependent ICAM-1-enriched-cup-like structures within minutes of binding in vitro to lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1)-bearing leukocytes. 14643123_Our data indicate an aetiological role for ICAM-1 in type 1 diabetes, which needs to be confirmed in future genetic and functional experiments. 14695458_Increased expression of ICAM1 may affect the development of initial atherosclerotic coronary stenosis, but not re-stenosis. 14714557_minor trauma to skin may induce expression of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and IL-8 14722298_community-circulating strains of Coxsackie virus A21 can infect target cells expressing either ICAM-1 or decay-accelerating factor alone and that such interactions extend tissue tropism and impact directly on viral pathogenesis. 14734737_Basal expression and colocalization of ICAM-1 with E-selectin and CCL17 chemokine in dermal vessels serves to recruit T cells to noninflamed human skin and provides a strong cutaneous immunosurveillance system and model interface with the environment. 14737745_positive marker for precinical type 1 diabetes in children 14741380_study demonstrates that overexpression of RORalpha1 and RORalpha4 inhibits TNF-alpha induced expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting the NF-B signaling pathway 14742996_beta2-AR agonists strongly inhibited the expression of ICAM-1 and CD40. 14763917_Data indicate that weight loss is more important than glycaemic control in regulating circulating levels of ICAM-1 in morbidly obese subjects. 14763979_Mutagenesis of domain 1 of ICAM-1 shows that the binding sites for different Plasmodium falciparum variants overlap to a large extent, but that there are subtle differences between them that correlate with their adhesive phenotypes. 14975197_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14984317_even a short-term exposure of endothelial cells (ECs) to high glucose concentration leads to their activation associated with increased expression of adhesion molecules such as ELAM-1, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1. 14993495_In patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, carotid atherosclerosis is associated with markers of inflammation, malnutrition and circulating levels of adhesion molecule ICAM-1. 15009098_Expresson is reduced in treatment with methotrexate in bullous pemphigoid. 15013836_Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 immunoreactivity in gray and white matter of the ACC in bipolar subjects was increased compared with control subjects (gray: p =.001; white: p <.001 and schizophrenic subjects p=".016;" white: study of gene-disease association. navigator in the spanish population argues against hypothesis that polymorphism at codon icam-1 gene is causally related to alzheimer disease. porphyromonas gingivalis enhanced expression intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on surface human umbilical vein endothelial cells a bacterial dose-dependent manner. molecule may play role asthma. an important inflammation-related plaque development. modifies inflammatory immune responses by changing cell-cell interaction then regulating apoptosis was processed distal arg441 indicating mmp-9 docking contributes sicam-1 shedding attenuation shear stress-induced upregulation icam-1. homozygote status for associated with protection primary sclerosing cholangitis. ie proteins stimulate villous trophoblasts paracrine release tnf alpha il1 beta as well direct effect infected cells. show muc1 mucin expressed can initiate calcium-based oscillatory signal contact association more efficient transmission factor hiv-1 bearing than combined gp120 icam-3 involvement virus-bound lfa-1 virus binding carriage confirmed lymphoid tissues. dcs owe part their outstanding ag-independent t cell stimulatory ability chemokines but not dc-specific icam-3-grabbing nonintegrin. visually normal peritoneal from women endometriosis early implantation endometriosis. serum level soluble bronchiolitis patients significantly higher healthy control infants microg vs concentration prevents thrombin-induced inhibiting p38 mapk activation which turn phosphorylation rela transcriptional activity bound nf-kappab. specific cd23-engagement lung induced significant decrease implicated plasmodium falciparum parasitized red blood cytoadherence help clarify essential requirements erythrocyte membrane protein data support linkage crohn disease suggest amino acid polymorphisms be ibd. s-1-p enhance both mrna levels cord vcam-1 e-selectin interleukin-6 are glucose regulated poly polymerase alone did increase either ros production or noted min reoxygenation. monocyte correlated coexpressing result flow-induced selective subset icam-1-expressing naturally occurring variant icam-1kilifi has altered characteristics respect different rhinovirus serotypes. lymphatic vessels beneficial judgement invasion metastasis colon cancer. mice were made express cell-surface receptor coxsackievirus a21 cav21 administered these via intramuscular route causes paralytic condition consistent poliomyelitis irish k469e ishemic heart pinpoint first time crucially involved small carcinoma cell-endothelial camp elevation activating pka able under pro-inflammatory conditions. combination transcription targeting account this augmentation. share common genetic modulation traits obesity insulin resistance hdl3 cholesterol. glycosylation regulate conformation functions icam receptors key immune-mediated processes thus critically diverse clinical disorders ranging asthma atherosclerosis. increased adhesiveness circulating leukocytes pathogenesis ulcerative colitis response tobacco smoke extract. molecules interacted only b streptococcus liquor strain while beta1 integrin gbs-iii gbs-v invasive strains myeloperoxidase-anca-positive microscopic polyangiitis selam-1 during active phase slower decline treatment period could prognostic risk chronic renal failure. gene-gene interaction. elevenfold simultaneous presence e469k kk genotype multiple system atrophy. monomeric profound changes alter clustering whereas oligomers microclustering. appears crucial induction itself sufficient confer ho-1 tumor induces such keratinocytes nf-kappab oral have immunostimulatory muocsa skin implication progression type diabetic retinopathy cannot supported. variants modulate atherosclerosis humans. influence independent plasma products. il-6 nasal lavage fluid allergic rhinitis controls. icam1 il6 pulmonary function. proximal tubule epithelial cd40 upregulates other pathway genes concomitant mononuclear mediated transduction pathway. mediating between parasitised vascular endothelium malaria had impact fibrinogen independently factors patient hypothesize biochemical g241a snp masked disease-related mechanism leading reduced schizophrenia. demonstrate mature form toxoplasma gondii adhesin mic2 activated host probably facilitates transmigration parasite metastatic breast lines. tnf-alpha acted through erk elicited synergistic effect. further cotreatment hepatocytes positive feedback loop involving htlv-1 tax formation virologic synapse t-cell tropism studies two senegalese villages located regions endemic showed no evidence variability malarial phenotypes studied. tnfalpha mainly nfkappab stat3 respectively rac1 central modulating cytokine-induced inhibits plus il-4 ige alterations scd23 scd54 engagement target leads recruitment mhc-i area enhances presentation cognate peptide complexes cytotoxic leukocyte-endothelial retinal microcirculation icam1. dc il-8 interacts constitutively decidual neutrophil trafficking into hemorrhagic inflamed trimester decidua nutrients physical exposure alcohol consumption endometrial stromal ischemic stroke e allele among guangxi zhuangs. trial gene-environment pharmacogenomic toxicogenomic. hybrid domain alphal beta2 affinity states crystallographic analysis its indicate haplotypes inverse relationship shown ratio icam1-expressing lymphocytes transforming growth concentrations stages acute rheumatic fever. destruction lfa-1-expressing takes place bile ductules also canal hering biliary cirrhosis antibodies produced after cardiac transplantation polymorphic residues contribute causing proinflammatory signaling pathways. frequencies apoe ppara pai-1 coronary artery donors arrangement differentiate groups process variation atresia. how lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 mediates rolling polystyrene particles flow postprandial ldl explain proatherogenic high lipemia. uveal melanoma cd54 caveolae required p. pneumoniae polyps group. measured enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays over years life children seroconverting positivity autoantibodies all susceptibility diabetes. gingival fibroblast stimulated monocytes resulting mmp-1 timp-1 contrast partly elements controlling uptake intracellular nanocarriers targeted up-regulation hours src pi3k migration endogenous transfected muc1. tace ectodomain cleavage diabetes mellitus navig> | ENSMUSG00000037405 |
Icam1 |
1967.147825 |
6.4614203835 |
2.691851 |
0.046094450 |
3698.595857 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3482.2488065 |
94.4376969 |
542.9026385 |
13.0449704 |
| ENSG00000090376 |
11213 |
IRAK3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y616 |
FUNCTION: Putative inactive protein kinase which regulates signaling downstream of immune receptors including IL1R and Toll-like receptors (PubMed:10383454, PubMed:29686383). Inhibits dissociation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 from the Toll-like receptor signaling complex by either inhibiting the phosphorylation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 or stabilizing the receptor complex (By similarity). Upon IL33-induced lung inflammation, positively regulates expression of IL6, CSF3, CXCL2 and CCL5 mRNAs in dendritic cells (PubMed:29686383). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K4B2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10383454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29686383}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Asthma;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase protein family. Members of this family are essential components of the Toll/IL-R immune signal transduction pathways. This protein is primarily expressed in monocytes and macrophages and functions as a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Mutations in this gene are associated with a susceptibility to asthma. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:11213; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001960]; negative regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045824]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0043242]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034122]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of macrophage tolerance induction [GO:0010933]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0043244]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to peptidoglycan [GO:0032494]; response to virus [GO:0009615] |
12054681_Identification and characterization of murine IRAK-M 14592437_Thus, our data indicate that IRAK-M could play a pivotal role in the process of endotoxin tolerance in human monocytes and provide evidence that PI3K is involved in regulating its expression. 15728517_IRAK-M is rapidly upregulated in human monocytes pre-exposed to tumor cells and could be involved in deactivation of tumor-infiltrating monocytes mediated by tumor cells. 16432636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16437636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17379480_These findings indicate that IRAK-M selectively attenuates p38 activation and inhibits innate immunity through stabilizing MKP-1. 17503328_IRAK-M is involved in the pathogenesis of early-onset persistent asthma. 17503328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17558906_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17558906_no evidence to suggest association between inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) or subsets of CD & UC and IRAK-M; an interaction was found between IRAK-M and CARD15 in UC patients 17982103_LPS tolerance in human endotoxemia models is associated with IRAK-M up-regulation. 18156187_Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide upregulates IRAK-M in macrophages. 18354163_observed striking up-regulation of IRAK-M in monocytes, but without concomitant proinflammatory cytokine production 18987746_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19013233_Analysis of single single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes did not reveal a significant association between polymorphisms in the IRAK-M gene and atopic dermatitis in this cohort. 19013233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19114913_Immunosuppression in sepsis caused by B. pseudomallei is associated with an upregulation of IRAK-M and an indicator of poor outcome. 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19372141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19414798_IRAK-M is a major mediator of globular adiponectin-induced endotoxin tolerance in primary macrophages 19423540_Nine SNPs distributed across eight genetic regions (ALOX5, IRAK3, ITGB2, NCF2, NFKB1, SELP, SOD1, and STAT1) were associated with risk of glioma with P value of |
ENSMUSG00000020227 |
Irak3 |
418.737054 |
0.3355596321 |
-1.575359 |
0.106593879 |
216.118955 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000063529012596239734875403721854796001096607772658081312352424515575195995071730683552492206839015910229229484440518539293304544485208040782708849292248487472534179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000013206876421415471956938101248896885215259502339859325106788197707409638429412830250864059151128925387109760774085574785725177848760836241126526147127151489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
197.1507408 |
30.4266632 |
594.0933523 |
65.5934915 |
| ENSG00000090382 |
4069 |
LYZ |
protein_coding |
P61626 |
FUNCTION: Lysozymes have primarily a bacteriolytic function; those in tissues and body fluids are associated with the monocyte-macrophage system and enhance the activity of immunoagents. |
3D-structure;Amyloid;Amyloidosis;Antimicrobial;Bacteriolytic enzyme;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes human lysozyme, whose natural substrate is the bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan (cleaving the beta[1-4]glycosidic linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine). Lysozyme is one of the antimicrobial agents found in human milk, and is also present in spleen, lung, kidney, white blood cells, plasma, saliva, and tears. The protein has antibacterial activity against a number of bacterial species. Missense mutations in this gene have been identified in heritable renal amyloidosis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:4069; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lysozyme activity [GO:0003796]; antimicrobial humoral response [GO:0019730]; cytolysis [GO:0019835]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; metabolic process [GO:0008152]; retina homeostasis [GO:0001895] |
10561612_a residue at the N-terminal of lysozyme is required for hydrogen bond networks with ordered water molecules and stabilization of the protein. 11887182_Local cooperativity in the unfolding of an amyloidogenic variant of human lysozyme 11927576_Positive contribution of hydration structure on the surface of human lysozyme to the conformational stability. 11986950_up-regulated by the AML1-MTG8 fusion protein, suggesting a role in the granulocytic maturation characteristic of the t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia 12183536_Streptococcal inhibitor of complement inhibits two additional components of the mucosal innate immune system: secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor and lysozyme. 12564923_Detailed comparison between the 35 degree C and 4 degree C structures of lysozyme revealed for the first time that an active site lobe has a structural ability to obstruct the polysaccharide-binding cleft only by temperature lowering without a substrate. 12709420_Structural and folding dynamic properties of human lysozyme T70N variant 14976184_promyelocytic leukemia protein, but not Sp100, induced the accumulation of MEF in PML nuclear bodies and MEF and PML physically interacted, stimulating MEF transcriptional activity, resulting in the up-regulation of endogenous lysozyme expression. 15155566_Hydrostatic pressure (3.5 kbar at 57 degrees C, pH 7.4) was used to make amyloidogenic states of WT & variant(Ile56Thr & Asp67His) lysozymes by inducing a conformational state of lysozyme that aggregates readily upon decompression. 15713462_amyloidogenic variants, I56T and D67H, show a specific, partly unfolded intermediate state under physiologically relevant conditions 16023673_the ensemble of reduced denatured conformers initially collapses into a large number of unstructured intermediates with one or two disulphide bonds, the majority of which then fold to form the native-like three-disulphide intermediate, des-[77-95] 16126226_Data suggest that partial unfolding is an intrinsic property of the human lysozyme structure, and suggest that the readiness with which it occurs is a critical feature determining whether or not amyloid deposition occurs in vivo. 16329101_A novel form of systemic ALys amyloidosis, caused by compound heterozygosity in exon 2 (p.T70N) and exon 4 (p.W112R) of the lysozyme gene (LYZ), with both mutations being present on the same allele. 16416029_Lysozyme functions as an antimicrobial peptide, with antibacterial activity. 16441658_findings indicate that a complex interplay between reduced native-state stability, lower secretion levels, and protein aggregation propensity influences the types of mutation that give rise to familial forms of amyloid disease 16799949_report a case of hepatic rupture secondary to hereditary lysozyme amyloidosis that was successfully treated by liver transplantation 17054380_The distortion of the hydrophobic core at the alpha- and beta-interface putatively results in the formation of the initial 'seed' for amyloid fibril. 17360367_The structure of the synthetic human lysozyme was confirmed by high-resolution x-ray diffraction, giving the highest-resolution structure (1.04 A) observed to date for this enzyme. 17407782_Clusterin, and perhaps other extracellular chaperones, could have a key role in curtailing the potentially pathogenic effects of the misfolding and aggregation of proteins that, like lysozyme, are secreted into the extracellular environment. 17524359_Thus, we provide a novel strategy for engineering the active site of enzymes. 18029788_The influence of mutant signal peptides on enzymatic activity of lysozyme at high pH or ionic strength were studied. 18344136_short-duration, high-intensity exercise increases the secretion rate of salivary Lysozyme despite no change in the saliva flow rate. 18434581_High salivary lysozyme levels are associated with the odds of hypertension. 19179970_Lysozyme activity in crevicular fluid and in unstimulated saliva correlated with periodontal pocket depth in donors and in patients with gingivitis or periodontitis. 19435495_Results show that the cationic nature is not a major determinant in the anti-HSV action of mucosal innate cationic polypeptides, since whereas human Lactoferrin inhibited HSV-1 infection efficiently, human lysozyme had no HSV-1 inhibiting activity. 19563039_There was no difference in the concentration of lysozyme in children with dental caries than that in controls. 20167661_Raised plasma lysozyme levels may be a useful biomarker of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and response to therapy. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21460390_increased production of the antibacterial enzyme lysozyme was found in collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis 21486364_Lysozyme is up-regulated in Barrett's mucosa 21574221_The degree of residual structure of lysozyme correlates with the ability of the protein to form amyloid fibrils. 21965601_We observed that expressing the destabilized F57I and D67H lysozymes triggers unfolded protein response activation, resulting in degradation of these variants. 22096116_When Lzm-S was located in close proximity to vascular smooth muscle cells, it could generate H(2)O(2) to produce lengthening in a human cell culture preparation. 23155290_Lysozyme is up-regulated in Barrett's mucosa 23264227_The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of chronic alcohol intoxication and smoking on the concentration and output of salivary lysozyme. 24121782_Both mRNA and protein levels of lysozyme were significantly higher in patients with biofilm associated chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) than those with CRS and no biofilm and controls. 24296430_Lzm-S can deposit in the systemic vasculature and kidneys in SS, where this deposition could lead to acute organ dysfunction. 24308818_Data suggest that the invariant loop of PliC (periplasmic inhibitor of c-type lysozyme) from Brucella abortus plays crucial role in inhibition of human c-type lysozyme via its insertion into the active site cleft of lysozyme. 24340941_The dynamics of changes in lysozyme activity and content of lactoferrin content of patients with chronic osteomyelitis 24495950_the protective action of lysozyme on the nephrotoxic effects of advanced glycation end products depend on ability to prevent the production and release of inflammatory mediators, such as IL-6 and to reduce macrophage recruitment in the inflammatory sites. 25217048_Hereditary amyloidosis associated with the p.Trp82Arg lysozyme variant in this new family is predominantly associated with mild upper gastrointestinal tract involvement and in some cases with inflammatory bowel disease. 25236863_Both the hLF and hLZ were expressed in the mammary gland of bi-transgenic pigs, as detected by western blotting.Interestingly, pig milk containing hLF and hLZ had synergistic antimicrobial activity 25575179_The determination of the structure of a low-population intermediate in the product release process by human lysozyme, is reported. 25659958_Accumulation of pathogenic lysozymes in the endoplasmic reticulum caused ER stress and the unfolded protein response mainly via the IRE1alpha pathway. 25706123_Data show that transgenic hens with stable expression of recombinant human lysozyme proteins can be created by microinjection of lentiviral vectors. 25914748_Tear lysozyme, lactoferrin and lipocalin concentrations were determined via electrophoresis and the results for patients with or without eyelid tumors were compared. 26366224_the possible relationship between ocular symptomatology, tear volume and tear break-up time (TBUT) and lipocalin, lactoferrin and lysozyme concentrations in the tear film were explored in a group of symptomatic dry-eyed postmenopausal (PM) women. 26961596_The preliminary results from the milk yield and milk compositions from a naturally lactating transgenic cloned cow 0906 were also tested. These results provide a solid foundation for the large-scale production of rhLZ in the future. 27177644_lysozyme cannot be used as a marker of acinar differentiation in salivary tumors. However, lysozyme expression can be helpful to distinguish mammary analog secretory carcinoma from acinic cell carcinoma 27294141_The purpose of this study is to understand the oral mucosal immune status of cancer patients and to make clear whether antibacterial proteins such as salivary secretory immunoglobulin (SIgA) and lysozyme in saliva were influenced by patients' health status and certain medical treatment therapy. 27428539_The findings suggest that the F57I mutation affects the aggregation process of lysozyme resulting in the formation of cytotoxic species and that SAP is able to prevent cell death in the F57I flies by preventing accumulation of toxic F57I structures. 27825804_Data show that hen lysozyme aggregates faster than the human lysozyme. 27926837_the location of specific mutations is an important factor in determining the native-state dynamical properties of human lysozyme 27931094_rhamnolipid (RL) secreted by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) accelerates proteolysis of lysozyme. 28419103_Data show increased levels of lysozyme C (LYZ), lacritin (LACRT) and zinc-alpha-2 glycoprotein 1 (AZGP1) in pooled tear fluid sample from Graves' disease (GD) patients with moderate-to-severe Graves' orbitopathy (GO) compared with GD patients without clinical signs of GO. 29446150_Three AMP genes, histatin 3 (HTN3), alpha-defensin 4 (DEFA4) and lysozyme C (LYZ), presented different expression levels in periodontitis patients compared with healthy subjects. The relative expression level of DEFA4 appeared to be a protective factor against periodontitis. 31391320_Lysozyme elicits pain during nerve injury by neuronal Toll-like receptor 4 activation and has therapeutic potential in neuropathic pain. 31694163_These results of the RNA-seq experiment show that lysozyme induces transcriptional modulation of the TNF-alpha/IL-1beta pathway genes in U937 monocytes. 31978114_Serum amyloid P component promotes formation of distinct aggregated lysozyme morphologies and reduces toxicity in Drosophila flies expressing human F57I lysozyme. 32522553_Analyses of displacements resulting from a point mutation in proteins. 33640796_Characterisation of the structural, dynamic and aggregation properties of the W64R amyloidogenic variant of human lysozyme. |
ENSMUSG00000069515+ENSMUSG00000069516+ENSMUSG00000020177 |
Lyz1+Lyz2+9530003J23Rik |
272.434377 |
0.4488941142 |
-1.155553 |
0.094078945 |
154.102036 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000002200037533738618975664721239469455542053567323063765570635080336133906561888745768464262328890229669653422206465620547533035278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000328005595939212282672643999305556773127791321928968001870976748258128360877253917421799605039223202140874491306021809577941894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
171.9917225 |
10.3392041 |
386.2038746 |
14.7645679 |
| ENSG00000090530 |
55214 |
P3H2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVL5 |
FUNCTION: Prolyl 3-hydroxylase that catalyzes the post-translational formation of 3-hydroxyproline on collagens (PubMed:18487197). Contributes to proline 3-hydroxylation of collagen COL4A1 and COL1A1 in tendons, the eye sclera and in the eye lens capsule (By similarity). Has high activity with the type IV collagen COL4A1, and lower activity with COL1A1 (PubMed:18487197). Catalyzes hydroxylation of the first Pro in Gly-Pro-Hyp sequences where Hyp is 4-hydroxyproline (PubMed:18487197). Has no activity on substrates that lack 4-hydroxyproline in the third position (PubMed:18487197). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CG71, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18487197}. |
Alternative splicing;Dioxygenase;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Signal;TPR repeat;Vitamin C |
|
This gene encodes a member of the prolyl 3-hydroxylase subfamily of 2-oxo-glutarate-dependent dioxygenases. These enzymes play a critical role in collagen chain assembly, stability and cross-linking by catalyzing post-translational 3-hydroxylation of proline residues. Mutations in this gene are associated with nonsyndromic severe myopia with cataract and vitreoretinal degeneration, and downregulation of this gene may play a role in breast cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:55214; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; L-ascorbic acid binding [GO:0031418]; procollagen-proline 3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0019797]; collagen metabolic process [GO:0032963]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; peptidyl-proline hydroxylation [GO:0019511] |
18487197_P3H2 is responsible for the hydroxylation of collagen IV, which has the highest 3-hydroxyproline content of all collagens. It is thus possible that P3H2 mutations may lead to a disease with changes in basement membranes. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19436308_The restriction of silencing in P3H2 to breast carcinomas, and its association with oestrogen-receptor-positive cases, suggests that P3H2 may be a breast-cancer-specific tumour suppressor. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21757687_P3H2 has preferred substrate sequences among the classes of 3Hyp sites in clade A collagen chains 21885030_High myopia is caused by a mutation in LEPREL1, encoding prolyl 3-hydroxylase 2. 24172257_LEPREL1 plays an important role in eye development and homozygous loss-of-function mutation of this gene can cause severely high myopia and early-onset cataract. 25469533_Recessive LEPREL1 mutations should be recognized as part of the differential diagnosis of lens subluxation. 25525168_mutation in LRPAP1 is associated with high myopia. Further studies are expected to evaluate the pathogenicity of the variants in CTSH, LEPREL1, ZNF644, SLC39A5, and SCO2. 29956121_Data identified an enhancer region within the TP63/LEPREL1 locus containing genetic variants associated with bladder cancer risk. 30608193_Mutation in the LEPREL1 gene is associated with ectopia lentis. 33918807_Prolyl 3-Hydroxylase 2 Is a Molecular Player of Angiogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000038168 |
P3h2 |
1332.768863 |
69.6121427738 |
6.121267 |
0.124392604 |
3743.179484 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2584.4297757 |
230.5412950 |
37.4611046 |
3.0820542 |
| ENSG00000090565 |
9727 |
RAB11FIP3 |
protein_coding |
O75154 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of endocytic traffic by participating in membrane delivery. Required for the abcission step in cytokinesis, possibly by acting as an 'address tag' delivering recycling endosome membranes to the cleavage furrow during late cytokinesis. Also required for the structural integrity of the endosomal recycling compartment during interphase. May play a role in breast cancer cell motility by regulating actin cytoskeleton. Acts as an adapter protein linking the dynein motor complex to various cargos and converts dynein from a non-processive to a highly processive motor in the presence of dynactin. Facilitates the interaction between dynein and dynactin and activates dynein processivity (the ability to move along a microtubule for a long distance without falling off the track) (PubMed:25035494). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17394487, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19327867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25035494}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport |
|
Proteins of the large Rab GTPase family (see RAB1A; MIM 179508) have regulatory roles in the formation, targeting, and fusion of intracellular transport vesicles. RAB11FIP3 is one of many proteins that interact with and regulate Rab GTPases (Hales et al., 2001 [PubMed 11495908]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:9727; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; postsynaptic recycling endosome membrane [GO:0098944]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; negative regulation of adiponectin secretion [GO:0070164]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
15158446_Rab11-FIP3 localises to a Rab11-positive pericentrosomal compartment during interphase and to the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis 15601896_FIP-3 and RAB11 protein complex regulates recycling endosomes targeting to the cleavage furrow during late cytokinesis. 17030804_Results describe the distinct C-terminal binding regions of FIP3 and FIP4 for Rab11 and ARF5/ARF6, and the crystal structure of Rab11 in complex with the Rab11-binding domain (RBD) of FIP3. 17394487_Necessary for the structural integrity of the pericentrosomal endosomal recycling compartment. 17628206_FIP3 is a scaffolding protein that, in addition to regulating endosome targeting to the cleavage furrow, also is required for Arf6 recruitment to the midbody during late telophase. 19327867_Rab11-FIP3 is a Rab11-binding protein that regulates breast cancer cell motility by modulating the actin cytoskeleton.(325-41) 20214888_FIP3 was identified as the first membrane-associated interacting-partner for DLIC-2. 20736163_CART1 might be a cytoplasmic, testis-specific derepressor of RAR 25673879_Rab11-FIP3 coordinates the interactions of ASAP1 and Rab11a with Rabin8. 27154205_Rac1-Rab11-FIP3 regulatory hub coordinates vesicle traffic with actin remodeling and T-cell activation 28215104_RAB11FIP3 combines with Eps15 homology domain 1 to promote the endocytosis recycling of phosphorylation of epithelial growth factor receptor. |
ENSMUSG00000037098 |
Rab11fip3 |
164.261782 |
0.4207588444 |
-1.248934 |
0.171843358 |
52.196445 |
0.00000000000050216954769739909142089504168068917172151194305840249398897867649793624877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003047706629939806918334834179730594638183666100772484242042992264032363891601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
104.3185278 |
13.8718379 |
249.5176419 |
23.4264447 |
| ENSG00000090661 |
79603 |
CERS4 |
protein_coding |
Q9HA82 |
FUNCTION: Ceramide synthase that catalyzes formation of ceramide from sphinganine and acyl-CoA substrates, with high selectivity toward long and very-long chains (C18:0-C22:0) as acyl donor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17977534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23530041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26887952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29632068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31916624}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17977534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23530041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26887952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29632068}. |
Enables sphingosine N-acyltransferase activity. Involved in ceramide biosynthetic process. Predicted to be located in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Predicted to be active in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79603; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; N-acyltransferase activity [GO:0016410]; sphingosine N-acyltransferase activity [GO:0050291]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148] |
20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21757428_The linkage and association of phospholipid transfer protein activity to LASS4 were studied. 23538298_Co-expression of CerS2 with CerS4/CerS6 reversed the inhibitory effect of long chain ceramides on cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis. we detected no effect on cell proliferation. 25779024_mRNA level of CerS4 is higher in cancerous cell lines and decreases following the induction of apoptosis. 26887952_These results suggest that the phosphorylation of ceramide synthases may be a key regulatory point in the control of the distribution and levels of sphingolipids of various acyl-chain lengths. 29738550_nine SNPs in the ceramide synthase 4 (CERS4) region were associated with circulating C23:0 levels (adjusted P |
ENSMUSG00000008206 |
Cers4 |
172.186874 |
0.1753264699 |
-2.511884 |
0.372651405 |
40.890132 |
0.00000000016103217827783121626254124820673812451543582824342593085020780563354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000821013800131533310897692349184396470862523642608721274882555007934570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.2559858 |
18.9455618 |
287.5593666 |
78.9184581 |
| ENSG00000090776 |
1947 |
EFNB1 |
protein_coding |
P98172 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface transmembrane ligand for Eph receptors, a family of receptor tyrosine kinases which are crucial for migration, repulsion and adhesion during neuronal, vascular and epithelial development (PubMed:8070404, PubMed:7973638). Binding to Eph receptors residing on adjacent cells leads to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells (PubMed:8070404, PubMed:7973638). Shows high affinity for the receptor tyrosine kinase EPHB1/ELK (PubMed:8070404, PubMed:7973638). Can also bind EPHB2 and EPHB3 (PubMed:8070404). Binds to, and induces collapse of, commissural axons/growth cones in vitro (By similarity). May play a role in constraining the orientation of longitudinally projecting axons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52795, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7973638, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8070404}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Craniosynostosis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane protein and a ligand of Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinases. It may play a role in cell adhesion and function in the development or maintenance of the nervous system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1947; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098] |
12084815_Human platelets express EphA4 and EphB1, and the ligand, ephrinB1. Forced clustering of EphA4 or ephrinB1 led to cytoskeletal reorganization, adhesion to fibrinogen, and alpha-granule secretion. 12136247_Expression profile of this ligand of EPHB2 in gastric cancer 12209731_The expression of ephrin-B1 was correlated with a poorer clinical prognosis. Ephrin-B1 protein was expressed by osteosarcoma cells and blood vessels. 12475948_Ephrin B1 induces human aortic endothelial cells migration in a pathway that involves Crk adaptor protein 12919674_conclude that ephrinB1 and B class Eph receptors provide positional cues required for the normal morphogenesis of skeletal elements 14576067_Eph/ephrin signaling enhances the ability of platelet agonists to cause aggregation by activating Rap1 and these effects require oligomerization of ephrinB1 but not phosphotyrosine-based interactions with the ephrinB1 cytoplasmic domain. 14642617_Ephrin-B1 may be involved in in vivo tumor progression by promoting neovascularization in hepatocellular carcinoma 15124102_Mutations of the ephrin-B1 gene cause craniofrontonasal syndrome 15351694_ephrin-B1 internalization is an active receptor-mediated process that utilizes the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway 15725075_On ephrinB1 stimulation, the small GTPases Rho and Ras are activated and Rap1 is inactivated. 15959873_EFNB1 mutations have a role in familial and sporadic craniofrontonasal syndrome (CFNS) 17204606_EphB/ephrin-B molecules play a role in restricting dental pulp stem cell attachment and migration to maintain Dthesse cells within their stem cell niche under steady-state conditions. 17567680_C-terminus of ephrin-B1 regulates activation of the extracellular release of MMP-8 without requirement of de novo protein synthesis. 17591954_Our results suggest that tyrosine phosphorylation of ephrin-B1 promotes invasion of cancer cells in vivo 17906625_Silencing of EphB expression is associated with colorectal tumorigenesis. 17942634_EphrinB1 may play an important role in the inflammatory states of rheumatoid arthritis, by affecting the population/function of T cells. 18043713_EFNB1 mutant transcripts with nonsense codons are degraded by the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway and lead to craniofrontonasal syndrome. 18314490_Ephrin-B1 is likely to play an important role in the regulation of malignant T lymphocytes through the control of lipid-raft-associated signaling, adhesion, and invasive activity 18627045_Several new EFNB1 mutations have been identified in craniofrontonasal syndrome. 19672298_combination of SDF-1, PTN, IGF2, and EFNB1 mimics the DA phenotype-inducing property of SDIA and was sufficient to promote differentiation of hESC to functional midbrain DA neurons 20308325_study reports that the expression of ephrin-B1 is controlled by a feedback loop involving posttranscriptional regulatory mechanisms 20565770_The impact of craniofrontonasal syndrome-causing EFNB1 mutations on ephrin-B1 function is reported. 20643727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734337_Unreported mutation in EFNB1 predicts occurrence of congenital diaphragmatic hernia, phenotypic differences between males and female. 21542058_X-linked cases resembling Teebi hypertelorism may have a similar mechanism to CFNS, and that cellular mosaicism for different levels of ephrin-B1 (as well as simple presence/absence) leads to craniofacial abnormalities. 22279592_Data show that EphrinB1, a PTPN13 substrate, interacts with ErbB2, and Src kinase mediates EphrinB1 phosphorylation and subsequent MAP Kinase signaling. 22718351_These results indicate a novel function of Nm23-H1 to control contact inhibition of locomotion, and its negative regulation by ephrin-B1. 23335590_we report the identification of mosaic EFNB1 mutations in every individual with craniofrontonasal syndrome, confirming the suggested diagnosis and supporting the hypothesis of cellular interference in humans. 23811940_High EFNB1 expression is associated with squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. 24240587_EphrinB1 expression is related to the metastasis of breast cancer and its enhanced expression confers a poor prognosis, suggesting that EphrinB1 may be a relevant therapeutic target in breast cancers. 24281372_Patients with EFNB1 mutations have a clear phenotype. This study will facilitate genetic counseling of parents and patients, and contribute to the diagnostic and screening process of patients with suspected CFNS. 24825906_CNK1 mediates ephrinB1 signaling that promotes cell migration through RhoA and JNK activity. 25258252_Results indicate that EphrinB1 is uniquely dysregulated in medulloblastoma and promotes oncogenic responses in medulloblastoma cells, implicating ephrinB1 as a potential target 25436983_that EphrinB1 (EFNB1) co-localizes with microtubules (MTs) during all phases of the cell cycle. 25486017_we report a family with a G151S mutation in the EFNB1 gene. The mutation was identified in two severely affected sisters and paradoxically in their clinically unaffected father. 25643922_EphB2/ephrin-B1 were invoked in dental pulp stem cells with TNF-alpha treatment via the JNK-dependent pathway, but not NF-kB, p38 MAPK or MEK signalling. 25779027_T cells from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients expressed higher EFNB1 mRNA levels, which correlated with RA symptoms and laboratory findings. Expression of EFNB1 in T cells might be a parameter for monitoring RA disease activity and treatment responses. 26580852_While ephrin-B1 deficiency leads to abnormal visual pathways in mice, it leaves the human visual system, apart from deficits in binocular vision, largely normal. 27039370_that expression of EFNB1 and EFNB2 is implicated in Th cell differentiation and migration to inflammatory sites in both EAE and MS 27650623_one novel (IVS2+3G>T) and one previously reported mutation (p.Gly151Ser) in EFNB1 Both patients were de novo cases without a family history of Craniofrontonasal syndrome. 28238796_we demonstrate that mosaicism for EPHRIN-B1 expression induced by random X inactivation in heterozygous females results in robust cell segregation in human neuroepithelial cells, thus supplying experimental evidence that Eph/ephrin-mediated cell segregation is relevant to pathogenesis in human CFNS patients. 28747399_This study showed that EphB2 cells have a transient increase in migration after heterotypic activation, which underlies a shift in the EphB2-ephrinB1 border but is not required for segregation or border sharpening. 29215649_Pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in non-FGFR genes were identified in 43 individuals, with diagnostic yields of 14% and 15% in retrospective and prospective cohorts, respectively. Variants were identified most frequently in TCF12 (N = 22) and EFNB1 (N = 8), typically in individuals with nonsyndromic coronal craniosynostosis or TWIST1-negative clinically suspected Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. 29602834_Through interactions with nephrin, ephrin-B1 maintains the structure and barrier function of the slit diaphragm. Moreover, phosphorylation of ephrin-B1 and, consequently, JNK are involved in the development of podocyte injury. 30006524_Lymphomas with low UTX expression express high levels of Efnb1, and cause significantly poor survival. 30058095_Chronic hypoxia-induced slug promotes invasive behavior of prostate cancer cells by activating the expression of ephrin-B1. 30262919_Analysis of the association of EPHB6, EFNB1 and EFNB3 variants with hypertension risks in males with hypogonadism 30326247_the results of this study confirm that EfnB1 contributes to the stromal support of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) function and maintenance and may be an important factor in regulating the HSPC niche. 31285555_Four novel mutations in EFNB1 in Indian patients with craniofrontonasal syndrome. 32022998_Extracranial midline defects in a patient with craniofrontonasal syndrome with a novel EFNB1 mutation. 32240825_Severe craniofrontonasal syndrome in a male patient mosaic for a novel nonsense mutation in EFNB1. 32337793_EPH receptor B2 stimulates human monocyte adhesion and migration independently of its EphrinB ligands. 33356837_Peripheral EphrinB1/EphB1 signalling attenuates muscle hyperalgesia in MPS patients and a rat model of taut band-associated persistent muscle pain. 35603962_Construction of three-gene-based prognostic signature and analysis of immune cells infiltration in children and young adults with B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000031217 |
Efnb1 |
105.485957 |
0.4526247612 |
-1.143613 |
0.152944242 |
57.036185 |
0.00000000000004278665376754812691966211326748812276602558155036426512651814846321940422058105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000277474081550531782524991282556840356131495906044648336319369263947010040283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.5316176 |
6.4508704 |
145.8451058 |
9.2319322 |
| ENSG00000090924 |
64857 |
PLEKHG2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H7P9 |
FUNCTION: May be a transforming oncogene with exchange activity for CDC42 (By similarity). May be a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RAC1 and CDC42. Activated by the binding to subunits beta and gamma of the heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) (PubMed:18045877). Involved in the regulation of actin polymerization (PubMed:26573021). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6KAU7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18045877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26573021}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Intellectual disability;Leukodystrophy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a RhoGTPase that can activate CDC42 by promoting exchange of GDP for GTP on CDC42. The encoded protein is activated by binding to the beta and gamma subunits of heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Defects in this gene have been associated with leukodystrophy and acquired microcephaly with or without dystonia. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:64857; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833] |
11839748_Activation of clg, a novel dbl family guanine nucleotide exchange factor gene, by proviral insertion at evi24, a common integration site in B cell and myeloid leukemias 18045877_signaling pathway by which G(i)-coupled receptor specifically induces Rac and Cdc42 activation through direct interaction of Gbetagamma with FLJ00018. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23000341_The binding of Rho family specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor(FLJ00018), at least two actin binding regions of FLJ00018, and actin negatively regulates for FLJ00018 function. 23811570_These results suggest that FLJ00018 is targeted via its pleckstrin homology domain to cellular membranes. 24001768_PLEKHG2 may serve as a key Gbeta-gamma-stimulated RhoGEF that regulates lymphocyte chemotaxis via Rac and Cdc42 activation and actin polymerization. 24378532_The tyrosine phosphorylation of PLEKHG2 plays an important role in EphB2 signaling, which is closely related to cell growth and the proliferation of tumor. 24554703_results provide evidence that stimulation of the Ras/MAPK pathway by EGFR results in FLJ00018 phosphorylation at Thr-680, which in turn controls changes in cell shape. 25213431_Autoantibodies binding to Plekhg2 were found in 19 of 29 patients (66%) with active mycobacterial infections. 26573021_Role of PLEKHG2 in actin polymerization and clinical and radiological findings in PLEKHG2 deficiency. 27765816_results provide evidence that FHL1A interacts with PLEKHG2 and regulates cell morphological change through the activity of PLEKHG2. 28108261_This is the first report to show that PLEKHG2 is a novel effector of Galphas, and is negatively regulated by the Galphas subunit through direct interaction. 28489964_results suggest that FHL1A specifically interacts with PLEKHG2 to regulate a function of PLEKHG2 that is modified by the interaction of Gbetagamma and Galphas. |
ENSMUSG00000037552 |
Plekhg2 |
981.146916 |
0.3780448606 |
-1.403371 |
0.286142228 |
23.223133 |
0.00000144251652515769050560935030796949618547841964755207300186157226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005012133689107229676221351433174078238153015263378620147705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
521.9300071 |
121.2677897 |
1387.1248045 |
232.7367844 |
| ENSG00000090975 |
57605 |
PITPNM2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZ72 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine between membranes (in vitro). Binds calcium ions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10022914}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
PITPNM2 belongs to a family of membrane-associated phosphatidylinositol transfer domain-containing proteins that share homology with the Drosophila retinal degeneration B (rdgB) protein (Ocaka et al., 2005 [PubMed 15627748]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:57605; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; membrane [GO:0016020]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; phosphatidylcholine binding [GO:0031210]; phosphatidylcholine transporter activity [GO:0008525]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol transfer activity [GO:0008526]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015] |
28195573_PITPNM2 was associated with bipolar disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000029406 |
Pitpnm2 |
139.264639 |
0.1250412753 |
-2.999524 |
0.887141960 |
9.600370 |
0.00194538183479821312829582957704133150400593876838684082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004308152420348330784161117179564826074056327342987060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.4099395 |
21.7588392 |
223.6167458 |
123.2906512 |
| ENSG00000091409 |
3655 |
ITGA6 |
protein_coding |
P23229 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-6/beta-1 (ITGA6:ITGB1) is a receptor for laminin on platelets (By similarity). Integrin alpha-6/beta-1 (ITGA6:ITGB1) is present in oocytes and is involved in sperm-egg fusion (By similarity). Integrin alpha-6/beta-4 (ITGA6:ITGB4) is a receptor for laminin in epithelial cells and it plays a critical structural role in the hemidesmosome (By similarity). ITGA6:ITGB4 binds to NRG1 (via EGF domain) and this binding is essential for NRG1-ERBB signaling (PubMed:20682778). ITGA6:ITGB4 binds to IGF1 and this binding is essential for IGF1 signaling (PubMed:22351760). ITGA6:ITGB4 binds to IGF2 and this binding is essential for IGF2 signaling (PubMed:28873464). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22351760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28873464}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Epidermolysis bullosa;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The gene encodes a member of the integrin alpha chain family of proteins. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain that function in cell surface adhesion and signaling. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate light and heavy chains that comprise the alpha 6 subunit. This subunit may associate with a beta 1 or beta 4 subunit to form an integrin that interacts with extracellular matrix proteins including members of the laminin family. The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin may promote tumorigenesis, while the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin may negatively regulate erbB2/HER2 signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. |
hsa:3655; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; insulin-like growth factor I binding [GO:0031994]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; neuregulin binding [GO:0038132]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; cell-substrate junction assembly [GO:0007044]; ectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0010668]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; nail development [GO:0035878]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; skin morphogenesis [GO:0043589] |
11728829_Mechanisms involved in alpha6beta1-integrin-mediated Ca(2+) signalling 11809527_Reduction in integrin alpha6beta4 is related to changes seen during immortalization and malignant progression 11852236_The PDZ domain of TIP-2/GIPC interacts with the C-terminus of the integrin alpha5 and alpha6 subunits. 11861761_These results demonstrate that integrin-dependent cell to extracellular matrix adhesion reinforces E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion in Caco-2 cells. 11959811_Production of the alpha(6p) variant from alpha(6) integrin may involve a post-translational processing event at the cell surface. 11988844_Human prostate tumors display on their cell surface the alpha6beta1 and/or alpha3beta1 integrins 12105188_Integrin (alpha 6 beta 4) regulation of eIF-4E activity and VEGF translation (Integrin alpha6beta4) 12364323_role in mediating pro-angiogenic activity of CYR61 12429829_Data suggest that the stability of the interaction between alpha6beta4 and laminin-5 is influenced by the clustering of alpha6beta4 through the deposition of laminin-5 underneath the cells. 12499048_Results suggest that alpha6beta4 integrin-mediated interactions of astrocytes with beta(ig)-h3 transduce intracellular signals through the focal adhesion proteins, which may regulate certain aspects of astrocyte response to brain injury. 12826661_integrin alpha 6 beta 1 binds to CCN1 12909644_alpha6beta1 integrins have roles as thrombospondin receptors in microvascular and large vessel endothelial cells 12919677_Data show that macrophage stimulating protein (MSP) and its receptor (Ron) induce phosphorylation of both Ron and alpha6beta4 integrin, and result in activation of alpha3beta1 integrin. 12931024_In pancreatic cancer, IL-1alpha enhanced alpha(6)beta(1)-integrin expression, probably via increased IL-1RI levels. 14517202_compartmentalization in lipid rafts is necessary to couple the alpha6beta4 integrin to a palmitoylated src family kinases and promote EGF-dependent mitogenesis. 14602071_Data demonstrate that alpha6beta4 integrin mediates pancreatic epithelial cell adhesion to Netrin-1, whereas recruitment of alpha6beta4 and alpha3beta1 regulate the migration of putative pancreatic progenitors on Netrin-1. 14607975_ligand-binding specificities of integrin alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta1 14707725_Results indicate that alpha6-containing integrin expression can be a significant marker of malignancy in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors (IPMTs). 15161909_alpha(6)beta(4) has a generic influence on the invasion of carcinoma cells that is not specific to Met 15194479_Results suggest that bacterial heat shock protein 60 may promote epithelial cell migration through activation of epidermal growth factor receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinases, and inhibition of alpha6beta4 integrin expression. 15302884_cAMP-Epac-Rap1 pathway regulates cell spreading and cell adhesion to laminin-5 through the alpha3beta1 integrin but not the alpha6beta4 integrin 15557282_CD82 attenuates integrin alpha6 signaling during a cellular morphogenic process 15579904_alpha6beta4 can augment cell-cell adhesion and slow down haptotaxis over laminin-5 15679046_Enhanced expression of Integrin alpha6 is associated with liver metastases from gastrointestinal tumours 15885076_adhesion to laminin-1 through alpha6-integrin represents a protective mechanism for melanocytes to withstand UVB damage 15897878_alpha6beta4 integrin potentiates autotaxin expression through the upregulation and activation of NFAT1. 15983209_alpha3, alpha5, and alpha6 beta1 integrins are expressed in ductal cells at 8 weeks, before glucagon- and insulin-immunoreactive cells bud off in fetal pancrea. 16228294_the signals induced by integrin alpha6beta1 modulate at the level of PI3K and Cdc42 activity to allow platelets to actively form filopodia 16258729_alpha6beta4 integrin is mobilized and activated durign carcinoma progression [review] 16339173_Data show that alpha6 and alpha3 integrin subunits interact with laminin 5 to increase expression of E-cadherin, and suggest that phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) activation plays a key role in this cross-talk. 16424229_A peptide is identified within the extracellular domain of integrin alpha 6 molecule, to which antibodies in the sera from patients with oral pemphigoid (OP) bind, and which may play an important role in the pathogenesis of OP. 16436605_PMP22 forms a complex with alpha6beta4 integrin in cultured colonic adenocarcinoma cells. 16504015_IL-1alpha can induce selective upregulation of alpha6beta1-integrin and uPA/uPAR in pancreatic cancer cells and these changes may modulate the aggressive functions of pancreatic cancer. 16537545_EWI proteins EWI-2 and EWI-F, alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrins, and protein palmitoylation have contrasting effects on cell surface CD9 organization 16571677_Both integrin alpha3beta1- and alpha6beta4-dependent cell adhesion to laminin-5 were also impaired in CD151-silenced cells. 16732726_Acquisition of multiple antitumor drugs was accompanied by a drastically reduced expression of alpha6beta1 in the adenocarcinoma cells. 16870608_Ln-5 is an important regulator of ADPKD cell proliferation and cystogenesis; Ln-5 gamma(2) chain and Ln-5-alpha(6)beta(4) integrin interaction both contribute to these phenotypic changes 16940506_in natural HPV infection, proliferating keratinocytes expressing alpha6 integrin at the site of epithelial wounding might be targeted by virions adsorbed transiently to LN5 secreted by migrating keratinocytes 16965770_The role of PTHrP in breast cancer growth and metastasis may be mediated via upregulation of integrin alpha6beta4 expression and Akt activation, with consequent inactivation of GSK-3. 16973601_The role of integrin alpha6beta4 in keratinocyte migration via laminin-332 matrix organization is reported.[integrin alpha6beta4; laminin-332] 17085437_alpha6 integrin might play a role in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis. 17303120_These data taken together suggest that the uPA-mediated cell surface cleavage of the alpha6 integrin extracellular domain is involved in tumor cell invasion and migration on laminin. 17332515_Keratinocytes expressing elevated levels of alpha6 integrin expanded over 200-fold during the 33-week in vivo study. 17475774_Integrin-mediated adhesion via alpha3beta1, but not alpha6beta4 integrin, supports cell survival through EGFR by signaling downstream to Erk. 17652716_Laminin repressed transcription, directed by the alpha6 gene promoter, by altering the nuclear levels of Sp1 and Sp3 17935134_alpha-6 integrin is required for the growth and survival of breast cancer cells 17979890_VEGFR2 up-regulation had no effect on VEGF-induced cell proliferation, but significantly enhanced endothelial progenitor cells migration and pseudotubes formation dependent on integrin alpha(6) subunit overexpression. 18155160_These results indicate that the alpha(6)(bri)/CD71(dim) subpopulation enriched corneal epithelial stem cells. 18270579_the alpha6beta4 integrin strongly influence Akt phosphorylation through ErbB-3 protein regulation 18436868_Subepicardial localization of CD117-positive cells and expression of laminin-1 and alpha(6) integrin subunits may all correspond to the activation of regeneration involving an epithelial-mesenchymal transition in adult heart 18451146_CD151-alpha(6) integrin complexes play a functional role in basal-like mammary tumor progression. 18550570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18614994_LPS or peritoneal dialysis effluent stimulated the adherence of T cells to mesothelial cells, a process mediated by the integrins alpha6beta1 and alpha4beta1 18687805_Extracellular Cyr61 interacts with alpha(5), alpha(6), and beta(1) integrins 18814027_alpha6beta4 integrin-FAK-p38MAPK pathway is invloved in modulation of LDH expression. 18818395_PODXL(hi)/CD49f(hi) MSCs were less prone to produce lethal pulmonary emboli 18831072_CD49f is commonly overexpressed in p-B-ALL, and represents a potentially useful marker for the immunophenotypic detection of MRD. 18842099_Blockade of the alpha6-integrin enhanced bone marrow (BM) homing of human and nonhuman primate BM-derived hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. 18958175_Tumor cells within the bone expressing the integrin mutation prevented cancer induced spontaneous flinching, tactile allodynia, and movement evoked pain. 18971471_Integrin alpha6beta4 plays an essential role in axonal regeneration and subsequent myelination. 18974120_results identify Y1494 as a major regulatory site for signaling from the alpha6beta4 integrin to promote tumor development and progression 19107504_differential expression of the alpha6 subunits is involved in the intestinal epithelial cell renewal process. 19124484_Integrin alpha6beta4 and NET1 coexpression is independently associated with the development of distant metastasis in breast cancer. 19130304_alpha 3, alpha 6A, and beta 1 integrin expression in cancer cells at the invasive front are related to the mode of invasion and prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma 19138983_Curcumin inhibits breast cancer cell motility and invasion by directly inhibiting the function of alpha(6)beta(4) integrin, and suggest that curcumin can serve as an effective therapeutic agent in tumors that overexpress alpha(6)beta(4). 19491258_results suggest that alpha(6) integrin cleavage permits extravasation of human prostate cancer cells from circulation to bone and can be manipulated to prevent metastasis 19579970_Results assess uterine receptivity in women with unexplained infertility using beta1 integrin molecules VLA-4, -5, and -6 within endometrial tissue in comparison with fertile women. 19586553_the alpha6Bbeta4 integrin inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and c-Myc activity and is significantly down-regulated in colon cancer cells relative to its alpha6Abeta4 counterpart 19767753_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19775453_Integrin alpha6beta1 co-localizes and interacts with HAb18G/CD147 to mediate tumor invasion and metastatic processes. 19808905_These studies define a novel mechanism by which integrin alpha6beta4 promotes cancer cell motility and invasion, and provides insight into how S100A4 expression is regulated in cancer cells. 19827952_TGF-beta-mediated up-regulation of the expression of the integrin subunits alpha(2) and alpha(6) is mainly mediated in MSC by Smad2. 20432448_Laminins and their integrin receptors are necessary for the development and maintenance of the peripheral nervous system, indicating the potential role for integrin receptors in directing prostate tumor cell invasion on nerves during perineural invasion. 20441998_These data demonstrate that infection requires the binding of human papillomavirus type 16 viral particles to heparan sulfate followed by activation of focal adhesion kinase through integrin alpha 6. 20452317_Glioblastoma stem cell express high levels of integrin alpha6. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508204_Demonstrate a major role of alpha6 integrin in the proangiogenic properties of endothelial progenitor cells. 20564319_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20695903_Data show that integrin alpha(6)beta(4) interacts with ErbB3 but not with ErbB1, ErbB2 or ErbB4, and enhances the heregulin-induced, ErbB3/ErbB2 heterodimer-mediated DNA synthesis, but not cell motility, in A549 cells. 20855525_Data describe how alpha6beta4 integrin selectively activates Fyn in response to receptor engagement, and show that both catalytic and noncatalytic functions of SHP2 are required for Fyn activation by alpha6beta4. 20878950_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20927591_CD151, c-Met, and integrin alpha3/alpha6 were all overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. CD151 and c-Met might be new molecular markers to predict the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. 21115897_High Integrin alpha6beta4 is associated with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. 21182210_Mouse models have shown a role for ITGA6 in many developmental processes including cortical and retinal lamination, apical ectodermal ridge formation and organogenesis 21195710_Data suggest that the alpha5 laminins emerge as putative primary extracellular matrix mediators of melanoma invasion and metastasis via alpha3/alpha6beta1 and other integrin receptors. 21359644_Data suggest that integrin alpha6beta1 is an important cell surface receptor that mediates the adhesion of the SMMC-7721 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line to type IV collagen. 21388972_curcumin inhibits alpha6beta4 signaling and functions by altering intracellular localization of alpha6beta4, thus preventing its association with signaling receptors such as EGFR. 21474814_in endothelial cells, ligation of alpha2beta1 and alpha6beta1 integrins induces the Notch pathway, and we disclose a novel role of basement membrane proteins in the processes controlling tip vs stalk cell selection 21518455_A physiologic role for PMP22 on the expression of alpha6 integrin. 21558389_PHLDA1 expression marks the putative epithelial stem cells, downregulates ITGA2 and ITGA6, and contributes to intestinal tumorigenesis 21752283_Integrin subunits alpha5 and alpha6 regulate cell cycle by modulating the chk1 and Rb/E2F pathways to affect breast cancer metastasis. 21799154_The alpha6beta1 integrin is a netrin-4 receptor in endothelial cells. 21969027_Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia (JEB-PA) is a rare autosomal recessive disease with blister formation within the lamina lucida due to mutations in the integrin beta4 (ITGB4) and alpha6 (ITGA6) genes 22049212_signaling from integrin alpha6beta4 facilitates lysophosphatidic acid- stimulated chemotaxis through preferential activation of RhoA, which, in turn, facilitates activation of Rac1 22295105_increased expression of ITGA6 is associated with drug-resistance and increased cell adhesion 22311737_CD49f enhances multipotency and maintains stemness through the direct regulation of OCT4 and SOX2. 22328509_CD151 support of alpha6 random defined diffusion is specific and functionally relevant, and probably underlies diverse CD151 functions in skin, kidney and cancer cells. 22389315_P-cadherin is coexpressed with CD44 and CD49f and mediates stem cell properties in basal-like breast cancer. 22396498_The findings indicated that integrin a6b1 promotes the survival of brain endothelial cells by inhibiting prodeath signaling by TNF-R1, in part by inducing cellular FLICE inhibitory protein expression. 22493440_data indicate that the alpha6beta4 integrin is a master regulator of transcription and translation of other integrin subunits and underscore its pivotal role in wound healing and cancer 22514625_Epcam+CD44-CD49fHi (non-sphere-forming) basal cells with significantly increased tubule induction activity compared to Epcam+CD44-CD49fLo (true) luminal cells. 22592262_This study identifies modulation of ITGA6 during cell-free varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infection, and provides the first evidence linking ITGA6 with post-entry productive VZV gene expression. 22684562_Taken together, it was concluded that CD151 promotes the proliferation and migration of PC3 cells through the formation of CD151-integrin complex and the activation of phosphorylated ERK. 22843693_CD151 links alpha(3)beta(1)/alpha(6)beta(1) integrins to Ras, Rac1, and Cdc42 by promoting the formation of multimolecular complexes in the membrane, which leads to the up-regulation of adhesion-dependent small GTPase activation 23045288_the CD49f(-)CD133(+) phenotype appears to identify OSIC-like cells that possess strong tumorigenicity correlated with an impaired osteogenic fate. 23070965_Interaction between alpha6 integrin and E-cadherin drives liver metastasis of colorectal cancer cells through hepatic angiopoietin-like 6. 23071680_Data indicate that resistance to UVB induced apoptosis in the alpha6 integrin(high+)/CD44(+) cells involved increased expression of TAp63 and was overcome by PI-3 kinase inhibition. 23071686_CD49f is an efficient marker of monolayer- and spheroid colony-forming cells of the benign and malignant human prostate. 23106339_S-nitrosylation of ITGalpha6 increased the extent of prostate cancer cell migration, which could be a potential mechanism of NO- and iNOS-induced enhancement of prostate cancer metastasis. 23233446_Data indicate that long-term self-renewing leukemic stem cells reside within the CD34(+)/ITGA6(+) fraction. 23306848_Overexpression of integrin alpha6 is associated with a migratory and invasive phenotype of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 23436775_GLI1 regulates the neuropilin-2/alpha6beta1 integrin based autocrine pathway that contributes to breast cancer initiation. 23496044_A report on the broad spectrum of clinical and morphological epidermolysis bullosa manifestations associated with novel alpha6beta4 integrin mutations. 23499737_Integrin alpha6 promoter activity was elevated by 2.5-fold in PTHrP (Parathyroid hormone-related protein)-overexpressing vs. control PC-3 cells. 23611113_Necl-4 interacts in cis with integrin alpha6 beta4 through their extracellular regions and Necl-4 inhibited the phorbol ester-induced disassembly of hemidesmosomes 23708747_These findings demonstrated that CD49f is an important marker for identifying colorectal colon cancer-initiating cells(CSCs) and suggest that the CD49f cell fraction may be the best candidate for colorectal CSCs. 24015244_CD49f expressing cells from newly-dissected gastric cancers form tumors with histological features similar to the parent tumor. 24022922_alpha6-integrin is required for hemangioma stem cellsadherence to laminin, vessel formation in vivo, and for homing to the liver. 24042193_High ITGA6 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 24056178_the alpha6 integrin subunit in Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells is important for their ability to stimulate vessel morphogenesis. 24180592_alpha6beta4 integrin and c-Src activation is important early signaling events to lead mTOR activation and cap-dependent translation of VEGF. 24227711_The integrins, alpha6beta1 (and alpha7beta1) are the laminin-binding integrins required for axonal sorting. 24289209_Integrin alpha6beta4 contributes to the suppression of anoikis in a primarily alpha6 subunit-dependent manner in undifferentiated cells. 24304619_Knockdown integrin alpha6 can inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 24375374_Expression of alpha2-integrin and EZH2 in a small fraction of prostate cancer cells is supportive for their role as stem cell marker. alpha6-integrin was predictive for prostate cancer biochemical and local recurrence, and disease specific death. 24403311_Integrin alpha6A splice variant regulates proliferation and the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. 24418536_Cellular integrin alpha6beta4 complex is necessary for HPV16 infection in HaCaTs cells. 24564203_The data presented herein clearly show that down regulation of ITGA6 gene in the human thymic epithelium triggers a complex cascade of effects upon the expression levels of several other cell migration-related genes. 24681327_These results indicate that mAbs to the laminin a4 globular domain are able to inhibit tumor cell adhesion and migration on laminins 411 and 421, and that alpha6beta1 integrin and MCAM bind a4-laminins at very close sites on the globular domain 24739392_These data suggest that systemic targeting of the ITGA6-dependent function of established tumors in bone may offer a noncytotoxic approach to arrest the osteolytic progression of metastatic prostate cancer. 24802970_Primary osteosarcoma patient tumor cell populations expressing high levels of CD49f and low levels of CD90 produce an aggressive xenograft tumor in mice. 24860089_NLGN1 and alpha6 integrin preferentially colocalize in the mature retinal vessels, whereas NLGN1 deletion causes an aberrant VE-cadherin, laminin and alpha6 integrin distribution in vessels 24955499_Role of N-terminal residues in Abeta interactions with integrin receptor and cell surface 24982892_PIK3R3, ITGB1, ITGAL, and ITGA6, were involved in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton that link to triple-negative breast cancer migration. 25288800_Data indicate that integrin alpha6 repression by Kruppel-like factor-9 (KLF9) inhibits glioblastoma cell stemness and tumorigenicity. 25318615_Unique sites of interaction between alphavbeta6 and uPAR are most likely located in uPAR domains II and III. 25450398_Inhibition of actin, FAK, and ILK expression resulted in significantly increased uPAR expression and the variant ITGA6p production in aggressive prostate and breast cancer cell lines. 25472585_ITGA3, ITGA6, ITGB3,ITGB4 and ITGB5 are associated with GC susceptibility (rs2675), ITGA3, ITGA6, ITGB3, ITGB4 and ITGB5 are associated with gastric cancer susceptibility tumor stage and lymphatic metastasis in Chinese Han population. 25561492_Integrin alpha6B-beta1 preferentially binds laminin 511 and this ligand-integrin ligation induces the TAZ nuclear localization and transcriptional activity. 25825984_Amphiregulin enhances alpha6beta1 integrin expression and cell motility in human chondrosarcoma cells through Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK/AP-1 pathway. 25858144_our observations suggest that miR-25 is a key regulator of invasiveness in human prostate cancer through its direct interactions with av- and a6-integrin expression 26013602_CD49f is a marker of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and is correlated with changes in these stem cells under inflammatory conditions. 26108791_We here identify CD49f and CD34 as markers to permit selection of the stem/progenitor cell-like population from human myometrium 26239765_Schwann cells in the tumor-nerve environment affect tumor cell migration and invasion through regulation of the laminin receptor A6B1 and its variant A6pB1. 26350464_syndecans remain anchored to the alpha6beta4 integrin via its cytoplasmic domain, but the activation of cell motility is disrupted 26381405_integrin alpha6beta4 stimulates invasion by promoting autocrine EGFR signaling through transcriptional up-regulation of key EGFR family members and by facilitating HGF-stimulated EGFR ligand secretion 26674523_Genetic and Immunohistochemical Expression of Integrins ITGAV, ITGA6, and ITGA3 As Prognostic Factor for Colorectal Cancer 26749288_Platelet-enhanced endothelial colony forming cell angiogenesis requires platelet tetraspanin CD151 and alpha6beta1 integrin signaling. 26895101_High ITGA6 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 26930028_Human pluripotent stem cells promote the expression of integrin alpha6beta1, and nuclear localization and inactivation of FAK to supports stem cell self-renewal. 26992919_these findings identify CD151 and its interactions with integrins a3 and a6 as potential therapeutic targets for inhibiting stemness-driving mechanisms and stem cell populations in Glioblastoma. 26996297_Ahr ligand aminoflavone targets breast cancer cells with stem cell-like properties, at least in part by abolishing alpha6-integrin expression. 27001172_HIF-dependent regulation of ITGA6 is one mechanism by which sorting for CD49f (+) cells enhances cancer stem cells. 27107458_Increased integrin alpha6beta4 expression is associated with venous invasion and decreased overall survival in non-small cell lung cancers. 27155928_Positive Thy1 and CD49f expression is significantly associated with the progression and poor prognosis of chondrosarcoma. 27509031_Results provide evidence that alpha3 and alpha6 integrins have significantly different internalization kinetics and that coordination exists between them for internalization in prostate cancer cells. 27535718_alpha6-integrin is a matrix stiffness-regulated mechanosensitive molecule which confers an invasive fibroblast phenotype and mediates experimental lung fibrosis. 27562932_During the past decades, many studies have provided evidence for a role of laminin-binding integrins in tumorigenesis, and both tumor-promoting and suppressive activities have been identified. (Review) 27624978_ITGA6 might be involved in a mechanism that underlies radiation resistance and that ITGA6 could be a potential target for therapies aimed at overcoming radiation resistance in breast cancer. 27641064_N-glycosylation controlled the EGFR complex formation with integrin alpha5beta1 or alpha6beta4 27763564_The A380T Single Nucleotide Polymorphism of the ITGA6 gene was not associated with breast cancer development in the analyzed population of Misiones, Argentina. 27773610_The SALL4 - integrin alpha6 - integrin beta1 network promotes cell migration for metastasis via activation of focal adhesion dynamics in basal-like breast cancer cells. 27922761_alpha6beta4 integrin is a positive regulator of collective cell migration of A549 cells through influence on signal pathways in leader cells. 28036265_miR-92b/integrin alpha6/Akt axis controls the motility of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. 28131812_The translational blocking of alpha5 and alpha6 integrin subunits affects migration and invasion, and increases sensitivity to carboplatin of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cell line. 28134816_alpha6(high)/CD71(low) cells give rise to a thicker pluristratified epithelium with lower seeding density and display a low Ki67 positive cells number, showing that they have reached the balance between proliferation and differentiation. 28494186_Small interference ITGA6 gene targeting in the human thymic epithelium differentially regulates the expression of immunological synapse-related genes 28522907_ITGA6 mRNA can be detected in stools of patients with colorectal cancers using droplet digital PCR. 28656629_By directly binding to the 3'UTRs of ITGA6 and ITGB1, we found miR-30e-5p to suppress mainly the adhesion of ITGA6 in CRC cells to laminin.Taken together, miR-30e-5p is a novel effector of P53-induced suppression of migration, invasion and metastasis 28716111_In particular, methylation levels of ITGA4, RERG, and ZNF671 could distinguish Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients from non-cancer nasopharyngeal epithelium (NNE) subjects. We identified the DNA methylation rates of previously unidentified NPC candidate genes. 28795417_FACS analysis of primary human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia tissues confirms expansion of CD49f basal epithelia in patients with Basal cell hyperplasia. 28873464_IGF2 also requires integrin binding for signaling functions, and the IGF2 mutants that cannot bind to integrins act as antagonists of IGF1R. 28926098_RUNX1 regulates ITGA6 through a consensus RUNX1 binding motif in its promoter 28972104_alpha6 beta4 integrin promotes resistance of cancer cells to ferroptosis. 29416013_Results confirm that integrin alpha6 (ITGA6) acted as a direct target of miR-143-3p. 29573114_MiR-127-3p inhibits cell growth and invasiveness by targeting ITGA6 in human osteosarcoma. 29976561_In vimentin-deficient cells, Rac1 fails to cluster at sites enriched in alpha6beta4 integrin heterodimers. 30010110_This study found a significant association between Hepatitis B virus (HBV)and integrin A6, which may be responsible for early migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Thus, integrin A6 is a predictive marker for tumor recurrence and invasiveness of HBV-driven HCC 30076704_In this study, we discovered that AhR ligand AF inhibits the proliferation of TamR cells at least in part by reducing a6-integrin expression and inhibiting activation of down-stream Src and Akt signaling pathways. Our findings and that of others also suggest that elevated a6-integrin expression is linked to tamoxifen resistance. 30536996_MiR-143-3p acts as an anti-oncogene by downregulating ITGA6/ASAP3 protein expression and could offer new insight into potential therapeutic targets for CRC. 30772768_Our findings suggest the significance of activating NFAT1/ITGA6 signaling in aggressive NPC, defining a novel critical signaling mechanism that drives NPC invasion and metastasis and providing a novel target for future personalized therapy. 30894280_The development of drugs targeting both ITGA6 and RPSA may be an effective strategy for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. 30922568_These data indicate that the alpha 6 integrin 3'UTR is a key regulator of alpha6 beta4 integrin heterodimer assembly and incorporation at sites of cell-matrix adhesion. 31175464_The protein levels of integrin alpha6 in lung adenocarcinoma tissues were significantly higher than those in adjacent tissues (p |
ENSMUSG00000027111 |
Itga6 |
562.517445 |
4.8145022635 |
2.267387 |
0.090690078 |
642.038950 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000120364655635298594748906118623427432627130240656291830816772872787790837134941030485340599251238335150680396428706880934527457374480879268490742353662639398010250883096853881284136027439158 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000072218793381179159180075149674121066854704805475941922670211078235301656740814097418166354885154971382962891107357817111188850442137309265285922941955490720208077039105638794858375614063114 |
Yes |
No |
972.1956840 |
50.7611899 |
203.2221563 |
9.0681487 |
| ENSG00000091490 |
23231 |
SEL1L3 |
protein_coding |
Q68CR1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23231; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
17457313_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000029189 |
Sel1l3 |
200.860644 |
0.2805793594 |
-1.833519 |
0.200497390 |
79.883981 |
0.00000000000000000039705268418601038402244757864386356572626575289692077690845151138887558772694319486618041992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000003377808425697702034210958591796069424310327165549027762792011486681076348759233951568603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.0519859 |
11.7647578 |
303.0523561 |
29.5062585 |
| ENSG00000091513 |
7018 |
TF |
protein_coding |
P02787 |
FUNCTION: Transferrins are iron binding transport proteins which can bind two Fe(3+) ions in association with the binding of an anion, usually bicarbonate. It is responsible for the transport of iron from sites of absorption and heme degradation to those of storage and utilization. Serum transferrin may also have a further role in stimulating cell proliferation.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Serves as an iron source for Neisseria species, which capture the protein and extract its iron for their own use. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327295, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22343719}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Iron;Iron transport;Metal-binding;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a glycoprotein with an approximate molecular weight of 76.5 kDa. It is thought to have been created as a result of an ancient gene duplication event that led to generation of homologous C and N-terminal domains each of which binds one ion of ferric iron. The function of this protein is to transport iron from the intestine, reticuloendothelial system, and liver parenchymal cells to all proliferating cells in the body. This protein may also have a physiologic role as granulocyte/pollen-binding protein (GPBP) involved in the removal of certain organic matter and allergens from serum. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:7018; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal part of cell [GO:0045178]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extrinsic component of external side of plasma membrane [GO:0031232]; HFE-transferrin receptor complex [GO:1990712]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; ferric iron binding [GO:0008199]; ferrous iron binding [GO:0008198]; iron chaperone activity [GO:0034986]; transferrin receptor binding [GO:1990459]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; antibacterial humoral response [GO:0019731]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to iron ion [GO:0071281]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0048260]; regulation of iron ion transport [GO:0034756]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; retina homeostasis [GO:0001895]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395] |
11436564_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11445282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11703331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11725818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11785295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11800564_mutational analysis of the transferrin receptor reveals overlapping HFE and transferrin binding sites 11903051_Solute carrier 11a1 (Slc11a1; formerly Nramp1) regulates metabolism and release of iron acquired by phagocytic, but not transferrin-receptor-mediated, iron uptake 11920219_Proband serum contains two transferrin forms: one of 80 kD analogous to the normal one, and a smaller one of 50 kD, which may arise from a specific degradation or be the gene product of a modified allele. 11940510_These results suggest that wild-type HFE negatively modulates the endocytic uptake of transferrin. This inhibitory effect is attenuated in cells expressing C282Y-mutant HFE. 12044175_A series of mutations in the carbonate-binding threonine and arginine residues of the N-terminal and C-terminal lobes of full-length transferrin (and in the N-lobe by itself) substantially alters the synergistic anion-binding functions of transferrin. 12111369_Mutation 375glu-lys is predicted to cause a conformational change in the coiled region of the carboxyl-terminal iron-binding lobe. 12135367_differential effect of a his tag at the N- and C-termini: functional studies with recombinant human serum transferrin 12165535_high-capacity multivalent metal-inducible mechanism for Fe acquisition from transferrin and lactoferrin 12175089_Serum levels of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), ceruloplasmin (Cp), and transferrin (Tf) in rheumatoid arthritis. Serum Tf levels were significantly diminished and serum levels of sICAM-1 and Cp were significantly increased. 12207902_Binding patterns of vanadium ions with different valence states to human transferrin 12223217_a protein identical to or highly homologous with serum TF was purified from follicular fluid; follicular fluid transferrin significantly increased sperm motility 12450380_The roles of the two basic residues in the 'dilysine trigger' regions of transferrins have been clarified and their different behaviors compared to those of the lactoferrins. 12458193_The position of arginine 124 controls the rate of iron release from the N-lobe of the human protein. 12459033_E2 induces Tf gene expression through a nonconsensus distal ERE 12473103_a complex of Yb3+-transferrin is recognized by human transferrin receptor, a possible pathway for Yb3+ accumulation in cells 12617162_review of role in bacterial infections, iron homeostasis, and free radical generation; and implications for theraputic use. 12626412_analyses and comparison of the oligosaccharides present on the different isoforms of purified transferrin isolated from control and patients with severe alcohol abuse 12819023_These findings demonstrate that papillary thyroid carcinoma cells synthesize unique post-translationally modified thyroglobulin and transferrin variants in situ. 12884526_In the urban population, the loci TF (AvaI in exon5) and ACE (I/D polymorphism of the Alu repeat in intron16) were studied in 130 and 141 subjects.The polymorphic loci of the urban and rural populations did not differ in the allele frequencies 12939601_Transferrin and other target genes identified may play a functional role in the downstream pathway of GADD153. 12942785_The analysis involved the data on nine polymorphic codominant loci: HP, GC, TF, PI, PGM1, GLO1, C3, ACP1, and ESD. The loci were selected by significance of differences in genotype frequencies between tuberculosis patients and healthy controls 12951205_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12951205_Transferrin C1 homozygosity carriers had an increased risk of Alzheimer's in subjects > or =75 years of age, showing that homozygosity for the Transferrin C1 allele was associated with an approximately three-fold increased risk. 14523999_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14567694_examination of iron release to pyrophosphate from the isolated recombinant C-lobe and from that lobe in the intact protein, each free and bound to receptor 14580189_identification of C-lobe as binding site to receptor 14614458_holo-transferrin blocked apoptosis of N.1 cells that was induced by Myc-activation or by treatment with TNFalpha, FasL, and TRAIL 14643898_Recycling, degradation and sensitivity to the synergistic anion of transferrin in the receptor-independent route of iron uptake by human hepatoma (HuH-7) cells 14645044_dynamics simulation of the open form of human serum transferrin apoprotein shows that it is flexible enough to sample conformations that are consistent with iron binding 14757931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14980223_analysis of the structure of TfR-Tf complex explains differences in the iron-release properties of free and receptor bound Tf 15042587_apotransferrin can influence oligodendroglia gene expression and differentiation through multiple mechanisms depending on the maturation of the cell. 15060098_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15060098_The combination of the C2 allele of transferrin and the C282Y allele of the haemochromatosis gene increase susceptibility for developing Alzheimer's disease. 15111541_Urinary levels are increaed in normoalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patients. 15214509_In TfC1 homozygotes a shift was found toward higher sialylation, but in TfC1C2 heterozygotes the 5- and 6-sialylated bands were less concentrated 15214510_isolation of transferrin from plasma by ion exchange column chromatography produced a broad pink protein band that subsequently separated on a gel filtration column into three proteins containing many metals. 15271890_degraded by arg-gingipain and lys-gingiapin of Porphyromonas gingivalis, providing sources of iron and peptides which may contribute to tissue destruction by catalyzing the formation of toxic hydroxyradicals 15319290_Transfserrin receptor 2 mRNA levels do not change in cells exposed to diferric transferrin (diferric transferrin) 15327995_Tyr188 is a critical residue not only for iron binding but also for chelator binding and iron release in transferrin 15466165_mutational analysis of patients with atransferrinemia 15536627_fucosylation at the reducing-terminal GlcNAc (Fucalpha1-6GlcNAc) specifically occurred at Asn630, as demonstrated by treatment of the glycopeptides with alpha1-3/4-L-fucosidase 15634274_EGF-like domains of factor Xa and factor IXa are important for the activation of the factor VII--tissue factor complex 15648851_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15698609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15892129_This co-culture system represents a potentially powerful tool to study neuron-glia interactions that occur during myelinogenesis and the role of Transferrin in this process. 15924420_Binding experiments with HeLa S3 cells indicate that recombinant human TF, in which Tyr426 or His585 is mutated, favor a closed or nearly closed conformation while those with mutations of Asp392 or Tyr517 ligands appear to promote an open conformation. 15975770_The single amino acid substitution in Transferrin C2 variant (Pro 570 Ser) does not affect the general conformation of the protein nor the local structure of the iron binding sites, or their binding properties. 16047113_Transferrin polymorphism does not behave as a genetic risk factor for either sporadic or familial Parkinson disease. 16085060_The competitive interaction of aluminum or iron binding to transferrin prevent normal Fe incorporation into K562 cells and trigger the upregulation of Fe transport. 16288727_by generating oxygen radicals, activated U937 cells were able to oxidise LDL; the oxidising process was most pronounced in the presence of copper and could be blocked by Tf 16300393_Position 632 must have a positively charged residue to elicit a robust rate acceleration as a function of increasing salt. On the basis of these observations, a model for iron release from the hTF C-lobe is proposed 16331960_Results describe the detection of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin based on the premise that glycosylation may afford some degree of protection to proteolytic action. 16339299_Expression of mRNA transcripts for transferrin was increased despite protein expression being reduced by heat shock. 16373913_Increased levels in urine predicts development of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. 16497717_Our studies suggest that AEC I is not just a simple barrier for gas exchange, but a functional cell that protects alveolar epithelium from injury. 16538641_the serum changes in sialic acid and carbohydrate-deficient transferrin levels in the course of type 2 diabetes mellitus are associated with each other in the presence of microangiopathy 17008590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17011669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17047092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17116317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17119318_Our findings provide new insights into the molecular basis of OLGc differentiation and on the role played by Tf in this process. 17192785_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17206377_G277S mutation carriers did not show the usual inverse association between iron stores and non-haem iron absorption 17206377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17496814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17496814_no significant differences in genotype, allele or haplotype frequencies of the 6 SNPs were found between schizophrenia patients & controls; results suggest the transferrin gene is not related to development of schizophrenia in Japanese population 17573378_Serum level of sialic acid in patients with chronic alcohol abuse depends on the concentration of the most sialylated glycoproteins: alpha 1-antitrypsin, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, and transferrin. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17640392_This study identifies the PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-mTOR signaling pathway as a new regulator of iron-transferrin uptake 17711300_This work combines kinetic results with structural information to provide a more precise description of the steps leading to and immediately following iron release from the N-lobe of hTF. 17728504_Carbohydrate-deficient transferrin (CDT) is considered as the most reliable marker for detecting heavy drinking in Korean males. 17976429_The within-person biological variability of transferrin saturation and unsaturated iron-binding capacity limits their usefulness as an initial screening test for expressing C282Y homozygotes. 17980706_adjustment of reference intervals for disialotransferrin and carbohydrate-deficient transferrin in relation to ethnicity, age, gender, body mass index and smoking is not required 18022819_stable complex between these Cp and Hp and Tf does not occur under the experimental conditions used 18045615_Two haplotypes A-C and G-G constructed of rs4481157-rs3811655 revealed significant associations with schizophrenia (global P=0.0001). Our findings support that TF gene may be involved in susceptibility to schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population. 18067952_analysis of tissue factor changes and the effects of tissue factor pathway inhibitor on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats 18097132_A novel mutation in exon 4, a G-->A transition at cDNA 410(Cys137Tyr) was found in a child with atransferrinemia & her consanguineous parents. Another novel mutation at IVS10(-23)C-->T, presumably a polymorphism, was also documented. 18245657_that TFR2-related HH may occur at a young age and is characterized by high TS levels 18257091_Upregulation of transferrin is associated with brain metastases in lung cancer 18307987_Sialylation of transferrin and total serum proteins reflects the intensity of inflammatory response during acute pancreatitis and could be used as a prognostic parameter for disease severity. 18344013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18344013_increased frequency of transferrin C1C2 genotype found in cystic fibrosis. 18395717_HFE and TF genes together may influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, functioning at the pituitary or testes level. 18442477_di-tri-bridge cannot be explained by genetic transferrin variants in these samples 18509548_The role of transferrin in glial protection was investigated. 18597674_in the case of abnormal pregnancies, the fetus may require higher levels of transferrin in order to prevent iron depletion due to the stress from the placental dysfunction 18654083_changes in cerebrospinal fluid transferrin glycosylation may play an important role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease 18795173_The joint presence of variant alleles in the HFE and TF genes showed the greatest effect, suggesting a gene-by-gene-by-environment interaction 18813964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18830724_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18835036_Apo-transferrin enhanced IL-18 mRNA and IL-18 secretion 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19021568_A general mechanism for the interaction of five metal-loaded Transferrins [Fe(III), Al(III), Bi(III), Ga(III) and Co(III)] with transferrin receptor, is reported. 19084217_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19084217_The three variants in TF (rs3811647, rs1799852 and rs2280673) plus the HFE C282Y mutation explained approximately 40% of genetic variation in serum transferrin (p = 7.8 x 10(-25)). 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19165391_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19176989_Interactions between distinct pools of TF-expressing cells likely influence tumour progression. The release of TF microparticles into the circulation contributes to the systemic coagulopathies commonly observed in cancer patients. Review. 19219998_The inability to obtain crystals of the TF G65R mutant led to development of a novel crystallization strategy in which the G65R/K206E double mutation stabilizes a single closed pink conformer and captures Arg65 in a single position. 19228837_protective role of Tf in acute stroke and a possible ambivalent role of ceruloplasmin 19250966_we have discovered a novel mitochondrial iron transport system that goes awry in Parkinson's disease, and which may provide a new target for therapeutic intervention. 19254567_Because the HFE alpha3 domain interacts with receptor 2 (TfR2), these results supported the finding that TfR2/HFE complex is required for transcriptional regulation of hepcidin by holo-transferrin. 19281173_The role of the five C-lobe Trp residues in reporting the fluorescence change has been evaluated. 19290554_Iron release from the N-lobe of transferrin is very sensitive to the conformation of the C-lobe, but is insensitive to the presence of the soluble portion of the transferrin receptor or to changes in pH (between 5.6 and 6.4). 19515372_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19545871_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19572083_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19583819_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19650928_Found a modest association of transferrin saturation with peripheral arterial disease, particularly among those with high cholesterol levels. 19670106_Urinary excretion of IgG, transferrin, and ceruloplasmin may be more sensitive indicators of glomerular capillary pressure change than albuminuria in normoalbuminuric diabetic patients. 19693784_the N-lobe loop of human serum transferrin is critical for binding to the transferrin receptor as revealed by mutagenesis, isothermal titration calorimetry, and epitope mapping 19698254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19761807_Human growth hormone-transferrin fusion protein promoted a modest but statistically significant weight gain after oral dosing in hypophysectomized rats. 19828835_This shows for the first time that transferrin receptor(TFR)-mediated transferrin-bound iron uptake is mediated primarily via TFR1 but not TFR2 and that a high-capacity TFR-independent pathway exists in hepatoma cells. 19838776_C-lobes of apo TF and Fe(2)TF bind to the helical domain of transferrin receptor, and the N-lobes are sandwiched between the ectodomain of transferrin receptor and the cell membrane as previously reported. 19852572_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19852572_Transferrin C2 and hemochromatosis C282Y alleles are not associated with increased risk for developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD) in Israel. 19856410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19859668_Data suggested that Al(2)Tf cannot form specific ionic interresidual interactions, such as those formed by Fe(2)Tf, to bind to TfR, resulting in impossible complex formation between Al(2)Tf and TfR. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19916167_The energy transfer from the three Trp residues at positions 8, 128, and 264 within the human serum transferrin (hTF) N-lobe to the ligand to metal charge transfer band was investigated by monitoring changes in Trp fluorescence emission and lifetimes. 19917294_The four microscopic rate constants required to accurately describe the kinetics of iron removal are reported for hTF with and without the TFR. 19921860_Human serum transferrin and ascidian monolobal transferrin bind vanadium with similar strengths; ascidian transferrin requires a synergistic bicarbonate anion for vanadium binding, whereas human serum transferrin does not. 20029940_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20052609_TF showed some association with psychological distress. 20064616_Detailed characterization of the C-lobe of hTF includes a mass determination by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS), analysis of the spectral (absorbance and fluorescence) properties, as well as rate constants for iron release. 20066543_The levels of Tf in sarcoidosis are high in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, but low in serum. Increased levels of Tf in BALF may reflect the disease activity. 20096706_The association constant for the binding of diferric transferrin (Tf) to TfR2alpha is 5.6x10(6) M(-)(1), which is about 50 times lower than that for the binding of Tf to TfR1, with correspondingly reduced rates of iron uptake. 20113254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20118108_A significant association between blood alcohol concentration and both carbohydrate-deficient transferrin (CDT) values and CDT positivity was found. 20150920_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20188707_MRCKalpha takes part in transferrin(Tf)-iron uptake, probably via regulation of Tf-TfR endocytosis/endosome trafficking that is dependent on the cellular cytoskeleton. 20215856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20309589_High glucose conditions induces TM expression. 20371432_Almost all of the acute-phase proteins were closely related to rheumatoid arthritis activity (based on DAS28) and their places in the downgrade scale were as follows: CRP, Tf, AGP, Hp and AAT. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20397659_Identification of a kinetically significant anion binding (KISAB) site in the N-lobe of human serum transferrin 20410508_Human TF expression by both hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic mouse cells contributes to activation of coagulation in mice 8 hours after LPS administration. 20413850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20444258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20447458_The rice-derived recombinant human transferrin was shown to be structurally similar to the native human transferrin, and also functionally the same as native transferrin in terms of reversible iron binding and promoting cell growth and productivity. 20534741_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615872_a mechanistic basis for the antimicrobial activity of human transferrin 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20633231_Although substantial domain separation upon binding of Neisseria meningitidis TbpB cannot be excluded, the preferred model of interaction involves binding human transferrin C-lobe in the closed conformation. 20634490_transferrin receptor 2 and HFE are involved in holotransferrin-dependent signaling for the regulation of furin which involved Erk phosphorylation. Furin in turn may control hepcidin expression. 20659343_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20708639_The interaction between tamoxifen (TMX) and human serum transferrin (HTF) was for the first time studied at varying pH values by fluorescence spectroscopy, circular dichroism (CD) and resonance light scattering (RLS). 20721554_Data suggest that dysmetabolic hyperferritinemia is characterized by hyperferritinemia with normal transferrin saturation, elevated hepcidin levels, and mild liver iron overload in a subset of patients. 20738776_Transferrin saturation is a predictor of hepatic iron overload. 20817350_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20880607_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21049900_thermodynamics of the interactions of serum apotransferrin (T) and holotransferrin (TFe(2)) with ceruloplasmin (Cp) 21113232_Apotransferrin promotes oligodendroglial progenitor cell (OPC) maturation and myelin recovery in the hypoxic corpus callosum by decreasing iron-mediated toxicity and inducing new OPCs from the subventricular zone. 21320285_GSK3 acts as a molecular brake on the signaling pathway, leading to TF expression in monocytes interacting with activated platelets 21376789_Demonstrate a possible damaging impact of various hydrophobic pollutants, which can enter an organism by inhalation or ingestion, on the functionality of the transferrin. 21384276_No significant differences are found in genotype and allele frequencies between Parkinson's disease patients and controls for the transferrin polymorphisms studied. 21389980_The significantly different associations we observed in subgroups suggest that toxic consequences on cognitive function of age-related brain iron increases may differ substantially by gender and genotypes(transferrin c2). 21408069_CSF total-Tf, a new biomarker, when combined with the current biomarker total-tau, is a reliable pre-mortem diagnostic test for Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob-disease . 21422745_The A Allele of the -576G>A polymorphism of the transferrin gene is associated with the increased risk of age-related macular degeneration in smokers. 21459485_This suggests that the Tf-2/Tf-1 ratio could distinguish iNPH from Alzheimer's disease, and possibly other dementias. 21514009_Our results suggest the existence of a link between hemochromatosis and transferrin gene mutations and iron abnormalities that increases the probability of developing Alzheimer's disease when accompanied by a distress of the liver. 21643746_Transferrin gene C2 variants are not high-risk genetic variants for schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder in a Croatian population, nor do they impact on age at onset of the first psychotic symptoms. 21664032_TF antigen 1.94 times higher in the fetus than in the mother 21665994_Missense polymorphisms rs1049296 and rs1799899 in TF strongly affecting transferrin glycosylation. 21678080_Results describe competitive binding of Fe(3+), Cr(3+), and Ni(2+) to transferrin (Tf) at various physiological iron to Tf concentration ratios. 21788477_The structure elucidates how the TFR accelerates iron release from the C lobe, slows it from the N lobe, and stabilizes binding of apohTF for return to the cell surface. 21811575_Experimental meningococcal sepsis in congenic transgenic BALB/c mice expressing human transferrin, was studied. 21820158_Circulating active TF and FXIa can occur in patients with cerebrovascular ischemic events >/=6 months after the events. The presence of these factors is associated with worse functional outcomes, persistent hypercoagulable state in cerebrovascular disease. 21866866_Gene diversity for haptoglobin and transferrin classical markers among Hindu and Muslim populations of Aligarh City, India. 21873562_Elevated transferrin saturation confers a two- to threefold increased risk of developing any form of diabetes, as well as type 1 and type 2 diabetes separately. 21881004_These observations suggest that NHE6 regulates clathrin-dependent endocytosis of transferrin via pH regulation. 21904748_UV-VIS absorbance is employed here to monitor the iron content in human holo-transferrin (TF) under various solvent conditions, changing polarity, pH, ionic strength, and the ionic and hydrophobic environment of the protein. 22041858_The study reports the chemical association of Titanium to TF 'in vivo' under different chromatographic conditions by elemental mass spectrometry using double focusing inductively coupled plasma (DF-ICP-MS) as detector. 22159020_retinal function and gene expression of some of the iron-associated genes are significantly altered. 22191507_identification of a number of residues that are critical to formation of and release of iron from the hTF-TFR complex 22232660_study found that partially overlapping additive genetic factors influenced transferrin levels and brain microstructure; a commonly carried polymorphism (H63D at rs1799945) in the hemochromatotic HFE gene was associated with white matter fiber integrity 22323359_TF, TFR2 and TMPRSS6 polymorphisms are significantly associated with decreased iron status, but only variants in TMPRSS6 are genetic risk factors for iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia. 22327295_crystal structures of the TbpA-transferrin complex and of the corresponding co-receptor TbpB 22343719_transferrin-binding protein B stabilizes the holo form of human transferrin. 22356162_model in which a series of pH-induced events involving both TFR residue His318 and TF residue His349 occurs to promote receptor-stimulated release of iron from the C-lobe of TF 22424853_The lower inhibition of tissue factor and greater endothelial dysfunction in STEMI than in non-STEMI patients may enhance thrombosis at the culprit lesion and adjacent coronary plaques. 22458330_BfrA, BfrD and BfrE are catecholamine receptors and are involved in the utilization of iron liberated from transferrin by host catecholamine stress hormones. 22722730_study indicates that HIV-infected women in Rwanda with a TF CD phenotype have a significantly higher prevalence of certain opportunistic infections and significantly lower TF concentrations than subjects with the TF CC phenotype 22726553_We demonstrate that visfatin induces transcription of mRNA for TF by Real Time PCR. 22819264_Therefore, we envision that the antithrombotic activity of CORM-2 might be used as a pharmaceutical agent for the treatment of various inflammatory conditions. 22829284_Bovine prolactin improved the expression of human transferrin through such a possible mechanism that bovine prolactin activated STAT5a transcription expression. 22861364_Patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes have lower apoTf serum levels than healthy controls & patients with long-lasting disease. apoTf has a pivotal role in the perpetuation of type 1 diabetes pathology. 22873711_The study demonstrates for the first time that the protonation of Tyr188 is required for the release of metal from iron- and aluminum-loaded serum transferrin. 22923205_study of effect of occupational exposure to lead among metallurgy workers in Poland on blood levels of transferrin (TRF), ceruloplasmin (CER) and haptoglobin (HPG): Transferrin levels were unchanged in exposed group compared with control group. 22938499_TF translocates to the cell front in association with cytoskeleton proteins and regulates HVSMC migration by mechanisms dependent and independent of factor (F)VIIa/PAR2 23027680_Data suggest that there is no association between plasma level of carbohydrate-deficient transferrin and volume decrease of brain gray or white matter in male subjects as result of current/recent or lifetime alcohol drinking in the Netherlands. 23089144_We found that the serum transferrin was associated with the rs8177178 (p T & 1825 C>T. 24256706_Increased urinary excretion of plasma proteins such as IgG, ceruloplasmin and transferrin, with different molecular radii of 55 A or less and different isoelectric points precede development of microalbuminuria in patients with NIDDM and hypertension. 24350254_did not find any association between the c.-2G>A polymorphism and keratoconus; no association was found between transferrin polymorphisms and Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy occurrence 24599423_decreased circulating levels in abdominal aortic aneurysm 24972167_Understanding the interaction between [Cr(phen)3](3+) with transferrin is relevant because this protein could be a delivery agent of Cr(III) complex to tumor cells. 25000850_H2O2 induces the expression of transferrin, and consequently, decreased iron absorption, suggests a novel mechanism for iron deficiency in pediatric non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients. 25163484_Human transferrin is internalized across the mycobacterial cell wall in a GAPDH-dependent manner within infected macrophages. 25224454_significant associations between serum iron binding capacity levels and two SNPs around TF on chromosome 3 were identified. 25287020_Infants born to mothers with the HFE C282Y gene missense variant but not the TF P570S or HFE H63D gene missense variants had lower umbilical cord blood lead levels relative to those born to women who were wild-type. 25298206_apelin-13 has a role in inducing expression of prothrombotic tissue factor 25375118_Results show that higher TF expression in patients with hypereosinophilic disorders may contribute to increase the thrombotic risk. 25457201_identified the rs3811647 polymorphism in the TF gene as the only SNP significantly associated with iron metabolism through serum transferrin and iron levels 25486930_Hereditary hypotransferrinemia caused by novel transferrin mutations can lead to elevated transferri |
ENSMUSG00000032554 |
Trf |
71.383183 |
0.1621734218 |
-2.624391 |
0.675220834 |
13.099728 |
0.00029533867192314746264597546954178142186719924211502075195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000754578292813857793956688890801842717337422072887420654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.6545609 |
9.6853041 |
104.9994828 |
40.3211768 |
| ENSG00000091592 |
22861 |
NLRP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9C000 |
FUNCTION: Acts as the sensor component of the NLRP1 inflammasome, which mediates inflammasome activation in response to various pathogen-associated signals, leading to subsequent pyroptosis (PubMed:22665479, PubMed:12191486, PubMed:17349957, PubMed:27662089, PubMed:31484767, PubMed:33093214, PubMed:33410748, PubMed:33731929, PubMed:33731932, PubMed:35857590). Inflammasomes are supramolecular complexes that assemble in the cytosol in response to pathogens and other damage-associated signals and play critical roles in innate immunity and inflammation (PubMed:22665479, PubMed:12191486, PubMed:17349957). Acts as a recognition receptor (PRR): recognizes specific pathogens and other damage-associated signals, such as cleavage by some human enteroviruses and rhinoviruses, double-stranded RNA, UV-B irradiation, or Val-boroPro inhibitor, and mediates the formation of the inflammasome polymeric complex composed of NLRP1, CASP1 and PYCARD/ASC (PubMed:22665479, PubMed:12191486, PubMed:17349957, PubMed:25562666, PubMed:30291141, PubMed:30096351, PubMed:33243852, PubMed:33093214, PubMed:33410748, PubMed:35857590). In response to pathogen-associated signals, the N-terminal part of NLRP1 is degraded by the proteasome, releasing the cleaved C-terminal part of the protein (NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1, C-terminus), which polymerizes and associates with PYCARD/ASC to initiate the formation of the inflammasome complex: the NLRP1 inflammasome recruits pro-caspase-1 (proCASP1) and promotes caspase-1 (CASP1) activation, which subsequently cleaves and activates inflammatory cytokines IL1B and IL18 and gasdermin-D (GSDMD), leading to pyroptosis (PubMed:22665479, PubMed:12191486, PubMed:17349957, PubMed:32051255, PubMed:33093214). In the absence of GSDMD expression, the NLRP1 inflammasome is able to recruit and activate CASP8, leading to activation of gasdermin-E (GSDME) (PubMed:33852854, PubMed:35594856). Activation of NLRP1 inflammasome is also required for HMGB1 secretion; the active cytokines and HMGB1 stimulate inflammatory responses (PubMed:22801494). Binds ATP and shows ATPase activity (PubMed:11113115, PubMed:15212762, PubMed:33243852). Plays an important role in antiviral immunity and inflammation in the human airway epithelium (PubMed:33093214). Specifically recognizes a number of pathogen-associated signals: upon infection by human rhinoviruses 14 and 16 (HRV-14 and HRV-16), NLRP1 is cleaved and activated which triggers NLRP1-dependent inflammasome activation and IL18 secretion (PubMed:33093214). Positive-strand RNA viruses, such as Semliki forest virus and long dsRNA activate the NLRP1 inflammasome, triggering IL1B release in a NLRP1-dependent fashion (PubMed:33243852). Acts as a direct sensor for long dsRNA and thus RNA virus infection (PubMed:33243852). May also be activated by muramyl dipeptide (MDP), a fragment of bacterial peptidoglycan, in a NOD2-dependent manner (PubMed:18511561). The NLRP1 inflammasome is also activated in response to UV-B irradiation causing ribosome collisions: ribosome collisions cause phosphorylation and activation of NLRP1 in a MAP3K20-dependent manner, leading to pyroptosis (PubMed:35857590). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11113115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12191486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15212762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17349957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18511561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22665479, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22801494, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25562666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27662089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30096351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30291141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31484767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32051255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33093214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33243852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33410748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33731929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33731932, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33852854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35594856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35857590}.; FUNCTION: [NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1]: Constitutes the precursor of the NLRP1 inflammasome, which mediates autoproteolytic processing within the FIIND domain to generate the N-terminal and C-terminal parts, which are associated non-covalently in absence of pathogens and other damage-associated signals. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22087307}.; FUNCTION: [NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1, N-terminus]: Regulatory part that prevents formation of the NLRP1 inflammasome: in absence of pathogens and other damage-associated signals, interacts with the C-terminal part of NLRP1 (NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1, C-terminus), preventing activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome (PubMed:33093214). In response to pathogen-associated signals, this part is ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome, releasing the cleaved C-terminal part of the protein, which polymerizes and forms the NLRP1 inflammasome (PubMed:33093214). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33093214}.; FUNCTION: [NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1, C-terminus]: Constitutes the active part of the NLRP1 inflammasome (PubMed:33093214, PubMed:33731929, PubMed:33731932). In absence of pathogens and other damage-associated signals, interacts with the N-terminal part of NLRP1 (NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 1, N-terminus), preventing activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome (PubMed:33093214). In response to pathogen-associated signals, the N-terminal part of NLRP1 is degraded by the proteasome, releasing this form, which polymerizes and associates with PYCARD/ASC to form of the NLRP1 inflammasome complex: the NLRP1 inflammasome complex then directly recruits pro-caspase-1 (proCASP1) and promotes caspase-1 (CASP1) activation, leading to gasdermin-D (GSDMD) cleavage and subsequent pyroptosis (PubMed:33093214). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33093214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33731929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33731932}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: It is unclear whether is involved in inflammasome formation. It is not cleaved within the FIIND domain, does not assemble into specks, nor promote IL1B release (PubMed:22665479). However, in an vitro cell-free system, it has been shown to be activated by MDP (PubMed:17349957). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17349957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22665479}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ectodermal dysplasia;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Immunity;Inflammasome;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Necrosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the Ced-4 family of apoptosis proteins. Ced-family members contain a caspase recruitment domain (CARD) and are known to be key mediators of programmed cell death. The encoded protein contains a distinct N-terminal pyrin-like motif, which is possibly involved in protein-protein interactions. This protein interacts strongly with caspase 2 and weakly with caspase 9. Overexpression of this gene was demonstrated to induce apoptosis in cells. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene, but the biological validity of some variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:22861; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; inflammasome complex [GO:0061702]; NLRP1 inflammasome complex [GO:0072558]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity [GO:0140608]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0008656]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to UV-B [GO:0071493]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; NLRP1 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:1904784]; pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002221]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; response to muramyl dipeptide [GO:0032495]; self proteolysis [GO:0097264]; stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade [GO:0031098] |
12191486_inflammasome comprises caspase-1, caspase-5, Pycard/Asc, and NALP1; a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta 14691733_Related to susceptiblity to vitiligo and autoimmune diseases. 15212762_Over-expression of NALP1 stimulated cell death in both HeLa cells and cerebellar granule neurons. 17164409_NALP 1 and 3 show distinct but separate expression profiles in human tissues suggesting a site-specific role in the inflammatory response 17377159_DNA sequence variants in the NALP1 region are associated with the risk of several epidemiologically associated autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases, implicating the innate immune system in the pathogenesis of these disorders. 17418785_Antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L) bind and suppress NALP1, reducing caspase-1 activation and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) production. 17620097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17637824_NALP1 genetic variations are involved in predisposition to generalized vitiligo. 17637824_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18263805_Relative copy numbers for the inflammasome mRNAs for ASC, caspase-1, NALP1, and Pypaf-7 were significantly lower in patients with septic shock compared with critically ill control subjects. 18348116_The pyrin domain of the ASC and NALP1 proteins were simulated at two different pH values, 3.7 and 6.5, with two different force-field parameter sets, and the molecular dynamics simulation trajectories were compared to NMR experimental data 18946481_NALP1 and the innate immune system may be implicated in the pathogenesis of many autoimmune disorders, particularly organ-specific autoimmune diseases. 18946481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19001869_significant KPNA1-, NLRP1- and NLRP3-gene expression phenotypes associated with human genotypes of Crohn's disease, Huntington's disease and rheumatoid arthritis 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19120479_Genetic variations are associated with autoinflammatory disorders and increased susceptibility to microbial infection 19223160_gene polymorphism is associated with vitiligo 19727120_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19727120_three-way interaction effects of chromosome 7 SNP rs6960920, chromosome 9 SNP rs4744411, and NLRP1 SNP rs6502867 on vitiligo phenotype and autoimmune disease phenotype; effects of both chromosome 7 and NLRP1 SNP rs6502867 on the vitiligo phenotype 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20152874_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20152874_study confirms an association between the coding polymorphism in NLRP1 and Autoimmune Addison's disease 20370570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20403135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20502346_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574744_study found that 2 SNPs in the NALP1 extended promoter region, rs1008588 and rs2670660 were significantly associated with generalized vitiligo in Arab vitiligo patients; several other SNPs in the NALP1 region were at the margin of significant association 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20697295_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21098108_These findings suggest that the NALP1 inflammasome is critical for mediating innate immune responses to T. gondii infection and pathogenesis. 21149496_results establish NLRP1 as a new genetic susceptibility factor for systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary fibrosis and anti-topoisomerase-positive SSc phenotypes and provides new insights into the pathogenesis of SSc. 21245836_NALP1/NLRP1 inflammasomes may have a role in CD pathogenesis. 21252346_study found KSHV Orf63 is a viral homolog of NLRP1; Orf63 blocked NLRP1-dependent innate immune responses; during the course of evolution with its human host, KSHV has usurped and modified a cellular NLR gene to inhibit the host inflammasome response 21331694_None of the six SNPs in the NLRP1 region were significantly associated with disease susceptibility or the ocular, neurological, and dermatological manifestations of VKH. 21376416_No evidence for association of the polymorphisms in NLRP1 gene with type 1 diabetes in Poland 21946017_These findings provide evidence of an association between single nucleotide variations in the NLRP1 gene and Alzheimer disease 21976003_NLRP1 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Han Chinese. 22087307_results identify a function for the FIIND and show that CARD8 and NLRP1 are ZU5-UPA domain-containing autoproteolytic proteins, thus suggesting a novel mechanism for regulating innate immune responses 22117610_Polymorphisms in the innate immunity gene NLRP1 are implicated in some familial forms of vitiligo. Review. 22227487_Twelve single nucleotide polymorphisms within NLRP1, NLRP3, NLRC4, CARD8, CASP1, and IL1B genes were analyzed in 150 HIV-1-infected Brazilian subjects. 2 polymorphisms in NLRP3 and IL1B were significantly associated to the HIV-1 infection. 22235789_results demonstrated that NLRP1 rs2670660 SNP and the NLRP1 rs12150220-rs2670660 A-G haplotype were associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in our study population, and in particular with the development of nephritis, rash and arthritis 22507623_A haplotype, T-T-C-G-A-C, in the NLRP1 gene was associated with a higher risk for Kawasaki disease development. 22524199_NLRP3/NLRP1 polymorphisms are associated with melanoma susceptibility 22665479_Autolytic proteolysis within the function to find domain (FIIND) is required for NLRP1 inflammasome activity. 23053059_we performed a genetic association study in patients with pneumococcal meningitis and found that single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the inflammasome genes CARD8 and NLRP1 are associated with poor disease outcome. 23253924_NLRP1 shows a genetic association with giant cell arteritis. 23349227_We describe a new corneal intraepithelial dyskeratosis and how we identified its causative gene - NLRP1 23374100_study found that NLRP1 rs12150220 T allele and NLRP1 rs2670660 G allele were significantly associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders compared with controls; NLRP1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid disorders 23380025_Our results do not support the role of the NLRP1 rs8182352 in systemic sclerosis. 23382179_NLRP1 RNA and protein levels were not altered by the predominant high-risk haplotype, indicating that altered function of the corresponding multivariant NLRP1 polypeptide predisposes to autoimmune diseases by activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome 23508996_The charge surface of the NLRP1 CARD structure and a procaspase-1 CARD model suggests potential mechanisms for their association through electrostatic attraction. 23563199_Genetic variation in the inflammasome affects atopic dermatitis susceptibility. 23770116_Studied NLRP1 haplotypes associated with leprosy in Brazilian patients. 23773036_Results show that polymorphisms in NLRP1 may be risk factors for susceptibility and progression of vitiligo.The upregulation of NLRP1 mRNA in patients with susceptible genotypes advocates the crucial role of NLRP1 in vitiligo. 23940760_Stimulation with TNF-alpha is sufficient for activation of the NALP1 inflammasome. 24008734_the NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes have a major role in neuronal cell death and behavioral deficits in stroke. 24065540_TNF-alpha rs1800629 A/G, NLRP1 rs878329 C/G and NLRP1 rs6502867 C/T polymorphisms were not associated with risk of RA or AS. 24334646_These results indicated deregulation of NLRP3/NLRP1 inflammasomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, and suggested an important role for inflammasomes in the pathogenesis and progression of systemic lupus erythematosus. 24439873_Inflammatory plasma factors induce NLRP1 on endothelial cells in peripheral artery disease. 24699513_The NOD-like receptor NLRP1a/Caspase-1 pathway is the best candidate to mediate the parasite-induced cell death. 24909542_Our data support the involvement of NLRP1 and the NLRP1 inflammasome in psoriasis susceptibility and further support the role of innate immunity in psoriasis. 25064844_The crystal structure of the LRR domain of human NLRP1 in the absence of muramyl dipeptide. 25342284_Elevated expression of NLRP1 was associated with pemphigus vulgaris disease progression. 25556596_The NLRP1 variant rs12150220 (L155H) was associated with the development of preeclampsia (OR = 1.58), suggesting a role of this inflammasome receptor in the pathogenesis of this multifactorial disorder. 25611377_NALP1 is expressed low in colon cancer and associated with the survival and tumor metastasis of patients, and treatment with 5-aza-2-deoxycytidine can restore NALP1 levels to suppress the growth of colon cancer. 25626361_The data of this study suggested that NLRP1/caspase-1 signaling participates in the seizure-induced degenerative process in humans. 25725098_these data identify NLRP1 as an essential mediator of the host immune response during IBD and cancer. 25744023_Human central Nervous System neurons express NLRP1 inflammasomes, which activate Casp1 and subsequently Casp6. Casp1 activation generates interleukin-1-beta-mediated neuroinflammation and Casp6 activation causes axonal degeneration. 25814374_Letter: aspirin intake in peripheral arterial disease attenuates NLRP1 inflammasome gene expression in endothelial cells. 26079697_Ethanol-induced HMGB1 release is associated with NOX2/NLRP1 inflammasome signaling, which represents a novel mechanism of ethanol-associated neuron injury. 26232934_Nlrp1 inflammasome is downregulated in trauma patients 26715049_NLRP1 inflammasome is activated by extracellular acidosis through ASIC1a signal pathway. 26902715_The changes in the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) in human corneas with disease expression may reflect different susceptibility to infectious and non-infectious injuries in corneas with various diseases. 26925775_HO-1 inhibited expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), which is a transcription factor regulating NLRP1 expression 26939933_The NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are activated in Alzheimer's disease 27423725_Simvastatin intake in peripheral arterial disease patients increases in vitro reactivity of NLRP1 inflammasome gene expression in endothelial cells. 27626170_Data show that cyclic stretch activated the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor containing pyrin domain 1 and 3 (NLRP1 and NLRP3) inflammasomes and induced the release of IL-1beta and pyroptosis via a caspase-1-related mechanism in human periodontal ligament cells (HPDLCs). 27662089_these findings establish a group of non-fever inflammasome disorders, uncover an unexpected auto-inhibitory function for the pyrin domain, and provide the first genetic evidence linking NLRP1 to skin inflammatory syndromes and skin cancer predisposition. 27750030_mRNA expression levels of NLRP1 and NLRC4 were not altered in chronic hepatitis B patients, suggesting that these genes are not responsible for the impaired immune responses against HBV observed in these patients. 27965258_Two new mutations in NLRP1 (c.3641C>G, p.Pro1214Arg and c.2176C>T; p.Arg726Trp) were found to cause a new autoinflammatory syndrome, NLRP1-associated autoinflammation with arthritis and dyskeratosis. 28263976_NLRP1 promotes melanoma growth by enhancing inflammasome activation and suppressing apoptotic pathways. 28422993_Th17 micro-milieu via IL-17A regulates NLRP1-dependent CASP5 activity in psoriatic skin autoinflammation. 28503575_Our study demonstrated the potentially significant role of NLRP1 rs878329 (G>C) in developing susceptibility to the partial seizures in a Chinese Han population 28634744_not associated with obesity in this study 28653215_The CC genotype of NLRP1 rs878329 and TT genotype of PADI4 rs2240340 were associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis susceptibility in Asians. 28733143_Genetic variants in NLRP1 lead to autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases in both humans and mice. NLRP1 N-terminal domain (PYD in humans) is autoinhibitory, whereas the C-terminal cleavage fragment containing the CARD domain engages an ASC-dependent inflammasome. [review] 28808162_NLRP1 senses cellular infection by distinct invasive pathogens. 28988323_the analysis of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients from Canada failed to identify potentially pathogenic mutations in NLRP1, including the previously described p.G587S mutation. Further studies are necessary to confirm a role of NLRP1 in the pathophysiology of MS. 29031829_NLRP1 rs2670660 and rs11651270 polymorphisms were significantly associated with a decrease risk to develop diabetic kidney disease in type I diabetes, and rs11651270 also with a lower risk of new renal events during follow-up. 29150951_The focus of this article is to discuss the time-course and regulation of inflammasome assembly and activation during Traumatic brain injury (TBI) and spinal cord injury (SCI)and their targeting in designing therapeutic approaches. We particularly focus on the inflammasomes NLRP1 and NLRP3 which play a pivotal function during TBI and SCI in the central nervous system (CNS) 29214170_NLRP1 promotes cell line MCF-7 the proliferation, migration, and invasion through inducing EMT. 29265930_The NLRP1 rs12150220 missense variant (H155L) was significantly correlated with numbers of asbestos bodies (ABs) in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients. Specifically, a low number of ABs was detected in individuals carrying the NLRP1 rs12150220 A/T genotype. 29393464_Based on the data obtained from patients and in vitro cells, we concluded that both NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes are highly involved in the FLS inflammation and pyroptosis. 29438387_study results suggest variations in the inflammasome, particularly in NLRP1 and CARD11, may be associated with chronic Chagas cardiomyopathy 29528779_Suggest inflammasome protein NLRP1 appears to have a specific role in the development of occlusive aortic disease. 29850521_eight single nucleotide polymorphisms, four from NLRP1 (rs8079034, rs11651270, rs11657747, and rs878329) and NLRP3 (rs7512998, rs3806265, rs10754557, and rs10733113) each in 540 patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris and 612 healthy controls in the Chinese Han population, were genotyped. 30096351_these experiments showed an essential role of the NLRP1 rather than the NLRP3 inflammasome in UVB sensing and subsequent IL-1beta and -18 secretion by keratinocytes 30214011_the NLRP1 inflammasome is a key negative regulator of protective, butyrate-producing commensals, which therefore promotes inflammatory bowel disease 30872533_the results provide a unified mechanism for NLRP1B activation by diverse pathogen-encoded enzymatic activities. 31078283_AIM2, NLRP1, and P2RX7 promoted susceptibility to Leishmania braziliensis infection. 31121538_It discusses a newly proposed 'functional degradation' mechanism that explains activation and assembly of NLRP1 into an oligomeric complex called an inflammasome. 31293094_The study results suggest NLRP-1 (rs2670660) is significantly associated with increased risk of NSV susceptibility whilst TLR-4 (rs4986790) does not confer risk in South Indian population. 31396539_SNPs in the NLRP1 gene were associated with T1 Diabetes(T1D), as well as the age of onset in the Chinese Han T1D individuals. This indicates that the NLRP1 gene might play a pivotal role in the etiopathogenesis of T1D and could be applied to genetic screening of T1D in the Chinese Han population. 31484767_Homozygous NLRP1 gain-of-function mutation is associated with a syndromic form of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. 31601004_Coding polymorphisms in NLRP1 rs12150220 show an association with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease disease severity. Decreased lung function, measured by a forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1% predicted), was significantly associated with the minor allele genotypes (AT + TT) of NLRP1 rs12150220 (p = 0.0002). The same rs12150220 genotypes exhibited a higher level of serum IL-1beta compared to the AA genotype 31663353_Chronic Meth abuse could result in increases of NLRP1 and NLRP3 and induction of inflammation and apoptosis in the hippocampus 31694740_Expression of inflammasomes NLRP1, NLRP3 and AIM2 in different pathologic classification of lupus nephritis. 32135277_Double-edged sword of inflammasome genetics in colorectal cancer prognosis. 32922182_Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) upregulates expression of Inflammasome NLRP1 via ROS/NF-kappaB signaling in HaCaT Cells. 33093214_Enteroviral 3C protease activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome in airway epithelia. 33243852_Human NLRP1 is a sensor for double-stranded RNA. 33378691_NLRP1 variant M1184V decreases inflammasome activation in the context of DPP9 inhibition and asthma severity. 33385378_NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are up-regulated in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and may contribute to overexpression of caspase-1 and IL-beta in sclerotic hippocampi. 33410748_Diverse viral proteases activate the NLRP1 inflammasome. 33420028_Structural basis for distinct inflammasome complex assembly by human NLRP1 and CARD8. 33420033_Mechanism of filament formation in UPA-promoted CARD8 and NLRP1 inflammasomes. 33431827_Homotypic CARD-CARD interaction is critical for the activation of NLRP1 inflammasome. 33621312_Three Novel Genetic Variants in the FAM110D, CACNA1A, and NLRP12 Genes Are Associated With Susceptibility to Hypertension Among Dai People. 33658393_Low expression of NLRP1 is associated with a poor prognosis and immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma patients. 33731929_Structural and biochemical mechanisms of NLRP1 inhibition by DPP9. 33731932_DPP9 sequesters the C terminus of NLRP1 to repress inflammasome activation. 33785922_DPP9 restrains NLRP1 activation. 33854691_Autophagy in the HTR-8/SVneo Cell Oxidative Stress Model Is Associated with the NLRP1 Inflammasome. 33972620_Genetic polymorphisms of inflammasome genes associated with pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and clinical prognosis in the Brazilian Amazon. 34257569_Somatic Mutation of NLRP Genes in Gastric and Colonic Cancers. 34530705_Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease: Focus on NLRP1 and NLRP3 Inflammasomes. 35126351_The Expression of Inflammasomes NLRP1 and NLRP3, Toll-Like Receptors, and Vitamin D Receptor in Synovial Fibroblasts From Patients With Different Types of Knee Arthritis. 35238869_The NLRP1 Inflammasome Induces Pyroptosis in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. 35594856_Human NLRP1 is a sensor of pathogenic coronavirus 3CL proteases in lung epithelial cells. 35857590_ZAKalpha-driven ribotoxic stress response activates the human NLRP1 inflammasome. 36293159_NLRP1 in Cutaneous SCCs: An Example of the Complex Roles of Inflammasomes in Cancer Development. |
ENSMUSG00000070390+ENSMUSG00000069830 |
Nlrp1b+Nlrp1a |
41.169898 |
0.0558670004 |
-4.161860 |
0.529859710 |
58.823138 |
0.00000000000001725008111835836492373173624154217294278325540990426389953427133150398731231689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000114175424801331587057159321669218101556958835929300732914271065965294837951660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4144585 |
2.0374898 |
84.9973829 |
24.2686694 |
| ENSG00000091844 |
26575 |
RGS17 |
protein_coding |
Q9UGC6 |
FUNCTION: Regulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades, including signaling via muscarinic acetylcholine receptor CHRM2 and dopamine receptor DRD2. Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form (PubMed:15096504). Binds selectively to GNAZ and GNAI2 subunits, accelerates their GTPase activity and regulates their signaling activities. Negatively regulates mu-opioid receptor-mediated activation of the G-proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZB0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15096504}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;GTPase activation;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal transduction inhibitor;Synapse;Synaptosome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the regulator of G-protein signaling family. This protein contains a conserved, 120 amino acid motif called the RGS domain and a cysteine-rich region. The protein attenuates the signaling activity of G-proteins by binding to activated, GTP-bound G alpha subunits and acting as a GTPase activating protein (GAP), increasing the rate of conversion of the GTP to GDP. This hydrolysis allows the G alpha subunits to bind G beta/gamma subunit heterodimers, forming inactive G-protein heterotrimers, thereby terminating the signal. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:26575; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968] |
15096504_RGS17 is a new RZ member that preferentially inhibits receptor signaling via G(i/o), G(z), and G(q) over G(s) to enhance cAMP-dependent signaling and inhibit calcium signaling 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19244110_RGS17, an overexpressed gene in human lung and prostate cancer, induces tumor cell proliferation through the cyclic AMP-PKA-CREB pathway. 19351763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19351763_RGS17 is a major candidate for the familial lung cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 6q23-25. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20306291_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20420807_Taken together, these data have provided the first evidence of miRNA regulation of RGS17 expression in lung cancer. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21044322_Results establish RGS10 and RGS17 as novel regulators of cell survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer cells and suggest that their reduced expression may be diagnostic of chemoresistance. 21620966_RGS17 is differentially expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and plays a central role in regulating transformed hepatocyte tumorgenicity. 22006218_Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in the regulator of G-protein signaling 17 gene are associated with smoking initiation. 22591552_Variation in RGS17 was associated with risk for substance dependence diagnoses in both African American and European American populations. 28337960_data suggest that RGS17 is overexpressed in colorectal carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion 28921827_Taken together, the results suggested that expression of miR-203 inhibited non-small-cell lung cancer tumor growth and metastasis by targeting RGS17 29351497_A screen of over 60,000 small molecules led to the identification of five hit compounds that inhibit the RGS17-Galphao protein-protein interaction. 29559347_Results showed that RGS17 overexpression promoted hepatocarcinoma (HCC) cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and reversed the miR-199 mediated inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasion. 30940727_these findings suggest that Ca(2+) positively regulates RGS17, which may represent a general mechanism by which increased Ca(2+) concentration promotes the GAP activity of the RZ subfamily, leading to RZ-mediated inhibition of Ca(2+) signaling. 31081094_MiRNA-199 inhibits malignant progression of lung cancer through mediating RGS17. 31454494_Knock-down of Long non-coding RNA Linc00483 inhibited the development of cervical cancer by regulating miR-508-3p/RGS17 axis. 34002599_MiR-203 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of ovarian cancer through regulating RGS17. |
ENSMUSG00000019775 |
Rgs17 |
18.117904 |
0.4452570164 |
-1.167290 |
0.404036941 |
8.396538 |
0.00375936329450160056434016020432409277418628334999084472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007884917601097496397954955682507716119289398193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2918843 |
2.9448481 |
25.6378376 |
4.3369586 |
| ENSG00000092108 |
23256 |
SCFD1 |
protein_coding |
Q8WVM8 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in SNARE-pin assembly and Golgi-to-ER retrograde transport via its interaction with COG4. Involved in vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable syntaxin binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of autophagosome assembly; regulation of protein transport; and response to toxic substance. Located in cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23256; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi-associated vesicle [GO:0005798]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; negative regulation of autophagosome assembly [GO:1902902]; post-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006892]; regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0060628]; regulation of protein transport [GO:0051223]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0006890]; toxin transport [GO:1901998]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
19536132_Study shows that the SM protein, Sly1, interacts directly with the conserved oligomeric Golgi (COG) tethering complex; Sly1-COG interaction is mediated by the Cog4 subunit, which also interacts with Syntaxin 5 through a different binding site. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27455348_Mutation in SCFD1 gene is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 29260601_The found of this study confirmed the lack of association of SCFD1 rs10139154 with the risk for ALS in a large Chinese population. 31267315_SCFD1 rs10139154 is associated with a decreased risk of developing Alzheimer disease. 34785650_mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of VAMP8 and SCFD1 regulates autophagosome maturation. 35234271_Lack of an association between SCFD1 rs10139154 polymorphism and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. |
ENSMUSG00000020952 |
Scfd1 |
273.844274 |
2.4067358830 |
1.267078 |
0.152696746 |
67.604129 |
0.00000000000000019984864087518315027273869734706021975095137203654732660496051721565891057252883911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001484532430456820910978461723151935243495186844860100894294419049401767551898956298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
388.8217502 |
56.9066394 |
161.9706478 |
17.2822534 |
| ENSG00000092345 |
1618 |
DAZL |
protein_coding |
Q92904 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein, which is essential for gametogenesis in both males and females. Plays a central role during spermatogenesis. Acts by binding to the 3'-UTR of mRNA, specifically recognizing GUU triplets, and thereby regulating the translation of key transcripts (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Spermatogenesis;Translation regulation |
|
The DAZ (Deleted in AZoospermia) gene family encodes potential RNA binding proteins that are expressed in prenatal and postnatal germ cells of males and females. The protein encoded by this gene is localized to the nucleus and cytoplasm of fetal germ cells and to the cytoplasm of developing oocytes. In the testis, this protein is localized to the nucleus of spermatogonia but relocates to the cytoplasm during meiosis where it persists in spermatids and spermatozoa. Transposition and amplification of this autosomal gene during primate evolution gave rise to the DAZ gene cluster on the Y chromosome. Mutations in this gene have been linked to severe spermatogenic failure and infertility in males. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:1618; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation activator activity [GO:0008494]; 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA stabilization [GO:0070935]; germ cell development [GO:0007281]; positive regulation of translational initiation [GO:0045948]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
11499325_role of the autosomal candidate gene DAZLA (Deleted in AZoospermia Like Autosome) in male subfertility 11872225_The DAZL transcript and protein are present in human spermatozoa. 12029071_The distinct expression pattern of DAZL protein in the corpus luteum may play an important role in the regulation of luteal function. 12200456_These findings confirm that DAZL and DAZ can only substitute for early functions of the murine homologue resulting in the establishment of the germ cell population and partial progression into meiosis 12414900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12414900_findings provide strong evidence for the role of the autosomal DAZL gene in human spermatogenesis 12511597_DAZ/DAZL protein can form a stable complex with human PUM2. 15066460_Role in spermatogenesis. Decreased DAZ proteins in spermatogenic failure may be due to germ cell loss. Transcription of BOULE, DAZL, and DAZ not altered in degrees of spermatogenic failure. No increase of DAZL or BOULE found in DAZ deletion. 15220464_Data suggest that the T54A polymorphism of deleted-in-azoospermia-like (DAZL) protein might play a role in infertility only in Taiwanese or Asiatic individuals. 15220464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15520024_In a Caucasian population, the DAZL SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) 386 is completely absent and SNP 260 is not associated with spermatogenic failure and therefore does not represent a molecular marker for genetic diagnosis of male infertility. 15520024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15595957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15607425_PUM2 and DAZL, are capable of binding the same mRNA sequences in the 3'UTR of human SDAD1 mRNA. 15879466_DAZL transcripts are present in the last stages of oocyte maturation, in embryoic cell stems, and throughout the preimplantation development. 16001084_DAZL activates translationally silent mRNAs during germ cell development through the direct recruitment of polyA-binding proteins. 16123080_The Thr54-->Ala polymorphism in exon 3 of DAZL has no major role in Japanese males with azoospermia or oligozoospermia. 16328470_SNPs in the DAZL gene may act jointly to affect common reproductive characteristics in the human population. 16573709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573709_study demonstrates the absence of the A386G (T54A) mutation in Indian subcontinent and two mutations A260G (T12A) and A437G (I71V) are polymorpic... these mutations in the DAZL gene are not associated with male infertility in Indian subcontinent 16730721_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16884537_Novel missense mutations of DAZL may be associated with age at menopause and/or sperm count and warrant further biochemical and genetic investigation. 17918711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18023443_Our results suggest that human amniotic fluid represents a new source for the isolation of human DAZL-, C-kit-, SSEA-4-, and Oct-4-positive stem cells without raising the ethical issues associated with human embryonic research. 18062861_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18088417_In ovarian extracts a marked increase in expression of DAZL mRNA and protein occurred in the 2nd trimester. 18178196_Follicle-stimulating hormone receptor and DAZL gene polymorphisms do not affect the age of menopause. 18178196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19327014_Results suggest that DAZL-expressing (DE)cells, which possess some pluripotent/multipotent characteristics of ES cells express OCT-4 and SOX-2 genes, can be easily isolated from blood. 19342699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19342699_expression of spermatogenic phenotypes of partial AZFc deletions is independent of the variations in DAZL and BOULE in the Han population 19865085_human DAZL (deleted in azoospermia-like) functions in primordial germ-cell formation, whereas closely related genes DAZ and BOULE (also called BOLL) promote later stages of meiosis and development of haploid gametes 19881148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20008336_Dazl contributes to the differentiation of embryonic stem cells into germ cells. 20462796_386A-->G was significantly correlated with sperm count (Pt was marginally correlated with sperm morphology. 20685756_These results suggest that incorrect epigenetic marks in germline gene DAZL may be correlated with male gametogenic defects. 22162380_overexpression of VASA and or DAZL, in both embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells promoted differentiation into primordial germ cells, and maturation and progression through meiosis was enhanced. 22329245_results showed no significant differences in the frequency of DAZL AG (P = 0.58) and MTHFR CT (P = 0.44) between oligozoospermic infertile men and controls 22752612_study identified the core promoter of the DAZL gene; also provided preliminary evidence for the role of a novel SNP of the DAZL gene promoter in spermatogenic failure 23678708_The A260G and A386G polymorphisms of the DAZL gene are not correlated with astheno-teratozoospermia-induced male infertility in the Han Chinese population. 24015185_Abnormal DNA methylation of the DAZL promoter might represent an epigenetic marker of male infertility. 24086306_demonstrate that Boll is also transiently expressed during oogenesis in the fetal mouse ovary, but is simultaneously co-expressed within the same germ cells as Dazl 24459810_Amniotic fluid-derived stem cells (AFSc) seem to express Nodal, Nanog and DAZL and it speculated that the regulation of self-renewal in AFSc could be similar as in human embryonic stem cells. 24717865_analysis of T12A and T54A polymorphisms role in the development of male infertility (Meta-Analysis) 25323654_Neither the A260G nor the A386G polymorphism of DAZL appeared to be involved in male infertility. 25491317_DAZL was not expressed either in normal cultures or lesions from cervixes with papillomavirus infections and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. 25994644_analysis demonstrated that SNP260 of DAZL did not contribute to oligo/azoospermia while SNP386 was correlated to male infertility 26989066_Data suggest that DAZL may be one such factor in human female fertility 27358391_hypermethylation of DAZL and BOULE promoters in human sperm is associated with human infertility 27768780_data can be used to further elucidate the role of NANOS3 and DAZL in germ cell development both in vitro and in vivo 28364521_Through the translational regulation of novel RNA targets SMC1B and TEX11, DAZL may have a key role in regulating chromosome cohesion and DNA recombination; two processes fundamental in determining oocyte quality and whose establishment in foetal life may support lifelong fertility. 28388287_computational analysis of free energy change due to this point mutation using GROMOS96 indicated decreased stability of the DAZL protein. The N109T variant in an infertile male population may provide a genetic marker for mutational analysis of DAZL 32682409_Suppressing Dazl modulates tumorigenicity and stemness in human glioblastoma cells. 33542261_The marker of alkyl DNA base damage, N7-methylguanine, is associated with semen quality in men. 34653405_Direct reprogramming of human Sertoli cells into male germline stem cells with the self-renewal and differentiation potentials via overexpressing DAZL/DAZ2/BOULE genes. 36273819_DAZL regulates proliferation of human primordial germ cells by direct binding to precursor miRNAs and enhances DICER processing activity. |
ENSMUSG00000010592 |
Dazl |
39.525674 |
9.8752011874 |
3.303810 |
0.489911210 |
44.069822 |
0.00000000003168686533257850113102062612708892039292685183227149536833167076110839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000170010226211871564570983068538677970144012974174074770417064428329467773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
72.9096531 |
22.7580895 |
7.3838742 |
1.8947863 |
| ENSG00000092421 |
57556 |
SEMA6A |
protein_coding |
Q9H2E6 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor for PLXNA2 that plays an important role in cell-cell signaling. Required for normal granule cell migration in the developing cerebellum. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and plays an important role in axon guidance in the developing central nervous system. Can act as repulsive axon guidance cue. Has repulsive action towards migrating granular neurons. May play a role in channeling sympathetic axons into the sympathetic chains and controlling the temporal sequence of sympathetic target innervation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35464}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for P.sordellii toxin TcsL in the in the vascular endothelium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32302524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32589945}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The transmembrane semaphorin SEMA6A is expressed in developing neural tissue and is required for proper development of the thalamocortical projection (Leighton et al., 2001 [PubMed 11242070]).[supplied by OMIM, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:57556; |
axon [GO:0030424]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; negative regulation of cell adhesion involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0106089]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903671]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900747]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001224]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526] |
16436660_Strong expression of SEMA6A is associated with langerhans cells of histiocytosis or dermatopathic lymphadenitis 17671748_NANOG-, SOX2-, and POU5F1 (OCT3/OCT4)-binding sites within intron 1 of the SEMA6A gene 18187809_findings suggest for SEMA6A a novel function in the cytoskeleton and a role in modulating tubulin isotype composition and microtubule dynamics 19578876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22184411_Data show that miR-27a/b regulated the expression of the angiogenesis inhibitor semaphorin 6A (SEMA6A) in vitro and in vivo and targeted the 3'-untranslated region of SEMA6A. 23740775_We identified the SEMA6A and HLA-DP loci as significant contributors to risk for granulomatosis with polyangiitis. 25576923_Data suggest that Sema6A and Mical1 may represent new potential therapeutic targets in BRAFV600E melanoma. 26014517_our findings indicated that SEMA6A may be a potential prognostic biomarker in the treatment of Glioblastoma multiforme 27787863_describes the experiments and methods enabling the characterization of Semaphorin 6A as a critical regulator of endothelial cell survival and vessel function 28982852_miR-203 induces the apoptosis of YD-38 human oral cancer cells by directly targeting SEMA6A. 31511512_RNA-guided epigenetic editing of Sema6a gene promoters via a dCas9-SunTag system with C11orf46 binding normalized SEMA6A expression and rescued transcallosal dysconnectivity via repressive chromatin remodeling by the SETDB1 repressor complex. 31527696_Semaphorin 6A Attenuates the Migration Capability of Lung Cancer Cells via the NRF2/HMOX1 Axis. 31687947_The A alleles of SEMA6A and POMP genes are likely the risk factors of disease development in Georgians 32302524_Genome-Wide CRISPR Screen Identifies Semaphorin 6A and 6B as Receptors for Paeniclostridium sordellii Toxin TcsL. |
ENSMUSG00000019647 |
Sema6a |
21.426011 |
0.2273506806 |
-2.137009 |
0.490500760 |
18.612158 |
0.00001601956053590245727447950729871450903374352492392063140869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000048994760362602625544063000839756227833277080208063125610351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5612854 |
2.5077224 |
33.5702743 |
7.3070336 |
| ENSG00000092529 |
825 |
CAPN3 |
protein_coding |
P20807 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-regulated non-lysosomal thiol-protease. Proteolytically cleaves CTBP1 at 'His-409'. Mediates, with UTP25, the proteasome-independent degradation of p53/TP53 (PubMed:23357851, PubMed:27657329). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23357851, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23707407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27657329}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Thiol protease |
|
Calpain, a heterodimer consisting of a large and a small subunit, is a major intracellular protease, although its function has not been well established. This gene encodes a muscle-specific member of the calpain large subunit family that specifically binds to titin. Mutations in this gene are associated with limb-girdle muscular dystrophies type 2A. Alternate promoters and alternative splicing result in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms and some variants are ubiquitously expressed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:825; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; myofibril [GO:0030016]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004198]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ligase regulator activity [GO:0055103]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; sodium ion binding [GO:0031402]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; titin binding [GO:0031432]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; calcium-dependent self proteolysis [GO:1990092]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to salt stress [GO:0071472]; G1 to G0 transition involved in cell differentiation [GO:0070315]; muscle cell cellular homeostasis [GO:0046716]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; muscle structure development [GO:0061061]; myofibril assembly [GO:0030239]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of protein sumoylation [GO:0033234]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045862]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; positive regulation of satellite cell activation involved in skeletal muscle regeneration [GO:0014718]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein destabilization [GO:0031648]; protein localization to membrane [GO:0072657]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045661]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to muscle activity [GO:0014850]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; self proteolysis [GO:0097264] |
12075569_reduced expression of calpain 3 was associated with phenotypes related to obesity and insulin resistance 12461690_effects of type of mutation, amount of calpain in the muscle, gender and ethnicity of affected patients on clinical course (age of onset and ascertainment) were analysed 12482600_reaction analysis of calpain p94 autolysis and domains 12882647_The enzyme is preferentially expressed in B- and T-lymphocytes, whereas it is poorly expressed in natural killer cells and almost undetectable in polymorphonuclear cells. 14981715_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14981715_The 550delA mutation was present on 76% of CAPN3 (calpain 3) chromosomes that led us to screen general population for this mutation 15073171_Insertion sequence 1 of p94 acts as internal autoinhibitory propeptide, blocking the active site of p94 from substrates and inhibitors. 15221789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15221789_Ten novel CAPN3 mutations found in concentrated in several exons in Muscular Dystrophies patients 15351423_This study found that three novel mutations of calpain 3 gene in limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A (LGMD2A, calpainopathy). 15689361_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15725583_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16107503_the time- and concentration-dependent changes in [Ca2+]i that occurred during concentric exercise fall near but below the level necessary to cause autolysis of calpains in vivo 16141003_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16290124_Efficient and stable CAPN3 transgene expression in mouse muscle restores enzyme proteolytic activity without evident toxicity in a calpain 3-deficient mouse model of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. 16533054_Thus, the proteolytic activity of the core of p94 and its deletion mutant lacking NS and IS1 was shown to be strictly Ca(2+)-dependent. We propose a two-stage model of activation of the proteolytic core of p94. 16627476_the importance of p94-connectin interaction in the control of p94 functions by regulating autolytic decay of p94 16934440_This review summarizes the known biochemical and physiological features of calpain 3 and the mechanisms of the mutations that result in disease. 16971480_Study provides evidence of the pathogenetic effect of specific CAPN3 gene mutations on protein function in limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A muscle and offers insights into the protein regions that are crucial for the autolytic activity of calpain-3. 17157502_CAPN3 mRNAs which contain frame-shift mutations are degraded by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in cells of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A patients 17318636_Three novel and six recurrent mutations are identified in Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. 17585039_amount of autolyzed calpain-3 unchanged immediately and 3 h after eccentric exercise but increased markedly 24 h after 17596655_CAPN3 mutations may have a role in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 17702496_The c.550delA mutation in CAPN3 was found in 8.1% of limb girdle muscular dystrophy and 1.9% of hyperCKemia patients. Two mutations (Val509Phe and Gln565Stop) have not been reported before. 17979987_nonsense-mediated messenger RNA decay as a mechanism for under-expression of CAPN3 associated to some specific variations 18073330_IkappaB alpha is expressed following NF-kappaB activation independent of the CAPN3 status, whereas expression of c-FLIP is obtained only when CAPN3 is present. 18258189_These results highlight the importance of conserved amino acids in domain IIb as well as in the p94-specific IS2 region. 18299526_A mutation analysis of the CAPN3 gene (Athena Diagnostics) was performed and revealed a C > T transition at nucleotide position 551 leading to a Thr184Met substitution, a known disease-causing mutation. 18310072_implicate the dynamic nature of connectin molecule as a regulatory scaffold of p94 functions 18334579_AHNAK accumulates when calpain 3 is defective in skeletal muscle of calpainopathy patients; moreover, AHNAK fragments cleaved by CAPN3 have lost their affinity for dysferlin. 18337726_CAPN3 mutation is associated with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A 18563459_CAPN3 alternative splicing isoforms in white blood cells in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2A 18676612_CAPN3 degraded AldoA; however, no accumulation of AldoA was observed in total extracts from CAPN3-deficient muscles suggesting that AldoA is not an in vivo substrate of CAPN3 18854869_Data show a high predictive value for reduced-absent calpain-3 or lost autolytic activity, and the biochemical assays are powerful tools for otherwise laborious genetic screening of cases with a high probability of being primary calpainopathy. 18974005_Data show that loss of function of the full-length isoform of CAPN3, also known as p94, as the pathogenic isoform can explain the 'progressive' development of muscular dystrophy. 19048948_Finding its mutation is useful for genetic diagnosis of type2 limb-gardle muscular dystrophies. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19386580_calpain 3 variants can play a proapoptotic role in melanoma cells and its downregulation, as observed in highly aggressive lesions, could contribute to melanoma progression. 19556129_Immunohistochemistry with Calp3-2C4 has a similar pickup rate of LGMD2A as immunoblot and it may therefore be useful for distinguishing the majority of genuine CAPN3 defects from secondary protein reduction. 20139084_calpain 3 participates in the establishment of the pool of reserve cells by decreasing the transcriptional activity of the key myogenic regulator MyoD via proteolysis independently of the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway. 20477750_Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy patients carried a new splicing site mutation (c.1536+1G>T) in the CAPN3 gene, which leads to complete retention of intron 12 of the CAPN3 gene and total calpain3 deficiency. 20517216_The major c.550delA mutation in the CAPN3 gene was identified in 70% of Russian patients. 20533264_The findings suggest that mutation analysis of the CAPN3 cDNA should use skeletal muscle tissue as materials instead of peripheral blood. 20634290_Interactions with M-band titin and calpain 3 link myospryn (CMYA5) to tibial and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies. 20635405_5 different intronic variants (one novel) in CAPN3 that bioinformatic tools predicted would affect RNA splicing, underwent comprehensive studies which were designed to prove they are disease-causing. 20860623_CARP and its regulator calpain 3 appear to occupy a central position in the important cell fate-governing NF-kappaB pathway in skeletal muscle 21172462_Data show that direct sequencing of CAPN3, encoding calpain-3, identified a homozygous deletion c.483delG (p.Ile162SerfsX17). 21204801_The findings further confirm mutations in CAPN3 as a genetic cause of eosinophilic myositis and highlight eosinophilic infiltration as an early component (or event) of primary calpainopathy. 21386772_A homozygous transversion mutation in the CAPN3 gene confirms limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. 21836041_In resting human skeletal muscle, the majority (87%) of calpain-3 was present in myofibrillar fractions. 21984748_In our series of patients, six out of the 13 patients (P9-P14) carried mutations in genes not related to facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, that is, CAPN3 and VCP 22006685_The benign phenotype observed in association with combined pG222R and pR748Q mutations suggests that limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A may result from a compensatory effect of compound heterozygosity rather than the LGMD2A mutations themselves. 22158424_This is the first report on a potential pathogenic CAPN3 gene mutation resulting from an Alu insertion. 22443334_Evidence from patients with limb girdle muscular dystrophies suggests that calpain 3 is needed for the regenerative process. 22486197_An intronic mutation in CAPN3 causes severe Limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2A in a large inbred family belonging to a genetic isolate in the Italian Alps. 22505582_The decrease in CaMKII signaling in the absence of CAPN3 is associated with a reduction of muscle adaptation response. 22926650_All 18 mutations of Chinese LGMD2A patients are distributed along the entire CAPN3 gene; 11 of the mutations are novel, including 4 missense mutations, 5 deletions, and 2 splicing mutations. 22975586_Alterations in CAPN3 and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling contribute to muscle mass loss in congenital muscular dystrophy. 23414389_In LGMD2A muscles the activation of the atrophy programme appeared to depend mainly upon induction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system 23666804_Researchers identified 2 founder mutations in CAPN3, a missense (c.2338G>C; p.D780H) and a splice-site (c.2099-1G>T) mutation, on 2 different haplotype backgrounds in unrelated limb-girdle muscular dystrophy in the Indian Agarwal community. 23707407_Authors found that PLEIAD also interacts with CTBP1 (C-terminal binding protein 1), a transcriptional co-regulator, and CTBP1 is proteolyzed in COS7 cells expressing CAPN3. 23821418_Lobulated fibers were often encountered in the muscle biopsies of LGMD2A patients. Such fibers were more frequent in patients with 550delA mutation 23908349_Suppression of transgenic CAPN3 expression in cardiac tissue prevents cardiac toxicity in a model of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. 24126726_The results indicate that PDGF-C upregulation and calpain-3 downregulation are involved in the aggressiveness of malignant melanoma and suggest that modulators of these proteins 24715573_a heterozygous deletion of the entire CAPN3 gene was found in a patients with Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A 25252031_Phosphorylated CAPN3 is involved in the pathology of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A through defects in myofibril integrity and/or signaling pathways. 25512505_results provide evidence that WT CAPN3 can be formed by the iMOC of two different complementary CAPN3 mutants 25658320_Calpain-3 over-expression induces p53 activation and redox imbalance in melanoma A375 cells. 25877298_Cleavage of C-terminal titin by CAPN3 is associated with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2A and tibial muscular dystrophy. 26363099_Studies indicate that gene mutations causing muscle-specific calcium-activated neutral protease 3 protein (CAPN3) defects are responsible for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A (LGMD2A). 26484845_We analyzed 76 families affected with LGMD and identified 62 probands with mutations in the CANP3 gene. C.550delA was the most common mutation identified, being found in 78% of the LGMD2A families 26632398_We identified four novel CAPN3 mutations and demonstrated clinical and pathological heterogeneity in Korean patients with calpainopathy. 27020652_Genetic analysis of CAPN3 gene by whole exome sequencing revealed five causative variants which had not been reported in the Iranian population before including a novel 6 bp deletion (c.795_800delCATTGA) and four previously reported mutations (c.1939G > T, c.2243G > A, c.2257delGinsAA, and c.2380 + 2T > G) 27055500_CAPN3 deficiency leads to degradation of SERCA proteins and Ca2+ dysregulation in the skeletal muscle. 27142102_The allele frequency of CAPN3 gene mutation in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy patients was different in patients from Latvia and Lithuania. 27259757_Heterozygosity for c.643_663del21 in CAPN3 results in a myopathy resembling the recessive form. 27262448_Unrelated families with limb girdle muscular dystrophy shared common haplotypes with homozygote patterns in two families, and a compound heterozygote pattern in the third family. 27861222_Here, for the first time, we report a new variant in the CAPN3 gene that can be considered as a robust genetics factor causing limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A disease. 28103310_This study demonstrates that a cluster of patients with Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Type 2A in a small Mexican village arises from a novel CAPN3 founder mutation. 28332615_We conclude that integrative variants, haplotypes and diplotypes of the CAPN3 rs4344713 and FRMD5 rs524908, as well as DBP and BMI are associated with serum lipid variables in the Jing and Han populations. 28881388_This study provides further evidence for autosomal dominant calpainopathy associated with CAPN3 c.643_663del21. 30500922_Two novel homozygous mutations, c.2242C>G (p.Arg748Gly) and c.291C>A (p.Phe97Leu) were identified in 2 patients with Limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A 31540302_Studies provide evidence for a role of CAPN3 mutations in calcium homeostasis in patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy recessive [review] 31612648_NOVEL intronic CAPN3 Roma mutation alters splicing causing RNA mediated decay. 31788660_Almost all Serbian patients with calpainopathy had c.550delA mutation. In most of the patients, disease started in the childhood or early adulthood. The disease affected both shoulder girdle - upper arm and pelvic girdle - thigh muscles with similar frequency, although muscles of lower limbs are more severely impaired. None had cardiomyopathy, 21% mild conduction defects. Respiratory function impaired 21%. 32200007_Calpain-3 (CAPN3), a 94-kDa member of the calpain protease family, is abundant in skeletal muscle. Mutations in the CAPN3 gene cause limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, indicating that CAPN3 plays important roles in muscle physiology. 32342993_Novel CAPN3 variant associated with an autosomal dominant calpainopathy. 32448375_Frizzled related protein deficiency impairs muscle strength, gait and calpain 3 levels. 32668095_Splicing impact of deep exonic missense variants in CAPN3 explored systematically by minigene functional assay. 32896923_Heterozygous CAPN3 missense variants causing autosomal-dominant calpainopathy in seven unrelated families. 32994280_Molecular landscape of CAPN3 mutations in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type R1: from a Chinese multicentre analysis to a worldwide perspective. 33337384_Mutational Spectrum of CAPN3 with Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Type 2A/R1 (LGMD2A/LGMDR1) Patients in India. 33427631_[Calpainopathies: state of the art and therapeutic perspectives].', trans 'Calpainopathies - Etat des lieux et perspectives therapeutiques. 34355366_Clinical and genetic features of Calpainopathies in Saudi Arabia - a descriptive cross-sectional study. 34697879_A recurrent rare intronic variant in CAPN3 alters mRNA splicing and causes autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy-1 in three Pakistani pedigrees. 35731190_CAPN3 c.1746-20C>G variant is hypomorphic for LGMD R1 calpain 3-related. 35878425_An 86 amino acids motif in CAPN3 is essential for formation of the nucleolus-localized Def-CAPN3 complex. |
ENSMUSG00000079110 |
Capn3 |
238.761790 |
0.1331859191 |
-2.908487 |
0.279582249 |
98.047577 |
0.00000000000000000000004084501942426359105334009199646665178073126937494638494456335392826518138065239327261224389076232910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000405156241063259851357107563341551513618424121981610808035660815928924449735859525389969348907470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.6606140 |
11.7965043 |
443.5098606 |
60.7435308 |
| ENSG00000092607 |
6913 |
TBX15 |
protein_coding |
Q96SF7 |
FUNCTION: Probable transcriptional regulator involved in the development of the skeleton of the limb, vertebral column and head. Acts by controlling the number of mesenchymal precursor cells and chondrocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene belongs to the T-box family of genes, which encode a phylogenetically conserved family of transcription factors that regulate a variety of developmental processes. All these genes contain a common T-box DNA-binding domain. Mutations in this gene are associated with Cousin syndrome.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:6913; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; RNA polymerase II transcription repressor complex [GO:0090571]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell fate specification [GO:0001708]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19068278_TBX15 mutations cause craniofacial dysmorphism, hypoplasia of scapula and pelvis, and short stature in Cousin syndrome. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20935629_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20962579_TBX15 might be involved in the pathophysiology of placental diseases. 23670221_Genes within recently identified loci associated with waist-hip ratio (WHR) exhibit fat depot-specific mRNA expression, which correlates with obesity-related traits. Adipose tissue (AT) mRNA expression of 6 genes (TBX15/WARS2, STAB1, PIGC, ZNRF3, GRB14 24039145_We identified homozygosity for a novel nonsense mutation (c.841C>T) in TBX15 predicted to cause a premature stop (p.Arg281*) with truncation of the protein. 26105758_Two traits of ear pinna anatomic variation are associated with SNPs in a region overlapping the TBX15 gene. 26216026_The results indicate the antiapoptotic role of TBX15 in cancer cells, suggesting a contribution of TBX15 in carcinogenesis. 27327083_TBX15 and NF-kappaB found in this study may be important to understand cancer and development processes. 28007980_first genome-wide scan for selection in Inuit from Greenland. A region, with a deeply divergent haplotype that is closely related to the sequence in the Denisovan genome contains two genes, WARS2 and TBX15. our study suggests a complex multi-factorial regulation of TBX15 and WARS2. We show that the introgressed region is associated with regional changes in methylation and expression levels 28847884_These studies showed that Tbx15 differentially regulates oxidative and glycolytic metabolism within subpopulations of white adipocytes and preadipocytes. 31975641_Osteoporosis- and obesity-risk interrelationships: an epigenetic analysis of GWAS-derived SNPs at the developmental gene TBX15. 33453148_CircPVT1 promotes progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by sponging miR-145-5p and regulating TBX15 expression. 33622874_TBX15 rs98422, DNM3 rs1011731, RAD51B rs8017304, and rs2588809 Gene Polymorphisms and Associations With Pituitary Adenoma. 34340684_Identification of TBX15 as an adipose master trans regulator of abdominal obesity genes. 35090585_Harnessing tissue-specific genetic variation to dissect putative causal pathways between body mass index and cardiometabolic phenotypes. |
ENSMUSG00000027868 |
Tbx15 |
30.355751 |
2.0171956058 |
1.012351 |
0.297385193 |
11.739050 |
0.00061202246235416758214642474200672950246371328830718994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001480893695794674317159356213835508242482319474220275878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.9265454 |
7.5369869 |
20.4427441 |
2.9912135 |
| ENSG00000092621 |
26227 |
PHGDH |
protein_coding |
O43175 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible oxidation of 3-phospho-D-glycerate to 3-phosphonooxypyruvate, the first step of the phosphorylated L-serine biosynthesis pathway. Also catalyzes the reversible oxidation of 2-hydroxyglutarate to 2-oxoglutarate and the reversible oxidation of (S)-malate to oxaloacetate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25406093}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine biosynthesis;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-serine biosynthesis; L-serine from 3-phospho-D-glycerate: step 1/3. |
This gene encodes the enzyme which is involved in the early steps of L-serine synthesis in animal cells. L-serine is required for D-serine and other amino acid synthesis. The enzyme requires NAD/NADH as a cofactor and forms homotetramers for activity. Mutations in this gene have been found in a family with congenital microcephaly, psychomotor retardation and other symptoms. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found, however the full-length nature of most are not known. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:26227; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; L-malate dehydrogenase activity [GO:0030060]; NAD binding [GO:0051287]; phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004617]; brain development [GO:0007420]; G1 to G0 transition [GO:0070314]; gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolic process [GO:0009448]; glial cell development [GO:0021782]; glutamine metabolic process [GO:0006541]; glycine metabolic process [GO:0006544]; L-serine biosynthetic process [GO:0006564]; neural tube development [GO:0021915]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510]; taurine metabolic process [GO:0019530]; threonine metabolic process [GO:0006566] |
11751922_we conclude that this mutation impairs the folding and/or assembly of PHGDH but has minimal effects on the activity or stability of that portion of the V490M mutant that reaches a mature conformation 18627175_The crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase has been solved with bound effector, 1-serine, and substrate, hydroxypyruvic acid phosphate. The human enzyme was also examined. 19223009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19235232_These data suggest that missense mutations associated with 3-PGDH deficiency either primarily affect substrate binding or result in very low residual enzymatic activity. 19388702_Studies in bacteria showed that addition of substrate at the active site is ordered, with HPAP binding before NADH. Also, NADH can compete with the substrate for binding to the allosteric site and thereby eliminate the substrate inhibition. 19404161_a coding PHGDH SNP (rs543703) was weakly associated with the development of schizophrenia in Korean population 19497206_The frequency of antibodies to Phgdh is much higher in patients with autoimmune hepatitis than in patients with other types of hepatitis or normal controls. 19778996_PHGDH is expressed in cytoplasm of stromal and glandular cells in endometrium; expression is relatively high in proliferative phase and lower in secretory phase. Data suggest expression of PHGDH in endometrium is regulated by HOXA10. 21760589_results reveal that certain breast cancers are dependent upon increased serine pathway flux caused by PHGDH overexpression and demonstrate the utility of in vivo negative-selection RNAi screens for finding potential anticancer targets 21804546_in some cancer cells a relatively large amount of glycolytic carbon is diverted into serine and glycine metabolism through phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. 21981974_The potential mechanisms by which PHGDH promotes cancer are discussed. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 24247658_PHGDH overexpression is found in cervical cancer, in particular, in bigger tumors and with advanced stages. Its expression is positively correlated with squamous cell carcinoma antigen level 24836451_We report on the identification of homozygous mutations in PHGDH and serine deficiency in individuals with Neu-Laxova syndrome. This disorder thus seems to be an extremely severe expression of PHGDH deficiency. 25152457_Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase deficiency is associated with Neu-Laxova syndrome. 25404730_p53-mediated repression of PHGDH enhances the apoptotic response upon serine starvation in melanoma cells. 26026368_Overexpression of Phgdh may be generally associated with CK5 cells, and oncogenic function may be determined by isoform expression. 26439504_High expression of PHGDH is associated with Colon Cancer. 27836973_High PHGDH expression is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 28135894_This report present 6 individuals from 3 unrelated families with infantile serine biosynthesis defect due to PGDH deficiency. 28614715_Study provides evidence that a unique metabolic program is activated in a lung adenocarcinoma subset, described by PHGDH, which confers cell growth. 28698143_Therefore, we show for the first time that the nuclear localization of Cat L and its substrate Cux1can be positively regulated by Snail NLS and importin beta1, suggesting that Snail, Cat L and Cux1 all utilize importin beta1 for nuclear import. 28894120_These findings highlight the role of epigenetic regulation of the PHGDH gene in triglyceride metabolism, providing novel insights on putative intervention targets. 28951458_Data show there was a significant negative correlation between PHGDH copy-number alteration and EPAS1 (HIF2A) expression. 29128633_Data indicate that the expression of PHGDH is increased in pancreatic cancer and is an independent molecular prognostic factor for pancreatic cancer patients. In addition, PHGDH controls cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities. 29626321_PHGDH expression is regulated by PlncRNA-1 in breast cancer. 30157431_Authors find that PHGDH(high) breast cancer cell lines are exquisitely sensitive to inhibition of the NAD(+) salvage pathway. Further, authors find that PHGDH protein levels and those of the rate-limiting enzyme of NAD(+) salvage, NAMPT, correlate in ER-negative, basal-like breast cancers. 30250195_this study identifies a clinically-relevant role for PHGDH in the regulation of stemness-differentiation axis within cancer stem-like cells . 30575741_major fluxes affected upon PHGDH inhibition that alter nucleotide metabolism are related to central carbon metabolism, and not the serine synthesis pathway 30744688_Besides catalyzing serine synthesis, PHGDH promotes pancreatic cancer development through enhancing the translation initiations by interacting with eIF4A1 and eIF4E. 30905671_Increased Serine Synthesis Provides an Advantage for Tumors Arising in Tissues Where Serine Levels Are Limiting. 31331318_These data suggest increased PHGDH expression impacts normal melanocyte biology, but PHGDH expression alone is not sufficient to cause cancer. 31615983_phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), the first committed enzyme in the serine synthesis pathway (SSP), is a critical driver for Sorafenib (and other tyrosine kinase inhibitors ) resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31678070_Reduced Phgdh expression and serine levels are closely associated with the development of Fatty Liver Disease. 31903955_This study is the first description of PHGDH and PSAT1 mutations in Chinese Neu-Laxova syndrome patients, which strongly implicates them in the pathogenesis of Neu-Laxova syndrome. 32196970_Clinical, molecular, and pathological findings in a Neu-Laxova syndrome stillborn: A Brazilian case report. 32203214_Serine-dependent redox homeostasis regulates glioblastoma cell survival. 32386122_Characterization of PHGDH expression in bladder cancer: potential targeting therapy with gemcitabine/cisplatin and the contribution of promoter DNA hypomethylation. 32438862_High Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Expression Induces Stemness and Aggressiveness in Thyroid Cancer. 32478681_Parkin ubiquitinates phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase to suppress serine synthesis and tumor progression. 32579715_Expanding the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of severe serine biosynthesis disorders. 32664979_Down regulating PHGDH affects the lactate production of sertoli cells in varicocele. 33340488_In Vivo Evidence for Serine Biosynthesis-Defined Sensitivity of Lung Metastasis, but Not of Primary Breast Tumors, to mTORC1 Inhibition. 33625616_Prognostic significance of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase in breast cancer. 33753166_Dimerization of PHGDH via the catalytic unit is essential for its enzymatic function. 33758422_Serine biosynthesis defect due to haploinsufficiency of PHGDH causes retinal disease. 34720086_Cul4A-DDB1-mediated monoubiquitination of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via increased S-adenosylmethionine. 34971423_Biophysical and biochemical properties of PHGDH revealed by studies on PHGDH inhibitors. 35508105_PHGDH expression increases with progression of Alzheimer's disease pathology and symptoms. 36147463_PHGDH Inhibits Ferroptosis and Promotes Malignant Progression by Upregulating SLC7A11 in Bladder Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000053398 |
Phgdh |
66.883368 |
3.6671031536 |
1.874641 |
0.325946381 |
31.850938 |
0.00000001664692997485248279585706764147762237726624334754887968301773071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000070850255602313337532770925759201263716136054426897317171096801757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
101.0949697 |
19.8837985 |
27.5630594 |
4.1971311 |
| ENSG00000092929 |
201294 |
UNC13D |
protein_coding |
Q70J99 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in cytotoxic granule exocytosis in lymphocytes. Required for both granule maturation and granule docking and priming at the immunologic synapse. Regulates assembly of recycling and late endosomal structures, leading to the formation of an endosomal exocytic compartment that fuses with perforin-containing granules at the immunologic synapse and licences them for exocytosis. Regulates Ca(2+)-dependent secretory lysosome exocytosis in mast cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15548590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17237785}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Exocytosis;Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis;Lysosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the UNC13 family, containing similar domain structure as other family members but lacking an N-terminal phorbol ester-binding C1 domain present in other Munc13 proteins. The protein appears to play a role in vesicle maturation during exocytosis and is involved in regulation of cytolytic granules secretion. Mutations in this gene are associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3, a genetically heterogeneous, rare autosomal recessive disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:201294; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; secretory vesicle [GO:0099503]; Weibel-Palade body [GO:0033093]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; germinal center formation [GO:0002467]; granuloma formation [GO:0002432]; natural killer cell degranulation [GO:0043320]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway [GO:1903307]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043304]; secretion [GO:0046903] |
14622600_HMunc13-4 mutations were shown to cause familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; HMunc13-4 is essential for the priming step of cytolytic granules secretion preceding vesicle membrane fusion. 14699162_Rab27 regulates the dense core granule secretion in platelets by employing its binding protein, Munc13-4 15466010_MUNC13-4 mutations play a role in the development of familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis subtype 3 through a defective cytotoxic pathway 16278825_A large group of 63 unrelated patients with Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) was analysed for mutations in STX11, PRF1, and UNC13D. 16630545_These observations decisively prove that Rab27a inhibits ENaC function through a complex mechanism that involves GTP/GDP status, and protein-protein interactions involving Munc13-4 and SLP-5 effector proteins. 16778144_CD107a surface expression has a role in Munc13-4 defect in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 16825436_12 novel and 4 known Munc13-4 mutations spread throughout the gene were found in haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis patients. 17993578_Biallelic UNC13D mutations were found in 18% of the PRF1/STX11-negative familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis families. 18240215_girl with systemic juvenile arthritis without macrophage activation syndrome was found to have compound heterozygous mutations of UNC13D and reduced NK cell cytotoxic function 18311812_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18311812_The genes PRF1, GZMB, UNC13D, and Rab27a involved in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis do not confer a significant risk of association with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 18432499_Fatal sibling cases of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) with MUNC13-4 mutations 18453599_a role for Munc13-4 as a component of the secretory machinery in neutrophils. 18492689_UNC13D mutations leading to splicing errors represent the majority of mutations observed in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 18710388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18759271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18759271_The data suggest an association between MUNC13-4 polymorphisms and macrophage activation syndrome in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 19120489_mutated in type III hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, a severe inflammatory disease of infectious etiology with fatal outcome 19131769_UNC13D mutations are associated with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 19704116_Rab27a or Munc13-4 recruitment to lytic granules is preferentially regulated by different receptor signals, demonstrating that individual target cell ligands regulate discrete molecular events for lytic granule maturation. 20015888_rRecurrent splicing mutations in UNC13D gene is associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 20823128_Data show that all but one patient with atypical familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis carried at least one splice-site mutation in UNC13D or STXBP2. 21370424_Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with MUNC13-4 gene mutation or reduced natural killer cell function prior to onset of childhood leukemia. 21646258_study reports recurrent fetal hydrops caused by familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with Munc13-4 mutation 21674762_Seven novel mutations in PRF1, UNC13D, and XIAP were identified in Chinese EBV-HLH patients. Only a fraction of Chinese children with EBV-HLH have genetic defects in PRF1, UNC13D, and XIAP. 21693760_Data show that point mutations in the binding motif of munc13-4 have severely impaired rab27a binding, allowing dissection of rab27a requirements in munc13-4 function. 21755595_novel Dutch founder mutation leads to severe early onset of FHL3 due to misfolding and degradation of munc13-4(1-899). 21881043_Missense and splice-site sequence variants in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 were found in 25 (14%) of the adult patients. The A91V-PRF1 genotype was found in 12 of these patients (48%). 21931115_Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3 (FHL3) caused by deep intronic mutation and inversion in UNC13D. 22271450_Data indicate that Munc13-4 reinternalization is required for the maintenance of an intracellular pool that is functional to guarantee the serial killing potential. 22508512_study reports that Munc13-4 bound Ca(2 ) and restored Ca(2 )-dependent granule exocytosis to permeable cells (platelets, mast, and neuroendocrine cells) dependent on putative Ca(2 )-binding residues in C2A and C2B. 23180437_The deep intronic mutation UNC13D:c.118-308C>T accounts for the majority of previously missing mutations and is the most frequent mutation in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3 in Korea. 23672263_Novel deep intronic and missense UNC13D mutations are reported in familial haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 3. 23810987_Defects in cargo trafficking caused by mutations in RAB27A and UNC13D genes, encoding Rab27a and its effector Munc13-4, cause severe immunodeficiencies in humans. (Review) 23840885_These data suggest that rare loss-of-function variations of UND13D are risk factors for autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome development. 23924873_this is the first report of HLH in association with EVC syndrome, and the IVS13+5G>A mutation that we believe is causative of EVC in our patient is also unreported. 24043286_This patient the patient carried mutations in FAS, XIAP, and UNC13D genes inherited from his mother who had rheumatoid arthritis; UNC13D is involved in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 24470399_The prevalence of a 253-kb inversion and two deep intronic mutations, c.118-308C > T and c.118-307G > A, in UNC13D was determined in 1709 North American patients with type 3 hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 8 new mutations were also found. 24842371_Data indicate that Munc13-4 is highly expressed in differentiated NK cells and effector CD8(+) T lymphocytes. 25312756_These studies highlight the need for RAB27A sequencing in patients with FHL with normal pigmentation and identify a critical binding site for Munc13-4 on Rab27a, revealing the molecular basis of this interaction. 25573973_These data support an important role for Munc13-4 in human platelet degranulation 25980904_Synergistic defects of UNC13D and AP3B1 leading to adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 26377049_A newly defined mutation in the UNC13D (c.175G>C; p.Ala59Pro) was found in an asymptomatic heterozygote father and his homozygous daughter who had hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 26637270_Munc13-4 conveys Ca(2+) sensitivity to platelet SNARE-mediated membrane fusion and reveal a potential mechanism by which Munc13-4 bridges and stabilizes apposing membranes destined for fusion. 26637356_Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest Munc13-4 binds to Rab11 and regulates trafficking of Rab11-containing vesicles; Munc13-4 appears to regulate final steps of Rab11-positive vesicle docking at plasma membrane in exocytosis. 26959483_analysis of sudden infant death syndrome brains shows downregulation of MyD88 in tissue from SIDS brains, as well as the downregulation of the genes encoding CCL3 and UNC13 in the liver 27016801_A novel Rab27a mutation binds melanophilin, but not Munc13-4, causing immunodeficiency without albinism. 27799161_Gene-corrected human Munc13-4-deficient CD8+ T cells can efficiently restrict EBV-driven lymphoproliferation in immunodeficient mice 28450451_Findings indicate that Munc13-4 supports acute WPB exocytosis by tethering WPBs to the plasma membrane via AnxA2-S100A10. 29549174_the results presented herein show that the munc13-4 protein expression assay is a reliable tool for FHL3 screening. 29665027_The present study describes a distinct variant spectrum in Chinese patients with Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), whereby UNC13D is the most frequently mutated gene with missense variants that are the most common molecular defects. The variant profile of Chinese HLH patients is quite different from that of Western cohorts but similar to that of Korean patients, yet showing its own uniqueness 29767240_The results of the present study indicate that Munc132 may be an essential regulator of basal MUC5AC exocytosis, while Munc134 appears to be a Munc13 protein subtype that may to be sensitive to hNE stimulation during airway MUC5AC hypersecretion. 29783935_Compound heterozygosity in the UNC13D gene was identified in trans and considered a causative mutation in a female patient with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). The nonsense mutation (NM_199242.2:c.2206C > T, p.Gln736X) was novel in cases of HLH. This mutation along with the splicing mutation (NM_199242.2:c.2709 + 1G > A) were inherited from the parents. 29930202_Depletion of Munc13-4 in highly aggressive breast carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells reduced the size of CD63(+) multivesicular bodies (MVBs), indicating a role for Munc13-4 in MVB maturation. 30758854_Results indicate that haploinsufficiency of UNC13D required for lymphocyte cytotoxicity can predispose patients to lymphoma, suggesting the importance of cytotoxic lymphocyte-mediated surveillance of cancer. 30892133_Cross-regulation of defective endolysosome trafficking and enhanced autophagy through TFEB in UNC13D deficiency. 31171812_Defective Zn(2+) homeostasis in mouse and human platelets with alpha- and delta-storage pool diseases. 31651726_Different Clinical Presentation of 3 Children With Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With 2 Novel Mutations. 32245292_Five mutations were detected in UNC13D. 32253931_Lentiviral Gene Therapy for Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Type 3, Caused by UNC13D Genetic Defects. 32582217_Alternative UNC13D Promoter Encodes a Functional Munc13-4 Isoform Predominantly Expressed in Lymphocytes and Platelets. 33093239_Unc-13 homolog D mediates an antiviral effect of the chromosome 19 microRNA cluster miR-517a. 33867526_Germline variants in UNC13D and AP3B1 are enriched in COVID-19 patients experiencing severe cytokine storms. 34339548_Spectrum mutations of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 genes in Vietnamese patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 35293882_Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With Heterozygous STX11 and Homozygous UNC13D Mutations Diagnosed in the Neonatal Period. |
ENSMUSG00000057948 |
Unc13d |
267.994672 |
0.3986902224 |
-1.326660 |
0.128613852 |
104.757359 |
0.00000000000000000000000138046419584665584642954353466308153468198373109568248938162351655001280903434235369786620140075683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000014627172670995434643122233802402968103036033799057191986996368307516469542406412074342370033264160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
152.5074390 |
34.3671486 |
385.4563584 |
62.6858521 |
| ENSG00000092969 |
7042 |
TGFB2 |
protein_coding |
P61812 |
FUNCTION: [Transforming growth factor beta-2 proprotein]: Precursor of the Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-beta-2) chains, which constitute the regulatory and active subunit of TGF-beta-2, respectively. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202}.; FUNCTION: [Latency-associated peptide]: Required to maintain the Transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-beta-2) chain in a latent state during storage in extracellular matrix (By similarity). Associates non-covalently with TGF-beta-2 and regulates its activation via interaction with 'milieu molecules', such as LTBP1 and LRRC32/GARP, that control activation of TGF-beta-2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202}.; FUNCTION: [Transforming growth factor beta-2]: Multifunctional protein that regulates various processes such as angiogenesis and heart development (PubMed:22772371, PubMed:22772368). Activation into mature form follows different steps: following cleavage of the proprotein in the Golgi apparatus, Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-2 (TGF-beta-2) chains remain non-covalently linked rendering TGF-beta-2 inactive during storage in extracellular matrix (By similarity). At the same time, LAP chain interacts with 'milieu molecules', such as LTBP1 and LRRC32/GARP, that control activation of TGF-beta-2 and maintain it in a latent state during storage in extracellular milieus (By similarity). Once activated following release of LAP, TGF-beta-2 acts by binding to TGF-beta receptors (TGFBR1 and TGFBR2), which transduce signal (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22772368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22772371}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aortic aneurysm;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate a latency-associated peptide (LAP) and a mature peptide, and is found in either a latent form composed of a mature peptide homodimer, a LAP homodimer, and a latent TGF-beta binding protein, or in an active form consisting solely of the mature peptide homodimer. The mature peptide may also form heterodimers with other TGF-beta family members. Disruption of the TGF-beta/SMAD pathway has been implicated in a variety of human cancers. A chromosomal translocation that includes this gene is associated with Peters' anomaly, a congenital defect of the anterior chamber of the eye. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Loeys-Dietz syndrome. This gene encodes multiple isoforms that may undergo similar proteolytic processing. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:7042; |
axon [GO:0030424]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; transforming growth factor beta complex [GO:0099126]; transforming growth factor beta ligand-receptor complex [GO:0070021]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005160]; type II transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005114]; type III transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034714]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; ascending aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035910]; atrial septum morphogenesis [GO:0060413]; atrial septum primum morphogenesis [GO:0003289]; atrioventricular valve morphogenesis [GO:0003181]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0060317]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003215]; cardioblast differentiation [GO:0010002]; cell death [GO:0008219]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; cranial skeletal system development [GO:1904888]; dopamine biosynthetic process [GO:0042416]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; embryonic digestive tract development [GO:0048566]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; endocardial cushion fusion [GO:0003274]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; eye development [GO:0001654]; generation of neurons [GO:0048699]; glial cell migration [GO:0008347]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; heart valve morphogenesis [GO:0003179]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; membranous septum morphogenesis [GO:0003149]; negative regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity [GO:0010693]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:1905006]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; neural retina development [GO:0003407]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; positive regulation of cardioblast differentiation [GO:0051891]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:1905007]; positive regulation of heart contraction [GO:0045823]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of integrin biosynthetic process [GO:0045726]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of ossification [GO:0045778]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032874]; positive regulation of timing of catagen [GO:0051795]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of apoptotic process involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:1902256]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of timing of catagen [GO:0051794]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta2 production [GO:0032909]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; salivary gland morphogenesis [GO:0007435]; secondary palate development [GO:0062009]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; somatic stem cell division [GO:0048103]; substantia propria of cornea development [GO:1903701]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; uterine wall breakdown [GO:0042704]; uterus development [GO:0060065]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11716069_TGFB2 induces MMP-2 expression and suppresses TIMP-2 expression. It promotes invasion of cultured glioma cells in a dose-dependent way. 11795478_The main source of myofibroblast-like cells and ECM production in the liver is the perisinusoidal stellate cell, which responds to injury with a pleiotypic change termed activation. Activation is orchestrated by cytokines, like tgfb2 11895345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11991670_no correlation between the concentration of either isoform of TGFbeta in milk and the corresponding TGFbeta in plasma 12011061_a transcriptional target for Akt/protein kinase B via forkhead transcription factor. 12021923_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 isoforms are produced by chondrosarcomas and could have a potential role as autocrine growth stimulators in these neoplasms 12060054_present in diabetic foot ulcer 12060393_Involvement of transforming growth factor-beta2 in catagen induction during the human hair cycle. 12064833_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12420205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12489185_investigated TGF-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 latency-associated peptides (LAP)expression in sound and carious human teeth 12545247_Immunohistochemical double-staining of human renal sections revealed that most Tgfb2-positive cells in control glomeruli were podocytes with few Tgfb2-positive mesangial cells. 12607775_TGF-beta2 expression in peritoneal fibroblasts was increased by hypoxia plus TGF-beta1, but decreased by TGF-beta1 alone. 12772773_Glucocorticoids significantly inhibited TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 production and reduced expression of the up-regulated TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 mRNA induced by exogenous TGF-beta1, -beta2, or -beta3 12802400_Data report the location and level of interleukin (IL)-8 and TGF-beta2 expression in the fimbrial compartment of fallopian tubes and IL-10 expression in the endometrium of women with pyoinflammatory adnexal diseases. 12911534_All three TGF-beta isoforms have fibrogenic effects on renal cells. TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 effects may be partially mediated by TGF-beta1. Blockade of all isoforms together may yield best therapeutic effect in reducing renal fibrosis. 14507446_Biological dressing effect of cultured epidermal sheets(CESs) is mediated by EGF family, TGF-beta, and VEGF. 14510802_In the confluent state, TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 stimulated the cells to progress to the S-phase of the cell cycle through platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) chain production and protein kinase C. 15009106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15113633_increase of serum immunoglobulin A in newborns during 1 month of life was well correlated with levels of both transforming growth factor-beta1 and transforming growth factor-beta2 15290353_Repression of promoter activity by HPV type 16 E6 and E7 proteins. 15389580_PSA-mediated activation of latent TGFbeta2 may be an important mechanism for autocrine TGFbeta regulation in the prostate and may potentially contribute to the formation of osteoblastic lesions in bone metastatic prostate cancer. 15695166_Recombinant TGF-beta 2 passes through the mouse blood-brain barrier after peripheral injection and is widely distributed throughout the brain, with highest concentrations in the hypothalamus and nerves and lowest in the cerebral hemispheres. 15816823_upregulation of the potent catagen inducer, transforming growth factor beta2 (TGFbeta2) by BDNF in hair follicles 15896309_Human TGF-beta2 but not human TGF-beta1, or -beta3 promotes cardiac myocyte differentiation from mouse ES cells. 16210002_TGF-beta 2 may promote endometrial tissue repair through the inhibition of the proliferation, expansion, and migration of endometrial stromal cells, and through stimulation of contraction of the collagen gel matrix by these cells. 16260601_TGF-beta-dependent nuclear accumulation of Smad2 is caused exclusively by selective nuclear trapping of phosphorylated, complexed Smad2 16463680_The expression of TGF-beta2 mRNA was higher in cortex cataract than in nuclear cataract. 16467496_In conclusion, increased TGF-beta2 transcription in response to serum stimulation in KFs appears to be mediated by the p38 MAPK pathway. 16608413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16885354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16891397_TGF-beta2 is secreted in response to injury, significantly alters the bulk optical properties of the extracellular matrix, and its tight regulation may be required for normal collagen homeostasis. 16998703_The mRNA expressions of TGFbeta1 in hMSCs increased with the length of cell culture. 17192487_ombined effects of TGF-beta2 and connective tissue growth factor appear to be involved in the pathogenesis of proliferative vitreoretinal diseases 17201588_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17217916_The results presented in this paper provide evidence for the involvement of an oxidative process in the apoptosis elicited by TGF-beta(2) in HLECs. 17401695_BMP-2, TGF-beta2, and TGF-beta3 are involved in bone formation in heterotopic ossifications. 17431704_No evidence for association with susceptibility or progression of MS, but have demonstrated a trend towards association of the 5' region of the gene with susceptibility to PD. 17431704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17453002_TGF-beta2 triggers the malignant phenotype of high-grade gliomas by induction of migration, and that this effect is, at least in part, mediated by versican V0/V1. 17532297_These results suggest that FGF-2 suppresses the hMSCs cellular senescence dependent on the length of culture through down-regulation of TGF-beta2 expression. 17611697_Am-80-induced cell-type non-specific growth inhibition is mediated by TGF-beta2, where the total mass of RARalpha could be an important regulatory factor in hematologic malignant cells 17651146_TGF-beta(2) may therefore be involved in the development of childhood atopic asthma by means of functional genetic polymorphism. 17679942_The highest levels of active TGF-beta2 were found in keratoconus eyes. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17960115_TGF-beta2 promoted human lens epithelial cell adhesion and migration in vitro. Integrin beta1 and integrin-mediated signaling are necessary for TGF-beta2-promoted adhesion and migration in human lens epithelial cells. 18039789_TGF-beta2 and -beta3 are differentially expressed during the menstrual cycle and regulated by progesterone in epithelial vs stromal cells. 18040277_The early induction of TGF-beta1 at the point of SCI suggests a role in the acute inflammatory response and formation of the glial scar, while the later induction of TGF-beta2 may indicate a role in the maintenance of the scar. 18043895_TGFbeta2 and TbetaRII have roles in the antiestrogenic activity of tamoxifen metabolites in breast cancer 18078367_TGF-beta 2 is closely related to cellular differentiation in human developing teeth 18080134_TGF-beta 2 was detected since the bud stage of the salivary gland. Its expression was observed in ductal cells and increased along gland differentiation. 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18223299_TGF-beta(2) is a potent growth factor for lens epithelial cell(LEC) epithelial mesenchymal transition(EMT); TGF-beta(2)-induced EMT in LECs is mediated by the downregulation of connexin 43, which is regulated through the PI3K/Akt pathway 18292822_The endometria from women with idiopathic infertility TGFbeta2 expression was 2.8 fold higher than in endometria from control group and 2.1 fold higher in endometrial samples from women with unexplained recurrent miscarriage compared to the control group. 18348727_IL-13 may contribute to subepithelial fibrosis in asthma by stimulating biologically significant TGF-beta2 secretion from the airway epithelium. 18358889_may affect the growth and differentiation of dental pulp cells via an autocrine fashion by activation of the transforming growth factor beta receptor protein kinase/receptor regulated Smad proteins signal transduction pathways 18384390_in gingival crevicular fluid and peri-implant crevicular fluid did not change significantly after a period of de novo plaque accumulation 18431253_Taken together, these in vitro and in vivo results indicate that glioma-derived factors may induce MMPs and downregulate endothelial tight junction protein and, thus, play a key role in glioma-induced impairment of the blood-brain barrier. 18498721_study found different expression of the TGF-beta1, -2 and -3 isoforms in the human corneal epithelium; such differential expression of TGF-betas suggests that each of them may play a specific role in corneal tissue 18505915_the TGF-beta1-2-3/Smad3 pathway has a role in mediating ovarian oncogenesis by enhancing metastatic potential 18563556_Genes more highly expressed in BRCA1-associated tumors included stathmin, osteopontin, TGFbeta2 and Jagged 1 18694919_A dominant increase in TGF-beta2 expression in cord tissue was seen in Dupuytren's disease. 19031438_BMP4 blocked the TGF-beta2 induction of extracellular matrix proteins in optic nerve head cells; the BMP antagonist gremlin reversed this inhibition 19062040_TGF-beta cytokines may be involved in postsurgical adhesion formation 19161338_High-affinity binding of TGF-beta1/3 to TGF-betaRII is primarily due to hydrogen bonding between Arg25 and 94 of TGF-beta1/3, and Glu119 and Asp32 of TbetaR-II. Arg25 and 94 are substituted by Lys in TGF-beta2, which binds with low affinity to TbetaR-II. 19212830_Report expression of decorin in esophageal cancer in relation to the expression of three isoforms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1, -beta2, and -beta3) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. 19249525_Expression levels of Tgfb2 in circulating lymphocytes are not sufficiently specific to diagnose transitory postsurgical complications such as symptomatic infection after liver transplantation. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19438810_These results suggest an important role for TGF-beta(2) in hair follicle morphogenesis. 19444386_The TGF-beta2 signal pathway participates in the apoptotic signal transfer and might be an initiator of cellular apoptosis of human lens epithelial cells. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19472023_Variations of the stress distribution in cancellous bone correlate with the variation of the concentrations of TGF-beta2 and IGF-I in bone matrix. 19572226_PRDX6 attenuates oxidative stress- and TGFbeta-induced abnormalities of human trabecular meshwork cells. 19651985_Ladybird homeobox 1 (LBX1), a developmentally regulated homeobox gene, directs expression of the known EMT inducers ZEB1, ZEB2, Snail1, and transforming growth factor beta2 (TGFB2). 19710942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937272_Our data provide evidence that TGF-beta signaling patterns vary by age and pathologic features of prognostic significance including ER expression. 19959123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965872_Data show that TNF-alpha induces the formation of fibrotic foci by cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells through activation of transforming growth factor-TGF-beta signaling in a manner dependent on hyaluronan-CD44-moesin interaction. 20059631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20134268_high prechemotherapy serum levels associated with improved survival in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer 20142847_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, and TGF-beta3 mRNAs were detected in both normal and pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (PBK) corneas. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20543478_Carbachol can promote and atropine can inhibit the expression and secretion of TGF-beta2 in human retinal pigment epithelium cells. 20585394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20585394_results represent the first report on CM genetic risk factors in Angolan children and suggest the novel hypothesis that genetic variants of the TGFB2 and HMOX1 genes may contribute to confer a specific risk of developing the CM syndrome 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20630504_A variant in the fibrillin-3 gene is associated with TGF-beta and inhibin B levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20875417_TGF-beta2 suppressed macrophage cytokine production in the developing intestine and protected against inflammatory mucosal injury. 21034224_elevated levels of TGF-b2 within the anterior segment contribute to the development of glaucoma; the increased risk for developing glaucoma as one ages may in part be related to the rise of this cytokine 21087804_The TGF-beta1 mediated secretion of endothelin-1 and TGF-beta2 is mediated by Rho kinase activation in hepatic stellate cells. 21087928_autocrine stimulation of myeloid progenitors by Tgfbeta2 as one mechanism by which HoxA10 expands this population. 21088899_Data suggest that glioma stem cells are likely to be the major tumor source of immunosuppressive cytokines such as TGF-beta2 and IL-10 and thereby play a crucial role in determining glioma malignancy. 21106846_Aqueous humor regulates dendritic cell maturation and function by the combined actions of cortisol and TGF-beta2, a pathway that is likely to contribute to the maintenance of immune privilege in the eye. 21161068_Study revealed a correlation between the localization of transforming growth factor-beta2 and the development of intraocular hyaloid vascular network, its regression, formation of the vitreous body, and development of definite retinal vessels. 21207416_quantitative increase in promoter methylation levels of TGFbeta2 is associated with prostate cancer progression 21212630_BMP-2 and TGFbeta2 shared pathways regulate endocardial cell transformation 21305699_TGFbeta subtypes (1, 2 and 3) affect terminal differentiation of in vitro cultured hBMSCs differently 21360509_Degranulation of skin mast cells can be an important mechanism of TGFbeta secretion in systemic sclerosis. 21411746_Data show that TGF-beta pathways operate during ovarian fetal development, and fibrillin 3 is highly expressed at a critical stage early in developing human and bovine fetal ovaries. 21446058_differential expression pattern of TGFbeta2 in the lens and retina is correlated with the cell type and differentiation state. 21585337_The present paper showed that TGF-beta2 stimulates endothelial-mesenchymal transition through multiple signalling pathways. 21642622_Gremlin employs canonical TGFbeta2/Smad signaling to induce extracellular matrix protein genes and proteins in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells. 21693611_The present study reveals that TGFbeta2 and NGF are associated with idiopathic epiretinal membranes, suggesting a novel compensatory mechanism so far never proposed. 21738403_Transforming growth factor-beta2 increases extracellular matrix proteins in optic nerve head cells via activation of the Smad signaling pathway. 21917933_A total of 853 proteins were quantified. TGFbeta treatment significantly altered the abundance of 47 proteins, 40 of which have not previously been associated with TGFbeta signaling in the eye. 22180604_Myxomatous mitral valves are characterized by reduced levels of MT1/2 accompanied by an up-regulation of TGF-beta2. 22464821_The aim of the study was to determine temporal TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 gene expression profiles in the anterior lens capsule of paediatric patients with posttraumatic cataract. 22487836_The genotypic and allelic frequencies of transforming growth factor beta 2 gene rs6658835 were associated with VSD (P 0.05). 22504005_identified transforming growth factor-beta2 secreted by normal kidney and ADPKD cells as an inhibitor of cystogenesis in 3D culture system using ADPKD cells from kidneys 22582395_RFX1 reduces cell proliferation through inhibiting the TGFbeta2-ERK signaling pathway. RFX1 blocks TGFbeta2 expression through its direct action on TGFbeta2 transcription. 22653295_data permit us to suggest an important role of TbetaRII expression in the maintenance of chondrocyte phenotype, which is altered with age, and bring new insights in our understanding of chondrogenesis process. 22706080_TGF-beta2 is abundant in seminal plasma as a key agent in seminal plasma that signals induction of proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in cervical cells. 22736943_No significant associations were identified between FOXC1, TGFbeta2, and BMP4 alleles and haplotypes and primary open-angle glaucoma. 22739237_the microenvironment at the verge between inflammation (IL-1beta) and tissue remodeling (TGFbeta2) can strongly promote the process of EndMT. 22772368_report heterozygous mutations or deletions in the gene encoding the TGF-beta2 ligand for a phenotype within the Loeys-Dietz syndrome spectrum 22772371_haploinsufficiency for TGFB2 predisposes to thoracic aortic disease, suggesting that the initial pathway driving disease is decreased cellular TGF-beta2 levels leading to a secondary increase in TGF-beta2 production in the diseased aorta 22786655_Transcriptional profiling of human glioblastoma vessels indicates a key role of VEGF-A and TGFbeta2 in vascular abnormalization. 22823397_TGF beta-2 inhibits the expression of the clock genes Period (Per)1, Per2, and Rev-erb-alpha, and of the clock-controlled genes D-site albumin promoter binding protein (Dbp) and thyrotroph embryonic factor (Tef ) 22955109_TGF-beta may contribute to aneurysm formation by promoting the generation of myofibroblasts that mediate damage to the arterial wall through recruitment of pro-inflammatory cells. 23099432_TGFbetaRIIb expression is a regulatory mechanism for TGFbeta2 signal transduction. 23102774_TGFbeta2 protein and localization of mutations are identified in patients with thoracic aortic aneurysm and/or dissection. 23249391_TGF-beta decreases baseline and IL-13-stimulated mucin production by primary human bronchial epithelial cells. 23257207_TGF-beta(2) reduces proliferation but stimulates migration of cultured corneal endothelial cells via p38MAPK phosphorylation. 23297089_SDC-2 modulates TGFbeta2 transcriptional regulation via Smad2 signaling to facilitate fibrosarcoma cell adhesion. 23306609_the suppression of TGF-b1 induced TGF-b3 upregulation, and the suppression of TGF-b2 induced another unexpected downregulation of both TGF-b1 and TGF-b3. 23322721_TGFbeta2 increased NFkappaB reporter activity in control cells, but betaglycan expression suppressed both basal and TGFbeta2-stimulated NFkappaB activity. 23387555_Mutation or removal of the G-quadruplex sequence from the 5' UTR of the gene diminished the level of expression of this gene at the translational level. 23651239_Data show expression of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, BMP-4, and BMP-7 was increased in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) cocultured with pancreatic cancer cells, and vasohibin-1, VEGF-A, and vVEGF-C expression in pancreatic cancer cells was upregulated by TAMs. 23668958_Endothelial cells may play a role in the induction and maintenance of EMT in tumor cells by constitutively releasing TGFbeta1 and TGFbeta2 23687438_MMP-2 and -9 are involved in the translocation of MRTF-A in lens epithelial cellsduring TGFbeta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. 23690072_These data do not confirm a crucial role of TGF beta1 and TGF beta2 release in the development of posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus 23712828_germline mutation of the TGFbeta2 gene is not a common cause of CTD in humans and that the TGFbeta2 expression level may be less critical in humans than in animals for the pathogenesis of CTD. 23880103_Serum TGFB2 was elevated in patients with classic prolapse as compared with the control group and the non-classic mitral valve prolapse group. 24045946_HD3alpha directly interacts with HDAC3 and Akt1 and selectively activates transforming growth factor beta2 (TGFbeta2) secretion and cleavage. 24193348_TGFB2 is a rarely mutated gene in patients with syndromic TAAD, and the clinical features of our TGFB2 mutation-positive individuals fit in the scheme of LDS, rather than MFS-related disorders. 24223867_Data indicate that glioma cell migration is mediated by Thrombospondin-1 (THBS-1) and TGF-beta2. 24311892_The expression of TGFB1 and TGFB2 increase significantly in benign prostatic hyperplasia treated with 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. 24314882_Inhibition of miR-21 has no effect on thrombospondin (TSP)-1-stimulated expression of TGFbeta2. 24402195_Compared to controls, plasma levels of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 were significantly lower in patients with recurrent VTE (p |
ENSMUSG00000039239 |
Tgfb2 |
107.029943 |
0.2716083227 |
-1.880400 |
0.318066755 |
33.534838 |
0.00000000699989070946605446781962569678323116129092795745236799120903015136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000030942913109229997223402052614060764312853279989212751388549804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.0472871 |
9.2136566 |
167.8003387 |
23.3727072 |
| ENSG00000093010 |
1312 |
COMT |
protein_coding |
P21964 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the O-methylation, and thereby the inactivation, of catecholamine neurotransmitters and catechol hormones. Also shortens the biological half-lives of certain neuroactive drugs, like L-DOPA, alpha-methyl DOPA and isoproterenol. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11559542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21846718}. |
3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Catecholamine metabolism;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Neurotransmitter degradation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Schizophrenia;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Catechol-O-methyltransferase catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosylmethionine to catecholamines, including the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. This O-methylation results in one of the major degradative pathways of the catecholamine transmitters. In addition to its role in the metabolism of endogenous substances, COMT is important in the metabolism of catechol drugs used in the treatment of hypertension, asthma, and Parkinson disease. COMT is found in two forms in tissues, a soluble form (S-COMT) and a membrane-bound form (MB-COMT). The differences between S-COMT and MB-COMT reside within the N-termini. Several transcript variants are formed through the use of alternative translation initiation sites and promoters. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:1312; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; catechol O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016206]; L-dopa O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0102084]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008171]; orcinol O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0102938]; catecholamine catabolic process [GO:0042424]; cellular response to phosphate starvation [GO:0016036]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; dopamine catabolic process [GO:0042420]; dopamine metabolic process [GO:0042417]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; methylation [GO:0032259]; neurotransmitter catabolic process [GO:0042135] |
11054766_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11054777_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11058906_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11121168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11121178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11142424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11150892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11163295_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11166081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11171904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11381111_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11401913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11426511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11434504_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11443519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11525417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11525422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11556837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11577006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11581117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11597779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11693181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11705709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11706521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11772685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11773866_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11840516_A low-activity allele is associated with obsessive-compulsive bahavior in females, not in males as previously reported. 11865133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11873938_COMT activity may determine the individual response to levodopa and result in ethnic differences in Parkinson disease susceptibility. 11900601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11925305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11927842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11990384_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11992559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11992559_possible association between the prophylactic efficacy of lithium in mood disorders and the following gene variants: catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) G158A, monoamine oxydase A (MAO-A) 30-bp repeat, G-protein beta 3-subunit (Gbeta3) C825T 11992560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11992560_possible influence of monoamine oxydase A (MAO-A), catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), serotonin receptor 2A (5-HT2A), dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2), and dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene variants on timing of recurrence in mood disorders 12011284_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12029502_Association between catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism and vitiligo. 12029502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036914_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12082558_polymorphism associated with schizophrenia in Chinese families in China 12090821_allelic variants of COMT gene may modulate the risk for schizophrenia 12116182_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12126868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12168735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12192614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12192614_that self-reported schizotypy scores in both questionnaires were significantly related to COMT genotype (P = 0.028 for the PAS and P = 0.015 for the SPQ) with individuals homozygous for the high activity allele showing the highest scores. 12270650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12359690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12360102_Characterization of human soluble high and low activity allele-catalyzed catechol estrogen methylation. 12360111_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12372660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12385014_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12402217_A highly significant association between a COMT haplotype and schizophrenia 12402217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12402217_catalyzes the o-methylation inactivation pathway of the major metabolites of estrogen, 2- hydroxyestradiol (2-OHE2) and 4-hydroxyestradiol (4-OHE2). 12415427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12465073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12467945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12476424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12476424_Results suggested that liability to heroin-dependence was associated with -287 A/G polymorphism of COMT gene. 12497608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12535946_Contrary to expectations that COMT would be expressed predominantly in non-neuronal cells, the present study shows that neurons are the main cell populations expressing COMT mRNA in the prefrontal cortex and striatum. 12566168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12571159_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12571159_Serum estradiol levels significantly correlate with COMT genotype. Differences in COMT genotype might be involved in causing variable effects of estrogens on diseases and on efficacy of hormone replacement therapy. 12574216_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12579508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12595695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12595695_individuals homozygous for the met158 allele of the catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism (val158met) showed diminished regional mu-opioid system responses to pain compared with heterozygotes 12602902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12605099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12605099_There is an inherited difference in COMT polymorphism which is important in the pathogenesis of anxiety in women. 12611827_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12627475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12668354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12673581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12707935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12711403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12712467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12718576_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12727796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12727796_examination of gene polymorphism in postmenopausal cancer risk 12729939_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12729939_the risk of having both low activity catechol-O-methyltransferase and high angiotensin-converting enzyme genotypes was over 10 times higher in schizophrenics with poor response to conventional neuroleptics 12739038_COMT polymorphism is of potential pharmacological importance to individual differences in the metabolism of catechol drugs and may be involved in the pathogenesis and treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome. 12739038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12740593_val/met variants in novelty seeking behavior 12782971_This study does not support the involvement of tyrosine hydroxylase, catechol-O-methyl transferase and Wolfram syndrome 1 polymorphisms in mood disorders. 12799619_Disease-related laminar difference of COMT expression may be involved in dysregulation of dopamine signaling circuits in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. 12810635_Methylation of multiple promoters of the COMT gene can selectively inactivate MB-COMT and may contribute to endometrial carcinogenesis. 12815660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815735_Low COMT activity is associated with aggressive behavior in schizophrenia. 12815735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815736_No significant association was found in Japanese patients between COMT polymorphism and schizophrenia. 12815736_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815739_There is an association between Val108/158 Met polymorphism of the COMT gene in schizophrenia. 12815746_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12815746_There was a weak association with COMT genotype in neuroticism when the males and females were considered separately. There was no significant interaction between COMT and MAOA. 12842306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12842306_The functional polymorphism in the COMT gene may modify the phenotype of suicide attempts and anger-related traits. 12842307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12842307_The association of the frontal P300 amplitude with the G1947A COMT genotype further emphasizes the functional role of this single nucleotide polymorphism. 12900951_COMT gene polymorphism is not directly associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder 12900951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12903043_Data suggested that for the Han Chinese children with ADHD in the study, there was no association between ADHD and Val158Met polymorphism of COMT gene. 12903043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12963670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12971967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14504192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14504192_These findings indicate that COMT genotype is associated with several risk factors for breast cancer and suggest that the low-activity COMT*2 allele is associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer among premenopausal women. 14508827_COMT gene polymorphism significantly increased the risk of developing prostate carcinoma. 14508827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14520117_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14520706_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14575568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14582147_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14610521_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14612555_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14654758_Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT( deficiency in mice increases the availability of L-DOPA, leading to enhanced dopaminergic tone, which may be associated with resistance to salt-induced hypertension. 14656021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14656940_Compared with the COMT Val/Val wildtype genotype, the adjusted odds ratio of endometrial cancer for women with the COMT Val/ 14656940_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14673217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14681918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14706432_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14729580_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14744739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14745454_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14754787_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14754787_The catechol O-methyltransferase gene has been associated with cognitive and behavioral phenotypes in schizophrenia 14966473_The Met108 allozyme displayed a 70-90% decrease in immunoreactive protein when compared with WT, but there was no significant change in the level of immunoreactive protein for Thr52 14989982_The Catechol-o-methyltransferase gene polymorphism is not associated with the generation and the severity of pregnancy induced hypertension. 15005715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15005715_There were no observed differences in the frequencies of allele and genotype between obsessive-compulsive disorder patients and control groups for COMT polymorphisms. 15009906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009906_a role of the catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphism in the pathogenesis of panic disorder in women 15033250_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15098000_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15098000_We have typed the IVS 1 rs737865 and 3' rs615599 sites and also included a novel IVS 1 indel polymorphism. We report that the schizophrenia-associated haplotype is significantly heterogeneous in populations worldwide. 15108175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15115916_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15118357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15124004_COMT SNP rs4680, a functional Val/Met polymorphism, showed modest association with Irish familial schizophrenia. Haplotype A-G-A for SNPs rs737865-rs4680-rs165599 was preferentially transmitted to the affected subjects. 15127078_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15127078_The results of this study suggests that the comt Val/Val genotype is a protective factor against suicide in males. 15129369_COMT genotype was not associated with bone mass at baseline, bone loss in untreated women, or response to HRT. 15129369_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15182372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15199113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15203287_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15211623_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15211623_There was no evidence of epistatic interaction between MAOA, MOAB, and COMT genes on Overt aggression scale scores. 15211633_suggest that polymorphisms in the COMT gene may influence susceptibility to both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia 15229337_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15241822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15261699_Comt gene plays role in dopamine degradation in patients with schizophrenia. 15261699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15274053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15283009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15285606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15292670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15292670_functional catechol-O-methyltransferase Val158Met genetic polymorphism contributes to individual differences in the personality traits novelty seeking and reward dependence 15300652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15300652_The COMT val158met polymorphism, which regulate central nervous system dopaminergic transmission, can influence some of the phenotypic manifestations of PD. 15309313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15319576_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15319576_The COMT gene is a plausible candidate gene for memory functioning in adulthood and old age. 15337663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15337664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15340358_Nominal evidence was found for association of illness from three-marker haplotypes spanning the 3' portions of COMT and ARVCF, including Val(108/158)Met with Val(108/158) being the overtransmitted allele, consistent with previous studies. 15341023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15355491_Clinical trial of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15382051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15386537_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15388245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15388245_the COMT-L allele and COMT-LL genotype are genetic risk factors for sporadic breast cancer in premenopausal Turkish women 15450787_None of the cognitive measures was associated with catechol-O-methyltransferase valine158 methionine genotypes; however, there was an effect of high-activity allele loading on schizotypy, in particular the negative and disorganization dimensions. 15450787_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15450911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15455371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15457497_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15465976_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15488308_COMT polymorphism influences on the risk of psychosis since the early stages, and claims for the possibility to identify distinct phenotypes on genetic basis among AD patients. 15488308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15505638_Results indicate the Val/Met polymorphism is not disease-causing and is simply in strong linkage disequilibrium with a causative effect, which interacts with another as yet unidentified variant approximately 20 kb away. 15520843_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15522252_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15522252_Patients homozygous for the COMT met allele displayed significant improvement on the working memory task after treatment. 15537444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15537444_the COMT val158met polymorphism is associated with peak BMD in young adult men 15537663_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15538046_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15548428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15567073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15569909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15570503_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15572182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15583702_An association was found between the high-activity COMT Val allele, particularly the COMT Val/Val genotype and early-onset major depressive disorder. 15583702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15583953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15584875_COMT (Val158Met) leads to neurobiology differences in executive cognitive function, stress/anxiety response, and opioid function that increase susceptibility to alcoholism. 15591802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15596044_Up-regulation of catechol O-Methyltransferase is associated with bladder cancer 15613245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15626819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15626819_This study did not provide evidence supporting an association between BDNF and COMT genes and declarative memory phenotypes. 15645182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15652872_No statistically significant differences were found in allele or genotype frequencies between patient and normal control subjects, although a nonsignificant overrepresentation of the Val allele in schizophrenia patients was suggested. 15652872_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15654505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15654584_the slower clearance of dopamine associated with the methionine variant of the COMT gene polymorphism may be disadvantageous to cognition in attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity 15668497_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15668720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15668720_these findings do not support a major role for COMT in increasing susceptibility for schizophrenia or in mediating frontal lobe function 15673663_COMT genotype had no significant impact on brain activation by pleasant stimuli but was related to the neural response to unpleasant stimuli. 15673663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15717291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15734954_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15747357_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15753616_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15774541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824744_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824744_The results of this meta-analysis do not support an association between the COMT Val allele and schizophrenia case status. 15846854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15852364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15862471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15866551_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15896265_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15900212_Observational study and clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15900225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15900225_These data replicate previous findings suggesting association between the ValMet polymorphism and specific expressions of anxiety among females. 15900232_Catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphism is not associated with the development of alcohol dependence, but may affect the susceptibility to a clinical heterogeneity of alcohol dependence in the Korean population. 15900232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15901785_Effect of catechol-O-methyltransferase val158met genotype on attentional control. 15901995_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15927391_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15927391_These results suggest that genetic variation in the COMT gene may contribute to variability in the efficacy of morphine in cancer pain treatment 15935994_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15936529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15941945_Observational study and clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15941966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956988_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956988_The val158met polymorphism of COMT would be associated with both high neuroticism and low extraversion, making it a plausible candidate locus for anxiety susceptibility. 15965967_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15965967_Study suggests that the status the functional COMT(L) variant may be potentially useful to select PD patients for high dose pyridoxine therapy. 15965969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15973162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15979789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15979789_This study suggested that COMT genotype may contribute to differences in normal cognitive aging and to differences in some of the major personality traits in old age. 15985686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15985686_the COMT(LL) genotype results in increased free estradiol levels and earlier pubertal development 15987428_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16026865_This study investigated two dopaminergic candidate genes (COMT VAL158MET and DRD2 TAQ IA) for endophenotypes of cognitive functioning. Results showed associations of the COMT gene with attention and with time estimation. 16027741_COMT genetic variation is associated with risk of psychosis in Alzheimer's disease 16027741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16037677_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16037677_These results support the hypothesis that the COMT Val(158)Met polymorphism influences executive functions in schizophrenia and the neuromotor performance in the deficit subtype only. 16040257_mechanisms other than an enkephalin-dependent receptor turnover must be responsible for COMT-related differences in mu receptor binding site availability in the human brain 16043133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043283_These results do not support the hypothesis that the COMT Val158Met gene polymorphism is associated with liability to schizophrenia-obssessive compulsive disorder. 16077979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16077979_Results suggest that COMT polymorphism may be implicated as a genetic trait affecting the susceptibility to breast cancer in a Japanese population and be an important genetic risk factor in the development of breast cancer in post-menopausal women. 16092759_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16094249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16102234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16102234_The Catechol O-methyltransferase Val158Met polymorphism is associated with cognitive performance in nondemented adults. 16103451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16109444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16118784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16118784_Risk and protective haplotypes may carry molecular variations in the COMT gene or its vicinity that are relevant to the pathophysiology of restrictive anorexia nervosa in the Israeli-Jewish population. 16126332_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16127282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16130011_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16135635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142442_No association found between COMT polymorphism and breast cancer in older white women 16142442_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16191465_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16202920_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16214922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16231731_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16231731_Transmission disequilibrium test and the haplotype analysis suggested that there was no association between ADHD and the COMT gene in the Chinese population. 16233957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16234808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16234808_This study identified the catechol-O-methyltransferase low-activity allele (COMT(L)) as a risk factor for decline in prefrontal cortical volume and cognition, as well as for the consequent development of psychotic symptoms during adolescence. 16247488_A 39 kDa isoform of membrane-bound COMT was isolated, which may be differentially regulated in psychiatric disorders. 16257094_Modeling Neuropsychiatric Inventory symptom-endophenotype-genotype relationships, & taking into account possible confounds by latent variable models, COMT & 5-HTTLPR genetic variation correlated with frontal & psychosis endophenotypes in Alzheimer disease 16257094_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16260521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16275815_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16281377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284375_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16330500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16356553_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16360899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16361958_COMTL allele was related with increased tonic dopamine activity and cognitive 'stability', which may induce cognitive inflexibility in schizophrenia. 16361958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16362639_Genetic analysis revealed an association between the VAL allele of COMT and the inattention scale, the hyperactivity/impulsivity scale, and the total ASRS scale,with highest scores in carriers of the MET/MET genotype. 16387984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16395295_Obs |
ENSMUSG00000000326 |
Comt |
988.665527 |
2.1252985672 |
1.087666 |
0.081737440 |
175.251124 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000052767665188768684202148864759489324123499016014452189491801363962312305481194419024239523720713773181911765419727089465595781803131103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000008760975682634711464190094588010762902135162813935848901659604432701788680995844935448728311345746025060043926657726842677220702171325683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1352.9880087 |
75.8175612 |
641.1472584 |
26.6880422 |
| ENSG00000095015 |
4214 |
MAP3K1 |
protein_coding |
Q13233 |
FUNCTION: Component of a protein kinase signal transduction cascade (PubMed:9808624). Activates the ERK and JNK kinase pathways by phosphorylation of MAP2K1 and MAP2K4 (PubMed:9808624). May phosphorylate the MAPK8/JNK1 kinase (PubMed:17761173). Activates CHUK and IKBKB, the central protein kinases of the NF-kappa-B pathway (PubMed:9808624). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17761173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9808624}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a serine/threonine kinase and is part of some signal transduction cascades, including the ERK and JNK kinase pathways as well as the NF-kappa-B pathway. The encoded protein is activated by autophosphorylation and requires magnesium as a cofactor in phosphorylating other proteins. This protein has E3 ligase activity conferred by a plant homeodomain (PHD) in its N-terminus and phospho-kinase activity conferred by a kinase domain in its C-terminus. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:4214; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; MAP kinase kinase kinase activity [GO:0004709]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038095]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
11746500_Modulation of human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene enhancer and promoter activity by MEKK1 is under the control of the NFkappaB/rel sites. 11756439_MEK kinase 1 induces mitochondrial permeability transition leading to apoptosis 11782455_caspase cleavage of MEKK1 is a dynamic regulatory mechanism that alters the subcellular distribution of MEKK1, changing its function to pro-apoptotic signaling 11903060_Opposing roles of serine/threonine kinases MEKK1 and LOK in regulating the CD28 responsive element in T-cells 11971970_Results suggest that the conserved AR acetylation site contributes to a pathway governing prostate cancer cellular survival, as AR acetylation mutants are defective in MEKK1-induced apoptosis. 11971971_Results show that oncogenic ras provokes premature senescence by sequentially activating the MEK-ERK and MKK3/6-p38 pathways in normal, primary cells. 12079429_the NOx-induced cell proliferation via activation of MEKK1 might contribute to lung tissue damage caused by NOx 12185592_The difference of suppression in pancreatic cancer cells and non-pancreatic cancer cells suggested that the MEKK1 pathway mainly contributes to cell survival in pancreatic cancer cells 12228228_mechanism by which the MEKK1-dependent JNK/SAPK pathway is negatively regulated by PAK through phosphorylation of serine 67 12456688_Ubiquitylation of MEKK1 inhibits its phosphorylation of MKK1 and MKK4 and activation of the ERK1/2 and JNK pathways 12584189_MEKK1 is activated by GSK3beta 12600818_conclude that Ras regulates TNF-alpha-induced chemokine expression by activating the AP-1 pathway and enhancing transcriptional function of NF-kappaB, whereas MEKK1 activates both the AP-1 and NF-kappaB pathways 12878610_Axin utilizes distinct regions for competitive MEKK1 and MEKK4 binding and JNK activation. 14500727_subdomain VIII of MEKK1 is involved not only in binding to, but also in discrimination of, protein substrates 14612408_coexpression of constitutive-active MEKK1 inhibited orphan receptor TR3 transcriptional activity and TR3-induced proliferation in lung cancer cells 15205333_The G(i)-Ras-MEKK1 signaling pathway mediates lysophosphatidic acid-stimulated ovarian cancer cell migration by facilitating focal adhesion kinase redistribution to focal contacts. 15299005_glutathione s-transferaase Mu suppresses MEKK1-mediated apoptosis and functions as a negative regulator of MEKK1. 16044153_MEKK1 plays a key role in Bcr-Abl-induced STAT3 activation and in ES cells' capacity for LIF-independent self-renewal and may thus be involved in Bcr-Abl-mediated leukemogenesis in stem cells 16046415_Galpha13-induced VASP phosphorylation that involves activation of RhoA and MEKK1, phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB, release of PKA catalytic subunit from the complex with IkappaB and NF-kappaB, and subsequent phosphorylation of VASP 16434970_Induction of Nur77 nuclear export by MEKK1 required a prolonged MEKK1 activation and was attenuated by Akt activation. Expression of constitutively active Akt prevented MEKK1-induced Nur77 nuclear export. 16714289_Pge2 abolished the MEKK1-induced MMP-1 promoter luciferase activity. 16760432_MEKK1 transmits wound signals, leading to the transcriptional activation of genes involved in Extracellular Matrix homeostasis, epithelial cell migration, and wound reepithelialization. 17301822_Caspase-3 and the p38alpha MAP kinase were activated during TIMP-1-induced UT-7 cells erythroid differentiation. 17397260_The results suggest that multiple cellular signaling pathways can reactivate the virus in a genetically homogeneous cell population. Further analysis revealed that the Raf/MEK/ERK/Ets-1 pathway mediates Ras-induced reactivation. 17889508_A pathway comprising PKCs>Raf-1>MEK-1>ERK-1/-2 mediates the effect of gastrin on the CgA promoter, and strongly suggests that enhanced phosphorylation of Sp1 and CREB is crucial for CgA transactivation through the G protein-coupled CCK-B/gastrin receptor. 17997823_Heterozygote carriers and minor allele homozygote carriers for SNP rs889312 in the MAP3K1 gene were less likely to be lymph node positive at breast cancer diagnosis (P = 0.044) relative to major allele homozygote carriers. 17997823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18032450_reduction of upstream MEKK1 signals uncovers analogous but differential roles of JNK1 and JNK2 in a biological process 18287093_MEK functions to enhance GCN2-dependent eIF2alpha phosphorylation rather than suppressing dephosphorylation 18308848_Signaling pathways that augment or diminish beta-cell MEKK-1 activity may aid in the generation of novel therapeutic strategies in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. 18355772_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18355772_The differences in the effects of the FGFR2 and MAP3K1 SNPs between BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers point to differences in the biology of BRCA1 and BRCA2 breast cancer tumors and confirm the distinct nature of breast cancer in BRCA1 mutation carriers. 18420486_MEKK-1 mediates cytokine-induced JNK- and NF-kappaB activation, and this event is necessary for iNOS expression and cell death in pancreatic islet cells. 18434448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18437204_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18467339_MAP3K1 protects against acute lung injury induced by nickel. 18521924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18784253_The activation of TORC1 through MEKK1-mediated phosphorylation, is reported. 18785201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18973230_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18984593_IPS-1 requires TRAF6 and MEKK1 to activate NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinases that are critical for the optimal induction of type I interferons 19028704_FGFR2 and MAP3K1 are involved in breast cancer susceptibility and confer their effects primarily in ER+ and PR+ tumors. 19028704_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19232126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19262425_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19289468_Loss of MADD expression resulted in reduced Grb2 and Sos1/2 recruitment to the TNFR1 complex and decreased Ras and MEKK1/2 activation 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19513748_MEKK1 may be a potential target for development of anti-invasion and metastasis drugs. 19617217_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19789366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19843670_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20128690_These results of MAP3K1, previously reported as an Axin1 inter-actor in c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase pathway, is also involved in the canonical Wnt signalling pathway and positively regulates expression of Wnt target genes. 20145138_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20417875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605201_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20809358_MAP3K1 rs889312 polymorphism is associated with increased risk of breast cancer in BRCA1 mutation carriers 20809358_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20923779_MAP/ERK kinase kinase 1 (MEKK1) mediates transcriptional repression by interacting with polycystic kidney disease-1 (PKD1) promoter-bound p53 tumor suppressor protein 20940704_Han11 was required to allow coupling of MEKK1 to DYRK1 and HIPK2. 21048223_Data show that MEKK-1 plays an integral role in IL-1beta modulation of Caco-2 TJ barrier function by regulating the activation of the canonical NF-kappaB pathway and the MLCK gene. 21129722_mutations in MAP3K1 that result in 46,XY DSD with partial or complete gonadal dysgenesis implicate this pathway in normal human sex determination 21152872_The upstream molecule of the TRAIL-induced MAPK activation is MEKK, as opposed to ASK1, via the mediation of its signal through JNK/p38 in a caspase-8-dependent manner. 21364884_Apoptosis induced by cytoskeletal disruption requires distinct domains of MEKK1. 21921033_Novel phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of tristetraprolin by mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase kinase 1 (MEKK1) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) 22110214_High MEK1 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 22468730_We also observed that four Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) were associated with severe asthma 23225170_FGFR2 and MAP3K1 SNPs have an additive effect on an increased risk of familial breast cancer in a South-American population. 23634849_MAP3K1 single nucleotide polymorphism rs889312 was confirmed to be associated with breast cancer risk (P = 0.04, OR 1.15, 95% CI 1.01-1.30). 24135036_MAP3K1 mutations tilt the balance in the sex-determining pathways by downregulating SOX9 and FGF9. 24253898_MAP3K1 protein expression level in breast cancer cells was higher than that in normal mammary gland cells. 24595411_The present meta-analysis suggests that MAPKKK1 rs889312-C allele and rs16886165-G allele might be risk factors for breast cancer, especially in Europeans and Asians. 24759887_Results demonstrate that MAP3K1 rs889312 is closely correlated with outcome among diffuse-type gastric cancer in a Chinese population. 25352737_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in ALDOB, MAP3K1, and MEF2C are associated with cataract. 25529635_We propose that the cancer risk alleles act to increase MAP3K1 expression in vivo and might promote breast cancer cell survival. 25899310_There were 3 specimens with mutations in MAP3K1 (MEKK1), including two truncation mutants, T779fs and T1481fs; T1481fs encoded an unstable and nonfunctional protein when expressed in vitro. 26018553_Mekk1 mediates p53 protein stability in the presence of Mdm2 and reduces p53 ubiquitination, suggesting an interference with Mdm2-mediated degradation of p53 by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. 26019450_MiR-451 inhibited the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting CDKN2D and MAP3K1 expression. 26050649_BAALC conferred chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia cells by upregulating ATP-binding cassette proteins in an ERK-dependent manner, which can be therapeutically targeted by MEK inhibitor 26237449_CSN6 positively regulates c-Jun in a MEKK1-dependent manner 28029147_SNP variants at the MAP3K1/SETD9 gene boundary associate with somatic PIK3CA variants in breast cancers. 28178648_Polymorphism of MAP3K1 is associated with breast cancer. 28408616_Through a stratification analysis, 5q11.2/MAP3K1 (rs16886034, rs16886364, rs16886397, rs1017226, rs16886448) and 7q32.3/LINC-PINT (rs4593472) were associated with Luminal A, and 10q26.1/FGFR2 (rs35054928) was associated with Luminal B. 28504475_Identification of a MAP3K1 variant should prompt an evaluation for disorders of sex development in female siblings of the proband 28858533_findings show a robust association between the variant allele of rs832582 (MAP3K1906Val) and decreased VFDs in patients with ARDS and suggest that this variant may predispose individuals to a greater inflammatory response. 28925592_miR-101 expression and RISC binding is increased after cyclosporine treatment in kidney cells; targets and reduces expression of MAP3K1 in vitro 29372690_We have revealed significant association of FGFR2 and MAP3K1 polymorphisms with breast cancer. 29499695_CXCL12 activates the MEKK1/JNK signaling pathway, which in turn initiates SMAD3 phosphorylation, its translocation to nuclei, and recruitment of SMAD3 to the CTGF promoter, which ultimately induces CTGF expression in human lung fibroblasts. 30483764_Of note, the enforced expression of MEKK1 or the exposure of medulloblastoma cells to the MEKK1 activator, Nocodazole, resulted in a marked inhibitory effect on GLI1 activity and tumor cell proliferation and viability. Taken together, the results of this study shed light on a novel regulatory mechanism of HH signaling, with potentially relevant implications in cancer therapy. 30608580_These mutations increase the binding of the RHOA, MAP3K4 and FRAT1 proteins and generally decrease the binding of RAC1. Thus, pathologies in MAP3K1 disrupt the balance between the pro-kinase activities of the RHOA and MAP3K4 binding partners and the inhibitory activity of RAC1. 31318172_Combined elevation of TRIB2 and MAP3K1 indicates poor prognosis and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma. 32817551_A cryptic tubulin-binding domain links MEKK1 to curved tubulin protomers. 32986312_A novel missense heterozygous mutation in MAP3K1 gene causes 46, XY disorder of sex development: case report and literature review. 33060765_Nonsense-associated altered splicing of MAP3K1 in two siblings with 46,XY disorders of sex development. 33481368_[Gonadal dysgenesis 46,XY DSD associated with variants in the MAP3K1 gene]. 34112222_Characteristics and possible mechanisms of 46, XY differences in sex development caused by novel compound variants in NR5A1 and MAP3K1. 34154626_RNA-binding protein IMP3 is a novel regulator of MEK1/ERK signaling pathway in the progression of colorectal Cancer through the stabilization of MEKK1 mRNA. 34251884_MEKK1-Dependent Activation of the CRL4 Complex Is Important for DNA Damage-Induced Degradation of p21 and DDB2 and Cell Survival. 34404765_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 activated by c-Myc promotes cell proliferation via interacting with FUS to stabilize MAP3K1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 35290982_Pathogenic Variants in MAP3K1 Cause 46,XY Gonadal Dysgenesis: A Review. 35524422_MicroRNA-203a-3p may prevent the development of thyroid papillary carcinoma via repressing MAP3K1 and activating autophagy. 36102299_Identification of a novel MAP3K1 variant in a family with 46, XY DSD and partial growth hormone deficiency. |
ENSMUSG00000021754 |
Map3k1 |
440.348090 |
0.3345833853 |
-1.579562 |
0.096997849 |
265.254313 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001228130469371993113664907816524186147455746850634474372059119851833950114926287298819620500354468216784948402883347714435687689712522752862711134620374298087597253470448777079582214355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000313077819135243859252898155153756541812538651525135302405678023116705837405458780955503560984610688597423932884857216981409383845644086613753658693282133640423126053065061569213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
222.4458103 |
13.3643798 |
669.7024160 |
26.6310482 |
| ENSG00000095066 |
29911 |
HOOK2 |
protein_coding |
Q96ED9 |
FUNCTION: Component of the FTS/Hook/FHIP complex (FHF complex). The FHF complex may function to promote vesicle trafficking and/or fusion via the homotypic vesicular protein sorting complex (the HOPS complex). Contributes to the establishment and maintenance of centrosome function. May function in the positioning or formation of aggresomes, which are pericentriolar accumulations of misfolded proteins, proteasomes and chaperones. FHF complex promotes the distribution of AP-4 complex to the perinuclear area of the cell (PubMed:32073997). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17140400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17540036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32073997}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Hook proteins are cytosolic coiled-coil proteins that contain conserved N-terminal domains, which attach to microtubules, and more divergent C-terminal domains, which mediate binding to organelles. The Drosophila Hook protein is a component of the endocytic compartment.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. |
hsa:29911; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; FHF complex [GO:0070695]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport [GO:0030705]; early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:0045022]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; protein localization to perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:1905719]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
17540036_Hook2 contributes to the establishment and maintenance of the pericentrosomal localization of aggresomes by promoting the microtubule-based delivery of protein aggregates to pericentriolar aggresomes. 19793914_Results identify Hook2, a linker protein that is essential for regulation of the microtubule network at the centrosome, as a binding partner of CENP-F. 21998199_Hook2 localizes at the Golgi apparatus and centrosome/basal body, a strategic partitioning for ciliogenesis. Hook2 interacts with PCM1. 27624926_We first demonstrate that Hook2 is essential for the polarized Golgi re-orientation towards the migration front. Depletion of Hook2 results in a decrease of PAR6alpha at the centrosome during cell migration, while overexpression of Hook2 in cells induced the formation of aggresomes with the recruitment of PAR6alpha, aPKC and PAR3 29228058_differential methylation profile of the HOOK2 gene in individuals with T2D and obesity might be related to the attendant T2D, but further studies are required to identify the potential role of HOOK2 gene in T2D disease 32397755_Coding Variants in HOOK2 and GTPBP3 May Contribute to Risk of Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma |
ENSMUSG00000052566 |
Hook2 |
156.216908 |
0.4088888714 |
-1.290219 |
0.230896993 |
30.196047 |
0.00000003905045205287540383223306291946008705906479008262977004051208496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000160284947803237216504409698436539599697425728663802146911621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.4291644 |
22.1298754 |
217.4680570 |
39.4411674 |
| ENSG00000095209 |
55151 |
TMEM38B |
protein_coding |
Q9NVV0 |
FUNCTION: Monovalent cation channel required for maintenance of rapid intracellular calcium release. May act as a potassium counter-ion channel that functions in synchronization with calcium release from intracellular stores. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DAV9}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes an intracellular monovalent cation channel that functions in maintenance of intracellular calcium release. Mutations in this gene may be associated with autosomal recessive osteogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]. |
hsa:55151; |
nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; bone development [GO:0060348]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; cellular response to caffeine [GO:0071313]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0070278]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lung epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060487]; phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008654]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0014808]; secretion by lung epithelial cell involved in lung growth [GO:0061033] |
18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23054245_TMEM38B is a novel candidate gene for autosomal recessive Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). Future studies are needed to explore fully the contribution of this gene to autosomal recessive Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) in other populations. 23316006_A deletion mutation in TMEM38B associated with autosomal recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. 26911354_TMEM38B mutations could lead to a rare form of OI, with an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance. We identified two novel mutations (c.455-7T>G in intron 3 and c.507G>A in exon 4) in TMEM38B in three Chinese children with OI. The two mutations created a new acceptor splice site (p.R151_G152insVL) and a novel downstream termination codon (p.W169X), respectively 27441836_Absence of TMEM38B causes osteogenesis imperfecta by dysregulation of calcium flux kinetics in the endoplasmic reticulum, impacting multiple collagen-specific chaperones and modifying enzymes. |
ENSMUSG00000028420 |
Tmem38b |
151.269775 |
3.2090474369 |
1.682145 |
0.211689329 |
61.332899 |
0.00000000000000481959180173049533336128392958614207762838531345916948112062527798116207122802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000033025615131635149010655179664929057765433186022452360930401482619345188140869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
232.6889185 |
33.4248553 |
72.6870093 |
7.9735636 |
| ENSG00000095370 |
10044 |
SH2D3C |
protein_coding |
Q8N5H7 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an adapter protein that mediates cell signaling pathways involved in cellular functions such as cell adhesion and migration, tissue organization, and the regulation of the immune response (PubMed:12432078, PubMed:20881139). Plays a role in integrin-mediated cell adhesion through BCAR1-CRK-RAPGEF1 signaling and activation of the small GTPase RAP1 (PubMed:12432078). Promotes cell migration and invasion through the extracellular matrix (PubMed:20881139). Required for marginal zone B-cell development and thymus-independent type 2 immune responses (By similarity). Mediates migration and adhesion of B cells in the splenic marginal zone via promoting hyperphosphorylation of NEDD9/CASL (By similarity). Plays a role in CXCL13-induced chemotaxis of B-cells (By similarity). Plays a role in the migration of olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) into the forebrain and the innervation of the olfactory bulb by the OSN axons during development (By similarity). Required for the efficient tyrosine phosphorylation of BCAR1 in OSN axons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZS8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12432078, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20881139}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Important regulator of chemokine-induced, integrin-mediated T lymphocyte adhesion and migration, acting upstream of RAP1 (By similarity). Required for tissue-specific adhesion of T lymphocytes to peripheral tissues (By similarity). Required for basal and CXCL2 stimulated serine-threonine phosphorylation of NEDD9 (By similarity). May be involved in the regulation of T-cell receptor-mediated IL2 production through the activation of the JNK pathway in T-cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZS8}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: May be involved in the BCAR1/CAS-mediated JNK activation pathway. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZS8}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
This gene encodes an adaptor protein and member of a cytoplasmic protein family involved in cell migration. The encoded protein contains a putative Src homology 2 (SH2) domain and guanine nucleotide exchange factor-like domain which allows this signaling protein to form a complex with scaffolding protein Crk-associated substrate. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:10044; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
12486027_This protein positively regulates T cell receptor-mediated interleukin-2 production by Jurkat cells. 17270363_SH2D3C (SHEP1) is less highly expressed than BCAR3 and NSP1 in breast cancer cells, and the expression patterns suggest differential roles for the three genes during breast cancer progression. 17427198_NSP3 overexpression did not induce anti-estrogen resistance in breast tumor cell lines. 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22081014_The structure of the NSP3-p130Cas complex reveals that this closed conformation is instrumental for interaction of NSP proteins with a focal adhesion-targeting domain present in Cas proteins. |
ENSMUSG00000059013 |
Sh2d3c |
447.118171 |
0.4740382701 |
-1.076925 |
0.127742423 |
70.053683 |
0.00000000000000005771229023002306326900946089331429733150641416894802149251120226836064830422401428222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000442510859114358640281902580169565195498731032973036003674849325761897489428520202636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
298.9362819 |
23.4811879 |
634.4520058 |
34.9216513 |
| ENSG00000095397 |
25861 |
WHRN |
protein_coding |
Q9P202 |
FUNCTION: Involved in hearing and vision as member of the USH2 complex. Necessary for elongation and maintenance of inner and outer hair cell stereocilia in the organ of Corti in the inner ear. Involved in the maintenance of the hair bundle ankle region, which connects stereocilia in cochlear hair cells of the inner ear. In retina photoreceptors, required for the maintenance of periciliary membrane complex that seems to play a role in regulating intracellular protein transport. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80VW5}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Hearing;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Synapse;Usher syndrome |
|
This gene is thought to function in the organization and stabilization of sterocilia elongation and actin cystoskeletal assembly, based on studies of the related mouse gene. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness and Usher Syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2016]. |
hsa:25861; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; periciliary membrane compartment [GO:1990075]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilia ankle link [GO:0002141]; stereocilia ankle link complex [GO:0002142]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium tip [GO:0032426]; synapse [GO:0045202]; USH2 complex [GO:1990696]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; cerebellar Purkinje cell layer formation [GO:0021694]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound [GO:0050910]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; inner ear receptor cell differentiation [GO:0060113]; inner ear receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060122]; paranodal junction maintenance [GO:1990227]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; retina homeostasis [GO:0001895]; sensory perception of light stimulus [GO:0050953]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
12641734_This paper describes a PDZ domain protein and its role in synaptic transmission in the related rat gene. 12833159_Defects in whirlin, a PDZ domain molecule involved in stereocilia elongation, cause deafness in the whirler mouse and families with DFNB31. 16434480_This paper concludes that this protein plays a role in photoreceptor and hair cell synapse organization in the related rat gene. 17171570_analysis of a novel genetic subtype for Usher syndrome, USH2D, which is caused by mutations in whirlin 19724906_Overexpression of the signal peptide whirlin isoform 2 is related to disease progression in colorectal cancer patients. 20352026_DFNB31 is not a major cause of Usher syndrome. 20352026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21738389_A novel DFNB31 mutation associated with Usher type 2 syndrome showing variable degrees of auditory loss in a consanguineous Portuguese family. 22147658_Mutation found in USH2A, GPR98, or DFNB31 account for the vast majority of USH2 patients and their analysis provide a robust pathway for routine molecular diagnosis. 23441107_In Spain, USH2A and GPR98 are responsible for 95.8% and 5.2% of Usher syndrome 2 mutated cases, respectively. DFNB31 plays a minor role in the Spanish population. There was a group of patients in whom no mutation was found. 24022220_Data indicate that that CIB2 localizes to stereocilia and interacts with the USH proteins myosin VIIa and whirlin, suggesting CIB2 is a Ca2+-buffering protein essential for calcium homeostasis in the mechanosensory stereocilia of inner ear hair cells. 28137943_Protein-protein interaction assays and co-expression of complex partners reveal that pathogenic mutations in USH1G severely affect formation of the SANS/ush2a/whirlin complex. Translational read-through drug treatment, targeting the c.728C > A (p.S243X) nonsense mutation, restored SANS scaffold function. We conclude that USH1 and USH2 proteins function together in higher order protein complexes. 29270100_two novel mutations in the WHRN and TMC1 genes are responsible for founder effects of hereditary hemochromatosis, Wilson s disease, the long QT syndrome and autosomal recessive deafness in a Swedish pedigree 30831381_Usher syndrome and non-syndromic deafness: Functions of different whirlin isoforms in the cochlea, vestibular organs, and retina. 31638198_whirlin-espin interaction is important for the architecture of the USH2 complex and actin bundles cross-linked by espin. Our demonstration of whirlin N-terminal fragment interaction with espin, is significantly novel, providing insight into how these two proteins interact to form the USH2 complex. 33539879_Folding and Misfolding of a PDZ Tandem Repeat. 33626355_Phase separation-mediated condensation of Whirlin-Myo15-Eps8 stereocilia tip complex. |
ENSMUSG00000039137 |
Whrn |
291.911468 |
0.4111647693 |
-1.282211 |
0.199384131 |
40.461281 |
0.00000000020055120779569982483449814234937073550990582759823155356571078300476074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001014787736395107631560581728494187941924664642101561184972524642944335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
168.1794566 |
23.7453390 |
411.6708156 |
41.2582419 |
| ENSG00000095951 |
3096 |
HIVEP1 |
protein_coding |
P15822 |
FUNCTION: This protein specifically binds to the DNA sequence 5'-GGGACTTTCC-3' which is found in the enhancer elements of numerous viral promoters such as those of SV40, CMV, or HIV-1. In addition, related sequences are found in the enhancer elements of a number of cellular promoters, including those of the class I MHC, interleukin-2 receptor, and interferon-beta genes. It may act in T-cell activation. Involved in activating HIV-1 gene expression. Isoform 2 and isoform 3 also bind to the IPCS (IRF1 and p53 common sequence) DNA sequence in the promoter region of interferon regulatory factor 1 and p53 genes and are involved in transcription regulation of these genes. Isoform 2 does not activate HIV-1 gene expression. Isoform 2 and isoform 3 may be involved in apoptosis. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor belonging to the ZAS family, members of which are large proteins that contain a ZAS domain - a modular protein structure consisting of a pair of C2H2 zinc fingers with an acidic-rich region and a serine/threonine-rich sequence. These proteins bind specifically to the DNA sequence motif, GGGACTTTCC, found in the enhancer elements of several viral promoters, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and to related sequences found in the enhancer elements of a number of cellular promoters. This protein binds to this sequence motif, suggesting a role in the transcriptional regulation of both viral and cellular genes. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:3096; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20226436_HIVEP1 rs169713C allele was associated with venous thrombosis. 20226436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23975832_Downregulation of tumor suppressor MBP-1 by microRNA-363 in gastric carcinogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000021366 |
Hivep1 |
58.417948 |
2.0151436806 |
1.010883 |
0.410751303 |
5.701987 |
0.01694572247467561118550172238883533282205462455749511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.030894128424680339373153969972918275743722915649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
79.2482919 |
19.6456457 |
40.0571455 |
7.3697983 |
| ENSG00000095970 |
54209 |
TREM2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZC2 |
FUNCTION: Forms a receptor signaling complex with TYROBP which mediates signaling and cell activation following ligand binding (PubMed:10799849). Acts as a receptor for amyloid-beta protein 42, a cleavage product of the amyloid-beta precursor protein APP, and mediates its uptake and degradation by microglia (PubMed:27477018, PubMed:29518356). Binding to amyloid-beta 42 mediates microglial activation, proliferation, migration, apoptosis and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL6R and CCL3, and the anti-inflammatory cytokine ARG1 (By similarity). Acts as a receptor for lipoprotein particles such as LDL, VLDL, and HDL and for apolipoproteins such as APOA1, APOA2, APOB, APOE, APOE2, APOE3, APOE4, and CLU and enhances their uptake in microglia (PubMed:27477018). Binds phospholipids (preferably anionic lipids) such as phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol and sphingomyelin (PubMed:29794134). Regulates microglial proliferation by acting as an upstream regulator of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling cascade (By similarity). Required for microglial phagocytosis of apoptotic neurons (PubMed:24990881). Also required for microglial activation and phagocytosis of myelin debris after neuronal injury and of neuronal synapses during synapse elimination in the developing brain (By similarity). Regulates microglial chemotaxis and process outgrowth, and also the microglial response to oxidative stress and lipopolysaccharide (By similarity). It suppresses PI3K and NF-kappa-B signaling in response to lipopolysaccharide; thus promoting phagocytosis, suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine and nitric oxide production, inhibiting apoptosis and increasing expression of IL10 and TGFB (By similarity). During oxidative stress, it promotes anti-apoptotic NF-kappa-B signaling and ERK signaling (By similarity). Plays a role in microglial MTOR activation and metabolism (By similarity). Regulates age-related changes in microglial numbers (PubMed:29752066). Triggers activation of the immune responses in macrophages and dendritic cells (PubMed:10799849). Mediates cytokine-induced formation of multinucleated giant cells which are formed by the fusion of macrophages (By similarity). In dendritic cells, it mediates up-regulation of chemokine receptor CCR7 and dendritic cell maturation and survival (PubMed:11602640). Involved in the positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation (PubMed:12925681). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99NH8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10799849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11602640, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24990881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27477018, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29518356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29752066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29794134}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a membrane protein that forms a receptor signaling complex with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein. The encoded protein functions in immune response and may be involved in chronic inflammation by triggering the production of constitutive inflammatory cytokines. Defects in this gene are a cause of polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy (PLOSL). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:54209; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane raft [GO:0044853]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; apolipoprotein A-I binding [GO:0034186]; apolipoprotein binding [GO:0034185]; high-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0008035]; kinase activator activity [GO:0019209]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0071813]; lipoteichoic acid binding [GO:0070891]; low-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0030169]; peptidoglycan binding [GO:0042834]; phosphatidylethanolamine binding [GO:0008429]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; sulfatide binding [GO:0120146]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0034189]; amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process [GO:0150094]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to lipid [GO:0071396]; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid [GO:0071223]; cellular response to oxidised low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0140052]; cellular response to peptidoglycan [GO:0071224]; complement-mediated synapse pruning [GO:0150062]; CXCL12-activated CXCR4 signaling pathway [GO:0038160]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097028]; dendritic spine maintenance [GO:0097062]; detection of lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032497]; detection of lipoteichoic acid [GO:0070392]; detection of peptidoglycan [GO:0032499]; excitatory synapse pruning [GO:1905805]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; import into cell [GO:0098657]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; memory [GO:0007613]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; microglial cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002282]; microglial cell proliferation [GO:0061518]; negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905907]; negative regulation of astrocyte activation [GO:0061889]; negative regulation of autophagic cell death [GO:1904093]; negative regulation of autophagy [GO:0010507]; negative regulation of cell activation [GO:0050866]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of fat cell proliferation [GO:0070345]; negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process [GO:0034351]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032691]; negative regulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:1902227]; negative regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150079]; negative regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:1900226]; negative regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1903753]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0010891]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway [GO:0034136]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034144]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; phagocytosis, recognition [GO:0006910]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900223]; positive regulation of antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0002588]; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001171]; positive regulation of C-C chemokine receptor CCR7 signaling pathway [GO:1903082]; positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050850]; positive regulation of CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade [GO:1905291]; positive regulation of CD40 signaling pathway [GO:2000350]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0045960]; positive regulation of engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:1901076]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of establishment of protein localization [GO:1904951]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of high-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0010983]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of inward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:1901980]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:1905581]; positive regulation of macrophage fusion [GO:0034241]; positive regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903980]; positive regulation of microglial cell migration [GO:1904141]; positive regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010822]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0060100]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901800]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of synapse pruning [GO:1905808]; positive regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032008]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900015]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of hippocampal neuron apoptotic process [GO:0110089]; regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045088]; regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032675]; regulation of intracellular signal transduction [GO:1902531]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha production [GO:0071640]; regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1903376]; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050730]; regulation of plasma membrane bounded cell projection organization [GO:0120035]; regulation of resting membrane potential [GO:0060075]; regulation of toll-like receptor 6 signaling pathway [GO:0034151]; regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032006]; respiratory burst after phagocytosis [GO:0045728]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; social behavior [GO:0035176] |
12080485_Mutations in two genes encoding different subunits of a receptor signaling complex (TYROBP and TREM2) result in an identical disease phenotype 12645956_The human TREM gene cluster at 6p21.1 encodes both activating and inhibitory single IgV domain receptors and includes TREM2. 12754369_Nasu-Hakola disease with a novel genetic mutations in the TREM2 gene 12913093_results demonstrate a critical role for TREM-2 in the differentiation of mononuclear myeloid precursors into functional multinucleated osteoclasts 12925681_These results indicate an important role for DAP12-TREM2 signaling complex in the differentiation and function of osteoclasts. 15966270_Two healthy subjects heterozygous for one mutated TREM2 allele showed a deficit of visuospatial memory associated with hypoperfusion in the basal ganglia, whereas the homozygotes for the wild-type allele of TREM2 did not show any abnormalities. 16505336_Mutation in Nasu-Hakola disease. 17530208_Transcript analysis of DCs of PLOSL patients show that TREM2 deficient cells differentiated into DCs and responded to pathogenic stimuli. However, the DCs showed morphological differences due to defects in the actin filaments. 18546367_Mutations in TREM2 lead to pure early-onset dementia without bone cysts 18551625_TREM2 is induced and expressed in microglia associated with amyloid plaques where it may impact on their differentiation state and function in aged APP23 transgenic mice, an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. 19019460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19019460_the DAP12-TREM2 complex unlikely has a role in genetic susceptibility of multiple sclerosis 19079182_TREM-2 can function as a pattern-recognition receptor in the induction of the innate immune response to gonococci. 19230638_decreased percentages of TREM-2 positive monocytes in patients with multiple sclerosis 19457124_Treatment with Hsp60 was found to stimulate the best known TREM2-dependent process, phagocytosis, however, only in the microglial N9 cells rich in the receptor. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20421649_These findings indicate that DAP12, possibly through association with TREM2, contributes to alveolar macrophage chemotaxis and recruitment to the lung and may mediate macrophage accumulation in lung diseases such as emphysema. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20640189_TREM2 expression correlates positively with amyloid phagocytosis in a transgenic model of amyloid pathology. 21834902_This is the first report of a Japanese Nasu-Hakola disease family caused by a splicing mutation of TREM2 that induces both neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. 22939635_we have identified a common TREM2 variant associated with CRP in United States minority populations. 23150908_Our findings strongly implicate variant TREM2 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. 23150934_Heterozygous rare variants in TREM2 are associated with a significant increase in the risk of Alzheimer's disease. 23380991_An association is found between rs75932628-T variant of TREM2 and early-onset Alzheimer's disease. 23391427_A positive replication study in a Spanish population confirms that TREM2 rs75932628-T is associated with risk for Alzheimer's disease. 23407992_REVIEW: the recent epidemiological findings of TREM2 that related with late-onset AD and speculate the possible roles of TREM2 in progression of this disease 23533697_TREM2 is expressed on microglial cells, the resident macrophages in the CNS, and functions to stimulate phagocytosis on one hand and to suppress cytokine production and inflammation on the other hand. 23582655_Mutation in TREM2 may serve as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease in general, and that potentially this class of TREM2 variant carriers with dementia should be considered as having a molecularly distinct form of neurodegenerative disease. 23721075_TREM-2 plays an important role in the host defense response to sepsis by enhancing bacterial clearance. 23759145_Its mutations are rare in a French cohort of patients with frontotemporal dementia. 23800361_Our results suggest that the TREM2 p.R47H substitution is a risk factor for frontotemporal dementia and Parkinson's disease 23855982_R47H variant of TREM2 is an Alzheimer's disease risk factor. 23855984_It is significantly enriched for genes genetically implicated in Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, and motor neuron disease, implying that these diseases share common pathways centered on microglia. 23870839_Its homozygous mutations cause frontotemporal dementia. (review) 24002183_Higher levels of TREM2 mRNA (p = 0.002) and protein (p A, p.Asp87Asn missense mutation in exon 2 and c.428del, p.Phe143fs frameshift mutation in exon 3. 30152135_These findings suggest a role for TREM2 in the brain of HIV+ individuals may deserve more investigation as a biomarker for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders and as a possible therapeutic target 30157425_Data identify specific deficits in the ability of iPSC-MGLCs harboring TREM2 missense mutations to respond to specific pathogenic signals. 30185230_Trem2 R47H variant activates a cryptic splice site that generates miss-spliced transcripts leading to Trem2 haploinsufficiency only in mice but not in humans 30222607_The minor allele frequency of rs75932628-T was 0.009 in cases and was not found in any healthy controls which suggests a significant association between rs75932628-T and Late Onset AD risk in our sample (P=0.010). 30341064_Alzheimer's disease-associated TREM2 variants bind Abeta with equivalent affinity but show loss of function in terms of signaling and Abeta internalization. 30442540_In vitro phagocytosis of human pluripotent stem cell monocytes and transdifferentiated microglia-like cells was not affected by the TREM2(+/R47H) mutation but was significantly impaired in TREM2(+/-) and TREM2(-/-) progeny. 30458365_TREM2 in CSF as a marker of neuroinflammation across the spectrum of early clinical AD. 30482868_In conclusion, the authors demonstrate that, although cerebrospinal fluid progranulin is not a diagnostic biomarker for Alzheimer's disease, it may together with sTREM2 reflect microglial activation during the disease. 30485483_There was a significant association between increased serum soluble TREM2 levels and the risk of developing all-cause dementia. 30568991_Elevations in CSF sTREM2 levels, an indicator of macrophage/microglial activation, are a common feature of untreated HIV-1 infection that increases with CD4+ T-cell loss and reaches highest levels in HIV-associated dementia. 30630532_Amyloid-beta pathology (A) and tau pathology/neurodegeneration have differing associations with cerebrospinal sTREM2 in patients with Alzheimer's Disease 30705288_Study shows that rare coding variants in TREM2, PLCG2, and ABI3 modulate susceptibility to Alzheimer disease in populations from Argentina, and they may have a European heritage. 30883352_TREM2 Variants and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 30978656_CSF glial biomarkers YKL40 and sTREM2 are associated with longitudinal volume and diffusivity changes in cognitively unimpaired individuals. results suggest that glial biomarkers exert a relevant and distinct influence in longitudinal brain macro- and microstructural changes in cognitively unimpaired adults, which appears to be modulated by age. 31028072_Downregulating the expression of TREM2 can inhibit the release of inflammatory factors from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia. 31068200_the effect of the TREM2 variants on cerebrospinal fluid levels occurs at post-transcriptional level 31101881_Aminophospholipids are signal-transducing TREM2 ligands on apoptotic cells. 31350575_Impact of TREM2 risk variants on brain region-specific immune activation and plaque microenvironment in Alzheimer's disease patient brain samples. 31362167_No multiple sclerosis or healthy subjects carried the variant of TREM2 studied in the Greek population. 31464095_A rare heterozygous TREM2 coding variant identified in familial clustering of dementia affects an intrinsically disordered protein region and function of TREM2. 31481003_Role of TREM2 in Alzheimer's Disease and its Consequences on beta- Amyloid, Tau and Neurofibrillary Tangles. 31513029_To examine the potential association of TREM2 with various neurodegenerative diseases, we assessed the risk effect of the R47H variant using a large multicenter neurodegenerative disease cohort comprised of AD, FTD, MCI, CBS, PSP-S, and ALS patients. We found the strongest risk association in the AD series (OR =4.46, CI =2.35-8.48, P= 2.07E-06). We found no evidence of a risk association within FTD, MCI, PSP-S, and CBS. 31724242_Association Between Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) and Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells 2 (TREM2) Genetic Variants and Clinical Progression of Huntington's Disease. 31779670_Plasma levels of soluble TREM2 and neurofilament light chain in TREM2 rare variant carriers. 31812991_CSF sTREM2 and Tau Work Together in Predicting Increased Temporal Lobe Atrophy in Older Adults. 31833018_Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Soluble TREM2 and Polymorphisms in Sporadic Parkinson's Disease in a Chinese Population. 31847649_Association study of serum soluble TREM2 with vascular dementia in Chinese Han population. 31902528_studies identify TREM2 as a key transcriptional regulator of cholesterol transport and metabolism under conditions of chronic myelin phagocytic activity, as TREM2 loss of function causes pathogenic lipid accumulation in microglia. 31907987_A locked immunometabolic switch underlies TREM2 R47H loss of function in human iPSC-derived microglia. 31915256_Longitudinal Basal Forebrain Degeneration Interacts with TREM2/C3 Biomarkers of Inflammation in Presymptomatic Alzheimer's Disease. 31932797_a TREM2 requirement in both mouse and human Alzheimer's disease, is reported. 31958095_Soluble TREM2 and Inflammatory Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid. 31959733_An Altered Relationship between Soluble TREM2 and Inflammatory Markers in Young Adults with Down Syndrome: A Preliminary Report. 32000403_Systematic review and meta-analysis suggested that R47H in the TREM2 gene leads to an increased risk for developing Alzheimer disease, but not for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson disease, which adds evidence to the notion that diverse pathogenesis may be involved in different neurogenerative diseases. 32031293_Microglia-Related Gene Triggering Receptor Expressed in Myeloid Cells 2 (TREM2) Is Upregulated in the Substantia Nigra of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. 32065223_findings indicate that Cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 could serve as a surrogate immune biomarker o |
ENSMUSG00000023992 |
Trem2 |
863.367409 |
0.4590414735 |
-1.123304 |
0.070174567 |
255.986426 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000128648632713914406047976917683517177115789716864905941291342131156513152920782676474777259290352826793076254665784034897471861839452523299626943847906446194429008755832910537719726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031647563647622943548214356294143511788892296940474669782075244334284553509164480040213906338195103588364329199246943855254861538872402119612625703837238688720390200614929199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
542.2698181 |
23.9882779 |
1189.5908573 |
35.7683902 |
| ENSG00000096093 |
114327 |
EFHC1 |
protein_coding |
Q5JVL4 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated protein which regulates cell division and neuronal migration during cortical development. Necessary for mitotic spindle organization (PubMed:19734894, PubMed:28370826). Necessary for radial and tangential cell migration during brain development, possibly acting as a regulator of cell morphology and process formation during migration (PubMed:22926142). May enhance calcium influx through CACNA1E and stimulate programmed cell death (PubMed:15258581). Microtubule inner protein (MIP) part of the dynein-decorated doublet microtubules (DMTs) in cilia axoneme, which is required for motile cilia beating (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E1BKH1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15258581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19734894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22926142, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28370826}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes an EF-hand-containing calcium binding protein. The encoded protein likely plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with susceptibility to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy and juvenile absence epilepsy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:114327; |
axonemal microtubule [GO:0005879]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; cerebral cortex cell migration [GO:0021795]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; mitotic spindle organization [GO:0007052]; regulation of cell division [GO:0051302] |
14582146_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15258581_Mutation analyses identified five missense mutations in EFHC1 that cosegregated with epilepsy or EEG polyspike wave in affected members of six unrelated families with JME and did not occur in 382 control individuals 15258581_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16378686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16378686_The combination of these polymorphisms could not be found in any control individuals, suggesting that they might be involved in genetic predisposition to migraine in this family. 16824517_Deletion analyses revealed that the N-terminal region of EFHC1 is crucial for the association with the mitotic spindle and the midbody. Our results suggest that EFHC1 could play an important role during cell division. 16839746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17054699_We found no evidence that EFHC1 is a major genetic risk factor for JME susceptibility in Dutch patients. 17159113_Mutations in the EFHC1 gene may underlie different types of epilepsy syndromes. 17634063_report presents one novel and one previously described mutation in the EFHC1 gene in Italian families, reinforcing the role of this gene in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 17972043_In this case of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, A molecular genetic analysis led to the identification of a polymorphism (A-->G) in position 10 in the intron 3 (rs949626) of the EFHC1 gene. 18505993_Nine percent of consecutive juvenile myoclonic epilepsy cases from Mexico and Honduras clinics and 3% of clinic patients from Japan carry mutations in Myoclonin1/EFCH1 18593566_Under reducing condition Ca(2+) or Mg(2+) ions bind to EFHC1C in a 1/1 molar ratio, while under oxidizing condition this ratio is reduced, showing that EFHC1C dimerization blocks Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) binding 18823326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18823326_The results of this study show that four coding SNPs, rs3804506, rs3804505, rs1266787, and rs17851770, of EFHC1 may not be susceptibility alleles for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22226147_The juvenile myoclonic epilepsy-related protein EFHC1 interacts with the redox-sensitive TRPM2 channel linked to cell death. 22690745_homozygous Phe229Leu mutation associated with primary intractable epilepsy in infancy 22727576_we conclude that mutations in the Myoclonin1/EFHC1 gene are an important cause of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy in Mexican patients. 22926142_These results show how Myoclonin1/EFHC1 mutations disrupt brain development and potentially produce structural brain abnormalities on which epileptogenesis is established. 23756480_Myoclonin1/EFHC1 mutation was suggested releated to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. 23756481_Three SNP alleles in BRD2, Cx-36, and ME2 and microdeletions in 15q13.3, 15q11.2, and 16p13.11 also contribute risk to juvenile myclonic epilepsy. 25489633_some EFHC1 mutations may be pathogenic only when introduced into specific genetic backgrounds to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 27467453_NHGRI gene-level evidence and variant-level evidence establish EFHC1 as the first non-ion channel microtubule-associated protein whose mutations disturb R-type VDCC and TRPM2 calcium currents in overgrown synapses and dendrites within abnormally migrated dislocated neurons, thus explaining CTC convulsions and 'microdysgenesis' neuropathology of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 28370826_EFHC1 mutations cause microtubule-associated defects in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 33181902_Revisiting the clinical impact of variants in EFHC1 in patients with different phenotypes of genetic generalized epilepsy. 33969125_Mutational Analysis of Myoclonin1 Gene in Pakistani Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000041809 |
Efhc1 |
79.569387 |
0.4571295346 |
-1.129325 |
0.349088622 |
10.083110 |
0.00149634540998699861434617641720024039386771619319915771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003390552387382268859777889602469258534256368875503540039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.2117268 |
12.8351369 |
107.8851085 |
19.7172818 |
| ENSG00000096384 |
3326 |
HSP90AB1 |
protein_coding |
P08238 |
FUNCTION: Molecular chaperone that promotes the maturation, structural maintenance and proper regulation of specific target proteins involved for instance in cell cycle control and signal transduction. Undergoes a functional cycle linked to its ATPase activity. This cycle probably induces conformational changes in the client proteins, thereby causing their activation. Interacts dynamically with various co-chaperones that modulate its substrate recognition, ATPase cycle and chaperone function (PubMed:16478993, PubMed:19696785). Engages with a range of client protein classes via its interaction with various co-chaperone proteins or complexes, that act as adapters, simultaneously able to interact with the specific client and the central chaperone itself. Recruitment of ATP and co-chaperone followed by client protein forms a functional chaperone. After the completion of the chaperoning process, properly folded client protein and co-chaperone leave HSP90 in an ADP-bound partially open conformation and finally, ADP is released from HSP90 which acquires an open conformation for the next cycle (PubMed:27295069, PubMed:26991466). Apart from its chaperone activity, it also plays a role in the regulation of the transcription machinery. HSP90 and its co-chaperones modulate transcription at least at three different levels. They first alter the steady-state levels of certain transcription factors in response to various physiological cues. Second, they modulate the activity of certain epigenetic modifiers, such as histone deacetylases or DNA methyl transferases, and thereby respond to the change in the environment. Third, they participate in the eviction of histones from the promoter region of certain genes and thereby turn on gene expression (PubMed:25973397). Antagonizes STUB1-mediated inhibition of TGF-beta signaling via inhibition of STUB1-mediated SMAD3 ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:24613385). Promotes cell differentiation by chaperoning BIRC2 and thereby protecting from auto-ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasomal machinery (PubMed:18239673). Main chaperone involved in the phosphorylation/activation of the STAT1 by chaperoning both JAK2 and PRKCE under heat shock and in turn, activates its own transcription (PubMed:20353823). Involved in the translocation into ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment) of leaderless cargos (lacking the secretion signal sequence) such as the interleukin 1/IL-1; the translocation process is mediated by the cargo receptor TMED10 (PubMed:32272059). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16478993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18239673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19696785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20353823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24613385, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32272059, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25973397, ECO:0000303|PubMed:26991466, ECO:0000303|PubMed:27295069}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Binding to N.meningitidis NadA stimulates monocytes (PubMed:21949862). Seems to interfere with N.meningitidis NadA-mediated invasion of human cells (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21949862, ECO:0000305|PubMed:22066472}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Secreted;Stress response;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the heat shock protein 90 family; these proteins are involved in signal transduction, protein folding and degradation and morphological evolution. This gene encodes the constitutive form of the cytosolic 90 kDa heat-shock protein and is thought to play a role in gastric apoptosis and inflammation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes have been identified on multiple chromosomes. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. |
hsa:3326; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex [GO:0034751]; axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic growth cone [GO:0044294]; dynein axonemal particle [GO:0120293]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex [GO:1990565]; inclusion body [GO:0016234]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ooplasm [GO:1990917]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; sperm head plasma membrane [GO:1990913]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein binding [GO:0043008]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; CTP binding [GO:0002135]; dATP binding [GO:0032564]; disordered domain specific binding [GO:0097718]; DNA polymerase binding [GO:0070182]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; heat shock protein binding [GO:0031072]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; histone methyltransferase binding [GO:1990226]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity [GO:0030235]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein kinase regulator activity [GO:0019887]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; sulfonylurea receptor binding [GO:0017098]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; TPR domain binding [GO:0030911]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; UTP binding [GO:0002134]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; central nervous system neuron axonogenesis [GO:0021955]; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly [GO:0051131]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; negative regulation of complement-dependent cytotoxicity [GO:1903660]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901799]; negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032435]; negative regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051248]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta activation [GO:1901389]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell size [GO:0045793]; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:1904031]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032516]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042307]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000010]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of tau-protein kinase activity [GO:1902949]; positive regulation of telomerase activity [GO:0051973]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031396]; response to cocaine [GO:0042220]; response to salt stress [GO:0009651]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; supramolecular fiber organization [GO:0097435]; telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly [GO:1905323]; telomere maintenance via telomerase [GO:0007004]; virion attachment to host cell [GO:0019062] |
14532285_PKC-epsilon is specifically required in the signaling pathway leading to the induction of hsp90 beta gene in response to heat shock. 15284248_hsp90beta is repressed by p53 in UV irradiation-induced apoptosis 15581363_Mutations at the phosphorylation sites of HSP90-beta modulate the interaction with arylhydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and may negatively regulate formation of the functional AhR complex in the steady-state cytosol. 16248461_The overexpression of HSP70 and HSP90beta are probably correlated with the occurrence, development and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 16280321_JAK1/2 are client proteins of Hsp90 alpha and beta; Hsp90 and CDC37 play a critical role in types I and II interferon pathways 17764690_Hydrogen-exchange mass spectrometry was used to study structural & conformational changes undergone by full-length Hsp90beta in solution upon binding of the co-chaperone Cdc37 & 2 Hsp90 ATPase inhibitors: Radicicol & the anticancer drug DMAG 18239673_Results suggest that HSP90 beta prevents auto-ubiquitination and degradation of its client protein c-IAP1, whose depletion would be sufficient to inhibit cell differentiation. 18285346_GCUNC45 is required for the normal cellular distribution of Hsp90beta, but not Hsp90alpha. 18347946_The conversion of Thr(566) and Ala(629) of Hsp90alpha to Ala(558) and Met(621) is primarily responsible for impeded dimerization of Hsp90beta. 18400751_conformational analysis of hydrolysis by human Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta 18412542_Tah1 is specific for Hsp90, and is able to bind tightly the yeast Hsp90, and the human Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta proteins, but not the yeast Hsp70 Ssa1 isoform 18591256_These data provide an explanation for apoptosome inhibition by activated leukemogenic tyrosine kinases and suggest that alterations in Hsp90beta-apoptosome interactions may contribute to chemoresistance in leukemias. 19022436_Presence of ovarian autoantibodies to human HSP90 in sera of women with infertility could be involved in human ovarian autoimmunity and thereby be a causative factor in early ovarian failure. 19047110_Hsp90 overexpression correlates with several adverse parameters for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hsp90alpha seems more relevant to the aggressiveness of gastrointestinal stromal tumors than Hsp90beta 19254810_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19327008_Study points to a potential role for Hsp90beta in MSC biology. 19380486_Results show that heat shock protein 90 beta is cleaved by activated caspase-10 under UVB irradiation. 19576239_Expression profiling of Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta and its cochaperone proteins may be useful for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19802386_COMMD1 has a role in conjunction with HSP90beta/HSP70 in the ubiquitin and O(2)-independent regulation of HIF-1alpha 19858214_celastrol may represent a new class of Hsp90 inhibitor by modifying Hsp90 C terminus to allosterically regulate its chaperone activity and disrupt Hsp90-Cdc37 complex. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19996313_Data show that the small molecule celastrol inhibits the Hsp90 chaperoning machinery by inactivating the co-chaperone p23, resulting in a more selective destabilization of steroid receptors. 20226818_findings present novel Hsp90 mutants that render cells resistant to Hsp90 inhibitors; show that the resistance depends on the increased ATPase turnover due to enhanced interaction with Aha1 20451655_H. pylori induces the translocation of HSP90beta from the cytosol to the membrane and interaction of HSP90beta and Rac1, which leads to the activation of NADPH oxidase and production of ROS in gastric epithelial cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20705598_Results show that RPL4, RPLP0, and HSPCB were the most stable reference genes in ovarian tissues. 20946244_cyclophilin A and Hsp90 facilitate translocation of lethal factor(N) diphtheria toxin, but not of lethal factor, across endosomal membranes, and thus they function selectively in promoting translocation of certain proteins, but not of others 21602280_a possible role for HSP90AB1 in postentry HIV replication and may provide an attractive target for therapeutic intervention. 21689689_TRIM8 modulates translocation of phosphorylated STAT3 into the nucleus through interaction with Hsp90beta and consequently regulates transcription of Nanog in embryonic stem cells. 22019372_Data identify HSP90 as a pro-inflammatory molecule in retinal pigmented epithelial cell sterile inflammatory responses. 22185817_DNA sequencing of 101 human samples detects eight and seven unique single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at the HSP90AA1 and HSP90AB1 loci, respectively. 22848402_Using a proteomic analysis, we determined that the cleavage occurs in a conserved motif of the N-terminal nucleotide binding site, between Ile-126 and Gly-127 in Hsp90beta, and between Ile-131 and Gly-132 in Hsp90alpha. 22849407_results demonstrate that Hsp90 plays an essential role in regulating PTK6 stability and suggest that Hsp90 inhibitors may be useful as therapeutic drugs for PTK6-positive cancers, including breast cancer 22929401_The upregulation of Hsp90-beta was associated with poor post-surgical survival time and lymphatic metastasis of lung cancer patients 23200770_the transdominant effect of HSP90AB1 on capsid-spacer protein 1-mutant HIV infectivity suggests a potential role for this class of cellular chaperones in HIV core stability and uncoating. 23515950_HSP90beta may positively regulate angiogenesis, not only as a protein chaperone, but also as an mRNA stabilizer for pro-angiogenic genes, such as BAZF, in a PRKD2 activity-dependent manner. 23516526_differences in expression caused by the -144 polymorphism in the HSP90beta promoter are associated with cellular inflammatory responses and the severity of organ injury 23661493_Hsp90 is upregulated in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and is critical for TGF-beta signalling. 23711381_Here we describe the specific association of heat shock protein-90-beta (Hsp90beta) with EV71 viral particles by the co-purification with virions using sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation and colocalization as shown by immunogold EM. 24292678_CDC37 has an important role in chaperoning protein kinases; it stabilizes kinase clients by a mechanism that is not dependent on a substantial direct interaction between CDC37 and HSP90, but requires HSP90 activity 24466266_Hsp90 binds directly to fibronectin (FN) and inhibition reduces the extracellular fibronectin matrix in breast cancer cells. 24511009_The frequency of mutant CC genotype for HSP90AA1 (rs4947C/T), mutant AA genotype for HSP90AB1 (rs13296A/G) and mutant CC genotype for HSP90B1 (rs2070908 C/G) was significantly higher in the patient group than in controls. 24581495_Study obtained a structural model of Hsp90 in complex with its natural disease-associated substrate, the intrinsically disordered Tau protein. Hsp90 binds to a broad region in Tau that includes the aggregation-prone repeats. 24670792_HSP70 was massively up-regulated in all mast cells three months after irradiation whereas HSP90AB1 was up-regulated only in a portion of mast cells 24880080_A novel mechanism for human carcinogenesis via methylation of HSP90AB1 by SMYD2. 25191796_The proteins (HSP90b, TMS1 and L-plastin) in the current study may hold potential in differentiating between melanoma and benign nevi in diagnostically challenging cases. 25300907_The expression levels of Hsp90-beta and annexin A1 positively correlated and such co-overexpression of Hsp90-beta and annexin A1 contributed to lung cancer diagnosis. 25486457_These results suggest that differences in the middle domain of Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta may be responsible for the isoform-specific interactions with selected proteins. 25995454_Casein kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of Hsp90beta and stabilization of PXR is a key mechanism in the regulation of MDR1 expression. 26044951_This study identifies overexpression of HSP90 (especially isoform HSP90AB1) and its clients ATR, ATM, and NBS1 as promising markers for radioresistant, aggressive soft tissue sarcomas with particularly poor prognosis. 26134567_These results suggest a means by which the hsp90beta interaction could prevent apo-sGCbeta1 from associating with its partner sGCalpha1 subunit while enabling structural changes to assist heme insertion into the H-NOX domain. 26358502_HSP90AB1: Helping the good and the bad 26511315_Apart from these distinct Cdc37/Hsp90 interfaces, binding of the B-Raf protein kinase to the cochaperone is conserved between mammals and nematodes. 26651243_We revealed that Hsp90A and Hsp90B are partly colocalized with heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) on the cell surface and that this colocalization was sensitive to heparin. 26903158_The expression level of Hsp90AB1 in lung cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in normal lung tissue and was associated with lung cancer pathological type and overall survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients. 27258564_the expressions of HSP90AB1 can predict prognosis in astrocytic tumors 27620500_The authors find that the interaction between sB-Raf and the Hsp90 chaperone system is based on contacts with the M domain of Hsp90, which contributes in forming the ternary complex with Cdc37 as long as the kinase is not stabilized by nucleotide. 27756247_Data show that C allele of rs2282151 was associated with increased expression level of heat shock protein 90 alpha family class B member 1 (HSP90AB1). 27959448_High HSP90B expression is associated with laryngeal carcinoma. 28239659_Fibroblasts isolated from pulmonary fibrosis lesions showed heightened Hsp90 ATPase activity compared with normal fibroblasts. The loss of the Hsp90AB, but not the Hsp90AA isoform, resulted in reduced fibroblast proliferation, myofibroblast transformation, and ECM production. 28359326_Hsp90beta induced endothelial cell-dependent tumor angiogenesis by activating VEGFRs transcription. 28651008_We found that the nutrient value of the culturing medium and the length of induction had significant effect on Hsp90 production in Escherichia coli. Our fast, single-day purification protocol resulted in a stable, well-folded and pure sample that was resistant to degradation in a reproducible manner. 29386344_the intracellular form of HSP90beta stabilises LRP1, thus amplifying HSP90alpha extracellular action 29768689_Elevated expression of HSP90alpha and HSP90beta was found to correlate with poor prognosis of head and neck cancers cases. Thus, elevated levels HSP90alpha and HSP90beta in secreted vesicles are potential prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in metastatic oral squamous cell carcinoma. 29871907_The genomic region between SLC29A1 and HSP90AB1 and its role in regulating adenosine signaling are key targets for further investigation into the pathogenesis of bevacizumab-induced hypertension. 29968330_The production of IFN-gamma by T cells stimulated with citrullinated HSP90beta demonstrates a bias toward TH1 immune responses that are likely involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease. 30305727_the crosstalk between Hsp90ab1 and LRP5 contributed to the upregulation of multiple mesenchymal markers, which are also targets of Wnt/beta-catenin. Collectively, this study uncovers the details of the Hsp90ab1-LRP5 axis, providing novel insights into the role and mechanism of invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer (GC) . 31124601_Copy number variations and polymorphisms in HSP90AB1 and risk of systemic lupus erythematosus and efficacy of glucocorticoids. 31449053_Through a proteomics screen, we identified the heat shock protein 90 B (hsp90B) chaperone as a direct MAST1 binding partner essential for its stabilization. Targeting hsp90B sensitized cancer cells to cisplatin predominantly through MAST1 destabilization. Mechanistically, interaction of hsp90B with MAST1 blocked ubiquitination of MAST1 at lysines 317 and 545. 31801945_USP22-dependent HSP90AB1 expression promotes resistance to HSP90 inhibition in mammary and colorectal cancer. 31885746_Serum Hsp90beta and total Hsp90 levels were statistically significantly higher in overweight and obese children compared to controls. Also, Hsp90beta levels were higher in overweight and obese NAFLD patients. However Hsp90alpha to Hsp90beta ratio had better accuracy for NAFLD diagnosis in obese and overweight patients compared to individual biomarkers. 32962253_Discovery of Novel Hsp90 C-Terminal Inhibitors Using 3D-Pharmacophores Derived from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. 33040396_Molecular basis of the interaction of Hsp90 with its co-chaperone Hop. 33080545_HSP90 expression and early recurrence in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Potential for a novel therapeutic target. 33145341_Heat Shock Protein 90 Family Isoforms as Prognostic Biomarkers and Their Correlations with Immune Infiltration in Breast Cancer. 33179566_Human coronavirus dependency on host heat shock protein 90 reveals an antiviral target. 33639524_Selective HSP90beta inhibition results in TNF and TRAIL mediated HIF1alpha degradation. 34217296_Effect of HSP90AB1 and CC domain interaction on Bcr-Abl protein cytoplasm localization and function in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 34449539_Protective Role of Genetic Variants in HSP90 Genes-Complex in COPD Secondary to Biomass-Burning Smoke Exposure and Non-Severe COPD Forms in Tobacco Smoking Subjects. 34534637_CircVCAN/SUB1 up-regulates MYC/HSP90beta to enhance the proliferation and migration of glioma cells. 35008592_Neurodegeneration and Astrogliosis in the Human CA1 Hippocampal Subfield Are Related to hsp90ab1 and bag3 in Alzheimer's Disease. 35298351_LncRNA RP3-326I13.1 promotes cisplatin resistance in lung adenocarcinoma by binding to HSP90B and upregulating MMP13. 35929142_HSP90AB1 Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, and Glycolysis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 36114006_ALS-linked loss of Cyclin-F function affects HSP90. |
ENSMUSG00000023944 |
Hsp90ab1 |
9552.451521 |
2.0422894389 |
1.030187 |
0.015475167 |
4493.665238 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12964.3111738 |
122.1634423 |
6394.4555295 |
47.7122788 |
| ENSG00000096654 |
7738 |
ZNF184 |
protein_coding |
Q99676 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is predicted to be a Kruppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family member. Sequence analysis predicts that the protein contains two Kruppel associated box (KRAB) boxes in the N-terminus and highly conserved zinc finger motifs at the C-terminus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:7738; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19571809_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27565901_We found that 6p22.1 (rs6904596, ZNF184) was associated with both lung cancer and blood triglycerides. 32125537_Association between ZNF184 and symptoms of Parkinson's disease in southern Chinese. |
|
|
53.109829 |
0.2114300085 |
-2.241748 |
0.808246993 |
6.880361 |
0.00871479466776679291550866679472164832986891269683837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016893577687273668430645301441472838632762432098388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.2508163 |
13.1793114 |
70.3300200 |
42.0069620 |
| ENSG00000099139 |
5125 |
PCSK5 |
protein_coding |
Q92824 |
FUNCTION: Serine endoprotease that processes various proproteins by cleavage at paired basic amino acids, recognizing the RXXX[KR]R consensus motif. Likely functions in the constitutive and regulated secretory pathways. Plays an essential role in pregnancy establishment by proteolytic activation of a number of important factors such as BMP2, CALD1 and alpha-integrins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19764806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20555025, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22740495}. |
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Pregnancy;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family, which includes proteases that process protein and peptide precursors trafficking through regulated or constitutive branches of the secretory pathway. The encoded protein undergoes an initial autocatalytic processing event in the ER to generate a heterodimer which exits the ER. It then sorts to the trans-Golgi network where a second autocatalytic event takes place and the catalytic activity is acquired. This encoded protein is widely expressed and one of the seven basic amino acid-specific members which cleave their substrates at single or paired basic residues. It mediates posttranslational endoproteolytic processing for several integrin alpha subunits and is thought to process prorenin, pro-membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase and HIV-1 glycoprotein gp160. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, some of which encode distinct isoforms, including a protease packaged into dense core granules (PC5A) and a type 1 membrane bound protease (PC5B). [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:5125; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cytokine precursor processing [GO:0140447]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; embryonic digestive tract development [GO:0048566]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; heart development [GO:0007507]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; limb morphogenesis [GO:0035108]; peptide biosynthetic process [GO:0043043]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0051004]; renin secretion into blood stream [GO:0002001]; respiratory tube development [GO:0030323]; signal peptide processing [GO:0006465]; viral life cycle [GO:0019058] |
11723118_we investigated the specificity and potency of complete prodomains and short C-terminal prodomain peptides of each SPC on highly purified, soluble enzyme preparations of human SPC1, SPC6, and SPC7. 15522936_PC5/6 plays a key role for decidualization in human endometrium. 15601911_PC6 is an essential molecule in modulating uterine function to support the establishment of embryo implantation 15911696_furin and PC5 play a role in a MT-MMP-MMP-2 proteolytic cascade, involving provision of macrophage MT1-MMP for the activation of pro-MMP-2; furin and PC5 are expressed in monocytes and colocalize with MT1-MMP in macrophages in the atherosclerotic plaque 16912035_PCSK9 levels are finely regulated by the basic amino acid convertases furin and PC5/6A 17242158_in binding VEGFR-2, furin and PC5 promote cleavage of N-and C-terminal VEGF-D propeptides, whereas PC7 promotes cleavage of the C-terminal propeptide only 18039650_after stimulation, the protease activity of PC5A is enhanced, as evidenced by the cleavage of the PC5A substrates Lefty, ADAMTS-4, endothelial lipase, and PCSK9. 18096669_PC1/3 governs the endocrine and PC2 the neuronal processing of proCCK, whereas PC5/6 contributes only to a modest endocrine synthesis of CCK-22. 18245819_fibrates simultaneously decreased PCSK9 expression while increasing PC5/6A and furin expression, indicating a broad action of PPARalpha activation in proprotein convertase-mediated lipid homeostasis. 18519639_We propose that Pcsk5, at least in part via GDF11, coordinately regulates caudal Hox paralogs, to control anteroposterior patterning, nephrogenesis, skeletal, and anorectal development. 19764806_Results describe the mechanisms of PC6 action in decidualization and identify caldesmon as one of its physiological substrates. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031622_Variability at the PCSK5 locus influences high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20555025_The proteolytic activation and thus bioavailability of BMP2 is controlled by PC6. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21094132_PTPkappa was scissored by the processed form of proprotein convertase 5, and galectin-3 binding protein which is over-produced in colon cancer cells and tissues. 21273245_PC6 may have a role in uterine receptivity and its uterine lavage levels appear to be significantly lower in a subgroup of women with unexplained infertility 21700711_Latent transforming growth factor beta-binding proteins-2 and -3 inhibit the proprotein convertase 5/6A. 21971156_PC6 plays a key role in regulating fundamental cellular remodeling processes, such as plasma membrane transformation and membrane-cytoskeletal interface reorganization. 22740495_study implicates PC6 as a key regulatory protein essential for the attachment of the blastocyst to the endometrial epithelium through the processing of pro-integrin-alphas 23686857_overexpression of PCs, furin and PC5, but not PC7, which are all expressed in SMC, increase PKGI cleavage in a dose-dependent manner 25350918_PC5/6A is involved in squamous differentiation of human nasal epithelial cells, possibly through up-regulation of the BMP-2 signaling pathway. 25429785_Proprotein convertase 5/6 cleaves PDGFA in the human endometrium in preparation for embryo implantation. 26055999_Case Report: whole exome sequencing of a case with the VACTERL association uncovered a novel frameshift mutation in the PCSK5 gene. 26077903_full-length alpha-DG in the human endometrial epithelium is a barrier for embryo attachment and that removal of alpha-DG-N by proprotein convertase 5/6 (PC6; a protease critical for implantation 28468828_loss of the convertase furin or PC5/6 in hepatocytes results in a approximately 30% decrease in APC levels, with no significant contribution from PACE4. We conclude that prior convertase cleavage of protein C in hepatocytes is critical for its thrombin activation. 29126984_this study demonstrates that Pcsk5 is expressed in bone-forming cells, and that OPN is a novel substrate for PC5/6 35045102_Urine peptidome in combination with transcriptomics analysis highlights MMP7, MMP14 and PCSK5 for further investigation in chronic kidney disease. |
ENSMUSG00000024713 |
Pcsk5 |
78.712138 |
0.3801755643 |
-1.395262 |
0.209853612 |
44.507322 |
0.00000000002534076799608187215529848941079996702332999269913216267013922333717346191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000136806779671605128210295659466403089127295444882292940746992826461791992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.8983858 |
6.3084483 |
110.7327654 |
11.0438664 |
| ENSG00000099194 |
6319 |
SCD |
protein_coding |
O00767 |
FUNCTION: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase that utilizes O(2) and electrons from reduced cytochrome b5 to introduce the first double bond into saturated fatty acyl-CoA substrates (PubMed:15907797, PubMed:18765284). Catalyzes the insertion of a cis double bond at the delta-9 position into fatty acyl-CoA substrates including palmitoyl-CoA and stearoyl-CoA (PubMed:15907797, PubMed:18765284). Gives rise to a mixture of 16:1 and 18:1 unsaturated fatty acids (PubMed:15610069). Plays an important role in lipid biosynthesis. Plays an important role in regulating the expression of genes that are involved in lipogenesis and in regulating mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation (By similarity). Plays an important role in body energy homeostasis (By similarity). Contributes to the biosynthesis of membrane phospholipids, cholesterol esters and triglycerides (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15610069, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15907797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18765284}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes an enzyme involved in fatty acid biosynthesis, primarily the synthesis of oleic acid. The protein belongs to the fatty acid desaturase family and is an integral membrane protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum. Transcripts of approximately 3.9 and 5.2 kb, differing only by alternative polyadenlyation signals, have been detected. A gene encoding a similar enzyme is located on chromosome 4 and a pseudogene of this gene is located on chromosome 17. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:6319; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; palmitoyl-CoA 9-desaturase activity [GO:0032896]; stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase activity [GO:0004768]; monounsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:1903966]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; response to fatty acid [GO:0070542]; unsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006636] |
12061775_Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity by the cis-9,trans-11 isomer and the trans-10,cis-12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid in human breast cancer cells. 12401889_stearoyl-CoA desaturase influence on plasma triglycerides in hypertriglyceridemia 14683458_Of genes identified in the liver whose expression is modulated by leptin, stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 ranks at the top of the list, according to this review. 14967817_relationship between triglyceride levels and the ratio of plasma oleic acid to stearic acid (the 18:1/18:0 ratio), a plasma marker of SCD activity, and n-3 PUFAs in 411 Japanese, 418 Korean, and 251 Mongolian adults 14967823_increased palmitate and stearate desaturation by stearoyl-CoA desaturase was associated with the destabilization of ABCA1 by saturated fatty acids palmitate and stearate 15609334_loss of SCD expression is a frequent event in prostate adenocarcinoma 15610069_The identification and characterization of SCD2, and its relationship to human SCD1 and mouse SCD2, are reported. 15662557_No evidence that SCD sequence variation influences diabetes susceptibility or related traits. 15662557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15708362_Results suggest that stearoyl-CoA desaturase levels are associated with the events of neoplastic cell transformation and programmed cell death. 15851470_by globally regulating lipid metabolism, stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity modulates cell proliferation and survival and shows the role of endogenously synthesized monounsaturated fatty acids in sustaining the neoplastic phenotype of transformed cells 15855323_SCD activity index after rosiglitazone in PPARgamma mutation supports a pivotal role of PPARgamma function in SCD regulation. 16213227_the lipogenic gene, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1), is robustly up-regulated in skeletal muscle from extremely obese humans Elevated expression of SCD1 in skeletal muscle contributes to abnormal lipid metabolism and progression of obesity. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16723740_SCD1 was degraded constitutively irrespective of the cellular levels of unsaturated fatty acids, which strictly regulate SCD1 gene expression. 17614770_study demonstrated that the gene expression of COX-2 and stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase diminished in the chronic phase of Graves'ophthalmopathy in parallel with a decrease in clinical activity score 17636091_Genetic variations in the SCD1 gene are associated with body fat distribution and insulin sensitivity. 17636091_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17852835_The results indicate that when the supply of FA to HL60 cells is limited, the intracellular content of n-3 and n-6 FA decreases and this leads to upregulation of the desaturases, D9D is doubled. 18030445_Results show that elevated SCD activity within adipose tissue is closely coupled to the development of insulin resistance. 18286258_High hepatic SCD1 activity may regulate fat accumulation in the liver and possibly protects from insulin resistance in obesity. 18340007_Fatty acid desaturation index (a marker of SCD1 activity) is a highly heritable trait that is associated with the dyslipidemia observed in familial combined hyperlipidemia. 18499418_age-related reduction in polyunsaturated fatty acid composition was inversely correlated with SCD expression and activity resulting in elevations in monounsaturated fatty acid composition 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18697866_Changed expression of downstream PPARgamma targets after stearoyl CoA desaturase (SCD) knockdown suggests that PPARgamma up-regulation of SCD leads to increased lipogenesis and potentiation of adiponectin signaling. 18813799_SCD1 activity regulates Akt activation in human lung adenocarcinoma cells 18832746_Dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia are attenuated by deficiency of stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase. 18952834_Data show that human fatty liver is characterized by increases in hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD1) and lipogenic activities. 19130493_decrease in lipid accumulation in apoE-transfected cells was associated with a strong downregulation of PPARs gamma1 and gamma2 and stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 19154947_associations of Delta 9 with adiposity and plasma lipids in healthy female adolescents support the concept derived from rodent models that Delta 9 activity is independently reflective of higher body mass index and higher circulatory triglyceride levels 19478146_SCD1 inducibility by palmitate is an individual characteristic that modulates lipid storage, palmitate-induced inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and insulin resistance. 19710915_data suggest that cancer cells require active SCD1 to control the rate of glucose-mediated lipogenesis, and that when SCD1 activity is impaired cells downregulate SFA synthesis via AMPK-mediated inactivation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20032470_Exogenous palmitate up-regulated de novo lipogenesis concomitantly with SCD and elongation 20395685_SNPs in the fatty acid desaturase gene are associated with higher blood essential fatty acids and perinatal depression. 20565855_potential role in disease onset and development (Review) 20579763_lower expression in dendritic cells compared to macrophages 20599700_This study demonstrates that the foreign SCD1 gene was expressed with high efficiency and induced elevated c9t11-CLA, t10c12-CLA, and n-7 fatty acid levels in mammalian cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20713121_Oleic acid, the main product of SCD1 reaction, is the predominant fatty acid of human adipose tissue triacylglycerols, associating SCD1 with the development of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. (Review) 21045174_We provide novel information that SCD1 activity and mRNA expression appear not to be elevated in subjects with high liver fat 21060977_Data suggest that the regulation of SCD1 is altered in individuals with morbid obesity and that the SCD1 protein has a different regulation in the two adipose tissues, as well as being closely linked to the degree of insulin resistance. 21179554_stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 inhibition induces CHOP-dependent cell death in human cancer cells 21331774_stearoyl-CoA desaturase plays a key role in the regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity in prostate cancer cells 21544602_study showed cystic fibrosis cells exhibit increased metabolism along metabolic pathways leading to n-7 and n-9 fatty acids compared with wild-type cells; changes are accompanied by increased expression of Delta5, Delta6 and Delta9 desaturases and elongases 5 and 6 21658928_Repression of SCD1 by alpha-linolenic acid favorably increased cholesterol efflux and decreased cholesterol accumulation in foam cells. 21674150_Macrophage expression of CD36, scavenger receptor A (SR-A) and stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) was increased, most prominently in macrophages exposed to hypertriglyceridemic diabetic serum 21775116_The mRNA levels of LXRalpha and SREBP-1c, transcription factors that regulate SCD-1, were decreased by 10,12 conjugated linoleic acid in human adipocytes. 21831035_[review] muscle. This review evaluates the role of SCD-1 as a homeostatic check-point between glucose and fatty acid metabolism in the development and progression of obesity. 21898701_Low expressed SCD1 gene in colonic mucosa is associated with active ulcerative colitis. 22026420_Data from menopause/ovariectomy model suggest that loss of ovarian function alters fatty acids in hepatic triglycerides, and these changes are mediated by increases in liver SCD-1. Exercise (i.e., wheel running) attenuates these changes. 22046234_role for the lipogenic enzyme SCD in Alzheimer's disease 22049297_Genetic variation in the SCD1 gene may play a role in the development of metabolic syndrome. 22209225_SCD1 activity and genetic variation have an important role in modulating the relationship between fatty acids and inflammation in young adults 22457791_data outline an effective strategy to establish an unambiguous link between fatty acid synthesis and cancer cell survival, and point toward SCD1 as a key target in this pathway 22819528_In a large community-based prospective cohort study, the estimate of SCD-1 activity by SCD16c had the strongest association with incident diabetes. 22946088_data indicate that SCD activity may control lung cancer cell metabolism, proliferation and survival by modulating the EGFR-->Akt/ERK signaling platforms 23013158_findings show low SCD1 expression is linked to a decrease in proliferation rate of breast cancer cells; this was accompanied by an increase in GSK3 activity; nuclear translocation of beta-catenin was decreased and its transactivation capacity; this suggests a role of SCD1 in EMT and cancer progression 23015656_The individual hepatic SCD1 activity is a determinant of liver fat accumulation under lipogenic dietary conditions. 23019225_In human bladder cancer cell lines expressing constitutively active FGFR3, knockdown of SCD1 by siRNA markedly attenuated cell-cycle progression, reduced proliferation, and induced apoptosis. 23139775_There are no associations between common variants of SCD1 or its inferred haplotypes and the investigated metabolic risk factors. 23208590_Patients with primary breast cancers expressing high SCD1 levels had significantly shorter relapse-free survival and overall survival in multivariable analysis. 23221600_Thyroid hormone negatively regulates human SCD-1 gene expression in without direct binding of the TH receptor to the SCD-1 gene promoter. 23331615_Both SCD1 and HIF-2alpha are critical to promoting tumorigenesis by synergistically acting on maintaining cell survival, triggering cell migration, and enhancing the colony formation ability of ca 23613812_Human breast cancer tissues contain abundant phosphatidylcholine(36ratio1) with high stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 expression. 23633458_Increased SCD1 expression supports clear cell renal cell carcinoma cell viability. 23934750_Genetic variation of the SCD1 gene may contribute to the risk of obesity, interacting with the type of dietary fat. 24135379_SCD was strongly expressed in surgically resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (n = 64) and various human HCC cell lines 24309934_The results suggest that SCD1 is a critical target in lung cancer tumor-initiating cells. 24356954_This minireview summarizes the role of skin SCD1 in regulating skin integrity and whole body energy homeostasis and offers a discussion of potential pathways that may connect these seemingly disparate phenotypes. 24357007_The effect of fenretinide on stearoyl-CoA desaturase should be considered in its potential therapeutic role against cancer, type-2 diabetes, and retinal diseases. 24368438_genetic association studies in population of men in Sweden: Data suggest that SNPs in SCD1 are associated with cancer death, especially among men with low intake of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids. 24375980_These results demonstrate that cardiometabolic risk factors are modulated by genetic variations in the SCD1 gene alone or in combination with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation. 24769897_SCD1 is found upregulated upon renal cell transformation indicating that its activity, while not impacting proliferation, represents a critical bottleneck for tumourigenesis 24780075_An association with Graves ophthalmopathy was shown for SNP rs1393491 in SCD. 24827925_DNA methylation levels of the SCD1 promoter were associated with weight change and with adherence to a Mediterranean diet. 24864084_Stearoyl-CoA desaturase is encoded by an SCD gene, which, depending on the species, may exist as different isoforms. (review) 25122791_These data further support the idea that SCD1 is associated with hepatitis C virus replication complex and that its products may contribute to the proper formation and maintenance of membranous web structures during virus replication. 25264165_The data indicate a direct inhibitory interaction of polyunsaturated fatty acids with LXRalpha, a consequent reduction of SREBP-1 and of its binding to SCD1 promoter. 25528629_SCD1 negatively regulates autophagy-induced cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma through inactivation of the AMPK signaling pathway. 25880005_Both siRNA-mediated and pharmacological inhibition of SCD1 impaired tumor cells migration. 26022099_This study illustrates for the first time that, in contrast to hepatic and adipose tissue, estrogen induces SCD-1 expression and activity in breast carcinoma cells. These results support SCD-1 as a therapeutic target in estrogen-sensitive breast cancer. 26224474_stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 has a role in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 26391970_Chronic exposure to chewing tobacco induces carcinogenesis in non-malignant oral epithelial cells and SCD plays an essential role in this process. 27223066_high expression of SCD1 is more frequently observed in late stage lung adenocarcinoma patients and presents poor prognosis 27306423_Results provide evidence that SCD is a regulator of breast stemness. 27467133_Our results suggest that relatively common genetic variants in stearoyl CoA desaturase and SREBF1 attenuated the positive associations between intake of a traditional diet rich in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and increases in fasting cholesterol and HbA1c levels, as well as the waist-to-hip ratio among Yup'ik participants. 27562731_A relevant link between one-night sleep deprivation , hepatic SCD1 expression and de-novo fatty acid synthesis via epigenetically driven regulatory mechanisms was found. 27838812_Results provide evidence that the hepatic BSCL2 deficiency induces the increase and expansion of lipid droplets potentially via increased SCD1 activity. 27846372_ULK1 has a role in RPS6KB1-NCOR1 repression of NR1H/LXR-mediated Scd1 transcription and augments lipotoxicity in hepatic cells 27861513_high SCD1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for OS in patients with ccRCC. Our data suggest that the expression of SCD1 might guide the clinical decisions for patients with ccRCC. 28345489_Study results suggest that stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 activity is required for cumulus cell lipid storage and steroidogenesis. 28368399_these data demonstrate for the first time the involvement of SCD1 in the regulation of the Hippo pathway in lung cancer, and point to fatty acids metabolism as a key regulator of lung cancer stem cells. 28397284_Experimental models in mice and human epithelial cells suggest that inhibition of stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase activity leads to airway hyper-responsiveness and reduced antiviral defense. 28647567_SCD1 overexpression was found in Hepatocellular Carcinomas , which was associated with shorter disease-free survival. 28765876_CD36, also known as FA translocase (FAT), that functions as a transmembrane protein and mediates the uptake of FAs, is observed to be highly expressed in breast cancer tissues. Furthermore, the anti-proliferation effect caused by the SCD1 inhibitor can not be reversed by exogenous oleic acid supplementation in CD36 knockdown breast cancer cells 28768997_Our findings suggested that SCD1 plays a key role in the pathophysiology of leptin resistance in neuronal cells associated with obesity. 28797843_High SCD1 expression is associated with resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer. 28801090_alterations in leptin and SCD-1 in HCU patients 29396722_study has provided evidence supporting the potential role of SCD1 as a biomarker for human bladder cancer prognosis. 29530061_Our findings show that SCD1 promotes metastasis of CRC cells through MUFA production and suppressing PTEN in response to glucose, which may be a novel mechanism for diabetes-induced CRC metastasis. 30190473_Type 2 diabetes patients have lower SCD1, which does not associate with insulin resistance. 30517862_reducing the levels of unsaturated membrane lipids by inhibiting SCD reduced alpha-syn toxicity in human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) neuronal models. 30592142_SCD may serve as a novel marker for the prediction of tumour progression. 30754064_Association of the PNPLA2, SCD1 and Leptin Expression with Fat Distribution in Liver and Adipose Tissue From Obese Subjects. 30884788_Expression changes in secreted frizzled-related protein 2, stearoyl-CoA desaturase, and hypoxia inducible lipid droplet-associated (HILPDA) with weight loss were confirmed by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Dietary weight loss induces significant changes in the expression of genes implicated in lipid metabolism (SCD and HILPDA) and WNT-signaling (SFRP2) in subcutaneous adipose tissue. 30927246_sodium orthovanadate changed SFA and MUFA composition in THP-1 macrophages and increased expression of SCD. Sodium orthovanadate did not affect the amount of any PUFA. This was associated with a lack of influence on the expression of FADS1 and FADS2. 31119852_SCD1 activation impedes foam cell formation by inducing lipophagy in oxLDL-treated human vascular smooth muscle cells. 31235426_Herein, we report that RBM3 is crucial for the stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD)-circRNA 2 formation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, which not only provides mechanistic insights into cancer-related circRNA dysregulation but also establishes RBM3 as an oncogene with both therapeutic potential and prognostic value 31623522_SCD-1(16) and SCD-1(18) activity indices were 20% and 7% lower, respectively, in black compared with white women. Lower visceral fat and SCD-1(16) were important mediators of fasting TRLP concentrations. These factors may contribute to the paradoxical association of lower fasting and postprandial TRLP subfractions despite insulin resistance in black compared with white pre- and postmenopausal women. 31642233_Inhibition of SCD1 activity can inhibit cell cycle progression and impair cell proliferation in breast cancer calls 31708235_Associations of maternal and fetal SCD-1 markers with infant anthropometry and maternal diet: Findings from the ROLO study. 31903889_Lower proportions of minor SCD1 genotypes (rs2167444, rs508384) implicate the role of genetic factors in the pathogenesis of elevated levels of apoB-48. 31915810_Betulinic acid induces apoptosis of gallbladder cancer cells via repressing SCD1. 31993937_SCD1 activity promotes cell migration via a PLD-mTOR pathway in the MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cell line. 32350414_Stearoyl-CoA-desaturase-1 regulates gastric cancer stem-like properties and promotes tumour metastasis via Hippo/YAP pathway. 32392704_Expression of SCD and FADS2 Is Lower in the Necrotic Core and Growing Tumor Area than in the Peritumoral Area of Glioblastoma Multiforme. 32438926_Fatty acid profile and estimated desaturase activities in whole blood are associated with metabolic health. 32670392_miR-215 Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion via Targeting Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. 33264619_Concurrent Mutations in STK11 and KEAP1 Promote Ferroptosis Protection and SCD1 Dependence in Lung Cancer. 33430034_Targeting a Lipid Desaturation Enzyme, SCD1, Selectively Eliminates Colon Cancer Stem Cells through the Suppression of Wnt and NOTCH Signaling. 33511729_HIF-1alpha downregulation of miR-433-3p in adipocyte-derived exosomes contributes to NPC progression via targeting SCD1. 33612070_NF-kappaB pathway play a role in SCD1 deficiency-induced ceramide de novo synthesis. 33904180_Fatty acid desaturase activity in mature red blood cells and implications for blood storage quality. 34030117_Tumor resistance to ferroptosis driven by Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 (SCD1) in cancer cells and Fatty Acid Biding Protein-4 (FABP4) in tumor microenvironment promote tumor recurrence. 34171462_Polymorphisms rs55710213 and rs56334587 regulate SCD1 expression by modulating HNF4A binding. 34621052_Aramchol in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. 34680068_Sequential Dynamics of Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1(SCD1)/Ligand Binding and Unbinding Mechanism: A Computational Study. 34690112_Exosome long non-coding RNA SOX2-OT contributes to ovarian cancer malignant progression by miR-181b-5p/SCD1 signaling. 35358687_An SCD1-dependent mechanoresponsive pathway promotes HCC invasion and metastasis through lipid metabolic reprogramming. 35361481_Roles of miR-124-3p/Scd1 in urolithin A-induced brown adipocyte differentiation and succinate-dependent regulation of mitochondrial complex II. 35452750_Elevated stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 activity is associated with alcohol-associated liver disease. 35547771_SCD1/FADS2 fatty acid desaturases equipoise lipid metabolic activity and redox-driven ferroptosis in ascites-derived ovarian cancer cells. 35682900_Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Elevated Expression of a Potentially Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Associated SCD1 Variant. 35906508_Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 as a therapeutic target for cancer: a focus on hepatocellular carcinoma. 36008942_Selenocysteine Machinery Primarily Supports TXNRD1 and GPX4 Functions and Together They Are Functionally Linked with SCD and PRDX6. 36361811_Stearoyl CoA Desaturase-1 Silencing in Glioblastoma Cells: Phospholipid Remodeling and Cytotoxicity Enhanced upon Autophagy Inhibition. |
ENSMUSG00000025203+ENSMUSG00000050195 |
Scd2+Scd4 |
2448.797285 |
2.6781995987 |
1.421263 |
0.034500684 |
1724.998514 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3606.0954519 |
73.3404640 |
1356.2920127 |
22.3114965 |
| ENSG00000099250 |
8829 |
NRP1 |
protein_coding |
O14786 |
FUNCTION: Cell-surface receptor involved in the development of the cardiovascular system, in angiogenesis, in the formation of certain neuronal circuits and in organogenesis outside the nervous system. Mediates the chemorepulsant activity of semaphorins (PubMed:9288753, PubMed:9529250, PubMed:10688880). Recognizes a C-end rule (CendR) motif R/KXXR/K on its ligands which causes cellular internalization and vascular leakage (PubMed:19805273). It binds to semaphorin 3A, the PLGF-2 isoform of PGF, the VEGF165 isoform of VEGFA and VEGFB (PubMed:9288753, PubMed:9529250, PubMed:10688880, PubMed:19805273). Coexpression with KDR results in increased VEGF165 binding to KDR as well as increased chemotaxis. Regulates VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Binding to VEGFA initiates a signaling pathway needed for motor neuron axon guidance and cell body migration, including for the caudal migration of facial motor neurons from rhombomere 4 to rhombomere 6 during embryonic development (By similarity). Regulates mitochondrial iron transport via interaction with ABCB8/MITOSUR (PubMed:30623799). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10688880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19805273, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30623799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9288753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9529250}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a host factor for human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infection. Recognizes and binds to CendR motif RRAR on SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 which enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33082293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33082294}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Binds VEGF-165 and may inhibit its binding to cells (PubMed:10748121, PubMed:26503042). May induce apoptosis by sequestering VEGF-165 (PubMed:10748121). May bind as well various members of the semaphorin family. Its expression has an averse effect on blood vessel number and integrity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10748121, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26503042}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparan sulfate;Heparin-binding;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes one of two neuropilins, which contain specific protein domains which allow them to participate in several different types of signaling pathways that control cell migration. Neuropilins contain a large N-terminal extracellular domain, made up of complement-binding, coagulation factor V/VIII, and meprin domains. These proteins also contains a short membrane-spanning domain and a small cytoplasmic domain. Neuropilins bind many ligands and various types of co-receptors; they affect cell survival, migration, and attraction. Some of the ligands and co-receptors bound by neuropilins are vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and semaphorin family members. This protein has also been determined to act as a co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 (which causes COVID-19) to infect host cells. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2020]. |
hsa:8829; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; neurofilament [GO:0005883]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; semaphorin receptor complex [GO:0002116]; sorting endosome [GO:0097443]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; semaphorin receptor activity [GO:0017154]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; vascular endothelial growth factor binding [GO:0038085]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005021]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; angiogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis [GO:0060978]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axonal fasciculation [GO:0007413]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; basal dendrite arborization [GO:0150020]; basal dendrite development [GO:0150018]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; branchiomotor neuron axon guidance [GO:0021785]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:0035729]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; commissural neuron axon guidance [GO:0071679]; coronary artery morphogenesis [GO:0060982]; dichotomous subdivision of terminal units involved in salivary gland branching [GO:0060666]; dorsal root ganglion morphogenesis [GO:1904835]; endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:0035767]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542]; endothelial tip cell fate specification [GO:0097102]; facial nerve structural organization [GO:0021612]; facioacoustic ganglion development [GO:1903375]; gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuronal migration to the hypothalamus [GO:0021828]; hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048012]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; motor neuron migration [GO:0097475]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; nerve development [GO:0021675]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; neural crest cell migration involved in autonomic nervous system development [GO:1901166]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuropilin signaling pathway [GO:0038189]; otic placode development [GO:1905040]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048842]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of cytokine activity [GO:0060301]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:1902336]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; postsynapse organization [GO:0099173]; protein localization to early endosome [GO:1902946]; regulation of Cdc42 protein signal transduction [GO:0032489]; regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090259]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030947]; regulation of vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0060627]; renal artery morphogenesis [GO:0061441]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; retina vasculature morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0061299]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in neuron projection guidance [GO:1902285]; sensory neuron axon guidance [GO:0097374]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; substrate-dependent cell migration, cell extension [GO:0006930]; sympathetic ganglion development [GO:0061549]; sympathetic neuron projection extension [GO:0097490]; sympathetic neuron projection guidance [GO:0097491]; toxin transport [GO:1901998]; trigeminal ganglion development [GO:0061551]; trigeminal nerve structural organization [GO:0021637]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; VEGF-activated neuropilin signaling pathway [GO:0038190]; VEGF-activated neuropilin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902378]; ventral trunk neural crest cell migration [GO:0036486]; vestibulocochlear nerve structural organization [GO:0021649]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] |
11807987_A potential mechanism involved in hemangioma formation is the alteration of the NRP1 signaling pathway in endothelial and/or pericytic cells. 11953749_A neuronal receptor, neuropilin-1, is essential for the initiation of the primary immune response. 11976715_Neuropilin-1 is another neuronal molecule in the 'immunological synapse'. 12216067_results suggest that NRP-1 may be a multiple function protein in human breast and may be involved in the induction of local invasiveness of neoplasia and angiogenesis and have direct relevance to the progression of breast cancer 12577308_promoter regions of human and mouse NRP1 genes were cloned and sequenced; transfection demonstrated that two Sp1 elements are major contributors to constitutive and induced activity 12730958_human glioma cells express class 3 semaphorins and receptors for soluble and membrane-bound semaphorins, suggesting a possible role of the semaphorin/neuropilin system in the interactions of human malignant glioma with the nervous and immune systems. 12883660_neuropilin-1 is expressed in the prostatic stromal cells, not epithelial tumor cells, and this expression is significantly increased in the malignant phenotype 14500350_breast carcinoma cells support an autocrine pathway involving SEMA3A, plexin-A1, and neuropilin-1 that impedes their ability to chemotax. 14514674_independently promote cell signaling in endothelial cells and also demonstrate the importance of last three amino acids for its function 14760080_Np-1 and Np-2 contribute to autocrine-paracrine interactions in pancreatic cancer 15126502_NP-1 has a specific role in mediating neurotrophic actions of VEGF family members 15160992_NRP1 overexpression contributes to tumor progression and has clinical significance for glioma. 15161648_Effect of NRP-1 overexpression on angiogenesis and growth of human colon adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. 15166498_Increased expression of NRP1 is associated with an aggressive angiogenic phenotype in melanoma. 15233640_correlation between neuropilin-1 and vascularity in human astrocytic tumors and a possible role for neuropilin-1 as a receptor for VEGF-induced angiogenesis 15522955_dual role as an enhancer of VEGF activity and a mediator of endothelial cell adhesiveness 15613413_NP-1 mRNA was highly expressed in vascular endothelium and in stromal cells, but in these cells, NP-1 expression did not change during the menstrual cycle. 15920019_role for Npn-1 in regulating endothelial barrier dysfunction in response to VEGF. 15956974_Neuropilin-1 overexpression in pancreatic cancer cell lines is associated with (a) increased constitutive MAPK signalling, (b) inhibition of anoikis, and (c) chemoresistance 16330548_Down-regulation of NRP1 by NRSF overexpression reduced Sema3A activity. It was concluded that NRSF is a transcription factor that silences NRP1 expression and thereby diminishes the Sema3A mediated inhibition of HaCaT keratinocyte migration 16371354_Data show that tuftsin and a higher affinity antagonist, TKPPR, bind selectively to neuropilin-1 and block vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) binding to that receptor. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424390_Preferential receptor binding and internalization by a ligand are mechanisms by which the common receptor Npn-1 can play an essential role in prioritizing conflicting signals. 16513643_This study describes the first specific antagonist of VEGF-A165 binding to NP-1 and demonstrate that NP-1 is essential for optimum KDR activation and intracellular signaling. 16648151_Immunohistochemical staining showed that NRP-1 was mainly confined to stroma and blood vessels and only in late-proliferative endometrium, epithelial staining was also observed. 16763549_GAG modification of NRP1 plays a critical role in modulating VEGF signaling, and may provide new insights into physiological and pathological angiogenesis. 16809290_NRP1 is involved in HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 entry 16847823_depletion of neuropilin-1 production by aortic smooth muscle cells with specific short hairpin RNA prevents the PDGF-dependent migration of vascular smooth muscle cells 16849452_NRP1 transfer to T lymphocytes during the immune synapse can convert T lymphocytes into vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)165-carrying cells. 16990775_increased NRP-1 expression in acute myeloid leukemia with significant correlation to survival 17015762_down-regulation of the neuropilin-1 transcripts by short interfering RNA caused spontaneous synoviocyte apoptosis, which was associated with both the decrease in Bcl-2 expression and the increase in Bax translocation to mitochondria. 17017185_Neuropilin-1 was expressed in most of human laryngeal carcinoma specimens and cell lines but was not expressed in nonmalignant tissue. 17088944_These results suggest that the expression of VEGFRs and NRPs on keratinocytes may constitute important regulators for its activity and may possibly be responsible for the autocrine signaling in the epidermis. 17369353_NP-1/Sema-3A-mediated interactions participate in the control of human thymocyte development 17369861_Data suggest that tumor cell-expressed NRP1 promotes glioma progression through potentiating the activity of the HGF/SF autocrine c-Met signaling pathway and enhancing angiogenesis. 17376520_NRP-1 expression was augmented threefold during malignant transformation of ovarian epithelial cells with oncogene ras, suggesting an association between NRP-1 and oncogenesis. 17575273_VEGF(121) binds directly to NRP1; however, unlike VEGF(165), VEGF(121) is not sufficient to bridge the NRP1.VEGFR2 complex. 17726369_Np-1 confers a growth and survival advantage to pancreas cancer cells, and interacts with integrin beta1 to coordinate signaling events that promote cell adherence and invasiveness. 17891484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17917967_neoplastic cells in myeloid leukemias frequently express VEGFR including NRP-1 and NRP-2 17974973_These findings indicate that Np-1 is required for efficient activation of c-Met-dependent pathways that promote cell invasiveness. 18000534_This study, by elucidating the mechanisms that govern VPF/VEGF-induced EC survival signaling via NRP-1, contributes to a better understanding of molecular mechanisms of cardiovascular development 18065694_Both NRP1 and NRP2 function as proangiogenic coreceptors, potentiating the activity of at least 2 proangiogenic cytokines, VEGF-A and hepatocyte grwoth factor. 18088455_The higher level of NRP-1 mRNA is expressed in bone marrow mononuclear cells of leukemia patients and plays a pivotal role in proliferation and migration of myeloid leukemic cells. 18164591_Support a role for NP-1 in mediating synergistic effects between VEGF-A(165) and FGF-2, which may occur in part through a contribution of NP-1 to KDR stability. 18223683_Gal-1 can directly bind to NRP1 on endothelial cells, and can promote the NRP1/VEGFR-2-mediated signaling pathway as well as NRP1-mediated biological activities. 18231921_higher level of NRP-1 mRNA was expressed in leukemias and NRP-1 promoted proliferation and chemotaxis of leukemic cells in response to VEGF. 18272814_The sulfated polysaccharides dextran sulfate and fucoidan, but not others, reduce endothelial cell-surface levels of NRP1, NRP2, and to a lesser extent VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2, and block the binding and in vitro function of semaphorin3A and VEGF(165). 18284215_VEGF-A induction of VEGFR2-negative human aortic smooth muscle cell migration is mediated through a molecular cross-talk of neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), VEGFR1 (Flt-1), and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling kinase. 18403014_Neuropilin-1 is expressed by a subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. 18628209_binding of Neuropilin-1 to VEGFR-2 requires the PDZ-binding domain of neuropilin-1 18638267_None of the examined NRP1 polymorphisms showed a difference in their allelic distribution between leg ulcer patients and controls. 18638267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18704117_Data establish distinct roles for unmodified and chondroitin sulphate-modified protein in modulating a new NRP1-p130Cas (BCAR1) signalling pathway contributing to glioblastoma cell invasion. 18708346_hypoxia and nutrient deprivation stimulate the rapid loss of NRP1 expression in both endothelial and carcinoma cells. NRP2 expression, in contrast, is maintained under these conditions 18785001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18922901_SEMA3B is a potential tumor suppressor that induces apoptosis in SEMA3B-inactivated tumor cells through the Np-1 receptor by inactivating the Akt signaling pathway. 18974107_NRP-1 knockdown renal cell carcinoma cells exhibit a more differentiated phenotype, as evidenced by the expression of epithelial-specific and kidney-specific cadherins, and the inhibition of sonic hedgehog expression participated in this effect 18984674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996601_NRP-1 expression might act as a co-factor for VEGF(165) enhancing the angiogenic stimulus 19037249_Transcripts of both NRP1 and NRP2 were found to be decreased in renal biopsies from patients with diabetic nephropathy 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19270265_VEGF(165) is a selective competitor of HTLV-1 entry and HTLV-1 mimics VEGF(165) to recruit HSPGs and NRP-1 to function as HTLV-1 receptors 19364973_The onset of NRP-1 expression identifies endothelial precursors in murine and human stem cells 19474288_Intra-amniotic infection upregulates decidual cell vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and neuropilin-1 and -2 expression: implications for infection-related preterm birth. 19480842_Data show that the expression of Sema3A receptors (neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), NRP-2, plexin A1, plexin A2, and plexin A3) significantly increased during M-CSF-mediated differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. 19486891_Extracellular protein kinase CK2 binds to the extracellular domain of NRP1 which is also phosphorylated by CK2 both in vitro and in vivo. 19499532_In contrast to murine Treg, Nrp-1 cannot be used as a specific marker of human Treg, but might represent a novel activation marker of human T cells both in vitro and in vivo. 19736548_This is the first report suggesting a differential role of NRP1 and NRP2 in renal fibrogenesis. 19805273_Data of affinity chromatography showed that the CendR peptides bind to neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) on the target cells. 19837659_alphav beta3 integrin may, in part, negatively regulate VEGF signaling by sequestering NRP1 and preventing it from interacting with VEGFR2 19857463_These findings suggest that NRP-1-VEGFR-2-complex formation may contribute to effective cellular functions mediated by VEGF(165) in megakaryocytic cells. 20026901_The developmental functions of the neuropilins are influenced by such different contexts, are reviewed. 20043119_PLGF isoforms PLGF-1 and PGF-2 and indeed their receptor neuropilin, have an aberrant pattern of expression and high levels of the PLGF-1 and neuropilin are linked to a poor prognosis. 20053475_Minor alleles of two SNPs in intron 9 of the NRP1 gene, which encodes neuropilin-1, were found to be associated with type 1 diabetes (T1D) in children. Neuropilin-1 peptides were confined to islets in human pancreas. 20053475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085644_Activation of VEGF165-NRP1-c-MET signaling could confer prostate cancer (PCa) cells survival advantages by up-regulating Mcl-1, contributing to PCa progression. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20215856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20631636_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20675371_NRP-1 functions as a key determinant of the diverse responses downstream of TGF-beta1 that are mediated by distinct Smad proteins and promotes myofibroblast phenotype. 20950431_NRP-1 down-regulation by butyrate was associated with decreased binding affinity of Sp1 for canonical Sp-binding sites in the NRP-1 promoter. 20956519_soluble recombinant rNRP-1 is a VEGF-A(165)-independent agonist of VEGFR-2 and stimulates angiogenesis in endothelial cells 21063027_Results indicate that NRP-1 could potentially be used as a target for ligand-directed therapy in leukemias and lymphomas. 21111525_NRP-1 is expressed in human decidua and trophoblast, suggesting an important role for the VEGF co-receptor NRP-1 at the embryo-maternal interface during embryonic implantation and placentation 21186301_conclude that Nrp1 is a co-receptor for TGF-beta1 and augments responses to latent and active TGF-beta 21245381_Knockdown of NRP1 or P130Cas or expression of either NRP1DeltaC or a non-tyrosine-phosphorylatable substrate domain mutant protein (p130(Cas15F)) was sufficient to inhibit growth factor-mediated migration of glioma and endothelial cells. 21306301_These results indicate a role for NRP1 and NRP1 glycosylation in mediating PDGF-induced VSMC migration, possibly by acting as a co-receptor for PDGFRalpha and via selective mobilization of a novel p130Cas tyrosine phosphorylation pathway. 21338642_Our results indicate a specific role of NRP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma growth and vascular remodelling. 21401950_NRP-1 is inversely associated with levels of butyrate. 21525791_neuropilin-1 expression is under androgen receptor control 21586748_Our data establish a distinct role of NRP-1 in VEGFR-2 signaling and reveal a general mechanism for the function of coreceptors in modulating receptor tyrosine kinase signal output 21653826_VEGF binding to NRP1 is essential for VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell migration, complex formation between NRP1 and VEGFR2, and signaling via FAK Tyr407 phosphorylation. 21852397_cytoplasmic domain of neuropilin 1 is dispensable for angiogenesis, but promotes the spatial separation of retinal arteries and veins 21897119_Decrease of NRP1 expression is associated with upregulation of VEGF189 expression that resulted in increased cell apoptosis. 21951945_expression increased in lupus nephritis 21978468_High NRP1 is associated with acute myeloid and acute lymphoid leukemia. 22025255_These observations confirm NRP1 as a valid anti-angiogenic target in malignancy and confirm a role for NRP1 in physiological, VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. 22052678_CD304 was repeatedly expressed in patients with TEL-AML1 gene rearrangement 22134529_MiR-320a downregulated the expression of neuropilin 1 at both the mRNA and protein levels. 22251373_Data indicate the simultaneous analysis of CD64 together with CD304 (Neuropilin-1) or the combination of CD11b and CD38 was suitable for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)patients with high current activity in synovitis. 22318724_basis for the potent and selective binding of VEGF-A(164) to Nrp1 22393126_VEGFR2 is preferentially expressed on the cell surface of the CD133(+) glioma stem-like cells, whose viability, self-renewal, and tumorigenicity rely, at least in part, on signaling through the VEGF-VEGFR2-Neuropilin-1 axis. 22627768_The molecule recognized by PAL-E and anti-PV-1 antibodies is not NRP-1 but PV-1. 22875653_The expression of both sema3A and NP-1 on B cells from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients was significantly different in comparison with normal healthy individuals 22885184_Nrp1 plays a key role in mammosphere formation and this activity is linked to NF-kappaB activation. 23145112_We further show that Nrp1 and Nrp2 both bind Sema3F with similar affinity and that both Nrp2 and the chimeric Nrp1 can selectively sequester Sema3 23175449_Neuropilin-1 may contribute to tumor progression in a number of systemic malignancies and that it's down regulation may markedly decrease tumor growth. 23185562_The hypoxia-mediated HIF-1alpha-dependent up-regulation of NRP-1 is a critical molecular event involved in the vasculogenic mimicry and tumor formation by fibrosarcoma cells in vivo. 23222303_Neuropilin-1 identifies a subset of bone marrow Gr1- monocytes that can induce tumor vessel normalization and inhibit tumor growth. 23288161_Neuropilin-1/c-met signalling pathway mediates rhodocetin-alpha,beta restructuring of matrix contacts in endothelial cells. 23447383_NRP1 might be involved not only in angiogenesis but also in tolerance mechanisms in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 23452854_Study reveals that PlGF is produced in the cerebellar stroma via tumor-derived Sonic hedgehog (Shh) and show that PlGF acts through Nrp1-and not vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1-to promote tumor cell survival. 23551578_An increase in NRP1 and NRP2 epithelial/tumour expression, as well as in NRP1 vascular expression, may be associated with disease progression in colorectal cancer. 23585340_Dysregulated expression of NRP-1 likely contributes to altered angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, neurogenesis and immune function in endometriosis. 23621014_The expressions of neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) on glioma cell lines and glioma tissues, were investigated. 23685409_the results demonstrate that NRP-1 is involved in melanoma progression through VEGFR-2-dependent and -independent mechanisms and suggest NRP-1 as a target for the treatment of the metastatic disease. 23956271_Studied the expression and prognostic value of NRP1 in primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the esophagus. 24053763_NRP-1 upregulation may be a novel biomarker for the prediction of advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 24066029_Neuropilin-1, p-NF-kappaB p65 and VEGF are predictors for the overall survival of Chinese men with PC. 24079887_Data suggest that SEMA3F (semaphorin-3F) C-terminal domain exhibits high-affinity binding of NRP1 (thus inhibiting binding of vascular endothelial growth factor A to NRP1); this interaction may be involved in anti-angiogenic activity of SEMA3F. 24114198_these data show that miR-320 regulates the function of vascular endothelial cells by targeting NRP1 and has the potential to be developed as an anti-angiogenic or anti-cancer drug. 24338507_NRP-1 may serve as a prognostic marker for osteosarcoma patients 24386482_Nrp1 is a specific marker of Tfh cells cognate activation in humans 24521511_vascular NRP1 can variably serve as a receptor for two secreted glycoproteins, the VEGF-A and SEMA3A, but it also has a poorly understood role as an adhesion receptor. 24556756_SN induces MUC5AC hypersecretion in a dose- and time-dependent manner; moreover, the MUC5AC over synthesis induced by SN is strongly associated with the enhanced binding of EGF to NRP1 24627131_overexpression of NRP-1 may play an important role in the progression of bladder cancer. 24632553_Data indicate that neuropilin 1 is highly expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDACs), and is significantly correlated with angiogenesis, advanced tumor-node-metastasis stage, p T stage, node invasion, and poor postoperative overall survival. 24641672_NRP1-dependent FLK1 activation has a protective effect in respiratory epithelial cells exposed to hypoxia. 24719187_Gal-1 has a role in increasing vascular permeability through the NRP-1/VEGFR1 and Akt signaling pathway 24736504_miR-338 acts as a novel tumor suppressor gene in gastric cancervby targeting NRP1 expression 24737589_NRP-1 may act as a more aggressive and promising predictor for the poor prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia 24791743_Results indicate that Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) mRNA and protein was expressed in the suprabasal epithelial layers of the skin sections. 24850663_NRP-1 is a partner in the EMT process in EOC tumors 24858828_neuropilin 1 and plexin A1 transmembrane domains interaction 24992616_Knockdown of neuropilin-1 suppresses invasion, angiogenesis, and increases the chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in osteosarcoma cells 24999732_High NRP1 expression levels are associated with lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 25077433_Sox2 is required for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma growth in mouse and human, where it enhances Nrp1/Vegf signaling to promote the expansion of tumor initiating cells along the tumor-stroma interface. 25180605_LKB1 promotes RAB7-mediated neuropilin-1 degradation to inhibit angiogenesis 25204970_Data show that neuropilin1 (NRP1) was identified as a target of microRNA miR-338 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells and inversely correlated with miR-338 in OSCC tissues. 25231404_Calreticulin promotes migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by upregulating neuropilin-1 expression via STAT5A. 25233427_Data (including data from mouse mutant strains) suggest NRP1 in vascular endothelium contributes to angiogenesis via VEGFA-dependent and VEGFA-independent mechanisms; the latter involves ABL1 (ABL proto-oncogene 1) and extracellular matrix. [REVIEW] 25271625_NRP-1 is an obligate receptor for mononuclear phagocyte chemotaxis, bridging neural ischemia to an innate immune response in neovascular retinal disease. 25277522_neuropilin-1 has a role in the endocytosis pathway in neoplasms 25315821_Data show that the transmembrane (TM)domains of neuropilins 1 and 2 dimerize with themselves. 25333267_Multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis revealed that patients with high peritumoral expression of both NRP-1 and VEGFR-2 in liver tumors were more than 4 times less likely to have recurrence. 25343644_Nrp1 had no detectable role in the tolerant phenotype. 25351619_We report for the first time that NRP1 is highly expressed on CD3+CD4+ t-infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer liver metastases, compared to peripheral blood mononuclear cells 25586548_Helios could be considered a more reliable marker for distinguishing thymic derived Regulatory T (tTreg) cells or peripherally induced Treg cells than Nrp1. 25670642_NRP1 is identified as an Epstein-Barr virus entry factor. 25713110_Positional mapping of PRKD1, NRP1 and PRDM1 as novel candidate disease genes in truncus arteriosus 25738638_RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated NRP-1 silencing may induce proliferation suppression, apoptosis promotion, as well as enhanced sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents. 25744030_observations suggest that NRP-1 is involved in megakaryocytopoiesis through complex formation with PDGFRs, and that NRP-1-PDGFR-complexes may contribute to effective cellular functions mediated by thrombopoietin and PDGF in megakaryocytic cells 25772243_A positive correlation between GPNMB and NRP-1 levels in human breast tumors. 25845525_The present findings suggested that increased NRP1 expression may be associated with the development of epithelial ovarian carcinoma. 25889301_VEGF is an autocrine growth factor in NSCLC signaling, at least in part, through NP1. 25954957_Increased NRP1 expression is associated with disease progression and reduced survival in patients with melanoma. 25979342_Heparin influences VEGF receptor-1, VEGF receptor-2, and neuropilin-1 through distinct mechanisms and regulates VEGF-induced signaling. 25997710_findings define that miR-148b might play a critical role in maintenance of SP cells with CSC properties by targeting NRP1 in HCC. 26147006_The over-expression of NRP1 was correlated with growth, survival and radio-resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. 26191184_MiR-365 can decrease migratory, invasive and proliferative behavior of malignant melanomas by attenuating the expression of NRP1. 26371509_PDE4D interacts directly with Neuropilins, positive regulators of Hedgehog signal transduction pathway. 26406949_NRP1 over-expression in miR-365 expressing cells could rescue invasion and growth defects of miR-365. In addition, miR-365 expression inversely correlated with NRP1 protein levels in malignant melanoma 26408254_Data show that binding of pleiotrophin (PTN) to neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) stimulated the internalization and recycling of NRP-1 at the cell surface. 26409917_Study found significant down-regulation of placental NRP-1 expression in fetal growth restriction pregnancies complicated with absent end-diastolic flow in the umbilical artery. 26451046_Neuropilin has a role as an essential cell surface receptor [review] 26563279_High Expression of Neuropilin-1 Associates with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 26573160_NRP1 was targeted by miR130a and miR130b at the binding site of chromosome 10: 334668643466870, which was involved in the axon guidance signaling pathway. 26602825_Semaphorin-3a, neuropilin-1 and plexin-A1 are axonal guidance molecules that have been recently implicated in regulating bone metabolism. 26701889_Increased NRP-1 expression is associated with metastatic endometrial and lung cancers. 26708340_Both placental NRP1 and VEGF were expressed at lower levels in women with pre-eclampsia and homocysteine-treated mice, which may contribute to endothelial damage. 26795388_NRP-1 was found to be overexpressed in gastric cancer (GC) tissues, and its expression correlates with the clinical staging, tumor differentiation and pathological types of gastric cancer. 26804163_VEGF-A acts via interaction with NRP-1 to trigger intracellular events leading to ECS cell survival and formation of aggressive, invasive and highly vascularized tumors. 26804176_our data suggest a novel molecular mechanism by which tMUC1 may modulate NRP1-dependent VEGFR signaling in PDA cells. 26805761_VEGF/NRP-1axis promotes progression of breast cancer via enhancement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of NF-kappaB and beta-catenin. 26823738_miR-152 suppression in NSCLC cells might promote neuropilin-1 mediated cancer metastasis. 26846845_Studies suggest that the activation of NRP-1 by PlGF directly contributes to tumour aggressiveness and to melanoma escape from anti-VEGF-A therapies. 26849476_REVIEW: Nrp1 functions in the vasculature is critical for the development of targeted therapeutics for cancer and vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and retinopathies. 26877262_neuropilin-1 is regulated in the oral epithelium and is selectively up-regulated during epithelial dysplasia 26923176_This review provides a general overview of current knowledge of the signalling pathways that are modulated by NRP1, with particular focus on neuronal and vascular roles in the brain and retina. 26937865_The new observation that shows strong NP-1 immunoreactivity of these particles, and decreased NP1 expression in syncytiotrophoblast of preeclampsia (PET) placentas in comparison to the control group, may imply a role of NP-1 in PET. 26967387_High NRP1 expression is associated with metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. 27014911_Data indicate that miR-206 inhibits neuropilin-1 (NRP1) and SMAD2 gene expression by directly binding to their 3'-UTRs. 27117252_this study identified the NRP1 cytoplasmic domain as essential for acute vascular hyperpermeability induced by different NRP1 ligands: a ligand- blocking antibody against NRP1 and a CendR peptide. 27257039_By blocking neuropilin-1 receptor (NRP-1) in tumor-bearing mice, luciferase activity in tumors delivered by HK polyplexes was reduced by 96%, whereas activity in normal tissues was minimally reduced. 27351129_Results suggest that targeting the transmembrane domains (TMD) of neuropilin-1 (NRP1) in breast cancer is a potent new strategy to fight against breast cancer and related metastasis. 27481513_Upregulated expression of NRP1 is associated with glioma. 27486976_Data show that neuropilin 1 (NRP1) binds extracellular AGO2 (carrying miRNA or not), and internalizes AGO2/miRNA complexes. 27542226_Data suggest neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) as a therapeutic target to reduce tumor fibrosis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression. 27591257_These data identify a new molecular mechanism of brain microvascular endothelial inflammatory response through NRP1-IFNgamma crosstalk. 27598321_This study indicates that capsaicin application results in significant loss of epidermal NRP-1 receptor expression, whereas diabetic subjects presenting small fiber neuropathy show full epidermal NRP-1 expression in contrast to the basal expression pattern seen in healthy controls 27666723_This study suggests that NRP1 expression and LVD are independent factors that are likely to predict the risk of LN metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)of the tongue, whereas the expression of VEGFC, VEGFR3, CCR7, and SEMA3E are nonindependent predictive factors 27676403_NRP1 is an important niche component 27720589_Study revels the structural description of the neuropilin-1 ectopic region by reporting the crystal structure of its MAM domain. The domain adopts a jellyroll fold that is stabilized by a Ca2+ ion while forming a molecular surface that is distinct from its structural homologs. 27797376_Our findings identify aberrant active integrin b1-driven Src-Akt hyperactivation as a primary resistance mechanism to cetuximab in PDAC cells and offer an effective therapeutic strategy to overcome this resistance using an EGFR and NRP1 dual targeting antibody 27798666_This report is the first study characterizing the specific functions of NRP1-Delta7, a glycosaminoglycan-defective neuropilin-1 splice variant that displays anti-tumorigenic properties in vitro and in vivo. 27937055_Curcumin-loaded nanoliposomes linked to homing peptides for integrin targeting and neuropilin-1-mediated internalization reduced viability of breast cancer cells. 28092670_Data provide evidence that NRP1 functions to enhance the metastatic potential of prostate tumors. 28254885_this study shows that NRP1 can act as a co-receptor for PDGF-D-PDGFRbeta signaling and is possibly implicated in intercellular communication in the vascular wall 28468826_Data suggest that neuropilin-1 (NRP1) functions as a receptor for neutrophil elastase (NE), mediates uptake/absorption of NE, and facilitates cross-presentation of PR1 (a peptide fragment of NE) in breast cancer cells. 28552348_Study show that a high percentage of intratumoral NRP1(+) Tregs correlates with poor prognosis in melanoma and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 28607365_This work supports the importance of NRP-1-associated molecules in circulation to characterize poor prognosis breast cancer and emphasizes on their role as favorable drug targets. 28618167_miR-320/NRP-1 axis contributes to the growth and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma cells. 28636974_Results showed a preferential association of NRP1 with SEMA3A, suggesting that SEMA3A can partially reverse the effects caused by the VEGFA preventing its binding with the NRP1 receptor. 28835419_Nrp1 mediates the migratory behavior of mesangial cells. 28910136_NRP1, as a promoter of odontoblast differentiation, regulates dental pulp stem cells via the classical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 28938007_Results show that Nrp1 plays a critical role in balancing responsiveness to VEGF-A versus TGFbeta to regulate glioblastoma growth, progression, and recurrence after anti-vascular therapy. 29018205_the effects of NRP1 knockdown in cancer cells are dependent on the genetic status of KRAS. 29059172_High NRP1 expression promotes esophageal squamous cancer progression. 29138851_Study demonstrated that NRP1+ cells possess tumor-initiating cells (TIC) properties, including the preferential expression of stemness markers, higher clonogenic and self-renewal potential, and increased cell migration capacity. These findings support an important role for NRP1 in the biology of lung cancer TICs. 29363855_These findings support that diminished levels of NRP1 contribute to the development of TOF, likely through its function in mediating VEGF signal and vasculogenesis. 29432830_rs2228638 of NRP1 may have a role in tetralogy of Fallot risk in European and Chinese Han populations 29457037_clinical samples from apical periodontitis patients were obtained to analyse the expression of Sema3A/Nrp1. These results indicated that the bone destruction level expanded from days 7 to 35 29457830_we discovered that miR-124-3p acts as the upstream suppressor of NRP-1 which promotes GBM cell development and growth by PI3K/Akt/NFkappaB pathway. 29486132_NRP1 can form complexes with FYN and have the correlation changes in odontoblast differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). Therefore, the study surmise that in the progress of dental caries, NRP1 interacts with FY |
ENSMUSG00000025810 |
Nrp1 |
1388.033917 |
6.1102305898 |
2.611227 |
0.063206670 |
1734.472540 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2447.4291545 |
89.5069780 |
403.4376398 |
12.5302037 |
| ENSG00000099326 |
7593 |
MZF1 |
protein_coding |
P28698 |
FUNCTION: Binds to target promoter DNA and functions as transcription regulator. Regulates transcription from the PADI1 and CDH2 promoter. May be one regulator of transcriptional events during hemopoietic development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15541732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17851584}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity; and protein homodimerization activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II and positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7593; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
15453830_MZF-1 and FHL3 formed a complex of high molecular mass with some additional proteins in the nucleus. Transcriptional repression of FcepsilonRI by MZF-1 required FHL3 as a cofactor. 15528990_Sp1 and MZF1 are involved in the transcriptional regulation of the hST6GalNAc IV gene in Jurkat T cells 15541732_MZF1 are important transcription factors regulating N-cadherin promoter activity and expression in osteoblasts. 15670815_a transcription factor, MZF-1, was revealed to interact with LDOC1 and enhance the activity of LDOC1 for inducing apoptosis 16297876_PKCalpha expression may be modulated by Elk-1 and MZF-1 at the transcriptional level. 16950398_Structure of MZF1 SCAN domain homodimer has been determined and provides an initial view of the recognition elements that govern dimerization for this large family of transcription factors. 17851584_MZF1 and Sp1/Sp3 binding to the promoter region drive the PADI1 expression in keratinocytes 19196427_These data suggest that APO can enhance the biosynthesis and release of FGF-2 through the activation of the MZF-1 transcription factor in striatal astrocytes 20145042_Taken together, this is the first study to show that MZF1 induces invasion and in vivo metastasis in colorectal and cervical cancer, at least in part by regulating Axl gene expression. 22242952_association between the expression of PKCalpha and the expression of the transcription factors Elk-1 and MZF-1 in breast cancer cell lines 22464443_signaling network activates the transcription of cathepsin B gene via myeloid zinc finger-1 transcription factor that binds to an ErbB2-responsive enhancer element in the first intron of cathepsin B 22559731_Expression levels of Elk-1 and PKCalpha were the highest in 5637 cells, but the MZF-1 expression observed in all five cell lines showed no significant difference. 22846578_This study shows that MZF-1 represses MMP-2 transcription and suggests that this repression may be linked to inhibition of human cervical cancer cell migration and metastasis. 23241556_Selected single nucleotide polymorphisms in the MZF-1 gene exert a minor effect on the risk of Alzheimer's disease. 23509792_p55PIK is transcriptionally activated by MZF1, resulting in increased proliferation of colorectal cancer cells 24793789_MZF1-mediated MYC expression may promote tumor progression, resulting in poor outcomes in cases of lung adenocarcinoma with low-wild-type-LKB1 tumors. 25065746_MZF-1 binds to and positively regulates the GAPDH promoter. 25284586_Data indicate that elevated miR-492 expression in prostate tumors that resulted in diminished myeloid zinc-finger 1 (MZF-1) and ferroportin (FPN). 25425970_Data suggest that induction of foxhead box M1(FOXM1) by E6 oncoprotein through the transcription factors MZF1/NKX2-1 axis may be responsible for human papillomavirus 16/18-mediated tumor progression. 25877752_our results revealed that the loss of nuclear expression of MZF1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) samples can predict the progression of OSCC and the survival of OSCC patients in Taiwan 25884514_The aberrant decreases in Ik-1 and MZF1 contribute significantly to the pathogenesis of NPM-ALK(+) T-cell lymphoma through the upregulation of IGF-IR expression. 25899830_our results argue that MZF-1 regulates the CTGF and NOV genes in the hematopoietic compartment, and may be involved in their respective functions in the stroma. 25903835_Here we discuss the regulation of MZF1 that mediated its recruitment and activation in cancer, concentrating on posttranslational modification by phosphorylation, and sumoylation 26010542_These findings suggest that PKCalpha expression in HCC could be stimulated by the formation of MZF-1/Elk-1 complex, which directly binds to the PKCalpha promoter. 27259238_miR-337-3p directly binds to the MMP-14 promoter to repress MZF1-facilitatd MMP-14 expression, thus suppressing the progression of gastric cancer 27764784_PAX2 is involved in the carcinogenesis of endometrial cancer by stimulating cell growth and promoting cell motility; the overexpression of PAX2 in endometrial cancer is regulated by promoter hypermethylation and the transcription factor MZF1 27922669_MZF1 has a role in cellular migration of gastric cancer cells via promoting an increase in intracellular SMAD4 levels. This study might provide new evidence for the molecular basis of the tumor suppressive effect of the MZF1-SMAD4 axis, a new therapeutic target in advanced human gastric cancer. 28478957_SIRT6 over-expression establishes a condition whereby reconfiguration of the Hexokinase 2 promoter chromatin structure makes it receptive to interaction with MZF1/SIRT6 complex, thereby favouring a regulatory state conducive to diminished transcription 28634046_Tumor antigen PRAME is up-regulated by MZF1 in cooperation with DNA hypomethylation in melanoma cells. 28703907_TGF-beta1-induced CK17 enhances cancer stem cell-like properties rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition in promoting cervical cancer metastasis via the ERK1/2-MZF1 signaling pathway. 29048625_MZF1 gene expression was not significantly correlated with PYROXD2 protein expression in the samples of resected tumor tissues, which revealed that the PYROXD2 promoter transcription activity was determined by the aggregated effect of numerous transcription factors. This finding may be helpful in understanding the underlying mechanism which regulates the PYROXD2 expression. 29842885_Mechanistically, FTO enhanced MZF1 expression by reducing m(6)A levels and mRNA stability in MZF1 mRNA transcript, leading to oncogenic functions. 30301827_Metallothionein 2A (MT2A)/myeloid zinc-finger 1 (MZF1) may serve as a prognostic marker and a therapeutic target for human gastric cancer. 31366500_Exogenous expression of the acidic domain of MZF1 repressed the binding of endogenous MZF1 to IGF1R promoter via blocking the interaction with ETS-like gene 1 (ELK1). This blockage not only caused MZF1 protein degradation, but also restrained ELK1 nuclear localization in high-level MZF1-expressing TNBC cells. MZF1, but not ELK1, was necessary for the retention of mesenchymal phenotype by repressing IGF1R promoter activity 32449233_Cigarette smoke modulates binding of the transcription factor MZF1 to the VEGF promoter and regulates VEGF expression in dependence of genetic variation SNP 405. 34602532_MZF1 alleviates oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by rotenone in SH-SY5Y cells by promoting RBM3 transcription. 34773072_MZF1 mediates oncogene-induced senescence by promoting the transcription of p16(INK4A). |
ENSMUSG00000030380 |
Mzf1 |
134.555314 |
0.3983242527 |
-1.327985 |
0.136180459 |
97.770589 |
0.00000000000000000000004697735854753774576042109954579986232117131538975758125899066016545324586672904842998832464218139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000465672137113268742139874459380558205958797416489867683286147867494086938222608296200633049011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.8702173 |
6.5034469 |
194.3030528 |
10.1721166 |
| ENSG00000099330 |
79629 |
OCEL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H607 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79629; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830] |
32083572_Low OCEL1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in human non-small cell lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000002396 |
Ocel1 |
49.214915 |
0.4334145798 |
-1.206180 |
0.220573043 |
30.167067 |
0.00000003963834800782974664654044190219284171661229265737347304821014404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000162517226832101951324648461162658552581206095055676996707916259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
30.1848342 |
8.4196632 |
69.7926656 |
13.7600106 |
| ENSG00000099338 |
57828 |
CATSPERG |
protein_coding |
Q6ZRH7 |
FUNCTION: Auxiliary component of the CatSper complex, a complex involved in sperm cell hyperactivation. Sperm cell hyperactivation is needed for sperm motility which is essential late in the preparation of sperm for fertilization. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:C6KI89}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Flagellum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Spermatogenesis;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
CATSPERG is a subunit of the CATSPER (see CATSPER1; MIM 606389) sperm calcium channel, which is required for sperm hyperactivated motility and male fertility (Wang et al., 2009 [PubMed 19516020]).[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:57828; |
CatSper complex [GO:0036128]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sperm principal piece [GO:0097228]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;19516020_CATSPERG is predicted to be a single transmembrane-spanning protein with a large extracellular domain and a short intracellular tail. |
ENSMUSG00000049123+ENSMUSG00000049676 |
Catsperg2+Catsperg1 |
10.117019 |
0.2390249936 |
-2.064767 |
0.628814444 |
10.513834 |
0.00118484139592404621489640792475483976886607706546783447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002726151052819785446101885639791362336836755275726318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5060154 |
1.6470807 |
14.5321498 |
4.2917062 |
| ENSG00000099365 |
112755 |
STX1B |
protein_coding |
P61266 |
FUNCTION: Potentially involved in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. May mediate Ca(2+)-regulation of exocytosis acrosomal reaction in sperm (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Membrane;Neurotransmitter transport;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of proteins thought to play a role in the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Vesicle exocytosis releases vesicular contents and is important to various cellular functions. For instance, the secretion of transmitters from neurons plays an important role in synaptic transmission. After exocytosis, the membrane and proteins from the vesicle are retrieved from the plasma membrane through the process of endocytosis. Mutations in this gene have been identified as one cause of fever-associated epilepsy syndromes. A possible link between this gene and Parkinson's disease has also been suggested. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:112755; |
axon [GO:0030424]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; nuclear lamina [GO:0005652]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; spindle [GO:0005819]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter [GO:0048791]; exocytic insertion of neurotransmitter receptor to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098967]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; negative regulation of macropinocytosis [GO:1905302]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling [GO:1903422]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0001956]; positive regulation of spontaneous neurotransmitter secretion [GO:1904050]; regulation of exocytosis [GO:0017157]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of synaptic activity [GO:0060025]; regulation of synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0010807]; spontaneous neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0061669]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081]; synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0031629]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
18691641_The STX1B-Delta transmembrane domain is characterized as the first nucleoplasmic syntaxin with no transmembrane domain. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 25101798_Data indicate that single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPS) in the 3'-untranslated region of the fucosyltransferase 1 (FUT1) gene and intron of the syntaxin 1B (STX1B) gene were the top hits for Kawasaki disease (KD) susceptibility. 25362483_STX1B and the presynaptic release machinery may have a role in fever-associated epilepsy syndromes 25534083_The data of this study suggested that the STX1B polymorphisms are associated with Parkinson disease etiology. 26224037_Findings suggested that STX1B rs4889603, FAM47E rs6812193 and SCARB2 rs6825004 do not confer a significant risk for Parkinson's disease 26751406_529 adults (n = 325 European-Americans, 204 Egyptians) on a stable warfarin dose were genotyped for GGCX rs12714145 and rs10654848, FPGS rs7856096, and STX1B rs4889606. 27740732_genetic variations in STX1B, DNMT3A and CYP1A1 have roles in influencing warfarin maintenance dose 28855684_Strong deregulation of SNAP25 and STX1B has been found at both mRNA and protein levels suggesting impaired synaptic function through SNAP25 reduction as a possible cause of calcium elevation and glutamate excitotoxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 29101845_Transcranial magnetic stimulation measures of motor cortex excitability show normal excitability in adult STX1B mutation carriers with a history of seizures. 30378543_that a sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy phenotype can be associated with syntaxin-1B gene mutation 30737342_These data expand the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of STX1B-related epilepsies to a diverse range of epilepsies. More often, loss-of-function mutations were found in benign syndromes, whereas missense variants in the SNARE motif of syntaxin-1B were associated with more severe phenotypes. 33677401_Delineation of epileptic and neurodevelopmental phenotypes associated with variants in STX1B. 34764822_Syntaxin-1 and Insulinoma-Associated Protein 1 Expression in Breast Neoplasms with Neuroendocrine Features. |
ENSMUSG00000030806 |
Stx1b |
16.252059 |
0.0556201107 |
-4.168250 |
0.689879023 |
40.180900 |
0.00000000023150064738929155970915223793397345192213165887551440391689538955688476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001165796504764907296930681609796985609417419027522555552423000335693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4870189 |
0.8325456 |
28.0338876 |
9.0655586 |
| ENSG00000099377 |
80270 |
HSD3B7 |
protein_coding |
Q9H2F3 |
FUNCTION: The 3-beta-HSD enzymatic system plays a crucial role in the biosynthesis of all classes of hormonal steroids. HSD VII is active against four 7-alpha-hydroxylated sterols. Does not metabolize several different C(19/21) steroids as substrates. Involved in bile acid synthesis (PubMed:11067870). Plays a key role in cell positioning and movement in lymphoid tissues by mediating degradation of 7-alpha,25-dihydroxycholesterol (7-alpha,25-OHC): 7-alpha,25-OHC acts as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR183/EBI2, a chemotactic receptor for a number of lymphoid cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EQC1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11067870}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Intrahepatic cholestasis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroidogenesis;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; steroid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11067870}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme which is involved in the initial stages of the synthesis of bile acids from cholesterol and a member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily. The encoded protein is a membrane-associated endoplasmic reticulum protein which is active against 7-alpha hydrosylated sterol substrates. Mutations in this gene are associated with a congenital bile acid synthesis defect which leads to neonatal cholestasis, a form of progressive liver disease. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:80270; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; 3-beta-hydroxy-delta5-steroid dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003854]; cholest-5-ene-3-beta,7-alpha-diol 3-beta-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047016]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016616]; B cell chemotaxis [GO:0035754]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699] |
20531254_Mutations in the HSD3B7 gene account for autosomal recessive neonatal cholestasis caused by 3[beta]-hydroxy-[DELTA]5-C27-steroid dehydrogenase/isomerase deficiency. 21044367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22095780_Homozygosity mapping identifies a bile acid biosynthetic defect (3beta-HSD deficiency due to a frameshift mutation in HSD3B7) in an adult with cirrhosis of unknown etiology. 26450365_Expression of steroid sulfated transporters and 3beta-HSD activity in endometrium of polycystic ovary syndrome 26712441_Novel Mutations in the 3beta-hydroxy-5-C27-steroid Dehydrogenase Gene (HSD3B7) in a Patient with Neonatal Cholestasis. 29670816_In the classical pathway, HSD3B7 catalyzes the second step of bile acid formation and its mutations may reduce the synthetic capability. 34627351_Genetic spectrum and clinical characteristics of 3beta-hydroxy-Delta(5)-C27-steroid oxidoreductase (HSD3B7) deficiency in China. |
ENSMUSG00000042289 |
Hsd3b7 |
23.337981 |
0.4957277982 |
-1.012380 |
0.366880757 |
7.579699 |
0.00590293126102117097359078812246480083558708429336547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011875053211485958951088015567165712127462029457092285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7493874 |
3.6407268 |
31.9788688 |
4.8964291 |
| ENSG00000099725 |
5616 |
PRKY |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
This gene is similar to the protein kinase, X-linked gene in the pseudoautosomal region of the X chromosome. The gene is classified as a transcribed pseudogene because it has lost a coding exon that results in all transcripts being candidates for nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) and unlikely to express a protein. Abnormal recombination between this gene and a related gene on chromosome X is a frequent cause of XX males and XY females. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
|
|
19474452_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
165.675452 |
0.3630188820 |
-1.461884 |
0.376674412 |
14.450484 |
0.00014389290110969007747271364294761042401660233736038208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000386507592425664370152510462830264259537216275930404663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83.6971800 |
26.5143629 |
231.0336835 |
52.1923717 |
| ENSG00000099849 |
8045 |
RASSF7 |
protein_coding |
Q02833 |
FUNCTION: Negatively regulates stress-induced JNK activation and apoptosis by promoting MAP2K7 phosphorylation and inhibiting its ability to activate JNK. Following prolonged stress, anti-apoptotic effect stops because of degradation of RASSF7 protein via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Required for the activation of AURKB and chromosomal congression during mitosis where it stimulates microtubule polymerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20629633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21278800}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to be involved in apoptotic process; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization; and signal transduction. Located in centriolar satellite. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8045; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15098441_rare alleles of HRas1 minisatellite are associated with increased risk of papillary thyroid cancer formation in children and adolescents after Chernobyl accident 19367319_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20629633_RASSF7 regulates the microtubule cytoskeleton and is required for spindle formation, Aurora B activation and chromosomal congression during mitosis. 21278800_RASSF7 acts in concert with N-Ras to constitute a stress-sensitive temporary mechanism of apoptotic regulation. 22695170_The RASSF gene family members RASSF5, RASSF6 and RASSF7 show frequent DNA methylation in neuroblastoma. 26569555_truncated RASSF7 could act as an oncogene in a small subset of tumours where it is mutated in this way. 26884887_Suggest that loss of RASSF7 expression results in apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells in human intervertebral disc degeneration. 29729697_RASSF7 promotes cell proliferation through activating MEK1/MEK2-ERK1/ERK2 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30139745_RASSF7 competed with MAX in the formation of a heterodimeric complex with c-Myc and attenuated its occupancy on target gene promoters to regulate transcription. |
ENSMUSG00000038618 |
Rassf7 |
108.335519 |
0.4704560559 |
-1.087868 |
0.167967489 |
42.444333 |
0.00000000007272281637546502740697868142908852871764135983312371536158025264739990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000379155340763639684347750049713031764153647884540987433865666389465332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.5241630 |
7.8883424 |
157.8143592 |
11.0286462 |
| ENSG00000099860 |
4616 |
GADD45B |
protein_coding |
O75293 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the regulation of growth and apoptosis. Mediates activation of stress-responsive MTK1/MEKK4 MAPKKK. |
Apoptosis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is a member of a group of genes whose transcript levels are increased following stressful growth arrest conditions and treatment with DNA-damaging agents. The genes in this group respond to environmental stresses by mediating activation of the p38/JNK pathway. This activation is mediated via their proteins binding and activating MTK1/MEKK4 kinase, which is an upstream activator of both p38 and JNK MAPKs. The function of these genes or their protein products is involved in the regulation of growth and apoptosis. These genes are regulated by different mechanisms, but they are often coordinately expressed and can function cooperatively in inhibiting cell growth. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4616; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] |
12162804_participation of NF-kappaB in the regulation of Gadd45beta 12759252_Results suggest that GADD45beta, which is down-regulated in most cases of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), remains an ideal candidate for development as a molecular marker in the diagnosis of HCC and as a potential therapeutic target. 12855571_in B cells, Gadd45 beta is induced by CD40 through a mechanism that requires NF-kappa B and that induction suppresses Fas-mediated killing 14630914_SMAD3 and SMAD4 activate gadd45beta through its third intron to facilitate G2 progression following TGFbeta treatment 15509538_methylation might play a crucial role in the epigenetic regulation of GADD45beta in hepatocyte transformation that may be directed by p53 status 15546867_TGF-beta induces biglycan expression through ALK5 and GADD45beta 15642734_NF-kappaB, ERK, and GADD45beta are able to coordinate in a loop-like signaling network to defend cells against the cytotoxicity induced by ionizing radiation 16144844_GADD45beta plays an essential role during chondrocyte terminal differentiation and mediates MMP-13 gene expression 17437852_We found significant differences in gene expression, specifically with a group of genes, including GADD45beta, known to be responsive to estrogen or to interact with estrogen receptor. 17485467_Association of Gadd45beta with MKK7 involves a network of interactions mediated by its putative helices alpha3 and alpha4 and loops 1 and 2 17591973_our results suggest that GADD45beta induction by SAMe via NF-kappaB may represent a novel mechanism of SAMe-mediated hepatoprotection, with p53 playing an important role. 18343408_The results suggest the occurrence of a large complex containing at least an MKK7-Gadd45 beta:Gadd45 beta-MKK7 tetrameric unit whose complexity could be further increased by the dimeric nature of the isolated MKK7. 18515079_Haplotype (rs2024144-rs3783501) of GADD45B affected the thickness of inter-ventricular septum in patients with hypertrophy cardiomyopathy. 18576389_These observations suggest that GADD45beta might play an important role in regulating chondrocyte homeostasis by modulating collagen gene expression and promoting cell survival in normal adult cartilage and in early OA 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834918_The stress-mediated induction of gadd45b by distinct stressors is differentially regulated at the level of mRNA transcription or mRNA stability, which is largely distinct from gadd45a. 19877043_Deficient Gadd45beta expression in RA can contribute to activation of JNK, exacerbate clinical arthritis, and augment joint destruction. 20530689_Diminished Gadd45beta expression leads to aberrant cell cycle arrest and diminished DNA excision repair and is associated with HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinomas. 20558744_Findings suggest that Gadd45b mediates p38-induced Rb phosphorylation by enhancing the interaction between p38 and Rb during Fas-induced apoptosis in murine hepatocytes. 20942912_The association of GADD45beta expression and pathological grading of chondrosarcoma in the present study suggests that the immunohistochemical study of GADD45beta may be a specific diagnostic parameter for chondrosarcoma cell differentiation. 21062976_Findings suggest that GADD45beta induction contributes to sorafenib-induced apoptosis in HCC cells, prompting further studies to validate its potential value in predicting sorafenib efficacy. 21127053_PXR activates the GADD45beta gene, increasing p38 MAPK phosphorylation, and leading HepG2 cells to change morphology and migrate. 21810943_GADD45beta is a novel pituitary tumor suppressor whose reexpression blocks proliferation, survival, and tumorigenesis 22048458_finding show there is an increased expression and decreased promoter binding of GADD45b in psychotic subjects. 22096849_Cadmium chloride can induce DNA damage and increase expression levels of the gadd153 and gadd45beta promoters in HepG2 cells. 23110778_as such may play an unappreciated role in tumorigenesis. The exact mechanism of GADD45B inactivation and overexpression requires further investigation. GADD45B could be a potential therapeutic target for CRC treatment in future 24104471_The gadd45b gene has both tumor suppressor and tumor promoter functions, dependent on the tissue/cell type and transforming event. (Review) 24104474_Gadd45B protects the liver through two entirely different processes: binding MKK7 to block damaging signal transduction or binding CAR to coactivate anabolic transcription. (Review) 26896926_our data demonstrate that C/EBPbeta plays a central role in controlling Gadd45beta gene expression in articular chondrocytes 26993769_present study provides evidence that variations in GADD45B rs2024144T, MAPK14 rs3804451A and GADD45A rs581000C may predict platinum-based chemotherapy toxicity outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer 27208483_Nrf2-Gadd45b signaling axis exhibited a protective role in antimony trioxide-induced cell apoptosis. 27572311_We propose a signaling cascade involving ARID1A, GADD45B and DUSP1 as mediators of the romidepsin effects in GCC cells. 27852859_We used a new approach to search for human genes repressed by small nucleic acids (microRNAs) expressed by a gammaherpesvirus (KSHV), which identified a gene called GADD45B as a target of microRNAs. Repression of GADD45B, which is expressed in response to DNA damage, benefited survival of infected cells in response to a DNA damage response. This information could be used to design new treatments for herpesvirus infections 28214215_Gadd45beta could be a suitable biomarker of cardiomyocytes apoptosis in newborns experiencing hypoxia in the first day of life, as its highest tissue immunoexpression around at the first six hours after birth. 28870783_These findings demonstrate that 19p13.3-GADD45B rs7354 variant and interaction between 19p13.3-GADD45B rs3783501 and 19q13.3-CD3EAP rs967591 may play a role in association with smoke-exposed lung cancer among Chinese. 29279355_High GADD45B expression is associated with cancer. 29356020_Although GADD45B is elevated in prostate cancer tissues, levels of GADD45B in prostate tumor tissues are reduced at late stage of tumor invasion, and higher levels of GADD45B predict better survivals of prostate cancer patients. 29572137_The assessment of the interaction between GADD45beta and MKK7 and the elucidation of the recognition surfaces between DTP3 and MKK7 significantly advance the understanding of the mechanism underlying the inhibition of the GADD45beta/MKK7 interaction by DTP3 and pave the way to the design of small-molecule DTP3 analogues. 29741778_demonstrate the protective role of GADD45beta in sepsis and the results suggest that GADD45beta could be used as a novel therapeutic target to cure sepsis 30622144_We found that GADD45B is indispensable for DNA damage protection and survival in stem cells. Thus, we describe an easy and efficient protocol of DNA-free gene editing of hard-to-target transcripts and enrichment of gene-modified cells that are generally difficult to transfect. 30643065_Down-regulation of GADD45beta can reduce the colony-forming ability of PC9 cells, promote the cell apoptosis, and enhance the sensitivity of PC9 cells to gefitinib 32425887_GADD45B Transcript Is a Prognostic Marker in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients Treated With Total Thyroidectomy and Radioiodine Therapy. 34272424_Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible proteins (GADD45) in psoriasis. 34842321_Single-cell transcriptomics identifies Gadd45b as a regulator of herpesvirus-reactivating neurons. |
ENSMUSG00000015312 |
Gadd45b |
50.121907 |
0.4884102867 |
-1.033835 |
0.249001993 |
17.269469 |
0.00003243569171182764462749506528815857109293574467301368713378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000095737706535737530618226931444780802848981693387031555175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
34.1614542 |
7.6962647 |
70.5796180 |
11.2947912 |
| ENSG00000099889 |
421 |
ARVCF |
protein_coding |
O00192 |
FUNCTION: Contributes to the regulation of alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24644279}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Methylation;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Armadillo Repeat gene deleted in Velo-Cardio-Facial syndrome (ARVCF) is a member of the catenin family. This family plays an important role in the formation of adherens junction complexes, which are thought to facilitate communication between the inside and outside environments of a cell. The ARVCF gene was isolated in the search for the genetic defect responsible for the autosomal dominant Velo-Cardio-Facial syndrome (VCFS), a relatively common human disorder with phenotypic features including cleft palate, conotruncal heart defects and facial dysmorphology. The ARVCF gene encodes a protein containing two motifs, a coiled coil domain in the N-terminus and a 10 armadillo repeat sequence in the midregion. Since these sequences can facilitate protein-protein interactions ARVCF is thought to function in a protein complex. In addition, ARVCF contains a predicted nuclear-targeting sequence suggesting that it may have a function as a nuclear protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:421; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; messenger ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990124]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-cell junction assembly [GO:0007043]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
15340358_Evidence was found for association of illness to rs165849 in ARVCF, and a stronger signal from three-marker haplotypes spanning the 3' portions of COMT and ARVCF. Val(108/158)Met was in linkage disequilibrium with the markers in ARVCF. 15456900_Interactions with zona occludens-1 and zona occludens-2, in particular, may mediate recruitment of ARVCF to the plasma membrane and the nucleus 15509897_Results implicate a very close association of ARVCF with migrating neurons from the ganglionic eminence. 16118784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16118784_Two haplotypes covering the catechol-O-methyltransferase-ARVCF region show significant transmission disequilibrium in anorexia nervosa-restricting Israeli-Jewish families 18198266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18600340_Differential expression pattern of protein ARVCF in nephron segments of human kidney. 19508883_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the ARVGF gene are associated with the risk of schizophrenia. 19617637_Over-expression of TXNRD2, COMT and ARVCF affects incentive learning and working memory in transgenic mice. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20333729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20333729_The functional variant rs165815, which affects a critical region of ARVCF, is a considerable source of the genetic variability associated with the risk of developing schizophrenia. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21846818_Five SNPs were validated as being significantly associated with prostate cancer mortality, one each in the LEPR, CRY1, RNASEL, IL4, and ARVCF genes. 22053977_Schizophrenic patients with more copies of the haplotype T-G-A-T-T-G-G-C-T-G-T (ARVCF-Hap1) have lower white matter integrity in caudate nucleus and greater perseverative errors. 24644279_Data indicate that armadillo repeat protein ARVCF interacts with the splicing factors the splicing factor SRSF1 (SF2/ASF), the RNA helicase p68 (DDX5), and the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein hnRNP H2. 24819575_Carriage of the minor allele at rs2518824 in the armadillo repeat gene deleted in velocardiofacial syndrome (ARVCF) gene was associated with white matter abnormality. 25683624_observed ARVCF-dependent changes in small GTPase (mainly RhoA) activity in lung cancer cells. We confirmed that ARVCF plays an important role in the malignant phenotype 31827232_p53-induced ARVCF modulates the splicing landscape and supports the tumor suppressive function of p53. |
ENSMUSG00000118669 |
Arvcf |
20.043343 |
0.4101970099 |
-1.285611 |
0.480548386 |
7.033615 |
0.00799937192805052696420453628434188431128859519958496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015650945076620598195304978617059532552957534790039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.2605087 |
3.6807677 |
30.4019042 |
5.9092011 |
| ENSG00000099991 |
23523 |
CABIN1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6J0 |
FUNCTION: May be required for replication-independent chromatin assembly. May serve as a negative regulator of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling via inhibition of calcineurin. Inhibition of activated calcineurin is dependent on both PKC and calcium signals. Acts as a negative regulator of p53/TP53 by keeping p53 in an inactive state on chromatin at promoters of a subset of it's target genes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14718166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9655484}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
Calcineurin plays an important role in the T-cell receptor-mediated signal transduction pathway. The protein encoded by this gene binds specifically to the activated form of calcineurin and inhibits calcineurin-mediated signal transduction. The encoded protein is found in the nucleus and contains a leucine zipper domain as well as several PEST motifs, sequences which confer targeted degradation to those proteins which contain them. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding two different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:23523; |
aggresome [GO:0016235]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; nucleosome assembly [GO:0006334] |
12700764_Crystal structure of the MADS-box/MEF2S domain of human MEF2B bound to a motif of the transcriptional co-repressor Cabin1 and DNA at 2.2 A resolution 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15671033_there is a 13-amino acid region within CN that is essential for the interaction with NFAT and with two other CN-binding proteins, AKAP79 and Cabin-1 17531200_Here, we report that Cabin1 has additional CN binding domain in its 701-900 amino acid residues. 19668210_Cabin1 inhibits p53 function on chromatin in the quiescent state; the presence of inactive p53 on some promoters might allow a prompt response upon DNA damage. 19717561_the association of CAIN with intracellular domains involved in mGluR/G protein coupling provides a mechanism by which Group I mGluR endocytosis and signaling are regulated 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075944_CABIN1 may not confer increased susceptibility for schizophrenia in the Japanese population. 20075944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21807893_Data show that, like HIRA, UBN1, and ASF1a, CABIN1 is involved in heterochromatinization of the genome of senescent human cells. 22275266_Our findings demonstrate that hCABIN-1 plays a critical role in promoting apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in attenuating inflammation and cartilage and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. 22401310_NHRD domain of UBN1 as being an essential region for HIRA interaction and chromatin organization by the HUCA complex 23624525_Two new susceptibility loci for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the Han Chinese population in chromosome 1, CAMK1G and chromosome 22, SUSD2 and CABIN1. 23939952_Results indicate an important role for LMP1 and Cabin1 in regulating apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in response to genotoxic stress. 30082790_analysis of the trimeric HIRA, UBN1 and CABIN1 H3.3 histone chaperone complex |
ENSMUSG00000020196 |
Cabin1 |
528.151888 |
0.2304872532 |
-2.117241 |
0.100615211 |
435.232965 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000118018347828502367537522698361153633630822850355364578688336092238000547062911762898235281876846269705386905856368261521073451410395518693260449982914864995976722145580046852495255178783231532295861077498096417050948119714465711031087 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000047724679834210824872708497345825955587607920447602000777530738541470359179743875311597006463504620767481614674736354595928679714711926353736419788938115521703672966802583209408068396574943536488887654952319142967071370944185361114877 |
Yes |
Yes |
213.8997093 |
13.5926547 |
936.0833311 |
39.3864276 |
| ENSG00000099998 |
2687 |
GGT5 |
protein_coding |
P36269 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves the gamma-glutamyl peptide bond of glutathione and glutathione-S-conjugate such as leukotriene C4 (PubMed:21447318). Does not cleaves gamma-glutamyl compounds such as gamma-glutamyl leucine (PubMed:21447318). May also catalyze a transpeptidation reaction in addition to the hydrolysis reaction, transferring the gamma-glutamyl moiety to an acceptor amino acid to form a new gamma-glutamyl compound (PubMed:21447318). Acts as a negative regulator of geranylgeranyl glutathione bioactivity by cleaving off its gamma-glutamyl group, playing a role in adaptive immune responses (PubMed:30842656). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21447318, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30842656}. |
Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Glutathione biosynthesis;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Leukotriene biosynthesis;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zymogen |
PATHWAY: Sulfur metabolism; glutathione metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21447318}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; leukotriene D4 biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21447318}. |
This gene is a member of the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase gene family, and some reports indicate that it is capable of cleaving the gamma-glutamyl moiety of glutathione. The protein encoded by this gene is synthesized as a single, catalytically-inactive polypeptide, that is processed post-transcriptionally to form a heavy and light subunit, with the catalytic activity contained within the small subunit. The encoded enzyme is able to convert leukotriene C4 to leukotriene D4, but appears to have distinct substrate specificity compared to gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:2687; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; glutathione hydrolase activity [GO:0036374]; hypoglycin A gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity [GO:0102953]; leukotriene C4 gamma-glutamyl transferase activity [GO:0103068]; leukotriene-C(4) hydrolase [GO:0002951]; peptidyltransferase activity [GO:0000048]; amino acid metabolic process [GO:0006520]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; glutathione catabolic process [GO:0006751]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; leukotriene D4 biosynthetic process [GO:1901750]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
24847614_There is a significant association of GGT with individual metabolic syndrome components, except HDL and inflammatory parameters (hs-CRP, ferritin). 25377544_Report different pattern of expression of GGT1 and GGT5 in normal human tissues. 27436590_Formation of LTD4 was rapid when catalyzed by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)1 in the A549 epithelial lung cancer cell line, but considerably slower when catalyzed by GGT5 in primary bronchial epithelial cells. When A549 cells were cultured in the presence of IL-1beta, GGT1 expression increased about 2-fold. Also exosomes from A549 cells contained GGT1 and augmented LTD4 formation. 32640421_Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived gamma-glutamyltransferase 5 promotes tumor growth and drug resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. 34088745_Abcc1 and Ggt5 support lymphocyte guidance through export and catabolism of S-geranylgeranyl-l-glutathione. |
ENSMUSG00000006344 |
Ggt5 |
9.269809 |
0.1408929589 |
-2.827329 |
0.656165174 |
19.301285 |
0.00001116312148537852273158955257459368226591323036700487136840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000034812523372953094679370378283778109107515774667263031005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1612205 |
1.2156630 |
15.1008582 |
5.3122146 |
| ENSG00000099999 |
200312 |
RNF215 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6U7 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in Golgi to vacuole transport; protein targeting to vacuole; and ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be part of Golgi transport complex. Predicted to be active in endosome; membrane; and trans-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:200312; |
endosome [GO:0005768]; Golgi transport complex [GO:0017119]; membrane [GO:0016020]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; Golgi to vacuole transport [GO:0006896]; protein targeting to vacuole [GO:0006623]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
|
ENSMUSG00000003581 |
Rnf215 |
56.045063 |
0.4423156594 |
-1.176852 |
0.241176317 |
24.001623 |
0.00000096254535821549714198199984571679976852465188130736351013183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003409447921108888205526162712422078016061277594417333602905273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9046226 |
5.8569281 |
86.2316754 |
8.8552434 |
| ENSG00000100003 |
23541 |
SEC14L2 |
protein_coding |
O76054 |
FUNCTION: Carrier protein. Binds to some hydrophobic molecules and promotes their transfer between the different cellular sites. Binds with high affinity to alpha-tocopherol. Also binds with a weaker affinity to other tocopherols and to tocotrienols. May have a transcriptional activatory activity via its association with alpha-tocopherol. Probably recognizes and binds some squalene structure, suggesting that it may regulate cholesterol biosynthesis by increasing the transfer of squalene to a metabolic active pool in the cell. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipid-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a cytosolic protein which belongs to a family of lipid-binding proteins including Sec14p, alpha-tocopherol transfer protein, and cellular retinol-binding protein. The encoded protein stimulates squalene monooxygenase which is a downstream enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:23541; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; vitamin E binding [GO:0008431]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0045540] |
12429094_SPF has two domain topology, and the ligand binding cavity has a peculiar horseshoe-like shape 12454003_phosphorylation enhances its ability to stimulate microsomal squalene monooxygenase; phosphorylation may provide a means for the rapid short term modulation of cholesterol synthesis 12972248_Data report the three-dimensional crystal structure of human supernatant protein factor in complex with RRR-alpha-tocopherylquinone, the major physiological oxidation product of RRR-alpha-tocopherol, at a resolution of 1.95A. 15033454_Discusses cloning of rat SEC14-like protein 3 and mentions three human SPF-related genes, known as SEC14-like protein 1, 2 and 3. 16267002_TAP not only mediates vitamin E absorption to facilitate vitamin E antiproliferation effect in prostate cancer cells, but also functions like a tumor suppressor gene to control cancer cell viability through a non-vitamin E manner. 17334589_reduced expression of TAP was associated with the cell proliferation status of prostate cancer, adverse pathological parameters and the increased risk of recurrence 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19190344_Genetic variation in TTPA and SEC14L2 is associated with serum alpha-tocopherol but does not have a direct effect on prostate cancer when vitamin E is administered. 19190344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19305383_These findings are consistent with alpha-tocopherol-associated protein acting as an antiproliferative factor in estrogen-receptor-positive luminal cells in normal/benign breast tissue 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19909011_Fndings raise the possibility that TAP/Sec14L2 may serve as a tumor suppressor in breast carcinogenesis. 23401652_novel association between the rs737723 polymorphism (SEC14L2/TAP) and higher primary open-angle glaucoma risk 23411208_TAP expression was significantly correlated with Her2/neu receptor expression and breast cancer stage. 24983950_hTAP1 reduces the in vitro activity of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma (PI3Kgamma) indicating the formation of a stalled/inactive hTAP1/PI3Kgamma heterodimer. 25290554_PI3Kgamma-induced VEGF expression was reduced when the human tocopherol-associated protein 1 (hTAP1/SEC14L2) was overexpressed suggesting formation of an inactive PI3Kgamma/hTAP1 heterodimer. 26266980_SEC14L2 enabled RNA replication of diverse HCV genotypes in several human hepatoma cell lines 28463110_Here, the authors report that the zebrafish/human phosphatidylinositol transfer protein Sec14l3/SEC14L2 act as GTPase proteins to transduce Wnt signals from Frizzled to phospholipase C (PLC). 30472319_SEC14L2, a lipid-binding protein, regulates HCV replication in culture with inter- and intra-genotype variations. 31851620_Discovering master regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma: one novel MR, SEC14L2 inhibits cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000003585 |
Sec14l2 |
20.641120 |
8.1652510822 |
3.029497 |
0.769321442 |
13.245314 |
0.00027326218343032775788190025245683045795885846018791198730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000701452143901154317150170580674739539972506463527679443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
19.7126575 |
13.9991215 |
2.0308763 |
1.0309647 |
| ENSG00000100036 |
339665 |
SLC35E4 |
protein_coding |
Q6ICL7 |
FUNCTION: Putative transporter. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable antiporter activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:339665; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; antiporter activity [GO:0015297] |
|
ENSMUSG00000048807 |
Slc35e4 |
65.046446 |
4.7257498684 |
2.240543 |
0.227820823 |
102.644385 |
0.00000000000000000000000401046542260716100678331315234880370468283600037173147027969347892112361719796354009304195642471313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000041686246223719504921897295773730789624683169799645994027977307250926175541394513857085257768630981445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.3640180 |
14.7918292 |
22.8516938 |
2.7028145 |
| ENSG00000100065 |
29775 |
CARD10 |
protein_coding |
Q9BWT7 |
FUNCTION: Scaffold protein that plays an important role in mediating the activation of NF-kappa-B via BCL10 or EGFR. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27991920}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The caspase recruitment domain (CARD) is a protein module that consists of 6 or 7 antiparallel alpha helices. It participates in apoptosis signaling through highly specific protein-protein homophilic interactions. Like several other CARD proteins, CARD10 belongs to the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family and activates NF-kappa-B (NFKB; see MIM 164011) through BCL10 (MIM 603517) (Wang et al., 2001 [PubMed 11259443]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:29775; |
CBM complex [GO:0032449]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; CARD domain binding [GO:0050700]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090051]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981] |
15184390_CARMA1 and CARMA3 bind to Ikappa kinase gamma-NFkappaB in B and T lymphocytes 17101977_CARMA3/Bcl10/MALT1-dependent NF-kappaB activation mediates angiotensin II-responsive inflammatory signaling in hepatocytes. 17724468_Protein kinase C-CARMA3 signaling axis plays an essential role in lysophosphatidic acid-induced ovarian cancer cell in vitro invasion. 18349075_results further define the molecular mechanisms that control activation of NF-kappaB and reveal a function for A20 in the regulation of CARMA and BCL10 activity in lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18757306_Data demonstrate that lysophosphatidic acid stimulates thymic stromal lymphopoietin and CCL20 expression in bronchial epithelial cells via CARMA3-mediated NF-kappaB activation. 19112107_components of the CBM complex, Carma3, Bcl10, and Malt1 are key mediators of the CXCL8/IL8-induced NFkappaB activation and VEGF up-regulation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20695076_activation of NF-kappaB by CXCR4 occurs through Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1 (CBM) complex in OSCC. loss of components of CBM complex in HNSCC can inhibit SDF-1 alpha induced phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21307088_Polymorphisms of ATOH7, TGFBR3 and CARD10 influence the size of optic disc area. 21406399_Data show that CARMA3 and Bcl10 contributed to several characteristics of EGFR-associated malignancy, including proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion. 22615840_The overexpression of CARMA3 was significantly correlated with TNM stage (P = 0.022) and tumor status (P = 0.013). 22884800_this study found that CARMA3 is overexpressed in colon cancers and contributes to malignant cell growth by facilitating cell cycle progression through NF-kappaB mediated upregulation of cyclin D1. 22992343_miR-146a expression is up-regulated in a majority of gastric cancers where it targets CARD10 and COPS8, inhibiting GPCR-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. 23608917_Genetic variation within PARP1 and CARD10 was associated with rate of hippocampal neurodegeneration in APOE e3/e3 patients. 23708960_CARMA3 facilitates proliferation and inhibits apoptosis through nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. 23771851_Data show that CARMA3 may serve as a novel and prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and play a role during the development and progression of the disease. 23893382_overexpression of CARMA3 in human glioma and its correlation with tumor grade. 24018495_CARD10 may be involved in hepatic carcinogenesis associated with hepatitis C in Egyptian patients. 24443255_CARMA3 is overexpressed in bladder cancer and regulates malignant cell growth and NF-kappaB signaling. 24633921_CARMA3 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and regulates malignant cell growth, invasion, and NF-kappaB signaling, which was dependent on its association with Bcl10. 24833094_CARMA3 regulates the ovarian cancer cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and chemoresistance. 25541973_The study identified the DEP domain-containing protein DEPDC7 as cellular binding partner of CARMA2 and CARMA3 proteins. 25906011_A novel mechanism of CARMA3 in lung cancer stemness and metastasis through the negative regulation of NME2 was identified. 26252200_miR-24 inhibited cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer cells by downregulation of CARMA3 26526492_Findings indicate that CARMA3 may suppress the activation of the P38 MAPK signaling pathway to regulate invasion, migration and apoptosis of lung cancer cells by activating NF-small ka, CyrillicB (P65) in the nucleus. 26652023_Data indicate no association between caspase recruitment domain family, member 10 protein (CARD10) polymorphism rs6000782 and type 1 autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) in a Japanese population. 28301668_Card10 polymorphisms may not be linked with psoriasis vulgaris in the southern Han Chinese population. 28717989_The results suggest that the involvement of CARMA3 in DNA damage-induced NF-kappaB is through the recruitment of TRAF6. 29259013_High CARMA3 expression is associated with Breast Cancer. 29773596_Card10 is expressed in granulocytes and is a direct target of CEBPE with functions extending to myeloid differentiation. 30723269_The circINTS4/miR-146b/CARMA3 axis promotes tumorigenesis in bladder cancer. 31565867_Caspase recruitment domain family member 10 regulates carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 and promotes cancer growth in bladder cancer cells. 31576094_Higher expression of CARMA3 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was relevant to poor prognostic survival. Down-regulation of CARMA3 inhibited proliferation and colony formation and induced apoptosis in HCC cell lines, while increasing its expression promoted tumorigenesis. 31939627_CARD10 promotes the progression of renal cell carcinoma by regulating the NFkappaB signaling pathway. 32238915_Mutant CARD10 in a family with progressive immunodeficiency and autoimmunity. 34190011_CARMA3 Transcriptional Regulation of STMN1 by NF-kappaB Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion. |
ENSMUSG00000033170 |
Card10 |
11.102788 |
0.4395233112 |
-1.185988 |
0.458961858 |
6.713080 |
0.00957082620278634429999975452574290102347731590270996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018420314871968501008181462452739651780575513839721679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4910769 |
2.3812585 |
17.1844190 |
3.5391406 |
| ENSG00000100097 |
3956 |
LGALS1 |
protein_coding |
P09382 |
FUNCTION: Lectin that binds beta-galactoside and a wide array of complex carbohydrates. Plays a role in regulating apoptosis, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Inhibits CD45 protein phosphatase activity and therefore the dephosphorylation of Lyn kinase. Strong inducer of T-cell apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14617626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18796645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19497882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24945728}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Extracellular matrix;Lectin;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted |
|
The galectins are a family of beta-galactoside-binding proteins implicated in modulating cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. This gene product may act as an autocrine negative growth factor that regulates cell proliferation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3956; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; galectin complex [GO:1990724]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; myoblast differentiation [GO:0045445]; plasma cell differentiation [GO:0002317]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046598]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] |
11846886_Galectin-1 possesses a cell growth-inhibitory site which is not part of the beta-galactoside binding site: a surface loop, comprising amino acid residues 25-30 and joining two internal beta-strands, forms part of the growth-inhibitory site. 11850528_overexpressed in nasal polyps exposed to budesonide 11937561_Galectin-1 has the ability to activate NADPH oxidase in neutrophils that have been exposed to inflammatory mediators and stress during extravasation in vivo. 12008046_Receptor tyrosine phosphatase, CD45 binds galectin-1 but does not mediate its apoptotic signal in Jurkat cells 12125737_Galectin-1 expression of human glioblastoma xenografts from the brains of nude mice revealed a higher level of galectin-1 in invasive areas. Galectin-1 enhances migration of tumor astrocytes and, therefore, their biological aggressiveness. 12271131_Galectin-1 plays a role in binding to the pre-B cell receptor and forms a synapse 12527107_galectin-1 is likely to be involved in the extracellular matrix assembly affecting incorporation of some components important for smooth muscle cell behavior 12853445_galectin-1 induces surface exposure of phosphatidylserine and phagocytic recognition of leukocytes without inducing apoptosis 14507657_Endogenous Gal-1 may be part of novel anti-inflammatory loop in which endothelium is the source of protein and migrating neutrophils the target for its anti-inflammatory action. 14550305_Galectin-1 interacts with beta-1 subunit of integrin 14612929_Galectin-1 activation in human hepatocellular carcinoma involves methylation-sensitive complex formations at the transcriptional upstream and downstream elements 14617626_examined ability of stromal cells secreting galectin-1 to kill T cells. Although the stromal cells synthesized abundant galectin-1, the most of the galectin-1 remained bound to the cell surface, and stromal cell-associated galectin-1 killed bound T cells. 14693917_galectin-1 induces astrocyte differentiation and strongly inhibits astrocyte proliferation, and then the differentiated astrocytes greatly enhance their production of BDNF which may be a new mechanism for preventing neuronal loss after injury 14769876_Galectin-1 plays a role in both cell-matrix interactions and the inhibition of Colo201 tumor cell proliferation in vitro; galectin-1 expressed in cells may be associated with apoptosis. 15050916_Gal-1 signaling in activated T cells constitutes an important mechanism of tumor-immune escape 15297883_Galectin-1-induced cell death proceeds via a caspase-independent pathway that involves a unique pattern of mitochondrial events. 15556936_dGal-1 functions as a dimer to recognize terminal N-acetyllactosamine units on extended poly-N-acetyllactosamines on cell surfaces 15556941_Gal-1 induces mitochondrial coalescence, budding, and fission accompanied by an increase and/or redistribution of fission-associated molecules 15663199_Regulated expression of galectin-1 during T-cell activation involves Lck and Fyn kinases and signaling through MEK1/ERK, p38 MAP kinase and p70 S6 kinase. 15690107_map of polymorphic sites within an 11-kb region containing the gene, including 14 SNPs and two genetic variations of other types detected in a Japanese population sample 15778371_galectin-1 can cross-link HIV-1 and target cells and promote a firmer adhesion of the virus to the cell surface 15862866_findings suggest a possible role for galectin-1 in anchoring microbial and cancer cells known to be rich in T antigen, in high serum IgA1 turn over and in tissue sequestering of IgA1 immune complexes 15910247_galectin 1 may have a role in immunological functions of human mesenchymal stem cells 15929990_Transient Ca(2+) fluxes contribute to a sustained redistribution of phosphatidylserines on neutrophils activated with fMLP and dimeric galecstin-1. 15972675_gal-1 binds to specific N-glycans on Nipah virus (NiV) glycoproteins and aberrantly oligomerizes NiV-F and NiV-G, indicating a mechanism for fusion inhibition. 16033063_galectin-1 shows apoptotic potential in both the epithelial tumour cell lines examined only with additional stress stimuli 16051185_stable inhibition of galectin-1 expression alters the expression of a number of genes that either directly or indirectly influence adhesion, motility and invasion of human glioblastoma cells. 16247730_data indicate that IL-12 down-regulates the expression of both gal-1 and CD7 in the microsomal fraction of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and cord blood CD4(+) cells 16388708_HSV-1 may use galectin-1 as a weapon to kill activated T cells and evade specific immune responses 16530434_ANXA1 and Gal-3 changed in their content and localization when neutrophils adhere to endothelia. In contrast, a decrease in the total amounts of Gal-1 was detected in migrated compared to non-migrated neutrophils. 16636291_Results demonstrate that Galectin-1 is an endogenous factor that promotes the proliferation of neural stem cells in the 16751364_Murine dendritic cells engineered to express transgenic galectin-1 in vivo represent a novel tool for differential control of the afferent and efferent arms of the T cell response. 16785517_Galectin-1 binds to and activates monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDC) to become phenotypically and functionally mature DCs capable of enhanced chemotactic migration in an in vitro extracellular matrix model. 16818733_Galectin 1 binds to VLA-5 integrins on bone marrow stromal cells and to VLA-4, VLA-5, and alpha4beta7 integrins on pre-B cells, forming a homogeneous lattice at the contact area between bone marrow pre-B and stromal cells. 16940423_Galectin 1 induces surface phosphatidylserine exposure in a carbohydrate-dependent fashion in activated, but not resting, human neutrophils and in several leukocyte cell lines. 17043243_galectin-1 regulates tumor angiogenesis and is a target for angiostatic cancer therapy 17110462_galectin-1, is overexpressed in regulatory T cells, and that expression is increased after activation 17177840_galectin-1 expression on stromal cells increases with the histopathologic grade of cervical tissues 17182582_Our results provide evidence of a novel unrecognized role for galectin-1 in the control of monocyte/macrophage physiology with potential implications at the crossroad of innate and adaptive immunity. 17269744_Galectin-1 was found to be negatively regulated by transfection with TP53 in a glioblastoma cell line. 17304502_roles of galectin-1 in cancer-associated stroma and in tumor immune privilege 17390012_galectin-1 has a role in recurrence in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas 17438085_Galectin-1 mediated suppression of Epstein-Barr virus specific T-cell immunity is associated with Hodgkin lymphoma 17523619_investigated the solvation properties of the carbohydrate recognition domain of galectin-1 by means of molecular dynamics simulations 17535296_p16INK4a modulates glycomic profile and galectin-1 expression to increase susceptibility to carbohydrate-dependent induction of anoikis in pancreatic carcinoma cells 17537433_Data show that galectin-1, an endogenous lectin produced by arterial cells, binds lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] in situ. 17603562_This study sheds light on the molecular mechanisms whereby betaGBP can control cell proliferation and, by extension, may potentially control tumorigenesis by controlling PI3K. 17616672_galectin-1 has a role in O-glycosylation regulation of LNCaP prostate cancer cell susceptibility to apoptosis 17649808_MUC1, TF and galectin might have important roles in endometrial pathogenesis and malignant transformation. 17880528_Results suggest a possible role for galectin-1 in the pathogenesis of primary glomerulopathies in children as a kind of podocyte-related self-protective activity and probably involvement of epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule in inflammatory processes. 17884770_Galectin-1 can be involved in the development and progression of colorectal carcinoma, and may relate to the infiltration, differentiation and lymph node metastasis of colorectal carcinoma. 17984174_galectin-1, an endogenous lectin with immunoregulatory properties, plays a key role in human platelet activation and function. 18007053_X-ray diffraction data enabled assignment of unit-cell parameters for crystals grown under 2 conditions, one belongs to a tetragonal crystal system and the other was determined as monoclinic P2(1), representing 2 new crystal forms of human galectin-1. 18223683_Gal-1 can directly bind to NRP1 on endothelial cells, and can promote the NRP1/VEGFR-2-mediated signaling pathway as well as NRP1-mediated biological activities. 18258591_Galectin-9 and galectin-1 require different glycan ligands and glycoprotein receptors to trigger T cell death. 18292532_Gal-1 and Gal-3 induce differential responses in T cells and neutrophils; Gal-1 induces IL-10 production and attenuates interferon-gamma production in activated T cells. 18315601_An association was seen between the level of presence of galectins-1 and -7 and neoplastic progression of hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. 18431251_These results suggest that decreasing Gal-1 expression (e.g. through brain delivery of nonviral infusions of anti-Gal-1 siRNA in patients) can represent an additional therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma. 18519761_Gal1 and c-Jun serve as diagnostic biomarkers that delineate classical Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma from other lymphomas with shared morphologic and/or molecular features. 18570123_Placental galectin-1 mRNA expression was significantly higher in severe preeclampsia than in controls; Trophoblasts had the most intense galectin-1 immunostaining 18581052_Internalization of Gal-1 depends on its lectin activity and follows dual pathways involving clathrin-coated vesicles and raft-dependent endocytosis. 18630998_Serum levels of galectins-1 and -3 are relatively high in patients with thyroid malignancy but there is considerable overlap in serum galectin-3 concentrations between those with benign and malignant nodular thyroid disease 18633135_Dimeric galectin-1 (dGal-1) preferentially binds to and signals through glycoproteins containing complex-type N-glycans in at least some leukocyte subsets 18662664_carbohydrate-binding and the splicing activities of Gal1 can be dissociated and therefore, saccharide-binding, per se, is not required for the splicing activity 18671640_Galectin-1 appears to modulate migration and invasion in human glioma cell lines and may play a role in tumor progression and invasiveness in human gliomas 18691335_Chorioamnionitis is associated with an increased galectin-1 mRNA expression and strong immunoreactivity of the chorioamniotic membranes 18791848_Galectin-1 decreases Smad3-complex from binding to the SBE, down-regulating transcription of COL1A2 in TGF-beta1-stimulated renal epithelial cells. 18796645_The structure of cysteine-less Gal-1 is almost identical to that of wild-type human Gal-1 18802059_Galectin-1 plays a role in promoting immunoglobulin production during plasma cell differentiation. 18838383_GnT-Vb-mediated glycosylation of RPTPbeta promotes galectin-1 binding and RPTPbeta levels of retention on the cell surface. 18947333_Our results argue for the involvement of galectin-1 in the PKCepsilon/vimentin-controlled trafficking of integrin-beta1 18991278_These studies identify galectin-1 as a cross-regulatory cytokine that selectively antagonizes Th1 survival, while promoting TCR-induced Th2 cytokine production. 19011096_secretion of galectin-1 by dNKs and other decidual cells contributes to the generation of an immune-privileged environment at the maternal-fetal interface 19032754_These data suggest that HTLV-I Tax increases galectin-1 expression and that this modulation could play an important role in HTLV-I infection by stabilizing both cell-to-cell and virus-cell interactions. 19064001_promotes apoptosis in activated T cells, down-regulates pro-inflammatory cytokines 19103599_monomer-dimer equilibrium regulates Gal-1 sensitivity to oxidative inactivation and provides a mechanism whereby ligand partially protects Gal-1 from oxidation. 19116313_Gal-1 induces phosphatidylserine exposure and subsequent phagocytic removal of living cells. 19125585_galectin-1 is associated with the pathophysiology of diabetes and a novel diagnostic marker protein in T2D patients. 19128029_Use of ultraviolet resonance Raman spectroscopy and calculated water radial distribution functions show that, while no large structural changes in Gal-1 protein follow lactose binding, substantial solvent reorganization occurs. 19148478_Associations between MMP-9 and galectins-1 and -7 in situ indicate presence in hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. 19155496_A unique set of molecules, galectin-1 and Tcl1, defines distinct B cell receptor signaling cascades, dictating survival and death of human naive and immunoglobulin M-positive (IgM+) memory B cells. 19171142_Galectin-1 interaction with tissue plasminogen activator contributes to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression involving both transformed epithelial cells and tumor fibroblasts. 19287070_Both TRP-1 and galectin-1 were highly expressed in normal melanocytes and melanoma. There was no correlation between TRP-1 or galectin-1 expression and survival. 19287997_Increased expression of galectin-1 is associated with human oral squamous cell carcinoma development. 19363525_Study reports that Gal-1 mRNA levels positively correlated with TrkB expression and anticorrelated with TrkA expression in a cohort of 102 primary neuroblastoma. 19412433_Down-regulating Gal-1 expression provokes a marked decrease in the expression of the brain-expressed X-linked gene: BEX2 19454697_fodrin degradation occurs during galectin-1 T cell death and CD45 is essential for fodrin degradation to occur 19492862_Results confirm the importance of the conserved tryptophan residue in the affinity of the ligand and gives further insights into the mode of interaction between lactose derivatives and human Galectin-1. 19506091_showed the possibility of galectin-1-mediated trophectoderm binding to the endometrium within the window of implantation. 19520156_we report a novel pathway by which regulatory T-cells utilize betaGBP to control CD8(+) T cell responses partly activating TCR signaling but blocking PI3K. this leads to a loss of p21(ras), ERK and Akt activities despite activation of TCR proximal signals 19550395_expression of galectin-1 is upregulated in tumors of different origin (Review) 19561030_Galectin-1 may be involved in chemoattraction at sites of inflammation in vivo and may contribute to disease processes such as atherosclerosis. 19635795_Data show that galectin-1 binding to surface CD43 and CD45 on MDDCs induced an unusual unipolar co-clustering of these receptors. 19688976_Interactions between galectin-1 and intracellular glycoconjugates are not critical for malignant transformation in the thyroid gland. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19860718_Studies lead to production of a particular mono-disperse oxidized galectin-1 species that is anticipated most optimal for investigations requiring milligram/ml concentrations such as X-ray crystallography. 19886821_Results demonstrate the critical role of Galectin-1 and Sema-3A in mesenchymal stem cell functions and may open new perspectives in the understanding and treatment of various immune and neoplastic disorders. 19898636_Galectin-1 inhibits retinal pigment epithelial cell attachment, migration, and spreading in vitro with no apparent cytotoxicity. 19900702_Stimulation of trophoblasts (BeWo cells) with gal-1 showed a significant alteration of phosphorylation status in 3 receptor tyrosine kinases: JAK2, RET and VEGFR3. Phosphorylation of these kinases could be involved in gal-1-induced cell differentiation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20006954_the mode of interaction between human galectin-1 and five galactose-containing ligands 20053628_Gal-1 was also expressed in arterial walls and exhibited prominent cytosolic and nuclear staining in cultured human endothelial cells 20157731_Galectin-1 protein expression level increases in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), it may serve as a candidate marker for pathologic differentiation grade of OSCC. 20177845_The relationship between expression and staining intensity of CD24 and galectin-1 and clinicopathologic variables in gastric adenocarcinoma were assessed. 20200618_The expression analysis in humans of Galectin-1 (Gal-1), the protein encoded by LGALS1, showed a Gal-1 preferential accumulation in the stromal tissue around hepatocellular carcinoma tumors. 20332322_In B-ALL, Gal-1 is a highly sensitive and specific biomarker of MLL rearrangement that is likely induced by a MLL-dependent epigenetic modification. 20363255_These results suggest that oxidized Gal-1 inhibits inflammatory responses in macrophages and promotes Schwann cell migration directly and by macrophage activation. 20399482_Our data indicate that GAL1 is a powerful diagnostic marker that distinguishes chondroblastic osteosarcomas from conventional chondrosarcomas. 20525878_Results help us understand mechanism for hypoxia/HIF-1-mediated migration/invasion of colorectal cancer cells. 20549082_there is increased expression of genes coding for annexin-1 and galectin-1 in nasal polyps and when systemic corticosteroids are given, the mean gene expression of annexin-1 decreases significantly and the mean expression of galectin-1 remains unaltered 20570633_Data show that coculture with activated T cells upregulated expression of CD54 and CD58 and secretion of galectin-1 by MSCs. 20592339_galectin-1 has a role in vulvar neoplasia 20596638_Galectin-1 may serve a potential diagnostic marker or therapeutic target for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20644118_identify galectin-1 as the first lectin mediating the immunomodulatory effect of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells on allogeneic T cells 20657665_galectin-1 reduces NiV-F mediated fusion of endothelial cells, and endogenous galectin-1 in endothelial cells is sufficient to inhibit syncytia formation 20728947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20728947_This study suggested revealed interaction between LGALS1 and IL2Rbeta suggesting a role of these proteins in this autoimmune myasthenia gravis disease. 20828557_Two MAPK pathways are stimulated by increasing levels of Gal-1 in the high glucose condition, leading to suppression of COL1 expression and increase of MMP1 expression. 20873803_The interaction of native dimeric and monomeric mutants of rat and human galectin-1 with mono- and divalent small molecules, fetuin, asialofetuin, and human serum glycoproteins was analyzed. 21113146_Gal-1/alpha(5)beta(1)-integrin interaction participates in the control of epithelial integrity and integrin sialylation may enable carcinoma cells to evade this Gal-1-dependent control mechanism. 21122983_gal-1 silencing imparts colorectal cancer with the ability to proliferate and escape apoptosis. 21147166_Human galectin-1 immobilized in active form in vitro sugar-specifically captured IgA and IgA-containing immune complexes formed by cell wall antigen in serum but not IgG 21191065_The regulatory effect of galectin-1 is mediated in part through its ability to induce, in an inhibitor of DNA binding 3 (Id3)-dependent manner, the expression of IL-10 in monocytes and monocyte-derived dendritic cells of lung cancer patients. 21292557_In healthy pregnant women, significantly higher percentage of T and NK cells expressed galectin 1 in their cytoplasma than in healthy non-pregnant women; the proportion of galectin-1-expressing cells was markedly decreased in preeclampsia. 21372130_an anti-angiogenic peptide, anginex, greatly enhances galectin-1 binding affinity for glycoproteins 21378323_MUC1 and Gal-1 might be useful for evaluating the potential of leiomyoma to transform into leiomyosarcoma. 21385934_Gal-1 regulates CAF activation; targeting Gal-1 in CAFs inhibits OSCC metastasis by modulating MCP-1 expression 21391228_There is a role of Gal-1 in modulating hepatocellular carcinoma cell adhesion, polarization, and in vivo tumor growth, with critical implications in liver pathophysiology. 21397408_The intense immunoexpression of galectins-1, -3, and -7 suggests the participation of these proteins in oral carcinogenesis and their use as markers of biological behavior and tumor progression in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. 21505194_In addition to its functional role in classic Hodgkin lymphoma-induced immunosuppression, Gal-1 is also associated with an adverse clinical outcome in this disease. 21514365_Studies developed an ultimate rule for galectin recognition of disaccharides. 21614093_Gal-1 is broadly expressed in mucosal tissue and influences the viability of human and mouse enterocytes, an effect which might influence the migration of these cells from the crypt, the integrity of the villus and the epithelial barrier function. 21632118_Gal-1 is involved in RTK phosphorylation and the induction of syncytium formation in trophoblast cells. 21689853_The present study suggest a novel regulatory loop by which NF-kappaB induces expression of Gal-1 21724180_Data indicate that Gal-1, Gal-2, Gal-4, and partly Gal-3 bound to monocytes/macrophages. 21747316_identified activated pancreatic stellate cells as the primary source of highly expressed galectin-1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma stroma 21779348_hMSC -BD11 surface galectin-1 expression was required to bring about matrix-endothelial interactions and for xenografted hMSC -BD11 cells to optimally recruit host vasculature. 21780106_Our study suggests that the overexpression of Galectin-1 in PSCs induced T cell apoptosis and Th2 cytokine secretion, which may regulate PSC-dependent immunoprivilege in the pancreatic cancer microenvironment. 21807362_CD4(+) T helper lymphocytes from type 1 diabetes patients produce normal levels of the immunoregulator galectin-1 but its reduced synthesis by monocytes helps to maintain a skewed pro-inflammatory response. 21880716_the mechanisms for galectin-1 expression regulation and HIF-1alpha- and C/EBPalpha-induced leukemic cell differentiation. 21880749_The authors show here that galectin-1 directly binds to HIV-1 in a beta-galactoside-dependent fashion through recognition of clusters of N-linked glycans on the viral envelope gp120. 21986812_CD30-targeted therapy in combination with galectin-1 treatment may induce effective killing of ALCL cells but not of HL cells 21998324_Gal-1 regulates I(Ca,L) by decreasing the surface expression of Ca(V)1.2 channels in a splice variant selective manner. This may modulate vasoconstriction. Gal-1 binds the I-II loop only in the absence of alternatively spliced exon 9*. 22022970_Galectin 1 and galectin 8 promote influenza virus binding in dose dependent manner. 22028908_galectin-1-binding glycoforms of haptoglobin 22081313_Platelets gal-1 forms an intracellular complex with monomeric actin. 22155450_Galectin-1 and galectin-3 expression profiles in classically and alternatively activated human macrophages. 22156919_gal-1 binds galactomannans (GM) preferentially at alpha-d-galactopyranosyl doublets, randomly distributed over the GM backbone, and surrounded by regions of naked mannose residues. 22167721_DC-expressed Gal-1 and Gal-3 are regulatory molecules that favor the inhibition of T cell activation. 22174828_These findings qualify gal-1 as a member of human trophoblast cell invasion machinery. 22267483_Have identified galectin-1 and galectin-3 as novel partners for VWF, and these proteins may modulate VWF-mediated thrombus formation. 22271227_Psoriasis in humans is associated with down-regulation of galectins in dendritic cells. 22285770_The galectin-binding ability of a glycoprotein is not only a promising biomarker candidate but may also have a specific function when the glycoprotein encounters the galectin in tissue cells, and be related to the pathophysiological state of the patient. 22291012_Lung cancer-derived galectin-1 enhances tumorigenic potentiation of tumor-associated dendritic cells by expressing heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. 22353504_Overexpression of galectin-1 protein in colorectal carcinoma is derived possibly from secreted galectin-1 from other normal tissues that cumulate in the stroma. 22373585_Results suggest that high expression of galectin-1 was associated with advanced stage and metastasis and with shorter cumulative overall survival. 22383798_Galectin-1 inhibits the viability, proliferation, and Th1 cytokine production of nonmalignant T cells in patients with leukemic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 22386573_we demonstrated that miR610-mediated inhibition of VASP expression resulted in a significant reduction in the migration and invasion properties of gastric cancer cells. 22432916_Expression level of galectin-1 was of prognostic value in human hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy. 22447203_Significant correlations of several transcripts were detected with the protein level of galectin-1 in the cancer-associated fibroblasts. 22456341_identified alphaIIbbeta3 integrin as a functional galectin-1 receptor in platelets 22546645_Studies indicate that galectins Gal-1 and Gal-3 have both been shown to promote tumor angiogenesis, an essential step for cancer progression. 22561438_Galectin-1 can mediate high glucose peritoneal dialysis solution-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. 22583806_cells at the margin of glioblastoma, in comparison to tumor core cells, have enhanced expression of mediators of invasion. Galectin-1 is likely one such mediator. 22609846_Umbilical cord blood lymphocyte subsets express more galectin-1 than their adult peripheral blood counterparts. 22689223_Nanotechnology was used to inhibit galectin-1 gene expression in monocyte-derived macrophages infected with HIV-1. 22692729_Gal-1 may serve as an adhesion molecule to interact with both cells and laminins 22696230_Data show that p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, and COX-2 activation are mediators for the galectin-1-promoted tumor progression and chemoresistance in lung cancer. 22716213_Galectin-1 may play a role in RASSF1A signaling in a gastric neoplams cell line. 22777171_Data present that galectin-1, ataxin-3 and sprouty-related EVH1 domain-containing protein 2 (SPRED2) may be associated with the progression and development of Down syndrome. 22785208_Stromal galectin-1 expression is associated with long-term survival in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 22844466_galectin-1 is one of the critical factors in MSCs regulating tumor progression 22884463_Data indicate that the diffusion constant of avian galectin-1 (CG-1B) increased by 5.6% in the presence of lactose, as has been seen for the human galectin-1. 22939954_High galectin 1 expression in peritumoral stroma significantly correlates with depth of invasion in cervical lesions and lymph node metastasis of cervical cancer. 22942212_Gal-1 can act either as chemoattractant or, as a molecule that negatively regulates migration under acute inflammatory conditions 23002109_Galectin-1 plays a key role in pregnancy maternal immune regulation by modulating HLA-G expression on trophoblast cells. 23027923_Data indicatae that expression of galectin-1 (Gal-1) is a hallmark of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), and is directly induced by both herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8/KS-associated herpesvirus [KSHV]) and hypoxia. 23113677_combined use of galectin-1 and galectin-3 showed 98% specificity and 47% sensitivity for renal cell carcinoma 23121677_macrophages from sputum samples of asthma patients express low levels of galectin-1 and galectin-9, favouring the exacerbated immune response observed in this disease. 23124203_Hhydrophobic residues from the lambda5-UR is crucial for the interaction with GAL1 and for pre-BCR clustering. 23142379_Galectin-1 controls cardiac inflammation and ventricular remodeling during acute myocardial infarction. 23223580_CD146 and its novel ligand Galectin-1 in apoptotic regulation of endothelial cells 23359172_Gal-1 as a diagnostic biomarker and immunotherapeutic target for LSCC. 23389289_ectopic expression of galectin-1 in a low-metastatic CL1-0 lung cancer cell line promotes its migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 23431236_Results have provided evidence that galectin-1 and mainly annexin-A1 are overexpressed in both gastritis and gastric cancer, suggesting a strong association of these proteins with chronic gastric inflammation and carcinogenesis. 23444403_High Galectin-1 expression is associated with Hodgkin lymphoma. 23510298_The pH dependence of the beta-galactoside binding activity of human galectin-1 (hGal-1) was investigated by fluorescence spectroscopy using lactose as a ligand. 23599627_galectin-1 has a role in regulating VEGF expression in gastric cancer 23681112_Galectin-1 (GAL-1) expression is a useful tool to differentiate between small cell osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma. 23824536_High galectin-1 serum levels are associated with high-grade glioma. 23929302_High galectin-1 expression is associated with glioma. 24077937_The involvement of gal-1 in the regulation of different processes during the establishment, development and maintenance of pregnancy could be described as unique and it has emerged as an important lectin with major functions in pregnancy. 24211210_these findings indicate that soluble Gal-1 promotes invasiveness through enhancing collective cell migration and increasing the incidence of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 24241899_Both galectin-1 and VEGF can serve as independent prognostic indicators of poor survival for gastric cancer 24284396_As Gal-1 plays important roles in preventing neurodegeneration and promoting neuroprotection in the brain, the interaction between SelM' and Gal-1 displays a new direction for studying the biological function of SelM in the human brain. 24361865_Galectin 1 was identified as a potential diagnostic biomarker of malignant mesothelioma. 24407244_Knockdown of endogenous Gal-1 in epithelial ovarian cancer cells resulted in the reduction in cell growth, migration, and invasion. 24451991_data provide new insights into the structural basis of Gal-1 redox regulation with critical implications in physiology and pathology. 24468067_Myosin IIa activation and galectin-1 endocytosis are important in tumor associated tDC development 24503185_Interleukin-1-induced changes in the glioblastoma secretome suggest its role in tumor progression. 24503541_Gal-1 decreased the expression of collagen genes COL3A1 and COL5A1 but increased the expression of fibronectin and laminin 5. 24517166_Suggest that galectin-1 is a protective factor against the development of digital vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis. 24530443_The results presented here demonstrated that galectin-1 and galectin-3 expression have important roles in clinical progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 24560493_Gal-1 expression may be a useful biomarker for better prediction of the clinical outcome and management of NSCLC patients. 24589677_Results show that galectin-1 regulates cell death through inhibition of CD45 PTP activity of anaplastic large cell lymphoma cell line H-ALCL. 24595374_Galectin-1 expression in stromal cells of pancreatic cancer suggests that this protein plays a role in the promotion of cancer cells invasion and metastasis. 24637109_gestational diabetes is associated with a failure to increase circulating gal-1 levels during the second and third trimester, and overexpression of gal-1 in placenta. LGALS1 polymorphism was associated with the development of gestational diabetes. 24646142_overexpression associated with shorter survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 24684681_Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells display a novel interaction between P-selectin and galectin-1. 24717333_no difference in cord blood concentration correlated with restricted or increased fetal growth 24719187_Gal-1 has a role in increasing vascular permeability through the NRP-1/VEGFR1 and Akt signaling pathway 24719523_both the AnxA1 and Gal-1 anti-inflammatory proteins are deregulated in precancerous gastric lesions 24752896_these findings identify CD69 and galectin-1 to be a novel regulatory receptor-ligand pair that modulates Th17 effector cell differentiation and function. 2477 |
ENSMUSG00000068220 |
Lgals1 |
4870.747062 |
3.1305166218 |
1.646401 |
0.054316194 |
886.665159 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000777461561915181680882490532892901444694764358953171428711585868252246622109626721640860843264953742739297079923552373475867361202735774 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000687145667896292263516226925166419427286221917049636346386456406157692211684489120442607039167577689154914236771004075058246606871177900 |
Yes |
No |
7441.3572226 |
246.9730352 |
2393.8102446 |
59.2863100 |
| ENSG00000100105 |
23598 |
PATZ1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBE1 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator that plays a role in many biological processes such as embryogenesis, senescence, T-cell development or neurogenesis (PubMed:10713105, PubMed:25755280, PubMed:31875552). Interacts with the TP53 protein to control genes that are important in proliferation and in the DNA-damage response. Mechanistically, the interaction inhibits the DNA binding and transcriptional activity of TP53/p53 (PubMed:25755280). Part of the transcriptional network modulating regulatory T-cell development and controls the generation of the regulatory T-cell pool under homeostatic conditions (PubMed:31875552). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10713105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25755280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31875552}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays a positive role in viral cDNA synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31060775}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains an A-T hook DNA binding motif which usually binds to other DNA binding structures to play an important role in chromatin modeling and transcription regulation. Its Poz domain is thought to function as a site for protein-protein interaction and is required for transcriptional repression, and the zinc-fingers comprise the DNA binding domain. Since the encoded protein has typical features of a transcription factor, it is postulated to be a repressor of gene expression. In small round cell sarcoma, this gene is fused to EWS by a small inversion of 22q, then the hybrid is thought to be translocated (t(1;22)(p36.1;q12). The rearrangement of chromosome 22 involves intron 8 of EWS and exon 1 of this gene creating a chimeric sequence containing the transactivation domain of EWS fused to zinc finger domain of this protein. This is a distinct example of an intra-chromosomal rearrangement of chromosome 22. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants are described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23598; |
male germ cell nucleus [GO:0001673]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217] |
10949935_The short isoform of the Zinc finger Sarcoma Gene (ZSG) was isolated as a RNF4 interacting protein. 11744704_We report here the isolation and characterization of two novel nuclear BTB/POZ domain zinc finger isoformsthat are specifically expressed in early hippocampal neurons, cerebellar granule cells, and gliogenic progenitors as well as in differentiated glia 11751862_MAZR and MITF synergistically transactivated the mMCP-6 gene. MAZR appeared to play important roles in the normal phenotypic expression of mast cells in association with MITF 18401526_The results show that ZNF278 promotes cell growth, and its knockdown suppresses cell proliferation. ZNF278 could be a potential proto-oncogene in colorectal cancer. 20026299_these results showed a potentially novel mechanism of cAMP signaling mediated through the interaction of RIalpha with PATZ1. 20677143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22052190_PATZ1 may have an important role in the regulation of EC senescence through an ROS-mediated p53-dependent pathway and contribute to vascular diseases associated with aging. 24336083_The data support a PATZ1 tumour-suppressive function based on its ability to enhance p53-dependent transcription and apoptosis. 24380431_these results propose that Patz1 is important for ESC pluripotency. 25595894_Loss of PATZ1 expression is associated with thyroid cancer progression. 25755280_Results show that PATZ1 binds to p53 and inhibits p53-dependent transcription activation. 27494852_this study show that PATZ1 expression correlates positively with BAX and negatively with BCL6 and survival in human diffuse large B cell lymphomas 27932482_The derived allele of rs174557, which is the common variant in most populations, diminishes binding of PATZ1, a transcription factor conferring allele-specific downregulation of FADS1. 29039562_ZNF278 played a prominent role in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer (CRC), and promoted CRC cell proliferation via the ERK/MAPK pathway, suggesting that it may act as a potential target in the diagnosis or treatment of CRC 29926841_The results of IHC and qPCR analyses showed that the expression of PATZ1 in cancerous tissue was significantly lower than that in non-cancerous tissues. Meanwhile, PATZ1 expression was significantly associated with tumor differentiation and LN metastasis. 30379650_EWSR1-PATZ1 fusion positive spindle and round cell sarcomas show abundant intratumoral fibrosis and polyphenotypic differentiation 31060775_It has been shown that PATZ1 is a novel regulator of HIV-1 infection. 31875552_The Transcription Factor MAZR/PATZ1 Regulates the Development of FOXP3(+) Regulatory T Cells. 33012788_EWSR1-PATZ1-rearranged sarcoma: a report of nine cases of spindle and round cell neoplasms with predilection for thoracoabdominal soft tissues and frequent expression of neural and skeletal muscle markers. 33378126_Expanding the spectrum of EWSR1-PATZ1 rearranged CNS tumors: An infantile case with leptomeningeal dissemination. 34417833_PATZ1 fusions define a novel molecularly distinct neuroepithelial tumor entity with a broad histological spectrum. |
ENSMUSG00000020453 |
Patz1 |
116.059650 |
0.4720479955 |
-1.082995 |
0.154371175 |
49.662612 |
0.00000000000182592517188579960980000248412055441652943055252933390875114127993583679199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000010681987925895521785638609749170011096325305643972569669131189584732055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
75.2221109 |
7.4575984 |
160.3921068 |
10.6298828 |
| ENSG00000100106 |
11078 |
TRIOBP |
protein_coding |
Q9H2D6 |
FUNCTION: May regulate actin cytoskeletal organization, cell spreading and cell contraction by directly binding and stabilizing filamentous F-actin. The localized formation of TARA and TRIO complexes coordinates the amount of F-actin present in stress fibers. May also serve as a linker protein to recruit proteins required for F-actin formation and turnover. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18194665}. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Disease variant;Methylation;Mitosis;Non-syndromic deafness;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein with an N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain and a C-terminal coiled-coil region. The protein interacts with trio, which is involved with neural tissue development and controlling actin cytoskeleton organization, cell motility and cell growth. The protein also associates with F-actin and stabilizes F-actin structures. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a form of autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that would encode different isoforms have been found for this gene, however some transcripts may be subject to nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:11078; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; midbody [GO:0030496]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; stereocilium base [GO:0120044]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; myosin II binding [GO:0045159]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; actin modification [GO:0030047]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:0051016]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
16385457_Mutations in TRIOBP, which encodes a putative cytoskeletal-organizing protein, are associated with nonsyndromic recessive deafness. 16385458_Mutations in a novel isoform of TRIOBP that encodes a filamentous-actin binding protein are responsible for DFNB28 recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. 18194665_All these findings suggest that HECTD3 may facilitate cell cycle progression via regulating ubiquitination and degradation of Tara. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19996280_Data show that 4-oxo-4-HPR inhibited tubulin polymerization and modulated gene expression of spindle aberration associated genes Kif 1C, Kif 2A, Eg5, Tara, tankyrase-1, centractin, and TOGp. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22820163_the centrosomal localization of Tara depended on the Thr-457 phosphorylation and the kinase activity of Plk1. 24692559_TAP68 functions in mediating TRF1-tankyrase 1 localization to the centrosome and in mitotic regulation 25130170_High TRIOBP expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 25333879_TRIOBP-1 aggregates are implicated for the first time as a biological element of the neuropathology of a subset of chronic mental illness 27546710_Results reveal that Tara forms a functional complex with Ndel1 and alters its intracellular distribution. The Ndel1-Tara complex plays a role in regulating actin cytoskeleton organization, which is critical for cell migration. 27764096_We discovered two genome-wide significant SNPs. The first was novel and near ISG20. The second was in TRIOBP, a gene previously associated with prelingual nonsyndromic hearing loss. Motivated by our TRIOBP results, we also looked at exons in known hearing loss genes, and identified two additional SNPs, rs2877561 in ILDR1 and rs9493672 in EYA4 (at a significance threshold adjusted for number of SNPs in those regions). 28089734_Case Reports: novel TRIOBP mutations associated with moderate, stable hereditary hearing impairment. 28438837_TRIOBP-1 aggregation, therefore, appears to occur through one or more specific cellular mechanisms, which therefore have the potential to be of physiological relevance for the biological process underlying the development of chronic mental illness. 29197352_Based on whole exome analysis, we identified two TRIOBP pathogenic variants (c.802_805delCAGG, p.Gln268Leufs*610 and c.5014G>T, p.Gly1672*, the first of which was novel) causative of nonsyndromic, peri- to postlingual, moderate-to-severe hearing loss in three siblings from a Polish family. 29507111_TRIOBP-1 overexpression caused intracellular co-sequestration of hERG signal, reduced native IKr and disrupted action potential repolarization. 29890989_roles of TRIO and F-actin-binding protein in human diseases 36029164_Elucidation of repeat motifs R1- and R2-related TRIOBP variants in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss DFNB28 among indigenous South African individuals. 36232351_TRIOBP-1 Protein Aggregation Exists in Both Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia, and Can Occur through Two Distinct Regions of the Protein. |
ENSMUSG00000033088 |
Triobp |
354.115135 |
0.4657325343 |
-1.102426 |
0.125312070 |
76.935120 |
0.00000000000000000176667409529715449933274265450116279457886576309728638572993375532860227394849061965942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000014608464788003363697692667862474690006805966201934403325690681185733410529792308807373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
222.4285641 |
29.0498813 |
480.0667808 |
44.5757392 |
| ENSG00000100139 |
85377 |
MICALL1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N3F8 |
FUNCTION: Probable lipid-binding protein with higher affinity for phosphatidic acid, a lipid enriched in recycling endosome membranes. On endosome membranes, may act as a downstream effector of Rab proteins recruiting cytosolic proteins to regulate membrane tubulation. May be involved in a late step of receptor-mediated endocytosis regulating for instance endocytosed-EGF receptor trafficking. Alternatively, may regulate slow endocytic recycling of endocytosed proteins back to the plasma membrane. May indirectly play a role in neurite outgrowth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19864458, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20801876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21795389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23596323}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Endocytosis;Endosome;LIM domain;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport;Zinc |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity; phosphatidic acid binding activity; and small GTPase binding activity. Involved in several processes, including plasma membrane tubulation; protein localization to endosome; and slow endocytic recycling. Located in late endosome and recycling endosome membrane. Is extrinsic component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:85377; |
extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; plasma membrane tubulation [GO:0097320]; protein localization to endosome [GO:0036010]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; slow endocytic recycling [GO:0032458] |
19864458_These data implicate MICAL-L1 as an unusual type of Rab effector that regulates endocytic recycling by recruiting and linking EHD1 and Rab8a on membrane tubules. 21795389_novel insights into the MICAL-L1/Rab protein complex that can regulate EGFR trafficking at late endocytic pathways. 21951725_Rab35 is a critical upstream regulator of MICAL-L1 and Arf6, while both MICAL-L1 and Arf6 regulate Rab8a function. 23596323_Cooperation of MICAL-L1, pacsin 2 (syndapin2), and phosphatidic acid in tubular recycling endosome biogenesis. 24481818_MICAL-L1-mediated recruitment of EHD1 to Src-containing recycling endosomes is required for the release of Src from the perinuclear endocytic recycling compartment in response to growth factor stimulation. 25248744_DGKalpha generates phosphatidic acid to drive its own recruitment to tubular recycling endosomes via its interaction with MICAL-L1 25287187_suggesting an EHD1-independent function for MICAL-L1 earlier in mitosis 28714518_Findings found that ectopic expression of MICALL1 significantly inhibited the proliferation of HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. Also, MICALL1 expression was found to be suppressed in colorectal cancer with p53 mutations. 31615969_Data support the notion that a pool of centriolar gamma-tubulin and/or alpha-tubulin-beta-tubulin heterodimers anchor MICAL-L1 to the centriole, where it might recruit EHD1 to promote ciliogenesis. 33334886_Defining the protein and lipid constituents of tubular recycling endosomes. 33972531_A junctional PACSIN2/EHD4/MICAL-L1 complex coordinates VE-cadherin trafficking for endothelial migration and angiogenesis. 34100897_MICAL-L1 is required for cargo protein delivery to the cell surface. |
ENSMUSG00000033039 |
Micall1 |
402.092641 |
2.1786617096 |
1.123442 |
0.108551545 |
106.640781 |
0.00000000000000000000000053363683082539670369576065936460737886794814936534434583144396237750287093071221988793695345520973205566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000005740874360774676426376695051342286837242025778664150201259554488937564276085367964697070419788360595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
557.1462678 |
34.3440596 |
257.6065439 |
12.1261050 |
| ENSG00000100156 |
23539 |
SLC16A8 |
protein_coding |
O95907 |
FUNCTION: Probable retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)-specific proton-coupled L-lactate transporter (By similarity). May facilitate transport of lactate and H(+) out of the retina and could therefore play a role in pH and ion homeostasis of the outer retina (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35308, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q90632}. |
Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
SLC16A8 is a member of a family of proton-coupled monocarboxylate transporters that mediate lactate transport across cell membranes (Yoon et al., 1999 [PubMed 10493836]).[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:23539; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; lactate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015129]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; lactate transport [GO:0015727]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718] |
20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27966779_The expression level of LIPC, SLC16A8, and TIMP-3 was significantly associated with age-related macular degeneration pathology. 33477551_A Splice Variant in SLC16A8 Gene Leads to Lactate Transport Deficit in Human iPS Cell-Derived Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000032988 |
Slc16a8 |
20.610401 |
0.1432289098 |
-2.803605 |
0.543109767 |
25.455471 |
0.00000045271207856104138079832805915958537923415860859677195549011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001668422042337321027185887030441779899092580308206379413604736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6631556 |
2.0444840 |
39.6754370 |
8.6965620 |
| ENSG00000100197 |
1565 |
CYP2D6 |
protein_coding |
P10635 |
FUNCTION: A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in the metabolism of fatty acids, steroids and retinoids (PubMed:18698000, PubMed:19965576, PubMed:20972997, PubMed:21289075, PubMed:21576599). Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via cytochrome P450 reductase (NADPH--hemoprotein reductase) (PubMed:18698000, PubMed:19965576, PubMed:20972997, PubMed:21289075, PubMed:21576599). Catalyzes the epoxidation of double bonds of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) (PubMed:19965576, PubMed:20972997). Metabolizes endocannabinoid arachidonoylethanolamide (anandamide) to 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid ethanolamide (20-HETE-EA) and 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid ethanolamides (EpETrE-EAs), potentially modulating endocannabinoid system signaling (PubMed:18698000, PubMed:21289075). Catalyzes the hydroxylation of carbon-hydrogen bonds. Metabolizes cholesterol toward 25-hydroxycholesterol, a physiological regulator of cellular cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:21576599). Catalyzes the oxidative transformations of all-trans retinol to all-trans retinal, a precursor for the active form all-trans-retinoic acid (PubMed:10681376). Also involved in the oxidative metabolism of drugs such as antiarrhythmics, adrenoceptor antagonists, and tricyclic antidepressants. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10681376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16352597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18698000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19965576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20972997, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21289075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21576599}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Heme;Iron;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microsome;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism |
PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; retinol metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10681376}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19965576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20972997}.; PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism; cholesterol metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21576599}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and is known to metabolize as many as 25% of commonly prescribed drugs. Its substrates include antidepressants, antipsychotics, analgesics and antitussives, beta adrenergic blocking agents, antiarrythmics and antiemetics. The gene is highly polymorphic in the human population; certain alleles result in the poor metabolizer phenotype, characterized by a decreased ability to metabolize the enzyme's substrates. Some individuals with the poor metabolizer phenotype have no functional protein since they carry 2 null alleles whereas in other individuals the gene is absent. This gene can vary in copy number and individuals with the ultrarapid metabolizer phenotype can have 3 or more active copies of the gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:1565; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; anandamide 11,12 epoxidase activity [GO:0062188]; anandamide 14,15 epoxidase activity [GO:0062189]; anandamide 8,9 epoxidase activity [GO:0062187]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; monooxygenase activity [GO:0004497]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen [GO:0016712]; steroid hydroxylase activity [GO:0008395]; alkaloid catabolic process [GO:0009822]; alkaloid metabolic process [GO:0009820]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; coumarin metabolic process [GO:0009804]; estrogen metabolic process [GO:0008210]; heterocycle metabolic process [GO:0046483]; isoquinoline alkaloid metabolic process [GO:0033076]; long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042759]; monoterpenoid metabolic process [GO:0016098]; negative regulation of binding [GO:0051100]; negative regulation of cellular organofluorine metabolic process [GO:0090350]; organic acid metabolic process [GO:0006082]; oxidative demethylation [GO:0070989]; retinol metabolic process [GO:0042572]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; xenobiotic catabolic process [GO:0042178]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
11037800_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11037802_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11055624_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11097351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11097352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11147929_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11204351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11207030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11207032_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11214775_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11266079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11285084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11291049_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11294012_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11295783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11303596_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11372584_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11376189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11422605_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11422615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11442888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11470994_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11477317_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11505219_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11520401_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11549206_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11560558_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11668217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11682257_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11702057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11735606_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11741249_Clinical trial of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11750286_Anti-CYP2D6 antibodies detected by quantitative radioligand assay and relation to antibodies to liver-specific arginase in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. 11751440_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11753271_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11753272_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11763000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11778144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11791895_CYP2D6 catalyzes the major metabolic pathway of fluvoxamine. 11809184_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11816009_determination of phenotype in liver microsomes 11829201_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11895912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11901361_polymorphisms and atypical antipsychotic weight gain 11927839_CYP2D6 genotype is associated with antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal syndromes 11927839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11940091_treatment-resistant schizophrenia -duplication in the cytochrome P450IID6 (CYP2D6) gene 12063626_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12065557_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12077255_The antigenic constitution of CYP2D6, the major target of liver kidney microsomal antibody type 1 in type 2 autoimmune hepatitis and chronic hepatitis C virus infections, has been initially characterized. 12089164_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12106691_demonstrate constitutive expression of cytochrome P4502D in neuronal cell population in human brain, indicating its possible role in metabolism of psychoactive drugs directly at or near their site of action, in neurons, in human brain. 12107620_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12142727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12142727_results indicate a significant influence of environmental factors as an explanation for the difference in capacity for CYP2D6, but not CYP2C19 metabolism between Caucasians and Black Africans 12152006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12152006_lower activity observed in a black American population is in part attributable to the presence of variant alleles that occur at a higher frequency in this population than in white subjects 12171760_Patients who had homozygous (L/L) or heterozygous (Wt/L) mutant alleles developed manganism an average of 10 years later than those who were homozygous wildtype 12172215_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12172215_the pronounced effect of the CYP2D6 genotype persists during long-term therapy, affecting both metabolic ratio and metoprolol plasma concentration. 12172336_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12175908_Duplicated alleles of CYP2D6*10 exist in the Japanese population and that it may be one of the factors affecting the capacity of Japanese to metabolize various CYP2D6 substrate drugs. 12175908_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12187002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12191703_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12206675_Study of oxidation of non-amine ligands and substrates by cytochrome P450 2D6 reveals lack of an obligatory role for Asp-301 in substrate electrostatic bonding. 12207635_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12210290_This study suggests that these polymorphisms are not related to the development of tardive dystonia. 12360109_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12360109_contributes to the biotransformation of E- and X-doxepin in healthy volunteers 12386645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12386646_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12392820_an alteration in position of active-site residues in CYP2D6.17 as a possible explanation for the reduced activity of the enzyme. 12404686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12419832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12421483_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12422998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12426523_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12438554_The functional differences between CYP2D6.1, CYP2D6.2, CYP2D6.10, and CYP2D6.17 allelic isoforms toward three clinically important substrates have been compared, and alterations in their metabolic capacities have been demonstrated. 12439227_new allelic arrangement in a poor metabolizer in debrisoquine 12446689_role of glutatmate 216 and aspartate 301 in determining substrate specificity and product regioselectivity 12459840_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12468438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12486288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12486288_We have examined frequency of the CYP2D6*4 allele of debrisoquine hydroxylase (DBH) involving G/A transition at the intron 3-exon 4 junction in dementia with Lewy bodies[DLB]; this allele does not act as a risk factor for DLB 12490310_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12503836_patients with impaired CYP2D6 enzyme activity due to enzyme inhibition by thioridazine might be more prone to increased risk of sudden death due to torsade de pointes type cardiac dysrhythmia 12536989_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12548461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12569554_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12579870_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12589966_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12610741_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12616663_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12622923_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12629505_Male schizophrenics with at least one decreased or loss of function allele for CYP2D6 have a moderately greater chance of developing tardive dyskinesia than males with only wild-type alleles. 12629505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12651805_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12657030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12691769_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12728976_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12734765_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12743673_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12748560_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12766554_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12782969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12782969_These results do not support the hypothesis that CYP2D6 activity affects temperament and character. 12784098_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12861292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12879168_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12879776_CYP2D6 gene is a marker for genetic susceptibility to allergic perennial rhinitis 12879776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12883230_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12893130_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12900870_CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 provided enhanced formation of R-EDDP from methadone and CYP2D6 incubation resulted in the preferential conversion to S-EDDP. 12900872_CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 do not significantly contribute to the metabolism of Methaqualone; although interindividual differences in the monitored metabolic patterns were noted, no marked difference could be related to a CYP2D6 or CYP2C19 polymorphism. 12911679_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12915955_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12919180_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12942225_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12950145_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12950145_The prevalence of CYP2D6 mutations of allelic variants predict genotype frequency in the Croatian population. 12960748_Homozygotes of CYP2D6*2 and CYP2D6*10 appear to be a susceptibility factor for developing acute extrapyramidal symptoms in schizophrenic patients. 12960748_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12963435_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 13680033_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14499311_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14499440_CYP2D6 genotype has an impact on analgesia with tramadol. Pharmacogenetics may explain some of the varying response to pain medication in postoperative patients. 14499440_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14514498_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14515061_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14520122_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14557687_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14571354_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14602525_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14624403_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14635107_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14639062_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14640293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14652703_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14653957_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14658041_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14716707_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14726620_Cytochrome P(450)IID6's activity may play a role in the development of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. 14726986_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14748763_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14985156_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14991823_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15005635_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15048614_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15061826_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15068562_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15090156_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15108188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15115913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15116051_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15118351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15118351_The CYP2D6*10 C188T polymorphism may be associated with the susceptibility to the occurrence of TD induced by typical antipsychotics, especially in male patients, and may also be correlated with AIMS scores in TD patients. 15149890_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15149890_carriers with three functional CYP2D6 genes, CYP2D6*1 x 2/*2 or CYP2D6*1/*2 x 2, are ultrarapid metabolizer phenotypes and there is no gene-dose between carriers with two and three CYP2D6*10 mutated genes 15177309_CYP2D6,...expressed at rather low levels compared to... other human CYPs, plays an important role in metabolism, partially or to a major extent for the oxidative biotransformation of a variety of psychoactive and cardiovascular drugs. 15177309_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15205367_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15237854_polymorphic CYP2D6 may play an important role in the interconversions of these psychoactive tryptamines, including a crucial step in a serotonin-melatonin cycle (Review) 15256524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15260906_...the present results show that CYP2D6, but not CYP2C9, may be related to QTc lengthening during treatment with risperidone. pp 191-192. 15260906_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15289790_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15313161_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15330195_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15349705_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15349706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15382273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15469888_Results describe the effects of genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 2D6 on the metabolism of neuroactive steroids and amines in the brain. 15470329_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15484318_Three new alternative splicing variants of CYP2D6 mRNA have been identified. 15499201_Five novel nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms are reported and 65 other sequence variations detected from the gene coding for cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 in 254 Japanese subjects. 15538128_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15584944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15588859_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15590749_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15592325_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15618665_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15632378_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15646732_Poor CYP2D6 metabolizers may be at higher risk of adverse reactions to metoprolol. 15648054_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15651900_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15669884_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15690482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15691505_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15708542_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15708542_Our results demonstrate that the CYP3A5*1 allele, previously reported as a marker for CYP3A5 expression in human kidney, is associated with increased risk for BEN, while CYP3A4*1B and CYP2D6 genotypes do not significantly modify the risk for the disease. 15726636_CYP2D6*31, is characterized by mutations encoding three amino acid substitutions: Arg296Cys, Arg440His and Ser486Thr, altering the kinetics. 15729081_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15731591_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15764408_Reported CYP2D6 phenocopying is not due to dextropropoxyphene being a CYP2D6 substrate. 15768052_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15769360_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15770075_Definite differences in pharmacokinetics were observed between CYP2D6 genotypes in the pharmacokinetics of oral itraconazole. 15770075_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15774926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15813658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15817819_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15820320_CYP2D6 not associated with susceptibility to tardive dyskinesia in chronic schizophrenia subjects 15820320_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15843230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15855722_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15861039_CYP2D6 loss of function alleles may predispose to tardive dyskinesia in patients with schizophrenia under treatment 15861039_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15914211_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15932952_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15952058_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15970126_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15987423_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16024198_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16025294_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16037945_Hepatitis C positive/LKM1+ sera recognize a specific conformational epitope on cytochrome 2 D6 between amino acids 254 to 288, the region that contains the major linear epitope in type 2 autoimmune hepatitis patients. 16048566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16079496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16130179_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16130179_The frequency of the wild-type CYP2D6*1 allele was 31% in Spain 16141609_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16160620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16162505_analysis of active-site residues in quinidine binding to CYP2D6 16189709_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16198657_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16205777_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16220080_CYP2D6 genotype significantly affects circadian variations of beta-adrenergic inhibition induced by metoprolol 16220080_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16236141_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16239355_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16249913_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16249913_The observed frequency of the CYP2D6 alleles tested was unique for the Mexican Mestizo sample analyzed 16272752_researchers found a novel structure of the CYP2D6 gene, which might lead to incorrect genotyping for CYP2D6*5 16283274_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16294366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16315032_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16337409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16352597_Crystal structure of human cytochrome P450 2D6 16361630_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16415111_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16423440_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16459354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16466686_Replacement of Ile106 with Glu, engineered to cause electrostatic repulsion with Glu216, had a profound topological effect in the higher region within the active site cavity and impaired the catalytic activity towards CYP2D6 probe substrates. 16476126_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16478753_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16490169_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16493615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16534507_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16537246_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16544144_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16550211_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551910_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16584388_CYP2D6 genotype might be a significant predictor of liver fibrosis progression rate in chronic hepatitis C patients. 16584388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16595916_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16611538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16633140_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16633141_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16638736_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16638864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16642541_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16679388_Base sequence from commercial human hepatocytes - potential to identify and characterize dysfunctional alleles and their likely mechanisms affecting gene expression 16716118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16771603_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16775389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778723_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16812949_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16815318_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16819548_CYP2D6 genotypes predicting ultrarapid metabolism resulted in about 50% higher plasma concentrations of morphine and its glucuronides compared with the extensive metabolizers. 16833023_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16835697_A significant association of 2850C > T (P = 0.015)of CYP2D6 with generalized tonic clonic seizures 16835697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16845507_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16849011_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16855473_Data reported here is said to not support previously reported association between CYP2D6 genotype and personality trains using NEO Five-Factor Inventory. 16858124_Data provide additional information to the CYP2D6 sequence data that was obtained by the human genome project. 16864175_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16880622_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16924387_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16960721_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17038884_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17089107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17089107_Results show that the occurrence of hypersomnia increased as the number of CYP2D6 mutant alleles increased. 17102541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17113562_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17115111_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17178267_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17186005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17194620_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17224713_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17225875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17225875_Results indicated that the CYP2D6*3 and CYP2D6*4 alleles, in particular, would be linked to the onset of porphyrias. 17234366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17241532_Allelic distributions of the CYP2D6 gene copy number variation differ among Chinese from different regions, indicating ethnic variety in Chinese. 17241532_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17242628_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17244352_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17250723_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17259947_Duplications and multiplications of active CYP2D6 genes can cause ultrarapid drug metabolism and lead to therapeutic failure or unwanted side effects. 17270484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17289397_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17297618_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17301689_CYP2D6 diversity is far greater within than between populations and groups thereof, (ii) null or low-activity variants occur at high frequencies in various areas of the world, (iii) linkage disequilibrium is lowest in Africa and highest in the Americas. 17301689_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17304721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17311358_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17311358_The frequencies of functional variant alleles of CYP2D6 in the Czech population are in concordance with other Caucasian populations. 17324244_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17324244_no significant association between CYP2D6 activity and personality trait because of the small interindividual variability in CYP2D6 activity within the Japanese population 17325735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17325735_Shows lower frequency of CYP2D6 poor metabolizers in schizophrenic patients suppo |
ENSMUSG00000022445+ENSMUSG00000094559+ENSMUSG00000068086+ENSMUSG00000094806+ENSMUSG00000068085+ENSMUSG00000068083+ENSMUSG00000061740+ENSMUSG00000096852+ENSMUSG00000118516 |
Cyp2d26+Cyp2d34+Cyp2d9+Cyp2d10+Cyp2d11+Cyp2d40+Cyp2d22+Cyp2d12+Cyp2d13 |
10.185486 |
0.2866883066 |
-1.802445 |
0.601585702 |
8.962325 |
0.00275603951059320622860027150125006301095709204673767089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005948112761566855775929862915063495165668427944183349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5887758 |
2.1310407 |
15.6519153 |
4.6728223 |
| ENSG00000100211 |
25776 |
CBY1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3M2 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits the Wnt/Wingless pathway by binding to CTNNB1/beta-catenin and inhibiting beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation through competition with TCF/LEF transcription factors. Has also been shown to play a role in regulating the intracellular trafficking of polycystin-2/PKD2 and possibly of other intracellular proteins. Promotes adipocyte and cardiomyocyte differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12712206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15194699}. |
3D-structure;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Differentiation;Golgi apparatus;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Beta-catenin is a transcriptional activator and oncoprotein involved in the development of several cancers. The protein encoded by this gene interacts directly with the C-terminal region of beta-catenin, inhibiting oncogenic beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation by competing with transcription factors for binding to beta-catenin. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:25776; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; floor plate development [GO:0033504]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; protein localization [GO:0008104] |
12712206_Chibby inhibits beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation by competing with Lef-1 to bind to beta-catenin 15194699_PIGEA-14 plays an important role in regulating the intracellular location of polycystin-2 15245581_As no somatic mutation was detected in C22orf2 in 36 colorectal tumour DNA, our results do not support the implication of Chibby as a tumour suppressor in colorectal carcinogenesis. 16570344_Chibby is not likely to promote colorectal carcinoma tumor development or progression. 17403895_CBY promotes adipocyte differentiation through inhibition of beta catenin signaling. 17905836_intrinsically disordered TC-1 interacts with Cby via its transient helical structure 18573912_14-3-3epsilon and 14-3-3zeta are identified as Cby-binding partners. 18663750_genes including CHIBBY involved in pediatric ependymomas. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19435523_Alanine substitutions of two or more of four critical leucine residues within the C-terminal heptad repeats eliminate the Cby-Cby interaction. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940019_These findings unravel the molecular basis through which a combinatorial action of Cby and 14-3-3 proteins controls the dynamic nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of beta-catenin. 20096688_Chibby and clusterin were co-immunoprecipitated with NBPF1. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21182262_The N-terminal portion of the CBY1 is unstructured in solution, but the C-terminal half forms a coiled-coil structure. 22911743_Cby plays an important role in organization of both primary and motile cilia in collaboration with Cnx. 23645032_Results from the association analysis suggest that common variation in CBY is not a cause for obesity in the Belgian population. 23707389_Stable expression of CBY1 drives beta catenin cytoplasmatic translocation and impairs beta catenin signaling in BCR-ABL + cells. 23838289_C-terminal polycystin-2 influences the interaction with PIGEA14 24339928_the impact of BCR-ABL1 on Chibby1, a beta catenin antagonist involved in cell differentiation and transformation 25175341_Study showed that expression of Cby protein was strongly downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) tumor tissues in comparison to normal laryngeal mucosa samples. 25389112_Results show the hypermethylation of CBY1 and BCL2-like11 promoters proceeding from DNMT1 is a crucial component of their reduced expression, but it is not directly involved in chronic myeloid leukemia resistance to imatinib. 26147002_CBY1 downregulation in CML comes from reduced protein stability when bound to 14-3-3sigma adapter protein. Dissociation raises CBY1 protein levels by enhancing its stability. The ubiquitin proteasome system reduces 14-3-3sigma-bound CBY1 stability by SUMOylation. 27082063_Cby's C-terminal domain alone binds to TC-1 with significantly greater affinity compared to full-length Cby, implying that target binding of the coiled-coil domain is affected by the flanking disordered regions. 27528616_FAM92 proteins interact with Cby1 to promote ciliogenesis via regulation of membrane-remodeling processes. 28107095_chronic Cby1 knockdown in colon cancer cells may counteract tumor progression by promoting the mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition process. 29764469_Our study reveals an association between Chibby expression and cancer aerobic glycolysis, which highlights the importance of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in regulation of energy metabolism of NPC. These results indicate that Chibby and PDK1 are the potential target for NPC treatment. 30063079_Chibby expression was decreased in gastric cancer samples and altered beta-catenin localization in cultured gastric cancer cells. 33131181_Loss of CBY1 results in a ciliopathy characterized by features of Joubert syndrome. 33934099_A novel Lnc408 maintains breast cancer stem cell stemness by recruiting SP3 to suppress CBY1 transcription and increasing nuclear beta-catenin levels. |
ENSMUSG00000022428 |
Cby1 |
65.072944 |
0.2260341887 |
-2.145387 |
0.762086480 |
6.923114 |
0.00850886665881096446173437186644150642678141593933105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016527289364922995162920926759397843852639198303222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.6064577 |
12.7962458 |
112.0499174 |
39.6548315 |
| ENSG00000100271 |
25809 |
TTLL1 |
protein_coding |
O95922 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic subunit of a polyglutamylase complex which modifies tubulin, generating side chains of glutamate on the gamma-carboxyl group of specific glutamate residues within the C-terminal tail of tubulin (PubMed:34782749). Probably involved in the side-chain elongation step of the polyglutamylation reaction rather than the initiation step. Modifies both alpha- and beta-tubulins with a preference for the alpha-tail. Unlike most polyglutamylases of the tubulin--tyrosine ligase family, only displays a catalytic activity when in complex with other proteins as it is most likely lacking domains important for autonomous activity. Part of the neuronal tubulin polyglutamylase complex. Mediates cilia and flagella polyglutamylation which is essential for their biogenesis and motility. Involved in respiratory motile cilia function through the regulation of beating asymmetry. Essential for sperm flagella biogenesis, motility and male fertility. Involved in KLF4 glutamylation which impedes its ubiquitination, thereby leading to somatic cell reprogramming, pluripotency maintenance and embryogenesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91V51, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34782749}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Flagellum;Ligase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable tubulin binding activity and tubulin-glutamic acid ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in microtubule cytoskeleton organization and protein polyglutamylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including cerebellar Purkinje cell differentiation; mucociliary clearance; and regulation of blastocyst development. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm; extracellular region; and microtubule cytoskeleton. Predicted to be active in cilium. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25809; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; tubulin-glutamic acid ligase activity [GO:0070740]; cerebellar Purkinje cell differentiation [GO:0021702]; immune response in nasopharyngeal-associated lymphoid tissue [GO:0002395]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mucociliary clearance [GO:0120197]; protein polyglutamylation [GO:0018095]; regulation of blastocyst development [GO:0120222]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288] |
19767753_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20564319_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000022442 |
Ttll1 |
31.401346 |
0.4780695490 |
-1.064708 |
0.387178466 |
7.185662 |
0.00734884336426259391489290706545034481678158044815063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014481832851337235121280677674349135486409068107604980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.9027556 |
4.9544897 |
43.8788998 |
7.2118462 |
| ENSG00000100288 |
1120 |
CHKB |
protein_coding |
Q9Y259 |
FUNCTION: Has a key role in phospholipid metabolism, and catalyzes the first step of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19915674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21665002}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Kinase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Nucleotide-binding;Phospholipid biosynthesis;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis; phosphatidylethanolamine from ethanolamine: step 1/3. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:19915674}. |
Choline kinase (CK) and ethanolamine kinase (EK) catalyze the phosphorylation of choline/ethanolamine to phosphocholine/phosphoethanolamine. This is the first enzyme in the biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine in all animal cells. The highly purified CKs from mammalian sources and their recombinant gene products have been shown to have EK activity also, indicating that both activities reside on the same protein. The choline kinase-like protein encoded by CHKL belongs to the choline/ethanolamine kinase family; however, its exact function is not known. Read-through transcripts are expressed from this locus that include exons from the downstream CPT1B locus. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:1120; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; choline kinase activity [GO:0004103]; ethanolamine kinase activity [GO:0004305]; CDP-choline pathway [GO:0006657]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:0006656]; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006646]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] |
18820697_A single nucleotide polymorphism located between CPT1B and CHKB, was associated with narcolepsy in Japanese (rs5770917[C], odds ratio (OR) = 1.79, combined P = 4.4 x 10(-7)) and other ancestry groups (OR = 1.40, P = 0.02). 18820697_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19404393_Japanese CNS hypersomnias (essential hypersomnia: EHS) other than narcolepsy with cataplexy was significantly associated with SNP rs5770917 (located between CPT1B and CHKB) and HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype 19404393_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915674_ChoKalpha and ChoKbeta isoforms have different physiological roles and implications in human carcinogenesis 20299452_kinetic studies revealed that HC-3 is a much more potent inhibitor for ChoKalpha isoforms (alpha1 and alpha2) compared with ChoKbeta. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21665002_homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in the gene encoding choline kinase beta were identified in individulas with congenital muscular dystrophy. 22177342_The study extends on the observation of a strong multiethnic association of polymorphisms in the TCRA and P2RY11 with narcolepsy, but does not confirm the association of CPT1B/CHKB (rs5770917) in the Chinese population. 23692895_CHKB activity was reduced in all three patients, significant reduction in choline:N-acetyl aspartate and choline:creatine ratios in keeping with a general decrease in the amount of choline and phosphocholine-based substrate 23945283_CHKB encodes choline kinase beta, an enzyme that catalyzes the first de-novo biosynthetic step of phosphatidylcholine, the most abundant phospholipid in the eukaryotic membrane [review] 24291895_Its mutations cause congenital muscular dystrophy.[Review] 24571861_study identified a novel haplotype consisting of the indel variation, which had not been detected in previous studies in Japanese and Korean populations, and observed four single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CHKB/CPT1B 25740612_A novel silent variant in the choline kinase beta causing muscular dystrophy. 26067811_A new form of congenital muscular dystrophy with multisystem involvement and characteristic mitochondrial structural changes, due to choline kinase beta gene defects has been characterized. 27123443_The whole exome sequencing revealed a novel homozygous missense mutation in the Choline Kinase-Beta (CHKB) gene in exon 9. 27149373_findings suggest that CKbeta, in concert with CKalpha, and depending on its phosphorylation status, might play a critical role as a druggable target in carcinogenesis 30986505_Alteration of mitochondrial membrane inner potential in three Italian patients with megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy carrying new mutations in CHKB gene. 31926838_Megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy: Same novel homozygous mutation in CHKB gene in two unrelated Chinese patients. 33712684_Megaconial congenital muscular dystrophy secondary to novel CHKB mutations resemble atypical Rett syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000022617 |
Chkb |
231.636953 |
0.4167545545 |
-1.262730 |
0.160705456 |
61.166951 |
0.00000000000000524343562868265105911618615234868562338915298076669202487209986429661512374877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000035813563109373402991394710149295825372820281651264906486176187172532081604003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
142.3872057 |
13.7797808 |
344.4141139 |
22.6827166 |
| ENSG00000100290 |
638 |
BIK |
protein_coding |
Q13323 |
FUNCTION: Accelerates programmed cell death. Association to the apoptosis repressors Bcl-X(L), BHRF1, Bcl-2 or its adenovirus homolog E1B 19k protein suppresses this death-promoting activity. Does not interact with BAX. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8521816}. |
Apoptosis;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene shares a critical BH3 domain with other death-promoting proteins, such as BID, BAK, BAD and BAX, that is required for its pro-apoptotic activity, and for interaction with anti-apoptotic members of the BCL2 family, and viral survival-promoting proteins. Since the activity of this protein is suppressed in the presence of survival-promoting proteins, it is suggested as a likely target for anti-apoptotic proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:638; |
Bcl-2 family protein complex [GO:0097136]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981] |
11782349_Systemic tumor suppression by the proapoptotic gene bik. 11884414_The results identify BIK as an initiator of cytochrome c release from mitochondria operating from a location at the ER. 12853473_NBK mediates apoptosis entirely by BAX-dependent mitochondrial pathway. 12874789_Several sequence alterations of the BIK gene have been identified in peripheral B-cell lymphomas which may have a role in disease pathogenesis. 14983013_Bik is induced in MCF-7 cells in the absence of estrogen signaling and plays a critical role in the antiestrogen-provoked breast cancer cell apoptosis. 15731089_degraded in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells. 15767553_Bik and Bim have roles in bortezomib sensitization of cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL 15791210_Data show that BIK activates recruitment of DRP1 to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum in intact cells, resulting in mitochondrial fragmentation but little release of cytochrome c to the cytosol. 15809295_Endogenous cellular BIK, therefore, regulates a BAX,BAK-dependent ER pathway that contributes to mitochondrial apoptosis 15824729_Bik/NBK accumulation was caused by stabilization of the protein from degradation and was associated with bortezomib cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction. 16060964_Bik does not have a definitive role in development and progression of sporadic breast neoplasms in Mexican females 17027756_E2Fs transactivate bik by a p53-independent mechanism. 17047080_Results suggest that expression of BIK in human breast cancer cells is regulated at the mRNA level by a mechanism involving a nontranscriptional activity of p53 and by proteasomal degradation of BIK protein. 17574210_The activation of caspase-9 and depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential were induced by BIK, which were decreased concomitant with caspase-12 silenced. 17714764_Genes encoding KU70, MGST1 and BIK show age-related mRNA expression levels in hematopoietic stem cells. 18299962_The depletion of ER Ca2+ stores rather than the elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ or the extracellular Ca2+ entry contributed to Bik-induced Hep3B cells apoptosis. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632297_BIK might not play a major role in the susceptibility of schizophrenia in Japanese population. 19632297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19641504_BIK is mainly localized in the ER & induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. It is involved in mature B cell selection. It a pro-apoptotic tumor suppressor in several human tissues. Review. 19767753_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898928_genetic polymorphism in patients with ataxia telangiectasia is associated with the disease progression 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20564319_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21063407_Bik has a role in both, apoptosis induction and sensitivity to oxidative stress in myeloma cells. 21622563_GRP78 can decrease BCL-2 sequestration by BIK at the endoplasmic reticulum 22139380_Data show that association of study-wide significance (P |
ENSMUSG00000016758 |
Bik |
60.009700 |
0.2958298473 |
-1.757160 |
0.225352934 |
63.195025 |
0.00000000000000187220689518795663476454135616455040510658315230929638062207231996580958366394042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000013175476028407342679128169876365195146007518178787876195201533846557140350341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.0291511 |
3.8728640 |
91.9378128 |
7.9437185 |
| ENSG00000100299 |
410 |
ARSA |
protein_coding |
P15289 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10751093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24294900}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Ichthyosis;Leukodystrophy;Lipid metabolism;Lysosome;Metachromatic leukodystrophy;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene hydrolyzes cerebroside sulfate to cerebroside and sulfate. Defects in this gene lead to metachromatic leucodystrophy (MLD), a progressive demyelination disease which results in a variety of neurological symptoms and ultimately death. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:410; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; arylsulfatase activity [GO:0004065]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cerebroside-sulfatase activity [GO:0004098]; sulfuric ester hydrolase activity [GO:0008484]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] |
11333871_Multiple alleles in a subject unaffected with metachromatic leucodystrophy 11857580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11941485_contribution of mutations to enzyme activity reduction and metachromatic leukodystrophy severity 12459318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12459318_analysis of arylsulfatase A mutations demonstrates a lack of association with Alzheimer-type dementia or Down syndrome 12473917_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12788103_the reduced lysosomal half-life of some mutated forms of ARSA is related to deficient octamerization 12888274_Structures of human arylsulfatase A crystals soaked in solutions containing 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate and O-phospho-DL-tyrosine have been determined at 2.7- and 3.2-A resolution, respectively. Phosphate and calcium binding sites are identified. 15026521_Metachromatic leukodystrophy Molecular analysis revealed compound heterozygosity for two novel missense mutations affecting conserved residues in the arylsulphatase A (ASA) sulphatase and carboxyterminal domains, with 89% loss of enzymatic activity. 15375602_missense mutation in which actual pathogenic effect was splicing-related by disrupting a potential exonic splicing enhancer (ESE) and causing a complete exon 7 skipping 15710861_Genetic analysis revealed homozygosity for a novel mutation in exon 3 of ARSA (F219V). 15772092_Enzyme replacement therapy, using ARSA, improves nervous system pathology and function in a mouse model for metachromatic leukodystrophy. 16110195_Homozygote for mutation of the ARSA gene presents with a late-infantile form of metachromatic leukodystrophy 16140556_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16311251_Adeno-associated virus serotype 5-mediated brain delivery of ARSA is a potentially efficacious therapeutic strategy for metachromatic leukodystrophy patients, especially for those with rapidly progressive form of the disease. 16678723_Novel mutations in the arylsulfatase A gene in eight Italian families with metachromatic leukodystrophy 17329011_decidual levels of arylsulphatase A showed very low values at 41 weeks, which reduced to a half at 42 weeks of gestation 17560502_Six DNA variants of the arylsulfatase A gene were identified: two novel frameshift mutations (c.179_180dupCA and c.1338dupC), one known nonsense mutation (p.W318X), and three known missense mutations (p.R84Q, p.G99V, and p.R288C) 17660863_Induction of tolerance to human ARSA in a mouse model of metachromatic leukodystrophy is reported. 17845130_Safety of ARSA overexpression for gene therapy of metachromatic leukodystrophy was evaluated. 18248830_R95Q, G144R, H393P, & C521Y cause large structural changes, & are associated with the severe phenotype of mucopolysaccharidosis VI. G137V & Y210C are thought to cause small structural changes in a limited region resulting in the attenuated phenotype. 18693274_11 novel ARSA alleles in Italian patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy are described. 18768108_DNA sequencing revealed two novel disease-causing missense mutations in the arylsulfatase gene in patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy 19021637_the novel Metachromatic leukodystrophy- causing mutations in the exons 2, 5 and even in 8 of the ARSA gene described here can be classified as severe type 0, leading in homozygosity to the late infantile form Metachromatic leukodystrophy 19054018_We report on two patients with mental retardation, dysmorphic features and low catalytic activity of arylsulfatase A which is because of were explained, in each patients, by a deletion of 22q13 and, thereby, of one allele of ARSA. 19224915_Saposin B(Sap B) is not a limiting factor of the coupled Sap B-ASA reaction in mouse kidney cells even if sulfatide has accumulated to unphysiologically high levels 19606494_characterized eight newly identified ARSA mutations, through lentiviral vector-based expression studies on cell lines and ARSA defective murine fibroblasts. The residual activity associated with the new mutant allele correlates well with the phenotype 21167507_ARSA mutations in the Indian population were characterized. 4 new variant & 5 pseudodeficiency alleles were found. Protein modeling showed loss of interactions leading to conformation change. 21265945_case report of missense mutations p.G99D and p.T409I associated with adult-type metachromatic leukodystrophy 21454621_cationization of ASA and an increase of the mannose 6-phosphate content of the enzyme may promote blood-to-brain transfer of ASA, thus leading to an improved therapeutic efficacy of enzyme replacement therapy behind the BBB. 21648305_The presence of two most common mutations associated with Arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency was analyzed in 56 patients with diagnosis of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, by polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism method. 21695197_The purpose was to estimate the birth prevalence of Metachromatic leukodystrophy in Poland by determining population frequency of the common pathogenic ARSA gene mutations and to compare this estimate with epidemiological data. 21966540_This is the first report that human adipocytes express functional DAR and ARSA, suggesting a regulatory role for peripheral DA in adipose functions. 23192358_Studied brain uptake in the rhesus monkey of a fusion protein of arylsulfatase a and a monoclonal antibody against the human insulin receptor. 23209833_The interaction between SPAM1, ARSA and HSPA2 in a multimeric complex mediating sperm-egg interaction. 23247813_HSPA2 regulates the expression of sperm surface receptors involved in human sperm-oocyte recognition, such as arylsulfatase A and SPAM1. 23689179_Arylsulphatase A activity in human endometrial polyps inversely correlates with aging 24001781_Sixteen novel mutations that cause metachromatic leukodystrophy have been identified in the arylsulfatase A gene. 24989669_We report three families with Arylsulphatase A partial deficit in which we can find a high recurrence of parkinsonism among the siblings. 25297594_Data indicate a significant correlation between the mutation of c.622delC(p.His208Metfs*46) in the arylsulfatase A (ARSA) gene and the phenotype OF metachromatic leukodystrophy. 26462614_an extensive review of all the ARSA-causative variants published in the literature to date, accounting for a total of 200 ARSA allele types (review) 26577183_First report of arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency (ASA-PD) allele and haplotype frequencies in a North African population, reveals relatively high prevalence of the ASA-PD allele in the Tunisian population with an intermediate genetic structure between Africans, Middle-eastern and Europeans most probably linked to the particular geographic location of Tunisia and the several population incursions throughout its history 27374302_siblings exhibited compound heterozygous variants {[c.302G>T]+[c.1344dupC]} in the ARSA gene, and both of the variants have been reported as disease-causing mutations previouslyfa 28799099_The novel p.L113P mutation in a Pakistani family with late infantile MLD has a pathogenic and destructive effect on the protein structure and function of ARSA. 30083785_A novel homozygous missense mutation c.699C>A (p.His231Gln) in exon 4 of ARSA gene was identified in the three metachromatic leukodystrophy patients inherited from their heterozygous parents. 30362153_The expression of serum DRAM1 messenger RNA (mRNA), ARSA mRNA, hsa-miR-2053 and lncRNA-RP1-86D1.3 were positive in 78.3%, 90%, 85%, and 83.3% of MPM patients, respectively. 30657900_Due to their safety profile and higher therapeutic potential the engineered hARSA variants might represent major advances for future enzyme-based therapies of metachromatic leukodystrophy and stimulate analogous approaches for other enzyme therapeutics 30674982_The most common variation of ARSA was c.931 C > T(p.Arg311*), found in 11.4% (14 out of 122 alleles) of the tested individuals. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first of its kind in India with respect to the size of the cohort and the molecular diagnostic method used and one of the largest cohorts of metachromatic leukodystrophy studied till date 30834272_In one case, the homozygous pathogenic variant NM_000049.2:c.914C>A;p.Ala305Glu, which is previously reported in ClinVar, in the gene ASPA was identified causing Canavan disease. In the second case, the homozygous novel variant NM_000487.5:c.256C>G;p.Arg86Gly in the gene ARSA was identified causing metachromatic leukodystrophy. 31312839_Plasma ARSA protein levels were changed in Parkinson's disease patients. ARSA inhibited the in vitro fibrillation of alpha-synuclein in a dose-dependent manner. Ectopic expression of ARSA reversed the alpha-synuclein phenotypes in both cell and fly models of synucleinopathy, the effects correlating with the extent of the physical interaction between these molecules. ARSA is a molecular chaperone for alpha-synuclein. 31694723_Three novel arylsulfatase A (ARSA) gene mutations p.Asp281Asn, p.Asp283Asn and p.Ala344Asp were described from Sri Lankan patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD). 31922587_The proband with late infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy was found to harbor compound heterozygous variants of the ARSA gene [c.467G>A (p.Gly156Asp) and c.960G>A (p.Trp320*)], neither of which was reported previously 32431092_Arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency in Mexico: Enzymatic activity and haplotype analysis. 32470555_Genetic analysis of arylsulfatase A (ARSA) in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. 32617873_Chinese Cases of Metachromatic Leukodystrophy with the Novel Missense Mutations in ARSA Gene. 32632536_Metachromatic leukodystrophy genotypes in The Netherlands reveal novel pathogenic ARSA variants in non-Caucasian patients. 32792226_Safety of intrathecal delivery of recombinant human arylsulfatase A in children with metachromatic leukodystrophy: Results from a phase 1/2 clinical trial. 33385934_Novel disease-causing variants in a cohort of Iranian patients with metachromatic leukodystrophy and in silico analysis of their pathogenicity. 33498624_Arylsulfatase A Remodeling during Human Sperm In Vitro Capacitation Using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM). 34531044_Evaluating the role of ARSA in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. 34554397_Analysis of the HEXA, HEXB, ARSA, and SMPD1 Genes in 68 Iranian Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000022620 |
Arsa |
532.989873 |
0.4308825097 |
-1.214634 |
0.073721213 |
275.252024 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008133798571275117669941266053978980175880751094600032447459523569489444459263499718683597166718197677383510251679412571527190175205028120267181783655679756100953525788099796045571565628051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002140015452977196693910598723917938793119482965721764565951487908636112559224091617170439539142243394183647600679216359068749400788639997603153244292231716094931925908895209431648254394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
328.5077792 |
15.8379110 |
767.4168635 |
24.1892226 |
| ENSG00000100302 |
23551 |
RASD2 |
protein_coding |
Q96D21 |
FUNCTION: GTPase signaling protein that binds to and hydrolyzes GTP. Regulates signaling pathways involving G-proteins-coupled receptor and heterotrimeric proteins such as GNB1, GNB2 and GNB3. May be involved in selected striatal competencies, mainly locomotor activity and motor coordination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11976265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19255495}. |
Cell membrane;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene belongs to the Ras superfamily of small GTPases and is enriched in the striatum. The encoded protein functions as an E3 ligase for attachment of small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO). This protein also binds to mutant huntingtin (mHtt), the protein mutated in Huntington disease (HD). Sumoylation of mHTT by this protein may cause degeneration of the striatum. The protein functions as an activator of mechanistic target of rapamycin 1 (mTOR1), which in turn plays a role in myelination, axon growth and regeneration. Reduced levels of mRNA expressed by this gene were found in HD patients. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:23551; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein sumoylation [GO:0033235]; regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043949]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; synaptic transmission, dopaminergic [GO:0001963] |
16945334_Rhes is an imidazoline-regulated transcript in pancreatic beta-cells 17556863_Rhes can interfere with the functional activity of wt and mutated TSHr and with the respective hormone-stimulated cAMP production of FSHr and LHr. 18571626_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571626_The genes RASD2 might be vulnerability genes for neuropsychologically defined subgroups of schizophrenic patients. 18815223_The monomeric G proteins AGS1 and Rhes selectively influence Galphai-dependent signaling to modulate N-type (CaV2.2) calcium channels. 19255495_Binding to the Gbeta subunits involves the cationic regions of AGS1 and Rhes, and Data used Rhes-AGS1 chimeras to show that their different cationic regions determine the Gbeta-specificity of the interactions. 23583659_The sequestering of Rhes through its binding to mutant huntingtin may decrease the ability of Rhes to perform vital physiological functions in the striatum neurons of Huntington disease patients. (Review) 23999124_The findings of this study suggested that Rhes may play a crucial role in striatal iron homeostasis. 24324270_Rhes robustly binds the autophagy regulator Beclin-1, decreasing its inhibitory interaction with Bcl-2 independent of JNK-1 signaling. 25556834_Rhes is reduced in the brains of Huntington's disease patients. 25818655_Findings reveal that ras homolog enriched in striatum is localized also in striatal cholinergic interneurons and, most importantly, lack of this G-protein, significantly alters dopamine D2 receptor modulation of striatal cholinergic excitability. 26190541_Rhes influences striatal cAMP/PKA-dependent signaling and synaptic plasticity in a gender-sensitive fashion 26228524_Study demonstrated that variation in the gene coding for RASD2 (rs6518956) affects in vivo prefrontal and striatal phenotypes in healthy human subjects that are relevant to schizophrenia 30064488_results support the hypothesis that Rhes expression is regulated by miRNA and indicate that miR-101 may be a potent modulator of Rhes expression in striatal neurons. 31638189_These regions have been used to design peptides aimed at inhibiting RHES interactions and, therefore, mHtt sumoylation; in turn, these peptides will be used to develop small molecule inhibitors by both rational design and virtual screening of large compound libraries. 34070217_Involvement of the Protein Ras Homolog Enriched in the Striatum, Rhes, in Dopaminergic Neurons' Degeneration: Link to Parkinson's Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000034472 |
Rasd2 |
178.581397 |
0.3384278921 |
-1.563080 |
0.152984201 |
104.601827 |
0.00000000000000000000000149319027668652415103361911282281217916503364597206162164027414029129209316337778545857872813940048217773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000015798916475909028257697450794911014870244845758606974078216761067650075744950299849733710289001464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.5413313 |
10.2166145 |
275.4091685 |
20.4024810 |
| ENSG00000100307 |
23492 |
CBX7 |
protein_coding |
O95931 |
FUNCTION: Component of a Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC1-like complex, a complex class required to maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of many genes, including Hox genes, throughout development. PcG PRC1 complex acts via chromatin remodeling and modification of histones; it mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119', rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility. Promotes histone H3 trimethylation at 'Lys-9' (H3K9me3). Binds to trimethylated lysine residues in histones, and possibly also other proteins. Regulator of cellular lifespan by maintaining the repression of CDKN2A, but not by inducing telomerase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19636380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21047797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21060834, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21282530}. |
3D-structure;Chromatin regulator;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that contains the CHROMO (CHRomatin Organization MOdifier) domain. The encoded protein is a component of the Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1), and is thought to control the lifespan of several normal human cells. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:23492; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PcG protein complex [GO:0031519]; PRC1 complex [GO:0035102]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; developmental process involved in reproduction [GO:0003006]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0032968]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
14647293_controls cellular lifespan through regulation of both the p16(Ink4a)/Rb and the Arf/p53 pathways 17374722_CBX7 is a chromobox protein causally linked to cancer development 18686603_In human glioma, CBX7 is down-regulated by the inhibition of miR-9 at posttranscriptional level. 18701502_Loss of the CBX7 gene expression correlates with a highly malignant phenotype in thyroid cancer 18984978_Downregulation of CBX7 is associated with urothelial tumor progression. 19706751_the ability of CBX7 to positively regulate E-cadherin expression by interacting with HDAC2 and inhibiting its activity on the E-cadherin promoter would account for the correlation between the loss of CBX7 expression and a highly malignant phenotype 20541999_Data show that chromobox 7 (CBX7) within the polycomb repressive complex 1 binds to ANRIL, and both CBX7 and ANRIL are found at elevated levels in prostate cancer tissues. 20542683_data reported indicate that the evaluation of CBX7 expression may represent a valid tool in the prognosis of colon cancer since a reduced survival of colorectal cancer patients is associated with the loss of CBX7 expression. 20723236_CBX7 acts as an oncogene in the carcinogenesis and progression of gastric cancer, and it may regulate tumorigenesis, cell migration and cancer metastasis partially via p16(INK4a) regulatory pathway. 21060834_found that expression of CBX7 in gastric carcinoma tissues with p16 methylation was significantly lower than that in their corresponding normal tissues, which showed a negative correlation with transcription of p16 in gastric mucosa 22041561_cbx7 expression was significantly downregulated in multiple human cancer tissues. 22214847_These data suggest that CBX7 is a tumor suppressor and that its loss plays a key role in the pathogenesis of cancer. 22226354_MicroRNA regulation of Cbx7 mediates a switch of Polycomb orthologs during ESC differentiation. 24375438_we showed for the first time that CBX7 was associated with a decreased prognosis for clear cell adenocarcinoma of the ovary 24865347_Results suggest that the loss of CBX7 expression might play a critical role in advanced stages of carcinogenesis by deregulating the expression of specific effector genes. 25351982_CBX7-mediated epigenetic induction of DKK-1 is crucial for the inhibition of breast tumorigenicity, suggesting that CBX7 could be a potential tumor suppressor in breast cancer. 25595895_CBX7/HMGA1b/NF-kappaB could take part in the same transcriptional mechanism that finally leads to the regulation of SPP1 gene expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 25596753_Aberrantly expressed miR-9 contributes to T24 cells invasion, partly through directly down-regulating CBX7 protein expression in bladder transitional cell carcinoma 25881303_Cbx7 is downregulated in CCs, and Cbx7 expression-low tumors correlated with lymph metastasis and poor overall survival of CC patients. 26216446_these results suggest that the retention of CBX7 expression may play a role in the modulation of chemosensitivity of lung cancer patients to the treatment with irinotecan and etoposide 26343356_Data show that polycomb-group proteins BMI1, PHC3, CBX6 and CBX7 expression was significantly increased during imatinib treatment. 26416703_the miR-9 family of microRNAs (miRNAS) downregulates the expression of CBX7. In turn, CBX7 represses miR-9-1 and miR-9-2 as part of a regulatory negative feedback loop. 27291091_Study found that Cbx7 was downregulated in glioma cell lines and tumors and identifies it as an inhibitor of glioma cell migration through its inhibitory effect on YAP/TAZ-CTGF-hippo signaling axis and underscores the importance of epigenetic inactivation of Cbx7 in gliomagenesis. 27449098_Data suggest that miR-375 leads to the activation of oncogenic signatures and tumor progression by targeting chromobox homolog 7 protein (CBX7). 28030829_Suggest CBX7 is an important tumor suppressor that negatively modulates PTEN/Akt signaling during pancreatic tumorigenesis. 28388562_CBX7 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation and invasion in glioma 28460453_our results validate the assumption that CBX7 is a tumor suppressor of gliomas. Moreover, CBX7 is a potential and novel prognostic biomarker in glioma patients. We also clarified that CBX7 silences CCNE1 via the combination of CCNE1 promoter and the recruitment of HDAC2. 29422082_CBX7 positively regulates stem cell-like characteristics of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p16 and activating AKT-NF-kappaB-miR-21 pathway. 29717132_Potential role of CBX7 in regulating pluripotency of adult human pluripotent-like olfactory stem cells in stroke model has been demonstrated. 30759399_Mass spectrometry analysis revealed several non-histone protein interactions between CBX7 and the H3K9 methyltransferases SETDB1, EHMT1, and EHMT2. These CBX7-binding proteins possess a trimethylated lysine peptide motif highly similar to the canonical CBX7 target H3K27me3. 30826432_CBX7 and PRMT1 contribute to regulate E-cadherin expression through several mechanisms. 30990338_Decreased CBX7 expression levels were correlated with liver cirrhosis in HCC patients. Furthermore, the survival times of HCC patients who were CBX7-expression-negative were shorter than HCC patients who were CBX7-expression-positive. Results show that downregulation of CBX7 is related to HCC progression and a poor prognosis in HCC patients. 31211140_findings suggest that CBX4 rs2289728 and CBX7 rs139394 are protective SNPs against HCC. The two SNPs may reduce the risk of HCC while suppressing the expression of CBX4 and CBX7. 32205869_CBX7 binds the E-box to inhibit TWIST-1 function and inhibit tumorigenicity and metastatic potential. 32495862_MicroRNA-18a suppresses ovarian carcinoma progression by targeting CBX7 and regulating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 33245100_Regulation of circGOLPH3 and its binding protein CBX7 on the proliferation and apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. 33400401_Multiomics integrative analysis reveals antagonistic roles of CBX2 and CBX7 in metabolic reprogramming of breast cancer. 34035231_CBX7 suppresses urinary bladder cancer progression via modulating AKR1B10-ERK signaling. 34281957_Expression and correlation analysis of Skp2 and CBX7 in cervical cancer. 34353139_Neuroprotection of chromobox 7 knockout in the mouse after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/hemeoxygenase-1 signaling pathway. 35526483_CBX7 represses the POU2F2 to inhibit the PD-L1 expression and regulate the immune response in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000053411 |
Cbx7 |
159.369584 |
0.3723880200 |
-1.425121 |
0.189759833 |
55.287341 |
0.00000000000010413710921750189672902985053314049678754773381461617987042700406163930892944335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000658835718838546090069951764933599139880543438252402665966656059026718139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.0742255 |
13.1676810 |
236.5181412 |
24.9608035 |
| ENSG00000100372 |
10478 |
SLC25A17 |
protein_coding |
O43808 |
FUNCTION: Peroxisomal transporter for multiple cofactors like coenzyme A (CoA), flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and nucleotide adenosine monophosphate (AMP), and to a lesser extent for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate (PAP). May catalyze the transport of free CoA, FAD and NAD(+) from the cytosol into the peroxisomal matrix by a counter-exchange mechanism. Inhibited by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and bathophenanthroline in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12445829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22185573}. |
Cytoplasm;Membrane;Peroxisome;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a peroxisomal membrane protein that belongs to the family of mitochondrial solute carriers. It is expressed in the liver, and is likely involved in transport. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:10478; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; adenine nucleotide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0000295]; ADP transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015217]; AMP transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0080122]; ATP transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005347]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; coenzyme A transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015228]; FAD transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015230]; FMN transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0044610]; NAD transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0051724]; ATP transport [GO:0015867]; fatty acid alpha-oxidation [GO:0001561]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty acid transport [GO:0015908] |
12445829_Results describe the identification of PMP34, a peroxisomal membrane protein belonging to the mitochondrial solute carrier family, as an adenine nucleotide transporter. 22185573_SLC25A17 is a transporter for CoA and FAD, and to a lesser extent NAD 23266187_Compares and contrasts all the known human SLC25A* genes and includes functional information. 25002403_PEX16 mediates the peroxisomal trafficking of two distinct peroxisomal membrane proteins, PEX3 and PMP34, via the endoplasmic reticulum |
ENSMUSG00000022404 |
Slc25a17 |
110.631547 |
2.0129699296 |
1.009326 |
0.195374949 |
26.543635 |
0.00000025765224279271909127049240521845074880502579617314040660858154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000972372054109059995909971826910656034215207910165190696716308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.6028868 |
16.3532965 |
71.7076032 |
6.1147418 |
| ENSG00000100385 |
3560 |
IL2RB |
protein_coding |
P14784 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for interleukin-2. This beta subunit is involved in receptor mediated endocytosis and transduces the mitogenic signals of IL2. Probably in association with IL15RA, involved in the stimulation of neutrophil phagocytosis by IL15 (PubMed:15123770, PubMed:31040185). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15123770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31040184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31040185}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The interleukin 2 receptor, which is involved in T cell-mediated immune responses, is present in 3 forms with respect to ability to bind interleukin 2. The low affinity form is a monomer of the alpha subunit and is not involved in signal transduction. The intermediate affinity form consists of an alpha/beta subunit heterodimer, while the high affinity form consists of an alpha/beta/gamma subunit heterotrimer. Both the intermediate and high affinity forms of the receptor are involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis and transduction of mitogenic signals from interleukin 2. The protein encoded by this gene represents the beta subunit and is a type I membrane protein. The use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. The protein is primarily expressed in the hematopoietic system. The use by some variants of an alternate promoter in an upstream long terminal repeat (LTR) results in placenta-specific expression. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:3560; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; interleukin-2 receptor complex [GO:0005893]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-15 receptor activity [GO:0042010]; interleukin-2 binding [GO:0019976]; interleukin-2 receptor activity [GO:0004911]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; interleukin-15-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0035723]; interleukin-2-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038110]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11750878_Alternate signalling pathways from the interleukin-2 receptor 11856346_Here we show, in four cell lines of human adult T cell lymphoma/leukemia origin, that the three IL-2R subunits are compartmented together with HLA glycoproteins and CD48 molecules in the plasma membrane 12200137_SHB links IL2 receptor for signal transduction and mediates apoptosis 12230826_investigation of the presence of IL-2alpha, and IL-2beta receptors on fresh and isolated sperm 12676936_Peptide p1-30, which is composed of the 30 amino-terminal residues of human interleukin-2, binds as a tetramer to the dimeric IL-2Rbeta2 receptor 14680494_The development of breast tumour is associated with an increased expression of IL-2 receptor beta and this expression also seems to be associated with the malignancy of the tumour. 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15191519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15350462_Cultures in the presence of peptide epitopes to this receptor inhibited T cell proliferation. 16084898_Interleukin-2 receptor beta-627*C homozygote and C allele correlate with higher susceptibility to endometriosis. 16284400_IL-15R alpha, which bears most of the binding affinity for IL-15, behaves as a potent IL-15 agonist by enhancing its binding and biological effects through the IL-15R beta/gamma heterodimer. 16293754_the crystal structure, at 2.3 A resolution, of the quaternary complex of IL-2 with the extracellular domains of receptors IL-2R alpha, IL-2Rss, and gamma c. 16380905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17108990_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17108990_location of the G245R polymorphism next to the proximal cytokine receptor homology segment; suggestive of a genetic association with the development of visceral leishmaniasis. 17115417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17152005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18299274_IL-2Rbeta chains form IL-2 binding homodimers 18445679_these results indicate that precise sorting of IL-2Rbeta from early to late endosomes is mediated by Hrs, a known sorting component of the ubiquitin-dependent machinery, in a manner that is independent of UIM-ubiquitin binding 18490721_study found PI3K & STAT5 signaling pathways are required for granulysin expression & IL-2Rbeta induction & IL-2Rbeta induction is a prerequisite for granulysin expression; both signaling pathways are defective in CD4+ T cells from HIV-infected patients 18589435_Report the selective expansion of genetically modified T cells using an antibody/IL2RB receptor chimera. 18592269_High serum IL-2R level is associated with peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified. 18715339_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18774388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18791162_The uncleaved 12-kDa form of p12(I) resides in the ER and interacts with the beta and gamma(c) chains of the interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R), the heavy chain of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I, as well as calreticulin and calnexin. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18829468_the preformed complexes between gamma c and IL-2Rbeta or IL-9Ralpha promote signaling by the JAK3 A572V mutant without ligand, identified in several human cancers. 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19471255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19602517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19602517_The C627T polymorphism in the IL2RB gene is not associated with risk of endometriosis in Korean women. 19773451_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19822714_Results provide additional evidence for the association of IL2RB and IL2RA with RA by independent replication in a Dutch population, underlining the importance of the IL2 pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923221_Data indicate that ser/thr phosphorylation negatively regulates IL-2 receptor complex formation and JAK3/STAT5 activation, and that this regulation is counteracted by PP2A. 20049410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20179739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20179739_Polymorphisms in IL2, IL2RA and IL2RB subunit genes were studied in 430 multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and in 550 ethnically matched controls from Madrid (Spain). 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20495002_IL-2Rbeta is subject to ectodomain shedding generating an intracellular fragment biologically functional, because (i) it is phosphorylated, (ii) it associates with STAT5A, and (iii) it increases cell proliferation. 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20585888_Data show that co-expression of ZNF300 and Egr1 lead to enhanced IL-2Rbeta promoter activity, and suggest that ZNF300 is another regulator of the human IL-2Rbeta promoter. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20728947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20811626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20860503_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21345943_Lyn coimmunoprecipitates with the interleukin-2 beta receptor and JAK3 proteins in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected T-cells. 21674833_The researchers found evidence that there were significant differences between the D22S1045 locus in the Maghreb population and other populations. 21839273_Genetic variants of IL2RB may be associated with the development of acute rejection episodes and may help predict risk in kidney transplantation patients. 21865161_LTR of the THE1D retroelement family has been domesticated as an alternative promoter of human IL2RB, the gene encoding the beta subunit of the IL-2 receptor. 21984699_This study directly examines proximal signaling by transgenic IL-2 and IL-15 and CD8-positive T cell primary and memory responses as a consequence of varied CD122-dependent signaling. 22558434_sIL-2Ralpha and sIL-2Rbeta induce marked subunit- and soluble cytokine receptor-specific behavioral disturbances 22573796_Single nucleotide polymorphism in IL2RB is associated with lung cancer. 23341462_Data suggest that cross-talk occurs between cAMP/PKA and the IL-2R beta/Jak3/Stat5b cascade in T-cells. 23418630_Expression of the IL-2 receptor beta-chain forms functional, high-affinity receptors on naive CD4+ T cells that correlates with their increased responsiveness to IL-2. 23512675_Data indicate that the two genetic variants within IL-2RA and IL-2RB are not associated with genetic susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Han Chinese. 23628622_Data indicate that both CgammaCR-CD127(+)composed of Interleukin-7 (IL-7) tethered to IL-7Ralpha/CD127, and CgammaCR-CD122(+) CD8(+) T((E/CM)) engraft in mice and persist in an absence of exogenous cytokine administration. 23676143_specific IL2/IL21, IL2RA and IL2RB polymorphisms do not seem to play a significant role on the non-anterior uveitis genetic predisposition 23926072_This is the first report demonstrating that heterodimeric combinations of IL-2R and IL-6R subunits are functional for signaling. 23972291_IL2RA and IL2RB as promising candidate genes for inflammatory bowel diseases(IBD) and suggesting a potential role of IL2R in the pathogenesis of IBD, likely involves regulatory T cells. 24112992_MiniSTR marker D22S1045 (locus 22q12.3) is localized near the breakpoint region of the Ewing Sarcoma gene, but was found to be neutral related to EWS in a case-control study analyzing allele frequencies and linkage disequilibrium. 24200909_in anti-citrullinated protein antibody positive rheumatoid arthritis, the haplotype AC of IL-2RB was associated with a higher rate of erosions at baseline and at 1 year follow-up in comparison to other haplotypes. 24523387_Suggest that oxalate-induced activation of the renal IL-2Rbeta pathway may lead to a plethora of cellular changes, the most common of which is the induction of inflammation. 24648606_IL-2 receptor beta chain expression is drastically diminished on T cells in ANCA-associated vasculitis. 25352670_CD112 downregulation resulted in a reduced ability of DNAM-1 to bind to the surface of both virus-infected and gD-transfected cells. 26152718_IL2RB thr-450 phosphorylation is a positive regulator for receptor-IL-2 complex stability and activation of signaling molecules. 26203933_An association with the risk of erosion was observed for a haplotype of 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms of the IL-2RB gene in ACPA positive Rheumatoid arthritis patients. 27463037_Characterization of interleukin receptor beta/gamma-associated protein complex assembly in IL-2- and IL-15-activated T-cells has been reported. 28413914_Among patients with a low pretreatment sIL-2R level who exhibited a positive response to R-CHOP, the posttreatment sIL-2R level may help to identify those with a poor prognosis. 28497365_Studies indicate many potential uses of soluble interleukin-2 receptor measurement in the diagnosis and treatment of hemophagocytic syndromes. 28916655_Chimeric fusion protein of interleukin 2 (IL2) and its receptor interleukin 2 receptor, beta protein (IL2Rbeta) enhances antitumor activity of natural killer NK92 cells. 29400710_Here we have developed a novel CAR construct capable of inducing cytokine signaling after antigen stimulation. This new-generation CD19 CAR encodes a truncated cytoplasmic domain from the interleukin (IL)-2 receptor beta-chain (IL-2Rbeta) and a STAT3-binding tyrosine-X-X-glutamine (YXXQ) motif, together with the TCR signaling (CD3z) and co-stimulatory (CD28) domains (hereafter referred to as 28-DeltaIL2RB-z(YXXQ)). 29502070_This study shows that a PTPN2-rs7234029 polymorphism is associated with ocular Behcet's disease and is strongly influenced by gender. In addition, our results suggest that the genetic association with PTPN2 may involve the regulation of PTPN2 mRNA expression and cytokine secretion. 31040184_the early-onset autoimmunity and immunodeficiency are linked to functional deficits arising from altered IL-2Rbeta expression and signaling in T and Natural killer cells. 31040185_three homozygous mutations in the IL2RB gene of eight individuals from four consanguineous families that cause disease by distinct mechanisms, are reported. 31279323_results showed that the IL2Rb polymorphisms were associated with lung cancer risk in the Chinese Han population 31393896_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the genes IL-2, IL-2RB, and JAK3 in patients with cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (V.) guyanensis in Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil. 31685439_In a Chinese Han population, we identified ADRB2 polymorphisms (rs1042711 and rs1560642) that were associated with increased risk of lung cancer, and polymorphisms in IL33 (rs7025417) and IL2RB (rs5756523 and rs2284033) that were associated with decreased disease risk. 32248706_Value of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sarcoidosis. 33507447_Impact of genetic variants in IL-2RA and IL-2RB on breast cancer risk in Chinese Han women. 33844287_Human CD8 T-stem cell memory subsets phenotypic and functional characterization are defined by expression of CD122 or CXCR3. 33954185_Downregulation of miR-497-5p Improves Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Targeting IL2RB. 34970527_Liver Injury and Elevated Levels of Interleukins, Interleukin-2 Receptor, and Interleukin-6 Predict the Severity in Patients With COVID-19. 35381314_Interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta as a novel hub gene plays a potential role in the immune microenvironment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. 35458517_Soluble IL-2R Levels at Baseline Predict the Development of Severe Respiratory Failure and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. 35924269_Upregulated Expression of IL2RB Causes Disorder of Immune Microenvironment in Patients with Kawasaki Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000068227 |
Il2rb |
15.623613 |
3.7212797982 |
1.895799 |
0.424955821 |
20.914672 |
0.00000480202365919467897593941874134770841919817030429840087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000015667079842995903891803358143341995400987798348069190979003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.1115948 |
6.2041323 |
6.7814345 |
1.4348219 |
| ENSG00000100427 |
23209 |
MLC1 |
protein_coding |
Q15049 |
FUNCTION: Regulates the response of astrocytes to hypo-osmosis by promoting calcium influx. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22328087}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The function of this gene product is unknown; however, homology to other proteins suggests that it may be an integral membrane transporter. Mutations in this gene have been associated with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts, an autosomal recessive neurological disorder. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23209; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; caveolin-mediated endocytosis [GO:0072584]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; positive regulation of intracellular transport [GO:0032388]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of response to osmotic stress [GO:0047484]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
11935341_Identification of novel mutations in MLC1 responsible for megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. 12111645_a novel polymorphism in exon 11 of the gene shows no association with schizophrenia 12149273_physical and functional interaction with fortilin: its potential role as a fortilin chaperone 12497630_KIAA0027 alleles were evaluated for potential roles in susceptibility to megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy and schizophrenia. 12850517_A 41-year-old Japanese male with MLC, in whom a homozygous missense mutation, TCG to TTG at codon 93 resulting in S93L, was detected in the MLC1 gene 12939431_A broad spectrum of pathogenetic mutations (missense, splice site, insertion, and deletions) were identified in the MLC1 gene, enlarging the spectrum of allelic variants without a straightforward genotype-phenotype correlation. 14615938_MLC1 may have a role in van der Knaap disease; it is mutated in patients 15037685_Thirty-three affected individuals with MLC were screened. All were from northern India and included 31 known Agarwals. All Agarwal patients were positive for homozygous insertion of a cytosine in exon 2 15992519_Association of MLC1 with SCZ and BPAD suggests involvement of a common pathway. 15992519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16001658_MLC1 gene showed up-regulation expression at both the mRNA and protein levels in HCC tissues and that MLC1 plays an important role in the growth of hepatoma cell SMMC7721 in vitro and vivo. 16470554_analysis of novel variants in MLC1 in patients with vacuolating megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts 16652334_13 novel mutations are associated with Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. 17210142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18165104_in the human brain, MLC1 protein is expressed in astrocyte processes and ependymal cells, where it colocalizes with dystroglycan and syntrophin 18330867_Prenatal diagnosis of megalencephalic leukodystrophy. 19931615_Because pathological mutations prevent MLC1 membrane expression, the identification of substances regulating MLC1 intracellular trafficking is potentially relevant for the therapy of MLC. 20560255_We report two patients with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts with confirmed mutations in the MLC1 gene. The mutation in the second patient was novel. We also review identified mutations in the Turkish population. 20926452_through its interaction with ATP1B1, MLC1 is involved in the control of intracellular osmotic conditions and volume regulation in astrocytes, opening new perspectives for understanding the pathological mechanisms of MLC disease. 21145992_Study detected five novel nucleotide variations in the entire coding region of the MLC1 gene. 21160490_Identification of novel MLC1 mutations in Chinese patients with megalencephalic leukoencephlopathy with subcortical cysts is reported. 21440627_Reduction of MLC1 expression results in the appearance of astrocyte intracellular vacuoles. This vacuolation is reversed by the co-expression of human MLC1 21555057_The presence of the c.135_136insC mutation in 29 patients of the Agarwal community suggests a founder effect in Indian patients. 21624973_study presents more detailed characterization of the effect of mutations found in MLC1 and GLIALCAM megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts 22328087_that MLC1 plays a role in astrocyte osmo-homeostasis and that defects in intracellular calcium dynamics may contribute to MLC pathogenesis. 22416245_Data show that wildtype MLC1(wt) was localized to the cell periphery, whereas mutant R22Q, A32V, G73E, S69L and T118M were trapped in the lumen of endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 23495687_Proposed is a therapeutic approach for prevention of cardiac contractile dysfunction dependent on MLC1 phosphorylation and degradation. 23793458_results indicate GlialCAM is necessary for MLC1 protein expression, and its reduction affects the activity of volume-regulated anion currents (VRAC) which may cause astrocyte vacuolation; work extends the role of GlialCAM as a chaperone of MLC1 needed for proper VRAC activation 24315536_clinical spectrum, neuroimaging characteristics and gene involvement in Egyptian patients with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts; deletion/insertion mutation in exon 11 was recurrent in 2 families; a missense mutation in exon 10 was identified in the third family 24561067_This study shows that in astrocytes MLC1 is expressed in early endosomes and recycled through the Rab11+ perinuclear compartment 24824219_we demonstrate an evolutionary conserved role for MLC1 in regulating glial surface levels of GLIALCAM, and this interrelationship explains why patients with mutations in either gene (MLC1 or GLIALCAM) share the same clinical phenotype. 25497041_Eight novel mutations in MLC1 from 18 Iranian patients with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts 25919557_Gene sequencing identified two heterozygous mutations of MLC1, including missense mutation in exon 3 (c.217G>A, p.Gly73Arg) and splice site mutation in intron 9 (c.772-1G>C in IVS9-1). 26033718_The extracellular domain of GlialCAM is necessary for cell junction targeting and for mediating interactions with itself or with MLC1 and ClC-2. 26908604_Study discloses an important role for MLC1 in the control of astrocyte growth and in the regulation of pathways that trigger quiescent astrocytes into reactive ones in response to brain injury. It also shows that MLC1 pathological mutations cause loss of its function, opening new perspectives for the comprehension of MLC disease pathogenesis. 27322623_Out of 20 patients, macrocephaly, classic MRI features, motor development delay and cognitive impairment were detected in 20(100%), 20(100%), 17(85%) and 4(20%) patients, respectively. 20(100%) were clinically diagnosed with MLC. 19(95%) were genetically diagnosed with 10 novel mutations in MLC1, MLC1 and GlialCAM mutations were identified in 15 and 4 patients, respectively 27389245_Novel mutations were identified in MLC1 from a group of Egyptian patients with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy. 28840990_Three different MLC1 pathogenic variants from five MLC patients with seven alleles contained the p.Ala275Asp variant in exon 10, two frameshift variants p.(Cys46Alafs*12) and p.(Ile113Glyfs*4) were also identified. 29466841_Disturbed astrocyte regulation of ion and water homeostasis in MLC causes hyperexcitability of neuronal networks and seizures 29667716_The frequency of MLC1 c.736delA in multiple families with similar disease phenotype from the Nalband community suggests a founder effect. 30683112_three overlapping genes (FGFBP2, GFOD1 and MLC1) between two modules could potentially have a role in acute myocardial infarction and have diagnostic potential 31209783_MLC1 contributes to restore astrocyte homeostasis after inflammation. 31888684_misallocation of pathogenic mutant MLC1 may disturbs the stable cell-cell communication and the homeostatic regulation of astrocytes in patients with Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts. 31960914_Structural basis for the dominant or recessive character of GLIALCAM mutations found in leukodystrophies. 32209057_Novel and deleterious variants in VPS53, GLB1, and MLC1, genes previously associated with variable neurodevelopmental anomalies, were found to segregate with intellectual disabilities in the three families. 32521795_Megalencephalic Leukoencephalopathy with Subcortical Cysts Disease-Linked MLC1 Protein Favors Gap-Junction Intercellular Communication by Regulating Connexin 43 Trafficking in Astrocytes. 33040087_Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts 1 (MLC1) promotes glioblastoma cell invasion in the brain microenvironment. 34847774_Transmembrane topology and oligomeric nature of an astrocytic membrane protein, MLC1. 34918859_A homozygous missense variant in the MLC1 gene underlies megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts in large kindred: Heterozygous carriers show seizure and mild motor function deterioration. 35440380_Prevalent MLC1 mutation causing autosomal recessive megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy in consanguineous Palestinian families. |
ENSMUSG00000035805 |
Mlc1 |
120.804960 |
0.3429995256 |
-1.543722 |
0.147793410 |
112.430710 |
0.00000000000000000000000002875402719975819167491215492922917704430192516367236404569276866076020168772053864358895225450396537780761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000321522304142750687684978003322389757403813095347337075470209519765553418668702079230570234358310699462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
61.2674622 |
5.8321462 |
179.6777555 |
10.5982011 |
| ENSG00000100429 |
83933 |
HDAC10 |
protein_coding |
Q969S8 |
FUNCTION: Polyamine deacetylase (PDAC), which acts preferentially on N(8)-acetylspermidine, and also on acetylcadaverine and acetylputrescine (PubMed:28516954). Exhibits attenuated catalytic activity toward N(1),N(8)-diacetylspermidine and very low activity, if any, toward N(1)-acetylspermidine (PubMed:28516954). Histone deacetylase activity has been observed in vitro (PubMed:11861901, PubMed:11726666, PubMed:11677242, PubMed:11739383). Has also been shown to be involved in MSH2 deacetylation (PubMed:26221039). The physiological relevance of protein/histone deacetylase activity is unclear and could be very weak (PubMed:28516954). May play a role in the promotion of late stages of autophagy, possibly autophagosome-lysosome fusion and/or lysosomal exocytosis in neuroblastoma cells (PubMed:23801752, PubMed:29968769). May play a role in homologous recombination (PubMed:21247901). May promote DNA mismatch repair (PubMed:26221039). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11677242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11726666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11739383, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11861901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21247901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23801752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26221039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28516954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29968769}. |
Alternative splicing;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the histone deacetylase family, members of which deacetylate lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones. Histone deacetylation modulates chromatin structure, and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:83933; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acetylputrescine deacetylase activity [GO:0047609]; acetylspermidine deacetylase activity [GO:0047611]; deacetylase activity [GO:0019213]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; histone deacetylase activity [GO:0004407]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; protein lysine deacetylase activity [GO:0033558]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; homologous recombination [GO:0035825]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; peptidyl-lysine deacetylation [GO:0034983]; polyamine deacetylation [GO:0106047]; positive regulation of mismatch repair [GO:0032425]; protein deacetylation [GO:0006476]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; spermidine deacetylation [GO:0106048] |
11739383_another histone deacetylase 11861901_molecular cloning and characterization of a novel class II histone deacetylase 15305372_Reduced expression of histone deacetylase 10 is associated lung cancer 17892858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17892858_Results suggest that the 'T' allele of HDAC10-589C>T affect on the increased transcription activity, and might accelerate HCC development through increased expression of HDAC10. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20032463_Results not only show that HDAC10 regulates melanogenesis but also demonstrate that the transcriptional activities of Pax3 and KAP1 are intimately linked to their acetylation status. 20471694_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20680488_HDAC10 is involved in transcriptional downregulation of TXNIP, leading to altered reactive oxygen species signaling in human gastric cancer cells. 21247901_Histone deacetylases 9 and 10 are required for homologous recombination. 23801752_results demonstrate that HDAC10 protects cancer cells from cytotoxic agents by mediating autophagy and identify this HDAC isozyme as a druggable regulator of advanced-stage tumor cell survival 23897811_HDAC10 suppresses expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and 9 genes, which are known to be critical for cancer cell invasion and metastasis 24145760_this study is describing HDAC10 as a promoter of autophagy-mediated survival in neuroblastoma cells and identifying this HDAC isozyme as a druggable regulator of advanced-stage tumor cell survival. 25337229_Suggest HDAC10 expression as a prognostic marker for gastric cancer. 26221039_study identifies an HDAC10-mediated regulatory mechanism controlling the DNA mismatch repair function of MSH2. 26240284_HDAC10 regulates cyclin A2 expression by deacetylating histones near the let-7 promoter. 27449083_this study demonstrated that HDAC10 localizes and functions in the cytoplasm of lung cancer cells, thereby underscoring its potential role in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer 28516954_HDAC10 structure and molecular function as a polyamine deacetylase has been reported. 29968769_Authors show that depleting or inhibiting HDAC10 results in accumulation of lysosomes in chemotherapy-resistant neuroblastoma cell lines, as well as in the intracellular accumulation of the weakly basic chemotherapeutic doxorubicin within lysosomes. 30204052_The free modeled structure of HDAC10 and its complexes with quisinostat and the highest-ranked compound ZINC19749069 were submitted to molecular dynamics simulation. 30515817_HDAC10 upregulation contributed to IL-1beta-mediated inflammatory activation of SMSCs. 31862140_Histone deacetylase 10 knockout activates chaperone-mediated autophagy and accelerates the decomposition of its substrate. 31888084_Characterization of the Role of Host Cellular Factor Histone Deacetylase 10 during HIV-1 Replication. 33481334_Histone deacetylase 10 exerts antitumor effects on cervical cancer via a novel microRNA-223/TXNIP/Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 33493381_Oncogenic miRNA-1908 targets HDAC10 and promotes the aggressive phenotype of cervical cancer cell. |
ENSMUSG00000062906 |
Hdac10 |
285.572396 |
0.3601659750 |
-1.473266 |
0.145659556 |
100.903526 |
0.00000000000000000000000965744667897480145793237010094852124367866288561656384924393068877601642441277363104745745658874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000098851534661350954512814617551043668691742837943176251339958793100393119601676517049781978130340576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
144.7315718 |
13.7080618 |
404.3026124 |
26.2730649 |
| ENSG00000100439 |
63874 |
ABHD4 |
protein_coding |
Q8TB40 |
FUNCTION: Lysophospholipase selective for N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE). Contributes to the biosynthesis of N-acyl ethanolamines, including the endocannabinoid anandamide by hydrolyzing the sn-1 and sn-2 acyl chains from N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) generating glycerophospho-N-acyl ethanolamine (GP-NAE), an intermediate for N-acyl ethanolamine biosynthesis. Hydrolyzes substrates bearing saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated N-acyl chains. Shows no significant activity towards other lysophospholipids, including lysophosphatidylcholine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine and lysophosphatidylserine. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VD66}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase activity and lysophospholipase activity. Predicted to be involved in N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine metabolic process; lipid homeostasis; and phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process. Predicted to act upstream of or within N-acylethanolamine metabolic process. Predicted to be located in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Predicted to be active in lipid droplet and mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:63874; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; carboxylic ester hydrolase activity [GO:0052689]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase activity [GO:0042171]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; lipid catabolic process [GO:0016042]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine metabolic process [GO:0070292]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; phosphatidylethanolamine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036152] |
16818490_Lysophospholipase/phospholipase B (EC 3.1.1.5) specific for N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE) suggesting a role in the biosynthesis of N-acyl ethanolamines including the endocannabinoid anandamide. 22488300_ABHD4 is a novel genetic regulator of anoikis sensitivity. 32868797_ABHD4-dependent developmental anoikis safeguards the embryonic brain. |
ENSMUSG00000040997 |
Abhd4 |
563.517082 |
0.3220023527 |
-1.634857 |
0.158761579 |
102.354279 |
0.00000000000000000000000464294655154550878747888254384925182884810127282967962132977541049247416360401530255330726504325866699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000048124923525850924857535641291789988721775413097612712131774764627578644393679496715776622295379638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
275.8629490 |
29.1070869 |
862.2279653 |
64.2175944 |
| ENSG00000100448 |
1511 |
CTSG |
protein_coding |
P08311 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease with trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like specificity (PubMed:8194606, PubMed:29652924). Also displays antibacterial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria independent of its protease activity (PubMed:2116408, PubMed:2117044). Prefers Phe and Tyr residues in the P1 position of substrates but also cleaves efficiently after Trp and Leu (PubMed:29652924). Shows a preference for negatively charged amino acids in the P2' position and for aliphatic amino acids both upstream and downstream of the cleavage site (PubMed:29652924). Required for recruitment and activation of platelets which is mediated by the F2RL3/PAR4 platelet receptor (PubMed:3390156, PubMed:10702240). Binds reversibly to and stimulates B cells and CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells (PubMed:7842483, PubMed:9000539). Also binds reversibly to natural killer (NK) cells and enhances NK cell cytotoxicity through its protease activity (PubMed:9000539, PubMed:9536127). Cleaves complement C3 (PubMed:1861080). Cleaves vimentin (By similarity). Cleaves thrombin receptor F2R/PAR1 and acts as either an agonist or an inhibitor, depending on the F2R cleavage site (PubMed:10702240, PubMed:7744748). Cleavage of F2R at '41-Arg-|-Ser-42' results in receptor activation while cleavage at '55-Phe-|-Trp-56' results in inhibition of receptor activation (PubMed:7744748). Cleaves the synovial mucin-type protein PRG4/lubricin (PubMed:32144329). Cleaves and activates IL36G which promotes expression of chemokines CXCL1 and CXLC8 in keratinocytes (PubMed:30804664). Cleaves IL33 into mature forms which have greater activity than the unprocessed form (PubMed:22307629). Cleaves coagulation factor F8 to produce a partially activated form (PubMed:18217133). Also cleaves and activates coagulation factor F10 (PubMed:8920993). Cleaves leukocyte cell surface protein SPN/CD43 to releases its extracellular domain and trigger its intramembrane proteolysis by gamma-secretase, releasing the CD43 cytoplasmic tail chain (CD43-ct) which translocates to the nucleus (PubMed:18586676). Cleaves CCL5/RANTES to produce RANTES(4-68) lacking the N-terminal three amino acids which exhibits reduced chemotactic and antiviral activities (PubMed:16963625). During apoptosis, cleaves SMARCA2/BRM to produce a 160 kDa cleavage product which localizes to the cytosol (PubMed:11259672). Cleaves myelin basic protein MBP in B cell lysosomes at '224-Phe-|-Lys-225' and '248-Phe-|-Ser-249', degrading the major immunogenic MBP epitope and preventing the activation of MBP-specific autoreactive T cells (PubMed:15100291). Cleaves annexin ANXA1 and antimicrobial peptide CAMP to produce peptides which act on neutrophil N-formyl peptide receptors to enhance the release of CXCL2 (PubMed:22879591). Acts as a ligand for the N-formyl peptide receptor FPR1, enhancing phagocyte chemotaxis (PubMed:15210802). Has antibacterial activity against the Gram-negative bacteria N.gonorrhoeae and P.aeruginosa (PubMed:2116408, PubMed:1937776). Likely to act against N.gonorrhoeae by interacting with N.gonorrhoeae penA/PBP2 (PubMed:2126324). Exhibits potent antimicrobial activity against the Gram-positive bacterium L.monocytogenes (PubMed:2117044). Has antibacterial activity against the Gram-positive bacterium S.aureus and degrades S.aureus biofilms, allowing polymorphonuclear leukocytes to penetrate the biofilm and phagocytose bacteria (PubMed:2117044, PubMed:32995850). Has antibacterial activity against M.tuberculosis (PubMed:15385470). Mediates CASP4 activation induced by the Td92 surface protein of the periodontal pathogen T.denticola, causing production and secretion of IL1A and leading to pyroptosis of gingival fibroblasts (PubMed:29077095). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10702240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11259672, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15100291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15210802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15385470, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16963625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18217133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18586676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1861080, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1937776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2116408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2117044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2126324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22307629, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22879591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29077095, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29652924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30804664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32144329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32995850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3390156, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7744748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7842483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8194606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8920993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9000539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9536127}. |
3D-structure;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Membrane;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the peptidase S1 protein family, is found in azurophil granules of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. The encoded protease has a specificity similar to that of chymotrypsin C, and may participate in the killing and digestion of engulfed pathogens, and in connective tissue remodeling at sites of inflammation. In addition, the encoded protein is antimicrobial, with bacteriocidal activity against S. aureus and N. gonorrhoeae. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyadenylation signals exist for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:1511; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; caspase binding [GO:0089720]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; serine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008236]; angiotensin maturation [GO:0002003]; antibacterial humoral response [GO:0019731]; biofilm matrix disassembly [GO:0098786]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; immune response [GO:0006955]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050868]; neutrophil activation [GO:0042119]; neutrophil-mediated killing of gram-positive bacterium [GO:0070946]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:1901731]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; purinergic nucleotide receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035590] |
2116408_Cathepsin G is an antimicrobial protein with bacteriocidal activity against S. aureus and N. gonorrhoeae. 11502364_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11557685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11920276_high molecular mass kininogen down-regulates cathepsin G-induced platelet activation by forming a complex with cathepsin G and thus prevents binding of cathepsin G to platelets 11928814_UVA light stimulates the production of cathepsin G and elastase-like enzymes by dermal fibroblasts: a possible contribution to the remodeling of elastotic areas in sun-damaged skin. 11986950_up-regulated by the AML1-MTG8 fusion protein, suggesting a role in the granulocytic maturation characteristic of the t(8;21) acute myelogenous leukemia 12524437_cathepsin G enhances fibrin deposition under flow conditions by elevating the activation state of fibrinogen-adherent platelets rather than by cleaving coagulation factors 12784398_BPI and cathepsin G are the major antigenic targets of ANCA seen in patients with systemic sclerosis 14688365_Serine proteinases cathepsin G and neutrophil elastase cooperate for the proteolytic regulation of CD87/urokinase receptor on monocytic cells. 14737102_role in development of myelodi leukemia with promyelocytic features 15100291_Cathepsin G initializes and dominates the destruction of intact myelin basic protein (MBP) by B cell-derived lysosomal extracts, degrading immunodominant MBP epitope and eliminating both its binding to HLA-DRB1*1501 and MBP-specific T cell response. 15131125_neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G are inhibited by PAI-1 mutants 15140022_Release of cathepsin G from neutrophils specifically down-regulates the responsiveness of neutrophils to C5a, and this effect may play a role in the down-regulation of acute inflammation. 15385470_down-regulation of CatG in macrophages is advantageous to M. tuberculosis bacilli and possibly is an important mechanism by which M. tuberculosis is able to evade the host immune defenses 15967795_oxidants generated by myeloperoxidase regulate cathepsin G activity in vivo 16034099_Neutrophil cathepsin G is the principal protease to produce CCL15 proteolytic products released in the course of hemofiltration of blood from renal insufficiency patients 16317101_PF-4 acts as an inhibitor of the CTAP-III-processing enzymes cathepsin G and chymase without becoming cleaved itself as a competitive substrate. 16444434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16977463_the monocyte chemotactic activity of cathepsin G may have a role in the pathogenesis of RA synovial inflammation 17418861_cathepsin g may play a role in the progression to heart failure by activating angiotensin II, leading to detrimental effects on the heart 17653609_Substrate specificity for cathepsin G is greatly enhanced when an aromatic side chain and a strong positive charge are incorporated in residue P(1). 18217133_Cathepsin G from neutrophils and monocytes may provide some pro-coagulant effect by activating FVIII. 18586676_The cleavage of neutrophil leukosialin (CD43) by cathepsin G releases its extracellular domain and triggers its intramembrane proteolysis by presenilin/gamma-secretase 18835135_Cathepsin G increases MMP expression in normal human fibroblasts through fibronectin fragmentation, and induces the conversion of proMMP-1 to active MMP-1. 19036358_Data report that the two subsets of human dendritic cells differ in their cathepsin distribution, and suggest tha Cathepsin G may be of functional importance. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19250736_MC are immunoreactive to cathepsin-G in human cutaneous mastocytosis, as well as the co-localization of tryptase and cathepsin-G in MC secretory granules. 19528350_both Cat-G and PAR(4) play key roles in generating and/or amplifying relapses in ulcerative colitis 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19620298_Cathepsin G is one of the mediators responsible for complement-dependent opsonophagocytic killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae by human neutrophils. 19910052_Historical and recent data on CatG expression, distribution, function and involvement in disease will be summarized and discussed, with a focus on its role in antigen presentation and immune-related events. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20331476_CatG cleaves human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR in vitro. Cleavage occurred on the loop between fx1 and fx2 of the membrane-proximal beta2 domain. In vivo, however, the CatG cleavage site is sterically inaccessible or masked by associated molecules. 20589323_Neutrophil cathepsin G can either facilitate or impede coagulation via effects on thrombin generation. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21193413_distinct catK/C4-S interactions are necessary for the collagenolytic activity of the enzyme. 21488974_potential of HNE and CatG to be used as markers for early detection of infection. Significant differences in HNE and CatG levels in infected and non-infected wound fluids were observed. 21543057_CatG was found to be dispensable in invariant chain conversion within intact primary human B cells and dendritic cells. 21850236_Data suggested the notion that CatG plays a critical role in proinsulin processing and is important in the activation process of diabetogenic T cells. 22588119_major binding partners of LEKTI were found to be the antimicrobial peptide dermcidin and the serine protease cathepsin G and no kallikreins. 22641217_the targeting and suppression of CTSG by AML1-ETO in t(8;21) AML may provide a mechanism for leukemia cells to escape from the intracellular surveillance system by preventing degradation of foreign proteins. 22915586_NE and CG bind to the surface of cancer cells, presumably to a cell surface receptor, and subsequently undergo clathrin pit-mediated endocytosis. 23147993_A novel HLA-A*0201 restricted peptide derived from cathepsin G is an effective immunotherapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. 23454598_demonstrate that cathepsin G (CG), neutrophil elastase (NE), and to a lesser extent proteinase 3 (PR3), degrade endocan 23466190_Increased concentrations of cathepsins B, D and G in the proliferative eutopic endometrium may play a role in the implantation of endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity. 23940756_Neutrophil cathepsin G is a physiologic modulator of platelet thrombus formation in vivo and has potential as a target for novel anti-thrombotic therapies. 24532668_proteolytic cleavage of PLTP by cathepsin G may enhance the injurious inflammatory responses that occur in COPD 24877096_Elastase and cathepsin G are elevated in the plasma of HD patients, originating from primed PMNLs. In these patients, chronic elevation of these enzymes contributes to cleavage of VE-cadherin and possible disruption of endothelial integrity. 24929239_These in vivo data provide, for the first time, compelling evidence of the collateral involvement of cathepsin G, NE, and proteinase 3 in cigarette smoke-induced tissue damage and emphysema 25248056_expression levels of ELANE and CTSG were determined by quantitative real-time PCR 26270939_Patients with certain polymorphisms in the CTSG gene had lower risk for chronic postsurgical pain compared with wild-types. 26837514_CatG is an essential protease for regulating MHC I molecules 26986619_Data show that lactoferrin (LF) increases the catalytic activity of cathepsin G (CatG) at physiological concentration. 27666013_CatG can be used as a novel marker to distinguish different NK cell subsets and MARS116 is applicable to determine cell surface CatG activity by flow cytometry. 28053237_Cleavage of the alarmins by Human mast cell chymase and human neutrophil cathepsin G suggests a function in regulating excessive inflammation. 28544544_Results provide evidence that cathepsin G (GC) activates IGF-1R by stimulating IGF-1 release from MCF-7 cells, and that IGF-1R activation is required for CG-induced cell aggregation. 28797985_CTSG was increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and muscle tissues of dermatomyositis (DM) patients, and CTSG activity was higher in the serum of DM patients 29077095_The results demonstrate that cathepsin G is directly engaged in caspase-4 activation by a bacterial ligand, which is responsible for cell death and IL-1alpha secretion in HGFs. 29703634_Cathepsin G in human atherosclerotic lesions is largely derived from monocytes. Activated monocytes may contribute to atherogenesis by generating modified LDL particles with increased proteoglycan binding, to enhance LDL retention. 29976772_Neutrophil extracellular traps promote endothelial cell activation and increased thrombogenicity through concerted action of IL-1alpha and cathepsin G and tissue factor production. 30017196_The lung extracellular matrix is vulnerable to pathological structural changes upon upregulation of serine proteases, including cathepsin G (CG) and proteinase 3 (PR3). 30791695_High CTSG expression is associated with antidiastole of tuberculous pleural effusion. 31647805_Results show that cathepsin G (CTSG) N125S (AG) genotype was significantly more frequent among osteomyelitis patients than controls. 32194574_Cathepsin G-Not Only Inflammation: The Immune Protease Can Regulate Normal Physiological Processes. 32303641_Local structural plasticity of the Staphylococcus aureus evasion protein EapH1 enables engagement with multiple neutrophil serine proteases. 32813288_Role of DNA methylation on human CTSG in dermatomyositic myoideum. 33132312_Cathepsin G-Induced Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Elevation in MCF-7 Medium Is Caused by Proteolysis of IGF Binding Protein (IGFBP)-2 but Not of IGF-1. 33245176_Gene body methylation facilitates the transcription of CTSG via antisense lncRNA AL136018.1 in dermatomyositic myoideum. 34376113_Downregulation of interleukin 36gamma and its cleaver cathepsin G following treatment with narrow-band ultraviolet B phototherapy in psoriasis vulgaris. 35462067_Cathepsin G-induced malignant progression of MCF-7 cells involves suppression of PAF signaling through induced expression of PAFAH1B2. |
ENSMUSG00000040314 |
Ctsg |
9.394820 |
0.0398057437 |
-4.650880 |
0.985382844 |
34.449786 |
0.00000000437390924871923491297358614019602507383410738839302211999893188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000019730715315127111806271147185359859932418657990638166666030883789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7941817 |
0.5780500 |
19.5259174 |
5.1317393 |
| ENSG00000100462 |
10419 |
PRMT5 |
protein_coding |
O14744 |
FUNCTION: Arginine methyltransferase that can both catalyze the formation of omega-N monomethylarginine (MMA) and symmetrical dimethylarginine (sDMA), with a preference for the formation of MMA (PubMed:10531356, PubMed:11152681, PubMed:11747828, PubMed:12411503, PubMed:15737618, PubMed:17709427, PubMed:20159986, PubMed:20810653, PubMed:21258366, PubMed:21917714, PubMed:22269951, PubMed:21081503). Specifically mediates the symmetrical dimethylation of arginine residues in the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins Sm D1 (SNRPD1) and Sm D3 (SNRPD3); such methylation being required for the assembly and biogenesis of snRNP core particles (PubMed:12411503, PubMed:11747828, PubMed:17709427). Methylates SUPT5H and may regulate its transcriptional elongation properties (PubMed:12718890). Mono- and dimethylates arginine residues of myelin basic protein (MBP) in vitro. May play a role in cytokine-activated transduction pathways. Negatively regulates cyclin E1 promoter activity and cellular proliferation. Methylates histone H2A and H4 'Arg-3' during germ cell development (By similarity). Methylates histone H3 'Arg-8', which may repress transcription (By similarity). Methylates the Piwi proteins (PIWIL1, PIWIL2 and PIWIL4), methylation of Piwi proteins being required for the interaction with Tudor domain-containing proteins and subsequent localization to the meiotic nuage (By similarity). Methylates RPS10. Attenuates EGF signaling through the MAPK1/MAPK3 pathway acting at 2 levels. First, monomethylates EGFR; this enhances EGFR 'Tyr-1197' phosphorylation and PTPN6 recruitment, eventually leading to reduced SOS1 phosphorylation (PubMed:21917714, PubMed:21258366). Second, methylates RAF1 and probably BRAF, hence destabilizing these 2 signaling proteins and reducing their catalytic activity (PubMed:21917714). Required for induction of E-selectin and VCAM-1, on the endothelial cells surface at sites of inflammation. Methylates HOXA9 (PubMed:22269951). Methylates and regulates SRGAP2 which is involved in cell migration and differentiation (PubMed:20810653). Acts as a transcriptional corepressor in CRY1-mediated repression of the core circadian component PER1 by regulating the H4R3 dimethylation at the PER1 promoter (By similarity). Methylates GM130/GOLGA2, regulating Golgi ribbon formation (PubMed:20421892). Methylates H4R3 in genes involved in glioblastomagenesis in a CHTOP- and/or TET1-dependent manner (PubMed:25284789). Symmetrically methylates POLR2A, a modification that allows the recruitment to POLR2A of proteins including SMN1/SMN2 and SETX. This is required for resolving RNA-DNA hybrids created by RNA polymerase II, that form R-loop in transcription terminal regions, an important step in proper transcription termination (PubMed:26700805). Along with LYAR, binds the promoter of gamma-globin HBG1/HBG2 and represses its expression (PubMed:25092918). Symmetrically methylates NCL (PubMed:21081503). Methylates p53/TP53; methylation might possibly affect p53/TP53 target gene specificity (PubMed:19011621). Involved in spliceosome maturation and mRNA splicing in prophase I spermatocytes through the catalysis of the symmetrical arginine dimethylation of SNRPB (small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated protein) and the interaction with tudor domain-containing protein TDRD6 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CIG8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10531356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11152681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11747828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12411503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12718890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15737618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17709427, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19011621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20421892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20810653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21081503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21258366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21917714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22269951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25092918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25284789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26700805}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Chromatin regulator;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Golgi apparatus;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme that belongs to the methyltransferase family. The encoded protein catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups to the amino acid arginine, in target proteins that include histones, transcriptional elongation factors and the tumor suppressor p53. This gene plays a role in several cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, and the assembly of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. A pseudogene of this gene has been defined on chromosome 4. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:10419; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; histone methyltransferase complex [GO:0035097]; methylosome [GO:0034709]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; histone arginine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008469]; histone H4R3 methyltransferase activity [GO:0044020]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein-arginine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016274]; protein-arginine omega-N symmetric methyltransferase activity [GO:0035243]; ribonucleoprotein complex binding [GO:0043021]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; DNA-templated transcription termination [GO:0006353]; endothelial cell activation [GO:0042118]; Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090161]; histone arginine methylation [GO:0034969]; histone H4-R3 methylation [GO:0043985]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; peptidyl-arginine methylation [GO:0018216]; peptidyl-arginine N-methylation [GO:0035246]; positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:1904992]; positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048026]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; regulation of DNA methylation [GO:0044030]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796]; spliceosomal snRNP assembly [GO:0000387] |
14559996_Data show that PRMT5 can be found in association with hSWI/SNF complexes and is involved in regulating the expression of carbamoyl-phosphate synthase-aspartate carbamoyltransferase-dihydroorotase. 15485929_suppressor of tumorigenicity 7 (ST7) and nonmetastatic 23 (NM23) are direct targets of PRMT5-containing BRG1 and hBRM complexes 15654770_It was found that is the recruitment of methylarginine-specific protein(s) to cytokine promoter regions that regulates their gene expression. 15670829_found that FCP1 is a genuine substrate of PRMT5-methylation both in vivo and in vitro, and FCP1-associated PRMT5 can methylate histones H4 in vitro 15701830_Up-regulation of SKB1 is associated with gastric cancer 15737618_contrast to PRMT3, DAL-1/4.1B was found to mediate PRMT5 by either inhibiting (Sm proteins) or enhancing (myelin basic protein) protein methylation. 16087681_Lsm10 and Lsm11, which replace the Sm proteins D1 and D2 in the histone RNA processing U7 snRNPs, associate with pICln in vitro and in vivo without receiving sDMA modifications and with PRMT5 and SMN complexes 16712789_SUZ12 might have a role in transcriptional regulation through physical interaction with MEP50 that can be an adaptor between PRMT5 and its substrate H2A 17437848_results suggest distinct functions of the nuclear and the p44/protein arginine methyltransferase 5 complexes in the developing fetal testis and in the oncogenesis of testicular tumors. 17627275_aberrant expression of PRMT5 leads to altered epigenetic modification of chromatin, which in turn impacts transcriptional performance of anti-cancer genes and growth of transformed lymphoid cells 17709427_that in human cells, PRMT5 and PRMT7 are required for Sm protein sDMA modification, and that Sm protein symmetric dimethylarginine modification is required for snRNP biogenesis in human cells. 18347060_identification of the protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) as an effector recruited to SNAIL through an interaction with AJUBA that functions to repress the SNAIL target gene, E-cadherin 18694959_These results indicate that PRMT5 overexpression epigenetically alters the transcription of key tumor suppressor genes. 18992153_BLIMP1 and PRMT5 were expressed and arginine dimethylation of histones H2A and H4 was detected in human male gonocytes and intratubular germ cell neoplasia unclassified and most seminomas, while downregulated in embryonal carcinoma. 19032343_These results indicate that Ski complexes serve to maintain a TGF-beta-responsive promoter at a repressed basal level via the activities of histone deacetylase and histone arginine methyltransferase. 19086919_FGF-2 is a new substrate of PRMT5. 19234465_Loss of the H4 arginine 3 methylation mark through short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of PRMT5 leads to reduced DNMT3A binding, loss of DNA methylation and gene activation. 19741270_ZNF224 recruits the arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 on the transcriptional repressor complex of the aldolase A gene 20421892_The protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) localizes to the GA and forms complexes with several components involved in GA ribbon formation and vesicle tethering. 20495075_PRMT5 induces multiprotein repressor complex containing the histone modifying enzymes SUV4-20h1, casein kinase 2alpha in silencing fetal globin gene expression resulting in beta-thalassemia and sickle cell disease. 20951943_Increased PRMT5 activity mediates key events associated with cyclin D1-dependent neoplastic growth, including CUL4 repression, CDT1 overexpression, and DNA rereplication. 21081503_RioK1, a new interactor of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5), competes with pICln for binding and modulates PRMT5 complex composition and substrate specificity. 21159818_loss of Prmt5 function is early embryonic-lethal due to the abrogation of pluripotent cells in blastocysts 21262773_The activity of SHP is also increased by posttranslational methylation at Arg-57 by protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5). 21316606_results indicate that phosphorylation of PRMT5 contributes to the mutant JAK2-induced myeloproliferative phenotype 21592330_COX2-dependent and independent activation of CK2alpha-Akt/uPA signal is mainly involved in urothelial carcinoma cell survival 21700716_results reveal a new cofactor for PDCD4 that alters its tumor suppressor functions and point to the utility of PDCD4/PRMT5 status as both a prognostic biomarker and a potential target for chemotherapy 21917714_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ERK1/2 signal transduction amplitude and cell fate through CRAF. 21975038_The results not only provide insight into the molecular mechanisms by which PRMT5 contributes to growth control, but also justify therapeutic targeting of PRMT5. 22143770_analysis of structural insights into protein arginine symmetric dimethylation by PRMT5 22199349_PRMT5 inhibits the PKCdelta- or 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-dependent increase in human involucrin expression, and PRMT5 dimethylates proteins in the p38delta complex. 22231400_Here the authors report that H3R2 is also symmetrically dimethylated (H3R2me2s) by PRMT5 and PRMT7 and present in euchromatic regions. 22266372_PRMT5 probably promotes tumor growth by stimulating cell proliferation and by participating in the construction of a tumor-favorable microenvironment via HIF-1 activation. 22269951_HOXA9 is required for TNF-alpha-dependent binding of PRMT5 to the E-selectin promoter in endothelial cells. 22708516_Data suggest that PRMT5 is highly expressed in lung cancer cells; PRMT5 expression is not detectable in benign lung tissues. Silencing PRMT5 expression strongly inhibits proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells in culture and in a xenograft model. 22726390_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 is a potential oncoprotein that upregulates G1 cyclins/cyclin-dependent kinases and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling cascade. 22952863_These results imply a novel mechanism by which PRMT5 controls cell growth and contributes to prostate tumorigenesis. 23071334_structure of the surprising hetero-octameric complex reveals the close interaction between the seven-bladed beta-propeller MEP50 and the N-terminal domain of PRMT5, and delineates the structural elements of substrate recognition. 23133559_type II protein arginine methyltransferase 5 has a role in the regulation of Circadian Per1 and CRY1 genes 23261437_PRMT5 triggers the symmetric dimethylation of EBNA2 RG domain to coordinate with EBNA2-mediated transcription. 23292799_These results suggest that overexpression of PRMT5 correlates with an aggressive malignant phenotype and may constitute a novel prognostic factor for epithelial ovarian cancer. 23671120_PRMT5 modulates the metabolic response to fasting signals. 23904475_PRMT5 dimethylates R30 of the p65 subunit to activate NF-kappaB. 23912080_results show that protein arginine methyl transferase (PRMT)-3 and -5 methylate NaV1.5 in vitro, interact with NaV1.5 in human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells, and increase NaV1.5 current density 24098663_PRMT5 is upregulated in malignant and metastatic melanoma and regulates expression of MITF and p27(Kip1.). 24121109_These results demonstrate that PRMT1 and PRMT5 are involved in hypoxia and ischemia-induced apoptosis via p-p38 MAPK and p-JNK in in vitro and in vivo models. 24189068_PRMT5 knockdown in non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines and primary lymphoma cells leads to RBL2 derepression and RB1 reactivation, which in turn inhibit PRC2 expression. 24326178_PRMT5 is significantly overexpressed in neoplastic lung tissues supporting its role in lung tumorigenesis. 24453002_The tumor suppressor ST7 is a key gene silenced by PRMT5. 24477620_PRMT5 functions in human embryonic stem cels to regulate proliferation in the self-renewing state by regulating the fraction of cells in Gap 1 (G1) of the cell cycle. 24664369_The results of this study indicated that PRMT5 is a marker of malignant progression in glioma tumors and plays a pivotal role in tumor growth. 24753255_We found that depletion of PRMT5 results in significantly reduced levels of CXCL10 mRNA, demonstrating a positive role for PRMT5 in CXCL10 induction. 25012667_findings indicate that PRMT5 is an essential regulator of myocardial hypertrophic signaling and suggest that strategies aimed at activating PRMT5 in the heart may represent a potential therapeutic approach for the prevention of cardiac hypertrophy 25220593_Our data suggest that LCE1 is a novel p53 downstream target that can be directly transactivated by p53 and is likely to have tumor suppressor functions through modulation of the PRMT5 activity. 25234597_Based on these results, we propose that PRMT5 determines cell fate by regulating 5'-cap dependent translation of proteins essential for proliferation and survival. 25281873_The PKC-c-Fos-NF-Y signaling pathway may be responsible for PRMT5 overexpression in a subset of human cancer patients. 25324546_PRMT5-mediated repression represents a novel mechanism of negative regulation of Cyp24a1. 25457166_PRMT5 is directly involved in genome defense during preimplantation development and in primordial germ cells at the time of global DNA demethylation. 25475372_These studies implicate PRMT5 in a novel mode of MYCN post-translational regulation. 25485739_data confirm that MEP50 plays a key role in substrate recognition and activates PRMT5 activity by increasing its affinity for protein substrates. 25582697_PRMT5 is required for lymphomagenesis triggered by multiple oncogenic drivers 25704480_TRAF4 upregulated PRMT5 expression, which occurred predominantly in the nucleus, on which TRAF4 promotion of cell proliferation in breast cancer is mainly dependent. 25713080_Data indicate that MEP50 WD repeat protein is essential for methylation of histones H4 and H2A by PRMT5 arginine methyltransferase. 25721668_PRMT5 enhances transcriptional activity of constitutive androstane receptor.PRMT5 is a gene-selective co-activator for CAR. 25742700_Data indicate that protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is overexpressed in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)+ primary lymphomas, EBV-transformed and EBV-immortalized B cells. 25870105_The G tract-mediated exon skipping creates a shorter PRMT5 protein (PRMT5S) that exhibits distinct localization and promotes cell cycle arrest at interphase. 25927346_PRMT5- mediated symmetric arginine dimethylation is attenuated by mutant huntingtin and is impaired in Huntington's disease. 26069323_PRMT5 role in the U snRNP assembly machinery 26078354_Findings provide new evidence that PRMT5 plays an important role in CRC pathogenesis through epigenetically regulating arginine methylation of oncogenes such as eIF4E and FGFR3. 26086249_PRMT5 is down-regulated by beta-amyloid in primary neurons and SH-SY5Y cells. This up-regulates E2F-1. PRMT5 knockdown in SH-SY5Y cells over-expressing the Swedish mutant form of human amyloid-beta precursor protein caused activation of apoptotic pathways. 26151339_The novel PRMT5S likely contributes to the observed diverse effects of PRMT5 in cells. 26248553_high nuclear expression of Protein arginine methyltransferase-5 is a potentially useful marker for estimating submucosal invasion of early colorectal carcinomas in endoscopically resected specimens 26482848_PRMT5 co-localizes with RASSF1A on stabilized microtubules.RASSF1A promotes the translocation of cytosolic PRMT5 to microtubules. 26536822_Increased PRMT5 activity enhanced acute myeloid leukemia growth. 26541651_PRMT5 plays an important role in human hepatocellular carcinoma growth via the downregulation of beta-catenin 26554819_arginine residues within the third intracellular loop of the D2 dopamine receptor were methylated by protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) 26563484_Data show that Omomyc protein co-localized with proto-oncogene protein c-myc (c-Myc), protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) and histone H4 H4R3me2s-enriched chromatin domains. 26597461_UHRF1 could form a complex with PRMT5 to contribute to the endometrial carcinogenesis. 26658161_Data show that the E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP interacts with protein arginine methyltransferase-5 (PRMT5) both in vivo and in vitro. 26708443_Our results indicate that PRMT5 is a marker of poor prognosis in NPC patients. PRMT5 promoted the radioresistance of NPC cells via targeting FGFR3, at least partly if not totally. 26729154_PRMT5 expression was upregulated during HTLV-1-mediated T-cell transformation. 26759235_PRMT5-induced methylation prevented phosphorylation of SREBP1a on S430 by GSK3beta 26763441_PRMT5 gene is silencing gene expression by histone arginine methylation in keratinocytes. 26912360_these findings reveal PRMT5 as a potential vulnerability across multiple cancer lineages augmented by a common 'passenger' genomic alteration. 26912361_methylthioadenosine accumulation in 5-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase-deleted cancers creates a hypomorphic PRMT5 state that is selectively sensitized toward further PRMT5 inhibition. 26912789_PRMT5 as an ASK1-binding protein.PRMT5 mediates arginine methylation of ASK1. 26990556_Data suggest that the protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5)-E2F1 transcription factor (E2F-1) pathway may act as a common target for exogenous lectins including Anguilla japonica lectin 1 (AJL1), and the cellular response to exogenous AJL1 may suggest a novel agent for cancer gene therapy. 27068473_methionine adenosyltransferase II alpha (MAT2A), and the arginine methyltransferase, PRMT5, as vulnerable enzymes in cells with MTAP deletion. 27183006_ERG signaling in prostate cancer is driven through PRMT5-dependent methylation of the androgen receptor. 27292259_Results provide evidence that PRMT5 differentially regulates self-renewal, survival and proliferation of primary glioblastoma neurosphere cells (GBMNS) 27315569_Study showed that PRMT5 mRNA levels were significantly higher in gastric cancer (GC) tissues and were independent of tumor depth, differentiation and lymph node metastasis. Findings indicate that PRMT5 acts as an oncogene in GC by enhancing the malignant phenotype of a cancer cell line. 27480244_Results provide evidence that PRMT5 and p44 regulate gene expression of growth and anti-growth factors to promote lung tumorigenesis. 27546619_High PRMT5 expression is associated with prostate cancer. 27643437_PRMT5 knockdown reduces growth, survival, and colony formation of chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cells. 27708221_PRMT5 inhibited the interaction between CDK4 and CDKN2A and then activated the CDK4-RB-E2F pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells under glucose induction. 27860244_PRMT5 regulated the production of inflammatory factors, cell proliferation, migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 28031468_The C-terminal motif of PRMT5 is required for plasma membrane association, and loss of this switching capacity is not compatible with life. This signaling phenomenon was recently reported for the HPV E6 oncoprotein but has not yet been observed for mammalian proteins 28074910_he phosphorylation of the MP inhibitory MYPT1(T850) and the regulatory PRMT5(T80) residues as well as the symmetric dimethylation of H2A/4 were elevated in human hepatocellular carcinoma and in other types of cancers. 28087667_findings show that PRMT5 is an important modulator of CD4(+) T cell expansion; PRMT5 was transiently upregulated during maximal proliferation of mouse and human memory Th cells; data implicate PRMT5 in the regulation of adaptive memory Th cell responses 28101581_our results indicate that PRMT5 may act as a putative oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma 28107179_High nuclear PRMT5 expression is associated with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 28115626_PRMT5 regulates internal ribosome entry site-dependent translation via methylation of hnRNP A1. 28238654_Methylation of RUVBL1 by the arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 is required for homologous recombination-mediated double-strand break repair by promoting TIP60-mediated histone H4K16 acetylation. 28381188_high expression of PRMT5 in primary and metastatic breast cancer lesions and indicated its function in cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and apoptosis. 28591716_Data indicate the significant potential of PRMT5 as a therapeutic target in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and colorectal cancer (CRC). 28854561_SFN treatment of tumors results in reduced MEP50 level and H4R3me2s formation, confirming that that SFN impacts this complex in vivo. These studies suggest that the PRMT5/MEP50 is required for tumor growth and that reduced expression of this complex is a part of the mechanism of SFN suppression of tumor formation. 28874563_These kinetic studies suggest a biochemical explanation for the interplay between PRMT5- and PRMT7-mediated methylation of the same substrate at different residues and also suggest a general model for regulation of PRMTs. 28945229_The polymerase-associated factor complex regulates Prmt5 to facilitate leukemic progression and is a potential therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukemias. 28977470_Data indicate that ZNF326 is an interaction partner and substrate of the PRMT5/WDR77 complex. 28987382_PRMT1 inhibition prevents gastric cancer progression by downregulating eIF4E and targeting type II PRMT5. 29106602_High PRMT5 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 29154828_These results could be helpful in discovering new potent and specific inhibitors of PRMT5, as well as in designing mutant residue assay to modulate the catalytic activity of PRMT5. 29185119_Study demonstrated that PRMT5 regulates OCT4/A, KLF4, and C-MYC in breast cancer to govern stemness and affects the doxorubicin resistance of breast cancer. 29227283_identified a LUBAC-independent role for SHARPIN in enhancing PRMT5 activity that contributes to melanomagenesis through the SKI/SOX10 regulatory axis. 29262329_PRMT5 as a key in vitro and in vivo regulator of breast cancer stem cells proliferation. PRMT5 epigenetically regulates FOXP1. 29441724_PRMT5 knockdown markedly inhibited in vitro HCC proliferation and in vivo tumorigenesis. Authors revealed that the mechanism of PRMT5-induced proliferation was partially mediated by BTG downregulation, leading to cell cycle arrest during the G1 phase in HCC cells. 29501774_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) was identified to be responsible for Eno-1 methylation. Overexpression of PRMT5 and caveolin-1 enhanced levels of membrane-bound extracellular Eno-1 and, conversely, pharmacological inhibition of PRMT5 attenuated Eno-1 cell-surface localization. 29518110_A 3.7 A structure of PRMT5, solved in complex with regulatory binding subunit MEP50 (methylosome associated protein 50, WDR77, p44), by single particle (SP) cryo-Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) using micrographs of particles that are visibly crowded and aggregated. The catalytic PRMT5 subunits form a core tetramer and the MEP50 subunits are arranged peripherally in complex with the PRMT5 N-terminal domain. 29559659_Luciferase reporter assays using the promoter region of the LCE1C gene confirmed that the phosphorylations of TAp63-T46/T281 contributed to full transcriptional activation of the LCE1C gene. LCE1C interacted with protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) and translocated it from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. 29603824_PRMT5 may play a role from early oncogenesis through to the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma , particularly in the aggressive mode of stromal invasion 29679612_Studies suggest that the protein arginine N-methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5)/miR-99 family/fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) axis in regulating lung cancer progression and identifies PRMT5 as a promising prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. 29718323_Evidence for the importance of PRMT5 for the post-translational regulation of TDP1 and repair of topoisomerase I covalent complexes. 29721098_CAPG competes with the transcriptional repressor arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) for binding to the STC-1 promoter. 29749478_our results indicated that PRMT5 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)and colon cancer cells contributed to their acquisition of aggressive characteristics, such as invasiveness, thus presenting a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of these diseases 29802960_Expression of PRMT5 was significantly increased in human gastric cancer (GC) tissues compared with normal gastric mucosa. Multiple evidences suggested that PRMT5 repressed transcription of tumor suppressor IRX1 via recruitment of DNMT3A on promoter. 30054435_The findings therefore indicate that Pb exposure increasing the PRMT5 expression might be one of the contributing epigenetic factors in the lead-mediated disease processes. 30082494_Inhibition of PRMT5 in B-cell lymphoma lines led to significant upregulation of BCL6 target genes, and the concomitant inhibition of both BCL6 and PRMT5 exhibited synergistic killing of BCL6-expressing lymphoma cells. 30189247_these results indicate important functions for PRMT5 in the regulation of basal interferon gene expression in mesenchymal stromal cells. 30257864_CARM1-mediated asymmetric methylation of PRMT5 is critical for its dimerization and methyltransferase activity leading to the repression of gamma-globin expression. 30289978_High PRMT5 nuclear expression was also associated with higher nuclear liver kinase B1 (LKB1), suggesting that a functional relationship may occur. Consistently, several approaches provided evidence that PRMT5 and LKB1 interact directly in the cytoplasm of mammary epithelial cells. 30305293_CircPRMT5 exerts critical roles in promoting UCB cells' EMT and/or aggressiveness and is a prognostic biomarker of the disease, suggesting that circPRMT5 may serve as an exploitable therapeutic target for patients with UCB. 30392062_curcumin affects the PRMT5-MEP50 methyltransferase expression might be explored for its therapeutic application. 30429891_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) and WD repeat domain 5 (WDR5), both of which regulate histone post-translational modifications, were required for HOXC10-mediated VEGFA upregulation. Importantly, a significant correlation between HOXC10 levels and VEGFA expression was observed in a cohort of human gliomas. 30446222_LINC01138 interacts with PRMT5 to increase arginine methylation and protein stability of SREBP1, promoting lipid desaturation and cell proliferation in Clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 30461193_High PRMT5 expression is associated with lung cancer. 30635341_This study indicates that H4R3sme2 and PRMT5 may serve as potentially sensitive biomarkers for the prediction of BCP-ALL occurrence and bone marrow relapse. Moreover, H4R3sme2 and PRMT5 with its target genes may represent potential therapeutic targets against pediatric BCP-ALL. 30675521_These results suggest that MEP50/PRMT5 is important for HH signal-induced GLI1 activation, especially in cancers. 30704408_A low expression of the PRMT5 gene serves as an independent risk factor for the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction. 30800128_These experiments indicate that limiting PRMT5 function may promote tumor immunity by inhibiting Treg function and limiting Treg migration into tumors. PRMT5 levels and activity is reported to be elevated in several tumor cells and abnormal PRMT5 functions may contribute to some aspects of the malignant phenotype. 30922330_The present study demonstrated that PRMT5 epigenetically silenced the expression of the tumor suppressor FBW7, leading to increased cMyc levels and the subsequent enhancement of the proliferation of and aerobic glycolysis in pancreatic cancer cells. 30940768_analysis led to the identification of previously unknown PRMT5 substrates, thus both providing insight into the global effects of PRMT5 and its inhibition in live cells, beyond chromatin. 31123343_our data suggest that PRMT5 is required for AKT activation and forms a feedback regulatory loop with AKT to promote the survival and proliferation of DLBCL cells 31267554_PRMT5 binds and methylates DDX5 at its RGG/RG motif. PRMT5-deficient cells accumulate R-loops, resulting in increased formation of gammaH2AX foci. 31312965_The potency, small size, and synthetic accessibility of this compound class provide promising hit scaffold for medicinal chemists to further explore this series of PRMT5 inhibitors. 31439820_Regulation of PRMT5-MDM4 axis is critical in the response to CDK4/6 inhibitors in melanoma. 31473880_High PRMT5 expressions is associated with therapeutic resistance to mTOR inhibition in glioblastoma. 31498866_Metadherin-PRMT5 complex enhances the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the WNT-beta-catenin signaling pathway. 31533041_A PRMT5-RNF168-SMURF2 Axis Controls H2AX Proteostasis. 31611688_The catalytic activity of PRMT5 is needed for the survival of acute myeloid leukemia cells. The splicing regulator SRSF1 relies on its methylation by PRMT5 and loss of PRMT5 leads to changes in alternative splicing of multiple essential genes for leukemia cell survival. 31665911_PRMT5 Promotes Human Lung Cancer Cell Apoptosis via Akt/Gsk3beta Signaling Induced by Resveratrol. 31694585_Data suggest that targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) could be a potential therapeutic strategy for MYC-driven medulloblastoma. 31765670_Knockdown of PRMT5 expression or forced expression of HSP90A with alanine replacement of R345 or R386 induced apoptosis with the degradation of client proteins in NDRG2(low) ATL-related and other cancer cells 31822509_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 represses tumor suppressor miRNAs that down-regulate CYCLIN D1 and c-MYC expression in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. 31851779_PRMT5 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via EGFR-beta-catenin axis in pancreatic cancer cells. 31868234_Switches in histone modifications epigenetically control vitamin D3-dependent transcriptional upregulation of the CYP24A1 gene in osteoblastic cells. 32023548_PRMT5-TRIM21 interaction regulates the senescence of osteosarcoma cells by targeting the TXNIP/p21 axis. 32089501_Circ-PRMT5 enhances the proliferation, migration and glycolysis of hepatoma cells by targeting miR-188-5p/HK2 axis. 32191634_PRMT5 regulates T cell interferon response and is a target for acute graft-versus-host disease. 32292506_PRMT5-dependent transcriptional repression of c-Myc target genes promotes gastric cancer progression. 32301278_PRMT5 silencing selectively affects MTAP-deleted mesothelioma: In vitro evidence of a novel promising approach. 32392182_High PRMT5 expression is associated with poor overall survival and tumor progression in bladder cancer. 32456215_Regulation of a PRMT5/NF-kappaB Axis by Phosphorylation of PRMT5 at Serine 15 in Colorectal Cancer. 32555249_Genomic deregulation of PRMT5 supports growth and stress tolerance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 32623319_Methylation of the central transcriptional regulator KLF4 by PRMT5 is required for DNA end resection and recombination. 32709847_PRMT5 promotes cancer cell migration and invasion through the E2F pathway. 32747416_Genome-wide R-loop analysis defines unique roles for DDX5, XRN2, and PRMT5 in DNA/RNA hybrid resolution. 32759981_PRMT5 promotes DNA repair through methylation of 53BP1 and is regulated by Src-mediated phosphorylation. 32808744_Circular RNA PRMT5 confers cisplatin-resistance via miR-4458/REV3L axis in non-small-cell lung cancer. 32868396_Glutathionylation Decreases Methyltransferase Activity of PRMT5 and Inhibits Cell Proliferation. 32887644_PRMT5 inhibition attenuates cartilage degradation by reducing MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling. 32999000_Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Promotes pICln-Dependent Androgen Receptor Transcription in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. 33045527_Targeting methyltransferase PRMT5 retards the carcinogenesis and metastasis of HNSCC via epigenetically inhibiting Twist1 transcription. 33090401_Circ-PRMT5 stimulates migration in esophageal cancer by binding miR-203. 33097661_Targeted CRISPR screening identifies PRMT5 as synthetic lethality combinatorial target with gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells. 33220929_Long noncoding RNA ARRDC1-AS1 is activated by STAT1 and exerts oncogenic properties by sponging miR-432-5p/PRMT5 axis in glioma. 33274632_Characterization of the Kinetic Mechanism of Human Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5. 33277756_Circ-PRMT5 promotes breast cancer by the miR-509-3p/TCF7L2 axis activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. 33296647_Nuclear cGAS Functions Non-canonically to Enhance Antiviral Immunity via Recruiting Methyltransferase Prmt5. 33416213_PRMT5 promotes progression of endometrioid adenocarcinoma via ERalpha and cell cycle signaling pathways. 33450196_MAT2A Inhibition Blocks the Growth of MTAP-Deleted Cancer Cells by Reducing PRMT5-Dependent mRNA Splicing and Inducing DNA Damage. 33462997_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) activates WNT/beta-catenin signalling in breast cancer cells via epigenetic silencing of DKK1 and DKK3. 33495409_PRMT5 regulates colorectal cancer cell growth and EMT via EGFR/Akt/GSK3beta signaling cascades. 33579912_PRMT5 inhibition disrupts splicing and stemness in glioblastoma. 33624332_Biochemical Investigation of the Interaction of pICln, RioK1 and COPR5 with the PRMT5-MEP50 Complex. 33664859_PRMT5 functionally associates with EZH2 to promote colorectal cancer progression through epigenetically repressing CDKN2B expression. 33675123_PRMT5 promotes colorectal cancer growth by interaction with MCM7. 33782401_Profiling PRMT methylome reveals roles of hnRNPA1 arginine methylation in RNA splicing and cell growth. 33795785_Transcriptional perturbation of protein arginine methyltransferase-5 exhibits MTAP-selective oncosuppression. 33829865_PRMT5 Promotes EMT Through Regulating Akt Activity in Human Lung Cancer. 33896016_Myelocytomatosis-Protein Arginine N-Methyltransferase 5 Axis Defines the Tumorigenesis and Immune Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33972717_Arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 methylates and stabilizes KLF5 via decreasing its phosphorylation and ubiquitination to promote basal-like breast cancer. 34026434_PRMT5 Enables Robust STAT3 Activation via Arginine Symmetric Dimethylation of SMAD7. 34033176_An AKT/PRMT5/SREBP1 axis in lung adenocarcinoma regulates de novo lipogenesis and tumor growth. 34103528_PRMT5-mediated arginine methylation activates AKT kinase to govern tumorigenesis. 34358446_Molecular basis for substrate recruitment to the PRMT5 methylosome. 34476262_METTL3 Intensifies the Progress of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Modulating the m6A Amount of PRMT5 and PD-L1. 34476934_PRMT5 promotes inflammation of cigarette smoke extract-induced bronchial epithelial cells by up-regulation of CXCL10. 34522232_PRMT5 disruption drives antitumor immunity in cervical cancer by reprogramming T cell-mediated response and regulating PD-L1 expression. 34531375_PRMT5 regulates cell pyroptosis by silencing CASP1 in multiple myeloma. 34712735_Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Promotes the Migration of AML Cells by Regulating the Expression of Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor B4. 35046516_PRMT5 confers lipid metabolism reprogramming, tumour growth and metastasis depending on the SIRT7-mediated desuccinylation of PRMT5 K387 in tumours. 35111150_PRMT5 Inhibition Promotes PD-L1 Expression and Immuno-Resistance in Lung Cancer. 35305370_PRMT5 regulates ATF4 transcript splicing and oxidative stress response. 35333690_Cullin 4A/protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (CUL4A/PRMT5) promotes cell malignant phenotypes and tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 35339800_PRMT5-activated c-Myc promote bladder cancer proliferation and invasion through up-regulating NF-kappaB pathway. 35622143_PRMT5-mediated RNF4 methylation promotes therapeutic resistance of APL cells to As2O3 by stabilizing oncoprotein PML-RARalpha. 36041632_Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 is essential for oncogene product EWSR1-ATF1-mediated gene transcription in clear cell sarcoma. 36167829_TP53 mutations and RNA-binding protein MUSASHI-2 drive resistance to PRMT5-targeted therapy in B-cell lymphoma. 36232624_The Structural Effects of Phosphorylation of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 on Its Binding to Histone H4. |
ENSMUSG00000023110 |
Prmt5 |
415.053942 |
3.4550019017 |
1.788687 |
0.140711260 |
156.507665 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000655741556443606976574248024449590499085450959695395262377045986569399128534194448651341308046194833458741868525976315140724182128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000098863589102223068438468244260187241833646813288720393290918375027577842849239394750154950181064705816424975637346506118774414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
644.5830501 |
65.0185228 |
187.9915698 |
14.1646554 |
| ENSG00000100473 |
1690 |
COCH |
protein_coding |
O43405 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the control of cell shape and motility in the trabecular meshwork. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21886777}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hearing;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is highly conserved in human, mouse, and chicken, showing 94% and 79% amino acid identity of human to mouse and chicken sequences, respectively. Hybridization to this gene was detected in spindle-shaped cells located along nerve fibers between the auditory ganglion and sensory epithelium. These cells accompany neurites at the habenula perforata, the opening through which neurites extend to innervate hair cells. This and the pattern of expression of this gene in chicken inner ear paralleled the histologic findings of acidophilic deposits, consistent with mucopolysaccharide ground substance, in temporal bones from DFNA9 (autosomal dominant nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness 9) patients. Mutations that cause DFNA9 have been reported in this gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. Additional splice variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described but their biological validities have not been demonstrated. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:1690; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
11709536_Areas that express COCH mRNA as determined by in situ hybridization, and to the regions of the inner ear which show histological abnormalities in autosomal dominant sensorineural deafness and vestibular disorder, DFNA9. 12928864_findings suggest that COCH mutations are unlikely to cause abnormalities in secretion and suggest that extracellular events might cause autosomal dominant sensorineural deafness (DFNA9) pathology 14501450_A multigeneration Belgian family with late-onset progressive sensorineural hearing loss--Linkage to DFNA9 was confirmed and mutation analysis revealed a P51S mutation in the COCH gene. 15579465_Cochlin, a protein associated with deafness disorder DFNA9, is present in glaucomatous but absent in normal trabecular meshwork 16835921_A new COCH mutation is identified which causes autosomal dominant hearing impairment. 16951386_Cochlin-specific interferon-gamma-producing T cells are implicated in the etiopathogenesis of autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. 17138532_Haplotype analysis placed the late onset autosomal dominant hereditary non-syndromic hearing loss locus within a 7.6 cM genetic interval defined by marker D14S1021 and D14S70, overlapping with the DFNA9 locus 17264471_the phenotype associated with the novel COCH (G87W) mutation is largely similar to that associated with the P51S and G88E mutation carriers 17368553_Data analysis demonstrated a significant association between vertical corneal striae and the Pro51Ser and Gly88Glu mutations in the COCH gene in DFNA9 families 1, 2, and 3 with cochleovestibular dysfunction. 17561763_This is a report of the audiological and vestibular characteristics of a Dutch DFNA9 family with a novel mutation, I109T, in the LCCL domain of COCH 17926100_A prominent but previously unreported ribbon-like pattern of cochlin in the basilar membrane was demonstrated, suggesting an important role for cochlin in the structure of the basilar membrane. 17944208_All affected family members with a COCH mutation in the vWFA2 domain shared sensorineural hearing loss with full penetrance starting between the second and fifth decade of life. 18312449_novel mutations in the vWFA2 domain of the COCH gene were identified in Chinese families with autosomal dominant sensorineural non-syndromic hearing loss (HL) 9 19013156_The second von Willebrand type A domain of cochlin has affinity for type II collagen, as well as type I and type IV collagens whereas the LCCL-domain of cochlin has no affinity for these proteins. 19098315_These results support the finding that the observed increased cochlin expression in glaucomatous TM is due to relative elevated abundance of transcription factors. 19161137_causative mutation in the COCH gene in American families associated with superior semicircular canal dehiscence.(280-5) 19657184_By RT-PCR, we found that full-length cochlin was expressed in all organs examined, with a splice variant in the heart. By Western blot, we detected short isoforms (11-17 kDa) in the perilymph. 19933177_Cochlin expression was effective in decreasing outflow facility and increasing pressure in cultured anterior segment, suggesting possible involvement of cochlin in IOP elevation in vivo. 20105107_present in the perilymph, not in cerebrospinal fluid 20228067_study suggests a possible molecular mechanism underlying DFNA9 hearing loss and provides an in vitro model that may be used to explore protein-misfolding diseases in genera 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20447147_The causative gene of autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss in the Korean family and a recurrent mutation in the COCH gene, were identified. 21046548_The onset of the hearing loss, in the 2nd or 3rd decade of life, is earlier than in most DFNA9 families. The progression of hearing loss and vestibular dysfunction in the American family is typical of other DFNA9 families with mutations in this domain. 21774451_The phenotype associated with the I109N COCH mutation is largely similar to that associated with the I109T, P51S, G87W, and G88E mutation carriers. However, subtle differences seem to exist in terms of age of onset and rate of progression. 21886777_Cochlin interacts with TREK-1 and annexin A2. 22139968_The data cannot confirm the association described previously between superior semicircular canal dehiscence and the presence of mutations in COCH gene. 22610276_the instability of mutant cochlin is the major driving force for cochlin aggregation in the inner ear in DFNA9 patients carrying the COCH p.F527C mutation 22931125_Identification of a novel missense mutation in COCH in a Chinese family with autosomal dominant non-syndromic progressive sensorineural hearing loss. 23660400_COCH and SLC26A5 mRNA are expressed in specific structures and cells of the inner ear in archival human temporal bone 23993205_Chinese DFNA9 family associated with novel COCH mutation with genotype-phenotype correlation. 24063017_This study suggests lack of association of both COCH and TNFA with primary open-angle glaucoma pathogenesis. 24275721_new variants in genes such as COCH is associated with nonsyndromic deafness and vestibular dysfunction. 24662630_A new phenotypic and characteristic radiologic feature of DFNA9 has been discovered. 25049087_prominent in the incudomalleal joint, incudostapedial joint, and the pars tensa of the tympanic membrane 25230692_This is the first report showing failure of mutant cochlin transport through the secretory pathway, abolishment of cochlin secretion, and formation and retention of dimers and large multimeric intracellular aggregates 25780252_Targeted exon resequencing of selected genes using next-generation sequencing identified 3 COCH (one known, two novel) mutations in a cohort of hearing loss patients in Japan. 26256111_the impaired post-translational cleavage of cochlin mutants may be associated with pathological mechanisms underlying DFNA9-related sensorineural hearing loss. 26631968_This family is the first case of a truncating COCH variant and supports the hypothesis that COCH haploinsufficiency is not the cause of hearing loss in humans. 26758463_Distinct vestibular phenotypes depending on the location of COCH mutations were demonstrated, and this study correlates a genotype of p.G38D in COCH to the phenotype of bilateral total vestibular loss, therefore expanding the vestibular phenotypic spectrum of DFNA9 to range from bilateral vestibular loss without episodic vertigo to MD-like features with devastating episodic vertigo 27083884_This study showed that Mendelian sensorineural hearing loss exhibits vestibular dysfunction, including DFNA9, DFNA11, DFNA15 and DFNA28. 28005267_COCH expression is significantly downregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28099493_c.889G>A (p.C162Y) Mutation in COCH leads to vestibular dysfunction and autosomal dominant nonsyndromic deafness 9.The p.C162Y mutation causes either disruption of LCCL domain fragment cleavage or aggregation of mutant cochlin. 28116169_A missense mutation in the LCCL domain of COCH was associated with autosomal dominant nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss in a Chinese family. 29305555_Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients displayed lower levels of systemic cochlin LCCL domain with subsequently impaired macrophage response in infected wounds. 29449721_A homozygous nonsense c.292C>T(p.Arg98*) COCH variant was identified in two brothers with prelingual hearing impairment. 30806805_The aim of this study was to carry out a systematic review of all reported hearing and vestibular function data in P51S COCH mutation carriers and its correlation with age.[review] 30904974_we selectively filtered out several reports describing DFNA9 patients with MD-like symptoms caused by COCH mutation 31126177_In 3 families with hearing impairment, whole exome sequencing revealed 3 novel variants in KCNQ4, LHFPL5 and COCH genes. Another variant in a homozygous state (c.116T>A, p.L39X) was identified in the COCH gene which encodes a secretory protein. 32562050_Novel loss-of-function mutations in COCH cause autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. 32635986_Cochlin-cleaved LCCL is a dual-armed regulator of the innate immune response in the cochlea during inflammation. 32939038_Homozygote loss-of-function variants in the human COCH gene underlie hearing loss. 33421658_On the pathophysiology of DFNA9: Effect of pathogenic variants in the COCH gene on inner ear functioning in human and transgenic mice. 33710989_A Novel COCH Mutation Affects the vWFA2 Domain and Leads to a Relatively Mild DFNA9 Phenotype. 34369416_Genotype-phenotype Correlation Study in a Large Series of Patients Carrying the p.Pro51Ser (p.P51S) Variant in COCH (DFNA9): Part I-A Cross-sectional Study of Hearing Function in 111 Carriers. 35020687_Does Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex (VOR) Gain Correlate With Radiological Findings in the Semi-Circular Canals in Patients Carrying the p.Pro51Ser (P51S) COCH Variant Causing DFNA9? Relationship Between the Three-Dimensional Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) and MR/CT Imaging. 35204720_Genotype-Phenotype Correlations of Pathogenic COCH Variants in DFNA9: A HuGE Systematic Review and Audiometric Meta-Analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000020953 |
Coch |
30.611333 |
0.4332567668 |
-1.206706 |
0.271220821 |
20.288767 |
0.00000665903810738243152347014264247349046854651533067226409912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000021371472595121696687499313060953909371164627373218536376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.3835494 |
4.0457771 |
42.6257148 |
6.2375494 |
| ENSG00000100483 |
79609 |
VCPKMT |
protein_coding |
Q9H867 |
FUNCTION: Protein N-lysine methyltransferase that specifically trimethylates 'Lys-315' of VCP/p97; this modification may decrease VCP ATPase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22948820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23349634}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Methyltransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
Enables ATPase binding activity and protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity. Involved in negative regulation of ATPase activity and peptidyl-lysine trimethylation. Located in cytosol. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79609; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; negative regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032780]; peptidyl-lysine methylation [GO:0018022]; peptidyl-lysine trimethylation [GO:0018023]; protein methylation [GO:0006479] |
22948820_METTL21D is the methyltransferase responsible for lysine methylation of VCP. 23349634_METTL21D trimethylates Lys-315 in VCP/p97 in a ASPCR1-dependent manner |
ENSMUSG00000049882 |
Vcpkmt |
49.562053 |
2.0852189235 |
1.060199 |
0.243527276 |
19.043297 |
0.00001277858439536414218576972773311339892643445637077093124389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000039607708037709939488668631213386106537654995918273925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.6215357 |
9.2844683 |
31.6690821 |
3.5052395 |
| ENSG00000100504 |
5836 |
PYGL |
protein_coding |
P06737 |
FUNCTION: Allosteric enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in glycogen catabolism, the phosphorolytic cleavage of glycogen to produce glucose-1-phosphate, and plays a central role in maintaining cellular and organismal glucose homeostasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22225877}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycogen metabolism;Glycogen storage disease;Glycosyltransferase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a homodimeric protein that catalyses the cleavage of alpha-1,4-glucosidic bonds to release glucose-1-phosphate from liver glycogen stores. This protein switches from inactive phosphorylase B to active phosphorylase A by phosphorylation of serine residue 15. Activity of this enzyme is further regulated by multiple allosteric effectors and hormonal controls. Humans have three glycogen phosphorylase genes that encode distinct isozymes that are primarily expressed in liver, brain and muscle, respectively. The liver isozyme serves the glycemic demands of the body in general while the brain and muscle isozymes supply just those tissues. In glycogen storage disease type VI, also known as Hers disease, mutations in liver glycogen phosphorylase inhibit the conversion of glycogen to glucose and results in moderate hypoglycemia, mild ketosis, growth retardation and hepatomegaly. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:5836; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; AMP binding [GO:0016208]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; bile acid binding [GO:0032052]; glucose binding [GO:0005536]; glycogen phosphorylase activity [GO:0008184]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; linear malto-oligosaccharide phosphorylase activity [GO:0102250]; purine nucleobase binding [GO:0002060]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; SHG alpha-glucan phosphorylase activity [GO:0102499]; vitamin binding [GO:0019842]; 5-phosphoribose 1-diphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0006015]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; glycogen catabolic process [GO:0005980]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
15223230_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15223230_Susceptibility to excessive liver glycogen storage in patients with type 1 diabetes. 17705025_Deficiency of liver glycogen phosphorylase is predominantly the result of missense mutations affecting enzyme activity. There are no common mutations and the severity of clinical symptoms varies significantly. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 32126244_The vitamin B6-regulated enzymes PYGL and G6PD fuel NADPH oxidases to promote skin inflammation. 32268899_Description of two GSD VI patients expanding the spectrum of PYGL mutations. 32892177_Glycogen storage disease type VI can progress to cirrhosis: ten Chinese patients with GSD VI and a literature review. 33879691_Glycogen storage disease type VI with a novel PYGL mutation: Two case reports and literature review. 34516362_Long noncoding RNA KCNMB2-AS1 promotes the development of esophageal cancer by modulating the miR-3194-3p/PYGL axis. 34675331_Human hair follicles operate an internal Cori cycle and modulate their growth via glycogen phosphorylase. 35037470_Identification of PYGL as a key prognostic gene of glioma by integrated bioinformatics analysis. 35611851_miR-155-5p regulates hypoxia-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell function by targeting PYGL. |
ENSMUSG00000021069 |
Pygl |
249.870397 |
0.4604114542 |
-1.119004 |
0.111914375 |
100.464794 |
0.00000000000000000000001205202648564425388617077565443232432106020280278649230114742347489548146555193852691445499658584594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000122765984077370037030416455189244621723484127756421491536328134339117745810199266998097300529479980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
151.7383477 |
12.1963187 |
332.0674597 |
18.1138834 |
| ENSG00000100564 |
5283 |
PIGH |
protein_coding |
Q14442 |
FUNCTION: Part of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (GPI-GnT) complex that catalyzes the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine from UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to phosphatidylinositol and participates in the first step of GPI biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16162815, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9463366}. |
Autism spectrum disorder;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Glycolipid biosynthesis; glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16162815, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9463366}. |
This gene encodes an endoplasmic reticulum associated protein that is involved in glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis. The GPI anchor is a glycolipid found on many blood cells and which serves to anchor proteins to the cell surface. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the GPI N-acetylglucosaminyl (GlcNAc) transferase that transfers GlcNAc to phosphatidylinositol (PI) on the cytoplasmic side of the endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5283; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; glycosylphosphatidylinositol-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (GPI-GnT) complex [GO:0000506]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; GPI anchor biosynthetic process [GO:0006506]; protein modification process [GO:0036211] |
26288249_Results from a study on gene expression variability markers in early-stage human embryos shows that PIGH is a putative expression variability marker for the 3-day, 8-cell embryo stage. 29573052_Truncation of PIGH protein was consistent with the utilization of an in-frame start-site at codon 63. In summary, we describe siblings harboring a homozygous c.1A > T variant resulting in defective GPI-anchor biogenesis and highlight the importance of exploring low-coverage variants within autozygous regions. 29603516_This suggests that PIGH mutations may cause a syndrome with developmental delay and autism, but without an epileptic encephalopathy, and should increase the awareness of the potentially deleterious nature of biallelic variants in this gene. 30370942_The GPI-anchor negative phenotype results from loss of mRNA expression of the PIGH gene, which is involved in the first step of GPI-anchor synthesis. Loss of PIGH mRNA expression within these B-ALL cells follows epigenetic silencing rather than gene mutation or deletion. 33156547_PIGH deficiency can be associated with severe neurodevelopmental and skeletal manifestations. 34294787_An epigenetic GPI anchor defect impairs TLR4 signaling in the B cell transdifferentiation model for primary human monocytes BLaER1. |
ENSMUSG00000021120 |
Pigh |
62.496935 |
2.1050743279 |
1.073871 |
0.196724834 |
30.109916 |
0.00000004082384001153906772949050258368630661465203957050107419490814208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000167052918927174017372469820227887105090758268488571047782897949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.5463472 |
10.9389990 |
42.3830969 |
4.0754865 |
| ENSG00000100591 |
10598 |
AHSA1 |
protein_coding |
O95433 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a co-chaperone of HSP90AA1 (PubMed:29127155). Activates the ATPase activity of HSP90AA1 leading to increase in its chaperone activity (PubMed:29127155). Competes with the inhibitory co-chaperone FNIP1 for binding to HSP90AA1, thereby providing a reciprocal regulatory mechanism for chaperoning of client proteins (PubMed:27353360). Competes with the inhibitory co-chaperone TSC1 for binding to HSP90AA1, thereby providing a reciprocal regulatory mechanism for chaperoning of client proteins (PubMed:29127155). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27353360, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29127155}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Stress response;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables ATPase activator activity; Hsp90 protein binding activity; and chaperone binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of ATPase activity. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10598; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; ATPase activator activity [GO:0001671]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032781]; protein folding [GO:0006457] |
12504007_stimulates the inherent ATPase activity of Hsp90 17110338_Hsp90 cochaperones modulate Hsp90-dependent stability of CFTR protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum 20089831_Data propose a model for Aha1 in the Hsp90 ATPase cycle where Aha1 regulates dwell time of Hsp90, and suggest Aha1 activity integrates chaperone function with client folding energetics by modulating ATPase sensitive dimer structural transitions. 22504172_The interaction of Aha1 with Hsp90 and its co-chaperones in rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) and in HeLa cell extracts, was characterized. 22727666_Hsp90 phosphorylation on tyrosine313 promotes recruitment of AHA1, which stimulates Hsp90 ATPase activity, furthering the chaperoning process. 22859491_Modulation of Hsp90 activity by AHA1 regulates VEGF signaling to eNOS and angiogenesis. 25378400_Aha1 may promote disposal of folding defective proteins by the cellular protein quality control. 25486457_These results suggest that differences in the middle domain of Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta may be responsible for the isoform-specific interactions with selected proteins. 28827321_Aha1 colocalized with tau pathology in brain tissue, and this association positively correlated with Alzheimer disease progression. 31299134_Data support the multi-step nature of the Hsp90/Aha1-interaction, where the N-terminal domain of Aha1 interacts with both Hsp90 M domains upon induction of a partially closed conformation of the Hsp90 dimer. In addition, the data indicate that the C-terminal domain of Aha1 can adopt several conformations leading to a dynamic, polymorphic complex. 31782942_Aha-type co-chaperones: the alpha or the omega of the Hsp90 ATPase cycle? 33468990_AHA1 upregulates IDH1 and metabolic activity to promote growth and metastasis and predicts prognosis in osteosarcoma. 35034596_Identification of AHSA1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Breast Cancer: Bioinformatics Analysis and in vitro Studies. 35757728_The Prognostic and Immunotherapeutic Significance of AHSA1 in Pan-Cancer, and Its Relationship With the Proliferation and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000021037 |
Ahsa1 |
495.210484 |
2.0495563142 |
1.035312 |
0.086465546 |
142.801322 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000649637632939163934364786760103311404665023311196452200275519928583591641277009171462786946138479038381774444133043289184570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000091233600972236534826444667805450238711413307947725981222932099823542929155759031046440954426657299336511641740798950195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
649.0574791 |
60.2836840 |
318.5176940 |
21.7490402 |
| ENSG00000100599 |
79890 |
RIN3 |
protein_coding |
Q8TB24 |
FUNCTION: Ras effector protein that functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange (GEF) for RAB5B and RAB31, by exchanging bound GDP for free GTP. Required for normal RAB31 function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12972505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21586568}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;GTPase activation;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
Summary: This protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RIN family of Ras interaction-interference proteins, which are binding partners to the RAB5 small GTPases. The protein functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange for RAB5B and RAB31. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:79890; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; negative regulation of mast cell chemotaxis [GO:0060755]; negative regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002091]; regulation of vesicle size [GO:0097494]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12972505_RIN3 biochemically characterized as the stimulator and stabilizer for GTP-Rab5 plays an important role in the transport pathway from plasma membrane to early endosomes 18486601_Tyrosine-phosphorylation signals are involved in the RIN3 activation and translocation to early endocytic vesicles. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21586568_RIN3 specifically acts as a GEF for Rab31. 23185384_RIN3 is a negative regulator of mast cell responses to SCF 24945404_The study reports a novel association between a variant within RIN3 and lower limb-bone mineral density and note its previous association with risk of Paget's disease. 25701875_RIN3 may contribute to Paget's disease of bone susceptibility by affecting osteoclast function. 26296892_discovered novel interaction candidates for CD2AP and characterized subtle yet significant differences in the recognition preferences of its three SH3 domains for c-CBL, ALIX, and RIN3 28738127_RIN3 may be involved in endolysosomal transport-a process known to be important to development of early onset AD. 30726512_Genetic Variation in RIN3 in the Belgian Population Supports Its Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Paget's Disease of Bone and Modifies the Age of Onset. 35241726_The neuronal-specific isoform of BIN1 regulates beta-secretase cleavage of APP and Abeta generation in a RIN3-dependent manner. |
ENSMUSG00000044456 |
Rin3 |
168.222563 |
2.1962779094 |
1.135061 |
0.214209600 |
27.654276 |
0.00000014505107856432340394226389659881881755154608981683850288391113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000563260699713079051205975606581022319119256280828267335891723632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
227.9102108 |
27.8980511 |
104.2522065 |
9.6241370 |
| ENSG00000100626 |
57452 |
GALNT16 |
protein_coding |
Q8N428 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the initial reaction in O-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis, the transfer of an N-acetyl-D-galactosamine residue to a serine or threonine residue on the protein receptor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22186971}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lectin;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
Enables polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity. Involved in protein O-linked glycosylation via serine and protein O-linked glycosylation via threonine. Predicted to be located in Golgi membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57452; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0004653]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493]; protein O-linked glycosylation via serine [GO:0018242]; protein O-linked glycosylation via threonine [GO:0018243] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31286696_rs2105269 and rs72625676 were associated with higher breast cancer (BC) risk in younger patients with age =51. For rs1275678 polymorphism, there was a significantly decreased risk of BC among older patients. rs2105269 was associated with tumor size and lymph node metastasis. Study suggests that GALNT16 polymorphisms are associated with BC susceptibility in Chinese population. 34452628_Circ-GALNT16 restrains colorectal cancer progression by enhancing the SUMOylation of hnRNPK. |
ENSMUSG00000021130 |
Galnt16 |
74.157748 |
0.1084283866 |
-3.205186 |
0.596117579 |
25.028111 |
0.00000056500532253321891283621503446199518805315165081992745399475097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002054058758766086302191555823526414314983412623405456542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3719357 |
5.6539390 |
124.7763294 |
35.1022942 |
| ENSG00000100714 |
4522 |
MTHFD1 |
protein_coding |
P11586 |
FUNCTION: Trifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of three forms of one-carbon-substituted tetrahydrofolate: (6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate and (6S)-10-formyltetrahydrofolate (PubMed:1881876, PubMed:10828945, PubMed:18767138). These derivatives of tetrahydrofolate are differentially required in nucleotide and amino acid biosynthesis, (6S)-10-formyltetrahydrofolate being required for purine biosynthesis while (6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate is used for serine and methionine biosynthesis for instance (PubMed:25633902, PubMed:18767138). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10828945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18767138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1881876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25633902}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Amino-acid biosynthesis;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Histidine biosynthesis;Hydrolase;Ligase;Methionine biosynthesis;Multifunctional enzyme;NADP;Nucleotide-binding;One-carbon metabolism;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Purine biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: One-carbon metabolism; tetrahydrofolate interconversion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10828945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18767138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1881876}. |
This gene encodes a protein that possesses three distinct enzymatic activities, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase and 10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase. Each of these activities catalyzes one of three sequential reactions in the interconversion of 1-carbon derivatives of tetrahydrofolate, which are substrates for methionine, thymidylate, and de novo purine syntheses. The trifunctional enzymatic activities are conferred by two major domains, an aminoterminal portion containing the dehydrogenase and cyclohydrolase activities and a larger synthetase domain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4522; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase activity [GO:0004329]; methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activity [GO:0004477]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004487]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0004488]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity [GO:0004486]; 10-formyltetrahydrofolate biosynthetic process [GO:0009257]; embryonic neurocranium morphogenesis [GO:0048702]; embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis [GO:0048703]; heart development [GO:0007507]; histidine biosynthetic process [GO:0000105]; methionine biosynthetic process [GO:0009086]; methionine metabolic process [GO:0006555]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neutrophil homeostasis [GO:0001780]; one-carbon metabolic process [GO:0006730]; purine nucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0006164]; purine ribonucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0009152]; serine family amino acid biosynthetic process [GO:0009070]; serine family amino acid metabolic process [GO:0009069]; somite development [GO:0061053]; tetrahydrofolate interconversion [GO:0035999]; transsulfuration [GO:0019346] |
12015164_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12384833_Genetic variation in the MTHFD1 gene is associated with an increase in the risk that a woman will bear a child with NTD. 12384833_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14632302_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14647408_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15122597_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15503105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15633187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15633187_Results conclude that women who are 'QQ' homozygote for the MTHFD1 1258G --> A (R653Q) polymorphism are almost three times more likely to develop severe abruptio placentae during their pregnancy than women who are 'RQ' or 'RR.' 15719048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15797993_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15861780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15937947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15953655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16123074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16123074_Women who are MTHFD1 1958AA homozygous are at increased maternal risk for unexplained second trimester pregnancy loss. 16236726_carriers of the MTHFD1-1958A gene allele were more likely to develop choline deficiency on the low-choline diet unless treated with folic acid; premenopausal women carriers showed 15 times increased susceptibility to organ dysfunction on low-choline diet 16315005_Heterozygosity and homozygosity for the MTHFD1 1958G > A polymorphism are genetic determinants of neural tube defect risk. 16315005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16328059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16552426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16712703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17035141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17114913_MTHFR C677T gene polymorphism associated with a predisposition to increased plasma homocysteine levels could constitute a useful predictive marker for macroangiopathy in Chinese Type 2 diabetic patients. 17417062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17417062_Since MTHFD genes are located in 14q24 loci, our findings support the significance of chromosome 1q in etiopathogenesis of schizophrenia. 17436311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17438114_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17449906_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17530705_Observational study of gene-disease association, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17533396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17548676_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17691219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17691219_The results indicate that of the enzymes studied the polymorphisms of folate-dependent enzyme MTHFD1 have pointed to significant differences in intensity of turnover of circulating thiols between AD and PD patients. 17894836_The methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (MTHFD1) 1958G>A variant is not associated with spina bifida risk in the Dutch population. 18221821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18261183_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18261183_The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of two polymorphisms of the methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 (MTHFD1) gene, the A1958G and the G401A variants, on the risk of cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Italian population. 18277167_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18427977_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18635682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18767138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18767138_The Arg653Gln polymorphism decreases enzyme stability and increases risk for congenital heart defects. 18771981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18801628_Data did not show differences in the distribution of MTR 2756A>G and MTHFD1 1958G>A polymorphic variants postmenopausal women with and without depression. The MTR GG genotype exhibited a 5.750-fold increased risk of depression in postmenopausal women. 18801628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18988749_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020309_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19064578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19112534_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19130090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19130090_SNP rs1076991 C > T as a potential risk factor for neural tube defects in a large homogenous Irish population 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19167960_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19167960_These data suggest that polymorphisms in MTHFD1 genes relevant to choline metabolism modulate parameters of choline status when folate intake is restricted. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19493349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19533788_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19619240_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19649727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19649727_The polymorphism distribution of genes encoding MTR, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase and MTHFD1 and MTHFR in patients with larynx cancer, was examined. 19651439_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19683694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706844_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706888_Induction of MTHFD1 antigen is associated with relapsed chronic myeloid leukemia. 19737740_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19774638_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19858780_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19936946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19946345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056620_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20209990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20217437_No significant difference of allele and genotype contributions of the MTHFD1 polymorphism between Alzheimer's disease cases and controls was detected in total samples. 20217437_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20334533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20334533_c.1958 G>A polymorphism unlikely to play a major role in recurrent spontaneous abortion 20374669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20386493_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20447924_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20458436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20544798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20565774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20570913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20594233_G1793A gene polymorphism, HHcy, folate deficiency and low vitamin B(12) concentration were associated with ulcerative colitis in central China. 20615890_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20737570_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20824655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20852008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20890936_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21055808_Data show that a significant association with NHL was observed only for MTHFD1 G1958A. 21055808_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21090237_Polymorphic variants of folate metabolizing genes (C677T and A1298C MTHFR, C1420T SHMT1 and G1958A MTHFD) are not associated with the risk of breast cancer in West Siberian Region of Russia 21254748_the frequencies of MTHFD1 alleles, as well as the frequencies of MTHFD11958 genotypes (GG, GA, AA, GA+AA) do not correlate with Down syndrome pregnancies 21271780_Mutation in Methylenetetrahydrofolate Dehydrogenase gene is associated with thrombosis. 21349258_The genotype and allele frequencies of the MTR Asp919Gly, MTHFR Ala222Val, MTHFD1 Arg653Gln and MTRR Ile22Met gene variants did not display statistical differences between patients with cervical cancer and controls. 21360829_This is the first implication of chr14q23.2-23.3 in the etiology of autism and points to MTHFD1, PLEKHG3, and CHURC1 as potential candidate genes contributing to autism risk. 21537707_MTHFD1 1958GA or AA genotypes were associated with smoking (p = 0.04) and alcoholism (p = 0.03) and were more often found in more advanced stage tumors (p = 0.04) and in patients with a shorter survival (p = 0.03). 22074251_An important role of polymorphisms and gene-gene interactions within the folate pathway in high dose methotrexate-related toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 22339736_Our results among the Brazilian population did not support an association between MTHFD1 G1958A polymorphism and risk for Down synrome. 23685927_Our findings demonstrated the susceptible role of the mutant-type MTHFR C677T, MTHFR A1298C, and MTHFD G1958A in recurrent miscarriage. 23894459_MTHFD1 G1958A polymorphism might be associated with a decreased risk of ALL and other cancers. Meanwhile, the MTHFD1 G401A might play a protective role in the development of colon cancer. 24197977_This meta-analysis suggests that MTHFD1 G1958A polymorphism might not be a risk factor for prostate cancer 24287951_suggested that G401A polymorphism of MTHFD1 was not associated with ovarian cancer risk when using additive 24368157_Prematurity and 1958G>A (MTHFD1)were not associated. Increases in the inflammatory marker CRP (logistic regression, p = 0.055) and BMI (chi-square, p = 0.0113) were associated with AA genotype in women with low folate. 24668664_neither MTHFD G1958A nor TC C776G polymorphisms are an independent risk factor for Down syndrome. However, the combined MTHFD/MTHFR, TC/MTHFR genotypes play a role in the risk of bearing a Down syndrome child in the Chinese population. 24977710_The MTHFD1 G1958A polymorphism might be associated with maternal risk for neural tube defects. 25039261_We find no evidence for association of the MTHFD1 R134K and R653Q polymorphisms with migraine in our Australian case-control population 25079255_methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase gene variants in the cognitive function of ADHD 25099943_ACAT1, ACACA, ALDH6A1 and MTHFD1 represent novel biomarkers in adipose tissue associated with type 2 diabetes in obese individuals. 25118499_Mutated 401A allele of MTHFD1 gene is essential risk factor of fetal hypotrophy in population of Polish women. 25129243_The results indicated the MTHFD1 1958G>A polymorphism to be one of the important genetic determinants of NSCLP risk in South Indian subjects 25213861_methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 (MTHFD1), an enzyme that generates methylenetetrahydrofolate from formate, ATP, and NADPH, functions in the nucleus to support de novo thymidylate biosynthesis. 25304051_G1958A (MTHFD1) polymorphisms showed no association with ischemic heart disease in patients from Yucatan, Mexico 25502174_the present meta-analysis provided evidence of the association between maternal MTHFD1 G1958A polymorphism and neural tube defects susceptibility. 25524527_MTHFD1 1958G > A is significantly associated with the susceptibility of neural tube defects in a Chinese population. 25544792_The MTRR c.66A>G (rs1801394) polymorphism and MTHFD1 c.1958G>A (rs2236225) are associated with increased maternal risk for Down syndrome. [Meta-analysis] 25548164_impact of MTHFD1 loss of function on folate-dependent purine, dTMP, and methionine biosynthesis in fibroblasts with MTHFD1 deficiency 25730024_We found that the compound mutation genotypes MTHFD-G1958A, MTR-A2756G, and RFC1-G80A increased the risk of preterm birth (OR = 2.88, 95%CI = 1.08-7.72, P = 0.028). 26299783_Data suggest impaired folate metabolism down-regulates placenta trophoblast proliferation, viability, invasive capacity, and progesterone secretion; silencing MTHFD1 gene down-regulates cell proliferation but does not alter progesterone secretion. 26343515_polymorphism of SNP loci rs1956545 and rs56811449 as well as a haplotype in MTHFD1 gene could have a role in the occurrence of neural tube defects in the Chinese population 26394717_Paternal, rather than a maternal, transmission bias of MTHFD1 G1958A variant for neural tube defects susceptibility in the offspring. 26803590_B vitamin treatments modify the risk of myocardial infarction associated with a MTHFD1 polymorphism in patients with stable angina pectoris. 26853819_impairments in MTHFD1 activity compromise both homocysteine remethylation and de novo thymidylate biosynthesis, and provide evidence that MTHFD1-associated disruptions in de novo thymidylate biosynthesis lead to genome instability that may underlie folate-associated immunodeficiency and birth defects 27597531_Results propose that MTHFD1 synthetase deficiency does not contribute to tumor initiation in the normal colon, but it limits tumor growth by reducing purine pools and altering expression of genes involved in cell proliferation and inflammation. 27872106_2 common and functional MTHFD1 polymorphisms (rs2236225 and rs1076991) modulate the risk associations of plasma serine and glycine with acute myocardial infarction in patients with stable angina pectoris. 28299500_Our study suggests no significant genetic association of MTHFR (rs1801131, rs1801133) and MTHFD1 (rs8006686) polymorphisms in South Indian Pseudoexfoliation syndrome patients. 28398708_MTHFR 1298CC was significantly associated with AE risk. The MTHFR haplotypes 677C-1298C/677T-1298A and 677T-1298C conferred risk in a progressive manner. MTHFD1 1958G>A was not associated with disease susceptibility. Children with the rs2236225 GA and the rs1801131 CC genotypes were at an increased risk as compared to the reference genotype of rs2236225 GG and rs1801131 28865601_The AA and GA genotypes of MTHFD1 G1958A, TT and GT genotypes of eNOS G894T and the AA and GA genotypes of ACE A2350G are risk factors for congenital heart defects. 28968444_MTHFD1 1958AA genotype is linked to a significantly reduced cancer risk. The 1958GG genotype is associated to PBMCs DNA hypomethylation as compared to the A allele carriership that may exert a protective effect for cancer risk by preserving from DNA hypomethylation 29392422_This study verified three SNPs in three genes (MTHFD1, MTHFR, and MTRR) were associated with neural tube defects risk in an independent Chinese population. 30183434_Our results showed that the differences in MTHFD1 methylation levels were statistically significant between control and essential hypertension subjects. 30343310_Authors found that MTHFD1 expression in the tumor tissues and cells was higher than that of adjacent normal tissues and cells. The survival time of patients with high MTHFD1 expression was shorter than those with low MTHFD1 expression. 30388610_This study is the first to show associations between MTHFD1 1958G>A, RFC-1 80G>A, MTHFR 677C>T, and MTHFR 1298A>C polymorphisms and UPL and to compare the effects of maternal and fetal samples on unexplained pregnancy loss using mother-abortus matched samples of Korean origin. 30459299_MTHFD1 was underexpressed in CCRCC tissue when compared with normal renal tissue. MTHFD1 transfection of human CCRCC Caki-1 cells in vitro inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis, associated with reduced expression of cyclin D1, reduced Akt phosphorylation, and increased expression of Bax/Bcl-2 and p53. 30814086_Hypomethylation of the MTHFD1 promoter is associated with stroke in Chinese hypertensive populations. 30882176_the polymorphism in MTHFD1 G1598A gene could be considered as an important genetic disorder associated with the etiology of male infertility. 30997850_High MTHFD1 expression in HCC indicated poorer prognosis. Combining MTHFD1 with serum AFP improved the accuracy of prognostic prediction. 31099277_Association of methionine synthase (rs1805087), methionine synthase reductase (rs1801394), and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 (rs2236225) genetic polymorphisms with recurrent implantation failure. 31133746_Our finding that MTHFD1 and other metabolic enzymes are chromatin associated suggests a direct role for nuclear metabolism in the control of gene expression. 32238907_CpG-SNP site methylation regulates allele-specific expression of MTHFD1 gene in type 2 diabetes. 32414565_Biochemical analysis of patients with mutations in MTHFD1 and a diagnosis of methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 deficiency. 32443475_Independent and Interactive Influences of Environmental UVR, Vitamin D Levels, and Folate Variant MTHFD1-rs2236225 on Homocysteine Levels. 33382484_A comprehensive association analysis between homocysteine metabolic pathway gene methylation and ischemic stroke in a Chinese hypertensive population. 34544865_Orthogonal genome-wide screens of bat cells identify MTHFD1 as a target of broad antiviral therapy. 34904448_Association Between MTHFD1 1958G > A Variant and non-Syndromic Cleft lip and Palate: An Updated Meta-Analysis. 35100977_Association of MTHFD1 gene polymorphisms and maternal smoking with risk of congenital heart disease: a hospital-based case-control study. 35894196_[Association of maternal MTHFD1 and MTHFD2 gene polymorphisms with congenital heart disease in offspring].', trans 'MTHFD1MTHFD2. |
ENSMUSG00000021048 |
Mthfd1 |
410.833305 |
2.9002439718 |
1.536174 |
0.176665825 |
72.792697 |
0.00000000000000001440087182312694800742176078688552821936371301251786358754714001406682655215263366699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000114032654565103957271448475856980168747924588631276199279795946495141834020614624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
598.6084566 |
67.7684022 |
208.1015753 |
17.3929532 |
| ENSG00000100767 |
89932 |
PAPLN |
protein_coding |
O95428 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable metalloendopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in extracellular matrix organization. Predicted to be located in basement membrane. Predicted to be active in extracellular matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:89932; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198] |
19724244_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30388611_ADAMTS-2, collagen type-1, TIMP-3 and papilin levels of the uterosacral ligament play essential roles in the etiopathogenesis of pelvic organ prolapse among postmenopausal women without stress urinary incontinence. |
ENSMUSG00000021223 |
Papln |
190.860626 |
0.3080041378 |
-1.698978 |
0.230774966 |
51.467721 |
0.00000000000072784029928821615996416448648750248677681551345841626243782229721546173095703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004368817737899175093224497740908423832999207814253850301611237227916717529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.3287242 |
13.9708053 |
293.0576515 |
32.0236634 |
| ENSG00000100802 |
60686 |
C14orf93 |
protein_coding |
Q9H972 |
|
Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within anatomical structure development; cell differentiation; and positive regulation of gene expression. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:60686; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628] |
27864143_RTFC promotes thyroid cancer cell survival under starving conditions, and thyroid cancer cell migration. The R115Q, V205M and G209D RTFC mutants enhance the colony forming capacity of thyroid cancer cells, and are able to transform normal thyroid cells. In summary, our data suggest the roles of RTFC in thyroid carcinogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000022179 |
4931414P19Rik |
45.996266 |
0.3987320767 |
-1.326508 |
0.305668612 |
18.563890 |
0.00001643035650829082839133321591873482248047366738319396972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000050209536658876320722351416225848197427694685757160186767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
26.9556664 |
7.3227055 |
67.7705485 |
12.7755844 |
| ENSG00000100852 |
394 |
ARHGAP5 |
protein_coding |
Q13017 |
FUNCTION: GTPase-activating protein for Rho family members (PubMed:8537347). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8537347}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Membrane;Nitration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Rho GTPase activating protein 5 negatively regulates RHO GTPases, a family which may mediate cytoskeleton changes by stimulating the hydrolysis of bound GTP. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:394; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
14610059_A cell cycle-regulated reduction in endogenous p190 levels is linked to completion of cytokinesis and generation of viable cell progeny. 16469769_precise control of p190-B Rho GTPase-activating protein activity is critical for normal branching morphogenesis during mammary gland development 18996642_ARHGAP5 (the gene encoding p190-B RhoGAP) is a probable target for the amplification at 14q12, and p190-B RhoGAP promotes cells spreading and migration by negatively regulating RhoA activity in Huh-7 hepatocellular carcinoma cells 19822667_Results link Cdk5 to Rho-ROCK signaling via Src and p190RhoGAP and implicate Cdk5 in the regulation of cell contraction, attachment, and migration. 23474761_The expression level of miR-486-5p was inversely correlated with that of ARHGAP5. 23552690_RhoA is down-regulated at cell-cell contacts via p190RhoGAP-B in response to tensional homeostasis. 23653363_Data indicate a role for p120-catenin (amino acids 820-843) domain in the p120-catenin.p190RhoGAP signaling complex assembly and membrane targeting. 24316134_Ectopic expression of p190B suppressed the miR-494-induced EGFR upregulation. 25961434_This newly identified miR-744/ARHGAP5 pathway provides further insight into the progression and metastasis of NPC and indicates potential novel therapeutic targets for NPC. 27231093_only collagen-IV elicits the formation of proteolytically active podosomes through a mechanism involving increased Src phosphorylation, p190RhoGAP-B (also known as ARHGAP5) relocalisation and MT1-MMP (also known as MMP14) cell surface exposure at podosome sites. 28100790_Brazilian Amerindian ancestry compared to Asian, European, and African Genomes.SNPs within or proximal to CIITA (rs6498115), SMC6 (rs1834619), and KLHL29 (rs2288697) were most differentiated in the Amerindian-specific branch. SNPs in ADAMTS9 (rs7631391), DOCK2 (rs77594147), SLC28A1 (rs28649017), ARHGAP5 (rs7151991), and CIITA (rs45601437) in the Asian comparison. 30250020_These results indicate that SIRT1 suppresses migration and invasion of gastric cancer by downregulating ARHGAP5 through an interaction with c-JUN, and these phenomena represent a novel mechanism of the antitumor action of SIRT1. 32483433_Investigation of the role and mechanism of ARHGAP5-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis. |
ENSMUSG00000035133 |
Arhgap5 |
15.032439 |
0.4362584572 |
-1.196745 |
0.498154045 |
5.623472 |
0.01772150841088617964635965051911625778302550315856933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032161498111973441105249094107421115040779113769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6126747 |
2.7136539 |
19.8109246 |
4.4842296 |
| ENSG00000100985 |
4318 |
MMP9 |
protein_coding |
P14780 |
FUNCTION: Matrix metalloproteinase that plays an essential role in local proteolysis of the extracellular matrix and in leukocyte migration (PubMed:2551898, PubMed:1480034, PubMed:12879005). Could play a role in bone osteoclastic resorption (By similarity). Cleaves KiSS1 at a Gly-|-Leu bond (PubMed:12879005). Cleaves NINJ1 to generate the Secreted ninjurin-1 form (PubMed:32883094). Cleaves type IV and type V collagen into large C-terminal three quarter fragments and shorter N-terminal one quarter fragments (PubMed:1480034). Degrades fibronectin but not laminin or Pz-peptide. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P41245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12879005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1480034, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2551898, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32883094}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMP's are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. The enzyme encoded by this gene degrades type IV and V collagens. Studies in rhesus monkeys suggest that the enzyme is involved in IL-8-induced mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells from bone marrow, and murine studies suggest a role in tumor-associated tissue remodeling. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4318; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to cadmium ion [GO:0071276]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular response to UV-A [GO:0071492]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cation channel activity [GO:2001258]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001268]; negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation involved in kidney development [GO:2000697]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; ossification [GO:0001503]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of keratinocyte migration [GO:0051549]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of receptor binding [GO:1900122]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150077]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] |
11168762_involvement of MMPs in microinvasive carcinomas 11410119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11486009_125-kDa urinary gelatinase as being a complex of MMP-9 and NGAL and provides evidence that NGAL modulates MMP-9 activity by protecting it from degradation. 11546917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11557670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11576356_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11688724_secretion in primary human monocytes induced by chemokines 11708786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11742492_Significant association with poor survival by MMP-9. 11756567_results indicate that two kinds of pro-form and active-form matrix metalloproteinases, MMP-2 and MMP-9, and their degradation products, are present in human seminal plasma 11781819_Multiple signaling pathways involved in activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in breast cancer cells 11813159_The CC chemokines CCL2 (MCP-1), CCL3 (MIP-1alpha), and CCL5 (RANTES) stimulated the release of monocyte MMP-9 protein in a bell-shaped dose-dependent manner. 11827968_Exposure of cryptic domains in the alpha 1-chain of laminin-1 by elastase stimulates macrophages urokinase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. 11830485_overexpression of MMP-9 in HTLV-I- infected cells may be in part responsible for the invasiveness of adult T-cell leukemia cells. 11833938_in differentiating trophoblasts Nitric Oxide regulates the induction of MMP-2 and MMP-9 required for invasion during embryo 11839588_shed as membrane vesicle associated components by endothelial cells and this may be a mechanism for regulating focalized proteolytic activity vital to invasive and morphogenic events during angiogenesis 11839746_gelatinolytic activity in situ, in tissue sections of term placenta, is co-localized with gelatinase B 11854622_in pancreatic cancer, invasion into large veins and destroyed type veins could be a risk factor for liver metastasis and that increased expression MMP-2 and MMP-9 were related to such invasion. 11875051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11876767_MMP-9 activity is significantly elevated in SLE patients and correlated with disease activity in males but not females. These results suggest that MMP-9 plays a role in the pathogenesis of SLE. 11890521_Respiratory syncytial virus infection of HEp-2 cells induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression 11916008_C/C homozygosity at the C-1562T polymorphism of the promoter may be protective against coronary artery disease in Koreans. 11916008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11920503_increasing expression and endometrial carcinoma appear closely related 11920505_significantly increased activity seen in plasma of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients 11935310_activity significantly higher in lung cancer cells than uninvolved lung parenchyma; may be involved in tumor progression 11940298_The expression of MMP-9 was significantly increased in mesangial proliferative glomeruli and interstitial vascular walls of IgA nephropathy patients. 11956628_expression of MMP-9 in cervical cancer 11958288_The plasma MMP-9 levels in patients with HCC were significantly higher than those in the normal controls 11971760_Results suggest that gastrin increases MMP-9 expression, which is associated with increased invasion, and this is a putative mechanism regulating remodelling of the gastric epithelium. 11986939_Production of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in early stage B-CLL is suppressed by interferons alpha and gamma. 11994547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11994547_We have determined the functional significance of a variable number tandem repeat and a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the MMP-9 gene on promoter activity and their association with preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM). 11999552_REVIEW: Role of gelatinase B in leukocytosis and stem cell mobilization. 12004062_novel regulation for the proteolytic activation of MMP-9 in human tissue (tissue-associated chymotrypsin-like proteinase, pM9A). 12029498_Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in squamous cell carcinomas of immunosuppressed patients. 12034345_destruction of the surrounding matrix by endometriosis might be caused by various MMPs, which are mainly produced in stromal cells. 12050187_ox-LDL and HDL lipoproteins regulate the production by activated monocytes 12051944_Crystal structure of human MMP9 in complex with a reverse hydroxamate inhibitor 12054499_FGF-2 and TPA induce matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in MCF-7 cells through PKC activation of the Ras/ERK pathway. 12062817_signalling pathways involved in MMP-9 regulation at the maternal-fetal interface 12063180_roughly constitutive TIMP-1 expression opposed to an inducible MMP-9 synthesis in Epstein--Barr virus-immortalized B lymphocytes 12077439_The X-ray crystal structure of the proform of human matrix metalloproteinase MMP9 has been solved to 2.5 A resolution 12081477_evaluation of the effect of increased levels of active MMP-9 in the central nervous system 12082590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12084167_Expression of MMP9 is elevated during PBSC mobilization by G-CSF. 12103254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12105194_Interferons inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation via interferon regulatory factor-1 binding competition with NF-kappa B 12126625_structural basis of the adaptive molecular recognition by MMP9 12127674_No allelic associations have been found between multiple sclerosis and the CA microsatellite marker in the promoter region of the gelatinase B gene in Belgian study populations. 12127674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12183836_plasma levels are increased during G-CSF induced hematopoietic stem cell mobilization 12193399_data indicate the involvement of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and matrix metalloproteinase 9 in the cervical ripening 12205736_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12208863_role of MMP9 in aortic aneurysms 12219015_Fibroblasts promote breast cancer cell invasion by upregulating tumor matrix metalloproteinase-9 production. 12231534_Primary GBMs were significantly more likely than secondary GBMs to contain active MMP-9. Active MMP-9 expression occurred in 83% of the EGFRvIII-immunopositive tumors only. 12235127_Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction inhibits migration of osteoclast-like cells by down-regulating MMP-9. 12235151_MMP9 activation is increased by Eph B4 receptor stimulation in human cells 12356580_mmp-9 production in bronchial epithelial cells is inhibited by S-nitrothiols 12372334_Bombesin-dependent pro-MMP-9 activation in prostatic cancer cells requires beta1 integrin engagement 12376362_MMP-9 level and TIMP-1 levels increased after birth but are not linked to bronchopulmonary dysplasia outcome; low MMP-2 level at birth is associated with the development of BPD 12398893_Block of mmp9 induction via vegfr-1 inhibition could be useful for the prevention of tumor metastasis in lung. 12414663_PTEN suppresses hyaluronic acid-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in U87MG glioblastoma cells through focal adhesion kinase dephosphorylation. 12431239_MMP-9 expression showed a tendency toward an adverse outcome of Hodgkin's lymphoma 12431981_MMP9 expression is regulated by MTA1 via histone-dependent and independent mechanisms in human cells 12437116_ILK activity is aassociated with upregulation of MMP-9 mRNA levels during podocyte stress 12443715_thrombospondin-1 plays a role in the up-regulation of MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer 12444074_data indicate that matrix metalloproteinase-9 is produced by the amnion but not the chorion in response to lipopolysaccharide; tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta appear to upregulate its production by the amnion 12452001_The expression of MMP-9 was positively related to the tumor invasiveness and metastasis in gastric cancers 12464265_HBV infection of hepatocytes and HepG2 cells affected the upregulation of MMP-9 expression and MMP-9 activation and, increased the invasion potential by plasmin, this is a report showing that an HBV infection is linked to the upregulation of MMP-9 in HCC 12471459_MMP-9 plays an important role in inflammatory peripheral neuropathy probably as means for inflammatory cell invasion 12479097_The over-expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 may play a key role in invasion and lymph-node metastasis of in squamous carcinoma of the cervix. 12479099_Increase of CD44s, MMP-9, and Ki-67 were involved in the growth and local invasion of osteosarcoma. 12559990_data demonstrated a moderate elevation of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and significant upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 in stable cell lines overexpressing gamma-synuclein 12586837_Details of cleavage of pro-MMP-9 by MMP-26, facilitating the efficient cleavage of fibronectin by MMP-9, and promoting invasiveness of ARCaP cells across fibronectin or type IV collagen 12587534_matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 and membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase mRNA expression in endometriosis was higher than in normal endometrium whereas E-cadherin, alpha- and beta-catenin mRNA expression was not suppressed in endometriosis 12589095_MMP-9 may contribute to eosinophil and mast cell migrations into nasal polyp tissue. 12606037_Arfaptin 1 inhibits ADP-ribosylation factor-dependent secretion of this enzyme induced by phorbol ester in fibrosarcoma cells. 12612199_significant increase of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the urine of children with acute pyelonephritis. 12615834_In the recurrent implantation failure group, the MMP score and IL-1beta concentration were significantly higher than those in the control group, whereas concentrations of IFN-gamma and IL-10 were significantly lower. 12626459_elevated pro-MMP-9 enzyme during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease may reflect vascular remodeling or an inflammatory response to a microbial agent, suggesting a pathophysiological role for MMP-9 in coronary aneurysm formation. 12642591_triple-helical peptides are highly selective substrates for and are hydrolyzed by human MMP2 and MMP9 12651627_not expressed by intestinal myofibroblasts in inflammatory bowel disease. 12663332_Membrane-bound MMP-9 on PMN may play pathogenetic roles in inflammatory lung diseases 12668489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12671895_MMP-9 induction by H. pylori may play an important role in gastric inflammation, ulcer formation, and carcinogenesis. 12704537_The purpose of this study was to evaluate the roles of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) with regard to varicose veins (VVs). 12712078_Chorioamnionitis is associated with increased lung type IV collagenase levels in the ventilated preterm infant. Antenatal lung inflammation with up-regulation of MMP-9 may be important in the pathogenesis of chronic lung disease. 12717622_MMP9 is activated through an oxidative pathway in pneumococcal meningitis 12717827_The interaction between MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in the processes of gastric tumor invasion and metastasis is that MMP-9 mainly promotes tumor invasion and metastasis and TIMP-1 inhibits functions of MMP-9. 12724312_matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation and association with integrin are inhibited by ganglioside GM3 12727228_Data demonstrate that blockade of the ERK pathway suppressed the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 3, 9, and 14, and CD44, and markedly inhibited the invasiveness of tumor cells. 12728308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12728308_Polymorphisms of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene influences the development of coronary artery disease. 12745093_Requirement for PKC-dependent NF-kappaB activation for induction of MMP-9 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 12750540_MMP-9 plasma level was significantly higher in patients undergoing thrombolytic therapy whose arteries were not recanalized; MMP-9 may be associated with the formation of a thrombolytics-resistant thrombus 12753719_MMP-9 and LM-R are useful indexes for predicting the metastasis and prognosis of breast cancer. 12769333_MMP9 is activated by SDF1 in bone marrow cells, causing release of soluble Kit-ligand and transfer of hematopoietic stem cells from a quiescent to a proliferative niche 12789238_Subepithelial basement membrane immunoreactivity for matrix metalloproteinase 9: association with asthma severity, neutrophilic inflammation, and wound repair. 12791318_PBMCs from SLE patients expressed a significantly higher activity of MMP-9 and spontaneously released higher levels of MMP-9, as compared to healthy donors 12810681_NF kappa B plays a in the regulation of MMP-9 expression and the ability of dykellic acid to suppress phorbol myristate acetate induction of MMP-9, with decreased MMP-9 promoter activity and mRNA expression. 12811828_results strongly support that sTNF up-regulates in an autocrine manner PAI-1 and MMP-9 syntheses during promyelocyte to monocyte differentiation; in more advanced differentiated stages, released sTNF is not a major determinant of PAI-1 and MMP-9 syntheses 12824186_a negatively charged peptide motif within the catalytic domain of MMP9 mediates binding to leukocyte beta 2 integrins 12830465_2.2 kb of the promoter region and all 13 exons (3.3 kb) of MMP9 genomic DNA were scanned for polymorphisms. There is a possible role for the (CA)n repeat in renal disease. 12830465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12847101_proMMP-9 has a novel role in providing a cellular switch between stationary and migratory cell phases 12850503_vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in osteolytic lesions of bone co-relates well with the extent of bone destruction and local recurrence 12861851_MMP-9 released from neutrophils may be involved in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma and COPD. 12865405_HGF, SDF-1, and MMP-9 have roles in stress-induced human CD34+ stem cell recruitment to the liver 12866035_high levels of plasma MMP-9 activity is associated with evidence of recurrence in breast cancer 12874388_integrin alphavbeta3 cooperates with metalloproteinase MMP-9 in regulating migration of metastatic breast cancer cells 12914776_Ultraviolet A downregulates MMP-9 in keratinocytes. 12921631_MMP-9 may not only play a role in the pathogenesis of COPD, but also relate to FEV(1.0)% of prediction and RV/TLC%. 12947332_GDNF upregulates expression and enzymatic activity of MMP-9 through different signaling pathways. GDNF modulates MMP-9 expression and activation, and this may promote pancreatic cancer invasion. 12949792_Upregulation of mmp-9 ia assiciated with neoplasm invasiveness in Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancers 12952836_The present results indicate that MMP-2 can be helpful in diagnosing Takayasu arteritis [TA] and that MMP-3 and MMP-9 can be used as activity markers for TA 12958623_oxidative stress-dependent MMP-9 induction in brain capillary endothelial cells was accompanied by a significant increase in the NF-kappaB localized in the nuclei 12960156_monocyte matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -9 are differentially regulated by interferon gamma through tumor necrosis factor-alpha and caspase 8 12960961_Data show that tissue plasminogen activator upregulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 in cell culture and in vivo, and that this is mediated by the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. 12967855_Both active gelatinases were detected in tears of severe corneal ulcer or severe ocular burn cases. The active form of gelatinase expression may be related to the severity of ulceration. 12970724_palpable tumours demonstrated significantly more MMP-2 and significantly less MMP-9 expression than nonpalpable tumours 14500349_MMP9 plays a role in the release of biologically active VEGF and consequently in the formation of ascites in ovarian cancer. 14520690_Increased plasma MMP-9 is associated with colorectal cancer 14550288_gelatinase B and neutrophil collagenase cleave MIG and IP-10 14550924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14551878_specific up-regulation of MMP-9 in the erythema migrans skin lesions of patients with acute Lyme disease; may play a role in the dissemination of B. burgdorferi. 14561155_an overview of mmp-9 gene expression in different cell types, from the triggering of cell-surface receptors, to the activation of cytoplasmic mediators and transcription factors responsible for the activation of MMP-9 promoter--REVIEW 14581136_Induction of MMP-9 secretion is related to the inflammation including apoptosis of keratinocytes resulting from UVB irradiation. 14605329_Although MMP-9 level predicts parenchymal brain hemorrhages after tPA treatment, no relationship exists with the C-1562T polymorphism, probably because this mutation is not functional in response to cerebral ischemia in vivo 14605329_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14607966_MMP-9 within tuberculous granuloma is associated with tissue destruction; monocytic cells packed together at the center of tuberculous granuloma exhibit strong cytoplasmic staining for MMP-9, but not TIMP-1. 14624478_first report to show that cultured HUVE constitutively express MMP9 and that this secretion is restricted to very early-passage cells 14633819_Plasma MMP-9 concentrations decrease aafter insulin infusion. 14644158_RhoA induced the expression of MMP-9; clustering of MMP-9 was observed in advancing lamellipodia at the forefront of endothelial cells, where this proteinase colocalized with RhoA and CD44 14661062_MMP-9 inhibition activity of resveratrol and its inhibition of JNK and PKC-delta may have a therapeutic potential in cancer. 14661256_effect of titanium, zirconia and alumina ceramics on activity and secretion in human osteoblasts 14668033_MMP-9 and su PAR levels might be used as a marker for disease activity and may contribute to blast cell dissemination. MMP-9 and suPAR may be target molecules in the strategy of treatment of AML. 14675172_in wounded keratinocytes, upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 depends on two distinct pathways: Rac1 and/or Cdc42 that control the activation of p38[MAPK] and RhoA activation that is required for stimulation of JNK. 14676438_Data show that matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human lung parenchyma is associated with cigarette smoking and with obstruction of airflow, suggesting that MMP-9 may play a role in the pathogenesis of COPD. 14681642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14687896_The analysis of MMP-9 in synovial fluid samples can reveal the inflammatory condition of the knee joints with gouty arthritis 14697951_Serum MMP-9 does not relate to the late phase of hepatic ischmeic reperfusion injury after human orthotopic liver transplantation. 14705229_stimulated expression of MMP-1 and MMP-9 may contribute to the invasive activity and the bone and cartilage loss in pigmented villonodular synovitis 14719079_The presence of MMP-9 was found in endometrial cancer, correlating with estrogen receptor alpha and uteroglobin levels. 14744773_MMP-26 was colocalized with MMP-9, TIMP-2, and TIMP-4 in breast cancer cells. 14766231_MMP-9 release from eosinophils is regulated by signaling through p38 MAP kinase 14767860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14767860_The -1562C-->T polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinase-9 was associated with bone mineral density in Japanese men 14963289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14973177_MMP and TIMP may be involved in the feto-neonatal development and may contribute to the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and/or intraventricular hemorrhage in critically ill preterm neonates 14981939_Various growth factors induce migration of human non-small cell lung cancer cells in the presence of extracellular matrix (ECM) components MMP-2 and MMP-9. 14982353_polymorphism in the promoter region may not have a relationship with implant loss 14983226_MMP-9 seems to be involved in ischemia/reperfusion injury during human liver transplantation 14990702_downregulated by Cytomegalovirus IL-10 activity in uterine microvascular endothelial cells and differentiating-invading cytotrophoblasts 15009705_the coordinated modulation of MMP-9 transcription via the TRE and the KRE-M9 elements is important in epidermal and mesenchymal tissues. 15015767_MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions are prognostic factors predicting the recurrence of meningioma, independent of proliferative potential. 15022328_Elevated serum MMP-9 in systemic lupus erythematosus may reflect neuropsychiatric involvement, particularly cognitive dysfunction. Serum MMP-9 concentration may be associated with small-vessel cerebral vasculopathy and risk of cerebral ischemia. 15033492_MMP3, MMP9, and TGFbeta1 are important for the modulation, composition, and maintenance of the ECM in oral squamous cell carcinoma 15034761_MMP-9 may have a role in the higher migrational capacity of CB CD34(+) cells, which may be beneficial to homing of these cells to the BM environment. 15064242_Nitric oxide concentrations could impact on capillary formation via a combination of direct effects on MMP activation and by altering the distribution or abundance of Cav-1 in tumor angiogenesis. 15067014_MMP-2 or MMP-9 mediated tumor cell invasion requires integrin cytoplasmic-tail motif EKQKVDLSTDC 15070833_cleave IGFBP-1 at (145)Lys/Lys(146), resulting in a small (9-kDa) C-terminal peptide of IGFBP-1 in first trimester decidua 15075244_membrane location can influence MMP9 activity in vitro and in vivo, and confirmation of the relevance of stromal-associated, but not tumor-bound MMP9 in mediating tumor-induced angiogenesis 15084374_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15085249_Observational study of gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15094060_sICAM-1 was processed distal to Arg441, indicating that MMP-9, docking to ICAM-1, contributes to sICAM-1 shedding and attenuation of the shear stress-induced upregulation of ICAM-1. 15105396_Endometriosis-associated increase in proteolysis and imbalance between of MMP-9 and of TIMP-1 in culture medium of endometrial tissue may reflect in vivo enhanced capacity of this tissue to break down the extracellular matrix in host tissues. 15118287_MMP-9 was increased regionally in the infarct-related coronary artery, at 11.8 ng/ml vs 8.2 ng/ml in the ascending aorta (p |
ENSMUSG00000017737 |
Mmp9 |
17472.430772 |
25.1645565694 |
4.653321 |
0.023326944 |
55790.540004 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33976.0597837 |
516.2186144 |
1359.7501665 |
19.4257609 |
| ENSG00000100994 |
5834 |
PYGB |
protein_coding |
P11216 |
FUNCTION: Glycogen phosphorylase that regulates glycogen mobilization (PubMed:27402852). Phosphorylase is an important allosteric enzyme in carbohydrate metabolism (PubMed:3346228). Enzymes from different sources differ in their regulatory mechanisms and in their natural substrates (PubMed:3346228). However, all known phosphorylases share catalytic and structural properties (PubMed:3346228). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27402852, ECO:0000303|PubMed:3346228}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Allosteric enzyme;Carbohydrate metabolism;Direct protein sequencing;Glycogen metabolism;Glycosyltransferase;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a glycogen phosphorylase found predominantly in the brain. The encoded protein forms homodimers which can associate into homotetramers, the enzymatically active form of glycogen phosphorylase. The activity of this enzyme is positively regulated by AMP and negatively regulated by ATP, ADP, and glucose-6-phosphate. This enzyme catalyzes the rate-determining step in glycogen degradation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5834; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; glycogen phosphorylase activity [GO:0008184]; linear malto-oligosaccharide phosphorylase activity [GO:0102250]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; SHG alpha-glucan phosphorylase activity [GO:0102499]; glycogen catabolic process [GO:0005980] |
17393985_Brain-type glycogen phosphorylase is expressed in non-small-cell lung carcinoma, particularly adenocarcinomas, and is an independent poor prognostic factor. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20482380_Significant increase in plasma glycoprotein BB in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22818785_GPBB is a valuable biological marker to predict the prognosis in patient with acute coronary syndrome. 22838188_H-FABP and GPBB can contribute to early acute myocardial infarction diagnosis and can distinguish acute myocardial infarction from acute coronary syndrome 27402852_the bGP structures reveal molecular features unique to the brain isozyme that provide a deeper understanding of the differences in the activation properties of these allosteric enzymes by the allosteric effector AMP. 27660393_disulfide bond acts as a redox switch that precludes the allosteric activation of the enzyme by AMP without affecting its activation by phosphorylation. This unique regulatory feature of bGP sheds new light on the isoform-specific regulation of glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen metabolism. 27965358_Using cysteine chemical labeling, mass spectrometry, and site-directed mutagenesis approaches, we show that thiram (and certain of its metabolites) alters the activity of bGP through the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond (Cys(318)-Cys(326)), known to act as a redox switch that precludes the allosteric activation of bGP by AMP. 29030420_The mean plasma GPBB levels were higher in acute ischemic stroke cases than in controls. 29845265_PYGB siRNA exerted an inhibitory effect on the cell viability of the human osteosarcoma cells MG63 and HOS by blocking the Caspase/Bcl and CDK1 signaling pathway, highlighting novel potential therapeutic methods for treating osteosarcoma. 30106110_PYGB silencing suppressed the growth and promoted the apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by affecting the NFkappaB/Nrf2 signaling pathway. 31536495_we identify PYGB as a novel metabolic target with potential applications in the management and/or prevention of metastasis in breast cancer. 31627092_Authors showed that PYGB was upregulated in ovarian cancer tissue and high level of PYGB expression is markedly correlated with poor prognosis of ovarian cancer patients. PYGB knockdown significantly suppressed ovarian cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration. 31678828_This method allows absolute quantitative measurement when conventional calibration curve fails to provide accurate estimation of cardiac biomarkers, especially at low and high concentration ranges. Under an optimised condition, the LOD of our SERS-based muPAD was identified at 8, 10, and 1pgmL(-1), for GPBB, CK-MB and cTnT, respectively, which is well below the clinical cutoff values. 32191839_PYGB facilitates cell proliferation and invasiveness in non-small cell lung cancer by activating the Wnt-beta-catenin signaling pathway. 32462986_PYGB Promoted Tumor Progression by Regulating Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Gastric Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000033059 |
Pygb |
1162.774264 |
2.0926621881 |
1.065339 |
0.051049034 |
438.980263 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018045999998083178356748273951383490650576404153691609574165503806678678328535890470338495173391982527451056733995445235085358706500351525494981396622240637045287402997750256301629569111259073776341958901222714865542134178395328915418 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007419469637094922054461537236295680589636428149322265948443938749097873670889877177298539418708115107504329149404056342342030508814504392531808412122186942038001600112690233436563796975317979643935507069792474277094108487342704908395 |
Yes |
Yes |
1609.4973758 |
50.5964169 |
774.5837664 |
19.1115375 |
| ENSG00000101004 |
22981 |
NINL |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2I6 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the microtubule organization in interphase cells. Overexpression induces the fragmentation of the Golgi, and causes lysosomes to disperse toward the cell periphery; it also interferes with mitotic spindle assembly. May play a role in ovarian carcinogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12852856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16254247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18538832}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in microtubule anchoring at centrosome. Located in cytosol; intercellular bridge; and microtubule cytoskeleton. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22981; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; microtubule anchoring at centrosome [GO:0034454] |
16254247_Overexpression of ninein and the ninein-like protein NIP induces fragmentation of the Golgi and causes lysosomes to disperse toward the cell periphery. 17403670_results indicate that ninein-like protein expression is cell cycle-dependent and regulated by anaphase-promoting cyclosome complex-mediated protein degradation 18538832_Overexpression of Nlp in ovarian tumors raises the possibility that Nlp may play a role in ovarian carcinogenesis. 18826961_Nlp(isoB)interacts with USH2A and lebercilin. 19509300_BRCA1 interaction of Nlp might be required for the successful mitotic progression, and abnormalities of Nlp lead to genomic instability. 19724857_Nlp overexpression might contribute to the development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 20093778_Nlp abnormalities may contribute to genomic instability and tumorigenesis and might serve as a potential biomarker for clinical diagnosis and as a therapeutic target. 20864540_regulation of Nlp by Aurora B is critical for the completion of cytokinesis, providing novel insights into understanding the machinery of cell cycle progression. 20890132_findings demonstrate that Cdc2/cyclin B1 is a key regulator in maintaining appropriate degradation and subcellular localization of Nlp, providing novel insights into understanding on the role of Cdc2/cyclin B1 in mitotic progression 21505454_This review summarises our current knowledge of physiological roles of Nlp, with an emphasis on its potentials in tumourigenesis. 22353935_Breast cancer patients with high expression of Nlp were likely resistant to the treatment of paclitaxel. 26485645_these data support a model where CC2D2A associates with NINL to provide a docking point for cilia-directed cargo vesicles, suggesting a mechanism by which transition zone proteins can control the protein content of the ciliary compartment. 26805762_Upon UVC radiation, Nlp interacts with XPA and ERCC1, and enhances their association |
ENSMUSG00000068115 |
Ninl |
156.779873 |
0.0719381818 |
-3.797098 |
0.820208590 |
16.895712 |
0.00003949070191020192746199010680463459266320569440722465515136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000115148708058984683682418603822839031636249274015426635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.8118593 |
15.5688980 |
268.3990669 |
154.2327401 |
| ENSG00000101017 |
958 |
CD40 |
protein_coding |
P25942 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFSF5/CD40LG (PubMed:31331973). Transduces TRAF6- and MAP3K8-mediated signals that activate ERK in macrophages and B cells, leading to induction of immunoglobulin secretion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P27512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31331973}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. The encoded protein is a receptor on antigen-presenting cells of the immune system and is essential for mediating a broad variety of immune and inflammatory responses including T cell-dependent immunoglobulin class switching, memory B cell development, and germinal center formation. AT-hook transcription factor AKNA is reported to coordinately regulate the expression of this receptor and its ligand, which may be important for homotypic cell interactions. Adaptor protein TNFR2 interacts with this receptor and serves as a mediator of the signal transduction. The interaction of this receptor and its ligand is found to be necessary for amyloid-beta-induced microglial activation, and thus is thought to be an early event in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Mutations affecting this gene are the cause of autosomal recessive hyper-IgM immunodeficiency type 3 (HIGM3). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:958; |
CD40 receptor complex [GO:0035631]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; B cell mediated immunity [GO:0019724]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; CD40 signaling pathway [GO:0023035]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002768]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000353]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes [GO:0048304]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090037]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035666] |
11042507_Review. In some cases of CLL the malignant cells express both CD40 and CD154. Implications for autoimmunity and therapy are discussed. 11714772_The capacity of natural killer cells to induce B cell activation is dependent on the interaction of CD40 with its ligand CD154. 11714804_A CD40 molecule with mutated nonfunctional signaling domains acts as a dominant negative inhibitor and effectively prevents NF-kB activation and the induction of gene expression changes. 11751974_Ceramide-rich membrane rafts mediate CD40 clustering in b lymphocytes 11792123_CD40 ligation induces macrophage IL-10 and TNF-alpha production: differential use of the PI3K and p42/44 MAPK-pathways. 11817328_CD40:CD40L interactions in X-linked and non-X-linked hyper-IgM syndromes. 11826760_CD40 and CD40L are important in autoimmunity and other immune processes. At least 5 signal transduction pathways are involved. 11830495_CD40 activation induces p53-dependent VEGF secretion and cell migration in multiple myeloma cells. 11830590_Critical role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and NF-kappa B in interferon-gamma -induced CD40 expression in microglia/macrophages. 11867568_Dissection of B cell differentiation during primary immune responses in transgenic mice expressing the human CD40 antigen 11870634_The selective triggering of CD40 on keratinocytes in vivo enhances cell-mediated immunity. 11876766_High constitutive expression of CD40 on salivary gland epithelial cells from Sjogren syndrome indicated their intrinsic activation. It was also expressed by lymphocytes, ductal epithelium and endothelium, but not other cells. 11877469_Short-circuiting long-lived humoral immunity by the heightened engagement of CD40. 11891278_Latent sensitivity to Fas-mediated apoptosis after CD40 ligation may explain activity of CD154 gene therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia 11981834_Absence of CD40/CD40L interactions results in increased susceptibility to disseminated infection with C. albicans through decreased NO-dependent killing of Candida by macrophages. 12011072_clustering of CD40 ligand is required to form a functional contact with CD40 12039918_IL-1 plays a prominent role in the inflammatory response initiated by CD40 ligation in intact human skin. 12070030_Studies of the mechanism of CD40-mediated apoptosis of human Burkitt lymphoma cell lines revealed an increase in bax messenger RNA with a subsequent increase in Bax protein in the mitochondria. 12089335_Endogenous Act1 is recruited to the CD40 receptor in human intestinal (HT29) and cervical (HeLa) epithelial cells upon stimulation with CD40 ligand, indicating that Act1 is involved in this signaling pathway. 12093796_plasmin induction of CD40 in human monocytes 12122011_mediates activation of NF-kappa B in airway epithelial cells 12149421_CD40 and CD80 molecules were observed to play a specific role in the induction of cytotoxic function but not in IFN-gamma production of IL-2-activated NK effectors. 12165546_Efficient generation of antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells using retrovirally transduced CD40-activated B cells. 12209089_CD40-mediated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation is required for immunoglobulin class switch recombination to IgE 12209092_CD40 engagement enhances eosinophil survival through induction of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 expression: implications for allergic inflammation 12220533_results suggest that in DG75 cells, TRAF3-induced MEK1 activation may be involved in CD40-mediated upregulation of IL-4-driven germline C epsilon transcription 12223522_Treatment of human gingival fibroblasts with human leukocyte elastase down-regulated CD40 expression & binding to CD40 ligand. CD40 reduction by direct proteolysis by HLE was seen in skin & lung fibroblasts (not monocytes, macrophages, & dendritic cells). 12324477_CD27 and CD40 co-stimulatory signals regulated the p53-amplified apoptotic pathway in B cells through the inhibition of p53-independent apoptotic pathway primarily induced by BCR ligation 12433678_CD40 induces human multiple myeloma cell migration via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/NF-kappa B signaling. 12437073_CD40 is a surface receptor through which the activity of Btk can be stimulated in human B cells. 12488500_CD40 ligation on monocytes accelerates the maturation of dendritic cells in the presence of GM-CSF/IL-4 12507785_Incubation of vascular endothelium with CD40L resulted in increased expression of cell adhesion molecules. Consequently, the adhesion of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes to CD40L treated endothelium was increased. 12510151_CD40 has pro- and anti-apoptotic functions in malignant B-cells and epithelial cancers [review] 12576427_CD40 is present in ovarian cancer cells and can be used for targeted gene delivery in a Coxsackie adenovirus receptor-independent. manner 12576441_Expression of this antigen may identify prognostically favorable subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 12593727_the CD40 gene was a new susceptibility gene for GD within certain families because it was both linked and associated with Graves disease 12604404_CD40 triggering enhances fludarabine-induced apoptosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B-cells through autocrine release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gama and tumor necrosis factor receptor-I-II upregulation. 12624779_Expression of CD40, CD54 and HLA-DR were seen in the hair structure including the dermal papilla in alopecia areata. 12626576_CD40L enhances the capacity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-responsive CD8+ T cells to produce IFN-gamma by increasing the number of IFN-gamma-producing CD8+ T cells and the amount of IFN-gamma produced per cell. 12637493_endothelial CD40, through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, regulates cell survival, proliferation, migration, and vessel-like structure formation, all steps considered critical for angiogenesis 12672076_CD40 can costimulate memory T cells and favors IL-10 secretion. 12676820_CD40 is constitutively expressed on platelets and provides a novel mechanism for platelet activation. 12686591_CD40 ligation induced a rise in NF-kappaB activity in hepatocytes 12764232_Patients with acute cerebral ischemia show upregulation of the CD40 system, which might contribute to the known proinflammatory, proatherogenic, and prothrombotic milieu found in these patients. 12778475_A synergistic role is played by the TLR9/CD40 system in the orchestration of CpG-ODN-induced responses in B lymphocytes. 12799532_REVIEW: positive feedback loop linking NFkappaB and CD40 plays an important role in the control of the adaptive immune response, with fundamental implications for immunity and tolerance in vivo. 12810728_CD40 is processed by the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme 12829914_expression profiles and relative contribution in the porcine-human xenogeneic response 12855571_in B cells, Gadd45 beta is induced by CD40 through a mechanism that requires NF-kappa B and this induction suppresses Fas-mediated killing 12857749_Interleukin-10 induction of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression attenuates CD40-mediated interleukin-12 synthesis in human endothelial cells. 12874247_Treatment of cultured human endothelial cells with anti-CD40 antibody (to ligate CD40) results in the expression of several other angiogenesis factors, e.g., fibroblast growth factor-2 and vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptors Flt-1 and Flt-4. 12893749_CD40-deficient dendritic cells from patients with hyper IgM disease exhibit severe impairment of DC maturation that may contribute to the defect of T-cell-mediated immunity 12905492_Immature dendritic cells engulfed apoptotic and necrotic neutrophils, resulting in up-regulation of CD83 and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules, but down-regulation of CD40, CD80, and CD86 14515262_All the apoptotic events induced by BCR triggering are completely reversed by CD40 ligation with anti-CD40 antibody. 14517219_LTbetaR, CD40 and TANK interact with TRAF3 at sites that promote molecular interactions driving specific signaling 14557256_stoichiometry of TRAF1-TRAF2 heteromeric complexes ((TRAF2)2-TRAF1 versus TRAF2-(TRAF1)2) determines their capability to mediate CD40 signaling but has no major effect on TNF signaling 14568936_A distinct response from naive and memory B cells is observed in vitro related to the duration of CD40 stimulation, reflecting the role of each subset in primary and secondary immune responses. 14611700_5'-untranslated region of the CD40 gene may confer genetic susceptibility to Graves' disease in Koreans 14611700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14612943_CD40 expression on gastric carcinoma may be associated with cell survival and elevation of cell motility 14617752_Results indicate that patients with active lupus nephritis exhibit B cell abnormalities that are consistent with intensive germinal center activity, are driven via CD154-CD40 interactions, and may be involved in the production of autoantibodies. 14633128_CD40 may be involved in peritonitis and in the development of late phase mononuclear predominance. 14644094_natural CD40 signaling pathways in B cells 14651941_Signal transduction and transcription factors inducing CD40 expression are described, as are the cis-elements in the CD40 promoter. Mechanisms underlying suppression of CD40 in macrophages/microglia by immunomodulatory agents are also discussed. 14665433_in human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells, CD40 and its downstream MAPKs are located in membrane rafts and that disruption of caveolae or dislodgment of signaling proteins and diminishes MAPK activation and IL-8 and MCP-1 production. 14687897_Patients with diabetes show increased coexpression of CD40 system, especially CD40L, which may create a proinflammatory and prothrombotic milieu for aggravating the development of atherosclerosis. 14695541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14699489_Activation of the CD40/CD40L system in the gut mucosa may trigger a self-sustaining loop of immune-nonimmune cell interactions leading to an antigen-independent influx of T cells that contributes to chronic inflammation. 14742996_beta2-AR agonists strongly inhibited the expression of ICAM-1 and CD40. 14747545_Epstein Barr virus LMP1 drives bfl-1 promoter activity through interactions with components of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)/CD40 signaling pathway; evidence presented that this process is NF-kappa B dependent 14764664_Platelet activation modulates the constitutive expression of CD40 on the surface of platelets; CD40 expression remains constant as demonstrated by flow cytometric analysis. 14976003_During an inflammatory response, CD40-CD154 mediated T helper cell-endothelial cell interaction results in an increased ciruclating monocyte recruitment & activation of these cells on their crossing of the endothelial cell barrier. 14991615_The CD4+ T lymphocyte-dependent antibody response to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides requires CD40-CD40 ligand interaction. 15001471_After CD40-activation, acute lymphocytic leukemia cells released substantial amounts of interleukin-10 (IL-10) but were unable to produce bioactive IL-12. 15069543_reduction in anti-IgM-induced growth inhibition due to altered N-glycosylation may enhance CD40-CD40L-mediated cell survival through TRAF2 which interacts with both IgM and CD40 in HBL-2 cells 15078922_upregulated by HIV-1 vpu in endothelial cells 15102691_CD40 has a role in progression of soft tissue sarcomas 15113760_demonstrate that the strength and persistence of CD40 signaling can induce migration to lymph nodes and secretion of cytokines 15153777_REVIEW: CD40-CD154 interaction can upregulate costimulatory molecules, activate antigen-presenting cells, influence T-cell priming and T-cell-mediated effector functions as well as participate in the pathogenic processing of chronic inflammatory diseases 15187129_ligation of CD40 on EC increased association of Ras with its effector molecules Raf, Rho, and PI3K. But, it was determined that only PI3K was functional for Ras-induced VEGF transcription. 15272925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15290728_CD40-CD154 interaction augments the expression of inflammatory cytokines and MMP in chondrocytes and contributes to an intrinsic process of cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis. 15291139_Soluble form of CD40 is increased in uremic patients (review) 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15307939_unable to confirm a role for CD40 in Graves' disease pathogenesis in our U.K. population 15331443_Germinal cell expansion occurs in the absence of CD40 signaling, which may act only in the initial and final stages of the GC reaction. 15339846_CD40 ligation induces CLL cells to express the proapoptotic molecule Bid and the death receptors CD95 and DR5 15367912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15375484_Loss of CD40 expression is associated with prostate cancer progression 15578091_Data show that specific NEMO mutations impair CD40-mediated c-Rel activation and B cell terminal differentiation. 15634933_These studies help to identify the TRAF binding domains in CD40 and to establish affinities between CD40 and the different TRAF proteins. 15670770_These results indicate a distinction between TNF Receptor family members CD40 and TNFR1 in their utilization of MAP3Ks, and demonstrate TRAF-dependence of Tpl2 association with the CD40 receptor complex. 15690148_CD40 may have a role in processes associated with islet autoimmunity and transplantation. 15708600_CD40 ligation strongly synergized with Tax to activate NF-kappaB, suggesting that CD40 signals may costimulate Tax-mediated NF-kappaB activation. 15753667_the majority of thyroid cancers express CD-40 and CD-40 ligand 15795333_CD40/CD40L signaling contributes to inflammatory and prothrombogenic responses and brain infarction induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion. 15808676_role of recipient CD40 and CD154 in the rejection process of concordant and discordant islet xenotransplantation 15817705_GPI(+) T lymphocytes showed a significant increase of all these parameters, and the analysis of CD40-dependent pathways revealed a functional persistence of CD154 expression on the CD48(+)CD4(+) lymphocytes. 15838273_LOX-1 and CD40 synergistically, but through a distinct pathway, work to induce endothelin-1 expression in endothelial cells. 15883744_Retinoic acid inhibits CD40 plus IL-4 mediated IgE production through alterations of sCD23, sCD54 and IL-6 production 15994291_anti-CD40 monoclonal antibodies, by rapidly inducing apoptosis, may reduce the capacity of inflammatory signal-matured immunogenic dendritic cells to generate an effective T-cell response 16033859_CD40 signals may simultaneously induce antiapoptotic genes for cytoprotection of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells 16091748_study provides evidence to support a role for constitutive CD40 signalling in cell neoplastic transformation 16127217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16127217_single nucleotide polymorphism of CD40 gene is associated with susceptibility to later onset of Graves disease in Japanese 16142355_CD40 expression may have a role in cyclophosphamide resistance in cervical squamous cell carcinoma 16149136_High CD40 expression in the ileal pouch mucosa could be implied in the pathogenesis of pouchitis following proctocolectomy for ulcerative colitis 16213477_both mouse and human renal carcinoma cells (RCC) constitutively express functional CD40 16221206_Platelets from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus can activate mesangial cells through CD40/CD154 interactions 16246299_This binding was not competed by either HSP70 or the biotin entity itself. Interestingly, the biotinylated HSP70 also elicited the production of CC-chemokine RANTES independent of CD40 signaling. 16260598_TRAF2-dependent CD40 signal transduction requires TRAF6 in nonhemopoietic cells 16279844_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16279844_results support the notion that CD40 C-1T polymorphism has a modest effect on genetic susceptibility to sporadic Graves disease 16356505_CD40 expression stimulated by chylomicron remnants in THP-1 cells is dependent on ERK 1/2-mediated pathway 16356539_Soluble CD40L was significantly elevated in patients with more advanced symptomatic PAD and might be an indicator for disease extent stratification. 16357329_Possible use of CD40-B cells as cellular adjuvant for cancer immunotherapy. 16429118_TRAF3 stabilization, JNK activation and caspase-9 induction define a novel pathway of CD40-mediated apoptosis in carcinoma cells. 16494885_higher inflammatory status of coronary lesions as well as involvement of the CD40-CD154 signaling cascade in chronic renal failure patients, especially in cases of calcified atherosclerotic lesions 16504636_Genetic variation of the CD40 gene is associated with coronary artery calcium in a diabetic population. 16504636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16644731_CD40 is present not only in the plasma membrane and cytoplasm but also in the nucleus of normal and neoplastic B-lymphoid cells 16756465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16756465_the CD40 gene may be involved in susceptibility for Graves' disease in the Japanese population 16864989_15d-PGJ2 significantly decreased CD40 and RANTES expression in HK-2 cells, which were partially mediated by PPAR-gamma-dependent pathways. 16901543_Anti-apoptotic signaling of CD40 involves induction of c-FLIP proteins. 16936191_Islet beta-cells responded to CD40-CD40L interaction by secreting IL-6, IL-8, MVP-1, & MIP-1beta. CD40-CD40L interaction activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 & nuclear factor-kappaB pathways in insulinoma NIT-1 cells. 16964404_Results suggest that hepatocyte over-expression of CD40 might play an important role in regulating hepatocyte survival and death in HCV-associated chronic liver diseases. 17012138_results indirectly suggest that sCD40 concentrations are related to cellular cholesterol levels 17026470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17026470_Single cytidine/thymine nucleotide polymorphism has no association with disease susceptibility or disease course in multiple sclerosis. 17043147_Review discusses the important role of CD40 in the angiogenic process of tumor-prone transgenic mice that is coupled to carcinogenesis. 17077013_the involvement of CD40 and its ligand CD40L in liver disease 17154264_BAFF-R and CD40 enhance B cell responsiveness to transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI)-mediated suppression. 17199090_Our results reveal the higher levels of maternal and umbilical sCD40L serum levels in pregnancy complicated by pre-eclampsia with and without intrauterine growth retardation. 17202327_reveal potent biologic functions for T cell CD40 and suggest an additional means for amplification of autoimmune responses 17225862_Data show that C4BP does not bind CD40, but it forms stable high molecular weight complexes with soluble CD40 ligand (sCD154). 17237414_Compared with healthy controls, CD4(+) T cells from HIV-1(+) patients had impaired induction of CD154 when T cell activation was mediated by CD40(+) APCs. In contrast, T cell activation in the absence of these cells resulted in normal CD154 expression 17237417_Ligation of cell surface CCR5 receptors by CCL3 or CD40 by CD40L activated the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways that induced APOBEC3G mRNA expression and production of the APOBEC3G protein 17255560_CD40 gene polymorphisms exert a genetic effect on IgE production in patients with asthma through translational regulation of CD40 expression on B cells 17255560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17302995_The level of CD40 was associated with late restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention indicating that restenosis is an inflammatory disorder 17319699_substitution of a D-prolyl residue for the glycyl within the Lys-Gly-Tyr-Tyr CD40-binding motif of CD40L leads to a complete loss of cooperativity in the interaction of the mimetic with its cognate receptor. 17344890_CD40 Kozak SNP is specific for thyroid antibody production involved in the etiology of Graves' disease 17344890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17376892_induction of the short c-FLIP isoforms inhibits the onset of CD95-induced apoptosis in primary CD40-stimulated ALL cells despite high CD95 expression. 17446175_Data demonstrate that CD40 signals B cell survival in part via transcriptional activation of the RelB NF-kappaB subunit. 17459878_CD40-40L signaling has a role in vascular inflammation 17534894_CD40 ligation may represent a novel mechanism for elimination of CRC cells and render CD40 a promising therapeutic target for the eradication of colorectal tumours. 17553307_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17599408_These data together uncovers a new signaling pathway regulating APE/Ref-1 nuclear translocation involving CD40-crosslinking, TRAF2 and p38. 17678876_upon CD40 ligand stimulation, endogenous and exogenous CD40 receptor is rapidly mobilized into lipid rafts compared with unstimulated Aortic Endothelial Cells. 17687557_High expression of CD40 is reported on skin fibroblasts from patients with systemic sclerosis. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17721998_CD40 stimulation can transiently induce RANTES and MCP-1 expression in LMP1-negative epithelial cells. 17786592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17786592_The CD40 gene seems to be not associated with Graves' disease in the Tunisian population 17805323_A possible role of CD40-CD40L interactions between monocytes and T4 helper cells in the pathogenesis of bone marrow failure in myelodysplastic syndromes was shown. 17884785_Prolactin plays an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE by increasing CD154 expression on the PBMCs, and bromocriptine produces no significant inhibitory effect on either endogenous or exogenous prolectin. 17904146_Chronic atrial fibrillation acutely upregulates CD40 expression as well as platelet adhesion to the endocardium 17925605_CD40, CD80 and CD86 are upregulated in cultured monocyte-derived dendritic cells of patients with coronary artery disease 17949264_For susceptible genes, the CC genotype in the CD40, the GG genotype in the CTLA-4 exon 1, and the CC genotype in the CTLA-4 promoter region have shown no significant association with clinical outcome after antithyroid drug withdrawal in Grave's disease. 17949264_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17967972_Cyclic stretch thus increases the abundance of CD40 in endothelial cells through transforming growth factor-beta1/Alk-1 signaling 17989345_CD40 expression was up-regulated on the circulating monocytes in septic subjects on Day 1 17999420_Activation of CD40 on cholangiocytes by activated macrophages provides a molecular mechanism to amplify chronic inflammation and bile duct destruction in liver disease. 18037736_In acute phase of myocardial infarction (MI), the circulating level of CD40 ligand, an index of platelet activation, is predictive of angiographic morphologic features that indicate high-burden thrombus formation (HBTF) in infarct-related artery (IRA). 18064390_Our results suggested that in the cardiovascular system, ghrelin not only has an anti-inflammatory effect, but also has a significant immunoregulatory effect that may be mediated through the GHSR-1a receptor. 18097708_Women with the TT genotype in rs1883832 SNP affecting to Kozak consensus sequence of CD40 gene had lower BMD at FN and at LS sites and increased risk of osteopenia or osteoporosis. 18159101_sCD40L level is similar in patients with aspirin-resistant and aspirin-sensitive platelet aggregation 18217399_the CD40/CD154 interaction has a role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune process leading to inflammatory infiltration in Graves' ophthalmopathy 18253927_Results suggest that anti-CD40 agonists decrease CD40 surface protein t(1/2) via a mechanism that involves TRAF6 but not TRAF2/3. 18287517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18287517_These results suggest that the TNFRSF5 -1C>T polymorphism may increase follicular lymphoma susceptibility through mechanisms that hinder cellular immune responses. 18289643_activated neutrophils release superoxides in a PI3 kinase-dependent manner, contributing to platelet activation and sCD40L release in a redox-controlled positive feed-back loop 18437082_N-acetylcysteine may be considered as a useful tool to prevent immune and inflammatory responses in pancreatic disorders by interfering with the CD40 pathway in pancreatic duct cells. 18445342_further evidence of the importance of the CD40 signal in developing efficient human DC vaccines for cancer immune therapy 18446002_C/T polymorphism in CD40 gene is not associated with susceptibility and phenotype of Graves' disease in Taiwanese. 18446002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18487509_CD40 signaling rapidly disrupts the ability of BCL6 to recruit the SMRT corepressor complex by excluding it from the nucleus, leading to histone acetylation, RNA polymerase II processivity, and activation of BCL6 target genes 18495129_inhibition of JNK and p38 activation interrupts CD40 induced endothelial cell activation and apoptosis 18548529_CD40 expression in tumors is associated with a poor prognosis and that the juxtacrine interaction of CD40-CD154 among cancer cells facilitates the development of malignant potential in nonsmall cell lung cancer. 18552209_very high expression of CD40 on BCP-ALL blasts is an independent prognostic marker indicative of superior relapse-free survival that may in part be due to CD40-dependent death receptor up-regulation 18591382_signaling via CD40-P227A stably expressed in B-cells led to increased phosphorylation of c-Jun, increased secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 and TNF-alpha, and increased Ig production, compared with wild-type CD40 18593367_reversion of Fas resistance is mediated through CD40/CD40L ligation rather than IFN-gamma stimulation by inhibiting synthesis of c-FLIP 18603231_Theses results suggest that CD40 is present in colon cancer, and recombinant soluble human CD40 ligand may be of clinical use to inhibit human colon cancer growth. 18606651_antiapoptotic signaling of CD40, which interferes with TRAIL-induced apoptosis in follicular lymphomas B cells, involves NFkappa-B-mediated induction of c-FLIP & Bcl-xL which can interfere with caspase 8 activation or mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18669876_endothelial CD40 involvement in the transcriptional regulation of gene networks associated with adhesion and motility, immunity, cell fate control, hemostasis, and metabolism 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18694960_These data reveal a novel 'feed-forward' mechanism induced by NF-kappaB which ensures that acutely synthesized IRF-1 operates in concert with NF-kappaB to amplify the immunoproteasome and antigen-processing functions of CD40. 18705404_CD40 expression was detected in 60.3% of paraffin-embedded ovarian cancer tissues and 73.3% of fresh ovarian cancer tissues, but not in normal ovarian tissues. CD40 expression was significantly correlated with FIGO stage of ovarian cancer. 18713981_maturation of human DC with OK432 induces direct tumor cell killing by DC by interaction of tumor cell CD40 with dendritic cell CD40L 18755875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18755875_the T/T genotype and T allele in the CD40 gene are more likely to be associated with late-onset Graves disease in Taiwanese patients 18794853_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18794853_Variant at the CD40 gene locus is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. 18796631_prolonged in vitro CD40 stimulation, resulted in up-regulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-xL, A1/Bfl-1, and Mcl-1 proteins, and afforded resistance to various classes of drugs 18835787_study demonstrated that Abeta(1-40), levels of sCD40 and sCD40L are increased in Alzheimer's disease and declining MMSE scores correlated with increasing sCD40L, which in turn, correlated positively with Abeta(1-42) 18849075_sCD40 natural isoforms encompassing either three or four CRDs might exert different antagonistic effects from known CD154 antibodies by recognition of only membranous CD154. 18996438_findings show that CD40-signalling might play a role in the pathogenesis of early Alzheimer's disease 19002156_CD40 signals regulate DC-derived IL-7 production that, in turn, may instruct CD8(+) T cells at the time of TCR engagement for survival leading to an increased expansion of antigen-specific T cells 19018001_mTORC2 and Akt facilitate CD40-inducible expression of VEGF in endothelial cells 19023113_in the absence of CD40-CD154 interactions, there is a marked reduction in SHM and, specifically, mutations of AICDA-targeted G residues in RGYW motifs along with a decrease in transversions normally related to UNG2 activity. 19086656_The upregulated level of costimulatory molecules CD28/B7-2 and CD40/ CD40L on T cells and B cells may play an important role in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. 19099972_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19118532_LPS induced CD40 expression on human PBMCs through activation of NFkappaB and JNK, and partially through the induction of IFNgamma production. 19159017_Data show that there were non-association and non-additional effects of TLR4/CD40 gene polymorphisms and haplotypes upon asthma risk. 19159017_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19171874_C1q augments the production of IL-12p70 by mouse and human DCs after CD40 triggering and plays important roles in sustaining the maturation of DCs and guiding the activation of T cells 19180477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19183933_CD40 expression was upregulated during adipocyte differentiation. CD40 mRNA levels were significantly higher in subcutaneous adipose tissue than in visceral adipose tissue of obese patients. 19221099_Pre-eclamptic woman had increased CD40 on monocytes. Preeclampsia is associated with activation of the CD40-CD40L system, which may contribute to the proinflammatory & prothrombotic milieu found in preeclampsia. 19246174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19268365_CD40 and B-cell receptor signalling induce MAPK family members that can either induce or repress Bcl-6 expression. 19272596_Pre-eclampsia is associated with activation of the CD40-CD40L system; activation of this system may contribute to the development or maintenance of proinflammatory & prothrombotic responses, increased cytokine production, & endothelial cell dysfunction 19336218_These results suggest that CD40 up-regulation by HBxAg may play a facilitating role in the pathogenesis causing hepatocellular carcinoma. 19397878_These results suggest that CD40 signaling plays a critical role in the survival and proliferation of EBV-infected epithelial cells, as well as in the virus-infected lymphocytes. 19419774_reduced BDNF secretion from PBMCs and defective regulation effect of CD40 stimulation on BDNF levels in untreated relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis are reversible by therapy with IFN-beta1a. 19421221_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19421221_Single nucleotide polymorphism in CD40 is associated with pemphigus foliaceus. 19422822_Data suggest that CD40/CD40L interaction modulates amyloid protein precursor processing independently of TRAF signaling. 19435719_strong association of the CD40 gene |
ENSMUSG00000017652 |
Cd40 |
227.286724 |
3.4318795074 |
1.778999 |
0.142214139 |
155.985747 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000852672254308856209240691395571198626501074701961987852084123329233008439959770677102271886713819037950656820612493902444839477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000128161328651718103479814956278411274170209865663765502632647739877120869321714509792570625516805460364366808789782226085662841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
351.0170511 |
29.6827417 |
103.0557403 |
6.9318871 |
| ENSG00000101096 |
4773 |
NFATC2 |
protein_coding |
Q13469 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the inducible expression of cytokine genes in T-cells, especially in the induction of the IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, TNF-alpha or GM-CSF. Promotes invasive migration through the activation of GPC6 expression and WNT5A signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21871017}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) family. The product of this gene is a DNA-binding protein with a REL-homology region (RHR) and an NFAT-homology region (NHR). This protein is present in the cytosol and only translocates to the nucleus upon T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation, where it becomes a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells transcription complex. This complex plays a central role in inducing gene transcription during the immune response. Alternate transcriptional splice variants encoding different isoforms have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:4773; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; transcription factor AP-1 complex [GO:0035976]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0033173]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; myotube cell development [GO:0014904]; ncRNA transcription [GO:0098781]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:1905064]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
11231878_Recombinant NFATp binds DNA on its own and cooperatively with AP-1 proteins, activates transcription in vitro, is phosphorylated, can be dephosphorylated by calcineurin, and exhibits regulated association with nuclei in vitro. 11911478_C-terminal one third of DNA binding domain confers different binding specificity of NFATc and NFATp to an NFAT site in the TNF-alpha promoters 12594826_NF-ATc2 induces apoptosis in Burkitt's lymphoma cells through signaling via the B cell antigen receptor 14657699_Differential responsiveness of cord blood T cells cannot be attributed to differences at the level of NFAT1 expression. 15117942_sumoylation has a dual role in the nuclear localization and transcriptional activation of NFAT1 15121840_identify a conserved docking site for casein kinase 1 (CK1) in NFAT proteins and show that mutation of this site disrupts NFAT1-CK1 interaction and causes constitutive nuclear localization of NFAT1 15184502_Nuclear factor of activated T cells balances angiogenesis activation and inhibition. 15271374_role in activating interleukin-5 receptor 15292278_These results suggest a novel and unexpected role for members of the NFAT transcription factor family in the hematopoietic system. 15347678_Interleukin (IL)-15 and IL-2 reciprocally regulate expression of the chemokine receptor CX3CR1 through selective NFAT1- and NFAT2-dependent mechanisms 15471864_the nuclear factor of activated T cell-dependent transactivation pathway has a role in viral protein A238L inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression 15632146_Expression of NFATc1 and NFATc2 wild type protein or the active catalytic subunit of calcineurin transactivates COX-2 promoter activity, whereas a dominant negative mutant of NFAT inhibited COX-2 induction in colon carcinoma cell lines. 15668245_CAML is an important signal transducer for the actions of Ang II in regulating the calcineurin-NFAT pathway and the interaction of CAML with ATRAP may mediate the Ang II actions in vascular physiology 15857835_NFAT and SRF may interact to cooperatively regulate smooth muscle cell-specific gene expression and NFAT may have a role in the phenotypic maintenance of smooth muscle 15897878_alpha6beta4 integrin potentiates autotaxin expression through the upregulation and activation of NFAT1. 16455648_NFATc2 activity is regulated by caspase-3 16497967_NFKB and NFAT regulate BLyS expression via at least one NFKB and 2 NFAT BLYS promoter binding sites. Constitutive activation of NFKB and BLyS in NHL-B cells forms a positive feedback loop associated with lymphoma cell survival and proliferation 16505480_NFAT promotes breast cancer cell invasion through the induction of COX-2 and the synthesis of prostaglandins 16690925_results indicate that HIV-1 Tat interacts with NFAT, affecting its cooperation with AP-1, without altering independent binding of these transcription factors to DNA 16849457_Studies with NFAT1-sufficient and -deficient double-transgenic bone marrow chimeric mice demonstrate that the transcription factor NFAT1 is involved in B cell anergy. 16888000_Constitutive expression of NFAT1/NFATc2 in transgenic mice controls bone resorption in vivo by stimulating differentiation and functioning of osteoclasts but not their survival. 17082665_In Wiskott-Aldrich CD8+ T cells, a block in cytokine production correlates with reduced nuclear levels of both NFAT-1 and NFAT-2. 17237388_Ral is activated upon BCR stimulation and mediates BCR-controlled activation of AP-1 and NFAT transcription factors. 17237447_the amount of NF-ATc2 bound to the promoters of CD154 (CD40L) and IL-2 genes in SLE; although high NF-ATc2 levels translated into higher CD154 transcription in SLE, IL-2 transcription was decreased 17398070_MAP3K8 and PRKCZ cooperate in the regulation of the transcriptional activity of NFATC2 through the phosphorylation of its amino-terminal domain. 17463169_NFAT1 could explain low FOXP3 expression and diminished Treg frequency in aplastic anemia. 17584983_NFAT1 mediates proinflammatory gene expression in response to mechanotransduction 17588603_Changes in AP-1 composition and the level of participating NFAT proteins can differentially influence cytokine gene expression, resulting in biological consequences for the modulation and dynamics of the immune response. 17711847_the WIP-WASP complex plays an important role in WASP stabilization and NFAT activation 17785820_NFAT1 is a critical regulator of CTLA-4 gene expression that binds to the CTLA-4 promoter in human T cells. 17882263_O-GlcNAc modification might be required for nuclear translocation of the transcription factors NFkappaB and NFAT 18097033_The promoter/enhancer activity of the NFAT-binding site in the TNF-alpha gene was up-regulated by NFATc2 but not by NFATc1, whereas both NFATs associated similarly with this region. 18218901_study found that Homer2 and Homer3 are negative regulators of T cell activation; this is achieved through binding of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and by competing with calcineurin 18246125_Unexpected coupling of PML with NFAT reveals a novel mechanism underlying the diverse physiological functions of promyelocytic leukemia. 18641302_accumulation of HIF-1alpha in activated mast cells requires up-regulation of HIF1A gene transcription and depends on the calcineurin-NFAT signaling pathway 18676376_NFAT and MyoD cooperation regulates myogenin expression and myogenesis 18710929_NFATc2 has a role in colitis by controlling mucosal T cell activation in an IL-6-dependent manner 18931684_Normalization of the constitutive VEGFR2 signaling in hemangioma endothelial cells with soluble VEGFR1 or antibodies that neutralize VEGF or stimulate beta1 integrin 18962896_our results establish crucial roles for enhancer element CNS-9, and NFAT1 and IRF4 that bind to it, for IL-10 expression in differential T helper subsets. 18973208_Children with type 1 diabetes show decreased insudtion of MFATc2 in T cells. 19192391_Lck regulated the activity of PKD2 by tyrosine phosphorylation, which in turn may have modulated the physiological functions of PKD2 during T cell receptor-induced T cell activation. 19286996_Endogenous expression of miR-184 in cord blood is 58.4-fold higher compared with adult blood CD4+ T cells, and miR-184 blocks production of NFAT1 protein through its complementary target sequence on the NFATc2 mRNA without transcript degradation. 19318479_A new translocation involving EWSRI and NFATc2 was cloned from Ewing sarcoma patients. 19318584_The extent of central tumor necrosis was decreased in the tumors in NFATc2((-/-)) mice, and this finding was associated with reduced tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-2 (IL-2) production by CD8(+) T cells. 19458075_SFRP2 is a novel stimulator of angiogenesis that stimulates angiogenesis via a calcineurin/NFAT pathway and may be a favorable target for the inhibition of angiogenesis in solid tumors. 19833725_3BP2 induces the protein complex with cellular signaling molecules through phosphorylation of Tyr(183) and SH2 domain leading to the activation of NFAT in B cells 19843528_the direct involvement of NFAT1 in the transcriptional regulation of hTERT. 19900447_Serum promotes pancreatic cancer growth through induction of the proproliferative NFAT/c-Myc axis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20093726_the the calcineurin/NFAT pathway has a role in lymphoma/leukemogenesis [review] 20097868_Data demonstrate that NFAT1 mediates PlGF-induced myelomonocytic cell recruitment via the induction of TNF-alpha. 20219685_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20367554_BAI2 is a functional GPCR regulated by proteolytic processing and activates the NFAT pathway 20368097_GATA3-NFAT1 complex may play an important role in the regulation of IL-13 transcription in human T cells.GATA3-NFAT1 complex may play an important role in the regulation of IL-13 transcription in human T cells. 20379146_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20448330_essential for the expression of a glioblastoma multiforme related IL-13Ra2 transcript 20557936_A region of NFATc2 C-terminal of the DNA binding domain was necessary and sufficient for interaction with cJun in the absence of DNA, and this same region of NFATc2 was required for the synergistic activation of IL-2 transcription in T cells. 20609354_High Wnt/Ca2+/NFAT signaling maintains survival of Ph+ leukemia cells upon inhibition of Bcr-Abl. 20628086_Genetic variation at the NFATC2 locus contributes to edema among individuals who receive rosiglitazone. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Statistical analysis indicated that six genes, NFATC2, SCP2, CACNA1C, TCRA, POLE, and FAM3D, were associated with narcolepsy. 20834230_Data show that NFATc2 inhibits polyQ aggregation in cells and is required for HSF1-mediated suppression of aggregation, and that HSF1 and NFATc2 cooperatively induce expression of PDZK3 and alphaB-crystallin, which facilitate degradation of polyQ. 21047202_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21282105_minocycline selectively impairs NFAT-mediated transcriptional activation, a result of increased phosphorylation and reduced nuclear translocation of the isoform NFAT1 21325277_Kinetic analyses of each step linking Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channel activation to NFAT1 nuclear residency reveals that the rate-limiting step is transcription factor exit from the nucleus 21576369_Data demonstrate that IRF-2BP2 is a negative regulator of the NFAT1 transcription factor and suggest that NFAT1 repression occurs at the transcriptional level. 21628454_a critical role of the GSK-3beta-HDM2 signaling loop in the regulation of NFATc2 protein stability and growth promotion 21799768_the prolonged IL-4 expression in NFAT1 deficient Th2 cells is mediated by preferential binding of JUNB/SATB1 to the IL-4 promoter with permissive chromatin architecture 21803625_The binding of NFAT1 to the NKX2-3 promoter region with rs1190140 was confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. 21964595_a novel negative cross talk between the NFAT1- and Stat5-signaling cascades that may affect breast tumor formation, growth, and metastasis 22045870_calcium responsiveness of IL-31 promoter required NFAT binding sites that bind NFATc1 and NFATc2 in vitro and in vivo. 22116621_Inhibition of NFAT or targeting of NFATc3 with small interfering RNA (siRNA) lowers the AIF-1/IRT-1 ratio and favours an anti-proliferative outcome for atherosclerosis. 22333584_NFAT1 directly binds to distal sites in the c-Myc promoter with different affinities. 22363514_The present study investigated the effect of heart failure aetiology on Ca(+2) handling proteins and NFAT1, MEF2C and GATA4 (transcription factors) in the same cardiac tissue. 22627363_NFAT1 and NFAT2 facilitated IL-17A expression in human T cells, though distinct mechanisms might be involved in these effects 22699055_Transfection with HCV C gene up-regulates NFAT1 expression and promotes the cell cycle progression and proliferation of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells. 22718120_Here we show that the calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells c2 (NFATc2) pathway has an antiapoptotic role in melanoma cells. 22767506_LCN2 and TWEAKR-TWEAK as crucial downstream effectors of NFAT1 that regulate breast cancer cell motility and invasive capacity. 22787160_Transcription factor NFAT1 activates the mdm2 oncogene independent of p53. 22911897_haplo-insufficiency of NFATC2 cooperates with activation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of JAK2V617F-positive ET with del(20q). 22986745_Data elucidate a previously unidentified mechanism by which galectin-3 regulates autotaxin and assign a novel role for NFAT1 during melanoma progression. 23060442_Endorepellin affects angiogenesis by antagonizing diverse VEGFR2-evoked signaling pathways: transcriptional repression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and VEGFA and concurrent inhibition of NFAT1 activation. 23359789_Both WNT5A and NFATc2 proteins are highly expressed in human pancreatic cancer tissues. 23665382_Data suggest a model in which IL-2 transcriptional synergy is mediated by the unique recruitment of a cJun homodimer to the -45 NFAT site by NFATc2, where it acts as a co-activator for IL-2 transcription. 23762456_Overexpressed NFAT1 in glioblastoma multiforme cells was mainly located in the nucleus, where it acted as a transcription factor. 24106272_in vivo biochemical or genetic inhibition of NFATc2 activity in megakaryocyte diminishes platelet CD40L implicates the NFATc2/EGR-1 axis as a key regulatory pathway of inflammatory and immunomodulatory activity in platelets 24136923_Translocation of NFAT1 to the cell nucleus is a direct, sensitive, reproducible and quantitative pharmacodynamic readout for tacrolimus action. 24173147_NFAT1 is differentially expressed in stimulated CD4-positive vs CD8-positive T cells. 24477908_Using a human CTL system model based on a CD8(+)/CD103(-) T cell clone specific of a lung tumor-associated Ag, we demonstrated that the transcription factors Smad2/3 and NFAT-1 are two critical regulators of this process. 24486774_Data suggest involvement of SALL4 (sal-like 4) and NFATC2(nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 2 ) genes disruption in cardiac and skeletal anomalies. 24551078_NFATc2 exhibited a higher relative affinity for binding site DS3 as compared with members of the C/EBP family (C/EBP alpha and beta). 24561192_USP22 deubiquitinates and stabilizes NFATc2 protein levels thereby promoting IL2 expression. 24931237_NFAT-1, STAT-1 and AP-1 might be the central transcription factors in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 25376468_no significant correlation of genetic polymorphisms with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Poland 25735562_NFAT1-mediated IL8 production promotes the migration of primary human neutrophils in vitro and also promotes neutrophil infiltration in tumor xenografts 25797200_inhibits CCR7 expression during the course of dendritic cell maturation 25818645_Results show that two protein isoforms NFAT1 and NFAT4 are both cytosolic and stimulated by the same Ca2+ messenger but require distinct subcellular Ca2+ signals for activity. 25987655_In multivariate logistic regression, the intronic rs6021191 variant in nuclear factor of activated T cells 2 (NFATC2) had the strongest association with hypersensitivity to asparaginase. 26238508_These data suggest that NFATc2 expression is regulated by intracellular calcium and in vitro stretch, and that the stretch response in human myometrial cells is dependent upon intracellular calcium signalling pathways. 26374065_two NFAT isoforms (NFAT4 and NFAT1) have shifted band-pass windows for the same receptor in the GPCR signaling pathway 26387540_the expression of NFATc2 promotes melanoma dedifferentiation and immune escape 26527057_Data indicate that RNA interference of NFAT isoforms NFATc1, NFATc2, NFATc3 and NFATc4 regulate gene expression differentially in human retinal microvascular endothelial cells (HRMEC). 26823495_we describe a novel mechanism by which GSK-3beta fine-tunes NFATc2 and STAT3 transcriptional networks to integrate upstream signaling events that govern pancreatic cancer progression and growth. 26903518_Up-regulation of Store-operated Ca2+ Entry and Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells Promote the Acinar Phenotype of the Primary Human Salivary Gland Cells. 27013197_NFAT1 overexpression is associated with Melanoma Tumor Growth and Metastasis. 27399331_These results demonstrate a repressor role for NFAT1 in cell cycle progression and Cyclin E expression in B lymphocytes, and suggest a potential function for NFAT1 protein in B cell malignancies. 27637333_revealed more than 170 NFAT-associated proteins, half of which are involved in transcriptional regulation. Among them are many hitherto unknown interaction partners of NFATc1 and NFATc2 in T cells, such as Raptor, CHEK1, CREB1, RUNX1, SATB1, Ikaros, and Helios. 27859969_FOXP1 has protein-protein interaction with NFAT1 on DNA and enhances breast cancer cell migration by repressing NFAT1 transcriptional activity. 27863227_NFAT1 is stimulated by subplasmalemmal Ca2+ microdomains, whereas NFAT4 additionally requires Ca2+ mobilization from the inner nuclear envelope by nuclear InsP3 receptors. 28024290_NFAT1 silencing could suppress cell migration and invasion through MMP-3. 28240604_An interaction of NFAT1 and the beta-catenin pathway, validate lysophosphatidic acid as an in vivo activator of beta-catenin-dependent transcription during allograft fibrogenesis. 28504924_Our results indicate that NFATc2 may be used as an early diagnostic or predictive biomarker for colorectal carcinoma as well as a therapeutic target 28526484_Our data have shown for the first time the regulation of CacyBP/SIP gene expression by NFAT1. Since NFAT transcription factors are involved in processes related to immune response, these results indicate potential involvement of CacyBP/SIP in the immune system. 28737489_NFATc2 enhances tumor-initiating phenotypes through the NFATc2/SOX2/ ALDH1A1 axis in lung adenocarcinoma. 28774282_NFATc2 and Sp1 are co-localized in cell nuclei and physically interact at the NFAT target sequence termed NFAT-responsive promotor construct. Sp1 increases the functional activity of its binding partner NFATc2. 28927426_Results show that NFAT1 expression is regulated by ASIC2 under acidosis and that NFAT1, binds to genes clustered in pathways involved in Rho GTPase signaling and calcium signaling. 29258522_NFAT1-regulated IL6 signalling contributes to aggressive phenotypes of glioma 29626598_Case Report: EWSR1-NFATC2 fusion tumor with round cell morphology and prominent myxoid to fibrous stroma. 29969451_The data indicate that expression of CRTh2 is regulated through the competitive action of GATA3 and NFAT1. 30459241_NFAT1 overexpression in melanoma-conditioned Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) promoted CD68(+)-macrophage infiltration, tumor growth, and metastasis in vivo NFAT1 may play a critical role in enhancing the TAM-mediated promotion of growth and metastasis in malignant melanoma. 30696421_NFATc2 and Sp1 seem to play a key role in the progression of pancreatic cancer. 30710146_A targetable vulnerability associated with NFATc2 and EZH2 expression in melanoma cells belonging to different mutational subsets. 30772768_Our findings suggest the significance of activating NFAT1/ITGA6 signaling in aggressive NPC, defining a novel critical signaling mechanism that drives NPC invasion and metastasis and providing a novel target for future personalized therapy. 30895378_URCS with EWSR1-NFATc2 fusion share a distinct DNA methylation signature and carry characteristic copy number alterations, which emphasizes that these sarcomas should be considered separately from EwS. 30940662_NFAT1 controls the growth and invasion of GSCs, partially by regulating NDEL1. 30994538_EWSR1-NFATC2 sarcoma is a novel translocation-associated sarcoma. It presents as either a primary bone or soft tissue tumor, usually exhibits distinctive histopathologic features, and has predilection for long bones of adult men. 31181312_Results found that NFATc2 expression was significantly increased in both GBM tissues and cultured cell lines and predicted to be a target gene of miR-454. 31304984_Data identified NFAT1-positive and NFAT1-negative melanoma subgroups, wherein NFAT1 expression correlates with melanoma stage and metastatic potential. Integrative bioinformatics revealed that genes coding for mitochondrial- and redox-related proteins are under NFAT1 control. NFAT1 are associated with poor disease outcome. 31464639_Nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 (NFAT1) expression and nuclear translocation are regulated by stromal interaction molecule2 (STIM2) in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. NFAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and upregulates transforming growth factor-beta1 expression and secretion in breast cancer cells. 32329053_Nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 and 2 are required for vertebral homeostasis. 32339381_CD147 regulates melanoma metastasis via the NFAT1-MMP-9 pathway. 32601188_STIM2 targets Orai1/STIM1 to the AKAP79 signaling complex and confers coupling of Ca(2+) entry with NFAT1 activation. 32991339_FUS-NFATC2 or EWSR1-NFATC2 Fusions Are Present in a Large Proportion of Simple Bone Cysts. 33079489_Role of nuclear factor of activated T cells 2 (NFATc2) in allergic asthma. 33507149_Induction of the IL-1RII decoy receptor by NFAT/FOXP3 blocks IL-1beta-dependent response of Th17 cells. 33754043_FGF19/SOCE/NFATc2 signaling circuit facilitates the self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells. 33941685_The N terminus of Orai1 couples to the AKAP79 signaling complex to drive NFAT1 activation by local Ca(2+) entry. 34081036_Expanding the Spectrum of EWSR1-NFATC2-rearranged Benign Tumors: A Common Genomic Abnormality in Vascular Malformation/Hemangioma and Simple Bone Cyst. 34089379_The role of molecular diagnostics in aneurysmal and simple bone cysts - a prospective analysis of 19 lesions. 34311033_TRPC3 promotes tumorigenesis of gastric cancer via the CNB2/GSK3beta/NFATc2 signaling pathway. 34332425_NFAT indicates nucleocytoplasmic damped oscillation via its feedback modulator. 34491912_Identification of direct transcriptional targets of NFATC2 that promote beta cell proliferation. 34584155_Expression and clinical significance of IL7R, NFATc2, and RNF213 in familial and sporadic multiple sclerosis. 34648001_Genetic inhibition of nuclear factor of activated T-cell c2 prevents atrial fibrillation in CREM transgenic mice. 35789258_Human complete NFAT1 deficiency causes a triad of joint contractures, osteochondromas, and B-cell malignancy. 35818214_STIM2 promotes the invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells through the NFAT1/TGF-beta1 pathway. 36394458_PARP1 Is a Prognostic Marker and Targets NFATc2 to Promote Carcinogenesis in Melanoma. |
ENSMUSG00000027544 |
Nfatc2 |
239.317973 |
0.3864309887 |
-1.371717 |
0.110927867 |
155.881475 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000898603036820560825599597444159047673723933926377938476434929997783338778266523671323153665694075109549032731592888012528419494628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000134790455523084119830792551485563681847785388229467953242444179509927769797072312457875088373415728426607529399916529655456542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
134.0136487 |
9.4370838 |
349.2898952 |
15.6530131 |
| ENSG00000101152 |
80331 |
DNAJC5 |
protein_coding |
Q9H3Z4 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a general chaperone in regulated exocytosis (By similarity). Acts as a co-chaperone for the SNARE protein SNAP-25 (By similarity). Involved in the calcium-mediated control of a late stage of exocytosis (By similarity). May have an important role in presynaptic function. May be involved in calcium-dependent neurotransmitter release at nerve endings (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P60904, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q29455}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is a member of the J protein family. J proteins function in many cellular processes by regulating the ATPase activity of 70 kDa heat shock proteins. The encoded protein plays a role in membrane trafficking and protein folding, and has been shown to have anti-neurodegenerative properties. The encoded protein is known to play a role in cystic fibrosis and Huntington's disease. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 8. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:80331; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; chromaffin granule membrane [GO:0042584]; clathrin-sculpted gamma-aminobutyric acid transport vesicle membrane [GO:0061202]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; ATP-dependent protein binding [GO:0043008]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; regulated exocytosis [GO:0045055]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693]; synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:0016079] |
10194413_Has a role in exocytosis of large dense core vesicles. 12039948_Csp has a role in regulated CFTR trafficking at the plasma membrane. [CYSTEINE STRING PROTEIN] 14570907_Cysteine string protein inhibits N-type calcium channels, but is blocked by mutant huntingtin 15972823_CSP modulates G protein function by preferentially targeting the inactive GDP-bound form of G alpha(s) and promoting GDP/GTP exchange; the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of full-length CSP is regulated by Hsc70-SGT 16469739_Cysteine string protein monitors late steps in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator biogenesis 18314541_First evidence that CSP and HSP70, and their interactions with MARCKS, are involved in mucin secretion from airway epithelium. 18596047_palmitoylation of CSP is enhanced specifically by co-expression of the Golgi-localized palmitoyl transferases DHHC3, DHHC7, DHHC15, or DHHC17 19098309_Csp not only regulates the exit of CFTR from the ER, but this action is accompanied by Hsc70/Hsp70 and CHIP-mediated CFTR degradation. 21820099_A neuroprotective role for CSPalpha in humans is confirmed. 22073189_This is the first replication study of the identification of DNAJC5 as the disease-causing gene for autosomal dominant ANCL. The identification of the novel gene in ANCL will allow us to gain a better understanding of the pathological mechanism of ANCLs 22235333_association of DNAJC5 mutations with autosomal dominant Kufs disease 22902780_Palmitoylation-induced aggregation of mutant CSP-alpha proteins may underlie the development of adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis 22978711_Results indicate of a p.L116del mutation in DNAJC5 from families with autosomal dominant Kufs disease. 24126164_Missense mutations in DNAJC5 does not play a major role in PD in the Chinese population. 25631211_the presynaptic vesicle protein CSPalpha is a key player in synaptic degeneration and protection in Alzheimer's disease. 26610600_These results suggest that the degeneration seen in the patients with AD-ANCL reported here might be a consequence of both the early effects of CSPalpha mutations at the cellular soma. 26659577_This study demonstrated that Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis with DNAJC5/CSPalpha mutation has PPT1 pathology and exhibit aberrant protein palmitoylation. 27261198_In fact, DnaJC5 overexpression induced tau release in cells, neurons, and brain tissue, but only when activity of the chaperone Hsc70 was intact and when tau was able to associate with this chaperone. 27452402_Phosphorylation of CSP triggers a major conformational switch that modulates its protein interactions. 28127059_The importance of specific residues in the cysteine-string domain was investigated, revealing that a central core of palmitoylated cysteines is essential for aggregation of adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis CSPalpha L115R/L116 mutants. 28424476_Results indicate that by assisting local lysosome/proteasome processes, CSPalpha-mediated removal of toxic proteins via extracellular vesicles plays a central role in synaptic proteostasis. 28740222_Study demonstrate that primary dermal fibroblasts from asymptomatic mutation carriers recapitulate features of adult-neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (AD-ANCL) in vitro including CSPalpha-p.L115R/CSPalpha-WT aggregates and the structural and functional lysosomal dysfunction found in the brains of AD-ANCL patients. Further findings support a gain-of-function mechanism for CSPalpha mutations leading to AD-ANCL. 29506599_This report describes the clinical history of autosomal dominant Kufs disease, the genetic mutation within the DNAJC5 gene, and the neuropathological findings demonstrating depletion of choline acetyltransferase in the brain. 30561534_Clinical distinction of type A (progressive myoclonus epilepsy) and type B (dementia with motor disturbance) Kufs disease was supported by molecular diagnoses. Type A is usually caused by recessive pathogenic variants in CLN6 or dominant variants in DNAJC5. Type B Kufs is usually associated with recessive CTSF pathogenic variants. 31919451_Autosomal-dominant adult neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis caused by duplication in DNAJC5 initially missed by Sanger and whole-exome sequencing. 32042150_Point mutations in cysteine string protein-alpha (CSP alpha) cause dominantly inherited adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (ANCL). Normally palmitoylated cysteine string region of cysteine string protein alpha loses palmitoylation in ANCL mutants. 32783189_Autosomal dominant neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis: Clinical features and molecular basis. 33662413_DNAJC5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells proliferation though regulating SKP2 mediated p27 degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000000826 |
Dnajc5 |
528.327155 |
4.9758722968 |
2.314949 |
0.507309178 |
17.722310 |
0.00002556111252972851437237876426333826884729205630719661712646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000076357421764580631637700514069422297325218096375465393066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
997.2832013 |
356.9615502 |
205.4243029 |
52.9701006 |
| ENSG00000101187 |
28231 |
SLCO4A1 |
protein_coding |
Q96BD0 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the Na(+)-independent transport of organic anions such as the thyroid hormones T3 (triiodo-L-thyronine), T4 (thyroxine) and rT3, taurocholate, estrone 3-sulfate, estradiol-17beta-glucuronide and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (PubMed:10873595, PubMed:19129463). Shows a pH-sensitive substrate specificity T4 and estrone 3-sulfate which may be ascribed to the protonation state of the binding site and leads to a stimulation of substrate transport in an acidic microenvironment (PubMed:19129463). Hydrogencarbonate/HCO3(-) acts as the probable counteranion that exchanges for organic anions (PubMed:19129463). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10873595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19129463}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity and thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in sodium-independent organic anion transport. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:28231; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; organic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008514]; prostaglandin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015132]; sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015347]; thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015349]; sodium-independent organic anion transport [GO:0043252] |
15994332_oligomerization of Oatp1a1 with PDZK1 is critical for its proper subcellular localization and function 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21486766_Compared with the adult cerebral cortex, mRNAs encoding OATP1A2, OATP1C1, OATP3A1 variant 2, OATP4A1, LAT2 and CD98 were reduced in fetal cortex at different gestational ages, whilst mRNAs encoding MCT8, MCT10, OATP3A1 variant 1 and LAT1 were similar. 25301452_High OATP4A1 expression is associated with small cell lung cancer. 26349991_our results revealed altered OATP3A1 and OATP4A1 mRNA levels and novel mechanisms that might be involved in their regulation in colorectal cancer 28378090_SLCO4A1 may be a valuable marker of poor prognostic for colorectal cancer (CRC). Furthermore, SLCO4A1 plays an important role in CRC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and carcinogenesis 29734253_Abundance of the Organic Anion-transporting Polypeptide OATP4A1 in Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer Patients: Association With Disease Relapse. 34638773_Placental Expression of Bile Acid Transporters in Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. |
ENSMUSG00000038963 |
Slco4a1 |
958.729103 |
8.4773695764 |
3.083617 |
0.095143507 |
1023.442834 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001441110275909177181025170880328049356115442989282224750915486261537317001168648267687146022773778359544090 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001530272494418665983666980250159329105912196751868694009759739531244841451838169809795223557025199347856750 |
Yes |
Yes |
1783.5176777 |
116.3915352 |
211.9733980 |
11.1600145 |
| ENSG00000101210 |
1917 |
EEF1A2 |
protein_coding |
Q05639 |
FUNCTION: This protein promotes the GTP-dependent binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the A-site of ribosomes during protein biosynthesis. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Autism spectrum disorder;Disease variant;Elongation factor;Epilepsy;GTP-binding;Intellectual disability;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes an isoform of the alpha subunit of the elongation factor-1 complex, which is responsible for the enzymatic delivery of aminoacyl tRNAs to the ribosome. This isoform (alpha 2) is expressed in brain, heart and skeletal muscle, and the other isoform (alpha 1) is expressed in brain, placenta, lung, liver, kidney, and pancreas. This gene may be critical in the development of ovarian cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:1917; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of lysosomal membrane [GO:0098574]; eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 complex [GO:0005853]; synapse [GO:0045202]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; translation elongation factor activity [GO:0003746]; translation factor activity, RNA binding [GO:0008135]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of lipid kinase activity [GO:0090218]; regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy [GO:1904714]; translation [GO:0006412]; translational elongation [GO:0006414] |
12053177_This is a putative oncogene in ovarian cancer. 14588074_Review. EEF1A2 is an important ovarian oncogene. The protein elongation network can activate tumorigenesis and inhibit apoptosis. 15893736_These results indicate that the use of cellular promoters such as those for EF-1alpha and ubiquitin C might direct prolonged gene expression in hematopoietic and mesenchymal progenitor cells. 16156888_eEF1A2 may have a role in cytoskeletal remodelling or apoptosis in breast neoplasms 16369491_Overexpression of EEF1A2 and KCIP-1 is associated with lung adenocarcinoma 17088255_there is a physical and functional relationship between eEF1A2 and PI4KIIIbeta 17130842_Regulates oncogenesis through Akt-dependent cytoskeletal remodeling. 17437010_The oncogenicity of eEF1A2 may be related either to its role in protein synthesis or to potential non-canonical functions. 17825975_The expression level of EEF1A2 correlates with cell growth but not apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with different differentiation grades. 17908984_EEF1A2 is highly homologous and functionally similar to the EEF1A1 oncogene, and was found to be restricted only to the normal tissues of the heart, brain, and skeletal muscle 18322813_overall, this study does not support an associated between statin use and prostate cancer but a reduced risk cannot be ruled out. 18474610_Study finds that eEF1A2 stimulates formation of filopodia by increasing the cellular abundance of cytosolic and plasma membrane-bound phosphatidylinositol-4,5 bisphosphate. 18978249_this population-based study of individuals with incident AD, use of statins and beta-blockers was associated with delay of functional decline. 19138673_eEF1A2 might play an important role in pancreatic carcinogenesis, possibly by acting as a tumour oncogene. 19636410_created and validated comparative three-dimensional (3-D) models of eEF1A1 and eEF1A2 on the basis of the crystal structure of homologous eEF1A from yeast 19723040_Studies indicate that the EEF1A2 abnormal expression in cancers correlates with a poor prognosis. 19966453_the interaction of ZPR1 and eEF1alpha 20505761_EEF1A2 may play contribute to the induction or progression of some plasmacytomas and a small percentage of multiple myeloma. 20819441_Levels of eEF1A2 and alpha-actinin-4 mRNA appeared to be unrelated to breast tumour size, except for a significant down-regulation of alpha-actinin-4 mRNA in T3 cases. 20864512_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21851817_The eEF1A2 likely plays an important role in mammary neoplasia and acinar development. 22095224_Pilot evaluation in archive prostate tissues showed the presence of EEF1A2 mRNA in near all neoplastic and perineoplastic but not in normal samples or in benign adenoma; in contrast, EEF1A1 mRNA was everywhere detectable 23444377_Data conclude that the interaction of p16(INK4a) with eEF1A2, and subsequent downregulation of the expression and function of eEF1A2 is a novel mechanism explaining the anti-proliferative effects of p16(INK4a). 23608534_a role for a RACK1/JNK/eEF1A2 complex in the quality control of newly synthesized polypeptides in response to stress 23695020_miR-663 and miR-744 mediate inhibition of the proto-oncogene eEF1A2 expression that results in retardation of the MCF7 cancer cells proliferation. We also observed upregulation of miR-663 and miR-744 with corresponding downregulation of eEF1A2 in resveratrol-treated MCF7 cells, suggesting that resveratrol may influence eEF1A2 expression through a miRNA-dependent pathway. 23739844_results provide evidence of eEF1A2 as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of aggressive pancreatic cancer 24285179_The activation level of the EEF1A2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MDM4 axis significantly influences the survival probability of hepatocellular carcinoma patients 24510995_There was no significant correlation between eEF1A2 protein and mRNA expression levels. Negative immunostaining of eEF1A2 predicted for poor prognosis of NSCLC. 24697219_De novo EEF1A2 mutations in patients with characteristic facial features, intellectual disability, autistic behaviors and epilepsy. 24853801_Our data suggests that eEF1A2 plays an important role in prostate cancer development, especially in inhibiting apoptosis. 25394965_Finally, a strong association between the expression of EEF1A2, phosphorylated AKT and MDM4 was observed in human HCC samples. Strong activation of the EEF1A2/PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MDM4 signaling pathway was observed in HCC patients 25436608_Both eEF1A1 and eEF1A2 colocalise with all eEF1B subunits, in such close proximity that they are highly likely to be in a complex. 25601347_Overexpression of eEF1A2 was correlated with worse outcomes in gastric cancer patients, suggesting its critical roles in the carcinogenesis of gastric cancer. 26212729_Our results provide novel information on the intracellular distribution and interaction of eEF1A isoforms. 26682508_In both cases, a de novo recurrent heterozygous mutation in EEF1A2 [c.364G>A (p.E122K)] was identified by whole-exome sequencing. CONCLUSION: This report provides clinical data on epileptic encephalopathy in patients with EEF1A2 mutation. Continuous high-voltage delta activity seen over both parietal areas may be a unique manifestation of EEF1A2 mutation. 27082702_Differential gene expression analysis demonstrated significant upregulation of PDZK1IP1, EEF1A2 and RPL41 (ENSG00000279483) genes in the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma samples when compared with the matched paratumor samples. 27122673_eEF1A2 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. Its silencing significantly decreases HCC tumorigenesis, likely by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling. 28911200_We report a pair of siblings carrying a homozygous missense mutation p.P333L in EEF1A2 who exhibited global developmental delay, failure to thrive, dilated cardiomyopathy and epilepsy, ultimately leading to death in early childhood. EEF1A2 appears to be critical for normal heart function in humans, and its deficiency results in clinical abnormalities in neurologic function as well as in skeletal and cardiac muscle defects 28923030_The overexpression of EEF1A2 is a frequent event in localized prostate cancer and is associated with histopathology features and a shorter biochemical recurrence-free survival. Due to its independence from serum PSA levels, EEF1A2 could serve as valuable biomarker in risk-stratification of localized prostate cancer 30132996_EEF1A2 expression is associated with colorectal cancer metastasis. 30370994_The central functional component of the complex is eEF1A, which occurs as two independently encoded variants with reciprocal expression patterns: whilst eEF1A1 is widely expressed, eEF1A2 is found only in neurons and muscle. 30381327_Data demonstrate for the first time that TCTP inhibits EF1A2 dimer formation and facilitates the interaction of EF1A2 with other elongation factors. 30782564_Here, the authors showed that HIV-1 reverse transcriptase interacted more strongly with eEF1A1 than with eEF1A2 in immunoprecipitation assay. 31220107_data showed a negative prognostic role of eEF1A2 protein in triple-negative breast cancer, sustaining further investigations to confirm this result by wider and independent cohorts of patients 31876369_SNX16 activates c-Myc signaling by inhibiting ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of eEF1A2 in colorectal cancer development. 32032648_expression pattern, histological analysis and functional role as a promoter of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in brain tumors 32062104_EEF1A2 mutations in epileptic encephalopathy/intellectual disability: Understanding the potential mechanism of phenotypic variation. 32160274_Recapitulation of the EEF1A2 D252H neurodevelopmental disorder-causing missense mutation in mice reveals a toxic gain of function. 32196822_Damaging de novo missense variants in EEF1A2 lead to a developmental and degenerative epileptic-dyskinetic encephalopathy. 32347192_Dimethylation of eEF1A at Lysine 55 Plays a Key Role in the Regulation of eEF1A2 on Malignant Cell Functions of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 32881299_EEF1A2 and ERN2 could potentially discriminate metastatic status of mediastinal lymph node in lung adenocarcinomas harboring EGFR 19Del/L858R mutations. 33035587_EEF1A2 triggers stronger ERK mediated metastatic program in ER negative breast cancer cells than in ER positive cells. 33121982_Whole-proteome analysis of mesonephric-derived cancers describes new potential biomarkers. 33144545_Hepatitis B Virus DNA Polymerase Displays an Anti-Apoptotic Effect by Interacting with Elongation Factor-1 Alpha-2 in Hepatoma Cells. 33473168_EEF1A2 interacts with HSP90AB1 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via enhancing TGF-beta/SMAD signalling. 34475047_Preclinical Activity of Plitidepsin Against Clear Cell Carcinoma of the Ovary. 35594436_eEF1A2 knockdown impairs neuronal proliferation and inhibits neurite outgrowth of differentiating neurons. 35741005_Analysis of the Expression and Subcellular Distribution of eEF1A1 and eEF1A2 mRNAs during Neurodevelopment. |
ENSMUSG00000016349 |
Eef1a2 |
27.885015 |
0.2608233901 |
-1.938855 |
0.335801584 |
35.179148 |
0.00000000300726372593119088476270875040247815279670362542674411088228225708007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000013754946574138326463362445146142165608438290291815064847469329833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8700818 |
2.5082366 |
45.7829876 |
5.3829343 |
| ENSG00000101294 |
81502 |
HM13 |
protein_coding |
Q8TCT9 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes intramembrane proteolysis of some signal peptides after they have been cleaved from a preprotein, resulting in the release of the fragment from the ER membrane into the cytoplasm. Required to generate lymphocyte cell surface (HLA-E) epitopes derived from MHC class I signal peptides (PubMed:11714810). May be necessary for the removal of the signal peptide that remains attached to the hepatitis C virus core protein after the initial proteolytic processing of the polyprotein (PubMed:12145199). Involved in the intramembrane cleavage of the integral membrane protein PSEN1 (PubMed:12077416, PubMed:11714810, PubMed:14741365). Cleaves the integral membrane protein XBP1 isoform 1 in a DERL1/RNF139-dependent manner (PubMed:25239945). May play a role in graft rejection (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D8V0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11714810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12077416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12145199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14741365, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25239945}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene, which localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum, catalyzes intramembrane proteolysis of some signal peptides after they have been cleaved from a preprotein. This activity is required to generate signal sequence-derived human lymphocyte antigen-E epitopes that are recognized by the immune system, and to process hepatitis C virus core protein. The encoded protein is an integral membrane protein with sequence motifs characteristic of the presenilin-type aspartic proteases. Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:81502; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0098554]; Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex [GO:0036513]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0098553]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; aspartic endopeptidase activity, intramembrane cleaving [GO:0042500]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; membrane protein proteolysis [GO:0033619]; membrane protein proteolysis involved in retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol [GO:1904211]; regulation of heme oxygenase activity [GO:0061960]; signal peptide processing [GO:0006465] |
12077416_identified human signal peptide peptidase as a polytopic membrane protein with sequence motifs characteristic of the presenilin-type aspartic proteases [SPP] 12139484_identification and molecular cloning; expression analysis of the hIMP1 gene (located on chromosome 20) was performed in human cell tissues and transfected cell cultures [IMP1] 12972007_widespread expression of SPP in many tissues 14704149_signal peptide peptidase forms a homodimer that is labeled by an active site-directed gamma-secretase inhibitor 14741365_IMP1 is a bi-aspartic polytopic protease capable of cleaving transmembrane proteins such as presenilin 2. 14988012_The peptide structure corresponding to the C-terminal residues from H13 ribosomal protein was determined using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. 15385547_SPP, SPPL2a, -2b, -2c, and -3 probably cleave type II-oriented substrate peptides as shown by consensus analysis 16730383_Compares a variant from the mouse ortholog to the human gene. 16738546_data implicate SPP in the US2 pathway and indicate the possibility of a previously unknown function for this intramembrane-cleaving aspartic protease in dislocation from the endoplasmic reticulum 16834339_Upon isolation of membranes and solubilization with detergent, the biochemical characteristics of SPP are remarkably similar to gamma-secretase. 21636854_structure of human SPP [SPP] 28198167_This study identifies that SPP affects EGFRvIII secretion profiles and thus promotes tumor progression, providing further understanding of the formation of secreted vesicles and driving role of EGFRvIII in Glioblastoma. 28624439_Though far from complete, our knowledge on pathophysiological functions of SPP/SPPL proteases, in particular based on studies in mice, has been significantly increased over the last years. Based on this, inhibition of distinct SPP/SPPL proteases has been proposed as a novel therapeutic concept e.g. for the treatment of autoimmunity and viral or protozoal infections, as we will discuss in this review. 29155886_The domains involved in HO-1 translocation have been identified, and it was shown that SPP-mediated HO-1 cleavage is isoform-specific (HO-1 vs HO-2) and independent of heme oxygenase activity. 29343547_Preproinsulin signal peptide epitopes are processed by SPP and loaded for HLA-guided immune recognition via pathways that are enhanced during type 1 diabetes pathogenesis. 30348988_Study demonstrates that SPP is highly induced in lung and breast cancers and promotes tumor progression, at least in part, by facilitating the degradation of mTOR inhibitor FKBP8. 36153332_Histocompatibility Minor 13 (HM13), targeted by miR-760, exerts oncogenic role in breast cancer by suppressing autophagy and activating PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000019188 |
H13 |
2532.933074 |
2.1439547556 |
1.100274 |
0.046206082 |
562.633818 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022473847716673739942404410177433939673108752838726098364792102361252640334866668736452161643808746147753921615518666179506150157282374932761946311271855816509698030217772507110811900632350056420127090853563 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011932157996334690509913244898030717559075997148899838424747973789987987281258701790424370683175921430900323581650828011547122014364990115157937121404523760701717697771963168216175151894691586932165972045177 |
Yes |
Yes |
3550.7470444 |
91.3887165 |
1667.8965788 |
33.0769850 |
| ENSG00000101307 |
10326 |
SIRPB1 |
protein_coding |
O00241 |
FUNCTION: Immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. Participates also in the recruitment of tyrosine kinase SYK. Triggers activation of myeloid cells when associated with TYROBP (PubMed:10604985). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10604985}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the signal-regulatory-protein (SIRP) family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP family members are receptor-type transmembrane glycoproteins known to be involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. This protein was found to interact with TYROBP/DAP12, a protein bearing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. This protein was also reported to participate in the recruitment of tyrosine kinase SYK. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009]. |
|
cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
16081415_SIRP beta 1 is a disulfide-linked homodimer in leukocytes that regulates neutrophil transepithelial migration 19034380_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the temporal lobe from patients with schizophrenia. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19893026_SIRPbeta1 is a novel IFN-induced microglial receptor that supports clearance of neural debris and Abeta aggregates by stimulating phagocytosis. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 25039969_SIRPB1 copy-number polymorphism was significantly associated with impulsive-disinhibited personality scores in a dose-dependent manner. 31349540_Deletions in Genes Participating in Innate Immune Response Modify the Clinical Course of Andes Orthohantavirus Infection. |
ENSMUSG00000095788+ENSMUSG00000095028+ENSMUSG00000074677+ENSMUSG00000037902+ENSMUSG00000078780+ENSMUSG00000078783 |
Sirpb1a+Sirpb1b+Sirpb1c+Sirpa+Gm5150+Gm9733 |
62.613370 |
2.7431111350 |
1.455813 |
0.442978675 |
9.756177 |
0.00178721182206431562951298719355008870479650795459747314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003987792364878200122857432319278814247809350490570068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
89.8375831 |
23.7743888 |
32.7839757 |
6.4670713 |
| ENSG00000101336 |
3055 |
HCK |
protein_coding |
P08631 |
FUNCTION: Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase found in hematopoietic cells that transmits signals from cell surface receptors and plays an important role in the regulation of innate immune responses, including neutrophil, monocyte, macrophage and mast cell functions, phagocytosis, cell survival and proliferation, cell adhesion and migration. Acts downstream of receptors that bind the Fc region of immunoglobulins, such as FCGR1A and FCGR2A, but also CSF3R, PLAUR, the receptors for IFNG, IL2, IL6 and IL8, and integrins, such as ITGB1 and ITGB2. During the phagocytic process, mediates mobilization of secretory lysosomes, degranulation, and activation of NADPH oxidase to bring about the respiratory burst. Plays a role in the release of inflammatory molecules. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and actin polymerization, formation of podosomes and cell protrusions. Inhibits TP73-mediated transcription activation and TP73-mediated apoptosis. Phosphorylates CBL in response to activation of immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptors. Phosphorylates ADAM15, BCR, ELMO1, FCGR2A, GAB1, GAB2, RAPGEF1, STAT5B, TP73, VAV1 and WAS. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10092522, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10779760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10973280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11741929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11896602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12411494, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15010462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15952790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15998323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17310994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17535448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19114024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19903482, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20452982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21338576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7535819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8132624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9406996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9407116}. |
3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Exocytosis;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phagocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Src family of tyrosine kinases. This protein is primarily hemopoietic, particularly in cells of the myeloid and B-lymphoid lineages. It may help couple the Fc receptor to the activation of the respiratory burst. In addition, it may play a role in neutrophil migration and in the degranulation of neutrophils. Multiple isoforms with different subcellular distributions are produced due to both alternative splicing and the use of alternative translation initiation codons, including a non-AUG (CUG) codon. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:3055; |
caveola [GO:0005901]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; innate immune response-activating signaling pathway [GO:0002758]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; leukocyte degranulation [GO:0043299]; leukocyte migration involved in immune response [GO:0002522]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; localization [GO:0051179]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050764]; regulation of podosome assembly [GO:0071801]; respiratory burst after phagocytosis [GO:0045728]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060333] |
1875927_Alternate use of a non-AUG (CUG), and an in-frame, downstream AUG translation initiation codon, results in the production of 2 isoforms in mouse and human. 10967098_Alternate use of a non-AUG (CUG), and an in-frame, downstream AUG translation initiation codon, results in the production of two isoforms with different subcellular localization. 11500821_A dominant negative form of Hck, in an interaction that is SH3 domain dependent, blocks HIV-1 Nef induced MHC class I downregulation. 11976726_SH3-dependent stimulation of Src-family kinase autophosphorylation without tail release from the SH2 domain in vivo 12592324_The interaction of the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase with this protein is mediated by multiple binding domains. 12900520_These results suggest that CSF-induced and HIV-1-mediated regulation of Hck and C/EBPbeta represent the heterogeneous susceptibility of tissue macrophages to HIV-1 infection. 14551197_C3G and Hck interact physically and functionally in vivo to activate kinase-dependent and caspase-mediated apoptosis, which is independent of catalytic domain of C3G 14969582_SRC kinases LYN & HCK let engaged b2 integrins form focal-adhesion-like structures needed for stable shear-resistant PMN adhesion. SRC-dependent outside-in signalling is needed for integrin adhesiveness triggered by a classical chemoattractant like IL-8. 15010462_Gab2 docking proteins in IL-6-induced proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. 15263807_In humans, the cytoplasmic domain of ADAM15v2 strongly interacts with Lck and Hck and regulates leukocyte function. 15626739_HIV-1 Nef interferes with M-CSF receptor signaling through Hck activation and thereby inhibits M-CSF functions in monocytes/macrophages. 16210316_data support the existence of multiple active conformations of Src family member Hck kinase that may generate unique downstream signals 16271895_The free energy surface shows that the N-terminal end of HCK acts as a reversible two-state conformational switch coupling the catalytic domain to the regulatory modules. 17024369_Data suggest that the insertion/deletion polymorphism could be a functional polymorphism of the Hck gene, may contribute to COPD pathogenesis and modify COPD-related phenotypes. 17024369_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17141806_The structure of the HckSH3:PD1 complex reveals novel features of SH3 ligand binding and yields new insights into the structural basics of SH3-ligand interactions. 17535448_p73 is identified as a novel substrate and interacting partner of Hck and it regulates p73 through mechanisms that are dependent on either catalytic activity or protein interaction domains. 17668209_hematopoietic cell kinase (hct) phosphorylates fems-like tyrosine kinase 3(FLT3) in the JM region and inhibits its maturation 17893228_Nef perturbs the intracellular maturation and the trafficking of nascent Fms, through a unique mechanism that required both the activation of Hck and the aberrant spatial regulation of the active Hck 18794796_Hck has a nonredundant function as a key downstream signaling partner for Bcr-Abl and may represent a potential drug target in CML 19211505_HCK and BIN1 plays critical roles in AHI-1-mediated leukemic transformation of cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. 19585521_This finding establishes an intriguing link between the pathogenesis of Nef and a newly emerging concept that the Golgi-localized Src kinases regulate the Golgi function. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20181660_Taken together, PKR and Hck were critical for DON-induced ribosomal recruitment of p38, its subsequent phosphorylation, and, ultimately, p38-driven proinflammatory cytokine expression. 20488787_Nef participates in HIV-1-induced multinucleated giant cells formation via a p61Hck- and lysosomal enzyme-dependent pathway 20670214_Identification and biophysical assessment of the molecular recognition mechanisms between the human haemopoietic cell kinase Src homology domain 3 and ALG-2-interacting protein X. 20798061_BSS-SAXS reconstruction is used to reveal the structural organization of Hck in solution and the different shifts in the equilibrium population of assembly states upon the binding of different signaling peptides 20810664_Data show that the structures and relative orientations of the SH2 and SH3 domains down-regulated Hck. 21567396_Hck activation at the Golgi apparatus causes the HIV-1 Nef-induced c-Fms proto-oncogene N-glycosylation defect. 21878628_Hck acts as a key regulator controlling gene expression in alternatively activated monocytes/macrophages. 21993313_Loss of HCK is associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. 22021612_we show that Hck, has a pre-eminent role in LPS/TLR4-induced TNF and IL-6 production. 22185326_There were significant differences in the genotype and allele distribution of -627 G/T polymorphism in Hck gene between cases and controls. 22393415_the activation of Hck, Lyn and c-Src by Nef is highly conserved among all major clades of HIV-1 22641034_This particular binding mode enables Hck SH3 to sense a specific non-canonical residue situated in the SH3 RT-loop of the kinase. 23439650_The SRC family tyrosine kinase HCK and the ETS family transcription factors SPIB and EHF regulate transcytosis across a human follicle-associated epithelium model. 23896410_Data indicate that combined treatment using SFK (LYN, HCK, or FGR) and c-KIT inhibitor dasatinib dasatinib and chemotherapy provides a novel approach to increasing p53 activity and enhancing targeting of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) stem cells. 24051604_Interaction between Nef and Hck is important for Nef-dependent modulation of viral infectivity. 25122770_Interaction with the Src homology (SH3-SH2) region of the Hck structures the HIV-1 Nef dimer for kinase activation and effector recruitment. 25972488_we provide evidence for involvement of HCK and FGR in FCRL4-mediated immunoregulation and for the functional importance of posttranslational modifications of the FCRL4 molecule. 27143257_HCK represents a novel target for therapeutic development in MYD88-mutated Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia and activated-B cell diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and possibly other diseases driven by mutated MYD88. 27485399_three-dimensional (3D) QSAR pharmacophore models were generated for Hck based on experimentally known inhibitors. A best pharmacophore model, Hypo1, was developed with high correlation coefficient (0.975), Low RMS deviation (0.60) and large cost difference (49.31), containing three ring aromatic and one hydrophobic aliphatic feature 27531930_Lysophosphatidylcholines prime polymorphonuclear neutrophil through Hck-dependent activation of PKCdelta, which stimulates PKCgamma, resulting in translocation of phosphorylated p47(phox). 28399411_High HCK levels correlate with reduced survival of colorectal cancer patients and is associated with activated macrophages gene signature. 29331674_HIV infection induced Hck activation.Myeloid cells require Hck for ADAM17 activation and secretion 29962266_These results suggest that the estrogen-autophagy-STAT3-HCK axis participates in the differentiation of PTGS2(high) IFNG(low) PRF1(low) GZMB(low) FCGR3(-) NK cells in ectopic lesion microenvironment. 31790499_These studies show that Hck and Fgr expression influences inhibitor sensitivity and the pathway to acquired resistance in Flt3-ITD+ AML. 31877324_Membrane Anchoring of Hck Kinase via the Intrinsically Disordered SH4-U and Length Scale Associated with Subcellular Localization. 32226298_Nucleotide binding domain and leucine-rich repeat pyrin domain-containing protein 12: characterization of its binding to hematopoietic cell kinase. 32484210_HCK promotes glioblastoma progression by TGFbeta signaling. 32591642_Identification of the SRC-family tyrosine kinase HCK as a therapeutic target in mantle cell lymphoma. 33162805_HCK can serve as novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for Breast Cancer patients. 33617879_Selective targeting of the inactive state of hematopoietic cell kinase (Hck) with a stable curcumin derivative. 33894273_miR-181b and miR-204 suppress the VSMC proliferation and migration by downregulation of HCK. 34167558_HCK maintains the self-renewal of leukaemia stem cells via CDK6 in AML. 35255496_A new role for the SRC family kinase HCK as a driver of SYK activation in MYD88 mutated lymphomas. 35280440_HCK is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker that Correlates with Immune Cell Infiltration in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 35639855_Kinase-deficient BTK mutants confer ibrutinib resistance through activation of the kinase HCK. |
ENSMUSG00000003283 |
Hck |
167.627642 |
4.8969194518 |
2.291874 |
0.147476305 |
253.700024 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000405344391542452526348867082667156482139218262943381949092771848726132877489177286033757657713253940525839464509967455901872361386269629608073566950920962881355080753564834594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000098564797679845142520756613582705882425749885561154779070614210050142947611288208627973452353978304536487392468703965685797500413906245737317990407433399013825692236423492431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
284.7018728 |
23.6663612 |
58.5528425 |
4.2323914 |
| ENSG00000101342 |
140711 |
TLDC2 |
protein_coding |
A0PJX2 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in response to oxidative stress. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:140711; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
|
ENSMUSG00000074628 |
Tldc2 |
6.494371 |
0.0611496280 |
-4.031512 |
0.997833527 |
22.750025 |
0.00000184501757245797855866767649829496278357510163914412260055541992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006336077098529493772070819712638467535725794732570648193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7447960 |
0.5491813 |
11.8669216 |
3.5013202 |
| ENSG00000101350 |
9371 |
KIF3B |
protein_coding |
O15066 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-based molecular motor that transport intracellular cargos, such as vesicles, organelles and protein complexes. Uses ATP hydrolysis to generate force to bind and move along the microtubule (By similarity). Plays a role in cilia formation (PubMed:32386558). Involved in photoreceptor integrity and opsin trafficking in rod photoreceptors (PubMed:32386558). Transports vesicles containing N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit GRIN2A into neuronal dendrites (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32386558}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Synapse |
|
The protein encoded by this gene acts as a heterodimer with kinesin family member 3A to aid in chromosome movement during mitosis and meiosis. The encoded protein is a plus end-directed microtubule motor and can interact with the SMC3 subunit of the cohesin complex. In addition, the encoded protein may be involved in the intracellular movement of membranous organelles. This protein and kinesin family member 3A form the kinesin II subfamily of the kinesin superfamily. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9371; |
axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; kinesin II complex [GO:0016939]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; midbody [GO:0030496]; plus-end kinesin complex [GO:0005873]; spindle [GO:0005819]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; intraciliary transport particle B binding [GO:0120170]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008574]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; anterograde axonal transport [GO:0008089]; anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex [GO:0098971]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; mitotic centrosome separation [GO:0007100]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; mitotic spindle organization [GO:0007052]; opsin transport [GO:0036372]; plus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule [GO:0072383]; positive regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032467]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
15345558_both motor domains of KIF3A/B coordinate for processive motility and move at different speeds 16298999_Interaction of KIF3A/3B with KAP3 may be important for the proper progression of mitosis. 17008358_kinesin-2 is a linker between polycystin-2(PC2) and fibrocystin and mediates the regulation of PC2 channel function by fibrocystin 18957512_Rip11/FIP5-kinesin-II complex plays a key role in the routing of internalized receptors through the perinuclear recycling endosomes. 19339549_Data indicate that p0071 and Ect2 are transported via distinct motors and identify a novel pathway implicating KIF3 in the regulation of actin organization during cytokinesis 19940036_Interaction with KIF3B alters CLC-5 cell surface expression, chloride current, and alters albumin endocytosis. Interaction with KIF3B facilitates microtubular transport and endocytosis of CLC-5-containing vesicles away from cell surface. 21871436_KIF3B is involved in the trafficking of kAE1 to the plasma membrane of human kidney alpha-intercalated cells. 24368420_Results suggest that KIF3B expression was upregulated in HCC tumor tissues and proliferating HCC cells, and an increasd KIF3B expression was associated with poor overall survival. 25588831_These data suggest that GLI interactions with KIF3A-KIF3B-KAP3 complexes are essential for proper GLI transcriptional activity. 28161539_High KIF3B expression is associated with seminoma. 28761002_The rate of transport is set by an equilibrium between a faster state, where only kinesin family member 17 protein (KIF17) motors move the train, and a slower state, where at least one kinesin family member 3A/B protein (KIF3AB) motor on the train remains active in transport. 30720171_miR-127-3p was downregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues and was associated with malignant clinicopathological features and poor prognosis. KIF3B was confirmed to be a direct target of miR-127-3p. Upregulation of KIF3B observed in OSCC promoted tumorigenesis. miR-127-3p targeted KIF3B to inhibit the development of OSCC by suppressing cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 31157987_High KIF3B expression is associated with Pancreatic Cancer. 31746486_Kif3b mutation reduces NMDAR subunit NR2A trafficking and causes schizophrenia. 31773695_LEF-AS1 participates in occurrence of colorectal cancer through adsorbing miR-505 and promoting KIF3B expression. 32237034_Identification of kinesin family member 3B (KIF3B) as a molecular target for gastric cancer. 32386558_Mutations in the Kinesin-2 Motor KIF3B Cause an Autosomal-Dominant Ciliopathy. 33153390_Circular RNA circ_0032462 Enhances Osteosarcoma Cell Progression by Promoting KIF3B Expression. 34918036_KIF3B gene silent variant leading to sperm morphology and motility defects and male infertilitydagger. |
ENSMUSG00000027475 |
Kif3b |
265.885986 |
2.0124655594 |
1.008964 |
0.099362319 |
104.079992 |
0.00000000000000000000000194310528413149531317287469478169507917483578566587200603015263516808175392469593134592287242412567138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000020456657627518450829499744607459268482176572801145893102487630793584472144175379071384668350219726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
357.3320761 |
20.6197829 |
178.9072057 |
8.1640409 |
| ENSG00000101384 |
182 |
JAG1 |
protein_coding |
P78504 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for multiple Notch receptors and involved in the mediation of Notch signaling (PubMed:18660822, PubMed:20437614). May be involved in cell-fate decisions during hematopoiesis (PubMed:9462510). Seems to be involved in early and late stages of mammalian cardiovascular development. Inhibits myoblast differentiation (By similarity). Enhances fibroblast growth factor-induced angiogenesis (in vitro). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18660822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20437614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9462510}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Deafness;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Notch signaling pathway;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The jagged 1 protein encoded by JAG1 is the human homolog of the Drosophilia jagged protein. Human jagged 1 is the ligand for the receptor notch 1, the latter is involved in signaling processes. Mutations that alter the jagged 1 protein cause Alagille syndrome. Jagged 1 signalling through notch 1 has also been shown to play a role in hematopoiesis. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2019]. |
hsa:182; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035909]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; cardiac neural crest cell development involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0061309]; cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003215]; cardiac septum morphogenesis [GO:0060411]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; ciliary body morphogenesis [GO:0061073]; distal tubule development [GO:0072017]; endocardial cushion cell development [GO:0061444]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inhibition of neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0002085]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; loop of Henle development [GO:0072070]; morphogenesis of an epithelial sheet [GO:0002011]; myoblast differentiation [GO:0045445]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022408]; negative regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001953]; negative regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045602]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000737]; nephron development [GO:0072006]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuroendocrine cell differentiation [GO:0061101]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; Notch signaling involved in heart development [GO:0061314]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; podocyte development [GO:0072015]; positive regulation of cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0062043]; positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045639]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; pulmonary artery morphogenesis [GO:0061156]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050678]; regulation of reproductive process [GO:2000241]; response to muramyl dipeptide [GO:0032495]; T cell mediated immunity [GO:0002456] |
11745040_a cell surface protein that functions in an ambryologically important signaling pathway 11964309_interaction with Notch1 on tumor cells dramatically induces proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis in vitro 11999354_inhibits proliferation of cd34+ macrophage progenitors 12022040_Familial deafness, congenital heart defects, and posterior embryotoxon caused by cysteine substitution in the first epidermal-growth-factor-like domain of jagged 1. 12297837_JAG1 gene abnormality may be an aggravating factor in extrahepatic biliary atresia 12357247_experiments in vitro showed that Jagged1 signaling inhibited process outgrowth from primary human oligodendrocytes 12370358_Activation of Notch-1 signaling by Jagged-1 induces monocyte-derived dendritic cell maturation in vitro. 12427653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12442286_Results of this study are consistent with the proposal that either haploinsufficiency for wild-type JAG1 and/or dominant negative effects produced by mutated JAG1 are responsible for the AGS phenotype. 12496248_identification of C-terminal PDZ-ligand is essential for cellular transformation 12497640_Identification of novel Jagged1 mutations in patients with Alagille syndrome. 12649809_Conditional mutation of this protein shows the developing heart is more sensitive than developing liver to JAG1 dosage. 12684674_suppresses the self-renewal capacity and long-term growth of two myeloblastic leukemia cell lines 12826675_Delta and Jagged undergo ADAM-mediated ectodomain processing followed by PS-mediated intramembrane proteolysis to release signaling fragments 12842995_Notch activation by JAG1 in the presence of alloantigen-presenting cells may therefore be a means of inducing specific regulatory T cells while preserving other T-cell functionality 14726396_Notch receptors 1&2 and their ligand Jagged1 are highly expressed in cultured and primary MM cells, suggesting Notch signaling is involved in the tight interactions between neoplastic plasma cells and their bone marrow microenvironment 14769803_induced an attenuation of cell motility which is accompanied by a decrease in actin stress fibers and an increase in adherence junctions and induces a NIH 3T3 cell tranformed phenotype mediated by FGF signaling. 15254769_Delta-1 and Jagged-1 have roles in growth suppression in two myeloid leukemia cell lines 15258909_soluble form of Jagged1, when present in the cell culture medium, was sufficient to induce keratinocyte differentiation 15280477_upregulated in Papillomavirus-mediated cervical neoplasia and required for notch activation. 15358557_structured in solution, as suggested by circular dichroism and NMR spectroscopy, and displays an EGF-like disulfide bond topology, as determined by disulfide mapping 15466172_Dysregulation of JAGGED1 protein levels plays a role in prostate cancer progression and metastasis and suggest that JAGGED1 may be a useful marker in distinguishing indolent and aggressive prostate cancers. 15712272_12 new mutations are described: 5 frameshifts, 3 nonsense, 2 missense, and 2 splice site. 15781650_Down-regulation of Notch-1, Delta-like-1, or Jagged-1 by RNA interference induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in multiple glioma cell lines. 15905075_Jagged1 and GDNF/Ret/GFRalpha1 interact and have a role in regulating ureteric budding and branching 15919944_observed that Jagged1 is preferentially upregulated in human cervical tumors and sustains tumor progression by HPV 16 oncogenes 16013021_Identification of novel Jagged1 mutations in patients with Alagille syndrome. 16307184_Data describe the immunohistochemical staining pattern of four Notch receptors (Notch1-4) and their ligands (Delta1 and Jagged1) in synovial tissues obtained from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 16403414_Wild-type JAG1 is inhibitory for hepatocyte growth factor gene expression; mutant JAG1 reverses the inhibition 16575836_83 novel mutations within the JAG1 gene are associated with Alagille syndrome. 16791277_data indicate a role for JAGGED/Notch signaling in the process of thymic involution 16934875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301032_Increased expression of Notch3, Jagged1, Hes1, and Hes6 gene transcripts were observed during differentiation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells. 17359939_results reveal that Jagged1, which is regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein, may contribute to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma 17368936_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17368936_absence of correlation between mutations in specific JAG1 gene exons and clinical features in patients with leukoencephalopathy CADASIL-like phenotype 17507991_patients with tumors expressing high levels of JAG1 protein had a worse outcome than those with tumors expressing low levels 17661408_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17720887_Mutations in JAGGED1 is associated with Notch signaling inhibition and Alagille syndrome 17822320_Overexpression of jagged1 is associated with breast cancer 17984306_Aberrant expression of Jagged1 and Notch1 are associated with poor outcome in breast cancer 17990101_JAG1 expression is associated with a basal phenotype and recurrence in lymph node-negative breast cancer. 18060036_IL-6 treatment triggered Notch-3-dependent upregulation of the Notch ligand Jagged-1 and promotion of MS and MCF-7-derived spheroid growth 18079963_Notch-1 and the Notch ligand Jagged-1 were expressed at significantly higher levels in CCRCC tumors than in normal human renal tissue, and the growth of primary CCRCC cells was attenuated upon inhibition of Notch signaling. 18192230_The results thus showed that Jag-1-mediated Notch signaling in human bone marrow stromal cells was necessary to initiate chondrogenesis, but it must be switched off for chondrogenesis to proceed. 18266235_This is the first study that explores the possible interaction between JAG1, NOTCH2, and Hey2 in the variable phenotypes observed in patients with Alagille syndrome 18354251_Data show that Jagged1 are abundantly expressed in osteoarthritis. 18563556_Genes more highly expressed in BRCA1-associated tumors included stathmin, osteopontin, TGFbeta2 and Jagged 1 18593716_Two mutations in the NOTCH1 found in patients with left ventricular outflow tract defects reduce JAGGED1 induced signaling. 18632624_Jagged-1 is the primary Notch3 ligand in ovarian carcinoma and Jagged-1/Notch3 interaction constitutes a juxtacrine loop promoting proliferation and dissemination of ovarian cancer cells within the intraperitoneal cavity 18784255_These data demonstrate the existence of novel cross-talk between thrombin, FGF, and Notch signaling pathways, which play important roles in vascular formation and remodeling. 19150223_Delta1 and Jagged1 are expressed in human umbilical cord epithelial cells at the mRNA and protein level. 19150886_NOTCH3 expression is induced in mural cells through an autoregulatory loop that requires endothelial-expressed JAGGED1. 19181211_These hematopoiesis-supportive clones also showed high gene expression of Jaggedl, a Notch ligand, as well as high potential to deposit calcium after osteogenic induction. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19393188_TNF induction of jagged-1 in endothelial cells is NFkappaB-dependent 19398721_the 3' untranslated regions of WNT1 and JAG1 were functional targets of miR-34a and miR-21 and provide evidence that these targets were translationally suppressed 19430482_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19542446_Of two Notch ligands (Jagged 1 and Delta-like 1) expressed by follicular dendritic cells, Jagged 1 appears to have a dominant role in germinal center B lymphocyte survival in tonsillar tissue. 19586525_A single, evolutionary conserved exon defines an autonomous structural unit that, despite the minimal structural context, closely matches the structure of the same region in the entire receptor binding module. 19603167_Jagged1 was marginally lower patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura. 19728763_Decreased jagged1 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 19780835_study of tetralogy of Fallot associated G274D mutation in the second epidermal growth factor repeat of Jagged-1; found the G274D mutation impairs correct folding of the epidermal growth factor module & cannot be rescued by compensative mutations 19816565_possible complementary role for JAG1 and DLL4 in the context of Kaposi sarcoma. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915977_We show that JAG1 down-regulation reduces direct binding of Notch to the cyclin D1 promoter 19935714_The expression of Jagged1, a ligand for canonical Notch signaling, was restricted to enteroendocrine cells or undetectable in the mucosa of the human small and large intestine, respectively. 19948535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20038814_Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates murine and human cell differentiation through STAT3/p63/Jagged/Notch cascade. 20040020_Notch signaling may participate in controlling cell differentiation and proliferation in normal bone and COF of the jaws. Notch signaling disorder may be a molecular incident in COF occurrence and development. 20096396_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20096396_These results identify the JAG1 gene as a candidate for bone mineral density regulation in different ethnic groups, and it is a potential key factor for fracture pathogenesis. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20437614_Data identified one frameshift and two missense mutations in the tetralogy of Fallot cases, one frameshift and two missense mutations in cases with pulmonic stenosis/peripheral pulmonary stenosis/pulmonary valve atresia with intact ventricular septum. 20437614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20517681_A Jagged-1-Notch-1 activation loop between tumor cells in head and neck cancer may function to promote tumor formation and progression. 20554499_Jagged protein 1 is involved in the cytodifferentiation of squamous odontogenic tumors of the mandible. 20580881_JAG1 expression was significantly increased in patient with Schizophrenia. 20586101_the interaction between the PDZ domain of afadin (AF6_PDZ) and a series of polypeptides comprising the PDZ-binding motif, was studied. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20683201_Sequence analysis of the genes identified 27% cholestasis subjects with missense, nonsense, deletion, and splice site variants associated with disease phenotypes based on the type of mutation in the JAG1, ATP8B1, ABCB11, or ABCB4 genes. 20800871_Our results indicate importance of NOTCH1 and JAGGED1 expression in plasma cell neoplasia and a possible diagnostic value of their immunohistochemical evaluation of bone marrow infiltrates for multiple myeloma. 20812035_Notch1, Jagged1 and Delta1 expression appear to be relevant prognostic markers in intermediate risk acute myeloid leukemia. 20819075_Jagged1 is shed by ADAM17 in a lipid-raft-independent manner, and the cytosolic domain of the former protein is not a pre-requisite for either constitutive or regulated shedding shedding. 20819128_Jagged1 was significantly more highly expressed in lymph node metastasis-positive tongue carcinoma. 20829885_Jagged1 protein inhibits the effects of SCF on erythroid cell expansion. 20833210_data suggest that Jagged/Notch signalling is required for a subset of TGFbeta1-responsive genes, and that complex signalling pathways are involved in the crosstalk between TGFbeta1 and Notch cascades in kidney epithelia 20870935_Jagged1 is an RBP-J target gene that is activated in a binary manner by TLR and Notch pathways. 20953350_expression regulated by Notch3 and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in ovarian cancer 21062756_High Jagged1 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma 21103979_Results suggest that common variants in JAG1 are not strongly associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes among white individuals. Findings cannot exclude these genes from involvement in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 21145176_Notch1 and Jagged1 are up-regulated in human colon adenocarcinoma and suggests that Notch1/Jagged1 signaling might play a role in the development of colon adenocarcinoma. 21199807_data suggest that JAG1-induced Notch activation results in breast cancer progression through upregulation of the plasminogen activator system, directly linking these 2 important pathways of poor prognosis 21266409_suggest that the prosensory function of Jag1 resides in its ability to generate discrete domains of Notch activity that maintain Sox2 expression within restricted areas of an extended neurosensory-competent domain 21602525_The stromal cell-mediated antiapoptotic effect on B- ALL cells is mediated by Notch-3 and -4 or Jagged-1/-2 and DLL-1 in a synergistic manner. 21637926_RUNX3 expression suppressed JAG1 expression and resulted in downregulation of tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 21639801_NOTCH2 expression and activation, independent of JAGGED1 expression, may contribute to the pathogenesis of hepatoblastoma. 21685392_miR-143/145 as activated independently by Jag-1/Notch and SRF in parallel pathways. 21752016_JAG1 mutations were identified in 59/135 (44%) probands with Alagille syndrome. 21753153_Jagged1 plays dual roles in cancer progression through an angiogenic function in tumor endothelial cells and through proliferation and chemoresistance in tumor cells. 21757656_Endothelial JAGGED1 controls hemangioma stem cell-to-pericyte differentiation in a murine model of infantile hemangioma. Pericytes have a fundamental role in formation of blood vessels in IH. 21810559_Notch signaling molecules, Notch1 and Jagged1, are morphogenesis regulation factors closely related to cytological differentiation in neoplastic cells of ameloblastoma. 21820430_The Jagged-1 intracellular domain (JICD) inhibits Notch1 signaling via a reduction in the protein stability of the Notch1 intracellular domain (Notch1-IC). 21866461_Epigallocatechin-3-gallate upregulated JAG1 gene expression in HT29 and HCT-8 cells, more so in HCT-8 cells. 21893051_Disease-associating novel JAG1 gene variations were found in TOF patients, and seem to play an important role in the causation of the disease 21911304_as compared to MSC, OP9 cells were more efficient at inducing self-renewal and/or de novo generation of primitive (CD34(+) CD38(-) Lin(-)) cells, and suggest that such effects were due, at least in part, to the presence of Jagged-1 and DL1. 22020917_DLL4 and Jagged1 siRNA gene therapy mediated by adenovirus may be useful for inhibiting growth and invasion of SGC7901 through a Notch/VEGF pathway. 22040217_Several JAG1 mutations were found in patients with tetralogy of Fallot. 22080880_Notch1, Jagged1, and Delta1 expressions might be useful markers for clinical prognosis of ovarian carcinomas. Jagged1 could be a marker for tumor grades. 22174012_We did not find an association of rs2273061 polymorphism in JAG1 in Mexican-Mestizo postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. 22204979_Both Notch3 and vascular smooth muscle cells differentiation marker proteins were upregulated, which were abrogated by Jagged1-specific siRNA. 22296176_Dll4 and Jag1 are expressed in glioblastoma vasculature. 22348356_The Notch1-JAG1 axis may enhance the invasive properties of endometrial carcinomas, which suggests the Notch pathway may be a promising target for the treatment of this malignancy. 22357466_The activation of Notch1 signal is common in children with acute leukemia. 22405927_These alterations were located in the extracellular domain of JAG1, in particular in the DSL and EGF-like repeat domain. 22465068_Data show that the PDZ binding motif is preceded by four alpha-helical segments and that, despite the extensive interaction between intracellular region of Jagged-1 J1_tmic and the micelle, the PDZ binding motif remains highly flexible. 22487239_Study suggest the requirement for cell-surface localization of Jagged1 for cis-inhibition activities. 22526456_immunohistochemical analysis of NOTCH1-3, JAGGED1, cMET, and phospho-MAPK in 100 carcinomas of unknown primary 22618231_these results reveal a regulatory interplay between miR-21, JAG1 and E2 that is important for advancing understanding of how the oncogenic potential of miR-21 and JAG1 manifests in different sub-types of breast cancer. 22847978_The ability to control differentiation of human periodontal ligament derived mesenchymal stem cells using modified surfaces containing the affinity immobilized Notch ligand, Jagged-1, was investigated. 22871495_High jagged 1 expression is associated with glioma. 23086448_Here we identified the Notch family member Jagged1 as a physiological ligand for CD46. 23157415_Jagged1 may be involved in differentiation and proliferation of tongue cancer. Targeting Jagged1 RNA interference lentiviral vector can effectively lower Jagged1 mRNA and protein expression levels of Tca8113 cells preventing proliferation of TSCC cells. 23300864_Overexpresion of JAG1 in endothelial cells inhibited cell proliferation, but did not affect cell migration, sprouting angiogenesis or cell adhesion. 23339193_Data indicate that a Notch-1-specific monoclonal antibody blocks binding with Jagged-1/Serrate. 23375636_High soluble form of Jagged-1 is associated with liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. 23379739_derived mesenchymal stem cells (hPDLSCs) on a Jagged-1-modified surface had increased expression of Notch signaling target genes, Hes-1 and Hey-1, suggesting the involvement of Notch signaling in hPDLSCs. 23416080_the juxtamembrane region of Jagged-1, one of the Notch ligands, behaves as a structured module and is cleaved by ADAM17 catalytic domain at E1054. 23752887_The role of NOTCH2 and JAG1 in formation of proximal nephron structures and podocytes might explain the observed phenotypes of renal dysplasia and proteinuria in patients with Alagille syndrome and renal tubular acidosis. 23758219_Overexpression of Jagged-1 and its intracellular domain in human mesenchymal stromal cells differentially affect the interaction with hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. 23934482_our results indicate that NF-kappaB has a non-cell-autonomous role in regulating cancer stem cell populations by forming intratumoural microenvironments composed of JAG1-expressing non-cancer stem cells with a basal-like subtype. 23956173_We hypothesize that a similar mechanism could be present in this patient with del22q11.2 syndrome associated with a JAG1 missense mutation acting as possible modifier factor for tetralogy of Fallot 24138322_3D coculture induced an upregulation of Notch3 receptor in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells and its ligand Jagged1 in human coronary artery endothelial cells. 24239355_the N terminus of human Jagged-1 is a C2 phospholipid recognition domain that binds phospholipid bilayers in a calcium-dependent fashion. 24573085_Short-term activation of Notch signaling by jagged-1 enhances store-operated calcium entry in pulmonary artery smooth muscle. 24604720_A random population of LNCaP prostate cancer cells comprises a heterogeneous group of cells with different androgen-deprivation sensitivities and potential for invasiveness; expression levels of 2 genes known to be regulated by miR-21, an androgen-regulated microRNA, SPRY1 and JAG1 were lower in an androgen insensitive clone, than an androgen sensitive clone. 24659709_Study suggests that the epigenetic silencing of miR-199b-5p during tumor progression is significantly associated with acquired chemoresistance in ovarian cancer through the activation of JAG1-Notch1 signaling. 24708907_This study demonistrated that NOTCH ligands JAG1 and JAG2 as critical pro-survival factors in childhood medulloblastoma. 24722295_downregulation of Jagged1 with lentiviral Jagged1-shRNA resulted in decreased colon cancer cell viability in vitro. 24748328_JAG1 gene mutations are associated with Alagille syndrome. 24788939_Data suggest that extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1/2 signaling can cross-interact with the transforming growth factor beta2/Smad2/3 and the Jagged-1/Notch-3 signaling in retinal pigment epithelium cells epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 24844362_Data show that the median expression of Jagged-1 protein and delta-like 1 protein (Dll-1) was significantly higher in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts than in peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCs). 24861552_Results show an association between sequence variants close to JAG1 at 20p12.2 and the risk of urinary bladder cancer. 24907271_Although Jag1 shares a high degree of homology with Jag2 in the ectodomain region, BACE1 fails to cleave Jag2 effectively, indicating a selective cleavage of Jag1. 25176314_our results suggest that the JAG1/Notch1/OPN cascade represents a potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. 25257302_silencing prevents Notch2-driven osteoclast development and bone destruction in multiple myeloma 25368251_High cytoplasmic Jagged1 expression is associated with laryngeal cancer. 25380486_Data indicate the role for endothelial Jagged1 protein to promote breast tumor through notch protein activation. 25400810_Report no significant association between jagged 1 polymorphisms and bone mineral density in Chinese postmenopausal women. 25424769_Jagged1 expression may be used as an independent prognosis factor in patients with glioblastoma 25514871_EGFRvIII-mediated radioresistance, but not chemoresistance, was also modulated by JAGGED1 25596152_On complete gene sequencing of JAG1 gene as described before, the patient was shown to be heterozygous for a known pathogenic mutationc.270delG (p.C92AfsX69) in exon 2 25676721_AGS is caused by mutations in one of two genes, namely, JAG1 or NOTCH2. These genes are part of the Notch signaling pathway, which is involved in cell fate determination. JAG1 mutations have been identified in 70-94% of individuals with clinically diagnosed AGS 25825216_Vehicular exhaust particles activate an AhR-Jag1-Notch1 cascade to promote allergic airway inflammation in concert with proasthmatic alleles. 25842263_It is also proved that Notch1 and JAGD1 expression were to be associated with cervical cancer invasion, lymph node metastasis, and FIGO system. 25903338_Transient expression of the human cytomegalovirus tegument proteins of pp71 and UL26 reduced NICD1 and Jag1 protein levels endogenously and exogenously. 26076142_JAG1 mutations are present in the majority of Chinese pediatric patients with clinical features of Alagille syndrome, and the mutations concentrate on different exons from other reports. 26276215_Jagged1 is a novel binding partner of Fe65, and Fe65 may act as a novel effector of Jagged1 signaling. 26339425_Case Report: JAGGED1 gene variations in Chinese twin sisters with Alagille syndrome. 26341090_High Jagged1 expression is associated with Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia. 26350262_PKCalpha Attenuates Jagged-1-Mediated Notch Signaling in ErbB-2-Positive Breast Cancer to Reverse Trastuzumab Resistance 26387946_Anti-estrogen resistance in human breast tumors is driven by JAG1-NOTCH4-dependent cancer stem cell activity. 26406415_High Jagged1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 26546995_DLL4 and JAG1 may have opposing effects on tumor angiogenesis in glioblastoma. 26548814_Expression and conditional gene knockout studies of JAG1 (Jag1) have correlated with tissue-specific disease phenotypes and have provided insight into both disease pathogenesis and human development 26618708_Data do not support association of biliary atresia with JAG1 mutations, at least in Czech patients. Rapid testing for JAG1 mutations could prevent misdiagnosis of Alagille syndrome in early infancy and improve their outcome. 26646450_findings provide evidence for a novel cell-autonomous pro-inflammatory Jagged1-Notch1 pathway in endothelial cells 26648562_these findings demonstrate that 50 microM EGCG protects against ox-LDL-induced endothelial dysfunction through the Jagged-1/Notch signaling pathway. 26679605_Our collective results clearly indicate that miR-186 functions as a tumor suppressor in MM, supporting its potential as a therapeutic target for the disease. 26721293_Jagged1 expression was correlated with higher tumor grade and invasion of breast carcinomas. 26760175_Alagille syndrome type 1 patients have an increased risk of nonautoimmune hypothyroidism, and that variations in JAG1 gene can contribute to the pathogenesis of variable congenital thyroid defects. 26779814_Jag1 is upregulated preferentially in pulmonary capillary endothelial cells in individuals with interstitial pulmonary fibrosis compared to normal lung. 26921446_bone marrow stroma induces Jagged1 expression in bone metastatic prostate cancer PC3 cells, and this enhanced expression is mechanistically linked to the promotion of cell migration 26926447_Immunohistochemical panel of CDX2, p120ctn, c-Myc, and Jagged1 proteins would be to distinguish between low/high grade dysplasia in histologically challenging cases of Barrett's esophagus. 26930648_SCC patients with higher JAG1 transcription had poor overall survival. 26971121_JAG1 protein expression was significant positive correlation with lymph node metastasis, pathological grades invasive ductal carcinoma of breast.JAG1 gene methylation level in breast cancer. 27118257_Low levels of Notch pathway genes Notch1, Notch2, Notch4 and Jagged1 correlated with poor prognostic factors such as larger tumor size, positive lymph-node status, tumor phenotype and infiltrating tumor Treg cells. 27174628_Positive Jagged1 and DLL4 expression is closely correlated with severe clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in patients with gallbladder cancers. 27216293_Data indicate that jagged 1 protein (JAG1)-mediated Notch signaling regulates differentiation of basal cells (BC) into secretory cells. 27270422_Results showed that JAG1 was significantly downregulated in miR-26a-overexpressing osteosarcoma cells and is a direct target of miR-26a. 27315779_amplification of Jagged1 contributed to mRNA expression that activates the Jagged1-Notch signaling pathway in liver cancer and led to poor outcome. 27487663_Expression of Jag-1 in dermal microvessels was enhanced from 20 weeks of gestation to 85 years. 27532668_By studying leprosy as a model, we provide evidence that upregulation of JAG1 on endothelium instructs monocytes to differentiate into M1 macrophages with antimicrobial activity. 27589478_expression of JAG1 is regulated by various pathways and is associated with poor prognosis through promoting the epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell proliferation or maintaining cell survival in colorectal cancer 27612417_A three-molecule score based on the expression of Notch pathway molecules: Jagged1, intracellular Notch1 (ICN1) and Hes1 (JIH score) to assess prognostic value in non-metastasis clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). 27832779_miR-199a-3p targets YAP1, downregulates Jagged1 and suppresses the Notch signaling to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell proliferation and promote apoptosis. These findings provide new insights into the mechanism by which miR-199a-3p suppresses HCC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis. 27846321_Human Jagged-1 induced the proliferation and differentiation of CD133+ cord blood progenitors compared with hDll-1. Thus, hJagged-1 signaling in the bone marrow niche may be used to expand EPCs for therapeutic angiogenesis 27919854_Positive Jagged1 and DLL4 expression is closely correlated with severe clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal carcinoma. 27941324_Jagged1 activation of Notch3 resulted in a significant decrease in cell proliferation while concomitantly promoting Hemangioma-pericyte maturation. 27957826_These findings imply that miR-199b-5p performs an inhibitory role in osteogenic differentiation in ligamentum flavum cells by potentially targeting JAG1 and influencing the Notch signalling pathway. 28111308_these results show that the Notch signaling pathway in T cells is crucial for the induction of TH2-mediated allergic airway inflammation in an house dust mite -driven asthma model but that expression of Jagged 1 or Jagged 2 on DCs is not required 28161537_High Jag1 expression is associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer. 28376567_HIF1A potentiates Jagged 1-mediated angiogenesis by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. 28445154_Data show that Delta-like 4 (DLL4) and Jagged1 (JAG1) displayed equal potency in stimulating Notch target genes in HMEC-1 dermal microvascular endothelial cells but had opposing effects on sprouting angiogenesis in vitro. 28472949_the Notch signaling and atherosclerosis relevant markers in lesions from femoral arteries of symptomatic peripheral artery disease patients, were characterized. 28476798_Specific Notch3 and Jag1 subcellular localization patterns may provide clues for the behavior of the corresponding tumors and could potentially be applied in the clinic for Jag1 targeting in triple-negative breast cancer patients. 28498402_Lower positive expression rate of RUNX3 and higher positive expression rate of Notch1 and Jagged 1 were observed in CRC tissues than those in normal adjacent tissues with a negative correlation, and the expression levels were associated with the differentiation degree, TNM staging, lymph node metastasis and tumor invasion depth (all P |
ENSMUSG00000027276 |
Jag1 |
526.627737 |
2.1850028377 |
1.127635 |
0.225095245 |
24.486678 |
0.00000074825407279949538803316038196311588137632497819140553474426269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002682591720796830556046734181374624483851221157237887382507324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
776.2949199 |
104.9071227 |
356.5957515 |
35.4702311 |
| ENSG00000101439 |
1471 |
CST3 |
protein_coding |
P01034 |
FUNCTION: As an inhibitor of cysteine proteinases, this protein is thought to serve an important physiological role as a local regulator of this enzyme activity. |
3D-structure;Age-related macular degeneration;Amyloid;Amyloidosis;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Thiol protease inhibitor |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and the kininogens. The type 2 cystatin proteins are a class of cysteine proteinase inhibitors found in a variety of human fluids and secretions, where they appear to provide protective functions. The cystatin locus on chromosome 20 contains the majority of the type 2 cystatin genes and pseudogenes. This gene is located in the cystatin locus and encodes the most abundant extracellular inhibitor of cysteine proteases, which is found in high concentrations in biological fluids and is expressed in virtually all organs of the body. A mutation in this gene has been associated with amyloid angiopathy. Expression of this protein in vascular wall smooth muscle cells is severely reduced in both atherosclerotic and aneurysmal aortic lesions, establishing its role in vascular disease. In addition, this protein has been shown to have an antimicrobial function, inhibiting the replication of herpes simplex virus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding a single protein. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:1471; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004869]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; defense response [GO:0006952]; negative regulation of blood vessel remodeling [GO:0060313]; negative regulation of collagen catabolic process [GO:0010711]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:2000117]; negative regulation of elastin catabolic process [GO:0060311]; negative regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0010716]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; regulation of tissue remodeling [GO:0034103]; supramolecular fiber organization [GO:0097435] |
2153254_CST3 exhibits an antimicrobial activity against herpes simplex virus. 10993992_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11074789_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11468325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11681790_localization, targetting and trafficking of cystatin C is investigated in cultured human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells 11711204_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11750287_Relationship between serum cystatin C and creatinine in kidney and liver transplant patients. 11815350_Associated with exudative age related macular degeneration. 11815350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11865157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12038606_Serum concentration of cystatin C is not affected by cellular proliferation in patients with proliferative haematological disorders. 12101112_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12479412_Enhancement of proteinase inhibitory activity of recombinant human cystatin C 12483523_role in invasiveness of human glioblastoma cells 12589965_decrease of cystatin C in the CSF might contribute in the process of metastasis and spread of the cancer cells in the leptomeningeal tissues 12663624_May be a better marker of glomerular filtration rate in IDDM than creatinine. 12670666_A significant elevation in the content of cystatin C is measured in the cerebrospinal fluid of human patients experiencing persistent pain of strong intensity. 12738401_most sensitive marker at routinely used cutoff values and would be more clinically useful than B2M or serum creatinine in diabetic patients at risk for nephropathy 12758063_In fibroblasts from donors carrying A/A, A/B, and B/B CST3 pulse-chase experiments demonstrated that release of the B variant of cystatin c [CysC] has a different temporal pattern compared to that of the A. Fibroblasts B/B homozygous secreted less CysC 12787072_Cystatin C physically associates with A beta precursor protein (A beta PP), and may play a novel role in the pathogenesis of sporadic inclusion body myositis by influencing A beta PP processing and A beta deposition 12938144_levels of serum cystatin C may predict early prognostic stages of patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy 14672279_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14672279_a synergistic association of CST3 and APOE4 alleles was observed in predicting vascular dementia patients so CST3 might interact with APOE4 on conferring vascular pathologies. 14714581_cystatin C level is a useful and convenient parameter of renal function, and may also prove to be an early marker of the severity of end-organ damage in patients with essential hypertension 14726415_7 polymorphisms, all in strong-linkage disequilibrium, were identified in the cystatin C gene. The mutant haplotype was associated with a higher average number of stenoses per coronary artery segment, implying an important role in coronary artery disease. 15013312_Serum creatinine is a more efficacious marker than serum cystatin C to assess renal function after renal transplantation. 15034766_presence of a susceptibility locus for Alzheimer's disease in the vicinity of CST3 for very elderly subjects. 15037657_Identification of CystC as a novel TGF-beta receptor antagonist, as well as a novel CystC-mediated feedback loop that inhibits TGF-beta signaling. 15086483_Serum cystatin C appears to be influenced by factors other than renal function alone. 15122877_In a yeast two-hybrid system cystatin C has been identified as a neuroglobin-interacting protein. 15212828_Cystatin C association with betaAPP resulted in increased sbetaAPP but did not affect levels of secreted Abeta. Analysis of the association of cystatin C and Abeta demonstrated a specific, saturable an 15223845_ystatin C is an important regulator for normal and pathological proteolysis in the male reproductive system. 15336605_In calvarial bone explants recombinant human cystatin C decreases calcium release into the medium significantly. 15350470_A valid serum marker for glomerular filtration rate in renal transplantation. 15479453_an age-related macular degeneration-associated cystatin C variant is associated principally with mitochondria rather than the Golgi apparatus 15719405_An excellent blood marker for screening of renal dysfunction in children with liver disease and after liver transplantation. 15728313_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15829557_The difference in localization of CyC and of CatS, -L, and -H in immature and mature DC shows that the regulatory potential of CyC toward CatS, -L, and -H inside DC is limited 15832773_Protein and mRNA levels of stefin B (p= 0.007), but not cystatin C, were significantly lower in atypical compared with benign meningiomas 15860739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15860739_The major haplotype -82G/-5G/+4A of the cystatin C gene determines plasma levels of cystatin C with homozygous persons having the highest plasma levels, but there was no association with secondary cardiovascular events in this study. 15882666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16005452_No effect of sex on serum cystatin C levels was observed, but average levels increased with age 16049933_The cystatin C expression is altered during the chronic phase of epilepsy and suggest that cystatin C plays a role in network reorganization in the epileptic dentate gyrus, especially in granule cell dispersion. 16131730_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16170782_full-length cystatin C when crystallized in a new, tetragonal form, dimerizes by swapping the same secondary structure elements but with a very different overall structure generated by the flexibility of the hinge linking the moveable elements 16188386_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16213753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16213753_the present findings represent the first demonstration of relationships between the AD genetic risk factor CST3 B and global neurophysiological phenotype 16386559_Cystatin C is an endogenous marker of glomerular filtration rate in kidney transplantation patients. 16437581_Cleavage of cystatin C to form a 12.5 kDa protein may identify a subgroup of patients with MS. 16443201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16446102_Conformational differences between the monomeric forms of wild-type cystatin C and its L68Q variant may be responsible for the higher tendency of the L68Q cystatin C to be amyloidogeneic. 16481598_Cystatin C is a novel cerebrospinal fluid protein whose content is altered by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and may therefore serve as a biomarker for this disease. 16608402_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16612982_hereditary cystatin C amyloid angiopathy is a rare, fatal amyloid disease in young people in Iceland caused by a mutation in cystatin C {REVIEW} 16612983_Accumulating data suggest involvement of cystatin C in the pathogenic processes leading to amyloid deposition in cerebral vasculature and most significantly to cerebral hemorrhage in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy {REVIEW} 16640527_Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) is equivalent to cystatin C measurement as a measure of glomerular filtration rate. 16838182_The conclusion of this review is that the association of serum cystatin C with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality most likely reflects early renal dysfunction. 16979980_A more sensitive serum marker than creatinine of glomerular filtration rate fter kidney transplantation. 17130480_Linkage analysis of renal function, measured as glomerular filtration rate (GFR), in 63 extended families with multiple members with type 2 diabetes estimated from serum concentrations of cystatin C. 17192785_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17210589_Although a gold standard of kidney function is lacking, this analysis suggests that cystatin C captures an association of mildly impaired kidney function with increased inflammation. 17310123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17310123_Plasma cystatin C levels were lower in the AD patients than in the control group. Plasma cystatin C levels were associated positively with age and negatively with CST3A allele in the control group. 17353786_Plasma cystatin C has no clear advantage over serum creatinine to detect renal failure in heart transplanted patients. 17394021_Increased CST3 is associated with an enhanced cardiovascular risk factor profile in Aboriginal youth. 17470433_human cystatin C oligomers are formed by propagated domain swapping 17537416_Increased urinary cystatin C reflects structural and functional renal tubular impairment independent of glomerular filtration rate. 17552057_There is a relative deficiency of circulating cystatin C (CysC) in systemic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Interaction between CysC and serum amyloid A protein explains this CysC deficiency and suggests CysC is regulating inflammatory responses. 17636214_Circulating levels of cystatin C in mothers, fetuses, and neonates from intrauterine growth-restricted and appropriate-for-gestational-age pregnancies. 17660266_In individuals with type 1 diabetes, cystatin C blood levels modestly predicts subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. 17668246_Serum creatinine levels are lower in malnourished children and lead to overestimation of glomerular filtration rate, but cystatin C levels are unaffected. 17718592_molecular dynamics simulations were conducted to investigate the conformational fluctuations of monomeric L68Q and wild-type cystatin Cs at various combinations of temperature (300 and 500K) & pH (2 & 7) to gain insights into the domain swapping mechanism 17728092_cystatin C levels were significantly higher in breast cancer patients than in controls or patients with osteoporosis; cystatin C was more elevated in prostate cancer patients than in controls or BPH patients 17822797_In Korean type 2 diabetic patients, cystatin-c based glmoerular filtration rate may be more valuable than creatinine-based GFR in the prediction of the microalbuminuric stage. 17826782_mild renal impairment detected by elevated cystatin C is associated with both the occurrence and the severity of coronart artery disease, independent of the other risk factors 17852800_The cystatin C, beta2-microglobulin and beta-trace protein levels displayed changes with increased levels in the third trimester but unaltered levels during the first and second trimesters. 17852801_There was good correlation between eGFRCystC and iohexol clearance (r = 0.88) in patients with iohexol clearance |
ENSMUSG00000027447+ENSMUSG00000033156 |
Cst3+Cst10 |
1601.294868 |
0.4742567362 |
-1.076260 |
0.045252454 |
568.688885 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001082729584207455681817620161085732608552180508441220333286264652168428759278053666628005331147800878939000073409209652598408211693242949246756977744909603296202801101311223884064498176594363303531363102205 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000579024951554421991856037527232504717396431942072474908167067556770186827355699000463602984905120791642897731146818003695136699251725663580280240567419801317225289538683394987810931744459856532902060928035 |
Yes |
Yes |
1040.1584583 |
28.2385711 |
2209.4372286 |
39.6110224 |
| ENSG00000101489 |
56853 |
CELF4 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZC1 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein implicated in the regulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing. Mediates exon inclusion and/or exclusion in pre-mRNA that are subject to tissue-specific and developmentally regulated alternative splicing. Specifically activates exon 5 inclusion of cardiac isoforms of TNNT2 during heart remodeling at the juvenile to adult transition. Promotes exclusion of both the smooth muscle (SM) and non-muscle (NM) exons in actinin pre-mRNAs. Activates the splicing of MAPT/Tau exon 10. Binds to muscle-specific splicing enhancer (MSE) intronic sites flanking the alternative exon 5 of TNNT2 pre-mRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11158314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12649496, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14973222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15009664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15894795}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
Members of the CELF/BRUNOL protein family contain two N-terminal RNA recognition motif (RRM) domains, one C-terminal RRM domain, and a divergent segment of 160-230 aa between the second and third RRM domains. Members of this protein family regulate pre-mRNA alternative splicing and may also be involved in mRNA editing, and translation. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56853; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; BRE binding [GO:0042835]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity [GO:0000900]; pre-mRNA binding [GO:0036002]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000380]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060079]; germ cell development [GO:0007281]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; mRNA splice site selection [GO:0006376]; negative regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0090394]; negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048025]; positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048026]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of retina development in camera-type eye [GO:1902866] |
14973222_Determination of CELF4 protein domains required for RNA splicing. 17672918_validated occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 6 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19911421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26811534_Authors report a modifying effect of a polymorphism of CELF4 on the dose-dependent association between anthracyclines and cardiomyopathy, which possibly occurs through a pathway that involves the expression of abnormally spliced TNNT2 variants. 28407444_The present study refines the molecular and neuropsychiatric phenotype associated with 18q12.2 deletion leading to CELF4 haploinsufficiency and provides evidence for a role for CELF4 in brain development and autism spectrum disorders. 33930674_An intronic variant in the CELF4 gene is associated with risk for colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024268 |
Celf4 |
21.731324 |
0.0667907284 |
-3.904208 |
0.532619144 |
78.998896 |
0.00000000000000000062144641972381585372758825943299400574773216850865036400830554441654385300353169441223144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000005238463252497728649998248845218353350989045469067407687080439870896952925249934196472167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9597341 |
1.1291677 |
44.6219235 |
6.9792955 |
| ENSG00000101605 |
8736 |
MYOM1 |
protein_coding |
P52179 |
FUNCTION: Major component of the vertebrate myofibrillar M band. Binds myosin, titin, and light meromyosin. This binding is dose dependent. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Muscle protein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Thick filament |
|
The giant protein titin, together with its associated proteins, interconnects the major structure of sarcomeres, the M bands and Z discs. The C-terminal end of the titin string extends into the M line, where it binds tightly to M-band constituents of apparent molecular masses of 190 kD (myomesin 1) and 165 kD (myomesin 2). This protein, myomesin 1, like myomesin 2, titin, and other myofibrillar proteins contains structural modules with strong homology to either fibronectin type III (motif I) or immunoglobulin C2 (motif II) domains. Myomesin 1 and myomesin 2 each have a unique N-terminal region followed by 12 modules of motif I or motif II, in the arrangement II-II-I-I-I-I-I-II-II-II-II-II. The two proteins share 50% sequence identity in this repeat-containing region. The head structure formed by these 2 proteins on one end of the titin string extends into the center of the M band. The integrating structure of the sarcomere arises from muscle-specific members of the superfamily of immunoglobulin-like proteins. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8736; |
M band [GO:0031430]; striated muscle myosin thick filament [GO:0005863]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010737] |
12972258_Results identify muscle-type creatine kinase as a binding partner of a central portion of myomesin and the closely related M-protein. 15890201_visco-elastic properties of myomesin might be crucial for the stability of the sarcomere 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21069531_EH-myomesin levels were up-regulated at least 10 times in dilated cardiomyopathy patients compared to controls. 21256114_This missense mutation caused significant changes of biochemical and biophysical properties of myomesin fragments indicating a role in the pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy . 21794030_Our results suggest that the downregulation of MBNL proteins should lead to the abnormal splicing of MYOM1 exon 17a in DM1 muscle. 22347812_myomesin could act as a highly elastic ribbon to maintain the overall structural organization of the sarcomeric M-band. 25152160_individual subfragments of titin and myomesin composed of Fn type III and Ig-like domains can activate expression of two IGF-1 splice forms in cultured myoblasts 27989621_Crystal structure of the obscurin(-like-1):myomesin complex reveals a trans-complementation mechanism whereby an incomplete immunoglobulin-like domain assimilates an isoform-specific myomesin interdomain sequence. 33452765_Knockout of MYOM1 in human cardiomyocytes leads to myocardial atrophy via impairing calcium homeostasis. |
ENSMUSG00000024049 |
Myom1 |
18.404167 |
4.0412362516 |
2.014797 |
0.604951164 |
10.358013 |
0.00128913895313602974018740709993835480418056249618530273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002950944625975155007069350432402643491514027118682861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
32.0575751 |
14.2845549 |
7.9635366 |
2.5403832 |
| ENSG00000101638 |
29906 |
ST8SIA5 |
protein_coding |
O15466 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the synthesis of gangliosides GD1c, GT1a, GQ1b, GP1c and GT3 from GD1a, GT1b, GM1b and GD3 respectively. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9199191}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9199191}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that may be present in the Golgi apparatus. The encoded protein, which is a member of glycosyltransferase family 29, may be involved in the synthesis of gangliosides GD1c, GT1a, GQ1b, and GT3 from GD1a, GT1b, GM1b, and GD3, respectively. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:29906; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; alpha-N-acetylneuraminate alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase activity [GO:0003828]; sialyltransferase activity [GO:0008373]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; glycosphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0006688]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491]; oligosaccharide metabolic process [GO:0009311]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
20930939_Chol-1alpha antigens (cholinergic neuron-specific gangliosides), such as GT1aalpha and GQ1balpha, which are minor species in the brain, are increased in the double-transgenic mouse brain. 33174041_Upregulated lncHRK2:1 prompts nucleus pulposus cell senescence in intervertebral disc degeneration. |
ENSMUSG00000025425 |
St8sia5 |
244.932928 |
0.3819623034 |
-1.388498 |
0.175995245 |
60.769348 |
0.00000000000000641693406803282069854979310809399834191331336505359494992717372952029109001159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000043546642227202038091012315351640229416454487554322128062267438508570194244384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
132.2868837 |
17.0393140 |
347.9605997 |
31.2044987 |
| ENSG00000101665 |
4092 |
SMAD7 |
protein_coding |
O15105 |
FUNCTION: Antagonist of signaling by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) type 1 receptor superfamily members; has been shown to inhibit TGF-beta (Transforming growth factor) and activin signaling by associating with their receptors thus preventing SMAD2 access. Functions as an adapter to recruit SMURF2 to the TGF-beta receptor complex. Also acts by recruiting the PPP1R15A-PP1 complex to TGFBR1, which promotes its dephosphorylation. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11163210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12023024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14718519, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17327236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9892009}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear protein that binds the E3 ubiquitin ligase SMURF2. Upon binding, this complex translocates to the cytoplasm, where it interacts with TGF-beta receptor type-1 (TGFBR1), leading to the degradation of both the encoded protein and TGFBR1. Expression of this gene is induced by TGFBR1. Variations in this gene are a cause of susceptibility to colorectal cancer type 3 (CRCS3). Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:4092; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; heteromeric SMAD protein complex [GO:0071144]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; activin binding [GO:0048185]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; I-SMAD binding [GO:0070411]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034713]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; adherens junction assembly [GO:0034333]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of chondrocyte proliferation [GO:1902731]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010719]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; negative regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060394]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010801]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of T cell cytokine production [GO:0002725]; negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation [GO:2000320]; negative regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:2000317]; negative regulation of transcription by competitive promoter binding [GO:0010944]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; negative regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0051444]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022409]; positive regulation of chondrocyte hypertrophy [GO:1903043]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein-containing complex localization [GO:0031503]; regulation of activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032925]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0055117]; regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010717]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0017015]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane depolarization [GO:0060373]; response to laminar fluid shear stress [GO:0034616]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055010]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
12151385_plasma membrane localization of Smad7 by Smurf1 requires the C2 domain of Smurf1 and is essential for the inhibitory effect of Smad7 in the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway 12202987_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12397035_Smad7 is activated in injured podocytes in vitro and in human glomerular disease and participates in negative control of TGF-beta/Smad signaling in addition to its pro-apoptotic activity. 12407115_Smad6 and Smad7 regulate thrombomodulin-dependent activation of protein C 12519765_CRM1-dependent nuclear export of Smurf1 is essential for the negative regulation of TGF-beta signaling by Smad7. 12589052_Smad7 may act as a scaffolding protein and facilitate TAK1- and MKK3-mediated activation of p38 12947087_attenuation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling by activating Smad7 transcription may proceed not only through TGF-beta receptor-regulated Smad proteins but also an independent pathway involving transcription factor ER81 and TAK1 protein kinase 12952364_Smad7 was overexpressed in ARO anaplastic cell line, the most malignant follicular thyroid carcinoma. 14718519_GADD34-PP1c recruited by Smad7 inhibits TGFbeta-induced cell cycle arrest. 14722617_Smad7 and Smurf1 have roles in regulation of TGF-beta signaling in scleroderma fibroblasts 14988821_In Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa, interferon-gamma induces expression of Smad7, which then prevents endogenous TGF-beta 1 from down-regulating ongoing tissue-damaging Th1 response. 14993265_Jab1/CSN5 as an adapter that targets Smad7 for degradation, thus releasing Smad7-mediated suppression of TGF-beta1 signaling. 15023526_Overexpression of SMAD7 inhibited the activity of the proliferation-specific promoters for the keratin 14 and cdc2 genes and reduced the expression of the mRNA for the proliferation-specific genes cdc2 and E2F1. 15033458_tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate down-regulates Smad6 expression presumably via PKCmu-ERK-dependent pathway and up-regulates Smad7 expression via PKCmu-dependent mechanism(s) which need no MAPK and NF-kappaB activation 15033661_Enhanced expression of the TGF-beta signaling inhibitor Smad7 may present one of the novel mechanisms of TGF-beta resistance in human gastric carcinomas. 15075243_novel role for Smad7 in TGF-beta-dependent activation of Rho GTPases 15128733_Smad7 is repressed by ski 15132952_dual signaling pathways involving TGF-beta1, an antiapoptotic pathway mediated by the Smad pathway involving p21, and an apoptosis-permissive pathway mediated in part by p38 MAPK. 15221015_WWP1 negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling in cooperation with Smad7. 15498852_identified target genes regulated by Smad7 in primitive hematopoietic cells that may control process of modulating the cell fate decisions of primary multipotent human repopulating cells 15529348_The regulation in chondrocytes of Smad6 and Smad7 expression by IL-1beta suggests a potentially important role of IL-1beta signaling in chondrocytes, via indirect influencing of the bone morphogenetic protein/TGFbeta signaling cascade. 15579469_induction of Smad7 gene expression by UV irradiation is mediated via induction of the transcription factor AP-1 in human skin fibroblasts 15632190_Abeta1-42 may play an important role in the negative regulation of TGF-beta1-induced MMP-2 production via Smad7 expression 15661223_Smad7 appears to be upregulated in endometrial cancers compared to normal endometrium. 15684397_Physical association of Smad7 and beta-catenin was found to be important for TGF-beta-induced apoptosis. 15708859_expression of Smad7 is crucial for 2-ME-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells 15736400_Smad6 and Smad7 expression affects the progression of early lesions of esophageal SCC and indicates a poor prognosis. 15788410_autocrine TGF-beta/Smad signaling is involved in contractility and matrix gene expression of fibroblasts from normal and hypertrophic scars; Smad7 inhibits these processes and may exert beneficial effects on excessive scar formation 15811425_UV-induced down-regulation of TbetaRII and the concerted over-expression of Smad7 may trigger the inhibition of the TGF-beta-induced phosphorylation of Smad2. 15811853_Smad7 acts to functionally inactivate RB and de-repress E2F without blocking the activation of TbetaRI and the nuclear translocation of Smad2/3, allowing TGF-beta1 to exert effects in a cancer cell that is resistant to TGF-beta1-mediated growth inhibition 15831498_the degradation of Smad7 is regulated by the balance between acetylation, deacetylation and ubiquitination 15877825_In mature human B cells, BMP-6 inhibited cell growth, and rapidly induced phosphorylation of Smad8. 15922743_SMAD7 induces tumorigenicity by blocking TGF-beta-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. 16007121_Various cellular functions implicated in melanoma development may be under control of autocrine TGF-beta and may be inhibited by Smad7 expression 16187293_TGF-beta1 and bleomycin intracellular signaling through autocrine regulation of Smad 3 binding to the proximal promoter of the Smad 7 gene 16260615_TGF-beta is involved in the physiological loss of gastric epithelial cells by activating apoptosis mediated by Smad7, Bim, and caspase-9 16285943_Smad7 is not transcriptionally regulated in gut but its increase in inflammatory bowel disease is due to posttranscriptional acetylation and stabilization by p300, which prevents Smad7 ubiquitination and degradation in the proteasome 16288847_TGFbeta-mediated phosphorylation of IkappaB-alpha and NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity are inhibited by Smad7 16442497_SnoN also seems to regulate negatively the TGF-beta-responsive smad7 gene by binding and repressing its promoter in a similar way to Ski 16601693_Axin and Arkadia cooperate with each other in promoting Smad7 ubiquitination. 16641086_analysis of the WW domain recognition motif for the interaction of Smad7 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 16714330_TGFbeta rapidly induces nuclear translocation of Smad proteins and subsequently stimulates Smad-Sp1 complex formation which increases Sp1 binding to promoter boxes in a pancreatic cancer cell line. 16718778_results suggest that inhibition of cell growth by activin is regulated by the negative feedback effect of Smad7 on the activin signaling pathway, and is mediated through p21(CIP1/WAF1) activation in SNU-16 cells 16720724_These findings indicate a new inhibitory function of FKBP12 as an adaptor molecule for the Smad7-Smurf1 complex to regulate the duration of the activin signal through activin type I receptors. 17009056_UVA1 phototherapy demonstrated the alteration of SMAD7 gene expression in localized scleroderma, as SMAD7 mRNA levels normalized after UVA1. The pathogenetic relevance of SMAD7 levels with respect to clinical improvement needs further investigation. 17172861_Smad7 plays a crucial role upstream of ATM and p53 to protect the genome from insults evoked by extracellular stress. 17230494_Smad7 appears to be important in colonic inflammation. 17332363_Stable overexpression of Smad7 in human melanoma cells impairs bone metastasis. 17377371_Smad7 expression was upregulated by IL-10 plus either IL-5 or GM-CSF. IL-10 inhibited the expression of TGF-beta-inducible early gene, which is known to downregulate Smad7 expression. 17438144_SMAD7 antagonizes TGFB1 signaling in the nucleus by interfering with functional Smad-DNA complex formation. 17510063_Arkadia induces degradation of SnoN and c-Ski in addition to Smad7. 17657819_Smad7 overexpression in cultured hepatocytes abrogated TGF-beta-dependent and intrinsic CTGF expression. 17704440_In this review, Smad7 inhibits the signaling response to transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta by a variety of mechanisms associated with peritoneal membrane failure during chronic peritoneal dialysis. 17928287_the up-regulation of TCF11/MafG binding could be suppressed by overexpression of the TGF-beta inhibitor Smad7, and a small interfering RNA to TCF11 blocked the suppression of iNOS by TGF-beta. 17931948_Gene variants may weakly contribute to a particular genetic background that increases the susceptibility to development of type 2 diabetes. 17934461_Single nucleotide polymorphism in SMAD7 is associated with colorectal cancer 18041647_high levels of Smad7 interferes with TGF-beta/activin-induced Smad/MAPK signaling and erythro-differentiation and promotes megakaryocytic differentiation, possibly by blocking autocrine TGF-beta. 18163503_up-regulation of Smad7 by IL-1beta is mediated through the NF-kappaB pathway, especially the p65 subunit in chondrocytes 18231913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18231913_variation at SMAD7 does not significantly contribute to an inherited susceptibility to CLL 18445023_A case-control study in Afro-Caribbeans found SMAD7 SNPs were not strongly associated with increased risk of developing keloids. 18445023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18593713_rather than being translocated to the nucleus for regulating the target gene transcription, Smad7-stabilized-beta-catenin is shunted to the E-cadherin complex to modulate cell-cell adhesion. 18616749_Although the levels of Smad7 were similar between hypertrophic skin fibroblasts and normal skin fibroblasts, TGF-beta1 up-regulated the expression of Smad7 for NSFs only, with no discernible effect on HSFs. 18683731_The expressions of TGF-beta1 and Smad7 were significantly increased in epithelia of oral lichen planus compared to normal oral mucosa. 18684712_ALK2(R206H) with Smad1 or Smad5 induced osteoblastic differentiation that could be inhibited by Smad7 or dorsomorphin. 18762808_The level of Smad7 is modulated by its physical interaction with Hic-5 and targeted to a degradation pathway not likely to be proteasomal 19032343_These results indicate that Ski complexes serve to maintain a TGF-beta-responsive promoter at a repressed basal level via the activities of histone deacetylase and histone arginine methyltransferase. 19192480_Smad7 makes CD4+ T cells resistant to Tregs-mediated suppression thus fine-tuning their proinflammatory potential. 19288000_Mutations and variants of Smad7 are unlikely to be of major significance to the pathogenesis of HPV-induced cervical cancer. 19288000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19341727_Results suggest a mechanism by which a balance between Smad4 and Smad7 in human gastric cancer is critical for differentiation, metastasis, and apoptosis of tumor cells. 19352540_Overexpression of Smad7 has been shown to antagonize TGF-beta-mediated fibrosis, carcinogenesis, and inflammation, suggesting a therapeutic potential of Smad7 to treat these diseases. 19357349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19357349_genetic variants of SMAD7 are markers predisposing to colon cancer, specifically in women. 19395656_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19395656_Study propose that the novel SNP we have identified is the functional change leading to CRC predisposition through differential SMAD7 expression. 19505925_None of the single nucleotide polymorphisms studied in SMAD7, GREM1 or CRAC1 were associated with breast cancer risk in our study 19505925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19562778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19624886_Smad7 expression was related with tumor differentiation and Lauren classification of gastric cancer. 19693466_Smad signaling pathway plays in important role in the progress of glomerular sclerosis, renal tubular injury and interstitial fibrosis in children with IGA nephropathy. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19758997_Mechanistically, in addition to interfering with the complex formation between the type I and type II receptors, hBAMBI cooperates with Smad7 to inhibit TGF-beta signaling 19843678_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19861282_Smad7 over-expression inhibits Smad2/3 phosphorylation, and decreases the expression of collagen I and alpha-SMA in HSC-T6 cells induced by TGF-beta1 to inhibit the progression of liver fibrosis. 19875456_Akt modulates TGF-beta signaling by temporarily adjusting the levels of two TGF-beta pathway negative regulators, Ski and Smad7 19878580_Smad7 mRNA expression correlated significantly with TGF-beta concentration, Col I and Col III expression, and the amount of fibrosis. 19885573_Adenovirus E1A oncoprotein is sufficient to induce Smad7 expression, an inhibitor of TGF-beta signalling. 20040761_Recombinant human SMAD7 overexpression abolishes hepcidin activation in mouse liver cells by BMPs & TGF-beta. A distinct SMAD regulatory motif (GTCAAGAC) within the hepcidin promoter is involved in SMAD7-dependent hepcidin suppression. 20124488_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20124488_Statistically significant association between both rs4939827 and rs12953717 and colon cancer, but not the rs4464148 SNP. 20165854_The expression of TGF-beta1, its receptor TGFbetaRII, and signaling proteins Smad4 and Smad7 was observed in the majority of colorectal cancer specimens. 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354004_Smad7 is up-regulated in peripheral CD4-positive cells in multiple sclerosis during relapse but not remission, and expression of Smad7 correlates with T helper type (Th)1 cell responses. 20416076_nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells are not sensitive to growth suppression by TGF-beta1, but the TGF-beta/Smad signaling transduction is functional 20437058_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20501757_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20514018_both ZEB1 downregulation and Smad7 overexpression contribute to resistance to TGF-beta1-mediated growth suppression in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. 20530476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551054_Data provide evidence that hypoxia could convert Smad7 function from an invasion inhibitor into an activator of invasion. Furthermore, they might shed light as to why increased Smad7 expression is detected in cancers. 20638935_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20648012_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20658468_Smad6 and Smad7, inhibitors of BMP signaling, were up-regulated in HFE-mutant hereditary hemochromatosis compared to controls, disruptin bone morphogenic protein signaling. 20659471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20663871_Smad7 thus has an additional mode of interaction with TGF-beta family type I receptors not possessed by Smad6, which may play roles in mediating the inhibitory effects unique to Smad7. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20738806_Smad7 suppresses beta-catenin degradation and promotes interaction with N-cadherin, stabilizing association with neighboring dermal fibroblasts, thus mitigating invasion. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20863724_in human liver, not only HAMP, but also SMAD7 and Id1 mRNA significantly correlate with the extent of hepatic iron burden. However, this correlation is lost in patients with HFE-HC, but maintained in subjects with non-hemochromatotic iron overload. 21054221_Smad7 overexpression is effective in blocking gingival myofibroblast transformation and activation. 21071539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21075068_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21075068_SMAD7 rs4464148 variant genotype was associated with increased cancer incidence 21221812_These outcomes suggest that rs12953717 is a common risk marker of colorectal, gastric, and lung cancers in the Han Chinese. 21258410_Data show that the WWP2-N isoform interacts with Smad2 and Smad3, whereas WWP2-C interacts only with Smad7. 21445336_Pro-inflammatory cytokine IL1B repress gastrin expression by activating Smad 7 and subsequent inhibition of nuclear localization of Smad 3/4 complex. Polymorphic promoter variants of IL1B gene can modulate the IL1B expression which 21883230_data confirm TGF-beta1 expression related to molecular events associated with CsA-induced gingival overgrowth.suggest Smad7 overexpression effective in blocking these events, including proliferation, type I collagen synthesis and MMP-2 activity. 21900845_LIR was able to induce gains in 1RM and quadriceps CSA similar to those observed after traditional HI. These responses may be related to the concomitant decrease in MSTN and increase in FLST isoforms, GASP-1, and SMAD-7 mRNA gene expression. 21910156_Results show SMAD7 variants known to be important for CRC risk were associated with disease-specific survival among prediagnostic NSAID users. 21931165_CYLD regulates TGF-beta signaling function in T cells and the development of Tregs through deubiquitination of Smad7 22028324_Data show that Smad7 is downregulated in inflamed colon of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-related colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC). 22033246_smad7 inhibits TGF-beta1 as well as the EGF signaling pathway in SKBR3 cells. 22229264_Smad-7 expression in breast neoplasms in positively correlated with tumor size, stage, and lymph node status. 22232431_nanoscale topographic features modulate TGFbeta-induced myofibroblast differentiation and alphaSMA expression, possibly through upregulation of Smad7. 22286770_This same cluster can additionally target the inhibitory Smad7 protein. 22457752_Results from our case-control study and the meta-analysis collectively confirmed the significant association of the SMAD7 variant rs4939827 with increased risk of colorectal cancer 22496417_The Smad7-APC complex links the TGFbeta type I receptor to the microtubule system to regulate directed cellular extension and migratory responses evoked by TGFbeta. 22641218_TGF-beta and RELA activation promoted SMAD7 expression. In turn, SMAD7 preferentially suppressed TGF-beta-induced SMAD and NF-kappaB reporters when compared with constitutive or TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB reporter gene activation 22751114_Targeting Stat3 or Smad7 for knockdown results in resensitization of TGF-beta's cytostatic regulation in vivo. 22841502_MTA1 appears to regulate a key inhibitor of TGFbeta signalling, SMAD7. By regulating molecules like SMAD7 MTA1 might assist the process of tumourigenesis and metastasis. 22876112_Smad7 plays an important role in regulating extracellular matrix proteins in the aqueous humor outflow pathway. 22921829_Smad7 binds YAP, Smurf1, Smurf2, and Nedd4L constitutively, the binding involving a PY motif in Smad7 and no phosphorylation. 23034881_SMAD7, a cell-intrinsic inhibitor of Activin/Nodal and BMP signaling, is sufficient to confer an anterior neural fate on pluripotent human embryonic stem cells. 23049692_Upregulation of Smad7 in cancer cells is sufficient to escape the negative effects of Bone morphogenetic proteins. 23104301_Single nucleotide polymorphism in smad7 is associated with colorectal cancer. 23244128_High Smad7 expression is associated with cholangiocarcinoma. 23255602_Smad7 was able to activate the caspase 8 promoter through recruitment of the interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) transcription factor to the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) site. 23258148_Four genes were significantly associated with proliferative vitreoretinopathy: SMAD7, PIK3CG,TNF locus, and TNFR2. In the European sample, replication was observed in SMAD7 and the TNF locus. 23390194_Data indicate that miR-21 potentiates TGF-beta signaling in hematopoietic cells via downregulation of SMAD7. 23435373_MiR-25 may function as a tumor suppressor by targeting Smad7 in colon cancer. 23472153_rs12953717 polymorphismof SMAD7 is associated with susceptibility to cancer [meta-analysis] 23560096_SMAD7 SNPs were associated with colorectal cancer risk in the Colon Cancer Family Registry. 23567938_IHG-1 expression is associated with repression of the endogenous TGF-beta1 inhibitor Smad7. 23625826_Smad7 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by inhibiting proliferation and G1 -S phase transition and inducing apoptosis through attenuation of NF-kappaB and TGFbeta signalling. 23804438_a detailed computational model for TGF-beta signalling that incorporates elements of previous models together with crosstalking between Smad1/5/8 and Smad2/3 channels through a negative feedback loop dependent on Smad7. 23949881_SMAD7 rs12953717 polymorphism contributes to increased risk of colorectal cancer. 23998914_The expression of TGF-beta1 is increased while the Smad7 expression is diminished in dendritic cell infiltration decrease in liver gastrointestinal cancer metastasis. 24039762_Genetic variants in SMAD7 influence susceptibility to congenital heart disease risk. 24066093_The results show association of SMAD7 variant rs4939827 with colorectal cancer risk in Croatian population. 24090133_Breast tumour cells down-regulate CCN2 gene expression in co-cultured fibroblasts in a Smad7- and ERK-dependent manner. 24259667_Smad7 enhanced ubiquitylation of Myc through direct interaction with Myc and recruitment of Skp2. Ablation of Smad7 resulted in less sensitivity to the growth inhibitory effect of TGF-beta by inducing stable Myc expression. 24317436_Smad7 can interact with other intracellular proteins and regulate also TGF-beta-independent signaling pathways thus making a valid contribution to the neoplastic processes in various organs. 24343358_Ids suppressed cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, and re-upregulated invasion and metastasis-related genes matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2), MMP9, CXCR4 and osteopontin, shown previously to be downregulated in response to Smad7 24345480_results demonstrated that miR-181c inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth and metastasis-related traits through the suppression of Smad7, functioning as a tumor suppressor 24369345_findings define a novel mechanism of Smad7 and YY1 to antagonize TGF-beta signaling 24394555_miR-181a promotes TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via repression of Smad7. 24448986_a SMAD7 variant may be associated with colorectal cancer risk in East Asians 24480808_Loss of smad7 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 24556688_Report role for Smad7 in sustaining colon tumorigenesis. 24557062_Genetic variation of SMAD7 in the Han Chinese population was significantly correlated with susceptibility to colorectal cancer. 24636138_Smad3 and phospho-Smad3 protein levels gradually decreased while TGF-beta1 mRNA level gradually decreased and the Smad7 mRNA level gradually increased from normal anterior pituitaries, noninvasive NFPAs, to invasive NFPAs. 24641900_acetaldehyde up-regulates COL1A2 by modulating the role of Ski and the expression of SMADs 3, 4, and 7. 24659668_Smad7 expression was significantly more frequent in intestinal type and well differentiated gastric adenocarcinomas and significantly correlated with the duration of disease-free survival. 24752577_BAMBI alone or in combination with Smad7 was significantly associated with the OS and DFS. These findings suggest that BAMBI and Smad7 may cooperatively inhibit the TGF-beta signaling, and thus promote the progression of gastric cancer. 24887517_miR-21 overexpression can contribute to TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting target smad7. 24935472_Studies indicate that as an inhibitor of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling, SMAD family member 7 (SMAD7) is overexpressed in numerous cancer types and its abundance is positively correlated to the malignancy. 24939309_Data suggest that ubiquitin specific peptidase 15 (USP15) may play a role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis through regulating the type I TGFbeta receptor (TbetaR-I)/Smad7 pathway. 24969865_There was no significant association between SMAD7 rs2337107 and the risk of colorectal cancer. 25060766_By targeting SMAD7, miR-17-5p promoted nuclear translocation of beta-catenin, enhanced expression of COL1A1 and finally facilitated the proliferation and differentiation of HMSC-bm cells. 25107916_Overexpression of smad7 blocks primary tumor growth and lung metastasis development in osteosarcoma. 25207745_The expression levels of collagens type I/III, TGF-beta1, Smad2/3/4/7 and PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1) in gluteal muscle contraction (GMC) patients were measured. 25333457_Smad7 maintains epithelial phenotype of ovarian cancer stem-like cells and supports tumor colonization by mesenchymal-epithelial transition. 25375357_Data propose that the associated colorectal cancer risk at 18q21.1 is due to four functional variants that regulate SMAD7 expression and potentially perturb a BMP negative feedback loop in TGFbeta/BMP signaling pathways. 25501551_Suggest novel role of leptin-NADPH oxidase induction of miR21 as a key regulator of TGF-beta signaling and fibrogenesis in experimental and human NASH. 25518932_Results suggest that Itch is a positive regulator of the TGF-beta-mediated Smad signaling pathway via Smad7 ubiquitination and protein degradation. 25540364_Authors demonstrated that hepatitis B virus can upregulate the level of Smad7 and inhibit TGF-beta signaling by downregulating miR-15a. 25554686_Data show PTEN protein frameshift mutation and a SMAD7 protein missense mutation occurring in a father and son who had a syndrome of gastrointestinal hamartomatous and ganglioneuromatous polyposis, and who both developed esophageal adenocarcinoma. 25602745_Data indicate that SMAD family member 7 protein (Smad7) transcripts were elevated in 41.4% of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples as compared with adjacent tissue. 25640388_The study found a significant association between colorectal cancer risk and rs4464148 AG genotype of the SMAD7 gene in affected women, but did not detect the same association in colorectal cancer male patients. 25867271_Study identified miR-367 as a negative regulator of Smad7 expression in pancreatic cancer cells by directly targeting its 3'-UTR. 25983322_SMAD7 is a target of miR-132 in glioma cells. 26055326_Overexpression of Smad7 in human HaCaT keratinocyte cells and mouse skin tissues elevated EGF receptor (EGFR) activity by impairing ligand-induced ubiquitination and degradation of activated receptor, which is induced by the E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl. 26071245_Increased miR-16 expression promotes liver fibrosis through downregulation of HGF and Smad7 in hepatitis C patients. 26278416_The expression of Smad7 increased. 26303523_The decrease in miR-195 led to an increase in Smad7 expression and corresponding up-regulation of p65 and the AP-1 (activator protein 1) pathway, which might explain the mechanism of steroid resistance in ulcerative colitis patients 26390174_MiR-185-3p and miR-324-3p can modulate NPC cell growth and apoptosis, at least partly through targeting SMAD7. 26445225_TGF-beta/Smad signalling pathway and VEGF-A participate in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. 26579801_Meta-analysis showed that for SMAD7 gene, rs4939827 and rs4464148 are risk factors for colorectal cancer (CRC) among Caucasians whereas rs12953717 could elevate the susceptibility to CRC in both Caucasians and Asians. 26608417_Suggest that greater tumor associated macrophage density, strong Hexim1 expression, strong SMAD2 expression, and mild SMAD7 expression play important roles in the progression of prostate adenocarcinoma. 26651974_Data indicate that, in irritable bowel disease, high Smad7 contributes to sustain detrimental immune responses and knockdown of this molecule can help attenuate the ongoing mucosal inflammation in patients with such disorders 26701726_Data show that protein kinase LKB1 physically interacts with BMP type I receptors and requires Smad7 protein to promote downregulation of the receptor. 26759305_Results showed that SMAD7 was up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and was found to be the target of UPF1. 26779637_Polymorphisms in the SMAD7 rs4939827 is associated with rectal cancer. 26818761_The inverse correlation between Smad7 and AhR expression helps to propagate inflammatory signals in the gut in Crohn's disease. 26856334_SMAD7 overexpression might represent a mechanism limiting TGF-beta-mediated fibrogenesis in human hepatic diseases; therefore, SMAD7 induction likely represents a candidate for novel therapeutic approaches. 26859364_Smad7 expression in necrotizing enterocolitis macrophages interrupts TGF-beta signaling and promotes NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory signaling in these cells through increased expression of IKK-beta 26892629_miRNA-181a appears to play a potential role in pancreatic beta-cells dysfunction via SMAD7. 26982322_Study founds the levels of CYLD and SMAD7 significantly decreased in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSSC) cells and proposes a model that CYLD suppresses OSCC metastases through SMAD7. Downregulation of CYLD appears to directly contribute to the distal metastases of primary OSCC and subsequently poor prognosis. 26989026_Our data revealed the SMAD7 loci is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility and its clinicopathologic development. 26997760_study suggested that TGF-beta1/Smad3/smad7 is a major pathway which plays an important role in the regulation of the IUA and specific inhibitor of Smad3 (SIS3) may provide a new therapeutic strategy for IUA. 27185036_Carboplatin may upregulate SMAD7 through suppression of miR-21 to inhibit TGFbeta receptor signaling mediated non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion. 27192628_miR-590-5p promotes osteoblast differentiation by indirectly protecting and stabilizing the Runx2 protein by targeting Smad7 gene expression. 27303812_microRNA-497 modulates breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and survival by targeting SMAD7. 27473823_Transforming Growth Factor beta inhibitor peptide P144 downregulates SKI and an upregulates SMAD7 at both transcriptional and translational levels in glioblastoma cell lines. 27572168_Furthermore, MERS coronavirus induced apoptosis through upregulation of Smad7 and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) expression in both kidney and lung cells. 27619676_Downregulation of Smad 7 promotes migration and invasion through enhancing epithelial mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 27628042_miR-424-5p -SMAD7 pathway contributed to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion and metastasis. 27861825_this study shows that in refractory celiac disease, high Smad7 associates with defective TGF-beta1 signaling and sustains inflammatory cytokine production 27996004_Mechanistic studies reveal that TGFbeta activates the expression of microRNA-182 (miR-182), which suppresses SMAD7 protein. miR-182 silencing leads to SMAD7 upregulation on TGFbeta treatment and prevents TGFbeta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of cancer cells. 28070019_this large-scale meta-analysis indicated that SMAD7 polymorphisms (rs4464148, rs4939827, and rs12953717) correlate with CRC. 28108300_the findings show that TIEG1 is highly expressed in human keloids and that it directly binds and represses Smad7 promoter-mediated activation of TGF-beta/Smad2 signaling 28192117_NR2F2 could promote TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal carcinoma cells and inhibit Smad7 expression via transactivation of miR-21. 28218435_Missense variant in smad7 gene is associated with colorectal cancer. 28292929_RNF11 sequestration of the E3 ligase SMURF2 on membranes antagonizes SMAD7 down-regulation of transforming growth factor beta signaling 28300830_Smad7 inhibition diminishes interaction of PKR with protein kinase inhibitor p58 (p58(IPK)). 28349818_A significant association was found between the low expression of inhibitory protein SMAD-7 and both zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70-negative cells (p = 0.04) and lower apoptotic index (p = 0.004). No differences were observed in SMAD-2/3 expression. In conclusion, our results demonstrate a significant correlation between greater SMAD-1/8 and lower SMAD-4 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells 28374902_Studied expression of microRNA-375 and its target gene SMAD-7 polymorphisms (rs4939827) in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients in comparis |
ENSMUSG00000025880 |
Smad7 |
308.951615 |
2.4883120246 |
1.315167 |
0.096961801 |
186.665067 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000169944836000659849271236462526797063716489840543844932988920705189311123266924334017534125187841108239097378737603172282888408517464995384216308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000030221515414093245269889407014603122382312404716009385401157814342613274402316645929804568564172088615017719437361165546462871134281158447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
443.6907057 |
24.3672618 |
179.5196410 |
8.0166575 |
| ENSG00000101670 |
9388 |
LIPG |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5X9 |
FUNCTION: Exerts both phospholipase and triglyceride lipase activities (PubMed:12032167, PubMed:10318835, PubMed:10192396). More active as a phospholipase than a triglyceride lipase (PubMed:12032167). Hydrolyzes triglycerides, both with short-chain fatty acyl groups (tributyrin) and long-chain fatty acyl groups (triolein) with similar levels of activity toward both types of substrates (PubMed:12032167). Hydrolyzes high density lipoproteins (HDL) more efficiently than other lipoproteins (PubMed:12032167, PubMed:10192396). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10192396, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10318835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12032167}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has substantial phospholipase activity and may be involved in lipoprotein metabolism and vascular biology. This protein is designated a member of the TG lipase family by its sequence and characteristic lid region which provides substrate specificity for enzymes of the TG lipase family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9388; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; 1-acyl-2-lysophosphatidylserine acylhydrolase activity [GO:0052740]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; lipase activity [GO:0016298]; lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0004465]; phosphatidylserine 1-acylhydrolase activity [GO:0052739]; phospholipase A1 activity [GO:0008970]; phospholipase activity [GO:0004620]; triglyceride lipase activity [GO:0004806]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006633]; high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034375]; lipid catabolic process [GO:0016042]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; phospholipid catabolic process [GO:0009395]; phospholipid homeostasis [GO:0055091]; positive regulation of cholesterol transport [GO:0032376]; positive regulation of high-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0010983]; regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process [GO:0050746]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; reverse cholesterol transport [GO:0043691]; triglyceride catabolic process [GO:0019433] |
12164779_EDL mediates both HDL binding and uptake, and the selective uptake of HDL-CE, independently of lipolysis and CLA-1. 12569156_Endothelial lipase has a role in HDL metabolism [review] 12601178_EL is a major determinant of HDL concentration in humans 12867537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12884003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14517167_Expression of human endothelial lipase in mice results in dose-dependent increase in postheparin plasma phospholipase activity, catabolic rate of HDL-apolipoprotein, and uptake of apoA-I in both kidney and liver 15117821_Hepatic expression of human EL in mice resulted in markedly decreased levels of VLDL/LDL cholesterol, phospholipid, and apoB accompanied by significantly increased LDL apolipoprotein and phospholipid catabolism. 15342690_N-linked glycosylation has a role in the secretion and activity of endothelial lipase 15485805_results suggest that endothelial lipase (EL) on the endothelial cell surface can promote monocyte adhesion to the vascular endothelium through the interaction with heparan sulfate proteoglycans 15576837_The Endothelial lipase (EL) is a recently discovered member of the triglyceride-lipase family that is involved in plasma HDL metabolism. 15961789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16023652_LIPG variants are associated with HDL related risk factors, and may play a role in susceptibility to cardiovascular disease in this population. 16023652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16039280_regulatory elements in 11.4 kb of 5' and 9.9 kb of 3' region express in small intestine, ovary, testis, mammary gland, brain, lung, aorta, adipose tissue and adrenals; those between 27.4 and 11.4 kb of 5' or 9.9 and 48.7 kb of 3' region in kidney 16877778_the presence of apoA-II on HDL particles inhibits the ability of endothelial lipase to influence the metabolism of HDL in vivo 16940551_maternal type 1 diabetes is associated with TG accumulation and increased EL and HSL gene expression in placenta 16980590_strong association between proinflammatory cytokines and plasma EL concentrations among healthy people with low or high visceral adipose tissue (VAT) levels 17016617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17093291_suppression of either LPL or EL decreases proinflammatory cytokine expression and influences the lipid composition of THP-1 macrophages. 17322565_N-linked glycosylation at Asn-116 reduces the ability of EL to hydrolyze lipids in LDL and HDL2 17356047_EL is the predominant TLG family member in the human placenta present at both interfaces; EL and LPL are dysregulated in growth restricted pregnancy 17495604_endothelial lipase plays a role in the etiology of the atherogenic plasma lipoprotein profile characteristic of the metabolic syndrome [review] 17526978_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17526978_The 584C/T polymorphism of the EL gene was associated with AMI independently of HDL-C levels and thus may be involved in the pathogenesis of acute myocardial infarction 17545692_phospholipase activities of EL N118A, EL N375A, & EL N473A were significantly diminished relative to that of wild-type EL, with greatest reduction being apparent for (E3)rHDL. activity of EL N62A was increased up to 6X relative to that of wild-type EL 17570372_macrophages in advanced atherosclerotic lesions display high levels of endothelial lipase (EL) expression and the level of EL expression varies greatly during transformation of blood monocytes into foam cells 17644777_atorvastatin reduces LPL and EL expression by reducing the activation of LXRalpha and NF-kappaB, respectively 17651673_adiponectin is a significant metabolic concomitant of HTGL activity in African Americans 17700364_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17822686_Endothelial lipase expression promotes the binding and uptake of native and oxidized LDL in THP-1 macrophages in a heparan sulfate proteoglycan-dependent manner. 17986713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986713_The endothelial lipase 584C/T allele at codon 111 is associated with protection from coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. 18039650_after stimulation, the protease activity of PC5A is enhanced, as evidenced by the cleavage of the PC5A substrates Lefty, ADAMTS-4, endothelial lipase, and PCSK9. 18193043_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18683147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18988890_Endothelial lipase appears to promote apolipoprotein A-I-mediated cholesterol efflux through catalytic and noncatalytic-dependent mechanisms in maacrophages. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19136670_SR-BI-mediated selective uptake of HDL cholesteryl ester is essential for the remodeling of large alpha-migrating HDL particles by EL. 19148283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287092_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287092_the low-frequency Asn396Ser variant is significantly associated with increased HDL-C, while the common Thr111Ile variant is not 19380136_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19380136_significant gene-physical inactivity interaction for HDL & some LDL measures for LIPG i24582 polymorphism. Higher levels of physical activity may be protective for HDL-C concentrations & low activity detrimental in LIPG i24582 TT women. 19411665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19411665_analysis among healthy Caucasian men and women from three independent studies does not support an association between the T111I variant and HDL-C, other plasma lipids, or risk of Coronary Heart Disease. 19411705_Thus, this N-terminal variant results in reduced secretion of endothelial lipase, plausibly leading to increased HDL-C levels. 19567873_The active form of EL is a homodimer in head-to-tail conformation. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19780863_LPL and LIPG are reported in the human testis and in germ cell neoplasms. 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20045866_Statins can reduce EL expression in vitro and in vivo via inhibition of RhoA activity. The inhibition of EL expression in the vessel wall may contribute to the anti-atherogenic effects of statins. 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20370913_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20394740_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20466371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20466371_common genetic variation in endothelial lipase (LIPG) does not appear to have a role in risk for coronary artery disease and deep venous thrombosis 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20621031_It seems that plasma endothelial lipase levels in individuals with atherosclerosis might be higher than that measured in healthy individuals. [review] 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20679960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20688330_Sulforaphane inhibits endothelial lipase expression via inhibition of NF-kappaB which may have a beneficial effect on HDL cholesterol levels 20691829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20923576_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20923576_The LIPG 584T allele is associated with increased serum HDL-C, TC and ApoB levels. 20972250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21122200_Treatment of patients with coronary artery disease with lipid-modulation and/or antiplatelet drug may significantly decrease the expression of endothelial lipase. 21130993_Endothelial lipase and EL-generated lysophosphatidylcholines promote endothelial IL-8 synthesis. 21145773_The c.584C>T EL polymorphism is associated with a higher risk of diabetic retinopathy that could be linked to modifications in HDL-cholesterol metabolism and blood pressure levels 21816559_results suggest that the subjects with TT endothelial lipase genotype benefit more from alcohol consumption than the subjects with CT and CC genotypes in increasing serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein (Apo) AI levels 21852675_study tested the hypothesis that placental EL expression is affected by obesity in pregnancy and gestational diabetes; metabolic inflammation with high leptin and increased TNF-alpha concentration at fetal-placental interface regulates placental EL expression 21957202_a reduction in nascent HDL formation may be partly responsible for reduced HDL-C during inflammation when both EL and SAA are known to be upregulated 22174694_we found that a common nonfunctional coding variant associated with HDL-C (rs2000813) is in linkage disequilibrium with a 5' UTR variant (rs34474737) that decreases LIPG promoter activity 22464213_Common and rare genetic variants in CETP and LIPC, but not LIPG, were more commonly found in the Thai HALP group, which could potentially contribute to high high-density lipoprotein cholesterol phenotypes in this population. 22723003_the EL -384A/C gene polymorphism might be associated with ACS in Chinese Han population, suggesting that the variant might be involved in the pathogenesis of ACS. 22740344_Endothelial lipase plays a role in thyroid and adipocyte biology in addition to its well-known role in endothelial function and HDL metabolism. 22952570_analysis of LIPG, CETP, and GALNT2 mutations in Caucasian families with extremely high HDL cholesterol 22972429_EL expression modulates vascular remodeling as well as plasma HDL-C levels 23075452_Endothelial lipase supplies cells with free fatty acids and HDL-derived lysophosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylethanolamine species resulting in increased cellular triglycerides and phosphatidylcholine (PC) content and decreased PC synthesis. 23102786_Starvation regulates endothelial lipase expression via SREBP-2. 23109900_Several lipid-related gene polymorphisms interact with overweight/obesity to modulate blood pressure levels. 23243195_Complete loss-of-function mutation of LIPG had higher plasma high-density cholesterol levels compared with partial loss-of-function mutation carriers. 23510199_Urinary endothelial lipase is a highly accurate gastric cancer biomarker that is potentially applicable to the general screening with high sensitivity and specificity. 23673478_T allele of LIPG -584C/T polymorphism might play a potential role in the susceptibility to atherogenesis in the Turkish population. 23991054_Results indicate the spatial consensus catalytic triad 'Ser-Asp-His', a characteristic motif in lipoprotein lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. 24115033_Interleukin-6 stimulates the translocation of HDL through the endothelium, the first step in reverse cholesterol transport pathway, by enhancing EL expression. 24458708_EL activity was higher in metabolic syndrome and in obesity. It was negatively associated with high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and apolipoprotein A-I in control and metabolic syndrome, respectively. 24634127_Genetic studies of patients with early onset of coronary artery disease (CAD) in the Chinese Han population show that the EL 584C/T variant is not always involved in the pathogenesis of early-onset CAD. 24852509_Studied if a specific variant of the endothelial lipase gene was more specifically linked to the severity of diabetic retinopathy. 24886585_The results of the present meta-analysis suggest that the carriers of EL 584 T allele have a higher HDL-C level in Caucasian populations. Whereas, it might not be a protective factor for CHD. 25250890_Results showed that the protein levels of endothelial lipase (EL), NF-kappaB p65, MAPK p38 protein levels, in addition to the proliferation of umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), were increased by angiotensin II (AngII). 25291260_EL-384A/C polymorphism was significantly associated with the ACS and lipids profile in an elderly Uygur population in Xinjiang. 26124511_results suggested that the SNP -384A/C in the LIPG gene may be associated with risk for coronary artery disease(CAD)and the LIPG gene may play a role in CAD in the Han Chinese 26447519_Endothelial lipase protein expression was increased in skeletal muscle of middle-aged men with high oxygen consumption. 27045898_FoxA1, FoxA2, and LIPG control the uptake of extracellular lipids for breast cancer growth. 27430252_Endothelial lipase is upregulated in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by interleukin-6 partly via the p38 MAPK and p65 NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 27431295_We identified a missense Asn396Ser mutation (rs77960347) in the endothelial lipase (LIPG) gene, occurring with an allele frequency of 1% in the general population, which was significantly associated with depressive symptoms (P-value=5.2 x 10-08, beta=7.2). 27590083_LIPG Polymorphisms are associated with Hyperlipidemia. 27600285_Endothelial lipase (EL) 2037T/C and 2237 G/A polymorphisms might not affect the lipid-owing effects of rosuvastatin in Chinese coronary artery disease patients 27612170_the EL 2237 A allele might be associated with an increased Apo A1 level in Coronary Artery Disease subjects. 28546217_Increased hepatic expression of endothelial lipase attenuates cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and protects against atherosclerosis. 29350614_In this study, the authors show that endothelial lipase (LIPG) is aberrantly overexpressed in basal-like triple-negative breast cancer. They demonstrate that LIPG is required for in vivo tumorigenicity and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells. 29748333_Hepatic overexpression of endothelial lipase lowers high-density lipoprotein but maintains reverse cholesterol transport via SR-BI/ABCA1-dependent pathways. 30150432_the LIPG polymorphism (584 C/T) - CAD correlation study in Turkish people living in Turkey. Results of this study suggest that the CC genotype may be a genetic risk factor for CAD and carrying T allele may be protective against CAD. 30621702_The differences in serum lipid profiles between the Maonan and Han populations might partly be attributed to LIPG SNPs, their haplotypes and gene-environmental interactions. 30651409_High LIPG expression is associated with Coronary Artery Disease. 30653260_The role for LIPG in enabling oxidative stress-induced lipid droplet accumulation in tumour cells. 30657227_Data indicate the association between the endothelial lipase gene (LIPG) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and serum lipid levels in the two ethnic groups in China. 31020688_Association of 584C/T polymorphism in endothelial lipase gene with risk of coronary artery disease. 31216999_Participants with elevated plasma endothelial lipase levels have a higher adjusted odds ratio of cognitive impairment than those with lower endothelial lipase levels. 31220617_This study examined the antioxidative capacity of Endothelial lipase (EL) modified high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (EL-HDL). EL-HDL exhibited increased resistance to copper ion-induced oxidation. 31473149_Serum total endothelial lipase mass could be a predictor for major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease. 31923467_Endothelial lipase - high-density lipoprotein exhibited increased capacity to induced eNOS Ser1177 phosphorylation and activity. 32572177_LIPG: an inflammation and cancer modulator. 32667032_Gene polymorphism associated with angiotensinogen (M235T), endothelial lipase (584C/T) and susceptibility to coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. 32893849_Significant association between the endothelial lipase gene 584C/T polymorphism and coronary artery disease risk. 33479916_Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis of the Association Between LIPG rs9958947 SNP and Stroke Risk. 33882321_Roles of endothelial lipase gene related single nucleotide polymorphisms in patients with coronary artery disease. 34001944_LIPG endothelial lipase and breast cancer risk by subtypes. |
ENSMUSG00000053846 |
Lipg |
29.273501 |
2.0227656472 |
1.016329 |
0.283361426 |
12.876403 |
0.00033275120569237583764005128372787112311925739049911499023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000843449733130597159060093392923818100825883448123931884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.5510743 |
6.0133420 |
16.7285411 |
2.2780059 |
| ENSG00000101811 |
1478 |
CSTF2 |
protein_coding |
P33240 |
FUNCTION: One of the multiple factors required for polyadenylation and 3'-end cleavage of mammalian pre-mRNAs. This subunit is directly involved in the binding to pre-mRNAs (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9199325}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;mRNA processing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear protein with an RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain. The protein is a member of the cleavage stimulation factor (CSTF) complex that is involved in the 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation of pre-mRNAs. Specifically, this protein binds GU-rich elements within the 3'-untranslated region of mRNAs. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1478; |
cleavage body [GO:0071920]; mRNA cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor complex [GO:0005847]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; mRNA polyadenylation [GO:0006378]; pre-mRNA cleavage required for polyadenylation [GO:0098789] |
9736695_Describes the induction of CSTF2 in the growth phase of cells. 15769465_dynamics of the CstF-64 RNA-binding domain, both free and bound to two GU-rich RNA sequences that represent polyadenylation regulatory elements, by NMR Spectroscopy 16207706_CstF64 (cstf2) and not other CstF subunits induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in murine macrophages and changes polyA site use 18272196_The inactivity of the RSV poly(A) site was at least in part due to poor CstF binding since tethering CstF to the RSV substrate activated polyadenylation. 19887456_The Hinge domain is necessary for CstF-64 interaction with CstF-77 and consequent nuclear localization. 21119002_nuclear accumulation of CstF-64 depends on binding to CstF-77 not symplekin; interaction between CstF-64/CstF-64Tau and CstF-77 are important for maintenance of nuclear levels of CstF complex components and intracellular localization, stability, function 21813631_CSTF2 is likely to play an important role in lung carcinogenesis and be a prognostic biomarker in the clinic. 23112178_CstF64 binds to thousands of dormant intronic PASs that are suppressed, at least in part, by U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins 24149845_CstF64 and CstF64tau modulate one another's expression and play overlapping as well as distinct roles in regulating global alternative polyadenylation profiles. 25266659_CstF64 is central to the function of a heat-labile factor, composed of cleavage/polyadenylation specificity factor, symplekin, and cleavage stimulation factor 64 and appears to be at least partly responsible for its cell cycle regulation. 25409906_CstF64, an essential polyadenylation factor, is a master regulator of 3'-UTR shortening across multiple tumour types. 26496945_CstF-64 is dispensable for the expression/3'-end processing of Star-PAP target mRNAs.CstF-64 and 3'-UTR cis-element determine Star-PAP specificity for target mRNA selection by excluding poly A polymerase. 28180311_hnRNP H binds to two specific G-runs in exon 5a of ACHE and activates the distal alternative 3 splice site (ss) between exons 5a and 5b. Furthermore, hnRNP H competes for binding of CstF64 to the overlapping binding sites in exon 5a, and suppresses the selection of a cryptic polyadenylation site, which additionally ensures transcription of the distal 3 ss required for the generation of AChET isoform. 29583087_The findings demonstrate that constitutive Tip110 expression in human cord blood CD34(+) cells is regulated, at least in part, through its interaction with CstF64, recruitment of CstF64 to, and selective usage of two polyadenylation sites within its 3'UTR. 30143523_CSTF2 exerts critical roles in activation of RAC1 by promoting 3'UTR shortening of RAC1 mRNAs through two transcription elongation factors, AFF1 and AFF4, in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder pathogenesis 30257008_Reverse genetics and nuclear magnetic resonance studies of recombinant CstF-64 (RRM-Hinge) and CstF-77 (monkeytail-carboxy-terminal domain) indicate that the last 30 amino acids of CstF-77 increases the stability of the RRM, thus altering the affinity of the complex for RNA. These results provide new insights into the mechanism by which CstF regulates the location of the RNA cleavage site during Cleavage/polyadenylation. 32816001_A missense mutation in the CSTF2 gene that impairs the function of the RNA recognition motif and causes defects in 3' end processing is associated with intellectual disability in humans. 34607841_CstF64-Induced Shortening of the BID 3'UTR Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Disrupting ceRNA Cross-talk with ZFP36L2. 35412944_Cleavage stimulation factor 2 promotes malignant progression of liver hepatocellular carcinoma by activating phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. 36113752_Alternative polyadenylation writer CSTF2 forms a positive loop with FGF2 to promote tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000031256 |
Cstf2 |
108.914950 |
2.8550491582 |
1.513516 |
0.172866316 |
76.965775 |
0.00000000000000000173946348340726686360310085194597277011085749377685555350225854454038199037313461303710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000014399596755519496111108152431081224894296466477517683346665222643423476256430149078369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
161.0356373 |
17.3075345 |
56.8532207 |
4.7471867 |
| ENSG00000101849 |
6907 |
TBL1X |
protein_coding |
O60907 |
FUNCTION: F-box-like protein involved in the recruitment of the ubiquitin/19S proteasome complex to nuclear receptor-regulated transcription units (PubMed:14980219). Plays an essential role in transcription activation mediated by nuclear receptors. Probably acts as integral component of corepressor complexes that mediates the recruitment of the 19S proteasome complex, leading to the subsequent proteasomal degradation of transcription repressor complexes, thereby allowing cofactor exchange (PubMed:21240272). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14980219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21240272}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Congenital hypothyroidism;Deafness;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;WD repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has sequence similarity with members of the WD40 repeat-containing protein family. The WD40 group is a large family of proteins, which appear to have a regulatory function. It is believed that the WD40 repeats mediate protein-protein interactions and members of the family are involved in signal transduction, RNA processing, gene regulation, vesicular trafficking, cytoskeletal assembly and may play a role in the control of cytotypic differentiation. This encoded protein is found as a subunit in corepressor SMRT (silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors) complex along with histone deacetylase 3 protein. This gene is located adjacent to the ocular albinism gene and it is thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of the ocular albinism with late-onset sensorineural deafness phenotype. Four transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. This gene is highly similar to the Y chromosome TBL1Y gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:6907; |
histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
15601853_TBL1 and TBLR1 are functionally redundant and essential for transcriptional repression by unliganded thyroid hormone receptors (TR) but not essential for transcriptional activation by liganded TR 16258276_Mutations within the LisH (LIS1 homology)motif of TBL 1X are likely to result in pathogenic consequences in genes associated with genetic diseases. 18193033_Wnt signalling induced the interaction between beta-catenin and TBL1-TBLR1, as well as their binding to Wnt target genes. Importantly, the recruitment of TBL1-TBLR1 and beta-catenin to Wnt target-gene promoters was mutually dependent on each other. 23665419_We localized proteins encoded by the top two regulated genes, TBL1X and USH1C, using immunohistochemistry to placental stem and anchoring villi associated with active contractile function. 26070566_TBL1 is required to protect GPS2 from degradation, with methylation of GPS2 by arginine methyltransferase PRMT6 regulating the interaction with TBL1 and inhibiting proteasome-dependent degradation. 26070712_Here, the authors show that transcriptional co-factor Transducin beta-like (TBL) 1 was over-expressed in both human and murine pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and TBL1 deficiency both prevented and reversed pancreatic tumor growth. 27129164_Targeted SUMOylation of TBL1 and TBLR1 may be a useful strategy for therapeutic treatment of androgen-independent prostate cancer. 27603907_TBL1X mutations are associated with central hypothyroidism and hearing loss. 28348241_missense mutations in the gene for TBLR1 that are associated with intellectual disability also prevent MeCP2 binding 30160833_TBL1X deletion is associated with Ocular albinism with infertility and late-onset sensorineural hearing loss. 30463081_TBL1X mRNA and protein expression were significantly increased in the gestational diabetes mellitus placenta. TBL1X is a potential target of miR-138-5p contributed to the abnormal growth of the placenta by enhancing the proliferation of trophoblasts. 33054136_Transducin beta-like protein 1 controls multiple oncogenic networks in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. |
ENSMUSG00000025246 |
Tbl1x |
62.255042 |
0.3631551872 |
-1.461342 |
0.197284396 |
57.205165 |
0.00000000000003926386525569238048106168090370440995975648973415061959713057149201631546020507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000255752273245374928821701169132432212042702057708254415047122165560722351074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.4344460 |
4.3976173 |
95.5426525 |
7.3456248 |
| ENSG00000101916 |
51311 |
TLR8 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR97 |
FUNCTION: Endosomal receptor that plays a key role in innate and adaptive immunity (PubMed:25297876, PubMed:32433612). Controls host immune response against pathogens through recognition of RNA degradation products specific to microorganisms that are initially processed by RNASET2 (PubMed:31778653). Recognizes GU-rich single-stranded RNA (GU-rich RNA) derived from SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV-1 and HIV-1 viruses (PubMed:33718825). Upon binding to agonists, undergoes dimerization that brings TIR domains from the two molecules into direct contact, leading to the recruitment of TIR-containing downstream adapter MYD88 through homotypic interaction (PubMed:23520111, PubMed:25599397, PubMed:26929371, PubMed:33718825). In turn, the Myddosome signaling complex is formed involving IRAK4, IRAK1, TRAF6, TRAF3 leading to activation of downstream transcription factors NF-kappa-B and IRF7 to induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and interferons, respectively (PubMed:16737960, PubMed:17932028, PubMed:29155428). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16737960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17932028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23520111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25297876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25599397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26929371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29155428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31778653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32433612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33718825}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This gene is predominantly expressed in lung and peripheral blood leukocytes, and lies in close proximity to another family member, TLR7, on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51311; |
endolysosome membrane [GO:0036020]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; single-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003727]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; immunoglobulin mediated immune response [GO:0016064]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001932]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; toll-like receptor 8 signaling pathway [GO:0034158]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224] |
12032557_Human TLR7 or TLR8 independently confer responsiveness to the antiviral compound R-848. 14976262_mediates species-specific recognition of GU-rich single-stranded RNA (ssRNA); data suggest that ssRNA represents a physiological ligand for TLR8 16008579_CBV-induced inflammatory response is mediated through TLR8. 16025564_TLR8 acts as a host sensor for human parechovirus 1, and activates signalling that leads to the synthesis of pro-inflammatory molecules by the host. 16123302_a mechanism described linking Toll-like receptor (TLR) 8 signaling to the control of CD4+ regulatory T cell function; results suggest that TLR8 signaling could play a critical role in controlling immune responses to cancer and other diseases 16737960_TLR8-mediated MEKK3-dependent IKKgamma phosphorylation might play an important role in the activation of IKK complex, leading to IkappaBalpha phosphorylation 16857668_analysis of human toll-like receptor 8 extracellular domain features that are essential for pH-dependent signaling 16935934_TLR3 agonist poly(I:C) activated epithelial cells, primary endothelial cells, and two types of primary human smooth muscle cells (airway [ASMC] and vascular) directly, while the TLR7/8 agonist R848 required the presence of leukocytes to activate ASMC 17023556_These data lead us to suggest that ongoing viral activation of TLR7/8 could alter the adaptive immune response by modifying DC differentiation and by down-regulating DC responsiveness to a subsequent bacterial TLR4-mediated signal. 17040905_TLR8 inhibits TLR7 and TLR9, and TLR9 inhibits TLR7 but not vice versa in HEK293 cells transfected with TLRs in a pairwise combination. 17090647_analyzed the expression of Toll-like receptors 1 to 9 on myeloid dendritic cells generated from X-linked agammaglobulinemia patients and evaluated their response to activation by specific Toll-like receptor agonists 17301562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17698957_Both types of compounds induced IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10, but only the 7-deazaguanosine-containing compound that activated both TLR7 and TLR8 induced IFN-alpha in monkeys 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17724596_Ciprofloxacin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced toll-like receptor-4 and 8 expression on human monocytes derived from adult and cord blood. 17868034_analysis of modification and regulation of TLR8 in HEK-293 cells stimulated with imidazoquinoline agonists 17932028_Btk as a key signaling molecule that interacts with and acts downstream of TLR8 and TLR9. 17964520_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18406377_TLR7-9 recognize single-stranded RNA, nucleoside analogs and single-stranded CpG-DNA, respectively, and their activation initiates the immune response against viruses and bacteria [review] 18431484_These results delineate the complex effects of triggering TLR7/8 for an efficient antiviral defense. 18605904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18605904_This first report of a functional TLR8 variant associated with a different clinical course of an RNA viral disease may have implications for the individual risk assessment of RNA virus infections as well as for future HIV vaccine development. 18682521_replicated association was obtained for SNPs or haplotypes of TLR7 and TLR8, suggesting these genes as novel disease genes for asthma and related disorders. 18686608_Human epidermal keratinocytes constitutively express all TLR 1-10 mRNA, which may enable human keratinocytes to respond to a wide range of pathogenic micro-organisms. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18927625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18927625_four polymorphisms in the TLR8 gene on chromosome X showed evidence of association with TB susceptibility in males, including a non-synonymous polymorphism rs3764880 (Met1Val; P = 0.007, odds ratio (OR) = 1.8, 95% c.i. = 1.2-2.7) 18942751_TLR8 is an X-linked IBD susceptibility gene with both common predisposing and protecting haplotypes. 18985439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18985439_These results do not support an involvement of SNPs rs3764879 and rs3764880 of TLR8 in predisposition to coronary artery disease. 18985539_Expression of TLR-8, but not Tollip, is highly up-regulated in the colonic epithelium from patients with active IBD. 19017992_TLR8 may play a role in driving TNF production in rheumatoid arthritis 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19028959_DCIR is an antigen presenting cell receptor that is endocytosed efficiently in a clathrin-dependent manner and negatively affects TLR8-mediated cytokine production. 19164127_the Jak/STAT signaling pathway was involved in CD40 expression and cytokine production in TLR7-stimulated DCs but negatively regulated CD83 expression and cytokine secretion in DCs activated through TLR8 19164128_TLR3, TLR4, and TLR8 ligands induce synergistic multiple signaling pathways leading to cytokine mRNA expression and protein production in human monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19265114_Synergy between TLR4 and TLR7/8 controls the sequential production of regulatory and proinflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-10, interferon (IFN)-gamma, and IL-17A by naive CD4-positive T cells. 19381167_The ligand-induced activation of TLR 8 leads to the accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein in THP-1 human myeloid macrophages via redox- and reactive nitrogen species-dependent mechanisms. 19406482_exptressed on Fallopian tube and uterus 19437550_Activation of TLR8 by double-stranded RNA (poly-I:C) or single-stranded RNA induced IFN-alpha/beta expression. Such activation done prior to HSV-1 infection reduced the susceptibility of the neuronal cells to infection. 19454678_In monocytes, the response to RNA oligonucleotides was mediated by either TLR8 or RIG-I. TLR8 was responsible for IL-12 induction upon endosomal delivery of ssRNA oligonucleotides 19505919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527497_TLR8-mediated neutrophilic responses are markedly potentiated by oxidative stress, and the potentiation is mediated by enhanced NF-kB activation. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19614650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19637197_Results show that TLR8 activation may be an important, novel pathway for targeted treatment of Th1-mediated diseases, such as Crohn's disease. 19841637_Activation of endosomal TLRs 7, 8 and 4 leads to downregulation of degradative HIF-1 alpha prolyl hydroxylation. 19850743_Fanconi anemia, complementation group C suppresses TNF-alpha production in mononuclear phagocytes by suppressing TLR8 activity 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915052_When dendritic cells were triggered with the potent synergistic combination of TLR4 and TLR7/8 in conjunction with a TLR2 ligand, there was a clear shift to more Th2- and Th17-prone responses in the naive and memory T cell subpopulations 20004021_A five-amino-acid motif in the undefined region of the TLR8 ectodomain is required for species-specific ligand recognition. 20100933_Studies show substantial decreases in older compared with young individuals in cytokine production in response to TLR1/2, TLR6, TLR3, TLR5, and TLR8, TLR7 and TLR9 in DCs. 20124101_Data show that TLR activation was associated with significantly increased production of IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and CCL3. 20194452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237413_Triggering of TLR7 and TLR8 expressed by human lung cancer cells induces cell survival and chemoresistance. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364151_exploited by in HIV-1virus for productive infection of dendritic cells 20399690_In individuals affected by primary Sjogren's syndrome, TLR8 mRNA levels were not elevated. 20412752_TLR7 contributes to lung inflammation, NSCLC progression, cell survival via BCL-2 production & resistance to antineoplastic agents. Review. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20595247_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20652908_TLR8 sensing can be activated following bacterial phagocytosis, and rs3764880 may play a role in the modulation of TLR8-dependent microbicidal response of infected macrophages. 20674764_These findings suggest that TLR8 Met1Val, TLR8 -129C/G, and TLR9 -1486T/C polymorphisms are important on clinical course of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever disease. 20829351_C/EBP{delta} and STAT-1 are required for TLR8 transcriptional activity. 20832340_Human CD14dim monocytes patrol and sense nucleic acids and viruses via TLR7 and TLR8 receptors. 20946625_Lower toll-like receptor 8 expression was observed in monocytes from infants with respiratory syncytial virus infection. 20977567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21061265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21092001_Suppressed G-CSF production in the presence of IFN-alpha may contribute to IFN-alpha-induced neutropenia. However, a TLR7/8 agonist elicits G-CSF secretion even in the presence of IFN-alpha. 21321205_Phagosomal signaling involves a cooperative interaction between TLR2 and TLR8 in pro- and antiinflammatory cytokine responses, whereas TLR8 is solely responsible for IRF7-mediated induction of IFN-beta. 21354862_TLR 7 and TLR8 expressions are associated with poor outcome and greater inflammatory response in acute ischemic stroke. 21499082_Quantitative polymerase chain reaction showed significantly higher expression of LEAP-1 (P = 0.002) and TLR-8 (P = 0.023) and TLR-10 (P = 0.014) in viral keratitis and LEAP-2 (P = 0.034) in dry eye, versus controls. 21677671_Toll-like receptors (TLRs) 6, 7, and 8 are upregulated in keloid scars 21734241_monoclonal antiphospholipid antibodies as well as IgG fractions from patients with antiphospholipid syndrome increase mRNA expression of the intracellular TLR7 in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and TLR8 in monocytes 21947541_we found no evidence of any functional effects of TLR7 or TLR8 polymorphisms on receptor expression, measles-specific cellular responses or measles vaccine antibody responses. 21977996_Data suggest that the response pattern of human and rhesus B cells and pDCs to TLR7/8 and TLR9 is similar, although some differences in the cell surface phenotype of the differentiating cells exist. 22022576_Variations in TLR7 and TLR8 genes might impair immune responses during hepatitis C virus infection. 22065095_analyzed the frequency of TLR7 rs179008, TLR8 rs3764880, TLR9 rs5743836 and rs352140 in 370 patients with SLE and 415 healthy controls from southern Brazil 22164301_UNC93B1 physically associates with human TLR8 and regulates TLR8-mediated signaling 22196370_Dual or triple activation of TLR7, TLR8, and/or TLR9 by single-stranded oligoribonucleotides. 22210629_Responsiveness to TLR7/8 stimulation, which have been shown to recognize HIV-1 ssRNA, did not decrease in chronic infection, and may represent a contributing factor to ongoing T-cell immune activation in the setting of chronic viremic HIV-1 infection. 22243920_The study provides evidence that the TLR7 and TLR8 triggering can suppress HIV replication in monocytes and lead to postpone HIV disease progression. 22289837_Human TLR8 detectS viral single-stranded RNA and imidazoquinoline compounds. Review. 22340042_Expression of TLR8 is significantly increased in HeLa cells. TLR8 agonist may influence tumor development. 22363482_Segments 1, 2, 3 and 4 may be major determinants of the stimulatory activity exerted on human TLRs 7 and 8. 22393042_Epigenetic regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) release in human macrophages by HIV-1 single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) is dependent on TLR8 signaling 22525943_Authors demonstrate the use of ImageStream in DCs to assess TLR7/8 activation-mediated increases in phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of a key transcription factor. 22730373_These results suggest that expression of TLR7, but not TLR8, may be a predictor for rheumatoid arthritis disease activity 22768144_IL10 production after TLR9 ligands or HSV-1 stimulation was significantly related with plasma levels of sex hormones, whereas no correlation was found in cytokines produced following TLR7 and TLR8 stimulation. 22795647_cooperative activation of DCs with NOD1 and NOD2 agonists and TLR7/8 ligands results in a synergistic release of pro-inflammatory mediators which promote the activation of IL-17-producing T cells. 22857391_Single nucleotide polymorphism in the TLR8 gene is associated with allergic rhinitis. 23221735_Cervical tumor Langerhans cells lacked TLR9 expression and were functionally anergic to all the 3: TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 ligands, which may play a crucial role in immune tolerance. 23223421_This study demonstrates profibrotic properties of circulating monocytes from patients with systemic sclerosis and a key role for TLR signalling, particularly TLR8, in TIMP-1 secretion and matrix remodelling. 23369718_Studies indicate that the nucleic acid-sensing toll-like receptors (TLRs), which include TLRs 3, 7, 8 and 9 are completely localized within the endosomal compartments of immune cells and recognize RNA and DNA from pathogens. 23386618_Complement receptor 3 influences toll-like receptor 7/8-dependent inflammation 23425350_Impaired TLR3 and TLR7/8-mediated cytokine responses may contribute to aggressive HCV recurrence postliver transplantation 23520111_crystal structures of unliganded and ligand-induced activated TLR8 dimers were elucidated; ligand binding induces reorganization of the TLR8 dimer, which enables downstream signaling processes 23685782_Data indicate that TLR8 stimulation of NK-DC co-cultures significantly increased DC priming of EGFR-specific CD8(+) T cells in the presence of cetuximab. 23787171_TLR8 expression and signaling is impaired in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with multiple sclerosis 23826189_Study evaluated innate immune profiles following TLR stimulation in HIV-1-infected mothers and newborns, found significantly compromised cytokine responses upon extracellular and intracellular TLR activation. Myeloid dendritic cell (DC) responsiveness appeared to be less impaired than plasmacytoid DCs, and might be enhanced through TLR7/TLR8 activation. 23906644_Bb RNA is a TLR8 ligand in human monocytes and that transcription of IFN-beta in response to the spirochete is induced from within the phagosomal vacuole through the TLR8-MyD88 pathway. 24046015_Data indicate that TLR-induced IL-1beta overproduction in FANCA- and FANCC-deficient mononuclear phagocyte cell lines and primary cells requires activation of the inflammasome. 24205871_Variations in TLR8 genes may modulate immune responses during HCV infection. 24227841_A-to-I editing of structured viral RNAs facilitated the activation of TLR7 and TLR8. 24254490_The mechanisms of action of Aldaratrade mark are complex. Imiquimod is an effective ligand for TLR7 (and TLR8 in humans) and also interferes with adenosine receptor signaling. 24445780_non-synonymous TLR8 SNP rs3764880-G allele was a risk factor for oral ulcer and pericardial effusion, with significant additive effects 24525049_TLR8 is a novel estrogen target gene that can lower the inflammatory threshold and implicate an IFNalpha-independent inflammatory mechanism that could contribute to higher systemic lupus erythematosus incidence in women. 24771848_Differently, costimulation of TLR2, TLR4, and TLR7/8 enhances IL-1beta secretion but severely inhibits IL-1Ra production. 24773332_In vitro treatment of PBMCs with R484 hijacks the pro inflammatory immune process triggered by TLRs7/8 to mediate anti-inflammatory response. 24782650_The mRNA expression level of TLR8 in the patients with cervical cancer and Hela cells were up-regulated, it consistent with the increased expression of VEGF and Bcl-2. 24813206_TLR7 and TLR8 can signal in two different 'modes' depending on the class of ligand. 24919757_Carriage of the G-allele of TLR8-rs3764879 was associated with the occurrence of SLE in Danish women, but not men. 24939850_HIV-1 infection induced the expression of pro-IL-1beta via TLR8-mediated mechanisms and activated caspase-1 through the NLRP3 inflammasome to cleave pro-IL-1beta into bioactive IL-1beta 25102141_Data indicate 4-methyl-1-pentyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-amine a pure toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) agonist, evoking proinflammatory cytokine and Type II interferon responses in mononuclear leukocytes. 25126563_TLRs 3, 7, and 8 are prime biomarker candidates for HCV infection mRNA expression analysis which might improve current therapeutic approaches. 25187660_the UNC93B1 tyrosine-based motif regulates trafficking and TLR responses via separate mechanisms. 25204046_Data show that a differential mRNA expression of Toll-like receptors 7 & 8 is associated with different responses to pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN) alpha-2b antiviral therapy in patients with hepatitis C infection. 25229618_Humanized TLR7/8 expression drives proliferative multisystemic histiocytosis in C57BL/6 mice 25231413_Data show that activation of toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) signaling in tumor cells can block the induction and reverse the suppression of senescent naive and tumor-specific T cells in vitro and in vivo, resulting in enhanced anti-tumor immunity. 25253287_Data show that a total of nine single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TLR1, TLR4, TLR6 and TLR8 in Caucasians, and two other SNPs, one each in Toll-like receptors TLR4 and TLR8, in African Americans were significantly associated with HIV status. 25283842_TLR8 activation has direct anti-leukemic effects independent of its immunomodulating properties. 25297876_The insertion loop between leucine-rich repeats 14 and 15 in TLR8 is indispensable for the receptor cleavage in endosomes. 25430040_No significant associations have been found between TLR8 polymorphisms and susceptibility to Graves' disease in Chinese Cantonese. 25464115_The minor allele of TLR8 rs3764879 of the donor is associated with outcome after myeloablative conditioned allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. 25476907_Increased miR-K-10b and miR-K12-12 are functionally involved in sepsis as agonists of TLR8, forming a positive feedback that may lead to cytokine dysregulation. 25572425_Met1Val of TLR8 is significantly associated with risk of pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility in southern Punjab population. This effect was highly pronounced among males. 25667415_Data indicate that treatment with toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8) agonists elicited granzyme B production. 25785446_an important role of 2'-O-methylation for shaping differential TLR7 or TLR8 activation 25877926_TLR8, but not TLR7, is involved in priming of human neutrophil reactive oxygen species production by inducing the phosphorylation of p47phox and p38 MAPK. 26085680_This study demonstrates a physiological role of TLR8 in the sensing of entire S. aureus in human primary phagocytes, including the induction of IFN-beta and IL-12 production via a TAK1-IKKbeta-IRF5 pathway that can be inhibited by TLR2 signaling. 26101323_TLR8 is identified as receptor for bacterial RNA in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages. Moreover, TLR8-dependent detection of bacterial RNA was critical for triggering monocyte activation in response to infection with Streptococcus pyogenes. 26134824_Study show a stage-dependent upregulation of both TLR7 and TLR8 expression in pancreatic cancer and point to their significant role in chronic inflammation-mediated TLR7/TLR8 signaling leading to tumor cell proliferation and chemoresistance. 26160538_Sex-specific associations for TLR8 polymorphisms in tuberculosis. 26202481_the activation of TLR8 by bi-specific si-RNA for the production of INFbeta, was investigated. 26315138_Results show that TLR7 and TLR8 on trophoblastic cells play an important role in the prevention of intrauterine HBV transmission by inhibiting HBV translocation across trophoblasts. 26455634_TLR8 polymorphisms seem to be related to non-progression of liver fibrosis in HIV/HCV coinfected patients, particularly in males and those patients infected with GT1. 26466955_Knockdown of LRRC59 reduced TLR3-, 8-, and 9-mediated, but not TLR4-mediated, signaling. 26483222_TLR7 and TLR8 may be involved in the pathogenesis of brain and lung damages caused by severe EV71 infection. 26486764_Results suggest a relationship between the TLR8 and the susceptibility to Crohn's disease and Behcet's disease. 26545385_Identified human TLR8 as functional TLR13 equivalent that promiscuously senses ssRNA. 26556310_Comparison of present and previous association studies reveals contradictory results for common variants. Thus, no associations exist between genetic variation in TLR8 and AR. 26725554_TLR7 and 8 polymorphisms may play a considerable role in the pathogenesis of asthma. 26762473_Our meta-analysis suggests that TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 polymorphisms are associated with the development of systemic lupus erythematosus in Caucasian, Asian, and African populations 26929371_TLR8 with the uncleaved Z-loop is unable to form a dimer. The uncleaved Z-loop located on the ascending lateral face prevents the approach of the dimerization partner by steric hindrance. 27003259_The ER-stress inducing property of IMQ is possibly of importance for its efficacy in treating basal cell carcinoma, in situ melanoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Our data could potentially be harnessed for rational design of even more potent ER-stress inducers and new anti-cancer drugs. 27156628_TLR7 and TLR8 genetic polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, and the link is shaped by less effective MTB phagocytosis and impaired TLR signaling. 27385120_Study demonstrates that Hepatitis C virus (HCV) genomic RNA harbours specific sequences that initiate an anti-HCV immune response through TLR7 and TLR8 in various antigen presenting cells. 27392462_interferon alpha (IFN-alpha) secretion induced by Toll-like receptor 7 and Toll-like receptor 8 (TLR7/TLR8) activation was observed in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), which was recovered with Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) signaling. 27677832_Conditioned media or microparticles released from obese omental adipose tissue increased CD16 and CCR5 expression on CD14(+)CD16(-) monocytes and augmented their migratory capacity towards the conditioned media from obese omental adipose tissue, itself. 27729782_COPD lung tissue explants showed a greater pro-inflammatory response to TLR3 or TLR7/8 activation than control smokers. 27772795_TLR8 gene rs3764880 polymorphisms might be associated with susceptibility to ischemic stroke and involved in the inflammatory reaction and lipid metabolism of ischemic stroke in southern Chinese Han. 27793997_combination adjuvant systems demonstrate markedly different immune activation with age, with combined DC activation via Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin and TLR7/8 representing a novel approach to enhance the efficacy of early-life vaccines. 27810904_the current study shows that motolimod ( selective small-molecule agonist of TLR8, stimulates natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, and monocytes))can be safely administered in combination with cetuximab with an acceptable toxicity profile 28039018_Demonstrate STAT1-dependent transcriptional activation of TLR8 with estrogen stimulation. 28062211_this study shows that TLR8 gene polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to HIV and HCV co-infection 28122964_this study identified TLR8 as mediator of monocyte differentiation and M2 macrophage polarization during hepatitis C virus infection 28245863_Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) replication activating the toll like receptor 8 (TLR8) molecular pathway in primary monocytes. 28403045_TLR8 polymorphisms were associated with an increased risk and TLR7 polymorphisms with a decreased risk of recurrent rhinovirus infections. 28472897_MBZ-induced IL-1beta release was found to be dependent on NLRP3 inflammasome activation and to involve TLR8 stimulation. 28606989_Data indicate a mechanism in which Toll-like receptors TLR7/8 signaling, through shedding of FcgRIIA, shifts neutrophil function from phagocytosis to a programmed necrosis pathway, neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis). 28626766_Positive rates of iNOS in cervical tissues were 72.1%, 28.2%, and 3.1% in the -HPV-positive patients with cervical cancer (CC group), HR-HPV group, and controls, respectively (P |
ENSMUSG00000040522 |
Tlr8 |
156.659819 |
6.7145685457 |
2.747295 |
0.171157336 |
273.453203 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020059316369333920181990282469268628358579817640089863606720065693697408189377500171211921701210450674529971962506529518301819060779646059787928947520528784320692494702598196454346179962158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005268247501981649007817652499172572005787825852623094899635499838587733772475397620217823479597898855489443400949420906803233071133097057857858021333655185181044089404167607426643371582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
275.3396762 |
30.5819094 |
41.3364255 |
3.9012711 |
| ENSG00000101974 |
286410 |
ATP11C |
protein_coding |
Q8NB49 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of aminophospholipids, phosphatidylserines (PS) and phosphatidylethanolamines (PE), from the outer to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane (PubMed:25315773, PubMed:32493773, PubMed:24904167, PubMed:26567335). Major PS-flippase in immune cell subsets. In erythrocyte plasma membrane, it is required to maintain PS in the inner leaflet preventing its exposure on the surface. This asymmetric distribution is critical for the survival of erythrocytes in circulation since externalized PS is a phagocytic signal for erythrocyte clearance by splenic macrophages (PubMed:26944472). Required for B cell differentiation past the pro-B cell stage (By similarity). Seems to mediate PS flipping in pro-B cells (By similarity). May be involved in the transport of cholestatic bile acids (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZW0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24904167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25315773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26944472, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32493773}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity and phosphatidylserine flippase activity. Predicted to be involved in phospholipid translocation; positive regulation of B cell differentiation; and pre-B cell differentiation. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane. Is integral component of plasma membrane. Implicated in X-linked congenital hemolytic anemia. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:286410; |
early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity [GO:0090555]; phosphatidylserine flippase activity [GO:0140346]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332] |
24904167_ATP11C and CDC50A are required for aminophospholipid translocation from the outer to the inner plasma membrane leaflet; that is, they display flippase activity. 26399598_Atp11c mediates the transport of bile acids and organic anions across the sinusoidal membrane by regulating organic anion transporting polypeptides. 26944472_our analyses of a patient with mild hemolytic anemia identified ATP11C as a major flippase in human erythrocytes and showed that genetic mutation of ATP11C causes congenital mild hemolytic anemia inherited as an X-linked recessive trait. 29123098_A characteristic di-leucine motif (SVRPLL) in the C-terminal cytoplasmic region of ATP11C becomes functional upon PKCalpha activation. Moreover, endocytosis of ATP11C is induced by Ca(2+)-signaling via Gq-coupled receptors. 29276178_results indicated that the extracellular domain of CDC50A has important roles both in CDC50A's ability to chaperone ATP11C to the plasma membrane and in inducing ATP11C's ATP hydrolysis-coupled flippase activity. 31253392_Data show that P4-ATPase flippase complex alpha subunit ATP11C (ATP11C) was absent in the patient's erythrocyte membranes. 31371488_The cytoplasmic C-terminal region of the ATP11C variant determines its localization at the polarized plasma membrane. 32493773_Crystal structure of a human plasma membrane phospholipid flippase. 32997992_Transport Cycle of Plasma Membrane Flippase ATP11C by Cryo-EM. 33103382_Reduction in flippase activity contributes to surface presentation of phosphatidylserine in human senescent erythrocytes. 34651249_The ratio of ATP11C/PLSCR1 mRNA transcripts has clinical significance in sickle cell anemia. |
ENSMUSG00000062949 |
Atp11c |
244.839292 |
2.0020982822 |
1.001513 |
0.101136568 |
99.187976 |
0.00000000000000000000002296370520591403967209875315515785543547976383092940522504915275628367687943409691797569394111633300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000230574346149177674235708255433783772115265447036483945289909829046148814768457668833434581756591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
327.0599538 |
29.0899991 |
164.4528857 |
11.1054852 |
| ENSG00000102007 |
5355 |
PLP2 |
protein_coding |
Q04941 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in cell differentiation in the intestinal epithelium. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes an integral membrane protein that localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum in colonic epithelial cells. The encoded protein can multimerize and may function as an ion channel. A polymorphism in the promoter of this gene may be linked to an increased risk of X-linked cognitive disability. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 5. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:5355; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemokine binding [GO:0019956]; ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015075]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; ion transport [GO:0006811] |
15474493_PLP2/A4 has a role in the chemotactic processes via CCR1 17416750_PLP2 is expressed abundantly in the pyramidal cells of hippocampus and granular cells of the cerebellum in the brains of a cohort of males with probable X-linked mental retardation. 24278019_This work ascribes a critical function to PLP2 for viral ligase activity and underlines the power of non-lethal haploid genetic screens in human cells to identify the genes involved in pathogen manipulation of the host immune system. 24604726_PLP2 and RAB5C are binding partners of TPD52. 26287415_PLP2 specifically binds to phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase to activate the protein kinase B pathway to enhance cell proliferation, adhesion, and invasion in melanoma cells. 29509055_Up-regulation of miR-422a attenuated microsphere formation, proliferation and tumor formation of breast cancer stem cells via suppressing the PLP2 expression. 30373180_Higher PLP2 immunohistochemistry staining significantly correlated with more advanced tumor grades and poorer prognosis in human gliomas. 31778016_Reduced expression of proteolipid protein 2 increases ER stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma. 31901870_MiR-765 functions as a tumour suppressor and eliminates lipids in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by downregulating PLP2. 32596309_PLP2 Expression as a Prognostic and Therapeutic Indicator in High-Risk Multiple Myeloma. 33859750_CD45RO(-)CD8(+) T cell-derived exosomes restrict estrogen-driven endometrial cancer development via the ERbeta/miR-765/PLP2/Notch axis. 34409455_PLP2 drives collective cell migration via ZO-1-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling at the leading edge in human colorectal cancer cells. 35190586_PLP2-derived peptide Rb4 triggers PARP-1-mediated necrotic death in murine melanoma cells. |
ENSMUSG00000031146+ENSMUSG00000057762 |
Plp2+Gm6169 |
908.228265 |
2.2301903982 |
1.157167 |
0.056264555 |
426.781583 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008154217716219939666286168025595958607635509655086666153453902610897394452601529880796192340910569712019566529551842587488537875306828951377481240947251512697280374521877217687873237835165153101695222369975351755435543227369427250750267 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003244103867692892711814777878091511116836333347107122675252825611759238607062474383692852058389598202366484777555111138215283842336575356592310715707899333293820743731155282159710228744164583100283750406497497996282186149934190222410280 |
Yes |
No |
1268.1913806 |
40.4621926 |
572.6699053 |
14.5489828 |
| ENSG00000102024 |
5358 |
PLS3 |
protein_coding |
P13797 |
FUNCTION: Actin-bundling protein found in intestinal microvilli, hair cell stereocilia, and fibroblast filopodia. May play a role in the regulation of bone development. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Plastins are a family of actin-binding proteins that are conserved throughout eukaryote evolution and expressed in most tissues of higher eukaryotes. In humans, two ubiquitous plastin isoforms (L and T) have been identified. Plastin 1 (otherwise known as Fimbrin) is a third distinct plastin isoform which is specifically expressed at high levels in the small intestine. The L isoform is expressed only in hemopoietic cell lineages, while the T isoform has been found in all other normal cells of solid tissues that have replicative potential (fibroblasts, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, melanocytes, etc.). The C-terminal 570 amino acids of the T-plastin and L-plastin proteins are 83% identical. It contains a potential calcium-binding site near the N terminus. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:5358; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; actin filament bundle [GO:0032432]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; actin filament network formation [GO:0051639]; bone development [GO:0060348] |
14567899_expression of T-plastin in the placental context may indeed be associated with the enhanced replicative potential of placental trophoblasts. 14612505_T-plastin has the potential to be a Sezary cell-specific marker valuable for diagnostic and treatment of Sezary syndrome. 15741236_T-plastin increases Arp2/3-mediated actin-based movement 16142308_T-fimbrin has a role in the response to DNA damage 18440926_unaffected SMN1-deleted females exhibit significantly higher expression of PLS3 than their spinal muscular atrophy-affected counterparts 18569641_Increased T-plastin is associated with leukemic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma 20937953_The PLS3 gene may be an age- and/or puberty-specific and sex-specific modifier of spinal muscular atrophy. 22495182_PLS3 is expressed in the majority of SS patients and provide insight into the molecular regulation of PLS3 expression in CTCL 22627769_T-plastin is a marker restricted to malignant lymphocytes from Sezary syndrome patients and plays a role for cell survival and migration. 23263861_PLS3 over-expression led to a stabilization of axons which, in turn, results in a significant delay of axon pruning, counteracting poor axonal connectivity in spinal muscular atrophy neuromuscular junctions. 23378342_Overexpression of PLS3 is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer 23429988_PLS3, Twist, KIR3DL2 and NKp46 gene expression can model efficient molecular Sezary syndrome diagnosis. 23549633_study identified a common gene variant in PLS3 as an independent prognostic marker in female patients with stage II and III colon cancer 24088043_Plastin 3 (PLS3) appears to be important in human bone health, on the basis of pathogenic variants in PLS3 in five families with X-linked osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures that we report here. 24170770_Data suggest that several single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the plastin genes PLS3 and LCP1 could serve as gender- and/or stage-specific molecular predictors of tumor recurrence in stage II/III colorectal cancer as well as therapeutic targets. 24172247_PLS3 gene may have an age- and gender-specific role in the clinical severity of SMA in children afflicted with this condition. 24217791_PLS3 overexpression is associated with colorectal cancer. 24271012_Loss of PLS3 is associated with spinal muscular atrophy. 24284364_PLS3 expression and SMA phenotype: a commentary on correlation of PLS3 expression with disease severity in children with spinal muscular atrophy. 25209159_results confirm the role of PLS3 mutations in early onset osteoporosis. The mechanism whereby PLS3 affects bone health is unclear, but it may be linked to osteocyte dendrite function and skeletal mechanosensing 25226517_T-plastin expression downstream to the calcineurin/NFAT pathway is involved in keratinocyte migration. 25880010_PLS3 was expressed in circulating tumor cells undergoing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in patients with breast cancer; an excellent biomarker for identifying groups at risk of recurrence or with a poor prognosis 26048141_plastin 3 is a regulator of actin microfilament bundles at the ES in which it dictates the configuration of the filamentous actin network 26114395_Measurements of SMN and PLS3 transcript and protein levels in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons show limited value as Spinal muscular atrophy biomarkers. 26134627_High levels of recombinant hPLS3 mRNA were expressed in motor neurons of SMA mice and an increased level of PLS3 protein in total spinal cord, yet neither survival nor the fundamental electrophysiological aspects of the neuromuscular junction improved. 26146096_t is beyond doubt that PL S3 must be further investigated to determine its role in diagnostics, prediction, treatment and monitoring of treatment of colorectal cancer. 26573968_PLS3 is a genuine spinal muscular atrophy protective modifier in SMN1-deleted individuals 27260405_We show that genes of the classical apoptosis pathway are involved in the smn-1-mediated neuronal death, and that this phenotype can be rescued by the expression of human SMN1, indicating a functional conservation between the two orthologs. Finally, we determined that Plastin3/plst-1 genetically interacts with smn-1 to prevent degeneration, and that treatment with valproic acid is able to rescue the degenerative phenotype 27279027_PLS3 expression does not always modify SMA phenotype 27499521_findings emphasize the power of genetic modifiers, PLS3 and CORO1C, to unravel the cellular pathomechanisms underlying spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)--and the power of combinatorial therapy based on splice correction of SMN2 and endocytosis improvement to efficiently treat SMA 27732335_Patients with PLS3 mutation-related osteoporosis respond to teriparatide treatment. 28218996_T-plastin mediates the hypoxia-induced membrane trafficking 28379384_PLS3 mutation plays a role in low turnover osteoporosis pathophysiology. 28694070_In this study, the authors found that the actin filament bundling abilities of PLS1 and PLS2 were similarly sensitive to Ca(2+) (pCa50 ~6.4), whereas PLS3 was less sensitive (pCa50 ~5.9). 28748388_PLS3 sequencing in childhood-onset primary osteoporosis identifies two novel disease-causing variants. 28777485_PLS3 deletions lead to severe childhood-onset osteoporosis resulting from defective bone matrix mineralization. 29736964_PLS3 mutation is associated with X-linked osteoporosis. 30204862_Regulation of osteoclastogenesis and bone remodeling via the PLS3-NKRF-NFkappaB-NFATC1 axis unveils a novel possibility to counteract osteoporosis. 30829071_study identifies PLS3 as a potential target for enhancing the p38 MAPK-mediated apoptosis induced by paclitaxel. 30837644_PLS3 polymorphisms are genetic loci for osteoporosis in postmenopausal Chinese women. 31293151_A Novel Peptide Probe for Identification of PLS3-Expressed Cancer Cells. 31347706_A novel nonsense variant in PLS3 causes X-linked osteoporosis in a Chinese family. 32239705_PLS3 predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer and promotes cancer cell proliferation via PI3K/AKT signaling. 32453450_Unique, Gender-Dependent Serum microRNA Profile in PLS3 Gene-Related Osteoporosis. 32655496_PLS3 Mutations Cause Severe Age and Sex-Related Spinal Pathology. 32938453_Genetic modifiers ameliorate endocytic and neuromuscular defects in a model of spinal muscular atrophy. 33802838_Expression and Localization of Thrombospondins, Plastin 3, and STIM1 in Different Cartilage Compartments of the Osteoarthritic Varus Knee. 34946798_X-Linked Osteogenesis Imperfecta Possibly Caused by a Novel Variant in PLS3. 35752817_Identification of a novel splicing mutation and genotype-phenotype correlations in rare PLS3-related childhood-onset osteoporosis. |
ENSMUSG00000016382 |
Pls3 |
116.302510 |
2.7531352965 |
1.461076 |
0.200617328 |
52.134933 |
0.00000000000051814902302699613173255089803563458537155606009605435247067362070083618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003138235363101544395059289568011768104243558452637330447032582014799118041992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
169.8102564 |
22.6831638 |
61.7718691 |
6.3436400 |
| ENSG00000102096 |
11040 |
PIM2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P1W9 |
FUNCTION: Proto-oncogene with serine/threonine kinase activity involved in cell survival and cell proliferation. Exerts its oncogenic activity through: the regulation of MYC transcriptional activity, the regulation of cell cycle progression, the regulation of cap-dependent protein translation and through survival signaling by phosphorylation of a pro-apoptotic protein, BAD. Phosphorylation of MYC leads to an increase of MYC protein stability and thereby an increase transcriptional activity. The stabilization of MYC exerted by PIM2 might explain partly the strong synergism between these 2 oncogenes in tumorigenesis. Regulates cap-dependent protein translation in a mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)-independent manner and in parallel to the PI3K-Akt pathway. Mediates survival signaling through phosphorylation of BAD, which induces release of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-X(L)/BCL2L1. Promotes cell survival in response to a variety of proliferative signals via positive regulation of the I-kappa-B kinase/NF-kappa-B cascade; this process requires phosphorylation of MAP3K8/COT. Promotes growth factor-independent proliferation by phosphorylation of cell cycle factors such as CDKN1A and CDKN1B. Involved in the positive regulation of chondrocyte survival and autophagy in the epiphyseal growth plate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18593906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18675992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20307683}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a protooncogene that acts as a serine/threonine protein kinase. Studies determined the encoded protein functions to prevent apoptosis and to promote cell survival.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:11040; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346]; response to virus [GO:0009615] |
12954615_pim-2 functions similarly to pim-1 as a pro-survival kinase; BAD is a legitimate PIM-2 substrate 15291354_hPim-2 mRNA expression in NHL was 1.5 to 2.6 times higher in involved splenic foci compared to nearby uninvolved regions. hPim-2 mRNA was increased 3-folds in B-CLL over normal B-cells 15548703_transcriptional induction of Pim-2 initiates a novel NF-kappaB activation pathway that regulates cell survival 15721354_EBV-induced upregulation of Pim kinases and Pim-stimulated EBNA2 transcriptional activity may contribute to the ability of EBV to immortalize B-cells and predispose them to malignant growth. 16015593_Up-regulation of Pim-2 is associated with disease progression and perineural invasion in prostate cancer. 16403219_All three Pim kinase family members predominantly phosphorylate Bad on Ser112 and in addition are capable of phosphorylating Bad on multiple sites associated with the inhibition of the pro-apoptotic function of Bad in HEK-293 cells 18216297_expression of the Myc and Pim proto-oncogenes by Jak2V617F was found to be FERM domain dependent. 18424697_Foxp3 can regulate pim 2 expression. 18593906_Pim kinases promote cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis by down-regulating p27(Kip1) expression at both transcriptional and posttranslational levels. 18675992_pim-2 acts as a pro-survival kinase to inhibit apoptosis and keep liver cell survival in IL-3-deprived medium. Pim-2 might participate in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma induction through its downstream molecules 4E-BP1 and Bad. 19821157_we infer that Pim-2 could activate API-5 to inhibit the apoptosis of liver cells, and NF-kappaB is the key regulator 19841674_structural analysis of the PIM2 kinase in complex with an organoruthenium inhibitor 20465571_PIM2 controls the expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6. 20592892_Data show that Pim-2 can induce malignant transformation of human liver cell line L02. 20939820_A cell-based test system useful for rapid and inexpensive pre-screening of compounds capable of preventing Pim-mediated phosphorylation is discussed. 21299464_Pax-5 may act as a transcription factor to modulate the expression of Pim-2 in B-cells 21475253_IL-6 and TNF family cytokines upregulate Pim-2 in bone marrow stromal cells and osteoclasts in multiple myeloma. This appears to be a novel anti-apoptotic mechanism for MM cell survival. 21859846_Targeting cap-dependent translation blocks converging survival signals by AKT and PIM 1, 2 kinases in lymphoma 22506047_While PIM-2 can function as a potent survival factor, it can, under certain circumstances, exhibit pro-apoptotic effects as well. 23209281_PIM kinases promote the production of IFNgamma, the hallmark cytokine produced by Th1 cells. 23749639_our results identify eIF4B as a critical substrate of Pim kinases in mediating the activity of Abl oncogenes 23752607_Our data indicate that PIM-2 and NF-kappaB gene expression is increased in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. High PIM-2 expression is associated with complete remission rate in AML patients. 23760264_Data indicate that PIM-2 is an upstream activator of E2F-1 and ATM in the ultraviolet damage response. 23813671_Overexpression of pim-2 may inhibit the apoptosis of prostate cancer cells through phosphorylation of eIF4B, thus promoting tumorigenesis. 23818547_Pim2 directly phosphorylates TSC2 on Ser-1798 and relieves the suppression of TSC2 on mTOR-C1, leading to multiple myeloma cells proliferation. 24142698_PIM2 could directly phosphorylate PKM2 on the Thr-454 residue, resulting in an increase of PKM2 protein levels. Compared with wild type, PKM2 with the phosphorylation-defective mutation displayed a reduced effect on glycolysis. 24505470_HIF-1A induced PIM2 expression in HepG2 cells via binding to the hypoxia-responsive elements (HREs) of the PIM2 promoter. 24799066_Blocking the activities of PIM kinases(PIM1, PIM2 and PIM3) could prevent pancreatic cancer development. PIM kinases(PIM1, PIM2 and PIM3) may be a novel target for cancer therapy 25238262_Data demonstrate the role of PIM kinases in driving myeloid leukemia, and as candidate molecules for therapy against human malignancies. 25854938_Persistent activation of STAT3 by PIM2-driven positive feedback loop for epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. 26064888_our findings will help to uncover novel signaling pathways between inflammations and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis development and imply that Pim-2/mTORC1 pathway may be critical for the initiation of inflammatory reactions. 26078709_Our findings suggest that Pim-2-mediated aerobic glycolysis is critical for monitoring Warburg effect in colorectal tumor cells, highlighting Pim-2 as a potential metabolic target for colorectal tumor therapy. 26500282_We show that Pim2 inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors, such as bortezomib, have additive effects to inhibit the growth of myeloma cells, suggesting that Pim2 could be an interesting target for the treatment of multiple myeloma. 26551340_A high percentage of urothelial carcinomas express Pim kinases. Pim expression differs in NILG, NIHG, and IHG lesions. 26643319_PIM2 gene knockdown enhances the anti-proliferative effect of AZD1208 in non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell line. 26764044_the elevated expression of PIM2 in blastic cells is associated with poor prognosis of AML patients and their resistance to induction therapy. 27448973_show that PIM1 contributes to melanoma cell proliferation and tumor growth in vivo; however, the presence of PIM2 and PIM3 could also influence the outcome. 27564460_Our data provide evidence for a novel role for Pim2 in the regulation of the DNA damage response (DDR). Knockdown of Pim2 upregulates several downstream DDR markers, mimicking the effects of doxorubicin (Dox) treatment of MM cells, and suggesting a role for the kinase as a negative regulator of this pathway. 27826617_High PIM2 expression is associated with osteosarcoma. 27901106_data suggest that PIM1/2 kinase overexpression is a common feature of male reproductive organs tumors, which provoke tissue alterations and a large inflammatory response that may act synergistically during the process of tumorigenesis. 28698206_PIM kinases in classical Hodgkin lymphoma exhibit pleiotropic effects, orchestrating tumor immune escape and supporting Reed-Sternberg cell survival. 28729093_These results demonstrate the involvement of PIM kinases in LIF-induced regulation in different trophoblastic cell lines which may indicate similar functions in primary cells. 28914261_we showed that RPS6KA3 knockdown reduced the propagation of human AML cells in vivo in mice. Our results point to RSK2 as a novel Pim2 target with translational therapeutic potential in FLT3-ITD AML. 28944837_Inhibition of PIM2 attenuated asthma symptoms and increased expression levels of interleukin (IL)10 and forkhead box protein 3 (FOXP3) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. 29124675_High PIM2 expression is associated with Malignant Grade in Prostate Cancer. 29570932_These findings demonstrate an important role for the PIM2-TTP complex in breast cancer tumorigenesis. 29665227_PIM2 is associated with unfavourable chronic lymphocytic leukaemia prognosis.PIM-2 role in the CXCR4-induced chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cell migration. 29985480_our findings indicated that PIM2 was a novel regulator of HK2, and suggested a new strategy to treat breast cancer. 30096294_PIM2 is upregulated by strongly activated tumor suppressor protein p53. 30340823_PIM2 might function as an important oncogene in gastric cancer 31358902_Phosphorylation of AMPKalpha1 by PIM2 led to decreasing AMPKalpha1 kinase activity, which in turn promoted aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth. In addition, PIM2 expression positively correlated with AMPKalpha1 Thr467 phosphorylation in Endometrial cancer tissues. Insights into the role of PIM2 and AMPKalpha1 in Endometrial cancer suggest that combination targeting of these proteins may represent a new strategy for tre... 31409638_HSF1 protein stability is regulated by PIM2-mediated phosphorylation of HSF1 at Thr120. PIM2, pThr120-HSF1, and PD-L1 expression positively correlated with each other in breast cancer tissues. 31501481_TRAF3 regulates the oncogenic proteins Pim2 and c-Myc to restrain survival in normal and malignant B cells. 31894300_Inhibition of PIM2 in liver cancer decreases tumor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo primarily through the modulation of cell cycle progression. 32641749_PIM2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression through activating NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 32754266_Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase 1 interacts with NF-kappaB p65 to regulate breast tumorigenesis via PIM2 induced phosphorylation. 33931981_Positive regulation of PFKFB3 by PIM2 promotes glycolysis and paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. 34511042_Long non-coding RNA SOX21-AS1 modulates lung cancer progress upon microRNA miR-24-3p/PIM2 axis. 35108359_PIM2 kinase has a pivotal role in plasmablast generation and plasma cell survival, opening up novel treatment options in myeloma. 36109523_Phosphorylation of PFKFB4 by PIM2 promotes anaerobic glycolysis and cell proliferation in endometriosis. |
ENSMUSG00000031155 |
Pim2 |
148.768604 |
3.5113903878 |
1.812042 |
0.139073026 |
179.453483 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000006378933164894518449499231817191922006236917120478247099171778284383368693479086492787449609575428801202037765172292438364820554852485656738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000001088474607096451951246267825681165171351133772034475459150721451364346764872190972418849552274771447755996600648131789057515561580657958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
237.1329705 |
19.7993873 |
68.0718298 |
4.8827364 |
| ENSG00000102100 |
7355 |
SLC35A2 |
protein_coding |
P78381 |
FUNCTION: Transports uridine diphosphate galactose (UDP-galactose) from the cytosol into Golgi vesicles where glycosyltransferases function, including galactosyltransferases that catalyze globotriaosylceramide/globoside (Gb3Cer) synthesis from lactosylceramide. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23561849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30834435}. |
Alternative splicing;Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the nucleotide-sugar transporter family. The encoded protein is a multi-pass membrane protein. It transports UDP-galactose from the cytosol into Golgi vesicles, where it serves as a glycosyl donor for the generation of glycans. Mutations in this gene cause congenital disorder of glycosylation type IIm (CDG2M). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:7355; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; UDP-galactose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005459]; carbohydrate transport [GO:0008643]; galactose metabolic process [GO:0006012]; UDP-galactose transmembrane transport [GO:0072334] |
21918738_localization of the UDP-Gal transporter may depend on the presence of the partner splice variant 23561849_Mosaicism of the UDP-galactose transporter SLC35A2 causes a congenital disorder of glycosylation. 23583405_The data further supports the hypothesis that UGT and NGT cooperate in the UDP-Gal delivery for glycosyltransferases located in the Golgi apparatus. 24115232_De novo mutations in SLC35A2 encoding a UDP-galactose transporter cause early-onset epileptic encephalopathy. 25451267_The short N-terminal region composed of 35 N-terminal amino-acid residues of UGT was crucial for galactosylation of N-glycans. 25944901_UDP-galactose (SLC35A2) and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (SLC35A3) Transporters Form Glycosylation-related Complexes with Mannoside Acetylglucosaminyltransferases (Mgats). 29679388_nonsynonymous variants in SCL35A2 were detected in the brains of 2 males with intractable epilepsy 29907092_SLC35A2 missense mutation is associated with congenital disorder of glycosylation. 30746764_Although normal glycosylation studies together with clinical variability and genetic results complicate the diagnosis of SLC35A2-CDG, the data indicate that the combination of these three elements can support the pathogenicity of mutations in SLC35A2. 30817854_Data characterize 26 new variants in the single largest study involving SLC35A2-congenital disorders of glycosylation. These variants had normal transferrin glycosylation. The biochemical assay assess SLC35A2-dependent UDP-galactose transport activity in primary fibroblasts of the patients that seems to be directly correlated to the ratio of wild-type to mutant alleles. 32605344_[Clinical characteristics of SLC35A2 gene variants related congenital disorders of glycosylation type]. 33407896_Frequent SLC35A2 brain mosaicism in mild malformation of cortical development with oligodendroglial hyperplasia in epilepsy (MOGHE). 34161696_SLC35A2-CDG: novel variants with two ends of the spectrum. 34384782_A three-pocket model for substrate coordination and selectivity by the nucleotide sugar transporters SLC35A1 and SLC35A2. |
ENSMUSG00000031156 |
Slc35a2 |
162.765163 |
2.2652843056 |
1.179692 |
0.156854663 |
56.010482 |
0.00000000000007208565292387733857948270726146366375181040453412606439087539911270141601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000461598367529904294485242782619968825619412300387267578116734512150287628173828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
228.3276949 |
21.4245244 |
101.4190555 |
7.3342360 |
| ENSG00000102144 |
5230 |
PGK1 |
protein_coding |
P00558 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes one of the two ATP producing reactions in the glycolytic pathway via the reversible conversion of 1,3-diphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate (PubMed:30323285, PubMed:7391028). In addition to its role as a glycolytic enzyme, it seems that PGK-1 acts as a polymerase alpha cofactor protein (primer recognition protein) (PubMed:2324090). May play a role in sperm motility (PubMed:26677959). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2324090, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26677959, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30323285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7391028}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycolysis;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Hydroxylation;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; pyruvate from D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate: step 2/5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30323285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7391028}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1,3-diphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate. The encoded protein may also act as a cofactor for polymerase alpha. Additionally, this protein is secreted by tumor cells where it participates in angiogenesis by functioning to reduce disulfide bonds in the serine protease, plasmin, which consequently leads to the release of the tumor blood vessel inhibitor angiostatin. The encoded protein has been identified as a moonlighting protein based on its ability to perform mechanistically distinct functions. Deficiency of the enzyme is associated with a wide range of clinical phenotypes hemolytic anemia and neurological impairment. Pseudogenes of this gene have been defined on chromosomes 19, 21 and the X chromosome. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:5230; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; phosphoglycerate kinase activity [GO:0004618]; protein-disulfide reductase (NAD(P)) activity [GO:0047134]; canonical glycolysis [GO:0061621]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; plasminogen activation [GO:0031639] |
2324090_Generif: Phosphoglycerate kinase is a moonlighting protein that functions as both a glycolytic enzyme and a primer recognition protein of DNA polymerase alpha. 11130727_Phosphoglycerate kinase is a moonlighting protein that functions as both a glycolytic enzyme and a disulfide reductase. 11745195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12080078_Phosphorylates pyrimidine L-deoxynucleoside analog diphosphaates 12174867_Overexpression induces a multidrug resistance phenotype. 12869554_3-phosphoglycerate kinase has a role in the activation of L-nucleoside analogs 14764427_These results demonstrate that phosphpglycerate kinase regulates uPAR expression at the post-transcriptional level. 15053920_production and secretion of PGK are regulated separately and oxygen and the protein hydroxylases can control not only gene expression but also protein secretion 15255553_phosphoglycerate kinase does not appear to have a role in the development or progression of neoplasms [letter] 16363799_During domain closure, Lys 215 in 3-phosphoglycerate kinase possibly moves together with the transferring phosphate, and this group is being positioned properly for catalysis. 17565005_The impact of hypoxic treatment on the expression of PGK1 and the cytotoxicity of troxacitabine and gemcitabine are reported. 17661373_our study indicates that inhibition of the transcription mechanism is the cause of PGK deficiency. 18096512_Aa steady state kinetic and biophysical study of the interaction of the model compound l-MgADP with hPGK, is presented. 18288812_Although L-ADP is almost as catalytically competent as D-ADP, under our experimental conditions (buffer containing 30% methanol, 4 degrees C) phosphoglycerate kinase binds D- and L-ADP with similar kinetics. 18453750_overexpression of PGK1 and its signalling targets may be a expression-pathway in diffuse primary gastric carcinomas promoting peritoneal dissemination 18540639_transmission path of the nucleotide effect toward the main hinge of phosphoglycerate kinase is described for the first time at the level of interactions existing in the tertiary structure[ 3-phosphoglycerate kinase] 18603805_PGK1 was selectively overexpressed in human colon tumor cells by treating with hydrogen peroxide as oxidative stress, while its expression was suppressed by co-treatment with antioxidants. 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19688824_Data show that PGK1 regulates the expression of CXCR4 and beta-catenin at the mRNA and protein levels. 19778949_Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) showed a difference between follicular cells from follicles leading to a pregnancy or developmental failure. 19854185_Results suggest that conformational rearrangements in the hinge generated by binding of both substrates provide the main driving force for domain closure overcoming the slightly unfavourable contact interactions between the domains. 21349853_PGK domain movement and catalysis is regulated by a spring-loaded release mechanism 21505655_enzyme kinetics studies show that the absence of the ribose OH-groups with is better tolerated for the purine than for the pyrimidine containing compounds in phosphoglycerate kinase 1 21549683_Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out with four different nucleotides (D-/L-ADP and D-/L-CDP) in complex with PGK and 1,3-bisphospho-d-glycerate. The binding affinities of CDPs were very weak while D- and L-ADP were better substrates. 21780947_two key (hub) PPARgamma direct target genes, PRKCZ and PGK1, were experimentally validated to be repressed upon PPARgamma activation by its natural ligand, 15d-PGJ2 in three prostrate cancer cell lines 22348148_All findings indicate that the different clinical manifestations associated with PGK1 deficiency chiefly depend on the distinctive type of perturbations caused by mutations in the PGK1 gene 22619369_carbonic anhydrase I, phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and apolipoprotein A-I appeared to be the most significant variations of proteins in patients with osteopenia and osteoarthritis 22742733_Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 was up-regulated significantly in radioresistant astrocytomas and also seems to be correlated with the negative prognosis following radiotherapy. 23130662_Glycolytic enzymes PGK1 and PKM2 are novel transcriptional targets of PPARgamma in breast cancer. 23336698_the low kinetic stability displayed by PGK1 protein mutations is causing human PGK1 deficiency 23684636_Conformational dynamics in the catalytic cycle of phosphoglycerate kinase, molecular details provided by structural analysis. [Review] 23727790_increased expression of PGK1 in colon cancer tissue is associated with metastasis. 24284928_PGK1 could promote radioresistance in U251 human cells. 24376734_PGK1 appears to play an important role for neuroblastoma 24721582_different factors contributing to hPGK1 thermodynamic and kinetic stability 24838780_mutations associated with hPGK1 deficiency lead to increased aggregation and proteolysis rates in vitro and inside cells due to protein thermodynamic destabilization 24934115_Phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency due to a novel mutation (c. 1180A>G) manifesting as chronic hemolytic anemia in a Japanese boy. 25175369_Suppression of PGK1 enhanced the radiosensitivity of U251 xenografts and suggest that PGK1 may serve as a useful target in the treatment of radioresistant glioma. 25867275_Results show that PGK1 mRNA and protein expression were significantly increased in breast cancer tissues and can be considered as a prognostic biomarker of chemoresistance to paclitaxel treatment in breast cancer. 26356530_PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway regulates HDAC3 S424 phosphorylation, which promotes HDAC3-PGK1 interaction and PGK1 K220 deacetylation 26396085_Retinal dystrophy may be one of the clinical manifestations of phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency. 26510737_In neuroblastoma cells, CAIX and PGK1 expression is up regulated under hypoxia and correlates with response to targeted anti-proliferative treatment. 26942675_Mitochindrial PGK1 acts as a protein kinase in coordinating glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, which is instrumental in cancer metabolism and tumorigenesis. 27342824_PGK1, a glycolytic enzyme catalyzing the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate into 2-phosphoglycerate, has increased expression in synovial tissues and blood of rheumatoid arthritis, which may be involved in pro-inflammation and synovial hyperplasia of the disease 28238651_Acetylated PGK1 binds to and phosphorylates Beclin1 at S30, leading to activation of the VPS34-Beclin1 complex to initiate autophagosomal formation. 28457968_Data suggest that, in breast cancer cells, MYC acts as an upstream regulator leading to PGK1 activation. (MYC, proto-oncogene c-myc; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase 1) 28749413_PGK1 is used to indicate the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 28763863_PGK1 is involved in the regulation of metastasis and invasion of HCC[ hepatocellular carcinoma] cells and can promote the migration and invasion of HCC cells. Therefore, PGK1 may be an important predictor of prognosis and postoperative recurrence in patients with liver cancer. 28923857_Data show that LINC00963 (MetaLnc9) interacted with the glycolytic kinase PGK1 and prevented its ubiquitination in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, leading to activation of the oncogenic AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. 29199648_The results indicate that ALDOA and PGK1 may indicate resistance to cisplatin in osteosarcoma 29995887_PGK1 mutated variants display different catalytic activity and conformational stability compared to the native enzyme. 30029001_PGK1 T243 phosphorylation regulates the direction of PGK1-catalyzed reaction. Inhibition of PGK1 T243 phosphorylation abrogates protumoral function of macrophages. PGK1 T243 phosphorylation correlates with grades and prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme patients 30111548_Lower glycolytic capacity in PGK1 deficiency seems to result in multisystem involvement and increased susceptibility to exertional rhabdomyolysis. 30392930_CDC7-bound PGK1 converts ADP to ATP, thereby abrogating the inhibitory effect of ADP on CDC7-ASK activity, promoting the recruitment of DNA helicase to replication origins, DNA replication, cell proliferation, and brain tumorigenesis. 30471866_Mechanistic investigations showed that Rab11-FIP2 interacted with the glycolytic kinase PGK1 and promoted its ubiquitination in NSCLC cells, leading to inactivation of the oncogenic AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. 30537744_High PGK1 expression was associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer, because PGK1 and HIF-1alpha formed a positive feed-forward loop and thus stimulated breast cancer progression and metastases. 30887539_Phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency: A nationwide multicenter retrospective study. 30925862_We propose that PGK1 mediates DNA repair and methylation through the HSP90/ERK pathway, and eventually enhances the chemoresistance to cisplatin. The results provide new insights on functions of PGK1 and HSP90, which might make them as promising targets for endometrial cancer chemotherapy. 30951021_Therapeutic Benefit of Blood Transfusion in a Patient With Novel PGK1 Mutation (c.461T>C [p.L154P]). 31222833_MicroRNA-450b-3p inhibits cell growth by targeting phosphoglycerate kinase 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31424298_Identification of a novel variant in phosphoglycerate kinase-1 (PGK1) in an African-American child (PGK1 Detroit). 31492635_The protein phosphatase activity of PTEN dephosphorylates and inhibits autophosphorylated PGK1, thereby inhibiting glycolysis, ATP production, and brain tumor cell proliferation 31578148_These findings highlight the potential use of PGK1 mRNA level, PGK1 promoter hypomethylation, and PGK1 pS203 and PDHK1 pT338 levels as biomarkers for cancer progression and prognosis, and the promising significance of PGK1 as a target in cancer treatment. 31649264_ACTL6A regulates follicle-stimulating hormone-driven glycolysis in ovarian cancer cells via PGK1. 31767834_PGK1 depletion activates Nrf2 signaling to protect human osteoblasts from dexamethasone. 31827081_Transcription factor NFAT5 contributes to the glycolytic phenotype rewiring and pancreatic cancer progression via transcription of PGK1. 32565733_miR-6869-5p Inhibits Glioma Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Targeting PGK1. 32582960_GBP1 promotes erlotinib resistance via PGK1activated EMT signaling in nonsmall cell lung cancer. 32705252_Activation of PGK1 under hypoxic conditions promotes glycolysis and increases stem celllike properties and the epithelialmesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via the AKT signalling pathway. 33096483_Novel PGK1 determines SKP2-dependent AR stability and reprograms granular cell glucose metabolism facilitating ovulation dysfunction. 33438023_Downregulation of long non-protein coding RNA MVIH impairs glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasion through an miR-302a-dependent mechanism. 33940159_FOXO3A-induced LINC00926 suppresses breast tumor growth and metastasis through inhibition of PGK1-mediated Warburg effect. 34445528_Pathological Role of Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1 in Balloon Angioplasty-Induced Neointima Formation. 34473315_PGK1 : An Essential Player in Modulating Tumor Metabolism. 34667156_Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 silencing by a novel microRNA microRNA-4523 protects human osteoblasts from dexamethasone through activation of Nrf2 signaling cascade. 34882921_HPV16 E6/E7 stabilize PGK1 protein by reducing its poly-ubiquitination in cervical cancer. 34893542_Molecular mechanism of glycolytic flux control intrinsic to human phosphoglycerate kinase. 35058442_PGK1 represses autophagy-mediated cell death to promote the proliferation of liver cancer cells by phosphorylating PRAS40. 35121728_PGK1 contributes to tumorigenesis and sorafenib resistance of renal clear cell carcinoma via activating CXCR4/ERK signaling pathway and accelerating glycolysis. 35123484_LncRNA NEAT1 facilitates glioma progression via stabilizing PGK1. 35183535_The basic functions of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and its roles in cancer and other diseases. 35715622_Long non-coding RNA NRSN2-AS1, transcribed by SOX2, promotes progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the ubiquitin-degradation of PGK1. 36229482_Loss of stability and unfolding cooperativity in hPGK1 upon gradual structural perturbation of its N-terminal domain hydrophobic core. |
ENSMUSG00000062070 |
Pgk1 |
2785.217878 |
2.4889181770 |
1.315519 |
0.047906128 |
742.123454 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020704185307569456534762242235325381695587982534566132179304079809545006850454816693125093249462543820916325342487844743623513456476632611059539734283569796474666497364 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014980087016653196985529514307259180701060227407619246576487435272805090289500988763765205149521209036498273950295362772780506971752020803083463424885202200462829553271 |
Yes |
No |
3969.9584837 |
159.4382715 |
1604.9761512 |
47.7869687 |
| ENSG00000102271 |
56062 |
KLHL4 |
protein_coding |
Q9C0H6 |
|
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the kelch family of proteins, which are characterized by kelch repeat motifs and a POZ/BTB protein-binding domain. It is thought that kelch repeats are actin binding domains. However, the specific function of this protein has not been determined. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56062; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; actin binding [GO:0003779] |
32753315_KLHL4, a novel p53 target gene, inhibits cell proliferation by activating p21(WAF/CDKN1A). |
ENSMUSG00000025597 |
Klhl4 |
34.425469 |
0.4009700738 |
-1.318434 |
0.278263901 |
22.978057 |
0.00000163861064105005078233559447781209073013997112866491079330444335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005662817387473366782834390681378167187176586594432592391967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.8828562 |
3.5262418 |
47.4252256 |
5.6883111 |
| ENSG00000102359 |
27286 |
SRPX2 |
protein_coding |
O60687 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a ligand for the urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor. Plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing endothelial cell migration and the formation of vascular network (cords). Involved in cellular migration and adhesion. Increases the phosphorylation levels of FAK. Interacts with and increases the mitogenic activity of HGF. Promotes synapse formation. May have a role in the perisylvian region, critical for language and cognitive development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16497722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18718938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19065654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24179158}. |
Angiogenesis;Cell adhesion;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Sushi;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a secreted protein that contains three sushi repeat motifs. The encoded protein may play a role in the development of speech and language centers in the brain. This protein may also be involved in angiogenesis. Mutations in this gene are the cause of bilateral perisylvian polymicrogyria, rolandic epilepsy, speech dyspraxia and cognitive disability. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:27286; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; hepatocyte growth factor binding [GO:0036458]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042325]; vocalization behavior [GO:0071625] |
209648_The SRPX2 protein contains the P-DUDES structural domain in its C-terminal region. This domain has significant albeit remote sequence similarity to thioredoxin-like domains, and is predicted to possess an oxidoreductase function. 16497722_The involvement of SRPX2 in these disorders suggests an important role for SRPX2 in the perisylvian region critical for language and cognitive development. 17942002_The R75K human-specific variation occurred in an important functional loop of the first sushi domain of SRPX2, indicating that this evolutionary mutation may have functional importance 18718938_Interaction of SRPX2 with uPAR involved in the functioning, the development and disorders of the speech cortex. 19065654_the biological functions of SRPX2 include cellular migration and adhesion to cancer cells. 19667118_These findings suggest that Srpx2 regulates endothelial cell migration and tube formation and provides a new target for modulating angiogenesis. 20236627_acts as regulator of ICAM1 and E-selectin during endotoxemia 20858596_The FOXP2-SRPX2/uPAR network provides exciting insights into molecular pathways underlying speech-related disorders. 22242148_SRPX2 is a novel chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that is overexpressed in gastrointestinal cancer cells. 23115050_Hypomethylation of SRPX2 appeared at the transition from adenoma to carcinoma, and was correlated with adenocarcinoma histology, microsatellite stability, and poor differentiation. 24179158_SRPX2 is an epilepsy- and language-associated gene that is a target of the foxhead box protein P2 (FoxP2) transcription factor. 24700475_High SRPX2 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 24995671_In rolandic epilepsy patients no major role was found for an association with SRPX2 or ELP4 genes. 25737434_Increased Sushi repeat-containing protein X-linked 2 is associated with progression of colorectal cancer. 28654796_SRPX2 potentially acts as an independent prognostic predictor and a drug-target for hepatocellular carcinoma patients. 28867754_This study suggests that SRPX2 promotes angiogenesis of HUVECs through the cooperation of the uPAR and integrin/FAK pathway. 30393191_We explore the contribution of SRPX2 variants to clinical phenotype in our patients and conclude that these variants at least partially explain the phenotype. Further studies are necessary to establish and confirm the association between SRPX2 and neurodevelopment particularly speech and language development. 30551519_Knockdown of SRPX2 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis, and promotes chemosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. 32455867_Sushi Repeat Containing Protein X-linked 2 Is a Downstream Signal of LEM Domain Containing 1 and Acts as a Tumor-Promoting Factor in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 32550700_SRPX2 promotes cell proliferation and invasion via activating FAK/SRC/ERK pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. 34093874_Local administration of liposomal-based Srpx2 gene therapy reverses pulmonary fibrosis by blockading fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition. |
ENSMUSG00000031253 |
Srpx2 |
134.538156 |
4.2538648327 |
2.088774 |
0.231125579 |
79.463023 |
0.00000000000000000049133553511562352218293537871051852604342486892485927958695857142856766586191952228546142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000004167880746153219698005363534607735112567474873606536769909958195512444945052266120910644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
226.0303505 |
30.8727362 |
53.1848110 |
5.8093200 |
| ENSG00000102362 |
94121 |
SYTL4 |
protein_coding |
Q96C24 |
FUNCTION: Modulates exocytosis of dense-core granules and secretion of hormones in the pancreas and the pituitary. Interacts with vesicles containing negatively charged phospholipids in a Ca(2+)-independent manner (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the synaptotagmin like protein family. Members of this family are characterized by an N-terminal Rab27 binding domain and C-terminal tandem C2 domains. The encoded protein binds specific small Rab GTPases and is involved in intracellular membrane trafficking. This protein binds Rab27 and may be involved in inhibiting dense core vesicle exocytosis. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:94121; |
endosome [GO:0005768]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet alpha granule membrane [GO:0031092]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; neurexin family protein binding [GO:0042043]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; lysosome localization [GO:0032418]; multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0071985]; negative regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0046676]; plasma membrane repair [GO:0001778]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; regulation of plasma membrane repair [GO:1905684] |
11773082_Synaptotagmin-like protein 4 (Slp4)/granuphilin-a contains an N-terminal Slp homology domain (SHD) (PMID: 11327731). The SHD of Slp4 specifically and directly binds the GTP-bound form of Rab3A, Rab8, and Rab27A. 16831872_in insulin-producing cells adequate levels of mir-9 are mandatory for maintaining appropriate Granuphilin levels and optimal secretory capacity 23140275_Slp4 and Rab8 are expressed and interact in human platelets, and might be involved in dense granule release. 24184645_the mechanisms of granuphilin plasma membrane targeting and release 24700782_Recruitment of STXBP1 by the Rab27A effector SYTL4 promotes Weibel-Palade body exocytosis. 25595293_Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate binds to the concave surface of granuphilin-C2A domain. The key residues involved in the binding were validated by mutation analysis. 26553929_GLUT5 required an interaction cascade of Rab11, Myo5B, Slp4a, Munc18-2, and Vamp7 with Stx3. 27032672_Granuphilin makes granules immobile and fusion-reluctant beneath the plasma membrane. Those granuphilin-positive, docked granules release a portion of granuphilin upon fusion, and fuse at a frequency and time course similar to those of granuphilin-negative undocked granules. Granuphilin forms a 180-nm cluster at the site of each docked granule, along with granuphilin-interacting Rab27a and Munc18-1 clusters. 28906046_Determined the solution structure of human synaptotagmin-like protein 4 (Slp4). Through modification of cysteine residues, found Slp4 binding of two zinc atoms is required for correct folding. 31930596_LMP1 upregulates SDC2 and SYTL4. 33042263_SYTL4 downregulates microtubule stability and confers paclitaxel resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. 33277360_Multivalent lipid targeting by the calcium-independent C2A domain of synaptotagmin-like protein 4/granuphilin. |
ENSMUSG00000031255 |
Sytl4 |
21.760177 |
0.2924616468 |
-1.773681 |
0.428710310 |
17.143592 |
0.00003465766461528425862849769889528772637277143076062202453613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000101658809563115202297296779665458643648889847099781036376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.4439179 |
2.8039969 |
32.5326370 |
6.2998828 |
| ENSG00000102393 |
2717 |
GLA |
protein_coding |
P06280 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids and participates in their degradation in the lysosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10838196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8804427}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Lysosome;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;RNA editing;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a homodimeric glycoprotein that hydrolyses the terminal alpha-galactosyl moieties from glycolipids and glycoproteins. This enzyme predominantly hydrolyzes ceramide trihexoside, and it can catalyze the hydrolysis of melibiose into galactose and glucose. A variety of mutations in this gene affect the synthesis, processing, and stability of this enzyme, which causes Fabry disease, a rare lysosomal storage disorder that results from a failure to catabolize alpha-D-galactosyl glycolipid moieties. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2717; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; alpha-galactosidase activity [GO:0004557]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; galactoside binding [GO:0016936]; galactosylgalactosylglucosylceramidase activity [GO:0017041]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; raffinose alpha-galactosidase activity [GO:0052692]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; glycoside catabolic process [GO:0016139]; glycosphingolipid catabolic process [GO:0046479]; glycosylceramide catabolic process [GO:0046477]; negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045019]; negative regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051001]; oligosaccharide metabolic process [GO:0009311] |
11668641_novel mutations in patients of European origin with Fabry disease 11775551_Missense mutation (1280A to G, N34S) was detected in exon 1 of alpha-galactosidase gene. 11828341_Alternative splicing in the alpha-galactosidase A gene: increased exon inclusion results in the Fabry cardiac phenotype. 12033283_Overexpression of human alpha-galactosidase A did not affect cellular morphology, which indicates that its overexpression in gene therapy endeavors should be safe. 12360742_Review. Alpha-galactosidase-A deficiency causes Fabry disease, transmitted as an X-linked recessive trait. As the gene shows various mutations, the establishment of phenotype-genotype correlations is limited. 12360745_Review. The GLA gene has been cloned and more than 200 mutations have been identified. 12370426_The adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector containing the alpha-gal A gene was injected into the right quadriceps muscles of Fabry knockout mice. 12471562_Occurrence of edited alpha-gal A transcripts in humans 12938095_Fifteen novel GLA mutations were identified in 22 Spanish Fabry disease patients. 15339079_A previously unreported deletion mutation (c.1072_1074delGAG) in exon 7 of alpha-Gal A gene on Xq22 in a Taiwanese family with Fabry disease is reported. 15712228_2 new intronic polymorphisms, c.640-16A>G and c.1000-22C>T, were detected with frequencies of 0.14 and 0.25 in both normal individuals and Fabry patients, respectively. 15776423_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15776423_analysis of mutations in the GLA gene in 121 patients with Fabry disease 16531566_Data show the usefulness of 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin for correction of the lysosomal storage in Fabry fibroblasts harboring different alpha-galactosidase A mutations with residual enzyme activity. 16595074_Studies further define the molecular heterogeneity of the alpha-Gal A mutations in classical Fabry disease, permit precise heterozygote detection and prenatal diagnosis. 16754800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16899426_DNA analysis of the alpha-galactosidase A gene confirmed the diagnosis of Fabry disease, showing a de novo point mutation at position 691 of exon 5. 17555407_results indicate that a large proportion of mutant GLA enzymes in Fabry disease patients with residual enzyme activity are kinetically active 17592721_Because of lack of functionality of rescued mutant alpha-galactosidase A, 4-phenylbutyrate seems to be of limited use as a chemical chaperone for Fabry disease. 17804462_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18023222_There is a significant correlation between the types of mutations of GLA and total Gb3 excretion in Fabry patients. 18205205_62 Fabry patients in Japan were examined and 24 GLA mutations were found, including 11 novel ones. 18456533_The negative effect of antibody formation in Fabry disease could be overcome by increasing the dose of enzyme administered to mice. 18472290_Two novel different deletions were detected using MLPA assay on two Fabry patients. 18560446_a correlation between this new intronic mutation and the unbalanced alpha-galactosidase A mRNAs ratio, which could therefore be responsible for the reduced enzyme activity causing Fabry disease. 18633574_Structural characterization of mutant alpha-galactosidases causing Fabry disease. 18698230_Mutated alpha-galactosidase A did not respond to a pharmacological chaperone 18724168_We report here a new mutation in Fabry disease. The hemizygote did not show corneal manifestations as opposed to heterozygotes in the described family. 18849176_Novel disease-causing mutations were found in 15 unrelated Hungarian families diagnosed with Fabry disease. 18979178_Case Report: suggest that the g.1170C>T SNP may be co-dominantly associated with a relatively decreased GLA expression at the transcription and/or translation level. 18979223_Mean alpha-Gal leukocyte activity was higher in subjects with the g.1170C or CC genotype than in those with the alternative genotypes. 19037253_Downregulation of alpha-galactosidase A upregulates CD77 19287194_The results of this study suggest that the chemical chaperone 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin enhances GLA enzyme activity and protein expression in milder mutations associated with the atypical form of Fabry disease. 19357250_Fabry disease is marked by deficiency of this enzyme, and enzyme replacement therapy may stabilize kidney function in these patients. 19404287_identified a new intronic mutation, g.9273C>T, located 5 nucleotides upstream of the alternative 3' splicing junction in Fabry disease 19468850_Results show that the unpredictable amino-acid pairs of human alpha-galactosidase A are more sensitive to mutation. 19621417_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940122_Data show that the high resolution structures of each step in the catalytic cycle will allow for improved drug design efforts on alpha-GAL. 19941952_Study in alpha galactosidase mutations that may be helpful in clarifying the consequences of the missense genetic lesions detected in Fabry disease. 19949670_Data show that alpha-Gal epitopes can be removed from the porcine aortic valve and pericardial tissue using recombinant human alpha-galactosidase A as effectively as using green coffee bean alpha-galactosidase. 20031620_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20110537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20110537_Screening for GLA mutations should probably be considered in different types of stroke; restricting investigation to patients with cryptogenic stroke may underestimate the true prevalence of Fabry disease in young stroke patients. 20122163_The R118C mutation was present in 60% of unrelated patients with alpha-galactosidase A causal mutations. 20444686_the active sites of human lysosomal enzymes alpha-galactosidase and alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase have interconvertible specificites 20505683_Mutations of the GLA gene is associated with Fabry disease. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20821055_Cardiovascular, renal and ocular abnormalities are highly prevalent in adult Taiwan Chinese subjects with the Fabry GLA mutation IVS4 + 919G-->A. 20860754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21305660_Novel deletions were identified and confirmed in the three unrelated women establishing their heterozygosity and risk for offspring with Fabry disease. 21333496_these data suggest that MLPA analysis and cDNA sequence should be considered in genetic testing surveys of patients with Fabry disease. 21517827_A novel missense mutation within GLA is associated with Fabry disease. 21569768_The kinetics of alpha-galactosidase A and beta-glucocerebrosidase deficient in Fabry and Gaucher diseases, respectively, is reported. 21569769_Two new mutations, M11V and R190X, were identified in alpha-galactosidase A. 21643977_Data suggest that insufficient alpha-galactosidase A activity may contribute to the pathogenesis of sporadic Parkinson's disease. 21683120_The sequence variant may affect GLA gene expression by altering transcription factor binding sites, contributing to the pathogenesis of sporadic Parkinson disease. 21755431_Case Report: Progressive renal failure despite long-term biweekly enzyme replacement therapy in a patient with Fabry disease secondary to a new alpha-galactosidase mutation of Leu311Arg (L311R). 21859400_The MGP gene Glu60X and Thr83Ala polymorphisms were significantly associated with chronic kidney disease. 22008442_A novel missense mutation in the GLA gene is important not only for a precise diagnosis of heterozygous status, but also for confirming relatives who are negative for this mutation. 22187137_analysis of synergy between pharmacological chaperone 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin and the human recombinant alpha-galactosidase A in cultured fibroblasts from patients with Fabry disease 22260214_Recent molecular studies of GLA have demonstrated the existence of atypical variants in Fabry disease, suggesting significant genotype-phenotype correlations. 22305854_alpha-Galactosidase with E66Q amino acid substitution is not a pathogenic mutation but is a functional polymorphism in Fabry disease. 22307442_Case Report: novel GLA mutation in mother/daughter/son with Fabry disease and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. 22341397_Alpha Galactosidase A deletions/duplications are asssociated with Anderson-Fabry disease. 22465271_Data inhicate that patients with alpha-galactosidase A (GLA) gene c.614delC mutation show classical clinical manifestations of Fabry disease (FD). 22551898_New mutations in the GLA gene that were found in Brazilian families with Fabry disease included 17 missense mutations, 7 nonsense mutations, 7 deletions, 6 insertions and 1 in the splice site. 22558451_Deregulation of key endothelial pathways as observed in Fabry disease vasculopathy is likely caused by intracellular Gb3 accumulation rather than deficiency of GLA 22563919_The current definition of Fabry disease is a measured decrease or deficit of alpha-Gal A enzyme activity or the detection of any mutation of the alpha-Gal A gene. 22768187_Sortilin is a new alpha-Gal A receptor expressed in renal endothelial cells and that this receptor together with the M6PR is able to internalize circulating alpha-Gal A. 22773828_alpha-Galactosidase aggregation is a determinant of pharmacological chaperone efficacy on Fabry disease mutants 22841442_Mutant alpha-galactosidase A with M296I does not cause elevation of the plasma globotriaosylsphingosine level. 23190516_These findings provide, for the first time, data regarding the prevalence of a-GalA deficiency (0.24%) in Turkish males receiving hemodialysis. 23393592_results provide evidence that GLA D313Y is potentially involved in neural damage with significant WML, demonstrating the necessity of evaluating patients carrying D313Y more thoroughly. 23608164_A novel missense mutation of GLA was identified at codon 220 in exon 5 23724928_GLA p.E66Q mutation is a genetic risk factor for cerebral small-vessel occlusion in elderly Japanese 23756194_A novel mutation in the GAL gene associated with Fabry disease. 23867994_Missense mutation p.R112C ablates the activity of the alpha-gal A gene and results in the development of Fabry disease with renal damage in a Chinese family. 24386359_residues important for expression of the GLA activity 24398019_A Fabry disease patient and his daughter had the mutation c.493 G > C in the 3d exon of the GLA gene. D165H substitution affects protein folding. This highly conserved AA may be a key amino acid for enzyme functionality. 24679964_The novel mutation p.M187R/g7219 T>G is associated with a particularly malignant cardiac phenotype in males and females over 40 years. 24718812_This study indicated that the p.E66Q variant of GLA does not affect the progression of chronic kidney disease. 25068814_OC follows a gene duplication strategy while MGP variability was obtained mostly by the use of multiple promoters and alternative splicing, leading to proteins with additional functional characteristics and alternative gene regulatory pathways. [review] 25101867_It is clear that a certain intronic haplotype in males with cryptogenic stroke is associated with reduced GLA expression and function. 25281798_Some clinical cases of some members of a Sicilian family to express phenotypical variability of Anderson-Fabry disease in subjects with the same genetic mutation in alpha galactosidase A gene, are reported. 25295576_Case Report: immunohistologically detected synaptopodin upregulation in foamy podocytes in Fabry disease due to novel alpha-galactosidase A mutation. 25382311_These data confirmed that the specific approach can effectively contribute to the identification of pathological mutations in GLA. 25423912_In Fabry disease patients, the alpha-galactosidase A-10T allele appears to be causal for neurological manifestations. 25468652_data strongly suggest that the GLA p.(Arg118Cys) variant does not segregate with Fabry disease clinical phenotypes in a Mendelian fashion, but might be a modulator of the multifactorial risk of cerebrovascular disease 26070511_GLA gene variations correlate with globotriaosylceramide and globotriaosylsphingosine analog levels in urine and plasma 26288249_Results from a study on gene variability markers in early-stage human embryos shows that GLA is a putative variability marker for the 3-day, 8-cell embryo stage. 26297554_The present study confirms the heterogeneity of mutations in Fabry disease and the importance of molecular analysis for genetic counseling, female heterozygotes detection as well as therapeutic decisions. 26334996_Thus, inheritance of the CIH caused an mRNA deregulation altering the GLA expression pattern, producing a tissue glycolipid storage. 26415523_We conclude that a mild GLA variant is typically characterized by high residual enzyme activity and normal biomarker levels. We found evidence that these variants can still be classified as a distinctive, but milder, sub-type of FD. 26456105_results directly implicated the GLA mutation p.E66Q as the genetic etiology of the Chinese renal variant FD pedigree. 26564084_Fabry disease, an X-linked disorder of glycosphingolipids that is caused by mutations of the GLA gene that codes for alpha-galactosidase A, leads to dysfunction of many cell types and includes a systemic vasculopathy. 26691501_Study describes 5 novel mutations found in the GLA gene of patients with clinical diagnosis of Fabry disease. 26869469_alpha-galactosidase A mutation, IVS4-type Fabry disease has features similar to those of classic Fabry disease and a higher frequency of deep white matter hyperintensities and a higher incidence of infarctions and pulvinar signs than in healthy controls 26971403_Case Report: Kidney transplantation from a mother with unrecognized Fabry disease to her son with low alpha-galactosidase A activity. 26981927_No pathogenic mutations in the coding regions of the GLA gene were identified in this group of patients and thus no Fabry disease was found in this study. 27059467_The results of the current study suggest that the GLA haplotype D313Y does not lead to severe organ manifestations as seen in genotypes known to be causal for classical Fabry disease. 27100101_High desphospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein level, reflecting a poor vitamin K status, seems to be associated with kidney damage and may be also a marker of cardiovascular risk in CKD patients 27156739_We report a case of Fabry disease with a p.R301X (c.901 C>T) mutation in a 39-year-old man who was being treated for chronic sclerosing glomerulonephritis for 2 years. Family screening tests showed that the proband's mother, sister, and daughter had the same mutation with different phenotypes. 27160240_Case Report: hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy with Fabry disease with the GLA E66Q mutation. 27195818_we review the various types of GLA variants and recommend that pathogenicity be considered only when associated with elevated globotriaosylceramide in disease-relevant organs and tissues as analyzed by mass spectrometry. 27238910_Enzyme activities (acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), galactocerebrosidase (GALC), glucocerebrosidase (GBA), alpha-galactosidase A (GLA), alpha-iduronidase (IDUA) and sphingomyeline phosphodiesterase-1 (SMPD-1)) were measured on ~43,000 de-identified dried blood spot (DBS) punches, and screen positive samples were submitted for DNA sequencing to obtain genotype confirmation of disease risk 27510433_This longitudinal Fabry Registry study analyzed data from patients with Fabry disease to determine the incidence and type of severe clinical events following initiation of enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) with agalsidase beta, as well as risk factors associated with occurrence of these events 27531472_we presented the clinical characters of a Chinese FD pedigree mimicking familial episodic pain. Furthermore, our finding suggests that a novel double mutation of GLA (c.273_276del TGAT in cis with c.281G>T) is associated with FD 27595546_We demonstrate that the wild-type sequence harbors an hnRNP A1 and hnRNP A2/B1-binding exonic splicing silencer (ESS) overlapping the 5'splice site (5'ss) that prevents pseudoexon inclusion.we demonstrate that splice switching oligonucleotide (SSO) mediated blocking of the pseudoexon 3'ss and 5'ss effectively restores normal GLA splicing 27834756_Four patients had non-amenable mutant forms of a-Gal based on the validated cell-based assay conducted after treatment initiation and were excluded from primary efficacy analyses only. 27916943_we reviewed other small molecules that were reported to have a stabilizing effect on some GLA missense mutations in vitro and might be developed to act in synergy or as an alternative to 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin 28087245_Results found a novel heterozygous stop codon mutation in exon 1 of the GLA gene in female patients with Fabry Disease with methylation in the non-mutated allele thought to be associated with the clinical severity of the disease. 28098348_Mesenchymal stem cells with reduced GLA activity are prone to apoptosis and senescence due to impaired autophagy and DNA repair capacity. 28152533_family study with the classical phenotype of Fabry disease due to the novel nonsense mutation c.607G>T (p.E203X) of the GLA gene; the Fabry disease phenotype is highly variable in heterozygote females, even within the same family 28166746_Similar central nervous system manifestations in patients with the IVS4 mutation or classical Fabry mutations. 28225726_p.M187R GLA mutation in Fabry disease causes a severe systemic and ophthalmologic phenotype, in both male and female patients. 28275245_GLA c.196G>C variant is a genetic risk factor for cerebral small-vessel occlusion and non-cardioembolism in Japanese males but not in females. 28276057_The mutation p.D313Y in the GLA gene may lead to organ manifestations and elevation of the Fabry-specific biomarker lyso-globotriaosylsphingosine. 28377241_Results showed that most Fabry disease patients carrying GLA IVS4+919A did not show abnormal cardiac phenotypes. The near-absence of GLA IVS4+919A in heart disease cohort suggested that this variant is not a frequent cause of overt heart diseases in Taiwan. 28430823_findings revealed the alternative splicing mechanism of GLA (IVS4+919G>A), and a potential treatment for this specific genetic type of Fabry disease by amiloride in the future 28615118_Loss of GLA activity is associated with Fabry disease. 28723748_Study described the demographic data, wide clinical spectrum of phenotypes, and GLA mutation spectrum of Fabry disease in Korea. Most of the patients had classical Fabry disease, with a 4 times higher incidence than that of late-onset Fabry disease, indicating an underdiagnosis of mild, late-onset Fabry disease. 28892806_Kidney histological changes, including tubulointerstitial fibrosis, may predate albuminuria and glomerular filtration rate changes in adult women with novel missense mutation 28988177_Four novel GLA pathogenic mutations are reported and evidence of pathogenicity of the D313Y mutation is provided. 29018006_alpha-Galactosidase A genotype N215S does not lead to the development of a classical Fabry phenotype but induces a specific cardiac variant of Fabry disease mimicking nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 29037082_The D313Y variant in the GLA gene was not Fabry disease causative in 2 Danish families. 29227985_GLA variants found included R118C (n = 2), D83N, and D313Y (n = 7); IVS6-22 C>T, IVS4-16 A>G, IVS2+990C>A, 5'UTR-10 C>T (n = 4), IVS1-581 C>T, IVS1-1238 G>A, 5'UTR-30 G>A, IVS2+590C>T, IVS0-12 G>A, IVS4+68A>G, IVS0-10 C>T, IVS2-81-77delCAGCC, IVS2-77delC. We found that patients with common heart disease did not contain a substantial number of patients with undiagnosed Fabry disease. 29330335_Of 67 studies, 63 that screened 51363patients (33943M and 17420F) and provided GLA mutations were reanalysed for disease-causing mutations. Of reported GLA mutations, benign variants occurred in 47.9% of males and 74.1% of females 29653899_It negatively regulates calcification of human aortic valve interstitial cells. 29794742_Presence of isolated heterozygous -10C >T SNP is not associated with clinically relevant symptoms or organ manifestations as seen in Fabry disease. 29982630_the GCS inhibitor lucerastat provides a viable mechanism to reduce Gb3 accumulation and lysosome volume, suitable for all Fabry patients regardless of genotype 30048710_Erosion of the inactivated X chromosome developed heterogeneously among clones, and mono-allelic expression of the GLA gene was maintained for a substantial period in a subset of iPSC clones. Gb3 accumulation was observed in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (iPS-CMs) from GLA activity-deficient iPSCs by mass-spectrometry and immunofluorescent staining. 30099469_GLA DNA screening protocols starting from the dialysis population and upstream extended to families of affected individuals may be an effective strategy to maximize the early identification of subjects with Fabry disease. 30242261_The etiology of alpha-Gal syndrome in humans. 30470436_Disruption of GLA in a human endothelial cell line by siRNA and CRISPR/Cas9 resulted in a 3-fold and 5-fold increase in VWF secretion, respectively. The increase in VWF levels was associated with decreased eNOS activity in both in-vitro models. Results suggest that GLA deficiency promotes VWF secretion through eNOS dysregulation, which may contribute to the vasculopathy of Fabry disease. 30587147_A novel loss-of-function mutation of the GLA gene has been identified in a Chinese Han family with Fabry disease. 30723321_In conclusion, migalastat, a first-in-class oral pharmacologic chaperone, has previously demonstrated clinical benefits in patients with Fabry disease and amenable GLA variants. The data reported here establish that migalastat benefited male patients with the classic phenotype 30762167_Study presents the first case of maternal germline mosaicism in Fabry disease. Study reports on a family of five members: unaffected parents, one unaffected son, and another son and daughter both carrying the same mutation (p.G138E) in the GLA gene. 30830284_GLA-gene variant p.D313Y causes peripheral neuropathy with increased dorsal root ganglia volume. 31067829_FD is a rare complex multisystem disease with high heterogeneity of its manifestations, causing various clinical symptoms in both heterozygous and hemizygous individuals. In this paper, we report a new GLA gene mutation (c.270C>G (p. Cys90Trp) in one Lithuanian family with two different phenotypes: a predominantly cardiac variant in heterozygous women and a classic form of Fabry disease in a hemizygous man 31103344_Circulating phylloquinone, inactive Matrix Gla protein and coronary heart disease risk: A two-sample Mendelian Randomization study. 31321922_A novel GLA missense mutation, c.280T>C (Cys94Arg), was found in a Chinese family with predominant renal manifestations of FD. Our study reveals the pathogenesis of c.280T>C mutation to FD and provides scientific foundation for accurate diagnosis and precise medical intervention for FD. 31393666_Strong increase of leukocyte apha-galactosidase A activity in two male patients with Fabry disease following oral chaperone therapy. 31841972_Generation of a GLA knock-out human-induced pluripotent stem cell line, KSBCi002-A-1, using CRISPR/Cas9. 31899485_Extensive characterization of the effective Proteostasis regulators revealed inhibition of the proteasome and elevation of GLA gene expression as paramount effects 31907047_Higher rate of rheumatic manifestations and delay in diagnosis in Brazilian Fabry disease patients. 31949022_Cardiomyopathy associated with the Ala143Thr variant of the alpha-galactosidase A gene. 31996269_Correlation between GLA variants and alpha-Galactosidase A profile in dried blood spot: an observational study in Brazilian patients. 32161151_Use of a rare disease registry for establishing phenotypic classification of previously unassigned GLA variants: a consensus classification system by a multispecialty Fabry disease genotype-phenotype workgroup. 32234567_Prevalence of GLA gene mutations and polymorphisms in patients with multiple sclerosis: A cross-sectional study. 32246049_The Fabry disease-causing mutation, GLA IVS4+919G>A, originated in Mainland China more than 800 years ago. 32246457_Is the alpha-galactosidase A variant p.Asp313Tyr (p.D313Y) pathogenic for Fabry disease? A systematic review. 32313061_Matrix Gla protein is an independent predictor of both intimal and medial vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. 32418857_A comprehensive testing algorithm for the diagnosis of Fabry disease in males and females. 32512878_Ultra-Deep DNA Methylation Analysis of X-Linked Genes: GLA and AR as Model Genes. 32602245_High expression of Matrix Gla Protein in Schnyder corneal dystrophy patients points to an active role of vitamin K in corneal health. 32797665_Recurrent fever of unknown origin: An overlooked symptom of Fabry disease. 32813676_Analysis of the alpha galactosidase gene: mutation profile and description of two novel mutations with extensive literature review in Turkish population. 32888778_Detailed epitope mapping of neutralizing anti-drug antibodies against recombinant alpha-galactosidase A in patients with Fabry disease. 33527381_Accuracy diagnosis improvement of Fabry disease from dried blood spots: Enzyme activity, lyso-Gb3 accumulation and GLA gene sequencing. 33531072_DNA methylation impact on Fabry disease. 33543778_Assessment of small fiber neuropathy in patients carrying the non-classical Fabry variant p.D313Y. 33673551_Reversal of the Inflammatory Responses in Fabry Patient iPSC-Derived Cardiovascular Endothelial Cells by CRISPR/Cas9-Corrected Mutation. 34205365_Plasma Globotriaosylsphingosine and alpha-Galactosidase A Activity as a Combined Screening Biomarker for Fabry Disease in a Large Japanese Cohort. 34768768_alpha-Galactosidase a Deficiency in Fabry Disease Leads to Extensive Dysregulated Cellular Signaling Pathways in Human Podocytes. 34785703_Detection of single nucleotide and copy number variants in the Fabry disease-associated GLA gene using nanopore sequencing. 34905550_Nationwide screening for Fabry disease in unselected stroke patients. 36334502_A theoretical study on binding and stabilization of galactose and novel galactose analogues to the human alpha-galactosidase A variant causing Fabry disease. |
ENSMUSG00000031266 |
Gla |
470.928430 |
3.8267812433 |
1.936131 |
0.096602079 |
402.281458 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001755066000330709574932887799370993391858556870914869051061772360350266573721884414823915491921144657241512944055300916775346708055020548622963501873678401558277663917680457774885320658587815322847650607381639605727671228641018075222746119834 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000662526193475224398225425305663534142038125243441065439423101429873986970282164840799484088294126374351552440252551012297340306251673770203766946613206025284313859283474402057888603289480687042878339847360700420224668971691528440715046599507 |
Yes |
No |
749.0607413 |
41.4372790 |
197.2023513 |
8.8478887 |
| ENSG00000102445 |
80183 |
RUBCNL |
protein_coding |
Q9H714 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of autophagy that promotes autophagosome maturation by facilitating the biogenesis of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) in late steps of autophagy (PubMed:28306502, PubMed:30704899). Acts by antagonizing RUBCN, thereby stimulating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity of the PI3K/PI3KC3 complex (PubMed:28306502). Following anchorage to the autophagosomal SNARE STX17, promotes the recruitment of PI3K/PI3KC3 and HOPS complexes to the autophagosome to regulate the fusion specificity of autophagosomes with late endosomes/lysosomes (PubMed:28306502). Binds phosphoinositides phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P), 4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P) and 5-phosphate (PtdIns(5)P) (PubMed:28306502). In addition to its role in autophagy, acts as a regulator of lipid and glycogen homeostasis (By similarity). May act as a tumor suppressor (Probable). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TD16, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28306502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30704899, ECO:0000305|PubMed:23522960}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Autophagy;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lipid metabolism;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a cysteine-rich protein that contains a putative zinc-RING and/or ribbon domain. The encoded protein is related to Run domain Beclin-1-interacting and cysteine-rich domain-containing protein, which plays a role in endocytic trafficking and autophagy. In cervical cancer cell lines, this gene is expressed at low levels and may function as a tumor suppressor. Promoter hypermethylation of this gene is observed in cervical cancer cell lines and tissue derived from human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:80183; |
autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; autophagosome maturation [GO:0097352]; autophagosome-endosome fusion [GO:0061910]; autophagosome-lysosome fusion [GO:0061909]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; regulation of glycogen metabolic process [GO:0070873]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216] |
18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987618_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19843677_Methylation of C13orf18 in cervical scrapings is strongly associated with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer. 21796628_Data suggest that the four-gene methylation panel might provide an alternative triage test after primary high-risk papillomavirus (hr-HPV) testing. 23522960_Re-activation of C13ORF18 led to partial demethylation of the C13ORF18 promoter and decreased repressive histone methylation. 25169519_MethyLight data demonstrated that C13orf18 and C1orf166 could not be considered as specific, sensitive and suitable prognostic biomarkers in cervical dysplasia related Papillomavirus Infections. 28306502_Pacer localizes to autophagic structures and positively regulates autophagosome maturation. 30704899_mTORC1 and GSK3-TIP60 signaling converge to modulate autophagosome maturation and lipid metabolism through Pacer. |
ENSMUSG00000034959 |
Rubcnl |
302.542733 |
0.4238362011 |
-1.238421 |
0.100510431 |
153.272655 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000003339527175932490564882910539559995156048470029203384414349979947482515218143626108324964647799948380679779802449047565460205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000496889325773826175384009844487025320169481222851076814988193307642565536455152555452127651619553816431107406970113515853881835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
173.9905600 |
11.9369483 |
413.2626242 |
18.9217748 |
| ENSG00000102468 |
3356 |
HTR2A |
protein_coding |
P28223 |
FUNCTION: G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) (PubMed:1330647, PubMed:18703043, PubMed:19057895). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) (PubMed:28129538). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors (PubMed:28129538). Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways (PubMed:28129538). Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores (PubMed:18703043, PubMed:28129538). Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood (PubMed:18297054). Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1330647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18297054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18703043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19057895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21645528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22300836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28129538}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24089568}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Behavior;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes one of the receptors for serotonin, a neurotransmitter with many roles. Mutations in this gene are associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia and obsessive-compulsive disorder, and are also associated with response to the antidepressant citalopram in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD). MDD patients who also have a mutation in intron 2 of this gene show a significantly reduced response to citalopram as this antidepressant downregulates expression of this gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:3356; |
axon [GO:0030424]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cell body fiber [GO:0070852]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor complex [GO:0098666]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; 1-(4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine binding [GO:0071886]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0004993]; Gq/11-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0001587]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; serotonin binding [GO:0051378]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; aging [GO:0007568]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; behavioral response to cocaine [GO:0048148]; cell death [GO:0008219]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050966]; detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050965]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0098664]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of potassium ion transport [GO:0043267]; negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051967]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; phospholipase C-activating serotonin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007208]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045821]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0010513]; positive regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045907]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; protein localization to cytoskeleton [GO:0044380]; regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0014059]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; serotonin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007210]; sleep [GO:0030431]; temperature homeostasis [GO:0001659]; urinary bladder smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014832] |
11121184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11121191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11121202_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11121203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11172633_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11300730_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11311507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317227_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317230_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11378836_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11409694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11421130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11431075_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11444684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11489292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11490436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11525423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11526993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11526996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11566166_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11702051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11702051_polymorphism of 5-HT2A receptor gene promoter may be causally related to the development of bipolar disorder 11702058_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11702058_promoter region of the 5-HT2A receptor gene does not contribute to a predisposition to anorexia nervosa for Japanese 11725820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11732859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11771315_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11803452_A multicenter European family-based transmission disequilibrium study found no evidence for a significant role of the 5-HT(2A) gene in anorexia nervosa. 11803534_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803534_Patients carrying 5-HT(2A)-C allele had more than five times the risk for attempting suicide than noncarriers. 11814537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11842624_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11891796_Differential expression of the 'C' and 'T' alleles of the 5-HT2A receptor gene in the temporal cortex of normal individuals and schizophrenics. 11918989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11920858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11920859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11956670_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11983190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11989622_Molecular dynamics of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A serotonin receptors with methylated buspirone analogues. 11992560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11992560_possible influence of monoamine oxydase A (MAO-A), catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), serotonin receptor 2A (5-HT2A), dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2), and dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) gene variants on timing of recurrence in mood disorders 12057029_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12063151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12079891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12105278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12109966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12109966_no association seen between T102C polymorphism of 5-HT2a receptor gene and onset of schizophrenia in Kuwaiti Arabs 12140776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140776_association between polymorphism of serotonin-2A receptor gene and schizophrenia among south Indians 12167522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12167522_possible association seen between variation in HTR2a, childhood ADHD, and later development of SAD in women 12202283_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12231269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12231269_The A allele of the 5-HT 2A gene has bee associated with anorexia nervosa. 12454564_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 12475403_For the ADHD combined subtype, the T102T genotype is a protective factor and the T102C genotype is a risk factor. 12476319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12476319_THe promotr is -1438G/A polymorphic in children and adolescents with obsessive-compulsive disorders. 12522576_In upper epidermis in eczematous skin; more evenly distributed in epidermis of control skin. In inflammatory dermal mononuclear cells and vessel walls. In basal epidermal layer of eczematous and control skin. 12532038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12585698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12605580_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12606840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12606842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12607287_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12624948_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12624948_The results did not support the association between the 5-HTR2A polymorphism and verbal fluency in normalcy, and agree with the assumed contribution of genotype A2A2 to the severity of schizophrenia 12650952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12685303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12695524_The interaction of a constitutively active arrestin with the arrestin-insensitive 5-HT(2A) receptor induces agonist-independent internalization. 12707936_An association was found between the presence of major depressive illness in Alzheimer's disease and both the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C polymorphisms. 12711403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714112_A generally decreased neocortical binding potential of 5-HT2A receptor is found in Alzheimer's brains with a significant regional reduction in orbitofrontal, prefrontal, lateral frontal, cingulate, sensorimotor, parietal inferior, and occipital region. 12759158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12759158_The study showed a positive association between panic disorder and the HTR2A gene, suggesting that HTR2A plays an important role in the pathogenesis of panic disorder. 12815744_An association was found between the HTR2A gene promoter polymorphism and depressed mood in elderly Swedish males. 12815744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12830506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12874600_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12875919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12877392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12886034_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12898571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12927326_-1438 G/A and T102C polymorphisms of the 5-HT2A receptor gene are not associated with increased risk of obsessive-compulsive disorder. The TT genotype of T102C and the AA genotype of the -1438 G/A polymorphism might be a factor in clinical severity 12927326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12957335_No association of the HTR2A polymorphism has been found in the overall sample of 142 unipolar affective disorder-control pairs regarding allele and genotype frequencies and homo-heterozygote distributions. 12957335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14508013_Review. Hyperactive platelet 5-HT2A receptor signal transduction occurs in depression. A possible mechanism for increased cardiac morbidity & mortality in depression may be this hyperreactivity & serotonin hyperresponsiveness of the platelet 5-HT2AR. 14514498_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14531760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14531760_To examine whether variation at two common polymorphisms, T102C and -1438AG, of the serotonin 2A gene (5HT2A) are involved in the puerperal triggering mechanism of bipolar affective puerperal psychosis 14566219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14566344_This study investigated a functional variation of a memory-related serotonin receptor in 349 healthy young volunteers, and found 21% poorer memory performance in subjects with the rare variant. 14610521_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14623359_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14668201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14681967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14698468_5-HT(2A) receptor gene polymorphism (A-1438G) appears to be associated with self-determinism and self-transcendence 14698468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14699448_absence of any interindividual variability in relative mRNA allele ratio suggests that the HTR2A locus is unlikely to contain common polymorphisms or epigenetic modification that alter HTR2A mRNA levels in adult brain 14730199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14730199_The results of this study support the hypothesis that the -1438A/G polymorphism of the promoter region of the 5-HTR2A gene is associated with MDD patients in a Korean population. 14741324_HTR2A gene is associated with schizophrenia 14741324_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14744461_5-HT(2A) receptor binding in the hippocampus was reduced by 29% in depressed subjects 14744462_Alterations in 5-HT(1A,) 5-HT(1B), and 5-HT(2A) mRNA levels in the brains of subjects with both mood disorders and schizophrenia add further support for hypothesis of dysregulation of the serotonergic system in these psychiatric disorders. 14967409_Single nucleotid polymorphism is associated with serotonin induced platelet aggregation. 15000807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15005715_A statistically significant difference between obsessive-compulsive patients and controls was observed on the genotypic distribution and allelic frequencies for the C516T variant of the serotonin receptor type gene. 15005715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15037867_Impulsive subjects exhibited decreased serotonin-induced calcium release by platelets, while fenfluramine-induced prolactin release was not affected. 15037867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15048642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15048642_These data did not provide evidence for a contribution of the 102T/C SNP of HTR2A gene to susceptibility to the southern Han Chinese schizophrenia. 15048655_No clear association was found between 5-HT2A variants and psychosis. 15048655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15052272_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15052272_Study assessed genetic factors influencing antidepressant response to fluoxetine. Results implicate HTR2A in the specificity of response to fluoxetine. 15083167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15140279_Observational study of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15167698_No allele differences were detected regardless of whether the bulimia nervosa patients had suffered prior anorexia nervosa episodes. 15167698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15190056_5-HT(2A) serotonin receptors are regulated by Caveolin-1 15211529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15211639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15211639_genotype distribution suggests that T102C polymorphism is associated with maintenance, but not with initiation of the smoking habit. The CC genotype was more frequent in the current smokers 15232358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15232358_Patients with homozygote C allele of the 102 T/C polymorphisms or homozygote A allele of the -1438 G/A polymorphism of the 5-HT2A receptor gene, have a high risk of IBS. T/T genotype of 102 T/C polymorphism may be associated with more severe pain. 15241435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15245785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15274035_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15285608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15309313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15313842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15313842_The 102T genotype of the 5-HT2A receptor was significantly associated with delusions and agitation/aggression in Alzheimer Disease patients with psychiatric symptoms. 15341275_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15383158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15469201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15476175_The results suggested that the 5-HT2A may play some roles in the effects of drug treatment on obsessive-compulsive disorder. 15483560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15533210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15550673_the serotonergic receptor 5HT2A could act as the cellular receptor for JCV on human glial cells 15562295_(+/-)-1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane hydrochloride (DOI), significantly increased arachidonic acid incorporation in widespread brain areas containing 5-HT2A/2C receptors. 15564892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15564892_Single nucleotide polymorphism might not be associated with susceptibility to a risk factor for developing smoking behavior. 15581469_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15659047_In this first report on the T102C genetic polymorphism of the 5-HT2A receptor in Chinese hypertensive patients, no correlation exists between T102C polymorphism and hypertension. 15659047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15717291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15722190_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15722953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15722960_No evidence for statistically significant associations between 5-HT2A polymorphisms and personality traits. 15722960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15826503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15826503_Potential genetic relationship between the serotonin receptor gene polymorphism and the HDL-cholesterol serum levels. 15857569_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15857569_genetic variability in HTR(2A) contributes a small but significant degree of risk for the expression of TD, particularly in older patients and specifically for the non-orofacial (limb-truncal) type. 15891581_Age strongly modulates the effect of the 5-HT2a receptor polymorphism at residue 452 on episodic memory. 15891581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15893580_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15915764_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15950062_the 5-HT(2A) receptor subtype is fully expressed in the human choriocarcinoma cell lines JEG-3 and BeWo as well as in normal human placental tissue 15965969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15999344_Findings indicate that women with bulimia nervosa who are HT2A GG homozygotes on the -1438G/A promoter polymorphism are characterized by increased impulsiveness. 15999344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16087994_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16127283_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16179957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16187138_PET study of the 5-HT2AR status in subjects at increased risk for schizophrenia; distribution volume ratios as a proxy for 5-HT(2A)R availability were reduced in prefrontal cortex regions of at-risk subjects 16215954_5-HTR2A gene -1438G/A polymorphism was probably not associated with APS-induced weight gain in Chinese Han patients with schizophrenia in the study. 16215954_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16231475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16258205_Genotypes and allele frequencies of 102T/C polymorphism of the HTR2A and 796G/C polymorphism of the HTR2C did not differ between controls and patients with obstructive sleep apnea. 16258205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16272956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16281377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16302021_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16314884_5-HT(2A)-serotonin receptor SNPs exert statistically significant effects on the affinity and functional effects of several currently approved atypical antipsychotics. 16328014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16362639_The C-allele of 5-HT2a was significantly associated with the hyperactivity/impulsivity scale and the total ASRS scale with highest scores in carriers of the TT genotype. 16382194_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16397402_No significant difference was found in the 5-HTTLPR frequency between AN patients and controls; however, there was a statistical trend towards a higher frequency of the A allele of the -1438 A/G polymorphism in patients. 16397402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16434999_A possible effect on synaptic plasticity or neurodevelopment might explain the influence of the His452Tyr polymorphism on temporal brain structures, and this might be the basis for poorer memory performance in 452Tyr carriers. 16443280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16449821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16464220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16491645_it is unlikely that the--1438 G/A polymorphism of serotonin receptor 2A gene may influence obesity in a Spanish children population 16545942_N376 to D mutation in the conserved NPxxY motif within the carboxy terminal tail domain (CT) of the 5-HT2A receptor alters the binding preference of GST-fusion protein constructs of the CT domain from ARF1 to an alternative isoform, ARF6. 16580628_5-HT exerts this positive growth effect on MCF-7 cells through, in part, the 5-HT(2A) receptor subtype, which is fully expressed in this cell line. 16633140_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16640790_In normal aging patients, 5-HT2A label was observed in large pyramidal cells, but to a lesser in small pyramidal cells and in stellate cells of cortical layers II-VI. In AD, density of positive cells was significantly reduced by 33%. 16642436_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16642436_Taken together with prior neurobiological findings, these new genetic data make a compelling case for a key role of HTR2A in the mechanism of antidepressant action. 16699051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16701945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16710319_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16710319_Persons with a GG genotype of the 5HT2A -1438 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) were significantly more likely to be categorized as having sexual dysfunction than persons with a GA or AA genotype 16741915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16741915_The -1438A>G polymorphism was found to be related to remission in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 16762419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16762419_results suggest that the 5HTR2A -1438 A/G polymorphism is possibly related to seasonality in the Korean population 16762472_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16767413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16767413_results suggest the possible involvement of the A-1438A polymorphism of the 5-HT2A receptor gene in impulsive behavior 16770336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778329_the 5-HT2A T102C and ET-1 G/T polymorphisms are interactively associated with hypertension 16806099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16856120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16874005_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16876316_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16899354_The results suggest a possible role for the 5-HT(2A)T102C polymorphism in the development of social anxiety disorder. 16958038_No evidences for biased transmissions of both HTR2A -1438 A > G and SLC6A4 polymorphisms to ADHD youths were observed. 16958038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16967466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16967466_lack of influence of the T102C polymorphism of the 5HT-2A receptor on the emergence of psychotic symptoms in Alzheimer's disease 17000047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17003810_Results suggest that a polymorphism of a gene related to the serotonergic system affects eating behavior, influencing food choices in a population with a stable diet. 17056873_The phosphorylation of Galpha protein represents a novel mechanism involved in regulation of receptor signaling. 17092965_5-HT2A receptors are involved spatial memory function. 17093889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17093889_investigate seven genetic variants in three genes (serotonin transporter (5-HTT), serotonin receptor 1B (5-HTR1B) and serotonin receptor 2A (5-HTR2A)), which have previously been shown to be associated with ADHD 17098333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17102980_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17185512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17203304_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17221840_No association between the 5-HT2A C102T polymorphism and suicidal behavior in major psychoses. 17221846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17221846_investigation of association between the T102C polymorphism on the 5HT2A gene and cognitive function in patients with schizophrenia; findings suggest that the TC genotype might be related to certain cognitive impairments in patients with schizophrenia 17225991_Observational study of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17240119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17240119_this replication study provides further evidence for association between the 5-HTR2A receptor T102C polymorphism and schizophrenia 17280648_Haplotype analysis and global chi(2) test for haplotype transmission revealed a significant association between some SNPs of HTR2A and autism. 17280648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17291660_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17291660_The 5-HT2A -1438A (or 102T) allele was significantly more frequent in patients than controls (0.53 and 0.45, respectively; corrected p=0.028, OR=1.39 (95% CI=1.11-1.75)). 17339524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17401157_The 102T/C sinngle nucleotide polymorphism in the 5-HT2A receptor gene may be an independent risk factor for developing stroke. 17406648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17407792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17407792_no genetic association between HTR2A T102C with either schizophrenia or bipolar disorder under the assumption of a parent-of-origin effect 17420819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17420819_Results suggest that the C516T polymorphism of the 5-HT2A receptor gene is not related to the susceptibility for schizophrenia in a Brazilian sample. 17440930_15 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the gene coding for the serotonin-receptor 2A (HTR2A) in patients suffering from PD and a control sample, is reported. 17440930_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17481814_a mechanism for the generation of different neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease from a single nucleotide polymorphism with reduced receptor binding in T102C 5-HT2A 17487576_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17487576_T102C polymorphism of the HTR2A gene may be involved in the development of temperament by moderating the influence of environmental conditions. 17503984_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17504248_Male carriers of T/T genotype of 5HTR2A who were rated hyperactive by their mothers expressed a high level of hostility, especially that of cynicism, in adulthood. For men with other genetic variants, such an association was not seen. 17504248_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17506229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17506229_results suggest that the 5-HT(2A) gene polymorphism (102T/C) is not involved in genetic susceptibility to suicidal behavior in schizophrenic patients 17510953_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17521439_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17521439_replicate the association between 5-HT2A T102C polymorphism and response to typical neuroleptics in schizophrenia patients 17525976_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17525976_Psychosis onset in Alzheimer disease is strongly associated with severity of depressive symptoms, an association that may be modified by HTR2A polymorphism 17544547_We conclude that widespread reductions in 5-HT(2A) receptor binding were found in amnestic MCI, pointing at the presence of serotonergic dysfunction in prodromal AD. 17564514_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17590256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17590256_This studt conclude that 5-HT(2A) SNPs may marginally modulate personality traits. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17614196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17614196_These data might suggest that 5-HT2A polymorphisms are not major susceptibility factors of psychotic symptoms in PD patients. 17617023_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17617023_study demonstrates a higher frequency of 5-HTR2A -1438A and 102T alleles in schizophrenia patients compared to healthy volunteers 17622759_sarpogrelate, a selective 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist, inhibited platelet aggregation in patients with ischemic stroke. 17625040_Human serum albumin-advanced glycation end products stimulate phosphatidylserine externalization in platelets via 5-HT 2A/2C receptors. 17655760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17688403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17688403_The results of the present study seem to indicate that HTR2A gene polymorphism influences the tendency to express tardive dyskinesia following prolonged antipsychotic drug exposure in Turkish schizophrenia patients. 17697394_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17713649_An independent significant association was found between the TT genotype (35.7%) and urinary incontinence (OR = 2.06, 95%CI = 1.16-3.65). 17713649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17715398_The relative importance of two serine residues located near the top of transmembrane helix 5 of the human 5-HT(2A) receptor, comparing the wild type with S5.43(239)A or S5.46(242)A mutations, was assesed 17728663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17728663_association between polymorphisms in this serotonin gene suggests that these genetic factors can modulate vulnerability to puerperal psychosis in female bipolar participants. 17804117_Although the -1438G>A polymorphism in the serotonin 2A receptor is not a relevant marker for obesity risk, this variant may play a role in determining BMI in obese subjects 17804117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17899021_These results suggest a progressive reduction of cortical 5-HT(2A)R density as a surrogate biological measure of increased risk for schizophrenia, irrespective of conversion. 17922252_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17922252_This study suggests the possibility that an abnormal production rate of the 5-HT(2A)R c.1438A>G gene product might lead to the development of abdominal obesity in men but not in women. 17924589_Clinical trial of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17924589_the HTR2A T102C could be a potential indicator of clinical improvement after risperidone treatment in patient with schizophrenia. 17938636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17938636_the 5HT2A gene showed e |
ENSMUSG00000034997 |
Htr2a |
10.122889 |
0.2205635841 |
-2.180733 |
0.700334330 |
9.708291 |
0.00183438525237574921386562998293356940848752856254577636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004081942759696375981615101835586756351403892040252685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6989456 |
1.8571826 |
16.9687017 |
5.3095865 |
| ENSG00000102539 |
2862 |
MLNR |
protein_coding |
O43193 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for motilin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11322507}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Motilin is a 22 amino acid peptide hormone expressed throughout the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The protein encoded by this gene is a motilin receptor which is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family. This member is a multi-pass transmembrane protein, and is an important therapeutic target for the treatment of hypomotility disorders. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:2862; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] |
12054506_The motilin pharmacophore in CHO cells expressing the human motilin receptor 16531413_motilin receptor extracellular domains have roles in peptide and non-peptidyl agonist binding and activity 18032475_action by different chemical classes of agonists that are known to interact with distinct regions of the motilin receptor likely yield a common activation state of the cytosolic face of this receptor 18183601_The motilin receptor is expressed in human colonic and ileal smooth muscle. Further, motilin receptor expression was also shown in the mucosa. 18420306_Desensitization and internalization of MLNR is independent of the C-terminal tail. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22465164_The data suggested that in species expressing both motilin-MR and ghrelin-GHSR, there is a compensatory relationship in vivo. 23142315_data support important roles of new regions in the TM domains of the motilin receptor for erythromycin action, suggesting differential mechanisms of actions by peptidyl and non-peptidyl ligands 30934667_human motilin receptor transgenic (Tg) mice were tested with experiments evaluating the effects of motilin, erythromycin (EM), and ghrelin. |
|
|
12.960031 |
0.2064999434 |
-2.275787 |
0.489312951 |
23.703944 |
0.00000112352070696494973866782270816022659687405393924564123153686523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003954021372151325598633814228932692458329256623983383178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4491994 |
1.6238401 |
21.9854841 |
4.6286847 |
| ENSG00000102755 |
2321 |
FLT1 |
protein_coding |
P17948 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFB and PGF, and plays an essential role in the development of embryonic vasculature, the regulation of angiogenesis, cell survival, cell migration, macrophage function, chemotaxis, and cancer cell invasion. Acts as a positive regulator of postnatal retinal hyaloid vessel regression (Ref.11). May play an essential role as a negative regulator of embryonic angiogenesis by inhibiting excessive proliferation of endothelial cells. Can promote endothelial cell proliferation, survival and angiogenesis in adulthood. Its function in promoting cell proliferation seems to be cell-type specific. Promotes PGF-mediated proliferation of endothelial cells, proliferation of some types of cancer cells, but does not promote proliferation of normal fibroblasts (in vitro). Has very high affinity for VEGFA and relatively low protein kinase activity; may function as a negative regulator of VEGFA signaling by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and preventing its binding to KDR. Modulates KDR signaling by forming heterodimers with KDR. Ligand binding leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leading to activation of phosphatidylinositol kinase and the downstream signaling pathway. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Phosphorylates SRC and YES1, and may also phosphorylate CBL. Promotes phosphorylation of AKT1 at 'Ser-473'. Promotes phosphorylation of PTK2/FAK1 (PubMed:16685275). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11141500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11312102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11811792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12796773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14633857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15735759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16685275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18079407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18515749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18583712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18593464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20512933, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20551949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21752276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7824266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8248162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8605350, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9299537, ECO:0000269|Ref.11}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Phosphorylates PLCG. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9299537}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: May function as decoy receptor for VEGFA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21752276}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: May function as decoy receptor for VEGFA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21752276}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: May function as decoy receptor for VEGFA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21752276}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 7]: Has a truncated kinase domain; it increases phosphorylation of SRC at 'Tyr-418' by unknown means and promotes tumor cell invasion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20512933}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) family. VEGFR family members are receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) which contain an extracellular ligand-binding region with seven immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, a transmembrane segment, and a tyrosine kinase (TK) domain within the cytoplasmic domain. This protein binds to VEGFR-A, VEGFR-B and placental growth factor and plays an important role in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. Expression of this receptor is found in vascular endothelial cells, placental trophoblast cells and peripheral blood monocytes. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Isoforms include a full-length transmembrane receptor isoform and shortened, soluble isoforms. The soluble isoforms are associated with the onset of pre-eclampsia.[provided by RefSeq, May 2009]. |
hsa:2321; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; placental growth factor receptor activity [GO:0036332]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005021]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048514]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; embryonic morphogenesis [GO:0048598]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; hyaloid vascular plexus regression [GO:1990384]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905563]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling pathway [GO:0036323] |
11693202_vitronectin increased the presence of all four growth factor receptors and most notably, VEGFR-1; in contrast, fibrin decreased all four receptors, especially FGFR-1 and FGFR-2 11806246_presence of an sVEGFR-1 in human serum and plasma of normal male and female donors strongly suggests that it plays an important role as a naturally occurring VEGF antagonist in the regulation and availability of VEGF-mediated biological activities in vivo 11807987_A potential mechanism involved in hemangioma formation is the alteration of the FLT1 receptor signaling pathway in endothelial and/or pericytic cells. 11811792_Effect of placenta growth factor-1 on proliferation and release of nitric oxide, cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in human epithelial cells expressing the FLT-1 receptor 11824379_Involvement of VEGFR-2 (kdr/flk-1) but not VEGFR-1 (flt-1) in VEGF-A and VEGF-C-induced tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells in fibrin matrices in vitro. 11839635_VEGF and flt-1 are upregulated in blood vessels in many organs of acute Kawasaki Disease 11852061_In this study we give evidence of Flt-1 and KDR receptors in platelets. 11862609_expression, purification and detection of biological activity 11877075_Overexpression of Flt-Ig significantly inhibited the growth of K562 leukemia cells. 11908876_VEGF, Flt1, and Flk1 can be considered as indicators of the malignancy potential of diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. The expression of VEGF and the two receptors may be affected by the proliferative activity of tumor cells. 11986954_CLL B cells consistently express VEGFR1 mRNA; co-expression of angiogenic molecules and receptors suggest autocrine pathways of stimulation. 12091880_Placental growth factor promotes recruitment of VEGFR1(+) hematopoietic stem cells from a quiescent to a proliferative bone marrow microenvironment, favoring differentiation, mobilization and reconstitution of hematopoiesis. 12133473_Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor (Flt-1) in breast carcinoma 12406876_results suggest that in the hematopoietic microenvironment an autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor loop contributes to optimal megakaryocytic maturation through Flt1 12426207_In human umbilical vein endothelial cells, the Flt-1 receptor appears to act as a decoy receptor, tempering the response to lower concentrations of VEGF. 12439912_The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors KDR and Flt-1 by gastric carcinoma tissues and cell lines was detected to elucidate the molecular mechanism of this growth factor in promoting tumor growth. 12543719_This protein is a novel therapeutic target for angiogenic disorders (REVIEW) 12607599_Staining for the receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 was positive in large lymphoid cells in stage IV non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 12651930_expression system is involved in angiogenesis in inflamed synovial tissue in the temporomandibular joint 12670505_VEGF secreted by retinal pigment epithelial cells upregulates pigment epithelium-derived factor expression via VEGFR-1 in an autocrine manner. 12727995_findings may point to an involvement of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in the pathophysiology of preeclampsia possibly by antagonizing vascular endothelial growth factor effects 12824880_Aberrant methylation of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 gene is associated with prostate cancer 12865438_VEGFR-1 secreted by endothelial cells becomes a matrix-associated protein that is able to interact with the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin; a new role of VEGFR-1 in angiogenesis 12949011_in humans: 1) VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA are increased by acute systemic exercise; 2) the time course of the VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA responses are different from those previously reported in rats 14512169_Postmortem brain tissue analysis demonstrates VEGFR1 localized as paracellular deposits in Durck's granulomas of patients with cerebral malaria. 14585871_mRNA expression of VEGF and its receptor flt-1 in the hydrosalpinx was significantly higher than that in the healthy oviduct. 14602804_overproduction of soluble VEGFR-1 may lead to suppression of VEGF-A and PlGF and the down-regulation of its membrane bound form (VEGFR-1) in the placental bed, may result in the defective uteroplacental development. 14607815_Data suggest that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor flt-1 is expressed by eosinophils whose activation with VEGF stimulates directed migration and release of eosinophil cationic protein. 14654077_VEGF, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 are concomitantly expressed in pre-B ALL cells. Expression of the receptors is limited to the intra-cytoplasmic compartment and may suggest either internalization or a block in trafficking of the receptor to the surface. 14674128_changing of transcriptional activity of VEGF gene and its receptor FLT-1 indicates an autocrine mechanism of regulation of angiogenic gene activity in the first step of carcinogenesis--low-grade intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix 14684734_crystal structure of placental growth factor in complex with domain 2 of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 14687619_Specific VEGFR1 expression, examined in 27 B-CLL samples, was positive in all of them. The VEGF transduction pathway may be very active in CLL cells. Both its paracrine & autocrine pathways may contribute to their enhanced survival. 14760936_in systemic lupus erythematosus patients the levels of VEGF and sVEGFR-1 are higher in patients with active SLE than in inactive disease or healthy persons 14967383_flt-1 appears to be important in the temporal regulation of oviductal secretion. 14996703_VEGF receotor signaling regulates survival signals in CLL cells and that interruption of this autocrine pathway results in caspase activation and subsequent leukemic cell death. 15135240_vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is strongly expressed in villous cytotrophoblast cells and subsequently in Hofbauer cells while its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1 are found on vasculogenic and angiogenic precursor cells 15160911_C-Myc over-expression was significantly associated with high sVEGF and normal sFlt-1 level in DLBCL patients, suggesting a complex interrelationship between c-Myc oncogene expression and angiogenic regulators 15166498_Increased expression of FLT1 is associated with an aggressive angiogenic phenotype in melanoma. 15183893_VEGFR1 initiates a clonogenic response in myeloid leukemia cells that is PI3-kinase dependent. 15272021_a basis for understanding molecular recognition between PlGF-1 and VEGFR1 15284201_cytotrophobasts possess a unique property to enhance sFlt-1 production under reduced oxygen 15329326_Increased soluble VEGFR-1 level is an important parameter in lung cancers. 15472115_Preeclamptic placental villous explants showed a four-fold increase in sVEGFR-1 over normal pregnancies. Elevated levels of sVEGFR-1 in preeclampsia are responsible for inhibiting angiogenesis. 15492987_There was a significant positive correlation between the level of expression of VEGF and VEGF-R1 (P = 0.04) in both control groups and lung bearing tumorlets. 15503825_During tumour progression there is a change in the relative amounts of sFIt-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in the circulation. 15589171_Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and monocytes play a vital role in angiogenesis through the regulation of VEGF and sVEGFR-1 15610240_VEGF and sFLT-1 can actively take part in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy 15610528_These data support the involvement in melanoma growth and survival of a VEGF-dependent internal autocrine loop mechanism, at least in vitro. 15649874_Subjects with acute mountain sickness have lower levels of soluble VEGF receptor (Flt-1) at both low and high altitude compared with well subjects. 15665766_Blocking VEGF and PDGF receptor signaling in cardiac allografts has distinctive effects on inflammation and survival. 15705187_in vivo EPO does not affect the functionality and/or production of components of the VEGF/Flt-1 system in diabetics with normal or reduced renal function 15711751_Relative to human VEGF165, the binding affinity of Pm venom VEGF to the human VEGFR-1 was 1.7-fold higher while affinity to the VEGFR-2 was 17-fold lower. But it did not bind the VEGFR-3 or neuropilin-1. 15735759_In contrast to the previous paradigm that VEGFRs are not present on tumor cells of epithelial origin, we found that VEGFR-1 is present and functional on CRC cells. 15817508_fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, a circulating antiangiogenic protein, may play an important role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia [review] 15817662_When used individually, FGFR1 partially prevented goiter and sVEGFR1 partially reduced vascular volume. 15886253_role for sFlt-1 in the maternal manifestations of preeclampsia 16005848_These findings are consistent with the idea that the chemotactic effect of VEGF-A on mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC) is mediated via VEGFR-1, and that VEGF-A and PlGF-1, have a functional role for recruitment of osteoprogenitor cells. 16021053_Increased sFlt-1 secretion in first versus second pregnancies may account in part for the increased risk of preeclampsia among nulliparous women. 16021077_Increased soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 is more likely to be present in women with severe preeclampsia, but it is not present in all women with preeclampsia. 16095053_In vitro stimulation of blood samples with bacteria-derived antigens resulted in a significant increase in soluble VEGF (p |
ENSMUSG00000029648 |
Flt1 |
115.809951 |
0.1688110082 |
-2.566519 |
0.180046092 |
222.280598 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002876990535670176440429072562325385056876129358795296016967995307699396391437629183189232852139520227761895176764304561908597475394788745006735553033649921417236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000617214830036218105280345563990543329529007903837783878852038315649812177731909497217684233713136966816681530159287144001682007266040841386711690574884414672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.1768554 |
4.2221880 |
210.2111937 |
13.8309322 |
| ENSG00000102781 |
84056 |
KATNAL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BW62 |
FUNCTION: Regulates microtubule dynamics in Sertoli cells, a process that is essential for spermiogenesis and male fertility. Severs microtubules in an ATP-dependent manner, promoting rapid reorganization of cellular microtubule arrays (By similarity). Has microtubule-severing activity in vitro (PubMed:26929214). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0T4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26929214}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Isomerase;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity and microtubule-severing ATPase activity. Involved in microtubule severing. Located in cytoplasm; microtubule; and spindle pole. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84056; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; katanin complex [GO:0008352]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; isomerase activity [GO:0016853]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule severing ATPase activity [GO:0008568]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; microtubule severing [GO:0051013]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
20519956_KL1-mediated microtubule severing is utilized to generate microtubule seeds within the poles and loss of this activity alters the normal balance of motor-generated forces that determine spindle length. 24664804_microdeletion 13q12.3 represents a novel clinically recognizable condition and that the microtubule severing gene KATNAL1 and the chromatin-associated gene HMGB1 are candidate genes for intellectual disability inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. 24913027_KATNAL1 gene sequence variants are not associated with azoospermia. 35752927_Common genetic variation in KATNAL1 non-coding regions is involved in the susceptibility to severe phenotypes of male infertility. |
ENSMUSG00000041298 |
Katnal1 |
44.070199 |
3.1650965769 |
1.662250 |
0.361582714 |
20.375029 |
0.00000636550283182016853251485033471368524260469712316989898681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000020460544816564828635987657867723044091690098866820335388183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.7526375 |
16.4840196 |
18.5688550 |
3.9822741 |
| ENSG00000102878 |
3299 |
HSF4 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULV5 |
FUNCTION: Heat-shock transcription factor that specifically binds heat shock promoter elements (HSE) (PubMed:22587838, PubMed:23507146). Required for denucleation and organelle rupture and degradation that occur during eye lens terminal differentiation, when fiber cells that compose the lens degrade all membrane-bound organelles in order to provide lens with transparency to allow the passage of light (By similarity). In this process, may regulate denucleation of lens fiber cells in part by activating DNASE2B transcription (By similarity). May be involved in DNA repair through the transcriptional regulation of RAD51 (PubMed:22587838). May up-regulate p53/TP53 protein in eye lens fiber cells, possibly through protein stabilization (PubMed:28981088). In the eye lens, controls the expression of alpha-crystallin B chain/CRYAB and consequently may be involved in the regulation of lysosomal acidification (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5CZP2, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R0L1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22587838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23507146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28981088}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform HSF4A]: Transcriptional repressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10488131}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform HSF4B]: Transcriptional activator. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10488131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16371476}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cataract;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Heat-shock transcription factors (HSFs) activate heat-shock response genes under conditions of heat or other stresses. HSF4 lacks the carboxyl-terminal hydrophobic repeat which is shared among all vertebrate HSFs and has been suggested to be involved in the negative regulation of DNA binding activity. Two alternatively spliced transcripts encoding distinct isoforms and possessing different transcriptional activity have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3299; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell development [GO:0048468]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; histone H3-K9 demethylation [GO:0033169]; lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:0070306]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12089525_Mutant DNA-binding domain of HSF4 is associated with autosomal dominant lamellar and Marner cataract. . We suggest that HSF4 is critical to lens development. 15277496_This is the first report describing association of an autosomal recessive cataract with the HSF4 locus on 16q21-q22.1 and the first description of HSF4 splice variants 15308659_HSF4 binds to alphaB-crystallin, Hsp70, and Hsp82 promoters and has a role in interacting with the canonical heat shock element of the alphaB-crystallin gene 15959809_Findings confirm that mutations in HSF4 may result in both autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive congenital cataract, and highlight the locus heterogeneity in autosomal recessive congenital cataract. 16552721_The results indicate that in the absence of Hsf1 and Hsf2, Hsf4b expression in cells leads to increased ability of Hsf4b to bind HSE during G1, leading to enhanced synthesis of inducible Hsp70. 16876512_These results identified a novel missense mutation R74H in the transcription factor gene HSF4 in a Chinese cataract family and expand the spectrum of HSF4 mutations causing cataract. 18941546_This result indicates that HSF4 mutations account for only a small fraction of age-related cataracts. 19014451_we have shown the first nonsense mutation in HSF4 causing autosomal recessive cataracts in a large consanguineous family from Pakistan 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564821_Hsf4b could interact with and phosphorylated by MAP kinase P38. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20670914_two missense mutations that have been associated with age-related cataract did not or only slightly alter HSF4 activity, implying that other genetic and environmental factors affect the functions of these mutant proteins. 21258402_HSF2 and HSF4 regulate transcription of HIF-1a and that a critical balance between these HSF is required to maintain HIF-a expression in a repressed state. 21792930_our findings suggest novel mechanisms of HSF2 regulation controlled by HSF4a. 22103961_we report the absence of mutations in all studied genes in four families with phenotypes associating cataract, mental retardation and microcephaly. 22587838_Presents the first evidence demonstrating that HSF4 plays a role in DNA damage repair and may contribute a better understanding of congenital cataract formation. 23264262_This comparative analysis with CRYAB and HSP70 demonstrates that differential heat shock response is controlled by cell-type-dependent access of HSF1 and HSF4 to specific promoters, independent of the promoter architecture. 23329665_HSF4 and WRN CNVs might be involved in ARC pathogenesis in the Han Chinese. 23507146_HSF4 exerts its function on lens differentiation via positive regulation of DLAD expression. 24045990_the transcriptional activation of HSF4 is mediated by interactions between activator and repressor domains within the C-terminal end. 24637349_This is the first report of the novel missense mutation, c.69 G-->T (p. K23N), in exon 3 of the HSF4 locus on 16q21-q22 associated with bilateral congenital cataracts in a Chinese family. 24975927_HSF4 p.Arg116His recreates the childhood lamellar cataract in mice suggesting that incomplete penetrance associated with early cataracts may not be an absence but a limitation of the detection of the phenotype 25088997_We found that HSF4 downregulation led to decrease of HIF1alpha mRNA expression 25877371_concluded that the new mutation of c.331C>T in HSF4 DNA may be responsible for the autosomal dominant congenital cataract in this family 25940838_HSF4 may work as a switch between lens epithelial cell proliferation and secondary fiber cell differentiation, a process which mainly depends on p53. 26003728_Nuclear HSF2 and HSF4 bound to HSF1 only after heat shock. 26319152_BCAS2 interacts with HSF4 and negatively regulates its protein stability via ubiquitination. 26490182_report on a novel homozygous HSF4 mutation (c.521T>C, p.Leu174Pro) in two sibs with congenital cataracts 28981088_In the cultured human lens epithelial cells, HSF4 could stabilize and retain p53 in the nucleus to activate its target genes such as fas cell surface death receptor (Fas) and Bcl-2-associated X apoptosis regulator (Bax). 29131521_High HSF4 expression is an independent indicator of poor overall survival and recurrence free survival in patients with primary colorectal cancer. 29164525_Ectopic UAP56 upregulated HSF4-controlled HSP25 and alpha B-crystallin proteins expression, while knocking down UAP56 by shRNA reversed it. 29243736_We have identified a novel mutation in HSF4 in a large British pedigree causing dominant congenital lamellar cataract 29454088_HMOX-1, an anti-oxidase, is a bona fide transcriptional target gene of HSF4 in HLECs (human lens epithelial cells). HSF4 directly binds to the HSE element in HMOX-1 promoter to mediate its mRNA transcription and protein accumulation. 30143024_The results expand the spectrum of HSF4 mutations causing congenital cataracts. 34345029_Variants in PAX6, PITX3 and HSF4 causing autosomal dominant congenital cataracts. |
ENSMUSG00000033249 |
Hsf4 |
99.689393 |
0.2415485712 |
-2.049615 |
0.424896143 |
21.451634 |
0.00000362866750100490457353217751967910942312300903722643852233886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000012000701840652564390127254867479678068775683641433715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.5586659 |
13.1308011 |
160.6453239 |
38.3861496 |
| ENSG00000102900 |
9688 |
NUP93 |
protein_coding |
Q8N1F7 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the nuclear pore complex (NPC) assembly and/or maintenance (PubMed:9348540). May anchor nucleoporins, but not NUP153 and TPR, to the NPC. During renal development, regulates podocyte migration and proliferation through SMAD4 signaling (PubMed:26878725). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15229283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15703211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26878725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9348540}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Membrane;mRNA transport;Nuclear pore complex;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Translocation;Transport |
|
The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure that extends across the nuclear envelope, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nucleoporins are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. This gene encodes a nucleoporin protein that localizes both to the basket of the pore and to the nuclear entry of the central gated channel of the pore. The encoded protein is a target of caspase cysteine proteases that play a central role in programmed cell death by apoptosis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:9688; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear periphery [GO:0034399]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; structural constituent of nuclear pore [GO:0017056]; nuclear envelope organization [GO:0006998]; nuclear pore complex assembly [GO:0051292]; nucleocytoplasmic transport [GO:0006913]; poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0016973]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395] |
16286466_Caspases target only Nup93 and Nup96 within the core structure of the nuclear pore complex 26878725_NUP93 and exportin 5 interact with the signaling protein SMAD4 and that NUP93 mutations abrogated interaction with SMAD4 27593162_we show that knockdown of Nup188 or its binding partner Nup93 leads to a loss of cilia during embryonic development while leaving NPC function largely intact. Many data, including the localization of endogenous Nup188/93 at cilia bases, support their direct role at cilia. Super-resolution imaging of Nup188 shows two barrel-like structures 29869118_Apart from a high etiological fraction of NPHS2 and WT1 genes, study has identified an unexpectedly high frequency of a limited set of presumably ancestral NUP93 causative mutations a longitudinal collection of Central European (Czech and Slovak) patients with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 30741391_Two rare compound heterozygous variants of NUP93 were identified by whole exome sequencing in two brothers with isolated cerebellar atrophy 30943371_The expression of nsp1 in HEK cells disrupts Nup93 localization around the nuclear envelope without triggering proteolytic degradation, while the nuclear lamina remains unperturbed. 31774908_This study verified that Nup93 is an important gene in cervical cancer, which could promote an aggressive behavior. 31959624_Nup93 regulates breast tumor growth by modulating cell proliferation and actin cytoskeleton remodeling. 33085133_Molecular and structural analysis of central transport channel in complex with Nup93 of nuclear pore complex. 34746948_Nup93 and CTCF modulate spatiotemporal dynamics and function of the HOXA gene locus during differentiation. 34767927_Nucleoporin 93 mediates beta-catenin nuclear import to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis. 35196484_Nucleoporin-93 reveals a common feature of aggressive breast cancers: robust nucleocytoplasmic transport of transcription factors. 35211795_Exploring the relevance of NUP93 variants in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome using next generation sequencing and a fly kidney model. |
ENSMUSG00000032939 |
Nup93 |
265.237567 |
2.1225471026 |
1.085797 |
0.139237147 |
60.356635 |
0.00000000000000791373489449527418787619229319068779990493673476281699663559265900403261184692382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000053360770691069093677527923590914705796815330901550211706307891290634870529174804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
364.8844859 |
30.9379910 |
172.9917923 |
11.0285382 |
| ENSG00000102931 |
23568 |
ARL2BP |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2Y0 |
FUNCTION: Together with ARL2, plays a role in the nuclear translocation, retention and transcriptional activity of STAT3. May play a role as an effector of ARL2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18234692}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)-like proteins (ARLs) comprise a functionally distinct group of the ARF family of RAS-related GTPases. The protein encoded by this gene binds to ARL2.GTP with high affinity but does not interact with ARL2.GDP, activated ARF, or RHO proteins. The lack of detectable membrane association of this protein or ARL2 upon activation of ARL2 is suggestive of actions distinct from those of the ARFs. This protein is considered to be the first ARL2-specific effector identified, due to its interaction with ARL2.GTP but lack of ARL2 GTPase-activating protein activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23568; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; spindle [GO:0005819]; GTPase regulator activity [GO:0030695]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; maintenance of protein location in nucleus [GO:0051457]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
19368893_Crystal structure of the ARL2-GTP-BART complex reveals a novel recognition and binding mode of small GTPase with effector. 21665939_overexpression of the amino (N)-terminal region of G3BP, including the binding region for BART mRNA, dominant-negatively inhibits formation of the complex between endogenous G3BP and BART mRNA, and increases the expression of BART. 21833473_Our results imply that BART increases active RhoA by inhibiting ARL2 function, which in turn inhibits invasiveness of cancer cells. 21901094_We identify a subset of BART miRNAs that are restricted to Latency III in normal infection but are up regulated in tumors that express Latency I and II. 22532868_These results imply that BART contributes to regulating PKCalpha activity through binding to ANX7, thereby affecting the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. 22745590_Our results imply that BART regulates actin-cytoskeleton rearrangements at membrane ruffles through modulation of the activity of Rac1, which, in turn, inhibits pancreatic cancer cell invasion. 23685147_EBV-miR-BART1 could influence the expression of metabolism-associated genes and might be involved in cancer metabolism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 23849777_Mutations in ARL2BP cause autosomal-recessive retinitis pigmentosa. 24899173_EBV also downregulates two immediate early genes by miR-BART20-5p. 26135619_Alteration of EBV encoded miR-BART1 expression results in an increase in migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and causes metastasis in vivo. EBV-miR-BART1 directly targets the cellular tumour suppressor PTEN. 27790702_Subsequent analysis of 844 index cases did not reveal further pathogenic chances in ARL2BP indicating that mutations in ARL2B are a rare cause of arRCD (about 0.1%) in a large cohort of French patients. 30210231_This study identified two homozygous variants in ARL2BP as a rare cause of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Further studies are required to define the underlying disease mechanism causing retinal degeneration as a result of mutations in ARL2BP and any phenotype-genotype correlation associated with residual levels of the wild-type transcript. 31425546_Study identified multiple ciliopathy phenotypes associated with mutations in ARL2BP in human patients and in a mouse knockout model. Spermiogenesis is impaired, resulting in abnormally shaped heads, shortened and mis-assembled sperm tails, and loss of axonemal doublets. ARL2BP is required for the structural maintenance of cilia as well as of the sperm flagellum, and that its deficiency leads to syndromic ciliopathy. 33438581_ARL3 activation requires the co-GEF BART and effector-mediated turnover. 34681596_Epstein-Barr Virus miR-BART1-3p Regulates the miR-17-92 Cluster by Targeting E2F3. |
ENSMUSG00000031776 |
Arl2bp |
331.395832 |
2.1029963125 |
1.072446 |
0.306654721 |
11.964258 |
0.00054230793980983012063379344880331700551323592662811279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001322801563729604848451693044353305594995617866516113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
511.9397993 |
99.0126004 |
245.5308611 |
34.3135634 |
| ENSG00000102934 |
51090 |
PLLP |
protein_coding |
Q9Y342 |
FUNCTION: Appears to be involved in myelination. Could also participate in ion transport events as addition of plasmolipin to lipid bilayers induces the formation of ion channels, which are voltage-dependent and K(+)-selective (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to be a structural constituent of myelin sheath. Predicted to be involved in myelination. Predicted to be located in compact myelin and membrane raft. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Biomarker of schizophrenia. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51090; |
compact myelin [GO:0043218]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; structural constituent of myelin sheath [GO:0019911]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; myelination [GO:0042552]; response to wounding [GO:0009611] |
26002055_These data support a model in which PLLP functions in myelin biogenesis through organization of myelin liquid-ordered membranes in the Golgi complex. 35015148_Integrative omics analysis identifies biomarkers of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000031775 |
Pllp |
25.227714 |
0.4876191338 |
-1.036173 |
0.381420538 |
7.235582 |
0.00714726422305630559178579730428282346110790967941284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014145028148607009105264253889799874741584062576293945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.2986948 |
5.4041781 |
35.3232932 |
7.6413027 |
| ENSG00000102984 |
55565 |
ZNF821 |
protein_coding |
O75541 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein with two C2H2 zinc finger motifs and a score-and-three (23)-amino acid peptide repeat (STPR) domain. The STPR domain of the encoded protein binds to double stranded DNA and may also contain a nuclear localization signal, suggesting that this protein interacts with chromosomal DNA. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:55565; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000031728 |
Zfp821 |
50.103171 |
0.4317298713 |
-1.211799 |
0.221936994 |
30.215914 |
0.00000003865247727003570249265122977556929928510953686782158911228179931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000158695567317309313277421019272583890824535046704113483428955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.3604529 |
4.3201776 |
73.2419128 |
6.6865523 |
| ENSG00000103150 |
23417 |
MLYCD |
protein_coding |
O95822 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA. In the fatty acid biosynthesis MCD selectively removes malonyl-CoA and thus assures that methyl-malonyl-CoA is the only chain elongating substrate for fatty acid synthase and that fatty acids with multiple methyl side chains are produced. In peroxisomes it may be involved in degrading intraperoxisomal malonyl-CoA, which is generated by the peroxisomal beta-oxidation of odd chain-length dicarboxylic fatty acids. Plays a role in the metabolic balance between glucose and lipid oxidation in muscle independent of alterations in insulin signaling. May play a role in controlling the extent of ischemic injury by promoting glucose oxidation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10455107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15003260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18314420, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23482565}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Cytoplasm;Decarboxylase;Disulfide bond;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Mitochondrion;Peroxisome;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Metabolic intermediate biosynthesis; acetyl-CoA biosynthesis; acetyl-CoA from malonyl-CoA: step 1/1. |
The product of this gene catalyzes the breakdown of malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA and carbon dioxide. Malonyl-CoA is an intermediate in fatty acid biosynthesis, and also inhibits the transport of fatty acyl CoAs into mitochondria. Consequently, the encoded protein acts to increase the rate of fatty acid oxidation. It is found in mitochondria, peroxisomes, and the cytoplasm. Mutations in this gene result in malonyl-CoA decarboyxlase deficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23417; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; malonyl-CoA decarboxylase activity [GO:0050080]; acetyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0006085]; acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0006637]; fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006633]; fatty acid oxidation [GO:0019395]; malonyl-CoA catabolic process [GO:2001294]; positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation [GO:0046321]; regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0031998]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931] |
12955715_Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency may result from MLYCD mutations that result in protein mistargeting. 16434556_The concentration of malonyl-CoA is diminished in muscle after physical training, most likely because of PGC-1alpha-mediated increases in MCD expression and activity. 17186413_analysis of nine novel MLYCD mutations in patients with malonyl-coenzyme A decarboxylase deficiency 18314420_MCD silencing suppresses lipid uptake and enhances glucose uptake in primary human myotubes. 18614968_Data suggest that increased expression of malonyl CoA decarboxylase, and the decreased expression of acetyl CoA carboxylase and 5'-AMP activated protein kinase are important regulators of the maturation of fatty acid oxidation in the newborn human heart. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20702857_This study of fatty acid oxidation and malonyl-CoA decarboxylase identifies a critical role for metabolism in both the normal pulmonary circulation (hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction) and pulmonary hypertension 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22778304_Our case emphasizes the need for ongoing cardiac disease screening in patients with MCD deficiency and the benefits and limitations of current dietary interventions. 23482565_Structural asymmetry and disulfide bridges among subunits modulate the activity of human malonyl-CoA decarboxylase. 23791943_The MLYCD catalytic domain is structurally homologous to those of the GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase superfamily. 26858006_Our result expands the phenotype of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency and suggests attentions should be paid to the mild form of disorders, for example, malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency, which usually present a severe disease course. 26948533_To identify the active site of MCD, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations were performed to explore the interactions of human mitochondrial MCD (HmMCD) and CoA derivatives. The findings reveal that the active site of HmMCD indeed resides in the prominent groove which resembles that of curacin A. |
ENSMUSG00000074064 |
Mlycd |
74.365987 |
2.2732255771 |
1.184741 |
0.447842026 |
6.734487 |
0.00945664481808650668470672684406963526271283626556396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018217185788952861696943230640499677974730730056762695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
108.4809410 |
33.2712759 |
48.3551527 |
10.6075273 |
| ENSG00000103197 |
7249 |
TSC2 |
protein_coding |
P49815 |
FUNCTION: In complex with TSC1, this tumor suppressor inhibits the nutrient-mediated or growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation of S6K1 and EIF4EBP1 by negatively regulating mTORC1 signaling (PubMed:12271141, PubMed:28215400, PubMed:35772404). Acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for the small GTPase RHEB, a direct activator of the protein kinase activity of mTORC1 (PubMed:15340059). May also play a role in microtubule-mediated protein transport (By similarity). Also stimulates the intrinsic GTPase activity of the Ras-related proteins RAP1A and RAB5 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P49816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12271141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15340059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28215400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35772404}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;GTPase activation;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the growth inhibitory protein tuberin. Tuberin interacts with hamartin to form the TSC protein complex which functions in the control of cell growth. This TSC protein complex negatively regulates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling which is a major regulator of anabolic cell growth. Mutations in this gene have been associated with tuberous sclerosis and lymphangioleiomyomatosis. [provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. |
hsa:7249; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; TSC1-TSC2 complex [GO:0033596]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; anoikis [GO:0043276]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; heart development [GO:0007507]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of mitophagy [GO:1901525]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032007]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046626]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
11112665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11403047_missense mutation in the GTPase activating protein homology region in families with tuberous sclerosis complex 11686512_negative regulators of cell division; control of transition from G0/G1 to S phase 11781698_Detected two sequence changes involving the TSC2 stop codon. 11811958_calmodulin signaling in the propagation of this TSC2 activity 11836366_Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis in a patient with an acrofacial dysostosis-like phenotype, tuberous sclerosis, and polycystic kidney disease shows a microdeletion of approximately 280 kb including the TSC2 gene on chromosome 16p13.3. 12015165_Novel TSC1 and TSC2 mutations in Japanese patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. 12062115_TSC1 and TSC2 mutations in tuberous sclerosis - used DHPLC analysis to facilitate the detection of a mosaic mutation, in the presence of a coexisting constitutional polymorphism. 12127687_effect on EHEN-induced renal and hepatocarcinogenesis in the suppressor gene transgenic rats 12172553_TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. 12176984_tuberin binds with 14-3-3 zeta to regulate phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 12271141_hamartin and tuberin function together to inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated signaling to eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) 12364343_associates with 14-3-3 in vivo 12468542_TSC2 expression is regulated by 14-3-3 beta in human cells 12547695_A link exists between this protein and kidney diseases 12581886_Estrogen action induces tyrosine phosphatase activity that regulates stability of tuberin, which may play a crucial role in cellular specific functions such as endocytosis. 12582162_MK2 phosphorylates TSC2, which creates a 14-3-3 binding site and thus regulates the cellular function of the TSC2 tumor suppressor protein 12711473_Mutation in TSC2 and activation of mammalian target of rapamycin signalling pathway in renal angiomyolipoma. 12766909_We conclude that the hamartin/tuberin complex exerted a direct effect on the morphology and adhesive properties of 293 cells through regulation of the level and/or activity of cellular E-cadherin/beta-catenin 12773159_mutated in suberous sclerosis (REVIEW). 12773162_Mutated in tuberous sclerosis. 12773163_mutated in sporadic tumors (REVIEW) 12820960_TSC2 is a GAP for rheb and insulin-mediated rheb activation is PI3K dependent. 12842888_TSC2 binds to rheb and has a role in S6 kinase activation 12869586_Rheb GTPase is a direct target of TSC2 GAP activity and regulates mTOR signaling. 12894220_Human TSC2 triggers mammalian cell size reduction and a dominant-negative TSC2 mutant induces increased size. 14551205_data support a model in which phosphorylation of hamartin regulates the function of the hamartin-tuberin complex during the G2/M phase of the cell cycle 14559897_the TSC1.TSC2 complex is regulated by pam and its ortholog highwire 14680818_Western blot analyses confirmed the deregulation of 14-3-3 proteins upon ectopic overexpression of TSC1 and TSC2. 14756965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14756965_TSC2 gene, which is responsible for tuberous sclerosis was identified, and all the exons of TSC2 were analyzed by using polymerase chain reaction-single strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) from peripheral blood of 28 patients . 14871804_A novel mechanism of post-translational inactivation of the TSC2 protein, tuberin, by physiologically inappropriate phosphorylation is demonstated. 14985384_people with TSC2 mutations were significantly more likely than those with TSC1 mutations to have autistic disorder, a low IQ, and a history of infantile spasms; low IQ was independently associated with both TSC2 mutations and a history of infantile spasm 15059224_Down regulation or loss of tuberin and/or hamartin expression may be permissive to fibrocyte proliferation or promote collagen production leading to fibroepithelial polyp formation. 15066998_Tuberin (TSC2) interact with smad2/smad3 during TGF-beta1 growth regulation. 15072102_tsc2 gene expression is reduced in the majority of subependymal giant cell astrocytomas 15150271_inhibition of B-Raf kinase via Rheb is an mTOR-independent function of tuberin 15175323_Binding with HPV16 E6 causes the proteasome-mediated degradation of Tuberin 15231735_Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and other benign tumor syndromes could be caused by dysregulation of the TSC2 pathway 15340059_To investigate the function of TSC2 and Rheb in mTOR signaling, we analyzed the TSC2-stimulated Rheb GTPase activity. 15355997_Tuberin has a role in binding p27 and negatively regulating its interaction with Skp2 15477556_Cortical tuber giant cells in a case of epileptogenic tuberous sclerosis showed predominantly nuclear hamartin, cytosolic tuberin, and hyperphosphorylation of S6. 15579767_data suggest that PGE2 signaling may promote endometrial tumorigenesis by inactivation of tuberin after its phosphorylation via the Akt signaling pathway 15595939_A total of 12 mutations were detected in 24 Indian TSC families in TSC genes. 15624760_Five of 6 subependymal giant cell astrocytomas(SEGAs) also showed evidence of biallelic mutation of TSC1 or TSC2, suggesting that SEGAs develop due to complete loss of a functional tuberin-hamartin complex. 15647351_monitored 14 previously uncharacterized and six known phosphorylation events after phorbol ester stimulation in the ERK/p90 ribosomal S6 kinase-signaling targets, TSC1 and TSC2, and a protein kinase C-dependent pathway to TSC2 phosphorylation 15798777_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15851026_Erk may modulate mTOR signaling and contribute to disease progression through phosphorylation and inactivation of TSC2. 15874888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15963462_identified three sites of TSC2 phosphorylation and a novel site of TSC1 phosphorylation, and investigated the roles of these sites in regulating the activity of the TSC1-TSC2 complex 16053916_investigation of the ability of different opioid receptors to regulate the phosphorylation and degradation of tuberin 16192644_Growth of smooth muscle cells derived from TSC2-renal angiomyolipoma demonstrates that epidermal growth factor is required. 16211238_study provides new insights into cellular roles of TSC proteins and promotes discussion on whether separable functions of these proteins might be associated with clinical differences of TSC1- and TSC2-associated disease 16213898_Reduced expression of tuberin might be involved in the progression of pancreatic cancer. 16237225_patient should be considered as having Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma that developed from two somatic hit mutations in TSC2 16258273_Tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressors TSC1 and TSC2 form a protein complex that integrates and transmits cellular growth factor and stress signals to negatively regulate checkpoint kinase TOR activity, as described in this review. 16341938_Data show that tuberin protein levels are decreased in the frontal cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. 16388022_TSC2 may play a critical role in modulating cell migration and invasiveness, which contributes to the pathobiology of LAM. 16537497_Overexpression of TSC2 rescues the migration phenotype of myr-Akt1-expressing tumor cells, and high levels of TSC2 in breast cancer patients correlate with increased metastasis and reduced survival. 16554133_Denaturing high performance liquid chromatography and DNA sequencing analysis of TSC1 and TSC2 revealed 13 types of mutations (30%). Nine novel mutations of TSC2 were identified. 16624901_The genome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe contains tsc1(+) and tsc2(+), homologs of human Tsc1 and Tsc2, respectively. Deletion of either tsc1(+) or tsc2(+) affects gene induction upon nitrogen starvation. 16835931_mutation in the TSC2 gene has a role in acrochordons and pancreatic islet-cell tumors in tuberous sclerosis [case report] 16897363_According to Knudson's two-hit model of tumorigenesis, second-hit mutation and resulting loss of heterozygosity of a tumor suppressor gene (tsc1 and tsc2) is necessary for tumor formation 16905638_Fractionation of synchronized airway smooth cells showed that tuberin enters the nucleus in late G(1), and passage through the cell cycle is necessary for nuclear entry. 16940165_documents the incidence, natural history, and outcome of cardiac tumors in patients with TSC in the largest series yet reported and provides a comparison of these features with TSC1 versus TSC2 mutation 17018601_The TSC/Rheb/mTOR pathway plays a critical role in the regulation of E(2)-induced proliferation. 17114181_mTOR-dependent pathways have roles in IFN signaling and 4E-BP1 and TSC1-TSC2 are key components in the generation of IFN-dependent biological responses 17114346_These findings suggest a link between tuberin nuclear localization and a variety of intracellular signaling events that have direct implications with respect to the role of tuberin in the pathology of tuberous sclerosis and lymphangioleiomyomatosis. 17234746_These functional data indicate that the Crumbs complex is a potential regulator of the mTORC1 pathway, cell metabolism and survival through a direct interaction with TSC1/2. 17273797_During conditions of cell stress, GADD34 forms a stable complex with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) 1/2, causes TSC2 dephosphorylation, and inhibits signaling by mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR). 17287951_We conclude that large deletions in TSC1 and TSC2 account for about 0.5 and 6% of mutations seen in TSC patients, respectively, and MLPA is a highly sensitive and accurate detection method, including for mosaicism. 17304050_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373211_implications for the development of cystic kidney disease [REVIEW] 17458623_study presents the cytoplasmic/nuclear distribution of tuberin in cell lines 17470459_p27 localization during the mammalian cell cycle is under the control of the tumor suppressor tuberin 17592551_Angiomyolipoma-derived smooth muscle TSC2-/- cells express survivin when exposed to IGF-1. Survivn expression is also triggered whenever culture conditions perturb normal TSC2-/- cell function. 17632432_Pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis can appear sporadically or be associated with tuberous sclerosis with abnormalities of the TSC2 suppressor gene. 17671177_Erk-mediated TSC2 phosphorylation occurred at a high incidence and positively correlated with mitogen activated protein kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin activation in Tuberous Sclerosis and cancers 17888633_novel tandem-duplication mutation od TSC2 in Chinese tuberous sclerosis patient 17922028_This is the first description of a functional interaction between the tumor suppressor tuberin and the oncogene Ras in regulating apoptosis. 17975002_CD44v6-positive sorted lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells showed loss of heterozygosity at the TSC2 locus; binding of CD44v6 antibody resulted in loss of cell viability. 17989114_Tuberin regulates a specific DNA repair enzyme, OGG1. This regulation may be important in the pathogenesis of kidney tumors in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. 18032745_Patients with a TSC1 mutation are more likely to have a less severe neurologic and cognitive phenotype than those with a TSC2 mutation. 18060739_Analysis of 15 tuberous sclerosis patient samples in which deletions in TSC2 extended into PKD1 showed no evidence of clustering of breakpoints near the polypyrimidine tract 18085521_Our observations of frequent deletion of TSC2 and the mTOR signalling pathway provide evidence that the oncogenetic lineage of PEComa, as a distinct TSC2-linked neoplasm, is similar to that of angiomyolipoma. 18094073_IFNbeta augments TSC2-dependent inhibition of TSC2-null ELT3 and human lymphangioleiomyomatosis-derived cell proliferation. 18302728_Functional characterisation of TSC2 variants can help identify pathogenic changes in individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex, and assist in the diagnosis and genetic counselling of the index cases and/or other family members 18320306_Results suggest that tuberin dysfunction may represent a mechanism for neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease with dementia (PD/DLB), and a mouse model of PD. 18342602_Data show that loss of TSC1 or TSC2 in cell lines and mouse or human tumors causes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and activates the unfolded protein response (UPR). 18368626_loss of tuberin in balloon cells of both cortical dysplasia type IIB in tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)-related and sporadic patients suggests that Focal cortical dysplasia type IIB may represent the focal form of TSC. 18381890_Results indicate that FBW5-DDB1-CUL4-ROC1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase regulating TSC2 protein stability and TSC complex turnover. 18411301_the TSC1-TSC2 complex inhibits mTORC1 and activates mTORC2, which through different mechanisms promotes Akt activation 18451215_Inactivation of TSC2 via loss of expression or phosphorylation occurred frequently in endometrial carcinoma to activate mTOR signaling 18538015_Involvement of TSC genes and other members of the mTOR signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. LOH and promoter methylation are two important mechanisms for downregulation of TSC genes. 18794342_in addition to the kinase LKB1, the Tsc1-Tsc2 complex, acting through TORC1, also modulates SAD to regulate axon formation 18794346_results reveal key roles of TSC1/TSC2 in neuronal polarity, suggest a common pathway regulating polarization/growth in neurons and cell size in other tissues, and have implications for the understanding of the pathogenesis of TSC 18807177_This study suggests a pivotal role of PI3 K, MAPK and mTOR pathways, via tuberin, in post-transcriptional control of CXCR4 18848473_These data identify the TSC2-mTOR pathway as a key regulator of innate immune homeostasis with broad clinical implications for infectious and autoimmune diseases, vaccination, cancer, and transplantation. 18926585_Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway may cause not only tumor development but also metabolic disorders such as diabetes and its comp 18958173_Anti-EGFR antibody efficiently and specifically inhibits human TSC2-/- smooth muscle cell proliferation. 18974095_a novel interaction between DAPK and TSC2 proteins that has revealed a positive link between growth factor stimulation of DAPK and mTORC1 signaling that may ultimately affect autophagy, cell survival, or apoptosis. 19005330_TSC2 which codes for tuberin plays a central role in regulating cell survival and proliferation signaling pathways 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19175396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19250671_Hypermethylation and downregulation of TSC2 gene is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 19259131_Data suggest that the three mutations were most likely de novo, as parents of affected patients did not present any features of TSC. 19265534_The data suggest that tuberin and OGG1 are important proteins in the pathogenesis of angiomyolipoma in tuberous sclerosis complex patients. 19332694_Cyst-like cortical tubers in the brain are strongly associated with TSC2 gene mutation in tuberous sclerosis complex. 19332694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19357198_A hypomorphic allele of Tsc2 highlights the role of TSC1/TSC2 in signaling to AKT and models mild human TSC2 alleles 19357198_AKT activity is downregulated when Tsc1/Tsc2 function is reduced. 19395678_found increased MMP-2 expression in cells lacking TSC1/TSC2 compared with their respective controls 19419980_Conducted a retrospective review of the chest computed tomography (CT) of 45 female and 20 male patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and found cysts consistent with Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) in 22 (49%) women and two (10%) men. 19422538_mineralized focal cortical dysplasias with balloon cells revealed an increased frequency of TSC2 allelic variants but not TSC1 19443708_that methylation of the TSC2 promoter might cause a complete loss of tuberin in TSC2 cells. 20042714_Tuberin-null cells become nonadherent and invasive and these nonadherent cells express cleaved forms of beta-catenin. 20145209_ARD1 functions as an inhibitor of the mTOR pathway and that dysregulation of the ARD1-TSC2-mTOR axis may contribute to cancer development 20146692_In the brain, TSC2 has been implicated in cell body size, dendritic arborization, axonal outgrowth and targeting, neuronal migration, cortical lamination, and spine formation [REVIEW]. 20160076_results identify a cytoplasmic pathway for ROS-induced ATM activation of TSC2 to regulate mTORC1 signaling and autophagy, identifying an integration node for the cellular damage response 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219685_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237422_These findings link TACC3 to novel structural and cell division functions of TSC2. 20304964_p22(phox)-based Nox oxidases maintain HIF-2alpha protein expression through inactivation of tuberin and downstream activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1/4E-BP1 pathway 20354165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363874_AMPK functions to inhibit IGF-I-stimulated PI3K pathway activation through stimulation of IRS-1 serine 794 phosphorylation. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530489_TSC2 has a role in controlling cell polarity and migration by regulating CDC42 and RAC1 activation 20605525_The rare occurrence of complete loss of TSC1/TSC2 function in human tumors suggests that retaining growth suppressor activity might be beneficial during tumour evolution, perhaps by promoting survival when cells grow in a nutrient-limited environment. 20622004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639436_Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), occurring sporadically (S-LAM) or in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), results from abnormal proliferation of LAM cells exhibiting mutations or loss of heterozygosity (LOH) of the TSC genes, TSC1 or TSC2. 20658316_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20658316_analysis of polymorphic variants in TSC1 and TSC2 and their association with breast cancer phenotypes 20671064_One of the targets of HtrA1 activity during fetal development is the TSC2-TSC1 pathway. 20818424_Rheb controls proliferation of TSC2-deficient cells by a mechanism that involves regulation of AMPK and p27, and that Rheb is a potential target for TSC/LAM therapy. 20882401_These findings establish a mouse model for TSC-related anxiety phenotypes and suggest that anxiety disorders in TSC have a biological foundation. 21036916_Lymphangioleiomyomatosis is characterized by cystic lung destruction, resulting from proliferation of smooth-muscle-like cells, which have mutations in the tumor suppressor gene TSC2. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21134130_TSC2 binds to the death domain of DAPK. This interaction is required for TSC2 to reduce DAPK protein levels and half-life. DAPK is regulated by the lysosome pathway. Lysosome inhibition blocks TSC2-mediated degradation of DAPK. 21145542_Increased expression of tuberin in human uterine leiomyoma. 21243421_Rattus norvegicus and Mus musculus TSC1 and TSC2 showed very high similarity to the human sequences, this was not the case for Danio rerio, Drosophila melanogaster, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, Schizosaccharomyces pombe or Disctyostelium discoideum. 21252315_study identified six TSC2 mutations, one indel, one nonsense, and four missense in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors 21309039_Functional assessment of variants in the TSC2 genes identified in individuals with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 21329690_REVIEW: TSC signaling in the CNS 21332470_TSC2 R1200W variant, and four other TSC2 missense variants associated with a mild TSC phenotype, confirmed that the changes disrupted the TSC1-TSC2 function. The TSC1-TSC2 interaction was not affected by the amino acid substitution. 21345208_results support the possibility that allele-specific variation in TSC mRNA expression contributes to the variable severity of symptoms in tuberous sclerosis complex patients 21407201_Human TSC2-null fibroblast-like cells induce hair follicle neogenesis and hamartoma morphogenesis. 21412983_TSC1, TSC2 and Rheb function independently of TORC1 in tuberous sclerosis complex.[Review] 21419848_Tuberous sclerosis complex protein TSC2 plays a critical role in Purkinje cell survival by regulating endoplasmic reticulum and oxidative stress. 21449900_In a cohort of tuberous sclerosis patients, there was a trend towards greater severity for patients with TSC2 mutations compared with their TSC1 counterparts, particularly for autistic spectrum disorder 21533174_presence of TSC2 mutations, in addition to TSC1 mutations, underlines the involvement of mTOR signaling in urothelial carcinoma 21555252_This study suggested that allelic imbalances of TSC2 in nonlesional focal epileptic tissue. 21784859_Redox regulates mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity by modulating the TSC1/TSC2-Rheb GTPase pathway. 21795849_ULK1 negatively regulates the kinase activity of mTORC1 and cell proliferation in a manner independent of Atg5 and TSC2 21846442_Eighty percent of cardiac rhabdomyomas are associated with tuberous sclerosis. In this case, molecular testing for tuberous sclerosis identified two variants in the TSC2 gene. 21900748_Tuberin regulates the cellular localization of cyclin B1. 21910228_Two females cases with typical manifestations of Tuberous sclerosis complex, horseshoe kidney, and an identical variant c.5138G>A in exon 39 (p.Arg1713His) of TSC2 gene. 21949787_Mutations in TSC2 is associated with angiomyolipoma. 22090422_study found tuberin and PRAS40 to be potent anti-apoptotic gatekeepers in early mammalian stem-cell differentiation; data allow new insights into the regulation of early stem-cell maintenance and differentiation and identify a new role of the tumor suppressor tuberin and the oncogenic protein PRAS40 22189265_TSC2 protein-truncating mutations and small in-frame mutations are associated with distinctly different intelligence profiles, providing further evidence that different types and locations of TSC germline mutations 22251200_Patients with mutations in TSC2 tended to have a higher frequency of hepatic angiomyolipomas than those with mutations in TSC1 or those with no mutations detected. 22287548_The results defined the TSC2-mTOR pathway as a key determinant in the differentiation of monocytes into M2 phenotype tumor-associated macrophages that promote angiogenesis. 22456611_Perivascular epithelioid cell tumors with TFE3 gene fusions demonstrated intact, robust tuberin protein labeling and no TSC2 loss of heterozygosity. 22490766_This study presented that the mutation rate of the TSC1 and TSC2 genes in Korean patients with tuberous sclerosis complex was 100%. 22608477_TSC2 mutations are more frequent in patients with retinal findings than in those without retinal findings. 22707510_Patient with TSC2 1801A>G mutation was found to have five facial features of TSC, including a rash of facial angiofibromas, a shagreen patch, a forehead plaque, gingival fibromas, and dental pitting. 22795129_The TSC1-TSC2-TBC1D7 (TSC-TBC) complex is the functional complex that senses specific cellular growth conditions and possesses Rheb-GAP activity. 22867869_Missense mutations located in the central region of TSC2 (exons 23-33) are associated with significantly reduced incidence of infantile spasms. 22903760_Data suggest that different, nonterminating TSC2 mutations can have distinct effects on TSC1-TSC2 function, and therefore, on Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) pathology. 23217510_Genetic investigation of the coding exons of TSC1 and TSC2 revealed a 4 bp deletion at nucleotides 3693-3696 in exon 30 of the TSC2 gene. 23254740_Two novel TSC2 mutations in Chinese patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. 23348097_Our results suggest that XLID CUL4B mutants are defective in promoting TSC2 degradation and positively regulating mTOR signaling in neocortical neurons. 23389244_No differences emerged in mutation distributions and types in precedent studies, excepting low frequency of the TSC2 nonsense mutation 23689538_Our results suggest that tuberin and p27 are aberrantly expressed in malignant breast tissue 23818547_Pim2 directly phosphorylates TSC2 on Ser-1798 and relieves the suppression of TSC2 on mTOR-C1, leading to multiple myeloma cells proliferation. 23846400_An increased frequency of C>G/G>C and C>T/G>A mutations in the coding strand was found in TSC2. 23867796_OPG stimulated proliferation of cells cultured from explanted LAM lungs, and selectively induced migration of lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells identified by the loss of heterozygosity for TSC2. 23878245_Data indicate a nitrosative-stress signaling pathway that engages ATM, LKB1, AMPK and TSC2 tumor suppressors to repress mTORC1 and regulate autophagy. 23878397_Data indicate that sunitinib inhibited TORC1 in endothelial cells in a Tsc1/Tsc2-dependent manner 23947572_Data show growth-inhibitory and proapoptotic effects of simvastatin on TSC2-null lymphangioleiomyomatosis cells compared with atorvastatin. 24075384_Prenatal diagnosis of an intrathoracic lesion with a family history of parental epilepsy should raise a suspicion of fetal cardiac rhabdomyoma and tuberous sclerosis. 24077282_Alpha B-crystallin has an essential role in TSC1/2 complex deficiency-mediated tumorigenesis. 24271014_TSC2 somatic second-hit mutations are associated with angiofibroma development in tuberous sclerosis. 24318044_This work indicates a novel role for this TSC2 gene, which encodes an activator of cell proliferation in response to androgen stimulation. 24398473_Covalent modification of TSC2 by iNOS-derived NO is associated with impaired TSC2/TSC1 dimerization, mTOR pathway activation, and proliferation of human melanoma. 24444419_oxidative stress induces Tnfaip8 l1/Oxi-beta, which results in increased autophagy by its exclusive binding with FBXW5 to stabilize TSC2 24529380_These data suggest that regulation of TSC2 subcellular localization may be a general mechanism to control its activity and place TSC2 in the amino-acid-sensing pathway to TORC1. 24599401_Findings indicate that neuronal Tsc1/2 complex activity is required for the coordinated regulation of autophagy by AMPK. 24606538_The features of alpha-smooth muscle cells of a patient affected by lymphangioleiomyomatosis associated with Tuberous sclerosis complex, named LAM/TSC cells, bearing a TSC2 mutation and an epigenetic defect causing the absence of tuberin, were investigated. 24683199_Two novel gross deletions of TSC2 gene in Malay patients with tuberous sclerosis complex and TSC2/PKD1 contiguous gene deletion syndrome, respectively. 24698169_In children with tuberous sclerosis complex, nonsense mutations in the TSC2 gene had a correlation with autistic behavior. 24748662_TSC2 also functions as a transcription factor. 24794161_study describes 2 cases of genetically proven TCS2, sharing the same genotype; detected a novel, small and in frame deletion/insertion TSC2 mutation on exon 30 (c.3664_3665delinsTT-p.Asp1222Phe) 24917535_TSC2 mutations are associated with a more severe, earlier presenting tuberous sclerosis complex phenotype. 25114899_Studied conditions that increase the sensitivity of cancer cells to MK-2206. and found reduction by salinomycin of Akt and downregulation of pAkt, pGSk3beta, pTSC2, and p4EBP1 by cotreatment with MK-2206. 25185584_This study demonstrates that TSC2-deficient tumor cells are hypersensitive to oxidative stress-dependent cell death, and provide critical proof of concept that TSC2-deficient cells can be therapeutically targeted 25281918_This is the first mutation and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) analyses of TSC2 in Korean Angiomyolipomas that focus on tuberous sclerosis complex. 25355409_A short segment of chromosome 16 encodes the tumor suppressor gene tuberin as well as the protein polycystin 1, which are responsible for tuberous sclerosis complex type 2 and autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease type 1, respectively. 25432535_Multiple mutations in TSC2 during kidney development lead to severe phenotype of multifocal renal cell carcinoma. 25476905_In TSC2-deficient angiomyolipoma patient cells, IRF7 is a pivotal factor in the Rheb/mTOR pathway. 25498131_Compared to patients with TSC1 mutations, individuals with TSC2 mutations had a significantly higher frequency of epilepsy and tended to have a higher frequency of infantile spasms. 25563326_a novel frame shift Tuberous Sclerosis Complex-2 Mutation in three patients with Tuberous sclerosis complex but with different severity of symptoms 25565629_PLK1 protein levels are increased in hamartin and tuberin deficient cells and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis patient-derived specimens, and that this increase is rapamycin-sensitive. 25654764_TSC2/mTORC1 signaling contributes to the maintenance of intestinal epithelium homeostasis by regulating Notch activity. 25724664_Data shows frequent loss of TSC2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCC) and that TSC2-null cell lines were more sensitive to mTOR inhibition by everolimus suggesting that TSC2 loss is a predictive biomarker for the response to everolimus in HCC patients. 25780943_these results demonstrate that TSC2-deficient cells have enhanced choline phospholipid metabolism and reveal a novel function of the TSC proteins in choline lysoglycerophospholipid metabolism 25782670_Results confirm strong association between TSC2 mutation and angiomyolipoma burden, and they indicate that everolimus response occurs regardless of mutation type or location or when no mutation in TSC1 or TSC2 has been identified. 25927202_previously unidentified TSC1 and TSC2 mutations in tuberous sclerosis complex 25972538_pUL38 can activate mTORC1 in both TSC2-dependent and -independent manners. 26252095_A novel frame-shifting mutation c.4258-4261delTCAG in the TSC2 gene is associated with tuberous sclerosis in a Chinese family. 26318033_AKT3 has a role in prostate cancer proliferation through regulation of Akt, B-Raf, and TSC1/TSC2 26393489_Tuberous sclerosis is a syndrome caused by dominant mutations in Tuberin (TSC2),causing Autism spectrum disorder - like behaviors, seizures, intellectual disability and characteristic brain and skin lesions. 26408672_IQ/DQ correlates inversely with predicted levels and/or deleterious biochemical effects of mutant TSC1 or TSC2 protein in tuberous sclerosis complex. 26412398_PAK2 is a direct effector of TSC1-TSC2-RHEB signaling and a new target for rational drug therapy in TSC. 26540169_TSC-related tumors can increase the mutation detection rate, indicate that it is not likely that a third TSC gene exists, and enable provision of genetic counseling to the substantial population of TSC individuals who are currently NMI 26563443_results confirm the consistent finding of TSC2 mutations in LAM samples, and highlight the benefit of laser capture microdissection and in-depth allele analyses for detection, such as NGS 26703369_Our evidence suggests that variants in TSC2 exons 25 or 31 are very unlikely to cause classical TSC, although a role for these exons in tissue/stage specific development cannot be excluded. 26728384_Data show that 10 pathogenic mutations were quickly identified, 7 were located in tuberous sclerosis 1 protein (TSC1) and 3 were observed in tuberous sclerosis 2 protein (TSC2). 26742086_By interfering with TSC-Rheb complex, arginine relieves allosteric inhibition of Rheb by TSC. Arginine cooperates with growth factor signaling which further promotes dissociation of TSC2 from lysosomes and activation of mTORC1. 26831717_Mutations in MTOR, TSC1, or TSC2 were more common in patients who experienced clinical benefit from rapalogs than in those who progressed. 26868506_Lysosomal recruitment of TSC2 is a universal response to stimuli that inactivate |
ENSMUSG00000002496 |
Tsc2 |
628.781281 |
0.4223228980 |
-1.243582 |
0.362033080 |
11.138516 |
0.00084553500019136961299293098193174955667927861213684082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001997454641937358808118085917726602929178625345230102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
417.4340093 |
89.5528302 |
994.3549526 |
153.9852759 |
| ENSG00000103257 |
8140 |
SLC7A5 |
protein_coding |
Q01650 |
FUNCTION: The heterodimer with SLC3A2 functions as sodium-independent, high-affinity transporter that mediates uptake of large neutral amino acids such as phenylalanine, tyrosine, leucine, histidine, methionine, tryptophan, valine, isoleucine and alanine (PubMed:9751058, PubMed:10049700, PubMed:11557028, PubMed:10574970, PubMed:11564694, PubMed:12117417, PubMed:12225859, PubMed:25998567, PubMed:30867591, PubMed:18262359, PubMed:15769744). The heterodimer with SLC3A2 mediates the uptake of L-DOPA (By similarity). Functions as an amino acid exchanger (PubMed:11557028, PubMed:12117417, PubMed:12225859, PubMed:30867591). May play a role in the transport of L-DOPA across the blood-brain barrier (By similarity). May act as the major transporter of tyrosine in fibroblasts (Probable). May mediate blood-to-retina L-leucine transport across the inner blood-retinal barrier (By similarity).Can mediate the transport of thyroid hormones diiodothyronine (T2), triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) across the cell membrane (PubMed:11564694). When associated with LAPTM4B, the heterodimer formed by SLC3A2 and SLC7A5 is recruited to lysosomes to promote leucine uptake into these organelles, and thereby mediates mTORC1 activation (PubMed:25998567). Involved in the uptake of toxic methylmercury (MeHg) when administered as the L-cysteine or D,L-homocysteine complexes (PubMed:12117417). Involved in the cellular activity of small molecular weight nitrosothiols, via the stereoselective transport of L-nitrosocysteine (L-CNSO) across the membrane (PubMed:15769744). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63016, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10049700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10574970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11557028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12117417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12225859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15769744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18262359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25998567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30867591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9751058, ECO:0000305|PubMed:18262359}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of hepatitis C virus/HCV infection, the complex formed by SLC3A2 and SLC7A5/LAT1 plays a role in HCV propagation by facilitating viral entry into host cell and increasing L-leucine uptake-mediated mTORC1 signaling activation, thereby contributing to HCV-mediated pathogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30341327}. |
3D-structure;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Isopeptide bond;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables L-leucine transmembrane transporter activity; L-tryptophan transmembrane transporter activity; and thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in carboxylic acid transport; thyroid hormone transport; and xenobiotic transport. Located in cytosol; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle; and plasma membrane. Is integral component of membrane. Part of amino acid transport complex; apical plasma membrane; and microvillus membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8140; |
amino acid transport complex [GO:1990184]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of apical plasma membrane [GO:0098591]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; antiporter activity [GO:0015297]; aromatic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015173]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; L-leucine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015190]; L-tryptophan transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015196]; neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015175]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015349]; alanine transport [GO:0032328]; amino acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0089718]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; cellular response to L-arginine [GO:1903577]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; isoleucine transport [GO:0015818]; L-histidine transport [GO:1902024]; L-leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:1903801]; L-tryptophan transmembrane transport [GO:1904556]; leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:0098713]; leucine transport [GO:0015820]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; methionine transport [GO:0015821]; negative regulation of autophagy [GO:0010507]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:1905460]; neutral amino acid transport [GO:0015804]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; phenylalanine transport [GO:0015823]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:1905534]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; proline transport [GO:0015824]; response to hyperoxia [GO:0055093]; response to muscle activity [GO:0014850]; thyroid hormone transport [GO:0070327]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; tryptophan transport [GO:0015827]; tyrosine transport [GO:0015828]; valine transport [GO:0015829]; xenobiotic transport [GO:0042908] |
12925876_study indicates the functional interaction between CD98 and CD147 in the regulation of cell fusion 15178563_Increased LAT1 expression can be induced by lipid oxidation products relevant to inflammatory responses in atherogenesis. LAT1 mediates lysophosphatidylcholine-enhanced cytokine production by endothelial cells. 15200428_Differences in L-DOPA handling between SHR and WKY cells may result from over-expression of LAT1 and LAT2 transporters in the former. 15589117_studies demonstrate that the only known SNP in the open reading frame of human LAT1 has no effect on the kinetics of large neutral amino acid transport via this carrier 15769744_identify LAT1 and LAT2 as members of system L that mediate transmembrane movement of l-CSNO 15900591_In vivo efforts focusing on LAT1/CD98 as a potential therapeutic target in liver cells. 16175382_LAT1 expression may increase with the upregulation of metabolic activity and cell proliferation in high-grade atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. 16496379_Findings suggest that LAT1 could be one of the molecular targets in glioma therapy. 17558306_Genetic variation in LAT1 and LAT2 does not appear to be a major cause of inter-individual variability in pharmacokinetics and of adverse reactions to melphalan. 17558306_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17622555_expression of LAT1 protein and mRNA in 124 cases of transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract was examined; detection of the active form LAT1 protein appears to be of value in informing the risk of progression 18095110_The expression of LAT1 was always higher in infiltrating glioma cells than in cells located in the center of the tumor. 18253116_Overexpression of L-type amino acid transporter 1 is associated with nonsmall cell lung cancer 18262359_This study demonstrated that LAT1 is involved in 90% of total uptake of tyrosine and also around 51% of alanine. Not more than 10% can be accounted for by LAT2, LAT3 and LAT4 isoforms. 18294274_Comparative immunohistochemical analyses of normal human tissues with anti-CD98 hc and anti-LAT1 revealed LAT1 to be an excellent molecular target for antibody therapy, possibly even superior to CD98 hc. 18382329_LAT1 may play an important role in enhancing the rates of tumor cell proliferation and growth in vivo. 18440724_Expression of LAT1 tended to increase from low-grade to high-grade neuroendocrine tumors. 18813831_Inhibition of system L (LAT1/CD98hc) reduces the growth of cultured human breast cancer cells. 19018776_LAT1 expression in primary and metastatic neoplasms is reported. 19068093_Elevated expression of CD98 is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. 19121087_elevated LAT1 expression in prostate cancers is a novel independent biomarker of high-grade malignancy 19171406_over expression of Lat1 is a pathological factor to predict the prognosis in patients with resectable stage I pulmonary adenocarcinoma 19184136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19347882_LAT1 is frequently expressed in thymic carcinomas but is absent in thymomas 19430419_the percentage of lung carcinoma patients remaining unclassifiable by TTF-1/TP63 was twice that of the five-antibody (TRIM29, CEACAM5, SLC7A5, MUC1, and CK5/6) test 19559497_higher mRNA levels in non-small-cell lung carcinomas compared to normal lung tissues 19635099_Multivariate analysis confirmed that positive expression of LAT1 was an independent factor for predicting a poor prognosis in surgically resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer. 19777189_High LAT1 expression is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer with lymph node metastases. 20091333_High expression of LAT1 and increased L-methyl-11C-methionine uptake is associated with high-grade gliomas. 20374249_Host protein CD98 contributes to protection against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-mediated cytotoxicity by interacion with bacterial sepZ protein. 20375792_upregulation of LAT1 is associated with ovarian cancer. 20510678_LAT1 increased expression in human ovarian cancer cell lines makes it a possible target for combination therapy with anti-proliferative aminopeptidase inhibitors. 20601542_LAT1 may have a critical and complex role in regulating human leiomyoma cell growth. 20680301_LAT1 mRNA was detectable only in fresh-frozen tissues of TSC, and it was upregulated in the cortical tuber lesion 21055621_LAT1 expression is a stronger prognostic factor than (18)F-FAMT uptake in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer 21371427_All these results indicate essential roles of LAT1 in the cell proliferation and occurrence of malignant phenotypes. 21439283_Data shwo that SLC7A5 is a direct target of miR-126. 21486766_Compared with the adult cerebral cortex, mRNAs encoding OATP1A2, OATP1C1, OATP3A1 variant 2, OATP4A1, LAT2 and CD98 were reduced in fetal cortex at different gestational ages, whilst mRNAs encoding MCT8, MCT10, OATP3A1 variant 1 and LAT1 were similar. 21501294_LAT 1 expression may be linked with cell proliferation and prognosis of gastric carcinomas. 21530999_LAT1 expression decreases because of human papillomavirus infection as reflected by p16 overexpression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, whereas LAT1 expression in invasive carcinoma is associated with acquired malignant potential 21798283_Variations in the ability of LAT1/DMT1/MTF1/MT1a to process and transport Hg may not play a significant role in the etiology of autism. 22007000_Data show that signaling via the androgen receptor and ATF4 pathways regulates expression of the amino acid transporters LAT1 and LAT3, thereby coordinating their increased expression in prostate cancer cells. 22077314_study revealed that LAT1 and CD98 expression are positively correlated with breast cancer proliferation and negatively correlated with ER and PgR status; show that LAT1 and CD98 expression are prognostic factors in triple negative breast cancer 22110199_High LAT1 expression is associated with drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. 22199264_analysis of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma 22736142_The LAT1 promoter has a canonical c-Myc binding sequence and overexpression of c-Myc increased LAT1 promoter activity. 22813728_LAT1 aberrant overexpression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas predicts poor prognosis, independent of Ki-67 LI, and offers a potential target for future anticancer therapy with its inhibitors. 23103253_HIF-2alpha/mTORC1/SLC7A5 pathway mediates proliferation and tumor promoting properties of HIF-2alpha. 23221699_L-theanine is transported mostly via the system L transport pathway and its isoforms 23270998_This study demonstrates that LAT1, primarily responsible for the uptake of large neutral amino acids, is functionally active in PC-3 cells. 23516127_Studied the clinicopathological significance of LAT1 expression in adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC). 23696029_LAT1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and could serve as a potential prognostic marker. 23809372_LAT-1 may function as an oncogene in gastric cancer. 23824658_LAT1 was expressed in gonad tissues and several kinds of cells having special functions, as well as being discovered to be an aspect of oncofetal protein. 23912240_The high yield expression of the human LAT1 transporter has been obtained for the first time using E. coli. The hLAT1 cDNA was amplified from HEK293 cells, cloned in pH6EX3 vector and expressed in E.coli. 24131658_LAT1 expression was a significant independent predictor of biliary tract cancer survival by multivariate analysis. 24168110_Increased expression of system large amino acid transporter (LAT)-1 mRNA is associated with invasive potential and unfavorable prognosis of human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 24606907_Polymorphisms of the LAT1 gene, there was no evidence for either allelic and/or genotypic association with the risk of NSCL/P in the Polish population. 24694899_L-type amino acid transporter 1 expression increases in well-differentiated but decreases in poorly differentiated endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma and shows an inverse correlation with p53 expression. 24704384_Seven SNPs in SLC7A5 and 20 in SLC7A8 were genotyped. Multiple analyses indicated that 1 SNP in the first intron of SLC7A5, rs4240803, was significantly associated with TPN use. 24726839_LAT1 and its associated protein, 4F2hc, are up-regulated and miR-7 expression was regulated by LAT1. 24890221_aberrant overexpression of LAT1 in bile duct adenocarcinoma predicts poor prognosis, suggesting that LAT1 may be a potential target of anticancer therapy. 25089027_CD147 and CD98 might play important roles in cyclophilin-induced cell migration. 25220100_The study shows that the expression of LAT1 on myeloma cells is significantly associated with high proliferative activity as well as poor prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. 25385314_data, therefore, suggest that FET is trapped within cells due to the asymmetry of its intra- and extracellular recognition by LAT1. 25597310_Metabolic changes accompanying activation of T cells must occur simultaneously with the reorganization of LAT1 and other transporters that are capable of providing sufficient nutrients to the cell. (Review) 25701737_CAP-D3 down-regulates transcription of genes that encode amino acid transporters (SLC7A5 and SLC3A2) to promote bacterial autophagy by colon epithelial cells. 25835180_Independently of Gleason score, aberrant overexpression of LAT1 in prostatic adenocarcinoma could predict LP under EM. Although prostate biopsy samples are small, LAT1 may be a novel prognostic biomarker of LP. 25908107_These results suggest that LAT1 expression is associated with disease progression in gastric carcinoma. 25979827_shRNA-mediated knockdown of Lat1 results in tumor growth inhibition and points to Lat1 as a potential therapeutic target. 25998567_LAPTM4b recruits LAT1-4F2hc to lysosomes, leading to uptake of leucine into lysosomes. 26050671_LAT1 and LAT2 are present and functional in the syncytiotrophoblast MVM, whereas LAT2 is also expressed in the BM and in the fetal capillary endothelium. 26054677_miR-126 plays a pivotal role in GC (gastric cancer) suppressing the process of GC cell, and this function is at least partly taken to implement by miR-126s's post-transcriptional effect on LAT-1. 26237765_LAT1 can serve as a significant prognostic factor to predict a poor outcome and it may therefore play an important role in the aggressiveness of cutaneous melanoma. 26256001_LAT1 is the transport competent unit of the LAT1/CD98 heterodimeric amino acid transporter. 26437640_CD98 promotes cell spreading and tumorigenicity by triggering integrin clustering and enhancing cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix. 26608079_Propose regulation of placental SNAT2/LAT1 ubiquitination by mTORC1 and Nedd4-2. 26621329_exposure to diesel exhaust particle extract induces functional overexpression of the amino acid transporter LAT1/CD98hc in lung cells 26657287_High SLC7A5 expression is associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. 26724922_LAT1 is not a leucine sensor. 26850337_the discovery of CD98 protein on the cell surface of the majority of malignant melanomas, is reported. 26944194_Proliferation of breast cancer cells is dependent on the expression of both LAT1 and AHR. 27224648_LAT1 and LAT2 were overexpressed in both pheochromocytoma and medullary thyroid carcinoma by comparison with normal tissues. 27276226_LAT1 overexpression was common in Brain Metastases and was specific for Brain Metastases as compared to healthy brain. These results could explain the specific Brain Metastases uptake on PET-AA. 27550420_This study shows the utility of (18)F-FBPA as a tumor-specific probe of LAT1 with low accumulation in the inflammatory lesions. 27566573_LAT1-NAD+-SIRT1 signaling is activated in tumor tissues of patients with non-small cell lung cancer; NAD+ synthesis regulates the SIRT1-FOXO1 apoptotic pathway in response to NQO1 27567475_Authors demonstrate that LAT1 is a critical transporter for human thymic carcinoma cells. LAT1 was strongly expressed in human thymic carcinoma tissues. 27834933_Expression levels of CD98 and beta1-integrin-A (the activated form of beta1-integrin) were significantly increased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues relative to those of normal liver tissues. 27846244_he findings in this study indicate a regulation relationship between CRKL and SLC7A5, and provide useful evidence for gastric cancer therapeutic strategies. 27912058_Study shows that the solute carrier transporter 7a5 (SLC7A5), a large neutral amino acid transporter localized at the blood brain barrier (BBB), has an essential role in maintaining normal levels of brain branched-chain amino acids; also identified several patients with autistic traits and motor delay carrying deleterious homozygous mutations in the SLC7A5 gene. 28052681_The expression level of LAT1 was not significantly correlated with prognosis in patients with cutaneous angiosarcoma. 28190014_The LAT1 isoform was confirmed as the major tyrosine transporter in patients with schizophrenia. However, the kinetic parameters (maximal transport capacity, affinity of the binding sites, and diffusion constant of tyrosine transport through the LAT1 isoform) did not differ between patients with schizophrenia and controls. 28320871_These results demonstrate a novel fundamental role of LAT1 to support the protein expression of 4F2hc via a chaperone-like function in chorionic trophoblasts. 28347255_Our study demonstrates that suppression of l-type amino acid transporter-1 activity using JPH203 might be used as a new therapeutic strategy for cholangiocarcinoma treatment. 28626091_SLC7A5 gene plays a role in promoting tumor development, which is regulated by the TGF-beta1 signaling pathway. 28739699_MTA1 expression was positively correlated with LAT1 (p=0.013) and CD34 (p=0.034) expression, but not with Ki-67 (p=0.078). MTA1 shows promise as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in esophageal cancer, and we anticipate that the gene will also prove to be a good therapeutic target. 28784848_this study shows that IL-2-induced expression of CD98 is a prerequisite for NKG2D-mediated activation of NK cells 28937983_Study showed that a positive [18F] FDOPA uptake in PET was associated with a minimal threshold of LAT1 expression, but did not find a linear correlation between intensity of [18F] FDOPA uptake and level of LAT1 expression. 29149426_LAT1 as an independent prognostic marker is a potential molecular targeting gene to reduce chemoresistance and tumor growth in patients with PDAC, supported by our in vitro study 29198077_L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) is overexpressed in the synovium of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Suppressing the LAT1 genes by using RNA interference and the LAT inhibitor, BCH reduces the phosphorylation of mTOR and its downstream target 4EBP1, radiolabeled leucine uptake, and migration of RA FLS. Treatment of cells with Interleukin-17 stimulates the expression of LAT1. 29277611_Thus, our results indicated that lncRNA-PVT1-5 may function as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-126 to promote cell proliferation by regulating the miR-126/SLC7A5 pathway, suggesting that lncRNA-PVT1-5 plays a crucial role in lung cancer progression and lncRNA-PVT1-5/miR-126/SLC7A5 regulatory network may shed light on tumorigenesis in lung cancer. 29278358_LAT1 is located close to the plasma membrane in skeletal muscle fibres and in close proximity to the microvasculature. Note a greater immunoreactivity of this protein in the sarcoplasm of type II fibres, potentially supporting the greater anabolic potential in these fibres. 29326164_Data suggest that amino acid uptake via ASCT2/SLC1A5 is required for cell proliferation/tumor growth independently of LAT1/SLC7A5; in part, these studies were conducted in lung and colon adenocarcinoma cell lines and involved gene knockout techniques. (ASCT2/SLC1A5 = solute carrier family-1 member-5; LAT1/SLC7A5 = solute carrier family-7 member-5) 29367342_High SLC7A5 expression is associated with gastric cancer growth and metastasis. 29422900_the expression of SLC7A5 on circulating monocytes from RA patients positively correlated with clinical parameters, suggesting that SLC7A5-mediated AA influx is related to inflammatory conditions. 29566741_SLC7A5 appears to play a role in the aggressive highly proliferative ER+ subtype driven by MYC and could act as a potential therapeutic target. Functional assessment is necessary to reveal the specific role played by this transporter in the ER+ highly proliferative subclass and HER2+ subclass of Breast cancer 30029480_These data collectively establish that in an in vitro context, human epithelial and mesenchymal hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines adapt to ASCT2 or LAT1 knockout. 30103560_review the upstream regulators of LAT1 and the downstream effects caused by the overexpression of LAT1 in cancer cells. 30241549_These preclinical results show that LAT1 inhibition is a novel therapeutic approach in the context of thyroid cancers, and more interestingly in untreatable thyroid cancers. 30300664_LAT1 and 4F2hc were identified as significant independent markers for predicting a worse prognosis in patients with pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma 30480742_The results of the present study demonstrated that SLC7A5 might be the potential candidate gene associated with central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC), indicating a previously unidentified molecular mechanism of CSC. 30528230_Dysfunction of MINCR, miR-126 and SLC7A5 predicted poor prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 30591441_rs4240803 impacted the expression of SLC7A5, thus contributing to the clinical response of multiple myeloma patients to melphalan therapy. 30591453_JPH203 treatment significantly reduced the viability of all gastric and colon cancer cells. While LAT1 expression levels and inhibitory potencies of JPH203 on LAT1 functions were comparable among the cells, all the esophageal cells were resistant to JPH203 30670494_We found that CD98hc-associated signaling mechanisms play a central role in the regulation of HNSCC radioresistance and may be a promising target for tumor radiosensitization. 30784173_Down-regulation of LAT1 arrests the growth of medulloblastoma cancer cells. 30867591_cryo-electron microscopy structures of human LAT1-4F2hc alone and in complex with the inhibitor 2-amino-2-norbornanecarboxylic acid at resolutions of 3.3 A and 3.5 A, respectively 31092450_LAT1 was closely associated with the expression of 4F2hc and phosphorylation of the mTOR pathway. LAT1 is a significant molecular marker used to predict prognosis after surgical resection of colorectal cancer patients. 31160781_This study reports the cryo-EM structure of the human LAT1-CD98hc heterodimer at 3.3-A resolution. 31282475_SLC7A5 and SLC3A2 structures are analyzed together with lower resolution cryo-EM structure, and multibody 3D auto-refinement against single-particle cryo-EM data was used to characterize the dynamics of the interaction of CD98hc and LAT1. 31605740_Deletion or inhibition of LAT1 efficiently controls IL-23- and IL-1beta-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mTOR activation independent of T-cell receptor signaling. 31636293_Rigorous sampling of docking poses unveils binding hypothesis for the halogenated ligands of L-type Amino acid Transporter 1 (LAT1). 31701662_Abnormalities in the genes that encode Large Amino Acid Transporters increase the risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder. 31728037_Ubiquitylation and endocytosis of the human LAT1/SLC7A5 amino acid transporter. 31748583_Characterization of the expression of LAT1 as a prognostic indicator and a therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma. 31963507_Glioblastoma Exhibits Inter-Individual Heterogeneity of TSPO and LAT1 Expression in Neoplastic and Parenchymal Cells. 31992742_LAT1 significantly contributed to bladder cancer progression. Targeting LAT1 by JPH203 may represent a novel therapeutic option in bladder cancer treatment. 32093034_Co-Expression Effect of SLC7A5/SLC3A2 to Predict Response to Endocrine Therapy in Oestrogen-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. 32144539_Correlation of high LAT1 expression with the prognosis of endometrioid carcinoma of the uterine corpus. 32240722_Regulation of Melanogenesis by the Amino Acid Transporter SLC7A5. 32359697_Positive correlation of expression of L-type amino-acid transporter 1 with colorectal tumor progression and prognosis: Higher expression in sporadic colorectal tumors compared with ulcerative colitis-associated neoplasia. 32405891_Hemocompatible LAT1-inhibitor can induce apoptosis in cancer cells without affecting brain amino acid homeostasis. 32410110_Prognostic Value of L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) in Various Cancers: A Meta-Analysis. 32458655_LAT1 (SLC7A5) Overexpression in Negative Her2 Group of Breast Cancer: A Potential Therapy Target. 32469987_Prognostic value of LAT-1 status in solid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. 32821949_The amino acid transporter Slc7a5 regulates the mTOR pathway and is required for granule cell development. 32867828_Intervening upregulated SLC7A5 could mitigate inflammatory mediator by mTOR-P70S6K signal in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. 33001560_Small molecule inhibitors provide insights into the relevance of LAT1 and LAT2 in materno-foetal amino acid transport. 33066406_The Heavy Chain 4F2hc Modulates the Substrate Affinity and Specificity of the Light Chains LAT1 and LAT2. 33164746_Control of Slc7a5 sensitivity by the voltage-sensing domain of Kv1 channels. 33256804_Amino acid transporter LAT1 in tumor-associated vascular endothelium promotes angiogenesis by regulating cell proliferation and VEGF-A-dependent mTORC1 activation. 33436954_L-type amino acid transporter 1 is associated with chemoresistance in breast cancer via the promotion of amino acid metabolism. 33657992_Fetal sex modulates placental microRNA expression, potential microRNA-mRNA interactions, and levels of amino acid transporter expression and substrates: INFAT study subpopulation analysis of n-3 LCPUFA intervention during pregnancy and associations with offspring body composition. 34091991_Amino acid transporters as emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. 34102206_Circular RNA circ-FAM158A promotes retinoblastoma progression by regulating miR-138-5p/SLC7A5 axis. 34182526_Expression of LAT1 and 4F2hc in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. 34201429_The Adipose Tissue-Derived Secretome (ADS) in Obesity Uniquely Induces L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 (LAT1) and mTOR Signaling in Estrogen-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. 34681614_L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1 Regulates Cancer Stemness and the Expression of Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1 in Lung Cancer Cells. 34737339_Expression of L-type amino acid transporter 1 is a poor prognostic factor for Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. 34759371_CD98-induced CD147 signaling stabilizes the Foxp3 protein to maintain tissue homeostasis. 34792178_SLC7A5 is linked to increased expression of genes related to proliferation and hypoxia in estrogenreceptorpositive breast cancer. 34836160_LAT1 and SNAT2 Protein Expression and Membrane Localization of LAT1 Are Not Acutely Altered by Dietary Amino Acids or Resistance Exercise Nor Positively Associated with Leucine or Phenylalanine Incorporation in Human Skeletal Muscle. 34856000_Increased expression of LAT1 in basal cell carcinoma: implications for tumour cell survival. 34942513_Expression profile of CD98 heavy chain and L-type amino acid transporter 1 and its prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. 35035814_circRNA LDLRAD3 Enhances the Malignant Behaviors of NSCLC Cells via the miR-20a-5p-SLC7A5 Axis Activating the mTORC1 Signaling Pathway. 35121373_First-in-human assessment of the novel LAT1 targeting PET probe (18)F-FIMP. 35176108_Management precautions for risk of obesity are necessary among infants with PKU carrying the rs113883650 variant of the LAT1 gene: A cross-sectional study. 35177712_Association of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) with the immune system and prognosis in invasive breast cancer. 35269556_Overexpression of miR-375 and L-type Amino Acid Transporter 1 in Pheochromocytoma and Their Molecular and Functional Implications. 35301401_Vitamin D stimulates placental L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) in preeclampsia. 35346864_SLC7A5 expression is up-regulated in peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus patients, associating with renal damage. 35848618_The role of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (Slc7a5) during in vitro myogenesis. 36192404_Co-expression effect of LLGL2 and SLC7A5 to predict prognosis in ERalpha-positive breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000040010 |
Slc7a5 |
1097.743515 |
4.2012679061 |
2.070825 |
0.054405496 |
1522.514170 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1808.0616255 |
60.2058752 |
433.7415914 |
12.2333333 |
| ENSG00000103260 |
79006 |
METRN |
protein_coding |
Q9UJH8 |
FUNCTION: Involved in both glial cell differentiation and axonal network formation during neurogenesis. Promotes astrocyte differentiation and transforms cerebellar astrocytes into radial glia. Also induces axonal extension in small and intermediate neurons of sensory ganglia by activating nearby satellite glia (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Meteorin regulates glial cell differentiation and promotes the formation of axonal networks during neurogenesis (Nishino et al., 2004 [PubMed 15085178]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:79006; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; glial cell differentiation [GO:0010001]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; radial glial cell differentiation [GO:0060019] |
15085178_Meteorin plays important roles in both glial cell differentiation and axonal network formation during neurogenesis. 26121675_The joint measurements of circulating METRN levels in the first trimester and systolic blood pressure and weight in the second trimester significantly increase the probabilities of predicting preeclampsia. 31859449_Over expression of METRN predicts poor clinical prognosis in colorectal cancer. 33867829_Identification of low-dose radiation-induced exosomal circ-METRN and miR-4709-3p/GRB14/PDGFRalpha pathway as a key regulatory mechanism in Glioblastoma progression and radioresistance: Functional validation and clinical theranostic significance. |
ENSMUSG00000002274 |
Metrn |
35.683393 |
0.4640714454 |
-1.107581 |
0.284750255 |
15.201589 |
0.00009662208783200959365516230503700967346958350390195846557617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000266269980657293076596603409456065492122434079647064208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.9989509 |
5.3498671 |
52.3703841 |
7.7764910 |
| ENSG00000103264 |
79791 |
FBXO31 |
protein_coding |
Q5XUX0 |
FUNCTION: Component of some SCF (SKP1-cullin-F-box) protein ligase complex that plays a central role in G1 arrest following DNA damage. Specifically recognizes phosphorylated cyclin-D1 (CCND1), promoting its ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome, resulting in G1 arrest. May act as a tumor suppressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16357137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19412162}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;DNA damage;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene is a member of the F-box family. Members are classified into three classes according to the substrate interaction domain, FBW for WD40 repeats, FBL for leucing-rich repeats, and FBXO for other domains. This protein, classified into the last category because of the lack of a recognizable substrate binding domain, has been proposed to be a component of the SCF ubiquitination complex. It is thought to bind and recruit substrate for ubiquitination and degradation. This protein may have a role in regulating the cell cycle as well as dendrite growth and neuronal migration. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:79791; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; cyclin binding [GO:0030332]; anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process [GO:0031145]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0031571]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; positive regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001224]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] |
16357137_Loss of FBXO31 is associated with breast cancer 19412162_ectopic expression of FBXO31 acts through a proteasome-directed pathway to mediate the degradation of cyclin D1, an important regulator of progression from G1 to S phase, resulting in arrest in G1 21537837_CGH array indicated that cases having cyclin D1 with increased copy number were significantly associated with elevated FBXO31 expression levels (P |
ENSMUSG00000052934 |
Fbxo31 |
172.442939 |
0.3768014514 |
-1.408124 |
0.479992902 |
8.219876 |
0.00414340352477424525567961666183691704645752906799316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008613610707840543834201696427044225856661796569824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
109.8374645 |
33.6045348 |
293.3731707 |
64.7422525 |
| ENSG00000103269 |
9028 |
RHBDL1 |
protein_coding |
O75783 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in regulated intramembrane proteolysis and the subsequent release of functional polypeptides from their membrane anchors. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Serine protease;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein similar to Rhomboid in Drosophila which is involved in signalling in the Spitz/epidermal growth factor receptor/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. The Rhomboid family of proteins consists of intramembrane serine proteases containing several transmembrane domains. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:9028; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
|
ENSMUSG00000025735 |
Rhbdl1 |
16.187752 |
0.2787057089 |
-1.843186 |
0.406979953 |
21.786848 |
0.00000304681486394570425391050555452565617997606750577688217163085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010176733965113962117983101296481152076012222096323966979980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1212353 |
1.9079141 |
22.1881113 |
4.2738965 |
| ENSG00000103313 |
4210 |
MEFV |
protein_coding |
O15553 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the regulation of innate immunity and the inflammatory response in response to IFNG/IFN-gamma (PubMed:10807793, PubMed:11468188, PubMed:17964261, PubMed:18577712, PubMed:19109554, PubMed:19584923, PubMed:16037825, PubMed:27030597, PubMed:28835462, PubMed:16785446, PubMed:17431422, PubMed:26347139). Organizes autophagic machinery by serving as a platform for the assembly of ULK1, Beclin 1/BECN1, ATG16L1, and ATG8 family members and recognizes specific autophagy targets, thus coordinating target recognition with assembly of the autophagic apparatus and initiation of autophagy (PubMed:16785446, PubMed:17431422, PubMed:26347139). Acts as an autophagy receptor for the degradation of several inflammasome components, including CASP1, NLRP1 and NLRP3, hence preventing excessive IL1B- and IL18-mediated inflammation (PubMed:16785446, PubMed:17431422, PubMed:26347139). However, it can also have a positive effect in the inflammatory pathway, acting as an innate immune sensor that triggers PYCARD/ASC specks formation, caspase-1 activation, and IL1B and IL18 production (PubMed:16037825, PubMed:27030597, PubMed:28835462). Together with AIM2, also acts as a mediator of pyroptosis, necroptosis and apoptosis (PANoptosis), an integral part of host defense against pathogens, in response to bacterial infection (By similarity). It is required for PSTPIP1-induced PYCARD/ASC oligomerization and inflammasome formation (PubMed:10807793, PubMed:11468188, PubMed:17964261, PubMed:18577712, PubMed:19109554, PubMed:19584923). Recruits PSTPIP1 to inflammasomes, and is required for PSTPIP1 oligomerization (PubMed:10807793, PubMed:11468188, PubMed:17964261, PubMed:18577712, PubMed:19109554, PubMed:19584923). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JJ26, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10807793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11468188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16037825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16785446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17431422, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17964261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18577712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19109554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19584923, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26347139, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27030597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28835462}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Amyloidosis;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein, also known as pyrin or marenostrin, that is an important modulator of innate immunity. Mutations in this gene are associated with Mediterranean fever, a hereditary periodic fever syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4210; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; inflammasome complex [GO:0061702]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032691]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; negative regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha production [GO:0071641]; negative regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:1900226]; pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002221]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:2001056]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; pyroptosome complex assembly [GO:1904270]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341] |
11139244_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11175300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11464248_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11484206_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11588211_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11781702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12077709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12105243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12105243_mutational spectrum in the genes in patients suffering from AA amyloidosis and recurrent inflammatory attacks 12124996_The effects of I591T mutation imply possibly a mild mutation, benign polymorphism, or a variant influenced by another modifier. 12180071_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12384939_MEFV message levels are related to both the genotype and the phenotype, and suggest that the pathophysiology of FMF relies on a quantitative defect of MEFV mRNA expression. 12401847_In phenotype II amyloidosis patients, the distribution of the four common MEFV mutations was not significantly different from that found in all FMF patients with typical symptoms who do or do not develop amyloidosis. 12401847_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12461684_penetrance of paired recognised pathogenic MEFV mutations may frequently be incomplete 12615073_there is a cryopyrin signaling pathway activated through the induced proximity of ASC, which is negatively regulated by pyrin 12687559_Disease severity and the development of amyloidosis in failial Mediterranean Fever are differentially affected by genetic variations within and outside the MEFV gene. 12687559_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12700594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12762136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12905488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12929299_In 412 FMF patients genotyped for MEFV mutations, M694V/M694V was the most common genotype (27%), followed by M694V/V726A (16%). The full genotype could be assessed in 57% of the patients, and one disease-causing mutation in an additional 26%. 12929299_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12955725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12966608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14578967_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14595024_Pyrin binds the PSTPIP1/CD2BP1 protein 14615741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14636645_S1791 was in compound heterozygosity with MEFV mutation M694V 14727057_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14727457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14985395_cellular location of mutant isoforms, in the presence or absence of ASC protein 15018633_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15071491_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15122067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15146467_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15458961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15643295_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15667491_MEFV mutations are not associated with Crohn Disease susceptibility, yet the presence of these mutations appears to be associated with a stricturing disease pattern and extraintestinal disease manifestations of Crohn Disease. 15667491_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15674370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15717684_E148Q mutation is significantly frequent in familial Mediterranean fever 15717684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15724392_In Egyptian familial Mediterranean fever patients, the M694V mutation was detected in 20 patients (100%) and V726A mutation in 17 patients (85%). 15805719_FMF is caused by mutations in the MEFV gene that encodes pyrin/marenostrin. 15903027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15903027_The occurrence of frequent MEFV mutations in BD patients suggests that the MEFV gene is involved in the pathogenesis of Behcet's disease. 15942916_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15958759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16037825_data suggest that both pyrin and cryopyrin are capable of assembling independent inflammasome complexes with ASC and procaspase-1, and activating caspase-1 via ASC oligomerization 16118480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16225401_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16234278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16245224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16245224_Our results indicate a relationship between some HLA-DR/DQ alleles and MEFV mutations in Mediterranean fever patients. 16255051_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16378925_MEFV protein mutations are associated with Familial Mediterranean fever 16378925_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16387839_Carrying the proinflammatory M694V pyrin allele increases the risk for myocardial infarction. Conversely, the wild-type pyrin genotype leads to longevity in a modern environment with reduced pathogen load and improved infection control. 16387839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16439335_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16523434_The gene coding the disease (MEFV) is identified on the 16th chromosome. The most common MEFV mutations are M694V, M680I, V726A and M694I located on exon 10 and E148Q located on exon 2. 16523438_MEFV protein mutations are associated with Familial Mediterranean fever 16614989_MEFV gene mutation show correlation between ulcertive colitis and familial mediterranean fever gene alteration. 16614989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16627024_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16627024_The severity of the disease and development of amyloidosis seem to have an association with M694V, the most common mutation in Syrian FMF patients. 16707534_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16721494_MEFV mutations may act as a genetic susceptibility factor for vasculitides in familial mediterranean fever patients. 16730661_A putative novel MEFV missense mutation, S702C, was localized on the constructed 3-D model. 16785446_The C-terminal B30.2 domain of pyrin is necessary and sufficient for the interaction with caspase-1 to modulate IL-1beta production. 16907704_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17067442_one MEFV mutation may indeed be conferring a heightened inflammation as suggested by the increased frequency in inflammatory symptoms; the carrier status for MEFV mutations seem to be unique, in that they cause an alteration in the state of 'health'. 17067447_in Ethiopian Jews in Israel, comon polymorphism in MEFV locus was found and a relatively high rate of mutation E148Q was detected 17090974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17102945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17102945_Though the effects of the MEFV genotypes seem clear, there are definitely other modifying factors or genes such as MICA on the development of amyloidosis and on the course of the disease 17195238_Reduced expression of the MEFV gene is associated with inflammation and that it may be one of the pathogenic mechanisms of the attacks of inflammation in familial Mediterranean fever patients. 17276496_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17276496_The profile of the MEFV gene mutations in the Tunisian population is concordant with other Arab populations but with some differences. 17454935_MEFV appears to be a susceptibility and modifier gene in Behcet's disease. 17454935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17469185_Country of recruitment, rather than MEFV genotype, is the key risk factor for renal amyloidosis in familial Mediterranean fever. 17489852_spectrum of MEFV alterations in familial Mediterranean fever patients and healthy individuals in Greece 17520284_The onset of UC in infants should prompt a search for MEFV mutations as this association may influence the management of the disease. 17566872_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17566872_spectrum of the MEFV mutations among our sampled Lebanese Familial Mediterranean Fever patients shows the high heterogeneity at the allelic level when compared to Arab and non-Arab populations 17594097_A novel mutation of the MEFV gene in a Greek family related to a non-classical, variably expressed FMF phenotype is reported. 17665427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17665427_This study shows a high prevalence of mutations of the MEFV gene in patients with anti-citrullinated protein antibody-negative palindromic rheumatism. 17696266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17696266_critically ill patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis have increased pyrin mutations, and patients with SIRS and sepsis carrying the pyrin mutation seem to be susceptible for a severe disease course 17697637_A review of familial Mediterranean fever caused by pyrin mutations. 17710881_familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) heterozygote mutation and nail-patella syndrome (NPS) in 3 members of a family with no pathologic mutation in the LMX1B gene 17711558_Familial Mediterranean Fever in Lebanon: founder effects for different MEFV mutations. 17711558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17889261_intermittent hydroarthrosis may be autoinflammatory diorder associated with MEFV mutation 17938136_study found Iranian Jews with familial Mediterranean fever have a unique spectrum of mutations including a newly described mutation, G632S, with a non-typical phenotype 17964261_PSTPIP1 mutants require pyrin to induce formation of ASC pyroptosome, a molecular platform that recruits and activates caspase-1. 18000697_mutation R761H should be included in the mutation scanning analysis researches or considered if the patient has M694V/? mutation especially in Turkish Mediterranean fever patients 18006045_Common Mediterranean mutations are frequent in the Azeri Turkish FMF patients but with some differences in the frequency of individual mutations. 18006045_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18035151_study confirms that alterations in the MEFV gene are important susceptibility factors for the development of posyarteritis nodosa 18061974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18061974_in Turkish Mediterranean Fever patients and their families, frequency of carriers was 27%, and the M694V/M694V genotype was more common in patients with amyloidosis 18097735_The allele frequencies of disease-causing mutations of MEFV(Mediterranean fever), even M694I, were C), and V726A, accounted for 48.4, 16.5, 13.5, and 9.7%, respectively. 21819621_The relation between reduced MEFV expression level and Familial Mediterranean Fever was confirmed. 21833519_Letter/Case Report: describe clinical response to thalidomide and colchicine in two siblings with Behcet's disease carrying a single mutated MEFV allele. 21901355_Report no significant relationship between the MEFV mutations in the Behcet's disease group and clinical findings. 22019805_study describes the MEFV mutational spectrum and distribution in the Algerian population; it shows that p.M694I is the most common MEFV mutation in Algerians 22037353_Our findings confirmed that homozygous M694V is associated with amyloidosis in the Turkish population as well similar to Armenia, Israel, and Arabian countries. 22207183_The rate of MEFV mutation among male and female patients were 56.78 and 48.88%, respectively. 22281876_Mutation in MEFV R717H and mutations in TNFRSF1A IVS2-17_18del2bpCT and IVS3+30:G-->A are novel in Hispanic Chilean patients with hereditary periodic fever syndrome. 22337722_The MEFV gene appears to be another immunologically relevant gene locus which contributes to multiple sclerosis susceptibility. 22351163_high frequency of inherited variants in the MEFV gene in patients with MDS and AML. 22368275_Human pyrin is required to detect intracellular Burkholderia cenocepacia leading to IL-1beta processing and release. 22451026_The prevalence of the two allele-MEFV mutations in patients with Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP) was found higher than that of the general population. 22453916_This is a review, which summarizes the current state of knowledge of the relationship between inherited variants in the MEFV gene and hematologic neoplasms. [review] 22467954_Data showed prevalence of familial Mediterranian fever gene mutations in Japanese people. 22532615_MEFV mutation carriage appears to modify the systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease phenotype in that it contributes to an excess of inflammatory manifestations. 22580583_This clinical observation supports recent findings contrasting the notion of periodic fever being a pure autosomal recessive disorder associated with rec |
ENSMUSG00000022534 |
Mefv |
52.880454 |
0.2680375289 |
-1.899493 |
0.228816996 |
73.080764 |
0.00000000000000001244515805678700230236362336887536193258116269108127030507127130931621650233864784240722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000098917896024865997415164491130338778174261452134745364883627871677163057029247283935546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.2969762 |
3.5735159 |
87.5231663 |
7.9798661 |
| ENSG00000103335 |
9780 |
PIEZO1 |
protein_coding |
Q92508 |
FUNCTION: Pore-forming subunit of a mechanosensitive non-specific cation channel (PubMed:23479567, PubMed:23695678). Generates currents characterized by a linear current-voltage relationship that are sensitive to ruthenium red and gadolinium. Plays a key role in epithelial cell adhesion by maintaining integrin activation through R-Ras recruitment to the ER, most probably in its activated state, and subsequent stimulation of calpain signaling (PubMed:20016066). In the kidney, may contribute to the detection of intraluminal pressure changes and to urine flow sensing. Acts as shear-stress sensor that promotes endothelial cell organization and alignment in the direction of blood flow through calpain activation (PubMed:25119035). Plays a key role in blood vessel formation and vascular structure in both development and adult physiology (By similarity). Acts as sensor of phosphatidylserine (PS) flipping at the plasma membrane and governs morphogenesis of muscle cells. In myoblasts, flippase-mediated PS enrichment at the inner leaflet of plasma membrane triggers channel activation and Ca2+ influx followed by Rho GTPases signal transduction, leading to assembly of cortical actomyosin fibers and myotube formation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E2JF22, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20016066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23479567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23695678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25119035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29799007}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a mechanically-activated ion channel that links mechanical forces to biological signals. The encoded protein contains 36 transmembrane domains and functions as a homotetramer. Defects in this gene have been associated with dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:9780; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cation channel activity [GO:0005261]; mechanosensitive ion channel activity [GO:0008381]; cation transport [GO:0006812]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; detection of mechanical stimulus [GO:0050982]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033634]; positive regulation of integrin activation [GO:0033625]; positive regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010831]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391] |
18311491_The MIB index was strongly correlated with disease progression in papillary urothelial neoplasms in the urinary bladder. 20016066_siRNA knockdown in epithelial cells inactivates endogenous beta1 integrin, reducing cell adhesion 22529292_Data show that the transmission of PIEZO1 mutations and cosegregation with the disease phenotype in all affected persons in both kindreds. 22790451_Piezo1 responses in a patch emulate many of the responses seen in whole-cell mode, there are significant differences, presumably in the force transfer structures. 22792288_Loss of Fam38A expression may cause increased cell migration and metastasis in lung tumours. 23479567_R2456H and R2488Q mutations in PIEZO1 alter mechanosensitive channel regulation, leading to increased cation transport in erythroid cells. 23487776_Xerocytosis is caused by mutations that alter the kinetics of the mechanosensitive channel PIEZO1. 23581886_study reports two unrelated families with hereditary xerocytosis where probands presented fetal hydrops for which the same heterozygous mutation in PIEZO1 was identified 23695678_The gain-of-function PIEZO1 phenotype provides insight that helps to explain the increased permeability of cations in red blood cells of dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis patients. 23972840_gating and inactivation as a function of pressure 24157948_PIEZO1 stretch sensitivity is modulated by polycystin-2. 24314002_Hereditary xerocytosis and familial haemolysis due to mutation in the PIEZO1 gene have been found in a Danish pedigree. 24798994_Piezo1 is a novel TFF1 binding protein that is important for TFF1-mediated cell migration in gastric cancer cells. 25037583_family of mechanically activated channels that counts only two members in human, piezo1 and 2, has emerged recently. [review] 25044010_The R2488Q PIEZO1 mutation is an apparent major cause of familial hereditary xerocytosis. 25349416_the mechanically gated ion channel Piezo1 is an important determinant of mechanosensitive lineage choice in neural stem cells and may play similar roles in other multipotent stem cells. 25561736_Protonation of the human PIEZO1 ion channel stabilizes inactivation. 25666479_a possible role of Piezo1 in invasion and metastatic propagation. 25955826_PIEZO1 is permeable to monovalent ions (K+, Na+, Cs+, Li+) and most divalent ions (Ba2+, Ca2+ and Mg2+), but not to Mn2+. 26001274_Mechanically activated Piezo1 plays an essential role in red blood cell volume homeostasis. 26001275_Piezo1 is amenable to chemical activation and thus there is a possibility that endogenous Piezo1 agonists might exist. 26333996_Homozygous and compound heterozygous mutations in PIEZO1, result in an autosomal recessive form of generalized lymphatic dysplasia with a high incidence of non-immune hydrops fetalis and childhood onset of facial and four limb lymphoedema. 26351678_Piezo1 channels are likely to function in normal RBCs and suggest a previously unidentified mechanotransductive pathway in ATP release. 26387913_Mutations in PIEZO1 is associated with persistent lymphoedema caused by congenital lymphatic dysplasia. 26646186_Piezo1 responds to lateral membrane tension with exquisite sensitivity as compared to other mechanically activated channels and that resting tension can drive channel inactivation, thereby tuning overall mechanical sensitivity of Piezo1. 26963637_When the 'split protein' is coexpressed, the parts associate to form a normal channel. 26971963_correlation between HPCHA and PIEZO1-gene mutated findings raise an important question as to whether any of the high phosphatidylcholine hemolytic anemia cases previously diagnosed in Japan may have in fact been the form of hemolytic anemia known as hereditary xerocytosis or dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis with PIEZO1 gene mutation 27160899_differential regulation of PKA and cell stiffness in unconfined versus confined cells is abrogated by dual, but not individual, inhibition of Piezo1 and myosin II. 27515482_MiR-103a might be a potential biomarker of myocardium infarction and could be used as an index for the diagnosis of AMI. It may be involved in the development of HBP and onset of AMI through regulating the Piezo1 expression. 27694883_analysis of Piezo1 domains by using localized force on magnetic nanoparticles 27743844_The Piezo1 convert a variety of mechanical stimuli into channel activation and subsequent inactivation, and what molecules and mechanisms modulate Piezo function. 27797339_data demonstrate that PIEZO1 is required for the regulation of NO formation, vascular tone, and blood pressure. 28164706_In the absence of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins Piezo1 receptors are relatively insensitive to mechanical forces pushing the cellular membrane, whereas they can hardly be activated by mechanically pulling the membrane. Yet, if conjugated with Matrigel, a mix of ECM proteins, the receptors become sensitized. 28199303_Because Piezo1 senses both mechanical crowding and stretch, it may act as a homeostatic sensor to control epithelial cell numbers, triggering extrusion and apoptosis in crowded regions and cell division in sparse regions. 28416610_platelets and Meg-01 cells express the MS cation channel Piezo1, which may contribute to Ca(2+) entry and thrombus formation under arterial shear. 28619848_present study was designed to evaluate in hereditary xerocytosis the functional link between mutated Piezo1 and KCNN4 28698554_Results find that Ucn1 exerts its chondroprotective effect by maintaining Piezo1 in a closed conformation. 28716860_Additional alterations in mutant PIEZO1 channel kinetics, differences in response to osmotic stress, and altered membrane protein trafficking, predicting variant alleles that worsen or ameliorate erythrocyte hydration. 28905417_The structural dynamics of the PIEZO1 channel activation and inactivation by coarse-grained modeling has been reported. 29065102_Piezo1-shRNA could inhibit the invasion of the osteosarcoma cells. 29191841_rare genetic variation accounts for a genetic phenotype-modifier role in dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis 29210095_A family with clinical and laboratory characteristics of hereditary xerocytosis (HX) had an apparently conservative novel variant, L2023V, in PIEZO1. Functional analyses demonstrated a gain-of-function phenotype for the mutant PIEZO1 channel, confirming the pathogenicity of the variant and its causative role for HX. 29330322_we discovered a hitherto unknown regulatory mechanism for human T cell activation and provide the first evidence, to our knowledge, for the involvement of Piezo1 mechanosensors in immune regulation. 29545531_Both vertebrate and invertebrate mechanosensitive PIEZO ion channels are polymodal, being voltage modulated, and can even be directly voltage gated following a preceding mechanical stimulus. 29683214_PIEZO1 exhibited an upregulation in most of the Gastric Cancer cell lines and primary samples compared with non-tumorous gastric epithelial tissues. Increase of PIEZO1 was associated with poor disease specific survival. PIEZO1 knockdown led to inhibitory effect by suppressing cell proliferation and invasion and inhibiting xenograft formation. 29757938_the knockdown of PIEZO1 significantly reduced the cell-viability of SW982 cells. 29799007_Cell surface flip-flop of phosphatidylserine acts as a molecular switch for PIEZO1 activation that governs proper morphogenesis during myotube formation. 29945412_Piezo1 protein was extensively expressed in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the nucleus pulposus cells 30085186_Piezo1 channels are Ca2+-permeable non-selective cationic channels which are critical for shear stress sensing and maturation of murine embryonic vasculature 30105803_in vivo evidence that a common PIEZO1 deletion allele is associated with RBC dehydration in sickle cell disease patients. 30244526_we report the use of prenatal ES to identify novel PIEZO1 variants as a cause of severe in utero onset of GLD. 30250223_We observed that over-expression of PIEZO1 in HEK293 cells increased cell migration velocity ~10-fold, and both enantiomeric A-beta peptides and GsMTx4 independently inhibited migration, demonstrating involvement of PIEZO1 in cell motility. 30260030_ShRNA-Piezo1 can protect cells by reducing the level of intracellular Ca(2+) and the change of mitochondrial membrane potential. 30324494_the presence of both Piezo1 and 2 in enteric neurons throughout the gastrointestinal tract from guinea pigs, mice and humans, were studied. 30344046_A stiffer mechanical tumor microenvironment elevates PIEZO1 expression to promote glioma aggression. 30462693_Whole-cell current from coexpressed PIEZO1/PIEZO2 also fit as a linear combination of homomer currents. High-resolution optical images of fluorescently-tagged channels support this interpretation because coexpressed subunits segregate into discrete domains. 30480546_The membrane footprint amplifies the sensitivity of piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 (Piezo1) to changes in membrane tension, rendering it exquisitely responsive. 30628892_identify a functionally conserved inactivation gate in the pore-lining inner helix of mouse Piezo1 and Piezo2 that is distinct from the two constrictions 30655378_PIEZO1-hereditary xerocytosis was characterized by compensated hemolysis in most cases, perinatal edema of heterogeneous severity in more than 20% of families and a major risk of post-splenectomy thrombotic events, including a high frequency of portal thrombosis; demonstrate the genetic bases of PIEZO1-hereditary xerocytosis. 30741991_Functional expression of the mechanosensitive PIEZO1 channel in primary endometrial epithelial cells and endometrial organoids. 30745454_Results indicate the critical prognostic values of the piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel components PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 30867417_Study using cultured human and mouse cells found that margaric acid, a saturated fatty acid present in dairy products and fish, inhibits Piezo1 activation and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), present in fish oils, modulate channel inactivation. 30885080_The results showcase the use of droplet-hydrogel bilayer for future experiments allowing simultaneous measurements of Piezo1 bilayer gating while visualising the channel proteins using fluorescence. 30916365_rapid amplification of cDNA ends identified a novel PIEZO1-RSPO2 fusion in one traditional serrated adenoma 31290742_Piezo1 functions as a key mechanotransducer for conferring mechanosensitivity to osteoblasts. 31298594_Mild erythrocytosis as a presenting manifestation of PIEZO1 associated erythrocyte volume disorders. 31322184_The expression Piezo1 was demonstrated to be significantly elevated in prostate cancer (PCa) cell lines and in human prostate malignant tumor tissues. Downregulation of Piezo1 significantly suppressed the viability, proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro, and inhibited prostate tumor growth in vivo. Piezo1 may also serve as a biomarker of PCa. 31340627_stomatocytosis with PIEZO1 gene mutations 31396578_Piezo1 Ca(2+) flickers allow spatial segregation of mechanotransduction events, and mobility allows Piezo1 channels to explore a large number of mechanical microdomains and thus respond to a greater diversity of mechanical cues. 31413092_PIEZO1 activation delays erythroid differentiation of normal and hereditary xerocytosis-derived human progenitor cells. 31451220_The study investigated the role of Piezo1 in mediating the intracellular calcium response of HEK293T cells in response to pulsed Ultrasound (US). The elicited calcium response depends critically on the pulse repetition frequency or burst duration of the US, as well as the presence of the Piezo1. Significantly higher increase was produced in the Piezo1-transfected than in the Piezo1-knockout cells. 31586031_Multiplex kinase activity profiling combined with kinase inhibitor experiments and phosphospecific immunoblotting established that Piezo1 activation stimulates IL-6 secretion via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase downstream of Ca(2+) entry. In summary, cardiac fibroblasts express mechanically activated Piezo1 channels coupled to secretion of the paracrine signaling molecule IL-6. 31611621_Coordination of WNT signaling and ciliogenesis during odontogenesis by piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1. 31624108_PIEZO1 gain-of-function mutations delay reticulocyte maturation in hereditary xerocytosis. 31685811_Activation of Piezo1 sensitizes cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through mitochondrial outer membrane permeability. 31737919_This is the first demonstration of a direct link between PIEZO1 and iron metabolism, which defines the channel as a new hepatic iron metabolism regulator and as a possible therapeutic target of iron overload in DHS and other iron-loading anemias. 31968259_Inactivation Kinetics and Mechanical Gating of Piezo1 Ion Channels Depend on Subdomains within the Cap. 31968281_Identification of PIEZO1 polymorphisms for human bone mineral density. 32109669_Heterogeneous phenotype of Hereditary Xerocytosis in association with PIEZO1 variants. 32112123_Targeted next-generation sequencing identified 8 missense variants in the PIEZO1 gene in 7 unrelated Indian hereditary xerocytosis patients. 3 of the 8 variants are novel (c.1795G > C, c.2915G > A, c.7372 T > C). Autosomal dominant mutation (c.7372 T > C) is associated with iron refractory iron deficiency anemia. Structural-functional analysis of the novel variants was investigated by molecular modeling software. 32152662_Overexpressing Piezo1 and silencing MCU could promote colon cancer cell migration and metastasis, reduce mitochondrial membrane potential, and promote each other's expression. 32265284_Red blood cells heterozygous for PIEZO1 E756del are not dehydrated and can support the intracellular growth of P. falciparum like wild-type cells. However, surface expression of the P. falciparum virulence protein PfEMP-1 was significantly reduced in infected cells heterozygous for PIEZO1 756del. Study findings demonstrate that PIEZO1 is an important innate determinant of malaria susceptibility in humans. 32323761_The roles of mechanosensitive ion channels and associated downstream MAPK signaling pathways in PDLC mechanotransduction. 32481599_Functional Expression of Piezo1 in Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) Neurons. 32526681_Piezo1 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in nucleus pulposus cell-mediated by Ca(2+)/NF-kappaB pathway. 32579474_Active modulation of human erythrocyte mechanics. 32675337_Effect of Piezo1 Overexpression on Peritumoral Brain Edema in Glioblastomas. 32697107_Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Represents an Anti-Inflammatory Therapy Via Reduction of Shear Stress-Induced, Piezo-1-Mediated Monocyte Activation. 32826342_Targeting Piezo1 unleashes innate immunity against cancer and infectious disease. 32959903_Analyzing the shear-induced sensitization of mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo-1 in human aortic endothelial cells. 32985688_YAP signaling induces PIEZO1 to promote oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation. 32999349_Identification of PIEZO1 as a potential prognostic marker in gliomas. 33149214_Investigation of associations between Piezo1 mechanoreceptor gain-of-function variants and glaucoma-related phenotypes in humans and mice. 33181827_Increased incidence of germline PIEZO1 mutations in individuals with idiopathic erythrocytosis. 33204718_Mechanism of Abnormal Chondrocyte Proliferation Induced by Piezo1-siRNA Exposed to Mechanical Stretch. 33210711_Piezo1 regulates migration and invasion of breast cancer cells via modulating cell mechanobiological properties. 33226641_Piezo1 channels mediate trabecular meshwork mechanotransduction and promote aqueous fluid outflow. 33298523_Piezo1 acts upstream of TRPV4 to induce pathological changes in endothelial cells due to shear stress. 33439514_Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 facilitates gastric cancer omentum metastasis. 33559992_The prognostic value of Piezo1 in breast cancer patients with various clinicopathological features. 33571427_A role of PIEZO1 in iron metabolism in mice and humans. 33575334_A New Hope in Spinal Degenerative Diseases: Piezo1. 33597646_Mechanical stretch induces Ca(2+) influx and extracellular release of PGE2 through Piezo1 activation in trabecular meshwork cells. 33610907_Piezo1 impairs hepatocellular tumor growth via deregulation of the MAPK-mediated YAP signaling pathway. 33628392_Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Activated by Matrix Stiffness Regulates Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence and Apoptosis in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. 33636174_Piezo1 regulates intestinal epithelial function by affecting the tight junction protein claudin-1 via the ROCK pathway. 33649312_Mechanical stretch promotes hypertrophic scar formation through mechanically activated cation channel Piezo1. 33657092_Up-down biphasic volume response of human red blood cells to PIEZO1 activation during capillary transits. 33658557_Adherent cell remodeling on micropatterns is modulated by Piezo1 channels. 33690597_PIEZO1 and the mechanism of the long circulatory longevity of human red blood cells. 33809739_Piezo1 Channels Contribute to the Regulation of Human Atrial Fibroblast Mechanical Properties and Matrix Stiffness Sensing. 33813851_Upregulation of Piezo1 (Piezo Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1) Enhances the Intracellular Free Calcium in Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells From Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients. 33848364_Recent advances in the pathophysiology of PIEZO1-related hereditary xerocytosis. 33973227_Characterisation of Asp669Tyr Piezo1 cation channel activity in red blood cells: an unexpected phenotype. 33974928_Piezo1 and BKCa channels in human atrial fibroblasts: Interplay and remodelling in atrial fibrillation. 34031557_Shear-stress sensing by PIEZO1 regulates tendon stiffness in rodents and influences jumping performance in humans. 34201899_Complex Modes of Inheritance in Hereditary Red Blood Cell Disorders: A Case Series Study of 155 Patients. 34217619_Piezo 1 is involved in intraocular pressure regulation. 34230590_Human genetic variant E756del in the ion channel PIEZO1 not associated with protection from severe malaria in a large Ghanaian study. 34358671_Association of varicose veins with rare protein-truncating variants in PIEZO1 identified by exome sequencing of a large clinical population. 34411418_Piezo1 initiates platelet hyperreactivity and accelerates thrombosis in hypertension. 34454425_G protein coupled estrogen receptor attenuates mechanical stress-mediated apoptosis of chondrocyte in osteoarthritis via suppression of Piezo1. 34489534_Modified N-linked glycosylation status predicts trafficking defective human Piezo1 channel mutations. 34606042_Piezo1 mediates endothelial atherogenic inflammatory responses via regulation of YAP/TAZ activation. 34656527_Digenic Inheritance of a FOXC2 Mutation and Two PIEZO1 Mutations Underlies Congenital Lymphedema in a Multigeneration Family. 34669509_Endothelial upregulation of mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 in pulmonary hypertension. 34781417_Mechanosensing by Piezo1 and its implications for physiology and various pathologies. 34913176_Piezo1 controls cell volume and migration by modulating swelling-activated chloride current through Ca(2+) influx. 34979904_Compression enhances invasive phenotype and matrix degradation of breast Cancer cells via Piezo1 activation. 34985971_PIEZO1 mediates a mechanothrombotic pathway in diabetes. 35082286_Microskeletal stiffness promotes aortic aneurysm by sustaining pathological vascular smooth muscle cell mechanosensation via Piezo1. 35139384_Tethering Piezo channels to the actin cytoskeleton for mechanogating via the cadherin-beta-catenin mechanotransduction complex. 35151521_[Involvement of the Piezo1 and TRPV4 stretch-activated channels in pulmonary hypertension].', trans 'Implication des canaux mecanosensibles Piezo1 et TRPV4 dans l'hypertension pulmonaire. 35173527_Emerging Piezo1 signaling in inflammation and atherosclerosis; a potential therapeutic target. 35181897_A Piez-o the jigsaw: the Piezo1 channel in skin biology. 35274124_Piezo1 activation attenuates thrombin-induced blebbing in breast cancer cells. 35283177_Fatty acids as biomodulators of Piezo1 mediated glial mechanosensitivity in Alzheimer's disease. 35409116_Store-Operated Ca(2+) Entry Contributes to Piezo1-Induced Ca(2+) Increase in Human Endometrial Stem Cells. 35436566_The role of mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel in diseases. 35559724_Piezo1 regulates shear-dependent nitric oxide production in human erythrocytes. 35606793_Excessive mechanical stress-induced intervertebral disc degeneration is related to Piezo1 overexpression triggering the imbalance of autophagy/apoptosis in human nucleus pulpous. 35608274_High-throughput membrane-anchored proteome screening reveals PIEZO1 as a promising antibody-drug target for human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35619555_Self-amplifying loop of NF-kappaB and periostin initiated by PIEZO1 accelerates mechano-induced senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and intervertebral disc degeneration. 35706029_Microglial amyloid beta clearance is driven by PIEZO1 channels. 35767143_The Piezo1 ion channel in glaucoma: a new perspective on mechanical stress. 35869052_A critical role of the mechanosensor PIEZO1 in glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells. 35968892_Mechanosensitive cation currents through TRPC6 and Piezo1 channels in human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. 36047858_Piezo1 Response to Shear Stress Is Controlled by the Components of the Extracellular Matrix. 36112948_Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 contributes to melanoma malignant progression through AKT/mTOR signaling. 36181398_Activation of Piezo1 contributes to matrix stiffness-induced angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 36208662_Piezo1 act as a potential oncogene in pancreatic cancer progression. |
ENSMUSG00000014444 |
Piezo1 |
3100.542335 |
0.4712123163 |
-1.085551 |
0.103258814 |
108.370082 |
0.00000000000000000000000022299859831907197737230844815050138368126624435458405809410375897241900211565024392257328145205974578857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000002429121262870481574134366455710213224522182228379609169595694523205789416842037553578848019242286682128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1988.4202585 |
169.2825644 |
4250.7187302 |
261.5034459 |
| ENSG00000103342 |
2935 |
GSPT1 |
protein_coding |
P15170 |
FUNCTION: Involved in translation termination in response to the termination codons UAA, UAG and UGA (By similarity). Stimulates the activity of ETF1 (By similarity). Involved in regulation of mammalian cell growth (PubMed:2511002). Component of the transient SURF complex which recruits UPF1 to stalled ribosomes in the context of nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) of mRNAs containing premature stop codons (PubMed:24486019). Required for SHFL-mediated translation termination which inhibits programmed ribosomal frameshifting (-1PRF) of mRNA from viruses and cellular genes (PubMed:30682371). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8IYD1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24486019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2511002, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30682371}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;GTP-binding;Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay;Nucleotide-binding;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
Enables translation release factor activity. Involved in regulation of translational termination. Acts upstream of or within protein methylation. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be part of translation release factor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2935; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; translation release factor complex [GO:0018444]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation release factor activity [GO:0003747]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay [GO:0000184]; protein methylation [GO:0006479]; regulation of translational termination [GO:0006449]; translation [GO:0006412]; translational termination [GO:0006415] |
12865429_GSPT1/eRF3 is proteolytically processed into an IAP-binding protein 15908960_Human translation termination factor eRF3/GSPT1 is an interacting partner of RNase L. 15987717_Polyglycine expansions in eukaryotic translation release factor 3 are associated with gastric cancer susceptibility 15987998_eRF3a controls the formation of the termination complex by modulating eRF1 protein stability. 16452507_Further, we describe a novel complex that contains the NMD factors SMG-1 and Upf1, and the translation termination release factors eRF1 and eRF3 (SURF). an association between SURF and the EJC is required for SMG-1-mediated Upf1 phosphorylation and NMD. 17562865_These results strongly suggest that the G1 arrest and the decrease in translation induced by eRF3a depletion are due to the inhibition of mTOR activity and hence that eRF3a belongs to the regulatory pathway of mTOR activity. 17700517_GSTP1 inhibits the binding of MAP kinase kinase kinase 5 (MAP3K5) to the 14-3-3 protein, a MAP3K5 inhibitor, while a novel role of GSPT1 is revealed in the regulation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-mediated apoptosis. 18083835_eRF3a is degraded by the proteasome when not associated with eRF1; proteasomal degradation of eRF3a controls translation termination complex formation by adjusting the eRF3a level to that of eRF1. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19424636_eRF3a/GSPT1 12-GGC allele increases the susceptibility for breast cancer development. 19963113_GSPT1 GGC(12) allele was present in 2.2% of colorectal cancer patients but was absent in Crohn disease patients and in the control group 20418951_crystal structures of the MLLE domain from PABPC1 in complex with the two PAM2 regions of eRF3 22101789_Our results show that the presence of the longer allele of eRF3a is correlated with threefold increased risk of breast cancer development 23019593_A biological role for the overlapping ERF3 PAM2 motifs in the regulation of deadenylase accessibility to PABPC1 at the 3' end of poly(A). 23054082_ERF3 is targeted for caspase-mediated proteolytic cleavage and degradation during DNA damage-induced apoptosis. 23377885_The survivin and eRF3 complex may function in spindle formation and segregation of chromosomes and cytokinesis. 24569073_The proteolytic cleavage of eRF3a and eRF3b into p-eRF3 leads to release an amino-terminal fragment containing nuclear export signal to allow the relocalization of eRF3 into the nucleus to interact with the p14ARF. 25028095_Overexpression of ID1 in two different cell lines induced STMN3 and GSPT1 at the transcriptional level, while depletion of ID1 reduced their expression. 26503584_GAB2, GSPT1, TFDP2 and ZFPM1 are four new susceptibility loci for testicular germ cell tumor. 26818177_Data found that the N-terminal glycine repeat of eRF3a influences eRF3a-PABP interaction and that eRF3a 12-GGC allele has a decreased binding affinity for PABP. 27418677_PABP enhances the productive binding of the eRF1-eRF3 complex to the ribosome, via interactions with the N-terminal domain of eRF3a which itself has an active role in translation termination. 30024602_miR-144 was found to be down-regulated in gastric cancer tissues while GSPT1 expression level was markedly increased; GSPT1 was a direct target of miR-144. 30867251_Data show that G1 to S phase transition 1 protein (GSPT1)-rs33635C was a predictor for lamivudine (LAM) therapy. 31539861_miR-27b-3p suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via negative expression regulation of GSPT1. 33819920_Identification of GSPT1 as prognostic biomarker and promoter of malignant colon cancer cell phenotypes via the GSK-3beta/CyclinD1 pathway. 35839920_Vimentin binds to a novel tumor suppressor protein, GSPT1-238aa, encoded by circGSPT1 with a selective encoding priority to halt autophagy in gastric carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000062203 |
Gspt1 |
709.221000 |
2.1894524212 |
1.130570 |
0.077935895 |
209.541925 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001729040713809807137223472959754078487485147517114689650452607626065511032019732700484568262438091041890197565125165957145014772322610951960086822509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000346747838802075453062750827255029870588054040117022000552724029357703027617000742651524830891117170900805924745209912057886114666871435474604368209838867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
954.3569274 |
45.0552701 |
439.1721544 |
15.8061423 |
| ENSG00000103365 |
23062 |
GGA2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UJY4 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in protein sorting and trafficking between the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and endosomes. Mediates the ARF-dependent recruitment of clathrin to the TGN and binds ubiquitinated proteins and membrane cargo molecules with a cytosolic acidic cluster-dileucine (DXXLL) motif (PubMed:10747088). Mediates export of the GPCR receptor ADRA2B to the cell surface (PubMed:27901063). Regulates retrograde transport of phosphorylated form of BACE1 from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network (PubMed:15615712). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10747088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15615712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27901063}. |
3D-structure;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Golgi-localized, gamma adaptin ear-containing, ARF-binding (GGA) family. This family includes ubiquitous coat proteins that regulate the trafficking of proteins between the trans-Golgi network and the lysosome. These proteins share an amino-terminal VHS domain which mediates sorting of the mannose 6-phosphate receptors at the trans-Golgi network. They also contain a carboxy-terminal region with homology to the ear domain of gamma-adaptins. This family member may play a significant role in cargo molecules regulation and clathrin-coated vesicle assembly. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23062; |
clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0043001]; Golgi to plasma membrane transport [GO:0006893]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; protein localization to cell surface [GO:0034394] |
12135764_endocytosis and intracellular transport of memapsin 2, mediated by its cytosolic domain, may involve the binding of GGA1 and GGA2 15615712_GGA proteins function with the phosphorylated ACDL in the memasin 2-recycling pathway from endosomes to trans Golgi on the way back to the cell surface. 17451558_Results demonstrate that cargo proteins contribute to the recruitment of GGA2 onto membranes and to the formation of GGA-positive clathrin-coated vesicles. 17494868_These results show that the dual roles of PI4P can promote specific GGA targeting and cargo recognition at the trans-Golgi network. 17596511_p56 tightly cooperates with the GGAs in the sorting of cathepsin D to lysosomes, probably by enabling the movement of GGA-containing transport carriers. 18431031_GGA2 is recruited to the trans-Golgi network independently of the other Golgi-localized, gamma-ear-containing, ARF-binding proteins and is required for the efficient sorting of lysosomal enzymes 19788741_GGA overexpression causes various sorting defects as measured by recycling of CD-MPR, internalization of transferrin receptor, and the subcellular localization of proteins like Tsg101, ubiquitin, and Hrs. 22291915_GGA2 mediates a vital function that cannot be compensated for by GGA1and/or GGA3. 24407285_These data indicate that clathrin is required for the function of AP-1- and GGA-coated carriers at the trans-Golgi network but may be dispensable for outward traffic en route to the plasma membrane. 27901063_full length alpha2B-AR associated with GGA2 but not GGA1, its third intracellular loop was found to directly interact with both GGA1 and GGA2. More interestingly, further mapping of interaction domains showed that the GGA1 hinge region and the GGA2 GAE domain bound to multiple subdomains of the loop. 28289207_PI4KIIIbeta interaction with the VHS domain of GGA2 affected PI4KIIIbeta localization. 29358589_Study shows that reduced expression of GGA3 resultes in accumulation of endocytosed EGFR within enlarged endosomes. GGA2 interacts with EGFR cytoplasmic domain to stabilize the receptor expression and promote cell growth. Finally, GGA2 was upregulated in 30.8% of human hepatocellular carcinomas and 23.3% of colorectal cancers. 30578931_Data suggest that overexpression of GGA2 in LUAD tumors results in the accumulation of EGFR protein and increased EGFR signaling, which helps drive tumor progression. 31076515_GGA2 and RAB13 are important specificity determinants for integrin activity-dependent traffic. 33206455_Inactivation of the three GGA genes in HeLa cells partially compromises lysosomal enzyme sorting. |
ENSMUSG00000030872 |
Gga2 |
718.014275 |
0.4984505196 |
-1.004478 |
0.230022015 |
18.558072 |
0.00001648058622204919018250195150709913605169276706874370574951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000050342188045829064293058136003722324858244974166154861450195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
468.1701447 |
74.2039723 |
943.9473052 |
107.9980841 |
| ENSG00000103485 |
23475 |
QPRT |
protein_coding |
Q15274 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the catabolism of quinolinic acid (QA). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17868694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24038671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9473669}. |
3D-structure;Glycosyltransferase;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; nicotinate D-ribonucleotide from quinolinate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17868694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24038671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9473669}. |
This gene encodes a key enzyme in catabolism of quinolinate, an intermediate in the tryptophan-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide pathway. Quinolinate acts as a most potent endogenous exitotoxin to neurons. Elevation of quinolinate levels in the brain has been linked to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, and Huntington's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:23475; |
catalytic complex [GO:1902494]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase (carboxylating) activity [GO:0004514]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435]; NAD metabolic process [GO:0019674]; quinolinate catabolic process [GO:0034213] |
19321014_QPRT is a potential new marker for the immunohistochemical screening of follicular thyroid nodules. 24038671_Report of the crystal structure of human QPRT bound to its inhibitor phthalic acid (PHT) and kinetic analysis of PHT inhibition of human QPRT. 26805589_The structural features, size distribution, heat aggregation and ITC studies of the full-length enzyme and the enzyme lacking helix alpha1 strongly suggest that human QPRT acts as a hexamer for cooperative reactant binding via three dimeric subunits and maintaining stability. 27889611_WT1 knock-down gave a corresponding decrease in QPRT gene and protein expression. Chromatin-immunoprecipitation revealed WT1 binding to a conserved site in the first intron of the QPRT gene. 28724915_Hepatic QPRT thus likely served as a cellular factor that dampened productive hepatitis c virus replication. 30443311_Our data suggest that QPRT may play an important role in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders in Chr16p11.2 deletion carriers. 32238439_Targeting NAD(+) Biosynthesis Overcomes Panobinostat and Bortezomib-Induced Malignant Glioma Resistance. 32716908_Silencing DSCAM-AS1 suppresses the growth and invasion of ER-positive breast cancer cells by downregulating both DCTPP1 and QPRT. |
ENSMUSG00000030674 |
Qprt |
407.695975 |
0.3437959253 |
-1.540376 |
0.099387691 |
239.298264 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000559392085827920294010592332105937321135686199441310314586558187642832267859246564964590533204017711979771388914015971663947534547309042504692477848493581404909491539001464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000128208496689753158493668057993918017392130321481764404354148416289086582855688399729407195057027202556949048804598976705524056689537888698016132593693328090012073516845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
211.5453618 |
13.7745560 |
620.7223502 |
26.8937533 |
| ENSG00000103489 |
64131 |
XYLT1 |
protein_coding |
Q86Y38 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate proteoglycans, such as DCN. Transfers D-xylose from UDP-D-xylose to specific serine residues of the core protein (PubMed:15461586, PubMed:17189265, PubMed:24581741, PubMed:23982343). Required for normal embryonic and postnatal skeleton development, especially of the long bones (PubMed:24581741, PubMed:23982343). Required for normal maturation of chondrocytes during bone development, and normal onset of ossification (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q811B1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15461586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17189265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23982343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24581741}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Glycan metabolism; chondroitin sulfate biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17189265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23982343}.; PATHWAY: Glycan metabolism; heparan sulfate biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17189265}. |
This locus encodes a xylosyltransferase enzyme. The encoded protein catalyzes transfer of UDP-xylose to serine residues of an acceptor protein substrate. This transfer reaction is necessary for biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycan chains. Mutations in this gene have been associated with increased severity of pseudoxanthoma elasticum.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:64131; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein xylosyltransferase activity [GO:0030158]; chondroitin sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030206]; chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0050650]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0006024]; glycosaminoglycan metabolic process [GO:0030203]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012]; ossification involved in bone maturation [GO:0043931]; proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0030166] |
15294915_DXD motifs in human xylosyltransferase I are required for enzyme activity 16133423_Elevated XYLT1 activities in pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients is a marker of proteoglycan biosynthesis. 16164625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16164625_xylotransferase genes might be potential candidate genes predisposing to diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients 16225459_Over 80% of the nucleotide sequence of the XT-I-cDNA is necessary for expressing a recombinant enzyme with full catalytic activity. 16569644_recombinant expression and cloning of active full-length xylosyltransferase I (XT-I) and characterization of subcellular localization of XT-I and XT-II 16571645_Variations in the XYLT-II gene are genetic co-factors in the severity of PXE. 16759312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778156_Increased levels of xylosyltransferase I correlates with the formation of extracellular matrix during chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. 17003309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17003309_The XYLT-I c.343G>T polymorphism contributes to the genetic susceptibility to development of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients. 17635914_TGF-beta(1) and mechanical stress induce xylosyltransferase I expression in cardiac fibroblasts and have impact for ECM remodeling in the dilated heart. 17980567_For the rate-limiting enzyme in glycosaminoglycan synthesis XT-I, maximal mRNA expression and enzyme activity were observed 10 days after osteogenic induction of mesenchymal stem cells, simultaneously to the beginning of ECM mineralization. 18294457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18294457_results show that XT-I polymorphisms potentially confer to the genetic susceptibility of abdominal aortic aneurysm 18763033_These results point to skeletal growth and tissue remodeling as a cause of the high XT activity in children 19014925_Data show that the xylosyltransferase I SNP is associated with a decreased glycosaminoglycan amount in the serum of healthy blood donors. 19014925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19197251_No statistically significant association was found between four XYLT variants and hypertension or blood pressure, suggesting that they do not play a significant role in the development of essential hypertension. 19197251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19762916_AP-1 Sp1 family of transcription factors are necessary for the transcriptional regulation of the XYLT1 gene. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22479506_Xylosyltransferase-I regulates glycosaminoglycan synthesis during the pathogenic process of human osteoarthritis 23223231_AP-1 and Sp3 are key regulators of IL-1beta-mediated modulation of xylosyltransferase I expression. 23747722_XYLT1 activity increased time-dependently in response to progressive myofibroblast transformation. 23982343_A family study shows that functional alterations of XYLT1 cause an autosomal recessive short stature syndrome associated with intellectual disability. 24581741_five distinct homozygous XYLT1 mutations may have a role in Desbuquois dysplasia type 2 25476526_These results suggest that XT-1 expression is refractory to the disease process and to inhibition by inflammatory cytokines and that signaling through AP-1, Sp1, and Sp3 is important in the maintenance of XT-1 levels in NP cells. 25480529_Human XYLT1 promoter sequence analysis and description. 26601923_XYLT1 mutation is associated with short limb skeletal dysplasia. 27030147_Our study describes the first case of DBQD2 resulting from compound heterozygous XYLT1 mutation, expands the mutational spectrum of the disease and provides evidence that the severe growth retardation and microsomia observed in DBQD2 patients may result not only from the skeletal dysplasia itself but also from GH and IGF-1 deficiency. 27881841_Novel and recurrent XYLT1 mutations in two Turkish families with Desbuquois dysplasia, type 2, have been reported. 28085539_In conclusion, we identified two genes, DZIP1 and XYLT1, potentially associated with nonsyndromic high myopia using whole exome sequencing and subsequent mutation screening analysis. 29681470_Study has provided detailed mechanistic insight into the initiation of glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis by showing how the unique active-site architecture of XT1 selects particular serine residues for xylosylation. 30542210_Due to the decrease in XYLT1 promoter activity after Sp1 binding site mutation. 30554721_GGC Repeat Expansion and Exon 1 Methylation of XYLT1 Is a Common Pathogenic Variant in Baratela-Scott Syndrome 31677793_HEK293 cells lacking both XT-isoforms are not viable 31973761_Expression of xylosyltransferases I and II and their role in the pathogenesis of arthrofibrosis. 31973816_microRNA-145 mediates xylosyltransferase-I induction in myofibroblasts via suppression of transcription factor KLF4. 32295230_Activin A-Mediated Regulation of XT-I in Human Skin Fibroblasts. 32920014_Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 5 transactivation of TGFBR1 stimulates the mRNA expression of proteoglycan synthesizing genes XYLT1 and CHST3. 33609631_Development of a xylosyltransferase-I-selective UPLC MS/MS activity assay using a specific acceptor peptide. 33662666_Cytokine-mediated induction of human xylosyltransferase-I in systemic sclerosis skin fibroblasts. |
ENSMUSG00000030657 |
Xylt1 |
482.386367 |
3.3021200377 |
1.723393 |
0.090170966 |
366.461747 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000110304033622326435754026061988769092380496371319505442052983881249121789955548157426732179516120661768016762670201262566895276235324175728733546031836621119587511202512050952154726454341758802310069585012053394734721223358064889907836914062500000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000037774652813585571864202617922788669654261577663472075218274265324087697931964201879863886468408916254353287525288675416408917448898446579506379134318212990844254130222331736078503385852658448963280884980164842090744059532880783081054687500000000000 |
Yes |
No |
720.7536274 |
64.7516841 |
220.0655200 |
14.8706377 |
| ENSG00000103494 |
23322 |
RPGRIP1L |
protein_coding |
Q68CZ1 |
FUNCTION: Negatively regulates signaling through the G-protein coupled thromboxane A2 receptor (TBXA2R) (PubMed:19464661). May be involved in mechanisms like programmed cell death, craniofacial development, patterning of the limbs, and formation of the left-right axis (By similarity). Involved in the organization of apical junctions; the function is proposed to implicate a NPHP1-4-8 module. Does not seem to be strictly required for ciliogenesis (PubMed:19464661). Involved in establishment of planar cell polarity such as in cochlear sensory epithelium and is proposed to implicate stabilization of disheveled proteins (By similarity). Involved in regulation of proteasomal activity at the primary cilium probably implicating association with PSDM2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CG73, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19464661}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Joubert syndrome;Meckel syndrome;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tight junction |
|
The protein encoded by this gene can localize to the basal body-centrosome complex or to primary cilia and centrosomes in ciliated cells. The encoded protein has been found to interact with nephrocystin-4. Defects in this gene are a cause of Joubert syndrome type 7 (JBTS7) and Meckel syndrome type 5 (MKS5). [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:23322; |
axonemal microtubule [GO:0005879]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary rootlet [GO:0035253]; ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; thromboxane A2 receptor binding [GO:0031870]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; establishment of planar polarity [GO:0001736]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lateral ventricle development [GO:0021670]; liver development [GO:0001889]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; neural tube patterning [GO:0021532]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; nose development [GO:0043584]; olfactory bulb development [GO:0021772]; pericardium development [GO:0060039]; regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0008589]; retinal rod cell development [GO:0046548] |
17558407_Responsible for Joubert syndrome, affecting cilia and basal bodies. 17558409_Mutations can cause the multiorgan phenotypic abnormalities found in cerebello-oculo-renal syndrome or Meckel syndrome. 17960139_T615P mutation represents the most common mutation in the RPGRIP1L gene causing disease in about 8-10% of Joubert syndrome type B patients negative for NPHP1, NPHP6, or AHI1 mutations 18256137_Discuss Fto/Ftm gene expression regulation via CUTL1. 18281315_Mutations in RPGRIP1L: extending the clinical spectrum of ciliopathies. Review. 18426861_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18565097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18565097_RPGRIP1L mutations are largely confined to the cerebello-renal subgroup, while they overall represent a rare cause of JSRD ( |
ENSMUSG00000033282 |
Rpgrip1l |
57.461056 |
4.3200936879 |
2.111063 |
0.816125338 |
5.815174 |
0.01588847948577313054507875733634136850014328956604003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029114085314712778024270889432045805733650922775268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
78.6907657 |
51.1308688 |
19.2544091 |
8.8444115 |
| ENSG00000103522 |
50615 |
IL21R |
protein_coding |
Q9HBE5 |
FUNCTION: This is a receptor for interleukin-21. |
3D-structure;Chromosomal rearrangement;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine receptor for interleukin 21 (IL21). It belongs to the type I cytokine receptors, and has been shown to form a heterodimeric receptor complex with the common gamma-chain, a receptor subunit also shared by the receptors for interleukin 2, 4, 7, 9, and 15. This receptor transduces the growth promoting signal of IL21, and is important for the proliferation and differentiation of T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. The ligand binding of this receptor leads to the activation of multiple downstream signaling molecules, including JAK1, JAK3, STAT1, and STAT3. Knockout studies of a similar gene in mouse suggest a role for this gene in regulating immunoglobulin production. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:50615; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-21 receptor activity [GO:0001532]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; immunoglobulin mediated immune response [GO:0016064]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101] |
12700598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15146416_IL-21R is associated with the activated phenotype of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts independently of the major proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and TNFalpha, but not with the destruction of articular cartilage and bone. 15751077_The up-regulation of IL-21R in keratinocytes indicates that its expression pattern is not only altered but it appears to be independent of key cytokines that are operant in systemic scleosis. 16260592_TCR-induced IL-21R expression is driven by TCR-mediated augmentation of Sp1 protein levels and may partly depend on the dephosphorylation of Sp1 16391014_surface IL-21 receptor is expressed at variable levels by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells 16867043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17015683_IL-21 differentially regulates IL-4-induced IgE production, via its growth- and differentiation-promoting capacities on isotype- committed B cells, & via its ability to induce IFNg production; the outcome depends on the presence of a IL-21R polymorphism. 17032244_IL-21R is overexpressed in the inflamed synovial membrane and in peripheral blood or synovial fluid leukocytes of RA patients. Thus, blockade of IL-21R signalling pathway may have a therapeutic potential in acute RA patients. 17462506_Data suggest a contribution of IL21 and IL21R to genetic susceptibility to type 1 diabetes and possible involvement of IL-21 and its receptor system in the disease pathogenesis. 17462506_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17624663_Follicular lymphoma cells showed exceptionally high IL-21R expression. IL-21 induced apoptosis in follicular lymphoma cells expressing high levels of IL-21 receptor. 19075398_These results suggest an important role for IL-21R in the mobilization of skin dendritic cells to draining lymph nodes and the subsequent allergic response to epicutaneously introduced antigen. 19230867_analyzed the transcriptional differences between B-cell subsets by gene expression profiling, and identified 15 genes significantly correlated to survival/proliferation. Among them, IL-21R and TCL1 were highly expressed in naive B cells. 19322899_Increased IL-21R is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 19617351_Tax1 transactivates the interleukin-21 (IL-21) and its receptor (IL-21R) genes in human T-cells. 19644854_A polymorphism within IL21R confers risk for systemic lupus erythematosus. 19644854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19874204_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19874204_parathyroid hormone (PTH) and interleukin 21 receptor (IL21R), achieved consistent association results for bone mineral density in both discovery and replication samples. 20059963_This report provides the first evidence that WSB-2 is a regulator of IL-21R expression and IL-21-induced signal transduction. 20072140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20193734_IL-21R is expressed in follicular lymphoma cells from early diagnosed, untreated patients. It mediates apoptosis. It is heterogenously expressed by human FL cell lines bearing the t(14;18) translocation. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21281812_These findings suggest role(s) for IL-21 in both the acute and chronic stages of multiple sclerosis via direct effects on T and B lymphocytes and, demonstrated for the first time, also on neurons. 21524651_IL21R and vezatin were also cleaved in apoptotic HeLa cells with the cleavage sites Asp344, Asp655 and Asp53. 21531891_Data suggest that the association of 2009 H1N1 vaccine-induced Ab responses with IL-21/IL-21R upregulation and with development of memory B cells and plasmablasts has implications for future research in vaccine design. 22032620_For risk-factor studies, anti-citrullinated peptide antibody-positive (CCP)-negative rheumatoid arthritis patients can be studied as one group via measurement of their IL-21 and IL-21 receptor levels. 22235133_Crystal structure of IL-21 binding to IL-21R reveals that the WSXWS motif of IL-21R is C-mannosylated at the first tryptophan. 23098230_Abundant expression of interleukin-21 receptor in follicular lymphoma cells is associated with more aggressive disease. 23296193_IL-21R gene polymorphisms and serum IL-21 levels predict virological response to interferon-based therapy in Asian chronic hepatitis C patients. 23354321_Data suggest that IL21 rs2221903 and IL21R rs3093301 polymorphisms may, independently or interactively, affect the susceptibility to and/or persistence of HBV infection potentially through altering IL-21 and IgE production. 23396946_Human monocyte-like THP-1 cells express two IL-21 receptor components, CD132 (gammac) and IL-21Ralpha, on their cell surface, as assessed by flow cytometry. 23440042_human IL-21R deficiency causes an immunodeficiency and highlights the need for early diagnosis 23830147_The IL-21R/STAT3 pathway is required for many aspects of human CD8(+) T-cell behavior but in some cases can be compensated by other signals. 24728504_Human neutrophils in peripheral blood express functional IL-21 receptors. 25007029_IL-21R on B cells is upregulated in allergic rhinitis patients when compared to controls. IL-21/IL-21R may be involved in the regulation of allergic reactions through the inhibition of IgE. 25398835_interleukin-21 receptor deficiency is associated with Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. 25500255_IL-21/IL-21R could act as potential biomarkers presenting early systemic sclerosis skin lesions severity. 25647271_expression of IL-21 and IL-21R were up-regulated in autoimmune thyroid disease and may be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease through augmenting aberrant immune cascade 25941256_STAT3 signaling downstream of IL-23R and IL-21R has a role in controlling human mucosal-associated invariant T cells and NKT cell numbers 26705256_Report increased levels of IL-21R in the skeletal muscle endothelial cells of patients with peripheral arterial disease compared to control individuals. 28057743_bone marrow monocytes from multiple myeloma patients show distinct features compared to those from patients with indolent monoclonal gammopathies, supporting the role of IL21R over-expression by bone marrow CD14(+) cells in enhanced osteoclast formation. 28303891_The number of IL-2-dependent FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells is increased in the peripheral blood of human patients with loss-of-function mutations in the IL-21 receptor (IL-21R). 30387833_Results showed the upregulation of IL-21R in gastric cancer (GC) associated with tumor size and lymphatic metastasis and acted as an independent prognostic factor of a poor survival and recurrence in GC. IL-21R functioned as an oncogenic factor and alleviated the suppressive effects of miR-125a in GC cells. 30639626_in IL-21R (rs3093390C/T) gene polymorphism, allele frequency of T is statistically different in the hepatitis B virus spontaneous clearance group compared to chronic hepatitis B virus infection cases 30758075_IL-21R rs2285452 AA genotype increases the risk of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese patients. 31573051_The IL21/IL21R axis reduced the growth and invasion of NSCLC cells via inhibiting Wnt/betacatenin signaling and PDL1 expression. The present results may provide a novel molecular target for NSCLC diagnosis and therapy. 33692795_WSB1 and IL21R Genetic Variants Are Involved in Th2 Immune Responses to Ascaris lumbricoides. 33710028_HIV-1 infection and the lack of viral control are associated with greater expression of interleukin-21 receptor on CD8+ T cells. 33929673_Genomic Spectrum and Phenotypic Heterogeneity of Human IL-21 Receptor Deficiency. 36189580_Expression of Interleukin-21 and Interleukin-21 receptor in lymphocytes derived from tumor-draining lymph nodes of breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000030745 |
Il21r |
213.108094 |
3.0223788056 |
1.595684 |
0.147321784 |
116.783570 |
0.00000000000000000000000000320167105125053513239201287541454554850127359335393408983262373326433597887225035449887400318402796983718872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000037327539270503865242471586823795195992415052889170999624769220489955111330626635890439501963555812835693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
326.2012189 |
26.5540902 |
108.2826977 |
7.1192433 |
| ENSG00000103528 |
51760 |
SYT17 |
protein_coding |
Q9BSW7 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003}. |
3D-structure;Differentiation;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable several functions, including calcium ion binding activity; phospholipid binding activity; and syntaxin binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of dendrite extension. Predicted to be located in trans-Golgi network. Predicted to be active in exocytic vesicle and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51760; |
exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861]; regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0017158]; regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0014059]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
16672768_The results suggest that B/K proteins play a role as potential substrates for PKA in the area where they are expressed. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000058420 |
Syt17 |
42.509945 |
0.1531194173 |
-2.707271 |
0.489221427 |
28.009662 |
0.00000012071121616664954099198817961957619360191529267467558383941650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000472223045486283425365017047889426571316562331048771739006042480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1974476 |
4.9247466 |
79.5830598 |
21.3530895 |
| ENSG00000103642 |
114294 |
LACTB |
protein_coding |
P83111 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial serine protease that acts as a regulator of mitochondrial lipid metabolism (PubMed:28329758). Acts by decreasing protein levels of PISD, a mitochondrial enzyme that converts phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) to phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn), thereby affecting mitochondrial lipid metabolism (PubMed:28329758). It is unclear whether it acts directly by mediating proteolysis of PISD or by mediating proteolysis of another lipid metabolism protein (PubMed:28329758). Acts as a tumor suppressor that has the ability to inhibit proliferation of multiple types of breast cancer cells: probably by promoting decreased levels of PISD, thereby affecting mitochondrial lipid metabolism (PubMed:28329758). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28329758}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Protease;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene encodes a mitochondrially-localized protein that has sequence similarity to prokaryotic beta-lactamases. Many of the residues responsible for beta-lactamase activity are not conserved in this protein, suggesting it may have a different enzymatic function. Increased expression of the related mouse gene was found to be associated with obesity. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:114294; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216] |
12164938_Differential expression of a novel gene, G24, in response to hsp27 and cell differentiation in human keratinocytes.(G24 PROTEIN) 18538381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26603571_MiR-125b-5p attenuates the secretion of MCP-1 by directly targeting inhibiting LACTB in LPS-stimulated THP-1 macrophages. 28329758_observations uncover a novel mitochondrial tumour suppressor, LACTB--and demonstrate a connection between mitochondrial lipid metabolism and the differentiation program of breast cancer cells, thereby revealing a previously undescribed mechanism of tumour suppression 28835318_LACTB was downexpressed in gliomas. Downregulation of LACTB predicted poor survival of glioma and promoted cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis of gliomas 29899406_our findings successfully demonstrate for the first time that LACTB is a novel epigenetic silenced tumor suppressor through modulating the stability of p53, supporting the pursuit of LACTB as a potential therapeutic target for colorectal cancer 33152401_LACTB promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activation of ERBB3/EGFR-ERK signaling resulting in unfavorable patient survival. 33507917_LACTB mRNA expression is increased in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and high expression indicates a poor prognosis. 33675985_LACTB suppresses melanoma progression by attenuating PP1A and YAP interaction. 34362477_[Alternative Splicing Analysis of LACTB Gene and Expression Characteristics of Different Transcripts in Leukemia Cell Lines]. 35247327_Structural basis for the catalytic activity of filamentous human serine beta-lactamase-like protein LACTB. 36088805_LACTB suppresses migration and invasion of glioblastoma via downregulating RHOC/Cofilin signaling pathway. 36375842_LACTB exerts tumor suppressor properties in epithelial ovarian cancer through regulation of Slug. |
ENSMUSG00000032370 |
Lactb |
278.249127 |
2.7579051782 |
1.463573 |
0.105107466 |
198.766125 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000388235434712271021314319877909138730492389248161767364098495107607218160472212037144932418851342998798768502472411774661953387521862168796360492706298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000073278197140065476931029845956281523460911069665873576492637535149403516450609857073347397587308717390570246650195046500542161993507761508226394653320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
414.9422306 |
25.5572555 |
151.5514236 |
7.7762464 |
| ENSG00000103742 |
57722 |
IGDCC4 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDY8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57722; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609] |
20658536_identified Nope as a novel oncofetal surface marker for murine and human HCC. Nope is specifically expressed by epithelial tumor cells but not in preneoplastic stages and is a promising marker 32986656_First evaluation of Neighbor of Punc E11 (NOPE) as a novel marker in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 35246597_Expression of Neighbor of Punc E11 (NOPE) in early stage esophageal adenocarcinoma is associated with reduced survival. |
ENSMUSG00000032816 |
Igdcc4 |
24.343268 |
7.8835318960 |
2.978842 |
0.529279438 |
32.930205 |
0.00000000955274796616744306738840786892216772052677242754725739359855651855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000041678557487623844526756562061178823519469460734399035573005676269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.6595043 |
12.7866170 |
5.4495697 |
1.4710401 |
| ENSG00000103811 |
1512 |
CTSH |
protein_coding |
P09668 |
FUNCTION: Important for the overall degradation of proteins in lysosomes. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Thiol protease;Zymogen |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a lysosomal cysteine proteinase important in the overall degradation of lysosomal proteins. It is composed of a dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. The encoded protein, which belongs to the peptidase C1 protein family, can act both as an aminopeptidase and as an endopeptidase. Increased expression of this gene has been correlated with malignant progression of prostate tumors. Alternate splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:1512; |
alveolar lamellar body [GO:0097208]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; multivesicular body lumen [GO:0097486]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; aminopeptidase activity [GO:0004177]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0008656]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; HLA-A specific activating MHC class I receptor activity [GO:0030108]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; thyroid hormone binding [GO:0070324]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation [GO:0019882]; bradykinin catabolic process [GO:0010815]; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0097067]; dichotomous subdivision of terminal units involved in lung branching [GO:0060448]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; immune response-regulating signaling pathway [GO:0002764]; membrane protein proteolysis [GO:0033619]; metanephros development [GO:0001656]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; neuropeptide catabolic process [GO:0010813]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001235]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010952]; protein destabilization [GO:0031648]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process [GO:0051603]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129]; T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001913]; zymogen activation [GO:0031638] |
12034564_involvement in processing of hydrophobic surfactant-associated protein C in type II pneumocytes 12589965_production of cathepsins B and H by tumor cells along with concomitant decrease of their inhibitor, cystatin C, in the CSF might contribute in the process of metastasis and spread of the cancer cells in the leptomeningeal tissues 12615673_Cathepsin H could contribute to the transformation of LDL to an atherogenic moiety; the process might involve a self-sustaining amplifying circle. 14515996_kinetic data on substrates hydrolysis and enzyme inhibition show the role of the mini-chain as a framework for transition state stabilization of free alpha-amino groups of substrates and as a structural barrier for endopeptidase-like substrate cleavage. 14662023_AKR1B1 and CTSH may be good markers for prediction of sensitivity to certain drugs 14766755_cathepsin H is involved in maturation of the biologically active surfactant associated protein B 15646835_cathepsin H has a role in progression of colorectal cancer that is distinct from that of cathepsins B and L 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18216060_A general defect in napsin A or cathepsin H expression or activity was not the specific cause for abnormal surfactant accumulation in juvenile pulmonary alveolar proteinosis 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18949742_cathepsin B, cathepsin H, cathepsin X and cystatin C may have roles in inflammatory breast cancer 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19073967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19404922_In contrast to cathepsin S, cathepsin H values did not correlate with markers of inflammation, indicating a specific role for cathepsin H in the pleural host response. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20647273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881085_These data indicate that cathepsins B, L and S may act as cell-death mediators in in monocytic cells infected with ICP4 and Us3 deletion mutant herpes simplex virus type 1. 21217776_CTSH overexpression in a subset hepatoma may be thyroid hormone receptor dependent and suggests that this overexpression has an important role in hepatoma progression. 22704610_The processing of procathepsin H is an autocatalytic, multistep process proceeding from an inactive 41kDa pro-form, through a 30kDa intermediate form, to the 28kDa mature form. 23204516_CtsH-mediated processing of talin might promote cancer cell progression by affecting integrin alphaVbeta3 activation and adhesion strength 23483898_Quantification of immunohistochemistry showed that there is no difference in the global expression of CTSD, CTSH and CTSK between asthmatics and non-asthmatics. 24982147_The data provide strong evidence that CTSH is an important regulator of beta-cell function during progression of T1D 25525168_mutation in LRPAP1 is associated with high myopia. Further studies are expected to evaluate the pathogenicity of the variants in CTSH, LEPREL1, ZNF644, SLC39A5, and SCO2. 26245339_In conclusion, CTSH/rs3825932 and ERBB3/rs2292239 SNPs were associated with reduced risk of progression to proliferative diabetic retinopathy and two-step progression of diabetic retinopathy on the ETDRS scale accordingly. 26429317_Especially, rs3825932 in CTSH has integrative functional evidence supporting the association with type 1 diabetes mellitus. 26960148_p41 fragment is also shown to reduce the secretion of interleukin-12 (IL-12/p70) during the subsequent maturation of treated dendritic cells. 28157489_the up-regulation of MMP genes is mediated through degradation of class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs) by certain cysteine cathepsins (Cts). 30044821_Study presents the crystal structures of human procathepsin H at 2.00 A and 1.66 A resolution. These structures allow us to explore in detail the molecular basis for the inhibition of the mature domain by the prodomain. Comparison with cathepsin H structure reveals how mini-chain reorients upon activation. Results demonstrate that procathepsin H is not auto-activated but can be trans-activated by cathepsin L. 32814070_The Rac2 GTPase contributes to cathepsin H-mediated protection against cytokine-induced apoptosis in insulin-secreting cells. 33992646_Genetic and environmental factors regulate the type 1 diabetes gene CTSH via differential DNA methylation. |
ENSMUSG00000032359 |
Ctsh |
2680.930947 |
3.8132043708 |
1.931004 |
0.037267295 |
2723.955896 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4257.4170157 |
95.4239164 |
1124.4830040 |
20.5339290 |
| ENSG00000103855 |
80381 |
CD276 |
protein_coding |
Q5ZPR3 |
FUNCTION: May participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. May play a protective role in tumor cells by inhibiting natural-killer mediated cell lysis as well as a role of marker for detection of neuroblastoma cells. May be involved in the development of acute and chronic transplant rejection and in the regulation of lymphocytic activity at mucosal surfaces. Could also play a key role in providing the placenta and fetus with a suitable immunological environment throughout pregnancy. Both isoform 1 and isoform 2 appear to be redundant in their ability to modulate CD4 T-cell responses. Isoform 2 is shown to enhance the induction of cytotoxic T-cells and selectively stimulates interferon gamma production in the presence of T-cell receptor signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11224528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12906861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14764704, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15314238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15682454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15961727}. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily, and thought to participate in the regulation of T-cell-mediated immune response. Studies show that while the transcript of this gene is ubiquitously expressed in normal tissues and solid tumors, the protein is preferentially expressed only in tumor tissues. Additionally, it was observed that the 3' UTR of this transcript contains a target site for miR29 microRNA, and there is an inverse correlation between the expression of this protein and miR29 levels, suggesting regulation of expression of this gene product by miR29. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:80381; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
12055244_A novel structural variant of B7-H3 (named B7-H3b) with four Ig-like domains, is the major isoform expressed in several tissues and results from gene duplication and differential splicing. 15188059_B7-H3 enhances T lymphocyte proliferation and IL-10 secretion when expressed in E. coli in vitro 15314238_data suggest that 4Ig-B7-H3 molecules expressed at the neuroblastoma tumor cell surface can exert a protective role from natural killer-mediated lysis by interacting with a still undefined inhibitory receptor expressed on natural killer cells 16274630_B7-H3 might be another valuable molecule marker for dendritic cells derived from monocytes 17406098_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the B7H3 gene are not associated with autoimmune myasthenia gravis. 17851789_Disease-free survival or overall survival of the gastric carcinoma patients with positive B7-H3 expression were significantly longer than those with negative B7-H3 expression. 18292521_B7-H3 may be important for the interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes and T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases; the outcome of such interactions depends on the activation state of the T cell. 18650384_analysis of an interaction between B7-H3 and TLT-2 that preferentially enhances CD8(+) T cell activation 18676751_B7-H3 is highly expressed in urothelial cell carcinoma across tumor stages, whereas B7-H1 and PD-1 expression are associated with advanced disease 18690846_Overexpression of B7H3 is associated with tumor cell migration and invasion. 18694993_Both tumor cell and tumor vasculature B7-H3 expression convey important information to predict clear cell renal cell carcinoma outcomes 18941196_Progenitor cells from the anterior pituitary gland containing 4Ig-B7-H3 may play a critical role in the immunoendocrine network. 19269710_results suggest circulating B7-H3 is a valuable biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and an elevated level of circulating B7-H3 suggests a poor clinical character for NSCLC. 19544488_Data do not point to a role for TREML2 as a receptor for B7-H3. 20035626_tumor-associated B7-H3 expression significantly correlates with prolonged postoperative survival;B7-H3 might play an important role as a potential stimulator of antitumor immune response in pancreatic cancer. 20333377_higher expression in human colorectal carcinoma correlates with tumor progression 20696859_B7-H3 functions as a costimulator of innate immunity by augmenting proinflammatory cytokine release from bacterial cell wall product-stimulated monocytes/macrophages and may contribute positively to the development of sepsis. 21107115_B7-H3 protein expressed by primary breast cancer cells is associated with extent of regional nodal metastasis. 21127709_role of B7-H3 in the regulation of T-cell response; its potential role in antitumor immunity (Review) 21251161_B7-H3 appears to be a useful blood marker for predicting tumor progression in gastric cancer 21344157_B7-H3 plays a crucial role in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression, tumor metastasis resulting in poor prognosis and might be involved in the negative regulation of T-cell-mediated tumor immune response. 21518725_silencing of B7-H3 increased the sensitivity of multiple human breast cancer cell lines to paclitaxel as a result of enhanced drug-induced apoptosis. 21597388_Upregulation of B7-H3 is associated with induction of immunosuppressive phenotype of dendritic cells in Non-small cell lung cancer microenvironment. 21671471_our findings indicate a novel role for B7-H3 in the regulation of the metastatic capacity of melanoma cells 21784485_B7-H3 is aberrantly expressed in prostate cancer. In addition to modulating tumor immunity, B7-H3 may have a novel role in regulating PC-3 cell progression 21792917_Analysis of B7-H3 protein expression indicates that comparable levels of B7-H3 are expressed on both primary human mesothelial and malignant mesothelial cell types. 21893365_regulates differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to osteoblasts 21982044_B7-H3 expression on cancer cells is correlated with the number of T cells infiltrating the tumor. Endometrium tumor development and progression may be associated with downregulation of T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity through B7-H3. 22187944_The reduced expression of B7-H3 in the livers might temper the inhibition of T-cell responses mediated by B7-H3 expressed on hepatocytes and thus promote the hepatic inflammation and hepatitis progression in the chronic HBV-infected patients. 22473715_B7-H3 expression in tumor-associated vasculature and fibroblasts was observed in the majority of samples. 22487487_high expression level in prostate cancer correlates with the expression of the proliferation marker Ki-67, biochemical failure and clinical relapse 22729558_The data suggested that B7-H3 was abundantly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and was associated with adverse clinicopathologic features and poor outcome. 22863596_In myasthenia gravis (MG) patients, down-regulation of sB7-H3 is finely correlated to the severity of the disease. 22910694_A review of B7-H3 and B7-H4 immune molecules and the role their overexpression plays in ovarian cancer. 22996270_Membrane B7-H3 may be a promising biomarker that associates with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. 23107341_Data suggest that the immunomodulatory proteins B7-H1, B7-H3, and HLA-G5 are secreted from early and term placenta via exosomes and have important implications in mechanisms by which trophoblast immunomodulators modify maternal immunological milieu. 23128494_High B7-H3 expression in human breast cancer tissues may be important in tumor progression and invasiveness. This expression appeared to be correlated with the ability of B7-H3 to promote IL-10 secretion 23242015_The study investigates the role of B7-H3 in pancreatic cancer progression and shows that this protein promotes cancer cell migration and invasiveness in vitro and in vivo. 23474948_B7-H3 is a significant factor in melanoma progression and events of metastasis. 23746248_The level of sB7-H3 in HCC patients was significantly higher than that in healthy people, and B7-H3 expression was correlated with clinical pathological indexes. 23916610_miR-187 plays a tumor suppressor role in clear cell renal cell carcinoma in a pathway involving B7-H3 23940627_B7-H3 expression in osteosarcoma cells is a potential mechanism controlling tumor immunity and invasive malignancy. 24139879_Soluble B7-H3 maybe plays an important role in immunopathogenesis of M. pneumoniae pneumonia, especially for increasing TNF-alpha concentration and activation neutrophils. 24140000_PD-1 expression is upregulated in urothelial bladder carcinoma versus normal urothelium. 24194851_High level of serum B7-H3 in patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma is caused by the increased expression of a newly discovered spliced soluble B7-H3 isoform in carcinoma and peritumor tissues. 24236063_B7H3 and ATP1B3 are overexpressed in tumor endothelial cells, favoring an angiogenic phenotype. 24577056_We identified miRNAs efficiently downregulating B7-H3 expression. The expression of miR-29c correlated with survival in breast cancer patients, suggesting a tumour suppressive role for this miRNA. 24630518_B7-H3 is aberrantly expressed in CD133-positive colorectal cancer cells 24787022_Thus, B7-H3 may have a critical role in primary hepatocellular carcinoma and it may enhance tumor escape from the immune surveillance of CD8(+) T cells. 24892449_Study shows that CD276 can be used to discriminate ECs from malignant tissue from ECs from normal tissue. In addition, CD276(+) CEC do occur in higher frequencies in patients with advanced cancer. 25001942_Data indicate that the expression of membrane B7-H3 (mB7-H3) in peri-tumor normal tissues was higher than that in tumor tissues, and it can serve as an assistant diagnostic marker for hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV-HCC). 25089268_IL-2/IL-2R and B7-H3 pathways may be involved in the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma 25130683_These results demonstrated that B7-H3 expression in acute leukemia predicts an unfavorable outcome. 25139714_The study confirms the overexpression of B7-H3 in colorectal cancer and shows the main localization of the protein in cytoplasm and cell membrane. 25200161_Data indicate that six sites of co-stimulatory molecule B7-H3 gene have single nucleotide polymorphisms variations and five sites are related to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 25370943_B7-H3-mediated STAT3 signaling pathway is an important mechanism for inducing M2-type polarization of tumor associated macrophages. 25416051_Overexpression of B7-H3 in CD14+ monocytes is associated with renal cell carcinoma progression.B7-H3 might play an important role in angiogenesis of renal cell carcinoma mediated by CD14(+) monocytes. 25609202_B7-H1 and B7-H3 are independent predictors of poorer survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 25675190_Our results indicate that B7-H3 expression in cervical invasive squamous cell carcinoma may play an important role in overcoming CD8(+) T-cell immunoregulation to acquire aggressive growth. 25684945_The overexpression of B7-H3 induces resistance to apoptosis in colorectal cancer cell lines by upregulating the Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. 25872657_Study shows that B7-H3 promotes mantle cell lymphoma progression and its knockdown significantly enhances the chemosensitivity. 25931383_B7-H3 was significantly up-regulated on monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis patients, while soluble B7-H3 in serum was decreased. A polymorphism variant, B7-H3-T-A-C-T, was shown to be associated with the incidence of RA and the decreased release of sB7-H3. 26108069_B7-H3 may play an important role in asthma exacerbation and was a useful clinical biomarker to evaluate asthma exacerbation. 26149216_Data show that immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4) increases the expression of the co-inhibitory molecule B7-H3 through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling. 26151358_B7H3 promotes cell migration and invasion through the Jak2/Stat3/MMP9 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer 26376842_B7-H3 is one of the most strongly expressed B7-family molecules in AML and merits further investigation. 26411671_B7-H3 and B7-H4 are involved in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and development and their coexpression could be valuable prognostic indicators. 26438868_found that the N-glycans of B7-H3 from Ca9-22 oral cancer cells contain the terminal alpha-galactose and are more diverse with higher fucosylation and better interaction with DC-SIGN and Langerin on immune cells than that from normal cells 26702052_findings demonstrate that activation-induced B7-H3 expression on synovial monocytes has the potential to inhibit Th1-mediated immune responses and immunomodulatory roles affecting RA pathogenesis. 26771843_The results provide novel insights into the function of B7-H3 in cancer, and suggest that targeting of B7-H3 may be a novel alternative to improve current anticancer therapies. 26787540_High expression of B7-H3 is associated with Colorectal cancer. 26823710_Suggesting that B7-H3 and Tregs may act cooperatively in tumor immune evasion, leading to poor outcomes for NSCLC patients. 27071700_Upregulated sB7-H3 expression in MPEs is correlated with TNM stage of NSCLC and may serve as a potential biomarker for NSCLC-derived MPEs 27145365_B7-H3 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transformation in colorectal cancer cells by activating the PI3K-Akt pathway and upregulating the expression of Smad1. 27175567_BRCC3 may play a role in B7-H3-induced 5-Fu resistance. 27188891_Children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia had significantly higher levels of sB7-H3 and IL-36 compared to control subjects. 27197253_We found that B7-H3 promoted the Warburg effect, evidenced by increased glucose uptake and lactate production in B7-H3-expressing cells. B7-H3 also increased the protein levels of HIF1alpha and its downstream targets, LDHA and PDK1, key enzymes in the glycolytic pathway 27273624_these results demonstrate that sB7-H3 promotes invasion and metastasis through the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway in pancreatic carcinoma 27459969_Plasma B7-H3 levels were decreased significantly in children subjected to pediatric general and cardiac surgery, which is closely associated with the severity of surgical stress. The negative correlation of plasma B7-H3 levels at day 1 and day 3 after surgery with surgical stress scoring implicates that the plasma B7-H3 level might be a useful biomarker for monitoring stress intensity during pediatric surgery. 27626927_Elevated B7-H3 expression is significantly associated with poor survival in cancer patients. (Meta-analysis) 27764786_Study reportes that B7-H3 and B7-H4 are highly expressed in human esophageal cancer tissues and significantly associated with tumor invasion. 27801901_Higher B7-H3 expression correlates with Gleason grade, prostate cancer stage and poor oncologic outcomes in prostatectomy cohorts. B7-H3 expression appears to be related to androgen signaling as well as the immune reactome. 27835582_Review/Meta-analysis: High B7-H3 expression was a significant indicator of lymph node metastasis and advanced TNM stage in non-small cell lung cancer. 27939887_B7-H3 hijacks SREBP-1/FASN signaling mediating abnormal lipid metabolism in lung cancer 28399408_CD276 is broadly expressed by tumor cells and tumor vasculature but Is dispensable for tumor growth. 28465042_Study using human melanoma skin samples and keratinocytes primary and cell line culture suggest that a basal expression of B7-H3 on keratinocytes may contribute to a constitutive immunological function of human epidermis. 28513992_metastatic melanoma cells with knockdown expression of B7-H3 showed modest decrease in proliferation and glycolytic capacity. 28539467_B7-H3 protein is expressed in the majority of NSCLCs and is associated with smoking history. High levels of B7-H3 protein have a negative prognostic impact in lung carcinomas. Coexpression of B7-H3 with PD-L1 and B7-H4 is relatively low, suggesting a nonredundant biological role of these targets. 28627681_High B7-H3 expression is associated with cervical cancer invasiveness. 28676400_B7-H3 promotes the oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells upregulating the expression of XRCC1 via PI3K-AKT pathway. 28685773_Inhibition of the B7-H3 immune checkpoint limits tumor growth by enhancing cytotoxic lymphocyte function 28765941_Our findings revealed that B7-H3 affect ovarian cancer progression through the Jak2/Stat3 pathway, indicating that B7-H3 has the potential to be a useful prognostic marker. 29299639_it is likely that B7-H3 plays an important role in cancer diagnosis and treatment, aside from its role as a co-stimulatory molecule--{REVIEW} 29423417_this study shows reduced sB7-H3 expression in the peripheral blood of systemic lupus erythematosus patients 29484464_Tumor B7-H3 expression was significantly higher in immunocompetent vs. immunosuppressed patients, largely driven by very low expression in HIV+ patients. 29696716_results suggest that B7-H3 may be a valuable biomarker in determining tumor progression and prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 29871819_IDH1 and B7H3 cannot be used as independent prognostic factors, co-expression of IDH1 and B7H3 significantly correlated with the prognosis of CRC patients and may serve as a combined predictive marker. Thus, the correlation between IDH1 and B7H3 has been proven in vivo and in vitro. 29924389_Evidence for B7-H3 mediating tumor glycolysis, via interacting with ENO1. 30027617_characterization of the expression pattern and biological function of B7-H3 in brain gliomas; B7-H3 expression is regulated by multiple mechanisms and is potentially involved in the T-cell receptor signaling pathway; higher B7-H3 expression indicates a worse prognosis for glioma patients 30075787_The axis of miR-29c/B7-H3 plays an important role in children with asthma through regulating Th2/Th17 cell differentiation and may provide new targets for treatment of asthma. 30082909_B7-H3 is associated with the major vault protein (MVP) and activates MEK through MVP-enhancing B-RAF and MEK interaction. B7-H3 expression increases stem cell population by binding to MVP which regulates the activation of the MAPK kinase pathway. Depletion of MVP blocks the activation of MEK induced by B7-H3 and dramatically inhibits B7-H3 induced stem cells. 30089601_HIV-infected lung cancer patients had significantly higher tumor B7-H3 expression compared to HIV-uninfected controls, and importantly similar tumor PD-L1 expression, and PD-1and PD-L1 expression on TII. 30099052_The expression of B7-H3 and B7-H4 favored an immunosuppressive microenvironment by promoting the production of IL-10 and TGFB1, thereby resulting in progression of cervical carcinogenesis. 30131660_Colorectal cancer (CRC) patients expressing both high B7-H3 and high B3GALT4 contributed to a significant decrease in overall survival. The expression of B3GALT4 in CRC is positively correlated with B7-H3 expression in vitro. B7-H3/B3GLAT4 may be used as dual prognostic biomarkers for CRC. 30132557_High expression level of B7H3 in muscleinvasive bladder cancer (MIBC) tissues is associated with a poor clinico-pathological status and poor prognosis, and promotes the development of MIBC in vitro and in vivo. 30226585_Study indicates that breast cancer patients have detectable circulating epithelial tumor cells (CETCs) with a high frequency of B7-H3 expression regardless of the stage of the disease. B7-H3 seems to be an important factor in immune evasion and may thus be a promising target for anticancer therapies. 30328478_B7-H3 might be an independent risk factor for 5-year mortality for Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) patients. Serum levels of B7-H3 were related to long-term major cardiovascular events and 5-year mortality of CHD patients. 30379377_CD276 (B7-H3) is enriched on the cell membrane of LEPCs. CD276 knockdown reduced proliferation and migration of LEPCs by increasing cell cycle inhibitors such as p21(cip1) and pRb and decreasing pErk1/2 and pAkt but promoted angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation by elevating vascular endothelial growth factor-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 and p-p38. 30481143_Soluble form of B7-H3 was positively correlated with the frequency of Treg cells in acute and chronic hepatitis B (HBV) infection, and hepatocellular carcinoma patients with HBV infection. B7-H3 might contribute to the progression of HBV infection by triggering inhibitory signals in effector T cells and it was closely associated with the progression and poor prognosis during HBV infection. 30486739_High B7-H3 expression is associated with phyllodes tumors. 30553455_miR-506 functions as a tumor suppressor miRNA and plays a significant role in inhibiting human mantle cell lymphoma cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing B7H3 expression. 30573782_High CD276 expression is associated with multiple myeloma. 30664982_the importance of BRD4/B7-H3/TLR4 pathway 30813210_Increased B7 protein expression by infiltrating immune cells was associated with disease progression, and specifically, the level of B7-H3 expression and localization of B7-H4 expression differed significantly among different stages of gastric carcinogenesis. 30851900_Overexpression of B7H3 contributes to malignant biliary strictures. 30914782_Investigated the expression of the CD276 molecule (B7H3) gene and protein in gliomas, as well as the expression of other genes in relation to B7H3 expression. 30952834_B7-H3 increased glucose consumption and lactate production by promoting hexokinase 2 expression in colorectal cancer cells, and we also found that HK2 was a key mediator of B7-H3-induced CRC chemoresistance. 31043272_results revealed B7-H3 was highly expressed in craniopharyngiomas and targeting B7-H3 might therefore be an effective therapeutic strategy against craniopharyngioma 31044564_rs2127015 of CD276 were associated with acute liver allograft rejection. rs2127015 influences CD276 expression. 31075138_CD276 and the gene signature composed of GATA3 and LGALS3 enable prognosis prediction of glioblastoma multiforme. 31100711_Plasma sB7-H3 level might serve as biomarker for predicting the severity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia and treatment efficacy. 31104673_Expression of B7H3 and B7H4 is closely corelated with clinicopathological parameters and prognosis of patients with T-LBL/ALL, suggesting that B7H3 and B7H4 expression play an important role in the development of T-LBL/ALL. 31267380_T cell cytotoxicity toward hematologic malignancy via B7-H3 targeting. 31292886_B7-H3, a costimulatory molecule, may be involved in angiogenesis in autoimmune diseases such as RA and SLE. Our results show that B7-H3 plays an important role in endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. 31412888_B7-H3 could promote inflammation and induce apoptosis of human salivary gland epithelial cells by activating NF-kappaB pathway, which might be a promising therapeutic target for pSS. 31611650_Tumor-expressed B7-H3 mediates the inhibition of antitumor T-cell functions in ovarian cancer insensitive to PD-1 blockade therapy. 31731055_NEAT1 promoted M2 macrophage polarization by sponging miR-214 and then regulating B7-H3, thus accelerating multiple myeloma progression 31948091_CD276-Positive Circulating Endothelial Cells Do Not Predict Response to Systemic Therapy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. 31950059_hsa_circ0021347 was selected and validated to be significantly downregulated in OS tissues and cell lines and showed a strong negative relationship with B7-H3 expression in OS. In addition, clinicopathological features showed that hsa_circ0021347 in OS tissues was negatively associated with Enneking stage and positively associated with patients' survival 31974361_B7-H3 promotes colorectal cancer angiogenesis through activating the NF-kappaB pathway to induce VEGFA expression. 32088722_B7-H3 and B7-H4 Expression in Breast Cancer and Their Association with Clinicopathological Variables and T Cell Infiltration. 32145124_MiR-1253 exerts tumor-suppressive effects in medulloblastoma via inhibition of CDK6 and CD276 (B7-H3). 32447027_Effects of B7-H3 expression on tumour-infiltrating immune cells and clinicopathological characteristics in non-small-cell lung cancer. 32576886_Clinical relevance of B7H3 expression in retinoblastoma. 32633367_The expression and clinical significance of B7-H3 and miR-145 in lung cancer patients with malignant pleural effusion. 32719950_B7-H3 is spliced by SRSF3 in colorectal cancer. 32787907_Evaluation of the role of B7-H3 haplotype in association with impaired B7-H3 expression and protection against type 1 diabetes in Chinese Han population. 32800541_Knocking down B7H3 expression enhances cell proliferation of SHEDs via the SHP1/AKT signal axis. 32856542_MicroRNA-199a Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion and Activates AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway by Targeting B7-H3 in Cervical Cancer. 32874188_The MDM2 ligand Nutlin-3 differentially alters expression of the immune blockade receptors PD-L1 and CD276. 32953890_sB7H3 in Children with Acute Appendicitis: Its Diagnostic Value and Association with Histological Findings. 32992699_B7-H3 in Medulloblastoma-Derived Exosomes; A Novel Tumorigenic Role. 33011740_B7-H3 regulates KIF15-activated ERK1/2 pathway and contributes to radioresistance in colorectal cancer. 33049447_B7-H3 expression in upper tract urothelial carcinoma associates with adverse clinicopathological features and poor survival. 33051306_B7-H3: An Attractive Target for Antibody-based Immunotherapy. 33119798_B7-H3 confers resistance to Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in human colon cancer cells via the STAT3/ULBP2 axis. 33306717_Serum soluble B7-H3 is a prognostic marker for patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. 33426073_B7-H3-Induced Signaling in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines with Divergent Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation Patterns. 33492448_miR-34a induces immunosuppression in colorectal carcinoma through modulating a SIRT1/NF-kappaB/B7-H3/TNF-alpha axis. 33531429_Preclinical Evaluation of B7-H3-specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 33533945_Mast cell proliferation in the cerebrospinal fluid after intraventricular administration of anti-B7H3 immunotherapy. 33558663_Tumor B7-H3 expression in diagnostic biopsy specimens and survival in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. 33669921_Gastric Carcinomas with Stromal B7-H3 Expression Have Lower Intratumoural CD8+ T Cell Density. 33743142_B7-H3, Negatively Regulated by miR-128, Promotes Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration. 33795387_Multiparametric flow cytometry highlights B7-H3 as a novel diagnostic/therapeutic target in GD2neg/low neuroblastoma variants. 33798549_A regulatory loop among CD276, miR-29c-3p, and Myc exists in cancer cells against natural killer cell cytotoxicity. 33815356_Immune Checkpoint-Associated Locations of Diffuse Gliomas Comparing Pediatric With Adult Patients Based on Voxel-Wise Analysis. 33845814_Expression patterns of the immune checkpoint ligand CD276 in urothelial carcinoma. 33875234_MiR-29c downregulates tumor-expressed B7-H3 to mediate the antitumor NK-cell functions in ovarian cancer. 33925968_In Vitro Evaluation of CD276-CAR NK-92 Functionality, Migration and Invasion Potential in the Presence of Immune Inhibitory Factors of the Tumor Microenvironment. 33976130_FUT8-mediated aberrant N-glycosylation of B7H3 suppresses the immune response in triple-negative breast cancer. 34100183_MicroRNA miR-29a Inhibits Colon Cancer Progression by Downregulating B7-H3 Expression: Potential Molecular Targets for Colon Cancer Therapy. 34104078_Immune checkpoint molecules are regulated by transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34125445_Immune checkpoint B7-H3 protein expression is associated with poor outcome and androgen receptor status in prostate cancer. 34290311_CD276 is an important player in macrophage recruitment into the tumor and an upstream regulator for PAI-1. 34431237_Fibronectin enhances tumor metastasis through B7-H3 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 34542756_Soluble B7-H3 in Ovarian Cancer and Its Predictive Value. 34552155_Reduced B7-H3 expression by PAX3-FOXO1 knockdown inhibits cellular motility and promotes myogenic differentiation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 34555253_Association analysis of B7-H3 and B7-H4 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in eastern Chinese Han population. 34562306_Integrated analysis reveals distinct molecular, clinical, and immunological features of B7-H3 in acute myeloid leukemia. 34565408_Gene clusters based on OLIG2 and CD276 could distinguish molecular profiling in glioblastoma. 34671026_B7-H3 regulates osteoclast differentiation via type I interferon-dependent IDO induction. 34787059_Expression characteristic of 4Ig B7-H3 and 2Ig B7-H3 in acute myeloid leukemia. 34799346_B7-H3 Suppresses Antitumor Immunity via the CCL2-CCR2-M2 Macrophage Axis and Contributes to Ovarian Cancer Progression. 34825713_B7H3 expression and significance in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 34979195_B7-H3 blockade decreases macrophage inflammatory response and alleviates clinical symptoms of arthritis. 35029291_B7H3 promotes the epithelialmesenchymal transition of NSCLC by targeting SIRT1 through the PI3K/AKT pathway. 35045656_[Preliminary study on the effect of B7H3 interaction with fibronectin on apoptosis of human chronic myeloid leukemia cells]. 35115487_LINC01123 promotes immune escape by sponging miR-214-3p to regulate B7-H3 in head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma. 35312883_B7 homolog 3 induces lung metastasis of breast cancer through Raf/MEK/ERK axis. 35333400_Association of B7-H3 expression with racial ancestry, immune cell density, and androgen receptor activation in prostate cancer. 35563359_Elevated Expression of the Immune Checkpoint Ligand CD276 (B7-H3) in Urothelial Carcinoma Cell Lines Correlates Negatively with the Cell Proliferation. 35777267_Clinical significance of B7-H3 and HER2 co-expression and therapeutic value of combination treatment in gastric cancer. 36175880_Comprehensive analysis of alternative polyadenylation regulators concerning CD276 and immune infiltration in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000035914 |
Cd276 |
2730.851665 |
2.2688996091 |
1.181993 |
0.045935531 |
656.307596 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000094916894395066287481966834070983926261849752062485983985988575471694889703419369608566361339891099398811522220861672397343359779465728476278883229984425379464960046580616281365004972610 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000058864426944167160124898627440965063780632494267507359539657012065480653185501633154881533340780771942792266390735411653362533669762586567734226122272874767105888420179236303881509829186 |
Yes |
No |
3910.0466501 |
114.3053623 |
1735.8127023 |
38.5729034 |
| ENSG00000103876 |
2184 |
FAH |
protein_coding |
P16930 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Phenylalanine catabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tyrosine catabolism |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-phenylalanine degradation; acetoacetate and fumarate from L-phenylalanine: step 6/6. |
This gene encodes the last enzyme in the tyrosine catabolism pathway. FAH deficiency is associated with Type 1 hereditary tyrosinemia (HT). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2184; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; fumarylacetoacetase activity [GO:0004334]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; arginine catabolic process [GO:0006527]; homogentisate catabolic process [GO:1902000]; L-phenylalanine catabolic process [GO:0006559]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; tyrosine catabolic process [GO:0006572] |
11476670_A missense mutation in the fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase gene, responsible for hereditary tyrosinemia, acts as a splicing mutation. 15465000_Data describe the metabolism of fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase mRNA harboring a nonsense mutation, W262X, in lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from hereditary tyrosinemia type I patients. 15638932_identification of an alternative nonsense transcript of the fah gene, which despite being subjected to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, produces a protein in different human tissues 15759101_An immunopositive liver nodule was found in a patient with tyrosinemia having a mosaic pattern of FAH. 18072279_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21764616_We detected 11 novel and 6 previously described pathogenic mutations in the fumarylacetoacetase gene in a cohort of 43 patients originating from the Middle East with the acute form hereditary tyrosinemia type I 22554029_Identification of novel mutations in the fumarylacetoacetase gene in Hereditary tyrosinaemia type I. 22884142_Compound mutations (R237X and L375P) in the fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase gene causing tyrosinemia type I in a Chinese patient. 23895425_Four splicing mutations affecting exonic or intronic nucleotides of the FAH gene were identified in two hereditary tyrosinemia type I patients. 24016420_Two siblings have been described with tyrosinemia type 1 complicated by reversible hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in infancy due to a FAH homozygous mutation. 26565546_FAH gene mutation is associated with tyrosinemia type 1. 27397503_Results from whole exome sequencing revealed a novel homozygous missense variant in FAH causing tyrosinemia type I . This novel variant involves the catalytic pocket of the enzyme, but does not result in increased succinylacetone or tyrosine. 28755182_molecular aspects of the FAH gene and its corresponding protein and a complete listing of all the mutations identified to date; highlight of the importance of splicing mutations in hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 29497141_Altogether these findings elucidate the molecular basis of HT1 caused by the frequent FAH c.1062+5G>A mutation, and demonstrate the compensatory effect of the c.1061C>A change in promoting exon definition, thus unraveling a rare mechanism leading to FAH immune-reactive mosaicism. 30843237_A liver-humanized mouse model of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1-deficiency. 31568711_We identified pathogenic variants in 15/16 studied alleles (93.8%). Nine different variants were found. The most commonly detected HT1-causing allele was NM_000137.2(FAH):c.3G > A or p.(?) [rs766882348] (25%, n = 4/16). We also identified a novel missense variant NM_000137.2(FAH):c.36C > A or p.(Phe12Leu) in a homozygous patient with an early and fatal acute form. 31584309_Genetic Analysis of Tyrosinemia Type 1 and Fructose-1, 6 Bisphosphatase Deficiency Affected in Pakistani Cohorts. 33218190_E3 Ubiquitin Ligase APC/C(Cdh1) Negatively Regulates FAH Protein Stability by Promoting Its Polyubiquitination. 33670179_Therapeutic Targeting of Fumaryl Acetoacetate Hydrolase in Hereditary Tyrosinemia Type I. 34382351_Survival-Assured Liver Injury Preconditioning (SALIC) Enables Robust Expansion of Human Hepatocytes in Fah(-/-) Rag2(-/-) IL2rg(-/-) Rats. 34678209_Fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase gene as a knockout target for hepatic chimerism and donor liver production. |
ENSMUSG00000030630 |
Fah |
83.685467 |
2.0302079658 |
1.021628 |
0.196157465 |
26.920242 |
0.00000021202665477420440481172274078264239349778108589816838502883911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000807616367604453383338713491623739315627972246147692203521728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
104.9435194 |
12.5892573 |
52.0097039 |
4.7116397 |
| ENSG00000103888 |
57214 |
CEMIP |
protein_coding |
Q8WUJ3 |
FUNCTION: Mediates depolymerization of hyaluronic acid (HA) via the cell membrane-associated clathrin-coated pit endocytic pathway. Binds to hyaluronic acid. Hydrolyzes high molecular weight hyaluronic acid to produce an intermediate-sized product, a process that may occur through rapid vesicle endocytosis and recycling without intracytoplasmic accumulation or digestion in lysosomes. Involved in hyaluronan catabolism in the dermis of the skin and arthritic synovium. Positively regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and hence tumor cell growth, invasion and cancer dissemination. In collaboration with HSPA5/BIP, promotes cancer cell migration in a calcium and PKC-dependent manner. May be involved in hearing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23509262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23990668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269685}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coated pit;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Hyaluronic acid;Hydrolase;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Enables several functions, including clathrin heavy chain binding activity; hyaluronic acid binding activity; and hyalurononglucosaminidase activity. Involved in several processes, including hyaluronan catabolic process; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation; and positive regulation of transport. Located in clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle; endoplasmic reticulum; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57214; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle [GO:0045334]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; clathrin heavy chain binding [GO:0032050]; ER retention sequence binding [GO:0046923]; hyaluronic acid binding [GO:0005540]; hyalurononglucosaminidase activity [GO:0004415]; hyaluronan biosynthetic process [GO:0030213]; hyaluronan catabolic process [GO:0030214]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; positive regulation of protein kinase C activity [GO:1900020]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
14577002_three possibly disease-causing point mutations 19434458_KIAA1199 was highly expressed in gastric cancer, and was associated with prognosis and lymph node metastasis in multivariate analyses. Taken together, KIAA1199 may be a novel gene that plays an important role in progression of gastric cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21443102_KIAA1199 is upregulated in gastric adenocarcinoma and is associated with tumor progression. 21772334_KIAA1199 transcript and protein are highly expressed in the majority of CRCs. KIAA1199 probably participates in Wnt-signalling, affecting cell proliferation, motility, adhesion. Also, KIAA1199 has a clinical correlation to outcome in stage-II CRC patients 22276102_KIAA1199 is differentially expressed in neoplastic tissues and KIAA1199 transcripts are more abundant in the plasma of patients with either cancer or adenoma compared to controls. 23509262_KIAA1199 is a new hyaluronan binding protein involved in hyaluronan depolymerization. 23936024_proteins that might interact with KIAA1199 and molecular pathways in which it might play roles, were identified. 23990668_KIAA1199 serves as a novel cell migration-promoting gene and plays a critical role in maintaining cancer mesenchymal status. 24269685_Results suggest that the N-terminal portion of KIAA1199 functions as a cleavable signal sequence required for proper KIAA1199 translocation and KIAA1199-mediated HAhyaluronan depolymerization. 24573670_KIAA1199 influences the proliferation, adhesion, motility, invasiveness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells, is a likely target gene of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway[review] 24628760_Findings indicate that KIAA1199 may play an important role in breast tumor growth and invasiveness. 25051373_KIAA1199 plays an important role in glycogen breakdown and cancer cell survival 25366117_oncogenic protein induced by HPV infection and constitutive NF-kappaB activity that transmits pro-survival and invasive signals through EGFR signalling 26009875_Results provide insight into the upregulation of CEMIP within cancer and can lead to novel treatment strategies targeting this cancer cell migration-promoting gene. 26045799_We present evidence that high expression of KIAA1199 is associated with tumor invasion depth, TNM stage, and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer 26437221_CEMIP directly facilitates colon tumor growth, and high CEMIP expression correlates with poor outcome in stage III and in stages II+III combined cohorts. 26518873_Regulation of Hyaluronan (HA) Metabolism Mediated by HYBID (Hyaluronan-binding Protein Involved in HA Depolymerization, KIAA1199) and HA Synthases in Growth Factor-stimulated Fibroblasts. 27922049_KIAA1199 is overexpressed in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. 28012880_Overexpression of KIAA1199 may contribute to increased migration of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and predict shorter survival after surgical resection. 28179576_Results suggest a possible link between inflammation, induced KIAA1199 expression, and enhanced migration during pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression. 28213952_Elevated KIAA1199 protein expression is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis in colorectal cancer. 28422983_KIAA1199 promotes migration and invasion by Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and matrix metalloproteinase-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression, and serves as a poor prognosis marker in gastric cancer. 28901311_Our findings revealed that KIAA1199 protein could be applied in predicting nonsmall cell lung cancer patient's outcome 29024602_the in-vitro anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in colorectal cancer cells that were induced by silencing cell migration inducing hyaluronan binding protein may be associated with GRP78 repression and UPR attenuation 29467409_CEMIP showed a diagnostic yield of 86.1% (68/79) in CA 19-9 negative pancreatic cancer. 29505302_Upregulation of CEMIP promotes migration and invasion in anoikis-resistant prostate cancer cells by enhancing PDK4-associated metabolic reprogramming. 29808799_CEMIP expression was increased in retinoblastoma tissues and cells. miR-140-5p inhibited CEMIP expression possibly by targeting the 3'-UTR. 29886655_expression of KIAA1199 is up-regulated in primary hepatocellular carcinoma, which is significantly correlated with the clinicopathological features and prognosis, high expression of KIAA1199 increased the risk of death in patients with primary hepatocellular carcinom 29915160_Here, we demonstrate that BRAF(V600E) -mutated colorectal cancers acquire resistance to MEK1 inhibition by inducing expression of the scaffold protein CEMIP through a beta-catenin- and FRA-1-dependent pathway 29935163_High HYBID expression is associated with osteoarthritis. 30166321_CEMIP expression in lung fibroblasts (FB) was downregulated in a glioma-associated oncogene homologue-dependent manner and CEMIP silencing in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis FB reduced collagen production and attenuated cell proliferation and migration. 30202098_study reveals that KIAA1199 promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via microtubule destabilization regulated by a PP2A/stathmin pathway, and suggests that KIAA1199 may be a promising target for preventing metastasis in colorectal cancer. 30241936_Findings indicate that hyaluronan-binding protein (HYBID) is indispensable for KIAA1199 (CEMIP)-mediated hyaluronan-B (HA) depolymerization in skin fibroblasts, but transmembrane protein 2 (TMEM2) is not involved in the HYBID-mediated process as a catalytic hyaluronidase. 30478628_KIAA1199 overexpression is an independent prognostic marker in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). KIAA1199 expression directly influences the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers. KIAA1199 promotes invasion and migration in NSCLC via PI3K-Akt mediated EMT. 30755597_KIAA1199 is a mobilizing factor that interacts with P38 and Wnt signaling, and induces changes in actin cytoskeleton, as a mechanism mediating recruitment of hMSC to bone formation sites. 30925458_CEMIP may promote the development of ovarian cancer by regulating PI3K/AKT signaling. 30980868_Studies showed that KIAA1199 promoted the migration, invasion, and metastasis of sorafenib-resistant HCC cells. Mechanistically, KIAA1199 is required for EGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in sorafenib-resistant HCC cells by aiding in EGFR phosphorylation. 31011255_CASC19 expression was upregulated in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues and CRC cell lines. Higher CASC19 expression was associated with poorer prognoses. CASC19 positively regulates CEMIP expression through targeting miR-140-5p. CASC19 may regulate the proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasizing ability of CRC cells by regulating microRNA-140-5p, as well as cell migration by inducing CEMIP. 31103876_Expression of KIAA1199 was highly upregulated in osteoarthritic cartilage. KIAA1199 knockdown exerted anti-catabolic and anti-inflammatory effects on IL-1beta-induced human chondrocytes via regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Therefore, pharmacological inhibition of KIAA1199 may represent a promising therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. 31501407_The miR-486-5p/KIAA1199/epithelial-mesenchymal transition axis might play a critical role in Papillary Thyroid Cancer invasion and metastasis. 31685984_Tumor exosomal CEMIP protein promotes cancer cell colonization in brain metastasis. 31746434_Data indicate that CEMIP is regulated by HCP5 and modulates the growth of prostate cancer cells. 31810922_Although overall survival rates (OSR) of patients, who underwent surgery did not correlate with KIAA1199 expression, patients who underwent adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 and had high KIAA1199 levels displayed significantly lower OSR. KIAA1199 expression appears to be a promising prognostic marker in patients with locally advanced GC, who underwent postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1. 31949043_HYBID (alias KIAA1199/CEMIP) and hyaluronan synthase coordinately regulate hyaluronan metabolism in histamine-stimulated skin fibroblasts. 32084364_The present study found that HYBID is up-regulated in knee osteoarthritis synovial tissue. 32207314_CEMIP regulates the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis through the WNT-beta-catenin signaling pathway. 32519472_Downregulation of KIAA1199 by miR-486-5p suppresses tumorigenesis in lung cancer. 32648226_A novel metastatic promoter CEMIP and its downstream molecular targets and signaling pathway of cellular migration and invasion in SCLC cells based on proteome analysis. 32757700_Cell migration inducing hyaluronidase 1 (CEMIP) activates STAT3 pathway to facilitate cell proliferation and migration in breast cancer. 33197891_Serum KIAA1199 is an advanced-stage prognostic biomarker and metastatic oncogene in cholangiocarcinoma. 33327261_Co-expression of KIAA1199 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a biomarker for an unfavorable prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33473125_Secreted KIAA1199 promotes the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by mediating hyaluronic acid degradation in an ANXA1-dependent manner. 33669634_The Attenuated Secretion of Hyaluronan by UVA-Exposed Human Fibroblasts Is Associated with Up- and Downregulation of HYBID and HAS2 Expression via Activated and Inactivated Signaling of the p38/ATF2 and JAK2/STAT3 Cascades. 33773462_The emerging role of KIAA1199 in cancer development and therapy. 33887254_HYBID derived from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages contribute to the glioblastoma growth. 33928604_LncRNA LINC00958 promotes tumor progression through miR-4306/CEMIP axis in osteosarcoma. 34058990_CircHYBID regulates hyaluronan metabolism in chondrocytes via hsa-miR-29b-3p/TGF-beta1 axis. 34455220_MiR-148a-3p targets CEMIP to suppress the genesis of gastric cancer cells. 34521918_Hypoxia increases KIAA1199/CEMIP expression and enhances cell migration in pancreatic cancer. 34608265_CEMIP, a novel adaptor protein of OGT, promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through glutamine metabolic reprogramming via reciprocal regulation of beta-catenin. 35013120_ATF4/CEMIP/PKCalpha promotes anoikis resistance by enhancing protective autophagy in prostate cancer cells. 35474501_CEMIP (KIAA1199) regulates inflammation, hyperplasia and fibrosis in osteoarthritis synovial membrane. 35543351_Cell migration inducing hyaluronidase 1 promotes growth and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 36241903_Expression and regulation of recently discovered hyaluronidases, HYBID and TMEM2, in chondrocytes from knee osteoarthritic cartilage. 36395406_Concurrent Overexpression of Two Hyaluronidases, KIAA1199 and TMEM2, Strongly Predicts Shorter Survival After Resection in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. 36419650_KIAA1199 Correlates With Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Infiltration in Lung Adenocarcinoma as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker. |
ENSMUSG00000052353 |
Cemip |
3754.090684 |
3.5223068542 |
1.816521 |
0.046177760 |
1506.202441 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6038.2582682 |
173.5473269 |
1726.0681502 |
38.2203301 |
| ENSG00000103942 |
9455 |
HOMER2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NSB8 |
FUNCTION: Postsynaptic density scaffolding protein. Binds and cross-links cytoplasmic regions of GRM1, GRM5, ITPR1, DNM3, RYR1, RYR2, SHANK1 and SHANK3. By physically linking GRM1 and GRM5 with ER-associated ITPR1 receptors, it aids the coupling of surface receptors to intracellular calcium release. May also couple GRM1 to PI3 kinase through its interaction with AGAP2. Isoforms can be differently regulated and may play an important role in maintaining the plasticity at glutamatergic synapses (PubMed:9808459). Required for normal hearing (PubMed:25816005). Negatively regulates T cell activation by inhibiting the calcineurin-NFAT pathway. Acts by competing with calcineurin/PPP3CA for NFAT protein binding, hence preventing NFAT activation by PPP3CA (PubMed:18218901). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18218901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25816005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9808459}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Disease variant;Hearing;Membrane;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the homer family of dendritic proteins. Members of this family regulate group 1 metabotrophic glutamate receptor function. The encoded protein is a postsynaptic density scaffolding protein. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Two related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosome 14. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:9455; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; intracellular organelle [GO:0043229]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; stereocilium tip [GO:0032426]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; G protein-coupled glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035256]; synaptic receptor adaptor activity [GO:0030160]; behavioral response to cocaine [GO:0048148]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; chemical homeostasis within a tissue [GO:0048875]; G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007216]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032703]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; regulation of store-operated calcium entry [GO:2001256]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
12815733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16314758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16314758_Polymorphism in the Homer2 gene is not a potential risk factor for the development of cocaine dependence in an African American population. 18218901_study found that Homer2 and Homer3 are negative regulators of T cell activation; this is achieved through binding of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and by competing with calcineurin 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914345_This study supports a role for HOMER2 gene in schizophrenia susceptibility. 20333726_Haplotypes of the HOMER 1 and 2 genes are unlikely to play a major role in the pathophysiology of alcohol dependence. 20333726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21885651_monitored Homer1 and Homer2 expression and subcellular localization in skeletal muscle biopsies following 60 days of bedrest 25649652_This study showed that HOMER2 (rs1256429; intronic, p = 8.7 x 10(1)) associated with Alzheimer disease. 25816005_These data provide compelling evidence that HOMER2 is required for normal hearing and that its sequence alteration in humans leads to ADNSHL through a dominant-negative mode of action 27832625_Homer1 and Homer2 might be considered as novel diagnostic biomarkers for large-artery atherosclerosis stroke. 29891190_that HOMER2 may be involved in tumourigenesis of endometrioid uterine tumours 30047143_we have identified a distinct, novel insertion variant in HOMER2, which provides validating evidence that HOMER2 is indeed required for normal hearing. Its sequence alteration is responsible for late-onset, autosomal dominant, non-syndromic, SNHL in humans. 33809266_A Novel Truncating Mutation in HOMER2 Causes Nonsyndromic Progressive DFNA68 Hearing Loss in a Spanish Family. |
ENSMUSG00000025813 |
Homer2 |
175.863889 |
0.3850903150 |
-1.376731 |
0.124992007 |
125.220228 |
0.00000000000000000000000000004554852440044264519426041849900634436054901084553781089894616637230907808310022277797912693131365813314914703369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000567817753505518114561758416048595069473612128326371909938530738125193810406782235489231425162870436906814575195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.4758079 |
7.4722976 |
241.9429005 |
11.9795289 |
| ENSG00000104177 |
50804 |
MYEF2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2K5 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor of the myelin basic protein gene (MBP). Binds to the proximal MB1 element 5'-TTGTCC-3' of the MBP promoter. Its binding to MB1 and function are inhibited by PURA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;RNA-binding;Transcription;Ubl conjugation |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in myotube differentiation and neuron differentiation. Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:50804; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; post-mRNA release spliceosomal complex [GO:0071014]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; myotube differentiation [GO:0014902]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; regulation of mRNA stability involved in response to oxidative stress [GO:2000815]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20709755_RNA-binding protein Muscleblind-like 3 (MBNL3) disrupts myocyte enhancer factor 2 (Mef2) {beta}-exon splicing 27866970_both polymorphisms (rs1426654 and rs2470102) play an important role in the skin pigmentation diversity of South Asians 27871913_This study demonstrated that none of the associations between time-frequency phenotypes and MYEF2 were significant. |
ENSMUSG00000027201+ENSMUSG00000049230 |
Myef2+Myef2l |
120.604995 |
0.4834054437 |
-1.048694 |
0.183641844 |
32.475908 |
0.00000001206793458093518253175109567441880553673172471462748944759368896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000052189485618108202159426552927540265969241772836539894342422485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
78.3292195 |
12.9044114 |
162.8516996 |
18.8910557 |
| ENSG00000104312 |
8767 |
RIPK2 |
protein_coding |
O43353 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses (PubMed:9575181, PubMed:9642260, PubMed:17054981, PubMed:21123652, PubMed:21887730, PubMed:28656966). Upon stimulation by bacterial peptidoglycans, NOD1 and NOD2 are activated, oligomerize and recruit RIPK2 through CARD-CARD domains (PubMed:17054981, PubMed:21123652, PubMed:28656966). Contributes to the tyrosine phosphorylation of the guanine exchange factor ARHGEF2 through Src tyrosine kinase leading to NF-kappa-B activation by NOD2 (PubMed:21123652). Once recruited, RIPK2 autophosphorylates and undergoes 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination by E3 ubiquitin ligases XIAP, BIRC2 and BIRC3. The polyubiquitinated protein mediates the recruitment of MAP3K7/TAK1 to IKBKG/NEMO and induces 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of IKBKG/NEMO and subsequent activation of IKBKB/IKKB (PubMed:18079694). In turn, NF-kappa-B is released from NF-kappa-B inhibitors and translocates into the nucleus where it activates the transcription of hundreds of genes involved in immune response, growth control, or protection against apoptosis (PubMed:18079694). Also plays a role during engagement of the T-cell receptor (TCR) in promoting BCL10 phosphorylation and subsequent NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:14638696). Plays a role in the inactivation of RHOA in response to NGFR signaling (PubMed:26646181). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14638696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17054981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18079694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21123652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21887730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26646181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28656966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9575181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9642260}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the receptor-interacting protein (RIP) family of serine/threonine protein kinases. The encoded protein contains a C-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD), and is a component of signaling complexes in both the innate and adaptive immune pathways. It is a potent activator of NF-kappaB and inducer of apoptosis in response to various stimuli. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8767; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; CARD domain binding [GO:0050700]; caspase binding [GO:0089720]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; JUN kinase kinase kinase activity [GO:0004706]; LIM domain binding [GO:0030274]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097202]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0035739]; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid [GO:0071223]; cellular response to muramyl dipeptide [GO:0071225]; cellular response to peptidoglycan [GO:0071224]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033080]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 signaling pathway [GO:0070427]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway [GO:0070431]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:2000563]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001961]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033092]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045627]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002827]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of xenophagy [GO:1904417]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to interleukin-12 [GO:0070671]; response to interleukin-18 [GO:0070673]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852]; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway [GO:0034134]; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034142]; xenophagy [GO:0098792] |
11894097_Involvement of receptor-interacting protein 2 in innate and adaptive immune responses 11894098_Rip2 transduces signals from both innate and adaptive immune responses. Functions downstream of the TLR2/3/4, IL-1 and IL-18 receptors. 12138198_These results implicate RIP2 in a previously unrecognized role: a checkpoint for myogenic proliferation and differentiation. 12755636_equilibrium and kinetic folding of a unique protein domain, caspase recruitment domain (CARD), of the RIP-like interacting CLARP kinase (RICK) (RICK-CARD), which adopts a alpha-helical Greek key fold 12775719_role in CARD6 modulation of NF-kappa B activation 14638696_Rip2 has an important role in TCR-induced NF-kappaB activation and T-cell function 15620648_NOD2-dependent ubiquitinylation of NEMO (a key component of the NF-kB signaling complex) is dependent on the scaffolding protein kinase RIP2. 16354923_Caspase-1-mediated cell death is regulated, at least in part, by the balance of Rip2 and Cop; alterations of this balance may contribute to aberrant caspase-1-mediated pathogenesis in Huntington's disease. 16418290_CARD6 is a regulator of NF-kappaB activation that modulates the functions of RICK protein 16492792_NOD2-S interacts with both, NOD2 and receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 and inhibits the 'nodosome' assembly by interfering with the oligomerization of NOD2 16582588_review of the regulation of interactions of CARD6 with RICK and microtubules [review] 16824733_Results indicate that S176 is a regulatory autophosphorylation site for RIP2 and that S176 phosphorylation can be used to monitor the activation state of RIP2. 16920334_Cop inhibition of cell death, at least to a certain extent, results from its interference with the activation of caspase-1 and caspase-4. 17054981_mutational analysis shows that interaction of NOD1 with RICK is critically dependent on 3 acidic residues on NOD1 CARD & 3 basic residues on RICK CARD & is likely to have a strong electrostatic component 17075290_Although polymorphisms in RIP2 are not likely to be associated with the development of asthma, the genetic variants might contribute to asthma severity in the Japanese population 17355968_NOD2 is responsible for the membrane recruitment of RICK to induce a regulated NF-kappaB signaling and production of proinflammatory cytokines. 17851464_RIPK2 is a marker for resolution of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis. 18079694_Data show that RICK polyubiquitination links TAK1 to IKK complexes, a critical step in Nod1/Nod2-mediated NF-kappaB activation. 18359207_The encapsulation efficiency of RIPK2 is reported. 18426885_We conclude that the endogenous IL-8 response induced by C. trachomatis infection is dependent upon NOD1 signaling through RIP2 as part of a signal system requiring multiple inputs for optimal IL-8 induction. 18566542_upregulation of RIP2 expression is required for rapid resolution of peritonitis 19121870_alternative mRNA splicing may be involved in the regulation of RIP2 actions, underlying the complexity of RIP2-dependent pathways regulating stress signaling and apoptosis. 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19406482_detected on all female reproductive tract tissues 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667203_Data suggest a role for XIAP in regulating innate immune responses by interacting with NOD1 and NOD2 through interaction with RIP2. 19693652_Elevated RIP-2 protein levels promote NF-kappaB function via interaction with IKK gamma 19721713_the NOD2/RIP2 pathway has a role in recognition of Yersinia, but caspase-12 does not modulate innate host defense against Y. pestis 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19911254_MS80 inhibits CD40-NF-kappaB pathway via targeting RIP2. 20018961_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20025869_Data suggest that inhibition of rip2 upregulation after wounding might contribute to the reduced and delayed wound re-epithelialization phenotype seen in glucocorticoid-treated patients. 20645315_RIP2 polymorphisms are not associated with inflammatory bowel diseases. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21123652_RIP2 undergoes autophosphorylation on Tyr 474 and this event is necessary for effective NOD2 signaling 21757725_Tri-DAP interacts directly with the LRR domain of NOD1 and consequently increases RICK/NOD1 association and RICK phosphorylation activity 21862576_the CARD of procaspase-1 is differently involved in the formation of procaspase-1 activating platforms and procaspase-1-mediated, RIP2-dependent NF-kappaB activation. 21887730_GEF-H1 mediated the activation of Rip2 during signaling by NOD2, but not in the presence of the 3020insC variant of NOD2 associated with Crohn's disease. GEF-H1 functioned downstream of NOD2 as part of Rip2-containing signaling complexes. 22075569_RIP2 gene polymorphisms may be associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in the Chinese population. 22484241_IL-4 failed to up-regulate expression of RP105 at the cell surface. In conclusion, the anti-inflammatory actions of IL-4 occur independently of IL-10, RP105, and the kinase activity of RIPK2 22504414_Association has been found between RIPK2 (rs42490) and cancer risk. 22615316_These findings mechanisms whereby HBeAg modulates intracellular signaling pathways by targeting RIPK2, supporting the concept that HBeAg could impair both innate and adaptive immune responses to promote chronic HBV infection. 22665475_RIP2 tyrosine kinase activity is not only required for NOD2-dependent autophagy but plays a dual role in this process. 22685397_we demonstrate that Porphyromonas gingivalis infection of human aortic endothelial cells resulted in the rapid cleavage of RIPK1 and RIPK2 22815893_inositol phosphatase SHIP-1 inhibits NOD2-induced NF-kappaB activation by disturbing the interaction of XIAP with RIP2 22828789_regulates reduced prostaglandin E2 production in chronic periodontitis 22993319_RIPK2 might play an important role in hepatic cell migration. These findings could shed new light on carcinogenesis and on liver regeneration. 23300079_Data suggest that ubiquitin (Ub) binding provides a negative feedback loop upon NOD1 and NOD2 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing proteins)-dependent activation of receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIP2). 23333941_In an attempt to explore TRAF3 binding partners that may be involved in TRAF3-regulated signaling, a yeast two-hybrid screen of a human spleen cDNA library was undertaken. RIP2 was identified as a TRAF3 binding partner. 23892723_Our findings identify RIP2 as a substrate for Pellino3 and Pellino3 as an important mediator in the Nod2 pathway and regulator of intestinal inflammation. 24015287_LRRK2 and RIPK2 variants in the NOD 2-mediated signaling pathway are associated with susceptibility to Mycobacterium leprae in Indian populations. 24366254_The Nod1/2-Rip2 axis was critical to induce optimal cytokine and chemokine responses to A. baumannii infection. 24642040_Data indicate that receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIP2) is an activator of the NF-kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways. 24658576_Receptor interacting protein-2 plays a critical role in human lung epithelial cells survival in response to Fas-induced cell-death. 24670424_NOD2 downregulates colonic inflammation by IRF4-mediated inhibition of K63-linked polyubiquitination of RICK and TRAF6. 24746552_NOD1 and RIP2 interact with bacterial peptidoglycan on endosomes to promote autophagy and inflammatory signaling. 24958724_the NOD1-RIP2 signaling axis is more complex than previously assumed, that simple engagement of RIP2 is insufficient to mediate signaling 25374171_RIP2 protein, human is involved in human colon tumorigenesis and could be a predictive marker for colon carcinoma progression 26040030_Changes in the expression levels of IRS1, IRS2, RIPK2, RSPO1, and DNA JC15 genes might contribute to the development of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in the obese boys. 26130752_that Rip2 modifies VEGF-induced signalling and vascular permeability in myocardial ischaemia 26297639_RIPK1 and RIPK2 are targets of HIV-1 Protease activity during infection, and their inactivation may contribute to modulation of cell death and host defense pathways by HIV-1 26463597_up-regulated in failing hearts 26466644_Barettin has inhibitory activity against two protein kinases related to inflammation, namely the receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (RIPK2) and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1alpha (CAMK1alpha). 26646181_RIP2 and RhoGDI bind to p75(NTR) death domain at partially overlapping epitopes with over 100-fold difference in affinity, revealing the mechanism by which RIP2 recruitment displaces RhoGDI upon ligand binding. 27122187_a new function of PAX5 in regulating RIP1 and RIP2 activation, which is at least involved in chemotherapeutic drug resistance in B-lymphoproliferative disorders, is reported. 27651416_Together, the data demonstrate that the NOD2-RIP2 pathway is activated in murine and human visceral leishmaniasis and plays a role in shaping adaptive immunity toward a Th1 profile. 27830463_this study reveals that LRRK2 is a new positive regulator of Rip2 and promotes inflammatory cytokine induction through the Nod1/2-Rip2 pathway. 27939575_Data indicate that receptor-interacting protein 2 (Rip2) polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of subclinical atherosclerosis (SA) and with some clinical and metabolic parameters. 28114344_study provides structural and dynamic insights into the NOD1-RIP2 oligomer formation, which will be crucial in understanding the molecular basis of NOD1-mediated CARD-CARD interaction in higher and lower eukaryotes 28545134_RIP2 kinase auto-phosphorylation is intimately coupled to dimerization. 29421659_Together, these data show that RIP2 promotes survival of breast cancer cells through NF-kappaB activation and that targeting RIP2 may be therapeutically beneficial for treatment of TNBC. 29659823_We analyzed a family with dominant inheritance of early-onset Osteoarthritis found that affected individuals harbored a rare variant allele encoding a significant amino acid change (p.Asn104Asp) in the kinase domain of receptor interacting protein kinase 2 (RIPK2) 29693188_Results showed that the expressions of RIP2 and BclxL were positively correlated with the malignant grade of astrocytoma. RIP2 promoted human glioblastoma cell proliferation by inducing expression of BclxL. 30026309_study exemplifies how targeting of the ATP-binding pocket in RIPK2 can be exploited to interfere with the RIPK2-XIAP interaction for modulation of NOD signaling. 30052281_These data illustrate that RIP2 can be activated by a relevant allergic stimulus and that such activation can contribute to allergic airway inflammation 30088101_Nine compounds from the ZINC database show satisfactory results, yielding among those selected, the compound ZINC01540228, as the most promising RIPK2 inhibitor. After binding free energy calculations, the following molecular dynamics simulations showed that the receptor protein's backbone remained stable after the introduction of ligands. 30279485_can form long filaments mediated by its caspase recruitment domain (CARD), in common with other innate immune adaptor proteins; NOD2 tandem CARDs bind to one end of the RIP2 CARD filament 30332343_Two Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms associated with susceptibility to develop dengue in NOD1 or RIPK2 genes were observed Children from Colombia. 30478312_molecular mechanisms how RIP2 is activated and self-propagating signal, are reported. 31044631_these results point to a plausible role for genetic polymorphisms in IL23R and RIPK2 in the development and severity of acute pancreatitis. 31279003_findings firstly exhibit that the G allele of rs39509 in nearGene-3 region of RIPK2 might serve as a hazard for TB in this Western Chinese Han population 31350258_Results demonstrate an essential role of phosphorylation of RIPK2 at Y474 for the inflammatory function and cytosolic RIPosome formation, whereas lack of phosphorylation at S176 can facilitate complex formation. 31903123_Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer by Activating Autophagy Signaling via the Upregulation of CARD3 Expression. 32041789_Porphyromonas gingivalis Cell Wall Components Induce Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression on Human Oral Carcinoma Cells by a Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 2 (RIP2)-Dependent Mechanism. 33204717_Autophagy Regulatory Genes MET and RIPK2 Play a Prognostic Role in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Bioinformatic Analysis Based on GEO and TCGA. 33413510_Hepatic NOD2 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis via a RIP2-mediated proinflammatory response and a novel nuclear autophagy-mediated DNA damage mechanism. 33790054_RIPK2 is an unfavorable prognosis marker and a potential therapeutic target in human kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. 34152391_14-3-3 and erlin proteins differentially interact with RIPK2 complexes. 34356990_Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase-2 as a Potential Prognostic Factor in Colorectal Cancer. 34587513_RIP2 knockdown inhibits cartilage degradation and oxidative stress in IL-1beta-treated chondrocytes via regulating TRAF3 and inhibiting p38 MAPK pathway. 34825931_Activation of RIPK2-mediated NOD1 signaling promotes proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via NF-kappaB pathway. 35033591_Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the NOD1/RIPK2/NF-kappaB pathway. 35099539_RIP2 Knockdown Attenuates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Activation via Negative Regulating Myocardin Expression. 35115556_Receptor-interacting protein kinase 2 (RIPK2) stabilizes c-Myc and is a therapeutic target in prostate cancer metastasis. 35409172_Transcriptional Regulation of RIP2 Gene by NFIB Is Associated with Cellular Immune and Inflammatory Response to APEC Infection. 35473583_A pancancer analysis of the carcinogenic role of receptor-interacting serine/threonine protein kinase-2 (RIPK2) in human tumours. 35477477_High expression of RIPK2 is associated with Taxol resistance in serous ovarian cancer. 35508972_Pan-cancer analysis reveals RIPK2 predicts prognosis and promotes immune therapy resistance via triggering cytotoxic T lymphocytes dysfunction. 36184801_Mechanism of RIP2 enhancing stemness of glioma cells induces temozolomide resistance. |
ENSMUSG00000041135 |
Ripk2 |
137.446149 |
2.9556317050 |
1.563467 |
0.143097279 |
122.572029 |
0.00000000000000000000000000017301858993645463525302945936565718156805031258053076351186839926713658359544098508386866797081893309950828552246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000002105321011922564362313669241781406506693950598143568116064121828318847669259117338924625073559582233428955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
206.7589978 |
18.5041217 |
70.5068755 |
5.1414133 |
| ENSG00000104332 |
6422 |
SFRP1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N474 |
FUNCTION: Soluble frizzled-related proteins (sFRPS) function as modulators of Wnt signaling through direct interaction with Wnts. They have a role in regulating cell growth and differentiation in specific cell types. SFRP1 decreases intracellular beta-catenin levels (By similarity). Has antiproliferative effects on vascular cells, in vitro and in vivo, and can induce, in vivo, an angiogenic response. In vascular cell cycle, delays the G1 phase and entry into the S phase (By similarity). In kidney development, inhibits tubule formation and bud growth in metanephroi (By similarity). Inhibits WNT1/WNT4-mediated TCF-dependent transcription. {ECO:0000250}. |
Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the SFRP family that contains a cysteine-rich domain homologous to the putative Wnt-binding site of Frizzled proteins. Members of this family act as soluble modulators of Wnt signaling; epigenetic silencing of SFRP genes leads to deregulated activation of the Wnt-pathway which is associated with cancer. This gene may also be involved in determining the polarity of photoreceptor cells in the retina. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:6422; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; bone trabecula formation [GO:0060346]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to heparin [GO:0071504]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to vitamin D [GO:0071305]; cellular response to X-ray [GO:0071481]; convergent extension involved in somitogenesis [GO:0090246]; digestive tract morphogenesis [GO:0048546]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; dorsal/ventral axis specification [GO:0009950]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; female gonad development [GO:0008585]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; hematopoietic stem cell differentiation [GO:0060218]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060766]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045578]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of bone remodeling [GO:0046851]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in controlling type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:2000080]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010719]; negative regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process [GO:2000270]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0046676]; negative regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043508]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033689]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050732]; negative regulation of planar cell polarity pathway involved in axis elongation [GO:2000041]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral axis specification [GO:2000054]; neural crest cell fate commitment [GO:0014034]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in axis elongation [GO:0003402]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in neural tube closure [GO:0090179]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902043]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process [GO:2000271]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000052]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; prostate epithelial cord arborization involved in prostate glandular acinus morphogenesis [GO:0060527]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis [GO:0060687]; regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010564]; regulation of midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904956]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; stromal-epithelial cell signaling involved in prostate gland development [GO:0044345]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in somitogenesis [GO:0090244] |
11741940_In this study, the disulfide linkages of recombinant sFRP-1 were determined 12413893_These results indicate that the human secreted frizzled-related protein (hsFRP) gene probably functions as a tumor suppressor in normal cervical epithelium and down-regulation of hsFRP contributes to development of cervical cancer. 14581477_the constitutive up-regulation of SFRP1 could be an adaptive cell survival mechanism 15235574_Our data, so far, exclude SFRP1 as a molecular cause of RD (retinal dystrophies) 15335268_Some hyperplastic polyps from patients with hyperplastic polyposis coli syndrome show a secreted Frizzled receptor protein 1 immunophenotype that could indicate alterations of cellular growth control. 15677765_findings suggest that Secreted frizzled-related proteins 1 (SFRP1) modulates glucocorticoid-induced bone loss 15886250_orbital adipogenesis is enhanced in Grave's ophthalmopathy and elevated levels of sFRP-1 in the orbit may be involved in stimulating this pathogenic process 16007200_SFRP 1 gene is frequently downregulated by promoter hypermethylation and suppresses tumor growth activity of lung cancer cells, which suggests that SFRP 1 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene for lung cancer 16149051_These results establish sFRP-1 as an important negative regulator of human osteoblast and osteocyte survival. 16288033_Data suggest that overexpression of SFRP1 by prostatic tumor stroma may account for the previously reported capacity of prostatic tumor stroma to provide a pro-proliferative paracrine signal to adjacent epithelial cells. 16328026_Results indicate that SFRP1 is the Hedgehog target to confine canonical WNT signaling within stem or progenitor cells. 16407829_Inactivating SFRP1 methylation occurred in all Barrett esophagus samples and in 96% of esophageal adenocarcinomas. 16410684_SFRP1 transcripts were shown to be downregulated in 90% (45/50) of the bladder tumors as compared with the normal bladder tissue. 16410723_These findings suggest that frequent downregulation of SFRP1 expression in breast cancer can be attributed, in large part, to aberrant promoter hypermethylation in conjunction with or without histone deacetylation. 16423993_Significant methylation and silencing of SFRP1 in CLL samples suggests its potential as a major contributor to leukomogenesis 16449975_promoter hypermethylation is the predominant mechanism of SFRP1 gene silencing in human breast cancer 16523202_study identifies sFRP1 inactivation at the premalignant stage of colorectal cancer development, indicating that these pathways may be useful targets for chemoprevention strategies in this common solid tumour 16532032_Represses Wnt signaling in breast tissue, and its downregulation contributes to the activation of Wnt signaling. 16609023_The SFRP1 protein gene plays an important role in the pathogenesis of bladder tumor and can be detected using cellular DNA extracted from urine samples. 16775427_Epigenetic SFRP1 inactivation is associated with urothelial carcinoma 17035233_sFRP-1, a target gene of the hedgehog pathway, is involved in cross-talk between the hedgehog pathway and the Wnt pathway 17353908_Promoter hypermethylation seems to be the predominant mechanism of SFRP1 gene silencing in renal cell carcinoma and may contribute to initiation and progression of this disease. 17443492_knocking down SFRP1 by RNA interference in beta-catenin-deficient cell lines (SK-Hep1) stimulated Wnt signaling and promoted cell growth. Data suggested that SFRP1 suppressed liver cancer cells growth through Wnt canonical signaling 17465504_SFRP1 inactivation is a common and early event caused mainly by hypermethylation in gastric cancer. SFRP1 expression loss may be correlated with tumor metastasis in primary gastric cancer. 17471511_Structure-function analysis of SFRP1 for its Wnt antagonist function is reported. 17485441_DKK1 and SFRP1 inhibit the transformed phenotype of breast cancer cell lines, and DKK1 inhibits tumor formation. 17500071_sFRP-1 is post-translationally modified by tyrosine sulfation at tyrosines 34 and 36, which is inhibited by the treatment of heparin 17544413_Wnt3A treatment significantly activated human hepatic stellate cells, while this was inhibited in secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (sFRP1) overexpressing cells. 17626620_Down-regulation of SFRP1 as a candidate tumor suppressor gene, triggered by the epigenetic and/or genetic events, could contribute to the oncogenesis of hepatic cell carcinoma. 17699851_The data support a role for sFRP1 as a tumor suppressor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and perhaps loss of sFRP1 is an early, aberrant molecular event in renal cell carcinogenesis. 18035687_Epigenetic inactivation by methylation is the predominant mechanism of SFRP1 gene silencing in breast cancer. 18156211_sFRP-1 can interact with Wnt receptors Frizzled 4 and 7 on endothelial cells to transduce downstream to cellular machineries requiring Rac-1 activity in cooperation with GSK-3beta 18274669_increased expression of sFRP1 in trabecular meshwork (TM) appears to be responsible for elevated IOP in glaucoma and restoring Wnt signaling in the TM may be a novel disease intervention strategy for treating glaucoma. 18371946_Forced expression of SFRP1 in cultured prostatic epithelial cells led to sustained activation of JNK that was essential for SFRP1-induced epithelial proliferation. 18497987_Loss of SFRP1 is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma 18528941_Hypermethylation and aberrant expression of SFRP genes are common in pancreatic cancer, which may be involved in pancreatic carcinogenesis. 18592156_Ectopic expression of SFRPs downregulated T-cell factor transcriptional activity in liver cancer cells, while overexpression of a beta-catenin mutant and depletion of SFRP1 using siRNA synergistically upregulated TCF/LEF transcriptional activity. 18639284_SFRP1 is hypermethylated in renal cell carcinoma. 18706212_Data shows that aberrant expression of Wnt antagonist SFRP1 in pancreatic cancer 18774388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18795670_All colorectal neoplasms samples showed hypermethylation in the promoter region of SFRP1 18941195_The soluble frizzled-related protein (FRP)1 family is implicated as possible mediators in hormone down-regulation of the earliest events in lymphopoiesis. 18949430_methylation-associated silencing of SFRP1 frequently occurs in renal cell carcinoma and plays a pivotal role in early carcinogenesis 19053830_sFRP1 can be inhibited by diarylsulfone sulfonamides, affecting osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, and bone mineral density, quality, and strength 19095296_Restoration of the expression of SFRP1 and SFRP2 attenuated Wnt signaling in CaSki cells, decreased abnormal accumulation of free beta-catenin in the nucleus, and suppressed ovarian cancer cell growth. 19118898_sFRP1 promoter methylation is associated with persistent Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myeloid leukemia. 19277043_Secreted Frizzled-related protein-1 is a negative regulator of androgen receptor activity in prostate cancer. 19299079_In multiple myeloma cell lines, aberrant promoter hypermethylation of the secreted Frizzled-related protein genes was a common event, and hypermethylation of SFRP1 was associated with transcriptional silencing. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473496_WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231 xenograft growth 19543515_increased frequency of promoter hypermethylation in SFRP1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia compared to chronic myeloid leukemia. 19565266_Inclusion of the SFRP1 gene into a set of 11 genes has improved the bladder cancer detection. 19569235_Down-regulation of SFRP1 can be triggered by epigenetic and/or genetic events and may contribute to the tumourigenesis of human breast cancer through both canonical and non-canonical WNT signalling pathways. 19690140_Wnt antagonist sFRP1 inhibits Wnt signaling and exerts potent antitumor activity by increasing the apoptosis rate in tumor cells and by impairing tumor vascularization 19702942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19702942_These results suggest that the SFRP1 may be a candidate gene for a BMD determinant 19723665_SFRP1 plays a role in the metastatic potential of renal cell carcinomas 19730886_SFRP1 and SFRP4 appear to be candidate markers for colorectal carcinoma. Unlike SFRP1 as a negative regulator for CRC carcinogenesis, SFRP4 may play quite different biological role in CRC. 19737074_The overall results of this study suggest that although the inhibitors of Wnt pathway promote early chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), they do not provide an ultimately enhancing role in the cartilage tissue engineering of MSCs. 20030932_Hypermethylation of SFRP1 and 2 was present in nine malignant hematopoietic cell lines. 20162454_Methylation of the SFRP1 gene was the major cause of reduced SFRP1 expression which led to Cytoplasm/Nucleus accumulation of beta-catenin and was associated with tumor malignancy. 20208569_Loss of WNT pathway inhibition due to SFRP1 gene silencing is associated with medulloblastoma. 20353273_epigenetic inactivation of SFRP1 is a common event contributing to lung carcinogenesis and maybe used as a potential biomarker for NSCLC in Chinese population. 20471677_Transcriptional down-regulation of the Wnt antagonist SFRP1 in haematopoietic cells of patients with different risk types of MDS. 20595636_Data demonstrate that SFRP1 promotes normal alveolar formation in lung development, although its expression in the adult up-regulates proteins that can cause tissue destruction. 20596629_SFRP1 promoter methylation is aberrant in mesothelioma. 20685720_Downregulation of SFRP1 is associated with recurrence in meningiomas. 20811686_This study suggests that a cause of catenin delocalization in oral cancer could be due to WNT pathway activation, by epigenetic alterations of SFRP-1, SFRP-2, SFRP-4, SFRP-5, WIF-1, DKK-3 genes 20823417_integrative genomics approach to a large cohort of medulloblastomas has identified four disparate subgroups (SFRP1) with distinct demographics, clinical presentation, transcriptional profiles, genetic abnormalities, and clinical outcome. 20848536_reduced SFRP1 expression has been associated with malignancy, low myofibroblast expression of this Wnt inhibitor may be implicated in increased risk of cancer in ulcerative colitis. 20856206_SFRP-1 and the SFRP-like molecule V3Nter can inhibit tumor growth of beta-catenin-activated tumor cells in vivo 21046672_Reduced expression of the sFRP1 protein was frequently observed in Chinese patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, which may at least partially result from the genetic instability, especially loss of heterozygosity. 21344486_WNT1 and SFRP1 mRNA levels were higher in DU145 cells compared to non-osteotropic cells. 21402050_The association of thrombospondin-1 and FRP1 is primarily mediated by the amino-terminal N-module of thrombospondin-1 and the netrin domain of FRP1. 21567192_Promoter hypermethylation of SFRP1 is a frequent event in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 21830441_significant decrease in the expression of SFRP1 and SFRP5 was observed in gastric cancer compared with corresponding normal gastric tissues 22031861_Data identified SFRP1 as a transcriptional repression target of the t(8;21) fusion protein and demonstrated a novel mechanism of Wnt activation in a specific subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 22178351_study reports data of association studies with osteoporosis related parameters and sFRP1 in men; also show significant associations between genetic variation in sFRP1 and adiposity related parameters 22246241_Sodium butyrate may modulate the SFRP1/2 expression through histone modification and promoter demethylation causing anti-tumor effects in gastric neoplasms. 22296502_Promoter hypermethylation of FRP1 leading to gene inactivation is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 22351518_Epigenetic silencing of sFRP1 activates the canonical Wnt pathway and contributes to increased cell growth and proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma 22576962_our study identified Gremlin 1, FRP, and Dkk-1 as natural brakes on hypertrophic differentiation in articular cartilage. 22927647_evidence presented suggesting that SFRP1 functions as a secreted mediator of senescence through inhibition of Wnt signaling and activation of the retinoblastoma pathway and that cancer-associated SFRP1 mutants are defective for senescence induction 23159077_SFRP1 gene methylation is closely associated with carcinogenesis and development of non-small cell lung cancer. 5-Aza-CdR may reverse the methylation of SFRP1, p16 and MGMT genes, and facilitate the re-expression of the anti-oncogenes. 23215838_Concomitant epigenetic silencing of SOX1 and SFRPs through promoter hypermethylation is frequent in hepatocellular carcinoma, and this might contribute to abnormal activation of canonical Wnt signal pathway. 23441124_Evidence that tear-protein SFRP1 levels are altered in keratoconus (KC) suggests the involvement of SFRPs in the pathogenesis of KC. 23449484_Increased expression of SFRP-1 and LC3 was observed in keratoconus corneas. 23467623_The basal-like subtype is associated with low methylation levels of the SFRP1 gene. 23572277_Studied the expression of TCF/LEF and SFRP family members (SFRP1 and SFRP3) to gain a better understanding of biological signaling pathways responsible for epidemiology and clinical parameters of clear cell RCC (cRCC). 23698475_The SFRP1 promoter region is hypermethylated in systemic sclerosis patients' fibroblasts and PBMCs compared to controls, leading to decreased SFRP1 expression and aberrant Wnt signalling. 23770846_HCV core-induced epigenetic silencing of SFRP1 may lead to the activation of the Wnt signaling pathway and thus contribute to HCC aggressiveness through induction of EMT. 23802127_sFRP1, an endogenous antagonist of the Wnt pathway, inhibits TGF-beta1-induced EMT. 23927957_sFRP1 is a biomarker for aggressive subgroups of human gastric cancer and a prognostic biomarker for patients with poor survival. 24080158_secreted FRP1 either inhibits or enhances signaling in the Wnt3a/beta-catenin pathway 24096618_We observed strong up-regulation of SFRP1 expression in all meningiomas with AKT1E17K mutation 24127655_Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces reexpression of the transcriptionally silenced SFRP1 gene in hepatoblastoma cells. 24133576_This is the first study to describe an association of the SFRP1 SNP rs3242 and bladder cancer risk as well as the influence of rs3242 on genotype-dependent microRNA capacity on SFRP1 mRNA. 24305703_Low SFRP1 expression is associated with glioma. 24374650_Epigenetic silencing of SFRP1 by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances hepatoma cell tumorigenicity through Wnt signaling pathway 24386373_Polymorphisms in several genes involved in the Wnt signaling pathway were associated with hepatic fibrosis or inflammation risk in HCV-infected males. 24454902_Hypermethylation of SFRP1 predicts poorer survival in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 24504368_Data suggest genistein exerts its anti-tumour effect via downregulation of miR-1260b that targeted sRRP1 and Smad4 genes in prostate cancer cells. Expression of sFRP1 and Smad4 was modulated via DNA methylation or histone modifications in PC. 24594839_results demonstrate that SFRP1 is a favorable prognostic factor for human BTC and that its expression inversely correlates with that of beta-catenin 24625818_miR-27a induced gene silencing contributes to bone metabolism in hFOB cells in vitro, which is partly affected by the post-transcriptional regulation of sFRP1, during osteoblast proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. 24643460_Results provide evidence that SFRP1 is a clinically important determinant of taxanes resistance in human advanced lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) cells, suggesting that it might be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of taxane-resistant LAD patients. 24695522_Our study provided the first evidence that SNPs in CTNNB1 and SFRP1 were associated with tuberculosis risk, and genetic variants in Wnt signaling pathway might participate in genetic susceptibility to tuberculosis in Chinese Han population. 24761891_High SFRP1 gene methylation is associated with ovarian cancer infected with high risk human papillomavirus. 24929326_Studies indicate that secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1) promoter methylation was strongly correlated with colorectal carcinogenesis among both Asians and Caucasians (all P T, CTNNB1 rs2293303 C > T, and WISP1 rs16893344 C > T were all strongly correlated with myocardial infarction (MI) susceptibility. 27420949_SFRP1 expression was significantly lower in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma tissues than that in tissues of control subjects. Histopathological differentiation in CSCC negatively correlated with SFRP1 expression. 27434867_miR-1303 promotes neuroblastoma (NB) proliferation by targeting GSK3beta and SFRP1, and might be a target for NB therapy. 27459115_This study suggested mechanistic relationship between miR-940 and Wnt/beta-catenin in the development and progression of pancreatic carcinoma through regulation of GSK3beta and sFRP1. 27570179_In prostate cancer decreased SFRP1 expression can be due to occupancy of H3K27me3 or to promoter DNA hypermethylation. 27599467_The secreted frizzled-related protein and disheveled protein family members appear to be actively involved in the pathogenesis of primary testicular germ cell tumors. 27739564_Genetic variants in the 3' untranslated region of sFRP1 gene is associated with risk of gastric cancer. 28077379_SFRP1 mRNA expression was reduced by both resistant starch and polydextrose. Resistant starch and polydextrose did not affect SFRP1 methylation or alter the expression of 10 microRNAs predicted to target SFRP1. 28099945_Data suggest that microRNA miR-27a may activate the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by negatively regulating SFRP1 to promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer (BC) cells. 28107193_Data indicate that microRNA miR-744 activated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by targeting multiple negative regulators of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, including SFRP1, GSK3beta, TLE3 and NKD1, and that NKD1 is a major functional target of miR-744. 28169332_sFRP1 overexpression in gastric cancer cells leads to increased cell proliferation and angiogenesis. 28178355_Our results indicate that DKK1 and SFRP1 may be potentially useful biomarkers for evaluating the beneficial effects of long-term exercise on physical fitness and metabolism as well as the prognosis of patients with cancer. 28218291_Study determined that SFRP1 is downregulated during tumor formation probably by DNA methylation, and associates consistently with tumor suppressive functions. 28230864_The expression of Dicer negatively correlated with that of SFRP1 and it appeared to promote CCA cell proliferation. 28398872_H2O2-induced SFRP1 gene demethylation contributes to H2O2-induced apoptosis in human U251 glioma cells. 28435069_Taken together, our results suggest that canonical Wnt signaling and its antagonist, sFRP1, regulate proliferation of human CSCs. Furthermore, excess sFRP1 in elderly patients causes CSC aging. 28605875_miR-1254 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting the expression of SFRP1. 28687085_Loss of SFRP1 likely contributes to tumor progression by altering the expression of a critical transcription factor in both the epithelium and the immune system. 28738713_active involvement in placental development and important role in pathology of pregnancy 28753106_Methylation of SFRP1, SFRP2, SDC2, and PRIMA1 promoter sequences was observed in 85.1%, 72.3%, 89.4%, and 80.9% of plasma samples from patients with Colorectal cancer and 89.2%, 83.8%, 81.1% and 70.3% from adenoma patients, respectively. 28812223_KL and SFRP1 methylation were more predominant in nasopharyngeal tumors. 29146058_preliminary data show loss of SFRP1 protein expression caused by the SFRP1 promoter hypermethylation in a subset of high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas 29358129_miR-1301-3p promoted the expansion of prostate cancer stem cells by inhibiting GSK3beta and SFRP1, and activating the Wnt pathway. 29455276_lost SFRP1 expression-induced Wnt/beta-catenin signaling due to the hypermethylation of the SFRP1 promoter could associate with keloid development 29731501_Methylation level of the SFRP1 promoter region is increased in patients with RCC compared to normal controls and might be involved in the occurrence and development of RCC. 29886152_MiR-208a enhances cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting SFRP1 and negatively regulating MEG3 29984924_Patients with chronic periodontitis exhibit elevated expression of SFRP1 and beta-catenin in gingival tissues, and this event is related to the degree of periodontal destruction. Abnormal expression of SFRP1 and beta-catenin may promote the development of periodontitis. 30055306_WNT5b rs3803164, and SFRP1 rs3242 were significantly associated with lumbar spine BMD. 30158579_Rab37-mediated SFRP1 secretion suppresses cancer stemness. 30235453_co-transfection of sFRP1 siRNA with miR- 191 inhibitor sequence, it was found that the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway was reactivated and the colony formation ability of RBE cells was restored. 30368728_Our results confirmed that promoter methylation of SFRP1 and SFRP2 contributed to the risk of colorectal cancer 30377735_FRP1 expression was upregulated in the clinical heart samples of doxorubicin cardiomyopathy compared with healthy hearts. 30394013_SFRP1 gene was epigenetically silenced in glioblastomas when compared to low astrocytoma grades, which may suggest that the lack of its protein is involved in astrocytoma progression. 30542739_sFRP1 overexpression promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by activating TGFbeta signaling; however, sFRP1 limits the growth inhibitory effect of TGFbeta signaling via Rac1 and GSK3beta. 31072914_Findings suggest that silencing miR-27a dampens osteosarcoma progression, which might be achieved through the inactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by up-regulating secreted frizzled related protein 1 (SFRP1). 31115543_Functional experiments demonstrated that miR144 promoted proliferation, inhibited apoptosis and induced the osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrowderived mesenchymal stem cells by targeting Sfrp1. It was also shown that miR144 may help regulate Osteoporosis (OP) by activating the Wnt/betacatenin pathway. These data suggest miR144 as a novel target for preventing and treating OP 31128064_Promoter methylation of SFRP1 gene is associated with lymph-node metastasis. 31140870_SFRP1 expression is strongly correlated with TNBC on protein level. Associations with age and tumor grade support the role of SFRP1 as a biomarker for chemotherapy response in TNBC. 31215318_Highly specific role of the Wnt inhibitor SFRP1 in maintaining the nonmineralized state of Periodontal ligament progenitors. 31248446_Loss of SFRP1 expression is a significant regulator of transcriptional profiles in AH and acts, in part, to limit estrogen signaling. These results support a broader role for SFRP1 in coordinating estrogen-induced responses and WNT signaling in normal breast epithelial cells. 31609675_Ectopic miR-196a-1 expression promoted invasion of low-invasive gastric cancer (GC) cells by targeting SFRP1. Conclusion: miR-196a-1 was delivered from high-invasive GC into low-invasive GC cells via exosomes and promoted metastasis to the liver in vitro and in vivo. 31770484_SFRP1 inhibited epithelial ovarian cancer through inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 31830937_Hypermethylation of SFRP1 gene in tumor tissue of postoperative CRC pateints is associated with favorable clinical outcome. 31928951_SFRP1 in Skin Tumor Initiation and Cancer Stem Cell Regulation with Potential Implications in Epithelial Cancers. 31947616_Role of Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 in Early Mammary Gland Tumorigenesis and Its Regulation in Breast Microenvironment. 32007530_SFRP1 promotor methylation analysis of FTA card touch-prep samples derived from colonic polyps. 32189106_Data demonstrate that the epigenetic suppression of the WNT/beta-catenin antagonist SFRP1 has an important impact on the malignant behavior of HB cells. 32572894_Effects of Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 on inhibiting cardiac remodeling. 32764696_Increased expression of secreted frizzled related protein 1 (SFRP1) predicts ampullary adenocarcinoma recurrence. 32799225_[sFRP1 Expression Induces miRNAs That Modulate Wnt Signaling in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells]. 33186588_Loss of SFRP1 expression is a key progression event in gastrointestinal stromal tumor pathogenesis. 33207226_Stromal SOX2 Upregulation Promotes Tumorigenesis through the Generation of a SFRP1/2-Expressing Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Population. 33230782_High-risk HPV infection modulates the promoter hypermethylation of APC, SFRP1, and PTEN in cervical cancer patients of North India. 33290588_Wnt antagonist secreted frizzled-related protein I (sFRP1) may be involved in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells in chronic apical periodontitis. 33965401_Transcription factor FOXC1 positively regulates SFRP1 expression in androgenetic alopecia. 34030621_sFRP1 Expression Regulates Wnt Signaling in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia K562 Cells. 34083850_Concurrent Evaluation of the Expression and Methylation of secreted frizzled-related protein 2 along with beta-catenin Expression in Patients with non-M3 Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 34572140_Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 Promotes Odontoblastic Differentiation and Reparative Dentin Formation in Dental Pulp Cells. 34617573_Silencing of MBD2 and EZH2 inhibits the proliferation of colorectal carcinoma cells by rescuing the expression of SFRP. 35210419_Single-cell profiling of human subventricular zone progenitors identifies SFRP1 as a target to re-activate progenitors. 35343265_LINC00092 Suppresses the Malignant Progression of Breast Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Through Modulating SFRP1 Expression by Sponging miR-1827. 35589066_Mechanical stress reduces secreted frizzled-related protein expression and promotes temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 35657114_UVB-induced SFRP1 methylation potentiates skin damage by promoting cell apoptosis and DNA damage. 35892344_Expression of Tumor Suppressor SFRP1 Predicts Biological Behaviors and Prognosis: A Potential Target for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 36368958_The H2A.Z-KDM1A complex promotes tumorigenesis by localizing in the nucleus to promote SFRP1 promoter methylation in cholangiocarcinoma cells. |
ENSMUSG00000031548 |
Sfrp1 |
64.981478 |
0.1554818149 |
-2.685182 |
0.254650503 |
120.375141 |
0.00000000000000000000000000052360767261275748745165375560288037748050429813460539680725450773494632759376410380269817324005998671054840087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000006257853641914413215442032165535062742603939956654874225661267764500621463633067698140166612574830651283264160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.9191989 |
3.2927642 |
122.3608111 |
12.0363175 |
| ENSG00000104356 |
10940 |
POP1 |
protein_coding |
Q99575 |
FUNCTION: Component of ribonuclease P, a ribonucleoprotein complex that generates mature tRNA molecules by cleaving their 5'-ends (PubMed:8918471, PubMed:30454648). Also a component of the MRP ribonuclease complex, which cleaves pre-rRNA sequences (PubMed:28115465). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28115465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30454648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8918471}. |
3D-structure;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;tRNA processing |
|
This gene encodes the protein subunit of two different small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein complexes: the endoribonuclease for mitochondrial RNA processing complex and the ribonuclease P complex. The encoded protein is a ribonuclease that localizes to the nucleus and functions in pre-RNA processing. This protein is also an autoantigen in patients suffering from connective tissue diseases. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:10940; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; multimeric ribonuclease P complex [GO:0030681]; nucleolar ribonuclease P complex [GO:0005655]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ribonuclease MRP complex [GO:0000172]; ribonuclease P activity [GO:0004526]; ribonuclease P RNA binding [GO:0033204]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis, endonucleolytic [GO:0090502]; tRNA 5'-leader removal [GO:0001682]; tRNA catabolic process [GO:0016078]; tRNA processing [GO:0008033] |
16723659_A transient association of protein subunits may be inversely correlated to its involvement in pre-rRNA processing. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21053045_Data idenified two cleavage sites for RNase MRP/RNase P in the coding sequence of viperin mRNA. 21509594_POP1 gene expression is increased in classic variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 22991464_Mitochondrial ribonuclease P structure provides insight into the evolution of catalytic strategies for precursor-trna 5' processing. 25839653_S-palmitoylation alters conformation or secondary structure of Trx1, as well as decreases the ability of Trx1 to transfer electrons from thioredoxin reductase to S-nitrosylated protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B and S-nitroso-glutathione 26275995_by inhibiting inflammasome assembly, provides a regulatory feedback loop that shuts down excessive inflammatory responses; Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome patients exhibit reduced expression 27380734_we reported the third case with POP1-related AAD. This phenotype may appropriately be termed AAD type 2. 28067412_Biallelic POP1 mutations were identified in both. A missense mutation and a novel single base deletion were detected in proband 1, p.[Pro582Ser]:[Glu870fs*5]. Markedly reduced abundance of RMRP and elevated levels of pre5.8s rRNA was observed. In proband 2, a homozygous novel POP1 mutation was identified 32134183_The novel R211Q POP1 homozygous mutation causes different pathogenesis and skeletal changes from those of previously reported POP1-associated anauxetic dysplasia. 36084948_Clinical significance for diagnosis and prognosis of POP1 and its potential role in breast cancer: a comprehensive analysis based on multiple databases. 36225929_POP1 inhibits MSU-induced inflammasome activation and ameliorates gout. |
ENSMUSG00000022325 |
Pop1 |
205.970183 |
2.7671276939 |
1.468389 |
0.128323296 |
132.077719 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000143874817033721030028186337724990330520957623699949658721584441346053350066510711884049111830563560943119227886199951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000018677153029179615775488640936368042625004522019222657642232614497435265010598370860606109999935142695903778076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
305.5633535 |
25.2856150 |
110.8895103 |
7.3073386 |
| ENSG00000104490 |
83988 |
NCALD |
protein_coding |
P61601 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the calcium-dependent regulation of rhodopsin phosphorylation. Binds three calcium ions. |
Calcium;Lipoprotein;Metal-binding;Myristate;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) family of calcium-binding proteins. The protein contains an N-terminal myristoylation signal and four EF-hand calcium binding loops. The protein is cytosolic at resting calcium levels; however, elevated intracellular calcium levels induce a conformational change that exposes the myristoyl group, resulting in protein association with membranes and partial co-localization with the perinuclear trans-golgi network. The protein is thought to be a regulator of G protein-coupled receptor signal transduction. Several alternatively spliced variants of this gene have been determined, all of which encode the same protein; additional variants may exist but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:83988; |
clathrin coat of trans-Golgi network vesicle [GO:0030130]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003073]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
7852401_The author characterizes the biochemical properties of recombinant bovine neurocalcin delta, whose protein sequence is identical to the human ortholog 17671797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17671797_association of the landmark SNP with the progression of diabetic nephropathy in a 8-year prospective study 18500817_Studies show that a fold recognition based model of the catalytic domain of ROS-GC1 was built, and neurocalcin delta docking simulations were carried out to define the three-dimensional features of the interacting domains of the two molecules. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23156397_It is presumed that NCALD is related to diabetic nephropathy by promoting epithelial mesenchymal transform. 28132687_Neurocalcin delta is a protective spinal muscular atrophy modifier in five asymptomatic SMN1-deleted individuals carrying only four SMN2 copies. 30076541_Coffee consumption is causally associated with an increased risk of osteoarthritis. SNPs in NCALD, POR, CYP1A1 and NRCAM were identified. 31109331_high expression of NCALD gene is a poor prognostic factor for cytogenetic normal acute myeloid leukemia. 32030795_NCALD affects drug resistance and prognosis by acting as a ceRNA of CX3CL1 in ovarian cancer. 32228639_Low expression of NCALD is associated with chemotherapy resistance and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000051359 |
Ncald |
68.921948 |
0.1341270602 |
-2.898328 |
0.277361283 |
114.296055 |
0.00000000000000000000000001122358215301116340653528127994092470935550366955789633703888085281637123497011643280529824551194906234741210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000127430825060342143606872697821546855976435289926042655494224922551682946392226369880518177524209022521972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.1558858 |
3.6906316 |
127.9673967 |
16.5572635 |
| ENSG00000104518 |
79792 |
GSDMD |
protein_coding |
P57764 |
FUNCTION: [Gasdermin-D]: Precursor of a pore-forming protein that plays a key role in host defense against pathogen infection and danger signals (PubMed:26375003, PubMed:26375259, PubMed:27281216). This form constitutes the precursor of the pore-forming protein: upon cleavage, the released N-terminal moiety (Gasdermin-D, N-terminal) binds to membranes and forms pores, triggering pyroptosis (PubMed:26375003, PubMed:26375259, PubMed:27281216). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26375003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26375259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281216}.; FUNCTION: [Gasdermin-D, N-terminal]: Promotes pyroptosis in response to microbial infection and danger signals (PubMed:26375003, PubMed:26375259, PubMed:27418190, PubMed:28392147, PubMed:32820063). Produced by the cleavage of gasdermin-D by inflammatory caspases CASP1, CASP4 or CASP5 in response to canonical, as well as non-canonical (such as cytosolic LPS) inflammasome activators (PubMed:26375003, PubMed:26375259, PubMed:27418190). After cleavage, moves to the plasma membrane where it strongly binds to inner leaflet lipids, including monophosphorylated phosphatidylinositols, such as phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, bisphosphorylated phosphatidylinositols, such as phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate, as well as phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-bisphosphate, and more weakly to phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylserine (PubMed:27281216, PubMed:29898893). Homooligomerizes within the membrane and forms pores of 10-15 nanometers (nm) of inner diameter, allowing the release of mature interleukin-1 (IL1B and IL18) and triggering pyroptosis (PubMed:27418190, PubMed:27281216, PubMed:29898893, PubMed:33883744). Gasdermin pores also allow the release of mature caspase-7 (CASP7) (By similarity). Exhibits bactericidal activity (PubMed:27281216). Gasdermin-D, N-terminal released from pyroptotic cells into the extracellular milieu rapidly binds to and kills both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, without harming neighboring mammalian cells, as it does not disrupt the plasma membrane from the outside due to lipid-binding specificity (PubMed:27281216). Under cell culture conditions, also active against intracellular bacteria, such as Listeria monocytogenes (By similarity). Also active in response to MAP3K7/TAK1 inactivation by Yersinia toxin YopJ, which triggers cleavage by CASP8 and subsequent activation (By similarity). Strongly binds to bacterial and mitochondrial lipids, including cardiolipin (PubMed:27281216). Does not bind to unphosphorylated phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylethanolamine nor phosphatidylcholine (PubMed:27281216). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D8T2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26375003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26375259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27281216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27418190, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28392147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29898893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32820063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33883744}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Immunity;Inflammasome;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Necrosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Transmembrane;Transmembrane beta strand |
|
Gasdermin D is a member of the gasdermin family. Members of this family appear to play a role in regulation of epithelial proliferation. Gasdermin D has been suggested to act as a tumor suppressor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:79792; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; NLRP3 inflammasome complex [GO:0072559]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; cardiolipin binding [GO:1901612]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; wide pore channel activity [GO:0022829]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; pore complex assembly [GO:0046931]; pore formation in membrane of another organism [GO:0035915]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 production [GO:0032732]; positive regulation of interleukin-18 production [GO:0032741]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269] |
19051310_Study investigated the expression pattern of the GSDM family genes in the upper gastrointestinal epithelium and cancers. 26375003_caspase-1 and caspase-4/5/11 specifically cleaved the linker between the amino-terminal gasdermin-N and carboxy-terminal gasdermin-C domains in GSDMD, which was required and sufficient for pyroptosis 26611636_Gene deletion of GSDMD demonstrated that GSDMD is required for pyroptosis and for the secretion but not proteolytic maturation of IL-1beta in both canonical and non-canonical inflammasome responses. 27339137_GsdmD p30 kills cells by forming pores that compromise the integrity of the cell membrane. 27383986_GSDMD N-terminal cleavage product oligomerizes in membranes to form pores that are visible by electron microscopy 27418190_Overall, these data demonstrate that GSDMD is the direct and final executor of pyroptotic cell death. 27460194_Studies show that the membrane-pores composed of gasdermin D-N domains (GSDMD-N domain) are required for pyroptosis. 27557502_the gasdermin-D pore: Executor of pyroptotic cell death 27573174_This study reveals the pore-forming activity of GSDMD and channel-forming activity of MLKL determine different ways of plasma membrane rupture in pyroptosis and necroptosis. 27604419_Studies indicate that gasdermin D (GSDMD) is cleaved by the activated caspases-1/4/5/11 between its N-terminal and C-terminal domains. 27932073_The pyroptosis is redefined as gasdermin D-mediated programmed necrosis. Gasdermin D are associated with various genetic diseases, and their cellular function and mechanism of activation. 28679757_Remarkably, the Enterovirus 71 protease 3C directly targets GSDMD and induces its cleavage, which is dependent on the protease activity. 28726636_Data, including data from studies using recombinant fusion forms of GSDMD, suggest that GSDMD participates in inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis of macrophages in response to various stimuli; this mechanism involves proteolysis of GSDMD by caspase-1 and caspase-11. 28928145_These findings reveal that GSDMD-C acts as an auto-inhibition executor and GSDMD-N could form pore structures via a charge-charge interaction upon cleavage by caspases during cell pyroptosis. 29108122_Results implicate pyroptosis induced by the CASP11/4-GSDMD pathway in the pathogenesis of alcoholic hepatitis 29195811_Pyroptosis regulator gasdermin D was necessary for IL-1beta secretion from living macrophages that have been exposed to inflammasome activators, such as bacteria and their products or host-derived oxidized lipids 29273476_Gasdermin D plays a key role in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) by regulating lipogenesis, the inflammatory response, and the NF-kB signaling pathway, revealing potential treatment targets for NASH in humans. 29365280_GSDMD regulates the release of microparticulate active caspase 1 from monocytes essential for induction of cell death and thereby may play a critical role in sepsis-induced endothelial cell injury. 29576317_Study reports the crystal structure of GSDMD C-terminal domain. Two interaction sites mediate the association of C and N domains. Mutations of GSDMD C-domain residues predicted to locate at its interface with the N-domain enhanced pyroptosis. Results suggest that GSDMDs may employ a distinct mode of intramolecular domain interaction and autoinhibition, which may be relevant to its unique role in pyroptosis. 29891674_The present study not only contributes to our understanding of GSDMD recognition by inflammatory caspases but also reports a specific inhibitor for these caspases that can serve as a tool for investigating inflammasome signaling. 29898893_Once inserted, the N-terminal domain of GSDMD assembles arc-, slit-, and ring-shaped oligomers, each of which being able to form transmembrane pores. This assembly and pore formation process is independent on whether GSDMD has been cleaved by caspase-1, caspase-4, or caspase-5. 30106450_High GSDMD expression is associated with tumor-node-metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. 30143555_GSDMD is proteolytically activated by neutrophil proteases and, in turn, affects protease activation and nuclear expansion in a feed-forward loop. In addition to the central role of GSDMD in pyroptosis, we propose that GSDMD also plays an essential function in NETosis. 30226619_lncRNA RP185F18.6 and DeltaNp63 may be considered unfavorable biomarkers, whereas GSDMD may be a favorable biomarker in colorectal cancer (CRC) ; these markers may prove valuable in the future diagnosis and prognosis of CRC 30391945_T. vaginalis inflammasome activation induces macrophage inflammatory cell death by pyroptosis, known to occur via caspase-1 cleavage of the gasdermin D protein, which assembles to form pores in the host cell membrane. We found that T. vaginalis-induced cytolysis of macrophages is attenuated in gasdermin D knockout cells 30392072_role of GSDMD in the stretch-induced inflammatory response in human periodontal ligament cells 30404007_Shiga toxin 2 (Stx2)/Lipopolysaccharide complex, from pathogenic enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli, activates caspase-4, gasdermin D (GSDMD), and the NLRP3 inflammasome in human THP-1 macrophages. 30547277_our current work demonstrates that IL-1beta release from stimulated THP1 cells is regulated by GSDM-D, and P2X7 is a dual-step process 30596757_findings suggest that NLRP3 is central to the activation/release of active caspase-1/GSDM-D encapsulated in microparticles (MP) by Francisella. 30634142_Our findings provide the first demonstration of GSDMD-determined pyroptotic cell death responsible for I/R induced release of IL-1beta and this would provide a mandate to better understand the unconventional mechanisms of cytokine release in the sterile innate immune system. 31276977_GSDMD is required for an optimal cytotoxic t-lymphocyte response to cancer cells 31461796_Gasdermin D: Evidence of pyroptosis in spontaneous preterm labor with sterile intra-amniotic inflammation or intra-amniotic infection. 31480859_alpha-NETA also significantly increased expression of pyroptosis-associated molecules including caspase-4 and GSDMD in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. 31492708_The GSDMD promotes IL-1 release from hyperactive or pyroptotic cells, with a specific focus on defining how these distinct cell fates associated with GSDMD activity can be regulated. 31548300_Gasdermin D (GSDMD) ontrols the release of the proinflammatory cytokines and pyroptotic cell death [Review]. 31802832_The expression of gasdermin D N terminal domain was significantly increased in the liver during human acute liver failure (ALF), in a D-galactose/lipopolysaccharide (D-Galn/LPS)-induced ALF mouse model and in D-Galn/LPS-treated AML12 hepatocytes. GSDMD-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis expanded the inflammatory response by upregulating MCP1/CCR2 to recruit macrophages. 31877317_Inactivation of the Cytoprotective Major Vault Protein by Caspase-1 and -9 in Epithelial Cells during Apoptosis. 31988247_Human polymorphisms in GSDMD alter the inflammatory response. 32109412_Structural Mechanism for GSDMD Targeting by Autoprocessed Caspases in Pyroptosis. 32149134_CD147 Expression Is Associated with Tumor Proliferation in Bladder Cancer via GSDMD. 32420343_High Glucose Induces the Loss of Retinal Pericytes Partly via NLRP3-Caspase-1-GSDMD-Mediated Pyroptosis. 32554464_Extended subsite profiling of the pyroptosis effector protein gasdermin D reveals a region recognized by inflammatory caspase-11. 32820063_Succination inactivates gasdermin D and blocks pyroptosis. 32851082_Rapamycin Inhibited Pyroptosis and Reduced the Release of IL-1beta and IL-18 in the Septic Response. 33208231_Zika virus protease induces caspase-independent pyroptotic cell death by directly cleaving gasdermin D. 33259938_Vitamin D/VDR attenuate cisplatin-induced AKI by down-regulating NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD pyroptosis pathway. 33359850_MicroRNA-204-GSDMD interaction regulates pyroptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in ankylosing spondylitis. 33587329_Pyroptosis executive protein GSDMD as a biomarker for diagnosis and identification of Alzheimer's disease. 33609534_Involvement of TFAP2A in the activation of GSDMD gene promoter in hyperoxia-induced ALI. 33761363_Gasdermin D mediates the maturation and release of IL-1alpha downstream of inflammasomes. 33883744_Gasdermin D pore structure reveals preferential release of mature interleukin-1. 34289345_Control of gasdermin D oligomerization and pyroptosis by the Ragulator-Rag-mTORC1 pathway. 34296442_SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid suppresses host pyroptosis by blocking Gasdermin D cleavage. 34407544_Gasdermin D inhibition prevents multiple organ dysfunction during sepsis by blocking NET formation. 34418095_Association of serum Gasdermin D with anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis. 34700129_Pan-cancer analysis reveals the expression, genetic alteration and prognosis of pyroptosis key gene GSDMD. 34752417_Gasdermin D inhibition confers antineutrophil-mediated cardioprotection in acute myocardial infarction. 34841669_Establishment and validation of a gasdermin signature to evaluate the immune status and direct risk-group classification in luminal-B breast cancer. 34955116_GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis: a critical mechanism of diabetic nephropathy. 35013201_Gasdermin D pores are dynamically regulated by local phosphoinositide circuitry. 35115408_Electrostatic influence on IL-1 transport through the GSDMD pore. 35119941_Epithelial Gasdermin D shapes the host-microbial interface by driving mucus layer formation. 35303042_The colonic pathogen Entamoeba histolytica activates caspase-4/1 that cleaves the pore-forming protein gasdermin D to regulate IL-1beta secretion. 35521691_The macrophage-associated microRNA-4715-3p / Gasdermin D axis potentially indicates fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: evidence from transcriptome and biological data. 35532120_GSDMD-dependent pyroptotic induction by a multivalent CXCR4-targeted nanotoxin blocks colorectal cancer metastases. 35580164_New Insights Relating Gasdermin B to the Onset of Childhood Asthma. 35749514_Gasdermin D-mediated release of IL-33 from senescent hepatic stellate cells promotes obesity-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. 36030524_Translocation of gasdermin D induced mitochondrial injury and mitophagy mediated quality control in lipopolysaccharide related cardiomyocyte injury. 36057231_Macrophages promote growth, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma by regulating GSDMD/IL-1beta axis. 36155610_USP25 UPREGULATION BOOSTS GSDMD -MEDIATED PYROPTOSIS OF ACINAR CELLS IN ACUTE PANCREATITIS. |
ENSMUSG00000022575 |
Gsdmd |
510.819206 |
0.3492759405 |
-1.517561 |
0.151010892 |
97.662379 |
0.00000000000000000000004961600772580722587842876895639218253755190130721994698483284878115506799645118007902055978775024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000491498170491889003946034673257874735615571984760943930316354905096787319962459150701761245727539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
274.4433274 |
27.6090431 |
791.9531790 |
56.2543631 |
| ENSG00000104549 |
6713 |
SQLE |
protein_coding |
Q14534 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the stereospecific oxidation of squalene to (S)-2,3-epoxysqualene, and is considered to be a rate-limiting enzyme in steroid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10666321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30626872}. |
3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;FAD;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Microsome;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Terpene metabolism; lanosterol biosynthesis; lanosterol from farnesyl diphosphate: step 2/3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24449766, ECO:0000305|PubMed:10666321, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30626872}. |
Squalene epoxidase catalyzes the first oxygenation step in sterol biosynthesis and is thought to be one of the rate-limiting enzymes in this pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6713; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; squalene monooxygenase activity [GO:0004506]; cellular aromatic compound metabolic process [GO:0006725]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; lipid droplet formation [GO:0140042]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126] |
12083769_functional promotor regions involved in transcription was determined 17316888_A cDNA library consisting of 220 upregulated genes in tumour tissue was established and named as LSCC. Differential expression was confirmed in five of these genes, including IGFBP5, SQLE, RAP2B, CLDN1, and TBL1XR1. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18728668_Distant metastasis-free survival in stage I/II breast cancer cases was significantly inversely related to SQLE mRNA in multivariate Cox analysis in two independent patient cohorts of 160 patients each 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 24449766_MARCH6 and squalene monooxygenase (SM) physically interact, and consistent with MARCH6 acting as an E3 ligase, its overexpression reduces SM abundance in a RING-dependent manner. 24840124_Data suggest that unsaturated fatty acids (oleate; oleoyl-CoA) stabilize SM/SQLE (which catalyzes 1st oxygenation step in cholesterol synthesis) most likely via inhibition of poly-ubiquitination by MARCH6 (membrane-associated ring finger [C3HC4] 6). 25787749_overexpression of SQLE in HCC cells promoted cell proliferation and migration, while downregulation of SQLE inhibited the tumorigenicity of Hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. 26434806_this study have identified a Squalene Monooxygenase region integrally associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane that is likely to interact with cholesterol or respond to cholesterol-induced membrane effects. 26777065_our results pinpoint SQLE as a bona fide metabolic oncogene by amplification, and as a therapeutic target in BC. These findings could have implications in other cancer types. 28069586_Data indicate that microRNA miR-133b-dependent squalene epoxidase (SQLE) plays a critical role in the potential metastasis mechanisms in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 28342963_Both HMGCR and SQLE promoters have two SREs that may act as a homing region to attract a single SREBP-2 homodimer. 28595267_Higher Gleason grade was associated with lower LDLR expression, lower SOAT1 and higher SQLE expression. Besides high SQLE expression, cancers that became lethal despite primary treatment were characterized by low LDLR expression (odds ratio for highest versus lowest quintile, 0.37; 95% CI 0.18-0.76) and by low SOAT1 expression (odds ratio, 0.41; 95% CI 0.21-0.83). 28972164_Taken together, our results support a model whereby the amphipathic helix in squalene monooxygenase N100 attaches reversibly to the ER membrane depending on cholesterol levels; with excess, the helix is ejected and unravels, exposing a hydrophobic patch, which then serves as a degradation signal. 29596888_Increasingly growing evidence underlines the positive correlation between SE over-expression and poor prognosis in different malignances. SE promotes tumor cell proliferation and migration via many pathways suggesting its oncogenic role. [review] 30734525_Further survival analysis indicated that high expression of SQLE indicated poor prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Our study presents novel evidence of potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets for lung SCC therapy and prognosis. 30792392_The shape of squalene epoxidase expands the arsenal against cancer. Review. 30940729_findings reveal the degron architecture of SM N100, introducing the role of non-canonical ubiquitination sites and deepening our molecular understanding of how SM is degraded in response to cholesterol. 31356817_OSBPL2 deficiency upregulates SQLE expression and increases the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesteryl ester by suppressing AMPK signalling, which provides new evidence of the connection between OSBPL2 and cholesterol synthesis. 31471528_VCP plays a key role in ERAD that contributes to the cholesterol-mediated regulation of Squalene monooxygenase. 32170014_squalene directly bound to the N100 region, thereby reducing interaction with and ubiquitination by MARCH6 32755570_The MARCH6-SQLE Axis Controls Endothelial Cholesterol Homeostasis and Angiogenic Sprouting. 32946903_Reduction of Squalene Epoxidase by Cholesterol Accumulation Accelerates Colorectal Cancer Progression and Metastasis. 33933449_The mammalian cholesterol synthesis enzyme squalene monooxygenase is proteasomally truncated to a constitutively active form. 34268906_Squalene epoxidase promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation through accumulating calcitriol and activating CYP24A1-mediated MAPK signaling. 34417456_MiR-205-driven downregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis through SQLE-inhibition identifies therapeutic vulnerability in aggressive prostate cancer. 34715817_Ferroptosis regulators, especially SQLE, play an important role in prognosis, progression and immune environment of breast cancer. 34939274_Squalene synthase predicts poor prognosis in stage I-III colon adenocarcinoma and synergizes squalene epoxidase to promote tumor progression. 35638462_SQLE facilitates the pancreatic cancer progression via the lncRNA-TTN-AS1/miR-133b/SQLE axis. 35720314_SQLE, A Key Enzyme in Cholesterol Metabolism, Correlates With Tumor Immune Infiltration and Immunotherapy Outcome of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. 35962621_Downregulated ferroptosis-related gene SQLE facilitates temozolomide chemoresistance, and invasion and affects immune regulation in glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000022351 |
Sqle |
4245.489638 |
3.1047670041 |
1.634485 |
0.031386154 |
2716.515293 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6618.4623669 |
144.8491080 |
2147.6113821 |
36.6592076 |
| ENSG00000104635 |
23516 |
SLC39A14 |
protein_coding |
Q15043 |
FUNCTION: Electroneutral transporter of the plasma membrane mediating the cellular uptake of the divalent metal cations zinc, manganese and iron that are important for tissue homeostasis, metabolism, development and immunity (PubMed:15642354, PubMed:27231142, PubMed:29621230). Functions as an energy-dependent symporter, transporting through the membranes an electroneutral complex composed of a divalent metal cation and two bicarbonate anions (By similarity). Beside these endogenous cellular substrates, can also import cadmium a non-essential metal which is cytotoxic and carcinogenic (By similarity). Controls the cellular uptake by the intestinal epithelium of systemic zinc, which is in turn required to maintain tight junctions and the intestinal permeability (By similarity). Modifies the activity of zinc-dependent phosphodiesterases, thereby indirectly regulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathways important for gluconeogenesis and chondrocyte differentiation (By similarity). Regulates insulin receptor signaling, glucose uptake, glycogen synthesis and gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes through the zinc-dependent intracellular catabolism of insulin (PubMed:27703010). Through zinc cellular uptake also plays a role in the adaptation of cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress (By similarity). Major manganese transporter of the basolateral membrane of intestinal epithelial cells, it plays a central role in manganese systemic homeostasis through intestinal manganese uptake (PubMed:31028174). Also involved in manganese extracellular uptake by cells of the blood-brain barrier (PubMed:31699897). May also play a role in manganese and zinc homeostasis participating in their elimination from the blood through the hepatobiliary excretion (By similarity). Also functions in the extracellular uptake of free iron. May also function intracellularly and mediate the transport from endosomes to cytosol of iron endocytosed by transferrin (PubMed:20682781). Plays a role in innate immunity by regulating the expression of cytokines by activated macrophages (PubMed:23052185). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q75N73, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15642354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23052185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27231142, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27703010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29621230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31028174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31699897}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Dystonia;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Parkinsonism;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the the SLC39A family of divalent metal transporters that mediates the cellular uptake of manganese, zinc, iron, and cadmium. The encoded protein contains eight transmembrane domains, a histidine-rich motif, and a metalloprotease motif, and is expressed on the plasma membrane and the endocytic vesicle membrane. It is an important transporter of nontransferrin-bound iron and a critical regulator of manganese homeostasis. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation and early-onset parkinsonism-dystonia with hypermanganesemia. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:23516; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; anion:cation symporter activity [GO:0015296]; cadmium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015086]; ferrous iron transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015093]; iron ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005381]; manganese ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005384]; solute:bicarbonate symporter activity [GO:0140410]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; import across plasma membrane [GO:0098739]; inorganic cation transmembrane transport [GO:0098662]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; iron import into cell [GO:0033212]; iron ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034755]; manganese ion homeostasis [GO:0055071]; manganese ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071421]; negative regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0051344]; positive regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045745]; regulation of hormone levels [GO:0010817]; zinc ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0071578]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577] |
15642354_ZIP14 (SLC39A14)was shown to function as a zinc influx transporter in a temperature-dependant manner. 15863613_Zip14 expression is up-regulated through IL-6 18524764_HFE decreases the stability of Zip14 and therefore reduces the iron loading in HepG2 cells 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682781_These results suggest that endosomal ZIP14 participates in the cellular assimilation of iron from transferrin, thus identifying a potentially new role for ZIP14 in iron metabolism. 20938052_Alternative splicing of SLC39A14 was identified in colorectal tumors and found to be regulated by the Wnt pathway. 21373779_ZIP14 downregulation is likely involved in the depletion of zinc in the hepatoma cells in Hepatocellular cancer 21462106_The transporter ZIP14 is up-regulated along the entire gastrointestinal tract by proinflammatory conditions. 22137264_Data suggest that Zip-14 mRNA level in enterocytes increases with iron or zinc depletion; Zip-14 transcript level in enterocytes decreases with zinc supplementation. 22173985_the SLC39A14-exon4B transcript variant is a colorectal cancer biomarker with high sensitivity and organ-confined specificity. 22318508_Observations indicate that ZIP14 and ZIP8 are both broad-scope metal-ion transporters that can mediate the cellular uptake of nutritionally important metals as well as the toxic heavy metal cadmium. 23052185_Zip14 expression induced by lipopolysaccharides in macrophages attenuates inflammatory response 23110240_Data show the role of ZIP14 in the hepatocyte is multi-functional since zinc and iron trafficking are altered in the Zip14(-/-) mice and their phenotype shows defects in glucose homeostasis. 24514587_Polymorphisms in SLC39A14 and SLC39A8 seemed to affect blood cadmium concentrations, for SLC39A14 this effect may occur via differential gene expression. 24576911_These results suggest that both the up-regulation of ZIP14 and the down-regulation of ZnT10 by IL-6 might have enhanced the accumulation of manganese in SH-SY5Y cells. 24927598_Asparagine-linked (N-linked) glycosylation of ZIP14, particularly the glycosylation at N102, was required for efficient membrane extraction of ZIP14 and therefore is necessary for its iron sensitivity. 26711644_Integrative analysis of four RNA-Seq datasets and differential expression revealed for the first time, splicing alterations of SLC39A14 and NR1I3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 27231142_Missense mutations solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 14 (SLC39A14) impair manganese uptake. 28673968_Zip14 activity is needed for adaptation to endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver. 28789954_Study shows that individuals harboring loss-of-function mutations in SLC30A10 or SLC39A14 develop inherited forms of Mn-induced neurotoxicity. 29292794_These results suggest that the wild type p53 plays a role in regulating ZIP14, but not DMT1 in HepG2 cells. 29333637_Increased free Zn(2+) correlates with induction of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum stress via altered expression levels of Zn(2+) -transporters, Zip8, Zip14, and ZnT8, in heart failure. 29685658_SLC39A14 mutation is associated with dystonia. 29895370_Expression of zinc transporters ZIP4, ZIP14 and ZnT9 in hepatic carcinogenesis-An immunohistochemical study 31261654_Both ZIP8 and ZIP14 have roles in manganese metabolism of alveolar epithelial cells. 31699897_solute carriers ZIP8 and ZIP14 regulate manganese accumulation in brain microvascular endothelial cells and control brain manganese levels 32392784_The Functions of ZIP8, ZIP14, and ZnT10 in the Regulation of Systemic Manganese Homeostasis. 32729666_Circular RNA circ_001842 plays an oncogenic role in renal cell carcinoma by disrupting microRNA-502-5p-mediated inhibition of SLC39A14. 33146651_Human placental cell line HTR-8/SVneo accumulates cadmium by divalent metal transporters DMT1 and ZIP14. 33658057_Knockdown of Circ_SLC39A8 protects against the progression of osteoarthritis by regulating miR-591/IRAK3 axis. 34198528_HIF-1alpha Dependent Upregulation of ZIP8, ZIP14, and TRPA1 Modify Intracellular Zn(2+) Accumulation in Inflammatory Synoviocytes. 34924116_Manganese transport in mammals by zinc transporter family proteins, ZNT and ZIP. 35787370_Calcium and the Ca-ATPase SPCA1 modulate plasma membrane abundance of ZIP8 and ZIP14 to regulate Mn(II) uptake in brain microvascular endothelial cells. 36062189_Circ_000829 Plays an Anticancer Role in Renal Cell Carcinoma by Suppressing SRSF1-Mediated Alternative Splicing of SLC39A14. 36361624_Hereditary Disorders of Manganese Metabolism: Pathophysiology of Childhood-Onset Dystonia-Parkinsonism in SLC39A14 Mutation Carriers and Genetic Animal Models. |
ENSMUSG00000022094 |
Slc39a14 |
1111.286926 |
5.6380160023 |
2.495188 |
0.067427534 |
1388.317107 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000072636365622304215964096783 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000108294217836889919804605770 |
Yes |
No |
1896.8340723 |
69.1112290 |
338.8168904 |
10.5839750 |
| ENSG00000104814 |
11184 |
MAP4K1 |
protein_coding |
Q92918 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase, which may play a role in the response to environmental stress (PubMed:24362026). Appears to act upstream of the JUN N-terminal pathway (PubMed:8824585). May play a role in hematopoietic lineage decisions and growth regulation (PubMed:8824585, PubMed:24362026). Able to autophosphorylate (PubMed:8824585). Together with CLNK, it enhances CD3-triggered activation of T-cells and subsequent IL2 production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24362026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8824585}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables ATP binding activity and MAP kinase kinase kinase kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including JNK cascade; cellular response to phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate; and protein phosphorylation. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:11184; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; MAP kinase kinase kinase kinase activity [GO:0008349]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate [GO:1904628]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
12522005_The catalytic activity of a hematopoietic cell-restricted, Ste20-related S/TPK, HPK1, is positively regulated by exposure to physiological concentrations of PGE2. HPK1 is a negative regulator of PGE2-induced FOS gene transcription. 15364934_PP4 is a positive regulator for HPK1 and the HPK1-JNK signaling pathway 15743830_Full activation of HPK1 is dependent on autophosphorylation of threonine 165 and phosphorylation of serine 171, which is a target site for protein kinase D (PKD) in vitro. 16341093_suppression or activation of NFkappaB by HPK1 determines sensitivity to activation-induced cell death 16449643_Pdcd4 suppresses tumor progression in colon carcinoma cells by the novel mechanism of down-regulating MAP4K1 transcription, with consequent inhibition of c-Jun activation and AP-1-dependent transcription. 17024227_Our work explains growth factor-independent survival during monocytic differentiation by caspase-mediated processing of HPK1 towards HPK1-N. 17353368_A novel negative feedback loop involves HPK-1-dependent serine phosphorylation of SLP-76 and 14-3-3 protein recruitment, which tunes T cell activation. 17712048_HPK1-C as a suppressor of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 proteins and provide a molecular basis for our understanding of CD95L-independent activation-induced cell death of lymphocytes. 17895239_Prostaglandin E2 activates HPK1 kinase activity via a PKA-dependent pathway 19141650_Restoring wild-type HPK1 protein in pancreatic cancer cells led to the increase in p21 and p27 protein expression and cell cycle arrest. HPK1 may function as a novel tumor suppressor and its loss plays a critical role in pancreatic cancer. 19706536_Results suggest HPK1-mediated phosphorylation of CARMA1 as an additional regulatory mechanism tuning the NF-kappaB response upon TCR stimulation. 21915030_The purpose of the study was to investigate the potential contribution of HPK1, MEKK1, TAK1, p-MKK4 to the development of extramammary Paget disease 22105350_HPK1 negatively regulates T cell activation by reducing the persistence of signaling microclusters. 22421156_results indicate that uncleaved HPK1 is a positive regulator of vitamin D-induced differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia cells, but the cleaved HPK1 fragment inhibits differentiation 22541691_QVD and 1,25D-induced differentiation was accompanied by increased signaling by Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1(HPK1), and the expression of transcription factors known to be involved in monocytic differentiation was increased. 22801218_Pdcd4 knockdown up-regulates MAP kinase kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP4K1) expression and increases phosphorylation of c-Jun. 23460610_HPK1 is critically involved in LFA-1-mediated polymorphonuclear neutrophils trafficking during acute inflammation. 24362026_CUL7/Fbxw8 ubiquitin ligase-mediated HPK1 degradation revealed a direct link and novel role of CUL7/Fbxw8 ubiquitin ligase in the MAPK pathway, which plays a critical role in cell proliferation and differentiation. 28765906_HPK1 protein expression, which is expressed at significantly higher levels in NATs compared with paired IDC-NOS tissues, is significantly negatively associated with ER positivity and is positively associated with OS duration, suggesting that HPK1 may exhibit anticancer activities. 28901492_Interactions between HPK1 and its adaptor proteins related to immunity has been discussed (Review). 31959629_Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 down-regulates the oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase AXL in pancreatic cancer. 32640226_MAP4K Interactome Reveals STRN4 as a Key STRIPAK Complex Component in Hippo Pathway Regulation. 32860752_Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase1 (HPK1) Mediates T Cell Dysfunction and Is a Druggable Target for T Cell-Based Immunotherapies. 33439152_Using yeast surface display to engineer a soluble and crystallizable construct of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1). 34166980_MAP4K1 functions as a tumor promotor and drug mediator for AML via modulation of DNA damage/repair system and MAPK pathway. 34908452_The Kinase MAP4K1 Inhibits Cytosolic RNA-Induced Antiviral Signaling by Promoting Proteasomal Degradation of TBK1/IKKepsilon. 35099066_Decoding the signaling profile of hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) in innate immunity: A proteomic approach. |
ENSMUSG00000037337 |
Map4k1 |
37.810219 |
0.2663955992 |
-1.908358 |
0.329210391 |
35.004188 |
0.00000000328996885088343179836784518227116996813563787327439058572053909301757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014996893217739177012666913204816387938933530676877126097679138183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.4307627 |
5.2337721 |
61.1814070 |
13.0728052 |
| ENSG00000104825 |
4793 |
NFKBIB |
protein_coding |
Q15653 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits NF-kappa-B by complexing with and trapping it in the cytoplasm. However, the unphosphorylated form resynthesized after cell stimulation is able to bind NF-kappa-B allowing its transport to the nucleus and protecting it to further NFKBIA-dependent inactivation. Association with inhibitor kappa B-interacting NKIRAS1 and NKIRAS2 prevent its phosphorylation rendering it more resistant to degradation, explaining its slower degradation. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the NF-kappa-B inhibitor family, which inhibit NF-kappa-B by complexing with, and trapping it in the cytoplasm. Phosphorylation of serine residues on these proteins by kinases marks them for destruction via the ubiquitination pathway, thereby allowing activation of the NF-kappa-B, which translocates to the nucleus to function as a transcription factor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:4793; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cytoplasmic sequestering of NF-kappaB [GO:0007253]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12475944_IkappaBbeta may be a novel target for transcription factors of the HMG-box SRY/Sox family and imply a potential role for NF-kappaB/IkappaBbeta in spermatogenesis 12651903_Data show that increased nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kB) activity in the amnion during labor is associated with an increase in the expression of NF-kBp65 and of the NF-kB binding proteins IkBa, IkBb-1 and IkBb-2. 15308628_VEGF increased Mn-superoxide dismutase promoter activity, an effect that was dependent on a second intronic NF-kappaB consensus motif. 15919917_data indicate that inhibition of NFkappa-B activity by the hepatitis C virus core protein might be related to its physical interaction with and interrupted nuclear localization of IKKbeta 17463416_None of the NFKBIB SNPs are associated with pneumococcal susceptibility. 17463416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18356846_NF-kappaB, IkappaB-alpha, IkappaB-beta mRNA decreased significantly after weight loss. 18434448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18950638_increased I-kappaBbeta expression reversed NF-kappaB activation in cancer cells, compensating for the loss of I-kappaBalpha via TGase 2 polymerization. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19500386_NFKBIA and NFKBIB are not likely to harbor ovarian cancer risk alleles. 19500386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20448286_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25326706_NFKBIBrs3136641TT single nucleotide polymorphism was associated with a significantly decreased risk of developing wheezing. 26227166_our data establish the importance of a novel tumor suppressive IKBB gene in abrogating angiogenesis in NPC via the NF-kappaB signalling pathway. 28314790_The subcellular distributions of IkappaB and NFkappaB are indicative of carcinogenesis. Inhibition of XPO1 results in intranuclear retention of IkappaB, which inhibits NFkappaB and thereby provides a novel mechanism for drug therapy in sarcoma. This effect can be further enhanced in relatively selinexor-resistant sarcoma cell lines by pretreatment with the proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib. 28448456_data suggest that miRNA-4776 modulates Influenza A virus production in infected cells through NFKBIB expression, possibly through the modulation of NF-kappaB. 32017069_The NF-kappaB regulator IkappaBbeta exhibits different molecular interactivity and phosphorylation status from IkappaBalpha in an IKK2-catalysed reaction. |
ENSMUSG00000030595 |
Nfkbib |
117.470704 |
2.0504834316 |
1.035964 |
0.139463013 |
55.896038 |
0.00000000000007640637312825843587373665153740276297339006211783996036501775961369276046752929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000488418392106147497338487314517953502644026508860974900017026811838150024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
158.7215755 |
14.1581789 |
77.8631559 |
5.4521621 |
| ENSG00000104859 |
11129 |
CLASRP |
protein_coding |
Q8N2M8 |
FUNCTION: Probably functions as an alternative splicing regulator. May regulate the mRNA splicing of genes such as CLK1. May act by regulating members of the CLK kinase family (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in RNA splicing and mRNA processing. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:11129; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30832715_Data identified a significantly differentially methylated cg26985354 near gene CLASRP to be associated with cleft lip and cleft palate. |
ENSMUSG00000061028 |
Clasrp |
265.429814 |
0.3936585429 |
-1.344983 |
0.188494770 |
49.758353 |
0.00000000000173896237842880929583112992324175693570689760214520447334507480263710021972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000010181310870927896940589345378403292275912295217210612463532015681266784667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
150.5259126 |
20.1160478 |
386.1434817 |
36.6875129 |
| ENSG00000104863 |
64130 |
LIN7B |
protein_coding |
Q9HAP6 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in establishing and maintaining the asymmetric distribution of channels and receptors at the plasma membrane of polarized cells. Forms membrane-associated multiprotein complexes that may regulate delivery and recycling of proteins to the correct membrane domains. The tripartite complex composed of LIN7 (LIN7A, LIN7B or LIN7C), CASK and APBA1 associates with the motor protein KIF17 to transport vesicles containing N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit NR2B along microtubules (By similarity). This complex may have the potential to couple synaptic vesicle exocytosis to cell adhesion in brain. Ensures the proper localization of GRIN2B (subunit 2B of the NMDA receptor) to neuronal postsynaptic density and may function in localizing synaptic vesicles at synapses where it is recruited by beta-catenin and cadherin. Required to localize Kir2 channels, GABA transporter (SLC6A12) and EGFR/ERBB1, ERBB2, ERBB3 and ERBB4 to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells. May increase the amplitude of ASIC3 acid-evoked currents by stabilizing the channel at the cell surface (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11742811}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Exocytosis;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Synapse;Tight junction;Transport |
|
Enables protein domain specific binding activity. Predicted to be involved in maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity; neurotransmitter secretion; and protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be part of MPP7-DLG1-LIN7 complex. Predicted to be active in basolateral plasma membrane; cell-cell junction; and synapse. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64130; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; MPP7-DLG1-LIN7 complex [GO:0097025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; synapse [GO:0045202]; L27 domain binding [GO:0097016]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045199]; neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0007269]; protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane [GO:1903361]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
14596909_LIN7B is a partner of IRSp53 anchoring the actin-based membrane cytoskeleton at cell-cell contacts. 15317815_PSD-95 and Lin-7b interact with acid-sensing ion channel-3 and have opposite effects on H+- gated current 16979770_Lin-7B is a binding partner for Rhotekin in the human brain cDNA library 18286632_Allelic and haplotype association was found between both BDNF and adult ADHD, and LIN-7 and adult ADHD. 20720508_Data suggest that decreased cortical LIN7b expression may contribute to abnormal corticostriatal connectivity in Huntington disease. 25196215_functional deficiency in Lin-7B could be implicated in clinical phenotypes in some autism spectrum disorders patients through bringing about abnormal cortical architecture |
ENSMUSG00000003872 |
Lin7b |
13.479862 |
0.3921600554 |
-1.350486 |
0.421745583 |
10.477775 |
0.00120819201555854693203029270875958900433033704757690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002777279886255124528859905552735654055140912532806396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6501216 |
2.0793958 |
19.5316648 |
3.3142716 |
| ENSG00000104870 |
2217 |
FCGRT |
protein_coding |
P55899 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor that transfers passive humoral immunity from the mother to the newborn. Binds to the Fc region of monomeric immunoglobulin gamma and mediates its selective uptake from milk (PubMed:7964511, PubMed:10933786). IgG in the milk is bound at the apical surface of the intestinal epithelium. The resultant FcRn-IgG complexes are transcytosed across the intestinal epithelium and IgG is released from FcRn into blood or tissue fluids. Throughout life, contributes to effective humoral immunity by recycling IgG and extending its half-life in the circulation. Mechanistically, monomeric IgG binding to FcRn in acidic endosomes of endothelial and hematopoietic cells recycles IgG to the cell surface where it is released into the circulation (PubMed:10998088). In addition of IgG, regulates homeostasis of the other most abundant circulating protein albumin/ALB (PubMed:24469444, PubMed:28330995). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10933786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10998088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24469444, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28330995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7964511}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as an uncoating receptor for a panel of echoviruses including Echovirus 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 25 and 29. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30808762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31104841}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;IgG-binding protein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a receptor that binds the Fc region of monomeric immunoglobulin G. The encoded protein transfers immunoglobulin G antibodies from mother to fetus across the placenta. This protein also binds immunoglobulin G to protect the antibody from degradation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:2217; |
endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; beta-2-microglobulin binding [GO:0030881]; IgG binding [GO:0019864]; IgG immunoglobulin transcytosis in epithelial cells mediated by FcRn immunoglobulin receptor [GO:0002416] |
11717196_Human FcRn binds selectively to human, rabbit and guinea pig IgG but not significantly to rat, bovine, sheep or mouse IgG (except for weak binding to mouse IgG2b). 12006623_Assembly of the FcRn alpha-chain with beta(2)microglobulin is important for both transport of FcRn from the ER to the cell surface and efficient pH-dependent IgG binding. 12023961_Functional reconstitution in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells requires co-expressed human beta 2-microglobulin 12144784_although a secreted soluble form of human FcRn does not dimerize, the membrane-anchored receptor can form both non-covalent and covalent dimers; dimerization of human FcRn occurs in the absence of its ligand, IgG 12538789_Expression of FcRn is demonstrated along the human fetal intestine and in a human nonmalignant fetal intestinal epithelial cell line (H4), which by location indicates that FcRn could play a role in the uptake and transport of IgG in the human fetus. 12972260_data show that it is possible to confer binding of mouse immunoglobulin G on human FcRn by mutagenesis of selected residues; observations are of direct relevance to understanding the molecular nature of the human FcRn-IgG interaction 14764666_Analysis of the dynamics and properties of trafficking of FcRn in live microvascular endothelial cells shows that the primary site at which FcRn sorts IgGs for either salvage or lysosomal degradation is the sorting endosome. 14767057_strong cell surface polarity displayed by hFcRn results from dominant basolateral sorting by motifs in the cytoplasmic tail that nonetheless allows for a cycle of bidirectional transcytosis 15258288_FCRN is involved in IgG exocytosis. 15644205_residues encompassing and extending away from the interaction site on the alpha2 helix of FcRn play a significant and most likely indirect role in FcRn-IgG interactions 15654966_expression of a functional FcRn in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. 15689494_FcRn leaves sorting endosomes in Rab4(+)Rab11(+) or Rab11(+) compartments 16229888_These transport and localization data are in accordance with efficient hFcRn-mediated apical IgG recycling and basolateral directed IgG transcytosis in placental trophoblasts. 16549777_FcRn binds IgG and albumin, salvages both from a degradative fate, and maintains their physiologic concentrations 16805790_a variable number of tandem repeats promoter polymorphism influences the expression of the FcRn receptor, leading to different IgG-binding capacities 16849638_FcRn fulfills a major role in IgG-mediated phagocytosis 17046328_FcRn-mediated recycling is a major contributor to the high endogenous concentrations of IgG and serum albumin, two important plasma proteins. 17048273_Our results show clear evidence that the conserved H166 is a key player in the FcRn-albumin interaction. 17384151_Elucidation of intracellular recycling pathways leading to exocytosis of FCRN was facilitated by using multifocal plane micoscopy. 17674040_Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) was expressed in various cells of the human skin (including keratinocytes, melanocytes, and histiocytes). 17703228_This review summarizes FcRn biology. 17709515_These data provide the first evidence that NF-kappaB signaling via intronic sequences regulates FcRn expression and function. 18003977_These results suggest a novel mechanism for regulation of IgG transport by calmodulin-dependent sorting of FcRn and its cargo away from a degradative pathway and into a bidirectional transcytotic route. 18566411_JAK/STAT-1 signaling pathway was necessary and sufficient to mediate the down-regulation of FcRn gene expression by IFN-gamma 18599440_A previously undescribed role for FcRn in mediating the presentation of antigens by dendritic cells when antigens are present as a complex with antibody, is shown. 18637944_The impact of two free cysteine residues (C48 and C251) of the FcRn heavy chain on the overall structure and function of soluble human FcRn is explored. 18684948_Intracellular trafficking of FcRn is regulated by its intrinsic sorting information and/or an interaction with major histocompatibility (MHC) class II invariant chain (Ii). 18843053_Results indicate that FcRn-dependent internalization of IgG may be important not only in cells taking up IgG from an extracellular acidic space, but also in endothelial cells participating in homeostatic regulation of circulating IgG levels. 19164298_N-glycans in FcRn contribute significantly to the steady-state membrane distribution and direction of IgG transport in polarized epithelia. 19362735_The role of hFcRn in IgG transport and trafficking in syncytiotrophoblasts cultures in vitro. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19451275_a single structurally and functionally heterogeneous recycling endosome compartment that traffics FcRn to both cell surfaces while discriminating between recycling and transcytosis pathways polarized in their direction of transport 19462839_It plays a role in intracellular IGG transfer and immune surveillance. (review) 19772792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19772792_VNTR polymorphisms within the FCGRT promoter are not associated with LN in the Chinese population. 20006594_A recombinant truncated HSA variant, HSA(Bartin), does not interact with FcRn, which gives a molecular explanation for the low serum levels. 20018855_No binding of albumin was observed at physiological pH to neonatal Fc receptor. At acidic pH, a 100-fold difference in binding affinity was observed. 20083659_Affinities to FcRn of clinically used therapeutic proteins are closely correlated with the serum half-lives reported from clinical studies, and suggest an important role of FcRn in regulating the serum half-lives of the therapeutic proteins. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452034_promoter polymorphism is not associted with the rate of maternal-fetal IgG transfer 20592032_the x-ray crystal structure of a representative monomeric peptide in complex with human FcRn 20627700_influence of FcRn expression on disease phenotype and the catabolism of therapeutically administered intravenous immunoglobulins in 28 patients with common variable immunodeficiency 20930418_Thirty-three genetic variations of FCGRT, including 17 novel ones, were found. 21256596_Methionine (Met) oxidation can result in a significant reduction of the serum circulation half-life and the magnitude of the change correlates well with the extent of Met oxidation and changes in FcRn binding affinities. 21368166_These studies demonstrate that FcRn-mediated transport is a mechanism by which IgG can act locally in the female genital tract in immune surveillance and in host defense against sexually transmitted diseases. 21690327_FcRn transgene blockade is a primary contributing factor toward reduction in arthritis severity; engineering of antibody Fc regions to generate potent FcRn blockers holds promise for the therapy of antibody-mediated autoimmunity in experimental arthritis. 22215085_Structure-based mutagenesis reveals the albumin-binding site of the neonatal Fc receptor 22453095_This mAb panel provides a powerful resource for probing the biology of human FcRn and for the evaluation of therapeutic FcRn blockade strategies. 22570488_Serum half-life of IgG is controlled by the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) that interacts with the IgG Fc region and may be increased or decreased as a function of altered FcRn binding. 23220220_Human FcRn was visualized in epithelial cells of Tg276 mice, but low serum hIgG levels were obtained 23286945_genetic polymorphism is associated with the efficiency of Ig replacement therapy in common variable immunodeficiency 23384837_Data indicate that Fc-neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) interaction is pH dependent. 23741050_Only the unbound receptor or FcRn bound to monomeric IgG is sorted into recycling tubules emerging from early endosomes. 23751752_The FCGRT promoter VNTR may influence mAbs' distribution in the body. CNV of FCGRT cannot be used as a relevant pharmacogenetic marker because of its low frequency. 23765230_Analytical FcRn chromatography allows differentiation of IgG samples and variants by peak pattern and retention time profile. 23917469_Studies indicate that high levels of endogenous IgG can compete with the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for binding to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). 24057047_Molecular dynamic simulations of human FcRn-Fc binding structures proposed that the protein-protein binding interface is composed of three subsites. 24072267_In intestine, there was an increasing proximal-distal gradient of mucosal FcRn mRNA and protein expression. 24278022_The Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) enhances human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) transcytosis across epithelial cells. 24469444_analysis of neonatal Fc receptor-based recycling mechanisms through identification of the human Fc interaction with human FcRn 24550358_FcRn has the potential to interact with IgG-Fc domains in the ciliary epithelium and retinal and choroidal vasculature, which might affect the half-life and distribution of intravitreally injected Fc-carrying molecules. 24652290_Extending serum half-life of albumin by engineering neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binding. 24764301_A cluster of conserved tryptophan residues of FcRn is required for binding to albumin and anti-FcRn albumin blocking antibodies. 24802048_Characterization and screening of IgG binding to the neonatal Fc receptor. 25030041_These results suggest that hFcRn Tgm are a valuable and useful tool for pharmacokinetic screening of mAbs and Fc-fusion proteins in the preclinical stage. 25344603_domain I and III of albumin required for optimal pH-dependent binding to the neonatal Fc receptor 25652137_These data indicate that human FcRn facilitates the transepithelial transport of IgE in the form of IgG anti-IgE/IgE ICs. 25658443_The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binds independently to both sites of the IgG homodimer with identical affinity. 25823782_none of the three functional polymorphisms in FcgammaR genes explored here, the FCGR3A F158V and FCGR2B I232T nsSNPs and the VNTR in FCGRT, showed an association with the response to TNFi in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 26252948_analysis of binding motifs in the hFCGRT promoter that interact with their corresponding (Sp1, Sp2, Sp3, c-Fos, c-Jun, YY1, and C/EBPbeta or C/EBPdelta) transcription factors (TFs) suggests their involvement in regulation of human FCGRT gene expression 26254986_FcRn binding activity of a large set of Fc-fusion samples after thermal stress, was investigated. 26260795_Critical Role of the Neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn) in the Pathogenic Action of Antimitochondrial Autoantibodies Synergizing with Anti-desmoglein Autoantibodies in Pemphigus Vulgaris. 26337808_Data indicate improved pharmacokinetics through enhanced neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) interactions were apparent for a complementarity-determining region (CDR) charge-patch normalized monoclonal antibody (mAb) which was affected by non-specific clearance. 26634928_the localization of FcRn alpha-chain in fixed nasal tissue, was studied. 27016466_This review summarizes the main findings on Fc Receptor neonatal biology, function and distribution throughout different tissues. 27469170_The results suggest that regardless of hyperglycemia degree, it decreases FcRn expression in placenta and blood cells and compromises the production and transfer of antibodies from maternal blood to newborns. 27836572_FcRn is involved in transport of aflibercept through REC in vitro. 27974681_we have demonstrated that loss of FcRn expression promotes tumor cell growth and proliferation. Our data support a model in which FcRn-mediated recycling of albumin reduces amino acid availability to fuel metabolic pathways. 28081504_this study shows that FcRn may be associated with the transport and metabolism of IgG in thyrocytes and that transport is independent of IgG type, and that FcRn may be involved in Hashimoto's thyroiditis pathogenesis 28637874_Data suggest that, unlike albumin with low FcRn-binding affinity, albumin with high FcRn-binding affinity (due to genetic variation/genetic engineering) is directed less to lysosomes and more to endosomes, suggestive of FcRn-directed albumin salvage from lysosomal degradation. (FcRn = neonatal Fc receptor) 28760885_these findings establish a novel mechanism of humoral protection in the eye involving FcRn and may facilitate vaccine and therapeutic development for other ocular surface diseases 28991504_Domains distal from the Fc could contribute to FcRn binding of IgG and alter antibody pharmacokinetics. 28991911_An arginine-to-histidine replacement at residue 435 in the binding domain of IgG3 to FcRn increases the transplacental transfer and half-life of malaria-specific IgG3 in young infants and is associated with reduced risk of clinical malaria during infancy. 29302759_Regulation of the Human Fc-Neonatal Receptor alpha-Chain Gene FCGRT by MicroRNA-3181. 29523681_As expected, recombinant factor IX (without albumin fusion) and an FcRn interaction-defective albumin variant localized to the lysosomal compartments of both FcRn-expressing and nonexpressing cells. These results indicate that FcRn-mediated recycling via the albumin moiety is a mechanism for the half-life extension of rIX-FP observed in clinical studies. 29540212_the presence of human serum albumin (HSA) or immunoglobulin G (IgG), which are both protected from intracellular degradation by the interaction with the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), results in a decreased amount of internalized fibrinogen. 29745444_this study shows that the IgG transfer from maternal serum to the fetus is positively correlated with FcRn expression in placental tissue throughout gestati 29782488_small molecule binds into a conserved cavity of the heterodimeric, extracellular domain composed of an alpha-chain and beta2-microglobulin 29908223_Down-regulation of FcRn is speculated to play a protective role in Hashimoto's thyroiditis pathogenesis by mainly reducing IgG1 transport in thyrocytes. 30326650_the measurement of FcRn protein may be preferred to FcRn mRNA for quantitative applications. Significant differences were found in FcRn expression in transgenic mice, Swiss Webster mice, and human tissues, which may have implications for the use of mouse models in the assessment of monoclonal antibody disposition, efficacy, and safety. 30808762_We show that loss of expression of FcRn or its binding partner beta 2 microglobulin (b2M) renders cells resistant to infection by a panel of echoviruses at the stage of virus attachment, and that a blocking antibody to b2M inhibits echovirus infection in cell lines and in primary human intestinal epithelial cells 30893823_This is the first time that FcRn expression and mAb transcytosis has been shown in a model of human nasal respiratory epithelium in vitro. 30955709_Placental FcRn expression in endothelial cells and macrophages is analogous to the expression pattern in other organs. FcRn expression suggests an involvement of FcRn in IgG transcytosis and/or participation in recycling/salvaging of maternal IgG present in the fetal circulation. FcRn expression in placental macrophages may account for recycling of monomeric IgG and/or processing and presentation of immune complexes. 31089170_Reduced FcRn-mediated transcytosis of IgG2 due to a missing Glycine in its lower hinge. 31209240_Contribution of DNA methylation to the expression of FCGRT in human liver and myocardium. 31289263_Study shows that human cytomegalovirus US11 inhibits the assembly of FcRn with beta2m and retains FcRn in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), consequently blocking FcRn trafficking to the endosome. US11 recruits the ubiquitin enzymes Derlin-1, TMEM129 and UbE2J2 to engage FcRn, consequently initiating the dislocation of FcRn from the ER to the cytosol and facilitating its degradation. 32461366_FcRn, but not FcgammaRs, drives maternal-fetal transplacental transport of human IgG antibodies. 32658257_FcRn is a CD32a coreceptor that determines susceptibility to IgG immune complex-driven autoimmunity. 33025844_Functional humanization of immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1 Fc domain human FCGRT transgenic mice. 33077645_V Region of IgG Controls the Molecular Properties of the Binding Site for Neonatal Fc Receptor. 33360096_Demonstration of fibrinogen-FcRn binding at acidic pH by means of Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. 34634960_Neonatal Fc receptor expression in lymphoid and myeloid cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. 34704415_Research progress on neonatal Fc receptor and its application. 34753797_An Expanded Genome-Wide Association Study of Fructosamine Levels Identifies RCN3 as a Replicating Locus and Implicates FCGRT as the Effector Transcript. 34996950_Human IgE does not bind to human FcRn. 35862785_Human FcRn Is a Two-in-One Attachment-Uncoating Receptor for Echovirus 18. |
ENSMUSG00000003420 |
Fcgrt |
3673.583925 |
0.3090941711 |
-1.693882 |
0.032821861 |
2688.633907 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1766.4197460 |
36.3585236 |
5755.3266952 |
75.5197027 |
| ENSG00000104885 |
84444 |
DOT1L |
protein_coding |
Q8TEK3 |
FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase. Methylates 'Lys-79' of histone H3. Nucleosomes are preferred as substrate compared to free histones (PubMed:12123582). Binds to DNA (PubMed:12628190). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12123582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12628190}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;DNA-binding;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a histone methyltransferase that methylates lysine-79 of histone H3. It is inactive against free core histones, but shows significant histone methyltransferase activity against nucleosomes. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:84444; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone H3K79 methyltransferase activity [GO:0031151]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; histone methyltransferase activity [GO:0042054]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0000077]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; heterochromatin formation [GO:0031507]; histone H3-K79 methylation [GO:0034729]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046425]; regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000677]; telomere organization [GO:0032200] |
15851025_mistargeting of hDOT1L to Hoxa9 plays an important role in MLL-AF10-mediated leukemogenesis 17094487_Altered phosphorylation of histone-H3 is associated with hepatocarcinogenesis 17855633_Identification of ENL-associated proteins by mass spectrometry revealed enzymes with a known role in transcriptional elongation: pTEFb and DOT1L. 18285465_suggesting a widespread mechanism for parallel or sequential recruitment of DOT1L and MLL to genes in their normal 'on' state 18449190_demonstration, using chemically ubiquitylated H2B, of a direct stimulation of hDot1L-mediated intranucleosomal methylation of H3 K79 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19443658_the CALM-AF10 fusion protein can also greatly reduce global H3K79 methylation in both human and murine leukemic cells by disrupting the AF10-mediated association of hDOT1L with chromatin 19734945_Impaired recruitment of the histone methyltransferase DOT1L contributes to the incomplete reactivation of tumor suppressor genes upon DNA demethylation. 19799466_titration of the level of ubiquitylated histone H2B within the nucleosome revealed a 1:1 stoichiometry of Dot1L activation. 19864429_AF17 competes with AF9 to bind Dot1a, decreases Dot1a nuclear expression by possibly facilitating its nuclear export, and relieves Dot1a.AF9-mediated repression of alpha-ENaC and other target genes. 20203130_study describes for the first time the components of DotCom and links the specific regulation of H3K79 trimethylation by Dot1 and its associated factors to the Wnt/Wingless signaling pathway 20208522_This permitted structure-activity studies of ubiquitylated mononucleosomes that revealed plasticity in the mechanism of hDot1L stimulation and identified surfaces of ubiquitin important for activation. 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21741597_These data point to DOT1L as a potential therapeutic target in MLL-rearranged leukemia. 22002246_a novel STAT1-DOT1L interaction that is required for the regulation JAK-STAT-inducible gene expression 22190683_down-regulation of DOT1L-mediated H3K79 methylation disturbs proliferation of human cells 22373577_These findings identify a novel role for Bat3 in regulating DOT1L function, which plays a critical role in DNA damage response. 22566624_These data are a further step to better understand the role of Wnt-signaling during chondrogenesis and cartilage homeostasis. DOT1L may represent a therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. 22619169_Data show that histone monoubiquitylation H2Aub did not influence histone methyltransferase Dot1L activity. 23012353_a functional interaction between hDOT1L and RNAPII targets hDOT1L and subsequent H3K79 methylations to actively transcribed genes. 23505243_In male subjects, the rs12982744 polymorphism in DOT1L is associated with hip osteoarthritis. 23891621_Interaction with CBX8 precludes AF9-DOT1L binding. 23996074_Functional studies show that the mapped AF9/ENL interacting site is essential for immortalization by MLL-AF9, indicating that DOT1L interaction with MLL-AF9 and its recruitment are required for transformation by MLL-AF9. 24486544_PITX2 forms complex with histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase. PITX2 complex methylates H3K4. 24816405_DOT1L Regulates IL-22 Dependent Colon Cancer Stemness via H3K79 Methylation 24854991_Establishing the precise function of DOT1L in normal adult hematopoiesis and understanding its mode of action will aid in our understanding of the use of DOT1L as a therapeutic target in MLL-rearranged leukemia. 24858818_inhibition of DOT1L, in combination with DNA damaging chemotherapy, represents a promising approach to improving outcomes for MLL-rearranged leukemia. 24916648_A genome-wide association study identifies PLCL2 and AP3D1-DOT1L-SF3A2 as new susceptibility loci for myocardial infarction in Japanese 25005768_DOT1L rs12982744 G to C change and variant C genotype may contribute to knee OA risk in a Chinese Han population. 25417107_Studies identified the evolutionarily conserved Af9 YEATS domain as a novel acetyllysine-binding module and established a direct link between histone acetylation and DOT1L-mediated H3K79 methylation in transcription control. 25464900_Results provide evidence that transformation driven by MLL fusions as well as the recurrent AML-associated NUP98-NSD1 fusion oncogene is critically dependent on the ability of AF10 to stimulate DOT1L activity. 25576241_Three candidate variants were identified: p.Glu1313Lys in Insulin receptor (INSR), p.Arg81Pro in F-box protein 24 (FBXO24) and p.Pro1146Leu in DOT1-like histone H3K79 methyltransferase 25921540_The graded reduction of the DOT1L interaction with MLL-AF9 results in differential loss of H3K79me2 and me3 at MLL-AF9 target genes. 26118503_Targeting DOT1L and HOX gene expression in MLL-rearranged leukemia and beyond. 26199140_expression associated with poorer survival and aggressiveness of breast cancers 26240340_analysis of a functional hotspot on ubiquitin that is required for the stimulation of human Dot1 26385168_Report drug formulation/delivery of DOT1L inhibitor pinometostat in leukemia. 26439302_The PZP domain of AF10 senses unmodified H3K27 to regulate DOT1L-mediated methylation of H3K79. 26830124_These data converge on a possible mechanism for hDot1L stimulation in which histone H2B physically 'corrals' the enzyme into a productive binding orientation. 26914852_study demonstrates the development of potent DOT1L inhibitors with novel scaffolds 26923329_this indicates that DOT1L function, like MLL, does not completely rely on its methyltransferase activity. Nevertheless, the small molecule DOT1L inhibition is sufficient to block the proliferation of MLL fusion-induced leukemia cells of murine and human origin 26927674_MLL1 and DOT1L cooperate with meningioma-1 to induce acute myeloid leukemia. 27002147_these findings strongly support the contention that histone methyltransferase, DOT1L-associated epigenetic changes induced by HA play pivotal roles in miR-10 production leading to up-regulation of RhoGTPase and survival proteins. 27294782_DOT1L, via dimethylated histone H3 K79, facilitates histone H4 acetylation, which in turn regulates the binding of BRD4 to chromatin in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 27335278_DOT1L may play a critical role in DNMT3A-mutant leukemia. 27626484_DOT1L cooperates with transcription factor ETS-1 to stimulate the expression of VEGFR2, thereby activating ERK1/2 and AKT signaling pathways and promoting angiogenesis. 27713173_this study shows that Dot1l expression predicts adverse postoperative prognosis of patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma 28076791_MLL-AF4 spreading gene expression is downregulated by inhibitors of the H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L. 28114995_findings demonstrate that DOT1L over-expression has important clinical significance in ovarian cancer and also clarify that it drives cell cycle progression through transcriptional regulation of CDK6 and CCND3 through H3K79 methylation 28209620_our results identify DOT1L as a novel cofactor in N-Myc-mediated transcriptional activation of target genes and neuroblastoma oncogenesis. Furthermore, they characterize DOT1L inhibitors as novel anticancer agents against MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. 28394257_These results reveal a cooperative transcriptional activation mechanism of AEP and DOT1L and suggest a molecular rationale for the simultaneous inhibition of the MLL fusion-AF4 complex and DOT1L for more effective treatment of MLL-rearranged leukemia. 28627522_DOT1L limits Wnt signalling to maintain cartilage homeostasis and protects against osteoarthritis. 28781076_human mammary epithelial cells reprogramming is dependent on gene silencing by the DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A and loss of histone transcriptional marks following downregulation of the methyltransferase DOT1L. 29161537_The present study identifies H3K79me1 and DOT1L upregulation as a novel epigenetic signature of arsenic-exposed humans who have characteristic dermatological lesions. 29234911_Gene and protein expression of DOT1L was increased in synovial tissues of both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis patients. 29343685_facilitates DNA damage repair; plays a protective role in ultraviolet radiation-induced melanomagenesis 29463719_Each C-Nap1 ring at the proximal end of the two centrioles organizes a rootletin ring and, in addition, multiple rootletin/CEP68 fibers. 29631608_DOT1L is essential for activation of NKX2.5 during the cardiac differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. 29972300_DOT1L, LSD1, and HDAC Class I Inhibitors Reduce HOXA9 Expression in MLL-AF9 Rearranged Leukemia Cells, But Dysregulate the Expression of Many Histone-Modifying Enzymes 30171029_Myeloma cells with histone modifier mutations or lower IRF4/MYC expression were less sensitive to DOT1L inhibition, but with prolonged treatment, anti-proliferative effects were achieved in these cells. 30616689_Study provides evidence that DOT1L plays an important role in an early DNA damage response and repair of DNA double-strand breaks via the homologous recombination pathway. 30651276_High DOT1L expression is associated with Leukemia. 30765112_Authors find that contacts mediated by Dot1L and the H4 tail induce a conformational change in the globular core of histone H3 that reorients K79 from an inaccessible position, thus enabling this side chain to insert into the active site in a position primed for catalysis. 30770869_The authors present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the catalytic domain of human DOT1L (residues 1-416) in complex with an H2BK120ub1 nucleosome core particle at an overall resolution of 4.1 A and determined the cryo-electron microscopy structure of DOT1L in complex with an unmodified nucleosome core particle at an overall resolution of 5.0 A. 30923167_results establish the molecular basis of the cross-talk between H2B ubiquitination and H3 Lys79 methylation as well as nucleosome destabilization by DOT1L 30981630_We report cryo-EM structures of human Dot1L bound to (1) H2BK120Ub and (2) unmodified nucleosome substrates at 3.5 A and 4.9 A, respectively. Comparison of both structures, complemented with biochemical experiments, provides critical insights into the mechanism of Dot1L stimulation by H2BK120Ub. 31525340_MiR-133b regulates CRC stemness and chemoresistance through targeting DOT1L. 31527241_the oligomerization ability of the DOT1L-AF10 complex is essential for MLL1-AF10's leukemogenic function 31727944_The DOT1L inhibitor Pinometostat decreases the host-response against infections: Considerations about its use in human therapy. 31888761_Data found that DOT1L was highly expressed in colorectal cancer and was negatively related to the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). DOT1L epigenetically promotes the transcription of c-Myc via H3K79me2. Its silencing or inhibition induces cell cycle arrest at S phase. These results suggest that DOT1L is a potential marker for colorectal cancer. 31939604_The role of DOT1L in the proliferation and prognosis of gastric cancer. 31952940_Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) is involved in breast cancer metastasis via transcriptional regulation of MALAT1 and ZEB2. 31999490_Analysis of Polymorphisms in the MATN3 and DOT1L Genes and CTX-II Urinary Levels in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis in a Northeast Mexican-Mestizo Population. 32450905_Therapeutic strategies against hDOT1L as a potential drug target in MLL-rearranged leukemias. 32552847_The lncRNA LAMP5-AS1 drives leukemia cell stemness by directly modulating DOT1L methyltransferase activity in MLL leukemia. 32814769_Histone methyltransferase DOT1L coordinates AR and MYC stability in prostate cancer. 33077595_DOT1L-controlled cell-fate determination and transcription elongation are independent of H3K79 methylation. 33484127_Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Thyroid Function Traits Identifies Novel Associations of fT3 With KLF9 and DOT1L. 33493351_Genome-wide association study on Northern Chinese identifies KLF2, DOT1L and STAB2 associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. 34037658_DOT1L modulates the senescence-associated secretory phenotype through epigenetic regulation of IL1A. 34187895_DOT1L complex regulates transcriptional initiation in human erythroleukemic cells. 34215314_AF10 (MLLT10) prevents somatic cell reprogramming through regulation of DOT1L-mediated H3K79 methylation. 34253616_Role of Dot1L and H3K79 methylation in regulating somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes. 34263728_Non-canonical H3K79me2-dependent pathways promote the survival of MLL-rearranged leukemia. 34414607_Computational modeling reveals key molecular properties and dynamic behavior of disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) and partnering complexes involved in leukemogenesis. 35135840_DOT1L Is a Novel Cancer Stem Cell Target for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 35172132_DOT1L activity in leukemia cells requires interaction with ubiquitylated H2B that promotes productive nucleosome binding. 35292818_The epigenetic enzyme DOT1L orchestrates vascular smooth muscle cell-monocyte crosstalk and protects against atherosclerosis via the NF-kappaB pathway. 35309733_DOT1L affects colorectal carcinogenesis via altering T cell subsets and oncogenic pathway. 35350907_Histone methyltransferase Dot1L inhibits pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis by promoting NUPR1 expression. 35850772_Combinatorial targeting of a chromatin complex comprising Dot1L, menin and the tyrosine kinase BAZ1B reveals a new therapeutic vulnerability of endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer. 36417856_DOT1L regulates lipid biosynthesis and inflammatory responses in macrophages and promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability. |
ENSMUSG00000061589 |
Dot1l |
1168.443148 |
2.2642125661 |
1.179009 |
0.051625519 |
524.879529 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003672358586604919789099748075228780396602156197330308902765681765502462336426766093495608921647535721435051388078901645773815503943834703146735757251268588652196104078137988730929924616193556338423190497564443717673 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001843673902662878384799555387347069280823533523239148055513482520203498124827097085742543414036856977797134606440932675309889940062877280506905038724114086595279690546038827665150791520614972860979174482254222249671 |
Yes |
No |
1663.9455383 |
52.5510419 |
740.2012930 |
18.2737753 |
| ENSG00000104888 |
57030 |
SLC17A7 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2U7 |
FUNCTION: Multifunctional transporter that transports L-glutamate as well as multiple ions such as chloride, proton, potassium, sodium and phosphate (PubMed:10820226). At the synaptic vesicle membrane, mainly functions as an uniporter which transports preferentially L-glutamate but also phosphate from the cytoplasm into synaptic vesicles at presynaptic nerve terminals of excitatory neural cells (By similarity). The L-glutamate or phosphate uniporter activity is electrogenic and is driven by the proton electrochemical gradient, mainly by the electrical gradient established by the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase across the synaptic vesicle membrane (By similarity). In addition, functions as a chloride channel that allows a chloride permeation through the synaptic vesicle membrane that affects the proton electrochemical gradient and promotes synaptic vesicles acidification (By similarity). Moreover, may function as a K(+)/H(+) antiport allowing to maintain the electrical gradient and to decrease chemical gradient and therefore sustain vesicular glutamate uptake (By similarity). The vesicular K(+)/H(+) antiport activity is electroneutral (By similarity). At the plasma membrane, following exocytosis, functions as a symporter of Na(+) and phosphate from the extracellular space to the cytoplasm allowing synaptic phosphate homeostasis regulation (PubMed:10820226). The symporter activity is driven by an inside negative membrane potential and is electrogenic (By similarity). Is necessary for synaptic signaling of visual-evoked responses from photoreceptors (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TXX4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10820226}. |
Alternative splicing;Antiport;Cell membrane;Chloride;Chloride channel;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Neurotransmitter transport;Phosphate transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a vesicle-bound, sodium-dependent phosphate transporter that is specifically expressed in the neuron-rich regions of the brain. It is preferentially associated with the membranes of synaptic vesicles and functions in glutamate transport. The protein shares 82% identity with the differentiation-associated Na-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter and they appear to form a distinct class within the Na+/Pi cotransporter family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57030; |
chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; clathrin-sculpted glutamate transport vesicle membrane [GO:0060203]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; L-glutamate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005313]; L-glutamate uniporter activity [GO:0140788]; neurotransmitter transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005326]; phosphate ion uniporter activity [GO:0140787]; potassium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015386]; sodium:inorganic phosphate symporter activity [GO:0015319]; sodium:phosphate symporter activity [GO:0005436]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; anion transport [GO:0006820]; brain development [GO:0007420]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; L-glutamate transmembrane transport [GO:0015813]; neural retina development [GO:0003407]; neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicle [GO:0098700]; neurotransmitter transport [GO:0006836]; phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0055062]; phosphate ion transport [GO:0006817]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; regulation of synapse structure or activity [GO:0050803]; regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:1900242]; sodium-dependent phosphate transport [GO:0044341]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249] |
15653259_In schizophrenia, VGLUT1 mRNA was decreased in hippocampal formation and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. In the hippocampus, the loss of VGLUT1 mRNA supports data indicating that glutamatergic presynaptic deficits are prominent. 15961236_Alterations in the pattern of vesicular glutamate transporter 1-immunoreactivity that perfectly matched the neuronal loss and gliosis, as well as the decrease in the number of asymmetrical synapses identified by electron microscopy in this tissue 17531353_Our results suggest that VGLUT1 expression in the prefrontal cortex could be used as a valuable neurochemical marker of dementia in AD. 17660252_Docking and homology modeling explain the inhibition of VGLUT1. 18155679_We found increased VGLUT1 transcript and reduced VGLUT1 protein expression in the ACC, but not DLPFC, in schizophrenia. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19720501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720501_this study suggests that the common genetic variants of the VGLUT1 gene appear not play a major role in conferring susceptibility to schizophrenia in Han population of Taiwan. 19839996_This study found decreased VGLUT1 mRNA expression in both major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder in the entorhinal cortex. 21396926_We examined the ratio of excitatory to inhibitory vesicular neurotransmitter transporter mRNAs (VGluT1 to VGAT) and their ratio in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during normal human development and in people with schizophrenia 22510271_Data indicate that GABAergic axons were labeled with vesicular inhibitory aa transporter (VIAAT) antibodies, whereas glutamatergic axons were detected with antisera against the major vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT) isoforms, VGLUT1 and VGLUT2. 23022470_Depressed patients showed significant decreases in synaptophysin (SYN) and VGLUT1 expression, whereas in bipolar patients, decreases in VGLUT1 expression have also been found. 25749033_Loss of SLC17A7 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 26836159_Results suggest that activation of JNK in Alzheimer's disease (AD) inhibits insulin signaling which could lead to a decreased expression of VGLUT1, therefore contributing to the glutamatergic deficit in AD 27029226_This study was the first to demonstrate an association between genetic polymorphism at rs7417284 SNP in the promoter region of the SLC17A7 gene and concussion severity and duration. Based upon these findings, rs74174284 is a potential predictive genetic marker for identifying athletes who are more susceptible for altered recovery times and worse motor speed ImPACT scores after sport-related concussion. 27258819_Study revealed susceptibility of glutamatergic nerve terminals to Abeta induced toxicity and underlined the importance of VGLUT1 in the progression of Alzheimer's disease, as the decrease of this protein levels could increase the susceptibility to subsequent deleterious inputs by exacerbating Abeta induced neuroinflammation and synaptic plasticity disruption. 29890994_The findings of this study indicate that Slc17A7 located on 1p/19q may simultaneously influence tumor development. 31663854_In mammals, VGLUT1 gained a proline-rich sequence that recruits endophilinA1 and turns the transporter into a regulator of synaptic vesicles organization and spontaneous release. |
ENSMUSG00000070570 |
Slc17a7 |
79.823300 |
4.2052024269 |
2.072175 |
0.211779517 |
100.126725 |
0.00000000000000000000001429515083536106527102672312071741074451973367021899365824640732933192843745473510352894663810729980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000144915127973852552533274485183199475091305240457161923641458446676555382737205945886671543121337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
135.0476768 |
16.3068806 |
32.1398630 |
3.3719613 |
| ENSG00000104894 |
951 |
CD37 |
protein_coding |
P11049 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. This encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins and other transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins. It may play a role in T-cell-B-cell interactions. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:951; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
14978098_CD37 cross-linking on human T cells transduces signals that lead to complete inhibition of CD3-induced T cell proliferation. 17182550_CD37 is important for dectin-1 stabilization in APC membranes and controls dectin-1-mediated IL-6 production. 17440052_provide strong justification for CD37 as a therapeutic target and introduce small modular immunopharmaceuticals as a novel class of targeted therapies for B-cell malignancies 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20709950_In the absence of both CD37 and Tssc6, immune function is further altered when compared with CD37- or Tssc6-deficient transgenic mice, demonstrating a complementary role for these two molecules in cellular immunity. 22624718_Identify two tyrosine residues in tetraspanin CD37 directly mediating transduction of survival and apoptotic signals. 23883821_Data indicate that enhanced antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC) is observed against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and is sustained at concentrations of SMIP-016(GV) as low at 5E(-6) microg/mL on cells expressing minimal CD37 antigen. 24445867_The CD37-targeted antibody-drug conjugate IMGN529 is highly active against human CLL and in a novel CD37 transgenic murine leukemia model. 25934707_Data indicate that cell differentiation antigen 37 (CD37) is well expressed and a potential drug target in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 27760757_CD37 is a critical determinant of rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 30089630_CD37 is highly expressed in human lymphoma. 30185523_tetraspanin CD37 controls CLEC-2 membrane organization and provides new molecular insights into the mechanisms underlying CLEC-2-dependent dendritic cell migration. 30854931_Low CD37 expression is associated with brain metastasis in lung cancer. 31089249_The anti-CD37 antibody BI 836826 in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 31366619_From a cohort of 137 primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) samples. CD37 mutations were exclusively identified in immune-privileged site-associated DLBCL (IP-DLBCL) cases but absent in non-IP-DLBCL cases. Modeling and functional analysis of CD37 missense mutations revealed loss of function by impaired CD37 protein expression at the plasma membrane of human lymphoma B cells. 32400873_CD37 high expression as a potential biomarker and association with poor outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. 35171311_CD37 expression in follicular lymphoma. |
ENSMUSG00000030798 |
Cd37 |
1094.396095 |
0.4352316835 |
-1.200145 |
0.063323563 |
358.937525 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004796623861007863432533110549649109122465088514599614731972895312619785665091204026860075397438327322136299378567702110527195096441575764255126350266907086372493748592551942896323911152602578359749677106016463312698761001229286193847656250000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001612714537322916997272084659196085539431353224998549126201613559261408210274558226575255156438747984354652009217773469079534356819865192916829756269340286679496815440226203375025262080315476779374117555221346265170723199844360351562500000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
682.6400214 |
26.0392594 |
1580.0133580 |
40.3377043 |
| ENSG00000104921 |
2208 |
FCER2 |
protein_coding |
P06734 |
FUNCTION: Low-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (IgE) and CR2/CD21. Has essential roles in the regulation of IgE production and in the differentiation of B-cells (it is a B-cell-specific antigen). |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;IgE-binding protein;Lectin;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Palmitate;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a B-cell specific antigen, and a low-affinity receptor for IgE. It has essential roles in B cell growth and differentiation, and the regulation of IgE production. This protein also exists as a soluble secreted form, then functioning as a potent mitogenic growth factor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:2208; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; IgE binding [GO:0019863]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; positive regulation of humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin [GO:0002925]; positive regulation of killing of cells of another organism [GO:0051712]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; sequestering of metal ion [GO:0051238] |
11920534_cd23 negativity is rare in typical b-cell CLL; negativity in patients with CD19+/CD5+ is suggestive of mantle cell leukemia 12002758_prognostic significance of soluble CD23 in advanced stages of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its role as an indicator for aggressive or indolent courses of disease. 12022472_a review on the domains and functions of the cd23 receptor 12070780_upstream regions of the CD23a and CD23b isoform coding sequences show distinct sensitivities to agents which induce CD23 protein expression at the plasma membrane 12127553_Investigation of several stimulators to promote CD23a expression on CLL vs. normal B-cells confirmed a different CD23 regulation in B-CLL. CD23a is always predominantly expressed (constant ratio of CD23a:CD23b). 12127555_CD23 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia was 53.9 times higher than in mantle-cell llymphoma. 12149502_At term, the percentage of CD21(+) and CD23(+) B cells was comparable to the adult 12379312_promoter is a target for NF-AT transcription factors in B-CLL cells 12456589_The data show that monocyte-derived DC express the P2X7 receptor whose activation opens a cation-selective channel, and which leads to rapid and near complete shedding of CD23. 12576441_Expression of this antigen may identify prognostically favorable subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 12731041_Pax-5 is a key regulator of the B-cell-restricted expression of the CD23a isoform. 12777399_ADAM8, ADAM15, and MDC-L, but not ADAM17, catalyzed ectodomain shedding of CD23, the low affinity IgE receptor. 15272865_role of the CD23/nitric oxide pathway in the control of the cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized red blood cells on endothelial cells 15469741_Data show that gamma-irradiation not only induced CD23 expression, but also augmented the interleukin-4-induced surface CD23 levels. 15565166_Downregulation of CD23 antigens activity are early steps in PI-induced apoptosis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes and may be part of the full apoptotic response. 15569053_Results suggest that CD23 should be included in the panel of antibodies currently used to characterize mediastinal large B-cell lymphomas. 15621797_review of mechanisms leading to the upregulation of CD23 in the leukemic cells and review of the potential functions of CD23 as well as its regulation by Notch2 in B-CLL 15795251_CD21 and CD23a are common targets for B lymphotropic gammaherpesviruses. 15843555_In humans, in contrast to what was previously found in mice, intestinal cells coexpress CD23a and CD23b, and the two splice forms show different localizations in polarized cells. 15883744_Retinoic acid inhibits CD40 plus IL-4 mediated IgE production through alterations of sCD23, sCD54 and IL-6 production 16009564_marked inhibition of cell cluster formation and proliferation is achieved by antibody treatment against the CD23 mature B cell surface marker expressed in LCL41 cells 16083870_Results describe the production of a recombinant form of human soluble CD23 with similar proinflammatory properties as the native protein. 16143132_CD23 encodes a functional IgE receptor on human intestinal epithelial cells and this epithelial receptor is likely to play an important role in food allergies. 16172256_CD23 is involved in both up- and down-regulation of IgE; CD23 can bind both its ligands, IgE and CD21, simultaneously. 16765898_The high-resolution crystal structures of the human CD23 lectin domain in the presence and absence of Ca2+ was solved. 16831589_CD23a is expressed normally on human IECs, and in the presence of IgE can function as an antigen-sampling mechanism capable of activating subepithelial mast cells. 16896156_low levels of c-Rel are the underlying cause of aberrant CD23 expression in non-X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome B cells 16899715_Our results indicate that CD23 expression in these human intestinal epithelial cells is mediated through the p38 MAPK pathway. 17301828_R62W influences the stability of membrane CD23 molecules due to possibly diminished N-glycosylation. 17493235_There is an unexpectedly high frequency of CD23 expression in follicular lymphomas in general, which is even more pronounced in inguinal nodes. 17540777_The interaction between alphavbeta5 and sCD23 indicates that integrins deliver to cells important signals initiated by soluble ligands without the requirement for interactions with RGD motifs in their common ligands. 17570115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17576766_the CD23 monomers inhibit and the oligomer stimulates IgE synthesis in human B cells after heavy chain switching to IgE 17635803_Transgenic CD23 enhances antibody and T-cell responses to IgE-complexed antigen, while it negatively regulates the total antibody response to a variety of antigens. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17980418_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18032710_lumiliximab may be an effective treatment alone or in combination with rituximab or chemotherapy agents in chronic lymphocytic leukemia or other CD23-overexpressing B-cell malignancies 18183502_correlation of CD23 expression in B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemia & clinical parameters; CD23 expression is significantly decreased in patients with extremely high lymphocyte counts (PBL counts of >100 x 10(9)/l) & in the advanced stages of disease 18568448_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18616759_The distinct punctate CD23 staining for Merkel cell carcinoma may be helpful in differentiating it from small cell carcinoma. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18657051_higher expression levels in adenoid tissue of children with house dust mite allergies 18697825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19223373_CD23 is a useful marker in distinguishing mediastinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma in mediastinal biopsies. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19290077_The absolute number of B lymphocytes and the percentage of naive cells (CD23-/CD27-) decreased with age whereas there was an increase in memory cells (CD27+). 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19635918_MyD88-dependent Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 agonists may enhance allergic responses by inducing the production of both CD23 and MMP9, resulting in increased cleavage of membrane CD23 and soluble CD23 accumulation. 19663668_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19805542_This study reveals a new human immune response mechanism to counter mycobacterial infection involving CD23 and its related ligands. 19845913_Interaction of functional FCER2 promoter polymorphism and phenotype-associated haplotypes 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20359104_CD23 and CD19 are important factors that associated with serum total IgE in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20805040_Data suggest that the CD23-mediated signal transduction pathways in human B cells and human monocytes are different. 20831712_Data indicate that the regions of CD23 responsible for interaction with ligands have been identified and help to explain the structure-function relationships within the CD23 protein. 21160045_A model of CD23-bound IgE-mediated amplification of immunity by B cells is demonstrated in schistosomiasis. 21241315_show for the first time that CD9 and CD81 act as molecular partners of trimeric FcvarepsilonRI on human antigen-presenting cell 21307287_CD23-mediated immunoglobulin (Ig)E transcytosis in human airway epithelial cells may play a critical role in initiating and contributing to the perpetuation of airway allergic inflammation. 21328056_All subtypes of juvenile arthritis have reduced circulating levels of sCD21 and sCD23. 21526166_IgE may be considered as immune mediator during antiprotozoal activity of human macrophages through its ability to trigger CD23 signaling. 21686206_Report the role of CD23 SNPs in IgE dependent signaling in B-lymphocytes. 21724429_Findings suggest that patients with t(11;14)(+)/CD23(+) plasma cell myelomas (PCM) present with lower platelet counts and may have a shorter overall survival than those with t(11;14)(+)/CD23(-) PCM. 21860351_The association of CD23 and CD30 antigen blood levels with the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in HIV patients is reported. 21889131_SPR analysis revealed a progressive increment in affinity of soluble fragments for IgE, upon increasing length of CD23 'stalk' domain, exCD23>sCD23>derCD23. 21958076_Our results suggest that the FCER2 T2206C variant might be a useful pharmacogenetic predictor of steroid refractory patients. 22059556_Transfectants expressing the single nucleotide polymorphism in FCER2 exhibited increased IL-4Ralpha expression after stimulation through CD23 compared with wild-type. 22304573_Variation at GLCCI1 and FCER2 could lead personalized asthma treatment. 22348662_Soluble CD23 promoted the release of cytokines from the THP-1 model cell line. In both model cell lines and primary tissue, cytokine release was more pronounced in immature monocyte cells than in mature cells. 22393152_mIgE & mCD21 cooperate in sCD23-mediated positive regulation of IgE synthesis on committed B cells. Feedback regulation may occur when the secreted-IgE level is big enough to allow binding to mCD23. This prevents further sCD23 release. 22560905_Binding of sCD23-derived peptides to av integrins and their biological activities are tolerant of some substitution in the recognition motif. 22767513_Downregulation of CD23 attenuated AIMP1-induced TNF-alpha secretion and AIMP1 binding. 22802656_Structural comparisons with both free IgE-Fc and its FcepsilonRI complex reveal not only that the conformational changes in IgE-Fc required for CD23 binding are incompatible with FcepsilonRI binding, but also that the converse is true. 22815482_CD23 and FcepsilonRI interaction sites are at opposite ends of the Cepsilon3 domain of IgE, but that receptor binding is mutually inhibitory, mediated by an allosteric mechanism 23229638_The interplay of free IgE with IgE-allergen immune complexes of different sizes and composition with CD23 binding represents a mechanism for the modulation of CD23-mediated immune responses. 23583387_Results support the complex model of CD23 induction by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). 23689700_The results are consistent with the suppression of parasite and allergen-specific IgE levels by sCD23. 23697368_Data indicate that upon sialylation, the affinities for Fcgamma receptors are reduced, whereas those for alternative cellular receptors, such as dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN)/CD23, are increased. 23775083_Results suggest that binding of Ca(2+) brings an extra degree of modulation to CD23 function. 23933509_Data indicate that the interaction of IgE with CD23 on B-cells regulates IgE production. 24010859_CD23b-R62W-expressing human B cells bind IgE with greater affinity than wild-type cells and display differences in kinetics of CD23-mediated ERK1/2 activation 24102092_data indicate that the studied FCER2 variations are strongly associated with asthma susceptibility and might be risk factor among north Indian asthmatic children 24354852_FCER2 polymorphism rs3760687 affects moderately elevated total serum IgE levels, especially in the absence of homozygosity for the risk allele of FCER1A SNP rs2427837. 24598915_Crystal structure of the CD23-Fc3-4 complex with different molecular-packing constraints. 24639354_we have demonstrated that PU.1, GATA1, and GATA2 are involved in the expression of FcepsilonRI in a human mast cell line and primary human mast cells using siRNA with high transfection efficiency, and by ChIP assay. 25155463_Human and murine P2X7 activation induces the rapid shedding of CD23 from B cells, with a potential role for ADAM10 in this process. 25567136_Elevated serum sCD23 is associated with increased risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 25802003_Data suggest that the protective immune response involving CD23-IgE-mediated nitric oxide release in cutaneous leishmaniasis (LCL). 26119874_there is a high CD23a/CD23b ratio of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, which demonstrates that in a subset of CLL cases, low CD23 expression together with high CD20 and CD38 expressions may serve as a surrogate for trisomy 12 26801967_Binding of CTLA4Fcepsilon to FcepsilonRII/CD23 appeared stronger than that of IgE 26965583_Report a variant of t(14;18) negative nodal diffuse follicular lymphoma with CD23 expression, 1p36/TNFRSF14 abnormalities, and STAT6 mutations. 27406841_found a higher frequency of LIN1(-) CCR3(+) eosinophils, and decreased expression of CD23 and CD62L receptors in eosinophils of AD patients 28108506_High CD23 expression is associated with B-cell Lymphoma. 29295972_Data show that each IgE Fc is targeted by two single-domain antibodies (sdabs) having an epitope largely distinct from the FcepsilonRI binding site but overlapping significantly with the CD23-binding site. 29724998_IL-3 transcriptionally regulates surface levels of Fcepsilon RI in human primary basophils. 29750316_The findings of our study indicate a positive association of circulating sCD23 level and B-NHL risks and highlight the possibility of sCD23 as a predictive marker of B cells non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. 29763855_these data confirm that CD23 protein is phosphorylated in B cells of B-CLL patients, report the identification of new CD23 phosphorylation sites, and suggest a possible role(s) of such phosphorylations in the activation of CD23 during the process of lymphocytic activation in B-CLL. 31054894_CD23 is associated with leukocytosis, a leukemic presentation, bone marrow involvement 31292524_Human DC-SIGN and CD23 do not interact with human IgG. 31309641_FCER2 T2206C variant associated with FENO levels in asthmatic children using inhaled corticosteroids: The PACMAN study. 31437490_IgE-ICs are noninflammatory through reduced engagement by FcepsilonRI but increased targeting of the CD23 pathway. 33108776_Correlations between exhaled nitric oxide, rs28364072 polymorphism of FCER2 gene, asthma control, and inhaled corticosteroid responsiveness in children with asthma. 33150420_Plasmablasts derive from CD23- activated B cells after the extinction of IL-4/STAT6 signaling and IRF4 induction. 33470651_CD23 mediated the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factors-alpha in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis. 34050993_An FCER2 polymorphism is associated with increased oral leukotriene receptor antagonists and allergic rhinitis prescribing. 34075727_Reviving lost binding sites: Exploring calcium-binding site transitions between human and murine CD23. 35046106_Bidirectional Transport of IgE by CD23 in the Inner Ear of Patients with Meniere's Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000005540 |
Fcer2a |
21.419300 |
0.1929406906 |
-2.373771 |
0.415042751 |
35.123464 |
0.00000000309449584035028792408792782016053318772108582379587460309267044067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014149553470746669219589284379866994667551693964924197643995285034179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.0047909 |
1.8692863 |
36.6434661 |
5.3529199 |
| ENSG00000104951 |
259307 |
IL4I1 |
protein_coding |
Q96RQ9 |
FUNCTION: Secreted L-amino-acid oxidase that acts as a key immunoregulator (PubMed:17356132, PubMed:32818467, PubMed:32866000). Has preference for L-aromatic amino acids: converts phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr) and tryptophan (Trp) to phenylpyruvic acid (PP), hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid (HPP), and indole-3-pyruvic acid (I3P), respectively (PubMed:17356132, PubMed:32818467, PubMed:32866000). Also has weak L-arginine oxidase activity (PubMed:26673964). Acts as a negative regulator of anti-tumor immunity by mediating Trp degradation via an indole pyruvate pathway that activates the transcription factor AHR (PubMed:32818467, PubMed:32866000). IL4I1-mediated Trp catabolism generates I3P, giving rise to indole metabolites (indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and indole-3-aldehyde (I3A)) and kynurenic acid, which act as ligands for AHR, a ligand-activated transcription factor that plays important roles in immunity and cancer (PubMed:32818467, PubMed:32866000). AHR activation by indoles following IL4I1-mediated Trp degradation enhances tumor progression by promoting cancer cell motility and suppressing adaptive immunity (PubMed:32818467). Also has an immunoregulatory function in some immune cells, probably by mediating Trp degradation and promoting downstream AHR activation: inhibits T-cell activation and proliferation, promotes the differentiation of naive CD4(+) T-cells into FOXP3(+) regulatory T-cells (Treg) and regulates the development and function of B-cells (PubMed:17356132, PubMed:25446972, PubMed:25778793, PubMed:28891065). Also regulates M2 macrophage polarization by inhibiting T-cell activation (By similarity). Also has antibacterial properties by inhibiting growth of Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria through the production of NH4(+) and H2O2 (PubMed:23355881). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17356132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23355881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25446972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25778793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26673964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28891065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32818467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32866000}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;FAD;Flavoprotein;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Lysosome;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-tryptophan degradation via pyruvate pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32818467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32866000}. |
This gene encodes a secreted L-amino acid oxidase protein which primarily catabolizes L-phenylalanine and, to a lesser extent, L-arginine. The expression of this gene is induced by the cytokine interleukin 4 in B cells. This gene is also expressed in macrophages and dendritic cells. This protein may play a role immune system escape as it is expressed in tumor-associated macrophages and suppresses T-cell responses. This protein also contains domains thought to be involved in the binding of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactor. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Some transcripts of this gene share a promoter and exons of the 5' UTR with the overlapping NUP62 gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:259307; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; L-amino-acid oxidase activity [GO:0001716]; L-phenylalaine oxidase activity [GO:0106329]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; polyamine oxidase activity [GO:0046592]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; amino acid catabolic process [GO:0009063]; L-phenylalanine catabolic process [GO:0006559]; negative regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050868]; negative regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell [GO:0002841]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045591]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045577]; tryptophan catabolic process [GO:0006569]; tryptophan catabolic process to indole-3-acetate [GO:0019440]; tyrosine catabolic process [GO:0006572] |
12031486_genomic structure, cDNA sequence, chromosome location and RNA expression in immune tissues 12446450_is activated in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, which might be due to a constitutive activation of a cytokine signaling pathway 17356132_hIL4I1 inhibited the proliferation of CD3-stimulated T lymphocytes with a similar effect on CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. In contrast, memory T cells were more strongly affected by hIL4I1 and its catabolite H(2)O(2) than naive T cells 19436310_strong IL4I1 expression is associated with B-cell lymphomas. 20683900_participates in the downregulation of Th1 inflammation 23355881_IL4I1 plays a distinct role compared to other antibacterial enzymes produced by mononuclear phagocytes. 24307243_IL4I1 upregulation in human Th17 cells limits their TCR-mediated expansion not only by blocking the molecular pathway involved in the activation of the IL-2 promoter, but also by maintaining high levels of Tob1, which impairs entry into the cell cycle. 25446972_The immunosuppressive enzyme IL4I1 expressed differentially in human induced Aiolos+, but not natural Helios+, FOXP3+ Treg cells. 26673964_reviewed SNPs of the IL4I1 isoform 1, which is expressed in lymphoid tissue; the N92D SNP leads to a hyperactive enzyme, while the R102G mutation is hypomorphic; show that IL4I1 activity is not only directed against phenylalanine, as initially described, but also at a lower level against arginine 28891065_the presence of IL4I1 during T-cell activation decreases early signaling events downstream of t-cell receptor stimulation, resulting in global T-cell inhibition which is more pronounced when there is CD28 costimulation. 28951444_Data showed proteome changes in alveolar epithelial cells type II exposed to an infection with A. fumigatus with IL4I1 showing the most prominent increase in abundance both, in terms of relative abundance as well as activity. Also, in the infected lungs, there was levels of IL4I1 metabolic products. 30048651_these data show that IL4I1+ cells shape the T-cell compartment and are associated with a higher risk of poor outcome in melanoma, supporting a key role for IL4I1 in immune evasion. 31379854_Lnc-C/EBPbeta Modulates Differentiation of MDSCs Through Downregulating IL4i1 With C/EBPbeta LIP and WDR5. 32818467_IL4I1 Is a Metabolic Immune Checkpoint that Activates the AHR and Promotes Tumor Progression. 33692337_IL4I1-driven AHR signature: a new avenue for cancer therapy. 34026337_What role for AHR activation in IL4I1-mediated immunosuppression ? 34134578_Integrated analysis reveals the participation of IL4I1, ITGB7, and FUT7 in reshaping the TNBC immune microenvironment by targeting glycolysis. 34717685_Single-cell analysis revealed that IL4I1 promoted ovarian cancer progression. 35952516_Pan-cancer analysis combined with experimental validation revealed IL4I1 as an immunological and prognostic biomarker. 36131918_IL4I1 binds to TMPRSS13 and competes with SARS-CoV-2 spike. |
ENSMUSG00000074141 |
Il4i1 |
1435.545186 |
4.2316033116 |
2.081204 |
0.046844418 |
2078.439545 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2340.6320277 |
64.5315874 |
557.3220278 |
13.1573724 |
| ENSG00000104967 |
4858 |
NOVA2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UNW9 |
FUNCTION: Functions to regulate alternative splicing in neurons by binding pre-mRNA in a sequence-specific manner to activate exon inclusion or exclusion (PubMed:32197073). It binds specifically to the sequences 5'-YCAY-3' and regulates splicing in only a subset of regulated exons (PubMed:10811881). Binding to an exonic 5'-YCAY-3' cluster changes the protein complexes assembled on pre-mRNA, blocking U1 snRNP binding and exon inclusion, whereas binding to an intronic 5'-YCAY-3' cluster enhances spliceosome assembly and exon inclusion. With NOVA1, they perform unique biological functions in different brain areas and cell types. Uniquely regulates alternative splicing events of a series of axon guidance related genes during cortical development, being essential for central nervous system development by regulating neural networks wiring. Regulates differentially alternative splicing on the same transcripts expressed in different neurons. This includes functional differences in transcripts expressed in cortical and cerebellar excitatory versus inhibitory neurons where is required for, respectively, development of laminar structure and motor coordination and synapse formation. Also the regulation the regulation of intron retention can sequester the trans-acting splicing factor PTBP2, acting as a variable cis-acting scaffolding platform for PTBP2 across various natural conditions (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A1W2P872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10811881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32197073}. |
3D-structure;Autism spectrum disorder;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables sequence-specific mRNA binding activity. Involved in neuron differentiation and regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4858; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; sequence-specific mRNA binding [GO:1990825]; central nervous system neuron development [GO:0021954]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of axon guidance [GO:1902667]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of RNA metabolic process [GO:0051252] |
17436242_SCN1A polymorphism has a dramatic effect on the proportions of neonate and adult alternative transcripts of SCN1A in adult brain tissue and, the effect of the polymorphism also appears to be modified by Nova2 expression levels. 30829570_Here, the authors report that endothelial cells (ECs) express a novel isoform of the cell-surface adhesion molecule L1CAM, termed L1-DeltaTM. The splicing factor NOVA2, which binds directly to L1CAM pre-mRNA, is necessary and sufficient for the skipping of L1CAM transmembrane domain in ECs, leading to the release of soluble L1-DeltaTM. 31014480_Authors identify a mechanism whereby Nova2-regulated splicing constrains Erk signaling, thus limiting lymphatic progenitor cell specification. 31832068_MiR-7-5p suppresses tumor metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting NOVA2. 32197073_The NOVA2 variant protein shows decreased ability to bind target RNA sequences. 34990795_PART1 destabilized by NOVA2 regulates blood-brain barrier permeability in endothelial cells via STAU1-mediated mRNA degradation. 35239092_Circ_0016760 Serves as a Cancer Promoter in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Through miR-876-3p/NOVA2 Axis. 35607920_De novo truncating NOVA2 variants affect alternative splicing and lead to heterogeneous neurodevelopmental phenotypes. |
ENSMUSG00000030411 |
Nova2 |
20.110519 |
0.1650569952 |
-2.598964 |
0.604136883 |
17.445030 |
0.00002957364446175671243515446773297838944927207194268703460693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000087704840718410496513274265950599328789394348859786987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1146589 |
1.6381050 |
18.0593966 |
6.0474396 |
| ENSG00000104970 |
|
KIR3DX1 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.685009 |
0.0393001403 |
-4.669322 |
0.906670376 |
26.135973 |
0.00000031820024580385667942316750729514485129811873775906860828399658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001187818823486323831106910818566912979576954967342317104339599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8540903 |
1.8707936 |
27.8019277 |
35.1860002 |
| ENSG00000104972 |
10859 |
LILRB1 |
protein_coding |
F6RVM3 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;FUNCTION: May act as receptor for class I MHC antigens. Becomes activated upon coligation of LILRB3 and immune receptors, such as FCGR2B and the B-cell receptor. Down-regulates antigen-induced B-cell activation by recruiting phosphatases to its immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitor motifs (ITIM). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10327049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10611342, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9482905}. |
Disulfide bond;Immunity;Membrane;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene is a member of the leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor (LIR) family, which is found in a gene cluster at chromosomal region 19q13.4. The encoded protein belongs to the subfamily B class of LIR receptors which contain two or four extracellular immunoglobulin domains, a transmembrane domain, and two to four cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs). The receptor is expressed on immune cells where it binds to MHC class I molecules on antigen-presenting cells and transduces a negative signal that inhibits stimulation of an immune response. It is thought to control inflammatory responses and cytotoxicity to help focus the immune response and limit autoreactivity. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
membrane [GO:0016020] |
11751964_effect on cytokine production by antigen-stimulated T cells 12130517_Engagement of ILT2/CD85j found in Sezary syndrome cells inhibits their CD3/TCR signaling. 12847262_Increased binding to influenza virus-infected cells is observed in leukocyte Ig-like receptor-1 (LIR1) that is functional and possibly results from the generation of complexes of class I MHC proteins after influenza virus infection. 12853576_inhibitory receptors Ig-like transcript 2 (ILT2) and ILT4 compete with CD8 for MHC class I binding and bind preferentially to HLA-G 15100307_Invariant receptor CD85j expressed on CD8+ T cells mediates the specific recognition of an infectious antigen component and provides a novel example that extends the characteristics of innate immunity to cells mainly involved in adaptive immunity. 15474475_C-terminal Src kinase is regulated by the leukocyte inhibitory receptor CD85j 15585844_Cell surface expression of immunoglobulin-like inhibitory MHC class I receptor CD85j is associated with T cell engagement into various stages of the cytolytic differentiation pathway. 15670976_report that ILT2 receptor, ILT3 receptor, ILT4 receptor, and KIR2DL4 receptor expression is up-regulated by HLA-G histocompatibility antigen in antigen-presenting cells, natural killer cells, and T cells 15905516_CD85j prevents the rescue from apoptosis and the cooperation between dendritic cells and antigen-specific T cells that is mediated by human osteoclast-associated receptor (hOSCAR). 16014635_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16014635_Polymorphism in LILRB1 is associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope negative subjects 16210603_Coexpression of ILT2 with killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) in human natural killer (NK) cells may compensate for weak interactions between particular KIR and major histocompatibility complex-I (MHC-I). 16305801_Kinetic studies demonstrated that LILRB1 binds to MHCIs with fast association and dissociation rates, typical of cell-cell recognition receptors. 17400057_Blocking HLA-G receptors ILT2 and ILT4 prevents HLA-G inhibitory effects, leading to the conclusion that that HLA-G acts mainly through these receptors. 17601702_results show that the peripheral blood mononuclear cells from some patients with systemic lupus erythematosus show a defective expression of ILT2, and that most of them exhibit a poor function of this inhibitory receptor 17998301_Progenitor mast cells expressed cell surface inhibitory LILRB1. Mature cord-blood-derived mast cells had detectable mRNA encoding multiple LILRs, none were expressed on the cell surface. 18094328_ligation of LILRB1 on dendritic cells by self-HLA molecules may play a key role in controlling the balance between the induction and suppression of adaptive immune responses 18398485_CD85j(+) NK cell inhibition of HIV-1 replication in MDDC is mainly mediated by CD85j interaction with an unknown ligand 18538388_The presence of LILRB1 in placental stromal cells and LILRB2 in vascular smooth muscle strongly suggest that HLA-G has novel functions in regulation of placental immunity, development and function of the extraembryonic vasculature. 18632577_The 2.2-A structure of a LIR-1/UL18/peptide complex reveals increased contacts and optimal surface complementarity in the LIR-1/UL18 interface compared with LIR/MHCI interfaces, resulting in a >1,000-fold higher affinity. 18684926_Natural killer (NK) cells are targets which express relatively high amounts of inhibitory ILT2/CD85j receptors on the cell surface, capable of shaping interferon-gamma release in response to viral products and during NK and dendritic cell cross-talk. 18802077_Expressed on cultured osteoclast precursor cells derived from peripheral blood monocytes; LILRB1 could be inhibitory for osteoclast development in presence of receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) and macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF). 18821690_CD85j(leukocyte Ig-like receptor 1) is expressed in Polymyositis and sporadic Inclusion body myositis at the sites of partial invasion and in Dermatomyositis in perivascular inflammation 18946352_Human inhibitory receptor immunoglobulin-like transcript 2 amplifies CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells that promote long-term survival of allografts. 19136885_soluble HLA-G dimer up-regulates inhibitory receptor ILT2 on alloreactive CD8+ T cells 19304799_Cross-linking with anti-LILRB1 or anti-KIR2DL4 resulted in up-regulation of a small subset of mRNAs including those for IL-6, IL-8, and TNFalpha 19841038_ILT2/HLA-G interaction impairs NK-cell functions through the inhibition of the late but not the early events of the NK-cell-activating synapse. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20139023_alloreactivity of a significant fraction of KIR(-) NK cells leads to killing of acute myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia blasts that is mediated by NKG2A and LIR-1. 20194892_cell-specific mechanisms allow tailoring of CD85j levels to the distinct roles it plays in different hematopoietic lineages. 20580616_the proportions of CD8+ T cells displaying LILRB1, an inhibitory NKR expressed at late stages of T cell differentiation, were directly related with age and MS duration 20600445_level of expression on NK cells varies depending on genetic polymorphism 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631139_Blockade of LILRB1 and LILRB3 receptors by monoclonal antibodies or short interfering RNA (siRNA) abrogated the specific antigen-presenting properties of dendritic cells, implying an important regulatory role of these molecules. 21092455_The rate of HLA-G receptor ILT-2 on CD4(+)T cell, CD8(+)T cell and B cell in acute rejection group was statistically lower than that in stable kidney function group after renal transplantation. 21213105_High affinity soluble ILT2 receptor is a potent inhibitor of CD8(+) T cell activation. 21233315_show that mAb 256 does not target a TCR ligand but blocks key interactions between non-TCR molecules on effector gammadelta T cells and ILT2 molecule, expressed by tumor targets 21242521_T cells require ILT2-positive cells to upregulate cell-surface ILT2 upon activation, evidence that sensitivity to modulatory molecules can be acquired from other cells. 21270408_LILRB1 exhibits a lower binding affinity for a subset of HLA-A alleles expressed by myeloid cells. 21551166_The abnormal expression and function of ILT2 detected in autoimmune thyroid disease suggests that this receptor may participate in the pathogenesis of this condition. 21559424_LILRA3 binds both classical and non-classical HLA class I molecules but with reduced affinities compared to LILRB1/LILRB2 21817101_Association of overt and subclinical atherosclerotic disease with LILRB1+ NK and T-cells reflects a relationship between the immune challenge by infections and cardiovascular disease risk, without attributing a dominant role for human cytomegalovirus. 22028331_[review] This review of LILR during HIV-1 infection focuses on the dynamic interplay between LILR and HLA class I molecules in determining HIV-1 disease progression, and the effects of HIV-1 mutational escape on LILR-mediated immune recognition. 22242197_The expression of CD85j, NKG2D, NKp30, NKp44, KIR2DL1/S1 and KIR2DL2/L3/S2 receptors at the cell surface evolves between 8 and 12 weeks of gestation. 22296096_The carriage of the HLA-G minus 14-bp polymorphism, LILRB1 single nucleotide polymorphism rs1061680, and activating and inhibitory KIRs are different in different ethnic groups but generally is not correlated with susceptibility to HIV-1. 22574131_expression of CTLA-4 and LIR-1 by peripheral T. cruzi antigen-responsive IFN-gamma-producing and total T cells from chronically T. cruzi-infected subjects with different clinical forms of the disease 22623953_A significant correlation was identified between miR-7 expression and tumor grade in high-risk ER+ breast cancer. 22802125_Data show that the leukocyte antigen G HLA-G alpha1-alpha3 structure, which constitutes the extracellular part of HLA-G2 and HLA-G6, binds the immunologic receptor LILRB2 but not LILRB1. 22844324_study concludes LIR-1 alone does not directly influence NK-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against multiple myeloma (MM); work provides investigation of inhibitory capability of LIR-1 in NK-92-mediated cytotoxicity against MM and the functional evaluation of LIR-1 on MM and LBCL lymphoblastoid cell line 23208495_MiR-7 is a novel miRNA with tumor suppressive function in colon cancer by targeting oncogenic YY1. 23348966_Cis association of leukocyte Ig-like receptor 1 with MHC class I modulates accessibility to antibodies and HCMV UL18. 23404538_miR-7 efficiently silenced some genes involved in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway and achieved favorable effects in treating glioma in vivo and in vitro 23756160_these results suggest that ILT2 participates in the defective immune-regulation observed in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 23955630_we report the crystal structures of the D3D4 domains of both LILRB1 and LILRB2. 23997222_HLA-G5 could be responsible, at least in part, via its interaction with ILT2, for decidual T cell IL-4 production, known to be crucial for successful pregnancy. 24038602_Binding of specific AP-1 factors, we found JunD associated with the LILRB1 distal promoter. 24156302_These data show that S100A9 protein, through ligation with CD85j, can stimulate the anti-HIV-1 activity of NK cells. 24453251_This B cell regulatory mechanism involving ILT2-HLA-G interaction brings important insight to design future B cell-targeted therapies aimed at reducing inappropriate immune reaction in allotransplantation and autoimmune diseases. 24550301_To escape antiviral response, antibody-opsonized dengue virus coligates LILRB1 to inhibit FcgammaR signaling for type-I IFN-stimulated gene expression. 24909369_Increased frequency of ILT2-expressing CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cells correlates with disease severity of pulmonary tuberculosis. 25070049_MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells by down regulating the STAT3 pathway 25726929_Patients expressing high levels of CD85j had an impaired ability to lyse triple negative breast cancer cells in the presence of Cetuximab. We also found that CD85j overexpression was associated with HLA-I and soluble HLA-G expression by tumors. 25853899_Our findings offer new insights into the immunopathology of rheumatoid arthritis(RA) patients with long-lasting anti-RA-treatment and highlight the importance to also measure the binding capability of sHLA-G to LILRB1 25855135_One SNP in LILRB1 (5724G>A) influenced the risk of NSCLC. 5724G>A was associated with protection from tumor cell infiltration of regional lymph nodes. Expression in tumor tissue correlated with tumor stage. 26314621_LIR-1 expression on CD8+ T cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients was higher than that in healthy controls. 26739048_Surprisingly, the ability of LIR1(+) natural killer cells to control virus spread differed between human cytomegalovirus strains, and this phenomenon was dependent on amino acid sequences within the viral ligand UL18. 26776460_this study shows that in the tuberculosis with pleural effusion -PE cases, ILT-2 expressing cells are reduced at the local disease site 26874236_this study shows that elevated levels of plasmatic sILT2 are present in non-muscle-infiltrating bladder cancer patients 26973020_a woman's heterozygosity in HLA-G and LILRB1 might be an advantage for a success of reproduction, but the partner's heterozygosity in 9A/10A KIR2DL4 alleles might not 27109306_the results support that a regulated assembly of these noncanonical HLA-I conformers during the immune response may enhance the avidity of their interaction with LILRB1. 27129285_LILRB1 ligation during the differentiation of monocytes to dendritic cells in vitro results in increased ABIN1 expression. ABIN1 mediates the effects of LILRB1 ligation-induced inhibitory effects on immune responses. 27417393_The exosomes-containing miR-7-5p is a crucial mediator of bystander autophagy. 27430434_miR7 negatively regulates PAK1 protein expression but has no effect on PAK1 mRNA expression. Knockdown of PAK1 expression markedly suppressed thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 27764812_The miR-7 can inhibit the activation of ERK/MAPK signaling pathway by down-regulating FAK expression, thereby suppressing the proliferation, migration and invasion of NSCLC cells. The miR-7 and its target gene FAK may be novel targets for the diagnosis and treatment of NSCLC. 27901488_we confirmed that the RASSF2-PAR-4 axis was mainly responsible for miR-7 functions in CAFs using bioinformatics methods. Overexpression of miR-7 in CAFs led to down-regulation of RASSF2, which dramatically decreased the secretion of PAR-4 from CAFs and then enhanced the proliferation and migration of the co-cultured cancer cells. 28646700_Serum miR-7 was significantly elevated in the T2DM patients [(401.0+/-34.37) fmol/L, PC and no association with insertion/deletion polymorphisms of LILRA3 with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) 30925324_these findings demonstrate that the ciRS-7/miR-7 axis can possibly serve as a regulator in mediating proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocytes in the process of osteoarthritis development 31451484_CD8(+)PD-1(-)ILT2(+) T Cells Are an Intratumoral Cytotoxic Population Selectively Inhibited by the Immune-Checkpoint HLA-G. 31501273_Results represent a novel branch of insulin action through the HNRNPK-miR-7 axis and highlight the possible implication of these posttranscriptional regulators in a range of diseases underlying metabolic dysregulation in the brain, from diabetes to Alzheimer's disease. 32390601_Immunosuppressive receptor LILRB1 acts as a potential regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrating with SHP1. 32534335_Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor subfamily B member 1 potentially acts as a diagnostic and prognostic target in certain subtypes of adenocarcinoma. 32650338_Structural basis for RIFIN-mediated activation of LILRB1 in malaria. 32918786_Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B1 and B4 (LILRB1 and LILRB4): Highly sensitive and specific markers of acute myeloid leukemia with monocytic differentiation. 32973812_Soluble HLA-G and HLA-G Bearing Extracellular Vesicles Affect ILT-2 Positive and ILT-2 Negative CD8 T Cells Complementary. 33342344_IncRNA ZFAS1 contributes to the radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by sponging hsa-miR-7-5p to upregulate ENO2. 33505397_Inhibition of iNKT Cells by the HLA-G-ILT2 Checkpoint and Poor Stimulation by HLA-G-Expressing Tolerogenic DC. 34054869_Prognostic Significance of Immune Checkpoints HLA-G/ILT-2/4 and PD-L1 in Colorectal Cancer. 34160005_LILRB1: A Novel Diagnostic B-Cell Marker to Distinguish Neoplastic B Lymphoblasts From Hematogones. 34186161_Tumor infiltrating and peripheral CD4(+)ILT2(+) T cells are a cytotoxic subset selectively inhibited by HLA-G in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. 34396443_miR125a5p and miR7 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of vascular smooth muscle cell by targeting EGFR. 34659215_B Cells Control Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cell Responses to Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Infection Through the CD85j HLA-G Receptor. 35041051_HLA-G-ILT2 interaction contributes to suppression of bone marrow B cell proliferation in acquired aplastic anemia. 35347579_Down-regulation of miR-7-5p and miR-548ar-5p predicts malignancy in indeterminate thyroid nodules negative for BRAF and RAS mutations. 35754199_Genetic diversity of the LILRB1 and LILRB2 coding regions in an admixed Brazilian population sample. 35917968_Increased ILT2 expression contributes to dysfunction of CD56(dim)CD16(+)NK cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. 36004818_Natural killer cell profiles in recurrent pregnancy loss: Increased expression and positive associations with TACTILE and LILRB1. 36104364_A LILRB1 variant with a decreased ability to phosphorylate SHP-1 leads to autoimmune diseases. 36389667_Dual checkpoint blockade of CD47 and LILRB1 enhances CD20 antibody-dependent phagocytosis of lymphoma cells by macrophages. |
ENSMUSG00000081665+ENSMUSG00000030427+ENSMUSG00000074417+ENSMUSG00000089942+ENSMUSG00000074419+ENSMUSG00000070873+ENSMUSG00000058818 |
Pira1+Lilra6+Pira12+Pira2+Pira13+Lilra5+Pirb |
194.926760 |
0.3181223701 |
-1.652346 |
0.177996635 |
84.680710 |
0.00000000000000000003506549997901634359962600585157905045368652790407616942972013340806824999162927269935607910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000313297082136974103751284017390872221818251884733124790552438732049722602823749184608459472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
99.0627836 |
11.4493113 |
313.5463320 |
24.7947013 |
| ENSG00000105063_ENSG00000180089 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
235.703460 |
0.2546420800 |
-1.973457 |
0.116537550 |
301.675142 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014217315512322235187381920706619111460200876992242637897349505309392401565405692091545597376313211872126102709430087858567759326268383364687160245568818924297521013428401148726010205791681073606014251708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004130857814210161343077676199700333117782376487279480367541306810710747137377090759888672667011508251143049519902608877910362325550672943904015279099233744539206177569246047909246044582687318325042724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
98.0887705 |
13.8888354 |
389.2099416 |
37.9478448 |
| ENSG00000105136 |
79744 |
ZNF419 |
protein_coding |
Q96HQ0 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79744; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27826023_previously unreported alternative splicing patterns in the genes ZNF419 and DKKL1 |
ENSMUSG00000053211+ENSMUSG00000000103 |
Zfy1+Zfy2 |
69.779142 |
0.4735194036 |
-1.078505 |
0.206244837 |
27.505442 |
0.00000015665311237561922467752283973096982805373045266605913639068603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000605287942058675283957085155872590576109359972178936004638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.8255283 |
7.1403321 |
97.3640513 |
10.3639989 |
| ENSG00000105246 |
10148 |
EBI3 |
protein_coding |
Q14213 |
FUNCTION: Associates with IL27 to form the IL-27 interleukin, a heterodimeric cytokine which functions in innate immunity. IL-27 has pro- and anti-inflammatory properties, that can regulate T-helper cell development, suppress T-cell proliferation, stimulate cytotoxic T-cell activity, induce isotype switching in B-cells, and that has diverse effects on innate immune cells. Among its target cells are CD4 T-helper cells which can differentiate in type 1 effector cells (TH1), type 2 effector cells (TH2) and IL17 producing helper T-cells (TH17). It drives rapid clonal expansion of naive but not memory CD4 T-cells. It also strongly synergizes with IL-12 to trigger interferon-gamma/IFN-gamma production of naive CD4 T-cells, binds to the cytokine receptor WSX-1/TCCR. Another important role of IL-27 is its antitumor activity as well as its antiangiogenic activity with activation of production of antiangiogenic chemokines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12121660}. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene was identified by its induced expression in B lymphocytes in response Epstein-Barr virus infection. It encodes a secreted glycoprotein belonging to the hematopoietin receptor family, and heterodimerizes with a 28 kDa protein to form interleukin 27 (IL-27). IL-27 regulates T cell and inflammatory responses, in part by activating the Jak/STAT pathway of CD4+ T cells. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:10148; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-27 receptor binding [GO:0045523]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; leptin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033210]; positive regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046641]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0042088] |
12121660_a new heterodimeric cytokine that consists of EBI3, an IL-12p40-related protein, and p28, a newly discovered IL-12p35-related polypeptide (IL-27) 15170639_results suggest that increased numbers of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells in areas of active inflammatory bowel disease are secondary to influx or local proliferation of inflammatory cells & do not contribute significantly to local production of EBI3 18167155_findings indicate that the restricted Th1 responses in newborns owing to deficient IL-12 production may be compensated for, in part, by enhanced IL-27 secretion 18336908_The genome-wide mRNA expression profile under the condition of short-term stimulation (4h) with IL-18 using the Affymetrix GeneChip((R)) Array System, was characterized. 19556516_Our data support a possible role of Ebi3 in atherogenesis 21285006_This study demonstrated that interleukin-35 expression could be detected in the CD4(+) T cells from peripheral blood of chronic hepatitis B patients. 21931777_Data show that Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) is differentially expressed among Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 22343630_IL-27 expression is one host immune factor produced in response to influenza A virus infection and that elevated IL-27 levels inhibit viral replication. 22438968_in contrast to TGF-beta, IL-35 is not constitutively expressed in tissues but it is inducible in response to inflammatory stimuli 22836044_The findings of this study support the potential role of regulatory T cells and genetic variations in the regions around FOXP3 and EBI3 genes in modifying the risk for AR development in Chinese patients. 23154182_these results reveal a novel functional role for IL-35 in suppressing cancer activity, inhibiting cancer cell growth, and increasing the apoptosis sensitivity of human cancer cells through the regulation of genes related to the cell cycle and apoptosis. 23562195_The findings of this study suggest that SNPs in FOXP3 and EBI3 genes modify the risk for development of chronic rhinosinusitis. 23619469_expressed by trophoblast cells 23845089_EBI3-overexpression in MRL/lpr mice induces generation of regulatory T cells, causing suppression of autoimmune and inflammatory reactions by affecting the T helper (Th)1 cell/Th2 cytokine balance. 23904441_the findings from the past decade identify IL-27 as a critical immunoregulatory cytokine, especially for T cells, whereas some controversy is fueled by results challenging the view of IL-27 as a classical silencer of inflammation. 24121041_circulating IL-35 in PDAC patients significantly increased, suggesting that regulating the expression of IL-35 may provide a new possible target for the treatment of PDAC patients, especially for the resectable ones. 24376289_The increased expression of IL-35 in chronic and aggressive periodontitis suggests its possible role in pathogenesis of periodontitis. 24743305_Interleukin-35 induces regulatory B cells that suppress autoimmune disease. [il-35] 24782489_ingestion of apoptotic cells by DCs leads to increased expression of IL-12p35 and Ebi3 without affecting IL-12p40. 24970690_The results suggest that the decreased expression of IL-35 could be involved in the pathogenesis of childhood asthma. 24994465_IL-35 levels are dramatically decreased in immune thrombocytopenia patients, suggesting that IL-35 may be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease. 25323532_IL-17 and IL-35 may be critically involved in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B-related LC. 25575066_The levels of EBI3 and IL-12p35 mRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in moderate or hyper-responders were significantly higher than those in non- or hypo-responders. 25640666_IL35 appears to contribute to the loss of immunological self-tolerance in ITP patients by modulating T cells and immunoregulatory cytokines. 25869609_IL-35 is highly expressed in chronic HBV CD4(+) T-cells and plays an important role in the inhibition of the cellular immune response in chronic HBV. 25935866_IL-35 mRNA and protein were higher in tuberculous pleural effusions than in malignant ones. 25937126_EBI3 gene rs4740 polymorphism is closely associated with susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis and the elevation and enrichment of EBI3 in the lung derived from macrophages may contribute to the exacerbation of mycobacterial infection. 26044961_IL-35 can effectively suppress the proliferation and IL-4 production of activated CD4+CD25- T cells in allergic asthma, and that IL-35 may be a new immunotherapy for asthma patients. 26204444_Elevated circulating IL-35, particularly at early phase, its decrease after treatment initiation, and a positive association between synovial fluid IL-35 and disease activity support an involvement of IL-35 in the pathogenesis of RA. 26303210_Data suggest that the toll like receptor 3 (TLR3)-interferon regulatory factor 6 protein (IRF6)-interleukin-23 subunit p19 (p19)/EBI3 protein axis may regulate keratinocyte functions in the skin. 26355156_EBI3 Downregulation Contributes to Type I Collagen Overexpression in Scleroderma Skin. 26431888_IL-35 was elevated in bone marrow of adult AML patients and this increase was correlated with the clinical stages of malignancy, suggesting that IL-35 is involved in pathogenesis of AML. 26472010_higher decidual mRNA expression in preeclampsia 26844658_Data show that interleukin-35 (Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) and the interleukin-12 Subunit p35 (p35) subunit) levels were significantly elevated in the patients with influenza infection. 27699510_The plasma levels of interleukin-35 were significantly higher in the hepatocellular carcinoma patients than the controls. 27855302_this study introduces IL-35 as a new treatment for pemphigus 28211781_The study revealed that post-therapeutic recovery of circulating IL-35 concentration might be an independent predictor for effective response to IST in pediatric AA. 28351328_over-expression of EBI3 could reduce the apoptosis of Treg/CD4(+)T/CD8(+)T cells and prevent radiation-induced immunosuppression of cervical cancer HeLa cells by inhibiting the activation of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway 28644966_IL-35 expression was significantly increased in patients with chronic hepatitis C and was positively correlated with the levels of viral RNA 28752680_Letter: circulating IL-35 is significantly higher than healthy controls and associate with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. 28989066_Pancreatic ductal carcinoma cells produce IL35 to recruit monocytes via CCL5 and induce macrophage to promote angiogenesis via expression of CXCL1 and CXCL8. 29343013_IL-35 may be involved in the inflammatory process of sarcoidosis and play an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. 29371247_IL-35 is induced during atherosclerosis development and inhibits mitochondrial reactive oxygen species-H3K14 acetylation-AP-1-mediated endothelial activation. 29445068_IL-35 may be involved in the pathogenesis of Primary biliary cirrhosis. 29729445_IL-35 is a relatively newly discovered member of the IL-12 family which are unique in structure as they are dimer formed by two subunits; recent findings have shown abnormal expression of IL-35 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and functional analysis suggested that IL-35 is critical in the onset and development of these diseases. [Review] 29738342_CC genotype of rs428253 in EBI3 was related to an increased risk of coronary heart disease in the Chinese Zhuang population. 29739077_Data suggest that reduced mRNA expression of forkhead box P3 (FoxP3) and circulating level of IL-35 (a heterodimer of EBI3 and IL12A ) are of significance in the context of coronary artery disease (CAD) pathogenesis. 29938865_The IL-35 levels in CagA(+) H. pylori-infected participants from peptic ulcer and H. pylori-infected asymptomatic groups were lower than individuals infected with CagA(-) strains. 30054763_IL-35 may have the effect on inhibiting inflammatory process in Kawasaki disease and further preventing Kawasaki disease patients from coronary artery lesion. 30218063_Tumor associated macrophages secrete interleukin-35 (IL-35) to facilitate metastatic colonization through activation of JAK2-STAT6-GATA3 signaling to reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer cells. 30257721_Researchers have constructed IL-35 gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)and explored their functions and mechanisms in some disease models. In this review, we discuss the potential tolerance-inducing effects of MSCs in transplantation and briefly introduce the immunoregulatory functions of the IL-35 gene-modified MSCs. 30513021_Regarding the significant negative correlation between EBI-3 gene expression and plasma levels of neopterin, it can be concluded that the altered gene expression of EBI-3 may play a role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 30589451_A decrease in the IL-35 (IL-12A+EBI3) serum levels may play an important role in the pathogenesis of primary Sjogren's syndrome. 30681737_this review describes the role of IL-35 in immune-related diseases 30805894_Analysis for EBI3 (rs4740) genotyping showed a significant association of 'GG' genotypie with reduced risk for disease. 30914441_IL-35 in inducing the activation of an anti-inflammatory M2-like macrophage phenotype, promoting early stent endothelialization after stent implantation. 31013577_The polymorphism of rs4740 of IL-35 encoding gene is associated with the occurrence of renal disorder and hematological disorder of SLE patients. 31955243_Epigenetic histone modulation contributes to improvements in inflammatory bowel disease via EBI3. 32763760_Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) single nucleotide polymorphisms and their association with central obesity and risk factors for cardiovascular disease: The GEA study. 33141778_Reduced IL-35 in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. 33259477_Lack of evidence for expression and function of IL-39 in human immune cells. 33407151_Analysis for interaction between interleukin-35 genes polymorphisms and risk factors on susceptibility to coronary heart disease in the Chinese Han population. 34069352_Epigenetic DNA Methylation of EBI3 Modulates Human Interleukin-35 Formation via NFkB Signaling: A Promising Therapeutic Option in Ulcerative Colitis. 34603342_A Chaperone-Like Role for EBI3 in Collaboration With Calnexin Under Inflammatory Conditions. 34884474_Multifaceted Analysis of IL-23A- and/or EBI3-Including Cytokines Produced by Psoriatic Keratinocytes. 34969761_Epstein-Barr Virus-induced Gene 3 as a Novel Biomarker in Metastatic Melanoma With Infiltrating CD8(+) T Cells: A Study Based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). |
ENSMUSG00000003206 |
Ebi3 |
1240.012091 |
23.3003524927 |
4.542280 |
0.093109726 |
2815.242083 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2403.1869354 |
130.0563572 |
103.9135317 |
5.3172254 |
| ENSG00000105281 |
6510 |
SLC1A5 |
protein_coding |
Q15758 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent amino acids transporter that has a broad substrate specificity, with a preference for zwitterionic amino acids. It accepts as substrates all neutral amino acids, including glutamine, asparagine, and branched-chain and aromatic amino acids, and excludes methylated, anionic, and cationic amino acids (PubMed:8702519, PubMed:29872227). Through binding of the fusogenic protein syncytin-1/ERVW-1 may mediate trophoblasts syncytialization, the spontaneous fusion of their plasma membranes, an essential process in placental development (PubMed:10708449, PubMed:23492904). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10708449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23492904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29872227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702519}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a cell surface receptor for Feline endogenous virus RD114. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10051606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10196349}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a cell surface receptor for Baboon M7 endogenous virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10196349}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a cell surface receptor for type D simian retroviruses. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10196349}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sodium;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The SLC1A5 gene encodes a sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter that can act as a receptor for RD114/type D retrovirus (Larriba et al., 2001 [PubMed 11781704]).[supplied by OMIM, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:6510; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; L-aspartate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015183]; L-glutamine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015186]; L-serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015194]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015175]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; glutamine secretion [GO:0010585]; glutamine transport [GO:0006868]; L-aspartate import across plasma membrane [GO:0140009]; L-glutamine import across plasma membrane [GO:1903803]; neutral amino acid transport [GO:0015804]; protein homotrimerization [GO:0070207]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
12050356_used as receptor by HERV-W Env glycoprotein 12175968_level of amino acid transporter B(0)(ACST2) mRNA expression was lower in forskolin treated BeWo cells 12555937_in the six unrelated Hartnup pedigrees studied, examination of linkage at 19q13.3, polymorphisms in the coding sequence and quantitation of expression of SLC1A5 did not suffice to explain the defect in neutral amino acid transport 12584318_results strongly suggest that combinations of amino acid sequence changes and N-linked oligosaccharides in a critical carboxyl-terminal region of extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) control retroviral utilization of both the ASCT1 and ASCT2 receptors 12757936_Hypoxia alters expression and function of syncytin and its receptor (amino acid transport system B(0)) during trophoblast cell fusion of human placental BeWo cells: implications for impaired trophoblast syncytialisation in pre-eclampsia. 14520239_ASCT2 messenger RNA was not altered significantly in hypoxia in cytotrophoblasts or in perfused placental cotyledons. 15848195_up-regulation of ASCT2 by S-nitroso-N-acetyl-DL-penicillamine might be partially associated with an increase in the density of transporter protein via de novo synthesis 16197915_These results show that the stimulation of ASCT2 expression in response to glutamine in part involves binding of FXR/RXR to the ASCT2 promoter. 16435221_analysis of SLC1A5 mutations on 19q13 in cystinuria patients 16516348_the activity of glutamate transporter GLAST/EAAT1 can effectively regulate the cell surface expression of glutamine/neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2 in human fetal astrocytes 16820059_evaluation of the interaction of the HERV-W envelope with the hASCT2 receptor; a region consisting of the N-terminal 124 amino acids of the mature glycoprotein surface subunit was determined as the minimal receptor-binding domain 17329400_ASCT2 silencing inhibits mTORC1 (mTOR/raptor) signaling and leads to growth repression, followed by enhanced survival signaling via mTORC2 (mTOR/rictor comples) and apoptosis of hepatoma cells. 17676482_Localisation and distribution of RDR/ASCT2 in human placental villi suggests that the fusion of placental trophoblast cells is not regulated by local or temporal variations of RDR/ASCT2 expression in villous cytotrophoblast cells. 18157695_In human entrocytes, glutamine transport and ASCT2 surface expression induced by short-term EGF are MAPK, PI3K, and Rho-dependent. 18638388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18638388_SLC1A5 gene is associated with schizophrenia. 19321927_In primary term human trophoblasts, ASCT2 mRNA levels were preserved at normoxia and downregulated at 1% O(2) after 48 h. 22238282_Cx43-mediated GJIC and SLC1A5 interaction play important functional roles in trophoblast cell fusion. 22804921_These data suggest that intracellular replication of Francisella tularensis depends on the function of host cell SLC1A5. 23213057_SLC1A5 plays a key role in Gln transport controlling lung cancer cells' metabolism, growth, and survival. 23507704_HER2- type breast cancer had the highest expression of stromal GLS1, tumoral GDH, stromal GDH, and tumoral ASCT, while TNBC had the lowest tumoral GDH expression. 23636801_stromal expression of the glutamine-metabolism-related proteins GLS1, GDH, ASCT2 increases with worsening histological phyllodes tumor grade. 24531984_the expression of LAT1 and ASCT2 is significantly increased in human melanoma. The importance of ASCT2 expression in melanoma was confirmed by shRNA knockdown, which inhibited glutamine uptake, mTORC1 signaling and cell proliferation. 24603303_ASC amino-acid transporter 2 expression has a crucial role in the metastasis of pulmonary AC, and is a potential molecular marker for predicting poor prognosis after surgery. 24687878_ASCT-2 is expressed in human oocytes.ASCT-2 is localized at the acrosomal region and equatorial segment of the spermatozoa. 24845232_ASCT2 expression plays an important role in tumour cell growth, and is a promising pathological marker for predicting a worse outcome in pancreatic cancer. 25052780_analysis of the kinetic mechanism of the transport catalyzed by the human glutamine/neutral amino acid transporter hASCT2 25142020_ASCT2 expression, which correlates with that of N-Myc and ATF4, is markedly elevated in high-stage neuroblastoma 25337245_Report the differential expression of SLC1A5 in human colorectal cancer and normal tissues, and a functional link between SLC1A5 expression and growth and survival of colorectal cancer. 25693838_ASCT2-mediated glutamine uptake is essential for multiple pathways regulating the cell cycle and cell growth. 25862406_The results demonstrate that N-glycosylation of SLC1A5 is critical for trafficking. 25987094_Genetic Variants in ASCT2 Gene are Associated with response to therapy in Hepatocelluar Carcinoma 26024742_LAT1, 4F2hc and ASCT2 were highly expressed in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer. 26455325_Both stable and inducible shRNA-mediated ASCT2 knockdown confirmed that inhibiting ASCT2 function was sufficient to prevent cellular proliferation and induce rapid cell death in TN basal-like breast cancer cells, but not in luminal cells. 26492990_Cys is a potent competitive inhibitor of hASCT2 but is not a substrate 26936531_High expression of LAT1 and ASCT2 correlates with metastasis and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 27129276_In the absence of SLC1A5 there is a crucial role of SNAT1 in supplying glutamine for glutaminolysis with SNAT2 acting as a 'backup' for glutamine transport. 27143784_Data show that SERT associates with ASCT2 (alanine-serine-cysteine-threonine 2), a member of the solute carrier 1 family co-expressed with SERT in serotonergic neurons and involved in the transport of small neutral amino acids across the plasma membrane. 27450723_ASCT2 is an EGFR-associated protein that can be co-targeted by cetuximab, leading to sensitization of cetuximab-treated cells to ROS-induced apoptosis. 28036362_The tumor metabolism status determined by expression of GLUT1 and ASCT2. 28419191_we found that PPARdelta directly regulated neutral amino acid transporter SLC1-A5 (solute carrier family 1 member 5) and glucose transporter-1 (Glut1) gene transcription, leading to uptake of glucose and amino acid, activation of mTOR signaling, and tumor progression. In contrast, silence of PPARdelta or its antagonist inhibited this event. 28507054_AR signaling promoted glutamine metabolism by increasing the expression of the glutamine transporters SLC1A4 and SLC1A5, genes commonly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Correspondingly, gene expression signatures of AR activity correlated with SLC1A4 and SLC1A5 mRNA levels in clinical cohorts. 28609484_Data suggest that both heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein type M (HNRPM) and solute carrier 1A5 (SLC1A5) have role in the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer. 28749408_These results indicated that ASCT2 (SLC1A5) could be a novel therapeutic target against KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. 28784848_this study shows that IL-2-induced expression of SLC1A5 is a prerequisite for NKG2D-mediated activation of NK cells 28807674_Results suggest that ASCT1/2 may play an important role in regulating extracellular d-serine and NMDA receptor-mediated physiological effects and that ASCT1/2 inhibitors have the potential for therapeutic benefit. 28823958_High ASCT2 expression is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 28885889_intronic variants of the ASCT2 gene have roles in hampering the splicing process and in longevity 29020998_Our data confirm the heterogeneity of breast tumors at a functional proteomic level and dissects the relationship between metabolism-related proteins, pathological features and patient survival. These observations highlight the importance of SHMT2 and ASCT2 as valuable individual prognostic markers and potential targets for personalized breast cancer therapy 29151270_Results provide evidence that ASCT2 enhances glutamine uptake in glycolipid-enriched microdomain/rafts in GD2(+) small-cell lung cancer cells, leading to the enhancement of cell proliferation and migration. 29326164_Data suggest that amino acid uptake via ASCT2/SLC1A5 is required for cell proliferation/tumor growth independently of LAT1/SLC7A5; in part, these studies were conducted in lung and colon adenocarcinoma cell lines and involved gene knockout techniques. (ASCT2/SLC1A5 = solute carrier family-1 member-5; LAT1/SLC7A5 = solute carrier family-7 member-5) 29334372_Herein we report the preclinical development of V-9302, a competitive small molecule antagonist of transmembrane glutamine flux that selectively and potently targets the amino acid transporter ASCT2. 29363109_This study provides the metabolic molecule SLC1A5 as a potential therapeutic target to increase the efficacy of cetuximab on colorectal cancer 29435734_ASCT2 was significantly overexpressed in the gastric cancer (GC) samples compared with adjacent non-cancerous gastric mucosa, in contrast, a significantly higher level of glutamine synthetase (GS) expression was observed in normal tissues than in GC samples compared with adjacent non-cancerous gastric mucosa. 29455869_Our results indicate that overexpression of SLC1a5 is associated with shorter overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer 29495336_the experimental data allowed identifying C467 residue as crucial for substrate binding and for transport activity modulation of hASCT2. 29563155_data reveal a role for SNX27 in glutamine uptake and amino acid-stimulated mTORC1 activation via modulation of ASCT2 intracellular trafficking 29872227_Relative to structures of other SLC1 members, ASCT2 is in the most extreme inward-oriented state, with the transport domain largely detached from the central scaffold domain on the cytoplasmic side 30029480_These data collectively establish that in an in vitro context, human epithelial and mesenchymal hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines adapt to ASCT2 or LAT1 knockout. 30071532_SLC1A5 expression is increased in tumor samples from esophageal cancer patients, and downregulation of SLC1A5 inhibited cell cycle progression and esophageal cancer growth. 30272366_Results demonstrated that ASCT2 and pmTOR protein levels were significantly higher in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) tissues and predicting a poor prognosis. The expression levels of ASCT2 and pmTOR in EOC were positively correlated indicating a synergistic effect on the growth and development of early EOC. 30635397_The ASCT2 deficiency was compensated by increased levels of sodium neutral amino acid transporter 1 (SNAT1 or SLC38A1) and SNAT2 (SLC38A2) in ASCT2ko 143B cells, mediated by a GCN2 EIF2alpha kinase (GCN2)-dependent pathway, but this compensation was not observed in ASCT2ko HCC1806 cells. 30668314_ASCT2 regulates gastric cancer proliferation via reactive oxygen species induced mitochondrial pathway. 30935948_that binding of galectin-12 to SLC1A5 significantly reduced glutamine uptake 31409775_the data show that ABHD11-AS1 acts as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to exert malignant properties in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) through the miR-199a-5p/SLC1A5 axis. 31535081_Critical role of ASCT2-mediated amino acid metabolism in promoting leukaemia development and progression. 31580259_These structures reveal insights into the conformation of the critical ECL2a loop which connects the two domains, thus allowing rigid body movement of the transport domain throughout the transport cycle. Furthermore, the structures provide new insights into substrate recognition, which involves conformational changes in the HP2 loop. 31685994_CD9 promoted the plasma membrane localization of the glutamine transporter ASCT2, enhancing glutamine uptake in Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. 31819178_The downregulation of ASCT2 significantly decreased the intracellular glutamine level, leading to attenuated growth and proliferation, increased apoptosis and autophagy, inactivation of the mTORC1 pathway, increased oxidative stress and an improved response to cetuximab in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 31826641_Chronic heart failure has profound effects on myocardial AA homeostasis, down-regulating myocardial SLC1A5 expression and impairing glutamine homeostasis. 31866442_A Variant of SLC1A5 Is a Mitochondrial Glutamine Transporter for Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells. 31959741_NEDD4L downregulates autophagy and cell growth by modulating ULK1 and a glutamine transporter. 32162845_ASCT2 overexpression is associated with poor survival of OSCC patients and ASCT2 knockdown inhibited growth of glutamine-addicted OSCC cells. 32242892_Interaction of the neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2 with basic amino acids. 32658600_Circular RNA circ-LDLRAD3 serves as an oncogene to promote non-small cell lung cancer progression by upregulating SLC1A5 through sponging miR-137. 32996252_SLC38A2 Overexpression Induces a Cancer-like Metabolic Profile and Cooperates with SLC1A5 in Pan-cancer Prognosis. 33039171_Topotecan induces hepatocellular injury via ASCT2 mediated oxidative stress. 33162818_NDRG2 ablation reprograms metastatic cancer cells towards glutamine dependence via the induction of ASCT2. 33841424_Flagellin From Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Stimulates ATB(0,+) Transporter for Arginine and Neutral Amino Acids in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. 34132956_Circ_0072995 Promotes Ovarian Cancer Progression Through Regulating miR-122-5p/SLC1A5 Axis. 34282517_SLC1A5 co-expression with TALDO1 associates with endocrine therapy failure in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. 34525179_The STAT3-MYC axis promotes survival of leukemia stem cells by regulating SLC1A5 and oxidative phosphorylation. 34662550_The pro-proliferative effect of interferon-gamma in breast cancer cell lines is dependent on stimulation of ASCT2-mediated glutamine cellular uptake. 34738502_Knockdown of circular RNA septin 9 inhibits the malignant progression of breast cancer by reducing the expression of solute carrier family 1 member 5 in a microRNA-149-5p-dependent manner. 34741534_The involvement of sodium in the function of the human amino acid transporter ASCT2. 34811815_Circ_0000463 contributes to the progression and glutamine metabolism of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting miR-924/SLC1A5 signaling. 35089546_Discoidin domain receptor 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulation of SLC1A5 and the mTORC1 signaling pathway. 35163050_Cysteine 467 of the ASCT2 Amino Acid Transporter Is a Molecular Determinant of the Antiport Mechanism. 35284960_Circ_0062558 promotes growth, migration, and glutamine metabolism in triple-negative breast cancer by targeting the miR-876-3p/SLC1A5 axis. 35320491_A novel miR-338-3p/SLC1A5 axis reprograms retinal pigment epithelium to increases its resistance to high glucose-induced cell ferroptosis. 35487063_Targeting of the glutamine transporter SLC1A5 induces cellular senescence in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 36273140_circ_0025033 promotes ovarian cancer development via regulating the hsa_miR-370-3p/SLC1A5 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000001918 |
Slc1a5 |
995.519032 |
2.4119466289 |
1.270198 |
0.051403988 |
622.044435 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002685969811076994332929143294573303461590597178045326944726452116436309839780653667019613031752724513008008477119450613344713363108361945904997873084580188710210573357701866819546771827996571834 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001536624589592885199714261203034659521363569073739009552526096773277413046609598341649997421127883073021963267136707623612527728210496506172525380323572704362180917974630618673511602898080936706 |
Yes |
No |
1423.5954990 |
42.5252055 |
594.4124766 |
14.4308523 |
| ENSG00000105329 |
7040 |
TGFB1 |
protein_coding |
A0A499FJK2 |
FUNCTION: Transforming growth factor beta-1 proprotein: Precursor of the Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-beta-1) chains, which constitute the regulatory and active subunit of TGF-beta-1, respectively. {ECO:0000256|ARBA:ARBA00002007}. |
Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Growth factor;Mitogen;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate a latency-associated peptide (LAP) and a mature peptide, and is found in either a latent form composed of a mature peptide homodimer, a LAP homodimer, and a latent TGF-beta binding protein, or in an active form consisting solely of the mature peptide homodimer. The mature peptide may also form heterodimers with other TGFB family members. This encoded protein regulates cell proliferation, differentiation and growth, and can modulate expression and activation of other growth factors including interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha. This gene is frequently upregulated in tumor cells, and mutations in this gene result in Camurati-Engelmann disease. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:7040; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005160]; adaptive immune response based on somatic recombination of immune receptors built from immunoglobulin superfamily domains [GO:0002460]; aging [GO:0007568]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; branch elongation involved in mammary gland duct branching [GO:0060751]; bronchiole development [GO:0060435]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus [GO:1990314]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; columnar/cuboidal epithelial cell maturation [GO:0002069]; connective tissue development [GO:0061448]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; embryonic liver development [GO:1990402]; enamel mineralization [GO:0070166]; endoderm development [GO:0007492]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; extracellular matrix assembly [GO:0085029]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; frontal suture morphogenesis [GO:0060364]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; germ cell migration [GO:0008354]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; Langerhans cell differentiation [GO:0061520]; lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:0070306]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; mammary gland branching involved in thelarche [GO:0060744]; muscle cell cellular homeostasis [GO:0046716]; myelination [GO:0042552]; negative regulation of biomineral tissue development [GO:0070168]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of immune response [GO:0050777]; negative regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032700]; negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007406]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051280]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; phospholipid homeostasis [GO:0055091]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090190]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of exit from mitosis [GO:0031536]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of histone acetylation [GO:0035066]; positive regulation of histone deacetylation [GO:0031065]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of microglia differentiation [GO:0014008]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071677]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of odontogenesis [GO:0042482]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of receptor clustering [GO:1903911]; positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045591]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051152]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; regulation of branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060762]; regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061035]; regulation of DNA binding [GO:0051101]; regulation of interleukin-23 production [GO:0032667]; regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042306]; regulation of sodium ion transport [GO:0002028]; regulation of striated muscle tissue development [GO:0016202]; regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045066]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to immobilization stress [GO:0035902]; response to laminar fluid shear stress [GO:0034616]; response to salt [GO:1902074]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; tolerance induction to self antigen [GO:0002513]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway involved in heart development [GO:1905313]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055010]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11008076_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11176807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11192323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11266927_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11266928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11267084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11267423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11316069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11345594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11357939_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11374867_downregulates expression of integrin alpha6 in lens epithelial cells; gene expression regulation 11389394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11391236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11391238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11401606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11404167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11436536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11453244_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11496247_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11528523_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11557193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11568166_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11576951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11694328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11715070_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11740340_Association of polymorphisms with genetic susceptibility to osteoporosis 11750277_Association of polymorphisms of the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene with the rate of progression of HCV-induced liver fibrosis. 11750277_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11769974_Transforming growth factor beta-1 stimulates invasivity of hepatic stellate cells by engagement of the cell-associated fibrinolytic system 11771728_Ectopic expression of eIF-4E in human colon cancer cells promotes the stimulation of adhesion molecules by transforming growth factorbeta 11776328_PAI-1 gene activation by TNF-alpha apparently is yet to be defined for the location of the response element and/or the signaling pathway, while TGF-beta is the most important cytokine for PAI-1 transcriptional activation through its 5' proximal promoter. 11784716_decrease in p21cip1 levels was mediated by a TGFbeta-initiated Ras-dependent, but smad-independent post-transcriptional mechanism 11800227_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803605_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803605_effect on renal function of polymorphism in heart transplant recipients 11810274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11824477_Human TGF-beta1 induces an accumulation of connexin43 in a lysosomal compartment in bovine endothelial cells. 11826761_TGF-beta1 is the predominant isoform in lymphoid organs and regulates autoimmunity and inflammation. Smad proteins 2,3,4,6,& 7 are involved in its signal transduction pathways. 11830340_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11836565_The induction of apoptosis by a combined 1,25(OH)2D3 analog, EB1089 and TGF-beta1 in NCI-H929 multiple myeloma cells. 11839086_induction in keratinocytes after gamma irradiation 11867550_TGFbeta can promote DNA instability through down-regulation of Rad51 and inhibition of DNA repair. 11876742_Dendritic cells exposed in vitro to TGF-beta1 ameliorate experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis.TGF-beta1 promotes dendritic cell differentiation and maturation. 11876761_S. stercoralis patients with HTLV-I showed a high frequency of expression of TGF-beta-1, but those without HTLV-I did not. 11906036_decreased levels of active TGFb in HIV, and immunosuppresed patients, and in patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia 11906646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11908736_REVIEW: role of TGFB1 as an anti-differentiating factor and modulator of gene expression and differentiation potential of hematopoietic elements. 11911944_TGFbeta1-induced parathyroid hormone-related protein(PTHrP)mRNA stability might be, in part, the result of cis-acting sequences within the coding region of the PTHrP mRNA. 11912197_Molecular mechanism of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced glutathione depletion in alveolar epithelial cells. Involvement of AP-1/ARE and Fra-1. 11924651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11924651_common TGF-beta1 polymorphisms are not associated with a risk of developing Dupuytren's disease. 11925630_TGF-beta 1 expression level can be a risk factor for alcoholic liver disease and might be related to the inflammatory activity and fibrosis of the liver in patients. 11928807_down-regulated UPA in normal and dystrophic myoblasts; was the only growth factor tested able to exceptionally up-regulate PAI-1, mainly in dystrophic satellite cells; and induced a dose-dependent increase of Matrigel invasion only in dystrophic myoblasts 11934870_results suggest the importance of alphaEbeta7 expression by TGF-beta in selective localization of intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes 11966931_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11981433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11991670_no correlation between the concentration of either isoform of TGFbeta in milk and the corresponding TGFbeta in plasma 11991675_production by different populations of erythroid cells derived from human embryonal liver 11992481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11998866_Transforming growth factor-beta1 enhanced smooth muscle actin expression in TR-PCT1 cells, but this expression was reduced by subsequent treatment with basic fibroblast growth factor. 12000722_TGF-beta(1) expression was significantly correlated with both hepatic fibrosis and the percentage of portal tracts showing histological abnormalities associated with cystic fibrosis liver disease. 12009575_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12020803_TGF beta 1 was able to suppress the expression of Id-1, a helix-loop-helix (HLH) protein, which plays important roles in the inhibition of cell differentiation and growth arrest. 12021923_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 isoforms are produced by chondrosarcomas and could have a potential role as autocrine growth stimulators in these neoplasms 12032592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12032592_results suggest that the TGF-beta1 gene at chromosome 19q13.1 may be a candidate susceptibility locus for hypertension in Japanese women 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12041672_Signaling transduction induced by PF4 in erythroleukemia cells was compared with that induced by TGFB1, which is also a potent inhibitor of HEL growth. 12046078_TGF beta1 expression and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer tissue. 12050565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12055267_TGF-beta 1 induces apoptosis of primary cultured bronchiolar epithelial cells via caspase-3 activation and down-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. 12057905_Direct stimulation of tubular epithelial cells with TGF-beta(1)/epithelial growth factor results in an increased migratory capacity across bovine tubular basement membranes preparations. 12060054_present in diabetic foot ulcers 12061838_induced in cicatricial pemphigoid: possible role(s) in dermal fibrosis 12068984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12068984_TGF-beta polymorphisms do not have a strong influence on disease onset or clinical progression in sarcoidosis and tuberculosis, although this polymorphism might have an effect on the immune response in a tuberculosis host 12081893_p38 MAP kinase regulation of AP-2 binding in TGF-beta1-stimulated chondrogenesis of human trabecular bone-derived cells 12081894_TGF-beta1-stimulated osteoblasts require intracellular calcium signaling for enhanced alpha5 integrin expression 12082048_No significant variations in the distribution of the genotypes and haplotypes were observed between Alzheimer patients and controls. 12082048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085100_distribution of intracellular and extracellular expression in human testis and its association with spermatogenesis 12089714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12095061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12097320_HTLV-1 tax represses Smad-mediated TGF-beta signaling. 12099698_Transforming growth factor-beta-induced transcription of the Alzheimer beta-amyloid precursor protein gene involves interaction between the CTCF-complex and Smads 12101112_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12107734_Angiotensin II induces its promoter activation; has a similarity to hyperglycemia. 12117671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12133353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140283_TGFbeta1 regulates BGN expression and is part of a cell growth regulation pathway 12150293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12150293_TGF-beta1 gene are not suitable genetic markers of MVP in Taiwan Chinese. 12160532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12161098_TGF-beta1 has a role in activation of endothelial cell apoptosis along with TNF-alpha 12161428_Data suggest that SMAD3 interactions with the positive regulators NKX2.1 and HNF-3 underlie the molecular basis for TGF-beta-induced repression of surfactant protein B gene transcription. 12163012_Results demonstrate that TGF-beta1 stimulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 production and promoter activity in a process that depends of the activation of the Ras-ERK1,2 MAP kinase pathway. 12163055_Differential effects of FGF4, EGF and TGFB1 on functional development of stromal layers (progenitor cell-outputs) in acute myeloid leukemia 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12168782_TGFB1 has a smaller role than TGFB3 in endometrial differentiation 12170265_activation of TGF-beta1/Smad2 signaling is associated with airway remodeling in asthma 12171249_TGFbeta1 regulates GM-CSF induced human myelopoiesis 12172787_This protein increases E. coli K1 adherence, invasion, and transcytosis in cultured human brain microvascular endothelial cells. 12174377_transforming growth factor-beta1 is closely related to the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer 12175481_Decrease of TGF-beta1 plasma levels and increase of nitric oxide synthase activity in leukocytes as potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease 12176809_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12182464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12186868_TGF-beta1 inhibition of COL2A1 gene transcription in articular chondrocytes is mediated by an increase of the Sp3/Sp1 ratio and by the repression of Sp1 transactivating effects on that gene 12189134_TGF-beta1 regulates human enhancer of filamentation-1 expression 12202478_TGF-beta mediated G1 arrest requires P27, Kip1, in cancer cell line 12202987_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12207584_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12209716_In this study, the expression of Smad4 protein appeared to be correlated with the depth of invasion of esophageal SCC 12219028_Resistance to transforming growth factor-beta occurs in the presence of normal Smad activation. 12223346_1,25(OH)(2)D(3) treatment of Caco-2 cells results in activation of latent TGF-beta 1 facilitated by the enhanced expression of IGF-II receptor 12232842_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12234017_TGFbeta1 stimulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of SiHa cells, indicating a positive role in the invasive transition of tumors. 12352892_relationship to intragraft messenger RNA expression of angiotensinogen and to chronic allograft nephropathy in kidney transplant patients 12358852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12366695_expression of mRNA for IL-4, IL-5, TGF-beta1, IFN-gamma in patients with cicatricial pemphigoid 12370400_TGF-beta 1 in combination with IL-13 increases production of eotaxin-1 in airway fibroblasts from asthmatic and normal subjects. 12370804_A role for TGF-beta in estrogen and retinoid mediated regulation of the nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. 12374793_MKK3 activation is required for subsequent p38alpha and p38delta MAPK activation and collagen stimulation by TGF-beta1 12376363_TGF-beta1 is a potent inducer of HO-1 and examined the signaling pathway by which TGF-beta1 regulates HO-1 expression in human lung epithelial cells 12379307_induces TGFBI in pancratic cancer cell lines and in pancreatic cancer cells in vivo 12382579_Substance P up-regulates the TGF-beta 1 mRNA expression of human dermal fibroblasts in vitro 12393416_Levels of phosphorylated Smad2/3 are sensors of the interplay between effects of retinoic acid and TGF-beta or vitamin D3 on monocytic and granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells. 12393612_HTLV1 Tax inhibits TGF-beta1 signaling by reducing the Smad3 DNA binding activity 12410804_children with active celiac disease have an altered expression of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3 in the small intestine 12411321_involvement of Furin gene regulation in the maturation of TGFB1 in differentiating megakaryoblastic cells 12413771_TGF-beta(1) might regulate the TARC-related inflammatory processes, which may be important for understanding the pathogenesis of allergic diseases. 12420205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12421823_the molecular mechanisms by which autocrine TGF-beta may selectively contribute to tumor cell motility 12431651_Polymorphism in this gene affects immunosuppression in stable kidney transplantation. 12431652_Codon 10 and codon 25 polymorphism affect gene expression and protein synthesis in stable renal allograft recipients. 12432546_The role of TGF-beta1 and -beta3 in generating a high TIFP was investigated in xenografted experimental anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) derived from the human ATC cell line 12438348_decreased ability to modulate Th1 response in mucosal leishmaniasis 12441075_LMP1 inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1-mediated induction of MAPK/p21 in Epstein-Barr virus infected gastric epithelial cell line GT38 12451269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12453980_Urinary TGF-beta1 and Amadori albumin were elevated in patients with micro- or macroalbuminuria 12454225_Localization of TGF-beta(1) mRNA and protein within tubular epithelial cells, with its increased urinary excretion in nephrotic syndrome, suggest the activation of these cells by filtered protein towards increased TGF-beta(1) production. 12457461_Data demonstrate that Egr-1, AP1 and Smad are part components of the transforming growth factor beta signal transduction pathway that regulates PPAR gamma expression. 12478192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12479636_may contribute to a reduction of proteolytic activity of human gingival fibroblasts in Cyclosporin A-induced gingival overgrowth which favors the accumulation of extracellular matrix 12485831_Exposure of human skin diploid fibroblasts to repeated subcytotoxic doses of ultraviolet-B induces its mRNA overexpression 12485877_cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress and TGF-beta(1) modulate expression of the cell cycle inhibitor p21(waf1/cip1) 12489179_TGF beta 1 signaling and stimulation of osteoadherin in human pulpal fibroblasts and in early secretory and mature odontoblasts. 12489185_investigated TGF-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 latency-associated peptides (LAP)expression in sound and carious human teeth 12491092_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12493411_An examination of quantitative gene expression of this protein in the renal artery wall of chronically rejected human renal allografts. 12493741_mutations in the signal peptide and latency-associated peptide of TGF-beta1 facilitate TGF-beta1 signaling 12500218_Genetic variation at the TGF-beta 1 locus is unlikely to confer significant susceptibility to advanced diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. 12500218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12507818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12514788_results indicate that cervical cancer cells affect the amount and the composition of the intratumoral stroma and the tumor infiltrate by the production and secretion of transforming growth factor-beta(1) 12515830_transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling is modulated by endogenous sphingolipid mediators 12525765_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12529270_TGF-beta signal transduction and mesangial cell fibrogenesis. Review. 12531695_the role of Smad proteins in TGF-beta1-mediated fibroblast-myofibroblast terminal differentiation 12531696_downregulated Notch2 expression in cultured human dental slices 12531888_TGF-beta1 up-regulates expression of integrins and fibronectin, an effect that is associated with autophosphorylation/activation of focal adhesion kinase. 12540377_Data show that high glucose alters endothelial cell growth, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression, but not apoptosis and endoreduplication, via a transforming growth factor-beta1 autocrine pathway. 12547711_fibroblast transcriptional programming in response to TGF-beta1 during development, oncogenesis, tissue repair, and fibrosis 12548199_transforming growth factor-beta1 was produced in follicular and luteal phases and stimulated cell proliferation mainly in leiomyoma cells 12559970_Results suggest that the destabilization of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) mRNA induced by transforming growth factor beta leads to the inhibition of antiviral activity and IFN-gamma production in interleukin-18-stimulated LNK5E6 cells 12560323_TGF-beta1 signaling potentiates renal tubular epithelial cell apoptosis by a Smad-independent, p38 MAP kinase-dependent mechanism. 12560674_Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) plays a central role in wound healing and fibrosis and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of keloid disease and hypertrophic scar. 12569017_Association of transforming growth factor beta-1 single nucleotide polymorphisms with radiation-induced damage to normal tissues in breast cancer patients. 12569017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12572925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579267_Transforming growth factor beta overexpression is associated with advanced stage gallbladder cancer 12579348_TGFB1 treatment of ECV304 cells increased bacterial cell adhesion. 12589095_TGF-beta1 may contribute to eosinophil and mast cell migrations into nasal polyp tissue. 12590978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12591385_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12595498_by inhibition of cell migration, increased expression of TGF-beta1 after ischemia delays recovery of proximal tubule structure and function. 12595908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12598898_Dysregulation of TGF-beta activation contributes to pathogenesis in Marfan syndrome. 12601022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12607775_TGF-beta1 expression in peritoneal fibroblasts was increased by hypoxia and/or TGF-beta1 stimulation, favoring adhesion development. 12615364_TGF-beta1 inhibited IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha-induced TARC production in HaCaT cells via Smad2/3. Modulation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway may be beneficial for treatment of atopic dermatitis. 12626500_TGF-beta1 potentiates Abeta production in astrocytes and may enhance the formation of plaques burden in the brain of Alzheimer's disease patients 12630751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12637138_Hip, lumbar spine and wrist fracture incidence for women with the TGF-beta1 Leu/Leu genotype was not significantly different when compared with that for women with Leu/Pro genotype. 12649573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12649573_Pro10 allele in the TGF-beta(1) gene pathway might contribute to prevalent diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. 12654639_expressed in acute respiratory distress syndrome 12667558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12667558_The C(-1348)-T and T(29)-C polymorphisms were distributed similarly in osteoporotic patients and normal controls, however, the rare genotypes were associated with higher bone mass at the hip. 12669309_G2 arrest induced by TGF beta1 in the Rb-negative hepatoma cell line and compared with G1 arrest in the Rb-positive hepatoma cell line 12675860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12675860_Our results suggest that TGF-beta T869C (Leu 10Pro) gene polymorphism is associated with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese. 12682078_TGFb has a role in stimulating Sp1, which results in up-and down-regulation of UGDH 12700666_Distortion of autocrine transforming growth factor beta signal accelerates malignant potential by enhancing cell growth as well as PAI-1 and VEGF production in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 12707335_THP-1 monocytic cells cultured in the presence of TGFB1 show decreased phagocytosis toward IgG-coated sheep red blood cells, suppressed expression of common gamma-subunit and signaling properties of FcgammaR, and downregulated MCP-1 production. 12727482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12743121_Transforming growth factor-beta1 produced by ovarian cancer cell line HRA stimulates attachment and invasion through an up-regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. 12746254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12747448_may be one of the most important factors in the regulation of the [gingival inflammatory} infiltrate and in the production of tissue repair with a stimulation of fibroblasts and endothelial cells 12751024_role in genetic susceptibility of tuberculosis 12753290_TGF-beta 1 increases glucocorticoid binding and signaling in inflammatory cells through a Smad 2/3- and AP-1-mediated process. 12754205_TGFbeta transcriptionally regulates tristetraprolin in human T cells 12772773_Glucocorticoids significantly inhibited TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 production and reduced expression of the up-regulated TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 mRNA induced by exogenous TGF-beta1, -beta2, or -beta3 12775566_TGF-beta1-controlled reduction in SDF-1 expression influences bone marrow cell migration and adhesion, which could affect the motility of cells trafficking the bone marrow. 12787424_Certain specific cytokine genotypes for TGF-beta1, IL-10, and TNF-alpha are not associated with chronic allograft dysfunction. Normal kidney with low TGF-beta1 genotype at codon 10 had lower TGF-beta1 mRNA. 12787424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12794244_TGF-beta1 may be involved in activation of cdk inhibitor p21WAF1 in gastric adenocarcinoma 12795790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12795790_promoter may have a small effect on the modulation of the inflammatory process during periodontitis 12802498_An increased concentration of wild-type GFAT in mesangial cells is enhanced both TGF-beta1 and fibronectin. 12810668_This is a novel mechanism of TGF-beta 1 inhibition requiring early G(1) induction and stabilization of p21 protein, which binds to and inhibits cyclin E-CDK2 and cyclin A-CDK2 kinase activity rather than direct modulation of cyclin or CDK protein levels. 12815042_transforming growth factor-beta signaling is regulated by protein inhibitor of activated STAT, PIASy through Smad3 12817760_TGF-beta and IGF-II in the bone microenvironment coordinately amplify IGF-I bioavailability through controlled IGFBP-4 proteolysis, which may be a means to promote bone formation. 12821938_TGF-beta1 upregulates VDUP1 12824005_gene expression profiling in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita 12838101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12838101_Transforming growth factor-[beta]1 polymorphism is not a factor associated with the occurrence of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament [OPLL], but related to the area of the ossified lesion. The 'C' allele might be a risk factor 12843182_the R218C mutation increases TGFbeta1 bioactivity and enhances osteoclast formation in vitro 12850832_a time-dependent release of TGFB and PDGF-AB occurred at neutral and alkaline pH, but not pH5, 15 min and 12h after platelet activation, suggesting relevance to wound healing 12857600_Serum levels of both bFGF and TGF-beta1 were found to be significantly higher in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 12858019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12858451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12858451_TGFbeta1 polymorphisms do not play a role in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis, but they may be a risk factor for genetic susceptibility to pulmonary fibrosis. 12859695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12874450_TGF-beta1-mediated collagen I accumulation is associated with cytoskeletal rearrangement and Rho-GTPase signaling 12875973_These data provide evidence for a functional role for integrin alphavbeta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta in control of human airway epithelial proliferation in vivo. 12879019_the antiproliferative effect of TGFbeta is decreased by epidermal growth factor in primary human ovarian cancer cells 12879228_After acceleration of regenerative response by HGF, subsequent elevation of TGF-beta1 synergistically controls graft size, regulating uncontrolled proliferation of hepatocytes. 12893825_TGF-beta1-mediated MAP kinase activation controls WNT-7A gene expression and Wnt-mediated signaling through the intracellular beta-catenin-TCF pathway 12894997_Neutralizing anti-TGF-beta1 antibody reversed the inhibition of keratinocyte proliferation. 12898374_low serum leptin, high serum TGF-beta1 and sOb-R levels, and elevated urine leptin concentrations were observed at the onset of minimal change nephrotic syndrome 12902338_the ligand-binding domain of GR, but not the DNA-binding domain or the N-terminal activation domain, is required for GR-mediated transrepression of TGF-beta transactivation 12909463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911534_All three TGF-beta isoforms have fibrogenic effects on renal cells. TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 effects may be partially mediated by TGF-beta1. Blockade of all isoforms together may yield best therapeutic effect in reducing renal fibrosis. 12911563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911563_Polymorphisms in TGF-beta1 influence risk for hemodialysis access failure. By inducing synthesis of extracellular matrix proteins, overproduction of TGF-beta1 may accelerate intimal hyperplasia, resulting in fistula stenosis and subsequent access failure. 12917425_transforming growth factor-beta signaling is inhibited by interferon gamma through direct interaction of YB-1 with Smad3 12938093_Four novel polymorphisms in TGFB1 are found not associated with spinal bone mineral density in postmenopausal Korean women. 12938093_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12938195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12943995_TGF beta1 regulates cell cycle proteins and may induce multiple independent signals to check the proliferative potential of human trophoblastic cells and allow their functional differentiation 12944979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12953061_a new function of TGF-beta1, which is to promote undifferentiated keratinocyte amplification 12960355_Genetic and immunohistochemical studies convincingly suggest a link between TGF-beta 1 and the pathogenesis of autoimmune-associated congenital heart block. 12960355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12974899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13678774_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13679381_TGF-beta1 in cartilage is active in periods of skeletal immaturity and is closely associated with increases in chondrocyte UDPGD activity 14504277_signaling in keratinocytes is regulated by glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins 14504444_Plasma TGF-beta1 levels of thrombocytopenic neonates were significantly lower than those of healthy nonthrombocytopenic neonates but did not differ significantly from nonthrombocytopenic neonates with similar perinatal risk factors for thrombocytopenia. 14507446_Biological dressing effect of cultured epidermal sheets(CESs) is mediated by EGF family, TGF-beta, and VEGF. 14510802_In the confluent state, TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 stimulated the cells to progress to the S-phase of the cell cycle through platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) chain production and protein kinase C. 14514699_sumoylation of Smad4 was strongly enhanced by TGF-beta-induced activation of the p38 MAP kinase pathway but not the Smad pathway 14514772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14525983_DACH1 bound to endogenous NCoR and Smad4 in cultured cells; Smad4 was required for DACH1 repression of TGF-beta induction of Smad signaling 14529885_Found in renal artery of kidney allografts in chronic rejection. 14531781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14531804_a signal transduction cascade of the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway, which is activated in the GEC, appears to be involved in the development of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis 14532743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14557872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14566095_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14576166_there is a TGF-beta1-activated pro-survival/anti-apoptotic signaling pathway in mesenchymal cells/fibroblasts 14576954_Mortal and early immortal stages of both cell lineages displayed growth reduction upon exposure to TGF-beta1. 14583433_ANG II-induced activation of latent TGF-beta1 in human mesangial cells operates via TSP-1 14585325_effect of restoring the growth-inhibitory autocrine circuit in epithelial cancer cells that have retained sensitivity to growth inhibition by TGF-beta1 but which produce and secrete insufficient amounts of endogenous peptide 14595120_TGF-beta 1 also activates the mitochondrial pathway showing Bid-mediated loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and subsequent cytochrome c release associated with the activations of caspase-9 and the effector caspases. 14596813_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14597484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14600158_TGF-beta1 is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB activation in the gut 14604900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14604900_transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene polymorphism is associated with prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia 1460733 |
ENSMUSG00000002603 |
Tgfb1 |
3429.464398 |
2.2276210186 |
1.155504 |
0.058114065 |
389.038128 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001340536215347022708405831893861503807787382376820508457522374137593431033974550224001629487463344952365151730982160183106646566062963864964678003804576107397661683221129474501516391265798015504991387863486246713289051779582905510324053466320038 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000490975546861589491114995358985480632229840542640061647693340541206600515766203184170623407508469460751096146794534328443575549365042100476986242667119225990653663390376700333875432942615306838453043928612419891099882818252808647230267524719238 |
Yes |
Yes |
4829.4261671 |
169.8575252 |
2183.6492573 |
57.1281385 |
| ENSG00000105339 |
22898 |
DENND3 |
protein_coding |
A2RUS2 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activating RAB12. Promotes the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound RAB12 into its active GTP-bound form (PubMed:20937701). Regulates autophagy in response to starvation through RAB12 activation. Starvation leads to ULK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of Ser-472 and Ser-490, which in turn allows recruitment of 14-3-3 adapter proteins and leads to up-regulation of GEF activity towards RAB12 (By similarity). Also plays a role in protein transport from recycling endosomes to lysosomes, regulating, for instance, the degradation of the transferrin receptor and of the amino acid transporter PAT4 (PubMed:20937701). Starvation also induces phosphorylation at Tyr-858, which leads to up-regulated GEF activity and initiates autophagy (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2RT67, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937701}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in cellular protein catabolic process; endosome to lysosome transport; and regulation of Rab protein signal transduction. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in cytoplasmic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22898; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; regulation of Rab protein signal transduction [GO:0032483] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25925668_a novel signaling pathway identified whereby starvation-induced activation of ULK leads to phosphorylation of endogenous DENND3, with subsequent activation of Rab12 and initiation of membrane trafficking events required for autophagy 28249939_DENND3 is the exchange factor for the small GTPase Rab12 regulated through an intramolecular interaction 29352104_show that DENND3 binds actin through a surface of positively charged residues on the PHenn domain of Ran12 |
ENSMUSG00000036661 |
Dennd3 |
3194.687866 |
0.4093684875 |
-1.288528 |
0.094107076 |
181.387442 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000002412635866754832151877751847539528454429299594784286040717140461697080019462110668854122690783500902614398114787164217887038830667734146118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000417473685736240584336836175730899672324081008215660384922121041348916539669528058272183986052063169145016907624068380755488760769367218017578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1854.8432205 |
117.0367331 |
4563.3482628 |
207.4414919 |
| ENSG00000105376 |
7087 |
ICAM5 |
protein_coding |
Q9UMF0 |
FUNCTION: ICAM proteins are ligands for the leukocyte adhesion protein LFA-1 (integrin alpha-L/beta-2). |
3D-structure;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM) family. All ICAM proteins are type I transmembrane glycoproteins, contain 2-9 immunoglobulin-like C2-type domains, and bind to the leukocyte adhesion LFA-1 protein. This protein is expressed on the surface of telencephalic neurons and displays two types of adhesion activity, homophilic binding between neurons and heterophilic binding between neurons and leukocytes. It may be a critical component in neuron-microglial cell interactions in the course of normal development or as part of neurodegenerative diseases. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7087; |
glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051963] |
16434609_study does not confirm association between ICAM 5 V3001 polymorphism and breast cancer risk 16733712_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17293864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18223167_ICAM-5 is involved in immune privilege of the brain and acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20644561_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22781129_A specific microenvironment facilitating ARF6-mediated mobilization of TLN that contributes to promotion of dendritic spine development. 23079714_ICAM5 V301I and rs281439 variants may contribute to the susceptibility of breast cancer. [Meta-analysis] 27923705_Here the authors identify neuron-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 5 (ICAM-5/telencephalin) as a cellular receptor for sialic acid-dependent and -independent entry of enterovirus D68. |
ENSMUSG00000032174 |
Icam5 |
52.712281 |
6.1936228432 |
2.630784 |
0.299441415 |
79.681007 |
0.00000000000000000044001019402079463912704792961071317386164206131304865721176611259579658508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000003741100497550074416951033620421093124961657289654802169276415213516884250566363334655761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.5120416 |
14.4359753 |
14.2855252 |
2.0553433 |
| ENSG00000105419 |
56917 |
MEIS3 |
protein_coding |
Q99687 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator which directly modulates PDPK1 expression, thus promoting survival of pancreatic beta-cells. Also regulates expression of NDFIP1, BNIP3, and CCNG1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97368}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a homeobox protein and probable transcriptional regulator. The orthologous protein in mouse controls expression of 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase 1, which promotes survival of pancreatic beta-cells. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:56917; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; brain development [GO:0007420]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; eye development [GO:0001654]; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001234]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20553494_This work suggests that the transcriptional activity of all members of the Meis/Prep Hth protein family is subject to autoinhibition by their Hth domains, and that the Meis3.2 splice variant encodes a protein that bypasses this autoinhibitory effect. 26354419_Findings support a model in which Meis3 is required for neural crest proliferation, migration into, and colonization of the gut such that its loss leads to severe defects in enteric nervous system development. 33376716_Inhibition of MEIS3 Generates Cetuximab Resistance through c-Met and Akt. |
ENSMUSG00000041420 |
Meis3 |
16.962350 |
2.0266680561 |
1.019110 |
0.381872150 |
7.186216 |
0.00734657636378044029412670568035537144169211387634277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014481232255528752803086511846686335047706961631774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.7378773 |
5.3689627 |
10.3166629 |
2.1048646 |
| ENSG00000105447 |
83743 |
GRWD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQ67 |
FUNCTION: Histone binding-protein that regulates chromatin dynamics and minichromosome maintenance (MCM) loading at replication origins, possibly by promoting chromatin openness (PubMed:25990725). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25990725}. |
Chromosome;DNA replication;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a glutamate-rich protein that contains five WD-repeat motifs. The encoded protein may play a critical role in ribosome biogenesis and may also play a role in histone methylation through interactions with CUL4-DDB1 ubiquitin E3 ligase. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:83743; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA replication origin binding [GO:0003688]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; nucleosome assembly [GO:0006334]; nucleosome disassembly [GO:0006337]; ribosome biogenesis [GO:0042254] |
27552915_Cdt1-binding protein GRWD1 promotes chromatin fluidity by influencing nucleosome structures, e.g., by transient eviction of H2A-H2B, and thereby promotes efficient MCM loading at replication origins. 27856536_GRWD1 overexpression in combination with HPV16 E7 and activated KRAS confers anchorage-independent growth and tumorigenic capacity on normal human fibroblasts. Consistent with this, GRWD1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients. 31545368_findings suggest a novel oncogenic function of GRWD1 as a transcriptional regulator of p53 and that GRWD1 might be an attractive therapeutic target and prognostic marker in cancer therapy 31891681_GRWD1 promotes cell proliferation and migration in non-small cell lung cancer by activating the Notch pathway. 34616846_Comprehensive Analysis of Glutamate-Rich WD Repeat-Containing Protein 1 and Its Potential Clinical Significance for Pancancer. 34933446_GRWD1-WDR5-MLL2 Epigenetic Complex Mediates H3K4me3 Mark and Is Essential for Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Induced Cellular Transformation. |
ENSMUSG00000053801 |
Grwd1 |
215.495761 |
2.0616863903 |
1.043825 |
0.136237825 |
58.521997 |
0.00000000000002010306651760416723696481300069811340143575290051458637208270374685525894165039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000132761190961895974209910016909589927625555405565904720788239501416683197021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
300.4765193 |
26.2591933 |
146.6447660 |
9.6951073 |
| ENSG00000105514 |
9545 |
RAB3D |
protein_coding |
O95716 |
FUNCTION: Protein transport. Probably involved in regulated exocytosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell membrane;Exocytosis;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Enables myosin V binding activity. Involved in bone resorption and positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway. Located in cytoplasmic microtubule and secretory vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9545; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory vesicle [GO:0099503]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; zymogen granule [GO:0042588]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTP-dependent protein binding [GO:0030742]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; myosin V binding [GO:0031489]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; peptidyl-cysteine methylation [GO:0018125]; positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway [GO:1903307]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; regulation of exocytosis [GO:0017157]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904] |
15257287_mutant Rab3D proteins interfere with the formation of bona fide Weibel-Palade bodies and consequently the acute, histamine-induced release of von-Willebrand factor 20038531_MIST1 binds to highly conserved CATATG E-boxes to directly activate transcription of 6 genes, including those encoding the small GTPases RAB26 and RAB3D. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21702009_Our findings indicate that Rab3D regulates the exocytosis of many components critical for the maintenance of oral physiology. 23526941_The presence of Rab3D(N135I) decreases the restriction of maturing secretory granules (SGs) to the F-actin-rich cell cortex, blocks the removal of the endoprotease furin from SGs and impedes the processing of the luminal SG protein secretogranin II. 25823663_High expression of small GTPase Rab3D promotes cancer progression and metastasis. 27046094_increased Rab3D expression is associated with invasiveness of CRC cells 28472755_targeting the Rab3D may be a potential therapeutic target for treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33891267_Long non-coding RNA FGD5-AS1 enhances osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration by targeting miR-506-3p/RAB3D axis. 33982832_Rab3 proteins and cancer: Exit strategies. 34551092_GDP/GTP exchange factor MADD drives activation and recruitment of secretory Rab GTPases to Weibel-Palade bodies. 35549813_Hsa_circ_0103232 promotes melanoma cells proliferation and invasion via targeting miR-661/RAB3D. 35616807_Hsa_circ_0006732 regulates colorectal cancer cell proliferation, invasion and EMT by miR-127-5p/RAB3D axis. |
ENSMUSG00000019066 |
Rab3d |
29.655557 |
0.2581259554 |
-1.953853 |
0.329205355 |
36.950298 |
0.00000000121179202234390344292186768142011860094342523552768398076295852661132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005754842422714290587223387885701386679215829644817858934402465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.7970318 |
2.4641082 |
46.0157651 |
5.6230755 |
| ENSG00000105516 |
1628 |
DBP |
protein_coding |
Q10586 |
FUNCTION: This transcriptional activator recognizes and binds to the sequence 5'-RTTAYGTAAY-3' found in the promoter of genes such as albumin, CYP2A4 and CYP2A5. It is not essential for circadian rhythm generation, but modulates important clock output genes. May be a direct target for regulation by the circadian pacemaker component clock. May affect circadian period and sleep regulation. |
Activator;Biological rhythms;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the PAR bZIP transcription factor family and binds to specific sequences in the promoters of several genes, such as albumin, CYP2A4, and CYP2A5. The encoded protein can bind DNA as a homo- or heterodimer and is involved in the regulation of some circadian rhythm genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:1628; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20174623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21411511_Lean individuals exhibited significant (P |
ENSMUSG00000059824 |
Dbp |
33.728557 |
0.4422598794 |
-1.177034 |
0.291978384 |
16.495281 |
0.00004877130197112099837131876656215467846777755767107009887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000140653461722107457187308510171419584366958588361740112304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.3870831 |
3.8714181 |
46.4057420 |
5.7310912 |
| ENSG00000105519 |
828 |
CAPS |
protein_coding |
Q13938 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-binding protein. May play a role in cellular signaling events (Potential). {ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a calcium-binding protein, which may play a role in the regulation of ion transport. A similar protein was first described as a potentially important regulatory protein in the dog thyroid and was termed as R2D5 antigen in rabbit. Alternative splicing of this gene generates two transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:828; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556] |
18729184_Results demonstrated the ubiquitous overexpressions of E-FABP and CAPS in EC and the correlations to the clinicopathologic parameters. CAPS might be a potential prognostic factor for survival in patients with EC 18775726_These results describe the crystal structure of Ca(2+)-loaded calcyphosine up to 2.65 A resolution and reveal a protein containing two pairs of Ca(2+)-binding EF-hand motifs. 19275752_The calcyphosine crystal diffracted to 2.8 A and belonged to space group P2(1)2(1)2, with the unit cell parameters a=70.39 A, b=132.02 A, c=46.20 A. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30339840_The results indicated that the autosomal recessive homozygous mutation, p.Leu127Trpfs, in CAPS might be a maternal effect causative mutation of RPL pathogenesis. 34370292_Calcyphosine promotes the proliferation of glioma cells and serves as a potential therapeutic target. |
|
|
84.011747 |
0.1307220895 |
-2.935425 |
0.303327125 |
90.025855 |
0.00000000000000000000235068000599960501973425078847923871062709515209165088477170219016798569100501481443643569946289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000021945627380489671922852678412714264156130275924666088438724081965958134787797462195158004760742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.2840227 |
4.1828819 |
163.2131317 |
20.6961378 |
| ENSG00000105643 |
27106 |
ARRDC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8TBH0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in protein transport. Located in cytoplasmic vesicle and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:27106; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
|
ENSMUSG00000002910 |
Arrdc2 |
290.457511 |
0.4679725092 |
-1.095504 |
0.098138724 |
125.711038 |
0.00000000000000000000000000003556802687759791029741813080656187046914207495529949812114624348473093041664815083802153594660921953618526458740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000445657110962092703774658955677461143482565601149070047646458926186496324805749735809001776942750439047813415527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
189.6692136 |
14.9275850 |
407.9872789 |
22.1919276 |
| ENSG00000105650 |
5143 |
PDE4C |
protein_coding |
Q08493 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17727341, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7843419}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;cAMP;Cell projection;Cilium;Hydrolase;Manganese;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; 3',5'-cyclic AMP degradation; AMP from 3',5'-cyclic AMP: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:7843419}. |
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) family, and PDE4 subfamily. This PDE hydrolyzes the second messenger, cAMP, which is a regulator and mediator of a number of cellular responses to extracellular signals. Thus, by regulating the cellular concentration of cAMP, this protein plays a key role in many important physiological processes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:5143; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cAMP catabolic process [GO:0006198]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23043089_PDE4A and PDE4C work in redundant fashion to mediate the loss of inhibitory PGE2 signaling in lung fibroblasts. 24842301_Data show that PDE4C is downregulated through promoter hypermethylation in glioma. |
ENSMUSG00000031842 |
Pde4c |
12.978621 |
0.1685520588 |
-2.568734 |
0.720192249 |
12.283403 |
0.00045700424850132932708124400278393295593559741973876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001130826941807144998819456560568141867406666278839111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7405928 |
1.7392900 |
21.8533015 |
6.3964148 |
| ENSG00000105662 |
23373 |
CRTC1 |
protein_coding |
Q6UUV9 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional coactivator for CREB1 which activates transcription through both consensus and variant cAMP response element (CRE) sites. Acts as a coactivator, in the SIK/TORC signaling pathway, being active when dephosphorylated and acts independently of CREB1 'Ser-133' phosphorylation. Enhances the interaction of CREB1 with TAF4. Regulates the expression of specific CREB-activated genes such as the steroidogenic gene, StAR. Potent coactivator of PGC1alpha and inducer of mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. In the hippocampus, involved in late-phase long-term potentiation (L-LTP) maintenance at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses. May be required for dendritic growth of developing cortical neurons (By similarity). In concert with SIK1, regulates the light-induced entrainment of the circadian clock. In response to light stimulus, coactivates the CREB-mediated transcription of PER1 which plays an important role in the photic entrainment of the circadian clock. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q157S1, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q68ED7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23699513}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays a role of coactivator for TAX activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) long terminal repeats (LTR). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16809310}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables cAMP response element binding protein binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in cytosol; nuclear body; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23373; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; cAMP response element binding protein binding [GO:0008140]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of membrane hyperpolarization [GO:1902631]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793]; positive regulation of dendrite development [GO:1900006]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; postsynapse to nucleus signaling pathway [GO:0099527]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511] |
12539049_cloning and functional analyses of the t(11;19) fusion oncogene: t(11;19)(q21;p13) translocation in mucoepidermoid carcinoma creates a novel fusion product that disrupts a Notch signaling pathway. 14720503_cloning of a novel fusion gene in mucoepidermoid carcinomas & benign Warthin's tumors; the fusion, which results from a translocation, creates a chimeric gene in which exon 1 of a novel gene designated WAMTP1 is linked to exons 2-5 of MAML2 [WAMPT1] 16652146_mutant Mect1-Maml2 expression plasmid carried silent nucleotide changes within the RNAi target sequence and observed that co-transfection of this mutant, but not wild-type Mect1-Maml2, could partially rescue RNAi growth inhibition in the MEC tumor line 16809310_Thus, both TORC1/2 and p300 families of coactivators are essential for optimal activation of HTLV-1 transcription by Tax. 16818685_The MECT1-MAML2 fusion transcript may be specific to mucoepidermoid carcinoma and associated with a distinct mucoepidermoid carcinoma subset that exhibits favorable clinicopathologic features and an indolent clinical course. 16980408_These results strongly suggest that TORCs play a key role in linking these external signals to the transcriptional program of adaptive mitochondrial biogenesis by activating PGC-1alpha gene transcription. 17334997_The present and previous observations indicate that the CRTC1-MAML2 fusion is etiologically linked to benign and low-grade malignant tumors originating from diverse exocrine glands rather than being linked to a separate tumor entity. 17437281_CRTC1/MAML2 transcript may be detected in both low and high grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC), that fusion negative tumors may define a subset of biologically aggressive MEC's tumors 17565599_the basic leucine zipper domain has a role in the regulation of transcriptional activity of CREB with TORC and salt inducible kinase [review] 18181164_CRTC1/MAML2 translocation and fusion transcript is asscociated with Warthin's tumor and mucoepidermoid carcinoma 18206539_The presence of the t(11;19)(q21;p13) rearrangement favors a diagnosis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 18717645_Stimulation by lithium of the interaction between CREB and TORC1 is reported. 18784253_The activation of TORC1 through MEKK1-mediated phosphorylation, is reported. 19164581_demonstrate that CRTC1-Maml2 oncoprotein, which causes mucoepidermoid carcinomas, binds and activates both c-Jun and c-Fos. 19269006_MAML2 and MECT1 fusion product can be detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction analysis performed on low- and high-grade primary bronchopulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma 19438452_Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) of the skin harbours CRTC1 rearrangements, a molecular finding that reflects morphological similarities between glandular and cutaneous MEC. 19521953_Mucoepidermoid carcinomas are often characterized by the fusion gene CRTC1-MAML2. The mean expression level of an embryonic stem cell marker, HMGA2 was studied and found to be higher in fusion negative than in positive tumors. 19531414_CRTC1-MAML2 fusion was associated with favorable clinicopathologic tumor features and was useful in predicting the overall survival of patients with salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010869_Data show that somatic loss of LKB1 is associated with underphosphorylation of endogenous Crtc1, enhanced Crtc1 nuclear localization. 20588178_MECT1/MAML2 translocation status may be important prognostically in salivary mucoepidermoid carcinomas, but it does not seem to override traditional clinicopathologic parameters. 20625861_We report an example of intraosseous mucoepidermoid carcinoma with positive TORC1/MAML2 gene fusion transcript and discuss the clinical implications. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21074686_The t(11;19) translocation and its CRTC1/MAML1 fusion transcript have been identified in mucoepidermoid carcinomas at different sites and are believed to be associated with the development of a subset of these tumors. 21668476_mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands positive for CRTC1-MAML2 or CRTC3-MAML2 fusion formed a favourable tumour subset that was distinct from fusion-negative cases 21706049_de-regulated LKB1-CRTC signaling might represent a crucial mechanism for esophageal cancer progression. 21798997_clear-cell renal cell carcinoma become refractory to REDD1-induced mTORC1 inhibition and shed light into the development of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma 22236576_The results of this study suggested that CRTC1 dysfunction caused by Abeta accumulation underlies changes in gene expression required for hippocampal-dependent memory in AD transgenic mice. 22457329_Studies indicate that phospholipase D (PLD) as a mediator of nutrients to mTORC1. 22627671_Inhibition of TORC1 retards, and to some extent reverses, phenotypic indicators of cellular senescence. 22749528_We demonstrate that glutamine in combination with leucine activates mammalian TORC1 (mTORC1) by enhancing glutaminolysis and alpha-ketoglutarate production. 22805177_These observations indicate that brain malformations in TSC are likely a consequence of increased TORC1 activation during embryonic brain development. 23074285_CRTC1-NEDD9 signaling axis mediates lung cancer progression caused by LKB1 loss. 23699513_The data of this study raise the prospect that CRTC1 plays a role in fundamental aspects of SCN clock timing and entrainment. 23925723_findings suggest that CRTC1 contributes to the genetics of human obesity in psychiatric patients and the general population. 23975434_aberrantly activated AREG-EGFR signaling is required for CRTC1-MAML2-positive MEC cell growth and survival, suggesting that EGFR-targeted therapies will benefit patients with advanced, unresectable CRTC1-MAML2-positive MEC. 24121173_Metaplastic Warthin tumor and metaplastic pleomorphic adenoma of salivary glands did not harbor CRTC1-MAML2 and CRTC3-MAML2 fusion transcripts, respectively, or MAML2 gene rearrangement. 24468654_Lacrimal and salivary gland PAs and Ca-ex-PAs have similar genomic profiles and frequently overexpress the PLAG1 oncoprotein. Copy number gains involving 9p23-p22.3 (NFIB) and 22q12-qter (PDGFB) may be of importance for disease progression. 24771140_Translocation t(11;19)(q14-21;p12-13) in patients with Salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma was reported , which results in fusion between exons 1 and 2 of CRTC1 on chromosome 19p13. 25071166_Malignant mucoepidermoid salivary gland tumors can arise from a recurrent t (11, 19)(q21;p13.1) translocation that generates an unusual chimeric CRTC1/MAML2 oncoprotein. 25083993_describe fundamental metabolic requirements of senescent primary human CD8+ T cells and demonstrate that p38 MAPK blockade reverses senescence via an mTOR-independent pathway 25300488_This study showed that CREB-regulated transcriptional coactivator 1 (CRTC1) is required for HBV transcription and replication. 25465874_CRTC1 activation is a key event that drives the LKB1-null mRNA signature in lung cancer. We also identified a positive feedback LKB1/CRTC1 signaling loop for COX-2/PGE2 regulation. 26300003_CRTC1 as new mediator of PGE2 signaling 26503699_A specific CRTC1-MAMl2-induced transcriptional program was identified in mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells. 26796488_Detection of the CRTC1/MAML2 fusion transcript provides useful information for MEC diagnosis but is not associated with differences in survival outcomes. 27002284_CRTC1 polymorphisms seem to play a role with obesity markers in individuals with MDD rather than non-depressive individuals. 27094739_DNA methylation levels within two distinct promoter regions of the CREB regulated transcription coactivator 1 gene were decreased in human hippocampus affected by Alzheimer disease. 27166823_Consistent with our findings in Drosophila, through the characterization of a wdr24-/- knockout HeLa cell line we determined that Wdr24 promotes lysosome acidification and autophagic flux in mammalian cells 27385002_modulation of rDNA transcription initiation, elongation and rRNA processing is an immediate, co-regulated response to altered amino acid abundance, dependent on both mTORC1 activation of S6K1 and MYC activity 27402217_revealing neither correlation between the cellular composition and CRTC1-MAML2 fusions nor presence of CRTC3-MAML2 fusions in cutaneous hidradenoma 27869139_CRTC1 negatively regulates lipogenic gene expression in liver. 28343305_MECT1-MAML2 fusion transcript is a driver genetic event in the pathogenesis of primary bronchopulmonary mucoepidermoid carcinoma 28438292_findings suggest further characterization of MECs is needed before considering the CRTC1/3-MAML2 gene fusion as a prognostic biomarker 28729415_High TORC1 expression is associated with meningioma and schwannoma. 29080681_mTORC1 hyperactivation in melanocytes results in hypopigmentation. 29240581_CRTC1-TRIM11 fusion appears to be specific of an unpigmented nodular tumor combining a melanocytic phenotype and low-grade tumor behavior. 29353885_LINC00473 acts as a promising biomarker and therapeutic target for human CRTC1-MAML2-positive Mucoepidermoid carcinomas. 29408765_This work reveals a regulatory circuit in which SIK1 suppresses gluconeogenic gene transcription by inducing ubiquitination and degradation of CRTC1. 29533464_Case Reports: identify a novel recurrent gene fusion, CRTC1-SS18, in undifferentiated small round cell sarcoma. 29713984_SNP located in CRTC1 has been shown in GWAS studies to be significantly associated with the risk of Barrett's esophagus. 29925665_Pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 by rapamycin in PHA-stimulated PBL reduced viral replication to the level found in unstimulated lymphocytes, indicating that mTORC1 activity supports MV replication as a proviral host factor. 30138216_Pancreatic mucoepidermoid carcinoma does not have CRTC1/3-MAML2 fusion gene and MAML2 gene rearrangement. 30380176_Two cases of breast mucoepidermoid carcinomas harboring CRTC1-MAML2 fusions are reported 30521840_These data suggest that increased CRTC1 in maladaptive hypertrophy presents a compensatory mechanism to delay disease progression in part by enhancing Rgs2 gene transcription. 31153815_Our data support the known role of CRCT1 regulating energy metabolism in brain. Here, we highlight relevance of CRTC1 regulation in blood and adipose tissue 31878957_Study identified a methylation change during the first month of psychotropic treatment in the CRTC1 gene, which was associated with early weight gain during the same period. This epigenetic modulation was dependent on a genetic variant (rs4808844A>G) in the same genetic region, which plays a considerable regulatory role. 32388919_Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3034c regulates mTORC1 and PPAR-gamma dependant pexophagy mechanism to control redox levels in macrophages. 32759469_Mislocalization of TORC1 to Lysosomes Caused by KIF11 Inhibition Leads to Aberrant TORC1 Activity. 32996262_TORC1 selectively regulates synaptic maturation and input convergence in the developing visual system. 33473104_Targeting Notch and EGFR signaling in human mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 33556406_Structural Insights into the Interaction Between CRTCs and 14-3-3. 33561653_mTORC1 silencing during intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell differentiation is mediated by the activation of the AMPK/TSC2 pathway. 33830080_The CRTC1-MAML2 fusion is the major oncogenic driver in mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 34657306_Salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma: histological variants, grading systems, CRTC1/3-MAML2 fusions, and clinicopathological features. 35993578_Cutaneous Melanocytic Tumor With CRTC1::TRIM11 Translocation : An Emerging Entity Analyzed in a Series of 41 Cases. 36115844_Oncogenic RAS commandeers amino acid sensing machinery to aberrantly activate mTORC1 in multiple myeloma. |
ENSMUSG00000003575 |
Crtc1 |
146.350040 |
0.4991937085 |
-1.002328 |
0.139639960 |
51.926125 |
0.00000000000057628527136483126614308340655082939858917800979298817765084095299243927001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003481772658757638148827570626419376125567500812607590887637343257665634155273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.5744075 |
8.8602775 |
200.9093301 |
11.8147882 |
| ENSG00000105808 |
10156 |
RASA4 |
protein_coding |
O43374 |
FUNCTION: Ca(2+)-dependent Ras GTPase-activating protein, that switches off the Ras-MAPK pathway following a stimulus that elevates intracellular calcium. Functions as an adaptor for Cdc42 and Rac1 during FcR-mediated phagocytosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448776}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the GAP1 family of GTPase-activating proteins that suppresses the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in response to Ca(2+). Stimuli that increase intracellular Ca(2+) levels result in the translocation of this protein to the plasma membrane, where it activates Ras GTPase activity. Consequently, Ras is converted from the active GTP-bound state to the inactive GDP-bound state and no longer activates downstream pathways that regulate gene expression, cell growth, and differentiation. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10156; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0034260]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580] |
11448776_CAPRI (Ca2+-promoted Ras inactivator) a Ca2+-dependent Ras GTPase-activating protein (Ras GAP). Switches off the Ras-MAPK pathway following G protein-coupled receptor stimulated intracellular Ca2+ elevation that recruits CAPRI to the plasma membrane. 16009725_CAPRI seems to low-pass filter the Ca2+ signal, converting different intensities of stimulation into different durations of Ras activity. 21460216_Ca2+-dependent monomer and dimer formation switches CAPRI Protein between Ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and RapGAP activities 25147919_RASA4 isoform 2 promoter methylation correlated with clinical parameters predicting poor prognosis (older age, elevated fetal hemoglobin), with higher risk of relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and with PTPN11 mutation. 34094999_Treponema denticola-Induced RASA4 Upregulation Mediates Cytoskeletal Dysfunction and MMP-2 Activity in Periodontal Fibroblasts. 34675073_Ras inhibitor CAPRI enables neutrophil-like cells to chemotax through a higher-concentration range of gradients. 34752201_RASA4 inhibits the HIFalpha signaling pathway to suppress proliferation of cervical cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000004952 |
Rasa4 |
317.356270 |
2.8065541768 |
1.488800 |
0.342512875 |
18.170862 |
0.00002019449636051122575646811496685728570810169912874698638916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000061180370747361596957779317218495407360023818910121917724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
429.8709431 |
91.9363063 |
154.1377606 |
24.0208424 |
| ENSG00000105825 |
7980 |
TFPI2 |
protein_coding |
P48307 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in the regulation of plasmin-mediated matrix remodeling. Inhibits trypsin, plasmin, factor VIIa/tissue factor and weakly factor Xa. Has no effect on thrombin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7872799}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood coagulation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Kunitz-type serine proteinase inhibitor family. The protein can inhibit a variety of serine proteases including factor VIIa/tissue factor, factor Xa, plasmin, trypsin, chymotryspin and plasma kallikrein. This gene has been identified as a tumor suppressor gene in several types of cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:7980; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; cellular response to fluid shear stress [GO:0071498] |
11840337_highly expressed in non-invasive cells but undetectable in highly invasive human glioma cells 12606321_the villous cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast are both important sites of TFPI-2 synthesis in the human placenta 12632077_methylation of TFPI-2 gene is not the sole cause of its silencing 12738994_induced by various pathways in human glioma cells 12757776_the minimal TFPI2 promoter is located between -166 and -111 from the translation start site; three transcription initiation sites and several putative transcription factor binding sites were identified, and potential regulatory regions were characterized. 12787920_These data provide evidence that tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 does not bind to matrix metalloproteinases-2, -9 or -1, or regulate matrix metalloproteinase-1, in the extracellular matrix. 12876637_The expression of TFPI-2 diminishes with an increasing degree of malignancy, which may suggest a role for TFPI-2 in the maintenance of tumor stability and inhibition of the growth of neoplasms. 12881707_These studies establish that TFPI-2 is transcriptionally silenced through promoter methylation in SNB19 cells. 12921785_Bovine TFPI2 was compared to human TFPI2. 14525759_secretion of inhibitory TFPI-2 by a highly metastatic tumor cell markedly inhibits its growth and metastasis 14558946_Expression of TFPI-2 may strongly inhibit the invasive ability of ovarian tumor cells in vitro, but has no effect on the migratory ability. 14623891_thrombin, through PAR-1 signaling, up-regulates the synthesis of TFPI-2 via a MAPK/COX-2-dependent pathway 14678821_Computer model of the interaction of human TFPI-2 Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor with human plasmin [letter] 14970225_analysis of the reactive site in the first Kunitz-type domain of TFPI2 14983234_human and murine TFPI-2 have different functions in liver regulation during inflammation in the two species 15183047_variations in the TFPI-2 gene and its promoter region 15221977_TNF treatment at 41 degrees C significantly reduced clotting activity, TF protein and mRNA as well as TFPI-2 mRNA. 15467913_data suggest that gC1qR may participate in tissue remodeling and inflammation by localizing TFPI-2 to the pericellular environment to modulate local protease activity and regulate High Molecular Weight Kininogen activation 15592528_Restored expression of the TFPI-2 gene in nonexpressing pancreatic cancer cells resulted in marked suppression in their proliferation, migration, and invasive potential. 15685245_These results suggest that silencing of the TFPI-2 gene by hypermethylation might contribute to tumour progression in NSCLC. 15932872_x-ray crystallographic analysis of Kunitz domain 1 of TFPI-2 in complex with trypsin 16247609_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16580726_Preeclampsia and IUGR showed distinct distributions of TFPI-2. 16641089_role of TFPI-2 as a maintenance factor of extracellular remodeling suggests the indirect function of ADAMTS1 as an additional homeostatic player by its ability to alter the extracellular location of TFPI-2 16965396_Aberrant methylation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 is associated with pancreatic carcinoma. 17023682_data suggest that VEGF-upregulation of TFPI-2 expression in endothelial cells may represent a mechanism for negative feedback regulation and modulation of its pro-angiogenic action on endothelial cells. 17138934_Our data suggest that TFPI-2 may be an important regulator of aberrant angiogenesis associated with tumor growth/metastasis, cardiovascular diseases, chronic inflammation, or diabetes. 17208328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17352822_A new 289-nucleotide splice variant of the TFPI-2 transcript consists of complete exons II & V, fused with several nucleotides derived from exons III & IV, & 6 nucleotides derived from intron C. It lacks either a 5'-TR) or a 3'-poly (A)+ tail. 17372906_Results showed that TFPI-2 is silenced in malignant melanomas by methylation of its promoter CGI and suggested that its silencing is involved in melanoma metastasis. 17464989_TFPI-2 is frequently silenced in hepatocellular carcinoma via epigenetic alterations, including promoter methylation and histone deacetylation; ectopic overexpression of TFPI-2 significantly suppressed the proliferation and invasiveness of HCC cells 17558445_The detailed conformational changes of the heated protein observed by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, circular dichroism and Raman spectroscopy revealed that hTFPI-2/KD1 was thermally stable 18053161_The CpG islands in TFPI-2 promoter was hypermethylated in highly invasive breast cancer cell line, and DNA methylation in the entire promoter region caused TFPI-2 repression by inducing inactive chromatin structure and decreasing KLF6 binding. 18097563_keratoepithelin induces elevated TFPI2 transcript levels in neuroblastoma cells without alterations of MYCN expression. 18401718_Collectively, our results demonstrate that treatment of HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cells exogenously with either TFPI-2 or its first Kunitz domain mutant R24K activates caspase-mediated, pro-apoptotic signaling pathways resulting in apoptosis. 18480470_Results reveals a novel placenta-specific transcript, TFPI2, which is expressed from the maternal allele. 18810851_Genotyping for MspI gene polymorphisms may be clinically relevant to define the predisposition to the major clinical manifestations in mixed cryoglobulinemic syndrome. 19081094_Tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 gene methylation is associated with low expression in carotid atherosclerotic plaques. 19102937_The expression of TFPI-2 is correlated with clinical stage and differentiation of pancreatic carcinoma. 19103149_Initial description of TFPI-2 internalization and translocation to the nucleus in a number of cells. 19212621_epigallocatechin gallate inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma through TFPI-2 overexpression 19288010_Methylation of CLDN6, FBN2, RBP1, RBP4, TFPI2, and TMEFF2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19435926_Potential of TFPI2 as a biomarker for the early detection of CRC using stool DNA-based assays. 19571260_Paternal imprinting (maternal expression) at TFPI2 is conserved among humans, mice and swine. 19763915_TFPI-2 plays a significant role in the invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma cell in vitro and in vivo. TFPI-2 is an independent prognostic factor for pancreatic carcinoma. 19902129_It was found that heparin calcium induced b-strands in hTFPI-2/ KD3C to different extents depending on the ratio of hTFPI-2/KD3C and heparin calcium. 19936309_TFPI-2 expression may strongly inhibit the migration ability of human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts in vitro. 20015200_study provides evidence that inactivation of TFPI-2 synthesis might promote tumour invasion by a mechanism dependent on regulation of MMP-1, -2, -3, -7 and of ERK signalling pathway 20018303_TFPI-2 plays a significant role in the growth, invasion, and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma cell in vitro and in vivo, and has potential in anticancer therapy. 20113832_Aberrant methylation of TFPI2 promoter CpG island occurred not only in gastric cancer (GC) cells but also in primary GC tissues at a high frequency, suggesting that epigenetic silencing of TFPI2 may contribute to gastric carcinogenesis. 20335518_Expression, DNA methylation and histone modifications of TFPI2, a presumed tumor suppressor, and that of other genes in the 7q21 imprinted gene cluster in prostate cancer, were analysed. 20347477_Placenta may be the main site of the high level of TFPI-2 production in maternal circulation 20377370_these data indicate that TFPI-2 inhibits esophageal tumor invasion and angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. 20530429_TFPI2 may act as a tumour suppressor in colorectal carcinomas and TFPI2 methylation may present a potential risk of malignancy in colorectal cancer. 20537494_TFPI-2 influences smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis in vitro in response to fluid shear stress. 21036731_Aberrant methylation of the TFPI2 gene was detected in 7 out of 38 (18%) primary gastric carcinomas, suggesting that the methylation of TFPI2 is frequently observed in gastric carcinomas. 21062455_Epigenetic inactivation of TFPI-2 by promoter hypermethylation is a frequent and tumor specific event in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 21224345_Findings define a functional involvement for miR-616 and TFPI-2 in the development and maintenance of androgen-independent prostate cancer. 21515313_Results showed that TFPI2 expression was not affected by with VLDL lipoproteins, but was induced by thrombin in THP-1 and monocyte-derived macrophages. 21530612_Our findings underscore the important role of TFPI-2 as a tumor suppressor gene 21621497_Results demonstrate the feasibility of using TFPI2 methylation and quantify human long DNA with fluorescent quantitative Alu PCR in fecal samples as a new noninvasive test for CRC. 21820798_TFPI2 methylation was significant in the sera of patients with large, poorly differentiated carcinoma, deep invasion, lymph node metastasis, or distant metastasis. TFPI2 methylation was observed more frequently according to the progression of TNM stage. 21983100_TFPI-2 methylation is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 21984372_inverse expression of CD24 and TFPI-2 was observed by immunohistochemical analysis of primary breast cancers (N = 1,174). TFPI-2 expression was highest in CD24 negative samples and lowered with increasing CD24 expression 22052167_Promoter hypermethylation of TFPI-2 is frequent and specific event in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. 22110206_Serum TFPI2 methylation is associated with gastric cancer. 22203034_TFPI-2 expression caused invasion and proliferation impair and induced apoptosis in TFPI-2 regulated BeWo and JEG-3 cells. It provides a clue for potential role of TFPI-2 in trophoblast. 22208663_There was a close association between the expression of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) and tumor cell apoptosis and angiogenesis in patients with cervical cancer. 22232300_recombined plasmid pEGFP-C1-TFPI-2 actually interacted with native RASSF1C 22399594_results confirm that detection of methylated TFPI2 in serum DNA was derived from colorectal cancer and could serve as a marker of surgical outcome 22449186_Methylation was found in 28.2, 33.3 and 33.3% of grade 1, 2 and 3 esophageal dysplasia, and 67% of primary esophageal cancer, but no methylation was found in normal mucosa. 23032906_The present work demonstrated that the epigenetic inactivation of TFPI-2 by promoter hypermethylation was a frequent and tumor-specific event in glioblastoma, and TFPI-2 promoter methylation might be considered as a prognostic marker in glioblastoma. 23108564_TFPI2 methylation in serum tended to be detected more easily in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and might be used as a predictor of HCC progression. 23300768_The C-terminus of TFPI-2 encodes for antimicrobial activity, and may be released during wounding. 23497249_Low or negative expression of TFPI-2 is associated with breast cancer progression, recurrence and poor survival outcome after breast cancer surgery. TFPI-2 expression in breast tumors is a potential prognostic tool for breast cancer patients. 23805888_TFPI2 is a novel serum marker for ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma and neoplastic transformation from endometriosis. 24591127_TFPI-2 downregulation can contribute to tumor invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through alteration in the expression of metastasis-related genes. 25036127_regulation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) expression by lysine-specific demethylase 1 and 2 25179542_TFPI-2 is a down-regulated tumor suppressor gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma, probably involving epigenetic silencing mechanisms. The loss of TFPI-2 expression is a key event for oral tumorigenesis, especially in the process of tumor metastasis. 25262870_TFPI-2 in platelets from normal or pregnant subjects and in plasma from pregnant women binds FV/Va and regulates intrinsic coagulation and fibrinolysis 25414083_TMPRSS4 is upregulated by silencing of TFPI-2 through aberrant DNA methylation and contributes to oncogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. 25755719_Our finding suggests that the decreased expression of TFPI-2 may play an important role in the carcinogenesis and progression, and may become a new adjunct marker in the diagnosis and prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma 25755762_our findings suggested that the differential expression of MMP-2 and TFPI-2 have a negative correlation in pancreatic carcinoma 25902909_Hypermethylation of TFPI2 promoter is increased in inflamed colon tissue. 25973077_DNA methylation of TFPI2 may play an important role in the carcinogenesis of cervical cancer and that the differential methylation of TFPI2 may at least partially explain the disparity in cervical cancer incidence between Uygur and Han women. 26313014_Its methylation is a prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. 26318044_Data show that silencing tumor-endothelial cells (EC) for trypsinogen 4 accumulated tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 (TFPI-2) in the matrix. 27797450_Tissue factor pathway Inhibitor 2 potencies differ between antifibrinolytic agents against human and mouse enzymes plasmin, factor XIa, and kallikrein 27798689_TFPI2 is a useful serum biomarker for preoperative clinical diagnosis of CCC. 27840051_This TPR-dependent PP5 inhibition shown by Ro 90-7501 is a unique and novel inhibitory mechanism, which might be a useful tool for studies of PP5 on both regulatory mechanism and drug discovery. 28039717_TFPI-2 expression was decreased in bladder cancer. TFPI-2 expression was decreased with progression in tumor grade and stage and was correlated to decreased apoptosis. 28088469_estrogen induced TFPI-2 expression in MCF7 cells is mediated by ERalpha and also by the action of LSD1. 28208084_Over-expression of TFPI-2 and aberrant promoter methylation status presented in the preeclampsia placentas, suggesting that epigenetic mechanism might contribute to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 28351398_TFPI2 hypermethylation is associated with colorectal cancer. 29051606_TFPI-2 role in the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells.Translocation of TFPI-2 into nucleus affects the promoter activity of the MMP-2 gene.TFPI-2 suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through the regulation of MMP-2 gene expression. 29845195_These results suggest that LSD2 achieves a promoting effect on small cell lung cancer by indirectly regulating TFPI2 expression through the mediation of DNMT3B expression or through the regulation of the demethylation of H3K4me1 in the promoter region of the TFPI2 gene. 30028057_MiR-616-3p binds specifically to the 3'-UTR region of TFPI2 mRNA. 30254643_TFPI-2 Protects Against Gram-Negative Bacterial Infection. 30258071_results suggest that TFPI-2 suppresses cancer cell proliferation and invasion partly through the regulation of the ERK1/2 signaling and through interactions with myosin-9 and actinin-4. 30343349_investigated association between 4 SNPs within TFPI-2 gene and coronary atherosclerosis risk in Chinese Han 30442884_further investigation revealed that lncRNA AC003092.1 regulates TFPI-2 expression through miR-195 in glioblastoma (GB). Taken together, these data suggest that lncRNA AC003092.1 could inhibit the function of miR-195 by acting as an endogenous CeRNA, leading to increased expression of TFPI-2; this promotes TMZ-induced apoptosis, thereby making GB cells more sensitive to TMZ. 30591460_Proliferation, mRNA level of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TFPI2), and cell invasion were evaluated using anti-Ki-67 antibody staining, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and xCELLigence system. 30651599_Mono-ADP-ribosylation of H3R117 upregulated methylation of TFPI2 by impact TET1. 30803712_localized to the cytoplasm of syncytiotrophoblast 31405379_Results found that TFPI2, SOX17, and GATA4 are frequently hypermethylated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines and tumors. The aberrant hypermethylation of these genes was associated with transcriptional silencing in OSCC cells. More importantly, the methylation status of TFPI2, GATA4, and SOX17 was significantly associated with OSCC patients' overall survival through TCGA DNA methylation database. 31839043_expression of TFPI-2 gene in PEGFP-N1-TFPI-2 can inhibit the growth of SHI-1 cells 31984574_Low abundance of TFPI-2 by both promoter methylation and miR-27a-3p regulation is linked with poor clinical outcome in gastric cancer. 32132611_Indirect regulation of TFPI-2 expression by miR-494 in breast cancer cells. 32196834_TFPI2 and NDRG4 gene promoter methylation analysis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells are novel epigenetic noninvasive biomarkers for colorectal cancer diagnosis. 32248791_TFPI2 suppresses breast cancer progression through inhibiting TWIST-integrin alpha5 pathway. 32559232_Two ways of epigenetic silencing of TFPI2 in cervical cancer. 32891505_TFPI-2 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer cells. 34009487_Validation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 as a specific biomarker for preoperative prediction of clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. 34184357_Toward an understanding of tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 as a novel serodiagnostic marker for clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. 34502355_Mechanisms of Systolic Cardiac Dysfunction in PP2A, PP5 and PP2AxPP5 Double Transgenic Mice. 35039572_MEG8 regulates Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2 (TFPI2) expression in the endothelium. 35227195_The methylation of SDC2 and TFPI2 defined three methylator phenotypes of colorectal cancer. 35404184_m(6)A RNA demethylase FTO promotes the growth, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through inhibiting TFPI-2. 35501390_MBD3 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through negative regulation of tumour suppressor TFPI2. 35613543_Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor 2: A Novel Biomarker for Predicting Asymptomatic Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. 35940082_Exosomal miR-195 in hUC-MSCs alleviates hypoxia-induced damage of trophoblast cells through tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2. |
ENSMUSG00000029664 |
Tfpi2 |
1273.035429 |
28.1281897034 |
4.813945 |
0.094065427 |
3461.669083 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2447.1033217 |
142.4286400 |
87.4493676 |
4.8374943 |
| ENSG00000105835 |
10135 |
NAMPT |
protein_coding |
P43490 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the condensation of nicotinamide with 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate to yield nicotinamide mononucleotide, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of NAD. It is the rate limiting component in the mammalian NAD biosynthesis pathway. The secreted form behaves both as a cytokine with immunomodulating properties and an adipokine with anti-diabetic properties, it has no enzymatic activity, partly because of lack of activation by ATP, which has a low level in extracellular space and plasma. Plays a role in the modulation of circadian clock function. NAMPT-dependent oscillatory production of NAD regulates oscillation of clock target gene expression by releasing the core clock component: CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer from NAD-dependent SIRT1-mediated suppression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99KQ4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24130902}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Biological rhythms;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Glycosyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; nicotinamide D-ribonucleotide from 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate and nicotinamide: step 1/1. |
This gene encodes a protein that catalyzes the condensation of nicotinamide with 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate to yield nicotinamide mononucleotide, one step in the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. The protein belongs to the nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRTase) family and is thought to be involved in many important biological processes, including metabolism, stress response and aging. This gene has a pseudogene on chromosome 10. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:10135; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase activity [GO:0047280]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; NAD biosynthesis via nicotinamide riboside salvage pathway [GO:0034356]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15124023_PBEF1 is upregulated in neutrophils by IL-1beta and functions as a novel inhibitor of apoptosis in response to a variety of inflammatory stimuli. 15947248_These findings identify PBEF1 as a regulator of NAD+-dependent reactions in smooth muscle cells (SMCs), reactions that promote, among other potential processes, the acquisition of a mature SMC phenotype. 16021090_Although PBEF had no chemotaxic effects, it was antiapoptotic for both amniotic epithelial cells and fibroblasts and may protect these cells against apoptosis that is induced by chronic distension, labor, or infection. 16186392_visfatin plasma concentrations and visceral visfatin messenger RNA expression correlated with measures of obesity but not with visceral fat mass or waist-to-hip ratio 16188281_PBEF contributes to acute lung injury susceptibility 16234302_visfatin may play a role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus 16394088_A true adipokine, but it is not regulated by thiazolidineidones and, thus unlikely to contribute to the insulin-sensitizing actions of these drugs. 16496121_increased macrophage population in obese human visceral white adipose tissue might be responsible for the enhanced production of chemokines as well as resistin and visfatin 16531748_Visfatin/pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor appears to be preferentially produced by the visceral adipose tissue and has insulin mimetic actions 16636125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16636125_data suggest that genetic variation in the visfatin gene may have a minor effect on visceral and subcutaneous visfatin messenger RNA expression profiles but does not play a major role in the development of obesity or type 2 diabetes mellitus 16701870_These data show that an inflammatory stimulus in the fetal membranes inducing NF-kappaB and AP-1 would up-regulate PBEF as well as IL-8. 16720654_findings show that, in human obesity, plasma visfatin is reduced, whereas visfatin mRNA is differentially regulated in adipose tissue 16736128_Circulating visfatin concentrations are increased by hyperglycaemia. This effect is suppressed by exogenous hyperinsulinaemia or somatostatin infusion. 16783377_FK866 is bound in a tunnel at the interface of the NMPRTase dimer, and mutations in this binding site can abolish the inhibition by FK866, providing a starting point for the development of new anticancer agents. 16802343_Pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor (PBEF) is regulated via IL-6 trans-signaling and the IL-6-related cytokine OSM. PBEF is also actively expressed during arthritis. 16814166_results show that there are decreased concentrations of plasma visfatin in gestational diabetes mellitus subjects and this may indicate that visfatin plays a role in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus 16828081_visfatin is a new hypoxia-inducible gene of which expression is stimulated through the interaction of HIF-1 with HRE sites in its promoter region. 16868228_visfatin has a local metabolic role in the recovery period following exercise. 16922702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16956691_The results indicate that hyperglycemia causes an increase in plasma visfatin levels and, as in people with diabetes mellitus type 2 but not with impaired glucose tolerance, this increase gets more prominent as the glucose intolerance worsens. 17003355_circulating visfatin is increased with progressive beta-cell deterioration. 17003359_A significant association was found between two SNPs of visfatin (rs9770242 and rs1319501), in perfect linkage disequilibrium, and fasting insulin levels (P = 0.002). 17003359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17090638_visfatin is highly expressed in lean, more insulin-sensitive subjects and is attenuated in subjects with high intramyocellular lipids, low insulin sensitivity, and high levels of inflammatory markers 17177135_potential link with pathogenesis of glucose resistance and type 2 diabetes 17189536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17237424_In patients with inflammatory bowel disease, plasma levels of visfatin are elevated and its mRNA expression is significantly increased in colonic tissue of Crohn's and ulcerative colitis patients 17261426_Circulating levels of the cytokine visfatin/PBEF-1 are influenced by renal function, but are not associated with fat mass or surrogate markers of insulin resistance in patients with chronic kidney disease. 17261426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17284735_Visfatin is down-regulated by overfeeding 17307730_Nampt is a longevity protein that can add stress-resistant life to human smooth muscle cells by optimizing SIRT1-mediated p53 degradation 17327330_Serum visfatin concentration is significantly associated with parameters of iron metabolism, especially in subjects with altered glucose tolerance. 17334748_An increase in fasting visfatin, the levels of which correlate with both fasting and post-glucose-load insulin concentrations, accompanies worsening glucose tolerance in the third trimester of pregnancy. 17335820_Women with PCOS exhibit higher plasma visfatin levels than control subjects of similar body mass index. 17340225_the regulation of glucose uptake, proliferation, and type I collagen production by visfatin in human osteoblasts involves IR phosphorylation, the same signal-transduction pathway used by insulin 17392604_This review summarizes current knowledge of the various functions of PBEF/visfatin towards involvement in the pathophysiology of several diseases. 17408594_Taken together, these results demonstrate that visfatin promotes angiogenesis via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK-dependent pathway. 17429683_PBEF/NAMPT/visfatin level is an indicator of beneficial lipid profile in non-diabetic Caucasian subjects 17512309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17556870_Plasma visfatin levels are increased in overweight and obese subjects with metabolic syndrome. 17582143_Visfatin has a role in insulin resistance and markers of hyperandrogenism in lean PCOS patients 17889652_During fasting, increased Nampt provides protection against cell death and requires an intact mitochondrial NAD(+) salvage pathway as well as the mitochondrial NAD(+)-dependent deacetylases SIRT3 and SIRT4. 17904242_Circulating visfatin may be related with some proinflammatory condition even in a nondiabetic state 17931620_Rosuvastatin induced a significant decrease in plasma visfatin levels in patients with primary hyperlipidemia. 17952840_Visfatin, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 mRNA expressions are increased in peripheral mononuclear-monocytic cells from women with type 2 diabetes. 17984105_Circulating levels of visfatin and adiponectin are associated with endothelial dysfunction in all stages of chronic kidney disease, independently of inflammation and insulin resistance. 18034779_Serum levels of the adipokine visfatin are increased in pre-eclampsia. 18083357_Severely obese women have higher than normal blood levels of visfatin. 18239648_As a good surrogate marker, plasma visfatin level can predict the visceral adipose tissue area in obese children. 18241953_Results show that visfatin levels may decrease with age and be related to the HDL metabolism in obese adolescents. 18248642_A probable new role of visfatin in inflammation reflected in PBMCs, in the context of obesity. 18252866_PBEF is shown to exert three distinct activities of central importance to cellular energetics and innate immunity.[REVIEW] 18270432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18270432_The -1535 promoter variant of the visfatin gene is associated with serum triglyceride and HDL-cholesterol levels in Japanese subjects. 18272217_Chronic stretching of the amniotic epithelial cells increases PBEF expression, which protects them from apoptosis. 18356846_C-reactive protein, migration inhibitor factor (MIF), leptin, and visfatin levels decreased after weight loss. 18363885_Our results showed that serum visfatin was increased in patients with metabolic syndrome, especially in those with carotid plaques. Visfatin may be an inflammatory marker of MetS 18410550_Circulating visfatin is independently associated with diabetes & resistin concentration, but is not related to adiponectin multimers or other metabolic covariates. data are suggestive of a potential role of visfatin in subclinical inflammatory states. 18486613_These results may reveal a novel role of PBEF in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury; it interacts with ND1, IFITM3, and ferritin light chain involved in oxidative stress and inflammation. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18686225_change of plasma visfatin concentration by intensive glycemic control may be a compensatory mechanism to ameliorate insulin deficiency due to pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes 18691043_analysis of the structure and function of visfatin and its relation to diabetes mellitus and other dysfunctions [review] 18714344_Circulating visfatin are significantly increased in HLA DR2 positive narcoleptic patients compared to controls. 18728403_PBEF1/NAmPRTase/Visfatin is a potential malignant astrocytoma/glioblastoma serum marker with prognostic value. 18728403_PBEF1/NAmPRTase/Visfatin may have a role in progression of malignant astrocytoma/glioblastoma 18787378_Results show that women with gestational diabetes mellitus have significantly decreased visfatin concentrations in the third trimester. 18823127_Although the weak energetic coupling of ATP hydrolysis appears to be a nonoptimized enzymatic function, closer analysis of this remarkable protein reveals an enzyme designed to capture NAM with high efficiency at the expense of ATP hydrolysis. 18940394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18940394_The visfatin (PBEF1) G-948T gene polymorphism is associated with increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in obese subjects. 18957417_cartilage-specific gene expression in human chondrocytes is regulated by SirT1 and nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase 18996492_Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase may play a critical role as an inflammatory cytokine in the development of pulmonary inflammation and dysregulation of pulmonary vascular endothelial and alveolar epithelial cell barriers. 19005759_Visfatin plasma concentrations could predict the presence of portal inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. 19009499_Visfatin upregulate secretion of MCP-1and IL-6 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 19073361_After a lifestyle intervention in patients with metabolic syndrome plasma visfatin concentrations were directly associated with inflammatory markers. 19074645_Plasma levels of PBEF/Nampt/visfatin are decreased in patients with liver cirrhosis. 19087564_Elevated expression of VF mRNA has a strong correlation with gestational diabetes mellitus and obesity. 19093738_Circulating visfatin levels are not affected by the presence of chronic malnutrition in anorexia nervosa or binge/purge eating behavior in bulimia nervosa. 19095760_Visfatin levevns in human cerebrospinal fluid decrease with rising body fat, supporting the assumption that visfatin transport is impaired in obesity and that central nervous visfatin insufficiency is linked to pathogenetic mechanisms of obesity. 19099366_maternal gestational diabetes mellitus, as well as delivery of large for gestational age neonate were independently associated with a higher maternal plasma visfatin concentrations. 19100714_These data further suggest an integral role for visfatin-FGF-2 signaling axis in modulating endothelial angiogenesis. 19111298_Circulating visfatin levels were higher in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome than healthy controls 19166999_PBEF/visfatin induces secretion of MCP-1 in human endothelial cells: role in visfatin-induced angiogenesis 19185944_Circulating visfatin was significantly lower in the gestational diabetes mellitus than in the NGT subjects at term, although no differences in its mRNA expression in fat and placental tissues were observed. 19200966_The follicular fluid visfatin concentrations are correlated to the number of oocytes retrieved. 19222486_Data suggest that visfatin may play a role in the hormone stabilization process independent of anthropometric, inflammatory or insulin resistance variables. 19284295_median maternal plasma concentration of visfatin peaks between 19-26, has a nadir between 27-34 weeks of gestation. Normal and overweight/obese pregnant women differed in the pattern of changes in circulating visfatin concentrations with gestational age 19300429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19300429_a visfatin gene (NAMPT/PBEF1) variant is associated with protection from obesity 19302375_Enhancing endothelial Nampt activity may thus be beneficial in scenarios requiring EC-based vascular repair and regeneration during aging and hyperglycemia, such as atherosclerosis and diabetes-related vascular disease. 19389865_Loss of renal function is accompanied by increased circulating active visfatin concentrations. Furthermore, decreased HDL cholesterol may hint at an increased probability of cardiovascular events in HD patients with elevated serum visfatin. 19402217_High serum visfatin is associated with endothelial dysfunction in kidney diseases. 19403191_Metabolic syndrome X is not significantly associated with serum visfatin. 19408173_plasma visfatin levels are associated with HDL-C and markers of hyperandrogenism, but it is not associated with proinflammatory markers and insulin resistance in lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome 19488934_Increased maternal levels of leptin and visfatin may be involved in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 19498324_The effects of hyper- and hypothyroidism on various metabolic parameters may be partly mediated by visfatin. 19513556_Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase and prostaglandin H2 synthase 2 are up-regulated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells after stimulation with interleukin-1. 19533482_Asian PCOS women had significantly higher serum visfatin. Their levels were significantly correlated with 2-hour post-load glucose and blood pressure in PCOS women and with fasting insulin and blood pressure in PCOS women with glucose intolerance. 19571557_plasma visfatin concentrations are lower in patients with type 1 DM and related to glycemic control reflected by HbA1c. 19572235_preterm labor with intra-amniotic infection is characterized by high maternal circulating visfatin concentrations 19583971_This is the first report demonstrating a potential role for this important cytokine/enzyme in inflammation-related bone disease. 19650786_The dynamics of Nampt/visfatin and high molecular weight adiponectin during oral glucose tolerance test appear to be linked with insulin and adiposity. 19654329_a novel role of PBEF in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury and other inflammatory disorders via AP-1 dependent mechanism 19666527_crystallographic analysis of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase 19727662_Visfatin is a cause of vascular inflammation, a feature of atherothrombotic diseases linked to metabolic disorders.isfatin appears to be a direct contributor to vascular inflammation, a feature of atherothrombotic diseases linked to metabolic disorders. 19751774_Visfatin through STAT3 activation enhances IL-6 expression that promotes endothelial angiogenesis. 19765775_findings suggest that visfatin/PBEF/Nampt is a proinflammatory marker of adipose tissue associated with systemic insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia 19804767_results suggested that Visfatin -1535C>T polymorphism might be associated with reduced risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population 19811274_adiponectin, ghrelin and visfatin levels were higher in the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus than in controls 19819277_These data suggest a contributory and multifunctional role for visfatin in prostate cancer progression, with particular relevance and emphasis in an obese population. 19819904_crystal structure and reaction mechanism 19834878_high nampt serum levels are significantly associated with advanced carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 19855187_The role of Nampt in regulating autophagy and potential mechanisms by which NAD(+) regulates autophagy in the heart, is discussed. 19887595_exercise increases skeletal muscle NAMPT expression and that NAMPT correlates with mitochondrial content 19900033_elevated in plasma of women with a small-for-gestational-age neonate; not significantly different from normal in women with pre-eclampsia 19912992_these results demonstrate that human hepatocytes are a potential source of circulating NAMPT. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19929281_The elevation of visfatin observed in children and adolescents with metabolic syndrome was proportionate to number of components of MetS but was not associated with insulin resistance. 19936064_activated, but not resting, T lymphocytes undergo massive NAD(+) depletion upon FK866-mediated Nampt inhibition 19948877_High visfatin in chronic kidney disease patients may constitute a counter-regulatory response to central visfatin resistance in uremia. 20019453_Plasma levels do not correlate with coronary calcification. 20046156_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20046156_Significant differences were found in LDL- & HDl-cholesterol, total cholesterol, & fasting serum insulin among visfatin genotypes (TT, GG, & GT). Circulating visfatin levels correlated with weight, BMI, hs-CRP & fasting insulin in the TT genotype. 20059442_Visfatin levels are higher in plasma of pregnant women with gestational diabetes, and in a pregestational diabetic state. 20085562_These findings suggest that visfatin/PBEF may play a role in the regulation of the complex and dynamic crosstalk between inflammation and metabolism during pregnancy. 20091460_These data suggest a differential role for visfatin and resistin in linking metabolic diseases to atherosclerosis with visfatin/PBEF/Nampt being more important in patients with type 2 diabetes and resistin in obese but nondiabetic human subjects. 20106640_Circulating levels of NAMPT and gene expression of NAMPT in human peripheral blood cells are increased in morbidly obese patients. 20121389_visfatin concentration was lower in umbilical cord blood than in maternal circulation, in normal pregnancy, Small for gestational age, and pre-eclampsia 20220292_Visfatin levels were significantly elevated in women with gestational diabetes mellitus and during the course of pregnancy and increased visfatin concentrations were reduced within 6 to 10 weeks after delivery. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20346233_Positive correlation between levels of visfatin and resistin may suggest that visfatin plays a role in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis 20346239_In rheumatoid arthritis patients on TNF-alpha blocker treatment, circulating visfatin levels are unrelated to disease activity, adiposity or metabolic syndrome 20358348_visfatin/Nampt/PBEF1 does not have direct insulin-like action in human adipocytes 20383745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20383745_the -1535C>T polymorphism of visfatin is associated with decreased plasma levels of inflammatory markers in coronary artery disease patients 20392873_sed on these findings, we suggest a role for decreased NAMPT/visfatin levels in hepatocyte apoptosis in NAFLD-related disease 20409603_Findings suggest that visfatin synthesis is activated from adipose tissue in a diabetic environment, induces NF-kappaB activation and leads to activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and systemic inflammation. 20451405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20451405_The involvement of the NAMPT gene in the development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in the Greek population, was evaluated. 20470278_Elevated visfatin related to markers of inflammation might represent a novel link between inflammation and adipocytokines in dialyzed patients. 20470283_Plasma visfatin levels are related to the endothelial functions, inflammation and the severity of proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy. Ramipril decreased visfatin levels and improved proteinuria, endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. 20482384_In patients with osteoarthritis, infrapatellar fat pad and synovium were important sources of visfatin, while osteophytes released largest amounts of visfatin. 20486883_higher in large-for-gestational age newborns 20506278_Data suggest that Nampt/SIRT1 pathway could be a novel therapeutic tool for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. 20586547_Visfatin levels in obese and overweight patients with polycystic ovary syndrome were higher than that found in females without concomitant disease with similar BMI, and visfatin had positive correlation with BMI, waist circumference and insulin resistance 20598369_Cyclic stretch/release of amniotic epithelial cells increased both intracellular and secreted PBEF. 20605615_both vaspin and visfatin/Nampt might play an important role in the pathogenesis of T2DM. 20606733_This is the first report demonstrating Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase overexpression in ovarian serous adenocarcinomas 20608974_PPARgamma ligands increase visfatin gene expression in a PPARgamma-dependent manner in primary human resting macrophages and in adipose tissue macrophages, but not in adipocytes 20621376_investigation of the main source of circulating visfatin (apparently placenta) and visfatin's potential role in pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20720266_A significant decline in visceral adipose tissue visfatin level was found to be associated with degree of steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients 20724478_analysis of inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase and how cellular bioenergetics reveals a mitochondrial insensitive NAD pool 20817637_Provide evidence of Notch1-dependent endothelial FGF-2 induction by visfatin and of Notch1 activation in visfatin-stimulated endothelial angiogenesis. 20823688_Even though the expression of NPY, omentin and visfatin was comparable between obese individuals and controls, we have to consider differences in the total production rate of adipose tissue-derived factors 20848232_visfatin plays an important role in breast cancer progression 20850423_Decreased vaspin and increased visfatin serum levels were observed in asymptomatic patients with coronary artery disease. 20885390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20951014_Suggest that increased circulating visfatin concentration is associated with insulin sensitivity improvement achieved after energy restricted diet intervention induced weight loss. 20956937_Our results suggest important roles of concomitant upregulation of NAMPT and SIRT1 along with increased FOXO3a protein level for prostate carcinogenesis 21061834_The administration of olmesartan improved blood pressure, insulin, HOMA, visfatin and lipid profile in hypertensive obese women. 21122936_Elevation of visfatin in T2DM is independent of obesity and insulin resistance and is mainly determined by fasting glucose and triglycerides. 21144000_CHS-828 and TP201565 are competitive inhibitors of NAMPT and that acquired resistance towards NAMPT inhibitors can be expected primarily to be caused by mutations in NAMPT. 21145308_these results identify visfatin as a gene oppositely regulated by the LXR and PPARgamma pathways in human macrophages. 21225497_Our study showed a positive association between visfatin and the fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 21246369_synovial fluid visfatin might involved in cartilage matrix degradation. 21296365_LDL cholesterol and C-reactive protein levels are positively correlated with visfatin levels. Weight is negatively correlated with visfatin levels, in an independent way and adjusted by age, sex and dietary intake. 21298414_Leucocytes are a major source of enzymatically active NAMPT, which may serve as a biomarker or even mediator linking obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance. 21327328_visfatin enhances atheroma inflammation through the NAMPT-MAPK (p38, ERK1/2)-NF-kappaB-EMMPRIN/MMP-9 pathway 21332548_Serum visfatin was correlated with disease severity and metabolic syndrome in chronic hepatitis C patients. 21375135_Weight reduction after a 2 months on a hypocaloric diet is not associated with a significant change in circulating visfatin in morbidly obese patients. 21375196_The present study confirms the association of visfatin with chronic kidney disease (CKD), however further studies at molecular level to check its expression within renal tissue may clarify its definitive role in CKD 21406189_Nampt and RBP4 serum concentrations did not correlate with the maximum percentage of carotid stenosis 21484571_This chapter summarizes the various functional aspects of Nampt and discusses its potential roles in diseases, with special focus on type 2 diabetes mellitus--REVIEW 21492230_expression of NAMPT was generally high in the more aggressive malignant lymphomas, with >80% strong expression, whereas the expression in the more indolent follicular lymphoma was significantly lower 21494798_Visfatin levels were significantly lower in patients with Behcet's disease whose illnesses were active or inactive than the control group. 21500554_Visfatin may be involved in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus. 21517777_role of NAMPT in human metabolism 21518975_Results demonstrate that PBEF can prime for PMN respiratory burst activity by promoting p40 and p47 translocation to the membrane. 21524918_In patients with active rheumatoid arthritis, serum visfatin levels are related to the number of B cells. 21542902_Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) activates visfatin expression in cultured human coronary arterial endothelial cells. HBO-induced visfatin is mediated by TNF-alpha and at least in part through JNK pathway. 21625240_Elevations in serum visfatin and C-reactive protein (CRP) may contribute to accelerated atherogenic processes in a spinal cord-injured population. 21631570_data suggest that the NAMPT -3186C>T polymorphism is significantly associated with plasma levels of post-prandial serum insulin and total cholesterol in Chinese T2DM patients with repaglinide monotherapy 21634360_Similar to IGF-I levels, determination of visfatin levels can be a predictive marker of retinopathy of prematurity, but more studies are needed. 21664630_The expression of visfatin is closely associated with the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in FFA-induced inflammation and is significantly decreased by NF-kappaB inhibition in HepG2 cells. 21677044_Insulin and GLP-1 are responsible for the rapid suppression of visfatin levels upon an oral glucose uptake in healthy probands. 21687707_transcriptional regulation of FTO and NAMPT in preadipocytes and adipocytes by metabolic regulators 21694775_These findings suggest that visfatin may represent a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is influenced by insulin/insulin sensitivity via the NF-kappaB and JNK pathways. 21697093_IL-1beta induces dedifferentiation of articular chondrocytes by up-regulation of SIRT1 activity enhanced by both NAMPT and ERK signaling. 21712732_Results support an association between serum visfatin/nicotinamide phosphoribosyl-transferase and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. 21726671_PBEF is partially responsible for the increased expression of inflammatory cytokines and apoptosis factors in infected human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. 21738955_Data indicating a possible role of leptin, adiponectin, visfatin, chemerin and vaspin in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis are summarized. 21777266_Compared with healthy girls, serum VISF concentrations are decreased in girls with anorexia nervosa. 21839801_visfatin activates pro-inflammatory cytokine release and phospholipid metabolism in human placenta via activation of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway 21840905_visfatin mRNA concentration in omental adipose tissue is closely correlated with BMI and insulin resistance 21906432_NAMPT rs9770242 and rs59744560 polymorphisms are not markers of disease susceptibility and cardiovascular disease disease in rheumatoid arthritis. 21939650_Visfatin level was increased in type 2 diabetes mellitus, possibly related to hyperglycemia 21963513_Results support a role for visfatin in the detection of subjects with many metabolic abnormalities, which result in increased CVD risk. 21975728_role in LPS-induced inflammatory responses of human monocytes 22024288_first-degree relatives of subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus showed a significant association with lower visfatin levels which may suggest a pathophysiological role for visfatin in beta cell dysfunction in this group. 22090280_A regulatory impact of Nampt rhythmicity on glucose homeostasis. 22137121_This study indicates that plasma visfatin levels are significantly higher in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients. 22147201_Report potential mechanistic link between the visfatin -1535C>T polymorphism and reduced coronary artery disease risk. 22151390_serum level increased in psoriasis 22167446_Plasma visfatin concentrations are lower in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and related to glycemic control reflected by HbA1c. 22186408_These data demonstrate that curcumin down-regulates visfatin gene expression and suggest that visfatin may contribute to breast cancer cell invasion and link obesity to breast cancer development and progression. 22228719_association of the common variants of IL6, LEPR, and PBEF1 with obesity in Indian children. 22251423_NAMPT rs1319501 minor allele associates with increased MI risk in young women. In young men a protective effect of the AKT1 rs3730358 minor allele was suggested, possibly related to an attenuated inflammation 22261365_Further prospective and longitudinal studies are needed to determine whether serum visfatin could be used as a prognostic tool in the armamentarium of postmenopausal breast cancer monitoring and management in conjunction with other biomarkers. 22272940_Visfatin serum concentration seems to be increased in preeclampsia as compared with uncomplicated pregnancy. 22293189_these results showed that visfatin promoted IL-8 production by upregulation of TXAS, leading to angiogenic activation in endothelial cells. 22313145_Data suggest that serum visfatin levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) correlate with risk factors for cardiovascular diseases but not with other metabolic factors in PCOS (i.e., obesity, insulin resistance). 22319029_Data suggest that increased serum NAMPT levels in patients with active acromegaly negatively correlate with adiposity in limbs/total body. NAMPT induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in mature adipocytes suggesting role in adipose inflammation. 22377803_P2X7-dependent release in LPS-activated monocytes following treatment with ATP 22380724_expression of VEGF and visfatin was significantly decreased in the preeclampsia group compared with the normotensive control group 22397743_Plasma visfatin level is not a useful biomarker of insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism. 22399297_the proinflammatory actions of visfatin in chondrocytes involve regulation of IR signaling pathways, possibly through the control of Nampt enzymatic activity 22425808_Physical exercise was reflected by a significant increase in lactate (p=0.01), insulin (p=0.01), visfatin concentrations (p=0.01, p |
ENSMUSG00000020572 |
Nampt |
571.592551 |
5.3072474305 |
2.407964 |
0.095252733 |
641.273159 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000176622803586336053197565680589419998522981201638510227328086545644798698783944109795365914745768692109010907214281775466932535592454242457698474985637147936626263439761785002312081247443752 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000105544638904223497360132203858561975968480295361585444578206698896975719535366053232036195223688115044680945125366080521477104450945723800263699629437941356790351964434399487771733690911361 |
Yes |
Yes |
963.0219313 |
57.6262344 |
182.9888440 |
8.9474621 |
| ENSG00000105854 |
5445 |
PON2 |
protein_coding |
Q15165 |
FUNCTION: Capable of hydrolyzing lactones and a number of aromatic carboxylic acid esters. Has antioxidant activity. Is not associated with high density lipoprotein. Prevents LDL lipid peroxidation, reverses the oxidation of mildly oxidized LDL, and inhibits the ability of MM-LDL to induce monocyte chemotaxis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11579088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15772423}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the paraoxonase gene family, which includes three known members located adjacent to each other on the long arm of chromosome 7. The encoded protein is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues, membrane-bound, and may act as a cellular antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress. Hydrolytic activity against acylhomoserine lactones, important bacterial quorum-sensing mediators, suggests the encoded protein may also play a role in defense responses to pathogenic bacteria. Mutations in this gene may be associated with vascular disease and a number of quantitative phenotypes related to diabetes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5445; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; acyl-L-homoserine-lactone lactonohydrolase activity [GO:0102007]; arylesterase activity [GO:0004064]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; aromatic compound catabolic process [GO:0019439]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636] |
11206400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11257265_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11512679_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11676977_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11676977_study suggested a gene-gene interaction between the PON1 and PON2 polymorphisms for CAD risk; may have linkage disequilibrium with a tightly linked PON3 locus or significant atherosclerotic alleles of nearby genes 11692002_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11768721_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11768721_association between left ventricular hypertrophy and the C825T allele of the G-protein beta3 subunit gene in Arabs. (G PROTEIN BETA3) 11803456_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11803456_PON2*S and apoE4 alleles have interactive effect on the development of the two most common forms of dementias AD and VD, and further support the hypothesis that cardiovascular factors contribute to the development of AD. 11918623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11918623_diabetic microangiopathy is genetically heterogeneous; PON1 Leu/Leu increases the risk for retinopathy and PON2 Ser/Ser increases the risk for microalbuminuria 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12151850_REVIEW: The paraoxonase gene family and coronary heart disease 12433026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12442067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12454802_Association between the severity of angiographic coronary artery disease and paraoxonase gene polymorphisms in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-sponsored Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) study 12454802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12561466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12588779_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12778447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12939804_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12955589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12955589_Polymorphisms of paraoxonase 1 and 2 genes, alone or in combination is associated with with bone mineral density 14636952_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14741412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14741412_These results suggested that the PON2 polymorphism might be a risk factor for LOAD independent of ApoE epsilon4 status in Chinese. 14984433_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14996478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15001326_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15039125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15232408_Genotyping for polymorphisms of PON1 Q192R, PON2 A148G, and PON2 S311C finds no association between mother's PON1 and PON2 genotypes and preterm delivery, but finds infant's PON1 RR and PON2 CC genotypes are associated with preterm delivery. 15232408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15256524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15345661_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15359538_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15544923_PON2 stimulation may represent a compensatory mechanism against the increase in cellular superoxide anion production and atherogenesis 15772423_PON1, PON2, and PON3 are lactonases with overlapping and distinct substrate specificities 15776585_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16030523_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16078734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16080611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16117861_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16135439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16141008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16164576_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16185677_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16319130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16411107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16614106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16767666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16767666_PON1 55 LM genotype and M allele, PON2 148 GG/AG genotype and G allele are the risk factors for coronary artery disease, and the activity of plasma PON is also markedly reduced in individuals with above genotypes. 16776623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16822964_A haploblock of high linkage disequilibrium (LD) spanning PON2 and PON3 was associated with SALS. 16822964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16822965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16822965_the C311S polymorphism was associated with sALS in dominant and additive models. 16891303_Plays a protective role against atherosclerosis in vivo. 16926679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17096118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17096118_PON2 variants have, at best, a small effect on the risk of renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. 17137217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17299970_Gene polymorphisms of PON1 55 Met/Leu, PON2 148 Ala/Gly and MnSOD 9 Ala/Val seemed to involve in the morbidity of CHD by influencing the plasma activities of PON and MnSOD. 17299970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17309646_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17404154_Here, we analyzed the ROS-reducing capability of paraoxonase-2 (PON2) in different vascular cells and its involvement in the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway known as the unfolded protein response. 17406108_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17406108_genotypes with the C allele of the PON2 gene C311S polymorphism is a risk factor for large vessel disease stroke in a Polish population 17412306_The rates of hydrolysis of estrogen esters by the paraoxonases is PON3 > PON1 > PON2, with the exception of 17beta estradiol, 3-acetate, 17-cyclopentylpropionate which is hydrolyzed at a slightly faster rate by PON2 compared to PON1. 17428620_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17436100_In Ashkenazi Jewish population, carriage of PON1 R192 allele may confer protection against the development of IBD. 17436100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17557249_C311S polymorphism of PON2 has no significant correlation with stroke in Han people of Chinese Hunan area and allele C/S is not an independent risk factor for stroke,neither is G148A. 17557249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17664137_PON1/2/3 may have extracellular functions as part of the host response in inflammatory bowel diseases and celiac disease 17854416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17916643_These observations demonstrate that the human intestine is preferentially endowed with a marked PON2 expression compared with the rat intestine and this expression shows a developmental and intracellular pattern of distribution. 17940058_Cys(311)Ser variant of PON2 may contribute to albumin excretion rate 18020951_PON2 expression is upregulated in unesterified cholesterol enriched macrophages through activation of the PI(3)K signal pathway 18063859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18063859_There was no significant correlation between the C311S and G148A polymorphisms of PON2 and stroke in the Chinese population. 18258817_We demonstrate that PON2 mRNA and protein are decreased in plaques versus plaque-adjacent tissue, mammary arteries, and fetal carotids. Our data indicate that the protective effect of PON2 could fail during atherosclerosis exacerbation. 18347034_The hydrolytic effects of PON1, PON2, and PON3 on the key quorum sensing compound of P.aeruginosa are reported. 18361900_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18361900_results indicate that PON2-311 polymorphism is an independent risk factor of AMI 18413200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18427977_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18436804_Urokinase plasminogen activator upregulates paraoxonase 2 expression in macrophages via an NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanism. 18513389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18569577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18635682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18691157_Data suggest that independent mechanisms mediate the degradation of paraoxonase-2 mRNA and protein after disturbance of calcium homoeostasis. 18695162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18720901_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18759523_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18759523_major effect of the paraoxonase-2 polymorphism on coronary artery disease risk in patients 18776646_This study revealed a significant association between Ser311Cys variation in the paraoxonase 2 gene and type 2 diabetes in northern Chinese. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977341_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19082953_The anti-atherogenic biological activities were studied in vitro using serum or cell cultures, and also in vivo, using PON 1/2/3 knockout or transgenic mice, as well as humans - healthy volunteers and atherosclerotic patients. 19091699_Data suggest that PON2 attenuates macrophage triglyceride accumulation and foam cell formation via inhibition of microsomal DGAT1 activity, which appears to be sensitive to oxidative state. 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19151417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19152805_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19166692_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19254215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19371607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401157_Oxidative stress and proinflammatory agents selectively affect the expression of PONs. 19479237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19497963_Urokinase activates macrophage PON2 gene transcription via the PI3K/ROS/MEK/SREBP-2 signalling cascade mediated by the PDGFR-beta. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19540141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19540141_a possible role for PON2 C311S polymorphism in the pathogenesis of cardiac ischemic damage 19546579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19575027_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19587357_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19654933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19654933_the allele and genotype frequencies of PON polymorphisms were described in a south-western Korean population 19818126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19840942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19840942_impaired lactonase activity may play a role in innate immunity, atherosclerosis, and other diseases associated with the PON2 311 SNP. 19865538_Quercetin supplementation increases PON2 levels in cultured monocytes in vitro but not in human volunteers in vivo. 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19930448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19930448_The PON2 311C allele is suggested as a possible predisposing factor for severe cases of ischemic stroke. 19939821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20099504_Serum paraoxonase 1, arylesterase activities and total free sulphydryl group levels were significantly lower in endometrial cancer patients compared to controls 20381198_The data of this study suggested that PON2 polymorphisms are not involved in ALS pathogenesis in an Italian population. 20430392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20458436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503442_differences between PON2 mRNA and protein distributions could be due to missence mutations in the PON2 gene, causing nontranslation of mRNA to protein in some tissues 20529763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530481_PON2 prevents mitochondrial superoxide formation and apoptosis independent from its lactonase activity 20536507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536507_genetic variants, including Ala/Ala of SCYA11 (eotaxin) Ala23Thr, Cys/Cys or Cys/Ser of PON2 (paraoxonase 2) Ser311Cys and Arg/Arg of ADRB3 (beta3-adrenergic receptor) Trp64Arg, were independently associated with incident cardiac end-point. 20565774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20582942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20582942_We now report that in genomic DNA from individuals with familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, we have identified at least 7 gene mutations that are predicted to alter PON1, PON2, and PON3 function. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20839225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20839225_These functional effects of PON1, PON2, PON3 variation should be considered in protecting vulnerable subpopulations from organophosphate pesticides and other inducers of oxidative stress. 20934178_paraoxonase components PON1, PON2, and PON3 are regulated by diverse nutritional molecules and pharmacological agents and pathophysiological events, such as oxidative stress and inflammation [review] 20980077_Low serum paraoxonase activity is a risk factor for Alzheimer disease; furthermore, multiple variants in PON influence serum paraoxonase activity and their effects may be synergistic. 20980077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21118365_in hemodialysis patients, frequency distribution of PON ratio showed 3 PON phenotypes: 74% oshowed PON1, 21% PON2, and 5% PON3. Compared to hemodialysis patients with PON1, patients with PON2 or 3 showed higher conversion rates for 4-nitrophenylacetate 21127310_the PON1 55M and PON1 192R alleles were associated with decreased sperm motility whereas the PON2 311C allele was associated with decreased concentration, supporting the significance of PON genes in semen quality. 21146823_This meta-analysis suggested no association between the PON2 polymorphisms and coronary heart disease risk. 21223581_PON2 genetic variation is significantly and independently associated with variation in serum PON activity and no obvious association between PON2 tagSNPs and SLE risk. 21368884_Deficiency of PON2 caused apoptosis of selective tumor cells. 21561808_Polymorphisms within Pon1, Pon2, and GSTM1 are associated with male infertility. 21620813_polymorphisms of pon1 gene affect PON1 paraoxonase activity while S311C polymorphism of pon2 gene might be associated with coronary heart disease 21672555_Both paraoxonases are expressed in the human frontal cortex; PON2 but not PON1 mRNA levels are up-regulated in Alzheimer disease. 21757906_the studied PON2 polymorphism is not associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease 21765051_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in PON2 is associated with chronic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes. 22016051_The association of PON2, with Parkinson's disease among Indians may point toward an inherent population-specific genetic predisposition 22183305_The aim of this study was to perform a meta-analysis to investigate a more authentic association between PON2 Ser311Cys polymorphism and ischemic stroke. 22534874_PON2 acts as a QS-quenching factor in keratinocytes and may have an important role in cutaneous defense against bacterial infections. 22744335_Paraoxonase (PON) family members seem central to a wide variety of human illnesses, but appreciation of their antioxidative function in the gastrointestinal tract is in its infancy 22860094_lower PPARgamma and PON2 gene expression in the BALF of children with CF is associated specifically with P. aeruginosa infection and neutrophilia. 22964087_Data suggest that mRNA expression and activity of PON-2 enzyme in monocytes and macrophages can be modulated by dietary factors (here, traditional Brazilian beverages/tea made from green or roasted yerba mate). 23053877_In the presence of metabolic syndrome and diabetes, PON2-311CC was associated with an increased risk of significant coronary stenosis. 23225229_hypertension, HDL-cholesterol concentration, and the presence of C allele in PON2 gene were independently associated with atherothrombotic events; study sheds light on role of PON2 as a possible cofactor in determining risk of events together with the well-known risk markers HDL-cholesterol and hypertension 23327886_A case-control study of Chinese workers exposed to occupational noise, PON2 gene polymorphisms(rs7493, rs12026, rs7785846 and rs7786401)was associated with a higher risk to noise-induced hearing loss. No higher risk was found for genotype rs12704796. 23487294_The polymorphisms of the PON genes studied are not related to increased risk of MS in the Polish population. 23742759_Individuals homozygous for the R allele of the PON1 gene and the C allele of the PON2 gene are more likely to have an increased risk of coronary artery disease. 24088404_No significant differences were found for PON2-311 genotypes or allele frequencies in patients with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. 24100645_The current metaanalysis highlighted results for the risk of association of PON155L with diabetic retinopathy (DR) and that PON2 gene polymorphisms, as well as PON1Q192R, may not confer major genetic risk to diabetic nephropathy or DR. 24301778_We conclude that the PON1 55M and PON2 311C alleles are independent risk factors for CAAD in essential hypertension patients from the Xinjiang Han population. 24421402_Data indicate that paraoxonase 2 (PON2) is a transmembrane protein that localizes to the plasma membrane in small intestinal tissue. 24636586_There were no statistically significant differences among all comparisons in pon2 mutation in patient with ischemic stroke. 24727057_S311C PON2 polymorphism is associated with the accelerated decline in kidney function in the chronic glomerulonephritis patients. 24807171_A modest dose-dependent allele effect between the PON2 c.311C > G polymorphism, increased triglyceride concentrations and decreased LDL particle size distribution. 24816800_changes in PON2 in the placenta in labour 24845160_Maternal genetic susceptibility GSTT1 and PON2 rs12026 could significantly modify the association of organic solvents with gestational age. 25038992_PON2 and PON3 (i) are associated with mitochondria and mitochondria-associated membranes, (ii) modulate mitochondria-dependent superoxide production, and (iii) prevent apoptosis. 25210784_Taken together, our data suggest a model by which DJ-1 exerts its antioxidant activities, at least partly through regulation of PON2. 25708945_PON2 levels reflect the cells' irradiation sensitivity. 25740199_D1-like receptors inhibit ROS production by altering PON2 distribution in membrane microdomains in the short-term, and by increasing PON2 expression in the long-term. 25913154_Newborns with PON2 148AG/GG genotype and exposed to high concentrations of MBP and MEHP had higher risks of LBW and SBL 25953737_Data suggest cigarette smoke leads to inhibition of hydrolytic activity of paraoxonase isoenzymes (PON1, PON2, PON3) by modification of thiol groups, by interactions with free radicals/heavy metals, or by decreasing HDL level in blood. [REVIEW] 25991559_Haplotype containing two risk alleles of PON1 and PON2 genes was significantly associated with disease diabetes mellitus, type 2. 26056385_PON2 is a central regulator of host cell responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa N-(3-oxo-dodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone 26227792_PON2 SNPs rs12026 and rs7493 were associated with intracerebral hemorrhage. The C alleles of rs12026 and rs7493 contributed to a decreased risk of ICH. 26656916_Data indicate the relationship between ubiqutination of lysine (Lys) 168 and paraoxonase 2 (PON2) catalytic activity. 26978533_Thi study found that the CC genotype of the PON2 S311C polymorphism is a risk factor for ischemic stroke. 27322774_PON2 is a new potential biomarker for therapy resistance or a prognostic tumor marker. 27578362_Data show that the mRNA levels of both paraoxonases PON2 and PON3 were significantly upregulated whereas PON1's mRNA was absent in transgenic mouse hearts. 27609416_The PON2 Ser311Cys polymorphism is associated with coronary heart disease risk in Caucasians. 27623343_High soluble expression levels were achieved with a yield of 76 mg of fully human PON2 variants per liter of culture media 27771368_Studies indicate that three paraoxonases PON1, PON2, and PON3 genes are clustered on chromosome 7, and that PONs possess numerous atheroprotective properties. 28108734_Results suggest that valproic acid (VPA) reduces paraoxonase 2 (PON2) expression in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells, which in turn increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and induces Bim protein production that inhibits cancer progression via the PON2-Bim cascade. 28430636_these results showed that PON2 could represent a molecular biomarker for bladder cancer and suggest a potential role of the enzyme as a prognostic factor for this neoplasm 28433610_Data suggest that paraoxonases (PON1, PON2, PON3) play roles in innate immunity, inflammatory response, and protection against oxidative stress; these factors are associated with the body's response to infectious diseases; low serum PON1 activities are associated with poor survival in patients with severe sepsis. [REVIEW] 28509526_No significant differences were observed between PON2 and PON3 gene expression in psoriatic lesional and non lesional skin compared with healthy controls 28566152_Study observed a genetic effect in ischemic stroke patients of the north area of the Gran Canaria island linked to the rs7493 variant in the PON2 gene with worse atherogenic ultrasonographic profile in ischemic stroke patients. Conversely, the Cys311Cys homozygosity, which is usually associated with an increased risk of stroke in the general population, was also related to a better ultrasonographic profile. 28637359_The decrease in monocyte/macrophage PON2 enzymatic activity observed in type 2 diabetes cannot be totally explained by abdominal obesity and insulin resistance. 28768768_PON-2 regulates ENaC activity by modulating its intracellular trafficking and surface expression 28803777_Paraoxonase 2 facilitates pancreatic ductal cancer growth and metastasis by stimulating GLUT1-mediated glucose transport. 28862184_In donor retina from patients with diabetes, all three PON1, PON2 and PON3 were expressed, and there was a significant increase in PON3 expression compared to control. This might be the reason for the increased thiolactonase activity observed in diabetic retina compared to control 29308836_Paraoxonase 2 (PON2) possesses antiatherogenic properties and is associated with lower Reactive Oxygen Species levels. PON2 is involved in the antioxidative and anti-inflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells. 29439952_These experiments delineate a PON2 redox-dependent mechanism that regulates endothelial cell TF activity and prevents systemic coagulation activation and inflammation. 29531225_PON2 decreases OC cell proliferation by inhibiting insulin like growth factor-1 expression and signaling. 29729330_suggesting that PON2 is necessary for proper mitochondrial function 30138371_Microarray analysis revealed differential expression of three vitamin D associated genes in the aortic adventitia in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and non-RA patients with coronary artery disease: while the expression of GADD45A and NCOR1 was higher, the expression of PON2 was lower in RA patients. 30607774_SOD2 A16V, but not PON2 S311C, polymorphism may be one of the genetic determinants for polycystic ovary syndrome in Chinese women 31338708_it is a oncogene which promotes gastric cancer. 31835890_Effect of High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress on Paraoxonase 2 Expression and Activity in Caco-2 Cells. 32306677_The rs7785846 (CT+TT) genotype carriers of PON2 gene are more susceptible to hearing impairment when exposed to high noise intensity. 32382056_WTAP and BIRC3 are involved in the posttranscriptional mechanisms that impact on the expression and activity of the human lactonase PON2. 33210737_Paraoxonase-2: A potential biomarker for skin cancer aggressiveness. 33531346_PON2 subverts metabolic gatekeeper functions in B cells to promote leukemogenesis. 34710487_Paraoxonase 2 protects against the CML mediated mitochondrial dysfunction through modulating JNK pathway in human retinal cells. 34987135_Insights into the role of paraoxonase 2 in human pathophysiology. 35092416_Insights into the role of paraoxonase 2 in human pathophysiology. 35286330_Airway epithelial Paraoxonase-2 in obese asthma. 35460610_Paraoxonase 2 C311S single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with type C lesions in coronary atherosclerosis. 36076661_Association of Paraoxonase-2 (C1053G) Gene Polymorphism with the Expression of Paraoxonase-2 Gene in Patients of Ischemic Stroke - A Pilot Study in Indian Population. |
ENSMUSG00000032667 |
Pon2 |
79.304606 |
2.6346841516 |
1.397630 |
0.196515994 |
51.201194 |
0.00000000000083367899210511940639753086632165847229790356376355475731543265283107757568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004983840390227445627827805496003744337336904823843042322550900280475616455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
112.3366556 |
17.7303404 |
42.9942288 |
5.2215579 |
| ENSG00000105855 |
3696 |
ITGB8 |
protein_coding |
P26012 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-V:beta-8 (ITGAV:ITGB8) is a receptor for fibronectin (PubMed:1918072). It recognizes the sequence R-G-D in its ligands (PubMed:1918072). Integrin alpha-V:beta-6 (ITGAV:ITGB6) mediates R-G-D-dependent release of transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-beta-1) from regulatory Latency-associated peptide (LAP), thereby playing a key role in TGF-beta-1 activation on the surface of activated regulatory T-cells (Tregs) (Probable). Required during vasculogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q0VBD0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1918072, ECO:0000305|PubMed:22278742}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the integrin beta chain family and encodes a single-pass type I membrane protein with a VWFA domain and four cysteine-rich repeats. This protein noncovalently binds to an alpha subunit to form a heterodimeric integrin complex. In general, integrin complexes mediate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interactions and this complex plays a role in human airway epithelial proliferation. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3696; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; integrin alphav-beta8 complex [GO:0034686]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; extracellular matrix protein binding [GO:1990430]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; ganglioside metabolic process [GO:0001573]; hard palate development [GO:0060022]; immune response [GO:0006955]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; Langerhans cell differentiation [GO:0061520]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta activation [GO:1901388]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
12324452_induced alpha(v)beta(8) integrin expression mediated Fas-stimulated migration 12875973_These data provide evidence for a functional role for integrin alphavbeta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta in control of human airway epithelial proliferation in vivo. 16702213_periostin has an active role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and metastasis that requires cross-talk between integrin and EGFR signaling pathways 18549475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19920174_Fusion of epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus proteins is triggered by binding of viral glycoproteins gHgL to integrins alphavbeta6 or alphavbeta8. 20019187_Reduced expression of integrin beta8 may be involved in the pathogenesis of sporadic brain arteriovenous malformations. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20519498_Transcription of the transforming growth factor beta activating integrin beta8 subunit is regulated by SP3, AP-1, and the p38 pathway 20942236_The mRNA levels of IntegrinalphaV and Integrinbeta8 were significantly higher in LSCC tissues than that in corresponding adjacent normal tissues. 20956944_miR-93 promotes the growth of, and angiogenesis in astrocytomas, by suppressing, at least in part, integrin-beta8 expression. 21178476_The authors demonstrated that both integrins alphavbeta6 and alphavbeta8 can serve as specific receptors for Epstein-Barr virus gHgL proteins. 21646718_Data suggest that lung fibroblast chemokine secretion directs dendritic cell trafficking, in a manner that is critically dependent on alphavbeta8-mediated activation of TGF-beta by fibroblasts. 21859829_Highly angiogenic and poorly invasive glioblastomas expressed low levels of beta8 integrin, whereas highly invasive glioblastomas with limited neovascularization expressed high levels of beta8 integrin. 21878622_Interleukin-1beta induces increased transcriptional activation of the transforming growth factor-beta-activating integrin subunit beta8 through altering chromatin architecture. 22279205_Deletion of the Itgb8 gene from retinal ganglia cells and Mu ller glia, but not astrocytes, results in highly abnormal vascular patterning and instability. 22753015_ITGB8 silencing may change lung cancer cells to a less invasive phenotype through alteration in the expression of metastasis-related genes. 23283986_alphavbeta8 integrin, via interactions with RhoGDI1, regulates activation of Rho proteins to promote glioblastoma multiforme cell invasiveness. 23874518_Desmoglein-2 co-localizes with integrin-beta8 in N-MVECs. 24294359_Brain metastases ITGB8 expression exhibits considerable heterogeneity according to tumor origin. 24367260_alphavbeta6- and alphavbeta8-integrins acted independently and are thus interchangeable as receptors for Herpes simplex type 1 virus entry. 25079481_data show that integrin beta 8, but not integrin beta 5 or integrin beta 6, protein expression is increased in liver specimens of patients with biliary atresia 25190218_overexpression of integrin alphav induces integrin alphavb8 heterodimer formation and the binding of integrin alphavbeta8 to type collagen might enhance the proliferation and invasion of SCC cells via the activation of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. 25886373_Integrin Beta8 plays a role in the motility of prostate cancer cells. 26157134_Herpes simplex virus entry is enabled by gH/gL interaction with alphavbeta6- or alphavbeta8-integrin receptors. 26901152_Integrins alphavbeta6 and alphavbeta8 were expressed in non-overlapping patterns by keratinocytes and maintained the epidermal residence of Langerhans cells and tissue resident memory T cells by activating latent TGF-beta. 27157394_Integrin beta8 was differentially expressed between Fibromyalgia patients and healthy controls. 27476161_Among Greek and Polish patients with intracerebral hemorrhage, heterozygous individuals with the rs10251386 and the rs10239099 of the ITGB8 gene had significantly lower age of ICH onset compared to the wild-type genotypes. 27782111_this study uncovers a novel pathway by which the TGFbeta-activating integrin alphavbeta8 is expressed in the human intestine on dendritic cell subsets, which is upregulated in patients with inflammatory bowel disease 28484027_Although Mn(2+) potently activates other integrins and increases affinity of alphaVbeta6 for pro-TGF-beta1 25- to 55-fold, it increases alphaVbeta8 affinity only 2- to 3-fold. 29204818_In cellular model, the microRNA-513a-3p was identified as a novel element targeting ITG-beta8, thereby controlling the protein level and its molecular function in the controlling of migration and pro-inflammatory environment. 29337055_The results demonstrated that the hsa_circ_0046701/miR-142-3p/ITGB8 axis might play critical regulatory roles in the pathogenesis and development of glioma. 29436681_our results indicate that miR-199a-3p enhances cisplatinsensitivity of ovarian cancer cells through downregulating ITGB8 expression, and miR-199a-3p may serve as a therapeutic target for the treatment of ovarian cancer patients with cisplatin-resistance. 29746867_ITGB8 is identified as a novel target of miR-26a-5p. 30061598_findings with the alphavbeta3 integrin suggests that our model of stabilizing the extended-closed conformation is generalizable to other integrins. 30520100_Data uncovered that ITGB8 was a target gene of miR-106b. ITGB8 mRNA and protein levels decreased in colon cancer cells overexpressing miR-106b. 30531684_ITGB8 was significantly upregulated in ovarian cancer tissues compared to that in normal ovary tissues. High-grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma patients with high ITGB8 expression had significantly shorter overall survival and recurrence-free survival compared to their low-expression counterparts. Increased ITGB8 expression might be an independent prognostic indicator of unfavorable overall survival 31033358_ITGB8 gene SNPs may be implicated in the risk of hemorrhagic event after a traumatic brain injury. 31792290_Lack of a binding site for one of three betaI domain divalent cations and a unique beta6-alpha7 loop conformation in beta8 facilitate movements of the alpha1 and alpha1' helices at the ligand binding pocket toward the high affinity state. 32196629_Circular RNA TTBK2 regulates cell proliferation, invasion and ferroptosis via miR-761/ITGB8 axis in glioma. 32202906_The long non-coding RNA PVT1/miR-145-5p/ITGB8 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 34371180_lncRNA ITGB8-AS1 functions as a ceRNA to promote colorectal cancer growth and migration through integrin-mediated focal adhesion signaling. 35238496_Integrin subunit beta 8 contributes to lenvatinib resistance in HCC. 35676251_Paradoxical role of beta8 integrin on angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry in glioblastoma. 36008481_Specificity of TGF-beta1 signal designated by LRRC33 and integrin alphaVbeta8. |
ENSMUSG00000025321 |
Itgb8 |
134.522223 |
10.8394144115 |
3.438215 |
0.201222057 |
358.162619 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007074101544925591818206809898967137599709107144662050848955100847129809528123175780377065217212684700692765479516688265291630441346160287586417061180428608733726116106398349661496899889635841954596551239831114799017086625099182128906250000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002367658476260810381530890503386687935505780347902622826094979454042349098342212115306190913281498239509182812085670986493775269429009975157685043146015569700956867783597524637818431454530166465483054238916338363196700811386108398437500000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
256.6535903 |
31.6431463 |
23.8094316 |
2.7433240 |
| ENSG00000105926 |
51678 |
PALS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZW5 |
|
Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
Members of the peripheral membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family function in tumor suppression and receptor clustering by forming multiprotein complexes containing distinct sets of transmembrane, cytoskeletal, and cytoplasmic signaling proteins. All MAGUKs contain a PDZ-SH3-GUK core and are divided into 4 subfamilies, DLG-like (see DLG1; MIM 601014), ZO1-like (see TJP1; MIM 601009), p55-like (see MPP1; MIM 305360), and LIN2-like (see CASK; MIM 300172), based on their size and the presence of additional domains. MPP6 is a member of the p55-like MAGUK subfamily (Tseng et al., 2001 [PubMed 11311936]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:51678; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003] |
33034629_Multi-ethnic GWAS and meta-analysis of sleep quality identify MPP6 as a novel gene that functions in sleep center neurons. 35902094_MPP6 stimulates both RRP6 and DIS3 to degrade a specified subset of MTR4-sensitive substrates in the human nucleus. |
ENSMUSG00000038388 |
Pals2 |
84.071764 |
0.2780786498 |
-1.846435 |
0.618158223 |
8.231625 |
0.00411666575622366467251955768347215780522674322128295898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008562850417398716607042530313265160657465457916259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.9506436 |
15.1522521 |
130.8326518 |
39.2324794 |
| ENSG00000105967 |
22797 |
TFEC |
protein_coding |
O14948 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator that acts as a repressor or an activator. Acts as a transcriptional repressor on minimal promoter containing element F (that includes an E-box sequence). Binds to element F in an E-box sequence-specific manner. Acts as a transcriptional transactivator on the proximal promoter region of the tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) E-box containing promoter (By similarity). Collaborates with MITF in target gene activation (By similarity). Acts as a transcriptional repressor on minimal promoter containing mu E3 enhancer sequence (By similarity). Binds to mu E3 DNA sequence of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene enhancer (By similarity). Binds DNA in a homo- or heterodimeric form. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11467950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9256061}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the micropthalmia (MiT) family of basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factors. MiT transcription factors regulate the expression of target genes by binding to E-box recognition sequences as homo- or heterodimers, and play roles in multiple cellular processes including survival, growth and differentiation. The encoded protein is a transcriptional activator of the nonmuscle myosin II heavy chain-A gene, and may also co-regulate target genes in osteoclasts as a heterodimer with micropthalmia-associated transcription factor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:22797; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11467950_Two alternatively spliced TFEC isoforms have been found to be sequence-specific transcriptional activators of the nonmuscle myosin II heavy chain-A gene in transfected cells. |
ENSMUSG00000029553 |
Tfec |
236.146636 |
2.2267705783 |
1.154953 |
0.208311785 |
30.221496 |
0.00000003854140213307372982405469012852361476717533150804229080677032470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000158327607983347670542217163619502784399628581013530492782592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
309.4650055 |
52.1796580 |
140.0395751 |
17.3377593 |
| ENSG00000105971 |
858 |
CAV2 |
protein_coding |
P51636 |
FUNCTION: May act as a scaffolding protein within caveolar membranes. Interacts directly with G-protein alpha subunits and can functionally regulate their activity. Acts as an accessory protein in conjunction with CAV1 in targeting to lipid rafts and driving caveolae formation. The Ser-36 phosphorylated form has a role in modulating mitosis in endothelial cells. Positive regulator of cellular mitogenesis of the MAPK signaling pathway. Required for the insulin-stimulated nuclear translocation and activation of MAPK1 and STAT3, and the subsequent regulation of cell cycle progression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15504032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18081315}. |
Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a major component of the inner surface of caveolae, small invaginations of the plasma membrane, and is involved in essential cellular functions, including signal transduction, lipid metabolism, cellular growth control and apoptosis. This protein may function as a tumor suppressor. This gene and related family member (CAV1) are located next to each other on chromosome 7, and express colocalizing proteins that form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. Additional isoforms resulting from the use of alternate in-frame translation initiation codons have also been described, and shown to have preferential localization in the cell (PMID:11238462). [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:858; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; caveola [GO:0005901]; caveolar macromolecular signaling complex [GO:0002095]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; D1 dopamine receptor binding [GO:0031748]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; basement membrane organization [GO:0071711]; caveola assembly [GO:0070836]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001935]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation [GO:0014859]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; positive regulation by host of viral process [GO:0044794]; positive regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060161]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell [GO:0019065]; regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051480]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088]; skeletal muscle cell proliferation [GO:0014856]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050]; viral release from host cell [GO:0019076] |
12138116_Data show that ER alpha and not ER beta silences caveolin-1/-2 expression in an epigenetic fashion in neuronal cells. 12414992_In Caco-2 cells, a polarized cell line derived from human colon cancer that does not express caveolin 1 (Cav-1), there was no detectable expression of caveolin 2 (Cav-2). 12648214_caveolin-2 may play a role in lamellar granule assembly, trafficking, and/or function. 12813462_PPARgamma ligands increased the levels of caveolin-2 2-5-fold in a concentration-dependent manner within 24 h. Nonthiazolidinedione PPARgamma ligands elevated caveolin-2 protein 3-4-fold. 15504032_New evidence demonstrating that Cav-2 undergoes phosphorylation at both tyrosines 19 and 27 also reveals that tyrosine phosphorylation of Cav-2 has no effect on its targeting to lipid rafts, but clearly disrupts hetero-oligomerization of Cav-2 with Cav-1. 15569306_Heterologously and endogenously expressed D1 dopamine receptors in renal cells are associated with and regulated by caveolin-2. 15583422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15703204_Actin cytoskeleton is involved as part of a caveolar complex in the regulation of myometrial maxi-K channel function. 15968725_increased expression of caveolins in proliferating bile ductules in primary biliary cirrhosis may be related to the homeostasis of cholesterol transport in regenerating bile ductules in liver 16244790_Overexpression of caveolin-2 is associated with inflammatory breast cancer 16521037_CAV2 identified and immunolocalized in the caveola-vesicle complexes (CVC )present in erythrocytes infected with P. vivax 16904002_caveolae and caveolins are integral membrane components in basal and ciliated epithelial cellsin rats, mice, and humans, indicating a crucial role in these cell types; in addition to their physiological role, they may be involved in airway infection 17615539_The presence of different caveolin isoforms in many cell types of the human retina, is reported. 17671707_Positive staining resulted in shorter survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 17898556_Caveolin-2 was expressed in the sinusoidal endothelial cells and the smooth muscle cells of the unparied arteries of hepatpcellular carcinoma specimens. 17912630_CAV2 is preferentially expressed in basal-like cancers and is associated with poor prognosis 18081315_Data suggests a possible involvement of serine 36-phosphorylated caveolin-2 in modulating mitosis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20062060_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20209490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20835238_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20835238_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in CAV2 is associated with primary open-angle glaucoma. 21178094_We found preliminary evidence that CAV2 rs2270188 interacts with dietary fat to affect risk of type 2 diabetes. 21321670_data and observations imply that a primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) risk allele at the 7q31 locus that contains the caveolin genes CAV1 and CAV2 is not strongly associated with glaucoma in an Iowa population 21373752_cav-2 acts as a modulator of cancer progression. 21489836_The combination of the expression of the genes for PPARgamma, STMN1 and CAV2 was significantly predictive for early recurrence of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer 21551225_CAV1 mRNA and protein levels are reduced by both NFBD1 knockdown and knockout independently of IR and p53 21873608_The identified single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with primary open-angle glaucoma in the Caucasian US population and that specific haplotypes located in the CAV1/CAV2 intergenic region are associated with the disease. 22236542_Stromal caveolin-2 expression were more frequent in anaplastic carcinoma and diffuse sclerosing variant of papillary carcinoma compared to conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma. 22819829_In contrast to wild-type-Cav-2, retroviral re-expression of Y19/27F-Cav-2 in Cav-2 knockout endothelial cells did not affect anti-proliferative effect of TGF-beta compared to empty vector. 23056496_CAV1 and -2 potentiate epsilon-toxin induced cytotoxicity by promoting toxin oligomerization 23667606_This study does not support an association between CAV2 variation and kidney transplant survival. 23743525_Our findings did not correspond with previous positive results, suggesting that CAV1-CAV2 variants studied in the present study are not important risk factors for Normal Tension Glaucoma. 24034151_This meta-analysis suggests that rs4236601[A] is associated with increased risk for POAG in Caucasian and Asian populations. 24572674_CAV1/CAV2 SNPs were associated significantly with primary open-angle glaucoma overall, particularly among women. 25525164_The implication of the caveolin genes, CAV1/CAV2, as a common genetic factor influencing both IOP variations and POAG may provide new insights of the underlying mechanism leading to glaucoma and glaucomatous visual field loss. 25556234_Results present initial characterization of key proteins Cav2 and CFL1 as cellular factors that colocalize with M in viral inclusions and filaments and ZNF502 protein which appears to interact with RSV M in the nucleus. 26015768_The minor allele G of rs17588172 in the CAV1-CAV2 locus is associated with decreased expression of CAV1 and CAV2 in some tissues, marginally with intraocular pressure elevation, and consequently with increased susceptibility to high-tension glaucoma. 26047157_variant in CAV2 is associated with increased age-of-onset of P. aeruginosa airway infection in cystic fibrosis cohort. 26480297_Caveolin-2 expression is necessary for the control of E2-dependent cellular proliferation of MCF-7 cells. 26543085_CAV-1 and -2 have roles in progression of prostate neoplasms 26930711_High CAV2 expression is associated with lung cancer. 27297022_this study confirmed the association of rs4236601 with primary open-angle glaucoma in different Chinese cohorts, and also found a common single-nucleotide polymorphism rs3801994 of diverse associations with primary open-angle glaucoma between Chinese and Japanese 27552914_A-type lamin-dependent Caveolin-2 homo-oligomerization in the inner nuclear membrane microdomain is a precondition for pY19-Caveolin-2-mediated insulin-response epigenetic activation at the nuclear periphery. 28857238_Results verified the presence of transcript III of cav-2 for the first time, but no protein associated was found. Also, a decreasing trend of cav-2 (transcripts I and II) were observed in tumoral tissues especially in stages I and II and seem to be associated with the incidence and promotion of breast cancer, especially in the initial stages of breast cancer. 29111846_No differences were observed for genotype and allele distributions in relation to rs4236601 in the CAV1/CAV2 region. The association of rs2157719 (CDKN2B-AS1) with the primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) phenotype corroborates previously published results, reinforcing the importance of this variant in POAG etiology. 29604334_Cav-2beta isoform yielded by alternative translation initiation desensitizes insulin receptor (IR) via dephosphorylation by PTP1B, and subsequent endocytosis and lysosomal degradation of IR, causing insulin resistance. 29850392_stromal expression of CAV1 in primary tumors was not associated with clinical outcome whereas the stromal expression of especially CAV2 in the metastatic lymph nodes could be associated with lung cancer pathogenesis. 29978477_MiR-29a was negatively correlated with both MUC16 expression and serum CA125 levels. 31889028_Genetic prediction models for primary open-angle glaucoma: translational research. 32109845_Caveolin proteins electrochemical oxidation and interaction with cholesterol. 32162426_Association of the CAV1-CAV2 locus with normal-tension glaucoma in Chinese and Japanese. 33975060_A genetic variant conferred high expression of CAV2 promotes pancreatic cancer progression and associates with poor prognosis. 34078402_Identification of prognostic lipid droplet-associated genes in pancreatic cancer patients via bioinformatics analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000000058 |
Cav2 |
16.219226 |
0.3562919631 |
-1.488868 |
0.379057208 |
16.055312 |
0.00006151879060394799367435247905433470805292017757892608642578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000174854101543283713213888797000095109979156404733657836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.7120254 |
2.2188287 |
24.6803249 |
3.8428017 |
| ENSG00000105974 |
857 |
CAV1 |
protein_coding |
Q03135 |
FUNCTION: May act as a scaffolding protein within caveolar membranes (PubMed:11751885). Forms a stable heterooligomeric complex with CAV2 that targets to lipid rafts and drives caveolae formation. Mediates the recruitment of CAVIN proteins (CAVIN1/2/3/4) to the caveolae (PubMed:19262564). Interacts directly with G-protein alpha subunits and can functionally regulate their activity (By similarity). Involved in the costimulatory signal essential for T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated T-cell activation. Its binding to DPP4 induces T-cell proliferation and NF-kappa-B activation in a T-cell receptor/CD3-dependent manner (PubMed:17287217). Recruits CTNNB1 to caveolar membranes and may regulate CTNNB1-mediated signaling through the Wnt pathway (By similarity). Negatively regulates TGFB1-mediated activation of SMAD2/3 by mediating the internalization of TGFBR1 from membrane rafts leading to its subsequent degradation (PubMed:25893292). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P49817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17287217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19262564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25893292}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Cell membrane;Congenital generalized lipodystrophy;Diabetes mellitus;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The scaffolding protein encoded by this gene is the main component of the caveolae plasma membranes found in most cell types. The protein links integrin subunits to the tyrosine kinase FYN, an initiating step in coupling integrins to the Ras-ERK pathway and promoting cell cycle progression. The gene is a tumor suppressor gene candidate and a negative regulator of the Ras-p42/44 mitogen-activated kinase cascade. Caveolin 1 and caveolin 2 are located next to each other on chromosome 7 and express colocalizing proteins that form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. Alternatively spliced transcripts encode alpha and beta isoforms of caveolin 1.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:857; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; caveola [GO:0005901]; caveolar macromolecular signaling complex [GO:0002095]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; inward rectifier potassium channel inhibitor activity [GO:0070320]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; nitric-oxide synthase binding [GO:0050998]; patched binding [GO:0005113]; peptidase activator activity [GO:0016504]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; angiotensin-activated signaling pathway involved in heart process [GO:0086098]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; basement membrane organization [GO:0071711]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; caveola assembly [GO:0070836]; caveolin-mediated endocytosis [GO:0072584]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0071360]; cellular response to hyperoxia [GO:0071455]; cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus [GO:0071375]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol transport [GO:0030301]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001935]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; glandular epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0002067]; insulin receptor internalization [GO:0038016]; lactation [GO:0007595]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; maintenance of protein location in cell [GO:0032507]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; mammary gland involution [GO:0060056]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; membrane depolarization [GO:0051899]; muscle cell cellular homeostasis [GO:0046716]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001960]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030857]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of inward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:1903609]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; negative regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060546]; negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045019]; negative regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051001]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:1900085]; negative regulation of pinocytosis [GO:0048550]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901380]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061099]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046426]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042532]; nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0006809]; nitric oxide homeostasis [GO:0033484]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol [GO:0010524]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043085]; positive regulation of cell adhesion molecule production [GO:0060355]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of ER-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:1903071]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; positive regulation of gap junction assembly [GO:1903598]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway [GO:0034141]; positive regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045907]; post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression [GO:0010608]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein localization to basolateral plasma membrane [GO:1903361]; protein localization to plasma membrane raft [GO:0044860]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; receptor internalization involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000286]; receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell [GO:0019065]; regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030193]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in regulation of contraction [GO:0098909]; regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction [GO:1901844]; regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051480]; regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell [GO:2000535]; regulation of fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0019217]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential [GO:0098903]; regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0052547]; regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900027]; regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006940]; regulation of the force of heart contraction by chemical signal [GO:0003057]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098911]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641]; tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0007260]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; vasoconstriction [GO:0042310]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050] |
11748236_Caveolin-1 expression enhances endothelial capillary tubule formation 11845324_CAV1 was found in liver endothelial cells and in Kupffer cells (liver non-parenchymal cells). 11915322_forms a cholesterol complex and transports it from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell membrane; activates signal transduction molecules 11920460_over-expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and worse prognosis after surgery in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 12011038_Neu3 functions as a caveolin-related signaling molecule within caveolin-rich microdomains 12138116_Data show that ER alpha and not ER beta silences caveolin-1/-2 expression in an epigenetic fashion in neuronal cells. 12176037_Some protein tyrosine phosphatases form molecular complexes with caveolin-1 in lipid rafts 12185081_regulation of expression and secretion by a protein kinase c epsilon signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells 12186899_data show that coexpression of caveolin can markedly inhibit expression of HIV proviral DNA and establish that the inhibition is mediated by the hydrophobic, membrane-associated domain 12235142_Data show that IL-6/raft/STAT3 signaling is a chaperoned pathway that involves caveolin-1 and HSP90 as accessory proteins and suggest a mechanism for the preservation of this signaling during fever. 12354760_both the caveolin-1/EGFR association and EGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 are modulated by ganglioside GM3 12359771_Endostatin associates with integrin alpha5beta1 and caveolin-1, and activates Src via a tyrosyl phosphatase-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. 12368209_data clearly implicate loss of functional Cav-1 in the pathogenesis of mammary epithelial cell hyperplasia 12372346_Caveolin-1 phosphorylation in human squamous cell carcinoma is dependent on ErbB1 expression and Src activation. 12401329_In the cerebral cortex caveolin-1 is expressed by all the cell types that form the vascular wall, endothelial cells, pericytes, and vascular astrocytes in vivo. 12414512_Up-regulated caveolin-1 accentuates the metastasis capability of lung adenocarcinoma by inducing filopodia formation. 12562842_basal and SR-BI-stimulated free cholesterol efflux to HDL and liposomes and SR-BI-mediated selective uptake of HDL cholesteryl ester are not affected by caveolin-1 expression 12606314_Caveolae plays a role in signal-transducing function of cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase. 12648214_caveolin-1 may play a role in lamellar granule assembly, trafficking, and/or function. 12694195_interacts with endothlin b receptor 12711000_ERalpha co-activator caveolin is negatively regulated by the steroid receptor itself 12716887_Caveolin-1 may modify the biosynthetic pathway of sugar chains via the regulation of the intra-Golgi subcompartment localization of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase III 12730243_caveolin has a role in recovery from cell sensecence 12732636_Caveolin-1 contributes to assembly of store-operated Ca2+ influx channels by regulating plasma membrane localization of TRPC1. 12737162_Caveolin-1 expression is an independent positive prognostic factor for survival in extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. 12810205_A statistically significant difference in the expression of caveolin-1 between oncocytoma with a mean labeling index of 91.7 and other malignant renal tumors with a lower mean labeling index possibly implicates this peptide in oncocytoma pathogenesis. 12813462_PPARgamma & caveolin-1 may coexist in a complex. PPARgamma participates in the regulation of caveolin gene expression in human carcinoma cells. Caveolin-1 may mediate some of the phenotypic changes induced by PPAR-G in cancer cells. 12816877_Caveolin-1 is an inhibitor of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) proliferative responses and might be capable of transforming PDGF-induced proliferative signals into death signals. 12888893_CAV-1 gene can be inactivated through mutations and does not play a role in the development of cervical cancer 14612902_cytoplasmic overexpression of caveolin-1 predicts a poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma 14645548_Akt activities are largely responsible for cav-1-mediated cell survival 14660607_caveolin-1 has a role in mediating astrocyte responses to MCP-1 14706341_negative regulation of caveolin-1 plays a central role in the complex cellular changes leading to metastasis 14707126_caveolin-1 associates with CD147, in a complex distinct from CD147-alpha(3) integrin complexes, thereby diminishing both CD147 clustering and CD147-dependent MMP-1-inducing activity 14719121_inactivation of Caveolin-1 by a mutation or by reduced expression may play a role in the pathogenesis of oral cancer 14729661_overexpression of caveolin-1 in hepatic cells stimulates cholesterol efflux by enhancing transfer of cholesterol to cholesterol-rich domains in the plasma membrane. 14963033_Ouabain assembles signaling cascades through the caveolar Na+/K+-ATPase. 14981899_Cav-1 haploinsufficiency in human breast epithelial cells can lead to partial transformation. 15064242_Nitric oxide concentrations could impact on capillary formation via a combination of direct effects on MMP activation and by altering the distribution or abundance of Cav-1 in tumor angiogenesis. 15069532_caveolin-1 is overexpressed in experimental colon adenocarcinoma by comparison to adjacent normal mucosa, and its expression in human colon cancer cells is directly associated with the growth rate 15190056_Cav-1 has a role in regulating the functional activity of 5-HT(2A) serotonin receptors and Galpha(q)-coupled receptors 15201341_caveolin-1 can inhibit the conversion of LG-CD147 (low glycoform-CD147) to HG-CD147 (high glycoform-CD147) 15205342_Results suggest different roles for CAV1 in SCLC, where CAV1 acts like a tumor suppressor gene, and NSCLC, where it appears required for survival and growth. 15219854_phosphorylation was found in both the acetylated and non-acetylated variants of caveolin-1beta. This variability in modifications is consistent with critical involvement of the N-terminal domain of caveolin in the regulation of caveolae 15234566_review of coordination of caveolin-1 gene expression regulation with that of MDR1 in cancer cells 15234575_In four different groups of marrow samples (20 normal, 56 acute myeloid leukemias (AML) at diagnosis, 48 AMLs at relapse, and 51 regenerating marrows), caveolin-1 and MDR-1 gene expressions were positively correlated 15240128_Our data demonstrate for the first time that the reduction of the plasma membrane cholesterol level induced by overexpressing caveolin-1 may indirectly inhibit P-gp transport activity by increasing plasma membrane fluidity. 15263006_caveolin-1 plays an important role in senescence-associated morphological changes by regulating focal adhesion kinase activity and actin stress fiber formation in the senescent cells. 15274335_Aberrant promoter methylation of the caveolin-1 gene may occur at the precancerous stage, regulated by gender-related factors and is associated with gene silencing of caveolin-1 in the development of colorectal cancer. 15314095_a functional peroxisome proliferator response element in the cav-1 promoter is activated upon rosiglitazone treatment in THP-1 macrophages 15334058_Caveolin-1 regulates primary breast tumor growth and spontaneous metastasis of breast cancer. 15353589_results suggest that CD26-caveolin-1 interaction plays a role in the up-regulation of CD86 on TT-loaded monocytes and subsequent engagement with CD28 on T cells, leading to antigen-specific T cell activation 15375584_role of aberrant promoter methylation in the regulation of caveolin-1 gene in breast cancer correlated with clinical findings 15458387_caveolin-1 expression was increased upon induction or over-expression of FOXO factors at both mRNA and protein levels 15466865_association of MT1-MMP with phosphorylated caveolin-1 occurs in caveolae membranes and involves the cytoplasmic domain of MT1-MMP 15466889_Caveolin-1 and MAL are located on prostasomes secreted by prostate cancer cells 15485671_Caveolin-1 clusters at cell-cell contacts after assembly of alpha-hemolysin into heptameric oligomers 15485672_facile penetration of alpha-HL's beta-barrel might occur through protein-protein interactions with the surrounding 7 alpha-helices of Caveolin-1 15496150_Overexpression of caveolin-1 in mesangial cells suppresses MAP kinase activation and cell proliferation induced by bFGF and PDGF, two major cytokines in mesangioproliferative nephritis(MN). Caveolin-1 expression vector is potential therapy for MN. 15504729_potential role of caveolin polarity in lamellipod extension and cell migration. 15531587_identiication of KLF11 as a dominant repressor of calveolin-1 gene 15590415_The caveolin 1 was found in the endothelial cells of 10-week-old human placenta. 15592498_Caveolin-1 in human breast cancer cells enhances matrix-independent cell survival that is mediated by upregulation of IGF-I receptor expression and signaling. 15657086_Caveolin-1 inhibits the activation of BMP type IA receptor in preformed hetero-oligomer complexes by binding to BMP type II receptor. 15665033_caveolin-1 (CAV-1) functions as a scaffolding protein for phosphofructokinase (PFK) 15691837_Results demonstrate that a branched signaling pathway involving MEK, ERK, PKCepsilon, PKCalpha, and caveolin-1 regulates collagen expression in normal lung tissue and is perturbed during fibrosis. 15703204_Actin cytoskeleton is involved as part of a caveolar complex in the regulation of myometrial maxi-K channel function. 15769846_The downregulation of caveolin-1 in HCT 116 cells inhibited degradation of the extracellular matrix protein collagen IV and the invasion of these cells through Matrigel. 15811424_When we overexpressed caveolin-1 in young mesenchymal stem cells, not only insulin signaling but also adipogenic differentiation was significantly suppressed with down-regulated PPARgamma2. 15817451_caveolin regulates the inhibition by cell-bound TFPI of the active protease production by the extrinsic pathway of coagulation 15948133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15948133_This is the first report providing evidence for CAV-1 being involved in predisposition to aggressive prostate cancer 15958730_unique features of CAV1 phosphorylation on oxidative stress observed implicate an important role of CAV1 in placental endothelial cell biology during pregnancy. 15968725_increased expression of caveolins in proliferating bile ductules in primary biliary cirrhosis may be related to the homeostasis of cholesterol transport in regenerating bile ductules in liver 15969750_Cav-1 expression inhibits ras homolog gene family, member C GTPase activation and subsequent activation of the p38 MAPK pathway in primary pancreatic cancer cells thus restricting migration and invasion 16202996_Caveolin-1 is more expressed in cancer tissues than normal colon and related with Akt-1, not with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor expression in colorectal cancer tissues, which suggests that signaling for caveolin-1 affects Akt-1 activation. 16225848_These results suggest that caveolae could represent an intracellular site that contributes to differentiate IR and IGF-IR activity, and demonstrate the role of caveolin-1 in the eNOS activation by Insulin and IGF-I. 16244790_Overexpression of caveolin-1 is associated with inflammatory breast cancer 16251425_data suggest that caveolin-1 expression indirectly promotes cell-cell adhesion in ovarian carcinoma cells by a mechanism involving inhibition of src-related kinases 16263077_structure activity relationship 16324201_CAV1 is down-regulated and inversely correlated with HER2 and EGFR expression status in DCIS of the breast. 16328005_aberrant methylation and abnormal protein expression of the caveolin-1-gene is involved in the formation of nonurothelial carcinomas of the urinary bladder 16332692_EGF-based signaling cascades phosphorylate Cav1 and have roles in caveolae assembly 16338968_It is therefore concluded that caveolin-1 facilitates the hypotonicity-induced release of Cl(-), taurine, and ATP. 16405917_These novel findings provide insight into possible signaling mechanisms of Nf1 and suggest that together Nf1 and Cav-1 may coordinately regulate cell growth and differentiation. 16407214_Epidermal growth factor receptor exposed to oxidative stress undergoes Src- and caveolin-1-dependent perinuclear trafficking 16443388_Two clones of cells expressing caveolin-1 were investigated for their lipoprotein metabolism activity, showing an increase in ldl liprotein degradation and an increase in HDL lipoprotein activity. 16480767_Cell-cell contact is required for BeWo trophoblasts to exhibit plasmalemmal caveolin-1. 16501093_interacts with rotavirus NSP4 and contributes to NSP4 intracellular trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface. 16541313_CAV1 has a role in both hereditary and sporadic breast cancer 16601146_Expression of caveolin is sufficient to drive the formation of caveolae in cell lines normally lacking caveolin, such as human colon cancer cells (Caco-2). 16601841_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16601841_The 22285 C-22375-22375 del (Cd) haplotype of CAV1 gene, but not the NOS3-CAV1 interaction, is associated with low levels of blood pressure and protects against metabolic syndrome 16608879_Results suggest that anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic properties of caveolin-1 may be attributed to reduced survivin expression via a mechanism involving diminished beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription. 16616146_Homocysteine induced impairment of nitric oxide production through through a modulation of Caveolin-1 expression. 16617096_As such, caveolae and caveolin-1 coordinate PDGF receptor signaling, leading to myocyte proliferation, and inhibit constitutive activity of p42/p44 MAPK to sustain cell quiescence. 16713605_PSMA binds to caveolin-1 and undergoes internalization via a caveolae-dependent mechanism in microvascular endothelial cells 16723714_Cav-1-deficient mammary acini displayed increased ERalpha levels and enhanced sensitivity toward estrogen-stimulated growth, with specific up-regulation of cyclin D1 16790997_important roles for VCAM-1 and Caveolin- 1 in the regulation of metastatic potential of gastric tumor cells 16807357_A ternary complex between NOSTRIN, caveolin-1, and eNOS mediates translocation of eNOS, with important implications for the activity and availability of eNOS in the cell. 16820915_CAV1, either alone or together with eNOS alleles, might modify colorectal cancer heritability. 16820915_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16822931_Thus, these results demonstrate a crucial role of caveolin-1 scaffolding domain interaction with TRPC1 in regulating Ca2+ influx via SOC. 16850311_Increased immunoexpression of the Cav-1 seems to be associated with the biological aggressiveness of meningiomas, reflecting a worse prognosis. 16857240_Inhibits apoptosis and promotes survival signaling in cancer cells. 16877379_the Sprouty/Caveolin-1 interaction modulates signaling in a growth factor- and Sprouty isoform-specific manner 16897435_Breast cancer patients with higher caveolin-1 expression may benefit from ABI-007 therapy. 16904002_caveolae and caveolins are integral membrane components in basal and ciliated epithelial cellsin rats, mice, and humans, indicating a crucial role in these cell types; in addition to their physiological role, they may be involved in airway infection 16920641_Results describe the expression of caveolin-1 in human fetal tissues during mid and late gestation. 16931572_The interaction of the GLP-1R with caveolin-1 regulates subcellular localization, trafficking, and signaling activity. 16979166_Cav-1 induced the cytoplasmic sequestration of BRCA1. 17014845_transcriptional activation of the IGF-IR gene by Cav-1 requires an intact p53 signaling pathway 17047056_Loss of CAV1 expression inhibited the anchorage-independent growth of EWS cells and markedly reduced the growth of EWS cell-derived tumors in nude mice xenografts, indicating that CAV1 promotes the malignant phenotype in EWS carcinogenesis. 17111160_The role of caveolin-1 as a factor contributing to the severity of the tubulointerstitial process resulting from obstructive nephropathy could be suggested. 17178917_Results indicate a pivotal role for cav-1 in the regulation of extracellular matrix production and suggest a novel therapeutic target for patients with pulmonary fibrosis. 17179151_activated EGF receptor transiently modulates integrin alpha2 cell surface expression and stimulates integrin alpha2 trafficking via caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis 17190831_CAV1 phosphorylation on Tyr-14 increases the induction of apoptosis by taxanes in breast cancer cells. 17197700_the Cav-1 scaffolding domain bound significantly to the gp41 expressed in mammalian cells 17200343_Caveolin 1 has a role in progression of a subset of basal-like and metaplastic breast carcinomas 17202321_Prolonged stimulation of isolated human thyrocytes by TSH/cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits caveolin-1 expression. 17237399_overexpression of caveolin-1 overcame the VEGF-mediated inhibition of adhesion and restored ICAM-1 clustering 17245131_Caveolin-1, as a negative regulator of endothelial cell proliferation, may be a potential target for the control of angiogenesis. 17272740_role of caveolin-1 in preventing ischemia-reperfusion injury 17284246_These results suggest that caveolin-1 regulates GD3-mediated malignant signals by altering GD3 distribution and leading edge formation 17287217_Ligation of CD26 by caveolin-1 recruits a complex, including CD26 and CARMA1, which functions in lymphocyte activation. 17299799_Over-expression of Caveolin-1 was associated with established features of prostate cancer and aggressive PSA recurrence. 17314510_This review suggests that caveolin-1 plays an essential role in regulating liver regeneration and that it is implicated in regulation of triglyceride accumulation, an essential process that plays a critical role in the regulation of liver regeneration. 17334644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17341888_Aberrant methylation of CAV1 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 17359972_These data suggest that in ovarian carcinoma cells cav-1, localized in transcriptionally inactive chromatin, exerts a functional activity mediated, at least in part, by directly binding to sequences of genes involved in proliferation. 17379346_the rotavirus NSP4 binding site was localized to caveolin-1 residues 2-22 and 161-178, at the amino- and carboxyl-termini, respectively 17460461_among astroglial tumors cav-1 expression varies in distribution, pattern & intensity specifically according to tumor types & grades 17478448_These data suggested that loss of caveolin-1 is associated with abnormal re-epithelialization in lung fibrosis. 17537407_glucocorticoids modulate the expression of caveolin-1 and caveolae biogenesis within alveolar epithelial cells via both transcriptional and translational modifications 17556531_Appropriate caveola-membrane organization by caveolin-1 and detection of estrogen receptor beta in the plasma membrane are directly reflected by MAP kinase phosphorylation and consequent vitamin D receptor expression. 17594718_Results indicated that caveolin-1 expression may have potential both as a diagnostic marker in the differential diagnosis of renal tumors and as a therapeutic target, especially for clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. 17609206_EMP2 regulates caveolin-1 transcription and more substantially its protein levels. 17615539_The presence of different caveolin isoforms in many cell types of the human retina, is reported. 17626097_HPV type 31 (HPV31) entry and initiation of early infection events require both caveolin 1 and dynamin 2 and occur independently of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. 17662641_Downregulation of caveolin-1 expression affects bleomycin-induced cell cycle arrest and subsequent cellular senescence that is driven by p53 and p21. 17671707_Positive staining resulted in shorter survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 17699771_Data suggest that Cav-1 down-modulation might function as a permissive mechanism, which, by unleashing c-Src and Met signaling, enables osteosarcoma cells to invade neighboring tissues. 17707459_These positive correlations provide new evidence for the involvement of prostate cancer cell derived cav-1 in mediating angiogenesis during prostate cancer progression. 17713785_These internalization data were highly suggestive of the predominant use of the clathrin-mediated pathway by NK1-R, even though NK1-R tended to reside constitutively in lipid raft/caveolae microdomains. 17785436_Re-expression of E-cadherin in HT29(US) cells restored the ability of caveolin-1 to down-regulate beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription and survivin expression, as seen in HT29(ATCC) cells. 17786288_The present data suggest that promoter methylation of the 14-3-3 sigma and CAGE-1 genes plays a crucial role during the phenotypical morphogenesis of vesical adenocarcinomas including signet ring cell carcinomas by an epigenetic mechanism. 17803693_Findings show for the first time the upregulation of mRNA CAV-1 expression levels in VAT and SAT of obese NG and obese T2DM patients compared with lean controls, suggesting a role for CAV-1 in obesity and T2DM development. 17848177_PAR1 localization in the caveolin-enriched membrane microdomain, bound to caveolin-1, represents a crucial requirement for TF induction in endothelial cells. 17850762_Our studies indicate that the conformational changes are probably initiated at the Caveolin-1 binding moti. 17851687_COX-2 is localized within caveolae compartment and colocalized with CAV-1 protein in lobular intraepithelial neoplasia of the breast. 17855368_caveolin-1 is a novel Id-1 binding partner that mediates the function of Id-1 in promoting prostate cancer progression through activation of the Akt pathway leading to cancer cell invasion and resistance to anticancer drug-induced apoptosis 17898556_Caveolin-1 was expressed in the sinusoidal endothelial cells and the smooth muscle cells of the unparied arteries of hepatpcellular carcinoma specimens. 17906498_Caveolin-1 inhibits the growth of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma HEp2 cell line. CAV1 interacts with EGFR and inhibits phosphorylation of EGFR and Erk1/2. 17933968_PCB77 induces eNOS phosphorylation in endothelial cells through a Src/PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism, regulated by functional caveolin-1. 17935714_p53 is an indispensable component of cellular signaling system which is regulated by caveolin-1 expression, involving Akt activation and increase in cyclin D1, thereby promoting proliferation of breast cancer cells. 17936759_Caveolin-1, specifically localized in cholesterol-enriched lipid rafts, appears to regulate constitutive and agonist-stimulated cell surface levels of 5-HT7 receptors via a clathrin-independent mechanism. 17942630_results show that there is a close association of AT(1), AT(2), and ERalpha with Cav-1 in human arterial smooth muscle cells in culture 17952758_caveolin-1(CAV1) was observed in most cells in myomas and in only few cells in controls; CAV1 was localized with oxytocin receptor and sex hormone binding globulin in myomas 18053095_caveolin-1 travels to late endosomes and is replaced by newly synthesized caveolin-1 at the plasma membrane 18054388_CBD1 but not CBD2 binds cells and forms large aggregates at the plasma membrane by colocalizing with cytofacial caveolin-1. 18065769_Caveolin-1 interacts and cooperates with the transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor ALK1 in endothelial caveolae. 18081315_The knockdown of caveolin-1 in endothelial cells decreases caveolin-2 phosphorylation at serine 23 and upregulation of serine 23 phosphorylation depends on caveolin-1-driven targeting to plasma membrane lipid rafts and caveolae. 18162583_The Cx43/Cavs association occurs during exocytic transport, and they clearly indicate that caveolin regulates gap junctional intercellular communication. 18180853_We observed that in the Glu/Asp and Asp/Asp mutant genotypes, the amount of NOS3 associated with Cav-1 was significantly lower. 18203815_low caveolin-1 levels in fibrotic lungs in scleroderma cause their overexpression of collagen, tenascin-C, and alpha actin 18211975_CAV1 as a new Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy (BSCL)-related gene and support a critical role for caveolins in human adipocyte function. 18237401_Very rare CAV1 frameshift mutations appear to be associated with atypical lipodystrophy and hypertriglyceridemia. 18245088_AnxA6 interferes with caveolin transport through the inhibition of cPLA(2). 18258603_Interactions of acetylcholinesterase with caveolin-1 and subsequently with cytochrome c appear to be indispensable for apoptosome formation in a colon cancer cell line. 18282163_an association between cav-1 expression and neoangiogenesis in meningiomas 18296864_Alteration of store-operated Ca(2+) entry by caveolin-1 expression changes could be one of the mechanisms contributing to the progression of breast cancer. 18300018_caveolin-1 plays a tumor-promoting role in advanced-stage cancer. (review] 18301242_a novel and unexpected pattern of Cav-1 expression in human skeletal muscle suggests a role for Cav-1 in terminal differentiation processes 18308897_Caveolin mediates rapid glucocorticoid effects and couples glucocorticoid action to the antiproliferative program. 18312604_Androgen dependent prostate growth in benign prostate hyperplasia may be linked to the interaction of androgen binding protein and oxytocin receptor, associated with caveolin 1 18332144_focal adhesion kinase mediates caveolin-1 up-regulation during epithelial to mesenchymal transition 18406871_Downregulation of CAV1 is associated with primary prostate carcinoma 18434090_Cav-1 increases the basal and TGF-beta1-induced expression of type I procollagen by regulating two opposite signaling pathways: inhibiting TGF-beta1/smad signaling and activating a PI-3 kinase/Akt/mTOR-dependent pathway in human dermal fibroblasts. 18437015_caveolin-1 may play an important role in the progression of transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract 18439424_This is the first evidence of increased nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of caveolin 1 during establishment of H(2)O(2)-induced premature senescence. 18444242_Wild-type APC regulates CAV1 expression in human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines via FOXO1a and C-myc. 18458534_Human breast cancer-associated fibroblasts show CAV1 down-regulation and RB tumor suppressor functional inactivation. 18510854_Growth and proliferation related Akt and Erk1/2 pathways were inhibited after caveolin-1 down-regulation. 18543249_Concluded that IL-6/sIL-6R enhances cathepsin B and L production via IL-6/sIL-6R-mediated Cav-1-JNK-AP-1 pathway in human gingival fibroblasts. 18561140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18561140_We report a novel polymorphic purine complex stretching approximately 150 bp of genomic DNA at the 1.5 kb upstream region of the human CAV1 gene, alleles and genotypes of which are associated with sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 18596970_the relationships between Cav-1 abundance, atherosclerotic plaque characteristics and clinical manisfestations of atherosclerotic disease. 18598695_These data indicate that caveolin-1 specifies filamin A as a novel target for Akt-mediated filamin A Ser-2152 phosphorylation thus mediating the effects of caveolin-1 on IGF-I-induced cancer cell migration. 18635971_These findings suggest that FASN and Cav-1 physically and functionally interact in PCa cells. 18667513_Caveolin-1-dependent infectious entry of human papillomavirus type 31 in human keratinocytes proceeds to the endosomal pathway for pH-dependent uncoating 18667611_Caveolin-1 may provide an effective target to protect against human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) protein Tat-induced brain microvascular endothelial cell dysfunction and disruption of the blood-brain barrier in HIV-1-infected patients. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18681962_There is a role for caveolin-1 in degenerative rather than age-induced changes in the nucleus pulposus. A positive correlation was identified between gene expression of caveolin-1 and p16INK4a (biomarker of cellular senescence). 18698612_A new subtype of congenital generalized lipodystrophy is not associated with the CAV1 gene. 18759267_Caveolin 1 appears to participate in the pathogenesis of tissue fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. 18789131_irradiation triggered caveolin-1 dependent Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor internalization into caveolae. 18793348_caveolin-1 is expressed in cardiac myocytes, localized to both caveolae and non-caveolar domains in the plasma membrane 18802406_Co-expression of fatty acid synthase and caveolin-1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 18836420_variations of caveolin-1 expression may have an important role in the progression of human breast lobular cancer 18922892_a feedback loop between Rho/ROCK, Src, and phosphorylated Cav1 in tumor cell protrusions, identifying a novel function for Cav1 in tumor metastasis that may contribute to the poor prognosis of some Cav1-expressing tumors. 18923542_Data indicate that HERG channels interact with caveolin-1 and are negatively regulated by this interaction. 18936967_Absence of significant correlations between cav-1 expression and other pathological parameters, such as the stage of disease or the patients overall survival, indicates that the role of cav-1 in GC is neither stage-specific nor related to prognosis. 18957516_Caveolin-1 plays a dual role in the fibronectin assembly regulated by uPAR signaling. 18985008_Findings suggest that hOAT4 and caveolin-1 share a cellular expression in the plasma membrane and caveolin-1 up-regulates the organic anionic compound uptake by hOAT4 under the normal physiological condition. 18992284_The phenotypic changes observed after caveolin-1 modulation were mediated by alpha(5)beta(1) integrins. 18992712_These results reveal a new mechanism by which caveolin-1 negatively regulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma cells. 19002186_In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, cav-1 may play an inhibitory role in tumorigenesis and lung metastasis through regulating integrin beta1- and Src-mediated cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. 19002697_Caveolin-1 is the membrane protein that forms part of the caveolae.The main functions of caveolae are transcytosis of both large and small molecules across cell membrane. 19015640_Caveolin-1 was upregulated and beta-catenin was recruited to the plasma membrane when xCT was deficient, which were followed by the inhibition of beta-catenin transcriptional activity. 19032226_Caveolin-1 expression is a distinct feature of chronic rejection-induced transplant capillaropathy. 19038362_Reviews recent studies in adipocytes, the specialized cell type for fatty acid storage, which suggest a role for caveolins in the formation, maintenance or mobilization of lipid droplet stores. 19052258_Caveolin-1 scaffold domain interacts with TRPC1 and IP3R3 to regulate Ca2+ store release-induced Ca2+ entry in endothelial cells. 19059381_hepaCAM is partially localized in the lipid rafts/caveolae and interacts with Cav-1 through its first immunoglobulin domain. 19061949_The data suggested that autophagy played a key role in Cd2+ induced endothelial dysfunction; integrin beta4, caveolin-1 and PC-PLC might be the targets of Cd2+ in vascular endothelial cells. 19104007_GTPCH I is targeted to caveolae microdomains in vascular endothelial cells, and tetrahydrobiopterin production occurs in proximity to endothelial NO synthase. The regulation of GTPCH I activity involves the caveolar coat protein, caveolin-1. 19116988_In prostate cancer cells in culture, delta-catenin was co-localized with caveolin-1 and CD59, suggesting its potential excretion into extracellular milieu through exosome/prostasome associated pathways. 19121286_These data suggest that flotillin-1 regulates caveolin-1 level by preventing its lysosomal degradation in intestinal epithelial cells. 19123976_caveolin-1 is essential in the down-regulation of MT1-MMP activity by promoting internalization from the cell surface 19160064_Data show that Cav-1 expression in tumor tissues was correlated with both the Ki-6 |
ENSMUSG00000007655 |
Cav1 |
42.685463 |
0.4414382104 |
-1.179717 |
0.256038206 |
21.389507 |
0.00000374816833128508245044142356550143091453719534911215305328369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000012379271552868163387283069465372165041117114014923572540283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.3050615 |
4.0250711 |
57.5938493 |
5.9284558 |
| ENSG00000105976 |
4233 |
MET |
protein_coding |
P08581 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding to hepatocyte growth factor/HGF ligand. Regulates many physiological processes including proliferation, scattering, morphogenesis and survival. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3-kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. Recruitment of these downstream effectors by MET leads to the activation of several signaling cascades including the RAS-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, or PLCgamma-PKC. The RAS-ERK activation is associated with the morphogenetic effects while PI3K/AKT coordinates prosurvival effects. During embryonic development, MET signaling plays a role in gastrulation, development and migration of muscles and neuronal precursors, angiogenesis and kidney formation. In adults, participates in wound healing as well as organ regeneration and tissue remodeling. Promotes also differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells. May regulate cortical bone osteogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P16056}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Listeria monocytogenes internalin InlB, mediating entry of the pathogen into cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11081636, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17662939, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19900460}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chromosomal rearrangement;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Membrane;Non-syndromic deafness;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase family of proteins and the product of the proto-oncogene MET. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate alpha and beta subunits that are linked via disulfide bonds to form the mature receptor. Further processing of the beta subunit results in the formation of the M10 peptide, which has been shown to reduce lung fibrosis. Binding of its ligand, hepatocyte growth factor, induces dimerization and activation of the receptor, which plays a role in cellular survival, embryogenesis, and cellular migration and invasion. Mutations in this gene are associated with papillary renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and various head and neck cancers. Amplification and overexpression of this gene are also associated with multiple human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]. |
hsa:4233; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; hepatocyte growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005008]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; semaphorin receptor activity [GO:0017154]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; endothelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0001886]; establishment of skin barrier [GO:0061436]; liver development [GO:0001889]; negative regulation of autophagy [GO:0010507]; negative regulation of guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:1905098]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-mediated programmed cell death [GO:1901299]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; negative regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051497]; negative regulation of thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway [GO:0070495]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; pancreas development [GO:0031016]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:2001028]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031116]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11750879_Role of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, in oncogenesis and potential for therapeutic inhibition 11839685_Modulation of the c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in small cell lung cancer 11864613_Met sequesters Fas, preventing apoptosis. 11894096_The endophilin-CIN85-Cbl complex mediates ligand-dependent downregulation of c-Met 11895493_Increased c-Met expression participates in cholangiocarcinogenesis and in the early developmental stages of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 11948964_high expression seen in intermediate cells in normal and malignant prostate epithelium indicates they are prone to stromal invasion in prostate carcinoma 12168776_HGF and HGFR have an alternative role activating the via STAT3 transdution and operating on placental tissues, overall in organogenesis alteration conditions 12183053_a signal transduction cascade or cross-talk emanating from CD44 to c-Met 12233882_Overexpression of HGF/c-met appears to be a biological feedback response to the fibrotic process of systemic sclerosis. 12244174_MET signaling is negatively regulated by c-Cbl which induces ubiquitination of its cytoplasmic domain. 12460923_MET may be one of the long sought oncogenes controlling progression of primary cancers to metastasis. 12524084_immunoexpression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met in the eutopic endometrium of patients with pelvic endometrioisis is possibly useful to predict greater activity of the ectopic endometrium 12538453_HGF may have a role in the pathogenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma 12594808_Radiation stimulates HGF receptor/c-Met expression that leads to amplifying cellular response to HGF stimulation via upregulated receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and MAP kinase activity in pancreatic cancer cells. 12595309_up-regulated during the in vitro recapitulation of several steps of angiogenesis; expression increased shortly after switching to angiogenic growth conditions & remained high during the first steps of angiogenesis, including cell migration & proliferation 12611639_Activation of the c-Met pathway targets the PI3K pathway in small cell lung cancer 12646256_These results indicate that overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase in renal carcinoma cells participates in rapid tumor growth in vivo. 12651912_Ki-ras mutations and HGF signaling cooperate to enhance tumor growth by increased duration of MAPK activation and decreased apoptosis in human carcinoma cells. 12682635_Met is expressed by the majority of MM cell lines and by approximately half of the primary plasma cell neoplasms tested.The hepatocyte growth factor/Met pathway controls proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma. 12686592_Endosomal dynamics of Met determine signaling output. 12707786_Autocrine and paracrine support of HGF-c-Met system attenuates degeneration of anterior horn cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Disruption of neuronal HGF-c-Met system at advanced stage accelerates cellular degeneration and cell death. 12709413_Role of the HGF receptor in proliferation and invasive behavior of osteosarcoma cell lines. 12716900_data define a protein kinase c-controlled traffic pathway for c-Met that operates independently of its degradative pathway 12726861_hypoxia promotes tumor invasion by sensitizing cells to hepatocyte growth factor stimulation, providing a molecular basis to explain Met overexpression in cancer 12766170_Gab1 and the Met receptor interact in a novel manner, such that the activated kinase domain of Met and the negative charge of phosphotyrosine 1349 engage the Gab1 MBD as an extended peptide ligand 12793903_Met can be detected in the axillary fluids of patients who undergo conservative operations for breast cancer, and its expression in the axillary drainage may have potential as a prognostic factor. 12847110_N-terminal domain of HGF inhibits angiogenesis not by disrupting the HGF/c-met interaction but rather by interfering with the endothelial glycosaminoglycans. 12856716_Activation of c-Met in colorectal carcinoma cells leads to constitutive association of tyrosine-phosphorylated beta-catenin 12883672_hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met/HGF receptor have roles in prostate neoplasm progression 12884908_c-Met signaling has roles in scattering, angiogenesis, proliferation, enhanced cell motility, invasion, and eventual metastasis [review] 12915129_These data suggest that coexpression of the MET and RON receptors confer a selective advantage to ovarian cancer cells and might promote ovarian cancer progression. 14508824_C-met expression is a significant marker for tall cell variant papillary carcinoma of the thyroid gland. 14509156_MUC1 and Met can be detected in the axillary fluids of patients with breast cancer; the expression of both tumor markers in the axillary drainage is strongly associated with unfavorable tumor features and can be used as a prognostic factor 14519655_Retroviral ribozyme transgenes targeting HGF/SF in fibroblasts or its receptor cMET in mammary cancer cells can reduce the growth of mammary cancer and associated angiogenesis by inhibiting paracrine stromal-tumor cell interactions. 14524531_c-Met and HGF-SF have roles in the growth and progression of human and canine osteosarcoma 14528000_establish by deletion mutagenesis that the HGF/SF and heparin-binding sites of MET are contained within a large N-terminal domain spanning the alpha-chain (amino acids 25-307) and the first 212 amino acids of the beta-chain (amino acids 308-519) 14627992_Mutation present in a notable subset of patients with oropharyngeal cancer and may interfere with radioresponsiveness. 14719064_Differentially expressed in gastric cancer and intestinal metaplasia. 15075332_Ser-985 phosphorylation of c-Met is bi-directionally regulated through PKC and PP2A 15123609_Data identify a DpYR motif including tyrosine(1003) as being important for the direct recruitment of the c-Cbl tyrosine kinase binding domain and for ubiquitination of the Met receptor. 15123705_Results provide an explanation for cell surface receptor cross-talk involving the Met receptor and link G protein-coupled receptors and the epidermal growth factor receptor to the oncogenic potential of Met signaling in human carcinoma cells. 15161909_the invasive function of Met can be independent of alpha(6)beta(4); alpha(6)beta(4) has a generic influence on the invasion of carcinoma cells that is not specific to Met 15173072_c-Met oncogene is a novel tumor rejection antigen recognized by cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and expressed on a broad variety of epithelial and hematopoietic malignant cells 15184888_MET receptor can interact with each of the three members of class B Plexins and control tumor invasive growth. 15192042_Met is frequently activated in these carcinomas and may favor tumor growth, and abundance of Met expression may differently regulate cell growth, morphogenesis, and migration in response to HGF. 15254691_Stat3 mediated by c-Met is frequently associated with the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma 15287857_HGF-specific immunostaining of proliferating cholangioles in the absence of HGF RNA suggests c-Met-mediated uptake of HGF and paracrine stimulation of cholangiocellular proliferation 15302591_Compared to IOSE-29, IOSE-Ov29 and IOSE-Ov29/T4 exhibited higher levels of the HGF receptor Met and an increasing duration of ERK1/2 activation with malignant progression, in conjunction with other neoplastic properties. 15314156_Results suggest that MUC20 is a novel regulator of the Met signaling cascade which has a role in suppression of the Grb2-Ras pathway. 15327888_Review. The role of Met in normal human prostate epithelium, and underlying mechanisms of deregulated Met expression in localized and metastatic prostate cancer are discussed. 15339794_TGF-beta1 significantly induced c-met expression in human kidney cells, which primarily took place at the gene transcriptional level. 15448002_Met proto-oncogene and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 have roles in metastasis of well-differentiated pancreatic endocrine neoplasms 15466866_K48R-linked polyubiquitin is required for Met endosomal trafficking 15492846_The autocrine mechanism between over-expressed c-Met and HGF/SF in malignant tumors is part of the process of pleural metastatic spread. 15504247_These results indicate that c-Met is actually activated in gastric carcinoma tissue, and may trigger proliferation/anti-apoptotic signals. 15516982_findings expand our understanding of tumor promoter/suppressor inter-relationships and downstream transcriptional effects of PTEN loss and c-Met overexpression in malignant gliomas 15579033_mutated in papillary renal cell carcinoma. 15590419_The role of HGFR signal in colon tumorigenesis is associated to progression of adenoma into carcinoma. 15596854_role of coreceptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) infection by facilitating AAV2 internalization into the cytoplasm 15632204_demonstrate that Sema4D is angiogenic in vitro and in vivo and that this effect is mediated by its high-affinity receptor, Plexin B1, and that biologic effects elicited by Plexin B1 require coupling and activation of the Met tyrosine kinase 15659325_in chronic skin ulcers, decreased biological activity of endogenous HGF and overexpression of c-met may have roles in fibrosis and delayed recovery 15672865_overexpression of c-Met is associated with advanced stage colorectal cancer 15678502_Cell proliferation, invasion, and morphological characteristics may be induced independently from the HGF/SF-Met pathway in C31/Tag metastatic prostate cancer cells. 15717924_Through promoting Met-Integrin association, HGF-FN and HGF-VN complexes coordinated and enhanced endothelial cell migration through activation of the PI-3 kinase pathway involving a Ras-dependent mechanism 15720819_c-Met is overexpressed in esophageal adenocarcinoma. 15760460_HGF/MET signalling protects Plasmodium sporozoite-infected host cells from apoptosis. 15772665_Targeting the activated, human MET oncogene to adult mouse liver caused slowly progressing hepatocarcinogenesis 15828871_Analysis with phospho-specific antibodies indicates that 3 kinases generate a signal-specific, combinatorial phosphorylation profile of the Hrs-STAM complex, with the potential of diversifying tyrosine kinase receptor signalling through a common element. 15849510_IGF-I and HGF cooperate to induce migration and invasion of colorectal carcinoma cells, and c-Met and uPA/uPAR are required for IGF-I-mediated migration and invasion. 15870272_negative feedback regulation in which Met activation leads to transcriptional induction of Notch function, which in turn limits HGF activity through repression of the Met oncogene 15911745_cMet/Fas interaction may inhibit self-association of Fas receptor such that reduced DISC formation occurs in these cells after Fas receptor ligation. cMet/Fas interaction may help explain why endothelial cells are resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis. 15980634_Deregulation of the interaction between HGF and its receptor c-met during placentation may be the cause responsible for the growth retardation of the fetus due to the impaired placental functions. 16039997_It is concluded that level and duration of MAPK activation by Met receptor are crucial for the induction of a full HGF-dependent mitogenic and invasive program in KS cells. 16099863_Induction of Met expression by low-oxygen tension may play an important role in the physiology of early pregnancy by promoting the invasion of trophoblast cells into the decidua of the uterus. 16139245_These results suggest that CD151 forms a structural and functional complex with c-Met and integrin alpha3/alpha6, and exerts its oncogenic functions through excessive activation of the HGF/c-Met signalling pathway. 16158056_hepatocyte growth factor signaling and Ki-ras oncogene activation have roles in colorectal cancer 16186806_upregulation of the MET pathway may contribute to the poor outcome of esophageal adenocarcinoma patients and that therapeutic agents targeting this pathway may help improve patient survival 16192631_HGFR signaling mediates the anti-fibrotic action of alitretinoin in glomerular mesangial cells. 16216128_expression of hepatocyte and keratinocyte growth factors and their receptors is preserved in patients with lung emphysema as compared to patients without emphysema 16278380_XIAP expression in colorectal cancer is regulated by hepatocyte growth factor/C-met pathway via Akt signaling 16403482_using RT-PCR for the detection of c-Met or mucin 1 mRNA may be a promising tool for the early detection of micro-metastatic circulating tumor cells in gastric carcinoma patients 16426920_study showed that c-Met overexpression may be important for the progression of cervical adenocarcinomas 16455654_c-Met expression is regulated by Mitf in the melanocyte lineage 16498238_The consistent expression of HGF and c-met during the perinatal period supports a physiological role for HGF in human lung development. 16537444_crystal structure, at 2.15-A resolution, of the autoinhibited form of the kinase domain, revealing an intricate network of interactions involving c-Met residues 16547140_Antibodies efficiently down-regulates HGF receptor through a molecular mechanism involving a double proteolytic cleavage 16627020_Liver cancer patients had a significantly higher level of serum hepatocyte growth factor than normal controls 16709175_As discussed in this review, receptor tyrosine kinase Met and its ligand HGF/SF (hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor) are essential in the signalling pathways required for embryogenesis and tissue regeneration. 16710476_Results reveal that a subset of human hepatocellular carcinomas and all liver metastases shared the Met-induced expression signature. 16804974_Overexpression of c-met occurs during the early stage of pancreatic carcinogenesis, and a single alteration of c-met expression is not sufficient for progression of chronic pancreatitis-affected epithelial cells to pancreatic cancer cells. 16857786_c-Met ectodomain shedding has a role in cancer's malignant potential 16867270_c-met-siRNA can down-regulate the expression of c-met and inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, motility and invasiveness. 16870139_results suggest that activation of c-Met signaling in prostate cancer cells may lead to induction of spontaneous mutations or genomic instability, which may lead to progression of androgen-independent state 16891453_IGF-IR and c-Met cooperate to induce migration and invasion of human pancreatic carcinoma cells. 16912172_Processing of the Met receptor results in the release of the cytoplasmic domain and its translocation to the nucleus in cells at low density. 16951184_Mimp expression reduces hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced proliferation and scattering by attenuating and altering the downstream signaling of met proto-oncogene. 16953230_A functional crosstalk between hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) and beta-catenin signaling sustains and increases colorectal carcinoma cell invasive properties. 17053076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17053076_genetic association (P = 0.0005) of a common C allele in the promoter region of the MET gene in 204 autism families 17062641_Serum-independent growth of 5637 cells involves the transmembrane signaling cascade via EGFR ligand(s) (but not HGF), EGFR, Src and p145(met). 17062664_Met activation induces changes consistent with early invasion, such as down-regulation of E-cadherin and anchorage-independent growth of esophageal adenocarcinoma. 17079873_The alternatively-spliced form of MET may contribute to the development and progression of human cancer. 17132227_c-Met has a role in progression of esophageal adenocarcinoma 17215249_glycosphingolipids, particularly GM2, form a complex with CD82, and this complex interacts with Met and thereby inhibits HGF-induced Met tyrosine kinase activity, as well as integrin to Met cross-talk 17243166_Plays a role in the progression of rhabdomyosarcoma. 17322284_HGF stimulation of c-Met-overexpressing H69 small cell lung cancer cells (40 ng/ml, 15 min) resulted in an increase of reactive oxygen species 17332337_Met is necessary for lung cancer cell lines growth and survival. 17372204_although serine proteases and HGF have quite distinct functions in proteolysis and Met signal transduction, respectively, they share a similar activation mechanism 17459054_In lung adenocarcinoma, c-Met activation may take place either ligand-dependently or ligand-independently via c-Met. overexpression. 17463250_findings show that amplification of MET causes gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by driving ERBB3 (HER3)-dependent activation of PI3K, a pathway thought to be specific to EGFR/ERBB family receptors 17593080_Imbalance in c-Met expression between tumour and surrounding normal tissue is associated with aggressive ductal carcinoma in situ phenotype. c-Met and HGF/SF may contribute to tumour development by different means than those controlled by Her2/neu. 17611703_c-met is an essential factor in the processes of migration and invasion of hepatocarcinoma cells 17662939_The crystal structure of the complex between a large fragment of the human Met ectodomain and the Met-binding domain of InlB. 17673463_c-MET is associated with FAS and when activated enhances drug-induced apoptosis in pediatric B acute lymphoblastic leukemia with TEL-AML1 translocation 17684486_persistent expression of the MET oncogene is mandatory until the advanced phases of cancer progression. 17689924_These results demonstrate that lysophosphatidic acid regulates c-Met function through PKC delta and E-cadherin. 17696172_Altered expression of MET and related molecules suggests dysregulation of signaling that may contribute to altered circuit formation and function in autism spectrum disorder 17702746_CD44 is an important regulator of HGF/c-Met-mediated in vitro and in vivo barrier enhancement, a process with essential involvement of Tiam1, Rac1, dynamin 2, and cortactin. 17704785_Fas antagonism by Met is abrogated in human fatty liver disease. 17804715_The tumor suppressor activity of GPx3 seems to relate to its ability to suppress the expression of c-met. 17981731_HGF and c-MET are potential orchestrators of invasive growth in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [review] 17992475_This study was designed to investigate the roles of HGF/c-Met in tumor progression and metastasis in HepG2 and Hep3B hepatoma cell lines 18024311_Co-expression of HGF and c-Met in gastric cancer may promote the progression of gastric cancer. 18025083_a novel mechanism by which plexin-mediated signaling can be regulated and explains how Sema4D can exert different biological activities through the differential association of its receptor with ErbB-2 and Met. 18053801_These results demonstrated that VPA inhibited two critical processes of tumor-stromal interaction, induction of fibroblastic HGF production and HGF-induced invasion of HepG2 cells. 18059365_cooperative role for c-Met and c-Myc in large-cell anaplastic medulloblastoma formation 18063891_HGF/c-Met were expressed in serum-starved ARPE-19 cells. 18093943_MET amplification occurs independently of EGFR(T790M) mutations in lung adenocarcinoma 18159174_The expression of c-met was closely related to the invasiveness of cholangiocarcinoma. 18172343_The expression rate of c-met was higher in adenocarcinomas than adenomas. 18180459_oncogenic EGFR and c-Met have roles in pathways mediating drug response 18187039_p100 MET, corresponding to the entire extracellular region of the MET receptor still spanning the membrane is able to bind HGF/SF and to prevent HGF-dependent signaling downstream of full MET, demonstrating its function as a decoy receptor. 18192688_Selectivity for specific adaptor protein involvement may be the key that determines the tissue- and cell-type specificity of Met-mediated tumorigenicity in human cancers 18258742_Src family kinases activity is important for the growth of colorectal cancer cell lines, although only low activity levels are required 18272501_a previously uncharacterized GM2/GM3 heterodimer complexed with CD82 inhibits cell motility through CD82-cMet or integrin-cMet pathway 18273647_Report renal expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and c-Met in children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. 18291418_NK1 variants have no detectable agonistic activity on, behave as bona fide receptor antagonists by blocking cell migration and DNA synthesis in target cells and have strong prospects as therapeutics for human cancer. 18316611_Met receptor contributes to trastuzumab resistance of Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cells 18379349_MET amplification associated with EGFR amplification is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 18395971_c-Met gene amplification is linked to metastatic progression, and is a viable target for a significant subset of advanced CRC. 18451158_A Met/c-Src-mediated signaling pathway is a mediator of EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation and cell growth in the presence of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 18451162_Usefulness of Frzb in modulating Met signaling as a new treatment strategy for soft tissue sarcomas. 18456660_the MET proto-oncogene and the downstream extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) are regulated by MicroRNA miR-199a* 18471412_High glucose can induce the expression of c-met, and Radix Astragali can up-regulate the expressions of c-met mRNA and protein in human kidney fibroblasts. 18495663_analysis of the hepatocyte growth factor-binding site in the immunoglobulin-like region of Met 18497076_Amplification of MET is associated with type I endometrial carcinoma tumors 18497953_overexpression of c-met is associated with gastric carcinoma 18504429_Met-driven invasive growth involves transcriptional regulation of Arhgap12. 18559601_The relative subcellular distribution of Met may be a valuable biomarker for estimating colon cancer prognosis. 18564920_identification of HGF/MET mutations in primary lymphedema, lymphedema/lymphangiectasia, and breast cancer-associated secondary lymphedema suggests that the HGF/MET pathway is causal or alters susceptibility for a broad range of lymphedema phenotypes 18578997_Disruption of lipid rafts inhibits the activation of PLCr1/PKC and PI3K/PKB signaling pathways by c-Met. 18593989_CXCR4 and c-Met are widely expressed in rhabdomyosarcoma and, at higher levels, in isolated marrow-infiltrating tumor cells 18625714_Phosphorylation of MUC1 by Met modulates interaction with p53 and MMP1 expression.( 18628208_the HGF/c-MET axis has a role in guiding stem cells toward brain injury 18628476_a novel splice variant of the Met receptor, Cgen-241A, is a potent antagonist of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-Met pathway 18636147_germline c-met missense mutation g.3522G--> A in exon 16 and somatic missense mutation g.3997 T-->C in exon 19 were identified in papillary renal cell carcinoma patients identified 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18709663_Mutations in the nonkinase regions of MET might play an important role in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. 18779368_STAT3 activation and nuclear accumulation in response to Hepatocyte Growth Factor requires nuclear-proximal activated c-Met. 18813782_HGF and c-Met have roles in growth of aggressive adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells 18819921_PTP1B and TCPTP play distinct and non-redundant roles in the regulation of the Met receptor-tyrosine kinase 18836087_MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitnib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients are reported. 18839537_The abnormal expression of c-met and PCNA protein was related with the oncogenesis of gastric carcinoma. 18930356_TFE3-renal carcinoma in an adult patient: a case with strong expression of phosphorylated hepatocyte growth factor (HGFR)/Met. 18938767_The epithelial expression of HGFR is elevated in mildly active UC. 18973760_Steric hindrance of the interaction between HGF beta domain binding to Met is sufficient for inhibiting full-length HGF-dependent Met signaling and cell migration. 18990695_ability of the leucine-rich repeat fragment to promote Met recycling could account for the increased cell motility induced by this ligand 18992144_c-Met kinase activity can up-regulate death receptor expression and thereby sensitize tumor cells to the death receptor ligand TRAIL 19002214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19002214_our findings provide further evidence that MET may play a role in autism susceptibility. 19006648_miR-34a has a role in tumor migration and invasion through modulation of the c-Met signaling pathway 19037978_a critical role of Met gene dose in non-small cell lung cancer , suggesting that Met may be a specific molecular therapeutic target in selected non-small cell lung cancer patients with increased Met copy number. 19050584_Perinuclear translocation of c-Met is confirmed in hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated cells; the increase in size of the 50 kDa subunit of c-Met may indicate the involvement of the [alpha]-chain in c-Met intracellular trafficking in chordoma cells. 19065669_The combination of CD151/c-Met is a novel marker in predicting the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and a potential therapeutic target. 19074879_This work identifies three miRNAs that negatively regulate MET expression. Inhibition of these endogenous miRNAs, by use of antagomiRs, resulted in increased expression of MET protein. 19096300_Activation of MET by gene amplification or by splice mutations deleting the juxtamembrane domain is associated with primary resected lung cancers. 19096301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19100682_MET receptor tyrosine kinase is a therapeutic anticancer target [review] 19107227_Ret/ptc1 cross talks with Met at transcriptional and signaling levels and promotes beta-catenin transcriptional activity to drive thyrocyte neoplastic transformation. 19109251_Distinct recruitment of Eps15 via Its coiled-coil domain is required for efficient down-regulation of the met receptor tyrosine kinase. 19117057_MET amplification is present in untreated NSCLC and EGFR mutation or MET amplification activates MET protein in NSCLC 19118941_NmU may be involved in the HGF-c-Met paracrine loop regulating cell migration, invasiveness and dissemination of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 19121849_c-Met plays an important role in bladder cancer development 19126036_Lack of oncogenic mutations in the c-Met catalytic tyrosine kinase domain in acral lentiginous melanoma 19139719_study determined PAX5 could regulate transcription of c-Met; the phospho-c-Met (active form) & PAX5 were both localized to the same intra-nuclear compartment in hepatocyte growth factor treated small-cell lung cancer cells and interacted with each other 19151767_MET as a target of YB-1 that work in concert to promote Basal-like breast cancers (BLBC) growth. 19165419_Expression of c-Met can be inhibited by RNA interference in flioma cells, which can inhibit the growth and metastasis of glioma cells and induce cell apoptosis. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19186126_molecular mechanism of activation and the functional role of cancer mutations in altering protein kinase structure, dynamics, and stability. 19190120_PTEN loss amplifies c-Met-induced glioblastoma malignancy. 19220894_C-met has a role in endometrial receptivity through its interaction with Plexin B1. 19255034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19255034_These results suggest that disrupted MET signaling may contribute to increased risk for autism spectrum disorder that includes familial gastrointestinal dysfunction. 19255323_MET increased gene copy number is an independent negative prognostic factor in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer 19297528_Met is processed in epithelial cells by presenilin-dependent regulated intramembrane proteolysis (PS-RIP) independently of ligand stimulation. 19302530_c-MET expression was observed in most spinal chordomas and correlated with the expression of CAM5.2, suggesting a relationship to an epithelial phenotype. 19318497_the relatively infrequent expression of HGF and Met in Wilms' tumor tumorigenesis reflects their roles in nephrogenesis, particularly the mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition, rather than a dependence on oncogenic signaling pathways. 19321255_SMYD3 has a role in regulation of c-Met expression and in cell migration and invasion induced by HGF 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19353596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19357348_The constitutive activation of nuclear Met-signaling pathway in MDA-MB231 cells, possibly determined at genetic or epigenetic levels of WWOX gene, might participate in breast carcinoma progression influencing invasive/metastatic phenotype. 19359592_HGF-induced activation of the Met receptor results in TF expression by MB cells and that this event probably contribute to tumor proliferation by enabling the formation of a provisional fibrin matrix. 19360663_data further support our hypothesis that genetic susceptibility impacting multiple components of the MET signaling pathway contributes to autism spectrum disorder risk 19380521_Combination of MET and EGFR inhibitors triggered stronger inhibition on cell proliferation and invasion of MPM cells than that of each in vitro. 19381876_EGFR T790M mutation and c-MET amplification can occur in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer with wild-type EGFR. These genetic defects might be related to different survival outcome. 19403030_HBx induces the expression of c-met through the activation of AP-2 and SP-1 activity at the promoter region in HepG2 cells. 19432801_CD44v6 is required for InlB-induced c-Met activation in Listeria invasion. 19433454_Decorin suppresses intracellular levels of beta-catenin, a known downstream Met effector, and inhibits Met-mediated cell migration and growth 19450681_An inverse relationship was found between generation of cytoplasmic fragment of MET protein and phosphorylation of MET protein, with a direct involvement of phosphorylated Tyrosine 1001 in protecting MET against its caspase cleavage. 19470725_Results show that blocking the HGF/c-Met pathway may be clinically useful for the treatment of HNSCC. 19471602_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19472090_MET protein is found to be highly expressed in alveolar soft part sarcoma patients, most commonly in the lower extremity (thigh, lower leg, and foot). 19483716_Data show that c-Met is the substrate of ST6Gal-I, and that the hyposialylation of c-Met can abolish cell motility in ST6Gal-I-KD HCT116 cells. 19490101_Results show that overexpression of miR-23b leads to uPA and c-met downregulation and to decreased migration and proliferation abilities of HCC cells. 19500853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19500853_Our data implicate the involvement of cMET in the pathogenesis of myopia in general, as well as more rapid progression in refractive error regardless of the initial refractory ability. 19502802_The downstream signaling in tumor cells overexpressing Met is not stably suppressed by Met tyrosine kinase inhibitors, even though Met remains fully inhibited. 19539981_Results demonstrated the presence of c-Met in osteogenic and chondrogenic tissues of developing human mandibles, which indicates possible functions for this receptor during mandibular development. 19546160_link between the PAR(2) and Met receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in promoting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell invasion. 19548256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19548256_the MET C allele influences at least two of the three domains of the autism triad 19549766_Urinary met may provide a noninvasive biomarker indicative of metastatic prostate cancer and may be a central regulator of multiple pathways involved in prostate cancer progression. 19556890_MACC1 acts via a specific consensus sequence of the Met promoter, described as an Sp1 binding site. 19567831_MET may play a critical role in the development of the most aggressive breast cancers and may be a rational therapeutic target. 19617568_Met induces mammary tumors with diverse histologies and is associated wi |
ENSMUSG00000009376 |
Met |
117.818402 |
6.5943135863 |
2.721222 |
0.255552366 |
110.547047 |
0.00000000000000000000000007435955522780294972642574990087826042201478308181356330752585548403768567204963346739532425999641418457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000820289263947960877185926179077645507848610673469639091699530920550643975364124571569846011698246002197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
210.7590264 |
31.1221237 |
31.7329082 |
3.9381323 |
| ENSG00000106004 |
3202 |
HOXA5 |
protein_coding |
P20719 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. Also binds to its own promoter. Binds specifically to the motif 5'-CYYNATTA[TG]Y-3'. |
Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. Methylation of this gene may result in the loss of its expression and, since the encoded protein upregulates the tumor suppressor p53, this protein may play an important role in tumorigenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3202; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; bronchiole development [GO:0060435]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell signaling involved in mammary gland development [GO:0060764]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060441]; intestinal epithelial cell maturation [GO:0060574]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lung goblet cell differentiation [GO:0060480]; lung-associated mesenchyme development [GO:0060484]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; mesenchymal-epithelial cell signaling [GO:0060638]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045647]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045639]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033599]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; respiratory system process [GO:0003016]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878]; trachea cartilage morphogenesis [GO:0060535] |
14701762_engineered a p53-mutant breast cancer cell line, Hs578T, to inducibly express HOXA5. Expression of HOXA5 can induce apoptosis through an apoptotic mechanism mediated by caspases 2 and 8. 15545268_loss of HOXA5 expression could lead to the functional activation of Twist resulting in aberrant cell cycle regulation and promoting breast carcinogenesis 15757903_analysis of transcriptional targets of HOXA5 by microarray hybridization 16379594_Hox A5 expression is inconsistent with an angiogenic phenotype; expression of Hox A5 may help to maintain existing vessels in a quiescent, differentiated state. 16756717_HOXA5 is a transcriptional regulator of hMLH1 in breast cancer cells 17167183_HOXA5 expression was maintained at stable levels at different reproductive stages of a woman's life, except during lactation. HOXA5 protein expression levels in breast carcinomas inversely co-relates with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor expression. 17785556_Study identified hypermethylation and gene inactivation of HOXA4 and HOXA5 was frequently observed (26-79%) in all types of leukemias studied. 17804711_HOXA5 acts directly downstream of RARbeta and may contribute to retinoid-induced anticancer and chemopreventive effects. 17957028_miR-130a is a regulator of the angiogenic phenotype of vascular endothelial cells largely through its ability to modulate the expression of GAX and HOXA5 18538349_The promoter methylation status of a panel of critical growth regulatory genes, RASSF1A, RARbeta2, BRCA1 and HOXA5, in 54 breast cancers and 5 distant normal breast tissues of Indian patients, was analyzed. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19554572_Epigenetic inactivation of Homeobox A5 gene is associated with nonsmall cell lung cancer. 19938081_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20846263_HOXA5 is hypermethylated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 20890077_The methylation percentage of HOXA5 in AML patients was higher than that of HOXA5 in control patients. 21311178_Androgen receptor mutations are associated with altered epigenomic programming as evidenced by HOXA5 methylation. 21546695_Studies suggest that HOXA4, HOXA5 and HOXB4 provide the spatial information needed to restrict the response to signals from the notochord, and not up regulated in pancreatic cancer. 22227861_since lower levels of HOXA5 predict poor prognosis, this gene may be a novel candidate for development of therapeutic strategies in OSCC. 22464764_HOXA5 can suppress keratinocytes growth and epidermal formation. 22876840_Our analysis showed that miR-196a suppressed the expression of HOXA5 both at the mRNA and protein levels; knockdown of HOXA5 expression in A549 cells using RNAi was shown to promote NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 25549794_Our findings present that decreased HOXA5 could be identified as a poor prognostic biomarker in nonsmall cell lung cancer and regulate cell proliferation and invasion 25585874_The NK AML patients with NPM1 mutations exhibited elevated HOXA4 methylation and expression levels of HOXA5 and MEIS1 compared with the NPM1 wildtype patients. 25875824_Ectopic expression of HOXA5 in highly invasive cancer cells suppressed cell migration, invasion, and filopodia formation in vitro and inhibited metastatic potential in vivo. 25979369_Among the mechanosensitive genes, the two transcription factors, HoxA5 and Klf3, contain cAMP-response-elements methylation of which could serve as a mechanosensitive master switch in gene expression in atherosclerosis. (Review) 25987065_Increased expression of HOXA5 is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 26219418_HOXA5-induced apoptosis was p53-independent. 26397212_Downregulation of HOXA5 by shRNA may trigger apoptosis and overcome drug resistance in leukemia cells. 26678341_In colon cancer, HOXA5 is downregulated, and its re-expression induces loss of the cancer stem cell phenotype, preventing tumor progression and metastasis. 26846409_high expression levels of HOXA5 mRNA and protein in children with ALL indicate that HOXA5 is closely associated with childhood ALL. 27052693_ATRA may inhibit the proliferation of K562 cells and promote apoptosis by upregulating the HOXA5 mRNA and protein expression. 27157614_loss of HOXA5 in mammary cells leads to loss of epithelial traits, an increase in stemness and cell plasticity, and the acquisition of more aggressive phenotypes. 27418136_lung cancer stem-like cells have plasticity under a condition of oxidative stress, and HOAX5 has a critical role in dedifferentiation 27960137_Knockdown of HOXA5 suppressed the proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell cancer cells. 28338293_HOXA5 could bind in the promoter of linc00312 and up-regulated the expression of it. 28423732_HOXA5 was identified as a tumor suppressor gene, which inhibited non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis by regulating cytoskeletal remodeling. Its expression is repressed by linc00673 through binding with EZH2. 28482119_The present study demonstrates that HOXA5 can be silenced in the psoriatic stratum corneum due to DNA methylation of the CGI located in the 5' region of HOXA5. 28833816_Research demonstrated that depletion of HOXA5 inhibited osteogenic differentiation and repressed cell proliferation by arresting cell cycle progression at the S phase via p16(INK4A) , p18(INK4C) , and Cyclin A in SCAPs, indicating that HOXA5 has a significant role in maintaining the proliferation and differentiation potential of dental-tissue-derived MSCs. 29174371_homeobox A5 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 were physically associated and appeared interdependent in activating PD-L1 transcription. Functional studies showed that HDAC8-mediated regulation of PD-L1 expression participated in modulating anti-melanoma T-cell responses. 29412790_The study demonstrated that MPP8 was associated with non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation through regulation of HOXA5. 29532406_HOXA5, HOXB6, and GLTP were direct target genes of MIR196B in CRC cells. 29632085_study implicates HOXA5 as a chromosome 7-associated gene-level locus that promotes selection for gain of whole chromosome 7 and an aggressive phenotype in glioblastoma. 30015922_Low HOXA5 expression is associated with Gastric cancer. 30046127_we demonstrate that HOXA3 and HOXA5 genes are markedly upregulated when NAP1L3 is suppressed in umbilical cord blood (UCB) haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Taken together, our findings establish an important role for NAP1L3 in haematopoietic stem cells homeostasis and haematopoietic differentiation. 30201235_LncRNA GAS5 depressed OA development by targeting miR-196a-5p and thereby down-regulating HOXA5 expression, providing substance for developing lncRNA-based strategies to treat OA. 30267809_HOXA5 functions as a tumor suppressor in regulating tumor growth of gastric cancer (GC) under regulation of miR-196a, supporting its potential utility as a therapeutic target for GC. 30483748_Study revealed that HOXA5 inhibits cervical cancer progression by regulating AKT/p27, proposing the potential role of HOXA5 in the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer. 30521886_HOXA5 overexpression in U2OS and MG63 cells markedly reduced cell survival and proliferation and elevated cell apoptosis and caspase-3 activity. 31159758_A novel transcript named HOXA5 short RNA could regulate colon cancer cell proliferation as a functional lncRNA both in vitro and in vivo. HOXA5 short RNA may have activated EGFR signaling in both colon cancer cell lines and xenograft tumors. 31779094_Study proposes that in progressive multiple sclerosis patients, the physiological spinal cord overexpression of HOXA5 combined with the age-dependent decline in AR ligands may favor the slow progression of TGFB1-mediated gliosis. 31959759_miR-130a and Tgfbeta Content in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from the Serum of Subjects at High Cardiovascular Risk Predicts their In-Vivo Angiogenic Potential. 32499530_HOXA5 inhibits the proliferation and neoplasia of cervical cancer cells via downregulating the activity of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and transactivating TP53. 32675397_MiR-196a promoted cell migration, invasion and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting HOXA5 in osteosarcoma. 32721103_Aberrant DNA methylation at HOXA4 and HOXA5 genes are associated with resistance to imatinib mesylate among chronic myeloid leukemia patients. 33136093_New insights in the clinical implication of HOXA5 as prognostic biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. 33414417_HOXA5 counteracts the function of pathological scar-derived fibroblasts by partially activating p53 signaling. 33461426_Homeobox A5 and A9 expression and beta-thalassemia. 33547267_An aging and p53 related marker: HOXA5 promoter methylation negatively correlates with mRNA and protein expression in old age. 34027794_Homeobox A5 activates p53 pathway to inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis of adrenocortical carcinoma cells by inducing Aldo-Keto reductase family 1 member B10 expression. 34098726_HINT1 (Histidine Triad Nucleotide-Binding Protein 1) Attenuates Cardiac Hypertrophy Via Suppressing HOXA5 (Homeobox A5) Expression. 34362486_[Effect of MiR-142-3p Targeting HOXA5 on Proliferation, Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis of Acute B Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells]. 34369713_MiR-301b-3p Promotes the Occurrence and Development of Breast Cancer Cells via Targeting HOXA5. 34646379_Interruption of neutrophil extracellular traps formation dictates host defense and tubular HOXA5 stability to augment efficacy of anti-Fn14 therapy against septic AKI. 35203377_Epigenetic Dysregulation of the Homeobox A5 (HOXA5) Gene Associates with Subcutaneous Adipocyte Hypertrophy in Human Obesity. 35219772_HOXA5 is amplified in glioblastoma stem cells and promotes tumor progression by transcriptionally activating PTPRZ1. 35370463_Expression Landscape and Functional Roles of HOXA4 and HOXA5 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000038253 |
Hoxa5 |
10.400283 |
0.2209180888 |
-2.178417 |
0.518102483 |
19.799522 |
0.00000860042040315139555927120146305853154444776009768247604370117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027194131351866880760489997292950192786520346999168395996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0084963 |
1.4058175 |
18.1987965 |
3.3828878 |
| ENSG00000106031 |
3209 |
HOXA13 |
protein_coding |
P31271 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific, AT-rich binding transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis.; FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. |
3D-structure;Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. Expansion of a polyalanine tract in the encoded protein can cause hand-foot-uterus syndrome, also known as hand-foot-genital syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3209; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis [GO:0060442]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic hindgut morphogenesis [GO:0048619]; endothelial cell fate specification [GO:0060847]; endothelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0001886]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; mesenchymal cell apoptotic process [GO:0097152]; mitotic nuclear division [GO:0140014]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell apoptotic process [GO:2001055]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030510]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to testosterone [GO:0033574]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281] |
11830496_a NUP98 primer and a degenerate primer corresponding to the third helix of the NUP98 was fused in-frame to HOXA13 in the patient with MDS(myelodysplastic syndrome). 11968094_A novel 2-bp deletion in the HOXA13 gene's highly conserved promoter region alters a key residue in the recognition helix of the homeodomain and is likely to perturb HOXA13's DNA-binding properties, resulting in both a loss and specific gain of function. 12073020_A novel stable polyalanine [poly(A)] expansion in the HOXA13 gene associated with hand-foot-genital syndrome: proper function of poly(A)-harbouring transcription factors depends on a critical repeat length? 12112533_The chromosome translocation t(7;11)(p15;p15) in acute myeloid leukemia results in fusion of the NUP98 gene with HOXA13. 14675924_There seems to be no evidence that isolated hypospadias is commonly caused by mutations in HOXA13. 17274802_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17935235_analysis of HOXA13 polyalanine expansion proteins in hand-foot-genital syndrome 18245445_Maintenance of appropriate HOX transcriptional program in adult fibroblasts may serve as a source of positional memory to differentially pattern the epithelia during homeostasis and regeneration. 18483557_In the absence of HOXA13 function, placental endothelial cell morphology is altered, causing a loss in vessel wall integrity, edema of the embryonic blood vessels, and mid-gestational lethality. 19145497_The expression of HOXA13 can be detected in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and is a negative independent predictor of disease-free survival. 19423998_Vaginal HOXA13 (homeobox A13) expression is diminished in women with pelvic organ prolapse compared with women with normal support 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19491265_results showed that HOXA13 expression enhanced tumor growth in vitro and in vivo, and was a negative independent predictor of disease-free survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 19591980_A novel mutation of HOXA13 in a family with hand-foot-genital syndrome. 21626505_Overexpression of HOXA13 mRNA is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 21829694_conclude that the non-conserved residue, V373 is critical for structurally recognizing TAA in the major groove, and that HOXA13 dimerization is required to activate transcription of target genes 21893383_Results provide an additional support to a hypothesis that HOXA13 might participate in the carcinogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 21971947_Hoxa9 and Hoxa13 are involved in the early and organised patterning of ENS development in the zebrafish model. 23376215_A total of 14 DNA sequence variations (10 novel and 4 known) within exonic and untranslated regions were detected in HOXA10 and HOXA13 among our cohorts of female genital malformations. 23532960_two de novo cases of hand-foot-genital syndrome associated with polyalanine expansions in HOXA13 were identified. 23592225_Validated HOXA13 as a novel prognostic marker in gastric cancer based on immunohistochemistry and statistical analysis. HOXA13 expression was significantly up-regulated in cancerous tissues compared with the corresponding non-cancerous mucosa. 24114970_Our study highlights the key role of HOTTIP and HOXA13 in hepatocellular carcinoma development. 24626613_the present study demonstrated that ANXA2 and SOD2 are potential target genes of HOXA13 and their coexpression predicts the poor prognosis of Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 25341685_serum HOXA13 may serve as a biomarker for early hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosing and predicting outcome. 25889214_HOTTIP/HOXA13 axis is a potential therapeutic target and molecular biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 26043692_study demonstrates that aberrant reduction of HOTTIP and HOXA13, which have a bidirectional regulatory loop, may play an important role in the pathogenesis of HSCR 26356815_HOXA13 promotes glioma progression in part via Wnt- and TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition 26485220_This pregnancy-maintaining regionalization of myometrial function may be mediated by HoxA13 26590955_Atypical hand-foot-genital syndrome and developmental delay due to de novo mutations in HOXA13 and NRXN1 26695677_Transfection of HOXA13 in HKCs could inhibit the degree of EMT induced by albumin-overload, possibly by increasing BMP-7 expression. 26982635_HoxA13 increases myometrial cell contractility by enhancing the secretion of IL-1beta, resulting in an up-regulation of CAP and other proinflammatory cytokine expression. 27064878_Down-regulation of HOTTIP and HOXA13 was associated with cell growth and cell cycle, and exerts tumor-suppressive functions in the genesis and progression of prostate cancer, providing a potential attractive therapeutic approach for this malignancy. 27108607_expression levels of HOTTIP and HOXA13 were both higher in gastric cancer which was poorly differentiated, at advanced TNM stages and exhibited lymph node-metastasis. Spearman analyses indicated that HOTTIP and HOXA13 had a highly positive correlation both in non-tumor mucosae and cancer lesions. Collectively, these findings suggest that HOTTIP and HOXA13 play important roles in gastric cancer progression. 27144338_Knockdown of HoxA13 caused the downregulation of long non-coding RNA HOTTIP and insulin growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) genes, indicating that both were targets of HoxA13. 27176855_HOXA13 is involved in HSAinduced EMT in HKC cells and upregulation of HOXA13 exerts a beneficial effect in EMT, which may be associated with the GR signaling pathway. 27830363_The results of our study show that high expression of HOXA13 is associated with the progression of bladder cancer and that HOXA13 might serve as a biomarker for prognosis of bladder cancer. 28384324_using both knockdown and knockout approaches we show that Hottip expression is required for activation of the 5' Hoxa genes (Hoxa13 and Hoxa10/11) and for retaining Mll1 at the 5' end of Hoxa. Moreover, we demonstrate that artificially inducing Hottip expression is sufficient to activate the 5' Hoxa genes and that Hottip RNA binds to the 5' end of Hoxa 28534516_Findings indicated that HOTTIP modulated HOXA13 at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels in ESCC cells. 28766961_HOXA13 is an unfavorable prognostic factor and a novel oncogene for prostate cancer. 28782268_Findings indicate that the recruitment of HOXA13-HOTTIP and HOXA13-HOTAIR to different sites in the BMP7 promoter is crucial for the oncogenic fate of human gastric cells. 28947713_Our study indicated that alteration of EPHA7 promoter transactivation produced by missensemutations of HOXA13 provided a molecular basis for HFGS. 29035381_Data suggest that patients with HOXA13-positive hepatocellular carcinomas experience worse overall survival than those with HOXA13-negative HCC; HOXA13 and HOTTIP (know regulator of HOXA13 expression) are expressed in the same neoplastic hepatocyte populations. (HOTTIP = long noncoding RNA HOTTIP) 29436749_Homeobox A13 (HOXA13) played a role of carcinogenesis through directly down-regulating dehydrogenase/reductase 2 (DHRS2) to increase proto-oncogene proteins c-mdm2 (MDM2). 29678634_prognostic value of HOXA13 in solid tumors 29757528_High HOXA13 expression was associated with inferior tumor regression grade and poor overall survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. HOXA13 increased cisplatin-resistance and promoted epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ESCC cells. 30550979_Significant decrease in the expression of the genes HOXA13 and COL3A in the uterosacral ligaments in advanced stages of prolapse, indicates that these gene expressions may play a role in the development of uterine prolapse. 30649340_Our data also reveal a specific role for Hoxa13 in the urogenital sinus, which is in part mediated by Gata3, as well as Hoxa13 requirement for the proper organization of the ureter. Finally, we provide evidence that Hoxa13 provides positional and temporal cues during the development of the lower urogenital system, a sine qua non condition for the proper function of the urinary system. 31957853_Downregulated long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of cardiomyocyte via miR-612/HOXA13 pathway in chronic heart failure. 32222541_Forced expression of HOXA13 confers oncogenic hallmarks to esophageal keratinocytes. 32444962_Knockdown of HOXA13 significantly suppressed cell proliferation of KIRC in vitro, increased the protein level of p53 and decreased the protein level of cyclin D1 in KIRC cells. Over-expression of HOXA13 had the opposite effects on KIRC cells. 32589328_Serum exosomal microRNA-766-3p expression is associated with poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32822724_HOXA13 promotes colon cancer progression through beta-catenin-dependent WNT pathway. 33629307_Long non-coding RNA UCA1 mediates proliferation and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating miR-185-5p/HOXA13 axis. 33896818_Homeobox-A13 acts as a functional prognostic and diagnostic biomarker via regulating P53 and Wnt signaling pathways in lung cancer. 34075028_IGF1-mediated HOXA13 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through upregulating ACLY and IGF1R. 34099670_HOXA13 in etiology and oncogenic potential of Barrett's esophagus. 34140506_3D genome alterations associated with dysregulated HOXA13 expression in high-risk T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 34979376_MiR-369-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by down-regulating HOXA13 expression. 35076814_Identification of a Novel circ_0010235/miR-1249-3p/HOXA13 Axis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000038203 |
Hoxa13 |
37.142793 |
0.1229806769 |
-3.023496 |
0.323358612 |
104.917349 |
0.00000000000000000000000127338095346623196398981607309689828924187251531335858035469709760318518521060582315840292721986770629882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000013511935926068715208800175610150617756308707337072369430244100267993201391902857722016051411628723144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0014745 |
1.7873996 |
65.5371705 |
7.4005394 |
| ENSG00000106066 |
54504 |
CPVL |
protein_coding |
Q9H3G5 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the digestion of phagocytosed particles in the lysosome, participation in an inflammatory protease cascade, and trimming of peptides for antigen presentation. |
Carboxypeptidase;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Zymogen |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a carboxypeptidase and bears strong sequence similarity to serine carboxypeptidases. Carboxypeptidases are a large class of proteases that act to cleave a single amino acid from the carboxy termini of proteins or peptides. The exact function of this protein, however, has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:54504; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; serine-type carboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004185]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20460425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21911749_genetic association studies in a Chinese population with type 2 diabetes: An SNP in CPVL (rs39059) is associated with diabetic retinopathy in a Chinese population of type 2 diabetic patients. |
ENSMUSG00000052955 |
Cpvl |
217.206960 |
0.3378792876 |
-1.565420 |
0.120874958 |
172.769979 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000183739840452072453872205170390424954723621428801298664996550805508788979626850800894278276265468932432894932915701247111428529024124145507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000030234114214856070223227146078758222281545732289936570536581275452328605171215474204559195892436486777232751421706780092790722846984863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
112.7872655 |
8.7823788 |
336.4964874 |
16.0916914 |
| ENSG00000106089 |
6804 |
STX1A |
protein_coding |
Q16623 |
FUNCTION: Plays an essential role in hormone and neurotransmitter calcium-dependent exocytosis and endocytosis (PubMed:26635000). Part of the SNARE (Soluble NSF Attachment Receptor) complex composed of SNAP25, STX1A and VAMP2 which mediates the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane. STX1A and SNAP25 are localized on the plasma membrane while VAMP2 resides in synaptic vesicles. The pairing of the three SNAREs from the N-terminal SNARE motifs to the C-terminal anchors leads to the formation of the SNARE complex, which brings membranes into close proximity and results in final fusion. Participates in the calcium-dependent regulation of acrosomal exocytosis in sperm (PubMed:23091057). Also plays an important role in the exocytosis of hormones such as insulin or glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23091057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26635000}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Exocytosis;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Neurotransmitter transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation;Williams-Beuren syndrome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the syntaxin superfamily. Syntaxins are nervous system-specific proteins implicated in the docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane. Syntaxins possess a single C-terminal transmembrane domain, a SNARE [Soluble NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein)-Attachment protein REceptor] domain (known as H3), and an N-terminal regulatory domain (Habc). Syntaxins bind synaptotagmin in a calcium-dependent fashion and interact with voltage dependent calcium and potassium channels via the C-terminal H3 domain. This gene product is a key molecule in ion channel regulation and synaptic exocytosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:6804; |
actomyosin [GO:0042641]; axon [GO:0030424]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a complex [GO:0070044]; synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a-complexin I complex [GO:0070032]; synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a-complexin II complex [GO:0070033]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; ATP-dependent protein binding [GO:0043008]; calcium channel inhibitor activity [GO:0019855]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; chloride channel inhibitor activity [GO:0019869]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; myosin head/neck binding [GO:0032028]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0045956]; positive regulation of catecholamine secretion [GO:0033605]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0001956]; positive regulation of norepinephrine secretion [GO:0010701]; protein localization to membrane [GO:0072657]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0010807]; response to gravity [GO:0009629]; secretion by cell [GO:0032940]; SNARE complex assembly [GO:0035493]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081]; synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0048488]; synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:0016079]; synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0031629]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
11719842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12114505_SNAP-25 traffics to the plasma membrane by a syntaxin-independent mechanism. 12198139_Munc18b binds to syntaxins 1A, 2, and 3 and regulates vesicle transport to the apical plasma membrane 12209004_CFTR channels are coordinately regulated by two cognate t-SNAREs, SNAP-23 (synaptosome-associated protein of 23 kDa) and syntaxin 1A. 12446681_interacts with CFTR protein differently from interactions with SNARE. 15175344_Syntaxin/Munc18 interactions in the late events during vesicle fusion and release in exocytosis 15202772_interacts with dopamine transporter 15219469_A significant genetic association was found between schizophrenia and an intron 7 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) tested. Haplotype analysis supported the association with several significant values that appear to be driven by the intron 7 SNP. 15316009_cleavage of APP but not syntaxin 1 is independent of cell surface regulation by extracellular ligands 15339904_Syn-1A binds both NBFs of SUR1 and SUR2A but appears to exhibit distinct interactions with NBF2 of these SUR proteins in modulating the KATP channels in islet beta cells and cardiac myocytes 16672225_Syntaxin-1A actions on sulfonylurea receptor 2A blocks acidic pH-induced cardiac K(ATP) channel activation 17032905_Norepinephrine transpossrter/syntaxin 1A complex rapidly redistributes, upon amphetamine treatment, when mechanisms supported by the transporter's NH2 terminus are eliminated. 17264080_analysis of the spatially distinct modes of munc18-syntaxin 1 interaction 17506992_the mechanisms involved in Syn1A-K(v) interactions vary significantly between K(v) channels, thus providing a wide scope for Syn1A modulation of exocytosis and membrane excitability 17543282_the H(abc) domain has a role in membrane trafficking and targeting of syntaxin 1A 17912268_A lower frequency of the PRM -352T allele of the STX1A gene in overweight/obese subjects impaires glucose regulation, particularly among individuals with combined glucose intolerance and overt diabetes. 17912268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18065728_We have identified a new three-gene classifier that is independent of and improves on stage to stratify early-stage NSCLC patients with significantly different prognoses. 18457912_The expression of the SNARE protein SNAP-25 and its cellular homologue SNAP-23, as well as syntaxin1 and VAMP (vesicle-associated membrane protein) in samples of normal parathyroid tissue, chief cell adenoma, and parathyroid carcinoma, was examined. 18512733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18512733_SNARE complex-related genes STX1A, VAMP2 and SNAP25 do not play a major role in susceptibility to schizophrenia in the Japanese population 18593506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18593506_STX1A might influence the serotonergic system during neurodevelopment 19004828_Direct interaction of otoferlin with syntaxin 1A, SNAP-25, and the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.3. 19129200_Homology with vesicle fusion mediator syntaxin-1a predicts determinants of epimorphin/syntaxin-2 function in mammary epithelial morphogenesis.( 19368856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19368856_This analysis revealed significant differences in both allele frequencies and genotype distributions of the STX1A gene in migraine. 19557857_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20385907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385907_We confirmed the involvement of syntaxin 1A in migraine susceptibility regarding rs941298. In addition, we found rs6951030 to also be associated in Portuguese migraine patients. 20422020_syntaxin 1A, a neuronal regulator of presynaptic vesicle release, may play a role in WS and be a component of the cellular pathway determining human intelligence. 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20564318_Results suggest that variants in RNASEL contribute to susceptibility to early onset and familial forms of prostate cancer. 21118708_association of STX1A with autism in a trio association study; in the anterior cingulate gyrus region, STX1A expression in the autism group was found to be significantly lower than controls; suggests a possible role of STX1A in pathogenesis of autism 21173146_ATP regulates pancreatic beta-cell K(ATP) channel activity, not only by its direct actions on Kir6.2 pore subunit, but also via ATP modulation of Syn-1A binding to SUR1. 21669024_Exocytotic dysfunctions in schizophrenia are probably related to an imbalance of the interaction between munc18-1a and SNARE (mainly syntaxin-1A) complex. 21789195_Recombinant alpha-SNAP-M105I has greater affinity for the cytosolic portion of immunoprecipitated syntaxin than the wild type protein. 21916482_Forming an acceptor SNARE complex between syntaxin-1A and SNAP-25 weakens but does not abrogate cholesterol-controlled cluster formation and indicates that the reconstitution process results in equal incorporation of protein at either lipid composition. 21976501_Syntaxin 1A effects may be additive but can be blocked at different concentration ranges of calmodulin, suggesting selective presynaptic targeting to directly regulate exocytosis. 22130660_A Ca(v)3.2/syntaxin-1A signaling complex controls T-type channel activity and low-threshold exocytosis. 22250207_Our results provide support for the hypothesis that STX1A represents a susceptibility gene for migraine 22264512_DrrA activation of the Rab1 GTPase on plasma membrane-derived organelles stimulated the tethering of endoplasmic reticulum-derived vesicles, resulting in vesicle fusion through the pairing of Sec22b with the plasma membrane syntaxin proteins. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22404429_Nesca directly binds KIF5B, kinesin light-chain and syntaxin-1 22411134_Direct interaction between syntaxin 1A and the Kv2.1 C-terminus is required for efficient insulin exocytosis and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. 22571925_The histone modification marks were significantly increased in bipolar disorder and major depression and this effect was correlated with significant increases in Syn1a gene expression. 22791290_Platelets deficient in Munc18b from a Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis type 5 had secretion defect. 23242284_In dementia with Lewy bodies patients there were lower levels of syntaxin in visual cortex compared to controls. 23403573_syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 cooperate as SNARE proteins to support neuron survival. 23572023_The clinical relevance of STX1A variants in CF 23801330_the preferential binding of CAPS1 to open syntaxin-1 can contribute to the stabilization of the open state of syntaxin-1 during its transition from 'closed' state to the SNARE complex formation. 23858467_N-peptide and LE mutation have no effect on the global conformation of the Munc18a-Syx1a complex. 24164654_no associaton with idiopathic generalized epilepsy was found regarding Intron 7 rs1569061 of Syntaxin 1A gene, MnlI rs3746544 and DdeI rs1051312 polymorphisms of SNAP-25 gene compared with healthy subjects 24218570_Prefusion structure of syntaxin-1A suggests pathway for folding into neuronal trans-SNARE complex fusion intermediate. 24375629_We described clinical, genetic, and functional data from 17 families with a diagnosis of benign familial neonatal epilepsy caused by KCNQ2 or KCNQ3 mutations and we showed that some mutations lead to a reduction of Q2 channel regulation by syntaxin-1A. 24429282_PIP2 affects islet beta-cell KATP channels not only by its actions on Kir6.2 but also by sequestering Syn-1A to modulate Syn-1A availability and its interactions with SUR1 on PM. 25445064_SNARE complex genes and their interactions may play a significant role in susceptibility and working memory of ADHD. 25803850_Blockade of the SNARE protein syntaxin 1 inhibits glioblastoma tumor growth. 26918652_Mislocalization of syntaxin-1 was found in pluripotent stem cells from epileptic encephalopathy patient. 27072493_Our results suggest that, as in the CNS, CADM1 interactions drive exocytic site assembly and promote actin network formation. These results support the broader hypothesis that the effects of cell-cell contact on beta-cell maturation and function are mediated by the same extracellular protein interactions that drive the formation of the presynaptic exocytic machinery. These interactions may be therapeutic targets for re... 27458546_A significant interactive two-locus model of STX1A_rs4363087|VAMP2_rs2278637 (presynaptic genes) was observed among SVC variants in all epilepsy cases. 28235601_Some Autism spectrum disorder patients had haploidy of STX1A gene and lower STX1A gene expression. 28722652_Analysing protein mobility, cluster size and accessibility to myc-epitopes the authors show that forces acting on the transmembrane segment produce loose clusters, while cytoplasmic protein interactions mediate a tightly packed state. 30916996_The N-terminal of the SNAP25 loop region binds with membrane, and this interaction induced a disorder-to-order conformational change of the loop, resulting in enhanced interaction between the C-terminal of the SNAP25 loop and syx-1. SNARE-complex assembly efficiency decreased when the electrostatic interaction between C-terminal of the SNAP25 loop and syx-1 was disrupted. 30976917_Using a case-control study to explore the association between STX1A gene and children with ADHD in Chinese Han population, our results suggest STX1A genetic variants might contribute to the susceptibility of children ADHD. 31192914_Results suggest a role of Stx-1A rs4717806 SNP in ischemic heart disease, possibly due to its influence in Stx-1A expression and, at cascade, to insulin secretion and to glucose dependent metabolism. 32059362_Syntaxin 1: A Novel Robust Immunophenotypic Marker of Neuroendocrine Tumors. 32815282_De novo STXBP1 mutation in a child with developmental delay and spasticity reveals a major structural alteration in the interface with syntaxin 1A. 33217562_Oligomeric alpha-Syn and SNARE complex proteins in peripheral extracellular vesicles of neural origin are biomarkers for Parkinson's disease. 34764822_Syntaxin-1 and Insulinoma-Associated Protein 1 Expression in Breast Neoplasms with Neuroendocrine Features. |
ENSMUSG00000007207 |
Stx1a |
176.383977 |
2.7003524794 |
1.433148 |
0.142973751 |
100.570765 |
0.00000000000000000000001142415697494329144617306266730579888335430318239731668217928721702908445578827922872733324766159057617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000116692426955130103985848048733883627699591679046750048354981867462787370470778114395216107368469238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
268.7533236 |
23.1766101 |
100.3841908 |
6.7337190 |
| ENSG00000106123 |
2051 |
EPHB6 |
protein_coding |
F8WCM8 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Kinase-defective receptor for members of the ephrin-B family. Binds to ephrin-B1 and ephrin-B2. Modulates cell adhesion and migration by exerting both positive and negative effects upon stimulation with ephrin-B2. Inhibits JNK activation, T-cell receptor-induced IL-2 secretion and CD25 expression upon stimulation with ephrin-B2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
ATP-binding;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Proteomics identification;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of transmembrane proteins that function as receptors for ephrin-B family proteins. Unlike other members of this family, the encoded protein does not contain a functional kinase domain. Activity of this protein can influence cell adhesion and migration. Expression of this gene is downregulated during tumor progression, suggesting that the protein may suppress tumor invasion and metastasis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:2051; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005003]; activated T cell proliferation [GO:0050798]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of T cell costimulation [GO:2000525]; type IV hypersensitivity [GO:0001806] |
11466354_Cross-linking of EphB6 alters profiles of lymphokine secretion, inhibits proliferation, induces Fas-mediated apoptosis of Jurkat leukemic T cells, and transduces signals into the cells via proteins it associates with. 12393850_interaction between EphB6 and its ligands facilitates T cell responses to antigen 12517763_EphB6 may play an important role in regulating thymocyte differentiation and modulating responses of mature T cells. 14612926_lower EphB6 expression has a role in melanoma progression to metastatic disease 15955811_EphB6 can both positively and negatively regulate cell adhesion and migration 16364251_The potential significance of EphB6 to serve as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator is discussed. 18754880_the two peptides derived from EphB6v might be appropriate targets for peptide-based specific immunotherapy for HLA-A2(+) patients with various cancers 18819711_CLL B-cells showed a more heterogeneous Eph/EFN profile, specially EFNA4, EphB6 and EphA10. EphB6 and EFNA4 were further related with the clinical course of CLL. 19234485_EphB6 receptor significantly alters invasiveness and other phenotypic characteristics of human breast carcinoma cells. 19513565_The kinase defective EPHB6 receptor tyrosine kinase activates MAP kinase signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. 20086179_Findings suggest a new role for EphB6 in suppressing cancer invasiveness and cell attachment through c-Cbl-dependent signaling. 20181626_The loss of EPHB6 expression in more aggressive breast carcinoma cell lines is regulated in a methylation-dependent manner. The EPHB6 methylation-specific PCR has clinical implications for the prognosis and/or diagnosis of breast and other cancer types 20952760_expression of more than 70 proteins was altered in EphB6-transfected MDA-MB-231 cells; proteins are involved in glycolysis, cell cycle regulation, tumor suppression, cell proliferation, mitochondrial metabolism, mRNA splicing, DNA replication and repair 21351276_Nonsynonymous variants of EPHB6 is associated with familial colorectal cancer. 21737611_results indicate that tumor invasiveness-suppressing activity of EPHB6 is mediated by its ability to sequester other kinase-sufficient and oncogenic EPH receptors 21811619_The alterations in miRNAs and their target mRNAs also suggest indirect involvement of EphB6 in PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. 21935409_Data found significant correlations between ephA2, ephA4, ephA7, ephB4, and ephB6 and overall and/or recurrence-free survival in large microarray datasets. 22039307_Our work shows that EphB3 is consistently expressed by malignant T lymphocytes, most frequently in combination with EphB6, and that stimulation with their common ligands strongly suppresses Fas-induced apoptosis in these cells. 24836890_We demonstrate that EphB6 reexpression forces metastatic melanoma cells to deviate from the canonical migration pattern observed in the chick embryo transplant model 24912672_Results suggest that erythropoietin-producing hepatocyte (Eph) receptor B6 (EphB6) may represent a useful tissue biomarker for the prediction of survival rate in colorectal cancers (CRCs). 25152371_EphB6 also interacts with the Hsp90 chaperone. 25239188_These findings implicate EphB6 as a negative regulator of EphA2 oncogenic signaling. 25331796_Studies clearly demonstrate an inverse relationship between the levels of phospho-ERK and the abundance of cadherin 17, beta-catenin and phospho-GSK3beta in EPHB6-expressing MDA-MB-231 cells. 26220827_Enhanced EphB6 expression was significantly associated with Thyroid Lesions. 26468391_EphB6 is a new biomarker for distinguishing high- and low-grade ovarian serous carcinoma, and may be a potential prognostic marker in ovarian serous carcinomas. 26617870_EphB6 protein may be used as a new marker for prognosis for tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 27145271_Study is the first to demonstrate that EphB6 overexpression together with Apc gene mutations may enhance proliferation, invasion and metastasis by colorectal epithelial cells. 27191502_Melanomas from geographically different regions in New Zealand have markedly different mutation frequencies, in particular in the NRAS and EPHB6 genes, when compared to The Cancer Genome Atlas database or other populations. These data have implications for the causation and treatment of malignant melanoma in New Zealand. 27418135_SRC kinase is a synthetic lethality partner of EPHB6 in triple-negative breast cancer cells 27788485_Authors provide evidence that an intrinsically kinase-inactive member of the Eph group of receptor tyrosine kinases, EPHB6, induces marked fragmentation of the mitochondrial network in breast cancer cells of triple-negative origin, lacking expression of the estrogen, progesterone and HER2 receptors. 28262839_using an EphB6 mouse knockout model we found that the loss of EphB6 does not initiate intestinal tumorigenesis and is not involved in the early tumor progression through the adenoma-to-carcinoma transition. 28453458_Data indicate that EphB6 protein was decreased in gastric carcinoma compared with normal mucosa. Analytic results based on pathological parameters suggests that EphB6 protein may inhibit metastasis of gastric carcinoma. 28826721_Low EPHB6 expression is associated with prostate cancer metastasis. 29116180_observations highlight a novel role for EphB6 in reducing drug resistance of T-ALL and suggest that doxorubicin treatment should produce better results if personalised based on EphB6 levels 29700392_It may be beneficial to enhance EPHB6 action concurrent with applying a conventional DNA-damaging treatment. 30262919_Analysis of the association of EPHB6, EFNB1 and EFNB3 variants with hypertension risks in males with hypogonadism. 31160603_This study demonstrated that EPHB6-mutated cells acquire cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) in association with CDH11 expression and RhoA/focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation. Targeted inhibition of EPHA2 or CDH11 reversed the acquired paclitaxel resistance, suggesting its potential clinical utility. 31241800_LncRNA DGCR5 regulates the non-small cell lung cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion through regulating miR-211-5p/EPHB6 axis. 32053275_Cataloguing the dead: breathing new life into pseudokinase research. 32754286_DNA methylation maintains the CLDN1-EPHB6-SLUG axis to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy and inhibit lung cancer progression. 32819434_The gut microbiota regulates autism-like behavior by mediating vitamin B6 homeostasis in EphB6-deficient mice. 33770085_Structure of the EphB6 receptor ectodomain. |
ENSMUSG00000029869 |
Ephb6 |
42.199499 |
0.2809393590 |
-1.831669 |
0.472900294 |
14.103948 |
0.00017298035718676748229323536509838277197559364140033721923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000458547067542508653918004180027878646797034889459609985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.4610639 |
5.5179592 |
59.1946002 |
13.5495745 |
| ENSG00000106211 |
3315 |
HSPB1 |
protein_coding |
P04792 |
FUNCTION: Small heat shock protein which functions as a molecular chaperone probably maintaining denatured proteins in a folding-competent state (PubMed:10383393, PubMed:20178975). Plays a role in stress resistance and actin organization (PubMed:19166925). Through its molecular chaperone activity may regulate numerous biological processes including the phosphorylation and the axonal transport of neurofilament proteins (PubMed:23728742). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10383393, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19166925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20178975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23728742}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Chaperone;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Host-virus interaction;Methylation;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Stress response |
|
This gene encodes a member of the small heat shock protein (HSP20) family of proteins. In response to environmental stress, the encoded protein translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and functions as a molecular chaperone that promotes the correct folding of other proteins. This protein plays an important role in the differentiation of a wide variety of cell types. Expression of this gene is correlated with poor clinical outcome in multiple human cancers, and the encoded protein may promote cancer cell proliferation and metastasis, while protecting cancer cells from apoptosis. Mutations in this gene have been identified in human patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and distal hereditary motor neuropathy. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:3315; |
axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; cornified envelope [GO:0001533]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; proteasome complex [GO:0000502]; spindle [GO:0005819]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein kinase C inhibitor activity [GO:0008426]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; anterograde axonal protein transport [GO:0099641]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902176]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:2001028]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038033]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; protein refolding [GO:0042026]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001932]; regulation of translational initiation [GO:0006446]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; retina homeostasis [GO:0001895] |
11740592_Phosphatase inhibitors prevent HSP27 dephosphorylation, destruction of stress fibrils, and morphological changes in endothelial cells during ATP depletion 11779227_Characterization of proteins associated with heat shock protein hsp27 in the squamous cell carcinoma cell line A431 11836590_HSP27 expression is cell differentiation and oral squamous cell carcinoma 12482203_in asthmatic subjects the basal epithelium cells express a high level of Hsp27 but no apoptotic morphology. 12489163_Expression of heat-shock protein 25 in dental pulp and enamel organ during odontogenesis in the rat molar. Hsp 25 is related to the formation and maintenance of the ruffled border of ruffle-ended ameloblasts and enamel-free-area cells. 12506142_Has specific actions in renal epithelia subjected to energy depletion, including interacting with actin to preserve architecture in specific intracellular domains. 12740362_Hsp27 has a role in regulating apoptosis through control of Akt activity 12838549_Maps to chromosome 7q11.23. Deletion may be resonsible for cognitive features of Williams syndrome. 12855565_Hsp27 is overexpressed in both dexamethasone resistant multiple myeloma cell lines and primary patient cells. 12917439_HSP27-dependent thermotolerance is suppressed by mumps virus infection through the destruction of STAT-1. 14715258_Taken together, our findings demonstrate that constitutively activated Stat3 up-regulates HSP27 and may facilitate phosphorylation of HSP27 at serine residue 78. 15013707_HSP27 expression was reduced in metaplasia and then significantly increased with neoplastic progresssion in Barrett esophagus. Gender-related differences were obnserved and HSP27 expression was higher in poorly-differentiated adenocarcinoma. 15122254_missense mutation in the gene encoding 27-kDa small heat-shock protein B1 (HSPB1, also called HSP27) that segregates in a family with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 15265704_HSP27 is involved in the UVC-resistance of human cells, at least those tested, possibly via functioning in nucleotide excision repair. 15272315_Hsp27 expression and cell survival are regulated by the POU transcription factor Brn3a 15274119_Results showed significant increases in expression and in HSP27 isoform numbers in renal cell carcinoma compared to normal kidney. 15542604_definition of the binding-competent oligomeric state of human Hsp27 15581903_wild-type protein forms smaller oligomers than previously believed, define the roles played by various structural domains in Hsp27 oligomerization 15649839_Hsp27 protects against cytotoxic effects induced by oxidative stress in cultured mammalian cells 15662019_HSP27, an ERbeta-associated protein, shows attenuated expression with coronary atherosclerosis and modulates estrogen signaling. 15728188_Ser(82) in the human heat shock protein Hsp27 is a novel substrate for PKD 15790570_MEK6E activates p38 and results in phosphorylation of its downstream substrate, heat shock protein 27 15806174_HSP25 downregulates PKCdelta, which is a key molecule for radiation-induced ROS generation and mitochondrial-mediated caspase-dependent apoptotic events. 15969449_particularly in conditions of enhanced oxidative stress, lymphomonocytes from liver disease patients present an increased expression of HSP27 16039988_Taken together, our results indicated that expanded ataxin-7 that leads to neurodegeneration significantly impaired the expression of Hsp27 and Hsp70 protein. 16087758_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16087758_One Hsp27 missense mutation, C379T, was detected in 4 autosomal dominant families with CMT disease type 2, and haplotype analysis indicated that the 4 families probably had a common founder. 16114012_Our results suggest that forms of stress that upregulate HSP27 and its phosphorylation may be useful as novel approaches to prevent adverse ocular effects arising from UV exposure in humans. 16126176_increased level of Hsp27 may reflect a dynamic process of the survived cells to unfold and remove mutant ataxin-3 16215937_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16215937_The first report of HSP27 gene mutation in Chinese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease , but it may be not common(0.90%). The C379T mutation in HSP27 gene also causes CMT2 except for distal hereditary motor neuropathy. 16240287_A tumor marker for hepatocellular hepatoma. 16339078_Hsp27 is an active participant in the (de)phosphorylation cascade controlling the activity of the splicing regulator SRp38. 16340246_findings provide a model system for the study of metastatic potential of tumors and are suggestive of an earlier unrecognized role for Hsp25 in tumor migration 16368711_A mutation in the small heat-shock protein HSPB1 leading to distal hereditary motor neuronopathy disrupts neurofilament assembly and the axonal transport of specific cellular cargoes. 16400691_Up-regulation of Hsp27 protein is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 16407830_Both MAPKAPK2 and HSP27 are necessary for TGFbeta-mediated increases in MMP-2 and cell invasion in human prostate cancer. 16436384_Hsp27 can exploit a large number of oligomerization states 16487519_Heat-shock protein 27 of endothelial cells is modified by methylglyoxal, which may contribute to changes in endothelial cell function associated to diabetes.. 16574891_Can be degraded by enzymes released from atherosclerotic plaques. May reflect proteolytic imbalance. Downregulation decreases vascular smooth muscle cell resistance to proteolytically-induced apoptosis. Might play role in prevention of plaque rupture. 16598774_KNG modulate bone marrow derived stromal/preosteoblast cell proliferation and suppress etoposide-induced apoptosis through ERK and HSP27 activation, respectively. 16624816_HSP25 and HSP70i activate HSF1 and have roles in inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation 16790501_Acidic pH exposure protects HEMEC through induction of Hsps and activation of MAPK and PI3 kinase pathway. 16840786_Data show that the suppression of NF-kappaB activation by Entamoeba histolytica in intestinal epithelial cells is mediated by heat shock protein 27. 16906418_Overexpression of HSP27 in Hep-2 cells confers chemoresistance which is associated with the delay in cell growth. 16923754_Hsp27 expression is increased in the normal-appearing vessel adjacent to carotid atherosclerotic plaque. 16935933_A mutation (S135F) in HSP27 that is also associated with these inherited peripheral motor neuron disorders showed increased interaction with wild-type HSP22 also, suggesting linkage of these two etiologic factors, HSP22 and HSP27, into one common pathway. 17004241_Exposure to low-level radiofrequency field up to 800 mW/kg does not induce phosphorylation of hsp27 or expression of hsp gene family. 17202147_HSP27 is required for both IL-1 and TNF-induced signaling pathways for which the most upstream common signaling protein is TAK1. 17206383_Plasminogen bound to hsps 27, 60, and 70 and Angiostatin predominantly bound to hsp 27 and to hsp 70 in a concentration- and kringle-dependent manner. 17213227_The muscle of patients undergoing haemodialysis undergoes some adaptive responses in total glutathione content, heat shock protein content and catalase activity that are potentially related to chronic oxidative stress. 17277149_Hsp27 regulates neutrophil chemotaxis and exocytosis 17342744_The function of CD10 in prostate cancer is largely unknown. In the C4-2 CaP cell line, CD10 was found to interact with both HSP27 and HSP70. 17350752_These data highlight an extranuclear interaction between ERbeta and HSP27 that may be of potential importance in modulating estrogen signaling. 17446863_Hsp27 facilitates actin-based Listeria monocytogenes motility through a phosphorylation cycle that shuttles actin monomers to regions of new actin filament assembly. 17522120_HSPs play a role in skeletal muscle recovery and remodeling/adaptation processes to high-force exercise 17570131_Neurotensin induces a striking increase in Hsp27 phosphorylation on Ser-82 in PANC-1 cells through convergent p38 MAPK, PKD, and PKD2 signaling. 17576382_Photodynamic therapy resistant HT29 cell variants are differentially sensitized to UVA compared with UVC due, in part at least, through the altered expression levels of BNip3, Hsp27 and mutant p53. 17597071_caspase-3 prodomain binding to heat shock protein 27 regulates monocyte apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 proteolytic activation 17616692_heat shock protein 27-mediated resistance to DNA damaging agents is inhibited by a novel PKC delta-V5 heptapeptide 17622316_These data suggest a potential dynamic and antagonistic interaction between HIV-1 Vpr and a host cell HSP27, suggesting that HSP27 may contribute to cellular intrinsic immunity against HIV infection. 17623484_This study suggests that the functional HSPB1 variant may represent a genetic modifier in the pathogenesis of motor neuron disease 17650072_Contributes to an increased chaperone capacity of cells by binding unfolded proteins that are hereby kept competent for refolding by Hsp70 or that are sorted to nuclear granules if such refolding fails. 17661346_HSP27 expression is modulated in concordance with migration dependent parameters in trophoblast cells. 17673262_activation of protein kinase C delta regulates the phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase 17823891_HSP-27 has the potential to redirect monocyte differentiation, derange dendritic cells (DC) and/or macrophage (Mphi)activation, and distort DC or Mphi interaction potential by altering receptor expression, signal transduction, or cytokine production. 17915561_During mitosis, HSF2 is bound to the HSE promoter elements of other heat shock genes, including hsp90 and hsp27, and the proto-oncogene c-fos. The presence of HSF2 is important for expression of these genes. 17916631_A novel pathway regulating human myometrial contraction at labor with HSP27 and alphaB-crystallin as potential targets for future tocolytic studies. 17928890_P38MAP kinase and HSP27 are phosphorylated in pemphigus skin 17949744_Alterations in HSP27 may give early evidence for intracellular differences in aortic aneurysm of patients with bicuspid aortic valve and tricuspid aortic valve. 17974989_These data identify novel nongenomic mechanisms involving androgen, AR, and Hsp27 activation that cooperatively interact to regulate the genomic activity of AR. 18007587_Hsp27 plays a protective role in regulating inflammatory responses in skin 18031542_In response to UBV irradiation, HSP27 in melanocytes translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. The HSP27 responses may provide some protective role against UVB-induced cell damage in the skin. 18066588_HSP27 identified as a differentiation and prognostic marker in neuroblastoma but not in Ewing's sarcoma 18089808_Hsp27 may play a general role in regulation of cellular senescence by modulating the p53 pathway. 18096692_hsp27 not only causes hormone resistance in New World primates but is also crucial to normal estrogen signaling in human cells. 18167130_Heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) was also verified as a downstream common activated protein of PKC beta-ERK(1/2) and PKC beta-p38 MAPK in hepatocellular carcinoma. 18167217_Hsp27 inhibits oxidative stress-induced H9c2 damage and inhibition of ROS generation and the augmentation of Akt activation may be involved in the protective signaling. 18320359_Beta-catenin co-immunoprecipitated with Hsp27B1 in breast cancer biopsy samples. Beta-catenin was coexpressed in the same tumor areas & in the same tumor cells that expressed Hsp27. 18344398_Here we report a novel mutation, G84R, in an elderly patient presenting with strikingly asymmetrical weakness. Expression of this and other known mutations in cell culture demonstrated enhanced aggregation of mutant HSPB1 protein compared with wild-type. 18390476_expression of phosphomimicking HSP27 was sufficient for retaining microfilament formation even when co-expressed with dominant-negative RhoA (EGFP-RhoN17). Thus, HSP27 activation is necessary for microfilament stability independently of RhoA activation 18418731_Sequential measurement intraoperatively of the levels of the heat shock proteins HSP70 and HSP27 in the cerebrospinal fluid can predict those patients who are at greatest risk for paralysis during thoracic aneurysm surgery. 18423118_HSP27 is highly expressed in K562/VCR cells, and the suppression of its expression by HSP27 ASO could enhance chemosensitivity of K562/VCR cells to vincristine. 18442089_HSP27 is a novel downstream effector of SPARC-regulated cell morphology and cell migration. 18465403_Hsp27, which is phosphorylated by MK2 in the MAPK pathway, protects epithelial cells from oxidant stress. 18472181_HSP27 regulates cell adhesion and invasion via modulation of focal adhesion kinase and MMP-2 expression. 18477563_phosphorylated heat shock protein 27 up-regulated the levels of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1, an inhibitory protein of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 18573886_Chaperone Hsp27 is a novel subunit that is itself an AU-rich elements (ARE)-binding protein essential for rapid ARE-mRNA degradation. 18587268_Ser135Phe mutation is associated with distal hereditary motor neuropathy type 2 phenotype in a large Korean family 18692580_Data report the expression patterns of HSP27 in the human testes and show differential expression during normal spermatogenesis, and altered expression abnormal spermatogenesis, suggesting that it may be related to the pathogenesis of male infertility. 18720982_Results reveal a novel post-translational modification of Hsp27 involving truncation of the N-terminal Met and acetylation of the penultimate Thr. 18800238_These results suggest that lower lymphocyte Hsp27 levels might be associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. 18832141_Mutations in the HSP27 (HSPB1) gene cause dominant, recessive, and sporadic distal HMN/CMT type 2. 18949417_HSP27 is closely connected with 5-FU resistance in colon cancer 18950704_Heat shock protein 27 physically interacts with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 and promotes ubiquitination. 18952241_K141Q mutation appears linked with the late-onset clinical phenotype as distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type II 19020532_induction of HSP27 in renal tubular cells protects against necrosis in vitro, but its systemic increase counteracts this protection by exacerbating renal and systemic inflammation in vivo. 19088045_findings show a significant association between low HSP27 expression and nonresponse to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in esophageal adenocarcinoma patients 19176359_RNA interference strategies confirmed the necessity for heat shock protein 27 to confer cytoprotection through a beta 2-adrenergic receptor agonist-initiated complex with beta-arrestin. 19214136_Serum HSP27 is increased in both chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma, and it should not be recommended as a diagnostic marker for pancreatic carcinoma. 19335999_The purified PEP-1-HSP27 fusion proteins can be transduced efficiently into neuronal cells and protect against cell death by enhancing mutant SOD1 activity. 19350847_Investigated serum contents of HSP27, HSP70 and HSP90 alpha; levels were significantly altered in patients suffering from COPD as compared to controls. HSP27 and HSP70 are potential novel serum markers for the diagnosis of COPD in the smoking population. 19373869_Modulation of HSP27 alters hypoxia-induced endothelial permeability and related signaling pathways. 19384818_Argpyrimidine-modification of Hsp27 is increased in diabetic failing heart. 19461484_Transfection of this human protein protects mice agains hepatiic ischemia and reperfusion injury. 19506078_These data suggest that n-6 dietary fatty acids stimulate a set of interactions that regulates cell adhesion through RhoA and ROCK II via a p38 MAPK-dependent association of HSP27 and p115RhoGEF. 19540014_downregulation of expression sensitizes lung adenocarcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 19597476_HSP27-induced HSF1 modification by SUMO-2/3 takes place downstream of the transcription factor phosphorylation on S303 and S307 and does not affect its DNA-binding ability 19643972_Low-to-negative HSP-27 protein expression in uveal melanoma correlates strongly with monosomy 3. 19656944_These results indicate that nuclear HSP27 can modulate SP1-dependent transcriptional activity to promote neuronal protection. 19675578_the DLK-ERK signaling pathway may act as a regulator of the interaction that occurs between Hsp27 and the cytoskeleton during the formation of the cornified cell envelope, a process conferring to the skin its crucial barrier function 19707199_Hsp-27 expression at diagnosis predicts poor clinical outcome in prostate cancer independent of ETS-gene rearrangement. 19767773_Hsp27 is a mediator of repression of androgen receptor function by PKD1 in prostate cancer cells. 19842058_HSP27 might be a potential biomarker for early diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring in the therapy of colorectal carcinoma. 19952398_There was no change in HSP27 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma following radiotherapy. 19955928_An immunological response to Hsp27 is increased in women with ovarian carcinoma. 19961396_Detection of serum HSP27 concentrations by ELISA may be useful for screening for gastric adenocarcinoma 20007907_This study aimed to investigate the localization of Hsp72, Hsp90, and Hsp27 in leukocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and age-matched control subjects. 20054128_procedure for obtaining diffraction-quality crystals of the alpha-crystallin domain of Hsp27 is presented. Initially, limited proteolysis was used to delineate the corresponding stable fragment (residues 90-171) 20093746_Data suggest that direct interactions between tumour and normal cells influence the expression of HSP27, HSP72 and MRP, and alter IL-6 and NO production. 20149037_phosphorylation of Hsp27 might be induced by p38 and ERK in placentas from patients with pre-eclampsia. 20178975_Increased monomerization of mutant HSPB1 leads to protein hyperactivity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy. 20209605_findings suggest that the p38 MAPK pathway plays a crucial role in miR-17-5p-induced phosphorylation of HSP27 and, as a consequence, phosphorylated HSP27 enhances the migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells 20231684_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20231684_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in HSPB1 promoter is asociated with lung cancer. 20299368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304146_Heat shock protein 27 is upregulated is a mediator of human esophageal epithelial cell proliferation and growth. 20363977_Heat shock protein 27 could act as an autoantigen of a streptococcal-induced autoimmune response and represents a target of the exaggerated T cell response in psoriasis. 20378850_In vascular smooth muscle cells, LDL modulates HSP27 phosphorylation and subcellular localization, affecting actin polymerization and cytoskeleton dynamics. 20382164_Lysine to arginine mutations of the identified SUMO acceptor sites drastically inhibited LEDGF/p75 SUMOylation and significantly increased its transcriptional activity on the heat shock protein 27 promoter. 20385876_Hsp27 is a critical regulator of normal CD8-positiveCD57-positive lymphocytes' lifespan; Hsp27 expression is significantly lower in CD8positiveCD57positive lymphocytes than in CD8positiveCD57negative cells. 20410505_Data suggest that HSP27 plays a role in the fine-tuning of terminal erythroid differentiation through regulation of GATA-1 content and activity. 20439495_These results identify a conserved and novel function for Hsp27 with potential as a target for interrupting signaling from estrogen receptor alpha and androgen receptors to tumor biology in hormone-responsive cancers. 20462503_Constitutive expression of HSP25 may prevent ectopic expression of tyrosine hydroxylase in zebrin II immunopositive Purkinje cell subsets. 20491124_Interaction of the wild type (wt) heat shock protein Hsp27 and its three-dimensional (3D) mutant (mimicking phosphorylation at Ser15, 78, and 82) with rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase (PhK) has been studied under crowding conditions. 20514530_This review will focus on the role of HspB1 in the retina, emphasizing effects on retinal ganglion cells. 20540527_Data show that siRNA knockdown of Hsp27 decreased metastatic behaviors of UM-SCC-22B by 3- to 4-fold in migration and 2-fold in cell invasion reducing cell invasion and migration to levels similar to the primary HNSCC UM-SCC-22A. 20557877_increases lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in macrophages 20694452_Studies indicate HSP90, HSP70, HSP27 interact directly or indirectly with the proteasome, assuring quite selectively the proteasomal degradation of certain proteins under stress conditions. 20694586_High gene expression of Hsp27 is associated with leukemia. 20714862_Plasma Hsp27 levels were increased in coal miners compared to non-coal miners. 20863832_Over-expression or knockdown of HSPB1, a related sHSP, affects the solubility, stability, and degradation of aggregation-prone CryAB mutants. 21081267_These results provide evidence that the expression of hsp27 and its phosphorylation by p38-mitogen-activated kinases are required for keratinocyte differentiation and for the formation of a regularly stratified epidermis. 21084594_In transgenic heat shock protein 27 mice increased levels of tau protein were found in hippocampus with reduced levels in wild-type mice. 21107776_The present findings indicate that serum anti-Hsp27 titers may be associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease. 21119665_High HSP27 expression in the cytoplasm is associated with uterine cervix carcinogenesis. 21208199_A marked elevation in HSP27 levels is observed during the relapse phase in patients with multiple sclerosis. 21245386_These results suggest that the p38 MAP kinase (MAPK)-MK2-Hsp27 signaling axis may target AUF1 destruction by proteasomes, thereby promoting AU-rich element mRNA stabilization. 21335933_increased expression level of Hsp27 might be correlated with the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. 21423207_report the isolation and characterization of Hsp27-targeted molecules interfering with its structural organization 21427224_Data show that osteocalcin synthesis was significantly reduced in the stable HSP27-transfected MC3T3-E1 cells and normal human osteoblasts. 21469165_Small heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) and superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] were down-regulated while cofilin-1 was up-regulated significantly in keratinocytes in response to the chemical challenge. 21514288_In this review, we will focus on the possible protective and immuno-modulatory roles of Hsp27 in atherogenesis with special emphasis on their changes following acute coronary events and their potential as diagnostic and therapeutic targets 21566277_HSP27 expressed higher in the right sided colon cancer than in the left sided colon cancer. 21585617_Proteomics showed that the expression of Hsp27 and cyclophilin A was upregulated in smokers, and this upregulation was particularly marked in COPD smokers. 21641913_Nevertheless, in solution, both alpha-crystallin domain proteins form stable dimers via the symmetric antiparallel interaction of beta7 strands. 21670152_results suggest that sequestration of oligomers by HspB1 constitutes a novel cytoprotective mechanism of proteostasis 21679777_Hsp27 is degraded through the autophagic pathway and that Hsp27 may have a protective role in myoclonic epilepsy associated with ragged-red fibers syndrome cells 21731611_Overexpression of HSPB1, as well as HSPB6, HSPB7 and HSPB8 independently protect against tachycardia remodeling by attenuation of the RhoA GTPase pathway at different levels. 21784846_HSF-1 inhibition and depletion of Hsp27 is a trigger, at least in part, for the accumulation of transcriptionally active mutant p53, which can either directly or NF-kappaB-dependently induce an MDR1/P-gp phenotype in MCF-7 cells. 21888831_Hsp27 inhibits cisplatin- induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell death through autophagy activation. 21909836_High serum HSP27 levels were associated with better nerve function and fewer neuropathic signs in persons with normal glucose tolerance, impaired glucose tolerance, and type 2 diabetes. 21931298_both high glucose and Ang II contribute to HSPB1 upregulation. 21937138_The CG/GG genotypes of HSPB1 rs2868371 were associated with lower risk of RIET, compared with the CC genotype in patients with NSCLC treated with radio(chemo)therapy. 21961414_higher concentration of HSP 27 in adjacent distal normal mucosa can be a response to stress factors related with metabolic changes of colorectal adenocarcinoma tissues or can be a protective function to stress factors of the tumour. 21967197_degradation of ubiquitinated HSP27 through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway mediated by SMURF2 21983720_The R127W mutant of HSPB1 may have reduced capacity to serve as a chaperone to prevent aggregate formation. 21989268_phosphorylated HSPB1 may play an important role in 5-FU resistance. 22004109_This study suggests a role for HSP27 as a prognostic and predictive marker in pancreatic cancer. 22019951_high anti-Hsp-27-antibody levels in obese-subjects without established coronary disease may be related to a heightened state of immunoactivation associated with obesity 22023707_Hsp27 participates in the maintenance of breast cancer stem cells through regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition 22031759_the results highlight a novel role for RSK1/2 and HSP27 phosphoproteins in P. aeruginosa-dependent induction of transcription of the IL-8 gene in human bronchial epithelial cells. 22031878_The results of this study could confirm the enhanced interaction of mutant HSPB1 with tubulin. Increased stability of the microtubule network was also clear in neurons isolated from these mice. 22032827_provide evidence for elevated HSP27 concentrations in serum and urine and increased HSP70 excretion levels in patients suffering from CKD 22050627_melatonin enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis via the inactivation of ERK/p90RSK/HSP27 cascade 22057845_Studied three Hsp27 truncation variants to assess the functional contributions of the nonconserved N- and C-terminal sequences. 22114076_Loss of the EGF-like module suppresses the enhanced HSP27 protein stability conferred by SPARC. 22176143_We studied the HSPB1 and HSPB8 mutation occurrence in patients with distal hereditary motor neuropathy and those with the axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 22179576_Hsp27 silencing suppresses proliferation by causing PEA-15 to bind and sequester extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), resulting in reduced translocation of ERK to the nucleus. 22185976_Silencing Hsp25/Hsp27 gene expression augments proteasome activity and increases CD8+ T-cell-mediated tumor killing and memory responses 22210387_Subunit exchange kinetics leading to HspB1-HspB5 or HspB4-HspB5 hetero-complex formation revealed that HspB5 exchanges more rapidly subunits with HspB1 than with HspB4. 22238643_Knock down of heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) induces degradation of several putative client proteins. 22264079_This first structural analysis of human small Hsp27 (HspB1) dissociation supports a model of chaperone activity wherein unstructured and highly flexible regions in the N-terminal domain are critical for substrate binding. 22272318_Data show that among the three small heat shock proteins, Hsp27, alphaA- and alphaB-crystallin, the R12A mutation improved the chaperone function of only alphaA-crystallin. 22350794_the key contribution of HSPB1-VEGF interactions in the balance between physiological and pathological angiogenesis. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22362414_HSP27 is involved in the regulation of androgen receptor mRNA in prostate cancer cells. 22465083_data suggest that serum HSP27 levels might serve as a possible tool to discriminate between early and advanced stages of non-small cell lung cancer 22521462_Overexpression of HSPB1 in neurons is sufficient to cause pathological and electrophysiological changes in transgenic mice that are seen in patients with hereditary motor neuropathy. 22534325_Data suggest that higher levels of HSP27 in tumor tissue from patients with epithelial ovarian cancer are associated with peritoneal metastasis; thus, tumor HSP27 level may be useful prognostic marker of poor survival. 22535481_High HSP70 and HSP27 expression is associated with worse clinical outcome in colon cancer. 22569359_This study demonistrated that Overexpression of human HSP27 protects sensory neurons from diabetes 22608953_results demonstrate significant associations between overall survival and SNPs in HSPB1 rs2868371 in USA patients with NSCLC after radio(chemo)therapy. 22647853_the involvement of LEDGF-mediated elevated expression of Hsp27-dependent survival pathway(s) in prostate cancer 22677112_TDP plays apoptosis-inducing roles by strongly suppressing the Hsp27 expression that is specifically associated with the mitochondrial death of the caspase-dependent pathway 22734906_we present a family with a novel mutation in the C-terminus of HSP27 (p.Glu175X) with a motor predominant distal neuropathy but with definite sensory involvement compatible with axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 22742457_our results demonstrate that p-HSP27 provides significant protection when cells are exposed to different stresses in the cell model of MERRF syndrome 22886594_HSP27 expression in gastric mucosae is inversely correlated with intraepithelial neoplasia, a probable precursor to gastric cancer, and HSP27 expression in cancer is positively correlated with poor differentiation. 22887120_HSPB1 is an intracellular antiviral factor against hepatitis B virus. 22907762_Hsp27 downregulated cells showed a significant increased MW 76 and 55 kDa PTEN forms and immunoprecipated with PTEN protein in cytoplasm. 22971995_Tubular expression of heat-shock protein 27 inhibits fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy. 22974980_These results suggest that Hsp27 dissociates from cytochrome c following PKCdelta-mediated phosphorylation at Ser78, which allows formation of the apoptosome and stimulates apoptotic progression. 22982087_HSP27 expression in colorectal cancer was strongly associated with the co-presence of wildtype KRAS and activated PI3K/AKT, indicating a possible role of HSP27 in overcoming PI3K/AKT induced oncogene induced senescence in tumours. 22993064_The HSP27 proteins suppress the increase in thioflavin T fluorescence associated with SOD1 aggregation, primarily through inhibiting aggregate growth, not the lag phase in which nuclei are formed. 23026841_Phosphorylation of HSP27 at Ser-78 is correlated with the acceleration of platelet aggregation induced by ADP in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. 23080524_Increased HSP 27 expression and associated improved right ventricle function and systemic perfusion supports a cardio-protective effect of HSP 27 in cyanotic tetralogy of Fallot. 23155000_HSP27 mediated F508del CFTR degradation is linked to its SUMOylation and to RNF4-mediated targeting to the ubiquitin-proteasome system. 23165430_Our data indicate CpG methylation of the first HSPB1 intron to be an important biomarker that identifies aggressive prostate cancers otherwise regarded as low risk 23185379_activation of PP2A or inactivation of the p38MAPK-MAPKAPK2-Hsp27 has a role in survival of cancer stem cells under hypoxia and serum depletion via decrease in PP2A activity 23264215_Hsp27 could have an impact on tumor malignancy. 23357534_The phosphorylated Hsp27 attenuates Dox-induced cell toxicity by regulating the transcriptional activity of p53 and up-regulating p21, which leads to the cell cycle arrest and cell survival. 23374503_We found that the CC genotype of HSPB1 rs2868371 was associated with higher risk of severe (grade >=3) RP in patients with NSCLC treated with radiation (chemo) therapy. 23404246_These results support the theory that Hsp27 plays a contributory role in the pathogenesis of pediatric AML-M4/M5. Therefore, Hsp27 may be exploited as a new target for enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs against leukemia. 23425286_Both HSP27 and HSP70 impact on the |
ENSMUSG00000004951 |
Hspb1 |
1014.598315 |
0.3911305859 |
-1.354278 |
0.061353371 |
488.570174 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000291693614754992847468925916492084346363935149373719663026715775869021497438699729049142555810336757637050840015717709566045453318800401703955172440905461958424357507785504083802814257748844799237797997610110173481819534157 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000135389866471185368239287825179054896596437767436088165135159214595022598200958622887440075950725359348337310780545132069053041314465352556848763438429326135802262191279765313254136283386319272742581799772836615959183158560 |
Yes |
No |
576.3398188 |
20.8337992 |
1483.7560271 |
34.6933538 |
| ENSG00000106244 |
11333 |
PDAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q13442 |
FUNCTION: Enhances PDGFA-stimulated cell growth in fibroblasts, but inhibits the mitogenic effect of PDGFB. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a phosphoprotein that may upregulate the PDGFA-stimulated growth of fibroblasts and also downregulate the mitogenicity of PDGFB. The encoded protein in rodents has been shown to bind PDGFA with a low affinity. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:11333; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
27448842_PDAP-1 as an effecter of PDGF signaling in glioma cells 29656114_AG1024+U0126 acted synergistically to downregulate 'synergy' genes, especially STAT6 and PDAP1, which displayed significant expression codependency and a common expression pattern linked with other key 'synergy' genes, supporting their predicted role in an STAT6-ERK-nuclear factor kappa beta (NF-kappaB) network. Daunorubicin and PDAP1 loss were synergistic, so PDAP1 is important for the response to this anthracycline. 35143476_RFX transcription factors control a miR-150/PDAP1 axis that restrains the proliferation of human T cells. |
ENSMUSG00000029623 |
Pdap1 |
483.771507 |
2.0470671900 |
1.033558 |
0.235474313 |
18.735516 |
0.00001501595680182038125820981333546910718723665922880172729492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000046078071183964411752006368194756191769556608051061630249023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
603.8834710 |
96.1033435 |
295.7271593 |
34.1478014 |
| ENSG00000106266 |
29886 |
SNX8 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5X2 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in several stages of intracellular trafficking. May play a role in intracellular protein transport from early endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19782049}. |
Endosome;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity and phosphatidylinositol binding activity. Involved in early endosome to Golgi transport and intracellular protein transport. Located in early endosome membrane. Colocalizes with retromer complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:29886; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; early endosome to Golgi transport [GO:0034498]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886] |
21973056_SNX4, but not SNX1 and SNX8, is associated with the Rab11-recycling endosomes and that a high frequency of SNX4-mediated tubule formation is observed as endosomes undergo Rab4-to-Rab11 transition. 24311514_SNX8: A candidate gene for 7p22 cardiac malformations including tetralogy of fallot. 29180417_SNX8 mediates IFNG-triggered non-canonical signaling pathway and host defense against Listeria monocytogenes. 34231239_Fatty Acid Synthase-Suppressor Screening Identifies Sorting Nexin 8 as a Therapeutic Target for NAFLD. 34524084_A PX-BAR protein Mvp1/SNX8 and a dynamin-like GTPase Vps1 drive endosomal recycling. |
ENSMUSG00000029560 |
Snx8 |
207.461830 |
2.1202413073 |
1.084228 |
0.139616019 |
59.954188 |
0.00000000000000970911943864748652464446997758702953963509674206733279788750223815441131591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000065228312660189756736536915845817681341121951898998077012947760522365570068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
266.0351135 |
26.3286863 |
126.6066273 |
9.3338138 |
| ENSG00000106404 |
24146 |
CLDN15 |
protein_coding |
P56746 |
FUNCTION: Claudins function as major constituents of the tight junction complexes that regulate the permeability of epithelia. While some claudin family members function as impermeable barriers, others mediate the permeability to ions and small molecules. Often, several claudin family members are coexpressed and interact with each other, and this determines the overall permeability. CLDN15 forms tight junctions that mediate the paracellular transport of small monovalent cations along a concentration gradient, due to selective permeability for Na(+), Li(+) and K(+) ions, but selects against Cl(-) ions. Plays an important role in paracellular Na(+) transport in the intestine and in Na(+) homeostasis. Required for normal Na(+)-dependent intestinal nutrient uptake. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12055082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:13129853}. |
Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Ion transport;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the claudin family. Claudins are integral membrane proteins and components of tight junction strands. Tight junction strands serve as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space between epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, and also play critical roles in maintaining cell polarity and signal transductions. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:24146; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; calcium-independent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell-adhesion molecules [GO:0016338]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; ion transport [GO:0006811] |
27869798_Data show that alterations in myosin light chain kinase activity, claudin-15 and claudin-2 expression are associated with gluten-induced symptomatology and intestinal permeability changes in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). 28863193_analysis of claudin-15 tight junction paracellular architecture by molecular dynamics simulations 31605016_Differential regulation of claudin-2 and claudin-15 expression in children and adults with malabsorptive disease. 32469152_Twist1 accelerates tumour vasculogenic mimicry by inhibiting Claudin15 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. 34131154_CLDN15 is a novel diagnostic marker for malignant pleural mesothelioma. 35650657_Tight junction channels claudin-10b and claudin-15: Functional mapping of pore-lining residues. 36114674_Unique structural features of claudin-5 and claudin-15 lead to functionally distinct tight junction strand architecture. |
ENSMUSG00000001739 |
Cldn15 |
47.250033 |
0.2457887681 |
-2.024509 |
0.293608878 |
49.915559 |
0.00000000000160506799396927273522757678952103564326558959862722986144945025444030761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000009408579662822266102836239387515626002647661785260879696579650044441223144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.8185084 |
4.2835836 |
73.1515722 |
11.1618118 |
| ENSG00000106479 |
643641 |
ZNF862 |
protein_coding |
O60290 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity and protein dimerization activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:643641; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
35142290_A novel gene ZNF862 causes hereditary gingival fibromatosis. |
|
|
177.605274 |
0.3187187862 |
-1.649644 |
0.275533200 |
34.500138 |
0.00000000426221031654499240264617274521856404856379185730475001037120819091796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000019250374624297458347097590026023028464408071158686652779579162597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
81.8750850 |
16.0091971 |
258.6313504 |
35.7655437 |
| ENSG00000106484 |
4232 |
MEST |
protein_coding |
Q5EB52 |
|
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily. It is imprinted, exhibiting preferential expression from the paternal allele in fetal tissues, and isoform-specific imprinting in lymphocytes. The loss of imprinting of this gene has been linked to certain types of cancer and may be due to promotor switching. The encoded protein may play a role in development. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been identified for this gene. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on the short arm of chromosomes 3 and 4, and the long arm of chromosomes 6 and 15. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:4232; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498] |
9192843_MEST gene is imprinted, with preferential expression from the paternal allele in fetal tissues. 10631159_MEST gene is imprinted in an isoform-specific manner in adult lymphocytes. 11754049_Findings suggest that PEG1/MEST can be excluded as a major determinant of Silver-Russell syndrome. 11821432_An imprinted PEG1/MEST antisense expressed predominantly in human testis and in mature spermatozoa. 11920156_Mutation screening and imprinting analysis of candidate genes for autism in the 7q32 region 12023987_a novel mechanism /promoter switch/ leading to biallelic expression in invasive breast cancer 12095916_An intron contains a sequence, MESTIT1, which is transcribed only from the paternal allele, may be involved in MEST regulation 15547750_Lof imprinting of PEG1/MESTOI may be related to tumorigenesis and malignant transformation, especially in NSCLC 16338457_PEG1 isoform 2 is in fact imprinted in a large subset of human placentae. 17450433_Hypermethylation of paternally expressed genes including PEG1/MEST, which have growth-promoting effects, may be relevant to low birth weight in subjects conceived by assisted reproduction techniques. 18585117_Type of epimutation at the PEG1/MEST locus does not play a relevant role in Silver-Russell syndrome. 18644838_MEST is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi apparatus where its putative enzymatic properties as a lipase or acyltransferase, predicted from sequence homology with members of the alpha/beta fold hydrolase superfamily. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20339302_data demonstrated that tumorigenesis of leiomyoma is associated with overexpression of isoform 1 of PEG1/MEST gene, but not with loss of imprinting of the gene 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21575949_Regardless of conception method, the PEG1 methylation percentage in chorionic villus from spontaneous abortions is significantly higher than in villus from induced abortions and multifetal reduction. 22249249_Data indicate that ARMCX2, COL1A1, MDK, MEST and MLH1 genes acquired methylation in drug-resistant ovarian cancer-sustaining (side population) cells. 22456293_In cortices, the MEST promoter was hemimethylated, as expected for a differentially methylated imprinting control region, whereas the COPG2 and TSGA14 promoters were completely demethylated, typical for transcriptionally active non-imprinted genes. 22531794_MEST showed tissue-specific imprinting, being paternally expressed in skeletal muscle, fat, pituitary gland, heart, kidney, lung, stomach and uterus, and maternally expressed in spleen and liver. 23209187_These results support the idea that intrauterine exposure to gestational diabetes mellitus has long-lasting effects on the epigenome of the offspring. 23229728_The expression levels of miR-335 significantly correlated with those of MEST, supporting the notion that the intronic miR-335 is co-expressed with its host gene 23343754_DNA methylation level at the H19 and MEST differentially methylated regions (DMRs)is reduced in placentas from pregnancies conceived by IVF/ICSI when compared with placentas from spontaneous conception. 23415968_Paternal methylation aberrations at imprinting control regions of DLK1-GTL2, MEST (PEG1), and ZAC (PLAGL1) and global methylation levels are not associated with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous miscarriages. 23775149_altered DNA methylation at imprinted domains including IGF2/H19 and PEG1/MEST may mediate the association between human papillomavirus infection and invasive cervical cancer 27697227_strongly expressed in invasive extravillous trophoblasts during the first trimester 28052120_G4 formation at motifs not previously identified through bioinformatic analysis of the MEST promoter, is reported. 28854270_Some growth-regulating imprinted genes such as MEST and MEG3, are susceptible to non-imprinted allele during development and differentiation, whereas the intergenic differentially methylated region of others (i.e. PEG3) are strictly maintained. 29157033_We conclude methylation changes at some CpG sites of MEST and DLK differentially methylated regions in preeclamptic group 29721103_Study provides evidence that MEST mediates the impact of prenatal bisphenol A exposure on long-term body weight development in offspring by triggering adipocyte differentiation. 30707743_Imprinting methylation in SNRPN and MEST1 in adult blood predicts cognitive ability. 30903102_MEST induces Twist-1-mediated EMT through STAT3 activation in breast cancers. 31574234_Long intergenic noncoding RNA (LINC00) 284 (LINC00284) is involved in angiogenesis during ovarian cancer (OC) development by recruiting nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB1) and down-regulating mesoderm-specific transcript (MEST). 32241207_The effect of folic acid deficiency on Mest/Peg1 in neural tube defects. 32375885_The sperm epigenome does not display recurrent epimutations in patients with severely impaired spermatogenesis. 34560900_MEST promotes lung cancer invasion and metastasis by interacting with VCP to activate NF-kappaB signaling. 34625606_Hypermethylation of Mest promoter causes aberrant Wnt signaling in patients with Alzheimer's disease. 34686504_miR-145-5p Modulates Gefitinib Resistance by Targeting NRAS and MEST in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 34997218_Human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-503-3p inhibits progression of human endometrial cancer cells through downregulating MEST. 35042621_Increased co-expression of MEST and BRCA1 is associated with worse prognosis and immune infiltration in ovarian cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000051855 |
Mest |
25.686533 |
0.3994577507 |
-1.323885 |
0.409129848 |
10.046474 |
0.00152639853896433539195975903624002967262640595436096191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003453348012739667575315971603799880540464073419570922851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.7705742 |
3.8881964 |
34.0430619 |
6.3467682 |
| ENSG00000106546 |
196 |
AHR |
protein_coding |
P35869 |
FUNCTION: Ligand-activated transcription factor that enables cells to adapt to changing conditions by sensing compounds from the environment, diet, microbiome and cellular metabolism, and which plays important roles in development, immunity and cancer (PubMed:30373764, PubMed:23275542, PubMed:7961644, PubMed:32818467). Upon ligand binding, translocates into the nucleus, where it heterodimerizes with ARNT and induces transcription by binding to xenobiotic response elements (XRE) (PubMed:30373764, PubMed:23275542, PubMed:7961644). Regulates a variety of biological processes, including angiogenesis, hematopoiesis, drug and lipid metabolism, cell motility and immune modulation (PubMed:12213388). Xenobiotics can act as ligands: upon xenobiotic-binding, activates the expression of multiple phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes (such as the CYP1A1 gene) (PubMed:7961644). Mediates biochemical and toxic effects of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons (PubMed:7961644, PubMed:34521881). Next to xenobiotics, natural ligands derived from plants, microbiota, and endogenous metabolism are potent AHR agonists (PubMed:18076143). Tryptophan (Trp) derivatives constitute an important class of endogenous AHR ligands (PubMed:32866000, PubMed:32818467). Acts as a negative regulator of anti-tumor immunity: indoles and kynurenic acid generated by Trp catabolism act as ligand and activate AHR, thereby promoting AHR-driven cancer cell motility and suppressing adaptive immunity (PubMed:32818467). Regulates the circadian clock by inhibiting the basal and circadian expression of the core circadian component PER1 (PubMed:28602820). Inhibits PER1 by repressing the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer mediated transcriptional activation of PER1 (PubMed:28602820). The heterodimer ARNT:AHR binds to core DNA sequence 5'-TGCGTG-3' within the dioxin response element (DRE) of target gene promoters and activates their transcription (PubMed:28602820). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23275542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28602820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30373764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32818467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32866000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34521881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7961644, ECO:0000303|PubMed:12213388, ECO:0000303|PubMed:18076143}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;ADP-ribosylation;Biological rhythms;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Retinitis pigmentosa;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a ligand-activated helix-loop-helix transcription factor involved in the regulation of biological responses to planar aromatic hydrocarbons. This receptor has been shown to regulate xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes such as cytochrome P450. Before ligand binding, the encoded protein is sequestered in the cytoplasm; upon ligand binding, this protein moves to the nucleus and stimulates transcription of target genes. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:196; |
aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex [GO:0034751]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; cytosolic aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex [GO:0034752]; nuclear aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex [GO:0034753]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; TBP-class protein binding [GO:0017025]; TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding [GO:0001094]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine [GO:1904613]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to forskolin [GO:1904322]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell [GO:0002841]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030888]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
11207035_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11393538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11408954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11505220_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11689007_polymorphisms that result in loss of CYP1A1 induction 11698344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11742002_Phylogenetic analysis shows that AHRR, AHR1, and AHR2 are distinct genes, members of an AHR gene family; these three vertebrate AHR-like genes descended from a single invertebrate AHR 11756572_The female reproductive tract expresses AHR and ARNT mRNA, and changes in expression at target sites in conditions such as endometriosis and uterine leiomyomas suggest a potential role for these factors in the pathogenesis of these conditions. 11768231_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/dioxin receptor in human monocytes and macrophages 11805098_Functional involvement of the Brahma/SWI2-related gene 1 protein in cytochrome P4501A1 transcription mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex 11835227_Arg554Lys was investigated and no association with micropenis was found. 11866883_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12024042_SRC-1, NCoA-2, and p/CIP are capable of independently enhancing TCDD-dependent induction of a luciferase reporter gene by the AHR/ARNT dimer. 12065584_Two parallel pathways mediate cytoplasmic localization 12139968_The silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors can interact with the aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor but fails to repress Ah receptor-dependent gene expression. 12200463_functional AhR are present in endometrial and endometriotic stromal cells and that TCDD up-regulates the expression of RANTES, providing a possible mechanistic link between dioxin exposure and chemokine expression in endometriosis. 12213390_Polymorphisms that regulate the phenotype of AHR-mediated responses, especially differences among ethnic groups. 12480531_Possible involvement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) leukemogenesis: constitutive activation of AhR in ATL. 12520072_AhR gene expression associates with individual variation of CYP1A1 inducibility and CYP1B1 expression in cultivated lymphocytes 12566446_Binding of ligands such as TCDD, beta-naphthoflavone, and benzopyrene metabolites to the Ah receptor is involved in human UGT1A1 induction. 12586752_experiments revealed a complex distribution of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator mRNAs and proteins in rat and human testis 12592376_DNA damage and cell cycle arrest induced by 2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl)-5-fluorobenzothiazole (5F 203, NSC 703786) is attenuated in aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficient MCF-7 cells 12612060_Inhibitory AhR-ERalpha cross talk is linked to a new pathway for degrading ERalpha in which TCDD initially induces formation of a nuclear AhR complex which coordinately recruits ERalpha & the proteasome complex, resulting in degradation of both receptors. 12637498_results confirm that the Ah receptor plays a critical role in B[a]P-7,8-dihydrodiol-induced apoptosis 12730383_In mice transgenic to this receptor, there is a lessened susceptibility to dioxin-induced toxicity. 12774124_estrogen receptor-mediated estrogen signalling is modulated by a co-regulatory-like function of activated AhR/Arnt, giving rise to adverse oestrogen-related actions of dioxin-type environmental contaminants 12837759_the dioxin receptor is stabilized by XAP2 12852830_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14560034_Results describe the recruitment of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and associated proteins to the human cytochrome P4501A1 gene promoter in vivo. 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14973392_interactions between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and estrogen receptor have a role in development of breast neoplasms [review] 14978034_AhR tyrosine 9, which is not a phosphorylated residue itself but is required for DNA binding, appears to play a crucial role in AhR activity by permitting proper phosphorylation of the AhR. 14985336_cell density regulates the intracellular localization and function of AhR, because of modulation of nuclear export activity 15026081_Inhibitory AHR-androgen receptor crosstalk was studied in the LNCaP prostatic tumor cell line. 15069065_AhR activation causes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, especially through expression changes in genes related to apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. 15123621_Results describe a mechanism whereby the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, a known transcriptional activator, mediates gene repression through interactions at E2F-responsive promoters, leading to the repression of E2F-dependent, S phase-specific genes. 15190133_nucleotide preference of the heterodimers of AHR and Arnt 15342792_Promoters and long-distance regulatory regions of AhR-responsive genes were analyzed by the genetic algorithm and a variety of other computational methods. 15474075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15499202_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15499202_Thirty-two single nucleotide variations have been identified in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene, including 25 novel ones and a GGGGC repeat polymorphism in the promoter region. 15572374_MEK1 facilitates ligand-initiated transcriptional activation while targeting the Ah receptor for degradation 15641800_Folding of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor transactivation domain modulates protein-protein interactions, such as the binding of transcription factor TATA-binding protein (TBP). 15728486_AhR activation in the T-lineage cells is directly involved in thymocyte loss and skewed differentiation; AhR activation in T cells and not in B cells suppresses the immunization-induced increase in both T cells and B cells. 15758562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15774926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15837795_ER alpha-AHR-ARNT protein-protein interactions mediate estradiol-dependent transrepression of dioxin-inducible gene transcription 15863442_AHR pathway plays important role in cigarette smoke-mediated COX-2 and prostaglandin production in human lung fibroblasts and may contribute to tobacco-associated inflammation and lung disease. 15897893_Induction of c-jun depends on activation of p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) by an AhR-dependent mechanism. 15917307_Expression of BCRP is most likely aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) dependent in Caco-2 cells. 15964790_AHR-mediated transcription: ligand-dependent recruitment of Era to TCDD-responsive promoters was studied. 16084889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16091746_AhR influences the expression of c-Myc, a protein critical to malignant transformation 16103451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16109480_Results provide evidence for a cross-talk between CYP3A4 and aryl hydrocarbon receptor, and show that conclusions drawn from experiments carried out in cell lines may lead to erroneous in vivo predictions in man. 16153594_This short review summarizes recent advances in the study of AhR activation and inducible expression of target gene cytochrome P450 (CYP1) and other CYP families 16337337_enhanced AhR expression and especially its nuclear translocation may be a favorable factor for gastric cancer formation presumably via up-regulating CYP1A1 expression 16403814_The increased AR gene activity observed in precious pubertyas indicated by the reduced AR gene methylation pattern, might lead to hypersensitivity of the hair follicles to steroid hormones and therefore to the premature development of pubic hair. 16480812_The aryl hydrocarbon receptor activates the retinoic acid receptoralpha through SMRT antagonism 16481407_Maternal smoking in combination with maternal AhR genetic polymorphisms may adversely affect infant birth size. 16538170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16619036_findings show that Ahr activation is functionally connected to a signaling cascade leading to dramatic alterations of cell plasticity and increase in cell motility 16675542_AhR-estrogen receptor 1/Sp1 transcription factor cross talk is due, in part, to enhanced association of AhR and estrogen receptor 1 16762319_a functional interaction between NcoA4 and AhR that may alter AhR activity to affect disease development and progression is demonstrated 16891617_The data presented support a major role for calpain in the AhR transformation, transactivation, and subsequent down-regulation, and provide a possible explanation for many of the reported phenomena of ligand-independent activation of AhR. 16922649_This review discusses the role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, a ligand-activated transcription factor that regulates the transcription of a wide range of genes, including some drug metabolizing enzymes. 16952353_Results suggest that the aryl hydrocarbon receptor participates in Slug induction, which, in turn, regulates cellular physiology including cell adhesion and migration. 16985026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16985033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17053541_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17053541_This study is the first to show an interaction between the CYP1A1 T3801C and AHR G1661A polymorphisms; this interaction could explain the difference in blood pressure level between smokers and non-smokers/ex-smokers 17140257_A truncated Ah receptor blocks the hypoxia and estrogen receptor signaling pathways. 17174437_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17200336_AhR overexpression up-regulates the expression of CYP1B1 in the early stage of lung adenocarcinoma 17223712_these observations support the hypothesis that there is a specific coordination between the activation of the cytosolic Ah receptor and the c-Src- and cdc37-containing HSP90 complex. 17244640_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17244640_investigated which roles the AR polymorphisms as well as the R554K and P185A in the AHR and AHRR genes, respectively, may play in modifying the effect of exposure to organohalogen pollutants in regard to sperm Y : X ratio 17311112_Proliferation of breast cancer cells is accompanied not only by expression of genes encoding cytochromes involved in estrogen metabolism, but also by changes in the expression of other genes, such as AHR. 17392787_findings uncover a function for AhR as an atypical component of the ubiquitin ligase complex and demonstrate a non-genomic signalling pathway in which fat-soluble ligands regulate target-protein-selective degradation through a ubiquitin ligase complex 17429315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17490615_Taken together, these data establish beta7 ITG as a new molecular target of PAHs, whose up-regulation by these environmental contaminants most likely requires activation of co-operative pathways involving both AhR and c-maf. 17498780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17502624_role of the AhR in the UVB stress response was confirmed in vivo by studies employing AhR KO mice 17511620_AHR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) agonists induce ERalpha promoter occupancy at AHR target genes through indirect activation of oestrogen receptor alpha(ERalpha), and support a role for ERalpha in AHR transactivation 17552871_evidence presented for regulatory cross-talk between aryl hydrocarbon receptor and glucocorticoid receptor alpha in HepG2 cells. 17559847_Allele and genotype frequencies of AHR and ARNT polymorphisms were similar between infertile men and controls. 17559847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17596880_Role of AhR in drug metabolism demonstrates in vivo up-regulation of androstane receptor through chemical exposure. 17642299_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17823287_AhR activation and COX-2 overexpression likely represent a mechanism of resistance to apoptosis in lymphoma cell lines that might be relevant for the development of lymphoma in vivo. 17823304_AhR with NF-kappaB RelB signaling pathways represent a new mechanism of cross talk between the two transcription factors 17900530_The interaction of AhR with RelB binding on a novel type of NF-kappaB binding site represents a new regulatory function of the AhR. 17963696_Hence the anti-inflammatory effect of PPARalpha overrides the pro-inflammatory effect of AhR. 18037991_in response to PAHs, Ahr-mediated activation of the harakiri, BCL2 interacting protein (contains only BH3 domain), was necessary for execution of cell death. 18059014_studies suggest that constitutively active AhR mediates different molecular outcomes than environmental chemical-activated AhR, and further implicate the AhR in mammary tumorigenesis 18065768_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates laminar fluid shear stress-induced CYP1A1 activation and cell cycle arrest in vascular endothelial cells. 18259752_AhR, a transcription factor, can bind specifically to AD1 in the C-terminal region of BRCA1 and affect BRCA1's ability to regulate transcription activity. 18302886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18302886_The polymorphism of aryl hydrocarbon receptor G1661A has no significant impact on levels of urinary 1-hydroxypyrene in coke oven workers. 18303622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18303622_SNPs rs6960165 or haplotypes of AHR were associated with the chromosome-defective micronuclei frequencies in coke-oven workers. 18358233_These findings indicate that the cross-talk function of the AhR with estrogen or androgen receptors is an intrinsic function of the AhR. 18359762_Reduction in VEGF correlates with inhibited prostate carcinogenesis in Ahr transsgenic mice. 18433817_AhR-mediated regulation of the human UGT1A4 gene by two xenobiotic response elements and a modulation by single nucleotide polymorphisms is demonstrated 18483242_analysis of how inflammatory signaling and aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediate synergistic induction of interleukin 6 in MCF-7 cells 18510611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515748_After high glucose stimulation, AhR was found in complex with Egr-1 & activator protein-2. The activity of the DNA-binding complex was regulated by glucose (a physiological stimulus) via activation of hexosamine pathway & intracellular glycosylation. 18524851_AHR binds to E2F1 and inhibits E2F1-induced apoptosis 18628420_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18628420_polymorphisms of AhR gene were associated with the level of 1-OHP among PAH-exposed workers, suggesting that AhR-mediated signaling might contribute to individual susceptibility to PAH exposure. 18632753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18677463_These data demonstrate xenobiotic induced regulation of the UGT1A3 gene by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, which shows genetic variability 18708059_CyP40 is found in the cell nucleus after 3-methylchloranthrene treatment and appears to promote the dioxin response element binding form of the AhR/Arnt heterodimer. 18708364_AhR is a master regulator of c-raf and propose cross-talk between AhR and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. 18818557_AHR polymorphisms and potential gene-smoking interaction may be involved in the etiology of lung cancer. 18818557_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18923163_Prunella vulgaris extract activities were probably related to an ability to function as an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonist in ECC-1 cells. 18990750_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19013013_broccoli-derived SUL can directly induce Cyp1a1 gene expression in an AhR-dependent manner and represents a novel mechanism by which sulforaphane induces this enzyme 19018768_Curcumin attenuates cytochrome P450 induction in response to TCDD by ROS-dependently degrading AhR and ARNT. 19027718_This review examines the impact of transient versus sustained receptor activation on AhR biology and explores the potential role for cytochrome P450 expression in regulating AhR activity among various tissues. 19034627_Bioactive terpenoids and flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba extract induce the expression of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes through pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated pathways. 19114668_AhR activation plays an essential part in the development of Th17 cells. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19255421_mechanism by which 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin is able to disrupt epidermal homeostasis and identify EGFR signaling as a regulator of the AHR 19333233_These results establish a role for AHR in inflammatory signaling within the liver, presenting a new therapeutic opportunity, and signify AHR's ability to function in a DNA-independent manner. 19340314_data identify novel roles for CREB and AhR as major, specific regulators of FSCN-1 transcription in human carcinoma cells but do not support the hypothesis that beta-catenin signaling has a central role 19356061_these data imply the existence of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) cross-talk in HeLa cells 19356098_This is the first report showing direct induction of UGT1A1 by a bilirubin through AhR pathway. 19358281_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and overexpression is associated with upregulation of fibroblast growth factor-9 resulting in lung adenocarcinomas. 19360915_Data show that aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression was significantly increased in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. 19371443_Results provide insight into the mechanism and function of the AhR pathway and its impact on gastric cancer progression. 19380484_Results identify aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) repressor (AHRR) Delta8 as the active form of human AHRR and reveal novel aspects of its function and specificity as a repressor of AHR. 19415745_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19415745_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor is associated with breast cancer. 19447902_The AhR is a potential drug target for treatment of ER-negative breast cancer. 19460354_AF2 domain contributes to dioxin-induced recruitment of ERalpha to AHR target genes, but that both the AF1 and AF2 domains are required for ERalpha-dependent increases in AHR activity. 19463884_AhR functionally cross-reacts with the GR, through which transactivation activity of the GR is further enhanced, and in contrast, transactivation activity of the AhR is inhibited. 19465936_pathogenesis of glioma formation may involve altered AhR regulation of the TGF-beta/Smad pathway, and AhR may represent a promising target for the treatment of human malignant gliomas and other diseases associated with pathological TGF-beta activity 19535631_AhR agonist signaling exerts specific effects on monocyte/dendritic cell subset differentiation of myeloid progenitor cells via interfering with lineage-determining transcriptional processes. 19536146_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling is an integral part of the induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms by ozone. 19556287_AHR signalling may be differentially affected according to pituitary adenoma phenotype. 19574409_demonstrate not only that dioxin induces the recruitment of ERalpha to AHR target genes but that AHR is recruited to estrogen-responsive regions in a gene-manner, suggesting that AHR utilizes these mechanisms to modulate estrogen-dependent signaling 19592671_EGF repressed the transcriptional activity of aryl hydrocarbon receptor. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19690180_study showed that AhR expression was higher in patients with a family history of upper gastrointestinal tract cancer; such individuals may be more susceptible to the deleterious effects of PAH exposure, including PAH-induced cancer 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19726680_AhR shuttles PAH o-quinone genotoxins to the nucleus and enhances oxidative DNA damage. 19736056_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19755661_Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway enhances cancer cell invasion by upregulating the MMP expression and is associated with upper urinary tract urothelial cancer. 19789301_Treatment of UVR sensitized human keratinocytes with an Hsp90 inhibitor caused a marked decrease in levels of AhR 19815066_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) modulation of androgen receptor activity is differentially altered by the level of FHL2 and AhR present in the cell. 19821039_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19821039_the AHR gene may play a role in determining the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with exposure to organochlorines, and highlight the importance of understanding gene-environment interactions. 19917880_AHR binds to CDK4 to facilitate cell cycle progression. The interaction is disrupted by exogenous ligands to induce G1 cell cycle arrest. 19917880_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells through functional interaction with cyclin-dependent kinase 4. 19941898_We hypothesize that it is the interaction of L-tryptophan and its metabolites with AHR that induces Th17 cell differentiation and autoinflammation in eosinophilic fasciitis, eosinophilia-myalgia-syndrome and toxic oil syndrome . 20000589_Prolonged activation of the AHR by indoxyl-3-sulfate may contribute to toxicity observed in kidney dialysis patients and thus represent a possible therapeutic target. 20032195_AhR agonists inhibited cell invasiveness and anchorage-independent growth in human breast cancer cells regardless of ER, PR, or HER2 status. 20032195_Knockdown of the AhR using siRNA increased the invasiveness of human breast cancer cells. 20032195_Ligand activation of AhR promotes differentiation & inhibits aspects of metastatic process in cell line panel representing major breast cancer subtypes. Aspects inhibited include cell invasiveness, colony formation, & anchorage-independent growth. 20032195_The inhibition of invasiveness and anchorage-independent growth in human breast cancer cells correlated with the ability of AhR agonists to promote differentiation. 20044593_Compared to the mAHR(b), the hAHR may play contrasting roles in TCDD-induced toxicity and endogenous AHR-mediated gene regulation. 20053997_Cellular protection by glucuronidation is inducible by xenobiotics via AhR and by oxidative metabolites via Nrf2 linking glucuronidation to cellular protection and defense against oxidative stress. 20064835_The AhR and p53 signaling pathways were the most significant canonical pathways activated by benzo(a)pyrene. 20130088_I3C is a novel anticancer agent in human cancers that coexpress ERalpha, GATA3, and AhR, a combination found in a large percentage of breast cancers but not in other critical ERalpha target tissues essential to patient health 20140206_Data show that shRNA targeted against beta-TrCP reduced prostate cancer cell growth, upregulated the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, and suggest that AhR activation may be a cancer counteracting mechanism in the prostate. 20146706_Emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the generation of regulatory T cells. 20171126_The AhR has a role in regulating the cell cycle, inflammation, & the hematopoietic and immune systems in health and disease. Triggering by xenobiotic ligands may be associated with leukemia. Review. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20301892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20301892_Survival time, metastasis and occurrence of second primary tumors were compared in carriers of wild type and Arg554Lys variant AHR. 20354149_In the placentas, the AHR immunoreactivity was present primarily in syncytiotrophoblasts. AHR is also expressed in the majority of human fetal tissues. 20395535_Findings indicate that AhR and Nrf2 play important roles in regulating hepatocyte MRP4 expression. 20401977_identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the AHR from six ethnic populations 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460431_AHR is a direct transcriptional regulator of human BCRP and provide an unprecedented role of AHR in cellular adaptive response and cytoprotection by up-regulating an important ATP-binding cassette efflux transporter 20511231_AHR-mediated priming is not restricted to the IL6 promoter and may contribute to the expression of a variety of genes, which do not have consensus dioxin response elements 20619336_AhR plays a crucial role in both basal and TCDD-induced expression of target genes in human hepatocytes. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20676092_AhR activation promoted the differentiation of CD4(+)Foxp3(-) T cells, which produce IL-10 and control responder T cells through granzyme B 20709182_results suggest that the AhR-induced increase of mucin production is partially mediated by reactive oxygen species generation 20804740_A novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor-responsive element (AhRE5) mediates transcriptional activation of ABCG2 gene expression. 20823264_The AhR pathway is constitutively activated and functional in human KGN granulosa cells. The constitutively activated AhR suppressed aromatase expression and estrogen synthesis and enhanced proliferation of KGN cells. 20878756_Abnormal AhR pathway activation in the intestinal mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease patients may promote chronic inflammation 20973933_AHR is able to modulate melanogenesis by controlling the expression of melanogenic genes. 21072210_Data show that the anti-cancer effects of tranilast are AHR dependent. 21081473_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21205295_The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling is the primarily affected pathway by the E6/E7 oncoproteins expression and this pathway is also deregulated in human small cell lung cancer. 21262915_Results suggested that therapeutic effects of RA-induced leukemia differentiation depend on AhR and its ability to downregulate the stem cell factor Oct4. 21316925_benzo(a)pyrene induces oxidative stress-mediated interleukin-8 production in human keratinocytes via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway 21357676_AHR detects xenobiotics, such as polycyclic aryl hydrocarbons found in roasted coffee, and induces transcription of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. 21374063_These findings about the role of AhR activators in epithelial immune regulation aid in understanding mucosal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and suggest that AhR activation has therapeutic value for the treatment of IBD. 21441140_CXCR2 mediates the atherogenic activity of environmental pollutants, such as dioxins, and contributes to the development of atherosclerosis through the induction of a vascular inflammatory response by activating the AhR-signaling pathway. 21462134_No association between AhR 1661G/A and ARNT 567G/C genetic polymorphisms and endometriosis was found in the southern Han Chinese women in this study. 21486221_Data indicate that overexpression of AhR alone is sufficient to induce carcinogenic transformation in mammary epithelial cells; data provide evidence for a direct role of AhR in progression of breast carcinoma. 21490707_Both the AHR and CYP1A2 genes are biologically plausible candidates as CYP1A2 metabolizes caffeine and AHR regulates CYP1A2. 21600206_AhR is down-regulated in intestinal tissue in inflammatory bowel disease. AhR signaling, via IL-22, inhibits inflammation and colitis in the gastrointestinal tract. 21613234_The AHR polymorphism might be associated with individual risk of male infertility in Chinese. 21627536_in the absence of exogenous ligands, the AhR promotes cell cycle progression in HaCaT keratinocytes 21640702_AHR overexpression is found among estrogen receptor (ER)alpha-negative human breast tumors and that its overexpression is positively correlated to that of the NF-kappaB subunit Rel-B and Interleukin 8. 21689841_There is a higher level of Aryl hydrocarbon Receptors in Infertile men in Iran 21742528_The homozygote variant genotype of AHR Lys554Lys is associated with a significantly lower AHR, ARNT and CYP1B1 mRNA expression. 21804081_Present data demonstrate for the first time that activation of the AhR by TCDD suppressed the development of Th2-mediated food allergic responses. 21828262_results demonstrate that SULT1E1 expression in MCF10A breast epithelial cells cells is transcriptionally regulated by confluence through a suppressive action of the AhR, which is not mediated through a dioxin response element at nt -3476 21878739_The role of AhR as a transcription factor is related to the low-glucose response. 21976023_tryptophan catabolite kynurenine is an endogenous ligand of the human AHR that is constitutively generated by human tumour cells via tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase, a liver- and neuron-derived Trp-degrading enzyme not yet implicated in cancer biology 21996739_AhR, without exposure to a ligand, associates with RelA, which then positively modulates NFkappaB activity and then upregulates IL-6 expression in human lung cells; a new mechanism for lung tumorigenesis 22052373_cancer tissues did not contain mutations in the AhR transactivation domain region when the DNA sequences were compared with those from normal tissues. 22053597_The expression of AhR mRNA in PBMCs and IL-22 protein in plasma of patients with allergic asthma were higher than those in controlled asthma cases. 22071320_Highlight the importance of cross-regulation between AhR and ERalpha and a novel mechanism by which AhR controls, through modulating the recruitment of RIP140 to ERalpha-binding sites, the kinetics and magnitude of ERalpha-mediated gene stimulation. 22123295_Data show that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation suppressed mammosphere formation of MCF-7 cells and decreased the proportion of cells with high aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH-1) activity. 22138065_Benzyl butyl phthalate-induces granulosa cell necrosis is AhR and CYP1B1 dependent. 22235307_the specific functions of AHR and ARNT in estrogen-dependent signaling 22273977_our data demonstrated that AhR protected lung adenocarcinoma cells against cigarette sidestream smoke particulate-induced oxidative stress and promoted post-exposure clonogenicity 22296396_A significant association between tumoral levels of glycodelin and AhR (p=0.002) in breast cancers. 22311706_data show that the AhR promotes proliferation of medulloblastoma (MB) cells, suggesting that this pathway should be considered as a potential therapeutic target for MB treatment 22361730_These data support novel observations that, in human colon cancer cells, Src-mediated cross talk between aryl hydrocarbon and EGFR results in ERK1/2 activation, thereby stimulating cell proliferation. 22388733_aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression is not required for the proliferation, migration, invasion, or estrogen-dependent tumorigenesis of breast cancer. 22486318_The activity and expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in hepatic stellate cells are regulated by chronic ethanol. 22495716_Results showed that AhR was highly expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues and cell lines when compared with its expression in normal tissue. 22495806_These results suggested that SUMOylation of AhR might play an important role in the regulation of its function, and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-d |
ENSMUSG00000019256 |
Ahr |
438.250125 |
3.8191410869 |
1.933248 |
0.092679094 |
443.737327 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001663671512416248952875804446808757615226597113552326248273311775763623528151224989246892485791900754986778621557301809094228250617164746238511784274560068180830001394219145286365858665383236340002003112250925325444782683148057237601 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000687837297570415588710808870196551515879239287967060748251535845925988426583973654726757824006113027323664561210258109481955288029419381534820992055495024587603929777768188434335729886824497072288574899196454800595601818862828738025 |
Yes |
No |
702.1300361 |
39.9383116 |
185.2343252 |
8.6191682 |
| ENSG00000106628 |
5425 |
POLD2 |
protein_coding |
P49005 |
FUNCTION: Accessory component of both the DNA polymerase delta complex and the DNA polymerase zeta complex (PubMed:22801543, PubMed:17317665, PubMed:24449906). As a component of the trimeric and tetrameric DNA polymerase delta complexes (Pol-delta3 and Pol-delta4, respectively), plays a role in high fidelity genome replication, including in lagging strand synthesis, and repair (PubMed:12403614, PubMed:16510448, PubMed:19074196, PubMed:20334433, PubMed:24035200). Pol-delta3 and Pol-delta4 are characterized by the absence or the presence of POLD4. They exhibit differences in catalytic activity. Most notably, Pol-delta3 shows higher proofreading activity than Pol-delta4 (PubMed:19074196, PubMed:20334433). Although both Pol-delta3 and Pol-delta4 process Okazaki fragments in vitro, Pol-delta3 may also be better suited to fulfill this task, exhibiting near-absence of strand displacement activity compared to Pol-delta4 and stalling on encounter with the 5'-blocking oligonucleotides. Pol-delta3 idling process may avoid the formation of a gap, while maintaining a nick that can be readily ligated (PubMed:24035200). Along with DNA polymerase kappa, DNA polymerase delta carries out approximately half of nucleotide excision repair (NER) synthesis following UV irradiation (PubMed:20227374). Under conditions of DNA replication stress, required for the repair of broken replication forks through break-induced replication (BIR) (PubMed:24310611). Involved in the translesion synthesis (TLS) of templates carrying O6-methylguanine or abasic sites performed by Pol-delta4, independently of DNA polymerase zeta (REV3L) or eta (POLH). Facilitates abasic site bypass by DNA polymerase delta by promoting extension from the nucleotide inserted opposite the lesion. Also involved in TLS as a component of the DNA polymerase zeta complex (PubMed:24449906). Along with POLD3, dramatically increases the efficiency and processivity of DNA synthesis of the DNA polymerase zeta complex compared to the minimal zeta complex, consisting of only REV3L and REV7 (PubMed:24449906). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16510448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19074196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20227374, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20334433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24035200, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24310611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24449906}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;DNA damage;DNA excision;DNA repair;DNA replication;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes the 50-kDa catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase delta. DNA polymerase delta possesses both polymerase and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity and plays a critical role in DNA replication and repair. The encoded protein is required for the stimulation of DNA polymerase delta activity by the processivity cofactor proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Expression of this gene may be a marker for ovarian carcinomas. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene, and a pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:5425; |
delta DNA polymerase complex [GO:0043625]; DNA polymerase complex [GO:0042575]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; zeta DNA polymerase complex [GO:0016035]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA biosynthetic process [GO:0071897]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication [GO:0006271]; DNA-templated DNA replication [GO:0006261]; error-prone translesion synthesis [GO:0042276] |
11986310_the interaction of PCNA with DNA polymerase delta is mediated through the small subunit of the enzyme 12522211_The association of PDIP38 with pol delta was shown to occur in calf thymus tissue and mammalian cell extracts by GST-PDIP38 pull-down and coimmunoprecipitation experiments. 18765914_As a first step towards understanding the functional importance of their regulatory subunit interactions, the three-dimensional structure of the p50-p66 heterodimer of human Pol delta has been solved using X-ray crystallography. 18818516_the crystal structure of p50*p66(N) complex featuring oligonucleotide binding and phosphodiesterase domains in p50 19237606_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20226869_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574454_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21079801_Results suggest that POLD2 and KSP37 might be potential prognostic biomarkers. 21372597_DNA polymerase delta catalytic subunit p125 induced by mutant type p53 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. 25662213_The results show that the FF483-484 amino acids in the human Poleta (designated F1 motif) are necessary for the interaction of this polymerase with POLD2, the B subunit of the replicative DNA polymerase delta, both in vitro and in vivo. 25924900_Inhibition of DNA polymerases a, delra and e by AFP promoter-driven artificial microRNAs may lead to effective growth arrest of AFP-positive HCC cells,as novel strategy for gene therapy 28934474_The proofreading activity of DNA polymerase delta plays a role in shunting DNA mismatch repair to an EXO1-dependent excision pathway as opposed to directly participating in gap formation via its 3'-5' exonuclease activity. 31326365_The role in cellular processes (DNA replication, DNA repair, homologous recombination) and cell cycle regulation of 2 forms of human DNA polymerase delta: delta3 and delta4 was reviewed. (REVIEW) 31449058_In patients from 2 independent pedigrees, we have identified what we believe to be a novel syndrome with reduced functionality of the polymerase delta complex caused by germline biallelic mutations in POLD1 or POLD2 as the underlying etiology of a previously unknown autosomal-recessive syndrome that combines replicative stress, neurodevelopmental abnormalities, and immunodeficiency. 31954770_ShRNA-based POLD2 expression knockdown sensitizes glioblastoma to DNA-Damaging therapeutics. 33077594_Polymerase delta promotes chromosomal rearrangements and imprecise double-strand break repair. 34116171_Exome sequencing reveals novel rare variants in Iranian familial multiple sclerosis: The importance of POLD2 in the disease pathogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000020471 |
Pold2 |
317.884659 |
2.2472079132 |
1.168134 |
0.117643325 |
98.106980 |
0.00000000000000000000003963791878496504276477336163545090165682311391439097232340709126355293712151706131407991051673889160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000393446994798980494791624207759962386091200537157687362799284112174769134639973344746977090835571289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
442.8513876 |
31.9694342 |
198.4791524 |
10.9973008 |
| ENSG00000106772 |
158471 |
PRUNE2 |
protein_coding |
Q8WUY3 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in regulating differentiation, survival and aggressiveness of the tumor cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16288218}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Manganese;Metal-binding;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 and adenovirus E1B 19 kDa interacting family, whose members play roles in many cellular processes including apotosis, cell transformation, and synaptic function. Several functions for this protein have been demonstrated including suppression of Ras homolog family member A activity, which results in reduced stress fiber formation and suppression of oncogenic cellular transformation. A high molecular weight isoform of this protein has also been shown to colocalize with Adaptor protein complex 2, beta-Adaptin and endodermal markers, suggesting an involvement in post-endocytic trafficking. In prostate cancer cells, this gene acts as a tumor suppressor and its expression is regulated by prostate cancer antigen 3, a non-protein coding gene on the opposite DNA strand in an intron of this gene. Prostate cancer antigen 3 regulates levels of this gene through formation of a double-stranded RNA that undergoes adenosine deaminase actin on RNA-dependent adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:158471; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; pyrophosphatase activity [GO:0016462]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915] |
16288218_BMCC1 is a new member of prognostic factors for NBL and may play an important role in regulating differentiation, survival and aggressiveness of the tumor cells 17360660_OBSCN and C9orf65 comprise a highly accurate two-gene classifier for differentiating gastrointestinal stromal tumors and leiomyosarcomas. 17961507_Our results suggest that the caspase-mediated cleavage of BNIP-2 and BNIP-XL could result in the release of the BCH domain or smaller fragments that are crucial for their proapoptotic activities. 18445682_findings show the BNIP2 & BCH domain of BNIPXL interacts with specific conformers of RhoA & mediates association with catalytic DH-PH domains of Lbc, a RhoA-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor; BNIPXL inhibits Lbc-induced oncogenic transformation 19319183_the longer BMCC1-1 isoform is upregulated in PCa tissues and metastases 19760627_The androgen regulation of PRUNE2 expression in prostate cancer cells was found to not be of any diagnostic value. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21234814_The nerve tissue-specific and post-development expression of PRUNE2/Prune2 suggests that PRUNE2 may contribute to the maintenance of mature nervous systems. 22967466_PRUNE2 expression is correlated with the survival of leiomyosarcoma patients. Non-coding RNA PCA3 has a significant positive correlation with PRUNE2 and may play an important role in the pathogenesis of leiomyosarcoma. 23059019_We showed that Olfaxin, a novel Prune2 isoform contains a BCH motif and localizes predominantly to the synaptic cytosol in the olfactory bulb and layer Ia of the piriform cortex. 24040105_BMCC1 is an AP-2 associated endosomal protein in prostate cancer cells. 25387265_recurrent germ line and somatic mutations in PRUNE2 were found in parathyroid carcinoma and computationally predicted to be deleterious; in addition, recurrent mutations in kinase genes related to cell migration and invasion were found. 25611382_BMCC1 negatively regulates phosphorylation pathway of AKT, resulted in apoptosis and the BNIP2 homology region of BMCC1 interacts with BCL2. 26080435_Results show prostate cancer antigen 3 (PCA3) as a dominant-negative oncogene and PRUNE2 protein as an unrecognized tumor suppressor gene in prostate cancer. 27453342_E2F1 directly facilitated BMCC1 transcription. These results also suggest that BMCC1 induced by E2F1 acts as a tumor suppressor through its pro-apoptotic function, resulted in favorable prognosis of neuroblastoma. 31170959_The programmed expression of full-length BMCC1 in human neuroblastoma cells undergoing DNA damage-induced apoptosis. 35929169_FOXF2 Regulates PRUNE2 Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Colorectal Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000039126 |
Prune2 |
16.656986 |
0.0331825808 |
-4.913430 |
0.772845947 |
63.487663 |
0.00000000000000161374285274990930824890214082692689609496836024987720392687151615973562002182006835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000011440367198169386612887877415743737530851313784208134194386730086989700794219970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0934087 |
0.6351606 |
33.0307872 |
7.5867713 |
| ENSG00000106785 |
9830 |
TRIM14 |
protein_coding |
Q14142 |
FUNCTION: Plays an essential role in the innate immune defense against viruses and bacteria (PubMed:30150992, PubMed:32404352). Facilitates the type I IFN response by interacting with MAVS at the outer mitochondria membrane and thereby recruiting NF-kappa-B essential modulator IKBKG/NEMO to the MAVS signalosome, leading to the activation of both the IFN regulatory factor 3/IRF3 and NF-kappa-B pathways (PubMed:24379373). Positively regulates the CGAS-induced type I interferon signaling pathway by stabilizing CGAS and inhibiting its autophagic degradation (PubMed:27666593). Acts as a scaffold between TBK1 and STAT3 to promote phosphorylation of STAT3 and resolve interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) expression (PubMed:32404352). Inhibits the transcriptional activity of SPI1 in a dose-dependent manner (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BVW3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24379373, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27666593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29053956, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30150992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32404352}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. The protein localizes to cytoplasmic bodies and its function has not been determined. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:9830; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of viral transcription [GO:0032897]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046596] |
18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24379373_Upon virus infection, TRIM14 recruits NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO) to the MAVS complex via ubiquitin chains. 25948474_stable enhanced expression of trim14 gene in cells activates the transcription of many immunity genes and suppresses Sindbis virus reproduction, but Sindbis virus infection of HEK-trim14 cells promotes inhibition of some genes involved in innate immunity. 26799420_Data suggest that tripartite motif containing 14 protein (TRIM14) might play an important role in the malignant progression of tongue squamous cells carcinoma (TSCC) and in regulation of the NF_Kappa B (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway. 27578425_In searching for mechanisms how TRIM14 exerts its antiviral function we found that TRIM14 interacted with HCV encoded non-structural protein NS5A and could strongly induce its degradation dependent on the NS5A1 subdomain. Interestingly extensive domain mapping analyses revealed that NS5A degradation was mediated by the highly conserved SPRY domain of TRIM14, which might involve the K48 ubiquitination pathway 28059079_Study shows that tripartite Motif 14 (TRIM14) is a putative tumor suppressor and regulator of innate immune response in non-small cell lung cancer. The functional data establishes a novel tumor suppressive role for TRIM14 in non-small cell lung cancer progression. 28205534_Our findings collectively suggest that TRIM14 functions as an oncogene by upregulating the AKT signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells, supporting its potential utility as a therapeutic target for this disease. 28350138_MiR-15b degrades TRIM14 in oral tongue squamous cell cancer.TRIM14 role in oral tongue squamous cell cancer resistance to cisplatin. 28476934_study identifies new gene-type zinc finger protein 125 (RNF125) as a negative regulator of TRIM14 in the innate antiviral immune response 28631557_survival of xenograft mice was prolonged by BsAbBmi/TRIM treatment compared to either AbBmi-1 or AbTRIM-14 treatment. In conclusion, these results provided new evidence that BsAbBmi/TRIM inhibited the progression of osteosarcoma, which suggest that BsAbBmi/TRIM may be a novel anti-cancer agent for osteosarcoma therapy 29053956_findings define the WHIP-TRIM14-PPP6C mitochondrial signalosome required for RIG-I-mediated innate antiviral immunity. 29204446_we identify the tripartite motif-containing protein (TRIM14) as a target of miR-195-5p. Therefore, we reason that the tumor suppressor role of miR-195-5p in oral squamous cell carcinoma is dependent on the interaction with TRIM14. 29562956_TRIM14 was upregulated in both tissues and cell lines of human breast cancer. Knockdown of TRIM14 inhibited cell proliferation but increased cell apoptosis. 29867201_TRIM14 promotes chemoresistance in gliomas by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling via stabilizing Dvl2 30150992_this study demonstrates that TRIM14 is a STAT1-dependent IFN-stimulated gene, and that the IFN-I-TRIM14-HBx axis shows an alternative way to understand the mechanism by which IFN-I inhibits virus replication 30272351_Results showed that TRIM14 is increased in gastric cancer (GC) tissues and cell lines and associated with malignant features and unfavorable prognosis. Gain and lossoffunctional data confirmed that TRIM14 promotes migration, invasion and EMT progression by activating AKT signaling. TRIM14 was found to function as an oncogene in regulating EMT and metastasis of GC via AKT signaling, which was regulated by miR195. 30728039_these findings provide insight into the specific biological role of TRIM14 in tumor invasion, and suggest that targeting the TRIM14/ZEB2 axis might be a novel therapeutic approach for blocking glioblastoma. 30973643_The crystal structure of the TRIM14 PRYSPRY domain was solved, and found a positively charged surface that may mediate its partner specificity. TRIM14 PRYSPRY domain binds to acidic peptides, and the analysis of the reported partners of TRIM14 is consistent with this assumption. 31150153_Knockdown of IRF-1 reduces the stimulation of TRIM14 transcription by IFN-alpha, suggesting that IRF-1 is involved in the activation of TRIM14 by IFN-I. IRF-2 has little effect on IFN-alpha-induced TRIM14 transcription but is essential for the basal transcription of TRIM14. 31322007_the function of TRIM14 and NF-kappaB signalling and might 31668806_TRIM14 may be a prognostic factor and oncogene in papillary thyroid carcinoma 32096264_Trim14 promotes autophagy and chemotherapy resistance of gastric cancer cells by regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway. 33174608_Tripartite motifcontaining 14 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in cervical cancer via the Akt signaling pathway. 33864033_Human TRIM14 protects transgenic mice from influenza A viral infection without activation of other innate immunity pathways. 33982666_TRIM14 regulates melanoma malignancy via PTEN/PI3K/AKT and STAT3 pathways. 34051007_miR-4443 targets TRIM14 to suppress metastasis and energy metabolism of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) in vitro. 34292652_miR-671-5p repressed progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma via TRIM14. 34656078_Human mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes inhibit the growth of acute myeloid leukemia cells via regulating miR-23b-5p/TRIM14 pathway. 34787066_Circular RNA circ_0048764 promotes the development of breast cancer by regulating microRNA-1296-5p/tripartite motif containing 14 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000039853 |
Trim14 |
208.413558 |
0.4675553792 |
-1.096791 |
0.113208693 |
95.244166 |
0.00000000000000000000016829338008642646246367267695930171047329390656814185589959759030420638481473361025564372539520263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001630998220666877474184330385465621759496405749505897984778009929263120625364535953849554061889648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
132.8385596 |
8.9473527 |
286.1957063 |
12.2918887 |
| ENSG00000106789 |
7464 |
CORO2A |
protein_coding |
Q92828 |
|
Actin-binding;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. This protein contains 5 WD repeats, and has a structural similarity with actin-binding proteins: the D. discoideum coronin and the human p57 protein, suggesting that this protein may also be an actin-binding protein that regulates cell motility. Alternative splicing of this gene generates 2 transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7464; |
transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556] |
12628926_This protein is one of 10-12 associated proteins in the purified N-CoR complex. 19654210_Coronin 2A and cofilin regulate a subset of focal-adhesion-turnover events. 20526340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23490283_The candidate marker CORO2A rs1985859 and the putative marker FAM101A rs7955740 may be of value for the prediction of radiosensitivity to preoperative colorectal tumors. 26373535_increased expression of coronin 2A is associated with the malignant phenotype of human colon carcinoma. 27129179_The regulation of CORO2A through the deubiquitinating activity of USP19 affected the transcriptional repression activity of the retinoic acid receptor (RAR), suggesting that USP19 may be involved in the regulation of RAR-mediated adipogenesis. 34884487_Molecular Pathogenesis of the Coronin Family: CORO2A Facilitates Migration and Invasion Abilities in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000028337 |
Coro2a |
65.375769 |
0.2045529913 |
-2.289453 |
0.227526784 |
109.414961 |
0.00000000000000000000000013163225970495930890407319524220816096301448342845619688441244529676036473242461966037808451801538467407226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000001444529481966691122777872593501570770196871541827445896122386083653549304628427307761739939451217651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.7603235 |
3.4332085 |
112.1672967 |
9.5612623 |
| ENSG00000106804 |
727 |
C5 |
protein_coding |
P01031 |
FUNCTION: Activation of C5 by a C5 convertase initiates the spontaneous assembly of the late complement components, C5-C9, into the membrane attack complex. C5b has a transient binding site for C6. The C5b-C6 complex is the foundation upon which the lytic complex is assembled.; FUNCTION: [C5a anaphylatoxin]: Derived from proteolytic degradation of complement C5, C5a anaphylatoxin is a mediator of local inflammatory process. Binding to the receptor C5AR1 induces a variety of responses including intracellular calcium release, contraction of smooth muscle, increased vascular permeability, and histamine release from mast cells and basophilic leukocytes (PubMed:8182049). C5a is also a potent chemokine which stimulates the locomotion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and directs their migration toward sites of inflammation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8182049}. |
3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Complement alternate pathway;Complement pathway;Cytolysis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane attack complex;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a component of the complement system, a part of the innate immune system that plays an important role in inflammation, host homeostasis, and host defense against pathogens. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate multiple protein products, including the C5 alpha chain, C5 beta chain, C5a anaphylatoxin and C5b. The C5 protein is comprised of the C5 alpha and beta chains, which are linked by a disulfide bridge. Cleavage of the alpha chain by a convertase enzyme results in the formation of the C5a anaphylatoxin, which possesses potent spasmogenic and chemotactic activity, and the C5b macromolecular cleavage product, a subunit of the membrane attack complex (MAC). Mutations in this gene cause complement component 5 deficiency, a disease characterized by recurrent bacterial infections. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:727; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane attack complex [GO:0005579]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; complement activation [GO:0006956]; complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0006957]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; cytolysis [GO:0019835]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010760]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575] |
3624902_Regulation of murine contact sensitivity to urushiol components by serum factors. 12488432_function in regulating the inhibitory/activating FcgammaRII/III receptor pair to connect complement and FcgammaR effector pathways in immune inflammation 12881318_Specific inhibition of the C5a moiety of C5 before cleavage prohibited CR3 up-regulation, phagocytosis, and oxidative burst but had no effect on C5b-9 (TCC) formation, lysis, and bacterial killing. 12937147_Absence of C5 resulted in fiber loss and extensive scarring, whereas presence of C5-favored axonal survival and more efficient remyelination. 14556080_HMG-CoA inhibition with cerivastatin reduced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and C5b-9-induced ERK1/2 activation 14662858_Expressed in a bacterial system, a recombinant C5 segment of C345C module has substantial beta-sheet structure and internal disulfide bonds, and binds to complement components C6 and C7 with dissociation constants of 10 and 3 nM, respectively. 15278436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15383587_A model is suggested for an irreversible membrane attack complex assembly in which the complement 7 factor I modules, but not those in complement 6, are bound to the C345C (netrin receptor) domain of complement 5 within the fully assembled complex. 15488949_first report of a whole molecular characterization of C5 deficiency found homozygosity for a double mutation in the exon 40 of the C5 gene, leading to a premature stop codon 15550394_analysis of binding mode for C5a to the C5aR 15585680_C5a is a key mediator of meconium-induced neutrophil activation 15598652_analysis of multifunctional C345C domain of C5 of complement 15879120_The interaction between the C345C domain at the C terminus of the C5 alpha-chain and the factor I domain of C7 plays an essential role in complement membrane attack complex formation and complement lytic activity. 16670089_C5b-9 regulation of the cell cycle activation in aortic endothelial cells through Akt pathway is dependent on inactivation of FOXO1 16823297_C3a is acutely elevated after human ischemic stroke, C5a shows delayed elevations 7 to 14 days after cerebral ischemia, and sC5b-9 is acutely depressed after stroke. (Complement 3a, c5a, and C5b-9) 16879222_C5a and its receptor have roles in PAI-1 production 17023413_analysis of the structural constraint for C5a docking with the complement factor 5a (C5a) receptor N terminus 17322907_data indicate that C5L2 can function as a positive modulator for both C5a- and C3a-anaphylatoxin-induced responses 17428459_C5 gene variants and Gc-globulin levels co-define the proinflammatory and profibrogenic effects of C5 in patients at-risk for progression of liver fibrosis 17482181_Impairment of the mechanisms involved in the regulation of activation of complement system factors C5b-9 may be important in the pathogenesis of endometriosis and endometriosis-associated infertility. 17498719_in stenotic aortic valves, complement is activated leading to generation of the anaphylatoxin C5a 17505301_in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, C5a activates the p38 cascade, and this pathway plays a major role in the C5a enhancement of LPS-induced IL-6 and TNF-alpha production 17634448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17644516_the amount of C5b-9-AF488 bound to K562 cells after complement activation was highly heterogeneous and inversely correlated with the CD59 level of expression 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17880261_A polymorphism in the TRAF1/C5 region produces an increased genetic risk in susceptibility to and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. 17880261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18039528_C3a and C5a can bring about eosinophil extravasation and increase in vascular permeability that facilitates eosinophil accumulation at sites of allergic inflammation. 18300128_Glomerular TGF-beta1 may induce tubular expression of C5b-9. Increased tubular C5b-9 expression may result in interstitial fibrosis through increased TGF-beta1 production. 18411281_PLCbeta3 may provide a selective target for inhibiting Ca(2+) responses to mediators of inflammation, including C5a, UDP, PAF, and LPA 18576341_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18576341_TRAF1-C5 locus genetic variant SNP rs3761847 is associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis 18644651_There is no evidence that these C5 single nucleotide polymorphisms are genetic risk factors for the development of advanced fibrosis in chronic HCV infection or other chronic liver diseases. 18714034_release of C5a from human C5 by a serine protease (ASP) of Aeromonas sobria that induced neutrophil migration 18759306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18953960_Anaphylatoxin C5a may be involved in the pathogenesis of COPD. 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116907_The risk of death in rheumatoid arthritis is increased in TRAF1/C5 rs3761847 GG homozygotes 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19162005_Cell cycle induction by C5b-9 in aortic endothelial cells is RGC-32 dependent and this is in part through regulation of Akt and growth factor release. 19180477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19230171_Glomerular deposition of C5b-9 may participate in the development of glomerulosclerosis in primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19265162_In mesenchymal stem cells both C3a and C5a cause prolonged and robust extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 and proto-oncogene protein c-akt (Akt) kinase phosphorylation. 19324972_C5a recapitulates impaired peripheral blood neutrophil phagocytosis and significantly down-regulates neutrophil CD88 (complement component 5a receptor) expression in vitro 19336421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19375167_The absence of component C5 in the serum of 3 siblings from a Brazilian family with history of consanguinity, was observed. 19401279_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19414197_The characterization of these new mutations is interesting in order to elucidate structure-function relationships in the C5 gene and it also helps to understand the molecular basis of this uncommon deficiency. 19416238_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19479237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19559392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19565500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19674979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19741008_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19843088_Robust generation of both C3a and C5a by either the alternative pathway or classical pathway alone were observed with both mouse and human sera, after adherent IgG-induced complement activation. 19864026_Complement C5b-9 induce a JNK/Bid-dependent and JNK-independent necrotic cell death. 19902201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19909405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19909405_The tagging SNP rs17611 of the C5 gene and smoking may be associated with periodontitis among the Hong Kong Chinese population. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19918040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19918040_Results showed no influence of rs10818488 and rs2900180 TRAF1/C5 gene polymorphisms in susceptibility to and clinical expression of giant cell arteritis. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20022638_No consistent significant associations between C5 SNPs and age-related macular degeneration were found in any of these studies. 20022638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20030635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20049410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20109314_sinus mucosa expression is increased in chronic rhinosinusitis patients 20124699_desArg-C5a crystallizes as a dimer and each monomer in the dimer has a three-helix core instead of the four-helix bundle noted in the NMR structure determinations. 20133685_the crystal structure of the C5-SSL7 complex confirms that binding of SSL7 to C5 occurs exclusively through the C-terminal beta-grasp domain of SSL7 leaving the OB domain free to interact with IgA. 20143644_plasma protein levels correlate with asthma severity 20205706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20233754_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424189_C5a contributes to hemodialysis-associated thrombosis, stimulating TF and GCSF production. 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20479942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20545943_Staphylococcal superantigen-like 7 affects all three pathways of complement activation and inhibits the cleavage of C5 by interference of its binding to C5 convertases. 20591742_Excessive C5a in sepsis functions as a critical inflammatory mediator to enhance IL-8 production mainly through MAPK signaling pathways. 20603037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20797713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20813982_Data show that the colocalization of C5a, MMP-1, and MMP-9 in coronary plaques. 20822712_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20822712_Our results do not show that the PTPN22, STAT4 and TRAF1/C5 gene polymorphisms may confer a direct risk of cardiovascular disease disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 20880552_C5 complement inhibitor pexelizumab was associated with a nonsignificant 6.7% reduction in the primary composite endpoint of death or myocardial infarction at postoperative day 30 in coronary artery bypass graft patients. 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21393613_Single nucleotide polymorphism in complement 5 is associated with lower renal allograft function. 21926466_performed a robust prospective nationwide genetic association study in patients with bacterial meningitis and found that a common nonsynonymous complement component 5 (C5) SNP (rs17611) is associated with unfavorable disease outcome 22244896_Data show that incubation of C5 with cathepsin D resulted in generation of C5a, which was inhibited by the aspartate protease inhibitor pepstatin A. 22258234_Serum levels of the complement activation products C3a and C5a were significantly elevated throughout the entire observation period and correlated with the severity of traumatic brain injury and survival 22284611_We confirmed the positive association of rs10818488 A allele with rheumatoid arthritis in Tunisia. 22308306_A high correlation between FSAP activity and C5a was found in multiple trauma patients 22452399_Polymorphism of the complement 5 gene and cardiovascular outcome in patients with atherosclerosis 22496247_Intestinal epithelial cells express C5aR apically and directly respond to C5a through the ERK signaling pathway. 22500023_Crystal structure of C5b-6 suggests structural basis for priming assembly of the membrane attack complex. 22528500_Caveolin-1 and dynamin-2 are essential for removal of the complement C5b-9 complex via endocytosis. 22802338_Thrombin efficiently cleaved C5 at a newly identified, highly conserved R947 site, generating previously undescribed intermediates C5(T) and C5b(T). 22812419_The functional and structural aspects of complement C5 and its fragments. [Review] 22820624_An association was found between the rs10818488 polymorphism of TRAF1-C5 and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythemaosis in Europeans [Meta-analysis] 23028051_Evidence is provided for the capacity of C5a to generate a tumor microenvironment that favors lung cancer progression: lung cancer cell lines generate C5a; levels of anaphylatoxin are increased in plasma of non-small cell lung cancer patients. 23071133_provide evidence that complement factor C5a-induced mast cell activation is highly involved in vein graft disease 23235303_Serum level of initiating complement factor (C1q) but not complement regulator C5 is deficient in schizophrenic patients. 23321589_complement component 5 is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in North Africa group and rheumatoid arthritis in European population. 23371790_deletion mutation results in meningococcal infections in a Saudi family 23401592_Evolution-related complement protein C5 is a substrate of prostate-specific antigen as potential immunoregulatory protein in diseased prostates and prostatic fluid. 23602531_Letter: serum C5a was not elevated in chronic spontaneous urticaria. 23662819_The presence of a deleterious allele in the C5 and CFH single nucleotide polymorphisms may predispose patients to exhibit cognitive dysfunction after carotid endarterectomy. 23792503_Patients who receive living-related liver transplantation due to inherited metabolic diseases are prone to higher oxidative stress, complement 5a activity, and serum transforming growth factor-ss1. 23833239_C5 was synthesized but not secreted by lung or skin mast cells. 24060963_C5a, but not C5a-des Arg, was able to induce further heteromer formation between complement C5a receptors. 24316322_a significant up-regulation (173 fold increase, p A and C3 gene polymorphism in 220 Chinese patients 27381421_tumoral C5a is an independent adverse prognostic biomarker for clinical outcome of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma patients after nephectomy. 27444648_these results not only confirm the critical role of C5b-9 in complement-mediated hemolysis and but also highlight the critical role of C5b-9 in inflammasome activation. 27461873_The complement activation factors Bb, C3a, C5a, and MAC were increased significantly in early-onset severe pre-eclampsia (EOSPE) (all P<.01 and late-onset severe pre-eclampsia value: .027 .001 respectively compared with e c1q c4d were increased significantly in lospe .003 .014 l-control. synergises p. aeruginosa lps both pd-l1 expression the production of il-10 tgf-beta. determined genotypes five polymorphisms rs17611 rs4837805 rs7026551 rs1017119 c5 gene. univariate analysis was associated ischemic stroke additive model dominant recessive model. this sample patients genetic variation is higher prevalence is. cerebrospinal fluid preterm newborns enriched clear cell renal carcinoma had a poorer overall survival recurrence free after nephrectomy. found gg variant contributing to risk laa-subtype but unable find an association between functional outcome at days variants. therapeutic management neonatal hemochromatosis cannot only be based on c5b9 liver samples as it not specific disease. c5a inflammation cystic fibrosis. study provides preclinical rationale for combined blockade pd-1 restore antitumor immune responses inhibit tumor growth improve outcomes lung cancer results provide evidence that intrinsic generation may fully blocked by eculizumab various disease settings. controlling blocking induced signaling humans therefore warrants targeted approach findings together data from genomic databases indicate complement factor p.a252t mutation heterozygosity sub-saharan africa. have relevant role meningococcal susceptibility geographical area. response lie active fragments c3a acting through their receptors c3ar c5ar1 c5ar2 direct cellular inflammation. show neoepitope which exposed binding vivo. addition vitro experiment revealed c5ar deficiency promoted development regulatory t cells whereas activation abolished differentiation cells. shows c5a-induced changes neutrophil morphology during identified peripheral mrna levels two genes serping1 made unique contributions variance superior frontal cortical thickness. vertex-wise maps gene thickness across cortex suggested relationship especially strong region. sc5b-9 thrombotic microangiopathy allogeneic stem transplantation. potentiated tnfalpha-induced nf-kappab tubular epithelial pathway promotes gastric pathogenesis suppressing p21 via pi3k signaling. emerging roles progression treatment placental contributed pre eclampsia regulating trophoblasts dysfunctions. aureus-induced coagulation human whole blood mainly attributable upregulation monocyte tissue factors plasma tf activity. depression schizophrenia. granulocyte cd11b separation c5-dependent. apigenin reduced proliferation npc triggered negative regulation axis. these might new insight into function also potential strategy treating inhibition demonstrate mesenchymal pathogenic up-regulation fh improves our understanding immunomodulatory mechanisms mscs lupus nephritis. fumigatus conidial metalloprotease mep1p cleaves host major components c3 c4 c5. correlates degree kidney donor acute injury. absence clinical aki urinary concentrations associate recipient delayed graft function. there baseline intracellular normal cd4 t-cell rather down regulated. dna methylation involved senescence injury cord il-6 could used independent markers predict retinopathy prematurity laser models predicting rop good accuracy. traf1 locus developing neurocysticercosis mexican population. pivotal axis propagating diabetic disrupting mitochondrial agility thereby establishing immunometabolic dkd. contributes brain subarachnoid hemorrhage. induce cytokine release thrombin challenged gram-positive bacteria. killing requires anchoring membrane attack complex precursor c5b-7. protein mbl2 are dengue severity. induces pro-inflammatory microvesicle shedding severely injured patients. c5a-c5ar1 gpcr covid-19 therapeutics. type activating stat3 gut-kidney abdominal aortic aneurysm has prognostic growth. disseminated gonococcal infection japanese man novel mutation. significance metalloproteinase chemokine cxc ligand component different stages anca vasculitis. tenocytes under influence anaphylatoxin c5a. drives envenomation immunopathology snake naja annulifera. concentration future venous thromboembolism. system hellp syndrome. formation extracellular traps myeloid-derived suppressor promote metastasis. adaptation fibrosis increases recruitment. srgap3 linked paediatric allergic asthma italian cystitis enhancement adhesion colonization uropathogenic e. coli. adipsin maternal serum follicular implantation successful pregnancy obese women. elevation convalescents early c3bbbp or c4d.> | ENSMUSG00000026874 |
Hc |
128.122059 |
0.3346326337 |
-1.579350 |
0.243805768 |
40.835336 |
0.00000000016561132344996069311838651938624793896748244037553376983851194381713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000843195286002559373949568113091376092560480515203380491584539413452148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.2106315 |
11.3539202 |
205.2050416 |
23.6000626 |
| ENSG00000106829 |
7091 |
TLE4 |
protein_coding |
Q04727 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional corepressor that binds to a number of transcription factors. Inhibits the transcriptional activation mediated by PAX5, and by CTNNB1 and TCF family members in Wnt signaling. The effects of full-length TLE family members may be modulated by association with dominant-negative AES. Essential for the transcriptional repressor activity of SIX3 during retina and lens development and for SIX3 transcriptional auto-repression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
Predicted to enable transcription corepressor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within Wnt signaling pathway; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor; and negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. Part of beta-catenin-TCF complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7091; |
beta-catenin-TCF complex [GO:1990907]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
17060451_Gbx2 and Otx2 interact with the WD40 domain of Groucho/Tle corepressors 18258796_Knockdown of TLE1 or TLE4 levels increased the rate of cell division of the AML1-ETO-expressing Kasumi-1 cell line, whereas forced expression of either TLE1 or TLE4 caused apoptosis and cell death. 19714205_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19893608_germ cell-specific RBMY and hnRNP G-T proteins were more efficient in stimulating TLE4-T incorporation than somatically expressed hnRNP G protein. 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22169276_Grg4 recruits the arginine methyltransferase PRMT5 to chromatin resulting in symmetric H4R3 dimethylation. 22927467_Displacing coactivators CREB-binding protein/p300 while promoting the recruitment of a corepressor, Grg4. 24099773_Groucho related gene Grg4 robustly activates the expression of a BMP reporter gene, as well as enhancing and sustaining the upregulation of the endogenous Id1 gene induced by BMP7. 25631048_PPM1B interacts with Groucho 4 and is localized to DNA in a Groucho-dependent manner, and phosphatase activity is required for transcriptional silencing. 26701208_the results suggested that TLE4, a potential prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer, plays an important role in the development and progression of human colorectal cancer. 27486062_the loss of TLE4 confers proliferative advantage to leukemic cells, simultaneous with an upregulation of a pro- inflammatory signature mediated through aberrant increases in Wnt signaling activity 28262390_Genes TGFB1, TLE4 and MUC22 are associated with the risk of childhood asthma in Chinese population. 35099008_TLE4 regulates muscle stem cell quiescence and skeletal muscle differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000024642 |
Tle4 |
1191.367618 |
0.4160388357 |
-1.265210 |
0.073496174 |
291.044361 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002944427201685436795151788156765253207443349563921603415058480475126833860411822695867723586593404610264982253910884807195356812770222038351853102126839337786766946647443177198510966263711452484130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000829384456047271870165616483894025850721767071278520677900000007713537407548974507857366177560178079846411821038653738609423131546440478289952426638960265533641325053082482554600574076175689697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
701.2230432 |
38.5675395 |
1697.2396186 |
66.0358122 |
| ENSG00000106976 |
1759 |
DNM1 |
protein_coding |
Q05193 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated force-producing protein involved in producing microtubule bundles and able to bind and hydrolyze GTP. Most probably involved in vesicular trafficking processes. Involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Endocytosis;Epilepsy;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Methylation;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nitration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the dynamin subfamily of GTP-binding proteins. The encoded protein possesses unique mechanochemical properties used to tubulate and sever membranes, and is involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and other vesicular trafficking processes. Actin and other cytoskeletal proteins act as binding partners for the encoded protein, which can also self-assemble leading to stimulation of GTPase activity. More than sixty highly conserved copies of the 3' region of this gene are found elsewhere in the genome, particularly on chromosomes Y and 15. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1759; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane coat [GO:0030117]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; photoreceptor ribbon synapse [GO:0098684]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic endocytic zone membrane [GO:0098835]; synapse [GO:0045202]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; synaptic vesicle budding from presynaptic endocytic zone membrane [GO:0016185]; synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0048488]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
11782545_These findings suggest that dynamin is part of a protein network that controls nucleation of actin from membranes. 12896979_dynamin-dependent endocytosis is inhibited by syntaphilin 14739229_serglycin-bound granzyme B in high-molecular-weight degranulate material from cytotoxic T lymphocytes predominantly followed a dynamin-dependent pathway to kill target cells 15004222_Point mutations were made in the GTPase effector/assembly domain (GED)of dynamin 1 and tested for their effects on self-assembly and clathrin-mediated endocytosis. 15123615_dynamin-1 interacts with Sumo-1, Ubc9, and PIAS-1, all of which are members of the sumoylation machinery 15262989_Dynamin GTPase domain is important for GTP binding, GTP hydrolysis, and clathrin-mediated endocytosis 15872089_dynamin, Cbl, and Src coordinately participate in signaling complexes that are important in the assembly and remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton, leading to changes in osteoclast adhesion, migration, and resorption 16432212_S-nitrosylation of dynamin regulates endocytosis through nitric oxide 16622417_PLD functions as a GTPase activating protein (GAP) through its phox homology domain (PX), which directly activates the GTPase domain of dynamin and increased epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) endocytosis at physiological EGF concentrations. 16938290_Data show that swapping the highly homologous GTPase domain of dynamin-2 into dynamin-1 is sufficient to confer caspase-3 activation. 17170701_Two mutations in middle domain, R361S and R399A, disrupt the tetrameric structure of dynamin in the unassembled state and impair its ability to stably bind to and nucleate higher-order self-assembly on membranes. 17910478_Pockets of short-range transient order and restricted topological heterogeneity in the guanidine-denatured state ensemble of GED of DNM1. 18836734_Data show that dynamin-1 is an inclusion body component in neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease identified by anti-SUMO-1-immunocapture. 18987626_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987626_our findings indicate that DNM1 is likely involved in the etiology of nicotine dependence and represents a plausible candidate for further investigation in independent samples 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19515832_Data suggest that the components of the GTPase-GED interface act as an intramolecular signaling module, which we term the bundle signaling element, that can modulate dynamin function in vitro and in vivo. 19666604_The ability of dynamin to alter the local distribution of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) could be crucial for the role of this GTPase in promoting membrane scission during clathrin-mediated endocytosis. 19776347_Results demonstrate that, in concert with dynamin-1 self-assembly, pleckstrin homology domain membrane insertion is essential for fission and vesicle release in vitro and for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in vivo. 19859085_Endocytosis of FcalphaR is clathrin- and dynamin-dependent, but is not regulated by Rab5, and the endocytic motif is not located in the cytoplasmic domain of FcalphaR. 20428113_2.0 A resolution crystal structure of a human dynamin 1-derived minimal GTPase-GED fusion protein, which was dimeric in the presence of the transition state mimic GDP.AlF(4)(-) 20690924_In conclusion, Clostridium botulinum C2 toxin is endocytosed by dynamin-dependent mechanisms and we provide evidence for involvement of clathrin and Rho. 21056892_The authors find that HIV-1 entry into macrophages is sensitive to inhibitors of Na(+)/H(+) exchange, actin rearrangement, dynamin, Rac1, and Pak1. 21460182_A new role for the dynamin-1 GTPase in the regulation of fusion pore expansion 21927000_crystal structure of human dynamin 1 in the nucleotide-free state with a four-domain architecture comprising the GTPase domain, the bundle signalling element, the stalk and the pleckstrin homology domain. 21962517_Study presents the GMPPCP-bound structures of the truncated human dynamin 1 helical polymer at 12.2 A and a fusion protein, GG, linking human dynamin 1's catalytic G domain to its GTPase effector domain (GED) at 2.2 A. 22022400_Herpes simplex virus type 1 can enter human keratinocytes by alternative entry pathways that require dynamin and host cholesterol. 23024787_dyn1 affects amyloid generation through regulation of BACE-1 subcellular localization and therefore its enzymatic activities. 23705820_analysis of how the membrane interactions of disease-related dynorphin A variants cause differences in cell toxicity 23793749_The discovery that the pre-mRNA sequence of dnm1 in humans has sequence features similar to that of the alternative splicing patterns observed in insects greatly expands the applicability of the docking site-selector sequence pairing model to bilaterian animals. 23908769_activity-dependent acceleration is only prominent at physiological temperature and that the mechanism of this modulation is based on the dephosphorylation of dynamin 1 24478459_Alternate pleckstrin homology domain orientations regulate dynamin-catalyzed membrane fission. 24486840_Dynamin1 is associated with both preserved cognition and regenerative responses in older people with cerebrovascular disease and may represent a novel treatment target. 24616919_Data suggest that dynorphin A (DynA) is ligand for opioid receptor kappa (KOR); upon DynA binding, only small chemical shifts observed in second extracellular loop of KOR; chemical shift changes of DynA show conclusively that DynA interacts with KOR. 24673776_Data show that the classical dynamin DNM1 and DNM3 genes reach their maximum expression levels (100% of maximal expression) in all normal central nervous system tissues studied. 24970086_findings show NDPKs (NM23-H1/H2/H4) interact with and provide GTP to dynamins, allowing these motor proteins to work with high thermodynamic efficiency for membrane remodeling 25031323_determined the alpha-synuclein-binding domain of beta-III tubulin and demonstrated that a short fragment containing this domain can suppress alpha-synuclein accumulation in the primary cultured cells 25048004_This study identified and confirmed DNM1 protein changes within the postsynaptic density in schizophrenia. 25116793_Dynamin 1 and dynamin 2 activity are not essential for Chlamydia trachomatis internalization but is required for normal development. 25262651_De novo mutations in synaptic transmission genes including DNM1 cause epileptic encephalopathies. 25450229_The rare variants in DNM1 were significantly associated with smoking status. 25690657_Data suggest that by binding to both clathrin and F-actin, mammalian actin-binding protein 1 (mAbp1; HIP-55 or SH3P7) is specifically recruited at a late stage of clathrin-coated pits (CCPs) formation, which subsequently recruits dynamin to CCPs. 26123023_molecular simulations corroborate the bimodal character of dynamin action and indicate radial and axial forces as dominant, although not independent, drivers of hemi-fission and fission membrane- transformations, respectively 26139537_CRISPR-Cas9n-mediated knockout and reconstitution studies establish that dynamin-1 is activated by Akt/GSK3beta signaling in H1299 non-small lung cancer cells. 26165689_findings support a role for HTT on dynamin 1 function and ER homoeostasis. Proteolysis-induced alteration of this function may be relevant to disease. 26479317_Data indicate the dynamics of a dynamin 1-catalysed GTP hydrolysis and tube-severing reaction in real time using fluorescence microscopy. 26611353_study reports 2 patients with early onset epileptic encephalopathy possessing de novo DNM1 mutations; detected the novel mutation c.127G>A (p.Gly43Ser) in a patient with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, and a recurrent mutation c.709C>T (p.Arg237Trp) in a patient with West syndrome 26659814_Data indicate that stimulation of the dynamin GTPase activity by SH3 domains is determined by its middle domain. 26795593_Three genes in our epilepsy cohort (COQ4, DNM1, and PURA), accounting for 14% (3/21) of all novel genetic etiologies identified in patients with epilepsy, were subsequently confirmed in independent publications. 27094744_Hypoxic down-regulation of constitutive endocytosis is HIF-independent, and involves caveolin-1-mediated inhibition of dynamin-dependent, membrane raft endocytosis. 27449069_Down-regulation of Dyn1 activity enhances extracellular Nme1 in human colon tumor cell lines. 27788222_interation of DG with laminin and dynamin is involved in the regulation of AQP4 internalization 28049841_Dynamin isoforms differentially regulate the endocytosis and apoptotic signaling downstream of TRAIL-death receptor (TRAIL-DR) complexes in cancer cells. TRAIL stimulation activates ryanodine receptor-mediated calcium release from endoplasmic reticulum stores, leading to calcineurin-mediated dephosphorylation and activation of Dyn1, TRAIL-DR endocytosis, and increased resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 28171750_CLCb/Dyn1-dependent adaptive clathrin-mediated endocytosis selectively altered EGF receptor trafficking. 28667181_Study delineates the phenotypic spectrum of DNM1 encephalopathy, an emerging disease of synaptic vesicle fission characterized by severe to profound developmental delay, infantile-onset epilepsy beginning with infantile spasms, and movement disorder. The genetic landscape of DNM1 encephalopathy is notable for the recurrent c.709C>T (p.Arg237Trp) variant and localization of mutations to specific domains of the protein. 28933693_Together, these observations suggest that while endophilin helps shape endocytic tubules and recruit dynamin to endocytic sites, it can also block membrane fission when present in excess by inhibiting inter-dynamin interactions. 29022874_The authors show that in fibroblasts, dynamin GTP hydrolysis occurs as stochastic bursts, which are randomly distributed relatively to the peak of dynamin assembly. Thus, dynamin disassembly is not coupled to GTPase activity, supporting that the GTP energy is primarily spent in constriction. 29357276_The data show that the dynamin-amphiphysin helices are rearranged to form clusters upon GTP hydrolysis and membrane constriction occurs at protein-uncoated regions flanking the clusters. 29397573_The twin siblings exhibit mild to moderate intellectual disability and autistic symptoms but no epileptic encephalopathy. Exome sequencing revealed a genetic variant, c.1603A>G (p.Lys535Glu), in the PH domain of dynamin 1. The twin sisters studied here share the de novo variant, c.1603A>G (p.Lys535Glu) in exon 15 of DNM1, classified as likely pathogenic. 29800726_Cellular fluorescein hyperfluorescence is dynamin-dependent. 30069048_3.75 A resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the membrane-associated helical polymer of human dynamin-1 in the GMPPCP-bound state 34172529_Loss-of-function variants in DNM1 cause a specific form of developmental and epileptic encephalopathy only in biallelic state. 34274446_Dynamin regulates L cell secretion in human gut. 34518553_CryoEM structure of the super-constricted two-start dynamin 1 filament. |
ENSMUSG00000026825 |
Dnm1 |
218.790164 |
0.2629887222 |
-1.926927 |
0.598944607 |
9.176155 |
0.00245188586328231108990571840422489913180470466613769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005329872657149765415030007176255821832455694675445556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.8458961 |
30.6834227 |
387.9618400 |
84.9880013 |
| ENSG00000107020 |
55848 |
PLGRKT |
protein_coding |
Q9HBL7 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for plasminogen. Regulates urokinase plasminogen activator-dependent and stimulates tissue-type plasminogen activator-dependent cell surface plasminogen activation. Proposed to be part of a local catecholaminergic cell plasminogen activation system that regulates neuroendocrine prohormone processing. Involved in regulation of inflammatory response; regulates monocyte chemotactic migration and matrix metalloproteinase activation, such as of MMP2 and MMP9. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21940822}. |
Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Plasminogen activation;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of plasminogen activation. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55848; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010756] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21795689_Plg-R(KT) was highly expressed in bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cells, human pheochromocytoma tissue, PC12 pheochromocytoma cells, and murine hippocampus. 21940822_Plg-R(KT) plays a key role in the plasminogen-dependent regulation of macrophage invasion, chemotactic migration, and recruitment in the inflammatory response. 31316511_Plasminogen and the Plasminogen Receptor, Plg-RKT, Regulate Macrophage Phenotypic, and Functional Changes. 32842150_Exposure of plasminogen and a novel plasminogen receptor, Plg-RKT, on activated human and murine platelets. 34897983_The plasminogen receptor Plg-RKT regulates adipose function and metabolic homeostasis. 35454092_Plg-RKT Expression in Human Breast Cancer Tissues. |
ENSMUSG00000016495 |
Plgrkt |
144.111416 |
3.0297000753 |
1.599175 |
0.136594948 |
141.223102 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000001437995513225607073548451421599915379959777276679369553072174533398247928927145809514104302095915954851079732179641723632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000200045370171630171931905408828368899300729572384129928946763832898242136649055646514111517220158020791132003068923950195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
216.2239416 |
17.9579991 |
71.8204293 |
4.9014285 |
| ENSG00000107175 |
10488 |
CREB3 |
protein_coding |
O43889 |
FUNCTION: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-bound sequence-specific transcription factor that directly binds DNA and activates transcription (PubMed:9271389, PubMed:19779205, PubMed:10984507, PubMed:15845366, PubMed:16940180). Plays a role in the unfolded protein response (UPR), promoting cell survival versus ER stress-induced apoptotic cell death (PubMed:15845366, PubMed:16940180). Also involved in cell proliferation, migration and differentiation, tumor suppression and inflammatory gene expression. Acts as a positive regulator of LKN-1/CCL15-induced chemotaxis signaling of leukocyte cell migration (PubMed:19779205, PubMed:15001559, PubMed:17296613). Associates with chromatin to the HERPUD1 promoter (PubMed:16940180). Also induces transcriptional activation of chemokine receptors (PubMed:18587271, PubMed:17296613). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10984507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15001559, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15845366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16940180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17296613, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18587271, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19779205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9271389}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays a role in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) virus protein expression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17054986}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: (Microbial infection) May play a role as a cellular tumor suppressor that is targeted by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10675342}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: (Microbial infection) Plays a role in herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) latent infection and reactivation from latency. Represses the VP16-mediated transactivation of immediate early genes of the HSV-1 virus by sequestering host cell factor-1 HCFC1 in the ER membrane of sensory neurons, thereby preventing the initiation of the replicative cascade leading to latent infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10623756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15705566}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Functions as a negative transcriptional regulator in ligand-induced transcriptional activation of the glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1 by recruiting and activating histone deacetylases (HDAC1, HDAC2 and HDAC6). Also decreases the acetylation level of histone H4. Does not promote the chemotactic activity of leukocyte cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19779205}.; FUNCTION: [Processed cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3]: This is the transcriptionally active form that translocates to the nucleus and activates unfolded protein response (UPR) target genes during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response. Binds the cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AG][AG]-3') and C/EBP sequences present in many promoters to activate transcription of the genes. Binds to the unfolded protein response element (UPRE) consensus sequences sites. Binds DNA to the 5'-CCAC[GA]-3'half of ERSE II (5'-ATTGG-N-CCACG-3'). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16940180}.; FUNCTION: [Processed cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3]: (Microbial infection) Activates transcription of genes required for reactivation of the latent HSV-1 virus. It's transcriptional activity is inhibited by CREBZF in a HCFC1-dependent manner, by the viral transactivator protein VP16. Binds DNA to the cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AG][AG]-3') and C/EBP sequences present in many viral promoters. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10623756}.; FUNCTION: [Processed cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3]: (Microbial infection) It's transcriptional activity is inhibited by CREBZF in a HCFC1-dependent manner, by the viral transactivator HCV core protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10675342}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Signal-anchor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Unfolded protein response |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor that is a member of the leucine zipper family of DNA binding proteins. This protein binds to the cAMP-response element and regulates cell proliferation. The protein interacts with host cell factor C1, which also associates with the herpes simplex virus (HSV) protein VP16 that induces transcription of HSV immediate-early genes. This protein and VP16 both bind to the same site on host cell factor C1. It is thought that the interaction between this protein and host cell factor C1 plays a role in the establishment of latency during HSV infection. This protein also plays a role in leukocyte migration, tumor suppression, and endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated protein degradation. Additional transcript variants have been identified, but their biological validity has not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:10488; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; cAMP response element binding protein binding [GO:0008140]; CCR1 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031726]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cytoplasmic sequestering of transcription factor [GO:0042994]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; establishment of viral latency [GO:0019043]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902236]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of deacetylase activity [GO:0090045]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in unfolded protein response [GO:0006990]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; release from viral latency [GO:0019046]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
12138176_Data show that Luman is processed by regulated intramembrane proteolysis. The site 1 protease (S1P), a Golgi-resident enzyme, may be involved in the processing of Luman. 12271126_HCF-1 contains an activation domain (HCF-1(AD)) required for maximal transactivation by VP16 and its cellular counterpart LZIP. 15001559_LZIP binds to CCR1 and the interaction between CCR1 and LZIP participates in regulation of Lkn-1-dependent cell migration without affecting the chemotactic activities of other CC chemokines that bind to CCR1. 15705566_the host cell factor-binding transcription factor Luman is inhibited by Zhangfei 16940180_Results report the identification of Herp, a gene involved in ER stress-associated protein degradation (ERAD), as a direct target of Luman. 17192849_LZIP functions as a positive regulator in the NF-kappaB activation pathway that is triggered by Lkn-1 without affecting the transcriptional activation of NF-kappaB induced by other CCR1-dependent chemokines 17296613_factor NF-kappaB plays an important role in regulation of LZIP expression, and LZIP expression regulates the monocyte cell migration induced by Lkn-1 18189280_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18391022_Luman/CREB3 recruitment factor inhibits Luman activation of the unfolded protein response 19779205_sLZIP functions as a negative regulator in glucocorticoid-induced transcriptional activation of GR by recruitment and activation of HDACs 20473547_These findings suggest that HDAC3 selectively represses CREB3-mediated transcriptional activation and chemotactic signalling in human metastatic breast cancer cells. 20546900_DC-STAMP interacts with ER-resident transcription factor LUMAN which becomes activated during DC maturation. 22004728_sLZIP-regulated ARF4 expression in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate is involved in breast cancer cell migration. 22009750_sLZIP plays a critical role in MMP-9 expression and is probably involved in invasion and metastasis of cervical cancer 23023215_GSK3beta was downregulate in all samples and CREB3 did not show a significant decrease or increase in its mRNA expression, but the results were significant in mucoepidermoid carcinoma and salivary duct carcinoma. 23583719_propose that JAB1 is a novel binding partner of Luman, which negatively regulates the activity of Luman by promoting its degradation 24185178_A CREB3-ARF4 signalling cascade may be part of a Golgi stress response set in motion by stimuli compromising Golgi capacity. 24441043_Findings indicate that sLZIP negatively regulates AR transactivation in androgen-dependent PCa cells and functions as a positive regulator in tumor progression of androgen-independent PCa. sLZIP contributes to the malignant phenotype of PCa. 24481121_These results indicate that sLZIP plays a role in expression of c-Jun, and migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells via regulation of MMP-9 transcription. 25077563_human sLZIP plays a critical role in development of atherosclerosis and can be used as a therapeutic target molecule for treatment of atherosclerosis 25358080_INHA gene expression is upregulated by cAMP via CRE in human trophoblasts, and TFAP2 regulates this expression by interacting with CRE. 27405867_The authors found that the CREB3/Herp pathway limited the increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and apoptosis early in poliovirus infection and this may reduce the extent of poliovirus-induced damage to the central nervous system during poliomyelitis. 28179603_The essential parts of the Golgi stress response from the perspective of the organelle autoregulation. The pathways of the mammalian Golgi stress response have been identified, specifically the CREB3 pathway. 28205568_Luman, a ubiquitous, non-canonical unfolded protein response (UPR), is identified as a novel regulator of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced PRNP expression. 28246167_These findings indicate that LZIP is a novel modulator of APOA4 expression and hepatic lipid metabolism. 28662179_sLZIP is a novel co-repressor of ERalpha, and plays a negative role in ERalpha-mediated cell proliferation in breast cancer 28840565_In summary, the authors show here that hepatitis C virus infection is associated with an upregulation of ARF4, which promotes hepatitis C virus replication. Upon hepatitis C virus infection, CREB3 was redistributed to nucleus and activated ARF4 transcription. 29249802_CREB3 was identified as a transcriptional regulator of upregulated ER-Golgi trafficking genes ARF4, COPB1, and USO1, and silencing of these genes attenuated the metastatic phenotype in vitro and lung colonization in vivo. Modulation of ER-Golgi trafficking plays an important role in metastatic progression. 30940151_Results show that CREB3 is a direct target of miR-203a and is considered an oncogene in osteosarcoma tumors and cell lines. 31291699_Endogenous full-length CREB3 was identified as a novel substrate for ERAD in HEK293 cells. 31612863_Knockdown of CREB3 activates endoplasmic reticulum stress and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma. 31941600_The stability of CREB3/Luman is regulated by protein kinase CK2 phosphorylation. 33355643_Role of small leucine zipper protein in hepatic gluconeogenesis and metabolic disorder. 33803345_Comparative Analysis of CREB3 and CREB3L2 Protein Expression in HEK293 Cells. 35746643_CREB3 Plays an Important Role in HPSE-Facilitated HSV-1 Release in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000028466 |
Creb3 |
262.065367 |
2.0991412413 |
1.069799 |
0.108782667 |
97.193845 |
0.00000000000000000000006286174957487728569482519281314423258118002094986317286274743725699165608489238366018980741500854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000619385463100926973454397585146475959554214347853164694421919563016576404379520681686699390411376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
361.1730152 |
22.1252382 |
173.3600002 |
8.3097371 |
| ENSG00000107249 |
169792 |
GLIS3 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEA6 |
FUNCTION: Acts as both a repressor and activator of transcription. Binds to the consensus sequence 5'-GACCACCCAC-3' (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Congenital hypothyroidism;Diabetes mellitus;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene is a member of the GLI-similar zinc finger protein family and encodes a nuclear protein with five C2H2-type zinc finger domains. This protein functions as both a repressor and activator of transcription and is specifically involved in the development of pancreatic beta cells, the thyroid, eye, liver and kidney. Mutations in this gene have been associated with neonatal diabetes and congenital hypothyroidism (NDH). Alternatively spliced variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described but the full-length nature of only two have been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:169792; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
16715098_results demonstrate a major role for GLIS3 in the development of pancreatic beta cells and the thyroid, eye, liver and kidney 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18840781_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19430480_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20081858_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378605_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20419449_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21515849_Children and adolescents carrying glucose-raising alleles of G6PC2, MTNR1B, GCK, and GLIS3 also showed reduced beta-cell function, as indicated by homeostasis model assessment of beta-cell function. 21543335_Glis3 interacts with Suppressor of Fused (SUFU) 21747906_the associations of GLIS3-rs7034200 and CRY2-rs11605924 with fasting glucose, beta cell function, and type 2 diabetes 21949744_Alleles of single nucleotide polymorphisms in GLIS3 and ADCY5 may confer risk of type 2 diabetes. 23737756_The present data suggest that altered expression of the candidate gene GLIS3 may contribute to both type 1 and 2 type diabetes by favouring beta cell apoptosis 23856252_analysis of a GLIS3 variant that may have a role in resistance to Japanese type 1 diabetes 25122662_Whole exome sequencing followed by immunohistochemistry of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and tumors showed two structural variants resulting in fusion transcripts: DNAJB1-PRKCA and CLPTM1L-GLIS3. 26147758_It may play a role in a number of physiological processes controlled by Glis3. 26259131_New findings with GLIS3 phenotype including craniosynostosis, hiatus hernia, atrial septal defect, splenic cyst, and choanal atresia and confirm further cases with sensorineural deafness and exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. 27148679_we describe the common facial dysmorphism consisting of bilateral low-set ears, depressed nasal bridge with overhanging columella, elongated, upslanted palpebral fissures, persistent long philtrum with a thin vermilion border of the upper lip in a cohort of seven patients with GLIS3 mutations and report the emergence of a distinct, probably recognizable facial gestalt in this group which evolves with age. 27862917_Replication of lead type 2 diabetes mellitus SNPs in GLIS3, KCNK16, and ZFAND3 was observed in American Indians. Sex-specific T2DM signals in GLIS3 and ZFAND3, which are distinct from the East Asian GWAS signals, were also identified. 28597135_Individually the rs7020673 and rs10758593 SNPs are not significantly associated with T1DM but seem to interact in the predisposition for this disease. 28648506_Given the role of GLIS3 in transcriptional activation and repression during embryogenesis, in humans, GLIS3 mutations present with multisystem involvement that also includes renal cystic dysplasia, progressive liver fibrosis and osteopenia. Thyroid findings in GLIS3 patients include thyroid aplasia, diminished colloid with interstitial fibrosis at post-mortem.[review] 28846454_GLIS3 polymorphism is not associated with Dermatomyositis /Polymyositis in the Chinese Han population 29436472_We detect a genome-wide significant association at rs10116772 with knee and/or hip total joint replacement; for allele A, an intronic variant in GLIS3, which is expressed in cartilage of osteoarthritis patients. 29606121_Data did not show any associations of GLI similar 3 protein (GLIS3) gene polymorphisms rs806052, rs143051164, and rs149840771 with carbohydrate metabolism disorders among patients with maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) in Russia. 29992946_Data show that loss of zinc finger protein GLIS3 (GLIS3) causes beta-cell death. 30242153_RNA interference-mediated knockdown of the Drosophila ortholog of GLIS3 in insulin-producing cells, a model for mammalian beta cells, conferred reduced insulin output. 30376208_Authors show that GLIS3 binds to and directly regulates the transcription of several WNT genes, including the strong posteriorizing factor WNT3A, and that inhibition of WNT signaling is sufficient to abrogate GLIS3-induced posterior specification. 30399154_The SNP rs3753841 in COL11A1, rs1258267 in CHAT and rs736893 in GLIS3 are associated with PACG in northern Chinese people, and the association of genetic markers manifests a tendency of ethnic diversity. Larger population-based studies are warranted to reveal additional primary angle-closure glaucoma loci and ethnic aspects of primary angle-closure glaucoma. 30648929_GLIS rearrangements, particularly PAX8-GLIS3, are highly prevalent in hyalinizing trabecular but not in papillary thyroid carcinoma 31273314_PAX8-GLIS3 gene fusion is a pathognomonic genetic alteration of hyalinizing trabecular tumors of the thyroid. 31415576_Rare missense variants in GLIS3 associates nominally with increased level of HbA1c and increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In contrast, the rare p.I28V variant associate with reduced level of fasting plasma glucose and may be protective against type 2 diabetes. 32281515_Evaluation of the association between five genetic variants and primary open-angle glaucoma in a Han Chinese population. 32383186_Oncogenic properties and signaling basis of the PAX8-GLIS3 fusion gene. 32681364_Association study of the functional variants of the GLIS3 gene with risk of knee osteoarthritis. 32693112_Transcription factor GLIS3: Critical roles in thyroid hormone biosynthesis, hypothyroidism, pancreatic beta cells and diabetes. 32699115_Gene of the month: GLIS1-3. 33667596_Molecular and clinical genetics of the transcription factor GLIS3 in Chinese congenital hypothyroidism. 33852861_Neonatal diabetes mutations disrupt a chromatin pioneering function that activates the human insulin gene. 34093443_Case Report: Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Caused by a Novel GLIS3 Mutation in Twins. 34403660_GLIS family zinc finger 3 promoting cell malignant behaviors and NF-kappaB signaling in glioma. 34943978_GLIS3: A Critical Transcription Factor in Islet beta-Cell Generation. 36114444_A circular RNA derived from GLIS3 accelerates the proliferation of glioblastoma cells through competitively binding with miR-449c-5p to upregulate CAPG and GLIS3. 36206155_Gli-similar 3 (GLIS3) rs7020763 (C>G) polymorphism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. |
ENSMUSG00000052942 |
Glis3 |
496.287525 |
8.9095237056 |
3.155348 |
0.119924866 |
699.417983 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040019126580485518271694903115438489209417671219570607821658937513915484755350369969815521583122219179451364368405561503389961661711255028010236366756462409481797261624414120057 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000027601977024671317837851160383791816970108741680731241263722059022614259638468965136706313263616225812427878970972570167418929550027341115318230309554645871098842739141462481140 |
Yes |
No |
933.1494660 |
64.5319024 |
105.2413765 |
6.2687694 |
| ENSG00000107281 |
56654 |
NPDC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQX5 |
FUNCTION: Suppresses oncogenic transformation in neural and non-neural cells and down-regulates neural cell proliferation. Might be involved in transcriptional regulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56654; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
15229225_NPDC-1 has a role in regulating neuronal proliferation and is degraded by the ubiquitin/proteasome system through a PEST degradation motif 15563841_Human gene mapped to chromosome 9q34.3. |
ENSMUSG00000015094 |
Npdc1 |
1294.567189 |
0.2082948877 |
-2.263301 |
0.133083285 |
268.162938 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000285294871173808975837493013848141473338304297713123394969085961543998820457527836786633013804131165440641693796394516548265096673741028257748502435908050101076582905079703778028488159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000073361538301836600735198389602652397454983061025067499352809826183476376753864007172206922894032184041240758341348203110839933359635536606031957379027430565798795214504934847354888916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
461.5987898 |
43.3458255 |
2226.8363851 |
148.0587908 |
| ENSG00000107331 |
20 |
ABCA2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZC7 |
FUNCTION: Probable lipid transporter that modulates cholesterol sequestration in the late endosome/lysosome by regulating the intracellular sphingolipid metabolism, in turn participates in cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:15238223, PubMed:21810484, PubMed:24201375) (Probable). May alter the transbilayer distribution of ceramide in the intraluminal membrane lipid bilayer, favoring its retention in the outer leaflet that results in increased acid ceramidase activity in the late endosome/lysosome, facilitating ceramide deacylation to sphingosine leading to the sequestration of free cholesterol in lysosomes (PubMed:24201375). In addition regulates amyloid-beta production either by activating a signaling pathway that regulates amyloid precursor protein transcription through the modulation of sphingolipid metabolism or through its role in gamma-secretase processing of APP (PubMed:22086926, PubMed:26510981). May play a role in myelin formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P41234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15238223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21810484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22086926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24201375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26510981, ECO:0000305|PubMed:15999530}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Endosome;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Lysosome;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intracellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the ABC1 subfamily. Members of the ABC1 subfamily comprise the only major ABC subfamily found exclusively in multicellular eukaryotes. This protein is highly expressed in brain tissue and may play a role in macrophage lipid metabolism and neural development. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:20; |
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex [GO:0043190]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; ceramide floppase activity [GO:0099038]; endopeptidase regulator activity [GO:0061135]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; cellular sphingolipid homeostasis [GO:0090156]; central nervous system myelin formation [GO:0032289]; ceramide translocation [GO:0099040]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; ganglioside metabolic process [GO:0001573]; glycosphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006687]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; negative regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0090370]; negative regulation of intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032384]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905598]; negative regulation of phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0071072]; negative regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:1905601]; negative regulation of sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0090155]; negative regulation of steroid metabolic process [GO:0045939]; positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process [GO:0042986]; positive regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902993]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process [GO:0032805]; regulation of intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032383]; regulation of post-translational protein modification [GO:1901873]; regulation of protein glycosylation [GO:0060049]; regulation of protein localization to cell periphery [GO:1904375]; regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000008]; regulation of steroid metabolic process [GO:0019218]; response to cholesterol [GO:0070723]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sphingomyelin metabolic process [GO:0006684]; sphingosine biosynthetic process [GO:0046512]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
12363033_roles for this largest known ABC protein in neural transmembrane lipid export 12560508_Reciprocal regulation of expression of the ABCA2 promoter by the early growth response-1 and Sp-family transcription factors. 15093135_It is likely that expression of ABCA2 by two independent promoters constitutes locus of regulation controlling expression of the protein to meet requirements in different tissues. 15155565_Increased expression of ABCA2 may be causally linked with altered expression of genes associated with the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. 15649702_Among the 45 ABCA2 single nucleotide polymorphisms(SNPs) we tested, one synonymous SNP (rs908832) was found significantly associated with AD in both samples. 15850583_the expression patterns of ABCA2 in combination with other markers showed phenotypic heterogeneity in schwannomas 16752360_Data suggest that ABCA2 may exert population-dependent effects on the genetic risk for sporadic Alzheimer's disease and support a role of ABC lipid transporters in the pathogenesis of this disease. 16752360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18336955_No association of ABCA2 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism on chromosome 9 with Alzheimer's disease. 18336955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20704561_A possible biochemical mechanism links ABCA2 expression, amyloid precursor protein processing, and Alzheimer's disease. 21041019_we demonstrate that ABCA2-deficiency inhibits prostate tumor metastasis in vivo and decreases chemotactic potential of cells 21072184_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21707071_SLC2A1/GLUT1, SLC1A3/EAAT1, and SLC1A2/EAAT2 were the main SLC proteins whereas ABCG2/BCRP, ABCB1/MDR1, ABCA2 and ABCA8 were the main ABC quantified in isolated brain microvessels 22086926_Down-regulation of the ATP-binding cassette transporter 2 (Abca2) reduces amyloid-beta production by altering Nicastrin maturation and intracellular localization. 24145140_Our findings indicate a considerable and direct relationship between mRNA expression levels of ABCA2, ABCA3, MDR1, and MRP1 genes and positive minimal residual disease (MRD) measured after one year of treatment. 29224028_The analyses results suggested ABCA2 mRNA expression was upregulated significantly in AD compared with controls in all datasets. 29630744_High expression of ABCA2 is associated with drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 32752121_Results from a Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) in Mastocytosis Reveal New Gene Polymorphisms Associated with WHO Subgroups. |
ENSMUSG00000026944 |
Abca2 |
838.198425 |
0.2932152956 |
-1.769968 |
0.145859849 |
140.778659 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000001798632141750620136677805227496403080804348834901578708257088502813050986703229691763411546290285514260176569223403930664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000249509496355631122386755147948073659319959212527652805742847869099951127819510634554822647857008632854558527469635009765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
380.9579627 |
38.3818551 |
1308.4203286 |
93.8670372 |
| ENSG00000107438 |
9124 |
PDLIM1 |
protein_coding |
O00151 |
FUNCTION: Cytoskeletal protein that may act as an adapter that brings other proteins (like kinases) to the cytoskeleton (PubMed:10861853). Involved in assembly, disassembly and directioning of stress fibers in fibroblasts. Required for the localization of ACTN1 and PALLD to stress fibers. Required for cell migration and in maintaining cell polarity of fibroblasts (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P52944, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10861853}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the enigma protein family. The protein contains two protein interacting domains, a PDZ domain at the amino terminal end and one to three LIM domains at the carboxyl terminal. It is a cytoplasmic protein associated with the cytoskeleton. The protein may function as an adapter to bring other LIM-interacting proteins to the cytoskeleton. Pseudogenes associated with this gene are located on chromosomes 3, 14 and 17. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]. |
hsa:9124; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; filamentous actin [GO:0031941]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; muscle alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051371]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; establishment or maintenance of actin cytoskeleton polarity [GO:0030950]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; heart development [GO:0007507]; maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0030011]; muscle structure development [GO:0061061]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; stress fiber assembly [GO:0043149] |
10861853_Enigma protein shown to interact with alpha actinin 2 by yeast two-hybrid screening and immunochemistry (co-localization at myocardial Z-disks). 11110697_CLP-36 contains a PDZ- and LIM domain, is widely expressed, interacts with actinin-1, actinin-2 and actinin-4, and localizes to actin stress fibers. The gene (7 exons) is localised to contig NT_008878.2 on chromosome 10. 11973348_results establish the CLP-36 PDZ-LIM protein as an adapter, recruiting the Clik1 kinase to actin stress fibers in nonmuscle cells, and suggest that Clik1 represents a novel regulator of actin stress fibers 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16609848_We present evidence for the exclusive protein expression of CLP36 in proliferative and early post-proliferative trophoblast cells. 17213842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21651830_PDLIM1 showed moderate parent-of origin effects for some single nucleotide polymorphisms in attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. 21680739_Alpha-actinin-4 and CLP36 protein deficiencies contribute to podocyte defects in multiple human glomerulopathies 22851037_Robust co-regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation sites has been revealed on novel protein interactions between EGFR and PDLIM1. 22922308_Femtomolar Zn2+ affinity of LIM domain of PDLIM1 protein uncovers crucial contribution of protein-protein interactions to protein stability. 24662836_Our results identify CLP36 as an important regulator of breast cancer cell migration and metastasis, and shed light on how increased CLP36 expression contributes to the progression of breast cancer. 26119933_PDLIM1 was shown to interact with p75(NTR) in highly invasive patient-derived glioma stem cells/tumor-initiating cells and shRNA knockdown of PDLIM1 in vitro and in vivo results in complete ablation of p75(NTR)-mediated invasion. 26701804_downregulation of PDLIM1 in colorectal cancer samples correlated with reduced E-cadherin and membrane beta-catenin levels 27068564_High titers of both TYMS and PDLIM1 serum autoantibodies were significantly more prevalent in breast cancer cases than in controls. 31509262_PDLIM1 Inhibits Tumor Metastasis Through Activating Hippo Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 31986893_MicroRNA-370-3p inhibits cell proliferation and induces chronic myelogenous leukaemia cell apoptosis by suppressing PDLIM1/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 33022122_Distribution of PDLIM1 at actin-rich structures generated by invasive and adherent bacterial pathogens. 33181636_Hyperprogression on immunotherapy with complete response to chemotherapy in a NSCLC patient with high PD-L1 and STK11: A case report. |
ENSMUSG00000055044 |
Pdlim1 |
27.872904 |
0.1716157988 |
-2.542746 |
0.364768920 |
54.633999 |
0.00000000000014520175952586005112697831495423938968675377225725497964958776719868183135986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000909668069015999349543018212849001185660649526631971184542635455727577209472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2884206 |
2.1501809 |
48.8329853 |
6.8423384 |
| ENSG00000107551 |
83937 |
RASSF4 |
protein_coding |
Q9H2L5 |
FUNCTION: Potential tumor suppressor. May act as a KRAS effector protein. May promote apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15574778}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor |
|
The function of this gene has not yet been determined but may involve a role in tumor suppression. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants; however, most of the variants have not been fully described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:83937; |
cell cycle [GO:0007049]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19066393_Single nucleotide polymorphism in RASSF4 gene is associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 23954638_expression of SPRR1B is upregulated in oral CSCs/CICs and SPRR1B has a role in cell growth by suppression of RASSF4 25701784_RASSF4 promotes EV71 replication and the production of viral progeny to accelerate the inhibition of the phosphorylation of AKT. 26526576_the present study suggested that RASSF4 serves as an important tumor suppressor in human nonsmall cell lung cancer . 28081736_RASSF4 overexpression inhibits proliferation, invasion, EMT, and Wnt signaling pathway in osteosarcoma cells. 28600435_RASSF4 controls store operated calcium entry and endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane junctions through ARF6-dependent regulation of PM PI(4,5)P2 levels, pivotal for a variety of physiological processes. 29259009_Loss of RASSF4 Expression in Multiple Myeloma Promotes RAS-Driven Malignant Progression. 31508857_RASSF4 is required for skeletal muscle differentiation. 34121238_Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway participates in the effect of miR-626 on oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RASSF4. |
ENSMUSG00000042129 |
Rassf4 |
220.915039 |
0.2124066137 |
-2.235099 |
0.197745873 |
122.550979 |
0.00000000000000000000000000017486400928725319585396514393868222842093559627899360639872070637773233676807993486335135457920841872692108154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000002126023704349141213080051513638191026128166331381772853460024154875285598564893518869212130084633827209472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
74.7788615 |
10.1857757 |
354.4584558 |
33.0614499 |
| ENSG00000107614 |
1787 |
TRDMT1 |
protein_coding |
O14717 |
FUNCTION: Specifically methylates cytosine 38 in the anticodon loop of tRNA(Asp). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16424344}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;tRNA processing |
|
This gene encodes a protein responsible for the methylation of aspartic acid transfer RNA, specifically at the cytosine-38 residue in the anticodon loop. This enzyme also possesses residual DNA-(cytosine-C5) methyltransferase activity. While similar in sequence and structure to DNA cytosine methyltransferases, this gene is distinct and highly conserved in its function among taxa. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:1787; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; tRNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016428]; tRNA methyltransferase activity [GO:0008175]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; tRNA C5-cytosine methylation [GO:0002946]; tRNA methylation [GO:0030488]; tRNA modification [GO:0006400]; tRNA stabilization [GO:0036416] |
12794065_identification of residual DNA-(cytosine-C5) methyltransferase activity 16173030_cDNA microarray analysis identified several genes involved in DNA methylation, such as DNMT2 and DNMT3a that were more highly expressed in LNCaP-r (an androgen sensitive prostate cancer cell line). 16424344_genetic and biochemical approach revealed that DNMT2 did not methylate DNA but instead methylated aspartic acid transfer RNA (tRNA(Asp)) and that DNMT2 specifically methylated cytosine 38 in the anticodon loop 17533396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_An association study of 45 folate-related genes in spina bifida: Involvement of tRNA aspartic acid methyltransferase 1 (TRDMT1) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19246518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19763880_The expression of DNMT1, DNMT2, DNMT3A and DNMT3B in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients, was investigated. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20147412_Hepatitis B virus-induced overexpression of DNMTs leads to viral DNA methylation and decreased viral gene expression and also leads to methylation of host CpG islands. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20864816_the role of Dnmt2 in stress granules could represent a primitive cellular defense mechanism against viral infection. 22591353_Mapped is the tRNA binding site of DNMT2 by systematically mutating surface-exposed lysine and arginine residues to alanine and studying the tRNA methylation activity and binding of the corresponding variants. 22942708_DNMT1, DNMT2 and DNMT3A may play important roles in gastric cancer carcinogenesis. 25747896_The strong effect of some of the somatic cancer mutations on DNMT2 activity suggests that these mutations have a functional role in tumorigenesis. 28476776_Data suggest that, upon HIV-1 infection, DNMT2 is re-localized from the nucleus to cytoplasmic stress granules where DNMT2 methylates HIV-1 messenger RNA; this methylation increases the stability of the HIV-1 RNA genome and up-regulates virus replication; thus, DNMT2 appears to facilitate HIV-1 infection. 31570165_TRDMT1 has a role in 5-methylcytosine modification of mRNA and in HEK293 cell proliferation and migration 33331537_Trdmt1 3'-untranslated region functions as a competing endogenous RNA in leukemia HL-60 cell differentiation. 33369458_Decoding the Genetic Alterations in Genes of DNMT Family (DNA Methyl-Transferase) and their Association with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 34100772_TRDMT1 participates in the DNA damage repair of granulosa cells in premature ovarian failure. 34139673_The lack of functional DNMT2/TRDMT1 gene modulates cancer cell responses during drug-induced senescence. 34871455_Position 34 of tRNA is a discriminative element for m5C38 modification by human DNMT2. |
ENSMUSG00000026723 |
Trdmt1 |
50.927148 |
5.0344227145 |
2.331826 |
0.866381069 |
5.533516 |
0.01865557515505925079146720690914662554860115051269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.033690968957380953985314420151553349569439888000488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.8071400 |
26.2406393 |
8.5603515 |
3.7507140 |
| ENSG00000107731 |
219699 |
UNC5B |
protein_coding |
Q8IZJ1 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for netrin required for axon guidance. Mediates axon repulsion of neuronal growth cones in the developing nervous system upon ligand binding. Axon repulsion in growth cones may be caused by its association with DCC that may trigger signaling for repulsion (By similarity). Functions as netrin receptor that negatively regulates vascular branching during angiogenesis. Mediates retraction of tip cell filopodia on endothelial growth cones in response to netrin (By similarity). It also acts as a dependence receptor required for apoptosis induction when not associated with netrin ligand (PubMed:12598906). Mediates apoptosis by activating DAPK1. In the absence of NTN1, activates DAPK1 by reducing its autoinhibitory phosphorylation at Ser-308 thereby increasing its catalytic activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08722, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K1S3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12598906}. |
Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the netrin family of receptors. This particular protein mediates the repulsive effect of netrin-1 and is a vascular netrin receptor. This encoded protein is also in a group of proteins called dependence receptors (DpRs) which are involved in pro- and anti-apoptotic processes. Many DpRs are involved in embryogenesis and in cancer progression. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:219699; |
membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; netrin receptor activity [GO:0005042]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; anterior/posterior axon guidance [GO:0033564]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068] |
12359238_Modulation of G(ialpha(2)) signaling by the axonal guidance of this protein 12655055_may represent tumor suppressor that inhibit tumor extension outside the region of netrin-1 availability by inducing apoptosis 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18469807_PIKE-L acts as a downstream survival effector for netrin-1 through UNC5B in the nervous system 18719102_Knockdown of Netrin-4 expression in EC increased their ability to form tubular structures; Netrin-4 bound only to neogenin but not to Unc5B or Unc5C receptors 19273616_In this study, we show that Unc5B, a member of the netrin receptor family, interacts with neogenin as a coreceptor for RGMa. 19570425_Netrin-1 can promote the potential of proliferation and invasion of extravillous trophoblasts in vitro through its receptors neogenin and UNC5B. 19822088_Stronger expression of UNC5B and UNC5C receptors in synovial fibroblasts might contribute to the disordered phenotype of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. 19826074_UNC5B receptor is localized to villous and extravillous cytotrophoblasts proximal to anchoring areas during the first trimester. 20092749_Down-regulation of UNC5b gene expression is related to angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21172653_The recruitment of PP2A to UNC5H2/B allows the activation of DAPk via a PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation and that this mechanism is involved in angiogenesis regulation. 21238923_Robo4 specifically binds to UNC5B, a vascular Netrin receptor, revealing unexpected interactions between two endothelial guidance receptors. 21922135_The mRNA expression analysis using tissue samples revealed that UNC5B mRNA was down-expressed in about 20% of CRC patients, and the patients with low-UNC5B-expression tumors showed a significantly higher recurrence rate after curative surgery. 22252496_Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 controls the expression of the uncoordinated-5-B receptor, but not of netrin-1, in first trimester human placenta 23055195_Low UNC5B expression was an independent risk factor for postoperative recurrence in patients with different stages and grades bladder cancer. 23312517_Reducing Unc5b levels in Sip1 knockout slices and brains rescues cell migration in cortical interneurons. 23526078_UNC5B was downregulated in kidney carcinoma. 23599441_UNC5B protein expressed in macrophages in hypoxic regions of atherosclerotic regions in human. 23666553_Higher netrin-1 and lower UNC5B expression in all prostate carcinoma cell lines indicated that netrin-1 and UNC5B could be used to predict metastasis. 24122613_Data indicate that dysregulation of expression of netrin-1 NTN1 in smooth muscle cell (SMC) and its chemorepulsive receptor UNC5B in macrophages are involved in the development of atherosclerosis and unstable plaques. 24528886_UNC5B expression is decreased in bladder cancer cells compared to normal bladder cell lines. 24584118_unc5b expression is greater in adipose tissue of obese versus lean subjects. 27846823_Our results suggest that UNC5B overexpression inhibits the proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cells by inducing cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. 27910960_Negative regulation of Naa10 towards NTN1 and its receptor UNC5B were also detected upon treatment of all-trans retinoid acid, which was often used to induce morphological differentiation. 29158083_These findings point to a new important function of UNC5B and provide a potential basis for hASCs-mediated bone regeneration. 29893424_LncRNA TNRC6C-AS1 regulates UNC5B in thyroid cancer to influence cell proliferation, migration, and invasion as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-129-5p. 30805847_UNC5B-AS1 plays an important role in tumourigenesis and metastasis of PTC and may be a potential therapeutic target for PTC. 31769036_Netrin-1 and its receptor Unc5b may have essential roles in periodontal inflammation 31884526_Netrin-1 works with UNC5B to regulate angiogenesis in diabetic kidney disease. 31914695_silencing of UNC5B, an NTN4 receptor, abrogated the NTN4-induced cellular activities of SEPCs in vitro and blood-flow recovery and neovascularization in vivo in ischemic muscle by reducing EPC homing and incorporation. 32196578_LncRNA UNC5B-AS1 promotes malignant progression of prostate cancer by competitive binding to caspase-9. 32231305_Netrin-1 promotes naive pluripotency through Neo1 and Unc5b co-regulation of Wnt and MAPK signaling. 32372016_UNC5B mediates G2/M phase arrest of bladder cancer cells by binding to CDC14A and P53. 32404521_Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Induces Apoptosis in Mammalian Cells through the UNC5B Pathway in a PP2A-Dependent Manner. 32762046_UNC-5 netrin receptor B regulates adipogenesis of human adipose-derived stem cells through JNK pathway. 33345442_The intracellular domain of UNC5B facilities proliferation and metastasis of bladder cancer cells. 33706585_Long non-coding RNA PITPNA-AS1 regulates UNC5B expression in papillary thyroid cancer via sponging miR-129-5p. 34239689_UNC5B Promotes Vascular Endothelial Cell Senescence via the ROS-Mediated P53 Pathway. 34381052_A ligand-insensitive UNC5B splicing isoform regulates angiogenesis by promoting apoptosis. 34470826_Delta40p53 isoform up-regulates netrin-1/UNC5B expression and potentiates netrin-1 pro-oncogenic activity. 35974411_Netrin-1 induces the anti-apoptotic and pro-survival effects of B-ALL cells through the Unc5b-MAPK axis. |
ENSMUSG00000020099 |
Unc5b |
119.866221 |
4.3873493875 |
2.133350 |
0.161547372 |
185.185009 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000357609473850230164462465612148813990324951934504750112470549704485807866917811192542669014550174105535106181680271575373808445874601602554321289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000062987062458584698815104020639271129645622163414064525388064801339903152629570000564990943308011902488892722051794237358990358188748359680175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
199.6266678 |
19.1200380 |
45.8457334 |
3.7723098 |
| ENSG00000107736 |
64072 |
CDH23 |
protein_coding |
Q9H251 |
FUNCTION: Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins. They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells. CDH23 is required for establishing and/or maintaining the proper organization of the stereocilia bundle of hair cells in the cochlea and the vestibule during late embryonic/early postnatal development. It is part of the functional network formed by USH1C, USH1G, CDH23 and MYO7A that mediates mechanotransduction in cochlear hair cells. Required for normal hearing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11138009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16679490}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Hearing;Membrane;Metal-binding;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Usher syndrome;Vision |
|
This gene is a member of the cadherin superfamily, whose genes encode calcium dependent cell-cell adhesion glycoproteins. The encoded protein is thought to be involved in stereocilia organization and hair bundle formation. The gene is located in a region containing the human deafness loci DFNB12 and USH1D. Usher syndrome 1D and nonsyndromic autosomal recessive deafness DFNB12 are caused by allelic mutations of this cadherin-like gene. Upregulation of this gene may also be associated with breast cancer. Alternative splice variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:64072; |
catenin complex [GO:0016342]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cochlear hair cell ribbon synapse [GO:0098683]; kinocilium [GO:0060091]; membrane [GO:0016020]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; photoreceptor ribbon synapse [GO:0098684]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium tip [GO:0032426]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; equilibrioception [GO:0050957]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; post-embryonic animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0048563]; regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051480]; response to stimulus [GO:0050896]; sensory perception of light stimulus [GO:0050953]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11857743_Three novel CDH23 mutations have been identified in patients with Usher syndrome type 1D. 12075507_patients with mutations in CDH23 display a wide range of hearing loss and retinitis pigmentosa phenotypes 12485990_the shaping of the hair bundle relies on a functional unit composed of myosin VIIa, harmonin b and cadherin 23 that is essential to ensure the cohesion of the stereocilia 12522556_Mutations in the calcium-binding motifs of CDH23 and the 35delG mutation in GJB2 cause hearing loss in one family 15537665_CDH23 and PCDH15 play an essential long-term role in maintaining the normal organization of the stereocilia bundle. 15660226_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15882574_Describes cloning of human and mouse isoforms B1, B2, C1 and C2. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16550584_Missense mutations in CDH23 have been associated with presbycusis and nonsyndromic prelingual hearing loss (DFNB12), whereas null alleles cause the majority of Usher syndrome (Usher 1D). 16598924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16598924_individuals with the rs1227049 CC genotype, rs3802711 TT genotype and GG genotype in the terminal position of exon 7 of CDH23 might be more susceptible to noise induced hearing loss. 16679490_Disease causing mutations were identified in 31 of the 34 families referred: 17 in MYO7A, 6 in CDH23, 6 in PCDH15, and 2 in USH1C. 17672918_the apparent occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 11 is discussed 17850630_analysis of CDH23 mutations in Japanese patients with non-syndromic hearing loss 18273900_Four missense mutations have been described in USH1 patients in a homozygous state. 18323324_Molecular genetic analysis was performed in 11 patients and pathogenic mutations were identified in all cases: (mutation in cadherin 23 gene in 6 cases). Two new mutations in the CDH23 gene never reported were found. 18348277_35 SNP-s were identified. The nonsynonymous SNPs localized to the part of the gene encoding the extracellular domain of Cadherin 23, (ectodomains 5, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, and 22). One amino acid change occurred at a conserved position in ectodomain 5. 18368581_Screening revealed that in Japanese, mutation in CDH23 is the major causes of hearing loss. 18429043_Based on our results it is estimated that about 20% of patients with Usher syndrome type I have CDH23 mutations. 18957941_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19268276_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19297620_The structures of the harmonin N-domain alone and in complex with the cadherin 23 internal peptide fragment uncovered the detailed binding mechanism of this interaction between harmonin and cadherin 23. 19683999_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20498078_determined the structure of the extracellular cadherin (EC)1-EC2 domains of cadherin 23, which binds to protocadherin 15 to form tip links of mechanosensory hair cells. 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20844544_Five mutations (three in MYO7A and two in CDH23) were identified in four of five unrelated patients with Usher syndrome type 1. 21940737_One non-syndromic deafness allele (DFNB12) in trans configuration to an Usher syndrome allele (USH1D) of CDH23 preserves vision and balance in deaf individuals, indicating that the DFNB12 allele is phenotypically dominant to an USH1D allele. 22413011_cadherin-23 is up-regulated in breast cancer tissue versus normal tissue and we propose that cadherin-23-mediated heterotypic adhesion between invading tumor cells and stromal fibroblasts may play a role in the metastatic cascade. 22581638_Despite that the Ahl allele of Cdh23 had been implicated with ARHI in mice, we found no positive association of the CDH23 tag SNP in intron 7 with ARHI in Han Chinese. 22879593_Large protein assemblies formed by multivalent interactions between cadherin23 and harmonin suggest a stable anchorage structure at the tip link of stereocilia 22899989_mutations of the CDH23 gene are an important cause of non-syndromic hearing loss. 23770805_Hearing loss was found to co-segregate with locus-specific STR markers for CDH23 in 1 Pakistani family. 24416283_Description of the spectrum of mutations in CDH23 in 374 families with autosomal recessive, non-syndromic hearing loss from India. 24448297_The results of this study confirm that CDH23 genetic variant may modify the susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss development in humans 24767429_mutations in the CDH23 gene are one of the most important causes of non-syndromic hearing loss in East Asians. 25493955_possible role in the deterioration of kidney function [meta-analysis] 25963016_The results revealed that CDH23 mutations are highly prevalent in patients with congenital high-frequency sporadic or recessively inherited hearing loss 26264712_Four (3.1 %) of 128 children carried two CDH23 mutant alleles, and SLC26A4 and GJB2 accounted for 18.0 and 17.2 %, respectively and showed profound nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss with minimal residual hearing. 26878454_A new diagnosis of sector retinitis pigmentosa was found to have two novel compound heterozygous mutations in CDH23, including one missense (c.8530C > A; p.Pro2844Thr) and one splice-site (c.5820 + 5G > A) mutation. 27349180_data suggest that CDH23-C is a CAMSAP3/Marshalin-binding protein that can modify MT networks indirectly through its interaction with CAMSAP3/Marshalin. 27792758_an important contribution of CDH23 mutations to poslingual Sensorineural Hearing Loss 28413019_We have identified CDH23 mutations as a genetic risk factor for both familial and sporadic pituitary adenoma. 29148562_19 variants including 6 pathogenic missense mutations were identified among South Indian assortative mating hearing-impaired individuals 30033219_Crystal structures showing 18 CDH23 extracellular cadherin (EC) repeats, including the most and least conserved, a fragment carrying disease mutations, and EC repeats with non-canonical Ca(2+)-binding motif sequences and unusual secondary structure. Deafness mutations' effects on stability and affinity for Ca(2+). Additionally, contiguous CDH23 EC repeats reveals helicity and potential parallel dimerization faces. 30747484_data indicate the role of Cdh23 as a suppressor of cell migration. 32276436_High-Throughput Sequencing Identifies 3 Novel Susceptibility Genes for Hereditary Melanoma. 32306668_Gene polymorphisms in CDH23 might associate significantly with the risk of noise-induced hearing loss 32468012_A novel highly frequent singlenucleotide polymorphism site of cadherin 23 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation based on whole exome sequencing. 32835555_A novel missense mutation locus of cadherin 23 and the interaction of cadherin 23 and protocadherin 15 in a patient with usher syndrome. 32911884_[Study on syndromic deafness caused by novel pattern of compound heterozygous variants in the CDH23 gene]. 33205915_Novel homozygous variants in the TMC1 and CDH23 genes cause autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. 33794607_[Nonsyndromic deafness due to compound heterozygous mutation of the CDH23 gene]. 34252883_Methylation silencing CDH23 is a poor prognostic marker in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 34752165_Cochlear Implantation Outcomes in Children With CDH23 Mutations-Associated Hearing Loss. 35786118_Association between genetic polymorphisms of cadherin 23 and noise-induced hearing loss: a meta-analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000012819 |
Cdh23 |
51.099211 |
0.2437606593 |
-2.036463 |
0.269256412 |
58.377416 |
0.00000000000002163605139557943879743755460335874977729998455688864567036944208666682243347167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000142629798391582190295570210926687901753680265404256033434648998081684112548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.7922519 |
4.5333050 |
78.5698928 |
12.5516596 |
| ENSG00000107738 |
64115 |
VSIR |
protein_coding |
Q9H7M9 |
FUNCTION: Immunoregulatory receptor which inhibits the T-cell response (PubMed:24691993). May promote differentiation of embryonic stem cells, by inhibiting BMP4 signaling (By similarity). May stimulate MMP14-mediated MMP2 activation (PubMed:20666777). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20666777, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24691993}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables endopeptidase activator activity; enzyme binding activity; and identical protein binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of cytokine production; positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process; and regulation of T cell activation. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64115; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endopeptidase activator activity [GO:0061133]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:0046636]; negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:2000562]; negative regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:2000565]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032700]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of collagen catabolic process [GO:0120158]; positive regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010950]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045591]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; zymogen activation [GO:0031638] |
20666777_Results suggest that GI24 contributes to tumor-invasive growth in the collagen matrix by augmenting cell surface MT1-MMP. 25279955_overexpression of the newly described co-stimulatory molecule, PD1 homologue (PD-1H) in human monocyte/macrophages is sufficient to induce spontaneous secretion of multiple cytokines. 26228159_p53-induced expression of DD1alpha prevents persistence of cell corpses and ensures efficient generation of precise immune responses in mice. 28236118_Taken together, the results indicated that the VISTA high and CD8 low group, as an immunosuppressive subgroup, might be associated with a poor prognosis in primary OSCC. These findings indicated that VISTA might be a potential immunotherapeutic target in OSCC treatment. 28258694_this review describes the functions of VISTA in the context of cancer immunotherapy 28776578_This study is the first to describe the expression of VISTA-expressing lymphocytes in melanoma samples and in the context of acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors 29203588_The immunomodulatory role of VISTA in human NSCLC. 29216931_VISTA expression supports immune-complex inflammation in collagen antibody-induced arthritis and VISTA is expressed in human synovium 29720116_VISTA protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma showed cell specific and displayed different prognosis 29737375_High VISTA expression is associated with primary cutaneous melanoma. 29771768_Data indicate that VISTA is predominantly expressed and up-regulated in the high-density infiltrated immune cells but minimal in pancreatic cancerous cells. 30106102_EGFR may be involved in immune evasion, possibly through regulation of B7H5 expression in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. 30128738_High VISTA expression is associated with colorectal carcinoma. 30220083_this study shows that VSIG-3 as a ligand of VISTA inhibits human T-cell function 30306644_This study is the first to demonstrate that in the CNS, VISTA is expressed by microglia, and that VISTA is differentially expressed in CNS pathologies. 30382166_The data suggest that VISTA is a novel immunosuppressive factor within the tumour microenvironment, as well as a new target for cancer immunotherapy. 30635425_VISTA may be a relevant immunotherapy target for effective treatment of patients with pancreatic cancer. 31088847_Hypoxia-Induced VISTA Promotes the Suppressive Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. 31363159_Expression of V-set immunoregulatory receptor in malignant mesothelioma. 31484064_Structure and Functional Binding Epitope of V-domain Ig Suppressor of T Cell Activation. 31537897_V-domain Ig-containing suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA), a potentially targetable immune checkpoint molecule, is highly expressed in epithelioid malignant pleural mesothelioma. 31645726_findings identify a mechanism by which VISTA may engender resistance to anti-tumour immune responses, as well as an unexpectedly determinative role for pH in immune co-receptor engagement 31781843_VISTA was detected in 51.4% of all samples and 46.6% of PD-L1-negative samples in patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Furthermore, VISTA expression was associated with pathologic type and PD-L1 expression. Moreover, VISTA expression in tumor cells, but not in immune cells, was associated with prolonged progression-free and overall survival in patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. 31883303_Overexpression of B7H5/CD28H is associated with worse survival in human gastric cancer. 31901178_VISTA protein (B7-H5) is a ligand for transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 2 protein (CD28H) and is widely expressed in tumor cells. B7-H5 expression is closely related to the prognosis of the tumor [Review]. 31940493_FOXD3 Regulates VISTA Expression in Melanoma. 31949051_VISTA is therefore a distinctive negative checkpoint regulator of naive T cells that is critical for steady-state maintenance of quiescence and peripheral tolerance. 32060343_Prognostic value of VISTA in solid tumours: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 32117584_Expression of TIM3/VISTA checkpoints and the CD68 macrophage-associated marker correlates with anti-PD1/PDL1 resistance: implications of immunogram heterogeneity. 32205423_Galectin-9 and VISTA Expression Define Terminally Exhausted T Cells in HIV-1 Infection. 32266446_Low VISTA expression is associated with breast cancer. 32600443_VISTA: an immune regulatory protein checking tumor and immune cells in cancer immunotherapy. 32873829_The prognostic significance of VISTA and CD33-positive myeloid cells in cutaneous melanoma and their relationship with PD-1 expression. 33086339_High VISTA Expression Correlates With a Favorable Prognosis in Patients With Colorectal Cancer. 33178206_VISTA Re-programs Macrophage Biology Through the Combined Regulation of Tolerance and Anti-inflammatory Pathways. 33250890_The Expression Pattern and Clinical Significance of the Immune Checkpoint Regulator VISTA in Human Breast Cancer. 33329552_Ligand-Receptor Interactions of Galectin-9 and VISTA Suppress Human T Lymphocyte Cytotoxic Activity. 33396515_LAG-3, TIM-3 and VISTA Expression on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma-Potential Biomarkers for Targeted Therapy Concepts. 33770210_Expression of VISTA on tumor-infiltrating immune cells correlated with short intravesical recurrence in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. 33889438_VISTA and PD-L1 synergistically predict poor prognosis in patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. 34106206_VISTA is an activating receptor in human monocytes. 34465822_Superpixel image segmentation of VISTA expression in colorectal cancer and its relationship to the tumoral microenvironment. 34660778_Soluble B7-H5 Is a Novel Diagnostic, Severity, and Prognosis Marker in Acute Pancreatitis. 34728682_The immune checkpoint VISTA exhibits high expression levels in human gliomas and associates with a poor prognosis. 34752423_Kidney VISTA prevents IFN-gamma/IL-9 axis-mediated tubulointerstitial fibrosis after acute glomerular injury. 35056382_VISTA, PDL-L1, and BRAF-A Review of New and Old Markers in the Prognosis of Melanoma. 35187955_Different clinical significance of novel B7 family checkpoints VISTA and HHLA2 in human lung adenocarcinoma. 35521773_Expression and clinical significance of VISTA and PD-L1 in adrenocortical carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000020101 |
Vsir |
66.504644 |
0.3942863315 |
-1.342684 |
0.230212000 |
34.345731 |
0.00000000461411265887218241674104830135107191413368354915292002260684967041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000020788859232281262583391065771817873830684675340307876467704772949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.3116619 |
5.8265541 |
100.3082499 |
9.5332625 |
| ENSG00000107816 |
84445 |
LZTS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BRK4 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of katanin-mediated microtubule severing and release from the centrosome. Required for central spindle formation and the completion of cytokinesis. May negatively regulate axonal outgrowth by preventing the formation of microtubule bundles that are necessary for transport within the elongating axon. Negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway. Represses beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation by promoting the nuclear exclusion of beta-catenin. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17000760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17351128, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17950943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18490357}. |
Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Mitosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the leucine zipper tumor suppressor family of proteins, which function in transcription regulation and cell cycle control. This family member can repress beta-catenin-mediated transcriptional activation and is a negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway. It negatively regulates microtubule severing at centrosomes, and is necessary for central spindle formation and cytokinesis completion. It is implicated in cancer, where it may inhibit cell proliferation and decrease susceptibility to tumor development. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:84445; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; midbody [GO:0030496]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; microtubule severing [GO:0051013]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; nuclear export [GO:0051168]; spindle midzone assembly [GO:0051255]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17000760_LZTS2 is a beta-catenin-interacting protein and modulates beta-catenin signaling and localization 17950943_The reciprocal crosstalk between beta-catenin/Tcf pathway and NF-kappaB signaling in hMSCs is mediated through the regulation of lzts2 expression. 18490357_LAPSER1 C terminal domain inhibits katanin(p80/p60)-mediated microtubule severing in vitro. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23275340_deletion of Lzts2 increases susceptibility to spontaneous and carcinogen-induced tumor development. 23761130_LZTS2 could inhibit cell proliferation and cell cycle transition at the G1/S phase and was implicated in the regulation of proteins associated with the canonical Wnt pathway, including GSK3B and beta-catenin through inactivating the Akt pathway. 29409973_Study found that LZTS2 was downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients and predicted poor prognosis. Functionally, we showed that LZTS2 suppresses tumorigenesis and radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a p85-dependent manner. 29499699_LZTS2 promoter hypermethylation is associated with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 33420362_beta-Trcp and CK1delta-mediated degradation of LZTS2 activates PI3K/AKT signaling to drive tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35287088_LZTS2: A novel and independent prognostic biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000035342 |
Lzts2 |
319.975199 |
0.3255810320 |
-1.618911 |
0.096698673 |
289.214065 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007375732052064905258253598832839786622600052814325183504494889132965301152133509260718860486171680918394647516334061577052998926792030081122847216922598282242209966064194759383099153637886047363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002061852369099962133338146900086936177909321874515052211662775049308450552847044626784920509850775877532394000008680367220467681638419068990743869133692360660209397238418205233756452798843383789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
154.1574230 |
9.4791304 |
476.9010956 |
17.9837207 |
| ENSG00000107829 |
6468 |
FBXW4 |
protein_coding |
P57775 |
FUNCTION: Probably recognizes and binds to some phosphorylated proteins and promotes their ubiquitination and degradation. Likely to be involved in key signaling pathways crucial for normal limb development. May participate in Wnt signaling. |
Developmental protein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway;WD repeat;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene is a member of the F-box/WD-40 gene family, which recruit specific target proteins through their WD-40 protein-protein binding domains for ubiquitin mediated degradation. In mouse, a highly similar protein is thought to be responsible for maintaining the apical ectodermal ridge of developing limb buds; disruption of the mouse gene results in the absence of central digits, underdeveloped or absent metacarpal/metatarsal bones and syndactyly. This phenotype is remarkably similar to split hand-split foot malformation in humans, a clinically heterogeneous condition with a variety of modes of transmission. An autosomal recessive form has been mapped to the chromosomal region where this gene is located, and complex rearrangements involving duplications of this gene and others have been associated with the condition. A pseudogene of this locus has been mapped to one of the introns of the BCR gene on chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6468; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12913067_a complex rearrangement associated with a approximately 0.5 Mb tandem duplication ion containing a disrupted extra copy of the DACTYLIN gene and the entire LBX1 and beta-TRCP genes. 16235095_results indicate that genomic rearrangement of SHFM3 is rare among non-syndromic SHFM patients and emphasize the importance of screening for genomic rearrangements even in sporadic cases of SHFM 16761290_Genomic rearrangements involving the SHFM3 locus at chromosome 10q24 is associated with syndromic and non-syndromic split-hand/foot malformation 23658844_biochemical characterization of the novel F-box and WD40 containing protein, FBXW4 |
ENSMUSG00000040913 |
Fbxw4 |
91.667665 |
0.4891625837 |
-1.031614 |
0.301157301 |
11.404747 |
0.00073256689249609691690773294325822462269570678472518920898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001747363822437361094083718704439434077357873320579528808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.8538591 |
11.3548770 |
121.2148563 |
16.5527954 |
| ENSG00000107833 |
10360 |
NPM3 |
protein_coding |
O75607 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of diverse cellular processes such as ribosome biogenesis, chromatin remodeling or protein chaperoning (PubMed:22362753, PubMed:20073534). Modulates the histone chaperone function and the RNA-binding activity of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23/NPM (PubMed:22362753). Efficiently mediates chromatin remodeling when included in a pentamer containing NPM3 and NPM (PubMed:15596447). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15596447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20073534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22362753}. |
Acetylation;Chaperone;Direct protein sequencing;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is related to the nuclear chaperone phosphoproteins, nucleoplasmin and nucleophosmin. This protein is strongly expressed in diverse cell types where it localizes primarily to the nucleus. Based on its similarity to nucleoplasmin and nucleophosmin, this protein likely functions as a molecular chaperone in the cell nucleus. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:10360; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; rRNA transcription [GO:0009303] |
19710011_Acetylation of transition protein 2 (TP2) by KAT3B (p300) alters its DNA condensation property and interaction with putative histone chaperone NPM3. 20073534_NPM3 lacks intrinsic histone chaperone activity, inhibits histone assembly activity of NPM1 in vitro, and dramatically enhances transcription in a cellular system. 22362753_Characterization of the sperm chromatin decondensation and nucleosome assembly activities of homo- and hetero-oligomers of NPM1,NPM2 and NPM3. 22968912_Studies indicate that histone chalerones nucleoplasmin (NPM2/NPM3) preferentially associated with histones H2A-H2B in the egg and the nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP) families. |
ENSMUSG00000056209 |
Npm3 |
28.018437 |
3.8426263973 |
1.942093 |
0.304487459 |
42.728704 |
0.00000000006288273852013487609209977339538117854789156524475401965901255607604980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000329715531281417660847140784364638771419819818220275919884443283081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
47.1889633 |
9.3941044 |
12.2863442 |
2.0256209 |
| ENSG00000107937 |
23560 |
GTPBP4 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZE4 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the biogenesis of the 60S ribosomal subunit (PubMed:32669547). Acts as TP53 repressor, preventing TP53 stabilization and cell cycle arrest (PubMed:20308539). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20308539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32669547}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;GTP-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis;Ubl conjugation |
|
GTP-binding proteins are GTPases and function as molecular switches that can flip between two states: active, when GTP is bound, and inactive, when GDP is bound. 'Active' in this context usually means that the molecule acts as a signal to trigger other events in the cell. When an extracellular ligand binds to a G-protein-linked receptor, the receptor changes its conformation and switches on the trimeric G proteins that associate with it by causing them to eject their GDP and replace it with GTP. The switch is turned off when the G protein hydrolyzes its own bound GTP, converting it back to GDP. But before that occurs, the active protein has an opportunity to diffuse away from the receptor and deliver its message for a prolonged period to its downstream target. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23560; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; preribosome binding [GO:1990275]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000463]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022408]; negative regulation of collagen binding [GO:0033342]; negative regulation of DNA replication [GO:0008156]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17210637_NGB is a tumor suppressor that regulates and requires merlin to suppress cell proliferation 27720713_GTPBP4 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by disrupting actin cytoskeleton, which is mediated by the reduced RhoA activity.Up-regulation of GTPBP4 in colorectal carcinoma is responsible for tumor metastasis. 33134380_Determining the Clinical Value and Critical Pathway of GTPBP4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Using a Bioinformatics Strategy: A Study Based on Datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas. 33204302_An Integrating Immune-Related Signature to Improve Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 34783233_LncRNA FGD5-AS1 functions as an oncogene to upregulate GTPBP4 expression by sponging miR-873-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma. 36116159_GTPBP4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via the PKM2 dependent glucose metabolism. |
ENSMUSG00000021149 |
Gtpbp4 |
241.410775 |
2.0983396602 |
1.069248 |
0.165810305 |
40.983009 |
0.00000000015355844824389135363209247169224936843678896991605142829939723014831542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000785350899542562772215390751477312458739277190034044906497001647949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
316.3447042 |
46.2471197 |
152.4085455 |
16.4241755 |
| ENSG00000108175 |
57178 |
ZMIZ1 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULJ6 |
FUNCTION: Acts as transcriptional coactivator. Increases ligand-dependent transcriptional activity of AR and promotes AR sumoylation. The stimulation of AR activity is dependent upon sumoylation (PubMed:14609956, PubMed:26522984). Also functions as a transcriptional coactivator in the TGF-beta signaling pathway by increasing the activity of the SMAD3/SMAD4 transcriptional complex (PubMed:16777850). Involved in transcriptional activation of a subset of NOTCH1 target genes including MYC. Involved in thymocyte and T cell development (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of postmitotic positioning of pyramidal neurons in the developing cerebral cortex (PubMed:30639322). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P1E1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14609956, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16777850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26522984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30639322}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the PIAS (protein inhibitor of activated STAT) family of proteins. The encoded protein regulates the activity of various transcription factors, including the androgen receptor, Smad3/4, and p53. The encoded protein may also play a role in sumoylation. A translocation between this locus on chromosome 10 and the protein tyrosine kinase ABL1 locus on chromosome 9 has been associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:57178; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030521]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; developmental growth [GO:0048589]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of nucleic acid-templated transcription [GO:1903508]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; pyramidal neuron migration to cerebral cortex [GO:0021852]; regulation of protein sumoylation [GO:0033233]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; vitellogenesis [GO:0007296] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16777850_First line of evidence demonstrates a physiological role for endogenous Zimp10 in regulating Smad3/4-mediated transcription. 17512505_(RAI17) was found to be upregulated in WT-Add1 vs MUT-Add1 overexpressing cells, possibly representing a key molecule/axis for the functional Add1-induced effect 17584785_Expression of exogenous hZimp10 enhances the transcriptional activity of p53 and knockdown of endogenous hZimp10 reduces the transcriptional activity of p53. 17967885_provides evidence to demonstrate a crucial role for Zimp10 in vasculogenesis 18007576_Fusion of ZMIZ1 to ABL1 is associated with a B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a t(9;10)(q34;q22.3) translocation 19795399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19929986_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20473688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23161489_ZMIZ1 and activated NOTCH1 are coexpressed in a subset of human T-ALL patients and cell lines. 23426136_ZMIZ1 is overexpressed in a significant percentage of human breast, ovarian, and colon cancers in addition to human squamous cell carcinomas, suggesting that ZMIZ1 may play a broader role in epithelial cancers. 24667117_ZMIZ1 is a susceptibility gene for vitiligo in Chinese population. 26163108_This case represents the first constitutional balanced translocation disrupting and fusing both MIZ-type containing and proline-rich 12 and provides clues for the potential function and effects of these in the central nervous system. 26403403_the expression of SENP8, SAE1, PIAS1, PIAS2 and ZMIZ1 is deregulated in the majority of PTC tissues, likely contributing to the PTC phenotype. 26522984_Targeting the NOTCH1-ZMIZ1 interaction might combat leukemic growth. 26624892_At the ZMIZ1 locus, we show that perturbation of ZMIZ1 expression in human islets and beta-cells influences exocytosis and insulin secretion, highlighting a novel role for ZMIZ1 in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. 28063629_we have identified a molecular phenotype of MS defined by expression of the MS risk gene ZMIZ1 in blood, and by other genes, especially transcription factors. ZMIZ1 expression is affected by, and interacts with, the environmental risk factors EBV and Vitamin D. 28447608_In a two-stage genome-wide association study and subsequent replication study to identify genetic factors associated with primary dysmenorrhoea in Chinese women, analysis provided evidence of a significant (P |
ENSMUSG00000007817 |
Zmiz1 |
794.559474 |
2.3540384720 |
1.235138 |
0.061496979 |
407.193160 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000149660974849385196773585211064127711737297168491153513893278023263554668986748344365074516648074482328170821197837496789868381964304650180640267862731922947299450114553071335687838890493850840236535643101420536460673690968420368463398517633 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000056786529274471087972334475359116918529267223127316600817379287540439594178131143226434279875680261165247058594377339515525327858474224490228854354896274263553687030007940943450377982973390770593160708595044856770138203688746969532985531259 |
Yes |
No |
1125.7150627 |
38.8179975 |
481.6536569 |
13.2780411 |
| ENSG00000108179 |
10105 |
PPIF |
protein_coding |
P30405 |
FUNCTION: PPIase that catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and may therefore assist protein folding (PubMed:20676357). Involved in regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) (PubMed:26387735). It is proposed that its association with the mPTP is masking a binding site for inhibiting inorganic phosphate (Pi) and promotes the open probability of the mPTP leading to apoptosis or necrosis; the requirement of the PPIase activity for this function is debated (PubMed:26387735). In cooperation with mitochondrial p53/TP53 is involved in activating oxidative stress-induced necrosis (PubMed:22726440). Involved in modulation of mitochondrial membrane F(1)F(0) ATP synthase activity and regulation of mitochondrial matrix adenine nucleotide levels (By similarity). Has anti-apoptotic activity independently of mPTP and in cooperation with BCL2 inhibits cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis (PubMed:19228691). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99KR7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19228691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20676357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22726440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26387735}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Isomerase;Mitochondrion;Necrosis;Reference proteome;Rotamase;S-nitrosylation;Transit peptide |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) family. PPIases catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and accelerate the folding of proteins. This protein is part of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Activation of this pore is thought to be involved in the induction of apoptotic and necrotic cell death. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10105; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex [GO:0005757]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; cyclosporin A binding [GO:0016018]; peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity [GO:0003755]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; cellular response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0071243]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in programmed cell death [GO:1902686]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of ATP-dependent activity [GO:0032780]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0090324]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler activity [GO:2000276]; negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090201]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization [GO:0000413]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability [GO:0046902]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in programmed necrotic cell death [GO:1902445]; regulation of necrotic cell death [GO:0010939]; regulation of proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0010849]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931] |
12077116_Cyclophilin D protects cell from cell death. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18076075_Crystal structure of human cyclophilin D in complex with its inhibitor, cyclosporin A at 0.96-A resolution, using a K133I mutant of human CypD 18614807_There was increased [Ca(2+)](c), [Ca(2+)](m), mCICR, MPTP opening, and expression of cyclophilin D and decreased DeltaPsim in POAG TM cells compared with control cells. 19735641_Cyclophilin D may play a role as a redox sensor in mitochondria of mammalian cells transmitting information on the redox environment to target proteins. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20978188_Data show that show that the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) directly associates with cyclophilin D (CypD). 21121808_adult viable human brain and liver mitochondria possess an active CypD-sensitive mitochondrial permeability transition 22013052_Human coronavirus-induced neuronal programmed cell death required cyclophilin d but not caspase 3 caspase 9 activities. 22892127_These results suggest Cyp-D's critical role in UVB/oxidative stress-induced skin cell death. 23303179_CypD directs mitochondria-to-nuclei inflammatory gene expression in normal and tumor cells 23845906_cisplatin-induced non-apoptotic death requires mitochondria Cyp-D-p53 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells 24343341_The p53/Cyp-D mitochondrial complexation was prevented by CsA or Cyp-D silencing. 24946211_In summary, the results of the present study provide mechanistic evidence that both apoptosis and programmed necrosis attribute to berberine's cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells. 25445707_molecular determinants necessary for Cyclophilin D activity regulation and binding to proposed pore constituents thereby regulating the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. 25837584_Cyp-D silencing down-regulated mitochondrial transcripts initiated from the heavy strand promoter 2 [i.e., NADH dehydrogenase 1 (ND1) by 11-fold; cytochrome oxidase 1 (COX1) by 4-fold; and ATP synthase subunit 6 (ATP6) by 6.5-fold. 26387735_Results show that CypD interacts with SPG7 and VDAC to form the mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex (PTP)and its CsA-binding region is necessary for PTP formation. 27515399_The influx of unfolded p53 into the mitochondrial matrix in response to oxidative stress indirectly activates the normally inhibited CypD by displacing it from Trap1 complexes. This activates CypD's isomerase activity. Liberated CypD then isomerizes multiple proteins including p53 (causing p53 aggregation) and the structural components of the mPTP pore, inducing pore opening. 27864141_cyclophilin D may modify mitochondrial features by inducing the translocation of molecules to the mitochondria through the mechanism associated with cellular energy metabolism 27916505_CyPD regulates mitochondrial metabolism, and likely cell survival, by promoting more efficient electrons flow through the respiratory chain via increased supercomplex formation 27993675_The present study is to investigate the role of CypD in regulating the mitochondrial dynamics relevant to oxidative stress induced neuron dysfunctions. 28351946_Binding of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) to cyclophilin D (CypD) was important for reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production after oxidative stress. 28378042_This review discusses previous studies to provide comprehensive information on the physiological role of cyclophilin D as well as PTP opening in the cell that can be taken into consideration for the development of new PTP inhibitors. [review] 30558250_the important yet enigmatic nature of CyPD (PPIF) somehow makes it a master regulator, yet a troublemaker, for mitochondrial function. 31884421_Targeting cyclophilin-D by miR-1281 protects human macrophages from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced programmed necrosis and apoptosis. 32041924_microRNA-1203 targets and silences cyclophilin D to protect human endometrial cells from oxygen and glucose deprivation-re-oxygenation. 32275395_RNase T1 Refolding Assay for Determining Mitochondrial Cyclophilin D Activity: A Novel In Vitro Method Applicable in Drug Research and Discovery. 33495413_Overexpression of TICRR and PPIF confer poor prognosis in endometrial cancer identified by gene co-expression network analysis. 34681682_Formation of High-Conductive C Subunit Channels upon Interaction with Cyclophilin D. |
ENSMUSG00000021868 |
Ppif |
1345.554781 |
6.1961579617 |
2.631374 |
0.063908359 |
1720.330848 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2329.3074500 |
77.7962400 |
378.4223476 |
11.0297997 |
| ENSG00000108379 |
7473 |
WNT3 |
protein_coding |
P56703 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors (Probable). Functions in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway that results in activation of transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family (PubMed:26902720). Required for normal gastrulation, formation of the primitive streak, and for the formation of the mesoderm during early embryogenesis. Required for normal formation of the apical ectodermal ridge (By similarity). Required for normal embryonic development, and especially for limb development (PubMed:14872406). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14872406, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26902720, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It encodes a protein which shows 98% amino acid identity to mouse Wnt3 protein, and 84% to human WNT3A protein, another WNT gene product. The mouse studies show the requirement of Wnt3 in primary axis formation in the mouse. Studies of the gene expression suggest that this gene may play a key role in some cases of human breast, rectal, lung, and gastric cancer through activation of the WNT-beta-catenin-TCF signaling pathway. This gene is clustered with WNT15, another family member, in the chromosome 17q21 region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7473; |
endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [GO:0044338]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904954]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in osteoblast differentiation [GO:0044339]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in stem cell proliferation [GO:1905474]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; dorsal/ventral axis specification [GO:0009950]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; gamete generation [GO:0007276]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; head morphogenesis [GO:0060323]; limb bud formation [GO:0060174]; mammary gland epithelium development [GO:0061180]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of collateral sprouting in absence of injury [GO:0048697]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; Spemann organizer formation at the anterior end of the primitive streak [GO:0060064]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089] |
11788904_Regulation of WNT3 and WNT3A mRNAs in human cancer cell lines NT2, MCF-7, and MKN45 15293277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15588944_Wnt3 plays an important role in regulating characteristics and activity of stromal cells. 16890161_The Wnt-3a triggers the interaction of LRP6 with caveolin and promotes recruitment of Axin to LRP6 phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and that caveolin thereby inhibits the binding of beta-catenin to Axin. 18044981_an internally truncated LRP5 receptor is strongly implicated in deregulated activation of the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hyperparathyroid tumors 18309246_The results indicated that HBx induction in the CCL13-HBx stable cell line downregulated Wnt-3/beta-catenin expression and suppressed cell growth by repressing cell proliferation or triggering cell apoptosis. 18313787_a functional interaction between Wnt3 and FZD7 leading to activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in HCC cells and may play a role during hepatocarcinogenesis. 18413325_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18563180_CTLA-4 is a direct target of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and is expressed in human melanoma tumors 18606139_WNT3 regulates distinct internalization pathways of LRP6 to tune the activation of beta catenin signaling. 18787224_mantle cell lymphoma highly and consistently expressed Wnt3 and Wnt10. 19365403_WNT activity regulates the self-renewal of prostate cancer cells with stem cell characteristics independently of androgen receptor activity. 19421142_RNA samples from 21 neuroblastoma showed a highly significant FZD1 and/or MDR1 overexpression after treatment, underlining a role for FZD1-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in clinical chemoresistance. 19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19863181_Results demonstrated significant up-regulation of WNT-3, WNT-4, WNT-5B, WNT-7B, WNT-9A, WNT-10A, and WNT-16B in patients with CLL compared to normal subjects. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20709709_Abnormalities of the Wnt3/3a pathway (located in the apical ectodermal ridge) include tetra-amelia and loss of the distal phalanges/nails. 20890934_Individuals carrying variant alleles in WNT3 presented an increased risk for cleft lip/palate (p = 0.0003; OR, 1.61; 95% CI, 1.29-2.02) in the Brazilian population studied. 20890934_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21314951_Extracellular domain of FZD7 (sFZD7) was tested for its functional activity to interact with Wnt3, its ability to inhibit Wnt3-mediated signaling. 21789800_SNP rs415430 in the WNT3 gene was not associated with the risk of development of Parkinson disease 22070884_The apoptotic index was significantly lower in high-Wnt3 tumors than in low-Wnt3 tumors (P=0.0245). 22112025_The findings of a significant association between lip and/or palate clefts and two markers in the WNT3 and COL11A2 genes were the most consistent and were observed in all groups analysed and stratified. 22288914_study confirmed the involvement of polymorphisms in the WNT3 gene in NCL/P aetiology in the tested population. 23071104_Knockdown of Wnt3 by siRNA restored cytoplasmic expression of beta-catenin. 24052941_mRNA level of WNT3 in hESCs correlates with their definitive ectoderm differentiation efficiency. 24162018_Colorectal tumors express elevated levels of Wnt3 and GPR177. 24303070_WNT3 inhibits cerebellar granule neuron progenitor proliferation and medulloblastoma formation via MAPK activation. 24344732_WNT3 and WNT5B are critical factors, secreted from mesenchymal cancer cells, for instigating the epithelial cancer cell invasion. 24647585_Data show that the WNT/beta-CATENIN signaling cascade components, including WNT ligands WNT3 and WNT5A, is crucial for early odontogenesis. 24852367_Genome association study shows a highly conserved 32 kb intergenic region containing regulatory elements between WNT3 and WNT9B in patients with classic bladder exstrophy. 26105184_WNT3 involvement in human bladder exstrophy and cloaca development in zebrafish 26108805_WNT3 and membrane-associated beta-catenin regulate trophectoderm lineage differentiation in human blastocysts. 26505415_Two SNPs (rs3809857 and rs9890413) in the WNT3 gene were subjected to case-control and case-parent analysis 27463143_Wnt3 is associated with cholesterol-dependent domains 27630294_PRKX, WNT3 and WNT16 genes, belonging to the WNT signaling pathway, are involved in the tumorigenic process of nodular basal cell carcinoma 27651098_analysis of WNT3 expression in CLL patients demonstrated that (i) untreated patients with more aggressive disease (with a notable exception of patients with 11q deletion) express less WNT3, (ii) WNT3 declines with disease progression in a significant proportion of patients and (iii) low WNT3 was identified as a strong independent marker indicating shorter treatment-free survival in CLL patients with IGHV mutation. 28337662_Our data demonstrated an important interdependence between TGF-beta and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways inducing EMT in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Twist served as a linkage between the two pathways during TGF-beta-induced EMT. A83-01 could inhibit the TGF-beta-initiated pathway interactions and enhance HER2-cells response to trastuzumab treatment 28586038_High expression of WNT3 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 28971890_Demonstrate a significant change in miRNA profile dependent on the assisted reproductive technology outcome affecting Wnt pathway. 29269485_YAP maintains human embryonic stem cells pluripotency by preventing WNT3 expression in response to Activin, thereby blocking a direct route to embryonic cardiac mesoderm formation. 29662193_The importance of the SPAG5/AKT-mTOR/Wnt3 axis identified in BUC cell models. 30355643_Based on the findings of our current study, the rs3809857 and rs9890413 polymorphisms of WNT3 appeared to be associated with non-syndromic cleft lip (CL) with or without cleft palate (NSCL/P) . Limited evidence is found to support the association between other WNT3 polymorphisms and risk of NSCL/P. 32392180_Identification of candidate lncRNAs and circRNAs regulating WNT3/beta-catenin signaling in essential hypertension. 32534708_Concurrent Wnt pathway component expression in breast and colorectal cancer. 32548991_Circulating miR-374b-5p negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation in the progression of osteoporosis via targeting Wnt3 AND Runx2. 34608506_WNT3 hypomethylation counteracts low activity of the Wnt signaling pathway in the placenta of preeclampsia. |
ENSMUSG00000000125 |
Wnt3 |
50.673396 |
2.9544056649 |
1.562868 |
0.258892674 |
36.845900 |
0.00000000127844662502353931110465097841259393685042766719561768695712089538574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006053856973162477295718934355937129732083690214494708925485610961914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.9748696 |
11.6684202 |
26.1568284 |
3.1892103 |
| ENSG00000108387 |
5414 |
SEPTIN4 |
protein_coding |
O43236 |
FUNCTION: Filament-forming cytoskeletal GTPase (Probable). Pro-apoptotic protein involved in LGR5-positive intestinal stem cell and Paneth cell expansion in the intestines, via its interaction with XIAP (By similarity). May also play a role in the regulation of cell fate in the intestine (By similarity). Positive regulator of apoptosis involved in hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis; via its interaction with XIAP (By similarity). Negative regulator of repair and hair follicle regeneration in response to injury, due to inhibition of hair follicle stem cell proliferation, potentially via its interaction with XIAP (By similarity). Plays an important role in male fertility and sperm motility (By similarity). During spermiogenesis, essential for the establishment of the annulus (a fibrous ring structure connecting the midpiece and the principal piece of the sperm flagellum) which is a requisite for the structural and mechanical integrity of the sperm (By similarity). Involved in the migration of cortical neurons and the formation of neuron leading processes during embryonic development (By similarity). Required for dopaminergic metabolism in presynaptic autoreceptors; potentially via activity as a presynaptic scaffold protein (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28661, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform ARTS]: Required for the induction of cell death mediated by TGF-beta and possibly by other apoptotic stimuli (PubMed:11146656, PubMed:15837787). Induces apoptosis through binding and inhibition of XIAP resulting in significant reduction in XIAP levels, leading to caspase activation and cell death (PubMed:15029247). Mediates the interaction between BCL2 and XIAP, thereby positively regulating the ubiquitination and degradation of BCL2 and promoting apoptosis (PubMed:29020630). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11146656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15029247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15837787, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29020630}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Flagellum;GTP-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Synapse;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the septin family of nucleotide binding proteins, originally described in yeast as cell division cycle regulatory proteins. Septins are highly conserved in yeast, Drosophila, and mouse, and appear to regulate cytoskeletal organization. Disruption of septin function disturbs cytokinesis and results in large multinucleate or polyploid cells. This gene is highly expressed in brain and heart. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. One of the isoforms (known as ARTS) is distinct; it is localized to the mitochondria, and has a role in apoptosis and cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:5414; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell division site [GO:0032153]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; septin complex [GO:0031105]; septin ring [GO:0005940]; sperm annulus [GO:0097227]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis [GO:0061640]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis [GO:0061484]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of exocytosis [GO:0017157]; spermatid differentiation [GO:0048515] |
12032658_role of Bradeion in colorectal neoplasms 12695511_Sept4 is involved in the formation of cytoplasmic inclusions as well as induction of cell death in alpha-synuclein-associated neurodegenerative disorders. 15029247_Data suggest that ARTS induces apoptosis by antagonizing IAPs, including XIAP. 15116257_SEPT8 and SEPT4 are localized surrounding alpha-granules. Activation of platelets by agonists resulted in the translocation of SEPT4 and SEPT8 to the platelet surface indicating a possible functional role of these proteins in platelet granular secretion 15122323_ARTS can function as a tumor suppressor protein in childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia. 15214843_We studied the assembly of three human septins, SEPT4, SEPT5 and SEPT8, with each other (heterotypic) and with themselves (homotypic) using a yeast two-hybrid system. 15837787_high cellular levels of ARTS protein sensitize cells toward apoptosis 16376484_The data presented here suggest that ARTS P-loop is not frequently mutated in gastric, lung, and hepatocellular carcinomas, and that apoptosis deregulation in cancers is not dependent on the mutation of ARTS gene. 16464805_Finds somatic mutation in P-loop domains of proapoptotic ARTS genes uncommon in colon cancers. 17105210_define explicitly and characterize the domains of human SEPT4 17296554_The Sept4 may be involved in PD as a dual susceptibility factor, as its insufficiency can diminish dopaminergic neurotransmission and enhance alpha-synuclein neurotoxicity. 17383018_interaction of kaposin A protein and the septin 4 variant was suggested as playing a possible role in the development of HHV-8-associated malignancies 17546647_SEPT9 sequence alternations causing hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy are associated with altered interactions with SEPT4/SEPT11 and resistance to Rho/Rhotekin-signaling 17644312_This protein may play an important role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia and could be used as a marker for this disease. 17764158_Data report an intermediate structure of the GTPase domain of human SEPT4 (SEPT4-G) during unfolding transitions induced by temperature. 18617022_The stability and aggregation properties of the GTPase domain from human SEPT4. 18951507_Sporadic PD cases showed a statistically significant decrease of the fold change (FC) of SEPT4 (FC = 0.67, P = 0.054) gene expressions in the substantia nigra & amygdala (SEPT4: FC = 0.32, P = 0.007) versus healthy controls. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19221096_structural defects in sperm are not caused by abnormal transcription or point mutations of the TAT1 and SEPT4 genes; however, although both proteins are expressed, they are not properly localized at sperm annulus 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21824006_ARTS is localized at mitochondria and promotes programmed cell death (apoptosis). 21898991_The expression of SEPT4 is significantly decreased in the ejaculated sperm of idiopathic asthenozoospermia patients. 21938432_SEPT4 is a Notch target gene. 21952823_these data suggests a tumor suppressor role of SEPT4_i1 in HCC through regulating hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis. 22503047_Bradeion/SEPT4 transcript levels are significantly increased in patients with transitional cell bladder cancer.We hypothesize that Bradeion is directly involved in bladder cancer pathogenesis with the highest expression at early cancer stages. 23180367_results suggest that Septin4 may be involved in the process of activation of hepatic stellate cells by lipopolysaccharide stimulation. 23479728_Identification of a novel anti-apoptotic E3 ubiquitin ligase that ubiquitinates antagonists of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins SMAC, HtrA2, and ARTS. 25527525_The data suggest that Sept4_i1 induces hepatic stellate cell apoptosis by inhibiting Akt and Bcl-2 expression and up-regulating PPAR-gamma expression. 28224479_carnosic acid induces parkin by enhancing the ubiquitination of ARTS, leading to induction of XIAP. 29366480_Septin4 is a novel essential factor involved in oxidative stress induced vascular endothelial cell injury by interacting with apoptosis-related protein PARP1. 29991349_In this review, we will discuss the recent advances of the tauopathy research, primarily focusing on its association with the early axonal manifestation of axonal transport defect, axonal mitochondrial stress, autophagic vesicle accumulation and the proceeding of axon destruction, and the pathogenic Tau spreading across the synapse. 31924572_Role of WW domain E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 in modulating ubiquitination and Degradation of Septin4 in oxidative stress endothelial injury. 32626973_Septin4 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in melatonininduced osteoblasts. 33627621_p53 induces ARTS to promote mitochondrial apoptosis. |
|
|
86.700035 |
0.0509911446 |
-4.293609 |
0.368076484 |
142.308701 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000832496877261907681269726768591579623425429134481054208577586666328033403979191029410048680015066224768816027790307998657226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000116802793805948252027355368696032206024178187519682461870786377034663027706142533236610692171097980462945997714996337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9891791 |
2.8101890 |
197.8294150 |
32.6678637 |
| ENSG00000108423 |
51174 |
TUBD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UJT1 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a positive regulator of hedgehog signaling and regulates ciliary function. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R1K7}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;GTP-binding;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity. Predicted to be a structural constituent of cytoskeleton. Predicted to be involved in microtubule cytoskeleton organization; mitotic cell cycle; and positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51174; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; cell projection organization [GO:0030030]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28137601_our data suggest that TUBD1 mRNA isoform expression profile in peripheral blood could be an accessible biomarker for predicting the risk for diabetic retinopathy development. 28906251_Here, the authors report that centrioles in delta-tubulin and epsilon-tubulin null mutant human cells lack triplet microtubules and fail to undergo centriole maturation. |
ENSMUSG00000020513 |
Tubd1 |
28.310385 |
0.4556676493 |
-1.133946 |
0.318201363 |
12.560339 |
0.00039402030530416348643590884748277858307119458913803100585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000985885693556442241694548478392334800446406006813049316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.2992440 |
3.2205175 |
36.0783012 |
4.8771594 |
| ENSG00000108465 |
80279 |
CDK5RAP3 |
protein_coding |
Q96JB5 |
FUNCTION: Substrate adapter for ufmylation, the covalent attachment of the ubiquitin-like modifier UFM1 to substrate proteins, in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress (PubMed:23152784, PubMed:30635284). Negatively regulates NF-kappa-B-mediated gene transcription through the control of RELA phosphorylation (PubMed:17785205, PubMed:20228063). Probable tumor suppressor initially identified as a CDK5R1 interactor controlling cell proliferation (PubMed:12054757, PubMed:12737517). Also regulates mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint and mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint (PubMed:15790566, PubMed:19223857). Through its interaction with CDKN2A/ARF and MDM2 may induce MDM2-dependent p53/TP53 ubiquitination, stabilization and activation in the nucleus, thereby promoting G1 cell cycle arrest and inhibition of cell proliferation (PubMed:16173922). May also play a role in the rupture of the nuclear envelope during apoptosis (PubMed:23478299). May regulate MAPK14 activity by regulating its dephosphorylation by PPM1D/WIP1 (PubMed:21283629). Required for liver development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99LM2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12054757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12737517, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15790566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16173922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17785205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19223857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20228063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21283629, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23152784, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23478299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30635284}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May be negatively regulated by hepatitis B virus large envelope protein mutant pre-s2 to promote mitotic entry. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21971960}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that has been reported to function in signaling pathways governing transcriptional regulation and cell cycle progression. It may play a role in tumorigenesis and metastasis. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 20. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:80279; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cyclin binding [GO:0030332]; MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding [GO:0097371]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding [GO:0044389]; apoptotic nuclear changes [GO:0030262]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; definitive erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0060318]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; liver development [GO:0001889]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; mitotic G2/M transition checkpoint [GO:0044818]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity by regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0044387]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071901]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901798]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein ufmylation [GO:0071569]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of phosphatase activity [GO:0010921]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
12054757_IC53 is a novel gene, mainly expressed in vascular endothelial cells and mediates cell proliferation 15790566_results strongly indicate that in response to genotoxic stress, Cdk5 activator-binding protein C53(C53) serves as an important regulatory component of DNA damage checkpoint through modulating cyclin dependent kinase 1-cyclin B1 function 16173922_It is suggested that LZAP can regulate ARF biochemical and biological activity; additionally, LZAP has p53-dependent cell-cycle effects that are independent of ARF. 17549666_it is concluded that CDK5RAP3, CCNB2, and RAGE genes may be used as a very reliable biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma 17785205_LZAP has a role in NF-kappaB regulation and tumor suppression. 19223857_CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 3 promotes checkpoint kinase 1 activation and mitotic entry in both unperturbed cell-cycle progression and DNA damage response. 19541669_Endothelium-specific overexpression of human IC53 downregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and elevates systolic blood pressure in mice. 20228063_found that C53/LZAP and DDRGK1 became more susceptible to the proteasome-mediated degradation in RCAD knockdown cells, whereas their ubiquitination was significantly attenuated by RCAD overexpression 21283629_the ability of LZAP to alter p38 phosphorylation depended, at least partially, on the p38 phosphatase, Wip1 21385901_Findings reveal that CDK5RAP3 is widely overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and that overexpression of CDK5RAP3 promotes HCC metastasis through PAK4 activation. 21394385_Data indicate that IC53 is a positive mediator for colon cancer progression, and IC53-rs2737 may serve as protection from the onset of colorectal cancer. 21465471_Nuclear gamma-tubulin interacts with tumor suppressor protein C53 that is involved in regulation of DNA damage 21971960_our results strongly suggest that the binding of hepatitis viral pre-S2 LHBs with C53 is a novel negative regulator of the checkpoint response 22028922_LZAP may play an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma progression 22860085_our findings provide the new evidence that overexpression of CDK5RAP3 promotes HCC metastasis via downregulation of p14(ARF). 23478299_C53/LZAP protein bound indirectly to the microtubule (MT), and expression of the C53/LZAP cleavage product caused abnormal MT bundling and NE rupture. 27793695_CDK5RAP3 negatively regulates the beta-catenin signaling pathway by repressing GSK-3beta phosphorylation in gastric neoplasms. 29540196_Our results demonstrated that CDK5RAP3 negatively regulates the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by repressing AKT phosphorylation, which leads to better survival of patients with gastric cancer. 30228783_Prognostic analysis showed that the co-expression of CDK5RAP3 and DDRGK1 was an independent prognostic factor correlating with the overall survival of gastric cancer patients. 30864700_Study demonstrated that CDK5RAP3/C53 isoform d (IC53d) was upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and was associated with tumor Tstage. Furthermore, overexpression of IC53d promoted the proliferation, colony formation and G1/S phase transition of gastric cancer cells, leading to enhancement of tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo. 30954448_The current findings advance innovation in drug discovery and highlight C53 as a novel pGC-B activator with sustained in vivo activity and anti-fibrotic actions in vitro. 31061682_CDK5RAP3 is associated with autophagy and down-regulated in renal cancer. 32606358_CDK5RAP3 as tumour suppressor negatively regulates self-renewal and invasion and is regulated by ERK1/2 signalling in human gastric cancer. 35219640_CDK5RAP3 acts as a putative tumor inhibitor in papillary thyroid carcinoma via modulation of Akt/GSK-3beta/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000018669 |
Cdk5rap3 |
861.361143 |
0.4990538441 |
-1.002733 |
0.079992234 |
156.559160 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000638969607247137207495621801572025929450505355763926608001807031288265229381801551253924204010203879988694097846746444702148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000096433449928095544963350775139753626962615348982666242029790031605548732317808726922125678489294831052802692283876240253448486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
586.8806481 |
35.1086912 |
1183.5534056 |
49.3607019 |
| ENSG00000108469 |
9400 |
RECQL5 |
protein_coding |
O94762 |
FUNCTION: DNA helicase that plays an important role in DNA replication, transcription and repair (PubMed:20643585, PubMed:22973052). Binds to the RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2A during transcription elongation and suppresses transcription-associated genomic instability (PubMed:20231364). Associates also with POLR1A and enforces the stability of ribosomal DNA arrays (PubMed:27502483). Plays an important role in mitotic chromosome separation after cross-over events and cell cycle progress (PubMed:22013166). Mechanistically, removes RAD51 filaments protecting stalled replication forks at common fragile sites and stimulates MUS81-EME1 endonuclease leading to mitotic DNA synthesis (PubMed:28575661). Required for efficient DNA repair, including repair of inter-strand cross-links (PubMed:23715498). Stimulates DNA decatenation mediated by TOP2A. Prevents sister chromatid exchange and homologous recombination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20231364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20348101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20643585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22013166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22973052, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23715498, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23748380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27502483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28575661}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA replication;Helicase;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a helicase that is important for genome stability. The encoded protein also prevents aberrant homologous recombination by displacing RAD51 from ssDNA. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:9400; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II, holoenzyme [GO:0016591]; 3'-5' DNA helicase activity [GO:0043138]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; DNA helicase activity [GO:0003678]; four-way junction helicase activity [GO:0009378]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; RNA polymerase II complex binding [GO:0000993]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to camptothecin [GO:0072757]; cellular response to ketone [GO:1901655]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; chromosome separation [GO:0051304]; DNA duplex unwinding [GO:0032508]; DNA metabolic process [GO:0006259]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication [GO:0006268]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:2000042]; negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0034244]; replication-born double-strand break repair via sister chromatid exchange [GO:1990414] |
15241474_RECQ5 is a protein with DNA helicase and strand-annealing activities in a single polypeptide. 17003056_RECQ5beta promotes strand exchange between arms of synthetic forked DNA structures resembling a stalled replication fork in a reaction dependent on ATP hydrolysis. 18003859_RECQL5 binds the Rad51 recombinase and inhibits Rad51-mediated D-loop formation. 18290761_The novel intramolecular modulation of RECQ5beta catalytic activity mediated by the zinc-binding motif may represent a universal regulation mode for all RecQ family helicases. 18419580_RecQ5beta has suppressive roles in events associated with RNAP II-dependent transcription 18562274_RECQ5 appears to be the only member of the human RECQ family of helicases that associates with RNAPII. 19570979_RECQL5 inhibits reconstituted, promoter-driven RNAPII transcription in a dose-dependent manner. 20081208_RECQL5beta dramatically stimulates the rate of FEN1 cleavage of flap DNA substrates. 20231364_Data suggest that RecQL5 promotes genome stabilization by participation in homologous recombination-dependent DNA repair as a RecQ helicase and by regulating the initiation of Pol II to reduce replication impairment and recombination. 20348101_Physical interaction of RECQ5 helicase with RAD51 facilitates its anti-recombinase activity. 20643585_propose that RECQL5 stabilises the replication fork allowing replication to overcome the effects of thymidine and complete the cell cycle 21210765_RECQL5 as a major determinant for camptothecin resistance in colorectal cancer cells. 21402780_study provides novel insights into a mechanism by which RECQ5 regulates the transcription machinery via its dynamic interaction with RNAPII, thereby preventing genome instability 22633600_the recruitment of RECQL5 to laser-induced DSB sites is independent of functional activities of its interacting partners, MRE11 and RNA polymerase II. 22645136_Data indicate taht BRC repeat is a common RAD51 recombinase interaction module that can either promote homologous recombination (HR), as in the case of BRCA2, or to suppress HR, as in RECQL5 helicase. 22973052_RECQL5 modulates and/or directly participates in base excision repair of endogenous DNA damage. 23180761_The study provides insight into the recruitment and retention dynamics of RECQL5 at DNA double-strand breaks sites and its functional interplay with BLM protein and Werner syndrome protein. 23627586_This article reviews the established roles of RECQL5 at the cross roads of DNA replication, recombination and transcription, and propose that human RECQL5 provides important backup functions in the absence of other DNA helicases.[review] 23748380_RECQL5 contacts the Rpb1 jaw domain of Pol II at a site that overlaps with the binding site for the transcription elongation factor TFIIS. Binding of RECQL5 to Pol II interferes with the ability of TFIIS to promote transcriptional read-through in vitro. 24213927_The present study indicated that RECQL5 genetic polymorphism and haplotypes were associated with larynx cancer in a Chinese population. 24287950_RECQL5 genetic polymorphisms were associated with osteosarcoma in a Chinese population. 24319145_The findings suggest that RECQ5 acts during the post-synaptic phase of synthesis-dependent strand annealing to prevent formation of aberrant RAD51 filaments on the extended invading strand, thus limiting its channeling into potentially hazardous crossover pathway of homologous recombination. 24836610_The data presented here provide evidence that RECQL5 plays a general role in the control of transcript elongation in human cells. In its absence, transcript elongation rates increase, the distribution profile of RNAPII is markedly altered across the genome, and higher levels of RNAPII pausing or arrest (i.e., transcription stress) are detected. 25394896_The present study indicated that the RECQL5 genetic polymorphism and haplotypes were associated with breast cancer in a Chinese population. 25851487_RecQ5 prevents transcription associated genome instability by facilitating PIAS1-SRSF1 ligase complex sumoylation of DNA topoisomerase 1. 25867335_The RECQL5 genetic polymorphism was associated with osteosarcoma in a Chinese population. 26391948_PARylation is involved in the recruitment of RECQL5 and WRN to laser-induced DNA damage and RECQL5 and WRN have differential responses to PARylated PARP1 and Poly(ADP-ribose). 26499077_results suggested RECQL5 as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma and may be a potential therapeutic target for osteosarcoma treatment 26586793_Expression of RECQL5 in breast cancer can drive proliferation supporting an oncogenic function for RECQL5 in breast cancer. RECQL5 is a promising biomarker in breast cancer. 26686625_RECQL5 is a critical regulator of genome stability in myeloproliferative neoplasms and demonstrate that replication stress-associated cytotoxicity can be amplified specifically in JAK2V617F mutant cells through RECQL5-targeted synthetic lethality. 26717024_RECQL5 has unique strand annealing properties relative to the other human RecQ helicase proteins 26844521_mutation associated with early myocardial infarction 27332117_Study characterized the G-quadruplex (GQ) unfolding activity of RECQ5 for different DNA constructs under different salt conditions, showed that RECQ5 is overall a weak GQ destabilizer compared to Bloom and Werner 27502483_interaction between RECQ5 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) promotes RAD18-dependent PCNA ubiquitination and the helicase activity of RECQ5 promotes the processing of replication intermediates. 27764811_we have shown that increased expression of RECQL5 protein occurs and is likely to contribute to tumourigenesis in UCC and that the pharmacological targeting of the helicase activity of RECQL5 is a strong target for future small molecule inhibitor development. 28100692_the open and closed forms of RECQL5 were used together with a quantitative comparison of all current RecQ family structures to construct a mechanistic model for RECQL5 helicase activity 28575661_RECQ5 removes RAD51 filaments stabilizing stalled replication forks at common fragile sites and hence facilitates CFS cleavage by MUS81-EME1. 30006506_It has been shown that conjugation of SUMO2, but not SUMO1 or SUMO3, to the essential replication factor PCNA is induced on transcribed chromatin by the RNAPII-bound helicase RECQ5. 30107528_increased RECQ5 levels stimulated 'alternative' HDR by single-stranded DNA donors, which is normally suppressed by RAD51; this was accompanied by stimulation of mutagenic end-joining. These results suggest that in some tumors, RECQ5 gene amplification may have profound consequences for genomic instability 30817846_These results prompt us to propose RECQL5 as a gene that would be worth to analyze in larger studies to explore its possible implication in BC susceptibility. 32497619_Mining the role of RECQL5 in gastric cancer and seeking potential regulatory network by bioinformatics analysis. 33197722_RECQL5 KIX domain splicing isoforms have distinct functions in transcription repression and DNA damage response. 33217443_Human RECQL5 promotes metastasis and resistance to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer. 33332547_Single-molecule visualization of human RECQ5 interactions with single-stranded DNA recombination intermediates. 33431668_ATRX and RECQ5 define distinct homologous recombination subpathways. 33567180_Human RecQ helicases in transcription-associated stress management: bridging the gap between DNA and RNA metabolism. 34822842_The deubiquitinase USP28 stabilizes the expression of RecQ family helicases and maintains the viability of triple negative breast cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000020752 |
Recql5 |
170.307530 |
0.3760357779 |
-1.411058 |
0.249571342 |
31.091193 |
0.00000002461858653070733902342006943139707253465076064458116888999938964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000103200890994956078060922045024072613017551702796481549739837646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.5318997 |
17.6633951 |
246.8164830 |
33.5474969 |
| ENSG00000108506 |
57508 |
INTS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0H0 |
FUNCTION: Component of the Integrator (INT) complex, a complex involved in the small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) U1 and U2 transcription and in their 3'-box-dependent processing. The Integrator complex is associated with the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II largest subunit (POLR2A) and is recruited to the U1 and U2 snRNAs genes (Probable). Mediates recruitment of cytoplasmic dynein to the nuclear envelope, probably as component of the INT complex (PubMed:23904267). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23904267, ECO:0000305|PubMed:16239144}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
INTS2 is a subunit of the Integrator complex, which associates with the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II large subunit (POLR2A; MIM 180660) and mediates 3-prime end processing of small nuclear RNAs U1 (RNU1; MIM 180680) and U2 (RNU2; MIM 180690) (Baillat et al., 2005 [PubMed 16239144]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:57508; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; integrator complex [GO:0032039]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0034243]; snRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0034472]; snRNA processing [GO:0016180] |
26811494_Mutation in INTS2 gene is associated with gastric cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis. |
ENSMUSG00000018068 |
Ints2 |
136.771981 |
2.0280058114 |
1.020062 |
0.237729830 |
18.002406 |
0.00002206259274461062715503266440375540469176485203206539154052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000066539409258367979670134584324614479555748403072357177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
206.8052395 |
29.5272132 |
102.8125390 |
10.7782752 |
| ENSG00000108515 |
2027 |
ENO3 |
protein_coding |
P13929 |
FUNCTION: Glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate. Appears to have a function in striated muscle development and regeneration. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15429}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycogen storage disease;Glycolysis;Lyase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; pyruvate from D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate: step 4/5. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15429}. |
This gene encodes one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. This isoenzyme is found in skeletal muscle cells in the adult where it may play a role in muscle development and regeneration. A switch from alpha enolase to beta enolase occurs in muscle tissue during development in rodents. Mutations in this gene have be associated glycogen storage disease. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:2027; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phosphopyruvate hydratase complex [GO:0000015]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphopyruvate hydratase activity [GO:0004634]; canonical glycolysis [GO:0061621]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096] |
19472918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21347838_Pyridoxamine and carnosine protected enolase against the total loss of catalytic activity. 25267339_Molecular genetic analysis of ENO3 gene revealed two novel homozygous missense mutations, (p.Asn151Ser and p.Glu187Lys)in patients presenting with recurrent rhabdomyolysis. 25918939_tRK1 forms a complex with human enolases and interacts with tRK1 and human pre-lysyl-tRNA synthetase (preKARS2) 31697874_Enolase 3 (ENO3) overexpression under serine/threonine kinase 11 (STK11) loss-of-function mutations implies that ENO3 might be a selective anticancer target in STK11-mutant cancer. 35477821_ENO3 promotes colorectal cancer progression by enhancing cell glycolysis. |
ENSMUSG00000060600 |
Eno3 |
13.740400 |
0.2837996723 |
-1.817055 |
0.543419465 |
10.791548 |
0.00101964570922675828133774356132335014990530908107757568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002368582100753376280810602594328884151764214038848876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6777199 |
1.8602495 |
20.8782458 |
4.2621931 |
| ENSG00000108561 |
708 |
C1QBP |
protein_coding |
Q07021 |
FUNCTION: Is believed to be a multifunctional and multicompartmental protein involved in inflammation and infection processes, ribosome biogenesis, protein synthesis in mitochondria, regulation of apoptosis, transcriptional regulation and pre-mRNA splicing. At the cell surface is thought to act as an endothelial receptor for plasma proteins of the complement and kallikrein-kinin cascades. Putative receptor for C1q; specifically binds to the globular 'heads' of C1q thus inhibiting C1; may perform the receptor function through a complex with C1qR/CD93. In complex with cytokeratin-1/KRT1 is a high affinity receptor for kininogen-1/HMWK. Can also bind other plasma proteins, such as coagulation factor XII leading to its autoactivation. May function to bind initially fluid kininogen-1 to the cell membrane. The secreted form may enhance both extrinsic and intrinsic coagulation pathways. It is postulated that the cell surface form requires docking with transmembrane proteins for downstream signaling which might be specific for a cell-type or response. By acting as C1q receptor is involved in chemotaxis of immature dendritic cells and neutrophils and is proposed to signal through CD209/DC-SIGN on immature dendritic cells, through integrin alpha-4/beta-1 during trophoblast invasion of the decidua, and through integrin beta-1 during endothelial cell adhesion and spreading. Signaling involved in inhibition of innate immune response is implicating the PI3K-AKT/PKB pathway. Required for protein synthesis in mitochondria (PubMed:28942965). In mitochondrial translation may be involved in formation of functional 55S mitoribosomes; the function seems to involve its RNA-binding activity. May be involved in the nucleolar ribosome maturation process; the function may involve the exchange of FBL for RRP1 in the association with pre-ribosome particles. Involved in regulation of RNA splicing by inhibiting the RNA-binding capacity of SRSF1 and its phosphorylation. Is required for the nuclear translocation of splicing factor U2AF1L4. Involved in regulation of CDKN2A- and HRK-mediated apoptosis. Stabilizes mitochondrial CDKN2A isoform smARF. May be involved in regulation of FOXC1 transcriptional activity and NFY/CCAAT-binding factor complex-mediated transcription. May play a role in antibacterial defense as it can bind to cell surface hyaluronan and inhibit Streptococcus pneumoniae hyaluronate lyase. May be involved in modulation of the immune response; ligation by HCV core protein is resulting in suppression of interleukin-12 production in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Involved in regulation of antiviral response by inhibiting RIGI- and IFIH1-mediated signaling pathways probably involving its association with MAVS after viral infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10022843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10479529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11086025, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11859136, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15243141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16140380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16177118, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17881511, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18676636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19004836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19164550, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20810993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21536856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21544310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22700724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28942965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8662673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8710908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9461517}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Involved in HIV-1 replication, presumably by contributing to splicing of viral RNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12833064}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In infection processes acts as an attachment site for microbial proteins, including Listeria monocytogenes internalin B (InlB) and Staphylococcus aureus protein A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10747014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12411480}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Involved in replication of Rubella virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12034482}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Adaptive immunity;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Complement pathway;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Mitochondrion;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis;Secreted;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transit peptide |
|
The human complement subcomponent C1q associates with C1r and C1s in order to yield the first component of the serum complement system. The protein encoded by this gene is known to bind to the globular heads of C1q molecules and inhibit C1 activation. This protein has also been identified as the p32 subunit of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2, as well as a hyaluronic acid-binding protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:708; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; adrenergic receptor binding [GO:0031690]; complement component C1q complex binding [GO:0001849]; hyaluronic acid binding [GO:0005540]; kininogen binding [GO:0030984]; mitochondrial ribosome binding [GO:0097177]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; transcription factor binding [GO:0008134]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; cytosolic ribosome assembly [GO:0042256]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050687]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; negative regulation of MDA-5 signaling pathway [GO:0039534]; negative regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048025]; negative regulation of RIG-I signaling pathway [GO:0039536]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000510]; positive regulation of mitochondrial translation [GO:0070131]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of trophoblast cell migration [GO:1901165]; regulation of complement activation [GO:0030449]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
11870091_increase in expression over the rostral portion of the sperm head after capacitation; may play a role in human fertilization 12220632_demonstrate that MT1-MMP via its cytoplasmic tail directly associates with a chaperone-like compartment-specific regulator gC1qR 12443542_presence of homologous sequences of HABP1 cDNA, termed processed HABP1 pseudogene, in humans 12538033_Maturation-dependent expression of this protein in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. 12574814_gC1qR expressed on activated platelets may contribute directly to thrombosis, inflammation, and endovascular infections. 15163734_binds with Hepacivirus core protein on CD8+ and CD4+ positive t-cells and inactivates lck and akt. 15243141_Human p32 functions as a corepressor of CCAAT-binding factor-mediated transcription activation. 15467913_data suggest that gC1qR may participate in tissue remodeling and inflammation by localizing TFPI-2 to the pericellular environment to modulate local protease activity and regulate High Molecular Weight Kininogen activation 16039650_HABP1 expression in Schizosaccharomyces pombe induces growth inhibition, morphological abnormalities like elongation, multinucleation and aberrant cell septum formation, implicating its role in cell cycle progression and cytokinesis 16140380_C1q functions as a chemotactic factor for immature dendritic cells, and migration is mediated through ligation of both gC1qR and cC1qR/CR. 16164755_These studies suggest that HCV core protein can lead to enhanced p38- and gC1qR-dependent IL-8 expression. 16177118_gC1qR down-regulates interleukin-12 production by signaling through 1-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. This is the first report to identify signaling pathways used by gC1qR-mediated immune suppression. 16641292_p32 overexpression effectively blocks mRNA accumulation from the adenovirus major late transcription unit (MLTU) and stimulates RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain phosphorylation in virus-infected cells. 16871385_we speculate that the epitope of gC1qR is unmasked in the germ cell lineage; by reducing gC1qR by siRNA, an increase was observed in the number of apoptotic cells in ITO-II & TCam-2 cell lines showing an antiapoptotic property of gC1qR in the germ cells 16893067_Data suggest that gC1qR serves as a molecular bridge between the complement and contact activation systems and is an important catalyst in inflammation. 17881511_Engagement of gC1qR on dendritic cells by hepatitis C virus core protein limits the induction of Th1 responses by inhibiting TLR-induced IL-12 production and may contribute to viral persistence. 17892212_These data suggest a role for gC1qR in the initial stages of Bacillus cereus spore attachment and/or entry. 17907801_P. falciparum-infected red blood cells use the 32-kDa human protein gC1qR/HABP1/p32 as a receptor to bind to human brain microvascular endothelial cells. 18358546_Data demonstrated a direct and specific interaction between vasopressin V2 receptor and GC1q-Rthese two proteins via the arginine cluster of vasopressin V2 receptor. 18460468_Differential isoform expression and interaction with the P32 regulatory protein controls the subcellular localization of the splicing factor U2AF26 18538737_Mitochondrial p32/C1QBP is a critical mediator of p14ARF-induced apoptosis. 18676636_Failure of p32 to interact with FOXC1 containing the disease-causing F112S mutation indicates that impaired protein interaction may be a disease mechanism for AR malformations. 18757437_results establish p32, particularly its cell-surface-expressed form, as a new marker of tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages/myeloid cells in hypoxic/metabolically deprived areas of tumors 19004836_Evidence for inhibitory interaction of hyaluronan-binding protein 1 (HABP1/p32/gC1qR) with Streptococcus pneumoniae hyaluronidase. 19164550_gC1qR is a physiological inhibitor of the RIG-I and MDA5-mediated antiviral signaling pathway 19190731_Cryoglobulins were present in over 90% of Chikungunya infection patients. Cryoglobulin frequency and levels decreased with time in recovering patients. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473882_results suggest that HCV infection expands gC1qR+CD4+ T cells, which increase the susceptibility to core-mediated immune dysregulation and facilitate the establishment of HCV persistency 19565630_HABP1 mRNA expression level was a significant factor for predicting breast cancer prognosis 19828637_Dysregulated shedding of C1q-R molecules contributes to vascular cryoglobulin-induced damage via the classic complement-mediated pathway in chronically hepatitis C-infected patients, with and without mixed cryoglobulinemia. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20100866_Knocking down p32 expression in human cancer cells strongly shifts their metabolism from oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to glycolysis. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21156793_the potential of p32 for antibody-based tumor targeting strategies and the utility of the 2.15 antibody as targeting moiety for the selective delivery of imaging and therapeutic agents to tumors. 21205079_p32 is highly expressed in prostate tumor samples and its expression is significantly associated with the Gleason score, pathological stage and relapse 21248045_The data presented suggest that p32 fulfills an essential function for rubella virus replication in directing trafficking of mitochondria near sites of viral replication to meet the energy demands of the virus. 21536672_cell-surface gC1qR regulates lamellipodia formation and metastasis via receptor tyrosine kinase activation. 21536856_p32 is a new rRNA maturation factor involved in the remodeling from pre-90S particles to pre-40S and pre-60S particles that requires the exchange of FBL for Nop52. 21559373_there is a a role for platelet-mediated clumping, rosetting and adhesion to gC1qR in the pathogenesis of severe malaria 21627988_HABP1 interacts with cell surface receptor integrin alphaVbeta3 that induces cell migration and tumor growth mediated by transcription factor NF-kappa B, membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase and matrix metalloprotease-2. 21725590_gC1qR could play an important role in HPV-16-induced cervical cancer immune evasion depending on its level of expression and subcellular localisation. 22008525_we have identified a mitochondrial protein p32 as a novel interactor of parkin in the brain 22101277_C1qbp is upregulated in human lung and colon cancer cell lines and tumors. 22451658_Overexpression of hyaluronan-binding protein 1 (HABP1/p32/gC1qR) in HepG2 cells leads to increased hyaluronan synthesis and cell proliferation by up-regulation of cyclin D1 in AKT-dependent pathway. 22700724_C1q/gC1qR may regulate dendritic cells differentiation and function through the DC-SIGN-mediated induction of cell-signaling pathways. 22771308_in ovarian serous carcinoma, HABP1 overexpression was correlated to histological-differentiation, residual tumor-size, serum CA-125 and stage; increased expression associated with cisplatin resistance; HAPBP1 overexpression in primary ovarian carcinomas is related to decrease in overall survival and progression free survival 22960332_polymorphisms in HABP1 are potentially involved in glaucomatous neurodegeneration. 23692256_Studies highlight the critical contributions of the p32 protein to the morphology of mitochondria and ER under normal cellular conditions, as well as important roles of the p32 protein in cellular metabolism and various stress responses. 23924515_C1QBP was observed to be overexpressed in breast cancer tissues, and its expression level was closely linked with distant metastasis and TNM stages. 23929393_Data indicate that hyaluronic acid binding protein 1 (HABP1)/P32/C1QBP overexpression correlated with peritoneal dissemination and lymph node metastasis in EOC. 23990920_RNase H1 and protein P32 are involved in mitochondrial pre-rRNA processing 24174616_this data suggest a novel protective mechanism of p33 in modulating innate immune response by neutralizing cytotoxic AMPs at the host cell surface. 24874554_The data suggest that p32 expression is important for trophoblast proliferation, via a mechanism involving regulation of normal mitochondrial function. 25061661_This suggests the importance of HABP1 induced HA cable formation in enhancing tumor potency by maintaining the oxidant levels and subsequent autophagic vacuolation. 25091479_By binding to p32, Mcl-1 can interfere with the uniporter function, thus inhibit the mitochondrial Ca(2+) uploading. This may provide a novel mechanism to explain the anti-apoptotic function of Mcl-1. 25355318_Interaction between HSV-1 ICP34.5 and p32 leads to the disintegration of nuclear lamina and facilitates the nuclear egress of HSV-1 particles. 25355598_Our results indicated that overexpression of HABP1 may serve as a new biomarker to predict the progression and prognosis of endometrial cancer. 25497084_data suggest that C1QBP is a novel regulator of YBX1, and the expression of C1QBP and the nuclear expression of YBX1 could both be used as independent prognostic makers for cancer progression in the RCC patients 25528767_Data show that p32 hyaluronan binding protein (p32) is a direct transcriptional target of oncogene Myc and that high level of Myc in malignant brain cancers correlates with high expression of p32. 25573962_our findings suggest that the C1QBP protein could be a potential proliferative marker in breast cancer 25794640_HABP1 protein high expression may contribute to the tumor progression and poor prognosis of TNBC, especially in predicting prognosis in TNBCs without lymph node metastasis. 25909887_Findings highlight a cytoprotective role of p32 under starvation conditions by regulating ULK1 stability, and uncover a crucial role of the p32-ULK1-autophagy axis in coordinating stress response, cell survival and mitochondrial homeostasis. 26085152_p32 appeared to be a core component of herpesvirus nuclear egress complexes, like UL31 and UL34 homologs in other herpesviruses, and to play multiple roles in herpesvirus nuclear egress. 26497555_Sp1-ZNF32-C1QBP axis protects against oxidative stress/apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 26753982_C1QBP interacts with DLAT and regulates the enzyme activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase. 27183919_Hepatitis C virus core protein ligates gC1qR to induce A20 expression in macrophages via P38, JNK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways, which leads to a low-grade chronic inflammation during HCV infection. 27328359_The authors identified Importin-alpha1 to bind to Coxiella burnetii AnkG and concluded that binding of AnkG to p32 and Importin-alpha1 is essential for its migration into the nucleus. 27835682_This study supports a key role for gC1qR in malaria-associated endovascular pathogenesis 28039537_HABP1 overexpression is associated with cervical cancer. 28107702_these data suggest that C1QBP could regulate YBX1 to suppress the AR-enhanced RCC cell invasion. Targeting this newly identified C1QBP/YBX1/AR/MMP9 signal pathway may provide a new potential therapy to better suppress RCC metastasis. 28108744_single nucleotide polymorphism srs2285747 of HABP1 increased breast cancer risk and elevated its protein expression in northern Chinese women 28428626_C1QBP may regulate L1CAM expression in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) through the Wnt/beta-Catenin pathway, thus affecting RCC cell adhesion, migration and metastasis. 28576489_results implicate p32 as a key host factor for RSV virus production, and bring to light the potential importance of mitochondria in RSV infection 28842250_The RAP80 deficiency reduces the protein level of p32 and p32 dependent mitochondrial translating proteins such as Rieske and COX1. 28942965_Mutation in C1QBP gene is associated with Severe Neonatal-, Childhood-, or Later-Onset Cardiomyopathy Associated with Combined Respiratory-Chain Deficiencies. 29035880_these results demonstrate that host-derived p32 has an important immunomodulating function that helps to counterbalance an overwhelming danger-associated molecular patterns response 29358188_We propose that endogenous gC1qR/p33 physically interacts with MCP-1 causing stabilization of the MCP-1 protein and stimulation of its activity in human periodontal ligament cells, suggesting a novel gC1qR/p33-mediated pro-inflammatory mechanism of action. 29670170_YBAP1/C1QBP regulates the nucleo-cytoplasmic distribution of YB-1 and its cytoplasmic functions, are consistent with a model that YBAP1/C1QBP acts as an mRNP remodeling factor. 30159917_these results highlight a novel mechanism underlying hi-FGF2-induced, mitochondria-driven cell death involving the direct interaction between hi-FGF2 and C1QBP and the upregulation of C1QBP expression. 31155612_Arginase II activity-dependent production of spermine augments Ca(2+) transition from the cytosol to the mitochondria in a mitochondrial p32 protein -dependent manner and regulates CaMKII-dependent constriction in vascular smooth muscle cells. 31293051_The primary mechanism contributing to the observed action of p32 is the ability of p32 to interact with the p53 tetramerization domain and to block p53 tetramerization, which in turn enhances nuclear export and degradation of p53, leading to defective p53 transactivation. 31844661_4-methylumbelliferone does not disrupt DUX4-C1QBP binding and has only a limited effect on DUX4 transcriptional activity, establishing that HA signaling has a central function in pathology and is a target for Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) therapeutics 32652806_Homozygous mutations in C1QBP as cause of progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO) and mitochondrial myopathy with multiple mtDNA deletions. 33515804_Loss of Mucosal p32/gC1qR/HABP1 Triggers Energy Deficiency and Impairs Goblet Cell Differentiation in Ulcerative Colitis. 34003581_Mitochondrial cardiomyopathy and ventricular arrhythmias associated with biallelic variants in C1QBP. 34494203_gC1qR Antibody Can Modulate Endothelial Cell Permeability in Angioedema. 35128841_Identification of Mitofusin 1 and Complement Component 1q Subcomponent Binding Protein as Mitochondrial Targets in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. |
ENSMUSG00000018446 |
C1qbp |
267.806193 |
2.2288628092 |
1.156308 |
0.107875336 |
115.548349 |
0.00000000000000000000000000596859903722390233411343555125100061607359928615103083631768495493480873592684332606950192712247371673583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000068557604505388953080005824513319888421919355800062545916854246003428133976465019827628566417843103408813476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
367.8218762 |
22.9942860 |
166.2151961 |
8.2216021 |
| ENSG00000108588 |
57003 |
CCDC47 |
protein_coding |
Q96A33 |
FUNCTION: Component of the PAT complex, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident membrane multiprotein complex that facilitates multi-pass membrane proteins insertion into membranes (PubMed:32814900). The PAT complex acts as an intramembrane chaperone by directly interacting with nascent transmembrane domains (TMDs), releasing its substrates upon correct folding, and is needed for optimal biogenesis of multi-pass membrane proteins (PubMed:32814900). WDR83OS/Asterix is the substrate-interacting subunit of the PAT complex, whereas CCDC47 is required to maintain the stability of WDR83OS/Asterix (PubMed:32814900). The PAT complex favors the binding to TMDs with exposed hydrophilic amino acids within the lipid bilayer and provides a membrane-embedded partially hydrophilic environment in which the first transmembrane domain binds (PubMed:32814900). Component of a ribosome-associated ER translocon complex involved in multi-pass membrane protein transport into the ER membrane and biogenesis (PubMed:32820719). Involved in the regulation of calcium ion homeostasis in the ER (PubMed:30401460). Required for proper protein degradation via the ERAD (ER-associated degradation) pathway (PubMed:25009997). Has an essential role in the maintenance of ER organization during embryogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25009997, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30401460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32814900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32820719}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables protein folding chaperone and ribosome binding activity. Involved in ERAD pathway; endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis; and protein insertion into ER membrane. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. Is integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57003; |
chaperone complex [GO:0101031]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0030867]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0032469]; ER overload response [GO:0006983]; ERAD pathway [GO:0036503]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; protein insertion into ER membrane [GO:0045048]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
25009997_these findings suggested that calumin serves to maintain the yolk sac integrity through participation in the ERAD activity, contributing to embryonic development. |
ENSMUSG00000078622 |
Ccdc47 |
626.073043 |
2.6456322125 |
1.403613 |
0.066266033 |
457.210942 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001944654633019580997992177714945084612914281450296146108941403831296967189925523643998430849177439545434826537746029007103420124391300231611012178884022148938151891846864973471378389704825968809767160510487862251183549929973335880 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000846699185350118530607364210680654444086091568169622716587140300501189075659170658499968791267125572207923832405237045053253919571704406193832107842673866552758745727040921429583516438539942025318792754408616890558902862085069087 |
Yes |
Yes |
900.1486679 |
39.2188058 |
342.9002890 |
11.8828370 |
| ENSG00000108679 |
3959 |
LGALS3BP |
protein_coding |
Q08380 |
FUNCTION: Promotes integrin-mediated cell adhesion. May stimulate host defense against viruses and tumor cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11146440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8034587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9501082}. |
3D-structure;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The galectins are a family of beta-galactoside-binding proteins implicated in modulating cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. LGALS3BP has been found elevated in the serum of patients with cancer and in those infected by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It appears to be implicated in immune response associated with natural killer (NK) and lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell cytotoxicity. Using fluorescence in situ hybridization the full length 90K cDNA has been localized to chromosome 17q25. The native protein binds specifically to a human macrophage-associated lectin known as Mac-2 and also binds galectin 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3959; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11867635_structural and functional properties of M2BP 11980646_Expression of 90K (Mac-2 BP) correlates with distant metastasis and predicts survival in stage I non-small cell lung cancer patients. 14758079_REVIEW: role in tumor progression and metastasis 15231701_90K plays an important role in the maintenance of an appropriate level of immune response. 16518858_a possible mechanism by which Tumor-associated antigen 90K may contribute to colon cancer progression is by modulating tumor cell adhesion to extracellular proteins, including galectin-3 17091455_There is no difference in Gal-3 expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with papillary thyroid cancer 17131321_Elevated Mac-2 binding protein is associated with distant metastasis and higher tumor stage in gastric cancer 17949550_serum galectin 3 binding protein (G3BP) levels were increased in Behcet's patients when compared with healthy controls and patients with inactive disease 18450743_galectin-3-binding protein as a factor secreted by neuroblastoma cells that stimulates the expression of interleukin-6 in bone marrow stromal cells and provides a novel function for this protein in cancer progression. 18490383_identified extracellular endosialin ligands and identified Mac-2 BP/90K as a specific interaction partner 18594176_EGF signal is critical for the Mac-2BP expression, and more importantly, STAT3 protein could work as a negative regulator, while human telomerase reverse transcriptase as a positive regulator in Mac-2BP transcription. 18646789_Mac-2 binding protein was found to be overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) specimens and significantly elevated in the sera of OSCC patients compared to healthy controls 19017490_NGF induces Mac-2BP expression via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. 19153476_High serum 90K (median value >or=1,249.50 ng/ml) showed a significant association with stage III/IV, >or=2 extranodal involvements and risk of high/high-intermediate international prognostic index 19291534_the Mac-2 BP may play a role in the development and progression of mucinous ovarian tumours 19544526_Engineered enhancement of LGALS3BP expression in EWS cells resulted in inhibition of anchorage independent cell growth/reduction of cell migration and metastasis. Silencing of LGALS3BP expression reverted cell behavior with respect to in vitro parameters 20019050_Initial assessment showed that serum Mac-2BP is significantly elevated in patients with NET (neuroendocrine tumors) and is expressed by the majority of NET tissues. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20583127_Serum Mac-2BP does not appear to originate in the prostate and it is unlikely that Mac-2BP can be used for the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer versus benign prostatic hyperplasia. 21094132_These results suggest that galectin-3 binding protein may be a potential therapeutic target for treatment of, at least, colon cancer patients with high expression of galectin-3 binding protein. 21474793_serum changes of three glycoproteins, galectin-3 binding protein, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, and thrombospondin 1, was associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma 21515679_Mac-2BP was detected as a predominant DC-SIGN ligand expressed on some primary colorectal cancer tissues 21660451_LGALS3BP gene was expressed by neuroblatoma cell lines and patients' neuroblasts 22447108_results show that NF-kappaB regulated the expression of G3BP and that G3BP increased the adhesion of T47D breast cancer cells to fibronectin 22496229_Adeno-associated virus type 6 interacts with G3BP in human and dog sera but not in macaque serum. 22864925_LGALS3BP induces vascular endothelial growth factor in human breast cancer cells and promotes angiogenesis. 22970241_breast cancer cells express Mac-2BP as a novel E-selectin ligand, potentially revealing a new prognostic and therapeutic target for breast cancer 23184915_The expression of serum Mac-2 binding protein is a potential therapeutic target and biomarker for lung cancer. 23233740_MIR596 is frequently observed in oral squamous cell carcinoma and regulates expression of LGAL3BP. 23443559_LGALS3BP suppresses assembly of centriolar substructures. 23775887_Serum Mac-2 binding protein levels as a novel diagnostic biomarker for prediction of disease severity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis 23830458_Recombinant 90K showed an apparent molecular weight of approximately 78kDa which was much smaller than that ( approximately 97kDa) of the natural 90K. It is suggested that recombinant 90K has small N-glycans with about half the molecular weight of N-glycans of natural 90K. 23899964_Studied levels of galectin-3 binding protein in milk from 247 HIV-infected Zambian mothers. Levels were higher in those mothers who transmitted HIV through breast-feeding. 24156545_Thus, 90K constitutes a novel antiviral factor that reduces the particle infectivity of HIV-1, involving interference with the maturation and incorporation of HIV-1 Env molecules into virions. 24302979_LGALS3BP is enriched in human ovarian carcinoma exosomes. 24362527_LGALS3BP-mediated integrin activation results into signal transmission via Akt, JNK and the Ras cascade via the Raf-ERK axis while p38 activity is kept at baseline levels 25013204_Gal-3BP levels in patients with haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome correlated with increased complement activation and with clinical variables reflecting the severity of acute hantavirus infection. 25320078_These findings suggest a novel immunoinhibitory function for LGALS3BP that might be important for immune evasion of tumor cells during cancer progression. 26070204_Post-Tx WFA+-M2BP (> 2.0 COI) is associated with the risk for development of HCC among patients with SVR. The WFA+-M2BP values could be a new predictor for HCC after SVR. 26124285_Results provide direct evidence for the involvement of CALU and LGALS3BP as potential negative regulators in the virus-triggered induction of the typeI interferons. 26168351_study elucidates the specificity of Gal-3BP interacting with galectin-1 and the role of Gal-3BP in cancer cell aggregation and metastasis 26219351_These results provide evidence that low expression of LGALS3BP participates in malignant progression of colorectal cancer. 26448934_90K/Mac-2BP correlated with the size of colorectal cancer. 26502662_findings may help clarify the molecular mechanism of the tumor-suppressive effect through down-regulation of LGALS3BP by miR-596 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma 26503549_three uniquely identified proteins (CDK6 , galectin-3-binding protein and LDH C) were found, which show tight connection with prostate cancer and presence of all of them was previously linked to certain aspects of prostate cancer 27176937_In this study, we addressed this question by analysing sLex expression together with two glycoproteins (BST-2 and LGALS3BP).Concomitant high expression of BST-2 with sLex defined a sub-group of patients with ER-negative tumours displaying higher risks of liver and brain metastasis and a 3-fold decreased survival rate 27240351_Results showed that in acute febrile phase, galectin-9 and galectin-3BP were induced in dengue patients compared to healthy controls suggesting that both molecules might be important inflammatory mediators in acute dengue virus infection. 27344370_serum M2BP may reflect silent atherosclerosis in apparently healthy subjects 27588936_the serum M2BP-adiponectin complex is elevated in men with coronary artery disease 27604950_M2BP inhibits both HIV-1 Env processing and virion production.M2BP traps HIV-1 Gag to vimentin filaments to inhibit the transportation of HIV-1 Gag to the plasma membrane. 27665173_Serum M2BP can be a useful biomarker for the diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and the prediction of disease progression since it potentially reflects altered pro-oncologic glycosylation enzymes 27668402_Our present results highlight the action of 90K on promoting degradation of mutant beta-catenin lacking the phosphorylation sites in the N-terminus. 28008658_WFA + -M2BP from hepatic stellate cells induces Mac-2 expression in Kupffer cells, which in turn activates hepatic stellate cells to be fi brogenic. 28336809_the combination of 17-AAG and PI3K/Akt inhibitor would effectively suppress acquired resistance to 17-AAG. In conclusion, targeting of LGALS3BP-mediated-specific survival signaling pathway in resistant cells may provide a novel therapeutic model for the cancer therapy. 28537900_A higher pre-treatment WFA+-M2BP level was associated with an increased risk of HCC development in patients with undetectable HBV DNA under NA therapy. 28731888_Elevated plasma M2BP levels might be predictive of unstable plaque and were associated independently with poor cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. 28756229_The Mac-2BP may have a role in regulating the extracellular spreading and storage of the Wnts, thereby modulating their bioavailability and stability. 28811008_Serum Mac-2-binding protein expression predicts disease severity in chronic hepatitis C patients. 29207493_Results showed that 90K destabilizes E-cadherin and affects cell adhesion and invasion in subconfluent cancer cells via dissociation of the E-cadherin-p120-catenin complex, suggesting that 90K drives less confluent tumor cells into the early steps of cancer metastasis. 29233037_Serum M2BP might contribute to the inflammatory process in systemic lupus erythematosus. 29288305_M2BPGi is a very useful, easily applicable clinical indicator associated with hepatocellular carcinoma development in chronic hepatitis B patients virologically well controlled with nucleot(s)ide analogues therapy; higher levels of serum M2BPGi at 48 weeks was independent risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma development. 29318378_M2BPGi is a surrogate marker for assessing hepatic stellate cells (HSC) activation. These findings may reveal the roles of HSCs in extrahepatic fibrotic disease progression. [Review] 29679552_Data suggest that serum levels of RBP4 and LGAL3BP are up-regulated after menopause when complicated by NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease); RBP4 and LGAL3BP may serve as biomarkers of NAFLD in postmenopausal women. (RBP4 = retinol binding protein 4; LGAL3BP = galectin-3 binding protein) 29679592_that Multiple coagulation factor deficiency protein 2 promotes cancer metastasis by regulating lectin mannose binding 1 and level of galactoside-binding soluble 3 binding protein expression levels 29743357_Low LGALS3BP expression is associated with HIV infections. 29882603_Gal-3BP expression is induced in viral infection and by a multitude of molecules that either mimic or are characteristic for an ongoing inflammation and microbial infection. It belongs to the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain-containing protein family, by virtue of its N-terminal SRCR domain. Review. 30101431_Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer is a novel liver fibrosis marker 30161179_In a large cohort of patients with the full spectrum of NAFLD, WFA+ -M2BP levels predicted the presence of advanced disease and correlated strongly with fibrosis stage. 30306612_Serum M2BPGi level significantly decreases after nucleoside analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B patients. 30530049_M2BP is highly expressed in advanced carotid artery plaques and significantly correlated with clinical ischemic manifestations. 30585730_adhesion protein LGALS3BP was found to be significantly enriched in circulating EVs from a cohort of EC patients with a high risk of recurrence by targeted proteomics (multiple reaction monitoring), highlighting its potential in liquid biopsy in EC. 30775897_Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi] might be able to detect liver fibrosis with great sensitivity 30786068_useful to identify high risk patients on antiviral treatment for subsequent hepatocellular carcinoma development 30848102_Results showed that LGALS3BP was upregulated at both RNA and protein levels in glioblastoma (GBM) tissue and generally associated with shorter overall survival (OS) in GBM patients. 30918432_High serum levels of Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) increased hepatocellular carcinoma risk by 4-5 folds. If M2BPGi is below the threshold (0.68 cut-off index), there is > 99% chance that the patient will not develop liver cancer in the subsequent 15 years. 31019124_Our results showed that serum Gal-3 and Gal-9 should not be considered biomarkers of inflammatory bowel disease. Despite not being a specific marker for Crohn's Disease, serum Gal-3BP might be used as an adjuvant biomarker for disease activity. 31302247_Increased LGALS3BP promotes proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma via PI3K/AKT pathway. 31393964_Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2-binding protein had a good performance in distinguishing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. 31653515_Elevated serum M2BP levels reflects one of the contributors to the progression of silent atherosclerosis. 31681284_Stimulation of Mononuclear Cells Through Toll-Like Receptor 9 Induces Release of Microvesicles Expressing Double-Stranded DNA and Galectin 3-Binding Protein in an Interferon-alpha-Dependent Manner. 31752995_High Gal3BP levels were associated with female sex, increasing sCD163 and total cholesterol levels, and decreasing HDL-cholesterol levels in patients with type 1 diabetes. The prevalence of high Gal3BP was more than twice as high in the women as in the men. 31894262_The GALNT6LGALS3BP axis promotes breast cancer cell growth. 31996371_Galectin 3-binding protein suppresses amyloid-beta production by modulating beta-cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. 32221402_Investigating LGALS3BP/90 K glycoprotein in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurological diseases. 32444247_Serum Mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer predicts esophagogastric varices in cirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection treated with IFN-free direct-acting antiviral agent: M2BPGi levels predict varices in SVR patients. 32455631_Wisteria floribunda Agglutinin-Positive Mac-2 Binding Protein but not alpha-fetoprotein as a Long-Term Hepatocellular Carcinoma Predictor. 32550761_M2BPGi for assessing liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C treated with direct-acting antivirals. 32847841_Serum levels of mac-2 binding protein are associated with diabetic microangiopathy and macroangiopathy in people with type 2 diabetes. 33208911_Plasma exosomes from endometrial cancer patients contain LGALS3BP to promote endometrial cancer progression. 33247961_Serum Mac-2 binding protein glycosylation isomer as a biomarker of fibrosis in living donor liver transplant graft. 33337998_Galectin-3-binding protein is a novel predictor of venous thromboembolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. 33354779_Microvesicles in active lupus nephritis show Toll-like receptor 9-dependent co-expression of galectin-3 binding protein and double-stranded DNA. 33686953_90K predicts the prognosis of glioma patients and enhances tumor lysate-pulsed DC vaccine for immunotherapy of GBM in vitro. 33910911_Serum galectin-3BP as a novel marker of obesity and metabolic syndrome in Chinese adolescents. 34052527_LGALS3BP/Gal-3 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. 34192302_N-glycan structures of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac2 binding protein in the serum of patients with liver fibrosisdagger. 34565385_Role of galectin 3 binding protein in cancer progression: a potential novel therapeutic target. 34728600_Extracellular LGALS3BP regulates neural progenitor position and relates to human cortical complexity. 34858323_Association of Serum Galectin-3-Binding Protein and Metabolic Syndrome in a Chinese Adult Population. 34874835_Human herpesvirus infections and circulating microvesicles expressing galectin-3 binding protein in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 34969731_Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer as a Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Sustained Virological Response. 35038949_Lectin galactoside-binding soluble 3 binding protein mediates methotrexate resistance in choriocarcinoma cell lines. 35346341_Urinary galectin-3 binding protein (G3BP) as a biomarker for disease activity and renal pathology characteristics in lupus nephritis. 35895036_LGALS3BP in Microglia Promotes Retinal Angiogenesis Through PI3K/AKT Pathway During Hypoxia. |
ENSMUSG00000033880 |
Lgals3bp |
175.988339 |
0.1761839086 |
-2.504846 |
0.238268608 |
105.081756 |
0.00000000000000000000000117199072332546072654062011664221403410803383193980672304634340578216589179305628931615501642227172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000012462956106832708612241176608818992380340163889669040533817066991086053295845204047509469091892242431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.2543420 |
7.7735067 |
292.6050514 |
29.1609003 |
| ENSG00000108691 |
6347 |
CCL2 |
protein_coding |
P13500 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a ligand for C-C chemokine receptor CCR2 (PubMed:9837883, PubMed:10587439, PubMed:10529171). Signals through binding and activation of CCR2 and induces a strong chemotactic response and mobilization of intracellular calcium ions (PubMed:9837883, PubMed:10587439). Exhibits a chemotactic activity for monocytes and basophils but not neutrophils or eosinophils (PubMed:8627182, PubMed:9792674, PubMed:8195247). May be involved in the recruitment of monocytes into the arterial wall during the disease process of atherosclerosis (PubMed:8107690). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10529171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10587439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8107690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8195247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8627182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9792674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9837883}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is one of several cytokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines are a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine is a member of the CC subfamily which is characterized by two adjacent cysteine residues. This cytokine displays chemotactic activity for monocytes and basophils but not for neutrophils or eosinophils. It has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases characterized by monocytic infiltrates, like psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. It binds to chemokine receptors CCR2 and CCR4. Elevated expression of the encoded protein is associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) infection. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:6347; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; CCR2 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031727]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; astrocyte cell migration [GO:0043615]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; helper T cell extravasation [GO:0035684]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process [GO:0034351]; negative regulation of natural killer cell chemotaxis [GO:2000502]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905563]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of apoptotic cell clearance [GO:2000427]; positive regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090280]; positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000353]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor activity [GO:1904783]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; viral genome replication [GO:0019079] |
11500196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11750041_Differential production of RANTES and MCP-1 in synovial fluid from the inflamed human knee. 11751881_These studies demonstrate that PEIPC and PECPC isomers are potent activators of endothelial cells increasing synthesis of IL-8 and MCP-1. 11776402_Contact hypersensitivity are significantly enhanced in the hMCP-1 Tgm, which appears to result from a constitutive activation of LC with the systemic presence of large amount of hMCP-1. 11844145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11912219_overexpression in mesangial cells by advanced glycation end products 11929421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11989790_Inflammatory cytokines mediate C-C (monocyte chemotactic protein 1) and C-X-C (interleukin 8) chemokine expression in human pleural fibroblasts. 11999660_Increased expression in atherectomy specimens from patients with restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty 12009356_Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor production by peritoneal macrophages may contribute to paracrine and autocrine activation and to macrophage accumulation in peritoneal cavity of women with endometriosis. 12022754_LPS-stimulated production of MCP-1 was significantly less in infected patients. Serum concentrations of both mediators were higher in infected patients and the highest concentrations of MCP-1 were in patients who died 12067898_Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces proliferation and interleukin-6 production in smooth muscle cells by differential activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein-1. 12078856_expression of MCP in aiway epithelial cells after injury enhances cell migration and proliferation 12082252_Fluid shear stress induces the secretion of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells 12093796_plasmin induction of MCP-1 in human monocytes 12117737_Simvastatin reduces expression of the proinflammatory cytokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in circulating monocytes from hypercholesterolemic patients. 12127997_MCP1 is upregulatied in Peyronie's disease 12183528_Induction of the gene encoding macrophage chemoattractant protein 1 by Orientia tsutsugamushi in human endothelial cells involves activation of transcription factor activator protein 1. 12186702_enhances the migration of bone marrow stromal cells 12195705_upstream signaling events in platelet-induced NF-kappa B activation that induce secretion of NF-kappa B-regulated chemokine MCP-1. 12204371_Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites induced MCP-1 expression and secretion in infected fibroblasts 12234797_Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 directly induces human vascular smooth muscle proliferation. 12239249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12239249_Recipients of renal transplants homozygous for the -2518 G mutation of the MCP-1 gene are at risk for premature kidney graft failure. 12351486_may be a marker of early development of nephropathy in IDDM 12358851_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372466_first report of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression in mesothelial cells induced by oxidized LDL, and provides direct evidence of inflammatory action of peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis 12374865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12374865_influence of genetic variation in MCP-1 on HIV-1 pathogenesis in large cohorts of HIV-1-infected adults and children 12391099_Circulating ICAM-1, IL-8, and MCP-1 in untreated obstructive sleep apnea were significantly greater than in controls. nCPAP therapy could reduce OSAS-induced hypoxia and generation of inflammatory mediators. 12391196_MCP-1 modulates the differentiation of monocytes into dendritic cells and may thereby inhibit Th1 cell development. 12393171_We used specific pharmacologic inhibitors to identify the signalling molecules which lead to interleukin (IL)-8 and MCP-1 production in human monocytes in response to M. tuberculosis infection 12397639_MCP-1 may play a role in progression of human esophageal carcinoma through its role in angiogenesis 12399623_Results show that high ambient glucose does not affect mesangial monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 release and decreases its chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) receptor expression. 12408680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12408680_homozygosity for G at -2518 in the MCP-1 gene might be a candidate for the genetic marker of Carpal-tunnel syndrome development in Japanese hemodialysis patients 12410798_some heat-stable component of P. gingivalis, including LPS, may be responsible for the induction of IL-8 and MCP-1 in HUVECs by a CD14-dependent mechanism 12413001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12413001_The polymorphisms of the MCP-1 and MIP-1A genes do not play a substantial role in genetic predisposition for sarcoidosis or in clinical manifestations of sarcoidosis in this Japanese population. 12419245_mechanism of gamma-Herpesvirus MCP-1 sequestration 12443832_induction of MCP-1 by Porphyromonas gingivalis in endothelial cells could enhance atherosclerosis progression by contributing to the recruitment of monocytes 12460032_A genetic polymorphism in the 5' flanking region of the MCP-1 gene is associated with nephritis in lupus through modulating MCP-1 expression. 12460032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12462338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12470469_Escherichia coli activates kidney proximal tubular cells to generate MCP-1 that promotes migration of monocytes in vitro. 12488502_IL-10 has two contrasting actions on MCP-1 production of monocytes/macrophages, between the resting and activated conditions. 12505750_results suggest that monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is produced in renal tubular cells and released into urine in proportion to the degree of proteinuria (albuminuria), and its increased expression in renal tubuli contributes to renal tubular damage 12520153_Myxomas with both high tumor and high stromal MCP-1 expression had a higher macrophage count than other myxomas. In cardiac myxoma, MCP-1 and thymidine phosphorylase may be important angiogenic signals accompanying growth. 12520365_results revealed that Porphyromonas gingivalis induces the expression of IL-8 and MCP-1 mRNAs in vascular endothelial cells, but bacterial proteases degrade both chemokines 12540965_The ability of activated protein C to upregulate the production of MCP-1 is most likely by increasing the stability of MCP-1-mRNA rather than by transcriptional activation via NF-KB 12632067_MCP-1 produced by human gastric carcinoma cells plays a role in angiogenesis via macrophage recruitment and activation 12651071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12665582_interacts with the transcriptional repression domain of MBD1 12724308_human monocytes require PKCbeta for the chemotactic response to MCP-1 12753088_MCP-1 may play a novel role as a protective agent against the toxic effects of glutamate and HIV-1 tat; neuronal and astrocytic apoptosis in culture was significantly inhibited by co-treatment with MCP-1 or RANTES but not IP-10 12758167_transcription regulated by Tat and the Smad-3 and-4 transcription factors whose activities are induced by the TGFbeta-1 pathway in human astrocytic cells 12787135_Estradiol-bound estrogen receptor beta may inhibit MCP-1 gene expression by inhibiting Sp1 and AP-1 transcriptional activities in keratinocytes. 12805068_CCL2 may represent an autocrine factor important for enhancing HIV-1 virion production likely by affecting the macrophage cytoskeleton. 12826189_a marker for acute rejection after liver transplantation 12826377_MCP-1 polymorphism is slightly associated with the susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in patients lacking the HLA shared epitope 12826377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12846738_that integrin-mediated cell adhesion to the ECM can induce MCP-1 expression through activation of FAK, and suggest a role for altered extracellular matrix deposition in the progression of glomerular diseases by affecting gene expression. 12904997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12944979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12946945_Proapoptotic stimuli upregulate MCP-1 expression by vascular smooth muscle cells through caspase- and calpain-dependent release of interleukin-1alpha. 12957789_differential glycosylation allows one to obtain highly effective short-lived CCL2 or less-effective long-lived CCL2 and may thus represent a novel mechanism of adaptation to pathological versus physiological conditions 12960255_ANF mediates the inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced expression of MCP-1. 14517168_MCP-1 mRNA levels were increased by 40-fold in left ventricle of myocardial infarction model mice; a transfected N-terminal deletion mutant of the human MCP-1 gene improved the survival rate and symptomology 14517792_Inheritance of the -2518 MCP-1 G allele, which appears to affect hepatic MCP-1 expression, may predispose HCV patients to more severe hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. 14517792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14571188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14576080_ROS such as superoxide and H(2)O(2) derived from Rac1-activated NADPH oxidase mediate TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression in endothelial cells. 14597108_Cerebrospinal fluid MCP-1 activity may be a sensitive marker for neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 14602575_Expression in the CNS of transgenic mice is a major pathogenic factor that drives macrophage accumulation in the development of CNS inflammatory disease. 14620921_MCP-1 genotype was an independent determinant of plasma MCP-1 level; findings indicate plasma MCP-1 associated with carotid atherosclerosis; -2518 SNP is associated with plasma level of MCP-1, but was not directly associated with carotid atherosclerosis 14620921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14647058_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14651522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14660607_MCP-1 has an effect on astrocytes that is mediated by caveolin-1 14687706_RANTES is more involved than MCP-1 in recruiting inflammatory cells in rhinological disease and may reflect the degree of local inflammation as consequence of the specific chemoattractant properties of RANTES 14733721_MCP-1 is substantially regulated upon monocyte contact with various cell wall components from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. 14767014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15005768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15016614_Unlike in cells exposed to proinflammatory cytokines, all three MAPKs (ERK, p38 MAPK, and JNK) were required to induce CCL2 secretion in response to activin. 15022320_Oncostatin M induces CCL-2 expression in osteoblasts. Activation of MEK/ERK and STAT pathways, which leads to c-Fos expression and AP-1-DNA binding, is involved in process. Signaling requires tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C but not COX-2. 15034225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15034225_The present study suggests that the MCP1 promoter -2518 polymorphism may not confer susceptibility to BID itself, but could have an influence on the clinical heterogeneity of BID, at least in the Korean population. 15041705_Up-regulation of MCP-1 in myeloma cells which express the relevant receptor C-C chemokine receptor 2. 15077296_Collagen II-reactive T cells in rheumatoid arthritis joints can increase the production of chemokines such as IL-8, MCP-1, and MIP-1 alpha through interaction with synoviocytes. 15081318_MCP-1 is induced by 13-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoic acid in the vasculature via activation of NF-kappa B 15082170_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15082170_The MCP-1 (-2518) gene polymorphism is unlikely to confer genetic susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease in this large Spanish population. 15110609_The capacity of in vitro factors to decrease human islet MCP-1 release suggests strategies to increase the success of islet transplantation. 15115316_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15123743_Eight tested neuroblastoma cell lines secreted a range of CCL2 (0-21.6 ng/ml. 15135805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15167690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15167690_Role of the MCP-1 promoter -2518 polymorphism in clinical heterogeneity of schizophrenia. 15188361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15188361_an A/G or G/G genotype may predispose to the development of systemic lupus erythematosus and further indicate that the patients with these genotypes may be at higher risk of developing lupus nephritis. 15191525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15191525_no association between the MCP-1 -2518 polymorphism and susceptibility to or clinical disease course in multiple sclerosis 15191888_SphK1 mediates TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 gene expression through a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway and may participate in oscillatory flow-mediated proinflammatory signaling pathway in the vasculature. 15191916_The induction of IL-13 and MCP-1 gene expression by IL-1beta was accompanied by the activation of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase and translocation of the transcription factor NF Kappa B into the nucleus. 15203564_Elevation of MCP-1 in the circulation of peripheral arterial disease(PAD) patients implicates this CC chemokine ligand 2 in inflammatory processes contributing to PAD clinical symptomatology. 15226634_An increase in MCP-1 may be an important factor in the progression of atherosclerosis in non-diabetic hemodialysis patients. 15257681_Our findings suggest a limited role for CCL2/CCR2 in early active multiple sclerosis 15280531_A strong upregulation of MCP-1 and RANTES was observed in all the cases, mainly in tubular cells, and there was a strong correlation between the expression of these chemokines and NF-kappaB activation in the same cells. 15288699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15296827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15302103_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15312962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15312962_The A-2518G polymorphism in MCP-1 gene does not seem to be a risk factor for the development of AD, but its presence correlates with higher levels of serum MCP-1, which can contribute to increase the inflammatory process occurring in AD. 15349727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15349727_Single nucleotide polymorphism in this gene supports role for MCP-1 in pathologies associated with hyperinsulinaemia. 15389752_Data suggest that the A-2518G variant of the SCYA2 has not a major role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. 15389752_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15466648_HIV-infected patients with the MCP-1-2518G allele have a 5-fold increased risk for atherosclerosis. 15466648_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15468376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15488313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15492853_Two codons of this human gene suppressed hepatic fibrosis in rats, thus providing feasible gene threapy. 15529362_MCP-1, MIP-1beta, and IL-8 elevated in relapsing polychondritis(RP) are proinflammatory chemokines, characteristic of activation of monocytes and macrophages and, in the case of IL-8, also of neutrophils. Role for cell-mediated immune response in RP. 15545821_MCP-1 is involved in the regulation of chemotaxis and function of monocytes during and early after the end of cardiopulmonary bypass 15579297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15599324_The surgical team and the enzyme were independently associated with in vitro CCL2/MCP-1 islet release in islet transplantation. 15602730_Role in the development of bronchiolitis associated with influenza and RSV infections in infants and children. 15607028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15611878_Association between presence of G at position -2518 in MCP-1 promoter region and presence of arthritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 15611878_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15627719_new role of MCP-1 as an arteriogenic factor in hemodialysis patients with cardiovascular disease. 15654958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15654958_The A -2518G polymorphism of the MCP-1 gene appears to affect MCP-1 expression of skin fibroblasts of patients with systemic sclerosis; the G/G genotype may predispose patients 15677312_stretching of mesangial cells stimulates their monocyte chemoattractant activity via an NF-kappaB-mediated, MCP-1-dependent pathway 15722361_MCP-1 significantly increased the number of TRAP-positive multinuclear bone-resorbing osteoclasts 15740484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15745922_increased CXCL10 especially in hypothyroid patients with a more aggressive disorder, and normal CCL2 serum levels in autoimmune thyroiditis 15780578_MCP-1 expression is upregulated in P. gingivalis-infected endothelial cells via reactive oxygen species, p38 MAP kinase, JNK, NF-kappaB, and AP-1. 15832427_MCP-1 mainly down-regulates the expression of chemotactic genes influencing neutrophilic granulocyte expression 15848524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15866653_Lack of involvement of polymorphism at position -2518 (A/G) of the MCP-1 gene on the susceptibility to acute allograft rejection among liver transplantation recipients. 15866653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15880317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15880317_Our aim was to determine whether the MCP-1 -2518 A/G polymorphism affects the severity of acute pancreatitis 15883814_Increased expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 is associated with invasive ductal breast carcinoma 15900302_CCL2 may play role in pathobiology of ovarian cancers 15919935_expression induced in macrophages by SARS-CoV infection 15976326_the production of MCP-1 and IL-8 in vascular endothelial cells was induced by mast cell granules and amplified by tryptase 15979992_IL-8 and MCP-1 may contribute to the pathophysiology of adenomyosis 16003740_results therefore identify MCP-1 as a target of the beta-catenin/TCF/LEF pathway in breast tumour cells, a regulation which could play a key role in breast tumour progression 16004967_These results indicate that interaction between the Arp2/3 complex and WASP stimulates actin polymerization and integrin beta-1-mediated adhesion during MCP-1-induced chemotaxis of THP-1 cells. 16009177_Biologically active MCP-1 secreted into both the uterine lumen and underlying stroma mediates the presence of monocytes, macrophages, and other immune cells in the uterine endometrium. 16009638_findings suggest that monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) may play a role in preterm labor regardless of the presence of intra-amniotic infection (IAI) 16020745_MCP-1/CCR2 may play a role in Ca2+ influx-dependent TF regulation in the monocyte-endothelial cell interaction in the impairment of nitric oxide synthesis 16050950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16078996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16095529_The results indicate that pulmonary CCR2+ T cells and MCP-1 contribute to the pathogenesis of pediatric ILD and might provide a novel target for therapeutic strategies. 16105652_These results suggest that hypoxia is an important negative regulator of monocyte chemotaxis to the renal inflamed interstitium, by reducing MCP-1 expression. 16116069_MCP-1 is involved in the pathogenesis of human atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction 16116069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16129702_MCP-1 overexpressed in tuberous sclerosis lesions acts as a paracrine factor for tumor development. 16164699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16195477_Human perivascular white adipose tissue has chemotactic properties through the secretion of chemokines 16204411_Basal secretion of IL-8 and MCP-1 was not changed in CTGF-silenced renal cells. 16206198_The transcription factor NF-kappaB, and possibly NF-I, contribute to the upregulation of CCL2 chemokine production during the differentiation of human progenitor cells toward an astrocyte phenotype. 16213182_The level of CCL2 in cultured fibroblasts was increased 3 h post-stimulation by purified or recombinant SAG1. 16214031_MCP-1 is upregulated by oxidized cholesterol. 16230097_no polymorphic sequence deletion in chronic hepatitis C. 16249002_IL-4 up-regulates the expression of MCP-1 and decreases NO bioavailability through activation of NADPH oxidase in endothelial cells 16278381_MCP1 has a role in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis of gastric carcinoma 16280328_the MCP-1-induced TRAP(+)/CTR(+) multinuclear cells represent an arrested stage in osteoclast differentiation, after NFATc1 induction and cellular fusion but prior to the development of bone resorption activity 16280979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16280979_Our data suggest that the CCL2 -2518A>G polymorphism may play a role in HLA-B27 associated acute anterior uveitis. 16307829_Significantly increased MCP-1 levels are found in patients with mild cognitive impairment and in mild Alzheimer's disease (AD), but not in severe AD patients as compared with controls. 16309586_In heme oxygenase-1 overexpressing cells, VEGF and the prostaglandin transporter were greatly increased while MCP-1 levels were decreased 16318581_MCP-1 and M-CSF, critical for monocyte recruitment, activation, and differentiation, differentially regulate VEGF-A expression and may play an important role in monocyte/macrophage- mediated tumor angiogenesis 16351713_probiotic E. coli Nissle 1917 specifically upregulates expression of proinflammatory genes and proteins MCP-1, MIP-2alpha, and MIP-2beta in human and mouse intestinal epithelial cells. 16352737_A functional promoter polymorphism in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is associated with increased susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis. 16352737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16356504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16358960_Increased MCP-1 levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid is associated with Lyme borreliosis 16359995_The VEGF level was detected in endometrial stromal cell culture media and was increased significantly when E2 or MCP-1 was added to the media, especially in the presence of E2 plus MCP-1 16362156_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16362156_The AA genotype at MCP-1 -2518 was an independent risk factor for the progression of renal disease in Japanese patients with IgA nephropathy, and was closely associated with renal survival 16397773_The MCP-1 mRNA expression was increased following exposure to calcium oxalate crystals in renal epithelial cell line 16415174_These data suggest that fibrogenic processes in Mo regulated by MCP-1/CCR2 may be novel, therapeutic targets for combating organ fibrosis. 16427785_Our data show that CT-1 induces in a concentration and time dependent manner MCP-1 mRNA and protein in HUVEC. 16436595_data suggest that CCL2, but not other chemokines, plays a key role in infiltration of HIV-infected leukocytes into the CNS and the subsequent pathology characteristic of NeuroAIDS 16439461_MCP-1 may represent a molecular link in the negative cross-talk between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle assigning a completely novel important role to MCP-1 besides inflammation 16439481_Macrophage-specific chemokine MCP-1, but not MIP1alpha, is present at higher concentrations in follicular fluid of ovulating follicles of both menstrual and in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles, in comparison with that of blood plasma. 16439891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16445900_Plasma MCP-1 concentration is genetically determined and associated with age and smoking habit and it also correlates with subclinical atherosclerosis in HIV-infected patients 16474202_Induction of HO-1 inhibits MCP-1 mRNA expression in U937 cells. 16479072_Data indicates that no association exists between the -2518A/G polymorphism of the MCP-1 gene and susceptibility to alopecia areata. 16479072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16504689_Monitoring cell excretion and mcp1 content may be utilized for early detection of polyomavirus-induced nephropathy after kidney transplantation. 16516290_Central nervous system involvement in acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with significantly higher levels of MCP1 in cerebospinal fluid during therapy. 16518346_Stretch-induced CCR2 downregulation may favour MCP-1 paracrine activity in mesangial cells. 16524739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16597919_findings show that in type II alveolar cells intrinsic and extrinsic peptide CGRP inhibits IL-1-induced MCP-1 secretion in an autocrine/paracrine mode 16609683_Albuminuria triggers tubular MCP-1/CCL2 expression with subsequent macrophage infiltration. 16631114_Our data suggest that elevated serum MCP-1 levels and increased monocyte CCR2, CD36, CD68 expression correlate with poor blood glucose control and potentially contribute to increased recruitment of monocytes to the vessel wall in diabetes mellitus. 16636247_study identifies significant correlations between MCP-1 in plasma and tissue alterations in all studied regions of deep white matter and basal ganglia of patients with HIV infection. 16636603_MCP-1 -2518 G allele does not significantly alter susceptibility to chronic pancreatitis. 16636603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16672419_found relevant markers in the MCP1 gene associated with HCMV reactivation 16697212_CXC chemokine CXCL10 and CC chemokine CCL2 serum levels increase with normal aging 16697654_monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 has a role in carotid atherosclerosis in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy 16705739_MCP-1 acts as a paracrine and autocrine factor for prostate cancer (CaP) growth and invasion. 16712788_intracellular ascorbate in vitro protects THP-1 cells from oxidative damage and inflammatory responses 16719905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16730843_results suggest that MCP-1, under the regulation of NF-kappaB, is involved in the pathogenesis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy 16733654_Results suggest that MCP-1/CCL2 and IP-10/CXCL10 produced by astrocytes may activate astrocytes in an autocrine or paracrine manner and direct reactive gliosis followed by migration and activation of microglia/macrophages in demyelinating lesions. 16741188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16751386_MCP-1 markedly enhances CX3CR1 expression on freshly isolated human peripheral blood monocytes or monocytic cell lines and stimulates the adhesion of these cells to immobilized CX3CL1/fractalkine. 16781696_The mRNA expressions of MCP-1 of all post-kidney transplant patients were significantly higher than controls. 16795034_These results suggest that lysophospholipid released by activated platelets might enhance the IL-8- and MCP-1-dependent chemoattraction of monocytes toward the endothelium through an IL-1-dependent mechanism. 16802342_CDK-4/6 modulated the production of MMP-3 and MCP-1. 16804844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16814297_A functional polymorphism within the TNF bloc could modulate MCP-1 concentration and seems more likely to be near to the LTA 252A>G polymorphism than to the TNF -308G>A one 16825597_Elevated systemic levels of the chemokines MCP-1, IL-8, and IP-10 precede coronary heart disease but do not represent independent risk factors. 16828028_Polymorphism in the promoter is related to increased susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis. 16835702_MCP-1 gene polymorphism might slightly associate with patients with systemic juvnile rheumatoid arthritis 16835702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16867220_CCL2 recruits prostate cancer epithelial cells to the bone microenvironment and regulates their proliferation rate 16872505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16873204_MCP1 is significantly elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid in HIV-1 infected patients. 16903979_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16934270_the MCP-1 gene -2578A>G polymorphism is associated with an excess risk of coronary atherosclerosis in an asymptomatic population and is a risk factor. 16939660_Adiponectin-mediated induction of IL-6, CCL2 and CXCL8 is disturbed in monocytes from type I diabetes patients. 16980310_Elafin inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in monocytes by inhibiting AP-1 and NF-kappaB activation. 16988194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16997300_Women with endometriosis-associated infertility have a poor IVF outcome. 17008880_C uptake is increased in UVB-irradiated keratinocytes through the translocation of SVCT-1 and regulates inflammatory response in the skin via the downregulation of IL-8 and MCP-1 production 17032917_MCP-1 functions as a chemoattractant to stimulate migration of VSMCs and mesenchymal cells toward ECs 17052731_serum MCP-1 levels are directly correlated, and cell-mediated immunity inversely correlated, with the severity of surgical stress 17062130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065190_genetic markers in the MCP-1 gene do not demonstrate significant genetic associations with the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and do not discriminate polymyositis from dermatomyositis in a UK Caucasian population 17082648_CCL2 expression by transgenic mouse pancreatic beta cells promotes recruitment of monocytes and dendritic cells into the islets of Langerhans. 17091019_In our cohort of white Spaniards, homozygosity for the variant CCL2-2518GG genotype is overrepresented in HIV-1-infected subjects 17091019_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17098977_findings show increased permeability & disrupted tight junctions of vascular endothelium cells in dengue haemorrhagic fever/dengue shock syndrome were effected by a mechanism partially dependent on MCP-1 secreted by DV2-infected monocytes & lymphocytes 17138827_HHV-8-induced MCP-1 may play an important role in promoting inflammation and pathogenic angiogenesis typical of HHV-8-associated lesions. 17169533_CCL2-2578G/G genotype could influence melanoma growth 17187019_Serum levels of MCP-1 were increased in Down's syndrome (DS) children and adults, but not in older DS patients. 17202846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17202846_frequency of homozygotes for the MCP1-2518A allele (MCP1-2518A/A) among chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) carrier patients was significantly higher than that among spontaneously recovered (SR) subjects 17207568_CD14+ cells producing TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-10, MCP-1, and IL-8 were significantly higher in peripheral blood than peritoneal fluid mononuclear cells of women with endometrio |
ENSMUSG00000035385 |
Ccl2 |
27.921477 |
28.8799599529 |
4.851997 |
0.570129952 |
101.527445 |
0.00000000000000000000000704801255778926153510696099901281151877759893185362409050115177749223915881771063141059130430221557617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000072493843451546693433941172624953226960959695362624927269913437631598807087129898718558251857757568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.0339215 |
19.0693624 |
1.7806683 |
0.6231200 |
| ENSG00000108702 |
6346 |
CCL1 |
protein_coding |
P22362 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that is chemotactic for monocytes but not for neutrophils. Binds to CCR8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1557400}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This antimicrobial gene is one of several chemokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines form a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CC subfamily, is secreted by activated T cells and displays chemotactic activity for monocytes but not for neutrophils. It binds to the chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 8. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:6346; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; viral process [GO:0016032] |
12393595_After stimulation via high-affinity FcepsilonRI, the transcriptional levels of I-309 (CCL1), MIP-1alpha (CCL3) and MIP-1beta (CCL4) were found among the 10 most increased human and mouse transcripts from approximately 12 000 genes 12645948_Transfected human CCL1 up-regulated ERK1/2 MAPK phosphorylation in BW5147 cells. CCL1 activates the MAPK pathway in CCR8-transfected CHO cells. 12949249_CCL1 is an antimicrobial protein with bacteriocidal activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 15814739_the axis CCL1-CCR8 links adaptive and innate immune functions that play a role in the initiation and amplification of atopic skin inflammation 16540498_CC chemokine ligand 1 may play a role in lymphocyte recruitment in bronchial asthma 16679317_Benzo(a)pyrene and an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist enhance activitity of te Ccl1 promoter. 16735693_Thus, CCL1 is a CC chemokine with a unique pattern of regulation associated with a distinct form of M2 (Type 2, M2b) monocyte activation, which participates in macrophage-dependent regulatory circuits of innate and adaptive immunity. 16864713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16864713_Variants in the CCL1 gene are associated with susceptibility to AEs through their potential implication in the host defense mechanisms against AEs. 17122780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17641040_The mechanisms underlying the mast cell-CD4-positive T lymphocyte axis is determined by mast cell-derived CCL1 and a subset of CD4-positive T cells expressing CCR8. 17672898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17693327_The combination of 17beta-E(2) with the environmental pollutant TCDD is involved in the pathogenesis of endometriosis via up-regulating the chemokine CCR8-I-309. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17845580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19057661_6 single nucleotide polymorphisms in CCL1 were found to be associated with tuberculosis in a case-control genetic association study with 273 TB cases and 188 controls 19117730_serum CCL1 levels were slightly, but statistically significantly, correlated with serum IgE levels in patients with bullous pemphigoid. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19372141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19776237_The authors show here that PRV-gG binds to the human chemokine CL1 and several CC and CXC human chemokines with high affinity. 19865101_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21849907_ACEI is effective in downregulating LPS-induced TNF-alpha, I-309, and IP-10, which play important roles in the pathogenesis of inflammation 22147355_There was a borderline association between a single nucleotide polymorphism located within the CCL1 gene and predisposition to tuberculosis using a singlepoint analysis 22479563_C-terminal clipping of chemokine CCL1/I-309 enhances CCR8-mediated intracellular calcium release and anti-apoptotic activity 22948508_CCL1, CCL26, and IgE may be associated with pruritus in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 23811304_CCL1-CCR8 interaction may play a critical role in lymphocytic recruitment in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis, leading to duct-centred inflammation and obliterative phlebitis. 23878309_These data identify a novel function for CCL1-CCR8 in metastasis and lymph node LECs as a critical checkpoint for the entry of metastases into the lymph nodes. 26548923_The results of the present study demonstrated that GAS5 was able to suppress bladder cancer cell proliferation, at least partially, by suppressing the expression of CCL1. 26722451_was to evaluate the possible association between CCL1 rs2072069 G/A or/and TLR2 rs3804099 T/C (T597C) polymorphisms and pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) or/and tuberculous meningitis (TBM) in a sample of the Chinese adult population 28972028_downregulation of miR-20a-5p is caused by promoter hypermethylation. MiR-20a-5p could also suppress the production of IL-17 by targeting OSM and CCL1 production in CD4(+) T cells in patients with active VKH. 29202792_Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 ( CCL1) is preferentially Plasma levels of CCL1 were significantly higher in patients with HAM/TSP. Minocycline inhibited the production of CCL1 in HTLV-1-infected T-cell lines. 30572845_Both CCL1 and CCL22 were expressed in most breast cancer tissues. CCL1 was significantly over-expressed in invasive breast cancer as compared to normal breast tissue. CCL1, but surprisingly not CCL22, showed a significant correlation with the number of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Treg 31063909_Comparison of the chemokine profiles in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid between IgG4-related respiratory disease and sarcoidosis: CC-chemokine ligand 1 might be involved in the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. 32447247_The utility of serum C-C chemokine ligand 1 in sarcoidosis: A comparison to IgG4-related disease. 34001131_CCL21 activation of the MALAT1/SRSF1/mTOR axis underpins the development of gastric carcinoma. 34413269_Hsa_circ_0134111 promotes osteoarthritis progression by regulating miR-224-5p/CCL1 interaction. 34691031_Serum Biomarker Profile Including CCL1, CXCL10, VEGF, and Adenosine Deaminase Activity Distinguishes Active From Remotely Acquired Latent Tuberculosis. |
|
|
116.469309 |
119.5228956405 |
6.901143 |
0.530879122 |
536.406575 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011407206753759543336697475319267223329828479166263589944219154640000022781326200595231861927714045967271114216389784633753996856841023009682148109836774528327703488942413747504828007671442533133682709376452028148 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005825964418183074403572780701355279102542627828366274459871108910638416170402071855701408491378691575559990044595597912762828005583852474328434472617873782781235972583767740166055358499118841106874760485572110740 |
Yes |
No |
233.4646346 |
85.9092778 |
1.9691127 |
0.7166752 |
| ENSG00000108799 |
2145 |
EZH1 |
protein_coding |
Q92800 |
FUNCTION: Polycomb group (PcG) protein. Catalytic subunit of the PRC2/EED-EZH1 complex, which methylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3, leading to transcriptional repression of the affected target gene. Able to mono-, di- and trimethylate 'Lys-27' of histone H3 to form H3K27me1, H3K27me2 and H3K27me3, respectively. Required for embryonic stem cell derivation and self-renewal, suggesting that it is involved in safeguarding embryonic stem cell identity. Compared to EZH2-containing complexes, it is less abundant in embryonic stem cells, has weak methyltransferase activity and plays a less critical role in forming H3K27me3, which is required for embryonic stem cell identity and proper differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19026781}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Isopeptide bond;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
EZH1 is a component of a noncanonical Polycomb repressive complex-2 (PRC2) that mediates methylation of histone H3 (see MIM 602812) lys27 (H3K27) and functions in the maintenance of embryonic stem cell pluripotency and plasticity (Shen et al., 2008 [PubMed 19026780]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:2145; |
chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; ESC/E(Z) complex [GO:0035098]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone H3K27 methyltransferase activity [GO:0046976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; heterochromatin formation [GO:0031507]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; histone H3-K27 trimethylation [GO:0098532]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; subtelomeric heterochromatin formation [GO:0031509] |
19026781_EZH1 maintains repressive chromatin through different mechanisms. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25578878_The related enzymatic subunits EZH1 and EZH2 undergo an expression switch during blood cell development. 27127229_EZH1, SUZ12 and UXT work synergistically to regulate pathway activation in the nucleus. 27311868_These evidences suggest that EZH2 and EZH1 are important in the counter-balancing mechanisms controlling proliferation/resting of lymphoid cells. The disruption of the balanced EZH2/EZH1 ratio may play important roles in the pathogenesis of lymphomas 27500488_a hot-spot mutation in EZH1 is the second most frequent genetic alteration in autonomous thyroid adenomas; the association between EZH1 and TSHR mutations suggests a 2-hit model for the pathogenesis of these tumors, whereby constitutive activation of the cAMP pathway and EZH1 mutations cooperate to induce the hyperproliferation of thyroid cells 27630126_Expression of the EZH2 homolog EZH1 is reduced in EZH2-deficient CML LICs, creating a scenario resembling complete loss of PRC2. EZH2 dependence of CML LICs raises prospects for improved therapy of TKI-resistant CML and/or eradication of disease by addition of EZH2 inhibitors 28346433_The authors report a novel PRC2-Ezh1 function that utilizes Ezh1beta as an adaptive stress sensor in the cytoplasm, thus allowing postmitotic cells to maintain tissue integrity in response to environmental changes. 28701475_pVHL loss causes the transcriptional activation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) target genes, including many genes that encode histone lysine demethylases. 28939884_Data show that embryonic stem cells with deletion of EZH1 or EZH2 fail to differentiate into ectoderm lineages. 29342143_identification of EZH1 as a repressor of haematopoietic multipotency in the early mammalian embryo 29723601_EZH1 mutations predominantly occurred in clinically benign follicular neoplasms without RAS mutations. 30688289_Overexpression the EZH1 gene inhibited HK-2 cell apoptosis, reduced ROS levels, and down-regulated the expressions of IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, Bax and Cyt C mRNA and protein, and increased the expressions of Bcl-2 and NFKBIA, CXCL8 and cyclin D1, indicating that overexpression of EZH1 suppressed NF-kappaB signaling in aristolochic acid-injured HK-2 cells. 30867289_functions mostly within canonical PRC2 and exhibits proliferation-dependent redundancy that shapes mutational signatures in cancer 31699991_Findings highlight the role of EZH1 in non-histone lysine methylation, indicating that cooperation between AML1-ETO and EZH1 and AML1-ETO site-specific lysine methylation promote AML1-ETO transcriptional repression in leukemia. 31747604_Targeting Excessive EZH1 and EZH2 Activities for Abnormal Histone Methylation and Transcription Network in Malignant Lymphomas. 33514705_Structures of monomeric and dimeric PRC2:EZH1 reveal flexible modules involved in chromatin compaction. 34856418_TRIM21 improves apatinib treatment in gastric cancer through suppressing EZH1 stability. |
ENSMUSG00000006920 |
Ezh1 |
317.778901 |
0.3582022240 |
-1.481154 |
0.174211986 |
70.506406 |
0.00000000000000004587742015656865206426246213100581776976756418926980951589200685702962800860404968261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000353418956947261603850727768997625785409116919979707893695319853577530011534690856933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
161.7012128 |
17.5294662 |
455.3764282 |
34.2708808 |
| ENSG00000108813 |
1748 |
DLX4 |
protein_coding |
Q92988 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in determining the production of hemoglobin S. May act as a repressor. During embryonic development, plays a role in palatogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11909945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25954033}. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Many vertebrate homeo box-containing genes have been identified on the basis of their sequence similarity with Drosophila developmental genes. Members of the Dlx gene family contain a homeobox that is related to that of Distal-less (Dll), a gene expressed in the head and limbs of the developing fruit fly. The Distal-less (Dlx) family of genes comprises at least 6 different members, DLX1-DLX6. The DLX proteins are postulated to play a role in forebrain and craniofacial development. Three transcript variants have been described for this gene, however, the full length nature of one variant has not been described. Studies of the two splice variants revealed that one encoded isoform functions as a repressor of the beta-globin gene while the other isoform lacks that function. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1748; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11792834_Genomic structure and functional control of the Dlx3-7 bigene cluster 11909945_BP1, a homeodomain-containing isoform of DLX4, represses the beta-globin gene. 15308321_involvement of BP1 in the mechanism of the negative regulation of beta-globin transcription. 17003054_BP1 can negatively modulate adult beta-globin gene expression and definitive erythroid cell differentiation, and suggest that BP1 could play a role in thalassemia. 17062780_Increased expression of homeobox gene DLX4 may be a contributing factor to the developmental abnormalities seen in the FGR-affected placentae. 17260014_we were able to show that enforced expression of the DLX4 homeobox gene markedly inhibited in vitro motility and invasion as well as in vivo metastasis via both hematogenous and lymphogenous routes. 17999690_results support the notion that BP1 might contribute to breast neoplastic transformation or tumor progression and suggest for the first time that BP1 mRNA level has potential as a prognostic predictor for breast cancer 18026954_BP1 may regulate bcl-2 and c-myc expression 18420035_BP1 may be part of a pathway contributing to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) development and/or progression and mRNA level could be a novel prognostic marker for NSCLC. 18931648_BP1 is an important upstream factor in the carcinogenic pathway of prostate cancer and that the expression of BP1 may reflect or directly contribute to tumor progression and/or invasion. 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18992636_Other mechanisms in addition to gene amplification play a role in BP1 protein expression om breast camcer/ 19242057_High BP1 expression is associated with inflammatory breast cancer and tumor aggressiveness 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21297662_The ability of DLX4 to counteract key transcriptional control mechanisms of the TGF-beta cytostatic program could explain, in part, the resistance of tumors to the antiproliferative effect of TGF-beta. 21602546_findings suggest that decreased expression of homeobox protein DLX-4 leads to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in trophoblasts 23091415_DLX4 induces cancer cells to undergo epithelial to mesenchymal transition through TWIST, enhancing tumor migration, invasion and metastasis. 23158431_All trans retinoic acid can inhibit the proliferation and the expression of BP1 in breast cancer cells. 24824934_The results suggest that high expression of DLX4 predicts hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. 24947980_DLX4 increased copy number was observed in 21.6% of the primary breast tumors and 24.3% of the sentinel lymph node metastasis 25471527_DLX4 can functionally replace c-MYC. 25614457_Aberrant DNA methylation of the DLX4 and SIM1 genes may be a novel progression marker for uterine cervical low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. 25823567_a DLX4 overexpression vector lacking the 3'UTR was shown to abolish miR-122-induced inhibition of proliferation in the HCC cell line Hep3B. 25825198_Methylated DLX4 is a potential biomarker that predicts poor prognosis after curative resection of pathologic stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 25924901_DLX4 promotes ovarian tumor angiogenesis in part by stimulating iNOS expression. 25954033_This first finding of a DLX4 mutation in a family with Cleft lip and/or palate establishes DLX4 as a potential cause of human clefts 26067154_DLX4 induces CD44 by stimulating IL-1beta-mediated NF-kappaB activity, thereby promoting peritoneal metastasis of ovarian cancer 26208636_Collectively, our findings indicate that DLX4 exerts opposing effects on the megakaryocytic and erythroid lineages in part by inducing IL-1beta and NF-kappaB signaling. 26325005_Our study reveals that BP1 overexpression serves as an independent risk factor in de novo AML patients. 26485746_study indicated that DLX4 hypermethylation was a frequent event and acted as an independent prognostic biomarker in de novo myelodysplastic syndrome patients 26524685_indicate that gains of DLX4 and ERBB2 occur in South African breast cancer patients irrespectively of their race and factors known to influence prognosis 27449292_Beta protein 1 (BP1) binds to and regulates estrogen receptor. 29575937_the role of BP1 protein in tumorigenesis of breast cancer and four other malignancies 29738288_indicated the hypothesis that DLX4 variants contributing to nonsyndromic orofacial cleft risk should be interpreted with caution 31100338_Results demonstrate that high expression of BP1 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with endometrial cancer and promotes cell proliferation and migration. 32281175_Homeodomain protein DLX4 facilitates nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via up-regulation of YB-1. 35883028_DNA methylation-mediated differential expression of DLX4 isoforms has opposing roles in leukemogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000020871 |
Dlx4 |
25.821886 |
0.2216727237 |
-2.173497 |
0.334376016 |
45.698780 |
0.00000000001379086119029502707797783868725287467413287423312340251868590712547302246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000075782990010705348450295436837562384341238086449266120325773954391479492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6321065 |
1.9191647 |
39.2154707 |
4.9310162 |
| ENSG00000108829 |
55379 |
LRRC59 |
protein_coding |
Q96AG4 |
FUNCTION: Required for nuclear import of FGF1, but not that of FGF2. Might regulate nuclear import of exogenous FGF1 by facilitating interaction with the nuclear import machinery and by transporting cytosolic FGF1 to, and possibly through, the nuclear pores. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22321063}. |
Acetylation;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Microsome;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables RNA binding activity and cadherin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction and signal transduction. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial nucleoid. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55379; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
22321063_LRRC59 facilitates transport of cytosolic FGF1 through nuclear pores by interaction with Kpns and movement of LRRC59 along the ER and NE membranes 25833693_we provide a novel therapeutic mechanism for inhibiting CIP2A function in cancerous cells via targeting the CIP2A-LRRC59 interaction. 26466955_Endosomal localization of endogenous TLR3 was decreased by silencing of LRRC59, suggesting that LRRC59 promotes UNC93B1-mediated translocation of NA-sensing TLRs from the ER upon infection. 30650545_the mechanisms of membrane integration of LRRC59 and its targeting to the inner nuclear membrane (INM), were investigated. 31068071_LRRC59 modulates type I interferon signaling by restraining the SQSTM1/p62-mediated autophagic degradation of pattern recognition receptor DDX58/RIG-I. 32788342_Quantitative Proteomics Links the LRRC59 Interactome to mRNA Translation on the ER Membrane. |
ENSMUSG00000020869 |
Lrrc59 |
658.884753 |
2.1173314136 |
1.082247 |
0.073148601 |
218.903525 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000015687562667018060002047795144087660958562563973247478662872649756415966121964166972790794337797061601652318744018106309938117085001074713090929435566067695617675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003307834642359808139033010321356670495097487209941403938392250721835941219900800865093195429492043570609937188385113205355350651792889493663096800446510314941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
892.8892713 |
39.8478044 |
424.6638263 |
14.6437297 |
| ENSG00000108840 |
10014 |
HDAC5 |
protein_coding |
Q9UQL6 |
FUNCTION: Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Involved in muscle maturation by repressing transcription of myocyte enhancer MEF2C. During muscle differentiation, it shuttles into the cytoplasm, allowing the expression of myocyte enhancer factors. Involved in the MTA1-mediated epigenetic regulation of ESR1 expression in breast cancer. Serves as a corepressor of RARA and causes its deacetylation (PubMed:28167758). In association with RARA, plays a role in the repression of microRNA-10a and thereby in the inflammatory response (PubMed:28167758). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24413532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28167758}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the class II histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. It coimmunoprecipitates only with HDAC3 family member and might form multicomplex proteins. It also interacts with myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) proteins, resulting in repression of MEF2-dependent genes. This gene is thought to be associated with colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10014; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; histone deacetylase activity [GO:0004407]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein lysine deacetylase activity [GO:0033558]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; epigenetic regulation of gene expression [GO:0040029]; heterochromatin formation [GO:0031507]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090051]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010832]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein deacetylation [GO:0006476]; regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010830]; regulation of protein binding [GO:0043393] |
11929873_Class II histone deacetylases are directly recruited by BCL6 transcriptional repressor 12019172_Histone deacetylase 5 is not a p53 target gene, but its overexpression inhibits tumor cell growth and induces apoptosis. 12242305_MITR, HDAC4, and HDAC5 associate with heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1), an adaptor protein that recognizes methylated lysines within histone tails and mediates transcriptional repression by recruiting histone methyltransferase 12626519_HDAC5 binds to Ca(2+)/calmodulin and inhibits MEF2a binding 15194749_ICP0 of herpes simplex virus Type 1 is able to overcome the HDAC5 amino-terminal- and MITR-induced MEF2A repression in gene reporter assays 15590418_The HDAC5, a class II HDAC involved in myogenesis, was not detected in the tissues. 16221676_G betagamma binds HDAC5 and inhibits its transcriptional co-repression activity 16236793_novel transcriptional pathway under the control of class II HDACs and suggest a role for these transcriptional repressors as signal-responsive regulators of antigen presentation 17975112_NO-dependent PP2A activation plays a key role in nuclear translocation of class II HDACs HDAC4 and HDAC5 18184930_AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulates GLUT4 transcription through the histone deacetylase (HDAC)5 transcriptional repressor. 18218981_Chronic upregulation/activation of CaMKIID, and PKD in heart failure shifts HDAC5 out of the nucleus, derepressing transcription of hypertrophic genes. 18288090_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18332134_Protein kinase D-HDAC5 pathway plays an important role in VEGF regulation of gene transcription and angiogenesis 19071119_These results indicate that HDAC4 and HDAC5 increase the transactivation function of HIF-1alpha by promoting dissociation of HIF-1alpha from FIH-1 and association with p300. 19351956_HDAC5 represses angiogenic genes, such as FGF2 and Slit2, which causally contribute to capillary-like sprouting of endothelial cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20042720_phosphorylation-dependent derepression of HDAC5 mediates flow-induced KLF2 and eNOS expression as well as flow anti-inflammation, and suggest that HDAC5 could be a potential therapeutic target for the prevention of atherosclerosis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20716686_Findings identify HDAC5 as a substrate of PKA and reveal a cAMP/PKA-dependent pathway that controls HDAC5 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and represses gene transcription. 21047791_differentiation-dependent GLUT4 gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is dependent on the nuclear concentration of a class II histone deacetylase (HDAC) protein, HDAC5 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21081666_Ser279 is a critical phosphorylation within the NLS involved in the nuclear import of HDAC5 21146494_in addition to activation of protein kinase D isozymes by phosphorylating Ser744 and Ser748 at their activation sites, PKCdelta may also play a role in the regulation of HDAC5 by phosphorylation of Ser259 21508384_Significantly increased methylation of the HDAC5 gene was associated with astrocytomas. 22243750_The results of this study suggested that suggest that HDAC5 provides a delayed braking mechanism on gene expression programs that support the development, but not expression, of cocaine reward behaviors. 22301920_HDAC5 in the maintenance/assembly of pericentric heterochromatin structure and demonstrate that class IIa HDAC5 can represent a potential target for anticancer therapies. 22914591_Loss of HDAC5 impairs memory function but has little impact in a transgenic mouse model of amyloid pathology. 22941650_The current study identified the class II deacetylase HDAC5 as a novel promoting factor of CTG*CAG expansions. 22991226_Data suggest that HDAC5 regulates muscle glucose metabolism and insulin action and that HDAC inhibitors can be used to modulate these parameters in muscle cells. 23297420_Dephosphorylation at a conserved SP motif governs cAMP sensitivity and nuclear localization of class IIa histone deacetylases HDAC4, 5 and 9 23364788_Nuclear calcium signaling is a regulator of nuclear export of HDAC4 and HDAC5. 23615070_Data indicate there was a link between baseline viral load, age (40 years), IL-28B (rs12979860), HDAC2 (rs3778216), HDAC3 (rs976552) and HDAC5 (rs368328) with sustained virological response (SVR). 23729589_HDAC5 is essential for the length maintenance of long telomeres and its depletion is required for sensitization of cancer cells with long telomeres to chemotherapy. 23812427_findings show N-Myc upregulated HDAC5 expression in neuroblastoma cells; HDAC5 repressed NEDD4 gene expression,increased Aurora A gene expression and consequently upregulated N-Myc protein expression;data identify HDAC5 as a novel co-factor in N-Myc oncogenesis 24092570_At the molecular level, we demonstrated that HDAC5 promoted mRNA expression of twist 1, which has been reported as an oncogene 24120667_These findings suggest that HDAC5 is a key determinant of p53-mediated cell fate decisions in response to genotoxic stress. 24191246_we show that Stat3 binds to the promoter region of PTPN13 and promotes its activity through recruiting HDAC5. Thus, our results suggest a previously unknown Stat3-PTPN13 molecular network controlling squamous cell lung carcinoma development 24594363_In erythroid cells, pull down experiments identified the presence of a novel complex formed by HDAC5, GATA1, EKLF and pERK which was instead undetectable in cells of the megakaryocytic lineage. 24706304_HDAC5 promoted the Six1 expression. 24732133_In C2C12 myoblasts, recombinant human HDAC5 phosphorylation by PKD regulated the expression of diverse metabolic genes and glucose metabolism. 24920159_Studied phosphorylation sites within functional HDAC5 domains, including the deacetylation domain (DAC, Ser755), nuclear export signal (NES, Ser1108), and an acidic domain (AD, Ser611). 25096223_Data reveal a novel role of HDAC5 in modulating the KLF2 transcriptional activation and eNOS expression. 25129440_mRNA and protein levels of HDAC5 were up-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 26059794_These results suggest a strong regulatory function of HDAC5 in the pro-inflammatory response of macrophages. 26261519_Formononetin-combined therapy may enhance the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin in glioma cells by preventing EMT through inhibition of HDAC5. 26747087_HDAC5 and HDAC6 were highly expressed in melanoma cells but exhibited low expression levels in normal skin cells. 26847592_HDAC5 promotes cellular proliferation through the upregulation of cMet, and may provide a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of patients with Wilms' tumor. 27177225_HDAC5 was extensively expressed in human BC tissues, and high HDAC5 expression was associated with an inferior prognosis. 27212032_these results suggest that HDAC5 is critical in regulating LSD1 protein stability through post-translational modification, and the HDAC5-LSD1 axis has an important role in promoting breast cancer development and progression. 27482699_The expression of HDAC5 was significantly increased in endothelial cells (ECs) from patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) compared to healthy control endothelial cells. Silencing of HDAC5 in SSc ECs restored normal angiogenesis. HDAC5 knockdown followed by ATAC-seq assay in SSc ECs identified key HDAC5-regulated genes involved in angiogenesis and fibrosis, such as CYR61, PVRL2, and FSTL1. 27614433_HDAC5 inhibits hepatic lipogenic genes expression by attenuating the transcriptional activity of liver X receptor. 27900262_Hdac5 and Hdac6 expression are required for the adequate expression of Icer and adipocyte function. Altered adipose expression of the two Hdacs in obesity by hypoxia may contribute to the development of metabolic abnormalities. 28235630_HDAC5 is a negative predictor of disease-free and overall survival in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor patients. 28414307_Interference with both glucose and glutamine supply in HDAC5-inhibited cancer cells significantly increases apoptotic cell death. 28440397_These findings demonstrate a novel mechanism for deregulation of HDAC5 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)and suggest that miR5895p/HDAC5 pathway may represent a new prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target against NSCLC. 28653891_the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells were impaired by knockdown of histone deacetylase 5 or hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha but rescued when eliminating homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, which suggested the critical role of histone deacetylase 5-homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2-hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway in hypoxia-induced metastasis. 29223407_Latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA) patients showed stronger binding of p-STAT3, HDAC5 and DNMT1 than controls. 29339432_Collectively, these data indicate that vIRF3 alters global gene expression and induces a hypersprouting formation in an HDAC5-binding-dependent and lymphatic endothelial cell-specific manner, ultimately contributing to Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-associated pathogenesis. 29508277_It identified BMAL1 as a cAMP-responsive coactivator of HDAC5 to regulate hepatic gluconeogenesis 29620443_HDAC5 expression was positively correlated with miR-2861 in lung cancer stem cells (LCSCs), and knockdown of miR-2861 decreased the expression of HDAC5, which implied that HDAC5 may be involved in the differentiation of LCSCs mediated by miR-2861. 29886060_HO-1 plays a key role in protecting tumor cells from apoptosis, in a process that involves Smad7 and HDAC4/5 in apoptosis of B-ALL cells 30013077_These results demonstrate a previously unknown negative epigenetic regulation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) homing and engraftment by HDAC5, and allow for a new and simple translational strategy to enhance HSC transplantation. 30066893_High HDAC5 expression is associated with invasion of lung cancer. 30110565_in hISMC from resected Crohn's strictures, we observed a significantly reduced contractile phenotype compared with patient-matched intrinsic controls that was associated with increased patient-specific expression of DNA methyltransferase 1, HDAC2, and HDAC5. 31052182_HDAC5 overexpression in urothelial carcinoma cell lines decreases cell proliferation but can promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 31690832_This study reveals that HDAC5 regulated by C-MYC is essential for SOX9 deacetylation and nuclear localisation, which is critical for tamoxifen resistance. These results indicate a potential therapy strategy for ER(+) breast cancer by targeting C-MYC/HDAC5/SOX9 axis. 31784580_HDAC4 and 5 repression of TBX5 is relieved by protein kinase D1. 33414476_METTL14-regulated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway via PTEN affects HDAC5-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular cells in diabetic kidney disease. 33419772_HDAC5 Loss Impairs RB Repression of Pro-Oncogenic Genes and Confers CDK4/6 Inhibitor Resistance in Cancer. 33673279_Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies APCDD1 and HDAC5 Genes as Potentially Cancer Predisposing in Familial Colorectal Cancer. 34036344_Impairment of human terminal erythroid differentiation by histone deacetylase 5 deficiency. 34125448_HDAC5 promotes intestinal sepsis via the Ghrelin/E2F1/NF-kappaB axis. 34502418_Neddylation Regulates Class IIa and III Histone Deacetylases to Mediate Myoblast Differentiation. 34740611_Histone deacetylase 5 deacetylates the phosphatase PP2A for positively regulating NF-kappaB signaling. 35265200_HDAC5 modulates PD-L1 expression and cancer immunity via p65 deacetylation in pancreatic cancer. 35574707_HDAC5, negatively regulated by miR-148a-3p, promotes colon cancer cell migration. 35900603_HDAC5 inactivates CYR61-regulated CD31/mTOR axis to prevent the occurrence of preeclampsia. 36175163_Epigenetic master regulators HDAC1 and HDAC5 control pathobiont Enterobacteria colonization in ileal mucosa of Crohn's disease patients. 36257380_METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification and HDAC5/YY1 promote IFFO1 downregulation in tumor development and chemo-resistance. 36263180_HDAC5-mediated Smad7 silencing through MEF2A is critical for fibroblast activation and hypertrophic scar formation. |
ENSMUSG00000008855 |
Hdac5 |
951.721644 |
0.4220170483 |
-1.244627 |
0.127979122 |
92.301305 |
0.00000000000000000000074435200818288986890426217869380390581301718244706938773166959855132063239580020308494567871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000007056284933063232656566709585724378540664156596592437636818878621269846007635351270437240600585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
560.8963276 |
51.1747535 |
1338.1335478 |
87.5364679 |
| ENSG00000108846 |
8714 |
ABCC3 |
protein_coding |
O15438 |
FUNCTION: ATP-dependent transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family that binds and hydrolyzes ATP to enable active transport of various substrates including many drugs, toxicants and endogenous compound across cell membranes (PubMed:11581266, PubMed:15083066, PubMed:10359813). Transports glucuronide conjugates such as bilirubin diglucuronide, estradiol-17-beta-o-glucuronide and GSH conjugates such as leukotriene C4 (LTC4) (PubMed:15083066, PubMed:11581266). Transports also various bile salts (taurocholate, glycocholate, taurochenodeoxycholate-3-sulfate, taurolithocholate- 3-sulfate) (By similarity). Does not contribute substantially to bile salt physiology but provides an alternative route for the export of bile acids and glucuronides from cholestatic hepatocytes (By similarity). Can confer resistance to various anticancer drugs, methotrexate, tenoposide and etoposide, by decreasing accumulation of these drugs in cells (PubMed:11581266, PubMed:10359813). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10359813, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11581266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15083066}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Lipid transport;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MRP subfamily which is involved in multi-drug resistance. The specific function of this protein has not yet been determined; however, this protein may play a role in the transport of biliary and intestinal excretion of organic anions. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8714; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ABC-type bile acid transporter activity [GO:0015432]; ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity [GO:0015431]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity [GO:0008559]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0043225]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; glucuronoside transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015164]; icosanoid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0071714]; xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042910]; bile acid and bile salt transport [GO:0015721]; leukotriene transport [GO:0071716]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855]; xenobiotic transport [GO:0042908] |
11820781_Expression of MRP3 can be induced by certain nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., indomethacin) in a reactive oxygen species-dependent but cyclooxygenase-2-independent manner. 11850532_tissue distribution and induction in normal human tissues and in cholestasis 12220224_possible role in the removal of bile acids from the liver in cholestasis 12628490_down- and up-regulation of MRP1 (and MRP3) expression can influence cellular folate homeostasis, in particular when cellular retention by polyglutamylation of folates is attenuated. 12704183_MRP3 active transport of estradiol-17-beta-d-glucuronide and MRP3 ATPase characteristics in isolated, inside-out membrane vesicles 15167703_Genetic polymorphisms in the MRP3 is associated with liver neoplasms 15688370_Upregulation of MRP3 expression is associated with pancreatic carcinoma 15824121_VDR has a role in the protection of colon cells from bile acid toxicity through regulation of the Mrp3 expression 16278398_MRP3, BCRP, and P-glycoprotein have roles in progression of adult acute myeloid leukemia 16424827_a polymorphism -211C>T in the promoter region of MRP3 does not determine the expression level of the gene in acute leukemia 16460798_evidence that clearly indicates that glyburide is preferentially transported by BCRP and MRP3 16946557_The mRNA induction of MDR1, MRP1, MRP2 and MRP3 by rifampicin (Rif), dexamethasone (Dex) and omeprazole (Ome) was investigated in primary cultures of cryopreserved human and rat hepatocytes. 17272513_our results indicate that activator Sp1 and repressor RXRalpha:RARalpha act in concert to regulate MRP3 expression. loss of RXRalpha:RARalpha may lead to upregulation of MRP3/Mrp3 expression in cholestatic liver injury. 17300812_The ABCC3 -211C>T polymorphism does not affect promotor activity nor FTF transcription factor binding. 17485564_Mrp2 and Mrp3 provide alternative routes for the excretion of a glucuronidated substrate from the liver in vivo. 17494643_MRP1-Pro(1150), MRP2-Pro(1158), and MRP3-Pro(1147) in the cytoplasmic loop 7 differ in their influence on substrate specificity but share a common role in the nucleotide interactions at nucleotide binding domain 2 of these transporters. 17495421_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17495421_in this study, the 31 ABCC3 exons and their flanking introns were comprehensively screened for genetic variations in 89 Japanese subjects; forty-six genetic variations, including 21 novel ones, were found 18038766_induction of ABCC2 and ABCG2 by tBHQ is mediated by the Nrf2/Keap1 system, whereas the induction of ABCC1 may involve a Keap1-dependent but Nrf2-independent mechanism. 18207572_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18207572_Polymorphisms in ABCC3 is associated with acute myeloid leukemia 18313914_No significant association was found between the two ABCC3 polymorphisms and colorectal cancer risk. 18313914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18593940_ABCC3 is a mediator of taxane resistance in HER2-amplified breast cancer. 18604784_MRP3 could be a novel molecular marker for localized non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, whose expression increases during the early progression of tumourigenesis 18698235_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the ABCC3 gene is associated with acquisition of hepatotoxicity, due to their poor ability to transport toxic compounds 18799096_the expression of MRP(multiple drug resistance-associated protein)1, MRP2, and MRP3 molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus mononuclear cells was not different from normal 19077464_MRP3, MRP4, and MRP5 are upregulated in 5-fluorouracil-resistant cells, and MRP5 contributes to 5-FU resistance in pancreatic carcinoma cells. 19107936_ABCC3 C-211T and ABCG2 C421A as candidate transporter SNPs to be further investigated as possible predictors of the clinical outcome of chemotherapy in lung cancer patients. 19107936_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19114588_Vectorial transport of resveratrol metabolites is mediated by multidrug resistance protein 3 (MRP3, ABCC3) located in the basolateral membranes of enterocytes. 19334674_analysis of positive allosteric cooperativity for ABCC3-mediated substrate translocation 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19345732_MRP3 induction was dependent upon the transcription factor Nrf2 19480556_Application of multivariate statistical procedures to identify transcription factors that correlate with MRP2, 3, and 4 mRNA in adult human livers. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937796_Immunohistochemical evaluation of human gliomas to determine the localization of MRP3 antigen using scFvs M25 and M58 showed a dense cytoplasmic and membranous staining pattern 19956884_MDR1, MRP2, MRP3 and MRP5 levels are decreased by tetramethylpyrazine in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20563633_Used a spin-labeled ATP analog, SL-ATP, to study nucleotide binding to highly purified human multidrug resistance protein 3, MRP3. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20922799_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21512263_study identified genetic polymorphisms of ABCC3 and evaluated their effects on ABCC3 expression and MRP3 function; 61 genetic variants were identified in three ethnic populations; of these variants 17 were novel 21606946_MRP3 A-189 T polymorphism was associated with treatment responses in acute lymphoblastic leukemia , likely due to the change in MRP3 efflux. 21780830_investigation of vectorial transport across enterocytes: Data from Caco-2 cell monolayers, models for intestinal absorption, suggest that MRP3 mediates fexofenadine/zwitterion efflux across basolateral membrane. 21799180_Low ABCC3 expression was associated with reduced event-free survival of neuroblastoma patients. 22016816_effect of ABCB1 and ABCC3 polymorphisms on osteosarcoma survival after chemotherapy 22089114_We demonstrate direct involvement between nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 and the MRP3 promoter, which leads to the up-regulation of the MRP3 gene. 22105759_up-regulation of hepatic MRP3/ABCC3 expression in human obstructive cholestasis is likely triggered by TNFalpha, mediated by activation of JNK/SAPK and SP1. 22272278_Findings show that the gene expression of ATP-dependent efflux transporters MRP1, -3, -4, -5, and p-gp fluctuated during stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelial cells (hESC-RPE) maturation. 22585709_Amplification and overexpression of the ABCC3 gene is associated with primary breast cancer. 22699933_Anti-ABCC3 IgA and IgG were determined using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) approach. 22767273_Increased MRP3 gene expression correlates with NRF2 mutations in lung squamous cell carcinomas. 23069916_human cornea models possessed MRP3 and BCRP expression, whereas no functional expression was found in rabbit and porcine corneas. 23176825_Stimulation of ATPase and substrate translocation show positive cooperativity. Maximal stimulation of ATPase activity is substrate independent. 23443122_These results suggest that carboplatin and paclitaxel may induce drug resistance mediated by MDR1 and MRP3, which may be enhanced by the simultaneous use of both drugs. 23588304_A predictive model combining variants in TPMT, ABCC3, and COMT with clinical variables significantly improved the prediction of hearing-loss development as compared with using clinical risk factors alone 23692149_The ABCC3 -211C/T polymorphism seems not to be associated with altered antiplatelet effects and clinical outcomes in clopidogrel-treated patients. 23747343_Induction of MRP3 expression by 17alpha-ethynylestradiol requires recruitment of estrogen receptor-alpha and activator protein-1. 24083708_ABCC3 rs4148416 TT polymorphism is associated with poor response to chemotherapy in bone tumors. 24176985_ABCC3 expression may serve as a marker for MDR and predictor for poor clinical outcome of NSCLC. 24272336_our results suggest that fusion protein scFvM58-sTRAIL with specificity for MRP3 is a highly selective therapeutic agent and may provide an alternative therapy for human Glioblastoma multiforme . 24996541_variants of ABCB1 rs128503, ABCC3 rs4148416, and GSTP1 rs1695 are associated with response to chemotherapy and survival of osteosarcoma patients 25088576_Aberrant expression of MRP3 in rectal cancer confers chemo-radioresistance. 25143454_Renal function of MRP3 is related to renal cell proliferation and cyst formation and that restoring MRP3 may be an effective therapeutic approach for polycystic kidney disease. 25155932_Our data suggest that besides bodyweight, OCT1 and ABCC3 genotypes play a significant role in the pharmacokinetics of intravenous morphine and its metabolites in children 25162314_for ABCC3 variants, little evidence, if any, was found for an association of drug response to genetic variants 25349122_A functional Nrf2 response element within the eighth intron of the ABCC3 gene. 25666946_Epidermal growth factor - mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition induces ABCC3 mRNA in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells. The process is calcium dependant. 25788542_Data suggest that hepatic expression of MRP3 is up-regulated and canalicular localization of MRP2 is altered in pediatric patients with advanced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; these alterations may be involved in changes observed in drug metabolism. 25985567_ABCC3 promoter methylation does not seem to exhibit any impact on maximum platelet aggregation and clopidogrel response at all 26107220_ABCC3 rs4148416 polymorphism was significantly associated with poor osteosarcoma response. 26337276_This report is the first to describe liver overexpression of Abcc3 during the cancer initiation, promotion, and progression periods in rat hepatocarcinogenesis model and in human hepatocellular carcinoma 26733163_ABCC3 is an important oncoprotein involved in glycolysis and drug resistance 26769852_High MRP expression is associated with sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. 26810133_ABCC3 genetic variants are associated with postoperative morphine-induced respiratory depression and morphine pharmacokinetics in children. 27171227_This study highlights the importance of ABCC3 transporters in drug resistance to chemotherapy in the context of breast cancer. 27709738_Wnt signaling regulates ABCC3 expression in colon cancer cells, with the ABCC3 locus being a target of the transcription factors TCF7L2 and beta-catenin. 27739315_Histological subtype of epithelial ovarian cancer correlated with the expression of PgP, MRP1, and MRP3. The lowest level of Pgp and MRP1 expression was found in endometrioid ovarian cancers 28356150_PXR is a potential biomarker for predicting outcome and activates MRP3 transcription by directly binding to its promoter resulting in an increased L-OHP efflux capacity, and resistance to L-OHP or platinum drugs in CRC. 28575098_miR-148a-siRNA and rifampin inhibited estradiol upregulation of MRP3 expression. miR-148a may be involved in the estrogen induction in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy via PXR signaling. MRP3 may be involved. 28586062_Data show that bladder cancer is associated with perturbed expression of MRP3 and BCRP. 29437875_CGI may function as an enhancer of the transcription of ABCC3. 29464551_Low expression of MRP3 is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and in Cholangiocarcinoma. 29545174_Data suggest that inhibition of sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (a) impairs cell survival and cell migration and (b) down-regulates expression of P-glycoprotein and MRP3 (ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 3). 30218633_OATPB1/B3 and MRP3 immunohistochemistry and signal intensity on hepatobiliary phase Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI can help to stratify hepatocellular adenoma according to their risk of malignant transformation. 30959153_The glucuronides of inactive androgens, androsterone glucuronide and etiocholanolone glucuronide were preferentially transported by MRP3, whereas the glucuronides of active androgens, Testosterone glucuronide and dihydrotestosterone glucuronide were mainly transported by MRP2 in liver. 31053501_ABCC3 is a novel target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. 32212330_Prevalence of ABCC3-1767G/A polymorphism among patients with antiretroviral-associated hepatotoxicity. 33582321_Effect of bile acids on the expression of MRP3 and MRP4: An In vitro study in HepG2 cell line. 33811842_CircABCC3 knockdown inhibits glioblastoma cell malignancy by regulating miR-770-5p/SOX2 axis through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 35008510_The Role of TRIP6, ABCC3 and CPS1 Expression in Resistance of Ovarian Cancer to Taxanes. 35328066_Association Study of SLCO1B3 and ABCC3 Genetic Variants in Gallstone Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000020865 |
Abcc3 |
381.680072 |
2.0970465880 |
1.068359 |
0.149582958 |
50.363605 |
0.00000000000127741437910202824721122788768492775516097403887272321298951283097267150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007553940799497571059714042377099447751059857480981918342877179384231567382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
548.5109330 |
57.7925925 |
263.4954917 |
20.5014883 |
| ENSG00000108932 |
9120 |
SLC16A6 |
protein_coding |
O15403 |
FUNCTION: Proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter. Catalyzes the rapid transport across the plasma membrane of many monocarboxylates such as lactate, pyruvate, branched-chain oxo acids derived from leucine, valine and isoleucine, and the ketone bodies acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in monocarboxylic acid transport. Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9120; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718] |
16174808_MCT6 is involved in the disposition of various drugs, including bumetanide. 32232919_Genetic variants in PDSS1 and SLC16A6 of the ketone body metabolic pathway predict cutaneous melanoma-specific survival. 35257743_Mammalian monocarboxylate transporter 7 (MCT7/Slc16a6) is a novel facilitative taurine transporter. |
ENSMUSG00000041920 |
Slc16a6 |
22.359444 |
8.2076205966 |
3.036964 |
0.432720130 |
57.183440 |
0.00000000000003969999229861349374840647396306214759613461076637186408788693370297551155090332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000258251161889614418899107603586544918013688520996851138988859020173549652099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.0870474 |
10.4669207 |
4.9155986 |
1.1732199 |
| ENSG00000108984 |
5608 |
MAP2K6 |
protein_coding |
P52564 |
FUNCTION: Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. With MAP3K3/MKK3, catalyzes the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in the MAP kinases p38 MAPK11, MAPK12, MAPK13 and MAPK14 and plays an important role in the regulation of cellular responses to cytokines and all kinds of stresses. Especially, MAP2K3/MKK3 and MAP2K6/MKK6 are both essential for the activation of MAPK11 and MAPK13 induced by environmental stress, whereas MAP2K6/MKK6 is the major MAPK11 activator in response to TNF. MAP2K6/MKK6 also phosphorylates and activates PAK6. The p38 MAP kinase signal transduction pathway leads to direct activation of transcription factors. Nuclear targets of p38 MAP kinase include the transcription factors ATF2 and ELK1. Within the p38 MAPK signal transduction pathway, MAP3K6/MKK6 mediates phosphorylation of STAT4 through MAPK14 activation, and is therefore required for STAT4 activation and STAT4-regulated gene expression in response to IL-12 stimulation. The pathway is also crucial for IL-6-induced SOCS3 expression and down-regulation of IL-6-mediated gene induction; and for IFNG-dependent gene transcription. Has a role in osteoclast differentiation through NF-kappa-B transactivation by TNFSF11, and in endochondral ossification and since SOX9 is another likely downstream target of the p38 MAPK pathway. MAP2K6/MKK6 mediates apoptotic cell death in thymocytes. Acts also as a regulator for melanocytes dendricity, through the modulation of Rho family GTPases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10961885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11727828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15550393, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20869211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8622669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8663074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9218798}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the dual specificity protein kinase family, which functions as a mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals. This protein phosphorylates and activates p38 MAP kinase in response to inflammatory cytokines or environmental stress. As an essential component of p38 MAP kinase mediated signal transduction pathway, this gene is involved in many cellular processes such as stress induced cell cycle arrest, transcription activation and apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5608; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; MAP kinase kinase activity [GO:0004708]; phosphatase activator activity [GO:0019211]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060048]; cellular response to sorbitol [GO:0072709]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; DNA damage induced protein phosphorylation [GO:0006975]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing signaling pathway [GO:0070423]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; ovulation cycle process [GO:0022602]; p38MAPK cascade [GO:0038066]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032308]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0051403] |
11727828_active MKK6 in HepG2 cells enhanced basal activity or IL-6-induced transcriptional activation of a SOCS3 promoter 11971971_Results show that oncogenic ras provokes premature senescence by sequentially activating the MEK-ERK and MKK3/6-p38 pathways in normal, primary cells. 12509443_MKK6 is involved in a positive feedback loop regulating macrophage signaling with p38 MAP kinase 15375157_a specific requirement for p150(Glued)/dynein/functional microtubules in activation of MKK3/6 and p38 MAPKs in vivo. 15492008_role in cardioprotection 15516490_MAP kinase kinase3- and 6-dependent activation of the alpha-isoform of p38 MAP kinase is required for the cytoskeletal changes induced by neutrophil adherence and influences subsequent neutrophil migration toward endothelial cell junctions 15550393_PAK6 kinase activity was repressed by a p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase antagonist and could be strongly stimulated by constitutively active MAP kinase kinase 6 (MKK6) 15677464_H-Ras-specific activation of Rac-MKK3/6-p38 pathway has a role in invasion and migration of breast epithelial cells 15722372_MKK6 promotes the development of cardiomyopathy by activation of a kinase cascade 15778394_MKK3 and MKK6 make individual contributions to p38 activation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes after cytokine stimulation 15790570_MEK6E activates p38 and results in phosphorylation of its downstream substrate, heat shock protein 27 16342939_selectivity pocket compounds prevent MKK6-dependent activation of p38alpha in addition to inhibiting catalysis by activated p38alpha 16728640_findings show that Yersinia YopJ acted as an acetyltransferase, using acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) to modify the critical serine and threonine residues in the activation loop of MAPKK6 and thereby blocking phosphorylation 16960152_Conditional induction of a dominant active form of MAPK kinase 6, a direct upstream kinase of p38, in Langerhans cells induces up-regulation of costimulatory molecules & enhances their T-cell stimulatory capacity. 18327563_Data suggest that sequence variations of ASK1 and MAP2K6 lead to partially sex-specific changes in the levels and/or phosphorylation states of p38 and p38-regulated proteins that might contribute to the observed delaying effects in the age of onset of HD. 18327563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19047046_as a mediator of SF- and Src-stimulated NF-kappaB activity. Finally, the Src/Rac1/MKK3/6/p38 and Src/TAK1/NF-kappaB-inducing kinase pathways exhibited cross-talk at the level of MKK3. 19141286_Gel filtration and small-angle X-ray scattering analysis confirm that the crystallographically observed ellipsoidal dimer is a feature of MEK6/DeltaN/DD and full-length unphosphorylated wild-type MEK6 in solution 19672773_Data provide evidence that p38 Map kinase pathway is activated leading to increased upregulation of mixed lineage kinase 3, MKK3/6, MSK1, and Mapkapk2, upon treatment of BCR/ABL expressing cells with dasatinib. 19846005_MKK6 p38 alpha signaling pathway regulates the expression of RAGE induced by mechanical stretch in A549 cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20162623_These results demonstrate that activin A induces erythroid differentiation of K562 cells through activation of MKK6-p38alpha/p38beta pathway and follistatin inhibits those effects. 20364819_Mechanism of oxidative stress-induced ASK1-catalyzed MKK6 phosphorylation.( 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20805296_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20869211_we demonstrated that MKK6 has a role for regulation of dendricity in melanocytes. 21078955_MKK6 and other MAP2Ks are a distinct class of cellular redox sensors 21308746_Results suggest that the p38alpha, MAPK, and MKK6 play prominent roles in IL-1beta and C/EBP-beta-mediated C3 gene expression in astrocytes. 21368234_Impaired cytokine production in natural killer (NK)T cells is demonstrated from MKK3-deficient6+/- mice. 21926646_activation by mechanical stretch induces HMGB1 and cytokine expression in A549 cells 22154358_Data suggest aberrant MAP2K protein (MKK3, MKK4, MKK6, and MKK7) expression indicates that altered cellular signal transduction mediated via JNK and p38 may be common in bladder cancer. 22164285_the balance between MKK6 and MKK3 mediates p38 MAPK associated resistance to cisplatin in NSCLC 22383536_crystal structure of human non-phosphorylated MAP2K6 (npMAP2K6) complexed with an ATP analogue was determined at 2.6 A resolution and represents an auto-inhibition state of MAP2K6 23744074_The models confirmed the reaction order, revealed processivity in the phosphorylation of MEK6 by ASK1, and suggested that the order of phosphorylation is dictated by both binding and catalysis rates. 24085465_Serine phosphorylation of p66shc is carried out by active MKK6. beta-Amyloid-induced ROS production and apoptosis increased in the presence of MKK6 and p66shc, which directly associate. 24936062_uncover a new mechanism of deactivation of MKK6-p38 and substantiate a novel regulatory role of FBXO31 in stress response 25019214_Data show significant increase in the expression of MKK6 in Esophageal, Stomach, and Colon cancers as compared to controls. 25214442_Data indicate that mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MKK6) levels were substantially higher in monocytes than in neutrophils. 27181679_MEK2 was essential for the phosphorylation of MKK3/MKK6 and p38 MAPK that directly impacted on cyclin D1 expression. 27526785_Data show that miR-625-3p induces oxaliplatin resistance by abrogating MAP2K6-p38-regulated apoptosis and cell cycle control networks. 29021624_acts as a repressor of UCP1 expression, suggesting that its inhibition promotes adipose tissue browning and increases organismal energy expenditure 29669288_The loss of MKK6 protein diminishes p38 activation, leading to further degradation of the remaining TRIM9 in glioblastoma cells. The disruption of the TRIM9s-MKK6 mutual stabilization loop ultimately leads to the inactivation of p38 signaling and promotes tumor progression. 30245131_Data suggest that mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 (MAP2K6) might be an important regulator of leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR)-induced radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells (NPC). 30305582_Advanced glycation end products significantly activated ASK1, MKK3, and MKK6, which led to activation of p38 MAPK, resulting in upregulated fibrotic response in human coronary smooth muscle cells. 30663248_Based on the experimentally determined models and parameters, dynamics of the p38alpha-MKK6-MKP5 system were explored, demonstrating for the first time that bistability can arise with this model at biologically feasible parameter values 30837379_USP22 could interact directly with MKK6 promoter. Down-regulation of USP22 led to the decreased MKK6 mRNA expression 33554397_The interaction of p38 with its upstream kinase MKK6. 34709743_A novel tumour suppressor protein encoded by circMAPK14 inhibits progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by competitively binding to MKK6. 35192930_MiR-1298-5p level downregulation induced by Helicobacter pylori infection inhibits autophagy and promotes gastric cancer development by targeting MAP2K6. 36205565_APEX1 promotes the oncogenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of MAP2K6. |
ENSMUSG00000020623 |
Map2k6 |
45.220039 |
13.7386453355 |
3.780168 |
0.566829424 |
36.736087 |
0.00000000135252456164877201196079574782192220250287562066660029813647270202636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006390288902028129325619453324084165424245895792410010471940040588378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
62.4971298 |
22.9101065 |
4.4255509 |
1.2258993 |
| ENSG00000109062 |
9368 |
SLC9A3R1 |
protein_coding |
O14745 |
FUNCTION: Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin family and thereby helps to link them to the actin cytoskeleton and to regulate their surface expression. Necessary for recycling of internalized ADRB2. Was first known to play a role in the regulation of the activity and subcellular location of SLC9A3. Necessary for cAMP-mediated phosphorylation and inhibition of SLC9A3. May enhance Wnt signaling. May participate in HTR4 targeting to microvilli (By similarity). Involved in the regulation of phosphate reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules. Involved in sperm capacitation. May participate in the regulation of the chloride and bicarbonate homeostasis in spermatozoa. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10499588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18784102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9096337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9430655}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a sodium/hydrogen exchanger regulatory cofactor. The protein interacts with and regulates various proteins including the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and G-protein coupled receptors such as the beta2-adrenergic receptor and the parathyroid hormone 1 receptor. The protein also interacts with proteins that function as linkers between integral membrane and cytoskeletal proteins. The protein localizes to actin-rich structures including membrane ruffles, microvilli, and filopodia. Mutations in this gene result in hypophosphatemic nephrolithiasis/osteoporosis type 2, and loss of heterozygosity of this gene is implicated in breast cancer.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:9368; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cell periphery [GO:0071944]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane protein complex [GO:0098797]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; stereocilium tip [GO:0032426]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding [GO:0031698]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; chloride channel regulator activity [GO:0017081]; dopamine receptor binding [GO:0050780]; gamma-aminobutyric acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015185]; growth factor receptor binding [GO:0070851]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; myosin II binding [GO:0045159]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; protein-membrane adaptor activity [GO:0043495]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; type 2 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031799]; type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031800]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007191]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; bile acid secretion [GO:0032782]; cellular phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0030643]; cerebrospinal fluid circulation [GO:0090660]; cilium organization [GO:0044782]; establishment of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045198]; establishment of Golgi localization [GO:0051683]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; gamma-aminobutyric acid import [GO:0051939]; gland morphogenesis [GO:0022612]; glutathione transport [GO:0034635]; import across plasma membrane [GO:0098739]; maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045199]; microvillus assembly [GO:0030033]; morphogenesis of an epithelium [GO:0002009]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010764]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045930]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0010642]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of sodium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0032416]; nuclear migration [GO:0007097]; phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060158]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034767]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045859]; regulation of renal phosphate excretion [GO:1903402]; regulation of sodium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0032415]; renal absorption [GO:0070293]; renal phosphate ion absorption [GO:0097291]; renal sodium ion transport [GO:0003096]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11882663_structural determinants in interaction of beta 2 adrenergic and platelet-derived growth factor receptors 11893083_Epithelial cells expressing ezrin generally co-express EBP50. These results document a preference for co-expression of EBP50 with ezrin in polarized epithelia. 11956211_Protein kinase C epsilon-dependent regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator involves binding to a receptor for activated C kinase (RACK1) and RACK1 binding to Na+/H+ exchange regulatory factor 12004055_EBP50/NHERF binds to the C terminus of FLAG-hkor and blocks the down-regulation of FLAG-hkor 12080081_epithelial iNOS binds to EPB50 which directs vectorial nitric oxide output 12145337_Estrogen receptor inducibility of the human Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor/ezrin-radixin-moesin binding protein 50 (NHE-RF/EBP50) gene involving multiple half-estrogen response elements. 12193606_role in regulating GTP-binding protein alpha q signaling 12626493_EBP50 has the capacity to inhibit receptor endocytosis 12651858_Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor has a role in the functional expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in nonpolarized cells and epithelia 12830000_the EBP50/beta-catenin complex promotes Wnt signaling, and over-expression of EBP50 may work cooperatively with beta-catenin in the development of liver cancer. 12920119_NHERF1 acts as a molecular switch that legislates the conditional efficacy of PTH fragments 14608357_A putative RUNX1 binding site variant of SLC9A3R1 is associated with susceptibility to psoriasis 15070904_binding of the KOR to NHERF-1/EBP50 facilitates oligomerization of NHERF-1/EBP50, leading to stimulation of NHE3. 15161943_NHERF links the betaPDGFR to the actin cytoskeleton through its interaction with MERM proteins and regulates cell spreading and migration 15467753_NHERF to be a candidate tumor suppressor gene in human breast carcinoma that may be interconnected to the SYK and MERLIN suppressors 15805108_results, using both endogenous and overexpressed cellular models, indicate a novel function for NHERF-1 and RAMP3 in the internalization of the adrenomedullin receptor and suggest additional regulatory mechanisms for receptor trafficking 16129695_ezrin binding activates the second PDZ domain of NHERF to interact with the cytoplasmic tails of CFTR (C-CFTR), so as to form a specific 2:1:1 (C-CFTR)(2).NHERF.ezrin ternary complex 16519819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16615918_analysis of NHERF recognition by ERM proteins 17078868_the tumour suppressor activity of NHERF1 in breast may be related to its regulatory effect on the cell cycle to suppress cell proliferation. 17237149_Modulation of the expression of CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) protein partners, like NHE-RF1, can rescue sequence-deleted CFTR activity. 17242191_An intramolecular conformation of NHERF1/EBP50 (ERM-binding phosphoprotein 50) in which the C-terminal EB region binds to the PDZ2 domain is described. 17332506_NHERF1 overexpression enhances the invasive phenotype in breast cancer cells, both alone and in synergy with exposure to the tumor microenvironment, via the coordination of PKA-gated RhoA/p38 signaling. 17593079_Oestrogen-responsive EBP50 may play an important role in tumour progression and might be a potential marker of invasiveness for breast cancer. 17602283_The interaction of PDZ proteins with hOAT4 may be cell-specific. In placenta, a different set of interacting proteins from PDZK1 and NHERF1 may be required to modulate hOAT4 activity. 17613530_C-terminal domain of NHERF functions as an intramolecular switch that regulates the binding capability of PDZ2, and thus controls the stoichiometry of NHERF to assemble protein complexes. 17884816_that NHERF1 inhibits endocytosis without affecting PTH1R recycling 17895247_serine 77 phosphorylation plays a key role in modulating NHERF-1 association with plasma membrane targets 17911601_Acts as a scaffold that assembles the cyclic AMP pathway in lipid rafts of the cell membrane during T cell activation. 17982258_These results indicate that NHERF1 plays a role in the turnover of CFTR at the cell surface, and that rDeltaF508 CFTR at the cell surface remains highly susceptible to degradation. 18184109_Beta-oestradiol-dependent up-regulation of NHERF1 significantly increases F508CFTR functional expression in CFBE41o(-) cells. 18588753_Relatively high level of expression of mRNA for SLC9A3RI was detected wheres lower level of S100A7 and GPRA were found. 18754678_Affinity of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) PDZ domain for the CFTR C-terminus is much weaker than that of the NHERF1/NHERF2 domains, enabling wild-type CFTR to avoid premature entrapment in the lysosomal pathway. 18784102_We identified three distinct mutations in seven patients with a low TmP/GFR value. The mutants expressed in cultured renal cells increased the generation of cyclic AMP (cAMP) by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and inhibited phosphate transport. 19034380_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the temporal lobe from patients with schizophrenia. 19073137_These data establish NHERF1 as a major determinant of MRP4 trafficking to apical membranes of mammalian kidney cells. 19091402_While the presence of forskolin results in an increase in OCTN2 protein expression, the increase in uptake capacity may be compensated by the decreased expression of PDZK1, NHERF1 or NHERF2. 19139211_no evidence was found for association of SNPs mapping to the NAT9, SLC9A3R1 and RAPTOR loci with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19173579_The tail of PDZK1 interacts with the PDZ domains of EBP50, and this interaction is negatively regulated by the intramolecular association of the tail of PDZK1 with its first PDZ domain. 19188335_NHERF1 inhibited beta-arrestin2 binding to wtPTH1R but had no effect on beta-arrestin2 association with pdPTH1R. Such an effect may protect against PTH resistance or PTH1R down-regulation in cells harboring NHERF1. 19234136_Expression and distribution of EBP50 are regulated by estrogens and contribute to the proliferative response in biliary epithelial cells. 19308292_these results provide the first evidence for NHERF-1 as a participant in the highly invasive phenotype of malignant gliomas 19581308_a transient association of PKD1 and PKD2 with NHERF-1 in live cells that is triggered by phorbol ester stimulation and, importantly, differs strikingly from the sustained translocation to plasma membrane. 19591839_Upon binding to ezrin, NHERF1 undergoes significant conformational changes in the region linking PDZ2 and its CT ezrin-binding domain, as well as in the region linking PDZ1 and PDZ2, involving very long range interactions over 120 A. 19912366_Breast cancerogenesis is characterized by increased cytoplasmic expression of NHERF1 as the tumour progresses. 20012548_Data indicate EBP50 plays a role in inhibiting breast cancer cell proliferation via promoting cell apoptosis and inhibiting ERK activation. 20031577_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20042604_a conformational switch in the scaffolding protein NHERF1 controls autoinhibition and complex formation 20140636_The down-regulation of hOAT4 activity by activation of protein kinase C and the up-regulation of hOAT4 activity by NHERF-1 are mediated through alteration of hOAT4 internalization. 20203292_NHERF1 was underexpressed in bronchi of cystic fibrosis patients. 20237154_Data show that PDZK1/EBP50/ezrin form a regulated ternary complex in vitro and in vivo. 20395446_Data show that podocalyxin overexpression in human embryonic kidney cells up-regulates Rac1 activity, which depends on a complex formed by podocalyxin, ERM-binding phosphoprotein 50, ezrin, and ARHGEF7, a Rac1 activator. 20404332_NHERF-1 binds to Mrp2, and plays a critical role in the canalicular expression of Mrp2 and its function as a determinant of glutathione-dependent, bile acid-independent bile flow 20442317_Data show that the last 4 residues of PIP5KIbeta constitute an atypical PDZ-binding motif, which steers PIP5KIbeta to the uropod by binding to both EBP50 PDZ domains. 20562104_NHERF1 and NHERF2 exhibit isotype-specific effects on G protein activation. 20571032_The phosphorylation of Thr(95) facilitates the phosphorylation of Ser(77). This, in turn, results in the dissociation of NHERF-1 from Npt2a and a decrease in phosphate transport in renal proximal tubule cells. 20656684_NHERF1 may serve as an adaptor, bringing beta-arrestin2 into close proximity to the PTHR, thereby facilitating beta-arrestin2 recruitment after receptor activation. 20736378_Findings define a tumor suppressor role for NHERF1 at the plasma membrane, and reveal a novel mechanism for PI3K/Akt activation through PTEN inactivation caused by a loss of membrane-localized NHERF1. 20801883_Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor-1 is involved in chemokine receptor homodimer CCR5 internalization and signal transduction but does not affect CXCR4 homodimer or CXCR4-CCR5 heterodimer. 20802536_Taken together, these results provide a novel insight into the regulation of Wnt signaling in normal and neoplastic breast tissues, and identify NHERF1 as an important regulator of the pathogenesis of breast tumors. 20937695_EBP50 is a critical factor that regulates microvilli assembly and whose activity is regulated by signaling pathways and occupation of its PDZ2 domain. 21160026_NHERF-1 mediates sodium-potassium-ATPase alpha1 subunit regulation by dopamine through its PDZ-2 protein-interaction domain. 21170265_NHERF1 alterations correlate with the progression and enhanced invasiveness of human colorectal cancer and implicates NHERF1 as an important regulator of epithelial morphology. The expression of NHERF1 may be used as diagnostic marker for CRC. 21191106_Data show that both NHERF2 and NHERF1 are involved in setting NHE3 activity. 21203899_Gene expression profiling of luminal B breast cancers reveals NHERF1 as a new marker of endocrine resistance 21496870_negative membranous Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 1 expression (odds ratio, 7.686; 95% confidence interval, 1.876-31.483) significantly correlated with family history of breast cancer. 21672215_To our knowledge, this represents the first study comparing the immunohistochemical profiles of EBP50 in PCa and Mets to specimens of HGPIN, BPH, NDP, and NAC and suggests that EBP50 expression is decreased in Mets. 21680517_HPV16-mediated NHERF-1 degradation correlates with the activation of the phosphatidylinositol-3'-OH kinase/AKT signaling pathway, which is known to play a key role in carcinogenesis 21707710_We propose that NHERF1 measurements in circulatory lymphocytes of breast cancer patients may be a valid method for the prediction of breast cancer occurrence and prognosis. 21804599_show for the first time a significant disruption of all three members of the PTEN-NHERF1-PHLPP1 tumor suppressor network in high-grade tumors, correlating with Akt activation and patient's abysmal survival 21822312_These findings indicate that loss of EBP50 at the plasma membrane in tumor cells may contribute to biliary carcinogenesis through EGFR activation. 21832055_Dynamic Na+-H+ exchanger regulatory factor-1 association and dissociation regulate parathyroid hormone receptor trafficking at membrane microdomains 21971156_PC6 cleavage of a crucial scaffolding protein EBP50, thereby profoundly regulating membrane-cytoskeletal reorganization 21983488_NHERF-1 digestion is a marker of a pathological calpain function in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells of cystic fibrosis patients 21990315_E2 failed to increase PTEN expression when NHERF1 was knocked down 22028271_role in the regulation of HIV-1 entry and replication 22366766_EBP50 gene transfection promotes 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through Bax- and Bcl-2-triggered mitochondrial pathways. 22440733_Results suggest the oncogenic role of NHERF1 and promote nuclear NHERF1 as a potential new biomarker of advanced colorectal cancer (CRC). 22446018_altered expression of peroxiredoxin 1 and radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 may be used as prognostic markers in cholangiocarcinoma. 22466651_nuclear EBP50 facilitates colon tumorigenesis by modulating the interaction between beta-catenin and TCF-1. 22476347_EBP50 can suppress EGF-induced proliferation of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EGFR phosphorylation and blocking EGFR downstream signaling in breast cancer cells. 22496422_These findings identify NHERF1 as an important signaling nexus for coordinating cell structure with metastatic behavior. 22506049_A patient with inappropriate renal phosphate reabsorption a previously unidentified mutation (E68A) located in the PDZ1 domain of NHERF1. 22610101_Findings suggest a novel model by which arrestin can serve as an adaptor to promote NHERF1 interaction with a GPCR to facilitate effective NHERF1-dependent receptor internalization. 22622406_Our results suggest that EBP50 may function as a potential tumor suppressor 22628548_Data report that NHERF1, a modular PDZ domain scaffolding protein, coordinates the assembly of an obligate ternary complex with Npt2a and the PKA-anchoring protein ezrin to facilitate PTH-responsive cAMP signaling events. 22766563_Nuclear NHERF1 expression, present in the early stages of carcinogenesis and related with poor prognosis, may contribute to the onset of malignant phenotype in colorectal adenocarcinoma. 22801783_It was shown that EBP50 was highly dynamic, turning over within seconds. EBP50 turnover was reduced by mutations that inactivate its PDZ domains and was enhanced by protein kinase C phosphorylation. 22964850_significant role for the multiprotein complex CFTR-NHERF1-ezrin-actin in maintaining tight junction organisation and barrier function 23284683_functional regulation of C3aR by NHERFs in human mast cells 23454118_Taken together, these data suggest that NHERF-1 plays a more central role in cell proliferation by modulating Gq-mediated signalling pathways. 23483729_The overexpression of EBP50 could inhibit the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and promote apoptosis by modulating beta-catenin, E-cadherin. 23583913_The study shows that ligand-induced structural and dynamic changes coupled with sequence variation at the putative PDZ binding site dictate ligand selectivity and binding affinity of the two PDZ domains of NHERF1. 23775624_cdc2/cyclin B-mediated EBP50 phosphorylation may play a role in the regulation of various cell functions by affecting actin cytoskeleton reorganization. 23985317_Data indicate that the tails promote different microvillar localizations for EBP50 and E3KARP, which localized along the full length and to the base of microvilli, respectively. 24012959_Breast cancer-derived K172N, D301V mutations abolish Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 1 inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling 24201803_Results show that the loss of nuclear NHERF1 expression is associated with reduced survival, and the link between nuclear NHERF1 and ER expression may serve as a prognostic marker for the routine clinical management of breast cancer patients. 24339979_New conformational state of NHERF1-CXCR2 signaling complex captured by crystal lattice trapping. 24642259_This study provides an understanding of the structural basis for the PDZ-mediated NHERF1-PLCbeta3 interaction that could prove valuable in selective drug design against CXCR2-related cancers. 24728453_PDZK1 and NHERF1 regulate the transport function of OATP1A2 by modulating protein internalization via a clathrin-dependent pathway and by enhancing protein stability. 24768637_the structural basis for the PDZ domain-mediated NHERF1-CXCR2 interaction and probable modes of PDZ domain dimerization 24788249_VIP regulates CFTR membrane expression and function in Calu-3 cells by increasing its interaction with NHERF1 and P-ERM in a VPAC1- and PKCepsilon-dependent manner. 24862762_These findings reveal an essential role of NHERF1 in epithelial morphogenesis and polarity and validate this 3D system for modeling the molecular changes observed in CRC. 25163515_NHERF1 is essential for maintaining the localization and function of Mrp-2. 25555876_EBP50 expression was decreased in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 25744438_conclude that FNACs provide useful material for detection of NHERF1 localization and expression, and that high nuclear NHERF1 expression may be a potential marker of aggressiveness in NSCLC 25756512_the activation of PTEN and NHERF-1 may impede the evolution of macrophages beyond the M1 into M2 phenotype in tumor microenvironment. 25775275_These data highlight a role for NHERF1 in ependymal morphogenesis with direct application to the diagnosis of ependymal tumors. 25789870_deuterium uptake profiles of isolated PDZ1 and PDZ2 were similar to those of full-length EBP50. Interestingly, PDZ1 was more dynamic than PDZ2, and these PDZ domains underwent different conformational changes upon ligand binding 25990958_A molecular switch in the scaffold NHERF1 enables misfolded CFTR to evade the peripheral quality control checkpoint. 26126066_Nuclear NHERF1 expression is associated with drug resistance in in advanced gastric cancer patients treated with epirubicin/oxaliplatin/capecitabine first line chemotherapy. 26142394_autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease is associated with a decrease in NHERF1 protein and mRNA levels. 26218645_The decrease in BECN1 degradation induced by SLC9A3R1 resulted in the activity of autophagy stimulation in breast cancer cells 26432781_This study identified alpha-actinin-4 as a novel NHERF1 interaction partner and provided new insights into the regulatory mechanism of the actin cytoskeleton by NHERF1. 26491017_activation of the Nherf1-PP1alpha-TAZ pathway in osteoblasts is targeted by histone deacetylase inhibitors 26531778_Results showed that EBP50 specifically scaffolds the interaction of PTEN with EGFR and enhances the inhibition of PTEN on EGF-induced AKT activation. These results elucidated a novel mechanism regulating EGF-induced AKT signaling. 26789121_Interaction of ABCB4 with EBP50 through its PDZ-like motif plays a critical role in the regulation of ABCB4 expression and stability at the canalicular plasma membrane. 26862730_This study sheds light on a possible therapeutic strategy targeting at the aberrant nuclear expression of EBP50 without affecting the normal physiological function of EBP50 at other subcellular localization. 26977012_A novel NHERF1 mutation in human breast cancer cells inactivates inhibition of EGFR signaling by NHERF1 promoting disease progression. 27097111_The present results suggest a role for NHERF1 in the progression of breast cancer mediated by the nuclear distribution of the NHERF1 protein, as determined by the truncation or key site mutation of the PDZ-I domain. 27206858_This interaction is promoted by EPAC1 activation, triggering its translocation to the plasma membrane and binding to NHERF1. Our findings identify a new CFTR-interacting protein and demonstrate that cAMP activates CFTR through two different but complementary pathways - the well-known PKA-dependent channel gating pathway and a new mechanism regulating endocytosis that involves EPAC1. 27448983_Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF1) expression level positively associates with G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) activation in ER-positive breast cancer. 27509846_High EBP50 expression is associated with cervical cancer. 27566107_we show here that NHERF1 loss from the PM is oncogenic in vivo through its influence on Wnt-APC-beta-catenin and Hippo-YAP pathways. 27765918_-catenin was predominantly associated with Na+/H+ exchanger regulating factor 1 (NHERF1) in a dynamic context and an increase of its oncogenic function through RAS-association domain family 1, isoform A (RASSF1A) inactivation in liver metastases. 27793802_COOH-terminal sequences mediate enhanced NHERF1 interaction and facilitate the localization of CFTR. 27823775_the distribution of NHERF1 in ovarian cancer and reveals a different regulation of NHERF1 and EZRIN expression in ovarian tumors which represents the complexity of the molecular changes of this disease 27871951_NF2 localizes in nucleus when Ser518 is not phosphorylated, while phosphorylated form is present in cytoplasm and plasma membrane. Data suggest that binding of NF2 to TIMAP and EBP50 is critical in nuclear localization of NF2. (NF2 = neurofibromin 2; TIMAP = TGF-beta-inhibited membrane-associated protein; EBP50 = Ezrin-Radixin-Mosein binding phosphoprotein 50) 27999191_The up-regulation of NHERF1 induced by the exposure to hypoxia in colon cancer cells depends on the activation of VEGFR2 signaling. 28011475_Wild-type NHERF1 acts as a tumour suppressor, while NHERF1 A190D mutation abolishes the tumour-suppressive effect in cancer cells, due to A190D mutation-mediated nuclear NHERF1 translocation and induction of YAP phosphorylation. 28068322_NHERF1/EBP50 encompasses the regulation of several major signaling pathways engaged in cancer, including the receptor tyrosine kinases PDGFR and EGFR, PI3K/PTEN/AKT and Wnt-beta-catenin pathways. 28085111_Na/H exchanger regulatory factor 1 (NHERF1) expression Is downregulated in cisplatin-resistant HeLa cells. 28235801_NHERF1 acts with PMCA2 to regulate HER2 signaling and membrane retention in breast cancers 28285124_Using neutron spin echo spectroscopy (NSE), the authors show salt-concentration-dependent excitation of nanoscale motion at the tip of the C-terminal tail in the phosphomimic S339D/S340D mutant. 28376304_data highlight sequences in PTHR that contribute to NHERF1 interaction and can be altered to prevent phosphorylation-mediated inhibition 28392297_Studies support a role for NHERF-1 and NHERF-2 (Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factors 1 and 2) in regulating the distribution of Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluRs) in the murine brain, while conversely the effects of the mGluR2/3 PDZ-binding motifs on receptor signaling are likely mediated by interactions with other PDZ scaffold proteins beyond the NHERF proteins. 28535016_High expression of NHERF-1 is associated with triple-negative breast cancer. 28684865_Taken together, these findings suggest that the high dynamics of cytosolic NHERF1 provide cancer cells with a means of controlling chemotactic migration. 28739728_Data demonstrated that EBP50 overexpression inhibited the adhesion and migration of breast and cervical cancer cell lines and suppressed MMP-2 activity in these cells; while its knockdown promoted cell adhesion and migration, and enhanced the activity of MMP-2.This study reveals the anti-metastatic effect and a new mechanism of EBP50 action in breast and cervical cancer cells. 28739734_Data provide evidence for an important role of NHERF1 in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells, as well as migration. 28960081_found that NHERF1 was associated with trophoblast differentiation and motility; stepwise experimental platform to explore new functions of ambiguously denoted candidate proteins 29126251_Low NHERF1 expression is associated with hypophosphatemia in calcium stone formers. 29551770_NHERF1 role in the colorectal cancer apoptosis.CTNNB1 represses NHERF1 expression by associating with TCF4 in colorectal cancer. 29846905_loss of EBP50 may therefore be a surrogate biomarker for high-risk human papilloma virus infection in oropharyngeal tumours. 29867145_NHERF1 inhibits Wnt signaling-mediated proliferation of cervical cancer via suppression of ACTN4, and NHERF1 downregulation may contribute to the progression of cervical cancer. 29901158_DNMT1 contributes to promoter hypermethylation and epigenetic NHERF1 silencing in colon cancer. 30230542_NHERF1 was found to be downregulated by HPV16 E6 rather than by HPV18 E6, leading to enhancement of ACTN4-mediated actin cytoskeleton organization, motility and invasion of cervical cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Thus, the enhancement of cell migration and invasion induced by HPV16 E6-mediated degradation of NHERF1 might be an important cause of cervical cancer carcinogenesis. 30581004_The results suggested that NHERF1 played an essential role in regulating liver cancer progression, and repressing NHERF1 expression exhibited significant anticancer effects via the induction of G0/G1 phase arrest, apoptosis and reactive oxygen species generation. 30696771_Dephosphorylated NHERF1 exhibited faster exchange at C-terminal residues suggesting that NHERF1 dephosphorylation precedes Ser(290) rephosphorylation 31042404_assessed the role of NHERF1 in regulating cAMP-mediated signaling and immunomodulatory functions in airway smooth muscle 31171716_findings provide important insight into the modulation of the intrinsic flexibility of NHERF1 by disease-associated point mutations that alter the dynamic assembly of signaling complexes 32014995_In vivo crystals reveal critical features of the interaction between cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and the PDZ2 domain of Na(+)/H(+) exchange cofactor NHERF1. 32164629_Alteration in the sensitivity to crizotinib by Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor 1 is dependent to its subcellular localization in ALK-positive lung cancers. 33092043_Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger Regulatory Factor-1 (NHERF1) Regulates Fetal Membrane Inflammation. 33499384_Noncanonical Sequences Involving NHERF1 Interaction with NPT2A Govern Hormone-Regulated Phosphate Transport: Binding Outside the Box. 33639163_Multisite NHERF1 phosphorylation controls GRK6A regulation of hormone-sensitive phosphate transport. 33952618_Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger Regulatory Factor 1 Mediates the Pathogenesis of Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of House Dust Mite-Induced Asthma. 33965858_Nuclear expression of NHERF1/EBP50 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 34323956_Cytoplasmic EBP50 and elevated PARP1 are unfavorable prognostic factors in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. 35140182_Cotranslational interaction of human EBP50 and ezrin overcomes masked binding site during complex assembly. 35307350_RGS14 regulates PTH- and FGF23-sensitive NPT2A-mediated renal phosphate uptake via binding to the NHERF1 scaffolding protein. |
ENSMUSG00000020733 |
Slc9a3r1 |
151.997931 |
0.3611859070 |
-1.469186 |
0.201542613 |
52.089785 |
0.00000000000053020037965699404921005790919124155548096399837021408529835753142833709716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003207277706449685489537313615250103439324735887794304289855062961578369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
81.5258853 |
11.7790882 |
227.5491244 |
22.9355016 |
| ENSG00000109084 |
27346 |
TMEM97 |
protein_coding |
Q5BJF2 |
FUNCTION: Intracellular orphan receptor that binds numerous drugs and which is highly expressed in various proliferating cancer cells (PubMed:28559337). Corresponds to the sigma-2 receptor, which is thought to play important role in regulating cell survival, morphology and differentiation (PubMed:23922215, PubMed:25620095). Under investigation for its potential diagnostic and therapeutic uses (PubMed:23922215, PubMed:25620095). May play a role as a regulator of cellular cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:19583955). May function as sterol isomerase (PubMed:25566323). May alter the activity of some cytochrome P450 proteins (PubMed:22292588). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19583955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28559337, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22292588, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23922215, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25620095, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25566323}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
TMEM97 is a conserved integral membrane protein that plays a role in controlling cellular cholesterol levels (Bartz et al., 2009 [PubMed 19583955]).[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:27346; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0030867]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558] |
15375745_MAC30 mRNA and protein expression in normal and cancerous tissue samples of the esophagus, stomach, colon and pancreas 17143516_MAC30 protein may play a role in development of colorectal cancer, and can be considered as a prognostic factor. 18070364_The most up-regulated gene was TMEM97 which encodes a transmembrane protein of unknown function (MAC30). 21079401_expression of MAC30 in the cytoplasm markedly increased from normal oral epithelial cells to primary oral squamous cell carcinoma; MAC30 expression in primary tumors with lymph node metastasis exceeded levels in those without metastasis 22024687_As the tumor penetrated the wall of the colon/rectum, MAC30 mRNA expression notably increased in colorectal tumors with T3+T4 stage compared to tumors with T1+T2 stage. 23229099_Overexpression of MAC30 is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer. 23254963_MAC30 may serve as a new molecular marker to predict the lymph node metastasis and prognosis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer 24853233_The down-regulation of MAC30 expression efficiently inhibited the proliferation of gastric cancer cells. Furthermore, the mobility of gastric cancer cells was also inhibited by down-regulation of MAC30. 26002575_High expression of TMEM97 is associated with glioma. 27268655_Overexpression of MAC30 is associated with Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Lung. 27378690_knockdown of TMEM97 also increases levels of residual NPC1 in NPC1-mutant patient fibroblasts and reduces cholesterol storage in an NPC1-dependent manner. Our findings propose TMEM97 inhibition as a novel strategy to increase residual NPC1 levels in cells and a potential therapeutic target for Niemann-Pick type C disease (NP-C). 27688262_MAC30 could be a useful biomarker of tumor differentiation and outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Overexpression of MAC30 predicts a worse tumor differentiated stage and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. 28559337_TMEM97 possesses the full suite of molecular properties that define the sigma2 receptor, and Asp29 and Asp56 are essential for ligand recognition 28644012_Study generated a series of sigma1R and sigma2R/Tmem97 agonists and antagonists and tested them for efficacy in the mouse spared nerve injury model. Results show robust antineuropathic pain effects of sigma1R and sigma2R/Tmem97 ligands, demonstrate that sigma2R/Tmem97 is a novel neuropathic pain target, and identify sigma2R/Tmem97 agonist UKH-1114 as a lead molecule for further development. 28972404_we not only confirmed the elevated MAC30 mRNA, but also demonstrated that GC with overexpression of MAC30 resisted to adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy. 29599847_TMEM97 was found to be overexpressed in prostate cancer, and identified as a novel miR-152 target gene. 30443021_These data indicate that the formation of a ternary complex of LDLR-PGRMC1-TMEM97 is necessary for the rapid internalization of LDL by LDLR. 32572762_The Sigma-2 Receptor/TMEM97, PGRMC1, and LDL Receptor Complex Are Responsible for the Cellular Uptake of Abeta42 and Its Protein Aggregates. 33618021_TMEM97 facilitates the activation of SOCE by downregulating the association of cholesterol to Orai1 in MDA-MB-231 cells. 34233061_Histatin-1 is an endogenous ligand of the sigma-2 receptor. 34615853_Transmembrane protein 97 exhibits oncogenic properties via enhancing LRP6-mediated Wnt signaling in breast cancer. 35373413_Inhibition of MAC30 exerts antitumor effects in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via affecting the Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway. 35907137_TMEM97 is transcriptionally activated by YY1 and promotes colorectal cancer progression via the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 35970844_GPCR/endocytosis/ERK signaling/S2R is involved in the regulation of the internalization, mitochondria-targeting and -activating properties of human salivary histatin 1. |
ENSMUSG00000037278 |
Tmem97 |
139.594097 |
3.5979313212 |
1.847168 |
0.144852011 |
169.488934 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000956730155723314155748692054669881069173267450792399712414966384420061545628692351095242947657093079277812464056296448688954114913940429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000155521333683657672456449770254963798190088283797082164832367626079766771427193478982643757478837934216109317731024930253624916076660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
220.5925639 |
18.4908522 |
61.7468870 |
4.3843797 |
| ENSG00000109133 |
55161 |
TMEM33 |
protein_coding |
P57088 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of the tubular endoplasmic reticulum (ER) network by modulating intracellular calcium homeostasis. Mechanistically, stimulates PKD2 calcium-dependent activity (By similarity). Suppresses the RTN3/4-induced formation of the ER tubules (PubMed:25612671). Positively regulates PERK-mediated and IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response signaling (PubMed:26268696). Plays an essential role in VEGF-mediated release of Ca(2+) from ER stores during angiogenesis (PubMed:30760708). Also plays a role in the modulation of innate immune signaling through the cGAS-STING pathway by interacting with RNF26 (PubMed:32614325). Participates in lipid metabolism by acting as a downstream effector of the pyruvate kinase/PKM. Forms a complex with RNF5 to facilitate polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation of SCAP on the ER membrane (PubMed:34487377). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CR67, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25612671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26268696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30760708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32614325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34487377}. |
Acetylation;Endoplasmic reticulum;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response; regulation of endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization; and response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Located in endoplasmic reticulum membrane; melanosome; and nuclear envelope. Is integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55161; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization [GO:0071786]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; positive regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903896]; positive regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903899]; regulation of endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization [GO:1903371]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
26268696_TMEM33 is a novel regulator of the PERK-eIE2alpha-ATF4 and IRE1-XBP1 axes of the UPR signaling. 34487377_PKM2-TMEM33 axis regulates lipid homeostasis in cancer cells by controlling SCAP stability. |
ENSMUSG00000037720 |
Tmem33 |
940.299128 |
2.0983665604 |
1.069267 |
0.133308516 |
62.574258 |
0.00000000000000256585379360107132387929454297969011788795360394510591817152089788578450679779052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000017872582347122138566980342454661401452108799789431081705970427719876170158386230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1318.3973651 |
107.1075535 |
632.5123850 |
37.6694935 |
| ENSG00000109265 |
57482 |
CRACD |
protein_coding |
Q6ZU35 |
FUNCTION: Involved in epithelial cell integrity by acting on the maintenance of the actin cytoskeleton. Positively regulates the actin polymerization, by inhibiting the interaction of actin-capping proteins with actin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30361697}. |
Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in negative regulation of barbed-end actin filament capping. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57482; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; epithelial structure maintenance [GO:0010669]; maintenance of gastrointestinal epithelium [GO:0030277]; negative regulation of barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:2000813]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838] |
30361697_CRAD (Cancer-related Regulator of Actin Dynamics, previously KIAA1211) binds to and inhibits capping proteins, which leads to actin polymerization. CRAD is ubiquitously expressed in epithelial cells and is required for the maintenance of epithelial cell integrity. Genetic ablation of this gene deregulates Wnt signaling and induces the development of tumors in mouse models. 30361697_Datam indicate that cancer-related regulator of actin dynamics (CRAD) as frequently mutated or transcriptionally downregulated and as a tumour suppressor in colorectal cancer (CRC). 31699089_The overall survival of small cell lung cancer patients carrying KIAA1211 mutation was significantly longer than those with wild-type KIAA1211. 33006362_Knockdown of CRAD suppresses the growth and promotes the apoptosis of human lung cancer cells via Claudin 4. 35172140_Substrate rigidity dictates colorectal tumorigenic cell stemness and metastasis via CRAD-dependent mechanotransduction. |
ENSMUSG00000036377 |
Cracd |
39.713794 |
2.0599884598 |
1.042636 |
0.252811642 |
17.207556 |
0.00003351008198317000454959091459983255845145322382450103759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000098566921098363751438733992848995058011496439576148986816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.5802554 |
8.7779787 |
25.7026798 |
3.4081618 |
| ENSG00000109321 |
374 |
AREG |
protein_coding |
P15514 |
FUNCTION: Ligand of the EGF receptor/EGFR. Autocrine growth factor as well as a mitogen for a broad range of target cells including astrocytes, Schwann cells and fibroblasts. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the epidermal growth factor family. It is an autocrine growth factor as well as a mitogen for astrocytes, Schwann cells and fibroblasts. It is related to epidermal growth factor (EGF) and transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha). The protein interacts with the EGF/TGF-alpha receptor to promote the growth of normal epithelial cells, and it inhibits the growth of certain aggressive carcinoma cell lines. It also functions in mammary gland, oocyte and bone tissue development. This gene is associated with a psoriasis-like skin phenotype, and is also associated with other pathological disorders, including various types of cancers and inflammatory conditions. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:374; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030297]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; dichotomous subdivision of terminal units involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060598]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in mammary gland duct elongation [GO:0060750]; ERBB2-EGFR signaling pathway [GO:0038134]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mammary gland branching involved in thelarche [GO:0060744]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0045741]; positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010838]; response to cAMP [GO:0051591]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434] |
11719440_(TARP) expression in prostate cancer cells leads to an increased growth rate and induction of caveolins and amphiregulin. 11859273_mRNA expression in atrophic gastritis before and after Helicobacter pylori eradication 12356750_H358 cells secrete a high level of amphiregulin that, in combination with IGF1, prevents serum deprivation apoptosis 12568494_Review. The activation of EGFR in response to smoke involves cleavage of amphiregulin by ADAM 17. 12711607_amphiregulin binds to EGF receptor and has a role in stimulation of lung epithelial cells upon exposure to tobacco smoke 12743035_Data show that in squamous cell carcinoma cells, stimulation with G protein-coupled receptor agonists specifically results in cleavage and release of amphiregulin (AR) by TACE. 14633617_Amphiregulin(AR) overexpressing cells (HaCaT-AR) displayed autonomous proliferation in serum-free media. HaCaT-AR cells formed rapidly growing tumors with AR expression similar to keratoacanthoma. 15186320_epidermal AR expression as a possible mediator of innate cutaneous immunity and epidermal proliferation and also as a potential trigger of both cutaneous psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. 15254267_amphiregulin- and ErbB1-dependent mechanism by which autocrine ERK activation is maintained in normal keratinocytes 15284208_AR is under strong regulation by the cAMP pathway in various cell types 15474502_upregulation of the epiregulin and amphiregulin expression is part of the signal transduction pathway which leads to ovulation and luteinization in the human ovary 15685553_an early-response growth factor that may contribute to the initial phases of liver regeneration. 15696081_Amphiregulin was secreted by human mast cells after aggregation of FcepsilonRI. Amphiregulin may be new target molecule for treatment of overproduction of sputum in bronchial asthma. 15696083_Mast cells secreted amphiregulin on IgE cross-linking, and amphiregulin induced proliferation of lung fibroblasts. Local release of amphiregulin by mast cells could play role in lung fibrosis by promoting proliferation of lung fibroblasts. 15735670_AREG gene expressed by purified primary myeloma cells, and expression higher than in normal bone marrow (BM) plasma cells or plasmablastic cells; AREG plays an important role in biology of multiple myeloma 15767261_AR and IGF1 cooperate to prevent apoptosis by activating a specific PKC-p90(rsk)-dependent pathway, which leads to Bad and Bax inactivation. 15955087_Enhanced transmigration of human neutrophils through polarized epithelial cell monolayers of MDCK cells after administration of AR, further supporting aspecific role for AR in pathogenesis of psoriasis. 16088955_Data suggest that parathyroid hormone-induced amphiregulin mRNA expression is mediated primarily through cyclic AMP-protein kinase A-CREB signaling. 16207795_Results suggest that hypoxia promotes intestinal epithelial amphiregulin expression in a CREB-dependent manner, an event that may contribute to increased proliferation. 16213893_The mechanism of deoxycholic acid-induced epideermal growth factor receptor activation is ligand-dependent and is controlled, at least in part, at the level of amphiregulin release from the basolateral cell membrane. 16336275_HAT induces amphiregulin production through the PAR-2 mediated ERK pathway, and then causes amphiregulin release by a TACE-dependent mechanism 16470170_Amphiregulin and HB-EGF mediate retinoic acid-mediated epidermal hyperplasia 16641105_results show that TACE undergoes phosphorylation that regulates release of amphiregulin upon GRP treatment; a signaling cascade of GRP-Src-PI3-K-PDK1-TACE-amphiregulin-EGFR with multiple points of interaction, translocation & phosphorylation is suggested 16888076_findings demonstrated that PGE2 may mimic LH action at least in part by the activation of amphiregulin and epiregulin biosynthesis in human granulosa cells 17035230_Amphiregulin (AR) up-regulates a number of genes involved in cell motility and invasion in MCF10A cells, suggesting that an AR autocrine loop contributes to the aggressive breast cancer phenotype. 17525275_AREG is up-regulated in tumor cells of SCC but not BCC of the skin. AREG is also overexpressed in asymptomatic epidermis adjacent to both SCC and BCC, relative to normal skin. 17548638_MIP-3alpha-mediated ERK1/2 activation in Caco-2 cells appeared to require metalloproteinase-dependent release of the endogenous EGFR ligand amphiregulin and transactivation of the EGFR. 17942395_After exposure to cisplatin, the resistant breast cancer cells secrete amphiregulin protein by short interfering RNA resulting in a nearly complete reversion of the resistant phenotype. 17960400_TNFalpha may play a key role in cooperation with HB-EGF and AREG in the proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes at the psoriatic skin lesions. 17962208_AREG is preferentially expressed in breast tumors co-expressing HER2/HER4. AREG is associated with estradiol receptors, small tumour size, low histoprognostic grading, high HER4 levels. 18045238_amphiregulin-specific EGF-R fate results from decreased hSprouty2 degradation and reduced Cbl recruitment to underphosphorylated EGF-R, two effects that impair EGF-R trafficking to lysosomes 18325497_Amphiregulin was expressed most dominantly among EGF receptor ligands tested and may mediate the hCG signal in human oocyte maturation. Elaborate interaction between AR and hCG may be required for an optimal oocyte maturation. 18560449_The expression of amphiregulin was increased in the secretory phase of human endometrium, and may play an important role in human implantation. 18811692_serum amphiregulin in patients with advanced non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer 18835871_Amphiregulin has a protective effect against apoptosis in the human corpus luteum. 18946024_plasma-membrane-anchored growth factor pro-amphiregulin binds A-type lamin and regulates global transcription 18955794_interleukin-4 and amphiregulin have roles in the proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells and cytokine release 19003995_Amphiregulin plays a crucial role in UV-induced EGFR activation and is overexpressed in skin cancer cell lines 19070973_Use of AREG as a biomarker in non-small cell lung cancershould be encouraged since AREG is correlated with a poor prognosis, resistance to treatments and to apoptosis. 19337692_These findings suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction induced Ca(2+) mobilization, and reactive oxygen species overproduction, which modulated the chemo-resistance and migration of hepatoma cells through the induction and activation of amphiregulin. 19344731_Amphiregulin is a key molecule among epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ligands and may play a pivotal role in the development or maturation of placenta. 19494503_eosinophils produce and release AREG, and participate in some physiological and pathological conditions in vivo. 19587163_may play a significant role in the proliferation of osseous dysplasia 19609315_lentivirus-mediated expression of soluble HB-EGF, but not soluble AREG, strongly enhanced keratinocyte migration, even in the presence of metalloproteinase inhibitors 19735466_The results of these studies identify CXCL12 as a novel inducer of amphiregulin ectodomain shedding and show that both basal and CXCL12-mediated amphiregulin shedding are ADAM10- and Src kinase-dependent in non-transformed N15C6 cells 19825997_Taken together, we provide evidence that AREG stimulation of EGFR results in high levels of PTHrP gene expression, contributing to cancer-associated bone pathology. 19895983_Acute asthma attacks are associated with hypersecretion of EGF and amphiregulin in the airway 19915156_Results describe the role of amphiregulin in an experimental model of bleomycin-induced pneumopathy in mice. 19935651_identify the gene for the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ligand amphiregulin (AREG) as a transcriptional target of YAP, whose induction contributes to YAP-mediated cell proliferation and migration, but not mesenchymal transition. 20103632_data build the connection between BRCA1 loss of function and AREG upregulation-a change in gene expression often observed in breast cancer. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428186_autocrine human KC growth is highly dependent on the AREG transmembrane precursor protein and strongly suggest a previously unreported function of the metalloproteinase-processed carboxy (C)-terminal domain of AREG 20567134_is not essential for the induction of contact hypersensitivity 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20651071_ATP released from tumor cells might exert a tumorigenic action by stimulating the secretion of AREG from dendritic cells. 20651357_the inhibition of amphiregulin expression, which impairs EGFR response to its exogenously available ligands, may represent an alternative anti-EGFR therapeutic strategy in breast cancer. 20719813_AREG accumulation is a useful marker of gonadotrophin stimulation and oocyte competence. 20726858_Data show that blockade of amphiregulin suppressed the activities of EGFR, HER3, and Akt and the expression of amphiregulin itself. 20811902_Amphiregulin expression was found to be increased in salivary glands of Sjogren's syndrome patients. 20856199_Data suggest that PHD2/HIF-2/amphiregulin signaling has a critical role in the regulation of breast tumor progression and propose PHD2 as a potential tumor suppressor in breast cancer. 21036386_human subjects with asthma contained significantly higher numbers of amphiregulin-producing basophils 21161326_Data suggest that expression status of AR and EPI mRNAs might be evaluated as dynamic predictors of response in KRAS WT patients receiving any cetuximab-based therapy. 21245963_AREG and GDF15 produced in response to UVB exposure can affect the growth and protein synthesis of lens epithelial cells 21258428_estrogen and progeterone increased cell proliferation in normal gland and mammary cancers through the increased production of amphiregulin 21298020_the infection of N. gonorrhoeae causes an alternative amphiregulin processing, subcellular distribution and release in human epithelial cervical cells that likely contribute to the predisposition cellular abnormalitiesof N. gonorrhoeae infections. 21302279_AREG functions in regulating the invasive breast cancer phenotype, perhaps through altered signaling that occurs when AREG activates plasma membrane localized epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). 21377153_Oocyte competence is linked to granulosa cell AR secretion. 21439861_may play a significant role in the proliferation of human bone marrow stromal cells 21454516_AGR2 induction of AREG is mediated by activation of the Hippo signaling pathway co-activator, YAP1. 21514161_Amphiregulin exosomes increase cancer cell invasion. 21653755_AREG expression is essential for efficient hepatitis C virus assembly and virion release. 21742971_Lung tumor-associated dendritic cell-derived amphiregulin increased cancer progression. 21917092_AP-1B is required for efficient recycling of amphiregulin to the basolateral surface 21917092_Polarized transport of amphiregulin is dependent on a novel EEXXXL basolateral sorting motif in its cytoplasmic domain 22395988_Low AREG is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 22425981_These results suggested that pro-AREG monoubiquitination and the subsequent trafficking to intracellular organelles is a novel shedding regulatory mechanism that contributes to the secretion of EGFR ligands in growth factor signaling. 22438584_proAREG-annexins-ADAM17 complex needs to localize at the cell surface for shedding of proAREG to occur 22445895_these data demonstrate a novel function mediated by the intracellular domain of proAREG and suggest a significant role for nuclear envelope-localized proAREG in driving human breast cancer progression. 22570239_Polycystin-1 regulates amphiregulin expression through CREB and AP1 signalling, which has implications in ADPKD cell proliferation 22581387_concentrations in colostrum/milk were higher on days 1 and 2 and rapidly declined to below 1 ng/ml on day 5 22641668_We conclude that the expression of Amphiregulin in a primary colorectal tumor is useful as an indicator of prognosis and as a predictor of recurrence. 22825057_AREG functions in a non-cell-autonomous manner to mediate EGF-independent growth and malignant behavior of mammary epithelial cells. 22967896_Amphiregulin is cleaved at Lysine 187, a site homologous to the cleavage site reported in the mouse protein and distinct from the Lysine 184 site previously reported for the human protein. 23263765_AREG plays pro-neoplastic roles in colorectal carcinogenesis 23285165_Regulation of amphiregulin gene expression by beta-catenin signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 23430747_Human antigen R-mediated mRNA stabilization is required for ultraviolet B-induced autoinduction of amphiregulin in keratinocytes. 23594797_These findings provide mechanistic insight into the regulation of YAP and AREG by RASSF1A in human multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. 23624749_Promoter methylation of AREG is associated with glioblastoma. 23625463_EREG-AREG and NRG1, which are members of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, seem to modulate Behcet's disease susceptibility through main effects and gene-gene interactions 23844004_Exosome-bound WD repeat protein Monad inhibits breast cancer cell invasion by degrading amphiregulin mRNA. 23851501_Self-reinforcing loop of amphiregulin and Y-box binding protein-1 contributes to poor outcomes in ovarian cancer. 23885463_we did not find a correlation between the presence of a K-ras mutation and the presence of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin in colon cancer tissue. 23975434_aberrantly activated AREG-EGFR signaling is required for CRTC1-MAML2-positive MEC cell growth and survival, suggesting that EGFR-targeted therapies will benefit patients with advanced, unresectable CRTC1-MAML2-positive MEC. 24092824_Data suggest that AREG (amphiregulin), BTC (betacellulin), and EREG (epiregulin) induced prostaglandin E2 production by induction of COX-2 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2) through MAP kinase signaling in granulosa cells. 24196392_IL-1beta-induced amphiregulin release may be involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 24816162_AREG shedding occurs through a TNF-alpha-converting enzyme-dependent mechanism in diacetyl treated pulmonary epithelial cells. 24860833_AREG expression was significantly correlated with Edmondson stage and serum AFP level. 24921206_During high-pressure ventilation, Nrf2 becomes activated and induces AREG, leading to a positive feedback loop between Nrf2 and AREG, which involves the p38 MAPK and results in the expression of cytoprotective genes. 25203737_AREG rs1615111, located in the AREG genomic region, can significantly define different prognostic cohorts in locally advanced GC 25261255_AREG induces ovarian cancer cell invasion by down-regulating E-cadherin expression 25454348_Expression profiling demonstrated that AREG-activated EGFR regulates gene expression differently than EGF-activated EGFR 25744849_AR induces hHSC fibrogenic activity via multiple mitogenic signaling pathways, and is upregulated in murine and human NASH, suggesting that AR antagonists may be clinically useful anti-fibrotics in NAFLD. 25825984_Amphiregulin enhances alpha6beta1 integrin expression and cell motility in human chondrosarcoma cells through Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK/AP-1 pathway. 25862847_The applied drugs showed remarkable suppression of mTOR expression, which might delay tumor progression. Interestingly, sorafenib and sunitinib increased AREG in HNSCC 11A and 14C 25869072_This study shows that TGF-alpha uses common and divergent molecular mediators to regulate E-cadherin expression and cell invasion. 25911599_Altered AREG expression induced by diverse luteinizing hormone receptor reactivity in granulosa cells may provide a useful marker for oocyte developmental competency 26047642_Bradykinin (BK) stimulation of human airway smooth muscle cell increases amphiregulin secretion in a mechanism dependent on BK-induced COX-2 expression. 26201903_Findings show the involvement of amphiregulin and semaphorin-3A in the improvement of skin innervations and penetration of nerve fibers into the epidermis. 26234682_results demonstrate that AREG controls G2/M progression and cytokinesis in keratinocytes via activation of a FoxM1-dependent transcriptional program, suggesting new avenues for treatment of epithelial cancer 26451607_High expression of amphiregulin is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 26503469_High Amphiregulin enhances intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and promotes tumor metastasis in osteosarcoma. 26519132_keratinocyte expression of hAREG elicits inflammatory epidermal hyperplasia 26527289_Our findings implicate amphiregulin as a critical mediator of the estrogen response in ERalpha-positive breast cancer 26742492_RYR2, PTDSS1 and AREG are autism susceptibility genes that are implicated in a Lebanese population-based study of copy number variations in this disease. 26884344_Low AREG expression is associated with gastric cancer. 27040371_Regulatory T-cell-intrinsic amphiregulin is dispensable for suppressive function. 27113901_AREG mediates hCG-induced StAR expression and progesterone production in human granulosa cells, providing novel evidence for the role of AREG in the regulation of steroidogenesis. 27272216_EREG and AREG are strongly regulated by methylation, and their expression is associated with CIMP status and primary tumour site. 27393417_AREG expression may be useful for identifying CRTC1-MAML2-positive mucoepidermoid carcinomas and as a marker for favorable prognosis. 27432879_These findings demonstrate the posttranslational regulation of Foxp3 expression by AREG in cancer patients through AREG/EGFR/GSK-3beta signaling, which could lead to Foxp3 protein degradation in Treg cells and a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. 27709733_EGF-AREG interplay in airway basal cell stem/progenitor cells is one of the mechanisms that mediates the interconnected pathogenesis of all major smoking-induced lesions in the human airway epithelium. 27713123_over-expression of AREG could serve as a novel GC biomarker, and active surveillance of its expression could be a novel approach to GC diagnosis and monitoring. 27826039_Amphiregulin enhances VEGF-A production in human chondrosarcoma cells and promotes angiogenesis by inhibiting miR-206 via FAK/c-Src/PKCdelta pathway. 27835572_Sprouty2 inhibits amphiregulin-induced down-regulation of E-cadherin and cell invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. 28256068_Results show that AREG expression is up-regulated in gastric tumor and its co-expression with TROP2 protein is associated with TNM stage, tumor size, lymph node metastases, and distant metastases. 28351301_blocking soluble amphiregulin with a neutralizing antibody also significantly increased apoptotic cell death of HepG2 cells due to treatment with methyl methanesulfonate, cisplatin, or a recombinant p53 adenovirus, suggesting that the function of amphiregulin involved in inhibiting apoptosis may be a common mechanism by which hepatoma cells escape from stimulus-induced apoptosis 28430338_No significant correlations emerged for YAP or AREG expression and VIII CN schwannoma volume. 28476786_Amphiregulin plays an important role in lung neoplasm resistance to amrubicinol 28600504_Amphiregulin contained in non-small-cell lung carcinoma-derived exosomes induces osteoclast differentiation through the activation of EGFR pathway. 28733611_Whole genome bisulfite sequencing revealed that integrin alpha6beta4 signaling promotes an overall hypomethylated state and site specific DNA demethylation of enhancer elements within the proximal promoters of AREG and EREG in pancreatic neoplasm cells as well as their expression. Additionally, base excision repair (BER) pathway is required to maintain the expression of AREG and EREG. 29112457_FOSL1 is a determinant of lung cancer in vivo and regulates tumor cell proliferation and survival, largely in the context of KRAS mutations through amphiregulin and cell survival gene regulation. 29261670_secretion of IL-13 and amphiregulin suggests Intrahepatic Innate lymphoid cells may be recruited to promote resolution and repair and thereby they may contribute to ongoing fibrogenesis in liver disease. 29421153_Results show that Areg is involved in the nuclear accumulation of IGF1R induced by gefitinib and preventing the induction of apoptosis of lung cancer cells. 29483579_The studies indicate that HIF2-alpha induces myocardial AREG expression in cardiac myocytes, which increases myocardial ischemia tolerance. 29550478_Cullin 3 regulates ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of AREG. 30087106_High-circulating AREG (>/=33 pg/mL) reclassifies patients into HR subgroups and thereby further refines the Minnesota aGVHD clinical risk score. 30230033_Data showed that AR was highly expressed and secreted in mobile and Doxorubicin (Dox)-resistant cells. AR can promote migratory activity and Dox resistance through activation of the MAPK pathway. 30252132_Retrospective comparison of the predictive power of AREG gene-body methylation versus AREG gene expression using samples from colorectal cancer patients treated with anti-EGFR inhibitors with complete clinical follow-up revealed that AREG expression is superior to AREG gene methylation. 30291869_AREG potentiated particulate matter-induced inflammation and mucus hypersecretion by activating EGFR-PI3Kalpha-AKT/ERK pathway in bronchial epithelial cells. 30323299_We concluded that YAP may play an important role in the regulation of abnormal keratinocyte proliferation via an AREG-dependent pathway and that YAP could be a new target in the treatment of psoriasis. 30411380_AREG-EGFR signaling protects from cholestatic injury and participates in physiological regulation of bile acid synthesis 30440051_We found that CRB3-induced proliferation is epidermal growth factor (EGF)-independent and occurs through a mechanism that involves secretion of the EGF-family ligand, amphiregulin (AREG)..We identified the FBD-containing protein, EPB41L4B, as an essential mediator of CRB3-driven proliferation and observed that the CRB3-dependent changes in endocytic trafficking were also dependent on EPB41L4B 30621731_AREG is packed into Multiple myeloma-derived exosomes and implicated in osteoclast differentiation through an indirect mechanism mediated by osteoblasts. 30790501_These results indicate that AR occurs through the Src/MEK/ERK/STAT-3 pathway, activating VEGF-C expression and contributing to lymphangiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma. Thus, AR could be a therapeutic target in metastasis and lymphangiogenesis of chondrosarcoma. 31040043_This study suggested that AREG and the AR were co-expressed in invasive breast cancer and may be valuable prognostic biomarkers in invasive breast cancer and promising therapeutic targets, especially in ER-negative breast cancer 31059536_novel finding that AREG mediates BPAF-induced ER-RTK crosstalk in ER+ breast cancer cells supports future studies to characterize the impact of BPAF on human ER+ breast cancer risk and to assess the safety profile of BPAF. 31087779_Our results showed that the increased activity of the TGF-beta1 pathway is strongly associated with the expression of AREG, denoting a direct and positive relationship between the TGF-beta1 and YAP1 pathways. It seems that, unlike the TGF-beta1 and SHH pathways, the YAP1 pathway does not play a significant role in the development of liver cirrhosis. 31092430_Treatment with lapatinib reduced BeWo cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis. Moreover, AREG treatment stimulated BeWo cell proliferation by activating ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, which was blocked by lapatinib. Targeting EGFR/HER2 might be a useful therapeutic strategy for human choriocarcinoma 31187330_Collectively, PAPPA, LHCGR, and AREG mRNA levels in CC may be able to identify oocytes with the best odds of resulting in a live birth, and HSD3B1 mRNA levels may be able to identify oocytes capable of producing euploid embryos 31370819_the results indicated that amphiregulin may potentially serve as biomarker and therapeutic approach for chemotherapy regimens in glioblastoma multiforme 31466817_over expression of AREG in gastric cancer cells promoted malignant procession via activation of ERK/JNK/p38 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. 31485602_Results indicated that AREG expression can regulate vincristine (VCR) resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells; overexpression of AREG increased VCR resistance in parental cells, whereas AREG knockdown decreased the VCR resistance of resistant cells. In addition, the glycogen synthase kinase3beta pathway may be involved in AREGinduced VCR resistance. 31519572_AREG and EREG mRNA expression levels in left-sided CRC were higher than in right-sided tumors. This may help explain why left-sided CRC is more responsive to anti-EGFR antibodies. 31553790_Human chorionic gonadotropin-induced amphiregulin stimulates aromatase expression in human granulosa-lutein cells: a mechanism for estradiol production in the luteal phase. 31630583_Serum amphiregulin and cerebellin-1 levels in severe preeclampsia. 32124941_Aberrant expression of the UPF1 RNA surveillance gene disturbs keratinocyte homeostasis by stabilizing AREG. 32187551_Mesenchymal Stem and Stromal Cells Harness Macrophage-Derived Amphiregulin to Maintain Tissue Homeostasis. 32323797_AREG mediates the epithelialmesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells via the EGFR/ERK/NFkappaB signalling pathway. 32472393_Knockdown of Amphiregulin Triggers Doxorubicin-Induced Autophagic and Apoptotic Death by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Glioblastoma Cells. 32616537_Amphiregulin Aggravates Glomerulonephritis via Recruitment and Activation of Myeloid Cells. 32943459_Amphiregulin Expression Is a Predictive Biomarker for EGFR Inhibition in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Combined Analysis of Three Randomized Trials. 32958255_Microbiota-derived short chain fatty acid promotion of Amphiregulin expression by dendritic cells is regulated by GPR43 and Blimp-1. 33775193_Immunohistochemical evaluation of the prognostic and predictive power of epidermal growth factor receptor ligand levels in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. 33941693_Dysregulation of Amphiregulin stimulates the pathogenesis of cystic lymphangioma. 33941851_Targeting autocrine amphiregulin robustly and reproducibly inhibits ovarian cancer in a syngeneic model: roles for wildtype p53. 34062166_Amphiregulin increases migration and proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by inducing its own expression via PI3-kinase signaling. 34290392_The combined detection of Amphiregulin, Cyclin A1 and DDX20/Gemin3 expression predicts aggressive forms of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 34329970_Amphiregulin stimulates human chorionic gonadotropin expression by inducing ERK1/2-mediated ID3 expression in trophoblast cells. 34468540_Expression of Amphiregulin in Enchondromas and Central Chondrosarcomas. 34843542_Microglial-stimulation of glioma invasion involves the EGFR ligand amphiregulin. 34893673_Amphiregulin can predict treatment resistance to palliative first-line cetuximab plus FOLFIRI chemotherapy in patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. 35109967_Interrelationships between amphiregulin, kisspeptin, FSH and FSH receptor in promotion of human ovarian cell functions. 35224759_High cutaneous amphiregulin expression predicts fatal acute graft-versus-host disease. 35500933_Profound Defect of Amphiregulin Secretion by Regulatory T Cells in the Gut of HIV-Treated Patients. 35732465_Loss of Amphiregulin drives inflammation and endothelial apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension. 36054710_Nuclear AREG affects a low-proliferative phenotype and contributes to drug resistance of melanoma. |
ENSMUSG00000029378 |
Areg |
140.546060 |
10.8402407593 |
3.438325 |
0.205370612 |
313.896504 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000030932445606034975975763415408557890163201971247941166337512198392791788443159601424217371479943041949215679048361223403977116501841698808634159658082799872071728795060971710026431757967202429426833987236022949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009279733681810492664040084885866644095486787037590125686044169986971965853287687249675559454605964437177113743200132291418133932115516526494658811803722210415761321913169501485185719502624124288558959960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
262.1633410 |
30.1115130 |
24.3526717 |
2.5922309 |
| ENSG00000109339 |
5602 |
MAPK10 |
protein_coding |
P53779 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in various processes such as neuronal proliferation, differentiation, migration and programmed cell death. Extracellular stimuli such as pro-inflammatory cytokines or physical stress stimulate the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAP/JNK) signaling pathway. In this cascade, two dual specificity kinases MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 phosphorylate and activate MAPK10/JNK3. In turn, MAPK10/JNK3 phosphorylates a number of transcription factors, primarily components of AP-1 such as JUN and ATF2 and thus regulates AP-1 transcriptional activity. Plays regulatory roles in the signaling pathways during neuronal apoptosis. Phosphorylates the neuronal microtubule regulator STMN2. Acts in the regulation of the amyloid-beta precursor protein/APP signaling during neuronal differentiation by phosphorylating APP. Participates also in neurite growth in spiral ganglion neurons. Phosphorylates the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer and plays a role in the photic regulation of the circadian clock (PubMed:22441692). Phosphorylates JUND and this phosphorylation is inhibited in the presence of MEN1 (PubMed:22327296). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11718727, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22441692}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biological rhythms;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as integration points for multiple biochemical signals, and thus are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is specifically expressed in a subset of neurons in the nervous system, and is activated by threonine and tyrosine phosphorylation. Targeted deletion of this gene in mice suggests that it may have a role in stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. A recent study provided evidence for translational readthrough in this gene, and expression of an additional C-terminally extended isoform via the use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]. |
hsa:5602; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; JUN kinase activity [GO:0004705]; MAP kinase activity [GO:0004707]; MAP kinase kinase activity [GO:0004708]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038095]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; response to light stimulus [GO:0009416]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12436199_Shares a promoter region with the tightly linked gene encoding Fas-associated phosphatase-1. 16737965_interaction of free arrestins with JNK3 and Mdm2 and their ability to regulate subcellular localization of these proteins may play an important role in the survival of photoreceptors and other neurons 17680991_Arrestin in all conformations binds JNK3 comparably, whereas Mdm2 preferentially binds cone arrestin 'frozen' in the basal state. 18408005_JNK3 recruits MKK4 to the beta-arrestin-2 scaffold complex by binding to the MAPK docking domain (D-domain) located within the N terminus of MKK4. 19001375_the molecular interactions of arrestin2 and arrestin3 and their individual domains with the components of the two MAPK cascades, ASK1-MKK4-JNK3 and c-Raf-1-MEK1-ERK2 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20525557_JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3 are involved in P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 21041242_The results suggest the possible involvement of CaMKII and JNK3 in soman-induced long-term neurotoxicity. 21166945_results suggest that MAPK10 may have a proapoptotic function and could function as a tumor-suppressor gene in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma 21321401_[review] This review focuses on delineating the role of scaffold proteins, especially that of JNK3 as a target, on the regulation of JNK signaling in neurons. 22047447_Arrestin-3 acts as a 'true' scaffold, facilitating JNK3alpha2 phosphorylation by bringing it and MAP kinase kinase (MKK)4 together. 22523077_Silent scaffolds: inhibition OF c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 activity in cell by dominant-negative arrestin-3 mutant. 23142346_Subtle structural mechanisms for allosteric signaling between the peptide-binding site and activation loop of human JNK3. 23329067_reduced JNK3 activity has potentially deleterious effects on neuronal function via altered regulation of a set of post-synaptic proteins. 24412749_Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 JNK3 alpha (JNK3apha2)binds to both domains of arrestin-3. 24767251_miR-29b mRNA, MAPK10 protein expression, and ATG9A protein expression are closely related to chemosensitivity of ovarian carcinoma. 25025079_JNK3 is required for the antiapoptotic effects of exendin 4 25178256_analysis of the unique mechanisms by which JNK1beta1 is regulated 25455349_Study found that JNK3 levels are increased in brain tissue and CSF from patients with Alzheimer disease and CSF levels could reflect the rate of cognitive decline 25475894_Data indicate that tetra-substituted pyridinylimidazoles were designed as dual inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) 3 and p38alpha mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, and both kinases may be involved in the progression of Huntington's disease. 26868142_Peptide mini-scaffold facilitates JNK3 activation in cells. 28393229_Mapk10 expression was regulated by miR27a-3p in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Mapk10 gene was down-regulated in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 30591558_phosphorylation rate of JNK3 at Thr-221 by MKK7 is two orders of magnitude faster than the corresponding phosphorylation of Tyr-223 by MKK4 with or without arrestin-3 31080119_Structural mechanisms of the arrestin-3/JNK3 interactions have been reported. 31432180_the present study identified a novel significant association between the increased expression levels of MAPK10, TUBB2B and RASL11B, and neuroblastoma cells. 32040807_Identification and neuroprotective evaluation of a potential c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 inhibitor through structure-based virtual screening and in-vitro assay. 32066630_MicroRNA-4516-mediated regulation of MAPK10 relies on 3' UTR cis-acting variants and contributes to the altered risk of Hirschsprung disease. 32468043_Propofol suppresses the progression of nonsmall cell lung cancer via downregulation of the miR215p/MAPK10 axis. 32572915_Circ_0000515 drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating MAPK10. 32998477_JNK3 as Therapeutic Target and Biomarker in Neurodegenerative and Neurodevelopmental Brain Diseases. 33774030_Genetic variants in MAPK10 modify renal cell carcinoma susceptibility and clinical outcomes. 34502556_The Roles of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) in Infectious Diseases. |
ENSMUSG00000046709 |
Mapk10 |
49.418705 |
8.3117361468 |
3.055150 |
0.359649859 |
72.657219 |
0.00000000000000001542416595030519225808437872074498976063339089896848943528340214470517821609973907470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000121678615407004072084777880533609073085415732697577018139867277568555437028408050537109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
80.2496969 |
15.9295289 |
9.4937398 |
1.6609028 |
| ENSG00000109381 |
1998 |
ELF2 |
protein_coding |
Q15723 |
FUNCTION: Isoform 1 transcriptionally activates the LYN and BLK promoters and acts synergistically with RUNX1 to transactivate the BLK promoter.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 may function in repression of RUNX1-mediated transactivation. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated; and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in cytosol and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1998; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11967990_angiopoietin-1 regulates expression of NERF2 and its own receptor in hypoxic cells. 12447867_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14970218_NERF/ELF-2 physically interacts with AML1 and mediates opposing effects on AML1-mediated transcription of the B cell-specific blk gene 17368566_These findings indicate that ELF2/NERF promotes VCP transcription and that ELF2/NERF-VCP pathway might be important for cell survival and proliferation under cytokine stress. 18544453_ELF2 transactivates VCP promoter through binding to two motifs, with a predominant contribution of the upstream one. 18754678_Affinity of the CAL PDZ domain for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) C-terminus is much weaker than that of the NHERF1/NHERF2 domains, enabling wild-type CFTR to avoid premature entrapment in the lysosomal pathway. 26968954_Our findings collectively support a potential role of triiodothyronine and its receptor in tumor growth inhibition through regulation of ELF2 28728844_PCAT7 contributed to the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through regulating miR-134-5p/ELF2 signaling pathway. 29632131_Mutations in eIF2B genes cause vanishing white matter disease due to translation defects. 35239093_Circ_0028007 Aggravates the Malignancy of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating miR-656-3p/ELF2 Axis. |
ENSMUSG00000037174 |
Elf2 |
261.718620 |
0.4010705293 |
-1.318072 |
0.104625873 |
161.494514 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000053348744578916115124035708564213132377718517243349863507350011640939501091178050222289977564272406285184047192160505801439285278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000008271296953621868850388619299540291060968804459532761311376697373894696259641744842450125391620369130762924214650411158800125122070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
146.1321179 |
10.1183677 |
367.3515300 |
16.4381605 |
| ENSG00000109458 |
2549 |
GAB1 |
protein_coding |
Q13480 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein that plays a role in intracellular signaling cascades triggered by activated receptor-type kinases. Plays a role in FGFR1 signaling. Probably involved in signaling by the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the insulin receptor (INSR). Involved in the MET/HGF-signaling pathway (PubMed:29408807). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29408807}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Deafness;Disease variant;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the IRS1-like multisubstrate docking protein family. It is an important mediator of branching tubulogenesis and plays a central role in cellular growth response, transformation and apoptosis. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:2549; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; signaling adaptor activity [GO:0035591]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; endothelial cell chemotaxis to vascular endothelial growth factor [GO:0090668]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell migration by vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038089]; response to hepatocyte growth factor [GO:0035728]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084] |
11606067_Unique phosphorylation mechanism of Gab1 using PI 3-kinase as an adaptor protein. 11701952_comparative FISH mapping of Gab1 and Gab2 genes in human, mouse and rat 11896055_ERK negatively regulates the epidermal growth factor-mediated interaction of Gab1 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase 12370245_Results indicate that Gab1 and SHP-2 promote the undifferentiated epidermal cell state by facilitating Ras/MAPK signaling. 12766170_Gab1 and the Met receptor interact in a novel manner, such that the activated kinase domain of Met and the negative charge of phosphotyrosine 1349 engage the Gab1 MBD as an extended peptide ligand 12808090_Gab1 is an integrator of cell death versus cell survival signals in oxidative stress 12855672_Gab1-SHP2 interaction plays a crucial role in gp130-dependent longitudinal elongation of cardiomyoctes and cardiac hypertrophy through activation of ERK5 14665621_results reveal that Gab1 protein recruits SHP2 protein tyrosine phosphatase to dephosphorylate paxillin 14701753_SHP-2/Gab1 association is critical for linking EGFR to NF-kappaB transcriptional activity via the PI3-kinase/Akt signaling axis in glioblastoma cells 15010462_Hck-mediated phosphorylation of Gab1 and Gab2 docking proteins in IL-6-induced proliferation and survival of multiple myeloma cells. 15351743_coupling of Gab1 to PI3K is important for biological responses in RET-expressing cells 15379552_extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 modulate insulin action via Gab1 by targeting serine and threonine residues beside YXXM motifs 15665327_Gab1 tyrosine phosphorylation is stimulated by flow shear stress to mediate protein kinase B and endothelial nitric-oxide synthase activation in endothelial cells 15940252_RAI associates with the Grb 2-associated binder 1 (GAB 1) adapter. This association is constitutive, but, in the presence of RET oncoproteins, both RAI and GAB 1 are tyrosine-phosphorylated, and the stoichiometry of this interaction remarkably increases 15952937_Gab2 plays a pivotal role in the EGF-induced ERK activation pathway and that it can complement the function of Gab1 in the EGF signalling pathway; Gab1 and Gab2 are critical signalling threshold proteins for ERK activation by EGF. 16687399_By amplifying positive interactions between survival and mitogenic pathways, GAB1 plays the critical role in cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. 16787925_Gab1 appears as a primary actor in coupling VEGFR-2 to PI3K/Akt, recruited through an amplification loop involving PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and its PH domain 16849525_Crk adaptor protein is required for the sustained phosphorylation of c-Met-docking protein Grb2-associated binder 1 (Gab1) in response to HGF, leading to the enhanced cell motility of human synovial sarcoma cell lines SYO-1, HS-SY-II, and Fuji. 17145761_Bisindolylmaleimide I abolishes the FGF2-mediated association of Shp2 tyrosine phosphatase with Frs2 and Gab1. 17178724_Gab1 is a novel critical regulatory component of endothelial cell migration and capillary formation with a key role in the activation of VEGF-evoked signaling pathways required for angiogenesis 17211494_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17625596_HGF signaling process from Gab1 to PI3K is negatively regulated by PKC-betaII, and its loss is critical for melanoma cells to gain invasive potential. 18003605_These results suggest that coupling of Grb2 to Gab1 mediates the hepatocyte growth factor-induced strong activation of the ERK pathway, which is required for the inhibition of HepG2 cell proliferation. 18192688_moderate level of Gab1 overexpression stimulated tumor growth 18577518_the Gab1-SHP2-ERK1/2 signaling pathway comprises an inhibitory axis for IGF-I-dependent myogenic differentiation. 19233262_These results underscore the non-redundant and essential roles of Gab1 and Gab2 in endothelial cells, and suggest major contributions of these proteins during in vivo angiogenesis. 19665053_Gab1 couples PI3K-mediated Erythropoietin signals with the Ras/Erk pathway and plays an important role in erythropoietin receptor-mediated signal transduction involved in the proliferation and survival of erythroid cells. 19881549_the phosphorylation of Gab1 by c-Src is important for hepatocyte growth factor -induced DNA synthesis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20005866_The binding of Grb2 adaptor to its downstream partners Sos1 and Gab1 docker is under tight allosteric regulation. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602450_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602450_We could not confirm a major association between Gab1 SNP (rs3805246) and the predisposition to H. pylori infection and CAG in this study populat 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20723025_PECAM-1-mediated inhibition of GPVI-dependent platelet responses result from recruitment of SHP-2-p85 complexes to tyrosine-phosphorylated PECAM-1, which diminishes the association of PI3K with activatory signaling molecules Gab1 and LAT 21282639_Gab1 is a critical upstream signaling component in VEGF-induced eNOS activation and tube formation, which is dependent on protein kinase A. 21782801_These data demonstrate that GAB1 is ubiquitinated by CBL and degraded by the proteasome, and plays a role in negative-feedback regulation of HGF/SF-MET signaling. 22366451_Met signals through a cortactin-Gab1 scaffold complex, to mediate invadopodia. 22536782_Data show that bivalent binding drives the formation of the Grb2-Gab1 signaling complex in a noncooperative manner. 22751113_that aberrant Gab1 signaling can directly contribute to breast cancer progression, and that negative feedback sites in docking proteins can be targeted by oncogenic mutations. 22851227_these data underscore the critical roles of Gab1 and Gab2 in IL-22-mediated HaCaT cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. 22865653_GAB1 plays an important role as part of the mechanism of by which EGFR induces induced activation of the MAPK and AKT pathway. 22915589_an anti-apoptotic role of caspase-cleaved GAB1 in HGF/SF-MET signaling. 23334917_Although Sos1 and Gab1 recognize two non-overlapping sites within the Grb2 adaptor, allostery promotes the formation of two distinct pools of Grb2-Sos1 and Grb2-Gab1 binary signaling complexes in lieu of a composite Sos1-Grb2-Gab1 ternary complex. 23612964_the acquired substrate preference for GAB1 is critical for the ERBB2 mutant-induced oncogenesis. 23805312_The model showed agreement at several key nodes, involving scaffolding proteins Gab1, Gab2 and their complexes with Shp2. VEGFR2 recruitment of Gab1 is greater in magnitude, slower, and more sustained than that of Gab2. As Gab2 binds VEGFR2 complexes more transiently than Gab1, VEGFR2 complexes can recycle and continue to participate in other signaling pathways. 24312291_expression of Gab1, VEGFR-2, and MMP-9 are significantly related to the malignant biological behavior of hilar cholangiocarcinoma 24374147_Gab1 as major target in linoleic acid-induced enhancement of tumorigenesis. 24391994_The combined GRB2 and GAB1 protein expression was significantly associated with aggressive tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 24787006_miR-150 can influence the relative expression of GAB1 and FOXP1 and the signaling potential of the B-cell receptor 24872569_Gab1 is an essential component of NRG1-type III signaling during peripheral nerve development. 24998422_Upregulations of Gab1 and Gab2 proteins associate with tumor progression of human gliomas. 25041730_C-SH3 of Grb2 mediates the interaction with mutant Htt and this interaction being stronger could replace Gab1, with mutant Htt becoming the preferred partner. This would have immense effect on downstream signaling events. 25078664_Galphai1/3 proteins lie downstream of KGFR, but upstream of Gab1-mediated activation of PI3K-AKT-mTORC1 signaling. 25144631_Endometrial GAB1 protein and mRNA expression are reduced in women with PCOS, suggesting that the endometrium of PCOS women have a defect in insulin signaling due to GAB1 down-regulation. 25217982_This study suggests potential effects of SNPs of Gab1 on the onset and susceptibility of biliary tract cancer. 25569504_Studied the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain of GAB1 for cancer treatment. Using homology models we derived, high-throughput virtual screening of five million compounds resulted in five hits which exhibited strong binding affinities to GAB1 PH domain. 25596749_Results suggest that Gab1 is an essential regulator of the EGF-mediated mTORC pathways and may potentially be used as a biomarker for urothelial carcinoma 25969544_EGFR-activated Src family kinases maintain GAB1-SHP2 complexes distal from EGFR. 25991585_Data demonstrate that miR-409-3p is a metastatic suppressor, and post-transcriptional inhibition of the oncoprotein GAB1 is one of its mechanisms of action. 26014518_We found that expression of Gab1, VEGFR-2, and MMP-9 was highly and positively correlated with each other and with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissues 26090437_Gab1 protein was upregulated in cyanotic compared to acyanotic hearts suggesting that Gab1 upregulation is a component of the survival program initiated by hypoxia in cyanotic children 26183772_CVB3 targets host GAB1 to generate a GAB1-N1-174 fragment that enhances viral infectivity, at least in part, via activation of the ERK pathway 26276357_Gab1 has a role in regulating SDF-1-induced progression via inhibition of apoptosis pathway induced by PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2/BAX pathway in human chondrosarcoma (CS). Gab1 can be recommended as a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in patients with CS. 26517531_These results demonstrate that cardiomyocyte Gab1 is a critical regulator of the compensatory cardiac response to aging and hemodynamic stress. 26871477_Knockdown of GAB1 mimicked the tumor-suppressive effects of miR-150 overexpression on HCC cells, whereas restoration of GAB1 expression partially abolished the inhibitory effects. 27241812_Gab1/SHP2/p38MAPK signaling pathway and Ang-2 have an essential role in regulating thrombin-induced monocyte adhesion and vascular leakage 27302321_Gab1 expression is correlated with poor prognosis of Epithelial ovarian cancer patients. 27475256_miR-5582-5p induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in cancer cells, but not in normal cells. GAB1, SHC1, and CDK2 were identified as direct targets of miR-5582-5p. 28081727_these data provide novel information for comprehending the tumor-suppressive role of miR-200a in HCC pathogenesis through inhibition of GAB1 translation. 28365441_onstitutive Gab1-dependent signalling in Jak2-V617F-expressing cells does not occur due to the constitutive association of Gab1 with PIP3 at the plasma membrane. 28619509_data suggested that miR-141-3p decreased the proliferation and migration of keloid fibroblasts by repressing GAB1 expression, providing a useful target for keloid management 28893350_These results suggested that Gab1 induced malignant progression of oral squamous carcinoma cells. 29408807_Modifier variant of METTL13 suppresses human GAB1-associated profound deafness. 29902453_Gab1 is required for H2O2-induced Akt activation in OB-6 osteoblasts. miR-29a inhibition upregulates Gab1 to protect OB-6cells from H2O2. Gab1 over-expression promotes Akt activation to inhibit H2O2-induced OB-6cell death. 30280777_Results identified GAB1 as a direct target of miR-590 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Its knockdown had the same effect as overexpression of miR-590 in NSCLC. Moreover, its overexpression partially reversed the suppressive effect of miR-590 on NSCLC. 30665442_Our findings indicate that elevated expression of Gab1 promotes Breast cancer metastasis by dissociating the PAR complex that leads to EMT, implicating a role of Gab1 as a potential biomarker of metastatic Breast cancer. Moreover, inhibition of Gab1 expression might be a promising therapeutic strategy for Breast cancer metastasis 30697991_Gab1 is associated with angiogenesis function of EA.hy926 endothelium cells via PI3K-Akt signaling pathway 31443923_Gab1 expression in Ewing sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma and synovial sarcoma may have prognostic significance 31505074_Increased expression of GAB1 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. 31651330_Gab1 enhances interleukin-6-induced MAPK-pathway activation in an SHP2-, Grb2-, and time-dependent manner 32650835_miR-183-3p suppresses proliferation and migration of keratinocyte in psoriasis by inhibiting GAB1. 32759334_Human Cytomegalovirus miR-US5-2 Downregulation of GAB1 Regulates Cellular Proliferation and UL138 Expression through Modulation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Pathways. 32859628_Recurrent Fusion of the GRB2 Associated Binding Protein 1 (GAB1) Gene With ABL Proto-oncogene 1 (ABL1) in Benign Pediatric Soft Tissue Tumors. 32888745_Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion while inhibits apoptosis of hypertrophic scarring fibroblasts by targeting miR-3187-3p/GAB1 axis. 33323827_Loss of GRB2 associated binding protein 1 in arteriosclerosis obliterans promotes host autophagy. 33393621_Circ_0061012 contributes to IL-22-induced proliferation, migration and invasion in keratinocytes through miR-194-5p/GAB1 axis in psoriasis. 33786575_FoxO1-GAB1 axis regulates homing capacity and tonic AKT activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 34732686_Association of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Gab1 Gene with Susceptibility to Meningioma in a Northern Chinese Han Population. 34929201_Macromolecular Crowding Induces a Binding Competent Transient Structure in Intrinsically Disordered Gab1. 35293807_Circ_0060531 knockdown ameliorates IL-22-induced keratinocyte damage by binding to miR-330-5p to decrease GAB1 expression. 35876480_Circ_0057452 sponges miR-7-5p to promote keloid progression through upregulating GAB1. 35894144_Interference of PTK6/GAB1 signaling inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of cervical cancer cells. 35967388_Molecular profile reveals immune-associated markers of medulloblastoma for different subtypes. |
ENSMUSG00000031714 |
Gab1 |
41.283632 |
0.3471439138 |
-1.526394 |
0.327037767 |
21.757238 |
0.00000309420247686853407278291180904084001213050214573740959167480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010325667772683600129633198216883016584688448347151279449462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.7282773 |
6.9830134 |
62.3429434 |
13.6558619 |
| ENSG00000109519 |
80273 |
GRPEL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HAV7 |
FUNCTION: Essential component of the PAM complex, a complex required for the translocation of transit peptide-containing proteins from the inner membrane into the mitochondrial matrix in an ATP-dependent manner (By similarity). Seems to control the nucleotide-dependent binding of mitochondrial HSP70 to substrate proteins (PubMed:11311562). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P38523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11311562}. |
Acetylation;Chaperone;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity and unfolded protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in protein import into mitochondrial matrix. Located in mitochondrial matrix and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80273; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; PAM complex, Tim23 associated import motor [GO:0001405]; TIM23 mitochondrial import inner membrane translocase complex [GO:0005744]; adenyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0000774]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein import into mitochondrial matrix [GO:0030150] |
12840016_The low resolution structure of human GrpE presented suggests that GrpE is a symmetric dimer when not bound to DnaK 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28848044_Data suggest that two putative NEF (nucleotide exchange factors) orthologs, GRPEL1 and GRPEL2, modulate function of mitochondrial HSP70 (mtHSP70); both GRPEL1 and GRPEL2 associate with mtHSP70 as hetero-oligomeric subcomplex and regulate mtHSP70 transport. (GRPEL = mitochondrial GrpE-like protein; HSP70 = heat-shock protein 70) 31636012_These data demonstrate that LIV-1-GRPEL1 axis dually regulates mitotic exit as well as apoptosis by interacting with PP2A B55alpha and AIF. |
ENSMUSG00000029198 |
Grpel1 |
242.185246 |
2.0792420915 |
1.056058 |
0.145093421 |
52.619934 |
0.00000000000040475995197039360089599037241156573064008658557888509221811546012759208679199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002476889258326289309529438075729496407904883792383543550386093556880950927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
323.8824308 |
31.3333144 |
157.0233746 |
11.3985692 |
| ENSG00000109686 |
152503 |
SH3D19 |
protein_coding |
Q5HYK7 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in regulating A disintegrin and metalloproteases (ADAMs) in the signaling of EGFR-ligand shedding. May be involved in suppression of Ras-induced cellular transformation and Ras-mediated activation of ELK1. Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14551139, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15280379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a multiple SH3 domain-containing protein, which interacts with other proteins, such as EBP and members of ADAM family, via the SH3 domains. This protein may be involved in suppression of Ras-induced cellular transformation and Ras-mediated activation of ELK1 by EBP, and regulation of ADAM proteins in the signaling of EGFR-ligand shedding. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:152503; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604] |
14551139_identified and characterized EBP, a novel EEN binding protein that interacts with the SH3 domain of EEN; normally expressed in cytoplasm but recruited to the nucleus by MLL-EEN [EBP] 15280379_yeast two-hybrid screening using the cytoplasmic domain of ADAM12 as bait identified a protein designated Eve-1. Eve-1 plays a role in positively regulating the activity of ADAMs in the signaling of EGFR-ligand shedding. 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 6 |
ENSMUSG00000028082 |
Sh3d19 |
19.613768 |
0.3340339282 |
-1.581933 |
0.435201004 |
13.541947 |
0.00023329025629537271250071861494745917298132553696632385253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000604098979459596722996206352718218113295733928680419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6298963 |
2.5619569 |
26.0286890 |
4.7360589 |
| ENSG00000109689 |
57620 |
STIM2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P246 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in mediating store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE), a Ca(2+) influx following depletion of intracellular Ca(2+) stores. Functions as a highly sensitive Ca(2+) sensor in the endoplasmic reticulum which activates both store-operated and store-independent Ca(2+)-influx. Regulates basal cytosolic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) concentrations. Upon mild variations of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) concentration, translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane where it probably activates the Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels ORAI1, ORAI2 and ORAI3. May inhibit STIM1-mediated Ca(2+) influx. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16005298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16860747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17905723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18160041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21217057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22464749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23359669}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium transport;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene is a member of the stromal interaction molecule (STIM) family and likely arose, along with related family member STIM1, from a common ancestral gene. The encoded protein functions to regulate calcium concentrations in the cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum, and is involved in the activation of plasma membrane Orai Ca(2+) entry channels. This gene initiates translation from a non-AUG (UUG) start site. A signal peptide is cleaved from the resulting protein. Multiple transcript variants result from alternative splicing. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. |
hsa:57620; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium channel regulator activity [GO:0005246]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; store-operated calcium channel activity [GO:0015279]; activation of store-operated calcium channel activity [GO:0032237]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; store-operated calcium entry [GO:0002115] |
198439_STIM2 is involved in spatial learning and plays an important role in ischemic-induced neuronal cell death during brain hypoxia. The absence of STIM2 reduces life expectancy in mice by sudden death. 11463338_Translation initiation from a non-AUG (UUG) start site. 16005298_STIM proteins function as Ca(2+) store sensors in the signaling pathway connecting Ca(2+) store depletion to Ca(2+) influx. 16860747_STIM2 is an inhibitor of store-operated channel (SOC) activation and plays a coordinated role with STIM1 in controlling SOC-mediated Ca(2+) entry signals. 17905723_STIM2 has two modes of activating CRAC channels: a store-operated mode activated through depletion of ER Ca2+ stores by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and store-independent activation mediated by cell dialysis; both regulated by calmodulin. 18160041_Study places STIM2 at the center of a feedback module that keeps basal cytosolic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ concentrations within tight limits. 18166150_Our biophysical studies reveal a structural stability difference in the EF-SAM region between STIM1 and STIM2, which may account for their different biological functions. 19019825_distinct oligomerization dynamics of STIM isoforms have evolved to adapt to differential roles in Ca(2+) homeostasis and signaling 19111578_Data demonstrate that cellular levels of STIM1 and STIM2, which are key players in capacitative Ca2+ entry, depend on presenilins. 19433064_results provide evidence for a role of STIM1 protein in the control of Ca2+ influx in neutrophils excluding a STIM2 involvement in this process 19487696_Results show that the 55-amino-acid STIM2 terminus substituted within STIM1 strikingly enhances both Orai1-mediated Ca(2+) entry and constitutive coupling to activate Orai1 channels. 19843959_STIM2 is involved in spatial learning and plays an important role in ischemic-induced neuronal cell death during brain hypoxia. The absence of STIM2 reduces life expectancy in mice by sudden death. 20172609_involved in both store-operated calcium entry and cell proliferation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20436167_STIM2 is a necessary partner of STIM1 for excitation-contraction coupling. 21217057_Data suggest that divergent Ca(2+)- and SAM-dependent stabilization of the EF-SAM fold contributes to the disparate regulation of store-operated Ca(2+) entry by STIM1 and STIM2. 21321120_STIM1 and STIM2 are located in the acidic Ca2+ stores and associates with Orai1 upon depletion of the acidic stores in human platelets. 21383014_a new model for STIM2-mediated regulation of ORAI1 in which two distinct proteins, STIM2 and preSTIM2, control store-dependent and store-independent modes of ORAI1 activation. 21906591_Stim1 and Stim2 were increased in brains of chronic epileptic rodents and strongly expressed in hippocampal specimens from medial temporal lobe epilepsy patients. 22125164_Stromal interaction molecule 2 is frequently overexpressed in colorectal tumors and confers a tumor cell growth suppressor phenotype. 22477146_The role of STIM2 in store operated calcium entry and its relevance in cellular physiology. [review] 22592407_It was shown that polyamines regulate intestinal epithelial restitution through TRPC1-mediated Ca2+ signaling by altering the ratio of STIM1 to STIM2. Overexpression of ornithine decarboxylase resulted in increased STIM1 but decreased STIM2 expression. 22914293_Studies indicate that in vertebrates, stromal interaction molecule proteins STIM1 and STIM2 are expressed ubiquitously 23359669_STIM2 regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry as a sensor of mild reductions in ER calcium levels. 24044355_Binding of the lysine rich domains of STIM1 and STIM2 to phosphatidylinositol 4,5 biphosphate rich liposomes depends on their oligomerization. 24472175_STIM2 is highly expressed and controls store-operated Ca(2+) entry in human melanoma. The invasive and migratory potential of melanoma cells was reduced upon silencing of STIM2. 24492416_While STIM1 is a full Orai1-agonist, leucine-replacement of this crucial residue in STIM2 endows it with partial agonist properties, which may be critical for limiting Orai1 activation stemming from its enhanced sensitivity to store-depletion 24603752_The higher amplitude of store-operated Ca2+ entry was associated to the over-expression for Stim2, Orai2-3, and TRPC1 while Stim2 levels remained constant and Stim1, Orai1, Orai3, TRPC1 and TRPC4 proteins were over-expressed in primary myelofibrosis. 25143380_the reciprocal shift in transient receptor potential channel 1 (TRPC1) and stromal interaction molecule 2 (STIM2) contributes to Ca2+ remodeling and cancer hallmarks in colorectal carcinoma cells 25533457_Imin channels are regulated by STIM2, TRPC3-containing INS channels are induced by STIM1, and TRPC1-composed Imax channels are activated by both STIM1 and STIM2. 25587190_STIM2 enhances receptor-stimulated Ca(2) signaling by promoting recruitment of STIM1 to the endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane junctions. 25896806_STIM2.1 cannot activate Orai1 due to splicing in residues within the channel-activating domain (CAD). STIM2.1 confers a calcium dependent dominant-negative function on both STIM1 and STIM2 (STIM2.2). Affinity of the STIM2.1 calmodulin binding site within the CAD domain is increased compared to STIM2.2. 25896806_These results imply that the splice variant STIM2.1 is an additional player tuning Orai1 activation in vivo. 26033257_STIM2beta does not by itself strongly bind Orai1, it is recruited to Orai1 channels by forming heterodimers with other STIM isoforms. 26911279_What is less clear is how the spatial and temporal spread of intracellular Ca(2+) is shaped and regulated by differential expression of the individual SOCE genes and their splice variants, their heteromeric combinations and pre- and posttranslational modifications. This review focuses on principle mechanisms regulating expression, splicing, and targeting of Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) channels. 28087881_With STIM2 being essential for life, but apparently not for development, newly available data demonstrate a complex and still intriguing behaviour that this review summarizes, updating current knowledge of STIM2 function [review] 28479254_The STIM2 protein play important roles in TGF-beta-induced EMT and these effects are related to both store-operated calcium entry and non-store-operated calcium entry. 29581306_Expression of full-length STIM1 with STIM2 in a 5:1 ratio causes suppression of sustained agonist-induced Ca(2+) oscillations and protects cells from Ca(2+) overload. 29642009_STIM2 is constitutively localized within ER-PM junctions in ER-Ca(2+) store replete cells. STIM2 traps STIM1 and triggers remodeling of STIM1 C terminus, causing STIM1/Orai1 coupling and enhancement of Orai1 function in cells with relatively high ER-[Ca(2+)]. 29783744_Stim2 deletion reduced SOCE by more than 90% in NIH 3T3 cells and abolishes STIM1 translocation to plasma membrane-associated ER membrane junctions. 30317585_Both STIM1 and STIM2 are necessary for cancer cell proliferation, but STIM1 is the dominant endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ sensor involved in cancer cell migration. 30444880_We identified the key structural determinants, especially the corresponding G residue in STIM1, which define the distinct activation dynamics of STIM2. The chimeric E470G mutation could switch STIM2 from a slow and weak Orai channel activator into a fast and potent one like STIM1 and vice versa. 30475382_STIM and FcgammaRII play an essential role in the regulation of diabetic kidney disease-induced podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition 30824535_Cross-talk between N-terminal and C-terminal domains in stromal interaction molecule 2 (STIM2) determines enhanced STIM2 sensitivity. 30967511_STIM1 is essential for IL-4 release after stimulation of FcepsilonRI, STIM2 mediates a delayed IL-3/IL-33-induced IL-4 release independent of STIM1. 31464639_Stromal interaction molecule2 (STIM2) overexpression promotes human breast cancer metastasis. STIM2 overexpression activated the nuclear factor of activates T cells 1 (NFAT1) and transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Knockdown of STIM2 inhibits the motility of breast cancer cells by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via specific suppression of NFAT1 and inhibits mammary tumor metastasis in mice. 32012922_Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Human STIM2 and ORAI1 in Neurons Exhibit Changes in Behavior and Calcium Homeostasis but Show No Signs of Neurodegeneration. 32186932_Treatment of CASR-transfected cells with Jag-1 further enhances CaSR-mediated increase in [Ca(2+)]cyt. Moreover, CaSR-mediated increase in [Ca(2+)]cyt was significantly augmented in cells co-transfected with CASR and STIM2. CaSR activation results in STIM2 clustering in CASR/STIM2-cotransfected cells. 32576932_Synergistic stabilization by nitrosoglutathione-induced thiol modifications in the stromal interaction molecule-2 luminal domain suppresses basal and store operated calcium entry. 32601188_STIM2 targets Orai1/STIM1 to the AKAP79 signaling complex and confers coupling of Ca(2+) entry with NFAT1 activation. 32641503_L-type Ca(2+) channel blockers promote vascular remodeling through activation of STIM proteins. 32794568_Functional role of TRPC6 and STIM2 in cytosolic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ content in resting estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. 33027906_Calmodulin Binding Proteins and Alzheimer's Disease: Biomarkers, Regulatory Enzymes and Receptors That Are Regulated by Calmodulin. 33086068_Oxidative Stress-Induced STIM2 Cysteine Modifications Suppress Store-Operated Calcium Entry. 35022238_Functional communication between IP3R and STIM2 at subthreshold stimuli is a critical checkpoint for initiation of SOCE. 35818214_STIM2 promotes the invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells through the NFAT1/TGF-beta1 pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000039156 |
Stim2 |
300.912492 |
0.4192095401 |
-1.254257 |
0.119242953 |
109.729643 |
0.00000000000000000000000011230974071544159690176602735929198313061018747709872997238375957689514306192535286754718981683254241943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000001233401616785653382062643774754748011605354499146557741247930690248711671497261477270512841641902923583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
194.1158353 |
32.5136353 |
466.6870173 |
56.4984504 |
| ENSG00000109743 |
683 |
BST1 |
protein_coding |
Q10588 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes both the synthesis of cyclic ADP-beta-D-ribose (cADPR) from NAD(+), and its hydrolysis to ADP-D-ribose (ADPR) (PubMed:7805847). Cyclic ADPR is known to serve as an endogenous second messenger that elicits calcium release from intracellular stores, and thus regulates the mobilization of intracellular calcium (Probable). May be involved in pre-B-cell growth (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7805847, ECO:0000305|PubMed:11866528, ECO:0000305|PubMed:7805847, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8202488}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;NAD;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase |
|
Bone marrow stromal cell antigen-1 is a stromal cell line-derived glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored molecule that facilitates pre-B-cell growth. The deduced amino acid sequence exhibits 33% similarity with CD38. BST1 expression is enhanced in bone marrow stromal cell lines derived from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The polyclonal B-cell abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis may be, at least in part, attributed to BST1 overexpression in the stromal cell population. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:683; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; uropod [GO:0001931]; ADP-ribosyl cyclase activity [GO:0061811]; cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase [GO:0061812]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0003953]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; phosphorus-oxygen lyase activity [GO:0016849]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050848]; regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001952]; regulation of cellular extravasation [GO:0002691]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2001044]; regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090022]; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050730]; regulation of superoxide metabolic process [GO:0090322]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11866528_crystal structures of the extracellular region of human BST-1 at atomic resolution in the free form and in complexes with five substrate analogues: nicotinamide, NMN, ATPgammaS, ethenoNADP, and ethenoNAD 12415565_CD157 molecule displays two distinct domains in its extracellular component. The first is implicated in the enzymic activities of the molecule and the second features adhesion/signalling properties [review] 15328157_Deficient in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinemia; crucial to regulation of innate immunity during inflammation. 18211745_The results confirm that CD157 physically interacts with CD11b/CD18 complex in human neutrophils 19052657_Results show that CD38 and CD157 are expressed constitutively by corneal cells: CD38 appears as a 45-kDa monomer, while CD157 is a 42- to 45-kDa doublet. 19915576_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639476_CD157 plays a pivotal role in the control of ovarian cancer cell migration and peritoneal invasion, and it may be clinically useful as a prognostic tool and therapeutic target. 20697102_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20697102_PARK16, PARK8, and PARK1 loci but not BST1 are found to be associated with Parkinson's disease. 20711177_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21044948_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21084426_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21084426_found converging evidence of association with Parkinson's disease on 12q24 (rs4964469, combined P = 2.4 x 10(-7)) and confirmed the association on 4p15/BST1 (rs4698412, combined P = 1.8 x 10(-6)), previously reported in Japanese data 21248740_Direct replication of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within SNCA and BST1 confirmed these two genes to be associated with the Parkinson's Disease in the Netherlands. 21478153_The CD157-integrin partnership provides optimal adhesion and transmigration of human monocytes. 22490479_The SNPs investigated in the BST1, PARK15 and PARK9 genes associated with PD susceptibility are not associated with PD in the northern Han Chinese population. 22916288_Findings implicate CD157 in the progression of EOC to metastatic disease and suggest that CD157 may represent a valuable therapeutic target. 23026536_BST1 SNPs rs11931532, rs12645693, & rs11724635 did not correlate with sporadic PD. The relationship of rs11724635 & sporadic PD had borderline significance. Smoking or caffeine intake did not correlate with SNP rs11724635 affecting sporadic PD. 23820587_This study confirmed the associations of BST1 with parkinson disease susceptibility and fail to show significant associations of alzheimer disease genome-wide association study (GWAS) top hits with PD susceptibility in a Korean population. 23827523_The results of this study showed that no causative mutation in the BST1 gene in patients with Parkinson's disease. 23853107_The results of this study indicated that the SNCA and BST1 SNPs generally increase the risk of developing PD and that SNCA rs11931074 in particular is associated with a higher risk of parkinson disease with family history. 24342025_BST1 rs11724635 polymorphism can interact with well water drinking to increase the risk of Parkinson's disease in a Taiwanese population. 24413464_A ligand-receptor complex SCRG1/BST1 axis facilitate mesenchymal stem cells migration, preserve OCT4 and CD271 expression, self-renewal and osteogenic differentiation. 24413464_Novel SCRG1/BST1 axis regulates self-renewal, migration, and osteogenic differentiation potential in mesenchymal stem cells. 24634087_Autism and with features of regression-previously acquired speech lost in the second year of life. The younger sister, who also had asthma, inherited a maternal deletion of 4p15.32 that results in a BST1-CD38 fusion transcript. 24753259_These findings indicate a central role of CD157 in cell-extracellular matrix interactions and make CD157 an attractive therapeutic target in inflammation and cancer. 24795584_These results demonstrate for the first time that CD157 plays a role as a neuro-regulator and suggest a potential role in pre-motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. 24896331_Studies indicate that vertebrate ADP-ribosyl cyclases (ARCs) Bst1 and CD38 with common gene structure of invertebrate ARC, suggesting the origin to the ancestor of bilaterian animals. 25250980_A pre-steady state and steady state kinetic analysis of the N-ribosyl hydrolase activity of hCD157. 25986899_the rs4698412 variant of BST-1 may increase the Parkinson disease susceptibility. [META-ANALYSIS] 29162908_Comparative phylogenetics indicate that exon 1b is a genomic innovation acquired during primate evolution, pointing to the importance of alternative splicing for CD157 function. 29216786_SNPs rs28532698 and rs4301112 in CD157 are not significantly associated with childhood autism spectrum disorder or the severity of the disease in a Chinese Han population. 30676692_BST1 rs4698412 allelic variant increases the risk of gait or balance deficits in patients with Parkinson's disease. 31423876_Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Blood Pressure Response to beta1-Blockers: Results From ICAPS (International Consortium of Antihypertensive Pharmacogenomics Studies). 31571381_Diagnosis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria with flowcytometry panels including CD157: Data from the real world. 31861847_The Roles of CD38 and CD157 in the Solid Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Immunotherapy. 33058446_Utility of FLAER and CD157 in a five-color single-tube high sensitivity assay, for diagnosis of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)-A standalone flow cytometry laboratory experience. 33397775_Novel Associations of BST1 and LAMP3 With REM Sleep Behavior Disorder. 33625657_Association of BST1 polymorphism with idiopathic restless legs syndrome in Chinese population. 34707185_CD157 signaling promotes survival of acute myeloid leukemia cells and modulates sensitivity to cytarabine through regulation of anti-apoptotic Mcl-1. |
ENSMUSG00000029082 |
Bst1 |
138.963041 |
0.3037266834 |
-1.719154 |
0.197892480 |
73.853890 |
0.00000000000000000841184522508905147940215160452679233246537946291389309383390582297579385340213775634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000067477628001257833366588351178780358881127019929618143789795681186660658568143844604492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.0710212 |
8.8639637 |
222.9802305 |
19.7586842 |
| ENSG00000109790 |
51088 |
KLHL5 |
protein_coding |
Q96PQ7 |
|
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable actin binding activity. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51088; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; actin binding [GO:0003779] |
14672410_Data report a novel splicing variant of KLHL5, named KLHL5b, and describe its expression pattern in many tissues. 31652307_KLHL5/Cul3-based E3 ubiquitin ligase complex is important for regulation of SK1 protein stability via Lys183 ubiquitination. |
ENSMUSG00000054920 |
Klhl5 |
894.950368 |
2.7208430121 |
1.444054 |
0.141064953 |
101.323625 |
0.00000000000000000000000781184905195233136849412970305868668729968749098700956511375306529770812247193134680856019258499145507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000080238616567026031987611641820211861478916577128444267507948405547535397630554143688641488552093505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1177.7983749 |
104.0080984 |
436.2580691 |
28.2313362 |
| ENSG00000109790_ENSG00000249685 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100.556001 |
2.9302294052 |
1.551014 |
0.218938663 |
49.873621 |
0.00000000000163974384039500313154014427191192782929177185202718192158499732613563537597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000009608026631294261513681550117116873929376530405477296881144866347312927246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
145.9436861 |
17.6855879 |
50.1358542 |
4.8216835 |
| ENSG00000109906 |
7704 |
ZBTB16 |
protein_coding |
Q05516 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional repressor (PubMed:10688654, PubMed:24359566). Transcriptional repression may be mediated through recruitment of histone deacetylases to target promoters (PubMed:10688654). May play a role in myeloid maturation and in the development and/or maintenance of other differentiated tissues. Probable substrate-recognition component of an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:14528312). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10688654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14528312, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24359566}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Intellectual disability;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene is a member of the Krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family and encodes a zinc finger transcription factor that contains nine Kruppel-type zinc finger domains at the carboxyl terminus. This protein is located in the nucleus, is involved in cell cycle progression, and interacts with a histone deacetylase. Specific instances of aberrant gene rearrangement at this locus have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7704; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; male germ cell nucleus [GO:0001673]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; PML body [GO:0016605]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035136]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; male germ-line stem cell asymmetric division [GO:0048133]; mesonephros development [GO:0001823]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045638]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; ossification involved in bone maturation [GO:0043931]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061036]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of NK T cell differentiation [GO:0051138]; positive regulation of ossification [GO:0045778]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11106752_two critical hits for promyelocytic leukemia 11920278_PLZF/RARalpha also binds the HD-NCR through the PLZF, which seems to be crucial for the t-RA resistance of t(11;17) APL patients 11964310_can interact with GATA-2 and can modify GATA-2 transactivation capacity 12145280_evidence of a functional interaction between the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein (PLZF) and DRAL/FHL2 12242665_PLZF plays a significant stimulatory role in megakaryocytic development, seemingly mediated in part by induction of TpoR expression at transcriptional level. 12802276_Hoxb2 is a direct target for regulation by PLZF in the developing CNS and suggest that deregulation of Hox gene expression may contribute to APL pathogenesis. 12970399_gene expression regulation in human endometrial stromal cells and myometrial smooth muscle cells 14527952_PLZF colocalizes with SUMO-1 in the nucleus; lysine 242 in the RD2 domain of human PLZF was identified as the sumoylation site 14645547_PLZF expression maintains a cell in a quiescent state by repressing c-myc expression and preventing cell cycle progression. 14657020_An inactive mutant of PLZF abolishes expression of p85 alpha PI3K followed by enhanced p70(S6) kinase. 15077196_a suppressor role in solid tumors 15467736_data indicate that recruitment of HDAC4 is necessary for PLZF-mediated repression in both normal and leukaemic cells 15623533_PLZF plays important roles in early osteoblastic differentiation as an upstream regulator of CBFA1 15964811_Histone acetyltransferase activity of p300 is required for transcriptional repression by PZLF. 15968309_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16637071_Androgen-independent cell line DU145 cells lack PLZF gene expression, resulting in the upregulation of Pbx1 and HoxC8 expression. The Pbx1-HoxC8 heterocomplex may lead to androgen-independent growth in prostate cancer. 16676348_These data suggest the existence of a mechanism that regulates ERK signaling via the C-terminus of ATP7B and the ATP7B-interacting hepatocytic PLZF. 16828757_potential tumor suppressor activity of CCS-3 may be mediated by its interaction with PLZF. 17082479_existence of a novel signal transduction pathway involving the ligand renin, renin receptor, and the transcription factor PLZF 17118363_The collapsin response mediator protein 1 and the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein interact with UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE). 17340613_TIMP1 regulates cell proliferation by interacting with the ninth zinc finger domain of PZLF. 17515885_Expression of PLZF in corneal endothelial cells is closely related to formation of cell-cell contacts, and PLZF may play role in suppressing their proliferation. 17537403_PLZF upregulates apoptosis-inducer TP53INP1, ID1, and ID3 genes, and downregulates the apoptosis-inhibitor TERT gene 17881917_PLZF mRNA was expressed in HCECs in vivo and in completely confluent HCECs but not in subconfluent HCECs in vitro. 18000064_supports an active role for PLZF and RARalpha-PLZF in leukemogenesis, identifies up-regulation of CRABPI 18262754_Activated Goalpha interacted directly with PLZF, and enhanced its function as a transcriptional and cell growth suppressor. 18348865_PLZF post-translational modification is controlled by intracellular ROS, and the biological function of PLZF is regulated by sumoylation and ubiquitination. 18417445_PLZF negatively regulates the expression of miR-221 and miR-222 18448589_observations suggest that PLZF is a negative regulator of ENaC in renal epithelial cells and might be part of a negative feedback loop that limits aldosterone's stimulatory effects on sodium reabsorption. 18568019_Data indicate that megakaryopoiesis is controlled by a cascade pathway, in which PLZF suppresses miR-146a transcription and thereby activates CXCR4 translation. 18611983_Our findings that PLZF is a key regulator of skeletal and male germline development. 18703361_study suggests that PLZF is a transcriptional signature of NKT cells that directs their innate-like effector differentiation during thymic development 18771349_Increased expression of the tumor suppressor PLZF in malignant melanomas is associated with long-term patient survival. 19421145_Data indicate a new mechanism of regulation of c-kit expression that involves a transcriptional control by PLZF in CD34(+) cells. 19444914_The 2 PLZF mutants are oncogenic, because they function as dominant negatives of wild-type PLZF, enhancing Myc phosphorylation and increasing Myc transcriptional and oncogenic activity. 19451220_PLZF/RARA expression leads to recruitment of the Polycomb-repressive complex 2 (PRC2) Polycomb group (PcG) complex to RA response elements 19648967_one mechanism for cells with altered LYRIC/AEG-1 expression to evade apoptosis and increase cell growth during tumourigenesis through the regulation of PLZF repression 19723763_During homeostasis, PLZF restricts proliferation and differentiation of human cord blood-derived myeloid progenitors to maintain a balance between the progenitor and mature cell compartments 19796243_The role of PLZF in human hematopoiesis was studied. 19855079_Data show that PLZF-RARalpha binds to a region of the c-MYC promoter, suggesting that PLZF-RARalpha may act as a dominant-negative version of PLZF by affecting the regulation of shared targets. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010871_Data indicate that deletions of PLZF are a common occurrence in MM and that downregulation of PLZF may contribute to MM pathogenesis by promoting cell survival. 20038602_a substantial number of fetal thymocytes and splenocytes express PLZF and acquire innate characteristics during their development in humans. 20098615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20945532_CUX1 interacts in vivo with multiple DNA-binding sites in the 5'-UTR and promoter of the PLZF gene in colorectal cancer cells 21547890_Small interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing of ZNF145 slowed down chondrogenesis, whereas overexpression of ZNF145 enhanced chondrogenesis. 21632718_Although PLZF is known to direct the effector program of natural killer (NK)T cells, this study shows that CD1d naive-like cells express it at a significantly lower amount than NKT cells. 21915328_PLZF appears to control the development and/or function of a wide variety of human lymphocytes that represent more than 10% of the total PBMCs. 22292015_Far infrared rays induce the nuclear translocation of PLZF which inhibits VEGF-induced proliferation in HUVECs. 22555178_Expression of the promyelocytic leukemia zinc-finger in T-lymphoblastic lymphoma and leukemia has strong implications for their cellular origin and greater association with initial bone marrow involvement. 23223428_Our findings identify a previously unknown pathway of regulation of innate-like T-cell homeostasis depending on XIAP and PLZF. 23280881_The p65 PLZF isoform is crucial to maintain colorectal cancer cell growth, adhesion and survival, and must occur independently of the traditionally viewed transcriptional role of PLZF in the course of these biological processes. 23416030_Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger and histone H1.5 differentially stain low- and high-grade pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors. 23804241_This study showed that reduced expression of PLZF was found to be common in nonsmall cell lung cancer; PLZF down-regulation was partially correlated with hypermethylation in the promoter region. 23898169_RARalpha-PLZF fusion protein inhibits myeloid cell differentiation through interactions with C/EBPalpha tethered to DNA in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 24339862_a PTEN/PLZF pathway and would shed new lights for developing therapeutic strategy of prostate cancer 24348178_overexpression of PLZF and exclusion of NK cells in dysplastic microenvironment are very early events in the stepwise sequence leading to CRC. 24359167_present study shows that ZBTB16 induced the expression of osteogenic differentiation markers independently of RUNX2. 24359566_Plzf was identified as a specific interacting protein of Znf179; the region containing the first two zinc fingers is critical for its interaction with Znf179. Cellular localization of Znf179 changed from cytoplasm to nucleus when Plzf was co-expressed. 24416448_TL1A, together with IL-12, IL-15 and IL-18, directly induces the production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha from PLZF leukocytes. 24424509_The aim of this study was to analyse the contribution of constitutive (P)RR activity to its cellular effects and the relevance of prorenin glycosylation on its ligand activity. 24764561_PLZF may have a role in the pathway of drug resistance associated with a TRAV1-2-TRAJ33 TCR-alpha rearrangement in peripheral T-cell lymphomas 24784718_When comparing benign and malignant uterine tumors, statistically significant differences were found in staining patterns for PLZF. 24816988_In dental follicle cells, a Runx2-independent differentiation mechanism exists that is regulated by ZBTB16. 24821727_PLZF can directly repress transcription of CDKN1A encoding p21 24990570_High cytoplasmic expression of PLZF is associated with capsular invasion and lymph node metastasis in thyroid neoplasms. 25023763_Data indicate that normal ovarian tissues strongly expressed histone H1.5, whereas ovarian granulosa cell tumors (GCTs) weakly expressed this protein; in contrast, PLZF protein expression was not significantly different between both study groups. 25178676_Data suggest that interleukin-32alpha (IL-32alpha) associates with leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) and protein kinase c epsilon (PKCvarepsilon), and then inhibits PLZF sumoylation, resulting in suppression of the transcriptional activity of PLZF. 25369784_Down-regulation of PLZF in human hepatocellular carcinoma.PLZF expression was positively correlated with the alkaline phosphatase level in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. 25705792_Authors found that PLZF mediates suppression of miR-146a to control increases of CXCR4 and TRAF6 protein levels in human primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes. 25807461_down-regulation of PLZF is an important molecular process for prostate tumor progression 25808865_PLZF loss enhances castration-resistant prostate cancer tumor growth in a xenograft model. 25833398_PLZF regulates CCR6 and is critical for the acquisition and maintenance of the Th17 phenotype in human cells. 26121690_NLRP7 is involved in Hydatidiform Molar Pregnancy (HYDM1) and interacts with the transcriptional repressor ZBTB16 26297253_These results support a prognostic value for loss of cytoplasmic PLZF expression in the stratification of non-small cell lung cancer and a possible role of cytoplasmic shift and down-regulation of PLZF in the pathogenesis of NSCLC. 26676652_Emerging evidence shows that PLZF regulates the balance of self-renewal and differentiation in stem cells. 26916077_ZBTB16 is a highly sensitive and specific marker for yolk sac tumors. 27035670_integration of PLZF ChIP-Seq and RNA Pol II RNA-Seq datasets revealed that the early growth response 1 (EGR1) transcription factor is a PLZF target for which its level of expression must be reduced to enable progesterone dependent hESC decidualization 28038473_Low ZBTB16 expression is associated with tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 28416638_High PLZF expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 28581124_ZBTB16 is a sensitive and specific marker for yolk sac tumour (YST) and is diagnostically superior to AFP and glypican-3 in metastatic and extragonadal settings. 28948827_Selected gene variants of the transcription factor ZBTB16 influence obesity-related parameters and serum lipid levels. 29186366_This study was conducted to identify the genome-wide transcriptional program that is controlled by PLZF during endometrial stromal cells decidualization using an established in vitro culture model, siRNA-mediated knockdown methods, and RNA-sequencing technology followed by bioinformatic analysis and validation. 29358655_These studies indicated PLZF inhibited the proliferation and metastasis via regulation of IFIT2. 29425303_We find that co-occupancy of PLZF and EZH2 on chromatin at PLZF target genes is not associated with SUZ12 or trimethylated lysine 27 of histone H3 (H3K27me3) but with the active histone mark H3K4me3 and active transcription. Removal of EZH2 leads to an increase of PLZF binding and increased gene expression. 30246336_We found that methylation of DNA in the promoter region of ZBTB16 and Twist1 genes might be one of the main mechanisms that controlling the gene expression during osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells 30431129_Study found that ANRIL expression in gastric cancer cell lines and tumor tissues was negatively associated with the level of PLZF and with ANRILrecruited polycomb repressive complex 2, which then drove PLZF silencing by collaborating between H3K27me3 and DNA methylation. 30672466_a latent enhancer within the ZBTB16/PLZF locus itself that became active, gained PLZF, p300 and Mediator binding and looped to the promoter of the nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) gene. 31065369_Study demonstrates that miR-4319 is expressed at a low level in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues, which predicts the poor clinical outcome of CRC. MiR-4319 regulates the proliferation, cell cycle, invasion and migration of CRC cells. Mechanically, miR-4319 is found to be transcriptionally regulated by PLZF, and acts as a tumour suppressor in CRC by targeting ABTB1. 31087222_Expression of the PTEN/FOXO3a/PLZF signalling pathway in pancreatic cancer and its significance in tumourigenesis and progression. 31126665_we summarize all variant translocations, their key features, their leukemogenic potential as well as recent advances in studies of PLZF-RARalpha-associated APL. Basic pathogenic differences between classical APL and PLZF-RARalpha-associated APL are further discussed 31378879_PLZF regulates apoptosis of leukemia cells by regulating AKT/Foxo3a pathway. 31554695_The express promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) transcription factor that distinguishes them from conventional CD8(+) T cells. 32517789_BTB/POZ zinc finger protein ZBTB16 inhibits breast cancer proliferation and metastasis through upregulating ZBTB28 and antagonizing BCL6/ZBTB27. 32773339_Verification of a ZBTB16 variant in polycystic ovary syndrome patients. 33206504_Cereblon Modulators Target ZBTB16 and Its Oncogenic Fusion Partners for Degradation via Distinct Structural Degrons. 34042280_Mutational profile of ZBTB16-RARA-positive acute myeloid leukemia. 34660783_Bioinformatics Analysis of ZBTB16 as a Prognostic Marker for Ewing's Sarcoma. 34764413_PLZF and its fusion proteins are pomalidomide-dependent CRBN neosubstrates. |
ENSMUSG00000066687 |
Zbtb16 |
15.390695 |
0.1114752488 |
-3.165205 |
0.616329409 |
28.620524 |
0.00000008804401618830471102078851029087980251119915919844061136245727539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000349148221101391092892460201596582791694345360156148672103881835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3322095 |
1.1849755 |
21.3171088 |
6.4782300 |
| ENSG00000109917 |
8882 |
ZPR1 |
protein_coding |
O75312 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a signaling molecule that communicates proliferative growth signals from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. It is involved in the positive regulation of cell cycle progression (PubMed:29851065). Plays a role for the localization and accumulation of the survival motor neuron protein SMN1 in sub-nuclear bodies, including gems and Cajal bodies. Induces neuron differentiation and stimulates axonal growth and formation of growth cone in spinal cord motor neurons. Plays a role in the splicing of cellular pre-mRNAs. May be involved in H(2)O(2)-induced neuronal cell death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11283611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17068332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22422766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29851065}. |
Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Differentiation;Dwarfism;Hypotrichosis;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is found in the cytoplasm of quiescent cells but translocates to the nucleolus in proliferating cells. The encoded protein interacts with survival motor neuron protein (SMN1) to enhance pre-mRNA splicing and to induce neuronal differentiation and axonal growth. Defects in this gene or the SMN1 gene can cause spinal muscular atrophy. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:8882; |
axon [GO:0030424]; Cajal body [GO:0015030]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Gemini of coiled bodies [GO:0097504]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; translation initiation factor binding [GO:0031369]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process involved in development [GO:1902742]; axon development [GO:0061564]; Cajal body organization [GO:0030576]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; DNA endoreduplication [GO:0042023]; inner cell mass cell proliferation [GO:0001833]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of motor neuron apoptotic process [GO:2000672]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of growth [GO:0045927]; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042307]; positive regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0033120]; positive regulation of transcription involved in G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0071931]; pre-mRNA catabolic process [GO:1990261]; regulation of myelination [GO:0031641]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510]; trophectodermal cell proliferation [GO:0001834] |
17068332_ZPR1 deficiency causes disruption of survival motor neurons and histone gene-specific transcription factor NPAT localization within the nucleus, blocks S phase progression, and arrests cells in both the G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20442857_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20691829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22623978_Significant associations of two SNPs (rs964184 and rs12286037) from ZNF259 with triglyceride levels in an Asian Indian cohort. 24178511_genetic polymorphism at the loci is associated with Factor VII and fibrinogen levels, and with plasma viscosity 24618354_Novel APOA5-ZNF259 haplotype manifesting sex-dependent effects on elevation of the TG:HDL-C ratio as well as the increased risk for metabolic syndrome. 24688311_These findings suggest that the association between ZNF259 rs2075290 SNP and serum lipid levels might have ethnic- and/or sex-specificity. 24780069_Single nucleotide polymorphism zinc finger protein 259 gene is associated with hyperlipidaemia. 24989072_Significant linkage disequilibria were noted among ZNF259, BUD13 and MLXIPL SNPs and serum lipid levels. 26118197_ZNF259 variants were associated with elevated Metabolic Syndrome risk in a Han Chinese population from the Jilin province of Northeastern China 26397108_Single nucleotide polymorphisms (Rs964184, rs3317316, rs6589566) of ZNF259 protein did not increase the risk of CHD in the Chinese population. 26634697_When the inter-dependence between alleles was examined using conditional models, five loci on BUD13, ZNF259, and ApoA5 showed possible independent associations. 27411854_Results suggest that ZPR1 plays an important role in the etiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and this gene might be involved in abnormal glucose metabolism. 29851065_provide genetic and molecular evidence that a homozygous missense mutation in ZPR1 is associated with a rare and recognizable multisystem syndrome 30902787_Identification of a relationship between a genetic variant in CETP and ZNF259 gene with coronary artery disease (CAD) and CAD and lipid profile, respectively. Further investigation in a larger population may help to investigate the value of emerging marker as a risk stratification marker in CAD and its risk factors. 31828288_ZPR1 prevents R-loop accumulation, upregulates SMN2 expression and rescues spinal muscular atrophy. 32807694_The ZPR1 genotype predicts myocardial infarction in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. 33567543_Implication between Genetic Variants from APOA5 and ZPR1 and NAFLD Severity in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia. 33986338_Kernel machine SNP set analysis finds the association of BUD13, ZPR1, and APOA5 variants with metabolic syndrome in Tehran Cardio-metabolic Genetics Study. |
ENSMUSG00000032078 |
Zpr1 |
311.446336 |
2.6206708065 |
1.389936 |
0.155223735 |
78.738994 |
0.00000000000000000070882544965944906798635397823779933973744993637477237319322043163083435501903295516967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000005968205155147443033637313293464327469324184775921558060440830217885377351194620132446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
443.4253761 |
42.7387777 |
170.3220728 |
12.3518159 |
| ENSG00000109929 |
6309 |
SC5D |
protein_coding |
O75845 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes a dehydrogenation to introduce C5-6 double bond into lathosterol in cholesterol biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10786622}. |
Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme of cholesterol biosynthesis. The encoded protein catalyzes the conversion of lathosterol into 7-dehydrocholesterol. Mutations in this gene have been associated with lathosterolosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6309; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; C-5 sterol desaturase activity [GO:0000248]; delta7-sterol 5(6)-desaturase activity [GO:0050046]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via desmosterol [GO:0033489]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via lathosterol [GO:0033490]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126] |
18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20144677_The EGR3 may not play a major role in schizophrenia susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27023786_The relationship between C-peptide concentrations and D5D enzyme activity estimates remained significant after adjusting for body mass index, waist circumference, and TNF-alpha. |
ENSMUSG00000032018 |
Sc5d |
406.469539 |
2.8117492040 |
1.491468 |
0.117040771 |
159.417569 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000151671470542342173424243488653859211699111851554458615419455337124502968056528589562396003157570406605358925844484474509954452514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000023174647051811288618464423452987791496077141501959148315069563560964579895475602790777273280557746470975644115242175757884979248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
581.6661746 |
61.8491984 |
208.6036437 |
16.4663422 |
| ENSG00000109971 |
3312 |
HSPA8 |
protein_coding |
P11142 |
FUNCTION: Molecular chaperone implicated in a wide variety of cellular processes, including protection of the proteome from stress, folding and transport of newly synthesized polypeptides, activation of proteolysis of misfolded proteins and the formation and dissociation of protein complexes. Plays a pivotal role in the protein quality control system, ensuring the correct folding of proteins, the re-folding of misfolded proteins and controlling the targeting of proteins for subsequent degradation (PubMed:21150129, PubMed:21148293, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661, PubMed:23018488). This is achieved through cycles of ATP binding, ATP hydrolysis and ADP release, mediated by co-chaperones (PubMed:21150129, PubMed:21148293, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661, PubMed:23018488, PubMed:12526792). The co-chaperones have been shown to not only regulate different steps of the ATPase cycle of HSP70, but they also have an individual specificity such that one co-chaperone may promote folding of a substrate while another may promote degradation (PubMed:21150129, PubMed:21148293, PubMed:24732912, PubMed:27916661, PubMed:23018488, PubMed:12526792). The affinity of HSP70 for polypeptides is regulated by its nucleotide bound state. In the ATP-bound form, it has a low affinity for substrate proteins. However, upon hydrolysis of the ATP to ADP, it undergoes a conformational change that increases its affinity for substrate proteins. HSP70 goes through repeated cycles of ATP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange, which permits cycles of substrate binding and release. The HSP70-associated co-chaperones are of three types: J-domain co-chaperones HSP40s (stimulate ATPase hydrolysis by HSP70), the nucleotide exchange factors (NEF) such as BAG1/2/3 (facilitate conversion of HSP70 from the ADP-bound to the ATP-bound state thereby promoting substrate release), and the TPR domain chaperones such as HOPX and STUB1 (PubMed:24318877, PubMed:27474739, PubMed:24121476, PubMed:26865365). Plays a critical role in mitochondrial import, delivers preproteins to the mitochondrial import receptor TOMM70 (PubMed:12526792). Acts as a repressor of transcriptional activation. Inhibits the transcriptional coactivator activity of CITED1 on Smad-mediated transcription. Component of the PRP19-CDC5L complex that forms an integral part of the spliceosome and is required for activating pre-mRNA splicing. May have a scaffolding role in the spliceosome assembly as it contacts all other components of the core complex. Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and mediates LPS-induced inflammatory response, including TNF secretion by monocytes (PubMed:10722728, PubMed:11276205). Participates in the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) quality control pathway in conjunction with J domain-containing co-chaperones and the E3 ligase STUB1 (PubMed:23990462). Interacts with VGF-derived peptide TLQP-21 (PubMed:28934328). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11276205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21148293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21150129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23018488, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23990462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24318877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24732912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27474739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27916661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28934328, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24121476, ECO:0000303|PubMed:26865365}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Methylation;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Spliceosome;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the heat shock protein 70 family, which contains both heat-inducible and constitutively expressed members. This protein belongs to the latter group, which are also referred to as heat-shock cognate proteins. It functions as a chaperone, and binds to nascent polypeptides to facilitate correct folding. It also functions as an ATPase in the disassembly of clathrin-coated vesicles during transport of membrane components through the cell. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:3312; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; chaperone complex [GO:0101031]; clathrin-sculpted gamma-aminobutyric acid transport vesicle membrane [GO:0061202]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; glycinergic synapse [GO:0098690]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lumenal side of lysosomal membrane [GO:0098575]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; photoreceptor ribbon synapse [GO:0098684]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic cytosol [GO:0099524]; postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0099634]; presynaptic cytosol [GO:0099523]; Prp19 complex [GO:0000974]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein disaggregase activity [GO:0140545]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; C3HC4-type RING finger domain binding [GO:0055131]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; clathrin-uncoating ATPase activity [GO:1990833]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; heat shock protein binding [GO:0031072]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; protein carrier chaperone [GO:0140597]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus [GO:0071383]; cellular response to unfolded protein [GO:0034620]; chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding [GO:0051085]; chaperone-mediated autophagy [GO:0061684]; chaperone-mediated autophagy translocation complex disassembly [GO:1904764]; late endosomal microautophagy [GO:0061738]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of supramolecular fiber organization [GO:1902904]; positive regulation by host of viral genome replication [GO:0044829]; positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048026]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein refolding [GO:0042026]; protein targeting to lysosome involved in chaperone-mediated autophagy [GO:0061740]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175]; regulation of protein complex stability [GO:0061635]; regulation of protein import [GO:1904589]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; slow axonal transport [GO:1990832]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
12421917_Tumor-derived HSP70 peptide complexes have the immunogenic potential to instruct dendritic cells to cross-present endogenously expressed, nonmutated, and tumor antigenic peptides shared among tumors of the melanocytic lineage for T cell recognition. 12840151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12850307_Hsc70 may be involved in androgen action on dermal papilla cells. 12890148_no abnormal levels of hsc70 and hsp60 were detectable in pediatric c-ALL pre B-cells at diagnosis nor at relapse. In contrast, developmentally regulated levels of hsc70 and hsp60 expression during B-cell ontogenesis were observed 14612456_tau binds to Hsc70, and its phosphorylation is a recognition requirement for the addition of ubiquitin 14684748_a novel nuclear export and nuclear localization-related signals in human Hsp70 14991745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15086793_a region of the TfR that can potentially interact with hsc70 15194794_sequestered in discrete foci in the nucleus of the infected cell in herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. 15292236_Hsp105alpha is suggested to regulate the substrate binding cycle of Hsp70/Hsc70 by inhibiting the ATPase activity of Hsp70/Hsc70, thereby functioning as a negative regulator of the Hsp70/Hsc70 chaperone system. 15336565_Expressed in colon cancer cells [NIP71] 15625011_The head shock protein 70 kD (HSP-70i) has been shown to protect cells, tissues, and organs from harmful assaults in vivo and in vitro experimental models. 15694383_In this study, we discovered that the U-box ubiquitin ligase carboxyl-terminus of Hsc70 interacting protein (CHIP) ubiquitylated Epsin. 15795242_Present in cells as part of the dengue virus receptor. 15972823_CSP modulates G protein function by preferentially targeting the inactive GDP-bound form of G alpha(s) and promoting GDP/GTP exchange; the guanine nucleotide exchange activity of full-length CSP is regulated by Hsc70-SGT 16100000_This study identified heat shock protein 70 protein 8 as being expressed on the cell surface and downregulated upon differentiation. 16817320_Histidine 89 is an essential residue for Hsp70 in the phosphate transfer reaction. 17022977_Hsc70 is directly associated with Influenza virus matrix protein 1 and therefore is required for viral production 17240362_Our results suggest that the widespread accumulation of Hsc70 and Hsp70 may occur in brains with MSA, and that Hsc70 and Hsp70 may be associated with the pathogenesis of MSA. 17284448_Hsc70 plays a defined role in reovirus outer capsid disassembly, during or soon after membrane penetration, to prepare the entering particle for gene expression and replication 17296233_serum Hsp70 concentrations are decreased in normal human pregnancy 17397964_Following co-immunoprecipitation, a specific interaction between the head domain of K5 with Hsc70, a chaperone also involved in vesicle uncoating, was verified. 17569659_FKBP38 is a co-chaperone of HERG and contributes via the Hsc70/Hsp90 chaperone system to the trafficking of wild type and mutant HERG potassium channels 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17636261_70-kDa heat shock proteins as a AQP2 interactors and have shown for hsc70 that this interaction is involved in AQP2 trafficking. 17785435_Important functions of recently activated dendritic cells are thus critically modulated by the newly discovered HSPA8-EWI-2 interaction. 17876681_Amino acid domains 280-297 of VP6 and 531-554 of VP4 are implicated in heat shock cognate protein hsc70-mediated rotavirus infection. 17878160_an association between Hsc70 and ASIC2 that may underlie the increased retention of ASIC2 in the endoplasmic reticulum of glioma cells. 17929041_HSP70 was a useful indicator of stressed neurons in acute phase of epilepsy, but not associated with neuronal death 17934269_Our data show that a mutation in hsp70-Hom gene is associated with higher incidence of Postoperative atrial fibrillation. 17954934_BAG-1 associates with Tau protein in an Hsc70-dependent manner. 18231578_propose that one function of the Hsc70 nuclear foci may be to serve to facilitate the process of clearing stalled RNAP II complexes from viral genomes during times of highly active transcription 18261988_Association between endogenous LAP2alpha and Hsp70 in non-transfected cells was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation. 18299791_Our results raise the possibility that HSP70 gene (i.e., haplotypes of rs2075799) might be implicated in the development of schizophrenia. 18307834_Cathepsin C propeptide interacts with intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP) and heat shock cognate protein 70. The propeptide of cathepsin C may stimulate the sorting to the lysosome contributing to the degradation of IAP in Caco-2 cells. 18380807_It was indicated that disruption of the HSC73-TAP association resulted in inhibition of TAP-dependent translocation of HSC73-bound peptides. 18434395_During the earliest stages of HSV-1 infection, the formation of Hsc70 foci adjacent to viral prereplicative sites occurs after PML bodies have been disrupted by ICP0. PML protein is not required for the formation of Hsc70 foci. 18493267_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18500754_hsc70 binds tau at two sites that are involved in tau aggregation, one of which is regulated by alternative splicing; hsc70 binding might directly inhibit tau-tau interactions that precede tau oligomerization and aggregation. 18600213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18600213_The variant allele of THBS2 is a risk factor for TAA in hypertensive patients, whereas the variant alleles of HSPA8, GPX1, AGT, and TNF are protective against this condition 18667436_the hydrophobicity of the TA region dictates whether a precursor is delivered to the ER via the Hsp40/Hsc70 or Asna-1/TRC40-dependent route. 18684711_Bag1 NEF increased refolding by Hsc70 and DJA2, as did the newly characterized NEF Hsp110 18772114_Simultaneously reducing the expression of both HSC70 and HSP72 induces proteasome-dependent degradation of HSP90 client proteins, G1 cell-cycle arrest, and extensive tumor-specific apoptosis in human tumor cell lines. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18988734_Cytosolic chaperone Hsc70 is required for the cytosolic reactivation of ricin A chain dislocated from the mammalian cell endoplasmic reticulum. 19009367_Identify Hsc70 as target for AGE modification in senescent human fibroblasts. 19014922_altered expression of proteins that underlie pathogenesis of SCA17 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19098309_Csp not only regulates the exit of CFTR from the ER, but that this action is accompanied by Hsc70/Hsp70 and CHIP-mediated CFTR degradation. 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19254810_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19321452_These findings suggest that histatin 3 may be involved in cell proliferation through the regulation of HSC70 and p27(Kip1) in oral cells. 19397879_These data indicate that Hsc70 may be involved in viral replication by regulating the intracellular distribution of X. 19551494_suggesting that HSP70 overexpression may regulate lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokines expression through NF-kappaB pathway. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19686046_Results identified heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) that showed elevated levels of protein carbonyls in inferior parietal lobule (IPL) from subjects with mild cognitive impairment. 19802014_Data show that Hsc70 appears active in breast cancer cells and hypersecreted by direct cath D inhibition. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20003465_surface located Hsc70 on trophoblast giant cells mediates the uptake of pathogenic bacteria and proteins containing the TPR domain inhibit the function of Hsc70 by binding to its EEVD motif 20018937_Heat shock protein 70 (Hsc70) plays a significant role in vascular endothelial cells via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. 20084477_Heteromeric complexes of Hsp70B', Hsp70, and Hsc70 were detected in differentiated human SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. 20300519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20300519_genetic variants in HSPA8 gene (especially promoter SNP rs2236659) contribute to the coronary heart disease susceptibility by affecting its expression level 20457599_PI 3-kinase and MEK kinase signaling as well as tyrosine dephosphorylation are essential for the accumulation of hsc70 in nucleoli of stressed cells 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20642807_The importance of Hsc70 in AtlE adhesin-mediated internalization was demonstrated by the inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus internalization with anti-Hsc70 antibodies. 20729196_the C331A mutant of neuronal nitric-oxide synthase is labilized for Hsp70/CHIP (C terminus of HSC70-interacting protein)-dependent ubiquitination 20804732_This is the first work reporting the localization of the GlcNAc-binding domain of a member of the HSP70 family. 20806039_The aim of this study is to examine the expression of HSP60, HSP72, and HSP90, and heat-shock cognate 70 (HCS70) at the mRNA and protein level in differentiating corneal cells from limbal stem cells following air exposure. 21050049_Immunocytochemical staining using this newly established antibody revealed that Hsc70 localizes predominantly in the cytoplasm in unstressed cells, whereas oxidative stress produced by H2O2 induces Hsc70 to translocate into the nucleus. 21103899_Partially unfolded states of AGXT strongly interact with Hsc70 and Hsp90 chaperones. 21148293_JB12 cooperates with cytosolic Hsc70 and the ubiquitin ligase RMA1 to target CFTR and CFTRDeltaF508 for degradation. 21565169_Apoptin induced the translocation of endogenous Hsc70 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, and both were co-localized in the nucleus. 21719532_The ability of the cytosolic cognate 70-kDa heat-shock protein (Hsc70) chaperone system to modulate cell surface expression of MC4R, was investigated. 22039833_Addition of Hsp70 to a mixture of oligomeric and fibrillar tau aggregates prevents the toxic effect of these tau species on fast axonal transport. 22074182_It is proposed that Az suppresses ubiquitination of DeltaF508-CFTR maybe by blocking interaction of the mutant with Hsc70 and CHIP, and, as a consequence, it enhances membrane trafficking of the mutant 22090113_Hsc70 is recruited to reovirus viral factories independently of its chaperone function. 22170045_downregulation of HSC70 resulted in increased levels of DeltaF508-CFTR complexes with the co-chaperone BAG3 that in addition appeared to co-localize with the mutated protein on the cell surface. 22743058_Hsc70 is a prerequisite for the surface translocation and angiogenic function of nucleolin, which suggests strategies to target both Hsc70 and NCL for more effective antiangiogenic therapies. 22842575_thise preliminary result indicated that HSP70 was related to the phosphorylation of MK2, a specific nuclear downstream target of p38, suggesting HSP70 is a potential chaperone for the nuclear translocation of p38. 22843682_the client binding domain of Hsc70 and Ssa1p binds two regions within alpha-Syn similar to a tweezer, with the first spanning residues 10-45 and the second spanning residues 97-102. 23065205_This case control study aims to investigate the role of HSP90 Gln488His (C > G), HSP70-2 P1/P2, HIF-1 alpha C1772T and HSPA8 intronic 1541-1542delGT polymorphisms as potential risk factors and/or prognostic markers for breast cancer. 23065523_Hsp73 sustains Hsp90 chaperone function and critically contributes to cell survival in multiple myeloma patients. 23071649_Studies suggest that Hsc70 and lysosome-associated protein 2A (LAMP-2A) through chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) play a role in the clearance of Htt and suggest a novel strategy to target the degradation of mutant huntingtin (Htt). 23224638_PKCiota knockdown sensitized cells to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis, whereas forced PKCiota expression counteracted the oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via Hsc70. 23235156_70-kDa heat shock cognate protein hsc70 mediates calmodulin-dependent nuclear import of the sex-determining factor SRY. 23333597_GLIPR1 interacts with Hsc70, and GLIPR1 overexpression or Hsc70 knockdown leads to transcriptional suppression of AURKA and TPX2. 23349634_Trimethylated at Lys-561 by METTL21A 23539416_Altered expression of Hsc70 and eIF5A-1 may cause defects in nucleocytoplasmic transport and play a role in esophageal carcinogenesis. 23569223_LAP1 and LULL1 as regulatory cofactors that are responsible for the activation of TorA's ATPase activity. 23865999_Relaxation-based NMR experiments on the Hsc70-CHIP complex determined that the two partners move independently in solution, similar to 'beads on a string 23880665_the ubiquitin ligase STUB1 is required for degradation of HIF1A in the lysosome by chaperone-mediated autophagy. 23948933_A significant downregulation of HSPA8 and HSPA9 was observed in AD across the three brain regions compared to the controls, suggesting their participation in AD pathogenesis. 23990462_the U-box mutation stimulated CHIP binding to Hsc70 while promoting CHIP oligomerization. CHIP binding to Hsc70 binding was also stimulated by the presence of an Hsc70 client with a preference for the ADP-bound state. 24056538_Cx43-Hsc70 interaction probably plays a critical role during G1/S progression. 24122553_the endogenous DNAJC12 and Hsc70 proteins interact in LNCaP cells. 24260102_These findings indicate that wild type ILK and the non-oncogenic ILK(R211A) mutation comprise a cardioprotective module with Hsp/c70. 24327656_These results demonstrate that Hsp70 recruits PP5 and activates its phosphatase activity which suggests dual roles for PP5 that might link chaperone systems with signaling pathways in cancer and development. 24361989_Results identify a systemic hsc70 reduction in Parkinson's disease patients. 24386440_H-ERG trafficking was impaired by H2O2 after 48 h treatment, accompanied by reciprocal changes of expression between miR-17-5p seed miRNAs and several chaperones (Hsp70, Hsc70, CANX, and Golga20) 24548631_HSP8A polymorphism is associated with drug-naive schizophrenia. 24736948_Results show that HSP72, HSC70 and HSP90 are overexpressed in human prostate cancer cells. 24801886_Hsc70 interacted with Rab1A in a chaperone-dependent mannerand Hsc70 knockdown decreased the level of Rab1A and increased the level of its ubiquitination under stress conditions. 24891511_Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of Niemann-Pick C1: evidence for the role of heat shock proteins and identification of lysine residues that accept ubiquitin. 25352667_LAP1 and LULL1 regulate Torsin ATPase activity through an active site complementation mechanism. 25527454_Data suggest that nhibition of nestin and heat shock protein HSPA8/HSC71 may be a useful molecular target in the treatment of glioblastomas. 25684577_CHIP docks onto Hsp70/Hsc70 and defines a bipartite mode of interaction between TPR domains and their binding partners. 25737151_HSP70 binds CD91 and TLR4 on decidual CD1a(+) dendritic cells, causes their maturation, and increases IL-15 in the context of Th1 cytokine/chemokine domination, which could support immune response harmful for ongoing pregnancy. 25882706_Active Hsc70 requires active tau to regulate microtubule assembly in vivo, suggesting that tau acts in some ways as a co-chaperone for Hsc70 to coordinate microtubule assembly. 25953005_HSC70 may serve as a molecular switch to modulate endocytic and autophagy pathways, impacting the source of antigens delivered for MHC class II presentation during cellular stress. (Review) 26010904_detailed and systematic investigation to characterize if there are significant differences in the CHIP in vitro ubiquitination of human Hsp70 and Hsc70. 26229111_heat shock cognate 70 (HSC70) is an essential component of Aes foci in colorectal cancer cells. 26232501_These results indicate that CHIP decreases the Kv1.5 protein level and functional channel by facilitating its degradation in concert with chaperone Hsc70 26335814_constitutive heat shock protein HSC70 forms granule-like structures in the cytoplasm of human cells several days after the exposure to heat stress 26425554_serum HSC71 was identified as a novel serum biomarker of renal cell carcinoma, particularly useful in early diagnosis of clear-cell type. 26481195_Cx43-Hsc70 interaction regulates cell cycle G1/S progression through a novel mechanism by which Cx43-Hsc70 interaction prevents the nuclear accumulation of p27 through controlling the nuclear translocation of cyclin D1-CDK4-p27 complex. 26526034_While cerebrospinal fluid Nrf2 and HSPA8 do not appear to offer diagnostic biomarkers for Parkinson's disease (PD), the associations between Nrf2 levels and UPDRS scores in LRRK2 + PD patients merit further investigation 26549849_HSPA8 maintains pluripotency of human pluripotent stem cells by binding to the master pluripotency regulator OCT4 and facilitating its DNA-binding activity. 26596547_LAP1 mutations are associated with severe dystonia, cerebellar atrophy and cardiomyopathy. 26775844_These findings provide further evidence that histatin 3 may be involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, particularly during G1/S transition, via the ubiquitin-proteasome system of p27(Kip1) and HSC70. 27225940_Downregulation of Hsc70, Hsp70, and IL-15 expression at gene and/or protein levels might support the retention of fertilization products in cases of missed abortion and blighted ovum. 27261198_In fact, DnaJC5 overexpression induced tau release in cells, neurons, and brain tissue, but only when activity of the chaperone Hsc70 was intact and when tau was able to associate with this chaperone. 27474739_These results suggest that Bag1 and Bag3 control the stability of the Hsc70-client complex using at least two distinct protein-protein contacts, providing a previously under-appreciated layer of molecular regulation in the human Hsc70 system. 28025138_HSPA1A and HSPA8 have roles in parturition through stimulating immune inflammatory and estrogen response 28026090_STRO-1 binds to immune-precipitated HSC70 and siRNA-mediated knock down of HSPA8 reduced STRO-1 binding. 28356524_study demonstrates a critical role of Hsc70 in SV40 endoplasmic reticulum-to-cytosol penetration and reveal how SGTA controls Hsc70 to impact this process 28559423_Synapsin is part of a multiprotein complex enriched in chaperones/cochaperones including Hsc70. Hsc70 chaperone activity is required for the cytosolic slow axonal transport of synapsin. 28603283_Taken together, by linking HSC70 and NF-kappaB signaling, TXNDC5 plays a pro-inflammatory role in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts, highlighting a potential approach to treat rheumatoid arthritis by blocking the TXNDC5/HSC70 interaction. 28731191_The roles of the E3 ubiquitin ligase, carboxy-terminus Hsc70 interacting protein (CHIP) in various types of cancers. 28814508_Engagement of the oligomer by LAP1 triggers ATP hydrolysis and rapid complex disassembly. Thus the Torsin complex is a highly dynamic assembly whose oligomeric state is tightly controlled by distinctively localized cellular cofactors. 28855508_Hsc70/Hsp90 chaperones contribute to the conformational and functional maintenance of DeltaF508-CFTR at 37 degrees C. 28978466_Post-transcriptional inhibition of HSPA8 expression leads to synaptic vesicle cycling defects in multiple models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 29107085_Hsp70participated in PINK1-mediated mitophagy by stabilizing PINK1. 29180285_These results demonstrate not only an important mechanism of Hsc70 in facilitating EV-A71 replication, but also a target for antiviral drug development. 29218503_This study demonstrated that particular distribution for HSC70 and PSMC4 in the cytoplasm and accumulation within Lewy body in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra in Parkinson patients. 29298892_Data suggest that both the small heat shock protein HspB1/Hsp27 and the constitutive chaperone Hsc70/HspA8 interact with tau to prevent tau-fibril/amyloid formation. Hsc70 is highly efficient at preventing tau-fibril elongation, possibly by capping ends of tau-fibrils. (HspB1 = heat shock protein family B small member 1; Hsc70 = heat shock protein family A Hsp70) 29300467_Taken together, these data suggest hat the altered hydrogen bonding observed in the Hsc70 C17W mutant (where the connectivity between Mg2+.nucleotide and E175 is also disrupted) could bring about changes to Hsc70 domain communication, affecting peptide association while also limiting ATP hydrolysis. 29875314_Study of intraventricular septum samples from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients and a panel of human MYBPC3 mutations expressed in neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes revealed suggest that wild type and mutant MYBPC3 proteins are clients for HSC70, and that the HSC70 chaperone system plays a major role in regulating MYBPC3 protein turnover. 30607818_Hsc70 Interacts with beta4GalT5 to Regulate the Growth of Gliomas. 30816582_Overexpression of Hsc70 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of human glioma cells. 31005254_identified HSPA1A and HSPA8 as the HSP70 family proteins that physically interact with DNAJA3, and established their requirement for the phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 31205025_intercellular antigen transfer of DBY is tightly regulated via binding to HSC70 and that this mechanism influences recognition and rejection of MHC-II-negative tumors in vivo. 31221799_HSC70 could bind independently to disordered CTA1, even in the absence of HOP. This indicated HSC70 recognizes distinct regions of CTA1, which was confirmed by the identification of a YYIYVI-binding motif for HSC70 that spans residues 83-88 of the 192-amino acid CTA1 polypeptide. 31276277_miR-26b-5p helps in EpCAM+cancer stem cells maintenance via HSC71/HSPA8 and augments malignant features in HCC. 31408507_overexpressing DNAJA2 but not DNAJA1 enhanced CFTR degradation at the endoplasmic reticulum by Hsc70/Hsp70 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP. Excess Hsp70 also promoted CFTR degradation, but this occurred through the lysosomal pathway and required CHIP but not complex formation with HOP and Hsp90. 31597739_The results identify HSC70 as a negative regulator of caspase-1 activation by the temperature-sensitive NLRC4-H443P mutant. 31663379_HSC70 expression is reduced in lymphomonocytes of sporadic ALS patients and contributes to TDP-43 accumulation. 32205407_Growth-Regulated Hsp70 Phosphorylation Regulates Stress Responses and Prion Maintenance. 32490574_Feedback regulation of heat shock factor 1 (Hsf1) activity by Hsp70-mediated trimer unzipping and dissociation from DNA. 32687490_Proteome-wide identification of HSP70/HSC70 chaperone clients in human cells. 32712350_HSPA8 knock-down induces the accumulation of neurodegenerative disorder-associated proteins. 32751253_Nuclear Accumulation of LAP1:TRF2 Complex during DNA Damage Response Uncovers a Novel Role for LAP1. 33077711_Hsc70/Stub1 promotes the removal of individual oxidatively stressed peroxisomes. 33186656_PRMT6 deficiency induces autophagy in hostile microenvironments of hepatocellular carcinoma tumors by regulating BAG5-associated HSC70 stability. 33320087_Torsin ATPases influence chromatin interaction of the Torsin regulator LAP1. 33390792_Clinical Implications of HSC70 Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 33493517_Heat shock transcription factor 1 is SUMOylated in the activated trimeric state. 33847413_Hspa8 and ICAM-1 as damage-induced mediators of gammadelta T cell activation. 33887528_Molecular mapping of platelet hyperreactivity in diabetes: the stress proteins complex HSPA8/Hsp90/CSK2alpha and platelet aggregation in diabetic and normal platelets. 33926391_High HSPA8 expression predicts adverse outcomes of acute myeloid leukemia. 34571256_Structural, thermodynamic and functional studies of human 71 kDa heat shock cognate protein (HSPA8/hHsc70). 34582004_HSPA8 Is Identified as a Novel Regulator of Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy by Modulating the beta-Arrestin1/A1AR Axis. 34685711_Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Markers LAMP2A and HSPA8 in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer after Neoadjuvant Therapy. 34798070_Binding with heat shock cognate protein HSC70 fine-tunes the Golgi association of the small GTPase ARL5B. 34932194_An association study of the HSPA8 gene polymorphisms with schizophrenia in a Polish population. 34965010_Inhibition of HSC70 alleviates hypertrophic cardiomyopathy pathology in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes with a MYBPC3 mutation. 35138165_Heat Shock Protein Member 8 (HSPA8) Is Involved in Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Attachment and Internalization. 35172151_FEZ1 phosphorylation regulates HSPA8 localization and interferon-stimulated gene expression. 35797800_Long noncoding RNA MAGI2-AS3 regulates the H2O2 level and cell senescence via HSPA8. 35886046_HSPA8 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Is Associated with Serum HSC70 Concentration and Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. 36246562_HSPA1A, HSPA2, and HSPA8 Are Potential Molecular Biomarkers for Prognosis among HSP70 Family in Alzheimer's Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000015656 |
Hspa8 |
8369.948534 |
2.3434518614 |
1.228635 |
0.027491595 |
1974.700462 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
11870.7263799 |
222.9238110 |
5100.1897487 |
72.0563033 |
| ENSG00000110011 |
3338 |
DNAJC4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NNZ3 |
|
Chaperone;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in response to unfolded protein. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:3338; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000024963 |
Dnajc4 |
118.002313 |
0.4014547797 |
-1.316691 |
0.309088706 |
17.680099 |
0.00002613466682576849275617715540054319944829330779612064361572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000077976082948927227431711040050998917649849317967891693115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
68.4508502 |
13.9991495 |
171.8954275 |
24.7373753 |
| ENSG00000110013 |
54414 |
SIAE |
protein_coding |
Q9HAT2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the removal of O-acetyl ester groups from position 9 of the parent sialic acid, N-acetylneuraminic acid. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine esterase;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme which removes 9-O-acetylation modifications from sialic acids. Mutations in this gene are associated with susceptibility to autoimmune disease 6. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms, found either in the cytosol or in the lysosome, have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:54414; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; sialate 4-O-acetylesterase activity [GO:0106331]; sialate 9-O-acetylesterase activity [GO:0106330]; sialate O-acetylesterase activity [GO:0001681]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; regulation of immune system process [GO:0002682] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20555325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20555325_odds ratio for inheriting defective SIAE alleles was 8.6 in all autoimmune subjects, 8.3 in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis, and 7.9 in subjects with type I diabetes 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21183218_SIAE expression is upregulated in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. 21615338_Functionally defective germline variant of sialic acid acetylesterase (Met89Val) is not associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus and Graves' disease. 21803834_These studies demonstrate that both SIAE and SOAT activities seem to be responsible for the enhanced level of Neu5,9Ac(2) in lymphoblasts, which is a hallmark in acute lymphoblastic leukemia 22257840_SIAE variants play a role in primary biliary cirrhosis. 22913750_There is no evidence for SIAE genetic variants affecting patients with vitiligo. 23011869_The analysis does not support a role for rare variants in SIAE in the pathogenesis of autoimmune Addison's disease. 23308225_SIAE may be associated with autoimmunity. 24748456_We found A467V SIAE variants (c.1400C>T, rs7941523) in a heterozygous state in all the patients with anti-PIT-1 antibody syndrome. 26535733_Authors determined whether mutations in the SIAE gene are responsible for RA in a Han Chinese population 28900629_analysis of whether SIAE rare variants associated with phenotype of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and autoimmunity risk in families with primary antibody deficiencies(PADS); 3 novel variants were found in patients with JIA and in their healthy relatives without autoimmunity; none of PAD patients or their relatives had SIAE defects; results show SIAE rare variants are not causative of autoimmunity as single defects |
ENSMUSG00000001942 |
Siae |
1267.731031 |
0.2377112089 |
-2.072718 |
0.057785107 |
1313.410176 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001377253408291266947676975864856426599591984 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001848023664216281916452343842590885054551566 |
Yes |
No |
489.5395050 |
18.3173415 |
2073.3009467 |
47.8529113 |
| ENSG00000110031 |
9404 |
LPXN |
protein_coding |
O60711 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional coactivator for androgen receptor (AR) and serum response factor (SRF). Contributes to the regulation of cell adhesion, spreading and cell migration and acts as a negative regulator in integrin-mediated cell adhesion events. Suppresses the integrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin (PXN). May play a critical role as an adapter protein in the formation of the adhesion zone in osteoclasts. Negatively regulates B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17640867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18497331, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20543562}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;LIM domain;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc |
|
The product encoded by this gene is preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and belongs to the paxillin protein family. Similar to other members of this focal-adhesion-associated adaptor-protein family, it has four leucine-rich LD-motifs in the N-terminus and four LIM domains in the C-terminus. It may function in cell type-specific signaling by associating with PYK2, a member of focal adhesion kinase family. As a substrate for a tyrosine kinase in lymphoid cells, this protein may also function in, and be regulated by, tyrosine kinase activity. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:9404; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; podosome [GO:0002102]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542]; negative regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050859]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033628]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
12674328_leupaxin may be a critical nucleating component of the osteoclast podosomal signaling complex 15786712_Leupaxin binding to tyrosine phosphatase PEP suggests that leupaxin may function as a signal-transducing complex with PEP. 17329398_These data demonstrate that LPXN forms a signaling complex with Pyk2, c-Src, and PTP-PEST to regulate migration of prostate cancer cells. 17640867_Leupaxin plays an inhibitory role in BCR signaling and B cell function. 18451096_leupaxin could serve as a potential progression marker for a subset of PCa and may represent a novel coactivator of the androgen receptor 18497331_Leupaxin is enriched in vascular smooth nuscle. It undergoes cytoplasmic/nuclear shuttling & functions as an serum response factor cofactor. It associates with CArG-containing regions. Its ectopic expression induces smooth muscle marker gene expression. 19760607_LPXN, a member of the paxillin superfamily, is fused to RUNX1 in an acute myeloid leukemia patient with a t(11;21)(q12;q22) translocation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917054_leupaxin functions as a paxillin counterpart that potently suppresses the tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin during integrin signaling. 20543562_first evidence of dynamic regulation of leupaxin localization and tyrosine phosphorylation by G-Protein Coupled Receptors 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 25955236_Results show that leupaxin has particular influence on the progression and invasion of breast cancer cells and may therefore represent an interesting candidate protein for diagnosis and therapeutic interventions. 26079947_Authors demonstrate that LPXN directly influences cytoskeletal dynamics via interaction with the actin-binding protein CaD and regulates CaD phosphorylation by recruiting ERK to highly dynamic structures within PCa cells. 26361959_this is the first demonstration of a role for the leupaxin in the regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma progression, at least in part, by enhancing beta-catenin transcription activity. 26866573_The full-length leupaxin binds to the Pyk2-focal adhesion targeting domain. 29975926_LPXN may facilitate bladder cancer progression by upregulating the expression of S100P via PI3K/AKT pathway. These results provide a novel insight into the role of LPXN in tumorigenesis and progression of bladder cancer and potential therapeutic target of bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024696 |
Lpxn |
1050.369326 |
11.9265106158 |
3.576100 |
0.075378171 |
2610.689827 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1962.9998864 |
87.2289115 |
165.7564519 |
6.8047500 |
| ENSG00000110047 |
10938 |
EHD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H4M9 |
FUNCTION: ATP- and membrane-binding protein that controls membrane reorganization/tubulation upon ATP hydrolysis. In vitro causes vesiculation of endocytic membranes (PubMed:24019528). Acts in early endocytic membrane fusion and membrane trafficking of recycling endosomes (PubMed:15020713, PubMed:17233914, PubMed:20801876). Recruited to endosomal membranes upon nerve growth factor stimulation, indirectly regulates neurite outgrowth (By similarity). Plays a role in myoblast fusion (By similarity). Involved in the unidirectional retrograde dendritic transport of endocytosed BACE1 and in efficient sorting of BACE1 to axons implicating a function in neuronal APP processing (By similarity). Plays a role in the formation of the ciliary vesicle (CV), an early step in cilium biogenesis. Proposed to be required for the fusion of distal appendage vesicles (DAVs) to form the CV by recruiting SNARE complex component SNAP29. Is required for recruitment of transition zone proteins CEP290, RPGRIP1L, TMEM67 and B9D2, and of IFT20 following DAV reorganization before Rab8-dependent ciliary membrane extension. Required for the loss of CCP110 form the mother centriole essential for the maturation of the basal body during ciliogenesis (PubMed:25686250). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q641Z6, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WVK4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15020713, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17233914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20801876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24019528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25686250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Endosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene belongs to a highly conserved gene family encoding EPS15 homology (EH) domain-containing proteins. The protein-binding EH domain was first noted in EPS15, a substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor. The EH domain has been shown to be an important motif in proteins involved in protein-protein interactions and in intracellular sorting. The protein encoded by this gene is thought to play a role in the endocytosis of IGF1 receptors. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:10938; |
ciliary pocket membrane [GO:0020018]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet dense tubular network membrane [GO:0031095]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034383]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010886]; positive regulation of endocytic recycling [GO:2001137]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659] |
12032069_A tubular EHD1-containing compartment involved in the recycling of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules to the plasma membrane 12121420_EHD3: a protein that resides in recycling tubular and vesicular membrane structures and interacts with EHD1. 15020713_a novel interacting partner for EHD1, rabenosyn-5, was revealed. 15710626_ATP binding is required for oligomerization of mRme-1/EHD1, which in turn is required for its association with endosomes 17284518_Data support a role for EHD1 in beta1 integrin recycling, and demonstrate a requirement for EHD1 in integrin-mediated downstream functions. 17507647_Rab8a and Myosin Vb colocalize to a tubular network containing EHD1 and EHD3, which does not contain Rab11a. 17899392_Solution structure of the 133 C-terminal residues of EHD1, which includes the EH domain, was solved. 18661112_Results show that EHD1 undergoes serine-phosphorylation, and suggest that EHD1 phosphorylation occurs between early endosomes and the endocytic recycling compartment. 19369419_Data show that EH domain mutant (K483E) that associates exclusively with punctate membranes displayed decreased binding to phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate and other phosphoinositides. 19798736_The results indicate that NPF is the preferred binding motif for the EHD1 EH-domain, but both the DPF and GPF motifs are capable of binding with lower affinity. 19864458_These data implicate MICAL-L1 as an unusual type of Rab effector that regulates endocytic recycling by recruiting and linking EHD1 and Rab8a on membrane tubules. 20489164_A new class of cardiac trafficking proteins(EHD1, EHD2, EHD3, EHD4) regulates cardiac membrane protein targeting. 20961375_EHD1 is involved in the control of CD59 transport from pre-sorting endosomes to the ERC in a PKC-dependent manner 22284051_Rabankyrin-5 interacts with EHD1 and Vps26 to regulate endocytic trafficking and retromer function 22456504_the lipid modifier cPLA2alpha and EHD1 are involved in the vesiculation of CD59-containing endosomes 24019528_evidence that the functions of both EHD1 and EHD4 are primarily in TRE membrane vesiculation, whereas EHD3 is a membrane-tubulating protein. 24481818_MICAL-L1-mediated recruitment of EHD1 to Src-containing recycling endosomes is required for the release of Src from the perinuclear endocytic recycling compartment in response to growth factor stimulation. 24946721_Data indicate that concordant transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGFbeta-1) positive and EH-domain containing 1 (EHD1) negative as a strong favorable prognosis factor in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 25287187_that Molecule Interacting with CasL Like-1 and Eps15 Homology Domain protein 1 differentially influence microtubule dynamics during early and late mitosis 25595798_Transport through recycling endosomes requires EHD1 recruitment by a phosphatidylserine translocase. 26378252_Authors found that Eps15-homology domain 1 (EHD1), a protein that associates with the endocytic recycling compartment (ERC), colocalizes with active R-Ras in transiently expressed HeLa cells. 26465136_van der Waals interactions should be the main consideration when we design peptide inhibitors of EHD1 EH domain with high affinities. 27411790_Results suggest that EHD1 is a cisplatin (CDDP)-resistant gene that suppresses DNA adduct-induced apoptosis by modulating intracellular CDDP concentrations. 27531895_this study shows that overexpression of EHD1 induced the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increased the metastatic potential of lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo 28215104_RAB11FIP3 combines with Eps15 homology domain 1 to promote the endocytosis recycling of phosphorylation of epithelial growth factor receptor. 29335527_Depletion of myosin-Va significantly inhibits the attachment of preciliary vesicles to the distal appendages of the mother centriole and decreases cilia assembly. Myosin-Va functions upstream of EHD1- and Rab11-mediated ciliary vesicle formation. 29549343_EHD1 may be an independent prognostic marker in lung cancer and that the NF-kappaB/miR-590/EHD1 signalling pathway might be a potentially effective therapy for overcoming EGFR-TKI resistance. 30683896_PACSIN1 and EHD1 assemble membrane tubules from the developing intracellular cilium that attach to the plasma membrane, creating an extracellular membrane channel to the outside of the cell. 30975166_The expression of EHD1 was negatively correlated with disease-free survival and overall survival of osteosarcoma patients. 31023336_the data obtained in this study suggest that EHD1 plays a critical role in Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) angiogenesis via b2AR signaling and highlight a potential target for antiangiogenic therapy. 31615969_Data support the notion that a pool of centriolar gamma-tubulin and/or alpha-tubulin-beta-tubulin heterodimers anchor MICAL-L1 to the centriole, where it might recruit EHD1 to promote ciliogenesis. 31707150_aberrant EHD1 signaling in the endometrium of RIF patients contributes to impaired decidualization and ultimately to implantation failure. EHD1 interacts with Wnt4, and this interaction leads to the suppression of Wnt4/beta-catenin signaling and impaired decidualization 31932478_RUSC2 and EHD1 function in a common pathway to positively regulate the basal traffic of Epidermal growth factor receptor from the Golgi compartment to the cell surface to ensure optimal surface receptor levels for subsequent ligand-mediated activation and cellular responses. 32138615_EHD1 Modulates Cx43 Gap Junction Remodeling Associated With Cardiac Diseases. 32800345_Identification of phostensin in association with Eps 15 homology domain-containing protein 1 (EHD1) and EHD4. 32966336_Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 4 (EHD4) is required for Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 1 (EHD1)-mediated endosomal recruitment and fission. 34217785_A feedback circuit comprising EHD1 and 14-3-3zeta sustains beta-catenin/c-Myc-mediated aerobic glycolysis and proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. 35149593_A Founder Mutation in EHD1 Presents with Tubular Proteinuria and Deafness. 35616188_EHD1 promotes the cancer stem cell (CSC)-like traits of glioma cells via interacting with CD44 and suppressing CD44 degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000024772 |
Ehd1 |
1122.807305 |
11.5152971826 |
3.525480 |
0.068692419 |
3163.616151 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2065.0592748 |
85.5559704 |
180.6445283 |
6.9331275 |
| ENSG00000110057 |
81622 |
UNC93B1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H1C4 |
FUNCTION: Plays an important role in innate and adaptive immunity by regulating nucleotide-sensing Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling. Required for the transport of a subset of TLRs (including TLR3, TLR7 and TLR9) from the endoplasmic reticulum to endolysosomes where they can engage pathogen nucleotides and activate signaling cascades. May play a role in autoreactive B-cells removal. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19006693}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is involved in innate and adaptive immune response by regulating toll-like receptor signaling. The encoded protein traffics nucleotide sensing toll-like receptors to the endolysosome from the endoplasmic reticulum. Deficiency of the encoded protein has been associated with herpes simplex encephalitis. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:81622; |
early phagosome [GO:0032009]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; Toll-like receptor binding [GO:0035325]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; T cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002457]; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway [GO:0034138]; toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway [GO:0034154]; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034162]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224] |
16111919_Haplotype H3 of the hUNC-93B1 gene seems related to E/A-ratio in elderly men. The relationship between the hUNC-93B1 gene and the age at onset of heart failure and mortality support a view of a clinically relevant impact of the gene. 16973841_findings elucidate a genetic etiology for herpes simplex virus encephalitis in two children with autosomal recessive deficiency in the intracellular protein UNC-93B, resulting in impaired cellular interferon-alpha/beta and -lambda antiviral responses 18082565_study confirms the function of UNC-93B for innate immunity in human beings, and extends the knowledge for this molecule to the analysis of its regulation and the subcellular localization of the endogenous protein 18241724_No UNC-93B1 mutations were foundin patients with MRS. 19006693_IRAK-4-, MyD88-, and UNC-93B-deficient patients did not display autoreactive antibodies in their serum or develop autoimmune diseases, suggesting that IRAK-4, MyD88, and UNC-93B pathway blockade may thwart autoimmunity in humans. 19120473_regulates ligand-induced trafficking of TLR7 and TLR9 from the ER to endolysosomes, potential therapeutic target for controlling dysregulated TLR7/9 responses in autoimmune diseases 19120481_Individuals with congenital mutations develop severe HSV-1 encephalitis 21173679_To date only 2 children with UNC-93B deficiencies have been identified after isolated HSV-1 encephalitis. 22164301_UNC93B1 physically associates with human TLR8 and regulates TLR8-mediated signaling 22611194_UNC93B1 expression is required for TLR3 cleavage and signaling. 23002119_IgM(+)IgD(+)CD27(+) but not switched B cells were strongly reduced in MYD88-, IRAK-4-, and TIRAP-deficient patients, but not UNC-93B-deficient patients. 23166319_TLR3 is the important regulator of UNC93B1 that in turn governs the responsiveness of all TLR3 as the important regulator of UNC93B1 that in turn governs the responsiveness of all NAS Toll-like receptors 25187660_the UNC93B1 tyrosine-based motif regulates trafficking and TLR responses via separate mechanisms. 26466955_Endosomal localization of endogenous TLR3 was decreased by silencing of LRRC59, suggesting that LRRC59 promotes UNC93B1-mediated translocation of NA-sensing TLRs from the ER upon infection. 29158474_Expression of a constitutively active STIM1 mutant, which no longer binds UNC93B1, restores antigen degradation and cross-presentation in 3d-mutated dendritic cells. 29852030_Our results suggest that rare protein-altering variants in the C10orf88 and UNC93B1 genes are associated with a worse response to anti-VEGF therapy in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration, but these results require further validation in other cohorts. 30935694_UNC93B1 regulates cell-cycle arrest at the G1 phase in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Down-regulated UNC93B1 stops granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. UNC93B1 may control tumors via granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. 33432245_Cryo-EM structures of Toll-like receptors in complex with UNC93B1. 33627833_Donor UNC-93 Homolog B1 genetic polymorphism predicts survival outcomes after unrelated bone marrow transplantation. 33837956_UNC93B1 curbs cytosolic DNA signaling by promoting STING degradation. 34223897_Dynamic control of nucleic-acid-sensing Toll-like receptors by the endosomal compartment. 34440442_Variants Affecting the C-Terminal Tail of UNC93B1 Are Not a Common Risk Factor for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 35577759_UNC93B1 attenuates the cGAS-STING signaling pathway by targeting STING for autophagy-lysosome degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000036908 |
Unc93b1 |
1090.987843 |
2.1024555454 |
1.072075 |
0.064951202 |
270.873852 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000073191074003211379825722310352962053891383255869774127324385055537677855045315611915481635742814043773640046532601977152814614448978479198341845500302895594080254682012309785932302474975585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018985944679919155461813957158981986687555986740360631544907461454323564511998745422026072999566045919550040748661277017226146172274867303512148423169994537751392726931953802704811096191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1498.7280385 |
53.1922103 |
718.1725631 |
19.7151393 |
| ENSG00000110090 |
1374 |
CPT1A |
protein_coding |
P50416 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of the acyl group of long-chain fatty acid-CoA conjugates onto carnitine, an essential step for the mitochondrial uptake of long-chain fatty acids and their subsequent beta-oxidation in the mitochondrion (PubMed:9691089, PubMed:11350182, PubMed:14517221). Plays an important role in hepatic triglyceride metabolism (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P32198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11350182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14517221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9691089}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nitration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid beta-oxidation. |
The mitochondrial oxidation of long-chain fatty acids is initiated by the sequential action of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (which is located in the outer membrane and is detergent-labile) and carnitine palmitoyltransferase II (which is located in the inner membrane and is detergent-stable), together with a carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase. CPT I is the key enzyme in the carnitine-dependent transport across the mitochondrial inner membrane and its deficiency results in a decreased rate of fatty acid beta-oxidation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1374; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0004095]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; palmitoleoyltransferase activity [GO:1990698]; carnitine metabolic process [GO:0009437]; carnitine shuttle [GO:0006853]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; eating behavior [GO:0042755]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0032000]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010883]; response to alkaloid [GO:0043279]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to tetrachloromethane [GO:1904772]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641] |
11001805_Human CPT1A, CPT1B, CPT2, CROT and CRAT are known to encode active carnitine acyltransferases. Earlier pfam annotations refer to the non-existing compound CARNITATE. In 2000 this has been changed to CARNITINE. 12111367_Mutations 1079A>G and 2028+2delAAGT result in an autosomal recessive mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation disorder. 12464674_hyperglycemia with hyperinsulinemia increases malonyl-CoA, inhibits functional CPT-1 activity, and shunts long-chain fatty acids away from oxidation and toward storage in human muscle 14517221_disease-causing CPT1A mutations can be divided into two categories depending on whether they affect directly or indirectly the active site of the enzyme 15647998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15846373_tBid decreases CPT-1 activity by a mechanism independent of both malonyl-CoA, the key inhibitory molecule of CPT-1, and Bak and/or Bax, but dependent on cardiolipin decrease 16246309_This inducible expression system should be well suited to study the roles of CPT1 and fatty acid oxidation in lipotoxicity and metabolism in vivo. 16271724_a conserved functional PPAR responsive element downstream of the transcriptional start site of the human CPT1A gene is localized; this sequence is fundamental for fatty acids or PGC1-induced transcriptional activation of the CPT1A gene 16697732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16697732_Patient with chronic hepatitis C, carrying the CPT1A minor allele are at the decreased risk of developing advanced liver fibrosis. 17089095_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17445541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17445541_neither haplotypes nor SNPs of CPT1A were found to be associated either with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus or with hepatic lipid content or insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients 17452323_structural analysis of two malonyl-CoA sites in carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A 18253084_The peculiar localization of CPT1 in the nuclei of human carcinomas and the disclosed functional link between nuclear CPT1 and HDAC1 propose a new role of CPT1 in the histonic acetylation level of tumors. 18385088_Accumulation of 3-hydroxylated intermediates of long-chain fatty acids may contribute to the pathogenesis of retinopathy in MTP deficiencies. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19181627_CPT1A p.P479L was associated with elevated plasma HDL and apoA-I levels. The association with increased levels of HDL and apoA-I suggest that the polymorphism might protect against atherosclerosis. 19181627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19217814_There is an astonishingly high frequency of CPT1 P479L variant and, judging from the enzyme analysis in the seven patients, also CPT-I deficiency in the areas of Canada inhabited by these families. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20124555_miR-370 acting via miR-122 may have a causative role in the accumulation of hepatic triglycerides by modulating initially the expression of SREBP-1c, DGAT2, and Cpt1alpha. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20638986_PPARalpha and PGC-1alpha stimulate transcription of the CPT-1A gene through different regions of CPT-1A gene. 20691246_Data show PEPCK-C and CPT-1 mRNAs are more abundant in non-tumoral tissues than in the tumoral counterpart, whereas the opposite occurred for the FAS gene. 20696606_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20696606_allele frequency and rate of homozygosity for the CPT1A P479L variant were high in Inuit and Inuvialuit who reside in northern coastal regions of Canada. 20843525_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20843525_The CPT1A c.1436C-->T variant is prevalent among some Alaska Native peoples, but newborn screening using current MS/MS cutoffs is not an effective means to identify homozygous infants 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20937660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20937660_Our data provide preliminary evidence that a highly prevalent CPT1A variant found among Alaska Native and other indigenous circumpolar populations may help explain historically high infant mortality rates. 21348853_These studies identified a favourable role for CPT1A in adipocytes to attenuate fatty acid-evoked insulin resistance and inflammation via suppression of JNK. 21484929_significant correlation between strong expression of CPT1A protein and poor outcome of ESCC patients 21763168_Impaired fasting tolerance among Alaska native children with a common carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A sequence variant. 21962599_carrier frequency of the c.1364A>C mutation of cpt1a in Finland is far lower than that of the variants found in Alaskan, Canadian, and Greenland native populations. 21990363_an environment-dependent structural switch underlies the regulation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A 22045927_Our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that the L479 allele of the CPT1A P479L variant confers a selective advantage that is both cardioprotective (through increased HDL-cholesterol) and associated with reduced adiposity 22278432_Data suggest that CPT1A, leptin receptor (LEPR), and insulin receptor (INSR) mRNA levels are higher in blood cells/blood from overweight children compared with normal weight children; INSR and CPT1A are increased only in males. 22533991_we have identified CPT1A as a novel transcriptional target of PAX3-FKHR and revealed the novel function of CPT1A in promoting cell motility. 22871568_Exposure to all-trans RA (ATRA) up-regulated the expression of carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT1-L) in HepG2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. 23090344_The CPT1A p.P479L variant is common to some coastal BC First Nations, and homozygosity for this variant is associated with unexpected death in infancy 23992672_The association of the arctic variant of CPT1A with infectious disease outcomes in children between birth and 2.5 years of age suggests that this variant may play a role in the historically high incidence 24037959_the structure of the regulatory domain of CPT1C was determined (residues Met1-Phe50) by NMR spectroscopy. 24118240_The results suggest the generality of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 inhibition under various stress conditions associated with ROS generation, providing an insight into a mechanism for oxidative dysfunction in mitochondrial metabolism. 24618825_High grade glioblastoma is associated with increased level of ZFP57, a protein involved in gene imprinting, and aberrant expression of CPT1A and CPT1C. 24711635_associations between methylation in CPT1A and lipoprotein measures highlight the epigenetic role of this gene in metabolic dysfunction. 24920721_CPT1A methylation was strongly associated with fasting very-low low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and trigylcerides. 25183267_CPT1A inhibition with RNAi resulted in triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells. The CPT1A promoter region was determined to contain two putative Sp1 binding sites, namely Sp1a and Sp1b, which might act as the GBE regulation response DNA element. 25501281_The present study was designed to evaluate the involvement of hexokinase and CPT-1 in the cell growth and proliferation of human prostate cancer cell lines, PC3, and LNCaP-FGC-10. 26041663_CPT1 is active on the outer surface of mitochondria and serves as a regulatory site for fatty acid oxidation due to its sensitivity for malonyl-CoA. CPT1a is the hepatic isoform. 26110892_This large-scale epigenome-wide study discovered and replicated robust associations between DNA methylation at CpG loci and obesity indices 26276667_Targeting the leukemia cell metabolism by the CPT1a inhibition 26716645_High CPT1A expression is associated with ovarian cancer. 26799588_High expression level of CPT1A is associated with breast cancer. 26808626_Methylation at 2 CpG sites in CPT1A on chromosome 11 was significantly associated with MetS. Significant associations were replicated in both European and African ancestry participants. 26820065_Homozygosity for the arctic variant is associated with increased risk of infant mortality, which may be mediated in part by an increase in infectious disease risk. Further studies are needed to determine whether the association we report represents a causal association between the CPT1A arctic variant and infectious disease-specific mortality 27195673_The recent findings and the current understanding of fatty acid oxidation and CPT1A in cancer have been summarized thus providing theoretical basis for this enzyme as an emerging potential molecular target in cancer therapeutic intervention. (Review) 27502741_this study shows that upregulation of the citrate pathway and down-regulation of carnitine palmitoyl-transferase 1 gene in cells from children with Down syndrome 27667153_Data show that in the absence of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibition, fatty acid oxidation increased along with increased activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I (CPT1). 27916548_our results proved CPT1A as a potential prognosticator and therapeutic target for AML. 28125087_We review here what is known and not known about the P479L variant and argue that public health action is premature. [review] 28139377_Methylation of a CpG site in CPT1A is associated with circulating adiponectin levels, likely in an obesity-dependent manner, in three population-based adult cohorts of European descent. 28330968_Furthermore, given the already low abundance of Cpt1b in white adipose tissue, it is unlikely that decreases in its expression can quantitatively decrease whole body energy expenditure enough to contribute to an obese phenotype. 28392417_These deleterious effects could be partially prevented by MCT-therapy and totally corrected by ETX. Inhibition of CPT1 may be view as a new therapeutic target for patients with a severe form of Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein deficiency. 28526869_We demonstrated that inhibition of CPT1 by systemic application of Etomoxir has beneficial effects in the treatment of depression in a highly validated CMS depression model. 28611031_The rs80356779, a p.Pro479Leu variant in CPT1A, was highly significantly associated with a range of fatty acid metabolism measures in a population-based sample from Greenland. 28671672_We provide evidence that the downregulation of hsa-miR-124-3p, hsa-miR-129-5p and hsa-miR-378 induced an increase in both expression and activity of CPT1A, CACT and CrAT in malignant prostate cells. 29107296_Targeted analysis of DNA methylation array revealed the mesenchymal stem cells in infants born to obese mothers had hypermethylation in genes regulating Fatty Acid Oxidation (PRKAG2, ACC2, CPT1A, SDHC) and corresponding lower mRNA content of these genes. Moreover, mesenchymal stem cells methylation was positively correlated with infant adiposity. 29596410_CPT1 is associated with anabolic processes that support healthy mitochondrial function and cancer cell proliferation independent of fatty acid oxidation. 29721083_Targeting CPT1A could be a beneficial regimen to improve the therapeutic effects of radiotherapy in NPC patients. 29795111_CPT gene upregulation increased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and led to cell apoptosis. 29930162_A reversible carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT1) inhibitor offsets the proliferation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. 29940537_CPT1A1A contributes to breast cancer-induced invasion and lymphangiogenesis of lymphatic endothelia cells via VEGF-C/VEGF-D/VEGFR-3 signaling. 29995871_CPT1A-mediated FAO activation induces CRC cells to resist anoikis. 30092766_the expression of CPT1A was higher in oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive, compared to ER-negative tumours and cell lines. Importantly, overexpression of CPT1A significantly decreased the proliferation and wound healing migration rates of MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells, compared to basal expression control 30107520_Three ubiquitous methylation loci were consistently and strongly associated with type 2 diabetes in Ghanaians: TXNIP, C7orf50 and CPT1A 30394687_CPT1A binds to and succinylates S100A10 at lysine 47, which promotes gastric cancer progression. 30823689_CPT1A methylation level is associated with body mass index in late gestation. 30945396_Data show that PPAR coactivator-1alpha (PGC1alpha) and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (CEBPB) form a complex and bind to the promoter of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 A (CPT1A). 31151054_We used metabolomics to demonstrate that inhibition of CDK9 leads to accumulation of acyl-carnitines, metabolic intermediates in fatty acid oxidation (FAO). Acyl-carnitines are produced by carnitine palmitoyltransferase enzymes 1 and 2 (CPT), and we used both genetic and pharmacological tools to show that inhibition of CPT-activity is synthetically lethal with CDK9 inhibition 31485672_High CPT1A expression is associated with breast cancer growth and metastasis. 31547059_CPT1A supports castration-resistant prostate cancer by supplying acetyl groups for histone acetylation, promoting growth and antiandrogen resistance. 31705849_Role of membrane curvature on the activation/deactivation of Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1A 31900237_Alteration of fatty acid oxidation by increased CPT1A on replicative senescence of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 31900483_mutations associated with hypoketotic hypoglycemia [review] 32088118_Inuit metabolism revisited: what drove the selective sweep of CPT1a L479? 32198139_Targeting Fatty Acid Oxidation to Promote Anoikis and Inhibit Ovarian Cancer Progression. 32561900_Genetic study of the Arctic CPT1A variant suggests that its effect on fatty acid levels is modulated by traditional Inuit diet. 32916992_LRRK2 Regulates CPT1A to Promote beta-Oxidation in HepG2 Cells. 32930325_Carbohydrate and fat intake associated with risk of metabolic diseases through epigenetics of CPT1A. 33273726_MSC-induced lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 promotes stemness and trastuzumab resistance through regulating CPT1 expression and fatty acid oxidation in breast cancer. 33378033_MiRNA-324-5p inhibits inflammatory response of diabetic vessels by targeting CPT1A. 33687587_Association of CPT1A gene polymorphism with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study. 33845545_[Clinical features and gene mutations of 6 patients with carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A deficiency]. 34045663_Fatty acid beta-oxidation promotes breast cancer stemness and metastasis via the miRNA-328-3p-CPT1A pathway. 34331935_Differential contributions of choline phosphotransferases CPT1 and CEPT1 to the biosynthesis of choline phospholipids. 34836312_Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Infant Feeding and DNA Methylation in Infancy and Childhood in a Population at Increased Risk for Type 1 Diabetes. 34963686_Overexpression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A promotes mitochondrial fusion and differentiation of glioblastoma stem cells. 35028612_Multiomic analysis identifies CPT1A as a potential therapeutic target in platinum-refractory, high-grade serous ovarian cancer. 35130611_Overexpression CPT1A reduces lipid accumulation via PPARalpha/CD36 axis to suppress the cell proliferation in ccRCC. 35273614_CPT1A-Mediated Fatty Acid Oxidation Promotes Precursor Osteoclast Fusion in Rheumatoid Arthritis. 36035217_Contribution of Adiponectin/Carnitine Palmityl Transferase 1A-Mediated Fatty Acid Metabolism during the Development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. 36180554_The role of CPT1A as a biomarker of breast cancer progression: a bioinformatic approach. 36233047_Augmented CPT1A Expression Is Associated with Proliferation and Colony Formation during Barrett's Tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000024900 |
Cpt1a |
250.229016 |
0.3726470173 |
-1.424118 |
0.102658954 |
197.715777 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000658134257011657275464284412106631278499703604526356391984058731277329736462786659676113303593421033138283408842972646568547645529179135337471961975097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000123431532827091004699957779735585439897473265493269083498922811429276724023703550120751311286000537535708742979678742557325676898472011089324951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
137.9431292 |
9.0308444 |
372.7503592 |
15.2909579 |
| ENSG00000110092 |
595 |
CCND1 |
protein_coding |
P24385 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory component of the cyclin D1-CDK4 (DC) complex that phosphorylates and inhibits members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulates the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition (PubMed:1833066, PubMed:1827756, PubMed:8114739, PubMed:8302605, PubMed:19412162, PubMed:33854235). Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complex and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase (PubMed:1833066, PubMed:1827756, PubMed:8114739, PubMed:8302605, PubMed:19412162). Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase (PubMed:1833066, PubMed:1827756, PubMed:8114739, PubMed:8302605, PubMed:19412162). Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals (PubMed:1833066, PubMed:1827756, PubMed:8302605, PubMed:19412162). Also a substrate for SMAD3, phosphorylating SMAD3 in a cell-cycle-dependent manner and repressing its transcriptional activity (PubMed:15241418). Component of the ternary complex, cyclin D1/CDK4/CDKN1B, required for nuclear translocation and activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex (PubMed:9106657). Exhibits transcriptional corepressor activity with INSM1 on the NEUROD1 and INS promoters in a cell cycle-independent manner (PubMed:16569215, PubMed:18417529). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15241418, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16569215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1827756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1833066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18417529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19412162, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33854235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8114739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8302605, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. |
3D-structure;Cell cycle;Cell division;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cyclin;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance throughout the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK4 or CDK6, whose activity is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein has been shown to interact with tumor suppressor protein Rb and the expression of this gene is regulated positively by Rb. Mutations, amplification and overexpression of this gene, which alters cell cycle progression, are observed frequently in a variety of human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2019]. |
hsa:595; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cyclin D1-CDK4 complex [GO:0097128]; cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity [GO:0016538]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; lactation [GO:0007595]; Leydig cell differentiation [GO:0033327]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033598]; mitotic cell cycle phase transition [GO:0044772]; mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0031571]; negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030857]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045737]; positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:1900087]; positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0010971]; positive regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033601]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; re-entry into mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000320]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to corticosterone [GO:0051412]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to iron ion [GO:0010039]; response to leptin [GO:0044321]; response to magnesium ion [GO:0032026]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; response to UV-A [GO:0070141]; response to vitamin E [GO:0033197]; response to X-ray [GO:0010165]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11470749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11642719_expression is related to apoptosis in thymus 11696452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11698342_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11739785_TGFbeta and PTHrP control chondrocyte proliferation by activating cyclin D1 expression 11751903_The ability of p21(Cip1) to inhibit cyclin D1 nuclear export correlates with its ability to bind to Thr-286-phosphorylated cyclin D1 and thereby prevents cyclin D1.CRM1 association 11813305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11815623_Endostatin causes G1 arrest of endothelial cells through inhibition of cyclin D1. 11836555_Immunohistochemistry of cyclin D1 and beta-catenin, and mutational analysis of exon 3 of beta-catenin gene in parathyroid adenomas 11838966_TSG101 expression in gynecological tumors: relationship to cyclin D1, cyclin E, p53 and p16 proteins. 11860939_Lower expression of p16 protein and overexpression of Cyclin D1 protein may be considered as prognostic biomarkers to skin carcinogenesis. 11870667_Cyclin D1 play important roles in esophageal carcinogenesis. 11872630_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11872630_This study was conducted to explore the association between the polymorphism and the susceptibility to and disease status of TCC of the bladder in 222 cases and 317 native Japanese controls 11884610_Reversal of growth suppression by p107 via direct phosphorylation by cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent kinase 4 11896626_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11902820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11923474_cyclin D1 may be a target gene for prolactin in normal lobuloalveolar development, as well as in the development and/or progression of mammary cancer. 11935308_analysis of expression improves differentiation of mantle cells from other lymphoma cells 11948404_Cyclopentenone causes cell cycle arrest and represses cyclin D1 promoter activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. 11958128_A/G polymorphism of CCND1 was associated with the susceptibility to NPC 11958128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11986316_expression affected by estrogen receptors alpha and beta 11992406_Activation of cyclin D1 and D2 promoters by human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein is associated with IL-2-independent growth of T cells 12002755_The expression of MIB-1 and prognosis in cyclin D1(CyD1)+ and CyD1- mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)were studied and compared to B-CLL/SLL. The CyD1- group (nodal MCL and CLL/SLL) had a longer median survival time than the CyD1+ group (nodal MCL and MLP). 12007188_Overexpression of cyclin D1 is found to be significantly correlated with increased chromosomal instability in patients with breast cancer. 12024041_The RASSF1A tumor suppressor blocks cell cycle progression and inhibits cyclin D1 accumulation (RASSF1A) 12036906_VHL-mediated hypoxia regulation of cyclin D1 in renal carcinoma cells. 12036934_Cyclin D1 is a candidate oncogene in cutaneous melanoma. 12036951_Overexpression of Icat induces G(2) arrest and cell death in tumor cell mutants for adenomatous polyposis coli, beta-catenin, or Axin. 12048199_cyclin D1 is a novel ligand-independent co-repressor 12067972_Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression and may provide a novel prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 12096344_The cyclin D1 high and cyclin E high subgroups of breast cancer: separate pathways in tumorogenesis based on pattern of genetic aberrations and inactivation of the pRb node. 12097293_Identification of cyclin D1 and other novel targets for the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene by expression array analysis and investigation of cyclin D1 genotype as a modifier in von Hippel-Lindau disease. 12101670_regulates cell cycle 12127555_Cyclin D1 expression in peripheral blood of 7 mantle-cell lymphoma pts was 1305.4 times higher than in 24 chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia pts. 12138206_Data suggest that one mechanism by which INI1/hSNF5 exerts its tumor suppressor function is by mediating the cell cycle arrest due to the direct recruitment of HDAC activity to the cyclin D1 promoter, causing its repression and G(0)-G(1) arrest. 12150453_overexpression of cyclin D1 sensitizes MCF7 cells to treatment with taxol 12151312_These data suggest that PKCdelta attenuates cyclin D1 promoter activity via the regulation of three distinct cis-acting regulatory elements. 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12203362_The CCND1 gene was rarely amplified in ILC in spite of showing overexpression of the protein in 41% of tumors. Hence, unlike IDC, increase in gene dosage did not account for the protein excess. 12209953_upregulation of cyclin D1 and Fra-1 in human colorectal adenocarcinomas is driven by abnormally expressed beta-catenin 12231535_Strong cyclin D1 mRNA overexpression was detected in mantle cell lymphomas, hairy cell leukemias,and multiple myelomas. Intermediate transcript levels were found in some multiple myelomas and hairy cell leukemias. 12237776_Amplifications of c-myc and CCND1 are associated with detrusor-muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma 12364325_inhibition of GSK3beta activity appears to trigger nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 and cell cycle progression 12376514_early use of oral contraceptives may be associated with subset of mammary tumors that overexpress cyclin D1 12379776_Marked intratumoral heterogeneity of c-myc and this but not of c-erbB2 amplification in breast cancer 12388769_These results indicate that estrogen-induced cyclin D(1) transcription can occur in HepG2 cells independently of the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptor. 12391146_Oct-1 potentiates CREB-dependent cyclin D1 transcriptional activity by a phospho-CREB and CREB binding protein-independent mechanism 12394763_Beta-catenin mutations correlate with over expression of C-myc and cyclin D1 Genes in bladder cancer 12439750_gene expression induced by galectin-3 12444551_CDK-independent transactivation of the estrogen receptor by cyclin D1 is, by itself, not sufficient to cause estradiol-independent growth of breast cancer cells. A vast overexpression of G1/S cyclins D1 A & E is able to do so by capturing CDK inhibitors. 12455063_AA genotype of cyclin d1 polymorphism is associated with increased risk of prostate cancer 12455063_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12480939_cyclin D1 expression initiates an apoptotic signal inhibited by different levels of cellular Bcl-2 at two points 12515730_Mantle cell lymphomagenesis results not only from direct consequences of inappropriate cyclin D1 expression but also from the ability of overexpressed cyclin D1 to buffer physiologic changes in p27 levels, rendering p27 ineffective as a growth inhibitor. 12554669_PRH, is a tissue-specific inhibitor of eIF4E-dependent cyclin D1 mRNA transport and growth 12557224_Clonal aberrations of CCND1 together with high mRNA expression suggest a role for deregulated CCND1 activity in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. 12569141_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12569141_The cyclin D1 A allele was associated with a diminished modulation of normal physiologic and treatment-induced decreased expression of cyclin D1. 12582032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12589056_cyclin D1 has a role in regulating mitogenic signaling with IKKalpha 12594215_retinoblastoma protein has cyclin D1-inducing activity that is abolished by adenovirus E1A and that involves multiple pocket sequences that are independently involved in cyclin D1 activation 12601350_increases of cyclin D1, cyclin-dependent kinase 4, cyclin E, cyclin A, and Wee1 play an important role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma from cirrhosis 12606305_gastrin appears to exert its mitogenic effects on gastric adenocarcinoma, at least in part, through changes in cyclin D1 expression. 12607604_Comparative study in the expression of p53, EGFR, TGF-alpha, and cyclin D1 in verrucous carcinoma, verrucous hyperplasia, and squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck region. 12634633_Cyclin G1 is frequently overexpressed in uterine leiomyoma in a p53-independent manner and that this abnormality could be attributed to the severe proliferation of human uterine leiomyomas. 12673692_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12673692_cyclin D1 (G870A) polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to esophageal and gastric cardiac carcinoma 12680219_Cells overexpressing cdk4 or cyclin D1 exhibited nuclear features characteristic of apoptosis. 12692418_These results indicate that the altered expression of beta-catenin, but not cyclin D1, in hepatocellular carcinoma may play an important role in tumor progression by stimulating tumor cell proliferation. 12694349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12694349_This study demonstrates that the CCND1 genotype may confer different risks for buccal squamous cell carcinoma (BSCC) and non-BSCC. 12707028_The activation of Stat 3 and the dysregulation of this protein are mutually exclusive events in multiple myeloma. 12738746_Cyclin d1 overexpression sensitizes breast cancer cells to fenretinide 12743597_Loss of von Hippel-Lindau protein causes cell density dependent deregulation of this protein through HIF. 12746453_Cyclin D1 splice variants have differential effects on localization, RB phosphorylation, and cellular transformation 12759391_LPA may directly increase the level of cyclin D1 in ovarian cancer cells, increasing their proliferation. 12761882_overexpression inhibits TNF-induced growth arrest 12778072_Presence is associated with high nuclear grade, large tumor size, and poor prognosis for glioma patients. 12807740_ccnd1 polymorphism is associated with early lung cancer and contributes to susceptibility to lung cancer 12808109_cyclin D1 transcription is repressed by p53 through down regulation of Bcl-3 and inducing increased association of the p52 NF-kappaB subunit with histone deacetylase 1 12824903_Deregulation of cyclin D1 is associated with early stages of plasma cell dyscrasia 12825853_Cyclin D1 could be indirectly induced by ErbB signalling through p21. ER-mediated upregulation of cyclin D1 seems to be a possible mechanism of maintaining cell proliferation in DCIS in case of EGFR- and HER-2/neu-negativity. 12883688_COX-2 or VEGF, but not cyclin D1 may play roles in breast cancer with poor prognosis 12883749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12894561_Data may suggest a possible role of the overexpression of cyclin D1 in the tumorigenesis of uveal malignant melanoma. 12896908_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12899785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12914697_Results describe how patterns of gene expression in human tumors have been deconvoluted to reveal a mechanism of action for the cyclin D1 oncogene. 12917336_The data are consistent with an oncogenesis model in which a lack of PTEN fuels the cell cycle by increasing the nuclear availability of cyclin D1 through the Akt/PKB pathway. 12917338_The cyclin D1 gene is overexpressed in human breast cancers and is required for oncogene-induced tumorigenesis 12921950_Up-Regulation of cyclin D1 and p21(Waf1/Cip1) is associated with differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cell lines 12930597_Study revealed a higher prevalence of both aberrant beta-catenin expression and cyclin D1 overexpression in papillary thyroid cancers around the Semipalatinsk nuclear test site than sporadic cases. 12937137_Localized to suprabasal cells of telogen bulge and anagen outer root sheath(ORS). May mediate proliferation of stem cells in bulge to more differentiated transient amplifying cells in the suprabasal ORS. 12955092_our data indicate that mutations of CCND1, which probably render the protein insensitive to degradation, represent a previously unreported mechanism of cyclin D1 overexpression in human tumors in vivo 12965081_the Cyclin D1/E2F1 pathway may be involved in apoptotic death of bone marrow cells in myelodysplastic syndromes 12972956_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14530270_cyclin D1 expression is regulated by Pak1 in mammary glands and tumors 14612904_cyclin D1, besides growth pattern, is a prognostic marker for local recurrence in DCIS 14645506_transcriptional regulation of the key cell cycle regulator cyclin D1 and roles of both STAT5 and Oct-1 in this process 14645576_stabilized by HSV-1 ICP0 through degradation of cdc34 14646596_significant difference in their biochemical properties between CDK4/cyclin D1 and CDK2/cyclin A affecting regulation of cellular RB function 14657069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14657069_These data provide strong evidence that the CCND1 870A allele may be associated with colorectal cancer, and particularly with forms of the disease that result in severe morbidity and mortality. 14666635_CCND1 G870A polymorphism has been reported as a genetic risk factor for some tumour types, it does not appear to be linked to the risk of breast and colorectal cancers. 14666635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14666673_The beta-catenin-cyclin D1 pathway might be involved in the growth of endometrial carcinomas. 14666699_In cervical cancers cyclin D3 may compensate for low levels of cyclin D1, whereas in corpus cancers both isoforms may contribute to the neoplastic phenotype. 14679024_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14679024_The CCND1 A870G polymorphism may increase risk for colorectal neoplasms. 14688016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14689059_Moderate amplification of the CCND1 gene in Paget's disease of breast 14701845_cyclin D1 binding to wild type Cdk4 is stimulated by Cdc37 14703063_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14720512_Cyclin D1 expression was evatuated in cell cycle responses to DNA mismatch repair-deficient cells upon methylation and UV-C damage. 14754892_cyclin D1/Cdk4 complexes are regulated by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I 14759115_There was no correlation between human papillomavirus status and cyclin D1 overexpression in human oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 14764597_cyclin D1 is inhibited by PPARgamma2 activation in hepatocytes via CREB-dependent and beta-catenin-independent pathways 14767060_cyclin D1 accumulation in G(1) phase is regulated by calcineurin 14966901_expression of Egr-1, c-fos and cyclin D1 varies in esophageal precancerous lesions and cancer tissues, suggesting an involvement of these genes in the development of esophageal carcinoma. 14981950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15059606_cyclin D1 has a role in tumorigenesis through interaction with C/EBPbeta 15060836_The expression patterns of cyclin D1, cyclin E, p21/waf1 and p27/kip1 in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may indicate their contribution in epithelial cell turnover and their possible implication in IBD-related dysplasia-carcinoma. 15063389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15090460_results indicate an effect of gene dosage as an alternative mechanism of cyclin D1 deregulation in MM 15128059_overexpression may be involved in the formation of the giant cells and the pathogenesis of central giant cell granuloma 15133490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15133490_The authors found a correlation between CCND1 genotype and the age of onset of hepatoblastoma. 15138714_Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and molecular analyses demonstrated involvement of the BCL1/CCND1 locus in a three-way translocation 15153436_Up-regulation of cyclin D1 is observed early in tumor formation, implying a possible role in tumor initiation. 15203873_Presence in bone marrow cells indicated diagnosis of multiple myeloma. 15225161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15226187_results suggest a model where RNA polymerase II bound at IgH regulatory sequences can activate the cyclin D1 promoter by either long-range polymerase transfer or tracking 15239347_cyclin D1-positive tumors tend to have perineural invasion more frequently.lymph vessel invasion is another factor related to cyclin D1 reactivity of the cells. 15245939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15245939_The CCND1 variant A allele may recessively increase the risk of carcinoma in situ incidence in patients with superficial bladder cancer. 15282324_Data show that CCND1 promoter activation by estrogens in human breast cancer cells is mediated by recruitment of a c-Jun/c-Fos/estrogen receptor alpha/progesterone receptor complex to the tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-responsive element of the gene. 15297421_Cyclin D1, p53, and p21Waf1/Cip1 have roles in progression of serous epithelial ovarian cancer 15350626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15355984_Data suggest that cyclin D1-Cdk2 complexes mediate some of the transforming effects of cyclin D1 and demonstrate that the cyclin D1-Cdk2 fusion protein is a useful model to investigate the biological functions of cyclin D1-Cdk2 complexes. 15375804_Review of Cyclin D1 overexpression in squamous cell head and neck neoplasms resulting from abnormalities in chromosome 11q13. 15377668_Synthesis is regulated by combined activity of ErbB2 and FGFR-4 that involves S6K1-mediated translation. 15378006_regulation by SNIP1 15498584_Tumor growth inhibition might be due to apoptosis caused by reduced cyclin D1 expression as revealed by immunohistochemical analysis of tumor samples. 15505422_Expression levels of CCND1 predict the cellular effects of mTOR inhibitors in ovarian carcinoma. 15513923_C-terminal sequences direct cyclin D1-CRM1 binding 15538282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15539430_cyclin D1 binding to the androgen receptor NH2-terminal domain inhibits activation function 2 association 15544931_estrogen receptor mediates cyclin D1 expression and growth of tamoxifen-resistant tumors. 15545188_CCND1 gains are early events in ovarian tumorogenesis. 15551329_CCND1 alternate transcripts encode proteins with differing functions: CCND1(tra) encodes protein involved in regulating mitogen responsive, anchorage-dependent progression; CCND1(trb) modulates ability of cell to grow in anchorage-independent manner 15557280_overexpression of FAK promoted exit from G(1) in glioblastoma cells, enhanced expression of cyclins D1 and E while reducing expression of p27(Kip1) and p21(Waf1), and enhanced the kinase activity of the cyclin D1-cyclin-dependent kinase-4 (cdk4) complex 15557752_In colorectal cancer, the CCND1 copy number increase was neither associated with the tumor phenotype (stage and grade) nor with the tumor localization (colon, rectum or sigmoid colon). 15558026_Cyclin D1 central domain could be exploited to develop novel prostate cancer therapeutics. 15578074_Cyclin D1 protein is upregulated in epithelioid sarcoma, suggesting a role in the pathogenesis of epithelioid sarcoma and appears to be regulated by translational and/or post-translational mechanisms. 15580291_Endogenously released IGF-I leads to constitutive cyclin D1 expression in human neuroendocrine tumour cells. 15621754_expression level of cyclin D1 RNA in bone marrow cells is predictive of the phase evolution in Chronic myeloid leukemia 15655836_Cyclin D1 may play a role in the early stage of gallbladder carcinoma. 15668481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15684604_experiments suggest that both catalytic and non-catalytic functions of cyclin D1 can collaborate to inactivate pRb-mediated cell cycle exit 15695117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15709184_Cyclin D1 may be a potential target for molecular intervention in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer. 15734847_We expressed cyclin D1 in the beta-cells of mice and islet hyperplasia developed in a time-dependent manner. 15735724_activation in breast cancer cells is mediated by mayven 15754315_An associative interaction between XPD protein and CCND1 genetic polymorphisms, tobacco exposure, and cancer risk. 15754315_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15755896_Cyclin D1, D2, or D3 expression appears to be increased and/or dysregulated in virtually all MM tumors despite their low proliferative capacity 15776189_marked expression in high-grade tumors supports its role in proliferative activity 15791567_data indicate that altered expression of beta-catenin may play an important role in oral cancer progression through increased proliferation and invasiveness under epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation but not mutation or cyclin D1 expression 15809880_cyclin D1 overexpression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 15811121_Bcl-1 staining was similar in all benign keratoses. 15824172_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15845652_AA genotype does not affect breast cancer risk. 15845652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15856299_Amplification of Bcl-1 is associated with the development of uterine cervical carcinoma 15861516_To explore the potential prognostic value of cyclin D1 in invasive breast cancer 15862753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15863141_CCND1 polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of endometrial cancer. 15863141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15870300_TAF1-dependent histone acetylation facilitates transcription factor binding to the Sp1 sites, thereby activating cyclin D1 transcription and ultimately G(1)-to-S-phase progression 15878868_exposure of cells to cadmium chloride results in cytotoxicity and cell death due to enhanced ubiquitination and consequent proteolysis of eIF4E protein, which in turn diminishes cellular levels of critical genes such as cyclin D1 15896460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15900590_Identification of mantle cell lymphoma with low cyclin D1 3'UTR is important because it seems to be associated with shorter overall survival. 15914210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15923181_PKC-mediated exclusion of LIMK2 from the nucleus might be a mechanism to relieve suppression of cyclin D1 expression by LIMK2 15943036_cyclin D1 was localized in cell nuclei 15949570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15951302_levels of cyclin D1a and D1b alternative transcripts in mantle cell lymphoma may depend more on sample origin than on CCND1 polymorphism 15951563_cyclin D1 plays an important role in cellular proliferation and differentiation through regulation of p300. 15971196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15981100_Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor can be misdiagnosed as a variety of tumors, including ependymoma that potentially harbors LOH 22q. Our data indicate that cyclin D1 is a target of hSNF5/INI1in primary tumors. 16051426_Increased cyclin D1 expression seen when earlier and later stage esophageal carcinomas stages compared 16115225_Cyclin D1 expression was significantly associated with tumour size and lymph node metastases in thyroid papillary microcarcinoma. 16123218_cases of cyclin D1-negative mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) do exist and are part of the spectrum of MCL 16131791_an activating mutation of the beta-catenin gene affected regulation of the cyclin D1 gene, resulting in the generation of intrathoracic sporadic desmoid tumor 16142313_the Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in carcinogenesis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas through overexpression of its target genes, particularly cyclin D1 16155412_STAT5b may mediate the transcriptional activation of cyclin D1 after hypoxic stimulation. 16163549_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16163738_cyclin D1 nuclear localization has a role in cancer [review] 16166625_SMAR1 regulates cyclin D1 by modification of chromatin through the SIN3/histone deacetylase 1 complex 16172916_The binding of STAT5 to the cyclin D1 promotor might up regulate cyclin D1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 16174239_expression of cyclin D1 and c-Myc in epithelial ovarian cancer reaffirms the notion that they are crucial components in the pathway of tumorigenesis 16207592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16226824_p38 kinase activation is linked temporally with cyclin D1 expression after PH and appears to exert cell cycle control in the adult liver. 16258726_integrin-dependent signal transduction events regulate the expression of cyclin D1 during G1 phase [review] 16258756_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16273238_Cyclin D1 expression may be a useful biomarker for assessing the risk of developing esophageal cancer. 16322291_Hypermethylation of cyclin d2 is asspciated with prostate tumorigenesis 16328437_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16328437_data support the hypothesis that the CCND1 A870G polymorphism may increase the risk of colorectal cancer in our Indian population 16334487_level of cyclin D1 negatively correlates with the proliferation properties of leukemic cells 16343742_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16399423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16406195_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16407831_TIMP-1-mediates cell-cycle arrest via cyclin D1 downregulation & p27KIP1 upregulation. 16461912_These studies indicate that the altered AR regulatory capacity of cyclin D1b contributes to its association with increased prostate cancer risk and provide evidence of cyclin D1b-mediated transcriptional regulation. 16488657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16490596_an association with alcohol consumption and the CCND1 gene or protein levels, in both esophageal and gastric cancers 16495921_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16507767_This study demonstrates for the 1st time the involvement of MAPK-cyclin D1-p21(cip)machinery during cell growth inhibition and apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells induced by cysthationine gamma-lyase overexpression. 16508013_we identified ZONAB-responsive elements in cyclin D1 promoter, cyclin D1 expression is regulated by ZONAB 16547504_Cyclin D1 overexpression alters the proliferation and differentiation behavior of HaCaT skin keratinocytes in organotypic co-cultures. 16552496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16552496_Our study suggests that the effect of cyclin D1 gene polymorphism on colorectal cancer risk is only observed in males and AA/AG genotype of cyclin D1 gene is associated with a higher risk of colorectal cancer 16568089_expression is repressed by SUMO modification of Sam68 16601140_the subtype 2 receptor-mediated antiproliferative effect of SRIH on TT cell proliferation may be exerted through a decrease in cyclin D1 and cdk4 levels 16614707_Cyclin D1 expression was not significantly different in normal cervix and in cervical cancer. 16614728_These findings suggest heterogeneous abnormalities of CCND and RB in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, in which dysregulated CCND and RB1 may lead to impaired cell cycle control. 16616093_Differences in oncoprotein expression between endometriotic and adenomyotic tissues provide further evidence that the pathogenesis of endometriosis is different from that of adenomyosis. 16638786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16644723_glucocorticoid receptor (GR) represses cyclin D1 via Tcf-beta-catenin 16645724_ionizing radiation is able to enhance cyclin D1 transcription induced by B[a]PDE, and NFAT3 is involved in the regulation of cyclin D1 transcription by B[a]PDE or B[a]PDE plus ionizing radiation 16672066_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16690963_Mantle cell lymphoma should be very sensitive to targeted therapy aimed at functional inhibition of the cyclin D1/CDK4 complex. 16691558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16691558_Results indicate that individuals carrying the CCND1 GG genotype have increased risk for the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 16691626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16699726_ERK1/2, JNK1/2 and p38 mapk pathways are all required for B[a]P-induced G1/S transition 16705174_Cyclin D1 promotes cellular motility through inhibiting ROCK signaling and repressing the metastasis suppressor TSP-1. 16723714_Cav-1-deficient mammary acini displayed increased ERalpha levels and enhanced sensitivity toward estrogen-stimulated growth, with specific up-regulation of cyclin D1 16732330_Cyclin D1 is often mutated in esophageal cancer. The mutations disrupt phosphorylation at Thr-286, causing its nuclear accumulation. An acidic residue in the C-terminus is needed for recognition & phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. 16758952_Cyclin D1 expression was higher in benzo(a)pyrene treated embryo lung fibroblasts than in controls. 16776827_cyclin D1 expression is deregulated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis through a RhoA dependent mechanism that influences lung fibroblast proliferation 16783567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16783567_Study evaluated associations odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals in polymorphisms of seven candidate genes in 1,172 non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cases and 982 population-based controls, the cyclin D1 splice variant G870A (rs603965) increased NHL risk. 16788380_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16804724_When the combinations of the variables were assessed in two separate multivariate models, the combined variables p21/Ki-67 or p21/cyclin D1 expression were independent predictors for overall survival. 16815198_CCND1 amplification is uncommon and appears to be late event in the development of ethmoid sinus adenocarcinoma. 16820873_Pin1 expression is correlated with cyclinD1 expression and may have a role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 16829689_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16829689_association between this CCND1 genotype and colorectal cancer risk in the Singapore Chinese Health Study. 16832876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16843438_telomerase reverse transcriptase has a novel role in the modulation of cyclin D1 expression 16860316_novel signaling pathway links BRCA1-IRIS to cellular proliferation through c-Jun/AP1 nuclear pathway; finally, this culminates in the increased expression of the cyclin D1 gene 16865250_High levels of cyclin D1 expression is associated with salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma 16870553_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16884382_Cyclin D1 overexpression is associated with endometrial carcinoma 16912209_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16916940_Cyclin D1 or cyclin D3 are differentially used in the distinct mitogenic stimulations by growth factors or TSH. 16924241_Expression of p27Kip1 in melanoma is regulated via cyclin D1 control of Cks1/Skp2-mediated proteolysis. 16940298_HBx and NF-kappaB2/BCL3 mediated-cyclin D1 up-regulation might play an important role in the HBx-mediated HCC |
ENSMUSG00000070348 |
Ccnd1 |
2499.522203 |
3.6943943419 |
1.885338 |
0.040743284 |
2164.342248 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3983.6082948 |
106.4069405 |
1086.6360272 |
23.3158954 |
| ENSG00000110104 |
79080 |
CCDC86 |
protein_coding |
Q9H6F5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Citrullination;Coiled coil;Host-virus interaction;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Located in chromosome; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79080; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA binding [GO:0003723] |
17300783_cyclon gene encodes a phosphorylated nuclear protein consisting of repetitive sequences in the amino-terminus and a coiled-coil domain in the carboxyl-terminus 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23439384_Cyclon/CCDC68 levels correlate with the clinical presentation of relapsed schizophrenia |
ENSMUSG00000024732 |
Ccdc86 |
130.985596 |
2.6110291353 |
1.384619 |
0.157938942 |
77.154631 |
0.00000000000000000158083553840401944096599415319836955813850045104014497773792236046119796810671687126159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000013101141239103497286989516030394219138967643906331077968685505652501888107508420944213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
193.6304773 |
17.7415038 |
74.5535035 |
5.4418858 |
| ENSG00000110218 |
24145 |
PANX1 |
protein_coding |
Q96RD7 |
FUNCTION: Structural component of the gap junctions and the hemichannels involved in the ATP release and nucleotide permeation (PubMed:16908669, PubMed:20829356, PubMed:30918116). May play a role as a Ca(2+)-leak channel to regulate ER Ca(2+) homeostasis (PubMed:16908669). Plays a critical role in oogenesis (PubMed:30918116). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16908669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829356, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30918116}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Differentiation;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Gap junction;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Oogenesis;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the innexin family. Innexin family members are the structural components of gap junctions. This protein and pannexin 2 are abundantly expressed in central nerve system (CNS) and are coexpressed in various neuronal populations. Studies in Xenopus oocytes suggest that this protein alone and in combination with pannexin 2 may form cell type-specific gap junctions with distinct properties. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:24145; |
bleb [GO:0032059]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; gap junction [GO:0005921]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; gap junction channel activity [GO:0005243]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; leak channel activity [GO:0022840]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; wide pore channel activity [GO:0022829]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cation transport [GO:0006812]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 alpha production [GO:0032730]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931] |
16682648_Data show that erythrocytes express the gap junction protein pannexin 1. 16690868_Pannexin-1 in pyramidal neurons is activated by ischemia and may play an important role ionic dysregulation 16908669_Overexpression of PanX1 results in the formation of Ca(2+)-permeable gap junction channels between adjacent cells, thus, allowing direct intercellular Ca(2+) diffusion and facilitating intercellular Ca(2+) wave propagation. 17036048_Panx1 in the plasma membrane of the macrophage couples to the purinergic P2X7 receptor and permeabilize the macrophage membrane, this signaling is required for the processing and release of interleukin-1beta in response to P2X7 receptor activation. 17036048_pannexin-1 is required for processing of caspase-1 and release of mature IL-1beta induced by P2X(7) receptor activation. 17240370_pannexin1 appears to be the molecular substrate for the permeabilization pore (or death receptor channel) recruited into the P2X(7)R signaling complex 17715132_PANX1 channels contain a glycosylation site that targets the hexamer to the cell membrane. 17925379_These studies show that Panx1 and Panx3 have many characteristics that are distinct from Cx43 and that these proteins probably play an important biological role as single membrane channels. 18596211_Explored the pharmacological action of compounds known to block gap junctions on Panx1 channels activated by the P2X(7)R and the mechanisms involved in the interaction between these two proteins. 19056988_It is demonstrated that pannexin-1 is activated by NMDA receptor stimulation and contributes to epileptic like bursting activity in the hippocampus. 19150332_In this study, they investigated whether endogenous panx-1 was activated and contributed to membrane current in osmotically swollen HEK-293 cells. 19213873_Pannexin 1 contributes to ATP release in airway epithelia. 20086016_although Panx1 and Panx3 share a common endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi secretory pathway to Cx43, their ultimate cell surface residency appears to be independent of cell contacts and the need for intact microtubules 20516070_Pannexin1 and Pannexin2 channels show quaternary similarities to connexons and different oligomerization numbers from each other 20622111_Pannexin 1 is the conduit for ATP release from erythrocytes in response to lowered O(2) tension. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20660288_T-cell receptor stimulation results in the translocation of P2X1 and P2X4 receptors and pannexin-1 hemichannels to the immune synapse. 20884646_immunostimulatory effects of hypertonic stress treatment are mediated by the controlled cellular release of ATP through Panx1 hemichannels . 20944749_data identify PANX1 as a plasma membrane channel mediating the regulated release of find-me signals and selective plasma membrane permeability during apoptosis, and a new mechanism of PANX1 activation by caspases 21606493_TRPV4 and Rho transduce cell membrane stretch/strain into pannexin 1-mediated ATP release in airway epithelia. 21659516_indicate that the oligomerization and trafficking of Panx1 are regulated by the C-terminal domain, whereas internalization of long lived Panx1 channels occurs in a manner that is distinct from classical endocytic pathways 21791690_MSR1 was significantly associated with the presence of Barrett esophagus/esophageal adenocarcinoma in derivation and validation samples 21865551_both P2X(7) and Panx-1 are required for GM-CSF promotion of multinucleated macrophages fusion 22311122_Panx1 assembles into a membrane anion channel with a relatively low single-channel conductance. 22311983_mechanism of PANX1 channel regulation 22753409_while Panx1 is present in skin melanocytes it is up-regulated during melanoma tumor progression, and tumorigenesis can be inhibited by the knockdown of Panx1 raising the possibility that Panx1 may be a viable target for the treatment of melanoma. 22947051_Panx1 level is modulated during keratinocyte differentiation and carcinogenesis and reveal distinct localization pattern for Panx1 in human adnexal structures. 22972801_These results suggest that panx1 contributes to pathophysiological ATP release in lipoapoptosis induced by saturated FFA; panx1 may play a role in hepatic inflammation by mediating an increase in extracellular ATP concentration in lipotoxic liver injury. 23033481_S-nitrosylation of Panx1 at Cys-40 and Cys-346 inhibits Panx1 channel currents and ATP release. 23456773_Blocking Panx1 hemichannels by reducing their opening or protein expression inhibited HIV replication in CD4(+) T lymphocytes 23549611_Overexpression of Panx1 in THP-1 cells also failed to increase the infl ammasome activity as revealed by similar IL-1beta and caspase-1 activity in comparison with normal THP-1 cells 23594276_Pannexin-1 immunoreactivity was mainly localized to enteric ganglia, blood vessel endothelium, erythrocytes, epithelial and goblet cells. In ulcerative colitis myenteric ganglia, there was a significant reduction in Panx1. 23700432_Panx1 localizes to chlamydial inclusions but its absence does not effect chlamydial development during infection of cells. 23798685_findings suggest that chemoattractant receptors require PANX1 to trigger excitatory and inhibitory signals that synergize to fine-tune chemotactic responses at the front and back of neutrophils 23918924_histamine induces ATP release from human subcutaneous fibroblasts, via pannexin-1 hemichannels, leading to [Ca(2+)]i mobilization and cell growth through the cooperation of H1 and P2 (probably P2Y1) receptors. 23936165_P2X4 assembles with P2X7 and pannexin-1 in gingival epithelial cells and modulates ATP-induced reactive oxygen species production and inflammasome activation during P. gingivalis infection. 24146091_Panx1 and Panx2 expression was detected in the temporal lobe cortex of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and in the control tissues. 24418937_The critical involvement of Panx1 despite its absence in epiplexus cells was while it was not surprising that ATP could activate the epiplexus cells. 24531690_These findings suggest that nonmetal hapten reactivity to thiol residues causes membrane disruption of keratinocytes and reactive oxygen species production that leads to ATP release through opening of Panx hemichannels. 24646995_data identify a novel linkage between an antibiotic, pannexin channels and cellular integrity, and suggest that re-engineering certain quinolones might help develop newer antibacterials 24655807_Panx1 is expressed on human platelets and amplifies Ca(2+) influx, ATP release and aggregation through the secondary activation of P2X1 receptors. 24671093_Pannexin-1 is not involved in the P2X7 mediated uptake of dye in Hek-293 cells. 25008946_Data suggest that both up-regulation and down-regulation of expression of pannexins (PANX1, PANX2, PANX3) are associated with disease onset and/or progression; examples include neoplasms, multiple sclerosis, migraine, and hypertension. [REVIEW] 25112874_Chemotherapeutic drugs also activated an alternative caspase- and Panx1-independent pathway for ATP release from Jurkat cells in the presence of benzyloxycarbonyl-VAD, a pan-caspase inhibitor. 25170954_These findings indicate that Panx1 participates in urothelial mechanotransduction and signaling by providing a direct pathway for mechanically-induced ATP release and by functionally interacting with P2X7Rs 25239622_Panx1 and Panx3 are co-expressed in human skeletal muscle myoblasts and play a pivotal role in dictating the proliferation and differentiation. 25301060_Pannexin-1 channel is involved in cigarette smoke-induced ATP release in the lung. 25947940_The frequency of Panx1-400C homozygotes was higher among cardiovascular patients with hyper-reactive platelets. The Panx1-400C variant encodes a gain-of-function channel that enhances collagen-induced ATP release and platelet aggregation. 26009197_This review focuses on the known roles of Panx1 related to purinergic signalling in the vasculature focusing on post-translational modifications and channel gating mechanisms that may participate in the regulated release of ATP. 26009198_Within this review, the regulation of Panx1 channels is discussed, with a focus on how they may contribute to platelet function. 26054298_Pannexin1-dependent pathophysiological eATP release in lipoapoptosis is capable of stimulating migration of human monocytes 26098574_Data show that mutation encoding a truncated form of the pannexin-1 (PANX1) channel, PANX1(1-89), as recurrently enriched in highly metastatic breast cancer cells. 26223428_The results of this study do not support a major contribution of PANX1-3 to disease risk of schizophrenia according to DSM-5. 26242575_Panx1 channels promote leukocyte adhesion and emigration through the venous wall during acute systemic inflammation. 26385361_PANX-1 plays an important role in the release of cytokines and glutamate in a tumor cell line. 26755773_CBX and other inhibitors, including probenecid, attenuate Panx1 channel activity through modulation of the first extracellular loop. 26823467_Decreased Panx1 function is a response to cell acidification mediated by IFN-gamma-induced up-regulation of Duox2. 27025600_Overactive Panx-1 promotes cancer cell survival in the context of mechanical deformation. Panx-1 inhibitors can be used to treat highly metastatic cancer. Mechanosensitive Panx-1 channels will be a new target for the prevention of metastasis and stress-induced diseases. 27109381_a pivotal role of P2X7 receptor-pannexin-1 in oxysterols toxicity in retinal cells 27129271_Data indicate that the consanguineous parents are each heterozygous for Pannexin1 (PANX1) but are not affected by the multiorgan syndromes. 27518505_Panx1 channels promote skeletal muscle myoblast differentiation and fusion. (Review) 27720686_Panx1 channels are involved in beta-toxin-induced cell death. 27741412_Pannexin1 is a mediator of inflammation and cell death. (Review) 27883084_These results elucidate for the first time PNX1-hemichannels as potentially main extracellular translocation pathway for NDKs from an intracellular pathogen. 28036289_Panx1 was mainly distributed in microcolumn neurons, dysmorphic neurons, balloon cells and reactive astrocytes in cortical lesions from intractable epilepsy patients with focal cortical dysplasia. 28134257_Progressive PANX1 channel opening is directly linked to permeation of ions and large and occurs during both irreversible and reversible forms of channel activation. This unique, quantized activation process enables fine tuning of PANX1 channel activity and may be a generalized regulatory mechanism for other related multimeric channels. 28142297_presence of the Panx1-400C allele was not associated with platelet reactivity in stable cardiovascular patients. 28389204_Pannexin1 (Panx1) was suggested to be functionally associated with purinergic P2X and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor channels. Activation of these receptor channels by their endogenous ligands leads to cross-activation of Panx1 channels. This in turn potentiates P2X and NMDA receptor channel signaling. 28735901_The ubiquitous expression, as well as its function as a major ATP release and nucleotide permeation channel, makes Panx1 a primary candidate for participating in the pathophysiology of CNS disorders. 28855161_ATP release from red blood cells is not mediated by the cAMP-mediated Panx1 pathway. 29222846_Influence of the three-dimensional culture of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells within a macroporous polysaccharides scaffold on Pannexin 1 and Pannexin 3. 29357945_All three pannexins Panx1, Panx2, and Panx3 mRNAs were expressed in all of the analyzed undifferentiated stem cell lines. 29393654_Stimulation of TRPV4 releases ATP via Pannexin channels in human pulmonary fibroblasts. 29676177_authors proposed a tentative intracellular signaling pathway of the acetylcholine-induced ciliary beat, in which the pannexin-1-purinergic P2X receptor unit may play a central role in ciliary beat regulation 29802622_Studies show that the Pannexin1 (Panx1) membrane channel responds to different stimuli with distinct channel conformations [Review]. 29848662_These data suggest a proepileptic role of pannexin-1 channels in chronic epilepsy. 29882918_These results newly identify Pannexin-1 as a protein highly expressed in human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells. 29932112_The pannexin 2 (Panx2) N86Q mutant is glycosylation-deficient and tends to aggregate in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)reducing its cell surface trafficking but it can still interact with pannexin 1 (Panx1). 30061676_ATP release was activated by TSPO ligands, and blocked by inhibitors of VDAC and ANT, while it was insensitive to pannexin-1 blockers. 30377218_hardly opens at a positive membrane potential, but its activity redoubles when a couple of specific amino acids (GS in particular) are inserted at the N terminus 30814251_This work implicates SRC-mediated PANX1 function in normal vascular hemodynamics and suggests that Tyr(198)-phosphorylated PANX1 is involved in hypertensive vascular pathology 30918116_Describe four independent families in which mutations in PANX1 cause familial or sporadic female infertility via a phenotype that we term 'oocyte death.' The mutations, which are associated with oocyte death, alter the PANX1 glycosylation pattern. 31110238_Role of pannexin-1 in the cellular uptake, release and hydrolysis of anandamide by T84 colon cancer cells. 31211503_Serum pannexin-1 levels were significantly lower in Behcet's syndrome. 31242494_Given the involvement of Panx1 at multiple steps of -inflammatory pathology, Panx1 could be a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of Acute kidney injury-{REVIEW} 31278290_A novel motif in the proximal C-terminus of Pannexin 1 regulates cell surface localization. 31410978_These data identify a novel signaling nexus between MLKL, RAB27, and PANX1 and propose ways to interfere with inflammation associated with necroptosis. 31694915_The Panx1 deletion protects against renal IRI by attenuating MAPK/ERK activation in a ferroptotic pathway. 31698505_Pannexin 1 activation and inhibition is permeant-selective. 32023876_A Genetic Polymorphism in the Pannexin1 Gene Predisposes for The Development of Endothelial Dysfunction with Increasing BMI. 32203128_Cryo-EM structure of human heptameric Pannexin 1 channel. 32231289_In combination with functional characterization, this work elucidates the previously unknown architecture of pannexin channels and establishes a foundation for understanding their unique channel properties. 32246089_Cryo-EM structures of human pannexin 1 channel. 32284561_Structural basis for gating mechanism of Pannexin 1 channel. 32312847_Endothelial Pannexin 1 Channels Control Inflammation by Regulating Intracellular Calcium. 32494015_Structures of human pannexin 1 reveal ion pathways and mechanism of gating. 32639715_Pannexin 1 Channels as a Therapeutic Target: Structure, Inhibition, and Outlook. 32688074_PANX1 in inflammation heats up: New mechanistic insights with implications for injury and infection. 32931038_The interplay between alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, pannexin-1 channels and P2X7 receptors elicit exocytosis in chromaffin cells. 33050989_Activation of pannexin-1 mediates triglyceride-induced macrophage cell death. 33052098_Single-cell dynamics of pannexin-1-facilitated programmed ATP loss during apoptosis. 33345473_[Regulatory effect of the pannexin1 channel on invasion and migration of testicular cancer Tcam-2 cells and its possible mechanism]. 33394272_Human Pannexin 1 channel: Insight in structure-function mechanism and its potential physiological roles. 33405952_Pannexin 1 mutation found in melanoma tumor reduces phosphorylation, glycosylation, and trafficking of the channel-forming protein. 33410749_ATP and large signaling metabolites flux through caspase-activated Pannexin 1 channels. 33495594_Homozygous variants in PANX1 cause human oocyte death and female infertility. 33499026_Restraint of Human Skin Fibroblast Motility, Migration, and Cell Surface Actin Dynamics, by Pannexin 1 and P2X7 Receptor Signaling. 33564071_Identification of pannexin 1-regulated genes, interactome, and pathways in rhabdomyosarcoma and its tumor inhibitory interaction with AHNAK. 33647315_Pannexin 1 binds beta-catenin to modulate melanoma cell growth and metabolism. 34067798_Pannexin 1 Transgenic Mice: Human Diseases and Sleep-Wake Function Revision. 34181173_Inhibiting of circ-TLK1 inhibits the progression of glioma through down-regulating PANX1 via targeting miR-17-5p. 34301959_Deacetylation as a receptor-regulated direct activation switch for pannexin channels. 34380770_Reduced pannexin 1-IL-33 axis function in donor livers increases risk of MRSA infection in liver transplant recipients. 34796785_PANX1 is a potential prognostic biomarker associated with immune infiltration in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A pan-cancer analysis. 35133866_Structures of human pannexin-1 in nanodiscs reveal gating mediated by dynamic movement of the N terminus and phospholipids. 35291811_Is the Pannexin-1 Channel a Mechanism Underlying Hypertension in Humans? a Translational Study of Human Hypertension. 35315432_Endothelial pannexin-1 channels modulate macrophage and smooth muscle cell activation in abdominal aortic aneurysm formation. 35325354_Novel insights into the SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis signaling pathways in preeclampsia patients: identifying pannexin 1 and toll-like receptor 4 as innovative prospective diagnostic biomarkers. 35373707_Pannexin1 inhibits autophagy of cisplatin-resistant testicular cancer cells by mediating ATP release. 35486697_Endogenous pannexin1 channels form functional intercellular cell-cell channels with characteristic voltage-dependent properties. 35563450_Pannexin-1 Activation by Phosphorylation Is Crucial for Platelet Aggregation and Thrombus Formation. 35834089_A novel heterozygous variant in PANX1 is associated with oocyte death and female infertility. 36012667_Mechanosensitive Pannexin 1 Activity Is Modulated by Stomatin in Human Red Blood Cells. 36037373_ER-resident STIM1/2 couples Ca(2+) entry by NMDA receptors to pannexin-1 activation. 36252698_A2A receptor-induced overexpression of pannexin-1 channels indirectly mediates adenosine fibrogenic actions by favouring ATP release from human subcutaneous fibroblasts. 36291086_Activity and Stability of Panx1 Channels in Astrocytes and Neuroblastoma Cells Are Enhanced by Cholesterol Depletion. |
ENSMUSG00000031934 |
Panx1 |
157.138697 |
6.7048109450 |
2.745197 |
0.209566545 |
168.466064 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000001600302613447763115195648314551598187908856716701582330602213038704909973805640787923314970838431199953721950635099346982315182685852050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000258147175677475219774016003110394969169868433673672993566725932793685780403127360173260220475074250279234888694190885871648788452148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
273.8844163 |
30.0455282 |
41.3283224 |
3.8618921 |
| ENSG00000110218_ENSG00000250519 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
410.983878 |
4.1477941083 |
2.052344 |
0.108824245 |
356.114564 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000019753269889892166783740943138119097819719853625616038234322445459860928193195008454958830667844270305618501347174556218054388997850156919961148987421693342763124699570396271480942154452542641458571981427638775130617432296276092529296875000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006566627557991179216363044530766422832775748053641237241001951621282110206158985918545748410481374450806559265699047822427778360149589956606746480401138821462021650080885726439186565178961771729881924386518221581354737281799316406250000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
670.1981513 |
42.1251091 |
162.8237032 |
8.3329903 |
| ENSG00000110237 |
9828 |
ARHGEF17 |
protein_coding |
Q96PE2 |
FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RhoA GTPases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12071859}. |
Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Acts upstream of or within actin cytoskeleton organization. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9828; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] |
12071859_a Rho-specific GEF with novel structural and regulatory properties and predominant expression in the heart 18677770_Identification of ARHGEF17, mutations in melanoma. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22911862_TEM4 contains a novel actin binding domain and binding to actin is essential for TEM4 subcellular localization and activity. 23195829_The rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 17 is drastically alter the effect of cGMP/cGK involving signaling pathways on RhoA-activated downstream effectors. 23825001_data implicate TEM4 as an essential regulator of the actin cytoskeleton that ensures proper membrane protrusion at the leading edge of migrating cells and efficient cellular migration via suppression of actomyosin contractility 26953350_Interaction of the central domain of ARHGEF17 with Mps1. 29997225_results provide compelling evidence that ARHGEF17 is a risk gene for Intracranial aneurysm. 33801779_RhoGEF17-An Essential Regulator of Endothelial Cell Death and Growth. |
ENSMUSG00000032875 |
Arhgef17 |
86.675791 |
0.2593216617 |
-1.947185 |
0.294590216 |
42.134134 |
0.00000000008522256344876616549550269090278729888776609868727973662316799163818359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000442605572309566748008230176398072885923795638518640771508216857910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9198893 |
7.3653580 |
147.0063101 |
19.5691627 |
| ENSG00000110328 |
374378 |
GALNT18 |
protein_coding |
Q6P9A2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the initial reaction in O-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis, the transfer of an N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc) residue from UDP-GalNAc to a serine or threonine residue on the protein receptor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22186971}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lectin;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:22186971}. |
Enables polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity. Involved in protein O-linked glycosylation. Predicted to be located in Golgi membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374378; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0004653]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33909026_Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 18 retains in endoplasmic reticulum depending on its luminal regions interacting with ER resident UGGT1, PLOD3 and LPCAT1. |
ENSMUSG00000038296 |
Galnt18 |
16.797872 |
12.7595466558 |
3.673505 |
0.601153747 |
41.428381 |
0.00000000012226929614711450063520728687090381378577141902042058063670992851257324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000628375630616786218831291075650937599794687571375106927007436752319335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.8953064 |
13.3874753 |
2.5530080 |
0.9019460 |
| ENSG00000110455 |
84680 |
ACCS |
protein_coding |
Q96QU6 |
FUNCTION: Does not catalyze the synthesis of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate but is capable of catalyzing the deamination of L-vinylglycine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11470512}. |
Alternative splicing;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in biosynthetic process. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84680; |
identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; transaminase activity [GO:0008483]; amino acid metabolic process [GO:0006520]; biosynthetic process [GO:0009058] |
20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000040272 |
Accs |
469.157182 |
0.2283216308 |
-2.130861 |
0.103568552 |
422.082652 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000085928079442106075434561286820662780651513820267668654378868796495992204507580424805008629428655088024396248797686207696210752144901949297317352557712582899490262474151939492253848688205889341281995839281397788208196941542687499922259509 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000033641868768315271747020973708481478050584757182510127644827497029551252043878716480229907605233791673819828679015841917374935906036882958218811793369342028572667095602307105183153103007829222243116603643470953009874418906770265902395067 |
Yes |
Yes |
168.4694457 |
17.3044322 |
740.5219475 |
52.5437502 |
| ENSG00000110492 |
4192 |
MDK |
protein_coding |
P21741 |
FUNCTION: Secreted protein that functions as cytokine and growth factor and mediates its signal through cell-surface proteoglycan and non-proteoglycan receptors (PubMed:18469519, PubMed:12573468, PubMed:12122009, PubMed:10212223, PubMed:24458438, PubMed:15466886, PubMed:12084985, PubMed:10772929). Binds cell-surface proteoglycan receptors via their chondroitin sulfate (CS) groups (PubMed:12084985, PubMed:10212223). Thereby regulates many processes like inflammatory response, cell proliferation, cell adhesion, cell growth, cell survival, tissue regeneration, cell differentiation and cell migration (PubMed:12573468, PubMed:12122009, PubMed:10212223, PubMed:10683378, PubMed:24458438, PubMed:22323540, PubMed:12084985, PubMed:15466886, PubMed:10772929). Participates in inflammatory processes by exerting two different activities. Firstly, mediates neutrophils and macrophages recruitment to the sites of inflammation both by direct action by cooperating namely with ITGB2 via LRP1 and by inducing chemokine expression (PubMed:10683378, PubMed:24458438). This inflammation can be accompanied by epithelial cell survival and smooth muscle cell migration after renal and vessel damage, respectively (PubMed:10683378). Secondly, suppresses the development of tolerogenic dendric cells thereby inhibiting the differentiation of regulatory T cells and also promote T cell expansion through NFAT signaling and Th1 cell differentiation (PubMed:22323540). Promotes tissue regeneration after injury or trauma. After heart damage negatively regulates the recruitment of inflammatory cells and mediates cell survival through activation of anti-apoptotic signaling pathways via MAPKs and AKT pathways through the activation of angiogenesis (By similarity). Also facilitates liver regeneration as well as bone repair by recruiting macrophage at trauma site and by promoting cartilage development by facilitating chondrocyte differentiation (By similarity). Plays a role in brain by promoting neural precursor cells survival and growth through interaction with heparan sulfate proteoglycans (By similarity). Binds PTPRZ1 and promotes neuronal migration and embryonic neurons survival (PubMed:10212223). Binds SDC3 or GPC2 and mediates neurite outgrowth and cell adhesion (PubMed:12084985, PubMed:1768439). Binds chondroitin sulfate E and heparin leading to inhibition of neuronal cell adhesion induced by binding with GPC2 (PubMed:12084985). Binds CSPG5 and promotes elongation of oligodendroglial precursor-like cells (By similarity). Also binds ITGA6:ITGB1 complex; this interaction mediates MDK-induced neurite outgrowth (PubMed:15466886, PubMed:1768439). Binds LRP1; promotes neuronal survival (PubMed:10772929). Binds ITGA4:ITGB1 complex; this interaction mediates MDK-induced osteoblast cells migration through PXN phosphorylation (PubMed:15466886). Binds anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) which induces ALK activation and subsequent phosphorylation of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS1), followed by the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and PI3-kinase, and the induction of cell proliferation (PubMed:12122009). Promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition through interaction with NOTCH2 (PubMed:18469519). During arteriogenesis, plays a role in vascular endothelial cell proliferation by inducing VEGFA expression and release which in turn induces nitric oxide synthase expression. Moreover activates vasodilation through nitric oxide synthase activation (By similarity). Negatively regulates bone formation in response to mechanical load by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in osteoblasts (By similarity). In addition plays a role in hippocampal development, working memory, auditory response, early fetal adrenal gland development and the female reproductive system (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P12025, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R1S9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10212223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10683378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10772929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12084985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12122009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12573468, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15466886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1768439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18469519, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22323540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24458438}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Growth factor;Heparin-binding;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of a small family of secreted growth factors that binds heparin and responds to retinoic acid. The encoded protein promotes cell growth, migration, and angiogenesis, in particular during tumorigenesis. This gene has been targeted as a therapeutic for a variety of different disorders. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:4192; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; chondroitin sulfate binding [GO:0035374]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparan sulfate binding [GO:1904399]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; adrenal gland development [GO:0030325]; behavioral fear response [GO:0001662]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cerebellar granular layer development [GO:0021681]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; defecation [GO:0030421]; dentate gyrus development [GO:0021542]; estrous cycle [GO:0044849]; glial cell projection elongation [GO:0106091]; leukocyte chemotaxis involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002232]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process [GO:1904036]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to wounding [GO:0106015]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; negative regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045590]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; positive regulation of artery morphogenesis [GO:1905653]; positive regulation of blood vessel branching [GO:1905555]; positive regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061036]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation [GO:2000347]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of inflammatory response to wounding [GO:0106016]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010838]; positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell [GO:1904996]; positive regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:1903039]; positive regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002690]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000179]; positive regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001224]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of neutrophil extravasation [GO:2000391]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell chemotaxis [GO:0071673]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905564]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; regulation of behavior [GO:0050795]; regulation of bone remodeling [GO:0046850]; regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032330]; response to auditory stimulus [GO:0010996]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; short-term memory [GO:0007614]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002286]; tissue regeneration [GO:0042246] |
11925507_Requirement of chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate recognition in midkine-dependent migration of macrophages 12077357_In a blood vessel model, midkine induced stratification of endothelial cells and increased their proliferation and glycosaminoglycan synthesis. Increased proliferation of endothelium also occurred by coculture with smooth muscle cells and midkine. 12122009_midkine binds to ALK and has a role in signal transduction for cell growth and survival 12127679_Midkine is expressed in astrocytes during the early period of human brain ischemia. 12147681_results suggest that the cell surface-expressed nucleolin serves as a low affinity receptor for midkine and could be implicated in its entry process 12175547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579281_Increased midkine expression is associated with superficial esophageal cancer 12841873_Increased preoperative serum midkine in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poor survival. 14970216_nuclear targeting growth factor midkine undergoes proteasomal degradation 15050737_a G to T substitution at the 62nd site of intron 3 in the midkine gene enhances the expression of truncated midkine in colon cancer 15138367_data showed that the midkine promoter activated a therapeutic gene in a wider range of human breast cancer than the c-erbB-2 promoter and suggest that MK promoter-mediated gene therapy is potentially more favorable in clinical settings 15146411_MK participates in each of the two distinct phases of rheumatoid arthritis development, namely, migration of inflammatory leukocytes and osteoclast differentiation, and is a key molecule in pathogenesis 15201962_Midkine promoter-based conditionally replicative adenovirus might be a promising new modality of gene therapy for malignant glioma. 15355893_Increased midkine levels are associated with tumorigenesis in neurofibromatosis type 1 15734764_MK may play roles, such as stimulation of endometriotic cell proliferation, in the development of endometriosis. 15781266_reported that human MK exclusively localized to the nucleus and nucleolus in HepG2 cells by using GFP as a tracking molecule 15897897_A survival molecule, midkine, was identified by cDNA array to be expressed only in drug-resistant neuroblastoma cells. 16895951_Midkine likely plays a key role in human fetal adrenal glandcdevelopment. 17066487_Resultsd suggested that truncated MK (tMK) has a greater ability of malignant transformation than full-length MK, and whether tMK is expressed or not will be useful information for improving cancer chemotherapy. 17171794_localized exclusively to the nucleus and accumulated in the nucleolus in the three kinds of cancer cell lines 17267033_Overexpression of midkine is associated with childhood B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia 17368428_Midkine, pleiotrophin (PTN), and their receptors syndecan-3 and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta, were highly expressed in the striatum during developmen 17451201_Antisense oligonucleotide targeting midkine suppressed the angiogenesis both in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (HEPG2)-induced chick chorioallantoic membrane and in situ human HCC tissues. 17493173_MK expression was increased along with tumor progression. 17607302_Midkine expression was detected in the glomeruli, tubular epithelium and interstitium of kidneys from patients with diabetic nephropathy 17845207_MK is involved in granulosa cell proliferation and estradiol production in developing follicles and may play a role as a local regulator in the human ovary. 17931612_IL-6 and IL-8, and probably midkine and VEGF-A, appear to participate in the development of cancer-related cachexia in gastroesophageal malignancies. 17971413_These data demonstrate a crucial role of MK-LRP1 signaling in anchorage-independent cell growth. 18176965_Midkine has anti-apoptotic and cytoprotective role during cadmium toxicity in hepatocytes 18195496_Midkine was expressed in choroid plexus of normal brain and released there; CSF MK levels were not high in patients with cerebral infarction but were increased in patients with meningitis 18329695_MK is considered to mediate growth activity of odontogenic tumors and cell differentiation of odontogenic mixed tumors through molecular mechanisms similar to those involved in morphogenesis of the tooth. 18422745_higher serum MK protein concentration was correlated with the presence of lymph node metastases and prognosis of endometrial carcinomas 18469519_Midkine induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Notch2/Jak2-Stat3 signaling in human keratinocytes. 18476626_Both TP and MK are important for angiogenesis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. The expression of TP, MK and CD105 were all correlated with T-stage and lymph node metastasis. 18657127_increased expression in the prefrontal cortex of chronic alcoholics 18682710_Increased serum midkine is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 18698021_midkine enhances soft-tissue sarcoma tumor growth 18712601_Quantitative analysis of MK mRNA may be a promising modality for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer and the prediction of its prognosis. 18851943_The major finding of this study is a novel MK-triggered signaling mechanism implicated in migration and invasiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. 18956201_midkine-mRNA expression was found in the majority of the neuroblastoma tissues. No correlation of MK status with survival, risk factors or disease stage was observed. 18985819_Midkine accumulated in nucleolus of HepG2 cells involved in rRNA transcription. 19016768_Plasma MDK level is a prognostic factor for human neuroblastoma. 19060126_Midkine prevents ventricular remodeling and improves long-term survival after myocardial infarction. 19112919_MK gene expression is increased with different levels in B-ALL patients. 19250738_MDK contributes to gastric cancer cell proliferation and suggest that it plays an important role in the development of human gastric cancer. 19409372_These results indicate that MK might be involved in the pathogenesis of leukemia and could be taken as an ideal diagnostic marker and molecular target for the treatment of acute leukemia. 19538527_High plasma midkine is associated with breast cancer. 19698107_The angiogenic factor midkine is regulated by dexamethasone and retinoic acid during alveolarization and in alveolar epithelial cells. 19728850_ulcerative colitis is associated with increased circulating midkine, which corresponds with clinical, endoscopic, inflammatory and angiogenic activity, and anemia. 20030927_High expression of MK and VEGF in bone marrow is correlated with angiogenesis and prognosis of multiple myeloma. 20030935_There is powerful drug efflux ability in lymphoblastic leukemia cells with high midkine gene expression. 20308059_Midkine and pleiotrophin have bactericidal properties: preserved antibacterial activity in a family of heparin-binding growth factors during evolution. 20350697_Serum midkine is a novel, reliable marker for risk-stratifying of heart failure patients with left ventricular systolic or diastolic dysfunction. 20442752_Midkine promotes self-renewal and proliferation of human embryonic stem cells. 20447063_Recombinant human MDK stimulates proliferation of articular chondrocytes. 20511550_Because of its wide expression in cancer tissues and its contribution to tumorigenesis, secreted MDK appears to be a novel attractive candidate for a cancer vaccine. 20525245_High serum midkine is associated with ovarian cancer. 20544404_there was powerful drug efflux ability in lymphoblastic leukemia cells with high MK gene expression. MK gene may take part in multidrug resistance. 20589434_Increased Serum Midkine Concentrations Correlate with Recurrence and Decreased Serum Midkine Level Correlates with Imatinib therapy in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 20811700_Midkine (MK) expression may affect prognosis via the p53 status and mutation of the p53 gene, and MK may be an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in patients with cancer cells with mutant p53. 21094842_Midkine levels are dependent on heart and kidney function, and might also represent a surrogate marker of subclinical inflammation in heart transplant recipients. 21208277_The level of midkine expression in breast cancer significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis (p = 0.001) and TNM staging (p = 0.003). 21212259_Premature ligand-receptor interaction during biosynthesis limits the production of growth factor midkine and its receptor LDL receptor-related protein 1. 21233844_selective targeting of the Mdk/ALK axis could help to improve the efficacy of antitumoral therapies for gliomas. 21787488_Quantitative analysis of MK messenger RNA expression revealed that periapical granulomas expressed significantly more MK than healthy gingival tissues. These findings suggest that MK is involved in the pathogenesis of periapical granulomas. 21826666_Increased midkine expression correlates with desmoid tumour recurrence. 21917682_Serum midkine levels can be useful to monitor hepatocellular carcinoma progression 21989914_Results demonstrate that the extent and timing of sympathetic neurogenesis is controlled by Midkine and Alk signaling. 22051879_Expression of MK and VEGF is increased in gastric cancer and increased expression is closely correlated with poor prognosis and survival 22249249_Data indicate that ARMCX2, COL1A1, MDK, MEST and MLH1 genes acquired methylation in drug-resistant ovarian cancer-sustaining (side population) cells. 22415659_The results showed that midkine expression in gastric tumor cells indirectly suppresses natural killer cytotoxicity by inducing MICA/B expression and suppressing NKG2D expression. 22417224_Letter: Plasma levels of midkine are not associated with plasma fibrinolytic potential or risk of venous thrombosis. 22562257_Midkine is differently expressed in tumors arising from colonic and rectal mucosa, where it may play diverse roles in carcinogenesis. 22669742_Estradiol induces the expression of midkine protein in lung cancer cells through the estrogen receptor beta activation pathway 22672821_Identify midkine interacting proteins in liver tumor cells. 22707563_Identify endothelial cells as the source of soluble midkine in the vascular system during hypoxia and defined midkine as a pivotal player of angiogenesis during ischemia in nonmalignant tissue. 22871361_Soluble rhMDK, rmMDK and rhPTN were expressed at a high-level and the protein was purified by a one-step purification using heparin affinity chromatography. Activity of purified rhMDK and rhPTN was confirmed by a cell proliferation assay. 23129424_MDK upregulation in castration resistant prostate cancer is associated with neuroendicrine differentiation (shown by its relation to CGA and TUBB3). 23212314_High MDK expression is associated with malignant pleural effusions. 23224432_High MDK expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 23243020_Findings indicate a critical role for the midkine-Notch2 signaling axis in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis, which implicates new strategies to treat neuroblastoma. 23391998_This study shows that airway epithelial cells of large airways and alveoli have a constitutive production of MK that is part of the bactericidal activity present in the air surface liquid, at least in vitro, and may thus be an important part of this arm of airway host defense. 23553629_The MDK signal peptide contains both subdominant and cryptic CD4+ T cell epitopes. 23719264_serum MDK level was significantly decreased in patients with hepatocellular carcinomas after curative resection and re-elevated when tumor relapse occurred. 23815177_High MK expression was found in cystic fibrosis lung tissue compared with control samples, involving epithelia of the large and small airways, alveoli, and cells of the submucosa (i.e., neutrophils and mast cells). 23899719_Circulating Midkine is significantly higher in malignant and non-malignant colorectal diseases than in apparently healthy individuals with more pronounced elevation in colorectal cancer than in non-malignant conditions. 24043271_Data shows the possibility that Staphylococcus aureus modulates and corrupts host airway defense lines such as MK by fragmentation in both immuno-competent and -suppressed patient groups. 24164595_MK might play an important role in the progression of HNSCC and may be a useful prognostic factor 24272599_Midkine is specifically expressed in papillary thyroid cancer tissues and is associated with clinicopathological features and BRAF mutation. 24500281_PKCdelta/midkine axis mediates hypoxic proliferation and differentiation of lung epithelial cells. 24516630_MK was expressed in adipocytes and regulated by inflammatory modulators. a significant increase in MK levels was observed in adipose tissue of obese ob/ob mice as well as in serum of overweight/obese subjects when compared with their respective controls. 24567526_Study presents novel MK functions and new upstream signaling effectors that induce its expression to promote PDAC. 24659893_frequently expressed in pancreatic cancer and associated with perineural invasion 25001988_MK expression in glioma was higher than in paratumor tissues. Overexpression was associated with the WHO grade, low Karnofsky score, time to recurrence, and poor survival. Co-expression of pleiotrophin and MK had a worse prognosis than either alone. 25017879_High expression levels of Midkine in gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma tissues may indicate a differentiation stage that is characteristic of malignancy, a late clinical stage and a poor prognosis. 25056169_High levels of midkine in severe peripheral artery disease patients introduce this cytokine as a possible novel effector in the advanced atherosclerotic process. 25283079_Midkine protein level is significantly higher in the papillary thyroid cancer than in the multi-nodular goiter patients. 25355294_Results from targeted sequencing in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia identified KMT2D and KIF1B as novel putative driver genes and a putative regulatory non-coding variant that coincided with overexpression of the growth factor MDK. 25428991_SP1 directly up-regulated the expression of midkine (MDK), and the SP1-MDK axis cooperated in glioma tumorigenesis. 25655295_Use hybrid-type modified chitosan derivative nanoparticles to deliver midkine-siRNA to HepG2 cells. 25787827_The Circulating Levels of Selenium, Zinc, Midkine, Some Inflammatory Cytokines, and Angiogenic Factors in Mitral Chordae Tendineae Rupture. 25817231_midkine is as good as or even better than thyroglobulin to screen patients with thyroid nodules for differentiated thyroid cancer before surgery, and to predict whether metastases exist 26159850_overexpression of midkine protein serves as an unfavorable prognostic biomarker in breast cancer patients 26297257_our results suggest that midkine expression could be a clinically useful marker in predicting the presence of multiple lymph node metastases in BRAFV600E papillary thyroid carcinoma. 26352402_MK high expression is an independent adverse prognostic factor in childhood ALL. Its level may be incorporated into an improved risk classification system for ALL and suggest the need of alternative regimens. 26566633_MK was significantly elevated in vitamin D deficiency and associated with anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies positivity which was significantly increased in vitamin D deficiency 26642712_PLSCR1 positively regulates hepatic carcinoma cell proliferation and migration through interacting with midkine 26656665_MDK plays an important role in non-small cell lung cancer progression and prognosis and may act as a convincing prognostic indicator for non-small cell lung cancer patients. 26798989_Study shows that overexpression of serum MK levels in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are associated with poor prognosis. 27089523_The concentration of MDK in amniotic fluid declined with gestational age.MDK concentrations in amniotic fluid were far higher than in maternal plasma. 27470002_midkine may be a good inflammatory marker in renal transplant recipients as in other inflammatory diseases. Moreover, it seems that it is not affected by factors other than inflammation during the post-transplantation period. 27497193_this paper shows that measurement of serum levels of MK is helpful in confirming the diagnosis of Henoch-Schonlein purpura and predicting related nephritis in Chinese children 27530994_Urinary midkine may be an effective biological marker for early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. 27692729_Midkine is involved in bowel inflammation in UC and lymph node metastasis in CRC, rendering midkine an attractive target for their treatment. 27813495_Results revealed that ectopic overexpression of midkine in HCC cell lines with IGF-1R inhibition markedly rescued inhibition of HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. These data imply that inhibition of IGF-1R suppresses HCC growth and invasion via down-regulating midkine expression. 27903979_Elevated plasma midkine and pleiotrophin levels in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients suggest their involvement in this disease. 28240744_we show that MK can potentially be used as a surrogate biomarker for predicting DTC metastases when Tg is not suitable due to TgAb positivity. 28559305_Data suggest that mature KLK9 (kallikrein 9) is a glycosylated chymotrypsin-like enzyme with strong preference for tyrosine over phenylalanine at P1 cleavage position; substrate specificity of KLK9 appears to extend to KLK10 and midkine; enzyme activity is enhanced by Mg2+ and Ca2+, but is reversibly attenuated by Zn2+; KLK9 is inhibited in vitro by many naturally occurring or synthetic protease inhibitors. 28656262_suppression of midkine gene promoted the antitumoral effect of cisplatin on human gastric cell line AGS in vitro and in vivo via Notch signaling pathway. 28686647_According to our results, serum MK has greater diagnostic value in diagnosing cancer, however, more reliable studies in larger cohort should be conducted to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of serum MK. 29113102_These results demonstrate that analysis of IHC expression patterns of MK and NANOG in pretreatment biopsy specimens during the work-up period can provide a more definitive prognosis prediction for each oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) patient that can help clinicians to develop a more precise individual treatment modality. 29164967_The data of this study showed that the serum MK concentration in ASD patients is significantly higher than healthy controls. 29344648_MDK promoted gemcitabine resistance of biliary tract cancer through inducing epithelial to mesenchymal transition via upregulating Notch1. 29355490_Midkine expression is not significantly linked to metastatic disease in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 29383694_Midkine can be considered as both a differentiating factor and a molecular-targeted therapy in odontogenic lesions 29486735_Positive expression of MK predicts poor prognosis in patients with resectable combined hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma. 29797475_Studied levels of mucin 16 (CA125), adenosine deaminase and midkine as tumor markers in nonsmall cell lung cancer-associated malignant pleural effusion. 29936723_High midkine expression is associated with invasion and metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 29984722_This study has demonstrated an important association between increased serum MK (midkine)levels and risk factors of atherosclerosis such as HT(Hypertension),increased total and LDL cholesterol. 30647120_NETosis substantially contributes to the pathogenesis of myocarditis and drives cardiac inflammation, probably via MK, which promotes PMN trafficking and NETosis. 31552013_Midkine Is Elevated After Multiple Trauma and Acts Directly on Human Cardiomyocytes by Altering Their Functionality and Metabolism. 31600291_MK has an excellent diagnostic value for hepatocellular carcinoma. 31639491_Midkine promotes articular chondrocyte proliferation through the MK-LRP1-nucleolin signaling pathway. 31648804_A combination of alpha-fetoprotein, midkine, thioredoxin and a metabolite for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma. 31801970_Midkine (MDK) growth factor: a key player in cancer progression and a promising therapeutic target. 31984657_Serum Midkine is a clinical significant biomarker for colorectal cancer and associated with poor survival. 32153561_Association of Midkine and Pleiotrophin Gene Polymorphisms With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Susceptibility in Chinese Han Population. 32308772_Midkine signaling maintains the self-renewal and tumorigenic capacity of glioma initiating cells. 32358581_NF1-mutant human and mouse brain neurons elaborate midkine to activate naive CD8(+ )T cells to produce Ccl4, which induces microglia to produce a key low-grade glioma growth factor (Ccl5) critical for low-grade glioma stem cell survival. 32587339_Growth Factor Midkine Aggravates Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension via Surface Nucleolin. 32879333_Serum Midkine, estimated glomerular filtration rate and chronic kidney disease-related events in elderly women: Perth Longitudinal Study of Aging Women. 33077955_Midkine rewires the melanoma microenvironment toward a tolerogenic and immune-resistant state. 33565751_Midkine: Utility as a Predictor of Early Diabetic Nephropathy in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus 33599989_Midkine-A potential therapeutic target in melanoma. 33625758_Shedding more light on the role of Midkine in hepatocellular carcinoma: New perspectives on diagnosis and therapy. 34689799_Diagnostic performance of Midkine ratios in fine-needle aspirates for evaluation of Cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. 34739899_Serum midkine level might be a diagnostic tool for COVID19 disease in pregnancy: From the disease severity, hospitalization and disease progression respects. 34916167_Extracellular vesicles derived from pancreatic cancer cells are enriched in the growth factor Midkine. 35028860_Midkine promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration by upregulating NR3C1 expression and activating the NF-kappaB pathway. 35236197_Maternal serum midkine level increases in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus: a case-control study. 35503453_Midkine Promotes Metastasis and Therapeutic Resistance via mTOR/RPS6 in Uveal Melanoma. 35588343_CAF-derived midkine promotes EMT and cisplatin resistance by upregulating lncRNA ST7-AS1 in gastric cancer. 36028490_Midkine expression by stem-like tumor cells drives persistence to mTOR inhibition and an immune-suppressive microenvironment. |
ENSMUSG00000027239 |
Mdk |
124.099278 |
0.1940339069 |
-2.365619 |
0.163316874 |
235.267548 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004232855479709366203980311139130414085852439536612442257274401426822560759431849833091651894057481317424558066387038915187477181479181603807049327770073432475328445434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000961183798161696098951992056112125893168799945947647419420649074423845194511498208744775962904652404681116695165593279238806087767278685252136938288458622992038726806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.7001502 |
4.4689907 |
211.2133137 |
12.3703756 |
| ENSG00000110660 |
54733 |
SLC35F2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IXU6 |
FUNCTION: Putative solute transporter. {ECO:0000305}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54733; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21874247_SLC35F2 was highly expressed in NSCLC tissues and the levels of expression, in particular the levels of the SLC35F2 transcript, were associated with NSCLC pathological staging. 29274137_Study showed that SLC35F2 was prominently upregulated in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) tissues at both protein and mRNA expression level and significantly associated with lymph node metastasis. These findings suggest that SLC35F2 exerts its oncogenic effect on PTC progression through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, with dependence on activation of TGFBR-1 and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. 33418944_SLC35F2, a Transporter Sporadically Mutated in the Untranslated Region, Promotes Growth, Migration, and Invasion of Bladder Cancer Cells. 34815782_USP32 confers cancer cell resistance to YM155 via promoting ER-associated degradation of solute carrier protein SLC35F2. |
ENSMUSG00000042195 |
Slc35f2 |
189.417019 |
3.2743882308 |
1.711225 |
0.128495835 |
181.604692 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000002163013875224856482677453622559205473187902787781310482293093648708477369849595527534419437398513823427623030404287618466696585528552532196044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000375142807613434080593969329679819791346584306438175806815933728734230006687647973254434928230444280935693135425879063404863700270652770996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
293.9225017 |
21.4668224 |
90.4504287 |
5.4832606 |
| ENSG00000110717 |
4728 |
NDUFS8 |
protein_coding |
O00217 |
FUNCTION: Core subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) which catalyzes electron transfer from NADH through the respiratory chain, using ubiquinone as an electron acceptor (PubMed:22499348). Essential for the catalytic activity and assembly of complex I (PubMed:22499348). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22499348}. |
3D-structure;4Fe-4S;Disease variant;Electron transport;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Respiratory chain;Transit peptide;Translocase;Transport;Ubiquinone |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, or Complex I, a multimeric enzyme of the respiratory chain responsible for NADH oxidation, ubiquinone reduction, and the ejection of protons from mitochondria. The encoded protein is involved in the binding of two of the six to eight iron-sulfur clusters of Complex I and, as such, is required in the electron transfer process. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Leigh syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:4728; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I [GO:0005747]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051539]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity [GO:0008137]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone [GO:0006120]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly [GO:0032981]; proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis [GO:0042776]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
15159508_2 new mutations (P85L upstream from the 2 cysteine motifs that coordinate the two [4Fe-4S] clusters which generate the complex I N2 clusters, & R138H between them)suggest that this subunit is essential for either the assembly or stability of complex I. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27516145_Results show that NDUFS8 protein and mRNA levels are up-regulated in lung neoplasm and correlate with poor overall survival. |
ENSMUSG00000059734 |
Ndufs8 |
269.473380 |
2.0835545771 |
1.059047 |
0.103350292 |
105.515233 |
0.00000000000000000000000094171177061652188712901581517226933943175163834463683342719020113922162584785269245912786573171615600585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000010043111079696431327482821642115139530909577970943722436662312483095227388929515655036084353923797607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
365.0830296 |
23.5130500 |
176.3144007 |
8.7574893 |
| ENSG00000110719 |
10312 |
TCIRG1 |
protein_coding |
Q13488 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of the V0 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons (By similarity). V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment (By similarity). Seems to be directly involved in T-cell activation (PubMed:10329006). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q29466, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q93050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10329006}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Membrane;Osteopetrosis;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of a large protein complex known as a vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase). The protein complex acts as a pump to move protons across the membrane. This movement of protons helps regulate the pH of cells and their surrounding environment. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. V-ATPase is comprised of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Mutations in this gene are associated with infantile malignant osteopetrosis. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:10312; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0033176]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0016471]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain [GO:0000220]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; dentin mineralization [GO:0097188]; enamel mineralization [GO:0070166]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; establishment of vesicle localization [GO:0051650]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis [GO:0061484]; immunoglobulin mediated immune response [GO:0016064]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lysosomal lumen acidification [GO:0007042]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; memory T cell activation [GO:0035709]; optic nerve development [GO:0021554]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; osteoclast proliferation [GO:0002158]; pH reduction [GO:0045851]; phagosome acidification [GO:0090383]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; protein catabolic process in the vacuole [GO:0007039]; protein localization to organelle [GO:0033365]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045667]; regulation of proton transport [GO:0010155]; response to silver ion [GO:0010272]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; ruffle organization [GO:0031529]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; T-helper 1 cell activation [GO:0035711]; tooth eruption [GO:0044691]; vacuolar acidification [GO:0007035] |
12054167_localization to chromosome 11q12-13 in autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type I 12161516_Sibling pair linkage and association studies between peak bone mineral density and the gene locus for the osteoclast-specific subunit (OC116) of the vacuolar proton pump on chromosome 11p12-13. 12552563_Four novel single nucleotide mutations in the TCIRG1 gene encoding the 116-kDa osteoclast specific subunit of ATP6I affecting splice acceptor or donor sites result in aberrant transcription products. 14523594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14523594_There is an association between a polymorphism affecting an API binding site in the promoter of the TCIRG1 gene and bone mass in Scottish women. 14584882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15300850_9 new TCIRG1 mutations were found in recessive osteopetrosis pts. 30% of the pts had c.1674-1G>A (aberrant splicing: r.1674_1884del) or c.2005C>T (protein variation: p.Arg669X). 40% were splicing regulatory sequence substitutions. 15809087_we validated by RT-PCR six new alternative splice events in TCIRG1 in most of the 28 human tissues studied 17082597_TIRC7 acts as an upstream regulatory molecule of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expression. 18270567_HLA-DR alpha 2 domain (sHLA-DRalpha2) induces negative signals by engaging TIRC7 on lymphocytes, inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells via activation of the intrinsic pathway 18715141_analysis of a novel Alu-Alu recombination-mediated genomic deletion in the TCIRG1 gene in five osteopetrotic patients 19172990_Linkage disequilibrium (LD) mapping of the OPTB locus at the TCIRG1 region and found a unique splice site mutation c.807+5G>A in all Chuvashian OPTB patients studied. 19172990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19371798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19507210_Mutations in TCIRG1, OSTM1, ClCN7, and TNFRSF11A genes were detected in nine, three, one, and one patientswith infantile malignant osteopetrosis, respectively. 20424301_That the CLCN7 mutations provoke a phenotype as severe as the one caused by TCIRG1 loss of function suggests the affected residues to be crucial for the function of the ClC-7 chloride channel or chloride/proton-exchanger 20525692_V-ATPase localization and activity in kidney cells is regulated via direct PKA-dependent phosphorylation of the A subunit at Ser-175 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21042819_The novel mutation c.242delC of TCIRG1 in infantile malignant osteopetrosis 22231430_Our data highlights the importance of two large genomic deletions and mutations in the 5' UTR with respect to patient management and, more critically, to prenatal diagnosis 23288846_The N termini of a-subunit isoforms are involved in signaling between vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) and cytohesin-2 24072707_The function of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) a subunit isoforms in invasiveness of MCF10a and MCF10CA1a human breast cancer cells. 24108692_analysis demonstrates that CLCN7 and TCIRG1 mutations differentially affect bone matrix mineralization, and that there is a need to modify the current classification of osteopetrosis 24526664_TIRC7 is involved in inflammation in multiple sclerosis and anti-TIRC7 mAb can prevent immune activation via selective inhibition of Th1- and Th17-associated cytokine expression. 24617318_TIRC7 might be associated with the pathogenesis of ITP, and TIRC7 levels could be used as an indicator to evaluate patients' response to HD-DXM treatment. 24753205_TCIRG1-associated congenital neutropenia. 24898387_Data indicate that the effects of epiregulin (EREG) and V-ATPase (TCIRG1) single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) on pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility, to the extent that they exist, are dependent on gene-gene interactions in West African populations. 24989235_An A to T transversion in the fourth base of the intron 2 donor splice site (c.117+4A-->T) in TCIRG1 in the Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) population was found to be responsible for osteopetrosis. 25623380_Increased expression of TIRC7 in plasma was associated with the severity of acute graft-versus-host disease. 25829125_an intronic region in TCIRG1 that seems to be particularly prone to splicing mutations, allowing the production of a small amount of protein sufficient to reduce the severity of the phenotype usually associated with TCIRG1 defects. 26049920_TIRC7 might be involved in the pathogenesis of aplastic anemia. 26906430_The highly invasive human breast cancer cell lines express higher levels of the a3 isoform than poorly invasive lines; knockdown of a3 reduces both expression of V-ATPases at the plasma membrane and in vitro invasion of breast tumor cells. (Review) 27187610_In this study, whole exome sequencing (WES) was successfully used in six patients with malignant infantile osteopetrosis (MIOP) and identified mutations in four MIOP-related genes (CLCN7, TCIRG1, SNX10, and TNFRSF11A). 27229898_Nine rare missense variants at evolutionarily conserved sites in TCIRG1 are associated with lower absolute neutrophil count. 28604959_TCIRG1 gene mutation in a Chinese family is associated with infantile malignant osteopetrosis. 28726516_The aim of this study was to develop a clinically applicable lentiviral vector expressing TCIRG1 to correct osteoclast function in Infantile malignant osteopetrosis 28738127_TCIRG1 may be involved in endolysosomal transport-a process known to be important to development of early onset AD. 28816234_Case Reports: TCIRG1-dependent osteopetrosis with a mild clinical course in Chinese patients. 29237407_Since a3 subunit of V-ATPase complex plays a crucial role in bone resorption process, structurally abnormal a3 subunit might have adversely affected bone resorption process, leading to infantile osteopetrosis in Pakistani family. 29303507_TCIRG1 functions as a metastasis-enhancing gene by modulating cellular growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 30431110_TCIRG1 mutation is associated with osteopetrosis. 30537558_mutations in SLC29A3 and TCIRG1 in patients with Sclerosing bone dysplasias with hallmarks of dysosteosclerosis. 30898715_The study revealed that five of the twelve cases of autosomal recessive osteopetrosis carry at least one mutation of TCIRG1 gene. 31111556_Novel c.G630A TCIRG1 mutation causes aberrant splicing resulting in an unusually mild form of autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. 32085585_The Vacuolar H(+) ATPase alpha3 Subunit Negatively Regulates Migration and Invasion of Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. 32319655_TIRC7 inhibits Th1 cells by upregulating the expression of CTLA4 and STAT3 in mice with acute graftversushost disease. 34545712_Clinical and molecular characterization of five Chinese patients with autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. 35981697_Osteoclast rich osteopetrosis due to defects in the TCIRG1 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000001750 |
Tcirg1 |
4416.406856 |
2.1534852522 |
1.106673 |
0.038364582 |
823.309251 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000046163682622264239375522845827800629874189786626957316849185953058542267084722773531851487514505327552760848143660158564397712866056310150573968988930 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000037645080414619900785584533513155077503653978233710043473830648413440570631656118044822865629666496184725318898888008461606801640397970471164657930085 |
Yes |
Yes |
6109.3895814 |
134.0103197 |
2856.9391132 |
47.2654850 |
| ENSG00000110721 |
1119 |
CHKA |
protein_coding |
P35790 |
FUNCTION: Plays a key role in phospholipid biosynthesis by catalyzing the phosphorylation of free choline to phosphocholine, the first step in phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis (PubMed:19915674, PubMed:34077757, PubMed:17007874). Also phosphorylates ethanolamine, thereby contributing to phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis (PubMed:19915674, PubMed:17007874). Has higher activity with choline (PubMed:19915674, PubMed:17007874). May contribute to tumor cell growth (PubMed:19915674). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17007874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19915674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34077757}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: This isoform plays a key role in lipolysis of lipid droplets following glucose deprivation (PubMed:34077757). In response to glucose deprivation, phosphorylated by AMPK, promoting localization to lipid droplets (PubMed:34077757). Phosphorylation is followed by acetylation by KAT5, leading to dissociation of the homodimer into a monomer (PubMed:34077757). Monomeric CHKA isoform 1 is converted into a tyrosine-protein kinase, which phosphorylates lipid droplet structural proteins PLIN2 and PLIN3, leading to lipolysis of lipid droplets (PubMed:34077757). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34077757}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Nucleotide-binding;Phospholipid biosynthesis;Phospholipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis; phosphocholine from choline: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:17007874, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19915674}.; PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis; phosphatidylethanolamine from ethanolamine: step 1/3. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:17007874, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19915674}. |
The major pathway for the biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine occurs via the CDP-choline pathway. The protein encoded by this gene is the initial enzyme in the sequence and may play a regulatory role. The encoded protein also catalyzes the phosphorylation of ethanolamine. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1119; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; choline kinase activity [GO:0004103]; cholinesterase activity [GO:0004104]; ethanolamine kinase activity [GO:0004305]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; CDP-choline pathway [GO:0006657]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; lipid droplet disassembly [GO:1905691]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:0006656]; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006646] |
11840339_activity regulated by Ras proteins through Ral-GDS and PI-3-kinase; has role in malignant transformation 12082619_ChoK overexpression was found in 17% of the samples. ChoK may be related to the development of human breast cancer, suggesting that this finding may suggest a novel antitumoral strategy. 12176020_upregulation of choline kinase is a frequent feature in human tumor-derived cell lines and in lung, prostate, and colorectal cancers 16820874_ChoK may have a role in carcinogenesis 17184542_Analyses showed genotype effects of CHKA genes on spina bifida risk, but did not show evidence of gene-nutrient. 17184542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18172309_These data suggest that HIF-1 activation of HREs within the putative chk-a promoter region can increase Chk-A expression within hypoxic environments, consequently increasing cellular PC and tCho levels within these environments. 18296102_The molecular basis to understand the connection between phospholipids metabolism and cell cycle regulation through choline kinase is reported. 19156696_The rates of choline kinase reaction in cell lysates of MDA-MB-231 breast, PC-3 prostate and HeLa cervical cancer cells and in solutions of purified human ChoK, was measured. 19448670_ChoKalpha plays a role in the aggressiveness of bladder tumors and constitutes a new approach for bladder cancer treatment. 19737740_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19855431_Data show that RNA silencing of choline kinase in HeLa cells completely abrogates the high concentration of phosphocholine, which in turn decreases phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidic acid and signaling through the MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways. 19915674_ChoKalpha and ChoKbeta isoforms have different physiological roles and implications in human carcinogenesis 20042122_From our data, we proposed that Choline kinase plays a key role in regulating Akt(ser473) phosphorylation, thereby promoting cell survival and proliferation 20299452_kinetic studies revealed that HC-3 is a much more potent inhibitor for ChoKalpha isoforms (alpha1 and alpha2) compared with ChoKbeta. 20662904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21822308_these results strongly implicate a new c-Src-dependent link between CHKA and EGFR, which contributes to the regulation of cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. 22038995_Data show choline kinase alpha (CHKalpha) expressed in both cytoplasm and nucleus in malignant lesions. 22515519_ASAH1 inhibition synergistically sensitizes lung cancer cells resistant to the antiproliferative effect of choline kinase alpha inhibitors. 22972156_CHKA SNPs (rs3794186 and rs11481) are not associated with HCC development; however, rs3794186 may correlate with serum AFP levels in HCC. 23071593_HK2 and CKA expression may have biologic and prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma, with tumor HK2 expression being a potential independent predictor of survival. 23416529_A combination of initial velocity and product inhibition studies, together with the kinetic and structural characterisation of a novel ChoKalpha inhibitor is used to support a mechanism of action for human ChoKalpha. 23762272_High choline kinase A expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 23775813_Chk-alpha expression and the effect of its downregulation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, is reported. 24281000_In EOC that CHKA downregulation significantly decreased the aggressive EOC cell. 24287694_pharmacological inhibition of ChoKalpha induces cancer cell death through a mechanism that involves the activation of exaggerated and persistent ER stress supported by CHOP overproduction. 24556997_Downregulation of Chk-alpha with siRNA increased PLD1 expression, and downregulation of PLD1 increased Chk-alpha expression. 24583375_Our data suggest that choline kinase and its product phosphocholine are required for the normal growth and mineralization of MG-63 cells. 25028471_choline kinase alpha is inhibited by a near-infrared fluorescent carbocyanine 25267063_The significance of CHKA overexpression on a TMA. 25522435_there is a role for the ChoKalpha protein in promoting cancer cell survival that is independent of its catalytic activity. 25768400_Chokalpha possessed oncogenic activity and could be a potential therapeutic target in T-cell lymphoma , as well as other hematological malignancies with interrupted Ras signaling pathways 25796169_Identify choline kinase alpha as a key regulator of glutathione-dependent antioxidant cell defense in ovarian carcinoma. 26041862_Increased expression of CHKA is seen in malignant lesions of prostate cancer 26496360_Downregulation of choline kinase-alpha enhances autophagy in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. 26503172_These data also support the approach of antitumor strategies that destabilize Chk-alpha protein or downregulate PtdCho in breast cancer treatment. 26657335_CHKA can act as an AR chaperone, providing, to our knowledge, the first evidence for kinases as molecular chaperones, making CHKA both a marker of tumor progression and a potential therapeutic target for PCa. 26769123_Study shows increased CHKA expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumors and may be a predictive marker of response to chemotherapy. 27489281_These findings demonstrate that hCKalpha forms a complex with hepatitis C virus NS5A and that hCKalpha activity enhances the targeting of the complex to the endoplasmic reticulum, where hCKalpha protein, not activity, mediates NS5A binding to NS5B, thereby promoting functional membranous viral replication complex assembly and viral RNA replication. 27556502_Results indicate that choline kinase alpha (CHKA) contributes to tumor progression and metastasis and may serve as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target in colorectal carcinoma (CRC). 28065789_We found levels of CHKA to be increased in human HCCs compared to nontumor tissues, and increased expression to be associated with tumor aggressiveness. Overexpression of CHKA in HCC cell lines increased their invasiveness, resistance to EGFR inhibitors, and ability to form metastatic tumors in mice by promoting interaction of EGFR with mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2. 28509322_There is no correlation between single CHKA rs7928739 polymorphism and the incidence of intrauterine fetal death. 28566381_hCKalpha functions as an indispensable regulator that bridges PI4KIIIalpha and hepatitis C virus NS5A and potentiates NS5A-stimulated PI4KIIIalpha activity, which then facilitates the targeting of the ternary complex to the endoplasmic reticulum for viral replication. 29389115_This study presents the detail the 2.35 A structure of choline kinase alpha in complex with inhibitor TCD-717. 29568919_miR-876-5p was able to significantly decrease the expression level of choline kinase alpha mRNA. 30629659_During proliferation, KDM2B binds to the Box2 located in the Chka promoter repressing its transcription. KDM2B knockdown enhances the levels of CKalpha expression in neuroblast cells and induces neuronal differentiation. These results suggest that KDM2B is required for the appropriate regulation of CKalpha during neuronal differentiation and to the maintaining of the undifferentiated stage of neuroblast cells. 32958130_[Knockdown of choline kinase alpha (CHKA) inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration of human U87MG glioma cells]. 34077757_Choline kinase alpha 2 acts as a protein kinase to promote lipolysis of lipid droplets. 34205960_DNA Methylation of Human Choline Kinase Alpha Promoter-Associated CpG Islands in MCF-7 Cells. 35202461_Bi-allelic variants in CHKA cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and microcephaly. |
ENSMUSG00000024843 |
Chka |
217.028796 |
0.3959261614 |
-1.336697 |
0.109293930 |
151.728923 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000007262269070267097806793805346673408861431609974729404465900698178981187065802585356948236836038823582839540904387831687927246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000001072983898670093652960102120634394934033889267574956946235508412604825535143805630096175071641617648765532067045569419860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
125.2128928 |
8.9017782 |
318.8323664 |
14.8696832 |
| ENSG00000110848 |
969 |
CD69 |
protein_coding |
Q07108 |
FUNCTION: Involved in lymphocyte proliferation and functions as a signal transmitting receptor in lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and platelets. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the calcium dependent lectin superfamily of type II transmembrane receptors. Expression of the encoded protein is induced upon activation of T lymphocytes, and may play a role in proliferation. Furthermore, the protein may act to transmit signals in natural killer cells and platelets. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:969; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466] |
12077230_CD69 engagement initiates protein tyrosine kinase-dependent signaling pathways in IL-2-activated NK cells by inducing selective activation of Syk, but not ZAP70, kinase. 12234263_CD69 transduces a Bcl-2-dependent death signal when ligated by a specific antibody. As the function of CD69 appears to be restricted to activated eosinophils, making an ideal target for therapeutic intervention in asthma. 12540017_a higher CD69 expression when atopic neutrophils were incubated with GM-CSF compared to non-atopic neutrophils 12718936_GM-CSF, IFN-gamma or IFN-alpha significantly induced CD69 expression on neutrophils. We demonstrated the capacity of CD69 to act as a costimulus for TNF-alpha production by neutrophils. 12865808_expression of CD69 on CD3+ and CD8+ peripheral blood T cells correlates closely with the presence of acute graft rejection in renal allograft recipients 14728878_Increased CD69 of T lymphocytes, along with abnormally elevated immunologically active molecules play an important role in immune pathogenesis of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome(MDS). 15893733_Our study has identified, by immunoprecipitation and direct protein sequencing (LC/MS/MS), binding of CD69 to an N-terminal protein fragment of calreticulin expressed on the cell surface of human PBMCs. 15952571_The expression of CD69 in T lymphocytes from nasal polyps was abnormally high. 16396693_The expression of CD69 and CD154 molecules depend partially on the prolactine. 16525420_CD69 forms a complex with and negatively regulates S1P1 and that it functions downstream of IFN-alpha/beta, and possibly other activating stimuli, to promote lymphocyte retention in lymphoid organs 16788832_Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II reduces CD69 expression in T cells. 17237603_data suggest unidentified natural ligands for CD69 and/or CD69 autoantibodies possibly affect joint-composing cell types through increased production of S100A9 in neutrophils, providing insight into functions of CD69 on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis 17541278_IL-3 is a central inducer of CD69 expression. Upregulated CD69 expression on locally accumulated basophils in bronchial asthma may be partly due to a combination of local cytokines, especially IL-3, plus IgE-cross-linking allergens. 17693977_Since induction of CD69 surface expression is dependent on the activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) activation pathway, it is suggested that in chronic fatigue syndrome there is a disorder in the early activation of the immune system involving PKC. 18593762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18627570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18627570_results do not support a major role for the CD69 gene polymorphisms in RA genetic predisposition in our population. 18959746_the physical, biochemical and in vivo characteristics of a highly stable soluble form of CD69 obtained by bacterial expression of an appropriate extracellular segment of this protein. 19383348_Expression of CD69 and IL8 is upregulated upon Bcr-Abl expression 19430480_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19543397_soluble factors in SSc plasma inhibit Treg function specifically that is associated with altered Treg CD69 and TGFbeta expression 19670272_analysis of CD69 molecules on human CD4+ T cell membrane 20054122_structure refined to 1.37 A resolution provides further details of the overall structure and the asymmetric interface between the monomers in the native dimer 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378605_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21152932_Caffeine does not appear to depress Natural killer cell CD69 expression. 21427408_Studies provide a mechanistic link between CD69 and the regulation of T(H)17 responses. 21557772_Increased CD4(+) CD69(+) CD25(-) T cells exert a critical role in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and might represent a clinically aggressive tumor phenotype. 21990950_Results suggest that H. pylori induces CD69 expression through the activation of NF-kappaB, and that cagPAI might be relevant in the induction of CD69 expression in T cells. CD69 in T cells may play a role in H. pylori-induced gastritis. 21993667_CD69 is significantly correlated with poor clinical and biological prognostic factors and is confirmed to be an independent disease prognosticator in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 22184722_T cells isolated from the hepatocellular carcinoma tissues expressed significantly more CD69 molecules than did those on paired circulating and nontumor-infiltrating T cells; these tumor-derived CD69(+) T cells could induce considerable IDO in monocytes 22456278_Intron I acts as an important regulatory element of CD69 expression. 22678911_Priming with apoptotic debris prevented DCs from establishing cytotoxicity toward live human tumor cells by inducing a Treg-cell population, defined by coexpression of CD39 and CD69 23454781_In patients with allergic rhinitis CD69 antigen is overexpressed on human peripheral blood natural killer cells reflecting their activation status. 23507197_CD69 overexpression is associated with the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection and adult T-cell leukemia. 23546309_This is the first report of the regulation of CD69 expression by LMP-1, and this novel finding may, thus, represent an important link between the EBV oncoprotein LMP-1 and its critical role in the development of EBV-associated diseases. 23758320_CD69 is induced by integrin alpha4beta1 outside-in signalling and T-cell receptor signalling. 23954168_REVIEW: CD69 exerts a complex immunoregulatory role in humans, and that it could be considered as a target molecule for the therapy of immune-mediated diseases 24044963_Following coculture with GTKO/CD46 pig mesenchymal stromal cells, it is possible that upregulation of CD69 on human T cells initiates signaling events that would regulate CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation and differentiation. 24668348_Human tumor-infiltrating CD4+CD69+ T cells suppress T cell proliferation via membarene -bound TGF-beta1. 24752896_these findings identify CD69 and galectin-1 to be a novel regulatory receptor-ligand pair that modulates Th17 effector cell differentiation and function. 24975965_Elevated expression of CD69 and CD161 on NK cells can be considered as immunological risk markers in RSA and IVF failure. 26100786_In vitro functional assays showed that CD69(+) Treg cells exerted an important suppressive effect on the activation of T effector cells 26296369_results demonstrate the functional and mechanistic interplays between CD69 and S100A8/S100A9 in supporting Treg-cell differentiation 26701728_Higher CD69 expression were less sensitive to bendamustine and is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 26846784_AIM expression in the kidney was associated with urinary protein and decline in kidney function. 28606013_this paper shows that decrease of CD69 levels on TCR Valpha7.2(+)CD4(+) innate-like lymphocytes is associated with impaired cytotoxic functions in chronic hepatitis B virus-infected patients 29663362_CD69 and CD24 partially inhibit apoptosis and erythroid differentiation in Chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 29749428_The frequency of CD69+ T cells was significantly higher in CD8+ and CD4+ T cells in nasal polyps compared with the peripheral blood of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. 29752720_CD69(+) T cells were associated with disease recurrence. 30015935_CD69 is a direct target of miR-367-3p. 30217447_In the presence of fusion protein-tyrosine kinases ITK-FER and ITK-SYK, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) was highly phosphorylated and early activation antigen CD69 (CD69) was significantly elevated. 30586697_Oxidized low-density lipoprotein binding to CD69 confers a regulatory phenotype to human T cells, dampening Th17 responses and ameliorating atherosclerosis. 31928947_Increased CD69 expression on activated eosinophils in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis correlates with clinical findings. 32408340_Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage as a biomarker for disease activity in Japanese children with IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. 33627405_T cells selectively filter oscillatory signals on the minutes timescale. 34344244_Prognostic Relevance of Concordant Expression CD69 and CD56 in Response to Bortezomib Combination Therapy in Multiple Myeloma Patients. 34427648_CD4+ T cells in inflammatory diseases: pathogenic T-helper cells and the CD69-Myl9 system. 35690994_Combined assessment of S- and N-specific IL-2 and IL-13 secretion and CD69 neo-expression for discrimination of post-infection and post-vaccination cellular SARS-CoV-2-specific immune response. |
ENSMUSG00000030156 |
Cd69 |
28.160688 |
0.1866585301 |
-2.421527 |
0.336077086 |
58.069172 |
0.00000000000002530610874455931149089405314086121213457743900354657284879067447036504745483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000166229712981617909615817315284517500433101450107997720806451980024576187133789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1470302 |
2.0525506 |
49.4418653 |
5.9351831 |
| ENSG00000110876 |
6404 |
SELPLG |
protein_coding |
Q14242 |
FUNCTION: A SLe(x)-type proteoglycan, which through high affinity, calcium-dependent interactions with E-, P- and L-selectins, mediates rapid rolling of leukocytes over vascular surfaces during the initial steps in inflammation. Critical for the initial leukocyte capture. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11566773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403782}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for enterovirus 71. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19543284}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sialic acid;Signal;Sulfation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a glycoprotein that functions as a high affinity counter-receptor for the cell adhesion molecules P-, E- and L- selectin expressed on myeloid cells and stimulated T lymphocytes. As such, this protein plays a critical role in leukocyte trafficking during inflammation by tethering of leukocytes to activated platelets or endothelia expressing selectins. This protein requires two post-translational modifications, tyrosine sulfation and the addition of the sialyl Lewis x tetrasaccharide (sLex) to its O-linked glycans, for its high-affinity binding activity. Aberrant expression of this gene and polymorphisms in this gene are associated with defects in the innate and adaptive immune response. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]. |
hsa:6404; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane raft [GO:0044853]; uropod [GO:0001931]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to interleukin-6 [GO:0071354]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; leukocyte adhesive activation [GO:0050902]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:0050901] |
11843835_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11916843_Comparison of PSGL-1 microbead and neutrophil rolling: microvillus elongation stabilizes P-selectin bond clusters 11929779_Human mast cell progenitors use alpha4-integrin, VCAM-1, and PSGL-1, E-selectin for adhesive interactions with human vascular endothelium under flow conditions 11961238_G-CSF down regulates PSGL-1 expression on the surface of neutrophils in humans 12036880_Attachment of the PSGL-1 cytoplasmic domain to the actin cytoskeleton is essential for leukocyte rolling on P-selectin. 12189248_Expression of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen by CD8(+) T cells specific for herpes simplex virus type 2(cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen) 12223514_Binding of two anti-human (KPL1 and PL1) and two anti-mouse (4RA10 and 2PH1) PSGL-1 mAbs to synthetic peptides of N-terminus of human and mouse PSGL-1 was found to be independent of tyrosine sulfation. 12354382_The epitope recognized by the M-DC8 MAb is 6-sulfo LacNAc, a novel carbohydrate modification of the P selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) 12377939_increased PSGL-1 expression on granulocytes from allergic-asthmatic subjects resulted in increased leukocyte recruitment on P-selectin under flow conditions 12387735_PSGL-1 engagement induces tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk and SRE-dependent transcriptional activity. 12393521_Inhibitors of glycosylation alter HECA-452 expression on human cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen-positive T-cells and prevent T-cell tethering and rolling on selectins under shear stress. 12529243_Stimulation of eosinophils with eotaxin-2 converts PSGL-1-P-selectin-dependent stationary adhesion to CD18-mediated shear-resistant stable attachment. Blocking eosinophil-platelet interactions may combat thrombotic disorders in hypereosinophilia. 12595306_Anti-P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) antibodies dramatically block the recruitment of CD8+ cells in brain vessels of patients with multiple sclerosis 12736247_L-selectin binds with high affinity to the N-terminal region of PSGL-1 through cooperative interactions with three sulfated tyrosine residues and an appropriately positioned C2-O-sLex O-glycan. 12736689_atomic force microscopy and flow-chamber experiments show that increasing force first prolonged and then shortened the lifetimes of P-selectin complexes with P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 12874338_Anaplasma phagocytophilum infected neutrophils showed reduced expression of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1, CD162) and L-selectin (CD62L) 12879153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12879153_results demonstrate that the PSGL-1 variable number of tandem repeat polymorphism is not a genetic risk factor for coronary heart disease 14507929_determination that PSGL-1 is an additional substrate for BACE1 14592840_PSGL1 is not essential for E-selection promotion of growth inhibition and apoptosis of human and murine hematopoietic progenitor cells 14615387_PSGL-1, by mediating monocyte-platelet interactions, plays a major role in secondary monocyte tethering. 14641238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14678816_platelet-monocyte complex formation is mostly dependent on PSGL-1 15001428_PSGL-1 and VLA-4 play an important role for leukocyte recruitment during intestinal inflammation. Therapeutic strategies designed to disrupt interactions mediated by PSGL-1 and/or VLA-4 may prove beneficial in treatment of chronic colitis. 15026421_core 2 beta1-6-N-glucosaminyltransferase and dimerization of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 have roles in rolling on P-selectin 15059608_platelet P-selectin and microparticle PSGL-1 have roles in thrombus formation [review] 15187162_binding of E-selectin to PMNs in suspension also elicited coclustering of L-selectin and PSGL-1 that was signaled via mitogen-activated protein kinase. 15217824_The interaction of PSGL-1 with P-selectin (CD62P) mediates tethering, rolling, and weak adhesion of leukocytes 15386532_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15459589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15466853_PSGL-1 interacts with CCL27 (CTACK/ILC/ESkine), a skin-associated chemokine that attracts skin-homing T lymphocytes 15488708_CLA and E-selectin are bound by T cells and have roles in skin inflammation [cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen, also called BE-2] 15497463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15522894_PG-M/versican binds to P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 and has a role in mediating leukocyte aggregation 15843584_Induced expression of cutaneous lymphocyte antigen on helper T cells determined a striking increase of rolling efficiency in inflamed brain venules. 15925831_immune response to alpha-streptococci may enhance expression on tonsillar T-cells in pustulosis palmaris et plantaris 15926890_A differential functional impact of N-glycosylation on C2GnT-1 and FucT-VII and disclose that a strongly reduced FucT-VII activity retains the ability to fucosylate PSGL-1 on the core2-based binding site(s) for the three selectins. 16024226_CLA is expressed in circulating mononuclear cells of patients with psoriasis 16039046_In conclusion, the C allele of the VNTR polymorphism in PSGL-1 is likely to be associated with PP-MS. 16039046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100264_biophysical analysis of PSGL-1/P-selectin neutrophil adhesion 16257118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16269612_CD43 is a T-cell E-selectin ligand distinct from PSGL-1 which expands the role of CD43 in the regulation of T-cell trafficking. 16501095_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are particularly potent inducers of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen on HSV-reactive memeory CD4 T cells 16547281_98% of CLA(+) effector memory T cells are resident in normal skin under resting conditions 16633357_rPSGL-Ig delays the aggregation process and increases the anti-aggregatory potency of GPIIb-IIIa antagonist 17181632_More than 50% of circulating CD4+CD25(high) regulatory T cells from both patients as well as healthy controls expressed cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen. 17221329_No significant association was found between PSGL-1 VNTR polymorphisms and in-stent restenosis. However, in patients with a family history of early CAD presence of PSGL-1 AB genotype might increase the risk of in-stent restenosis. 17221329_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17322099_ECs express functional PSGL-1 which mediates tethering and firm adhesion of monocytes and platelets to inflamed endothelium. 17346310_These data demonstrate a role for Anaplasma phagocytophilum-mediated ROCK1 phosphorylation in infection induced by PSGL-1 and mediated by Syk. 17372146_The association of PSGL-1 with lipid microdomains is essential for its redistribution induced by IL-8 stimulation and that the redistribution modulates neutrophil functions mediated by interactions with P-selectin. 17420019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17420019_Specific P-selectin and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 genotypes/haplotypes may have roles in coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke 17510705_activation of EphB4 enhances proangiogenic capacity through induction of PSGL-1 expression and adhesion to E selectin and P selectin 17545190_It is suggested that the VNTR polymorphism of PSGL-1 is a significant determinant of thrombotic predisposition in patients with APS. 17545190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17597069_ADAM28s promotes PSGL-1/P-selectin-mediated leukocyte rolling adhesion to endothelial cells and subsequent infiltration into tissue spaces through interaction with PSGL-1 17827388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17890399_A new method for determining receptor-ligand association/dissociation events across the interface of two surfaces (two-dimensional binding) by monitoring abrupt decrease/resumption in thermal fluctuations of a biomembrane force probe. 17910894_These findings suggest that 1,25D(3) can selectively downregulate CLA expression without influencing lymphocyte migration patterns to other tissues. 17947642_regulation of O-glycosylation controls sLe(x) expression, and also suggest that O-glycans may have a function in dendritic cells migration 18182036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18250165_a lectin domain residue in L-selectin has a role in binding to P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 but not to 6-sulfo-sialyl Lewis x 18363812_P-selectin-PSGL-1-induces TF and IL8 expression through Lyn phosphorylation, and part of the inhibitory effect of IL10 depends on reduced phosphorylation 18451333_Report complete downmodulation of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand in monocytes undergoing apoptosis. 18452987_Results suggest that the generation of C5a induced by hemodialysis membranes is responsible for the clustered redistribution of PSGL-1 in neutrophils leading to the increase in the platelet-neutrophil microaggregate formation. 18485118_These data fervently hint that specific recognition of the PSGL-1 N-terminus is crucial for optimal Anaplasma phagocytophilum AnkA delivery. 18497306_Our data suggest that in the absence of overt activation, PSGL-1 (P selectin ligand 1-P-selectin-dependent platelet binding to monocytes represents a normal physiological process with little impact on the potential of monocytes to cause vascular injury 18509085_cooperation of the alpha(M)beta(2)/GPIbalpha and to PSGL-1/P-selectin systems regulates the prothrombotic properties of PMN-derived microparticles and MP-induced platelet activation 18519846_PSGL-1 level was also higher on human CD14+CD16- monocytes than on CD14-CD16+ monocytes. 18713749_the role of PSLG1 decamers is to extend PSGL-1 N terminus far above the cell surface to support and stabilize leukocyte rolling on L- or P-selectin 18773738_HECA-452 could be of prognostic relevance in the early stage of mycosis fungoides 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19262138_P-selectin cross-links PSGL-1 and enhances neutrophil adhesion to fibrinogen and ICAM-1 in a Src kinase-dependent, but GPCR-independent mechanism. 19353220_This study shows that higher neutrophil PSGL-1 expression on admission may imply a higher risk for END and that monocyte Mac-1 expression on admission reflects the severity of ischemic stroke on admission. 19395438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19395438_Specific SELP and SELPLG polymorphisms were associated with cell surface measures of SELP and SELPLG in both whites and African Americans in the ARIC Carotid MRI Study 19404397_Flotillin-1 and -2 associate with PSGL-1 in resting and in stimulated neutrophils are importantly involved in neutrophil uropod formation and/or stabilization 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19542463_Follicular dendritic cells can efficiently activate HIV-1 replication in latently infected monocytic cells via an intercellular communication network mediated by the P-selectin/P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) interaction. 19543284_a role for PSGL-1-positive leukocytes in cell tropism and pathogenesis during the course of foot and mouth disease and other EV71-mediated diseases. 19628338_cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen expression might be an indicator of poor prognosis in non-nasal NK-cell lymphomas with nodal presentation 19665434_Activation of memory CLA(+) CD4(+) T cells results in increased PSGL-1 expression and consequently, increased binding to P-selectin, suggesting a more diverse tissue trafficking capacity. 19696154_Multiple sclerosis is associated with an expanding pool of PSGL-1 positive CD4+ T lymphocytes able to transmigrate the BBB endothelium in vitro and possibly contributing to brain pathology. 19875629_PSGL-1 may contribute to T-cell interaction with the inflamed blood brain barrier, and may be a therapeutic taarget in brain multiple sclerosis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913879_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20051472_The adhesion mediated by the P-selectin P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) couple is stronger for shorter PSGL-1 variants. 20376705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20376705_The present study demonstrated no evidence of association between individual SELP or PSGL-1 single nucleotide polymorphisms or haplotypes with incident coronary heart disease. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20445017_Human neutrophil rolling on E- or P-selectin induces the extended alpha(L)beta(2) integrin conformation through signaling triggered by PSGL-1 engagement. 20558823_Deficiency of Psgl-1 is associated with reduced IL-1 receptor-mediated adhesive properties of the endothelium. 20586826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20690162_There is a strong expression of both SELPLG and coronin-1C in the majority of primary effusion lymphomas, irrespective of their gene dosage. SELPLG is critical for cell migration and chemotaxis, while CORO1C regulates actin-dependent processes. 20705591_Results suggested that Syk plays a key role in signal transduction downstream of PSGL-1 in endothelial progenitor cells. 20943886_The results suggest that an adaptive mutation, along with a PSGL-1-binding phenotype, may facilitate efficient PSGL-1-dependent replication of enterovirus 71 strains in L-PSGL-1 cells. 21044367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21079683_Tyrosine sulfation of the amino terminus of PSGL-1 is associated with enterovirus 71 infection. 21144558_Healthy volunteers were genotyped and the adhesion of neutrophils expressing the PSGL-1 isoforms A/A, A/B and B/B were studied under static and physiologic flow conditions. 21292497_IL-6 induces neutrophilia and reduces CD162 expression on neutrophils in inflammation 21484243_Levels of P-selectin and L-selectin were decreased in AD and lowest in AD patients with highest cognitive decline. Our findings suggest that these molecules may induce alterations of endothelial regulation and influence neurodegenerative processes of AD 21768350_Data show that Pic, a class 2 SPATE protein produced by Shigella flexneri 2a targets a broad range of human leukocyte glycoproteins including CD43, CD44, CD45, CD93, CD162 and the surface-attached chemokine fractalkine. 21816455_Exceedingly high PMA in aortic stenosis are independent of SELPLG polymorphisms, and largely of the hemodynamic compromise caused by the stenotic valve. 21864485_PSGL-1 microparticles show a characteristic course during alloSCT and their possible association with relapse/progress requires further evaluation of the PSGL-1/P-selectin interaction in leukemias and lymphomas 21880775_Coxsackievirus A24 variant bound better to mouse L929 cells overexpressing human P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) than to mock-transfected cells, suggesting that PSGL-1 is a candidate receptor for the virus. 22021370_Studies indicate that PSGL-1, CD44, and ESL-1 on mature leukocytes are physiologic glycoprotein ligands for endothelial P-selectin and E-selectin. 22096244_Data show the contribution of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) to the regulation of growth, dissemination, and drug resistance in multiple myeloma (MM) cells in the context of the bone marrow microenvironment. 22229154_ADAM8 is both associated with PSGL-1 through the ezrin-radixin-moesin actin-binding proteins and able to cause the proteolytic cleavage of this adhesion receptor. 22307784_There is significant association between PSGL-1 Met62Ile polymorphism and advanced carotid atherosclerosis with stenosis in female patients from the Serbian population. 22311979_PSGL-1 EBS plays a critical role in recruiting leukocytes on selectins and in activating the MAPK pathway, whereas it is dispensable to phosphorylate Syk and to lead to alpha(L)beta(2)-dependent leukocyte slow rolling. 22366582_E- and P-selectins play a role in spontaneous metastasis formation both into bone marrow and lungs. 22535539_The aim of the study was to investigate the degree of platelet activation in NSCLC and the roles of PSGL-1 in the activation of platelets. 22947939_effect of mutation on binding affinity to P- and L-selectin 23192782_PSGL-1 has Janus-faced functions, being both adhesive and anti-adhesive. 23302872_These results indicated that SCARB2 is capable of viral binding, viral internalization, and viral uncoating and that the low infection efficiency of L-PSGL1 cells is due to the inability of PSGL1 to induce viral uncoating. 23601501_In conclusion, authors report PSGL-1 as a novel target for pneumococcal ZmpC and show that ZmpC inhibits neutrophil extravasation during pneumococcal pneumonia. 23750651_Psoriasis patients' tonsils have a higher frequency of skin-homing CLA [cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen] positive T cells, correlating significantly with their frequency of blood CLA+ T cells. 23760234_A receptor-dominated endocytosis of enterovirus 71 infection was observed: PSGL-1 initiates caveola-dependent endocytosis and hSCARB2 activates clathrin-dependent endocytosis. 23812215_Expression of CD11b and CD162 on monocytes has a temperature-dependent regulation, with decreased expression during hypothermia. 23935488_Data suggest that PSGL1 on leukocytes is binding site for VP1 (a capsid protein) in Enterovirus 71; conserved lysine residues on virus surface are responsible for interaction with sulfated tyrosine residues in PSGL1 N-terminus. 24055812_Specific phosphorylations on 130 and 153 tyrosine residues of p85-bound Rho-GDP dissociation inhibitor-2 are pivotal for P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1-induced beta1 integrin-mediated lymphocyte adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. 24122451_Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) is required for PSGL-1-induced beta1 integrin clustering which ultimately regulates beta1 integrin-mediated Jurkat cell adhesion to fibronectin. 24127491_The PSGL-1-L-selectin complex-induced signaling effects on neutrophil slow rolling and recruitment in vivo demonstrate the functional importance of this pathway. 24244398_These findings suggest one molecular mechanism by which bromelain may exert its anti-inflammatory effects is via selective cleavage of PSGL-1 to reduce P-selectin-mediated neutrophil recruitment 24312591_ligation of PSGL-1 on HL-60 cells activates beta2 integrin, for which lipid raft integrity and Syk activation are responsible 24583418_Up-regulation of PSGL-1 on CD14++CD16+ monocytes may play a crucial role in plaque rupture and thrombus formation. 24606340_P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 and L-selectin have roles in neutrophil recruitment and activate human endothelial colony-forming cells at the site of vessel injury 24840181_Staphylococcal SElX and SSL6 proteins bind cell surface receptors PSGL-1 and CD47, respectively. 24997419_SCARB2 and PSGL-1 in human gastrointestinal tract, lung, and brain tissues correlated with the distribution of pathological changes seen in EV71 infection. 25135296_lymphocyte trafficking into the CNS under VLA-4 blockade can occur by using the alternative adhesion molecules, PSGL-1 and MCAM, the latter representing an exclusive pathway for TH17 cells to migrate over the blood-brain barrier 25320329_Host membrane protein PSGL-1, CD43, and CD44 association with assembling HIV-1 Gag is driven by polybasic sequences present in the cytoplasmic tails of the membrane proteins and in Gag. 25405250_expression of P-selectin and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1, forming an auto-augmented loop of porcine aortic endothelial cells and platelet activation 25425738_Taken together, these results show that beta-adducin is a pivotal lipid raft-associated protein in PSGL-1-mediated neutrophil rolling on P-selectin. 25428141_Report influence of SELPLG variation on leukocyte-platelet interactions in cardiovascular disease. 25445472_CD162 staining and the staining degree, with the other standard immunohistochemical stains, were shown to be beneficial in the diagnosis of multiple myeloma disease. 26115234_The solution structure of CCL19 is reported. It contains a canonical chemokine domain. Chemical shift mapping shows the N-termini of PSGL-1 and CCR7 have overlapping binding sites for CCL19 and binding is competitive. 26124272_E-selectin interactions with glycoprotein ligands (CD44/hematopoietic cell E-/L-selectin ligand and PSGL-1) mediate the initial capturing of cells out of flow. 26332489_The significant presence of CLA+ T cells and E-selectin expressions in the OLPG suggests their involvement in the etiopathogenesis of OLP; however, only a weak correlation between CLA+ T cells and E-selectin was observed. 26539491_This study provides a better understanding of the biology of P-selectin and PSGL-1 and their roles in dissemination and resensitization of Multiple myeloma treatment. 26975045_PSGL-1 is a novel receptor for S. pneumoniae that contributes to protection against invasive pneumococcal disease. 27423570_Platelet-leukocyte aggregations increased in acute ischemic stroke patients rapidly within 3h. The I allele of PSGL-1 M62I was associated with risk of developing acute ischemic stroke, especially large artery atherosclerosis stroke and small artery occlusion stroke. Small artery occlusion stroke patients with the II genotype of PSGL-1 M62I have the higher level of platelet-neutrophil aggregates. 27625334_These data indicate that cardiac surgery influences the expression of CD162, CD166 and CD195 and that the intensity of the immune system response, displayed as the change in the CD162, CD166, CD195 expression, varies, depending on the surgical technique used. 27892504_PSGL1 mediated leukocyte rolling and the inflammatory response in general.PSGL1 is a ligand for Siglec-5 and interacts with Siglec-5 ectodomain. 28262471_Studies indicate that P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) PSGL-1 can negatively regulate T cell function. 28392462_The percentage of CXCR3(+) CD4(+) TEM cells negatively correlated with the severity of the cutaneous disease in psoriasis patients. Importantly CLA(+) CD4(+) TCM cells expressing CCR6(+) or CCR4(+)CXCR3(+) negatively correlated with psoriasis severity suggesting recruitment to the skin compartment. 28663244_c-Myc regulates P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 expression in monocytes during HIV-1 infection. 28680883_The Interaction of Selectins and PSGL-1 as a Key Component in Thrombus Formation and Cancer Progression. 28809090_PSGL-1 VNTR polymorphism may have limited contribution to the thrombotic tendency in patients with Behcet's disease. 29218606_PI3K is a signal linker between L-selectin and PSGL-1 in IL-18 transcriptional activation at the promoter level. 29703921_Consensus sequence analysis revealed enterovirus 71 with mutations at E145G and S241L and partial mutations at V146I of VP1, and a T to C substitution at nucleotide 494 of the 5'-UTR exhibited higher binding affinity for virus receptor, human P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (hPSGL-1). 29962384_PSGL-1 contributed to cytotoxic CD4 T cell homing to the culprit coronary artery and promoted plaque instability in ACS. 30395634_PSGL-1 polymorphisms (rs7137098 and rs8179137) were significantly associated with severe EV71 infection (OR 1.46, 95% CI 1.1-1.96; and OR 1.47, 95% CI 1.07-2.03, respectively). 30833724_PSGL-1 was identified as an HIV-1 restriction factor downregulated by HIV-1 Vpu, which binds to PSGL-1 and induces its ubiquitination and degradation through the ubiquitin ligase SCF(beta-TrCP2). 31645726_VISTA is an acidic pH-selective ligand for PSGL-1 31897593_Circulating P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand 1 and P-Selectin Levels in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients. 32193343_Virion-incorporated host transmembrane proteins PSGL-1 and CD43 inhibit attachment of HIV-1 particles to target cells. Co-clustering of HIV-1 structural protein Gag with PSGL-1 and subsequent progeny virion release contribute to depletion of PSGL-1 from an infected cell surface. In addition, study reports a previously unidentified role for Gag in viral down-regulation of antiviral proteins. 33244198_P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 deficiency prevents development of acute pancreatitis by attenuating leukocyte infiltration. 33432452_P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1 Deficiency Protects Against Aortic Aneurysm Formation Induced by DOCA Plus Salt. 34615372_Myeloid Mineralocorticoid Receptor Transcriptionally Regulates P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1 and Promotes Monocyte Trafficking and Atherosclerosis. 35153625_SELPLG Expression Was Potentially Correlated With Metastasis and Prognosis of Osteosarcoma. 35597982_P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1/CD162) is incorporated into clinical HIV-1 isolates and can mediate virus capture and subsequent transfer to permissive cells. 36199080_Lnc-SELPLG-2:1 enhanced osteosarcoma oncogenesis via hsa-miR-10a-5p and the BTRC cascade. |
ENSMUSG00000048163 |
Selplg |
46.302832 |
3.9078495134 |
1.966375 |
0.267529740 |
55.925339 |
0.00000000000007527609356878846443790235219533427825204258826419234651439182925969362258911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000481610377579244791719806477327003415883806269892630780304898507893085479736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
72.6660702 |
11.2566274 |
18.7035310 |
2.4432366 |
| ENSG00000110880 |
23603 |
CORO1C |
protein_coding |
Q9ULV4 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in directed cell migration by regulating the activation and subcellular location of RAC1 (PubMed:25074804, PubMed:25925950). Increases the presence of activated RAC1 at the leading edge of migrating cells (PubMed:25074804, PubMed:25925950). Required for normal organization of the cytoskeleton, including the actin cytoskeleton, microtubules and the vimentin intermediate filaments (By similarity). Plays a role in endoplasmic reticulum-associated endosome fission: localizes to endosome membrane tubules and promotes recruitment of TMCC1, leading to recruitment of the endoplasmic reticulum to endosome tubules for fission (PubMed:30220460). Endosome membrane fission of early and late endosomes is essential to separate regions destined for lysosomal degradation from carriers to be recycled to the plasma membrane (PubMed:30220460). Required for normal cell proliferation, cell migration, and normal formation of lamellipodia (By similarity). Required for normal distribution of mitochondria within cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUM4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25074804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25925950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30220460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34106209}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Involved in myogenic differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19651142}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2013]. |
hsa:23603; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; flotillin complex [GO:0016600]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; synapse [GO:0045202]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; endosome fission [GO:0140285]; endosome membrane tubulation [GO:0097750]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; membrane fission [GO:0090148]; negative regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010633]; negative regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051895]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity by regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0044387]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900025]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis [GO:2000394]; regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010632]; regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010762]; regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051893]; regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001932]; regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900027]; regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900024]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591] |
12377779_oligomerization, F-actin interaction and membrane association are mediated by carboxyl terminus 17274980_We show that coronin 3 similar to other coronins interacts with the Arp2/3-complex and cofilin indicating that this family in general is involved in regulating Arp2/3-mediated events. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19651142_Fndings postulate a role for CRN2 isoforms in the structural and functional organization of F-actin in highly ordered protein complexes. 19913511_Coronin 1C negatively regulates epithelial cell migration via FAK-mediated inhibition of cell-matrix adhesion. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20678442_Patients with higher coronin-1C expression had a more advanced stage of hepatocellular carcinoma. 20690162_There is a strong expression of both SELPLG and coronin-1C in the majority of primary effusion lymphomas, irrespective of their gene dosage. SELPLG is critical for cell migration and chemotaxis, while CORO1C regulates actin-dependent processes. 22974233_Coronin 3 promotes gastric cancer metastasis via the up-regulation of MMP-9 and cathepsin K. 23292607_Coronin-1C overexpression is associated withand hepatocellular carcinoma growth through enhancement of tumor cell proliferation and migration, which are correlated with Rac-1 activation. 25518741_Data indicate that coronin 1C protein (CORO1C) was a direct target of the microRNA miR-1/133a cluster in EBC-1 CORO1C was a direct target of the miR-1/133a cluster in lung-squamous cell carcinoma cell line EBC-1. 25862165_Coro1C mediated Rac1 trafficking through actin-rich vesicles. 27499521_findings emphasize the power of genetic modifiers, PLS3 and CORO1C, to unravel the cellular pathomechanisms underlying spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)--and the power of combinatorial therapy based on splice correction of SMN2 and endocytosis improvement to efficiently treat SMA 28302118_It would appear that YB-1 could regulate cell invasion and migration via downregulation of its indirect target coronin-1C. The association between YB-1 and coronin-1C offers a novel approach by which metastasis of breast cancer cells could be targeted and abrogated. 29074849_circBIRC6 and circCORO1C are functionally associated with the pluripotent state in undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells 30065298_These results identify coronin 1C as a novel player of the multi-faceted mechanism responsible for invadopodia formation, MT1-MMP surface exposure and invasiveness in breast cancer cells. 30150608_Coronin 1c protein and F-actin protein are highly expressed in breast cancer and their expression may be related to the metastasis of breast cancer cells. 30974047_CORO1C promoted both proliferation and metastasis, stimulated cellular mitosis and inhibited cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Gastric cancer patients with positive CORO1C expression were associated with poor prognosis and lower survival rate. 31595425_miR-26 suppresses renal cell cancer via down-regulating coronin-3. 32206066_MiR-206 may suppress non-small lung cancer metastasis by targeting CORO1C. 33511909_Circ_0003998 Regulates the Progression and Docetaxel Sensitivity of DTX-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by the miR-136-5p/CORO1C Axis. 34062216_Cytoplasmic RAD23B interacts with CORO1C to synergistically promote colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. 34534547_A peptide CORO1C-47aa encoded by the circular noncoding RNA circ-0000437 functions as a negative regulator in endometrium tumor angiogenesis. 35034254_Circ_0025039 acts an oncogenic role in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-636-dependent regulation of CORO1C. 35064359_CircRNA CORO1C Regulates miR-654-3p/USP7 Axis to Mediate Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. 35388975_Circ_0020123 plays an oncogenic role in non-small cell lung cancer depending on the regulation of miR-512-3p/CORO1C. 35593474_CORO1C, a novel PAK4 binding protein, recruits phospho-PAK4 at serine 99 to the leading edge and promotes the migration of gastric cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000004530 |
Coro1c |
1833.919646 |
2.7188827269 |
1.443014 |
0.046995192 |
940.771519 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001345234028620078211539747057546693747659915639326534435516384092834043181165447224934960996459877131969723053632292720682117 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001289328198859243814777916722677693270111638032990454003104095418323409752110943604703608667013061539332327039618396056182589 |
Yes |
No |
2638.6972684 |
101.1432946 |
977.3824180 |
28.3645722 |
| ENSG00000110911 |
4891 |
SLC11A2 |
protein_coding |
P49281 |
FUNCTION: Important in metal transport, in particular iron. Can also transport manganese, cobalt, cadmium, nickel, vanadium and lead. Involved in apical iron uptake into duodenal enterocytes. Involved in iron transport from acidified endosomes into the cytoplasm of erythroid precursor cells. May play an important role in hepatic iron accumulation and tissue iron distribution. May serve to import iron into the mitochondria. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17109629, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24448823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25326704, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25491917}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Iron;Iron transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the solute carrier family 11 protein family. The product of this gene transports divalent metals and is involved in iron absorption. Mutations in this gene are associated with hypochromic microcytic anemia with iron overload. A related solute carrier family 11 protein gene is located on chromosome 2. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:4891; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal part of cell [GO:0045178]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; paraferritin complex [GO:0070826]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; vacuole [GO:0005773]; cadmium ion binding [GO:0046870]; cadmium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015086]; cobalt ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015087]; copper ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005375]; ferrous iron transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015093]; inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022890]; iron ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005381]; lead ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015094]; manganese ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005384]; nickel cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015099]; retromer complex binding [GO:1905394]; solute:proton symporter activity [GO:0015295]; transition metal ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0046915]; vanadium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015100]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; cadmium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070574]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cobalt ion transport [GO:0006824]; copper ion transport [GO:0006825]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; detection of oxygen [GO:0003032]; erythrocyte development [GO:0048821]; heme biosynthetic process [GO:0006783]; iron import into cell [GO:0033212]; iron ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034755]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; lead ion transport [GO:0015692]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; manganese ion transport [GO:0006828]; multicellular organismal iron ion homeostasis [GO:0060586]; nickel cation transport [GO:0015675]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to iron ion [GO:0010039]; vanadium ion transport [GO:0015676] |
11891802_location was observed on or near the cell surface suggesting it might participate in surface membrane transport of iron 11897618_expression levels of human DCT1 mRNA, and to a lesser extent IREG1 mRNA, are regulated in an iron-dependent manner 11943663_airway epithelial cells increase mRNA and expression of the Nramp2/DMT1/DCT1 without an IRE after exposure to iron. The increase results in an elevated transport of iron and its probable detoxification by these cells. 12127992_DMT1 is a transporter for lead 12209011_iron regulation of DMT1 involves the expression of a previously unrecognized upstream 5' exon (exon 1A) of the human and murine DMT1 gene 12662899_Using the Xenopus oocyte expression system, human Nramp2, a human intestinal iron transporter, was shown to work as a cadmium transporter 12734107_These results demonstrate that DMT1 is a physiologically relevant Cu(1+) transporter in intestinal cells, indicating that intestinal absorption of copper and iron are intertwined. 12949888_in iron deficiency DMT-1 and mobilferrin concentrated in apical surface of duodenal villae; increase due to increased binding to mucin in vesicles near surfacel; localized in goblet cells and outside cell in luminal mucin 12973678_divalent metal ion transporter-1 may be of pivotal importance for the regulation of metal ion homeostasis within organs involved in absorption and excretion of ions 14768003_Increased expression of DMT1 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis-associated hepatic iron overload. 15024413_the G185R mutant DMT1 exhibits a new, constitutive Ca(2+) permeability 15139022_comparison of the regional distribution of SFT/UbcH5A and DMT1 mRNA in the adult brain 15223008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15459009_Mutation of DMT1 identified in a female with severe hypochromic microcytic anemia and iron overload. 15636493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15644277_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15792797_Intracellular localization of SLC11A2 to endosomal/lysosomal compartment is regulated by iron. 15880641_Transferrin receptor (TfR) and hemochromatosis factor, as well as TfR and DMT1 interact in placental trophoblast cells 16123094_DMT1 isoforms are expressed in first trimester human placenta and embryonic tissues 16439678_DMT1 mutations are responsible for severe hypochromic microcytic anemia in humans. 17109629_Specific signals or cues to direct DMT1 to the appropriate subcellular compartments (e.g. in erythroid cells) or the plasma membrane (e.g. in intestine). 17293870_Modulation of DMT-1 function by L-type calcium channel blockers is a pharmacological therapy for the treatment of iron overload disorders. 17510944_two DMT1 intronic SNPs showed positive association with restless legs syndrome in patients with a history of anemia, when compared to RLS patients without anemia. 17980698_These results demonstrate the importance of these regions in coupling of metal ions and protons as well as the possible proximity of I144 and F227 in the folded structure of DCT1. 18082289_Increased DMT1+IRE expression in MES23.5 cells caused the increased intracellular iron accumulation. This resulted in the increased oxidative stress leading to ultimate cell apoptosis. 18419598_Correlation between the expression of DMT1 and the content of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in hypoxic cells is reported. 18667808_DMT1 (NRAMP2/DCT1) genetic variability and resistance to recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in chronic kidney disease patients under haemodialysis. 19679638_These findings suggest both that DMT1 plays a critical role in ion-mediated neuropathogenesis in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and that pharmacological blockage of DMT1 may provide novel therapeutic strategies against AD. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20007457_Suggest a novel mechanism of regulation of intestinal iron absorption based on inward and outward fluxes at both membrane domains, and repositioning of DMT1 and FPN between membrane and intracellular compartments as a function of iron supply. 20152801_Ca2+ is a low-affinity noncompetitive inhibitor--but not a transported substrate--of DMT1, explaining in part the effect of high dietary calcium on iron bioavailability. 20164305_Findings demonstrate that the retromer recognizes the recycling signal of DMT1-II and ensures its proper endosomal recycling. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20410187_Data suggest that miR-Let-7d participates in the finely tuned regulation of iron metabolism by targeting DMT1-IRE isoform in erythroid cells. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20945371_DMT1 is a hypoxia-inducible gene. 21074515_Data show that the peptide can bind to Mn2+ and Co2+ ions by the side chains of the negatively charged residues in the motif and the C-terminal part of DMT1-TMD1. 21199652_An acute increase in hepcidin concentration reduces intestinal iron absorption through ubiquitin-dependent proteasome degradation of DMT1 21276595_Our findings support an implication for iron metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and suggest that the genotype of the SLC11A2 gene could modulate the duration of the disease 21777657_CC haplotype in DMT1 gene is a possible risk factor for Parkinson disease in this Han Chinese population. 21798283_Variations in the ability of LAT1/DMT1/MTF1/MT1a to process and transport Hg may not play a significant role in the etiology of autism. 21871825_Our data confirm the major role of SLC11A2 in the maintenance of iron homeostasis in humans and demonstrate that the mutation contributes to the development of anemia and hepatic iron overload. 21947861_DMT1 is likely involved in endosomal iron transport in placental STB and placental DMT1 + IRE expression was primarily regulated by the IRE/IRP mechanism 21948377_Homology implies that inverted structural symmetry facilitates Slc11 H(+)-driven Me(2+) import and provides a 3D framework to test structure-activity relationships in macrophages and study functional evolution of MntH/Nramp (Slc11) carriers. 22068728_Data show that both shRNA-DMT1 and shRNA-hCTR1 cells had lower apical Fe uptake, Cu uptake, and Zn content compared to control cells. 22137264_Data suggest that DMT-1 in enterocytes is delocalized from plasma membrane upon iron or zinc depletion; apical abundance of DMT-1 increases with zinc supplementation. 22154351_analysis of synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted pyrazoles as blockers of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) 22310887_DMT1 regulation in an isoform specific fashion can occur by ubiquitination and the events involved have implications for DMT1 function and disease processes. 22371024_These results suggest that the VS4+44C>A polymorphism of the DMT1 gene may interact with place of living and gender to modulate the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). 22383495_The data were consistent with PAP7 interacting with DMT1 and regulating DMT1 expression in K562 cells by modulating expression of DMT1 protein. 22509377_sequenced exons and exon-intron boundaries of SLC11A2 and TMPRSS6 in all 6 family members with iron-refractory iron deficiency anaemia; cannot exclude or confirm a gene-gene interaction between SLC11A2 and TMPRSS6; gene sequencing did not reveal causative rare mutations 22666436_that 1B/(-)IRE DMT1 expression and intracellular iron influx are early downstream responses to NF-kappaB/RelA activation and acetylation during brain ischemia and contribute to the pathogenesis of stroke-induced neuronal damage 22736759_Substrate profile and metal-ion selectivity of human divalent metal-ion transporter-1. 23016933_Identification and characterization of the first SLC11A2 isoform 1a mutation causing a defect in splicing process and an hypomorphic allele expression of the SLC11A2 gene. 23996061_Manganese (Mn) transport carriers DMT1 and FPN1 mediate the apical uptake and basolateral exit of Mn in colonic epithelial Caco-2 cells. 24120082_The DMT1 IVS4 C(+) allele occurred more frequently in WND than in the healthy controls. 24448823_DMT1 not only exports iron from endosomes, but also serves to import the metal into the mitochondria 24475238_In Parkinson's disease, increased iron levels are associated with increased Ndfip1 expression for the regulation of DMT1, including abnormal Ndfip1 activation in non-neuronal cell types such as astrocytes. 24914374_Six months after RYGB surgery, patients exhibit an increase in DMT1 expression in the enterocytes of the tips of the villi at the proximal jejunum 25562168_We propose that DMT1 deficiency negatively affects metabolism and life span of mature erythrocytes; two other aspects of defective erythropoiesis which contribute to the pathophysiology of the disease 25772431_Suggest role for divalent cation transporter DMT1 in the entry of Hg(II) into the intestinal epithelium. 25817364_the TT genotype and T allele of the 1254T>C polymorphism may be a risk factor for Parkinson disease 26067577_Gene silencing of either CTR1 or DMT1 did not affect copper accumulation in cells, but deficiency in both CTR1 and DMT1 resulted in a complete inhibition of copper uptake. 26289753_These data suggest that iron uptake induces the production of ROS, which modify DMT1 endocytic cycling, thus changing the iron transport activity at the apical membrane. 27117373_Divalent metal transporter-1 overexpression in endometriosis patients' endometrium can increase iron influx to endometrial cells, inducing oxidative stress-mediated proinflammatory signaling. In turn, endometriosis-related conditions, as iron overload and inflammation (IL-1beta), enhance endometriosis patients endometrial DMT1 expression, creating a vicious circle on DMT-1-modulated pathways. 27546461_the cellular iron importer, divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), is highly expressed in colorectal cancer through hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha-dependent transcription. 27889239_X-ray crystallographic analysis of a 4-component complex comprising the VPS26 & VPS35 subunits of retromer, sorting nexin SNX3, & recycling signal from the divalent cation transporter DMT1-II; analysis identifies a binding site for canonical recycling signals at the interface between VPS26 & SNX3; shows cooperative interactions among the VPS subunits, SNX3 & cargo that couple signal-recognition to membrane recruitment. 28367088_These results suggest that the increased expression of DMT1 induces iron overload and iron overload induces osteoblast autophagy and apoptosis, thus affecting the pathological processes of osteoporosis. Clarifying the mechanisms underlying the effects of DMT1 will allow the identification of novel targets for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. 28714470_DMT1 was increased in myelodysplastic syndrome patients. 28754960_E193 in hDMT1, is proposed to translocate protons in an inward-rectified manner by alternating contact with the solvent on each side of the membrane bilayer. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations provide insight into how H(+)-translocation through E193 is allosterically linked to intracellular gating, establishing a novel transport mechanism distinct from that of other H(+)-coupled transporters. 28762519_Results indicate that there is a dysregulation of DMT1 + IRE in IA testes, which might due to the up-regulation of IRP1 and HIF-1A. 29023457_celiac disease may unmask the contribution of the DMT1 IVS4+44C>A polymorphism to the risk of anemia. 29082606_SLC11A2 expression is increased in the intestine of patients with type 2 diabetes in association with iron stores and serum hepcidin levels. 29178181_A compound heterozygote with hereditary hypochromic microcytic anemia was found to have 2 new DMT1 mutations: a C > T transition at nucleotide 1429 of exon 15 (R477W) and a G > C substitution at position +1 bp of the splice-donor site within intron 4 (ivs4 + 1 G/C). R477W was inherited from proband's mother, while ivs4 + 1 G/C was of paternal inheritance. 30055235_We summarize DMT1 expression depending on the types of cell or tissue and the function and mechanism of one of the iron chaperones, PCBP2 30423260_PKCalpha promotes microvillus membrane DMT1 expression. 30527495_Low DMT1 expression associates with increased oxidative phosphorylation as well as glycolysis and identifies early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after surgical treatment. 30555088_Solute carrier family-11 member-2 (SLC11A2) homozygous CC genotype for IVS4+44C/A showed significant correlation with Type-2 diabetes (T2DM) risk, suggesting that presence of C allele of IVS4+44C/A plays pathological roles. 30870050_The results highlighted a protective association of A-T-T haplotype against the risk of Age-related cataract (ARC). 30959888_The loss of CTR1 resulted in a decrease in the level of COMMD1, XIAP, and NF-kappaB. Differently, the DMT1 deficiency induced increase of the COMMD1, HIF1alpha, and XIAP levels. 31092704_To better understand the mechanisms of zinc-induced iron absorption, we have studied the effect of zinc on iron uptake, iron transporter and iron regulatory protein (IRP 1 and 2) expression and the impact of the PI3K pathway in differentiated Caco-2 cells, an intestinal cell culture model. We found that zinc induces DMT1 protein and mRNA expression. 31721611_Enhanced expression of apical membrane- and basolateral membrane-localized DMT1 and FPN1 in UC human colon. 31804182_the interaction of aromatic bis-isothiourea-substituted compounds with human DMT1 and its prokaryotic homologue EcoDMT, is reported. 32379419_alpha-Synuclein Regulates Iron Homeostasis via Preventing Parkin-Mediated DMT1 Ubiquitylation in Parkinson's Disease Models. 33146651_Human placental cell line HTR-8/SVneo accumulates cadmium by divalent metal transporters DMT1 and ZIP14. 33781609_Mutation analysis of seven SLC family transporters for early-onset Parkinson's disease in Chinese population. 34626817_Evaluation of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) (rs224589) polymorphism on blood lead levels of occupationally exposed individuals. 35730874_DOES SLC11A2 GENE MUTATION ASSOCIATE WITH IRON-REFRACTORY IRON-DEFICIENCY ANEMIA AFTER BARIATRIC SURGERY? 35857262_Genotypic Effect of IVS4+44C>A and c.2044T>C DMT1 Gene Mutations on Pathophysiology of Iron-Deficiency Anemia. 35893933_The Associations between Metalloestrogens, GSTP1, and SLC11A2 Polymorphism and the Risk of Endometrial Cancer. 36047197_Regulation of Iron-Ion Transporter SLC11A2 by Three Identical miRNAs. |
ENSMUSG00000023030 |
Slc11a2 |
502.079426 |
2.7817805352 |
1.476009 |
0.081378515 |
333.352577 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001788968062602117476928141394161854375523093852516060045925481552450052266487123569665841043920128573325173948638300524967652426076796916952757029930101678468092809585964387608926994509273011857430901727639138698577880859375000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000565421169250690664288988508214986519536332896937074400598348314221750018988817400176932785196982027943657824359296889457612409527349262081182936188045763943147453088595912062025742803039740635995258344337344169616699218750000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
736.1295372 |
42.1687901 |
266.2480685 |
12.0242384 |
| ENSG00000110921 |
4598 |
MVK |
protein_coding |
Q03426 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of mevalonate to mevalonate 5-phosphate, a key step in isoprenoid and cholesterol biosynthesis (PubMed:9325256, PubMed:18302342, PubMed:9392419, PubMed:11278915). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11278915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18302342, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9325256, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9392419}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cataract;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Kinase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Peroxisome;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Isoprenoid biosynthesis; isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthesis via mevalonate pathway; isopentenyl diphosphate from (R)-mevalonate: step 1/3. {ECO:0000305}. |
This gene encodes the peroxisomal enzyme mevalonate kinase. Mevalonate is a key intermediate, and mevalonate kinase a key early enzyme, in isoprenoid and sterol synthesis. Mevalonate kinase deficiency caused by mutation of this gene results in mevalonic aciduria, a disease characterized psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and recurrent febrile crises. Defects in this gene also cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome, a disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of fever associated with lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, gastrointestinal dismay and skin rash. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:4598; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; mevalonate kinase activity [GO:0004496]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; isopentenyl diphosphate biosynthetic process, mevalonate pathway [GO:0019287]; isoprenoid biosynthetic process [GO:0008299]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] |
12444096_Mutations of MVK found in hyper-IgD and periodic fever syndrome patients affect the stability and/or maturation of MVK in vitro in a temperature-sensitive manner and may explain the chain of events leading to episodic inflammation and fever. 12477733_Isoprenoid and cholesterol biosynthesis still occurs in cells from mevalonate kinase-deficient patients. 12634869_Carrier frequency of 1:65 overestimates disease frequency, probably due to a reduced penetrance of V377I homozygosity. 12634869_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14730012_The subcellular localisation of human mevalonate kinase (MK) use a variety of biochemical and microscopical techniques. 14749336_LH receptor mRNA-binding protein (LRBP) is a a novel trans-factor for luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA from ovary. 15037710_Mevalonic aciduria, with psychomotor retardation, cerebellar ataxia, recurrent fever, and death in early childhood, and hyper-immunoglobulin D syndrome, with recurrent fever attacks without neurologic symptoms, are caused by mevalonate kinase deficiency 15188372_Mutations in the coding region of the MVK gene were detected in 6 hyperimmunoglobulinemia D patients, and the most common mutation was V377I. 16234278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17213252_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193043_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18302342_Several hydrophobic amino acid side chains are positioned near the polyisoprenoid chain of FSP & their functional significance has been evaluated in mutagenesis experiments with human MK, which exhibits highest reported sensitivity to feedback inhibition. 18494797_an intact active site of MVK is required for its binding to rat LHR mRNA and for its translational suppressor function 18512793_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18941711_homozygosity for the mutation of the MVK gene has been reported in an Asian patient, and indicated a need for differentiation. 19148283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19487539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605566_For the SNPs KCTD10_i5642G-->C and MVK_S52NG-->A, homozygotes for the major alleles (G) had lower HDL-cholesterol concentrations than did carriers of the minor alleles (P = 0.005 and P = 0.019, respectively). 19605566_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20159775_These data suggest MMAB is the most likely gene influencing high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels at MMAB-MVK locus. 20160193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20194276_A novel missense mutation in mevalonate kinase (Tyr116His) is associated with mevalonate kinase deficiency and dyserythropoietic anemia. 20430392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20714348_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20814828_Report mevalonate kinase deficiency compromized fiberoblast geranylgeranylation of RhoA and Rac1. 20972250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21124859_Results support that deleterious copy number alterations in MVK, NLRP3 and TNFRSF1A are rare or absent from the mutational spectrum of hereditary recurrent fevers. 21147848_data show that LH-regulated ERK1/2 signaling is required for the LRBP-mediated down-regulation of LHR mRNA 21430599_The farnesyltransferase inhibitors tipifarnib and lonafarnib inhibit cytokines secretion in a cellular model of mevalonate kinase deficiency. 21548022_Significant liver disease in a patient with Y116H mutation in the MVK gene. 22038276_hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome (HIDS) patients carried 11 different MVK mutations mostly in compound heterozygosity; the most frequent mutation was p.Val377Ile; in Germany, the incidence of HIDS is very low 22159817_Novel mutations of MVK gene in Japanese family members affected with hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome. This is the first case in which exon skipping mutation of the MVK gene has been certainly identified at the genomic DNA level. 22271696_This atypical presentation of MA suggests that it should be included in the differential diagnosis of unclassified patients with psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive or ataxia, even in the absence of febrile episodes. 22983302_MVK has a role in regulating calcium-induced keratinocyte differentiation and could protect keratinocytes from apoptosis induced by type A ultraviolet radiation. 23834120_Results identify a novel frameshift mutation in this gene implicated in disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis in 4 Chinese families 24008101_study reportstwo novel mutations of the MVK gene in Chinese patients with disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis 24064360_These results suggest that hCG-induced down-regulation of LHR mRNA expression is mediated by activation of cAMP/PKA/ERK pathways to increase miR-122 expression, which then increases LRBP expression through the activation of SREBPs. 24084495_In the current article, we add another phenotype to the spectrum of diverging disorders associated with mutations in MVK. 24411001_Results suggest that the effects of MVK mutations in Behcet's disease could be an additional genetic susceptibility factor for the patients with neurological involvement. 24551296_Report a novel missense mutation in mevalonate kinase responsible for disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis. 24708999_The testing for the Hyper IgD Syndrome was positive for the pV377I/c.1129 G>A heterozygosity in a patient with periodic fever. 24781643_mutations are responsible for porokeratosis of Mibelli development in Chinese families 25053464_results from this 4 generation family imply a causal relationship between MVK and perokeratosis. 25059119_study reports a novel mutation of the MVK gene in Chinese patients with disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP); result confirms the involvement of MVK gene in DSAP 25982894_Wild-type MK and the variant V261A, which is associated with HIDS, were recombinantly expressed in Escherichia coli. Enzyme activity was determined by formation of MVAP over time 26420133_predictive analysis of mutations in MVK to predict disease severity 26794421_this study extends the mutation spectrum of MVK; MVK protein stability and correct folding might be the molecular mechanism causing disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis 27213830_In a cohort of mevalonate kinase deficiency patients, ninety-six (84%) of the patients harbored at least 1 p.V377I mutation, 14 (12%) of which were homozygous. The second most frequent mutation was p.I268T, occurring in 29 (25%) of the patients. None of them were p.I268T homozygous. A p.C152Y mutation was found in 1 patient. 27716295_These findings suggest that rs11066782 in KCTD10, rs11613718 in KCTD10 and rs11067233 in MMAB may contribute to the susceptibility of coronary heart disease by altering plasma HDL-C levels in Han Chinese. 28095071_Mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD) can be associated with retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and early onset cataract. Most MKD patients developing RP carry the (p.Ala334Thr) mutation. 29148404_Case Report: homozygous missense p.Cys161Arg in MVK was identified in family members with familial Mediterranean fever. 29290516_this study demonstrates mevalonate kinase deficiency presenting as recurrent rectal abscesses and perianal fistulae 30101835_The findings suggest that the MVK rs2287218 SNP is likely to increase the risk of CHD and IS by decreasing serum HDL-C levels in our study populations. 30418111_In rare cases, periodic fever and inflammatory symptoms in adults can be attributed to mutations in NLRP3, MVK and TNFRSF1A. 30597534_Novel mutations in mevalonate kinase cause disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis. 31135083_In this study, we discussed the clinical effects of eight different variants we have detected in the MVK, TNFRSF1A and NLRP3 genes. Four of them were previously identified in patients with Periodic fever syndromes 31207227_Patients with disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis (DSAP) and linear porokeratosis (LP) exhibit monoallelic germline mutations in genes encoding mevalonate pathway enzymes, such as MVD or MVK 31474985_Defective Protein Prenylation in a Spectrum of Patients With Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency. 32822427_Spectrum of clinical features and genetic variants in mevalonate kinase (MVK) gene of South Indian families suffering from Hyperimmunoglobulin D Syndrome. 34145613_Phenotypic diversity, disease progression, and pathogenicity of MVK missense variants in mevalonic aciduria. 34751146_Novel missense mutations of MVK and FDPS gene in Chinese patients with disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis. |
ENSMUSG00000041939 |
Mvk |
67.277407 |
2.3264943786 |
1.218158 |
0.332713739 |
13.121502 |
0.00029192596159561602121856882519068676629103720188140869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000746375747990870056988721437107869860483333468437194824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
97.7189356 |
19.8091161 |
42.1262169 |
6.4986855 |
| ENSG00000110944 |
51561 |
IL23A |
protein_coding |
Q9NPF7 |
FUNCTION: Associates with IL12B to form the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-23 that plays different roles in innate and adaptive immunity (PubMed:11114383). Released by antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells or macrophages, binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R to activate JAK2 and TYK2 which then phosphorylate the receptor to form a docking site leading to the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT4 (PubMed:32474165, PubMed:29287995, PubMed:33606986). This process leads to activation of several pathways including p38 MAPK or NF-kappa-B and promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-17A/IL17A (PubMed:12023369). In turn, participates in the early and effective intracellular bacterial clearance (PubMed:32474165). Promotes the expansion and survival of T-helper 17 cells, a CD4-positive helper T-cell subset that produces IL-17, as well as other IL-17-producing cells (PubMed:17676044). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114383, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12023369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16424222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17676044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29287995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32474165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33606986}. |
3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Tissue remodeling |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of the heterodimeric cytokine interleukin 23 (IL23). IL23 is composed of this protein and the p40 subunit of interleukin 12 (IL12B). The receptor of IL23 is formed by the beta 1 subunit of IL12 (IL12RB1) and an IL23 specific subunit, IL23R. Both IL23 and IL12 can activate the transcription activator STAT4, and stimulate the production of interferon-gamma (IFNG). In contrast to IL12, which acts mainly on naive CD4(+) T cells, IL23 preferentially acts on memory CD4(+) T cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51561; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; interleukin-23 complex [GO:0070743]; interleukin-23 receptor complex [GO:0072536]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-23 receptor binding [GO:0045519]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; positive regulation of activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0010536]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation [GO:0043382]; positive regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032816]; positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation [GO:0032819]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of NK T cell activation [GO:0051135]; positive regulation of NK T cell proliferation [GO:0051142]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002827]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment [GO:2000330]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:2000318]; positive regulation of tissue remodeling [GO:0034105]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042509]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; tissue remodeling [GO:0048771] |
12162874_Elevated expression of mRNA for IL-23(p19)was found in trigeminal ganglia of BALB/C mice infected with HSV-1 from early acute infection to the beginning of the latent phase. 12847224_In BALB/c mice, single chain (sc) IL-23-transduced CT26 cells grow progressively until day 26, then the tumors start to regress in most animals; scIL-23 transduction also significantly suppresses lung metastases of CT26 and B16F1 tumor cells. 14707118_IL-23 plays a more dominant role than IL-12 in psoriasis, a Th1 type of human inflammatory disease. 15070757_Macrophages produce neither IL-23 nor IL-12 but predominantly secrete IL-10. 15583831_IL-23 p19 mRNA is inducible in colonic myofibroblasts by IL-1beta and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha 15731058_synthesis induced by Bordetella pertussis in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDC) 16300465_This overview provides the historical background and current understanding of the roles of IL-12, IL-23, and T-helper type 1 (TH1) cell development in inflammation and autoimmunity. 16339539_IL-23 plays an important role in the FasL-induced IL-17 production. 16424222_Augmented expression of IL-23 by keratinocytes and cutaneous antigen-presenting cells may contribute to the perpetuation of inflammatory lesions in psoriatic skin. 16670765_IL-23 and IL-17 have roles in inflammation [commentary] 16751425_An abnormal type-1 T helper (Th1) cell bias exists related to IL-23-expressing dendritic cells from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients, which may play an important role in the pathogenesis of human autoimmune diseases such as MS. 16772281_Increased concentrations of p40 subunit of IL-23 in follicles containing oocytes suggest an important role of this cytokine in reproduction. 17007011_This review summarizes information on the expression and role of IL-12 both in patients with Crohn's diease and experimental models of colitis, thus emphasizing differences between IL-12 and IL-23 activity on the development of intestinal inflammation. 17021762_Abnormal IL-23 expression may play a role in the pathogenesis and progression of mycosis fungoides to Sezary syndrome. 17182554_c-Rel controls IL-23 p19 gene expression through two kappaB sites in the p19 promoter, and propose a c-Rel-dependent enhanceosome model for p19 gene activation. 17187052_IL-22 is preferentially produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the acanthosis induced by IL-23 17236132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17564777_mRNA levels of IL23 subunit p19 in active SLE patients was significantly higher compared with those in the inactive SLE patients 17606463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17763202_Upregulated IL-23p19 in synovial fluid may be involved in joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. 17945537_results here show that IL-23 is elevated in children with malarial anemia, and that IL-10 and IL-12 appear to have important regulatory effects on IL-23 production during childhood malaria 18054783_Data suggest that the p38 MAP kinase and NF-kappaB signaling pathways play an important role in regulation of IL-23p19 expression on human microglia, and are thus potential therapeutic targets in the treatment of MS. 18180107_These data indicate that IL23R represents a novel shared susceptibility gene as its association with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has recently been verified. 18190588_an increased expression of IL-12 p40, IL-12 p35 and IL-23 p19 mRNA was observed in bone marrow mononuclear cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with aplastic anemia compared with the corresponding one in normal controls. 18311793_Immunohistochemical stainings of submandibular glands from C57BL/6.NOD-Aec1Aec2 mice and of salivary gland biopsy specimens from Sjogren's syndrome patients revealed IL-17 and IL-23 staining within lymphocytic foci and epithelial tissues. 18319400_NK cells require in vivo priming with IL-12/23 to acquire their full spectrum of functional reactivity, while T cells are dependent upon IL-12/23 signals for the differentiation and/or the maintenance of CD56(+) effector memory T cells 18373953_The activated IL-23/IL-17 axis is important for the inflammatory immunity in systemic lupus erythematosus. 18408745_IL-23 stimulates survival and proliferation of Th17 cells and thus serves as a key master cytokine regulator for psoriasis 18490716_findings show that lactic acid secreted by tumor cells enhances the transcription of IL-23p19 and IL-23 production in monocytes/macrophages and in tumor-infiltrating immune cells that are stimulated with TLR2 and 4 ligands 18497880_intestinal macrophages expressing CD14 contribute to the pathogenesis of Crohn disease via IL-23/IFN-gamma axis 18579762_Levels of IL-23, IL-17, and IFN-gamma are elevated in Behcet disease(BD) with active uveitis. IL-23/IL-17 pathway together with IFN-gamma is associated with active intraocular inflammation in BD patients. 18606709_study demonstrates that oxidative stress induced by soluble cigarette smoke components potently inhibits the production of IL-12 and IL-23 by maturing dendritic cells 18680750_Data suggest that the structure of interleukin-23 reveals the molecular basis of p40 subunit sharing with interleukin-12. 18708069_Results describe the crystal structures of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-23 and its complex with a high-affinity neutralizing antibody. 18752933_Serum levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and IL-23p19 were higher in psoriatic arthritis patients than in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 18754016_Identification of potentially functional splice variants of IL23 receptor (IL-23R) will aid in understanding possible pathogenic mechanisms of IL-23R's contribution to disease susceptibility. 18786233_The role of the IL23/IL17 axis in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation is reported. 18825388_The greatest upregulation of IL-23p19, Foxp3 and survivin mRNA was seen in colorectal carcinomas than normal mucosa. 19034457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19040306_Significant associations between Arg381Gln SNP and haplotypes encoding this variant were noted in psoriatic arthritis 19088061_IL-23 in synergy with IL-18 elicits IFN-gamma production in NK T cells but not in NK cells; upregulates IL-18Ra and CD56 expression 19169254_Expanded catalog of genetic loci implicated in psoriasis susceptibility. 19169254_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19201028_Fibroblast-like synoviocytes are potently regulated by inflammatory cytokines to specifically express IL-23 p19. 19247658_IL-23 and IL-17 may play critical roles in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis and IL-23-stimulated production of IL-17 by PBMCs may be responsible for the development of AS. 19262574_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19264456_Bioactive forms of IL-12 and IL-23 are highly expressed in various DC and macrophage subsets and their marked in situ production suggest that both cytokines have crucial pathogenic role in psoriasis. 19322214_The IL-23/Th17 axis has a role in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis [review] 19333939_overexpression of IL-23, but not IL-17, is a pivotal feature of subclinical gut inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis 19426392_Association of the CagA status of Helicobacter pylori and serum levels of interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-23 in duodenal ulcer patients. 19431078_This review summarizes the critical role of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in progressing to chronic destructive arthritis, as well as the dominant cell type in arthritis development and pathology. 19479806_IL-23 and IL-17 are up-regulated during acute hepatic rejection after liver transplantation. 19542049_Synergistic production of IL-23 by dendritic cells derived from cord blood in response to costimulation with LPS and IL-12 is reported. 19542431_Evaluating IL-23 production by dendritic cells (DC) in conjunction with IL-12p70 subunit may be important to elucidate the exact nature of DCs ability to regulate the immune response. 19587005_binding of NKG2D to UL-16 binding protein (ULB)1 contributes to IL-23-dependent IL-17 production by CD4(+) cells in human M. tuberculosis infection. 19605880_these results suggest that the IL-23-induced Th17 pathway is stimulated in inflammatory periodontal lesions 19657406_Levels of IFNgamma, TNFalpha, IL-6, IL-15, IL-18, and IL-23 were increased (above healthy controls) in both affected and unaffected areas from Inflammatory Bowel Diseas. 19705136_genes encoding components of the IL23-mediated inflammatory pathway are important determinants of psoriasis pathogenesis across multiple racial groups. 19797506_Results desceibe the gene expression of interleukins-17A, -23, and -12 and determine the proximity of IL-17A- and IL-23-producing cells in rheumatoid synovial tissue. 19845828_In the most severely affected group of Huntington's disease patients there were increased blood levels of IL-23. 19900478_induces RANKL expression in synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients via STAT3 and NF-kappaB signal pathways 19915944_the concentration of soluble form of vascular endothelial cadherin and IL-23 are raised in sera of patients with Behcet's disease compared with healthy controls 19929695_interleukin 17 and interleukin 23 were statistically significantly decreased in tuberculin skin test(TST)-positive individuals, compared with TST-negative individuals 20027291_The IL-23 induced cytokines allow for the subsequent production of IL-12 and amplify the IFN-gamma production in the type-1 cytokine pathway. 20054003_Data show that that 4-trifluoromethyl-celecoxib can inhibit secretion but not transcription of IL-12 (p35/p40) and IL-23 (p40/p19 heterodimers), and that this is associated with HERP function in the endoplasmic reticulum. 20071030_CD40-triggering of immature and mature DC but not of primary monocytes induced a rapid expression of high levels of IL-23, free p40, and minor levels of IL-12. 20106535_higher expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes and decidua of recurrent spontaneous abortion patients 20154336_IL23A may have undergone positive selection pressure directed towards conservation, suggesting that functional genetic variants within IL23A will have a significant impact on the host immune response. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428758_IL-23 up-regulates the growth and cell proliferation of oral cancer by promoting the nuclear transactivation of RelA. 20603238_Data from a large patient cohort rather suggest that high intra-tumoral expression levels of p35 mRNA and p19 mRNA are associated with a superior clinical outcome. 20624950_Data indicate dendritic cells from TLR7(-/-) animals showed activated IL-23, and neutralization of IL-17 in the TLR7(-/-) resulted in a significant decrease in the mucogenic response in the lungs. 20682175_serum IL-23 levels are significantly elevated in colorectal carcinoma (CRC) vs. control patients and are strongly associated with overexpression of VEGF, thus they may play an important role in carcinogenesis of CRC 20682672_Data show that IL-17 levels are elevated in SLE patients with elevated serum IL-23 in patients with inflammatory manifestations, but lack of correlation between Th17, Th1, and Th2 cytokines suggested independent regulatory mechanisms for these cytokines. 20701979_results suggest a possible regulatory role for IL-23 in the menstrual cycle and in early pregnancy, although the extent and function of this role are yet to be determined 20840651_SAA is a significant inducer of IL-23 and IL-1beta in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synoviocytes and potentially activates the IL-23/IL-17 pathway in the RA synovium. 20873540_IL-23 may contribute to the chronic inflammation and airway remodelling in allergic rhinitis. 20886035_Beta-glucan exposure in the cell wall of fungi is essential for the generation of IL-23 producing dendritic cells and TH-17 immune responses. 20956338_our results identify a critical functional role for IL-23 in psoriasis 21116820_IL-21 and IL-23 levels are increased in the plasma of spondyloarthritis (SpA) patients compared with healthy volunteers, but not that of IL-17A; no evidence is found that the level of any of these cytokines reflects SpA activity. 21145044_semiquinone glucoside derivative dose dependent study showed approximately similar level of induction in IL-12p40, IL-12p35, IL-23p19 and RelA proteins expression at all tested concentration (30-90 microg/ml) compared to control 21145111_Human periodontal ligament fibroblasts are a target of Th17, and that IL-17 appears to up-regulate the expression of IL-23 p19 via a homeostatic mechanism involving Akt-, p38 MAPK-, and ERK 1/2-dependent NF-kappaB signalling versus the JNK/AP-1 pathway. 21161669_Our results indicate increased serum IL-23 levels in ankylosing spondylitis patients 21227898_Expression of IL-23p19 was increased significantly in inflamed mucosa of crohn Disease. 21231819_IL-17 and IL-23 levels are increased in early as compared to established disease providing evidence that IL-17/IL-23 may play a crucial role in autoimmune diseases. 21302302_This work investigated, for the first time, the role of IL-23 in colorectal cancer resection and chemotherapy, showing no correlation with the severity of disease, tumor removal, and chemotherapeutic treatment. 21387004_IL-23 was an essential cytokine in mediating Th17 cell development by IFN-induced dendritic cells. 21402701_IL-23 induction by beta-glucans is due to activation of c-Rel associated with Ser-10-histone H3 phosphorylation in the il23a promoter mediated by MAPK and SAPK or PKA, and inhibition of il12a transcription 21515794_Data show that deletion of TTP completely abolishes IFN-gamma-mediated p19 mRNA degradation. 21516111_Data show that IL-23 induced a positive feedback loop whereby GM-CSF secreted by T(H)17 cells stimulated the production of IL-23 by antigen-presenting cells. 21518507_The imbalance of T cell subsets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpurapatients is mainly associated with IL-12, but not with IL-23 and IL-17. 21531892_Data indicate that Th17 cells convert to Th1 cells through IL-17 induction of mucosal innate IL-12 and IL-23 production. 21547355_The IL-23/IL-23R pathway is a potential route to facilitate the malignant progression of cancers. 21560441_IL-23 and IL-17 participates in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. IL-23 may play a critical role in the development of UC through inducing production of IL-17. 21576383_IL-23-responsive innate lymphoid cells are increased in inflammatory bowel disease 21623003_The IL23A and TNIP1 genes showed convincing evidence for association SNPs mapping to previously reported psoriasis loci show evidence for association to PSA. 21641076_IL-12 and IL-23 were found to be abundantly expressed by macrophages infiltrating papillary and reticular dermis of hidradenitis suppurativa lesional skin 21670317_Systemic IL-23 transgene exposure induces chronic arthritis, severe bone loss and myelopoiesis, which results in increased osteoclast differentiation and systemic bone loss. 21740501_Primary immunodeficiencies that impair interleukin-23 (IL-23)-dependent pathways are associated in humans with disseminated non-typhoidal Salmonella bloodstream infections (bacteraemia). 21747388_The individual contributions of these cytokines to specific pathologies require investigation and clinical evaluation of the role of IL-12- and IL-23-specific inhibitors. 21931205_IL-23 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis and is a marker of disease activity in these patients. 22003203_IL-23 and IL-1beta are identified as critical factors in the generation of egg antigen-specific transgenic T helper (Th)17 cells involved in the pathogenesis of severe schistosomiasis. 22127978_Patients with SLE display enhanced IL-23p19 expression as a result of hyperactivation of TBK-1, resulting in increased binding of IRF-3 to the promoter. 22144400_Since IL-23 is a maturation and growth factor for IL-17-producing cells, increased IL-23R expression may regulate the function of this putative pathogenic gamma-delta T cell population. 22174449_A new molecular mechanism for hepatitis B virus-induced IL-23 expression involves activation of the ERK/NF-kappaB pathway by hepatitis B x protein, leading to the transactivation of the IL-23 p19 and p40 promoters. 22177788_IL-23, a regulatory element that bridges the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system, might be involved in the inflammatory process observed in fetal abdominal aortic wall. 22209993_These data gives reason to believe there is an involvement of IL-23 in peripheral arterial disease. 22262980_These results demonstrate an involvement of IL-17/-23 system in the early primary Sjogren's syndrome pathogenesis. 22298331_study found a significant higher systemic IL-23 value in women with breast cancer compared to the control group; patients with shorter overall survival presented higher IL-23 values, suggesting a negative prognostic correlation 22417709_Production of IL-23 was increased in the peripheral mononuclear blood cells of primary Sjogren's syndrome patients compared to controls. 22505413_human IL-23 crystal belonged to space group P61 or P65, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 108.94, c = 83.79 A degrees , = 120 22559912_These data demonstrate that IL-23/IL-17 axis, stimulated independently of TGF-beta increase IL-17A gene polymorphism and antiphospholipid antibody production, might contribute to vascular manifestations of primary antiphospholipid syndrome. 22621182_IL-27 was found to be the only IL-12 family member that acts on antigen-presenting cells as a priming signal for IL-23. 22678234_IL-23 levels were higher in asthmatic than in healthy children (p 0.05). 27146815_High IL-23 expression is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 27155366_Interleukin 17A (Il17a) and interleukin-23 (IL-23) - dependent interleukin-17 Receptor C (IL-17RC) are expressed by sputum and neutrophils in deltaF508-CFTR protein (F508del) cystic fibrosis patients. 27240992_suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid significantly inhibited IL-12p40 and IL-23p19 mRNA synthesis and did not change IL-12p35 mRNA transcription. 27245439_An increase in CSF mean levels of IL-23 was observed in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. 27315572_TNF-alpha plays an important role for the autocrine stimulation of IL-23 production by 6-sulfo LacNAc(+) dendritic cells. 27343994_this study shows that double-negative T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients are more expanded when stimulated in vitro with recombinant IL-23 than controls 27388654_Data show that the number of interleukin 17 (IL-17) positive cells significantly correlated positively with the number of interleukin-23 (IL-23) positive cells in skin 27400195_our results suggest that IL-39 induces differentiation and/or expansion of neutrophils in lupus-prone mice. 27515793_The expression of IL-17 and IL-12 in patients with lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei is reported in patients and healthy controls. 27551155_IL-23 released by keratinocytes in response to endogenous TLR4 ligands caus |
ENSMUSG00000025383 |
Il23a |
134.984351 |
20.9892379488 |
4.391578 |
0.250902567 |
416.163264 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001669422253425632965134422219218684668866135223715522752694112529829800740509351524748591290423418841136615242015501260657566004993743446837530516671920265756001939402851718290453644888954492540081243407159790958009161233053033179807300712 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000643359594270557252545463148137447434174651923245697603354557861544632167073432505814583103833768094101322062575651131019864567700012585636116315398667697059739480439688310845762434762036448199929520795595383781900977954518183743459758261 |
Yes |
Yes |
264.8343831 |
41.3490477 |
12.7109668 |
1.8901060 |
| ENSG00000111012 |
1594 |
CYP27B1 |
protein_coding |
O15528 |
FUNCTION: A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in vitamin D metabolism and in calcium and phosphorus homeostasis. Catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the activation of vitamin D in the kidney, namely the hydroxylation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3/calcidiol at the C1alpha-position to form the hormonally active form of vitamin D3, 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3/calcitriol that acts via the vitamin D receptor (VDR) (PubMed:10518789, PubMed:9486994, PubMed:22862690, PubMed:10566658, PubMed:12050193). Has 1alpha-hydroxylase activity on vitamin D intermediates of the CYP24A1-mediated inactivation pathway (PubMed:10518789, PubMed:22862690). Converts 24R,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3/secalciferol to 1-alpha,24,25-trihydroxyvitamin D3, an active ligand of VDR. Also active on 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (PubMed:10518789). Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via FDXR/adrenodoxin reductase and FDX1/adrenodoxin (PubMed:22862690). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10518789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10566658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12050193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22862690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9486994}. |
Disease variant;Heme;Iron;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Hormone biosynthesis; vitamin D biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9486994}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to the inner mitochondrial membrane where it hydroxylates 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 at the 1alpha position. This reaction synthesizes 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, the active form of vitamin D3, which binds to the vitamin D receptor and regulates calcium metabolism. Thus this enzyme regulates the level of biologically active vitamin D and plays an important role in calcium homeostasis. Mutations in this gene can result in vitamin D-dependent rickets type I. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1594; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0004498]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; secalciferol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0062185]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; calcitriol biosynthetic process from calciol [GO:0036378]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; G1 to G0 transition [GO:0070314]; negative regulation of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0010956]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045618]; positive regulation of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity [GO:0010980]; positive regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway [GO:0070564]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280]; vitamin D catabolic process [GO:0042369]; vitamin D metabolic process [GO:0042359]; vitamin metabolic process [GO:0006766] |
12039697_CYP1alpha intron 6 polymorphism appears not to be associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus, Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 12050193_Novel gene mutations in patients with 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency that confer partial enzyme activity in vitro. 12137802_activity is diminished in human prostate cancer cells and is enhanced by gene transfer 12161526_Expression and activity of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha-hydroxylase are restricted in cultures of human syncytiotrophoblast cells from preeclamptic pregnancies. 12386916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12496369_Targeted disruption of this protein in ras-transformed keratinocytes demonstrates that this locally produced protein suppresses growth and induces differentiation in an autocrine fashion. 12746631_Polymorphism of this gene may be associated with NIDDM in Poland. 12855575_demonstrated constitutive expression of 25(OH)D3-1 alpha-hydroxylase in monocyte-derived dendritic cells, which was increased after stimulation with LPS. 14671156_mRNA in alveolar macrophages greater in lung cancer than controls. Advanced stage of lung cancer showed highest expression, followed by early group, then controls. 15225751_suggests that there are some minor structural and functional differences between the wild-type VDR and the Delta165-215 deletion mutant and that Y143 residue is more important for receptor function than residue S278 15243130_Down-regulation of 1alpha-hydroxylase promoter through NFkappaB signaling may contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammation-associated osteopenia/osteoporosis. 15296474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15296474_The CYP27B1 promoter (-1260) C/A polymorphism appears to be associated with endocrine autoimmune diseases but the CYP27B1 intron 6 (+2838) C/T polymorphism appears to be associated only with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 15331405_Increased expression of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1alpha-hydroxylase is associated with dysgerminomas 15589699_1Alpha-hydroxylase is found in both neurons and glial cells of the brain in a regional and layer-specific pattern. 15795327_evidence for the expression of an enzymatically active 25(OH)D3-1alpha-hydroxylase system in human VSMCs, which can be upregulated by parathyroid hormone and estrogenic compounds, an autocrine mechanism to curb changes in VSMC proliferation 15947108_GFI1 in prostate cancer cells acts as a repressor of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha hydroxylase gene. 15956353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16061850_CYP27B1 splice variants have roles in vitamin D(3) metabolism in human glioblastoma multiforme 16549446_first studies to demonstrate that nontransformed human mammary cells express 25 hydroxyvitamin D3-1-alpha hydroxylase(CYP27B1), and that they are growth inhibited by physiologically relevant concentrations of 25(OH)D3 16720713_Results describe the expression, localization and regulation of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3), 1alpha-hydroxylase in human cycling and early pregnant endometrium. 17023519_Expression, activity, and functionality of 1alpha-hydroxylase unequivocally demonstrates that vitamin D can act in an auto/paracrine manner in bone. 17079137_The overall data suggest that calcitriol downregulates CYP27B1 expression via a cAMP-dependent signaling pathway, whereas upregulates 24-hydroxylase gene expression through a VDR-dependent mechanism 17207990_expression of the 5'-flanking region for the CYP27B1 gene in osteoblast cells may be regulated differently to that previously described in kidney cells 17207994_growth factor independent 1 may play a significant role in the down regulation of endogenous production of 1,25D in prostate cancer cells and could provide a novel insight to future diagnosis and treatment 17223345_CYP27B1 gene could play a functional role in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes through modulation of its mRNA expression and influence serum levels of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) via the -1260 C/A polymorphism 17236759_modulation of the 25 hydroxyvitamin D(3)-1alpha-hydroxylase opens up a new target for vitamin D(3) related therapies in endometrial cancer 17254772_local 1,25D synthesis has paracrine effects in the bone microenvironment implying that vitamin D metabolism in human osteoblasts represents a physiologically important pathway 17267208_confirm a crucial role for STAT1alpha as well as for C/EBPbeta in the regulation of 1alpha-hydroxylase in monocytes 17287116_abundance of less active 1alpha-hydroxylase protein variants can alter the local synthesis of calcitriol in the cells and may explain variations of enzymatic activity in different cells and tissues 17368179_local synthesis of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) may be a preferred mode of response to antigenic challenge in many tissues 17395559_Evidence is presented for autocrine and paracrine activities of CYP27B1. 17395703_Data indicate that noncoding splice variants of CYP27b1 are functionally active and may play a significant role in the regulation of 1,25(OH)2D3 synthesis during normal physiology. 17426122_The identification of two new vitamin D response element-binding regions in the distal promoter that bind vitamin D receptor-retinoid X receptor complexes. 17488797_4 novel & 4 known mutations were identified in patients with 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency; new mutations included a nonsense mutation in exon 6; deletion of adenine in exon 9 ; substitution of thymine for cytosine in exon 2; & a splice site mutation 17606874_Common inherited variation in the vitamin D metabolism such as mutation in CYP27B1 affect susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. 17606874_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17878529_Seveeral splice variants are identified in breast cancer cell lines and malignant cells ma contain inactive variants. 17932346_Association between polymorphisms across the entire vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene and genes encoding for vitamin D activating enzyme 1-alpha-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) and deactivating enzyme 24-hyroxylase (CYP24A1) and prostate cancer risk. 17932346_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18476984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18495603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18689381_Significant associations of 2 CYP27B1 SNP variants and 25(OH)D concentrations were observed. The findings indicate important genetic influences on regulation of seasonal circulating 25(OH)D concentrations in MS twins. 18767073_Oncogenic transformation of mammary epithelial cellS was associated with reduced 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 synthesis, and reduced mRNA and protein levels of VDR and CYP27b1 18767934_CYP27B1 does not commonly serve as a classical tumor suppressor gene in the development of sporadic parathyroid adenomas or of refractory secondary/tertiary hyperparathyroidism 18768522_No evidence that CYP27B1 polymorphisms were associated with mammographic breast density among Caucasian premenopausal women of French descent. 18843020_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19154546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19219539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19255064_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19255064_Single nucleotide polymorphisms may be associated with risk of prostate cancer in men with low vitamin D status. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19454612_common genotypic variation found in VDR, CYP27B1, and CYP24A1 has little or no effect on overall prostate cancer risk 19505920_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19524013_Repression of CYP27B1 gene expression may be a common event but the novel inhibitory elements we have identified may be unique to osteoblasts. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667158_Compared to the benign cell line, the malignant cell lines showed a significantly higher expression of 1alphaOHase at the RNA level. A statistically lower expression of the 1alphaOHase protein was found in the malignant tissue 19706847_A possible interaction between CYP27B1 and UV-weighted sun exposure with proximal colon cancer was observed. 19706847_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19783860_No significant differences were observed in genotype or allele frequencies between case and control groups for VDR, CYP27B1 or CYP2R1 SNPs 19783860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19852851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19891555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19891555_a SNP in CYP27B1 was associated with congestive heart failure (odds ratio: 2.14 for subjects homozygous for the C allele; 95% CI: 1.05-4.39). 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951419_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19966181_Circulating 25OHD amplifies vitamin D signaling through IGF-I up-regulation, which in turn induces CYP27B1 in a feed-forward mechanism to potentiate osteoblast differentiation. 19998245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19998245_this study confirms the association of the CYP27B1 C(-1260)A polymorphism with autoimmune Addison's disease. 20007432_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20082271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20152900_analysis of 1alpha-hydroxylase and innate immune responses to 25-hydroxyvitamin D in colonic cell lines 20304056_human PBLs show only weak methylation in the upstream region of CYP27B1 and none in CYP24A1 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20518841_No significant differences in the allele and genotype frequencies of PDCD1 and CYP27B1 polymorphisms were found between Type 1 diabetes patients and controls. 20518841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20534770_A novel mutation in the CYP27B1 gene was found in patient with vitamin D dependent Rickets type I. 20619365_Studies indicate that vitamin D synthesis, a two-step process, starts with a 25-hydroxylation primarily by CYP2R1 and a subsequent 1alpha-hydroxylation via CYP27B1. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20648053_Associations with three single nulceotide polymorphisms in the Swedish materials between CYP27B1 gene multiple sclerosis was shown. 20648053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20654748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20687218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20701904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20809279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20831823_Low CYP27B1 is associated with invasive breast tumours. 20847308_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21107545_The data suggest that a common but functional variation within the CYP27B1 promoter gene is associated with fracture risk in the elderly. 21145801_Reduced 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and CYP27B1-1260 promoter polymorphism leading to reduced 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with failure to achieve response in HCV genotype 1, 2, and 3 infected patients 21440908_Findings fail to directly connect vitamin D metabolism gene 1-alpha-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) enzyme polymorphisms to multiple sclerosis susceptibility in Canadians. 21441443_Study confirms that variation in CYP27B1 is associated with predisposition to autoimmune disease type 1 diabetes. 21542014_CYP27B1 is required for the antiproliferative and prodifferentiation effects of 25(OH)D(3) on human marrow stromal cells. 21869486_Novel vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase gene mutations in a Chinese vitamin-D-dependent rickets type I patient 22190362_This study demonistrated that Rare variants in the CYP27B1 gene are associated with multiple sclerosis and more likely to be vitamin D deficient prior to disease onset. 22326730_the expression and distribution of the 1alpha-OHase in hyperplastic human parathyroid tissue, and regulation of the enzyme in cultured human parathyroid cells. 22443290_investigated CYP27B1 mutation in seven patients from four separate families and characterize the genotype-phenotype correlation 22446158_CYP27B1 expression in macrophage and platenta 22511602_The CYP27B1 expression was increased in follicular adenoma and differentiated thyroid cancer compared with normal thyroid. 22516854_A genetic study identify a rare mutation in CYP27B1 in a multiple sclerosis family 22547098_rare variants in CYP27B1, which encodes the enzyme that converts vitamin D to its active form, are strongly associated with MS risk supports a causal role of vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for MS 22588163_The study describes nine novel mutations in addition to 37 known mutations of CYP27B1 gene and shows the correlation between these mutations and the clinical findings of 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. 22612324_This study evaluatee the associations between vitamin D receptor, CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 gene polymorphisms with oral cancer risk and survival. 22963605_These results suggest that the CYP27B1-1260 promoter polymorphism is possibly associated with the persistence, but not susceptibility to HBV infection in Chinese HBV patients. 22995334_Reduction of CYP27B1 correlates with melanoma phenotype and behavior, and its lack affects the survival of melanoma patients, indicating a role in the pathogenesis and progression of this cancer. 23045480_IL-13 induces vitamin D-dependent hCAP18/LL-37 expression in bronchial epithelial cells most likely by increasing CYP27B1. 23063903_Finding suggest that GG genotype of CYP2R1 polymorphism and/or CC genotype of CYP27B1 polymorphism increased the risk of developing of type 1 diabetes in Egyptian children. 23149444_genetic association studies in population in Italy: Data suggest that 3 SNPs (CYP27B1, rs4646536; IL28B, rs8099917; SLC28A2 rs11854484) are associated with pharmacokinetics of ribavirin and thus, sustained virologic response in hepatitis C patients. 23286944_genetic polymorphism is associated with the frequency of dendritic cell subsets in patients with type 1 diabetes 23334593_This study demonistrated that CYP27B1 mRNA increase in white matter of brain with patient in multiple sclerosis. 23423976_CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 polymorphisms modulate vitamin D metabolism in colon cancer cells. 23444327_The results of this study suggested that no evidence of association between mutant alleles of the CYP27B1 gene and multiple sclerosis. 23483640_These results provide evidence against a major role for CYP27B1 mutations in multiple sclerosis. 23614044_The rs703842 A>G polymorphism of CYP27B1 may play a role in HLA-B27-associated uveitis. 23886824_The data do not support a major role for rare CYP27B1 variants in the etiology of multiple sclerosis. 23894780_Polymorphisms in genes connected to vitamin D--VDR (Vitamin D Receptor), CYP27B1 (1alpha-hydroxylase gene) and DBP (Vitamin D-Binding Protein) may predispose people to development of autoimmune thyroiditis. [review] 24029861_The increased cutaneous CYP27B1 levels in the CKD patients suggest that the loss of renal activity of this enzyme is at least partially compensated for by the skin. 24158849_Results show that CYP27B1 is predominantly expressed in dendritic cells (DCs). Its expression in these cells is necessary for their response to VitD, which is known to upregulate pathways involved in generating a tolerogenic DC phenotype. 24245571_Results show that upregulated gene expression of CYP27B1 may lead to misbalance of vitamin D metabolites and may contribute to the pathogenesis of RCC 24308945_Thias study providing additional support for CYP27B1 p.R389H in the pathogenicity of multiple sclerosis. 24371450_CYP27B1 activity in monocytes is higher among patients with active tuberculosis than those with frequent TB contact. 24471562_Higher maternal 25(OH)D during pregnancy was associated with significantly higher placental protein expression of CYP27B1 at term supportive of a link between substrate availability and placental production of calcitriol. 24535953_We now propose that the low potency of the intrinsic VDR-mediated activities of 25(OH)D3 can be augmented to the level of 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 without its activation through 1alpha-hydroxylation by CYP27B1, but by simply preventing its inactivation by CYP24A1. 24576880_ocular barrier epithelial cells express the machinery for vitamin D3 and can produce 1,25(OH)2D3. 24643654_Regulation of CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 hydroxylases limits cell-autonomous activation of vitamin D in dendritic cells. 25060765_The CYP27B1+2838 polymorphism may be useful as pretreatment factor to selection of patients with higher probability of response to therapy. 25284246_Data suggest compound heterozygous mutations in CYP27B1 (missense/frameshift mutations) in 2 brothers are associated with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1A; entering puberty urinary calcium is marker for secondary hyperparathyroidism. [CASE REPORT] 25371233_Case Report: novel pathogenic missense mutation (CYP27B1:Homozygous c.1510C > T(p.Q504X)) causing vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1. 25488826_Vitamin D-binding protein SNPs are associated with prostate cancer; low 25(OH)D metabolism score and CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 variants are associated with grade 25501638_Results suggest that local expression of CYP27B1 in ovarian tumor cells can modify their behavior and promote a less aggressive phenotype by affecting local concentrations of active of vitamin D levels within the tumor microenvironment. 25542806_Variants of CYP27B1 are associated with both multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica patients in Han Chinese population. 25544771_Data show that cytochrome P450 CYP27B1 and CYP24A1 expression were significantly different between tumor and normal tissues in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 26124321_LNCaP cells were stably transfected with CYP27B. 26241700_This study reveals no association between CYP27B1 polymorphisms and blood levels of 1alpha,25-hydroxyvitamin D. 26291067_Increased CYP27B1 expression and local duodenal 1,25(OH)2D3 production during puberty may be a metabolic adaptation that promotes dietary calcium absorption. 26466946_The multiple sclerosis-associated regulatory variant rs10877013 affects expression of CYP27B1 and VDR under inflammatory or vitamin D stimuli. 26575398_Reduced sinonasal levels of 1alpha-hydroxylase are associated with worse quality of life in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. 26607259_this study indicates rs8176345 in CYP27B1 gene is significantly correlated with erlotinib-induced skin rash in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer 27016371_primary human osteoblasts in the presence of high calcium concentrations increase their CYP27B1 mRNA levels by 1.3-fold 27074284_Vascular Calcification Induced by Chronic Kidney Disease Is Mediated by an Increase of 1alpha-Hydroxylase Expression in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells 27175669_We found that the C allele was associated with lowered Multiple Sclerosis risk in Caucasians. Whether the association holds for other ethnic groups needs further investigation. 27210415_Male placental cotyledons showed reduced basal CYP27B1 and cathelicidin gene expression compared to females. 27287609_A Case of Vitamin-D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A with Normal 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Caused by Two Novel Mutations of the CYP27B1 Gene. 27381199_IL-13 suppressed cyp27b1 expression in CD14(+) cells. IL-13 increased expression of miR-19a in CD14(+) cells. IL-13 suppresses cyp27b1 expression in peripheral CD14(+) cells via up regulating miR-19a expression. 27399352_Mutation in CYP27B1 is associated with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1. 27618536_The local regulation of vitamin D in sinonasal tissue during chronic rhinosinusitis may be independent of serum 25(OH)D levels. Vitamin D may be dysregulated at multiple levels, with decreased transcription of the metabolic gene CYP27B1 and increased transcription of the catabolic gene CYP24A1. 27904983_findings do not support a role of an independent effect of the investigated vitamin D-related gene variants, VDBP and CYP27B1, in the risk of Multiple Sclerosis 27922682_The aim of the present study was to investigate the mRNA expression levels of the CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 genes in malignant and normal breast tissues. The results demonstrated that the mRNA expression of CYP27B1 was downregulated in the tumor tissues, compared with the adjacent normal tissues (P |
ENSMUSG00000006724 |
Cyp27b1 |
13.437867 |
4.6321813131 |
2.211692 |
0.503975109 |
19.859306 |
0.00000833559339200673394567036450508723532948351930826902389526367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000026424690392186294209987684755702730399207212030887603759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6927662 |
6.0011331 |
4.6620601 |
1.1044387 |
| ENSG00000111058 |
79611 |
ACSS3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H6R3 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from short-chain fatty acids (PubMed:28003429). Propionate is the preferred substrate (PubMed:28003429). Can utilize acetate and butyrate with a much lower affinity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A0G2K047, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28003429}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Enables propionate-CoA ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in ketone body biosynthetic process. Located in mitochondrial matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79611; |
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; acetate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0003987]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; butyrate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047760]; propionate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0050218]; ketone body biosynthetic process [GO:0046951] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29493120_This report is the first to indicate ACSS3 as a biomarker of GCa prognosis and that targeting ACSS3 in GCa patients might be therapeutically valuable. 33391508_ACSS3 represses prostate cancer progression through downregulating lipid droplet-associated protein PLIN3. |
ENSMUSG00000035948 |
Acss3 |
33.068219 |
0.3781689184 |
-1.402897 |
0.470444641 |
8.357278 |
0.00384145634112158370840339749463510088389739394187927246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008040257458161455261791417115091462619602680206298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.6971042 |
5.2186251 |
39.2331655 |
9.5911103 |
| ENSG00000111077 |
23371 |
TNS2 |
protein_coding |
Q63HR2 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein phosphatase which regulates cell motility, proliferation and muscle-response to insulin (PubMed:15817639, PubMed:23401856). Phosphatase activity is mediated by binding to phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) via the SH2 domain (PubMed:30092354). In muscles and under catabolic conditions, dephosphorylates IRS1 leading to its degradation and muscle atrophy (PubMed:23401856, PubMed:30092354). Negatively regulates PI3K-AKT pathway activation (PubMed:15817639, PubMed:23401856, PubMed:30092354). Dephosphorylates nephrin NPHS1 in podocytes which regulates activity of the mTORC1 complex (PubMed:28955049). Under normal glucose conditions, NPHS1 outcompetes IRS1 for binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) which balances mTORC1 activity but high glucose conditions lead to up-regulation of TNS2, increased NPHS1 dephosphorylation and activation of mTORC1, contributing to podocyte hypertrophy and proteinuria (PubMed:28955049). Required for correct podocyte morphology, podocyte-glomerular basement membrane interaction and integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier (By similarity). Enhances RHOA activation in the presence of DLC1 (PubMed:26427649). Plays a role in promoting DLC1-dependent remodeling of the extracellular matrix (PubMed:20069572). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CGB6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15817639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20069572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26427649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28955049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30092354}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the tensin family. Tensin is a focal adhesion molecule that binds to actin filaments and participates in signaling pathways. This protein plays a role in regulating cell migration. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three transcript variants encoding three distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23371; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; collagen metabolic process [GO:0032963]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; multicellular organismal homeostasis [GO:0048871]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; response to muscle activity [GO:0014850] |
12470648_Interaction of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase with C1-TEN. 15817639_C1 domain-containing phosphatase and TENsin homologue (C1-TEN) appears to be a novel intracellular phosphatase that negatively regulates the Akt/Protein kinase B signaling cascade 17006924_variant 3 significantly promoted the cell growth and motility of HCC cells; clonal transfectants of variant 3 were more closely packed and resulted in a higher saturation density than in the control vector transfectants 19194507_Tensins may represent a novel group of metastasis suppressors in the kidney, the loss of which leads to greater tumor cell motility and consequent metastasis. 19440389_DLC1 interaction with tensin2 through this novel focal adhesion binding site contributes to the growth-suppressive activity of DLC1. 19747564_Differential proteolytic cleavage of Tensin2 can liberate domains with discrete localisations and functions, which has implications for the role of Tensins in cancer cell survival and motility. 19895840_Data suggest that the interaction between START-GAP1 and tensin2 occurs in a PTB domain-dependent manner. manner.ty=0 20069572_focal adhesion-localized tensin 2 negatively regulates DLC1 to permit Rho-mediated actomyosin contraction and remodeling of collagen fibers 20678486_Tensin2, in addition to regulating cytoskeletal dynamics, influences phosphoinositide-Akt signalling through its PTPase domain. 21461930_Here, we report complete chemical shift assignments of the SH2 domain of human tensin2 determined by triple resonance experiments. 21527831_Tensin2 is an important new mediator in TPO/c-Mpl pathway and has a positive affect on cellular growth, at least in part through its effect on the PI3K/Akt signaling. 21765928_Tensin2 SH2 domain was identified to interact with nonphosphorylated ligand (DLC-1) as well as phosphorylated ligand. 22019427_Results identified tensin2 as a Syk-binding protein. 22645138_The tumor suppressor DLC1 utilizes a novel binding site for tensin2 PTB domain interaction 23233134_Pulldown studies in human cells using Myc-tagged Tensin2 constructs revealed that DISC1 specifically interacts with the C-terminal PTB domain of Tensin2 in a phosphorylation-independent manner. 25101860_p62 expression increased but C1-Ten protein decreased during muscle differentiation, supporting a role for p62 as a physiological regulator of C1-Ten. 27203214_Patients with low TNS2 expression showed poor relapse-free survival rates for breast and lung cancers. These results strongly suggest a role of tensin2 in suppressing cell transformation and reduction of tumorigenicity. 28955049_Study observed significant increase in C1-Ten level in diabetic kidney and in high glucose-induced damaged podocytes. C1-Ten acts as a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPase) at the nephrin-PI3K binding site and renders PI3K for IRS-1, thereby activating mTORC1. These findings demonstrate the relationship between nephrin dephosphorylation and the mTORC1 pathway, mediated by C1-Ten PTPase activity. 30092354_Collectively,these findings suggest that the interaction between the C1-Ten/Tensin2 SH2 domain and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 produces a negative feedback loop of insulin signaling through IRS-1. 30419905_Axl binds to and phosphorylates TNS2 and that Axl/TNS2/IRS-1 cross-talk may potentially play a critical role in glucose metabolism of cancer cells. 33753854_Novel candidate factors predicting the effect of S-1 adjuvant chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000037003 |
Tns2 |
59.057051 |
0.0757972674 |
-3.721710 |
0.435689631 |
66.720831 |
0.00000000000000031281195325099547551076818810385944741408157949297264011079278134275227785110473632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002298210268782823789017351248373607411978967584448296790355925622861832380294799804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3536133 |
3.0529222 |
108.6574414 |
26.3516897 |
| ENSG00000111186 |
81029 |
WNT5B |
protein_coding |
Q9H1J7 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Probable developmental protein. May be a signaling molecule which affects the development of discrete regions of tissues. Is likely to signal over only few cell diameters (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It encodes a protein which shows 94% and 80% amino acid identity to the mouse Wnt5b protein and the human WNT5A protein, respectively. Alternative splicing of this gene generates 2 transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:81029; |
endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; lens fiber cell development [GO:0070307]; muscle cell differentiation [GO:0042692]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of convergent extension involved in gastrulation [GO:1904105]; positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000052]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
12165812_WNT5b is upregulated by beta-estradiol in tumor cell lines 15386214_WNT5B gene may contribute to conferring susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and may be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease through the regulation of adipocyte function. 15972578_In leiomyoma cells, the regulation of Wnt5b expression by retinoids appears to be attenuated. 18555673_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18555673_Variation in WNT5B predisposes to type 2 diabetes in the absence of obesity. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19863181_Results demonstrated significant up-regulation of WNT-3, WNT-4, WNT-5B, WNT-7B, WNT-9A, WNT-10A, and WNT-16B in patients with CLL compared to normal subjects. 21766608_This is significantly related to fat cell differentiation, suggesting its possible involvement in the onset of diabetes mellitus type 2 and metabolic syndrome. 21980498_Differentiation paralleled the activation of Wnt5/Calmodulin signalling by autocrine/paracrine intense secretion of Wnt5a and Wnt5b 23817222_This study shows that the WNT5B germline variant rs2010851 was significantly identified as a stage-dependent prognostic marker for CC patients after 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy. 24040439_TGF-beta/Smad, integrin/integrin-linked kinase (ILK) and wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways are involved in epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human renal fibrogenesis. 24220306_These results indicate that Wnt5b is involved in the migration ability of OSCC cells through active Cdc42 and RhoA. 24344732_WNT3 and WNT5B are critical factors, secreted from mesenchymal cancer cells, for instigating the epithelial cancer cell invasion. 24399733_Ursolic acid suppressed the expression of Wnt5alpha/beta and beta-catenin, inducing apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. 24564888_WNT5B is elevated in both in the tumor and the patients' serum from triple negative breast cancer. 24841200_Knocking down Wnt5b expression reduced phospho-PKCA levels and cell migration. 24944491_Report increased Wnt5b levels in adriamycin treated liver cancer stem cells within 4h of treatment. 25246426_Results demonstrate that the Wnt5B pathway may play an important role in atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor biology. 25425204_The interaction between Wnt isoforms and their LRP6 cognate receptor depends on the jutting loop present in Wnt3a but absent in Wnt5b. 26733379_This study identified WNT5B and CTNNBL1 for peak bone mineral density and body composition in males from the Han Chinese ethnic group. 26861993_these results suggest that TGF-beta1 stimulates HSC-4 cell invasion through the Slug/Wnt-5b/MMP-10 signalling axis. 27036869_WNT-5B induces IL-6 and CXCL8 secretion in pulmonary fibroblasts. 27121420_overexpression of WNT5B significantly increased cell proliferation, migration and invasion capacities of the COLO 205 cells in vitro. WNT5B may play an important role in the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. 27126693_exaggerated WNT-5B expression upon cigarette smoke exposure in the bronchial epithelium of COPD patients leads to TGF-beta/Smad3-dependent expression of genes related to airway remodelling 27593938_the data suggest that WNT5B induces tube formation by regulating the expression of Snail and Slug proteins through activation of canonical and non-canonical WNT signalling pathways. 27762090_results suggest that Wnt5b-associated exosomes promote cancer cell migration and proliferation in a paracrine manner 27932350_Noncanonical Wnt signaling via Wnt5a/5b/11 may have role in the pathogenesis of aortic valve calcification. 28078366_were not able to replicate or further verify the genetic association of polymorphisms in WNT4 and WNT5B with bone mineral density 29847788_IMP3 also facilitates the transcription of SLUG, which is necessary for TAZ nuclear localization and activation, by a mechanism that is also mediated by WNT5B. 31666682_WNT5B exerts oncogenic effects and is negatively regulated by miR-5587-3p in lung adenocarcinoma progression. 32092330_Up-regulated miR-374a-3p relieves lipopolysaccharides induced injury in CHON-001 cells via regulating Wingless-type MMTV integration site family member 5B. 32561739_The lncRNA RP11-142A22.4 promotes adipogenesis by sponging miR-587 to modulate Wnt5beta expression. 34536574_Exosome-mediated circ_0001846 participates in IL-1beta-induced chondrocyte cell damage by miR-149-5p-dependent regulation of WNT5B. 34906330_Estrogen receptor alpha and NFATc1 bind to a bone mineral density-associated SNP to repress WNT5B in osteoblasts. |
ENSMUSG00000030170 |
Wnt5b |
111.756624 |
9.3175465735 |
3.219950 |
0.208853924 |
272.107535 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000039408303025943171798066156768551138062115021968793553532478583511735516811333295892656740222637922926801986881208369659387665127685563049583833929103045268238503240354475565254688262939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010294983232972056348353961015809492891374860345916984816934345837977694281898976391323906413224893862112592450929232551855051011620024059111709407131340920926731996587477624416351318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
206.5375285 |
25.2606462 |
22.2270394 |
2.4996330 |
| ENSG00000111249 |
23316 |
CUX2 |
protein_coding |
O14529 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in the control of neuronal proliferation and differentiation in the brain. Regulates dendrite development and branching, dendritic spine formation, and synaptogenesis in cortical layers II-III. Binds to DNA in a sequence-specific manner. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70298}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Epilepsy;Homeobox;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a protein which contains three CUT domains and a homeodomain; both domains are DNA-binding motifs. A similar gene, whose gene product possesses different DNA-binding activities, is located on chromosome on chromosome 7. Two pseudogenes of this gene have been identified on chromosomes 10 and 4. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:23316; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular response to organic substance [GO:0071310]; cognition [GO:0050890]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061003]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; short-term memory [GO:0007614] |
19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26221032_results suggest that the persistent expression of CUX2 in postmitotic neurons contributes to the maintenance of genome integrity through its stimulation of oxidative DNA damage repair. 29459676_Significant allelic and genotypic associations were identified between NEURL variant rs6584555 and GJA1 variant rs13216675 and Atrial fibrillation (AF). Significant genotypic association was found between CUX2 SNP rs6490029 and AF 29630738_Patients with CUX2 p.Glu590Lys display a distinctive phenotypic spectrum, which is predominantly generalized epilepsy 29795476_De novo variant c.1768G>A; p.(Glu590Lys) in CUX2 was identifies in a patient with intellectual disability, seizures, and autism spectrum disorder. 30720667_this is the first study to explore and validate the relationships between seven SNPs in the FAM65B, AGBL4, and CUX2 genes and ATDH in a Chinese population. On the basis of this case-control study, SNP rs10946737 in FAM65B may be associated with susceptibility to ATDH in Chinese Han anti-TB treatment patients. 33093602_CUX2, BRAP and ALDH2 are associated with metabolic traits in people with excessive alcohol consumption. 35881915_CUX2/KDM5B/SOX17 Axis Affects the Occurrence and Development of Breast Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000042589 |
Cux2 |
368.883001 |
0.0103347404 |
-6.596354 |
0.918548827 |
32.351334 |
0.00000001286688785566897991466691990574550130688180615834426134824752807617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000055465906761002959027012925189922820656818203133298084139823913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
9.6076325 |
10.2969999 |
925.5014003 |
671.3124174 |
| ENSG00000111252 |
10019 |
SH2B3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UQQ2 |
FUNCTION: Links T-cell receptor activation signal to phospholipase C-gamma-1, GRB2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. {ECO:0000250}. |
Diabetes mellitus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of the SH2B adaptor family of proteins, which are involved in a range of signaling activities by growth factor and cytokine receptors. The encoded protein is a key negative regulator of cytokine signaling and plays a critical role in hematopoiesis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with susceptibility to celiac disease type 13 and susceptibility to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:10019; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; stem cell factor receptor binding [GO:0005173]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase adaptor activity [GO:0005068]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; cellular response to interleukin-3 [GO:0036016]; embryonic hemopoiesis [GO:0035162]; erythrocyte development [GO:0048821]; hematopoietic stem cell differentiation [GO:0060218]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; monocyte homeostasis [GO:0035702]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070100]; negative regulation of Kit signaling pathway [GO:1900235]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:0090331]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046426]; negative regulation of response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0060761]; negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042532]; neutrophil homeostasis [GO:0001780]; thrombopoietin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038163] |
16644735_Adaptor Lnk is a negative regulator in the TNFalpha-signaling pathway mediating ERK inhibition suggesta a role for Lnk in the interplay between PI3K and ERK triggered by TNFalpha in vascular endothelial cells. 17007883_TNF-alpha induces Lnk expression through PI3K-dependent signaling pathway in umbilical vein endothelial cells 18311140_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18588518_Data show that Lnk bound directly to c-Kit through Tyr(568) on juxtamembrane domain of c-Kit. 18593762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18805825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19073967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19198610_A nonsynonymous SNP at 12q24, in SH2B3, associated significantly with myocardial infarction in six different populations. 19198610_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19293402_Lnk is a potent inhibitor of JAK2V617F constitutive activity. 19375649_in parallel to binding wild-type JAK2 and c-KIT, Lnk associates with and is phosphorylated by mutant alleles of JAK2 and c-KIT. 19430479_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19430483_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19693089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19838195_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19860791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951419_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20190752_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20404132_myeloproliferative neoplasms patients bearing LNK mutations exhibited aberrant JAK-STAT activation, and cytokine-responsive CD34(+) early progenitors were abnormally abundant 20508602_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508602_rs3184504 in SH2B3 confers susceptibility for multiple sclerosis. 20546165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546165_The SH2B3 784T>C variant could contribute to the pathogenesis of T1 diabetes through impaired immune response that promotes activation and expansion of self-reactive lymphocytes in susceptible individuals. 20560212_Functional investigation of the effect of the SH2B3 genotype in response to lipopolysaccharide and muramyl dipeptide revealed that carriers of the SH2B3 rs3184504*A risk allele showed stronger activation of the NOD2 recognition pathway 20586186_Association of the polymorphisms of the ERBB3 and SH2B3 genes with type 1 diabetes 20586186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20724988_LNK mutation is associated with blast-phase myeloproliferative neoplasms. 20843259_The current study suggests that LNK mutations are part of the 'missing link' in the pathogenesis of JAK2 mutation-negative 'idiopathic' erythrocytosis or polycythemia vera. 20971364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21060863_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21310211_The Lnk is a negative regulator of PDGFR signaling. 21496118_Lnk is a potential candidate for the modulation of signaling pathways to protect vascular endothelial cells from inflammation in xenotransplantation. 21794913_LNK can also be mutated outside PH and SH2 domains in myeloproliferative neoplasms with and without V617FJAK2 mutation. 21922527_Study suggests that LNK mutations occur in low frequency in human MPN, and can occur in several regions of the LNK gene not only on a pleckstrin homology domain which have been regarded as a hot spot. 21990094_A nonsynonymous LNK polymorphism is associated with idiopathic erythrocytosis. 22028877_SH2B3 inhibits neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells and primary cortical neurons 22441983_Lnk adaptor is an effective regulator of the integrin-mediated signaling pathway that affects endothelial cell adhesion and migration processes. 22493691_Novel associations for hypothyroidism and autoimmune risk loci include SNPs near the SH2B3 gene. 22916186_observations suggest that genotyping of SNPs at this locus may be useful for the study of ALS risk in a high percentage of individuals and that ATXN2 and SH2B3 variants may interact in modulating the disease pathway 23812944_There was an infrequent occurrence of LNK mutations in patients with JAK2 mutation-negative erythrocytosis. 23844121_Thrombotic antiphospholipid syndrome shows strong haplotypic association with SH2B3-ATXN2 locus. 23908464_Overall, these results demonstrate a Knudson tumor suppressor role for SH2B3 in the pathogenesis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia 24297922_IL-11 therefore drives a pathway that enhances HSPC radioresistance and radiation-induced B-cell malignancies, but is normally attenuated by the inhibitory adaptor Lnk. 24704825_in contrast to the findings in hematologic malignancies, the adaptor protein LNK acts as a positive signal transduction modulator in ovarian cancers. 25231511_The single-nucleotide polymorphism in SH2B3 was significantly associated with Hypertension in an Algerian population sample. 26319099_Genetic variations in inflammation and its related subpathway components are keys to the development of lung, colorectal, ovary, and breast cancer, including SH2B3, which is associated with lung, colorectal, and breast cancer. 26522763_SH2B3 mutations occur infrequently, and exon 8 in SH2B3 may be the most frequent mutational area in BCR-ABL negative myeloproliferative neoplasms patients in Korea. 26535636_the minor allele A of rs3184504 (A vs G, OR = 1.18, 95%CI = 1.12-1.24, P |
ENSMUSG00000042594 |
Sh2b3 |
1821.794280 |
2.3692871235 |
1.244453 |
0.044126822 |
798.305839 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012600933468825686163507417601960957556518517188062719671703278777868287718952692360170610225261734968265062192254997888912866560075637198165204618552125139 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009788935684203533894171145868879620149501999872035479499479770764410972650093667050170651739879758725212745312485906141183035774783157478414894344918732257 |
Yes |
Yes |
2600.7883047 |
63.0798030 |
1105.2835598 |
21.3281767 |
| ENSG00000111261 |
54682 |
MANSC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H8J5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54682; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000032718 |
Mansc1 |
10.267272 |
0.2836509570 |
-1.817811 |
0.518046417 |
12.566628 |
0.00039269656584221688177746556469571714842459186911582946777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000982740134254174576775020533148108370369300246238708496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9927845 |
1.7691256 |
17.6131717 |
3.7970377 |
| ENSG00000111266 |
80824 |
DUSP16 |
protein_coding |
Q9BY84 |
FUNCTION: Dual specificity protein phosphatase involved in the inactivation of MAP kinases. Dephosphorylates MAPK10 bound to ARRB2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11489891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15888437}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase that is a member of the dual specificity protein phosphatase subfamily. These phosphatases inactivate their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues. The encoded protein specifically regulates the c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathways.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:80824; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; JUN kinase binding [GO:0008432]; MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0017017]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 binding [GO:0048273]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008330]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; MAPK export from nucleus [GO:0045204]; negative regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043508]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
14586399_context-dependent role for DUSP16 on cell transformation and apoptosis. 15689616_activation of the ERK pathway strongly blocks JNK activation through stabilization of MKP-7 mediated by phosphorylation 15888437_MKP7 binds beta-arrestin 2 via amino acids 394-443 of MKP7, the same region that interacts with JIP-1 19307591_identification of an intricate SDF-1alpha-induced signaling cascade that involves eNOS, JNK3, and MKP7and enhances endothelial migration 20122898_MKP-7 down-regulates ERK-dependent gene expression by blocking nuclear accumulation of phospho-ERK. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20551953_DUSP16 is a new epigenetically regulated determinant of JNK activation in BL. 22182512_MKP-7, a negative regulator of JNK, regulates VCAM-1 expression in activated endothelial cells through IRF-1 but not GATA6. 22245064_DUSPs 10 and 16 are positive regulators of activation, apparently acting by modulating cross-talk between the p38 and ERK pathways. 23077088_Data indicate that LRP6, BCL2L14, DUSP16, CREBL2, and CDKN1B were involed in centromeric (12p11.21-12p13.2) deletion in ETV6-RUNX1 B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL). 23233447_Data indicate that the activities of phosphoprotein phosphatases MKP5 and MKP7 were determined in the system. 23639976_PPARdelta-mediated messenger RNA stabilization of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase (MKP)-7 was responsible for the GW501516-mediated inhibition of JNK signaling. 23926106_analysis of the interaction of the MAPK binding domain of DUSP16 with p38alpha 26381291_The DUSP16 ablation leads to a G1/S transition arrest, reduced incorporation of 5-bromodeoxyuridine, enhanced senescence-associated beta-galactosidase activity, and formation of senescence-associated heterochromatic foci. 26988444_The crystal structure of JNK1 bound to the catalytic domain of MKP7 at 2.4-A resolution, providing high-resolution structural insight into the FXF-docking interaction, is reported. 29880481_Chemotherapy increased DUSP9 expression and decreased DUSP16 expression in a HIF1-dependent manner. 33077868_DUSP16 is a regulator of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and promotes their expansion ex vivo. 33326930_CircDUSP16 Contributes to Cell Development in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating miR-497-5p/TKTL1 Axis. 33863904_DUSP16 promotes cancer chemoresistance through regulation of mitochondria-mediated cell death. |
ENSMUSG00000030203 |
Dusp16 |
21.771755 |
2.2837777451 |
1.191422 |
0.326361918 |
13.573101 |
0.00022944996078424817259264201219082224270096048712730407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000594885196061040416419529730518434007535688579082489013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.9775723 |
6.3020404 |
13.2448078 |
2.2022924 |
| ENSG00000111341 |
4256 |
MGP |
protein_coding |
P08493 |
FUNCTION: Associates with the organic matrix of bone and cartilage. Thought to act as an inhibitor of bone formation. |
Alternative splicing;Chondrogenesis;Deafness;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Gamma-carboxyglutamic acid;Osteogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the osteocalcin/matrix Gla family of proteins. The encoded vitamin K-dependent protein is secreted by chondrocytes and vascular smooth muscle cells, and functions as a physiological inhibitor of ectopic tissue calcification. Carboxylation status of the encoded protein is associated with calcification of the vasculature in human patients with cardiovascular disease and calcification of the synovial membranes in osteoarthritis patients. Mutations in this gene cause Keutel syndrome in human patients, which is characterized by abnormal cartilage calcification, peripheral pulmonary stenosis and facial hypoplasia. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:4256; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; structural constituent of bone [GO:0008147]; cartilage condensation [GO:0001502]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; ossification [GO:0001503]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500] |
11073842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12207096_REVIEW: an important inhibitor of pathologic calcification, and deficiency contributes to pathogenesis of cardiovascular calcifications in dialysis patients. 12721790_Genetic variations at the MGP locus did not affect the rate of tooth loss in the elderly. However, the MGP locus may be associated with some determinants for tooth loss in elderly women. 12721790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14587031_the effect of MGP on calcification and osteogenic differentiation is determined by availability of BMP-2 14963895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15045141_Serum MGP levels were lower in patients with coronary artery calcification (CAC) than in those without. As the severity of CAC increased, there was a decrease in serum MGP levels, suggesting a role for MGP in the development of vascular calcification. 15280384_matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein and bone morphogenetic protein-2 processing and transport in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells is regulated by serum fetuin 15744522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15864013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15982861_MGP has a novel binding activity for vitronectin 16210837_Chronic kidney disease and hemodialysis patients have a different distribution of MGP gene polymorphism as compared to the normal population. 16210837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16392639_Finds increased frequencies of the MGP G-7A G allele and the G7-A GG genotype in Mexicans compared to Europeans. For the T-138C genotype, we found differences among the Mexicans. 16392639_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16735944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16973975_Matrix Gla protein is associated with individual coronary heart disease CHD) risk factors and the Framingham CHD risk score in men and women free of clinically apparent CHD. 17014561_accelerated vascular calcification observed in CKD have recently become clearer, leading to the hypothesis that a lack of natural inhibitors of calcification like matrix Gla may trigger calcium deposition 17509359_MGP gene polymorphism is associated with kidney stones and influences genetic susceptibility to kidney stones. 17509359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17643059_High expression of MGP in varicose veins may contribute to venous wall remodeling by affecting proliferation and mineralization processes probably through impaired carboxylation of MGP. 17670744_Matrix GLA protein is an inhibitory morphogen in pulmonary vascular development 17724449_lower ratio of Gla-MGP over Glu-MGP in pathological fibroblasts compared to controls suggests these cells may play an important role in the ectopic calcification in pseudoxanthoma elasticum 17848178_gamma-glutamyl carboxylation and serine phosphorylation of MGP contribute to its function as a calcification inhibitor and that MGP may inhibit calcification via binding to vascular smooth cell-derived vesicles. 17890861_Undercarboxylated MGP levels were inversely associated with phosphate, positively associated with serum fetuin-A levels, and inversely associated with the aortic augmentation index 18222176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18222176_Results suggest a role for the local calcification inhibitor matrix Gla protein in pseudoxanthoma elasticum manifestation. 18286307_Circulating levels of MGP and fetuin-A could not be identified as independent predictors of vascular stiffness or other carotid artery parameters in pediatric renal transplant recipients. 18369157_Suggest that BMP-4 and calcium binding in MGP are independent but functionally intertwined processes and that the BMP binding is essential for prevention of vascular calcification. 18401181_Developed ELISA for measuring serum matrix Gla. Serum matrix Gla may be used as a biomarker to identify those at risk for developing vascular calcification. 18841280_MGP is a potent inhibitor of arterial calcification 18971553_the kidney is able to extract matrix Gla-protein from the plasma at a constant level of 12.8%, independent of renal function in hypertensive subjects 19151998_We have investigated the synthesis and localization of fetuin-A and MGP in bone of hemodialysis patients 19190822_Uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein (ucMGP) is associated with coronary artery calcification in haemodialysis patients. 19327888_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19350115_Examine circulating Matrix Gla-Protein and anticoagulation status in patients with aortic valve calcification. 19352064_The results of this study suggest a role for MGP genetic variants in coronary atherosclerosis among men that is not reflected in serum MGP concentrations. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19661459_Heat shock protein 70 enhances vascular bone morphogenetic protein-4 signaling by binding matrix Gla protein. 19712474_Upregulation of MGP results in increased cell migration in glioblastoma. 19730704_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19730704_possible role of SNPs in the promoter region of MGP gene with relation to lead toxicity was investigated for the first time in the Indian population 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20133489_Plasma MGP increased progressively in a chronic kidney disease setting and was associated with the severity of aortic calcification. 20368306_matric gla protein is a potent inhibitor of calcification in vitro and may thus play a role in the regulation of peritoneal calcium homeostasis. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20479029_higher FGF23 and lower ucMGP levels are independently associated with mortality and cardiovascular disease events 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21143859_Report increased matrix Gla protein levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and/or ischemic heart disease. 21294711_a dysregulated MGP system could be involved in left ventricular dysfunction in patients with chronic heart failure 21724703_There may be an association between hand osteoarthritis and genetic polymorphism at the matrix Gla protein (MGP) locus that is not reflected by total MGP serum concentrations. 21765215_Mgp gene deletion may have a role in arteriovenous malformations 21870514_MGP A/A variant of MGP promoter G-7-->A polymorphism is a risk factor of ACS in Ukrainian population. 22115341_The change in serum fetuin-A, matrix Gla protein (MGP), and osteopontin (OPN) levels after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) indicates that these parameters play a role in the pathophysiological processes leading to an ICH. 22239033_MGP level correlated negatively with proinflammatory cytokines & acute phase proteins in acute pancreatitis, & positively with lipase, fetuin A, & albumin, indicating a possible role in calcium & phosphate metabolism disturbances in AP. 22796540_Angiotensin II exacerbates vascular calcification through activation of transcription factors, and regulation of MGP and inflammatory cytokine expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. 22819559_Circulating dp-ucMGP and t-ucMGP may serve as markers for the extent of coronary artery calcification, but these findings need to be confirmed 22992285_Higher circulating MGP levels could help identify minor carotid stenosis with calcification in a relatively homogenous risk population (i.e., postmenopausal women), regardless of underlying cardiovascular risk factors 23046575_findings showed that SNPrs4236 of the MGP gene is associated with kidney stones in the Chinese Han population, and influences the genetic susceptibility to kidney stones 23062766_Menaquinone supplementation dose-dependently decreases dephospho-uncarboxylated MGP concentrations, but does not affect other MGP species. 23110920_MGP is a multi-functional inhibitor of normal and abnormal angiogenesis that may function by coordinating with both Notch and BMP signaling pathways 23223140_MGP carboxylation remained much less in pseudoxanthoma elasticum fibroblasts. 23233942_the A/A-variant of MGP gene promotor is associated with an increased risk of ischemic atherothrombotic stroke in female persons in the Ukrainian population. 23307874_Increased risk of myocardial infarction associated with MGP ThrAla83 genotype observed elsewhere may be related to faster progression of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. 23504408_The MGP-138CC genotype may be associated with slower progression of vascular calcification in maintenance hemodialysis patients 23563003_rs1800802 (T > C) polymorphism within the MGP promoter is not related to stenosis of the coronary artery. 23677904_Genetic variants of MGP are associated with calcification on the arterial wall. 23877986_the findings of this prospective study among type 2 diabetic patients shows that high circulating dpucMGP levels are associated with increased cardiovascular diseases risk, especially with peripheral arterial disease and heart failure. 24029658_High MGP concentrations may be associated with more vascular calcification. 24210635_Vitamin K insufficiency, as assessed by high plasma matrix Gla protein concentrations, is associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease independent of classical risk factors and vitamin D status. 24228496_The A/A-variant of MGP gene is associated with an increased risk of ischemic atherothrombotic stroke in the Ukrainian women. 24281054_Matrix Gla protein gene functional polymorphisms is associated with loss of bone mineral density and progression of aortic calcification. 24445527_Based on the study results, the MGP protein did not play an important role in the development of stenosis of coronary arteries. 24458983_Both mutations predict complete loss of MGP function. 24762216_High matrix Gla protein levels are associated with below-knee arterial calcification score in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. 24804215_Extracellular matrix proteins expression profiling in chemoresistant variants of the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line. 24835435_circulating dp-ucMGP and dp-cMGP may have a role in increasing risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality 25190488_The concentration of dephosphorylated-uncarboxylated Matrix Gla protein was higher in hemodialysis patients treated with vitamin K. 25421980_Inactive nonphosphorylated and uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein levels were followed in a Flemish population. They correlated causally with non-cancer mortality and coronary events but not total cardiovascular mortality. 25458708_It is assumed that Lp-PLA2 is involved in vascular calcification and that dp-ucMGP is a more appropriate biomarker of residual risk than Lp-PLA2 itself. 25528106_Higher plasma dephosphorylated uncarboxylated MGP (reflective of lower vitamin K status) was associated with higher odds of meniscus damage, osteophytes, bone marrow lesions, and subarticular cysts. 25871831_Altering NOTCH1 levels affected MGP mRNA and protein. 25957430_Data shoed increased GAS6 and decreased MGP levels in hemodialysis patients, as mediators of induction or prevention of vascular calcification. 25974989_MGP expression is impaired in patients with ankylosing spondylitis 25987667_High levels of desphospho-uncarboxylated MGP are independently and positively associated with arterial stiffness after adjustment for common cardiovascular risk factors, renal function, and age. 25990696_MGP expression is significantly lower in diseased relative to normal aortic valve interstitial cells. Lack of this important 'anti-calcification' protein may contribute to calcification of the aortic valve. 26016598_Increased desphospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein, which is a circulating biomarker of vitamin K status and vascular calcification, is independently associated with aortic stiffness, but not with stiffness of distal muscular-type arteries. 26040031_The association has been found between the ischemic atherothrombotic stroke and polymorphic variants of genes MGP and VKORC1. 26771974_Uncarboxylated MGP in synovial fluid might serve as a novel biomarker for assessing knee osteoarthritis progression. 27009385_MGP is significantly repressed by miR-155 in breast cancer MCF-7 cells, and concomitantly there is a stimulation of cell proliferation and cell invasiveness. 27119839_The substitution of threonine by alanine due to MGP exon 4 Thr83Ala polymorphism is related to a decrease in the likelihood of arterial calcification in female persons in the Ukrainian population 27172275_ectopic expression of Mgp in murine and human osteosarcoma cells led to a marked increase in lung metastasis. Abrogation of Mgp prevented lung metastatic activity, an effect that was rescued by forced expression. Mgp levels dramatically altered endothelial adhesion, trans-endothelial migration in vitro and tumour cell extravasation ability in vivo 27348051_MGP rs4236 [A/G] gene polymorphism was not to be associated with subgingival dental calculus. Also, that GCF MGP levels were detected higher in patients with subgingival dental calculus than those without subgingival dental calculus independently of polymorphism, may be the effect of adaptive mechanism to inhibit calculus formation. 27951533_Correlations of plasma desphosphorylated uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein (dp-ucMGP) with vascular calcification and vascular stiffness in chronic kidney disease. Plasma dp-ucMGP was positively associated with vascular calcification and might be utilized as an early marker for vascular calcification in CKD patients. 28411264_Genetic variability in the MGP gene was associated with vascular recurrence in the Spanish population. 28605143_Studied serum levels of bone morphogenic protein-4 (BMP-4) and matrix Gla protein (MGP) in patients who were admitted to emergency department with the diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention. MGP and BMP-4 levels were significantly elevated when compared to subjects with normal coronary arteries. 28654853_This study concluded that diabetes coexisting with renal disease leads to extreme vascular calcification expressed by elevated MGP levels, resulting in higher frequency of cardiovascular disease in comparison to CKD patients without diabetes. 28734846_genetic association studies in population in Greece: Data suggest that an SNP in promoter region of matrix Gla protein (rs1,800,802; T-138C) is associated with diabetic angiopathy (as indicated by carotid intima media thickness) in patients with type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. 28821877_the MGP gene rs1800801 polymorphism is significantly associated with vascular calcification and atherosclerotic disease, especially in the Caucasian population. 28855172_Our results indicate that the association between the matrix Gla protein variant and increased risk for hand Osteoarthritis is caused by a lower expression of matrix Gla protein, which may increase the burden of hand Osteoarthritis by decreased inhibition of cartilage calcification. 29303985_Dp-ucMGP was high preoperatively, and further increased postoperatively in cardiovascular risk patients. 29529056_Study found an association between diastolic left ventricular function with circulating inactive desphospho-uncarboxylated MGP in two cohorts; undertook histological studies confirming the presence of MGP in the heart and determining its exact localization in healthy and diseased hearts, using conformation-specific MGP antibodies. 29635270_higher plasma dp-ucMGP concentrations found in African American hemodialysis patients may be associated with greater arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction. 29777408_The polymorphisms of OPN and MGP were not significantly associated with primary knee osteoarthritis in the codominant, dominant, and recessive models (p > 0.05). The study suggests that there are no associations between OPN and MGP polymorphisms with primary knee osteoarthritis in Mexican population. 29788226_Chronic kidney disease is associated with increased (inactive) dp-ucMGP, a vitamin K-dependent inhibitor of vascular calcification, which correlates with large artery stiffness. 30257426_This study observed increased expression of MGP in Paclitaxel and Topotecan Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines at both mRNA and protein level. 30617055_this study shows that MGP gene rs1800802 polymorphism is associated with increased risk for knee knee osteoarthritis (OA) in Chinese Han population and the rs1800802 polymorphism may be a diagnostic marker of radiographic knee OA. 30717170_MGLAP is the most powerful natural calcification inhibitor found in the human body, and is tightly associated with all types of calcification, mortality, and cardiovascular disease. (Review) 31025895_In people representative for the general population, higher inactive desphospho-uncarboxylated MGP was associated with greater PWV , central pulse pressure, forward pulse wave, and backward pulse wave. 31069456_High dephospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein concentrations, a plasma biomarker of vitamin K, in relation to frailty: the Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. 31215457_MGP expression is subject to cis-acting regulators that correlate with the OA association signal. These are active in a range of joint tissues but have effects which are particularly strong in cartilage 31264274_our results showed that the HOXC8-MGP axis played an important role in the tumorigenesis of Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and might be a promising therapeutic target for TNBC treatment 31510823_Renal Resistive Index Is Associated With Inactive Matrix Gla (gamma-Carboxyglutamate) Protein in an Adult Population-Based Study. 31589964_Study found that high expression level of MGP is related with a worst prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) and correlated with a worse prognosis and survival rate lower than five years. 31804541_Plasma dephosphorylated-uncarboxylated Matrix Gla-Protein (dp-ucMGP): reference intervals in Caucasian adults and diabetic kidney disease biomarker potential. 32086862_Intracellular matrix Gla protein promotes tumor progression by activating JAK2/STAT5 signaling in gastric cancer. 32092076_Inactive matrix gla protein plasma levels are associated with peripheral neuropathy in Type 2 diabetes. 32422228_Uncarboxylated matrix Gla-protein: A biomarker of vitamin K status and cardiovascular risk. 32584873_Matrix Gla protein polymorphism rs1800801 associates with recurrence of ischemic stroke. 32839405_The Association of dp-ucMGP with Cardiovascular Morbidity and Decreased Renal Function in Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease. 33359068_Suppression MGP inhibits tumor proliferation and reverses oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer. 33669806_Circulating Levels of Dephosphorylated-Uncarboxylated Matrix Gla Protein in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. 33984465_Characterization of dynamic changes in Matrix Gla Protein (MGP) gene expression as function of genetic risk alleles, osteoarthritis relevant stimuli, and the vitamin K inhibitor warfarin. 34809448_Matrix Gla Protein Levels Are Associated With Arterial Stiffness and Incident Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. 35025148_1,25-(OH)2D3 participates and modulates airway remodeling by reducing MGP and TGF-beta1 expression in TNF-alpha-induced airway smooth muscle cells. |
ENSMUSG00000030218 |
Mgp |
11.002475 |
0.0285433935 |
-5.130699 |
1.013693901 |
37.223554 |
0.00000000105333803021348158153884108173764869165189850264141568914055824279785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005029850962779355491498407609504694981694683519890531897544860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7077028 |
0.5266790 |
24.6894082 |
7.1683203 |
| ENSG00000111344 |
8437 |
RASAL1 |
protein_coding |
O95294 |
FUNCTION: Probable inhibitory regulator of the Ras-cyclic AMP pathway (PubMed:9751798). Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9751798}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Differentiation;GTPase activation;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is member of the GAP1 family of GTPase-activating proteins. These proteins stimulate the GTPase activity of normal RAS p21 but not its oncogenic counterpart. Acting as a suppressor of RAS function, the protein enhances the weak intrinsic GTPase activity of RAS proteins resulting in the inactive GDP-bound form of RAS, thereby allowing control of cellular proliferation and differentiation. This particular family member contains domains which are characteristic of the GAP1 subfamily of RasGAP proteins but, in contrast to the other GAP1 family members, this protein is strongly and selectively expressed in endocrine tissues. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been described [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:8437; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12221082_Galpha and Gbeta gamma require distinct Src-dependent pathways for its activation 16009725_RASAL preservs of Ca2+ frequency information 17640920_RASAL constitutes a tumor suppressor gene and therefore further emphasized the importance of Ca(2+) in the regulation of Ras signaling and has established that deregulation of this pathway is an important step in Ras-mediated tumorigenesis 18992247_Decreased expression of the RAS-GTPase activating protein RASAL1 is associated with colorectal tumor progression. 20473946_Reduced expression of RAS protein activator like-1 is associated with gastric cancer. 22825043_decreased RASAL1 expression is a characteristic of gastric cancer and regulated by epigenetic mechanisms 23251034_Ras GTPase activating (RasGAP) activity of the dual specificity GAP protein Rasal requires colocalization and C2 domain binding to lipid membranes. 23665422_Hypermethylations of RASAL1 and KLOTHO is associated with renal dysfunction in a Chinese population environmentally exposed to cadmium 24136889_We identified RASAL1 as a major tumor suppressor gene that is frequently inactivated by hypermethylation and mutations, providing a new alternative genetic background for thyroid cancer, particularly FTC and ATC. 24377515_Promoter hypermethylation of the RASAL1 gene was detected in MKN-28, SGC-790l and BGC-823 cancer cells. 24531877_It is a tumor suppressor gene which influences the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by regulating RAS/ERK signaling pathway. 24712574_Germline RASAL1 alterations are uncommon in patients with Cowden syndrome but may not be infrequent in patients with apparently sporadic follicular-variant papillary thyroid cancer. 24925056_large chromosome 12 rearrangement, spanning MDM2 and RASAL1, is the first recurrent molecular abnormality to be reported in juvenile ossifying fibroma 25616414_Transcriptional suppression of RASAL1 through aberrant promoter methylation contributes to endothelial-mesenchymal transition and ultimately to progression of cardiac fibrosis. 25735335_Loss of RASAL1 expression is associated with gastric carcinogenesis. 26008146_These findings suggest that Ebp1 suppressed thyroid cancer cell lines by upregulating RASRAL expression. 26997440_Report a new subtype of high-grade mandibular osteosarcoma with RASAL1/MDM2 amplification. 27012941_HIF1alpha and transforming growth factor (TGF)/SMAD signalling pathways synergistically regulate hypoxia-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition through both DNMT3a-mediated hypermethylation of RASAL1 promoter and direct SNAIL induction. 27124111_DNA methylation, TGFbeta1 and RASAL1 appear to have an interacting relationship. 27878301_RASAL1 role in in sorafenib-resistance of liver cancer cells 28011578_our study showed significantly longer overall survival times for oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma patients without RASAL1 expression 28885980_Domain topology of human Rasal |
ENSMUSG00000029602 |
Rasal1 |
7.658073 |
12.4253630261 |
3.635216 |
0.896445665 |
22.587033 |
0.00000200835567116010144152475798418056029959188890643417835235595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006871425523023435198656429928609767898706195410341024398803710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.1390463 |
8.5573117 |
1.1124478 |
0.6498229 |
| ENSG00000111424 |
7421 |
VDR |
protein_coding |
P11473 |
FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor for calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D3 which mediates the action of this vitamin on cells (PubMed:28698609, PubMed:16913708, PubMed:15728261, PubMed:10678179). Enters the nucleus upon vitamin D3 binding where it forms heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor/RXR (PubMed:28698609). The VDR-RXR heterodimers bind to specific response elements on DNA and activate the transcription of vitamin D3-responsive target genes (PubMed:28698609). Plays a central role in calcium homeostasis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P13053, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10678179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15728261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16913708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28698609}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes vitamin D3 receptor, which is a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily of ligand-inducible transcription factors. This receptor also functions as a receptor for the secondary bile acid, lithocholic acid. Downstream targets of vitamin D3 receptor are principally involved in mineral metabolism, though this receptor regulates a variety of other metabolic pathways, such as those involved in immune response and cancer. Mutations in this gene are associated with type II vitamin D-resistant rickets. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the initiation codon results in an alternate translation start site three codons downstream. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. A recent study provided evidence for translational readthrough in this gene, and expression of an additional C-terminally extended isoform via the use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2018]. |
hsa:7421; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; calcitriol binding [GO:1902098]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; lithocholic acid binding [GO:1902121]; lithocholic acid receptor activity [GO:0038186]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear retinoid X receptor binding [GO:0046965]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; small molecule binding [GO:0036094]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process involved in mammary gland involution [GO:0060057]; bile acid signaling pathway [GO:0038183]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; intestinal absorption [GO:0050892]; lactation [GO:0007595]; mammary gland branching involved in pregnancy [GO:0060745]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010839]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of apoptotic process involved in mammary gland involution [GO:0060058]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045618]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vitamin D 24-hydroxylase activity [GO:0010980]; positive regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway [GO:0070564]; regulation of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0060558]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; vitamin D receptor signaling pathway [GO:0070561] |
11028447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11033842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11043509_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11049814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11092401_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11134121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11136533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11167636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11174470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11204438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11224872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11230734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11248649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11251690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11257727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11306745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11316004_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11335187_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11353946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11355046_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11359741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11383910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11389055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423686_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11440415_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11445000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11456232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11461072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11484168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11489147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11489753_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11498732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11498733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11498736_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11522087_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11532853_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11552708_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11579931_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11598396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11678976_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11679916_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11684540_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11684548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11689145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11720436_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11744805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11744805_These data suggest that BsmI VDR polymorphism does not play an important role in the bone loss seen in hypercalciuric CSF patients. 11751444_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11776070_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11779241_critical role of helix 12 of the vitamin D3 receptor for the partial agonism of carboxylic ester antagonist, ZK159222 11782643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11786968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11789558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11800328_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11808760_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11834737_transactivation modulated by a central dinucleotide within vitamin D response elements 11846330_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11887173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11898916_Association of vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphisms in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 11898916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11909970_Stat1-vitamin D receptor interactions antagonize 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D transcriptional activity and enhance stat1-mediated transcription. 11910656_A clinically significant relationship between VDR and ER genotypes and biochemical markers of bone turnover or serum lipoproteins could not be demonstrated in healthy Danish postmenopausal women 11910656_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11913978_Regulation of calbindin-D9k expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) and parathyroid hormone in mouse primary renal tubular cells 11914750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11914750_polymorphism and risk of severe diabetic retinopathy. 11918225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11918225_data support the VDR gene as a quantitative trait locus(QTL)underlying spine bone mineral density variation 11918709_vitamin D receptor is required for the initiation of the postnatal hair follicular cycle 11920955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11942896_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11956476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11972301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11972530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11979895_its genetic polymorphism determines bone mineral density 11984699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11991441_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11991950_regulates expression of CYP3A4, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 in hepatocytes 12003670_polymorphism in type 1 diabetics in a Romanian population 12016314_functions as a receptor for the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid (LCA) 12016463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12018632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12037619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12040821_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12053022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12064837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12064837_results suggest that the vitamin D receptor Fok I start codon polymorphism is not related to patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan 12071154_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12073153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12073153_investigation of the genetic influence of Sp1 polymorphism on bone density in Irish women 12086963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12086963_levels in relation to vitamin D status, insulin secretory capacity, and VDR genotype in Bangladeshi Asians. 12087029_There is an association between genotype and age of onset in juvenile Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes. 12096841_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12111344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12111344_The VDR genotype contributes to the liver dysfunction in patients with psoriasis, although no correlation was found between VDR genotype and the skin eruptions of psoriasis. 12145331_retinoid X receptor regulates vitamin D receptor functions in part by regulating subcellular localization 12147248_alteration of cellular phosphorylation state affects vitamin D receptor-mediated CYP3A4 mRNA induction in Caco-2 cells 12150447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12154394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12162507_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12169981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12173074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12174912_expression is increased in ovarian carcinomas as compared to normal ovarian tissue 12181642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12181642_contribution of VDR genotypes to prostate cancer susceptibility might depend on the population studied and its geographic localization; VDR genotypes are important in the definition of the genetic risk profile of populations of southern Europe 12192493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12192493_This is the first report of an association between VDR gene polymorphism and psoriasis in a Caucasian population. 12195069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12200969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12203138_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12211444_Tryptophan missense mutation in the ligand-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor causes severe resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. 12219967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12237325_removal of the insertion domain between helices 2 and 3 of the receptor does not markedly influence the functionality of the Vitamin d receptor. 12324918_Determination of VDR genotype by analysis of BsmI endonuclease gene polymorphism may predict both hemoglobin level and erythropoietin requirement in hemodialysis patients with anemia. 12324918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12360016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12363051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12369133_Despite a slight increase in the number of urinary tract infections among children with the BB genotype for the vitamin D receptor, there is no statistically significant correlation with genetic susceptibility. 12369133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12369780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12369780_the VDR genotype polymorphism affects bone density of renal transplant recipients via its effects on the severity of secondary hyperparathyroidism. 12375338_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12391072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12391072_vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphism, which locates at the translation initiation site, matters in the adaptations of bone to long-term impact loading. 12402975_Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with renal cell carcinoma in Japanese. 12402975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12403843_A novel mutation in helix 12 of this receptor impairs coactivator interaction and causes hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-resistant rickets without alopecia. 12404162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12413773_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12413773_Polymorphisms of VDR gene are associated with Japanese patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Allelic variance in the VDR gene or other genes in linkage disequilibrium with this gene might predispose to the development of psoriasis vulgaris. 12429765_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12433736_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12434167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12434167_associations between BsmI-polymorphism of the VDR gene and bone mineral density and bone metabolism in 24 premenopausal (aged 22-45 years) and 69 postmenopausal (aged 48-65 years) Finnish women 12444895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12446192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12454321_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12457456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12468277_Novel mutation in the VDR, Q317X, is the molecular defect in a patient with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D resistant rickets 12470203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12470203_the FokI genotype of the vitamin D receptor gene is related to bone mass at the hip in Czech postmenopausal women, whereas the importance of remaining VDR genotypes was not evident. 12477580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12482639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12482639_VDR polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of type 1 diabetes in the Dalmatian population of South Croatia. 12490310_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12521655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12532336_Data suggest that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) actions on normal prostate cells may be mediated independently through androgen receptors and vitamin D receptors. 12540499_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12542560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12555245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12566913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12588283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12595908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12601576_(Is this the right receptor?) Start codon polymorphism is an independent predictor of lumbar, but not femoral neck bone density. 12601576_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12608943_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12649542_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12649542_The VDR genotype seems to slow the progression of secondary hyperparathyroidism needing parathyroidectomy in patients treated with hemodialysis. 12649563_VDR was expressed in all pancreatic cancers studied. 12656660_marked decreases in vitamin D receptor and calcium-sensing receptor expression could be responsible for the high proliferation of parathyroid cells and the pathological progression of hyperparathyroidism 12666703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12666703_VDR polymorphism is associated with oral bone loss, clinical attachment loss, and tooth loss in older men 12673591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12673591_Significant association between VDR genotype and postmenopausal osteoporosis in Chinese women was observed in this study. 12674768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12694466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12717384_human hepatocytes express very low VDR(n) messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels. 12753258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12759877_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12759877_VDR gene polymorphisms may jointly influence bone mass and the rate of bone loss in older African-American women-- 12778851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12786678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12792298_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12807755_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12814692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12814692_VDR genotype determination may provide a tool to identify individuals who are at risk for calcium nephrolithiasis. 12818464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12820934_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12829710_a previtamin D3 analog with genomic activities equivalent to 1,25(OH)2D3 12836289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12843155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12843155_association between the VDR gene polymorphism and type 1 diabetes and the onset pattern. 12843190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12843190_the VDR gene constitutes a locus for reduced bone mineral density in men. 12846052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12846052_VDR polymorphism do not play a major role in rheumatoid arthritis predisposition in german patients. 12868700_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12869402_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12874698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12874698_We found VDR genotype to be associated with frame size and bone mineral apparent density(BMAD)but the VDR genotype effects on stature and bone size seem to neutralize the effect on areal BMD. 12879219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12895309_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12896855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12899513_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12903041_Data show that the Achang and Han ethnic groups differ in the frequency distribution of VDR gene start codon polymorphism. 12903041_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12905734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12914574_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12915669_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12915669_interaction between ERalpha and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms leads to increased risk of osteoporotic vertebral fractures in women, largely independent of bone mineral density 12927786_ER-alpha and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms are related to bone mineral density in pre- and post-menopausal women 12927786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12957667_in a model of neoplastic cell transformation, irradiating the MCF-10F cell line followed by treatment with estrogen led to over-expression of the VDR gene, which contained single-base mutations within intron 8 and exon 9 12958689_Genetic variation in the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) is associated with BMD in premenopausal women. 12958689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12960019_For RXR heterodimerizing receptors like VDR, P-box requires redefinition and expansion to include DNA specificity element corresponding to arg-49 and lys-53 of hVDR. These residues are crucial for selective DNA recognition. 12968672_A Cdx-2 binding site polymorphism (G to A) in the promoter region of the vitamin D receptor gene was reported. investigated the relationship between the VDR Cdx-2 genotype and risk of fracture 12968672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12969965_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14505233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14527203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14527840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14527848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14528100_Children with bone cancer are significantly taller than the reference population, which may be influenced by the genotype for the Fok I polymorphism of the VDR gene 14528100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14530911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14557853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14572874_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14574802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14584884_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14597850_BsmI polymorphism of the VDR gene influences BP in healthy men. A positive relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and BP is present only in men with the BB genotype. 14597850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14634546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14634546_The VDR baTL haplotype allele is related to bone mass in Korean women. 14641002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14641002_Subjects were genotyped for vitamine D receptor (VDR)A (ApaI), VDRB (BsmI) and VDRF (FokI) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The SNPs analysed are unlikely to be associated with type 1 diabetes in the Finnish population. 14642064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14665637_results suggest that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 rapid effects require the presence of vitamin D receptor and control, in part, the vitamin D catabolism via increased expression of the 24-hydroxylase and ferredoxin genes 14688157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14691685_No relationship was observed between VDR allelic polymorphisms and osteomalacia. 14691685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693728_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693728_Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism are unlikely to be a major determinants of susceptibility to prostate cancer. 14693733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14714273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14714273_To fully determine whether sequence differences in VDR gene are susceptibility variants for type 2 diabetes mellitus, additional studies in different populations are required in a large study group. 14718481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14719475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14725686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14727381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14731356_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14731356_Results indicated that the individuals carrying the VDR B allele were more susceptible to lead poisoning. 14746673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14746673_Result suggested the possibility that vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism might be important in determining an individual's susceptibility to development of vitamin D deficiency rickets. 14748937_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14749534_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14749534_The prevalence of the VDR Taq I and Bsm I alleles and the genotype frequencies in patients with breast cancer was similar to that in the normal population 14963917_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14991752_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14997007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14999525_Data describe the influence of allelic variations of the vitamin D receptor and estrogen receptor genes on bone mineral density. 14999525_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15009617_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15012617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15037631_Vitamin D receptor has a role in p38 MAPK activation-selectively induced cell death in K-ras-mutated human colon cancer cells 15040830_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15050735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15057510_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15061984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15064717_Suppression of Sp1 expression by small interference RNA reduced the stimulation of p27Kip1 promoter activity by vitamin D3 in prostatic cancer cells. 15065089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15066214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15066918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15067191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083068_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083213_VDR TaqI polymorphism is associated with a group of men with benign prostatic hyperplasia who are at an increased risk of prostate cancer 15104566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15108066_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15129811_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15141345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15141734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15141734_Polymorphisms in the VDR and NRAMP1 gene are statistically associated with susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in the Chinese Han population. 15145445_resistance of acute monocytic leukemia cells to calcitriol-induced differentiation correlates with impaired nuclear localization of vitamin D receptor, but not with its total expression in the cells 15187348_VDR polymorphism associated with the risk of developing rosacea fulminans. 15205858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15205858_VDR genotypes may be associated with increased calcium excretion in hypercalciuric nephrolithiatic subjects. 15210908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15213319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15213514_Lead workers with the VDR B allele had significantly (P value |
ENSMUSG00000022479 |
Vdr |
81.923922 |
2.3528765732 |
1.234426 |
0.171519236 |
52.835658 |
0.00000000000036265722262731269257578687139972731018257995350140276968886610120534896850585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002227557472317576066538721786510045405008823005132967409736011177301406860351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
115.5327193 |
12.9833177 |
49.4745649 |
4.4286538 |
| ENSG00000111641 |
4839 |
NOP2 |
protein_coding |
P46087 |
FUNCTION: Involved in ribosomal large subunit assembly (PubMed:24120868). S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyltransferase that specifically methylates the C(5) position of cytosine 4447 in 28S rRNA (Probable). May play a role in the regulation of the cell cycle and the increased nucleolar activity that is associated with the cell proliferation (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24120868, ECO:0000305, ECO:0000305|PubMed:23913415}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Citrullination;Isopeptide bond;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis;RNA-binding;rRNA processing;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of cell population proliferation; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator; and ribosomal large subunit assembly. Located in nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4839; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA (cytosine-C5-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0009383]; maturation of LSU-rRNA [GO:0000470]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796]; ribosomal large subunit assembly [GO:0000027]; RNA methylation [GO:0001510]; rRNA base methylation [GO:0070475] |
25481415_Findings suggest a newly discovered role of Nop2 in both mature neurons and in cells possibly involved in the regeneration of nervous tissue 26196125_p120 has an rRNA:5-Methylcytosine-Methyltransferase activity. 26906424_NOL1 represents a new route by which telomerase activates transcription of cyclin D1 gene, thus maintaining cell proliferation capacity 32176734_Mechanistically, NOP2 associates with HIV-1 5' LTR, interacts with HIV-1 TAR RNA by competing with HIV-1 Tat protein, as well as contributes to TAR m5C methylation. RNA MTase catalytic domain (MTD) of NOP2 mediates its competition with Tat and binding with TAR. Overall, these findings verified that NOP2 suppresses HIV-1 transcription and promotes viral latency. 32554858_Long noncoding RNA LINC00963 induces NOP2 expression by sponging tumor suppressor miR-542-3p to promote metastasis in prostate cancer. 35381832_Upregulated expression of NOP2 predicts worse prognosis of gastric adenocarcinoma by promoting tumor growth. 36161484_Human NOP2/NSUN1 regulates ribosome biogenesis through non-catalytic complex formation with box C/D snoRNPs. |
ENSMUSG00000038279 |
Nop2 |
64.168082 |
2.0892145726 |
1.062961 |
0.306489165 |
11.955740 |
0.00054479276381902484553687582291559010627679526805877685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001328016712463882384107072276435701496666297316551208496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
92.1155141 |
17.1987171 |
44.4866196 |
6.3574558 |
| ENSG00000111644 |
84519 |
ACRBP |
protein_coding |
Q8NEB7 |
FUNCTION: [Acrosin-binding protein, mature form]: Acrosomal protein that maintains proacrosin (pro-ACR) as an enzymatically inactive zymogen in the acrosome. Involved also in the acrosome formation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3V140}. |
Cytoplasmic vesicle;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is similar to proacrosin binding protein sp32 precursor found in mouse, guinea pig, and pig. This protein is located in the sperm acrosome and is thought to function as a binding protein to proacrosin for packaging and condensation of the acrosin zymogen in the acrosomal matrix. This protein is a member of the cancer/testis family of antigens and it is found to be immunogenic. In normal tissues, this mRNA is expressed only in testis, whereas it is detected in a range of different tumor types such as bladder, breast, lung, liver, and colon. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:84519; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acrosome assembly [GO:0001675]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; spermatid development [GO:0007286] |
16301813_We showed identification of HLA-A24-binding OY-TES-1 peptide, TES(401-409) (KTPFVSPLL) recognized by CD8 T-cells. 20876808_High ACRBP expression correlated with reduced survival time and faster relapse among ovarian cancer patients. 22651134_The down-regulation of OY-TES-1 expression in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells caused cell growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction and migration ability attenuation. 24294369_OY-TES-1 is frequently expressed in colorectal carcinoma and is able to induce humoral immune response spontaneously in CRC patients. 25673160_OY-TES-1 downregulation in liver cancer cells caused 2 opposite effects on cell proliferation: promotion by upregulating CCND2 and CDCA3, and inhibition by CD9 upregulation and NANOG downregulation. OY-TES-1 may play multiple roles in liver cancer. 26189257_OY-TES-1 was expressed in ovarian cancer (OC) tissues with a high proportion, and some of OC tissues presented OY-TES-1 expression in high level vs OC adjacent tissues. 26339343_Down regulation of OY-TES-1 increased expression of apoptosis-regulated protein caspase-3, and decreased expression of cell cycle-regulated protein cyclin E, migration/invasion-regulated proteins MMP2 and MMP9. 32862383_Cancer-testis Antigen OY-TES-1 Expression and Immunogenicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33559934_CT23 knockdown attenuating malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma cell is associated with upregulation of metallothionein 1. |
ENSMUSG00000072770 |
Acrbp |
9.441032 |
0.2897889630 |
-1.786925 |
0.597086636 |
8.976721 |
0.00273440917822815286741811036108629195950925350189208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005903156277701849044547977030106267193332314491271972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4907330 |
1.6224645 |
12.4237354 |
3.6527874 |
| ENSG00000111671 |
84727 |
SPSB2 |
protein_coding |
Q99619 |
FUNCTION: Substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820, PubMed:21199876). Negatively regulates nitric oxide (NO) production and limits cellular toxicity in activated macrophages by mediating the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of NOS2 (PubMed:21199876). Acts as a bridge which links NOS2 with the ECS E3 ubiquitin ligase complex components ELOC and CUL5 (PubMed:21199876). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21199876}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a member of a subfamily of proteins containing a central SPRY (repeats in splA and RyR) domain and a C-terminal suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) box. This protein plays a role in cell signaling. This gene is present in a gene-rich cluster on chromosome 12p13 in the vicinity of the CD4 antigen and triosephosphate isomerase genes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:84727; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity [GO:1990756]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
19609018_Shows that this gene is associated with the regulation of cell proliferation in canine mammary cancer cell lines. 28549582_crystal structure of SPSB2 in complex with cyclic peptide inhibitor cR8, at a resolution of 1.34 A 31204687_C-terminal His6 tag of the recombinant protein binds to a shallow pocket adjacent to the iNOS-binding site on a crystallographically related SPSB2 molecule 31344133_Results demonstrated that cellular factor SPSB2 interacts with and decreases viral protein NS5A to inhibit HCV replication. SPSBP2 interacts with the HCV protein NS5A via its SPRY domain and inhibits HCV replication by ubiquitination and degradation of NS5A. 33862200_Structural basis for the regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase by the SPRY domain-containing SOCS box protein SPSB2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. |
ENSMUSG00000038451 |
Spsb2 |
31.951310 |
0.3965909842 |
-1.334276 |
0.386252792 |
11.815799 |
0.00058730220980264470805043419687763162073679268360137939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001425284547301387122475446744829241652041673660278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.7497240 |
4.1387436 |
45.2785273 |
7.0334630 |
| ENSG00000111679 |
5777 |
PTPN6 |
protein_coding |
P29350 |
FUNCTION: Modulates signaling by tyrosine phosphorylated cell surface receptors such as KIT and the EGF receptor/EGFR. The SH2 regions may interact with other cellular components to modulate its own phosphatase activity against interacting substrates. Together with MTUS1, induces UBE2V2 expression upon angiotensin II stimulation. Plays a key role in hematopoiesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11266449}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH2 domain |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. N-terminal part of this PTP contains two tandem Src homolog (SH2) domains, which act as protein phospho-tyrosine binding domains, and mediate the interaction of this PTP with its substrates. This PTP is expressed primarily in hematopoietic cells, and functions as an important regulator of multiple signaling pathways in hematopoietic cells. This PTP has been shown to interact with, and dephosphorylate a wide spectrum of phospho-proteins involved in hematopoietic cell signaling. Multiple alternatively spliced variants of this gene, which encode distinct isoforms, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5777; |
alpha-beta T cell receptor complex [GO:0042105]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004726]; phosphorylation-dependent protein binding [GO:0140031]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0005001]; abortive mitotic cell cycle [GO:0033277]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; epididymis development [GO:1905867]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042267]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin [GO:0002924]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of mast cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0033007]; negative regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050732]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050860]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; platelet formation [GO:0030220]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045577]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060338]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
11826756_The Lyn/CD22/SHP-1 pathway is important in autoimmunity. Naive and tolerant B-cells differ in their calcium signaling in response to antigenic stimulation. 11858824_peripheral blood monocytes treated for 5--8 days with GM-CSF (i.e. mature Mphi) acquired the capacity to assemble tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 with CD9, alpha3-beta1 integrin and their CD46. 11907066_SHP-1 is recruited to the NK cell immune synapse within 1 min in both cytolytic and noncytolytic conjugates, allowing clear distinction between noncytolytic and cytolytic interactions at this early time. 11986327_interacts with siglec-11 11987243_evidence of cytokine-regulated SHP-1 nuclear localization mediated by a bipartite nuclear localization signal, suggesting that SHP-1 regulates nuclear signaling in cell growth control. 12130517_ILT2 triggering on cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) cells leads to the recruitment of SHP-1 and to the specific inhibition of CTCL malignant cell proliferation in Sezary syndrome induced by CD3/T-cell receptor. (TCR) stimulation. 12145687_In the T cell line HUT-78, JAK3 was found to be highly phosphorylated. These results suggest that SHP-1 might be involved in maintaining the IL-2R/JAK3 signaling pathway under control and point towards a role of SHP-1 in the pathogenesis of the disease. 12438221_Functional loss of SHP1 is associated with the pathogenesis of leukemias/lymphomas. 12459556_participation in regulation of Stat6 dephosphorylation 12482860_crystal structure of the C-terminal truncated human SHP-1 in the inactive conformation at 2.8-A resolution and refined the structure to a crystallographic R-factor of 24.0% 12571228_SHP-1 may be involved in the regulation of beta-catenin transcriptional function and in the negative control of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation 12591278_show the existence of multiple transcripts of SHP-1 in human transformed T cells and normal PBMCs and give evidence supporting the concept that SHP-1 can negatively regulate growth of malignant T cells 12646642_SHP-1 plays a pivotal role in reorganization of cytoskeletal architecture by inducing actin dephosphorylation. 12734331_A blockade in early signaling events observed with TCR antagonists occurs via a negative intracellular signal that is mediated by SHP-1. 12832410_Associates with phosphorylated Fc gamma RIIa to modulate signaling events in myeloid cells 12917349_Vav1 trapping was independent of actin polymerization, suggesting that inhibition of cellular cytotoxicity occurs through an early dephosphorylation of Vav1 by SHP-1, which blocks actin-dependent activation signals. 14551136_SHP-1 inhibits PRL receptor and EPO receptor signaling by recruitment and targeting of SOCS-1 to Jak2, highlighting a new mechanism of SHP-1 regulation of cytokine-receptor signaling. 14630083_Down-regulation of SHP1 is associated with adult T-cell leukemia 14691303_SHP1 gene silencing is one of the events critical to the onset of malignant lymphomas/leukemias in humans. 14976049_hypermethylated in multiple myeloma 15070900_SHP-1 can dephosphorylate alpha-actinin in vitro and in vivo. 15197735_CNS myelination was significantly reduced in SHP-1-deficient mice relative to their normal littermates at multiple times during the active period of myelination. 15339845_Mice lacking SHIP-1 have defects in the erythroid and myeloid compartments similar to those in mice lacking Lyn or SHP-1. 15456853_inactivation of Ros by SHP-1-mediated dephosphorylation plays a role in the regulation of complex stability 15557341_TFG is a novel protein able to modulate SHP-1 activity. 15574429_transformation of TF-1 cells with FLT3/ITD mutations suppressed the activity of SHP-1 by approximately 3-fold 15579525_SHP-1 may be a novel target molecule to sensitize erythropoietin action in hemodialysis patients with hyporesponsive anemia 15701718_SHP-1 acts at multiple stages of hematopoietic differentiation to alter lineage balance. Expression of WT SHP-1 reduced myeloid colony numbers while increasing the numbers of secondary embryoid bodies and mixed hematopoietic colonies obtained 15746253_SRIF inhibitory effects on thyroid medullary carcinoma cell proliferation are mediated, at least in part, by SHP-1, which acts through a MAPK-dependent mechanism 15870198_STAT3 may transform cells by inducing epigenetic silencing of SHP-1 in cooperation with DNMT1 and histone deacetylase 1 16326706_Shp-1 mediates the antiproliferative activity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 16501054_Our results suggest an alteration of the SHP-1 modulation by GM-CSF in lipid rafts of PMN with aging. These alterations could contribute to the decreased GM-CSF effects on PMN. 17046078_SHP1 activation, association with Src and dephosphorylation of specific proteins were dependent on extracellular calcium and maintenance of a higher cytosolic calcium plateau. 17079228_Protein phosphatase 6 specifically down-regulates transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) through dephosphorylation of threonine-187 in the activation loop, suppressing inflammatory responses via TAK1 signaling pathways. 17142110_increased activity of inhibitory molecules, such as Src homology domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) and suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS), is responsible for age-related failure of GM-CSF to stimulate neutrophil functions 17218319_findings provide an insight into the structure of the hematopoietic cell-specific P2 promoter of the SHP-1 gene and identify PU.1 as the transcriptional activator of the P2 promoter 17227821_These data suggest a mechanism of IC-mediated inhibition of IFN-gamma signaling, which requires the ITAM-containing FcgammaRI, as well as the ITIM-dependent phosphatase SHP-1, ultimately resulting in the suppression of STAT1 phosphorylation. 17239936_SHP-1 loss correlates with, and may contribute to, progression of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma 17272397_novel mechanism regulating GH signaling in which estrogen receptor modulators enhance GH activation of the JAK2/STAT5 pathway in a cell-type-dependent manner by attenuating protein tyrosine phosphatase activities 17404032_In human erythrocytes SHP-1 is present in membranes from resting cells, but in 5% of the protein amount. SHP-1 ensures band 3 dephosphorylation. 17561098_SHP-1 and SHP-2, two structurally related cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine phosphatases with different cellular functions and cell-specific expression patterns, were compared for their intrinsic susceptibility to oxidation by H(2)O(2). 17579069_A novel 6-mer motif SKHKED within the carboxyl terminus of SHP-1 is necessary and sufficient for lipid raft localization and for the function of SHP-1 as a negative regulator of T-cell receptor signaling. 18086677_Thus the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of caspase-8, mediated by Lyn and SHP-1, respectively, represents a novel, dynamic post-translational mechanism for the regulation of neutrophil apoptosis 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18209728_Mononuclear leukocytes of multiple sclerosis patients have a deficiency in SHP-1 and increased inflammatory gene expression. 18441283_SHP-1 plays an important role in regulating oxidative stress. 18502033_TIMP1 functions as a differentiating and survival factor of GC B cells by modulating CD44 and SHP1 in the late centrocyte/post-GC stage, regardless of EBV infection. 18543080_Our results demonstrate putative roles of SHP-1 and SHP-2 in the progression of both Condyloma acuminatum and cervical cancer after HPV infection. 18948549_in HTLV-1-transformed CD4+ T cells, TIPS causes dissociation of transcription factors from the core SHP-1 P2 promoter, which in turn leads to subsequent DNA methylation, an important early step for leukemogenesis. 18952289_IL-10 suppresses the co-stimulatory effect of CD2 in T cells that have intact SHP-1, demonstrating an essential role of SHP-1 in IL-10-mediated direct T cell suppression. 19096001_Downregulation of platelet responsiveness upon contact with LDL by the protein-tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2. 19104650_Leishmania can exploit a host protein tyrosine phosphatase, namely SHP-1, to directly inactivate IRAK-1. 19166311_The kinetic and mechanistic details of reversible oxidation of SHP-1 and SHP-2, were investigated. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19234487_Lyn is downstream of Jak2, and Jak2 maintains activated Lyn kinase in CML through the SET-PP2A-Shp1 pathway. 19379557_5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine can re-express the silent SHP-1 gene, inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in K562 cells. 19398961_macrophages of multiple sclerosis patients display a deficiency of SHP-1 expression, heightened activation of STAT6, STAT1, and NF-kappaB and a corresponding inflammatory profile 19542910_Data suggest that age-specific interactions between Siglec-9 and SHP-1 may influence the altered inflammatory responsiveness and longevity of neonatal polymorphonuclear neutrophils. 19543515_increased frequency of promoter hypermethylation in SHP1 gene in acute myeloid leukemia compared to chronic myeloid leukemia. 19551406_Demethylation in HT-29 cells recovered the constitutive expression of SOCS-1 and SHP-1. 19591923_The SHP-1:PDK1 complex between the cytoplasm and the nucleus is dependent on a specific sequence of events; initial recruitment of PDK1 to perinuclear PIPs, followed by SHP-1 mediated entry via the nuclear pore complex and PDK-1 mediated nuclear export. 19619438_As(2)O(3) could cause demethylation and re-expression of SHP-1 in T2 lymphoma cells, and may inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis. 19749791_p53 repression of SHP-1 expression leads to trkA-Y674/Y675 phosphorylation and trkA-dependent suppression of breast-cancer cell proliferation. 19789387_SHP-1 is phosphorylated in a dynamic fashion after endorepellin stimulation. It is an essential mediator of endorepellin activity. A novel functional interaction between the integrin alpha2 subunit & SHP-1 is described. 19838216_Data show that SHP-1 knockdown increases p27stability, decreases the CDK6 levels, inducing retinoblastoma protein hypophosphorylation, downregulation of cyclin E and thereby a decrease in the CDK2 activity. 19874234_SHP-1 plays a minor role in determining autoimmune hemolytic anemia and its expression is upregulated in monocytes from these patients. 19950550_As2O3 can effectively cause demethylation and inhibit the growth of tumor by reactivating the SHP-1 gene transcription. 20068065_Plumbagin inhibits STAT3 activation pathway through the induction of SHP-1 and this may mediate the sensitization of STAT3 overexpressing cancers to chemotherapeutic agents. 20117097_SHP-1 plays an important role in airway mucin production through regulating oxidative stress. 20130595_Forced expression of SOCS3 and SHP-1 inhibits IFN-alpha signaling in psoriatic T cells. 20196786_5-aza-dc can induce SHP1 expression and inhibit JAK2/STAT3/STAT5 signalling 20351292_TonEBP/OREBP is extensively regulated by phosphatases, including SHP-1, whose inhibition by high NaCl increases phosphorylation of TonEBP/OREBP at Y143, contributing to the nuclear localization and activation of TonEBP/OREBP 20398180_These results suggest that calpain-dependent cleavage of SHP-1 and SHP-2 may contribute to protein tyrosine dephosphorylation in Jurkat T cell death induced by Entamoeba histolytica. 20424160_Results support the notion that the tumor suppressor effects of SHP1 on NPM-ALK are dependent on its ability to bind to this oncogenic protein. 20687222_SHP-1 may be a therapeutic target in prostate cancer, even when there is an IL-6-related growth advantage. 20696858_SHP-1 has disparate effects on subpopulations of responding CD8 T lymphocytes, reducing the number of short-lived effector cells generated without affecting the size of the memory precursor effector cell pool that leads to long-term memory formation. 20840866_SHP-1 negatively controls tyrosine phosphorylation of beta-catenin, thus inhibiting its association with TATA-binding protein and promotes beta-catenin degradation into the proteasome through a GSK3beta-dependent mechanism. 21291405_REVIEW: role of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 on cell-cycle regulation and its possible roles in tumour onset and progression 21357539_Transgenic SHP-1 inhibits signaling through multiple receptors and regulates NF-kappaB and transcription factor activator protein (AP)-1 signaling in dendritic cells. 21406173_an alteration in PTPN6/SHP1 may contribute to neutrophilic dermatoses 21465528_Crystal structure of human protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in the open conformation 21505184_Immunoreceptor-tyrosine-based-activation-motifs suppressive signals subvert the activating function of rafts to promote incorporation of receptors into supramolecular domains where signaling molecules are deactivated by SHP-1. 21505186_Inhibitory ITAM signaling traps activating receptors with the phosphatase SHP-1 to form polarized 'inhibisome' clusters. 21536801_Data indicate that CD300F is an active regulator of TLR-mediated macrophage activation through association with SHP-1 involving MyD88 and/or TRIF. 21604205_SHP-1 is expressed significantly higher in multisystem than single-system Langerhans cell histiocytosis 21719561_in serum- or IGF-1-stimulated breast cancer MCF-7 cells, JNK induces SHP1 expression through the binding of AP-4 and RFX-1 transcription factors to the epithelial tissue-specific SHP1 promoter. 21799016_SHP-1 antagonizes the action of receptor and non-receptor-tyrosine kinases on GIV and down-regulates the phospho-GIV-PI3K-Akt axis of signaling. 21806449_impaired signaling is associated with enhanced phagocytosis in neonatal monocyte-derived macrophages 21818116_data demonstrate that constitutive activation of STAT3 in Sezary syndrome is not due to the loss of SHP-1, but is mediated by constitutive aberrant activation of JAK family members 21821701_SHP-1 could be a new biologic indicator at baseline of IMA sensitivity in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. 21900501_These findings showed a novel role for SHP-1 in the regulation of Akt activity through the modulation of the ghrelin/GHSR1a system signaling 21964525_Methylation at the SHP-1 promoter in plasma is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 22043923_regulation of the TLR3/TRIF-mediated pathway required the combined action of SHP-1 and SHP-2, which could be accomplished by CD300f but not CD300a. 22180308_Data show that silencing of SHP-1 by RNA interference abolished the effects of dovitinib on p-STAT3, indicating that SHP-1, a protein tyrosine phosphatase, mediates the effects of dovitinib. 22210881_Data show that that SPL/RGS/SHP1 complexes are present in resting platelets where constitutive phosphorylation of SPL(Y398) creates an atypical binding site for SHP-1. 22258937_it is indicated that the SHP-1 methylation plays important role in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome via activating the JAK/STAT pathway probably 22371396_SHP-1 plays a critical role in abrogating M. pneumoniae-induced IL-8 production in nonasthmatic airway epithelial cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt and NF-kappaB activity, but it is defective in asthma. 22458809_Studies indicate that CD45, nonreceptor SH2 domain-containing PTP-1 (SHP-1) and PEST domain-enriched tyrosine phosphatase (PEP) are expressed at elevated levels in immune cells and play essential roles in T cell homeostasis. 22458980_Increased SHP-1 promoter methylation may relate in part to decreased SHP-1 expression and increased leukocyte-mediated inflammation in multiple sclerosis. 22488585_PTPN6 epigenetic silencing was recurrent in primary effusion lymphoma & diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, with a higher prevalence in the non-germinal centre subtype. It was associated with the activation of the Jak-Stat pathway. 22539788_Mice lacking protein tyrosine phosphatase Shp1 specifically in dendritic cells (DCs) develop splenomegaly associated with more CD11c+ DCs. 22589543_LST1 is expressed specifically in leukocytes of the myeloid lineage, where it localizes to the tetraspanin-enriched microdomains and it binds SHP-1 and SHP-2 phosphatases. 22730659_Abnormal methylation of SHP-1 gene promoter might have tentative role in the pathogenesis and progression of myelodysplastic syndrome. 22738830_IFN-beta and IFN-gamma/TNF-alpha decrease erythrophagocytosis by human monocytes in vitro, and this effect does not apparently require an increase in SIRP-alpha or SHP-1 expression. 22797910_Data suggest that protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 6 (SHP-1) may interact with EGF receptor (EGFR) to inhibit proliferation. 22960265_This study is the first to identify and define an interaction between SHP-1 and an SH3 domain-containing protein. Our findings provide an alternative way that SHP-1 can be linked to potential substrates. 23074279_Data show that TIMP-2-mediated inhibition of vascular endothelial cell permeability involves an integrin alpha3beta1-Shp-1-cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin cytoskeletal association. 23391724_The global role of SHP-1 in regulating CD8 positive T cell activation. 23406209_These results suggest the involvement of the ZAP70 and PTPN6 genes in the genetic component conferring a general susceptibility to Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, respectively. 23729600_Data suggest growth retardation in idiopathic short stature is related to delayed activation of JAK2 (Janus kinase 2) by PTP1B (protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 1) and SHP1 in response to GH/GHR (growth hormone/GH receptor) signaling. 23766558_The endothelial tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 plays an important role for vascular hemostasis in vivo, which is crucial in TNF alpha -induced endothelial inflammation. 23824557_A high level of SHP1P2 methylation of hilar lymph nodes from stage I NSCLC patients is associated with early relapse of disease. 23842094_SHP1 decreases the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells through affecting cell cycle distribution 23948750_results strongly suggest that expression of NTRK1-pY674/pY675 together with wild-type TP53 and low levels of PTPN6 expression are predictors of improved disease-free survival in breast cancer 23979523_studies have uncovered novel epigenetic mechanisms of PTPN6 suppression and suggest that PTPN6 may be a potential target of epigenetic therapy in DLBCL. 24100145_study identified novel SHP-1 transcripts in epithelial cancer cells; each product of ORF SHP-1 transcripts has phosphatase activity and isoforms with an N-SH2 deletion have increased phosphatase activity and novel protein-protein interactions; study documents utilization of promoter 2 by SHP-1 transcripts and a noncoding transcript in epithelial cells 24510345_PTPN6 expression may be a factor contributing to poor survival for anaplastic glioma patients. 24587194_hERG and hEAG channels are regulated by Src and by SHP-1 tyrosine phosphatase via an ITIM region in the cyclic nucleotide binding domain. 24647617_decreased expression levels of SHP-1 caused by aberrant promoter hypermethylation may play a key role in the progression of CML by dysregulating BCR-ABL1, AKT, MAPK, MYC and JAK2/STAT5 signaling. 24793756_SHP-1 expression ws lower in PBMCs from unmedicated schizophrenics. The promoter region was hypermethylated. Silencing SHP-1 induced IKK/NF-kB and pro-inflammatory cytokines. SHP-1 expression may explain 30% of the clinical negative symptom variance. 24824657_We demonstrated that the association and oxidation of c-Src and SHP-1 by ROS are key steps in enhancing OC survival, which are responsible for increased bone loss when ovarian function ceases. 24886428_A PKC-SHP1 signaling axis desensitizes Fcgamma receptor signaling by reducing the tyrosine phosphorylation of CBL and regulates FcgammaR mediated phagocytosis. 24952874_transcription factor RFX-1 regulates SC-2001-mediated SHP-1 Phosphatase transcription in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 25619838_SHP-1 is a potent suppressor of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25635370_SHP-1(I) presented concordance between unmethylated promoter region and tumor for breast or prostate. 25785436_Results show that dissociation of SHP-1 from spinophilin is followed by an increase in the binding of spinophilin to PP1. 25799543_Data show that SHP-1 promotes HIF-1alpha degradation under hypoxic conditions leading to a reduction in VEGF synthesis and secretion and impairing epithelial cells proliferation. 25824741_Inactivation of SHP1 is associated with myeloproliferative neoplasm. 25897665_Soluble egg antigens glycans are essential for induction of enhanced SOCS1 and SHP1 levels in dendritic cells via the mannose receptor. 25962492_Phosphorylation of ATR and CHK1 did not show significant differences in the three cell groups. Overexpression of SHP-1 in the CNE-2 cells led to radioresistance and the radioresistance was related to enhanced DNA DSB repair. 26081980_miR-4649-3p is downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines accompanied with SHP-1 upregulation. 26215037_SHP-1 has a critical role in radioresistance, cell cycle progression, and senescence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells 26334669_cAMP signalling of Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin through the SHP-1 phosphatase activates the BimEL-Bax pro-apoptotic cascade in phagocytes. 26373709_This study also found no correlation of SHP-1 expression at diagnosis with response to treatment, although a trend for lower SHP-1 expression was noted in the very small non-responders' group of the 3-month therapeutic milestone. 26473472_MiR-378g enhanced radiosensitivity partially by targeting SHP-1 in NPC cells. 26508024_Overexpression of SHP1 downregulates the JAK2/STAT3 pathway to modulate various target genes and inhibit cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer cells. 26565811_N225K and A550V PTPN6 mutations cause loss-of-function leading to JAK3 mediated deregulation of STAT3 pathway and uncover a mechanism that tumor cells can use to control PTPN6 substrate specificity. 26597461_Data demonstrate for the first time that SHP1 methylation has high specificity for diagnosis of endometrial carcinoma, while CDH13 promoter methylation plays a role in the earlier stage. 26679051_A combination of sorafenib and SC-43 is a synergistic SHP-1 agonist duo which reduces tumor size and prolonged survival time. 26742467_SYK, LYN and PTPN6 were markedly elevated in atherosclerotic plaques of carotid atherosclerosis patients. 26781335_Quinalizarin enhances radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells partially by suppressing SHP-1 expression 26878112_In addition to their role in NK cell activation by hematopoietic cells, the SLAM-SAP-SHP1 pathways influence responsiveness toward nonhematopoietic targets by a process akin to NK cell 'education'. 26959741_we demonstrated that SHP-1 dephosphorylates PKM2Y105 to inhibit the Warburg effect and nucleus-dependent cell proliferation, and the dephosphorylation of PKM2Y105 by SHP-1 determines the efficacy of targeted drugs for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment 27216862_this review focalizes upon the implication of SHP-1 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders, and addresses developing therapeutic strategies targeting SHP-1 27364975_Data suggest that SHP-1/p-STAT3/VEGF-A axis is a potential therapeutic target for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). 27572445_The results reveal that SHP1 is the long-sought phosphatase that can antagonize Helicobacter pylori CagA. Augmented Helicobacter pylori CagA activity, via SHP1 inhibition, might also contribute to the development of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer. 27585521_Hyperglycemia induces SHP-1 promoter epigenetic modifications, causing its persistent expression and activity and leading to insulin resistance, podocyte dysfunction, and DN. 27644671_study evaluated SHP1-P2 methylation levels in the lymph nodes of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients; hypothesized that SHP1-P2 methylation levels would be higher in metastatic lymph nodes 27814644_Analyzed gene expression profiles of monocytes from symptomatic congestive heart failure patients; there is a down-regulation of the phosphatase SHP-1 which induces a significant activation of TAK-1/IKK/NF-kB signaling. 27959415_Low SHP1 expression is associated with primary central nervous system lymphoma. 28182003_luteolin inhibited STAT3 activation through disrupting the binding of HSP-90 to STAT3, which promoted its interaction to SHP-1. 28187032_the absence of SHP-1 in immunohistochemical analysis might serve as a marker of poor prognosis for a subset of high-grade endometrial cancer. 28210822_SHP1 DNA methylation in in patients with B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma 28250424_we found that THEMIS directly regulated the catalytic activity of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. 28295507_crocin induced the expression of SHP-1, a tyrosine protein phosphatase, and pervanadate treatment reversed the crocin-induced downregulation of STAT3, suggesting the involvement of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. 28369102_Results provide evidence that repression of SHP-1, SHP-2 and SOCS-1 gene expression in patient plasma cells supports the constitutive activation of the JAK/STAT3 pathway and probably leads to higher degrees of bone marrow invasion. 28376405_these results indicate that DNMT1 mediates aberrant methylation and silencing of SHP-1 gene in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells 28378014_Biophysical assay for tethered signaling reactions reveals tether-controlled activity for the phosphatase SHP-1. 28416389_The Shp1 functions as a positive regulator and acts in a novel mechanism through promoting EGFR protein expression in human epithelial cells. 28465325_These findings show a novel role for Shp-1 in the regulation of IEC growth and secretory lineage allocation, possibly via modulation of PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling pathways. 28480959_PTPN6 is associated with progression of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Low expression level of PTPN6 was associated with DNA methylation and regulated by histone acetylation 28533521_this study provided strong in vivo and cellular evidences that hepatocyte SHP-1 plays a cardinal role in the production of inflammatory mediators that contribute to endotoxemia. 28606940_the role of Shp1 in myeloid cells and how its dysregulation affects immune function, which can impact human disease. 28692056_These findings have provided first lines of evidences that PDZK1 expression is negatively correlated with SHP-1 activation and poor clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) . PDZK1 was identified as a novel tumor suppressor in ccRCC by negating SHP-1 activity 28790195_these data highlight a signaling pathway in which SHP-1 acts through CrkII to reshape the pattern of Rap1 activation in the immunological synapse. 28978467_M. tuberculosis-initiated human mannose receptor signaling regulates macrophage recognition and vesicle trafficking by gamma Fc receptors, Grb2, and SHP-1. 29058147_observations suggest that Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) has the ability to induce host PTPN6 expression, and induction of PTPN6 may favour the attenuation of the pro-inflammatory immune response of the host, which is otherwise detrimental for the survival of CHIKV and establishment of an infection 29288235_Data suggest that targeting the ring finger 6 protein (RNF6)/protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 (SHP-1)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) axis provides a potential therapeutic option for RNF6-amplified tumors. 29298416_FcgammaRIIB expressed in neurons functions as a receptor for alpha-syn fibrils and mediates cell-to-cell transmission of alpha-syn. SHP-1 and 2 are activated downstream by alpha-syn fibrils through FcgammaRIIB and play an important role in cell-to-cell transmission of alpha-syn. 29449322_actomyosin retrograde flow controls the immune response of primary human Natural killer cells through a novel interaction between beta-actin and the SH2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1), converting its conformation state, and thereby regulating Natural killer cell cytotoxicity. 29466992_Our data revealed that HNF1A-AS1 is a direct transactivation target of HNF1alpha in HCC cells and involved in the anti-HCC effect of HNF1alpha. HNF1A-AS1 functions as phosphatase activator through the direct interaction with SHP-1. 29776962_The nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma 29931651_PTPN6 is required for the cell-surface expression of TRPM4 channels in HEK293 cells. 29961065_This study demonstrates that VB inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion while promoting apoptosis via SHP-1 activation and inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation. 30112836_Data show that E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF38 (RNF38) interacts with the nonreceptor tyrosine phosphatase SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP-1) and induces the polyubiquitination of SHP-1, which leads to destabilization of SHP-1. 30420593_These findings support the notion that control of pSTAT3 in TCL tumors is complex and involves epigenetic silencing of the tyrosine phosphatase PTPN6. 30470842_Study demonstrates that miR-152 can inhibit lymphoma growth via suppressing DNMT1-mediated silencing of SOCS3 and SHP-1. These data demonstrate a new mechanism for the development of NHL. 30674631_HoxA10 interacts with p38 MAPK to repress the activation of p38 MAPK and STAT3 and recruits and facilitates SHP-1 to catalyze the dephosphorylation of p38 MAPK and STAT3. 30764849_SHP1 and SHP2 are relevant mediators of differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia cells 30816454_PTPN6 may serve as tumor suppressor gene in ESCC and inhibit esophageal cancer cell proliferation and invasion. The P2 is frequently methylated in esophageal cancer cells and ESCC tissues, and this may be one of the epigenetic mechanisms implicated in PTPN6 silencing in ESCC. 31000475_A rare in-silico-predicted damaging variant (Ala455Thr) in the protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 6 (PTPN6) gene is shown to cause early-onset emphysema. 31427082_The Ang1 induced the dissociation of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 from the Tie2 receptor and increased the binding of SHP-1 to JAK1, JAK2, and STAT3, which are IL-6 downstream signaling proteins. 31550807_revealed that the SHP-1 methylation rate was positively correlated with the positive rate of STAT3 phosphorylation 31836852_SHP1 regulates a STAT6-ITGB3 axis in FLT3ITD-positive AML cells. 32004441_synapse formed by 4-1BB-encoding CAR recruits the THEMIS-SHP1 phosphatase complex that attenuates CAR-CD3zeta phosphorylationk 32343611_Decrease in SHP-1 enhances myometrium remodeling via FAK activation leading to labor. 32390601_Immunosuppressive receptor LILRB1 acts as a potential regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrating with SHP1. 32437509_PD-1 and BTLA regulate T cell signaling differentially and only partially through SHP1 and SHP2. 32454905_The Analysis of PTPN6 for Bladder Cancer: An Exploratory Study Based on TCGA. 32674045_Correlation between SHP-1 and carotid plaque vulnerability in humans. 32779804_SHP-1 suppresses the antiviral innate immune response by targeting TRAF3. 32917126_Vitamin D3-VDR-PTPN6 axis mediated autophagy contributes to the inhibition of macrophage foam cell formation. 33133093_Shp1 Loss Enhances Macrophage Effector Function and Promotes Anti-Tumor Immunity. 33264612_SHP-1 Regulates Antigen Cross-Presentation and Is Exploited by Leishmania to Evade Immunity. 33615510_PTPN6 promotes chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells via inhibiting the SP1/MAPK signalling pathway. 33639070_SHP1 Decreases Level of P-STAT3 (Ser727) and Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. 33736531_The role of Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 hypermethylation in the classification of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and its association with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation in skm-1 cells. 33990399_The Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-1 (PTPN6) but Not CD45 (PTPRC) Is Essential for the Ligand-Mediated Regulation of CD22 in BCR-Ligated B Cells. 34088320_The phosphatase Shp1 interacts with and dephosphorylates cortactin to inhibit invadopodia function. 34535085_Circular RNA-0007059 protects cell viability and reduces inflammation in a nephritis cell model by inhibiting microRNA-1278/SHP-1/STAT3 signaling. 34910686_METTL14 benefits the mesenchymal stem cells in patients with |
ENSMUSG00000004266 |
Ptpn6 |
1032.094052 |
2.3326920843 |
1.221996 |
0.060810256 |
404.629732 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000540896906615433374500485953083301371762765215690871857521168062801000539441195050971157504555045071513629691349708558510043429237645685222260458011834859547563113917904368538561483817889560480494526531982048589412322018091239250736634858185 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000204708675426764015848500891546501524524855451196068072883673762594479463194498514309128694993782927837827715122308990918868437862672161360445850364888988528144204862862231064295227741701720500767825174978954660390175618323027606493269558996 |
Yes |
No |
1465.7538913 |
49.2121376 |
632.5593854 |
16.9316078 |
| ENSG00000111711 |
51026 |
GOLT1B |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3E0 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles with the Golgi complex. |
Acetylation;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Involved in positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51026; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] |
|
ENSMUSG00000030245 |
Golt1b |
490.409487 |
2.3448220353 |
1.229478 |
0.074214299 |
278.105876 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001942510647993131797186027339035094380683904108160207314453902424899928111073021700597926071470416679943537878597961178055689060150973206024452312027166157263474710603645689843688160181045532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000514747884459221307060154155211993249550459482501130819069581007363142832288888576295414491125285046841910272564940641471374466653859192028852388607347134036329450168523180764168500900268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
683.5319974 |
41.0829938 |
293.9741550 |
13.5275838 |
| ENSG00000111732 |
57379 |
AICDA |
protein_coding |
Q9GZX7 |
FUNCTION: Single-stranded DNA-specific cytidine deaminase. Involved in somatic hypermutation (SHM), gene conversion, and class-switch recombination (CSR) in B-lymphocytes by deaminating C to U during transcription of Ig-variable (V) and Ig-switch (S) region DNA. Required for several crucial steps of B-cell terminal differentiation necessary for efficient antibody responses (PubMed:18722174, PubMed:21385873, PubMed:21518874, PubMed:27716525). May also play a role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression by participating in DNA demethylation (PubMed:21496894). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18722174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21385873, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21496894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21518874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27716525}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a RNA-editing deaminase that is a member of the cytidine deaminase family. AICDA is specifically expressed and active in germinal center-like B cells. In the germinal center, AICDA is involved in somatic hypermutation, gene conversion, and class-switch recombination of immunoglobulin genes. An epigenetic role in neoplastic transformation and lymphoma progression has been experimentally ascribed to AICDA using mouse models. Defects in this gene are the cause of autosomal recessive hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome type 2 (HIGM2). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:57379; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cytidine deaminase activity [GO:0004126]; deoxycytidine deaminase activity [GO:0047844]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cytidine to uridine editing [GO:0016554]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA cytosine deamination [GO:0070383]; DNA demethylation [GO:0080111]; isotype switching [GO:0045190]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0090310]; negative regulation of single stranded viral RNA replication via double stranded DNA intermediate [GO:0045869]; negative regulation of transposition [GO:0010529]; regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication [GO:0033262]; somatic diversification of immunoglobulins [GO:0016445]; somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes [GO:0016446] |
11823785_required for somatic hypermutation in the centroblast-like Ramos cells; sufficient to induce somatic hypermutation in hybridoma cells, which represent a later stage of B-cell differentiation that does not normally undergo SHM 12097915_AID mutates E. coli suggesting a DNA deamination mechanism for antibody diversification. 12114543_Internal IgH class switch region deletions are position-independent and enhanced by expression 12202747_Somatic hypermutation of the AID transgene in B and non-B cells 12511417_AID is highly regulated during normal B-cell development & is constitutively expressed in human germinal center B-NHL & in subsets of nongerminal center B-NHL. This constitutive expression may cause illegitimate recombination & somatic mutation in B-NHL. 12521993_Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells that express this enzyme display dissociation between class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation 12715918_has the function to induce spontaneous IgM production in B cells 12799424_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase causes transcription-dependent, strand-biased C to U deaminations. 12855567_data suggest that AID-mediated DNA alterations may occur in a variably sized, minor subset of B-CLL cells at any given time. 12873980_Expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase is confined to B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas of germinal-center phenotype. 12928399_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase plays a crucial role in the induction of DNA breakage during immunoglobulin class switch recombination. 12973929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14536088_there is an essential role for the C-terminal domain of AID in CSR that is independent of its cytidine deaminase activity and that is not required for either gene conversion or somatic hypermutation 14551145_AID transcripts, including a splice variant, were common to both unmutated or mutated VH genes in mantle cell lymphoma. 14769937_AID is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein with a bipartite nuclear localization signal and a nuclear export signal in its N and C termini, respectively 14990977_AID expression was associated with the ongoing mutation in follicular lymphoma (FL) fresh cells. Results suggest the switch off of AID expression may start in the B-lineage differentiation stage counterpart of FL after optimizing somatic hypermutation 15061213_expression of AID in 15 Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines by RT-PCR 15087440_Activation-induced cytosine deaminase (AID) is actively exported out of the nucleus but retained by the induction of DNA breaks 15148397_results suggested both AID and APOBEC-1 are equally likely to bind single-stranded DNA or RNA, which has implications for the identification of natural AID targets 15182647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15195091_separate domains of AID interact with specific cofactors to regulate these two distinct genetic events in a target-specific way 15304391_AID protein is specifically expressed in normal and transformed germinal center B cells 15371439_wild type AID retains its specificity for mutated hot spot motifs within the confines of a moving transcription bubble while introducing clusters of multiple deaminations predominantly on the nontranscribed strand 15372234_novel mutation found in the gene encoding for activation-induced cytidine deaminase in a Tunisian family with hyper-IgM type 2 syndrome 15448152_Aid and perhaps some of its family members may have roles in epigenetic reprogramming 15593119_AID overexpression by itself does not automatically lead to the onset of a mutator phenotype. 15613101_expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia L2 with t(14;18)(q32;q21) 15944282_Direct evidence is presented for the DNA deamination from Escherichia coli expressing AID; uracils are preferentially generated at cytosines in the nontranscribed strand during transcription. 15949042_AID-mediated deamination of DNA is a major cause of mutations at G-C base pairs in immunoglobulin genes during somatic hypermutation. Its intrinsic substrate specificity is a primary determinant of mutational hotspots at G-C base pairs during SHM. 16122802_AID can interact with MDM2, an oncoprotein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and targets p53 for nuclear export and degradation. 16269615_interfollicular large B cells and AID-expressing B lymphocytes of the thymic medulla could give rise to mature B-cell malignancies. 16314506_Somatic hypermutation on both DNA strands is the natural outcome of AID action on a transcribed gene. 16387847_control of T cell-dependent immune responses may be modulated, via AID, by signals that activate protein kinase A 16439679_The distribution of nuclear AID is consistent with the topography of somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination in activated B cells. 16541139_The AID expression and ASHM are associated with higher-grade transformation of CLL and provide further evidences that AID expression and ASHM may be activated during the clonal history of B-cell lymphomas. 16624806_review of the role of AICDA in producing high affinity isotype-switched antibodies [review] 16705187_AID binds DNA exposed by the transcribing polymerase, implicating the polymerase itself as the vehicle which distributes AID on DNA as it moves away from the promoter. 16785531_Features of activation-induced deaminase (AID) mapping within the noncatalytic domain, but outside the chromosome region maintenance 1-dependent nuclear export signal at the C-terminus, influence its function. 16999936_APOBEC3G is not a nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling protein like APOBEC-1 and AID 17060445_AID may persist on immunoglobulin and other target sequences after deamination, possibly acting as a scaffolding protein to recruit other factors 17066440_Findings suggest that the aberrant expression of AID is observed in human hepatocytes with several pathological settings, including chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. 17132718_cells may be the founder cells of the germinal center reaction (a pro-GC cell) and may be the normal counterpart of the mantle cell lymphoma cell 17161027_AID is alone unable to act processively on any of a number of DNA substrates 17485517_AID is a BCR-ABL1-induced mutator in Philadelphia chromosome(+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells, which may be relevant to the particularly unfavorable prognosis of this leukemia subset. 17638864_primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL), an immunoglobulin (Ig)-negative lymphoma that possesses hypermutated, class-switched Ig genes, expresses high levels of AID with an intact primary structure but does not do class switch recombination 17878393_AID retains its exclusive association with numerous, residual germinal centers in parotid Sjogren's syndrome-MALT lymphomas, whereas neoplastic marginal zone-like B cells are consistently AID negative 18213388_generation of phase 1 mutations is not a prerequisite for the expression of phase 2 mutations 18306229_The proinflammatory cytokine-induced aberrant production of AID might link bile duct inflammation to an enhanced genetic susceptibility to mutagenesis, leading to cholangiocarcinogenesis 18329947_aberrant AID expression can be triggered by several pathogenic factors, including Helicobacter pylori infection & proinflammatory cytokines, in human epithelial cells, but AID expression is absent in those cells under physiologic conditions[review]. 18390709_results obtained with activated CD19(+) B cells show that the expression of E47, activation-induced cytidine deaminase, and Iggamma1 circle transcripts progressively decrease with age 18391550_Aberrant expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase may contribute to the development of gastric cancers and induce p53 nuclear expression 18417471_analysis of the effect of phosphorylation and phosphorylation-null mutants on the activity and deamination specificity of activation-induced cytidine deaminase 18722174_The results, therefore, identify residues in AID involved in its in vivo targeting and suggest they might act through interaction with CTNNBL1, giving possible insight into the linkage between AID recruitment and target-gene transcription. 18757891_Results identify non-conservative homologous recombination as a novel DNA transaction pathway promoted by activation-induced cytidine deaminase. 18760480_AID and Ung generate staggered double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) not only by cleaving intact double-strand DNA, but also by processing blunt DSB ends. 18772346_AID can cause single-base substitutions or multiple clustered mutations depending on the transcriptional activity of T7 RNA polymerase. 18776814_expressed in bone marrow infiltrates of malignant lymphoma 18940926_results lead to a model for exonuclease 1 function in class switch recombination in which cleavage at activation-induced deaminase (AID)-initiated nicks produces gaps that become substrates for further attack by AID and subsequent repair 19017972_V(H)4 replacement in preimmune human B cells is mediated by an AICDA-independent mechanism resulting from inefficient but selective RAG activity. 19023113_in the absence of CD40-CD154 interactions, there is a marked reduction in SHM and, specifically, mutations of AICDA-targeted G residues in RGYW motifs along with a decrease in transversions normally related to UNG2 activity. 19139166_Estrogen regulates gene expression of AID at the transcriptional level. 19196959_class switch recombination activity of AID requires an ACF-like cofactor that specifically interacts with the carboxy-terminal domain of AID 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266080_sensitive gel electrophoresis (CSGE) and sequencing analysis of AICDA coding sequences demonstrated sequence heterogeneity due to 5923A/G and 7888C/T polymorphisms, but did not reveal any novel mutation that might explain the selective IgE deficit. 19309412_The expression of activation induced cytidine deaminase in follicular lymphoma is independent of prognosis and stage. 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19363484_HoxC4 directly activates the Aicda promoter 19380635_AID acts processively in naked DNA and DNA organized within transcribed nucleosomes. 19412186_Two other mechanisms involved in controlling AID subcellular localization, are identified. 19443686_AID targeting of hot and cold spots is a key part of the mutation process, our results suggest that the sequence environment plays an equally important role 19561087_When recognition loop of 9-11 amino acids is grafted from the donor APOBEC3F or 3G proteins into the acceptor scaffold of AID, the mutational signature of AID changes toward that of the donor proteins. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19575287_in hyper-IgM syndrome, one novel AICDA mutation (E122X) was detected 19578742_abnormal over-expression of GANP together with AID might be associated with rigorous DNA damage, potentially causing the malignant development of Cholangiocarcinoma (CCAs) during long-term inflammation. 19667096_Both mice and humans share a latent, AID-dependent pathway for the preimmune diversification of B lymphocytes. 19703021_The higher levels of AID expression in B cells of Reumatoid Arthritis patients correlate with the higher levels of T helper cell cytokines IFN-gamma and IL-17. 19732723_ACIDA promotes B lymphoid blast crisis and drug resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. 19734146_SLIP-GC is a replication-related protein in germinal center B cells whose reduction is toxic to cells through an AICDA-dependent mechanism. 19741596_However, no activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) expression (an absolute requirement for class switching) was detected in lamina propria 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19859091_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19898425_AID expression is an indicator of an unfavorable prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma patients 19911124_Studies indicate the APOBEC family consists of 11 members: APOBEC-1 (Apo1), APOBEC-2 (Apo2), activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID), APOBEC- 3A, -3B, -3C, -3DE, -3F, -3H (Apo3A-H) and APOBEC- 4 (Apo4). 19966806_Aicda is regulated by the balance between B cell-specific and stimulation-responsive elements and ubiquitous silencers. 20027182_data provide new evidence that mammalian AID is required for active DNA demethylation and initiation of nuclear reprogramming towards pluripotency in human somatic cells 20048284_Altering the spectrum of immunoglobulin V gene somatic hypermutation by modifying the active site of AID. 20117026_Expression of at least one AID-mRNA isoform predominated among mutated IgG vs. mutated IgMD. AID splice variants may inhibit somatic hypermutation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells of the unmutated subtype. 20118283_Findings underscore that AID splice variants are unlikely to have preservation of catalytic activity. 20233972_High expression of AID and active class switch recombination might account for a more aggressive disease in unmutated CLL patients: link with an activated microenvironment in CLL disease. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237507_Higher expression levels of activation-induced cytidine deaminase distinguish hairy cell leukemia from hairy cell leukemia-variant and splenic marginal zone lymphoma. 20338830_the sequence selectivity of APOBEC family of enzymes 20373075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20373075_The researchers found no evidence of an association between the AICDA 7888 C/T polymorphism and the risk of gastric atrophy or gastric neoplasms in the study group. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20491788_The ectopic expression of AICDA in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLS) causes TP53 somatic mutations & dysfunction, leading to acquisition of tumour-like properties by RA-FLS. 20507984_GANP may serve as an essential link required to transport AID to B-cell nuclei and to target AID to actively transcribed IgV regions 20637757_AID-mediated genotoxic effects appear to occur frequently at the CDKN2b-CDKN2a locus and contribute to malignant transformation of the gastric mucosa 20729863_14-3-3 proteins specifically bound 5'-AGCT-3' repeats, were upregulated in B cells undergoing class switch DNA recombination (CSR) and were recruited with AID to the switch regions that are involved in CSR events 20855884_Esr1 bind to and activate the HOXC4 promoter to potentiate HoxC4-mediated AID induction, immunoglobulin class switch and somatic hypermutation. 20864035_Exogenous and intrinsic AID-induced DNA strand breaks in B-cells activate ATM, which signals through an LKB1 intermediate to inactivate CRTC2, resulting in repression of germinal center B-cell differentiation, while opposing lymphomagenesis. 20878190_findings suggest that pro-inflammatory cytokine-mediated aberrant expression of AICDA in colonic epithelial cells plays a role as a genotoxic factor that enhances genetic instability during chronic colonic inflammation, leading to colorectal cancer 20927319_Low Cytidine Deaminase is associated with gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. 20974684_The constitutive expression of AID in ATL cells can be speculated to result from mutations induced by the Tax-activated AID and/or other Tax-associated mutagenic mechanisms 21041454_Hsp90 inhibition provides the first pharmacological means to down-regulate AID expression and activity. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21109971_AID and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in cancer cells may be modified by epigenetic mechanisms 21133730_AID overexpression promotes chromosomal abnormalities and is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression 21255825_Study implicates the RNA exosome, a cellular RNA-processing/degradation complex, in targeting AID to both DNA strands. 21268017_Ig class-switch recombination, as well as the stabilisation of AID, depend on an interaction between the AID C-terminal decapeptide and factor(s) additional to Crm1. 21290192_High expression and mutation-inducing activity of AID is associayed with human lung cancer. 21570118_Activation-induced deaminase (AID) expression is correlated with Bcr-Abl expression in chronic myelocytic leukemia-B-lymphoid blast cells. 21659520_Phosphorylation directly regulates the intrinsic DNA cytidine deaminase activity of activation-induced deaminase and APOBEC3G protein 21700883_identified a major and previously unsuspected role for AID in the removal of developing autoreactive B cells 21831295_Findings demonstrate that miR-93 and miR-155 constitutively suppress AID translation in MCF-7 cells, suggesting widespread roles for these miRs in preventing genome cytidine deaminations, mutagenesis, and oncogenic transformation. 21984922_Analysis of co-regularities and creation of AID-associated functional network gives an integrated view of biological processes and might be further applied to assess role of altered AID expression in etiology of other diseases. 22034886_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with inflammation in ulcerative colitis, whereas it may not specifically contribute to carcinogenesis 22080610_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase -induced decrease in Top1 is critical for somatic hypermutation. 22168746_AID may act as a negative regulator of cell survival in follicular lymphoma when sufficient c-myc is expressed 22198384_Data suggest that AID may generate DNA damage with variable efficiencies in different organisms, identify residues critical in regulating AID activity, and provide insights into the evolution of the APOBEC family of enzymes. 22234692_Data show that interaction between myeloma and dendritic cell (DC), but not monocytes, leads to rapid induction of the genomic mutator activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and AID-dependent DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in myeloma cell. 22308462_Along with known AID targets, this screen identified a set of unique genes (SNHG3, MALAT1, BCL7A, and CUX1) and confirmed that these loci accumulated mutations as frequently as Ig locus after AID activation 22363466_Lysine modification may represent a novel level of AID regulation. 22391874_Hypermutable bases (both paired and unpaired) are made accessible to activation-induced cytidine deaminase in stabilised DNA secondary structures formed with increasing transcription levels 22446380_The data suggested that the present-day human APOBEC3B enzyme retained the nuclear import mechanism of an ancestral activation-induced cytosine deaminase during the expansion of the APOBEC3 locus in primates. 22466889_aberrant AID expression may play an important role in the dysplasia-carcinoma sequence in the oral cavity 22469133_Findings suggest that activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) plays an integral role in inflammation-associated carcinogenesis and is therefore a potential target molecule for the prevention and treatment of cancers. 22492685_An ortholog of AID was, evolutionarily, the first enzyme to generate acquired immune diversity by catalyzing gene conversion and probably somatic hypermutation. (Review) 22715099_A structural analysis is presented that shows how localized defects in different regions of AID can contribute to loss of catalytic function. 22798497_While APOBEC3A was a strong deaminator of both C and 5-methylcytosine, AID was much weaker in it's ability to deaminate this modified base. 22843687_Spt6 is a unique histone chaperone capable of regulating the histone epigenetic state of both AID targets and the AID locus. 22899287_We suggest that duodenal follicular lymphoma cells are in the memory B-cell stage, and require BACH2 instead of AID for ongoing mutation. 22962683_DNA sequence preference may serve as an additional layer of AID regulation by restricting its mutagenic activity to specific sequences, despite the observation that AID has the potential to access the genome widely. 22992148_report of two siblings of a Tajik family with a hyper-immunoglobulin M (HIGM) syndrome phenotype in which a novel missense mutation in the activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AICDA) gene was detected 23008333_Data show that activation-induced deaminase (AID) associates with RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 (PAF1) through its N-terminal domain. 23017209_RBM5 promotes exon 4 skipping of AID pre-mRNA by competing with the binding of U2AF65 to the polypyrimidine tract. 23071276_Data suggest that the production of fully functional activation-induced deaminase (AID) protein by IGHV-unmutated (U-CLL) and IGHV-mutated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (M-CLL) cells could be involved in clonal evolution of the disease. 23133680_LINE-1 retroelements are complexed and inhibited by activation induced cytidine deaminase 23166356_Among BCL6 validated targets, miR-155 and miR-361 directly modulate AID expression, indicating that via repression of these miRNAs, BCL6 up-regulates AID. 23190037_B cell defects, as measured by the autonomous AID reporter, in IBD patients contribute to reduced humoral responses to the influenza vaccine, as we have previously shown for elderly individuals. 23198547_H. pylori infection induces ectopic AID expression in the gastric mucosal cells via NFkappaB activation, resulting in various gene mutations and aberrations in the gastric mucosal cells leading to gastric cancer development. 23212122_a critical role for AID activity in the initiation of reprogramming to iPSCs. 23263985_AID enzymatic activity is important for the fragility at the the human bcl-2 major breakpoint region. 23277564_identify a unique cofactor, RING finger protein 126 (RNF126), verify its interaction by traditional techniques, and show that it has functional consequences as RNF126 is able to ubiquitylate activation-induced cytidine deaminase 23341589_C-to-T and G-to-A mutations accumulated in hepatitis B virus (HBV) nucleocapsid DNA when AICDA was expressed in HBV-replicating hepatic cell lines. 23363221_LMP1 induces AID up-regulation and genomic instability via Egr-1. 23399385_High levels of AID specifically increased mutations at A, but not T, leading to strand bias. 23408445_genetic polymorphisms in AICDA and CASP14 are associated with risk for brain tumor in Korean children. 23476051_Both WGCW/WRC and CpG/CGC breaks at BCL6 are most likely initiated by AID in germinal center B-cells, and their differential use suggests subtle mechanistic differences between Ig-BCL6 and non-Ig-BCL6 rearrangements. 23589568_This reveals a novel antineoplastic role of AID that can be triggered by inhibition of homologous recombination. 23593411_5-FC combined gene therapy with TNF-alpha and CD suicide gene should be an effective treatment on Laryngeal carcinoma. 23634222_Aberrant AID expression in the oral epithelium would contribute to the initiation of oral squamous cell carcinoma 23652018_GANP-mediated chromatin modification promotes transcription complex recruitment and positioning at immunoglobulin variable loci to favour AID targeting. 23662991_Results show that activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID) expression may be associated with deletions in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). 23731676_There was no significant association between the previously reported genetic variant of AICDA gene and the development of Common variable immunodeficiency or selective IgA deficiency 23803409_Two patients, sisters from a consanguineous family, were diagnosed with HIGM2 syndrome, and found to be homozygous for a transversion mutation. 23820005_aberrant AID expression triggers an auto-activation circuit to consolidate self-expression 23882083_Data indicate that knockdown of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) suppresses expression of several key epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) transcriptional regulators and increased methylation of CpG islands of these genes. 23942124_data suggest a role for nucleotide sugar pucker in explaining the molecular basis for AID's DNA selectivity and, more generally, suggest how other nucleic acid-modifying enzymes may distinguish DNA from RNA 24025329_proinflammatory cytokines IL-1/TNFalpha trigger a novel antiviral mechanism involving AID to regulate host cell permissiveness to HBV infection. 24244169_findings reveal additional functions for AID in innate immune defense against KSHV with implications for a broader involvement in innate immunity to other pathogens. 24349193_DNA repair pathways which are in vitro activated by AID-induced lesions are reminiscent of those found during AID-induced in vivo immunoglobulin diversification. 24351917_findings suggest that AID has a role in the development of oral epithelial dysplasia and promotes progression of oral cancer 24434356_AID physically associates with the major spliceosome subunits (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, snRNPs), as well as other essential splicing components, in addition to the transcription machinery. 24507160_[review] In a B cell that produces AID protein and undergoes mutation of the V regions of the expressed Ig heavy and light chain genes, only some of the transcription complexes initiating at the active V-region promoters are associated with AID. 24684646_analysis of a possible association between AID expression and BRAF mutation in melanoma 24923561_B cells hijack to supply ssDNA substrates for AID to mutate at immunoglobulin V regions during somatic hypermutation. 24973444_AID lacking the C terminus is impaired in its ability to recruit nonhomologous end joining repair factors, resulting in accumulation of double-strand breaks that undergo aberrant resection. 25099163_demonstrates that intensity of malaria transmission correlates with AID expression levels in the presence of Epstein-Barr virus 25154417_Results show that both AID mRNA levels and DNA-cytosine deamination activities follow the same general pattern of increase and decline after stimulation in the two genetic backgrounds. 25179679_data demonstrate that AID is active in CLL in vivo and thus, AID likely contributes to clonal evolution of CLL. 25237741_In yeast, AID and the catalytic domain of APOBEC3G preferentially mutate transcriptionally active genes within narrow regions, 110 base pairs in width, fixed at RNA polymerase initiation sites. 25483776_Study reports that the majority of detectable AID off-target activity in a variety of mouse and human lymphoid or nonlymphoid cell types occurs within focal regions of overlapping sense/antisense transcription within intragenic super enhancers. 25483777_AID activity and its relationship to chromosome folding and the B cell regulome was studied; find that AID-mediated lesions occur predominantly within B cell super-enhancers and regulatory clusters; further show that the structural and transcriptional features of these domains help explain AID tumorigenic activity in the B cell compartment of mice and humans. 25486549_Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)-induced mutagenic U:G mismatches in DNA may be a fundamental and common cause of mutations in B-cell malignancies. 25849121_These findings indicated that TNF-alpha-induced AID expression is involved with class switch recombination in cancer. 25902538_hnRNP K and hnRNP L may serve as A1CF-like cofactors in AID-mediated class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation 25912253_HSP90 inhibitors indirectly target AID in vivo 25990957_Surges in ERK activity induced by extracellular cues enhance Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization to generate protrusion power phases sufficient to promote sustained cell motility. 26077666_High expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 26113087_Data indicate that both the amount and intensity of the activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) protein expression increased with the progression from precancerous to cancerous lesions in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues. 26166388_The high levels of memory and activated B cells and follicular helper T cells were positively associated with the progression of immunoglobulin A nephropathy. This may be mediated by the overexpression of AID, which is potentially regulated by IL21. 26219420_aberrant expression of AID may reflect continuous B cell activation and sustained survival signals in HCV-related CV patients. 26223652_Data show that microRNAs miR-155 and miR-16 downregulate activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and transcription factor E47 in B Cells through binding of the 3'-untranslated regions. 26355458_identify AID derivatives that accelerate somatic hypermutation with minimal impact on viability, which will be useful tools for engineering genes and proteins by iterative mutagenesis and selection 26365193_DNA methylation dynamics of germinal center B cells are mediated by AID. 26398702_AICDA/APOBEC family of cytidine deaminases is significant in innate immunity, as it restricts numerous viruses, including HBV, through hypermutationdependent and independent mechanisms. (Review) 26537386_Studies indicate that gene conversion mediated by activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) has been found to contribute to generation of the primary antibody repertoire. 26545377_AID mutations leading to AID deficiency are the most frequent underlying molecular basis of hyper IgM syndrome in consanguineous Tunisian patients. 26638776_Mutations in activation-induced cytidine deaminase is associated with indolent chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. 26867650_Data suggest novel mechanism in innate immunity allows cytokine TGF-beta to restrict viral circular DNA in hepatocyte nuclei via innate immunity; AID deaminates circular DNA of hepatitis B virus leading to DNA degradation; mechanism depends on UNG. 26936395_We also report that AID activity results in epigenetic, genetic and genomic damage in fallopian tube epithelial cells 26980048_AID protein is expressed in a large proportion of Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cases at levels detectable by immunohistochemistry. 27142677_Finnish founder allele causing HIGM2 identified. 27217538_These data, showing the direct targeting and induction of functional AID by EBNA3C, suggest a novel role for EBV in the etiology of B cell cancers, including endemic Burkitt lymphoma 27258794_Structural analysis of AID protein required in immunoglobulin diversification has been reported. 27716525_the His130Pro mutation allows the enzyme to retain its mutagenic activity and would prevent the interaction of AID with specific cofactors required for class switch recombination but not for somatic hypermutation. Thus, there would be no contradiction between maintaining the catalytic and mutagenic activity of AID and the presence of function defects at the genomic level. 27789066_this study reports a case of growth hormone deficiency with an autosomal recessive Hyper-immunoglobulin M syndrome by phenotype and genotype, with a novel mutation in AICDA that has not been reported formerly 28077417_silencing of AID in human bone marrow cells skews differentiation toward myelomonocytic lineage. However, in contrast to Tet2 loss, Aid loss does not contribute to enhanced HSC self-renewal or cooperate with Flt3-ITD to induce myeloid transformation. Genome-wide transcription and differential methylation analysis uncover the critical role of Aid as a key epigenetic regulator 28140712_we reported high AID, low miR-181b and high miR-155 expression in de novo adult B-ALL patients. Univariate high AID or low miR-181b expression was an unfavorable prognostic factor. High AID with low miR-181b or with low miR-155 expression is better in predicting unfavorable OS than univariate factor. High AID with low miR-181b and low miR-155 expression confers worst prognosis. 28388279_AID expression was increased in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with del17p or del11q who have poor prognosis. 28490810_induction of AID expression would result in chromosomal translocations in the process of differentiation from B cell derived induced pluripotent stem cells. 28757211_Data implicate intrinsic preference of AID for structured substrates and uncover the importance of G4 recognition and oligomerization of AID in class switch recombination. 28779685_The authors found that the viral epsilon RNA and C-terminus of AID are required for AID-mediated hepa |
ENSMUSG00000040627 |
Aicda |
6.792933 |
12.9704195608 |
3.697153 |
0.935969836 |
18.888902 |
0.00001385564213657858736539283533995003949712554458528757095336914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000042766473846905056173991338530626649117039050906896591186523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.6998296 |
7.2581443 |
0.9850487 |
0.5299348 |
| ENSG00000111788 |
|
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.882804 |
0.4575979520 |
-1.127847 |
0.389698094 |
8.473819 |
0.00360294270980806132301244026905351347522810101509094238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007590555865938765703337942625239520566537976264953613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.2527686 |
5.7296199 |
19.8620548 |
8.6087666 |
| ENSG00000111907 |
7164 |
TPD52L1 |
protein_coding |
Q16890 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins that contain coiled-coil domains and may form hetero- or homomers. The encoded protein is involved in cell proliferation and calcium signaling. It also interacts with the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5 (MAP3K5/ASK1) and positively regulates MAP3K5-induced apoptosis. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:7164; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001235]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406] |
12963375_These results identify 14-3-3 proteins as partners for hD53, and alternative splicing as a mechanism for regulating 14-3-3 binding. 14761963_a member of the tumor protein D52 family involved in cell proliferation and calcium signaling, up-regulates the ASK1-induced apoptosis [D53L1] 16620967_The results indicate that tumor protein D52-like 1 genes are not ubiquitously expressed in leukemic bone marrow in children, and that RNA sample parameters may influence measures of gene expression more than commonly appreciated. |
ENSMUSG00000000296 |
Tpd52l1 |
17.115298 |
0.2116812268 |
-2.240035 |
0.453859047 |
25.136145 |
0.00000053422082085215329971274698939165403999140835367143154144287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001953207658106956364928077224396574251841229852288961410522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0358367 |
1.9670910 |
23.3421790 |
5.8699503 |
| ENSG00000111913 |
9750 |
RIPOR2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y4F9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an inhibitor of the small GTPase RHOA and plays several roles in the regulation of myoblast and hair cell differentiation, lymphocyte T proliferation and neutrophil polarization (PubMed:17150207, PubMed:24687993, PubMed:23241886, PubMed:24958875, PubMed:25588844, PubMed:27556504). Inhibits chemokine-induced T lymphocyte responses, such as cell adhesion, polarization and migration (PubMed:23241886). Involved also in the regulation of neutrophil polarization, chemotaxis and adhesion (By similarity). Required for normal development of inner and outer hair cell stereocilia within the cochlea of the inner ear (By similarity). Plays a role for maintaining the structural organization of the basal domain of stereocilia (By similarity). Involved in mechanosensory hair cell function (By similarity). Required for normal hearing (PubMed:24958875). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80U16, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17150207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23241886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24687993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24958875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27556504}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Acts as an inhibitor of the small GTPase RHOA (PubMed:25588844). Plays a role in fetal mononuclear myoblast differentiation by promoting filopodia and myotube formation (PubMed:17150207). Maintains naive T lymphocytes in a quiescent state (PubMed:27556504). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17150207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25588844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27556504}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chemotaxis;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Hearing;Membrane;Myogenesis;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal transduction inhibitor |
|
This gene encodes an atypical inhibitor of the small G protein RhoA. Inhibition of RhoA activity by the encoded protein mediates myoblast fusion and polarization of T cells and neutrophils. The encoded protein is a component of hair cell stereocilia that is essential for hearing. A splice site mutation in this gene results in hearing loss in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:9750; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium membrane [GO:0060171]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of establishment of T cell polarity [GO:1903904]; negative regulation of protein localization to cell leading edge [GO:1905872]; negative regulation of Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:2001107]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; negative regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000405]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of neutrophil extravasation [GO:2000391]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of establishment of cell polarity [GO:2000114]; regulation of mitotic spindle assembly [GO:1901673]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741] |
17150207_C6ORF32 is a novel protein likely to play multiple functions, including promoting myogenic cell differentiation, cytoskeletal rearrangement and filopodia formation 21190562_PC3 tumors are sustained by a small number of tumor-initiating cells with stem-like characteristics, including strong self-renewal and pro-angiogenic capability and marked by the expression pattern FAM65Bhigh/MFI2low/LEF1low. 24687993_Fam65b expression is necessary for the complex to form. 24958875_show that wild-type Fam65b is expressed during embryonic and postnatal development stages in murine cochlea, and that the protein localizes to the plasma membranes of the stereocilia of inner and outer hair cells of the inner ear 25588844_These data together elucidate a mechanism for RHOA and pMLC polarization in stimulated neutrophils through direct inhibition of RHOA by FAM65B at the leading edge. 25953057_In our analyses of the DYX2 locus, we observed associations of KIAA0319, ACOT13, and FAM65B with developing cortical thickness and/or functional anisotropy. 27269051_Mouse Ripor2 forms ring-like structures at the base of stereocilia and interacts with RhoC 27556504_FAM65B has a role in controlling proliferation of transformed and primary T cells 30254631_results show that Fam65b expression and phosphorylation can finely tune the amount of active RhoA in order to favor optimal T lymphocyte motility. 30720667_this is the first study to explore and validate the relationships between seven SNPs in the FAM65B, AGBL4, and CUX2 genes and ATDH in a Chinese population. On the basis of this case-control study, SNP rs10946737 in FAM65B may be associated with susceptibility to ATDH in Chinese Han anti-TB treatment patients. |
ENSMUSG00000036006 |
Ripor2 |
20.876206 |
7.8954267507 |
2.981017 |
0.444661554 |
53.367717 |
0.00000000000027660534041982659946296805087304999861298054897318365874525625258684158325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001708240512383531608983015478053021381612056051046977245277957990765571594238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.6310024 |
10.6134665 |
4.7236865 |
1.2238544 |
| ENSG00000112137 |
221692 |
PHACTR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9C0D0 |
FUNCTION: Binds actin monomers (G actin) and plays a role in multiple processes including the regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics, actin stress fibers formation, cell motility and survival, formation of tubules by endothelial cells, and regulation of PPP1CA activity (PubMed:21798305, PubMed:21939755). Involved in the regulation of cortical neuron migration and dendrite arborization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q2M3X8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21798305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21939755}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Epilepsy;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the phosphatase and actin regulator family of proteins. This family member can bind actin and regulate the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. It plays a role in tubule formation and in endothelial cell survival. Polymorphisms in this gene are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease and cervical artery dissection. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:221692; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; synapse [GO:0045202]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; actomyosin structure organization [GO:0031032]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; dendrite arborization [GO:0140059]; regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001222]; stress fiber assembly [GO:0043149] |
19198609_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20971364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21798305_Findings suggest that PHACTR-1 is likely to be a key regulator of endothelial cell function properties. 21939755_Phactr-1 is a key component in the angiogenic process 22745674_Results from this GWAS support a central role of PHACTR1 in CAD susceptibility irrespective of lifestyle and ethnic divergences. 23042660_3 loci from related cardiovascular genomewide studies were significant: PHACTR1 in large-vessel disease (P=2.63e(-6)), PITX2 in cardioembolic stroke (P=4.78e(-8)), and ZFHX3 in cardioembolic stroke (P=5.50e(-7)). 23479725_a novel signaling route whereby TGF-beta silences the expression of miR-584, resulting in enhanced PHACTR1 expression, and further leading to actin rearrangement and breast cancer cell migration. 25420145_GWAS analysis of 1,393 cervical artery dissection cases and 14,416 controls showed that the rs9349379[G] allele was associated with lower risk. This was confirmed independent follow-up samples. 26086777_The rs12526453 CC homozygotes (previously associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction) showed, in 2 independent samples, better long-term survival. 26362351_our result highlighted the pivotal role of phactr-1 protein in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 27187934_PHACTR1 is a key atherosclerosis candidate gene since it is regulated by atherogenic stimuli in macrophages and endothelial cells 27517945_To evaluate the role of two polymorphisms (rs2026458 and rs9349379) of the PHACTR1 gene in the susceptibility to the risk of developing premature coronary artery disease (CAD) in the Mexican population. Results suggest that the PHACTR1 rs9349379 polymorphism plays an important role in the risk of developing premature CAD in the Mexican population. 27545877_Stimulation of Slack K(+) channels alters mass at the plasma membrane by triggering dissociation of Phactr-1. 27792790_the expression of PHACTR1 by genotypes in primary human fibroblasts showed higher expression in rs9349379-A carriers . Phactr1 knockdown in zebrafish resulted in dilated vessels indicating subtle impaired vascular development 27893421_our study suggests that several PHACTR1 and SLC22A3 gene polymorphisms may exert a protective effect against the CAD in the Chinese Han male population. 28287809_There was no significant association between the presence of risk alleles of rs12526453 and coronary heart disease in an Iranian population. 28753427_CRISPR-edited stem cell-derived endothelial cells demonstrate rs9349379, a common SNP in the 3 intron of the PHACTR1 gene, regulates expression of endothelin 1 (EDN1), a gene located 600 kb upstream of PHACTR1. The known physiologic effects of EDN1 on the vasculature may explain the pattern of risk for the five associated vascular diseases. 29884117_PHACTR1 splicing is associated with atherosclerosis. 30256902_The data of this study showed that the PHACTR1 mutations may cause morphological and functional defects in cortical neurons during brain development, which is likely to be related to the pathophysiology of West syndrome and other neurodevelopmental disorders. 30293016_silencing PHACTR1 alleviates the nuclear accumulation of p65 and NF-kappaB via interaction with MRTF-A, ensuing attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation in human coronary artery endothelial cells 30354304_Confirmation of Causal rs9349379- PHACTR1 Expression Quantitative Trait Locus in Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Endothelial Cells. 30621952_This study reports that rs9349379 PHACTR1/EDN1 genetic locus is the first genetic risk locus for spontaneous coronary artery dissection. 30772888_Phactr-1 was shown to have a role in the inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation and migration, promoted cell apoptosis, and regulated matrix metalloproteinases and apoptosis-associated proteins. 30777881_Our study indicate that the PHACTR1 rs9349379 polymorphism is associated with the increased risk for CAD in the female Chinese Han population. 31200082_Results suggest that PHACTR1 haplotypes inferred from the variants rs9349379, rs2026458 and rs2876300 affect PHACTR1 mRNA and bear the risk for carotid plaque presence in patients with advanced carotid atherosclerosis. 31204462_Phactr1 rs9349379 polymorphism is associated with an elevated susceptibility to coronary artery disease [meta-analysis] 32420588_Associations between PHACTR1 gene polymorphisms and pulse pressure in Chinese Han population. 32475314_Genetic Study of PHACTR1 and Fibromuscular Dysplasia, Meta-Analysis and Effects on Clinical Features of Patients: The ARCADIA-POL Study. 33460763_Association of PHACTR1 intronic variants with the first myocardial infarction and their effect on PHACTR1 mRNA expression in PBMCs. 33630758_Deficiency of macrophage PHACTR1 impairs efferocytosis and promotes atherosclerotic plaque necrosis. 33660664_The association of polymorphism in PHACTR1 rs9349379 and rs12526453 with coronary artery atherosclerosis or coronary artery calcification. A systematic review. 33727568_PHACTR1 genetic variability is not critical in small vessel ischemic disease patients and PcomA recruitment in C57BL/6J mice. 34109516_A Study of Associations Between rs9349379 (PHACTR1), rs2891168 (CDKN2B-AS), rs11838776 (COL4A2) and rs4880 (SOD2) Polymorphic Variants and Coronary Artery Disease in Iranian Population. 36091033_PHACTR1, a coronary artery disease risk gene, mediates endothelial dysfunction. |
ENSMUSG00000054728 |
Phactr1 |
36.130875 |
0.4808843877 |
-1.056238 |
0.286012201 |
13.675697 |
0.00021724779389010567516929417486437614570604637265205383300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000565234873579756672001828121665312210097908973693847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1501614 |
4.2516222 |
48.5183724 |
6.0970271 |
| ENSG00000112144 |
22858 |
CILK1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPZ9 |
FUNCTION: Required for ciliogenesis (PubMed:24797473). Phosphorylates KIF3A (By similarity). Involved in the control of ciliary length (PubMed:24853502). Regulates the ciliary localization of SHH pathway components as well as the localization of IFT components at ciliary tips (By similarity). May play a key role in the development of multiple organ systems and particularly in cardiac development (By similarity). Regulates intraflagellar transport (IFT) speed and negatively regulates cilium length in a cAMP and mTORC1 signaling-dependent manner and this regulation requires its kinase activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62726, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JKV2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24797473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24853502}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Eukaryotic protein kinases are enzymes that belong to a very extensive family of proteins which share a conserved catalytic core common with both serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinases. This gene encodes an intestinal serine/threonine kinase harboring a dual phosphorylation site found in mitogen-activating protein (MAP) kinases. The protein localizes to the intestinal crypt region and is thought to be important in intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation. Alternative splicing has been observed at this locus and two variants, encoding the same isoform, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:22858; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; intraciliary anterograde transport [GO:0035720]; intraciliary retrograde transport [GO:0035721]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15988018_ICK is the prototype for a new group of MAPK-like kinases requiring dual phosphorylation at TDY motifs. 16954377_PP5 (protein phosphatase 5)and CCRK (cell cycle-related kinase) are yin-yang regulators of T157 phosphorylation. ICK interacts with and phosphorylates human Scythe, an essential regulator of proliferation and apoptosis during mammalian development. 19185282_ICK may play a role in the development of multiple organ systems. R272Q has been associated with endocrine-cerebro-osteodysplasia and may explain loss of function since the R272Q mutant fails to localize at the nucleus and has diminished kinase activity 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19696144_Findings demonstrate an important role for ICK in proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells. 19696144_ICK plays an important role in the regulation of proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells. ICK may control G1 cell cycle progression by regulating expression of cell cycle regulators cyclin D1, c-Myc and p21Cip1. 20459822_ICK and FBX9 are divergently transcribed from a bidirectional promoter that is GC-rich and contains a CpG island. 22356909_an important role for ICK in modulating the activity of mTORC1 through phosphorylation of Raptor Thr-908. 22761715_High ICK expression is associated with prostate cancer. 23743448_In glioblastoma cells with deregulated high levels of CCRK, its depletion restores cilia through ICK and an ICK-related kinase MAK, thereby inhibiting glioblastoma cell proliferation. 24244486_the expressions of ICK/MAK/MOK proteins in the intestinal tract can be differentially and dynamically regulated, implicating a significant functional diversity within this group of protein kinases. 25184386_findings suggest that increased ICK expression/activity in response to protein deprivation likely provides a novel protective mechanism to limit apoptosis and support compensatory mucosal growth under nutritional stress. 27466187_These data identify ICK as an short rib polydactyly syndromes (SRPS)-associated gene and reveal that abnormalities in signalling pathways contribute to defective skeletogenesis 29539279_Our data provide evidence that heterozygous variants in ICK caused juvenile myoclonic epilepsy in 7% of the patients included in our analysis. Variant ICK affects cell processes that help explain microdysgenesis and polyspike networks observed on EEG in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. 31277411_Study demonstrates that human ICK (intestinal cell kinase) that authors herein call CAPK (ciliopathy-associated protein kinase) interacts with human KIF3A and phosphorylates a conserved site Thr672 both in vitro and in vivo. Long, unstructured, non-catalytic carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of CAPK is required for this interaction with and phosphorylation of KIF3A. 31506943_Previously known as intestinal cell kinase because it was cloned from that origin, CILK1 is now recognized as a widely expressed and highly conserved. Mutations in the human CILK1 gene have been associated with ciliopathies. Thus, CILK1 has a fundamental role in the function of the cilium. Several candidate substrates have been proposed for CILK1. [review] 32178256_Functional Alterations in Ciliogenesis-Associated Kinase 1 (CILK1) that Result from Mutations Linked to Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy. 32732286_Anterograde trafficking of ciliary MAP kinase-like ICK/CILK1 by the intraflagellar transport machinery is required for intraciliary retrograde protein trafficking. 35609210_BROMI/TBC1D32 together with CCRK/CDK20 and FAM149B1/JBTS36 contributes to intraflagellar transport turnaround involving ICK/CILK1. |
ENSMUSG00000009828 |
Cilk1 |
111.735562 |
0.4420848693 |
-1.177605 |
0.384752939 |
8.748899 |
0.00309789037264057666096195298166549036977812647819519042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006611460656474105537783181318900460610166192054748535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.4812591 |
49.5056824 |
123.3366852 |
73.5415540 |
| ENSG00000112149 |
9308 |
CD83 |
protein_coding |
Q01151 |
FUNCTION: May play a significant role in antigen presentation or the cellular interactions that follow lymphocyte activation. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a single-pass type I membrane protein and member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of receptors. The encoded protein may be involved in the regulation of antigen presentation. A soluble form of this protein can bind to dendritic cells and inhibit their maturation. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:9308; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation [GO:0043367]; defense response [GO:0006952]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; negative regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032713]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation [GO:0043372]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12072358_the soluble extracellular CD83 domain inhibits DC-mediated T-cell proliferation, representing the first report describing a functional role for CD83. 12182451_cloning and characterization of the promoter region of the human CD83 gene 12594843_Increased expression of DC-SIGN+IL-12+IL-18+ and CD83+IL-12-IL-18- dendritic cell populations in the colonic mucosa of patients with Crohn's disease 12857898_induction of the CD83 promoter by LMP1 of Epstein-barr virus is mediated by the activation of NF-kappaB signal pathway in B cells 14687618_20% of chronic lymphocytic leukemia & 5/7 mantle-cell lymphoma patients have significantly elevated levels of soluble CD83. sCD83 may have an immunoregulatory role in vivo & functional significance in hematological malignancies, like CLL and MCL. 14962896_infected mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells lose surface CD83 while maintaining intracellular protein expression in cytomegalovirus infection. 15320871_monocytes, macrophages and immature DCs contain preformed intracellular CD83, and its rapid surface expression upon activation is post-translationally regulated in a process involving glycosylation 15454113_combined treatment of phosphatidic acid and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induce expression of CD83 in KG1 cells. 15721284_analysis of monomeric and dimeric isoforms of CD83 15905506_Putative soluble forms of CD83 proteins are characterized by a partial deletion of the extracellular and transmembrane domains; the smallest CD83 splice product shows a strong inhibitory effect on T cell proliferation in mixed leukocyte reactions. 16012714_Results suggest the importance of tumor-infiltrating CD83(+) dendritic cells as a useful prognostic factor for patients with gallbladder carcinoma. 16484227_the HuR-CRM1 axis affects the nucleocytoplasmic translocation of CD83 mRNA under regular physiological conditions 17178712_the signal sequences in APRIL that mediate its intracellular trafficking and provide evidence that this protein ligand of HuR is an important player in the post-transcriptional regulation of CD83 expression 17197902_The mature dentritic cells express CD83 and high CD40/80/86, whereas the immature cells express CD1a and low CD40/80/86 17428858_HSV-1 induces CD83 degradation in mature dendritic cells with immediate-early kinetics via the cellular proteasome 17469160_The abundance of CD83+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs) in perivascular areas and the overexpression of CCL19 and CCL21 in perivascular cellular foci suggest plasmacytoid DCs are central to the muscle inflammation in juvenile dermatomyositis. 17535098_CD83 antigen was identified as a useful tumor marker for the diagnosis of pediatric large cell lymphoma. 17561858_mRNA can be measured by real-time polymerase chain reaction to determine removal of dendritic cells in whole blood 17628801_membrane expression of the dendritic cell maturation marker CD83 on tumor cells from lung cancer patients 18056445_CD83 gene polymorphisms increase susceptibility to human invasive cervical cancer 18056445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18292234_In rheumatoid arthritis patients, the number of CD304(+) plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) exceeded that of CD1c(+) myeloid DCs (mDCs), with the majority of infiltrating DCs being CD83(-) or DC-LAMP(-). 18625638_Data suggest that in systemic lupus erythematosus, the increased number of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs) supports a pathogenic role for these cells, and decreased myeloid DC and CD83 expression may explain susceptibility to infections. 18755511_GM-CSF can both synergize with TNFalpha in the case of expression of IL1-RA and antagonize in the case of CD83. 19130553_The CK2 alpha' phosphorylates APRIL and therefore is responsible for the regulation of the nucleocytoplasmic translocation of CD83 mRNA. 19195701_sCD83 release may play a regulatory role in CLL progression. 19234177_Overexpression of CD83 in transgenic mice suppresses the humoral response to both T cell-independent and T-cell dependent model antigens in a dose-dependent manner. 19257981_Data show high expression of CD86 and CD11C, moderate expression of CD1a and CD123, low levels of CD83 on dendritic cells after induction by GM-CSF and IL-4. 19317050_No CD83-positive Langerhans cells were detected in any epidermodysplasia verruciformis patients or normal controls. 19321495_CD1a and CD83 may be involved in pain generation and the pathogenesis of endometriosis 20118277_Data show that pollen grains triggered the production of IL-8, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and strongly upregulated the membrane expression of CD80, CD86, CD83, HLA-DR and caused only a slight increase in the expression of CD40. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20566323_Structure identification of recombinant CD83 mutant variant as a potent therapeutic protein is reported. 20861805_sCD83 is capable of attenuating dendritic cell maturation and function, and inducing donor-specific allograft tolerance, in the absence of toxicity. 21076370_Human solublee CD83 alone is capable of inducing kidney allograft tolerance in kidney transplantation in mice. 21469977_Suggest that impaired immune function, absence of CD83-positive mature and activated dendritic cells in cancer nodules may have a role in the pathogenesis of thyroid papillary carcinoma. 22065790_CD83-stimulated monocytes suppress T-cell immune responses through production of prostaglandin E2 22134374_Results do not suggest that the common genetic variation of CD83 is related to cervical or vulvar cancers. The association between tagSNP rs853360 and risk of cervical SCC is likely to be due to chance. 23246582_Data indicate that the frequencies of CD11c, CD11c/CD86, HLA-DR/CD86, CD83 and CD80 were significantly high, while CD11c/HLA-DR was low in Hepatitis E infection. 23339870_We identified IRF-1, IRF-2, IRF-5, p50, p65, and cRel to be involved in regulating maturation-specific CD83 expression in DCs. 24268989_IDO and CD83 are expressed differently in human epidermal Langerhans cells 24436459_the presence of CD83 in mDC membranes enhances T lymphocyte proliferation by boosting calcium release from intracellular stores in these cells. 24643878_HSV-1 ICP0 alone induces CD83 degradation independent of its E3 ubiquitin ligase function and of the ubiquitin machinery. 25151500_CD83(+) T cells share important features with regulatory T cells, identifying CD83 as a novel lineage marker to discriminate between different T cell populations. 25243645_suggesting that a negative feedback regulation may exist in monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells (DCs) based on sCD83 released from the mature DCs 25701785_GRASP55 interacts with CD83 shortly after induction of dendritic cells maturation and that this interaction plays a role in CD83 glycosylation as well as in surface expression of CD83 on dendritic cells. 25997495_Sustained expression of CD83 was observed when CD4+ T cells were induced by transforming growth factor-beta to differentiate into CD4+CD25+ forkhead box P3+ regulatory T (iTreg) cells. 26129803_These results suggest that HTLV-I induces CD83 expression on T cells via Tax1 -mediated NF-kappaB activation, which may promote HTLV-I infection in vivo. 26561569_Triple costimulation via CD80, 4-1BB, and CD83 ligand elicits the long-term growth of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells in low levels of IL-2. 26575844_nonspreading Rift Valley fever virus infection of monocyte-derived immature denditic cells results in incomplete maturation, associated with gradual downregulation of CD83. 27421624_this study shows that dendritic cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients have low expression levels of CD83 27702941_We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of plasma caffeine, paraxanthine, theophylline, theobromine and paraxanthine/caffeine ratio. A single SNP at 6p23 (near CD83) and several SNPs at 7p21 (near AHR), 15q24 (near CYP1A2) and 19q13.2 (near CYP2A6) met GW-significance (P |
ENSMUSG00000015396 |
Cd83 |
667.120451 |
4.8853081988 |
2.288450 |
0.075721313 |
952.809027 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003251854530842585552188297346679597052590782102410432219386259334098799454971820352750290656566126790723458379012350399070 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003221300192968896619132392664318742502080941211940622714321619508973806480962001265976499557334070996397378495482265460320 |
Yes |
No |
1122.3550341 |
50.0331636 |
231.5150558 |
8.8069329 |
| ENSG00000112186 |
10486 |
CAP2 |
protein_coding |
P40123 |
FUNCTION: May have a regulatory bifunctional role. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene was identified by its similarity to the gene for human adenylyl cyclase-associated protein. The function of the protein encoded by this gene is unknown. However, the protein appears to be able to interact with adenylyl cyclase-associated protein and actin. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10486; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; adenylate cyclase binding [GO:0008179]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; presynaptic actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0099140]; regulation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0045761]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
17000669_CAP2 is up-regulated in human cancers and that is possibly related to multistage hepatocarcinogenesis. 23022774_An important conserved function of CAP2 in higher vertebrates may be associated with the process of skeletal muscle development. 26374196_CAP2 overexpression is a novel prognostic marker in malignant melanoma. CAP2 expression seems to increase stepwise during tumor progression, suggesting the involvement of CAP2 in the aggressive behavior of malignant melanoma. 27573674_CAP2 is upregulated in breast cancer and is associated with the expression of progesterone receptor and patient survival 30047046_CAP2 is a Valuable Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognostic in Patients with Gastric Cancer. 30518548_CAP2 joins other regulators of actin dynamics demonstrated to cause human genetic diseases. Our study is the first to demonstrate a mutation in CAP2 in human and a direct role for mutated CAP2 and perturbation of actin dynamics in the pathogenesis of DCM and possibly also conduction abnormalities in humans. 31640951_CAP2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues in close relation with the tumor progression. CAP2 is an independent risk factor for 5-year survival rate after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. 31871199_Study used lysine-to-glutamine mutations to map the relevant lysines on actin for INF2 regulation. K50Q- and K61Q-actin, when bound to CAP2, inhibit full-length INF2 but not INF2 lacking inhibitory domain (DID). CAP WH2 domain binds INF2-DID with submicromolar affinity but has weak affinity for actin monomers, while INF2-C-terminal diaphanous autoregulatory domain binds CAP/K50Q-actin 5-fold better than CAP/WT-actin. 32211793_CAP2 expression in ovarian cancer is an independent prognostic factor for recurrence-free survival. 34294609_Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induces CAP2 Expression Promoting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Liver Cancer Cells. 35163460_Analysis of mRNA and Protein Levels of CAP2, DLG1 and ADAM10 Genes in Post-Mortem Brain of Schizophrenia, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Disease Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000021373 |
Cap2 |
81.120537 |
0.3292184248 |
-1.602883 |
0.199058965 |
66.413622 |
0.00000000000000036556713891935681502266715853779492723824525476743196872320140755618922412395477294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002675146737952258975052982271246309171944504756018856639343539427500218152999877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.5409185 |
5.0077252 |
120.9435724 |
9.5248508 |
| ENSG00000112210 |
51715 |
RAB23 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULC3 |
FUNCTION: The small GTPases Rab are key regulators of intracellular membrane trafficking, from the formation of transport vesicles to their fusion with membranes. Rabs cycle between an inactive GDP-bound form and an active GTP-bound form that is able to recruit to membranes different set of downstream effectors directly responsible for vesicle formation, movement, tethering and fusion. Together with SUFU, prevents nuclear import of GLI1, and thereby inhibits GLI1 transcription factor activity. Regulates GLI1 in differentiating chondrocytes. Likewise, regulates GLI3 proteolytic processing and modulates GLI2 and GLI3 transcription factor activity. Plays a role in autophagic vacuole assembly, and mediates defense against pathogens, such as S.aureus, by promoting their capture by autophagosomes that then merge with lysosomes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22365972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22452336}. |
Cell membrane;Craniosynostosis;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Endosome;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a small GTPase of the Ras superfamily. Rab proteins are involved in the regulation of diverse cellular functions associated with intracellular membrane trafficking, including autophagy and immune response to bacterial infection. The encoded protein may play a role in central nervous system development by antagonizing sonic hedgehog signaling. Disruption of this gene has been implicated in Carpenter syndrome as well as cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:51715; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; craniofacial suture morphogenesis [GO:0097094]; GTP metabolic process [GO:0046039]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; negative regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042308] |
17373734_Rab23 is overexpressed and/or activated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Rab23 may be both a HCC predictor and a target for treating HCC. 17503333_RAB23 mutations in Carpenter syndrome imply an unexpected role for hedgehog signaling in cranial-suture development. 18485483_Data show that RAB23 participates in central nervous system development. 18559507_RAB23 amplifications are associated with gastric cancer 20358613_A RAB23 mutation (c.86dupA) present in the homozygote state in four relatives of Comorian origin with Carpenter syndrome, is reported. 21412941_Carpenter syndrome: extended RAB23 mutation spectrum and analysis of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay 21540310_association of the 6p12.1 locus with sarcoidosis implicates this locus as a further susceptibility factor and RAB23 as a potential signalling component 22365972_Rab23 directly associates with Su(Fu) and inhibits Gli1 function in a Su(Fu)-dependent manner. 22452336_Rab9A and Rab23 GTPases play crucial roles in autophagy of Group A Streptococcus. 23007279_The inhibition of the Rab23 cycle decreases the expression and nuclear localization of Gli1. 23948406_Rab23 expression level was the highest in Bcap-37 cells. 25489984_Rab23 was a target gene of miR-367, and ectopic expression of Rab23 could reverse the invasion and migration inhibitory activity of miR-367. 25867419_Data indicate the essential role of GTP binding protein RAB 23 (Rab23) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) inva-sion, motility and metastasis. 26238143_Rab23 is expressed in breast cancer cells, and ectopic expression of Rab23 inhibits the growth and proliferation as well as induces cell apoptosis in breast cancer cells These effects may be due to the inhibition by Rab23 of Gli1 and Gli2 mRNA expression 26648292_Rab23 enhance squamous cell carcinoma cell invasion via up-regulating Rac1. 26715272_High Rab23 expression is associated with bladder cancer. 26897750_Rab23 serves as an important oncoprotein in human astrocytoma by regulating cell invasion and migration through Rac1 activity 27659550_Forced expression of MiR-92b decreased the mRNA and protein level of RAB23, and RAB23 rescued the biological functions of miR-92b. Taken together, this study revealed the oncogenic roles and the regulation of RAB23 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, suggesting RAB23 might be a therapeutic target 28277196_Down-regulation of Rab23 suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells. 29191386_miR-429 was down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and cells. Up regulation of miR-429 decreased the migratory capacity and reversed the EMT to MET in HCC cells. RAB23 was confirmed as a target of miR-429. 29416296_Genetic variants in RAB23 and ANXA11 genes were associated with an increased risk of sarcoidosis-associated uveitis. 29771408_miR-16 acts as a tumor repressor in osteosarcoma cells by reducing epithelial mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion by targeting RAB23 expression. 30191377_Rab23 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration Via Rac1/TGF-beta Signaling. 31465935_RAB family small GTP binding protein RAB 23 (Rab23) and ADP-ribosylation factor-like 13B (Arl13b) have been implicated in ciliopathy-associated human diseases and could regulate hedgehog proteins (Hh) signalling cascade in multifaceted manners [Review]. 31550546_This is the first report that HE4 can regulate the expression of the Rab23 protein, and that knockdown of RAB23 decreases the proliferation, invasion, and migration abilities as well as inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in ovarian cancer cells. 31635804_OSER1-AS1 acted as a ceRNA to sponge miR-372-3p, thereby positively regulating the Rab23 expression and ultimately acting as a tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma progression 32856288_miR-597-3p inhibits invasion and migration of thyroid carcinoma SW579 cells by targeting RAB23. 34278506_miR3673p downregulates Rab23 expression and inhibits Hedgehog signaling resulting in the inhibition of the proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells. 34748996_Expansion of the phenotypic and mutational spectrum of Carpenter syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000004768 |
Rab23 |
57.343032 |
3.1287016169 |
1.645564 |
0.263811746 |
38.996625 |
0.00000000042453875379107837850438120939281904514528420691021892707794904708862304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002090821490142248019153219028786437616584947818410000763833522796630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.6284995 |
13.9045151 |
28.4729981 |
3.5694115 |
| ENSG00000112249 |
10973 |
ASCC3 |
protein_coding |
Q8N3C0 |
FUNCTION: 3'-5' DNA helicase involved in repair of alkylated DNA (PubMed:22055184). Promotes DNA unwinding to generate single-stranded substrate needed for ALKBH3, enabling ALKBH3 to process alkylated N3-methylcytosine (3mC) within double-stranded regions (PubMed:22055184). Also involved in activation of the ribosome quality control (RQC) pathway, a pathway that degrades nascent peptide chains during problematic translation (PubMed:28757607, PubMed:32099016). Drives the splitting of stalled ribosomes, as part of the ribosome quality control trigger (RQT) complex (PubMed:28757607, PubMed:32099016). Part of the ASC-1 complex that enhances NF-kappa-B, SRF and AP1 transactivation (PubMed:12077347). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12077347, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22055184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28757607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32099016}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;DNA damage;DNA repair;Helicase;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to a family of helicases that are involved in the ATP-dependent unwinding of nucleic acid duplexes. The encoded protein is the largest subunit of the activating signal cointegrator 1 complex that is involved in DNA repair and resistance to alkylation damage. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:10973; |
activating signal cointegrator 1 complex [GO:0099053]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; DNA repair complex [GO:1990391]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 3'-5' DNA helicase activity [GO:0043138]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; DNA dealkylation involved in DNA repair [GO:0006307]; DNA duplex unwinding [GO:0032508]; rescue of stalled ribosome [GO:0072344]; ribosome disassembly [GO:0032790]; ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:1990116] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22055184_DNA unwinding by ASCC3 helicase is coupled to ALKBH3-dependent DNA alkylation repair and cancer cell proliferation. 23781071_Silencing of ASCC3 resulted in upregulation of multiple antiviral interferon-stimulated genes, which correlated with inhibition of infection of several positive-strand RNA viruses. 26536629_ASCC3 Gene Polymorphism was associated with Chronic Hepatitis B. 28215706_UV exposure results in spatial restriction of transcription and slower elongation, with the result that only the promoter-proximal 20-25 kb are efficiently transcribed; these events underlie a switch to expression of short mRNA isoforms and preferential use of alternative last exons in a number of genes, including ASCC3. 33139697_The interaction of DNA repair factors ASCC2 and ASCC3 is affected by somatic cancer mutations. 34217309_ALKBH3 partner ASCC3 mediates P-body formation and selective clearance of MMS-induced 1-methyladenosine and 3-methylcytosine from mRNA. |
ENSMUSG00000038774 |
Ascc3 |
499.456701 |
2.0442519069 |
1.031573 |
0.126750430 |
65.374097 |
0.00000000000000061947799417709316601008498196006652436938451963127638677519826160278171300888061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004484303675357477096641374627939972876042014435921112536220789479557424783706665039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
695.4039723 |
49.7321120 |
342.5108124 |
18.5265995 |
| ENSG00000112276 |
11149 |
BVES |
protein_coding |
Q8NE79 |
FUNCTION: Cell adhesion molecule involved in the establishment and/or maintenance of cell integrity. Involved in the formation and regulation of the tight junction (TJ) paracellular permeability barrier in epithelial cells (PubMed:16188940). Plays a role in VAMP3-mediated vesicular transport and recycling of different receptor molecules through its interaction with VAMP3. Plays a role in the regulation of cell shape and movement by modulating the Rho-family GTPase activity through its interaction with ARHGEF25/GEFT. Induces primordial adhesive contact and aggregation of epithelial cells in a Ca(2+)-independent manner. Also involved in striated muscle regeneration and repair and in the regulation of cell spreading (By similarity). Important for the maintenance of cardiac function. Plays a regulatory function in heart rate dynamics mediated, at least in part, through cAMP-binding and, probably, by increasing cell surface expression of the potassium channel KCNK2 and enhancing current density (PubMed:26642364). Is also a caveolae-associated protein important for the preservation of caveolae structural and functional integrity as well as for heart protection against ischemia injury. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5PQZ7, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ES83, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16188940, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26642364}. |
cAMP;cAMP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Glycoprotein;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the POP family of proteins containing three putative transmembrane domains. This gene is expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle and may play an important role in development of these tissues. The mouse ortholog may be involved in the regeneration of adult skeletal muscle and may act as a cell adhesion molecule in coronary vasculogenesis. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:11149; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell projection membrane [GO:0031253]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; cAMP binding [GO:0030552]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cell migration involved in heart development [GO:0060973]; epithelial cell-cell adhesion [GO:0090136]; heart development [GO:0007507]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; positive regulation of locomotion [GO:0040017]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of endocytic recycling [GO:2001135]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; sinoatrial node cell development [GO:0060931]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051146]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
18349282_Methylation of BVES was present in 80% of NSCLC tissues but only 14% of noncancerous tissues. 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627872_Frequent silencing of BVES is associated with promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. 21069264_Data suggest that POPDC gene expression is modified in end-stage heart failure in humans in a manner suggesting regulatory and/or functional differences between the three family members and that POPDC1 is particularly susceptible to this condition. 21283798_Bves expression and localization can regulate RhoA and ZONAB/DbpA activity. 21911938_BVES was found to be underexpressed in all stages of colorectal carcinoma and in adenomatous polyps, indicating its suppression occurs early in transformation. 22109561_Low Bves expression is associated with gastric cancer progression. 22354168_Popdc1 (Bves) modulates cardiac pacemaker activity in response to stress and displays high expression levels in the sinus node. The Popeye domain acts as a high-affinity cAMP binding domain and Popdc proteins interact with the ion channel TREK-1. 23403794_Coding sequence and splice junctions of BVES were sequenced in 114 unrelated patients with Tetralogy of Fallot and 400 unrelated healthy individuals.Four novel BVES mutations were identified in patients with TOF but not in the 400 controls. 24442236_These results suggest that down-regulation of BVES in hepatocellular carcinoma induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition, thus promoting invasion and metastasis in HCC cells. 26642364_Forced expression of POPDC1(S201F) in a murine cardiac muscle cell line (HL-1) increased hyperpolarization and upstroke velocity of the action potential 28389570_BVES plays a key role in maintaining the integrity of the colonic mucosa and protecting from inflammatory carcinogenesis. Results also suggest that BVES promotes the post-translational degradation of c-Myc. 28807821_Study shows that EGFR negatively regulates POPDC1 expression in breast cancer cell lines and that overexpression of POPDC1 can reduce EGFR-mediated cell migration and proliferation in breast cancer cells. 28939104_recently a novel family of cAMP effector proteins emerged and was termed the Popeye domain containing (POPDC) family, which consists of three members POPDC1, POPDC2 and POPDC3. POPDC proteins are transmembrane proteins, which are abundantly present in striated and smooth muscle cells. POPDC proteins bind cAMP with high affinity comparable to PKA 28954821_Functional suppression of POPDC1 promoted breast cancer cell migration and proliferation, cAMP interacts with POPDC1 and up-regulates its expression in breast cancer cells. 29907869_BVES plays a protective role both in ulcerative and infectious colitis. 31386585_c.385C>T (p.R129W) is a functional SNP of the BVES gene that reduces the transcriptional activity of BVES in vitro and in vivo in TOF tissues. This subsequently affects the transcriptional activities of GATA4 and NKX2.5 related to TOF. These findings suggest that c.385C>T may be associated with the risk of TOF in the Han Chinese population. 32843646_BVES downregulation in non-syndromic tetralogy of fallot is associated with ventricular outflow tract stenosis. 33261556_An interaction of heart disease-associated proteins POPDC1/2 with XIRP1 in transverse tubules and intercalated discs. 34069715_The Transition from Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia to Gastric Cancer Involves POPDC1 and POPDC3 Downregulation. 35660068_Proteomic and morphological insights and clinical presentation of two young patients with novel mutations of BVES (POPDC1). |
ENSMUSG00000071317 |
Bves |
128.443511 |
2.5660881732 |
1.359571 |
0.149953093 |
83.330212 |
0.00000000000000000006943032601319953621000405101867666114578291131254642000111831912079196627018973231315612792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000612547287480469358571106642444328768265159422359877102598479936546027602162212133407592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
188.1618421 |
15.8961683 |
73.7741009 |
5.0562038 |
| ENSG00000112294 |
7915 |
ALDH5A1 |
protein_coding |
P51649 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes one step in the degradation of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19300440}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Mitochondrion;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; 4-aminobutanoate degradation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12208142, ECO:0000305|PubMed:14635103, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19300440, ECO:0000305|PubMed:9683595}. |
This protein belongs to the aldehyde dehydrogenase family of proteins. This gene encodes a mitochondrial NAD(+)-dependent succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase. A deficiency of this enzyme, known as 4-hydroxybutyricaciduria, is a rare inborn error in the metabolism of the neurotransmitter 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In response to the defect, physiologic fluids from patients accumulate GHB, a compound with numerous neuromodulatory properties. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7915; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004777]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; gamma-aminobutyric acid catabolic process [GO:0009450]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536]; neurotransmitter catabolic process [GO:0042135]; nitrogen compound metabolic process [GO:0006807]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; succinate metabolic process [GO:0006105] |
12629812_High activity of this protein probably indicates disorders in lymphocyte energy state. 14981524_Higher SSADH activity is associated with higher intelligence across the general population. 14981524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15642443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16406321_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16786440_The unexpected pattern of human SSADH polymorphism compared to interspecific findings outlines the possibility of a recent positive selection on some variants relevant to new cognitive capabilities unique to humans. 17457693_Deficiency in humans causes ggamma-hydroxybutyric aciduria. 17913586_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18505418_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18505418_within the 65-85 years age range, the T/T genotype is overrepresented in subjects with impaired cognitive function 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19300440_Redox-switch modulation of human SSADH by dynamic catalytic loop 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667317_SSADH deficient patients have widespread reduction in benzodiazepine receptor (BZPR) binding, suggested by high endogenous brain GABA levels that downregulate GABA(A)-BZPR binding site availability. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363598_This study indicated that global disruption of cortical networks in SSADH KO mice, affecting both excitatory and inhibitory neurons. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20445195_Study seeks to determine whether cerebellar abnormalities are present in human succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency on volumetric MRI, compared with radiographic and histologic studies in the mouse model. 20659789_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21438145_the duplication (6)(p22.2) and corresponding hyperactive level of SSADH activity may have negative consequences for GABA metabolism 22437753_our study identified a novel homozygous ALDH5A1 gene mutation associated with SSADH deficiency. 23516105_Succinic semialdehyde dehydrognase deficiency is caused by a mutation of the Aldh5a1-gene resulting in a dysfunction of the enzyme succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase--{REVIEW} 23825041_Missense mutation in ALDH5A1 is associated with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency and severe intellectual disability. 23926001_Missense mutations of c.527G>A and c.691G>A in the ALDH5A1 gene are associated with pathogenesis of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. 24230997_Results show that opioid-dependent patients carrying the T allele of a functional variant in ALDH5A1 had a greater risk of being nonresponders to methadone maintenance treatment 24327614_The strongest association signal arose from an intronic region of the gene ALDH5A1, which encodes the mitochondrial enzyme succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH), an enzyme involved in gamma-aminobutyric acid metabolism. 25431891_Two novel ALDH5A1 mutations likely responsible for SSADH deficiency were identified, and DNA sequencing provided an accurate diagnosis for an at-risk fetus whose sibling had SSADH deficiency. Current study and literature review identified nine additional novel mutations in eight unrelated families bringing the number of unique mutations of ALDH5A1 resulting in SSADH deficiency to 44, occurring from exon 1 to exon 10. 25558043_Pearl et al. identify 3 new pathogenic mutations in the ALDH5A1 gene previously unreported in the literature. EXON: 1 Nucleotide change: c.412 C>T Change in protein: p.L138F EXON: 4 Nucleotide change: c.754G>T Change in protein: p.Q252X EXON: 8 Nucleotide change: c.1360G>A Change in protein: p.A454T 26422261_SSADH catalytic loop role in the SSADH redox-switch modulation 28186584_The proband was found to have compound heterozygous mutations of the succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH5A1) gene, namely c.398_399delAA (p.N134X) and c.638G>T (p.R213L), for which her parents were both heterozygous carriers. 28346042_ALDH5A1 mRNA expression was down-regulated in ovarian cancer patients compared with that in normal tissues. 28664505_By ALDH5A1 gene expression in transiently transfected HEK293 cells and enzyme activity assays, we demonstrate that the p.V500 L mutation, despite being conservative, produces complete loss of enzyme activity 29895405_ALDH5A1 nonsense mutation is associated with reduced Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity and stability resulting in Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. 31117962_Four Chinese patients (two males and two females) at the age of 86 days to 5 years were diagnosed with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (SSADH deficiency) with aldehyde dehydrogenase family 5 member A1 (ALDH5A1) gene mutations. 32223457_Novel mutations in a Chinese family with two patients with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. 32402538_Functional analysis of thirty-four suspected pathogenic missense variants in ALDH5A1 gene associated with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. 32575506_SSADH Variants Increase Susceptibility of U87 Cells to Mitochondrial Pro-Oxidant Insult. 32881051_ALDH5A1 acts as a tumour promoter and has a prognostic impact in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 32887777_Novel ALDH5A1 variants and genotype: Phenotype correlation in SSADH deficiency. 33203024_Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency: In Vitro and In Silico Characterization of a Novel Pathogenic Missense Variant and Analysis of the Mutational Spectrum of ALDH5A1. 33319393_Gene expression analysis in epileptic hippocampi reveals a promoter haplotype conferring reduced aldehyde dehydrogenase 5a1 expression and responsiveness. 34882073_Assessing Prevalence and Carrier Frequency of Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency. |
ENSMUSG00000035936 |
Aldh5a1 |
106.928442 |
0.2811729745 |
-1.830470 |
0.161601455 |
134.604982 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000040284731887100484075274022005652341257432744660406589635916711571293082782117974359470391476634176797233521938323974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000005366449843444071729363823529066615448689472197097851195474985129581821915184937192566660968395808595232665538787841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.2291126 |
5.2086515 |
172.7872372 |
11.2864722 |
| ENSG00000112394 |
117247 |
SLC16A10 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF71 |
FUNCTION: Sodium- and proton-independent thyroid hormones and aromatic acids transporter (PubMed:11827462, PubMed:18337592, PubMed:28754537). Mediates both uptake and efflux of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) and 3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine (T4) with high affinity, suggesting a role in the homeostasis of thyroid hormone levels (PubMed:18337592). Responsible for low affinity bidirectional transport of the aromatic amino acids, such as phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan and L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-dopa) (PubMed:11827462, PubMed:28754537). Plays an important role in homeostasis of aromatic amino acids (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3U9N9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11827462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337592, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28754537}. |
Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
SLC16A10 is a member of a family of plasma membrane amino acid transporters that mediate the Na(+)-independent transport of aromatic amino acids across the plasma membrane.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. |
hsa:117247; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; aromatic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015173]; L-phenylalanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015192]; L-tryptophan transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015196]; L-tyrosine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005302]; thyroid hormone transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015349]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; aromatic amino acid transport [GO:0015801]; thyroid hormone generation [GO:0006590]; thyroid hormone transport [GO:0070327]; thyroid-stimulating hormone secretion [GO:0070460] |
18337592_MCT10 is at least as active a thyroid hormone transporter as hMCT8, and that both transporters facilitate iodothyronine uptake as well as efflux. 20167367_Increased MCT8 and decreased MCT10 expression within placentae of pregnancies complicated by IUGR may contribute to aberrant development of the fetoplacental unit. 21315799_monocarboxylate transporter 10 facilitates bromoacetyl [(125)I] iodothyronine transport, but is not labeled by it 21486766_Compared with the adult cerebral cortex, mRNAs encoding OATP1A2, OATP1C1, OATP3A1 variant 2, OATP4A1, LAT2 and CD98 were reduced in fetal cortex at different gestational ages, whilst mRNAs encoding MCT8, MCT10, OATP3A1 variant 1 and LAT1 were similar. 21508134_The strong expression of MCT10 and OATP1C1 in the human hypothalamus indicates a possible role in the regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis. 26779635_High TAT1 expression is associated with metastasis and recurrence in endometrial cancer. 27492966_the aim of this study was to examine if MCT8 and MCT10 increase the availability of triiodothyronine for its nuclear receptor. 28754537_In the MCT10 modeled structure, N81 appeared to protrude into the putative trajectory of tryptophan. 31595333_Molecular predictor of TaT1 patients. 31820424_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Thyroid Hormone Transporter Genes MCT8, MCT10 and Deiodinase DIO2 Contribute to Inter-Individual Variance of Executive Functions and Personality Traits. |
ENSMUSG00000019838 |
Slc16a10 |
102.305427 |
27.8065005379 |
4.797350 |
0.264499658 |
448.522543 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000151235021955211453560223810763104740670591952015543604755495525490216201472180115176133491639935306767860940535808101876994439005221642529592613706989051946556769825166297523301520396191259614178281754957619597556664348087929906819 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000063777969258826314939296837633260676166803164428121146909495734627597665008164162598030318484199648377633793362638276901663537809038293244891232227470341299442134493590166508829007403745186213445024474892422358587464985558905775735 |
Yes |
Yes |
169.3022672 |
34.6870628 |
6.1772283 |
1.1093580 |
| ENSG00000112578 |
705 |
BYSL |
protein_coding |
Q13895 |
FUNCTION: Required for processing of 20S pre-rRNA precursor and biogenesis of 40S ribosomal subunits. May be required for trophinin-dependent regulation of cell adhesion during implantation of human embryos. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17360433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17381424}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis |
|
Bystin is expressed as a 2-kb major transcript and a 3.6-kb minor transcript in SNG-M cells and in human trophoblastic teratocarcinoma HT-H cells. Protein binding assays determined that bystin binds directly to trophinin and tastin, and that binding is enhanced when cytokeratins 8 and 18 are present. Immunocytochemistry of HT-H cells showed that bystin colocalizes with trophinin, tastin, and the cytokeratins, suggesting that these molecules form a complex in trophectoderm cells at the time of implantation. Using immunohistochemistry it was determined that trophinin and bystin are found in the placenta from the sixth week of pregnancy. Both proteins were localized in the cytoplasm of the syncytiotrophoblast in the chorionic villi and in endometrial decidual cells at the uteroplacental interface. After week 10, the levels of trophinin, tastin, and bystin decreased and then disappeared from placental villi. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:705; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; preribosome, small subunit precursor [GO:0030688]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; snoRNA binding [GO:0030515]; maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000462]; regulation of protein localization to nucleolus [GO:1904749]; ribosome biogenesis [GO:0042254]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; trophectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0001829] |
17381424_These results suggest that, while bystin may play multiple roles in mammalian cells, a conserved function is to facilitate ribosome biogenesis required for cell growth. 17917702_review of the roles of bystin in embryo implantation, assembly of ribosomes, and as a target of c-MYC 20805244_bystin is necessary for efficient cleavage of the internal transcribed spacer 1 at site 2 and for further processing of the pre-rRNA. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33628587_BYSL contributes to tumor growth by cooperating with the mTORC2 complex in gliomas. 34797290_DDX10 and BYSL as the potential targets of chondrosarcoma and glioma. |
ENSMUSG00000023988 |
Bysl |
178.421517 |
2.5238727404 |
1.335639 |
0.153326549 |
75.478130 |
0.00000000000000000369476641208600266087673538136217986315461338591944508158437798783779726363718509674072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000030113060321584424971337264173937541453727453812788672493638841842766851186752319335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
257.2684334 |
31.1517077 |
102.4935596 |
9.3973222 |
| ENSG00000112659 |
23113 |
CUL9 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWT3 |
FUNCTION: Core component of a Cul9-RING ubiquitin-protein ligase complex, a complex that mediates ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of BIRC5 and is required to maintain microtubule dynamics and genome integrity. Acts downstream of the 3M complex, which inhibits CUL9 activity, leading to prevent ubiquitination of BIRC5 (PubMed:24793696). Cytoplasmic anchor protein in p53/TP53-associated protein complex. Regulates the subcellular localization of p53/TP53 and subsequent function (PubMed:12526791, PubMed:17332328). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12526791, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17332328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24793696}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable several functions, including ATP binding activity; metal ion binding activity; and ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in microtubule cytoskeleton organization; protein ubiquitination; and regulation of mitotic nuclear division. Located in cytosol. Part of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23113; |
cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031461]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
12526791_Parc, a Parkin-like ubiquitin ligase,is a critical regulator in controlling p53 subcellular cytoplasmic localization and subsequent function. 16672220_FUBP1 is an authentic substrate of Parkin that might play an important role in development of Parkinson disease pathology along with aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase interacting multifunctional protein type 2 17298945_CPH domain interaction surface of p53 resides in the tetramerization domain and is formed by residues contributed by at least two subunits 17332328_PARC and CUL7 subcomplexes exhibit E3 ubiquitin ligase activity in vitro. 18230339_These studies suggest that PARC-interacting peptides are promising candidates for the enhancement of p53-dependent apoptosis in tumors with wt cytoplasmic p53. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22117079_the regulation of p53 subcellular localization and apoptosis by PARC as a contributing factor in CDDP resistance in OVCA cells and Ca(2+)/calpain in PARC post-translational processing and chemosensitivity. 25028716_PARC (also known as CUL9) was found to be the ubiquitin ligase responsible for the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of cytochrome c, thus promoting cell survival. 25028717_PARC-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of Cyt c is a strategy engaged by both neurons and cancer cells to prevent apoptosis during conditions of mitochondrial stress. 28481879_Results in U2OS cells demonstrate that the functions of CUL9 in regulating cell proliferation and maintaining genomic integrity are mainly mediated by p53, and that CUL9 is a critical p53 activator. 33705438_A proteomics approach for the identification of cullin-9 (CUL9) related signaling pathways in induced pluripotent stem cell models. |
ENSMUSG00000040327 |
Cul9 |
297.316055 |
0.3754319596 |
-1.413377 |
0.119605350 |
138.527782 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000005586831096113463803657007885415401723528319211110795311070857800289951971937788335886843071875773603096604347229003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000763533583135506690639406404239749257971170640311889290840893443612214857892575158200554330534259861451573669910430908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
167.9864574 |
17.7456471 |
451.0375433 |
33.6281472 |
| ENSG00000112667 |
10591 |
DNPH1 |
protein_coding |
O43598 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond of deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates to yield deoxyribose 5-phosphate and a purine or pyrimidine base. Deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates containing purine bases are preferred to those containing pyrimidine bases. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24260472, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25108359}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Nucleotide metabolism;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene was identified on the basis of its stimulation by c-Myc protein. The latter is a transcription factor that participates in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. The exact function of this gene is not known but studies in rat suggest a role in cellular proliferation and c-Myc-mediated transformation. Two alternative transcripts encoding different proteins have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10591; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphate N-glycosidase activity [GO:0070694]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate catabolic process [GO:0009159]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; nucleoside metabolic process [GO:0009116]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; purine nucleotide catabolic process [GO:0006195] |
18726892_characterization of the human Rcl gene, we cloned its promoter, Rcl is a bona fide target gene of ETV1. 20962348_analysis of human deoxynucleotide N-hydrolase Rcl and rat gene c6orf108 33833118_Targeting the nucleotide salvage factor DNPH1 sensitizes BRCA-deficient cells to PARP inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000040658 |
Dnph1 |
196.528536 |
2.1262756340 |
1.088329 |
0.120109401 |
82.745927 |
0.00000000000000000009330786074972606864997745231751112694750237023490747304173276166494588323985226452350616455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000816858852115039609177748203425130153393740007198214675074310342495209624757990241050720214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
269.1384389 |
18.8885747 |
127.5148565 |
7.0574380 |
| ENSG00000112685 |
55770 |
EXOC2 |
protein_coding |
Q96KP1 |
FUNCTION: Component of the exocyst complex involved in the docking of exocytic vesicles with fusion sites on the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12459492, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32639540}. |
Acetylation;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Exocytosis;Intellectual disability;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the exocyst complex, a multi-protein complex essential for the polarized targeting of exocytic vesicles to specific docking sites on the plasma membrane. Though best characterized in yeast, the component proteins and the functions of the exocyst complex have been demonstrated to be highly conserved in higher eukaryotes. At least eight components of the exocyst complex, including this protein, are found to interact with the actin cytoskeletal remodeling and vesicle transport machinery. This interaction has been shown to mediate filopodia formation in fibroblasts. This protein has been shown to interact with the Ral subfamily of GTPases and thereby mediate exocytosis by tethering vesicles to the plasma membrane. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:55770; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocyst [GO:0000145]; Flemming body [GO:0090543]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; Golgi to plasma membrane transport [GO:0006893]; membrane fission [GO:0090148]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell [GO:2000535]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904]; vesicle tethering involved in exocytosis [GO:0090522] |
12459492_SEC5 has been identified as a binding partner of deafness locus putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor. 12575951_Functional study of the Drosophila homolog. 14525976_evidence that mammalian exocyst components are present as distinct subcomplexes on vesicles and the plasma membrane and that Ral GTPases regulate the assembly interface of a full octameric exocyst complex through interaction with Sec5 and Exo84 17018283_These observations define the mechanistic contribution of RalGTPases to cancer cell survival and reveal the RalB/Sec5 effector complex as a component of TBK1-dependent innate immune signaling. 18697830_Localization of Exocyst and, by extension, targeting of Exocyst-dependent cargo, is dependent on Ral GTPases, which control association between Sec5 and paxillin. 20145037_shRNA-mediated knockdown of the Ral effector proteins Sec5 and Exo84, but less so in the case of RalBP1, reduced oncogenic RalGEF-mediated transformation and oncogenic Ras-driven tumorigenic growth of human cells. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20570966_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20616560_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21197618_Data show that Mc1R, HERC2, IRF4, TYR and EXOC2 are ranked highest in hair color prediction analysis. 22761837_We identified interactions between RalA and its effectors sec5 and exo84 in the Exocyst complex as directly necessary for migration and invasion of prostate cancer tumor cells. 23844030_Exocyst sec5 regulates exocytosis of newcomer insulin granules underlying biphasic insulin secretion. 26359301_data suggest that the induction of SGK1 through treatment with dexamethasone alters MT dynamics to increase Sec5-GEF-H1 interactions, which promote GEF-H1 targeting to adhesion sites. 32639540_Mutations in the exocyst component EXOC2 cause severe defects in human brain development. |
ENSMUSG00000021357 |
Exoc2 |
177.618546 |
4.4870474935 |
2.165766 |
0.884985322 |
5.465992 |
0.01939004879984135634729547348342748591676354408264160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034893577211126361459214706428610952571034431457519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
338.2836299 |
225.8072646 |
77.3340636 |
36.3750670 |
| ENSG00000112701 |
26054 |
SENP6 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZR1 |
FUNCTION: Protease that deconjugates SUMO1, SUMO2 and SUMO3 from targeted proteins. Processes preferentially poly-SUMO2 and poly-SUMO3 chains, but does not efficiently process SUMO1, SUMO2 and SUMO3 precursors. Deconjugates SUMO1 from RXRA, leading to transcriptional activation. Involved in chromosome alignment and spindle assembly, by regulating the kinetochore CENPH-CENPI-CENPK complex. Desumoylates PML and CENPI, protecting them from degradation by the ubiquitin ligase RNF4, which targets polysumoylated proteins for proteasomal degradation. Desumoylates also RPA1, thus preventing recruitment of RAD51 to the DNA damage foci to initiate DNA repair through homologous recombination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16912044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17000875, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20212317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20705237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21148299}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein sumoylation. |
Ubiquitin-like molecules (UBLs), such as SUMO1 (UBL1; MIM 601912), are structurally related to ubiquitin (MIM 191339) and can be ligated to target proteins in a similar manner as ubiquitin. However, covalent attachment of UBLs does not result in degradation of the modified proteins. SUMO1 modification is implicated in the targeting of RANGAP1 (MIM 602362) to the nuclear pore complex, as well as in stabilization of I-kappa-B-alpha (NFKBIA; MIM 164008) from degradation by the 26S proteasome. Like ubiquitin, UBLs are synthesized as precursor proteins, with 1 or more amino acids following the C-terminal glycine-glycine residues of the mature UBL protein. Thus, the tail sequences of the UBL precursors need to be removed by UBL-specific proteases, such as SENP6, prior to their conjugation to target proteins (Kim et al., 2000 [PubMed 10799485]). SENPs also display isopeptidase activity for deconjugation of SUMO-conjugated substrates (Lima and Reverter, 2008 [PubMed 18799455]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:26054; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SUMO-specific endopeptidase activity [GO:0070139]; protein desumoylation [GO:0016926]; protein modification by small protein removal [GO:0070646]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925]; regulation of kinetochore assembly [GO:0090234]; regulation of spindle assembly [GO:0090169] |
14563852_SENP1 localization is influenced by expression and localization of SUMO-1-conjugated target proteins within the cell. 16912044_SUSP1 plays an important role in the control of the transcriptional activity of RXRalpha and thus in the RXRalpha-mediated cellular processes 17000875_We have investigated the specificity of SUSP1 using vinyl sulfone inhibitors and model substrates. SUSP1 has a strong paralogue bias toward SUMO2/3 and acts preferentially on substrates containing three or more SUMO2/3 moieties 18799455_SENP6 and SENP7 exhibit lower rates for processing pre-SUMO1, pre-SUMO2, or pre-SUMO3 in comparison with SENP2 20212317_Results reveal a novel mechanism whereby the finely balanced activities of SENP6 and RNF4 control vertebrate kinetochore assembly through SUMO-targeted destabilization of inner plate components. 21148299_study of substrate specificity of SENP6; it is also capable of cleaving mixed chains of SUMO-1 and SUMO-2/3; mutation of catalytic cysteine of results in its accumulation in PML NBs; findings indicate SUMO-modified PML is a substrate of SENP6 21878624_Loop 1 insertion in SENP6 and SENP7 as a platform to discriminate between SUMO1 and SUMO2/3 isoforms in this subclass of the SUMO protease family. 24424631_the structure of SENP2-Loop1 in complex with SUMO2 was solved at 2.15 A resolution, and reveals the details of an interface exclusive to SENP6/7 and the formation of unique contacts between both proteins 28615201_LANA could bind to the promoter region of the SENP6 gene and inhibit SENP6 expression while the regulated SENP6 could in turn modulate the abundance of LANA through desumoylation. 30631152_The authors conclude that SENP6, a factor important for CENP-A maintenance and assembly, functions in protecting a portion of M18BP1 from PIAS4-mediated SUMOylation and subsequent SUMOylation-dependent ubiquitination and degradation. 30720688_SENP6 and FEM1C gene expression in liver transplantation predicts transplantation tolerance. 31485003_SUMO specific peptidase 6 (SENP6) deficient cells are severely compromised for proliferation, accumulate in G2/M and frequently form micronuclei. 31597105_The SUMO Isopeptidase SENP6 Functions as a Rheostat of Chromatin Residency in Genome Maintenance and Chromosome Dynamics. 31980633_SENP6 activity is required throughout the cell cycle, suggesting that a dynamic SUMO cycle underlies a continuous surveillance of the centromere complex. 35022408_Genetic alterations of the SUMO isopeptidase SENP6 drive lymphomagenesis and genetic instability in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 36292645_Single Cell RNA-Seq Identifies Immune-Related Prognostic Model and Key Signature-SPP1 in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000034252 |
Senp6 |
974.270723 |
0.2777084405 |
-1.848357 |
0.075305471 |
594.913203 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002139073650597930415170043373524089941613241176022853628253007703560306127062706265675983335228776787316558275567965286409615141613050164298566733505913403894454298996237119405474698037426818551560167 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001173707326499087539549149288315860161742777413258668347004697432061869172591221747061068108787419263532757866429348466111038251132428437314915431988521936149748569305548551850579605539459272952423486 |
Yes |
No |
409.4502533 |
25.0480418 |
1485.2440333 |
62.5478486 |
| ENSG00000112715 |
7422 |
VEGFA |
protein_coding |
P15692 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth. Induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. Binds to the FLT1/VEGFR1 and KDR/VEGFR2 receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. NRP1/Neuropilin-1 binds isoforms VEGF-165 and VEGF-145. Isoform VEGF165B binds to KDR but does not activate downstream signaling pathways, does not activate angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. Binding to NRP1 receptor initiates a signaling pathway needed for motor neuron axon guidance and cell body migration, including for the caudal migration of facial motor neurons from rhombomere 4 to rhombomere 6 during embryonic development (By similarity). Also binds the DEAR/FBXW7-AS1 receptor (PubMed:17446437). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q00731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11427521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16489009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17446437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25825981}. |
3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Heparin-binding;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It encodes a heparin-binding protein, which exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer. This growth factor induces proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells, and is essential for both physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Disruption of this gene in mice resulted in abnormal embryonic blood vessel formation. This gene is upregulated in many known tumors and its expression is correlated with tumor stage and progression. Elevated levels of this protein are found in patients with POEMS syndrome, also known as Crow-Fukase syndrome. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with microvascular complications of diabetes 1 (MVCD1) and atherosclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. There is also evidence for alternative translation initiation from upstream non-AUG (CUG) codons resulting in additional isoforms. A recent study showed that a C-terminally extended isoform is produced by use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon via a stop codon readthrough mechanism, and that this isoform is antiangiogenic. Expression of some isoforms derived from the AUG start codon is regulated by a small upstream open reading frame, which is located within an internal ribosome entry site. The levels of VEGF are increased during infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), thus promoting inflammation by facilitating recruitment of inflammatory cells, and by increasing the level of angiopoietin II (Ang II), one of two products of the SARS-CoV-2 binding target, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). In turn, Ang II facilitates the elevation of VEGF, thus forming a vicious cycle in the release of inflammatory cytokines. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2020]. |
hsa:7422; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; VEGF-A complex [GO:1990150]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; neuropilin binding [GO:0038191]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 binding [GO:0043183]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding [GO:0043184]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005172]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; basophil chemotaxis [GO:0002575]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell development [GO:0060948]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; cellular stress response to acid chemical [GO:0097533]; commissural neuron axon guidance [GO:0071679]; coronary artery morphogenesis [GO:0060982]; coronary vein morphogenesis [GO:0003169]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:0035767]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; eye photoreceptor cell development [GO:0042462]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lactation [GO:0007595]; lung development [GO:0030324]; lymph vessel morphogenesis [GO:0036303]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; motor neuron migration [GO:0097475]; negative regulation of adherens junction organization [GO:1903392]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability [GO:1905604]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000048]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903141]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048842]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903589]; positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090190]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell migration by vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038089]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038091]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038033]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of epithelial tube formation [GO:1905278]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of histone deacetylase activity [GO:1901727]; positive regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002687]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mast cell chemotaxis [GO:0060754]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:1900086]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090037]; positive regulation of protein kinase D signaling [GO:1903572]; positive regulation of protein localization to early endosome [GO:1902966]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002092]; positive regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:1902336]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia [GO:0061419]; positive regulation of trophoblast cell migration [GO:1901165]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900748]; positive regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043117]; post-embryonic camera-type eye development [GO:0031077]; primitive erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0060319]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0010749]; regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090259]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129]; tube formation [GO:0035148]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling pathway [GO:0036324]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084]; vascular wound healing [GO:0061042]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; VEGF-activated neuropilin signaling pathway [GO:0038190] |
11146397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11352659_Includes data regarding non-AUG translation initiation (CUG) of VEGF 11563986_Includes data regarding non-AUG translation initiation (CUG) of VEGF 11642726_upregulated in eye in experimental herpesvirus retinopathy 11686329_Thrombin induces increased expression and secretion of VEGF from human FS4 fibroblasts, DU145 prostate cells and CHRF megakaryocytes. 11705851_The VEGF levels were significantly higher in recurrent ALL compared with newly diagnosed ALL. 11705867_VEGF levels were elevated in patients with invasive cancer of ductal/no specific type, ductal carcinoma in situ, and estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors. 11731620_Includes data regarding non-AUG translation initiation (CUG) of VEGF 11741977_induction in human glioblastoma cells by acidic extracellular pH via ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway 11742492_Significant association with poor survival by VEGF. 11748975_Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in serous ovarian carcinoma: relationship with high mitotic activity and high FIGO stage. 11751905_both VEGF-induced PI 3-kinase activation and beta(1) integrin-mediated binding to fibronectin are required for the recruitment and activation of PKC alpha. 11783119_VEGF expression and intratumoral microvessel density (IMVD) can be considered as a biological indicator of malignant potential in brain astrocytoma. 11784713_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates neutrophil transendothelial migration via up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells 11784722_modulation of signaling and angiogenic effects by PTEN 11806247_upregulation by interleukin-1 beta in vascular smooth muscle cells via the P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 11809675_Vascular endothelial growth factor-A(165) induces progression of melanoma brain metastases without induction of sprouting angiogenesis. 11809713_Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase stimulates human glioma xenograft growth and angiogenesis. 11815711_essential for developmental angiogenesis and is also required for female reproductive functions and endochondral bone formation. 11819817_VEGF plays an important role in the oncogenesis of human gastric cancer. 11824377_Platelets and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a morphological and functional study. 11831981_VEGF is highly related to PVBE and angiogenesis of meningoma. 11832343_bFGF and VEGF were synergistic in terms of DAF expression, resulting in enhanced endothelial cytoprotection 11834731_A 40-bp RNA element that mediates stabilization of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by HuR. 11836562_Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor is useful in assessing progression of breast cancer post surgery and during adjuvant treatment. 11839635_VEGF and flt-1 are upregulated in blood vessels in many organs of acute Kawasaki Disease 11847008_Blood levels are elevated in myelodysplastic syndromes and in acute myeloid leukemia. VEGF corrected for the peripheral blood platelet count is a marker of disease progression in MDS. 11866530_NMR structure of a phage-derived peptide antagonist in complex with vascular endothelial growth factor 11866538_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates the Tie-2:Tie-1 receptor complex 11867956_free plasma VEGF levels are high in chronic renal impairment; may contribute to the endothelial dysfunction of uraemia 11875709_prognostic value of matched preoperative serum and plasma vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations in patients with colorectal cancer. 11877311_Prognostic significance of VEGF expression in bone marrow cells in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. 11877669_VEGF upregulates BCL-2 expression and is associated with decreased apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. 11882460_Chemoattractive and proliferative effects of VEGF-A have been demonstrated on primary human osteoblasts. 11891801_Plasma VEGF levels are significantly increased in chronic myeloproliferative disorders. The highest levles were found in CMD with essential thrombocythemia. Levels were significantly higher in CMD patients with vascular complications. 11908876_VEGF may act as a growth factor for both endothelial cells and tumor cells. 11912213_Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor A transcription in tumorigenic glioblastoma cell lines by an enhancer with cell type-specific DNase I accessibility 11912219_overexpression in mesangial cells by advanced glycation end products 11920479_tumor cell-VEGF induction may promote angiogenesis in adenocarcinoma of the lung; tumor cell expression may be important prognostic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung 11921018_expression of tissue factor (TF) and VEGF is frequently observed in colorectal cancer and TF expression is significantly related with VEGF expression and microvessel density 11930687_VEGF as a mediator of OHSS. 11930688_VEGF may play a role in pathogenesis of OHSS. 11940485_Cultured plasma cells from patients with advanced relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma who responded favorably to thalidomide secreted a significantly lower amount of VEGF than did plasma cells from resistant patients. 11956584_thrombin upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor 11956638_VEGF expression and vascular density in colon cancer 11957147_COX-2 is upregulated in endometrial cancer and facilitates tumor growth via angiogenesis produced in associated with VEGF and TP 11959648_copper sulfate induced VEGF expression in primary as well as transformed human keratinocytes 11960372_Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis 11961297_the role and intracellular signal pathway of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation induced by VEGF 11961303_VEGF and p53 are highly expressed in esophageal carcinomas 11964077_VEGF is down regulated in ovarian carcinoma cells and in serous effusions 11964307_HTLV-I-transformed T cells, but not HTLV-I-negative CD4(+) T cells, secrete biologically active forms of VEGF and bFGF and induce angiogenesis in vitro. 11972026_A dynamic shift of VEGF isoforms with a transient and selective progesterone-induced expression of VEGF189 regulates angiogenesis and vascular permeability in human uterus 11978184_Increased expression of VEGF may be responsible for gastric carcinogenesis and tumor aggressiveness of gastric cancer in northern China. 11978667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11980898_differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in bladder cancer cells (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, beta) 11986954_level spontaneously secreted by patient CLL B-cells quantified; secreted in 2/3 patient samples; co-expression of VEGF and VEGF receptors suggests autocrine pathways of stimulation. 11999550_REVIEW: Association of expression of VEGF and receptors in human leukemia and lymphoma, resulting in the generation of autocrine loops that may support cancer cell survival and proliferation 12012273_investigation of the immediate effect of ovulation induction with hCG on peripheral VEGF levels in 6 women with primary infertility enrolled in the IVF/ET program 12014632_Overexpression of cyclin DI contributes to malignant properties of esophageal tumor cells by increasing VEGF production and decreasing Fas expression. 12016145_modulation of synthesis by sodium butyrate in colon cancer cell line HT29 12023772_findings suggest that products secreted by schistosome eggs may promote angiogenesis within hepatic granulomas by up-regulating endothelial cell VEGF 12038454_VEGF and IL-6 were both independent prognostic factors for overall survival of aggressive lymphoma. 12039075_Data suggest that VEGF-A may be more than angiogenic in prostate cancer and hence favor tumor progression by affecting tumor cells. 12042276_relationship between serum VEGF levels, alpha(2)M levels and the development of OHSS in hyperstimulated subjects undergoing IVF 12058259_Genotype may influence tumour growth in malignant melanoma, possibly via effects on tumour angiogenesis 12058259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12062186_Comparison and modulation of angiogenic responses by FGFs, VEGF and SCF in murine and human fibrosarcomas. 12067896_VEGF-induced proliferation and angiogenesis requires activation of the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway, whereas vascular permeability is enhanced by PKC blockade. 12067976_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085210_Hyperthermia acts as an anti-angiogenic strategy by suppressing VEGF expression & thus inhibiting endothelial proliferation and blood vessel ECM remodeling. 12102661_results indicate opposite effects of IFN-gamma and IL-4 on VEGF expression from normal and activated keratinocytes and fibroblasts 12105188_Integrin (alpha 6 beta 4) regulation of eIF-4E activity and VEGF translation (Integrin alpha6beta4) 12114504_VEGF binds to CTGF and degrades MMPs, inducing physiological or pathologic angiogenesis 12117969_Induction of VEGF in THP-1 macrophages and human microvascular endothelial cells during Bartonella henselae infection 12119553_IL-10 gene expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer specimens was significantly correlated with VEGF121 gene expression. The results suggested that IL-10 stimulates angiogenic factor gene expression. 12127077_VEGF(121) contains a third interchain disulfide bond between Cys116 of each monomer. 12133473_VEGF promotes angiogenesis by paracrining in breast carcinoma, and takes part in tumor invasion and lymph node metastasis. 12133520_A new alternative splicing isoform of VEGF has been identified in the lung tissue of a legally aborted human fetus. 12133521_VEGF is associated with the development and prognosis of colorectal cancer. 12141529_effect of epidermal growth factor on vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by endometrial stromal cells 12149254_Data show that exposure of human colon carcinoma cells to insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) induces the expression of HIF-1 alpha, the regulated subunit of hypoxia-inducible factor 1, a known transactivator of the VEGF gene. 12151344_expression in colon carcinoma cells exposed to pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate 12151391_role of a variant in competitively and specifically antagonizing the mitogenic effect of the wild-type protein on endothelial cells 12163680_Green tea inhibits induction in human breast cancer cells. 12168088_PTEN modulates angiogenesis in prostate cancer by regulating VEGF expression. 12168808_vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been demonstrated to have a central involvement in the angiogenic process in rheumatoid arthritis 12168898_Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression correlates with p53 and ki-67 expressions in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 12174362_expressions of iNOS and VEGF may serve as indexes for evaluating staging of gastric carcinoma and forecasting its risk of metastasis 12174901_data suggest that mutations of p53 and activation of the Ras/MAPK pathway may play a role in the induction of VEGF expression in human colorectal cancer 12187074_High level of vascular endothelial growth factor in hemorrhagic pleural effusion of cancer. 12197476_regulation and expression profile of 884 human genes under the influence of either bFGF or VEGF-A alone in the context of human endothelial cells 12207021_cystine knot promotes folding and not thermodynamic stability 12208766_The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis. 12209585_VEGF isoforms and mutations in human colorectal cancer. 12209725_Women with ovarian carcinoma who reported higher levels of social well being had lower levels of VEGF 12213806_These results suggest that the expression of HIF-1 and VEGF induced by Cr(VI) may be an important signaling pathway in the Cr(VI)-induced carcinogenesis. 12213874_may play important roles in placental biology and chorionic villus vascular development and remodeling in an autocrine/paracrine manner 12213878_findings implicate altered VEGF and KDR signaling in pituitary tumorigenesis; PTTG stimulation of FGF-2 and VEGF expression in the presence of up-regulated growth factor receptors may account for angiogenic growth and progression of human pituitary tumors 12215337_expression in uterine leiomyoma 12232762_The prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor in 574 node-negative breast cancer patients who did not receive adjuvant systemic therapy. 12235106_plays a role in bone formation elicited by bone morphogenetic protein 4, and can significantly enhance BMP4-elicited bone formation and regeneration 12239588_vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human esophageal cancer 12358602_findings underline an essential role of AP-2/Sp1 recognition sites in UVB-mediated VEGF expression by the keratinocyte-derived cell line HaCaT 12391145_Data describe a novel mechanism by which vascular endothelial growth factor induces DNA synthesis in a pathway where sphingosine kinase mediates signaling from protein kinase C to Ras in a manner independent of Ras-guanine nucleotide exchange factor. 12391545_Hb-induced synthesis of VEGF in TF-bearing malignant cells is mediated by protein tyrosine kinase and by MAP-kinase pathways 12393542_Inhibition of p38 MAPK inhibits IL-6 and VEGF secretion in bone marrow stromal cells triggered by adherence of multiple myeloma cells. 12400015_These results demonstrate a novel pathogenic mechanism whereby mutations in BRCA1, via their interaction with ER-alpha, could promote tumorigenesis through the hormonal regulation of mammary epithelial cell proliferation and impaired VEGF function 12406876_results suggest that in the hematopoietic microenvironment an autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor loop contributes to optimal megakaryocytic maturation through Flt1 12413884_Data demonstrate that the paracrine interaction between endothelial and mesenchymal cells potentiates angiogenesis in vitro and that this occurs with vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) but not with growth factor-2 (FGF-2). 12425822_The VEGF expression and tumour angiogenesis are correlated with peritumoural brain edema. 12427739_mediation of proliferation of human pulmonary valve endothelial cells by NFATc1 12427750_vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated gene induction and angiogenic responses of endothelial cells is inhibited by NAB2 12428103_FGF2 and VEGF release by platelets support cell survival and cell growth of vascular endothelium cells in coculture. 12429966_up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with submucosal carcinoma of esophagus 12430738_The malignant transformation of endothelial cells may be characterized by VEGF expression in the presence of p53 gene mutation. 12439912_The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors KDR and Flt-1 by gastric carcinoma tissues and cell lines was detected to elucidate the molecular mechanism of this growth factor in promoting tumor growth. 12445161_close relationship of VEGF expression with macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression in human glioblastoma 12446667_VEGF might contribute to breast cancer metastasis by enhancing the transendothelial migration of tumor cells through the down-regulation of endothelial integrity 12451991_The in vitro invasive ability of ovarian tumor cells appeared to be positive correlated to high expression of VEGF and MMP-2. 12452000_The high expression of VEGF in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma may promote the tumor progression and lead to dismal prognosis. 12453880_In vivo administration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its antagonist, soluble neuropilin-1, predicts a role of VEGF in the progression of acute myeloid leukemia in vivo. 12453985_Vitreous levels are altered in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy 12456629_vascular endothelial growth factor does not discriminate ectopic from abnormal intrauterine pregnancies at 6 weeks gestation 12474525_Differential expression follows BCG immunotherapy in superficial papillary transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder 12481883_review discusses the impact of new vessel formation related to acute leukemia and the relation with various angiogenic factors with focus on VEGF/VEGF receptor signaling 12482858_VEGF is induced by p38 after stimulation by sodium arsenite 12482957_We show here that vascular endothelial growth factor but not basic fibroblast growth factor can induce gene expression of Notch1 and Dll4, in human arterial endothelial cells. The VEGF-induced specific signaling is mediated through VEGF receptors 1 and 2 12493399_This factor is transcribed and translated in chronic renal allograft rejection. 12496364_The induction of maximal neovascularization by VEGF requires the interaction between ephrin-A1 and EphA2. 12499259_Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. 12505748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12505748_results suggest that polymorphisms in the promoter region of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene together with the aldose reductase gene may be associated with the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy 12509426_regulation of transcription by oxidative stress via Sp1- and Sp3-dependent activation of two proximal GC-rich promoter elements 12509854_restoration of PTEN function in gliomas may induce therapeutic effect by downregulating VEGF. 12517803_PTEN mutation and epidermal growth factor receptor activation regulate mRNA expression in human glioblastoma cells by transactivating the proximal promoter 12545153_Stat3 directly regulates VEGF expression and hence angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer 12548213_VEGF impaired bradykinin-mediated dilatation and enhanced basal tone and permeability of isolated arteries which might indicate a potential role for VEGF in the development of endothelial dysfunction in pregnancy 12551914_A set of loop-1 and -3 structures in this protein family member, VEGF-ENZ-7, is essential for the activation of VEGFR-2 signaling. 12553038_Induction of VEGF seems to be regulated by the extent of the IL-6 receptor expression on pancreatic cancer cells. 12558813_We conclude that VEGF -460, -141 and +405 genotypes are not associated with susceptibility to childhood steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome 12563064_VEGF found in cerebrospinal fluid of SIDS infants (postmortem) suggests that a single or multiple hypoxic events may precede the SIDS event. 12568850_Progestins activate this gene transcription in endometrial adenocarcinoma cells 12574959_IL-6r and TNF-alpha increase in parallel to VEGF and FGF-2 with increasing stage of multiple myeloma. 12579315_VEGF-A is an estrogen responsive gene and modulation of this gene expression by estrogen is biphasic and can be mediated through ER-alpha dependent pathway. 12581744_exogenous VEGF-A(165) or VEGF-A(121) did not affect the rate of proliferation of either trophoblast cells or breast carcinoma cells, but did reduce their ability to invade through reconstituted ECM (Matrigel) 12590639_The relationship between pituitary tumour transforming gene (PTTG) expression and in vitro growth hormone and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion from human pituitary adenomas. 12591230_vascular endothelial growth factor indirectly stimulates smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through the modulation of basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta(1) released by endothelial cells 12591731_We have analyzed the impact of the common -460/+405 polymorphism on both basal and stimulated VEGF transcription using the human breast cancer cell line MCF7. 12593846_expression in pancreatic carcinoma cell line evoked by insulin-like growth factor I receptor 12594002_We studied the association of endometriosis with circulating levels of human leukocyte antigens and VEGF in two generations of a single family (mother and three daughters). These markers were expressed distinctly in women with familial endometriosis. 12594815_Malignant mesothelioma growth inhibition by agents that target the VEGF and VEGF-C autocrine loops. 12597245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12597245_Significant ethnic differences in C702T and G1612A allele frequencies, but C702T, C936T and G1612A polymorphisms in 3'-UTR of VEGF gene are not associated with risk of RCC in Japanese population. 12604407_A paracrine loop in the VEGF pathway triggers tumor angiogenesis and growth in multiple myeloma. 12607595_VEGF expression plays a role in promoting angiogenesis in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, and p53 is likely to be involved in regulating VEGF expression. 12607599_VEGF, but not bFGF, was associated with higher tumor grading of NHL and high-grade transformation of low-grade lymphoma. 12615701_Cyclooxygenase-1 is overexpressed and promotes vascular endothelial growth factor production in ovarian cancer. 12629515_We conclude that IL-6 may promote cervical tumorigenesis by activating VEGF-mediated angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. 12631341_IGF-I induces VEGF gene expression and protein secretion in human mesangial cells via a Src-dependent mechanism. 12637571_extracellular pH might play an important role in regulating vascular endothelial growth factor interactions with cells and the extracellular matrix 12646239_These results demonstrate that a seven amino acid VEGF exon 6-derived peptide is an effective inhibitor of ocular neovascularisation in vivo. 12651930_expression is involved in angiogenesis in inflamed synovial tissue in the temporomandibular joint 12654193_expression levels of VEGF and bFGF were correlated with the biological behavior of superficial transitional cell bladder carcinoma. 12654197_expression levels of VEGF and bFGF were correlated with the biological behavior of superficial transitional cell bladder carcinoma. 12660426_mast cells may play an active role in the angiogenesis of basal cell carcinoma through the production of VEGF 12666706_increased in gingival tissues of diabetic patients, especially those with periodontal disease 12667326_The expression of EGF in hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC underlies the overexpression of VEGF in HCC. 12668286_Local VEGF expression was correlated significantly with tumor size, advanced stage and lymph node metastasis, but not correlated with peripheral VEGF levels 12670505_VEGF secreted by retinal pigment epithelial cells upregulates pigment epithelium-derived factor expression via VEGFR-1 in an autocrine manner. 12684660_expressed during angiogenesis in human ovarian cancer cells in vivo 12684689_Results suggest that up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor enables and supports the pathogenesis of external ear canal cholesteatoma. 12687277_Serum VEGF activity may be used to evaluate angiogenic and metastatic activity in breast cancer patients. 12696078_With the progression of tumor grade, the positive rate of VEGF gene expression significantly increased. 12700666_Distortion of autocrine transforming growth factor beta signal accelerates malignant potential by enhancing cell growth as well as PAI-1 and VEGF production in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 12708473_The expression of VEGF was significantly correlated with gastric cancer differentiation & vascular invasion. 12710853_In pregnancies complicated by trisomy 21 VEGF levels were significantly lower than in healthy controls. May be sign of imbalance of placental vascularization and altered endothelial function. 12711260_vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression is suppressed by pigment epithelium-derived factor through anti-oxidative properties, which inhibits leptin-induced angiogenesis 12716475_heme oxygenase activity up-regulates VEGF production and augments the capability of endothelial cells to respond to exogenous stimulation 12716911_ADAMTS1 significantly blocks VEGFR2 phosphorylation due to direct binding and sequestration of VEGF165, with consequent suppression of endothelial cell proliferation. 12719950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12719950_Significant difference between normal individuals and stone patients in distribution of VEGF gene polymorphism as well as an odds ratio of 1.30 per copy of the 'T' allele. 12727858_Vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in colon cancer cells exposed to prostaglandin E2 is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. 12740269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12742981_Gene transfer of VEGF during PTCA and stenting shows that intracoronary gene transfer can be performed safely; no differences in restenosis rate or lumen diameter were present after 6-month follow-up, and increased myocardial perfusion was detected 12756808_possible blood biological marker of Yersinia infection and may be involved in the development of chronic conditions 12763746_Submaximal exercise, suitable for humans with low cardiovascular fitness, induces decrease in VEGF arteriovenous balance that is likely to be of clinical significance in promoting angiogenic effects. 12767510_VEGF-A might play a main role in the COX-2 angiogenic pathway. 12788875_In the luteal phase, VEGF and IP-10, in the normal human breast, exhibit a proangiogenic profile. This may be one mechanism by which sex steroids contribute to breast cancer development. 12800229_Expression of VEGF has a significant correlation with microvascular density in colorectal carcinoma. 12810642_The promoter of human vascular endothelial growth factor contains 7 consensus binding sites for beta-catenin/TCF. Transfection of normal colon epithelial cells with activated beta-catenin up-regulated levels of VEGF-A mRNA and protein. 12810677_Tumor-derived VEGF interacts with Angs/Tie-2 system in host stromal endothelial cells & induces in a paracrine manner the remodeling of host vasculature to support angiogenesis during tumor growth. 12827055_Pterygia exhibit significantly lower PEDF but higher VEGF levels than those in normal corneas and conjunctivae. 12839933_Bombesin stimulates nuclear factor kappa B activation and expression of this angiogenic factor in prostate cancer cells. 12844492_VEGF has a regulatory role in focal adhesion complex assembly in human brain microvascular endothelial cells via activation of FAK and RAFTK/Pyk2 12845559_VEGF is produced locally and plays a fundamental, but not specific, role in diabetic retinal neovascularisation and proliferation. 12845639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12847526_VEGF is a modifier of motoneuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 12850503_vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in osteolytic lesions of bone co-relates well with the extent of bone destruction and local recurrence 12855698_Vascular endothelial growth factor causes translocation of p47phox to membrane ruffles through WAVE1 12860293_human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells produce VEGF, which in turn regulates PEDF production, and this balance may be contributing to neovascularization in tumors. 12865814_expression or function in acute and chronic allograft rejection; an important proinflammatory cytokine after transplantation and its expression pattern might identify patients at risk for the development of GVD 12871382_thrombin-induced VEGF mRNA expression is associated with the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in vascular endothelial cells 12871881_Although VEGF seems to play a pivotal role locally in the implantation and development of endometriotic lesions, the disease is not associated with a significant modulation in the levels of circulating VEGF. 12883661_COX-2 and VEGF are expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and may have a role in tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis 12883688_COX-2 or VEGF, but not cyclin D1 may play roles in breast cancer with poor prognosis 12883692_VEGF is regulated by her2/neu and contributes to Wilms tumor angiogenesis in vivo 12888890_VEGF has a role in pathologic angiogenesis and is downregulated by antisense oligonucleotides 12890905_Serum VEGF concentration was increased in arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO) and thromboangitis obliterans, but increased concentration of M-CSF was seen only in ASO. 12893367_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12893367_VEGF gene C/T polymorphism is a suitable genetic marker of prostate cancer but cannot be used in the prediction of the outcome of patients who have received hormonal therapy. 12901801_Plasma VEGF levels are significantly higher than in gastric tumor patients than those in 10 healthy controls 12918061_Vascular endothelial growth factor expression correlates with matrix metalloproteinases MT1-MMP, MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human glioblastomas 12926153_In patients with advanced ovarian carcinoma, intense VEGF immunostaining was more often detected in peritoneal metastases than in primary tumors. 12937141_Secreted VEGF protein levels were significantly lower in IGF-IR dominant negative cells. Autocrine activation of IGF-IR system significantly affects VEGF expression and angiogenesis in human pancreatic cancer. 12949011_in humans: 1) VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA are increased by acute systemic exercise; 2) the time course of the VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA responses are different from those previously reported in rats 12957716_Our findings suggest that hyperhomocysteinemia could promote the development of atherosclerotic lesions through VEGF induction in macrophages. 14500349_Activated MMP9, and, to a lesser extent, MMP2, increased VEGF release by SKOV3 and OVCAR3 ovarian carcinoma cells. 14507446_Biological dressing effect of cultured epidermal sheets(CESs) is mediated by EGF family, TGF-beta, and VEGF. 14507641_High-level expression of angiopoietin-2 and VEGF receptors was observed in the endothelium of verruga peruana. Surprisingly, the major source of VEGF production in verruga peruana is the overlying epidermis. 14512169_Postmortem brain tissue analysis demonstrates activation of the proangiogenic VEGF signaling cascade in patients with cerebral malaria. 14512791_vascular endothelial growth factor expression is regulated by HIF1a and HIF2a, and has a role in nodular malignant melanomas of the skin 14513045_Progression of multiple myeloma to a vascular phase is accompanied by increase in microcirculation and and in VEGF. 14513053_Expressed in multiple myeloma cells and in bone marrow cells. 14514674_role of neuropilin-1 on endothelial cell migration 14530810_Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with myeloproliferative disorders 14532971_VEGF is upregulated by cyclooxygenase-2 in human gastric carcinoma 14555767_Hepatocyte growth factor mediates angiogenesis in cultured cancer cells by regulating the expression of this protein and thrombospondin 1. 14559444_VEGF may serve as an important modulator of mitogen-induced VSMC proliferation after vascular injury. 14572781_data suggest that human peritoneal mesothelial cells contribute to the development of peritoneal metastases and the accumulation of malignant ascites due to the production of vascular endothelial growth factor 14585871_VEGF may play an important role in the hydrosalpinx fluid formation, possibly by promoting vascular and epithelial permeability and therefore serum transudation. 14593238_in umbilical cord plasma, a developmental increase was evident in concentrations of vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF) and angiogenin during the last trimester of gestation, and VEGF level was lower in term fetuses born to mothers with diabetes 14602779_IGF-I stimulates VEGF synthesis in thyroid carcinomas in an Akt-dependent pathway via AP-1 and HIF-1 alpha 14604996_Both of the IRS proteins modulate VPF/VEGF expression in pancreatic cancer cells by different mechanistic pathways. 14607580_Intrauterine VEGF levels are regulated in a cycle-dependent way. Increasing levels in the late secretory phase are clearly correlated with decidualization. 14607712_the protein level of VEGF can reflect the compensation status of cirrhosis patients and may act as an anti-cirrhotic factor 14609725_VEGF express |
ENSMUSG00000023951 |
Vegfa |
204.089727 |
4.0558169867 |
2.019993 |
0.173029981 |
133.768863 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000061381155755960528176704159854062784813971703600094840852004590130455629048323196606667950803171152074355632066726684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000008132727638761017918297559866200083164208094996686600275292881881570937616847492140914610558866115752607583999633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
330.1248873 |
38.1993019 |
82.1111196 |
7.4248951 |
| ENSG00000112773 |
55603 |
TENT5A |
protein_coding |
Q96IP4 |
FUNCTION: Cytoplasmic non-canonical poly(A) RNA polymerase that catalyzes the transfer of one adenosine molecule from an ATP to an mRNA poly(A) tail bearing a 3'-OH terminal group and participates in the cytoplasmic polyadenylation (PubMed:33882302). Polyadenylates mRNA encoding extracellular matrix constituents and other genes crucial for bone mineralization and during osteoblast mineralization, mainly focuses on ER-targeted mRNAs (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3Z5S8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33882302}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Nucleotidyltransferase;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in mRNA stabilization. Predicted to act upstream of or within response to bacterium. Implicated in lung non-small cell carcinoma; osteoarthritis; and osteogenesis imperfecta type 18. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55603; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; RNA adenylyltransferase activity [GO:1990817]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; mRNA stabilization [GO:0048255]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
12054608_a candidate of human retinal disease on chromosome 6 16545789_A novel VNTR polymorphism in C6orf37 exists in Chinese population and is not associated with colorectal cancer risk 16545789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16924696_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17803723_Genetic analysis of FAM46A in Spanish families with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa: characterization of novel VNTRs is reported. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24625963_VNTR in the coding region of the FAM46A gene, FAM46A rs11040 SNP and BAG6 rs3117582 SNP are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis 25231575_Susceptibility to large-joint osteoarthritis (hip and knee) is associated with BAG6 rs3117582 SNP and the VNTR polymorphism in the second exon of the FAM46A gene on chromosome 6. 25884493_Genotype frequencies of cd (four and five VNTR repeats) and cc (four VNTR repeats homozygote) of the FAM46A gene were significantly decreased in the patients compared to the healthy controls in the Croatian and Norwegian subjects 26993346_This exploratory genome-wide association studies confirmed APOE and identified the novel loci: rs72907046 near FAM46A (P = 1 x 10(-9) OR = 3.2 [2.1-4.9]). 29234017_By functional analysis based on a set of 1129 proteins from 494 obese subjects study identified and validated FAM46A as a trans regulator for leptin. 29358272_We conclude that FAM46A mutations are responsible for a severe form of osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) with congenital bowing of the lower limbs and suggest screening this gene in unexplained OI forms. 33370626_FAM46A expression is elevated in glioblastoma and predicts poor prognosis of patients. 35137485_Tent5a modulates muscle fiber formation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis via maintenance of myogenin expression. |
ENSMUSG00000032265 |
Tent5a |
1478.214260 |
0.3039400972 |
-1.718141 |
0.044234558 |
1569.990853 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
684.5077779 |
20.3446791 |
2268.1052267 |
41.5019324 |
| ENSG00000112799 |
9450 |
LY86 |
protein_coding |
O95711 |
FUNCTION: May cooperate with CD180 and TLR4 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and cytokine production. Important for efficient CD180 cell surface expression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9450; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031666] |
16907704_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18001295_in the promoter region we identified 3 SNPs, rs1334710, rs4959389 and rs977785 that are associated with mite-sensitive allergy in Taiwanese children; results suggested that MD-1 could be a susceptible gene for mite-sensitive allergy in Taiwanese children 19255686_Identified MD-1 SNP (rs7740529) association with asthma in Taiwanese children and adults. 19255686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20935629_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21130168_In this study, we produced variants of MD-1 and MD-2 in Pichia pastoris. Contrary to previous reports, this study suggests that MD-1 can bind to LPS. 21426727_MD-1 may be a disease susceptibility gene for adult asthma in a Southern Han population in China. 21959264_Both mouse and human RP105/MD-1 exhibit dimerization of the 1:1 RP105/MD-1 complex, demonstrating a novel organization. 24735745_DNA methylation of the LY86 gene is associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and inflammation. 27209086_our results reveal that MD-1 deficiency is of critical importance in down-regulating induction and progression of colitis, thereby suggesting that MD-1 might be a target for future interventional therapies of inflammatory bowel disease. 32251450_LY86 knockdown results in reduced monocyte migration towards the chemokine MCP-1, thereby implying that this reduced migration may underlie the increased susceptibility to candidemia. 33394553_Genetic variability of immune-related lncRNAs: polymorphisms in LINC-PINT and LY86-AS1 are associated with pemphigus foliaceus susceptibility. |
ENSMUSG00000021423 |
Ly86 |
55.308591 |
0.4707098952 |
-1.087090 |
0.199758002 |
30.300543 |
0.00000003700223884902209742113609746046176685041473319870419800281524658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000152471536965819684481828442945694490617825067602097988128662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.9679997 |
4.6299656 |
76.8925562 |
6.3081905 |
| ENSG00000112972 |
3157 |
HMGCS1 |
protein_coding |
Q01581 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the condensation of acetyl-CoA with acetoacetyl-CoA to form HMG-CoA, which is converted by HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) into mevalonate, a precursor for cholesterol synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7913309}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasm;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Metabolic intermediate biosynthesis; (R)-mevalonate biosynthesis; (R)-mevalonate from acetyl-CoA: step 2/3. |
Enables protein homodimerization activity. Predicted to be involved in acetyl-CoA metabolic process and farnesyl diphosphate biosynthetic process, mevalonate pathway. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:3157; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase activity [GO:0004421]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; acetyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0006084]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; farnesyl diphosphate biosynthetic process, mevalonate pathway [GO:0010142]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] |
18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19088433_ACBP is a transcriptional regulator of the HMGCS1 and HMGCR genes encoding rate-limiting enzymes of cholesterol synthesis pathway. 20346956_The authors report high-resolution crystal structures of the human cytosolic (hHMGCS1) and mitochondrial (hHMGCS2) isoforms in binary product complexes. 28468827_Data suggest that HMGCS1 (HMG-CoA synthase 1) signals through ketogenesis/acetoacetate to promote cell proliferation and BRAF(V600E)-dependent MEK1 activation in BRAF(V600E)-positive melanoma and colon cancer cells; HMGCS1 co-localizes with HMGCL (HMG-CoA lyase) and BRAF(V600E) in cytosol of melanoma and colon cancer cells. (BRAF = proto-oncogene protein B-raf) 30537987_Study showed that 5'isomiRNA of miR-140-3p (miR-140-3p-1) was preferentially expressed during the entire spectrum of preneoplastic progression in the MCF10A-derived triple negative breast cancer model. miR-140-3p-1 and its novel direct gene targets, HMGCR and HMGCS1, key enzymes in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, were deregulated in the normal-to-preneoplastic transition. 32126890_A new genetic locus for antipsychotic-induced weight gain: A genome-wide study of first-episode psychosis patients using amisulpride (from the OPTiMiSE cohort). 32692762_The mevalonate precursor enzyme HMGCS1 is a novel marker and key mediator of cancer stem cell enrichment in luminal and basal models of breast cancer. 33120050_Umbilical cord plasma-derived exosomes from preeclamptic women induce vascular dysfunction by targeting HMGCS1 in endothelial cells. 33601148_HMGCS1 drives drug-resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through endoplasmic reticulum-UPR-mitochondria axis. 34347016_TDP-43 mediates SREBF2-regulated gene expression required for oligodendrocyte myelination. 34454908_Interaction of Gal-7 with HMGCS1 In Vitro May Facilitate Cholesterol Deposition in Cultured Keratinocytes. 34526098_circHMGCS1-016 reshapes immune environment by sponging miR-1236-3p to regulate CD73 and GAL-8 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 34549901_Pan-cancer analysis reveals the oncogenic role of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase 1. 36328117_Compartmentalized activities of HMGCS1 control cervical cancer radiosensitivity. |
ENSMUSG00000093930 |
Hmgcs1 |
661.238124 |
3.7310895165 |
1.899597 |
0.127545635 |
213.049918 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000296812673672478183132876526608641897127089314102848068388825740531918812366433728346833045186901527211234013848880616609146598783297577028861269354820251464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000060594122592057780429685019746198573879147639256943556825452246036344785184899874975378384227761637856249996092690060902133386555590277566807344555854797363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1013.7199139 |
80.9940946 |
273.3167626 |
16.5037510 |
| ENSG00000112983 |
10902 |
BRD8 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0E9 |
FUNCTION: May act as a coactivator during transcriptional activation by hormone-activated nuclear receptors (NR). Isoform 2 stimulates transcriptional activation by AR/DHTR, ESR1/NR3A1, RXRA/NR2B1 and THRB/ERBA2. At least isoform 1 and isoform 2 are components of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complex which is involved in transcriptional activation of select genes principally by acetylation of nucleosomal histones H4 and H2A. This modification may both alter nucleosome - DNA interactions and promote interaction of the modified histones with other proteins which positively regulate transcription. This complex may be required for the activation of transcriptional programs associated with oncogene and proto-oncogene mediated growth induction, tumor suppressor mediated growth arrest and replicative senescence, apoptosis, and DNA repair. NuA4 may also play a direct role in DNA repair when recruited to sites of DNA damage. Component of a SWR1-like complex that specifically mediates the removal of histone H2A.Z/H2AZ1 from the nucleosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10517671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14966270, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24463511}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Growth regulation;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene interacts with thyroid hormone receptor in a ligand-dependent manner and enhances thyroid hormone-dependent activation from thyroid response elements. This protein contains a bromodomain and is thought to be a nuclear receptor coactivator. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:10902; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex [GO:0035267]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleosome [GO:0000786]; Swr1 complex [GO:0000812]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0097067]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone acetylation [GO:0016573]; histone H2A acetylation [GO:0043968]; histone H4 acetylation [GO:0043967]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:1905168]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000779] |
16571680_SMAP gene family constitutes an important ArfGAP subfamily, with each SMAP member exerting both common and distinct functions in vesicle trafficking. 19787264_BRD8 expression is associated with tumor progression toward advanced stages 23064015_incorporation of the histone variant H2A.Z at the promoter regions of PPARgamma target genes by p400/Brd8 is essential to allow fat cell differentiation 26940039_miR-185 can attenuate androgen receptor function indirectly by suppressing BRD8 ISO2 30237520_Taken together, our results suggest that BRD8 is involved not only in p53-dependent gene suppression, but also in the maintenance of genome stability. 32860757_BRD8, which is negatively regulated by miR-876-3p, promotes the proliferation and apoptosis resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via KAT5. 33476703_The Bromodomain Containing 8 (BRD8) transcriptional network in human lung epithelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000003778 |
Brd8 |
333.555539 |
0.4197235301 |
-1.252489 |
0.136733217 |
82.344421 |
0.00000000000000000011432371802105377947287054755510806484334203704712360979978136299450852675363421440124511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000996114567881200564421853669483386801209007867793172787823641201043756154831498861312866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
201.0011848 |
20.1406720 |
484.0569257 |
34.1987981 |
| ENSG00000113070 |
1839 |
HBEGF |
protein_coding |
Q99075 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor that mediates its effects via EGFR, ERBB2 and ERBB4. Required for normal cardiac valve formation and normal heart function. Promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation. May be involved in macrophage-mediated cellular proliferation. It is mitogenic for fibroblasts, but not endothelial cells. It is able to bind EGF receptor/EGFR with higher affinity than EGF itself and is a far more potent mitogen for smooth muscle cells than EGF. Also acts as a diphtheria toxin receptor. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Heparin-binding;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables growth factor activity and heparin binding activity. Involved in several processes, including epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling; and positive regulation of wound healing. Located in cell surface and extracellular space. Implicated in glomerulosclerosis and perinatal necrotizing enterocolitis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1839; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030297]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; ERBB2-EGFR signaling pathway [GO:0038134]; ERBB2-ERBB4 signaling pathway [GO:0038135]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of elastin biosynthetic process [GO:0051545]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0045741]; positive regulation of keratinocyte migration [GO:0051549]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells [GO:0035313] |
11761337_Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor decreases inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide production after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. 11769972_Site-directed mutagenesis of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF): analysis of O-glycosylation sites and properties 11920609_HB-EGF mRNA and protein levels in gastric cancers were elevated, compared with normal gastric tissues, especially in the intestinal type. 11922634_The current study reveals that HB-EGF mRNA is abundantly expressed in human and mouse adipose tissue, plasma HB-EGF levels increase in parallel with fat accumulation in human, and subjects with coronary artery disease have higher plasma HB-EGF levels. 11943653_Bronchial epithelial compression regulates MAP kinase signaling and HB-EGF-like growth factor expression. 11983897_Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor mediates the biological effects of P450 arachidonate epoxygenase metabolites in epithelial cells 12095415_nardilysin (NRDc) is potently inhibited by heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) 12099696_Helicobacter pylori-stimulated EGF receptor transactivation requires metalloprotease cleavage of HB-EGF 12112577_data suggest that uterine receptivity may be regulated in part by the stromal-derived HB-EGF 12230876_HB-EGF cytoprotection is due, in part, to its ability to decrease reactive oxygen species production 12568494_Review. The mode of activation of EGFR in response to bacterial lipoteichoic acid involves cleavage of the transmembrane ligand HBEGF by ADAM 10. 12612909_Transgenic expression of HB-EGF accelerates the proliferation of hepatocytes after partial hepatectomy 12725245_the effect of N- and C-terminal residues of the EGF-like domain of HB-EGF in the binding affinity to the EGF receptor on A431 cells 12768307_Diffusely expressed throughout normal and psoriatic epidermis and sparsely colocalized with EGFr in all viable epidermal layers, with increased colocalization in psoriatic epidermis. 12835543_HB-EGF has an important role in the early pathogenesis of psoriasis. 12882762_HB-EGF and FGF-2 act in concert to regulate the synthesis of elastin in injury/repair situations in pulmonary fibroblasts. 12952982_proHB-EGF shedding induced by TPA and angiotensin II requires PACSIN3 as an upregulator 12958167_Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor has a role in Angiopoietin-mediated recruitment of vascular smooth muscle cells. 14573593_GnRH-induced transactivation of the EGF-R and the subsequent ERK1/2 phosphorylation result from ectodomain shedding of HBEGF. 14634113_HB-EGF blocks cytokine-induced NF-kappaB activation and decreases nitric oxide production, interferes with cytokine-induced IkappaB kinase activity, inhibits phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha, and suppresses release of proinflammatory IL-8. 14738873_Results suggest that epidermal growth factor receptor HER-mediated autocrine and paracrine signaling by heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor or other EGF family members induces cytotrophoblast differentiation to an invasive phenotype. 14764442_Cis-acting element mediating gastrin responsiveness was mapped to the -69 to -58 region of the HB-EGF promoter. Gastrin stimulation was PKC dependent and at least partially mediated by activation of the EGF receptor. 15062539_The spatial and temporal pattern of HB-EGF expression suggest that HB-EGF may an important local regulator of ovarian function and structure. 15169883_relevance of a p38-ADAM-HB-EGF-EGFR-dependent pathway and its potential significance for tumor cells in evasion of chemotherapeutic agent-induced apoptosis 15274392_HB-EGF might be a more important tumor growth regulator of malignant fibrous histiocytoma through autocrine or paracrine pathways, when compared with betacellulin. 15289334_HB-EGF is a potent inducer of tumor growth and angiogenesis 15331606_the heparin-binding domain serves as a negative regulator of heparin-binding EGF-like Growth Factor 15389565_Results indicate that pro-heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (pro-HB-EGF) shedding and subsequent HB-EGF C terminal fragment signaling are related with progression of the cell cycle. 15509542_ADAM12m is highly expressed in human glioblastomas and may play a role in the prominent proliferation of the glioblastomas through shedding of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor 15562026_HB-EGF has a function in endometrial maturation in mediating decidualization and attenuating TNF alpha- and TGF beta-induced apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells. 15755902_HB-EGF/HER-1 signaling is relevant to mesenchymal stem cell biology, by regulating both proliferation and differentiation 15827558_These results suggested that HB-EGF in peritoneal fluid might play a key role in cell survival and in the proliferation of OVCA. 15979989_HB-EGF may play a vital role in regulating luteal growth in a juxtacrine manner and through activating HER4 signalling 15988409_HB-EGF is one of the factors that are significantly upregulated in PVR (proliferative vitreoretinopathy) retinas. 16034135_Recombinant HB-EGF decreases proinflammatory cytokine-stimulated NF-kappa B activation and nitric oxide production via activation of the phosphoinositide-3-kinase signaling pathway. 16407398_A post-transcriptional mechanism induced in trophoblasts by low O(2) rapidly amplifies HBEGF signaling to inhibit apoptosis. 16470170_HB-EGF and amphiregulin mediate retinoic-acid induced epidermal hyperplasia 16557002_results suggest a novel role for the cytoplasmic domain of HB-EGF that is regulated by phosphorylation 16687414_lysophosphatidic acid-induced IL-8 secretion is partly dependent on EGFR transactivation regulated by PKCdelta-dependent activation of Lyn kinase and MMPs and proHB-EGF 16837648_Inward potassium current in bladder urothelial cells(BUC) can be modulated by EGF and HB-EGF. Changes in BUC membrane potassium conductance caused by altered levels of EGF and HB-EGF may therefore play role in pathophysiology of interstitial cystitis. 16901467_Glutamatergic neurotransmission plays a crucial role in regulating ectodomain shedding of transgenic HB-EGF in the brains of transgenic mice that overexpress human HB-EGF. 16923819_Nardilysin has an essential role in HB-EGF ectodomain shedding, which is regulated by the modulation of sheddase activity 16996055_Results demonstrate that mRNA stability and in particular the heparin binding epidermal growth factor like growth factor (HB-EGF) 3'-untranslated region is involved in HB-EGF mRNA induction. 17001310_Chemotherapy-induced HB-EGF activation represents a critical mechanism of inducible chemotherapy resistance. 17392284_HB-EGF carboxyl-terminal fragment is a potent regulator of gene expression via its interaction with the transcriptional repressor Bcl6. 17472728_These findings demonstrate that amino-terminally truncated, membrane-bound form of HB-EGF stimulates cell proliferation but lacks insulin-like signalling. 17525275_HB-EGF is up-regulated in tumor cells of SCC but not BCC of the skin. HB-EGF is also overexpressed in asymptomatic epidermis adjacent to both SCC and BCC, relative to normal skin. 17548351_Gbetagamma mediates UVB-induced human keratinocyte apoptosis by augmenting the ectodomain shedding of HB-EGF, which sequentially activates EGFR and p38 17637826_activation of PPARdelta is a major event in psoriasis, contributing to the hyperproliferative phenotype by induction of HB-EGF. 17654528_The maintenance of the activation level of EGFR, which determines the cellular invasive potential, operates through an autocrine loop involving the JNK-dependent production of uPA and HB-EGF activity. 17668298_Plasma/bladder concentrations of recombinant human rhHB-EGF equivalents were significantly lower following the intravesicular route than following intravenous administration. Histologic tissue examination indicated no toxicity attributable to rhHB-EGF. 17717322_HB-EGF regulated epithelial repair is enhanced by IL-13 from airway epithelial cells 17855771_Juxtacrine activation of EGFR by membrane-anchored HB-EGF may play an important role in the regulation of tight junction proteins and transepithelial resistance. 17928891_alters the phenotype of keratinocytes in a manner similar to that observed during epidermal repair 17960400_TNFalpha may play a key role in cooperation with HB-EGF and AREG in the proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes at the psoriatic skin lesions. 17962208_HBEGF was present in almost all breast cancers studied. High expression is related to the biological aggressiveness of breast cancer. 18093224_HB-EGF acts as a negative adipogenesis regulator during the early but not later stages of adipocyte differentiation, block the commitment of pluripotent mesenchymal cells to the adipocyte lineage triggered by bone morphogenic protein 4. 18463770_Review. HB-EGF is implicated in angiogenesis, wound healing, blastocyst implantation, atherosclerosis, & tumor formation. It is the diphtheria toxin receptor. 18686008_A novel hairless model on an atopic dermatitis-prone genetic background generated by DTR transgenesis is reported. 18691754_HBEGF-mediated signaling significantly reduces trophoblast cell death at term and its deficiency in preeclampsia could negatively impact trophoblast survival. 18725202_These results suggest that HB-EGF-Cys/Ser(134/143) antagonizes EGFRs. 18852147_The roles of HB-EGF in cell adhesion, invasion, and angiogenesis in ovarian cancer, were examined. 18925469_HB-EGF regulates endothelial cell function via stimulation of eNOS and nitric oxide production to promote eNOS dependent angiogenesis. 18929421_Pro-inflammatory stimuli induce the release of HB-EGF from mesenchyme cells, which stimulates DNA-replication in initiated/premalignant hepatocytes 19064678_At least three genes, orthologous to loci in this LD block, HBEGF, IK, and SRA1, result independently in a phenotype of myocardial contractile dysfunction when their expression is reduced with morpholino antisense reagents. 19127210_Preclinical neonatal rat studies of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in protection of the intestines from necrotizing enterocolitis. 19218109_Increased HB-EGF expression may be implicated in the pathogenesis and development of gastric carcinoma. 19389413_HBEGF is a potent dilator of terminal mesenteric arterioles. 19559571_These results demonstrate that HB-EGF-induced eNOS activation depends on p42/p44 MAPK, PI3K/Akt pathways and endogenous VEGF in HaCaT cells. 19609315_lentivirus-mediated expression of soluble HB-EGF, but not soluble amphiregulin, strongly enhanced keratinocyte migration, even in the presence of metalloproteinase inhibitors 19671876_Measuring HIF1a, HB-EGF, and VEGF-C expression may contribute to a better understanding of the prognosis of patients with soft tissue sarcoma and may even play a crucial role for the distribution of patients to multimodal therapeutic regimens. 19682489_Cellular senescence of human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) is associated with an altered MMP-7/HB-EGF signaling and increased formation of elastin-like structures. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19919524_This data suggests that ethanol-induced apoptosis was reduced by HB-EGF, while hESC pluripotency was maintained. 19961362_Increased serum HB-EGF is associated with heart hypertrophy and elevated blood cholesterol. 19996587_We demonstrated that human adrenocortical carcinoma cells express HB-EGF 20130271_HBEGF advances trophoblast extravillous differentiation through coordinate activation of PI3 kinase, ERK, MAPK14, and JNK, while only MAPK14 is required for its antiapoptotic activity. 20131286_reduction of antiphospholipid-mediated HB-EGF represents an mechanism that is responsible for the defective placentation and heparin protects from aPL-induced damage by inhibiting antibody binding 20332144_mAbs efficiently inhibited ectodomain shedding of proHB-EGF, and consequently prevented the cell growth of the EGFR-expressing cells in a co-culture system with proHB-EGF-expressing cells. 20351696_induces several genes characteristics of columnar phenotypes of esophageal squamous epithelium in a paracrine manner 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20586269_HB-EGF participate in transactivation of EGF receptor under oxidative stress. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20739660_Endothelial-derived PDGFB and HBEGF both are required to control pericyte motility, proliferation, and recruitment along the endothelial cell tube ablumenal surface. 20847549_Recombinant HB-EGF significantly promotes rat PC12 cell neurite outgrowth, an effect blocked by EGF receptor (EGFR) inhibition or mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibition, but not by tyrosine kinase inhibition. 20856931_Expression of HB-EGF is regulated by miR-212 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 20889674_Results suggest that LTD induces EGF receptor transactivation through the release of HB-EGF in human bronchial epithelial cells with downstream release of CXCL8. 20946474_MT1-MMP co-expressed with HB-EGF in ovarian carcinoma cells potentiates the activity of HB-EGF to promote invasive tumor growth and spreading in vivo. 21386996_PKCalpha and PKCdelta regulate ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of heparin binding-EGF through separate pathways. 21413023_ATP induces HB-EGF synthesis and release by interacting with the P2 purinergic receptor and through p38 and ERK1/2 signaling in response to a challenging environment. 21640162_brief exposure to HB-EGF, but not to EGF, is sufficient to induce prolonged activation of the EGF receptor and to enhance healing 21788507_Hypoxic induction of PAR-2 was found to elicit an angiogenic endothelial cell phenotype and to specifically up-regulate heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF). 22009535_findings indicate that HB-EGF and PDGF reciprocally mediate the interaction of cancer cells with cancer-associated fibroblasts, promoting cancer cell proliferation in a paracrine manner 22110740_LIV-1 is involved in prostate cancer progression as an intracellular target of growth factor receptor signaling which promoted EMT and cancer metastasis 22136955_These results confirm that polymorphisms in the HGEGF gene are associated with pre-eclampsia. 22209887_Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor is a potent autocrine regulator of invasion activity in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 22291012_Lung cancer-derived galectin-1 enhances tumorigenic potentiation of tumor-associated dendritic cells by expressing heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. 22319602_variant 1936T prevents hsa-miR-1207-5p from down-regulating HBEGF in podocytes 22402363_study is the first report demonstrating a role for the ADAM-HBEGF-EGF receptor axis in Ox-PAPC induction of IL-8 in HAECs. 22592159_expression of HB-EGF in human KCs triggers a migratory and invasive phenotype with many features of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which may be beneficial in the context of cutaneous wound healing. 22646534_HB-EGF-C nuclear translocation might be crucial in gastric cancer invasion. HB-EGF-C nuclear translocation may offer a prognostic marker and a new molecular target for gastric cancer therapy. 22718294_Results suggest that heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a target for oral cancer and that CRM197 is effective in oral cancer therapy. 23146907_results indicate that Abl kinases negatively regulate HNSCC invasive processes through suppression of an HB-EGF autocrine loop responsible for activating a EGFR-Src-cortactin cascade 23349913_Our results show that HB-EGF acts as a cell proliferation and cell survival factor in cancer cells. 23376846_HB-EGF overexpression and Kras(G12D) together, but neither alone, increase cancer cell proliferation. 23443317_Results suggest that HB-EGF plays a pivotal role in the acquisition of tumor aggressiveness in TNBC by orchestrating a molecular hierarchy regulating tumor angiogenesis. 23589494_Hypoxia increased the levels and activity of the ADAM12 metalloprotease in a Notch signaling-dependent manner, leading to increased ectodomain shedding of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR) ligand heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. 23597914_Correlation has been found between HB-EGF expression/immunostaining and the different types of analyzed soft tissue sarcomas. 23598347_visualized spatiotemporal regulation of proHB-EGF shedding in individual cells using a simple method that measures changes in fluorescence ratios 23787814_A reciprocal cross-talk between intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells and myofibroblasts through the HB-EGF/EGFR axis contributes to CCA progression. 23907942_The study suggest that one of the causes of unexplained miscarriages may result from the impaired expression of heparanase and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. 23917679_HB-EGF acts as a potent paracrine and/or autocrine chemotactic factor as well as a mitogen that mediates HER1 and/or HER4 in the invasion and metastasis of thyroid carcinoma cells. 24013225_Autocrine HBEGF expression promotes breast cancer intravasation, metastasis and macrophage-independent invasion in vivo. 24038577_Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor and CD9 are likely implicated in processes that are highly relevant for MS lesion formation 24043629_a mechanism of a probiotic-derived soluble protein in modulating intestinal epithelial cell homeostasis through ADAM17-mediated HB-EGF release, leading to transactivation of EGFR. 24116709_studies suggest disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 12(ADAM 12S) and heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor(HB-EGF) are involved in cellular plasticity resulting in production of brown adipose tissue-like cells 24346967_Knockdown of HSP27 by shRNA decreased HB-EGF plus CXCL5-mediated tumor spheroid formation in a three-dimensional culture system, suggesting that AKT/HSP27 was required for HB-EGF/CXCL5-mediated cancer progression 24828490_HB-EGF is a biomarker for LPA1 receptor activation in human breast and prostate cancers. 25138066_the relative expression of hyalurosome (CD44, HAS3, HB-EGF) genes was found to be reduced in patients prior to topical treatment and to be notably increased following treatment. 25201063_MiR-212 exerts suppressive effect on SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells through targeting HBEGF. 25359857_Suggest high levels of HB-EGF contribute to carotid plaque stabilization and reduce the incidence of acute coronary events. 25510766_Urinary levels of NGF and HB-EGF may be potential biomarkers for evaluating outcome of overactive bladder syndrome treatment. 25517307_Studies indicate that heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a therapeutic target in some types of cancers. 25589361_Data suggest that placental expression of HBEGF, EGF (epidermal GF), and TGFA (transforming GF alpha) is down-regulated in pre-eclampsia as compared to normal term birth; each growth factor blocks cell death/apoptosis of cytotrophoblast cell line. 25717241_Serum sHB-EGF is closely correlated with advanced stage gastric cancer and can be a promising serological biomarker for GC. 26572150_HB-EGF is a molecular target for the resistance of ovarian cancer to paclitaxel and CRM197 as a HB-EGF-targeted agent might be a chemosensitizing agent for paclitaxel-resistant ovarian carcinoma 26974561_These results indicate that this new anti-HB-EGF mAb 2-108 would be useful in the diagnosis of HB-EGF-related cancers and would be a strong tool in both basic and clinical research on HB-EGF. 26980026_Serous carcinomatous component championed by expression of HB-EGF predisposes to recurrence/metastasis in stage I metastasis and recurrence in stage I uterine malignant mixed mullerian tumor. 27097072_This antibody reacts with human HB-EGF but not mouse HB-EGF. No cross-reactivity to other EGFR ligands was observed by antigen ELISA. 27243144_Results support the idea that excess heparin binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF) leads to a significant elevation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and ventricular dilatation. These data suggest a potential pathophysiological mechanism that elevated HB-EGF can elicit VEGF induction and hydrocephalus. 27496793_Annexin A2 and HB-EGF are overexpressed and are being secreted into serum in Her-2 negative breast cancer patients. 27701455_Study demonstrates that HBEGF is post-transcriptionally regulated by low O2 (placental environment) through a mechanism involving interactions of miRNAs with its 3'UTR. 27888810_macrophage-secreted MMP-9 released HB-EGF from macrophages, which increased MMP9 in OVCA433, resulting in a positive feedback loop to drive HB-EGF release and increase proliferation in co-culture. 28013056_MMP14 plays an important mechanistic role in NSCLC progression, by supporting cancer invasiveness, promoting collagen degradation, and releasing HB-EGF, which accelerates lung tumor progression. 28174207_Heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparin derivatives further enhance HBEGF-induced differentiation by forming a complex with the epidermal growth factor receptor 28183528_Genome-wide significant (GWS) associations in single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based tests (P |
ENSMUSG00000024486 |
Hbegf |
875.815110 |
2.5374795687 |
1.343396 |
0.054928513 |
609.799283 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001237101883276135033194981495281987602176458227905597658492927121171731656010069993437262481925259817980268151729479755985982321201172860014865126247939776703132248403787707081069076519501026167112 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000694282273656112219964222096140789203367143105674177016763715697714475082013710365453641190201552923161074986708972722918487218467313441208350632031580848148610224261089669227051896761077840032642 |
Yes |
No |
1263.3999472 |
39.4274148 |
501.4551799 |
12.7864779 |
| ENSG00000113108 |
10307 |
APBB3 |
protein_coding |
O95704 |
FUNCTION: May modulate the internalization of amyloid-beta precursor protein. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the APBB protein family. It is found in the cytoplasm and binds to the intracellular domain of the Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) as well as to other APP-like proteins. It is thought that the protein encoded by this gene may modulate the internalization of APP. Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10307; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:0050750]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
|
ENSMUSG00000117679 |
Apbb3 |
96.978259 |
0.3881293497 |
-1.365391 |
0.291713323 |
21.108245 |
0.00000434056437745119608114527723352615851126756751909852027893066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000014227566113963947372106529087876225503350724466145038604736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.8656384 |
10.3785621 |
153.0606505 |
18.3769193 |
| ENSG00000113161 |
3156 |
HMGCR |
protein_coding |
P04035 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of (3S)-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) to mevalonic acid, the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of cholesterol and other isoprenoids, thus plays a critical role in cellular cholesterol homeostasis (PubMed:2991281, PubMed:21357570, PubMed:6995544). HMGCR is the main target of statins, a class of cholesterol-lowering drugs (PubMed:11349148, PubMed:18540668). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11349148, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18540668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357570, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2991281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6995544}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Metabolic intermediate biosynthesis; (R)-mevalonate biosynthesis; (R)-mevalonate from acetyl-CoA: step 3/3. |
HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol synthesis and is regulated via a negative feedback mechanism mediated by sterols and non-sterol metabolites derived from mevalonate, the product of the reaction catalyzed by reductase. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is suppressed by cholesterol derived from the internalization and degradation of low density lipoprotein (LDL) via the LDL receptor. Competitive inhibitors of the reductase induce the expression of LDL receptors in the liver, which in turn increases the catabolism of plasma LDL and lowers the plasma concentration of cholesterol, an important determinant of atherosclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:3156; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; coenzyme A binding [GO:0120225]; hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) activity [GO:0004420]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; coenzyme A metabolic process [GO:0015936]; isoprenoid biosynthetic process [GO:0008299]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900222]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
11716764_Mevastatin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase attenuates VCAM-1 expression in umbilical vein endothelial cells, but increases E-selectin expression, after TNF-alpha induction. 12213890_characterization of the coordinated regulation of cholesterol metabolism in human liver; regulation of its mRNA in liver 12477733_regulation of isoprenoid/cholesterol biosynthesis in cells from mevalonate kinase-deficient patients by presence of this enzyme 12778445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14556080_HMG-CoA inhibition with cerivastatin reduced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and C5b-9-induced ERK1/2 activation 15090540_3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase is ubiquinated in permeabilized cells mediated by cytosolic E1 and a putative membrane-bound ubiquitin ligase 15199031_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15233402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15473258_The present study demonstrated that both SOD1 and the metal-free form of enzyme (Apo SOD1) inhibit HMG-CoA reductase gene expression in HepG2 cells, in normal human fibroblasts, and in fibroblasts of subjects affected by familiar hypercholesterolemia 15811249_Competitive inhibitors of the reductase induce the expression of LDL receptors in the liver, which in turn increases the catabolism of plasma LDL and lowers the plasma concentration of cholesterol, an important determinant of atherosclerosis. 16054061_data indicate that buildup of cholesterol synthesis intermediates represses the pathway selectively at HMGCR and reveal a previously unappreciated link between feedback inhibition of HMGCR and carbon flow through the cholesterol synthetic pathway. 16930778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17284348_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17284348_polymorphism of the HMGCR gene appears to be linked to both Alzheimer's risk and disease progression 17652086_In Schwann cells neuregulin-1 increases the transcription of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarylcoenzyme A reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol biosynthesis. 17855807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17870053_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17870053_These results suggest that the HMGCR gene may serve as a modifier gene for hypercholesterolemia in Chinese diabetic patients. 18024962_The roles of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP)-dependent gene expression, side chain oxysterol biosynthesis, and cholesterol precursors in the short term regulation of endoplasmic reticulum cholesterol level and HMGR activity, is examined. 18056971_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18056971_acute myocardial infarction from information on functional gene variants that favor inflammation or modulate cholesterol metabolism: IL6 -174 G/C, TNF -308 G/A, IL10 -1082 G/A, SERPINA3 -51 G/T, IFNG +874 T/A, HMGCR -911 C/A, and APOE epsilon2/3/4 18261733_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18332269_snp and the common haplotypes inferred from them were tested for association with plasma LDL-C and LDL-C response to simvastatin in blacks and whites. Black carriers of H7 and/or H2 had lower baseline LDL-C and significantly attenuated LDL-C response 18354102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18459144_HIF-1alpha accumulation is able to increase level and activity of HMG-CoAR by stimulating its transcription 18559695_a common HMGCR SNP located within intron 13 was associated with variation in the proportion of HMGCR mRNA that is alternatively spliced 18622260_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18787507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18802019_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18802019_Identified variants in HMGCR that are associated with LDL-cholesterol across populations and affect alternative splicing of HMGCR exon13. 18815589_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19053857_Expression of the HMGCR gene was up-regulated by lovastatin (P A HMGCR affect the blood apoB levels which might be predictive of cardiovascular disease risk. [Meta- analysis] 30483734_HSP90 interacted with 3hydroxy3methylglutarylCoA reductase (HMGCR), the ratelimiting enzyme of mevalonate pathway, in the immunoprecipitation assay. 30537987_Study showed that 5'isomiRNA of miR-140-3p (miR-140-3p-1) was preferentially expressed during the entire spectrum of preneoplastic progression in the MCF10A-derived triple negative breast cancer model. miR-140-3p-1 and its novel direct gene targets, HMGCR and HMGCS1, key enzymes in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway, were deregulated in the normal-to-preneoplastic transition. 30588482_Anti-HMGCR myopathy can resemble limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD). Diagnosis of patients with a LGMD-like presentation of anti-HMGCR myopathy is critical because these patients may respond favorably to immunotherapy, especially those with shorter disease duration. 30692522_Statin treatment led to an upregulation of HMGCR mRNA and protein expression by up to sixfolds in the statin-resistant cells lines (p |
ENSMUSG00000021670 |
Hmgcr |
1098.429606 |
2.9902260592 |
1.580255 |
0.127174875 |
148.166861 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000043617043875412465855628635405664586940077632068825671251617708215461491532571447805074864312313565051226760260760784149169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000006348989818551163717510045091021147122305548970310436949763789572680841963552246106044889273345432911810348741710186004638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1683.6655584 |
129.3742335 |
566.9208831 |
32.3562711 |
| ENSG00000113273 |
411 |
ARSB |
protein_coding |
P15848 |
FUNCTION: Removes sulfate groups from chondroitin-4-sulfate (C4S) and regulates its degradation (PubMed:19306108). Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, cell migration and invasion in colonic epithelium (PubMed:19306108). In the central nervous system, is a regulator of neurite outgrowth and neuronal plasticity, acting through the control of sulfate glycosaminoglycans and neurocan levels (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P50430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19306108}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Ichthyosis;Leukodystrophy;Lysosome;Metachromatic leukodystrophy;Metal-binding;Mucopolysaccharidosis;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
Arylsulfatase B encoded by this gene belongs to the sulfatase family. The arylsulfatase B homodimer hydrolyzes sulfate groups of N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine, chondriotin sulfate, and dermatan sulfate. The protein is targeted to the lysozyme. Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder resulting from a deficiency of arylsulfatase B. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:411; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; arylsulfatase activity [GO:0004065]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase activity [GO:0003943]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; colon epithelial cell migration [GO:0061580]; lysosomal transport [GO:0007041]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010632]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to methylmercury [GO:0051597]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to pH [GO:0009268] |
11668612_Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI: Structural and clinical implications of mutations in N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase 14974081_Seven novel mutation were identified in ARSB in mucopolysaccharidosis type VI patients undergoing a Clinical trial of enzyme replacement therapy, 3 of these mutations resulted in truncated proteins. 16435196_analysis of novel mutations on the arylsulphatase B gene in South American Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI patients 17324393_Decreased arylsulfatase B activity is associated with cystic fibrosis 17458871_The identification of many novel mutations unique to individuals/their families highlighted the genetic heterogeneity of the mucopolysaccharidosis VI disorder. 17643332_Novel mutations in arylsulfatase B is associated with mucopolysaccharidosis VI 18285341_modification of expression of the lysosomal sulfatases ASB and GALNS regulates the content of CSs. 18299243_Reduced activity of arylsulfatase B enzymatic activity in children with cystic fibrosis 18406185_All the ARSB mutations studied had a significant effect on enzyme activity, protein processing and/or mRNA stability. 18486607_arylsulfatase B gene mutation profile in Taiwanese MPS VI patients may be different from MPS VI patients from other countries[mucopolysaccharidosis type VI ] 19306108_Arylsulfatase B regulates colonic epithelial cell migration by effects on MMP9 expression and RhoA activation. 19346317_IL-8 increases in bronchial epithelial cells after arylsulfatase B silencing due to sequestration with chondroitin-4-sulfate 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21378286_Altered ARSB immunostaining and reduced activity may be useful indicators of malignant transformation in human colonic tissue. 21996138_13 mucopolysaccharidosis type VI patients were found to be homozygous for the previously undescribed H178L ARSB mutation 22079206_investigation of substrate specificity of arylsulfatase B in colonic epithelial cells; competitive binding of complex polysaccharides/glycosaminoglycans with arylsulfatase B can affect generation of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory response 22428001_Hypoxia reduces arylsulfatase B activity and silencing arylsulfatase B replicates and mediates the effects of hypoxia. 22550062_Arylsulfatase B activity was significantly less in the polymorphonuclear leukocytes and mononuclear cells from the cystic fibrosis patients than controls. 22971959_PTC124 but not gentamicin, increases the level of ARSB activity. 23023219_Sequencing analysis revealed a novel homozygous missense mutation in the ARSB gene at c.1457A 23520469_results indicate that mammalian ARSB improves functional recovery after CNS injury. 23835622_ARSB activity was significantly higher in the normal tissues. 23855929_novel homozygous missense mutation, c.278 C>T, p.P93L, associated with mucopolysaccharidosis type VI 24240681_Arylsulfatase B regulates versican expression by galectin-3 and AP-1 mediated transcriptional effects. 24677745_Mutation analysis of the ARSB gene revealed seven missense and three frameshift mutations of which eight were novel. 24778176_These studies reveal how carrageenan exposure can lead to transcriptional events in colonic epithelial cells through decline in arylsulfatase B activity, with subsequent impact on C4S, galectin-3, Sp1, and Wnt9A 25511584_Silencing Wnt9A increased the expression of CHST11 in the colonic epithelial cells, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay demonstrated enhancing effects of Wnt9A siRNA and exogenous BMP4 on the CHST11 promoter 26609033_Nine novel mutations of ARSB were identified in MPS VI cases from India in the present study. The study also provides some insights into the genotype-phenotype association in MPS VI 27797586_Three novel mutations in ARSB were detected, expanding the mutational spectrum of ARSB causing MPS VI. A compound heterozygous for the c.464G>A (p.C155Y) and c.1163G>C (p.R388T) mutations, a 13.8-kb deletion encompassing exons 2 and 3, mutation c.479G>A (p.R160Q), and novel c.464G>A (p.C155Y) mutation. 27826022_Mutation analysis of 19 Indian mucopolysaccharidosis VI patients revealed the presence of a total of 15 different mutations of which twelve were novel. 28659610_The outcome of this study highlight a potential role for arylsulfatase B in promoting atherosclerosis-related stroke and warrants its further investigation as a therapeutic target that could be of potential clinical benefit. 28884960_Of the 20 patients included in the study, molecular genetic analysis was performed on 17 patients... molecular analysis results of four patients who was excluded from the overall study (three of which were another adult male siblings who did not receive ERT and one patient whose ERT duration was shorter than 6 months) were were included in determination of allele frequency of ARSB. 29081414_Findings indicate that lower arylsulfatase B (ARSB) is associated with prostate cancer recurrence. 29703589_Decreased ARSB expression is associated with cystic fibrosis. 29794138_Low ARSB expression is associated with prostate cancer. 30982216_Data of this study confirms the existence of mutational heterogeneity in the ARSB between Iranian patients. 31009684_Sequencing analysis of ARSB gene revealed four pathogenic homozygote mutations, including a novel nonsense mutation c.281C>A (p.Ser94X) in 9 patients, as well as, a known nonsense mutation c.753C>G (p.Try251X) in 3 cases, and two missense mutations c.904G>A (p.Gly302Arg) and c.454C>T (p.Arg152Trp) in two cases. The type of mutations affected the severity patient's phenotypes. 32664626_A Possible Role for Arylsulfatase G in Dermatan Sulfate Metabolism. 34435740_Deep intronic variant in the ARSB gene as the genetic cause for Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome (MPS VI). 34948256_Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VI, an Updated Overview of the Disease. 36361933_Profound Impact of Decline in N-Acetylgalactosamine-4-Sulfatase (Arylsulfatase B) on Molecular Pathophysiology and Human Diseases. |
ENSMUSG00000042082 |
Arsb |
514.363947 |
2.4792556154 |
1.309907 |
0.073085060 |
325.841697 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000077355003362241899488220550566011660847222424276766469398885427742978327138109126764817118865378265756307177028723789775003661125619121056740559349343433834130308582749266848248943448385084309393278090283274650573730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023786663533889385820628719083848332400232623620274715667433129430772082514233845730042313713147798194018912117473412557382242987054300961582829350792606957783315107281754691029643233868284823984140530228614807128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
745.9763629 |
36.3660055 |
303.2029881 |
11.6082064 |
| ENSG00000113302 |
3593 |
IL12B |
protein_coding |
P29460 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that can act as a growth factor for activated T and NK cells, enhance the lytic activity of NK/lymphokine-activated killer cells, and stimulate the production of IFN-gamma by resting PBMC. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114383}.; FUNCTION: Associates with IL23A to form the IL-23 interleukin, a heterodimeric cytokine which functions in innate and adaptive immunity. IL-23 may constitute with IL-17 an acute response to infection in peripheral tissues. IL-23 binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R, activates the Jak-Stat signaling cascade, stimulates memory rather than naive T-cells and promotes production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. IL-23 induces autoimmune inflammation and thus may be responsible for autoimmune inflammatory diseases and may be important for tumorigenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114383}. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of interleukin 12, a cytokine that acts on T and natural killer cells, and has a broad array of biological activities. Interleukin 12 is a disulfide-linked heterodimer composed of the 40 kD cytokine receptor like subunit encoded by this gene, and a 35 kD subunit encoded by IL12A. This cytokine is expressed by activated macrophages that serve as an essential inducer of Th1 cells development. This cytokine has been found to be important for sustaining a sufficient number of memory/effector Th1 cells to mediate long-term protection to an intracellular pathogen. Overexpression of this gene was observed in the central nervous system of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), suggesting a role of this cytokine in the pathogenesis of the disease. The promoter polymorphism of this gene has been reported to be associated with the severity of atopic and non-atopic asthma in children. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3593; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; interleukin-12 complex [GO:0043514]; interleukin-12 receptor complex [GO:0042022]; interleukin-23 complex [GO:0070743]; interleukin-23 receptor complex [GO:0072536]; late endosome lumen [GO:0031906]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; interleukin-12 alpha subunit binding [GO:0042164]; interleukin-12 receptor binding [GO:0005143]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101]; natural killer cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002323]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903588]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032700]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900747]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; positive regulation of activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0010536]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation [GO:0050671]; positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation [GO:0043382]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation [GO:0032946]; positive regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032816]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002860]; positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation [GO:0032819]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of NK T cell activation [GO:0051135]; positive regulation of NK T cell proliferation [GO:0051142]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0034393]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002827]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment [GO:2000330]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:2000318]; positive regulation of tissue remodeling [GO:0034105]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042509]; response to UV-B [GO:0010224]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; sexual reproduction [GO:0019953]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0042088]; T-helper cell differentiation [GO:0042093] |
11196715_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11753820_inherited interleukin-12 deficiency: IL12B genotype and clinical phenotype of 13 patients from six kindreds 11813133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11820460_Heparins (unfractionated heparin, UFH and low molecular weight heparin certoparin) had no effect on the release of IL-1ra, IL-10, and IL-12p40 from neutrophils or peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 11940489_STATE OF ART REVIEW. Malignant B-cells from follicular and marginal zone lymphomas expressed IL-12 p35 and p40 transcripts, whereas only p35 mRNA was detected in mantle cell lymphoma. 11972887_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11972887_The IL12B gene does not confer susceptibility to coeliac disease 11978670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12065887_results suggest that LPS stimulates the pituitary gland directly in vivo to increase IL-12 p40 gene expression 12100467_DISCUSSION FORUM: it is the p40 protein, either alone or paired with other polypeptides, rather than p75, that acts as an interface between the innate and adaptive immune responses 12117904_Leishmania priming of human dendritic cells for CD40 ligand-induced interleukin-12p40 secretion is strain and species dependent 12117918_The purified lipoprotein, Lpk, from Mycobacterium leprae, was found to induce production of interleukin-12 in human peripheral blood monocytes 12202149_results suggest that impaired IL-12 production in HIV-infected myeloid cells occurs, in part, via disruption of IL-12 p40 gene expression in a manner that requires cellular infection 12207325_ATPgammaS potentiated the IL-12p40 release induced by TNF-alpha. This potentiation was observed as long as the IL-12p40 concentration under agonist stimulation remained below a threshold value close to 10 ng/ml; inhibition was observed above this value. 12241719_IL12B promoter heterozygosity contributes to asthma severity rather than susceptibility per se. 12241719_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12270766_possible role of IL-12 and tissue antioxidants in development and progression of chronic sinusitis 12297341_role of CD28 and IL-12/IL-15 signaling impairment in T cell proliferative deficiency during senescence 12413772_IL12B SNP is associated with susceptibility to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris, presumably by affecting the Th1/Th2 balance. 12413772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12424624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12424627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12472178_IL-12 expression in PMN of SLE patients was less prominent than that of the normal controls. 12672403_A key mechanism in the pathogenesis of MS is the increased expression of CD86 and CD40L and the increased production of IL12 during disease progression. 12857749_Interleukin-10 induction of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression attenuates CD40-mediated interleukin-12 synthesis in human endothelial cells. 12876411_Diesel exhaust particles seem to inhibit the production of IL-12 p40 in lipopolysaccharide activated monocytes as a model for lung macrophages 12914676_These two potentially important candidate gene single nucleotide polymorphisms are not associated with susceptibility to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 14551880_IL-12B 3'untranslated region has no effect or has a negligible effect on human susceptibility to tuberculosis. 14551880_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14675396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14675396_The IL12B TaqI gene polymorphisms do not appear to be involved in susceptibility to celiac disease 14679201_interleukin-12 p40 transcription and NF-kappaB activation are inhibited by nitric oxide in macrophages and dendritic cells 14746806_Data show that reverse signaling via 4-1BB-ligand enhanced interleukin-12beta mRNA and the secretion of IL-12 p70 in various antigen-presenting cells, including monocytes. 14962816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14976188_identify erythroid Kruppel-like factor as a transcription factor in macrophages able to regulate IL-12 p40 transcription depending on the cellular activation status 15004750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007350_no evidence to support the presence of a heterozygote effect of the IL12B promoter polymorphism on the level of asthma in early childhood or adulthood 15057902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15102082_Frequencies of the various genotypes for the promoter region of the gene encoding IL-12p40 (IL12B) did not differ between psoriasis patients and controls. 15102082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15285014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15285014_The polymorphism of IL12B (1188A/C) appears to have some influence on the outcome of hepatitis c virus infection. 15295696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15295696_association between IL12B intron 2 polymorphism and tuberculosis and between specific IL12B haplotypes and TB found in Hong Kong Chinese population 15322986_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15322986_We found a strong association between the IL12B_4237 and IL12B_6402 polymorphisms and an asthma-severity phenotype in whites. 15356557_Decreased LPS-induced IL-12(p70) and IL-10 responses were associated with the TLR4 (Asp299Gly) polymorphism and independently with asthma, especially atopic asthma in school-age children 15448160_interleukin 12 and interferon gamma are involved in inhibition of cytotrophoblastic cell invasion 15464247_No association of IL12B polymorphisms and self-limited HCV infection could be demonstrated. 15464247_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15482860_p300 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of IL-12 p40, and IL-12 p40 is one of the target genes of p300 15483662_A direct role for IL12B in susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease is unlikely. 15483662_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15523691_study shows that PBMCs of patients with advanced gastric cancer show poor production of TNF and IL-12p40 in response to stimulation with tumor cells in vitro & this unresponsiveness is associated in some patients with diminished IRAK-1 expression in vivo 15603869_Heterozygosity of a polymorphism in the 3'untranslated region of the IL12B gene was associated with a delayed disease in late-onset diabetics. 15603869_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15620465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15620465_The IL12B 1188 (A-->C) gene polymorphism is not involved in defining the genetic basis of the susceptibility to and final outcome of peptic ulcer disease. 15644581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15837792_synthesis in RAW264.7 cells is induced by IRF-8 15858599_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15869883_reversible histone acetylation/deacetylation modification plays an important role in the transcriptional regulation of IL-12 15871664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15871664_chronically infected patients were significantly more likely than those with resolved HCV infection to be homozygous for the IL-12B 3'-UTR A allele 15937086_IL12B gene polymorphisms may affect the final steps of gastric carcinogenesis in H pylori infected subjects. 15941730_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15988104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15993716_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16005098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16005098_The IL-12B 3'UTR A-C polymorphism would be considered as a supplementary risk factor for Type 1 diabetes in conjunction with HLA haplotypes. 16039994_The pro-inflammatory nature of hResistin was further evident from the ability of this protein to induce the nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB transcription factor as seen from electrophoretic mobility shift assays. 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16210052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16216674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16514412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16514412_Our results provide evidence for anti-bacterial host response toward Th1-immunity mediated by IL-12B in patients with Adamantiades-Behcet's disease (ABD), and the possible insight into the genetic susceptibility that is independent of HLA background. 16574246_Among cytokines affecting T helper type 1 (Th1)-Th2 balance, the levels of IL-12 p40 and its autoantibody are specifically elevated in patients with myasthenia gravis complicated by thymoma. 16600026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16637265_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16681592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16712658_The 1188A/C exchange in the IL12B gene is associated with Th1-mediated infectious diseases such as tuberculosis and salmonellosis 16750991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16772281_Increased concentrations of p40 subunit of IL-12/IL-23 in follicles containing oocytes suggest an important role of this cytokine in reproduction. 16789008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16789008_The association of IL-12p40 A1188C polymorphism with the outcome of HCV infection is reported. 16948912_Th1-type cell and related cytokines might play an important role in the pathogenesis of HT and GD. 16966828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17148969_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17152005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17172248_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17236132_IL12B and IL23R genes play a fundamental role in psoriasis pathogenesis. 17236132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17327408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17388919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17392024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17403771_upon activation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies, only 25% of the CD4+ T cells from HIV-1 patients showed an increase in the IL-12beta2 when compared with 50% in healthy controls 17445208_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17445208_Polymorphic variants in the IL12B gene is associated with leprosy and tuberculosis 17477815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17504509_IL-12B-3'UTR polymorphism may contribute to silicosis severity rather than to susceptibility 17504509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17509455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17513774_IL-12p40-transgenic C57BL/6 mice characterized by overexpression of p40 show increased levels of serum IL-12p80 and enhanced disease susceptibility. 17564777_mRNA levels of IL12 subunit p40 in active SLE patients was significantly higher compared with those in the inactive SLE patients 17567674_downregulation of TLR2 and decreased production of interleukin-12 p40 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha following Mycobacterium avium or lipoteichoic acid stimulation may contribute to host susceptibility to nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease 17579859_IL-12 may have a role in progression of the colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence 17587057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17587057_Sequence variants in the genes for the interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R) and its ligand (IL12B) confer protection against psoriasis. 17644387_IL12B 3' UTR C allele was present at significantly higher frequency in cardiomyopathic as compared to asymptomatic. Results suggest that IL12B 3' UTR gene polymorphisms may influence the susceptibility to develop Chagasic cardiomyopathy. 17644387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17653830_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17846855_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17881511_Engagement of gC1qR on dendritic cells by hepatitis C virus core protein limits the induction of Th1 responses by inhibiting TLR-induced IL-12 production and may contribute to viral persistence. 17889143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17901940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17901940_four variants (rs11209026, rs7517847, rs1343151, rs10889677) of IL-23R and the A1188C polymorphism (rs3212227) of IL-12B are unlikely to be major contributors to the pathogenesis of myocardial infarction 17932439_IL -10 (-1082 G/A) and IL -12B 3'UTR (Taq I) (A/C) gene polymorphisms were not associated either with susceptibility or resistance to pulmonary tuberculosis in the south Indian population. 17932439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17945537_results here show that IL-23 is elevated in children with malarial anemia, and that IL-10 and IL-12 appear to have important regulatory effects on IL-23 production during childhood malaria 17993580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17994425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18034172_polymorphism associated with early onset psoriasis 18048021_A heightened, perhaps persistent, activational state of IL-12(p40)/Stat4 signaling may be present in active Chinese ulcerative colitis (UC) patients, and possibly involved in chronic inflammation in UC. 18075513_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18082575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18082575_no strong evidence was present in this study to support a role for the IL12B/IL23R psoriasis-associated SNPs in multiple sclerosis susceptibility; the potential role of other, unlinked SNPs in these genes with a very modest influence cannot be excluded 18086266_Homozygosity of high producer IL-12p40 genotype IL-12Bpro-11 and -GG had the highest genetic risk of silicosis development in Bulgarian miners. 18086266_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18092318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18163209_Association of interleukin-6, interleukin-12, and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms with essential hypertension in Tatars from Russia 18163209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18190588_an increased expression of IL-12 p40, IL-12 p35 and IL-23 p19 mRNA was observed in bone marrow mononuclear cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with aplastic anemia compared with the corresponding one in normal controls. 18192685_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18219280_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18219280_Polymorphisms of the IL12B and IL23R genes are associated with psoriasis. 18240960_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18300039_IL-12 p40 mRNA levels were significantly up-regulated in PHA-activated PBMCs. 18319400_NK cells require in vivo priming with IL-12/23 to acquire their full spectrum of functional reactivity, while T cells are dependent upon IL-12/23 signals for the differentiation and/or the maintenance of CD56(+) effector memory T cells 18341612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18367309_IL12B polymorphisms IVS2 -912GG genotype and IVS2 -912G:IVS4 +314A haplotype are associated with increased risk for cervical cancer in Korean women. 18367309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18369459_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18383521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18383521_Single nucleotide polymorphism in IL12B is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 18389618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18413324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18413324_The IL12B promoter polymorphism was associated with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. 18422730_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18438406_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18449199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18449199_This study characterized the genetic variation in IL12B in 215 individuals belonging to 34 families and evaluated linkage and association of parasitemia with IL12B polymorphisms and haplotypes. 18485489_IL-12 p40 3'UTR 1188 A/C polymorphism is associated with greater susceptibility to lepromatous leprosy in patients from western Mexico 18485489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18497679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18512797_interleukin 12B (IL12B) variants are not associated with rheumatoid arthritis. 18522869_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18557702_These results implicate IL-12 and IL-27 in regulating human macrophages, and IL-27 derived from macrophages during infection impedes control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth. 18563338_interleukin-12 has a role in the killing activity of lymphocytes on Hela cells 18588591_Genotypical variations of the IL-12B (40) gene have not been investigated for schizophrenic patients yet.We examined polymorphic variants of IL-12B (p40). 18588591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18606709_study demonstrates that oxidative stress induced by soluble cigarette smoke components potently inhibits the production of IL-12 and IL-23 by maturing dendritic cells 18619507_results demonstrate that IL-12 improves the cytotoxicity of NK cells in an NKG2D-dependent manner and augments the expression of cytotoxic effector molecules 18628242_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18631256_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18632587_Polymorphisms in the IL12B promoter region associate with two different clinical courses of steroid-sensitive childhood nephrotic syndrome. 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18680750_Data suggest that the structure of interleukin-23 reveals the molecular basis of p40 subunit sharing with interleukin-12. 18703108_results demonstrated that the production of IL-10 from PBMC depended on both -1082A*G in IL10 and +16974A*C in IL12B polymorphisms 18717726_IL-12 promotes disease development in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. 18800148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18800148_variants are not specific risk factors for arthritis, but relevant for susceptibility to psoriasis in general 18821674_in the presence of IL-18, cutaneous lupus erythematosus keratinocytes failed to express IL-12 18827961_Serum levels of p40 IL-12/23 may not be considered as a biologic tool of disease activity assessment in spondyloarthropathy (SpA) patients. Mean levels of synovial p40 IL12/23 were higher in SpA patients compared to osteoarthritis patients. 18834321_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19035472_Variation within IL23R and IL12B is associated with susceptibility to both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis 19118071_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19118071_These findings suggest that IL12A rs568408 and IL12B rs3212227 may individually and jointly contribute to the risk of cervical cancer and may modify cervical cancer risk associated with parity. 19134014_The IL-12/23p40 gene -6415CTCTAA/GC polymorphism is involved in cytokine production potential by affecting Sp1-mediated transcription activity. 19169254_Expanded catalog of genetic loci implicated in psoriasis susceptibility. 19169254_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19169255_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19169255_Strong replication for two known susceptibility loci MHC and IL12B in psoriasis. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19174780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19185507_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19210338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19210338_genetic variants at position +16974 are associated with susceptibility to chronic periodontitis [in Taiwan] 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19249008_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19262574_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19264456_Bioactive forms of IL-12 and IL-23 are highly expressed in various DC and macrophage subsets and their marked in situ production suggest that both cytokines have crucial pathogenic role in psoriasis. 19274925_In asthmatic patients, the effects of the IL-12B polymorphism on asthma, allergic rhinitis, familial asthma, eosinophilia and total IgE levels, are controversial. 19274925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19279357_IL12B polymorphisms were found to be both positively (susceptible) and negatively (protective) associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Macedonians. 19328947_IL12B 3'UTR polymorphism does not affect graft survival, delayed graft function or acute rejection, but it has impact on the occurrence of cytomegalovirus infection after kidney transplantation. 19328947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19342681_p40(2) participates in the pathogenesis of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and that neutralization of p40(2) may be beneficial in multiple sclerosis patients 19419334_Reduced IL-12p40 and IL-10 production of monocyte-derived dendritic cells generated from HIV infected patients who were receiving receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy or are therapy naive is reported. 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19435421_Polymorphismin the interleukin-12-3' untranslated region is associated with glioma. 19487916_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19487916_This is the first study to provide an evidence for the association of IL-12beta (1188A/C) gene polymorphism with the risk of cervical cancer. 19495883_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19505916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19516896_analysis of the link between the evolutionary conservation of Vpr and its ability to suppress IL-12 secretion by DC 19525409_data suggest that although IL23R contributes to Rheumatoid Arthritis aetiology, its effect is seemingly not the same as that reported in Crohn's disease. 19554267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19646340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19683555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19705136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19733878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773451_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19782084_Higher serum levels of IL-10 and IL-12 in HBeAg-positive patients are correlated with early, spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion 19819209_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19832040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19832040_Polymorphisms in IL12B were not associated with the development of colorectal carcinoma but IL-12p40 serum levels were associated with disease progression. 19838195_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19860911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956104_present the analysis of a set of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within and flanking the IL12B gene; no SNP showed individually significant association in the population as a whole. 20003322_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20003322_The existence of a significant association between the [IL12B promoter allele] CTCTAA allele and susceptibility to cerebral malaria was confirmed in Southeast Asian population, which was previously reported in African populations. 20014019_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20016509_Studies indicate that modulation of TH-17 cell function and/or differentiation has proceeded to the greatest extent with monoclonal antibodies to IL-12 p40. 20027321_Susceptibility to tuberculous infection is associated with AC genotype of the polymorphic region A-1188C in the IL12 gene. 20054003_Data show that that 4-trifluoromethyl-celecoxib can inhibit secretion but not transcription of IL-12 (p35/p40) and IL-23 (p40/p19 heterodimers), and that this is associated with HERP function in the endoplasmic reticulum. 20060272_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20061784_IL- 18 and IL-12p40 polymorphisms may have some effect on the onset age and deterioration of glycemic control in Turkish patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. 20105444_increased production by PBMC isolated from systemic lupus erythematosus patients 20145925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20217072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20236616_IL-2, IL-10 and IL-12B are regulated by 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20349123_TL1A increased cytotoxicity of IL-12/IL-18-activated NK cells against target cells dependent on NK activation for lysis and could function in vivo as a key co-activator of NK cytotoxicity. 20350312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20371868_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20372811_Data show that exosomes inhibited the expression of JAK3 and phosphorylation of STAT5 in high doses in T-cells, but not JAK2, while EXO/IL-12 had much less attenuated reduction of the expression of p-STAT5. 20387064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20387064_genotypic and haplotypic variation at IL12Bpro and IL12B 3' UTR in this population influences susceptibility to severe malaria and functional changes in circulating IL-12p40 and IFN-gamma levels. 20395963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20399512_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20483637_results indicate JNK1 negatively and JNK2 positively regulates IL-12 synthesis induced by LPS in THP-1 macrophages; PI3K p110beta affects JNK1 activity, but not JNK2 activity, as induced by LPS, resulting in positive regulation of IL-12 p40 production 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20521253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20525402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20544370_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20551083_Describe the successful construction, characterization and production of the heterodimeric immunocytokine F8-IL12. Engineered tumor-targeting heterodimeric immunocytokine F8-IL12 using different combinations of the two subunits (p35 and p40). 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20621951_Early treatment of multiple sclerosis with IFN-beta1b may stabilize clinical disease by attenuating level of Il-12p40. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20653817_The observed discordance in periodontal breakdown in the studied monozygotic twin population may be related to the relatively low levels of IL-12p40 secretion after ex vivo stimulation of whole-blood cell cultures. 20653995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20653995_The allelic as well as genotypic frequencies of interleukin-12B gene polymorphisms did not significantly differ between HIV-1/AIDS patients and negative healthy controls. 20658240_Genotype-22 of IL12Bpro was predominantly combined with genotype-AA of a single nucleotide polymorphism in 3'UTR among systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and this combination elevates the risk of SLE. 20658240_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20705102_inhibits acute myeloid leukemia cell growth 20711808_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20714168_Findings in this study suggest that adiponectin, IL-12p70, and IL-13 may play a role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802378_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20811626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navi |
ENSMUSG00000004296 |
Il12b |
9.246999 |
103.5133144122 |
6.693673 |
1.104990833 |
56.823640 |
0.00000000000004767012663607722469312604381501183406125805516739823985972179798409342765808105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000308330880433172588484386362435380836476226523723553896161320153623819351196289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.0098904 |
14.3694768 |
0.1751981 |
0.1363372 |
| ENSG00000113356 |
10622 |
POLR3G |
protein_coding |
O15318 |
FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Specific peripheric component of RNA polymerase III which synthesizes small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs (PubMed:20154270). May direct with other members of the RPC3/POLR3C-RPC6/POLR3F-RPC7/POLR3G subcomplex RNA Pol III binding to the TFIIIB-DNA complex via the interactions between TFIIIB and POLR3F. May be involved either in the recruitment and stabilization of the subcomplex within RNA polymerase III, or in stimulating catalytic functions of other subunits during initiation. Plays a key role in sensing and limiting infection by intracellular bacteria and DNA viruses. Acts as nuclear and cytosolic DNA sensor involved in innate immune response. Can sense non-self dsDNA that serves as template for transcription into dsRNA. The non-self RNA polymerase III transcripts, such as Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs), induce type I interferon and NF- Kappa-B through the RIG-I pathway (PubMed:19609254, PubMed:19631370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19609254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154270}. |
3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription |
|
Enables chromatin binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of innate immune response; positive regulation of interferon-beta production; and transcription by RNA polymerase III. Acts upstream of or within cell population proliferation. Located in cytosol and nuclear body. Part of RNA polymerase III complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10622; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase III complex [GO:0005666]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity [GO:0003899]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006359]; transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006383] |
21898682_Decreased levels of POLR3G result in loss of pluripotency and promote differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to all three germ layers but have no effect on cell apoptosis. 28494942_POLR3G regulates small non-coding RNAs and RNA splicing in human pluripotent stem cells. The primary function of POLR3G is in the maintenance rather than repression of transcription. 30820548_Depletion of POLR3G selectively triggers proliferative arrest and differentiation of prostate cancer cells, responses not elicited when POLR3GL is depleted. 30972912_FCER1A (rs7549785) and possibly POLR3G (rs7712322) are shown to be associated with peginterferon alfa-2a response in adult patients with chronic hepatitis B. 33626331_RNA polymerase III is required for the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by homologous recombination. 35637192_A cancer-associated RNA polymerase III identity drives robust transcription and expression of snaR-A noncoding RNA. |
|
|
105.456455 |
55.5157314394 |
5.794825 |
1.337877492 |
12.577521 |
0.00039041422230663989966295557287878636998357251286506652832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000978189428152436866656382896678678662283346056938171386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
245.3424301 |
213.1097562 |
4.5494324 |
2.7728166 |
| ENSG00000113361 |
1004 |
CDH6 |
protein_coding |
P55285 |
FUNCTION: Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins. They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells; cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the cadherin superfamily. Cadherins are membrane glycoproteins that mediate homophilic cell-cell adhesion and play critical roles in cell differentiation and morphogenesis. The encoded protein is a type II cadherin and may play a role in kidney development as well as endometrium and placenta formation. Decreased expression of this gene may be associated with tumor growth and metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:1004; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; catenin complex [GO:0016342]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; adherens junction organization [GO:0034332]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; cell-cell junction assembly [GO:0007043]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560] |
20634887_The chromatin modifications were determined at five PRC2 targets commonly underexpressed in multiple myeloma (CIITA, CXCL12, GATA2, CDH6 and ICSBP/IRF8). The selected genes were confirmed to be underexpressed in MM compared to normal plasma cells. 24069422_CDH6 is under the control of the transcription factor RUNX2, which we previously described as a crucial mediator of the Id1 pro-invasive function in thyroid tumor cells. 26285159_Data indicate that BRAFV600E, P-cadherin and cadherin 6 protein expressions were correlated with one another. 27593557_Tumor suppressor genes deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1), F-box/WD-repeat-containing protein 7 (FBXW7), and cadherin-6 (CDH6) were identified as presumed targets in Cholangiocarcinoma (CC).Inverse correlation between promoter methylation and expression suggested miR-129-2 and members of the miR-200 family (miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-429) as novel tumor suppressors and oncomiRs, respectively, in CC 29628305_our findings demonstrate that CDH6 exerts as an important independent biomarker that could predict human osteosarcoma clinical outcomes. miR-223-3p can inhibit cell invasion, migration, growth, and proliferation in osteosarcoma by directly targeting CDH6 30806528_The low endometrial expression of beta-catenin, E-cadherin and K-cadherin were associated to fertility-related problems, such as primary intertility and recurrent pregnancy loss. 32427856_CDH6 and HAGH protein levels in plasma associate with Alzheimer's disease in APOE epsilon4 carriers. 32600462_Characterization of the role for cadherin 6 in the regulation of human endometrial receptivity. |
ENSMUSG00000039385 |
Cdh6 |
6.127487 |
0.1748425503 |
-2.515872 |
0.777495605 |
11.948798 |
0.00054682634137939679572215645464439148781821131706237792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001332533729364354614307930368966026435373350977897644042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6581330 |
0.9578095 |
9.5875009 |
2.7601239 |
| ENSG00000113389 |
4883 |
NPR3 |
protein_coding |
P17342 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the natriuretic peptide hormones, binding with similar affinities atrial natriuretic peptide NPPA/ANP, brain natriuretic peptide NPPB/BNP, and C-type natriuretic peptide NPPC/CNP. May function as a clearance receptor for NPPA, NPPB and NPPC, regulating their local concentrations and effects. May regulate diuresis, blood pressure and skeletal development. Does not have guanylate cyclase activity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70180}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Chloride;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes one of three natriuretic peptide receptors. Natriutetic peptides are small peptides which regulate blood volume and pressure, pulmonary hypertension, and cardiac function as well as some metabolic and growth processes. The product of this gene encodes a natriuretic peptide receptor responsible for clearing circulating and extracellular natriuretic peptides through endocytosis of the receptor. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:4883; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chloride ion binding [GO:0031404]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; natriuretic peptide receptor activity [GO:0016941]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007194]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; osteoclast proliferation [GO:0002158]; pancreatic juice secretion [GO:0030157]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; positive regulation of urine volume [GO:0035810]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033688]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11556325_protein structure: ligand binding domains 12768436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12872042_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12872042_The novel Npr1 gene 3C variant and the Npr3 gene C(-55) allele are associated with hypertensive family history. 15017020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15459247_Atrial natriuretic paptide, purified from medium bathing cells expressing NPR-C, a receptor known to internalize natriuretic peptides, was degraded. 15785005_Novel six-nucleotide repeat polymorphism located 4 base pairs upstream of the major transcriptional initiation site. 15785005_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15911071_model of hormone recognition and allosteric receptor activation revealed from structural studies of NPR-C [review] 15911072_discussion of NPR-C receptor coupling to different signaling pathways and their regulation [review] 16870210_A structural comparison of complexes of NPC-C with each NP hormones (ANP, BNP, and CNP)reveals that NPR-C uses a conformationally inflexible surface to bind three different, highly flexible, NP ligands. 17890443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17890443_The NPRC polymorphism is not an independent determinant of NP concentration in HF. 17951249_Ostn is a naturally occurring ligand of the NPR-C clearance receptor and may act to locally modulate the actions of the natriuretic system in bone by blocking the clearance action of NPR-C, thus locally elevating levels of C-type natriuretic peptide. 18633189_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19326473_Genetic variation within the NPPA/NPPB and NPR3 genes is associated with risk of VnD after primary coronary artery bypass grafting 19326473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343178_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19352691_the NPR-C receptor is expressed in normal and neoplastic human alpha cells. 19458086_Data indicate that the familial ANP mutation associated with atrial fibrillation has only minor effects on natriuretic peptide receptor interactions but markedly modifies peptide proteolysis. 19570815_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19570815_results suggest that variation in the C-type natriuretic peptide signaling pathway, involving the NPPC and NPR3 genes, plays an important role in determining human body height. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20691218_The mRNA levels of natriuretic peptide receptor-C appear to be increased in epicardial adipose tissue independent of their plasma levels in coronary artery disease. 20700369_The data indicates that ANP, BNP, and CNP and natriuretic peptide receptor transcripts are expressed and are functional in human lens epithelial cells. 20823417_integrative genomics approach to a large cohort of medulloblastomas has identified four disparate subgroups (NPR3)with distinct demographics, clinical presentation, transcriptional profiles, genetic abnormalities, and clinical outcome. 21464461_Data found a consistent and significant association between the rs2270915 polymorphism of the NPR3 gene and SBP in diabetic patients. This genetic variation may affect pressure response to changes in dietary sodium. 22001395_Results demonstrate the opposite effects of NPR-A and NPR-C in LPS-mediated endothelial permeability and lung injury. 22421372_Report the presence of CNP and its receptors, NPR2/3 in atherosclerotic plaques of human carotid artery, with increased expression of NPR3 in histologically unstable plaques. 22559095_polymorphisms or haplotype in NPR3 gene may influence the risk of ischemic stroke or hypertension independently in Chinese population. 22995222_a NPR3 promoter gene variant could have a role on cerebrovascular disease susceptibility 23493048_The significant change in NPR3 protein was observed for the Arg146 variant allozyme, with 20% of wild-type protein, primarily because of autophagy-dependent degradation. 24465655_Data show that natriuretic peptide receptor 3 (NPR3) single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is independently associated with diastolic dysfunction and does not appear to be related to alterations in circulating levels of natriuretic peptides. 25711724_Angiotensin II downregulates vascular smooth muscle cell NPR-C gene expression by destabilizing its mRNA. 25736855_Results from this study point to a role for miR-100 in the regulation of NPR3 expression, and suggest a possible therapeutic target for modulation of NP bioactivity in heart disease. 26345810_This study focused on the natriuretic peptide receptor C gene (NPR3). The correlation analysis between NPR3 and hypertension was replicated in 450 Chinese Dai and 484 Chinese Mongolian individuals. 26782497_The NPRC genetic variant,Rs1847018, is a genetic marker of essential hypertension. 27191271_NPR-C gene single nucleotide polymorphisms significantly contribute to CAD susceptibility in the Chinese Han population 28497617_This study suggested that NPR3 rs2270915 polymorphism was associated with decreased systolic blood pressure level marginally in essential hypertension patients in a Chinese Han population; the polymorphism may function through decreasing NPR3 mRNA expression and ANP level. 28659173_NPR3 expression is downregulated by MRCCAT1 in the in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 29040610_study identifies novel, putative mechanisms for BP-associated variants at the NPR3 locus to elevate blood pressure. 29242602_loss of NPR-C reduces HRV due to perturbations in the regulation of the heart by the autonomic nervous system 29409758_It was the aim to investigate the expression of natriuretic peptide receptors NPR-A, NPR-B and NPR-C during adipocyte differentiation (AD), upon stimulation with fatty acids (FA), and in murine and human adipose tissue depots. 29523263_Suggest that pro-ANP/corin/NPR-C signaling is dominant in the vascular system in preeclampsia. 30591105_The levels of ANP, NPRA, IL-4 and GATA3 increased in peripheral blood of children with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. 31234560_A role of NPR-C mutation in pulmonary arterial hypertension is reviewed. 32251605_LncRNA FENDRR Upregulation Promotes Hepatic Carcinoma Cells Apoptosis by Targeting miR-362-5p Via NPR3 and p38-MAPK Pathway. 34229087_NPR3, transcriptionally regulated by POU2F1, inhibits osteosarcoma cell growth through blocking the PI3K/AKT pathway. 34668435_Oxygen and steroids affect the regulatory role of natriuretic peptide receptor-C on surfactant secretion by type II cells. |
ENSMUSG00000022206 |
Npr3 |
30.580962 |
0.0489379585 |
-4.352902 |
0.522259632 |
83.270829 |
0.00000000000000000007154766563440535840831504572435063859546443319386012610165692660046943274210207164287567138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000630473758067954002009375536356817826086340961439722892570292067659920576261356472969055175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1756098 |
1.2372252 |
65.3534006 |
12.1550463 |
| ENSG00000113494 |
5618 |
PRLR |
protein_coding |
P16471 |
FUNCTION: This is a receptor for the anterior pituitary hormone prolactin (PRL). Acts as a prosurvival factor for spermatozoa by inhibiting sperm capacitation through suppression of SRC kinase activation and stimulation of AKT. Isoform 4 is unable to transduce prolactin signaling. Isoform 6 is unable to transduce prolactin signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12580759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20032052}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a receptor for the anterior pituitary hormone, prolactin, and belongs to the type I cytokine receptor family. Prolactin-dependent signaling occurs as the result of ligand-induced dimerization of the prolactin receptor. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different membrane-bound and soluble isoforms have been described for this gene, which may function to modulate the endocrine and autocrine effects of prolactin in normal tissue and cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:5618; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; endosome lumen [GO:0031904]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor binding [GO:0005127]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; leukemia inhibitory factor receptor activity [GO:0004923]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; prolactin receptor activity [GO:0004925]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0042976]; activation of transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0007171]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; lactation [GO:0007595]; localization [GO:0051179]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; oncostatin-M-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038165]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; prostate gland growth [GO:0060736]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030856]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694] |
11721697_Review: Prolactin receptor signal transduction 11997178_results presented are consistent with a role of the PRL-PRLR system in bone/cartilage formation/repair processes 12021177_Genomic regions containing exons for human prolactin receptor, and 5'-flanking and intronic sequences, were determined and their order was established in chromosome 5p14-13. 12351696_Given its apparent widespread expression, this PRLr isoform may contribute to PRL action. 12391112_Plasma prolactin elevated in exercise and correlated with total prolactin-receptor expression per B lymphocyte. Increase in prolactin-receptor per B lymphocyte in response to exercise. Increased circulating B lymphocytes expressing prolactin receptor. 12477494_Results demonstrate a stimulatory effect of estradiol on the expression of human prolactin receptor mRNA species with alternative exons-1, hE1(3) and hE1(N1)in breast cancer cells. 12559630_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12559630_To evaluate a possible role of prolactin receptor genes in SLE & MS formed an association study of PRLR SNPs was done. No statistically significant difference in the prolactin allele distribution was observed for any of the tested variations. 12668872_the interaction between Cyclophilin A and the PRLR plays a differential regulatory role in the various signaling pathways leading from the PRLR. 12679477_results demonstrate a direct effect of prolactin, via functional prolactin receptors, in reducing the lipoprotein lipase activity in human adipose tissue 12819209_prolactin signaling is attenuated by phosphorylation of the prolactin receptor on Thr391 12937675_expression in hepatocytes was maximum in secondary liver cancer, high in obstructive jaundice, and less in cholelithiasis; expression in cholangiocytes was higher than in hepatocytes and was maximum during obstructive jaundice 15082796_data indicate that the prolactin receptor is a novel SCF(beta-TrCP) substrate and implicate beta-TrCP as an important negative regulator of prolactin signaling and cellular responses to this hormone 15119991_A150C (Leu-->Ile) transversion at exon 6 of PRLR was detected.Polymorphism of prolactin receptors might play a role in mammary carcinogenesis 15119991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15135067_transactivation occurs through an indirect interaction between erbB2 and prolactin or leptin receptors 15504038_Data support an 'induced-fit' model for prolactin receptor binding where binding of the first receptor to human prolactin induces a conformation change in the hormone creating the second receptor-binding site. 15618286_Prolactin receptor mediates the Vav2 and Nek3 interaction. 15700312_Responsiveness of ovarian carcinomas to prolactin suggest that the prolactin/prolactin receptor system may be a new therapeutic target of ovarian carcinomas. 16103113_prolactin binding initiates limited proteasomal cleavage of its receptor, generating a cell-associated fragment containing the extracellular domain; findings described new potential mediator of prolactin action 16278670_phosphorylation of prolactin receptor on Ser349 is decreased in breast cancer cells lines and primary cancer tissue that exhibit stabilization and accumulation of prolactin receptor 16434456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16556730_Prolactin acts on the preformed Long Form homodimer to induce active signal transduction, while Short Form heterodimer lacks cytoplasmic sequences essential for activation. 16651265_a novel Estradiol-regulated non-estrogen responsive element-dependent transcriptional mechanism that mediates hPRLR expression 16785991_The data suggest that prolactin synergistically augments epidermal growth factor signaling in T47D breast cancer cells at least in part by lessening EGF-induced epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation. 17177141_An analysis of changes in the the expression of the prolactin receptor in liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis. 17525486_The data revealed a widespread expresion of PRLR in normal and neoplastic human thyroid tissues. 17785459_residual agonism can be abolished either by further disrupting hormone site 2-receptor contacts by N-terminal deletion, as in Del1-9-G129R-human prolactin (hPRL), or by stabilizing hPRL and constraining its intrinsic flexibility, as in G129V-hPRL 18053149_In this comprehensive analysis covering 59 kb of the PRL locus and 210 kb of the PRLR locus, we found no significant association between common variation in these candidate genes and breast cancer risk or plasma PRL levels. 18053149_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18081308_Results demonstrate that altered extracellular domain conformation, and not just a change in bulk, produces altered conformation of the intracellular signaling region of the receptors. 18207134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18207134_The resulting pattern of findings confirmed the hypotheses of the significance of the genes involved in the development of affiliative behaviors in the manifestation of ASD, the strongest results were obtained for allelic associations with the PRLR genes. 18252943_Prolactin promotes phosphorylation of PRLr on Ser349 and accelerates endocytosis of PRLr. Prolactin stimulated PRLr phosphorylation, endocytosis, and degradation in Jak2-null cells reconstituted with wild type Jak2. 18316598_GSK3 beta is a bona fide PRLr kinase that phosphorylates PRLr on Ser(349) and is required for the recognition of PRLr by beta Trcp, as well as for PRLr ubiquitination and degradation 18573876_The results of experiments using forced expression of ubiquitin mutants indicate that PRLr polyubiquitination via K63-linked chains is important for efficient interaction of PRLr with AP2 as well as for efficient internalization. 18596217_Mechanisms controlling PRLR isoform expression in the fallopian tube. 18613925_Prolactin receptor is significantly more expressed in male breast carcinoma than in gynaecomastia, and with different patterns of reactivity, suggesting a role for prolactin in male breast carcinogenesis. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18681966_Autocrine prolactin appears to act as an inducible survival factor in a clonogenic subpopulation of breast cancer cells 18779591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18779591_a heterozygous single nucleotide polymorphism in exon 6 of the PrlR gene, encoding Ile(146)-->Leu substitution in its extracellular domain confers constitutive activity to the receptor variant 19056863_Data indicate that src family kinases are key mediators of ligand-initiated prolactin receptor internalization, down-regulation, and signal transduction in breast cancer cells. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19153125_Even a very low level of PRLR expression was found to be sufficient to mediate PRL responsiveness in breast cancer cell lines. 19273600_Results suggest that the prolactin receptor conformation as stabilized by S-S bonds is required for the inhibitory action of S1b on prolactin-induced LF-mediated function and JAK2 association. 19276348_Human mammary epithelial cells harboring degradation-resistant PRLr display accelerated proliferation and increased invasive growth. 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19739126_Increased expression of short form 1b prolactin receptor in prostate cancer cells decreases cell growth and cell migration and reduced invasive capacity. 19897676_Characterization of two constitutively active prolactin receptor variants in a cohort of 95 women with multiple breast fibroadenomas. 19897676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19906835_short form (sf)1b affects the end result of signaling through the long form(LF) receptor and the effects on cell number also support the concept that the LF:SF1b ratio may be relevant to tumor growth 20032052_four splice variants in spermatozoa 20053995_PRL structure will be a useful guiding tool for further investigations of the molecular mechanisms involved in PRLR dimerization and activation, as well as for the optimization of PRLR antagonists 20214633_Usually where breast STAT5a is present, PRLR is reduced; without STAT5a PRLR becomes abundant. Breast lesions lacking both were tested immunohistochemically for PRLR isoforms. The intermediate isoform was essentially only detected in these lesions. 20335148_The positive correlations in positivity rate between the PRL-R and ER/PR expressions are found only in CerbB-2 positive patients with breast cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20427283_Results strongly support a conformationally mediated obligate-ordered prolactin receptor binding for each of the three lactogenic hormones: prolactin, growth hormone, and placental lactogen. 20453834_prolactin receptor expression is common in colorectal cancer 20547007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20655519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20658264_Our study suggests the prolactin receptor gene is a molecular target that may be important in the pathogenesis and progression of lobular neoplasia 20716560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20826546_SIRPalpha modulates PRL receptor-associated signaling as a function of integrin occupancy by mediating integrin-PRL receptor cross-talk and contributing to breast cancer biology. 20846877_Blockade of the PRLR represents a novel treatment for patients with advanced breast or prostate cancer with limited therapeutic options. 20875426_This study allowed to visualize for the first time the loop L5 spanning PRLR2 residues Thr133-Phe140, revealing its central implication for the three intermolecular interfaces of the 1:2 complex between natural prolactin and two PRLR chains. 20889499_Two independent histidines, one in human prolactin and one in its receptor, are critical for pH-dependent receptor recognition and activation. 20962278_acetylation and deacetylation provide the rheostat-like regulation for the cytokine receptor PRLR in its cytoplasmic loop dimerization and subsequent STAT5 activation 21068074_Prolactin receptor signaling contributes to the local inflammatory response within the atherosclerotic plaque and thus to atherogenesis. 21125332_These findings suggest that the polymorphism rs10941235 in the PRLR gene is associated with breast cancer and cancer antigen 15-3 levels in Taiwanese women. 21144038_Rabbit antibodies have high titer and could specifically recognize each isoform of PRLR in breast cancer cell lines and human breast carcinoma biopsies. 21238538_Progesterone induces expression of the prolactin receptor gene through cooperative action of Sp1 and C/EBP transcription factors 21305610_Our results indicate no significant association of prolactin and PRLR polymorphisms with clozapine response, tardive dyskinesia diagnosis or its severity in patients with schizophrenia 21310852_Endogenous GH receptor(GHR) and PRLR associate, possibly as a GHR-PRLR heterodimer, in human breast cancer cells and GH signaling in these cells is largely mediated by the PRLR in the context of both PRLR-PRLR homodimers and GHR-PRLR heterodimers. 21470416_data provide limited support for an association between common variations in PRLR and breast cancer risk 21510945_both Zn(2+) and human PRLr binding influence human PRL conformers in an interdependent fashion 21591677_Functional impact of manipulation on the relative orientation of human prolactin receptor domains. 21670145_Enhanced complex formation of ERalpha dimer with SP1 and C/EBPbeta by E2 has an essential role in the transcriptional activation of the hPRLR gene. 21775057_Data show that cells expressing higher long:short PRLR ratios had increased growth, survival and migration in response to PRL and suggest that PRLR antagonists may be therapeutically beneficial in ovarian cancer. 21816901_The association of the PRLr with HMGN2 enables Stat5a-responsive promoter binding, thus facilitating transcriptional activation and promoting anchorage-independent growth. 21989556_PRL signaling through the long form prolactin receptor causes reduced fatty acid oxidation, increased lipid storage, glucose intolerance, and obesity. 22081226_These results demonstrate important contextual aspects of PRL-PRLR interactions with implications for the analysis of the role of PRL in breast cancer. 22325776_The structure of the human prolactin receptor reveals a structural link between the WSXWS motif, hormone binding, and receptor dimerization and we propose it as a general mechanism for class 1 receptor activation. 22577091_can be activated by three sequence-diverse human hormones: prolactin, GH, and placental lactogen [review] 22606260_PRLr isoforms expression and PRLr subcellular localisation are altered in parathyroid tumours 23159947_The prolactin receptor transactivation domain is associated with steroid hormone receptor expression and malignant progression of breast cancer 23192981_Our data suggest that prolactin receptor presence meaningfully affects growth hormone receptor use in breast cancer cells. 23651351_SNPs of the PRLR gene 5' UTR and promoter region are associated with increased risk for gestational diabetes in a population of Chilean subjects. 23775766_Results demonstrate a novel function for hepatic PRLR in the regulation of insulin sensitivity and provide important insights concerning the nutritional regulation of PRLR expression. 23849393_Data suggest that signal transduction via prolactin and prolactin receptor plays role in trophoblast cell migration and invasion; PRLR is expressed by extravillous cytotrophoblasts and first-trimester placental bed tissue. 24032713_Hypertrimethylation on H3K27 of the p53 gene promoter region due to elevated expression of DeltaS2 PRLR by alternative splicing of the pre-mRNA in its full-length form might serve as a new mechanism underlying prostate cancer 24142695_PRL-induced transient signaling in sensory neurons is governed by PI3K or PKCepsilon, mediated via the PRLR-S isoform, and transient effects mediated by PRLR-S are inhibited by presence of PRLR-L in these cells. 24195502_Thus, the familial hyperprolactinemia appears to be due to a germline, loss-of-function mutation in PRLR, resulting in prolactin insensitivity. 24249584_Negative/low expression is associated with poorly differentiated and larger breast tumors in Poland 24333596_PRL-R attenuation post-transcriptionally increased ZnT2 abundance and redistributed intracellular Zn pools into lysosomes and mitochondria. 24391856_High MFAB expression is associated with testicular germ cell tumor and glioblastomas. 24735798_Major changes in prolactin receptor conformation and dimerization affinity are triggered by single mutations in critical regions of D1. 24758841_PRL induced transient signaling pathways in neurons and modulated ion channels. [review] 24990775_There is a possible role for PRLR in the progression of cervical cancer. 24997655_exposure to prolactin increases TNF-alpha release from CD14(+) monocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients, which can be abolished by PRLR gene silencing or treating with MAPK inhibitor. 25524456_Study shows that position 146 plays a central role in directing intrinsic properties of the PRLR, including extracellular domain folding, PRL-responsiveness, and ligand-independent activity of the receptor. 25784554_a residue quartet in the extracellular membrane proximal domain of the homodimeric cytokine receptor prolactin receptor is a key regulator of intracellular signaling discrimination 25846210_Data suggest that (1) cell membrane/lipid bilayer binding of PRLR and (2) tyrosine phosphorylation of PRLR intracellular domain are independent. 26095602_long PRLR plays an important role in breast cancer metastasis. 26317306_results highlight PRLR as an independent predictor of favorable prognosis in human breast cancer 26513615_Two markers for the PRL peptide gene and three markers for the prolactin receptor (PRLR) gene were genotyped. 26586670_PRL-PRLR can escalate the impact of breast cancer on bone metastasis and the presence of PRLR in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer bone metastasis has the potential to modulate the microenvironment to induce lytic osteoclast formation. 26641246_This study identified 4 PRLR variations (p.Ile76Val, p.Ile146Leu, p.Glu108Lys and p.Glu554Gln) in 16 Sporadic Prolactinoma in Humans. 26844452_The prolactin receptor is constitutively expressed on regulatory T and effector T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients, and this expression is higher than in healthy individuals. 27480353_Low PRLR expression is associated with Triple Negative Breast Cancer. 27575941_PRLRI146L and PRLRI176V variants are not associated with breast cancer or multiple breast fibroadenomas risk. 27788487_Prl receptor is expressed at different levels in the majority of glioblastoma multiforme tumors. Prolactin stimulation resulted in increased STAT5 phosphorylation and increased cellular invasion. 28377489_These results illustrate promising antitumor activity against PRLR-positive breast cancer xenografts and support the evaluation of anti-PRLR antibody-drug conjugate as potential therapeutic agents in breast cancer. 28980840_In a replication study of the association between the prolactin receptor gene intron C/T polymorphism (rs37389) and recurrent miscarriage, no association was found. 29901521_Prolactin-PRLR signaling may play a crucial role for the progression of type I endometrial cancer (EC) without involving the PTEN mutation in young hyperprolactinemic women without insulin resistance. 30445560_our results identify an association between a gain-of-function PRLR variant and prolactinomas and reveal a new etiology and potential therapeutic approach for these neoplasms. 30987013_loss of the co-expression of PRLR, TGFbetaRI and TGFbetaRII is indicative of aggressiveness and poor patient survival outcomes in breast cancer. 31389293_Association between prolactin receptor expression and proliferation in the endometrium of obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 32116231_PRLR probably plays a different role in the development and progression of breast cancer. In luminal A and luminal B HER2-positive subtypes PRLR may act as an oncogen, and in luminal B HER2-negative and ER-, PR-negative subtypes can play a tumor suppressor role. 32199279_Prolactin receptor expression as a novel prognostic biomarker for triple negative breast cancer patients. 32286456_Prolactin Acts on Myeloid Progenitors to Modulate SMAD7 Expression and Enhance Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation into the NK Cell Lineage. 32360085_Upregulation of Prolactin Receptor Expression and Activation of Prolactin Signaling in an Aggressive Triple-Negative Breast Carcinoma During Pregnancy: A Case Report. 33259941_Immunohistochemical localization of prolactin receptor (PRLR) to Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's lymphoma. 33335078_Progesterone receptor isoform-dependent cross-talk between prolactin and fatty acid synthase in breast cancer. 33608185_Prolactin receptor expression and its role in trophoblast outgrowth in human embryos. 33664869_The short isoform of PRLR suppresses the pentose phosphate pathway and nucleotide synthesis through the NEK9-Hippo axis in pancreatic cancer. 33942735_Changes in prolactin receptor location in prostate tumors.', trans 'Cambios en la localizacion del receptor prolactina en tumores prostaticos. 35922139_Breast Cancer and Prolactin - New Mechanisms and Models. 36187116_Prolactin receptor gene transcriptional control, regulatory modalities relevant to breast cancer resistance and invasiveness. |
ENSMUSG00000005268 |
Prlr |
22.027658 |
0.4104795485 |
-1.284618 |
0.361667196 |
12.864366 |
0.00033489825385198633816291602371961744211148470640182495117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000848746261479278491131339468012129145790822803974151611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.4134081 |
5.1087254 |
25.0926539 |
8.5329690 |
| ENSG00000113555 |
51294 |
PCDH12 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPG4 |
FUNCTION: Cellular adhesion molecule that may play an important role in cell-cell interactions at interendothelial junctions (By similarity). Acts as a regulator of cell migration, probably via increasing cell-cell adhesion (PubMed:21402705). Promotes homotypic calcium-dependent aggregation and adhesion and clusters at intercellular junctions (By similarity). Unable to bind to catenins, weakly associates with the cytoskeleton (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O55134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21402705}. |
Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Primary microcephaly;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the protocadherin gene family, a subfamily of the cadherin superfamily. The encoded protein consists of an extracellular domain containing 6 cadherin repeats, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic tail that differs from those of the classical cadherins. The gene localizes to the region on chromosome 5 where the protocadherin gene clusters reside. The exon organization of this transcript is similar to that of the gene cluster transcripts, notably the first large exon, but no significant sequence homology exists. The function of this cellular adhesion protein is undetermined but mouse protocadherin 12 does not bind catenins and appears to have no affect on cell migration or growth. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51294; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; labyrinthine layer development [GO:0060711]; neuron recognition [GO:0008038] |
19054571_A putative association was also found between protocadherin 12 and cortical folding (asymmetry coefficient of gyrification index). 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21402705_PCDH12 may play an important role in human placental development, and proteolytic cleavage in response to external factors, such as cytokines and pathological settings, regulates its activity 27164683_Genome-wide analysis to determine the genetic cause of a microcephaly syndrome; found that loss of function of PCDH12 leads to recessive congenital microcephaly with profound developmental disability 29904113_WHSC1 gene variant is associated with dyskinetic cerebral palsy with epilepsy. 30178464_Autosomal-recessive malformation, diencephalic-mesencephalic junction dysplasia syndrome patients have biallelic mutations in PCDH12 and lack of protein expression. 30459466_Homozygous PCDH12 mutation is associated with cerebellar ataxia, dystonia, retinopathy, and dysmorphism. 33527719_Ophthalmic phenotypes associated with biallelic loss-of-function PCDH12 variants. 34773825_The phenotypic spectrum of PCDH12 associated disorders - Five new cases and review of the literature. 34929393_PCDH12 variants are associated with basal ganglia anomalies and exudative vitreoretinopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000024440 |
Pcdh12 |
117.700650 |
0.3253817810 |
-1.619795 |
0.242901044 |
43.061854 |
0.00000000005303629744900820261325299804953611621655129582109111652243882417678833007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000279377498339529270789855691284721619926934010891272919252514839172363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.4174016 |
11.8293116 |
168.2703808 |
25.5111422 |
| ENSG00000113643 |
5917 |
RARS1 |
protein_coding |
P54136 |
FUNCTION: Forms part of a macromolecular complex that catalyzes the attachment of specific amino acids to cognate tRNAs during protein synthesis (PubMed:25288775). Modulates the secretion of AIMP1 and may be involved in generation of the inflammatory cytokine EMAP2 from AIMP1 (PubMed:17443684). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17443684, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25288775}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative initiation;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Leukodystrophy;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Arginyl-tRNA synthetase belongs to the class-I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5917; |
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex [GO:0017101]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; arginine binding [GO:0034618]; arginine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004814]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; arginyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006420]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418] |
16055448_leucyl-tRNA synthetase requires its C-terminal domain for its interaction with arginyl-tRNA synthetase in the multi-tRNA synthetase complex 17443684_RARS over-expression impairs aminoacyl t-RNA synthetase interacting multifunctional protein (AIMP1) secretion by both HeLa and MCF7 cells. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20923763_Hemin binds to human cytoplasmic arginyl-tRNA synthetase and inhibits its catalytic activity 24777941_report describe 4 patients with hypomyelination and mutations in RARS 24859084_The crystal structures of the L-arginine-complexed, and L-canavanine-complexed forms of arginyl-tRNA synthetase from Homo sapiens. 24898251_The mRNA of human cytoplasmic arginyl-tRNA synthetase recruits prokaryotic ribosomes independently. 25288775_interactions between the N-terminal domains of ArgRS and AIMP1 are important for the catalytic and noncatalytic activities of ArgRS and for the assembly of the higher-order MSC protein complex with ArgRS-GlnRS-AIMP1 25724651_Data indicate that the N terminus of Pro-EMAP II binds to its C terminus, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, and the neurofilament light subunit. 28905880_Missense variant Ser456Leu and a de novo deletion Tyr616Leufs*6 cause disorder akin to Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. 29133573_we demonstrated the presence of the recurrent RARS-MAD1L1 gene fusion in NPC. Furthermore, we provided the first evidence showing that the RARS-MAD1L1 fusion gene enhances tumorigenicity, CSC-like properties, and therapeutic resistance 30006346_This study demonstrates that human mitochondrial AspRS, ArgRS, and LysRS, each have a specific sub-mitochondrial distribution, with ArgRS being exclusively localized in the membrane, LysRS exclusively in the soluble fraction, and AspRS being present in both. 31814314_RARS1-related hypomyelinating leukodystrophy: Expanding the spectrum. 33515434_Distinct pathogenic mechanisms of various RARS1 mutations in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease. |
ENSMUSG00000018848 |
Rars |
424.368836 |
2.2145224971 |
1.146996 |
0.086701694 |
175.695646 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000042198518560743363037144246483287141509193628421633408441277035022006932767973143983263182424452527501460008529932110832305625081062316894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000007045815994983847347379853044322967683908613107020565398203819116219439350837854835087324966595901830010428845696424104971811175346374511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
589.7213918 |
32.1449028 |
268.1236422 |
11.3765638 |
| ENSG00000113657 |
1809 |
DPYSL3 |
protein_coding |
Q14195 |
FUNCTION: Necessary for signaling by class 3 semaphorins and subsequent remodeling of the cytoskeleton. Plays a role in axon guidance, neuronal growth cone collapse and cell migration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables filamin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including actin filament organization; regulation of plasma membrane bounded cell projection organization; and response to axon injury. Predicted to act upstream of or within nervous system development. Predicted to be located in several cellular components, including cell body; growth cone; and lamellipodium. Predicted to be part of filamentous actin. Predicted to be active in synapse. Predicted to colocalize with exocytic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1809; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; filamentous actin [GO:0031941]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; synapse [GO:0045202]; chondroitin sulfate binding [GO:0035374]; filamin binding [GO:0031005]; hydrolase activity, acting on carbon-nitrogen (but not peptide) bonds [GO:0016810]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678] |
11771764_Aberrant expression of dihydropyrimidinase related proteins-2,-3 and -4 in fetal Down syndrome brain. 15933812_HUlip was expressed in late fetal and early postnatal brains in the neurons of the brain stem, basal ganglia/thalamus, and dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. HUlip expression was easily detected in tumor cells undergoing neuronal differentiation. [Ulip] 16611631_GSK3 alters phosphorylation of CRMP-1, -2, and -4 isoforms 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20543870_new function of CRMP4 as a metastasis-suppressor in lymph node metastasis of prostate cancer 20804502_Data show that two genes, LTB4DH and DPYSL3, were confirmed to be candidate genes for the predictor of a good immune response. 20977846_Ulip1 was downregulated and HIF1a was upregulated in hypoxic neuroblastoma cells. 21179545_CRMP4 is a key physiological substrate of GSK3 in regulating chromosomal alignment and mitotic progression through its effect on spindle microtubules 22805864_High collapsin response mediator protein 4 expression is associated with liver metastasis in pancreatic cancer. 23568759_study found the association between the rs147541241 variant and amyotrophic lateral scerosis was limited to the French population 24011394_Downregulation of MYCN by small interfering RNA (siRNA) increased DPYSL3 levels, while upregulation of MYCN in non-MYCN NB cells decreased DPYSL3 levels. 24339867_DPYSL3 as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-associated molecule that regulates cell adhesion and migration by stabilization of focal adhesion complex 24914979_structures provide further insight into the effects of medically relevant mutations of the DPYSL-3 gene encoding CRMP-4 and the putative enzymatic activities of CRMPs 25096402_Expression status of DPYSL3 in gastric cancer tissues may represent a promising biomarker for the malignant behavior of GC. 25173447_DPYSL3 expression levels inversely correlated with those of VEGF and FAK. Down-regulation of DPYSL3 expression in HCC tissues may serve as a predictive biomarker for HCC after curative resection. 27475326_Data indicate that CRMP4a and CRMP4b isoforms have opposite effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer. CRMP4a expression was reduced in gastric carcinoma tissues and cell lines and seems to act as a tumor suppressor in gastric carcinoma. CRMP4b expression was higher in tumor tissue and cell lines. 28382925_CRMP4 methylation levels >/=15% were significantly associated with a poor prognosis and their combination with CAPRA-S score accurately predicted tumor progression and metastasis 29196732_Data found a damaging de novo missense CRMP4 mutation in a male autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Accumulating evidence suggests that a disturbance in the regulatory function of CRMP4 in forming neuronal networks is an important aspect underlying some characteristics of ASD, including sexual differences. These findings provide CRMP4 as a novel candidate gene contributing to ASD. 30498031_DPYSL3 expression identifies claudin-low (CLOW) tumors that will be sensitive to approaches that promote vimentin phosphorylation during mitosis and inhibitors of PAK signaling during migration and EMT. 31980687_Diabetes, an independent poor prognostic factor of non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma, correlates with dihydropyrimidinase-like 3 promoter methylation. 32121246_Upregulation of Thr/Tyr kinase Increases the Cancer Progression by Neurotensin and Dihydropyrimidinase-Like 3 in Lung Cancer. 33655336_Collapsin response mediator protein 4 enhances the radiosensitivity of colon cancer cells through calciummediated cell signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000024501 |
Dpysl3 |
49.550777 |
5.6436079246 |
2.496618 |
0.296857437 |
69.732645 |
0.00000000000000006791275641311391551808015451594530810428195036774004500479406942758942022919654846191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000517230281041053301692145146332206153375217732443003271214365668129175901412963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
83.8334388 |
22.1310557 |
14.9796396 |
2.9671234 |
| ENSG00000113739 |
8614 |
STC2 |
protein_coding |
O76061 |
FUNCTION: Has an anti-hypocalcemic action on calcium and phosphate homeostasis. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hormone;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted, homodimeric glycoprotein that is expressed in a wide variety of tissues and may have autocrine or paracrine functions. The encoded protein has 10 of its 15 cysteine residues conserved among stanniocalcin family members and is phosphorylated by casein kinase 2 exclusively on its serine residues. Its C-terminus contains a cluster of histidine residues which may interact with metal ions. The protein may play a role in the regulation of renal and intestinal calcium and phosphate transport, cell metabolism, or cellular calcium/phosphate homeostasis. Constitutive overexpression of human stanniocalcin 2 in mice resulted in pre- and postnatal growth restriction, reduced bone and skeletal muscle growth, and organomegaly. Expression of this gene is induced by estrogen and altered in some breast cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8614; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040015]; regulation of hormone biosynthetic process [GO:0046885]; regulation of store-operated calcium entry [GO:2001256]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280] |
15367391_STC-2 can act as a potent growth inhibitor and reduce intramembranous and endochondral bone development and skeletal muscle growth, implying that these tissues are specific physiological targets of stanniocalcins 15486227_Recombinant human and fish STC2 proteins were generated and found to be N-glycosylated homodimers. STC2 is a functional homodimeric glycoprotein, and thecal cell-derived STC2 could play a paracrine role during follicular development. 17545519_NTN4, TRA1, and STC2 have roles in progression of breast cancer 17909264_The induction of GDF15 and STC2 is likely specific to MK-4, vitamin K2 analog. 18355956_elevated expression of STC-1 or STC-2 act as survival factors also for breast cancer cells and thereby contribute to tumor dormancy. 18394600_STC2 was aberrantly hypermethylated in human cancer cells. 18492817_Stanniocalcin 2 expression is regulated by hormone signalling and negatively affects breast cancer cell viability in vitro. 19298603_stanniocalcin 2 overexpression in a prostate cancer cell line promoted prostate cancer cell growth, indicating its oncogenic property 19415750_Increased STC2 gene expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 19582875_Stanniocalcin 2 promotes invasion and is associated with metastatic stages in neuroblastoma. 19786016_STC2 is a HIF-1 target gene and is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation. 20174869_Human stanniocalcin-1 or -2 expressed in mice reduces bone size and severely inhibits cranial intramembranous bone growth. 20422456_High expression level of Stanniocalcin 2 is associated with gastric cancer. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20619259_STC2 is a positive regulator in tumor progression at hypoxia. 20734150_High STC2 is associated with lymph node metastases in squamous cell esophageal carcinoma. 22503972_These findings point to three novel functions of STC2, and suggest that STC2 interacts with HO1 to form a eukaryotic 'stressosome' involved in the degradation of heme. 23187001_STC2 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and migration. 23548070_High STC2 expression levels are associated with disease recurrence in patients with gastric cancer. 23664860_Stanniocalcin-1 and -2 promote angiogenic sprouting in HUVECs via VEGF/VEGFR2 and angiopoietin signaling pathways. 23906305_High STC2 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinomas and adenocarcinoma of gallbladder. 24100594_Our results indicate that STC2 could be a useful molecular blood marker for predicting tumor progression by monitoring CTCs in patients with gastric cancer. 24375080_stanniocalcin 2 (STC2) was the most highly upregulated gene in anti-VEGF antibody-treated tumors 24503185_Interleukin-1-induced changes in the glioblastoma secretome suggest its role in tumor progression. 24606961_STC2 overexpression correlates to poor prognosis for nasopharyngeal carcinomas. 24729417_High STC2 expression is associated with glioma. 24743310_Circulating STC1 and STC2 mRNA are potentially useful blood markers for LSCC 25234931_The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical value of measuring expression levels of STC2 in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. 25463045_These findings suggest that STC2 can be a potential lung cancer biomarker and plays a positive role in lung cancer metastasis and progression. 25674244_Stanniocalcin 2 may contribute to tumor development and radioresistance in cervical cancer. 25771305_This study utilized ER+ IBC to identify a metagene including ABAT and STC2 as predictive biomarkers for endocrine therapy resistance. 25830567_STC2 may inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition at least partially through the PKC/Claudin-1-mediated signaling in human breast cancer cells. 26165228_The results showed that the expression of HMGA2 and STC2 was positively correlated. Furthermore, STC2 expression was significantly associated with tumor grade and histotype. 26361149_STC2 has a role in promoting cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer 26424558_Up-regulation of CDK2 and CDK4 and down-regulation of cell cycle inhibitors p16 and p21 were observed after the delivery of STC2. Furthermore, STC2 transduction activated pAKT and pERK 1/2 signal pathways. 26874357_Data suggest that stanniocalcin 1 and 2 (STC1, STC2) participate in inhibition of proteolytic activity of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) during folliculogenesis. 26983002_STC2 is involved in regulating PAPP-A activity during the development of atherosclerosis 27346255_Our results demonstrated the contrasting effects of STC1 and STC2-derived peptides on human macrophage foam cell formation associated with ACAT1 expression and on HASMC migration. 27662663_STC2 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression through activating ERK/MEK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. 27863406_Results show that STC2 promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, tumor growth, and metastasis through the PI3K/AKT/Snail pathway. 27878259_These findings indicated that STC2 may promote osteoblast differentiation and mineralization by regulating ERK activation 27939696_Mus81 knockdown suppresses proliferation and survival of HCC cells likely by downregulating STC2 expression, implicating Mus81 as a therapeutic target for HCC. 28887636_MiR-184 was confirmed to directly target STC2 in glioblastoma cells 28990324_STC2, is a possible early marker during development of diabetes mellitus. 29712555_In STEMI patients, Stanniocalcin-2 and IGFBP-4 emerged as independent predictors of all-cause death and readmission due to HF. The Stanniocalcin-2/PAPP-A/IGFBP-4 axis exhibits a significant role in STEMI risk stratification. 29748538_these findings newly identify STC2 as the first stanniocalcin responsible for mediating the immunomodulatory effects of MSCs on allogeneic T cells and STC2 contribute to MSC-based treatment for ACD mainly via reducing the CD8(+) Tc1 cells. 29956502_In conclusion, STC2 expression is abundant in male breast cancer where it is an independent prognostic factor for disease-free survival. 30661222_high-expression of STC2 is a negative prognostic factor, associated with increased risk of recurrence in endometrioid endometrial cancer 30962272_The high expression of STC2 mRNA and protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may be associated with the occurrence, development, and prognosis of HCC. STC2 may also be possible to help developing new therapeutic strategies for HCC. 31075234_LINC00460 and STC2 were highly expressed while miR-206 was poorly expressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma . Besides, miR-206 was found to bind to both LINC00460 and STC2. 31100207_Study shows for the first time an opposite effect of hSTC-1 and hSTC-2 on glyceride-glycerol generation from glucose in epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) of fed rats and provides evidence for a direct role of hSTC-1 and hSTC-2 in the regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism in eWAT of rats. 31103608_Total IGFBP 5, PAPPA, PAPPA2 and Stanniocalcin-2. 31173256_The results demonstrated that STC2 participates in the development and progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) by promoting CRC cell proliferation, survival and migration and activating the Wnt/betacatenin signaling pathway. 31236000_Study found that STC2 is overexpressed in colon adenocarcinoma tissues and positively correlated with poor prognosis. The binding site of the transcription factor Sp1 is widely located in the promoter region of STC2. Knocking down the expression of Sp1 significantly inhibited the transcription activity of STC2. 31845230_Results showed that the expression level of STC2 gene in breast cancer tissues was significantly higher than in normal breast tissues. The expression of STC2 gene was correlated with lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, TNM stage and histological grade. 31982135_STC2 modulates ERK1/2 signaling to suppress adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. 32296395_New Insights Into Physiological and Pathophysiological Functions of Stanniocalcin 2. 32445747_Stanniocalcin 2 contributes to aggressiveness and is a prognostic marker for oral squamous cell carcinoma. 32900244_Antioncogenic Effect of MicroRNA-206 on Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Inhibition of Proliferation and Promotion of Apoptosis and Autophagy. 33234031_BIRC7 and STC2 Expression Are Associated With Tumorigenesis and Poor Outcome in Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. 33774276_The novel prognostic risk factor STC2 can regulate the occurrence and progression of osteosarcoma via the glycolytic pathway. 33797657_Stanniocalcin-2 promotes cell EMT and glycolysis via activating ITGB2/FAK/SOX6 signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 33813422_Clinical Significance of Stanniocalcin2 mRNA Expression in Patients With Colorectal Cancer. 34099278_Prognostic Correlation of Glycolysis-Related Gene Signature in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer. 34612765_The significance of Stanniocalcin 2 in malignancies and mechanisms. 34881630_Blocking stanniocalcin 2 reduces sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35157929_Stanniocalcin2 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of trophoblasts via activation of autophagy under high-glucose conditions. 35501821_Stanniocalcin 2 (STC2): a universal tumour biomarker and a potential therapeutical target. 35796937_Preliminary investigation of gene expression levels of PAPP-A, STC-2, and HIF-1alpha in SARS-Cov-2 infected patients. |
ENSMUSG00000020303 |
Stc2 |
127.591914 |
0.1781128563 |
-2.489136 |
0.165597267 |
248.395608 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005810533203206236987640500773046265644278690524708708325736511610559425816163606216402481056896045972596799053995149667881855446474935486078465529669045963601092807948589324951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001378833924104888254425007352299891566736034384407978473413047992300116187120849376442594548593428146308186321441604431048567418824837426012674956865566855412907898426055908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9468455 |
4.1656616 |
214.6676629 |
13.0583199 |
| ENSG00000113790 |
1962 |
EHHADH |
protein_coding |
Q08426 |
FUNCTION: Peroxisomal trifunctional enzyme possessing 2-enoyl-CoA hydratase, 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and delta 3, delta 2-enoyl-CoA isomerase activities. Catalyzes two of the four reactions of the long chain fatty acids peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway (By similarity). Can also use branched-chain fatty acids such as 2-methyl-2E-butenoyl-CoA as a substrate, which is hydrated into (2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-methylbutanoyl-CoA (By similarity). Optimal isomerase for 2,5 double bonds into 3,5 form isomerization in a range of enoyl-CoA species (Probable). Also able to isomerize both 3-cis and 3-trans double bonds into the 2-trans form in a range of enoyl-CoA species (By similarity). With HSD17B4, catalyzes the hydration of trans-2-enoyl-CoA and the dehydrogenation of 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA, but with opposite chiral specificity (PubMed:15060085). Regulates the amount of medium-chain dicarboxylic fatty acids which are essential regulators of all fatty acid oxidation pathways (By similarity). Also involved in the degradation of long-chain dicarboxylic acids through peroxisomal beta-oxidation (PubMed:15060085). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07896, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DBM2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060085, ECO:0000305|PubMed:15060085}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Fatty acid metabolism;Isomerase;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Multifunctional enzyme;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid beta-oxidation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060085}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a bifunctional enzyme and is one of the four enzymes of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway. The N-terminal region of the encoded protein contains enoyl-CoA hydratase activity while the C-terminal region contains 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity. Defects in this gene are a cause of peroxisomal disorders such as Zellweger syndrome. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:1962; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003857]; delta(3)-delta(2)-enoyl-CoA isomerase activity [GO:0004165]; enoyl-CoA hydratase activity [GO:0004300]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; intramolecular oxidoreductase activity, transposing C=C bonds [GO:0016863]; long-chain-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0016509]; long-chain-enoyl-CoA hydratase activity [GO:0016508]; NAD+ binding [GO:0070403]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA oxidase [GO:0033540] |
18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24401050_Mistargeting of peroxisomal EHHADH disrupts mitochondrial metabolism and leads to renal Fanconi's syndrome; this indicates a central role of mitochondria in proximal tubular function. 33430801_EHHADH contributes to cisplatin resistance through regulation by tumor-suppressive microRNAs in bladder cancer. 33997049_Increased EHHADH Expression Predicting Poor Survival of Osteosarcoma by Integrating Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis and Experimental Validation. |
ENSMUSG00000022853 |
Ehhadh |
69.750977 |
0.4939595136 |
-1.017535 |
0.305051984 |
10.905452 |
0.00095881624199967087525398046210511893150396645069122314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002237490550500417785251272562163649126887321472167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.3954230 |
10.4670497 |
89.2437809 |
15.3614050 |
| ENSG00000113966 |
84100 |
ARL6 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0F7 |
FUNCTION: Involved in membrane protein trafficking at the base of the ciliary organelle. Mediates recruitment onto plasma membrane of the BBSome complex which would constitute a coat complex required for sorting of specific membrane proteins to the primary cilia (PubMed:20603001). Together with BBS1, is necessary for correct trafficking of PKD1 to primary cilia (By similarity). Together with the BBSome complex and LTZL1, controls SMO ciliary trafficking and contributes to the sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway regulation (PubMed:22072986). May regulate cilia assembly and disassembly and subsequent ciliary signaling events such as the Wnt signaling cascade (PubMed:20207729). Isoform 2 may be required for proper retinal function and organization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20207729, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20603001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22072986}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Intellectual disability;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Obesity;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Transport;Vision |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ARF-like (ADP ribosylation factor-like) sub-family of the ARF family of GTP-binding proteins which are involved in regulation of intracellular traffic. Mutations in this gene are associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS). A vision-specific transcript, encoding long isoform BBS3L, has been described (PMID: 20333246). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:84100; |
axonemal microtubule [GO:0005879]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane coat [GO:0030117]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; protein polymerization [GO:0051258]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192]; visual perception [GO:0007601]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
15314642_We uncovered four different homozygous substitutions in ARL6 in four unrelated families affected with Bardet-Biedl syndrome, two of which disrupt a threonine residue important for GTP binding and function of several related small GTP-binding proteins. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19236846_These findings implicate that Arl6 mutants are destabilized and eliminated by the proteasome in cells, probably due to the altered nucleotide-binding properties. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20142850_the first null mutation reported in BBS3 gene in patient with Bardet-Biedl syndrome 20207729_Bardet-Biedl syndrome-associated small GTPase ARL6 (BBS3) functions at or near the ciliary gate and modulates Wnt signaling. 20333246_These data demonstrate that the BBS3L transcript is required for proper retinal function and organization. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21282186_BBS3 A89V is sufficient to rescue the transport delays induced by the loss of BBS3 but was unable to rescue vision impairment 23219996_Mutations identified in the present study extend the body of evidence implicating the genes ARL6 and BBS10 in causing Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 23548655_Arl6 is indispensable in cilia signaling but dispensable in ciliogenesis (Review). 24939912_Results show that BBS1 and BBS3 regulates the ciliary traficking of PC1. 25402481_The BBSome is a coat-like ciliary trafficking complex composed of proteins mutated in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. ARL6 E108A mutation prevents BBSome recruitment to cilia. 25704570_Elevated levels of serum ARL6 were able to discriminate between excessive alcohol users and controls. 27271309_Mutations of the ARL6 gene cause Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a heterogeneous disorder that increases the risk of Hypertension and Diabetes mellitus. 29806606_In the 64 BBS patients (44 males, 20 females) were studied, mutations were predominant in BBS10 and ARL6 genes; the c.272T>C; p.(I91T) mutation in ARL6 gene was a recurrent mutation 31939736_Structure and activation mechanism of the BBSome membrane protein trafficking complex. 32361989_High prevalence of Bardet-Biedl syndrome in La Reunion Island is due to a founder variant in ARL6/BBS3. |
ENSMUSG00000022722 |
Arl6 |
23.509914 |
2.5588770863 |
1.355511 |
0.382275551 |
12.509813 |
0.00040482008115321074185471994510976401215884834527969360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001011364996246003717869643701021686865715309977531433105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.4233130 |
8.4088897 |
11.9951561 |
2.5083050 |
| ENSG00000114013 |
942 |
CD86 |
protein_coding |
P42081 |
FUNCTION: Receptor involved in the costimulatory signal essential for T-lymphocyte proliferation and interleukin-2 production, by binding CD28 or CTLA-4. May play a critical role in the early events of T-cell activation and costimulation of naive T-cells, such as deciding between immunity and anergy that is made by T-cells within 24 hours after activation (PubMed:7527824). Also involved in the regulation of B cells function, plays a role in regulating the level of IgG(1) produced. Upon CD40 engagement, activates NF-kappa-B signaling pathway via phospholipase C and protein kinase C activation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P42082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7527824}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Interferes with the formation of CD86 clusters, and thus acts as a negative regulator of T-cell activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7527824}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for adenovirus subgroup B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16920215}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a type I membrane protein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. This protein is expressed by antigen-presenting cells, and it is the ligand for two proteins at the cell surface of T cells, CD28 antigen and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4. Binding of this protein with CD28 antigen is a costimulatory signal for activation of the T-cell. Binding of this protein with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 negatively regulates T-cell activation and diminishes the immune response. Alternative splicing results in several transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:942; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; activation of protein kinase C activity [GO:1990051]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; CD40 signaling pathway [GO:0023035]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002639]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of lymphotoxin A production [GO:0032761]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation [GO:0045630]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] |
11196673_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11279501_Structure in complex with CTLA-4; may represent a distinct signalling mechanism available to dimeric cell-surface receptors. 11726649_Thus, this study is the first demonstration of a distinct signaling event induced by CD80 and CD86 molecules in B cell lymphoma. 11823047_In AML, CD86 is a marker of monocytic/dendritic lineage 11826754_The B7-CD28/CTLA-4 costimulatory pathway has a dominant role in regulating T-cell activation. Antagonists enable graft survival and suppress autoimmunity. 11986949_a soluble form of CD86 encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript is present at elevated levels in blood in some leukaemia patients 12015893_CD80 and CD86 molecules can substitute for each other in the initial activation of resting CD4(+) T cells and in the maintenance of their proliferative response 12071705_expression, refolding, purification, characterization, and crystallization of the receptor-binding domain of human B7-2 is described; glycosylation is not important for proper folding of the receptor-binding domain of B7-2 nor for its binding to CTLA-4 12097397_Leishmania major infection of macrophages cocultured with neutrophils results in a neutrophil-macrophage interaction via CD86 leading to IFN-gamma secretion and restriction of Leishmania growth. 12100033_Impaired up-regulation of CD70 and CD86 in naive B cells from patients with CVID suggests an intrinsic signalling or expression defect at the level of naive B cells in type I CVID. 12187923_polymorphisms have no association with type I diabetes among Finnish subjects 12213904_Intense expression is an unfavorable prognostic indicator for differentiated thyroid carcinoma of children and adolescents 12372936_After B7-1 and B7-2 induction, proximal tubular epithelial cells costimulate CD28 on T lymphocytes resulting in cytokine production. 12486098_Data show that interaction between iC3b-opsonized apoptotic cells and immature dendritic cells down-regulated the expression of CD86 and up-regulated expression of CC chemokine receptor 7. 12513711_The identical effects of B7-1 and B7-2 on regulation of human IL-2 gene transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. 12582153_c-MIR induced specific down-regulation of B7-2 surface expression through ubiquitination, rapid endocytosis, and lysosomal degradation 12606712_B7-2 dimer observed in the B7-2/CTLA-4 complex displays a very hydrophilic dimer interface which provides a mechanism for preventing the formation of B7-1/B7-2 heterodimers 12672403_A key mechanism in the pathogenesis of MS is the increased expression of CD86 and CD40L and the increased production of IL12 during disease progression. 12829914_expression profiles and relative contribution in the porcine-human xenogeneic response 12878356_results demonstrate that herpes simplex virus-2 infection effects the expression of B7 isoforms (B7-1 and B7-2) on monocytes in two ways with opposing outcomes 12905492_Immature dendritic cells engulfed apoptotic and necrotic neutrophils, resulting in up-regulation of CD83 and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules, but down-regulation of CD40, CD80, and CD86 14692664_results confirm that both the CD80 and CD86 molecules play an important role in the maintenance and amplification of the inflammatory process 14727087_Decreased expression of CD86 antigen is associated with melanoma 14871408_CD80 and CD86 activate T cells in IgA nephropathy, CD80/CD86 expressions correlated with renal function at the time of renal biopsy, and monocyte/macrophages and tubular epithelial cells act as antigen presenting cells 14975605_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14978077_CD86 and CD80 have opposite roles in the functioning of human regulatory T cells via CTLA-4 and CD28, an observation that has significant implications for manipulation of immune responses and tolerance in vivo. 15019278_PIII also promoted a significant increase in the percentage of cells expressing CD86 15034022_Engagement of B7-1/B7-2 molecules on human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-positive dendritic cells delivers a signal that is obligately required for the triggering of IDO activity during antigen presentation. 15045639_CTLA-4 gene polymorphism may not play a role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese. 15059478_CD86 may play an important role in asthma pathogenesis. 15110532_utilized as cellular attachment receptor by Adenovirus serotype 3 and thus may achieve both goals of cellular entry and evasion of the immune system 15163715_insertion of CD80 and CD86 antigens into HIV-1 virions increases virus infectivity by facilitating the attachment and entry process due to interactions with their two natural ligands, CD28 and CTLA-4 15280476_kK5 proteins of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herepsvirus does not affect class I expression but does downregulate human B7.2 molecules in a TAP/tapasin-independent manner 15623548_CD86 was found to be concentrated within the cytoplasmic vesicles of macrophages and dendritic cells. 15628695_Upregulation in the colonic mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis. 15895390_NF-kappaB signal plays a key role in LIGHT-mediated upregulation of CD86 expression. 15942292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15942292_There was no relationship between the B7 gene polymorphisms studied and disease susceptibility or BAL fluid cell profiles in Japanese sarcoidosis patients. 16002699_B7.1/B7.2 binding ultimately determines the formation of dimer-dependent CTLA-4 lattices that may be necessary for triggering B7-dependent T cell inactivation. 16115907_Results indicate the expression of functional B7.2 molecule may facilitate progression of acute myeloid leukemia. 16223675_CD86 AA genotype at +1057 position could be involved in liver transplant acceptance, given that its presence is related to a decrease of acute rejection frequency and to a graft survival increase. 16223675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16339520_in human T4 cells in the absence of TCR ligation, CD28/CD86 interaction induced lipid raft polarization, activation of Vav1, increase in intracellular calcium, and nuclear translocation of NFKBp65, but not T cell proliferation or cytokine production 16690948_While purified CD123+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells from adults up-regulated co-stimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 with IL-3 alone those from neonates required the addition of CpG-DNA to reach adult levels. 16712644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17386046_Expression of CD86 on keratinocytes from normal cervical epithelium but not on HPV-16 positive lesions could be a mechanism for evading host immune surveillance. 17513529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17513529_The CD86 gene, and specifically the Ile179Val polymorphism, may be a novel aetiological factor in the development of asthma and related allergic disorders. 17524139_Expression of CD86 and CD80 costimulatory molecules appears to be a marker of better clinical outcome and survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 17605869_The expression of CD80 and CD86 on peripheral lymphocytes from idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura patients were higher than that of the normal control. 17622942_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17919231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925605_CD40, CD80 and CD86 are upregulated in cultured monocyte-derived dendritic cells of patients with coronary artery disease 17947667_while CD86 does not stimulate an initial response as strongly as CD80, there is greater sustained activity that is seen even in the absence of continued costimulation 17963596_Abnormal expression of TLR3 and CD86 may relate to the persistence of HBV infection. 17977894_T cells that had become non-responsive to anti-CD3 could be reactivated to proliferate when costimulated with 4-1BBL, either alone or combined with CD80/CD86. 17989345_CD86 was constitutively expressed on circulating monocytes in healthy individuals and levels were decreased in septic subjects on Day 1 18005680_Results describe a two-pronged mechanism by which Nef removes CD80 and CD86 from the cell surface. 18069758_Dendritic cells obtained from Crohn's disease patients with mutations in the NOD2 gene display an activated phenotype characterized by high CD86 expression. 18301333_possible functional relationship between the enhanced incidence of precursor plasmacytoid dendritic cells, their comparatively high relative expression of the coinhibitory molecule PD-L1 18322188_Generation of a novel alternate transcript of the B7-2 costimulatory molecule (B7-2C) by the splicing of exon 4 appears to represent a mechanism for the fine tuning of full-length protein B7-2A-mediated costimulatory signals. 18506362_CD86 was differentially expressed in both macrophages and foam cells from subjects with atherosclerosis. 18506362_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18577795_The expression levels of B7.2 were low on day 1 in S7, S10 and H37Ra Mycobacterium tuberulosis infected monocyte derived macrophages 18580477_Monocytes of chronic graft-versus-host disease patients had greater CD86 mean fluorescence intensity in marrow. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18941200_A novel role is found for CD86 expression on the microvasculature, whereby ligation of CTLA-4 on CD4-positive T cells by CD86 on islet endothelial cells is key to the adhesion of recently activated T cells. 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19086656_The upregulated level of costimulatory molecules CD28/B7-2 and CD40/ CD40L on T cells and B cells may play an important role in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19257981_Data show high expression of CD86 and CD11C, moderate expression of CD1a and CD123, low levels of CD83 on dendritic cells after induction by GM-CSF and IL-4. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19299714_human APCs in which CREMalpha was selectively suppressed expressed more CD86 on the surface membrane 19430862_B7-2 expression in chronic B cell lymphocytic leukemia patients is significantly lower; interferon-gamma could induce B7-2 expression slightly 19550123_Data showed there was no significant differences between MoDCs from ovarian cancer women and healthy women in CD86 and CD80. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19735272_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19852851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20019769_Increased amount of CD86 or ICOS positive lamina propria mononuclear cells and enterocytes suggests that co-stimulatory molecules may play a role in the pathogenesis of Crohn disease. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20067533_increased expression on dendritic cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients 20100932_Data show that the expression of CD86 was different from other activation markers, because expression was delayed after in vitro TCR stimulation and required sufficient IL-2 signaling. 20118277_Data show that pollen grains triggered the production of IL-8, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and strongly upregulated the membrane expression of CD80, CD86, CD83, HLA-DR and caused only a slight increase in the expression of CD40. 20212510_In the absence of irradiated M. tuberculosis, dendritic cells consist in a major DC-SIGN(high)/CD86(low) and minor DC-SIGN(low)/CD86(high) subpopulations, whereas in the presence of bacteria, there is an enrichment of DC-SIGN(low)/CD86(high) population. 20230296_CD86 +1057G/A polymorphism may not be associated with coronary artery disease in the Chinese population. 20230296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20380573_Data suggest that CD86 and 1057G/A polymorphism may contribute to genetic susceptibility to colorectal neoplasms in a Chinese population. 20380573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20388394_In active ulcerative colitis CD86 and ICOS were over-expressed in the intestinal epithelial cells and lamina propria mononuclear cells. 20433886_Data show that CD86 1057G>A, CTLA4-1722T>C, CTLA4-318C>T, CTLA4(AT)n, CD28(CAA)n, and D2S72(CA)n were found associated with susceptibility to pemphigus foliaceus. 20433886_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20601595_Expansion of donor-derived lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV)-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is significantly impaired in B7.1/B7.2-deficient T cell receptor (TCR)transgenic recipients, compared with wild-type. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20732370_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20732370_genetic polymorphism is associated with risk or protection for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Chinese population 20802378_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20884055_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20884055_These results suggest that the polymorphisms of the CD86 gene may be used as genetic markers for making the diagnosis and prognosis of Graves' ophthalmopathy. 20971123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20979791_increased CD80 and CD86 expression with the progression of tubulointerstitial lesion might play an important role in the development of lupus nephropathy 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21469977_The low expression of CD80 and CD86 in thyroid papillary carcinoma may help them evade the immune system. 21474713_study shows CTLA-4 can capture its ligands (CD80, CD86)from opposing cells by trans-endocytosis; data reveal mechanism of immune regulation in which CTLA-4 acts as an effector molecule to inhibit CD28 costimulation by cell-extrinsic depletion of ligands 21525579_AA genotype and A allele of CD86 +1057G>A polymorphism may confer a protection against acute kidney allograft rejection in Tunisian patients. 21540807_After surgery the rate of monocytes expressing B7-2 decreased in all the patients 21563968_the +1057G/A polymorphism of the CD86 gene is associated with increased susceptibility to osteosarcoma 21628959_Allergen exposure needs to cause weak or moderate cytotoxicity for DD86 and CD54 expression. 21870962_The +1057G/A polymorphism of the CD86 gene is associated with increased susceptibility to Ewing's sarcoma. 21911468_Parasite-induced B7-2 is dependent on Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) but not extracellular signal-regulated kinase or p38 signaling; its expression on human peripheral blood monocytes is dependent on JNK signaling. 22074996_Data show that CD80 promoter and CD86 exon 8 allele frequencies vary significantly among populations of different ancestries. 22142817_Data suggest that expression of CD86, CD80, and CD40 on dendritic cells in normal endometrium is higher than on tumor infiltrating dendritic cells in endometrioid adenocarcinoma; this may reflect roles in antigen presentation/tumor escape. 22182632_primary liver disease could influence the pre-transplantation levels of sCD86 and sCD95L. High pre-transplantation serum levels of sCD86 could favor the development of episodes of acute rejection. 22199280_Yeast-derived beta-glucan lacks cytotoxic effects towards B-lymphoma cells but up-regulation of CD86 suggests maturation of the cells via dectin-1 by the carbohydrate 22246628_IL-2 upregulates CD86 expression on human CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells via a receptor-dependent mechanism that involves the NFAT and mammalian target of rapamycin pathways. 22371880_CD86 represents an important tool for subdividing HSCs in several circumstances, identifying those unlikely to generate a full spectrum of hematopoietic cells. 22379101_Phe119 and Ser120 in the MIR2 ITM region and Asp244 in the B7-2 JM region contribute to the recognition of B7-2 by MIR2. 22659416_these results reveal the critical importance of the cytoskeleton-dependent CD86 polarization to the IS and more specifically the K4 motif for effective co-signaling. 22732586_Interaction of CD28 with B7 costimulatory antigen promotes proliferation and survival of activated gammadelta T cells following Plasmodium infection. 22821131_The frequency of the CD86 gene +1057A allele was significantly higher in pancreatic cancer cases than in controls. 22962607_CD86 and IL-12p70 are key players for T helper 1 polarization and natural killer cell activation by Toll-like receptor-induced dendritic cells. 23175469_Myeloid leukemia cells with a B7-2(+) subpopulation provoke Th-cell responses and become immuno-suppressive through the modulation of B7 ligands. 23246582_Data indicate that the frequencies of CD11c, CD11c/CD86, HLA-DR/CD86, CD83 and CD80 were significantly high, while CD11c/HLA-DR was low in Hepatitis E infection. 23289444_Lower expression of B7-1 and B7-2 proteins on peripheral monocytes in pre-eclampsia might indicate a secondary regulatory mechanism in response to the ongoing systemic maternal inflammation. 23470321_Studies indicate co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors B7-1, B7-2, CD28 and TNFRSF14 have a pivotal role in T cell biology, as they determine the functional outcome of T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. 23661460_We failed to find any significant association of the 2 CD86 SNPs with RA. 23867827_Our results indicate that the methylation pattern in the CD86 promoter and CpG island is closely related to the expression of this co-stimulatory molecule in keratinocytes. 24202305_Provide evidence for an involvement of CD40+ and CD86+ B cells in the incidence of stroke and suggest that both pathogenic and protective B cell subsets exist. 24283754_the higher levels of sCTLA-4 and CD86 in B-ALL patients might be candidate parameters for poor prognosis and may serve to refine treatment stratification with intensification of therapy in those patients prone to relapse. 24298899_no statistically significant difference between brucellosis patients and controls in the allele and genotype distributions of CTLA4, +49A/G (P = 0.859) and CD86, +2379G/C (P = 0.476) was found. 24378263_Cirrhotic patients with type 2 diabetes have increased expression of monocytic CD86 in comparison with cirrhotic non-diabetic, diabetic and healthy controls. This increases significantly with increase of the stage of the Child-Pugh score. 24415757_NOTCH1 protein regulates CD80/CD86-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in interleukin-6 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase production by dendritic cells 24531620_PD-L1 expression and the PD-L1/CD86 ratio in CD14(++)CD16(+) monocytes were higher during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. 24845157_These findings reveal the distinct but complementary roles of CD80 and CD86 IgV and IgC domains in T cell activation. 24897540_CD86 +1057G/A polymorphism may be not associated with the genetic susceptibility to chronic immune thrombocytopenia in a Chinese population. 24930629_B7-2 costimulation and intracellular indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression is reduced in umbilical cord blood as compared to adult peripheral blood. 24951814_Expression of costimulatory molecules CD80/86 is an absolute requirement for efficient CD8 T cell priming by adenoviral vectors. 24981893_Meningococcal capsular polysaccharide-loaded vaccine nanoparticles induce expression of CD86. 25129060_Polymorphisms in CD86 gene have diverse effects on the pathogenesis of pneumonia-induced sepsis. 25369324_CD86 polymorphisms (rs1129055) may have protective effects on cancer risk in Asians and that CD86 polymorphisms (rs17281995) is likely to contribute to risk of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer in Caucasians. 25482673_TLR2, TLR4 and CD86 gene polymorphisms are associated with Recurrent aphthous stomatitis. 25892855_analysis of the expression of TLR-9, CD86, and CD95 in circulating B cells of patients with chronic viral hepatitis B or C before and after antiviral therapy 25896473_Results support a CTLA4-Ig/CD86 interaction on gammaIFN and IL-17 activated endothelial cells that modulates the expression of VEGFR-2 and ICAM1. 25912130_CD86 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to pneumonia-induced sepsis and may affect gene expression in monocytes. 26416278_Data show that induction of CD86 antigen expression on monocytes by human beta Defensin-3 (hBD-3) is suppressed by P2X7 purinoceptor (P2X7R) antagonist. 26795594_B-cells from patients tolerant to the graft maintained higher IL-10 production after CD40 ligation, which correlates with lower CD86 expression compared to patients with chronic rejection. 26901523_The SNP CD40 -1C>T was associated with the IgG response against PvDBP, whereas IgG antibody titers against PvMSP-119 were influenced by the polymorphism CD86 +1057G>A. 27348308_the upregulation of CD86 but not CD80 and PD-L1 on CD68+ cells in the liver of HBV-infected patients, observed in our study, suggest that the profile of CD68+ cells does not support the induction of proper Th1 responses that are needed to clear HBV infection. This might provide an explanation for the absence of potent HBV-specific T cells during chronic HBV infection. 27708164_Our results reveal a role for B7-2 as obligatory receptor for superantigens. B7-2 homodimer interface mimotopes prevent superantigen lethality by blocking the superantigen-host costimulatory receptor interaction. 27718302_CD73 and CD86 are the most relevant markers to incorporate in the routine MRD evaluation of BCPALL. 28056587_IL-6, DEC205, and CD86 can be predictive biomarkers for the respiratory and immune effects of ambient PM2.5. 28067225_Hepatitis C virus has a genetically determined lymphotropism through co-receptor B7.2. 28074067_Our data demonstrate that CML patients with high CD86(+)pDC counts have a higher risk of relapse after TKI discontinuation. 28079472_CD86 variants association with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis in Iranian population. 28274366_Our study reports a novel association of SNPs within CD86 and CTLA4 genes with pemphigus. The CD86 rs1129055 A allele appears to confer susceptibility to Pemphigus vulgaris but not to pemphigus foliaceus. 28338767_The expression of CD1d showed a significantly negative correlation with CD86 level in B cells from imiquimod (IMQ)-treated mice, B6.MRLlpr mice, and lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. 28904313_results strongly suggest that CD40 and CD86 play a role in the pathophysiology of oral inflammatory diseases such as OLP 29217299_DCreg resisted phenotypic and functional maturation and further upregulated PD-L1:CD86 expression. 29277562_Examining the mRNA expression levels of CD80 and CD86 genes between colon polyps with the rectal polyps shows that the enhanced level of CD86 in adenoma samples could be considered as a valuable biomarker for distinguishing the adenoma from hyperplastic polyps and the masses located in the colon from the rectum. 29577049_this study shows that recipients' CD86 gene polymorphisms influence the overall survival after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and, together with CTLA-4 polymorphisms, might be considered a risk factor for acute graft versus host disease 29599775_CD86 may be involved in immunoregulation by its association with CTLA-4 in asymptomatic patients. 30343689_CD86 gene rs1129055 and rs1915087 polymorphisms are significantly related to the risk of sepsis. For the rs1129055 polymorphism, the GA genotype and A allele are obviously correlated with increased risk of sepsis. Meanwhile, the carriers of the TT genotype and T allele of the rs1915087 polymorphism are more likely to develop sepsis. 30406401_Our results suggest that the use of CD86 molecule as a proliferation marker for chronic lymphocytic leukemia is highly questionable. However, the CD86 molecule may interfere with the immune system of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia by activating and depleting immune functions 31114583_Staphylococcal and Streptococcal Superantigens Trigger B7/CD28 Costimulatory Receptor Engagement to Hyperinduce Inflammatory Cytokines. 31485639_The findings of the present study suggested that dendritic cells from patients with allergic rhinitis express high levels of the co-stimulatory molecule CD86, but not of CD80. 31575740_The secreted M2 protein encoded by cowpox virus (CPXV) specifically interacts with human and murine B7.1 (CD80) and B7.2 (CD86). 31651850_AA genotype and A allele of CD86 polymorphism rs1129055 might be correlated with decreased sepsis susceptibility in Chinese Han population, but not rs2715267. AA genotype and A allele of CD86 polymorp 31755324_the expressions of CD80 on Bcells and of CD86 on monocytes were increased in peripheral blood from patients with autoimmune thyroid diseases, especially in severe cases, and their gene polymorphisms are associated with the susceptibility and the severity of Hashimoto's disease 32197584_A combination of the activation marker CD86 and the immune checkpoint marker B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) indicates a putative permissive activation state of B cell subtypes in healthy blood donors independent of age and sex. 32580776_Discovery of CD80 and CD86 as recent activation markers on regulatory T cells by protein-RNA single-cell analysis. 33363541_CD86 Is a Selective CD28 Ligand Supporting FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cell Homeostasis in the Presence of High Levels of CTLA-4. 33771483_PD-L1 induces macrophage polarization toward the M2 phenotype via Erk/Akt/mTOR. 34149691_Association of Polymorphisms in T-Cell Activation Costimulatory/Inhibitory Signal Genes With Allograft Kidney Rejection Risk. 34157285_Human and viral membrane-associated E3 ubiquitin ligases MARCH1 and MIR2 recognize different features of CD86 to downregulate surface expression. 34191384_Cryptic association of B7-2 molecules and its implication for clustering. 34486997_The myeloid cell biomarker EMR1 is ectopically expressed in colon cancer. 34656742_Multilocus evaluation of genetic predictors of multiple sclerosis. 34738707_Clinicopathological significance of CD28 overexpression in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. 35000467_Gene-environment interactions increase the risk of pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis associated with ozone pollution. 35380688_PDZ Proteins SCRIB and DLG1 Regulate Myeloma Cell Surface CD86 Expression, Growth, and Survival. 36051533_The Role of CD40, CD86, and Glutathione S-Transferase Omega 1 in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000022901 |
Cd86 |
20.317432 |
17.3849547996 |
4.119767 |
0.694201632 |
36.794983 |
0.00000000131227497114531600346057585589586158558716988409287296235561370849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006204093073063697545781803091829303964388486747338902205228805541992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.9022234 |
16.2927661 |
2.2885346 |
0.8493080 |
| ENSG00000114019 |
51421 |
AMOTL2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2J4 |
FUNCTION: Regulates the translocation of phosphorylated SRC to peripheral cell-matrix adhesion sites. Required for proper architecture of actin filaments. Inhibits the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, probably by recruiting CTNNB1 to recycling endosomes and hence preventing its translocation to the nucleus. Participates in angiogenesis. May play a role in the polarity, proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. Selectively promotes FGF-induced MAPK activation through SRC. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17293535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21937427, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22362771}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Endosome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
Angiomotin is a protein that binds angiostatin, a circulating inhibitor of the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Angiomotin mediates angiostatin inhibition of endothelial cell migration and tube formation in vitro. The protein encoded by this gene is related to angiomotin and is a member of the motin protein family. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:51421; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; establishment of cell polarity involved in ameboidal cell migration [GO:0003365]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
21832154_AMOTL2 is as a novel activator of LATS2. 21937427_Amotl2 plays a pivotal role in polarity, migration and proliferation of angiogenic endothelial cells 23525008_These results demonstrate a role for Amotl2 in synaptic maturation and support the involvement of podosomes in this process. 23911299_AMOTL2 interacts with TAZ and modulates transcriptional activity of TAZ. 24003252_Scaffold proteins angiomotin (Amot) and angiomotin-related AmotL1 and AmotL2 were recently identified as negative regulators of YAP and TAZ by preventing their nuclear translocation. 24225952_These results collectively suggest that the Hippo pathway negatively regulates the actin-binding activity of Amot family members through direct phosphorylation. 25080976_AmotL2 expression correlates with loss of tissue architecture in tumors from human breast and colon cancer patients. 25998128_mTORC2-mediated phosphorylation of AMOTL2 blocks its ability to inhibit YAP signaling. 26598551_study reports for the first time that USP9X is a deubiquitinase of Angiomotin-like 2 (AMOTL2) and that AMOTL2 mono-ubiquitination is required for YAP inhibition 28368415_these results provide novel insights into a dual tumor suppressive function of AMOTL2 by targeting both YAP and AKT in liver size control and cancer prevention 30794467_the localization of IQGAP1, AmotL2, and FKBP51 in malignant cells and tumor microenvironment of human GB tumors 32950569_AMOTL2 inhibits JUN Thr239 dephosphorylation by binding PPP2R2A to suppress the proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 34036399_AMOTL2knockdown promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma by regulating betacatenin nuclear localization. 34165350_AmotL2, IQGAP1, and FKBP51 Scaffold Proteins in Glioblastoma Stem Cell Niches. 34404733_AMOTL2 mono-ubiquitination by WWP1 promotes contact inhibition by facilitating LATS activation. |
ENSMUSG00000032531 |
Amotl2 |
12.622585 |
0.1296303147 |
-2.947525 |
0.614199816 |
25.836015 |
0.00000037168790054242874966783697320005241948592811240814626216888427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001379807196178633913152518711275895668677549110725522041320800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0832403 |
1.3293481 |
23.7161118 |
5.4103107 |
| ENSG00000114107 |
80321 |
CEP70 |
protein_coding |
Q8NHQ1 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the organization of both preexisting and nascent microtubules in interphase cells. During mitosis, required for the organization and orientation of the mitotic spindle. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome;TPR repeat |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cilium assembly and regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization. Located in centrosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80321; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507] |
20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21795687_These results thus report for the first time the identification of Cep70 as an important centrosomal protein that interacts with gamma-tubulin and underscore its critical role in the regulation of mitotic spindle assembly. 22427462_data showed that Cep70 increased the microtubule length without affecting the microtubule number in the purified system; results demonstrate that Cep70 could directly regulate microtubule assembly by promoting microtubule elongation instead of microtubule nucleation 26112604_findings suggest that Cep70 promotes microtubule stability by interaction with HDAC6 and regulation of tubulin acetylation 26893288_Cep70 overexpression stimulates pancreatic cancer by inducing centrosome abnormality and microtubule disorganization 28063737_these results demonstrate a critical role for Cep70 in the development and progression of breast cancer. 28632150_Cep70 interacts with tubulin, and promotes the ability of paclitaxel to stimulate microtubule assembly. These data demonstrate that Cep70 mediates paclitaxel sensitivity in breast cancer. 33980814_Loss of CEP70 function affects acrosome biogenesis and flagella formation during spermiogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000056267 |
Cep70 |
18.797715 |
0.4385193974 |
-1.189287 |
0.453166522 |
6.798658 |
0.00912263981935863485506210679432115284726023674011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017615144392168165243806043918084469623863697052001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.5749409 |
2.8518626 |
21.8713852 |
4.4828935 |
| ENSG00000114251 |
7474 |
WNT5A |
protein_coding |
P41221 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Can activate or inhibit canonical Wnt signaling, depending on receptor context. In the presence of FZD4, activates beta-catenin signaling. In the presence of ROR2, inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by promoting beta-catenin degradation through a GSK3-independent pathway which involves down-regulation of beta-catenin-induced reporter gene expression (By similarity). Suppression of the canonical pathway allows chondrogenesis to occur and inhibits tumor formation. Stimulates cell migration. Decreases proliferation, migration, invasiveness and clonogenicity of carcinoma cells and may act as a tumor suppressor (PubMed:15735754). Mediates motility of melanoma cells (PubMed:17426020). Required during embryogenesis for extension of the primary anterior-posterior axis and for outgrowth of limbs and the genital tubercle. Inhibits type II collagen expression in chondrocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P22725, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q27Q52, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15735754, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17426020}. |
Alternative splicing;Chondrogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene encodes a member of the WNT family that signals through both the canonical and non-canonical WNT pathways. This protein is a ligand for the seven transmembrane receptor frizzled-5 and the tyrosine kinase orphan receptor 2. This protein plays an essential role in regulating developmental pathways during embryogenesis. This protein may also play a role in oncogenesis. Mutations in this gene are the cause of autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:7474; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; chemoattractant activity involved in axon guidance [GO:1902379]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor binding [GO:0005115]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; anterior/posterior axis specification, embryo [GO:0008595]; atrial septum development [GO:0003283]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; cervix development [GO:0060067]; chemoattraction of serotonergic neuron axon [GO:0036517]; chemorepulsion of dopaminergic neuron axon [GO:0036518]; cochlea morphogenesis [GO:0090103]; convergent extension involved in axis elongation [GO:0060028]; convergent extension involved in organogenesis [GO:0060029]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; epithelial cell migration [GO:0010631]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in mammary gland duct elongation [GO:0060750]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; establishment of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045198]; establishment of planar polarity [GO:0001736]; excitatory synapse assembly [GO:1904861]; face development [GO:0060324]; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008543]; genitalia development [GO:0048806]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; hematopoietic stem cell proliferation [GO:0071425]; hindgut morphogenesis [GO:0007442]; hypophysis morphogenesis [GO:0048850]; inhibitory synapse assembly [GO:1904862]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lateral sprouting involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060599]; lens development in camera-type eye [GO:0002088]; lung development [GO:0030324]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; mammary gland branching involved in thelarche [GO:0060744]; meiotic nuclear division [GO:0140013]; melanocyte proliferation [GO:0097325]; mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0010463]; mesenchymal-epithelial cell signaling [GO:0060638]; mesodermal to mesenchymal transition involved in gastrulation [GO:0060809]; midgut development [GO:0007494]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell proliferation in midbrain [GO:1904934]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040037]; negative regulation of melanin biosynthetic process [GO:0048022]; negative regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0072201]; negative regulation of prostatic bud formation [GO:0060686]; negative regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051964]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0035567]; non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway via JNK cascade [GO:0038031]; notochord morphogenesis [GO:0048570]; olfactory bulb interneuron development [GO:0021891]; optic cup formation involved in camera-type eye development [GO:0003408]; paraxial mesoderm formation [GO:0048341]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in axis elongation [GO:0003402]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1904938]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0061350]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in cardiac right atrium morphogenesis [GO:0061349]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in gastrula mediolateral intercalation [GO:0060775]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904955]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in neural tube closure [GO:0090179]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0061347]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in pericardium morphogenesis [GO:0061354]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0061348]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061036]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000049]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of heart induction by negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090082]; positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell proliferation [GO:1902035]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043032]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045836]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0002053]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; positive regulation of neuron projection arborization [GO:0150012]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000052]; positive regulation of ossification [GO:0045778]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of protein kinase C activity [GO:1900020]; positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090037]; positive regulation of protein localization to synapse [GO:1902474]; positive regulation of response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0060760]; positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010820]; positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070245]; positive regulation of timing of anagen [GO:0051885]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060340]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; post-anal tail morphogenesis [GO:0036342]; postsynapse assembly [GO:0099068]; postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099170]; presynapse assembly [GO:0099054]; primary heart field specification [GO:0003138]; primitive streak formation [GO:0090009]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060762]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175]; regulation of postsynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0099566]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; secondary heart field specification [GO:0003139]; secondary palate development [GO:0062009]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070242]; type B pancreatic cell development [GO:0003323]; urinary bladder development [GO:0060157]; uterus development [GO:0060065]; vagina development [GO:0060068]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904953]; Wnt signaling pathway, calcium modulating pathway [GO:0007223]; Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:0060071]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11956659_Frequent up-regulation of WNT5A mRNA in primary gastric cancer. 12086864_Increased expression of WNT5a is associated with cell motility and invasion of metastatic melanoma 12165812_WNT5a is upregulated by TNF-alpha in tumor cell lines 12244165_Wnt-5a promotes T cell nuclear accumulation of the transcription factor NFAT in the presence of cyclosporin A. 12482967_These results suggest that the TAK1-NLK MAPK cascade is activated by the noncanonical Wnt-5a/Ca(2+) pathway and antagonizes canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 12805222_Results suggest that disabled-2 functions as a negative regulator of canonical Wnt signaling by stabilizing the beta-catenin degradation complex. 12841867_Down-regulation of Wnt-4 and up-regulation of Wnt-5a are possible markers of the malignant phenotype of human squamous cell carcinoma. 15067324_Altered mRNA expression is associated with prostate cancer recurrence. 15389636_Their different spatial expression patterns suggest that Wnt4 and Wnt5a proteins are not functionally linked to type II collagen and type X collagen synthesis in in vitro chondrogenic models of mesenchyme stem cells 15592517_Wnt-5a is involved in the response of malignant neuroblasts to retinoic acid. 15735754_Wnt-5a serves as an antagonist to the canonical Wnt-signaling pathway with tumor suppressor activity in differentiated thyroid carcinomas. 16169547_Over-expression of Wnt5a in transgenic mice disrupts epithelial-response to FGF10 and regulates Shh signaling. 16569699_The role of Wnt5A in the microenvironment of primary breast cancer and macrophage-induced breast cancer invasion. 16569699_function of Wnt 5a as either a suppressor or promoter of malignant progression seems to be modulated by intercellular interactions 16601243_WNT5A and FZD5 regulate the microbially induced interleukin-12 response of antigen-presenting cells and interferon-gamma production by mycobacterial antigen-stimulated T cells 16880514_NFAT1, a transcription factor connected with breast cancer metastasis, is activated by Wnt-5a through a Ca2+ signaling pathway in human breast epithelial cells which was simultaneously counteracted by a Wnt-5a-induced Yes/Cdc42 signaling pathway. 16914445_The Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision-like protein HuR, inhibited translation of Wnt-5a when bound to highly conserved AU-rich sequences in the 3'-untranslated region of the Wnt-5a mRNA. 16996564_The aberrant expression of WNT5A suggest that the Wnt signaling pathway may be abnormally regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), which provides insight into the molecular mechanisms of NPC. 17035633_Screening for Wnt5a-regulated genes in cultured endothelial cells identified several encoding angiogenic regulators, including matrix metalloproteinase-1, an interstitial collagenase, and Tie-2, a receptor for angiopoietins. 17227781_WNT5A is an important target of CUTL1 and mediator of invasiveness and tumor progression in pancreatic cancer. 17426020_Wnt5A can signal via protein kinase C (PKC), so the role of PKC in Wnt5A-mediated motility and epithelial to mesenchymal transition was also assessed using PKC inhibition and activation studies 17458904_Wnt3A/5A can function as mesenchymal regulatory factors by providing instructive cues for the recruitment, maintenance, and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. 17463182_Our findings demonstrate that APC status plays a key role as a determinant of Wnt5a secretion and suggest that CaSR-mediated secretion of Wnt5a will inhibit defective Wnt signaling in APC-truncated cells in an autocrine manner. 17486081_Hypomethylation of wingless-related MMTV integration site 5A (WNT5A), S100 calcium-binding protein P (S100P) and cysteine-rich protein 1(CRIP1) was confirmed in the cancer cells by bisulfite sequencing. 17525119_Ability of phenylmethimazole (C10) to decrease growth and migration of papillary thyroid cancer cells may be related to its suppressive effect on TLR3 and Wnt5a signaling. 17546602_These results suggest that Wnt signaling crosstalk and functional antagonism with the LRP5 co-receptor are key signaling regulators of mesenchymal stem cells maintenance and differentiation. 17709179_Data indicate that Wnt5a signaling is an important regulator in the proliferation of glioma cells. 17937436_did not detect submicroscopic deletion or duplication nor sequence alteration in either CACNA2D3 or WNT5A in ZLS-affected individuals 17952396_Review about the different influences and signaling pathways of Wnt5A in tumor progression. 17956663_The genesis of myelocytic leukemia is related to the down-regulated expression of Wnt5a. 17967789_Wnt5a and Wnt11 expression in EPC cells was induced by coculture with rat neonatal cardiomyocyte and was blocked by gamma-secretase inhibition. 17986384_Our findings suggest non-canonical Wnt signalling plays a role in regulating endothelial cell growth and possibly in angiogenesis. 17992121_These data show activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin-signalling pathway in uveal melanoma and suggest that components of this pathway might be useful prognostic markers as well as attractive therapeutic targets to treat this disease. 18032022_WNT5A, a putative tumour suppressor gene in ALL, is silenced by methylation in this disease and that this epigenetic event is associated with upregulation of CYCLIN D1 expression and confers poor prognosis in patients with ALL. 18172252_WNT5A is frequently inactivated in CRC by tumor-specific methylation, and thus, is a potential biomarker. 18174174_MT1-MMP-induced phenotypic changes were dependent upon up-regulation of Wnt5a, which has been implicated in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 18174455_Wnt5A is critically involved in inflammatory macrophage signaling in sepsis and is a target for antiinflammatory mediators like APC or antagonists like sFRP1. 18413325_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18420933_findings show cell-autonomous mechanisms allow Wnt5a to control cell orientation, polarity, and directional movement in response to positional cues from chemokine gradients 18456733_Wnt5a expressed in atherosclerotic lesions colocalizes with TLR-4. 18462958_study demonstrated that Wnt3a & Wnt5a can promote proliferation of HEK293 cells & inhibit serum starvation-induced apoptosis, which implies Wnt3a & Wnt5a can maintain survival of HEK293 cells under stress 18477650_negative correlation between expression of Wnt-5a & hepatitis B virus x gene(HBx) mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC); it is concluded that HBx mutants may participate in development & progression of HCC, at least in part through the Wnt-5a pathway 18541964_No mutation found in Zimmermann-Laband syndrome 18615587_both Wnt5a and Wnt3a bound Ror2, only Wnt5a induced Ror2 homo-dimerization and tyrosine phosphorylation in U2OS human osteoblastic cells. 18632632_Wnt3a and Wnt5a have roles in inducing BMP-4 and 6 expression in prostate cancer osteoblast differentiation 18656562_Data show that Wnt5a is highly expressed during osteoblastic differentiation, and that clusters of genes regulating cell cycle, cell proliferation and cell growth, and gene transcription are altered with absence of Wnt5a expression. 18703641_Expression of Wnt5a plasmid but not Wnt1 or Wnt3a increased caudal homeodomain factor CDX2 transcripts and protein in HT-29 adenocarcinoma cells. Wnt5a increased activity of a sucrase-isomaltase (SI) promoter in Caco-2BBE cells. 18794093_Cytoplasmic WNT5A increases with melanoma progression and strong expression is associated with poor outcome. 18990694_LRP1 stimulates a canonical Wnt5a signaling pathway that prevents cholesterol accumulation. 19048125_WNT5A is regulated by PAX2 and may be involved in blastemal predominant Wilms tumorigenesis 19061910_These data suggest that the epigenetic remodeling of the WNT5A promoter is correlated with its transcriptional activation and this upregulation likely participates in arsenical-induced malignant transformation. 19063862_Amino acid limitation in colon cancer cells induces phosphorylation of ERK1/2, which then down-regulates WNT5a expression. 19074888_Staining of a melanoma tissue array also highlighted the inverse relationship between MART-1 and Wnt5A expression. 19148501_pathways related to Wnt5a have an important role in ovarian malignant neoplasia. 19171330_Mutations in the coding sequence of WNT4, WNT5A, WNT7A, and WNT9B are not responsible for the Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome. 19177143_Wnt5A activates calpain-1, leading to the cleavage of filamin A, which results in a remodeling of the cytoskeleton and an increase in melanoma cell motility 19244247_Data show that Wnt-5a stimulation of breast epithelial cells leads to increased cell-cell adhesion, and that Wnt-5a/casein kinase Ialpha (CKIalpha)-specific phosphorylation of beta-catenin leads to increased complex formation of beta-catenin/E-cadherin. 19251946_WNT5A is a regulator of fibroblast proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. 19399181_Wnt5a regulates epidermal differentiation even in adult skin 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19467340_Expression of Wnt-5a protein significantly stimulated cell proliferation, and transfection with siRNA plasmids suppressed Wnt-5 expression and cell proliferation 19473452_may be an important marker during initial events of actinic cheilitis malignant transformation; might recruit other events in lip squamous cell carcinoma, such as matrix metalloproteinase 3 synthesis 19492056_Wnt5a enhances cardiac gene expressions of EPC via an activation of PKC delta 19520808_Wnt5A is a critical mediator of CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling and migration in human and murine T 19561643_Results indicate that Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling involves the activation of a SFK, leading to MMP-13 expression, and that constitutively active Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling confers invasive properties on osteosarcoma cells in a cell-autonomous manner. 19582886_Laminin gamma2 mediates Wnt5a-induced invasion of gastric cancer cells. 19651774_Phospho-DARPP-32 potentiates Wnt-5a-mediated CREB activity and suppresses filopodia formation. 19696445_syndecan 1 and 4 correlate to increased metastatic potential in melanoma patients and are an important component of the Wnt5A autocrine signaling loop 19760930_WNT5A gene has been methylated from the early stages of colorectal cancers. 19802008_Data show that ROR2 knockdown results in a decrease in signaling downstream of Wnt5A. 19849855_Differential expression of Wnt ligands in HCC cells is associated with selective activation of canonical Wnt signaling in well-differentiated, and its repression in poorly differentiated cell lines. 19874313_WNT5A, a putative tumor suppressor gene in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), is silenced by methylation in this disease and that this epigenetic event is associated with upregulation of CYCLIN D1 expression. 19878652_WNT5A negatively regulates both proliferation and migration of HDPCs, suggesting its important role in odontogenesis via controlling the HDPCs. 19910923_Wnt5a activated Rac in the beta-catenin-independent pathway, and Frizzled2 (Fz2) and Ror1 or Ror2 were required for this action. 19918918_A WNT5A/ROR2 signal transduction pathway is important in craniofacial and skeletal development and proper formation and growth of these structures is sensitive to variations in WNT5A function. 19940551_Data show that tumor spheroid cells express ABCG2, Bmi1, WNT5A, CD133, prox1 and VEGFR3. 19956879_Wnt-5a regulates proliferation in lung cancer cells 20008136_WNT5A signaling is important in modulating tumorigenic behaviors of enamel epithelium cells in ameloblastomas. 20032469_WNT-5a is necessary to maintain osteogenic potential of MSC and inhibition of WNT-5a signaling therefore plays a role in their determination into preadipocytes in humans 20083703_Wnt5A is not involved in the onset or progression of MCC and support other data that indicate that Wnt signaling is inactive in this cancer despite its neuroendocrine origins. 20101234_Wnt5a promotes the aggressiveness of prostate cancer and that its expression is involved in relapse after prostatectomy. 20376066_study suggest a shift away from canonical Wnt signaling toward noncanonical pathways driven by interactions between Wnt-5a and its cognate receptors in psoriasis, accompanied by impaired homeostatic inhibition of Wnt signaling by WIF-1 and dickkopf 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20429785_stimulator of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells osteogenic differentiation 20454608_A quantitative analysis of the expression of Wnt5A protein in human tissue arrays, containing 600 prostate tissue cores, showed >50% increase in malignant compared to benign cores (p |
ENSMUSG00000021994 |
Wnt5a |
30.677759 |
50.6832084483 |
5.663436 |
0.705368313 |
127.245002 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001641988664743225436961378371468357136222857038571819492105713335600017233317218443011675788056891178712248802185058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000207675687160325693904571867720810695947184026199095651377075398008307087764807985497128584029269404709339141845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.6530728 |
29.4715485 |
1.2320413 |
0.5764372 |
| ENSG00000114268 |
5210 |
PFKFB4 |
protein_coding |
Q16877 |
FUNCTION: Synthesis and degradation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Hydrolase;Kinase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is one of four bifunctional kinase/phosphatases that regulate the concentration of the glycolytic byproduct fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP). The encoded protein is highly expressed in cancer cells and is induced by hypoxia. This protein is essential to the survival of cancer cells under conditions of hypoxia, because it increases the amount of F2,6BP and ATP at a time when the cell cannot produce much of them. This finding suggests that this protein may be a good target for disruption in cancer cells, hopefully imperiling their survival. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:5210; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity [GO:0003873]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 2-phosphatase activity [GO:0004331]; fructose 2,6-bisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0006003]; fructose metabolic process [GO:0006000] |
15474002_Mechanisms of hypoxic regulation of PFKFB4 gene expression were studied in several cancer cell lines. 15642344_A detailed analysis of the 5'-flanking region of human gene pfkfb4 using different 5'-deletion promoter constructs was carried out; this gene is activated by serum and chemical hypoxia whereas beta-estradiol decreases its expression. 15925437_Overexpression of PFKFB-4 transcript levels in breast & colon malignant tumors correlates with enhanced expression of PFKFB-3, hypoxia-inducible factor(HIF)-1alpha & known HIF-1 dependent genes Glut1 & VEGF 17143338_PFKFB-4 and PFKFB-3 genes are expressed in gastric and pancreatic cancer cells, they strongly respond to hypoxia via a HIF-1alpha dependent mechanism and possibly have a significant role in the Warburg effect which is found in malignant cells 21396842_PFKFB4 has an important role in the progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer ( 21640852_Sulforaphane is a potent inducer of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via PFKFB4-inhibition pathways. 22056879_an essential role of PFKFB4 in the maintenance of brain cancer stem-like cells 22576210_we found that the glycolytic enzyme PFKFB4 is essential for prostate cancer cell survival by maintaining the balance between the use of glucose for energy generation and the synthesis of antioxidants. 22811469_Data suggest that molecular mechanism by which dihydrotestosterone induces Pfkfb4 (and thus glycolysis) during spermatogenesis involves stimulation of Sertoli cells to secrete FGF-2 (fibroblast growth factor 2); study uses recombinant human Pfkfb4. 22892400_PFKFB4 and HO-2 are expressed in a coordinated manner to maintain glucose homeostasis. 25115398_Data indicate that the PFKFB4 expressed in multiple transformed cells and tumors functions to synthesize F2,6BP. 25772235_PFKFB4 suppresses oxidative stress and p62 accumulation, without which autophagy is stimulated likely as a ROS detoxification response. 26221874_Inhibition of PFKFB4 suppresses glycolysis and proliferation of multiple human cancer cell lines. 27181362_HIF-1alpha transactivates hypoxia-responsive elements (HRE)-D of the promoter region of PFKFB4 in hypoxia condition. 27491149_The expression of PFKFB3, PFKFB4, NAMPT, and TSPAN13 is strongly up-regulated in pediatric glioma. 27614159_Our FD models could facilitate a better mechanistic understanding of FD and help develop effective therapeutics for FD and other fibrosis diseases. 27769068_Data show that PFKFB4 is the target gene of PPARgamma which modulates the transcriptional activity of its promoter. 28092678_High PFKFB4 expression is associated with colon and lung cancer. 28152500_This work has uncovered a novel function of the enzymes PFKFB3 and PFKFB4 in ovarian cancer cells during mitotic arrest 29208667_Epithelial and endothelial tyrosine kinase (Etk) interacts with 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 4 (PFKFB4) to promote small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) chemoresistance through regulation of autophagy. 29615789_findings suggest that the Warburg pathway enzyme PFKFB4 acts as a molecular fulcrum that couples sugar metabolism to transcriptional activation by stimulating SRC-3 to promote aggressive metastatic tumours 30415245_PFKFB4 enhances the invasiveness of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by inducing HA production and PFKFB4-induced expression of HAS2 depends upon the activation of p38 signaling. 30504385_Currently available anti-melanoma therapeutic strategies may significantly benefit from agents targeting PFKFB4 activity. 30613295_CD44ICD interacts with CREB and binds to the promoter region of PFKFB4, thereby regulating PFKFB4 transcription and expression. 30819197_This study aims to characterise the expression and phosphorylation of isozymes of the key glycolytic regulatory protein, 6-phosphofructokinase-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2/FBPase-2), in urinary exosomes of subjects with pre-eclampsia . 32299611_PFKFB4 is critical for the survival of acute monocytic leukemia cells. 33593309_PFKFB4 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via phosphorylating and activating transcriptional coactivator SRC-2. 34211613_PFKFB4 Overexpression Facilitates Proliferation by Promoting the G1/S Transition and Is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 34348486_Relocation of phosphofructokinases within epithelial cells is a novel event preceding breast cancer recurrence that accurately predicts patient outcomes. 34445551_Expression of Alternative Splice Variants of 6-Phosphofructo-2-kinase/Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-4 in Normoxic and Hypoxic Melanoma Cells. 34593007_PFKFB4 is overexpressed in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma promoting pentose phosphate pathway that mediates Sunitinib resistance. 35659173_Loss of PFKFB4 induces cell cycle arrest and glucose metabolism inhibition by inactivating MEK/ERK/c-Myc pathway in cervical cancer cells. 35813480_Hypoxia-inducible CircPFKFB4 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Facilitating the CRL4(DDB2) E3 Ubiquitin Ligase-mediated p27 Degradation. 35914811_PFKFB4 interacts with ICMT and activates RAS/AKT signaling-dependent cell migration in melanoma. 35926796_PFKFB4 modulated by miR-195-5p can boost the malignant progression of cervical cancer cells. 36109523_Phosphorylation of PFKFB4 by PIM2 promotes anaerobic glycolysis and cell proliferation in endometriosis. |
ENSMUSG00000025648 |
Pfkfb4 |
156.852847 |
4.8001640815 |
2.263084 |
0.175234360 |
169.346156 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000001027954796237159290553118934011632942811680679593386714268358301191634917663455035382653732537009154054952198009686981095001101493835449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000166548987842595727917248337786201944075290839423951811318558853739803159132988834181678835491720314099239885763381607830524444580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
258.8093222 |
26.1425873 |
54.2777738 |
4.6015797 |
| ENSG00000114268_ENSG00000114270 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.013782 |
12.2942530280 |
3.619912 |
0.714015842 |
23.314863 |
0.00000137533093432777906026857981519606610731898399535566568374633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004789968048767819289428943063668953072919975966215133666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.6343417 |
24.2818064 |
4.7059775 |
1.6234031 |
| ENSG00000114270 |
1294 |
COL7A1 |
protein_coding |
Q02388 |
FUNCTION: Stratified squamous epithelial basement membrane protein that forms anchoring fibrils which may contribute to epithelial basement membrane organization and adherence by interacting with extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins such as type IV collagen. |
Alternative splicing;Basement membrane;Cell adhesion;Collagen;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Epidermolysis bullosa;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
|
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type VII collagen. The type VII collagen fibril, composed of three identical alpha collagen chains, is restricted to the basement zone beneath stratified squamous epithelia. It functions as an anchoring fibril between the external epithelia and the underlying stroma. Mutations in this gene are associated with all forms of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. In the absence of mutations, however, an acquired form of this disease can result from an autoimmune response made to type VII collagen. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1294; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; collagen type VII trimer [GO:0005590]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle [GO:0030134]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; epidermis development [GO:0008544] |
11843659_glycine substitution mutations in COL7A1 are associated with dominant familial dystrophic toenail changes 11986329_bone morphogenetic protein-1 (BMP-1), which exhibits procollagen C-proteinase activity, cleaves the C-terminal propeptide from human procollagen VII 12060403_The epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen (type VII collagen) is present in human colon and patients with crohn's disease have autoantibodies to type VII collagen. 12353709_A novel splice site mutation in collagen type VII gene in a Chinese family with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa. 12485454_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12787118_May contribute to flexibility of linker of fibronectin type III domains and may affect interactions between noncollagenous 1 domain and extracellular matrix proteins. May have role in dermal-epidermal adhesion, wound healing, and skin remodeling. 14727126_R578X, 7786delG, and R2814X mutations are specifically limited to British patients, and the mutations 5818delC, 6573+1G-->C, and E2857X are frequent in Japanese patients. 15113589_identical COL7A1 glycine substitutions can cause remarkably heterogeneous clinical phenotypes 15365990_The predicted rates of AA substitutions for glycine were compared with missense mutations that have been observed to cause disease. Any Gly replacement will cause disease & the level of triple-helix destabilization determines clinical outcome. 15774758_collagen VII required for Ras-driven epidermal tumorigenesis by enhancing tumor cell invasion; retention of NC1 sequences in a subset of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients may contribute to their susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma 15810887_TNF-alpha and IL-1beta enhance the TGF-beta-mediated up-regulation of COL7A1 expression in HaCaT keratinocytes 15816848_Spectrum of mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa and cryptic splicing 15888141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16470588_COL7A1 hemizygosity and a missense mutation with complex effects on splicing may be causative in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 16500083_preimplantation genetic diagnosis for Hallopeau-Siemens recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 16923137_Two boys with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa and their fathers revealed a heterozygous nucleotide G to A transition at position 6109 and 6082 in 73 exon of COL7A1, which resulted in a glycine to arginine substitution (G2037R and G2028R), respectively. 16971478_Mutations from more than 1000 families with different forms of epidermolysis bullosa were analyzed. 242 mutations were distinct and 138 were novel, previously unreported mutations. 17106611_Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa due to a glycine substitution missense mutation in the COL7A1-gene 17229600_Glycine subsstitution in this protein underlies mild recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, showing that type VII collagen is tolefant of heterozygous glycine substitution. 17336503_description of a novel glycine substitution mutation in COL7A1 in a Chinese pedigree with dominant epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa 17425959_We report 14 Australian families with different forms of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) with 23 different COL7A1 allelic variants, nine of which were novel. 17495952_Individuals with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa can develop squamous-cell carcinoma regardless of type VII collagen expression and that additional factors have a role in explaining the high incidence of tumors complicating this genodermatosis. 17525268_Data show that the cartilage matrix protein subdomain of type VII collagen is pathogenic for epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. 17900868_Identify novel mutation in COL7A1 responsible for dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in a Chinese family. More severe phenotype observed in female members. 17916216_Mutational analysis revealed 30 pathogenic COL7A1 mutations among a total of 33 allels, identifying 10 novel and 14 previously adentified mutations. 18331784_The expression of COL7A1 mrna was higher in malignant tissue and was correlated with depth of tumor invasion and lymphatic invasion in ESCC. 18374850_Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa may present in generalized or localized forms and the disease may be inherited in either autosomal dominant or recessive mode. Genetic analysis shows mutations in COL 7A1 in this case 18429782_Mutations in the gene for collagen VII (COL7A1) have been documented in both types of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. 18440202_A p.Glu2857X mutation exhibits mild pathogenic effects in COL7A1, and its uniqueness enables detailed analysis and comparison of the destabilizing effects of missense mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients. 18450758_known recessive DEB C7 mutations perturb critical functions of the C7 molecule and may have a role in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 18496702_linked to dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in Tunisian consanguineous families 18558993_characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa [review] 19197535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19197535_The increased type VII collagen degradation was suspected to trigger an inflammatory response leading to itchy skin in EB pruriginosa. All 27 with EB pruriginosa were heterozygous for dominant-negative glycine substitution mutations in the COL7A1 gene. 19250433_novel glycine substitution mutation in the COL7A1 gene in three affected family members with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19422682_Results suggest that the down-regulation of alpha 6(IV) mRNA coincides with the acquisition of invasive growth properties, whereas alpha1(IV) and alpha1(VII) mRNAs were up-regulated already in dysplastic tissue. 19435799_Results describe the effect of loss of collage type VII on squamous cell carcinoma tumourigenesis using RNA interference in a 3D organotypic skin model. 19486043_new variants of COL7A1 mutations underlying epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa 19665875_Pseudosyndactyly occurs in approximately half of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB-O) patients when type VII collagen is strongly reduced. The prognosis in RDEB cannot always be simply predicted from the COL7A1 genotype. 19681861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19681861_Results disclosed 42 novel COL7A1 mutations, including the first large genomic deletion of 4 kb affecting only the COL7A1 gene, and three apparently silent mutations affecting splicing. 19945621_Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) emerged as a candidate for type VII collagen mutations becausing anchoring fibrils were shown to be morphologically altered, reduced in number, or completely absent in patients 20184583_Although the COL7A1 database indicates that most dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa mutations are family specific, the pathogenic mutation c.6527insC was highly recurrent in this cohort, this recurrence level has never previously been reported for COL7A1. 20555349_six new genetic mutations were found in collagen type VII for inversa dystropic epidermolysis bullosa 20598510_Analysis of the COL7A1 gene in Czech patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa reveals novel and recurrent mutations. 20920254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21113014_Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-I is associated with specific recessive arginine and glycine substitutions in the triple helix domain of type VII collagen. 21196708_novel compound heterozygous recessive COL7A1 missense mutations in 2 siblings presenting different Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa clinical subtypes 21448560_In screening the COL7A1 gene for mutations in individuals with dominant/recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa our data highlight that delineation of glycine substitutions in type VII collagen has important implications for genetic counselling. 21482078_NC1 and NC2 domains of type VII collagen have a role in of epidermolysis bullosa acquisita 21574979_Mutation in this gene results in skipping of exon 87 leading to aberrant splicing of this exon. 21658117_Two cases of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa revealed heteroallelic recessive mutations which resulted in premature termination codons. 21879237_we have identified three pathogenic COL7A1 mutations (G1773R, splicing site mutation of c.6900+1G>C, and G2701W) in 3 dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa families. 22070715_The infant's genomic DNA from blood was found to be heterozygous for a missense mutation on exon 54 of COL7A1 (c.5017G > A, p.G1673R) not previously described in bullous dermolysis of the newborn. 22209565_Letter: report novel and recurrent COL7A1 mutations in Chilean patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. 22266148_We present the first COL7A1 mutation analysis in Polish dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients. 22515571_The wide diversity of clinical phenotypes with one underlying genotype demonstrates that COL7A1 mutations are incompletely penetrant and strongly suggests that other genetic and environmental factors influence clinical presentation. 22757647_This study confirms unequivocally that the c.6527insC mutation in the COL7A1 gene, a cause of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, originated from a single ancestor. 22974128_Novel deletion mutation (c.3717del5) in COL7A1 in a patient with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. 23106673_We describe three families with multiple affected members in which epidermolysis bullosa prurigosa variant shows autosomal-dominance and all three previously unreported COL7A1 mutations were identified. 23226319_novel disease-causing mutations in the COL7A1 gene 23397949_We report six Chinese cases with Epidermolysis Bullosa Pruriginosa, who had four novel and two previously reported mutations leading to glycine substitutions of COL7A1. 23591773_Loss of collagen VII has a global impact on the cellular microenvironment in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients. 23624125_Mutation in COL7A1 caused a broad range of severity of disease in a family with pretibial epidermolysis bullosa. 23679163_We report the first case of HS-RDEB homozygous PTC mutations of 5818delC in both COL7A1 alleles. 23688405_Our long-term observational study showed that this in-frame exon skipping mutation was conversely highly predictive of the pruriginosa phenotype and characterized by a very variable phenotype in terms of severity of disease. 23769655_data further enhance the mutation spectrum of the LAMB3 and the COL7A1 genes, and also underscore the crucial roles of these genes in pathogenesis of epidermolysis bullosa 23834951_Data suggest that, of the five basement membrane types present in term placental tissue and fetal membranes, just one, that associated with amnion epithelium, expresses type VII collagen. 23947675_immortalized and cloned recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes carrying the c.6527insC mutation 24117545_Bullous dermolysis of the newborn (BDN) is a subtype of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa caused by mutations in type VII collagen resulting in disorganized anchoring fibrils and sublamina densa blister formation. 24127822_anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies fluctuated in parallel with disease activity in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita 24210835_The mutations detected in our 17 DEB patients highlight the presence of both mild (DDEB) and severe phenotypes (RDEB-O and RDEB-sev gen), confirming that a more severe involvement of the oropharyngeal mucosa occurs in RDEB. 24213372_analysis of COL7A1 mutations in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 24252097_Results suggest that In children with a moderate form of DEB with no or moderate skin fragility, a glycine substitution near the THD interruption domain of the collagen VII leading to thermolabile protein could explain this phenomenon 24317394_We show that revertant recessive dystrohic epidermolysis bullosa keratinocytes expressing functional C7 can be reprogrammed into induced pluripotent stem cells and self-corrected keratinocytes can be differentiated into epidermal or hematopoietic cells. 24357722_SLCO1B3 expression and promoter activity are modulated by COL7A1 in tumor keratinocytes isolated from recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. 24732400_TGM2 was identified as a stable interaction partner of collagen VII and is reduced in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. 24794830_Case Report: hot spot mutation c.6127G>A in COL7A1 leads to dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa associated with intracellular accumulation of pro-collagean VII. 24810542_The central collagenous domain of Col7 contains several interruptions of the collagen triple helix 24927163_Study demonstrated that versican, TGFbeta1, Col7A1 and ITGbeta3 are up-regulated in isolated Cancer stem cells. 25425313_COL7A1 mutation was diagnosed with next generation sequencing in patient with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. 25556825_This study is conducive to highlighting the phenotypic diversity of EBP, expanding the database on COL7A1 mutations in EBP and laying the foundation for this family's prenatal genetic counselling. 25566895_A novel dominantnegative heterozygous acceptor splice site mutation in the COL7A1 gene (IVS671G>T) was found in both our patient and his youngest son. 25639640_Collagen Type VII missense mutation is responsible for the development of recessive bullous epidermolysis. 25689103_autoantibodies to COL7, independent of the targeted epitopes, induce blisters both ex vivo and in vivo 26066885_Gene therapy is successful in the treatment of hereditary epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica. 26289024_A total of 50% of the pro-alpha1 (VII) procollagen chains will contain the dominant COL7A1 mutation if a DDEB patient carries one mutant COL7A1 in 100% of skin cells, which will lead to dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 26472200_In conclusion, we identified a Japanese founder recurrent mutation of c.6216 + 5G > T, inducing aberrant splicing of COL7A1 and tending to cause a mild phenotype of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa 26476432_Type VII collagen suppresses TGFbeta signaling and angiogenesis in cutaneous SCC (squamous cell carcinoma). Patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) SCC may benefit from anti-angiogenic therapy. 26568311_TANGO1 is thus pivotal in concentrating procollagen VII in the lumen and recruiting ERGIC membranes on the cytoplasmic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. 26586712_Novel dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa COL7a1 framshift mutation c.5493delG (p.K1831Nfs*10) in exon 64 leads to a premature termination codon located 10 amino acids downstream in exon 64 (p.K1831Nfs*10) and is expected to result in a loss of function. 26595603_The results in these two brothers show that COL7A1 mutation leads to persistent blistering in adulthood indicating that DEB may persist throughout life in a mild form. 26897595_COL7A1 mutations have a role in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa and can be corrected meganuclease-mediated homology-directed repair 27117059_expression restored to recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa skin by topical gene therapy 27328306_miR-29 Regulates COL7A1 in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa, directly through targeting its 3' untranslated region at two distinct seed regions and indirectly through targeting an essential transcription factor required for basal COL7A1 expression, SP1. 27790721_we have identified a novel glycine substitution mutation of the COL7A1 gene in two unrelated Scottish families with a DDEB phenotype. This mutation abolishes the donor splice site and results in in-frame exon skipping. This leads to dominant negative interference between the wild-type and truncated-type collagen proteins resulting in a mild phenotype. 27899325_COL7A1 harbored mutations in the overwhelming majority of patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, and most of them in this Iranian cohort were consistent with autosomal recessive inheritance. Ninety percent of these mutations were homozygous recessive, reflecting consanguinity in these families. 28126522_Patients with RDEB carry mutations in the COL7A1 gene encoding for type VII collagen, the main component of anchoring fibrils, microstructures responsible for the anchorage of the epidermis to the underlying dermis. [review] 28164502_Case Report: glycine substitution specific to COL7A1, exon 110, was identified in a Chinese family with epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa. 28800953_COL7A1 editing via CRISPR/Cas9 in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients' keratinocytes in vitro has been reported. 29182795_Case Report: Epidermolysis ullosa acquisita with previously unrecognized mild dystrophic EB and biallelic COL7A1 missense mutations. 29272047_three unrelated patients with two identical pathogenic compound heterozygous mutations in the COL7A1 gene developed different clinical forms of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa and mild recessive non-Hallopeau-Siemens. 29305555_specifically binds and sequesters the innate immune activator cochlin in the lumen of lymphoid conduits 29473190_In summary, we present 7 novel COL7A1 mutations in a cohort of 17 Mexican RDEB patients, expanding the mutation spectrum in this disease. 29490344_Type VII collagen is distributed particularly at the strained parts of the accommodation system. Type VII collagen was associated with various basement membranes and with ciliary zonules. 29499655_High chimeric COL7A1-UCN2 recurrence is associated with cancer stem cell transition, promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition in laryngeal cancer. 29504492_Case report of 2 potentially pathogenic variants in COL7A1 occurring on the same allele in members of a family with epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa and autosomal dominant inheritance. 29512192_In summary, we have found a novel mutation of COL7A1 gene in Chinese patients with DEBPr. 29512197_In both the cases, the variants p.G2692D, p.Q1571* and p.G1667E in the COL7A1 were not previously reported in 1000 genome, Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), Alleles in Middle East and North Africa (al mena) or in a in-house database of over 1000 exomes and genomes from South Asia. 29531004_Mutation in COL7A1 gene is associated with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. 29574987_Study reports novel COL7A1 mutation c.5327G>T (p.G1776V) in patient with dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa-bullous dermolysis of the newborn whose affected family members had typical dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, nails only. 30930113_Our strategy could potentially be extended to a large number of COL7A1 mutation-bearing exons within the long collagenous domain of this gene, opening the way to precision medicine for Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa 31709745_A novel mutation of COL7A1 in a Chinese DEB-Pt family and review of the literature. 32396230_What do we learn from dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, nails only? Idiopathic nail dystrophy may harbor a COL7A1 mutation as the underlying cause. 32484238_Next-generation sequencing through multigene panel testing for the diagnosis of hereditary epidermolysis bullosa in Chinese population. 32926178_Apparent Missense Variant in COL7A1 Causes a Severe Form of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa via Effects on Splicing. 33081018_Nonsequential Splicing Events Alter Antisense-Mediated Exon Skipping Outcome in COL7A1. 33258232_Self-improving dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: First report of clinical, molecular, and genetic characterization of five patients from Southeast Asia. 33974636_Rare functional genetic variants in COL7A1, COL6A5, COL1A2 and COL5A2 frequently occur in Chiari Malformation Type 1. 34286919_Novel and very rare causative variants in the COL7A1 gene of Vietnamese patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa revealed by whole-exome sequencing. 34435747_Ancestral patterns of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa mutations in Hispanic populations suggest sephardic ancestry. 34512204_Prognostic Value of Highly Expressed Type VII Collagen (COL7A1) in Patients With Gastric Cancer. 34543471_Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa: a new case series of a rare phenotype unveils skewed Th2 immunity. 34948168_Availability of mRNA Obtained from Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells for Testing Mutation Consequences in Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. 35163654_5'RNA Trans-Splicing Repair of COL7A1 Mutant Transcripts in Epidermolysis Bullosa. 35314946_Novel variants in LAMA3 and COL7A1 and recurrent variant in KRT5 underlying epidermolysis bullosa in five Chinese families. 35527172_Two cases of the intermediate phenotype of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa harboring the novel COL7A1 mutation c.3570G>A. 35560343_COL7A1 G2287R mutation with two clinical phenotypes in the same family: Bullous dermolysis of the newborn and dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa. 35979658_Analysis of COL7A1 pathogenic variants in a large cohort of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients from Argentina reveals a new genotype-phenotype correlation. |
|
|
797.639313 |
7.0246490539 |
2.812426 |
0.188990608 |
198.103022 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000541757071433819875878518033313089596659218038158371566611326013158983000429054429626425887960419730281895607878648798982901269027934176847338676452636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000101864132157492760402085612999752499594667376302981208074857130289519490542559329303826566574977505229629426430904004519106820225715637207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1459.4274240 |
160.0526498 |
208.6730420 |
17.3242635 |
| ENSG00000114315 |
3280 |
HES1 |
protein_coding |
Q14469 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor of genes that require a bHLH protein for their transcription. May act as a negative regulator of myogenesis by inhibiting the functions of MYOD1 and ASH1. Binds DNA on N-box motifs: 5'-CACNAG-3' with high affinity and on E-box motifs: 5'-CANNTG-3' with low affinity (By similarity). May play a role in a functional FA core complex response to DNA cross-link damage, being required for the stability and nuclear localization of FA core complex proteins, as well as for FANCD2 monoubiquitination in response to DNA damage. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18550849}. |
3D-structure;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This protein belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors. It is a transcriptional repressor of genes that require a bHLH protein for their transcription. The protein has a particular type of basic domain that contains a helix interrupting protein that binds to the N-box rather than the canonical E-box. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3280; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; HLH domain binding [GO:0043398]; JUN kinase binding [GO:0008432]; N-box binding [GO:0071820]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; adenohypophysis development [GO:0021984]; amacrine cell differentiation [GO:0035881]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; ascending aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035910]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; Cajal-Retzius cell differentiation [GO:0021870]; cardiac neural crest cell development involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0061309]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation [GO:0048667]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; comma-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072049]; common bile duct development [GO:0061009]; embryonic heart tube morphogenesis [GO:0003143]; establishment of epithelial cell polarity [GO:0090162]; forebrain radial glial cell differentiation [GO:0021861]; glomerulus vasculature development [GO:0072012]; hindbrain morphogenesis [GO:0021575]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; inner ear receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060122]; labyrinthine layer blood vessel development [GO:0060716]; lateral inhibition [GO:0046331]; liver development [GO:0001889]; lung development [GO:0030324]; metanephric nephron tubule morphogenesis [GO:0072282]; midbrain development [GO:0030901]; midbrain-hindbrain boundary morphogenesis [GO:0021555]; negative regulation of amacrine cell differentiation [GO:1902870]; negative regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090281]; negative regulation of cell fate determination [GO:1905934]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation [GO:2000978]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060253]; negative regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045608]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048715]; negative regulation of pancreatic A cell differentiation [GO:2000227]; negative regulation of pro-B cell differentiation [GO:2000974]; negative regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000737]; negative regulation of stomach neuroendocrine cell differentiation [GO:0061106]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; oculomotor nerve development [GO:0021557]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; pancreatic A cell differentiation [GO:0003310]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle, embryonic [GO:0045977]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050678]; regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045598]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046425]; regulation of secondary heart field cardioblast proliferation [GO:0003266]; regulation of timing of neuron differentiation [GO:0060164]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; renal interstitial fibroblast development [GO:0072141]; response to alkaloid [GO:0043279]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to thyroid hormone [GO:0097066]; S-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072050]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; stomach neuroendocrine cell differentiation [GO:0061102]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; trochlear nerve development [GO:0021558]; ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0060675]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
12065598_acid alpha-glucosidase gene is a novel target of the Notch-1/Hes-1 signaling pathway 12406868_HES-1 preserves the long-term reconstituting hematopoietic activity of 34-KSL stem cells ex vivo. 12535671_These results indicate that the molecular association between HES1-, HEY2- and SIRT1-related proteins is conserved among metazoans, from Drosophila to human, and suggest that the Sir2-bHLH interaction also plays important roles in human cells. 12972610_Hes1 transcription repression activity is inhibited by Hes6. 14722248_the estrogen receptor and AhR signaling pathways regulate HES-1, but with opposing effects, suggests the existence of a new pathway by which AhR represses E2-signaling. 15467735_HES-1 inhibits both estrogen- and heregulin-beta1-stimulated growth of breast cancer cells 15536134_IkappaBalpha is recruited to the promoter regions of the Notch-target gene, hes1 15563463_Notch1 inhibits the development of erythroid/megakaryocytic cells by suppressing GATA-1 activity through HES1 16214363_For marking and purifying neural stem cells to ascertain whether differences exist, we generated transgenic mice using promoters from Hes genes (pHes1 or pHes5) to drive expression of destabilized enhanced green fluorescent protein. 16253247_HES-1 is an upstream negative regulator of REST expression. 16322473_HES-1 alone is not able to substitute for Notch-1 signaling to induce T-cell differentiation of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. 16365048_Notch protein binding to Hes5-GFP is extinguished fast and recovered slowly, whereas Hes1-GFP is inhibited late and recovered quickly 16894395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17072841_Expression of HES1 increased significantly during chondrogenesis in chondrocytes while expression in mesenchymal stem cells was maintained at a low level. 17301032_Increased expression of Notch3, Jagged1, Hes1, and Hes6 gene transcripts were observed during differentiation of cultured human skeletal muscle cells. 17388915_expression significantly higher in squamous cervical carcinoma than in CIN as well as higher in CIN than normal cervical epithelia 17822320_Overexpression of hes1 is associated with breast cancer 18274550_Notch-mediated Hes1 expression contributes to the maintenance of the proliferative crypt compartment of the small intestine by transcriptionally repressing two CDK inhibitors. 18491256_lack of nuclear expression of HES1 may contribute to the abundance of ASCL1 and to tumorigenesis in the endocrine pancreas. 18524252_regulates brain development process.[review] 18550849_HES1 interaction with Fanconi anemia (FA) core complex members is dependent on a functional FA pathway. Cells depleted of HES1 exhibit an FA-like phenotype. 18599525_Inhibition of HES-1 expression using shRNA resulted in significantly reduced pancreatic beta-cell replication and dedifferentiation 18719287_it is concluded that HES1 safeguards against irreversible cell cycle exit both during normal cellular quiescence and pathologically in the setting of tumorigenesis 18821565_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19039095_These findings are consistent with a novel type of repressive estrogen response element in the distal 3' region of the HES-1 gene. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116245_The Notch signaling mediator, Hes1, potently suppressed V2 promoter activity through interaction with two Hes sites within the V2 exon. 19118200_ChIP-on-chip data reveal 3 oncogenic transcription factors, NOTCH1, MYC, and HES1, bind to several thousand target gene promoters 19321451_FA core complex interferes with HES1 binding to the co-repressor transducin-like-Enhancer of Split, suggesting that the core complex affects transcription both directly and indirectly. 19322650_we showed that SOX9 binding to the HES-1 enhancer was induced by retinoic acid 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19603167_Hes1 protein expression was also found elevated in immune thrombocytopenic purpura and Hes1 of ITP was found expressed higher in cellular nucleus than that of controls. 19724860_Notch1 signaling pathway was activated in laryngeal carcinoma accompanied with up-regulation of Notch1 and Hes1 expression 19808903_This study first reports HES1-dependent SRC/STAT3 pathway that provides a functional link between Notch signaling and hypoxia pathway. 19861684_Hes1 is a key molecule in blast crisis transition in CML. 19880519_Hyperactivation of BRAF-MEK signaling activates MAP2 expression in melanoma cells by two independent mechanisms, promoter demethylation or down-regulation of neuronal transcription repressor HES1. 19891787_Expression of Hes-6 resulted in induction of E2F-1, a crucial target gene for the transcriptional repressor Hes-1. 19935883_Data show that inhibition of Hes1 activity can promote insulin expression and glucose responsiveness in gall bladder epithelial cells. 20022559_HES1 repressed gene expression in part by recruiting histone deacetylases in tumor cells.[Review] 20091184_The expression of HES1 is increased in advanced ovarian serous adenocarcinomas, and HES1 high-expression probably is a potential poor prognostic factor for the patients. 20515776_data suggest IkappaBalpha regulates Hes1-mediated activity in osteoclast differentiation and resorption, which supports a cross-talk between NF-kappaB and Notch in osteoclast activity 20668890_Combining Hes1 knockout studies and ptf1a-Cre-mediated lineage tracing showed that the inactivation of Hes1 induced the misexpression of ptf1a in discrete regions of the primitive stomach and duodenum, as well as the common bile duct. 20816878_Data show that HES-1 Orange domain is well folded in all conditions, forms stable dimers, and greatly increases protein resistance to thermal denaturation. 20832754_Hes1, a canonical Notch target and transcriptional repressor, is responsible for sustaining IKK activation in T-ALL. Hes1 exerts its effects by repressing the deubiquitinase CYLD, a negative IKK complex regulator. 21103979_Results suggest that common variants in HES1 are not strongly associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes among white individuals. Findings cannot exclude these genes from involvement in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 21106062_The studies support coordinated regulation of delta-catenin expression by both the activating transcription factor E2F1 and repressive transcription factor Hes1 in prostate cancer progression. 21125297_HES1 gene expression was unchanged toward the terminal ileum. HES1-positive cells were found in the crypt base in all regions of the small intestine. 21169257_Notch may directly suppress Hedgehog via Hes1 mediated inhibition of Gli1 transcription, and targeting both pathways simultaneously may be more effective at eliminating glioblastoma multiform cells. 21224467_The novel interaction of HES1 and PARP1 in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia modulates the function of the HES1 transcriptional complex and signals through PARP1 to induce apoptosis 21238798_In this study, HES 1 transcription factor was detected in the lining epithelium of human periapical cysts with limited inflammation, showing Notch pathway activation in those cells. 21495212_Hes1 overactivation is associated with cell differentiation, thereby resulting in uterine carcinogenesis. 21866461_Epigallocatechin-3-gallate down-regulated HES1 gene expression in HT29 and HCT-8 cells very slightly. 21984123_These indicate that HES1 is uncoupled from Notch in ESFT, that EWS-FLI1-mediated inhibition of Notch contributes to ESFT aggressive cell growth, and support a role for Notch in ESFT tumour suppression 22036964_Data suggest that HEs-1/Hey-1 transcriptional modulation of insulin degrading enzyme may impact amyloid beta metabolism by providing a functional link between Notch signaling and the amyloidogenic pathway. 22333607_The expression of Hes1 is correlated with pathological types and differentiation types of colorectal cancer, but is not correlated with the long-term survival rate. 22411914_High Hes1 expression is associated with medulloblastoma. 22705236_Down-regulation of Notch1 and Notch3 in two hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines resulted in Hes1 down-regulation, CDKN1C/P57 up-regulation, and reduced cell growth. 22846929_High HES1 are associated with Glucocorticoid resistance of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. 22871495_High Hes-1 expression is associated with glioma. 23037857_Expression of Notch receptor and its target gene Hes-1 in bone marrow CD34+ cells from patients with psoriasis. 23235341_Notch1/Hes1-signaling pathway is activated during early pancreatic embryogenesis and reaches the highest at birth. 23379739_Data show that the periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hPDLSCs) on a Jagged-1-modified surface had increased expression of Notch signaling target genes, Hes-1 and Hey-1, suggesting the involvement of Notch signaling in hPDLSCs. 23423517_The Notch1-Hes1 signalling axis suppresses neuroendocrine differentiation and maintains tubular/acinar features in adenocarcinoma and non-neoplastic epithelium in the biliary tree. 23860410_Notch signaling can directly downregulate MUC5AC promoter activity through Hes1-dependent mechanisms. 23900217_HES1 was overexpressed in colorectal cancer tumors relative to normal colonic mucosa. 24342613_Hes1-mediated enhancement of IL-22-STAT3 signaling significantly increased the induction of genes encoding antimicrobial peptides, such as REG1A, REG3A and REG3G, in human intestinal epithelial cells. 24346283_HES1 was identified as a direct target of microRNA-9 in medulloblastoma, and restoration of microRNA-9 was shown to trigger cell cycle arrest, to inhibit clonal growth and to promote medulloblastoma cell differentiation 24486648_Hes1 upregulation contributes to the development of FIP1L1-PDGRA-positive leukemia in blast crisis. 24492635_The results from this study indicate that Hes1 plays a quantitative role in the development and progression of colon cancer and the maintenance of the stemness of cancer stem cells, which remains to be fully characterized. 24684754_In prostate tumors, the overexpression of PTOV1 was associated with decreased expression of HEY1 and HES1, and this correlation was significant in metastatic lesions. 24825862_Data indicate that chronic myelogenous leukemia blast crisis showed that MMP-9 was highly expressed in three, with two exhibiting high levels of HES1 expression. 24885297_The tumor suppressor function of LSAMP is most likely exerted by reducing the proliferation rate of the tumor cells, possibly by indirectly upregulating one or more of the genes HES1, CTAG2 or KLF10. 24894488_the present results revealed, for the first time, that Hes-1 could be SUMO-modified by PIAS1 and GADD45alpha is a novel target of Hes-1 25037575_Hes-1 protein expression was gradually increased from normal to dysplasia to oral carcinoma, revealing Hes-1 role in the progression of oral cancer. 25107895_This study revealed that Notch signaling-related molecules (including Notch1, Hes1, and others) are expressed in L929 and MRC-5 cells and that Notch signaling regulates the expression of col1alpha1 and col1alpha2 in both cell lines. 25139105_This study is the first report that elucidated the HES1 underexpression in ESCC and revealed its correlation with the invasiveness of ESCC. 25216517_CPEB1 specifically suppressed the translation of HES1 and SIRT1 by interacting with a cytoplasmic polyadenylation element. 25234168_Hes1 suppresses acute myeloid leukemia development through FLT3 repression. 25605780_Hes1 oscillation sustains a dynamic proliferation state that is well adapted for versatile fate decisions in both single- and two-cell neural progenitor systems. 25636905_HES1 has a role in metastasis and predicts poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer 25672829_Pancreatic stellate cells promoted Hes 1 expression in both PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cell lines and induced chemoresistance to gemcitabine. High Hes 1 expression was seen in pancreatic cancer patients with shorter overall and progression-free survival times. 25733872_Hes1 cooperated with CaMK2delta to modulate OA pathogenesis through induction of catabolic factors, including Adamts5, Mmp13, Il6, and Il1rl1 25781910_we summarize the recent data supporting the idea that Hes1 may have an important function in the maintenance of cancer stem cells self-renewal, cancer metastasis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process induction 25784680_Hairy and Enhancer of Split 1 (HES1), a transcriptional repressor controlled by NOTCH1, is a critical mediator of NOTCH1-induced leukemogenesis strictly required for tumor cell survival. 25817041_OR1A1 activation suppresses hepatic triglyceride metabolism by modulating HES-1, PPARG, and mtGPAT expression. 25849484_High Hes1 expression is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia. 25906782_HES1 DMROI methylation predicted differences in early infant behaviour, known to be associated with academic success. In vitro, methylation of HES1 inhibited ETS transcription factor binding, suggesting a functional role of this site. 25920606_Interference with Notch1 increased the expression level of Hes-1. 25987042_Decreased HES1 expression is associated with higher lung metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma 26092281_overexpression of HES1 in primary AML cells inhibited growth of AML in a xenograft mice model. In conclusion, we demonstrated the tumor suppressor role of HES1 in AML. 26448192_Suggest that loss of Hes1 could be used as a sensitive and specific marker to differentiate sessile serrated adenomas/polyps from hyperplastic polyps. 26452025_Results suggest that Hes1 plays an important role in the invasion and metastasis of NPC through inhibiting PTEN expression to trigger EMT-like phenotypes. 26452029_Results provide functional and mechanistic links between Hes1 and Bmi-1/PTEN/Akt/GSK3beta signaling in the development and progression of colon cancer. 26563369_PNA-antimiR-182 reduced the levels of NICD, Hes1, HIF-1alpha, and p-Akt in both cell groups, while it augmented the intracellular content of FOXO1 and Numb suppressor proteins. In other words, PNA-antimiR-182-mediated upregulation of Numb was associated with downregulation of HIF-1alpha and Hes1. Consequently, downregulation of miR-182 might find therapeutical value for overcoming trastuzumab resistance 26650241_High expression of Hes1 is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 26678889_Low HES1 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 26988248_we demonstrate for the first time an essential role of HPV oncoprotein E6 that selectively overexpresses in CaCxSLCs and participates in maintenance of stem cell phenotype and stemness through upregulation of Hes1 while preponderance of E7 leads to differentiation. 27353377_We demonstrated that ZNF70 interacts with ZFP64 and activates HES1 transcription by binding to the HES1 promoter. In addition, HES1 gene expression is increased in ILDR2-knockdown HepG2 cells, in which ZNF70 is translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, suggesting that ZNF70 migration to the nucleus after dissociating from the ILDR2-ZNF70 complex activates HES1 transcription. These results support a novel link betwee 27476040_Loss of nuclear expression of Hes1 occurs in 83% of colorectal adenocarcinomas and is associated with female sex, right-sided location, BRAFV600E mutation, microsatellite instability, larger tumor size, and significantly worse survival. 27567696_In SNSCC, the subgroup of patients with high expression (5th quintile) of HES1 mRNA was associated with better survival (P = .04); however these patients with high expression of HES1 mRNA had also a more favorable tumor stage and grade and more unfavorable resections representing potential confounders. 27612417_A three-molecule score based on the expression of Notch pathway molecules: Jagged1, intracellular Notch1 (ICN1) and Hes1 (JIH score) to assess prognostic value in non-metastasis clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). 27639167_Hes1 plays a key role in acinar cell integrity and plasticity on cellular insults. 27677287_High expression of Hes1 is associated with radiation resistance in pancreatic cancer. 28013292_Low Hes1 expression is associated with left ventricle hypertrabeculation/non-compaction and Menetrier-like gastropathy. 28079885_The phenotype was rescued by ectopic expression of miRNA182-5p in Delta182 cells. A bioinformatic analysis and Hes1 modulation data suggested that Hes1 could be a putative target of miRNA182-5p. A reciprocal relationship between miRNA182-5p and Hes1 was seen in the context of TK inhibition 28122586_miR-182 reveals its oncogenic capacity in medullary thyroid carcinoma by directly contributing to the invasive behavior through loss of the tumor suppressive HES1/Notch1 signaling circuit. 28245235_Cells could therefore regulate the proportion of Wnt- and Notch-mediated control of the Hes1 promoter to coordinate the timing of cell fate selection as they migrate through the intestinal epithelium and are subject to reduced Wnt stimuli. Furthermore, mutant cells characterised by hyperstimulation of the Wnt pathway may, through coupling with Notch, invert cell fate in neighbouring healthy cells, enabling an aberrant cel 28420872_Hes-1 knockdown promotes osteopontin expression in HUVECs and enhances OPN-induced angiogenesis. 28423527_These results suggest that HES1 promotes extracellular matrix protein expression and inhibits proliferative and migratory functions in the trabecular meshwork cells under oxidative stress, thereby providing a novel pathogenic mechanism underlying and a potential therapeutic target to primary open-angle glaucoma 28451898_In the present study, the authors reported the first observation of Hes1 oscillatory expression in human neural progenitor /stem cells, with an approximately 1.5 hour periodicity and a Hes1 protein half-life of about 17 (17.6 +/- 0.2) minutes. Human cytomegalovirus infection disrupts the Hes1 rhythm and down-regulates its expression. 28464285_GPR146 has an antiviral role in fighting against viral infection, although the GPR146-mediated protection is eliminated by IRF3/HES1-signalling. 28536281_Hes1 disruption leads to tumor regression without perturbing normal stem cell homeostasis, preclinically validating Hes1 as a cancer therapeutic target. 28750047_IE1 is involved in Hes1 degradation by assembling a ubiquitination complex and promoting Hes1 ubiquitination as a potential E3 ubiquitin ligase, followed by proteasomal degradation of Hes1. 28974640_Notch signaling and Id2/3 regulate neurogenesis in a complementary manner and ID factors can induce neural stem cell maintenance and quiescence in the absence of Notch. 29436668_Our results suggest that KN promotes goblet cell differentiation by regulating Wnt, Notch, and AhR signals and expression of Hes1 and Hath1. 29458175_The Sox17-Notch1-Hes1 pathway is critical for maintaining the undifferentiated state of IAHCs. 29463306_HES1 is mono-ubiquitinated in a Fanconi anemia core complex-dependent manner. 29491143_Depletion of HES1 increased cell death in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse and human cells, in a manner that depended on the pro-apoptotic gene growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34. 29523683_High HES1 expression is associated with pancreatic neoplasms. 29665790_The results of this study demonstrate that HES1 is a specific downstream gene of NOTCH1 and that it contributes to SACC proliferation, apoptosis and metastasis. 29981167_High HES1 expression is associated with invasiveness and tumorigenicity of non-small cell lung cancer. 30107165_MiR-182 alleviates the development of cyanotic congenital heart disease by suppressing HES1 30548309_Data indicate that hairy/enhancer of split-1 (Hes1) protein, overexpressed under the influence of Juglone, is apparently involved in Juglone-induced apoptosis among K562 cells. 30615540_Among all HPV-16-positive precancers the major HES1 protein expression positivity signal was present from cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 2 and 3 that develops into invasive squamous cell carcinoma. 30653033_Annexin A10 and HES-1 Immunohistochemistry in Right-sided Traditional Serrated Adenomas Suggests an Origin From Sessile Serrated Adenoma. 30895661_We defined the KK-LC-1/presenilin-1/Notch1/Hes1 as a novel signalling pathway that was involved in the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 31109645_The significant role of NK1R in mediating ESCC cell proliferation depended on the activation of SP and might be related to the downstream regulation of Hes1. 31232134_HES1 demonstrates uniform robust (+++) nuclear staining pattern in the tumor cells of all the neuroendocrine neoplasms (32/32), regardless of the origin of the system and the grade of the tumor. 31919081_HES1 and HES4 have non-redundant roles downstream of Notch during early human T-cell development. 32173531_Inhibition of NOTCH signaling pathway chemosensitizes HCC CD133(+) cells to vincristine and 5-fluorouracil through upregulation of BBC3. 32329442_Inhibition of HES-1 might play a protective role in endothelial cells under cholesterol stimulation via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 32879444_MYEOV increases HES1 expression and promotes pancreatic cancer progression by enhancing SOX9 transactivity. 32949667_High expression of miR-374a-5p inhibits the proliferation and promotes differentiation of Rencell VM cells by targeting Hes1. 32972441_microRNA-216b enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma MG63 and SaOS-2 cells by binding to JMJD2C and regulating the HIF1alpha/HES1 signaling axis. 33067264_Hes1 Is Essential in Proliferating Ductal Cell-Mediated Development of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. 33390847_HES1 promotes breast cancer stem cells by elevating Slug in triple-negative breast cancer. 33531431_Hes1 overexpression leads to expansion of embryonic neural stem cell pool and stem cell reservoir in the postnatal brain. 33544929_IL-6 and IL-8, secreted by myofibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment, activate HES1 to expand the cancer stem cell population in early colorectal tumor. 34278469_Sirt3 promotes the autophagy of HK2 human proximal tubular epithelial cells via the inhibition of Notch1/Hes1 signaling. 34354706_ILC2 Cells Promote Th2 Cell Differentiation in AECOPD Through Activated Notch-GATA3 Signaling Pathway. 34582650_LGR5, HES1 and ATOH1 in Young Rectal Cancer Patients in Egyptian. 34725165_Differential phase register of Hes1 oscillations with mitoses underlies cell-cycle heterogeneity in ER(+) breast cancer cells. 34738458_MicroRNA-361-5p Aggravates Acute Pancreatitis by Promoting Interleukin-17A Secretion via Impairment of Nuclear Factor IA-Dependent Hes1 Downregulation. 34804002_Oxidative Stress Leads to beta-Cell Dysfunction Through Loss of beta-Cell Identity. 35640677_Induction of Transcriptional Inhibitor HES1 and the Related Repression of Tumor-Suppressor TXNIP Are Important Components of Cell-Transformation Program Imposed by Oncogenic Kinase NPM-ALK. 35975741_Ischemic preconditioning/ischemic postconditioning alleviates anoxia/reoxygenation injury via the Notch1/Hes1/VDAC1 axis. 36037042_Identification and targeting of a HES1-YAP1-CDKN1C functional interaction in fusion-negative rhabdomyosarcoma. 36206597_Loss of Hes1 in embryonic stem cells caused developmental disorders in retinal pigment epithelium morphogenesis and specification. 36321463_HES1 promoter activation dynamics reveal the plasticity, stemness and heterogeneity in neuroblastoma cancer stem cells. |
ENSMUSG00000022528 |
Hes1 |
65.988732 |
2.8258271657 |
1.498673 |
0.195447221 |
60.736983 |
0.00000000000000652330299216706674719047753262094855316812922960134635275153414113447070121765136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000044248139781427344049174412477125595549861617611364650315408653113991022109985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
96.9624077 |
11.3149528 |
34.5416733 |
3.3362825 |
| ENSG00000114446 |
55081 |
IFT57 |
protein_coding |
Q9NWB7 |
FUNCTION: Required for the formation of cilia. Plays an indirect role in sonic hedgehog signaling, cilia being required for all activity of the hedgehog pathway (By similarity). Has pro-apoptotic function via its interaction with HIP1, leading to recruit caspase-8 (CASP8) and trigger apoptosis. Has the ability to bind DNA sequence motif 5'-AAAGACATG-3' present in the promoter of caspase genes such as CASP1, CASP8 and CASP10, suggesting that it may act as a transcription regulator; however the relevance of such function remains unclear. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17107665, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17623017}. |
Apoptosis;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA-binding;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Predicted to enable DNA binding activity. Acts upstream of or within activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process; apoptotic process; and regulation of apoptotic process. Predicted to be located in ciliary basal body. Predicted to be part of axoneme and intraciliary transport particle B. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus; centrosome; and cilium. Implicated in orofaciodigital syndrome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55081; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cilium [GO:0005929]; dendrite terminus [GO:0044292]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intraciliary transport particle B [GO:0030992]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; intraciliary anterograde transport [GO:0035720]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0043616]; left/right pattern formation [GO:0060972]; motile cilium assembly [GO:0044458]; negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010839]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
11788820_Results show that pro-apoptotic Hippi-Hip-1 heterodimers can recruit procaspase-8 into a complex of Hippi, Hip-1 and procaspase-8, and launch apoptosis through components of the 'extrinsic' cell-death pathway. 11807533_critical for the death-promoting effects of mutant huntingtin protein in cultured cells 12745083_Hippi interacts with the viral death protein Apoptin. 16364650_Hippi expression induced apoptosis by releasing AIF and cytochrome c from mitochondria, activation of caspase-1 and caspase-3, and altering the expression of apoptotic genes and genes involved in mitochondrial complex I and II. 17142908_Crystals of the pDED of HIPPI were grown in space group P4(1), with unit-cell parameters a = b = 77.42, c = 33.31 A and a calculated Matthews coefficient of 1.88 A3 Da(-1) (33% solvent content) with two molecules per asymmetric unit. 17173859_In summary, we showed that HIPPI could interact with the putative promoter sequence of caspase-1 and increased the expression of the downstream gene suggesting that HIPPI could act as transcription regulator. 18188704_Over-expression of BLOC1S2 in presence or absence of HIPPI does not induce apoptosis. However, BLOC1S2 & HIPPI sensitize NCH89 glioblastoma cells to pro-apoptotic actions of staurosporine & death ligand TRAIL. 21832040_novel transcription regulatory mechanism of REST by HIPPI may contribute to the deregulation of transcription observed in the cell model of Huntington disease. 21943362_HIPPI-P53 interaction was necessary for HIPPI mediated up-regulation of Caspase1 gene. 27060890_sequencing of IFT57 in 13 OFDS subjects and 12 subjects with Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome was negative. This report identifies the implication of IFT57 in human pathology and highlights the first description of a ciliary transport defect in OFDS, extending the genetic heterogeneity of this subgroup of ciliopathies. |
ENSMUSG00000032965 |
Ift57 |
64.568713 |
2.0772070882 |
1.054645 |
0.270757672 |
15.010933 |
0.00010689013902463966162927760938927690403943415731191635131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000292817084633199982944551376107256146497093141078948974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.1909066 |
15.7690442 |
41.7033597 |
5.7112823 |
| ENSG00000114554 |
5361 |
PLXNA1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UIW2 |
FUNCTION: Coreceptor for SEMA3A, SEMA3C, SEMA3F and SEMA6D. Necessary for signaling by class 3 semaphorins and subsequent remodeling of the cytoskeleton. Plays a role in axon guidance, invasive growth and cell migration. Class 3 semaphorins bind to a complex composed of a neuropilin and a plexin. The plexin modulates the affinity of the complex for specific semaphorins, and its cytoplasmic domain is required for the activation of down-stream signaling events in the cytoplasm (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable semaphorin receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including generation of neurons; regulation of GTPase activity; and regulation of cell shape. Predicted to act upstream of or within dichotomous subdivision of terminal units involved in salivary gland branching; neuron projection morphogenesis; and regulation of smooth muscle cell migration. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5361; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; semaphorin receptor complex [GO:0002116]; semaphorin receptor activity [GO:0017154]; dichotomous subdivision of terminal units involved in salivary gland branching [GO:0060666]; gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuronal migration to the hypothalamus [GO:0021828]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; neuron projection extension [GO:1990138]; olfactory nerve formation [GO:0021628]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014910]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287] |
14500350_Breast carcinoma cells support an autocrine pathway involving SEMA3A, plexin-A1, and NP1 that impedes their ability to chemotax. 17520388_Expression of Plexin A1 in gastric carcinoma was significantly higher than that in normal gastric mucosa. 18161927_PlexinA1 may play an important role in the occurrence and development of gastric carcinoma, and be related to tumor angiogenesis and proliferation. 19176370_In malignant pleural mesothelioma cells, plexin-A1 and VEGF-receptor 2 (VEGF-R2) are associated in a complex which are involved in survival pathways. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19480842_Data show that the expression of Sema3A receptors (neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), NRP-2, plexin A1, plexin A2, and plexin A3) significantly increased during M-CSF-mediated differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. 24858828_neuropilin 1 and plexin A1 transmembrane domains interaction 25518740_Data indicate that plexin A1-4 (PLXNA1-4) mediation of neuroanatomical traits can be detected using in vivo neuroimaging techniques. 26602825_Semaphorin-3a, neuropilin-1 and plexin-A1 are axonal guidance molecules that have been recently implicated in regulating bone metabolism. 26962861_a novel mutation in the PLXNA1 receptor (c.2587G>A) in newly established pancreatic cell line, is reported. 27506939_PLEXA1 has a developmental and tumor-associated pro-angiogenic role in brain neoplasms 28334861_We thus screened 250 patients for the presence of mutations in PLXNA1, and identified different nonsynonymous mutations (p.V349L, p.V437L, p.R528W, p.H684Y, p.G720E, p.R740H, p.R813H, p.R840Q, p.A854T, p.R897H, p.L1464V, p.K1618T, p.C1744F), all at heterozygous state, in 15 patients. 29091353_Data suggest that Fyn tyrosine kinase (Fyn)-dependent phosphorylation at two critical tyrosines is a key feature of vertebrate plexin A1 (PlxnA1) and plexin A2 (PlxnA2) signal transduction. 30467832_Our findings indicate that PLXNA1 variants cause not only anosmic but also normosmic IHH with a relatively high prevalence (3.9%). Heterozygous missense PLXNA1 variants appear to be involved together with other IHH gene variants in bringing about the IHH disease phenotype. 31383552_These findings demonstrate that cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumour metastasis of ESCC can be suppressed by overexpression of miR-134 through downregulating PLXNA1, which subsequently blocks the MAPK signalling pathway. 34054129_Biallelic and monoallelic variants in PLXNA1 are implicated in a novel neurodevelopmental disorder with variable cerebral and eye anomalies. 34636164_Analysis of PLXNA1, NRP1, and NRP2 variants in a cohort of patients with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. 35852441_Rare variant screening and burden analysis of PLXNA1 in Parkinson's disease. |
ENSMUSG00000030084 |
Plxna1 |
717.645494 |
2.9540564129 |
1.562697 |
0.114600301 |
180.542711 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000003689142780968726461393846511511631419718729004522364739262078752138110451443653787000324565981781647753829506131140192337625194340944290161132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000635376282929969656385295893355823642374999003215832660906882299004217992122975137005575145479039871998332145164312123597483150660991668701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1128.4488682 |
76.5658416 |
384.7793384 |
19.8723686 |
| ENSG00000114626 |
80325 |
ABTB1 |
protein_coding |
Q969K4 |
FUNCTION: May act as a mediator of the PTEN growth-suppressive signaling pathway. May play a role in developmental processes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10891360, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11494141}. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Elongation factor;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein with an ankyrin repeat region and two BTB/POZ domains, which are thought to be involved in protein-protein interactions. Expression of this gene is activated by the phosphatase and tensin homolog, a tumor suppressor. Alternate splicing results in three transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:80325; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; translation elongation factor activity [GO:0003746] |
18429817_Study showed that BPOZ-2 is a human counterpart of yeast Btb3p, which is a putative adaptor for Pcu3p-based ubiquitin ligase; BPOZ-2 bound to E3 ligase CUL3 in vitro and in vivo. 18459963_BPOZ-2 promoted eEF1A1 ubiquitylation and degradation, suggesting that eEF1A1 is a substrate of BPOZ-2. 31065369_Study demonstrates that miR-4319 is expressed at a low level in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues, which predicts the poor clinical outcome of CRC. MiR-4319 regulates the proliferation, cell cycle, invasion and migration of CRC cells. Mechanically, miR-4319 is found to be transcriptionally regulated by PLZF, and acts as a tumour suppressor in CRC by targeting ABTB1. |
ENSMUSG00000030083 |
Abtb1 |
360.378163 |
0.4698582319 |
-1.089703 |
0.105558995 |
106.480098 |
0.00000000000000000000000057870768820815192367959171735283215948003975873493983219214221227219910326233787145611131563782691955566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000006203141233080843496192879716105925256239604839440645164761705245091288896119863238709513098001480102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
231.6634626 |
18.1034320 |
496.0053286 |
26.5856075 |
| ENSG00000114698 |
57088 |
PLSCR4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRQ2 |
FUNCTION: May mediate accelerated ATP-independent bidirectional transbilayer migration of phospholipids upon binding calcium ions that results in a loss of phospholipid asymmetry in the plasma membrane. May play a central role in the initiation of fibrin clot formation, in the activation of mast cells and in the recognition of apoptotic and injured cells by the reticuloendothelial system. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3-binding;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables CD4 receptor binding activity and enzyme binding activity. Predicted to be involved in plasma membrane phospholipid scrambling. Predicted to act upstream of or within cellular response to lipopolysaccharide. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57088; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; CD4 receptor binding [GO:0042609]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; phospholipid scramblase activity [GO:0017128]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; plasma membrane phospholipid scrambling [GO:0017121] |
19333378_SLPI is a ligand for PLSCR1 and PLSCR4, which also interact directly with the CD4 receptor at the cell surface of T lymphocytes 19540310_Results show that binding affinities of the peptides are in the order hPLSCR1>hPLSCR3>hPLSCR2>hPLSCR4 for Ca2+ and in the order hPLSCR1>hPLSCR2>hPLSCR3>hPLSCR4 for Mg2+. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21690087_Crystallographic analysis of mammalian importin alpha1 in complex with the hPLSCR4-NLS reveals this minimal NLS binds specifically and exclusively to the minor binding site of importin alpha 23089641_biochemical and functional characterization of human phospholipid scramblase 4 27363667_the first report on the transcriptional regulation of hPLSCR4, where Snail was shown to downregulate the expression of Human phospholipid scramblase 4 31322545_LINC00641 suppressed cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis in NSCLC, indicating that LINC00641 exerted tumor-suppressive role in NSCLC. Through mechanism investigation, we determined that LINC00641 acted as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) in NSCLC by sponging miR-424-5p to upregulate phospholipid scramblase (PLSCR4) expression. 31409384_Specific DNA methylation signatures for aggressive choroid plexus carcinoma (CPC) revealed AK1, PER2, and PLSCR4 as potential biomarkers for CPC that can be used to improve molecular stratification for diagnosis and treatment. 33577029_LINC00641 induces the malignant progression of colorectal carcinoma through the miRNA-424-5p/PLSCR4 feedback loop. 34772994_Whole blood transcriptomic analysis reveals PLSCR4 as a potential marker for vaso-occlusive crises in sickle cell disease. 36077184_Phospholipid Scramblase 4 (PLSCR4) Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation via PIP3-Mediated AKT Activation. |
ENSMUSG00000032377 |
Plscr4 |
9.706872 |
0.0601774221 |
-4.054634 |
0.851074435 |
32.781954 |
0.00000001030975408772270613044072035601947390226484913000604137778282165527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000044875249287757930303192102595641332918319221789715811610221862792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0294269 |
0.6315491 |
17.2927569 |
4.0798308 |
| ENSG00000114735 |
51409 |
HEMK1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5R4 |
FUNCTION: N5-glutamine methyltransferase responsible for the methylation of the glutamine residue in the universally conserved GGQ motif of the mitochondrial translation release factor MTRF1L. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18541145}. |
Methyltransferase;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable DNA binding activity and methyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in DNA methylation and protein methylation. Predicted to be located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51409; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008170]; protein methyltransferase activity [GO:0008276]; protein-(glutamine-N5) methyltransferase activity [GO:0102559]; S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase activity [GO:0008757]; DNA methylation [GO:0006306] |
18541145_Human mitochondrial methyltransferase, HMPrmC, which methylates the glutamine residue in the GGQ tripeptide motif of HMRF1L, was identified. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 35260756_Mammalian HEMK1 methylates glutamine residue of the GGQ motif of mitochondrial release factors. |
ENSMUSG00000032579 |
Hemk1 |
103.966829 |
0.3414560966 |
-1.550228 |
0.276600142 |
30.373884 |
0.00000003562929317138241791716488462461731590025237892405129969120025634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000147142800002687316474951043261676364437562369857914745807647705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.1718839 |
10.7912785 |
159.0201587 |
21.9308264 |
| ENSG00000114745 |
64689 |
GORASP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQQ3 |
FUNCTION: Key structural protein of the Golgi apparatus (PubMed:33301566). The membrane cisternae of the Golgi apparatus adhere to each other to form stacks, which are aligned side by side to form the Golgi ribbon (PubMed:33301566). Acting in concert with GORASP2/GRASP55, is required for the formation and maintenance of the Golgi ribbon, and may be dispensable for the formation of stacks (PubMed:33301566). However, other studies suggest that GORASP1 plays an important role in assembly and membrane stacking of the cisternae, and in the reassembly of Golgi stacks after breakdown during mitosis (By similarity). Caspase-mediated cleavage of GORASP1 is required for fragmentation of the Golgi during apoptosis (By similarity). Also mediates, via its interaction with GOLGA2/GM130, the docking of transport vesicles with the Golgi membranes (PubMed:16489344). Mediates ER stress-induced unconventional (ER/Golgi-independent) trafficking of core-glycosylated CFTR to cell membrane (PubMed:21884936). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16489344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21884936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33301566}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Golgi apparatus;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;Zinc |
|
The Golgi complex plays a key role in the sorting and modification of proteins exported from the endoplasmic reticulum. The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane protein involved in establishing the stacked structure of the Golgi apparatus. It is a caspase-3 substrate, and cleavage of this encoded protein contributes to Golgi fragmentation in apoptosis. This encoded protein can form a complex with the Golgi matrix protein GOLGA2, and this complex binds to the vesicle docking protein p115. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:64689; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; establishment of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0061951]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; negative regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050774]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
9346242_Identification of GRASP65, and demonstration that it functions in the formation of stacked Golgi cisternae. 9628863_A study showing that GRASP65 binds directly to the coiled-coil vesicle tethering factor GM130, and targets it to Golgi membranes. 15576368_the GRASP domain alone of GRASP65 inhibits mitotic fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus 15834132_GRASP65 may function as a signal integrator controlling the cell growth 15888544_GRASP65 has a role in the regulation of spindle dynamics rather than a direct role in the stacking of Golgi cisternae 16489344_Ribbon formation requires the Golgi proteins GM130 and GRASP65. 19581411_Mitochondria bearing GRASP65 became tethered to one another, and this depended on a GRASP65 PDZ domain that was also required for GRASP65 self-interaction. 19840934_Data demonstrate that both GRASP55 and 65 are needed for the efficient transport to and through the Golgi complex, thus highlighting a novel role for the GRASPs in membrane trafficking. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083603_These results demonstrate that GRASP55 and GRASP65 stack mammalian Golgi cisternae via a common mechanism. 20214750_GRASP65 has a role in Golgi cisternal stacking and cell cycle progression 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20937827_the mechanism of phosphoinhibition as direct inhibition by PLK1 of the PDZ ligand underlying the GRASP65 self-interaction. 21368855_The C-terminal fragments of GRASP65 produced following caspase cleavage are targeted to mitochondria, and ectopic expression of these sensitises HeLa cells to Fas ligand. 23552074_propose that GRASP55/65 are negative regulators of exocytic transport and that this slowdown helps to ensure more complete protein glycosylation in the Golgi stack and proper sorting at the trans-Golgi network 24227884_Cisternal-specific functions of GRASP65 and GRASP55 in continuity, compartmentalization, and function of the Golgi ribbon. 26363069_Mutagenesis experiments support these structural observations and demonstrate that they are required for GRASP65-GM130 association. 26538023_In cells, Mena and actin were required for Golgi ribbon formation after nocodazole washout; in vitro, Mena and microfilaments enhanced GRASP65 oligomerization and Golgi membrane fusion. Thus Mena interacts with GRASP65 to promote local actin polymerization, which facilitates Golgi ribbon linking. 27703074_The authors determined that Golgi membrane ribbon fragmentation increased during the early cytoplasmic phase of cytomegalovirus virion assembly and that Golgi membrane fragmentation in infected cells was dependent on the phosphorylation of an integral cis-Golgi protein, Grasp65. 28782625_In situ proximity ligation assays of Golgi localization of alpha-mannosidase IA at giantin versus GM130-GRASP65 site, and absence or presence of N-glycans terminated with alpha3-mannose on trans-Golgi glycosyltransferases may be useful for distinguishing indolent from aggressive prostate cancer cells. 28814501_Results demonstrate a critical role for GRASP55 and GRASP65 in maintaining the stacked structure of the Golgi, which is required for accurate posttranslational modifications in the Golgi. Additionally, the GRASP knockout cell lines developed in this study will be useful tools for studying the role of GRASP proteins in other important cellular processes. 30566031_DjA1 interacts with GRASP65 to enhance Golgi structure formation through the promotion of GRASP65 trans-oligomerization. 31336000_GRASP65 modulates Golgi structure and microtubule organization during cell division. 32331836_Markers of malignant prostate cancer cells: Golgi localization of alpha-mannosidase 1A at GM130-GRASP65 site and appearance of high mannose N-glycans on cell surface. 32822731_Biophysical characterization of intrinsically disordered human Golgi matrix protein GRASP65. 33301566_Rapid degradation of GRASP55 and GRASP65 reveals their immediate impact on the Golgi structure. 35312866_GRASP depletion-mediated Golgi fragmentation impairs glycosaminoglycan synthesis, sulfation, and secretion. |
ENSMUSG00000032513 |
Gorasp1 |
300.910741 |
0.4214839136 |
-1.246451 |
0.110111676 |
127.741586 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001278513642330378251632198260156733945471281971303640414890710425165785773892303603394005051541171269491314888000488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000162120802068697442219796864627898156432376356690213122837150794911241388730413492957893595303175970911979675292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
169.6069203 |
28.2128506 |
406.9812848 |
48.5440077 |
| ENSG00000114757 |
51555 |
PEX5L |
protein_coding |
Q8IYB4 |
FUNCTION: Accessory subunit of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels, regulating their cell-surface expression and cyclic nucleotide dependence. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Enables peroxisome matrix targeting signal-1 binding activity and small GTPase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in protein import into peroxisome matrix, docking and regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling. Predicted to act upstream of or within maintenance of protein location and regulation of membrane potential. Located in cytosol. Part of receptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51555; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; intracellular cyclic nucleotide activated cation channel activity [GO:0005221]; peroxisome matrix targeting signal-1 binding [GO:0005052]; peroxisome targeting sequence binding [GO:0000268]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; protein import into peroxisome matrix, docking [GO:0016560]; regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043949] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21504900_increasing cAMP levels in cells antagonized the up-regulation of HCN1 channels mediated by a TRIP8b construct binding the CNBD exclusively. 22550182_TRIP8b interacts with the carboxyl-terminal region of HCN channels and regulates their cell-surface expression level and cyclic nucleotide dependence. 23077068_Seizure-dependent plasticity wound is not conditional upon TRIP8b in cerebral cortex. 24451387_Nedd4-2 plays an important role in the regulation of HCN1 trafficking and may compete with TRIP8b(1a-4) in this process 25197093_Data show that Rab8b-interacting protein TRIP8b does not compete with cyclic AMP for the same binding region of hyperpolarization activated cyclic nucleotide gated potassium channel 2 (HCN2). 25538232_the sequential formation of a highly stable trimeric complex involving cargo protein, PEX7 and PEX5L stabilizes cargo binding and is a prerequisite for PTS2-mediated peroxisomal import. 28864772_TRIP8b competes with a portion of the cAMP-binding site or distorts the binding site by making interactions with the binding pocket, thus acting predominantly as a competitive antagonist that inhibits the cyclic-nucleotide dependence of HCN channels. 28887304_allosteric coupling of the TRIP8b TPR domains both promotes binding to HCN channels and limits binding to type 1 peroxisomal targeting signal substrates. 35502931_Genetic variants in DDO and PEX5L in peroxisome-related pathways predict non-small cell lung cancer survival. |
ENSMUSG00000027674 |
Pex5l |
17.649239 |
4.2106469008 |
2.074042 |
0.453908401 |
20.553507 |
0.00000579874493738160180761722142794845069602160947397351264953613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000018703993722847996739174977753883410969137912616133689880371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.9000860 |
8.3680749 |
6.1690477 |
1.5270124 |
| ENSG00000114812 |
7433 |
VIPR1 |
protein_coding |
P32241 |
FUNCTION: This is a receptor for VIP. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase. The affinity is VIP = PACAP-27 > PACAP-38. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8926282}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a receptor for vasoactive intestinal peptide, a small neuropeptide. Vasoactive intestinal peptide is involved in smooth muscle relaxation, exocrine and endocrine secretion, and water and ion flux in lung and intestinal epithelia. Its actions are effected through integral membrane receptors associated with a guanine nucleotide binding protein which activates adenylate cyclase. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:7433; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptor activity [GO:0004999]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284] |
11812772_Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor-1 (VPAC-1) is a novel gene target of the hemolymphopoietic transcription factor Ikaros. 11834941_VPAC1 is a cellular neuroendocrine receptor expressed on T cells that actively facilitates productive HIV-1 infection. 11859928_Thus, the highly diverged chemical properties of the hydrophobic 'YL' motif and charged 'DR(Y)' motif could be a crucial difference between the Secretin Receptor Family and the Rhodopsin Family with respect to receptor activation and G-protein coupling. 11930171_VPAC1 receptor mRNA is expressed in the trigeminal, otic and superior cervical ganglia (prejunctional) and cerebral arteries (postjunctional). 11981043_a small sequence in the third intracellular loop of the VPAC(1) receptor is responsible for the efficient agonist-stimulated intracellular calcium concentration increase 12094871_Genetic complexity of HVR1 quasispecies of hepatitis C virus in patients with cirrhosis. 12133828_a selective filter; Identification of a critical domain for restricting secretin binding 12225791_Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) inhibits the proliferation of bone marrow progenitors through the VPAC1 receptor. 12690118_the role of charged residues in the intracellular loop 3 and the proximal C-terminal tail of hVPAC1 receptor for agonist-induced adenylyl cyclase activation 14599709_cloning and sequencing of 5' flanking region; VPAC1 may play a functional role in development of both cerebellum and adrenal medulla 15171718_Data suggest that vasoactive intestinal peptide directly stimulates cortisol secretion from H295 cells via activation of the VPAC1 receptor subtype. 15247290_the hVPAC1 receptor binds to vasoactive intestinal peptide at its N-terminal ectodomain 15451021_Interaction of different G proteins with the recombinant VPAC1 receptor involves different receptor sub-domains. 15932876_the VPAC1 receptor carboxyl terminus has a role in agonist-induced receptor phosphorylation, internalization, and recycling 16037943_Farnesoid X receptor agonists may increase gallbladder fluid secretion through transcriptional activation of VPAC1. 16520374_analysis of the two-step activation mechanism of VPAC receptor and of class II G protein-coupled receptors 16554109_Thr429 phosphorylation has a role in activation of human VPAC1 16888162_125I-[Bpa28-vasoactive intestinal peptide] was covalently bonded to the 121-133 fragment within the N-terminal ectodomain of the receptor 16888167_Photoaffinity experiments clearly indicated that the 6-28 part of VIP physically interacts with the N-terminal ectodomain of VPAC1 receptor 16888206_MCF-7 cells have VPAC1 receptors that bound the VIP chemotherapeutic conjugate 16888207_observations provide additional evidence for a role of proapoptotic caspase adaptor protein and PAC1 R in the events determining the outcome of prostate cancer 16934434_identification and characterization of novel five-transmembrane(5TM) isoforms of VPAC1 17077178_expression of VIP receptor-1 (VPAC1) and VPAC2 in CD4+ T cells changed reciprocally in the context of the activation state 17611633_The differential expression of VIPR1 in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease mucosa suggests that the VIP system plays different roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. 17651798_Both intra- and extracellular Ca2+ play a role in controlling pro-inflammatory functions stimulated by PACAP which acts through a VPAC-1, FPRL1/Galphai/PI3K/ERK pathway and a VPAC-1/Galphas/PKA/p38 pathway to fully activate monocytes 17883247_analysis of VIP 16gamma-glutamyl diamino derivative positive charges on hVPAC1 and hVPAC2 receptor function 17885205_Structural studies provide a detailed molecular understanding of the VIP-VPAC1 receptor interaction. 18000164_VPAC1 signaling tempers normal megakaryopoiesis, and inhibition of this pathway stimulates megakaryocyte differentiation. 18174366_Proinflammatory effect of VIP is mediated via the specific G protein-coupled receptor VIP/pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating protein (VPAC1) receptor as well as via FPRL1. 18351280_VIP and PACAP levels were decreased in anterior vaginal wall of stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse patients,they may participate in the pathophysiology of these diseases. 18383379_deficient expression of VPAC1 (vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1) in immune cells of Rheumatoid Arthritis was associated with the predominant proinflammatory Th1 mileu; reduced VPAC1 expression in RA is associated with genetic polymorphism 18597186_Results indicate that the N-terminal part of VIP physically interacts with the N-ted in the continuity of 6-28 VIP sequence; and the N-terminal part of VIP and its antagonist (PG97-269) have different sites of interaction with the VPAC1 receptor N-ted. 18663606_VIP acts in an autocrine fashion via VPAC1 to inhibit megakaryocyte proliferation and induce proplatelet formation 18668120_HLA-B (*)2705 and a functional polymorphism in VIPR1 gene, might be due to a founder effect or might be the result of a selective pressure. Consequent downregulation of this receptor in presence of a 'danger' signal might influence susceptibility to AS. 18668120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19309439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19309439_Patients with idiopathic achalasia show a significant difference in allele, genotype and phenotype of VIPR1 distribution of snps 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014941_We describe significant upregulation of the SPP1 gene, downregulation of VIPR1, and losses of the VIPR1 gene. 20026142_Results indicate that VPAC1, but not VPAC2 or PAC1, up-regulation in macrophages is a common mechanism in response to acute and chronic pro-inflammatory stimuli. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20691743_Moreover, we report the markedly nuclear localization of VPAC(1) receptors in estrogen-dependent (T47D) and independent (MDA-MB-468) human breast cancer cell lines 20706588_role of in MicroRNA 525-5p down-modulating VPAC1 expressio 20922191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20922191_The VIPR1 polymorphism, previously linked to gastrointestinal dysmotility disorders, does not represent a common risk factor for gallstones in the general or in an elderly population. 21711977_increased expression in patients with allergic rhinitis 21769421_mRNA expression of the VPAC1 receptor was detected in 51% of the tumor specimens, while the incidence of mRNA expression for VPAC2 was 46%. 21896307_silencing of VPAC1 receptor inhibits vasoactive intestinal peptide effects on both EGF receptor and HER2 transactivation and vascular endothelial growth factor secretion in human breast cancer cells 22166542_The genetic association reported here indicates that VIP/VPAC1 signaling can be a relevant pathway in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in females 22291440_hree residues play an important role in VPAC1 interaction with the first histidine residue of VIP. These data demonstrate that VIP and PG97-269 bind to distinct domains of VPAC1 22763881_The overexpression of VPAC1 and VPAC2 receptors and COX-2 in cancer tissue gives them a potential role as targets for diagnosis of prostate cancer. 23651810_VPAC1 receptor has a role in endotoxemia in peripheral blood mononuclear cells 24671823_These data suggest that VPAC1 overexpression is associated with poorer differentiation of colon cancer, which is likely caused by subsequent EGFR activation in cancer cells. 24788249_VIP regulates CFTR membrane expression and function in Calu-3 cells by increasing its interaction with NHERF1 and P-ERM in a VPAC1- and PKCepsilon-dependent manner. 25390694_variations at the 3'UTR of the VPAC-1 gene act synergistically to affect the expression of the luciferase as well as of the GFP reporter genes expressed in HEK293T cells. 26712708_VPAC1 rs9677 CC genotype could be correlated with a reduced response to statin therapy and seems to be involved in diabetes cardiomyopathy in female patients with type 2 diabetes. 26881970_The results reveal that more severe inflammation, based on high levels of IL-6, is associated with lower expression of VPAC1 and, conversely, with increased expression of VPAC2. 27381006_In vitro-polarized macrophages by GM-CSF (GM-MO), with a proinflammatory profile, expressed higher levels of VIP receptors, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptors 1 and 2 (VPAC1 and VPAC2, respectively), than macrophages polarized by M-CSF (M-MO) with anti-inflammatory activities. RA synovial macrophages, according to their GM-CSF-like polarization state, expressed both VPAC1 and VPAC2. 30407703_follicle-associated epithelium-adjacent villus epithelium in ileum of Crohn's disease possessed more mucosal mast cells and mucosal mast cells expressing VPAC1 but not VPAC2. 30583864_The promoter region of VIPR1 was methylated and DNA methylation inhibited VIPR1 gene transcription. Deacetylation of H3K27 in the promoter of VIPR1 inhibited the transcription of VIPR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Low expression of VIPR1 had an adverse prognostic impact on HCC, and such expression is at least partially mediated by epigenetic modification. 30692637_Enhanced expression of VPAC1 in primary gastric cancer correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis.VPAC1 activation induces Ca2+ signaling to promote migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. 30810849_3D structure prediction of VAPC1 and identification of dual natural inhibitors for VPAC1 and EGFR. 31089161_Activation of Th lymphocytes alters pattern expression and cellular location of VIP receptors in healthy donors and early arthritis patients. 31408534_S. Typhimurium infection exploits host VPAC1/VIP to gain survival advantage in human monocytes. 31560089_Findings point out the tumor suppressor roles of VIPR1 in human LUAD pathogenesis. 32807782_Cryo-EM structure of an activated VIP1 receptor-G protein complex revealed by a NanoBiT tethering strategy. 35864952_Activation of VIPR1 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating arginine and pyrimidine metabolism. 35869757_[VIPR1 promoter methylation promotes transcription factor AP-2alpha binding to inhibit VIPR1 expression and promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro]. 36430275_PAC1, VPAC1, and VPAC2 Receptor Expression in Rat and Human Trigeminal Ganglia: Characterization of PACAP-Responsive Receptor Antibodies. |
ENSMUSG00000032528 |
Vipr1 |
134.702152 |
0.1517937208 |
-2.719816 |
0.166990235 |
308.973898 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000365388818870185584560270735595548684544928890590280410818768737207073976209401779155323685107323734222154307994110983874249605304037361759635742043398882937594157424728274347058842863589234184473752975463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000108732640454111671692776286936472277982602633584462092888566305546550073553770275983288663845793808272793132088464192771001647257395583813926666662862586589399290653863011657520587505132425576448440551757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.0258045 |
4.2188373 |
245.6158671 |
14.3729414 |
| ENSG00000114853 |
92999 |
ZBTB47 |
protein_coding |
Q9UFB7 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92999; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20116376_Data show that ZNF651 is a ZNF652 paralogue that shares a common DNA binding sequence with ZNF652 and represses target gene expression through the formation of a CBFA2T3-ZNF651 corepressor complex. |
ENSMUSG00000013419 |
Zfp651 |
139.201757 |
0.4900165546 |
-1.029098 |
0.146427411 |
49.603982 |
0.00000000000188131452293624129582962839602528393092434333411233637889381498098373413085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000010992954219532430603350367416644534687003575967878532537724822759628295898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.3921091 |
8.7588984 |
189.6479859 |
12.0655476 |
| ENSG00000114857 |
4820 |
NKTR |
protein_coding |
P30414 |
FUNCTION: PPIase that catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and may therefore assist protein folding (PubMed:20676357). Component of a putative tumor-recognition complex involved in the function of NK cells (PubMed:8421688). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20676357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8421688}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Isomerase;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Rotamase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a membrane-anchored protein with a hydrophobic amino terminal domain and a cyclophilin-like PPIase domain. It is present on the surface of natural killer cells and facilitates their binding to targets. Its expression is regulated by IL2 activation of the cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4820; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cyclosporin A binding [GO:0016018]; peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity [GO:0003755]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization [GO:0000413] |
|
ENSMUSG00000032525 |
Nktr |
773.637263 |
0.4964109263 |
-1.010393 |
0.123454989 |
65.990697 |
0.00000000000000045305642053233326225512527042431873478442022054255011731527247320627793669700622558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000003302277909657895550321984907244957214595966303594121171727238106541335582733154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
534.7530510 |
42.9198064 |
1086.4217707 |
61.9875760 |
| ENSG00000114978 |
55233 |
MOB1A |
protein_coding |
Q9H8S9 |
FUNCTION: Activator of LATS1/2 in the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS1/2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration. Stimulates the kinase activity of STK38 and STK38L. Acts cooperatively with STK3/MST2 to activate STK38. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15197186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18362890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19739119}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the Hippo signaling pathway, which controls organ size and tumor growth by enhancing apoptosis. Loss of the encoded protein results in cell proliferation and cancer formation. The encoded protein is also involved in the control of microtubule stability during cytokinesis. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:55233; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; hippo signaling [GO:0035329]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15766530_Mats1 can rescue the lethality associated with loss of Mats function in Drosophila; As Mats1 is mutated in human tumors, Mats-mediated growth inhibition and tumor suppression is likely conserved in humans 17611689_MATS1 mRNA expression is suppressed in tumor tissue and its low expression is associated with tumor growth, invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer 19739119_hMOB1A and hMOB1B are 2 LATS-binding proteins that may function as tumor suppressors in human cancer cells. 19955215_Results suggest that Mob1 and the other mammalian orthologues of the mitotic exit network regulate mitotic progression by facilitating the timely mobilization of the chromosomal passenger complex to the spindle midzone. 22454515_Mob1A and Mob1B are needed for cell abscission and centriole re-joining after telophase and cytokinesis. 23652010_The RING ligase praja2 ubiquitylates and degrades Mob, a core component of NDR/LATS kinase and a positive regulator of the tumour-suppressor Hippo cascade. 25031347_No relationship has been found between the MOBKL1B-NS5A interaction and hepatitis C virus replication. 28373297_Through a comprehensive set of biochemical, biophysical, mutational and structural studies, we quantitatively assess how phosphorylation of MOB1A regulates its interaction with both MST kinases and LATS/NDR family kinases in vitro. 28373298_In this study, we investigated the mechanisms behind the recruitment of MST1 and MST2 kinases to MOB1, which facilitate signal transmission in the Hippo pathway by bringing the MST1 and MST2 kinases in close vicinity to their substrates, the LATS family kinases. 28675297_validated the functional importance of an identified interaction network by characterizing a distinct novel interaction between PTPN5 and Mob1a. 28947795_MOB1 binds differently to the NDR2 and LATS1 kinases.MOB1 interaction with Hippo and MST protein is not essential for development and tissue growth control. 32513747_The Legionella kinase LegK7 exploits the Hippo pathway scaffold protein MOB1A for allostery and substrate phosphorylation. 32780197_RNA-binding protein Musashi2 regulates Hippo signaling via SAV1 and MOB1 in pancreatic cancer. 34983617_Circular RNA circCCDC85A inhibits breast cancer progression via acting as a miR-550a-5p sponge to enhance MOB1A expression. 35349706_Oxidative stress-CBP axis modulates MOB1 acetylation and activates the Hippo signaling pathway. 36123327_CAF-derived exosomal WEE2-AS1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression via promoting degradation of MOB1A to inhibit the Hippo pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000043131 |
Mob1a |
1719.349360 |
2.3936346096 |
1.259203 |
0.040140507 |
987.349539 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100934010604197884059760026607698866551149762570918676276382020069112412909170106211414632964918731731912623090881 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000103457360869302822385188828696797205755591270795130104841733429646808465645708704083950464372082899021567368917533 |
Yes |
Yes |
2357.6580963 |
72.4229024 |
991.8749035 |
22.9278688 |
| ENSG00000115008 |
3552 |
IL1A |
protein_coding |
P01583 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine constitutively present intracellularly in nearly all resting non-hematopoietic cells that plays an important role in inflammation and bridges the innate and adaptive immune systems (PubMed:26439902). After binding to its receptor IL1R1 together with its accessory protein IL1RAP, forms the high affinity interleukin-1 receptor complex (PubMed:2950091,PubMed:17507369). Signaling involves the recruitment of adapter molecules such as MYD88, IRAK1 or IRAK4 (PubMed:17507369). In turn, mediates the activation of NF-kappa-B and the three MAPK pathways p38, p42/p44 and JNK pathways (PubMed:14687581). Within the cell, acts as an alarmin and cell death results in its liberation in the extracellular space after disruption of the cell membrane to induce inflammation and alert the host to injury or damage (PubMed:15679580). In addition to its role as a danger signal, which occurs when the cytokine is passively released by cell necrosis, directly senses DNA damage and acts as signal for genotoxic stress without loss of cell integrity (PubMed:26439902). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14687581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15679580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17507369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26439902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2950091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3258335}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Lipoprotein;Mitogen;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Pyrogen;Reference proteome;Secreted |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This cytokine is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in various immune responses, inflammatory processes, and hematopoiesis. This cytokine is produced by monocytes and macrophages as a proprotein, which is proteolytically processed and released in response to cell injury, and thus induces apoptosis. This gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2. It has been suggested that the polymorphism of these genes is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3552; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing [GO:0002248]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; fever generation [GO:0001660]; heart development [GO:0007507]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; keratinization [GO:0031424]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of establishment of Sertoli cell barrier [GO:1904445]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033092]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of neutrophil migration [GO:1902624]; positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032308]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0010893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; response to copper ion [GO:0046688]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to L-ascorbic acid [GO:0033591]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; response to ozone [GO:0010193]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
11065142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11079552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11138328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11145356_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11241561_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11264025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350506_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11423389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11427627_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11436125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11448121_The level of IL-1 alpha is significantly higher in sera of cicatricial pemphigoid patients with active disease before intravenous immunoglobulin therapy compared to the post-treatment level. 11453239_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11669478_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11703512_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737511_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11774556_Allele specific regulation of cytokine genes: monoallelic expression of the IL-1A gene. Review. 11774564_Interleukin-1 alpha and beta system in testis--quantitative analysis. Expression of immunomodulatory genes in male gonad. 11777547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11784248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11790645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11858158_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11895290_Meta-analysis of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11895546_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11911995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11921766_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11930657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11940570_Lipopolysaccharide-mediated reactive oxygen species and signal transduction in the regulation of interleukin-1 gene expression. 11956022_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11991668_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11991668_data indicate that IL-1 gene polymorphisms known to affect the inflammatory response are highly related to plasma levels of CRP and fibrinogen in patients referred for coronary angiography 12028539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12034804_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12037600_Cloning and functional analysis of the allelic polymorphism in the transcription regulatory region 12047332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12047332_Results suggest a role for the IL1A gene in modifying the clinical features of migraine. 12051868_Interleukin-1 system plays a role in sex steroid receptor gene expression in human endometrial cancer. 12052540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12052541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12070246_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12100571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12101079_TNF-alpha promoter polymorphism is associated with Il-1 beta synthesis capacity in human leukocytees 12102486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115182_Association of the interleukin-1 gene cluster on chromosome 2q13 with knee osteoarthritis. 12115182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12149413_Review.inheritance of a specific IL-1A gene polymorphism increases risk for development of Alzheimer's disease by as much as sixfold. Moreover, this increased risk is associated with earlier age of onset of the disease. 12161036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12195069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12209090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12209090_The IL1A genotype associates with atopy in nonasthmatic adults 12210881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12212456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12218254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12220547_Review. The IL-1 family consists of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta, 2 receptors, and a specific receptor antagonist, IL-1Ra. The balance between IL-1 & IL-1Ra in local tissues plays an important role in the susceptibility to & severity of many diseases. 12242547_IL-1A allele 2 is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD) in a dose-dependent manner, the risk of developing AD with two copies of the IL-1A allele 2 being approximately double that of one copy of the IL-1A allele 2. 12242547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12362317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12362317_relationship between interleukin-1A (IL-1A) gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility of chronic periodontitis in Uighur minority in Xingjiang province of China 12370389_IL1-alpha induced during in vitro activation of mast cells by cystic fibrosis-associated Pseudomonas aeruginosa stimulates neutrophil transendothelial migration. 12390476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12404162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12425801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445604_investigated interleukin polymorphisms in ovarian cancer but did not find any association between common polymorphisms of interleukin 1A, interleukin 1B, and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist and the occurrence of ovarian cancer 12453471_We have identified a novel regulatory sequence at -65 to -41 of the human IL-1alpha promoter 12519748_a 'defective' IL-1ra response to IL-1 may underlie, at least in part, the exaggerated prostaglandin-endoperoxide H synthase (PGHS)-2 induction in orbital fibroblasts 12528118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12528118_the CTG haplotype of the IL1A gene may be an important marker for the susceptibility to, and the severity of, systemic sclerosis 12528119_that a DNA binding protein containing the Ets domain is constitutively expressed in fibroblasts from the skin of systemic sclerosis patients and regulates transcription of the IL1A gene, contributing to the fibrogenic phenotype of fibroblasts 12530978_soluble form of the IL-1 receptor accessory protein (AcP) increases the affinity of binding of human IL-1alpha and IL-1beta to the soluble human type II IL-1 receptor 12558814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12558933_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12562360_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12598547_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12613995_In conjunctiva of keratoconjunctivitis sicca patients. 12622850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12626603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12631337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12631337_The association of the TN7(delTTCA)A haplotype with higher levels of IL-1 alpha expression and reduced risk for ESRD is consistent with involvement of cytokines in risk for developing nephropathy. 12641660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12651617_may enhance the local production of CCL3, which may interact with CCR1 expressed on hepatoma cells, in an autocrine and/or paracrine manner 12667716_Low levels of IL-1 alpha mrna expression are associated with an increased risk for cancer specific death in patients with bladder cancer. 12673844_TNF-alpha & IL-1 produced by sickle leukocytes are the primary factors responsible for the observed CAM expression. This & the subsequent endothelial adherence of sickle erythrocytes play roles in the pathophysiology of sickle-related complications. 12702109_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12710950_IL-1A was used to stimulate epidermal keratinocytes in organ culture. 12714264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714264_no one particular polymorphism in the IL-1 gene cluster yields an advantage for survival in the last decades of life 12729191_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12730545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12737276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12742380_Activation of vascular endothelial cells by IL-1alpha released by a pulmonary epithelial cell line infected with respiratory syncytial virus. 12746420_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12749050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12752101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12752325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12759172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12782964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12794386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12801479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12824054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12869004_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12874528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12890860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12899665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12901853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12913118_the constitutively up-regulated expression of pre-IL-1 alpha in the nuclei of systemic sclerosis (SSc) fibroblasts up-regulates proliferation and matrix production of SSc fibroblasts through binding necdin 12928052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12928381_Monoallelic expression of IL-1 alpha is observed in Th0, Th1, and Th2 cell clones from healthy individuals, as well as in synovial fluid of the knee joint derived from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 12930304_confirm the role of uPA in acantholysis and suggest an involvement of IL-1alpha/TNF-alpha in uPA induction 12930389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12931024_In pancreatic cancer, IL-1alpha enhanced alpha(6)beta(1)-integrin expression, probably via increased IL-1RI levels. 12946945_Proapoptotic stimuli upregulate MCP-1 expression by vascular smooth muscle cells through release of interleukin-1alpha. 12947160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12974682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13679381_IL-1alpha activity in chondrocytes is independent of any direct modification in UDPGD activity and manifests equally in human cartilage of all ages 14514232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14533660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14566095_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14584862_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14633625_Cancer cell-derived cytokines, such as IL-1 alpha, induce cachexia by affecting leptin-dependent metabolic pathways. 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14639688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14644395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14656692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14664464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14672899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14673470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14674121_serum IL-1 alpha and IL-1 soluble receptor type 2 levels in women with ovarian cancers were significantly higher than those in cervical cancer, and in patients with benign disorders, and in healthy control 14688369_In IL-1 alpha transgenic mice, which may overproduce membrane-associated (MA)IL-1 as well as soluble IL-1 alpha, severity of arthritis highly correlates with MA-IL-1 activity rather than with soluble IL-1 alpha activity or serum IL-1 alpha concentration. 14693849_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14705223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14705223_The IL-1alpha-889 polymorphism, previously shown to predispose to increased IL-1 protein expression, may be involved in susceptibility to systemic sclerosis 14735144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14974822_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14983027_Precursor form of IL-1alpha was overexpressed in various cells and assessed for activity in the presence of saturating concentrations of IL-1 receptor antagonist 14984963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14986816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14997019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007345_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15007345_polymorphisms of IL1A (G/T at +4845) and IL4RA (T/C at +22446) show an epistatic effect on the risk of atopy 15009111_cells of keratinocyte origin (SCC 12F) respond to a single physiologic dose of solar-simulated irradiation with both early (8 h) and late (72 h) peaks of IL-1alpha mRNA induction 15036245_The presence of high amounts of intracellular IL-1alpha in human dermal fibroblasts suggests that these cytokines may carry out important function inside cells 15039285_(125)I fibrinogen demonstrated no specific interaction of IL-1alpha with fibrinogen 15050696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15068111_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15082121_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15082121_The results suggest a possible contribution of the IL-1 gene locus polymorphisms to the pathogenesis of LBP. 15117956_IL-1beta is the critical regulator of tuberculosis-stimulated CCL5 secretion in the lung. 15130917_IL-1 evokes a complex gene expression program in endothelial cells that includes positive but also negative (feedback) regulators of diverse endothelial cell functions. 15170937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15190266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15219382_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15220553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15238767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15248873_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15270852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15338333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15341923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15351436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15361128_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15377701_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15381245_Potential in tissue repair for injured human keratinocytes 15465625_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15468358_Data show that interleukin 1-alpha (IL-1a) is an important autocrine fibrogenic factor in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and suggest that inhibition of intracellular IL-1a may be a novel strategy for the treatment of SSc. 15476179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15476179_The polymorphism distributions of IL-1alpha (-889C/T) showed no differences between the essential hypertension group and control group. 15489227_IL-1-inducible phosphorylation of p65 NFkB is mediated by multiple protein kinases including IKKalpha, IKKbeta, IKKepsilon, TBK1, and an unknown kinase and couples p65 to TAFII31-mediated IL-8 transcription 15514971_A potent cytokine stimulus for IL-8 RNA stabilization in breast cancer cells. 15551344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15561982_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15562658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15562910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15563458_SHP-2 has a role in regulating IL-1-induced Ca2+ flux and ERK activation via phosphorylation of PLCgamma1 15566952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15581980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15587751_serum IL-1 and TNF-alpha are reduced significantly by calcitriol during osteoporosis 15592292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15633328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15638425_Cellular and subcellular expression of TNF-alpha, IL-1alpha and IL-6 in hepatocytes inx chronic hepatitis C. 15679580_IL-1alpha, TNF-alpha, CCL20, CCL27, and CXCL8 alarm signals are induced in human cells after allergen and irritant exposure 15679582_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15694997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15723707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15726267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15727567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15732864_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15732864_polymorphisms may play an important role in determining generalized aggressive periodontits susceptibility in Chinese males 15733644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15737206_essential role for soluble factors, mainly IL-1alpha and bFGF, in the stimulation of dermal fibroblasts by human melanoma cells to secrete MMP-1. 15745939_The significant associations between VEGF and the levels of IL6 and IL1 alpha suggest an important role for these cytokines in the development of these tumours. 15777329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15797878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15830637_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15836820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15854776_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15931231_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15951664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15951664_White carriers of the (+484)T haplotype were at increase risk of spontaneous preterm birth. 15954918_Two polymorphisms within the IL-1 gene cluster are associated with ESRD independent of race 15974847_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15974847_individuals carrying the positive genotype have significantly greater risk for developing periodontitis 15986200_Polymorphisms associated with control of gene expression and protein levels were not associated with occurrence of chronic idiopaathic leukemia in adults and were not responsible for the increased cytokines. 16021081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16030091_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16046471_IKKbeta phosphorylates multiple p65 sites, as well as in an IkappaB-p65 complex, and S468 phosphorylation slightly reduces TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB activation 16078996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16101131_Data demonstrates that IL-1alpha and COX-2 mRNA are frequently co-expressed in human gastric cancer tissues, and suggest that the IL-1alpha-COX-2 pathway might be involved in tumor progression by regulating cancer cell proliferation. 16106254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16115908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16155691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16159520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16206345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16226351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16230423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246569_N-terminal IL-1alpha propiece increases ECV304 tumor cell motility. 16268484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16291395_The proteolytic activation of pro-MMP-9 in skin inflammatory diseases likely occurs via a pathway including IL-1alpha. 16304445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16317381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16318580_GBF1 is recruited to the endogenous IRF-9 promoter, and interacts with C/EBP-beta, IL-1, and IL-6 16361815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16378839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16378839_there is no genetic association between IL1A gene polymorphism and outcome after head injury 16384981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16389181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16403098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16410064_enhances tissue type plasminogen activator production in human pulp cells 16410066_induces alkaline phosphatase, osteonectin, and osteocalcin in tooth mineralization and may play a role in the cytoprotection of pulp cells via heme oxygenase-1 expression 16411061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16428739_significantly increases infective endocarditis incidence due to a platelet releasate-susceptible Streptococcus oralis strain, with rapidly increasing numbers of bacteria within the vegetations. 16433908_IL-1 alpha is secreted by middle ear epithelial cells upon exposure to NTHi components and that it can synergistically act with certain of these molecules to up-regulate beta-defensin 2 via the p38 MAP kinase pathway. 16464738_Genetic variations in pro-inflammatory IL-1alpha may predict the clinical outcome of breast carcinoma. 16464738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16478776_In conclusion, incubation of normal or GD thyrocytes with Th1 cytokines induces a significant reduction in TSH-increased expression of both TPO and ThOXs, an effect partially mediated by NO. 16504015_IL-1alpha can induce selective upregulation of alpha6beta1-integrin and uPA/uPAR in pancreatic cancer cells and these changes may modulate the aggressive functions of pancreatic cancer. 16508980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16510430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16517748_vitamin D modulates cutaneous inflammatory reactions, at least in part, by increasing the IL-1Ra to IL-1alpha ratio and suppressing IL-18 synthesis in keratinocytes 16546408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16564702_icIL-1ra1 does not act at an intracellular level to alter IL-1 mediated signalling, and is effective in inhibiting IL-1 responses only when released in an ATP-dependent and cell type specific manner 16564703_elevated production of IL-1alpha and TNF-alpha by in vitro stimulated whole blood cell cultures occurs in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease obese patients 16567828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16619041_studies demonstrate a novel role for IL-1alpha in mediating a proliferative response to TGF-beta signaling 16636934_Interleukin-1 alpha gene single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with negative response to cyclophosphamide therapy scleroderma patients with alveolitis 16636934_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16684536_NF-kappaB is probably the primary transcription factor by which cAMP counteracts the inhibition of erythropoietin gene expression by IL-1. 16702372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16708852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16719905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16720107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16733901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16788102_allele-specific expression of IL-1alpha in CD4+ cells is achieved, at least in part, by differential methylation of the promoter 16814297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16842617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16856121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16879223_the 4G/5G PAI-1 genotype influences the PAI-1 response to IL-1alpha and the modulatory effect of pravastatin 16885196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16888077_results suggest elevation of IL1 in myometrium at the end of pregnancy initiates process of down-regulation of oxytocin receptors in advanced labour resulting in desensitization of the myometrium to elevated levels of oxytocin in blood during lactation 16900886_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16905534_Tyr-542 of SHP-2 modulates IL-1-induced Ca2+ signals and association of the ER with focal adhesions 16907768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16911569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16918024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16930778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16931944_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16938461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16945028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16945028_composite genotype was found to be significantly associated with severe chronic periodontitis 16961803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16965524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16965825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16965825_a common polymorphism of the interleukin-1alpha gene is associated with the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome 16971486_These findings reveal that nuclear localization of pre-IL-1alpha depends on the binding to HAX-1 and that biological activities might be elicited by the binding to both HAX-1 and IL-1RII in SSc fibroblasts. 16978691_IL-1, FN, and FN-derivatives have interrelated roles in determining biomaterial-modulated macrophage function [review] 17002905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17012236_This study proposes a novel mechanism of TIMP-1 regulation, which ensures an increased supply of the inhibitor after brain injury, and limits extracellular matrix degradation. 17034724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17083033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17138334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17140155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17141301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17149369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17179726_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17197697_Through the study of IRAK modification mutants, two parallel IL-1-mediated signaling pathways for NFkappaB activation, TAK1-dependent and MEKK3-dependent, were uncovered. These two pathways bifurcate at the level of IRAK modification. 17205326_All the polymorphisms within the IL-1alpha gene are in strong linkage disequilibrium and not convincingly associated with fracture risk, BMD, or bone turnover. 17205326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17214636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17244613_IL1 induced NF-kappaB activation is NEMO-dependent but does not require IKKbeta 17257312_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17290104_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17290104_PARP-1 haplotypes increased the risk of AD by interaction with the IL-1A -889 allele 2. 17293495_Autocrine actions of endogenous IL-1 alpha, mediated via IL-1RI signaling, contribute to a proproliferative and proinflammatory phenotypic shift in toll like receptor-activated human vascular smooth cells. 17309781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17309781_the gene polymorphisms of the promotor region of IL-1 alpha at position (-889) are likely to play a pathogenic role in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in modification of its clinical presentation and severity 17331078_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17335370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335371_IL-1 genotypes are associated with cytokine levels in patients with aggressive periodontitis and chronic arthritis 17335371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335373_+4845 alleles may influence post-scaling values of salivary aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase 17335373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17348886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17353161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 1736 |
ENSMUSG00000027399 |
Il1a |
12.134534 |
48.5240747149 |
5.600629 |
1.078956138 |
57.616042 |
0.00000000000003186163873817499337757750230108585803666778127340997173178038792684674263000488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000208641432021057186295986473659085309509788122572793156450643436983227729797363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.5136135 |
19.0421318 |
0.5089186 |
0.3877660 |
| ENSG00000115009 |
6364 |
CCL20 |
protein_coding |
P78556 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a ligand for C-C chemokine receptor CCR6. Signals through binding and activation of CCR6 and induces a strong chemotactic response and mobilization of intracellular calcium ions (PubMed:11352563, PubMed:11035086, PubMed:20068036). The ligand-receptor pair CCL20-CCR6 is responsible for the chemotaxis of dendritic cells (DC), effector/memory T-cells and B-cells and plays an important role at skin and mucosal surfaces under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions, as well as in pathology, including cancer and various autoimmune diseases (PubMed:21376174). CCL20 acts as a chemotactic factor that attracts lymphocytes and, slightly, neutrophils, but not monocytes (PubMed:9038201, PubMed:11352563). Involved in the recruitment of both the pro-inflammatory IL17 producing helper T-cells (Th17) and the regulatory T-cells (Treg) to sites of inflammation. Required for optimal migration of thymic natural regulatory T cells (nTregs) and DN1 early thymocyte progenitor cells (By similarity). C-terminal processed forms have been shown to be equally chemotactically active for leukocytes (PubMed:11035086). Positively regulates sperm motility and chemotaxis via its binding to CCR6 which triggers Ca2+ mobilization in the sperm which is important for its motility (PubMed:23765988, PubMed:25122636). Inhibits proliferation of myeloid progenitors in colony formation assays (PubMed:9129037). May be involved in formation and function of the mucosal lymphoid tissues by attracting lymphocytes and dendritic cells towards epithelial cells (By similarity). Possesses antibacterial activity towards E.coli ATCC 25922 and S.aureus ATCC 29213 (PubMed:12149255). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O89093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11035086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11352563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12149255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20068036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23765988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25122636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9038201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9129037, ECO:0000303|PubMed:21376174}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This antimicrobial gene belongs to the subfamily of small cytokine CC genes. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. The protein encoded by this gene displays chemotactic activity for lymphocytes and can repress proliferation of myeloid progenitors. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:6364; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; CCR6 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031731]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell migration [GO:0072678]; thymocyte migration [GO:0072679] |
11877260_B-cell chemotaxis responsiveness to MIP-3alpha is profoundly suppressed by surrogate antigen. 11994436_MIP-3 alpha-induced calcium flux and chemotaxis can be enhanced significantly on peripheral blood and tonsillar B cells after activation by cross-linking surface antigen receptors. 12010510_Increased serum levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha in chronic viral hepatitis 12067311_MIP-3alpha, in periodontal diseased tissue appears to have an important role in the selective recruitment of T cells in the context of periodontal inflammation. 12149255_x-ray crystal structure of human MIP-3alpha refined to a resolution of 1.7 A compared with the crystal structures of human beta-defensin-1 and -2 12239608_LARC plays a crucial role in the tumor immunity of human malignant glioma 12356943_These results show that the concentration of MIP-3alpha in the endometrium is modulated by these inflammatory mediators. 12414801_co-ordinate activation and binding of ESE-1, Sp1, and NF-kappaB to the MIP-3alpha promoter is required for maximal gene expression by cytokine-stimulated Caco-2 human intestinal epithelial cells. 12496186_demonstrated that P. aeruginosa can provide a direct signal to stimulate CCL20 and GM-CSF production by human mast cells 12684696_Results describe the relationship between cancer-related factors and serum levels of macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma. 12760962_Cells were also exposed to small size-fractions of ambient particulate matter. Each of these stimuli induced MIP-3alpha/CCL20 gene and protein expression. 12821122_MIP-3alpha and BD-2 have the ability to stimulate odontoblast differentiation in addition to their more traditional role in inflammation 12949249_CCL20 is an antimicrobial protein with bacteriocidal activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14714554_Calcium triggers beta-defensin (hBD-2 and hBD-3) and chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha (MIP-3alpha/CCL20) expression in monolayers of activated human keratinocytes 15069060_in non-transformed human colonocytes, MEK activation following flagellin/TLR5 engagement is a key modulator for NFkappaB-independent, IL-8 and MIP3alpha expression. 15336571_rowth of a proportion of human hapatocellular carcinoma cells may be mediated by CCL20-CCR6 axis. 15474097_MIP-3alpha was present in follicular fluid and correlated with oocyte maturation, and was regulated by IL-1alpha and TNF-alpha. MIP-3alpha may play an important role in the human preovulatory process. 15618437_the alveolar epithelium is an important source of CCL20 in the lung and may play a critical role in controlling the movement of dendritic cells through the lung both under normal and inflammatory conditions 15671814_plays a role in the advancement of pulpal inflammation via the recruitment of Chemokine (C-C motif) Receptor 6-expressing lymphocytes 15679580_IL-1alpha, TNF-alpha, CCL20, CCL27, and CXCL8 alarm signals are induced in human cells after allergen and irritant exposure 16034074_MIP-3 alpha expression may be involved in the recruitment of CD45R0-positive T cell subsets into the intestinal lamina propria 16095490_MIP-3alpha/CCL20 has a role in amplification of the immune response during renal allograft rejection by attraction of CCR6+ inflammatory cells, which may include DC, to the site of inflammation 16215992_In conclusion, IEC and CRC express CCL20 and its receptor CCR6. CCL20 expression is increased in intestinal inflammation, while CCR6 is upregulated during cell differentiation. 16531471_Vaginal epithelial cells respond to factors present in semen by secreting CCL20, leading to the enhancement of langerhans cells recruitment during HIV transmission. 16764701_Of all chemokines found to be expressed in normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, CCL20 was the only chemokine showing significant upregulation in HCC tissues. 16820679_The structure of the human macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha has been determined at 1.81 angstroms resolution by X-ray crystallography 17075975_CXCR4 expression in colorectal liver metastases suggests it is a predictive factor. CCL20 and receptor CCR6 expression in hepatocellular carcinomas indicates a role of a CCL20/CCR6 ligand-receptor pair in liver carcinogenesis and progression. 17133360_Our results add new insight to the important role of the CCL20/CCR6, RANKL system in the bone tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. 17241869_Stimulation of intestinal epithelial cells with IL-21 resulted in enhanced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 and increased synthesis of macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha (MIP-3alpha), a T-cell chemoattractant 17295217_UTP up-regulated approximately 2- to 3-fold the antimicrobial chemokine CCL20 expression and release in primary airway epithelial cells 17545018_CCL20 and CXCR4 expressions are markedly down-regulated in epidermal condyloma acuminatum lesions. 17548638_MIP-3alpha can regulate mitogenic signaling in colonic epithelial cells. 17562763_Interaction between CCL20 and CCR6 may play a role in chemokine-mediated lymphocyte trafficking during gastric inflammation in Helicobacter infection. 17664181_the role of TGF beta 1 in high glucose-induced MIP-3 alpha expression 18047937_CCL19, CCL20 and CCL22 factors could play an additive role in the pathogenesis of the inflammatory process leading to bronchiolar fibro-obliteration in lung transplant patients 18086840_The C-terminal alpha-helical region of MIP-3alpha plays a significant part in its broad anti-infective activity 18512817_CCL20(macrophage inflammatory protein 3) concentrations were significantly higher in Synovial fluie (SF) compared with peripheal blood samples; SF mononuclear cells constitutively expressed CCL20 messenger RNA 18576931_exodus-1is a physiologic constituent of amniotic fluide; its concentration increases as term approaches;elevated levels are found in intraamniotic infection/inflammation 18684866_the Th2 cytokine IL-21 is abnormally expressed in Hodgkin lymphoma cells, which regulates STAT3 signaling and attracts Treg cells via regulation of MIP-3alpha 18703490_CCL20 is overexpressed in myeloma microenvironment related to osteolytic bone lesions. 18757306_Data demonstrate that lysophosphatidic acid stimulates thymic stromal lymphopoietin and CCL20 expression in bronchial epithelial cells via CARMA3-mediated NF-kappaB activation. 18980993_study provides evidence that MIP-3alpha is overexpressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells and that its serum level is significantly elevated in NPC patients and tightly associated with the disease status and treatment outcome of NPC 19006683_CCL20 mRNA and protein levels were significantly elevated in H. pylori-positive patients and substantially decreased after successful eradication 19233848_CCR6 regulation of the actin cytoskeleton orchestrates human beta defensin-2- and CCL20-mediated restitution of colonic epithelial cells 19295614_Th17 cytokines stimulate CCL20 production in vitro and in vivo, and thus provide a potential explanation of how CCR6-positive Th17 cells maintain their continual presence in psoriasis through a positive chemotactic feedback loop. 19303953_Investigated the regulation of ccl20 expression and found different NF-kappaB pathways modulate CCL20 transcription by operating on the same NF-kappaB binding site in the same cell type. 19305396_the CCR6-CCL20 axis in the choroid plexus controls immune surveillance of the CNS. 19324905_KSHV and K13-mediated induction of CCL20 and CCR6 may contribute to the recruitment of dendritic cells and lymphocytes into the Kaposi sarcoma lesions, and to tumor growth and metastases. 19340288_show that the chemokine receptor CXCR4 stimulates the production of the chemokine CCL20 and that CCL20 stimulates the proliferation and adhesion to collagen of various tumor cells 19350575_Prolactin may enhance basal and IL-17-induced CCL20 production in keratinocytes by AP-1 and NF-kappaB activation, which is partially mediated via MEK/ERK and JNK. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19479364_secretion in bronchial epithelial cells is induced during Chlamydophila pneumoniae infection 19492413_This study demonstrates a different expression of CCL20-positive osteoblasts in osteoarthritis versus rheumatoid arthritis disease that seem to be associated with the presence of infiltrating mononuclear cells. 19567485_expression in gingival epithelial cells is induced by trypsin via activation of protease-activated receptor 2 19644053_The expression of adipocyte CCL20 was positively correlated with BMI and increased in visceral compared to subcutaneous adipocytes. 19784662_Electric fields increased keratinocyte CCL20 expression. 19797510_Data suggest that therapeutic efficacy of biologic DMARD may result from the inhibition of CCL20 production in rheumatoid synovium. 19885605_adipocyte culture medium increased the production of TNF-alpha in MDA-MB-231 cells, which stimulated CCL20 expression in an autocrine fashion 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20023216_CCL20 (MIP3A) induces APOBEC3G expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and in CD4+ T lymphocytes via CCR6. The increased expression of APOBEC3G results in HIV inhibition. 20054338_As CCL20 is activated by Th17 cytokines, the upregulation of CCL20 production by Trim32 provides a positive feedback loop of CCL20 and Th17 activation in the self-perpetuating cycle of psoriasis 20064082_higher levels of expression on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chinese patients with inflammatory bowel disease 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400327_This study has shown that activation of OX40 induces CCL20 expression in the presence of antigen stimulation. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20420712_CCL3 and CCL20-recruited dendritic cells modified by melanoma antigen gene-1 have a role in anti-tumor immunity against gastric cancer 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20439195_CCL20 was preferentially expressed in adrenal tissues from patients with primary non-small-cell lung cancer who developed metastases 20459729_CCL20 and CCR6 play a role in the development and progression of pancreatic cancer and may constitute potential targets for novel treatment strategies. 20511548_Synergistically enhanced by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, the expression of CD54 in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) enables CCR6 chemokine ligand CCL20 to induce in vitro adhesion of T helper (Th)17 cells to MSCs. 20595617_Oxidative stress biases intestinal epithelial responses to flagellin, leading to increased production of IL-8 and decreased production of CCL20; suggesting that epithelial cells are capable of adjusting their antimicrobial responses. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20816914_These data demonstrate a role for the FP receptor in regulation of the chemokine CCL20, which can mediate proliferation of endometrial adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. 20819093_M. tuberculosis increases dramatically the expression of CCL20 in human monocytes. CCL20 inhibits M. tuberculosis-mediated apoptosis, possibly as a consequence of the down-regulation of ROS production. 20969772_increased expression of MIP-3alpha favors recruitment of immature DCs to the tumour bed, whereas de novo local expression of SLC and MIP-3beta induces accumulation of mature DCs at the tumour margin forming clusters with T-cells 21178014_Polarized, in situ-differentiated, skin-derived T helper cell (Th)17 clones activated via the T cell receptor-CD3 complex produce CCL20 in addition to interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22. 21178448_Human corneal eptihelial cells secret CCL20 in response to S. aureus exposure. 21248725_Gene expression of epithelial innate immune markers beta-defensin 2 and CC chemokine ligand 20 is increased following the inhibition of HDAC and DNMT 21300824_Binding of CCL20, a G protein-coupled receptor ligand to G protein-coupled receptor CCR6 induces MUC5AC mucin production in human airway epithelial (NCI-H292) cells. 21724701_CCL20/CCR6 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of RA by assembling the molecular and cellular components orchestrating synovitis. 21881590_Sorted keratinocytes had an early burst of upregulated gene expression, which included CCL20, IL-15, IL-23A, IFN-kappa, and several antimicrobial peptides. 21911466_The ability of Fusobacterium nucleatum cell wall and beta-defensins to produce proinflammatory cytokines and CCL20 suggests the broad role of F. nucleatum and human antimicrobial peptides in primary immune responses elicited by oral epithelium. 21912453_Data show that both CCL20 and CCR6 mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly increased in patients who received preoperative FOLFOX chemotherapy = 12 mo before liver surgery in comparison to patients who did not undergo FOLFOX treatment. 21935436_The CCL20-CCR6 axis mediates the migration of circulating Tregs into tumor microenvironment, which in turn results in tumor progression and poor prognosis in HCC patients. 21949768_The role of the CCL20/CCR6/IL-17 axis in non-small-cell-lung-cancer tumor growth, was investigated. 21961038_Data show that CORM-2 reduced the expression of inflammatory mediators IL-8, CCL2 and CCL20. 22001440_CCL20 is one of its target genes, which is related to the HPV16 E6 and E7 oncogenes. 22019504_Data show that IL-17A synergistically enhanced CCL20 production from IL-1beta-stimulated gingival fibroblasts (HGFs) in a concentration-dependent manner. 22048239_Data show IL-22 and CCL20, but not IL-17, expression is elevated in both sera and lesional skin in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and suggest that IL-22 may be important in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, which may prove to be a future therapeutic target. 22099878_miR-21 functionally interacts with the 3'UTR of CCL20 mRNA. 22286692_MIP-3alpha-driven recruitment of Th17 cells or CD45R0+ memory T lymphocytes is not affected in patients carrying heterozygous NOD2 variants. 22388957_CCL20 may be used for the detection of HCC in HCV-infected patients with comparable specificity and higher sensitivity than AFP. 22533972_PI16-positive Treg showed enhanced in vitro migration towards the inflammatory chemokines CCL17 and CCL20, suggesting they can migrate to sites of inflammation 22553918_These results suggest that Brucella induces only a weak proinflammatory response in gut epithelial cells, but produces a significant CCL20 secretion. 22715389_a differential regulation pattern for genes solely expressed in Th17 cells (IL17A and CCL20) compared to genes expressed in both Th17 and Th1 cells (IL23R and IL12RB2), where high levels of promoter methylation are correlated to near zero 22796894_CXCR3 promotes recruitment of Th17 cells from the blood into the liver in both human and murine liver injury. Their subsequent positioning near bile ducts is dependent on CCR6 and cholangiocyte-secreted CCL20. 22857950_CCL20 is a pivotal mediator of Langerhans cells recruitment into epidermis. 22860513_In fibroblasts, the commensal bacterium Streptococcus gordonii stimulated the mRNA of CCL20 after 24 h, while not in gingival epithelial cells. 22911498_identified CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta as a critical regulator of CCL20 gene expression in normal human keratinocytes; HPV8 E7 oncoprotein suppressed C/EBPbeta-inducible and constitutive CCL20 gene expression as well as Langerhans cell migration 22926691_Increased MIP-3a was significantly associated with synchronous liver metastases and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. 22926920_Our data suggest for the first time that CCL20 and CCR6 might play an important role in the regulation of aggressiveness in human gliomas 23011799_Data show that transfection of ORMDL3 in bronchial epithelial cells induced expression of MMP-9, ADAM-8, CCL-20, IL-8, CXCL-10, CXCL-11, oligoadenylate synthetases (OAS) genes, and selectively activated activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6). 23118497_Plasmin triggers release of the chemokine CCL20 from dendritic cells. 23460117_In summary, tumor cells exchange signals with the surrounding healthy cells modifying the extracellular matrix through enzyme secretion; thus, CCL20 might be a factor involved in the ontogeny of breast carcinoma. 23681234_results suggest that plasmin generated in inflamed tissues might elicit production of chemokine CCL20 by human macrophages leading to the recruitment of CCR6 positive Th17 cells to the inflammatory sites 23717583_results demonstrated that CCL20 might serve as a biomarker for GD and suggested the possible role of OPN in induction of CCL20 expression 23790181_results strongly suggest an association between CCL20/CCR6 expression and the induction of colorectal adenoma, colorectal adenocarcinoma and the development of colorectal liver metastases 23817679_High CCL20 expression in the microenvironment is associated with colorectal tumors. 23823618_results provide a potential explanation for involvement of the CCL20-CCR6 system in the trafficking of IL-17-producing cells to degenerated IVD tissues 24081898_IL-6 produced from IL-1beta-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells could increase CCL20 production. 24394994_genetic and biological role of the C-C chemokine ligand CCL20 and the C-C chemokine receptor CCR6in rheumatoid arthritis, is discussed.[review] 24395091_CCL20 rs6749704 polymorphism was associated with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. 24401998_Dendritic and T cells in psoriasis express CCL20 and CCR6 as part of the pathology. 24557363_1beta-stimulated HPDLCs. CONCLUSIONS: These data provide a novel mechanism through which genipin could be used to provide direct benefits in periodontal disease to inhibit IL-6 and CCL20 productions in periodontal lesions. 24627531_glucocorticoids enhance CCL20 production by bronchial epithelium, which may constitute a novel mechanism in Th17-mediated glucocorticoid-insensitive inflammation in asthma 24629487_CCL20 and 14-3-3 zeta are molecules that play a putative role during tumorgenesis in pancreas, and may therefore be new parameters for histological diagnosis and discrimination between pancreatic neoplasms and chronic pancreatitis. 24657657_CCL20 and CXCL8 synergize to promote colorectal metastatic progression by coordinated induction of EMT via PI3K/AKT-ERK1/2 signaling axis. 24699535_CCL20 levels were significantly elevated in the CSF of patients with pneumococcal meningitis. 24733189_Overexpression of CCL20 in human proximal tubular cells is inhibited by blockade of KCa3.1 under diabetic conditions through inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. 24743888_CCR6/CCL20 biological axis increased the capacity of proliferation and adhesion, as well as the chemotactic migration and the level of cytokines related to degraded extracellular matrix. 24851271_Data indicate that periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) express a functional P2X7 ATP receptor, whose activation is linked to the production of pro-inflammatory molecules IL8 and CCL20. 24866282_High CCL20 expression is associated with colon cancer. 24984269_CCL20 promotes the invasion and migration of thyroid cancer cells via NF-kappa B signaling-induced MMP-3 production. 25172034_We conclude that CCL 20 mRNA expression in the conjunctival epithelium plays a crucial role in regulating homeostasis at the ocular surface and in exacerbation of vernal keratoconjunctivitis . 25202827_identify Syk as an upstream signaling molecule in IL-17A-induced Act1-TRAF6 interaction in keratinocytes, and inhibition of Syk can attenuate CCL20 production 25352172_CCL20 could be an immune marker in ANCA-associated vasculitis. 25579056_two inflammatory cytokines, MIP-1delta and MIP-3alpha, are able to increase mesenchymal stromal cells migration in vitro 25593462_CCL20 expression is associated with HCC recurrence and patient survival and promotes HCC cell proliferation and migration by inducing EMT-like changes via PI3K/AKT and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways. 25661365_CCL20 cooperated with CCR6 could recruit T regulatory cells to tumor sites, and chemotherapy medicine docetaxel could decrease the expression of CCL20. 25768730_Th17 cells are recruited into tumor tissues preferentially through CCR6-CCL20 pathway 25864589_Results indicate that CCL20 is crucial for tobacco smoke-caused lung cancer, and anti-CCL20 could be a rational approach to fight against this deadly disease. 25882704_Induction of CCL20 requires IkappaKbeta, a component of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway; p65, a NF-kappaB transcriptional subunit, is recruited to the CCL20 gene promoter 25918170_A TGF-beta-responsive enhancer element required for efficient IL-1beta-dependent expression of the proinflammatory chemokine CCL20 by human lung fibroblasts. 26103626_CCL20 enhanced osteoblast-mediated osteoclastogenesis, partly via IL-6 production, suggesting that CCL20 may contribute to osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis by affecting bone cell communication. 26125463_stimulates leukocyte migration in ovary, may aid in final ovulatory events 26154142_Study provides evidence that tumor cells signal to the surrounding healthy cells through CCL20 inducing the modulation of the expression of molecules involved in EMT and promoting angiogenesis directly and indirectly through the secretion of VEGF, a major contributor to angiogenesis. 26156805_AEG-1 mediates CCL20/CCR6-induced EMT development via both Erk1/2 and Akt signaling pathway in cervical cancer, which indicates that CCL20/CCR6-AEG-1-EMT pathway could be suggested as a useful target to affect the progression of cervical cancer. 26284335_CCL4 and CCL20 recruit functionally different T lymphocyte subsets into oesophageal carcinoma. 26296735_ADAM10 activity contributes to house dust mite-induced shedding of chemokines, including CCL20 26345847_Tregs of unexplained recurrent miscarriage patients was significantly lower than that in controls. CCL20-CCR6 could drive immune activity of CD4(+)FOXP3(+) Tregs, followed by their migration to the feto-maternal microenvironment 26400278_High-risk HPV-type lesions might inhibit the chemokine CCL20 on Langerhans cells through E6 and E7 to escape the immune response. 26448160_human lung epithelial cells secrete CCL20 and BD2 in response to B. abortus and/or to cytokines produced by infected monocytes. 26536229_High CCL20 expression is associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 26634210_Both MIP-3alpha and cystatin A overexpressions in NPC tumor tissues were strong independent factors of poor prognosis in NPC patients. 26771764_There were early increased plasma concentrations of CCL20 and CCR6 in patients with sepsis. CCL20 and CCR6 correlate with severity of illness in ICU patients. 26789110_High expression of CCL20 is associated with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 26883727_CCR6(-) regulatory T cells blunt the restoration of gut Th17 cells along the CCR6-CCL20 axis in treated HIV-1-infected patients. 26910332_Cytomegalovirus replication in the allograft causes an intrapulmonary increase of CCL-18 and CCL-20 and a systemic rise of CCL-20 serum levels. 26968871_Production of CCL20 from lung cancer cells induces the cell migration and proliferation through PI3K pathway. 27015366_CCL20 contributed to invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of RANK over-expressed endometrial cancer cells 27018255_High CCL20 expression is associated with B-lymphoblastic lymphoma with inflammation. 27152707_These results showed that the higher levels of CXCL10, CCL20 and CCL22 were associated with ischemic heart disease. The serum levels of chemokines may influence by the certain traditional risk factors of IHD and some studied SNPs, but did not influence by treatment and gender of patients. 27173614_The strongest OR was for CXCL8 (interleukin-8) in serum (96.8, 95% CI: 11.9-790.2). Of these 15 markers, 6 were also significantly elevated in serum from Chile (CCL20, C-reactive protein, CXCL8, CXCL10, resistin, serum amyloid A). 27301951_MFSD2B, CCL20 and STAT1, or STARD7 and ZNF512 genes may be risk or protect factors in prognosis of ADC; HTR2B, DPP4, and TGFBRAP1 genes may be risk factors in prognosis of SQC. 27590109_mutually exclusive transcriptional regulation by AP-1 (cjun/cfos) and non-canonical NF-kappaB (RelB/p52) downstream of MEK-ERK and NIK-IKK-alpha-NF-kappaB2 (p100) phosphorylation, respectively was responsible for persistent Ccl20 expression in the colonic cells. 27797715_findings provide insight into the important role of macrophage-secreted CCL20 in pancreatic cancer and implicate CCR6/CCL20 as potential therapeutic targets 27834463_There was underexpression of the majority of genes after sunitinib treatment. The lower expression levels of IGFBP1, CCL20, CXCL6 and FGB were confirmed by qRT-PCR in all cases. The downregulation of gene expression leads us to search for methylation as a mechanism of action of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors 27916417_This study evaluated the role of CCL20 and CCR6 in the regulation of laryngeal neoplasms; it showed that these proteins acted on proliferation and metastasis via the p38 pathway and multiple microRNAs. 28188806_CCL20-recruited immune cells further increase TRAIL resistance of CCL20-producing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. 28283475_primary cultures of human bronchial epithelial cells and the BEAS-2B cell line were used to examine the effects of bacterial-viral coexposure, as well as each stimulus alone, on epithelial expression of CXCL8 and, in particular, CCL20. 28483840_Results demonstrated that F. nucleatum ssp. animalis and dysregulated CCL20 protein expression are important factors associated with human colorectal cancer progression. 28526351_A gut-specific endogenously produced mediator with the capacity to modulate the IL-17/Th17 signaling response. 28552941_HMC stimulated by IgA1 could produce CCL20 and consequently recruit inflammatory Th17 cells to the kidneys to induce further lesion in IgA nephropathy 28602508_CCN1 stimulates CCL20 production in vitro and in vivo, and thus supports the notion that overexpressed CCN1 in hyperproliferating keratinocyte is functionally involved in the recruitment of inflammatory cells to skin lesions affected by psoriasis. 28618084_CCL20 provoked a 2.5-fold increase of cell migration and invasion in human cancerous breast epithelial cells ; CCL20 also enhanced MMP- 2 and MMP-9 mRNAs/protein expression and activities. 28851919_CCL20, which is regulated by HuR and secreted into the bone microenvironment, enhances the metastatic ability and bone metastasis of breast cancer cells by stimulating cancer cells and osteoblastic cells in both autocrine and paracrine manners. 29229985_High CCL20 level is associated with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. 29362221_Our data highlight the synergistic interaction between melanoma tumor cells and prometastatic macrophages through a CCR6/CCL20 paracrine loop. Stromal levels of CCL20 in primary melanomas may be a clinically useful marker for assessing patient risk, making treatment decisions, and planning or analyzing clinical trials. 29535421_CCL20 role in glioblastoma.CCL20 expression in astrocytes during hypoxia.CCL20 up-regulates HIF-1alpha through NF-kappaB activation. 29690903_expression of CCL20, an important inflammatory mediator, is increased in Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis. 29880013_CCl20 and CXCL13 synergistically increased B-cell migration form peripheral blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients. 29946002_Elevated CCL20 production by airway smooth muscle cells, possibly resulting from dysregulated expression of the anti-inflammatory miR-146a-5p, may contribute to enhanced mucus production in asthma. 30048972_These results provide evidence that necrotic cells induce the expression of CCL2/MCP-1 and CCL20/MIP-3alpha in glioblastoma cells through activation of NF-kappaB and AP-1 and facilitate the infiltration of microglia into tumor tissues. 30052635_CCL20 can be a novel predictive marker for taxane response, and the blockade of CCL20 or its downstream pathway might reverse the taxane resistance in breast cancer patients. 30114340_We postulate CCL20 does not activate CCR6 through the canonical two-step/two-site mechanism of chemokine-chemokine receptor activation 30192865_S1P induced the expression of some asthma-related genes, such as ADRB2, PTGER4, and CCL20, in bronchial epithelial cells. The knock-down of SIPR3 suppressed the expression of S1P-inducing CCL20. 30287142_we identified HCV-induced CCL20 as a direct pro-angiogenic factor that acts on endothelial CCR6. These results suggest that the CCL20/CCR6 axis contributes to hepatic angiogenesis, promoting the hypervascular state of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 30399422_CCL20 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of MS. Both allelic variation of (rs6749704) within CCL20 gene and (rs763780) within IL-17F gene can be considered risk factor for development of MS in Egyptian patients. 30537747_CCL20 was upregulated in giant cell tumor of bone patients and correlated with tumor progression and poor prognosis. CCL20 recruited mononuclear cells and induced osteoclastogenesis by over-activating the AKT and NF-kappa B signaling pathways. 30655106_The serum CCL20 level was significantly elevated in patients with vitiligo. The level of serum CCL20 was higher in active than in the stable stage. Patients with active vitiligo had elevated numbers of circulating Th1/17 cells and Tc1/17 cells, and upregulated expression of CCR6 in PBMCs and lesions. 30760665_CCL20 enhanced doxorubicin resistance of OC cells by regulating ABCB1 expression 31010609_CCL20 and to a less extent CXCL8 may play a key role in triggering the Koebner phenomenon after scratch injury to keratinocytes. 31322256_High CCL20 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis. 31352173_Chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) expression increases with NAFLD stage and hepatic stellate cell activation and is regulated by miR-590-5p. 31395078_Colorectal cancer cell-derived CCL20 recruits regulatory T cells to promote chemoresistance via FOXO1/CEBPB/NF-kappaB signaling. 31497857_The rheumatoid synovial environment alters fatty acid metabolism in human monocytes and enhances CCL20 secretion. 31682009_CCL20 expression is significantly downregulated in healthy palatal mucosa of smokers 31682009_CCL20 expression significantly downregulated in healthy palatal mucosa of smokers 31852159_CCL20 and FOXP3+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes may have synergistic effects, and their upregulated expressions may lead to immune evasion in breast cancer. Combinatorial immunotherapeutic approaches aiming at blocking CCL20 and depleting FOXP3 might improve therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer patients. 31866467_Cisplatin-stimulated macrophages promote ovarian cancer migration via the CCL20-CCR6 axis. 31898342_Transcription factor RUNX3 promotes CD8(+) T cell recruitment by CCL3 and CCL20 in lung adenocarcinoma immune microenvironment. 32060846_REVIEW: CCL20 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment 32238601_Obesity status modifies the association between rs7556897T>C in the intergenic region SLC19A3-CCL20 and blood pressure in French children. 32412043_CCL20-CCR6 axis directs sperm-oocyte interaction and its dysregulation correlates/associates with male infertilitydouble dagger. 32480426_Systematic reassessment of chemokine-receptor pairings confirms CCL20 but not CXCL13 and extends the spectrum of ACKR4 agonists to CCL22. 32533638_CCL20 is a novel ligand for the scavenging atypical chemokine receptor 4. 32541785_Structural basis for chemokine receptor CCR6 activation by the endogenous protein ligand CCL20. 32596949_FDPS promotes glioma growth and macrophage recruitment by regulating CCL20 via Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. 32601464_EGFR/Ras-induced CCL20 production modulates the tumour microenvironment. 32732864_EN2 as an oncogene promotes tumor progression via regulating CCL20 in colorectal cancer. 33113266_Eomes promotes esophageal carcinoma progression by recruiting Treg cells through the CCL20-CCR6 pathway. 33165673_miR-19a mitigates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury by depressing CCL20 and inactivating MAPK pathway in human embryonic cardiomyocytes. 33483346_Structure and Functional Characterization of a Humanized Anti-CCL20 Antibody following Exposure to Serum Reveals the Formation of Immune Complex That Leads to Toxic |
ENSMUSG00000026166 |
Ccl20 |
415.017516 |
14.4697615336 |
3.854969 |
0.120681981 |
1345.207037 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000169522220537284934369173420400952053 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000240591151454839000815576214944157512 |
Yes |
Yes |
788.4759781 |
58.6532355 |
54.8984093 |
3.8718898 |
| ENSG00000115084 |
80255 |
SLC35F5 |
protein_coding |
Q8WV83 |
FUNCTION: Putative solute transporter. {ECO:0000305}. |
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80255; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000026342 |
Slc35f5 |
838.368297 |
2.5049162340 |
1.324762 |
0.088291246 |
221.180619 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004998775388551523290811340460442154002282397447542731566654146544858472831928655470866187294845509349357311234760233005352538741133949784511969482991844415664672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001066212785188157191578464695474216758683817409361709690831115695821770241547523708903231559778342941895741643992350877154532892698846069379214895889163017272949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1151.5673936 |
90.5084686 |
464.3653516 |
26.8956084 |
| ENSG00000115091 |
10096 |
ACTR3 |
protein_coding |
P61158 |
FUNCTION: ATP-binding component of the Arp2/3 complex, a multiprotein complex that mediates actin polymerization upon stimulation by nucleation-promoting factor (NPF) (PubMed:9000076). The Arp2/3 complex mediates the formation of branched actin networks in the cytoplasm, providing the force for cell motility (PubMed:9000076). Seems to contact the pointed end of the daughter actin filament (PubMed:9000076). In podocytes, required for the formation of lamellipodia downstream of AVIL and PLCE1 regulation (PubMed:29058690). In addition to its role in the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton, the Arp2/3 complex also promotes actin polymerization in the nucleus, thereby regulating gene transcription and repair of damaged DNA (PubMed:17220302, PubMed:29925947). The Arp2/3 complex promotes homologous recombination (HR) repair in response to DNA damage by promoting nuclear actin polymerization, leading to drive motility of double-strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:29925947). Plays a role in ciliogenesis (PubMed:20393563). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17220302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20393563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29058690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29925947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9000076}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
The specific function of this gene has not yet been determined; however, the protein it encodes is known to be a major constituent of the ARP2/3 complex. This complex is located at the cell surface and is essential to cell shape and motility through lamellipodial actin assembly and protrusion. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2013]. |
hsa:10096; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; Arp2/3 protein complex [GO:0005885]; brush border [GO:0005903]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actin polymerization-dependent cell motility [GO:0070358]; Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin nucleation [GO:0034314]; asymmetric cell division [GO:0008356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; meiotic chromosome movement towards spindle pole [GO:0016344]; meiotic cytokinesis [GO:0033206]; positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly [GO:0010592]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; spindle localization [GO:0051653] |
12036877_Arp2/3 complex is required for actin polymerization during platelet shape change. 12200375_Platelets activate Arp2/3 complex, assemble actin, and change shape in the absence of WASp, indicating a more specialized role for WASp in these cells. 12429845_Results suggest that recruitment of factors by Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASP) and Scar1 stimulates cellular actin-based motility and actin nucleation with the Arp2/3 complex. 12464680_Arp2/3 complex contribution to actin filament nucleation in platelets and fibroblasts importantly requires free barbed ends generated by severing and uncapping. 12672817_cortactin links receptor endocytosis to actin polymerization by binding both CD2AP and the Arp2/3 complex, which may facilitate the trafficking of internalized growth factor receptors 12791263_ARP3-mediated actin polymerization is regulated by phosphorylation of the WASP protein. 15242766_The interaction between cortactin and Arp2/3 complex plays an important role in S1P-mediated remodeling of endothelial cells. 15279900_Arp2/3 complex genes have roles in actin organization and possibly in cancer phenotypes 15385624_existence of an Arp2/3 complex-dependent event during the early phase of the life cycles of both primate lentiviruses and intracellular mature vaccinia virus 15469433_signalling pathways leading to Arp2/3-dependent actin nucleation play an important role in Salmonella typhimurium invasion, but are not involved in intracellular Salmonella-induced actin assembly 15741236_T-plastin increases Arp2/3-mediated actin-based movement 16004967_These results indicate that interaction between the Arp2/3 complex and WASP stimulates actin polymerization and integrin beta-1-mediated adhesion during MCP-1-induced chemotaxis of THP-1 cells. 16253999_the binding of the C terminus of SPIN90 with both the Arp2/3 complex (actin-related proteins Arp 2 and Arp 3) and G-actin activates the former, leading to actin polymerization 16403731_in activation of the Arp2/3 complex, the C domain first primes the complex by inducing a necessary conformational change and then initiates nucleus assembly by bringing an actin monomer into proximity of the primed complex 17085436_signal-induced relief of the autoinhibited fold of IQGAP1 allows activation of N-WASP to stimulate Arp2/3-dependent actin assembly 17501982_Data show that Chlamydia trachomatis activates Rac and promotes its interaction with WAVE2 and Abi-1 to activate the Arp2/3 complex resulting in the induction of actin cytoskeletal rearrangements that are required for invasion. 17524364_Taken together, our data suggest that Apr3 should play an important role in ATRA signal pathway. 17576929_p120 depletion led to dramatic loss of cortactin and its partner, Arp3, from the cell leading edges 18516090_Results suggest that WAVE and the Arp2/3 complex jointly orchestrate different types of actin-based plasma membrane protrusions by promoting ruffling and inhibiting mDia2-induced filopodia. 19262673_the exchange rate of N-WASP controls the rate of ARP2/3-complex-dependent actin-based motility by regulating the extent of actin polymerization by antagonizing filament capping 19286135_The Arp2/3 complex, an actin-nucleating factor, is recruited at the ring structure and is important for parasite entry. 19913427_Loss of Arp2/3 function led to defects in cell adhesion and actin assembly at the junction with the target cell (the lytic synapse) 20404198_key residues at this interface were crucial for actin nucleation and Y-branching, high-affinity F-actin binding, and Y-branch stability, demonstrating that the affinity of Arp2/3 complex for F actin independently modulates branch formation and stability. 20974812_The results identify Arp2/3 complex as a key factor in the generation of the dynamic actin cluster during mitosis. 21108927_the centrosome transiently recruits Arp2/3 to perform processes such as centrosome separation prior to mitotic entry. 22100162_Anthrax edema toxin induced transendothelial cell tunnels are resealed by MIM via Arp2/3-driven actin polymerization. 23051739_We demonstrate that WAVE2-Arp2/3 is a major nucleator of actin assembly at the zonula adherens and likely acts in response to junctional Rac signaling 23320827_Study suggested that positive CFL1 and Arp3 expression are closely related to tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis of gallbladder cancer. 24344184_The Arp2/Arp3 complex has a role in osmotic signaling. 24469447_Cortactin has a role as a scaffold for Arp2/3 and WAVE2 at the epithelial zonula adherens 24872192_study unveils an ARP2/3:VCA-independent function of nuclear-WASp in TH1 gene activation that is uncoupled from its cytoplasmic role in actin polymerization. 25264243_The loss of the Arp2/3 complex acts as a stress that initiates cell cycle arrest by triggering p16INK4a/p14Arf transcription. 26028144_Platelet actin nodule formation is dependent on WASp and the ARP2/3 complex. 26370503_Suggest alpha5beta1/Arp2/Arp3/FHOD3 pathway reprograms the actin cytoskeleton to promote invasive migration and local invasion in vivo. 26655834_demonstrate that the Arp2/3 complex in higher eukaryotes is actually a family of complexes with different properties 26848712_RARalpha regulates Arp2/3-mediated actin cytoskeletal dynamics through a non-genomic signaling pathway 26991540_miR-24-1*/let-7a*-ARP2/3 complex-RAC isoforms pathway may represent a novel pathogenic mechanism for Hirschsprung disease. 26997484_Kv3.3 regulates Arp2/3-dependent cortical actin nucleation mediated by Hax-1; resulting cortical actin structures interact with the channel's gating machinery to slow its inactivation rate during sustained membrane depolarizations; a mutation that leads to late-onset spinocerebellar ataxia type 13. 27052944_These findings indicate that inhibition of the Rac1WAVE2Arp2/3 signaling pathway may promote radiosensitivity, which may partially result from the downregulation of CFL1 in U251 human glioma cells. 27181356_Arp2 and Arp3 expression was increased under atherosclerotic conditions both in ApoE-/- mice and in oxidized low-density lipoproteins stimulated human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs). 27559607_evidence of a direct protein-protein interaction between PKD2 and Arp2/3 28170369_Authors found that ARP3 and profilin1 were 2 binding partners of LMO2, primarily in cytoplasm. LMO2. LMO2 mediated the assembly of a complex including ARP3, profilin1, and actin monomer, increased actin monomer binding to profilin1, and promoted lamellipodia/filopodia formation in basal-type breast cancer cells. 29636431_Collectively, our results demonstrate that palladin can functionally replace the Arp2/3 complex during bacterial actin-based cellular entry and intracellular motility of Listeria monocytogenes. 30049513_we conclude that ARP3 may be a potential prognostic indicator and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma 30489239_Proteins involved in actin-filament-based processes, specifically CDC42 and members of the ARP2/3 complex are crucial for establishment of Japanese encephalitis virus infection. 30792969_Overall, the authors demonstrate the active role of the Arp2/3 complex and WIPF2 in mediating the internalization of Aspergillus fumigatus conidia into human airway epithelial cells. 31698518_Partial loss of actin nucleator actin-related protein 2/3 activity triggers blebbing in primary T lymphocytes. 32169900_Proline-rich 11 (PRR11) drives F-actin assembly by recruiting the actin-related protein 2/3 complex in human non-small cell lung carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000026341 |
Actr3 |
5482.104285 |
2.3500305675 |
1.232680 |
0.042573998 |
823.518928 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000041563717837490542920829671232452640239565333024595381647392237242970405110122990567171933904405004091915755398614588036161635590151147593125416715525 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034082248626742242947619572150041641812529742515542359179036284705018491529915267489548281815956365867231811761834895749528299033743062813198086357019 |
Yes |
No |
7342.0378233 |
200.7047470 |
3146.4450563 |
63.6683338 |
| ENSG00000115107 |
55240 |
STEAP3 |
protein_coding |
Q658P3 |
FUNCTION: Endosomal ferrireductase required for efficient transferrin-dependent iron uptake in erythroid cells. Participates in erythroid iron homeostasis by reducing Fe(3+) to Fe(2+). Can also reduce of Cu(2+) to Cu(1+), suggesting that it participates in copper homeostasis. Uses NADP(+) as acceptor. May play a role downstream of p53/TP53 to interface apoptosis and cell cycle progression. Indirectly involved in exosome secretion by facilitating the secretion of proteins such as TCTP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15319436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16651434}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell cycle;Copper;Endosome;FAD;Flavoprotein;Glycoprotein;Heme;Ion transport;Iron;Iron transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a multipass membrane protein that functions as an iron transporter. The encoded protein can reduce both iron (Fe3+) and copper (Cu2+) cations. This protein may mediate downstream responses to p53, including promoting apoptosis. Deficiency in this gene can cause anemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:55240; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cupric reductase activity [GO:0008823]; ferric-chelate reductase (NADPH) activity [GO:0052851]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on metal ions, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016723]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; copper ion import [GO:0015677]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; transferrin transport [GO:0033572] |
12606722_TSAP6 may augment Myt1 activity and act downstream to p53 to interface apoptosis and cell-cycle progression 15319436_role for TSAP6 in the export of TCTP and indicate that this multipass membrane protein could have a general role in the regulation of vesicular trafficking and secretion. 18495927_The crystal structure of the human Steap3 oxidoreductase domain in the absence and presence of NADPH was determined. 19236508_Down-regulated expression of the TSAP6 protein in liver is associated with a transition from cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21871451_findings indicate that STEAP3 maintains iron storage in human malignant cells and tumor proliferation under the hypoferric condition 22624035_TSAP6 is a target of rhomboid protease RHBDD1-induced proteolysis. 26675350_heterozygous STEAP3 mutations are relatively common in humans and that their deleterious effect in humans remains to be confirmed 27825812_TSAP6 over expression is associated with poor survival in metastatic high-grade serous carcinoma. 28303916_In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), lower expression of the STEAP3 copper reductase and heavy Cu isotope enrichment have been reported for the tumor mass, relative to the surrounding tissue 31176711_this study identified oxidative stress-dependent upregulation of the iron-converting metalloreductase, STEAP3, as a key mediator of extracellular matrix production in wound healing 31350307_This article is the first report of a role of Steap3 in mature RBCs; it defines a new mechanism of redox biology in RBCs with a substantial effect upon RBC function and provides a novel mechanistic determinant of genetic variation of RBC storage. 34649092_Predictive potential of STEAP family for survival, immune microenvironment and therapy response in glioma. 34741044_STEAP3 promotes cancer cell proliferation by facilitating nuclear trafficking of EGFR to enhance RAC1-ERK-STAT3 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35275508_STEAP3 Affects Ferroptosis and Progression of Renal Cell Carcinoma Through the p53/xCT Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000026389 |
Steap3 |
95.022835 |
2.2390651377 |
1.162896 |
0.159928036 |
53.738714 |
0.00000000000022900588120131165227563456834569768384973070807220096867240499705076217651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001423810786238989024587788709837652513035335943847314865706721320748329162597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
133.8667113 |
12.7638404 |
60.2589213 |
4.5824436 |
| ENSG00000115129 |
9540 |
TP53I3 |
protein_coding |
Q53FA7 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of quinones (PubMed:19349281). Exhibits a low enzymatic activity with beta-naphthoquinones, with a strong preference for the ortho-quinone isomer (1,2-beta-naphthoquinone) over the para isomer (1,4-beta-naphthoquinone). Also displays a low reductase activity for non-quinone compounds such as diamine and 2,6-dichloroindophenol (in vitro) (PubMed:19349281). Involved in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (PubMed:19349281). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19349281}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is similar to oxidoreductases, which are enzymes involved in cellular responses to oxidative stresses and irradiation. This gene is induced by the tumor suppressor p53 and is thought to be involved in p53-mediated cell death. It contains a p53 consensus binding site in its promoter region and a downstream pentanucleotide microsatellite sequence. P53 has been shown to transcriptionally activate this gene by interacting with the downstream pentanucleotide microsatellite sequence. The microsatellite is polymorphic, with a varying number of pentanucleotide repeats directly correlated with the extent of transcriptional activation by p53. It has been suggested that the microsatellite polymorphism may be associated with differential susceptibility to cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:9540; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; NADPH:quinone reductase activity [GO:0003960]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H [GO:0016651]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; quinone binding [GO:0048038]; NADP metabolic process [GO:0006739] |
15067011_p53 activity and PIG3 gene function are uncoupled by UV-dependent alternative splicing through rapid proteolytic degradation 15192123_suppression of p53-C277Y by RNAi reduced pig3 promoter activity, RNA, and protein expression 15491642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18801469_numerous factors contribute to the normal alternative splicing of PIG3 exon 4 and UV-inducible increases in this process require that the splicing of this exon be maintained in a sufficiently weakened state under normal conditi 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19349281_PIG3 action is through oxidative stress produced by its enzymatic activity and provides essential knowledge for eventual control of apoptosis. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20023697_Results suggest that PIG3 is a critical component of the DNA damage response pathway and has a direct role in the transmission of the DNA damage signal from damaged DNA to the intra-S and G2/M checkpoint machinery. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603616_certain p53 mutatants activate PIG3, whereas the result of our study show increased full-length transcript expression in tumor counterparts 22461624_a novel signaling pathway of GPx3-PIG3 in the regulation of cell death in prostate cancer. 23241165_study provides evidence that the variant genotypes of (TGYCC)n repeats in the PIG3 promoter are functional and associated with risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in a non-Hispanic white population 24388982_prohibitin and prohibiton (PHB2) contribute to PIG3-mediated apoptosis by binding to the PIG3 promoter (TGYCC)15 motif 26133772_The results suggested that PIG3 plays an oncogenic role in PTC via the regulation of the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway and support the exploration of PIG3 as a novel biomarker for patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma 26464464_PIG3, which functions in DNA damage repair, uses an unexpected catalytic mechanism to suppress Rho-ROCK activity and impair tumor invasion in vivo. This regulation was suppressed by antioxidants. 26472723_Data indicate that knockdown of p53-induced gene 3 (PIG-3) expression by small interfering RNA (siRNA) treatment can inhibit the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). 27029070_Data suggest that PIG3 was involved in HIF-1alpha regulation, and indicate a signaling pathway of PIG3/HIF-1alpha in the regulation of cell migration in renal cell carcinoma. 28259183_Results revealed that PIG3 expression levels positively correlated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and indicate that PIG3 promotes NSCLC progression. 28351326_our data suggest that high expression of p53-inducible gene 3 is significant for glioblastoma inhibition and p53-inducible gene 3 independently indicates good prognosis in patients, which might be a novel prognostic biomarker or potential therapeutic target in glioblastoma. 30281878_Study found that PIG3 expression was positively associated with lymph node metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) but not from lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). Further data revealed a role for PIG3 in inducing LUAD metastasis, and its role as a new FAK regulator, suggesting that it could be considered as a novel prognostic biomarker. 30334411_expression of PIG3 is frequently reduced in gastric cancer (GC) tissue, and PIG3 suppressed human GC growth through p53- mediated apoptosis; PIG3 may act as a potential diagnostic marker and a potential therapeutic target of GC |
|
|
14.820889 |
0.3933816530 |
-1.345998 |
0.430124119 |
9.731855 |
0.00181101577255549268941070550908989389427006244659423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004037244042126427075178884962269876268692314624786376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.9444189 |
2.7055002 |
20.5237017 |
4.8618052 |
| ENSG00000115165 |
9595 |
CYTIP |
protein_coding |
O60759 |
FUNCTION: By its binding to cytohesin-1 (CYTH1), it modifies activation of ARFs by CYTH1 and its precise function may be to sequester CYTH1 in the cytoplasm. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains 2 leucine zipper domains and a putative C-terminal nuclear targeting signal, but does not have any hydrophobic regions. This protein is expressed weakly in resting NK and T cells. The encoded protein modulates the activation of ARF genes by CYTH1. This protein interacts with CYTH1 and SNX27 proteins and may act to sequester CYTH1 protein in the cytoplasm.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:9595; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155] |
12052827_observations suggest that CASP is a scaffolding protein that facilitates the function of at least one member of the cytohesin/ARNO family in response to specific cellular stimuli 16702224_Cybr not only regulates lymphocyte adhesion and cell-cell interaction but also contributes to the regulation of the signaling cascade and of the genetic program downstream of the T cell receptor. 17577583_These results suggest that endosomal SNX27 may recruit CASP to orchestrate intracellular trafficking and/or signaling complexes. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21562043_on infection of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), CYTIP is rapidly degraded and as a consequence beta-2 integrins, predominantly LFA-1, are activated 23223005_loss of DNA methylation enables HIF-driven cytohesin 1 interacting protein expression to protect cancer cells from death cytokine signals 23469018_a newly identified binding partner of CYTIP, SOCS-1, and confirm its function in regulating the degradation of CYTIP by the proteasome 25058460_CASP has a direct role in the secretion of IFN-gamma, and NK cell motility and ability to kill tumor cells. CASP polarizes to the leading edge of migrating NK cells, and to the immunological synapse when engaged with tumor cells. |
ENSMUSG00000026832 |
Cytip |
597.833535 |
4.2874052852 |
2.100105 |
0.107313099 |
371.976716 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006947119859108561854234402090462820678251174955868671607160218334908750825540999615643961715567059229723075868126971052489219556261189291159908435343730790509981575380848033785538772405211134021676857956684170147809709305875003337860107421875000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002418384177368923790287129530314404610829348484368535714599376988692130762221077625329153140293163047119685402189228214659479508863748492119591779564879223389862336081520416392027687568254508954893218508619412432381068356335163116455078125000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
959.8286400 |
58.5520711 |
225.4990390 |
10.8779867 |
| ENSG00000115170 |
90 |
ACVR1 |
protein_coding |
Q04771 |
FUNCTION: Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type I receptor that is involved in a wide variety of biological processes, including bone, heart, cartilage, nervous, and reproductive system development and regulation (PubMed:20628059, PubMed:22977237). As a type I receptor, forms heterotetrameric receptor complexes with the type II receptors AMHR2, ACVR2A or ACVR2B (PubMed:17911401). Upon binding of ligands such as BMP7 or GDF2/BMP9 to the heteromeric complexes, type II receptors transphosphorylate ACVR1 intracellular domain (PubMed:25354296). In turn, ACVR1 kinase domain is activated and subsequently phosphorylates SMAD1/5/8 proteins that transduce the signal (PubMed:9748228). In addition to its role in mediating BMP pathway-specific signaling, suppresses TGFbeta/activin pathway signaling by interfering with the binding of activin to its type II receptor (PubMed:17911401). Besides canonical SMAD signaling, can activate non-canonical pathways such as p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases/MAPKs (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P15261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17911401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20628059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22977237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25354296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9748228}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Magnesium;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Activins are dimeric growth and differentiation factors which belong to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily of structurally related signaling proteins. Activins signal through a heteromeric complex of receptor serine kinases which include at least two type I ( I and IB) and two type II (II and IIB) receptors. These receptors are all transmembrane proteins, composed of a ligand-binding extracellular domain with cysteine-rich region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain with predicted serine/threonine specificity. Type I receptors are essential for signaling; and type II receptors are required for binding ligands and for expression of type I receptors. Type I and II receptors form a stable complex after ligand binding, resulting in phosphorylation of type I receptors by type II receptors. This gene encodes activin A type I receptor which signals a particular transcriptional response in concert with activin type II receptors. Mutations in this gene are associated with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressive. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:90; |
activin receptor complex [GO:0048179]; apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; BMP receptor complex [GO:0070724]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; activin binding [GO:0048185]; activin receptor activity, type I [GO:0016361]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; transforming growth factor beta binding [GO:0050431]; transforming growth factor beta receptor activity, type I [GO:0005025]; transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004675]; activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032924]; acute inflammatory response [GO:0002526]; atrial septum primum morphogenesis [GO:0003289]; atrioventricular valve morphogenesis [GO:0003181]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; BMP signaling pathway involved in heart development [GO:0061312]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; cardiac muscle cell fate commitment [GO:0060923]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus [GO:0071385]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; dorsal/ventral pattern formation [GO:0009953]; embryonic heart tube morphogenesis [GO:0003143]; endocardial cushion cell fate commitment [GO:0061445]; endocardial cushion fusion [GO:0003274]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; gastrulation with mouth forming second [GO:0001702]; germ cell development [GO:0007281]; heart development [GO:0007507]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; mitral valve morphogenesis [GO:0003183]; negative regulation of activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032926]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; pharyngeal system development [GO:0060037]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of determination of dorsal identity [GO:2000017]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:1905007]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0048641]; smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051145]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; urogenital system development [GO:0001655]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
11969340_distribution in gestational tissues across human pregnancy and during labour 16642017_We mapped fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva to chromosome 2q23-24 by linkage analysis and identified an identical heterozygous mutation (617G --> A; R206H) in the glycine-serine (GS) activation domain of ACVR1 17351709_Study examined 3 Japanese patients with Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva for ACVR1 mutations and identified the 617G>A mutation in all 3 patients; results suggest that the mutation in the ACVR1 gene is common and recurrent in the global population. 17496924_knockdown of ALK2, but not TGFbetaRI (ALK5), abrogated endoglin-mediated decreases in cell motility and constitutively active ALK2 was sufficient to restore a low-motility phenotype in endoglin deficient cells 17572636_In both the wild-type ACVR1 model and template crystal structures (TbetaRI), the conserved arginine appears to form a salt bridge with an invariant aspartate residue. 18019378_Various mutations may occur in myositis ossificans nuclear families. 18234825_Together, these findings show that TGFbeta superfamily activation of Smad2/3 is required for repression of spontaneous differentiation under strain. 18292470_there was significant down-regulation of ALK-2 expression in asthma patients at baseline; allergy challenge was associated with upregulation 18684712_ALK2(R206H) with Smad1 or Smad5 induced osteoblastic differentiation that could be inhibited by Smad7 or dorsomorphin. 18830232_The novel amino-acid substitution is predicted to influence either the conformation/stability of the GS region or the binding affinity with FKBP12, resulting in a less stringent inhibitory control on the ACVR1 kinase activity. 18854405_ALK2 signalling contributes to the disturbed folliculogenesis in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients. 18854405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18952055_ALK2(G356D) activities found in Japanese fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva patient were weaker than those of ALK2(R206H), and they were suppressed by a specific inhibitor of the BMP-regulated Smad pathway. 19028479_The serum activin A level, increased in AMI, was positively correlated with peak CK and CK-MB levels which are measures of infarction size. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19085907_Study showed that all patients examined have heterozygous ACVR1 missense mutations in conserved amino acids. 19148527_activin inhibits the growth of SNU-16 cells by inducing apoptosis through caspase activation. 19299629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19300893_This study aimed to investigate the ACVR1 gene mutation in Chinese FOP patients. Direct sequence analysis of genomic DNA and restriction enzyme digestion demonstrated the presence of a single heterozygous mutation in the ACVR1 gene in both patients. 19330033_two further unique mutations (c.605G>T and c.983G>A) in this gene in two FOP patients; disparate missense mutations mapped to the GS and kinase domains of the protein supports the disease model of mild kinase activation 19335617_Data show that co-expressing constitutively active type I and type II receptors resulted in the phosphorylation of both R-Smad subclasses in a ligand-independent manner. 19400542_NOG & 617G>A activin A type I receptor(ACVRI)mutations in 27 fibrodysplasia ossificans patients; 5 NOG mutations found in 7 patients; 617G>A mutation in ACVR1 gene found in 14 patients; with 1 exception, 617G>A & NOG mutations were mutually exclusive 19506109_Dominant-negative ALK2 allele associates with congenital heart defects. 19543505_ACVR1 gene mutations were found heterozygous point mutation of c.617G>A; p.R206H in Myositis Ossificans. 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19736306_Endoglin is phosphorylated on cytosolic domain threonine residues by the TGF-beta type I receptors ALK2 in prostate cancer cells. In the presence of constitutively active ALK2, endoglin did not inhibit cell migration 19796185_a variant of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva phenotypes are associated with specific mutations in ACVR1 gene 19896889_The discovery of the FOP metamorphogene reveals a highly conserved target for drug development and identifies a fundamental defect in the BMP signaling pathway that when triggered by injury and inflammation transforms one tissue into another. 19929436_The R206H mutation in ALK2 confers constitutive activity to the mutant receptor, sensitizes mesenchymal cells to BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation, and stimulates new bone formation. 19996292_BMP9 acts as a proliferative factor for immortalized ovarian surface epithelial cells and ovarian cancer cell lines, signaling predominantly through an ALK2/Smad1/Smad4 pathway, the major BMP9 receptor in endothelial cells. 20011542_Of 51 microsatellite stable colon tumors, 7 (14%) lost ACVR2, 2 (4%) ACVR1, and 5 (10%) pSMAD2 expression. 20463014_The impact of ACVR1 R206H mutation on BMP signaling and its downstream signaling cascades in murine myogenic C2C12 cells and HEK 293 cells, was studied. 20577760_Progressive heterotopic ossification along with congenital malformation of the great toes, the two major clinical features that define classic FOP, led to a suspicion of FOP and to the definitive screening of the ACVR1 gene 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20716560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736820_in two cases of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, heterozygous missense mutation 617G>A (R206H) was found 21248739_These data indicate that in the context of a Down's syndrome background, ALK2-mediated reduction of BMP signaling may contribute to congenital heart defects. 21297076_ACVR1 is associated with acute lung injury in mice 21377447_These findings suggest that ALK2(L196P) is an activated BMP receptor equivalent to ALK2(R206H) and that ALK2(L196P) activity may be suppressed in vivo by a novel molecular mechanism in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva patients with this mutation. 21617230_Low activin A in the cytosol is associated with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. 21668474_copy number alterations at 2q24 can be involved in ACVR1 overexpression, which is associated with longer overall survival in laryngeal carcinomas 21878751_miR-30c expression was increased during adipogenesis of multipotent adipose-derived stem cells; miRNA target prediction revealed 2 putative direct targets of miR-30c, PAI-1 and ALK2, both inversely regulated to miR-30c during adipogenesis and responsive to miR-30c overexpression 22408438_miR-148a is an important mediator of ACVR1, thus offering a new potential target for the development of therapeutic agents against Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. 22630080_Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva has been linked to an autosomal dominant mutation on chromosome 2, to the gene encoding activin receptor-like kinase 2 (ALK2), a BMP type I receptor 22748444_Confirmation of the presence of this recurrent mutation facilitates diagnostic accuracy in affected persons in South Africa, and allows researchers to narrow the search for molecular targets for rational intervention to the ACVR1/ALK2 domain. 22884369_Luminal iron levels govern intestinal tumorigenesis after Apc loss in vivo. 22949078_Constitutive activation of ALK2 such as that caused by the Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva mutation inhibits the generation and maintenance of human induced pluripotent stem cells. 22971142_Presence of the 455C allele of BMP4 and the 8474T allele of ACVR1 gene was significantly associated with decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (p=0.0004 and p=0.046, respectively). 22977237_The crystal structure of the cytoplasmic domain of ALK2 in complex with the inhibitors FKBP12 and dorsomorphin. 23142694_ALK2 may be an important receptor in ET-1 production during BMPR2 knockdown 23169291_Study suggests that activin A contributes to the malignant phenotype of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) cells via regulation of cyclin D and may represent a valuable candidate for therapeutic interference. 23227223_Functional analysis of the 3'UTR region by Luciferase reporter assays showed that it plays an inhibitory role on ACVR1/Alk-2 gene expression. 23260810_Disease causing mutations in the ACVR1 gene identified in Turkish patients diagnosed as fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. 23918320_heterozygous mutation i.e., c.617(G>A)in ACVR1 was detected in patients with rare genetic disorder - Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva 24047559_The findings provide novel insights into the molecular mechanisms that regulate expression of the ACVR1 gene and that could be targets of new strategies for future therapeutic treatments. 24347165_Glucocorticoids recruit Tgfbr3 and Smad1 to shift transforming growth factor-beta signaling from the Tgfbr1/Smad2/3 axis to the Acvrl1/Smad1 axis in lung fibroblasts. 24705250_Recurrent somatic mutations in ACVR1 in pediatric midline high-grade astrocytoma. 24705251_Recurrent somatic mutations in ACVR1 found in diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. 24705252_Recurrent activating ACVR1 mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. 24705254_ACVR1 mutations in diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas were constitutively activating, leading to SMAD phosphorylation and increased expression of the downstream activin signaling targets ID1 and ID2. 24798338_ALK2 (R206H) mutation increases osteoclast formation through TGF-beta. The activation of activin-like kinase signaling enhanced osteoclast formation through TGF-beta expression during heterotopic ossification in muscle tissues. 25101911_compounds demonstrated consistent binding to a panel of mutant and wild-type ALK2 proteins 25271001_clinically aggressive stem cell-like subtype of hepatocellular carcinoma characterized by miR-148a-ACVR1-BMP-Wnt circuit 26058333_Genetic analysis of ACVR1 identified the recurrent allelic variant c.617 G>A; p.R206H in 12 of 14 Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP)patients. One of the remaining patients had a previously reported allele c.1067G>A; p.G356D in the 9th exon and the second allele c.983G>A; p.G328E in the 8th exon of ACVR1. 26097044_A report of two patients has been presented with multi-system involvement in a severe variant of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva caused by the ACVR1 c.772G>A; R258G mutation. 26133550_Changes in the binding site residue(e.g. pre-hinge region in ALK2) or side chain orientation (e.g. Tyr219 in caALK2 vs. wtALK2), or ligand modification (e.g. DMH1 vs. LDN193189) causes distinct binding profiles and selectivity among BMP inhibitors. 26597752_The higher PE activin A concentrations resulted in abnormal endothelial functions, which may contribute to the systemic maternal vascular endothelial cell dysfunction observed in the disorder. 26621707_Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva-ACVR1 abnormally transduces bone morphogenetic protein signaling in response to Activin-A. 26776312_Common mutations in ALK2/ACVR1, a multi-faceted receptor, have roles in distinct pediatric musculoskeletal and neural orphan disorders. 26869672_Activin-A is increased in the airway of asthmatics and peaks during asthma exacerbations.Activin-A signalling pathways are dysregulated in severe asthma. 27182040_The clinical manifestations, the disease course, and the molecular findings of involvement of ACVR1 gene in this family are suggestive of 'FOP variant' or an unusual ACVR1-related skeletal dysplasia 27256111_Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) syndrome is caused by mutation of the gene ACVR1. Developed is a simplified one-step procedure by simultaneously introducing reprogramming and gene-editing components into human fibroblasts derived from patient with FOP. The one-step-mediated ALK2 gene-corrected induced pluripotent stem cells restored global gene expression pattern. 27530160_The ACVR1 R206H mutation may not directly increase the formation of mature chondrogenic or osteogenic cells. 27565519_The effects of ACVR1/ALK2 mutations causing fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva are extended to the central nervous system. Brainstem hamartomatous lesions and dysmorphisms, variably associated with dentate nucleus and basal ganglia signal abnormalities and/or calcifications, may represent useful disease hallmarks. 27713089_the Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva mutation ACVR1(R206H) is more sensitive to a number of natural ligands. 27959431_Further investigation on clinical ESCC samples and non-tumorous adjacent tissue found that tumors with triple-positive BMP6, ALK2 and BMPRII had deeper growth than tumors with only BMP6 expression 28075462_Low ALK2 expression is associated with invasiveness of breast cancer. 28459464_Authors demonstrated that the BMP type I receptor ALK-2 (encoded by the ACVR1 gene) has crucial roles in apoptosis induction of patient-derived glioma-initiating cells (GICs), TGS-01 and TGS-04. 28476747_The role of an ALK2 mutation (R258S) in IRIDA development in a patient also bearing compound heterozygous mutations in TMPRSS6 was demonstrated by reconstructing in vitro the proband's genotype, expressing mutants TMPRSS6 and ACVR1 in the presence of hemojuvelin and assessing hepcidin activation. ALK2(R258S) maintained high hepcidin expression in the presence of MT2(I212T). 28646109_Data suggest BMP9/GDF2 and BMP10 synergize with TNFA to increase monocyte recruitment to vascular endothelial cells; process appears to be mediated mainly via ALK2/ACVR1 (which exhibits protein kinase activity). These studies used in vitro flow monocyte adhesion assay. (BMP9 = growth differentiation factor 2; BMP10 = bone morphogenetic protein 10; TNFA = tumor necrosis factor alpha; ALK2/ACVR1 = activin A receptor type 1) 28733457_both bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) and BMP6 are proangiogenic in vitro and ex vivo and that the BMP type I receptors, activin receptor-like kinase 3 (ALK3) and ALK2, play crucial and distinct roles in this process. 28847510_activation of AMPK upregulated Smad6 and Smurf1 and thereby enhanced their interactions, resulting in its proteosome-dependent degradation of ALK2. 29551750_this study characterized the ALK2 mutants R258G, G328V and F246Y, which were identified in patients with severe fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma and unusual hereditary skeletal dysplasia, respectively. 29587443_Study emphasizes about the role of ACVR1 which encoding a receptor for BMP proteins in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP). Most FOP patients carry the recurrent R206H substitution in the GS domain, whereas a few other mutations are responsible for limited cases. Mutations cause a dysregulation of the downstream BMP-dependent pathway making mutated ACVR1 responsive to a non-canonical ligand, Activin A. [review] 29693185_Results showed that ACVR1 was a direct target of miR-384 and was involved in the inhibitory effects of miR-384 on breast cancer progression. Furthermore, the study indicated that ACVR1 activated the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in breast cancer. 29739878_BMPR2 inhibits ALK2-mediated signaling by preventing ALK2 from oligomerizing with the type 2 receptors ACVR2A and ACVR2B. 30159679_Identification of small molecule inhibitors of ALK2: a virtual screening, density functional theory, and molecular dynamics simulations study. 30819221_AFAP1-AS1 functions as an endogenous RNA by competitively binding to miR-384 to regulate ACVR1, thus conferring inhibitory effects on pancreatic cancer cell stemness and tumorigenicity 31240838_We applied the same modeling and simulation methods to established Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) variants, to identify the detailed effects that they have on the ACVR1 protein, as well as to act as positive controls against which the effects of p.K400E could be evaluated. Our in silico molecular analyses support p.K400E as altering the behavior of ACVR1 31432174_the role of ALK2 in the process of Heterotopic ossification (HO) is introduced and the progress made towards the targeted inhibition of ALK2 is discussed. The present study aims to offer a platform for further research on possible targets for the prevention and treatment of HO. 31685442_These findings suggest that the PSMD14-ALK2 axis plays an essential role in initiation of the BMP6 signaling pathway and contributes to tumorigenesis and chemoresistance of colorectal cancers. 32142668_Pediatric glioma mutation Acvr1(G328V) arrests the differentiation of oligodendroglial lineage cells, and cooperates with Hist1h3b(K27M) and Pik3ca(H1047R) to generate high-grade diffuse gliomas. 32235336_Activins as Dual Specificity TGF-beta Family Molecules: SMAD-Activation via Activin- and BMP-Type 1 Receptors. 32273545_Differential kinase activity of ACVR1 G328V and R206H mutations with implications to possible TbetaRI cross-talk in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. 32437875_Functional characterization of a unique mutant of ALK2, p.K400E, that is associated with a skeletal disorder, diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. 32448372_Prophylactic treatment of rapamycin ameliorates naturally developing and episode -induced heterotopic ossification in mice expressing human mutant ACVR1. 32473755_Involvement of activin a receptor type 1 (ACVR1) in the pathogenesis of primary focal hyperhidrosis. 32512165_Design of primers for direct sequencing of nine coding exons in the human ACVR1 gene. 32641001_Association analysis of polymorphisms rs12997 in ACVR1 and rs1043784 in BMP6 genes involved in bone morphogenic protein signaling pathway in primary angle-closure and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma patients of Saudi origin. 33089331_A Three-Generation Pedigree of Multifocal Heterotopic Ossification With Bilateral Involvement. 33443061_Association of rs12997 variant in the ACVR1 gene: a member of bone morphogenic protein signaling pathway with primary open-angle glaucoma in a Saudi cohort. 33766507_MiR-130a Acts as a Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Regulates the Activity of the BMP/SMAD Pathway by Suppressing ACVR1. 33973349_Nonclassic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: A child from Angola with an ACVR1(G328E) variant. 34003511_Pathogenic ACVR1(R206H) activation by Activin A-induced receptor clustering and autophosphorylation. 34013359_Anti-Mullerian hormone concentration regulates activin receptor-like kinase-2/3 expression levels with opposing effects on ovarian cancer cell survival. 34311122_ACVR1(R206H) extends inflammatory responses in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages. 34400635_Structural basis for ALK2/BMPR2 receptor complex signaling through kinase domain oligomerization. 34490965_Upregulation of oncogene Activin A receptor type I by Helicobacter pylori infection promotes gastric intestinal metaplasia via regulating CDX2. 34755602_Modeling the ACVR1(R206H) mutation in human skeletal muscle stem cells. 34854557_An ACVR1(R375P) pathogenic variant in two families with mild fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. 35236255_MicroRNA-137 inhibits the inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human nucleus pulposus cells by targeting activin a receptor type I. 35587280_Recurrent ACVR1 mutations in posterior fossa ependymoma. 36131296_Recapitulation of pro-inflammatory signature of monocytes with ACVR1A mutation using FOP patient-derived iPSCs. |
ENSMUSG00000026836 |
Acvr1 |
140.157032 |
2.8633482490 |
1.517703 |
0.156508206 |
94.909705 |
0.00000000000000000000019927053371070780926371646940898967491350429339868507021371981692559050003410447970964014530181884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001926151327812735579034385016117035599704473140120420654301282292752972580274217762053012847900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
219.6786301 |
21.3981385 |
77.0782059 |
6.0067601 |
| ENSG00000115194 |
7781 |
SLC30A3 |
protein_coding |
Q99726 |
FUNCTION: Probable proton-coupled zinc ion antiporter mediating the import of zinc from cytoplasm into synaptic vesicles and participating to cellular zinc ion homeostasis in the brain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17349999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19521526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26647834}. |
Antiport;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Ion transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
Predicted to enable zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in regulation of sequestering of zinc ion. Located in late endosome and synaptic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7781; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; hippocampal mossy fiber [GO:0097457]; hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse [GO:0098686]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; positive regulation of transport [GO:0051050]; regulation of sequestering of zinc ion [GO:0061088]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043]; zinc ion import into synaptic vesicle [GO:0099180]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577] |
14662799_AIDL cells exhibited a lower expression of zinc transporter 1 (ZnT1) and higher expression of ZnT3 than LNCaP cells. 17971500_hZnT-3 is expressed at low levels in leukocytes. 18639746_Data show that ZNT3 is extensively present in the Abeta-positive plaques in the cortex of human AD brains. 19521526_SLC30A3 (ZnT3) oligomerization by dityrosine bonds regulates its subcellular localization and metal transport capacity 23849395_SNPs in SLC30A3 show a gender-specific association with schizophrenia in an East UK cohort. 24953873_this study provides the first evidence of a role for zinc in depression in people with dementia. 25104558_An association was found between reduced ZnT3 in the prefrontal cortex and cognitive impairment in patients with either dementia with Lewy bodies or Parkinson's disease dementia. 25284286_The results of this study suggested that ZnT3 protein levels are decreased in the spinal cords of sporadic ALS patients. 26867900_ZNT3 and ZNT8 (known to regulate insulin secretion) have opposite effects on insulin synthesis and secretion possibly by a transcriptional co-regulation since mRNA expression of ZNT3 was inversely correlated to ZNT8 and ZNT3 over-expression reduced insulin synthesis and secretion. 27661418_There was a significant decreased in protein levels of ZnT3 in the prefrontal cortex in Major depression disorder, relative to control subjects. 27678294_The level of ERK1/2 phosphorylation was significantly increased by tunicamycin treatment in control cells, not in SLC30A3 knockdown cells. The ERK1/2 pathway is thought to have an association with defensive effects of SLC30A3 on cellular stress such as ER stress. 27750116_SNPs in the SLC30A3 gene and adjacent region are associated with schizophrenia in female but not male cases. 29372370_ZNT3 was only detected in human beta-cells, but not in mouse beta-cells. 32925049_Increased Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentration of ZnT3 Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer's Disease. 33715270_Epigenetic targeting of SLC30A3 by HDAC1 is related to the malignant phenotype of glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000029151 |
Slc30a3 |
19.750745 |
4.4474651527 |
2.152983 |
0.584778329 |
12.653443 |
0.00037487464989440963912536997071356381638906896114349365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000941973073279108938371528836341894930228590965270996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.0739087 |
10.6007036 |
6.3863366 |
1.8237452 |
| ENSG00000115257 |
54760 |
PCSK4 |
protein_coding |
Q6UW60 |
FUNCTION: Proprotein convertase involved in the processing of hormone and other protein precursors at sites comprised of pairs of basic amino acid residues (By similarity). In males, important for ADAM2 processing as well as other acrosomal proteins with roles in fertilization and critical for normal fertilization events such as sperm capacitation, acrosome reaction and binding of sperm to zona pellucida (By similarity). Also plays a role in female fertility, involved in the regulation of trophoblast migration and placental development, may be through the proteolytical processing and activation of proteins such as IGF2 (PubMed:16040806). May also participate in folliculogenesis in the ovaries (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P29121, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16040806}. |
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Serine protease;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family, which includes proteases that process protein and peptide precursors trafficking through regulated or constitutive branches of the secretory pathway. The encoded protein undergoes an initial autocatalytic processing event in the ER to generate a heterodimer which exits the ER and sorts to subcellular compartments where a second autocatalytic even takes place and the catalytic activity is acquired. This gene encodes one of the seven basic amino acid-specific members which cleave their substrates at single or paired basic residues. The protease is expressed only in the testis, placenta, and ovary. It plays a critical role in fertilization, fetoplacental growth, and embryonic development and processes multiple prohormones including pro-pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating protein and pro-insulin-like growth factor II. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:54760; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; acrosome reaction [GO:0007340]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; reproductive process [GO:0022414]; sperm capacitation [GO:0048240] |
16040806_abnormal processing of IGF-II by PC4 may represent a previously uncharacterized mechanism involved in the pathophysiology of fetoplacental growth restriction 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21080038_Maturation by propeptide removal occurs very inefficiently when rat or human proPCSK4 is overexpressed in HEK293 cells where it interacts with BiP. |
ENSMUSG00000020131 |
Pcsk4 |
8.517778 |
0.2876857351 |
-1.797434 |
0.650957344 |
7.931084 |
0.00485926644993932115024204421160902711562812328338623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009967033463188489442186046574079227866604924201965332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5220668 |
1.7374600 |
12.5967109 |
3.6851818 |
| ENSG00000115306 |
6711 |
SPTBN1 |
protein_coding |
Q01082 |
FUNCTION: Fodrin, which seems to be involved in secretion, interacts with calmodulin in a calcium-dependent manner and is thus candidate for the calcium-dependent movement of the cytoskeleton at the membrane. Plays a critical role in central nervous system development and function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34211179}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin capping;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Spectrin is an actin crosslinking and molecular scaffold protein that links the plasma membrane to the actin cytoskeleton, and functions in the determination of cell shape, arrangement of transmembrane proteins, and organization of organelles. It is composed of two antiparallel dimers of alpha- and beta- subunits. This gene is one member of a family of beta-spectrin genes. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal actin-binding domain, and 17 spectrin repeats which are involved in dimer formation. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6711; |
axolemma [GO:0030673]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cuticular plate [GO:0032437]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; M band [GO:0031430]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; spectrin [GO:0008091]; spectrin-associated cytoskeleton [GO:0014731]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament capping [GO:0051693]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; central nervous system formation [GO:0021556]; common-partner SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0007182]; Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0043001]; membrane assembly [GO:0071709]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903076]; regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060390] |
12820899_High affinity and slow overall kinetics of association/dissociation of beta II-spectrin may suit it well to a role in strengthening cell junctions and providing stable anchorage for transmembrane proteins at points specified by cell-adhesion molecules. 15310273_Quantitative analysis of erythrocyte membrane proteins revealed increase in beta-spectrin from patients with homozygous and heterozygous forms of beta-thalassemia. 17074766_ankyrin-G and beta(2)-spectrin are functional partners in biogenesis of the lateral membrane of epithelial cells 17088250_because both the T2159E mutant and the wild-type allow neuritogenesis, we conclude that the short C-terminal betaII-spectrin is phosphorylated during this process 17546056_TGF-beta signaling and Smad adaptor embryonic liver fodrin (ELF) suppress human hepatocarcinogenesis, potentially through cyclin D1 deregulation. 17620337_E-cadherin thus requires both ankyrin-G and beta-2-spectrin for its cellular localization in early embryos as well as cultured epithelial cells. 17716929_Our results therefore indicate the importance of N-terminal region for lipid-binding activity of the beta-spectrin ankyrin-binding domain and its substantial role in maintaining the spectrin-based skeleton distribution. 17905835_analysis of the conformational change of erythroid alpha-spectrin at the tetramerization site upon binding beta-spectrin 18262053_Characterization of the 2p21 breakpoint identified the SPTBN1 gene in myeloproliferative disorders. 18704924_ELF, a TGF-beta adaptor and signaling molecule, functions as a critical adaptor protein in TGF-beta modulation of angiogenesis as well as cell cycle progression. 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20554715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20739274_Results suggest that epigenetic silencing of SPTBN1 (beta2SP) is a new potential causal factor in BWS patients. 20886430_reduced SPTBN1 expression correlated with shorter survival of pancreatic cancer patients, suggesting a tumor suppressor function of this gene 21412925_Results suggest that it is possible for cellular proteins to differentially associate with the C-termini of different beta-spectrin isoforms to regulate alpha- and beta-spectrin association to form functional spectrin tetramers. 22771809_These results suggest that alpha-synuclein modulates neurite outgrowth by interacting with cytoskeletal proteins such as SPTBN1. 22798246_genetic association study in population of 1,012 Han women in China: Data suggest that an SNP in SPTBN1 (rs11898505) is associated with osteoporotic fractures and bone mineral density of lumbar spine in aging women. 25096061_in human HCC tissues, SPTBN1 expression correlated negatively with expression levels of STAT3, ATF3, and CREB2; SMAD3 expression correlated negatively with STAT3 expression 25307947_decreased SPTBN1 and kallistatin gene expression associated with decreased relapse-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma 25632041_betaII spectrin is critical for normal myocyte electric activity. Dysfunction in the betaII spectrin-dependent cytoskeleton in cardiomyocytes contributes to human arrhythmia. 25880619_TGF-beta1 and ELF protein are potential and reliable biomarkers for predicting prognosis in HCC patients after hepatic resection. 27095047_Subjects whose head and neck tumors expressed spectrin were 4.60 times more likely (hazard ratio; 95% confidence interval: 1.88-11.25) to die at any given time when compared with those without spectrin (P = .001). 27496196_c-Met overexpression, HER-2 gene amplification, and SPTBN1-ALK gene fusion can coexist in lung adenocarcinoma and may become a potential biomarker of cancer refractory to crizotinib, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy as well as of a relatively poor prognosis. 29555987_beta2 spectrin induced the differentiation of liver cancer stem cells, and then repressed the CSCs properties in liver tumorinitiating cells. Transduction of beta2SP into liver CSCs resulted in a reduction in colony formation ability, spheroid formation capacity, invasive activity, chemo-resistance properties, tumorigenicity in vivo. 30690801_Data suggeset the novel mutation (c.5650G > C/p.Ala1884Pro) of beta-spectrin (SPTB) to be the genetic lesion in this family of hereditary spherocytosis (HS). 32516133_SPTBN1 suppresses the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer via SOCS3-mediated blockade of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. 33390831_betaII spectrin (SPTBN1): biological function and clinical potential in cancer and other diseases. 33754058_SPTBN1 inhibits inflammatory responses and hepatocarcinogenesis via the stabilization of SOCS1 and downregulation of p65 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33847457_Heterozygous variants in SPTBN1 cause intellectual disability and autism. 34211179_Pathogenic SPTBN1 variants cause an autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental syndrome. 34358482_SPTBN1 inhibits growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer by downregulating miR-21. 36444616_SPTBN1 attenuates rheumatoid arthritis synovial cell proliferation, invasion, migration and inflammatory response by binding to PIK3R2. |
ENSMUSG00000020315 |
Sptbn1 |
839.829893 |
0.2785963723 |
-1.843752 |
0.062019553 |
908.843267 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011733053871429193528514197748345400271240122272812171558225907872142310611531551909952230766794174808461402453290623102741592117000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010690115749524376924196349599530180684815433552750462131970247580730224373260818361378495465200381656637700257421235607277715521657 |
Yes |
Yes |
383.7736374 |
15.1668273 |
1386.7497514 |
33.9857747 |
| ENSG00000115363 |
84141 |
EVA1A |
protein_coding |
Q9H8M9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of programmed cell death, mediating both autophagy and apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17492404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19029833}. |
Apoptosis;Autophagy;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in apoptotic process and autophagy. Located in intracellular membrane-bounded organelle and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84141; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; autophagy [GO:0006914] |
17492404_TMEM166 is a novel regulator involved in both autophagy and apoptosis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22495369_TMEM166 expression was widely down-regulated in the cancer tissues. 23098460_Low TMEM166 mRNA and protein expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 24257118_The adenovirus-mediated increase of FAM176A inhibited the growth of the tumor cells. 27490928_EVA1A interacts with the WD repeats of ATG16L1 through its C-terminal and promotes ATG12-ATG5/ATG16L1 complex recruitment to the autophagic membrane and enhances the formation of the autophagosome. 28185834_Low EVA1A expression is associated with glioblastoma. 29749374_results suggest that miR-125b plays a role in the resistance of HCC cells to chemotherapy via a mechanism involving the downregulation of EVA1A-mediated autophagy. 31754186_Myc/Max dependent intronic long antisense noncoding RNA, EVA1A-AS, suppresses the expression of Myc/Max dependent anti-proliferating gene EVA1A in a U2 dependent manner. 31977009_Eva1a ameliorates atherosclerosis by promoting re-endothelialization of injured arteries via Rac1/Cdc42/Arpc1b. 32969138_Eva-1 homolog A promotes papillary thyroid cancer progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Hippo signalling pathway. 33006534_Transmembrane Protein 166 and its Significance. 33200377_TMEM166 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma via upregulating TP53. 33556710_Eva1a inhibits NLRP3 activation to reduce liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via inducing autophagy in kupffer cells. 36078115_The Degradation of TMEM166 by Autophagy Promotes AMPK Activation to Protect SH-SY5Y Cells Exposed to MPP(). 36273122_Down-regulation of EVA1A by miR-103a-3p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells proliferation and migration. |
ENSMUSG00000035104 |
Eva1a |
37.232033 |
93.3392680367 |
6.544412 |
0.868762616 |
114.065968 |
0.00000000000000000000000001260446846004943773217226685898132815556623398955721910417117242696319117864489633973335003247484564781188964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000142889365952634179401836074473311663549591090803065400907908707534227712998564641111443052068352699279785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
77.5306238 |
46.7248307 |
0.8241933 |
0.4877009 |
| ENSG00000115423 |
1768 |
DNAH6 |
protein_coding |
Q9C0G6 |
FUNCTION: Force generating protein of respiratory cilia. Produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Dynein;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene belongs to the dynein family, whose members encode large proteins that are constituents of the microtubule-associated motor protein complex. This complex is composed of dynein heavy, intermediate and light chains, which can be axonemal or cytoplasmic. This protein is an axonemal dynein heavy chain. It is involved in producing force for ciliary beating by using energy from ATP hydrolysis. Mutations in this gene may cause primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) as well as heterotaxy. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:1768; |
axonemal dynein complex [GO:0005858]; dynein complex [GO:0030286]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
26918822_DNAH6 role in heterotaxy and primary ciliary dyskinesia:DNAH6 is required for motile cilia function mediating airway clearance 29019003_DNAH6 gene expression is down regulated in blood samples of HD patients. 29323929_Genetic variants within DNAH6, DNAH14, and DNAAF3 are associated with variation in lung function among persons with cystic fibrosis. 31676830_Identification of DNAH6 mutations in infertile men with multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella. |
ENSMUSG00000052861 |
Dnah6 |
12.298590 |
0.3034844110 |
-1.720306 |
0.628449310 |
7.183308 |
0.00735849024498033427860166355571891472209244966506958007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014496329823091784472222087742920848540961742401123046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9104807 |
2.4805259 |
19.3966301 |
5.5627431 |
| ENSG00000115459 |
84173 |
ELMOD3 |
protein_coding |
Q96FG2 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) for ARL2 with low specific activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24039609}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Disease variant;GTPase activation;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the engulfment and cell motility family of GTPase-activating proteins that regulate Arf GTPase proteins. Members of this family are defined by a conserved engulfment and cell motility domain. In rat cochlea, the encoded protein is found in stereocilia, kinocilia and cuticular plate of developing hair cells suggesting a function for this protein in cochlear sensory cells. An allelic variant of this family has been associated with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness-88 in humans. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:84173; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; kinocilium [GO:0060091]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilium [GO:0032420] |
24039609_Collectively, our data provide the first insights into the expression and biochemical properties of ELMOD3 and highlight its functional links to sound perception and actin cytoskeleton. 24616099_The non-opioid sigma-1 receptor (S1R) was identified as a novel effector of GAP activity of ELMOD1-3 proteins as its direct binding to either ELMOD1 or ELMOD2 resulted in loss of GAP activity. 29713870_the analysis of the stability of the wild-type (WT) and mutant ELMOD3 protein shows that the decay of p.His171Arg is faster than that of the WT, suggesting a shorter halflife of the c.512A > G variant. A novel variant in the ELMOD3 gene, encoding a member of the engulfment and cell motility (ELMO) family 31800155_ELMOD3-SH2D6 gene fusion as a possible co-star actor in autism spectrum disorder scenario. |
ENSMUSG00000056698 |
Elmod3 |
115.431357 |
0.4083839523 |
-1.292002 |
0.172603589 |
55.589346 |
0.00000000000008930634482537329006166751048960108319313844910114497110953379888087511062622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000567439367035088076222196991756804943527262019564716410968685522675514221191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
64.3622057 |
7.4156876 |
159.1740369 |
12.6444108 |
| ENSG00000115461 |
3488 |
IGFBP5 |
protein_coding |
P24593 |
FUNCTION: IGF-binding proteins prolong the half-life of the IGFs and have been shown to either inhibit or stimulate the growth promoting effects of the IGFs on cell culture. They alter the interaction of IGFs with their cell surface receptors. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Enables insulin-like growth factor I binding activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to cAMP; regulation of smooth muscle cell migration; and regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation. Part of insulin-like growth factor ternary complex. Biomarker of pulmonary fibrosis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:3488; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex [GO:0016942]; insulin-like growth factor ternary complex [GO:0042567]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; insulin-like growth factor I binding [GO:0031994]; insulin-like growth factor II binding [GO:0031995]; aging [GO:0007568]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; mammary gland involution [GO:0060056]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of growth [GO:0045926]; negative regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043569]; negative regulation of muscle tissue development [GO:1901862]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy [GO:1904205]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014912]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043568]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904754]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043567]; response to growth hormone [GO:0060416]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051146]; type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0044342] |
11821401_Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) interacts with a four and a half LIM protein 2 (FHL2). 11923300_role in stimulating growth and IGF-I secretion in intestinal smooth muscle by ras-dependent activation of MAP kinase signaling pathways 11973331_c-Myb and B-Myb transactivate the IGFBP-5 promoter through binding-dependent and -independent mechanisms. 12005306_cDNA probes were used to analyze the gene expression of IGFBP-5 in luteinized granulosa cells from different-sized follicles after ovarian hyperstimulation. Transcript levels increased with increasing follicular fluid (FF) volume 12777377_IGFBP-5 is a potent growth inhibitor and proapoptotic agent in human breast cancer cells via modulation of cell cycle regulation and apoptotic mediators 14645245_Fibronectin and IGFBP-5 bind to each other, and this binding negatively regulates the ligand-dependent action of IGFBP-5 by triggering IGFBP-5 proteolysis. 15001525_The IGFBP-5 C-domain is necessary and sufficient for its nuclear localization, and residues K206, K208, K217, and K218 are particularly critical. The IGFBP-5 N-domain contains a putative transactivation domain. 15140223_IGF-II:VN and IGF-I:IGFBP-5:VN complexes may be useful in situations where enhanced keratinocyte cell migration and proliferation is required, such as in wound healing and skin regeneration. 15155755_exogenous IGFBP-5 increases apoptosis by binding to and inhibiting the activities of insulin-like growth factors 15534875_Understanding the mechanism of how cleavage of IGFBP-5 by this protease (IGFBPase) alters its activity will help to further our understanding of the biologic actions of the IGFs 15618969_Inhibition of expression of IGFBP-5 by micro and small interfering RNA has marked effect on neuroblastoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation 15650232_IGFBP-5 has a role in growth and differentiation of neuroblastoma cells 15661050_The expression of certain IGFBP is significantly altered in renal cell carcinoma 15681824_Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 5 are xpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and have a role in extracellular matrix deposition 15777798_Activation by C/EBP alpha and beta did not depend on their binding to the C/EBP site, since they still activated IGFBP-5 promoter. 15780948_In that IGFBP-5 is thought to stimulate transgenic bone formation, directly or via the action of insulin-like growth factor 1, such changes in bone IGFBP-5 may be important to ensure robust bone acquisition in the early postnatal period. 15802501_IGFBP-5 expression may influence extrinsic apoptotic pathways via a differential modulation of downstream cell survival and cell death pathways. 15930103_Igfbp5-mediated fibroblast growth factor receptor 2-IIIb signals regulate the genetic program that controls the structure of the hair shaft medulla in transgenic mice. 16007340_IGFBP-5 interacts with RASSF1C 16195401_Importance of the kinetics of association/dissociation in determining the enhancing or inhibiting effects of IGFBP-5 and the ability to generate an IGFBP-5 mutant with exclusively IGF-enhancing activity. 16311053_In conclusion, our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that FHL-2 and ADAM-9 are important modulators of IGFBP-5 actions and are, in part, regulated in a coordinated manner in bone 16543235_there are several conserved residues in the IGFBP-5 N-terminal region that are critical for transactivation and IGFBP-2 and -3 also have strong transactivation activity in their N-domains 16716263_IGF-I and -II are chemotactic factors for mesenchymal progenitor cells; IGFBP-5 both modulates the IGF-I effect and directly stimulates migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells 16865675_overexpression of IGFBP-5 may play a significant role in the malignant transformation of normal pancreatic epithelial cells 17067554_Inhibition of endogenously produced IGFBP-5 is associated with Bim-dependent apoptosis in NB cells. 17071587_Overexpression of IGFBP-5 in mouse lung results in fibroblast activation, increased extracellular matrix deposition, and myofibroblastic changes. 17242174_Promoter contains a CACCC-rich consensus sequence required for activation by MN1. 17290407_study shows that down-regulation of IGFBP-5 protein correlates with cervical carcinogenesis and does so at a preneoplastic stage 17312271_Ratios between the IGFBPs and IGF(insulin-like growth factor), different IGFBPs, sequential proteolytic cleavage of IGFBPs, and association of activating proteinases are elements in the regulation of IGF receptor stimulation. 17316888_A cDNA library consisting of 220 upregulated genes in tumour tissue was established and named as LSCC. Differential expression was confirmed in five of these genes, including IGFBP5, SQLE, RAP2B, CLDN1, and TBL1XR1. 17496250_Phosphorylation and O-glycosylation both affected IGFBP-5 binding to heparin but not insulin-like growth factor binding or ternary complex formation with the acid-labile subunit. 17595320_IGFBP-5 can interact with VDR to prevent RXR:VDR heterodimerization; IGFBP-5 may attenuate the 1,25(OH)2D3-induced expression of bone differentiation markers. 17651454_Overexpression of IGFBP5 was associated with breast cancer 17804819_IGFBP-5 plays a role in the regulation of cellular senescence via a p53-dependent pathway and in aging-associated vascular diseases 17823924_Androgen suppressive therapy increases IGFBP5 in the bone marrow microenvironment and thereby may facilitate the progression of prostate cancer. 17892529_Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 enters vesicular structures but not the nucleus 18085517_This suggests that IGFBP-5 possesses an IGF-independent suppressor function 18161051_IGFBP-5 inducible by gankyrin overexpression may be involved human hepatocarcinogenesis. 18210156_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18210156_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in IGFBP5 is associated with breast cancer 18311789_There is a novel function of ADAM-12m in chondrocyte proliferation and cloning in osteoarthritic cartilage through enhanced bioavailability of IGF-1 from the IGF-1-IGFBP-5 complex by selective IGFBP-5 digestion. 18373644_IGFBP2 and IGFBP5 play a role in the development of metastasis and may serve as useful markers to predict lymph node metastasis in patients with small (T1) invasive breast carcinomas. 18602100_A new approach for designing protein delivery systems using IGFBP-3/5 derived peptides based on the molecular mechanisms of IGF-independent activities of IGFBPs. 18624948_Expression in gingival epithelial cells is associated with anti-apoptosis, migration and differentiation 18665784_patients with poor diabetes control have lower levels of IGF-1, and greater IGFBP-1, IGFBP-5, and bone-specific alkaline phosphatase 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18710598_IGFBP-5 plays an important role in the biology of breast cancer, especially in breast cancer metastasis [review] 18762576_IGFBP-5 promotes muscle cell differentiation by binding to and switching on the IGF-II auto-regulation loop. 18775916_IGFBP-5 expression prevented tumor growth and inhibited tumor vascularity in a xenograft model of human ovarian cancer. These results are the first evidence showing that IGFBP-5 plays a role as tumor suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis 18805800_mRNA levels of IGFBP5, a specific substrate for PAPP-A2 protease activity, were also significantly increased, suggesting a potential role for IGFBP5 in fetal and placental growth suppression during pre-eclampsia. 18809517_Results suggest that NFI proteins are important regulators of IGFBP5 expression in human osteoblasts and thus in modulating IGFBP5 functions in bone. 18957933_IGFBP5 has a gender-specific association with adiponectin, which may modulate the development of metabolic syndrome 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19250630_PSA secreted by prostate cancer cells degrades IGFBP-5 and augments the IGF signal transduction. 19341485_Findings imply that the mutant form of IGFBP5 increases proliferation and motility of breast cancer cells and that mutation of the NLS in IGFBP5 results in localization of IGFBP5 in the cytoplasm. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19476635_Increased IGFBP-5 is associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical carcinoma. 19610136_These results indicate that IGFBP-5 expression affects the cell cycle and survival signal pathways and thus it may be an important mediator of pancreatic cancer cell growth. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19628764_IGFBP-5 induces a fibrotic phenotype via the activation of MAPK signaling and the induction of nuclear Egr-1 that interacts with IGFBP-5 and promotes fibrotic gene transcription. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19808657_Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 stimulates growth of human intestinal muscle cells by activation of Galphai3. 19843326_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19877176_OBSL1 modulates the expression of IGFBP2 and IGFBP5 proteins in 3-M syndrome. 19948051_Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. 19950226_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20345844_Decreased Cav-1 expression in fibrotic diseases likely leads to increased deposition of IGFBP-5 in the extracellular matrix. 20354179_insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 is a modulator of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20416304_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508032_Data indicate that retinal astrocytes enhance the proliferation of cone-like retinoblastoma cells by deploying IGFBP5, a factor that also provides trophic support to the tumor cells' non-neoplastic counterparts. 20583135_Data show that IGFBP5 expression is down-regulated during 4HPR-induced neuronal differentiation of human RPE cells through a MAPK signal transduction pathway involving C/EBPbeta. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20810604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20944648_IGFBP-5 has an effect on human hair shape. 20949447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20949447_The IGFBP5 polymorphism is functional and may potentially be a biomarker for susceptibility to late-stage risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 21029365_Data revealed a strong induction of several genes encoding components of the extracellular matrix, such as collagens, COMP, IGFBP5 and biglycan. 21191810_results suggest that PGE(2) may play an important role in controlling cellular senescence of HDFs through the regulation of IGFBP5 and therefore may contribute to inflammatory disorders associated with aging 21256825_the L-domain of IGFBP-5 is a novel TNFR1 ligand that functions as a competitive TNF-alpha inhibitor. 21460855_Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 is a novel marker that has an important role in the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. The loss of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 function may contribute to metastasis in osteosarcoma. 21852217_We genotyped single-nucleotide polymorphisms of IGF1, IGF2, IGF1R, IGF2R, IGFBP1, IGFBP3, IGFBP5, IRS1, IRS2, and IRS in pancreatic cancer patients 22246875_This study demonistrated that IGFBP5 was significantly decreased in skeletal muscel in patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 22252554_c-Src and IL-6 inhibit osteoblast differentiation and integrate IGFBP5 signalling 22328518_The IGFBP5 enhanced adhesion, it inhibited cell migration, although this was not evident using the truncated C-terminal mutant, suggesting that effects of IGFBP5 on adhesion and migration involve different mechanisms. 22571677_VEGF may play a regulator role in human ovarian physiology by modulating the expression of IGF-II and IGFBP-5 in luteinized granulosa cells. 23499909_IGFBP-5 modulates the efficiency of estrogen-triggered activation of the Akt/PKB signaling pathway which has been associated with growth factor/ ERalpha cross-talks. 23539739_IGFBP-5 overexpression is a poor prognostic factor in patients with urothelial carcinomas of upper urinary tracts and urinary bladder. 23576565_Data suggest that insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) regulation by calcium-dependent chloride channel DOG1. 23665505_IGFBP5 domains modulate tumorigenicity and metastasis of human osteosarcoma in different ways 24120850_IGFBP-5 is important in maintaining epithelial-mesenchymal boundaries and thus may limit metastasis and fibrosis by inducing an orderly repair mechanism, very distinct from the fibrotic disruption induced by TGFbeta1. 24379630_Serum IGFBP-5 concentrations were lower in Crohn's disease patients compared to healthy controls regardless of disease activity or the presence of stricture formation. 24551065_IGFBP-5 induces its pro-fibrotic effects, at least in part, via DOK5. IGFBP-5 and DOK5 are both increased in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts and tissues and may thus be acting in concert to promote fibrosis. 25007054_IGFBP-5 may be a negative modulator of RASSF1C/ PIWIL1 growth-promoting activities. 25248036_rs4442975 at 2q35 flanks a transcriptional enhancer that physically interacts with the promoter of IGFBP5. Evidence suggests that the g-allele confers increased breast cancer susceptibility through relative downregulation of IGFBP5. 25422220_IGFBP5 mRNA expression is a good indicator in clinical outcome of breast cancer patients. 25475528_Data indicate co-localization of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins IGFBP-4, IGFBP-5 in the syncytiotrophoblast layer of first trimester placental villi as early as 5 weeks of gestational age. 25548030_Our results suggest that rs6214 on the IGF1 gene and rs2854744 near the IGFBP3 gene potentially play an important role with ASMI in Taiwanese older adults in a metropolitan area. 25603050_miR-204-5p suppresses IGFBP5 expression by direct binding to the 3' untranslated region. 25827480_Demethylation of IGFBP5 by Histone Demethylase KDM6B Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Periodontal Tissue Regeneration by Enhancing Osteogenic Differentiation and Anti-Inflammation Potentials. 26010068_Results shed light on the mechanism of IGFBP5 as a potential tumor-suppressor in melanoma progression. 26103640_data provide further insights into the role of cellular compartmentalization in IGFBP-5-induced fibrosis 26762731_Data demonstrate that dysregulation of miR-143-3p:Igfbp5 interactions in satellite cells with age may be responsible for age-related changes in satellite cell function. 27050076_Co-ordinated and reciprocal alteration in IGFBP-2 and -5 expression may play a role in the acquisition of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. 27484838_IGFBP5 promoted osteogenic differentiation potentials of periodontal ligament stem cells and Wharton's jelly umbilical cord stem cells via the JNK and MEK/Erk signalling pathways. 27612043_IGFBP5 promoter and exon-I methylation did not have any differences between tumor and adjacent tissues so that IGFBP5 methylation did not change IGFBP5 gene regulation in breast cancer. 27752126_Factor Xa induced endothelial cell senescence through IGFBP-5. 28008951_These results suggest that the C-terminus of IGFBP-5 exerts anti-cancer activity by inhibiting angiogenesis via regulation of the Akt/ERK and NF-kB-VEGF/MMP-9 signaling pathway. 28049695_dysregulation of DNMT3A and IGFBP5 is relevant to preeclampsia. Thus, we propose that DNMT3A and IGFBP5 can serve as potential markers and targets for the clinical diagnosis and therapy of preeclampsia. 28554590_AMP-IBP5 markedly enhanced keratinocyte migration and proliferation. AMP-IBP5-induced keratinocyte activation was mediated by Mrg X1-X4 receptors with MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. 28835592_Data suggest that IGFBP5 nuclear import is mediated by KPNA5/KPNB1 complex; nuclear localization sequence of IGFBP5 is critical domain in this nuclear translocation. (IGFBP5 = insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5; KPNA5 = karyopherin subunit alpha-5; KPNB1 = karyopherin subunit beta-1/importin-beta) 29016699_MiR-137 inhibited cell proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via targeting IGFBP-5 and modulating the mTOR/STAT3 signaling. 29896299_The study exemplifies flow-dependent epigenetic regulation of endothelial gene expression, and also suggests that targeting the EZH2/H3K27me3/IGFBP5 pathway may offer novel therapeutics for inflammatory disorders such as atherosclerosis. 30542696_Study results demonstrated that miR-885 promoted metastasis of colorectal cancer (CRC) in vitro, and that von Willebrand factor (vWF) and IGFBP5 are potential novel target genes of miR-885, indicating that the miR-885/vWF and miR-885/IGFBP5 axes may serve roles in the metastasis of CRC. 30745575_PKNOX2 is a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer by activation of IGFBP5 and p53 signaling pathways 30810066_In vitro analyses revealed that ROS production was induced by recombinant and adenoviral vector-mediated IGFBP-5 (AdBP5) in a dose- and time-dependent manner, regulated through MEK/ERK and JNK signaling, and primarily mediated by NADPH oxidase (Nox). Silencing IGFBP-5 in systemic sclerosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis fibroblasts reduced ROS production. 31210318_MicroRNA-193a-3p participates in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis by regulating proliferation and apoptosis of MH7A cells through targeting IGFBP5. 31290273_Down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration via the ERK signalling pathway. 31401027_Birth weight and length Z-scores were negatively associated with Z-scores of intact IGFBP-4, PAPP-A, and PAPP-A2 levels 31404102_These data lend support for the idea that unidentified cortical proteins like IGFBP5, which may not manifest a known pathologic footprint, may contribute to motor and cognitive function in older adults. 31886201_IGFBP5 is down regulated in Kidney renal papillary renal cell carcinoma kidney tissues compared to its expression in control tissues and that the expression of IGFBP5 is negatively related to patient survival 32194505_Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-5 in Physiology and Disease. 32484228_Protein QTL analysis of IGF-I and its binding proteins provides insights into growth biology. 32585242_IGFBP5 modulates lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity through activating AMPK pathway in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 33010605_MiR-193b inhibits autophagy and apoptosis by targeting IGFBP5 in high glucose-induced trophoblasts. 33035436_Homocysteine downregulates cardiac homeobox transcription factor NKX2.5 via IGFBP5. 33823868_Single cell RNA sequencing identifies IGFBP5 and QKI as ciliated epithelial cell genes associated with severe COPD. 34146516_Functional annotation of the 2q35 breast cancer risk locus implicates a structural variant in influencing activity of a long-range enhancer element. 34362467_LncRNA-TUG1 promotes the progression of infantile hemangioma by regulating miR-137/IGFBP5 axis. 34655977_LncRNA HOXA11-AS aggravates the keloid formation by targeting miR-148b-3p/IGFBP5 axis. 34822133_Overexpression of long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via miR-143-3p/IGFBP5 axis. 34830489_Identification of Impacted Pathways and Transcriptomic Markers as Potential Mediators of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Transgenic Mice Expressing Human IGFBP5. 35151245_Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 5: an Important Regulator of Early Osteogenic Differentiation of hMSCs. 35513854_Insulin-like growth factor 5 associates with human Ass plaques and promotes cognitive impairment. |
ENSMUSG00000026185 |
Igfbp5 |
263.086981 |
3.1199055465 |
1.641502 |
0.105400508 |
249.369602 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003563467107085103232715012914533193081738306235711386144441938921430096487449592614010037789882834102754426312165426617049269862260804805041691789568858439452014863491058349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000851080493536830364066480592384878890860698204849637033076410352800047163354829169614574548930285500520981738593370278685079604129728547776828628812495480815414339303970336914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
403.1205497 |
25.1059158 |
130.1236496 |
6.6900495 |
| ENSG00000115507 |
5013 |
OTX1 |
protein_coding |
P32242 |
FUNCTION: Probably plays a role in the development of the brain and the sense organs. Can bind to the BCD target sequence (BTS): 5'-TCTAATCCC-3'. |
Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the bicoid sub-family of homeodomain-containing transcription factors. The encoded protein acts as a transcription factor and may play a role in brain and sensory organ development. A similar protein in mouse is required for proper brain and sensory organ development and can cause epilepsy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:5013; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; diencephalon morphogenesis [GO:0048852]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; metencephalon development [GO:0022037]; midbrain development [GO:0030901]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11901358_Fine mapping of the chromosome 2p12-16 dyslexia susceptibility locus candidate gene 18849347_OTR1, OTX2 and CRX act as positive modulators of the BEST1 promoter in the retinal pigment epithelium. 19018235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19414065_In the human fetal eye, OTX1 expression was confined to anterior retina. 19893048_This study identifies OTX1 as a molecular marker for high-grade germinal center derived Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma 20354145_The early expression of OTX1 in proliferative cell layers of the human fetal brain supports the concept that this homeobox gene is important in neuronal cell development and differentiation. 21478910_established that the p53 protein directly induces OTX1 expression by acting on its promoter 21750575_XPO1 and OXT1 may contribute to ASD in 2p15-p16.1 deletion cases and non-deletion cases of ASD mapping to this chromosome region. 24388989_overexpression of OTX1 results in accumulation of colorectal cancer (CRC) cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo, whereas ablation of OTX1 expression inhibits the proliferative and invasive capability of CRC cell lines 25203062_Genitalia defects in these patients could result from the effect of OTX1. 28348423_OTX1 and OTX2 genes might have a role in the pathogenesis of different types of sinonasal neoplasms. 28599093_We speculate that ACTR2 and MEIS1 might respectively play a role in the pathogenesis of the observed deafness and cardiomyopathy...the patient carrying a 2p14p15 deletion including OTX1 had normal kidneys and genitalia, thus confirming that OTX1 haploinsufficiency is not invariably associated with genitourinary defects. 30066897_High OTX1 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 30797919_The OTX1 gene was expressed in 52% of 60 Brazilian medulloblastoma patients. Expression varied with age (higher in adults), location (predominantly by hemisphere), and histological type (desmoplastic). 32325080_Long non-coding RNA HNF1A-AS1 upregulates OTX1 to enhance angiogenesis in colon cancer via the binding of transcription factor PBX3. 32419651_miR-3196 acts as a Tumor Suppressor and Predicts Survival Outcomes in Patients With Gastric Cancer. 32549762_MicroRNA-4516 suppresses pancreatic cancer development via negatively regulating orthodenticle homeobox 1. 32838760_OTX1 exerts an oncogenic role and is negatively regulated by miR129-5p in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 33015792_OTX1 is a novel regulator of proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma. 33336731_Long noncoding RNA MAFG-AS1 facilitates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting miR-3196/OTX1 axis. 34306176_miR-223-5p Suppresses OTX1 to Mediate Malignant Progression of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. 34559577_Orthodenticle homeobox OTX1 is a potential prognostic biomarker for bladder cancer. 35303522_Overexpression of OTX1 promotes tumorigenesis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35474406_Knockdown of circMYOF inhibits cell growth, metastasis, and glycolysis through miR-145-5p/OTX1 regulatory axis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 36177903_OTX1 promotes tumorigenesis and progression of cervical cancer by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000005917 |
Otx1 |
343.685771 |
0.2705444779 |
-1.886062 |
0.101314608 |
357.599854 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009380233114250779312371062105169092220876604114740127519714941689974450757836596378967574220443659759645876523092522752817014878309725136087281505879159566153140681732195040584756548189479970743537978750126171689771581441164016723632812500000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003125332748675880966152509813014258509726236866414480822588011967944426911495504644400959139704474265558275950956846974813268920924798472130255882024053641586733320046048668544828618530525188214802545516590726037975400686264038085937500000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
146.0328494 |
9.1211047 |
543.2584626 |
20.1852704 |
| ENSG00000115523 |
10578 |
GNLY |
protein_coding |
P22749 |
FUNCTION: Antimicrobial protein that kills intracellular pathogens. Active against a broad range of microbes, including Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Disulfide bond;Fungicide;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The product of this gene is a member of the saposin-like protein (SAPLIP) family and is located in the cytotoxic granules of T cells, which are released upon antigen stimulation. This protein is present in cytotoxic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells, and it has antimicrobial activity against M. tuberculosis and other organisms. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10578; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; phagocytic vesicle lumen [GO:0097013]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640] |
10644038_Peptides encoded by this gene display antimicrobial activity against S. typhimurium, L. monocytogenes, E. coli, S. aureus, C. neoformans, C. albicans, L. major, and M. tuberculosis. 11418670_This molecule activates a pathway of CTL- and NK cell-mediated death via disruption of cell and mitochondrial membranes. This is a distinct pathway from granzyme- and death receptor-induced apoptosis. 12145461_The megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line CMK, from a Down's syndromept, expressed granulysin mRNA, suggesting that GNLY is occasionally present in immature multilineage cells or may be characteristic of leukemic cells obtained from Down's syndrome pts. 12421959_Up-regulation of granulysin in primary CD8 T cells correlates with the acquisition of anticryptococcal activity, which can be blocked by specific inhibition of granulysin. 12483306_Sequence analysis of this gene do not support it as a candidate gene for familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 12488100_Data report the initial crystal structure of selenomethionyl granulysin by MAD phasing at 2A resolution. 12626573_Granulysin is detected in a granular pattern in the cytoplasm of alpha GalCer-activated NKT cells consistent with their presence within cytotoxic granules and suggests that these cells can mediate antimicrobial activity. 15223905_mRNA expression measurement of granulysin in urinary cells of renal allograft ents allows the early noninvasive detection of ongoing acute rejection. 15778384_granulysin was found exclusively in endosomal-phagosomal vesicles; lipid raft microdomains, enriched in the immunological synapse, may thus enhance uptake and transfer of granulysin into bacterial infected host cells 15843520_Granulysin not only contributes to innate immunity but also to adaptive immunity as it attracts and activates human monocytes, dendritic, natural killer (NK) and T cells. 16980658_Granulysin expression in CD8 cells seems to be correlated with steroid resistance in polymyositis 17038537_These cells use granulysin as the effector molecule, and priming is dysregulated in HIV-infected patients, which results in defective microbicidal activity 17596262_This study shows that the regulation of granulysin synthesis in response to IL-2 or bacterial antigen stimulation occurs at several levels: RNA expression, extensive alternative splicing and posttranslational processing. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18192122_Serum granulysin is elevated in patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 18490721_study found PI3K & STAT5 signaling pathways are required for granulysin expression & IL-2Rbeta induction & IL-2Rbeta induction is a prerequisite for granulysin expression; both signaling pathways are defective in CD4+ T cells from HIV-infected patients 18584314_Increased expression in pbmc and elevated serum levels correlated with the severity of primary biliary cirrhosis 18688023_granulysin is involved in spontaneous abortion. 19029983_Granulysin in the blister fluids was a 15-kDa secretory form 19106590_serum granulysin is a novel parameter of patients cancer immunity 19111751_Results demonstrate the localization and effect of intracellularly expressed granulysin on non-native cancer cells and indicate its potential utility in gene therapy for cancer. 19243819_High granulysin mrna expression is associated with systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19454696_Granulysin can target lysosomes to induce partial release of lysosomal contents into the cytosol; relocalized lysosomal cathepsin B can process Bid to active tBid to cause cytochrome c and apoptosis-activating factor release from mitochondria. 19687290_HIV-1 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells may reduce the antimicrobial profile of activated CD8+ T cells by disrupting signaling events that are critical for the induction of granulysin. 19861007_GLS/IL-12-modified Mycobacterium smegmatis as a novel anti-tuberculosis immunotherapeutic vaccine. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20660289_Both 9- and 15-kDa forms of recombinant GNLY-induced in vitro chemotaxis and activation of both human and mouse dendritic cells. 20889547_these data provide details about the complex regulation leading to granulysin expression and anticryptococcal activity in primary CD4(+) T cells. 21296981_Cytotoxic T- and natural killer (NK) cell-delivered transgenic granulysin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, activating caspase-7 and distinct apoptotic pathways in target cells. 21501511_Gene expression profiles of monocytes cultured with 15 kDa Granulysin or GM-CSF for 4, 12, 24 and 48 hours were analysed to unravel both similarities and differences between the effects of these stimulators. 21623991_All these data clearly show the abundant expression and spontaneous secretion of GNLY by decidual NK cells during first trimester pregnancy. 21819408_Granulysin is expressed at different levels in multiple cutaneous adverse drug reactions both by NKp46(+) cells and by CD8(+) T cells. 21967803_GNLY-expressing lymphocytes, probably attracted by IL-15, not only participate partially in myocardial cell apoptosis, but also hasten resolution of cardiac leukocyte infiltration in patients with myocardial infarction. 22045985_Findings suggest that Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell-mediated production of granulysin as an underestimated immune effector in malaria. 22216262_Proliferating memory T cells (CFSE(low)CD4(+)CD45RO(+)) were identified as main source of granulysin and these cells expressed both central and effector memory phenotype 22586033_recombinant 15 kDa granulysin is not cytolytic but is a potent inducer of monocytic differentiation to dendritic cells 22788687_GNLY polymorphism genotypes and diplotypes were associated with the chronicity of HBV 22890551_Granulysin is closely associated with the characteristics of NK-cell neoplasms and serum granulysin may serve as a novel biomarker for these disorders. 23399514_study to determine: expression of GNLY at the gene and protein levels at the maternal-fetal interface, relationship(s) between GNLY and perforin, and GNLY secretion by stimulated NK cells 23801887_suggested that the alteration of circulating granulysin has potential function in host immune response against TB and HIV/TB coinfection 24035442_Serum granulysin levels were significantly elevated in both acute and chronic alopecia areata patients. 24269628_It was concluded taht granulysin induces apoptosis on hematological tumor cells and on cells from B-cell lymphocytic leukemia patients, opening the door to research on its use as a new anti-tumoral treatment. 24906149_Human, but not rodent, cytotoxic granules also contain granulysin, an antimicrobial peptide in addition to granzymes; study shows that granulysin delivers granzymes into bacteria to kill diverse bacterial strains. 25644528_A three-way interaction between SNPs in HLA-DQ and GNLY was identified in terms of HBV clearance. 25921628_Carbamate pesticides significantly reduced the intracellular levels of perforin, GrA, GrB, Gr3/K, and GRN in NK-92CI cells. 26225678_High Granulysin expression is associated with Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma and Sezary Syndrome. 26314314_Studies indicate that cytotoxic mechanisms mediated by granulysin and TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand) seem to be less secondary effects on normal tissues. 26751807_serum GNLY is closely associated with the clinical characteristics of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and may be a potential biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma 26752517_GNLY delivers Gzms into three protozoan parasites (Trypanosoma cruzi, Toxoplasma gondii and Leishmania major), in which the Gzms generate superoxide and inactivate oxidative defense enzymes to kill the parasite. 27276051_These results suggest that the 15 kDa granulysin exhibits a novel mechanism in bacteria killing in a way that's different from most antimicrobial peptides. 27756230_Decreased blood granulysin at the protein level, is linked to the immunological condition of latent tuberculosis infection. 29896906_Increased seminal granulysin has a negative impact on spermatogenesis in infertile men in general and in infertility associated with varicocele in particular. 30151671_The results suggest granulysin as a novel marker for a subset of cytotoxic natural killer cell derived malignancies 30658247_These studies provide a deeper insight into the subcellular localization and release mechanisms of the individual GNLY species. 31449312_Granulysin+ cytotoxic cells are upregulated in blood and lesions of patients with psoriasis suggesting the involvement of granulysin mediated cytotoxicity in psoriasis pathogenesis. 31642954_GNLY mutation IS associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. 32066596_gammadelta T Cells Kill Plasmodium falciparum in a Granzyme- and Granulysin-Dependent Mechanism during the Late Blood Stage. 32271478_Association between seminal granulysin and malondialdehyde in infertile men with varicocele and the potential effect of varicocelectomy. 32511236_granulysin and granzyme B synergize to restore carbapenem bactericidal activity and overcome carbapenem resistance in E. coli. 32822574_Decidual NK Cells Transfer Granulysin to Selectively Kill Bacteria in Trophoblasts. 32913355_Contributions of IFN-gamma and granulysin to the clearance of Plasmodium yoelii blood stage. 32929333_Enhanced tuberculosis clearance through the combination treatment with recombinant adenovirus-mediated granulysin delivery. 33560872_The Role of IL-13, IL-15 and Granulysin in the Pathogenesis of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. 34093532_A Profound Membrane Reorganization Defines Susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum Infected Red Blood Cells to Lysis by Granulysin and Perforin. 34445098_Gran1: A Granulysin-Derived Peptide with Potent Activity against Intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 34691030_Identification of Diagnostic Signatures and Immune Cell Infiltration Characteristics in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Integrating Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine-Learning Strategies. 35066979_GNLY gene polymorphism: A potential role in understanding psoriasis pathogenesis. |
|
|
36.758530 |
7.4951631713 |
2.905960 |
0.326725353 |
91.565469 |
0.00000000000000000000107960613999771160720353806885881272399572753563250275082819815142265440499613760039210319519042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000010201655970785034736367352270824902785253661908321933069355297307723162703041452914476394653320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
66.8703375 |
13.5023971 |
9.0039719 |
1.6425329 |
| ENSG00000115541 |
3336 |
HSPE1 |
protein_coding |
P61604 |
FUNCTION: Co-chaperonin implicated in mitochondrial protein import and macromolecular assembly. Together with Hsp60, facilitates the correct folding of imported proteins. May also prevent misfolding and promote the refolding and proper assembly of unfolded polypeptides generated under stress conditions in the mitochondrial matrix (PubMed:7912672, PubMed:1346131, PubMed:11422376). The functional units of these chaperonins consist of heptameric rings of the large subunit Hsp60, which function as a back-to-back double ring. In a cyclic reaction, Hsp60 ring complexes bind one unfolded substrate protein per ring, followed by the binding of ATP and association with 2 heptameric rings of the co-chaperonin Hsp10. This leads to sequestration of the substrate protein in the inner cavity of Hsp60 where, for a certain period of time, it can fold undisturbed by other cell components. Synchronous hydrolysis of ATP in all Hsp60 subunits results in the dissociation of the chaperonin rings and the release of ADP and the folded substrate protein (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11422376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1346131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7912672, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25918392}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Chaperone;Direct protein sequencing;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Stress response |
|
This gene encodes a major heat shock protein which functions as a chaperonin. Its structure consists of a heptameric ring which binds to another heat shock protein in order to form a symmetric, functional heterodimer which enhances protein folding in an ATP-dependent manner. This gene and its co-chaperonin, HSPD1, are arranged in a head-to-head orientation on chromosome 2. Naturally occurring read-through transcription occurs between this locus and the neighboring locus MOBKL3.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:3336; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding [GO:0051085]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
11898127_Hereditary spastic paraplegia SPG13 is associated with a mutation in the gene encoding the mitochondrial chaperonin Hsp60. 12220543_The low stability of the monomeric unit suggests that folding and assembly reactions for cpn10 are coupled. 12483302_The genome structure of this gene has been established. 12703979_Cpn10 and placental lactogen are capable of stimulating the synthesis of type I collagen by human osteoblasts in culture 14525625_Identification of amino acids important for the assembly of the cpn10 heptamer. 15059967_complex mechanisms are involved in the protection by hsp10 against simulated ischemia and reoxygenation-induced myocyte death 15546885_Hsp10 exerts anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting Toll-like receptor signaling possibly by interacting with extracellular Hsp60 15590416_The HSP10 plays a role in bone marrow cell differentiation other than being a mitochondrial co-chaperonin. 15816004_Chaperonin 10 and calgranulin A are identified as markers for diagnosis and screening of endometrial carcinoma. 15978542_the cpn10 interfaces can adapt to structural alterations without loss of either subunit-subunit affinity or heptamer specificity 16100270_biophysical analysis of dissociation equilibrium for the heptameric co-chaperonin proteins 10 from Aquifex aeolicus and human mitochondria 16253146_HSP60 and HSP10 are expressed in large bowel carcinomas with lymph node metastases 16502466_proteomic analysis of possible role of heat shock protein 10 in colorectal cancer 16979655_Results describe the time-resolved folding and assembly mechanism of the heptameric co-chaperonin protein 10 (cpn10) in vitro. 17072495_Investigation of single-nucleotide variations in the Hsp10 gene and their disease-causing potential. 17278877_In this review, we revise the involvement of Hsp10 in signal transduction pathways and its possible role in cancer etiology. 17419711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18329043_Data show that Hhsp10 formed fibrils from only the acidic unfolded state and Core peptide regions of these protein fibrils were determined by proteolysis followed by a combination of Edman degradation and mass spectroscopy analyses. 18465204_The effects of cpn 10 on cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage, were assessed. 18500265_In patients with serous ovarian carcinomas, gene expression analysis coupled with immunohistochemistry allowed the identification of HSP10 as an independent factor of progression-free survival. 18987317_the GroEL-GroES chamber behaves as a passive 'Anfinsen cage' whose primary role is to prevent multimolecular association during folding. 19142874_Results describe a novel function of chaperonin 10 as a general differentiation factor, not limited to erythroid cells, and show how this biological effect is mediated by GSK-3alpha/beta. 19520060_HSP10 was identified as a new autoantigen in both autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. 19903031_HSP10 protein was detected only in oocytes from human preantral follicles, whereas in antral follicles, it was localised in oocytes, granulosa cells, theca cells and stroma cells. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21375247_Data show that that in presence of 300 mg/mL Ficoll the thermodynamic stability of each cpn10 monomer increases by over 30%, whereas the interfaces are stabilized by less than 10%. 25075042_Hsp10 and Hsp90 may be involved in large bowel carcinogenesis. 25355063_Hsp10 has a role in nuclear localization and lung cells response to cigarette smoke 26429916_Cpn10 has a role in the spatial regulation of NPAT signaling 26585937_Data indicate that on addition of the heat-shock proteins GroEL-GroES molecular chaperone system, the folding of the nascent chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) was significantly enhanced. 27491302_Hsp10 and Hsp60 may be implicated in carcinogenesis from its very early steps in colorectal cancer. 27840373_EPF induces the differentiation of regulatory T cells and increases their immunosuppressive activities. 27993580_High expression of HSP10 is negatively associated with estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor status and might be a novel independent biomarker for poor prognosis in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 28662100_miR-146a, miR-146b, and miR-155 are exerting anti-inflammatory properties by down-regulating IL-6 and IL-8, and influencing the expression of HSP10 in the activated endothelium 29028811_elevated expression of HSP10 protein inhibits apoptosis and associates with poor prognosis of astrocytoma 32060690_An inventory of interactors of the human HSP60/HSP10 chaperonin in the mitochondrial matrix space. 32317635_structural basis for active single- and double-ring complexes coexisting in the mHsp60-mHsp10 chaperonin reaction cycle 32986659_Overexpression of HSP10 correlates with HSP60 and Mcl-1 levels and predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. 34285302_Structural basis for the structural dynamics of human mitochondrial chaperonin mHsp60. |
|
|
392.057486 |
2.0521921987 |
1.037166 |
0.082733189 |
158.615348 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000227083719014760881451270676842498446408388130093480250759878425914680768461661010738987646645926227195744218079198617488145828247070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000034589842029492986180101215052563707781999550205846328253435878768830181864245082558743699281678107837478819419629871845245361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
530.5635848 |
26.4264216 |
260.4388015 |
10.1650001 |
| ENSG00000115590 |
7850 |
IL1R2 |
protein_coding |
P27930 |
FUNCTION: Non-signaling receptor for IL1A, IL1B and IL1RN. Reduces IL1B activities. Serves as a decoy receptor by competitive binding to IL1B and preventing its binding to IL1R1. Also modulates cellular response through non-signaling association with IL1RAP after binding to IL1B. IL1R2 (membrane and secreted forms) preferentially binds IL1B and poorly IL1A and IL1RN. The secreted IL1R2 recruits secreted IL1RAP with high affinity; this complex formation may be the dominant mechanism for neutralization of IL1B by secreted/soluble receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10975853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12530978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7989776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9862719}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin 1 receptor family. This protein binds interleukin alpha (IL1A), interleukin beta (IL1B), and interleukin 1 receptor, type I(IL1R1/IL1RA), and acts as a decoy receptor that inhibits the activity of its ligands. Interleukin 4 (IL4) is reported to antagonize the activity of interleukin 1 by inducing the expression and release of this cytokine. This gene and three other genes form a cytokine receptor gene cluster on chromosome 2q12. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants and protein isoforms. Alternative splicing produces both membrane-bound and soluble proteins. A soluble protein is also produced by proteolytic cleavage. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:7850; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-1 binding [GO:0019966]; interleukin-1 receptor activity [GO:0004908]; interleukin-1, type II, blocking receptor activity [GO:0004910]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 alpha production [GO:0032690]; negative regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000660]; negative regulation of protein processing [GO:0010955]; protein processing [GO:0016485] |
11804955_reduced levels of mRNA in the endometrium of women suffering from endometriosis reveals a profound defect in gene expression with reduced capability of endometrial tissue to down-regulate IL-1 activity 11846196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12356774_the unique sIL1R-II binding ability of human IL-1beta is due to a single amino acid difference compared with monkey IL-1beta 12363051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372465_findings point toward a deficiency in the mechanisms involved in the down-regulation of IL-1 actions at the systemic level and reveal soluble interleukin-1 receptor type II as a key factor involved in that process 12377932_to evaluate whether the interleukin (IL)-1 decoy receptor (R)is correlated with severity of infection in critically ill patients and reflects the activation of anti-inflammatory pathways by glucocorticoid hormones 12530978_soluble form of IL-1R AcP contributes to the antagonism of IL-1 action by the type II decoy receptor 12794127_The type II IL-1 decoy receptor acts as a scavenger of IL-1, representing a novel autoregulatory mechanism of the IL-1 system in neutrophils. 14674121_serum IL-1 alpha and IL-1 soluble receptor type 2 levels in women with ovarian cancers were significantly higher than those in cervical cancer, and in patients with benign disorders, and in healthy control 15653174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15705625_a reduced release of sIL-1RII by the endometrial tissue of women with endometriosis and revealed a proteolytic post-translational mechanism which may be involved in the down-regulation of IL-1RII levels 16596202_Increased circulating levels of interleukin 1 receptor, type II is associated with Hepatitis C virus positive patients and with those affected also by non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and cryoglobulinemia syndrome 16971486_These findings reveal that nuclear localization of pre-IL-1alpha depends on the binding to HAX-1 and that biological activities might be elicited by the binding to both HAX-1 and IL-1RII in SSc fibroblasts. 17307738_BACE1 and BACE2 may act as alternative alpha-secretase-like proteases in proteolytic processing of IL-1R2 and APP 17324958_decreased IL1R2 expression is predominant in the eutopic and ectopic endometrium of women with endometriosis when compared with normal women. 17413037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17482186_Suggest that IL-1RII can neutralize IL-1 beta and counteract its effect on endometrial stromal cells, and may provide a new clinical strategy for the treatment of endometriosis. 17517439_Abnormal interleukin 1 receptor types I and II gene expression in eutopic and ectopic endometrial tissues of women with endometriosis. 17702847_Chorionic gonadotropin down-regulates the expression of the decoy inhibitory interleukin 1 receptor type II in human endometrial epithelial cells. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17919610_Levels of interleukin-1beta and Il1R2in the peritoneal fluid of normal women and patients with endometriosis suffering from pelvic pain and infertility. 18096476_IL1R2 was greatly decreased with future rejection and FLT3, ITGAM, and PDCD1 showed borderline changes in future cardiac rejections. 18315432_was detected more often in chronic periodontitis gingival crevicular fluid than in aggressive periodontitis gingival crevicular fluid, and there was no correlation between gingival crevicular fluid concentration and clinical parameters. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19026558_Results suggest that interleukin-1 receptor type II overexpression is likely, through activation of the IL-1alpha precursor pathway, to enhance cell migration. 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401759_Alternate splicing of interleukin-1 receptor type II in vitro correlates with clinical glucocorticoid responsiveness in patients with autoimmune inner ear disease. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19489917_IL1R2 showed significant associations with Aspirin-intolerant asthma. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20062062_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20652271_ANTXR2 and IL-1R2 polymorphisms are not associated with ankylosing spondylitis in Chinese Han population. 20652271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20654748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21083841_As already reported in endometriotic cells, endometrioid ovarian cancer cells exhibit a decrease in the expression of IL-1RII. These findings highlight a common signature between endometrioid ovarian cancer and implants of endometriosis. 21683158_Results suggest that under atherogenic conditions, there is a decrease in IL-1R2 expression in monocytes/macrophages and in the vascular wall that may facilitate IL-1 signaling. 21704385_interactions between TLR4 and IL-1R2 are associated with cervical pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations. 22048455_The methylation statuses of the IL10 and IL1R2 genes were significantly reduced in the SLE patient samples relative to the healthy controls 23395675_Intracellular interleukin-1 receptor 2 binding prevents cleavage and activity of interleukin-1alpha, controlling necrosis-induced sterile inflammation. 24313836_Data indicate a significant increase in the levels of IL-8, TNF-alpha and IL-1R2 in the CSF of both meningitis groups as compared to controls, and the concentrations of IFN-gamma and IL-1 differed significantly only between the mumps group and control. 24411993_First study evaluating for associations between cytokine gene variations and the development of persistent breast pain in women following breast cancer surgery: 1 SNP (IL1R2 rs11674595) and 1 haplotype (IL10 haplotype A8) were associated with pain 24818754_A genetic susceptibility locus for AgP may lie within or close to the IL1R2 locus in Japanese aggressive periodontitis. 25432697_results suggested that IL1R2 could have oncogenic potential in osteosarcoma 25650410_Cerebrospinal fluid soluble interleukin-1 Receptor II, but not log interleukin-6, levels were positively correlated with a composite measure of aggression. 25736356_This is the first detection that the genetic variation rs2302589 in IL-1R2 gene was associated with ankylosing spondylitis in Northern Han Chinese. 25849954_Suggest IL-1R2 as potential biomarker of acute respiratory distress syndrome. 26209639_Data show that interleukin-1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) forms a complex with c-Fos proto-oncogene protein and activates the interleukin-6 (IL-6) and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) promoters. 26324711_Interleukin-1alpha Activity in Necrotic Endothelial Cells Is Controlled by Caspase-1 Cleavage of Interleukin-1 Receptor-2 26530134_these results reveal that the IL-1/IL-1R2 axis is differentially regulated in the remitting intestinal mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients 26590821_IL1R2 rs2310173 genotype GT was mildly protective against ankylosing spontylitis only in HLA-B27-negative patients. 26607028_reduced risk of preterm birth in Indian women with the minor allele of rs2072476 polymorphism 26888452_IL1R2 hypomethylation and androgen receptor hypermethylation may constitute an important determinant of disease severity, whereas NPR2 hypomethylation and SP140 hypermethylation may provide a biomarker for vulnerability to excessive daytime sleepiness in Obstructive Sleep Apnea 26967533_present study demonstrated the ability of Staphylococcus aureus to induce IL-1RII shedding in myeloid cells 27138824_No significant differences in the lymphocyte mRNA levels of IL-1R2, IL-6R, and Gp130 were observed between MDD patients and NC. These studies suggest abnormal gene expression of these cytokines and their membrane-bound receptors in the lymphocytes of MDD patients, and that their mRNA expression levels in the lymphocytes could be a useful biomarker for depression. 27461004_Data show that all the six inflammation-related CpG-SNPs genotypes including IL1B rs16944, IL1R2 rs2071008, PLA2G7 rs9395208, FAM5C rs12732361, CD40 rs1800686, and CD36 rs2065666 were associated with coronary heart disease (CHD), suggesting an important role of inflammation in the risk of CHD. 28341182_Expression level of IL1R2 was down regulated in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 29853279_Plasma levels of soluble IL-1R2 are independently associated with parameters of left ventricular adverse remodeling following ST-elevation myocardial infarction. 29901123_The expression of SLC22A4, IL1R2 and VNN3, were independently associated with elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in chronic heart failure patients. 30256493_Data indicate the association between genetic polymorphisms of interleukin 1 receptor type 1 (IL1R1) and interleukin 1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) and tuberculosis (TB) susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. IL1R1 and IL1R2 and TB susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 30460760_IL1R2 SNPs rs719250 and rs3218896 are significantly associated with cervical cancer risk among Uygur females from China. 30623603_rs11674595 was significantly associated with the risk of femur head osteonecrosis in the Chinese Han population. 30672138_rs2072472 was significantly associated with a 0.73-fold decreased risk of high-altitude pulmonary edema. 30895747_rs3218977-GG was associated with a decreased risk of lung cancer in Chinese population. rs2072472 had a significant risk-increasing effect in the dominant model. 30895748_Two SNPs (rs4851527 and rs3218896) and haplotypes TGTC and TACT were significantly associated with endometrial cancer risk in Chinese population. 31021479_our data suggest that rs3917225 in IL1R1 , rs2072472 and rs11674595 in IL1R2 were potential risk markers associated with thyroid cancer risk in the Chinese Han population. Our findings provided new insights into the roles of IL1R1 and IL1R2 and the etiology of thyroid carcinoma. 31744444_IL1R2 Polymorphisms are Associated with Increased Risk of Esophageal Cancer. 32252823_The association of genetic polymorphisms in interleukin-1 receptors type 1 and type 2 with age-related hearing impairment in a Taiwanese population: a case control study. 32402117_Association of IL1R2 rs34043159 with sporadic Alzheimer's disease in southern Han Chinese. 32447774_Cell surface IL-1alpha trafficking is specifically inhibited by interferon-gamma, and associates with the membrane via IL-1R2 and GPI anchors. 32727543_Platelet concentrate and type II IL-1 receptor are risk factors for allergic transfusion reactions in children. 33057899_LncRNA A2M-AS1 lessens the injury of cardiomyocytes caused by hypoxia and reoxygenation via regulating IL1R2. 33507149_Induction of the IL-1RII decoy receptor by NFAT/FOXP3 blocks IL-1beta-dependent response of Th17 cells. 33704402_IL-1R2 expression in human gastric cancer and its clinical significance. 33809042_Cytokine Signature of Dengue Patients at Different Severity of the Disease. 34244037_Association of ITPKB, IL1R2 and COQ7 with Parkinson's disease in Taiwan. 34636689_Influence of Sociodemographic Characteristics and Inflammation-Related Gene Variants on the Comfort Level of Caregivers of Patients With Head and Neck Cancer. 34664761_IL1R2 polymorphisms and their interaction are associated with osteoporosis susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 34865658_The association of genetic polymorphisms in interleukin-1 receptors type 1 and type 2 with sudden sensorineural hearing loss in a Taiwanese population: a case control study. 35087030_Cardiomyocyte IL-1R2 protects heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating IL-17RA-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. 35943312_Over-expression of IL1R2 in PBMCs of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Its Clinical Significance. |
ENSMUSG00000026073 |
Il1r2 |
41.876892 |
132.1684645031 |
7.046234 |
0.975801783 |
195.767423 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000001751955996260107731814458174334550261469247341413382930494310955026679882456260761671262980863089768207999139361993184982324578413681592792272567749023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000324452578479287173625064374168710694539821776653986736993799736376887533274814312587473026457038038489985473612417510302918799425242468714714050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
93.0894476 |
66.5264427 |
0.7063529 |
0.5020656 |
| ENSG00000115594 |
3554 |
IL1R1 |
protein_coding |
P14778 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for IL1A, IL1B and IL1RN (PubMed:2950091). After binding to interleukin-1 associates with the coreceptor IL1RAP to form the high affinity interleukin-1 receptor complex which mediates interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-kappa-B, MAPK and other pathways. Signaling involves the recruitment of adapter molecules such as TOLLIP, MYD88, and IRAK1 or IRAK2 via the respective TIR domains of the receptor/coreceptor subunits. Binds ligands with comparable affinity and binding of antagonist IL1RN prevents association with IL1RAP to form a signaling complex. Involved in IL1B-mediated costimulation of IFNG production from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells (PubMed:10653850). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10653850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10671496, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2950091}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Membrane;NAD;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin-1 receptor family. The encoded protein is a receptor for interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. It is an important mediator involved in many cytokine-induced immune and inflammatory responses. This gene is located in a cluster of related cytokine receptor genes on chromosome 2q12. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:3554; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-1 binding [GO:0019966]; interleukin-1 receptor activity [GO:0004908]; interleukin-1, type I, activating receptor activity [GO:0004909]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; positive regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000661]; positive regulation of neutrophil extravasation [GO:2000391]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell cytokine production [GO:2000556]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555] |
11040178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11083263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11127457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11197691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11220627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11380474_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11380940_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11390630_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11427627_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11506478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11508575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11527622_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11578018_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11665666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11742191_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11752505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11762793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11790645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11820460_Heparins (unfractionated heparin, UFH and low molecular weight heparin certoparin) had no effect on the release of IL-1ra, IL-10, and IL-12p40 from neutrophils or peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 11838837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11846196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11849463_Carriage of IL1beta and IL1RN*2, together with non-carriage of TNF2 is associated with increased susceptibility, but not with a prognosis of IgAN. 11849463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11851889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11956022_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12028539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12038885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12095061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12133437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12136897_Carriage of ILRN*2 alleles influences disease severity rather than susceptibility. 12138282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12145738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12212456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12240899_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12363051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12412204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12424621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12425801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12472674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12477576_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12558814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12595908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12729621_IL-1 receptor has a role in the pathway linking static compression to reduced proteoglycan synthesis 12752101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12804791_A decrease in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist expression in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic patients. 12890860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14557872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14563376_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14644395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14680589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14734209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14735144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14758530_high allele frequency of the IL1RN*2 allele may affect disease susceptibility in childhood nephrotic syndrome 14872281_IL-1RA gene polymorphism is not responsible for specific clinical characteristics in RA and SLE but that IL-1RN*2 is relevant in the susceptibility to RA. 14872281_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15170937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15188516_There is an association between polymorphisms of the promoter region -511C/T of IL-1B and IL-1RN intron 2 and chronic hepatitis B virus infection 15190266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15300624_Sixteen SNPs were identified through a 9643 bp sequencing of IL-1R1 gene. Four were in 5' flank region, four in intron region, one in coding region, and seven in 3' untranslated region. 15361128_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15375600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15388348_Data show that Exip, but not p38alpha, binds to Toll interacting protein, which is involved in interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling pathway, and impaired NF-kappaB activity. 15472211_the dysregulation of IL-1/IL-1-R system relates to immunological dysfunction in endometriosis 15481335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15653174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15723707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15789892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15797878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15866876_SIGIRR inhibits IL-1R and TLR4-mediated signaling through different mechanisms 15919456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16258158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16258158_Our findings indicate that the VDR FokI polymorphism and several VDR and IL-1-R1 haplotypes are associated with susceptibility to T1DM in the Dalmatian population. 16301860_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 16305343_data describe percentage of bone marrow cells expressing receptors for interleukin-1, platelet-derived growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, transforming growth factor-beta, epidermal growth factor and c-Fos and c-Myc in untreated lung & breast cancer 16323614_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16354686_Rac1 facilitated the recruitment of Nox2 into the endosomal compartment and subsequent redox-dependent recruitment of TRAF6 to the MyD88/IL-1R1 complex. 16564702_icIL-1ra1 does not act at an intracellular level to alter IL-1 mediated signalling, and is effective in inhibiting IL-1 responses only when released in an ATP-dependent and cell type specific manner 16573560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16911713_Distributions of single-base polymorphisms of the human IL-1RI gene were evaluated and a C-->A transition in exon 1C showed protective effect against endometriosis in heterozygotes. 16911713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16937503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16938461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17083033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17257312_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17324958_Our study showed an imbalance in the expression of IL1R1 and IL1R2 in eutopic, and particularly in ectopic, endometrial tissues of women with endometriosis 17413037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17477815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17480058_Conformational stability of rhIL1ra was monitored by equilibrium urea denaturation, and thermodynamic parameters of unfolding; conformational stability, monitored using the Cm value, has an effect on oxidation rates of buried methionines 17517439_Abnormal interleukin 1 receptor types I and II gene expression in eutopic and ectopic endometrial tissues of women with endometriosis. 17584583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17607501_rheumatic heart disease cases showed a significantly higher frequency of homozygous genotypes of IL-1Ra A1/A1. Cases with mitral valve disease showed higher frequencies of genotype IL-1Ra(VNTR) A1/A1. 17622942_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17627763_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17688691_This study shows an increase in gene and protein production for the IL-1 receptor type I in degenerate intervertebral discs. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17889143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18052726_results showed that there was a gender difference in IL-1Ra gene polymorphism expressed by a higher incidence of IL1RN*1/IL1RN*1 homozygotes and a lower occurrence of IL1RN*1/IL1RN*2 heterozygotes in men compared with women 18321953_The expression of the IL-1 receptor, a known regulator of SREBP-2, was also elevated after exercise. 18322311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18484169_polymorphism is not associated with the presence of pulmonary aspergillosis infection; but in combination with IL1a and IL1b genotypes may predict disease susceptibility 18576303_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18624935_Mild or intensive immunoreactivity for IL-1RI was observed in the epithelial cells in all cases, and in the endothelial cells and fibroblasts in five cases of keratocystic odontogenic tumors. 18632425_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18763028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18773331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18810365_IL-6 and IL-1Ra polymorphisms can be considered genetic markers for bronchial asthma susceptibility and/or severity among Egyptian children. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18996842_TRAF6 and interleukin receptor-associated kinase 2 are novel binding partners for PS1, and IL-1R1 is a new substrate for presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase cleavage 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19076825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19117745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19142372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19211154_Long-term, but not short-term memory is impaired in a transgenic mouse strain overexpressing human soluble interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) in the brain. 19232518_These results indicate that TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination of IL-1R1 has a decisive role in IL-1R1 signalling and propose a molecular mechanism whereby TRAF6 promotes ubiquitination and RIP of IL-1R1 through its ubiquitin ligase activity. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19290009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19408823_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19428986_IL-1ra was expressed within the length of the human fallopian tube only in menstrual cycle secretory phase and in the intraauterine pregnancies samples 19431193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19470040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19488045_This study indicated that statistically significant higher protein and mRNA levels of the il1r in frontal corte in bipolar disorder. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19594368_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19683555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19684156_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19702713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19702713_This the first study to show a positive correlation between polymorphisms in the IL-1alpha and IL-1RA genes and susceptibility to Graves' ophthalmopathy. 19716405_DSCR1-1S isoform positively modulates IL-1R-mediated signaling pathways by regulating Tollip/IRAK-1/TRAF6 complex formation. 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19738620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773451_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19801678_Data show that Nox2 and IL-1R1 localize to plasma membrane lipid rafts in the unstimulated state and that IL-1beta signals caveolin-1-dependent endocytosis of both proteins into the redoxosome. 19819943_Data show that activation of TLR2 in purified human beta-cells and islets stimulated the expression of proinflammatory factors, and IL-1RI activity increased the TLR2 response in human islets. 19822442_Data suggest that in the Brazilian population, the polymorphism of the IL-1ra gene is a relevant factor for rheumatic heart disease severity. 19844779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19860911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940113_Data suggest that TILRR is an IL-1RI co-receptor, which associates with the signaling receptor complex to enhance recruitment of MyD88 and control Ras-dependent amplification of NF-kappaB and inflammatory responses. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19950169_Data demonstrate that PKC-alpha is induced by several MyD88-dependent TLR/IL-1R ligands and regulates cytokine expression in human and murine DC. 19965648_Human Th17 cell differentiation is regulated via differential expression of IL-1RI, which is controlled by IL-7 and IL-15. 20066156_findings that human Tregs preferentially express receptors for TNF and IL-1 suggest a potential function in sensing and dampening local inflammation 20120526_No significant association of IL1R1 with retinopathy or nephropathy in Croatian patients with type I diabetes 20120526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20213229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20349753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353565_An association between severe hand osteoarthritis and IL1R1 gene. 20353565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20523065_Serum levels of ECP, IL-5, -6, -8 and -10, G-CSF, MCP-1, IL-1 ra and IP-10 were significantly elevated in acute compared with stable childhhood asthma. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603050_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20709104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20799037_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20806065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20811626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20818961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20956022_No association was found between recurrent spontaneous abortion and gene polymorphisms in the interleukin-1 receptor 1 gene. 20956022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21083841_IL-1RI expression was not altered in endometrioid carcinoma cells in comparison with endometrial cells, clear-cells, serous and mucinous ovarian cancer cells. 21086908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21281963_IL1RL1 polymorphisms are associated with serum IL1RL1-a, blood eosinophils, and asthma in childhood 21435443_Interleukin-1 receptor-mediated inflammation impairs the heat shock response of human mesothelial cells 21787753_This study found for the first time an epigallocatechin gallate-induced downregulation of the IL-1RI expression possibly being caused by NF-kappaB inhibition. 21858107_Data sshow that variants in SFTPD, CD46 and IL1R1 are associated with IPD in both EA and AA. 21998454_IL-1RI expression in regulatory T (Treg)cells identifies a subpopulation at an early stage of differentiation. 22031183_regulates S100A8/A9-dependent keratinocyte resistance to bacterial invasion 22173128_Data suggest that c-kit is an important regulator of IL-1 receptor 1/IL-1beta signaling and effector functions in mast cells; such signaling is IL-relevant for IL-6 release. 22262840_a role for TILRR in selective amplification of NF-kappaB responses through IL-1RI and suggest that the specificity is determined by changes in receptor conformation and adapter protein recruitment. 22267087_the LCAP related changes in sIL-1RI and IL-1Ra might impact the clinical outcome during treatment with an LCAP filter in patients with inflammatory bowel disease 22285486_data demonstrated that IL-1R polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis 22385245_findings demonstrate that neutrophils express IL-1R1 and that IL-1R1 is induced following extravasation and exists in a mobile intracellular compartment 22417897_No sufficient evidence was available to support any associations between IL1-Ra and IL6-147G/C polymorphisms and ischemic stroke. 22426547_The study presents the crystal structure of IL-1beta bound to its primary receptor IL-1RI and its receptor accessory protein IL-1RAcP. 22435759_Analysis of the data suggested that IL-1R1 expression in the neonatal period provides an additional level of Myd88-dependent signaling during this period of heighted susceptibility to infection. 22509941_The IL-1R1 1498T>C polymorphism is associated with early-stage endometriosis in Korean women. 22515947_This study demonistrated that Carriers of the minor allele for a single nucleotide polymorphism in interleukin (IL)1-receptor 1 (IL1R1) (rs2110726) were less likely to report breast pain prior to surgery 22574108_a genetic link between rs1921622 IL1RL1 polymorphism and disease severity in RSV bronchiolitis 22594576_The IL1R1 promoter SNP rs2192752 may contribute to the location of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), and the C allele of rs2192752 may be a risk factor for the development of PTC in both lobes. 23022958_The internalization of IL1RI after IL-1 binding is not a mechanism of feedback inhibition but of critical importance for the IL-1-induced gene expression. 23253688_genetic polymorphism is associated with atopic dermatitis in Iranian pediatric population 23375040_T allele of the 511 site of IL-1beta gene and V allele of the second introne of IL-1Ra gene are associated with the infertility occurrence of polycystic ovary syndrome patients 23407395_These results demonstrate that IL-1alpha and IL-1R1 signaling is essential for microabscess formation, neutrophil recruiting chemokine expression, and acanthosis in psoriasis-like skin inflammation induced by imiquimod. 23634226_Common IL-33 and IL1RL1 polymorphisms contribute to the risk of inflammatory bowel disease 23722873_The frequency of the IL-1RN rs315952 CT genotype was significantly lower among patients with systemic lupus erythematosus compared with healthy controls 24080160_These results provide evidence for a key role of Rac1 in a pathway that regulates IL-1-induced gene expression depending on receptor endocytosis. 24315345_). Findings provide evidence of subgroups of women with breast cancer who report distinct trajectories of attentional function and of a genetic association between subgroup membership and an IL1R1 promoter polymorphism. 24328419_Only the IL1RN tandem repeats polymorphism may be associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis susceptibility; TSHR and IL1RN polymorphisms may represent prognostic factors for predicting the severity of the disease. 24356554_No significant differences are detected in the Fcgamma-RIIa and IL1-Ra polymorphisms compared to controls in a study to search for associations between antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis and IL1R1 polymorphisms. 24458711_IL1R1- and IL1beta-related transcripts are elevated in the setting of obesity; IL1R1/IL1beta augment both megakaryocyte and platelet functions, promoting a prothrombotic environment during infection and obesity; potentially contributing to the development of atherothrombotic disease 24818754_Thirty-eight single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified within genomic regions containing all exons and relevant exon-intron boundaries in IL1R1 and IL1R2 in japanese aggressive periodontitis. 24842757_results demonstrate clear functional consequences of the rs917997 risk polymorphism; this polymorphism leads to a loss-of-function through decreased IL-18RAP, IL-18R1, and IL-1R1 protein expression, which impairs autocrine IL-18 and IL-1 signaling 24976267_IL-1 receptor gene polymorphisms could be one of the factors influencing the expression of membrane-bound IL-1 receptors on immunocompetent cells. 24988285_the NLRP3 inflammasome/IL-1RI axis is dispensable for PM10-facilitated allergic sensitization. 25014791_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in RBPJ, IL1R1, REV3L, TRAF3IP2, IRF1 and ICOS showed association with rheumatoid arthritis in black South Africans. 25108563_FcgammaRIIa cross-talk with TLRs, IL-1R, and IFNgammaR selectively modulates cytokine production in human myeloid cells. 25240697_severe forms of pancreatitis are associated with increased levels of IL-6, IL-10 and IL-1ra 25425640_SUMOylation is a novel mechanism in the regulation of beta-arrestin 2-mediated IL-1R/TRAF6 signaling 25453823_Blood monocytes from renal cell carcinoma patients displayed a tumor-promoting transcriptional profile that supported functions like angiogenesis and invasion. Induction of this protumor phenotype required an interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)-dependent mechanism. 25697140_TNF-alpha (-308) GG, IL-10 (-819) TT, IL-10 (-1082) GG and IL1R (+1970) CC genotypes are found to be predominant (p=0.01, p=0.02, p=0.0001 and p=0.001, respectively) in both tuberculoid as well as lepromatous leprosy patients. 25749018_This study found that the mRNA expression of IL-1R1, TNFR1, and TNFR2 was significantly higher in schizophreina 26076982_IL-1R1 expression appears to define a tissue regulatory T cell phenotype together with the expression of CD25, glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor family-related gene and CTLA-4. 26098632_investigated the association between four inflammatory cytokines (CD121a, interleukin [IL]-1beta, IL-8, and IL-11) and coronary heart disease 26279140_The results present identification of critical regions within the TIR domain of IL-1 receptor type in humans and mice. 26560040_Altered expression of EP2 in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease contributes to deficient induction of IL-1RI, reducing the capacity of IL-1beta to increase COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression, which results in low PGE2 production 26590148_salt-inducible kinase inhibition decreases proinflammatory cytokines in human myeloid cells upon IL-1R stimulation. 26902320_The work identifies a pathogenic role of postnatal IL1b/IL-1R1 pathway and subsequent prolonged prominent increase of endocannabinoid signaling in adult seizure susceptibility following prolonged febrile seizures, and highlights IL-1R1 as a potential therapeutic target for preventing the development of epilepsy after infantile febrile seizures. 26975823_IL1R1 SNP rs949963 is associated with the susceptibility to asthma in children from Central China and may increase the serum expression of IL1R1. 27072893_ligand-activation of GPER generates a feedforward loop coupling IL1beta induction by CAFs to IL1R1 expression by cancer cells, promoting the up-regulation of IL1beta/IL1R1 target genes such as PTGES, COX2, RAGE and ABCG2 27327966_the IL-1 receptor is translocated to lipid rafts where receptor endocytosis occurs to enable the internalization-dependent IL-1 signaling to activate the IL-1-induced gene expression. 27418552_interleukin-1 receptor 1/MyD88 signalling has roles in the development and progression of pulmonary hypertension 27717726_this study shows that IL-1a gene variants are not associated with susceptibility to juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Iranian population 27980229_Study highlights the association of genetic polymorphisms of IL1R1 with knee osteoarthritis susceptibility in the Northwestern Chinese Han population. 28027994_study confirmed that genetic variant in IL-1R1(rs3917267) has significant association with HBV infection and HBV breakthrough infection in children, which provides new clues for the study of pathogenesis of chronic HBV infection in children 28164491_Serum ST2 is elevated in heart failure patients and correlated with disease severity. 28659487_Since mumps virus SH coimmunoprecipitated with tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1), RIP1, and IRAK1, we hypothesize that SH exerts its NF-kappaB activation inhibitory function by interacting with TNFR1, interleukin-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1), and TLR3 complexes in the plasma membrane of infected cells. 29103994_this study shows that sputum cell IL-1 receptor expression level is a marker of airway neutrophilia and airflow obstruction in asthmatic patients 29284683_The finding that the informative microsatellite marker within intron 1 of IL1R detects a survival advantage for patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), revealed through a transmission disequilibrium in patient cohorts with a survivor-dependent recruitment bias, supports involvement of IL-1R in CF pathogenesis. 29548280_Two miRNAs, hsa-miR-205-3p and hsa-miR-3909 and their target genes IL-1beta and IL1R1 are specifically involved in the progression of rheumatic heart disease. 30093707_IL-1R signaling licenses effector cytokine production by memory CD4 T cells 30120937_the IL-1beta-IL-1R signaling pathway may contribute to skin inflammation and psoriasis pathogenesis via the direct regulation of dermal IL-17-producing cells and stimulation of keratinocytes for amplifying inflammatory cascade. 30256493_Data indicate the association between genetic polymorphisms of interleukin 1 receptor type 1 (IL1R1) and interleukin 1 receptor type 2 (IL1R2) and tuberculosis (TB) susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. IL1R1 and IL1R2 and TB susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 30623603_rs10490571 and rs3917225 were significantly associated with the risk of femur head osteonecrosis in the Chinese Han population. 31021479_our data suggest that rs3917225 in IL1R1 , rs2072472 and rs11674595 in IL1R2 were potential risk markers associated with thyroid cancer risk in the Chinese Han population. Our findings provided new insights into the roles of IL1R1 and IL1R2 and the etiology of thyroid carcinoma. 31104063_The mutant homozygous genotype in codominant model (AA versus GG, OR=2.37, 95% CI: 1.08-5.21, P=0.001) and in recessive model (AA versus GG/GA, OR=2.82, 95% CI: 1.30-6.12, P=0.005) of rs956730 were associated with an increased LDH risk in males, while rs956730 heterozygous genotype under codominant model (AG versus GG, OR=0.65, 95% CI: 0.46-0.92, P=0.001) was a protective genotype in males. 31317192_GAG positioning on IL-1RI; A mechanism regulated by dual effect of glycosylation 31476928_Methylation of Specific CpG Sites in IL-1beta and IL1R1 Genes is Affected by Hyperglycaemia in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. 32252823_The association of genetic polymorphisms in interleukin-1 receptors type 1 and type 2 with age-related hearing impairment in a Taiwanese population: a case control study. 32573694_Neuronal interleukin-1 receptors mediate pain in chronic inflammatory diseases. 32628975_Impact of IL1R1 polymorphisms on the risk of head and neck cancer in Chinese Han population. 32707076_Increased Expression of Interleukin-1 Receptor Characterizes Anti-estrogen-Resistant ALDH(+) Breast Cancer Stem Cells. 32739831_The effect of IL-1R1 and IL-1RN polymorphisms on osteoporosis predisposition in a Chinese Han population. 32778144_The IL1beta-IL1R signaling is involved in the stimulatory effects triggered by hypoxia in breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). 33956941_MyD88 oligomer size functions as a physical threshold to trigger IL1R Myddosome signaling. 34156282_Immune-related genes LAMA2 and IL1R1 correlate with tumor sites and predict poor survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 34159887_Association between the IL-1A, IL-1B and IL-1R polymorphisms and lymphoma. 34647846_IL-1R1 rs6755229 polymorphism is related to death in patients undergoing major surgery who develop septic shock: a retrospective study. 34865658_The association of genetic polymorphisms in interleukin-1 receptors type 1 and type 2 with sudden sensorineural hearing loss in a Taiwanese population: a case control study. 34923425_Association of IL1R1 gene (SNP rs2071374) with the risk of preeclampsia. 34995730_Expression of obesity- and type-2 diabetes-associated genes in omental adipose tissue of individuals with obesity. 35143941_IL1R1 gene variants associate with disease susceptibility to IgG4-related periaortitis/periarteritis in IgG4-related disease. 35460250_Expression-based Genome-wide Association Study Links OPN and IL1-RA With Newly Diagnosed Type 1 Diabetes in Children. |
ENSMUSG00000026072 |
Il1r1 |
127.513904 |
9.3834196704 |
3.230114 |
0.207461900 |
266.687312 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000598289573306635657132652246320861364153041372170796030345048896714854694937709208326167445311341418249509020437777162228731140192247813115424978581882026196225865533051546663045883178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000153045998301662775928043612645642979846834284131379836671794597995863939210548332579393074513686003060689943329377042054160579007368241187096870965442252376931264734594151377677917480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
234.4492042 |
29.5598590 |
25.2229527 |
2.8336560 |
| ENSG00000115596 |
7475 |
WNT6 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6F9 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for members of the frizzled family of seven transmembrane receptors. Probable developmental protein. May be a signaling molecule which affects the development of discrete regions of tissues. Is likely to signal over only few cell diameters. Together with CAV1 may promote chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells to DNA-damaging anthracycline drugs through the activation of the canonical Wnt receptor signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22370641}. |
Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It is overexpressed in cervical cancer cell line and strongly coexpressed with another family member, WNT10A, in colorectal cancer cell line. The gene overexpression may play key roles in carcinogenesis. This gene and the WNT10A gene are clustered in the chromosome 2q35 region. The protein encoded by this gene is 97% identical to the mouse Wnt6 protein at the amino acid level. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7475; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; axis specification [GO:0009798]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cornea development in camera-type eye [GO:0061303]; epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling [GO:0060684]; nephron tubule formation [GO:0072079]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of tooth mineralization [GO:0070172] |
16953426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20113781_Wnt6 plays an important role in tooth development by promoting human dental papilla cell differentiation, without significant effects on cell proliferation. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21547848_The WNT6 rs6747776 homozygous minor allele (CC) was associated with increased risk of colorectal adenoma. 22370641_WNT6 and Cav1 are upregulated by chemotherapeutics and enhance the resistance of GC cells to anthracycline drugs 24935540_WNT6 activates the JNK signaling pathway in HDPCs, leading to migration and differentiation. 25750203_analysis of missense mutation in WNT6 in couples with unexplained recurrent miscarriage 26617869_our results support the concept that WNT6 may play a role in tumor progression 30279739_The authors show that WNT6 is significantly overexpressed in glioblastoma, as compared to lower-grade gliomas and normal brain, at mRNA and protein levels. Functionally, WNT6 increases typical oncogenic activities in glioblastoma cells, including viability, proliferation, glioma stem cell capacity, invasion, migration, and resistance to temozolomide chemotherapy. 30431574_WNT6 may be a diagnostic and prognostic marker in osteosarcoma 30535429_Study results indicated that PLAGL2 was overexpressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) as a protooncogene and that it could active the Wnt/betacatenin pathway as a transcription factor by binding with the promoter region of Wnt6. 31618077_Secreted Wnt6 binds to FZD4 to activate the canonical Wnt6 signaling pathway, which is upstream of ROCK1 and 14-3-3sigma, and that this is the cell signaling pathway underlying diabetes-associated centrosome amplification. 31923345_A novel molecular link between HOXA9 and WNT6 in glioblastoma identifies a subgroup of patients with particular poor prognosis. 32572884_MiR-566 protects the malignant progression of breast cancer by negatively regulating WNT6. 34686698_Wnt6 plays a complex role in maintaining human limbal stem/progenitor cells. 35300692_Wnt4, Wnt6 and beta-catenin expression in human placental tissue - is there a link with first trimester miscarriage? Results from a pilot study. 35691114_The glycoprotein Wnt6 regulates human dental papilla cells differentiation by canonical Wnt signaling pathway. 36075327_WNT6 participates in the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer by upregulating/activating the typical Wnt pathway and Notch1 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000033227 |
Wnt6 |
38.044560 |
0.4985332773 |
-1.004238 |
0.275023137 |
13.481082 |
0.00024098081917959187649679042575456833219504915177822113037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000623357324060773930994583391651531201205216348171234130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.9663451 |
4.7698336 |
52.5019148 |
6.4142454 |
| ENSG00000115604 |
8809 |
IL18R1 |
protein_coding |
Q13478 |
FUNCTION: Within the IL18 receptor complex, responsible for the binding of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL18, but not IL1A nor IL1B (PubMed:8626725, PubMed:14528293, PubMed:25261253, PubMed:25500532). Involved in IL18-mediated IFNG synthesis from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells (PubMed:10653850). Contributes to IL18-induced cytokine production, either independently of SLC12A3, or as a complex with SLC12A3 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10653850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14528293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25261253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25500532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8626725}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Membrane;NAD;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine receptor that belongs to the interleukin 1 receptor family. This receptor specifically binds interleukin 18 (IL18), and is essential for IL18 mediated signal transduction. IFN-alpha and IL12 are reported to induce the expression of this receptor in NK and T cells. This gene along with four other members of the interleukin 1 receptor family, including IL1R2, IL1R1, ILRL2 (IL-1Rrp2), and IL1RL1 (T1/ST2), form a gene cluster on chromosome 2q. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:8809; |
interleukin-18 receptor complex [GO:0045092]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-1 receptor activity [GO:0004908]; interleukin-18 binding [GO:0042007]; interleukin-18 receptor activity [GO:0042008]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-18-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0035655]; natural killer cell activation [GO:0030101]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0038061]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell cytokine production [GO:2000556]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045063] |
14662834_Expression of the IL-18 receptor is demonstrated on dendritic cells (DC) in peripheral blood and epidermis; on monocyte-derived DC its expression is up-regulated by interferon-gamma. 14662859_The biologically active IL-8R complex requires the membrane-proximal third immunoglobulin-like domain in IL-18Ralpha for formation of IL-18R ternary complex as well as for signaling involved in IL-18-induced interferon-gamma in natural killer cells. 14734551_IL-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP in Jurkat cells. 15009178_the promoter region of IL-18 receptor has two novel single nucleotide polymorphisms 15044087_Thus, our results identified a functional region in the IL-1R AcP required for the recruitment and activation of PI 3-kinase. 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15202785_Transfection of C33A cervical cancer cells with the IL-18 receptor induced IL-18 expression, and enhanced intracellular reactive oxygen species and Fas expression. 15323361_review of structure, function and tissue distribution of IL-18R [review] 15760905_IL-18, IL-18 receptor alpha, and CD48 complex formation via glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor glycan triggers binding to IL-18 receptor beta, and thereby induces intracellular signal transduction and IFN-gamma production. 16043644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16236915_The overexpression of IL-18Ralpha predominantly by CD4+ T cells in sarcoidosis emphasizes crucial roles played by T-helper type 1 cells in the IL-18/IL-18Ralpha system in sarcoidosis 16467876_Two IFN-gammaR2 chains interact through species-specific determinants in their extracellular domains. Finally, these determinants also participate in the interaction of IFN-gammaR2 with IFN-gammaR1. 16971411_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16979683_our data show that variola virus IL-18BP prevents IL-18 from binding to IL-18R by interacting with three residues that are part of the binding site for hIL-18Ralpha. 17403771_A twofold increase in the percentage of CD4-resting T cells expressing IL-12Rbeta1 and IL-18Ralpha from HIV-1-infected patients; deregulation of the IL-12 and IL-18 pathways may play a role in the immunopathogenesis of HIV-1 infection. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18382474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18382474_There is a significant association between polymorphisms of interleukin 18 receptor 1 and asthma. 18715339_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18774397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774397_study provides suggestive evidence for associations of SNPs in the IL1RL1 gene and adjacently located family members IL18R1 and IL18RAP with asthma and atopy in 2 independent Dutch asthma populations 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19249008_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19394601_Interleukin-18 receptor expression may possibly be responsible for the pathologic process of adenomyosis. 19473509_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19473509_Our analysis suggests that the variability of IL18R1 genes is unlikely to contribute to modulate the risk of cardiovascular disease 19592492_a role for SOCS1 and -3 in the seemingly paradoxical hyperresponsive state in cells deficient in IL-18Ralpha, supporting the concept that IL-18Ralpha participates in both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879772_These results demonstrate how IL-18 activity is regulated by TNFalpha and TGF-beta1, and how IFNgamma production through regulation of IL-18 receptor and T-bet expression. 19910030_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19954659_The levels of plasma IL-18 and IL-18R on CD3(+) lymphocytes were significantly increased in active phase immune thrombocytopenia than in remission phase and controls. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354066_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354066_Report increased expression of IL18R1 in multiple sclerosis but did not find evidence of a genetic association with SNPs. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627039_IL-18 and IL-18Ralpha might upregulate the expression of Th1-cytokines in immune thrombocytopenia patients. 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20833839_These data suggest a role for IL-1F family members in psoriasis. 20860503_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21435242_The soluble IL-18Ralpha complex could be a potentially useful biomarker for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis 21742843_IL18 and IL18R1 genes as plausible genes regulating the humoral immune response to smallpox vaccine in both Caucasians and African Americans. 21965503_IL18 and its receptor may play an important role in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma. 22136483_Genetic variation in the promoter region of IL18, but not IL18R1, may be associated with knee osteoarthritis. 22289858_Data suggest that IL-18RAP and IL-18R1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms identify African-American infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 23103228_Our study reveals the important role of IL12/IL18-mediated transcriptional regulation of IFN-gamma production in leprosy. 23901078_Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms in the IL18R1, IL18 and interferon-gamma genes and smallpox vaccine induced adaptive immunity. 23963474_increased levels of soluble IL-18Ralpha complex in serum may also exert an antagonistic effect in vivo and play an important role in the inflammatory process in allergic asthma. 24842757_results demonstrate clear functional consequences of the rs917997 risk polymorphism; this polymorphism leads to a loss-of-function through decreased IL-18RAP, IL-18R1, and IL-1R1 protein expression, which impairs autocrine IL-18 and IL-1 signaling 24909718_There was no association between the rs917997 in IL18R gene and rs187238 in IL18 gene polymorphisms and risk for non-Hodgkin's malignant lymphomas in Novosibirsk population. 24963217_IL-18, IL-18BP, and IL-18R may have roles in the pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian carcinoma 25170117_IL-18R downregulates IFN-alpha production by activation-induced splicing of IL-18Ralpha into 2 isoforms: the full-length receptor (IL-18Ralpha1) and a novel, truncated variant (IL-18Ralpha2), a competitive molecular decoy inhibiting canonical IL-18Ralpha1/IL-18Rbeta signaling. 25261253_structural basis for the specific recognition of IL-18 by its alpha receptor 25269704_Human memory IL-18Ralpha and DR3 CD4+ T cells may contribute to antigen-independent innate responses at barrier surfaces. 25327457_PDGFB and IL18R1 represent plausible candidates for studying the pathophysiology of these disorders in the context of TLR4 activation 25360588_polymorphisms in the interleukin 18 receptor 1 gene and tuberculosis susceptibility among Chinese 25500532_The architecture of the IL-18 receptor second domain (D2) is unique among the other IL-1R family members, which presumably distinguishes them from the IL-1 receptors that exhibit a more promiscuous ligand recognition mode. 25729923_IL-37 requires the receptors IL-18Ralpha and IL-1R8 to carry out its multifaceted anti-inflammatory program upon innate signal transduction. 26561030_strong evidence that IL-18 and IL18Ralpha have important functions in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma 26566691_some SNPs of ST2-IL18R1-IL18RAP gene cluster might increase the risk of susceptibility of Graves' disease (GD) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) in Chinese Han population. 26600055_IL-18 and IL-18R polymorphisms may contribute to the development and lymph node metastasis of PTC. 26736035_IL18R1 rs1035130 may be associated with schizophrenia. 28395725_IL-18, IL-18R and IL-18BP expression in eosinophil are involved in the inflammatory reaction of asthma. 28922563_asthma is very likely to be determined by balance of IL-18/IL-18BP/IL-18R expression in inflammatory cells. 30990817_Our replicated associations with HK1 and IL18R1 suggest that variants in inflammatory pathways, such as the biologically-plausible NLRP3 inflammasome, may contribute to nocturnal hypoxemia. 32193584_IL-18/IL-18R1 promotes circulating fibrocyte differentiation in the aging population. 33522333_IL18-family Genes Polymorphism Is Associated with the Risk of Myocardial Infarction and IL18 Concentration in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000026070 |
Il18r1 |
155.421420 |
9.9066379386 |
3.308396 |
0.184584691 |
364.779754 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000256345079751210676934073321813900373747642818336085547281710017546577306251947564785213180969112285419189593403093114291186788634086729191075213916763001827471217555851566675122161737983944433829199341379201371182716684415936470031738281250000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000087584568914996976760187908750624244779790196201441877736728361827370040510165145903244002712913703014475850124767668387870155172940280155747871915642925459927472405568673984479018025811150626770695826195378685952164232730865478515625000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
283.9901664 |
31.9340259 |
28.8746198 |
2.9287078 |
| ENSG00000115607 |
8807 |
IL18RAP |
protein_coding |
O95256 |
FUNCTION: Within the IL18 receptor complex, does not mediate IL18-binding, but involved in IL18-dependent signal transduction, leading to NF-kappa-B and JNK activation (PubMed:9792649, PubMed:14528293, PubMed:25500532). May play a role in IL18-mediated IFNG synthesis from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14528293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25500532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9792649, ECO:0000305|PubMed:10653850}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Membrane;NAD;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an accessory subunit of the heterodimeric receptor for interleukin 18 (IL18), a proinflammatory cytokine involved in inducing cell-mediated immunity. This protein enhances the IL18-binding activity of the IL18 receptor and plays a role in signaling by IL18. Mutations in this gene are associated with Crohn's disease and inflammatory bowel disease, and susceptibility to celiac disease and leprosy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:8807; |
interleukin-18 receptor complex [GO:0045092]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-18 receptor activity [GO:0042008]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-18-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0035655]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092] |
15760905_IL-18, IL-18 receptor alpha, and CD48 complex formation via glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor glycan triggers binding to IL-18 receptor beta, and thereby induces intracellular signal transduction and IFN-gamma production. 16043644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17897836_Truncated forms of IL-18RAP may be involved in the complex mechanism of IL-18 activity regulation. 18092318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18311140_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18311140_Variations in IL18RAP is associated with celiac disease 18439550_CARD9 and IL18RAP are IBD loci important in innate immunity in the predisposition to both CD and UC. 18439550_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774397_study provides suggestive evidence for associations of SNPs in the IL1RL1 gene and adjacently located family members IL18R1 and IL18RAP with asthma and atopy in 2 independent Dutch asthma populations 18805825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19073967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19103669_IL18RAP is a novel predisposing gene for coeliac disease. 19103669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473509_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19473509_Our analysis suggests that the variability of IL18RAP genes is unlikely to contribute to modulate the risk of cardiovascular disease 19542083_Investigated the regions 2q12 (IL18RAP) and 3p21 (CCR3)in regards to celiac disease risk in the Spanish population.Two SNPs, rs917997 (2q12) and rs6441961 (3p21), were genotyped; Assoc'n was found w/rs6441961, a non-sign. result was obtained for rs917997. 19542083_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19693089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714583_The mechanism of the impaired natural killer cell function in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis involves a defect in IL-18Rbeta phosphorylation. 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20176734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22289858_Data suggest that IL-18RAP and IL-18R1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms identify African-American infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 22685567_Data indicate that MyD88 works together with the IL-1/IL-18 receptors, can interact with two distinct sorting adaptors, TRAM and Mal, in a conserved manner. 23891168_The SNP modified IL18RAP surface protein expression by NK cells. 24842757_results demonstrate clear functional consequences of the rs917997 risk polymorphism; this polymorphism leads to a loss-of-function through decreased IL-18RAP, IL-18R1, and IL-1R1 protein expression, which impairs autocrine IL-18 and IL-1 signaling 26289103_This meta-analysis provides robust estimates that IL18RAP rs917997 and chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 3 rs6441961 are potential risk factors for celiac disease in European populations. 26358252_These findings suggested that IL-18RAP rs917997, IL-32 rs2015620, IL-22 rs1179251, and interactions between these polymorphisms and H. pylori infection were associated with risks of gastric lesions 26566691_some SNPs of ST2-IL18R1-IL18RAP gene cluster might increase the risk of susceptibility of Graves' disease (GD) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) in Chinese Han population. 27775096_An association of IL18RAP single nucleotide polymorphism rs2058660 with Behcet's disease, but not Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease in Han Chinese. 29146643_Polymorphisms in IL18RAP influence susceptibility to obesity. We demonstrated that the A allele in rs7559479 increases MIR136 binding, which regulates IL-18 system activity. 31126849_There was no association between IL18RAP gene polymorphisms (rs1420106 and rs917997) with the risk of spondylotic myelopathy in Indian population. 31147177_IL18RAP polymorphisms and its plasma levels in patients with Lumbar disc degeneration. 32732242_Investigation of genetically regulated gene expression and response to treatment in rheumatoid arthritis highlights an association between IL18RAP expression and treatment response. 33522333_IL18-family Genes Polymorphism Is Associated with the Risk of Myocardial Infarction and IL18 Concentration in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. 33769074_Integrating disease and drug-related phenotypes for improved identification of pharmacogenomic variants. 33823154_A novel anti-human IL-1R7 antibody reduces IL-18-mediated inflammatory signaling. 35361972_Whole-genome sequencing reveals that variants in the Interleukin 18 Receptor Accessory Protein 3'UTR protect against ALS. |
ENSMUSG00000026068 |
Il18rap |
11.385089 |
10.2131539217 |
3.352357 |
0.634424481 |
35.313304 |
0.00000000280708017155052557515593065454347077025687440254841931164264678955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012871234337398494970645480893565310021031677933933679014444351196289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.7915398 |
8.7242013 |
2.0601114 |
0.7924125 |
| ENSG00000115657 |
10058 |
ABCB6 |
protein_coding |
Q9NP58 |
FUNCTION: ATP-dependent transporter that catalyzes the transport of a broad-spectrum of porphyrins from the cytoplasm to the extracellular space through the plasma membrane or into the vesicle lumen (PubMed:33007128, PubMed:27507172, PubMed:17661442, PubMed:23792964). May also function as an ATP-dependent importer of porphyrins from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria, in turn may participate in the de novo heme biosynthesis regulation and in the coordination of heme and iron homeostasis during phenylhydrazine stress (PubMed:17006453, PubMed:10837493, PubMed:23792964, PubMed:33007128). May also play a key role in the early steps of melanogenesis producing PMEL amyloid fibrils (PubMed:29940187). In vitro, it confers to cells a resistance to toxic metal such as arsenic and cadmium and against chemotherapeutics agent such as 5-fluorouracil, SN-38 and vincristin (PubMed:25202056, PubMed:21266531, PubMed:31053883). In addition may play a role in the transition metal homeostasis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10837493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17006453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17661442, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21266531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23792964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25202056, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27507172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29940187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31053883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33007128}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dyskeratosis congenita;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Lysosome;Membrane;Microphthalmia;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. This protein is a member of the heavy metal importer subfamily and plays a role in porphyrin transport. This gene is the molecular basis of the Langereis (Lan) blood group antigen and mutations in this gene underlie familial pseudohyperkalemia and dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:10058; |
ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex [GO:0043190]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endolysosome membrane [GO:0036020]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome membrane [GO:0033162]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial envelope [GO:0005740]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; multivesicular body membrane [GO:0032585]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vacuolar membrane [GO:0005774]; ABC-type heme transporter activity [GO:0015439]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; efflux transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015562]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; tetrapyrrole binding [GO:0046906]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cellular copper ion homeostasis [GO:0006878]; cellular detoxification of cadmium ion [GO:0098849]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; heme metabolic process [GO:0042168]; heme transmembrane transport [GO:0035351]; heme transport [GO:0015886]; melanosome assembly [GO:1903232]; porphyrin-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0006779]; porphyrin-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006778]; skin development [GO:0043588]; tetrapyrrole metabolic process [GO:0033013]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
11977179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791740_study of C-terminal nucleotide-binding domain of ABCB6 in nucleotide-free & ADP-bound states by NMR & homology modelling; results revealed localised dynamic cooperativity, which was proposed for a prokaryotic ABC MJ1267, also exists in a eukaryotic ABC 17006453_ABCB6 is uniquely located in the outer mitochondrial membrane and is required for mitochondrial porphyrin uptake 17661442_ABCB6 exists in two molecular weight forms, is localized to both the outer mitochondrial membrane and the plasma membrane, and plays a functional role in the plasma membrane. 18279659_ather, it localized in the ER-derived and brefeldin A-sensitive perinuclear compartments, mainly in the Golgi apparatus. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20823549_overall structure of ABCB6 is L-shaped and consists of two lobes, consistent with other reported nucleotide-binding domain structures 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21199866_Conserved intramolecular disulfide bond is critical to trafficking and fate of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters ABCB6 and sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1)/ABCC8. 21849266_ABCB6 plays a role in cell growth and proliferation by targeting the cell cycle. 22226084_The results demonstrated that ABCB6 mutations cause ocular coloboma. 22246506_It was established that ABCB6 encodes a new blood group system (Langereis, Lan). Targeted sequencing of ABCB6 in 12 unrelated individuals of the Lan(-) blood type identified 10 different ABCB6 null mutations. 22655043_Knock-down studies demonstrate that ABCB6 function is not required for de novo heme biosynthesis in differentiating K562 cells, excluding this ABC transporter as a key regulator of porphyrin synthesis. 22688660_High expression levels of ABCB6 are associated with glioma. 22761424_Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) mediate transcriptional activation of the ATP binding cassette transporter ABCB6 gene via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) 22958180_p.Arg192Trp is the first ABCB6 missense mutation causing the Lan- blood type and appears to be a relatively frequent cause of this rare blood type. 23180570_the two missense mutations in residue 375 of the ABCB6 polypeptide found in affected individuals of families with chromosome 2-linked FP could contribute to the red cell K(+) leak characteristic of this condition. 23483087_Aberrant mRNA and DNA methylation levels of ABCB6 may serve as useful predictive biomarkers for early intrahepatic recurrence of HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma 23519333_These findings suggest that ABCB6 may be a physiological factor for skin pigmentation. 23763549_To date, 19 ABCB6 alleles that encode Lan- or Lan+(w) /-, or Lan+(w) phenotypes have been described. 23792964_results suggest a direct interaction between mitochondrial ABCB6 and its transport substrates that is critical for the activity of the transporter 23793916_Data suggest that expression of ABCB6 varies widely in bone marrow and blood samples from patients with acute myeloid leukemia. [LETTER] 24192121_No significant associations were detected for the ABCB6 or ABCG1 gene. 24224009_data add new variants to the repertoire of ABCB6 mutations with dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria. 24456066_We describe eight new mutations in ABCB6 of which seven, including three missense mutations, underlie the Lan- phenotype and determine that a complete gene deletion of ABCG2 or ABCB6 is not responsible for the Jr(a-) or Lan- phenotype, respectively. 24498303_Data indicate ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 6 (ABCB6) as the disease candidate gene by discovering a coding mutation (c.1358C>T; p.Ala453Val) that co-segregates with the dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria phenotype. 24947683_a heterozygous substitution Arg723Gln in the ATP-binding cassette, Subfamily B, Member 6 protein that segregated with FP in the Cardiff family and was also present in both blood donors. Arg723Gln is listed in human variation databases 25202056_Expression of ABCB6 is related to resistance to 5-FU, SN-38 and vincristine. 25288164_Identified two novel ABCB6 mutations in two Chinese families affected with dyschromatosis universalis hereditaria (DUH), underscoring the causative role of the ABCB6 mutations in the molecular pathogenesis of DUH. 25360778_genetic variants linked to lower or absent cell surface expression of ABCB6/Langereis may be more common than previously thought. 25573285_These data indicate that the expression of ABCB6 in plasma membrane is important for porphyrin accumulation after ALA administration, including hypoxic conditions. 25627919_Data suggest N-terminal transmembrane domain of ABCB6 functions as independent folding unit and plays crucial role in lysosomal (rather than plasma membrane) targeting of ABCB6; this domain is dispensable for dimerization and ATP binding/hydrolysis. 27151991_ABCB6 missense mutations in red blood cells from subjects with familial pseudohyperkalemia show elevated potassium ion efflux. 27507172_Severely affected porphyria patients harbor variant alleles in the ABCB6 gene. 31053883_The human ABCB6 protein is the functional homologue of HMT-1 proteins mediating cadmium detoxification in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Caenorhabditis elegans. 31189171_Investigated whether 9 SNPs in ABCB1 (rs6946119, rs28401781, rs4148739, and rs3747802), ABCB6 (rs1109866, rs1109867, rs3731885, and rs3755047), and ABCG1 (rs182694); findings support an association between ABCG1 polymorphism and schizophrenia in a Han Chinese population; no association between schizophrenia and a specific allele or genotype among the SNPs of ABCB1 and ABCB6 was observed 32329696_UBE2L6 is Involved in Cisplatin Resistance by Regulating the Transcription of ABCB6. 32710948_Systematic analysis of the ABC transporter family in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals the importance of ABCB6 in regulating ferroptosis. 33007128_Cryo-electron microscopy structure of human ABCB6 transporter. 34392362_Substrate specificity of Chondroitinase ABC I based on analyses of biochemical reactions and crystal structures in complex with disaccharides. 34724702_ABCB6 polymorphisms are not overly represented in patients with porphyria. 35461746_ABCB6 knockdown suppresses melanogenesis through the GSK3-beta/beta-catenin signaling axis in human melanoma and melanocyte cell lines. |
ENSMUSG00000026198 |
Abcb6 |
17.992794 |
0.2070334801 |
-2.272064 |
0.756422808 |
8.336169 |
0.00388634541536478925541353568462454859400168061256408691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008120393308434923490546353264107892755419015884399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7443229 |
3.2689759 |
28.2649755 |
10.6706080 |
| ENSG00000115687 |
23178 |
PASK |
protein_coding |
Q96RG2 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in energy homeostasis and protein translation. Phosphorylates EEF1A1, GYS1, PDX1 and RPS6. Probably plays a role under changing environmental conditions (oxygen, glucose, nutrition), rather than under standard conditions. Acts as a sensor involved in energy homeostasis: regulates glycogen synthase synthesis by mediating phosphorylation of GYS1, leading to GYS1 inactivation. May be involved in glucose-stimulated insulin production in pancreas and regulation of glucagon secretion by glucose in alpha cells; however such data require additional evidences. May play a role in regulation of protein translation by phosphorylating EEF1A1, leading to increase translation efficiency. May also participate in respiratory regulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16275910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17052199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17595531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20943661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21181396, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21418524}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Lipid-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serine/threonine kinase family that contains two PAS domains. Expression of this gene is regulated by glucose, and the encoded protein plays a role in the regulation of insulin gene expression. Downregulation of this gene may play a role in type 2 diabetes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:23178; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045719]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of glucagon secretion [GO:0070092]; regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange [GO:0043576] |
11688972_molecular cloning, gene expression, and comparison with mouse protein 15148392_Results suggest that elevated glucose concentrations rapidly increase Per-Arnt-Sim kinase activity in pancreatic islet beta cells, followed by up-regulation by glucose of preproinsulin and pancreatic duodenum homeobox 1 gene expression. 17595531_identified the multifunctional eukaryotic translation elongation factor eEF1A1 as a novel interaction partner of PASKIN in the nuclei of testis germ cells and in the midpiece of sperm tails 20943661_Structural bases of PAS domain-regulated kinase (PASK) activation in the absence of activation loop phosphorylation. 21181396_PASK is involved in the regulation of glucagon secretion by glucose and may be a useful target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. 22065581_Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain-containing protein kinase (PASK) has a role in insulin hypersecretion 22219681_The role of PAS kinase in PASsing the glucose signal. 23721480_Mutations that affect PAS domain cause a severe protein trafficking defect and change the interactions with Kv11.1 channels. 23853095_PASK phosphorylates and inactivates GSK3beta, thereby preventing PDX-1 serine phosphorylation and alleviating GSK3beta-mediated PDX-1 protein degradation in pancreatic beta-cells. 30381292_we provide the first evidence for a role of USF1 in respiration since it appeared to complement Cbf1 in vivo as determined by respiration phenotypes. In addition, we confirmed USF1 as a substrate of human PAS kinase (hPASK) in vitro Combined, our data supports a model in which Cbf1/USF1 functions to partition glucose toward respiration and away from lipid biogenesis 31072927_MTORC1-PASK signaling is required for the rise of myogenin-positive committed myoblasts. 31529049_we show that the nuclear PASK associates with the mammalian H3K4 MLL2 methyltransferase complex and enhances H3K4 di- and tri-methylation. We also show that PASK is a histone kinase that phosphorylates H3 at T3, T6, S10 and T11. |
ENSMUSG00000026274 |
Pask |
69.660086 |
0.4958357753 |
-1.012066 |
0.274114404 |
13.300117 |
0.00026538961391407679072523828622820474265608936548233032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000682787293249393972480176806527651933720335364341735839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.4267864 |
9.1853513 |
102.8380551 |
13.1858061 |
| ENSG00000115756 |
3241 |
HPCAL1 |
protein_coding |
P37235 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the calcium-dependent regulation of rhodopsin phosphorylation. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myristate;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of neuron-specific calcium-binding proteins family found in the retina and brain. It is highly similar to human hippocalcin protein and nearly identical to the rat and mouse hippocalcin like-1 proteins. It may be involved in the calcium-dependent regulation of rhodopsin phosphorylation and may be of relevance for neuronal signalling in the central nervous system. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:3241; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] |
11173883_VILIP-3 immunostaining was found to be reduced in Alzheimer brains; immunoreactive material was detected in close association with amyloid plaques and neurofibrillar tangles, typical pathologic hallmarks of AD 14739275_visinin-like protein-3 interacts with microsomal cytochrome b5 in a Ca2+-dependent manner 15834280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16703469_The interaction of human VILIP1 and VILIP3 with divalent cations was explored using circular dichroism and fluorescence measurement. 21059989_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23873030_HPCAL1 did not appreciably influence the ability of WT PHOX2B. 25019684_Results show that in the presence of calcium, N-myristoylation significantly increases the kinetic rate of VILIP adsorption to the membrane. 26659654_Secreted HPCAL1 protein in the plasma dropped dramatically in hepatocellular carcinoma patients relative to controls. 27820860_The myristoylated VILIP-3 protein structure determined in this study is quite different. 30843345_These studies elucidate the tumour-promoting activity of HPCAL1. They also offer an innovative therapeutic strategy focusing on the HPCAL1-Wnt/b-catenin axis to regulate proliferation and development of Glioblastoma. 35102488_Hippocalcin-like 1 is a key regulator of LDHA activation that promotes the growth of non-small cell lung carcinoma. 36438486_Hippocalcin-Like 1 blunts liver lipid metabolism to suppress tumorigenesis via directly targeting RUVBL1-mTOR signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000071379 |
Hpcal1 |
1184.748129 |
2.1452374302 |
1.101137 |
0.051718523 |
455.173215 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005398772853627585408377958843182541676335254721549915113523950483332520531264443379655992185341240921240600028812508833687959641913939335892786535337307406745904482378388312279671890709433665662816783390857594178748835425971652661 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002336829540162555872203697763682306843261825578230596501932384459479858617988363126497152250279860185130284221961829179058241117011798932882344101844964265697034934572321348956041076083052667837483099864840021465156331718760261714 |
Yes |
No |
1642.4991055 |
52.6126024 |
771.3693368 |
19.1182454 |
| ENSG00000115828 |
25797 |
QPCT |
protein_coding |
Q16769 |
FUNCTION: Responsible for the biosynthesis of pyroglutamyl peptides. Has a bias against acidic and tryptophan residues adjacent to the N-terminal glutaminyl residue and a lack of importance of chain length after the second residue. Also catalyzes N-terminal pyroglutamate formation. In vitro, catalyzes pyroglutamate formation of N-terminally truncated form of APP amyloid-beta peptides [Glu-3]-amyloid-beta. May be involved in the N-terminal pyroglutamate formation of several amyloid-related plaque-forming peptides. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15063747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18486145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21288892}. |
3D-structure;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transferase;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes human pituitary glutaminyl cyclase, which is responsible for the presence of pyroglutamyl residues in many neuroendocrine peptides. The amino acid sequence of this enzyme is 86% identical to that of bovine glutaminyl cyclase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:25797; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase activity [GO:0016603]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; peptidyl-pyroglutamic acid biosynthetic process, using glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase [GO:0017186]; protein modification process [GO:0036211] |
12196024_Functional expression of human glutaminyl cyclase in Pichia pastoris reveals the presence of a disulfide bond with an important role in the stabilization of active protein structure. 14522962_human glutaminyl cyclase is a metal-dependent transferase 14680951_Glutaminyl cyclase was expressed as a fully active 37 kDa enzyme with kcat/Km values of 14.3, 9.3, and 2.4 mM(-1)s(-1) for the substrates Gln-Gln, Gln-NH(2), and Gln-t-butyl ester, respectively 15231017_Genetic variations in QPCT are important factors affecting the bone mineral density of adult women that contribute to susceptibility for osteoporosis. 15231017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16135565_structure of human QC in free form and bound to a substrate and three imidazole-derived inhibitors 17334644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17687619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17687619_Our results suggest that QPCT may be the QTL gene at chromosome 2p for spine BMD variation in the Chinese population 18072935_combined steady-state enzyme kinetic and X-ray structural analyses of 11 single-mutation human QCs to investigate the roles of the H-bond network in catalysis 18470930_The computations outline the important role of Trp329 in helping the substrate binding process and stabilizing the cyclization transition state. 18486145_Golgi apparatus retention implies a 'housekeeping' protein maturation machinery conducting glycosylation and pyroglutamyl formation. For these isoenzymes, apparently similar strategies evolved to retain the proteins in the Golgi complex. 19804409_Human isoQC proteins displayed a broad substrate specificity and preference for hydrophobic substrates, similar to the related QC. 20383514_This study demonstrated that glutaminyl cyclase expression and pE-Abeta formation in subcortical brain regions( Edinger-Westphal nucleus, locus coeruleus and nucleus basalis Meynert) affected in Alzheimer's disease. 21288892_Upon binding to PBD150, a large loop movement in gQC allows the inhibitor to be tightly held in its active site primarily by hydrophobic interactions. 21301857_The resilts of this studt provided histopathological evidence for QC being a prerequisite for pE-Abeta pathology in vivo and further underline the therapeutic potential of QC inhibition in Alzheimer Disease. 21671571_This study presents a first comparison of two mammalian QCs (human and mouse) containing typical, conserved post-translational modifications. 23183267_Upregulation of QPCT expression is associated with thyroid carcinomas. 23207485_this study demonistrated that QPCT mRNAand protein from mononuclear cells correlated with theseverity of dementia. 24164736_observations provide evidence for an involvement of QC in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis and cognitive decline by QC-catalyzed pGlu-Abeta formation 26492838_the genetic risk of QPCT gene for schizophrenia also exists in the Han Chinese population. 26572640_these findings demonstrate a significant association between common single nucleotide polymorphism within QPCT gene and schizophrenia risk in a Han Chinese population. 28587659_The addition of QC activity to core diagnostic CSF biomarkers may be of specific interest in clinical cases with discordant imaging and biochemical biomarker results. 32551535_Hydrazides Are Potent Transition-State Analogues for Glutaminyl Cyclase Implicated in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. 33774034_A Unique Carboxylic-Acid Hydrogen-Bond Network (CAHBN) Confers Glutaminyl Cyclase Activity on M28 Family Enzymes. 34036385_QPCT regulation by CTCF leads to sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma by promoting angiogenesis. 34309760_A glutaminyl cyclase-catalyzed alpha-synuclein modification identified in human synucleinopathies. |
ENSMUSG00000024084 |
Qpct |
217.084574 |
4.4228515439 |
2.144977 |
0.117630433 |
354.059666 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000055348280479649790413200209331174524126218723667061421621948184813031812968897190205459703082363179787048138664685391192469281899542793876326580440353980697029242031391399033295028270631736480415774348529112103278748691082000732421875000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018317054257390825388877948812234220342464679224775626950980973832927421044181789661054426061104729662719661243127605281604312064666733440449663975924762427286112228818602349064997389274482564314183719034190289676189422607421875000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
350.3962119 |
25.6812385 |
79.7791588 |
4.9770228 |
| ENSG00000115884 |
6382 |
SDC1 |
protein_coding |
P18827 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears both heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate and that links the cytoskeleton to the interstitial matrix. Regulates exosome biogenesis in concert with SDCBP and PDCD6IP (PubMed:22660413). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22660413}. |
3D-structure;Glycoprotein;Heparan sulfate;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane (type I) heparan sulfate proteoglycan and is a member of the syndecan proteoglycan family. The syndecans mediate cell binding, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal organization and syndecan receptors are required for internalization of the HIV-1 tat protein. The syndecan-1 protein functions as an integral membrane protein and participates in cell proliferation, cell migration and cell-matrix interactions via its receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. Altered syndecan-1 expression has been detected in several different tumor types. While several transcript variants may exist for this gene, the full-length natures of only two have been described to date. These two represent the major variants of this gene and encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6382; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; myoblast development [GO:0048627]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; positive regulation of exosomal secretion [GO:1903543]; positive regulation of extracellular exosome assembly [GO:1903553]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to cAMP [GO:0051591]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; Sertoli cell development [GO:0060009]; striated muscle cell development [GO:0055002]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
9857223_The detection of syndecan-1 in endometrial cancer of different clinical and histological stages could be of prognostic value in clinical diagnosis. 11168765_The loss of syndecan-1 expression evident in acantholytic conditions 11830493_mediates hepatocyte growth factor binding and promotes Met signaling in multiple myeloma 11877089_Serum levels of soluble syndecan-1 correlated with tumor mass in patients with multiple myeloma. 12091355_Soluble syndecan-1 promotes growth and dissemination of transplanted human myeloma tumors in vivo in SCID mice implanted with human bones. 12144130_review of structure, function, cell and tissue distribution 12660231_regulation of expression in isoform specific manner by farnesoid X receptor 12749851_Cells adherent via syndecan-1 do not spread, but can be induced to spread by Mn(2+), suggesting that activation of a beta(1) or beta(3) integrin partner is required. 12824007_TNF-alpha and IL-1beta are capable of down-regulating syndecan-1 expression 12879463_High syndecan-1 expression in breast carcinoma is related to an aggressive phenotype 12904296_shedding of syndecan-1 promoted by MT1-MMP through the preferential cleavage of Gly245-Leu246 peptide bond stimulates cell migration 12920224_The increased stromal syndecan-1 expression, coupled with its loss from the surface of carcinoma cells, may contribute to tumor cell invasion and the development of metastases 12947106_results demonstrate that the laminin alpha3 LG4/5 modules within unprocessed laminin-5 permit its cell binding activity through heparan and chondroitin sulfate chains of syndecan-1 12975379_the extracellular domain mediates an interaction that is necessary for dynamic cytoskeletal rearrangements whereas an interaction of the transmembrane domain is required for the initial spreading response 14630925_results demonstrate that cell-surface syndecan-1 is a degradative target of heparanase (HPSE-1), and syndecan-1 regulates HPSE-1 biological activity 14645569_serves as a primary human papillomavirus receptor protein in natural HPV11 infection of keratinocytes. 14701864_MT4-MMP and the proteoglycan form of syndecan-1 have roles in ADAMTS-4 activation on the cell surface 14744776_Growth-promoting loop exists between breast cancer cells and their stroma that depends on the activity of glycanated Sdc1. 14972511_Consistent with a possible biochemical role for syndecan-1 in prostate cancer progression and metastasis, syndecan-1 expression correlated with serologic recurrence in Gleason sum 7 prostate cancer and was highly expressed in soft-tissue metastases. 15126321_in hyperinflammatory lesions, ephrinB2 was predominantly expressed in macrophage-like cells and EphB4 in small venules; syntenin and syndecan-1 were up-regulated in EphB4-positive endothelial cells after stimulation with preclustered ephrinB2 15297422_syndecan-1 and glypican-1 have roles in progression of ovarian cancer 15383330_Altered matrix-dependent signaling due to increased levels of cell surface syndecan-1 may lead to epithelial cell invasion during early stages of tumorigenesis. 15459490_Concomitant expression of syndecan-1 in both epithelium and stroma may be a predictor of unfavourable prognosis in breast cancer, and in contrast with previous studies, loss of epithelial syndecan-1 was associated with a more favourable prognosis 15479743_syndecan-1 is likely to be a critical regulator of many cellular behaviors that depend on activated alpha(v)beta(3) integrins 15648090_constitutive shedding corresponding to the basal level of soluble syndecan-1 ectodomain was significantly increased when cells were stimulated with P. gingivalis lipopolysaccharide 15728209_osteoprotegerin affects monocyte mi-gration and protein kinase C and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt activation via syndecan-1. 15743035_syndecan-1 has a role in progression of invasive breast carcinomas through the remodeling of breast cancer tissue via interaction with other extracellular matrix components 15770719_Expression of paxillin and syndecan-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) may affect its invasive and metastatic ability. May be converse correlation between expression of paxillin and syndecan-1 protein in HCC. 15886501_Stromal syndecan-1 expression is an independent prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer, whereas epithelial syndecan-1 expression predicts better prognosis only in resectable disease. 15902740_Loss of syndecan-1 plays a role in the growth of G-type cancers of differentiated type gastric cancers at an early stage 16020957_Low epithelial syndecan-1 expression was associated with a higher histological grade and a more advanced clinical stage of the colorectal cancer 16132527_Malignant glioma cells express all types of syndecans. NF-kappaB participates in the upregulation of the syndecan-1 expression at the transcriptional level, and increased expression of syndecan-1 could associate with thrombospondin-1. 16247452_stromal fibroblast-derived Sdc1 stimulates breast carcinoma growth and angiogenesis in vivo 16286510_shed syndecan-1 or MMP7-syndecan-1 complexes may have roles in tumor progression 16636895_Syndecan-1 and syndecan-4 may have roles in progression of breast carcinoma 16720645_The ectodomain of the syndecan-1 core protein contains an active site that assembles into a complex with the alphavbeta5 integrin and regulates alphavbeta5 integrin activity. 16773719_Certain immunomarkers like syndecan-1, kappa and lambda light chains and IgA heavy chain could be of much help in identifying early stage immunoproliferative small intestinal disease (IPSID). 16778379_CD138 may have a role in progression of nodal diffuse large B cell lymphoma 16840194_syndecan-1 may have a role in progression of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia 16857657_increase of Syndecan-1 in all tissue compartments and a redistribution from epithelium to stroma may be a characteristic feature for dense breast tissue 16884912_syndecan-1 shedding may modulate the pathogenesis of specific microbes 16945147_the endocytic path taken by Syn-1 is clathrin-independent and relies upon lipid raft function 16982797_Lacritin targets the deglycanated core protein of SDC1 and not HS chains or SDC2 or SDC4. Binding requires partial or complete removal of HS chains by endogenous HPSE. This limits lacritin activity to HPSE release sites as an HPSE 'off/on switch'. 17149710_Syndecan-1 expression is uniquely influenced by changes in the phase and magnitude of the local stress field. 17314405_domain V of the gamma2 chain negatively regulates the integrin beta4 phosphorylation, probably through a syndecan-1-mediated signaling, leading to enhanced cell adhesion and suppressed cell motility 17339423_Heparanase influences expression and shedding of syndecan-1 17413980_In summary, ovarian carcinomas exhibit up-regulated expression of several extracellular matrix proteins, and syndecan 1 represents a novel tumor-associated marker in ovarian serous carcinomas. 17431390_Decreased syndecan-1 is asociated with thyroid cancer 17455248_upregulation of syndecan-1 may be a critical element for endometrial cancers in maintaining their viability 17579341_SDC1 interaction with the LG4/5 domain in kalinin is essential for keratinocyte migration. 17625591_syndecan-1 regulates keratinocyte proliferation differently during skin development and in healing wounds. 18006945_Results indicate a lack of association between SDC-1 polymorphisms and risk of squamous cell carcinomas of the cervix. 18064305_heparan sulfate and syndecan-1, the predominant intestinal epithelial heparan sulfate proteoglycan, are essential in maintaining intestinal epithelial barrier function. 18093920_syndecan TMD homodimerization and heterodimerization can be mediated by GxxxG motifs and modulated by sequence context 18190591_the association of circulating sCD138 levels in plasma with clinical behavior in 104 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia 18378436_Syndecan-1 and beta1 integrin signaling downstream of laminin alpha1-derived peptide AG73 regulate adhesion and MMP production by human salivary gland tumor cell lines (CAC2 and M1). 18386024_aberrant skin expression may be involved in the development of psoriasis 18413760_n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) upregulate SDC1 in breast cancer cellsbu activating PPARgamma, providing a chemopreventive effect. 18450428_In vitro reconstructed normal human epidermis expresses differentiation-related proteoglycans (CD44, syndecan-1, desmosealin, and 7C1). 18450755_syndecan 1 is up-regulated by n-3 fatty acids by a transcriptional pathway involving PPARgamma 18542065_loss of syndecan-1 epithelial expression was of strong prognostic value in breast carcinomas 18657535_Our findings thus suggest that a previously unknown link between integrin alpha2beta1 and syndecan-1 is important in regulating cell adhesion to collagen and in triggering integrin downstream signalling. 18694404_CD138 is a new simple non-invasive marker for predicting liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. 18957427_Rab5 is a critical regulator of syndecan-1 shedding that serves as an on-off molecular switch through its alternation between the GDP-bound and GTP-bound forms. 18997617_Expression of Galectin-3, CD138, p16INK4a, and TTF-1 in mucinous bronchioloalveolar adenocarcinoma after Hodgkin lymphoma. 19010933_Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-mediated stromal syndecan-1 shedding stimulates breast carcinoma cell proliferation. 19020713_syndecan-1 directly contributes to the growth and invasive ability of oral cancer cells 19029267_Plasma levels of syndecan-1 increased significantly during coronary artery bypass grafting, with or without the use of cardiopulmonary bypass. 19073610_Oxidative shedding of syndecan-1 is an underlying cause of neutrophil chemotaxis and aberrant wound healing that may contribute to pulmonary fibrosis. 19107206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126645_Proteolytic conversion of Sdc1 from a membrane-bound into a soluble molecule marks a switch from a proliferative to an invasive phenotype, with implications for breast cancer diagnostics and potential glycosaminoglycan-based therapies. 19228696_Data show that syntenin-1 binds to syndecan-1 and participates in the formation of membrane protrusions, and that syntenin-1 recruitment depends on the dephosphorylation of Tyr-309 located within syndecan-1 PDZ binding domain EFYA. 19251947_Shed syndecan-1 restricts neutrophil elastase from alpha1-antitrypsin in neutrophilic airway inflammation. 19255147_The active site within the Sdc1 core protein was identified and a peptide inhibitor called synstatin (SSTN) that disrupts Sdc1's interaction with alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) integrins was derived. 19305494_Results show that heparanase alters the level of nuclear syndecan-1. 19351365_The present results suggest that the decrease in syndecan-1 expression and increase in the Ki-67 index observed in ameloblastic carcinomas is in accordance with its higher aggressiveness as compared to the rare desmoplastic and peripheral ameloblastomas. 19420730_reduced syndecan-1/E-cadherin expression may be good indicators of recurrence and prognosis in extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma. 19450993_changes in the pattern expression of syndecan-1 and -2 indicate that both molecules may be involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumor progression of prostate cancer. 19456850_syndecan-1 is a co-receptor for APRIL and TACI at the cell surface of MMC, promoting the activation of an APRIL/TACI pathway that induces survival and proliferation in multiple myeloma cells 19473447_Results showed that epithelial syndecan-1 expression is reduced as lip carcinogenesis progresses (normal tissue>actinic cheilitis>lip squamous cell carinoma), suggesting that syndecan-1 could be a useful marker of malignant transformation in the lip. 19581738_Ressutls show that cystic tumors of the pancreas express syndecan-1 and tenascin differently and suggest that low syndecan-1 expression might serve as a predictive factor for malignancy. 19596856_the effects of syndecan-1 on myeloma survival, growth, and dissemination are due, at least in part, to its positive regulation of tumor-host interactions that generate an environment capable of sustaining robust tumor growth. 19632304_Study indicates that SDC-1 and -4 may be required for HepG2, Hep3B and Huh7 human hepatoma cell migration, invasion or spreading induced by the chemokine. 19696445_syndecan 1 and 4 correlate to increased metastatic potential in melanoma patients and are an important component of the Wnt5A autocrine signaling loop 19735958_Chronic inflammation and exogenous insulin usage increases the serum syndecan-1 level in type 2 diabetics. 19802384_syndecan-1 and FGF-2, but not FGFR-1 share a common transport route and co-localize with heparanase in the nucleus, and this transport is mediated by the RMKKK motif in syndecan-1 19822079_Data report that the bFGF, FGFR1/2 and syndecan 1-4 expressions are altered in bladder tumours. 19860843_syndecan-1 might contribute to urothelial carcinoma cell survival and progression 19866343_higher proportion of protein-expressing B-cells in the blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 19875451_ADAM17 may therefore be an important regulator of syndecan functions on inflamed lung epithelium. 20008145_Sdc1 has a protective effect during experimental colitis. 20013319_High CD138 serum levels are associated with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression. 20036233_Data substantiate the existence of a co-adhesion receptor system in tumor cells, whereby Sdc1 functions as a key regulator of cell motility and cell invasion by modulating RhoA and Rac activity. 20081059_Age-associated study of detailed characterization of circulating CD138-negative and CD138-positive plasma cells sorted by flow cytometry shows a typical plasma cell cytology with no obvious morphological differences. 20083849_all syndecans can interact with proteins of the actin-associated cytoskeleton--REVIEW 20097882_pathway driven by heparanase expression in myeloma cells: elevated levels of VEGF and shed syndecan-1 form matrix-anchored complexes that together activate integrin and VEGF receptors on adjacent endothelial cells thereby stimulating tumor angiogenesis 20193112_Decreased expression of Syndecan-1 mRNA and the increased expression of HPA-1 mRNA can promote the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 20200931_Syndecan-1 shed by tumor cells exerts biologic effects distal to the primary tumor and that it participates in driving osteoclastogenesis and the resulting bone destruction. 20204274_Syndecan-1 and versican expression status can serve as an indicator of prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. 20237901_Laminin-derived peptide AG73 regulates migration, invasion, and protease activity of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through syndecan-1 and beta1 integrin. 20307537_The presence of a less mature, more resistant CD138-negative myeloma cell fraction within bone marrow microniches might contribute to high incidence of relapse of myeloma patients. 20361982_Cell biological analysis established that Syndecan1 is a physiological binding partner of Tiam1 and that the PDZ domain has a function in cell-matrix adhesion and cell migration. 20398359_Expression of syndecan 1 in healthy breast tissue during menstrual cycle. 20430722_Results suggest a role for syndecan-1 and cathepsins D and K in growth and invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 20471559_This study confirms a direct relationship between suprabasal p35 localization together with down-regulation of syndecan-1 immunoexpression and dysplastic changes of oral lichen planus and hence the possibility for malignant transformation. 20477813_The prognostic value of intraepithelial and stromal CD3-, CD117- and CD138-positive cells in non-small cell lung carcinoma. 20598296_The syndecan- and alpha2beta1 integrin-binding peptides synergistically affect cells and accelerate cell adhesion. 20683626_multiple regression analysis showed that apolipoprotein A1 was a predictor of serum syndecan-1 levels in subjects with type 2 diabetes 20736897_A threshold of greater than six CD138+ metabolically active plasma cells is associated with poor kidney allograft function and survival. 20927321_Loss of SDC-1 is associated with prostate cancer. 20971705_couples the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor to inside-out integrin activation 21148276_These results demonstrate that syndecan-1 and syndecan-2 gene silencing by RNA interference reduces HSV-1 entry, plaque formation and facilitates cell survival. 21257720_SST0001, a chemically modified heparin, inhibits myeloma growth and angiogenesis via disruption of the heparanase/syndecan-1 axis 21265098_High glucose can decrease the expression of core protein Sydecan-1 and Glypican-1 in cultured human renal glomerular endothelial cells. 21317913_In benign samples, syndecan-1 was expressed in basal and secretory epithelial cells with basolateral membrane localisation. In prostate cancer samples syndecan 1 was expressed to granular-cytoplasmic localisation. 21320038_sCD138 may be applicable as a surrogate marker of disease activity. 21327984_A multiple regression analysis showed that BMI (beta = 0.783, P |
ENSMUSG00000020592 |
Sdc1 |
114.986459 |
2.9321778777 |
1.551973 |
0.192361131 |
65.046243 |
0.00000000000000073160893005216270300708373971466379605183602118784191858935628260951489210128784179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000005270155103743251219916499060094303156120043498539251558554497023578733205795288085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
173.7740986 |
19.3655523 |
59.7760170 |
5.2854279 |
| ENSG00000115896 |
5334 |
PLCL1 |
protein_coding |
Q15111 |
FUNCTION: Involved in an inositol phospholipid-based intracellular signaling cascade. Shows no PLC activity to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol. Component in the phospho-dependent endocytosis process of GABA A receptor (By similarity). Regulates the turnover of receptors and thus contributes to the maintenance of GABA-mediated synaptic inhibition. Its aberrant expression could contribute to the genesis and progression of lung carcinoma. Acts as an inhibitor of PPP1C. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17254016}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
Predicted to enable phospholipase C activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis and phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway; regulation of GABAergic synaptic transmission; and regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5334; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GABA receptor binding [GO:0050811]; inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate binding [GO:0070679]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; phospholipase C activity [GO:0004629]; gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway [GO:0007214]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of receptor binding [GO:1900122]; regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0032228] |
16952428_PRIP-1 plays an important role in type A receptor signaling for gamma-aminobutyric acid in the brain 18776929_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18776929_PLCL1 is a novel gene associated with variation in hip bone size, which has a role in the pathogenesis of hip fractures 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20030815_In postmenopausal women, our results suggest that the PLCL1 rs7595412 polymorphism has no obvious effect on hip bone size and bone mineral density but may be associated with increased proportion of vertebral fracture and increased levels of osteocalcin 20030815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22128345_effect of DZP on PRIP-1 knockout mice was reduced 23911386_PRIP interacts with the catalytic subunits of PP1 and PP2A and the interactions are regulated by phosphorylation. [review] 26603167_susceptibility gene for dermatomyositis in Chinese patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies 34115876_Identification of novel pleiotropic gene for bone mineral density and lean mass using the cFDR method. 35820936_PLCL1 regulates fibroblast-like synoviocytes inflammation via NLRP3 inflammasomes in rheumatoid arthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000038349 |
Plcl1 |
47.113686 |
3.2160367933 |
1.685284 |
0.231852640 |
54.926698 |
0.00000000000012510990364799022188693713128731843775413336283808263260652893222868442535400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000786466004192647222007080224405106211793201054227608892688294872641563415527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
64.2066849 |
24.7191286 |
20.0934404 |
5.6728562 |
| ENSG00000115902 |
6509 |
SLC1A4 |
protein_coding |
P43007 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent neutral amino-acid transporter that mediates transport of alanine, serine, cysteine, proline, hydroxyproline and threonine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14502423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26041762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8101838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8340364}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter for alanine, serine, cysteine, and threonine. Defects in this gene have been associated with developmental delay, microcephaly, and intellectual disability. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:6509; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-aspartate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015183]; L-cystine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015184]; L-glutamine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015186]; L-hydroxyproline transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034590]; L-proline transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015193]; L-serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015194]; L-threonine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015195]; neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015175]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; cognition [GO:0050890]; glutamine transport [GO:0006868]; hydroxyproline transport [GO:0034589]; L-alanine import across plasma membrane [GO:1904273]; L-alanine transport [GO:0015808]; L-aspartate import across plasma membrane [GO:0140009]; L-cystine transport [GO:0015811]; L-glutamate transmembrane transport [GO:0015813]; L-serine import across plasma membrane [GO:1903812]; L-serine transport [GO:0015825]; proline transport [GO:0015824]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; threonine transport [GO:0015826]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11824937_ASCT1 is able to mediate a concentrative transport of alanine, which is Na+-dependent but not coupled to the Na+ gradient 12050356_used as receptor by HERV-W Env glycoprotein 12584318_results strongly suggest that combinations of amino acid sequence changes and N-linked oligosaccharides in a critical carboxyl-terminal region of extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) control retroviral utilization of both the ASCT1 and ASCT2 receptors 17106422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18442140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18442140_This study revealed genetic associations of SLC1A4, SQSTM1, and EIF4EBP1 with MSA. These results may lend genetic support to the hypothesis that oxidative stress is associated with the pathogenesis of MSA. 18638388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18638388_SLC1A4 gene is associated with schizophrenia. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24808181_Na+ interactions with the neutral amino acid transporter ASCT1. 25930971_SLC1A4 disruption may impair brain development and function by decreasing the levels of L-serine in neurons. The identification of additional families with mutations in SLC1A4 would be necessary to confirm its involvement in intellectual disability. 26041762_ASCT1 is essential in brain serine transport. 26138499_SLC1A4 is the disease causing gene of a novel neurologic disorder manifesting with significant intellectual disability, severe postnatal microcephaly, spasticity and thin corpus callosum. 27193218_SLC1A4 deficiency should not be considered a population-specific disorder, and all patients with unexplained severe neurodevelopmental delay and the features outlined should be investigated regardless of ethnicity, as there are no known metabolic markers of this potentially treatable condition. 27909246_ANKRD50 simultaneously engages multiple parts of the SNX27-retromer-WASH complex machinery in a direct and co-operative interaction network that is needed to efficiently recycle the nutrient transporters 28807674_Results suggest that ASCT1/2 may play an important role in regulating extracellular d-serine and NMDA receptor-mediated physiological effects and that ASCT1/2 inhibitors have the potential for therapeutic benefit. 35605507_A rare cause of microcephaly, thin corpus callosum and refractory epilepsy due to a novel SLC1A4 gene mutation. |
ENSMUSG00000020142 |
Slc1a4 |
942.068207 |
2.0267689868 |
1.019182 |
0.076703577 |
175.043049 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000058587614809864413764197916057841738111001277988352134445580892454690352922713302223362740960777020273082815737808459743973799049854278564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000009705423059411882077778229472345241002886011655037752449058742040630601500535785516582778802624947899271856677216874231817200779914855957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1281.6855186 |
55.9075838 |
637.0808675 |
21.1037180 |
| ENSG00000115919 |
8942 |
KYNU |
protein_coding |
Q16719 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) and L-3-hydroxykynurenine (L-3OHKyn) into anthranilic acid (AA) and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-OHAA), respectively. Has a preference for the L-3-hydroxy form. Also has cysteine-conjugate-beta-lyase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11985583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17300176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8706755, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9180257}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-kynurenine degradation; L-alanine and anthranilate from L-kynurenine: step 1/1. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03017}.; PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; quinolinate from L-kynurenine: step 2/3. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. |
Kynureninase is a pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (pyridoxal-P) dependent enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of L-kynurenine and L-3-hydroxykynurenine into anthranilic and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acids, respectively. Kynureninase is involved in the biosynthesis of NAD cofactors from tryptophan through the kynurenine pathway. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:8942; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 3-hydroxykynureninase activity [GO:0061981]; kynureninase activity [GO:0030429]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process from tryptophan [GO:0034354]; anthranilate metabolic process [GO:0043420]; L-kynurenine catabolic process [GO:0097053]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435]; quinolinate biosynthetic process [GO:0019805]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; response to vitamin B6 [GO:0034516]; tryptophan catabolic process [GO:0006569]; tryptophan catabolic process to kynurenine [GO:0019441] |
16080802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16080802_The Lys412Glu polymorphism of the KYNU gene in a hypertensive candidate chromosomal region is associated with essential hypertension in Han Chinese. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22012986_A rare variant at the KYNU gene is associated with essential hypertension in the Han Chinese population. 26725996_Our results suggest that tryptophan metabolism might dichotomously modulate immune responses, with KYNU as a switch between immunosuppressive versus inflammatory outcomes. 31332944_A novel role of kynureninase in the growth control of breast cancer cells and its relationships with breast cancer. 34051337_TDO2 knockdown inhibits colorectal cancer progression via TDO2-KYNU-AhR pathway. 35054825_The TZM-bl Reporter Cell Line Expresses Kynureninase That Can Neutralize 2F5-like Antibodies in the HIV-1 Neutralization Assay. 35362267_Re-sequencing of candidate genes FOXF1, HSPA6, HAAO, and KYNU in 522 individuals with VATER/VACTERL, VACTER/VACTERL-like association, and isolated anorectal malformation. |
ENSMUSG00000026866 |
Kynu |
397.830255 |
7.8715552569 |
2.976649 |
0.108427123 |
813.759274 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005502738204487141295264774084680776702535154120233873369051288789628767877529888186126193209765903326313967493980082780054184068074053719496224728227321 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004390292751255687157962568371154477802724441205901761822391594444628971739515981949062652887571846414051756700438665618251969120547496798411157049889112 |
Yes |
No |
702.6407495 |
47.2747772 |
89.9474340 |
5.2673260 |
| ENSG00000115946 |
56902 |
PNO1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRX1 |
FUNCTION: Positively regulates dimethylation of two adjacent adenosines in the loop of a conserved hairpin near the 3'-end of 18S rRNA (PubMed:25851604). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25851604}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Located in nucleolus and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56902; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA binding [GO:0003723] |
30176151_A detailed characterization of PNO1 organization and its interaction with NOB1. 30862720_High PNO1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 31800162_Importance of PNO1 for growth and survival of urinary bladder carcinoma: Role in core-regulatory circuitry. 33664245_MYC-mediated upregulation of PNO1 promotes glioma tumorigenesis by activating THBS1/FAK/Akt signaling. 33728967_PON1 polymorphisms can predict generalized anxiety and depressed mood in patients with multiple chemical sensitivity. 33864661_Knockdown of PNO1 inhibits esophageal cancer progression. 34050137_PNO1 regulates autophagy and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via the MAPK signaling pathway. 35445733_Ribosome assembly factor PNO1 is associated with progression and promotes tumorigenesis in triplenegative breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000020116 |
Pno1 |
195.695237 |
2.0361867220 |
1.025870 |
0.116982577 |
77.498334 |
0.00000000000000000132834479625480525688930422523699476987414283174390164030120864424588944530114531517028808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000011045841798716013749472273026456764687808414402380146474014210866698704194277524948120117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
264.0108370 |
18.3698190 |
130.5318984 |
7.1369033 |
| ENSG00000115963 |
390 |
RND3 |
protein_coding |
P61587 |
FUNCTION: Binds GTP but lacks intrinsic GTPase activity and is resistant to Rho-specific GTPase-activating proteins. |
3D-structure;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein which is a member of the small GTPase protein superfamily. The encoded protein binds only GTP but has no GTPase activity, and appears to act as a negative regulator of cytoskeletal organization leading to loss of adhesion. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:390; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cortical cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030865]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
11940653_Socius is a novel Rnd GTPase-interacting protein involved in disassembly of actin stress fibers 15754346_RhoE is a tumor suppressor gene that is downregulated early in the development of prostate cancer 15777789_Rnd3/RhoE regulates the assembly of the apical junction complex and tight junction sealing when transfected to a rat tumor cell line. 16311049_The RND3 mRNA levels increased significantly after gestation in myometria. 17182035_RhoE plays an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation and survival and may be considered as an oncosupressor since it is capable to induce apoptosis in several tumor cell lines. 18045987_These results identify Rnd3 as a regulator of cross talk between the RAF/MEK/ERK and Rho/ROCK signaling pathways, and a key contributor to oncogene-mediated reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesions. 18204440_PDK1 competes directly with RhoE for binding to ROCK1. In the absence of PDK1, negative regulation by RhoE predominates, causing reduced acto-myosin contractility and motility. 18721871_Staphylococcal enterotoxin B-treated renal proximal tubule epithelial cells, show 32 differentially expressed transcripts; one of the down-regulated DETs matched the sequence for Rnd3, which normally inhibits Rho protein function. 18923151_Data show that RhoE integrates two processes essential for keratinocyte differentiation and stratification: regulation of proliferative status and integrin adhesion. 18946488_mutation of the RhoE effector region attenuates RhoE-mediated disruption of the actin cytoskeleton, indicating that RhoE exerts its inhibitory effects on ROCK-I through protein(s) binding to its effector region. 19101510_This study demonstrated that RhoE may promote the multidrug resistance phenotype of gastric cancer cells by decreasing the expression of Bax at posttranscriptional level, thus inhibiting vincristine-induced apoptosis. 19244113_Findings implicate Rnd3 as a major suppressor of RhoA-mediated actin cytoskeletal organization and in the acquisition of an invasive melanoma phenotype. 19850923_RhoE inhibits 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and eIF4E function impairing cap-dependent translation. 20683643_study demonstrates a novel role for mir-200b in cell cycle progression and identifies RND3 as a novel mir-200b target 21109974_RhoE expression in gastric cancer cells was regulated by histone deacetylation, but not by DNA methylation, at the epigenetic level. 21209796_Data show that the increased invasiveness of tumorigenic cells was associated with reduced expression of Rnd3. 21478267_Upregulation of FOXD3 expression following inhibition of B-RAF and MEK correlates with the downregulation of Rnd3, a Rho GTPase and inhibitor of RhoA-ROCK signaling. 21917148_Restoration of RND3 expression or RHOA knockdown attenuated the migratory ability of residual cells without affecting overall cell survival 22037464_This study identifies RhoE as a direct target for HIF-1 in gastric cancer cells. 22132820_the expression of miR-17 was negatively correlated with that of RND3 in colorectal cancer tissues and cells 22213123_expression of RhoE was significantly negatively associated with serum AFP (P = 0.013) and tumor grade (P = 0.016) 22234932_Rnd3 expression was significantly lower in invasive tumors with satellite nodules 22251971_The authors show that enteropathogenic Escherichia coli translocates EspH, which inactivates mammalian RhoGEFs and triggers cytotoxicity. 22272352_Results show that induction of RhoE by cAMP is mediated through protein kinase A (PKA) and promotes BeWo cell fusion but has no effect on functional differentiation. 22357615_role of the N-terminal region in signaling; Rnd1 and Rnd3 have a KERRA (Lys-Glu-Arg-Arg-Ala) sequence of amino acids in their N-terminus, which functions as the lipid raft-targeting determinant; the sequence mediates lipid raft targeting of p190 RhoGAP correlated with its activation 22454524_Loss of Rnd3 expression in keratinocytes results in altered colony morphology. 22477709_RhoE may play a driving role in the development and progression of ESCC, and targeting the RhoE may be an effective and feasible approach for treatment of ESCC. 22829315_frequently down-regulated in predominantly HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinomas 23546594_alteration of the malignant behavior of cancer cells by AES is related to RND3 regulation. 23622247_Study reports a high-affinity 14-3-3-binding site at the C terminus of Rnd3 consisting of both the Cys241-farnesyl moiety and a Rho-associated coiled coil containing protein kinase (ROCK)-dependent Ser240 phosphorylation site. 23630292_Rnd3 is a regulator of Notch1 signaling 23821457_Transfection of pre-miR-200c reduces RhoE expression. 24045951_a mechanism according to which proteasomal degradation of RhoE by Skp2 regulates its protein levels to control cellular proliferation. 24312338_CXCR4 might be a downstream effector for RhoE 24399089_RhoE may participate in human cancer progression and act as a candidate target of p53, and these findings also strongly suggest that RhoE may be a new candidate tumor suppressor and could serve as a potential target in the gene therapy of cancer. 24525741_define RhoE as a Notch1 target that is essential for recruitment of N1IC to promoters of Notch1 target genes, establishing a regulatory feedback loop in Notch1 signaling 24667864_MicroRNA-200b acts as a stimulant for the proliferation of HTFs by targeting p27/kip1 and RND3. 25372032_Rnd3 regulates lung cancer cell proliferation through notch signaling. 26108681_We conclude that downregulation of RND3 is responsible for the enhancement of Notch activity that promotes glioblastoma genesis. 26132659_the development and application of a novel data integration methodology reveals novel functions of RND3 in controlling glioma cell migration, invasion, proliferation, angiogenesis and clinical outcome. 26761524_constant degradation of RND3 by chaperone-mediated autophagy is required to sustain rapid proliferation of gastric cancer cells. 26976596_RhoA-ROCK-Rnd3 feedback loop determined the local reassembly sites of the actin cortex during membrane blebbing. 27213590_RhoE and ROCK2 regulate chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. 27555595_Studies provide evidence that Rnd3 plays a dual role in cells; on one hand, it regulates cell proliferation, on the other hand, Rnd3 plays an important role in regulating metastasis and invasion. [review] 27656111_plexin-B2 is a downstream target for Rnd3, which contributes to its cellular function. 27705942_RND3 promotes Snail 1 protein degradation in glioblastoma tumor cells, promoting cell migration and neoplasm invasiveness. 27721256_Our data supported that RhoE could inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis. Moreover, these tumor-suppressing effects might be acted through the negative regulation of EGFR/ERK signaling. 28040410_This study Gene-based tests suggest evidence of association with related genes, ZEB2, RND3, MCTP1, CTBP2, and beta EEG. 29022920_TUG1 can epigenetically inhibit the level of RND3 through binding to EZH2, thus promoting pre-eclampsia development. 29940177_Rnd3 is a MKL1-SRF target that plays a key role in the feedback loop described between the MKL1-SRF pathway and the organization of the actin cytoskeleton 30066855_miR200b and miR200c targeted the expression of RhoE and inhibited the malignancy of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, and the downregulation of miR200b and miR200c may contribute to the high expression of RhoE in NSCLC. 30402829_In pre-eclampsia, increased miRNA-182-5p expression could inhibit the migratory and invasive ability of trophoblast cells through targeted degradation of RND3 protein. 30586715_The study uncovers RhoE as a new fine-tuning factor modulating myocardial infarction-induced inflammation and promoting injured heart recovery. 31332862_RND3 bound p65 and promoted the ubiquitination of p65 protein, leading to reduced expression of p65 protein and inhibition of the NF-kappaB signalling pathway and its downstream target genes IL-8 and BCL-2 to promote apoptosis in GBM cells. 31672447_uncovered a novel differential expression of adipose RND3 in obesity and insulin resistance, which may at least partly depend on a causal effect of RND3 on adipocyte lipolysis. 34046947_Maternal RND3/RhoE deficiency impairs placental mitochondrial function in preeclampsia by modulating the PPARgamma-UCP2 cascade. 34231097_Serum levels of cytoskeleton remodeling proteins and their mRNA expression in tumor tissue of metastatic laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers. 34636197_Effect of RhoE expression on the migration and invasion of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 34767964_HOXD9 transcriptionally induced UXT facilitate breast cancer progression via epigenetic modification of RND3. 35256752_Silencing of RND3/RHOE inhibits the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma and is associated with reversible senescence. 35699481_RND3 Transcriptionally Regulated by FOXM1 Inhibits the Migration and Inflammation of Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis Through the Rho/ROCK Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000017144 |
Rnd3 |
225.343286 |
2.1550206744 |
1.107702 |
0.116321389 |
91.213620 |
0.00000000000000000000128969465335438311723412921137475155105200699642755297744849476981876534864568384364247322082519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000012147985375565217052861984909868941292229774198900380818106833902270125236100284382700920104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
306.1617973 |
21.0734296 |
142.8463260 |
7.7192153 |
| ENSG00000116016 |
2034 |
EPAS1 |
protein_coding |
Q99814 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in the induction of oxygen regulated genes. Heterodimerizes with ARNT; heterodimer binds to core DNA sequence 5'-TACGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters (By similarity). Regulates the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and seems to be implicated in the development of blood vessels and the tubular system of lung. May also play a role in the formation of the endothelium that gives rise to the blood brain barrier. Potent activator of the Tie-2 tyrosine kinase expression. Activation requires recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as CREBBP and probably EP300. Interaction with redox regulatory protein APEX1 seems to activate CTAD (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97481}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Angiogenesis;Congenital erythrocytosis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Host-virus interaction;Hydroxylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor involved in the induction of genes regulated by oxygen, which is induced as oxygen levels fall. The encoded protein contains a basic-helix-loop-helix domain protein dimerization domain as well as a domain found in proteins in signal transduction pathways which respond to oxygen levels. Mutations in this gene are associated with erythrocytosis familial type 4. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:2034; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; epithelial cell maturation [GO:0002070]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; lung development [GO:0030324]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; myoblast fate commitment [GO:0048625]; norepinephrine metabolic process [GO:0042415]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of protein neddylation [GO:2000434]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to oxidative stress [GO:0043619]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11823643_hypoxic induction of the COOH-terminal transactivation domain (CAD)occurs through abrogation of hydroxylation of a conserved asparagine in the CAD 12123724_enzymatic hydroxylation of a conserved prolyl residue in hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunits governs capture by the pVHL E3 ubiquitin ligase complex 12209691_expression related to increased angiogenesis in endometrial adenocarcinoma 12464608_HIF-2alpha and Ets-1 binding is required for transcriptional activation of Flk-1 in endothelial cells 12588875_MAPK signaling facilitates HIF1a and HIF2a activation through p300/CBP 12697324_HIF-2alpha regulates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression in vascular endothelial cells. 12823854_HIF2A is upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. 14512791_Hypoxia-inducible factors 1alpha and 2alpha have roles in vascular endothelial growth factor expression and in nodular malignant melanomas of the skin 14645546_hypoxic gene induction in cells expressing HIF-2alpha but not HIF-1alpha 14668441_HIF-2alpha PAS-B binds the analogous ARNT domain in vitro 14691554_HIF2alpha has a role in regulating pVHL-defective tumor growth 14744852_trans-regulation between HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha during hypoxia likely conveys target gene specificity 14966910_HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 is expressed in most of hepatocellular carcinoma with capsular infiltration and portal vein invasion, which indicates a possible role of HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 in HCC 14985465_deregulation of hypoxia-inducible genes in VHL-/- cells can be attributed mainly to deregulation of HIF and validate HIF as a therapeutic anticancer drug target 15039136_role of EPAS1 and Sp1 in the hypoxic response of cancer cells 15156561_siRNA targeted degradation of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha results in decreased hypoxia-induced PHD3 expression 15192019_EPAS1 may contribute to the construction of mature vessels by modulating the coordinated expressions of VEGF, Flt-1, Flk-1, and Tie2. 15217953_HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in renal cell carcinoma harboring VHL mutations do not have a major role in radiosensitivity 15240563_the complete EPO enhancer displayed dependency on HIF-2alpha regulation, indicating that additional cis-acting elements confer HIF-2alpha specificity within this region 15247232_HIF1a and HIF2a are regulated by PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 15598469_The HIF2A is a transcription factor that plays a key role in the response of cells to oxygen levels. 15652356_HIF-2alpha protein is selectively present in human fetal week 8.5 SNS paraganglia. HIF-2alpha was detected in hypoxic and in well-oxygenized neuroblastoma cells and tissue, presumably reflecting their embryonic features. 15653678_Results describe the specific interaction of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF)-2alpha, but not HIF-1alpha, with the NF-kappaB essential modulator (NEMO). 15964822_Enhanced expression of HIF2A suppressed HIF1A and vice-versa. 16098466_Overexpression of HIF-2alpha in glioma tumors enhances angiogenesis but reduces growth of these tumors, in part by increasing tumor cell apoptosis. 16208515_DNA variants in EPAS1 influence the relative contribution of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism and hence the maximum sustainable metabolic power for a given event duration 16208515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16263938_The role of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha on cell migration and proliferation in fibroblasts during hypoxia is reported. 16278385_androgen receptor is involved in VEGF and hypoxia sensing via hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1a, HIF-2a, and the prolyl hydroxylases in human prostate cancer 16284786_HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha mRNA levels are transiently increased in untrained human skeletal muscle in response to an acute exercise bout, but this response is blunted after exercise training. 16554418_In the normal, fully developed kidney, HIF-1alpha is expressed in most cell types, whereas HIF-2alpha is mainly found in renal interstitial fibroblast-like cells and endothelial cells 16760477_hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha stabilization and transactivation in a graded oxygen environment are regulated in a cell-specific manner 16826581_High HIF-2alpha expression is associated with head and neck cancer 16885164_HIF-P4H, HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha are effective oxygen sensors 16920734_knockdown of the HIF-2alpha gene demonstrated that HIF-2alpha regulates VEGF production, expression of which is essential in renal cell carcinoma 17097563_Results describe the differential recruitment of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha to common target genes in neuroblastoma, and show that HIF-2alpha promotes an aggressive phenotype. 17140440_MT1-MMP is a major mediator of tumor cell invasiveness and type I collagen degradation by VHL RCC cells that express either MT1-MMP or HIF-2alpha 17220275_HIF2alpha C-terminal transactivation domain, in contrast to the HIF1alpha C-terminal transactivation domain, is relatively resistant to the inhibitory effects of FIH1 under normoxic conditions 17285230_Overexpression of the HIF-2A is associated with astrocytomas 17417656_discovery of a conserved, functional iron-responsive element (IRE) in the 5' untranslated region of the messenger RNA encoding EPAS1 17437013_The late expression of HIF-2alpha in the Barrett's carcinogenesis sequence and its high expression in adenocarcinoma suggest it as a morker of disease progression. 17452775_The role of protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) in patients with colorectal adenocarcinomas. 17477366_There may be a hormonal and hypoxia-independent regulatory mechanism coordinating the expression of HIF-1alpha, HIV-2alpha, VEGF, the androgen receptor, and FOXP1 in prostate tumors. 17495954_HIF-2alpha was strongly expressed in both the epidermis and in capillary endothelial cells of the dermis in psoriasis. 17526729_Quantitative differences with respect to HIF deregulation are sufficient to account for the differential risks of kidney cancer linked to VHL mutations. 17555795_cytoplasmic expression of HIF-2alpha in ovarian carcinomas was higher than that in benign and borderline tumors; cytoplasmic expression of HIF-2alpha was significantly higher in stage III and IV tumors than stages I and II 17562539_hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in prostate cancer has been confirmed 17570486_both HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha play important and similar roles in hypoxia-mediated stimulation of PAI-1 expression in HTR-8/SVneo cells 17718430_Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha proteins are not transcriptionally regulated at the mRNA level but are probably regulated at the post-mRNA level. 17852557_high levels of the hypoxia regulated proteins HIF1alpha and CA9 in HNC predict resistance to platinum based radio-chemotherapy. 17907154_we provide the first evidence that HIF-2alpha is essential for hypoxic induction of the human articular chondrocyte phenotype via SOX9 18024825_HIF-1 and HIF-2 are detected in the endothelium and macrophages. Hypoxia-inducible factors in endothelial cells may induce VEGF, thereby contributing to the development of choroid neovascularization. 18055454_HIF-1 and HIF-2 have roles in SK1 upregulation during hypoxia in glioma cells 18077449_new hypoxia-inducible and SOX9-regulated genes, Gdf10 and Chm-I. In addition, Mig6 and InhbA were induced by hypoxia, predominantly via HIF-2alpha 18319549_The ratio of the HIF-2alpha positive cell in tumor infiltrative macrophages may be a new predictive indicator for prognosis before radiation therapy for uterine cervical cancer. 18378852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18420194_Data show that the specific contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha to hypoxic gene expression in vitro is limited and modulated by cell type-specific and exogenous factors. 18423372_HIF-2alpha differentially binds and regulates transcription under hypoxia. 18442887_the region between -3 kb and -1 kb is required for the minimal skeletal tissue-specific expression of Runx2, and that the region between -155 bp and -75 bp is important for its basal transcription, which may be in part mediated by HIF2A in bone tissues. 18508787_the HIF2A(M535I) gene mutation could induce hereditary erythrocytosis at a young age 18625704_an angiogenic signal-ETS1/HIF-2alpha axis regulates the VEGFR1 chromatin domain to induce VEGFR1 transcription in endothelial cells and in differentiating embryonic stem cells 18650473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18711622_HIF-2 alpha plays an important role in the regulation of Epo production. 18728663_Poorer survival of HIF-2 alpha and CA9 stromal-positive CRCs was associated with wild-type TP53, but not with BNIP3 methylation 18787502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18945681_expression of hypoxia-inducible factors 1 alpha and 2 alpha is dependent on mTORC1 and mTORC2 18957292_This study offers novel evidence supporting redox status regulation of HIF-2alpha accumulation under hypoxic conditions. 19010893_Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha correlates to distant recurrence and poor outcome in invasive breast cancer. 19021062_LDH5 is highly upregulated in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas and is in direct relation to factor HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha expression. LDH5 expression is linked with activated VEGFR2/KDR expression 19030186_HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha have divergent roles in colon cancer 19077391_Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha additively promote endothelial vasculogenic properties. 19080330_Data show that EPAS1 and VEGF, but not HIF1alpha, are overexpressed in pancreatic carcinoma. 19129502_crystal structures of the heterodimer formed by the C-terminal PAS domains from the HIF2alpha and ARNT subunits of the HIF2 transcription factor, both in the absence and presence of an artificial ligand 19208626_find that all result in impaired degradation and thus aberrant stabilization of HIF-2alpha 19238077_Pancreatic endocrine microadenomatosis in patients with von Hippel-Lindau disease: characterization by VHL/HIF pathway proteins expression. 19252526_Type 2B R167Q mutant pVhl produces a unique profile of HIF dysregulation, thereby promoting tissue-specific effects on cell growth, development and tumor predisposition. 19287200_the results of the present study revealed that only HIF-1alpha, but not HIF-2alpha dimerizes with HIF-1beta and then regulates expression of target genes in response to hypoxia. 19322701_Increased HIF-2alpha expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 19386601_Within a tiled promoter array we identified 546 and 143 sequences that bound, respectively, to HIF-1alpha or HIF-2alpha at high stringency. 19401348_Study concluded that in ccRCC, PAX2 reactivation is driven by HIF-dependent mechanisms following pVHL loss. 19436307_HIF-1alpha, but not HIF-2alpha, might be used as a marker of prognosis, in addition to methods currently used, to enhance rectal cancer patient management. 19477429_GSCs differentially respond to hypoxia with distinct HIF induction patterns, and HIF2alpha might represent a promising target for antiglioblastoma therapies. 19481479_Only the HIF2A haplotype was shared by individuals who exhibit the high altitude pulmonary edema phenotype 19483472_PTEN induces HIF-2alpha transcriptional activity by inhibiting expression of Yin Yang 1 (YY1), which acts as a novel corepressor of HIF-2alpha. 19498162_findings show that Sirt1 promotes HIF-2 signaling during hypoxia and likely other environmental stresses 19541651_Analysis of the A(2A) receptor gene promoter revealed a hypoxia-responsive element in the region between -704 and -595 upstream of the transcription start site, and by using a ChIP assay, we demonstrate that HIF-2alpha binding to this region is specific. 19590888_The localization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha supports concept that hypoxia is major stimulus for development of submacular wound healing and within this context choroid neovascularization is but one component of this process. 19660915_Report expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha with progression of keratinocytic neoplasms. (Letter) 19706526_Results correlate with altered p53 phosphorylation and target gene expression in untreated human tumor samples and show that HIF2alpha likely contributes to tumor cell survival including during radiation therapy. 19805377_HIF-2alpha as a marker of normoxic neural crest-like neuroblastoma tumor-initiating/stem cells (TICs) isolated from patient bone marrows. 19837976_Data show that EMMPRIN up-regulate hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha, VEGFR-2, and the soluble forms of VEGF in endothelial cells, thus directly regulating the angiogenic process. 19903792_HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha are differentially regulated in vivo in neuroblastoma 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914104_HIF-1alpha expression was an independent predictor of cancer-specific survival in clear cell RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation 19940151_Hsp70- and CHIP-dependent ubiquitination represents a molecular mechanism by which prolonged hypoxia selectively reduces the levels of HIF-1alpha but not HIF-2alpha protein. 19955413_HIF-2alpha is a potentially universal culprit in promoting the persistent proliferation of neoplastic cells 20015878_HIF2A is a newly identified regulator of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand (CXCL)12 expression in multiple myeloma plasma cells and a major contributor to multiple myeloma plasma cell-induced angiogenesis. 20028863_our findings recognize the PHD/HIF regulatory axis as a novel therapeutic target to disable a tumor's ability to adjust to hypoxic conditions and control cell survival 20032376_Detection of a loss-of-function HIF1A mutation in a primary RCC is consistent with HIF-1 and HIF-2 having different roles in renal tumourigenesis. 20039838_Findings present the first evidence that HIF-2alpha is critically involved in the ROS-regulated vascular remodeling processes. 20158574_Mitochondria and HIFs are intimately connected to regulate each other resulting in appropriate responses to hypoxia. 20204822_Uterine leiomyomas are severely and uniformly hypoxic, but do not induce HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, glucose transporter (GLUT)-1 or carbonic anhydrase (CA) IX. 20224786_preferential activation of PTPRZ1 by HIF-2 results at least in part from cooperative binding of HIF-2 and ELK1 to nearby sites on the PTPRZ1 promoter region 20304964_p22(phox)-based Nox oxidases maintain HIF-2alpha protein expression through inactivation of tuberin and downstream activation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1/4E-BP1 pathway 20354189_iron regulatory protein-1-mediated inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-2a translation is linked to the anti-inflammatory 15-deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 20375133_Hypoxia controls the expression of several tumor stem cell signature genes involved in the regulation of stemness as well as the stem cell properties of glioma cells, through HIF-2alpha. 20395290_HIF-2alpha-mediated activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor potentiates head and neck cancer cell migration in response to hypoxia. 20416395_Hypoxia upregulated transcription from all three alternative HIF-3alpha promoters. siRNA experiments showed that this induction is mediated specifically by HIF-1 and not by HIF-2. 20496369_Both HIF-1 and HIF-2 serve as negative regulators of ANK expression in the disc. We 20513003_The knockdown of HIF-2alpha raises autophagic activity and attenuates apoptosis by enhancing HIF-1alpha expression. 20534544_EPAS1 (HIF2alpha) is associated with low hemoglobin concentration in Tibetan highlanders 20534544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551700_HIF2alpha is regulated by hypoxia in the developing human lung. 20559021_present work suggested that HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha were involved in metastasis and invasion of gastric cancer cells under hypoxia, with the involvement of JNK signal pathway 20559438_Both HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha are activated in close correlation with retinal hypoxia but have contrasting cell specificities, consistent with differential roles in retinal ischaemia 20595611_SNP at EPAS1 shows a 78% frequency difference between Tibetan and Han samples, representing fastest allele frequency change observed to date; this SNP's association with erythrocyte abundance supports role of EPAS1 in adaptation to hypoxia 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20632821_Immunostaining results identified HIF-1alpha expression in five (5/20) varicose vein specimens, whereas no control saphenous vein specimens expressed HIF-1alpha. 20807755_The HIF-2alpha showed promoting roles in tumor angiogenesis and growth, and therapeutic outcome may benefit from combined targeting of HIF-2alpha 20824203_a novel mechanism by which EMMPRIN promotes tumor progression through HIF-2alpha/VEGFR-2 mediated mechanism 20856199_Data suggest that PHD2/HIF-2/amphiregulin signaling has a critical role in the regulation of breast tumor progression and propose PHD2 as a potential tumor suppressor in breast cancer. 20939709_prolyl hydroxylase domain protein (PHD) site-specifically hydroxylates the alpha-subunit of the transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor alpha (HIF-alpha), thereby targeting the latter for degradation by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor protein (VHL) 20961960_Observational study and genome-wide association study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20964835_Analysis of renal carcinoma cells for expression of HIF-1a and HIF-2a confirmed high levels of hypoxia inducible factor in cells lacking functional von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumour suppressor. 20965423_Studies indicate that HIF2alpha is selectively expressed in the CD133+ subpopulation of glioblastoma cells, whereas HIF1alpha expression is widespread among both tumorigenic and nontumorigenic cells. 20978319_HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha and CAIX were up-regulated in 88.2% (15/17), 100% (17/17) and 88.2% (15/17) of CCRCC tumors respectively and their expression is independent of VHL status. 21030426_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 21042786_Of specimens with VHL alterations 95.6% tested positive for EPO. EPO was identified in 96.2 and 94.2% of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha positive specimens, respectively, compared to 72.4 and 53.8% for HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha negative groups (p |
ENSMUSG00000024140 |
Epas1 |
83.037784 |
0.3320260918 |
-1.590631 |
0.196110464 |
67.202688 |
0.00000000000000024497987751704251287819350977228284914496452191225162042798046968528069555759429931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001811574645366506672202419044813534754968429273114249866694080992601811885833740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.3964074 |
5.2296734 |
135.6965092 |
9.3650459 |
| ENSG00000116032 |
116444 |
GRIN3B |
protein_coding |
O60391 |
FUNCTION: NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with reduced single-channel conductance, low calcium permeability and low voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. |
Calcium;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Ligand-gated ion channel;Magnesium;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. The encoded protein is found primarily in motor neurons, where it forms a heterotetramer with GRIN1 to create an excitatory glycine receptor. Variations in this gene have been proposed to be linked to schizophrenia. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:116444; |
neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex [GO:0017146]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; cation channel activity [GO:0005261]; glycine binding [GO:0016594]; ionotropic glutamate receptor activity [GO:0004970]; ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0015276]; ligand-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential [GO:0099507]; neurotransmitter binding [GO:0042165]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035235]; protein insertion into membrane [GO:0051205]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924] |
15722182_NR3B mRNA expression in the human hippocampal formation (CA1-CA4 and dentate gyrus) and adjacent neocortex may have implications for understanding the role of NMDA receptors for physiological and pathological processes in these forebrain regions. 17543277_cross-talk between NR3B and NR4A receptors is a mechanism modulating the transcriptional activities of these orphan nuclear receptors 17687115_We tested whether genetic dysfunction of GRIN3B is implicated in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20016182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20016182_These observations suggest that the genetic variation of the NR3B subunit of the NMDA receptor is not a risk factor for Alzheimer's dis pathogenesis 20153313_our findings suggest that the over-expression of NR3B subunit of NMDA receptor is a long lasting result of chronic opioid abuse. 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24814139_Rs2240158 of GRIN3B was significantly associated with mismatch negativity in healthy subjects. 25768306_Authors investigated the significance of a common human genetic variation of the NMDAR NR3B subunit 28132660_GRIN3B missense mutation is an inherited risk factor for schizophrenia. |
ENSMUSG00000035745 |
Grin3b |
37.584416 |
0.1144942832 |
-3.126653 |
0.336201188 |
95.036445 |
0.00000000000000000000018691221769828250644763630000205000619425217879798151173696132629209465392250422155484557151794433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001807879641695052151631749373451468319645863442397395673280971473140255056932801380753517150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2426367 |
1.8099931 |
72.3858238 |
8.6143325 |
| ENSG00000116039 |
525 |
ATP6V1B1 |
protein_coding |
P15313 |
FUNCTION: Non-catalytic subunit of the V1 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons (PubMed:16769747). V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment (PubMed:32001091). Essential for the proper assembly and activity of V-ATPase (PubMed:16769747). In renal intercalated cells, mediates secretion of protons (H+) into the urine thereby ensuring correct urinary acidification (PubMed:16769747). Required for optimal olfactory function by mediating the acidification of the nasal olfactory epithelium (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91YH6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16769747, ECO:0000303|PubMed:32001091}. |
ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c'', and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This encoded protein is one of two V1 domain B subunit isoforms and is found in the kidney. Mutations in this gene cause distal renal tubular acidosis associated with sensorineural deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:525; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0098850]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0016471]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain [GO:0000221]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; proton transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015078]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0055064]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; olfactory behavior [GO:0042048]; ossification [GO:0001503]; pH reduction [GO:0045851]; potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0055075]; prostaglandin metabolic process [GO:0006693]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; regulation of pH [GO:0006885]; renal sodium excretion [GO:0035812]; renal sodium ion transport [GO:0003096]; renal tubular secretion [GO:0097254]; renal water homeostasis [GO:0003091]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; synaptic vesicle lumen acidification [GO:0097401]; vacuolar acidification [GO:0007035]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex assembly [GO:0070072] |
16433694_Here, we describe the molecular findings of the first two Greek Cypriot families with recessive dRTA and the long-term clinical findings in four of five affected members. 17216496_This report describes a new mutation in the ATP6V1B1 gene responsible for distal renal tubular acidosis. 18180394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19008710_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19478356_Two siblings with distal renal tubular acidosis and sensorineural deafness having mutation in the first coding exon of the ATP6V1B1 gene , resulting in a non functional protein, are reported. The parents were found to be carriers for the mutation. 19639346_A mutation in ATP6V1B1 is associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct and early onset of sensorial hearing loss. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20233014_two novel mutations of a heterozygous 15 base-pair deletion (c.756_770del) in exon 7 and a heterozygous 1 base-pair insertion (c.1242_1243insC) in exon 12 in distal renal tubular acidosis and hearing loss 20622307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20622307_This study indicated that a significant percentage of the children with DRTA had sensorineural hearing loss and mutation in ATP6V1B1 gene. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20805693_Only two ATP6V1B1 mutations are found in a Cypriot population with distal renal tubular acidosis. 22509993_Data indicate that direct sequencing of the ATP6V1B1 gene showed one patient harbors two homozygous mutations and the other one is a compound heterozygous. 23729491_Mutations of the ATP6V1B1 gene is associated with primary distal renal tubular acidosis. 23923981_Rare and family-specific variants in ATP6V1B1 are responsible for distal renal tubular acidosis and sensorineural hearing loss syndrome in Turkey. 24252324_Three ATP6V1B1 mutations were observed: one frameshift mutation in exon 12; a G to C single nucleotide substitution, on the acceptor splicing site in intron 2, and one novel missense mutation in exon 11. 24975934_Two probands from different kindreds with mutations in ATP6V1B1 presented early onset profound sensorineural hearing loss 25164082_demonstration of renal acidification defects and nephrolithiasis in heterozygous carriers of a mutant B1 subunit that cannot be attributable to negative dominance; propose that heterozygosity may lead to mild real acidification defects due to haploinsufficiency 25285676_Two founder mutations in the ATP6V1B1 gene were found in 16/27 dRTA cases. 25498251_ATP6V1B1 genetic mutations were detected in more than half of the families studied. Mutations in this gene therefore seem to be the most common causative factors in hearing loss associated with distal renal tubular acidosis in these families. 26453614_Our data indicate that recurrent stone formers with the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase B1 subunit p.E161K SNP exhibit a urinary acidification deficit with an increased prevalence of calcium phosphate-containing kidney stones 27140593_A novel c.1169dupC frameshift mutation of ATP6V1B1 gene was identified in one family and the c.1155dupC North African mutation in 2 other families. Both mutations are located in exon 12 of ATP6V1B1 gene in Moroccan patients with recessive form of distal renal tubular acidosis associated with precocious hearing loss. 28233610_The aim of this work was to analyze the prevalence of genetic defects in SLC4A1, ATP6V0A4, and ATP6V1B1 genes and to assess the clinical phenotype of distal renal tubular acidosis patients that are eventually typical of the different genetic forms of the disease. 29024829_Distal renal acidosis patient carries two novel mutations, one in each of the genes ATP6V0A4 and ATP6V1B1. 29054531_RhCG and H+ATPases are located within the same cellular protein complex in the kidney and this interaction is required for maximal urinary acidification by H+-ATPases, a prerequisite for efficient NH3 secretion and urine excretion of NH4+. 29310826_Both B1 and B2 subunits of the V-ATPase are detectable in human urinary exosomes, and acid and alkali loading or distal renal tubular acidosis cause changes in the B1 but not B2 subunit abundance in urinary exosomes. 29993276_ATP6V1B1 is expressed in the early distal nephron. The physiological importance of H(+)-ATPase expression in these segments remains to be delineated. 30230413_The p. P137S and p. R302W mutations in ATP6V1B1 and p. S473F and p. R807X in ATP6V0A4, were novel disease-causing mutations of distal renal tubular acidosis. 30256676_In patient one, Two novel heterozygous missense mutations of the ATP6V1B1 gene (c.409C>T, p.Pro137Ser; c.904C>T, p.Arg302Trp) were identified. In patient III 2 novel heterozygous duplications (c.1504dupT, p.Tyr502Leufs*22; c.2351dupT, p.Phe785Ilefs*28) were found. 30821427_Serum autoantibodies to subunit B1 and subunit B2 of v-H(+) -ATPase in renal tubular acidosis patients may be responsible for impaired urinary acidification. 31733597_Our study indicates the importance contribution of ATP6V1B1 gene mutations to the pathogenesis of the dRTA in the Algerian population and will contribute to introducing principles to predict the characteristics of the dRTA in patients. 34157794_Identification of seven exonic variants in the SLC4A1, ATP6V1B1, and ATP6V0A4 genes that alter RNA splicing by minigene assay. 35301649_Genetic heterogeneity in GJB2, COL4A3, ATP6V1B1 and EDNRB variants detected among hearing impaired families in Morocco. |
ENSMUSG00000006269 |
Atp6v1b1 |
8.837407 |
0.2879251559 |
-1.796234 |
0.532510824 |
12.437798 |
0.00042073144348722018096009556131775752874091267585754394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001048100608585885188880904017594275501323863863945007324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0819654 |
1.6544289 |
14.2116182 |
3.3784562 |
| ENSG00000116095 |
65977 |
PLEKHA3 |
protein_coding |
Q9HB20 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in regulation of vesicular cargo transport from the trans-Golgi network (TGN) to the plasma membrane (PubMed:15107860). Regulates Golgi phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P) levels and activates the PtdIns(4)P phosphatase activity of SACM1L when it binds PtdIns(4)P in 'trans' configuration (PubMed:30659099). Binds preferentially to PtdIns(4)P (PubMed:11001876, PubMed:15107860). Negatively regulates APOB secretion from hepatocytes (PubMed:30659099). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11001876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15107860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30659099}. |
3D-structure;Golgi apparatus;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding activity. Predicted to be involved in ceramide transport and intermembrane lipid transfer. Located in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:65977; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; ceramide 1-phosphate binding [GO:1902387]; ceramide 1-phosphate transfer activity [GO:1902388]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; ceramide transport [GO:0035627]; intermembrane lipid transfer [GO:0120009] |
15107860_Data show that FAPP1 and 2 are essential components of a phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate- and ADP-ribosylation factor-regulated machinery that controls generation of constitutive post-Golgi carriers. 20300118_The micelle-bound structure of the FAPP1 pleckstrin homology domain reveals how its prominent wedge independently tubulates Golgi membranes by leaflet penetration. 21298564_We report the complete (1)H, (13)C and (15)N resonance assignments of the FAPP1-PH in its free state and those induced by PtdIns(4)P or detergent micelles. 21454700_Molecular basis of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and ARF1 GTPase recognition by the FAPP1 pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. 24462251_Binding sites on Fapp1 protein for Arf1 and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate minimally overlap 30659099_The activity of Sac1 across ER-TGN contact sites requires the four-phosphate-adaptor-protein-1. |
ENSMUSG00000002733 |
Plekha3 |
136.821857 |
2.2143379512 |
1.146875 |
0.189557049 |
36.059869 |
0.00000000191347193062519523082201869791478532345507801437634043395519256591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000008931956260603378754568301125995460898465694299375172704458236694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
165.7060910 |
22.9868534 |
75.3419109 |
7.5773371 |
| ENSG00000116120 |
10056 |
FARSB |
protein_coding |
Q9NSD9 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Ligase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a highly conserved enzyme that belongs to the aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase class IIc subfamily. This enzyme comprises the regulatory beta subunits that form a tetramer with two catalytic alpha subunits. In the presence of ATP, this tetramer is responsible for attaching L-phenylalanine to the terminal adenosine of the appropriate tRNA. A pseudogene located on chromosome 10 has been identified. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:10056; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phenylalanine-tRNA ligase complex [GO:0009328]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phenylalanine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004826]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; phenylalanyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006432]; protein heterotetramerization [GO:0051290]; translation [GO:0006412] |
20223217_Structure of human cytosolic phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase: evidence for kingdom-specific design of the active sites and tRNA binding patterns 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22137894_Human PheRS recognizes C74, the G1-C72 base pair, and the 'discriminator' base A73, proposed to contribute to tRNA(Phe) identity in the yeast mitochondrial enzyme. 29573043_Expression studies using fibroblasts isolated from the proband revealed a severe depletion of both FARSB and FARSA protein levels. These data indicate that the FARSB variants destabilize total phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase levels, thus causing a loss-of-function effect. 30014610_This study further implicates FARSB mutations in a multisystem, recessive, neurodevelopmental phenotype that share clinical features with the previously known aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-related diseases. 31355908_FARSA mutations mimic phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase deficiency caused by FARSB defects. 34159625_Contribution of upregulated aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis to metabolic dysregulation in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000026245 |
Farsb |
300.078642 |
2.2884348800 |
1.194361 |
0.108859310 |
120.711590 |
0.00000000000000000000000000044192721122721717915071866888898272809719439742770580722853856444124181351851277099740400444716215133666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000005316092614273615191337486574388769149867331065604538266864685476455372470372395810045418329536914825439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
423.4944632 |
27.6518202 |
186.3814103 |
9.4501749 |
| ENSG00000116133 |
1718 |
DHCR24 |
protein_coding |
Q15392 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reduction of the delta-24 double bond of sterol intermediates during cholesterol biosynthesis (PubMed:11519011, PubMed:21671375, PubMed:25637936, PubMed:22178193). In addition to its cholesterol-synthesizing activity, can protect cells from oxidative stress by reducing caspase 3 activity during apoptosis induced by oxidative stress (PubMed:11007892, PubMed:22010141). Also protects against amyloid-beta peptide-induced apoptosis (PubMed:11007892). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11007892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11519011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21671375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22010141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25637936}. |
Alternative splicing;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;FAD;Flavoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Signal;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; cholesterol biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11519011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21671375}. |
This gene encodes a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-dependent oxidoreductase which catalyzes the reduction of the delta-24 double bond of sterol intermediates during cholesterol biosynthesis. The protein contains a leader sequence that directs it to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Missense mutations in this gene have been associated with desmosterolosis. Also, reduced expression of the gene occurs in the temporal cortex of Alzheimer disease patients and overexpression has been observed in adrenal gland cancer cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1718; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; delta24(24-1) sterol reductase activity [GO:0000246]; delta24-sterol reductase activity [GO:0050614]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016628]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:0042987]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via desmosterol [GO:0033489]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via lathosterol [GO:0033490]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; plasminogen activation [GO:0031639]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; skin development [GO:0043588]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
15001630_seladin-1/DHCR24 is modulated by the ACTH/cAMP-driven pathway and its expression is reduced in adrenal cancer 15577914_unanticipated role for Seladin-1, previously implicated in Alzheimer's disease and cholesterol metabolism, in integrating cellular response to oncogenic and oxidative stress 15688385_High levels of DHCR24 gene expression is associated with melanoma metastases 15954227_seladin-1 has been isolated and found to be down-regulated in brain regions affected by Alzheimer disease--REVIEW 16762343_These original results demonstrate for the first time that seladin-1 is abundantly expressed by stem cells and appear to suggest that reduced expression in AD might be due to an altered pool of multipotent cells. 17510943_DHCR24 gene may be associated with Alzheimer's disease risk. 17579359_Preliminary results suggest the absence of an association between DHCR24/seladin-1 genotypes and Alzheimer's disease in the Italian population. 17855807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17984220_ablation of DHCR24/seladin-1 prevented apoptosis of primary neurons in a p53-dependent manner 18194465_DHCR24 protects neuroblastoma cells against Abeta toxicity by increasing membrane cholesterol content. 18499757_Seladin-1 may be considered a fundamental mediator of the neuroprotective effects of estrogen. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18762779_the seladin-1 gene is androgen regulated and has a higher level of expression in prostate cancer tissues compared to the normal prostate 18815215_Seladin-1/DHCR24 is an LXR target gene and that LXR may regulate lipid raft formation. 19325144_Results suggest that antiinflammatory effects of HDLs are mediated partly through an upregulation of DHCR24. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19520779_seladin-1 expression and intracellular localization are correlated with both the intensity and nature of ACTH-induced steroidogenesis and resultant oxidative stress. 19815556_seladin-1 downregulation increases BACE1 levels and activity through enhanced GGA3 depletion during apoptosis 19861417_DHCR24 is elevated in response to HCV infection and inhibits the p53 stress response by stimulating the accumulation of the MDM2-p53 complex in the cytoplasm and by inhibiting the acetylation of p53 in the nucleus. 20061631_Reduced expression of the enzyme that converts desmosterol into cholesterol, Alzheimer indicator 1 gene (seladin-1/dhcr24), in cortex and cerebellum may underlie increased desmosterol levels in 21 month-old amyloid-beta mutant mice. 20166102_Seladin-1 involvement in proliferation and secretion suggests that its downregulation may be a major mechanism causing prostate cancer evolution. 20465827_Promoter methylation could be involved in the altered pattern of seladin-1 gene expression in adrenal carcinoma. 20568014_DNA methylation and histone acetylation have roles in regulating the promoter region of the human DHCR24 gene 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21559050_affected individuals have a homozygous missense mutation in DHCR24 leading to dramatically augmented plasma desmosterol levels. We thus establish a clear consistent phenotype of desmosterolosis (MIM 602398). 21901424_Level of brain amyloid deposition on [(11)C]PiB PET was associated with rs7551288, an intronic SNP in DHCR24, in 103 participants. The minor allele was associated with lower PiB uptake with non-carriers showing higher PiB uptake in frontal regions. 21987590_This study describes Simvastatin modulates the Alzheimer's disease-related gene seladin-1. 22010141_DHCR24-overexpressed cells were protected from apoptosis in response to oxidative stress, which was accompanied by a decrease in DHCR24 content on the ER and activation of caspase-3. 22178193_a novel role for 24,25EC in cholesterol homeostasis, through its rapid inhibition of cholesterol synthesis at DHCR24. 22431021_Activation of Sp1 by oxidative stress is involved in the promotion of expression of DHCR24 by Hepatitis C virus. 22910610_a gender dependent effect of DHCR24 rs600491 polymorphism on the susceptibility to Alzheimer disease. 23050906_DHCR24 gene expression is regulation by cholesterol availability. 23123430_Inflammation is inhibited in coronary artery endothlial cells by increasing 3beta-hydroxysteroid-Delta24 reductase expression. 23416078_TR-beta and LXR-alpha competitively up-regulate the human Seladin-1 promoter, sharing the same response element, site A. 24363437_Data indicate a mechanism whereby 3beta-hydroxysterol Delta24-reductase (DHCR24) activity is regulated by signaling. 24489783_DHCR24 expression protects neuronal cells from apoptotic cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. 24562935_In vitro experiments showed that DHCR24 overexpression induced tumor proliferation. 24916565_Data (including data from studies using RNA from post-mortem brain tissue) suggest that expression of DHCR24 is up-regulated in parietal cortex of patients with Huntington's disease as compared to control subjects. 25637936_physical and functional interaction between DHCR24 and DHCR7 26288822_DHCR24 auto-antibody represents a potential noninvasive biomarker for hepatitis C virus-related liver disease and may facilitate the diagnosis of PIVKA-II and AFP-negative hepatocellular carcinoma. 27919032_the expanding database of post-translational modifications will be a valuable resource for mapping the topology of membrane-associated proteins, such as DHCR24, that is, flagging cytosolic residues accessible to modifying enzymes such as kinases and ubiquitin ligases. 28112250_The crucial role of the insulin/STAT3/DHCR24/PGR axis in the progression of endometrial carcinoma. 29093763_Study observed decreased methylation at the DHCR24 locus in offspring of women with active pregnancy eating disorders (ED) and increased methylation at the LGALS2 locus in offspring of women with past ED compared to controls. 29175559_Mutation in DHCR24 gene cause desmosterolosis presenting with multiple congenital anomalies with increased level of the cholesterol precursor desmosterol while disrupting development of cholesterol, impacting embryogenesis. 30278482_DHCR24 might be a therapeutic target for patients with bladder cancer 31100313_MiR-124 targeting Dhcr24 regulates oxidative stress and hypoxia induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. 31900429_A variant near DHCR24 associates with microstructural properties of white matter and peripheral lipid metabolism in adolescents. 31904814_the E3 ubiquitin ligase membrane-associated ring-CH-type finger 6 (MARCH6), known to control earlier rate-limiting steps in cholesterol synthesis, also control levels of LDM and the terminal cholesterol synthesis enzyme, 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase. 32286791_Amiodarone Alters Cholesterol Biosynthesis through Tissue-Dependent Inhibition of Emopamil Binding Protein and Dehydrocholesterol Reductase 24. 32641492_Hepatitis C virus NS3-4A protease regulates the lipid environment for RNA replication by cleaving host enzyme 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase. 32713162_24-Dehydrocholesterol reductase promotes the growth of breast cancer stem-like cells through the Hedgehog pathway. 33422461_Endothelial cells control vascular smooth muscle cell cholesterol levels by regulating 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase expression. 33710538_DHCR24 Knockdown Lead to Hyperphosphorylation of Tau at Thr181, Thr231, Ser262, Ser396, and Ser422 Sites by Membrane Lipid-Raft Dependent PP2A Signaling in SH-SY5Y Cells. 34624089_Oncogenic role of the SOX9-DHCR24-cholesterol biosynthesis axis in IGH-BCL2+ diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. 34949154_24-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase alleviates oxidative damage-induced apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells via regulating Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B activation. 35296367_The role of DHCR24 in the pathogenesis of AD: re-cognition of the relationship between cholesterol and AD pathogenesis. 36068004_Hsa_circ_0003221 facilitates the malignant development of bladder cancer cells via resulting in the upregulation of DHCR24 by targeting miR-892b. |
ENSMUSG00000034926 |
Dhcr24 |
1153.675223 |
2.2382749267 |
1.162387 |
0.050880292 |
526.204779 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001890711168698993284917511618586436465917706894536781654355845084646978939151204536795177238742606686749062078967747029854285406853766273206361940152418585861570299989731485068517400461344087668025513560068607626733 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000952453817406045815782326660108052027894429362327212852947703791984951767385983868904346007882204953563645784215479111573071779528850669721844923804952247535200887025433722488129396249334914690584456329743873202006 |
Yes |
No |
1610.9800694 |
48.2324917 |
724.7868017 |
17.1259684 |
| ENSG00000116157 |
2882 |
GPX7 |
protein_coding |
Q96SL4 |
FUNCTION: It protects esophageal epithelia from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. It suppresses acidic bile acid-induced reactive oxigen species (ROS) and protects against oxidative DNA damage and double-strand breaks. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22157330}. |
3D-structure;Oxidoreductase;Peroxidase;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Enables catalase activity. Predicted to be involved in cellular response to oxidative stress. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2882; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; catalase activity [GO:0004096]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; peroxidase activity [GO:0004601]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599] |
15294905_NPGPx plays an essential role in breast cancer cells in alleviating oxidative stress generated from polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21215271_GPx7 labeled as secreted glutathione peroxidase, is actually endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein disulfide isomerase peroxidase 23123197_NPGPx is essential for releasing excessive ER stress by enhancing GRP78 chaperone activity to maintain physiological homeostasis. 23454490_GPx7 is an unusual CysGPx catalyzing the peroxidatic cycle by a one Cys mechanism in which GSH and PDI are alternative substrates. 23580780_tumour suppressor functions in esophageal adenocarcinomas and silenced by location-specific promoter DNA methylation 23828861_NPGPx protects against fat accumulation in mice and human via modulating ROS 23919619_GPx7 promotes oxidative protein folding, directly utilizing Ero1alpha-generated hydrogen peroxide in the early secretory compartment. 24692067_Loss of glutathione peroxidase 7 promotes TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in Barrett's carcinogenesis. 25586538_SNPs most associated with Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy were in ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 4 (ABCC4) gene. 26708178_use GPX4 and GPX7 as possible markers for improving HCC diagnosis/prognosis. 32719007_Characterization of the endoplasmic reticulum-resident peroxidases GPx7 and GPx8 shows the higher oxidative activity of GPx7 and its linkage to oxidative protein folding. 34339889_MicroRNAs mediated regulation of glutathione peroxidase 7 expression and its changes during adipogenesis. 34626080_GPX7 Facilitates BMSCs Osteoblastogenesis via ER Stress and mTOR Pathway. 35440701_Comprehensive analysis of epigenetics regulation, prognostic and the correlation with immune infiltrates of GPX7 in adult gliomas. |
ENSMUSG00000028597 |
Gpx7 |
84.612361 |
0.4644845436 |
-1.106298 |
0.174633724 |
40.815853 |
0.00000000016727068028000961949589816721398497986750264487909589661285281181335449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000851350083080324861562333427521037307328377607973379781469702720642089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.7792175 |
5.8700211 |
118.8130267 |
8.1485815 |
| ENSG00000116183 |
60676 |
PAPPA2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXP8 |
FUNCTION: Metalloproteinase which specifically cleaves insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-5 at the '163-Ser-|-Lys-164' bond. Shows limited proteolysis toward IGFBP-3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11264294, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26902202}. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Sushi;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the pappalysin family of metzincin metalloproteinases. The encoded protein cleaves insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 and is thought to be a local regulator of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) bioavailability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:60676; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; response to salt stress [GO:0009651] |
18374411_Seven placental transcripts characterize HELLP-syndrome. 18805800_PAPP-A2 in syncytiotrophoblast cells was dramatically increased in pre-eclampsia. Maternal serum concentrations of PAPP-A2 were also significantly elevated in pre-eclampsia as compared with uncomplicated pregnancy. 18818296_Preeclampsia involves changes in the gene expression of PAPPA2 in placental cytotrophoblasts. 19474058_PAPPA2 is expressed in the syncytiotrophoblast layer of human placental villi and is also detected in some invasive extravillous trophoblasts in the first trimester 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20103653_Circulating IGFBP-5 is proteolyzed by PAPP-A2 during pregnancy, resulting in increased IGF bioavailability, which may have important consequences for the development of the fetus and/or the well-being of the mother. 20304771_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21496272_factors previously known to be highly expressed in preeclamptic placentae (PGE2 and TNF-alpha), contribute to the upregulation of PAPPA2. results are consistent with the hypothesis that PAPPA2 is upregulated as a consequence of placental pathology 22037112_Association of a single nucleotide polymorphism in pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A2 with developmental dysplasia of the hip 23484525_PAPPA2 may be upregulated in severe pre-eclampsia and, functionally, this may be mediated via increased placental hypoxia known to occur with this pregnancy disorder. 23804707_The existence of this assay will enable an assessment of the biomarker potential of PAPP-A2 in pre-eclampsia as well as other clinical conditions. 24336677_The upregulation of PAPP-A2 observed in preeclampsia at term occurs early in pregnancy, before the symptoms develop. 24672801_The association between this PAPPA2 single nucleotide polymorphism and developmental dysplasia of the hip was evaluated. 25154785_overexpression in Down syndrome from placental mRNA to maternal serum protein 26748159_PAPP-A2 is differentially expressed in different trophoblast populations and shows strong down regulation in the mid second trimester in chorionic villous samples. 26902202_These patients provide important insights into the regulation of longitudinal growth in humans, documenting the critical role of PAPP-A2 in releasing IGF-I from its binding proteins. 27525857_in situ hybridization (ISH) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were employed to examine the spatial and temporal expression of PAPPA2 in the human fetomaternal interface. 27648969_Short-term treatment with progressive doses of rhIGF1 (recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-1) improved growth in two siblings with deficiency of PAPP-A2 (pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A2) [due to a homozygous loss-of-function frameshift mutation in exon 3 of the PAPP-A2 gene (p.D643fs25*)] that resulted in postnatal growth failure due to resulting decrease in IGF1 bioavailability. [CASE REPORT] 28854436_PAPP-A2 is increased in Hemodialysis patients and interacts with PAPP-A on patients prognosis. 29144175_Pregnancy associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) appears to be a potentially useful biomarker for short-term risk stratification of patients presenting with chest pain of ischemic origin (Review). 29238946_This review evaluates the current data concerning PAPP-A2 function, and particularly the effect of PAPP-A2 mutation on growth. 29532882_The findings suggest a possible pathophysiological link between the development of Fetal growth restriction and the expression of PAPPA, PAPPA2 and PLAC-1. 29653372_PAPP-A2 mutation is associated with idiopathic short stature. 30816319_The potential role of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A2 in angiogenesis and development of preeclampsia. 31103608_Total IGFBP 5, PAPPA, PAPPA2 and Stanniocalcin-2. 31961798_PAPP-A2 consistently decreased throughout childhood. PAPP-A2 levels positively correlated with the percent free IGF-I and negatively with intact IGFBP-3. correlative findings suggest that PAPP-A2 is an important regulator of the percent free IGF-I which can be a marker of perturbations in the GH/IGF-I axis. 31994005_Uteroplacental Ischemia Is Associated with Increased PAPP-A2. 32004755_Netazepide Inhibits Expression of Pappalysin 2 in Type 1 Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors. 32739295_Disorders caused by genetic defects associated with GH-dependent genes: PAPPA2 defects. 32990126_PAPP-A2 and Inhibin A as Novel Predictors for Pregnancy Complications in Women With Suspected or Confirmed Preeclampsia. 33783375_Associations of plasma PAPP-A2 and genetic variations with salt sensitivity, blood pressure changes and hypertension incidence in Chinese adults. 34116346_Serum Inhibin-A and PAPP-A2 in the prediction of pre-eclampsia during the first and second trimesters in high-risk women. 34203285_Genetic Study of IL6, GDF5 and PAPPA2 in Association with Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. 34272725_Short stature with low insulin-like growth factor 1 availability due to pregnancy-associated plasma protein A2 deficiency in a Saudi family. 34476481_Dynamic Changes in Serum IGF-I and Growth During Infancy: Associations to Body Fat, Target Height, and PAPPA2 Genotype. |
ENSMUSG00000073530 |
Pappa2 |
19.752299 |
0.4897481570 |
-1.029888 |
0.370738463 |
7.738487 |
0.00540560865297244445837332449400491896085441112518310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010968763227642739158107509922501776600256562232971191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2842704 |
4.8732227 |
23.3682199 |
7.0110294 |
| ENSG00000116191 |
55103 |
RALGPS2 |
protein_coding |
Q86X27 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the small GTPase RALA. May be involved in cytoskeletal organization. May also be involved in the stimulation of transcription in a Ras-independent fashion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Alzheimer disease;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of Ral protein signal transduction; regulation of catalytic activity; and small GTPase mediated signal transduction. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55103; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of Ral protein signal transduction [GO:0032485] |
27149377_RALGPS2 is implicated in the control of cell cycle progression and survival in the in vitro growth of NSCLC cell lines. This function is largely independent of Ral GTPases and associated with modulation of Skp2, p27 and p21 cell cycle regulators 29208460_In fact the overexpression of RalGPS2 or of its PH-domain increased markedly the number and the length of nanotubes, while the knock-down of RalGPS2 caused a strong reduction of these structures. Moreover, using a series of RalA mutants impaired in the interaction with different downstream components (Sec5, Exo84, RalBP1) we demonstrated that the interaction of RalA with Sec5 is required for TNTs formation |
ENSMUSG00000026594 |
Ralgps2 |
67.357094 |
0.4294238236 |
-1.219526 |
0.184309328 |
44.370948 |
0.00000000002716891688488418543725629783156807432048518435863115882966667413711547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000146355187306894391848202966274370903643209373967692954465746879577636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.5274120 |
6.6193330 |
95.3345228 |
10.8244606 |
| ENSG00000116396 |
3749 |
KCNC4 |
protein_coding |
Q03721 |
FUNCTION: This protein mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a potassium-selective channel through which potassium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
The Shaker gene family of Drosophila encodes components of voltage-gated potassium channels and is comprised of four subfamilies. Based on sequence similarity, this gene is similar to the Shaw subfamily. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the delayed rectifier class of channel proteins and is an integral membrane protein that mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. It generates atypical voltage-dependent transient current that may be important for neuronal excitability. Multiple transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:3749; |
axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite membrane [GO:0032590]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body membrane [GO:0032809]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005251]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] |
15485486_Kv3.4 was overexpressed in early stages of Alzheimer disease and in advanced stages was present at high levels in neurodegenerative structures. This subunit regulates delayed-rectifier currents, primary determinants of spike repolarization in neurones 16449802_The characterization of a missense mutation in MiRP2 that affects its phosphorylation and consequent interactions with Kv3.4 is reported. 20093253_Kv3.4 channels exert a permissive role in the cell cycle progression of proliferating uterine vascular smooth cells. 21912965_Although all KV3 subunit transcripts are significantly expressed at embryonic age in whole mouse brain extracts, only KV3.1, KV3.2 and KV3.4 subunit transgenic proteins are present. 22473424_these data suggest that Kv3.4 and Cav1.2 may act together to control Ca(2) -dependent electrical activity of pioneer axons and play important roles during axon pathfinding. 23443853_Ionizing radiation-induced G2/M arrest was preceded by activation of Kv3.4-like voltage-gated potassium channels. 25609640_These results suggest a novel peripheral mechanism of post-spinal cord injury pain sensitization implicating Kv3.4 channel dysregulation and potential Kv3.4-based therapeutic interventions. 26648458_This study provides original evidence to demonstrate the early occurrence and high prevalence of abnormal Kv3.4 expression in oral leucoplakias. Our results support a role for Kv3.4 potassium channel in OSCC tumorigenesis rather than tumour progression and disease outcome. 31471334_HIF-1alpha regulates the invasion, migration and proliferation of oral cancer cells by regulating Kv3.4 expression. 33368632_PKCepsilon associates with the Kv3.4 channel to promote its expression in a kinase activity-dependent manner. |
ENSMUSG00000027895 |
Kcnc4 |
50.281961 |
2.9235928942 |
1.547742 |
0.547238315 |
7.522556 |
0.00609311773208456863848425655305618420243263244628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012224332978872941984915811985956679563969373703002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.9734921 |
20.2033682 |
20.4110832 |
5.0470072 |
| ENSG00000116514 |
127544 |
RNF19B |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMZ0 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBE2L3 and UBE2L6 in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates, such as UCKL1 (PubMed:16709802, PubMed:27485036). Involved in the cytolytic activity of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T-cells (PubMed:10438909). Protects against staurosporin-induced cell death (PubMed:27485036). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10438909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16709802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27485036}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a multi-pass membrane protein containing two RING-type and one IBR-type zinc finger motifs. The encoded protin is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that plays a role in the cytotoxic effects of natural killer (NK) cells. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. There are pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes X and Y in a possible pseudoautosomal region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:127544; |
cytolytic granule [GO:0044194]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042267]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
27570112_NKLAM is a positive regulator of STAT1-mediated transcriptional activity and is an important component of the innate immune response. |
ENSMUSG00000028793 |
Rnf19b |
205.899301 |
3.1219548170 |
1.642450 |
0.113751911 |
216.047962 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000065835278827293220710124295121576907458113989518001955389571081046380077917007994347826690998148562830876310331877221805694372358530586097913328558206558227539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000013667070541362137572953737952962416068051517066486743012662161991072803863182337472770631307228728666784055950790178102401128956699949412723071873188018798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
313.5567345 |
21.7664359 |
101.2009855 |
5.8170977 |
| ENSG00000116539 |
55870 |
ASH1L |
protein_coding |
Q9NR48 |
FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase specifically trimethylating 'Lys-36' of histone H3 forming H3K36me3 (PubMed:21239497). Also monomethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (H3K9me1) in vitro (By similarity). The physiological significance of the H3K9me1 activity is unclear (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99MY8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21239497}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Cell junction;Chromatin regulator;Chromosome;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Tight junction;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the trithorax group of transcriptional activators. The protein contains four AT hooks, a SET domain, a PHD-finger motif, and a bromodomain. It is localized to many small speckles in the nucleus, and also to cell-cell tight junctions. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55870; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone H3K36 methyltransferase activity [GO:0046975]; histone H3K4 methyltransferase activity [GO:0042800]; histone H3K9 methyltransferase activity [GO:0046974]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; histone H3-K36 dimethylation [GO:0097676]; histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051568]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002674]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; tarsal gland development [GO:1903699]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; uterine gland development [GO:1903709]; uterus morphogenesis [GO:0061038] |
17923682_These data suggest that ASH1L occupies most, if not all, active genes and methylates histone H3 in a nonredundant fashion at a subset of genes. 21239497_human ASH1L specifically methylates histone H3 Lys-36. 22140534_ASH1 and MLL1 synergize in activation of Hox genes. 22541069_Long Non-coding RNA, DBE-T recruits the Trithorax group protein Ash1L to the FSHD locus, driving histone H3 lysine 36 dimethylation, chromatin remodeling, and 4q35 gene transcription. 22696682_induction of Cdk5 activity is a novel mechanism through which hASH1 may regulate migration in lung carcinogenesis 24019522_all of the H3K36-specific methyltransferases, including ASH1L, HYPB, NSD1, and NSD2 were inhibited by ubH2A, whereas the other histone methyltransferases, including PRC2, G9a, and Pr-Set7 were not affected by ubH2A. 24244179_Our results uncover a novel regulatory cascade orchestrated by Ash1l with RAR and provide insights into mechanisms underlying the establishment of the transcriptional activation that counteracts Polycomb silencing 25238203_These data demonstrate that miR-142-3p downregulation has a role in thyroid tumorigenesis, by regulating ASH1L and MLL1. 26002201_Both ASH1L and SETD2 are H3K36 specific methyltransferases but only SETD2 can trimethylate this mark. 26292256_Structural features were identified in ASH1L related to its' function and enzymatic activity. 27154821_Epigenetic regulators play vital roles in cancer pathogenesis and represent a new frontier in therapeutic targeting. Our studies provide basic mechanistic insight into the role of H3K36me2 in transcription activation and MLL leukemia pathogenesis and implicate ASH1L histone methyltransferase as a promising target for novel molecular therapy. 27434206_Our data suggest a role for ASH1L, a methyl transferase protein and member of the trithorax (Trx) family, in regulation of the HBB gene and as a potential modifier of beta-thalassaemia severity. 28041684_suppresses matrix metalloproteinase through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in pulpitis 28394464_There has been increasing evidence that heterozygous mutation of ASH1L is associated with ID and autism spectrum disorders. We suggest that ASH1L abnormalities may cause a novel MCA/ID syndrome. 29109511_DDB2 promotes cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer excision by recruiting the histone methyltransferase ASH1L, which methylates lysine 4 of histone H3. In turn, methylated H3 facilitates the docking of the XPC complex to nucleosomal histone octamers. 29724719_Study shows that mutations associated with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) result both in loss of miR-142-3p function and in decreased miR-142-5p expression. During hematopoietic maturation, loss of Mir142 increased ASH1L protein expression and consequently resulted in the aberrant maintenance of Hoxa gene expression in myeloid-committed hematopoietic progenitors. 29753921_A novel loss of function mutation in ASH1L was identified in a patient with an emergent neurodevelopmental syndrome. 30827841_ASH1L activation by MRG15 represents a delicate regulatory mechanism for how a cofactor activates an SET domain HMTase by releasing autoinhibition 30827843_Ash1L stimulates H3K36 methyltransferase activity through Mrg15 binding 31673123_Mutations in ASH1L confer susceptibility to Tourette syndrome. 32398261_Novel role of ASH1L histone methyltransferase in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. 34373061_ASH1L mutation caused seizures and intellectual disability in twin sisters. 34782621_Deficiency of autism risk factor ASH1L in prefrontal cortex induces epigenetic aberrations and seizures. 35147301_Exploration of INSM1 and hASH1 as additional markers in lung cytology samples of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma with indeterminate neuroendocrine differentiation. 35307981_ASH1L may contribute to the risk of Tourette syndrome: Combination of family-based analysis and case-control study. |
ENSMUSG00000028053 |
Ash1l |
712.838730 |
0.4062076315 |
-1.299711 |
0.452560386 |
7.465841 |
0.00628806659989570530117086732957432104740291833877563476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012581247528054846640532815627011586911976337432861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
431.0508176 |
110.8109559 |
1073.1101148 |
199.1900257 |
| ENSG00000116667 |
81563 |
C1orf21 |
protein_coding |
Q9H246 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:81563; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000032666 |
1700025G04Rik |
327.189697 |
6.7478945004 |
2.754437 |
0.127157609 |
457.416631 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001754204767678250460652512385455841729506851595735930005969130475578506792412450840772666431793791533252817639420962188387730947184163575249577217799075691593310437808313568060105208556324553046952171319417180649458116668384627658 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000766037348252395726573299537336560761731453306270015754182093145435000616882966784724865422053518351416105193774404909298725554828345156854891918587556915688091616957013501565402973666289808144005736253485987125466741702188027708 |
Yes |
Yes |
509.3038549 |
57.2488485 |
75.6934781 |
6.4350632 |
| ENSG00000116668 |
54823 |
SWT1 |
protein_coding |
Q5T5J6 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54823; |
nucleus [GO:0005634] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000052748 |
Swt1 |
85.549353 |
0.4228586131 |
-1.241753 |
0.292503091 |
17.597206 |
0.00002729890831347239497158170540291877159688738174736499786376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000081285432057061235314003588836584413002128712832927703857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.7512484 |
10.5831773 |
125.6013111 |
17.7688725 |
| ENSG00000116701 |
4688 |
NCF2 |
protein_coding |
P19878 |
FUNCTION: NCF2, NCF1, and a membrane bound cytochrome b558 are required for activation of the latent NADPH oxidase (necessary for superoxide production). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12207919}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chronic granulomatous disease;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;TPR repeat |
|
This gene encodes neutrophil cytosolic factor 2, the 67-kilodalton cytosolic subunit of the multi-protein NADPH oxidase complex found in neutrophils. This oxidase produces a burst of superoxide which is delivered to the lumen of the neutrophil phagosome. Mutations in this gene, as well as in other NADPH oxidase subunits, can result in chronic granulomatous disease, a disease that causes recurrent infections by catalase-positive organisms. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:4688; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; NADPH oxidase complex [GO:0043020]; phagolysosome [GO:0032010]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; superoxide-generating NAD(P)H oxidase activity [GO:0016175]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; respiratory burst [GO:0045730]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] |
11483614_Transcriptional regulation of the p67phox gene: role of AP-1 in concert with myeloid-specific transcription factors. Identification of cis-regulatory elements regulating p67(phox), with identification of specific sequences of TF binding sites. 11705402_In a cell-free system, covalent binding between C-terminal-truncated p67phox and rac in the correct fusion order produces a more stable complex than the individual components and significantly influences the duration of fusion-produced oxidase activation. 11796733_detailed study of the protein-protein interactions that occur in the p40-p47-p67(phox) complex of the resting oxidase 11893732_p22(phox), gp91(phox), p47(phox), p67(phox), and p40(phox) existed as a functional complex in the cytoskeletal fraction. 11929750_Val204 in p67(phox), previously shown to be required for NADPH oxidase activity under cell-free conditions, was found to be essential for superoxide production by intact COS-phox cells. 12101222_effect of cPLA2 on its translocation 12130503_NAD(P)H oxidase subunits p47(phox) and p67(phox) are expressed in platelets; and NAD(P)H oxidase-dependent platelet superoxide anion release increases platelet recruitment. 12719414_p67phox and p47phox have roles in regulating a change of conformation in cytochrome b558, which initiates the electron transfer in NADPH oxidase activation 15181005_NOXO1, p47phox, and p67phox regulate Nox3 15256399_NAD(P)H oxidase activity is associated with increased protein levels of p22phox, p47phox, and p67phox, and increased p22phox and nox2 (gp91phox) mRNA expression. 16293794_Increased expression and activity of NAD(P)H oxidase subunits and xanthine oxidase, in part mediated through angiotensin II and PKC-dependent pathways, are important mechanisms underlying increased oxidative stress in human coronary artery disease 16297854_Here we show that the p47(phox)-p67(phox) interaction is disrupted not only by deletion of the PRR but also by substitution for basic residues in the extra-PRR (K383E/K385E). 16310324_Expression of p67(phox) is regulated through mechanisms that include modulation of transcription and translation. 16608528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16626305_These results indicate that Hcy (homocysteine)-stimulated superoxide anion production in monocytes is regulated through PKC-dependent phosphorylation of p47phox and p67phox subunits of NADPH oxidase. 16987007_NADPH oxidase assembly from p67phox was studies at the single-cell level. 17060455_chemoattractant-stimulated superoxide production can be amplified by a positive feedback loop in which p67(phox) targets Vav1-mediated Rac activation 17462995_These data clearly identify PLAGL2 as a novel regulator of NCF2/p67phox gene expression as well as NADPH oxidase activity and contribute to a greater understanding of the transcriptional regulation of NCF2. 17651608_There is an increased expression of NADPH oxidase p47(-PHOX) and p67(-PHOX) factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17712795_a novel single nucleotide polymorphism in the promoter region 17910042_Single nucleotide polymorphism leads to alternative splicing without altering gene expression or respiratory burst activity. 18029359_p40(phox) translocates p67(phox) to the region of the cytochrome and subsequently switches the oxidase to an activated state dependent upon PtdIns(3)P and SH3 domain engagement. 18424721_As(2)O(3) induced phosphorylation and membrane translocation of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47(phox) and it also increased translocation of Rac1 and p67(phox). 18546332_mutations in CYBB, NCF1, CYBA or NCF2 may play a role in chronic granulomatous disease 18625437_autosomal recessive CGD due to NCF-2 gene mutations, and a novel homozygous and hypomorphic NCF-2 gene mutation was found. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116138_p67(phox)-SH3(N) specifically functions in gp91(phox)/Nox2 activation probably via facilitating oxidase assembly. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19372141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Nine SNPs distributed across eight genetic regions (ALOX5, IRAK3, ITGB2, NCF2, NFKB1, SELP, SOD1, and STAT1) were associated with risk of glioma with P value of C) in NCF2 gene. We show that this mutation is responsible for a drastic decrease of p67phox mRNA and leads to the skipping of exon 3 detected in the low amount of residual mRNA. 27765769_Skeletal muscle protein expression of the NADPH oxidase subunits p22(phox), p47(phox), and p67(phox) was increased in obese relative to lean subjects, where p22(phox) and p67(phox) expression was attenuated by exercise training in obese subjects. 28035544_We analyzed the clinical and laboratory findings of CGD with mutations in the NCF2 gene from amongst our cohort of CGD patients. A homozygous mutation (c.835_836delAC, p.T279fsX294), a deletion in NCF2 gene was found in two cases. In the third case, two heterozygous mutations were detected, IVS13-2A>T on one allele and c.1099C>T (p.) on the other allele. 28096301_Phosphoinositol 3-phosphate regulates reactive oxygen species production by maintaining p40phox and p67phox at the phagosomal membrane. 29483646_Results show that NCF2 expression is highly upregulated in gastric cancer (GC) tumors. However, its mRNA is targeted by miR-532 and its expression repressed. More importantly, NCF2 can in turn upregulate LINC01410 expression via NF-kappaB in GC. 30323221_Activation of PAD4 by membranolytic insults that result in high levels of intracellular calcium (higher than physiological neutrophil activation) leads to rapid citrullination of p47(phox)/NCF1 and p67(phox)/NCF2, as well as their dissociation from PAD4 31245869_NCF2, MYO1F, S1PR4, and FCN1 as potential noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers in patients with obstructive coronary artery: A weighted gene co-expression network analysis. 31794672_Studies indicate that the G allele of neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) rs10911362 provided a protective role against tuberculosis (TB) risk in the Western Chinese Han population. 32666379_Novel NCF2 Mutation Causing Chronic Granulomatous Disease. 33145364_Association of NCF2, NCF4, and CYBA Gene Polymorphisms with Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Chinese Population. 33179520_Upregulation of glutaminase 2 and neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 is associated with the poor prognosis of glioblastoma. 33651148_Potentially functional variants of ERAP1, PSMF1 and NCF2 in the MHC-I-related pathway predict non-small cell lung cancer survival. 34708124_NCF1/2/4 Are Prognostic Biomarkers Related to the Immune Infiltration of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. 34971477_Neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) gene polymorphism is associated with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, but probably not with other autoimmune rheumatic diseases in children. |
ENSMUSG00000026480 |
Ncf2 |
102.564968 |
3.9224995894 |
1.971773 |
0.212772838 |
86.055546 |
0.00000000000000000001749517927954698552988705262268597065498625017128505389511425316406700858351541683077812194824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000157456613515922860741186859289005674694979645674718679408676802466970912064425647258758544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
161.6148026 |
21.2630654 |
41.4400348 |
4.3996197 |
| ENSG00000116711 |
5321 |
PLA2G4A |
protein_coding |
P47712 |
FUNCTION: Has primarily calcium-dependent phospholipase and lysophospholipase activities, with a major role in membrane lipid remodeling and biosynthesis of lipid mediators of the inflammatory response (PubMed:7794891, PubMed:8619991, PubMed:8702602, PubMed:9425121, PubMed:10358058, PubMed:14709560, PubMed:16617059, PubMed:17472963, PubMed:27642067, PubMed:18451993). Plays an important role in embryo implantation and parturition through its ability to trigger prostanoid production (By similarity). Preferentially hydrolyzes the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached at sn-2 position of phospholipids (phospholipase A2 activity) (PubMed:7794891, PubMed:8619991, PubMed:9425121, PubMed:10358058, PubMed:17472963, PubMed:18451993). Selectively hydrolyzes sn-2 arachidonoyl group from membrane phospholipids, providing the precursor for eicosanoid biosynthesis via the cyclooxygenase pathway (PubMed:18451993, PubMed:7794891, PubMed:9425121, PubMed:10358058, PubMed:17472963). In an alternative pathway of eicosanoid biosynthesis, hydrolyzes sn-2 fatty acyl chain of eicosanoid lysophopholipids to release free bioactive eicosanoids (PubMed:27642067). Hydrolyzes the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached at sn-1 position of phospholipids (phospholipase A1 activity) only if an ether linkage rather than an ester linkage is present at the sn-2 position. This hydrolysis is not stereospecific (PubMed:7794891). Has calcium-independent phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase activities in the presence of phosphoinositides (PubMed:12672805). Has O-acyltransferase activity. Catalyzes the transfer of fatty acyl chains from phospholipids to a primary hydroxyl group of glycerol (sn-1 or sn-3), potentially contributing to monoacylglycerol synthesis (PubMed:7794891). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P47713, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10358058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12672805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14709560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17472963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451993, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27642067, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7794891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8619991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8702602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9425121}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Glycerol metabolism;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Leukotriene biosynthesis;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phospholipid degradation;Phospholipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Prostaglandin biosynthesis;Prostaglandin metabolism;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Membrane lipid metabolism; glycerophospholipid metabolism. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P47713}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; arachidonate metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451993}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; prostaglandin biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451993}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; leukotriene B4 biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18451993}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytosolic phospholipase A2 group IV family. The enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids to release arachidonic acid which is subsequently metabolized into eicosanoids. Eicosanoids, including prostaglandins and leukotrienes, are lipid-based cellular hormones that regulate hemodynamics, inflammatory responses, and other intracellular pathways. The hydrolysis reaction also produces lysophospholipids that are converted into platelet-activating factor. The enzyme is activated by increased intracellular Ca(2+) levels and phosphorylation, resulting in its translocation from the cytosol and nucleus to perinuclear membrane vesicles. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:5321; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047498]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047499]; ceramide 1-phosphate binding [GO:1902387]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0008374]; phosphatidyl phospholipase B activity [GO:0102545]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; arachidonic acid secretion [GO:0050482]; cellular response to antibiotic [GO:0071236]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; glycerol metabolic process [GO:0006071]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; icosanoid metabolic process [GO:0006690]; leukotriene biosynthetic process [GO:0019370]; monoacylglycerol biosynthetic process [GO:0006640]; phosphatidylcholine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036151]; phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0034638]; phosphatidylglycerol catabolic process [GO:0034478]; platelet activating factor biosynthetic process [GO:0006663]; positive regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043032]; positive regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010572]; positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032308]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002827]; prostaglandin biosynthetic process [GO:0001516]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127] |
12048163_Expressed in human colorectal adenocarcinomas 12124392_PLA2G5 binds to PLA2G4 to induce leukotriene synthesis in neutrophils 12414998_Nuclear localisation was dependent on proliferation, with subconfluent cells containing higher levels of nuclear cPLA(2)-alpha than contact-inhibited confluent or serum-starved cells. 12765847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12765847_Polymorphisms in phospholipase A2 gene is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus 12885780_group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A(2) is activated by phosphorylation 14609334_The proposed model for membrane docking of the C2 domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2 is fully compatible with the biological function of the intact enzyme. 14686920_novel mechanisms involving accessory proteins at the target membrane play a role in the regulation of cPLA2-alpha 14726390_show that Phospholipase A(2) type IVA is present in red cells as a 90-kDa protein 14769798_cPLA2 has a role in B-Myb-dependent regulation of c-Myc expression 14963030_cPLA(2)alpha translocated to forming phagosomes, surrounding the zymosan particle and completely overlapping with early endosome and plasma membrane markers but only partially overlapping with resident endoplasmic reticulum proteins 15007070_Stable expression of human groups IIA and X secreted phospholipases A(2) (hGIIA and hGX) in CHO-K1 and HEK293 cells leads to serum- and interleukin-1beta-promoted arachidonate release. 15041036_SNP4 located in the 5'-flanking region of the PLA2G4A gene was associated with schizophrenia 15118355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15259375_The IValpha cytosolic phospholipase A2 at protein levels in articular cartilage from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and patients with non-arthritic joints. 15276701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15318030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15331599_cPLA2 has an influence on IL-8 and COX 2 gene and protein expression at least in part through PPAR-gamma 15358156_Results suggest that a protein kinase C delta-reactive oxygen species-NF-kappaB cascade plays a pivotal role in cytosolic phospholipase A(2)alpha induction by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. 15475363_cPLA(2)-alpha has a role in the regulation of neutrophil-mediated bacterial killing and the innate immune response to bacterial infection 15789617_Group X secretory phospholipase A2 induces potent arachidonic acid release without activation of cPLA2a. 15975962_Increased cPLA(2)alpha activity is associated with colon cancer 16181776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16221889_phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2] promotes translocation of cPLA2alpha to perinuclear membranes of intact cells in a manner that is independent of rises in the intracellular Ca2+ concentration 16407173_These results suggest that early cell death events promoted by an overload of calcium can be prevented by the activity of cytosolic Group IVA phospholipase A(2)alpha. 16409471_HCy led to the phosphorylation of cytosolic phospholipase A2; HCy promoted cPLA2 activation; cPLA2 phosphorylation and activation required p38 MAPK 16585943_This study reviews the evidence and discusses the potential roles of phospholipase A2 Group 4A for schizophrenia with particular emphasis on published association studies. 16603549_cytosolic and group IIA secreted phospholipases A(2) work together to liberate arachidonate from phospholipids in response to cytokines 16754327_This review summarizes the phenotypes resulting from genetic ablation of cPLA2alpha, and the properties of newly discovered enzymes in the cPLA2 family. 16829784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16963226_Our data suggest that PKCalpha, but not PKCbeta, is the predominant cPKC isoenzyme required for cPLA(2) protein phosphorylation and maximal induction of cPLA(2) enzymatic activity upon activation of human monocytes. 17178883_PPARdelta induces COX-2 expression and the COX-2-derived PGE(2) further activates PPARdelta via cPLA(2)alpha. which forms a growth-promoting signaling that may play a role in hepatocarcinogenesis. 17344094_The data presented link the stimulation of ERK-cPLA(2)-15-LO pathway by oxidized LDL to the prooxidant mechanism of the lipoprotein complex. 17417066_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17460547_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17629734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17672871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17685590_Residues specific for binding arachidonic and palmitic acids, preferred substrates for cPLA2 and PLB1, respectively, are identified. These results explan the differences in substrate specificity between lipases sharing the cPLA2 catalytic domain fold. 17873281_the confluence-dependent interaction of cPLA(2)alpha and annexin A1 at the Golgi acts as a novel molecular switch controlling cPLA(2)alpha activity and endothelial cell prostaglandin generation. 17901074_This study showed that cortisol increased PLA2G4A mRNA level via GR-dependent ongoing transcription in human amnion fibroblasts by activating the binding of GR to PLA2G4A promoter directly. 17971499_Cell surface ANXA1 synthesis is capable of blocking beta 2-integrin adhesion in PMNs. Fluticasone propionate does not cause ANXA1 synthesis or nuclear transport of cytosolic gIVaPLA2 & thus does not block beta2-integrin adhesion. 17976189_cytosolic phospholipase A2 and leukotriene B4 may have roles in acute myeloid leukemia 18280113_The mutation of Ser515 to Ala (S515A) did not change cPLA(2)alpha activity, although S228A and S505A completely and partially decreased the activity, respectively. 18388244_Role of cPLA2-alpha in the early action of TCDD through a nongenomic pathway in MCF10A cells is reported. 18451993_human cPLA(2alpha) deficiency is associated with impaired eicosanoid biosynthesis, small intestinal ulceration, and platelet dysfunctio 18471798_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18502815_Cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha activation induced by S1P is mediated by the S1P3 receptor in lung epithelial cells.( 18562188_BanI polymorphism of PLA2G4A showed a significant impact on mean age of the onset of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder in males, indicating lower mean age at admission in homozygous A2A2 males. 18562188_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18566601_Data show that activation of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) and production of lysophosphatidylcholine are initial events required for radiation-induced activation of Akt and ERK1/2 in vascular endothelial cells. 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18632668_a role of cPLA(2)alpha in the formation of nascent lipid droplets from the endoplasmic reticulum 18665843_the inhibition of cPLA(2)alpha activity affected many of the allergen-dependent, asthma-associated gene expression changes. 18686860_Many loci in the cPLA2 family genes were associated with schizophrenic. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18840708_cPLA2 and IIbbeta3 interact to reinforce each other's functions during IIbbeta3 signaling. 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19091957_Cytosolic phospholipase A2-alpha is an early apoptotic activator in PEDF-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. 19176526_Ser-505 phosphorylation and basic residues in the catalytic domain principally act to regulate cPLA(2)alpha hydrolytic activity 19237603_Cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) is identified as a central molecule in NKG2D-mediated cytolysis in cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 19280714_Cigarette smoke extract induces cytosolic expression via NADPH oxidase, MAPKs, AP-1, and NF-kappaB in human tracheal smooth muscle cells 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401382_TLR2 mediates augmented cPLA(2) activation and subsequent leukotriene biosynthesis. 19450127_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19560328_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625654_Phosphorylation of cPLA2-alpha on serine505 by c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinases is an important step for the proper binding of the enzyme to phagosomal membranes in an active manner in human macrophages. 19632995_Study provides a paradigm shift in how cPLA(2)alpha is activated during inflammation. 19675210_Data show that the redistribution of cPLA2alpha from the cytoplasm to the Golgi correlates with adherens junction maturation and occurs before tight junction formation. 19717620_The polybasic cluster of cPLA(2)alpha (Lys(488)/Lys(541)/Lys(543)/Lys(544)) regulates the subcellular localization of the enzyme in intact cells under physiologically relevant conditions. 19753100_These findings identify cPLA(2)alpha as the first component of the machinery that is responsible for the formation of intercisternal tubular continuities and support a role for these continuities in transport through the Golgi complex. 19778898_JNK and ceramide kinase govern the biogenesis of lipid droplets through activation of group IVA phospholipase A2 19795129_The cPLA ( 2 )alpha gene may be a possible disease modifier gene in familial adenomatous polyposis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20034614_Genetic variations in the COX2 and PLA2 genes increase the risk of IFN-alpha-induced depression, possibly by affecting the levels of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid . 20034614_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20066429_These results provide in vivo evidence for increased expression and activation of cPLA2 in motor neurons, reactive astrocytes, and activated microglia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 20069553_These results suggest that in human tracheal smooth muscle cells, activation of MAPKs, NF-kappaB, and p300 are essential for IL-1beta-induced cPLA(2) expression and PGE(2) secretion. 20112044_Data show that inhibition of cPLA(2)alpha activity with specific inhibitors blocked growth factor-induced membrane and actin dynamics, suggesting an important role for cPLA(2)alpha in these processes. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20203101_Cortisol activates the cAMP/protein kinase A/CREB-1 pathway via Galpha(s) induction, and the phosphorylated CREB-1 interacts with GR at the GRE to promote cPLA(2alpha) expression in amnion fibroblasts. 20211985_The study reports the first evidence for a correlation between cPLA(2)alpha enzymatic activity and overexpression of the HER2 receptor. 20227521_Decrease in expression or activity of cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha increases cyclooxygenase-1 action: A cross-talk between key enzymes in arachidonic acid pathway in prostate cancer cells. 20351714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20392485_higher expression in PBMCs of asthma patients 20435073_Data show that glycation end products (AGE) increase PIP2 production, arachidonic acid release and reactive oxygen species via cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation, and inhibit Na+ K+ ATPase surface expression via PIP5Kgamma. 20464283_data suggest that the BanI cPLA2 polymorphism may play a role in the susceptibility for late-onset Alzheimer disease a Brazilian sample. 20478385_Differential patterns in first-episode vs. chronic patients might be related to PLA(2)-increase at disease onset. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20635443_The study shows that cPLA2 and mPGES-1, in addition to COX-2, are constitutively overexpressed, and that 15-PGDH might be attenuated in colorectal cancer. Furthermore, cPLA2 and 15-PGDH as well as COX-2 could have an important role in tumor progression. 20643646_C. albicans engages both beta-glucan and mannan-binding receptors on macrophages that act with MyD88 to regulate the activation of cPLA(2)alpha and eicosanoid production. 20705608_Studies help determine the regulation and function of the cPLA(2) family members. 20802406_These preliminary data might suggest an influence of cPLA2alpha on GM-CSF gene expression in human lung cells. 20808133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20808133_There was no significant correlation between IFN-gamma or cPLA2 genotypes and AD 21097525_cytoplasmic phospholipase A(2)alpha is required for mediating P. aeruginosa-induced production of certain eicosanoids such as PGE2. However, neutrophil transepithelial migration induced by P. aeruginosa does not require cytoplasmic phospholipase A(2)alpha 21127289_Protease-activated receptor signaling in platelets activates cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha differently for cyclooxygenase-1 and 12-lipoxygenase catalysis. 21148506_Cellular invasion was shown to require activation of host cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2alpha) by Loops1 and 2 but not 3 of Escherichia coli OmpA. 21185392_Results suggest that low magnitude stretch can induce cPLA(2) phosphorylation through the MEK/ERK and PI3K-Akt pathways, independently. 21198294_There were relatively more cPLA2alpha positive tumors, as defined by positive staining in >10% of tumor cells 24 of 76 tumors (32%). 21247147_results show that the S111P mutation of cPLAhampers calcium binding and membrane translocation without affecting the catalytic activity. 21268080_Results demonstrated that cigarette smoke extract-induced cPLA(2) expression was mediated through NOX2-dependent p42/p44 MAPK and p38 MAPK/c-Fos and JNK1/2/c-Jun/p300 pathways in HTSMCs. 21315000_There is a possible relation between Leptin release and cPLA 2 activity in inflammatory cells induced by LPS. 21478406_data suggest that lipin-1 associates with lipid droplets and regulates the activation of cytosolic group IVA phospholipase A(2)alpha in monocyte-derived macrophages 21536681_cPLA(2)-dependent AA release is required for VEGF-induced Src-PLD1-PKCgamma-mediated pathological retinal angiogenesis 21771656_cPLA(2)alpha gene activation by IL-1beta is dependent on an upstream kinase pathway, enzymatic activation and downstream 15-lipoxygenase activity: a positive feedback loop 21825068_These findings demonstrate that specific host factors involving cPLAalpha and cysteinyl LTs contribute to type III GBS penetration of the blood-brain barrier and their contribution involves PKCalpha. 21862584_Mutation of HuR Thr-118 reduced the association between HuR and cPLA(2)alpha mRNA under IL-1beta treatment 21896865_findings indicate that cPLA2 in the lens epithelial cells is regulated by calcium mobilization and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) activation; both PDGF mitogenic action and calcium signaling are cPLA(2)alpha-dependent 22003202_A cPLA2-initiated lipid mediator pathway induces autophagy in a murine macrophage cell line and in human primary monocytes. 22138395_these results illustrated that cPLA(2)alpha-mediated actin filament rearrangements downstream of Akt activation is required for C. sakazakii invasion into brain endothelial cells. 22274867_Immunohistochemical expressions of cPLA(2)alpha in 23 species of human non-small lung cancer and 5 species of human normal lung to assess their clinicopathological relevance. 22378731_genetic association studies in populations in Costa Rica: An SNP in PLA2G4A (rs12746200) is associated with myocardial infarction; this association is modulated by dietary factors (i.e., omega-6 fatty acid intake). 22398721_A VE-cadherin-PAR3-alpha-catenin complex regulates the Golgi localization and activity of cytosolic phospholipase A(2)alpha in endothelial cells. 22456504_the lipid modifier cPLA2alpha and EHD1 are involved in the vesiculation of CD59-containing endosomes 22648535_The molecular and biological evidence of the involvement of cPLA2s in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease, is reviewed. 22728329_the regulation of HT-29 proliferation is mediated by cPLA(2)alpha-dependent PGE(2) production. PGE(2)via EP induces CREB phosphorylation by the PKA pathway and regulates beta-catenin and cyclin D1 cellular localization by PKB/Akt pathway. 22895089_The presence of a terminal sialic acid moiety, a rare modification of mammalian glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors, was essential in the activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and synapse damage induced by cross-linked PrPc. 22911431_study identified the MAPK/ERK regulated, cytosolic, calcium-dependent PLA2G4A as a novel hepatitis C virus dependency factor; inhibition of PLA2G4A activity reduced core protein abundance at lipid droplets, core envelopment and secretion of particles 23043861_results suggest that C2-di-ethyl-ceramide-1-phosphate appeared to inhibit cPLA(2)alpha, probably by interaction with a site in the catalytic domain of the enzyme. 23219238_Data detected statistically significant but weak impact of PLA2G4A and PTGS2 gene polymorphisms on niacin flush response in schizophrenia patients. 23268370_Mutations in PLA2G4A were identified as a cause of cryptogenic multifocal ulcerating stenosing enteritis in two affected siblings. 23307260_PLA2G4A might serve as a promising target for future therapeutic approaches to gastric cancer combined with COX-2 inhibitors. 23549331_data provide new and important contributions to the understanding of cPLA2alpha regulation at the transcriptional level, with implications for eicosanoid metabolism, cellular signaling, and disease pathogenesis 23801329_LacCer is a direct activator of cPLA2alpha. 23948114_Phospholipase A2 expression in coronary thrombus is associated with recurrence of cardiac events. 24349530_cPLA2alpha appears to be an important regulator of central effectors of inflammation and joint destruction, namely MMP3, IL8, COX2, and PGE2. 24366870_LMW HA was a potent stimulant of AA release in a time- and dose-dependent manner, induced cPLA2alpha, ERK1/2, p38, and JNK phosphorylation, as well as activated COX2 expression and prostaglandin (PG) E2 production 24721622_EGF stimulates platelet-activating factor production in ovarian cancer cells in a manner that requires cPLA2. 25102418_Data indicate 3-(1-Aryl-1H-indol-5-yl)propanoic acids a potent inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha (cPLA2alpha). 25102815_Case Report/Twin Study: syndromic form of deficiency of cPLA2a , characterised by recurrent GI ulcers and bleeding diathesis, associated with mild inherited deficiency of factor XI. 25365190_We conclude that cPLA2alpha is required for sustaining AKT phosphorylation at Ser473 and cell proliferation in colorectal cancer cells with PI3K mutation 25617738_Suggest retinal pigment epithelium metabolism of 7-ketocholesterol occurs by esterification to fatty acids via cPLA2alpha and SOAT1 followed by selective efflux to HDL. 25761116_alphaSN triggered synapse damage via hyperactivation of cPLA2 25904158_Letter: report instability of cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha variant resulting in severe impairment in platelet arachidonic acid metabolism. 25969996_Thymocyte maturation can occur independently of cPLA2-alpha. 26162318_These results indicate epigenetic regulation of cPLA2 and the potential of such regulation for treatment of chronic inflammation. 26183771_These studies constitute a definitive account, demonstrating the fundamental role of cPLA2alpha to eicosanoid formation and cellular responses within the human circulation. 26303530_The study reports the formation of a multiprotein complex at the G2-to-M transition in vitro and in vivo. Group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2-alpha) acts as a bridge in this complex to promote binding of SIRT2 to cyclin A-Cdk2. 26416244_cPLA2alpha plays an important role in cell cycle re-entry by quiescent prostate cancer cells 26525102_genetic association study in Quebec City population: Data suggest total plasma n-6 fatty acid phospholipid levels and C-reactive protein are modulated by SNPs in PLA2G4A and PLA2G6 alone or in combination with fish oil dietary supplementation. 27133131_Phospholipase activity is linked to energy metabolism, revealing cPLA2 as a central regulator of both lipidomics and energy flux. 27528014_present study indicates that among all cytosolic phospholipases A2, specific phospholipase A2 group IVA are the main enzymes involved in cigarette smoke induced anomalies in type I and type II lung epithelial cells 27554058_cPLA2alpha may play a key role in renal repair after injury through a PGE2-independent mechanism 28108057_Study provides evidence that BanI polymorphism of cPLA2 gene may be associated with somatic symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder in the Taiwanese population. 28383549_This study indicates the potential role of cPLA2alpha in breast cancer metastasis and indicates that this molecule is a promising therapeutic target for breast cancer. 28649002_cPLA2alpha activates PI3K/AKT and inhibits Smad2/3 during epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 28724385_The impaired phospholipid level and remarkable increased in cPLA2 concentration asserted their roles in the etiology of autism. 28887431_these studies suggests that cPLA2alpha expressed by neutrophils, but not epithelial cells, plays a significant role in infection-induced neutrophil transepithelial migration by mediating LTB4 synthesis during migration, which serves to amplify the magnitude of neutrophil recruitment in response to epithelial infection 29167338_cPLA2alpha, which releases fatty acid from the sn-2 position of membrane-associated glycerophospholipids, is critically involved in coronavirus replication, most likely by producing lysophospholipids that are required to form the specialized membrane compartments in which viral RNA synthesis takes place 29307829_These findings indicate the positive roles of cPLA2alpha in breast cancer cell growth, survival, migration and response to chemotherapy. Our work also highlights the therapeutic value of blocking cPLA2alpha to overcome chemoresistance in breast cancer. 29342349_A lipidomics-based LC/MS assay was used to define the specificity of cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 toward a variety of phospholipids. A unique hydrophobic binding site for the cleaved fatty acid dominates each enzyme's specificity rather than its catalytic residues and polar headgroup binding site. 29551681_results suggested that IFN-gamma induces autophagy-associated apoptosis in CRC cells via inducing cPLA2-dependent mitochondrial ROS production. 29893858_High PLA2G4A expression is associated with obesity. 30071514_PLA2G4A up-regulated the protein expression of E-cadherin and down-regulated the protein expression of vimentin, which inhibited ESCC cell mobility and invasiveness. 30103930_Results indicate that the BanI polymorphic variant contributes significantly to plasma glucose levels in female patients with schizophrenia. Females carrying the PLA2G4A-G allele (PLA2G4A-GG homozygous and PLA2G4A-AG heterozygous) presented with lower glucose levels than PLA2G4A-AA homozygous carriers, and the PLA2G4A genotype contributed approximately 6% of plasma glucose level variability in this group of patients. 30360807_The expression of cPLA2alpha varies in multiple glioblastoma cell lines and is associated with chemoresistance rather than tumor development. cPLA2alpha depletion moderately inhibits glioblastoma growth and survival but remarkably sensitizes chemo-resistant glioblastoma cells to several chemotherapeutic agents. 31003849_cPLA2a could promote osteosarcoma cell invasion via inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, indicating that cPLA2a was an independent prognostic biomarker and may be an effective drug target for osteosarcoma 31050338_Tyr96 plays a key role in lipid headgroup recognition via cation-pi interaction with the phosphatidylcholine trimethylammonium group. Mutagenesis analyses confirm that Tyr96 and Asn65 function in phosphatidylcholine binding selectivity by the C2-domain and in the regulation of cPLA2alpha activity. 31474631_It catalyzes the initial step in the generation of lipid mediators, including eicosanoids and lysophospholipids, in the progression of hepatic fibrosis. 32077754_PLA2G4A upregulation has multiple effects on the malignant phenotype of Acute Myeloid Leukemia cells together with its partners. 33023184_cPLA2alpha Enzyme Inhibition Attenuates Inflammation and Keratinocyte Proliferation. 33086624_Updating Phospholipase A2 Biology. 33550612_Protein dynamics analysis identifies candidate cancer driver genes and mutations in TCGA data. 33853093_Re-analysis of genetic polymorphism data supports a relationship between schizophrenia and microsatellite variability in PLA2G4A. 34131250_Quantitative proteomics analysis of glioblastoma cell lines after lncRNA HULC silencing. 34255137_Targeting cPLA2alpha inhibits gastric cancer and augments chemotherapy efficacy via suppressing Ras/MEK/ERK and Akt/beta-catenin pathways. 34283812_PLA2G4A promotes right-sided colorectal cancer progression by inducing CD39+gammadelta Treg polarization. 34474084_Omega-3 versus Omega-6 fatty acid availability is controlled by hydrophobic site geometries of phospholipase A2s. 34502319_A Multiplex CRISPR-Screen Identifies PLA2G4A as Prognostic Marker and Druggable Target for HOXA9 and MEIS1 Dependent AML. 34889025_Genetic polymorphism data support a relationship between schizophrenia and microsatellite variability in PLA2G4A in Northern Europeans not Han Chinese. 34946532_Inhibition of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2alpha Induces Apoptosis in Multiple Myeloma Cells. 34969839_A synergy between mechanosensitive calcium- and membrane-binding mediates tension-sensing by C2-like domains. 35705959_Calcium-dependent cytosolic phospholipase A2 activation is implicated in neuroinflammation and oxidative stress associated with ApoE4. |
ENSMUSG00000056220 |
Pla2g4a |
87.224041 |
0.3886448219 |
-1.363476 |
0.193251228 |
50.479768 |
0.00000000000120399610931246344423870206784998220309046423892596067162230610847473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007128352416145993019216353299974457636764557655340013297973200678825378417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.9730210 |
6.9725213 |
126.9036167 |
12.0204953 |
| ENSG00000116774 |
56944 |
OLFML3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRN5 |
FUNCTION: Secreted scaffold protein that plays an essential role in dorsoventral patterning during early development. Stabilizes axial formation by restricting chordin (CHRD) activity on the dorsal side. Acts by facilitating the association between the tolloid proteases and their substrate chordin (CHRD), leading to enhance chordin (CHRD) degradation (By similarity). May have matrix-related function involved in placental and embryonic development, or play a similar role in other physiological processes. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15280020}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the olfactomedin-like gene family which also includes genes encoding noelin, tiarin, myocilin, amassin, optimedin, photomedin, and latrophilin. The encoded protein is a secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein with a C-terminal olfactomedin domain that facilitates protein-protein interactions, cell adhesion, and intercellular interactions. It serves as both a scaffold protein that recruits bone morphogenetic protein 1 to its substrate chordin, and as a vascular tissue remodeler with pro-angiogenic properties. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:56944; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15280020_may have matrix-related function involved in human placental and embryonic development, or play a similar role in other physiological processes 23398349_This paper reports OLFML3 expression in human and baboon eye. The full coding DNA sequence has 1221 bp, from which an open reading frame of 406 amino acid was obtained. 31919052_Circadian Regulator CLOCK Recruits Immune-Suppressive Microglia into the GBM Tumor Microenvironment. 34686207_Surfaceome CRISPR screen identifies OLFML3 as a rhinovirus-inducible IFN antagonist. 34884869_Microglia-Derived Olfactomedin-like 3 Promotes Pro-Tumorigenic Microglial Function and Malignant Features of Glioma Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000027848 |
Olfml3 |
27.022057 |
0.0383033425 |
-4.706386 |
0.569987337 |
119.978337 |
0.00000000000000000000000000063955307980792132880067700581820044792615058106951915349679457327541548853321040635222516357316635549068450927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000007612744724165256635777555977755621980916211339814435036278213544606960783839300077602274541277438402175903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0777290 |
0.8339307 |
54.7764879 |
7.2793651 |
| ENSG00000116791 |
1429 |
CRYZ |
protein_coding |
Q08257 |
FUNCTION: Does not have alcohol dehydrogenase activity. Binds NADP and acts through a one-electron transfer process. Orthoquinones, such as 1,2-naphthoquinone or 9,10-phenanthrenequinone, are the best substrates (in vitro). May act in the detoxification of xenobiotics. Interacts with (AU)-rich elements (ARE) in the 3'-UTR of target mRNA species. Enhances the stability of mRNA coding for BCL2. NADPH binding interferes with mRNA binding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17497241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20103721}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. The former class is also called phylogenetically-restricted crystallins. This gene encodes a taxon-specific crystallin protein which has NADPH-dependent quinone reductase activity distinct from other known quinone reductases. It lacks alcohol dehydrogenase activity although by similarity it is considered a member of the zinc-containing alcohol dehydrogenase family. Unlike other mammalian species, in humans, lens expression is low. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. One pseudogene is known to exist. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:1429; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; NADPH:quinone reductase activity [GO:0003960]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; visual perception [GO:0007601]; xenobiotic catabolic process [GO:0042178] |
11295131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714703_up-regulation of quinone reductase can protect breast cells against oxidative DNA damage 20103721_zeta-Crystallin is a bcl-2 mRNA binding protein involved in bcl-2 overexpression in T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia. 20835842_novel enzymatic activity for human zeta-crystallin, the double- bond a,b-hydrogenation of 2-alkenals and 3-alkenones, was identified. 21276778_role of Zta1p in the yeast adaptation to some stress types and the general functional significance of zeta-crystallins 22843503_Our results suggest that genetic variants in TYW3/CRYZ and NDST4 loci may be involved in the regulation of circulating resistin levels 31563996_Zeta-crystallin is a moonlighting protein endowed with two main different functions: (1) mRNA binding with stabilizing activity; (2) NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase. Zeta-crystallin has been clearly demonstrated to stabilize mRNAs encoding proteins involved in renal glutamine catabolism during metabolic acidosis resulting in ammoniagenesis and bicarbonate ion production that concur to compensate such condition. [review] |
ENSMUSG00000028199 |
Cryz |
44.667019 |
2.1464094615 |
1.101925 |
0.230224048 |
23.281171 |
0.00000139963561316862226282620000616940814097688416950404644012451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004871167566698624649544797915456939563227933831512928009033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.2632413 |
8.3928476 |
28.7414462 |
3.1442509 |
| ENSG00000116815 |
965 |
CD58 |
protein_coding |
P19256 |
FUNCTION: Ligand of the T-lymphocyte CD2 glycoprotein. This interaction is important in mediating thymocyte interactions with thymic epithelial cells, antigen-independent and -dependent interactions of T-lymphocytes with target cells and antigen-presenting cells and the T-lymphocyte rosetting with erythrocytes. In addition, the LFA-3/CD2 interaction may prime response by both the CD2+ and LFA-3+ cells. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The encoded protein is a ligand of the T lymphocyte CD2 protein, and functions in adhesion and activation of T lymphocytes. The protein is localized to the plasma membrane. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:965; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757] |
11575926_CD2-CD58 binding site 12496412_Signal-dependent adhesion of resting NK cells initiated by expression of ICAM-1 is greatly enhanced by coexpression of LFA-3, even in the absence of cytokines. 12553064_The complement inhibitor CD59 and the lymphocyte function-associated antigen-3 (LFA-3, CD58) genes possess functional binding sites for the p53 tumor suppressor protein. 15093607_Transmembrane CD58 may trigger signaling independently of the GPI-linked isoform. 15963548_Human cells transformed with Ad12 demonstrated reduced expression of cell surface LFA-3. 16830383_The level of CD58 molecule (in both serum and PBMC form) of patients with hepatitis B is related to the degree of liver damage. 17085486_We use this analysis to determine that the 2D Kd for CD2-CD58 is 5.4-7.6 molecules/microm2. 2D Kd analysis provides a general and quantitative measure of the mechanisms regulating cell-cell adhesion. 17168569_T cell activation causes the CD58-bound CD2 to be recognized and immobilized at sites of cell-cell contact, thereby strengthening T cell-APC adhesion 18650830_Susceptibility gene for multiple sclerosis in Australians. 18820826_We found variable, but persistently elevated levels of sLFA-3 throughout the various phases and types of the hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome, which suggest that sLFA-3 levels have correlation with disease stages. 19109405_the synergistic synthesis of IL-8 occurs when lymphocytes are stimulated through the CD2 pathway by CD58 on HT-29 cells, resulting in TNF-alpha release that, in turn, augments IL-8 synthesis and CD58 expression by the HT-29 cells 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19237575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19237575_during clinical remission, increases in CD58 expression, mediated by the protective allele, up-regulate the expression of FoxP3 through engagement of the CD58 receptor, CD2, leading to the enhanced function of TREG cells that are defective in MS 19268704_Cross-linking of CD58 induces protein tyrosine phosphorylation of BLNK, Syk and PLCgamma, and activation of ERK and Akt/PKB. 19375175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19497873_Study reports additional genetic and transcriptomic evidence for the role of CD58 (LFA-3) in multiple sclerosis (MS) susceptibility using a Swedish case-control material, with a result that closely mimics that of De Jager et al. 19506219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834503_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834503_Studies indicate that five SNPs showed genome-wide significant association with MS: HLA-DRA, IL7R, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A. 19865102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19898481_Genetic variants at CD58, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis risk 19898481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20450971_Studies indicate that SNP in IL7RA, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A genes has been consistently associated with MS. 20570633_Data show that coculture with activated T cells upregulated expression of CD54 and CD58 and secretion of galectin-1 by MSCs. 20806065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21362770_Two large cohorts of systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients of European Caucasian ancestry do not support the implication of ITGAM, ITGAX, and CD58 genes in the genetic susceptibility of SSc, although they were identified as autoimmune disease risk genes. 21726122_Seven selected CD58 single-nucleotide polymorphisms were found to not affect aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease susceptibility in a Korean population. 22137796_In 21 percent of diffuse large B cell lymphoma cases, lesions involve the CD58 gene, which encodes a molecule involved in T and natural killer cell-mediated responses 24655566_Genetic variations in CD58 were associated with the susceptibility of neuromyelitis optica in a Korean population. 24727892_Results indicate that CD58 is a novel cell-surface marker that functionally regulates self-renewal of Colorectal tumor-initiating cells. 25197941_SNPs in CD58 are associated with increased risk of candidemia. 25795118_Linkage disequilibrium show evidence that mir-548ac rs1414273 variant is strongly associated with Multiple sclerosis (MS)-associated haplotype and confirms the single nucleotide polymorphisms within the first intron of CD58 been related too. [review] 25884075_The positive correlation is established between content of polymorphic nuclear monocytes and level of expression of molecules of LFA-1, ICAM-1, LFA-3, and PECAM-1. 25903733_This study demonstrated that the Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide of CD58 is associated with multiple sclerosis in man in Russia. 25984915_the fundamental mechanism of glycosylation of human CD2 is to promote CD2-CD58 binding by conformational adjustment of CD2 26041540_CD58/CD2 is the primary costimulatory pathway in human CD28-CD8+ T cells. 26137540_Cytometry analysis evidenced a specific expression profile on reticulocytes of SCA infants, with notably an increased expression of the adhesion molecules Lu/BCAM, ICAM-4 and LFA-3, both in percentage of positive cells and in surface density. 26194173_Frequent inactivating mutations of CD58 in classical Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines, but their rare occurrence in primary Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg cells. 27467287_data suggest that loss of CD58 is a potential immune escape mechanism of HL tumor cells, especially in clinically aggressive disease 27825110_Mutations and copy number loss of CD58 or TP53 are identified to be an independent negative prognostic factors for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 28601281_A new neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders susceptibility variant was identified, rs56302466, on the CD58 gene, in a Han Chinese population. 29500862_indicate that including both CD58 and CD81 markers in addition to CD19, CD34, CD20, CD38, and CD10 are helpful in minimal residual disease detection by flow cytometry 30006149_SNP rs1335532 associated with multiple sclerosis is located in active CD58 enhancer region and creates a strong functional Ascl2-binding site. 30128676_High-resolution melting curve analysis of polymorphisms within CD58, CD226, HLA-G genes and association with multiple sclerosis susceptibility in a subset of Iranian population: a case-control study. 30418605_We show that the Alu insertion promotes skipping of CD58 exon 3 and results in a frameshifted transcript, indicating that the Alu may be the causative variant for increased MS risk at this locus. Using RT-PCR analysis at the endogenous locus, we confirm that the Alu variant is a sQTL for CD58. 30730892_Across different global populations and data sets, carriers of the multiple sclerosis risk allele showed reduced CD58 mRNA levels but increased hsa-miR-548ac levels. 31505972_CD58 single nucleotide polymorphisms are involved in susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid diseases 32589698_Rosetting T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma are activated by immunological synapse components HLA class II and CD58. 33649592_Multimodal pooled Perturb-CITE-seq screens in patient models define mechanisms of cancer immune evasion. 34168659_CD58 Immunobiology at a Glance. 34738847_Higher Expression of WT1 With Lower CD58 Expression may be Biomarkers for Risk Stratification of Patients With Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 35881486_Multidimensional single-cell analysis identifies a role for CD2-CD58 interactions in clinical antitumor T cell responses. 36288878_High Expression of CD58 and ALDH1A3 Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Basal-like Breast Cancer. |
|
|
680.479112 |
2.1522736023 |
1.105861 |
0.088116243 |
155.968229 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000860221363977597039408009235374519864835215761558955163417500030810127729662877802203211410067909548082809578772867098450660705566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000129164469301213956786008059349630953100565765383482690366373840661415214612437969338140978346751719385565593256615102291107177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
943.2200961 |
48.3100309 |
441.3078236 |
16.7939443 |
| ENSG00000116819 |
339488 |
TFAP2E |
protein_coding |
Q6VUC0 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with inducible viral and cellular enhancer elements to regulate transcription of selected genes. AP-2 factors bind to the consensus sequence 5'-GCCNNNGGC-3' and activate genes involved in a large spectrum of important biological functions including proper eye, face, body wall, limb and neural tube development. They also suppress a number of genes including MCAM/MUC18, C/EBP alpha and MYC. AP-2-epsilon may play a role in the development of the CNS and in cartilage differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Activator;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in anatomical structure development; regulation of cell population proliferation; and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:339488; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20862309_These findings reveal that Tfap2 activity, mediated redundantly by Tfap2a and Tfap2e, promotes melanophore differentiation in parallel with Mitf by an effector other than Kit. 22216841_TFAP2E hypermethylation is associated with clinical nonresponsiveness to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. 23331625_AP-2epsilon indirectly interacts with the core promoter of COL2A1 and subsequently inhibits its transcriptional activity, thus modulating cartilage development. 24996990_AP-2E was frequently hypermethylated in tumors from patients with colorectal cancer 25810491_Hypermethylation of TFAP2E was associated with lack of response to fluorouracil-based chemotherapy, indicating that it might be a potential predictor of treatment response in patients with gastric cancer. 28260105_Results showed that lower expression levels of TFAP2E are significantly associated with a shorter survival of patients with neuroblastoma indicating that TFAP2E acts as a tumor suppressor of neuroblastoma. 29535127_TFAP2E methylation and expression may not play a major role in predicting response to 5-FU-based chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. 31115533_In the present study, it was demonstrated that hypermethylation of TFAP2E resulted in its reduced expression and 5FU chemoresistance in gastric cancer (GC) cells. miRNAs miR106a5p and miR421 were highly expressed and regulated the chemoresistance induced by TFAP2E methylation. |
ENSMUSG00000042477 |
Tfap2e |
53.857925 |
0.2124919897 |
-2.234520 |
0.617503985 |
11.704484 |
0.00062349682538720147938898774597760166216176003217697143554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001505695867590820403308926600516315374989062547683715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.6364524 |
7.5875455 |
81.0915525 |
25.6373646 |
| ENSG00000116833 |
2494 |
NR5A2 |
protein_coding |
O00482 |
FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that acts as a key metabolic sensor by regulating the expression of genes involved in bile acid synthesis, cholesterol homeostasis and triglyceride synthesis. Together with the oxysterol receptors NR1H3/LXR-alpha and NR1H2/LXR-beta, acts as an essential transcriptional regulator of lipid metabolism. Plays an anti-inflammatory role during the hepatic acute phase response by acting as a corepressor: inhibits the hepatic acute phase response by preventing dissociation of the N-Cor corepressor complex (PubMed:20159957). Binds to the sequence element 5'-AACGACCGACCTTGAG-3' of the enhancer II of hepatitis B virus genes, a critical cis-element of their expression and regulation. May be responsible for the liver-specific activity of enhancer II, probably in combination with other hepatocyte transcription factors. Key regulator of cholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A) expression in liver. May also contribute to the regulation of pancreas-specific genes and play important roles in embryonic development. Activates the transcription of CYP2C38 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P45448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15707893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15723037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15897460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16289203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159957}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Lipid-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA-binding zinc finger transcription factor and is a member of the fushi tarazu factor-1 subfamily of orphan nuclear receptors. The encoded protein is involved in the expression of genes for hepatitis B virus and cholesterol biosynthesis, and may be an important regulator of embryonic development. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:2494; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; acinar cell differentiation [GO:0090425]; bile acid metabolic process [GO:0008206]; calcineurin-mediated signaling [GO:0097720]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; homeostatic process [GO:0042592]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; pancreas morphogenesis [GO:0061113]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
11927588_role in regulating aromatase expression in preadipocytes (liver receptor homologue-1) 12820970_Ligands are dispensabe for LRH-1 activation. 12852843_LRH-1 is a nuclear receptor which can assume an active conformation in the absence of a ligand agonist. 12853459_Liver receptor homolog 1 controls the expression of carboxyl ester lipase in pancreas 12972592_PDX-1 regulates expression of LRH-1 during pancreas development. 14671206_LRH-1 is highly expressed in corpus luteum, and it plays an essential role in the regulation of HSD3B2. 14728801_hBIF and HNF1 are involved together in the viral gene expression regulation of the Hepatitis B virus. 15117876_role for LRH-1 in the induction of the progesterone but not the estrogen biosynthetic pathway during granulosa cell differentiation. 15121760_LRH-1 is a positive transcription factor for ABCG5 and ABCG8 and, in conjunction with studies on LRH-1 activation of other promoters, identify LRH-1 as a 'master regulator' for genes involved in sterol and bile acid secretion from liver and intestine 15143151_important functional role of helix 1 in cofactor recruitment and a novel molecular mechanism of transcriptional regulation and cofactor recruitment mediated by hLRH-1 15181096_LRH-1 could be the major transcription factor responsible for the rapid and significant increase in ovarian StAR gene expression after ovulation. 15205472_The liver receptor homolog-1 has emerged as an essential regulator for the expression of cyp7a1 gene. 15218078_LHR-1 regulgates apolipoprotein A-1 transscription, and affects cholesterol homeostasis. 15613430_CYP11A1 expression in human granulosa cells is regulated by LRH-1. 15707893_Human LRH-1 receptor binds phosphatidyl inositol second messengers;ligand binding is required for maximal activity. 15723037_hLRH-1's control of gene expression is mediated by phospholipid binding 15923626_Data show that sumoylated LRH-1 is exclusively localized in promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear bodies, and that this association is a dynamic process regulated in part by SUMO-1. 15963945_suppression of hLRH-1 resulted in cell cycle arrest mediated by the down-regulation of cyclin E1 16091743_LRH-1 is transcriptionally regulated by the estrogen receptor alpha reinforcing the hypothesis that LRH-1 could exert potential oncogenic effects in breast cancer formation. 16282330_LRH-1 and SHP1 regulate 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase promoter and have a role in regulation of cholesterol synthesis and uptake 16439367_phosphorylation of the hinge domain of the nuclear hormone receptor LRH-1 stimulates transactivation 16450584_siRNA interference studies suggested that nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (hLRH-1) acts as a negative regulator in farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase expression. 16469397_FTF and LRH-1 are two related but different transcription factors in human Caco-2 cells, suggesting that they may be homologues and not orthologues. 17095585_LRH-1 and SF-1 have qualitatively similar actions on FSH-stimulated estrogen and progesterone production. These factors may have overlapping actions in regulation of steroidogenesis that accompanies granulosa cell differentiation. 17522048_LRH-1 stimulation of the FAS LXR response is blocked by the addition of small heterodimer partner (SHP) and that FAS mRNA 17910058_LRH-1/phospholipid and LRH-1/SHP (fragments) interactions are analyzed by counting atomic contact number, identifying hydrogen bonds, and estimating binding free energies 17952562_The present study demonstrated for the first time the increased expression of hLRH-1v1 and hLRH-1 in human gastric cancer, an alteration which may implicate in tumorigenesis. 17977826_LRH-1 is a novel regulator of APOM transcription and further extend the role of this orphan nuclear receptor in lipoprotein metabolism and cholesterol homeostasis 18191017_Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces LRH-1 mRNA expression in MCF-7 cells in a prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-dependent manner. 18270374_Liver receptor homolog 1 (LRH-1) is a key transcriptional factor required for the hepatic expression of CYP7A1. 18385139_PGC-1alpha is an important co-activator for LRH-1 and that SHP targets the interaction between LRH-1 and PGC-1alpha to inhibit CYP7A1 expression. 18410128_a study, by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, the impact of the ligand on the receptor and the interaction with different cofactor peptides 18508634_Possible unexpected new class of nuclear receptor signaling molecules, but broader functional roles of LRH-1 and these new ligands remain to be established.[REVIEW] 18665078_Differential expression of steroidogenic factors 1 and 2, cytochrome p450scc, and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in the pancreas. 19015525_structure of the Dax-1:LRH-1 complex provides the molecular mechanism for the function of Dax-1 as a potent transcriptional repressor 19022561_both SF1 and LRH1 can transcriptionally cooperate with the AP-1 family members c-JUN and c-FOS, known to be associated with enhanced proliferation of endometrial carcinoma cells, to further enhance activation of the STAR, HSD3B2, and CYP19A1 PII promoters 19359379_The results indicate that LRH-1 could represent another key regulator of the steroidogenic lineage in MSCs and play a vital role in steroid hormone production in human Leydig cells. 19629617_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20101243_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20133449_results indicate that PGC-1alpha is involved in progesterone production in ovarian granulosa cells by potentiating transcriptional activities of LRH1 proteins. 20159957_selective synthetic agonists induce SUMOylation-dependent recruitment of either LRH-1 or LXR to hepatic APR promoters and prevent the clearance of the N-CoR corepressor complex upon cytokine stimulation 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20607599_Our findings extend this by highlighting LRH-1 as a key regulator of the estrogen response in breast cancer cells through the regulation of ER expression. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20817789_These findings suggest a new role of LRH-1 in promoting migration and invasion in breast cancer, independent of oestrogen sensitivity. 21129436_These results indicated that pluripotent stem cells could be differentiated into steroidogenic cells by the nuclear receptor 5A family of protein via the mesenchymal cell lineage. 21258413_Data indicate an important role of LRH-1 in colorectal tumor GC synthesis. 21392518_The results of this study support the hypothesis that suppression of LRH-1 may potentially be beneficial in the tissue specific regulation of aromatase expression in post menopausal breast cancer. 21536586_crucial role of the estrogen target gene nr5a2 in protecting human islets against-stressed-induced apoptosis 21614002_findings identify an LRH-1 dependent phosphatidylcholine signalling pathway that regulates bile acid metabolism and glucose homeostasis 21949357_LRH-1 transcription is activated up to 30-fold in pancreatic cancer cells compared to normal pancreatic ductal epithelium 21990348_findings demonstrate that signaling through RARs has critical roles in molecular reprogramming and that the synergistic interaction between Rarg and Lrh1 directs reprogramming toward ground-state pluripotency 22048972_NR5A2 modulates gene expression in osteoblasts and some allelic variants are associated with bone mass in Spanish postmenopausal women. 22125638_Data show that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in ABO, sonic hedgehog (SHH), telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), nuclear receptor subfamily 5, group A, member 2 (NR5A2) were found to be associated with pancreatic cancer risk. 22187462_The three-dimensional structure of a beta-catenin armadillo repeat in complex with the liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) ligand binding domain at 2.8 A resolution, is reported. 22359603_in ER-positive breast cancer cells, LRH-1 promotes cell proliferation by enhancing ERalpha mediated transcription of target genes such as GREB-1 22504882_The lipid-free receptor undergoes previously unrecognized structural fluctuations, allowing it to interact with widely expressed co-repressors. 23000165_this study indicates that LRH-1 acts as a transcriptional activator in the regulation of OCT4 gene expression through the cooperative interaction with three binding sites directly or/and indirectly. 23038264_HNF4alpha and LRH-1 promote active transcription histone marks on the Cyp7a1 promoter that are reversed by FGF19 in a SHP-dependent manner 23471216_Expression of human LRH-1 is regulated in a tissue-specific manner, and that the novel promoter region is controlled by the Sp-family, NR5A-family and PGC-1alpha in ovarian granulosa cells in a coordinated fashion. 23537609_Data conclude that SF-1 regulates aromatase expression in GCT; over-expression of LRH-1 suggests that this receptor may be involved in the pathogenesis of GCT by mechanisms other than the regulation of aromatase. 23667258_Experimental evaluation of the predicted ligands identified two compounds that inhibit the transcriptional activity of LRH-1 and diminish the expression of the receptor's target genes. 23737522_Data indicate that sequence divergence has differentially impacted ligand binding and protein dynamics in NR5A2. 23817023_Lrh-1 is necessary for maintenance of the corpus luteum, for promotion of decidualization and for formation of the placenta. 24520076_report the genome-wide location and molecular function of LRH-1 in breast cancer cells and reveal its therapeutic potential for the treatment of breast cancers, notably for tumors resistant to treatments currently used in therapies. 24564400_Data (including data from transgenic overexpression/gene silencing) suggest that NR5A2 modulates signal transduction/cell proliferation in mammary cells; mammary morphology exhibits significant reduction in lateral budding after NR5A2 overexpression. 24570488_during chronic colitis, TNF suppresses intestinal steroidogenic gene expression by inhibiting the activity of NR5A2, thus decreasing glucocorticoid synthesis and sustaining chronic inflammation. 24769073_LRH1 overexpression is associated with increased pancreatic cancer growth and metastatic spread 25435372_Analysis of breast cancer samples reveals that a high LRH-1 level is inversely correlated with CDKN1A expression in breast cancer patients and is associated with poor prognosis 25514243_the NR5A2 rs3790844 polymorphism is associated with increased OS of GC patients in the dominant model, and similar results were found among the female group and tumor size >5 cm group for NR5A2 rs3790843 polymorphism. 25675535_This study demonstrates a critical proproliferative role for LRH-1 in established colon cancer cell lines. 25869073_loss of LRH-1 by siRNA or miR-451 mimics significantly impaired Wnt/beta-catenin activity, leading to G0/G1 cell cycle arrest 25873311_Results identify LRH-1 as a critical component of the anti-inflammatory and fungicidal response of alternatively activated macrophages that acts upstream from the IL-13-induced 15-HETE/PPARgamma axis. 25896302_These findings demonstrate that in vitro LRH-1 can act like SF-1 and compensate for its deficiency. 25943101_AFPR may play a pivotal role in HBV-related hepatocarcinogenesis. 25951367_Studies indicate that liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) is critical involvement in multiple types of cancer, and represents a desirable target for therapeutic applications. 25987835_our findings present supportive evidence that ApoM is a regulator of human LRH-1 transcription, and further reveal the importance of ApoM as a critical regulator of bile acids metabolism 26241054_these data demonstrate that copper-mediated nuclear receptor dysfunction disrupts liver function in WD and potentially in other disorders associated with increased hepatic copper levels. 26241668_in spermatozoa the LRH-1 effects are closely integrated with the estrogen signaling, supporting LRH-1 as a downstream effector of the estradiol pathway on some sperm functions. 26320367_Down-regulation of MicroRNA-381 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in colon cancer cells through up-regulation of LRH-1. 26398198_SERBP1 is a component of the LRH-1 transcriptional complex. 26400164_LRH-1 drives colon cancer cell growth by repressing the expression of the CDKN1A gene in a p53-dependent manner. 26421305_These findings show that POD-1/TCF21 regulates SF-1 and LRH-1 by distinct mechanisms, contributing to the understanding of POD-1 involvement and its mechanisms of action in adrenal and liver tumorigenesis. 26530052_demonstrate aberrant expressions of SF-1 and LRH-1 in endometriotic granulosa-lutein cells 26553876_Data suggest LRH1/NR5A2 exhibits phospholipid-mediated allosteric control of protein-protein binding interface in interactions with TIF2 (co-activator; transcription intermediary factor 2) and SHP (co-repressor; small heterodimer partner protein). 26592175_The SNPs rs3790843 and rs3790844 in the NR5A2 gene are associated with pancreatic cancer risk in Japanese subjects. 26677080_The present study indicates that miR-381 may be a novel tumor suppressor that blocks HCC growth and invasion by targeting LRH-1. 26761123_NR5A2 may be important in the pathophysiology of preterm birth and exploring noncoding regulators of NR5A2 is warranted 27049310_miR-376c inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cell growth and invasion by targeting LRH-1 27586588_NR5A2-mediated cancer cell survival is facilitated through augmentation of GATA6 and anti-apoptotic factor BCL-XL levels. 27694446_The dramatic repositioning is influenced by a differential ability to establish stable face-to-face pi-pi-stacking with the LRH-1 residue His-390, as well as by a novel polar interaction mediated by the RJW100 hydroxyl group. The differing binding modes result in distinct mechanisms of action for the two agonists. 27809310_miR-27b-3p levels were found to be significantly negatively correlated with both NR5A2 and CREB1 levels in breast cancer tissues. 27983934_Our study suggests that miR-219-5p regulated the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human gastric cancer cells by suppressing LRH-1. 27984042_Additionally, the authors solved the structure of the human LRH-1 DNA-binding domain bound to a DR0 motif located within the Oct4 promoter. 27996162_The role of NR5A2 in regulating pancreatic cancer stem cell properties and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic carcinoma cells 28081303_The fusion transcript NR5A2-KLHL29FT was identified in normal and cancerous colonic epithelia. It is due to an uncharacterized polymorphic germline insertion of the NR5A2 sequence from chromosome 1 into the KLHL29 locus at chromosome 2, rather than a chromosomal rearrangement. NR5A2-KLH29FT expression levels were significantly lower in colon cancers than in matched normal colonic epithelia. 28363985_The first crystal structure of the LRH-1-PGC1alpha complex , which depicts hydrophobic contacts is identified and described. 28440426_Liver receptor homologue1 (LRH1) is a direct target of miR30d in colorectal carcinoma cells. 28531169_the expression level of LRH-1 can be used as a marker in the early diagnosis of unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. 28710032_Liver receptor homolog-1 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-136 29048619_our data indicated that miR-381 inhibited migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)by targeting LRH-1, and may represent a novel potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker for NSCLC. 29128635_Results show that LRH-1 is a direct target gene of miR-374b and that decreased miR-374b expression may contribute to the promotion of LRH-1-mediated tumorigenesis of colon cancer. 29237721_Rev-erbalpha regulates Cyp7a1 and cholesterol metabolism through its repression of the Lrh-1 receptor. 29438990_These findings not only demonstrate the significant role of the nuclear receptor LRH-1 in the promotion of intratumoral androgen biosynthesis in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) via its direct transcriptional control of steroidogenesis, but also suggest targeting LRH-1 could be a potential therapeutic strategy for CRPC management. 29443959_transcriptional regulation by NR5A2 links differentiation and inflammation in the pancreas; findings support the notion that, in the pancreas, the transcriptional networks involved in differentiation-specific functions also suppress inflammatory programs; under conditions of genetic or environmental constraint, these networks can be subverted to foster inflammation 29515023_LRH-1-deficient adult mice fed high-fat diet displayed macrovesicular steatosis, liver injury, and glucose intolerance, all of which were reversed or improved by expressing wild-type human LRH-1. Results suggest that LRH-1 maintains the pool of arachidonoyl phospholipids, thus ensuring phospholipid diversity and normal lipid homeostasis in the adult liver. 29545602_LRH1 is highly expressed in chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer.LRH1 enhanced breast cancer cell chemoresistance by upregulating MDC1 and attenuating DNA damage. 29669824_Lrh-1 transcriptionally regulates Oat2. 30044146_rs2816948 not significantly associated with recurrent abortions 30273983_The results of our study indicate that LRH1 predicts NSCLC progression, metastasis, and a dismal prognosis, emphasizing its promising role as a novel target in NSCLC therapies. 30305617_LRH-1 maintains intestinal epithelial health and protects against inflammatory damage. 30320362_Results found the mRNA and protein expression levels of LRH1 were significantly higher in HepG2 and HuH6 hepatoblastoma cell lines and results suggest that LRH1 may contribute to cell proliferation in hepatoblastoma. Hepatoblastoma cells with higher LRH1 expression levels more susceptible to LRH1 inhibition. 30638865_study identified LRH1-driven pathway as a circuitry responsible for hepatocyte identity by using cistromic analysis, improving our understanding of liver pathophysiology and identifying novel therapeutic targets. 30740909_we have provided convincing evidence in vitro and in vivo demonstrating that Nr5a2 can induce lung CSC properties and promote tumorigenesis and progression through transcriptional up-regulation of Nanog. 30923324_Regulation of liver receptor homologue-1 by DDB2 E3 ligase activity is critical for hepatic glucose metabolism. 31058195_Using the cells derived from the model, novel SF-1/Ad4BP- and LRH-1-regulated genes were identified by combined DNA microarray and promoter tiling array analyses. The interaction of SF-1/Ad4BP and LRH-1 with transcriptional regulators in the regulation of ovarian steroidogenesis was also revealed. 31328159_This study describes a novel and critical role of LRH-1 in T cell maturation, functions, and immopathologies and proposes LRH-1 as an emerging pharmacological target in the treatment of T cell-mediated inflammatory diseases. 32037723_GATA6 enhances the stemness of human colon cancer cells by creating a metabolic symbiosis through upregulating LRH-1 expression. 32572717_Impact of NR5A2 and RYR2 3'UTR polymorphisms on the risk of breast cancer in a Chinese Han population. 32931651_Nuclear-mitochondrial crosstalk: On the role of the nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 (NR5A2) in the regulation of mitochondrial metabolism, cell survival, and cancer. 33079429_Epithelial Nr5a2 heterozygosity cooperates with mutant Kras in the development of pancreatic cystic lesions. 33252195_Temporal activation of LRH-1 and RAR-gamma in human pluripotent stem cells induces a functional naive-like state. 33335203_Enantiomer-specific activities of an LRH-1 and SF-1 dual agonist. 34129175_LRH-1 high expression in the ovarian granulosa cells of PCOS patients. 34310734_NF-kappaB Regulation of LRH-1 and ABCG5/8 Potentiates Phytosterol Role in the Pathogenesis of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Cholestasis. 34561301_Nuclear receptor NR5A2 negatively regulates cell proliferation and tumor growth in nervous system malignancies. 34643922_Nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2 (NR5A2): role in health and diseases. 35801407_LRH-1/NR5A2 interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor to regulate glucocorticoid resistance. |
ENSMUSG00000026398 |
Nr5a2 |
91.869886 |
0.0870159757 |
-3.522576 |
0.249389755 |
250.607559 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001914198071105530963902872377680204145684943372947557937984643366445013716021223286330935009093763860433428204239656307629378229898423426530744070883649499137391103431582450866699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000460906419731119683076856550366376057770831578827713014264115333477058162013474522536418181743281073736915520491635081696920231983645395218082696509043216792633756995201110839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.6255252 |
2.5971309 |
157.8377079 |
16.0285514 |
| ENSG00000116852 |
23046 |
KIF21B |
protein_coding |
O75037 |
FUNCTION: Plus-end directed microtubule-dependent motor protein which displays processive activity. Is involved in regulation of microtubule dynamics, synapse function and neuronal morphology, including dendritic tree branching and spine formation. Plays a role in lerning and memory. Involved in delivery of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA(A)) receptor to cell surface. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QXL1}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the kinesin superfamily. Kinesins are ATP-dependent microtubule-based motor proteins that are involved in the intracellular transport of membranous organelles. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene are associated with inflammatory bowel disease and multiple sclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:23046; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
20007504_Comprehensive follow-up of the first genome-wide association study of multiple sclerosis identifies KIF21B as susceptibility loci 20587413_Data show the association of SNPs in KIF21B with multiple sclerosis in a Belgian study population. 20587413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24065353_KIF21B may play an important role in the pathogenesis of AS in the Chinese population and might be a new therapeutic target for AS. 25149646_KIF21B is associated with ankylosing spondylitis in a Chinese population of Shandong Province 28290984_Thus, KIF21B combines microtubule-binding and regulatory activities that together constitute an autonomous microtubule pausing factor. 32415109_Mutations in the KIF21B kinesin gene cause neurodevelopmental disorders through imbalanced canonical motor activity. 33346730_Kinesin-4 KIF21B limits microtubule growth to allow rapid centrosome polarization in T cells. 35341446_Targeting kinesin family member 21B by miR-132-3p represses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000041642 |
Kif21b |
948.220212 |
3.8982852148 |
1.962840 |
0.063903592 |
959.747903 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100879039073568839930101645384023367842271387926306506819704502711475410901202689898437297948497527669693414568457335412 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000101290790253460969773795796511292069569334261202981509618816045338158641499636743620081113476093121719575347990222449698 |
Yes |
No |
1535.3450584 |
58.0429454 |
396.4835002 |
12.3577159 |
| ENSG00000116874 |
10352 |
WARS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UGM6 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that activate and transfer the amino acids to their corresponding tRNAs during the translation of mitochondrial genes and protein synthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:28650581}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Dystonia;Ligase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Parkinsonism;Primary mitochondrial disease;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Two forms of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase exist, a cytoplasmic form, named WARS, and a mitochondrial form, named WARS2. This gene encodes the mitochondrial tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. Two alternative transcripts encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10352; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; tryptophan-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004830]; mitochondrial tryptophanyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0070183]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418]; tryptophanyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006436]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
14757836_tandem promoters provide a dual system to regulate expression and alternative splicing of human TrpRS in vivo 17726052_Mutations located at the appended beta1-beta2 hairpin and the AIDQ sequence of human TrpRS switch this enzyme to a tRNA-dependent mode in the tryptophan activation step. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20935629_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27389904_The data demonstrate a pro-angiogenic function for Wars2 both within and outside the heart. 28007980_first genome-wide scan for selection in Inuit from Greenland. A region, with a deeply divergent haplotype that is closely related to the sequence in the Denisovan genome contains two genes, WARS2 and TBX15. our study suggests a complex multi-factorial regulation of TBX15 and WARS2. We show that the introgressed region is associated with regional changes in methylation and expression levels 28236339_we found a compound heterozygous genotype of the mitochondrial tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (WARS2) gene, comprising a nonsense mutation (c.325delA, p.Ser109Alafs*15), which very likely entails nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and a missense mutation 28650581_Here we substantially extend and consolidate the symptomatology of WARS2 by presenting a patient with severe infantile-onset leukoencephalopathy, profound intellectual disability, spastic quadriplegia, epilepsy, microcephaly, short stature, failure to thrive, cerebral atrophy, and periventricular white matter abnormalities 28905505_This confidently implicates that mutations in WARS2 cause mitochondrial disease with a broad spectrum of clinical presentation. 28910573_An alternative conformation of human TrpRS suggests a role of zinc in activating non-enzymatic function. 29120065_This case expands the phenotypic spectrum of WARS2 deficiency and emphasizes the importance of mitochondrial protein synthesis in the pathogenesis of Parkinsonism. 33007465_A lead candidate functional single nucleotide polymorphism within the WARS2 gene associated with waist-hip-ratio does not alter RNA stability. 33721618_Mini-TrpRS is essential for IFNgamma-induced monocyte-derived giant cell formation. |
ENSMUSG00000004233 |
Wars2 |
70.951575 |
2.0473299334 |
1.033744 |
0.227098122 |
20.710610 |
0.00000534191994300991078599948058691637697847909294068813323974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017328953485456324764548904915351101863052463158965110778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.9933588 |
12.4660311 |
46.7827931 |
4.7340668 |
| ENSG00000116981 |
84618 |
NT5C1A |
protein_coding |
Q9BXI3 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ribonucleotide and deoxyribonucleotide monophosphates, releasing inorganic phosphate and the corresponding nucleoside (PubMed:11133996, PubMed:7599155, PubMed:8967393, PubMed:34814800). AMP is the major substrate but can also hydrolyze dCMP and IMP (PubMed:11133996, PubMed:7599155, PubMed:8967393, PubMed:34814800). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11133996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34814800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7599155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8967393}. |
Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Nucleotide metabolism;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Cytosolic nucleotidases, such as NT5C1A, dephosphorylate nucleoside monophosphates (Hunsucker et al., 2001 [PubMed 11133996]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:84618; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; 5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0008253]; IMP 5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0050483]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; XMP 5'-nucleosidase activity [GO:0106411]; adenosine metabolic process [GO:0046085]; allantoin metabolic process [GO:0000255]; AMP catabolic process [GO:0006196]; dAMP catabolic process [GO:0046059]; dGMP catabolic process [GO:0046055]; IMP catabolic process [GO:0006204]; nucleoside metabolic process [GO:0009116] |
15888028_overexpression of 5'-nucleotidase inhibits Natural Killer cell cytotoxicity to ameliorate rejection after xenotransplantation 17065091_deoxycytidine kinase, deoxyguanosine kinase, and cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase I are regulated in a cell cycle-dependent manner in MOLT-4 cells 19352542_There was no correlation between expression of cN-I and fiber type. 21873433_NT5C1A suppression promotes AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation and metabolism in human and mouse skeletal muscle 25857661_seropositivity to the NT5c1A antibody is associated with greater motor and functional disability in sporadic inclusion body myositis 25892010_Anti-NT5C1A is a common target of circulating autoantibodies in autoimmune diseases. 26906009_Individual missense changes in NT5C1A showed considerable variation in response to the different nucleoside analogs tested. 30709769_NT5C1A is robustly expressed in tumor cells of resected PDAC patients. Moreover, NT5C1A mediates gemcitabine resistance by decreasing the amount of intracellular dFdCTP, leading to reduced tumor cell apoptosis and larger pancreatic tumors in mice. 31024569_Anti-NT5c1A Autoantibodies as Biomarkers in Inclusion Body Myositis. |
ENSMUSG00000054958 |
Nt5c1a |
117.513534 |
0.0682478188 |
-3.873073 |
0.229919798 |
381.182011 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000068804990366657822208850612333463527512080374882469281348454914979844290083639016322910183230364845944077382221383054888596989852910195003430318682480059510811753264247140632234464294385519977715464741004308506233666520301994751207530498504638672 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000024649554801258967447090333762794359687572206329887056447966915811521606486467089976871467555193542784411770371322040010425602760239366815138197401695029705887238588225492830353632281335027668935499587233965701482674148792284540832042694091796875 |
Yes |
No |
14.8964183 |
2.3207350 |
219.8242399 |
14.8412890 |
| ENSG00000116983 |
51440 |
HPCAL4 |
protein_coding |
Q9UM19 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the calcium-dependent regulation of rhodopsin phosphorylation. {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Lipoprotein;Metal-binding;Myristate;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to human hippocalcin protein and hippocalcin like-1 protein. It also has similarity to rat neural visinin-like Ca2+-binding protein-type 1 and 2 proteins. This encoded protein may be involved in the calcium-dependent regulation of rhodopsin phosphorylation. The transcript of this gene has multiple polyadenylation sites. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:51440; |
calcium channel regulator activity [GO:0005246]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000046093 |
Hpcal4 |
24.327358 |
0.2550503778 |
-1.971146 |
0.364891781 |
30.332971 |
0.00000003638876875211430412283559587133252577473285782616585493087768554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000150069356463036343910227160547421476621821057051420211791992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7731775 |
2.4167474 |
38.5037689 |
5.7083559 |
| ENSG00000116991 |
57568 |
SIPA1L2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2F8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the signal-induced proliferation-associated 1 like family. Members of this family contain a GTPase activating domain, a PDZ domain and a C-terminal coiled-coil domain with a leucine zipper. A similar protein in rat acts as a GTPases for the small GTPase Rap. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:57568; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28380328_Our results suggest that rs329648 is associated with risk of developing PD in the Han Chinese population. Our findings should be verified in further studies, and they highlight the need for functional studies of MIR4697. 30706531_SIPA1L2 is a potential genetic modifier of CMT1A phenotypic expressions. |
ENSMUSG00000001995 |
Sipa1l2 |
70.726822 |
3.0983659550 |
1.631508 |
0.230970241 |
50.244636 |
0.00000000000135725199181776428790963640972705577815958510878857623538351617753505706787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007987655262850958442332243782264665108924783787358592235250398516654968261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.8777767 |
15.2191480 |
34.7389617 |
3.9765054 |
| ENSG00000116996 |
57829 |
ZP4 |
protein_coding |
Q12836 |
FUNCTION: Component of the zona pellucida, an extracellular matrix surrounding oocytes which mediates sperm binding, induction of the acrosome reaction and prevents post-fertilization polyspermy. The zona pellucida is composed of 3 to 4 glycoproteins, ZP1, ZP2, ZP3, and ZP4. ZP4 may act as a sperm receptor. |
Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Fertilization;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The zona pellucida is an extracellular matrix that surrounds the oocyte and early embryo. It is composed primarily of three or four glycoproteins with various functions during fertilization and preimplantation development. The nascent protein contains a N-terminal signal peptide sequence, a conserved ZP domain, a consensus furin cleavage site, and a C-terminal transmembrane domain. It is hypothesized that furin cleavage results in release of the mature protein from the plasma membrane for subsequent incorporation into the zona pellucida matrix. However, the requirement for furin cleavage in this process remains controversial based on mouse studies. Previously, this gene has been referred to as ZP1 or ZPB and thought to have similar functions as mouse Zp1. However, a human gene with higher similarity and chromosomal synteny to mouse Zp1 has been assigned the symbol ZP1 and this gene has been assigned the symbol ZP4. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57829; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; egg coat [GO:0035805]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; acrosin binding [GO:0032190]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; structural constituent of egg coat [GO:0035804]; acrosomal vesicle exocytosis [GO:0060478]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; negative regulation of binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:2000360]; positive regulation of acrosome reaction [GO:2000344]; positive regulation of humoral immune response [GO:0002922]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; prevention of polyspermy [GO:0060468] |
15805145_ZPB induces acrosomal exocytosis through a Gi independent pathway. 15950651_Binding sites for recombinant zona pellucida B (ZPB) glycoprotein are located both at the N- and C-terminus of proacrosin 16407501_Exposure of sperm to ZP proteins promoted acrosomal exocytosis and changed motility patterns. 18667750_induces acrosome reactions which are protein kinase-C, protein tyrosine kinase, T-type Ca2+ channels, and extracellular Ca2+ dependent 19004505_a significant decrease in acrosomal exocytosis mediated by both recombinant human ZP3 (p |
|
|
19.469311 |
0.0683388557 |
-3.871150 |
0.594950481 |
51.714277 |
0.00000000000064194240493327494273794716355869132979727192944707780952739994972944259643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003868954633244237981378126363070298369614685718431701388908550143241882324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5006078 |
1.0004975 |
36.7839743 |
6.6856094 |
| ENSG00000117009 |
8564 |
KMO |
protein_coding |
O15229 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-kynurenine (L-Kyn) to form 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine (L-3OHKyn) (PubMed:29429898, PubMed:23575632, PubMed:26752518, PubMed:28604669, PubMed:29208702). Required for synthesis of quinolinic acid, a neurotoxic NMDA receptor antagonist and potential endogenous inhibitor of NMDA receptor signaling in axonal targeting, synaptogenesis and apoptosis during brain development. Quinolinic acid may also affect NMDA receptor signaling in pancreatic beta cells, osteoblasts, myocardial cells, and the gastrointestinal tract (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23575632, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26752518, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28604669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29208702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29429898, ECO:0000305|PubMed:12402501}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;FAD;Flavoprotein;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Monooxygenase;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; quinolinate from L-kynurenine: step 1/3. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03018}. |
This gene encodes a mitochondrion outer membrane protein that catalyzes the hydroxylation of L-tryptophan metabolite, L-kynurenine, to form L-3-hydroxykynurenine. Studies in yeast identified this gene as a therapeutic target for Huntington disease. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:8564; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; kynurenine 3-monooxygenase activity [GO:0004502]; NAD(P)H oxidase H2O2-forming activity [GO:0016174]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process from tryptophan [GO:0034354]; aging [GO:0007568]; anthranilate metabolic process [GO:0043420]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; kynurenic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0034276]; kynurenine metabolic process [GO:0070189]; L-kynurenine metabolic process [GO:0097052]; NAD metabolic process [GO:0019674]; positive regulation of glutamate secretion, neurotransmission [GO:1903296]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; quinolinate biosynthetic process [GO:0019805]; response to salt stress [GO:0009651]; tryptophan catabolic process [GO:0006569] |
15950064_the function KMO AND indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase may change from a role in immunosuppression at the maternal-fetal interface in early pregnancy, to one associated with regulation of fetoplacental blood flow or placental metabolism in late gestation 16716206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16716206_Results suggest that kynurenine 3-monooxygenase is unlikely to be related to the development of schizophrenia in Japanese. 19626040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21030213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21030213_The present analysis of the combined Scandinavian sample did not reveal any allele frequency difference between patients and healthy controls 21693093_analyzed association between KMO gene polymorphisms and CSF concentrations of kynurenic acid in patients with schizophrenia and controls. results suggest that the nonsynonymous KMO SNP rs1053230 influences CSF concentrations of KYNA. 21727251_significant and correlated reduction in gene expression and enzyme activity in the frontal eye field in schizophrenia patients; rs2275163 has modest effects on predictive pursuit and visuospatial working memory endophenotypes 23459468_findings from five independent cohorts suggest that genetic variation in KMO influences the risk for psychotic features in mania of bipolar disorder patients. 24316190_Study reporting on the first successful bacterial (Escherichia coli) expression of active FLAGtrade mark-tagged human KMO enzyme expressed in the soluble fraction and progress towards its purification. 25464917_Results suggest that KMO variation influences a range of cognitive domains known to predict functional outcome in schizophrenia 25715464_Two KMO SNPs were observed more often in schizophrenia patient group compared with healthy controls. 26099564_These results suggest that KMO exhibits tumor-promoting effects towards hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and it may serve as a novel prognostic marker in HCC. 26589832_A comprehensive review of the molecular properties of KMO, including its kinetics, reaction mechanism, and inhibitor structure-activity relationship (SAR), is not currently available and, thus, is our focus here 27020856_Our data establish the candidacy of KMO as a causal factor for changes in the kidney leading to proteinuria and indicate a functional role for KMO and metabolites of the tryptophan pathway in podocytes 27077813_SiRNA knockdown of the pathway components Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase and quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase caused cells to revert to a state of susceptibility to 3HK-mediated apoptosis. 28139632_There is the association between the rs1053230 polymorphism and depression. 28319697_results show the incidence of Postpartum Depression in the Chinese population to be 7.3%, with PDS characterized by increased serum 3-HydroxyKinurenine concentration and 3-HK/Kynurenine ratio, versus matched postpartum women without PDS. Furthermore, polymorphisms of Kynurenine Monooxygenase rs1053230 are significantly associated with the incidence of PDS. 32268268_Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase upregulates pluripotent genes through beta-catenin and promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression. 32390008_Dysregulation at multiple points of the kynurenine pathway is a ubiquitous feature of renal cancer: implications for tumour immune evasion. 33170836_A novel role for kynurenine 3-monooxygenase in mitochondrial dynamics. 34440798_Kynurenine Monooxygenase Expression and Activity in Human Astrocytomas. 35011505_The Kynurenine Pathway and Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase Inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000039783 |
Kmo |
36.703843 |
8.2319199958 |
3.041229 |
0.409518745 |
53.363147 |
0.00000000000027724957583201981306413872122124110680772141046546153120289091020822525024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001711503027720875175165356466282233396502404643158001817937474697828292846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.7922197 |
18.3622087 |
7.3259086 |
1.7499542 |
| ENSG00000117036 |
2117 |
ETV3 |
protein_coding |
P41162 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor that contribute to growth arrest during terminal macrophage differentiation by repressing target genes involved in Ras-dependent proliferation. Represses MMP1 promoter activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12007404}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2117; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription repressor complex [GO:0090571]; DEAD/H-box RNA helicase binding [GO:0017151]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
14754893_PE-1/METS is an antiproliferative Ets repressor factor induced by CREB-1/CREM-1 during macrophage differentiation 17525531_Differential repression of c-myc and cdc2 gene expression by ERF and PE-1/METS. 18025162_The ETV3 expression was strongly induced by the STAT3 pathway regulated by IL-10 but not by STAT3 signaling activated by IL-6, which cannot activate the anti-inflammatory signaling pathway. 23329352_Frequent copy number gains at 1q21 and 1q32 are associated with overexpression of the ETS transcription factors ETV3 and ELF3 in breast cancer irrespective of molecular subtypes. 29877893_Case Reports/Review: indeterminate dendritic cell tumor lacking the ETV3-NCOA2 translocation. |
ENSMUSG00000003382 |
Etv3 |
507.934731 |
2.1333643169 |
1.093130 |
0.083873187 |
170.061432 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000717379849845241820937515515643847553773677355061974699128949258891289679265157718016042971327525740524166941725070500979200005531311035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000116871154345648657214770175589340414934426140978567154433209222815126497511681780657037321739181567198384570360758516471832990646362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
703.7118862 |
34.9808308 |
332.2361191 |
12.7856253 |
| ENSG00000117054 |
34 |
ACADM |
protein_coding |
P11310 |
FUNCTION: Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is one of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases that catalyze the first step of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation, an aerobic process breaking down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA and allowing the production of energy from fats (PubMed:1970566, PubMed:8823175, PubMed:21237683, PubMed:2251268). The first step of fatty acid beta-oxidation consists in the removal of one hydrogen from C-2 and C-3 of the straight-chain fatty acyl-CoA thioester, resulting in the formation of trans-2-enoyl-CoA (PubMed:2251268). Electron transfer flavoprotein (ETF) is the electron acceptor that transfers electrons to the main mitochondrial respiratory chain via ETF-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETF dehydrogenase) (PubMed:25416781, PubMed:15159392). Among the different mitochondrial acyl-CoA dehydrogenases, medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase acts specifically on acyl-CoAs with saturated 6 to 12 carbons long primary chains (PubMed:1970566, PubMed:8823175, PubMed:21237683, PubMed:2251268). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15159392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1970566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21237683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2251268, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25416781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8823175}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;FAD;Fatty acid metabolism;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2251268}. |
This gene encodes the medium-chain specific (C4 to C12 straight chain) acyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase. The homotetramer enzyme catalyzes the initial step of the mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway. Defects in this gene cause medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, a disease characterized by hepatic dysfunction, fasting hypoglycemia, and encephalopathy, which can result in infantile death. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:34; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003995]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; medium-chain-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity [GO:0070991]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; carnitine biosynthetic process [GO:0045329]; carnitine metabolic process, CoA-linked [GO:0019254]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA dehydrogenase [GO:0033539]; glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005978]; liver development [GO:0001889]; medium-chain fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0051793]; medium-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0051791]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to starvation [GO:0042594] |
11263545_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 11349232_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11517203_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12522104_MCAD is induced by PGC-1 in an ERRalpha-dependent manner 12914524_Interference between PPARA and ERRalpha and RXRA complex heterodimer and the nuclear receptor site of MCAD 14692513_single arginine residue is essential for the binding of electron transferring flavoprotein to MCAD, but the single histidine residue, although involved, is not 14970748_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15171999_first molecular identification of MCADD in an Arab patient and the first reported splice mutation in the MCAD gene that has been functionally characterized 15832312_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15896661_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15902558_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16128823_Two novel rare mutations, R256T and K364R, have been investigated to assess how far the biochemical properties of the mutant proteins correlate with the clinical phenotype of medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. 16291504_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17186412_analysis of MCAD deficiency (homozygous at c.985A>G (K329E)) complicated by acute liver failure in pregnancy [case report] 17539907_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18188679_Measurement of MCAD activity in leukocytes or lymphocytes using phenylpropionyl-CoA as a substrate can be regarded as the gold standard to diagnose MCAD deficiency upon initial positive screening test results. 18241067_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18241067_Six novel and seven previously reported medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase mutations were detected in newborns with medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18927092_Ethnic-specific homozygous adenin/guanine substitution in an ACADM birth prevalence from a large-scale United Kingdom newborn screening study. 19064330_study indicates that c.449-452delCTGA represents a common mutation in Japanese patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) 19224950_Protein misfolding of MCAD protein is the molecular basis in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. 19551636_In the medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, the 985G mutant and 985A normal alleles had allelic frequencies of 0.0020 and 0.9980, respectively. 19551636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19649258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20434380_classification of genotypes with at least one variant of unknown significance in individuals who are carriers of, or affected with, MCAD deficiency of the following genotypes: c.985A>G/wildtype, c.199T>C/c.985A>G and c.985A>G/c.985A>G 20567907_Identify an ACADM founder mutation for MCADD in Saudi Arabian population. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21083904_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21239873_The mutation in Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency is the first report of the c.461T>G mutation in the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene. 21968293_physiological concentrations of flavin adenine dinucleotide resulted in a spectacular enhancement of the thermal stabilities of MCADH and prevented enzymatic activity loss 22630369_Subjects with variant ACADM genotypes and residual MCAD enzyme activities G is a functional SNP, which leads to higher MCAD expression, perhaps due to improved splicing. This study is a proof of principle that synonymous SNPs are not neutral. 23829193_Segregation studies in the Gypsy families showed that 93/123 relatives were carriers of the acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase G985 allele, suggesting its high prevalence in this ethnic group. 24718418_mutations in the ACADM gene lower the temperature threshold at which medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency loss-of-function occurs. 24966162_our study demonstrates that not all mutations identified in children with abnormal NBS profiles suggestive of MCAD deficiency result in a total loss in MCAD activity and function 26223887_The c.600-18G > A variant activates a cryptic splice site, which competes with the natural splice site. 26947917_Study determined three mutations (p.R53C, p.R281S and p.G362E) in MCAD protein predisposing for MCAD deficiency which seems to be unique to Japanese population. 27148938_Exclusively breastfed neonates with MCAD are at risk for early metabolic decompensation. As breastfeeding rates increase, close management of feeding difficulties is essential for all neonates awaiting newborn screening results 27308838_17 VUS (37%; 7 in ACADM, 9 in GALT, and 1 in PAH) were reclassified from uncertain (6 to benign or likely benign and 11 to pathogenic or likely pathogenic). We identified common types of missing information that would have helped make a definitive classification and categorized this information by ease and cost to obtain 27477829_Subjects with neonatal symptoms, or neonatal abnormal labs, or neonatal triggers were more likely to have at least one copy of the severe c.985A>G ACADM gene mutation 27856190_Our study has revealed the unique genetic backgrounds of MCAD deficiency among Japanese, based on the largest series of non-Caucasian cases. 27871288_LCHAD and MCAD are differentially expressed in maternal and fetal tissues during normal late pregnancy, which may represent a metabolic adaptation in response to physiological maternal dyslipidemia during late pregnancy. 27976856_The in silico structural changes in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (hMCAD) p.K329E variant protein affect the disturbed oligomeric profile, thermal stability, and conformational flexibility, with respect to the wild-type. 31033143_In six unrelated Chinese patients with medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency, six mutations were found in acyl-CoA dehydrogenase medium chain (ACADM). One mutation (c.727C>T) was novel and the others (c.158G>A, c.387+1delG, c.449_452del, c.1045C>T, and c.1085G>A) have been previously reported. 33580884_Genotype and residual enzyme activity in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency: Are predictions possible? 33975883_Suppression of ACADM-Mediated Fatty Acid Oxidation Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Aberrant CAV1/SREBP1 Signaling. 34039636_Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Protects Mitochondria from Lipid Peroxidation in Glioblastoma. 34704412_Screening and follow-up results of fatty acid oxidative metabolism disorders in 608 818 newborns in Jining, Shandong province. |
ENSMUSG00000062908 |
Acadm |
733.646384 |
0.3951335481 |
-1.339588 |
0.083396221 |
256.684982 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000090600043583610624725216007426023806886172801805415845679111092585350259286788734396399747238757442611141611905221752006717280773864123520169627963583014462756182183511555194854736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022362151225653724101940274926591542373338995381153661872169502861980041759409740575552660490570130007431285663660772083341144816258129411862091984186662330102990381419658660888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
411.0110227 |
27.8869283 |
1047.0778452 |
49.3630419 |
| ENSG00000117091 |
962 |
CD48 |
protein_coding |
P09326 |
FUNCTION: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface glycoprotein that interacts via its N-terminal immunoglobulin domain with cell surface receptors including 2B4/CD244 or CD2 to regulate immune cell function and activation (PubMed:27249817, PubMed:12007789). Participates in T-cell signaling transduction by associating with CD2 and efficiently bringing the Src family protein kinase LCK and LAT to the TCR/CD3 complex (PubMed:19494291). In turn, promotes LCK phosphorylation and subsequent activation (PubMed:12007789). Induces the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic immunoreceptortyrosine switch motifs (ITSMs) of CD244 initiating a series of signaling events that leads to the generation of the immunological synapse and the directed release of cytolytic granules containing perforin and granzymes by T-lymphocytes and NK-cells (PubMed:9841922, PubMed:27249817). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12007789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19494291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27249817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9841922}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the CD2 subfamily of immunoglobulin-like receptors which includes SLAM (signaling lymphocyte activation molecules) proteins. The encoded protein is found on the surface of lymphocytes and other immune cells, dendritic cells and endothelial cells, and participates in activation and differentiation pathways in these cells. The encoded protein does not have a transmembrane domain, however, but is held at the cell surface by a GPI anchor via a C-terminal domain which maybe cleaved to yield a soluble form of the receptor. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:962; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; defense response [GO:0006952]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
12072193_CM1-induced apoptosis is achieved via different initiation pathways, which are cell-type dependent 12496412_Signal-dependent adhesion of resting NK cells initiated by expression of ICAM-1 is greatly enhanced by coexpression of CD48, even in the absence of cytokines. 15356144_Engagement of natural killer (NK) cell receptor 2B4 by its counterreceptor, CD48, expressed on target cells leads to an inhibition in NK cytotoxicity independent of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein (SAP) expression. 15760905_IL-18, IL-18 receptor alpha, and CD48 complex formation via glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor glycan triggers binding to IL-18 receptor beta, and thereby induces intracellular signal transduction and IFN-gamma production. 16081768_Review of recent studies suggests an important role for interactions between 2B4 and CD48 in the course of T cell activation and proliferation 16585556_2B4 (CD244) can stimulate NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine production by interacting with NK cell expressed CD48 and adds CD48 to the growing number of activating NK cell receptors 16785501_CD48 is an interleukin (IL)-3-induced activating receptor on eosinophils and may be involved in promoting allergic inflammation. 16803907_CD48 is a CD2 and CD244 (2B4)-binding protein 16866884_In conclusion, we cannot confirm a role of human endogenous retrovirus-K18 superantigen polymorphisms or of the CD48 CA repeat for type 1 diabetes susceptibility. 16866884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17222190_findings indicate that FimH induces host cell signalling cascades that are involved in E. coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) and CD48 is a putative HBMEC receptor for FimH 17599905_the mechanism of signal transduction by CD244 is to regulate FYN kinase recruitment and/or activity and the outcome of CD48/CD244 interactions is determined by which other receptors are engaged. 18617371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19494291_CD2 functions as the master switch recruiting CD48 and Lck 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164429_The ligand (CD48) of the 2B4 receptor can exert both activating and inhibiting signals; natural killer (NK) cells might be at risk for self-killing were it not for the inhibiting signals generated by the 2B4-CD48 interaction. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20833258_Stimulation of CD48 induces rearrangement of signaling factors in lipid rafts, Lck-kinase activity, and tyrosine phosphorylation. 22495247_replication study of association of 2 SNPs in HERV-K18 and 19 tagSNPs in CD48 with schizophrenia (SZ)and type 2 diabetes (T2D) in patients with SZ in 2 Danish samples; no association was found with SZ or with T2D among individuals with SZ for any of the SNPs 23225218_Monocyte-induced natural killer cell dysfunction was markedly attenuated by blocking CD48 receptor 2B4 on NK cells, but not by blockade of NKG2D and NKp30. 24505299_Blockade of 2B4/CD48 interaction resulted in improvement in function via perforin expression and degranulation as measured by CD107a surface mobilization on HTLV-1 specific CD8+ T cells. 24670806_we propose that SLAMF2 engagement regulates adaptive immune responses 25255823_These data demonstrate the important role of CD48 in SA/exotoxins-eosinophil activating interactions that can take place during allergic responses and indicate CD48 as a novel therapeutic target for allergy and especially of AD. 26836239_Our data indicate sCD48 as a SEB-induced 'decoy' receptor derived from eosinophil and therefore as a potential anti-inflammatory tool in S. aureus-induced eosinophil inflammation often associated with allergy. 26860368_The present study provides further insights into the role of the 2B4-CD48 interaction in the fine regulation of CD8(+) T-cell effector function upon antigenic stimulation. 26926492_CD48 expression was increased in patients with a short disease duration compared to both controls and patients with longer disease duration. In patients with short disease duration, increased CD48 expression was associated with alveolar inflammation. 27249817_Data show that 2B4 not only can bind to CD48 in trans but also interacts with CD48 in cis by using the same binding interface. Also, the results demonstrated that constitutive phosphorylation of 2B4 occurs only in the presence of CD48, and that cis binding is sufficient to induce substantial levels of baseline phosphorylation. 27859399_mCD48 and sCD48 are differentially expressed in the peripheral blood of asthma patients of varying severity. sCD48 inhibits CD244-mediated eosinophil activation. These findings suggest that CD48 may play an important role in human asthma. 30306094_soluble CD48 levels were significantly elevated in patients with nonallergic asthma compared to control and to the allergic asthma cohort 31115879_immune receptor CD48 is overexpressed on MM cells together with SLAMF7, and that CD48 may be considered as an alternative target for treatment of MM in cases showing weak expression of SLAMF7. 31419545_this study demonstrates recurrent inflammatory disease caused by a heterozygous mutation in CD48 31922199_CD48 mRNA expression was significantly lower in patients than in normal healthy individuals. 33219153_Human innate lymphoid cell precursors express CD48 that modulates ILC differentiation through 2B4 signaling. 34477021_sCD48 is elevated in non-allergic but not in allergic persistent rhinitis. 34489334_GDF15 induces immunosuppression via CD48 on regulatory T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000015355 |
Cd48 |
10.576822 |
117.4792304112 |
6.876262 |
1.125596982 |
54.331938 |
0.00000000000016932722870272061712910693942652432997697693750627223607807536609470844268798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001059012667649218771075398643131119962761468866752068151981802657246589660644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.5539432 |
17.3198148 |
0.1840316 |
0.1438804 |
| ENSG00000117114 |
23266 |
ADGRL2 |
protein_coding |
O95490 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-independent receptor of low affinity for alpha-latrotoxin, an excitatory neurotoxin present in black widow spider venom which triggers massive exocytosis from neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Receptor probably implicated in the regulation of exocytosis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88923}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the latrophilin subfamily of G-protein coupled receptors. The encoded protein participates in the regulation of exocytosis. The proprotein is thought to be further cleaved within a cysteine-rich G-protein-coupled receptor proteolysis site into two chains that are non-covalently bound at the cell membrane. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:23266; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; latrotoxin receptor activity [GO:0016524]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] |
30340542_The results of this study suggest that this ADGRL2 variation impedes the proper development of the cerebellum resulting in RES which is thought to occur when the cerebellar primordium develops and probably results from abnormal function of genes expressed during initial patterning of the mesencephalon-rhombencephalon 33798451_Adhesion GPCR Latrophilin-2 Specifies Cardiac Lineage Commitment through CDK5, Src, and P38MAPK. 34581723_LPHN2 inhibits vascular permeability by differential control of endothelial cell adhesion. |
ENSMUSG00000028184 |
Adgrl2 |
926.231070 |
0.3505228889 |
-1.512419 |
0.076441679 |
385.967918 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006247092440781003543611653414391664578785461416389564869496168506269424156403187041649188901084434242971965165824883376729472616599173425445000223608565587192951951597593032542313710565841227332941101621608011307262842137788538821041584014892578 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002265530329875371314166731867360809983719871701099865626193342661527874357320176305925386976046298789541471482683115562270179472175519515398611545907318306318136058293024072703661734907419905582200579712221291672769041269930312409996986389160156 |
Yes |
No |
496.3965623 |
23.6678014 |
1425.2690313 |
46.0027119 |
| ENSG00000117115 |
11240 |
PADI2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2J8 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the deimination of arginine residues of proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12392711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25621824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30044909}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl arginine deiminase family of enzymes, which catalyze the post-translational deimination of proteins by converting arginine residues into citrullines in the presence of calcium ions. The family members have distinct substrate specificities and tissue-specific expression patterns. The type II enzyme is the most widely expressed family member. Known substrates for this enzyme include myelin basic protein in the central nervous system and vimentin in skeletal muscle and macrophages. This enzyme is thought to play a role in the onset and progression of neurodegenerative human disorders, including Alzheimer disease and multiple sclerosis, and it has also been implicated in glaucoma pathogenesis. This gene exists in a cluster with four other paralogous genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11240; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; euchromatin [GO:0000791]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; histone H3R26 arginine deiminase activity [GO:0140798]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-arginine deiminase activity [GO:0004668]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070100]; negative regulation of lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:1901624]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762]; transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling [GO:0045815] |
12392711_molecular cloning and gene organization; expressed by all the living epidermal layers, suggesting that PAD type II is functionally important during terminal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes 15555572_first report to demonstrate a measurable response in the amounts of peptidylarginine deiminase type II mRNA, protein and activity in human astrocytes by prolonged hypoxic exposure 15629448_hPADI2 and hPADI4 have different roles under physiological and pathological conditions 17469138_The amount of peptidyl arginine deiminase type II enzyme and citrullinated myelin basic protein was increased in multiple sclerosis 17968929_PAD-2 & PAD-4 are only isotypes expressed in synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis & other arthritides; inflammatory cells are major source, but PAD-4 also comes from hyperplastic synoviocytes; both isotypes probably involved in citrullination of fibrin 18645041_These data provide new structure-function dimensions for chemokines in leukocyte mobilization, disclosing an anti-inflammatory role for PAD. 18668562_The citrullinating enzyme PAD-4 was detected in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondylarthritides. 18923545_Results describe the in vitro kinetic properties of the human peptidylarginine deiminase isoform 2 (hPAD2), and explore the putative inhibitory action of the methyl ester side chain of paclitaxel. 19478818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19478818_PADI2 does not contribute to genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. 19564157_PAD2 is expressed in human monocytic leukaemia THP-1 cells during differentiation into macrophages 20013286_PAD2 activation and aberrant citrullinated proteins could play a role in pathogenesis and have value as a marker for the postmortem classification of neurodegenerative diseases. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20806090_This is the first report demonstrating that like in primary open angle glaucoma, normal tension glaucoma also possesses elevated levels of both PAD2 and protein-bound citrulline. 21878453_Defective regulation of PAD2 in the periphery blood, without the immunological shelter of the blood-brain barrier, may contribute to the development of the autoimmune responses in MS. 22520816_Normal human and canine mammary epithelium showed strong cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of PAD2, but there was reduced PAD2 expression in mammary carcinomas from both species. 22614825_Contact between stimulated T cells and monocyte-macrophages or cytokine-activated monocyte-macrophages constitutes a highly likely source of PAD2 and PAD4, which are observed in inflamed synovial tissues. 22853951_17beta-estradiol stimulation induces the recruitment of PAD2 to target promoters by ERalpha, whereby PAD2 then citrullinates H3R26, which leads to local chromatin decondensation and transcriptional activation. 22911765_PAD2 binds directly to the promoters of the PTN and MAGEA12 genes and that the likely mechanism by which PAD2 regulates expression of these genes is via citrullination of arginine residues 2-8-17 on histone H3 tails. 23022892_These findings suggest that PAD2 and citrullinated proteins may play a key role in the brain pathology of prion diseases. [review] 23562679_Our observations show increased levels of protein deimination but not PAD2 in age related macular degeneration retinas and retinal pigment epithelium suggesting reduced rate of turnover of deiminated proteins. 24384061_Data suggest peptidylarginine deiminase 2 (PAD2) as a possible biomarker in various inflammatory diseases. 24594197_PAD2 and PAD4 have distinct substrate specificities. 24850148_PADI2 and vimentin participate in the apoptotic mechanisms of activated T lymphocytes. 24989433_PAD2 appears to use a substrate-assisted mechanism of catalysis in which the positively charged substrate guanidinium depresses the pKa of the nucleophilic cysteine 25213324_these studies provide the first genetic evidence that PAD2 functions as an oncogene and suggest that PAD2 may promote tumor progression by enhancing inflammation within the tumor microenvironment. 25475141_PAD2 activity was detected in synovial fluid samples from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 25621824_Protein arginine deiminase 2 binds six calcium ions in an ordered fashion. 25897949_Report increased levels of extracellular PAD2 in the lungs of smokers. 26245941_PAD2 activity was significantly higher in cell-free synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients compared to osteoarthritis patients. 26255191_We identified the presence of PADI3 mRNA expression in synovial tissue and PADI2 and PADI4 mRNA expressions in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 26927695_this study shows that a miR-4728 downregulates PADI2, a novel rheumatoid arthritis risk gene 27280713_Downregulation of PADI2 is an early event in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer associated with poor prognosis and points toward a possible role of citrullination in modulating tumor cells and their microenvironment. 27599511_Deimination of myelin basic protein (MBP) by peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) prevents its binding to the proteasome and decelerates its degradation by the proteasome in mammalian cells. Potential anticancer drug tetrazole analogue of chloramidine 2, at concentrations greater than 1 microM inhibits the enzymatic activity of PAD in vitro. 27818200_Multiple proteins citrullinated by hypoxia-induced PADs were identified. In addition, the extracellular domain of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 was citrullinated by human PAD2 in vitro. CONCLUSION: Our data may contribute to understanding of pathophysiology of malignant gliomas from the aspects of protein citrullination. 28403548_Data suggest that protein-arginine deiminase 2 (PADI2) suppresses the proliferation of colonic epithelial cells through catalysis of protein citrullination, and that downregulation of PADI2 expression might therefore contribute to colon carcinogenesis. 28766045_These data suggest that overexpression of the human PAD2 transgene in the epidermis of transgenic mice increases the malignant conversion rate of benign tumors by promoting an inflammatory microenvironment. 28819028_Peptidyl arginine deiminase 2 (PADI2) is required for activation of androgen receptor (AR) signaling under androgen-deprived condition. 29084334_Brain gene expression of PADI2, ZNF385A, PSD2, and A2ML1 and DNA methylation dysregulations are implicated in the alteration of brain tissue properties associated with late-life cognitive decline above and beyond the influence of common neuropathologic conditions. 29148420_the mRNA expression of PADI2, PADI4 and Sp1 is upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis bone marrow CD34+ cells independently of the systemic inflammation or treatment regimen. 30064459_Chronic gingival inflammation is associated with increased local citrullination and PAD2 and PAD4 expression in periodontitis. 30161253_In most rheumatoid arthritis patients, PAD2 and PAD4 are equally efficient in generating citrullinated target sites for anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) in fibrinogen and ENO1. The binding of autoantibodies to histone H3 was generally higher after citrullination with PAD4 than with PAD2. Citrullinated human serum albumin is not a target for ACPAs. 31243954_PAD2 translocates into the nucleus in response to calcium signaling. 31267364_Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase, Type II (PADI2) Is Involved in Urothelial Bladder Cancer. 31601253_PAD2 expression is upregulated in Tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells. 31730822_citrullination of fibrinogen by peptidylarginine deiminase 2 impairs fibrin clot structure 31940417_This study shows that ubiquitous or nervous system expression of human PAD2 or PAD4 in Drosophila melanogaster have minimal impact on Drosophila melanogaster lifespan, fecundity, and the response to acute heat stress. 32079300_Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 2 (PADI2)-Mediated Arginine Citrullination Modulates Transcription in Cancer. 32098295_Peptidylarginine Deiminase Isozyme-Specific PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 Inhibitors Differentially Modulate Extracellular Vesicle Signatures and Cell Invasion in Two Glioblastoma Multiforme Cell Lines. 32341463_PAD enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic effectors and autoimmune targets. 32785008_The Essential Role of Peptidylarginine Deiminases 2 for Cytokines Secretion, Apoptosis, and Cell Adhesion in Macrophage. 33157227_Citrullination as a novel posttranslational modification of matrix metalloproteinases. 33573274_Peptidylarginine Deiminase Inhibitor Application, Using Cl-Amidine, PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 Isozyme-Specific Inhibitors in Pancreatic Cancer Cells, Reveals Roles for PAD2 and PAD3 in Cancer Invasion and Modulation of Extracellular Vesicle Signatures. 34274450_PAD2-mediated citrullination of Fibulin-5 promotes elastogenesis. 34421923_PADI2 Polymorphisms Are Significantly Associated With Rheumatoid Arthritis, Autoantibodies Serologic Status and Joint Damage in Women from Southern Mexico. 34569542_The Clinical and Prognostic Significance of Protein Arginine Deiminases 2 and 4 in Colorectal Cancer. 35181688_Syndecan-2 regulates PAD2 to exert antifibrotic effects on RA-ILD fibroblasts. 35737372_Molecular Mechanism of Protein Arginine Deiminase 2: A Study Involving Multiple Microsecond Long Molecular Dynamics Simulations. 36076933_Peptidylarginine Deiminase 2 Gene Polymorphisms in Subjects with Periodontitis Predispose to Rheumatoid Arthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000028927 |
Padi2 |
19.079502 |
2.7236735918 |
1.445554 |
0.416064405 |
12.033595 |
0.00052250191005603842560323091248619675752706825733184814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001278535840919616623986843073623731470433995127677917480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.0995067 |
6.7434974 |
10.4588214 |
2.0054726 |
| ENSG00000117152 |
5999 |
RGS4 |
protein_coding |
P49798 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. Activity on G(z)-alpha is inhibited by phosphorylation of the G-protein. Activity on G(z)-alpha and G(i)-alpha-1 is inhibited by palmitoylation of the G-protein. |
Alternative splicing;Lipoprotein;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Schizophrenia;Signal transduction inhibitor |
|
Regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) family members are regulatory molecules that act as GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) for G alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. RGS proteins are able to deactivate G protein subunits of the Gi alpha, Go alpha and Gq alpha subtypes. They drive G proteins into their inactive GDP-bound forms. Regulator of G protein signaling 4 belongs to this family. All RGS proteins share a conserved 120-amino acid sequence termed the RGS domain. Regulator of G protein signaling 4 protein is 37% identical to RGS1 and 97% identical to rat Rgs4. This protein negatively regulate signaling upstream or at the level of the heterotrimeric G protein and is localized in the cytoplasm. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5999; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; G-protein alpha-subunit binding [GO:0001965]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; brain development [GO:0007420]; dorsal root ganglion development [GO:1990791]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0061052]; negative regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060160]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of glycine import across plasma membrane [GO:1900924]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901380]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; regulation of actin filament organization [GO:0110053]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to cocaine [GO:0042220]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to morphine [GO:0043278] |
12023979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12422374_cytosolic and membrane levels of RGS4 may contribute to the regional differences in the coupling of muscarinic M1 receptors in Alzheimer's disease 12436019_A significant decrease in the transcript encoding regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. 12642592_results suggest that palmitoylation of a Cys residue in the regulator of G protein signaling(RGS) box is critical for RGS16 and RGS4 GAPase activating protein activity and their ability to regulate G protein signaling in mammalian cells 14732600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14732600_The data of this research give modest support for the hypothesis that the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 is a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. 14755443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15182322_RGS4 mRNA distribution in human postmortem tissue from normal persons was very dense in most cortical layers examined, with lower density in the basal ganglia and thalamus. 15274033_Results could be interpreted as supporting evidence for the association between RGS4 and schizophrenia. 15369705_RGS4 and beta-tubulin modulate Galpha-GDP and Galpha-GTP states thus modulating MT1 melatonin receptor function. 15381923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15381923_RGS4 polymorphisms are associated with alterations in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (area 9) volumes among schizophrenic patients. 15383626_Although gross indices of signaling were unaffected by RGS4, it slowed the rate of increase in Ins(1,4,5)P3 levels. 15660667_In schizophrenia, significant case-control differences were not observed, though the TDT suggested transmission distortion. For bipolar disorder, an omnibus test suggested differences in the overall distribution of haplotypes bearing all four SNPs. 15660667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16082709_No association is identified between RGS4 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers, genotypes, or haplotypes and schizophrenia 16082709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16176390_Data do not directly replicate previous associations of RGS4, but association with SNP 7 in the Scottish population provides some support for a role in schizophrenia susceptibility. 16176390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246308_These results provide the first demonstration of a Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between RGS4 and CaM in vivo and show that association in lipid rafts of the plasma membrane might be involved in this physiological regulation of RGS proteins. 16380905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16508931_Finding weakens the evidence that mutations or variation in the RGS4 gene have an effect on schizophrenia susceptibility. 16508931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526029_Results fail to support the RGS4 as a candidate gene for schizophrenia when evaluated with three SNP markers from promoter region and intron 1. 16604300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16631129_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791139_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791139_this meta-analysis did not find statistically significant evidence for association between RGS4 and PRODH and schizophrenia on the basis of either allelic or genotypic analysis. 16860780_RGS4 is an example of a molecule that may underlie increased vulnerability through either genetic or non-genetic mechanisms, which we suggest may be typical of other genes in a complex, polygenic disorder such as schizophrenia. 16904822_Genetic polymorphisms within RGS4 are unlikely to confer an increased susceptibility to the etiology of schizophrenia. 16904822_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16905560_RGS4 mRNA was inversely correlated with COMT enzyme activity in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex 17006672_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17006672_SNPs in RGS4, G72, GRM3, and DISC1 showed evidence for significant statistical epistasis with COMT. 17055463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17092693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17106420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17220356_examined function, receptor specificity, and expression of R4 subfamily RGS proteins, RGS2, -3, -4, -5, and -8 via missense mutations introduced 17301167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301167_RGS4 single nucleotide polymorphism impacts frontal lobe blood oxygenation level-dependent response and network coupling during working memory and results in reductions in gray, white matter structural volume in individuals carrying the A allele. 17408693_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17410640_In RGS4, the G-allele of the previously reported SNP RGS4-1 (single and as part of haplotypes with SNP RGS4-18) was associated with non-deficit schizophrenia but not with deficit schizophrenia. 17410640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17515439_study identified all common RGS4 polymorphisms & evaluated patterns of linkage disequilibrium in relation to schizophrenia; 2 haplotypes reported to confer liability to SZ had significant promoter activity suggesting functional role for both haplotypes 17588543_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17588543_RGS4 genotypes predicted both the severity of baseline symptoms and relative responsiveness to antipsychotic treatment in patient with schizophrenia. 17707117_Full length cloning and expression analysis of splice variants of RGS4 were performed. 17707117_Multiple splice variant forms of RGS4 and Rgs4 are expressed in human and mouse brain and show differential expression across brain compartments. 17722013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17722013_the association of regulator of G-protein signalling 4 protein polymorphisms with the phenotypic subgroups of schizophrenia. 18031991_The isolation and characterization of a novel human RGS4 mutant which displays enhanced or gain-of-function (GOF) activity, is described. 18198266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204343_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18204343_RGS4 variances influence clinical manifestations of schizophrenia 18262772_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18434012_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18434012_RGS4 polymorphism was not associated with treatment response to electroconvulsive therapy in major depressive disorder 18443239_Transgenic overexpression of cardiac myocyte-specific RGS4 attenuates overexpression of hypertrophy-related genes in guanylyl cyclase A-knockout mice. 18470533_Data show that the expression of RGS4 decreases in the prefrontal cortex of postmortem brain samples spanning half a century of human aging (18-67 years). 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18584117_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18622782_Altered RGS4 expression is not universally present throughout the cortex of people with schizophrenia. 18804346_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18804346_We found evidence of a joint effect between IL3 (rs31400) and DTNBP1 18834502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19041089_results suggest the possibility that alterations in the expression of RGS4-3 contribute to the development of SCZ. 19059885_Regulator of G-protein signaling 4 suppresses LPS-induced MUC5AC overproduction in the airway. 19201815_Prostaglandin E(2) can induce MUC5AC overproduction via the EP(4) receptor and that RGS4 may have suppressive effects in controlling MUC5AC overexpression in the airway. 19282471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19282471_RGS4 polymorphisms are associated with variations in cognitive functions and contribute a small but statistically significant proportion of variance in a family-based sample. 19324084_RGS4 plays a key role in G protein coupling selectivity and signaling of the mu- and delta-opioid receptors. 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19416973_role for endogenous RGS4 protein in modulating delta-opioid receptor signaling in SH-SY5Y cells 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19549919_Findings point to the existence of a mechanism for posttranslational regulation of RGS4 function, which may have important implications for the acquisition of a metastatic phenotype by breast cancer cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937977_A homogeneous sample of 280 schizophrenia patients and 230 healthy controls of Hungarian, Caucasian descent were genotyped for polymorphisms in schizophrenia candidate genes NRG1, DTNBP1, RGS4, G72/G30, and PIP5K2A. 19937977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20414142_RGS4 is a potential susceptible gene for bipolar disorder. 20430014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20630860_A novel mechanism involving coordinated regulation of nuclear levels and acetylation of NF-YA and Bcl6 activates RGS4 transcription. 20712983_Localization of Sst2 to the projection prevents excess G-protein activation during the pheromone response. 20816714_RGS4 and RGS10 proteins are detected in postmortem prefrontal cortex. 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21209077_Opioid-induced down-regulation of RGS4: role of ubiquitination and implications for receptor cross-talk. 21674833_The researchers found evidence that there were significant differences between the D1S1656 locus in the Maghreb population and other populations. 21910931_RGS4 gene variations specifically disrupt prefrontal control of saccadic eye movements. 22157635_Lack of association between the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) rs951436 polymorphism and schizophrenia. 22253691_These studies indicate that increased RGS4 expression promotes a phenotypic switch of airway smooth muscle, evoking irreversible airway obstruction in subjects with severe asthma. 22753418_Cys-2 and Cys-12 play markedly different roles in the regulation of RGS4 membrane localization, intracellular trafficking, and G(q) inhibitory function via mechanisms that are unrelated to RGS4 protein stabilization. 23093381_The results suggest unaltered membrane RGS4 and cytosolic RGS10 proteins levels in schizophrenia and major depression. 23332465_genetic association study in Chinese Han population: Data suggest an SNP in RGS4 (rs10759) is associated with increased predisposition to schizophrenia via down-regulation of miroRNA (MIRN124) binding to 3-prime-untranslated region of RGS4 mRNA. 23630294_dramatic up-regulation of RGS4 expression in the nucleus accumbens of subjects treated with monoamine-directed antidepressants 23733193_Data indicate that Rab5, Rab7 and Rab11 are involved in RGS4 traffics through plasma membrane recycling or endosome. 23911251_RGS4 and COMT risk variants are associated with brain structural alterations in patient with schizophrenia. 24297163_ectopic expression of R4 subfamily members RGS2, RGS3, RGS4, and RGS5 reduced activated PAR1 wild-type signaling, whereas signaling by the PAR1 AKKAA mutant was minimally affected. 25289860_RGS2 and RGS4 are new interacting partners that play key roles in G protein coupling to negatively regulate kappa-OmicronR signaling. 26088132_RGS4 deletion results in a predisposition to atrial fibrillation from enhanced activity in the G-protein pathway, resulting in abnormal calcium release and corresponding electrical events. 26119705_After alphao dissociates from MOR, RGS4 remains bound to the C-terminal region of MOR 26640232_All of these results confirmed the critical role of RGS4 in NSCLC progression. 26910404_The results of this study demonstrated the association between the variation in the regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) gene, a putative candidate gene for psychosis previously associated with schizophrenia endophenotypes, and psychotic-like experiences (PLEs). 26987813_Data support the notion that the Galpha, but not Gbetagamma, arm of the Gi/o signalling is involved in TRPC4 activation and unveil new roles for RGS and RGS4 in fine-tuning TRPC4 activities. 28219718_Study investigated whether RGS4 could participate in signalling pathways to regulate neurotropic events. These observations suggest that RGS4 is implicated in opioid dependent neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth via a 'non-canonical' signaling pathway regulating STAT5B-directed responses. 31330059_MiR-21-3p modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis via targeting TGS4 in retinal pigment epithelial cells. 31386272_A highly conserved delta-opioid receptor region determines RGS4 interaction. 31587286_lncRNA RPL34-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion while promoting apoptosis by competitively binding miR-3663-3p/RGS4 in papillary thyroid cancer. 32199913_RGS4 promotes allergen- and aspirin-associated airway hyperresponsiveness by inhibiting PGE2 biosynthesis. 32386256_miR-874-3p inhibits cell migration through targeting RGS4 in osteosarcoma. 32392739_Targeting RGS4 Ablates Glioblastoma Proliferation. 32501280_RGS4 controls Galphai3-mediated regulation of Bcl-2 phosphorylation on TGN38-containing intracellular membranes. 32517689_Regulators of G-protein signaling, RGS2 and RGS4, inhibit protease-activated receptor 4-mediated signaling by forming a complex with the receptor and Galpha in live cells. 35628613_Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000038530 |
Rgs4 |
77.516926 |
8.7387187293 |
3.127422 |
0.252586816 |
169.661591 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000877159911333222154615841403700072564405847394635347880850204739546947268020615137485228669050231898977887379231788145261816680431365966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000142743994391161604071700454882416149703591193547737038672448736108089716026703457477192261606397088308240128640136390458792448043823242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
138.9588015 |
22.5141992 |
15.9982373 |
2.2770851 |
| ENSG00000117228 |
2633 |
GBP1 |
protein_coding |
P32455 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes GTP to GMP in 2 consecutive cleavage reactions (By similarity). Confers protection to several pathogens, including the bacterial pathogens Listeria monocytogenes and Mycobacterium bovis BCG as well as the protozoan pathogen Toxoplasma gondii (By similarity). Promotes IFN-gamma-mediated host defense against bacterial infections by regulating bacteriolytic peptide generation via its interaction with ubiquitin-binding protein SQSTM1, which delivers monoubiquitylated proteins to autolysosomes for the generation of bacteriolytic peptides (By similarity). Exhibits antiviral activity against influenza virus (PubMed:22106366). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22106366}. |
3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Immunity;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Secreted |
|
Guanylate binding protein expression is induced by interferon. Guanylate binding proteins are characterized by their ability to specifically bind guanine nucleotides (GMP, GDP, and GTP) and are distinguished from the GTP-binding proteins by the presence of 2 binding motifs rather than 3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2633; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032703]; negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903077]; negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900025]; negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050860]; protein localization to vacuole [GO:0072665]; regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050848]; regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903076] |
11598000_The helical domain of GBP-1 mediates the inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by inflammatory cytokines. 12414522_GBP-1 expression is selectively induced by inflammatory cytokines and is an activation marker of endothelial cells during inflammatory diseases. 12881412_The GBP-1 GTPase controls the invasive and angiogenic capability of endothelial cells through inhibition of MMP-1 expression. 14741045_NF-kappaB motif and ISRE co-operate in the activation of GBP-1 expression by inflammatory cytokines in endothelial cells. 15504415_designed point mutants in the phosphate-binding loop (P-loop) as well as in the switch I and switch II regions. These mutant proteins were analysed for their interaction with guanine nucleotides and for their ability to hydrolyse GTP. 15937107_Golgi targeting of human guanylate-binding protein-1 requires nucleotide binding, isoprenylation, and an IFN-gamma-inducible cofactor. 16005050_GBP-1 regulates anti-proliferative effect of inflammatory cytokines. It also mediates inhibition of endothelial cell invasiveness by down regulation of MMP-1[review] 16511497_crystal structures of the N-terminal G domain trapped at successive steps along the reaction pathway and biochemical data reveal the molecular basis for nucleotide-dependent homodimerization and cleavage of GTP 16873363_kinetic investigation of GTP hydrolysis catalyzed by interferon-gamma-induced hGBP1 16894355_Interferon-alpha upregulates GBP1 in cultured human vascular endothelial cells. 16936281_Human guanylate binding protein-1 may be a useful surrogate marker for diagnosis of bacterial meningitis 18260761_3 genes were upregulated in patients with chronic EBV infection: guanylate binding protein 1, tumor necrosis factor-induced protein 6, and guanylate binding protein 5; they may be associated with the inflammatory reaction or with cell proliferation. 18697200_GBP-1 may be a novel biomarker and an active component of a Th-1-like angiostatic immune reaction in colorectal carcinoma. 18697840_Inhibition of endothelial cell spreading and migration by inflammatory cytokines is mediated by GBP-1 through induction of ITGA4 expression. 19079332_GBP-1 is a novel marker of intestinal mucosal inflammation that may protect against epithelial apoptosis induced by inflammatory cytokines and subsequent loss of barrier function 19150356_The authors demonstrate for the first time that both the alpha-helix of the intermediate region and the (103)DXEKGD(108) motif play critical roles for the hydrolysis to GMP. 19223260_The results indicate that the GBP1, STAT1 and CXCL10 may be novel risk genes for the differentiation of PBM at the monocyte stage. 19463820_Positions of cysteine residues buried between the C-terminal domain of GBP1 and the rest of the protein are identified which report a large change of accessibility by the compound after addition of GTP. 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20450919_Results identify intramolecular contacts of guanylate binding protein 1, which relay nucleotide-dependent structural changes from the N-terminus to the C-terminus and thereby mediate tetramer formation of the protein. 20454519_Animals carrying murine mammary carcinoma cells that had been given doxycycline for induction of human GBP-1 expression revealed a significantly reduced tumor growth compared with mock-treated mice. 20483731_These findings identify a role for IFN-alphaA-mediated GBP-1 expression in the prevention of intestinal epithelial apoptosis by commensal bacteria. 20716116_Data indicate that GBP-1 contributes to vascular dysfunction in chronic inflammatory diseases by inhibiting endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) angiogenic activity via the induction of premature EPC differentiation. 20923658_hGBP-1, hGBP-2 showed dimerization-related GTPase activity for GMP formation. 21151871_GBP-1 cellular 1ocalization depends on prenylation and dimerization. 21714544_higher GBP1 level in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma tissue was associated with higher overall pathological stage, positive perineural invasion, and poorer prognosis 22059445_Data indicate that GBP1 guanine cap (i.e., C-terminal guanine-binding amino acid motif, particularly Arg240/Arg244) is key structural element responsible for dimerization and is essential for self-activation of GTPase activity. 22162832_establish GBP1 as a previously unknown link between EGFR activity and MMP1 expression and nominate it as a novel potential therapeutic target for inhibiting GBM invasion. 22607347_Data indicate that alpha12/13 represents a stable subdomain of guanylate-binding protein 1 (hGBP1). 22692453_Cytokine-induced GBP-1 retards cell proliferation by forming a negative feedback loop that suppresses beta-catenin / TCF signaling. 22859948_Thermodynamic insight as to how the stability of an intermediate catalytic complex regulates the product formation in hGBP1. 23042300_GBP1 inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor formation of colon tumor cells. 23042300_results suggested that GBP-1 acts directly as a tumor suppressor in CRC and the loss of GBP-1 expression might indicate tumor evasion from the IFN-gamma-dominated Th1 immune response. 23086406_GBP1/2 are critical effectors of antichlamydial interferon (IFN)gamma-mediated pathogen clearance via rerouting of bacterial inclusions in macrophages for lysosomal degradation. 23727578_Data indicate that among three deductive p53 response element (p53RE) present in the hGBP1 promoter region, two p53REs were found to be transactivated by p53. 24190970_GBP-1 is a novel member within the family of actin-remodeling proteins specifically mediating IFN-gamma-dependent defense strategies. 24190970_IFN-gamma-induced Guanylate Binding Protein-1 is a novel Actin Cytoskeleton Remodeling Factor. GBP-1 may induce actin remodeling via globular actin sequestering and/or filament capping. GBP-1 is a novel member within the family of actin remodeling proteins, specifically mediating IFN-gamma-dependent defense strategies. 24337748_GBP-1 is a downstream processor of IFN-gamma. 24991938_data show that dimer formation of hGBP1 involves multiple spatially distant regions of the protein, namely, the N-terminal LG domain and the C-terminal helices alpha13. 25081641_Molecular dynamics studies showed that only GTP decreases the formation of the GBP1:PIM1 complex through an allosteric mechanism, outlining the rational for the identification of new compounds potentially able to revert resistance to paclitaxel. 25098609_GBP1 overexpression is necessary for the radioresistant phenotype in clinically relevant radioresistant cells 26760981_GBP1 promotes lymph node metastasis and has a positive correlation with EGFR expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 26848767_GBP1 expression is elevated in human Glioblastoma multiforme tumors and positively correlates with EGFRvIII status in Glioblastoma multiforme specimens, and its expression is inversely correlated with the survival rate of Glioblastoma multiforme patients. Taken together, these results reveal that GBP1 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for Glioblastoma multiforme with EGFRvIII mutation. 26874079_A novel role for hGBP1 in cell-autonomous immunity that is independent of pathogen-containing vacuole translocation. 27071416_the study not only highlights the importance of hGBP1 tetramer in stimulated GMP formation, but also demonstrates its role in the antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus. 27422384_In insulitic islets from living patients with recent-onset T1D, most of the overexpressed ISGs, including GBP1, TLR3, OAS1, EIF2AK2, HLA-E, IFI6, and STAT1, showed higher expression in the islet core compared with the peri-islet area containing the surrounding immune cells 27590579_Elevated hGBP-1 RNA in ovarian tumors correlates with shorter recurrence-free survival. hGBP-1 does not confer paclitaxel resistance on MCF-7 and TMX2-28 breast cancer cells. 28123064_Results suggest that guanylate-binding protein 1 (GBP1) plays a pivotal role in anti-T. gondii protection of mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSCs) and may shed new light on clarifying the mechanism of host defense properties of hMSCs. 28272793_These findings confirm the involvement of caspase-1 in non-classical secretion mechanisms and open novel perspectives for the extracellular function of secreted GBP-1. 28580591_Previously reported tetrameric and dimeric species of hGBP-1 and hGBP-5 were unmasked as dimers and monomers, respectively, with their shapes depending on both the bound nucleotide and the ionic strength of the solution. 28592529_Taken together, these results provide a new understanding of the antiviral mechanism of human GBP1, which possesses potent anti-Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus activity, and suggest the critical role of viral RTA in the evasion of the innate immune response during primary infection by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. 28645896_hGBP1F acts as a nucleotide-controlled molecular switch by modulating the accessibility of its farnesyl moiety, which does not require any supportive proteins 29115931_Results show that GBP1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), under the control of EGFR and selectively affects the growth of TNBC cell lines. 29144452_Shigella flexneri infection induces rapid proteasomal degradation of human guanylate binding protein-1 (hGBP1); the mode of IpaH9.8 action highlights the functional importance of GBPs in antibacterial defenses 29233899_Here, we show that the human protein GBP1 acts as a cytosolic 'glue trap,' capturing cytosolic Gram-negative bacteria through a unique protein motif and preventing disseminated infections in cell culture models. To escape from this GBP1-mediated host defense, Shigella employs a virulence factor that prevents or dislodges the association of GBP1 with cytosolic bacteria. 29348519_we have found GBP1 was downregulated during osteogenic differentiation of hBM-MSCs. While knockdown of GBP1 promoted osteogenesis, overexpression of GBP1 suppressed osteogenesis of hBM-MSCs. 29350274_Proteomics analysis of the tumor cells revealed Guanylate-Binding Protein 1 (GBP1) as a key T lymphocyte-induced protein that enables breast cancer cells to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The GBP1 gene appeared to be up-regulated in breast cancer of patients who developed brain metastasis. Silencing of GBP1 reduced the ability of breast cancer cells to cross the in vitro BBB model. 29618166_we identified that the LG domains of hGBP-1 and hGBP-5 build an interaction site within the hetero dimer. Our in vitro study provides mechanistic insights into the homomeric and heteromeric interactions of hGBP-1 and hGBP-5 and present useful strategies to characterise the hGBP network further. 29991124_transfection of GBP1 revealed its regulation on migration and invasiveness of glioma cells, decreasing sensitivity of chemotherapeutic agent, shortening survival of tumor-bearing animals. These data demonstrate that GBP1 may serve as a novel prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target for gliomas. 30044945_In the salivary gland ducts from patients with IgG4-related disease there was significant infiltration of IgG-positive plasma cells, and expression of GBP-1, CLDN-7 and LSR was increased. 30120107_this demonstrated that the alpha9-helix is the proliferation inhibitory domain of GBP-1, which acts independent of the GTPase activity through the inhibition of the Hippo transcription factor TEAD in mediating the anti-proliferative cell response to IFN-gamma. 31268602_Data report that human GBP1 acts as an upstream regulator of diverse forms of cell death in macrophages and promotes the activation of microbe-specific downstream pathways. The access to or release of microbial ligands in infected macrophages required GBP1, which therefore acts a gatekeeper of microbe-induced cell death. 31421831_GBP-1 may enhance lung adenocarcinoma invasiveness by promoting cell motility, and control of GBP-1 expression has the potential to contribute to the development of new therapeutic strategies for lung adenocarcinoma. 31954926_The alpha helix of the intermediate region is required for substrate-induced oligomerization and enhanced GMP production. 32352209_Catalytic activity of human guanylate-binding protein 1 coupled to the release of structural restraints imposed by the C-terminal domain. 32433976_hGBP1 Coordinates Chlamydia Restriction and Inflammasome Activation through Sequential GTP Hydrolysis. 32510692_Direct binding of polymeric GBP1 to LPS disrupts bacterial cell envelope functions. 32581219_Human GBP1 binds LPS to initiate assembly of a caspase-4 activating platform on cytosolic bacteria. 32582960_GBP1 promotes erlotinib resistance via PGK1activated EMT signaling in nonsmall cell lung cancer. 32783936_Human GBP1 Differentially Targets Salmonella and Toxoplasma to License Recognition of Microbial Ligands and Caspase-Mediated Death. 33113220_Stimulation of GMP formation in hGBP1 is mediated by W79 and its effect on the antiviral activity. 33301214_Guanylate-binding protein 1 correlates with advanced tumor features, and serves as a prognostic biomarker for worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients. 33405388_Structural requirements for membrane binding of human guanylate-binding protein 1. 33552086_GBP1 Facilitates Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Extracellular Secretion to Promote the Malignant Progression of Lung Cancer. 33885766_The GBP1 microcapsule interferes with IcsA-dependent septin cage assembly around Shigella flexneri. 34022623_Healthy and preeclamptic pregnancies show differences in Guanylate-Binding Protein-1 plasma levels. 34194003_Upregulation of GBP1 in thyroid primordium is required for developmental thyroid morphogenesis. 34399626_Guanylate-Binding Protein-Dependent Noncanonical Inflammasome Activation Prevents Burkholderia thailandensis-Induced Multinucleated Giant Cell Formation. 35179710_Guanylate Binding Protein 1 (GBP1): A Key Protein in Inflammatory Pyroptosis. 35773466_Role of GBP1 in innate immunity and potential as a tuberculosis biomarker. |
|
|
50.001021 |
6.1506400386 |
2.620737 |
0.269198983 |
103.964126 |
0.00000000000000000000000206012637450491449246321336357011385158175558998782393363815093612068096717848675325512886047363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000021642324048179744187193364674020612867062159920874874233425800337110578297483698406722396612167358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.4154264 |
13.7014394 |
13.9323485 |
1.9880997 |
| ENSG00000117245 |
57576 |
KIF17 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2E2 |
FUNCTION: Dendrite-specific motor protein which, in association with the Apba1-containing complex (LIN-10-LIN-2-LIN-7 complex), transports vesicles containing N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit NR2B along microtubules. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99PW8}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable microtubule binding activity and plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity. Predicted to be involved in anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex and cell projection organization. Predicted to act upstream of or within microtubule-based process; protein-containing complex localization; and vesicle-mediated transport. Predicted to be located in microtubule cytoskeleton. Predicted to be part of intraciliary transport particle B and kinesin complex. Predicted to be active in cilium; microtubule cytoskeleton; and neuron projection. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57576; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; periciliary membrane compartment [GO:1990075]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008574]; anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex [GO:0098971]; cell projection organization [GO:0030030]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
14673085_KIF17b serves as a molecular motor component of a TB-RBP-mouse ribonucleoprotein complex transporting a group of specific CREM-regulated mRNAs. 19679349_The intense placental expression of KIFC1 in syncytiotrophoblast and KIF17 in vascular endothelium suggests that both proteins might be important in a cargo-transport system. KIFC1 and KIF17 expression are increased of both in preeclamptia and diabetes. 20378615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20530208_Data show that the homodimeric kinesin-2 motor KIF17 is kept in an inactive state in the absence of cargo, and define two molecular mechanisms that contribute to autoinhibition of KIF17. 20646681_This study suggested that disruption of KIF17, although rare, could result in a schizophrenia phenotype and emphasize the possible involvement of rare de novo mutations in this disorder. 20696710_Depletion of KIF17 from cells growing in three-dimensional matrices results in aberrant epithelial cysts that fail to generate a single central lumen and to polarize apical markers. 24072717_although EB1 and KIF17-Tail may coordinate KIF17 catalytic activity, our data reveal a novel and direct role for KIF17 in regulating MT dynamics. 26421900_Expression of KIF17 in schizophrenic postmortem brains was significantly lower than controls. Both genotypic distribution and allelic frequency of rs2296225 polymorphism were significantly different between the chronic schizophrenia subjects and controls. 26759174_KIF17 can modify RhoA-GTPase signaling to influence junctional actin and the stability of the apical junctional complex of epithelial cells. 26823018_The first evidence of an interaction between septins and a nonmitotic kinesin is provided and it is suggested that SEPT9 modulates the interactions of KIF17 with membrane cargo. 28077622_In mammalian cells, KIF17 is dispensable for ciliogenesis and IFT-B trafficking but requires IFT-B, as well as its NLS, for its ciliary entry across the permeability barrier located at the ciliary base. 28761002_The rate of transport is set by an equilibrium between a faster state, where only kinesin family member 17 protein (KIF17) motors move the train, and a slower state, where at least one kinesin family member 3A/B protein (KIF3AB) motor on the train remains active in transport. 33922911_Biallelic Variants in KIF17 Associated with Microphthalmia and Coloboma Spectrum. |
ENSMUSG00000028758 |
Kif17 |
143.982105 |
0.2997120181 |
-1.738351 |
0.159422589 |
121.447327 |
0.00000000000000000000000000030499225140861564376022466092616956528354004229161891851764067922798075627351110927776289827306754887104034423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000003695965214114259004910224984924437841134846737836728208822030017551165228043008603719954408006742596626281738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
65.9087705 |
6.7946554 |
221.8292287 |
14.2166315 |
| ENSG00000117266 |
5129 |
CDK18 |
protein_coding |
Q07002 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in signal transduction cascades in terminally differentiated cells. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable ATP binding activity; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity; and protein serine kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein phosphorylation and regulation of transcription involved in G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5129; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of transcription involved in G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000083] |
15019984_Expression of PCTAIRE 3a (474 amino acids) was evident throughout the brain and in the majority of tissues analyzed, while spliced isoform PCTAIRE 3b (504 amino acids) was limited to several subcortical nuclei of the basal gangli and the spinal cord. 16766195_PCTAIRE 3 is aassociated kinase that modulates tau phosphorylation in Alzeheimer's disease. 26885753_Increased levels of PCTAIRE3 is associated with Alzheimer's disease. 27382066_these data reveal a rate-limiting role for CDK18 in replication stress signalling and establish it as a novel regulator of genome integrity. 31266951_CDK18 knockdown or ATR inhibition in glioblastoma stem-like cells suppressed homologous recombination. 32164329_Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 18 Controls Trafficking of Aquaporin-2 and Its Abundance through Ubiquitin Ligase STUB1, Which Functions as an AKAP. |
ENSMUSG00000026437 |
Cdk18 |
150.312653 |
0.1919047233 |
-2.381538 |
0.210267425 |
125.861993 |
0.00000000000000000000000000003296277485203942819625395854223455567195924532858744268046034219852802069441501109370307176504866220057010650634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000413364959062108781232382217659768712470535988713544495828782197223246792786369163685833427734905853867530822753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.9899094 |
6.6646669 |
252.2771180 |
22.6519745 |
| ENSG00000117298 |
1889 |
ECE1 |
protein_coding |
P42892 |
FUNCTION: Converts big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9396733}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hirschsprung disease;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in proteolytic processing of endothelin precursors to biologically active peptides. Mutations in this gene are associated with Hirschsprung disease, cardiac defects and autonomic dysfunction. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:1889; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; Weibel-Palade body [GO:0033093]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; bradykinin catabolic process [GO:0010815]; calcitonin catabolic process [GO:0010816]; ear development [GO:0043583]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; endothelin maturation [GO:0034959]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; heart development [GO:0007507]; hormone catabolic process [GO:0042447]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; pharyngeal system development [GO:0060037]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by endothelin [GO:0003100]; regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0019229]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287]; substance P catabolic process [GO:0010814]; sympathetic neuron axon guidance [GO:0097492] |
11723113_ECE-1alpha is expressed at significant levels in various types of human skin cells (including keratinocytes) and that it plays a constitutive role in the processing and UVB-inducible secretion of ET-1 by human keratinocytes 11906289_Toward an optimal joint recognition of the S1' subsites of endothelin converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), and neutral endopeptidase (NEP). 12011762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12244060_identification of potential residues involved in phosphorylation 12393864_Data demonstrate that the targeting signals specific for endothelin-converting enzyme 1b constitute a regulatory domain that could modulate the localization and the activity of other isoforms. 12464614_ECE1 has a role in limiting Abeta accumulation in the mouse brain 12609744_It is suggested that endothelial cells sense shear stress as oxidative stress and transduce signal for the regulation of the gene expression of ECE. 14597855_Cis-acting elements bind CAAT-box binding protein NF-YB, GATA-2, E2F-2, and a GC-box binding factor associated with transcriptional start sites of ECE-1c. Three polymorphic dinucleotide repeats. Methylation suppressed ECE-1c promoter in endothelium. 15010576_The main isoform to increase in response to high glucose was ECE-1c and it may be one of the factors contributing to the elevated ET-1 peptide levels observed in diabetes. 15126915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15126915_This EVA-based study suggests that ECE1 interacts with ET1 to influence blood pressure in women. 15240857_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15340356_Neuronal ECE-1 expression was observed in various cortical regions of nondemented subjects. In a case-control study involving patients with late-onset AD, homozygous carriers of the A allele of ECE1 gene had a reduced risk of AD. 15665524_locally synthesized AII could be one of the mediators involved in the down-regulation of ECE-1 16023075_ECE-1 protein expression, prepro-endothelin-1 mRNA, and endothelin-1 peptide release were increased in response to native LDL or oxidized LDL. 16234608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16531800_Observations strongly suggest that the expression of ECE is enhanced in neointimal smooth muscle cells at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervention injury in human coronary arteries. 16567585_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16698938_increased neuronal PKCepsilon activity can promote Abeta clearance and reduce AD neuropathology through increased endothelin-converting enzyme activity 16986361_These findings suggest that endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE) is upregulated in the neointima at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervension (PCI) injury. ECE may be one of the mediators in the repair processes after PCI in humans. 17264805_Homozygous carriers of the ECE-1 -839G variant allele exhibited a decreased risk of coronary artery disease 17264805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17545092_Data show that CD133 and ECE expressions are associated with lymphoid metastasis and prognosis of NSCLC, and their overexpression often suggests unfavorable prognosis of NSCLC. 17592116_Endosomal peptidase ECE-1 degrades neuropeptides in endosomes to disrupt the peptide-receptor-beta-arrestin complex, thereby controlling postendocytic trafficking and signaling of receptors. 17618613_ECE-1b-338C to A variant might be associated with increased risk of CAD in Chinese population. 17618613_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17664854_genotyped 5 single nucleotide polymorphisms in the ECE1 gene in 1,873 individuals from a general Japanese population and identified one associated with hypertension in women 17701914_Endothelin-1 and endothelin-converting enzyme-1 have roles in human granulomatous pathology of eyelid 17712175_Spacio-temporal expression of two endopeptidases, ECE-1 and NEP, involved in the synthesis and degradation of ET-1, might regulate ET-1 action in human endometrium. 17761169_Results show catalytically active ECE-1 was detected in the media of human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and was confirmed by mass spectrometry based assays. 17977716_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18039931_A mechanism by which endosomal ECE-1 degrades neuropeptides in endosomes to disrupt the peptide/receptor/beta-arrestin complex, freeing internalized receptors from beta-arrestins and promoting recycling and resensitization, is proposed. 18334739_A allele was less present in LOAD patients than in controls, but an at limits statistically significant difference was achieved only in subjects aged less than 80 years 18334739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18781169_Transient ECE-1c overexpression increased PC-3 invasiveness through matrigel, whereas transient ECE-1a expression suppressed invasion 18974277_Enhanced ECE-1 expression induced by hyperglycemia is partly due to activation of the PKC-delta isoform. Thus, inhibition of this PKC isoform may prevent diabetes-related increase in ET-1. 18992253_The crystal structure of the extracellular domain (residues 90-770) of human ECE-1 (C428S) with the generic metalloprotease inhibitor phosphoramidon determined at 2.38 A resolution. 19222484_By degrading endocytosed SP, ECE-1 promotes the recycling and re-sensitization of NK(1) receptors in endothelial cells, and thereby induces re-sensitization of the pro-inflammatory effects of SP. 19289136_C-338 polymorphism of the ECE1 gene might be associated with increased risk of carotid atherosclerosis in the Chinese population. 19289136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19531493_Endosomal endothelin-converting enzyme-1 is a regulator of beta-arrestin-dependent ERK signaling 19889475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037208_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037208_study argues that the ECE1 338A allele is protective against late-onset Alzheimer disease in a Chinese population 20345647_any disease-specific contribution of ECE-1 to the accumulation of Abeta or reduction in local microvascular blood flow in Alzheimer disease or Vascular dementia is probably small. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20558134_These data indicate for the first time that PKC activation induces the trafficking and shedding of ECE to and from the cell surface, respectively. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20663017_ECE-1 is not correlated with amyloig beta or clinical diagnosis Alzheimer disease 20725143_ECE-1 influences prostate cancer cell invasion via both ET-1-mediated FAK phosphorylation and ET-1 independent mechanisms. 21554123_4,4'-dihydroxy-trans-stilbene strongly inhibits ECE-1 activity, whereas resveratrol is inactive. 21777246_Our results point to a regulatory function of ET-1, its type B receptor (ET(B)) and endothelin-converting enzyme-1 proteins in transendothelial passage of monocytes 21851036_Results of this study suggest lack of direct correlation of Lys198Asn ET-1 and Thr341lle ECE-1 gene polymorphisms with risk of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia in the studied population of Polish women 22027013_Te results of this study suggested taht genetic variations in MMEL1, ECE1, ECE2, AGER, PLG, PLAT, NR1H3, MMP3, LRP1, TTR, NR1H2, and MMP9 genes do not play major role among the Finnish AD patient cohort. 22322595_Degradation by ECE-1 is a novel mechanism by which CRF(1) receptor is protected from overactivation by physiologically relevant high concentrations of higher affinity ligand to mediate distinct resensitization and downstream signaling. 22416137_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) degrades NT in acidic conditions, and its activity is crucial for NTR1 recycling. 22693153_The Alzheimer's disease associated intronic haplotype is linked to the 338A variant of known ECE1b promoter variant, 338C>A (rs213045). 22728136_review of ECE-1 phosphorylation and other stimuli which act induce trafficking of ECE-1 to the cell surface [review] 22731820_results suggest that ECE1 polymorphisms may contribute to the susceptibility of sporadic congenital heart disease in a Chinese population 22972025_involved in the physiological degradation of atrial natriuretic peptide 23022525_The results complete a gap in our understanding of the mechanism(s) behind PKC induced trafficking of ECE-1. 23175834_we demonstrate that a CpG-CA repeat within the human ECE-1c promoter is highly polymorphic, harbors transcriptional start sites 23283972_Endothelin-converting enzymes degrade intracellular beta-amyloid produced within the endosomal/lysosomal pathway and autophagosomes 23360525_study suggests that the severity of periodontal disease may be associated with the expression of metalloendopeptidase genes, including NEP, ECE1 and ADAM17, in the buccal mucosal epithelium. 23816989_Although the presence of a soluble form of ECE-1 has been demonstrated in vitro, it is yet to be shown in any human biological fluid. This study, used a combination of mass spectrometry, Western blotting & quenched fluorescent substrate based enzyme assays & showed presence of catalytically active, soluble form of ECE-1 in CSF of subarachnoid hemorrhage subjects. 23863409_The altered expression of enzymes regulating the activity of ET-1, NEP and ECE-1, during parturition is controlled by inflammatory cytokines. 24000822_phosphoramidon and Abeta peptide binding to hECE-1 24026618_C-338A polymorphism of the ECE-1b gene was associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han population. 24497914_Data indicate endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) as a target for alternative polyadenylation (APA), a regulatory mechanism aberrantly activated in cancer cells, and the mechanisms leading to ECE-1 overexpression in malignant cells. 24595843_Compared with rs213045 G homozygote, rs213045 TG genotype and rs213045 TT/TG genotypes are in dominant model significantly increased the risk of ischemic stroke. 24812665_identify the neural peptidase ECE-1 as a negative regulator of itch on sensory nerves by directly regulating ET-1-induced pruritus 24898255_the primary function of betaARRs and ECE-1 in SP-dependent inflammatory signaling is to promote resensitization, which allows the sustained NK1R signaling from the plasma membrane that drives inflammation 25179465_An arterial-specific enhancer of the human endothelin converting enzyme 1 (ECE1) gene is synergistically activated by Sox17, FoxC2, and Etv2 25226840_Nitric oxide inhibits the production of soluble endothelin converting enzyme-1 by endothelial cells. 25268585_confirmed that endothelin-converting enzyme 1 (ECE1), EDN1, and EDNRB were involved in SP-induced pigmentation and found that EDN1 secretion was affected by ECE1 and EDN1 siRNAs, but not by EDNRB siRNA 25469848_Thus, our findings suggest that ECE-1 may be a novel hypoxia-inducible factor-target gene. 25501500_Structural analysis of membrane-bound hECE-1 dimer using molecular modeling techniques: insights into conformational changes and Abeta1-42 peptide binding. 26543229_CK2-increased ECE-1c protein stability is related to augmented migration and invasion of colon cancer cells, shedding light on a novel mechanism by which CK2 may promote malignant progression of this disease. 26806547_results indicate that PKC-phosphorylated ECE-1 is a TIMAP-PP1c substrate and this phosphatase complex has an important role in endothelin-1 production of EC through the regulation of ECE-1 activity. 27036146_These results indicated that the ECE1 rs212528 and rs213045 polymorphisms had no major role to play in the genetic susceptibility to intracerebral haemorrhage. 28171705_ECE-1 and ECE-2 levels were significantly reduced in post-mortem brains from dementia with Lewy body patients. 29978582_overexpression of ECE-1 in head and neck cancer is a predictor of poor tumor differentiation and prognosis 30626614_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 regulates glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signalling and resensitisation. 30926432_current evidence suggests that ECE-1c contributes to cancer aggressiveness and plays a putative role as a key regulator of cancer progression. 31777301_Effects of ECE-1b rs213045 and rs2038089 polymorphisms on the development of contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with acute coronary syndrome. 31788944_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1c promotes stem cell traits and aggressiveness in colorectal cancer cells. 32107880_Association of ECE1 gene polymorphisms and essential hypertension risk in the Northern Han Chinese: A case-control study. 32170981_The role of Candida albicans candidalysin ECE1 gene in oral carcinogenesis. 32278308_Placental endothelin-converting enzyme-1 is decreased in preeclampsia. 35645613_Association of Endothelin-Converting Enzyme and Endothelin-1 Gene Polymorphisms with Essential Hypertension in Malay Ethnics. |
ENSMUSG00000057530 |
Ece1 |
51.008086 |
4.5192802679 |
2.176093 |
0.657642320 |
9.068784 |
0.00260009917422008478629646965885058307321742177009582519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005631322642918335126538398327511458774097263813018798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.8737009 |
32.9562214 |
16.6980232 |
4.9313049 |
| ENSG00000117318 |
3399 |
ID3 |
protein_coding |
Q02535 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator (lacking a basic DNA binding domain) which negatively regulates the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors by forming heterodimers and inhibiting their DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Implicated in regulating a variety of cellular processes, including cellular growth, senescence, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and neoplastic transformation. Involved in myogenesis by inhibiting skeletal muscle and cardiac myocyte differentiation and promoting muscle precursor cells proliferation. Inhibits the binding of E2A-containing protein complexes to muscle creatine kinase E-box enhancer. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing the transcriptional activator activity of the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8437843}. |
3D-structure;Biological rhythms;Myogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a helix-loop-helix (HLH) protein that can form heterodimers with other HLH proteins. However, the encoded protein lacks a basic DNA-binding domain and therefore inhibits the DNA binding of any HLH protein with which it interacts. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:3399; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; leptomycin B binding [GO:1901707]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to leptomycin B [GO:0072750]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; heart development [GO:0007507]; metanephros development [GO:0001656]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; notochord development [GO:0030903]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of DNA replication [GO:0006275]; response to wounding [GO:0009611] |
12952978_nuclear Id protein acts by sequestering pools of transiently diffusing bHLH protein to prevent reassociation with chromatin domains 15370294_Fluvastatin did not regulate p21 and p27, but down-regulated Id3 and p53 slightly. 15494533_Overexpression of Id3 enhances expression of ICAM-1 and E-selectin, and induces angiogenic processes such as transmigration, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 expression, and tube formation in cultured vascular endothelial cells. 15583422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15645115_Id1, 2 and 3 might play a role in the early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis, but not in the development of advanced carcinoma, and might consequently be related to HCC dedifferentiation 16271072_Id1, 3 double-knockdown significantly impaired the ability of gastric cancer cells to form peritoneal metastasis 16449966_ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis of immortalized keratinocytes is at least in part due to Id3 upregulation in these cells 16682435_ID proteins (ID1, ID2, ID3 and ID4) were significantly increased in Mecp2-deficient Rett syndrome brain; ID genes are ideal targets for MeCP2 regulation of neuronal maturation that may explain the molecular pathogenesis of Rett syndrome 17537403_PLZF upregulates apoptosis-inducer TP53INP1, ID1, and ID3 genes, and downregulates the apoptosis-inhibitor TERT gene 18281048_estrogen-induced tube formation in vascular endothelial cells requires the presence of Id3, a member of the helix-loop-helix family of transcriptional factors and estrogen increases Id3 phosphorylation via a redox-dependent process 18374504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18477564_RhoA/Rho-associated kinase signaling plays positive and negative roles in myogenic differentiation, mediated by MRTF-A/Smad-dependent transcription of the Id3 gene in a differentiation stage-specific manner 19054058_There is a mechanism whereby reactive oxygen species upregulation of Id3 relieves repression of bax via E-box-binding factors. 19477940_RNA interference demonstrated that Id3 regulates differentiation and cell cycle (increased Neuro-D6 and p21 mRNA) in neuroblastoma cells 19515385_role in the development of peritoneal metastasis of pancreatic cancer 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20080245_The level of Id-3 protein expression was associated with the malignant potential of gastric tumors. 20185798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185798_Results provide novel evidence that Id3 is an atheroprotective factor and link a common SNP in the human ID3 gene to loss of Id3 function and increased carotid intima-media thickness. 20191379_Id1/3 peptide aptamer could represent a nontoxic exogenous agent that can significantly provoke antiproliferative and apoptotic effects in breast cancer cells, which are associated with deregulated expression of Id1 and Id3. 20512523_expression of vFLIP decreased the expression levels of Id2 and Id3 as well as cyclin E and cyclin A compared with the vFLIP-null cells 21030215_ID3 plays a role as an apoptosis inducer in response to X-ray irradiation via the regulation of endogenous beta-catenin level. 21191065_In serum samples of lung cancer patients, galectin 1-mediated Id3 induces expression of interleukin (IL)-10 in functionally altered signal pathways of monocytes and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. 21486943_Study uniquely identifies ID1 and ID3 as negative regulators of the hPSC-hematopoietic transition from a hemogenic to a committed hematopoietic fate, and demonstrates that this is conserved between hESCs and hiPSCs. 21498546_the data establish dysregulation of the Id/bHLH axis as an early and sustained feature of ductal pathogenesis 21837949_The ID3 protein is expressed in prostate cancer, and is elevated with the increase of Gleason score. 21975932_EGFR-AKT-Smad signaling promotes formation of glioma stem-like cells and tumor angiogenesis by ID3-driven cytokine induction. 21993163_Older muscle contained significantly more transcript for Forkhead Box O 1 (FoxO1, p=0.001), Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1, p=0.009), and Inhibitor of DNA Binding 3 (ID3, p=0.043) than young muscle. 22151756_Overexpression of Id3 triggered apoptosis in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, implicating Id3 in negative control of tumor growth. 22698403_Data show that regulation of p21 by ID1 and ID3 is a central mechanism preventing the accumulation of excess DNA damage and subsequent functional exhaustion of cancer-initiating cells (C-ICs). 22882857_Overexpression of Id3 markedly promoted the proliferation and invasive capacity of MCF-7 cells; however, these effects were significantly suppressed by the overexpression of FHL2. 23060149_These findings suggest an essential role of Id1 and Id3 in TGFbeta1 effects on proliferation and migration in prostate cancer cells. 23119064_Data indicate that ID2.K47A, ID2.Q55A and ID3.R52A, ID3.R60A had wildtype like expression levels in E. coli. 23143595_The findings suggested that cooperation between ID3 inactivation and immunoglobulin-MYC gene translocation is a hallmark of Burkitt lymphomagenesis. 23311395_Id1 and Id3 co-expression seems associated with a poor clinical outcome in patients with locally advanced NSCLC treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy 23342268_increased Id1 and Id3 expression attenuates all three cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKN2B, -1A, and -1B) resulting in a more aggressive PCa phenotype. 23768125_High ID3 expression is associated with medulloblastoma seeding and is a poor prognostic factor, especially in patients with Group 4 tumors 23771884_Id proteins, and particularly Id1 and Id3, are critical downstream effectors of BMP signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell. 24222112_ID3 mutations are recurrent events in double-hit B-cell lymphomas. 24292846_Importantly, the distinct ID3 expression patterns in acute leukemias (AL) indicate a specific deregulation of ID3 in the various types of AL and may support subtyping of AL. 24343358_study shows that Id2, Id3 and Id4 are each able to overcome TGF-beta dependence, and establish a role for Ids as key mediators of TGF-beta melanomagenesis 24493312_the combined immunohistochemical detection of VPREB3 and ID3 is applicable to the routine diagnostic in case of mature aggressive B-cell lymphomas. 24603695_Data indicate association of inhibitor of differentiation 3 (ID3) single nucleotide polymorphism rs11574 directly with coronary artery pathology. 24655651_Epigenetic changes in ID3, in combination with experiences of maltreatment, may confer risk for depression in children. 25090023_our data provide evidence that ID3 may play a critical role in regulating vascular endothelial cell survival and development of microvascular lesions induced by persistent environmental pollutants such as PCB153. 25239768_ID3 plays a potential role in the underlying regulatory mechanisms of metabolic health in human obesity. [Review] 25665868_ID3 has a role in the acquisition of molecular stem cell-like signature in microvascular endothelial cells 25778840_Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) acts as an inhibitor of ID-1, -2 and -3 and promotes basic helix loop helix (bHLH) E47 DNA binding and transcriptional activity. 26384138_Upon Id3 transfection, A549 cells displayed decreased migratory and invasive capabilities, however, co-transfection of miRId3 and Id3 into A549 cells reversed the Id3-induced inhibitions of migratory and invasive capabilities. 26992947_Immunohistochemical detection of inhibitor of DNA binding 3 mutational variants in mature aggressive B-cell lymphoma. 27044543_Results show that ID1, ID3 and IGJ genes are highly expressed in adult B-ALL and correlate with poor prognosis in Hispanic patients. 27176047_The results of the present study revealed that overexpression of Id3 may serve as a novel strategy for inhibiting cisplatinsensitive lung cancer. 28224680_Taken together, we found that Id3+ and CTLA-4+ endometrial cells were significantly higher in women with repeated implantation failure and recurrent miscarriage, suggesting the negative roles of these angiogenesis and immune tolerance markers involving in regulating endometrium receptivity. 29026069_The interactions between ID3 and the DNA damage mediator protein MDC1 suggest that ID3 participates in the DNA damage signaling pathway to maintain genomic stability. 29507860_This review will discuss the current understanding of ID3 in excess fat accumulation and the potential for Estrogenic Endocrine Disruptors to influence susceptibility to obesity or metabolic disorders via ID3 signaling 29593730_this study shows that CD5L promotes M2 macrophage polarization through autophagy-mediated upregulation of ID3 29907859_a critical role for highly altered Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL)-specific microRNA-10a in regulating the development of OPLL by modulating the ID3/RUNX2 axis. 30520117_blocks E47-mediated inhibition of beta-catenin transcription in choloangiocarcinoma cells 31215762_our results show that the suppressive effect of TGF-beta1 on the expression of MMP1 is mediated by a transcription factor, the inhibitor of differentiation 3 (ID3) protein. Our findings provide insights into the molecular interactions and mechanisms of TGF-b1 and ID3 during the regulation of MMP1 in human granulosa-lutein cells. 32039486_miR-212-5p exerts tumor promoter function by regulating the Id3/PI3K/Akt axis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 32305567_The HBx and HBc of hepatitis B virus can influence Id1 and Id3 by reducing their transcription and stability. 32536579_Correlation of the levels of DNA-binding inhibitor Id3 and regulatory T cells with SLE disease severity. 32760207_LEF1/Id3/HRAS axis promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33273801_Role of inhibitor of differentiation 3 gene in cellular differentiation of human corneal stromal fibroblasts. 34329970_Amphiregulin stimulates human chorionic gonadotropin expression by inducing ERK1/2-mediated ID3 expression in trophoblast cells. 34520124_ID1/ID3 mediate the contribution of skin fibroblasts to local nerve regeneration through Itga6 in wound repair. 34547407_Heme Oxygenase-1 (HMOX-1) and inhibitor of differentiation proteins (ID1, ID3) are key response mechanisms against iron-overload in pancreatic beta-cells. 34592230_Up-regulated DNA-binding inhibitor Id3 promotes differentiation of regulatory T cell to influence antiviral immunity in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. 34620174_EGF stimulates human trophoblast cell invasion by downregulating ID3-mediated KISS1 expression. 34718742_ID3 promotes homologous recombination via non-transcriptional and transcriptional mechanisms and its loss confers sensitivity to PARP inhibition. 34877804_Loss of ID3 in pancreatic cancer cells increases DNA damage without impairing MDC1 recruitment to the nuclear foci. 35219016_Expression of Id3 represses exhaustion of anti-tumor CD8 T cells in liver cancer. 35599595_Circadian Period 2 (Per2) downregulate inhibitor of differentiation 3 (Id3) expression via PTEN/AKT/Smad5 axis to inhibits glioma cell proliferation. 35678885_Brain infiltration of breast cancer stem cells is facilitated by paracrine signaling by inhibitor of differentiation 3 to nuclear respiratory factor 1. |
ENSMUSG00000007872 |
Id3 |
309.851847 |
0.1598448319 |
-2.645256 |
0.108110636 |
679.473813 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000869667000517552135435610651701178513240023148240465200272012056158758461013132177827199302133836829571599532667947106884693276350755036017490381680115224240561315843500084223277633 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000575618158190092725322195244629333425474197193816558421632152024351748644127037661757954798948742469478735016135437973135035991698939531911860739486619984872294909397593375544638880 |
Yes |
No |
86.7755122 |
7.1821266 |
545.9392515 |
26.3842761 |
| ENSG00000117394 |
6513 |
SLC2A1 |
protein_coding |
P11166 |
FUNCTION: Facilitative glucose transporter, which is responsible for constitutive or basal glucose uptake (PubMed:18245775, PubMed:19449892, PubMed:25982116, PubMed:27078104, PubMed:10227690). Has a very broad substrate specificity; can transport a wide range of aldoses including both pentoses and hexoses (PubMed:18245775, PubMed:19449892). Most important energy carrier of the brain: present at the blood-brain barrier and assures the energy-independent, facilitative transport of glucose into the brain (PubMed:10227690). In association with BSG and NXNL1, promotes retinal cone survival by increasing glucose uptake into photoreceptors (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P46896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10227690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18245775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19449892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25982116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27078104}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cataract;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Dystonia;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Hereditary hemolytic anemia;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation. |
This gene encodes a major glucose transporter in the mammalian blood-brain barrier. The encoded protein is found primarily in the cell membrane and on the cell surface, where it can also function as a receptor for human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) I and II. Mutations in this gene have been found in a family with paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesia. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013]. |
hsa:6513; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; female germ cell nucleus [GO:0001674]; female pronucleus [GO:0001939]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; midbody [GO:0030496]; photoreceptor inner segment [GO:0001917]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0055056]; dehydroascorbic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0033300]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; hexose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015149]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; long-chain fatty acid transporter activity [GO:0005324]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042910]; cellular hyperosmotic response [GO:0071474]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; dehydroascorbic acid transport [GO:0070837]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; glucose import [GO:0046323]; glucose import across plasma membrane [GO:0098708]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659]; L-ascorbic acid metabolic process [GO:0019852]; long-chain fatty acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0015911]; monosaccharide transmembrane transport [GO:0015749]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to Thyroglobulin triiodothyronine [GO:1904016]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11168944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11231353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11425315_GLUT1 mediates the transport of glucose across the plasma membrane down a concentration gradient without a specifc requirement for energy or hydrolysis of ATP, however, the ATP-binding domains are critical for transporter activity and kinetic properties. 11477169_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11681785_Review: structure of the human erythrocyte facilitative glucose transporter (GLUT1) 11747430_GLUT1 is a cooperative tetramer of proteins, each presenting a translocation pathway that alternates between uptake and export states in which, at any instant, two subunits must present sugar uptake and two subunits must present sugar exit states. 11836704_marker for discriminating hepatocellular carcinoma from other carcinomas 11920478_consistent marker of ovarian epithelial malignancy 11953883_Carcinoma samples displaying reduced levels of MCT1 were found to express the high affinity glucose transporter, GLUT1, suggesting that there is a switch from butyrate to glucose as an energy source in colonic epithelia during transition to malignancy 11991658_GLUT1 is expressed by normal articular chondrocytes. 12064911_observed differential response of individual isoforms GLUT1, GLUT3, & GLUT4 in neutrophils and granulocytes to hypoglycemia may represent a mechanism to protect the cells from the stress of glucose deprivation 12086959_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12086959_polymorphism has an effect on susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in IDDM 12112827_glucose transporter 1 and 3 in the placenta 12122099_Coexpression of glucose transporter 1 and matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human cancers 12133004_Results describe a possible non-genomic site of estrogen action near the hydrophilic pore of GLUT1. 12145475_The expression of the glucose transporter 1 was downregulated by up to 80% in the failing heart. 12379105_Cooperative nucleotide binding to GLUT1 and nucleotide modulation of GLUT1-mediated sugar transport are regulated by a proton-sensitive saltbridge (Glu329-Arg333/334). 12379106_TNP-ATP binding to glucose transporter GLUT1 has been modeled as a cooperative process in which each GLUT1 protein in a complex of four proteins (subunits) presents a single nucleotide binding domain. 12393496_HTLV receptor expression is an early marker of T-cell cell-cycle entry. Up-regulation of the HTLV receptor, via signals transmitted through the IL-7 cytokine receptor & the TCR, may contribute to mother-to-infant transmission & spreading of HTLV-1. 12583599_Basal membrane GLUT1 is upregulated over gestation, increased in diabetic pregnancy, and decreased in chronic hypoxia, while microvillous membrane GLUT1 is unaffected. (review) 12752470_To characterize seizure types and electroencephalographic features of glucose transporter type 1 deficiency syndrome (Glut-1 DS). 12849991_Data show that by using RNA interference, glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) mRNA and protein expression is reduced, leading to inhibition of a serum-mediated increase in glucose transport. 12942120_increased GLUT-1 expression in rectal tumours was an adverse prognostic factor 12969152_Overexpression of GLUT1 leads to cytosolic alkalinization of mesangial cells depending on functional Na+/H+ exchanger but not on Na+ independent H+ transport. 14622599_GLUT-1 is a receptor for HTLV 14674124_differences in GLUT1 receptor mRNA expression in two breast cancer cell lines with higher expression in MDA-MB-231; results show that invasiveness of cancer cells may be associated with the expression of glucose transporters, including GLUT1 14688257_description of two-dimensional models for the orientation of the 12 transmembrane helices and the conformation of the exofacial glucose binding site of GLUT1 14757434_Differentiation of THP-1 monocytes into macrophages was associated with marked induction of GLUT 3 and GLUT 5 protein expression, and high levels of GLUT 1, GLUT 3, and GLUT 5 were maintained after transformation to foam cells. 14991538_There are two fundamentally different hepatic vascular lesions in infants and young children: GLUT1-positive hepatic infantile hemangioma (HIH) and GLUT1-negative hepatic vascular malformation with capillary proliferation (HVMCP). 15073187_Relative proximity and orientation of helices 4 and 8 of the GLUT1 glucose transporter 15086844_Glut1 is a useful marker of intraneural perineurioma 15147968_hnRNP A2 acts on GLUT1 mRNA to inhibit expression of GLUT1 in a brain cancer cell line. 15331928_High GLUT1 mRNA levels were observed only in ovarian cancer. The intensity of GLUT1 expression in malignant ovarian neoplasms was associated neither with tumor characteristics nor with patient survival. 15454279_Basal or stimulated ROS production and Glut1 activity were significantly reduced by pretreating both cell lines with EUK-134 15502921_Levels of GLUT1 mRNA expression in skin fibroblasts from 'slow-track' patients were greater than those from 'fast-track' patients with diabetic nephropathy. 15682272_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15709778_Data support a GluT1-mediated red blood cell sugar transport mechanism in which newly bound sugars are transiently sequestered within the translocation pathway where they become inaccessible to extra- and intracellular water. 15745834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15745834_Oolymorphisms in the GLUT1 gene are associated with susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. 15767416_results provide additional evidence that glut-1 is a receptor for HTLV 15778389_it is reported in this study that TGF-beta induces binding of HTLV virions and expression of glucose transporter type 1 in primary CD4(+) T lymphocytes that remain quiescent 15823019_operational properties of GLUT1 are determined by host cell environment 15847702_CA IX and GLUT 1 as well as VEGF and IL 6 have roles in response of in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to radiotherapy +/- chemotherapy 15924676_bFGF and GLUT1 play important roles in the carcinogenesis and progression of ovarian epithelial carcinoma. 15955807_distinct domains of the glucose transporter GLUT1 mediate HTLV envelope binding and virus entry 15967114_Glut-1, HK-II, and PCNA expression are related to uptake of 18F-FDG uptake in lung cancer 16125330_We present an alternative hypothesis centring on presumed deficits in membrane bound glucose transporter proteins GLUT 1 and GLUT 3, either in absolute numbers or functional capacity. 16126902_during human thymopoiesis, GLUT1 is up-regulated after beta-selection 16136514_This review presents a model incorporating hypoxia responsive facilitative GLUT1 and GLUT3 as putative components of the glucose sensing apparatus in chondrocytes 16142350_HIF-1alpha may have a role in recurrence and survival in superficial bladder cancer, while Glut-1 may have a role in survival in invasive bladder cancer 16147855_GLUT1 may play a role in cementogenesis 16172126_the exoplasmic end of helix 4 lies outside the inner helical bundle in the exofacial configuration of Glut1 16195374_Glut1 has a role in vitamin C entry into mitochondria and confers mitochondrial protection against oxidative injury 16220828_The GLUT-1 expression in borderline and malignant ovarian epithelial tumors was analyzed against prognosis, no statistically significant difference was identified. 16273245_GLUT-1 may play an important role in the advancement of papillary carcinoma and lymph node metastasis. 16310037_basal membrane fractions GLUT1 was positively correlated with birth weight at high, but not low altitude 16407180_Data suggest that endocyclic hexose hydrogens, as with maltosaccharides in maltoporins, form pi-bonds with aromatic rings and slide between sites instead of being translocated via a single alternating site in GLUT1. 16443776_SGK1 regulates GLUT1 and may contribute to or account for the PI3 kinase-dependent but PKB-independent stimulation of GLUT1 by insulin. 16519917_results demonstrate the utilization of cell surface GLUT-1 in HTLV-1 infection of CD4(+) T lymphocytes and implicate a critical role for the ECL1 region in viral tropism 16681687_Altered expression of GLUT1 was found in head and neck squamous intraepithelial neoplasia. 16681688_In keratinizing carcinomas, GLUT1 was immunodetected peripherally, with loss of expression in central keratinized zones. 16800634_Some detergents stabilize while others destabilize GLUT1 quaternary structure but GLUT1 does not appear to exchange rapidly between protein/lipid/detergent micelles. 16842248_GLUT1 is expressed in the vast majority of endometrial intraepithelial and uterine serous papillary carcinoma, suggesting a biological role during the early steps of carcinogenesis in endometrial serous neoplasms. 17020877_helix 12 of Glut1 plays a passive stabilizing role in the structure of Glut1 and is not directly involved in the transport mechanism 17064664_GLUT1 may be a major pathway uptake of both inorganic and methylated arsenicals in erythrocytes or the epithelial cells of the blood-brain barrier, contributing to arsenic-related cardiovascular problems and neurotoxicity. 17071132_GLUT1 expression may provide useful prognostic information in patients with salivary gland carcinoma 17080242_The central part of the colorectal tumor, thought to be relatively hypoxic, had stronger GLUT-1 expression and a higher SUV than the periphery, in both the primary tumor and hepatic metastatic foci. 17167225_Icreased GLUT1 levels lead to excess glucose metabolism under normoglycemic conditions and altered gene expression of pathogenetic factors involved in diabetic kidney disease. 17192790_GLUT-1 is a sensitive and specific immunohistochemical marker enabling differential diagnosis of reactive mesothelium from malignant mesothelioma. 17294670_GLUT-1 expression have a role in gastric carcinoma, as shown by FDG uptake representing tumor metabolism 17387384_comparison of the expression of HIF-1alpha and GLUT-1 with various clinicopathological features of colorectal cancer 17404017_Significant coexpression of GLUT-1, Bcl-xL, and Bax points to cooperation of all three regulatory proteins in elimination due to irreversible injury, adaptation to hypoxia, reduction of further damage, and survival of colorectal cancer cells. 17442736_During trophoblast hypoxia glucose transporters (GLUT1/3) are upregulated via HIF-1 alpha pathway. 17451637_glycosylation change & decrease of transport activity of GLUT1 may be 1 possible mechanism of ER stress induced by down-regulating GnT-V, & GnT-V may contribute to the regulation of glucose uptake by modifying glycosylation of GLUT1 in some tumor cells. 17452775_The role of protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) in patients with colorectal adenocarcinomas. 17504522_Glut-1 is induced by TCR engagement, resulting in massive increases in glucose uptake and binding of HTLV-1 and -2 envelopes to both CD4 and CD8 T lymphocytes 17554865_The expression of Glut1 changes according to the metabolic need of infantile hemangioma cells. 17591274_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17611657_Findings suggest that characteristic differences in the patterns of glucose uptake can exist according to the histological type and that GLUT1, GLUT3 and GLUT4 could be related to tumor angiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. 17635959_Transport regulation involves ATP-dependent conformational changes in (or interactions between) the GLUT1 C terminus and the C-terminal half of GLUT1 cytoplasmic loop 6-7. 17727838_Gatifloxacin affects GLUT1 gene transcription, reduces GLUT1 mRNA expression and glucose transport in HepG2 cells. This may contribute to gatifloxacin induced dysglycemia especially in patients predisposed to disturbances of glycemic control. 17854396_Papillary thyroid cancers Papillary thyroid cancers with no 131I uptake had slightly reduced NIS, significantly reduced thyroglobulin,thyroperoxidase and pendrin and significantly increased GLUT-1 gene expression levels. 17991316_The positive rate of GLUT-1 was significantly higher in malignant and borderline serous ovarian carcinomas than in benign tumors and normal ovarian tissues. 18097583_GLUT-1 overexpression is to some extent regulated by HIF-1alpha and is also strongly associated with histological features. 18172662_GLUT1 expression was studied in normal and degenerate intervertebral discs. 18177733_GLUT1 and 9 are preferentially localized to the plasma membrane and thus can account for the transport activity. 18191496_Glut-1 plays a crucial role in determining FDG uptake in neuroendocrine (NE) lung tumors 18212354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18212354_single nucleotide polymorphisms on gene involved with glucose metabolism and obesity may be associated with increased susceptibility to spina bifida 18227718_in 5 cases of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma, study found diffuse intense positivity of the tumor cells for Glut-1 in all 5 cases and focal and weak immunoreaction for Claudin-1 in 3 cases 18245775_helix 6 of Glut1 contains amino acid side chains that are critical for transport activity and structurally analogous outer helices may play distinct roles in the function of membrane transporters 18246802_Abnormal expression of GLUT-1, p63 and DNA-Pkcs may perhaps participate in serous ovarian tumor occurrence. 18271924_the expression of Glut 1 with (18)F-FDG [(18)F]-2-fluro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake, indicating that Glut 1 is a major glucose transporter expressed inCholangiocellular carcinoma 18290322_A role for GLUT1 as an endogenous marker of tumor hypoxia is currently not supported by the available clinical data. 18311082_GLUT-1 XbaI gene polymorphism is associated with vascular calcifications in nondiabetic uremic patients. 18311082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18324916_In the ampulla of Vater, GLUT1 expression was associated with malignant change, and might be a useful marker of malignancy. 18343752_Glut 1 expression levels in tumor cell lines corresponds to 2-gluSNAP cytotoxicity. 18351386_Upregulation of HIF-1 alpha and its downstream targets GLUT1 and SDF-1 in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas may be due to hypoxia. 18387950_intracellular charges at the MFS TM2-3 and TM8-9 signature loops and flanking TMs 3, 5, and 6 are critical for the structure of GLUT1 as are TM glycines 18401196_GLUT-1 gene expression level and protein expression were correlated with lymph node metastasis, poor survival and clinical stage of head and neck carcinoma. 18410529_Data suggest that resistin causes activation of the ERK1 and 2 pathways in trophoblast cells, and that ERK1/2 activation stimulates GLUT-1 synthesis and increased placental glucose uptake. 18422279_Glut1 and HIF-1 alpha are highly expressed in non-small cell lung carcinoma, and their expressions are associated with tumor differentiation and clinical stage. 18451999_GLUT1 mutations are a cause of paroxysmal exertion-induced dyskinesias and induce hemolytic anemia by a cation leak 18565734_Expression of GLUT-1 in psoriasis and the relationship between GLUT-1 upregulation induced by hypoxia and proliferation of keratinocyte growth. 18577546_co-occurring PED and epilepsy can be due to autosomal dominant heterozygous SLC2A1 mutations, expanding the phenotypic spectrum associated with GLUT1 deficiency and providing a potential new treatment option for this clinical syndrome. 18613291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18613291_The TAT haplotype of the GLUT1 gene confers susceptibility to T2DM in the Tunisian population. 18614966_Functional studies of the T295M mutation causing Glut1 deficiency: glucose efflux preferentially affected by T295M. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18695903_No relationship between the immunohistochemical expression of Glut-1, -3, Hex I or II and glucose metabolism measured using [18F]FDG-PET in patients with high-grade glioma is observed. 18726700_Expression of GLUT-1 is significantly reduced in low-grade oligodendroglial tumors harboring LOH 1p. 18764953_results suggest that glucose transporter Glut-1 expression can significantly discriminate between human malignant melanoma and benign melanocytic nevi 18821326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18821326_The GLUT1 gene confers susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients in the Tunisian population. 18948400_GLUT1 expression is increased in human ESCs when decidualized in vitro with P(4) and dibutyryl cAMP, suggesting a similar role for P(4) in human endometrium. 18953257_Apigenin inhibits the GLUT-1 glucose transporter and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. 18973239_The altered GLUT1 mRNA expression in diseased cartilage with significance in osteoarthritis(OA) suggests that reduced GLUT1 may contribute to the failure of OA cartilage repair. 18981181_analysis of glucose transporter GLUT1 topology and structural dynamics 18987250_Erythrocyte GLUT1 transports alpha and beta sugars with equal avidity in an ATP independent manner. 18990414_Deficiency may result in cerebral hypoxia and hyperglycemia. 19016655_The C-terminal PDZ-binding motif of Glut1 plays a key role in growth factor regulation of glucose uptake by both allowing GIPC to promote Glut1 trafficking to the cell surface and protecting intracellular Glut1 from lysosomal degradation. 19020718_Glut-1 may have a role in progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma 19020742_lysyl oxidase and glucose transporter-1 expression have roles in prostate cancer progression 19085834_Glucose transporter-1 is expressed and has a role in pancreatic carcinogenesis 19142800_HIF-1 alpha and GLUT-1 could cooperate with TGF-beta1, and TGF-beta1 might mediate cross-talk between the inflammatory environment and tumour with a favourable impact on patient survival in colorectal cancer 19152396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19166280_role for the glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) in mediating the observed changes in the dielectric properties of human erythrocyte membranes as determined by dielectric spectroscopy 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19173807_Standard uptake value of 18F-FDG PET-CT is linearly correlated with the expression of GLUT1, but not with the expression of Ki67. 19234439_GLUT-1 is expressed in approximately half of the pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas and shows a strong correlation with neuroendocrine differentiation/grade 19286567_increased GLUT1 expression levels in hepatocellular cancer cells functionally affect tumorigenicity 19289587_EMA is a better marker than XIAP or GLUT-1 for the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma 19292042_The overexpression of Glut1 plays an important role in carcinogenesis and progression of breast carcinoma, and closely correlates with cell proliferation. 19303158_HCV replication down-regulates cell surface expression of GLUT2 partly at the transcriptional level, and possibly at the intracellular trafficking level as suggested for GLUT1, thereby lowering glucose uptake by hepatocytes. 19304421_phenotype of GLUT1-deficiency syndrome [review] 19347605_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19347605_The XbaIG > T and HaeIIIT > C GLUT1 polymorphisms were investigated in six different Brazilian populations. 19366592_Role of Ile(287) in GLUT1 was studied by its replacement with each of the other 19 amino acids. Ile(287) is a key residue for maintaining high glucose affinity and is located at or near the exofacial glucose binding site. 19386788_Report endofacial competitive inhibition of the glucose transporter 1 activity by gossypol. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19434538_In human gastric carcinoma, GLUT1 expression is associated with tumor aggressiveness. 19449892_Helix 9 of Glut1 plays an outer stabilizing role for the inner helical bundle predicted to form the exofacial substrate-binding site. 19465749_GLUT1 is a highly promising stage-independent, prognostic marker in adrenocortical carcinoma. 19490621_Osteoarthritis chondrocytes exposed to high glucose were unable to downregulate GLUT-1, thereby accumulating more glucose and producing more reactive oxygen species. 19533082_Rosiglitazone significantly increases glucose uptake in wild-type podocytes and this is associated with translocation of GLUT1 to the plasma membrane. 19533890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536037_study to evaluate the expression of glucose transporters (Gluts) 1 and 3 in Hodgkin and nonHodgkin lymphoma and to assess the association between their expression and the tumor intensity on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography 19554504_The expression pattern of GLUT1 is reported in newly diagnosed esophageal adenocarcinoma by means of immunohistochemistry. 19569052_Increasing GLUT expression is associated with poor response to chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. 19587357_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19619276_GLUT1 has a role in hypoxia in colorectal cancer 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19630075_2 new mutations (c.998G>A & c.274C>T) resulting in p.R333Q & p.R91W respectively were found in patients with sporadic paroxysmal exercise-induced dyskinesia. 19648108_Results show that 8-aminoadenosine reduces glucose consumption by regulating localization and expression of key glucose transporters GLUT1 and GLUT4. 19648882_Identified GLUT-1 as an additional marker that will be useful for differentiating thymic carcinoma from type B3 thymoma. 19655166_Expression of pAkt, GLUT1 and TKTL1 were higher in breast cancer and DCIS than in normal tissue. 19681047_At physiological glucose, GLUT1 and GLUT3 are the predominant active isoforms in HeLa cells and rat hepatocarcinoma AS-30D tumor cells, respectively. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19709351_GLUT-1 served as a marker indicating that tumors with deep invasion tended to result in a worse prognosis in patients due to either lymph node metastasis, a recurrence of the primary lesion or distant metastasis. 19798636_findings suggest GLUT1 deficiency underlies a significant proportion of early-onset absence epilepsy 19819644_GLUT1 expression in the ampulla of vater, extrahepatic bile ducts, and gall bladder carcinomas is associated with some prognostic factors, and GLUT1 expression is associated with a worse prognosis in the patients with gall bladder carcinomas. 19822956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19822956_XbaI GLUT1 gene polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes with nephropathy. 19883765_Purification and characterization of human glucose transporters GLUT1 expressed in Pichia pastoris. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19955252_Data show altered mRNA expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1, IRS-2, glucose transporter (GLUT)-1, GLUT-4 and glycogen synthase kinase-3 isoforms genes in adipose tissue in gestational diabetes mellitus women in comparison to pregnant controls. 20030103_GLUT-1 expression was positive in all the cases of infantile hemangioma on the face. 20063428_clinical survey indicates that gait disturbances and movement disorders are common in patients with Glut-1 deficiency. 20079187_Abnormal expression of beta-catenin and overexpression of Glut-1 may be the early events in tumorigenesis of endometrioid adenocarcinoma. 20113375_is a prognostic marker for mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary gland 20221955_Molecular analysis of the SLC2A1 gene identified a novel homozygous c1402C>T (p. Arg468Trp) mutation in exon 10 in the index patient 20375117_Suggest the GLUT1 glucose transporter could play an important role in the development of diabetic nephropathy. 20382060_All patients with severe Glut-1 deficiency syndrome had severe epilepsy, significant cognitive and motor delay, ataxia, and microcephaly. MRI changes, when present, were of greater severity than are typically associated with missense mutations in SLC2A1. 20395120_GLU-1 is expressed in peri-necrotic regions of tumors and non-malignant tissues and may be linked to hypoxia. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428049_GLUT1 and GLUT3 protein expression are indicators of poor prognosis outcome in oral squamous cell carcinoma, probably due to the enhanced glycolytic metabolism of more aggressive neoplastic cells. 20512538_GLUT-1 is a candidate as a diagnostic as well as a tissue prognostic marker in gallbladder carcinoma patients. 20526721_The expression of HIF-1alpha and GLUT1 proteins was increased after CoCl(2)-induced hypoxia in all breast cancer cell lines tested 20527231_The overexpression of glut1 may be a useful marker in distinguishing benign endometrial hyperplasia from endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia 20540786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20540786_SLC2A1 polymorphism was significantly associated with 2-[fluorine-18]-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-uptake in combination with the apurinic/apyimidinic endonuclease Asp148Glu (T>G) polymorphism in the squamous cell type of non-small-cell lung cancer. 20569445_Intratumoral hypoxia in breast cancer is marked by coordinated expression of such markers as HIF-1alpha, Glut-1, leptin and ObR. The relationships among these proteins can be altered by preoperative chemotherapy. 20574033_GLUT1 deficiency is an important monogenic cause of absence epilepsies with onset from early childhood to adult life. The phenotypic spectrum of GLUT1 deficiency is considerably greater than previously recognized. 20607826_High expression of GLUT-1 and LDH5, a tetramer of 4 lactate dehydrogenase A subunits, was confirmed by tissue microarray analysis of 249 renal cell carcinoma specimens 20630673_Data show that the phenotype of T295M-associated Glut1 deficiency is not significantly different from that of patients with a deficient 3-OMG uptake, indicating that T295M affects glucose transport at the blood-brain barrier as much as other mutations. 20679470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20679470_this genetic variant of glut1 might favor aggressive phenotypes by modulating the efficiency of cancer cells to recruit glucose and escalate growth rate 20687207_Glut1 deficiency syndrome may present as an autosomal recessive trait 20703861_Glut1 expression correlates significantly with (18)F-FDG uptake in lung neoplasms. 20730618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20803547_GPC3 plays a role in glucose transport by interacting with GLUT1. 20846124_The author searched extensively for the expression and influence of 3 markers included in chronic inflammation and early carcinogenesis, cell cycle regulation and tissue hypoxia: cyclooxygenase-2, p53 gene and glucose transporter-1 protein--REVIEW 20854211_Downregulation of Glut-1 inhibited the cellular glucose uptake, growth, and invasion of MG63 osteosarcoma cells in vitro. 20937822_WNK1 promotes cell surface expression of glucose transporter GLUT1 by regulating a Tre-2/USP6-BUB2-Cdc16 domain family member 4 (TBC1D4)-Rab8A complex 20947823_Increased vascular smooth muscle GLUT1 increased glucose uptake, impairing vascular contractility and accelerating proinflammatory, neutrophil-rich lesion in response to injury, as well as medial hypertrophy. 20965718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21029693_2-NBDG is taken up and accumulated in breast cancer cells that highly express GLUT-1. 21033220_GLUT1 expression(along with Bcl-xl and EPO) plays a role in promoting self survival of malignant cells under hypoxic conditions of colorectal cancer. 21075472_high expression in lung adenocarcinoma is associated with a poor survival 21109935_The relationship of the expression pattern of GLUT-1 with the localization and morphology of the tumor stroma was analyzed. 21135204_A 10 base pair (bp) deletion within intron 9 of Glut1 was genotyped for 457 patients with meningomyelocele (MM) and showed it to be more common in Caucasian MM patients than in Caucasian controls (P = .02). 21194153_The data suggested a crucial role of Glut1 in the development of the cerebral endothelial cells with BBB properties in vivo. 21206329_GLUT-1 seems to be playing a role in pancreatic tumorigenesis as well as in clear-cell pathogenesis. 21270293_Taken together, these observations indicate that 4F2hc is likely to be involved in GLUT1 stabilization and to contribute to the regulation of not only amino acid but also glucose metabolism. 21273616_Weak GLUT1 expression is associated with good radiotherapy response in rectal cancer 21281236_High GLUT-1 is associated with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 21294792_GLUT1 mRNA levels were detected by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in SurePath(TM) liquid-based cytology bronchial brushing specimens from patients with lung cancer and benign lung disease. 21295279_Gain and loss of function in glut1, the Drosophila ortholog, was associated with suppression and enhancement of Tau toxicity resulting in Alzheimer disease. 21306648_Data show that CA9, GLUT1 and LOX mRNA levels were equally and strongly correlated to hypoxic extent in FaDudd, and the same was observed for CA9 and GLUT1, but not LOX, in SCCVII tumors. 21317389_T helper (Th)type 1, Th2, and Th17 cells express high surface levels of glucose transporter Glut1 and are highly glycolytic; regulatory T cells, in contrast, express low levels of Glut1 and have high lipid oxidation rates. 21321933_The effect of insulin and IGF-I on GLUT expression and glucose transport in three well-characterized human osteosarcoma cell lines, was determined. 21332301_Data indicate that the SNP Rs710218 is not associated with a higher risk for HCC but rather for HCC progression, potentially via HIF-1alpha mediated increased GLUT1 expression. 21343253_Findings suggest that GLUT1 mRNA expression is essential for decidualization. 21384913_major determinants of ligand binding affinity and cooperativity at the GLUT1 endofacial site 21395180_GLUT1 may play an important role in tumorigenesis, development, differentiation, lymphatic metastasis and prognosis of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 21411785_p16 FISH is a more sensitive and specific test than GLUT-1 immunohistochemical analysis and can be a more reliable ancillary tool to support the diagnosis of mesothelioma. 21438910_Coexpression of high levels of HIF-1alpha and GLUT-1 is significantly correlated with prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. 21442770_Data sugget that a combination of GLUT1 and CAIX immunocytochemical staining can give a higher diagnostic performance. 21445818_We failed to detect any SLC2A1 mutations in the 23 patients analyzed, thus excluding mutations of this gene as a frequent cause of classical alternating hemiplegia of childhood. 21475039_expression patterns differ between keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma 21521642_Case Report: diagnosis of a congenital GLUT1-negative hepatic vascular malformation with capillary proliferation. 21528061_Results show a significant inverse correlation between GLUT1 expression and Apaf-1 expression in colorectal adenocarcinomas, and patients with GLUT1 expression demonstrate poor overall survival. 21546213_No SLC2A1 mutation was identified in 20 (60.6%) patients tested. 21555602_Diagnosis of GLUT1 deficiency is a strong indication for early use of the ketogenic diet, which may substantially improve outcome of this severe disorder. 21697701_GLUT1 expression is positive only in infantile hemangiomas, whereas WT1 positivity is found in all vascular neoplasms and in arteriovenous malformations. 21707071_SLC2A1/GLUT1, SLC1A3/EAAT1, and SLC1A2/EAAT2 were the main SLC proteins whereas ABCG2/BCRP, ABCB1/MDR1, ABCA2 and ABCA8 were the main ABC quantified in isolated brain microvessels 21786248_The patients with high-expressed GLUT1 had a worse prognosis than those with low-expressed GLUT |
ENSMUSG00000028645 |
Slc2a1 |
2528.962347 |
7.2199110179 |
2.851981 |
0.242298408 |
121.198618 |
0.00000000000000000000000000034572719633424983222691966168785798815035521399680855787747310394421085049873609840176413854351267218589782714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000004179306648561447375929935537539910076976059301552622766482621460308117177992470736569430300733074545860290527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4430.5421007 |
715.2480293 |
619.2874314 |
72.8576361 |
| ENSG00000117395 |
10969 |
EBNA1BP2 |
protein_coding |
Q99848 |
FUNCTION: Required for the processing of the 27S pre-rRNA. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in rRNA processing and ribosomal large subunit biogenesis. Located in chromosome and nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10969; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; nuclear periphery [GO:0034399]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; preribosome, large subunit precursor [GO:0030687]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] |
12768013_attaches to yeast mitotic chromosomes in a cell cycle-dependent manner and causes EBNA1 to attach to the mitotic chromosomes and effect EBV plasmid segregation 15923612_Data show that human EBNA1 binding protein 2 (hEBP2 is essential for the proliferation of human cells and that repression of hEBP2 severely decreases the ability of EBNA1 and EBV-based plasmids to bind mitotic chromosomes. 18959818_RNA and protein levels of cyclin E1, a dominant oncoprotein, were elevated in the EBP2- enhanced green fluorescent protein stable clones. 19170763_BXDC1 and EBNA1BP2 function in a dynamic scaffold for ribosome biogenesis. 24481446_EBP2 is a novel binding partner of c-Myc that regulates cell proliferation, and tumorigenesis via a positive feedback loop. 25501510_We further show that the primary tumors as well as metastasized lesions derived from EBV antigen-expressing cancer cells( EBNA3C or EBNA1 ) in nude mice model display EMT markers expression pattern 30224479_Targeted profiling of RNA translation reveals mTOR-4EBP1/2-independent translation regulation of mRNAs encoding ribosomal proteins. 33040459_EBP2, a novel NPM-ALK-interacting protein in the nucleolus, contributes to the proliferation of ALCL cells by regulating tumor suppressor p53. |
ENSMUSG00000028729 |
Ebna1bp2 |
308.455195 |
2.4236986474 |
1.277210 |
0.102654714 |
156.026433 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000835393795204769124476861905674209639616301599537296142805155882413843294558910904756133505898521574017934199218871071934700012207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000125692277443653337042569401985101663768501459173073434672950863810722781260512739043806794241031621339743651333265006542205810546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
437.8300730 |
25.8542041 |
181.8773152 |
8.5638531 |
| ENSG00000117400 |
4352 |
MPL |
protein_coding |
P40238 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for thrombopoietin that acts as a primary regulator of megakaryopoiesis and platelet production. May represent a regulatory molecule specific for TPO-R-dependent immune responses. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08351}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
In 1990 an oncogene, v-mpl, was identified from the murine myeloproliferative leukemia virus that was capable of immortalizing bone marrow hematopoietic cells from different lineages. In 1992 the human homologue, named, c-mpl, was cloned. Sequence data revealed that c-mpl encoded a protein that was homologous with members of the hematopoietic receptor superfamily. Presence of anti-sense oligodeoxynucleotides of c-mpl inhibited megakaryocyte colony formation. The ligand for c-mpl, thrombopoietin, was cloned in 1994. Thrombopoietin was shown to be the major regulator of megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet formation. The protein encoded by the c-mpl gene, CD110, is a 635 amino acid transmembrane domain, with two extracellular cytokine receptor domains and two intracellular cytokine receptor box motifs . TPO-R deficient mice were severely thrombocytopenic, emphasizing the important role of CD110 and thrombopoietin in megakaryocyte and platelet formation. Upon binding of thrombopoietin CD110 is dimerized and the JAK family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases, as well as the STAT family, the MAPK family, the adaptor protein Shc and the receptors themselves become tyrosine phosphorylated. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4352; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; thrombopoietin receptor activity [GO:0038164]; basophil homeostasis [GO:1990960]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; eosinophil homeostasis [GO:1990959]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; monocyte homeostasis [GO:0035702]; neutrophil homeostasis [GO:0001780]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation [GO:0050671]; positive regulation of platelet formation [GO:1905221]; thrombopoietin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038163] |
11961237_binding to platelet thrombopoietin receptor is directly involved in human thrombopoietin plasma level regulation 12010817_expressed in megakaryocytes in essential thrombocythemia 12091373_The expression pattern of c-mpl in megakaryocytes correlates with thrombotic risk in essential thrombocythemia. 12145691_A new mutation of MPL, Trp(508) to Ser(508) in the intracellular domain of MPL, induces factor-independent growth in Ba/F3 cells & constitutively activates 3 distinct signaling pathways, SHC-Ras-Raf-MAPK/JNK, JAK-STAT, and PI3K-Akt-Bad. 12200367_The cytoplasmic domain of Mpl receptor transduces exclusive signals in embryonic and fetal hematopoietic cells. 14764528_Asn505 is an activating mutation with respect to the intracellular signaling and survival of cells in familial essential thrombocythemia deriving from a dominant-positive activating mutation of the c-MPL gene. 14995067_the promoter activity of myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene is modulated by transcription through a PKC-dependent pathway 15210714_c-Mpl truncated isoform with an essential C-terminal peptide is required for a proteolytic process 15269348_K39N represents an identified functional Mpl polymorphism and is associated with altered protein expression of Mpl and a clinical phenotype of thrombocytosis. 15269348_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15307100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15452260_may play a role in hematopoietic inhibition during HIV-1 infection, and control of its expression levels may aid in hematopoietic recovery and thereby reduce the incidence of cytopenias occurring in infected individuals 15647951_expression of TPO receptor on platelets until 1 month after birth cause a decreased TPO clearance and keep a high level of free TPO in blood, resulting in the subsequent thrombocytosis in preterm infants. 15741216_a C-terminal AML1 mutation leads to a decrease in Mpl receptor expression in familial thrombocytopenia 15899890_Interaction with JAK2 or Tyk2 appears to protect the receptor from proteasome degradation. Sequences encompassing Box1 and Box2 regions of the receptor cytosolic domain and an intact JAK2 or Tyk2 FERM domain are required for these effects. 15951300_PRV-1 overexpression is associated with a significantly increased risk of thrombosis, whereas decreased c-Mpl expression is not 16088917_In this study, we report the binding of hNUDC to the extracellular domain of the thrombopoietin receptor (Mpl) as detected by the yeast two-hybrid system, GST pull-down, and co-immunoprecipitation. 16454716_in HIV infected patients, both the serum thrombopoietin (TPO) levels and the TPO-c-Mpl complexes on the platelet surface were significantly elevated 16470591_analysis of MPL mutations in patients suffering from congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia 16834459_Activation of JAK-STAT signaling via a somatic activating mutation in the transmembrane domain of MPL (MPLW515L) is an important pathogenetic event in patients with JAK2V617F-negative MF. 16868251_MPLW515L or MPLW515K mutations are present in patients with MMM or ET at a frequency of approximately 5% and 1%, respectively, but are not observed in patients with polycythemia vera (PV) or other myeloid disorders 16868251_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17052978_expression of JAK2 stabilizes mature TpoR and thus further increases its surface expression. This JAK2 effect depends on the Box 1 region, the only JAK2 interacting site in the TpoR 17157161_The expression of mRNA of C-MPL in platelets is a clear band by RT-PCR methods. 17379761_THPO upregulates c-mpl expression during formation of CD34+ cells. 17408398_it was concluded that the oncogenic event in idiopathic myelofibrosis associated with the MPLW515L/K mutations probably occurs in a progenitor cell common to both myeloid and lymphoid cells, such as the pluripotent haematopoietic stem cell 17408465_MPL mutation in myelofibrosis characterises patients with more severe anaemic phenotype 17507998_MPLW515K, but not JAK2V617F, is expressed in in vitro expanded CD4+ T lymphocytes from primary myelofibrosis patients 17540852_Clonal myelopoiesis antedates acquisition of JAK2V617F or MPLW515L/K mutations. 17658515_hNUDC binds to cell surface-captured Mpl.Co-expression of Mpl-EGFP and hNUDC-DsRed led to the release of hNUDC-DsRed into the culture medium 17666371_Mutations in MPL is associated with congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia 17709604_The MPL W515L or K mutation induces a spontaneous megakaryocyte (MK) differentiation. 17920755_MPL gene mutations were not associated with erythrocytosis, but segregated primarily with the phenotypes of thrombocytosis, extramedullary disease, myelofibrosis, and osteosclerosis. 17956691_Expression of c-mpl in CD34+ BMHCs and platelets of polycythemia vera patients was not obviously abnormal. 18040685_no MPL (myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene thrombopoietin recept) W515L/K mutations were found in any patients with refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts associated with marked thrombocytosis (RARS-T) 18174381_These data demonstrate that dimerization of a single cytokine receptor can deliver a profound expansion signal in both uncommitted and lymphoid-committed human hematopoietic progenitors. 18250227_diagnostic and prognostic value of JAK2 and MPL515 mutations in 241 SVT patients 18295514_Sp1 sites in the c-mpl promoter enhancer region and Ets elements in front of the transcription start site are critical for c-mpl gene expression. 18297515_review of roles of Jak2, Jak3, and MPL mutations in signal transduction and etiology of myeloid malignancies 18422784_a severe clinical course of congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia may be expected when mutations lead to absent Mpl expression or signalling in patients with missense mutations 18451306_MPL mutations lacked prognostic significance with respect to thrombosis, major hemorrhage, myelofibrotic transformation or survival. 18451306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18464114_MPL W515L mutations may contribute to the primary molecular pathogenesis of Chinese patients with ET 18464114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18487512_c-Mpl cytoplasmic YRRL motifs are responsible for both Tpo-mediated internalization via interactions with AP2 and lysosomal targeting after endocytosis. 18519816_MPLW515L/K mutations do not define a distinct phenotype in ET, although some differences depend on the JAK2V617F mutational status of the counterpart. 18528423_results demonstrate that only the detected MPL W515 mutations trigger spontaneous MPL activation leading to a G(1)/S transition activation 18566540_JAK2 and MPL mutations in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocytosis, and primary myelofibrosis [review] 18669880_A sensitive detection method for MPLW515L or MPLW515K mutation in chronic myeloproliferative disorders with locked nucleic acid-modified probes and real-time polymerase chain reaction is reported. 18669880_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18687690_AML1 can regulate the c-mpl promoter both positively and negatively by changing the binding partner according to cell types 18754026_role of mutant alleles of JAK2 & MPL in the pathogenesis of polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia & primary myelofibrosis [review] 19029146_35 MPLW515 mutations were detected in the 869 selected patients 19036112_study identified the novel MPL mutation p.Pro106Leu and obtained strong support for its association with development of thrombocytosis 19097174_Expression of c-MPL was associated with CD34+ AML and M2 FAB AML subtype. 19099657_A point mutation was detected in patients with essential thrombocythemia but not polycythemia vera, idiopathic myelofibrosis, or chronic myelogenous leukemia. 19099657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19175989_No MPL W515L/K expression was found in early myeloproliferative disorders. 19175989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19194467_MPLW515L mutation is associated with acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with myelofibrosis. 19194467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19196872_Mutations in MPL gene is associated with chronic myeloproliferative disease. 19261614_MPL(W515L)/JAK2 complex requires membrane localization for JAK2 phosphorylation, resulting in autonomous receptor signaling. 19274616_MPL W515L/K mutations are associated with chronic myeloproliferative disorders. 19302922_This research characterizes mutations of c-Mpl that lead to thrombocytopenia in a child with congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. 19341705_CD90 and CD110 are are useful positive-selection markers for the isolation of cancer stem cells in some cases of T-ALL. 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19372714_JAK2V617F or MPLW515 mutations do not seem to correlate with simple clinical parameters. ET patients with wild-type JAK2were significantly younger at diagnosis. 19372714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19469654_Increasing trend for MPL expression is associated with early to advanced stages of myelodysplastic syndrome. 19483125_The Asn505 mutation of the c-MPL gene, which causes familial essential thrombocythemia, induces autonomous homodimerization of the c-Mpl protein due to strong amino acid polarity. 19521067_No evidence of a clinico-pathological association was found between the presence of MPL W515K/L mutations & haematological indices, BM cellularity, megakaryocyte morphology & clustering, spleen size or thrombotic/haemorrhagic events 19521067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19560457_Mpl plays an important and specific role in mediating hNUDC-induced megakaryocyte proliferation and differentiation. 19608689_A recurrent MPL-S505N mutation found in Italian families with hereditary thrombocythemia is likely caused by a founder effect. 19643476_MPL gene mutations seem to be associated with thrombocytosis. 19643476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19713221_Patients with familial thrombocytosis caused by MPL serine505asparagine mutation have a high risk of thrombosis, and with aging, develop splenomegaly and bone marrow fibrosis, affecting life expectancy. 19728022_W515-P518delinsKT are missense mutations in essential thrombocythemia 19996410_Results suggest that TpoR cytosolic phosphorylated Y112 and flanking sequences could become targets for pharmacologic inhibition in MPNs. 20111067_Acquisition of a MPL mutation is not influenced by the presence of JAK2 46/1 haplotype frequency in myeloproliferative neoplasms. 20113333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20113333_lack of spontaneous STAT3 and STAT5 activation and the normal response to TPO is unexpected as MPLW515L leads to constitutive receptor activation and hypersensitivity to TPO in experimental models 20113830_Distinct patterns of cytogenetic and clinical progression in chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms with or without JAK2 or MPL mutations. 20113830_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20151976_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20166549_Protein kinase C plays the essential role in the modulation of c-mpl promoter activity of megakaryoblastic cells. 20232601_Propose a gene therapeutic strategy, with c-mpl as the major genetic component, to address the morbidity and mortality resulting from cytopenias in HIV infected patients. 20304805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304805_The JAK2 46/1 haplotype predisposes to MPL-mutated myeloproliferative neoplasms. 20331763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331763_The MPL W515L mutation and JAK2 exon 12 mutations can also be found in JAK2 V617F negative myeloproliferative disorders patients. 20410924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485371_MPLW515L mutation is not associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. 20508616_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20520633_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20529857_separate binding sites on the Mpl receptor for TPO and hNUDC identified 20823136_Studies demonstrate that progression to AML is part of the natural history of MPL W515L-associated disease. 20890078_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20890078_The frequencies of the MPL W515L/K mutations with essential thrombocythemia/post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis were 3.2%. 21051030_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21051030_The MPL W515L/K mutations are rare in Taiwanese patients with Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. 21174945_in megakaryoblastic cells, PKC plays the crucial role in the initiation of up-regulation of PMA-induced c-mpl promoter activity 21225925_Mutations in the thrombopoietin receptor gene, c-mpl is associated with congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia 21228032_double mutations in cis of MPL exon 10 in myeloproliferative neoplasms 21326037_mutations in exons 12 to 14 of Jak2 can be used to diagnose myeloproliferative disorders 21402716_Data suggest that signaling and inactive states of thrombopoietin receptor are related by receptor subunit rotations, rather than a simple monomer-dimer transition. 21489838_A founder mutation in the MPL gene c.79+2T>A causes congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia (CAMT) in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. 21489838_identification and characterization of a founder mutation in MPL in the Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) population. 21555228_BCR/ABL negative and JAK2V617F-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms patients have other mutations besides W515 mutation in MPL exon10 and mutations other than single nucleotide exchange also exist 21570117_MPL exon 10 mutations are associated with myeloproliferative neoplasms. 21605620_Data indicate that the precise mechanisms for the different biological effects regarding stimulation through the same receptor, Mpl, remain to be elucidated. 21674576_Of 168 pts, 149 with polycythemia vera (PV) and 19 with post-PV myelofibrosis (PV-MF), two pts (1.2%; 1 PV, 1 PV-MF) harbored MPL mutations. Data suggest PV is molecularly more complex than previously appreciated. (study from Mayo Clinic, MN, USA) 21691276_MPL mutation is not associated with primary myelofibrosis. 21841770_Thrombopoietin receptor agonist therapy in primary immune thrombocytopenia is associated with bone marrow hypercellularity and mild reticulin fibrosis but not other stromal abnormalities. 21858098_Results suggest that MPL mutations within the TM region could result in conformational changes including tilt and rotation (azimuthal) angles along the membrane axis. 21892137_Subtle differences in cytokine receptor dimerization provide a new layer of signalling regulation that is relevant for disease. 22093990_STAT5 phosphorylation levels of EPO and TPO receptors are elevated in bone marrow cells of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. 22102270_Studies indicate that in most of the cases the CAMT is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in the gene MPL. 22180433_This study shows for the first time a link between homozygous MPL mutations and familial aplastic anemia. It also highlights the important role of MPL in trilineage hematopoiesis. 22290824_Ligand-inducible dimerization of intracellular Mpl in human myeloerythroid progenitors induces progenitor expansion and erythropoiesis. 22337712_High MPL expression is associated with leukemia. 22338178_The expression of EPOR and TPOR on CD34+ CD59+ bone marrow cells are significantly higher than those on CD34+ CD59- cells of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patients. 22378845_Selection against TpoR antiproliferative signaling occurs by TpoR down-modulation and that restoration of down-modulated TpoR levels could become a biomarker for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms. 22565617_genetic association studies in Italian population: Data suggest that JAK2 GGCC haplotype is associated with JAK2 mutation (V617F) but is not associated with MPL mutation in exon 10 in myeloproliferative neoplasm subjects. [meta-analysis included] 22613795_Up-regulation of wild-type MPL levels promotes leukemia development and maintenance through activation of the PI3K/AKT axis. 23351976_Different mutations of the human c-mpl gene indicate distinct hematopoietic diseases. 23359689_Tryptophan at the transmembrane-cytosolic junction modulates thrombopoietin receptor dimerization and activation. 23441089_MPL W515L mutation in pediatric essential thrombocythemia. 23511495_MPL Baltimore mutation is associated with thrombocytosis. 23575445_Loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 1p involving the MPL location may represent a molecular mechanism of fibrotic transformation in MPL-mutated myeloproliferative neoplasms. 23747337_In migrating cancer stem cells isolated from primary human colorectal cancers, CD110(+) and CDCP1(+) subpopulations mediate organ-specific lung and liver metastasis. 23908116_Impaired transcriptional regulation of the MPL signaling that normally governs megakaryopoiesis and erythropoiesis underlies congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. 23986553_investigation of JAK2V617F, Exon12_JAK2 and MPLW515K/L was relevant for the diagnosis of 38.4% of patients suspected to have BCR-ABL1-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms 24043765_These experiments define a novel VEGF-miR-1-Mpl-P-selectin effector pathway in lung Th2 inflammation and herald the utility of miR-1 and Mpl as potential therapeutic targets for asthma. 24085601_The effects of inhibition of the TPO/c-MPL pathway on enhancing the chemotherapy sensitivity of AML cells. 24402162_The current study identifies 'CALR(-)ASXL1(+)' and 'triple-negative' as high-risk molecular signatures in PMF. 24931576_Both immature and mature Mpl reach the cell surface. 24986690_Data indicate that of the 617 subjects studied, 399 (64.7%) carried Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), 140 (22.7%) had a CALR (calreticulin gene) exon 9 indel, 25 (4.0%) carried an thrombopoietin receptor (MPL) mutation. 25103330_The phenotype and status of the commonly acquired JAK2 V617F, CALR exon 9 and MPL W515L/K mutations in affected individuals from a consecutive series of ten familial myeloproliferative neoplasms kindred are described. 25189720_Mutations in JAK2, MPL, and CALR appear to be the main driver mutations in the majority of myeloproliferative neoplasms. (Review) 25231745_Molecular monitoring of patients having undergone AHSCT for PMF should not be restricted to JAK2, MPL or CALR, but all mutations present in primary fibrotic neoplastic myeloproliferation should be included to interpret abnormal blood values after AHSCT 25343958_Amino acid substitutions in a thrombopoietin receptor (Mpl)--containing cell growth switch (CGS) extending receptor stability improve the expansion capacity of human cord blood CD34(+) cells in the absence of exogenous cytokines. 25398833_MPL mutation is associated with myeloproliferative neoplasms. 25468569_OTT1 regulates the alternative splicing of Mpl-TR, a truncated isoform of c-Mpl, which modulates Thrombopoietin-mediated signaling. 25482134_CALR mutation, MPL mutation and triple negativity may have roles in lowering vascular risk in primary myelofibrosis 25538044_The P106L mutation functionally separates The activity of c-Mpl in downstream signaling from that in maintaining platelet homeostasis. 25573593_MPL gene mutations are associated with essential thrombocythaemia and major thrombotic complications. 25637689_No individuals with either the MPL W515K mutation or the JAK2 exon 12 mutations were identified 25761530_Letter/Meta-analysis: thrombopoietin receptor agonists significantly increase the risk of portal vein thrombosis in liver diseases. 25911549_Flow cytometric detection of MPL (CD110) as a diagnostic tool for differentiation of congenital thrombocytopenias. 25970554_we describe a Mpl W515K somatic mutation in a paediatric case of ET who presented with Budd-Chiari syndrome. No paediatric patient harbouring a Mpl W515K mutation has been previously reported. 26071474_The data supports the proposal of including MPL exon 10 mutations as major diagnostic markers for myeloproliferative neoplasms. 26119186_Anagrelide proved effective among all molecular subsets, indicating that JAK2/CALR/MPL mutational status does not seem to represent a major determinant of choice of cytoreductive treatment among essential thrombocythemia therapies. 26159733_erythrocyte lineage enforces exclusivity through upregulation of EKLF and its lineage-specific cytokine receptor (EpoR) while inhibiting both FLI-1 and the receptor TpoR (also known as MPL) for the opposing megakaryocyte lineage 26314963_PARP-1 has an important role in the progression of acute myeloid leukemia by suppressing the myeloproliferative leukemia virus oncogene 26316487_A newborn girl with congenitcal amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia had a homozygous missense Trp154-to- Arg mutation in exon 4 of c-MPL. The same heterozygote mutation was detected in her mother, father, and 2 siblings. 26419289_identification of a higher frequency of co-existing JAK2 exon-12 or MPL exon-10 mutations in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms with a low JAK2V617F allelic burden compared to those with a higher allelic burden. 26437785_goals were: (i) to identify other MPL mutations that should be tested in MPN patients by mutation-specific PCR; and (ii) to determine the amino acid requirements at position 515 to prevent TpoR self-activation 26450985_this study has shown that in a fraction of the so-called triple-negative ETs a significant proportion of patients have mutations in signaling molecules, more particularly in MPL. 26505790_Using C-mannosylation defective mutant of c-Mpl, the C-mannosylated tryptophan residues at four sites (Trp(269), Trp(272), Trp(474), and Trp(477)) are essential for c-Mpl-mediated JAK-STAT signaling. 26614694_Compared to normal controls, the frequency of the JAK246/1 haplotype was significantly higher among patients with JAK2V617F, JAK2Ex12del, or MPL mutations, whereas no significant difference was found among CALR mutation-positive patients 26627830_His(499) regulates the activation of human TpoR and provides additional protection against activating mutations, such as oncogenic Asn mutations in the TM domain 26668133_Thrombopoietin receptor activation by myeloproliferative neoplasm associated calreticulin mutants. 26768689_Mutation status of JAK2, CALR, and MPL in essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis defines clinical outcome. 26817954_mutant CALR promotes myeloproliferative neoplasm development by activating c-MPL and its downstream pathway. 26890983_In essential thrombocythemia, MPL mutations might be associated with a higher risk of fibrotic transformation and the presence of JAK2/MPL mutations with higher risk of thrombosis. 26951227_we show that the positive charge of the CALR mutant C-terminus is necessary to transform hematopoietic cells by enabling binding between mutant CALR and the thrombopoietin receptor MPL. 27177927_In tumor cell cultures, exogenous expression of MPL led to constitutive activation of STAT3 and 5, ERK1/2, and AKT, cytokine-independent growth, and reduction of apoptosis similar to the effects seen in the spontaneously outgrown cells. 27519934_Concurrent MPL W515L and Y591D mutations in a patient with myelofibrosis. 27768091_MPL mutations and splenomegaly are risk factors for essential thrombocythemia progression into primary nyelofibrosis. 27855276_Coexisting mutations of the JAK2, CALR, and MPL genes in myeloproliferative neoplasms suggest that CALR and MPL should be analyzed not only in JAK2-negative patients but also in low V617F mutation patients. 27865175_MPL is up regulated in JAK2(V617F) ECs and contributes to the maintenance/expansion of the JAK2(V617F) clone over JAK2(WT) clone in vitro 27993871_Normal FLT3 and negative expression of CD34 and cMPL may predict a longer overall survival in aute myeloid leukemia. 28034873_these results demonstrate that MPL P106L is a receptor with an incomplete defect in trafficking. 28391042_A novel germ-line mutation of c-mpl gene in a sporadic case of essential thrombocythemia. 28625126_This study demonstrated that absence of MPL mutation in stroke. 28714945_In 136 patients with myelofibrosis and a median age of 58 years who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) for molecular residual disease, the percentage of molecular clearance on day 100 was higher in CALR-mutated patients (92%) in comparison with MPL- (75%) and JAKV617F-mutated patients (67%). 28741795_Results show that mutant CALR induces autocrine, but not paracrine activation of MPL in myeloproliferative neoplasm. [review] 28766534_Essential Thrombocythemia and Primary Myelofibrosis patients with MPL mutations are at high risk for Thrombotic Events. 28990497_In 94.9% of PV, 85.5% ET and 85.2% PMF, authors found mutations in JAK2, MPL or CALR. 74.9% carried JAK2V617F, 12.3% CALR mutations, 2.1% MPL mutations and 10.7% were triple negative. 29146710_JAK2, CALR, MPL and ASXL1 mutational status correlates with distinct histological features in Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms 29266414_MPL, CALR and JAK2 are considered driver mutations in myeloproliferative neoplasms.The occurrence of two driver mutations in the same patient was determined and the clinical presentation and disease progression were compared with those in patients with only one driver mutation. Co-occurrence of 2 driver mutations affects the presentation or evolution of MPN, especially essential thrombocythemia. 29274361_These results indicate that lusutrombopag acts on human TPOR to upregulate differentiation and proliferation of megakaryocytic cells, leading to platelet production. 29288169_Insights into the mechanism of the pathogenic mutant CALR-MPL interaction in myeloproliferative neoplasms. 29313460_The expression of TPO and c-Mpl was significantly decreased in the cITP group compared to the nITP group, suggesting that TPO and its receptor may play important roles in childhood cITP pathogenesis. 29384262_Frameshift mutation in the MPL gene is associated with congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. 29390868_JAK2V617F mutation was found in 37 (61.7%) patients with ET. Among 23 patients without JAK2V617F mutation, 7 (11.7%) had CALR mutation and 1 (1.7%) had MPL mutation. Fifteen (25.0%) patients were negative for all 3 mutations: JAK2V617F(-), CALR(-), and MPL(-). 29934356_MPL and CALR genotypes show a similar clinical picture at essential thrombocythaemia diagnosis. Bone marrow histology in MPL-mutated ET is characterized by prominent megakaryocytic proliferation. 30084272_This study explored the relationship between mutations in the Janus kinase 2 gene ( JAK2), MPL, and the calreticulin gene ( CALR) in Uygur and Han Chinese patients with BCR-ABL fusion gene-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. 30304655_Comprehensive genomic characterization identified distinct genetic subgroups and provided a classification of myeloproliferative neoplasms on the basis of causal biologic mechanisms. Mutations in JAK2, CALR, or MPL being the sole abnormality in 45% of the patients. 30635630_The S505A MPL mutation is associated with childhood hereditary thrombocytosis and essential thrombocythemia. 30770989_positive CD110 expression in PDAC was associated with poor prognosis and liver metastasis of human PDAC samples 31014934_indirubin may play a direct role in thrombopoiesis by activating cellular MPL and normalizing TNF expression to suppress inflammation in ITP. This study may thus improve our understanding of indirubin and provide important information for optimizing therapeutic strategies for ITP patients. 31128484_MPL is the requisite cytokine receptor for CALR mediated tumorigenic transformation, as has been demonstrated in a mouse model. 31135094_Recurrent concomitant classical and/or noncanonical JAK2- and MPL-mutations could be detected by NGS in 15.7% of JAK2V617F- and MPLW515-positive MF patients with genotype-phenotype associations. 31462733_Mutant calreticulin interacts with MPL in the secretion pathway for activation on the cell surface. 31548225_The Molecular Genetics of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. 31554376_MPL Mutation Associated with Essential Thrombocythemia. 31668145_The effects of mutational profiles on phenotypic presentation of myeloproliferative neoplasm subtypes in Bosnia: 18 year follow-up. 31697803_Transforming MPL exon 10 mutations are not limited to S505N and W515L/K/R/A, but are highly restricted by position and amino acid type. Many second-site mutations can enhance constitutive signaling by a canonical MPL exon 10 mutation and several are found in myeloproliferative disease patients. 31858134_Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm with Ring Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis with Cooccurrent SF3B1 and MPL Gene Mutations: A Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature. 32341206_c-Mpl and TPO expression in the human central nervous system neurons inhibits neuronal apoptosis. 32499240_Clinical acceleration of JAK2 p.V617F driven myeloproliferative disease due to a new uncommon homozygous MPL p.Y591D mutation. 32591258_JAK2, CALR, and MPL Mutations in Egyptian Patients With Classic Philadelphia-negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. 32703794_CAMT-MPL: congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia caused by MPL mutations - heterogeneity of a monogenic disorder - a comprehensive analysis of 56 patients. 33202112_JAK2V617F, CALR and MPL515L/K mutations and plateletcrit in essential thrombocythemia: A single centre's experience. 33255170_The Genetic Basis of Primary Myelofibrosis and Its Clinical Relevance. 33361847_MOLECULAR GENETIC ABNORMALITIES IN THE GENOME OF PATIENTS WITH Ph-NEGATIVE MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASIA AFFECTED BY IONIZING RADIATION AS A RESULT OF THE CHORNOBYL NUCLEAR ACCIDENT.', trans 'MOLEKULIaRNO-GENETYChNI ANOMALII U GENOMI KhVORYKh NA Rh-NEGATYVNI MIIeLOPROLIFERATYVNI NEOPLAZII, IaKI ZAZNALY DII IONIZUIuChOI RADIATsII VNASLIDOK AVARII NA ChAES. 33693786_An Asian-specific MPL genetic variant alters JAK-STAT signaling and influences platelet count in the population. 33770389_MPL exon 10 mutations other than canonical MPL W515L/K mutations identified by in-house MPL exon 10 direct sequencing in essential thrombocythemia. 33789164_Mutation Profile in BCR-ABL1-Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Single-Center Experience From India. 33909030_Mechanism of mutant calreticulin-mediated activation of the thrombopoietin receptor in cancers. 33921387_Low JAK2 V617F Allele Burden in Ph-Negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Is Associated with Additional CALR or MPL Gene Mutations. 34010413_CALR mutant protein rescues the response of MPL p.R464G variant associated with CAMT to eltrombopag. 34131895_Clinical course of myeloproliferative leukaemia virus oncogene (MPL) mutation-associated familial thrombocytosis: a review of 64 paediatric and adult patients. 34165774_MPL overexpression induces a high level of mutant-CALR/MPL complex: a novel mechanism of ruxolitinib resistance in myeloproliferative neoplasms with CALR mutations. 34210000_Thrombopoietin Contributes to Enhanced Platelet Activation in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. 34300032_Clinical and Laboratory Features of JAK2 V617F, CALR, and MPL Mutations in Malaysian Patients with Classical Myeloproliferative Neoplasm (MPN). 34756243_The MPL mutation. 34845187_MPL S505C enhances driver mutations at W515 in essential thrombocythemia. 35544613_Clinical and molecular characteristics of acute myeloid leukemia with MPL mutation. 35633552_Study of CALR, MPL, and c-kit Gene Mutations in Thai Patients with JAK2 V617F Negative Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. 35791502_Pro106Leu MPL mutation is associated with thrombocytosis and a low risk of thrombosis, splenomegaly and marrow fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000006389 |
Mpl |
10.527392 |
0.2320056685 |
-2.107768 |
0.488593364 |
20.017622 |
0.00000767317531617443743588696108970381715153052937239408493041992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024408635273003165272335049373886306511849397793412208557128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5716880 |
1.4623771 |
19.7380272 |
3.6697220 |
| ENSG00000117425 |
8643 |
PTCH2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6C5 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the control of cellular growth (PubMed:18285427). May have a role in epidermal development. May act as a receptor for Sonic hedgehog (SHH). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18285427}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor of the patched gene family. The encoded protein may function as a tumor suppressor in the hedgehog signaling pathway. Alterations in this gene have been associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, basal cell carcinoma, medulloblastoma, and susceptibility to congenital macrostomia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:8643; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; hedgehog family protein binding [GO:0097108]; hedgehog receptor activity [GO:0008158]; smoothened binding [GO:0005119]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; epidermal cell fate specification [GO:0009957]; hair cycle [GO:0042633]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; positive regulation of epidermal cell differentiation [GO:0045606]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; skin development [GO:0043588]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
14613484_PTCH2 isoforms have distinct roles in Hedgehog signalling. 18285427_PTCH2 (2157G-->A), a novel missense mutation, underlies NBCCS, resulting in the loss of PTCH2 inhibitory function in the Shh signalling pathway. 19208383_A susceptibility locus on 1p32-1p34 for congenital macrostomia in a Chinese family and identification of a novel PTCH2 mutation are reported. 19221557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19237606_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23479190_Frameshift mutation in the PTCH2 gene can cause nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. 29109083_Our data extend these observations and demonstrate a significant increase in Ptch2 expression in the obstructive UPJ segments in a subset of patients with congenital UPJO. 29230040_Combined heterozygous germline mutations in PTCH1 and PTCH2 were identified in a patient with embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. 30021865_The importance of the ATRX/DAXX pathway was confirmed by the first-ever pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pNEN)-specific protein-damaging hotspot mutation in DAXX. In this study, both novel genes, including the pro-apoptotic CYFIP2 gene and hedgehog signaling PTCH2, and novel pathways, such as the MAPK-ERK pathway, were implicated in pNEN. 31233836_Pds5b/Ptch2 axis regulates cell proliferation and invasion in pancreatic tumor cells. 33047712_[Exploring parent-of-origin effects for non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate on PTCH1, PTCH2, SHH, SMO genes in Chinese case-parent trios]. 34170463_PTCH2 is not a strong candidate gene for gorlin syndrome predisposition. 34990798_Inherited rare and common variants in PTCH1 and PTCH2 contributing to the predisposition to reproductive cancers. 36027694_Reduced PTCH2 expression is associated with glioma development through its regulation of the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000028681 |
Ptch2 |
7.658315 |
0.3315367048 |
-1.592759 |
0.666518129 |
5.806586 |
0.01596626380989557558720548513520043343305587768554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029249355074352577366081362697514123283326625823974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5642082 |
2.6276939 |
8.2219311 |
5.4451189 |
| ENSG00000117461 |
8503 |
PIK3R3 |
protein_coding |
Q92569 |
FUNCTION: Binds to activated (phosphorylated) protein-tyrosine kinases through its SH2 domain and regulates their kinase activity. During insulin stimulation, it also binds to IRS-1. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH2 domain |
|
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and similar compounds, which then serve as second messengers in growth signaling pathways. PI3K is composed of a catalytic and a regulatory subunit. The protein encoded by this gene represents a regulatory subunit of PI3K. The encoded protein contains two SH2 domains through which it binds activated protein tyrosine kinases to regulate their activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:8503; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IA [GO:0005943]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity [GO:0016303]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; immune response [GO:0006955]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0046854]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043551]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217] |
17360667_IGF2-PIK3R3 signaling axis is involved in promoting the growth of a subclass of highly aggressive human glioblastomas that lack EGF receptor amplification. 17452746_We have identified novel nonclassical mediators of the SREBP-1 response, including p55gamma, supporting the hypothesis that SREBP-1 regulates stress response and signaling genes. 20197460_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22722333_A fusion peptide containing the p55PIK amino terminus, TAT-N24, which not only inhibited cell proliferation, but also stimulated differentiation. 22876838_PIK3R3 was up-regulated in gastric cancer and promoted cell cycle progression and proliferation. 23135998_Data show that miR-7 inhibits the effects of TLR9 signaling on lung cancer cells through regulation of the PIK3R3/Akt pathway. 23509792_p55PIK is transcriptionally activated by MZF1, resulting in increased proliferation of colorectal cancer cells 23904382_Containing the N24 of PI3K-p55PIK. 23939377_our results show that the-PCNA interaction is important in regulating DNA synthesis and contributes to tumorigenesis. 24130211_p55PIK could be a substrate of activated caspase 6 during paraquat-induced apoptosis, leading to loss of original biological functions and redistribution to disturb cell cycle progression. 24469061_discovered that ERBB4 and S6K2 were the direct targets of miR-193a-3p and that PIK3R3 and mTOR were the direct targets of miR-193a-5p in non-small-cell lung cancer 24632606_study shows that the p53/miR-148b/p55PIK axis has an important role in cell proliferation and tumor growth, and may represent a novel therapeutic target for treating cancers containing p53 mutations or losses. 24837077_Overexpression of PIK3R3 depends on SNAI2, inducing significant epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). 24982892_PIK3R3, ITGB1, ITGAL, and ITGA6, were involved in the regulation of actin cytoskeleton that link to triple-negative breast cancer migration. 25371235_TGF-beta/NKX2.1/PIK3R3 axis is crucial in the TGF-beta-induced inhibition of cell proliferation, and the NKX2.1/PIK3R3 axis might become a target in TGF-beta receptor-repressed lung adenocarcinoma 25388664_p55gamma sequentially up-regulated p53 and p21, resulting in cell-cycle arrest in S phase; small-interfering RNA knockdown of either p53 or p21 blocked p55gamma-induced vascular smooth muscle cell growth arrest. 25608840_our findings provide new insights into tumor suppression by miR-511 by negatively regulating the PIK3R3/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway 26587973_p55PIK-PI3K signaling can contribute to imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors by increasing KIT expression. 26826873_The proliferation, migration and invasion was decreased in ovarian SKOV3 when HOTAIR or PIK3R3 was silenced. 27503199_miR-181a2/181b2 prominently dampened cell-cycle progression, suppressed cell growth, and promoted apoptosis of tumor cells in vitro They also effectively impeded tumor formation and growth in vivo miR-181a2/181b2 exert the tumor suppressor ability by depressing the direct target PIK3R3 (p55gamma) and consequently modulating the PIK3R3/Akt/FoxO signaling pathway 28260020_Study showed that PIK3R3 was a target of miR-365 and its expression was upregulated and inversely correlated with miR-365 expression in glioma tissues. 28944887_The findings suggest that miR-212 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by directly targeting PIK3R3. 28970114_p55PIK significantly stimulated the expression of AFP by activating NF-kappaB signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 29350678_PIK3R3 regulates the expression of PPAR-alpha in hepatocytes.The novel PIK3R3-HNF4alpha-PPAR-alpha signaling axis plays a significant role in hepatic lipid metabolism. 29370570_Database analysis indicates that better disease-free survival in colorectal cancer patients with higher expression of PIK3R3, but there is no significant difference in overall survival. Study in tumor cell lines showed that PIK3R3 could enhance 5-FU induced apoptosis by regulating the expression of thymidine phosphorylase. 29719293_PIK3R3 could promote the metastasis of Pancreatic Cancer by facilitating ZEB1 induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. 29802999_Using case-control study and functional analyses, study have identified SNP rs7536272 A > G, located in the promoter region of PIK3R3, acts as a risk factor of GC through enhancing the transcriptional activity of PIK3R3, contributing to increased expression of PIK3R3. 30664174_these results demonstrated that miR601 may inhibit the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)by directly targeting PIK3R3 and regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Therefore, miR601 may be an effective therapeutic target for the treatment of patients with HCC. 30823895_HOXD-AS1/miR-186-5p/PIK3R3 is a novel pathway to promote cell migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in epithelial ovarian cancer 30825222_miR-224-5p inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting PIK3R3/AKT3 in uveal melanoma. 32196574_MicroRNA-29c-3p inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation through targeting PIK3R3. 32473571_PIK3R3 regulates ZO-1 expression through the NF-kB pathway in inflammatory bowel disease. 32819600_miR-29a-3p suppresses hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis by modulating hepatic stellate cell proliferation via targeting PIK3R3 gene expression. 33142041_Inhibition of exosomal miR-24-3p in diabetes restores angiogenesis and facilitates wound repair via targeting PIK3R3. 33949204_p55PIK deficiency and its NH2-terminal derivative inhibit inflammation and emphysema in COPD mouse model. 34120890_MiR-513b-5p represses autophagy during the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PIK3R3. 34321458_PIK3R3, part of the regulatory domain of PI3K, is upregulated in sarcoma stem-like cells and promotes invasion, migration, and chemotherapy resistance. 34773593_LncRNA JHDM1D-AS1 Suppresses MPP + -Induced Neuronal Injury in Parkinson's Disease via miR-134-5p/PIK3R3 Axis. 35761259_PIK3R3, a regulatory subunit of PI3K, modulates ovarian cancer stem cells and ovarian cancer development and progression by integrative analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000028698 |
Pik3r3 |
92.613294 |
2.8260085768 |
1.498766 |
0.192977115 |
60.666493 |
0.00000000000000676112303374351018850394927374975379797089440614410449370552669279277324676513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000045819180889832049752861277609634649750109270521791771102471102494746446609497070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
141.6854676 |
16.8444289 |
50.5202869 |
4.7726605 |
| ENSG00000117479 |
10560 |
SLC19A2 |
protein_coding |
O60779 |
FUNCTION: High-affinity transporter for the intake of thiamine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10542220}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Deafness;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes the thiamin transporter protein. Mutations in this gene cause thiamin-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome (TRMA), which is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by diabetes mellitus, megaloblastic anemia and sensorineural deafness. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:10560; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; folic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008517]; thiamine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015234]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; thiamine transmembrane transport [GO:0071934]; thiamine transport [GO:0015888]; thiamine-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0042723]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
11286512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12065289_the effect of mutations in SLC19A2 identical to those found in thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome (TRMA), on functional activity and membrane expression of the transporter. 12227830_insertion of the thiamine transporter 1 linkers into reduced folate carrier (D215-R263 Delta) at position 215 restored 60-80% of wild-type levels of transport 12454006_correlate structure with cellular expression profile and reveal a critical dependence on backbone integrity and microtubule-based trafficking processes for functional expression 12900388_the importance of GKLF, NF-1, and SP-1 in regulating the activity of the SLC19A2 promoter 14615284_hTHTR-2 is expressed along the human gastrointestinal tract and that expression of its protein in intestinal epithelia is mainly localized to the apical brush-border membrane domain 14622275_this functional characterization of the D93H mutation of THTR1 provides a molecular basis for Rogers syndrome 14994241_Missense mutation in the SLC19A2 gene is associated with thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome 15952116_Findings indicate that the RFC1 genotype is a possible susceptible gene marker for an increased neural tube defects risk in Chinese population. 16015585_Three genetic variants of SLC19A2 gene were identified in Wernicke Korsakoff syndrome patients. 16055442_differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells is associated with an up-regulation in thiamin uptake process which is mediated via transcriptional regulatory mechanisms that involve the SLC19A2 and SLC19A3 genes 16371350_analysis of targeting and trafficking of hTHTR1 and hTHTR2 in epithelial cells 16373304_We have identified a novel missense mutation (T158R) that was excluded in 100 control alleles. 16705148_Thiamine uptake by HEK-293 cells is mediated via a specific pH-dependent process, which involves both the hTHTR-1 and hTHTR-2. 17331069_results show spectrum of mutant phenotypes, underlining that thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anaemia can result from decreased thiamine transport underpinned by changes in THTR1 expression levels, cellular targeting and/or protein transport activity 17463047_THTR1 is involved in thiamine transport by retinal pigment epithelium. Mutations found in thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia impaired THTR1 expression/function. 17659067_Three infants with thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia were homozygous, and the parents were heterozygous for a c.196G>T mutation in the SLC19A2 gene on chromosome 1q23.3, which encodes a high-affinity thiamine transporter. 19064610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19340000_findings suggest that the RFC G80A polymorphism may influence outcome in childhood ALL patients being treated with methotrexate 19423748_Pancreatic beta cells and islets take up thiamine by a regulated THTR1/2-mediated process. 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19731322_No SLC25A38 mutations were found among sixty CSA probands examined 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20466634_Data show that MTHFR 677C>T and MTRR 66A>G polymorphisms are two independent risk factors for DS pregnancies in young women, but RFC-1 80G>A and MTR 2756A>G polymorphism are not independent risk factor. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22369132_Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anaemia (TRMA), due to mutations in the thiamine transporter SLC19A2, is associated with the classical clinical triad of diabetes, deafness, and megaloblastic anaemia. 22876572_Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by diabetes mellitus, megaloblastic anemia and sensorineural hearing loss due to mutations in SLC 19A. 23285265_Glucose-induced decreased expression of thiamine transporters in the tubular epithelium may mediate renal mishandling of thiamine in diabetes. 23289844_study identified a compound heterozygous mutation p.Y81X/p.L457X (c.242insA/c.1370delT) in the SLC19A2 gene in two sisters with thiamine responsive megaloblastic anemia 23454484_A non-sense mutation SLC19A2 was found in four patients with Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia, indicating its high frequency in Persian population. 23589815_Thiamine transporter 2 deficiency is a recessive disease caused by mutations in the SLC19A3 genes. 23638917_Here we describe for the first time Leber's congenital amaurosis as the retinal phenotype and also report a novel point mutation in the SLC19A2 gene that co-segregated with the disease in a thiamine responsive megaloblastic anemia patient. 23642734_These findings demonstrate that the genes involved in dictating thiamine homeostasis, such as SLC19A2, SLC25A19 and TPK-1, were significantly up-regulated in clinical tissues and breast cancer cell lines. 24072090_study presents three thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia patients with a novel missense mutation in the SLC19A2 gene (c.382 G>A (p.E128K)). Administration of thiamine in patients with TRMA ameliorates the megaloblastic anemia and diabetes mellitus. 24355766_Missense mutations were found in the SLC19A2 gene of 4 Chinese patients with thiamine responsive megaloblastic anemia. 24357267_The present study confirms the variability of the clinical manifestations caused by the same mutation within patients with TRMA syndrome. 24509276_Allelic expression imbalance confirmed that cis variation at the human SLC35F3 locus influenced expression of that gene, and the allelic expression imbalance peak coincided with the hypertension peak. 24520986_the novel SLC19A2 mutation reported here may have contributed to the patient's psychotic manifestations by an unknown mechanism 24771227_Individuals with genotype A80A for the SLC19A1 gene have a poor absorption of folate, altering the metabolism of folate and compromising the process of cell division promoting development of neuroblastoma. 25707023_A novel homozygous SLC19A2 gene mutation c.[205G>T], p.[(Val69Phe)] causing thiamine responsive megaloblastic anemia syndrome. 28371426_SLC19A2 mutation is associated with permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus. 29969779_A Novel Mutation of SLC19A2 in a Chinese Zhuang Ethnic Family with Thiamine-Responsive Megaloblastic Anemia.( 30833467_Study demonstrate that SLC19A2 deficit causes impaired insulin secretion in conjunction with mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of protection against oxidative stress, and cell cycle arrest. These findings link SLC19A2 mutations to autosomal dominant diabetes and suggest a role of SLC19A2 in beta-cell function and survival. 31296181_TRMA syndrome with a severe phenotype, cerebral infarction, and novel compound heterozygous SLC19A2 mutation: a case report. 31951336_Besides reporting a novel mutation of the causative gene SLC19A2, we wanted to emphasize this syndrome in the aspect of coexistence of insulin dependent diabetes, transfusion dependent anemia and thrombocytopenia. 32498429_3'-UTR Polymorphisms of Vitamin B-Related Genes Are Associated with Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures (OVCFs) in Postmenopausal Women. 32683950_Posttranscriptional regulation of thiamin transporter-1 expression by microRNA-200a-3p in pancreatic acinar cells. 33008889_pH-dependent pyridoxine transport by SLC19A2 and SLC19A3: Implications for absorption in acidic microclimates. 33649974_The Effects of Genetic Mutations and Drugs on the Activity of the Thiamine Transporter, SLC19A2. 35686496_Whole-Exome Sequencing Revealed a Pathogenic Nonsense Variant in the SLC19A2 Gene in an Iranian Family with Thiamine-Responsive Megaloblastic Anemia. |
ENSMUSG00000040918 |
Slc19a2 |
66.073939 |
3.2168975139 |
1.685670 |
0.219101324 |
60.560417 |
0.00000000000000713544807607276244431005756928641559968531319496642950639397895429283380508422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000048245173432356374021697034222776905549950020313243470582165173254907131195068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.5688706 |
12.4030287 |
31.1981487 |
3.2360449 |
| ENSG00000117500 |
50999 |
TMED5 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3A6 |
FUNCTION: Potential role in vesicular protein trafficking, mainly in the early secretory pathway. Required for the maintenance of the Golgi apparatus; involved in protein exchange between Golgi stacks during assembly. Probably not required for COPI-vesicle-mediated retrograde transport. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19948005}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Involved in Golgi ribbon formation. Located in cis-Golgi network; endoplasmic reticulum exit site; and endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:50999; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle [GO:0030134]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070971]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090161]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886] |
18549622_Expression of cgi-100 mRNA decreased in a dose- and time-dependent manner in the K562 cells treated with matrine and over-expression of cgi-100 elevates the proliferation and the immaturity level of K562 cells. 24778190_The luminal alpha-helical but not GOLD domain of p24gamma2 was required for efficient GPI-AP transport. 34404391_Identification of a novel circ_0018289/miR-183-5p/TMED5 regulatory network in cervical cancer development. |
ENSMUSG00000063406 |
Tmed5 |
1125.564476 |
2.1476386235 |
1.102751 |
0.063623982 |
299.105940 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000051589103362626262112600033205571402694277734809072525039008555309863662309473995493638282681392138080843381950571643777338872497058693634699859479619317811879490424682020988100816794030833989381790161132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014959826436785139287291416708156097397958202472033203261500183785820573333000474763466138592031211567497201769642012370815009998960867666144985037752602086659676518254347143965787836350500583648681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1537.7713518 |
55.9550931 |
721.1407758 |
20.1642546 |
| ENSG00000117525 |
2152 |
F3 |
protein_coding |
P13726 |
FUNCTION: Initiates blood coagulation by forming a complex with circulating factor VII or VIIa. The [TF:VIIa] complex activates factors IX or X by specific limited proteolysis. TF plays a role in normal hemostasis by initiating the cell-surface assembly and propagation of the coagulation protease cascade. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12652293}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood coagulation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes coagulation factor III which is a cell surface glycoprotein. This factor enables cells to initiate the blood coagulation cascades, and it functions as the high-affinity receptor for the coagulation factor VII. The resulting complex provides a catalytic event that is responsible for initiation of the coagulation protease cascades by specific limited proteolysis. Unlike the other cofactors of these protease cascades, which circulate as nonfunctional precursors, this factor is a potent initiator that is fully functional when expressed on cell surfaces, for example, on monocytes. There are 3 distinct domains of this factor: extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic. Platelets and monocytes have been shown to express this coagulation factor under procoagulatory and proinflammatory stimuli, and a major role in HIV-associated coagulopathy has been described. Platelet-dependent monocyte expression of coagulation factor III has been described to be associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality. This protein is the only one in the coagulation pathway for which a congenital deficiency has not been described. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:2152; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; serine-type endopeptidase complex [GO:1905370]; serine-type peptidase complex [GO:1905286]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; activation of blood coagulation via clotting cascade [GO:0002543]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; activation of plasma proteins involved in acute inflammatory response [GO:0002541]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; blood coagulation, extrinsic pathway [GO:0007598]; blood coagulation, fibrin clot formation [GO:0072378]; blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway [GO:0007597]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0010641]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to wounding [GO:0009611] |
11583305_The complex between tissue factor and factor VIIa initiates coagulation and intracellular signaling, alters gene expression, and promotes metastasis. 11744662_selective activation of NF-kappaB (p50/p65) during intensive physical exercise does not result in the expression 11776298_TF-FVIIa interaction elicits intracellular signalling events implicated in sepsis, inflammation, angiogenesis, metastasis and atherosclerosis. These include the sequential activation of Src-like kinases, MAP kinases, small GTPases and calcium signalling. 11816707_tissue factor/tissue factor pathway inhibitor imbalance is associated with myocardial infarction at young age in Japanese men. 11816709_TF promotes metastasis by a pathway that does not involve high expression of known PARs by tumor cells. PAR1 enhances the metastatic potential of cells with high TF expression. 11858183_Resveratrol does not inhibit the activation or translocation of NF-kappaB/Rel proteins but inhibits NF-kappaB/Rel-dependent transcription of the gene for TF by impairing the transactivation potential of p65. 11858185_Endothelin-1 enhances TF expression in monocytes from health individuals. No additional stimulation was seen in monocytes from heart failure subjects, who nonetheless have 2.5 times as much TF as controls. 11858480_In children with sepsis-induced multiple organ failure, a cytokine-associated increase in circulating TF and systemic activity was predicted. Increased TF was associated with the development of coagulopathy and tended to be associated with mortality. 11876644_pH dependence of fVIIa amidolytic activity in complex with soluble tissue factor 11882315_differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages in culture enhances their tissue factor expression. 11921018_results suggest involvement of tissue factor in the process of metastasis and progression of colorectal cancer may depend on increased angiogenesis 11929768_Coronary no-reflow is caused by shedding of active tissue factor from dissected atherosclerotic plaque. 11943929_TF-apoprotein selectively binds Hb, most probably via the carbohydrate moieties (alpha-d-glucosyl; alpha-d-mannosyl and N-acetyl-beta-d-glucosaminyl residues) of TF, and enhances its procoagulant activity. 11973337_signaling increased transcription as well as mRNA stabilization leading to up-regulation of interleukin-8 synthesis 11994566_Enhanced monocyte tissue factor expression is implicated in the hemostatic diathesis characterizing hepatosplenic schistosomiasis. 12008961_Fluvastatin upregulated IkappaB alpha in unstimulated as well as in TNFalpha-stimulated HUVEC cells and also impaired the TNFalpha-induced Cdc42 prenylation, indicating that fluvastatin interferes with transcriptional activation of tissue factor gene. 12019261_TF cytoplasmic domain-independent stimulation of protein synthesis via activation of S6 kinase contributes to FVIIa effects in pathophysiology. 12028585_expression of TF and TFPI in human melanoma 12036889_Tissue factor is the receptor for plasminogen type 1 on 1-LN human prostate cancer cells; Plasminogen type 2, containing only one O-linked oligosaccharide chain, did not bind to tissue factor on 1-LN human prostate cancer cells 12070020_Thrombin functions studied during tissue factor-induced blood coagulation 12083487_Tissue factor activity is upregulated in human endothelial cells exposed to oscillatory shear stress. 12083501_expression on monocyte subpopulations during normal pregnancy 12095134_monocyte adhesion and transmigration induce tissue factor expression 12149215_data indicate that endothelial cell surface expression of TF and extrinsic clotting factors are critical in augmenting capillary leak following intravascular tumor necrosis factor administration 12152652_tissue factor expression by LPS-stimulated human monocytes is inhibited by adenosine and involves the adenosine A3 receptor, specifically 12152682_a three-dimensional model of the ternary complex between FVIIa:TF:FIX was built using a full-space search algorithm in combination with computational graphics 12172458_REVIEW:clotting-dependent and -independent mechanisms of TF-induced angiogenesis in cancer 12189027_non-activated and activated platelets contain an inactive form of TF that may develop functional activity following its release 12192302_effect of platelet-derived CD40L on the tissue factor activity of human CD40-positive melanoma cells and monocytes 12270558_levels of tissue factor in placenta and myometrium, over tissue factor in blood plasma may be clinically significant in obstetrics, for instance, in the etiology of DIC in placental abruption 12353085_15d-PGJ2 down-regulates LPS- and TNFalpha-induced TF activity through inhibition of TF gene transcription. 12356487_REVIEW: role of tissue factor-FVIIa complex in pathophysiological processes and effect of the inhibitors of the tissue factor:factor VII pathway 12408769_correlation between tissue factor (TF) expression and hepatic metastasis and prognosis in rectal cancer 12426405_Mice expressing low levels of human TF in an mTF(-/-) background had significantly shorter lifespans than wild-type mice, in part, because of spontaneous fatal hemorrhages. Low-TF mice had a selective heart defect with hemosiderin deposition & fibrosis. 12514112_Tissue factor initiates blood coagulation via circulating microvesicles and platelets. 12529356_the Gla and first epidermal growth factor-like domains of factor X play a role in the prothrombinase and tissue factor-factor VIIa complexes. 12540946_REVIEW: model of the intravascular TF pathway in which adhesive interactions of the TF bearing platelets and microvesicles to neutrophils and monocytes enable blood coagulation 12544727_The influence of several eicosanoids of the lipoxygenase pathway on regulation of LPS-induced tissue factor was examined in whole blood. 12603864_These data support a transcriptional role for both nuclear factor-kappaB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, but not MEK1, in tissue factor gene expression in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. 12654807_M type 1 and 3 strains of group A streptococci are potent inducers of TF synthesis; findings suggest that a novel interaction between group A streptococci and host cells contributes to the observed coagulopathy in Strep toxic shock syndrome 12871349_review of role of tissue factor in thrombosis 12883669_tissue factor has a role in affecting proliferative ability in meningioma 12903530_TF may influence tumor growth and metastasis by modulating VEGF expression and neoangiogenesis. 12920028_cell surface location-dependent phosphorylation of the TF cytoplasmic domain is regulated at multiple levels 12941032_demonstrate the occurrence of two forms of non-cell-bound TF. One form, which is microparticle-associated, supports thrombin generation via FVII. The other form, which is fluid-phase, does not stimulate thrombin formation 14597990_The ectopic expression of the acute promyelocytic leukemia-specific PML/RARalpha oncoprotein in U-937 cells results in induction of TF mRNA and promoter activity 14610342_The TF and TFPI levels depend significantly on the renal function; elevated TF and TFPI levels may be related to thrombosis and atherosclerosis in chronic renal failure patients on peritoneal dialysis 14675092_In response to endotoxin, there was an increase in IL-6, TF and CD11b expression and a procoagulant shift of clotting onset time, which was normalized by 4 mmol L-1 nicotinamide 14675093_superantigens from S. aureus activate the extrinsic coagulation pathway by inducing expression of TF in monocytes, and that the expression is mainly triggered by superantigen-induced IL-1 beta release 14678810_Tissue factor expression induced by local inflammation is involved in the pathogenesis of thrombosis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation 14738565_circulating microparticles from platelets, erythrocytes, and granulocytes exposed TF; microparticle-exposed TF antigen levels were higher in cardiac patients compared with healthy individuals. 14750502_model characterizes likely enzyme-binding exosites on FVIIa and Xa that may be involved in the ternary complex (sTF-VIIa-Xa) formation and the membrane binding region of the ternary complex. 14756558_Substitutions on the TF surface that contacts the protease domain of factor VIIa have nearly identical effects on the affinities for both factors VII and VIIa--hence zymogen VII can readily adopt a VIIa-like conformation required for binding to TF. 14961150_The TF-603A/G gene promoter polymorphism significantly influences constitutive TF gene expression in human monocytes but has no major effect on TF gene expression or on whole blood coagulation time in LPS stimulated conditions. 15016732_FVIIa/TF-interaction produces STAT5 phosphorylation, STAT5 nuclear translocation and transactivation of a reporter gene. 15034795_review: role of TF up-regulation in cancer pathogenesis and tumor angiogenesis 15034796_review: role of TF in hypercoagulability and clotting-dependent induction of tumor angiogenesis 15041276_some protease inhibitors might act as stress and induced TF expression with direct phosphorylation of JNK and p38, followed by phosphorylation and activation of AP-1 in monocytic cells 15117736_Review. This review focuses on the roles of TF in hemostasis, thrombosis, and vascular development. 15154603_the transfer of TF to monocytes is not simply an CD62P-mediated adhesion of platelets or platelet-derived microvesicles to monocytes, but may involve other not yet identified mechanisms 15161741_Pancreatic duct cells exert a potent factor VII-dependent procoagulant activity related to their expression of tissue factor. 15182581_TF/FVIIa complex up-regulates the transcription of u-PAR in human ovarian cancer cells. 15213840_EGFR, PYK2, Yes, and SHP-2 are involved in transduction of the TF/FVIIa signal possibly via transactivation of the EGF receptor. 15213854_TF expression in leukocytes plays an important role in various diseases but the expression level does not always correlate with plasma levels of TF antigen 15242552_Data suggest that Rac-dependent activation of the NFkappaB pathway may be a critical element promoting thrombin-induced tissue factor expression and activity, and thus a prothrombotic state in pulmonary hypertension. 15252050_Arg(74) mutant of TF was defective in enhancing both the amidolytic and proteolytic activity of fVIIa, suggesting that this residue may be required for the allosteric activation of the protease. 15304041_polymorphisms in the 5'-UTR of the tissue factor gene are associated with altered expression in human endothelial cells 15328160_membrane cholesterol functions as a positive regulator of TF function by maintaining TF receptors, probably in noncaveolar lipid rafts, in a high-affinity state for VIIa binding 15467908_TF and TFPI mRNA expression, protein levels and activity in trophoblast cells were determined and compared to human umbilical vein endothelial cells 15494427_Tissue factor expression by colorectal cancer cells appears to act as both a regulatory target and an important mediator of oncogene-driven tumor growth and neovascularization. 15562024_Progesterone-dependent up-regulation of tissue fasctor provides a survival advantage to burgeoning breast cancer cells. 15604222_the concentration of physiologically active TF in non-cytokine-stimulated blood from healthy individuals cannot exceed and is probably lower than 20 fM. 15630487_hyperchemotaxis towards PDGFRB is likely to depend in part on phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of TF 15814630_Tissue factor(TF) expression may contribute to the aggressiveness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by stimulating tumor invasiveness, and that evaluation of the primary tumor for TF expression may identify patients with a poor prognosis. 15835921_dissociation of fVIIai from TF occurred by a two-step mechanism 15842359_TF is enhanced by Shiga toxin and has a role in the coagulopathy observed in hemolytic uremic syndrome 15860742_The higher availability of surface TF antigen on mononuclear leukocytes from high responders and TF-containing microparticles might make these individuals more susceptible to hypercoagulation 15865421_Despite indistinguishable stability under physiological conditions of mutant tissue factor(R200W) and wild-type TF, important clues are revealed regarding misfolding and aggregation propensities of the mutant TF(R200W) to explain why it is lost in vivo. 15869604_FVIIa induces PRIM1 and ensuing cellular proliferation via a TF- and of the PARs entirely PAR-2-dependent pathway, in distinction to that of thrombin which is PAR-1-dependent and TF-independent 15892865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905465_tissue factor-mediated cellular signaling is relevant to cancer angiogenesis 15935832_in a model system, TGF beta-1 released from activated platelets contributes to the hemostatic imbalance at the sinusoidal endothelium in patients with hepatic VOD by increase of endothelial cell PAI-1 production and TF expression. 15996056_CRP regulation of monocyte TF could contribute to the higher than expected atherosclerotic vascular disease seen in patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease 16020745_MCP-1/CCR2 may play a role in Ca2+ influx-dependent TF regulation in the monocyte-endothelial cell interaction in the impairment of nitric oxide synthesis 16113798_human B lymphocytes can express a functional Tissue Factor in response to phorbol myristate acetate 16113838_EGF-mediated upregulation of TF results in its accumulation in caveolae-like membrane fractions and increased coagulative and invasive potential 16182846_Transmembrane glycoprotein involved not only in the onset of the coagulation cascade, but also in cell proliferation and anti-apoptotic processes, may play a role in the development of alloantibody-induced chronic rejection. 16215234_the transient, localized expression of TF is sufficient to sustain a TF-independent procoagulant response as long as flow persists 16217771_reports existence of novel TF transcript predominantly expressed in tumor cells; occurs as a result of alternative splicing and insertion of an additional exon 16236262_ability of epithelial cells to interact with the vascular system via expression of the TF gene (and other effectors) is under the control of complex alterations in cellular architecture 16239598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16239598_The 5466 AG genotype is a novel predictor of cardiovascular death in acute coronary syndrome and may act through a high TF response 16324758_A marker of endothelial damage/injury in the activation of vascular and coagulation abnormalities in acute coronary syndromes. 16363246_FVIIa/TF interaction on activated monocyte-derived macrophages could be relevant to prepare monocytes/macrophages for extravasation and may represent a novel amplification loop of leukocyte recruitment 16453151_TF can promote immune evasion in tumour cells expressing this protein leading to increased survival and therefore metastatic rate in such cells 16473535_review of differential pathways involving activated platelets for the TF-mediated coagulation start in blood. 16488980_protein S, which is well known as the cofactor of activated protein C, specifically inhibits TF activity by promoting the interaction between full-length TF pathway inhibitor (TFPI) and factor Xa (FXa) 16490369_review: tissue factor microparticles are present in a spectrum of cancer patients known to have a high incidence of thromboembolic complications 16493499_hypothesize that granulocytes take-up TF for transport to other locations in order to initiate fibrin formation or to induce pro-inflammatory gene expression upon interaction with factor VIIa 16507316_Among major red wine phenolics, quercetin appears to be the predominant suppressor of TF induction 16510984_structure-based drug design of specific inhibitors for Factor VIIa/Tissue factor. 16516912_TF induction in conjunction with TFPI suppression may be relevant for the increased frequency of myocardial infarction observed in cocaine consumers 16529959_show that increasing the lipid surface area available to each TF:VIIa increases the apparent k(cat) and that it approaches a maximum asymptotically, exhibiting a K(1/2) at a 40 nm lipid radius; the binding parameters of Xa were determined 16531802_Hypertensive individuals with carotid artherosclerosis had a significant increase in monocyte TF mRNA and activity levels compared with hypertensive individuals with no carotid lesions. 16634740_the TF-1208 polymorphism is functional in that it regulates basal TF-mRNA in circulating monocytes and circulating microparticle-associated TF-procoagulant activity in vivo 16697385_This and other proagulants are strongly atherogenic and therefore we suggest a mechanism for the involvement of Chlamydia pneumoniae in the onset and progression of vascular disease. 16794185_Paclitaxel increases endothelial TF expression via its stabilizing effect on microtubules and selective activation of JNK 16820938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16835245_Results indicate that proper positioning of the factor VII/VIIa binding site on tissue factor above the membrane surface is important for efficient rates of activation of factor X by this membrane-bound enzyme/cofactor complex. 16839353_FVIIa not only decreased thromboplastin sensitivity to plasma FVII, it surprisingly increased sensitivity to plasma levels of FV, FX and prothrombin. 16894464_formation of TF-FVIIa-FXa complex prevents apoptosis in breast cancer cells by a thrombin-independent pathway 16930953_Induction of macrophage TF expression by VT-1 may play an important role in the acceleration of the coagulation-inflammation-thrombosis circuit during infections by VT-producing E. coli. 16937466_Results suggest that soluble tissue factor might contribute to activation of the coagulation system in pancreatic cancer. 16949034_the inhibiting effect of celecoxib on endothelial TF expression does not extend to vascular smooth muscle cells 16959886_Data demonstrate that tissue factor-factor VIIa-mediated coagulation and cell signaling involve distinct cellular pools of tissue factor. 17008590_Admission coagulation factor VII and tissue factor antigen levels, partially predicted by polymorphisms, are independent predictors of mortality and reinfarction in patients with acute myocardial infarction. 17060476_Platelet-derived tissue factor contributes to the propagation and stabilization of a thrombus. 17066404_High expression of tissue factor is associated with lymphatic metastasis and gastric cancer with intestinal phenotype 17137581_The differential influence of TF is modified depending on the presence of other coagulation factors and ultimately acts as a deciding factor in the determination of cellular fate for vascular endothelial cells 17157899_The intersubject variability of F3 mRNA production in monocytes and its relation with TLR4 was studied. 17196206_atherosclerotic plaque tissue factor (TF) activity was higher in plaques from dyslipidemic patients than in non dyslipidemic ones. 17200119_local changes in phospholipid bilayer composition modulate the activity of the factor VIIa.tissue factor complex 17200762_review of properties of alternatively spliced tissue factor 17200764_no pro-coagulant activity (FX activation, thrombin generation) of alternatively-spliced human tissue factor was observed on the surface, in lysates, and on microparticles from TF transfected cells. 17234207_down-regulation of urokinase plasminogen activator in female low-tissue factor mice protects them from more severe cardiac fibrosis 17237436_SAA induced TF mRNA in PBMC within 30 min and optimal procoagulant activity within 4 h through activation of NF-kappaB via the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways. SAA-induced TF was partially inhibited by high-density lipoprotein. 17314141_monocyte-derived human dendritic cells stimulated with a P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) agonist undergo a large release of microparticles containing the membrane-bound form of tissue factor 17323935_These results suggest that both Arg-200 and Lys-201 of TF interact with EGF-1 domain of factor X to facilitate the optimal docking of the substrate into the catalytic groove of the protease in the activation complex. 17324918_The results suggest that estrogens may modulate T F expression and cytokine production by monocytes and may thus be involved, at least in part, in the pathophysiology of acute inflammatory processes associated with high estrogen levels. 17331567_The association between TF and uPA/suPAR system is significantly related to the presence of cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients 17334638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17347408_human platelets not only assemble the clotting reactions on their membrane, but also supply their own TF for thrombin generation in a timely and spatially circumscribed process 17384202_roles of PAR1 and PAR2 and F7 in tissue factor mobilization and endocytosis 17401435_1alpha,25-(OH)2DHT(3) blocks TNF-induced monocytic tissue factor expression by inhibition of AP1 and NF-kappa B. 17459125_Semen contains factor VII/tissue factor, reinforcing the concept of an active clotting system in semen. 17469034_An inadequate tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) concentration as a result of elevated tissue factor (TF):tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) ratio characterizes patients with clinical manifestations of nephrotic syndrome and mild proteinuria. 17470200_factor VIIa-tissue factor, PAR1 and PAR2 have roles in transcription in tumor cell lines 17483700_The high levels of intravascular TF present in neonates (prior and after LPS-stimulation) might help to explain the clinically observed efficient clotting of cord blood despite low levels of procoagulatory factors. 17536017_identification of TF as an important mediator of C5a-induced oxidative burst in neutrophils in antiphospholipid antibody-induced fetal injury provides a new target for therapy to prevent pregnancy loss 17549302_Nuclear factor of activated T cells and early growth response 1 are required for tissue factor upregulation in response to vascular endothelial growth factor in endothelial cells. 17577783_Leukemia patients showing parallel activation of the studied proteins trended to exhibit higher incidence of fatal outcome. 17586694_Expression of tissue factor (TF) was increased in the pulmonary arterioles and plexiform-like lesions of the rats. TF was also heavily expressed in the vessels and plexiform lesions of humans with pulmonary arterial hypertension. 17597988_review of cellular function of tissue factor: signal transduction, protein interactions 17598015_most abundant n-3 FA, docosahexaenoate, increases the release of TF-exposing microparticles from endothelial cells, accounting for decreased endothelial cell TF surface exposure. 17663729_tissue factor and thrombin signaling have roles in cancer progression [commentary] 17675290_Histone deacetylase inhibitors transcriptionally inhibit agonist-induced tissue factor expression in endothelial cells and monocytes by a TF-kappaB- and HDAC3-dependent mechanism. 17721619_proportion of TF-positive or both TF- and platelet antigen CD41a-positive leukocytes was increased markedly in pericardial blood obtained during CPB. 17724132_Metabolism of endocannabinoids by the endothelial cell COX-2 coupled to the prostacyclin (PGI(2)) synthase activates the nuclear receptor peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor delta, which negatively regulates the expression of tissue factor. 17726162_the present data undermine the recently proposed hypothesis that PDI-mediated disulfide exchange plays a role in regulating TF procoagulant and cell signaling functions. 17848177_PAR1 localization in the caveolin-enriched membrane microdomain, bound to caveolin-1, represents a crucial requirement for TF induction in endothelial cells. 17852460_is elevated in patients with cancer 17883594_Postdelivery increase in tissue factor-dependent activation of coagulation is likely to be a natural mechanism to prevent excessive blood loss during and after delivery, and may also increase risk of venous thromboembolism. 17883595_Tissue factor expression contributes to tumor growth/regulating properties of CD133-positive tumor stem cells. 17898544_Low concentrations of tissue factor increased endothelial cell proliferation and higher concentrations reduced cell proliferation/triggered apoptosis. 17900273_A novel monocyte phenotype characterized by high TF/low CD36 presentation could be further developed for use as a marker for detection of individuals prone to developing prothrombotic conditions. 17901245_tumor cell TF-PAR2 signaling is crucial for tumor growth 17920661_TF antisense oligomer suppresses the synthesis of biologically active endothelial TF and antisense oligomers may represent a useful tool in the investigation of endothelial TF function/biology. 17922809_Cisplatin induced the release of endothelial microparticles that showed TF-independent thrombin generation and procoagulant activity. 17938822_Factor VIIa/tissue factor-dependent gene regulation has a role in pro-coagulant activity 17939398_Expression of TF is inhibited by PTEN gene via inactivating PI3K/AKT pathway. 17947506_pinpoint monocytes as a major source of TF and provide solid experimental evidence for a direct transfer of TF protein from the monocytes to granulocytes in the blood 17977694_decrease in frequency domains of resting heart rate variability would be associated with elevated plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and soluble tissue factor (sTF) 17982314_the activation of monocytes and blood platelets is accompanied by the elevation of monocytic Tissue Factor expression in advanced liver cirrhosis 17991872_Tissue Factor/Activated Factor VII complex transactivates PDGFRbeta to regulate PDGF-BB-induced chemotaxis of monocytes and fibroblasts 18000605_whole blood tissue factor procoagulant activity and plasma FVIIa in ten patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and 11 non-diabetic patients at baseline and 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours (h) after presentation for acute stroke 18005233_Replacing the 1st 2 exons of mouse TF with the complete human coding sequence under the control of the mouse promoter mediated normal hemostasis. There may be a threshold TF level for prenatal development & a critical level for maintaining hemostasis. 18019946_4 models of coagulation including minimally altered whole blood induced to clot by tissue factor (TF) 18023707_alternative spliced TF expression promotes tumor growth, and is associated with increased tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer 18029910_Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase is required for protein translation of endothelial tissue factor in culture. 18031796_the anti-apoptotic signaling of TF/FVIIa and TF/FVIIa/FXa is abolished by simvastatin, which induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells in a NFkappaB-dependent manner 18091328_data support the role of TF in angiogenesis and disease progression of prostate cancer 18180609_Plasma Tissue Factor (TF) activity and percentage of TF-positive monocytes was signigficantly higher in hyperlipidemic diabetics and those with macrovascular complications 18217146_Found significant differences in frequency at which tissue factor was found in the plasma of patients with coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndromes. 18278195_Prothombinase/factor III induced clotting time was used to monitor heparinization during cardiopulmonary bypass. 18278454_TF may have a role in chemotherapy resistance in human neuroblastoma and its progression, at lest in part, by regulating doxorubicin-induced ap 18284603_Urotensin-induced expression of TF and of VCAM-1/ICAM-1 was mediated through the Rho A-activation of the transcription factor, NF-kappaB 18292391_In acute coronary syndrome patients the greater expression of tissue factor in platelets and platelet-leukocyte aggregates strengthens the link between platelet activation, blood coagulation, and thrombus formation. 18297283_phosphorylation of TF at Ser258 and to a lesser extent Ser253, plays an essential role in the protective influence of TF on immune evasion by tumour cells 18308368_Leptin induced functional TF and increased TF mRNA and protein expression in both neutrophils and mononuclear leukocytes 18310227_Levels of intra-alveolar TFPI in adult respiratory distress syndrome are not sufficient to block intra-alveolar TF procoagulant activity due to truncation and inactivation of intra-alveolar TFPI 18315555_ASF/SF2 and SRp55 appear to interact with the variable TF exon 5 through exonic splicing enhancers at bases 39 and 87-117. Weakening of the above ESE modulates splicing of TF exon 5. 18327399_Membrane-bound prothrombin fragment 1 is required to promote optimum Fva cofactor activity which in turn is translated by efficient initial cleavage of prothrombin by prothrombinase at Arg(320). 18363812_P-selectin-PSGL-1-induces TF and IL8 expression through Lyn phosphorylation, and part of the inhibitory effect of IL10 depends on reduced phosphorylation 18449421_Microparticle-associated vascular adhesion molecule-1 and tissue factor follow a circadian rhythm in healthy human subjects. 18490736_results confirm that the procoagulant properties of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome patients are the result of TF induction & indicate that BALF neutrophils are a main source of TF in intra-alveolar fluid 18495150_Viral myocarditis is a hypercoagulative state which is associated with increased myocardial TF expression and activity. Upregulation of TF contributes to a systemic activation of the coagulation cascade. 18508060_C-reactive protein and tissue factor in acute coronary syndrome 18612547_Studies suggest that TF-FVIIa-FXa-mediated signaling modulates mTOR pathway activation, which regulates in part breast cancer cell migration. 18641355_recombinant activated protein C-mediated up-regulation of IL-10 reduces TF in circulating monocytes 18642055_no significant difference in tissue factor expression between male and female subgroups; no correlation found between TF and age, BMI or total fat intake 18645927_in blood cells from patients with PV or ET, the presence of JAK2V617F mutation translates into activation of hemostasis, with increased expression of platelet-associated TF microparticles & formation of increased platelet/neutrophil aggregates.[review] 18665396_Certain levels of TF are required for the maintained viability and growth of endothelium and TF-expressing tumor cells. 18665928_no evidence for TF expression in high-purity preparations of immunologically isolated eosinophils 18677291_Elevated levels of TF and TFPI in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease can be independent risk factor for atherosclerotic complications. 18802362_Eosinophils are the cellular source of TF in chronic urticaria skin lesions. 18835104_Case Report: Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy caused by an ovarian cancer expressing tissue factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. 18846330_Homocysteine could significantly induce the expression of TF in vascular smooth muscle cells. 18848323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18983479_identify ROS originating in mitochondria as key mediators of the signaling pathways triggered by PAR1 and PAR2 engagement in endothelial cells; mechanisms downstream from PAR1 and PAR2 activation, different for the two receptors, also induced TF 18983492_Thrombin up-regulates TF activity in pleural mesothelial cells through the transcriptional activation of TF, whereas plasmin increases TF activity by inactivating the cell-associated TFPI by a limited proteolysis. 18983503_Insulin inhibits TF expression in monocytes and monocyte-derived microparticles through interference with G(i)alpha(2)-mediated cAMP suppression, which attenuates Ca(2+)-mediated TF synthesis. 18983524_heme induces TF expression by directly activating endothelial cells; the time-course of heme-mediated TF antigen expression paralleled the induction of procoagulant activity 18989544_Report increased tissue factor-bearing leukocytes after off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery. 19002040_Activation of clotting with less than 5 pmol/l of TF facilitates thrombin and fibrin generation at low, but not at supraphysiological rVIIa concentrations 19012190_PPROM is associated with specific changes in the hemo |
ENSMUSG00000028128 |
F3 |
53.129024 |
7.4274961576 |
2.892876 |
0.272963160 |
128.133284 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001049528649491490562829176967379436684793210095710839137237604829154600728682422000614948842667217832058668136596679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000133774118018086368399798846800882062142873963638608789653677609940732173160211210261039127544790972024202346801757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.2430131 |
15.5058475 |
12.5015290 |
1.8911754 |
| ENSG00000117569 |
58155 |
PTBP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKA9 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein which binds to intronic polypyrimidine tracts and mediates negative regulation of exons splicing. May antagonize in a tissue-specific manner the ability of NOVA1 to activate exon selection. In addition to its function in pre-mRNA splicing, plays also a role in the regulation of translation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91Z31, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11003644, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12667457}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Reduced affinity for RNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12213192}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
The protein encoded by this gene binds to intronic polypyrimidine clusters in pre-mRNA molecules and is implicated in controlling the assembly of other splicing-regulatory proteins. This protein is very similar to the polypyrimidine tract binding protein (PTB) but most of its isoforms are expressed primarily in the brain. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:58155; |
growth cone [GO:0030426]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; mRNA splice site selection [GO:0006376]; negative regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0033119]; regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000177]; regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0043484]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510] |
16002244_The nPTB proximal promoter, although rich in G+C content and presenting putative binding sites for the transcription factors Sp1, NF-1, NF-kB and Oct-1, lacks a typical TATA box. 17548433_Study shows that PTB can function as an anti-repressor molecule to counteract the splicing inhibitory activity of SRp30c. 20160105_present fluorescence, NMR, and in vivo splicing data in support of a role of PTB in inducing RNA loops. We show that the RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) 3 and 4 of PTB can bind two distant pyrimidine tracts and bring their 5' and 3' ends in close proximity 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21282112_Regulation of the mutually exclusive exons 8a and 8 in the CaV1.2 calcium channel transcript by polypyrimidine tract-binding protein. 23174904_Changes in miR-223/PTBP2 pathway could contribute of abnormal splicing in chronic myeloid leukemia. 24264039_Defining the multifunctional roles of PTB will contribute to the understanding of key regulatory events in gene expression. 24286314_In T98G glioma cells, the level of sumoylated PTBP2 was reduced compared to that of normal brain cells. Overall, this study shows that PTBP2 is posttranslationally modified by SUMO1. 25025966_MALAT1 binds to SFPQ releasing PTBP2 from the SFPQ/PTBP2 complex, the increased SFPQ-detached PTBP2 promotes cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer. 26416554_PTBP1 and PTBP2 impaired autoregulation of SRSF3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma cancer cells. 26657638_Data show that polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins nPTB and ROD1 interact with mitochondrial tRNA(Thr) in the cytoplasm outside of mitochondria. 27681424_It has been established that PTBP1 and PTBP2 are members of a family of cryptic exon repressors. 30726713_PTBP2 exon 10 inclusion is associated with the progression of CML and it is BCR-ABL1 dependent 34459124_LncRNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 shuttled by prostate cancer cells-secreted exosomes initiates osteoblastic phenotypes in the bone metastatic microenvironment via miR-205-5p/runt-related transcription factor 2/splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich/polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 2 axis. 34548489_SON drives oncogenic RNA splicing in glioblastoma by regulating PTBP1/PTBP2 switching and RBFOX2 activity. 35295960_Associations between Gene-Gene Interaction and Overweight/Obesity of 12-Month-Old Chinese Infants. |
ENSMUSG00000028134 |
Ptbp2 |
169.509390 |
0.4883578103 |
-1.033990 |
0.342965394 |
8.892499 |
0.00286344616307870978438865350312880764249712228775024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006156513527609870466139607714239900815300643444061279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
116.4197412 |
34.9895247 |
239.0507023 |
51.5157747 |
| ENSG00000117592 |
9588 |
PRDX6 |
protein_coding |
P30041 |
FUNCTION: Thiol-specific peroxidase that catalyzes the reduction of hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxides to water and alcohols, respectively (PubMed:9497358, PubMed:10893423). Can reduce H(2)O(2) and short chain organic, fatty acid, and phospholipid hydroperoxides (PubMed:10893423). Also has phospholipase activity, can therefore either reduce the oxidized sn-2 fatty acyl group of phospholipids (peroxidase activity) or hydrolyze the sn-2 ester bond of phospholipids (phospholipase activity) (PubMed:10893423, PubMed:26830860). These activities are dependent on binding to phospholipids at acidic pH and to oxidized phospholipds at cytosolic pH (PubMed:10893423). Plays a role in cell protection against oxidative stress by detoxifying peroxides and in phospholipid homeostasis (PubMed:10893423). Exhibits acyl-CoA-dependent lysophospholipid acyltransferase which mediates the conversion of lysophosphatidylcholine (1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine or LPC) into phosphatidylcholine (1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine or PC) (PubMed:26830860). Shows a clear preference for LPC as the lysophospholipid and for palmitoyl CoA as the fatty acyl substrate (PubMed:26830860). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10893423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26830860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9497358}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Antioxidant;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Lysosome;Multifunctional enzyme;Oxidoreductase;Peroxidase;Phosphoprotein;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Transferase |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the thiol-specific antioxidant protein family. This protein is a bifunctional enzyme with two distinct active sites. It is involved in redox regulation of the cell; it can reduce H(2)O(2) and short chain organic, fatty acid, and phospholipid hydroperoxides. It may play a role in the regulation of phospholipid turnover as well as in protection against oxidative injury. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9588; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; 1-acylglycerophosphocholine O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0047184]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047499]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peroxiredoxin activity [GO:0051920]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular oxidant detoxification [GO:0098869]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0048026]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
12121978_Data show that p29 is a novel protein that associates with p67, has peroxiredoxin activity, and has a potential role in protecting the NADPH oxidase by inactivating H(2)O(2) or altering signaling pathways affected by H(2)O(2) [neutrophil protein p29 ] 12193653_overexpression protects cells against phospholipid peroxidation-mediated membrane damage [1-cys peroxiredoxin] 12650976_The significant increase in peroxiredoxin 6 level in frontal cortex of patients with Pick's disease is useful in discriminating it from Down syndrome/Alzheimer's disease. 14751239_AOP2 protects hyperglycemia-induced lens epithelial cell apoptosis; this molecule may have the potential to prevent hyperglycemia-mediated complications in diabetes 15890616_Prdx6 is an important antioxidant enzyme and has a major role in lung phospholipid metabolism [review] 15941719_Protects HeLa cells from H(2)O(2)-induced cell death. 16186110_Saitohin interacts with peroxiredoxin 6, a unique member of that family that is bifunctional and the levels of which increase in Pick disease. 16330552_SP-A and Prdx6 directly interact, which provides a mechanism for regulation of the PLA(2) activity of Prdx6 by SP-A 17653765_overexpression of peroxiredoxin 6 is associated with oligodendroglioma 17980029_Overexpression of peroxiredoxin 6 leads to a more invasive phenotype and metastatic potential in human breast cancer, at least in part, through regulation of the levels of uPAR, Ets-1, MMP-9, RhoC and TIMP-2 expression. 18025307_PRDX6 is required for blood vessel integrity in wounded skin. 18386021_In brain tissue of patients with Alzheimer's disease , many blood vessels exhibited peroxiredoxin 6 staining that appeared to be due to the astrocytic foot processes. 18619034_two potential interaction partners of Prx6: the calcium-activated cysteine endopeptidase calpain and the p50RhoGAP protein of the family of Sec14-like proteins. 18826942_H2O2-mediated hyperoxidation of Prdx6 induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M transition through up-regulation of iPLA2 activity. 18973804_expression is upregulated during response to oxidative stress 19140803_The MAPKs can mediate phosphorylation of Prdx6 at Thr-177 with a consequent marked increase in its aiPLA(2) activity. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19236840_Prdx6 binds to reduced phospholipid at acidic pH but at cytosolic pH binds only phospholipid that is oxidized compatible with a role for Prdx6 in the repair of peroxidized cell membranes 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 19566940_Overexpression of peroxiredoxin I and is associated with breast carcinoma. 19572226_PRDX6 attenuates oxidative stress- and TGFbeta-induced abnormalities of human trabecular meshwork cells. 19700648_The localization of Prdx6 in acidic organelles and consequent PLA2 activity depend on a novel 10-aa peptide located at positions 31-40 of the protein. 19889963_Extrinsic PRDX6 prevents UV-triggered cell death and abnormal protein expression in PRDX6-deficient lens epitheial cells. 19937138_promotes lung cancer cell invasion by inducing urokinase-type plasminogen activator via p38 kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and Ak 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354123_This study is the first to define the functions of the enzymatic activities of PRDX6 in metastasis and to show the involvement of arachidonic acid in PRDX6 action in intact cells. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20532202_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20796224_It could be detected that PRDX6 is associated with tumorigenesis in tonge squamous cell carcinoma. 20829884_Prx6 modulates TRAIL signaling as a negative regulator of caspase-8 and caspase-10 in death-inducing signaling complex formation of TRAIL-resistant metastatic cancer cells. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21166495_The antioxidant Prdx 6 protects ovarian cancer cells against cisplatin-induced apoptosis via inactivation of the caspase signaling pathway. 21346153_Results suggest that ERK and p38 MAPK regulate subcellular localization of Prdx6 by activation of 14-3-3epsilon as a chaperone protein, resulting in its translocation to acidic organelles. 21415860_Results provide new insights into the distinct roles of bifunctional Prdx6 with peroxidase and PLA(2) activities in oxidative stress-induced and TNF-induced apoptosis, respectively. 21627785_Study revealed novel SNPs within the PRDX6 gene and its 5' and 3' flanking regions via direct sequencing. 22178385_Data suggest that Prdx6 serves an additional biochemical or structural role in supporting optimal NADPH oxidase activity. 22215146_Data suggest that SNPs of peroxiredoxin 1, 2 and 6 are not associated with esophageal cancer. 22236188_expression and function of Prdx1 and Prdx6 in MCF-7 and noncancerous MCF-10A cell lines; found elevated Prdx1 expression in MCF-7 cells and comparable expression of Prdx6; data suggest synergistic role for Prdx1 and Prdx6 in MCF-10A cells 22492841_decreased levels, combined with higher thiol oxidation (and probable inhibition) of PRDXs (particularly PRDX6), are noted when human sperm function is altered. 22663767_a change in the conformation of Prdx6 upon its phosphorylation is the basis for enhancement of PLA(2) enzymatic activity 22678913_(2) activity of Prdx6-PLA(2) in intact cells mediates its ability to enhance phox activity in response to fMLF 22985558_The protein and mRNA expressions of Prx1 and Prx6 increased significantly in the order of normal brain tissue, grade II astrocytoma, grade III astrocytoma and grade IV astrocytoma. 23113308_Drug resistance formation was accompanied by a significant increase in the expression of PRDX1, PRDX2, PRDX3, PRDX6 genes in all cancer cell strains, which confirms the importance of redox-dependent mechanisms into development of cisplatin resistance. 23158669_The level of Prx6 protein is lower in gastric cancer tissues than in normal para-cancer tissue. Prx6 expression is significantly correlated with the differentiation degree of GC. 23164639_Oxidation of the catalytic cysteine in Prdx6 is required for its interaction with PiGST, the interaction plays an important role in regenerating the peroxidase activity of Prdx6. 23643677_overexpression of PRDX6 promotes lung tumor growth via increased glutathione peroxidase and iPLA2 activities through the upregulation of the AP-1 and JNK pathways. 23815338_KGF can activate an antioxidant response element in a promoter without reactive oxygen species involvement and that KGF and Dex can synergistically activate the PRDX6 promoter and protect cells from oxidative stress 24316730_Hypoexpression of PRDX6 is associated with papillary thyroid carcinomas. 24391750_Apoptosis related proteins ERp29, PRDX6 and MPO were differentially expressed in placentas of pregnant women with intrahepatic cholestasis and in healthy pregnant women. 24512906_our findings indicate that PRDX6 promotes lung tumor growth via increased glutathione peroxidase and iPLA2 activities. 24910119_Reactive oxygen species-evoked aberrant sumoylation signaling affects Prdx6 activity by reducing Prdx6 abundance. 25748205_Several regions of reduced PRDX6 are in a substantially different conformation from that of the crystal structure of the peroxidase catalytic intermediate. The differences between the two structures likely reflect catalysis-related conformational changes. 25935550_High intensity of cytoplasmic Prx VI expression in pretreatment diffuse large B-cell lymphoma samples predicts worse outcome. 25938937_PRDX6 may serve as a biomarker for traumatic brain injury and that autoimmune profiling is a viable strategy for the discovery of novel biomarkers 26279427_PRDX6 protects ARPE-19 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. 26285655_AA (arachidonic acid) as a crucial effector of PRDX6-dependent proliferation and inducer of Src family kinase activation. 26293541_PRDX6 inhibited the carcinogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma, and the calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity of PRDX6 promoted cancer cell death induced by TNF-alpha. 26398495_PRDX6-anion exchanger 1 interaction contributes to the maintenance of anion exchanger 1 during cellular stress such as during metabolic acidosis. 26447207_Delivery of a protein transduction domain-mediated Prdx6 protein protected against oxidative stress-evoked neuronal cell death. 26560306_Our study provides new insight into the initial regulatory mechanisms of mitophagy and reveals the protective role of PRDX6 in the clearance of damaged mitochondria. 26647763_Prdx6 and its PLA2 activity have a protective role in donors after brain death livers. 26830860_Prdx6 is a complete enzyme comprising both PLA2and LPCAT activities 26891882_Peroxidase activity was markedly reduced by mutation at either of the Leu sites and was essentially abolished by the double mutation, while PLA2 activity was unaffected. Decreased peroxidase activity following mutation of the interfacial leucines presumably is mediated via impaired heterodimerization of Prdx6 with piGST that is required for reduction and re-activation of the oxidized enzyme. 26921317_Thr can substitute for Ser for the enzymatic activities of Prdx6 but not for its targeting to LB. These results confirm an important role for LB Prdx6 in the degradation and remodeling of lung surfactant phosphatidylcholine. 27094494_the transition-state substrate analogue inhibitor of Prdx6 phospholipase A2 activity (MJ-33) was shown to suppress Nox1 activity, suggesting Nox1 activity is regulated by the phospholipase activity of Prdx6. Finally, wild type Prdx6, but not lipase or peroxidase mutant forms, supports Nox1-mediated cell migration in the HCT-116 colon epithelial cell model of wound closure 27353378_Thus far only the crystal structure of Prx in the oxidized state has been reported. In this study, we present the crystal structures of human Prx6 in the reduced (SH) and the sulfinic acid (SO2H) forms. 27484502_These findings implicate miR-371-3p as a suppressor of PRDX6 and suggest that co-targeting of peroxiredoxin 6 or modulating miR-371-3p expression together with targeted cancer therapies may delay or prevent acquired drug resistance. 27554973_The constitutive elevations of Prdx6 and NF-kappaB during Clonorchis sinensis infection may be associated with more severe persistent hepatobiliary abnormalities mediated by clonorchiasis. 27932289_Peroxiredoxin 6 has a role in the repair of peroxidized cell membranes and cell signaling [review] 27934969_The increased HDL and plasma levels of PRDX6 in AAA patients support the potential of PRDX6 as a new biomarker of AAA. 28055018_Mutational analysis of functional sites showed that both peroxidase and PLA2 active sites were necessary for mutant Prdx6 function, and that Prdx6 phosphorylation (at T177 residue) was essential for optimum PLA2 activity.Mutant Prdx6 at its Sumo1 sites escapes and abates this adverse process by maintaining its integrity and gaining function 28293090_PRX6 protein is associated with fetal esophageal development and cancer differentiation. 28393051_the data demonstrate that Prdx6 interrupts the formation of TRAF6-ECSIT complex induced by TLR4 stimulation, leading to suppression of bactericidal activity because of inhibited mROS production in mitochondria and the inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in the cytoplasm. 28513872_These observations demonstrated that the expression and localization of NPM affected the homeostatic balance of oxidative stress in tumor cells via PRDX6 protein. The regulation axis of NPM/PRDX/ROS may provide a novel therapeutic target for cancer treatment. 29109765_The present data suggest that PS2 mutations suppress lung tumor development by inhibiting the iPLA2 activity of PRDX6 via a gamma-secretase cleavage mechanism and may explain the inverse relationship between lung cancer and Alzheimer's disease incidence. 29792351_These findings illuminate the effects of PRDX6 during osteogenic differentiation of hDPSCs, and also suggest that regulating PRDX6 may improve the clinical utility of stem cell-based regenerative medicine for the treatment of bone diseases. 29912414_The Ca2+-iPLA2 activity of PRDX6 is the most important and first line of defense against oxidative stress in human spermatozoa, maintaining cell viability and DNA integrity. 30104402_These results suggest that there are distinct prognostic values of PRDX family members in patients with ovarian cancer, and that the expression of PRDX3, PRDX5, and PRDX6 mRNAs are a useful prognostic indicator in the effect of chemotherapy in ovarian cancer patients. 30120980_These findings highlight the importance of Prdx6 as an essential regulator of oxidative stress in the eye. 30413111_we examined the therapeutic efficacy of the Ginkgolic acid (GA), a Sumoylation antagonist, to disrupt aberrant Sumoylation signaling in human and mouse lens epithelial cells (LECs) ...our study revealed an unprecedented role for GA in LECs and provided new mechanistic insights into the use of GA in rescuing LECs from aging/oxidative stress-evoked dysregulation of Sp1/Prdx6 protective molecules 30562740_These findings demonstrated that PRDX6 expression plays a characteristic growth-promoting role in Colorectal Cancer metastasis. 31036877_The findings reveal an essential role of PRDX6 in protecting cells against ferroptosis and provide a potential target to improve the antitumor activity of ferroptosis-based chemotherapy. 31519597_Patients with low Prx6 levels might be more prone to treatment-related adverse effects through elevated levels of oxidative stress. 31651026_PRDX6 contributes to the regulation of reactive oxygen species production and the PI3K/AKT pathway for the maintenance of sperm survival. 32018008_The anti-oxidant enzyme, Prdx6 might have cis-acting regulatory sequence(s). 32051828_PRDX6 Promotes the Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem (Stromal) Cells to Insulin-Producing Cells. 32643149_Peroxiredoxins are involved in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. 32784474_Clock Protein Bmal1 and Nrf2 Cooperatively Control Aging or Oxidative Response and Redox Homeostasis by Regulating Rhythmic Expression of Prdx6. 32798391_[Expression of Peroxiredoxin-6 Gene in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Clinical Significance]. 33035814_Knockout of PRDX6 induces mitochondrial dysfunction and cell cycle arrest at G2/M in HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cells. 33060708_Structural basis of peroxidase catalytic cycle of human Prdx6. 33547545_KLF9 regulates PRDX6 expression in hyperglycemia-aggravated bupivacaine neurotoxicity. 33561454_Peroxiredoxin 6 translocates to the plasma membrane of human sperm under oxidative stress during cryopreservation. 33631924_Identification of peroxiredoxin 6 as a potential lung-adenocarcinoma biomarker for predicting chemotherapy response by proteomic analysis. 33958651_pH induced conformational alteration in human peroxiredoxin 6 might be responsible for its resistance against lysosomal pH or high temperature. 34937537_Role of Innate Immunity and Oxidative Stress in the Development of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Peroxiredoxin 6 as a New Anti-Diabetic Agent. 35240453_Circular RNA hsa_circ_0011385 contributes to cervical cancer progression through sequestering miR-149-5p and increasing PRDX6 expression. 35645108_Effect of lentivirus-mediated peroxiredoxins 6 gene silencing on the phenotype of human gastric cancer BGC-823 cells. 35705035_Human peroxiredoxin 6 is essential for malaria parasites and provides a host-based drug target. 35723029_PRDX6 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and ferroptosis in periodontitis. 35929062_Activation of the JAK1/STAT1 signaling pathway is associated with peroxiredoxin 6 expression levels in human epididymis epithelial cells. 36008942_Selenocysteine Machinery Primarily Supports TXNRD1 and GPX4 Functions and Together They Are Functionally Linked with SCD and PRDX6. 36209344_PRDX6 knockout restrains the malignant progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 36222336_Integrated bioinformatics and machine learning strategies reveal PRDX6 as the key ferroptosis-associated molecular biosignature of heart failure. 36361777_Ferritin Heavy Chain Binds Peroxiredoxin 6 and Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Migration. |
ENSMUSG00000026701+ENSMUSG00000050114 |
Prdx6+Prdx6b |
1700.054977 |
0.4882662379 |
-1.034260 |
0.046051779 |
505.956419 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000048082718967991212969825099342886169367811833871457054067151047614727144843678741753719101181523703540348626487129803793490374145061439905262632704192745393267644344712536442731225036410053765789862461927840186810269465 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023117294200897401747013033089278089815354596204125254980313672285542074023435460504183690388079095672611425702557422951749303798672805407116454631774827013188326309525143585100714867972728277013593785255285323796636850 |
Yes |
No |
1124.3200262 |
34.9161798 |
2320.1832104 |
49.0648124 |
| ENSG00000117616 |
57035 |
RSRP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BUV0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:57035; |
|
26209438_Results show that C1orf63 expression was elevated in tumor tissues and correlated with better prognosis for breast cancers with advanced stage but the underlying mechanism is unknown. |
ENSMUSG00000037266 |
Rsrp1 |
613.395919 |
0.4680895018 |
-1.095144 |
0.219169852 |
24.276614 |
0.00000083446063412244649324056534542282115296529809711501002311706542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002975752345892077931966464982016518092677870299667119979858398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
395.6244092 |
61.4233363 |
847.2548945 |
94.7664540 |
| ENSG00000117643 |
57134 |
MAN1C1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR34 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the maturation of Asn-linked oligosaccharides. Trim alpha-1,2-linked mannose residues from Man(9)GlcNAc(2) to produce first Man(8)GlcNAc(2) then Man(6)GlcNAc and a small amount of Man(5)GlcNAc. |
Calcium;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P32906}. |
Predicted to enable mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase activity. Predicted to be involved in N-glycan processing. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57134; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-alpha-mannosidase activity [GO:0004571]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; Golgi apparatus mannose trimming [GO:1904381]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487] |
17727818_overexpression of Golgi alpha1,2-mannosidase IA, IB, and IC also accelerates ERAD of terminally misfolded human alpha1-antitrypsin variant null (Hong Kong) (NHK), and mannose trimming from the N-glycans on NHK in 293 cells 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32419574_Golgi alpha1,2-mannosidase I induces clustering and compartmentalization of CD147 during epithelial cell migration. |
ENSMUSG00000037306 |
Man1c1 |
134.820280 |
0.3504270626 |
-1.512814 |
0.164417690 |
85.401853 |
0.00000000000000000002434923590830689225928511405775328747533609745694548981377255958413741154799936339259147644042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000217947072168956799319949802846064527782407828750141170169596360750574604026041924953460693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.8612878 |
7.6608029 |
200.7036901 |
14.5314171 |
| ENSG00000118113 |
4317 |
MMP8 |
protein_coding |
P22894 |
FUNCTION: Can degrade fibrillar type I, II, and III collagens. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family of proteins. These proteins are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Proteolysis at different sites on this protein results in multiple active forms of the enzyme with distinct N-termini. This protein functions in the degradation of type I, II and III collagens. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:4317; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903980]; positive regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150078]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903428]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903978]; regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150077] |
11731274_expression in normal and malignant melanocytic cells 12101112_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12117418_MMP-8 cleaves TFPI following Ser(174) within the connecting region between the second and third Kunitz domains 14550288_gelatinase B and neutrophil collagenase cleave MIG and IP-10 15042023_Matrix metalloproteinase-8 is produced primarily by chorionic cells in human fetal membranes, and the level of matrix metalloproteinase-8 protein and messenger RNA expression in fetal membranes increases during labor. 15187163_membrane-bound MMP-8 on PMN cleaves types I and II collagens, and alpha(1)-proteinase inhibitor, but is substantially resistant to inhibition by tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) and TIMP-2. 15367487_Functionally significant single nucleotide polymorphisms of the MMP8 promoter haplotypes and preterm premature rupture of membranes were evaluated. 15367487_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15661397_in the later stages of myeloid development, MMP8 and other SGP genes are coordinately upregulated, and members of the C/EBP family, in particular C/EBPalpha and C/EBPepsilon, play specific and unique roles in upregulating their expression 15888067_Significantly elevated metalloproteinase 8 in broncho-alveolar lavage fluid is associated with Bronchiolitis obliterans 16134994_significantly elevated sinus mucus levels associated with elevated IL-8 levels in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP); IL-8 and MMP-8 seemingly form an inductive cytokine-proteinase cascade in CRSwNP pathogenesis 16242329_x-ray crystallographic analysis reveals that in a complex with MMP-8, N-hydroxyurea binds the catalytic zinc ion in a monodentate rather than bidentate mode and with high out-of-plane distortion of the amide bonds 16259988_MMP-8 has a role in carotid plaque progression 16432074_A localized increase in MMP-8 and -9, mediated by native mesenchymal cells, presents a potential pathway for collagen breakdown and abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture. 16872847_findings show that bacterial vaginosis is associated with increased levels of matrix metalloproteinase-8(MMP-8) in vaginal fluid 16877349_The expression of matrix-modeling genes in chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (cIMF) is not influenced by the JAK2 mutation status but is predominantly related to the stage of disease. 16928431_Immunofluorescence intensity, representing MMP-8 expression, in the periodontal tissues of smokers (30 fields from 6 subjects, mean 1154+/-124 units) was significantly higher than that in the periodontal tissues of non-smokers. 16940985_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17178858_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17418871_distinct deficits in NO production and elevations in MMP-8 and -9 expression in diabetic human skin fibroblasts compared to normal 17473191_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17567680_C-terminus of ephrin-B1 regulates activation of the extracellular release of MMP-8 without requirement of de novo protein synthesis. 17584650_Data show that serum MMP-8 concentration is closely associated with ACS, particularly AMI, and may serve as an indicator for predicting ACS and AMI. 17728507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17728507_Results show that -799C/T on the promoter region of MMP-8 lacks association with development of bronchiectasis in Koreans. 17932311_Serum MMP-8 concentrations are elevated in prevalent or subclinical atherosclerosis and associate with the worst cardiovascular outcome. 17974962_MMP8 gene variation may influence breast cancer prognosis and support the notion that MMP8 has an inhibitory effect on cancer metastasis. 17974962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18278188_In an in vitro atherosclerosis model neutrophil infiltration was mediated via IL-8-signalling and accompanied by release of MMP-8 and induction of endothelial cell apoptosis. 18366705_MMP8, but not MMP1 or MMP13, may affect the metastatic behaviour of breast cancer cells through protection against lymph node metastasis 18428024_Total MMP-8 immunoreactivity, the proportion of active MMP-9, and gelatinolytic activity in urine were significantly higher in diabetic nephropathy patients than in controls 18626311_high serum MMP-8 levels in melanoma patients were significantly related to presence of vascular invasion (P=0.001) in primary tumour, tumour ulceration (P=0.003) and tumour bleeding (P=0.033) 18700005_In patients with high-risk bacteria, MMP-8-, MMP-9- and TIMP-1-concentrations were higher than in patients with low-risk bacteria. 18768525_Functional polymorphisms in the promoter of MMP-8 do not significantly confer susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma in a southern Chinese population. 18768525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18980523_Non-surgical periodontal treatment was effective in reducing the levels of MMP8 in gingival crevicular fluid from diabetic patients with chronic periodontitis. 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19094243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19094243_a C/G polymorphism in MMP8 was associated with a statistically significant decreased risk of developing lung cancer, but does not seem to modify or be an independent prognostic factor for overall survival 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19159011_MMP-8 were identified at higher levels in lung secretions of pediatric ALI patients compared with controls. 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19330028_Expression of wild-type but not mutant MMP8 in human melanoma cells inhibited growth on soft agar in vitro and tumor formation in vivo, suggesting that wild-type MMP-8 has the ability to inhibit melanoma progression. 19358835_Obese children and adolescents had higher circulating MMP-8 concentrations, lower plasma TIMP-1 concentrations, and higher MMP-8/TIMP-1 ratios than non obese controls. 19442604_Primary cultures stromal cells from giant cell tumour of bone produce MMP-1 and MMP-13 but not MMP-8.. 19460733_Patients with coronary heart disease showed increased levels of MMP2 and MMP9. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19674746_plasma MMP-8 levels were found to be high in patients with unstable angina (UAP), suggesting that MMP-8 levels in UAP may reflect coronary plaque instability and that MMP-8 is a promising biomarker for UAP. 19708869_Reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR analysis revealed that Prevotella intermedia ATCC 25611 supernatant increased MMP-1 and MMP-8 mRNA expression in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. 19745165_Results indicate that MMP8 is an important player in atherosclerosis. 19751716_increased circulating MMP-8 and MMP-9 levels and proteolytic activity in periodontal disease patients that decrease after periodontal therapy 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19880617_Pneumolysin induces release of matrix metalloproteinase-8 and -9 from human neutrophils 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19995403_Higher levels of MMP-8 were found in the gingival crevicular fluid of chronic periodontitis patients compared with controls, and these markers decreased 3 months after periodontal therapy. 20042585_Soluble MMP-8 and membrane-bound MMP-8 on activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils can cleave and inactivate recombinant macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha in vitro. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20184870_MMP-8 and -9 are highest in T2DM UA patients. MMP-9, showed the strongest associations with clinical parameters related to diabetic nephropathy. 20356362_MMP-2 and -8 are elevated in serum and blister fluid in severe sepsis, implying that they may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of severe sepsis and organ dysfunctions 20371206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20442866_MMP-8 activity plays a crucial role in disassembly of cell junction components and cell adhesion during meningococcal infection 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453486_Pleural fluid MMP-2, MMP-8 and MMP-9 may provide useful information for differentiating between uncomplicated and complicated parapneumonic effusions. 20484597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20621951_Early treatment of multiple sclerosis with IFN-beta1b may stabilize clinical disease by attenuating level of MMP-8. 20626027_Compared and found plasma MMP-8 values were significantly higher in patients with carotid atherosclerosis compared with controls but did not differ signif'ly according to gender, smoking and hypertensive status, associated diseases, and use of statins. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20659259_MMP-8 levels in oral rinse samples were higher in subjects with the strongest periodontal inflammatory burden than in subjects with less inflammatory changes when oral rinse levels were adjusted to number of teeth. 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20708200_MMP-8 could be involved in the acute inflammatory reaction and may be a useful marker for the diagnosis of acute thoracic aortic dissection (TAD). 20809029_The MMP8 values in gingival crevicular fluid can be a marker of the gingival overgrowth onset. 20889295_Short-term use of statins is not associated in reducing levels of MMP 9 in areas of low and peak wall stress in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21196908_In patients with histological chorioamnionitis and funisitis, umbilical cord blood MMP-8 concentrations were not significantly changed. 21432777_differences in histological features between nasal polyposis and chronic rhinosinusitis might be related to the expression of MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-8 and their tissue inhibitor-2 21437624_Data indicate that the balance between MMPs and TIMPs in women with PCOS is altered, probably due to androgen excess found in these women. 21515330_We confirmed the decreased capacity of cell migration due to down-regulation of MMP-8 by apigenin. 21642878_Finding of this study indicates an influence of MMP8 gene variation on melanoma susceptibility. 21697883_MMP-8 is involved in sensory nerve growth within the interstitial CoL matrix through modulation by the axonal guidance molecules and/or extracellular matrix components 21784671_reduced risk on recurrence of superficial bladder cancer was observed in patients with MMP8 TT genotype 21857935_Data show that higher MMP-8 and active MMP-9 levels at 48 hours of disease onset are associated with a longer duration of mechanical ventilation and fewer ventilator-free days among pediatric patients. 21872914_MMP-3, MMP-8, and MMP-9 levels were significantly different between patients with Hyper-IgE syndrome and control subjects and might contribute to some of the characteristic features of Hyper-IgE syndrome 21906737_MMP-8 promoter -381A/G and -799C/T gene polymorphisms could be risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis. 21920499_Although none of the investigated SNPs in the MMP8 gene was individually associated with periodontitis, specific haplotype showed association with clinical manifestation of chronic periodontitis in a Czech population. 21925226_genetic variations are associated with increased risk of ulcerative colitis in Caucasians of New Zealand 21994255_gene polymorphism is associated with atherosclerosis in Finland 22092455_Multivariate logistic regression analysis with adjustment for age, gender and smoking indicated that increased risks of aggressive periodontitis and chronic periodontitis were associated with the -799 T allele of matrix metalloproteinase-8. 22113040_The allele and genotype frequencies of MMP8 rs11225395 were not associated with the development of gastric cancer development and lymph node metastasis. 22179173_The preliminary results indicate that this polymorphism may be a risk factor for tendinopathy and could be used as a genetic marker for the primary lesions of the posterior tibial tendon. 22257687_An increase of serum MMP-8 reflects plaque instability and tissue damage in acute coronary syndrome. 22311494_Serum level of MMP-8 in the carotid vulnerable plaque group was higher than that in the carotid stable plaque group. 22382449_results suggest that polymorphism in the promoter region of MMP-8 gene is associated with early implant failure. This polymorphism can be a genetic marker to risk of implant loss. 22487237_The polymorphism at position -799 of the gene for MMP-8 is associated with tendinopathy primary posterior tibial tendon in the population studied. The results suggest that individuals with the T allele are at greater risk of developing tendinopathy. 22808470_The content of MMP-8 an MMP-9 in oral fluid of patients with severe periodontium was slightly higher than that in other patients and subjects with the intact periodontium. 23054081_E-cadherin, EMMPRIN and MMP-8 median values were significantly increased in all chronic kidney disease children, as well as in all dialyzed patients versus controls 23259856_MMP-8 may be directly involved in hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and trafficking. 23313321_Children with febrile infection have significantly elevated levels of serum MMP8 compared to children with unprovoked generalized seizures. 23442769_Low levels of plasma MMP8 levels can rule out acute aortic dissection. 23512982_Suggest that MMP8 plays an important role in angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. 23632023_a causal connection between MMP-8 activity and the IL-6/IL-8 network, with an acute response to MMP-8 involving induction of the proinflammatory mediators, which may in part serve to compensate for the deleterious effects of MMP-8 on breast cancer 23851508_findings have shown that MMP-8 is able to modify the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells because of its ability to proteolytically cleave decorin and regulate miR-21 levels 23851938_Moderate-strength STS causes the highest TIMP-1/MMP-8 ratio, leading to appropriate conditions for reformation of the extracellular matrix 23865360_Evaluated gingival inflammation and the enzyme activity of MMP-8 in gingival crevicular fluid of pregnant women. The aMMP-8 values of pregnant subjects were higher compared with non-pregnant, but the difference was not statistically significant. 23953866_elevated levels of IL-6 and MMP-8 in amniotic fluid at mid-trimester are predictive of preterm delivery 23962148_Our results suggest that serum MMP-8, TIMP-1, and the ratio of MMP-9/TIMP-1 might be useful adjuncts as predictors of prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma 23967183_Baseline serum MMP-8 is a significant predictor of LV remodeling and cardiovascular outcome after MI 24065531_The C-799T polymorphism in the MMP8 promoter is part of the genetic variation underlying the susceptibility of individuals to the progression of thoracic aortic dissection. 24099107_suggests that binding of the HGF variants to the cell surface c-Met resulted in the downregulation of MMP-9, and upregulation of MMP-8 protein expressions might be key molecular signals against proliferation, migration, and invasion of A549 cells 24164993_Studied plasma MMP-8 levels and its correlates 20+/-3 months after acute myocardial infarction. 24170307_MMP8 rs1940475 SNP modifies the host response to inflammatory stimuli. 24267248_Plasmatic OxLDL and MMP-8 levels are associated with carotid atherosclerosis 24283658_it can be suggested that MMP-8 -799 C/T and TIMP-1 372 T/C, *429 T/G gene polymorphisms in males may be associated with the susceptibility to GAgP in the Turkish population. 24651234_MMP-8 levels were possibly higher in 90-day nonsurvivors but performed poorly in predicting outcome 24828408_Plasma and BALF MMP-8 levels are unlikely to serve as a prognostic biomarker for IPF patients. 25016699_Studied the plasma concentrations of MMP-8, TIMP1, C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, and WBCs in patients with acute coronary syndrome and found levels were significantly higher than those in the control group. 25034366_MMP-8 promoter gene polymorphism -799 T/T is significantly associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer in Mexican women. 25109362_The 799C/T polymorphism in the promoter region of MMP8 may be associated with the development of TAD and that the T allele may increase patient predisposition to the disease. 25319807_patients with high serum MMP-8 levels may benefit from adjuvant IFN-alpha therapy, but this observation should be further investigated. 25545245_MMP-8, MMP-9, and YKL-40 might serve as novel non-invasive biomarkers of CF lung disease and pulmonary exacerbations. 25550459_investigated whether MMP-8 affects the structure and antiatherogenic function of apolipoprotein (apo) A-I, the main protein component of HDL particles 25607396_The expression of MMP-7, -8, -9 and -13 in the gingiva of the young patients with aggressive periodontitis and type 1 diabetes mellitus was positive in all studied cases. 25633268_Strong associations of MMP-8 with components of Metabolic Syndrome X in univariate, bivariate and multivariate models suggest plasma MMP-8 as a potential cardiometabolic risk marker for Metabolic syndrome X. 25635689_Gender-specific analysis of MMPs demonstrated consistent increase in MMP-1 and -8 in tuberculosis, but MMP-8 was a better discriminator for TB in men. 25712810_increased levels in saliva and serum in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, and is potentiated in the presence of gingivitis 25841875_Positive results of the aMMP-8 test significantly correlate with generalized ChP. The aMMP-8 test may be used by physicians to detect periodontitis in their patients. 26132583_salivary levels of the analyzed biomarkers MMP-8, -9, MPO are associated with periodontal status. However, these biomarkers could not differentiate between patients with or without a MI. 26339374_miR-539 plays a key role in inhibiting osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration and can regulate MMP8 expression in osteosarcoma cells. 26418236_Sputum, serum, and urine MMP-8 were not significantly changed in COPD exacerbation compared to recovery values. 26462905_amniotic fluid concentrations in acute-chorioamnionitis distinctly decrease throughout preterm-gestation 26492282_Plasma MMP-8 and MMP-9 concentrations correlate with diabetic ketoacidosis severity and are known to degrade brain microvascular endothelial cell tight junctions. Thus, leukocyte-derived MMPs might contribute to DKA-associated cerebrovascular complications. 26577236_Initial analysis of the MMP8 gene showed suggestive association between rs1940475 and knee OA, but the finding did not replicate in other study cohorts, even though the trend for predisposing allele was similar in all five cohorts. MMP-8 is a good biological candidate for OA, but our study did not find common variants with significant association in the gene. 26773532_EMMPRIN, MMP8, hyaluronan, beta-defensing-2, and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) are elevated in women with vaginal inflammation 26872724_The reciprocal positive interplay between MMP-8 and TGF-beta1 contributes to HCC invasion and metastasis by inducing EMT mainly through the PI3K/Akt/Rac1 pathway. 26898119_The serum levels of IL-8, MIP-1 alpha, MIP-1 beta, MMP-8, Resistin, FLRG, and BCAM were significantly higher in breast cancer patients, but LAP and TSH-beta levels were lower. 26923392_Blood expression of matrix metalloproteinases 8 and 9 and of their inducers S100A8 and S100A9 supports diagnosis and prognosis of PDAC-associated diabetes mellitus 27296149_Obesity is associated with elevated circulating MMP-8 in young adults. MMP-8 is also increased in smokers. 27313452_Plasma levels of MMP-1, MMP-8, and MMP-9 are associated with COPD severity and can be used as a biomarker to better understand the characteristics of COPD patients. 27377304_Serum level patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-8 showed distinctive patterns for patients with spinal cord injury neurological impairment. MMP-8 and MMP-9 patterns showed significant differences regarding functional recovery. Our binary logistic regression model showed that, according to neurological damage, measuring peripheral serum levels can be used to monitor and predict locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury. 27442388_Suggest that MMP-8 polymorphism -799 C/T was a risk for developing chronic periapical lesions. 27561093_plasma concentrations of MMP-7, MMP-8, -9 and TIMP-1 within 96 h from the onset of acute pancreatitis symptoms are elevated in acute pancreatitis patients compared with healthy controls 27579896_a 7-gene signature was identified which correctly predicted the primary prefibrotic myelofibrosis group with a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 89%. The 7 genes included MPO, CEACAM8, CRISP3, MS4A3, CEACAM6, HEMGN, and MMP8 27631232_rs1940475 and rs11225395 associated with 1.32-fold increased risk of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head 27797337_infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis is characterized by impairements in the system MMP/inhibitors: the levels of MMP-1, -9 increased, MMP-3, -8, TIMP-1 remained at the reference values and a 2-macroglobulin was low. 27843200_there is a negative correlation between blood MMP8 and HDL-cholesterol levels, suggesting a contributory role of MMP8 in metabolic alterations in acne inversa 28278213_Low MMP-8/TIMP-1 reflects left ventricle impairment in takotsubo cardiomyopathy and high TIMP-1 may help to differentiate it from acute coronary syndrome 28283184_Suggest that Ang-(1-7) plays an important role in protecting against atherosclerosis via counter-regulation of Ang II-induced MMP-8. 28330493_MMP-8 is a vital component of the myoepithelial tumour-suppressor function. It restores MEC interaction with the matrix, opposes TGF-beta signalling and MMP-9 proteolysis, which contributes to inhibition of tumour cell invasion. 28423488_These results provide the first evidence that MMP8 SNP at the rs11225394 locus is associated with the increased risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese Han population. 28445942_among Chinese males, MMP-3 rs650108 and MMP-8 rs2012390 decrease alcohol-induced ONFH risk and MMP-8 rs11225394 increases it. 28652424_Our findings suggest that the polymorphisms at MMP-8 C-799T or Val436Ala may not play a major role in mediating personal risk of oral cancer; however, the detailed mechanisms require further investigation. 28734574_Reduction in serum levels of MMP8 predicted complete remission in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients following bariatric surgery. 28745526_Our study demonstrated that the MMP-8 C-799T is associated with the risk of developing severe preeclampsia during pregnancy. However, the MMP-8 C + 17G polymorphism might not be a risk factor for susceptibility to preeclampsia. 28772283_Our study provides evidence for the tumour-suppressive mechanisms of MMP-8 in OTSCC by interplay with TGF-b1 and VEGF-C. 29078079_Persistent oral human papillomavirus infection was associated with a low salivary MMP-8 concentration indicating eventually a failure in oral anti-inflammatory defence. 29102926_Our findings suggest that the polymorphisms at MMP-8 -799C/T, Val436Ala and Lys460Thr may not play a major role in determining the personal susceptibility to childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Taiwan. 29212897_Genetic polymorphism in S100A9-S100A12-S100A8 locus affects serum and plasma MMP-8 and shows a suggestive association with the risk of cardiovascular diseases. 29215835_Matrix metalloproteinase-1, -8, -9 and the risk of cardiovascular complications in patients with CHD before and after myocardial revascularization. 29263043_Reduced expression of types I and III collagen and TIMP-1 as well as the increased expression of MMP-1 and MMP-8 in the anterior vaginal wall tissues play important roles in the onset of pelvic organ prolapse. 29275297_Data show that polymorphism in the promoter region of matrix metallopeptidase 8 (MMP-8) (-799C/T) and two non-synonymous polymorphisms (Val436Ala and Lys460Thr) were not significantly associated with risk of pterygium.pterygium. 29292194_Data show that individuals with MMP-8 -799TT genotype and intermediate HIV disease stage are at higher risk for the advancement of HIV disease. MMP-8 polymorphism indicated a trend of elevated risk for the modulation of HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder (HAND) severity. MMP-8 -799TT genotype may facilitate the risk for the development of HAND with tobacco and alcohol usage. 29453088_Data demonstrate significantly higher serum concentrations of inflammatory biomarkers MMP-8, MPO and TIMP-1 in acute ischemic stroke cases. 29532899_MMP-1 and MMP-8 gene polymorphisms have a role in promoting the increase and remodeling of the collagen III and V in posterior tibial tendinopathy 29564945_Peri-implant sulcular fluid levels of MMP-8 and MMP-9 are significantly higher among waterpipe smokers compared with never-smokers with peri-implantitis. 29599337_MMP8 -799C/T, Val436Ala and Lys460Thr polymorphisms may only play an indirect role in determining personal cancer susceptibility to breast cancer in Taiwan. 29808017_High-serum MMP-8 levels are associated with systemic inflammation and adverse outcome in colorectal cancer. 29929486_MMP-8 and TIMP-1 in serum, but not MMP-9, identified colorectal cancer patients with bad prognosis 30170451_Five single nucleotide polymorphisms including rs3740938, rs2012390, rs1940475, rs11225394, and rs11225395 of MMP-8 gene were genotyped in a Chinese Han population. It was found rs3740938 of MMP-8 was associated with an increased risk of ankylosing spondylitis under the dominant model and additive model after adjustment for gender and age by performing logistic regression analysis. 30192205_Low MMP8 level is associated with gastric cancer. 30194163_Results suggest that MMP8 C-799T, Val436Ala and Lys460Thr may only play an indirect role in determining personal cancer susceptibility for bladder cancer in Taiwan. 30194384_data showed that polymorphisms of MMP8 and MMP9 may be associated with breast cancer risk in the Chinese Han population. 30300896_rs1939012 may play a potential role of gene regulation and/or epistasis in a complex etiology of vertigo. 30313082_The meta-analysis results showed a remarkable association between rs11225394 in MMP-8 gene and an increased risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head and a significant association between MMP-8 rs2012390 and the decreased risk of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. 30328228_A significant association of rs1799750 (MMP-1) and rs11225395 (MMP-8) polymorphism on early implant loss was demonstrated (P = 0.001). 30626536_With increased levels of MPO, MMP-8 and MMP-8/TIMP-1 ratio. 30755371_No significant interactions were noted between the MMP3, MMP8 and TIMP2 genes with ACLR susceptibility despite the known biological interactions between the proteins. 31067818_Two polymorphisms of MMP-8 and MMP-27 were significantly associated with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) risk, both individually and in combination. Therefore, these two polymorphisms are potential biomarkers for RPL susceptibility. 31263835_MMP-8 was identified only in myocardiocytes, while MMP-9 and TIMP-2 were present in both myocardiocytes and stroma, but with different intensity. The increasing intensity of MMP-8 and TIMP-2 immunoreactions was significantly associated with low HCS. 31444693_The modulation of the TREM-1/PGLYRP1/MMP-8 axis in peri-implant diseases. 31590330_The MMP-8 rs11225395 Promoter Polymorphism Increases Cancer Risk of Non-Asian Populations: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis. 31638929_MMP-8 C-799 T, Lys460Thr, and Lys87Glu variants are not participant with the susceptibility of cancer 31771979_Moonlighting matrix metalloproteinase substrates: Enhancement of proinflammatory functions of extracellular tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase upon cleavage. 31881666_Salivary IL-6, MMP-8 and GSS mRNA levels in combination with urine test analysis could be useful diagnostic tool for the very distributed disorder of pyelonephritis in childhood. 32108279_Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) through the ERK-mediated pathway. 32234890_Regression analysis adjusted by age showed that for MMP8 rs11225395 each minor A allele copy significantly reduced the odds for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) development (odds ratio=0.49, 95% confidence intervaI=0.04-2.19, p=0.048). MMP8 rs11225395 AA genotype was associated with smaller laryngeal tumour size (p=0.023). 32790178_Local and systemic levels of aMMP-8 in gingivitis and stage 3 grade C periodontitis. 32801681_Increased MMP8 Levels in Atopic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Study Testing Multiple Immune Factors in Atopic and Non-Atopic Patients. 32818670_LncRNA TP73-AS1/miR-539/MMP-8 axis modulates M2 macrophage polarization in hepatocellular carcinoma via TGF-beta1 signaling. 32944879_Torquetenovirus Titer in Vaginal Secretions from Pregnant and Postpartum Women: Association with Absence of Lactobacillus crispatus and Levels of Lactic Acid and Matrix Metalloproteinase-8. 33143325_MMP-8, TRAP-5, and OPG Levels in GCF Diagnostic Potential to Discriminate between Healthy Patients', Mild and Severe Periodontitis Sites. 33219886_Comparative Analysis of MMP-8 and MMP-9 Concentrations in Crevicular and Peri-Implants Sulcular Fluids. 33275619_Fibrosis regression is induced by AdhMMP8 in a murine model of chronic kidney injury. 33275641_Computational analysis of the metal selectivity of matrix metalloproteinase 8. 33375174_The Impacts of Fish Oil and/or Probiotic Intervention on Low-Grade Inflammation, IGFBP-1 and MMP-8 in Pregnancy: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Clinical Trial. 33556788_Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases-8, -9 and endogenous tissue inhibitor-1 in oral biofluids during pregnancy and postpartum. 33556789_Evaluation of active matrix metalloproteinase-8 (aMMP-8) chair-side test as a diagnostic biomarker in the staging of periodontal diseases. 33567492_Salivary Metalloproteinase-8 and Metalloproteinase-9 Evaluation in Patients Undergoing Fixed Orthodontic Treatment before and after Periodontal Therapy. 33894037_Causal associations of serum matrix metalloproteinase-8 level with ischaemic stroke and ischaemic stroke subtypes: a Mendelian randomization study. 33902302_Causal Effect of MMP-1 (Matrix Metalloproteinase-1), MMP-8, and MMP-12 Levels on Ischemic Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. 34043679_Matrix metalloproteinase MMP-8, TIMP-1 and MMP-8/TIMP-1 ratio in plasma in methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. 34353321_Origin of MMP-8 and Lactoferrin levels from gingival crevicular fluid, salivary glands and whole saliva. 34419758_Periodontitis and peri-implantitis tissue levels of Treponema denticola-CTLP and its MMP-8 activating ability. 34448550_Human leukocyte antigens are associated with salivary level of active MMP-8. 34550870_A Novel Protective Role for Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 in the Pulmonary Vasculature. 34571507_Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 and Myeloperoxidase Predict Survival after Resection of Colorectal Liver Metastases. 34800007_Active matrix metalloproteinase-8: A potential biomarker of oral systemic link. 35163727_The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13) in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Pathological Processes. 35328734_Matrix Metalloproteinase 8 Expression in a Tumour Predicts a Favourable Prognosis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. 35329310_Peri-Implant Surgical Treatment Downregulates the Expression of sTREM-1 and MM |
ENSMUSG00000005800 |
Mmp8 |
2049.308734 |
38.2314983189 |
5.256690 |
0.078601735 |
7515.898174 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4030.5697620 |
202.5591695 |
106.2085092 |
5.2013056 |
| ENSG00000118200 |
23271 |
CAMSAP2 |
protein_coding |
Q08AD1 |
FUNCTION: Key microtubule-organizing protein that specifically binds the minus-end of non-centrosomal microtubules and regulates their dynamics and organization (PubMed:23169647, PubMed:24486153, PubMed:24706919). Specifically recognizes growing microtubule minus-ends and autonomously decorates and stabilizes microtubule lattice formed by microtubule minus-end polymerization (PubMed:24486153, PubMed:24706919). Acts on free microtubule minus-ends that are not capped by microtubule-nucleating proteins or other factors and protects microtubule minus-ends from depolymerization (PubMed:24486153, PubMed:24706919). In addition, it also reduces the velocity of microtubule polymerization (PubMed:24486153, PubMed:24706919). Through the microtubule cytoskeleton, also regulates the organization of cellular organelles including the Golgi and the early endosomes (PubMed:27666745). Essential for the tethering, but not for nucleation of non-centrosomal microtubules at the Golgi: together with Golgi-associated proteins AKAP9 and PDE4DIP, required to tether non-centrosomal minus-end microtubules to the Golgi, an important step for polarized cell movement (PubMed:27666745). Also acts as a regulator of neuronal polarity and development: localizes to non-centrosomal microtubule minus-ends in neurons and stabilizes non-centrosomal microtubules, which is required for neuronal polarity, axon specification and dendritic branch formation (PubMed:24908486). Through the microtubule cytoskeleton, regulates the autophagosome transport (PubMed:28726242). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23169647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24486153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24706919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24908486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27666745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28726242}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables microtubule minus-end binding activity. Involved in several processes, including axon development; regulation of dendrite development; and regulation of organelle organization. Located in cytosol and microtubule end. Colocalizes with Golgi apparatus; centrosome; and microtubule minus-end. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23271; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; microtubule end [GO:1990752]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; microtubule minus-end binding [GO:0051011]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; axon development [GO:0061564]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of Golgi organization [GO:1903358]; regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031113]; regulation of organelle organization [GO:0033043] |
19508979_The CKK domain binds microtubules and represents a domain that evolved with the metazoa. 22116939_in a two-stage GWAS to identify common susceptibility variants of epilepsy in Chinese, the strongest signals were observed with two highly correlated variants, rs2292096 and rs6660197, with the former reaching genome-wide significance, on 1q32.1 in the CAMSAP1L gene 24148305_the rs2292096 G allele of CAMSAP1L1, which was associated with reduced risk of symptomatic epilepsy, tended to associate with increased expression of CAMSAP1L1, which represses neurite outgrowth. 24706919_These results show that members of the CAMSAP/Patronin family all localize to and protect minus-ends but have evolved distinct effects on microtubule dynamics. 24908486_The CAMSAP/Nezha/Patronin family protein CAMSAP2 specifically localizes to noncentrosomal microtubule minus-ends and is required for proper microtubule organization in neurons. 28726242_noncentrosomal MTs regulate autophagy through a cross-talk between CAMSAP2 and EB1 32084403_Microtubule Minus-End Binding Protein CAMSAP2 and Kinesin-14 Motor KIFC3 Control Dendritic Microtubule Organization. 32206120_CAMSAP2-mediated noncentrosomal microtubule acetylation drives hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. 33782614_A chemical genetics approach to examine the functions of AAA proteins. 35188072_CircRNA SOD2 motivates non-small cell lungs cancer advancement with EMT via acting as microRNA-2355-5p's competing endogenous RNA to mediate calmodulin regulated spectrin associated proteins-2. |
ENSMUSG00000041570 |
Camsap2 |
287.113624 |
2.9148324974 |
1.543413 |
0.146669167 |
108.178759 |
0.00000000000000000000000024559768038520827169715082324803970785334626877358575212518009879287400609726432776369620114564895629882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000002671349861817003581916879702404596306390225498067993185268637952199319296475721330352826043963432312011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
436.8337665 |
40.9321398 |
150.8396871 |
10.7826331 |
| ENSG00000118242 |
55686 |
MREG |
protein_coding |
Q8N565 |
FUNCTION: Probably functions as cargo-recognition protein that couples cytoplasmic vesicles to the transport machinery. Plays a role in hair pigmentation, a process that involves shedding of melanosome-containing vesicles from melanocytes, followed by phagocytosis of the melanosome-containing vesicles by keratinocytes. Functions on melanosomes as receptor for RILP and the complex formed by RILP and DCTN1, and thereby contributes to retrograde melanosome transport from the cell periphery to the center. Overexpression causes accumulation of late endosomes and/or lysosomes at the microtubule organising center (MTOC) at the center of the cell. Probably binds cholesterol and requires the presence of cholesterol in membranes to function in microtubule-mediated retrograde organelle transport. Binds phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate, but not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate or phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (By similarity). Required for normal phagosome clearing and normal activation of lysosomal enzymes in lysosomes from retinal pigment epithelium cells (PubMed:19240024). Required for normal degradation of the lipofuscin component N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E) in the eye. May function in membrane fusion and regulate the biogenesis of disk membranes of photoreceptor rod cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NVG5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19240024}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lipid-binding;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable phosphatidylinositol binding activity. Predicted to be involved in melanocyte differentiation; melanosome transport; and phagosome maturation. Predicted to act upstream of or within developmental pigmentation. Predicted to be located in late endosome membrane and melanosome membrane. Predicted to be intrinsic component of organelle membrane. Predicted to be part of protein-containing complex. Predicted to be active in melanosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55686; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; melanosome membrane [GO:0033162]; organelle membrane [GO:0031090]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318]; melanosome localization [GO:0032400]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; minus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule [GO:0072385]; phagosome maturation [GO:0090382] |
20463177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25301234_MREG-dependent processing links both autophagic and phagocytic processes in LC3-associated phagocytosis. MREG participates in coordinating the association of phagosomes with LC3 for content degradation with the MREG loss leading to phagosome accumulation. 28698135_Taken together, MREG regulates thyroid cancer cell invasion and proliferation through PI3K/Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. MREG may serve as a promising therapeutic strategy for thyroid cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000039395 |
Mreg |
26.480910 |
3.8218165977 |
1.934259 |
0.331443953 |
35.345316 |
0.00000000276131795737064030953576620141219633008944356333813630044460296630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012681099269069898507878982254083038982983566711482126265764236450195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
43.0578709 |
9.7134142 |
11.3119128 |
2.0643697 |
| ENSG00000118257 |
8828 |
NRP2 |
protein_coding |
O60462 |
FUNCTION: High affinity receptor for semaphorins 3C, 3F, VEGF-165 and VEGF-145 isoforms of VEGF, and the PLGF-2 isoform of PGF.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human cytomegalovirus pentamer-dependent entry in epithelial and endothelial cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30057110}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the neuropilin family of receptor proteins. The encoded transmembrane protein binds to SEMA3C protein {sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3C} and SEMA3F protein {sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3F}, and interacts with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). This protein may play a role in cardiovascular development, axon guidance, and tumorigenesis. This protein has also been determined to act as a co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 (which causes COVID-19) to infect host cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2021]. |
hsa:8828; |
axon [GO:0030424]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; semaphorin receptor complex [GO:0002116]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; semaphorin receptor activity [GO:0017154]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005021]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; dorsal root ganglion morphogenesis [GO:1904835]; facial nerve structural organization [GO:0021612]; facioacoustic ganglion development [GO:1903375]; gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuronal migration to the hypothalamus [GO:0021828]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; nerve development [GO:0021675]; neural crest cell migration involved in autonomic nervous system development [GO:1901166]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in neuron projection guidance [GO:1902285]; sensory neuron axon guidance [GO:0097374]; sympathetic ganglion development [GO:0061549]; sympathetic neuron projection extension [GO:0097490]; sympathetic neuron projection guidance [GO:0097491]; trigeminal ganglion development [GO:0061551]; ventral trunk neural crest cell migration [GO:0036486]; vestibulocochlear nerve structural organization [GO:0021649] |
12730958_human glioma cells express class 3 semaphorins and receptors for soluble and membrane-bound semaphorins, suggesting a possible role of the semaphorin/neuropilin system in the interactions of human malignant glioma with the nervous and immune systems. 14760080_Np-1 and Np-2 contribute to autocrine-paracrine interactions in pancreatic cancer 15613413_NP-2 mRNA, in endothelium, was expressed only by the endothelium of veins, and in these cells, its expression was hormonally regulated in the converse manner: it was very low during the proliferative phase and high during the secretory phase 16621967_NRP2 acts as a coreceptor that enhances human endothelial cell biological responses induced by VEGF-A and VEGF-C. 16816121_NP2 is directly involved in an active signaling complex with the key regulators of lymphangiogenesis. 17088944_These results suggest that the expression of VEGFRs and NRPs on keratinocytes may constitute important regulators for its activity and may possibly be responsible for the autocrine signaling in the epidermis. 17427189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17427189_The polymorphisms in the NRP2 gene are associated with autism, implying that the NRP2 gene may render individuals to be predisposed to autism. 17699524_that neuropilin-2 (NRP-2), a receptor for the semaphorin and vascular endothelial growth factor families in neurons and endothelial cells, respectively, is expressed on the surface of human dendritic cells and is polysialylated. 17891484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17917967_neoplastic cells in myeloid leukemias frequently express VEGFR including NRP-1 and NRP-2 18065694_Both NRP1 and NRP2 function as proangiogenic coreceptors, potentiating the activity of at least 2 proangiogenic cytokines, VEGF-A and hepatocyte grwoth factor. 18182619_NRP2 expression enhances cell survival, migration, invasion, and in vivo tumor growth and it may be a promising therapeutic target for colorectal cancer. 18307536_IL-8 might be a malignant factor in human pancreatic cancer by induction of vascular endothelial growth factor and NRP-2 expression and ERK activation. 18564921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18708346_hypoxia and nutrient deprivation stimulate the rapid loss of NRP1 expression in both endothelial and carcinoma cells. NRP2 expression, in contrast, is maintained under these conditions 18781179_In gliomas, SEMA3B, SEMA3G and NRP2 expressions were related to prolonged survival 18785001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19037249_Transcripts of both NRP1 and NRP2 were found to be decreased in renal biopsies from patients with diabetic nephropathy 19088020_Reduction of NRP-2 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells decreased survival signaling, migration, invasion, and ability to grow under anchorage-independent conditions. 19409892_Data suggest that neuropilin 2 may increase the response to VEGF, which is more significant in gastric tumor endothelial cells (TEC) than in normal cells, leading to gastric TEC with aggressive angiogenesis phenotypes. 19474288_Intra-amniotic infection upregulates decidual cell vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and neuropilin-1 and -2 expression: implications for infection-related preterm birth. 19480842_Data show that the expression of Sema3A receptors (neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), NRP-2, plexin A1, plexin A2, and plexin A3) significantly increased during M-CSF-mediated differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. 19580679_Neuropilin-2 in breast cancer has a role in lymph node metastasis, poor prognosis, and regulation of CXCR4 expression 19736548_This is the first report suggesting a differential role of NRP1 and NRP2 in renal fibrogenesis. 19790074_Soluble neuropilin-2 has no antirepellent activity but aggravates sympathetic nerve fiber repulsion and arthritis. Increased shedding of neuropilin-2 is probably an unfavorable sign in rheumatoid arthritis. 19855168_NRP2 is necessary to trigger Sema3A-induced glioma cell repulsion and attraction. 20488940_Polysialyted NRP2 enhances dendritic cell migration through the basic c-terminal region of CCL21. 20548225_BMSCs transfected with reconstructed plasmid pIRES-hBMP-2-VEGF165 could secret a high level of BMP-2 and hVEGF165. 20651020_Mutated soluble neuropilin-2 B domain antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor bioactivity and inhibits tumor progression. 20851535_Expression of Nrp2 protein is significantly correlated with tumor progression and angiogenesis in salivary adenoid cystic carcinomas. 21199821_dendritic cells express the NRP2 isoforms NRP2a and NRP2b, both are susceptible to polysialylation which is required to specifically enhance chemotaxis toward CCL21 21324919_A critical role of NRP2 in coordinated cell patterning and growth was confirmed using the coculture system. We conclude that NRP2 represents an important mediator of melanoma-endothelial interactions. 21474827_Vascular endothelial growth factor-D stimulates endothelial cell VEGF-A, stanniocalcin-1, and neuropilin-2 and has potent angiogenic effects. 21610314_It was concluded that hypoxia regulates VEGF and SE MA3F activities through transcriptional repression of their common receptor NRP2, providing a novel mechanism by which hypoxia induces tumor angiogenesis, growth and metastasis. 21747928_a direct role of NRP2 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and highlight a cross-talk between neuropilin-2 and TGF-beta1 signaling to promote cancer progression 21840568_In tumoral tissue, consistently strong staining of Neuropilin-2 was noted only in renal cell carcinoma but not in any of the other tumors studied. 21880798_Nrp2 expression was correlated with lymph node metastasis and VEGF-D expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Our data also showed a role for Nrp2 in regulating VEGF-D-induced invasion and migration in vitro. 22028766_tumor cell-derived NRP-2 mediates critical survival signaling in gastrointestinal cancer cells 22384800_In the majority of lung, breast and colorectal cancers, the effects of anti-neuropilin-2 are likely to be restricted to the vasculature 22777769_the VEGF receptor NRP2 is induced by PTEN loss and VEGF/NRP2 signaling regulates the expression of Bmi-1, a key effector of prostate tumorigenesis induced by PTEN deletion 22961441_NRP2 and VEGFR-3 mRNA levels were significantly higher in some of the vascular malformations endothelial cells. 22971992_Inhibition of VEGF by EGCG was associated with suppression of neuropilin-2. 23076131_Neuropilin 2 enables the function of specific integrins that contribute to tumor initiation and progression. [review] 23145112_Utilizing the information on Nrp ligand binding specificity, we demonstrate Nrp constructs that specifically sequester Sema3 in the presence of VEGF-A 23149913_These data suggest a link between the VEGF-C/NRP-2 axis and cancer cell survival 23436775_GLI1 regulates the neuropilin-2/alpha6beta1 integrin based autocrine pathway that contributes to breast cancer initiation. 23551578_An increase in NRP1 and NRP2 epithelial/tumour expression, as well as in NRP1 vascular expression, may be associated with disease progression in colorectal cancer. 23585340_Dysregulated expression of NRP-2 likely contributes to altered angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, neurogenesis and immune function in endometriosis. 23801331_ST8SiaIV synthesized polySia selectively on a NRP2 glycoform that was characterized by the presence of sialylated core 1 and core 2 O-glycans. 23892628_GATA2 and Lmo2 cooperatively regulate VEGF-induced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis via NRP2. 24121493_NRP2 contributes significantly to TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. 24359286_This preliminary study strongly supports the significance of NRP2 as a useful biomarker for malignant progression of melanoma, which may be useful for early identification of patients with melanoma at high risk. 24522185_Paxillin knockdown increases capillary endothelial cell migration and invasiveness, and thereby enhances microvessel ingrowth, by suppressing NRP2 expression. 24729581_This is the first report of a targeted MRI molecular probe based on USPIO and VEGF165-aptamer. 24862180_High NRP2 expression is associated with bladder cancer. 25068647_Data indicate that semaphorin 3F (SEMA3F) and its receptor neuropilin-2 (NRP2) are expressed in the thymus. 25315821_Data show that the transmembrane (TM)domains of neuropilins 1 and 2 dimerize with themselves. 25543087_Neuropilin-2 mediates lymphangiogenesis of colorectal carcinoma via a VEGFC/VEGFR3 independent signaling. 25890345_Neuropilin-2 expression is inhibited by secreted Wnt antagonists and its down-regulation is associated with reduced tumor growth and metastasis in osteosarcoma 26026587_This is the first study in the literature showing that neuropilin-2 and ezrin are related with prognosis in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. 26030152_the novel interplay between PAX8 and Neuropilin-2 26156437_SEMA3F-NRP2 interactions inhibit intracellular PI-3K activity, mTORC2-dependent signaling, RhoA activity and cytoskeletal stress fiber formation. 26286962_Data show significant increases in semaphorin3C, 3D and their receptor neuropilin-2 in degenerate samples which were shown to contain nerves and blood vessels, compared to non-degenerate samples without nerves and blood vessels. 26560516_NRP2/WDFY1 axis is required for maintaining endocytic activity in cancer cells, which supports their oncogenic activities and confers drug resistance. 26753562_the concurrent high expression of VEGF-C and NRP2 is predictive of the unfavorable prognosis in glioblastoma. 26881875_Authors found that NRP2 gene silencing in metastatic melanoma cell lines inhibited tumor cell growth in vitro; furthermore, knockdown of NRP2 expression in the metastatic melanoma cell line 1205Lu significantly inhibited in-vivo tumor growth and metastasis. 26884342_Sequence Requirements for Neuropilin-2 Recognition by ST8SiaIV and Polysialylation of Its O-Glycans. 27026195_NRP2 inhibits WDFY1 transcription by preventing the nuclear localization of a transcription factor, Fetal ALZ50-reactive clone 1 (FAC1). 27063000_NRP2 promotes tumourigenesis and metastasis in Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) through deregulation of ERK-MAPK-ETV4-MMP-E-cadherin signalling. 27159043_Study identifies NRP2 and ESL-1 as targets for polysialylation in murine microglia and human THP-1 macrophages and reveals a striking convergence in the regulation of the two polysialylated acceptors in the course of inflammatory activation. A pool of polysialylated NRP2 and ESL-1 is assembled after injury or in culture and its shedding is an early response to lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of microglia. 27527412_The summarizes the structure and function features of pathway-related molecules of VEGFC/D-VEGFR3/NRP2 axis, stages of various tumors and their molecular mechanisms and significances in tuthe expression changes of these molecules in different anatomic organs or histopathologic types or development lymphatic metastasis. 28065765_The authors also identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms in NRP2 and IGFBP4 loci that increase and reduce risk of lichen planus in hepatitis C virus-infected patients, respectively. 28096505_Neuropilin 2 isoform NRP2b contributed to the oncogenic response to transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) and correlated with tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. 28484884_The results of this study showed that there is a significant association betweenNPR2 rs849563 polymorphism and autism in the studied population 28893946_Sema3a-Nrp2 signaling along an unrecognized pancreatic developmental axis constitutes a chemoattractant system essential for generating the hallmark morphogenetic properties of pancreatic islets. 29130509_NRP2 protein was highly expressed in HPV (-) group compared to that in HPV (+) group. E7-HOTAIR-miR-331-3p-NRP2-E7 formed a regulatory loop, and could be involved in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer. 29227334_Overexpression of NRP2 is associated with spitzoid melanocytic lesions. 29339213_Neuropilin-2 (NRP-2) induces lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs)proliferation, reconstruction and lymphangiogenesis and subsequently promotes tumor cell migration, invasion and lymphatic metastasis via VEGF-C/D-NRP-2 axis [Review] 29717062_Data show that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) -neuropilin 2 (NRP2) signaling contributed to the activation of tafazzin protein (TAZ) in various breast cancer cells. 30057110_neuropilin-2 (Nrp2) is the receptor for HCMV-pentamer infection in epithelial/endothelial cells 30111533_Neuropilin-2 in macrophages promotes tumor growth by regulating efferocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells and orchestrating immune suppression 30656681_the XIST/miR-486 -5p/NRP-2 axis appeared to participate in the progression of colorectal cancer 30717262_The article highlights the diverse NRP1 and NRP2 ligands and interacting partners on endothelial cells, which are relevant in the context of the tumor vasculature and the tumor microenvironment. (Review) 30806307_In endometrial cancer cells, NRP2 expression increased with the degree of histological differentiation. 31013538_The Roles of Neuropilin 2/VEGF-C Axis in a Series of Recurrent Lymphangioma. 31235595_These findings reveal roles for VEGF-NRP2 and YAP/TAZ in DNA repair, and they indicate a unified mechanism involving VEGF-NRP2, YAP/TAZ, and Rad51 that contributes to resistance to platinum chemotherapy 31257576_NRP-2 is involved in small intestinal neuroendocrine tumor progression and metastasis. 31509606_High NRP2 expression is associated with acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate. 31541344_Our results confirmed that (1) rhVEGF165 was highly expressed in MSG cells and was secreted into the cocoon of S1-V165; (2) the dimeric form of rhVEGF165 could be easily dissolved from S1-V165 cocoons using an alkaline solution; (3) rhVEGF165 extracted from S1-V165 cocoons exhibited slightly better cell proliferative activity than the hVEGF165 standard in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 31664117_Silencing of Neuropilins and GIPC1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma exerts multiple cellular and molecular antitumor effects. 32174262_miR-331-3p Suppresses Cell Proliferation in TNBC Cells by Downregulating NRP2. 32350071_Influence of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein O Polymorphism on the Inhibitory Effect of Soluble Forms of Trimer- and Pentamer-Specific Entry Receptors. 32480134_Clinical significance of neuropilin-2 expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 32988871_Presence of the Transmembrane Protein Neuropilin in Cytokine-induced Killer Cells. 33212964_Segregation Analysis of Rare NRP1 and NRP2 Variants in Families with Lymphedema. 33299122_VEGF-C mediates tumor growth and metastasis through promoting EMT-epithelial breast cancer cell crosstalk. 33389349_Circ-LDLRAD3 Enhances Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion and Inhibits Apoptosis by Regulating MiR-224-5p/NRP2 Axis in Gastric Cancer. 33396906_MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells. 33461580_Neuropilin 1 and Neuropilin 2 gene invalidation or pharmacological inhibition reveals their relevance for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. 33528717_Influence of VEGF-A, VEGFR-1-3, and neuropilin 1-2 on progression-free: and overall survival in WHO grade II and III meningioma patients. 33918816_Neuropilin-2 and Its Transcript Variants Correlate with Clinical Outcome in Bladder Cancer. 33923753_The Role of Heparan Sulfate and Neuropilin 2 in VEGFA Signaling in Human Endothelial Tip Cells and Non-Tip Cells during Angiogenesis In Vitro. 34516335_lncRNA RMRP predicts poor prognosis and mediates tumor progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-613/ neuropilin 2 (NRP2) axis. 34636164_Analysis of PLXNA1, NRP1, and NRP2 variants in a cohort of patients with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. 35028975_NRP2 promotes atherosclerosis by upregulating PARP1 expression and enhancing low shear stress-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. 35473507_Effects of silencing neuropilin-2 on proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer HT-29. 35533267_MUC16 Promotes Liver Metastasis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Upregulating NRP2-Associated Cell Adhesion. 35776228_Role of Neuropilin-2-mediated signaling axis in cancer progression and therapy resistance. 35876388_Quantitative Assessment of the Apical and Basolateral Membrane Expression of VEGFR2 and NRP2 in VEGF-A-stimulated Cultured Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. 36306654_The activation of TGF-beta signaling promotes cell migration and invasion of ectopic endometrium by targeting NRP2. |
ENSMUSG00000025969 |
Nrp2 |
969.214716 |
2.7150628749 |
1.440986 |
0.062384462 |
534.867238 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000024664016886027756908374791892613169921696398395314858731725080420129719984198150412224932867010314140071441669334635196673863018590990935460190037419522696649108118953948400594883214717435911873965130015773180426 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012509996193737789738876510044074532836676753959320868417718544495607696313845166028477565157867379934568027517258135365133560003928790229695757137776950464330848221310274130734327312900180611912519285096126452178 |
Yes |
No |
1405.3479396 |
61.2541584 |
520.6959208 |
17.6154859 |
| ENSG00000118308 |
4033 |
IRAG2 |
protein_coding |
Q12912 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the delivery of peptides to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules; this occurs in a transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP)-independent manner. May play a role in taste signal transduction via ITPR3. May play a role during fertilization in pronucleus congression and fusion. Plays a role in maintaining nuclear shape, maybe as a component of the LINC complex and through interaction with microtubules. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60664}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fertilization;Immunity;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encode dby this gene is expressed in a developmentally regulated manner in lymphoid cell lines and tissues. The protein is localized to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4033; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; immune system process [GO:0002376]; nucleus organization [GO:0006997]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906]; vesicle targeting [GO:0006903] |
16410263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18299280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639392_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 31694064_Clinical variability and probable founder effect in oculocutaneous albinism type 7. 35676525_Jaw1/LRMP increases Ca(2+) influx upon GPCR stimulation with heterogeneous effect on the activity of each ITPR subtype. |
ENSMUSG00000030263 |
Irag2 |
563.230590 |
0.2177356120 |
-2.199351 |
0.211853389 |
100.392845 |
0.00000000000000000000001249787419103812433802927022885609315649206830818421529411492822483897846552736154990270733833312988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000127219740041188076387885169278085106695602818471907201400142913699786717529605084564536809921264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
207.8193758 |
29.3341698 |
961.3544984 |
96.2318999 |
| ENSG00000118407 |
27145 |
FILIP1 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z7B0 |
FUNCTION: By acting through a filamin-A/F-actin axis, it controls the start of neocortical cell migration from the ventricular zone. May be able to induce the degradation of filamin-A. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K4T4}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a filamin A binding protein. The encoded protein promotes the degradation of filamin A and may regulate cortical neuron migration and dendritic spine morphology. Mice lacking a functional copy of this gene exhibit reduced dendritic spine length and altered excitatory signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:27145; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
23087206_Data show that RhoD binds the actin nucleation-promoting factor WHAMM (WASp homologue associated with actin Golgi membranes and microtubules), as well as the related filamin A-binding protein FILIP1. 34000624_Clinically relevant aberrant Filip1l DNA methylation detected in a murine model of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000034898 |
Filip1 |
21.934904 |
0.2080543880 |
-2.264967 |
0.472716338 |
23.163926 |
0.00000148761948388638737505703171781767935044626938179135322570800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005159131480771399817189960118613001327503297943621873855590820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0839474 |
2.8059285 |
39.5494231 |
8.5310437 |
| ENSG00000118432 |
1268 |
CNR1 |
protein_coding |
P21554 |
FUNCTION: G-protein coupled receptor for endogenous cannabinoids (eCBs), including N-arachidonoylethanolamide (also called anandamide or AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), as well as phytocannabinoids, such as delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (PubMed:15620723, PubMed:27768894, PubMed:27851727). Mediates many cannabinoid-induced effects, acting, among others, on food intake, memory loss, gastrointestinal motility, catalepsy, ambulatory activity, anxiety, chronic pain. Signaling typically involves reduction in cyclic AMP (PubMed:1718258, PubMed:21895628, PubMed:27768894). In the hypothalamus, may have a dual effect on mitochondrial respiration depending upon the agonist dose and possibly upon the cell type. Increases respiration at low doses, while decreases respiration at high doses. At high doses, CNR1 signal transduction involves G-protein alpha-i protein activation and subsequent inhibition of mitochondrial soluble adenylate cyclase, decrease in cyclic AMP concentration, inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent phosphorylation of specific subunits of the mitochondrial electron transport system, including NDUFS2. In the hypothalamus, inhibits leptin-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and mediates cannabinoid-induced increase in SREBF1 and FASN gene expression. In response to cannabinoids, drives the release of orexigenic beta-endorphin, but not that of melanocyte-stimulating hormone alpha/alpha-MSH, from hypothalamic POMC neurons, hence promoting food intake. In the hippocampus, regulates cellular respiration and energy production in response to cannabinoids. Involved in cannabinoid-dependent depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI), a process in which depolarization of CA1 postsynaptic pyramidal neurons mobilizes eCBs, which retrogradely activate presynaptic CB1 receptors, transiently decreasing GABAergic inhibitory neurotransmission. Also reduces excitatory synaptic transmission (By similarity). In superior cervical ganglions and cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells, inhibits voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels in a constitutive, as well as agonist-dependent manner (PubMed:17895407). In cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells, cannabinoid-induced inhibition of voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels leads to vasodilation and decreased vascular tone (By similarity). Induces leptin production in adipocytes and reduces LRP2-mediated leptin clearance in the kidney, hence participating in hyperleptinemia. In adipose tissue, CNR1 signaling leads to increased expression of SREBF1, ACACA and FASN genes (By similarity). In the liver, activation by endocannabinoids leads to increased de novo lipogenesis and reduced fatty acid catabolism, associated with increased expression of SREBF1/SREBP-1, GCK, ACACA, ACACB and FASN genes. May also affect de novo cholesterol synthesis and HDL-cholesteryl ether uptake. Peripherally modulates energy metabolism (By similarity). In high carbohydrate diet-induced obesity, may decrease the expression of mitochondrial dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase/DLD in striated muscles, as well as that of selected glucose/ pyruvate metabolic enzymes, hence affecting energy expenditure through mitochondrial metabolism (By similarity). In response to cannabinoid anandamide, elicits a pro-inflammatory response in macrophages, which involves NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL1B and IL18 secretion (By similarity). In macrophages infiltrating pancreatic islets, this process may participate in the progression of type-2 diabetes and associated loss of pancreatic beta-cells (PubMed:23955712). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O02777, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P47746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15620723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1718258, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17895407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21895628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23955712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27768894, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27851727}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Binds both 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and anandamide. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15620723}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Only binds 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) with high affinity. Contrary to its effect on isoform 1, 2-AG behaves as an inverse agonist on isoform 2 in assays measuring GTP binding to membranes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15620723}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Only binds 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) with high affinity. Contrary to its effect on isoform 1, 2-AG behaves as an inverse agonist on isoform 3 in assays measuring GTP binding to membranes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15620723}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Obesity;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes one of two cannabinoid receptors. The cannabinoids, principally delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and synthetic analogs, are psychoactive ingredients of marijuana. The cannabinoid receptors are members of the guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (G-protein) coupled receptor family, which inhibit adenylate cyclase activity in a dose-dependent, stereoselective and pertussis toxin-sensitive manner. The two receptors have been found to be involved in the cannabinoid-induced CNS effects (including alterations in mood and cognition) experienced by users of marijuana. Multiple transcript variants encoding two different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2009]. |
hsa:1268; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; cannabinoid receptor activity [GO:0004949]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; aging [GO:0007568]; axonal fasciculation [GO:0007413]; cannabinoid signaling pathway [GO:0038171]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; maternal process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060135]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of action potential [GO:0045759]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; negative regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0033602]; negative regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0031999]; negative regulation of mast cell activation [GO:0033004]; negative regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051001]; negative regulation of serotonin secretion [GO:0014063]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002866]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045777]; positive regulation of fever generation [GO:0031622]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of feeding behavior [GO:0060259]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222]; regulation of penile erection [GO:0060405]; regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0099509]; regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0032228]; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051966]; response to cocaine [GO:0042220]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to morphine [GO:0043278]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; retrograde trans-synaptic signaling by endocannabinoid [GO:0098921]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; trans-synaptic signaling by endocannabinoid, modulating synaptic transmission [GO:0099553] |
15472222_the cannabinoid receptor CB1 was not identified in first trimester placenta 15562018_Human sperm express functional CB(1)-R, the activation of which negatively influences important sperm functions such as motility. 15620723_Identification of a splice variant of the human CB1 receptor. 15657045_lipid rafts control CB1R binding and signaling, and CB1R activation underlies the protective effect of methyl-beta-cyclodextrin against apoptosis 15668727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15668727_the presence of two long alleles in the cnr1 gene was associated with a reduced prevalence of depression in parkinson disease 15728830_Senile plaques in AD patients express CB1 receptors which show increased nitration. G-protein coupling and CB1 receptor protein expression are markedly decreased in AD brains. 15927811_CB1 and CB2 immunoreactivity was observed in cutaneous nerve fiber bundles, mast cells, macrophages, epidermal keratinocytes, and the epithelial cells of hair follicles, sebocytes and eccrine sweat glands. 15952782_Tole of cysteine residues in CB1 ligand binding and activation, and demonstrate a method for mapping key determinants in CB1 structure and function 16204352_No convincing association is found for cannabinoid receptor type 1 (Cnr1) in a systematic genetic association study in a human sample of postmenopausal osteoporosis patients and matched female controls 16204352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16263116_CB1R is associated with cholesterol- and sphyngolipid-enriched membrane domains (rafts). 16314880_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16365309_CB(1) receptors are stabilized in a conformation that enables G(q)11 signaling by the WIN55212-2 cannabinoid agonist, thus shifting the G protein specificity of the receptor 16623851_4 SNPs in the CNR1 gene are found to be positively associated with striatal response to happy faces (and not to disgust faces) in humans, using fMRI. 16634642_decreased thermal stability of T210I receptor & increased level of internalization of a T210I receptor-GFP chimera were also observed. Results suggest that T210 plays key role in governing transition between inactive & active CB(1) receptor states. 16712507_Sequential assignments of TM5 and intra-cellular loop 3 were accomplished. The obtained structure also showed alpha-helix in the TM5 region, but it was interrupted by a disordered region (Gly204_ILe206). 16715087_study shows that CB1 receptors are upregulated in the liver of cirrhotic individuals and expressed in liver fibrogenic cells 16741937_Findings fail to replicate the original report of an association between SNPs adjacent to an alternative CNR1 exon 3 transcription start site and polysubstance abuse. 16741937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16788767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16818376_analysis of human cannabinoid receptor 1 truncation 16917946_A common CNR1 haplotype is associated with developing fewer cannabis dependence symptoms among adolescents who have experimented with cannabis. 16917946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16962033_Antagonists may prove beneficial in the treatment of proliferative liver fibrosis. 17015679_lipid rafts control CB1R, but not CB2R, and endocannabinoid transport in immune and neuronal cells. 17041005_In summary, up-regulation of CB1 in T lymphocytes in response to CBs themselves may facilitate or enhance the various immunomodulatory effects related to CBs. 17065342_CB(1) mRNA expression was negatively correlated with visceral fat mass, fasting insulin and circulating 2-arachidonylglycerol. 17068343_apoptosis induced by cannabinoid receptor CB1 and CB2 agonists leads to activation of ERK1/2 leading to G1 cell cycle arrest in prostate cancer cells 17074588_High expression of CB1 receptor was observed in 29 (45%) in hepatocellular carcinoma. 17160086_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17160086_results show that the presence of the CB1 polymorphic allele was significantly associated with a lower body mass index 17270342_These data suggest that endocannabinoids regulate pathways affecting skeletal muscle oxidation, effects particularly evident in myotubes from obese individuals. 17284627_no association of human adipose tissue CNR1 mRNA expression with measures of body fat, metabolic parameters, fat cell function, or adiponectin expression. 17292652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17292652_There is no evidence for an association of CNR1 alleles with obesity in German children. 17370106_In major depression, CB(1) receptor immunopositive glial cells in the grey matter were decreased. Furthermore, our data show that different medications have an impact on the expression of CB(1) receptors in the ACC. 17384224_results clearly suggest that Ser7.39, but not Ser2.60, plays a crucial role in mediating ligand specific interactions at the CB(1) receptor; modeling studies predict that Ser7.39 in a g-chi1 conformation may induce a helix bend in transmembrane helix 7 17405839_Genetic variants at CNR1 are associated with obesity-related phenotypes in men 17405839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17449448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17508995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17509535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17533584_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17595161_CB1 cannabinoid receptor Helix 8 Leu contributes to selective signal transduction mechanisms 17655760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17669634_CNR1 gene polymorphisms could be a psychopharmacogenetic rather than a vulnerability factor regarding schizophrenia and its treatment 17678969_CB(1)R and CB(2)R are differentially linked to lipid rafts, specialized microdomains of the plasma membrane--REVIEW 17683024_Cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors and their respective ligands, the endocannabinoids, have a significant role in the modulation of food intake and motivation to consume palatable food. [REVIEW] 17684478_impaired CB1 receptor function promotes passive stress-coping behavior, which, at least in part, might relate to alterations in BDNF function. 17712725_The endocannabinoid system is activated in obese visceral adipose tissue as shown by decreased FAAH, Cb1, and adiponectin expression. 17873324_G1422A polymorphism in the CNR1 gene is associated with increased abdominal adiposity in obese men. 17873324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17881126_In conclusion, we could not detect a statistically significant association between mutations in the CNR1 gene and the predisposition to develop schizophrenia. 17881126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17923791_insulin may play a key role in the obesity-linked dysregulation of the adipose endocannabinoid system at the gene level 17942526_No associations were identified between CNR1 genetic variants and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis 17942526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17978319_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17978319_There was no evidence of association between schizophrenia and CNR1 (OR=0.97, 95% CI 0.82-1.13) or CHRNA7 (OR=1.07, 95% CI 0.77-1.49) genotypes, or of interactions between tobacco use and CHRNA7, or cannabis use and CNR1or COMT genotypes. 18064064_No significant difference was found between the schizophrenia and control cases in cannabinoid CB1 receptors binding in the superior temporal gyrus. 18092149_CB1 is densely located in glucagon-secreting alpha cells and less so in insulin-secreting beta cells. 18156315_Analysis of promoter regions regulating basal and Il-4-inducible expression of CB1 in T-lymphocytes is reported. 18165231_AEA is able to decrease differentiating gene expression by increasing DNA methylation in human keratinocytes, through a p38, and to a lesser extent p42/44, mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway triggered by CB1R. 18174385_The profound loss of function in the I2.62T-D2.63N double mutant suggests that, although these residues are not obligatory for agonist recognition, they play a synergistic and crucial role in modulating signal transduction. 18179391_Impulsivity was significantly associated with the 6-repeat allele of the triplet repeat polymorphism (AATn/A6; p A mutation in the CNR1 gene in patients with esophageal cancer. 19366584_CB1 helices 7 and 8 reconstituted into phospholipid bilayers are oriented in a transmembrane and in-plane (i.e., parallel to the phospholipid membrane surface) fashion, respectively. 19419760_Very low or absent FAAH and high CB1 levels correspond with spontaneous miscarriage. 19420965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19420965_a single nucleotide mutation in CNR1 has a role in colorectal cancer outcome 19443135_Case-control analysis identified a nominal association between single nucleotide polymorphism of CNR1 and having one or more cannabis dependence symptoms 19477951_analysis of anandamide-stimulated cannabinoid receptor signaling in human ULTR myometrial smooth muscle cells 19481011_The loss of CB(1) receptors in HD is also thought to be a compensatory mechanism due to evidence that endocannabinoids modulate the reuptake of GABA in the GP. 19485422_Synthetic CB1 peptide backbone dynamics and rotameric freedom are altered by the peptide's phospholipid bilayer environment, which exerts a dynamic influence on the conformation of a transmembrane helix critical to signal transmission by the CB1 receptor. 19539700_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19539700_Our results demonstrated a significant haplotypic effect of CNR1 on migraine headaches. 19547718_results demonstrate the expression and regulation of CB1 and CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase in retinal pigment epithelial cells 19596672_Blocking CB1 together with selective activation of CB2 may suppress pro-inflammatory responses of macrophages. 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19652957_This study suggested that antipsychotics induce down-regulation of CB1 receptors in brain. 19659925_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19661434_results suggest that spinal endocannabinoids and CB1 receptors on inhibitory dorsal horn interneurons act as mediators of heterosynaptic pain sensitization and play an unexpected role in dorsal horn pain-controlling circuits 19725030_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19725030_certain constellations of CB1-receptor and 5-HTT promoters yield extremely high or low synaptic 5-HT concentrations, and these are associated with an anxious phenotype 19730968_CB1 was markedly expressed in hepatocytes and biliary epithelial cells in the livers of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis 19730968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19766594_the NMR solution structure of a synthetic 40-mer (T(377)-E(416)) that encompasses human cannabinoid receptor-1 (hCB1) transmembrane helix 7 (TMH7) and helix 8 (H8) [hCB1(TMH7/H8)] in 30% trifluoroethanol/H(2)O was reported. 19801960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19837905_[REVIEW] CB(1) cannabinoid receptor highlights the contribution of two important aspects of GPCR function-orthosteric ligand binding and receptor heterodimerization-toward directed GPCR signaling 19839995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19854014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19858202_Cannabinoid receptor type 1- and 2-mediated increase in cyclic AMP inhibits T cell receptor-triggered signaling. 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19919870_The Cnr1 A3813G variant is associated with different levels of CB1 mRNA in perirenal visceral adipose tissue. 19938110_Report the ultrastructural compartmentalization of CB1-R in human sperm and a potential role in sperm suvival and acrosome reaction. 19942623_CB1 activation in cardiomyocytes may amplify the reactive oxygen/nitrogen species-MAPK activation-cell death pathway in pathological conditions 19944766_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956878_cannabinoid CB1 receptor may have a role in progression of human colon cancer, as its antagonists rimonabant and oxaliplatin inhibit growth 20007426_CNR1 genotypes could behave as risk factors for primary progressive multiple sclerosis. 20007426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010552_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20010552_The underlying mechanism of these genetic effects may be enhanced neural response in reward areas of the brain in carriers of the CNR1 G allele and FAAH C/C genotype in response to marijuana cues. 20010914_In Caucasians, long repeats (>or=14) of 18087-18131(TAA)(8-17) were associated with heroin addiction. 20010914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20015515_The levels of the CB1 receptors and the CB1 receptor-mediated G-protein signaling were significantly lower in the ventral striatum of CA compared to the control group. 20041802_Cyanidin and delphinidin are ligands with moderate affinity to human CB1and CB2. 20049372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20049372_The mutant genotype G1359A is associated with a better cardiovascular profile (weight, BMI, fat mass, waist circumference, insulin, HOMA and c reactive protein) than wild type group. 20080186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080186_These findings, although preliminary, suggest that the CNR1 gene variants may contribute to the susceptibility to mood disorders 20090845_high expression level of CB(1) and CB(2) receptors commonly found in malignant astrocytomas precludes the use of cannabinoids as therapeutics, unless AKT is concomitantly inhibited 20107430_In this study, we provide evidence that the CNR1 gene may be associated with antipsychotic-induced weight gain in chronic schizophrenia patients. 20107430_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20124735_Cannabinoid 1 receptor blockade reduces atherosclerosis with enhances reverse cholesterol transport 20192949_In line with the polygenic model, our meta-analysis supports a minor implication for CNR1 AAT polymorphism in illicit substance dependence vulnerability. 20192949_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20195480_Data show that the CNR1 p.Thr453Thr polymorphism appears to modulate UC susceptibility and the CD phenotype. 20195480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197196_The novel finding is the association of the mutant-type group G1359A and A1359A with a better cardiovascular profile (triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, insulin, and homeostasis model assessment levels) than the wild-type group. 20204253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20204253_The finding of this study is the lack of association of G1359A polymorphism of CB receptor 1 gene with obesity, cardiovascular risk factors and adipocytokines 20307616_results demonstrate opposite changes in cannabinoid receptor 1 and 2 protein expression in human gliomas 20369362_In the endometrium, CB1 and CB2 immunoreactivity was primarily restricted to the glandular epithelium and expression was unrelated to the phase of the menstrual cycle. 20391958_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20391958_Polymorphism G1359A in the CB1 receptor did not have a significant effect on biochemical and anthropometric improvements after biliopancreatic diversion surgery. 20406692_In conclusion, we found that [(11)C] OMAR can image human CB1 receptors in normal aging and schizophrenia. 20415562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20494466_expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors is upregulated in aortic valve stenosis 20505532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20505532_We found a different distribution of allelic frequency of AAT repeats in the CNR1 gene in healthy controls and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) patients, and a significant association between the CNR1 >10/ >10 genotype and IBS 20506110_Palmitic acid induced apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress via CB(1)R expression in human proximal tubule cells. CCB(1)R blockade may be a potential anti-diabetic therapy for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. 20555313_The cb1 receptor was down regulation in the prefrontal cortex in patient with schizophrenia. 20587580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587580_This study found a link between common variants of the endocannabinoid receptor 1 and body fat distribution in young men. 20602678_CB1/CB2 participate in the regulation of lipid metabolism in human-derived immortalized hepatocytes by regulating the expression of key enzymes of lipid synthesis and transport. 20606244_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20607655_Western-blot and immunohistochemical assays revealed the presence of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor protein in fetal and adult kidneys 20621164_The early expression pattern of cannabinoid receptor 1 in cortical development is confirmed, and a function is suggested for CB1 in the early stages of corticogenesis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631561_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20680268_These data point to in vivo changes in endocannabinoid transmission, specifically for CB1 receptors in the QA model, with involvement of the caudate-putamen, but also distant regions of the motor circuitry, including the cerebellum 20691427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20705472_CB1 expression is maintained by nerve fibers in painful human dental pulp; neurofilament fibers are significantly reduced in the dental pain group compared to non-painful controls, but there is no difference in the ratio of CB1 to neurofilaments. 20720046_CB1 levels in the brains of Huntington disease (HD) patients 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20808855_Tumour epithelial FAAH-IR is associated with prostate cancer severity and outcome at mid-range, but not high, CB(1)IR scores. 20838400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20838400_There is an association of the variants of CNR1 with obesity-related phenotypes in Polish postmenopausal women. 20851297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20852034_A posttranscriptional downregulation of CB and the absence of expression of CB characterize clear cell renal cell carcinomas . 20854251_This study demonistrated that CB! receptor expression in human platelets and predominantly localized inside the cell. 20862263_Hepatitis C virus infection induces the expression of cannabinoid receptor 1. 20863671_First-episode schizophrenia patients who use cannabis show a pronounced cortical thinning in brain regions with a high density of type 1 cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. 20885390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20929960_these results support the notion that downregulation of type 1 cannabinoid receptors is a key pathogenic event in Huntington's disease, and suggest that activation of these receptors in patients with Huntington's disease may attenuate disease progression. 21034788_CB1 receptors are intact in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and may play a role in preserving cognitive function. Therefore, CB1 receptors should be further assessed as a potential therapeutic target in AD. 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21044623_a bulky hydrophobic contact is largely sufficient to provide significant receptor function and binding affinity to cannabinoid CB(1) receptor ligands 21050275_our study provides strong evidence that endocannabinoids are a modulator for the proposed 'handshake' interactions between corticothalamic and thalamocortical axons, especially for fasciculation. 21062041_Conformational data indicate that regular turn structures in the central portion of hemopressin and biologically active fragment hemopressin(1-6) are critical for an effective interaction with cannabinoid CB1 receptor. 21129839_genetic association studies in Czech/Central European population: investigation of association of 3 SNP in CNR1 with pre-eclampsia; data indicate that rs806368 in CNR1 gene may act as susceptibility marker for pre-eclampsia 21148019_The results of the present investigation point to CB(1)R long AAT repeats as an important modulator of disease severity in relapsing multiple sclerosis subjects. 21156413_results suggest that allele G of the CNR1 gene could be associated with a lower susceptibility to glioma 21203460_high tumor CB(1) receptor expression at diagnosis augments the deleterious effects of a high pEGFR expression upon disease-specific survi 21209828_a CNR1 (cannabinoid receptor 1) haplotype may have a role in attenuating the decrease in HDL cholesterol that typically accompanies weight gain 21234731_These data offer new insight into CNR1 properties and support the concept that the membrane bilayer itself may serve as a mechanochemical mediator of G-protein coupled receptor signal transduction 21244428_This review focuses on both the functional roles of the CB1 receptor carboxyl-terminus in the binding of numerous proteins and regulation of receptor activation, signaling, and subcellular localization. 21251115_This study demonistrated that CB1 was expressed in neurons, injured axons, oligodendrocytes, macrophages/microglia, some astrocytes, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells and pericytes of brain in patient with multiple sclerosis. 21266946_Results indicate a possible role of CNR1 in the development of tardive dyskinesia. 21306178_truncation of arrestin-2 provides scope for positively charged residues in the polar core of the protein to interact with phosphates present in the loop of the CB1(5P)(454-473) peptide 21346174_The findings provide direct evidence for a functional interaction between CB1R and IR signaling involved in the regulation of beta-cell proliferation. 21373835_Activation of CB(1) receptors may play an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy by facilitating MAPK activation, oxidative stress and inflammatory signalling. 21396980_The findings suggest that AATn polymorphism modifies CNR1 translation, indicating a different modulation of CB1. 21420833_This study suggested that heavy cannabis use in the context of specific CNR1 genotypes may contribute to greater white matter volume deficits and cognitive impairment, which could in turn increase schizophrenia risk. 21442624_These results provide evidence that CB(1)R blockade through the recovery of FAAH 1 expression may be a potential anti-diabetic therapy for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. 21443454_CB1 receptor contributes to the rapid ischemic tolerance induced by electroacupuncture pretreatment against focal cerebral ischemia. 21450051_Our study indicates that expression of cannabinoid receptors CB1 AND CB2 occurs in glia in HIV encephalitis brains 21459482_Patients with Parkinson's disease show an absolute decrease in CB1 availability in the substantia nigra; by contrast, CB1 availability is relatively increased in nigrostriatal, mesolimbic, and mesocortical dopaminergic projection areas. 21471673_studies provide data to suggest that the ATT repeat in the CNR1 gene influences sweet taste in obese females. 21471953_Upregulated CB1 receptor expression in paranoid schizophrenia leads to increased CB1 receptor binding in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. 21472688_A differential association between the expression of CNR1/CNR2 and RAGE with morphological changes and expression of molecular markers of inflammation could be established in patients with inflammatory bowel disease 21472841_The novel finding of this study is the association of the G1359A and A1359A cannabinoid type-1 genotypes with a lower prevalence of metabolic syndrome than the G1359G genotype 21477106_CNR1 and FAAH are associated with altered gastric functions or satiation that may predispose to obesity. 21480765_Further genotyping of the endocannabinoid receptor gene cannot be used as a significant marker of predisposition to cardiovascular diseases in postmenopausal women. 21513772_This study demonistrated that variations within CNR1 may differentially alter the sensiti |
ENSMUSG00000044288 |
Cnr1 |
310.382163 |
5.9977354860 |
2.584418 |
0.693396915 |
12.261073 |
0.00046250538165973256298640903239061117346864193677902221679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001142906317310840970738472499590443476336076855659484863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
343.7410000 |
192.7668539 |
57.0384682 |
22.7960165 |
| ENSG00000118473 |
84251 |
SGIP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQI5 |
FUNCTION: May function in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Has both a membrane binding/tubulating activity and the ability to recruit proteins essential to the formation of functional clathrin-coated pits. Has a preference for membranes enriched in phosphatidylserine and phosphoinositides and is required for the endocytosis of the transferrin receptor. May also bind tubulin. May play a role in the regulation of energy homeostasis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VD37}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Endocytosis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
SGIP1 functions as an endocytic protein that affects signaling by receptors in neuronal systems involved in energy homeostasis via its interaction with endophilins (see SH3GL3; MIM 603362) (Trevaskis et al., 2005 [PubMed 15919751] and Uezu et al., 2007 [PubMed 17626015]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:84251; |
AP-2 adaptor complex [GO:0030122]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; clathrin coat assembly [GO:0048268]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; positive regulation of feeding behavior [GO:2000253]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0048260]; response to dietary excess [GO:0002021] |
17626015_SGIP1alpha plays an essential role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis by interacting with phospholipids and Eps15. 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20421487_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20946875_SGIP1 and the signaling adaptor Reps1 interact with ITSN1 in vivo. 21317682_The earlier implicated single nucleotide polymorphisms located in SGIP1 gene showed no association with alcohol dependence or theta electroencephalogram power. 21407171_Our results show association between genetic variants in SGIP1 and fat mass. We provide evidence that variation in SGIP1 is a potentially important determinant of obesity-related traits in humans 26822536_crystal structures of the SGIP1 mu homology domains in complex with peptides containing two DPF motifs, are reported. 28030933_The present study demonstrated a possible association of target P300 evoked theta and of alcohol dependence with SNPs from the gene SGIP1 in the region of rs10889635, but further studies are required. 30236986_Data indicate that cysteine C632 residue is important for the function of SH3 domain GRB2 like endophilin interacting protein 1 (SGIP1) during cellular endocytosis. 33118832_Plasma SGIP1 methylation in diagnosis and prognosis prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000028524 |
Sgip1 |
60.590970 |
0.3710996774 |
-1.430121 |
0.274837673 |
26.813305 |
0.00000022408923414192851394367270081303677997652812337037175893783569335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000850927989692530188207432711305910899568516470026224851608276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.6472246 |
5.8428059 |
93.9427015 |
10.7887278 |
| ENSG00000118507 |
9465 |
AKAP7 |
protein_coding |
Q9P0M2 |
FUNCTION: Probably targets cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) to the cellular membrane or cytoskeletal structures. The membrane-associated form reduces epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity, whereas the free cytoplasmic form may negatively regulate ENaC channel feedback inhibition by intracellular sodium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17244820}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) family, a group of functionally related proteins that bind to a regulatory subunit (RII) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) and target the enzyme to specific subcellular compartments. AKAPs have a common RII-binding domain, but contain different targeting motifs responsible for directing PKA to distinct intracellular locations. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]. |
hsa:9465; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse [GO:0098686]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; protein kinase A binding [GO:0051018]; protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding [GO:0034237]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; regulation of protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010738] |
12804576_AKAP7gamma is the first nuclear AKAP to bind RI and may be responsible for positioning PKA via RI and/or RII to regulate PKA-mediated gene transcription in both somatic cells and oocytes 17244820_AKAP15 regulates ENaC via a novel PKA-independent pathway 18082768_AKAP18 contains a phosphodiesterase domain that binds AMP. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22670899_Data from studies using recombinant proteins suggest that both AKAP7-gamma and AKAP7-alpha exhibit high-affinity interactions with isoenzymes of PKC (protein kinase C); AKAP7 could dictate PKC localization/function. 24302730_PKC tethered to AKAP7alpha was less susceptible to inhibition from the ATP-competitive inhibitor Go6976 and the substrate-competitive inhibitor PKC 20-28, but not the activation-competitive inhibitor calphostin C. 27487922_Malonate in the nucleotide-binding site traps human AKAP18-gamma in a novel conformational state. 28446746_AKAP7 expression levels may have clinical utility as a prognostic biomarker for post-stroke blood brain complications |
ENSMUSG00000039166 |
Akap7 |
34.980416 |
0.3992375798 |
-1.324681 |
0.296973030 |
20.096482 |
0.00000736320077878817446791377687720370204260689206421375274658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000023488403608150738654343145372926926484069554135203361511230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6202408 |
4.2807214 |
54.4163754 |
7.0691160 |
| ENSG00000118513 |
4602 |
MYB |
protein_coding |
P10242 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator; DNA-binding protein that specifically recognize the sequence 5'-YAAC[GT]G-3'. Plays an important role in the control of proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. |
Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein with three HTH DNA-binding domains that functions as a transcription regulator. This protein plays an essential role in the regulation of hematopoiesis. This gene may be aberrently expressed or rearranged or undergo translocation in leukemias and lymphomas, and is considered to be an oncogene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4602; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; myeloid cell development [GO:0061515]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:1901533]; negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0045653]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051571]; positive regulation of histone H3-K9 methylation [GO:0051574]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of T-helper cell differentiation [GO:0045624]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
11848471_Activation of c-MYC and c-MYB proto-oncogenes is associated with decreased apoptosis in tumor colon progression. 11896618_Friend murine erythroleukemia cells are held in an immature and proliferating state by a pathway that is dependent on Myb activity 11973331_c-Myb transactivates the IGFBP-5 promoter 12370369_c-Myb has no apparent effect on core binding factor/polyoma enhancer-binding protein 2 binding, but is critical for activation of enhancer-dependent transcription of the TCR delta enhancer. 12424255_role in regulating type I collagen alpha 2 chain gene 12529244_involvement of c-myb in the regulation of intestinal nutrient absorption 12631292_Data suggest that the negative influence on transactivation properties by the negative regulatory domain region of c-Myb depends on sumoylation sites. 15187020_NmU expression is related to Myb and that the NmU/NMU1R axis constitutes a previously unknown growth-promoting autocrine loop in myeloid leukemia cells 15221349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15509555_p53 antagonizes c-Myb by recruiting mSin3A to down-regulate specific Myb target genes 15687240_c-Myb activity is directly regulated by cyclin D1 and CDKs and imply that c-Myb activity is regulated during the cell cycle in hematopoietic cells 15747776_10 genes were down-regulated following treatment of the T-ALL cells with 0.15 and 1.5 microg/mL of metal ores at 72 h. 15778089_data suggest that amplification of c-myb in tumor cells may lead to robust GRP78 gene induction, which may in turn assist cells in survival under conditions of oxygen deprivation and nutrient stress 15927960_c-Myb has a longer half-life (at least 2-fold) in BCR/ABL-expressing than in normal hematopoietic cells 16299810_EGF-induced activation of B-Myb promoter required both E2F and EGFR target sites 16461764_point mutation are uncommon in patients with myeloproliferative disorders 16597594_c-Myb is a major factor that controls differentiation as well as proliferation of hematopoietic progenitor cells derived from hemogenic endothelial cells; appropriate levels of c-Myb protein are strictly defined at distinct differentiation steps 16631597_Together, these results show that the cAMP pathway blocks gamma-globin gene expression in K562 cells by increasing c-Myb expression. 16797705_The enhanced stability of c-Myb in CML blast crisis cells and perhaps in other types of leukemia is not caused by a genetic mechanism. 16861354_individuals with elevated HbF levels during adult erythropoiesis demonstrated simultaneous transcriptional down-regulation in cMYB and HBS1L 16977606_Among MYB regulation, the most dynamic is the control of transcriptional elongation by sequences within intron 1, this regulatory sequence is transcribed into an RNA stem-loop and 19-residue polyuridine tract, and is subject to mutation in colon cancer. 17095623_a lack of integrin engagement leads to the induction of cellular markers associated with myeloid differentiation 17242210_c-Myb protein plays a previously unappreciated role in the G(2)/M cell cycle transition of normal and malignant human hematopoietic cells 17363689_c-Myb regulates cell cycle-associated IP3R1 transcription in VSMCs via specific highly conserved Myb-binding sites in the IP3R1 promoter. 17435759_Duplication of MYB is an oncogenic event and we suggest that MYB could be a therapeutic target in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 17452517_The MYB(dup) alteration was associated with T-cell acute leukemia 17599807_Protein expression of c-Myb in human arterial vascular smooth muscle cells is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). 17690249_MYB is an effector of estrogen/estrogen signaling 17712044_The HBS1L-MYB intergenic region on chromosome 6q23.3 influences erythrocyte, platelet, and monocyte counts. 18070937_Alu--mediated MYB tandem duplication occurs at low frequency during normal thymocyte development and is clonally selected during the molecular pathogenesis of human T-ALL 18093978_TRAF6 is modified by small ubiquitin-related modifier-1, interacts with histone deacetylase 1, and represses c-Myb-mediated transactivation. 18195038_An array of variant transcripts, expressed in highly regulated, lineage-specific patterns were formed from alternate exons 8A, 9A, 9B, 10A, 13A, & 14A. They encoded c-Myb proteins with identical DNA binding domains but unique C-terminal domains. 18408764_c-Myb cooperates with FLASH in foci associated with active RNA polymerase II, leading to enhancement of Myb-dependent gene activation. 18476782_MYB is highly expressed in almost all estrogen-receptor-positive breast tumours & is a direct target of estrogen/ER signalling. It is required for tumor cell proliferation. Review. 18498763_These data provide evidence that c-Myb may serve a previously unappreciated role in the coupling between transcription and splicing. 18667440_c-Myb is an evolutionally conserved target of miR-150 and miR-150/c-Myb interaction is important for embryonic development and possibly oncogenesis 18667698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18708755_restoration of c-Myb levels partly alleviates tumors suppressive effects of miR-15a/16, suggesting that c-Myb is a key downstream target of this microRNA cluster 18765672_Fbxw7, the F-box protein of an SCF complex, targets c-Myb for degradation in a Wnt-1- and NLK-dependent manner. 18818396_these findings suggest the presence of a c-Myb-miR-15a autoregulatory feedback loop of potential importance in human hematopoiesis 18818702_a gain of the MYB locus, was found recurrently and only in the MYST3-linked AMLs (7/18 vs 0/34). MYST3-AMLs have also a specific a gene expression profile, which includes overexpression of MYB, CD4 and HOXA genes 19036881_The results indicate that c-Myb potentiates Stat5a-driven gene expression, possibly functioning as a Stat5a coactivator, in human breast cancer. 19148297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19198610_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19198610_SNPs at WDR36, IL33 and MYB that showed suggestive association with eosinophil counts were also associated with atopic asthma. 19427836_These findings suggest that c-myb stimulates cell growth, in part, by regulating expression of the components of IGF-IGFBP axis in K562 cells. 19615744_The mRNA expression of transcription factor MYB, the designated target of miR-150, was shown to correlate inversely with the miR-150 level 19646965_c-Myb appears to be phosphorylated by HIPK1 in its negative regulatory domain as supported by both in vivo and in vitro data. 19696200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19737967_Results show that mutation of single residues in the c-MYB transactivation domain important for CBP/p300 binding leads to complete loss of transforming ability. Double mutants show severely impaired transact'n and are also defective for CBP/p300 binding. 19841262_The MYB-NFIB fusion is a hallmark of adenoid cystic carcinomas (ACC) and deregulation of the expression of MYB and its target genes is a key oncogenic event in the pathogenesis of ACC.[MYB-NFIB fusion prtoein] 19843942_c-Myb does not appear to be required for commitment to B cell differentiation but is crucial for B cell differentiation to the CD19-positive pro-B cell stage as well as survival of CD19-positive pro-B cells. 19860791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19862010_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20027603_Enhanced expression of c-MYB is associated with ulcerative colitis-associated neoplasia. 20093773_c-Myb has the ability to transform hemtopoietic cells, which lends relevance to its role in mixed-lineage leukemia. 20142358_During differentiation, transgenic Myb-deficient CD4+CD8+ double-positive thymocytes undergo premature apoptosis due to decreased Bcl-xL expression; forced reintroduction of c-Myb restores Bcl-xL. expression. 20183929_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364308_MyoD and c-myb are involved in regulation of basal and estrogen-induced transcription activity of the BRCA1 gene 20472475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20472475_SNPs in BCL11A and the HBS1L-MYB region did not show statistically significant correlations with HbFlevels.This suggests that the BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB loci have a minor effect on HbF level compared to the XmnI QTL in beta-thalassemia intermedia patients. 20484083_c-Myb, GATA-3, and Menin form a core transcription complex that regulates GATA-3 expression and, with the recruitment of MLL, results in Th2 cell maturation. 20524209_PMA induces overexpression of lysozyme via ERK1/2 MAP kinase-c-Myb signaling pathways 20531406_The human B-cell interactome (HBCI), reveals a hierarchical, transcriptional control module, where MYB and FOXM1 act as synergistic master regulators of proliferation in the germinal center (GC). 20547751_Hep27 is regulated at the transcriptional level by the proto-oncogene c-Myb and is required for c-Myb-induced p53 stabilization. 20622260_Data show that the proto-oncogene c-Myb controls Slug transcription in tumor cells of different origin. Such a regulatory pathway contributes to the acquisition of invasive properties that are important for the metastatic process. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20647765_This study, together with previous and recent data showing rearrangements and copy number alterations of the MYB locus in T-cell leukemia and certain solid tumors, will be the main focus of this review. 20659323_Findings suggest MYB may be a viable therapeutic target in breast cancer. 20686118_Overexpression of either KLF1 or LMO2 partially rescued the defect in erythropoiesis caused by c-myb silencing, whereas only KLF1 was also able to repress the megakaryocyte differentiation enhanced in Myb-silenced CD34+ cells. 20702610_The findings suggest that MYB may be a specific novel target for tumor intervention in patients with salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. 20802522_SUMO binding was established as a mechanism involved in modulating the transactivation activity of c-Myb, and responsible for keeping the transforming potential of c-myb in check. 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20927387_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21046410_Increased expression of MYB may have a role in a subset of pediatric gliomas, through a variety of mechanisms in addition to MYB amplification and deletion. 21068433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21164292_MYB translocation and expression are useful diagnostic markers for a subset of adenoid cystic carcinomas, indicating local aggressive behavior. 21177182_The expression level of c-myb mRNA is closely related with the development of Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. 21190594_c-Myb has a functionally important role in the regulation of OPN expression in hepatocellular carcinoma 21205891_Data suggest that miR-15a, -16-1, and MYB may be important therapeutic targets to increase HbF levels in patients with sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia. 21261996_Results show that c-Myb associates with a surprisingly large number of promoters in human cells. 21296997_Evidence of oncogenic activities of MYB in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia that include its stimulatory role in MIR155HG transcription. 21338522_PIAS1 is a common partner for two cancer-related nuclear factors, c-Myb and FLASH. 21364958_Dramatic repositioning of c-Myb to different promoters during the cell cycle. 21376705_These suggest that c-Myb play an important role in the hMSCs differentiation too, which is consistent with the epigenetic control mechanism of c-Myb. 21385855_A 3-bp deletion in the HBS1L-MYB intergenic region on chromosome 6q23 is associated with HbF expression. 21469677_A G-quadruplex structure formed in a c-myb repeat by a mechanism of transcription-coupled DNA repair that may represent a transcription roadblock in vivo. 21572406_our studies show that MYB activation through gene fusion or other mechanisms is a major oncogenic event in adenoid cystic carcinoma 21590770_Micro Rna R-150 and its targeting of c-Myb may serve as a new mechanism underlying the colonic epithelial disruption in DSS-induced murine experimental colitis and in active human IBD. 21618541_study demonstrates that benign sporadic, dermal cylindromas express the MYB-NFIB gene fusion 21795403_GSK3beta inactivation induces apoptosis of leukemia cells by repressing the function of c-Myb 21853052_c-myb alternative RNA splicing was elevated and much more complex in leukemia samples. 21901247_1 of the 9 Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinomas (PLGA) expressed the adenoid cystic carcinoma-associated MYB-NFIB gene fusion; findings indicate that the PLGA genome is genetically stable 21953443_Breast cancer cells play a significant role in sustaining and amplifying the inflammation process through the activation of c-myb. 21960247_a c-Myb-Bmi1 transcription-regulatory pathway is required for p190(BCR/ABL) leukemogenesis. 21976542_study concludes conclude that: t(6;9) results in complex genetic and molecular alterations in adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC); MYB-NFIB gene fusion may not always be associated with chimeric transcript formation; noncanonical MYB-NFIB gene fusions occur in a subset of tumors; high MYB expression correlates with worse patient survival 22025269_MiR-150 interacts with the 3'UTR of c-Myb mRNA. 22039304_c-Myb critically regulates IL-13 expression via direct binding to the conserved GATA-3 response element 22101269_TGFbeta-induced c-Myb expression enhances invasion and aggressiveness of breast cancer cells. 22110127_TIP60 is a normal regulator of c-Myb function and that dysregulated or mutated TIP60 may contribute to c-Myb-driven leukemogenesis. 22391450_reveal a novel role for the MuvB complex in recruiting B-Myb and FoxM1 to promote late cell cycle gene expression and in regulating cell cycle gene expression from quiescence through mitosis. 22431717_study provides first experimental evidence for a functional role of Myb in growth and malignant behavior of prostate cancer cells and suggest a novel mechanism for castration resistance 22439866_c-Myb regulates matrix metalloproteinases 1/9, and cathepsin D: implications for matrix-dependent breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis. 22505352_Explored copy number alterations rearrangements in adenoid cystic carcinoma. 86% of the tumors expressed MYB-NFIB fusion transcripts and 97% overexpressed MYB mRNA. 22516378_These studies show the mutual importance of c-Myb and the GR in controlling survival of pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. 22714709_PUMA, c-Myb and p53 protein expression closely relates to the carcinogenesis, fast-progression, easy-metastasis, high-invasion, and poor-prognosis in gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 22739149_In acute leukemic cells and leukemic bone marrow stromal cells, c-myc expression positively correlated with c-myb expression. 22764095_c-Myb inhibition decreased cell proliferation, increased the number of cells in G(0) /G(1) phase of the cell cycle, increased the sensitivity of pre-B-ALL cells to cytotoxic agents, & delayed disease onset in a mouse model of leukemia. 22853316_Transgenic K562 cells have distinct gene expression profiles both in steady state and during terminal erythroid differentiation, with GATA1s expression characterised by lack of repression of MYB, CCND2 and SKI. 22880131_These results unravel a critical role of c-Myb in promoting Erbin transcription in G2/M phase and also predict an unappreciated function of Erbin in cell cycle progression. 22910413_Fbxw5 enhances sumoylation of nuclear c-Myb. 22936743_Studies indicate that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in regions of BCL11A and HBS1L-MYB intergenic polymorphism are the major modifiers of HbF in African Americans. 23340802_Analysis of gene expression profiling arrays from acute myeloid leukemia patients uncovered significant correlations between FLT3 expression level and that of MYB and CEBPA. 23398943_ChIP assays showed that in U937 cells MYB binds to a conserved element upstream of the DRAK2 transcription start site. 23475628_High expression of c-myb is associated with lymph node metastasis and invasion in gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 23483952_C-MYB can bind to the -709A allele of the MMP3 promoter, activate its transcription and lead to a higher expression of this gene. 23505388_These findings reveal an important and so far unknown connection between PRMT4 and the chromatin remodeller Mi2 in c-Myb signalling. 23658056_High c-myb expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 23725736_Rearrangements of MYB were detected in 8 of 13 analyzed cases of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the lacrimal gland. Our data also suggest that MYB and its downstream targets are potential therapeutic targets for these tumors. 23935942_NLK suppressed proliferation, induced apoptosis and mediated c-Myb degradation in MCF-7 cells. 23980173_Characterize the structure of the transition state of the binding-induced folding in the reaction between the KIX domain of the CREB-binding protein and the transactivation domain of c-Myb. 24013223_3'-LTR mutations may upregulate syncytin-1 expression, enabling it to participate in urothelial cell carcinoma tumorigenesis and development by interacting with c-Myb. 24067373_Activation of miR200 by c-Myb depends on ZEB1 expression and miR200 promoter methylation in breast cancer cells. 24121275_Data shows that MYB regulates the expression of endogenous human GFI1. 24174222_the hypomethylation of the c-Myb motif upregulates the S100A4 expression in laryngeal cancer. 24220303_reveals a complex network of proteins regulated by c-Myb. 24257756_of c-Myb, is detected preferentially in nonSUMOylated protein and has a negative effect on stress-induced SUMOylation of c-Myb. Stress-activated p38 MAPKs phosphorylate Thr(486) in c-Myb, attenuate its SUMOylation 24283570_Direct repression of MYB by ZEB1 suppresses proliferation and epithelial gene expression during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. 24302647_Myb gene over expression is useful for differential diagnosis of adenoid cystic carcinoma an pleomophic adenoma in salivary gland. 24486218_findings indicated that miR-195 functions as tumour suppressor in NSCLC, and the miR-195/MYB axis might represent a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC intervention 24504520_This study showed that the expression of miR34a negatively correlates with the expression of CDK4 and MYB and SIRT1 in pediatric patients with acute leukemia. 24576033_Using FISH testing for detecting MYB gene abnormalities in the salivary gland of FNA biopsies has the potential to provide additional, helpful ancillary information in diagnosing adenoid cystic carcinomas 24614105_Several HBS1L-MYB intergenic variants reduce transcription factor binding, affecting interactions with MYB and MYB expression levels. This may explain the genetic association of HBS1L-MYB intergenic polymorphisms with erythroid traits and HbF levels. 24667352_Genetic variants of MYB is associated with sickle cell disease. 24732452_Studied MYB oncogene in transformed adenoid cystic carcinomas.Data demonstrated that the MYB/NFIB translocation is not necessarily an early event or fundamental for the progression to adenoid cystic carcinoma with high-grade transformation. 24847116_new mechanism-based therapeutic approaches for PCa by targeting PARP and the DDR pathway involving c-Myb, TopBP1, ataxia telangiectasia mutated- and Rad3-related (ATR), and Chk1. 25103188_results show that a p63(-) Myb(+) population of airway epithelial cells represents a distinct intermediate stage of differentiation 25230975_High c-myb expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 25231743_MicroRNA-193b-3p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting the MYB oncogene in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 25394790_study found that heterozygous somatic mutations are acquired that introduce binding motifs for the MYB transcription factor in a precise noncoding site, which creates a super-enhancer upstream of the TAL1 oncogene; MYB binds to this new site 25457385_Genetic variant in the BCL11A (rs1427407), but not HBS1-MYB (rs6934903) loci associate with fetal hemoglobin levels in Indian sickle cell disease patients. 25488618_The study compares polymorphism at BCL11A to HBS1L-MYB loci and explains less of the variance in HbF in patients with sickle cell disease in Cameroon. 25522282_miR-150 is an important suppressor of pancreatic ductal carcinoma and acts as a regulator of c-Myb and MUC4 in aggressive progress. 25530421_our observations suggest that miR-103a functioned as a tumour suppressor by targeting c-Myb. These findings indicate that miR-103a might play a significant role in pathogenesis of gastric cancer 25587024_Authors observed that forced MYB-NFIB expression in human salivary gland cells alters cell morphology and cell adhesion in vitro and depletion of VCAN blocked tumor cell growth of a short-term ACC tumor culture. 25616133_c-MYB might target miR-143 in order to regulate stem cell properties, cell growth, apoptosis, and DNA damage repair. 25740244_Data show that Naphthol AS-E phosphate inhibits proto-oncogene protein Myb activity by disrupting its interaction with E1A binding protein p300. 25857263_The MYB/MAF co-silencing constrained the skewing of erythroid versus megakaryocyte lineage commitment in MYB-silenced CD34+ cells, by restraining the expansion of megakaryocyte lineage while partially rescuing the impairment of erythropoiesis. 25857824_In malignant spiradenocarcinoma, MYB expression was lost 25928412_conserved regulatory elements within the MYB core enhancer in individuals with sickle cell disease 25963073_Stage and margin status were important prognostic factors for ACC. Tumors with evidence of MYB-NFIB fusion were more likely to originate in minor salivary glands 26076064_Results indicate that cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinomas possess the same types of MYB alterations as ACCs of other anatomic sites. 26089205_Our results show that a subset of prostatic basal cell carcinoma s harbors rearrangement of MYB 26208222_Our data suggest that c-Myb is a transcription factor with multifaceted target regulation depending on cell type. 26462877_In summary, our results implicate that metastatic properties of some RMS subtypes might be linked to c-Myb function. 26657649_MYB is aberrantly overexpressed in PC cells and acts as a key determinant of pancreatic tumour growth and metastasis 26711711_All five successfully hybridized ACCs featured MYB rearrangement, whereas PLGAs did not show MYB rearrangement. Interestingly, one case of PLGA demonstrated a single intact copy of MYB in greater than 88% of the neoplastic cells. All ACCs exhibited consistent p63+/p40+ staining, whereas PLGAs demonstrated a p63+/p40- immunophenotype. 26810070_l genetic alterations were limited to two fusion genes, EWSR1-PATZ1 and SLMAP-NTRK2, both in gangliogliomas. Alterations in BRAF, FGFR1, or MYB account for most pathogenic alterations in low-grade neuroepithelial tumors 26829750_our study identifies super-enhancer translocations that drive MYB expression and provides insight into downstream MYB functions in alternate adenoid cystic carcinoma lineages. 26829751_MYB-QKI rearrangements promote tumorigenesis through three mechanisms: MYB activation by truncation, enhancer translocation driving aberrant MYB-QKI expression and hemizygous loss of the tumor suppressor QKI 26873484_Statistically significant negative association was found between the frequency of the c-Myb-positive tumor cells and the presence of distant metastases but not tumor differentiation, tumor stage, lymph node involvement, vascular invasion, tumor localization, age, and gender of the patients. No significant association between MYB mRNA and any clinicopathological characteristics was observed. 26934556_The expression levels of two target genes, Myb and VEGFR2, were affected significantly by miR-16, while glucose administration inhibited miR-16 expression and enhanced tumor cell proliferation and migration. 26969893_Molecular heterogeneity in the pathogenesis of sporadic and inherited cutaneous cylindromas, with convergence on MYB activation. 27032383_PIAS1 enhances p300 recruitment to c-Myb-bound sites through interaction with both proteins. In addition, the E3 activity of PIAS1 enhances further its coactivation 27107996_p38 and NOX1 are essential for the protective effect of c-Myb and that NOX1 acts upstream of p38 activation. 27160456_identification of SNPs within the IQCJ, NXPH1, PHF17 and MYB genes partly explaining the large interindividual variability observed in plasma triglyceride levels in response to an n-3 fatty acid supplementation 27174194_The study shows that MYB gene breaks occur in 65% of ACC cases. MYB status very likely plays a role in the biological nature of ACC, leading to differences in survival. 27197202_c-myb overexpression is associated with Breast Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. 27213588_Expression of the MYB-NFIB fusion oncogene in mammary tissue resulted in hyperplastic glands that developed into adenocarcinoma. 27220777_hsamiR495 was downregulated in glioma tissues and cell lines, and acts as a tumor suppressor gene in glioma via the negative regulation of MYB. 27246849_MYB as novel regulator of pancreatic tumor desmoplasia, which is suggestive of its diverse roles in Pancreatic Cancer pathobiology. 27566443_A trend toward superior PFS was noted with the MYB/NFIB rearrangement, although this was not statistically significant. NGS revealed three tumors with 4q12 amplification, producing increased copies of axitinib-targeted genes PDGFR/KDR/KIT. 27601730_Exosomes isolated from cultured AML or the plasma from mice bearing AML xenografts exhibited enrichment of miR-150 and miR-155. HSPCs cocultured with either of these exosomes exhibited impaired clonogenicity, through the miR-150- and miR-155-mediated suppression of the translation of transcripts encoding c-MYB 27662035_NFIB-associated gene rearrangement is a frequent genetic event in vulvar adenoid cystic carcinomas. Chromosome translocations involving NFIB but with an intact MYB indicate the presence of novel oncogenic mechanisms for the development of adenoid cystic carcinomas of the vulva. 27748374_MYB acts on MAPK signaling by directly regulating transcription of the gene encoding the negative modulator SPRY2. 27765671_HBXIP up-regulates YAP expression via activating transcription factor c-Myb to facilitate the growth of hepatoma cells. 27974718_c-Myb is overexpressed in tracheobronchial and pulmonary adenoid cystic carcinomas. 28085142_Rearrangement of MYB did not affect OS. 28098399_This study assesses MYB, CD117 and SOX-10 expression in cutaneous adnexal tumors. 28134766_A genome-wide association study (GWAS) identified loci associated with the plasma triglyceride (TG) response to omega-3 fatty acid (FA) supplementation in IQCJ, NXPH1, PHF17 and MYB. 28210977_Both cases harbored the MYB-NFIB gene fusion as demonstrated by FISH and RNA-sequencing 28323779_The coexpression of GATA3 and MYB might be helpful in the distinction of primary cutaneous adnexal carcinoma versus metastatic breast, salivary gland, or urothelial carcinoma 28332727_Studied association of BCL11A single nucleotide polymorphisms(snps) and HBS1L-MYB Intergenic snps with Hereditary Persistence of Fetal Hemoglobin (HPFH) in a cohort of sickle cell patients. 28344318_identified a high frequency of MYB rearrangements that promoted the MYB transcriptional activity in BPDCN. MYB split FISH analysis can constitute a valuable diagnostic tool for detecting MYB rearrangements 28361591_high-risk genotypes of six Hb F-associated SNPs, rs9376090, rs7776054, rs9399137, rs9389268, rs9402685 in the HBS1L-MYB intergenic region and rs189984760 in the BCL11A locus, showed association with high Hb F levels 28472346_A mutant of c-Myb, D152V, specifically affects c-Myb's ability to regulate genes involved in differentiation, causing failure in c-Myb's ability to block differentiation. 28790107_deficiency alters the expression of a crucial subset of TAL1- and NOTCH1-regulated genes, including the MYB and MYC oncogenes, respectively. 28973440_The data indicate that MAZ is essential to bypass MYB promoter repression by RB family members and to induce MYB expression. 29066854_genome-wide association analyses identified a new genome-wide significant locus on the HBS1L-MYB intergenic region for platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio 29084208_Low c-myb expression promotes breast cancer lung metastasis. 29135517_The presence of the MYB fusion in intermediate-grade and hybrid carcinomas that at least partially exhibit an epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma phenotype may in fact point to an adenoid cystic carcinoma. 29149504_Breast adenoid cystic carcinomas probably constitute a convergent phenotype, whereby activation of MYB and MYBL1 and their downstream targets can be driven by the MYB-NFIB fusion gene, MYBL1 rearrangements, MYB amplification, or other yet to be identified mechanisms. 29243184_Salivary gland ACC cases expressing the MYB-NFIB chimeric gene showed significantly higher blood vessels density compared to non-expressing cases, and suggested that higher VEGF production capability in the former cases may be the cause. The findings also suggested that MYB-NFIB chimeric gene expression may be related to the onset age of ACC. 29410490_In the present study, MYB or MYBL1 locus rearrangement was detected in nearly all adenoid cystic carcinoma cases, and therefore it would be a good diagnostic marker for adenoid cystic carcinoma. 29415639_These results indicated that low expression of Mda-7/IL-24 along with high expression of C-myb are predictors for poor prognosis of Burkitt lymphoma patients; this outcome suggests that Mda-7/IL-24 and C-myb might be potential targets for clinical treatment of Burkitt lymphoma. 29488168_Expression of c-Myb, a regulatory factor of B lymphocytes, is increased in B lymphocytes of AIHA/Evans patients, while miR-150 expression is decreased. c-Myb was negatively correlated with miR-150. 29517281_C-Myb expression in the laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.YB-1 regulates miR-155 expression via c-Myb in the laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 29760303_High c-myb expression is associated with In-Stent Restenosis in Peripheral Artery Disease. 29890118_Data observe that increasing and decreasing the helical stability of c-Myb over a broad range has a small effect on the binding affinity to KIX domain of CREB binding protein. To reduce the binding affinity by more than 1 kcal/mol, it was necessary to introduce glycine or proline in the middle of the c-Myb helix. 29954426_Data indicate a pioneer factor model in which c-Myb binds to regions of closed chromatin and then recruits histone acetyltransferases. By binding to histones, c-Myb facilitates histone acetylation, acting as a cofactor for p300 at c-Myb binding sites. The resulting H3K27ac leads to chromatin opening and detachment of c-Myb from the acetylated chromatin. 30076175_Transcriptional activation of the miR-17-92 cluster is involved in the growth-promoting effects of MYB in human Ph-positive leukemia cells. 30103947_The data demonstrate that c-Myb plays a critical role in the activation of NK cells and therefore is a therapeutic target for cancer and viral diseases. 30133116_LINC01287 exerted as a ceRNA and negatively regulated miR-298 expression. MYB was identified as a downstream target of miR-298. The miR-298/MYB axis mediated LINC01287's effect on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) 30158641_The role of the TGF-beta1/c-Myb/miR-520h/Smad7 axis in EOC metastasis. 30200835_found no significant differences in the genetic distribution and allelic frequency of MYB and SOX-6 gene polymorphisms 30454024_Data provide evidences supporting the role of Sema5A in melanoma progression and the involvement of Bcl-2, miR-204 and c-Myb in regulating its expression. 30502345_Collectively, our data showed that ZFAS1 contributed to the development of AML by sequestering miR-150 from Myb or Sp1, elucidating the central |
ENSMUSG00000019982 |
Myb |
202.265053 |
0.1673478209 |
-2.579078 |
0.139118798 |
372.347088 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005769850856981043009650384455479072524753601763200290693044580177062645011487558563906192158568904171696273100515454882425458241063808414790258178365604009085606472336369992415741565161704583830230545922999885188886537434882484376430511474609375000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002013309660733810743587651575197647569783452025613841861667373888496517829976486345431447121096916150760389527952506481819368265387174601790050895764964878055327076348049129670164286060092898239794688940162981083403792581520974636077880859375000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.9511302 |
7.2160061 |
344.3683640 |
28.0762377 |
| ENSG00000118515 |
6446 |
SGK1 |
protein_coding |
O00141 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase which is involved in the regulation of a wide variety of ion channels, membrane transporters, cellular enzymes, transcription factors, neuronal excitability, cell growth, proliferation, survival, migration and apoptosis. Plays an important role in cellular stress response. Contributes to regulation of renal Na(+) retention, renal K(+) elimination, salt appetite, gastric acid secretion, intestinal Na(+)/H(+) exchange and nutrient transport, insulin-dependent salt sensitivity of blood pressure, salt sensitivity of peripheral glucose uptake, cardiac repolarization and memory consolidation. Up-regulates Na(+) channels: SCNN1A/ENAC, SCN5A and ASIC1/ACCN2, K(+) channels: KCNJ1/ROMK1, KCNA1-5, KCNQ1-5 and KCNE1, epithelial Ca(2+) channels: TRPV5 and TRPV6, chloride channels: BSND, CLCN2 and CFTR, glutamate transporters: SLC1A3/EAAT1, SLC1A2 /EAAT2, SLC1A1/EAAT3, SLC1A6/EAAT4 and SLC1A7/EAAT5, amino acid transporters: SLC1A5/ASCT2, SLC38A1/SN1 and SLC6A19, creatine transporter: SLC6A8, Na(+)/dicarboxylate cotransporter: SLC13A2/NADC1, Na(+)-dependent phosphate cotransporter: SLC34A2/NAPI-2B, glutamate receptor: GRIK2/GLUR6. Up-regulates carriers: SLC9A3/NHE3, SLC12A1/NKCC2, SLC12A3/NCC, SLC5A3/SMIT, SLC2A1/GLUT1, SLC5A1/SGLT1 and SLC15A2/PEPT2. Regulates enzymes: GSK3A/B, PMM2 and Na(+)/K(+) ATPase, and transcription factors: CTNNB1 and nuclear factor NF-kappa-B. Stimulates sodium transport into epithelial cells by enhancing the stability and expression of SCNN1A/ENAC. This is achieved by phosphorylating the NEDD4L ubiquitin E3 ligase, promoting its interaction with 14-3-3 proteins, thereby preventing it from binding to SCNN1A/ENAC and targeting it for degradation. Regulates store-operated Ca(+2) entry (SOCE) by stimulating ORAI1 and STIM1. Regulates KCNJ1/ROMK1 directly via its phosphorylation or indirectly via increased interaction with SLC9A3R2/NHERF2. Phosphorylates MDM2 and activates MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of p53/TP53. Phosphorylates MAPT/TAU and mediates microtubule depolymerization and neurite formation in hippocampal neurons. Phosphorylates SLC2A4/GLUT4 and up-regulates its activity. Phosphorylates APBB1/FE65 and promotes its localization to the nucleus. Phosphorylates MAPK1/ERK2 and activates it by enhancing its interaction with MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Phosphorylates FBXW7 and plays an inhibitory role in the NOTCH1 signaling. Phosphorylates FOXO1 resulting in its relocalization from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Phosphorylates FOXO3, promoting its exit from the nucleus and interference with FOXO3-dependent transcription. Phosphorylates BRAF and MAP3K3/MEKK3 and inhibits their activity. Phosphorylates SLC9A3/NHE3 in response to dexamethasone, resulting in its activation and increased localization at the cell membrane. Phosphorylates CREB1. Necessary for vascular remodeling during angiogenesis. Sustained high levels and activity may contribute to conditions such as hypertension and diabetic nephropathy. Isoform 2 exhibited a greater effect on cell plasma membrane expression of SCNN1A/ENAC and Na(+) transport than isoform 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11154281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11410590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11696533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12397388, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12590200, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12634932, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12650886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12761204, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12911626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14623317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14706641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15040001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15044175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15234985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15319523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15496163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15733869, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15737648, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15845389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15888551, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16036218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16443776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16982696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17382906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18005662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18304449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18753299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19447520, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19756449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20511718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20730100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21865597}. |
3D-structure;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Kinase;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Stress response;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a serine/threonine protein kinase that plays an important role in cellular stress response. This kinase activates certain potassium, sodium, and chloride channels, suggesting an involvement in the regulation of processes such as cell survival, neuronal excitability, and renal sodium excretion. High levels of expression of this gene may contribute to conditions such as hypertension and diabetic nephropathy. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:6446; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium channel regulator activity [GO:0005246]; chloride channel regulator activity [GO:0017081]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004712]; sodium channel regulator activity [GO:0017080]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to aldosterone [GO:1904045]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; long-term memory [GO:0007616]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of transporter activity [GO:0032411]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; regulation of gastric acid secretion [GO:0060453]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796]; renal sodium ion absorption [GO:0070294]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814] |
12077559_Excessive transcription of the human serum and glucocorticoid dependent kinase hSGK1 in lung fibrosis 12215463_single nucleotide polymorphisms of SGK linked to variations in blood pressure 12376324_Glucocorticoidss stimulate sgk1 expression in human epithelial cells via activation of a GRE in the 5'-flanking region of sgk1. 12397388_Powerful stimulating effect of all three isoforms of SGK on K(+) channels. Those effects may participate in regulation of epithelial transport, cell proliferation, and neuromuscular excitability. 12417559_Sgk is a positive regulator of sodium transport. 12435876_Glomerulonephritis leads to glomerular and in some cases to epithelial up-regulation of hSGK1 transcription. 12444200_NHERF2 and SGK1 interact to enhance ROMK1 activity by enhancing abundance of channel protein in cell membrane, allowing integration of genomic regulation and activation of SGK1 and NHERF2 in control of ROMK1 activity and renal K(+) excretion. 12590200_The stimulating effect of SGK1 on the Xenopus oocyte Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase is mimicked by the isoforms SGK2 and SGK3. 12634932_All three members of the SGK family of kinases SGK1-3 and protein kinase B stimulate the slowly activating K(+) channel KCNE1/KCNQ1. The kinases may thus participate in the regulation of KCNE1-dependent transport and excitability. 12684516_SGK-1 phosphorylation of Kir1.1 drives expression on the plasmalemma. The results suggest a possible molecular mechanism for aldosterone-dependent regulation of the secretory potassium channel in the kidney. 12788082_SN1 is a target for the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2, which is inactivated by the serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase SGK1, its isoform SGK3, and protein kinase B. 12923071_up-regulation of SGK1 enhances cell surface epithelial sodium channel expression in collecting duct cells. 14623317_NHERF2, ROMK1, and SGK1 have roles in regulating protein abundance in the plasma membrane and K(+) current 14725621_SGK levels are increased in brains of Huntington's disease patients; SGK phosphorylates huntingtin at serine 421, protecting striatal neurons against polyQ-huntingtin-induced toxicity. 15044175_SGK1 stimulates the NaPi IIb, at least in part, by phosphorylating and thereby inhibiting Nedd4-2 binding to its target. 15166308_Na+-coupled glucose transporter 1 (SGLT1) was regulated by neuronal cell expressed developmentally downregulated 4-2 (Nedd4-2) and serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) 15167446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15208094_cAMP-stimulated Na+ transport in H441 distal lung epithelial cells does not affect levels of this enzyme. 15304560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15304560_These findings argue against important role of coding regions of Sgk1 in blood pressure regulation and hypertension and in the hypertension-related progression of renal diseases. 15328345_cAMP regulates ENaC in part by phosphorylation and inhibition of Nedd4-2. Moreover, Nedd4-2 is a central convergence point for kinase regulation of Na(+) transport. 15342340_Sgk1 may modulate insulin action on the cotranslational glycosylation of glycoproteins 15461589_results identify NDRG1 and NDRG2 as physiological substrates for SGK1, and demonstrate that phosphorylation of NDRG1 by SGK1 primes it for phosphorylation by GSK3 15496163_ClC-Ka/barttin channels are regulated by SGK1 and SGK3, which may thus participate in the regulation of transport in kidney and inner ear. 15576372_Nedd4-2 phosphorylation induces SGK ubiquitination and degradation 15578212_Co-expression of SGK1, but not of SGK2 or SGK3, increased Kv 4.3/KChIP2b channel currents. 15665527_demonstration of the significance of SGK1 and NHERF2 as TRPV5 modulators which are likely to participate in the regulation of calcium homeostasis by 1,25(OH)2D3 15695387_SGK acts as an oncogene in breast cancer cells through activation of the IKK-NF-kappaB pathway, thereby preventing apoptosis. 15721303_SGK1 activation has a role in oncofetal fibronectin expression 15737648_In conclusion, the kinases SGK1 and SGK3 increase EAAT5 activity by increasing cell surface abundance of the carrier. 16036218_SGK1 and SGK3 increase SLC6A8 activity by increasing the maximal transport rate of the carrier. Deranged SGK1 and/or SGK3 dependent regulation of SLC6A8 may affect energy storage particularly in skeletal muscle, heart, and neurons 16105029_The effects of high glucose on proximal tubular cells proliferation, reduced apoptosis and increased NHE3 mRNA levels are mediated by EGFR-dependent up-regulation of SGK-1 16125969_key role for sgk1 in the molecular pathway of cell death, in which sgk1 seems to exert a protective role. 16221215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16221215_SGK-1 risk carriers are at increased risk of hypertension and are more sensitive to the blood pressure elevating effects associated with hyperinsulinemia 16301823_SGK1 is upregulated in diabetic nephropathy and actively participates in the stimulation of matrix protein deposition in this common deleterious complication of diabetic hyperglycemia. 16301825_SGK1 regulates current amplitudes and kinetic properties of KCNQ4 channel activity, an effect sensitive to mutations in the SGK1 consensus sequence of the channel. 16443776_SGK1 regulates GLUT1 and may contribute to or account for the PI3 kinase-dependent but PKB-independent stimulation of GLUT1 by insulin. 16817852_constitutive ubiquitin-mediated degradation of SGK-1 is an important mechanism regulating its biological activity 16847254_SGK1 is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum-associated ubiquitin-conjugation machinery by an amphipathic helix 16971495_Acute effect of glucocorticoids on NHE3 is mediated by a glucocorticoid receptor dependent mechanism that activates SGK1 in a nongenomic manner. 17170520_Incubation with glucose, the Ca2+-ionophore ionomycin and the cytokine TGF-beta1 were all found to evoke significant and time-dependent increases in both SGK1 and alphaENaC protein expression. 17317952_Our data do not support that SGK1 gene variations are disease-causing factors in genetically unexplained pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1. 17360471_an SGK1 site in WNK4 regulates Na+ channel and K+ channel activity 17382906_SGK1 promotes glucose transporter membrane abundance via GLUT4 phosphorylation at Ser274. Thus, SGK1 may contribute to the insulin and GLUT4-dependent regulation of cellular glucose uptake. 17442044_In conclusion, maximal glutamate transport modulation by SGK1 is accomplished by direct EAAT4 stimulation and to a lesser extent by inhibition of intrinsic Nedd4-2. 17568772_SGK1 negatively regulates stress-activated signaling through inhibition of SEK1 function 17570343_The observations disclose that PIKfyve participates in the SGK1-dependent regulation of SLC5A1. 17571248_IL-2 induced regulation of Sgk1 and a role of the IL-2 receptor and Sgk1 in the regulation of epithelial tumor cell death and survival. 17595519_A kinase-dead SGK mutant (K127N) had a dominant-negative effect on CFTR, reducing CFTR Cl currents by 38%. 17640988_That SGK1 targets FOXO1 in differentiating human endometrium, together with its distinct temporal and spatial expression pattern and increased expression in infertile patients, suggest a major role for this kinase in early pregnancy events. 17932503_These data suggest that SGK-1 is an androgen-regulated gene that plays a pivotal role in AR-dependent survival and gene expression. 17965184_study reports the 1.9 A crystal structure of the catalytic domain of inactive SGK1 in complex with AMP-PNP 17982254_The present observations disclose the transcription of three distinct SGK1 splice variants, which are all markedly upregulated in tumor tissue but differentially upregulated following differentiation or hypoxia. 17982255_The observations suggest that SGK1 regulates the creatine transporter SLC6A8 at least partially through phosphorylation and activation of PIKfyve. 17985234_SGK1 mRNA is rapidly induced by glucocorticoid stimulation in HEK293 cells 18209482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18209482_The observations support the view that SGK-1 may participate in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. 18239069_Glucocorticoid (GC)-mediated down-regulation of urokinase plasminogen activator expression via the serum and GC regulated kinase-1/forkhead box O3a pathway. 18319604_In human renal fibroblasts, serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase1 (SGK1) and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) protein expression were enhanced by angiotensin II 18456663_Hsp90 activity is essential for regulating the PI3K/SGK-1 pathway. 18487207_SGK1 negatively regulates the pro-apoptotic transcription factor Forkhead box O3a (FoxO3a) via phosphorylation and exclusion from the nucleus. 18570873_SGK1 is an mTOR-raptor substrate and mTOR may promote G1 progression in part through SGK1 activation and deregulate the cell cycle in cancer. 18753299_A conserved NH2-terminal variant of Sgk1 shows improved stability, enhanced membrane association, and greater stimulation of epithelial Na+ transport in a heterologous expression system. 18801914_The role of aldosterone in sodium absorption by intestinal cells via multiple changes in cellular processes, including SGK1 NHE3 and sodium pump activity is reported. 18985156_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18985156_Study in three independent European populations supports the conclusion that SGK variability affects diabetes risk. 19068477_Coexpression with active Akt1 increased the phosphorylation of Ser397 and thereby SGK1 kinase activity. SGK1 activation was further augmented by coexpression with the protein kinase WNK1 (with no lysine kinase 1). 19088076_SGK1 phosphorylation of IkappaB Kinase alpha and p300 Up-regulates NF-kappaB activity and increases N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR2A and NR2B expression. 19088452_The present results reveal two novel PEPT2 posttranslational modulators, SGK1 and NHERF2, which might regulate transport of oligopeptides and peptidomimetic drugs. 19232516_PIKfyve is a potent stimulator of ClC-2-activity and contributes to SGK1-dependent regulation of ClC-2. 19380724_GILZ1 and SGK1 provide a physical and functional link between the PI3K- and Raf-1-dependent signaling modules 19447520_SGK1 expression during liver regeneration is a part of a signaling pathway that is necessary for enhancing ERK signaling activation through modulating the MEK/ERK complex formation. 19461886_SNP rs9493857 lies within a predicted binding site for Oct1, a transcription factor known to cooperate with the GR in the transactivation of target genes. 19584721_The outlined recent findings advanced our understanding of the molecular regulation of SGK1 as well as the role of the kinase in renal physiology--review 19617352_the SGK1/Nedd4-2 signaling pathway regulates both CFTR and ENaC trafficking in CF epithelial cells 19619128_Glucocorticoids can activate the alpha-ENaC gene promoter independently of SGK1. 19706464_c-Src inhibits SGK1-mediated phosphorylation hereby restoring the WNK4-mediated inhibition of ROMK channels thus suppressing K secretion. 19756449_Sgk1, a gene regulated by p53 at the transcriptional level,affects cell proliferation and differentiation and that the expression and the half-life of p53 is regulated by Sgk1 through MDM2 that directs p53 to ubiquitylation and proteosomal degradation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19961832_EPO protects from renal I/R injury and SGK1 might contribute to the mediation of EPO effects under ischemic conditions. 20041238_TRPV6-expressing oocytes I(H) was increased by coexpression of (S422D)SGK1. 20338997_interacted selectively with rictor but not with raptor 20438709_This study reveals that mTORC2 is a critical target of PLD-mediated survival signals and identifies SGK1 as a downstream target of mTORC2 for the stabilization of HDM2. 20466724_analysis of phosphorylatable residues that activate Nedd4-2 and may work together with residues targeted by inhibitory kinases (SGK1 and protein kinase A) to govern Nedd4-2 regulation of epithelial ion transport 20511718_Glucocorticoid inducible kinase isoforms SGK1-3 are novel potent stimulators of Slc6a19 and may thus participate in the regulation of neutral amino acid transport in vivo. 20525693_Data find that expression of the N termini of all four WNKs results in modest to strong activation of SGK1. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631247_Data support a physiological role for SGK1.1 in the regulation of delta-ENaC through a pathway that differs from the classical one and suggest that the kinase could serve as an integrator of different signaling pathways converging on the channel. 20832730_Rictor forms a complex with Cullin-1 to promote SGK1 ubiquitination and destruction. 20884880_Results suggest that SGK-1 is an injury-responsive kinase that could mediate mechanical stretch-induced proliferation of vascular cells in vein graft, leading to neointima formation. 20933037_SGK1 expression is enhanced in the temporal neocortex of patients with drug-refractory epilepsy. 20947508_GILZ1 inhibits SGK1 ubiquitinylation and subsequent proteasome-mediated degradation, thereby prolonging its half-life and increasing its steady-state expression. 21079778_Results show that even though partial methylation of the promoter region of SGK1 is present, this does not account for the different expression levels seen between normal and tumour tissue. 21147854_SGK1 inhibits the Notch1 signaling pathway via phosphorylation of Fbw7. 21224398_a crucial role for SGK1 induction in B-13 pancreatic cell transdifferentiation to B-13/H hepatocytes 21355052_PI3K-activating hormones inhibit ROMK by enhancing its endocytosis via a mechanism that involves phosphorylation of WNK1 by Akt1 and SGK1. 21430556_in 2 populations, observed an association between genetic variants in SGK1 and ischaemic stroke; this could imply that cerebrovascular amiloride-sensitive sodium channel or other SGK1-regulated proteins may be important for development of ischaemic stroke 21478911_SGK1 is a highly cytokine-responsive gene in myeloma cells promoting their malignant growth 21563193_SGK1 expression is high in most untreated prostate cancers and declines with androgen deprivation. However, these data suggest that relatively low expression of SGK1 is associated with higher tumor grade and increased cancer recurrence. 21691090_results suggest that testosterone up-regulates SGK-1 in the kidney contributing to sexual dimorphisms in the cell signalling machinery 21757730_mSIN1 protein mediates SGK1 protein interaction with mTORC2 protein complex and is required for selective activation of the epithelial sodium channel 21784856_the association of sgk1 with the apical cell membrane, where it interacts with ENaC, is a novel means by which sgk1 specifically enhances ENaC activity in aldosterone-stimulated collecting duct cells. 21900244_Neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 4-2 (Nedd4-2) regulation by 14-3-3 protein binding at canonical serum and glucocorticoid kinase 1 (SGK1) phosphorylation sites. 22001908_Data show that deregulated SGK1 activity in cycling endometrium interferes with embryo implantation, leading to infertility, or predisposes to pregnancy complications by rendering the feto-maternal interface vulnerable to oxidative damage. 22240294_This explorative analysis of SGK1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) samples highlights the potential role of this factor in NSCLC patients. prognosis 22250980_investigation of the role of SGK1 in the control of airway epithelial Na+ absorption (via up-regulation of the epithelial sodium channel [ENaCalpha, ENaCbeta, and ENaCgamma] under the control of glucocorticoid/dexamethasone in these experiments) 22309306_Data show that SGK1 regulates cell migration via vinculin dephosphorylation, a mechanism that is controlled by membrane androgen receptor function. 22590650_SGK1 is a gamma-secretase regulator presumably effective through phosphorylation and degradation of NCT. 22648267_Genotype status at SGK1 variants may identify individuals prone to salt-sensitive hypertension. 22704443_Cyclic hydrodynamic pressure stimulating the proliferation of human bladder smooth muscle cells cultured in scaffolds. The signal transduction mechanism for this process is involved with the PI3K/SGK1 and not the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 22809514_activation of platelets with thrombin stimulates the translation of SGK1. 22832853_Glucocorticoid-inducible genes GILZ and SGK-1 might be promising candidate markers for hippocampal volume changes relevant for diseases like MDD. 23012321_SGK1-dependent ion channel regulation may thus become pathophysiologically relevant primarily after excessive (pathological) expression. Therefore, SGK1 may be considered an attractive therapeutic target despite its broad range of functions. 23019294_SGK1 is activated in human heart failure. In hypertensive heart disease, total SGK1 but not phosphorylated SGK1 increased. The opposite occurred in dilated cardiomyopathy. 23034940_Renally expressed Sgk1 isoform, Sgk1_i3, stimulates ENaC activity when heterologously expressed in collecting duct cells. 23055545_Low SGK1 expression is related to ACTH-independent cortisol secretion in adrenocortical tumors and is a new prognostic factor in adrenocortical carcinoma. 23108393_Sgk1-dependent regulation of RANBP1 has functional consequences on both mitotic microtubule activity and taxol sensitivity of cancer cells. 23339546_Identification of polymorphisms rs1057293 and rs1743966 in the SGK 1 gene, and the Arg97Ile mutation, for the first time in patients with transient tachypnea of the newborn. 23363009_Neuronal expression of SGK1 in aged human brain and its nuclear compartmentalization suggest a possible neuroprotective role. 23392695_Transgenic mice with increased SGK1.1 activity shows diminished sensitivity to induced seizures. 23487453_Authors also demonstrate that SGK1 is required for influenza A virus ribonucleoprotein nuclear export. 23581296_Knockdown of SGK1 markedly reduces proliferation of Akt inhibitor-resistant, but not inhibitor-sensitive, cells. 23589291_SGK1,3 enhances the expression level of mature hERG channels by inhibiting Nedd4-2 as well as by promoting Rab11-mediated hERG recycling. 23650397_findings identify SGK1 as a mediator for the effects of cortisol on neurogenesis and GR function, with particular relevance to stress and depression. 23933686_Data suggest that overexpression of SGK1 participates in pathophysiology of several disorders, including metabolic syndrome, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, thrombosis, stroke, inflammation, autoimmune disease, fibrosis, and tumor growth. [REVIEW] 24043625_store-operated Ca(2+) entry regulates SGK1 expression in epithelial cells and suggest that SGK1-dependent cytoprotective signaling involves effects on maintaining mitochondrial function. 24043696_Orai1 is expressed in the human endometrium and is up-regulated by SGK1 and TGFbeta1. 24214981_PI3K-SGK1 pathway stabilizes Kv7.1 surface expression by inhibiting Nedd4-2-dependent endocytosis and thereby demonstrates that Nedd4-2 is a key regulator of Kv7.1 localization and turnover in epithelial cells. 24431232_These data suggest SGK1 plays a key role in regulating neutrophil survival signaling and thus may prove a valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory disease. 24586903_SGK1 selectively increases wild type-CFTR in the plasma membrane of human airway epithelia cells by inhibiting its endocytic retrieval from the membrane. 24602173_These results suggested that urinary SGK1 should be a good indicator of tubulointerstitial damage in patients of IgA nephropathy. 24685888_Numerical simulations of the model solutions yield a better understanding of the process and indicate the importance of the SGK1 gene in the development of medulloblastoma 24811177_SGK1 phosphorylated Shank2E, increasing CFTR abundance. 24864229_The role of distinct SGK1/FOXO3A-associated regulation in p53 versus ANXA7 responses were elucidated and proposed that aberrant SGK1 could affect reciprocal SGK1-FOXO3A-Akt regulation. 24878720_Significant associations between SGK1 and SBP. 24961472_Increased SGK-1 expression reduces oxidative stress and improves cell survival in endothelial cells. 25152363_Inhibition of SGK1 activity as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of occlusive vascular diseases. 25384981_C4-CER can replace the PI3K/mTORC2 pathway to directly induce SGK1 to autophosphorylate at Ser422, an initial step leading to activation of PDK1 and of SGK1 by PDK1. 25422956_MDD patients with low expression of SGK1 have significantly smaller CA2/3 and CA4/DG volumes compared to patients with high expression of SGK1 mRNA and to healthy controls with low/high expression of SGK1, respectively. 25614279_SGK1 plays a pivotal role in vascular inflammation during atherogenesis. SGK1 participates in the regulation of monocyte/macrophage migration and MMP-9 transcription via regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB. 25667458_PIN1-mediated SGK1 ubiquitination is a major regulator of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell growth and survival 25705664_we discuss the expression of DISC1, DBZ, and SGK1 , their roles in the regulation of oligodendrocyte function, possible interactions of DISC1 and DBZ in relation to SZ, and the activation of the SGK1 signaling cascade in relation to MDD. 25825522_SGK1 overexpression was found to decrease reactive oxygen species generation. 25849655_results indicate that SGK1.1 regulates gene transcription upon a different set of genes some of which participate in cell survival pathways (BAG-4) and others in intracellular vesicular traffic (Brox) 25993992_These findings have identified an anti-inflammatory function of SGK1, elucidated the underlying intracellular mechanisms 26034353_SGK1 inhibits intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and promotes proliferation via the MEK/ERK/p53 pathway in colitis. 26038830_mRNA levels of ARC and SGK1 did not differ significantly between the schizophrenia or control samples. 26188042_FE65 influences APP degradation via the proteasome, and phosphorylation of FE65 Ser(610) by SGK1 regulates binding of FE65 to APP, APP turnover and processing. 26230157_The results from this study may be of particular importance, because SGK1WT over-expression by activating telomerase and reducing reactive oxygen species levels may delay the processes of endothelial senescence. 26277930_After adjustment for multiple testing, single-nucleotide polymorphism rs9376026 was significantly associated with diastolic blood pressure and mean arterial pressure responses to low-sodium intervention 26359301_data suggest that the induction of SGK1 through treatment with dexamethasone alters MT dynamics to increase Sec5-GEF-H1 interactions, which promote GEF-H1 targeting to adhesion sites. 26429539_SGK1 was up-regulated in CD4 T cells 26491696_This review focuses on recent advances in understanding of the roles of Akt and SGK1 in the regulation of renal tubular transport. 26506154_Data suggest that SGK1 expression is down-regulated in prefrontal cortex neurons of post-traumatic stress disorders subjects (male and female; postmortem samples obtained from tissue bank). 26548813_SGK1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer.SGK1 positively regulates the growth, migration and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.SGK1 activates beta-catenin signaling in NSCLC cells. 26658840_Highly recurrent mutation of GSK1 is associated with nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. 26827666_SGK1 overexpression in tissues and serum was found in patients with endometriosis. 26840046_Increased expression of SGK1 is associated with Hydrosalpinx. 26869290_Study provides evidence that enhanced SGK expression and activity in multiple myeloma cells contributes to resistance to ER stress, including bortezomib challenge. 26942879_High SGK1 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 27020669_Potassium supplementation has a blocking effect against salt-loading-induced IL-17A production in T lymphocytes, and the protective effect was mediated through suppression of p38/MAPK-SGK1 pathway. 27251632_Up-regulated expression of SGK1 is associated with lung cancer. 27331901_miRNA-7-5p can regulate the expression of human alveolar ENaC by targeting the mTORC2/SGK-1 signaling pathway. 27451907_In cancer cells resistant to PI3Kalpha inhibition, PDK1 blockade restores sensitivity to these therapies. SGK1, which is activated by PDK1, contributes to the maintenance of residual mTORC1 activity through direct phosphorylation and inhibition of TSC2. 27488665_Human SMCT1 is regulated by insulin and SGK1. 27606670_LEFTY2 regulates the expression and activity of ENaC in endometrial epithelial cells via SGK1. 27664953_associated with risk of hypertension development in Chinese 27771704_SGK1 can mediate chemo- and radio-resistance during the treatment of various human tumors, both in vitro and in vivo. (Review) 28177128_SGK1 inhibitor SI113 induced a significant reduction in endometrial cancer cells viability, as a result of induction of autophagy, apoptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. 28336914_Here the authors show that SGK1 directly regulates NaV1.5 channel function. 28338770_Findings show that serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) protein dynamics can be an important part of intracellular signaling, directly influencing cellular response decisions. 28389565_Akt3 constitutively suppresses macropinocytosis in macrophages through a novel WNK1/SGK1/Cdc42 pathway. 28504714_Findings illustrate how cancer cells utilize a chromatin remodeling factor to engage a core survival pathway to support its cancerous phenotypes, and reveal new facets of MTA1-SGK1 axis by a physiologic signal in cancer progression. 28608480_Sgk1 stimulated OAT3 transport activity by interfering with the inhibitory effect of Nedd4-2 on the transporter. This study provides important insights into how OAT3-mediated drug elimination is regulated in vivo. 28634071_SGK1 promotes YAP/TAZ transcriptional activity. SGK1 enhances YAP/TAZ activity by upregulating YAP/TAZ. SGK1 is a transcriptional target of YAP. SGK1 stabilizes TAZ by inhibiting GSK3beta. 28733463_TLR4 and C5aR crosstalk in dendritic cells induces a core regulatory network of RSK2, PI3Kbeta, SGK1, and FOXO transcription factors. 28993509_The importance of the serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) for cellular survival was validated in multiple patient-derived GBM stem cell lines using shRNA, CRISPR, and pharmacologic inhibitors. 29055016_SGK1 was found to be essential for proliferation and survival of thyroid cancer cells harboring PI3K-activating mutations. 29328462_High SGK1 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 29346764_Data suggest that SGK1 also plays a critical role in IL-23R-mediated inhibition of Treg and development of Th17 cells. Authors demonstrate that SGK1 functions as a pivotal node in regulating the reciprocal development of pro-inflammatory Th17 and Foxp3(+) Treg cells during autoimmune tissue inflammation 29352074_Studies indicate that aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron (ASDN) expressed channels are up-regulated by serum and glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1). 29412164_Taken together, our results suggest that SGK1 inhibits PM2.5-induced cell apoptosis and ROS generation via ERK1/2 and AKT signaling pathway in human lung alveolar epithelial A549cells. 29604467_Decreased expression of SGK1 may play a critical role in increasing the expression of alpha-syn, which is related with dopaminergic cell death in the Substantia nigra of chronic MPTP-induced Parkinsonism mice and in SH-SY5Y cells. 29889103_In primary aortic vascular smooth muscle cells, overexpression of constitutively active SGK1S422D, but not inactive SGK1K127N, upregulated osteo-/chondrogenic marker expression and activity, effects pointing to increased osteo-/chondrogenic transdifferentiation. 29976632_Fewer Tumor Copy Number Segments of the SGK1 Gene Are Associated with Glioblastoma Multiforme. 30257988_Study reveals SGK1 inhibition with miR-576-3p or pharmacologically inhibits migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma. 30337371_Up-regulation of the kinase gene SGK1 by progesterone activates the AP-1-NDRG1 axis in both PR-positive and -negative breast cancer cells 30655532_Study finds that Src positively regulates SGK1 expression in triple negative breast cancer cells, which exhibit a prominent signalling network governed by Src family kinases. 30706178_SGK1 expression is upregulated by IL-18 in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), and SGK1 participates in the intracellular signaling of IL-18-induced osteo-/chondrogenic transdifferentiation of VSMCs. 30837283_SGK1 activation occurs at a distinct subcellular compartment from that of Akt and suggests a mechanism for the selective activation of these functionally distinct mTORC2 targets through subcellular partitioning of mTORC2 activity. 30920175_Newborns born via elective cesarean section exhibited a lower expression of ENaC, Na-K-ATPase, and SGK1. Significant correlations existed between the expressions of ENaC, Na-K-ATPase, and SGK1, and the concentration of norepinephrine in the cord blood, which points to the importance of birth stress in promoting lung fluid clearance during early postnatal pulmonary adaptation. 30966771_SGK1 is evidently downregulated in chronic MPTP-intoxication and acupuncture stimulation maintained SGK1 expression. 31203134_SGK1 mediates the effects of E2 on trophoblast viability. 31641423_the effect and molecular mechanisms of SGK1 in renal tubular cells upon oxidative stress injury, is reported. 31694887_Serum- and Glucocorticoid-inducible Kinase 1 is Essential for Osteoclastogenesis and Promotes Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis. 31725056_Low Circulating Levels of GR, FKBP5, and SGK1 in Medicated Patients With Depression Are Not Altered by Electroconvulsive Therapy. 32036218_Targeting SGK1 enhances the efficacy of radiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. 32106831_GR, Sgk1, and NDRG1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: their correlation with therapeutic outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 32323833_TCRP1 induces tamoxifen resistance by promoting the activation of SGK1 in MCF7 cells. 32597300_Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-mediated transfer of microRNA-133b boosts trophoblast cell proliferation, migration and invasion in preeclampsia by restricting SGK1. 32767771_SGK1 is a signalling hub that controls protein synthesis and proliferation in endothelial cells. 33003561_Role of SGK1 in the Osteogenic Transdifferentiation and Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Promoted by Hyperglycemic Conditions. 33093458_ClC-3/SGK1 regulatory axis enhances the olaparib-induced antitumor effect in human stomach adenocarcinoma. 33517828_The interaction of TEA domain transcription factor 4 (TEAD4) and Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) promoted the malignant process mediated by serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1). 33730592_SGK1 signaling promotes glucose metabolism and survival in extracellular matrix detached cells. 33988691_SGK1 mutations in DLBCL generate hyperstable protein neoisoforms that promote AKT independence. 34669124_SGK1, autophagy and cancer: an overview. 34715204_Mechanistic insights into the role of serum-glucocorticoid kinase 1 in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review. 34741867_Cross-regulation of notch/AKT and serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) in IL-4-stimulated human macrophages. 34826606_Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 regulates transforming growth factor beta1-connective tissue growth factor pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis. 34860160_Knockdown of Serum- and Glucocorticoid-Regulated Kinase 1 Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity of Gastric Cancer Through Suppressing the Nuclear Factor Kappa-B Signaling Pathway. 35106936_SGK1 mutation status can further stratify patients with germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma into different prognostic subgroups. 35202674_Identification of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 as a regulator of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling. 35222400_SGK1, a Critical Regulator of Immune Modulation and Fibros |
ENSMUSG00000019970 |
Sgk1 |
2044.458663 |
6.3248062355 |
2.661021 |
0.139706754 |
325.832614 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000077708184410894372110673659822514475146075453470179524120807023657570494051822930175733820878493001913900133568347965699710336529014410667988738061089783440867666380671856143062424179812630598007672233507037162780761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023845588397189208349188194654168141242497356797112781352036245399479141230812103450201584723068138233612596097812229247101779122313623870288942279741058036847203328352540093989023195497622964467154815793037414550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3611.1784007 |
305.1893710 |
574.2817453 |
36.0999709 |
| ENSG00000118523 |
1490 |
CCN2 |
protein_coding |
P29279 |
FUNCTION: Major connective tissue mitoattractant secreted by vascular endothelial cells. Promotes proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes. Mediates heparin- and divalent cation-dependent cell adhesion in many cell types including fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, endothelial and epithelial cells. Enhances fibroblast growth factor-induced DNA synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10614647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12553878}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;DNA synthesis;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a mitogen that is secreted by vascular endothelial cells. The encoded protein plays a role in chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, cell adhesion in many cell types, and is related to platelet-derived growth factor. Certain polymorphisms in this gene have been linked with a higher incidence of systemic sclerosis. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:1490; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; insulin-like growth factor binding [GO:0005520]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; aging [GO:0007568]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol [GO:0097553]; cartilage condensation [GO:0001502]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; chondrocyte proliferation [GO:0035988]; DNA biosynthetic process [GO:0071897]; epidermis development [GO:0008544]; extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0070278]; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008543]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lung development [GO:0030324]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; ossification [GO:0001503]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060452]; positive regulation of cell activation [GO:0050867]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of G0 to G1 transition [GO:0070318]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032330]; response to amino acid [GO:0043200]; response to anoxia [GO:0034059]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to fatty acid [GO:0070542]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to mineralocorticoid [GO:0051385]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894] |
11751417_Elevated levels of connective tissue growth factor, WISP-1, and CYR61 in primary breast cancers associated with more advanced features. 11818516_gene is expressed in granulosa-luteal cells (insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein-2; IGFBP-rP2) 11855859_Mechanical stress is required for high-level expression of connective tissue growth factor in fibroblasts. 11897682_the induction of FN by AGE is partly mediated by the AGE-induced up-regulation of cell-derived CTGF and is dependent on PKC activity 11967989_IL-4 interfered with the TGF-beta-induced transcriptional activation of the CTGF gene. 12016149_role in initiating angiogenesis in collaboration with matrix metalloproteinases 12036876_Identification of integrin alpha(M)beta(2) as an adhesion receptor on human peripheral blood monocytes for Cyr61 and connective tissue growth factor: immediate-early gene products expressed in atherosclerotic lesions. 12114504_CTGF has a role in binding to MMPs and VEGF-induced physiological or pathologic angiogenesis 12150969_enhancement of expression on chondrocytes by a novel cis-element 12217862_role in epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation 12218048_CTGF mediates a number of its biological effects by the induction of signaling processes via beta(3) integrin 12239232_CTGF is a hypertrophic factor for human mesangial cells. molecular mechanisms underlying this G(1) phase arrest appear to be due to the induction of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKI) p15(INK4), p21(Cip1), and p27(Kip1). 12398938_localization and expression during fracture healing 12470643_CTGF interacts with the cytoskeletal protein actin in chondrocytes. 12496395_In contrast to CD4+ alpha beta-T cells, gamma delta-T cells are capable of expressing CTGF mRNA and synthesizing its corresponding protein, which supports the concept that gamma delta-T cells contribute to wound healing or tissue fibrotic processes. 12535930_In brains from Alzheimer's patients, a strong tangle-associated CTGF immunoreactivity was observed in entorhinal cortex, hippocampus and temporal cortex. 12571253_Gene expression regulation requires tgf-beta2 in fibroblasts. 12595495_Alterations in alpha5beta1 levels induced by TGF-beta are mediated at least in part through the induction of CTGF in glomerular mesangium 12668285_CTGF acts as a negative regulator of the cell growth in oral squamous cell carcinoma possibly through its interaction with growth modifiers inside the cell 12760970_These results suggest that TGF-beta1-induced CTGF mRNA expression is mediated through the JNK-dependent pathway, whereas p38 MAP kinase and ERK pathways minimally contribute 12787426_Production of CTGF by peritoneal mesothelial cells and its presence in peritoneal cavity in peritoneal dialysis. Increase in CTGF in peritoneal membrane fibrosis suggests involvement in underlying pathophysiologic mechanism(s). 12811819_CTGF/Hcs24 produced in the hypertrophic region may act on chondrocytes in the proliferative and maturative zone via some heparan sulfate proteoglycan, such as perlecan. 12831056_Regulates angiogenesis and endothelial cell function. (review) 12888575_the constitutive overexpression of CTGF in SSc fibroblasts seems to be independent of TGFbeta signaling but dependent at least in part on Sp1 12941731_Magnitude of Urinary CTGF NH(2)-terminal fragment excretion is related to the severity of diabetic nephropathy 12951326_data link alterations in the microtubule and actin cytoskeleton to the expression of connective tissue growth factor 14512169_Postmortem brain tissue analysis demonstrates CTGF localized occasionally in astrocytes but not in macrophages/microglial cells of patients with cerebral malaria. 14633859_Cooperation between CTGF and IGF-I might be involved in glucose-induced matrix accumulation in tubulointerstitial fibrosis and might contribute to pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. 14684735_the sequence IRTPKISKPIKFELSG within CCN2is a unique binding domain for integrin alpha(v)beta(3) that is sufficient to mediate hepatic stellate cell adhesion 14758550_results suggest that connective tissue growth factor(CTGF) is involved in extracellular matrix production in parietal epithelial cells and that it is one of the mediators promoting the scarring process in glomerular crescents 14988298_The NH2-terminal CTGF fragment content is increased in the vitreous of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. 14996858_CTGF inhibits metastasis and invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma by a CRMP-1-dependent mechanism. 15003992_Fibroblast proliferation, differentiation into myofibroblasts, & increased collagen synthesis are regulated via a CTGF-dependent pathway. CTGF serves to control a pivotal switch point in the cascade for connective tissue formation. 15039132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15041728_CYR61 and CTGF may play a role in the progression of gliomas; their levels at diagnosis may have prognostic significance. 15045137_unstimulated platelets contain considerable amounts of CTGF; CTGF presence in platelets is a result of endocytosis from extracellular environment in bone marrow; agonist-stimulation of platelets resulted in release of CTGF from the storage granules 15053922_evidence that adenylate cyclase as well as one or several protein kinases might be involved in the mechanoregulation of Cyr61, CTGF and Nov genes 15090860_connective tissue growth factor seems to be an attractive alternative therapeutic target for combating renal fibrosis--REVIEW 15111539_Levels are elevated in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy and appear to be correlated with proteinuria and creatinine clearance. 15113833_Generated antibodies for functional analysis of CTGF. Showed antibody bound to the CT module neutralizes efficiently the stimulatory effect of CTGF on chondrocytic cell proliferation 15135656_CTGF may play a crucial role in the renal tubular epithelial-transdifferentiation and the following deposition/degradation process of extracellular matrix during tubulointerstitial fibrosis 15247510_CTGF has a role in scleroderma and in pathological fibrosis [review] 15298857_Simvastatin through a Rho signaling mechanism in lung fibroblasts can modulate CTGF expression and interaction with TGF-beta. 15345671_CTGF has a role in the reduced matrix degradation observed in diabetic nephropathy. 15377500_TGF-beta 1-stimulated CTGF expression is mediated by mechanisms involving ERK and JNK pathways and is downregulated by IL-4 and IL-13 through modulation of Smad and ERK signals. 15459777_CTGF plays a major role in the pathogenesis of progressive fibrosis in biliary atresia. 15526358_Cyr61 and CTGF genes may play an important role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis and correlate with recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 15536170_key dependence of the fibrogenic actions of CTGF on TGF-beta in kidney 15598883_CCN2 is one of the major functional components of platelets 15703175_sodium-hydrogen exchanger activity modulates connective tissue growth factor mRNA expression in transforming growth factor beta1- and Des-Arg10-kallidin-stimulated myofibroblasts 15761189_CTGF protein is significantly increased in complicated compared with fibrous plaques and may enhance monocyte migration into atherosclerotic lesions, thus contributing to atherogenesis. 15761249_CTGF upregulation in arterial vascular smooth muscle cells of the lung is associated with the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension. 15820145_indicate novel roles of M-CSF in articular cartilage metabolism in collaboration with CTGF/CCN2, particularly during an inflammatory response 15857887_data provide a molecular basis for the divergence of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) actions on connective tissue cell types 15940639_CTGF induction is important for robust oval cell response during liver regeneration after 2-AAF/partial hepatectomy treatment in rats 15941869_Negative regulation of CTGF by hCG during luteal rescue mediated by paracrine signals. 15950619_Under pathological conditions, where CTGF expression is elevated, CTGF blocks the negative feedback loop provided by Smad 7, allowing continued activation of the TGFbeta signaling pathway. 15956925_Human CTGF is a cysteine rich polypeptide that has similar structures to PDGF and has been implicated in connective tissue formation. PDGF and CTGF may play a role in the development of aneurysmal walls in both AAAA and IAAA. 16044512_Cis-acting element of structure-anchored repression of CTGF was investigated. 16186174_CTGF expression in the brain might have a role in Alzheimer's disease clinical progression and neuropathology 16204411_CTGF plays a specific role as a downstream mediator of TGF-beta(1)-induced renal fibrosis 16247469_Hypoxia increased the ctgf/ccn2 mRNA level by altering the 3'-untranslated region (UTR)-mediated mRNA stability without requiring de novo protein synthesis. 16255854_CTGF may play a role in the pathogenetic process of muscular dystrophy, and may be important for muscle repair and fibrosis. 16270194_increased glomerular expression of CTGF occurs from the earliest stage of diabetic nephropathy; CTGF is required for mesangial synthesis of fibronectin stimulated by high glucose or glycated albumin 16291159_In biliary atresia livers, novel biliary epithelia CTGF mRNA expression is high and correlates with severity of fibrosis; these data support a role for biliary epithelial cell signaling in fibrogenesis 16373901_Urinary CTGF may be a progression promoter in diabetic nephropathy. 16457822_CCN2/CTGF enhances chondrocyte adhesion to FN through direct interaction of its C-terminal CT domain with FN, and alpha5beta1 is involved in this adhesion. 16482098_Administration of losartan, but not amlodipine, to hypertensive patients improves structural abnormalities and prevents the production of CTGF and TGF-beta in small arteries. 16501850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16501850_The CTGF gene was resequenced to identify novel or known variants, and make an analysis of their association with diabetic nephropathy. 16528248_Tranilast is a potential effective antifibrotic compound in the kidney, exerting its effects via inhibition of TGF-beta1-induced CTGF expression and downstream activation of the Smad2 pathway in both PTCs and CFs. 16543635_Migration of HUVECs transfected with CTGF vector increased significantly compared with those transfected with vector control 16684954_Bradykinin and angiotensin II lower CTGF mRNA expression below basal levels over a span of 4 hours. 16731742_These findings suggest that CTGF may contribute to aberrant autocrine and paracrine pathways that promote pancreatic cancer cell growth, invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis 16790529_CTGF stimulated the phosphorylation and cytoplasmic translocation of p27(Kip-1) on serine 10; role of p27(Kip-1) as a mediator of actin rearrangement. 16813525_CCN2 was critically involved in osteolytic metastasis and was induced by PKA- and PKC-dependent activation of ERK1/2 signaling by PTHrP. 16820572_A delicate balance of collagen, elastin, & vascular smooth muscle cells in the aortic wall is clearly essential for a compliant aorta, and CTGF may play a vital role in this balance. 16858645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16877704_CTGF may behave as a secreted tumor suppressor protein in the normal lung, and its expression is suppressed in many NSCLCs. 16889607_CTGF has potential as a biomarker of CAN, and also a therapeutic target in managing graft fibrosis. 16899928_this study demonstrated that CTGF is released from platelets by high shear stress; furthermore, disturbed flow along atherosclerotic vessels may induce endothelial CTGF expression and contribute to the progress of atherosclerotic lesions 17093396_CTGF in trabecular meshwork is modulated by physiological agonists and by increased ocular pressure and mechanical stretch. Regulation of CTGF within outflow pathway may play role in homeostasis of intraocular pressure. 17116388_IFN-gamma interferes with stellate cell activation in the pancreas and suggest activated STAT1 as an inductor of a quiescent pancreatic stellate cells phenotype. 17119035_local factors, such as CTGF and genomic amplification, seem to be more important than germ line genetic variation in influencing PAI1 expression and its untoward effects in breast cancer 17170128_Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) was the highest overexpressed gene in B-cell ALL compared with the other groups, and displayed heterogeneous expression, suggesting it might have prognostic relevance. 17192487_Vitreous body cells may be a possible source of CTGF and thus might play a role in vitreoretinal interface diseases. 17215322_In endothelial cells CTGF gene transcription is controlled by alteration is cytoskeletal actin and serum response factor. 17224075_Expression of CTGF mRNA was up-regulated as early as 6 hours in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells after exposed to high glucose condition, followed by extracellular matrix components accumulation. 17239539_CTGF contributes to the extracellular matrix accumulation in wound healing and tissue fibrosis by enhancing the affinity of FN to fibrin. 17239853_CCN2 supplies essential, non-redundant functions required for fibroblasts to properly participate in features of embryogenesis, and further suggest that CCN2 may play essential roles in adult wound healing, tissue repair and fibrogenesis. 17375628_CTGF polymorphism at -447 G/C was not associated with biliary atresia and jaundice in the postoperative period in Thai children 17375628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17393107_Role of CTGF in extracellular matrix degradation in renal tubular epithelial cells is reported. 17399683_We thus conclude that CCN2 enhances hBMSC attachment via integrin-p38 MAPK signal pathway. 17399955_The up-regulation of angiotensin II receptor type 1 and the consequent increase of CTGF expression, independently of TGFbeta1, participate in high-glucose-induced fibronectin production in cultured human dermal fibroblasts 17437852_We found significant differences in gene expression, specifically with a group of genes, including CTGF, known to be responsive to estrogen or to interact with estrogen receptor. 17441427_The expression of CTGF and/or OPN might be important biological markers in reflecting the progression, biological behavior, metastatic potential and prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 17498677_Connective tissue growth factor (CTFG) induces the expression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) protein in HK-2 cells 17550972_Results suggest that CTGF plays a crucial role in migratory/invasive processes in human breast cancer by a mechanism involving activation of the integrin-alphavbeta3-ERK1/2-S100A4 pathway. 17579708_Downregulation of the CTGF is associated with lung cancer. 17580150_Sirolimus conversion provided a beneficial strategy to improve long-term graft survival in chronic allograft nephropathy; attentuation of CTGF expression may be an antiproliferative effect. 17602195_CTGF is a functional target of aldosterone in mesangial cells, but aldosterone-induced CTGF gene expression is not directly mediated by the mineralocorticoid receptor. 17622321_Overexpression of CTGF is one of the most important features of idiopathic portal hypertension. 17657819_Smad7 overexpression in cultured hepatocytes abrogated TGF-beta-dependent and intrinsic CTGF expression. 17671176_epigenetic silencing by hypermethylation of the CTGF promoter leads to a loss of CTGF function, which may be a factor in the carcinogenesis of ovarian cancer 17673559_Exercise with high mechanical loading induced the expression of CTGF in human skeletal muscle. 17681742_Basal expression of collagen, fibronectin and CCN2 and adhesion to matrix was not affected 17765657_Blocking experiments with the lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor-specific inhibitor Ki16425 suggest a general involvement of LPA receptors in bacteria-triggered CTGF expression. 17786299_CTGF induction is associated with pancreatic cancer 17876891_Gastrointestinal carcinoid tumor fibrosis is a CTGF/TGFbeta1-mediated stellate cell-driven fibrotic response. 17881752_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17881752_The G-945C substitution represses CTGF transcription, and the -945G allele is significantly associated with susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. 17908800_MMP-2 processing of HARP and CTGF released vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from angiogenic inhibitory complexes. 17915216_These data reveal a novel function for CTGF in the regulation of epithelial tissue repair beyond its established role in fibrosis, and further highlight the complexity of TGFbeta regulation of epithelial cell function. 17922682_CTGF is a useful prognostic marker for GC. High CTGF expression is associated with the risk of lymph nodes metastasis and a poor survival time in GC. 17944991_CTGF mRNA expression was induced in HUVSMCs after treatment with dl-homocysteine (50 micromol L(-1)) for 1 h, which remained at the elevated level for up to 8 h. 17951630_the interaction of CTGF and beta-catenin-TCF/Lef forms a positive feedback loop, which could contribute to the tumorigenicity of ESCC. 17951996_ILK mediated the effect of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in proximal tubular epithelial cells stimulated by CTGF 17996907_In conclusion, TGF-beta1-CTGF pathway may play a role in the fibrosis that is commonly observed in muscular dystrophy. 18080105_REVIEW: chemistry,biosynthesis, function of CCN2, and its relation to fibrosis and cancer 18172013_Heterochromatin protein gamma coordinately regulates CCN2/CTGF by interacting with MMP3, which affects the development, tissue remodeling, and pathology of arthritic diseases through this CCN2/CTGF regulation thus is suggested. 18212329_Increased expression of this protein correlates with the loss of VHL protein expression in renal cell carcinoma. 18245529_Expression levels at diagnosis may represent a useful molecular tool to early identification of patients with different prognosis in osteosarcoma 18264937_TGF-beta1 and CTGF mRNAs are correlated with urinary protein level in IgA nephropathy. 18266973_TGF-beta-dependent CTGF/CCN2 expression in hepatocytes cultured under completely TGF-beta-free conditions was analysed. 18287089_TGFbeta1 stimulates CCN2 expression in human gingival fibroblasts through a RhoA-independent, Rac1/Cdc42-dependent mechanism 18292194_Hypoxia enhances the production of CTGF in primary term human trophoblasts 18319604_In human renal fibroblasts, serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase1 (SGK1) and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) protein expression were enhanced by angiotensin II 18344285_Plasma CTGF contributes significantly to prediction of end-stage renal disease and mortality in patients with type 1 diabetic nephropathy. 18358427_connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 has roles in tissue repair, scarring and fibrosis [review] 18395916_CTGF may have a role in lymph node metastases in gastric cancer 18400984_Examine specific signals involved in the long-term maintenance of radiation-induced fibrogenic differentiation and suggest roles for CCN2 and TGF-beta1. 18451226_An unbiased analysis of the gallblader cancer transcriptome by serial analysis of gene expression has identified CTGF expression as a predictive biomarker of favorable prognosis in gallbladder cancer 18481257_These results suggest that connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) plays an important role in the development of persistent skin fibrosis and that CTGF may be a potential and specific therapeutic target in skin fibrosis. 18596209_Connective tissue growth factor inhibits adipocyte differentiation. 18622762_the influence of CTGF expression on the biological behavior and progression of various cancer cells, as well as its regulation on various types of protein signals and their mechanisms 18628999_CTGF is primarily a pro-fibrotic factor in the eye, and a shift in the balance between CTGF and VEGF is associated with the switch from angiogenesis to fibrosis in proliferative retinopathy 18639630_These results indicate a tight control of CTGF expression in pancreatic stellate cells at the transcriptional level. 18648180_the up-regulation of CTGF expression may be responsible for the fibrosis process of urethral tissues in US patients 18676875_Findings implicate the importance of CTGF in lung tissue repair and fibrosis and propose CTGF-induced migration of lung fibroblasts to the damaged tissue. 18683703_antisense oligonucleotides inhibit CTGF and fibronectin expression in human tenon' s capsule fibroblasts induced by transforming growth factor beta2. 18783549_CTGF is proposed as a fibrogenic master switch for epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 18787533_AZX100, an analogue of the small heat shock protein, HSP20, reduces TGF-beta1-induced CTGF expression in keloid fibroblasts 18805993_Regulation of CCN2/CTGF and related cytokines in cultured peritoneal cells under conditions simulating peritoneal dialysis. 18835464_These results suggest that CCN2 regulates the expression of VEGF at a transcriptional level by promoting HIF-1alpha activity. 18836231_Findings suggest that CCN2 induced by mechanical stress may therefore play some role in meniscus growth and regeneration. 18846327_High glucose-induced CTGF expression is mediated through the active SGK1 pathway in mesangial cells. 18922143_CCN2 expression occurred via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and the downstream transcription factor ATF-2. 18922980_These data suggest that CTGF protein induced by S1P2 might act as a growth inhibitor in Wilms' tumor. 18936953_plasma membrane S1P(1) receptors are rapidly internalized and subsequently translocated to nuclear compartment upon S1P stimulation; nuclear S1P(1) is able to regulate the transcription of Cyr61 and CTGF 19016368_CTGF expression in human intervertebral disc: implications for angiogenesis in intervertebral disk degeneration are reported. 19054816_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19054816_results do not confirm previous findings and suggest that the CTGF -945 promoter polymorphism does not play a major role in SSc susceptibility or clinical phenotype. 19054818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19054818_The results confirm the association between an SNP in the CTGF gene and susceptibility to Systemic sclerosis, especially in the presence of diffuse cutaneous SSc, interstitial lung disease and anti-topoisomerase I antibody. 19069651_CTGF and WISP-1 could play an important role in the progression of primary lung cancers by either individual gene itself or cointeraction. 19096030_miR-133 and miR-30 regulate connective tissue growth factor: implications for a role of microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. 19153601_activation of GPR30 by OHT also induces CTGF in fibroblasts from breast tumour biopsies, these pathways may be involved in promoting aggressive behaviour of breast tumours in response to endogenous oestrogens or to OHT being used for endocrine therapy. 19179545_Increased CCN2 staining in clinical pancreatic tumor tissue relative to stromal cells surrounding the tumor, supporting our assertion that tumor cell-derived CCN2 is important for pancreatic tumor growth. 19208517_HBx may facilitate liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cell proliferation and upregulating the expression of fibrosis-related molecules like CTGF 19210343_plays an important role in wound healing and in the regeneration of periodontal tissue 19218111_High glucose treatment can increase CTGF mRNA and protein expressions in cultured human renal tubular epithelial cells. 19233176_A regulatory role for miR-18a in chondrocytic differentiation through CCN2. 19243500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247157_strong CTGF expression in painful intervertebral discs may be related to disc fibrosis and degeneration 19253834_CTGF plays an important role in the pathogenesis of scleroderma and it is closely associated with the development of the pathologic fibrotic process. 19277979_Role of connective tissue growth factor and its interaction with basic fibroblast growth factor and macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 in skin fibrosis. 19298220_Results indicate that CCN2/CTGF binds to aggrecan through its N-terminal IGFBP and VWC modules, and this binding may be related to the CCN2/CTGF-enhanced production and secretion of aggrecan by chondrocytes. 19301259_Connective tissue growth factor enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the alphavbeta3 integrin, FAK, ERK, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 19333718_data demonstrated that preptin is involved in bone anabolism mediated by ERK/CTGF in human osteoblasts and may contribute to the preservation of bone mass observed in hyperinsulinemic states, such as obesity 19378419_Signal transduction is involved in CTGF-induced production of chemokines in mesangial cells. 19382180_Downregulation of connective tissue growth factor by three-dimensional matrix enhances ovarian carcinoma cell invasion. 19409809_Increased urinary CCN2 is associated with the early progression of diabetic nephropathy, whereas MCP-1 is associated with later stage disease. 19429239_The results suggest that 15d-PGJ(2) inhibits TGF-beta-induced CTGF expression by inhibiting the phosphorylation of Smad2. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19485899_[review] The TSP1/transforming growth factor beta/ connective tissue growth factor axis may contribute in the pro-inflammatory and pro-atherogenic state in patients affected with rheumatoid arthritis. 19494553_Ras/MAP kinase pathway, specifically through N-Ras, mediates TGFbeta1 auto-induction and TGFbeta1-induced CTGF expression in human renal tubule epithelial cells. 19549692_hypoxia inhibits CTGF synthesis in human proximal tubular epithelial cells, involving HIF-1alpha. 19565505_A direct profibrotic effect of CTGF and its contribution to lung fibrosis through transcriptional activation of Col1a2 has been demonstrated. 19589256_This study was designed to investigate the effect of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) 1 and 2 on TGF-beta(1)-regulated CTGF gene expression and corneal scar formation. 19625611_For the first time in any system, fatty acid is newly identified as a regulator of CTGF, and this work implicates autocrine CTGF as a mediator of adverse effects of high glucose and fatty acids in cardiomyocytes. 19641518_CTGF/CCN2 mediates collagen loss in chronologically aged human skin 19657322_Transforming growth factor-beta2 upregulates sphingosine kinase-1 activity, which in turn attenuates the fibrotic response to TGF-beta2 by impeding CTGF expression. 19670427_Production of elevated CCN2 levels in hepatocytes of transgenic mice in vivo does not cause hepatic injury or fibrosis per se but renders the livers more susceptible to the injurious actions of other fibrotic stimuli. 19673024_Data show that endogenous CCN2 is a mediator of basal or TGF-beta1-induced collagen I production in human HSCs and regulates entry of the cells into S phase. 19724859_CTGF and DUSP1 overexpression in residual breast cancer samples may be a reflection of resistance to further administration of doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide regimen 19730442_results identify caspase-3 activation in endothelial cells as a novel inducer of CTGF release and fibrogenesis 19762080_The enhancement of CTGF expression as well as serum CTGF levels in clinical conditions attributed to placental dysfunction suggests a role for this secretory protein in the pathophysiology of placental injury or its sequelae. 19764552_Rosiglitazone inhibits CTGF expression induced by TGF-beta1 in HLF-02 cells by activating PPARgamma through NF-kappaB and AP-1 signal transduction pathways. 19764567_The expression of collagen III and CTGF in pPROM group were decreased significantly when compared to their control groups. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19822645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19822645_The single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs9402373 that lies close to CTGF is associated with severe hepatic fibrosis in two Chinese samples, in Sudanese, and in Brazilians infected with either Schistosoma japonicum or S. mansoni. 19861250_CTGF is an important mediator of high glucose-induced tubular epithelial hypertrophy, and transfection with siRNA targeting CTGF can alleviate hypertrophy. 19863391_Specifically, the CTGF mRNA and protein levels were 50% and 48% of the control levels, respectively. These findings suggest that cyclic stretching of fibroblasts contributes to anti-fibrotic processes by reducing CTGF production. 19890996_The synovial cells with treatment of 0.1 mg/mL Hylan decreased the CTGF gene expression. 19893244_-beta1 shRNAs could obviously inhibit the expression levels of TGF-beta1, CTGF, FN and cellular proliferation stimulated by HSA in HK2 cells. 19895313_CTGF is involved in the wound-healing process and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of intraocular proliferative diseases. 19922639_aberrant connective tissue growth factor production induced by TNFalpha plays a central role for the abnormal osteoclastic activation in RA patients. 19955828_we discuss the biology of CCN2 with a focus on the regulation of CCN2 gene, cellular mechanisms of profibrotic CCN2 effects and the current in vivo and in vitro evidence for the role of CCN2 in the development of renal fibrosis[review] 20004937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20015945_Dialysate CTGF concentration could be a biomarker for both peritoneal fibrosis and membrane function in peritoneal dialysis patients. 20018872_Exposure to low oxygen tension or treatment with the hypoxia-mimetic dimethyloxalyl glycine (DMOG) stabilized HIF-1alpha and up-regulated CTGF in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and in a murine microvascular endothelial cell line. 20032097_CTGF gene polymorphisms may contribute to susceptibility to scleroderma. 20032097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20032117_Exposure to hypoxia decreased CTGF gene expression in cultured human tubular epithelial cells. 20050020_CTGF is preferentially expressed by human bulge cells, compared to differentiated hair follicle keratinocytes 20053285_plasma CCN2 has a role in right ventricular dysfunction and valvular regurgitation in neuroendocrine tumor patients 20056838_Fascin regulates the proliferation and invasiveness of ESCC cells by modulating the expression of CTGF and CYR61 via TGF-beta pathway. 20117462_In atrial fibrillation, angiotensin II activates CTGF via activation of Rac1 and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase, leading to up-regulation of Cx43, N-cadherin, and interstitial fibrosis. 20162579_Overexpression of CTGF caused the U343 glioblastom multiforme cells to survive for longer than 40 days in serum-free medium 20180416_Estradiol may induce hypospadias by upregulating the expressions of ATF3 and CTGF. 20201953_In dermal fibroblasts, CCN2 is required for the induction of MMP1 following Akt inhibition. CCN2 induces MMP1 expression via an Erk1/2 and Ets1-dependent pathway. 20222112_This study is the first to show that TGF-beta induces CTGF expression through activation of Smad3 and activator protein 1 (AP-1) signaling pathways in nucleus pulposus cells. 20237235_Filtered CTGF is normally reabsorbed almost completely in proximal tubules via megalin, and elevated urinary CTGF may largely reflect proximal tubular dysfunction. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20238043_There may be abnormal CTGF synthesis regulation in Age-related macular degeneration. 20305691_miR-17-92 and its target CTGF mediate effects of differentiation-promoting treatment on glioblastoma cells through multiple regulatory pathways. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20522428_Findings provide the first evidence that variants within the promoter region of the CTGF/CCN2 gene predisposes diabetic subjects to develop albuminuria. 20522428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20522536_Treatment of microalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease usin |
ENSMUSG00000019997 |
Ccn2 |
8.882164 |
2.8703717817 |
1.521238 |
0.522892873 |
8.718683 |
0.00314965461842739869596785595717847172636538743972778320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006712229593991973775057857665160554461181163787841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3166850 |
4.1580716 |
4.6766379 |
1.2111045 |
| ENSG00000118564 |
26234 |
FBXL5 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKA1 |
FUNCTION: Component of some SCF (SKP1-cullin-F-box) protein ligase complex that plays a central role in iron homeostasis by promoting the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of IREB2/IRP2. Upon high iron and oxygen level, it specifically recognizes and binds IREB2/IRP2, promoting its ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome. Promotes ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of DCTN1/p150-glued. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17532294, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19762596, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19762597}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Iron;Leucine-rich repeat;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbls class and, in addition to an F-box, contains several tandem leucine-rich repeats. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this locus. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:26234; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] |
17532294_Our findings provide a potential mechanism by which p150(Glued) protein function is regulated by SCFs. 19762596_iron homeostasis is regulated by a proteolytic pathway that couples IRP2 degradation to intracellular iron levels through the stability and activity of FBXL5 19762597_observations suggest a mechanistic link between iron sensing via the FBXL5 hemerythrin domain, IRP2 regulation, and cellular responses to maintain mammalian iron homeostasis 22253436_Detailed molecular and structural characterization of the ligand-responsive hemerythrin domain provides insights into the mechanisms by which FBXL5 serves as a unique mammalian metabolic sensor. 22648410_Data indicate that F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (FBXL5)-Hr (hemerythrin-like domain) undergoes substantive structural changes when iron becomes limiting, accounting for its switch-like behavior. 23135277_F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 5 (FBXL5) is required for maintenance of cellular and systemic iron homeostasis 24778179_results thus suggest that HERC2 regulates the basal turnover of FBXL5, and that this ubiquitin-dependent degradation pathway contributes to the control of mammalian iron metabolism 25832584_FBXL5 regulates cortactin through induction of its ubiquitylation, and FBXL5 similarly regulates Snail1. 25956243_FBXL5-mediated degradation of CITED2 leads to the activation of HIF-1alpha. 28131773_analysis of the redox sensing mechanism by which FBXL5 can serve as an iron metabolism regulator within mammalian cells 28714470_Transcriptomic analysis shows downregulation of FBXL5 expression in HSCs of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. 28768766_regulatory circuit involving FBXL5 and CIA acts through both IRPs to control iron metabolism and promote optimal cell growth 30219228_MiR-1306-3p directly targets FBXL5 and modulates FBXL5-meadiated snail protein stability in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30257389_this study demonstrated that FBXL5 functioned as an oncogene in the progression of colon cancer through regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling 30877170_Dysregulation of FBXL5-mediated cellular iron homeostasis was found to be associated with poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma, suggesting that FBXL5 plays a key role in defense against hepatocarcinogenesis. 31229404_We demonstrate that the CIA-targeting complex promotes the ability of FBXL5 to degrade iron regulatory proteins. In addition, the FBXL5-CIA-targeting complex interaction is regulated by oxygen (O2) tension displaying a robust association in 21% O2 that is severely diminished in 1% O2 and contributes to O2-dependent regulation of IRP degradation 32126207_This study has identified an iron-sulfur cluster within FBXL5, which promotes IRP2 polyubiquitination and degradation in response to both iron and oxygen concentrations. 33735560_Ferroportin and FBXL5 as Prognostic Markers in Advanced Stage Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000039753 |
Fbxl5 |
398.429516 |
0.4466455085 |
-1.162798 |
0.262314324 |
19.044919 |
0.00001276772763415060313253908408359649229169008322060108184814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000039582369224965951309824774284606974106281995773315429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
254.1362347 |
41.5296839 |
572.7054001 |
67.3012733 |
| ENSG00000118655 |
64858 |
DCLRE1B |
protein_coding |
Q9H816 |
FUNCTION: 5'-3' exonuclease that plays a central role in telomere maintenance and protection during S-phase. Participates in the protection of telomeres against non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)-mediated repair, thereby ensuring that telomeres do not fuse. Plays a key role in telomeric loop (T loop) formation by being recruited by TERF2 at the leading end telomeres and by processing leading-end telomeres immediately after their replication via its exonuclease activity: generates 3' single-stranded overhang at the leading end telomeres avoiding blunt leading-end telomeres that are vulnerable to end-joining reactions and expose the telomere end in a manner that activates the DNA repair pathways. Together with TERF2, required to protect telomeres from replicative damage during replication by controlling the amount of DNA topoisomerase (TOP1, TOP2A and TOP2B) needed for telomere replication during fork passage and prevent aberrant telomere topology. Also involved in response to DNA damage: plays a role in response to DNA interstrand cross-links (ICLs) by facilitating double-strand break formation. In case of spindle stress, involved in prophase checkpoint. Possesses beta-lactamase activity, catalyzing the hydrolysis of penicillin G and nitrocefin (PubMed:31434986). Exhibits no activity towards other beta-lactam antibiotic classes including cephalosporins (cefotaxime) and carbapenems (imipenem) (PubMed:31434986). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15467758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15572677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16730175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16730176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18468965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18469862, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19197158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19411856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20655466, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31434986}. |
3D-structure;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA damage;DNA repair;Dyskeratosis congenita;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Telomere;Ubl conjugation |
|
DNA interstrand cross-links prevent strand separation, thereby physically blocking transcription, replication, and segregation of DNA. DCLRE1B is one of several evolutionarily conserved genes involved in repair of interstrand cross-links (Dronkert et al., 2000 [PubMed 10848582]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:64858; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 5'-3' exodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0035312]; 5'-3' exonuclease activity [GO:0008409]; beta-lactamase activity [GO:0008800]; damaged DNA binding [GO:0003684]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:0006303]; interstrand cross-link repair [GO:0036297]; protection from non-homologous end joining at telomere [GO:0031848]; telomere capping [GO:0016233]; telomere maintenance [GO:0000723]; telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening [GO:0010833]; telomeric 3' overhang formation [GO:0031860]; telomeric loop formation [GO:0031627] |
15467758_siRNA knockdown of hSNM1B rendered cells sensitive to ionizing radiation, suggesting the possibility of hSNM1B involvement in homologous recombination repair of double-strand breaks arising as intermediates of ICL repair 16606622_the C terminus of Snm1B was shown to interact with the TRF homology domain of TRF2 indicating that Snm1B is likely recruited to the telomere via interaction with the double-stranded telomere-binding protein TRF2 16730175_SNM1B (Apollo) protein exhibits a 5'-to-3' DNA exonuclease activity and functions together with TRF2 to protect telomeres from damage and fusion. 16730176_SNM1B (Apollo) is an Artemis-like nuclease that is required for the protection of telomeres during or after their replication. [Apollo] 18468965_observations suggest an important role for hSNM1B in the response to ionizing radiation damage, a role that may be, in part, upstream of the central player in maintenance of genome integrity, ATM 18469862_Snm1B interacts with the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) complex and with FancD2 further substantiating its role as a checkpoint/DNA repair protein. 18593705_The protein hSnm1B is stabilized when bound to the telomere-binding protein TRF2 19197158_Results suggest that SNM1B/Apollo and Astrin function together to enforce the prophase checkpoint in response to spindle stress. 19411856_DCLRE1B protein binds to a C-terminal fragment of HSP72 Heat-Shock Proteins, known to contain the substrate binding domain. 20655466_TRF2, which binds preferentially to positively supercoiled DNA substrates, together with Apollo, negatively regulates the amount of TOP1, TOP2alpha, and TOP2beta at telomeres. 21478198_SNM1B functions epistatically to the central Fanconi anemia factor, FANCD2, in cellular survival after interstrand crosslinks damage and homology-directed repair of DNA double-strand breaks 22692201_differences in the substrate selectivities of SNM1A and SNM1B are likely to be relevant to their in vivo roles 22907656_The nuclease hSNM1B/Apollo is linked to the Fanconi anemia pathway via its interaction with FANCP/SLX4. 23189151_the N-terminal region of Snm1B forms a complex containing PSF2 and Mus81, while the C-terminal region is important for PSF2-mediated chromatin association. 23863462_The SNM1B/APOLLO DNA nuclease functions in resolution of replication stress and maintenance of common fragile site stability. 26582912_Different charge distributions along the DNA binding groove may account for the drastic difference in processivity and DNA digestion efficiency, including that of damaged substrates, between SNM1A and SNM1B. 34387694_A phosphate binding pocket is a key determinant of exo- versus endo-nucleolytic activity in the SNM1 nuclease family. 34387696_Structural and mechanistic insights into the Artemis endonuclease and strategies for its inhibition. |
ENSMUSG00000027845 |
Dclre1b |
124.264181 |
2.4311877822 |
1.281661 |
0.141946240 |
83.139687 |
0.00000000000000000007645520178437057560872697577142257674447033048951242735317979093423446101951412856578826904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000673316693518681252094814009176165594389640165745429013777201276980122202076017856597900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
178.9000272 |
16.1717017 |
74.1119464 |
5.3348294 |
| ENSG00000118690 |
84071 |
ARMC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEN0 |
FUNCTION: Required for sperm flagellum axoneme organization and function (By similarity). Involved in axonemal central pair complex assembly and/or stability (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3URY6}. |
Alternative splicing;Differentiation;Disease variant;Reference proteome;Repeat;Spermatogenesis |
|
Involved in sperm axoneme assembly. Implicated in spermatogenic failure 38. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84071; |
cilium organization [GO:0044782]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288] |
18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30686508_bi-allelic mutations in ARMC2 cause male infertility in humans and mice by inducing a typical 'multiple morphological abnormalities of the flagella' phenotype, indicating that this gene is necessary for sperm flagellum structure and assembly 34493464_A novel stop-gain mutation in ARMC2 is associated with multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella. |
ENSMUSG00000071324 |
Armc2 |
68.179664 |
0.2816179247 |
-1.828189 |
0.605764495 |
8.148875 |
0.00430878794785694105989870550388332048896700143814086914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008931008300852191078567088311501720454543828964233398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.6556520 |
12.2953371 |
106.2255446 |
31.1371919 |
| ENSG00000118733 |
118427 |
OLFM3 |
protein_coding |
Q96PB7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Synapse |
|
Predicted to be involved in eye photoreceptor cell development. Predicted to be located in Golgi apparatus; extracellular space; and synapse. Predicted to be part of AMPA glutamate receptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:118427; |
AMPA glutamate receptor complex [GO:0032281]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; synapse [GO:0045202]; eye photoreceptor cell development [GO:0042462]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12019210_identification of a novel olfactomedin-related gene, named optimedin, located on chromosome 1p21 in humans, expressed in brain and retina; may be a candidate gene for disorders involving the anterior segment of the eye and the retina (optimedin) 16115881_Pax6 regulation of Optimedin in the eye and brain may directly affect multiple developmental processes, including cell migration and axon growth 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22281030_This is the first instance of OLFM3 being linked with anoikis resistance in a human cancer cell line |
ENSMUSG00000027965 |
Olfm3 |
56.947912 |
0.2953576475 |
-1.759465 |
0.246307397 |
51.895348 |
0.00000000000058538956513230281743836919166097591089251844787000322867243085056543350219726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003533885472945926173625175045994046814454986327191932105051819235086441040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.3484173 |
4.5581626 |
86.8311561 |
10.0291975 |
| ENSG00000118777 |
9429 |
ABCG2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UNQ0 |
FUNCTION: Broad substrate specificity ATP-dependent transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family that actively extrudes a wide variety of physiological compounds, dietary toxins and xenobiotics from cells (PubMed:11306452, PubMed:12958161, PubMed:19506252, PubMed:20705604, PubMed:28554189, PubMed:30405239, PubMed:31003562). Involved in porphyrin homeostasis, mediating the export of protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) from both mitochondria to cytosol and cytosol to extracellular space, it also functions in the cellular export of heme (PubMed:20705604, PubMed:23189181). Also mediates the efflux of sphingosine-1-P from cells (PubMed:20110355). Acts as a urate exporter functioning in both renal and extrarenal urate excretion (PubMed:19506252, PubMed:20368174, PubMed:22132962, PubMed:31003562). In kidney, it also functions as a physiological exporter of the uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate (By similarity). Also involved in the excretion of steroids like estrone 3-sulfate/E1S, 3beta-sulfooxy-androst-5-en-17-one/DHEAS, and other sulfate conjugates (PubMed:12682043, PubMed:28554189, PubMed:30405239). Mediates the secretion of the riboflavin and biotin vitamins into milk (By similarity). Extrudes pheophorbide a, a phototoxic porphyrin catabolite of chlorophyll, reducing its bioavailability (By similarity). Plays an important role in the exclusion of xenobiotics from the brain (Probable). It confers to cells a resistance to multiple drugs and other xenobiotics including mitoxantrone, pheophorbide, camptothecin, methotrexate, azidothymidine, and the anthracyclines daunorubicin and doxorubicin, through the control of their efflux (PubMed:11306452, PubMed:12477054, PubMed:15670731, PubMed:18056989, PubMed:31254042). In placenta, it limits the penetration of drugs from the maternal plasma into the fetus (By similarity). May play a role in early stem cell self-renewal by blocking differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TMS5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11306452, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12477054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12682043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12958161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15670731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19506252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20110355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20368174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20705604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22132962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23189181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28554189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30405239, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31003562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31254042, ECO:0000305|PubMed:12958161}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lipid transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is included in the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the White subfamily. Alternatively referred to as a breast cancer resistance protein, this protein functions as a xenobiotic transporter which may play a major role in multi-drug resistance. It likely serves as a cellular defense mechanism in response to mitoxantrone and anthracycline exposure. Significant expression of this protein has been observed in the placenta, which may suggest a potential role for this molecule in placenta tissue. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:9429; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; external side of apical plasma membrane [GO:0098591]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity [GO:0008559]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; biotin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015225]; efflux transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015562]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; organic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008514]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; riboflavin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0032217]; urate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015143]; xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042910]; biotin transport [GO:0015878]; cellular detoxification [GO:1990748]; export across plasma membrane [GO:0140115]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; organic anion transport [GO:0015711]; renal urate salt excretion [GO:0097744]; riboflavin transport [GO:0032218]; transepithelial transport [GO:0070633]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; urate metabolic process [GO:0046415]; xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:1990962] |
11688982_role in transport of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38) in human lung cancer cells 11801536_ABCG2 protein effluxes hoechst 33342 in hematopoietic stem cells 11807788_homodimer formation is essential for BCRP drug resistance 11948115_There is no indication that elevated BCRP expression in breast carcinomas confers resistance to anthracyclines. 11986944_Increased expression in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia compared to level at diagnosis. 12145683_Expression of the BCRP gene reduces the response to chemotherapy in AML and that BCRP expression is higher at the time of relapse. 12208758_Overexpression of wild-type breast cancer resistance protein mediates methotrexate resistance. 12369998_involvement of ABCG2 in multidrug resistance in cancer, especially with regard to acute myeloid leukemia 12374800_characterization of different isoforms without possible endogenous dimerization partners 12393637_ABCG2 expression conferred resistance to mitoxantrone & topotecan, but not to idarubicin. High levels of ABCG2 mRNA expression in adult AML blast specimens are relatively uncommon. ABCG2 expression may be limited to a small cell subpopulation. 12429862_The breast cancer resistance protein protects against pheophorbide a, a major chlorophyll-derived dietary phototoxin, and protoporphyria. 12438926_In both normal and tumour brain tissue, BCRP is located at the blood-brain barrier, mainly at the luminal surface of microvessel endothelium. It may pose an additional barrier to drug access to the brain. 12459192_results showed that ABCG2 confers resistance to indolocarbazoles by transporting them in an energy-dependent manner 12479221_polymorphisms in BCRP1 result in low amounts of BCRP, which results in hypersensitivity of normal cells to such anticancer drugs as irinotecan and mitoxantrone 12576456_RNA expression of this protein in breast cancer correlates with response to chemotherapy. 12604403_Function of the ABC transporters, P-gp, multidrug resistance protein and BCRP, in minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia 12668685_BCRP may play a role in the transport of sterols in human, in addition to its ability to transport multiple drugs and toxins. 12682043_transports sulfated conjugates of steroids and xenobiotics 12741957_functional study on polymorphism and determination of critical role of arginine-482 in methotrexate transport 12810652_Wld-type as well as R482T BCRP mediates cellular efflux of 9-AC but not 9-NC. Zplar groups at the 9 or 10 position of the CPT A ring facilitate interaction with BCRP. 12874005_ABCG2 is a component of the energy-dependent efflux system for certain folates and antifolates. 12958161_ABCG2 is expressed and functions as a transporter in the brain. 12960109_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14566825_Single amino acid substitutions in the transmembrane domains of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) alter cross resistance patterns in transfectants 14576842_REVIEW: multidrug resistance in breast cancer 14613996_Higher ABCG2 expression is associated with T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia 15001581_human ABCG2 likely exists and functions as a homotetramer 15014021_BCRP may serve as a molecular target for reducing drug resistance to chemotherapy in advanced lung cancer patients. 15014037_VX-710 modulates Pgp, MRP-1, and BCRP(R482), and has potential as a clinical broad-spectrum multidrug resistance modulator in malignancies. 15027118_ABCG2 overexpression is associated with drug resistance to SN38 in colon cancer cells and in irinotecan-treated metastases 15044468_Bcrp/ABCG2 enhances hypoxic cell survival through interactions with heme 15146167_subcellular localization of ABCG2 in gallbladder adenocarcinoma 15170677_As a method of circumventing ABCG2-associated drug resistance, low-polarity camptothecin analogues are considered to be potent lead compounds. 15208643_BCRP mRNA levels, antibody staining and function correlated strongly in cell lines but not in acute myeloid leukemia samples, suggesting complex biology of BCRP in AML and incomplete modeling by cell lines 15229462_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15251980_imatinib is a substrate for BCRP; it competes with mitoxantrone for drug export 15260487_GXXXG motif promotes proper packing of the transmembrane segments in the functional ABCG2 homodimer, although it does not solely arbitrate dimerization 15355921_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15475413_Results suggest that 1) the predominant allelic expression pattern of BCRP in placental samples is biallelic, and 2) the mutation C421A is not a genetic variant acting in cis, but is considered to influence translation efficiency. 15557326_conformational changes of the ABCG2 multidrug transporter modify its interaction with a monoclonal antibody on the cell surface 15598974_Cyclosporin A is neither a substrate nor an inhibitor of the human ABCG2 transporter. 15607361_The breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) can be expressed in AML and BCRP mRNA expression was determined in samples from 40 AML patients by real-time RT-PCR. 15625123_The ABCG2, a member of the ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporters, has been identified as a molecular determinant for bone marrow stem cells and proposed as a universal marker for stem cells. 15670731_substrate specificity of the Arg (wild-type) form is unique and that amino acid replacements at position 482 induce major alterations in both the transport activity and substrate specificity of this protein 15769853_The ABCG2 (MXR/BCRP/ABCP) is associated with mitoxantrone resistance accompanied by cross-resistance to a broad spectrum of cytotoxic drugs. 15801936_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15807535_glycosylation of ABCG2 on asparagine 596 is not essential for expression, transport activity, or trafficking to the plasma membrane 15811555_ABCG2 might play a significant role in maintaining human neural stem cells in an undifferentiated state 15811951_Side populations amounting to A, did not appear to be associated with the altered pharmacokinetics of pitavastatin. 17460607_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17481587_During the exposure to anticancer drugs, an allele-specific Q141 ABCG2 gene amplification occurs that confers a drug resistance advantage when compared to the K141 ABCG2. 17494054_BCRP Guanine34Adenosine and Cytosine421Adenosine polymorphisms are associated with the risk and survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 17494054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17505995_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17518356_Suggest that BCRP could play a significant role in the pharmacokinetic interactions of ketoconazole or itraconazole with BCRP substrate drugs. 17519960_dose-dependent, reversible inhibition of ABCG2-mediated efflux in primary human and murine HSC by both imatinib and nilotinib; ABCG2-transduced K562 cells were protected from imatinib and nilotinib-mediated cell death and from downregulation of P-CRKL 17534875_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17569884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17595345_BCRP may play a hitherto unrecognized survival role in the placenta, protecting the trophoblast against cytokine-induced apoptosis and possibly other extrinsic activators via modulation of ceramide signaling 17622941_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17627617_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17662239_Membrane cholesterol selectively modulates the activity of the human ABCG2 multidrug transporter. 17671398_The absolute presence of ABCG2-positive cells in the tumor is a single independent prognostic factor, suggesting the underlying roles in malignant characteristics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma other than drug resistance. 17682070_Results suggest that Bcrp and Mrp4 are partly involved in the luminal efflux of edaravone sulfate and edaravone glucuronide, respectively. 17686774_wild type ABCG2 is degraded in lysosomes, and the misfolded ABCG2 lacking intramolecular disulfide bond undergoes ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation in proteasomes 17690695_imatinib does not interact at the ATP-binding sites of either Pgp or ABCG2 despite their strong affinity for the ATP-binding pocket of the tyrosine kinases; it behaves like a transport substrate as it stimulates ATP hydrolysis by these transporters 17701580_ABCG2 higher expression is associated with minimal residual disease in mantle cell lymphoma 17851787_ABCG2 expression is up-regulated in gastric carcinoma. 17875533_statistically significant correlations between MRP1 and LRP expression and between MRP1 or LRP expression and MDR1 expression 17916067_Human adult dental pulp tissue contains side population cells...that express ABCG2 17923155_This is the first evidence to clearly indicate that glyburide is preferentially transported by BCRP, in the brush border of the human placenta. 17925548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17927879_ABCG2 is overexpressed in glioma stem cells, glioma tissues of higher grades, and implanted glioma xenografts. 17934801_P-gp, rather than BCRP or OCT1, is partially responsible for the development of imatinib-resistance due to constitutive and functional overexpression, leading to reduced intracellular accumulation of imatinib in resistant K562 cells. 17938326_The expression of ABCG2 may explain in part the ineffectiveness of doxorubicin as a single modality treatment for anaplastic thyroid cancer or for treatment of metastatic follicular thyroid cancer. 17938643_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17976197_We describe a novel nonsense mutation in exon 10 of the ABCG5 gene in a 10-year-old girl showing clinical and biochemical features of sitosterolaemia 18042733_Progesterone receptor isoforms differentially regulate expression of ABCG2 in placental choriocarcinoma cells. 18055445_ABCG2 is a regulatory protein of early human hematopoietic development. 18056989_Pim-1 kinase phosphorylates BCRP/ABCG2 and thereby promotes its multimerization and drug-resistant activity in human prostate cancer cells 18094074_identify a steroid-binding element in the membrane domain of ABCG2 with a similarity to steroid hormone/nuclear receptors 18159130_Certain genetic polymorphisms and/or inhibition of ABCG2 by drugs can enhance the potential risk of photosensitivity. 18167504_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18180275_BCRP expression in lymphoblasts, liver and intestine is associated with novel promoter and intron 1 single nucleotide polymorphisms. 18200595_Determination of P-glycoprotein, MDR-related protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein, and lung-resistance protein expression in leukemic stem cells of acute myeloid leukemia. 18207572_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18221820_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18237272_certain genetic polymorphisms can affect the protein stability of ABCG2 18240903_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18245481_ABCG2 expression in MCF7 cells is regulated during an EMT, and that the EMT effect reflects posttranslational regulation of ABCG2 function by E-cadherin as well as transcriptional repression of the ABCG2 gene. 18249138_Results of molecular dockings of known BCRP substrates to the BCRP model indicate multiple binding sites in BCRP. 18255023_Breast cancer resistance protein is variably expressed and localized in human fetal membranes and decidua. 18256692_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18309947_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18315895_High expression of BCRP gene may induce clinical drug resistance, and may be an unfavorable factor for prognosis in adult patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia. 18370855_these aspects of the transporter warrant further research aimed at understanding ABCG2's structure, function and regulation of expression--REVIEW 18382425_Multidrug resistance (MDR) phenotype arises following low-dose, single-step exposure to doxorubicin, and further suggest that ABCG2 may mediate early stages of MDR development. 18392808_ABCG2, an efflux pump for xenobiotics/drugs, was expressed at much higher levels in failing hearts compared to nonfailing control hearts. ABCG2 was found in cardiac capillary endothelial cells and cardiomyocytes 18408567_Commonly occurring SNPs in BCRP linked with significantly increased oral sulfasalazine plasma exposure in humans. 18429968_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18430864_Three cysteine residues (Cys284, Cys374, Cys438) are required concurrently for the function of ABCG2 and potentially for intramolecular disulfide bond formation. 18509645_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18558430_BCRP actively transports glyburide. 18559609_Dasatinib is a substrate of both efflux proteins, ABCB1 and ABCG2. 18573883_The binding of a putative miRNA at the 3'UTR of ABCG2 suppresses the expression of ABCG2. 18588889_These results indicate that Pgp down-regulates BCRP expression in a drug-free state in which JNK/c-Jun is involved. 18644784_biochemical analysis of a model of the large extracellular loop of the ABCG2 protein 18668433_Human ABC transporters ABCG2 (BCRP) and ABCG4 18681776_Review highlights the influence of ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2 (ABCP, BCRP and MXR) polymorphisms on the absorption and disposition of a wide variety of drugs. 18695635_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18702307_in prostate cancer cells at least two mechanisms of drug resistance are interconnected. PTEN and mTOR signaling were shown: to be involved into regulation of MRP1 and BCRP 18710444_Increased exposure to amine 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP)may decrease survival, but the ABCG2 C421A polymorphism does not appear to increase the risk of prostate cancer. 18710444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18725232_Co-expression of cytokeratin 8 and breast cancer resistant protein indicates a multifactorial drug-resistant phenotype in human breast cancer cell line. 18775442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18775442_heterozygous carriers of the minor alleles of SNPs rs2622621 and rs1481012 had a decreased risk of colorectal cancer 18793608_High level functional expression of the ABCG2 multidrug transporter in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells is reported. 18806751_Lower expression of BCRP is associated with minimal residual disease. 18820285_results indicate the protective role of intrinsic ABCG2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 18823676_High BCRP expression was associated with drug resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. 18824712_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18829547_Lapatinib reverses ABCB1- and ABCG2-mediated MDR by directly inhibiting their transport function. 18834626_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18838068_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18841444_Cellular phototoxicity evoked through the inhibition of human ABC transporter ABCG2 by cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in vitro. 18841445_Curcumin may be used to enhance drug exposure when the rate-limiting step of drug absorption and/or tissue distribution is impacted by ABCG2. 18951337_The growth inhibitory effects of berberine treatment on MCF-7 cells may be partly via effects on side population (SP) cells and ABCG2 expression. 18958403_Major SNP (Q141K) variant of human ABC transporter ABCG2 undergoes lysosomal and proteasomal degradations. 18981009_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18991020_These findings suggested that there are differences between cell lines in the regulation mechanism of ABCG2 expression by sex hormone treatment. 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19032367_ABCG2 polymorphism is associated with chemotherapy-induced diarrhea in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who received frontline rituximab plus cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/vincristine/pred-nisone chemotherapy. 19032367_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19052456_Expression of both efflux transporters BCRP and MDR1 is reduced, but only in inflamed tissue of patients with active UC 19063604_evidence support a 6-transmembrane segment model for BCRP with the amino and carboxyl termini of the membrane-spanning domain located intracellularly 19074750_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19101070_ABCG2 expression is correlated neither to side population nor to hematopoietic progenitor function in human umbilical cord blood. 19107936_ABCC3 C-211T and ABCG2 C421A as candidate transporter SNPs to be further investigated as possible predictors of the clinical outcome of chemotherapy in lung cancer patients. 19107936_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19114588_Vectorial transport of resveratrol metabolites is mediated by breast cancer resistance protein 3 (BRCP, ABCG2) located in the apical membranes of enterocytes. 19131524_BCRP knockdown was reflected in significant reduction of the efflux ratio of E3S and PhA. Clone D in particular should be a useful model for identifying and characterizing P-gp substrates and inhibitors without interference from BCRP and/or MRP2 19139722_study found a small population of plasma cells expresses a high level of ABCG2; high expression of ABCG2 appeared to be induced by the synergistic action of IL-6 & endoplasmic reticulum stress, and could protect the plasma cells from apoptotic stimuli 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19165709_ABCG2 expression was limited to microvessel endothelial cells in infants born at 22 (0/7)-42 (0/7) weeks of gestation. 19167193_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19167193_This study suggests that genetic polymorphisms in ABCG2 transporters may not be significant predictors of drug response in epilepsy patients. 19172464_We have demonstrated the expression of BCRP in human corneal epithelial cells and, for the first time, demonstrated its functional activity leading to drug efflux. 19188929_Identification of MDR1 and BCRP as genes that confer tumor cell resistance to the aurora B kinase inhibitor, AZD1152. 19232821_Sensitization of ABCG2-overexpressing cells to conventional chemotherapeutic agent by sunitinib was associated with inhibiting the function of ABCG2. 19240161_Up-regulation of intracellularly localized BCRP in response to adaptation to low folate conditions may be a common feature within a panel of colon cancer cell lines. 19251825_ABCG2 transport of acridine compounds requires hydrogen bond formation via a hydroxyl group located at the external poly-cyclic acridine ring 19277036_in EGFR-expressing Caco-2 cells, BCRP is one of the determinants of gefitinib resistance but not of erlotinib resistance. 19333723_IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha induce ABCG2 mRNA and protein expression and increase its activity in breast cancer cell line MCF-7. In MCF-7/MX cells these cytokines modulate ABCG2 expression, but they have no influence on the transporter mRNA levels. 19340456_Increased ABCG2 expression is associated with the grade of glioma and resistance to mitoxantone. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19349540_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19367293_P-glycoprotein and BCRP might act to prevent the blood-borne Abeta 1-40 from entering the brain 19403814_ABCG2 may act as a gatekeeper at the blood-brain barrier to prevent blood Abeta from entering the brain. 19406100_arginine 383 is a crucial residue for ABCG2 biogenesis, where even the most conservative mutations have a large impact. 19421150_Results show that downmodulation of ABCG2 or ABCC2 resulted in the inability of Tie2 activation to induce a chemoresistant phenotype. 19442037_In this review, BCRP is an efflux transporter expressed in various human tissues and considered particularly important for intestinal drug absorption and hepatic drug elimination. 19474787_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19474787_These results indicate that the ABCG2 polymorphism markedly affects the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin and, even more so, of rosuvastatin-potentially affecting the efficacy and toxicity of statin therapy. 19477032_breast cancer resistance protei nmay be a molecular determinant of the outcome of Photofrin-photodynamic therapy. 19503597_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506252_ABCG2 is a urate efflux transporter and rs2231142 (Q141K) a loss-of-function mutation in its gene causes hyperuricemia and gout. 19506252_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19514121_BCRP expression is differentially regulated downstream of the MEK-ERK pathway, transcriptionally upregulated through the inhibition of the MEK-ERK-RSK pathway in breast cancer. 19523815_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19541926_Small intestinal efflux mediated by MRP2 and BCRP shifts sulfasalazine intestinal permeability from high to low, enabling its colonic targeting. 19546880_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19567678_Data show that the BLI-based assay is an efficient method to identify new inhibitors of ABCG2. 19584153_Data show that the GG genotype in ABCG2, AA genotype in CYP3A5 were associated with poor response to IM, whereas the GG genotype at SLC22A1 was correlated with high rate of loss of response or treatment failure to IM therapy. 19584153_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19593328_Sonic hedgehog protein, GLI1-3 and ATP-binding cassette G2 are aberrantly expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 19605531_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19605531_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in ABC-transporter genes may serve as pharmacogenetic markers associated with clinical response to Mitoxantrone therapy in multiple sclerosis. 19622290_High expression of MDR1, MRP1, ABCG2 proteins in gastric cancer is related with the resistance to epirubicin. 19629677_This in vitro study indicates that expression levels and activity of BCRP, and P-gp at the blood-brain barrier may be altered by acute inflammation, possibly affecting the penetration of their substrates into the brain. 19636001_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-environme |
ENSMUSG00000029299 |
Abcg3 |
5.618660 |
10.4922720723 |
3.391255 |
0.924693240 |
16.300307 |
0.00005405519954986903670727735327083962602046085521578788757324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000154833057511365596850202996925816023576771840453147888183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3709635 |
6.5741184 |
0.9937603 |
0.5668692 |
| ENSG00000118785 |
6696 |
SPP1 |
protein_coding |
P10451 |
FUNCTION: Major non-collagenous bone protein that binds tightly to hydroxyapatite. Appears to form an integral part of the mineralized matrix. Probably important to cell-matrix interaction. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31096}.; FUNCTION: Acts as a cytokine involved in enhancing production of interferon-gamma and interleukin-12 and reducing production of interleukin-10 and is essential in the pathway that leads to type I immunity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10923}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Biomineralization;Cell adhesion;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Sialic acid;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the attachment of osteoclasts to the mineralized bone matrix. The encoded protein is secreted and binds hydroxyapatite with high affinity. The osteoclast vitronectin receptor is found in the cell membrane and may be involved in the binding to this protein. This protein is also a cytokine that upregulates expression of interferon-gamma and interleukin-12. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:6696; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; ion binding [GO:0043167]; small molecule binding [GO:0036094]; androgen catabolic process [GO:0006710]; biomineral tissue development [GO:0031214]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to testosterone stimulus [GO:0071394]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of collateral sprouting of intact axon in response to injury [GO:0048685]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of estradiol secretion [GO:2000866]; response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor [GO:0036005]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280] |
11721059_upregulated transcripts in brain of patients with multiple sclerosis 11787071_mapping of functional epitopes that are important to cell adhesion and migration 11801541_Increased expression is associated with breast tumor metastasis 11807984_The osteopontin gene, which has a role in immunosurveillance, is a direct target of TP53. 11825898_Three SIBLINGs (small integrin-binding ligand, N-linked glycoproteins) enhance factor H's cofactor activity enabling MCP-like cellular evasion of complement-mediated attack. 11854181_OPN induced a profound level of synthesis of IL-12 from noninfected PBMCs. The major cellular source of OPN was monocytes. 11861425_PPARgamma ligands inhibit OPN gene expression through the interference with the binding of nuclear factors to A/T-rich sequence in THP-1 cells. 11926891_an association between levels of a biomarker, osteopontin, and ovarian cancer suggest its clinical usefulness 11928818_Osteopontin modulates prostate carcinoma invasive capacity through RGD-dependent upregulation of plasminogen activators. 11933203_A silent polymorphism (707C>T, rs1126616) of osteopontin was significantly associated with systemic lupus erythematosus 11940202_Osteopontin was suggested to play a role in HCC, especially in cancer-stromal interactions. 11968014_RT-PCR analysis of human bone marrow stromal cells during osteogenesis in vitro: the mRNA levels of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), bone sialoprotein-II (BSP), osteopontin (OP) and cbfa-1 increased with culture time in osteogenic medium. 11979972_has RGD sequence and role in osteoclast adhesion 12142743_Results provide the first evidence that osteopontin may play an important role in stone formation in chronic pancreatitis. 12456016_in human tumor cells, HGF and M-CSF stimulate osteopontin production (which is subsequently used as a substrate for cell adhesion) 12506143_crystal retention in the human kidney may depend on the expression of CD44-, OPN-, and-HA rich cell coats by damaged distal tubular epithelium. 12606946_OPN-induced migration of mammary epithelial cells also requires activation of the EGF pathway. EGF & OPN synergistically induced cell migration. Exogenous OPN increased ligand (TGFalpha> EGF) & EGFR mRNA expression, as well as EGFR kinase activity. 12620651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12640447_Osteopontin, which was identified as a lead gene in the signature, was over-expressed in metastatic HCC 12650610_Elevated osteopontin (OPN) transcription often correlates with increased metastatic potential of transformed cells, and in several model systems OPN--whether produced by the tumor cells or by stromal cells - has been shown to enhance metastatic ability. 12650611_osteopontin as the leading candidate clinical marker derived from a screen of approximately 12,000 named genes. 12761568_Association with disease course is detectable in patients with at least one wild-type OPN 1284A allele: these patients are less likely to have a mild disease course and are at increased risk for a secondary-progressive clinical type. 12761568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12771144_first report that osteopontin induces nuclear factor kappaB activity and urokinase secretion by activating phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/Akt protein/Ikappab kinase-mediated signaling pathways 12842452_study indicates the possibility that osteopontin plays an important role in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis via increased immune activity 12879219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12927044_OPN expression is significantly higher in malignant epithelial sources over normal and benign epithelial sources, but no difference in expression levels is evident between primary tumors with or without metastases. 12928913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12939547_In patients with previous anterior wall myocardial infarction(MI) osteopontin is released from heart into coronary circulation in proportion to left ventricular(LV) systolic function and volumes. Osteopontin may be associated with post-MI LV remodeling. 12949055_OPN binds to the alphavbeta3-integrin to increase plasma membrane CD44v6 expression and augment in vitro adhesion to hyaluronate 14517343_increased expression of the alpha(v)beta(3) integrin during breast cancer progression can make tumor cells more responsive to malignancy-promoting ligands such as OPN and result in increased tumor cell aggressiveness. 14524533_OPN is expressed in breast and prostate cancer and has a role in differentiation and activation of osteoclasts 14534308_platelet adhesion to osteopontin-coated surfaces requires an agonist-induced exposure of alpha v beta 3-binding sites for this ligand 14563350_Opn is among the most abundantly expressed proteins in a range of lung diseases and has been shown to regulate aspects of pulmonary granuloma formation, fibrosis, and malignancy (review) 14592838_Subjects carrying haplotype B and/or C had an 8-fold higher risk of developing Dianzani autoimmune/lymphoproliferative disease than haplotype A homozygotes. 14704150_induces alpha(v)beta(3) integrin-mediated AP-1 activity and urokinase type plasminogen activator secretion by activating c-Src/EGFR/ERK signaling pathways 14706653_OPN promoter region SNP at nt -433 may be a useful marker reflecting hepatitis activity in chronic hepatitis C patients. 14706653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14716823_Epidermal growth factor may regulate osteopontin gene expression through PI3K signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 14988426_Nurr1 activates the OPN promoter directly in osteoblastic cells and may have a role in the regulation of bone homeostasis 14990565_Beta-catenin, Lef-1, Ets transcription factors, and the AP-1 protein c-Jun each weakly enhanced luciferase expression from an OPN promoter. 14996707_Notch1 gene expression was decreased 5-fold in osteopontin-treated CD34+ cells 15003892_Myeloma cell lines adhere to OPN, so high stromal OPN expression may be partly responsible for retention of myeloma cells in bone marrow. The high plasma OPN levels may be due to OPN production by tumor cells & tumor-induced production by non-tumor cells. 15004750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15014008_The large increase in OPN expression in tumors compared with normal tissue and its association with survival suggest a role for OPN in lung tumorigenesis. 15019804_Osteopontin is expressed at high concentrations in secretory endometrium in epithelial cells and in decidua in stromal cells. Decidual stromal expression of osteopontin is up-regulated by decidualization. 15101999_Decreased expression of OPN is considered to be a reliable indicator of tumor aggressiveness and clinical outcome in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 15167446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15389974_Data demonstrate that early down-regulation of osteopontin in vitro inhibits human osteoclastogenesis. 15479859_osteopontin promoter polymorphisms affect its transcriptional activity 15494684_Review. OPN's role in bone and its role in adhesion, migration, cell survival, and tumorigenesis. 15501463_Molecular structure of OPN, evidence for its functional role in tumor cell metastasis, downstream signals that activate invasive mechanisms, and recent reports concerning regulation of OPN transcription [review] 15579312_analysis of osteopontin peptides and their roles in cell adhesion 15692970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15696579_highly phosphorylated human OPN-1 can stimulate trophoblastic cell migration and provides evidence for the involvement of the PI3K/mTOR/p70 S6 kinase pathway in the JAR cells response 15712659_OPN was higher in proliferated bile ductules of acute-form fulminant hepatitis than in cirrhotic and normal liver bile ducts. OPN in proliferated bile ductules was decreased in subacute form of fulminant hepatitis. 15731245_Rotavirus infection of intestinal epithelial cells caused marked increases in OPN mRNA levels and secreted OPN protein 15742429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15742430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15744522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15761492_Data show that mRNA expression of osteopontin (OPN) was elevated in CD4(+) synovial T cells derived from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, which correlated with increased OPN concentrations in synovial fluid (SF). 15776015_Even though the role of osteopontin in the cytopathogenesis of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor still needs to be determined, data support that overexpressed osteopontin is a potential diagnostic marker for atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor. 15845635_up-regulation of OPN expression by interlobular biliary epithelium in biliary atresia, which correlates with biliary proliferation and portal fibrosis 15855273_identify OPN as an important tissue-derived factor that DCs encounter when traveling from peripheral sites of activation to secondary lymphatic organs, which induces DC maturation toward a Th1-promoting phenotype 15857938_ability of Bcr-Abl to stimulate the expression of OPN 15863395_Circulating levels of osteopontin, but not IFN-gamma or IL-12, reflect disease activity in patients with tuberculosis. 15868370_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15868370_SNPs in the promoter region of the osteopontin gene as a marker predicting the efficacy of interferon-based therapies in patients with chronic hepatitis C. 15885319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15885319_Osteopontin (OPN) genotypes may influence multiple sclerosis development and progression due to their influence on OPN levels. 15949549_OPN has a role in foreign body giant cell formation in response to implantation 15954903_osteopontin is one of the crystal-associated urine proteins involved in the formation of the organic layers of the plaque particles in kidney stones 15956076_OPN and CEACAM1 may act as a functional complex involved in the regulation of placental invasiveness. 15970685_Increase in osteopontin is associated with pancreatic cancers and chronic pancreatitis 15993098_Overall these results show that OPN is deregulated by BCR-ABL oncogene and suggest that OPN could be involved in CML stem cell biology. 15998376_Granular cell tumor among Schwannian cell tumors consistently express OPN, but its biological significance requires further investigation. 15998773_CD44 and/or OPN may be molecular targets for therapeutic intervention in aggressive papillary thyroid carcinomas. 16000556_Osteopontin overexpression is common in primary non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and may be important in the cancer development and progression and osteopontin plasma levels may serve as a biomarker for diagnosing or monitoring patients with NSCLC. 16005200_integrin alphavbeta6, alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, alpha5beta1 and alpha9beta1 binding to osteopontin is controlled by specific structural motifs that are recognized by extracellular proteases 16009426_Three promoter polymorphisms of the human Eta-1 gene, -443T/C, -156delG/G, -66T/G, were investigated for possible influence on gene expression. 16047475_These data suggest that nitric oxide enhances hepatocellular cancer expression of OPN and, as a result, conveys a metastatic phenotype. 16100012_SPP1 mRNA increases during acute lung injury in mice 16136472_localizes with the follicular dendritic cell (FDC) network in lymphatic tissues in HIV-1 infection and has a role in lymphoid follicle pathology and repair and B cell regulation 16145474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16145474_Polymorphism at position 9,402 of the OPN gene is highly associated with urinary calcium stones, whereas polymorphism at position 9,171 of the OPN gene is not associated with urinary calcium stone disease. 16166420_Results support the hypothesis of an association between high osteopontin expression and poor survival of patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer, suggesting that osteopontin could be a candidate target for cancer therapy. 16204248_TIS7, a negative regulator of transcriptional activity, represses expression of OPN and beta-catenin/Tcf-4 target genes 16208410_silencing Runx2 with siRNA in myeloma cells suppressed OPN mRNA and protein expression, critical for the proangiogenic effect of myeloma cells 16299231_Results identify osteopontin as a marker and a potential therapeutic target in cases of aggressive laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. 16331611_increased OPN level may be involved in the malignant transformation of prostate epithelial cells and OPN expression level is an important determinant for patient survival 16373617_high plasma levels of OPN in patients with a history of percutaneous coronary intervention were associated with the presence of restenosis, suggesting that OPN may play a role in the development of restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention 16424021_osteopontin contributes to several steps in the process of prostate carcinogenesis and metastasis 16428483_Elevated osteopontin in urine is associated with ovarian cancer 16433860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16489073_Results suggest osteopontin is dependent on ERalpha for its expression. 16512757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16533775_High osteopontin expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancers 16571650_OPN acts downstream of PI3K in melanoma and PTEN loss contributes to melanoma development 16614705_Protein kinase B (Akt) gene regulated osteopontin expression at the RNA level and protein level. 16632752_has a pivotal role in the development of immune responses and in the tissue destruction and the subsequent repair processes associated with inflammatory diseases 16633066_study shows the expression pattern of osteopontin in cellular populations of normal endometrium and in endometrial carcinoma and its correlation with the expression of CEACAM1 16741188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16765311_results suggest that OPN might suppress multiplication of Plasmodium falciparum through T helper 1 cells-mediated immune responses 16786357_High Osteopontin is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 16797773_Real-time RT-PCR confirmed up-regulation of IL-8, osteopontin, and TNFRSF14 and down-regulation of SAMeS and CD209 in AH. 16807238_OPN-transfected cells express high levels of hyaluronan synthase 2, which is associated with increased HA production and matrix retention and is necessary for tumor cell adhesion to bone marrow endothelial cells and anchorage-independent growth 16817793_hyperphosphatemia or azotemia is associated with the expression of osteopontin in vascular smooth muscle cells in patients with ESRD 16830223_We found that the expression of OPN corroborates with the aggressive phenotype of the breast cancer cells i.e. the expression of OPN is acquired as the breast cancer cells become more aggressive. 16880782_The evaluation of Osteopontin expression is useful for predicting the malignant properties of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 16962083_The presence of OPN in the normal human and non-human primate SN coupled to its decreased expression following nigral cell degeneration suggests that it may play an important role in dopaminergic neurone survival. 17005603_Intranuclear OPN participates in the process of cell duplication and associates with Plk1. 17022822_Expression of SPP1 in osteosarcoma is associated with an inflammatory response and bone remodeling, making it a good biomarker. 17044113_OPN is produced in osteolytic lesions: MM-derived OPN plays a critical role in bone disease by protecting bone from destruction. 17110905_Increased blood levels in smokers with type 2 diabetes. 17130676_Review. Osteopontin plays a role in Th1 and IgE-mediated immune responses. 17170369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17188882_OPN is involved in Parkinson disease-associated neurodegeneration 17189522_Data suggest that transglutaminase 2 interactions with osteopontin lead to protein polymerization that facilitates macrophage adhesion to the calcified elastic lamellae to promote clearance of the ectopic mineral deposits. 17227585_Osteopontin a tumor-metastasis activator, a crucial downstream target of Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 is identified. 17244457_Osteopontin might enhance the expression of MMP-2 and uPA to promote malignant phenotypes of SMMC-7721 cells. 17245215_The plasma concentrations of OPN are elevated in patients with ulcerative colitis and that OPN expression is correlated with clinical activity. 17253181_The expressions of G3BP and OPN proteins have a close relationship with lymphoid metastasis and survival in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients. 17289872_Osteoclast-derived osteopontin and VEGF from myeloma cells cooperatively enhance angiogenesis and also induce osteoclastogenic activity by vascular endothelial cells 17316167_The immunocytochemical localization of OPN in the cytoplasm of pyramidal neurons. In AD brains, there was a significant 41 % increase in the expression of neuron OPN compared with age-matched control brain. 17332338_OPN-CD44(V) interaction promotes ECM-derived survival signal mediated through integrin activation, which may play an important role in the pathogenic development and progression of gastric cancer. 17343740_A possible role of OPN and its receptor(s)is mediating downstream signals in the progression of prostate cancer cells. OPN over expression increases the interaction of CD44 and MMP-9 on the cell surface. 17360982_Treatment of human macrophages with the PPARalpha ligands bezafibrate or WY14643 inhibited OPN expression and transcription. 17369493_demonstrated the role of OPN in two distinct aspects of macrophage accumulation: prevention from recirculation and protection from apoptosis 17384004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17418101_Thus, erythrocytes may be specialized cells for storing and supplying plasma S1P. 17439891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17439891_that the 795 polymorphism does not play an etiological role per se in multiple sclerosis 17441427_The expression of CTGF and/or OPN might be important biological markers in reflecting the progression, biological behavior, metastatic potential and prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 17444956_OPN-stimulated IL-10 production increases less in T-cell cultures from Crohn's disease (CD) patients than from healthy controls, indicating that IL-10 deficiency may be involved in the defective immune-regulation in CD. 17452979_Increased expression of an osteopontin splice variant was associated with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma 17464350_These data confirm the positive role of OPN in gastric-cancer-associated angiogenesis. 17482182_Osteopontin was found more prominently in glandular epithelium than in interstitial space of the endometrium. 17482311_OPN plays a crucial role for tumor growth and angiogenesis of human lung cancer cells in vivo by interacting with alphavbeta3 integrin. 17493236_Frequent osteopontin expression is typical of, but not specific for malignant pleural mesothelioma, whereas it appears to select pulmonary adenocarcinoma cases with p65 and MMP-9 expression, suggesting a link with EGFR signalling pathways. 17496055_Findings suggest that SPP1 polymorphisms might be among the genetic factors for HBV clearance and/or HCC occurrence. 17496055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17519954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17519954_significant association of two haplotypes located in the OPN promoter with the relative probability of nephrolithiasis; one of increased and one of reduced risk 17545592_Macrophage-derived OPN can compensate for the decrease of OPN and thereby restore the metastatic potential of OPN-knockdown tumor cells. 17548669_the possible mechanisms by which osteopontin may contribute functionally to malignancy, particularly in breast cancer {Review} 17565744_OPN (osteopontin) is a transcriptional target of aberrant Wnt signaling, and OPN expression alone predicts survival in human colon cancer. 17595250_Plasma OPN and mRNA expression of OPN in omental adipose tissue are increased in overweight/obese patients. 17620367_Data indicate that therapeutic targeting of tumor OPN molecules could reset metastatically relevant gene networks, resulting in clinical benefit. 17689681_In SW480 human colon cancer cells, we conclude that Sp1 mediated expression of the tumor metastasis protein, OPN, regulates in vitro functional correlates of tumor metastasis 17696803_OPN is involved in mediating hepatic inflammation and the ensuing liver toxicity --REVIEW 17706953_OPG but not OPN stimulated a dose-dependent increase in the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and E-selectin by endothelial cells in the presence of TNF-alpha 17721886_REVIEW of multi-faceted functional role of OPN in breast cancer, in particular the malignancy-promoting aspects of OPN 17848618_ING4 suppression in MM cells up-regulated IL-8 and OPN, increasing the HIF-1alpha activity and its target gene NIP-3 17852826_Reference intervals were established with a high analytic performance for OPN and an acceptable analytic performance for OPG and total sRANKL. The study revealed low biological variation for OPN and total sRANKL and high biological variation for hsCRP. 17884775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17884775_Osteopontin gene 9250 polymorphism appears to be associated with the susceptibility to lupus nephritis in southern Chinese Han population. 17896150_Increased expression of osteopontin is associated with gastric carcinoma 17898038_Whole urine from osteopontin, Tamm-Horsfall protein , or double-null mice all possessed a dramatically reduced ability to inhibit the adhesion of calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals to renal epithelial cells 17938278_These data suggest that OPN is associated with keratinocyte differentiation and that it is expressed in AK and SCC, which have metastatic potential, but minimally expressed in solid BCC. 17960616_overexpression of Osteopontin-c is associated with invasive, but not in noninvasive, breast tumor 17987038_Finding identify OPN and CD44v6 as predictive markers of recurrence or aggressiveness in laryngeal intraepithelial neoplasia, and overall, point out an important signalling complex in the evolution of laryngeal dysplasia. 18004082_Osteopontin protein expression was confirmed as a new independent predictor of tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. 18037740_Osteopontin expression of circulating CD4+ T cells and plasma osteopontin levels reflect the severity of heart failure. 18048491_Osteopontin expression in adipose tissue macrophages was strongly up-regulated by obesity. 18053633_specific recognition of membrane-bound Osteopontin sites on preosteogenic cell membrane 18072945_phosphorylation and glycosylation sites and N-terminal fragments present in urine are generated by proteolytic cleavage 18079410_OPN is required for the differentiation and activity of myofibroblasts formed in response to the profibrotic cytokine transforming growth factor-beta1. 18085382_Osteopontin as well as dystrophy within the tumor may be involved in the stromal calcification of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. 18155656_These are the first data to suggest a role for osteocytes and OPN in the recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to aid in fracture repair. 18158320_syndecan-4 is a critical intrinsic regulator of inflammatory reactions via its effects on OPN function 18160829_Results show that OPN is not valuable as a clinical marker for monitoring the treatment response in multiple myeloma patients because of inconsistency in its levels in multiple myeloma patients. 18162078_Real-time PCR showed that ETOH significantly altered the expression of genes involved in cell adhesion. There was an increase in the expression of alpha and beta Laminins 1, beta Integrins 3 and 5, Secreted phosphoprotein1 and Sarcoglycan epsilon. 18167187_OPN gene 9250 polymorphism appears to be associated with susceptibility to SLE in Chinese Han ethnic population. 18167187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18174176_osteopontin (OPN) is highly expressed and secreted by erythroblasts during differentiation 18178454_Demonstrated elevated serum OPN and OPG levels in patients with carotid stenosis and documented an independent association between these biochemical markers, pathology and carotid-induced symptomatology. 18181047_Osteopontin, cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor synergically promote angiogenesis and metastasis in gastric cancer. 18197854_production is associated with the inflammatory process of oral lichen planus development 18210151_plasma osteopontin levels are potentially useful as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for cervical cancer. 18210878_Osteopontin over-expression is considerably correlated with lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancers. 18317949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18317949_haplotypes of OPN gene contributed to determining risk factors as well as protective factors of large artery atherosclerosis. 18335026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18335026_osteopontin is associated with SLE, and this association is especially stronger in males. To our knowledge, this report serves as the first association of a specific autosomal gene with human male lupus 18353318_Infertile women with isolated polycystic ovaries are deficient in endometrial expression of osteopontin but not alphavbeta3 integrin during the implantation window. 18388057_Osteopontin levels are elevated in patients with peripheral arterial disease. 18393978_osteopontin expression is elevated in ovarian clear cell carcinoma 18396783_Compared with normal pregnancy, osteopontin expression and decidual killer cells accumulation were reduced significantly in recurrent pregnancy loss patients. 18406574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18410276_studied gene expression profile of brain lesions of a patient with Neuromyelitis optica by using DNA microarray; found marked up-regulation of interferon gamma-inducible protein 30 (IFI30), CD163, and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1, osteopontin) 18413297_OPN is a bona fide substrate for thrombin, and generation of thrombin-cleaved OPN with enhanced pro-inflammatory properties provides a molecular link between coagulation and inflammation 18442196_The most overexpressed gene in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is the gene encoding osteopontin. 18443355_Opn plays an important role in the development of albuminuria, possibly by modulating podocyte signaling and motility 18459127_Functional -443T/C osteopontin promoter polymorphism is associated with melanoma metastases. 18470911_OPN downregulation by BRMS1 may be responsible, at least in part, for BRMS1-mediated metastasis suppression by sensitizing cancer cells to stress induced apoptosis. 18474739_Osteopontin in the cerebrospinal fluid may be, in part, of central nervous system origin, and may play an important role in central nervous system inflammation. 18480255_osteopontin alternative translation generates intracellular and secreted isoforms that mediate distinct biological activities in dendritic cells 18493866_The overexpression of osteopontin protein in astrocytoma cells suggests its role in astrocytoma progression and angiogenesis. 18508510_Opn has pivotal role in cell adhesion, chemotaxis, prevention of apoptosis, invasion, migration and anchorage-independent growth of tumor cells. [REVIEW] 18524812_Data show that mRNA expression of OPN was significantly increased throughout the window of implantation. 18537194_Novel pathway by which OPN and possibly other Ets-1 target genes involved in tumor metastasis are regulated by TIP30. Mechanism for metastasis promoted by TIP30 deficiency. 18549690_osteopontin:alpha(v)beta(3)integrin complex untenable as marker of endometrial receptivity and implantation potential 18549897_RNA stability is a new, previously unrecognized mechanism that regulates osteopontin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma to convey metastatic function. 18550471_Osteopontin expression was significantly lower in long-term compared with short-term survivors of malignant pleural mesothelioma (P |
ENSMUSG00000029304 |
Spp1 |
61473.002199 |
2.1037277077 |
1.072948 |
0.005756405 |
35454.108800 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83651.0296947 |
296.3428069 |
40051.3427290 |
113.6089931 |
| ENSG00000118855 |
64747 |
MFSD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H3U5 |
FUNCTION: Lysosomal transporter which is essential for liver homeostasis. Required to maintain stability and lysosomal localization of GLMP. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DC37}. |
Alternative splicing;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable protein homodimerization activity. Predicted to be involved in protein localization to lysosome and protein stabilization. Predicted to be located in lysosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64747; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; protein localization to lysosome [GO:0061462]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821] |
21752829_MFSD1 protein localizes in lysosomes in HeLa cells |
ENSMUSG00000027775 |
Mfsd1 |
1542.316245 |
2.9385792748 |
1.555119 |
0.048101373 |
1057.020652 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000072505370387477353998151491867402019707106916150628784493069675157897489713246674833555011892586639 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000079864124396952662842009950178118420047026892419947122771127585105550072726846860173944522909034414 |
Yes |
No |
2374.1968846 |
66.2807041 |
813.7936946 |
18.4262201 |
| ENSG00000118894 |
196483 |
EEF2KMT |
protein_coding |
Q96G04 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the trimethylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (EEF2) on 'Lys-525'. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25231979}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
Enables protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity. Involved in peptidyl-lysine trimethylation. Located in cytoplasm. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:196483; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; peptidyl-lysine trimethylation [GO:0018023]; protein methylation [GO:0006479] |
25231979_Previously uncharacterized lysine-specific methyltransferase FAM86A and Yjr129c introduce a functionally important lysine methylation in eEF2. |
ENSMUSG00000022544 |
Eef2kmt |
78.932932 |
2.1978631998 |
1.136102 |
0.180602323 |
40.027390 |
0.00000000025042669417871997043727412939344463549407038271965575404465198516845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001257244219754390093647465593369380587596140230743912979960441589355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.2484287 |
12.2731811 |
49.1516948 |
4.4323843 |
| ENSG00000118939 |
7347 |
UCHL3 |
protein_coding |
P15374 |
FUNCTION: Deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) that controls levels of cellular ubiquitin through processing of ubiquitin precursors and ubiquitinated proteins. Thiol protease that recognizes and hydrolyzes a peptide bond at the C-terminal glycine of either ubiquitin or NEDD8. Has a 10-fold preference for Arg and Lys at position P3'', and exhibits a preference towards 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitin chains. Deubiquitinates ENAC in apical compartments, thereby regulating apical membrane recycling. Indirectly increases the phosphorylation of IGFIR, AKT and FOXO1 and promotes insulin-signaling and insulin-induced adipogenesis. Required for stress-response retinal, skeletal muscle and germ cell maintenance. May be involved in working memory. Can hydrolyze UBB(+1), a mutated form of ubiquitin which is not effectively degraded by the proteasome and is associated with neurogenerative disorders. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19154770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21762696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22689415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2530630, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9790970}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the deubiquitinating enzyme family. Members of this family are proteases that catalyze the removal of ubiquitin from polypeptides and are divided into five classes, depending on the mechanism of catalysis. This protein may hydrolyze the ubiquitinyl-N-epsilon amide bond of ubiquitinated proteins to regenerate ubiquitin for another catalytic cycle. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:7347; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; deNEDDylase activity [GO:0019784]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; post-translational protein modification [GO:0043687]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
15531586_1.45 A resolution crystal structure of human UCH-L3 in complex with the inhibitor ubiquitin vinylmethylester, an inhibitor that forms a covalent adduct with the active site cysteine of ubiquitin-specific proteases 16402389_Upregulation of UCH-L3 is associated with Uterine Cervical Neoplasms 19047059_Substrate filtering by the active site crossover loop in UCHL3 revealed by sortagging and gain-of-function mutations. 19154770_These results indicate that mono-Ub and Ub dimers may regulate the enzymatic functions of UCH-L1 and UCH-L3, respectively, in vivo. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19476499_Untangling the folding mechanism of the 5(2)-knotted protein UCH-L3 19636824_identification and the sequence-specific assignments for 186 out of the 218 UCH-L3 (230 less 12 prolines) backbone 15N and amide proton resonances 21762696_impaired UCH-L3 function may contribute to the accumulation of full length UBB(+1) in various pathologie 22679485_Data identified of UCHL3 as an essential deubiquitinase in adipogenesis. 25194810_UCH-L3 is a novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration in prostate cancer cells. 25369561_Using a series of engineered protein substrates, which are similar in size yet differ in secondary structure, we demonstrate that thermal stability is a key factor that significantly affects UCH-L3 hydrolysis. 27780264_Study demonstrated positive correlations between the level and activity of UCHL3 and sperm characteristics and function suggesting that UCHL3 may play a role in male infertility. 28583475_The authors find that UCHL3 regulates COPS5-dependent deneddylation of Cullin1, which is an essential component of SCF(beta-TrCP) complex and associated with SCF(beta-TrCP) activities. The authors further demonstrate that UCHL3 upregulates the levels of SCF(beta-TrCP) substrates including IFN-I receptor IFNAR1, which enhances IFN-I mediated signaling pathway and antiviral activity. 29898404_Depletion of UCHL3 increases TDP1 ubiquitylation and turnover rate and sensitizes cells to TOP1 poisons. Overexpression of UCHL3, but not a catalytically inactive mutant, suppresses TDP1 ubiquitylation and turnover rate. 30559450_UCHL3 facilitates cellular viability after DSB induction by antagonizing Ku80 ubiquitylation to enhance Ku80 retention at sites of damage. 31477831_Our results indicate that highly expressed UCHL3 enhances inflammation by stabilizing TRAF2, which in turn facilitates tumourigenesis in ovarian cancer, and that UCHL3 is a potential target for ovarian cancer patients with increased inflammation. 31642235_UCH-L3 might play a role in epithelial ovarian cancer pathogenesis and progression 32180254_UCH-L3 promotes non-small cell lung cancer proliferation via accelerating cell cycle and inhibiting cell apoptosis. 32486284_Ubiquitin Carboxyl-Terminal Hydrolases (UCHs): Potential Mediators for Cancer and Neurodegeneration. 32546741_The deubiquitylase UCHL3 maintains cancer stem-like properties by stabilizing the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. 32738097_Deubiquitylase UCHL3 regulates bi-orientation and segregation of chromosomes during mitosis. 33238157_K27-Linked Diubiquitin Inhibits UCHL3 via an Unusual Kinetic Trap. 33616859_UCHL3 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic cancer through upregulating LDHA expression. 34016790_Silencing UCHL3 enhances radio-sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting DNA repair. 35053210_Rational Development and Characterization of a Ubiquitin Variant with Selectivity for Ubiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase L3. 35088238_Knockdown of UCHL3 inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by reducing CRY2 methylation. |
ENSMUSG00000022111+ENSMUSG00000035337 |
Uchl3+Uchl4 |
140.686011 |
2.3546113122 |
1.235489 |
0.187327373 |
43.037496 |
0.00000000005370074556833342270418404402054638521052387645227099710609763860702514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000282776669492900940354072460099004934774846731215802719816565513610839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
202.6375379 |
22.1803131 |
86.5711563 |
7.2857543 |
| ENSG00000118946 |
27253 |
PCDH17 |
protein_coding |
O14917 |
FUNCTION: Potential calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the protocadherin gene family, a subfamily of the cadherin superfamily. The encoded protein contains six extracellular cadherin domains, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail differing from those of the classical cadherins. The encoded protein may play a role in the establishment and function of specific cell-cell connections in the brain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27253; |
GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; negative regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050805]; presynaptic active zone assembly [GO:1904071]; regulation of synaptic vesicle clustering [GO:2000807]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560] |
17672918_the apparent occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 2 is discussed 20180417_Azoospermic testis showed down-regulation of CDH18 and PCDH17. 20200074_results suggest that silencing of PCDH17 expression through hypermethylation of the promoter or other mechanisms leads to loss of its tumour-suppressive activity, which may be a factor in the carcinogenesis of a subgroup of ESCCs 21213369_statistical significant downregulation of PCDH17/PCH68 and PTPRD was observed 22207556_Our study clearly demonstrates that PCDH17 is transcriptionally downregulated in gastric cancer due to aberrant promoter CpG island methylation 22926751_PCDH17 acts as a tumour suppressor, exerting its anti-proliferative activity through inducing apoptosis and autophagy, and is frequently silenced in gastric and colorectal cancers. 23684785_This study demonistrated that critical role for PCDH17 in the synaptic development of specific corticobasal ganglia circuits and suggest the involvement of PCDH17 in such circuits in depressive behaviors. 24366498_PCDH17 promoter methylation was significantly associated with malignant behaviour and poor prognosis of bladder cancer 24567353_PCDH17 promoter methylation is closely associated with bladder cancer malignancy and may be used as an independent predictor of clinical outcomes in patients with bladder cancer. 26386721_PCDH-17 inhibited metastasis via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. 26404644_PCDH17 methylation occurred more frequently and was associated with malignant clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients 26683656_PCDH17 methylation in serum is a frequent event in early-stage prostate cancer, and it is an independent predictor of BCR after radical prostatectomy 26700620_DNA methylation in a combination of POU4F2/PCDH17 has yielded the highest sensitivity and specificity of 90.00% and 93.96% in all the 312 individuals, showing the capability of detecting bladder cancer effectively among pathologically varied sample groups. 27351130_PCDH17 functions as a tumor suppressor inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and metastasis in breast cancer but is frequently methylated in primary tumors which could be a potential biomarker. 27643535_Aberrant methylation of protocadherin 17 is associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 28070120_We report a genetic association with mood disorders within the genomic region spanning PCDH17. A consistent pattern of allelic association, involving cognition, neuroticism as personality trait, structural and functional imaging, was found in independent samples and in expression of the PCDH17 gene in brain tissues. 28688232_PCDH17 methylation in serum is a potential prognostic biomarker for patients with renal cell carcinoma after surgery. 29566279_PCDH17 methylation is detectable in serum of cancer patients. 29991130_Methylation of PCDH17 could play an important role in development and progression of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC)and has potential to become a target in the search for new clinical biomarkers 30165032_Aberrant hypermethylation in the promoter might be the explanation of PCDH17 downregulated in PCDH17 and promoted the development of nasopharyngeal cancer(NPC). 30213786_Study found elevated promoter methylation and decreased expression of PCDH10 and PCDH17 in advanced gastric lesions, suggesting that elevated PCDH10 and PCDH17 methylation may be an early event in gastric carcinogenesis. 30454973_PCDH17 is downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 30922328_PCDH17 gene was silenced by DNA methylation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Low PCDH17 expression is associated with distinct clinical and biological features and improves risk stratification in patients with AML. 31994011_MiR-23a-3p promoted G1/S cell cycle transition by targeting protocadherin17 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33896826_Repression of protocadherin 17 is correlated with elevated angiogenesis and hypoxia markers in female patients with breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000035566 |
Pcdh17 |
15.486697 |
2.9410813246 |
1.556347 |
0.477070780 |
10.753169 |
0.00104100897290408298499764239153364542289637029170989990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002414787433610602988831583814999248716048896312713623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.3450358 |
6.7877098 |
8.2321058 |
1.8721329 |
| ENSG00000118965 |
57539 |
WDR35 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2L0 |
FUNCTION: As a component of the IFT complex A (IFT-A), a complex required for retrograde ciliary transport and entry into cilia of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), it is involved in ciliogenesis and ciliary protein trafficking (PubMed:21473986, PubMed:28400947, PubMed:29220510). May promote CASP3 activation and TNF-stimulated apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20193664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21473986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28400947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29220510}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Ectodermal dysplasia;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. Two patients with Sensenbrenner syndrome / cranioectodermal dysplasia (CED) were identified with mutations in this gene, consistent with a possible ciliary function.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:57539; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cilium [GO:0005929]; intraciliary transport particle A [GO:0030991]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; intraciliary retrograde transport [GO:0035721]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512] |
20193664_These results indicated that naofen may function as a novel modulator activating caspase-3, and promoting TNF-alpha-stimulated apoptosis. 20817137_WDR35 is homologous to TULP4 (from the Tubby superfamily) and has previously been characterized as an intraflagellar transport component, confirming that Sensenbrenner syndrome is a ciliary disorder. 21473986_Through structural modeling, we show that WDR35 has strong homology to the COPI coatamers involved in vesicular trafficking and that short-rib polydactyly mutations affect key structural elements in WDR35. 22486404_report on the detection of novel WDR35 mutations in two unrelated cranioectodermal dysplasia patients 22987818_A pathogenic WDR35 mutation was identified in a family with a complex clinical presentation that includes significant overlap of the phenotypes described in Sensenbrenner syndrome and the unclassified short-rib polydactyly syndromes. 25908617_Splicing variants in WDR35, and possibly in other IFT-A components, underlie a number of Ellis-van Creveld syndrome cases by disrupting targeting of both the EvC complex and Smoothened to cilia. 27806291_Wdr35 regulates cilium assembly by selectively regulating transport of distinct cargoes. 28332779_Psychomotor development was apparently normal. Molecular analysis in one of the affected individuals identified compound heterozygosity for a nonsense (c.1922T>G, p.(Leu641*)) and missense (c.2522A>T, p.(Asp841Val)) variants in WDR35. We 28870638_A differential diagnosis of Sensenbrenner Syndrome was made after a novel homozygous missense mutation in WDR35 was identified in a patient with initial diagnosis of Jeune syndrome. 29134781_The observations of the Sensenbrenner syndrome patient in this study provide additional clinical data and expand the molecular spectrum of Sensenbrenner syndrome. Moreover, the two variants identified in the proband provide further evidence for the WDR35 mutations as the most common cause of this rare syndrome. 29174089_Homozygous missense mutation in WDR35 gene is associated with multiple congenital anomalies, including brain malformations and skeletal dysplasia suggestive of cranioectodermal dysplasia ciliopathy. 30570184_Over-expression of WDR35 results in decreased phosphorylation of ribosome S6 protein in a RagA-, RagB- and RagC-dependent manner. Thus, WDR35 is associated with RagA, RagB and RagC and might negatively influence mTORC1 activity. 30790652_Results demonstrated that copy number variation (CNV) of WDR35 may lead to skeletal dysplasia and fetal anomaly, and that down-regulated WDR35 may damage the cilia formation and sequentially indirectly regulate Gli signal, which would eventually result in negative regulation of osteogenic differentiation. 32804427_Prenatal genetic diagnosis of cranioectodermal dysplasia in a Polish family with compound heterozygous variants in WDR35. 33009702_Association study of genetic variants at TTC32-WDR35 gene cluster with coronary artery disease in Chinese Han population. 33421337_Interfamilial clinical variability in four Polish families with cranioectodermal dysplasia and identical compound heterozygous variants in WDR35. 33610917_WDR35 is involved in subcellular localization of acetylated tubulin in 293T cells. |
ENSMUSG00000066643 |
Wdr35 |
65.380524 |
2.2687659436 |
1.181908 |
0.252152818 |
21.855975 |
0.00000293899981673026385763829518293910325610340805724263191223144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009832193403204599499944048301980359383378527127206325531005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.6858683 |
14.6686713 |
39.3596240 |
4.9467726 |
| ENSG00000118985 |
22936 |
ELL2 |
protein_coding |
O00472 |
FUNCTION: Elongation factor component of the super elongation complex (SEC), a complex required to increase the catalytic rate of RNA polymerase II transcription by suppressing transient pausing by the polymerase at multiple sites along the DNA. Component of the little elongation complex (LEC), a complex required to regulate small nuclear RNA (snRNA) gene transcription by RNA polymerase II and III (PubMed:22195968). Plays a role in immunoglobulin secretion in plasma cells: directs efficient alternative mRNA processing, influencing both proximal poly(A) site choice and exon skipping, as well as immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) alternative processing. Probably acts by regulating histone modifications accompanying transition from membrane-specific to secretory IgH mRNA expression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20471948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22195968, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23251033}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Involved in snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. Part of transcription elongation factor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22936; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; transcription elongation factor complex [GO:0008023]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0032968]; snRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042795]; transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II promoter [GO:0006368] |
19749764_ELL2 addition regulates mRNA processing by enhancing poly(A) site choice and exon splice-site skipping 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22483617_Prostratin and HMBA, two well-studied activators of HIV transcription and latency, enhance ELL2 accumulation and SECs formation largely through decreasing Siah1 expression and ELL2 polyubiquitination. 25058508_Tax transactivates the ELL2 promoter in HTLV-1-infected T-cells. 25238757_Loss of ELL2 in B cells results in decreased Igh secretory mRNA and decreased expression of Ig light chain plus genes involved in the unfolded protein response like XBP1, ATF6, BiP, cyclin B2, OcaB (BOB1, Pou2af1). 26007630_multiple myeloma risk allele harbours a Thr298Ala missense variant in an ELL2 domain required for transcription elongation 28134250_Study reports the 2.0-A resolution crystal structure of the human ELL2 C-terminal domain bound to its 50-residue binding site on AFF4, the ELLBow. The ELLBow consists of an N-terminal helix followed by an extended hairpin and occupies most of the concave surface of ELL2. This surface is important for the ability of ELL2 to promote HIV-1 Tat-mediated proviral transcription. 28531325_Results provide the first evidence that ELL2 is a direct target of miR-299 and increased ELL2 expression and down-regulation of miR-299 are associated with GBM progression and poor prognosis in patients. 28858629_Selective expression of the transcription elongation factor ELL3 in B cells prior to ELL2 drives proliferation and survival 28870994_These results suggest that ELL2 and its pathway genes likely play an important role in the development and progression of prostate cancer. 28903037_expression is consistent with inherited genetic variation contributing to arrest of plasma cell development, facilitating multiple myeloma clonal expansion. 29179998_Knockdown of RNA polymerase II elongation factor ELL2 (ELL2) sensitized prostate cancer cells to DNA damage and overexpression of ELL2 protected prostate cancer cells from DNA damage. 29695719_Study in CD138+ plasma cells from 1630 multiple myeloma (MM) patients show that the MM risk allele at 5q15 lowers ELL2 expression in these cells, but not in peripheral blood or other tissues. 30009504_ELL2 protein was downregulated in prostate cancer specimens and was up-regulated by androgens in prostate cancer cell lines LNCaP and C4-2. ELL2 knockdown enhanced prostate cancer cell proliferation and motility. 30556882_MRCCAT1 is upregulated in glioma, predicting poor outcome for patients. MRCCAT1 promotes glioma cell proliferation and migration by activating p38-MAPK signaling. 34265249_Allosteric transcription stimulation by RNA polymerase II super elongation complex. 34948391_Characterizing the Interaction between the HTLV-1 Transactivator Tax-1 with Transcription Elongation Factor ELL2 and Its Impact on Viral Transactivation. |
ENSMUSG00000001542 |
Ell2 |
288.205707 |
2.4328241309 |
1.282632 |
0.136157437 |
87.430085 |
0.00000000000000000000873122677444865996432202614060743537958818547039050442975030574821460049861343577504158020019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000079502101906762625988904175701212123840327812822777040673363768696901843213709071278572082519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
386.7761735 |
34.4918760 |
160.2982123 |
10.7441229 |
| ENSG00000119048 |
7320 |
UBE2B |
protein_coding |
P63146 |
FUNCTION: Accepts ubiquitin from the E1 complex and catalyzes its covalent attachment to other proteins. In association with the E3 enzyme BRE1 (RNF20 and/or RNF40), it plays a role in transcription regulation by catalyzing the monoubiquitination of histone H2B at 'Lys-120' to form H2BK120ub1. H2BK120ub1 gives a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation, elongation by RNA polymerase II, telomeric silencing, and is also a prerequisite for H3K4me and H3K79me formation. In vitro catalyzes 'Lys-11'-, as well as 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination. Required for postreplication repair of UV-damaged DNA. Associates to the E3 ligase RAD18 to form the UBE2B-RAD18 ubiquitin ligase complex involved in mono-ubiquitination of DNA-associated PCNA on 'Lys-164'. May be involved in neurite outgrowth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16337599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17108083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17130289, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1717990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20061386}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;DNA damage;DNA repair;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00388}. |
The modification of proteins with ubiquitin is an important cellular mechanism for targeting abnormal or short-lived proteins for degradation. Ubiquitination involves at least three classes of enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes, or E1s, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, or E2s, and ubiquitin-protein ligases, or E3s. This gene encodes a member of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family. This enzyme is required for post-replicative DNA damage repair. Its protein sequence is 100% identical to the mouse, rat, and rabbit homologs, which indicates that this enzyme is highly conserved in eukaryotic evolution. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7320; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; HULC complex [GO:0033503]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; XY body [GO:0001741]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity [GO:0061631]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; chiasma assembly [GO:0051026]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; histone H2A ubiquitination [GO:0033522]; histone lysine demethylation [GO:0070076]; histone ubiquitination [GO:0016574]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; meiotic telomere clustering [GO:0045141]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043951]; negative regulation of developmental process [GO:0051093]; negative regulation of post-translational protein modification [GO:1901874]; negative regulation of reproductive process [GO:2000242]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of reciprocal meiotic recombination [GO:0010845]; postreplication repair [GO:0006301]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein K11-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070979]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070534]; protein monoubiquitination [GO:0006513]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of histone modification [GO:0031056]; response to UV [GO:0009411]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; synaptonemal complex organization [GO:0070193]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
14981545_MCF10A cells stably transfected with antisense RAD6B display hypersensitivity to damage-inducing drugs. 17050667_These data reveal a potentially important role for transcriptionally active beta-catenin in the regulation of Rad6B gene expression, and link aberrant beta-catenin signaling with transcriptional deregulation of Rad6B and breast cancer development. 18339854_Findings reveal a positive regulatory feedback loop between Rad6B and beta-catenin and a novel mechanism of beta-catenin stabilization/activation in breast cancer cells. 18363965_The SAP domain of RAD18 (residues 248-282) is crucial for binding of RAD18 complexed with RAD6B to DNA substrates. 18385908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18385908_deletions in this suspected promoter region are associated with increased binding affinity for SP1, and might represent one of several factors required for alteration of UBE2B gene expression 18497339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18497339_study suggests that the UBE2B gene is associated with male infertility in Indian men 19466589_Rad6B is a fundamental component of postreplication DNA repair and can be used as an independent marker for determining response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 19548583_Hydroquinone could upregulate the expression of Rad6B in L-02 hepatic cells. 20378615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041297_Ubc2/Rad6 ser(120) regulates ubiquitin-dependent N-end rule targeting by E3{alpha}/Ubr1 21549715_Data show that the homodimeric Rad18 RING domain can recruit two Rad6b E2 enzymes, whereas the full-length Rad18 homodimer binds only to a single Rad6b molecule. 22083959_RAD6 can form a ternary complex with MDM2 and p53 that contributes to the degradation of p53. 22547805_The Rad6-Rad18 enzyme plays an essential role in promoting replication through DNA lesions by translesion synthesis in mammalian cells. 22705350_beta-catenin and Rad6B interacting regions, were identified. 23079972_UBE2B polymorphisms g.-293T>G, g.20016A>G and g.9157A>G are not associated with male infertility, and the GA haplotype is likely a protective factor for male fertility in Northeast Chinese men. 23378580_UBE2B mRNA alterations are associated with severe oligozoospermia in infertile men. 23525009_RNF168, in complex with RAD6A or RAD6B, is activated in the DNA-damage-induced protein ubiquitination cascade. 25384975_RAD6 physically interacts with heterochromatin protein 1alpha and ubiquitinates HP1alpha at residue K154, thereby promoting heterochromatin protein 1alpha degradation through the autophagy pathway 26223869_A novel variant (Chr5.133706925 A > G) residing in the UBE2B gene promoter region confers a high risk for idiopathic azoospermia in a Chinese population. 26336826_Data show that the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 RAD6A/B-MDM2 ubiquitin ligase machinery regulates anti-silencing function 1A protein (ASF1A) degradation. 26679603_These findings show the importance of Rad6 in ovarian cancer and emphasize the need for further studies of Rad6 as a potential target for the treatment of ovarian cancer. 27235675_In conclusion, we reveal that miR-455-5p expression is regulated by the TGF-beta-dependent pathway, which subsequently leads to UBE2B down-regulation and contributes to oral cancer tumourigenesis. 27678051_These results point to an important role of the affinity between RNF4 and its cognate RAD6B or UBCH5B in governing the multiplicity of substrate ubiquitination. 28031328_RAD6 promotes proteasome activity and nuclear translocation by enhancing the degradation of PSMF1 and the lamin B receptor. 28490629_These data deepen insights into the vital role of RAD6/translesion synthesis in platinum drug tolerance and reveal clinical benefits of targeting RAD6 with SMI#9 for managing chemoresistant cancers. 28806395_RAD6 is upregulated in response to chemotherapy and significantly correlated with expression of ovarian cancer (OC) stem cell signaling genes ALDH1A1 and SOX2 and poor prognosis of OC patients. 31303644_MicroRNA-4268 inhibits cell proliferation via AKT/JNK signalling pathways by targeting Rab6B in human gastric cancer. 31639439_These RAD6B activities are unaffected by BRCA1 status. 31683936_Authors confirmed that RAD6BDeltaexon4 and RAD6Bintron5ins variants are expressed as 14 and 15 kDa proteins, respectively, with functional in vivo ubiquitin conjugating activity. 33109568_High Expression of UBE2B as a Poor Prognosis Factor in Patients With Rectal Cancer Following Chemoradiotherapy. 33181138_RAD6B Loss Disrupts Expression of Melanoma Phenotype in Part by Inhibiting WNT/beta-Catenin Signaling. 35313791_UBE2B promotes ovarian cancer growth via promoting RAD18 mediated ZMYM2 monoubiquitination and stabilization. 36162503_Mutations of Rad6 E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes at alanine-126 in helix-3 affect ubiquitination activity and decrease enzyme stability. |
ENSMUSG00000020390 |
Ube2b |
486.028454 |
0.4530538881 |
-1.142245 |
0.450037628 |
6.285380 |
0.01217379857412858278065126427236464223824441432952880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022936592667109761967125791670696344226598739624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
269.8519398 |
92.4456697 |
599.9442005 |
147.8381101 |
| ENSG00000119285 |
55127 |
HEATR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H583 |
FUNCTION: Ribosome biogenesis factor. Involved in nucleolar processing of pre-18S ribosomal RNA. Required for optimal pre-ribosomal RNA transcription by RNA polymerase I. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17699751}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribonucleoprotein;Ribosome biogenesis;rRNA processing;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of rRNA processing and positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I. Located in fibrillar center and mitochondrion. Implicated in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Biomarker of glioblastoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55127; |
90S preribosome [GO:0030686]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; small-subunit processome [GO:0032040]; t-UTP complex [GO:0034455]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; snoRNA binding [GO:0030515]; maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000462]; positive regulation of rRNA processing [GO:2000234]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I [GO:0045943] |
25126583_Glioma-associated antigen HEATR1 induces functional cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with glioma. 29143558_These findings reveal an important role for HEATR1 in ribosome biogenesis. 31785531_HEATR1 deficiency promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation and gemcitabine resistance by up-regulating Nrf2 signaling. 32634230_HEATR1 promotes proliferation in gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. 33894417_HEATR1, a novel interactor of Pontin/Reptin, stabilizes Pontin/Reptin and promotes cell proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000050244 |
Heatr1 |
565.908361 |
2.4122770115 |
1.270396 |
0.094339569 |
179.852831 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000005218593287874334182875312078404748614968263175072569355015600330482795244107636610589649858936604829955097084592807732406072318553924560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000894615992207028693759680399160369310029223296953342047641373420693598656994750363709214102255252873624816190023523176932940259575843811035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
811.0635519 |
52.1833072 |
338.8684792 |
16.5655585 |
| ENSG00000119411 |
54836 |
BSPRY |
protein_coding |
Q5W0U4 |
FUNCTION: May regulate epithelial calcium transport by inhibiting TRPV5 activity. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium transport;Cytoplasm;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transport;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein ubiquitination. Predicted to act upstream of or within cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor. Predicted to be located in cell leading edge; membrane; and perinuclear region of cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54836; |
cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
12615066_Expression analysis of the rat BSPRY ortholog and demonstration of its interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. 19929093_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000028392 |
Bspry |
11.868454 |
0.1281339735 |
-2.964275 |
0.660868119 |
22.263661 |
0.00000237661857715682919113065266203399517053185263648629188537597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008062259296445599071417008329998310500741354189813137054443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1739989 |
1.1126944 |
16.5076917 |
4.5645485 |
| ENSG00000119431 |
81932 |
HDHD3 |
protein_coding |
Q9BSH5 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Reference proteome |
|
Located in nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:81932; |
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634] |
|
ENSMUSG00000038422 |
Hdhd3 |
61.219014 |
0.3655326922 |
-1.451928 |
0.213969631 |
47.290805 |
0.00000000000611986323016050517211823753945023067653263826315424012136645615100860595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000034489950850389102201951377963984627858518017262667854083701968193054199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.5362483 |
4.4319541 |
89.5711636 |
7.6199429 |
| ENSG00000119508 |
8013 |
NR4A3 |
protein_coding |
Q92570 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator that binds to regulatory elements in promoter regions in a cell- and response element (target)-specific manner. Induces gene expression by binding as monomers to the NR4A1 response element (NBRE) 5'-AAAAGGTCA-3' site and as homodimers to the Nur response element (NurRE) site in the promoter of their regulated target genes (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of proliferation, survival and differentiation of many different cell types and also in metabolism and inflammation. Mediates proliferation of vascular smooth muscle, myeloid progenitor cell and type B pancreatic cells; promotes mitogen-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through transactivation of SKP2 promoter by binding a NBRE site (By similarity). Upon PDGF stimulation, stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by regulating CCND1 and CCND2 expression. In islets, induces type B pancreatic cell proliferation through up-regulation of genes that activate cell cycle, as well as genes that cause degradation of the CDKN1A (By similarity). Negatively regulates myeloid progenitor cell proliferation by repressing RUNX1 in a NBRE site-independent manner. During inner ear, plays a role as a key mediator of the proliferative growth phase of semicircular canal development (By similarity). Mediates also survival of neuron and smooth muscle cells; mediates CREB-induced neuronal survival, and during hippocampus development, plays a critical role in pyramidal cell survival and axonal guidance. Is required for S phase entry of the cell cycle and survival of smooth muscle cells by inducing CCND1, resulting in RB1 phosphorylation. Binds to NBRE motif in CCND1 promoter, resulting in the activation of the promoter and CCND1 transcription (By similarity). Also plays a role in inflammation; upon TNF stimulation, mediates monocyte adhesion by inducing the expression of VCAM1 and ICAM1 by binding to the NBRE consensus site (By similarity) (PubMed:20558821). In mast cells activated by Fc-epsilon receptor cross-linking, promotes the synthesis and release of cytokines but impairs events leading to degranulation (By similarity). Also plays a role in metabolism; by modulating feeding behavior; and by playing a role in energy balance by inhibiting the glucocorticoid-induced orexigenic neuropeptides AGRP expression, at least in part by forming a complex with activated NR3C1 on the AGRP- glucocorticoid response element (GRE), and thus weakening the DNA binding activity of NR3C1. Upon catecholamines stimulation, regulates gene expression that controls oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle (By similarity). Plays a role in glucose transport by regulating translocation of the SLC2A4 glucose transporter to the cell surface (PubMed:24022864). Finally, during gastrulation plays a crucial role in the formation of anterior mesoderm by controlling cell migration. Inhibits adipogenesis (By similarity). Also participates in cardiac hypertrophy by activating PARP1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51179, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZB6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20558821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24022864}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the steroid-thyroid hormone-retinoid receptor superfamily. The encoded protein may act as a transcriptional activator. The protein can efficiently bind the NGFI-B Response Element (NBRE). Three different versions of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas (EMCs) are the result of reciprocal translocations between this gene and other genes. The translocation breakpoints are associated with Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4, Group A, Member 3 (on chromosome 9) and either Ewing Sarcome Breakpoint Region 1 (on chromosome 22), RNA Polymerase II, TATA Box-Binding Protein-Associated Factor, 68-KD (on chromosome 17), or Transcription factor 12 (on chromosome 15). Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:8013; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; cellular respiration [GO:0045333]; cellular response to catecholamine stimulus [GO:0071870]; cellular response to corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulus [GO:0071376]; cellular response to leptin stimulus [GO:0044320]; common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation [GO:0035726]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; gastrulation [GO:0007369]; mast cell degranulation [GO:0043303]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced neuron death [GO:1903208]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010613]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation [GO:0046321]; positive regulation of feeding behavior [GO:2000253]; positive regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010828]; positive regulation of mast cell activation by Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038097]; positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production [GO:0032765]; positive regulation of monocyte aggregation [GO:1900625]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904754]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; pyruvate oxidation [GO:0009444]; regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048660]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0061469] |
12543801_The homeotic protein Six3 is a coactivator of the nuclear receptor NOR-1 and a corepressor of the fusion protein EWS/NOR-1 in human extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. 14525795_The genes identified here are novel candidates as key early mediators of VEGF-induced endothelial functions. 14962944_In vascular smooth muscle cells, LDL-induced mitogenesis involves NOR-1 upregulation through a CREB-dependent mechanism. Mutation of specific CRE sites in the NOR-1 promoter abolishes LDL-induced NOR-1 promoter activity. 15262426_Aberrant coexpression of NOR1 and SIX3 is a potential alternative mechanism underlying the development of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas 15523651_different SIX3 mutations in HPE2 may affect different signaling pathways, and that one of these pathways may involve the nuclear receptor NOR1 15949808_Neuron-derived orphan receptor-1 (NOR-1) is a transcription factor over-expressed in human atherosclerotic plaques that is involved in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. 15964844_NR4A nuclear receptors NR4A1, NR4A2, NR4A3 are potential transcriptional mediators of inflammatory signals in activated macrophages 16873729_Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 are expressed in human atherosclerotic lesion macrophages and reduce human macrophage lipid loading and inflammatory responses, providing further evidence for a protective role of these factors in atherogenesis. 16945922_platelet-derived growth factor-induced NOR1 transcription in smooth muscle cell is mediated through cAMP-response element-binding protein-dependent transactivation of the NOR1 promoter 17515897_NOR-1 is a critical tumor suppressor of myeloid leukemogenesis that is downregulated in leukemic blasts from acute myeloid leukemia patients. 17596136_NOR-1 up-regulation plays a key role in thrombin-induced endothelial cell growth 17981763_NOR-1 is over-expressed in human atherosclerotic plaques and in porcine arteries subjected to angioplasty, is induced by growth factors in vascular cells and it has been involved in cell migration and proliferation 18325999_NOR-1 is necessary for oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle. 19682370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19682370_common genetic variation within the NR4A3 locus determines insulin secretion 19720740_NOR-1 is a downstream effector of HIF-1 signaling involved in the survival response of endothelial cells to hypoxia. 19727524_NOR1 protein is frequently down-expressed in Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 19775727_These results suggest that FISH analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens using EWSR1 and NR4A3 probes is useful and convenient and may provide an ancillary method for the diagnosis of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. 20411565_Protein kinase C-regulated role in TCR-induced thymocyte apoptosis 20558821_A novel pathway is identified that establishes NOR1 orphan nuclear receptor in an atherogenic role by positively regulating monocyte recruitment to the vascular wall. 20659174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20659174_Results identified the NR4A3 gene is associated with the quantity of tobacco smoked in subjects with schizophrenia; this association was replicated in a population of individuals with bipolar disorder. 20668010_Loss of NR4A3 is associated with thyroid follicular neoplasia. 21621845_stimulation of peripheral blood mast cells caused a robust upregulation of NR4A2 and, in particular, NR4A3, while NR4A1 expression was only moderately affected 21725049_Data from patients with familial platelet disorder/acute myelogenous leukemia indicate a correlation between increased clonogenic potential of patient hematopoietic progenitor cells and NR4A3 expression. Data indicate NR4A3 is direct target of RUNX1. 21752397_Low expression of NR4A gene family members (NR4A1, NR4A3) and 1-alpha25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor (VDR) genes is demonstrated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of multiple sclerosis patients. 21873782_NOR1 isoform 1 and isoform 2 are both detected in fetal brain. NOR1 isoform 2 lacking exon 2 is the sole isoform in multiple tissues except for brain. 22143616_Data show altered adipose tissue expression of the NOR1 stress-responsive nuclear receptor in obesity, suggesting it may modulate pathogenic potential in humans. 22569967_The pathognomic rearrangement of NR4A3 is a useful diagnostic feature in identifying cellular extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. 22789442_Pin1 enhances the transcriptional activity of all three NR4A nuclear receptors and increases protein stability of Nur77 through inhibition of its ubiquitination. 23247046_present work is the first report of a novel mechanism of HDAC inhibitor-induced apoptosis in AML that involves restoration of the silenced nuclear receptors Nur77 and Nor1 23390133_Over-expression of neuron-derived orphan receptor-1 (NOR-1) exacerbates neointimal hyperplasia after vascular injury 23462179_Nor-1 and its gene targets are also up-regulated in human HCC samples. 23554459_Results indicate that miR-638 is a key molecule in regulating vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by targeting the NOR1/cyclin D pathway. 23588370_We molecularly confirmed NR4A3/EWSR1 rearrangements as myxochondroid sarcoma, either osseous or extraskeletal variants. 24005216_NR4A nuclear receptors are involved in negative selection of thymocytes, Treg differentiation and the development of Ly6C monocytes. Nur77 and Nurr1 attenuate atherosclerosis in mice whereas NOR-1 aggravates vascular lesion formation. 24626568_Results indicate that DNA hypomethylation of the CpG island at Nr4a3 exon 3 is associated with low Nr4a3 expression, and correlates with poor prognosis of neuroblastoma. 24630523_These results reinforce the role of NOR-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and in vascular remodelling 24657653_NOR1 suppresses slug/vimentin expression to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 24788728_NOR1 expression causes apoptosis of tumor cells in hypoxia by altering the expression of PDK1 expression and mitochondrial Bax-Bcl2 balance thus suppress tumor cell adaptation to hypoxia 24806827_Studies demonstrate that NOR1 deletion in hematopoietic stem cells accelerates atherosclerosis formation by promoting myelopoiesis in the stem cell compartment and by inducing local proatherogenic activities in the macrophage. 25089663_In this review, a concise overview of the current understanding of the important metabolic roles governed by NR4A members NR4A1, NR4A2 and NR4A3 including their participation in a number of diseases shall be provided 25118646_Study suggests that NOR1 modulates the proliferation and apoptosis of human prostate cancer PC3 cells through the MAPK signaling pathway. 25199433_placental expression not affected by obesity or gestational diabetes 25410408_The authors discuss the role of NR4A1 and NR4A3 as tumor suppressors in hematologic neoplasms.[Review] 25449536_identified 13 ADCC-activated genes. Six gene expression assays including 8 of the 13 genes (CCL3, CCL4/CCL4L1/CCL4L2, CD160, IFNG, NR4A3 and XCL1/XCL2) were analyzed in 127 kidney biopsies 25536180_Our data support a role for NOR-1 as a negative modulator of the acute response elicited by pro-inflammatory stimuli in the vasculature. 25809189_A2M is expressed in the vasculature and NR4A receptors modulate VSMC MMP2/9 activity by several mechanisms including the up-regulation of A2M. 25844690_NOR1 promotes the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 25852083_DNA-PK directly phosphorylates NOR-1, modulating vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. 25917081_NR4A2 is a key factor in multiple diseases, such as inflammation, cancer and cardiovascular diseases. 25941992_Data identify NOR1 as a transcription factor induced during alternative differentiation of human macrophages and demonstrate that NOR1 modifies the alternative macrophage phenotype. 26096603_accumulation of NR4A3 is specific to alpha-synucleinopathy. 26600038_miR-17 and -20a target NOR-1 thereby regulating NOR-1-dependent gene expression. 26634653_Identified Nur77/Nor1 as novel regulators of thrombomodulin expression and function in vascular endothelial cells. 27159982_Study found a marked down-regulated gene expression of the NR4A subfamily (NR4A1, NR4A2, and NR4A3) obtained from Parkinson's disease patients, but only a NR4A1 decrease in Alzheimer's disease patients compared to healthy controls. This study reports that the entire NR4A subfamily and not only NR4A2 could be systemically involved in Parkinson's disease. 27166283_Overexpression of NR4A3 in adipocytes produces a complex phenotype characterized by impaired glucose metabolism and low serum catecholamines due to enhanced degradation by adipose tissue. 27181368_Results indicate that NOR-1 regulate SMPX in human muscle cells and acts as a muscle regulatory factor to promote myotube differentiation. 27528092_aberrant JAK/STAT3 signaling epigenetically silences a potential tumor suppressor, NR4A3, in gastric cancer, plausibly representing a reliable biomarker for gastric cancer prognosis 27697661_the role of intragenic DNA hypermethylation in reducing the expression of NR4A3 in AML 27891591_NOR1 suppresses cancer stem-like cell properties in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inhibiting the AKT-GSK-3beta-Wnt/beta-catenin-ALDH1A1 signaling circuit. 28232113_NOR1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating Notch pathway. 28249774_In the 3 cases of the primary extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma (EMC) of bone we found the most frequent and specific chromosomal translocation t(9:22) EWSR1-NR4A3 of the extraskeletal counterpart. 28249906_Transcript analysis of four different aggressive lymphoma cell lines overexpressing either NR4A3 or NR4A1 revealed that apoptosis was driven similarly by induction of BAK, Puma, BIK, BIM, BID, and Trail. Overall, our results showed that NR4A3 possesses robust tumor suppressor functions of similar impact to NR4A1 in aggressive lymphomas 28637666_NR4A2 and NR4A3 are components of a downstream transcriptional response to PKA activation in the neutrophil, and that they positively regulate neutrophil survival and homeostasis. 28666984_VTN levels were increased in cell supernatants from vascular smooth muscle cells that overexpress NOR-1 28791396_NOR1 activates HSCs and contributes to liver fibrosis in vitro and this effect was achieved through the activation of the Wnt/betacatenin pathway. 28808448_NR4A sub-family of nuclear orphan receptors (Nor-1, Nurr-1 and Nur-77) may have a role in trophoblastic cell differentiation. 29377304_findings indicated that cAMP-PKA up-regulated STAT5B, followed by increase in syncytin2 expression through GCM1 and OVOL1, resulting in cell fusion and hCG production, while cAMP-PKA-up-regulated NR4A3 could decrease syncytin2 expression. 29695901_NOR1 upregulation is associated with hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling in COPD via promoting human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. 30076719_our study provides the first in vitro evidence highlighting the antiproliferative and antimigratory roles of miR-638 in human Abnormal airway smooth muscle cell (ASMC) remodeling and suggests that targeted overexpression of miR-638 in ASMCs may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for preventing ASM hyperplasia associated with asthma. 30096407_These results indicate that NOR-1 induces NOX1 in human vascular smooth muscle cells and participates in the complex gene networks regulating oxidative stress and redox homeostasis in the vasculature. 30227111_Long non-coding RNA BRE-AS1 represses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and survival via up-regulating NR4A3 30455429_NR4A3 is a novel target of p53 that contributes to apoptosis 30664630_It has been concluded that NR4A3 is upregulated through enhancer hijacking and has important oncogenic functions in acinic cell carcinomas of the salivary glands. 30696767_results uncover that Nor1 negatively regulates beta-cell mass. Nor1 represents a promising molecular target in diabetes treatment to prevent beta-cell destruction. 31020999_NR4A3 fusion proteins trigger an axon guidance switch that marks the difference between EWSR1 and TAF15 translocated extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas cells. 31094928_immunostaining is a highly specific and sensitive marker for acinic cell carcinoma of the salivary glands 31183633_Results indicated that NR4A3 directly activates the expression of GAP43 and induces differentiated phenotypes of NB cells, without affecting the upstream signals regulating GAP43 expression and NB differentiation. 31209222_study demonstrates that miR-665 upregulation is associated with metastasis and poor survival in BC patients, and mechanistically, miR-665 enhances progression of BC via NR4A3/MEK signaling pathway. 31701670_The pro-inflammatory effect of NR4A3 in osteoarthritis. 31936632_Disruption of Beta-Cell Mitochondrial Networks by the Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nor1/Nr4a3. 31985010_NOR-1 is involved in the transcriptional programme leading to Hypertensive cardiac hypertrophy. 32125766_Long non-coding RNA LINC00467 drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inhibiting NR4A3. 32241159_The tumor suppressor NOR1 suppresses cell growth, invasiveness, and tumorigenicity in glioma. 32323598_miR-106b-5p induces immune imbalance of Treg/Th17 in immune thrombocytopenic purpura through NR4A3/Foxp3 pathway. 32341238_Nuclear NR4A2 (Nurr1) Immunostaining is a Novel Marker for Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands Lacking the Classic NR4A3 (NOR-1) Upregulation. 32809265_Evaluation of NR4A3 immunohistochemistry (IHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization and comparison with DOG1 IHC for FNA diagnosis of acinic cell carcinoma. 33163142_SMARCB1 Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of NR4A3 via Direct Interaction Driven by ROS in Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury. 33221345_NR4A3 induces endothelial dysfunction through up-regulation of endothelial 1 expression in adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. 33241311_Nor1, a novel cytokine-responsive regulator of pancreatic beta-cell mass and function mediated by disruption of mitochondrial networks. 34248958_Transcriptional Profiling of Monocytes Deficient in Nuclear Orphan Receptors NR4A2 and NR4A3 Reveals Distinct Signalling Roles Related to Antigen Presentation and Viral Response. 34383980_Atypic SUMOylation of Nor1/NR4A3 regulates neural cell viability and redox sensitivity. 34437889_Minireview: What is Known about SUMOylation Among NR4A Family Members? 34565470_NR4A3 and CCL20 clusters dominate the genetic networks in CD146(+) blood cells during acute myocardial infarction in humans. 34657447_Knockdown of long noncoding RNA AC245100.4 inhibits the tumorigenesis of prostate cancer cells via the STAT3/NR4A3 axis. 34768801_NR4A3: A Key Nuclear Receptor in Vascular Biology, Cardiovascular Remodeling, and Beyond. 34873305_Analysis of clinicopathologic features and expression of NR4A3 in sinonasal acinic cell carcinoma. 35230891_MiR-501-5p alleviates cardiac dysfunction in septic patients through targeting NR4A3 to prevent its binding with Bcl-2. 35418692_Matriptase-2/NR4A3 axis switches TGF-beta action toward suppression of prostate cancer cell invasion, tumor growth, and metastasis. 36040481_Functional association of NR4A3 downregulation with impaired differentiation in myeloid leukemogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000028341 |
Nr4a3 |
12.656063 |
12.0718919569 |
3.593580 |
0.631214618 |
41.892621 |
0.00000000009642584638624207666564819140263319433015176684875768842175602912902832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000499559667483655011472651337304812929618336170278780627995729446411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.7911680 |
9.5172996 |
2.0005129 |
0.7504791 |
| ENSG00000119514 |
79695 |
GALNT12 |
protein_coding |
Q8IXK2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the initial reaction in O-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis, the transfer of an N-acetyl-D-galactosamine residue to a serine or threonine residue on the protein receptor. Has activity toward non-glycosylated peptides such as Muc5AC, Muc1a and EA2, and no detectable activity with Muc2 and Muc7. Displays enzymatic activity toward the Gal-NAc-Muc5AC glycopeptide, but no detectable activity to mono-GalNAc-glycosylated Muc1a, Muc2, Muc7 and EA2. May play an important role in the initial step of mucin-type oligosaccharide biosynthesis in digestive organs. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lectin;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
This gene encodes a member of a family of UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases, which catalyze the transfer of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) from UDP-GalNAc to a serine or threonine residue on a polypeptide acceptor in the initial step of O-linked protein glycosylation. Mutations in this gene are associated with an increased susceptibility to colorectal cancer.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:79695; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0004653]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493] |
12135769_cloning and characterization 15557789_The expression of pp-GalNAc-T12 seems to be a negative marker especially of metastatic gastric and colorectal cancer 19617566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19617566_inactivating GALNT12 mutations were identified as acquired somatic mutations in a set of 30 microsatellite stable colon tumors. 22461326_Inherited deleterious variants in GALNT12 are associated with CRC susceptibility. 24038392_we integrated different computational tools to perform the in silico analysis of clinically significant mutations (nsSNPs/single amino acid change) at both functional and structural levels, found in human GALNT3, GALNT8, GALNT12, and GALNT13 genes. 24115450_Results rule out GALNT12 as a major high familial colorectal cancer susceptibility gene. Additional studies are required to provide further evidence about its role as a moderate/low susceptibility gene in familial aggregation of cancer. 29095867_LOH analyses, glycosylation pattern tests and case-control studies, our results did not support the role of c.907G>A, p.(D303N) as a high-penetrance risk allele for polyposis CRC 29749045_The findings provide strong, independent evidence for the association of GALNT12 defects with CRC-susceptibility; underscoring implications for glycosylation pathway defects in CRC. 33593824_Interaction between G ALNT12 and C1GALT1 Associates with Galactose-Deficient IgA1 and IgA Nephropathy. 35461073_GALNT12 is associated with the malignancy of glioma and promotes glioblastoma multiforme in vitro by activating Akt signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000039774 |
Galnt12 |
84.747914 |
0.2133124592 |
-2.228960 |
0.276228340 |
63.599611 |
0.00000000000000152459253949273100741263811736902241217658663177680899991628393763676285743713378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000010813544393518841260367142503774967370668317820370241122418519807979464530944824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.5389485 |
5.9258938 |
144.4347934 |
18.8271061 |
| ENSG00000119522 |
57706 |
DENND1A |
protein_coding |
Q8TEH3 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) regulating clathrin-mediated endocytosis through RAB35 activation. Promotes the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound RAB35 into its active GTP-bound form. Regulates clathrin-mediated endocytosis of synaptic vesicles and mediates exit from early endosomes (PubMed:20154091, PubMed:20937701). Binds phosphatidylinositol-phosphates (PtdInsPs), with some preference for PtdIns(3)P (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K382, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937701}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transport |
|
Clathrin (see MIM 118955)-mediated endocytosis is a major mechanism for internalization of proteins and lipids. Members of the connecdenn family, such as DENND1A, function as guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for the early endosomal small GTPase RAB35 (MIM 604199) and bind to clathrin and clathrin adaptor protein-2 (AP2; see MIM 601024). Thus, connecdenns link RAB35 activation with the clathrin machinery (Marat and McPherson, 2010 [PubMed 20154091]).[supplied by OMIM, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:57706; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of Rab protein signal transduction [GO:0032483] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22180642_At least two of the PCOS susceptibility loci identified in the Chinese PCOS GWAS (DENND1A and THADA) are also associated with PCOS in European derived populations. 22504079_The rs2479106 G allele was associated with decreased PCOS susceptibility 22547425_Variants in DENND1A are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in women of European ancestry. 22902918_Our results suggest that SNPs rs2479106 in gene DENND1A and rs13405728 in gene LHCGR are associated with endometrioid adenocarcinoma. 23208300_THADA and DENND1A, carry risk alleles that are associated with endocrine and metabolic disturbances in PCOS patients of Han Chinese descent. 24086769_sequence analysis of the DENND1A gene of patients with PCOS did not identify alterations that alone could be responsible for the PCOS pathogenesis 24706793_DENND1A, plays a key role in the hyperandrogenemia associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 25626177_We demonstrated lack of association of DENND1A SNPs rs10818854, rs2479106, and rs10986105, previously associated with PCOS in Asians, with PCOS in Bahraini Arab women. 26055712_The guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity of connecdenn 1 and 2 are autoinhibited, and this is regulated by Akt activation downstream of insulin stimulation. 26757598_This meta-analysis suggested that rs2479106 and rs10818854 polymorphisms in the DENND1A gene were associated with increased risk of polycystic ovary syndrome 27297658_Genome-wide association studies have identified DENND1A as a candidate gene for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PCOS theca cells are shown to overexpress DENND1A splice variant 2 (V2), but not V1. Also, the genetic variation 330 bp upstream of exon 20A is not associated with VE variant expression. 27488699_DENND1A gene variant is likely to have influence on PCOS risk. 29325736_The association of DENND1A rs10818854 and rs10986105 variants with PCOS in Tunisian but not Bahraini women confirms the dependence of this association on the ethnic/racial origin of study subjects. 29727258_Genetic variants of PCOS (rs13405728 in LHCGR gene; rs13429458 in THADA gene and rs2479106 in DENND1A gene) may not be involved in the development of preeclampsia in Han Chinese women. 30232779_we evaluated the frequencies of CYP19A1 rs2414096 and DENND1A rs10818854 polymorphisms in overweight and normal individuals and didn't find any significant difference between these groups which demonstrates a lack of association between obesity risk and these SNPs 31184707_decreased miR-130b-3p expression in PCOS theca cells, which was correlated with increased DENND1A.V2, cytochrome P450 17alpha-hydroxylase (CYP17A1) mRNA and androgen biosynthesis. 31941453_The tagging SNPs rs2479106 and rs2468819 in the DENND1A gene are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in the Chinese population, whereas rs2670139, rs2536951 and rs2479102 are not correlated with PCOS in the same population 34320236_A Multi-center Genome-wide Association Study of Cervical Dystonia. |
ENSMUSG00000035392 |
Dennd1a |
126.823655 |
2.0964670654 |
1.067960 |
0.429470521 |
5.916145 |
0.01500274558707948881208782410112689831294119358062744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027673147321331324766102710555060184560716152191162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
181.0273300 |
54.8871443 |
86.3945288 |
18.8710389 |
| ENSG00000119535 |
1441 |
CSF3R |
protein_coding |
Q99062 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CSF3), essential for granulocytic maturation. Plays a crucial role in the proliferation, differientation and survival of cells along the neutrophilic lineage. In addition it may function in some adhesion or recognition events at the cell surface. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7514305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is the receptor for colony stimulating factor 3, a cytokine that controls the production, differentiation, and function of granulocytes. The encoded protein, which is a member of the family of cytokine receptors, may also function in some cell surface adhesion or recognition processes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Mutations in this gene are a cause of Kostmann syndrome, also known as severe congenital neutropenia. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:1441; |
endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; granulocyte colony-stimulating factor binding [GO:0051916]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response [GO:0006952]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045637]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11468284_the dimerization interface of the complete receptor complex is different from that in the x-ray structure of a partial complex. A model of the tetrameric G-CSF.G-CSF-R complex was prepared 11714811_The C-terminus of the G-CSF receptor, truncated in patients with severe congenital neutropenia/acute myeloid leukemia, is required for SH2-containing phosphatase-1 suppression of G-CSF-stimulated Stat activation. 11920194_Lack of STAT3beta function in a differentiation-competent murine cell line expressing human G-CSFR argues against its having a role in Kip1 expression or neutrophil differentiation. 12012328_Novel variant involved in induction of cell proliferation; myelodysplastic syndrome; a deletion of three nucleotides (2128-2130) in the juxtamembrane domain of the G-CSFR resulted in a conversion of Asn(630)Arg(631) to Lys(630). 12422946_abnormalities of primitive myeloid progenitor cells expressing G-CSFR may play an important role in the impairment of granulopoiesis in patients with severe congenital neutropenia 12586631_the carboxy-terminal region of hGCSFR plays a role in the phagocytosis and Syk and Hck kinase tyrosine phosphorylation is involved. 14737106_selective inhibition of G-CSF receptor expression by C/EBPalphap30-ER is due in part to its variable affinity for C/EBP sites 14751388_G-CSFR expression in some bladder cancers appears to be an early event during malignant transformation that increases beta1-integrin expression and adhesion and thereby may promote tissue invasion. 14992583_Thermodynamic data for the interaction of GCSF-GCSFR induced by GCSF binding suggest that the activated structure of GCSFR is a 2:2 complex structure. 15370243_reviewed the knowledge of the expression of G-CSFR and its role in the disorders of granulopoiesis, including myelodysplastic syndrome, and neutropenia in myelodysplastic patients 15644419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15644419_lifelong altered G-CSF response by the G-CSF-R_785Lys may render individuals susceptible to development of high-risk M 16033816_The Tyr 729 of the G-CSF-R is required for SOCS3-mediated negative regulation of G-CSF-R signaling and that the duration and intensity of G-CSF-induced Stat5 activation are regulated by two distinct mechanisms. 16492764_crystal structure of the signaling complex between human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) and a ligand binding region of GCSF receptor (GCSF-R), has been determined to 2.8 A resolution 16493051_Deleterious G-CSFR-mediated signaling events, such as aberrant Stat3 activation demonstrated in a subset of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients with poor prognosis, could be exploited for the treatment of AML patients. 16985178_CSF3R nonsense mutations (10 new) in SCN at 17 sites lead to a loss Tyr residues in the intracellular domain of the receptor. CSF3R mutation is an early event in leukemogenesis that has to be accompanied by as yet undefined cooperating molecular events 16985178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17024119_single-nucleotide polymorphism (Glu785Lys) is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia with multlineage dysplasia 17047971_The observed up-regulation of G-CSF receptors towards a role in the pathophysiology of human ischemic stroke. 17494858_that mutations of CSF3R may provide the 'activated tyrosine kinase signal' that is thought to be important for leukemogenesis. 17572226_The G-CSF/G-CSFR autocrine/paracrine signaling loop significantly promotes survival and growth of bladder cancer cells. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18536571_REVIEW: Congenital neutropenia patients with acquired CSF3R mutations define a group with high risk for development of leukemia; discussion of possible pathomechanism 18923646_results indicate ubiquitination required for regulation of G-CSFR-mediated proliferation & cell survival; mutation disrupting G-CSFR ubiquitination induce aberrant signaling & proliferative response to G-CSF; this may contribute to leukemic transformation 19099633_There was no significant difference in expression rate of G-CSFR on CD34+ cells between aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and controls. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453968_Data show that a lysine within the membrane-proximal region of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor is indispensable for ubiquitination and lysosomal sorting of the receptor. 19620628_identify an autosomal mutation in the CSF3R gene in a family with a chronic neutrophilia. This T617N mutation energetically favors dimerization of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor transmembrane domain. 19794089_Two cases of X-linked neutropenia are reported that evolved to acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplasia, with acquisition of G-CSF receptor mutations. 19833857_RAS and CSF3R mutations in severe congenital neutropenia. 20237318_a possible role of G-CSF in malignant transformation, particularly in patients with neutropenia harboring mutations in the gene encoding the G-CSF receptor. 20471446_G-CSF-induced upregulation of MT1-MMP in hematopoietic cells and its enhanced incorporation into membrane lipid rafts contributes to proMMP-2 activation, which facilitates mobilization of HSPC. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20557950_Transgenic Fn14/TWEAK receptor pathway in a mouse model is adversely involved in inflammatory and ischemic brain disease associated with the strongest increase of the endogenous neuroprotective G-CSF and the G-CSF receptor system. 20654748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20654748_The results reported in this study suggest a role for CSF3R in the determination of bone density in women. 20696205_Data from rna interference of G-CSFR messenger RNA demonstrated the limited specificity of antibodies for HuG-CSFR expressed on the cell surface. 20819538_CD123+CD34+CD38- cells exhibited lower expression of G-CSF receptors, which might partly explain why MDS clone responds worse to G-CSF in vitro and in vivo. 21129254_Gemcitabine can enhance in vitro the expression rate of bone marrow G-CSFR in chronic myeloid leukemia patients at chronic or blastic phases. 21641233_Pretreatment of PMNs with IFN-gamma or G-CSF for a long-time (22 h)induced a significant lower fungal damage against biofilms compared with planktonic cells. 22146088_An acquired CSF3R mutation in an adult chronic idiopathic neutropenia patient who developed acute myeloid leukaemia. 22796466_CSF3R gene polymorphism plays a significant role in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells for transplantation. 23159284_Certain missense single nucleotide polymorphisms, especially which are placed in the conserved regions of G-CSFR may possess the capacity to influence the response to G-CSF treatment. 23508011_The stimulating factor 3 receptor mutation (CSF3R-T595I) found in acute myeloid leukemia patients was found to have ligand independent activation properties. 23656643_Mutations in CSF3R are common in patients with CNL or atypical CML and represent a potentially useful criterion for diagnosing these neoplasms. 23687340_A subpopulation of GCSFR positive neuroblastoma cells exhibit enhanced tumorigenicity and a stem cell phenotype. 23774674_findings show CSF3R somatic mutations can be identified in 4 percent of the patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML); these mutations, which affect distinct residues in CSF3R are frequently associated with mutations in ASXL1 gene and have a poor prognostic impact on overall and AML-free survival 23820376_Fbw7 together with GSK3beta negatively regulates G-CSFR expression and its downstream signaling. 23897249_In myelodysplastic syndromes, altered CD114 distribution was more informative than density changes. In CML, CD114 density was significantly decreased on early blasts and expression was essentially limited to late blasts. 24081659_Mice transplanted with human CSF3R T618I-expressing hematopoietic cells developed a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by overproduction of granulocytes and granulocytic infiltration of the spleen and liver, which was uniformly fatal. 24403076_Thr-615 and Thr-618 sites of membrane-proximal mutations are part of an O-linked glycosylation cluster. Mutation at these sites prevents O-glycosylation of CSF3R and increases receptor dimerization. 24445868_concurrent CSF3R and SETBP1 mutations are associated with Chronic neutrophilic leukemia. 24523240_The detection of both RUNX1 and CSF3R mutations could be used as a marker for identifying Congenital neutropenia patients with a high risk of progressing to leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes. 24574781_The expression of G-CSFR before preoperative irradiation may predict the radiosensitivity of rectal cancer. 24614839_CSF3R T618I mutation as a disease-specific marker of atypical CML post allo-SCT in two patients. 24746896_frequency of CSF3R mutations is highly prevalent among acute myeloid leukemia patients secondary to severe congenital neutropenia compared to de novo AML. 24753537_this study describes a novel genetic Severe congenital neutropenia type in 2 unrelated families associated with recessively inherited loss-of-function mutations in CSF3R, encoding the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor. 25316523_mutation analysis of CSF3R, SETBP1 and CALR should be included in the diagnostic criteria for chronic neutrophilic leukemia 25404019_study to see if the CSF3R p.T618I mutation was present in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and solid tumors of Korean patients; data revealed that CSF3R p.T618I mutation occurred in an AML with myelodysplasia-related changes and a refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation 25533830_the incorporation of CSF3R mutation testing can be a useful point-of-care diagnostic to evaluate the presence of a clonal myeloid disorder, as well as providing the potential for genetically informed therapy. 25666388_In conclusion, rhCSF3 can promote melanocyte proliferation through CSF3R without affecting tyrosinase activity 25708716_CSF3R polymorphisms are associated with chronic neutrophilic leukemia. 25730818_The leukemogenic potential of G-CSFRIV is associated with the Stat5-dependent dysregulation of miR-155 and the target genes of this miRNA. 25850813_The SETBP1 and ASXL1 mutations have pathogenetic roles in CSF3R-mutated chronic neutrophilic leukemia. 25858548_No CSF3R mutations were found in cases of MDS, JMML or ET. The only mutation found in the CALR gene was a frameshift (p.L367 fs) in one ET patient. 25865944_A de novo CSF3R mutation was associated with the transformation of myeloproliferative neoplasm to atypical chronic myeloproliferative leukemia. 26324699_CSF3R mutations are associated with congenital neutropenia. 26475333_The Colony-Stimulating Factor 3 Receptor T640N Mutation Is Oncogenic, Sensitive to JAK Inhibition, and Mimics T618I 26956865_CSF3R mutations, mechanisms of mutations, and their contributions to the myeloid malignancies (Review) 27034432_Co-occurrence of mutations in CSF3R and CEBPA in a well-defined AML subset, which uniformly responds to JAK inhibitors; this paves the way to personalized clinical trials for this disease. 27056979_The quantitative methods used in this study have shown non-altered expression levels of different microglial markers (Iba-1, Cd11b and CD68), together with increased expression of IL6, IL10RA, colony stimulating factor 3 receptor and toll-like receptor 7 in the thalamus in FFI, which explains the seemingly contradictory results of the previous studies. 27143256_CSF3R mutations co-occur with CEBPA mutations in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. 27270496_biallelic CSF3R mutations were identified In the group of congenital neutropenia patients; CSF3R mutant clones are highly dynamic and may disappear and reappear during continuous granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) therapy. The time between the first detection of CSF3R mutations and overt leukemia is highly variable 27629739_Results indicate that granulocyte-colony stimulating factor receptor, tissue factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor bound vascular endothelial growth factor expression as well as their co-expression might influence breast cancer biology. 27984641_CSF3R T618I, ASXL1 G942 fs and STAT5B N642H trimutation co-contribute to a rare chronic neutrophilic leukaemia manifested by rapidly progressive leucocytosis, severe infections, persistent fever and deep venous thrombosis. 28005267_CSF3R expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28031554_a central role of enhanced Mapk signaling in CSF3R-induced leukemia. 28073911_This study proposes that acquisition of CSF3R mutations may represent a mechanism by which myeloid precursor cells carrying the ELANE mutations evade the proapoptotic activity of the Neutrophil Elastase mutants in SCN patients. 28209656_we report here for the first time changes in the allele frequencies of CSF3R-T618I and SETBP1-G870S with response to ruxolitnib as well as insights into the clonal evolution of CNL under selective pressure from ruxolitinib. 28209919_CSF3R T618I mutation is associated with Chronic neutrophilic leukemia. 28439110_we have expanded the region of the CSF3R cytoplasmic domain in which truncation or missense mutations exhibit leukemogenic capacity, which will be useful for evaluating the relevance of CSF3R mutations in patients and helpful in defining targeted therapy strategies. 28578910_our data demonstrates that E6AP facilitates ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of G-CSFR leading to attenuation of its downstream signaling and inhibition of granulocytic differentiation. 28652245_study aimed to identity and characterize novel CSF3R extracellular missense mutations from exome sequencing of leukemia patients; results show the structural and functional importance of conserved extracellular cysteine pairs in CSF3R 29305046_CSF3R genetic polymorphism occurred more frequently in the individuals with Septic Arthroplasty failure - Periprosthetic Joint Infection. 29338593_Expression and role of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (GM-CSFR) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSFR) on Ph-positive acute B lymphoblastic leukemia. 29501745_G-CSF-R is C-mannosylated at W318 and that this C-mannosylation has role(s) for myeloid cell differentiation through regulating downstream signaling. 29572350_expanded the regions of the CSF3R extracellular and transmembrane domains in which missense mutations exhibit leukemogenic capacity and have further elucidated the mechanistic underpinnings that underlie altered CSF3R expression, dimerization, and signaling activation 29920840_We identified two pathogenic and 10 loss-of-function (LOF) candidate variants, accounting for 4.74% (12 out of 253) of all the. In burden tests, rare missense variants in three genes (CSF3R, DSP, and LAMA3) were identified that have a statistically significant relationship with Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 29932212_An in-depth understanding of the interaction between these genetic alterations could facilitate a clearer understanding of the role of CSF3R mutations in acute myeloid leukemia development and may be used for disease classification, prognosis, and the development of targeted therapy. 30348809_analysis of germline variants in CSF3R at amino acid N610, which may be potently oncogenic and activate the receptor independently of its ligand GCSF 31041512_The prevalence of CSF3R mutations was high in AML patients with CEBPA(dm), which indicated a poor prognosis, and CSF3R mutations may be a new potential candidate for prognostically re-stratifying AML patients with CEBPA(dm). 31462738_these data are the first to demonstrate expression of the CSF3R-V3 splice variant in primary human myeloid cells and a role for SRSF2 in modulating CSF3R splicing 31692115_Next-generation sequencing reveals unique combination of mutations in cis of CSF3R in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. 31697825_CSF3R T618I mutation is associated with familial chronic neutrophilic leukemia. 31784538_Activating mutations in the granulocyte colony stimulating factor receptor (CSF3R), cooperate with loss of function mutations in the transcription factor CEBPA to promote acute myeloid leukemia development. 32329128_Promoter hypermethylation in CSF3R induces peripheral neutrophil reduction in benzene-exposure poisoning. 32821971_Cooperating, congenital neutropenia-associated Csf3r and Runx1 mutations activate pro-inflammatory signaling and inhibit myeloid differentiation of mouse HSPCs. 32966608_Loss-of-function mutations in CSF3R cause moderate neutropenia with fully mature neutrophils: two novel pedigrees. 33108454_Heterozygous germ line CSF3R variants as risk alleles for development of hematologic malignancies. 33511998_Effect of the unfolded protein response and oxidative stress on mutagenesis in CSF3R: a model for evolution of severe congenital neutropenia to myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia. 33606788_Colony-stimulating factor 3 signaling in colon and rectal cancers: Immune response and CMS classification in TCGA data. 33707412_CSF3R T618I mutant chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) defines a proliferative CMML subtype enriched in ASXL1 mutations with adverse outcomes. 34818692_The clinical characteristics and prognosis of Chinese acute myeloid leukemia patients with CSF3R mutations. 34975010_Differential Implications of CSF3R Mutations in t(8;21) and CEBPA Double Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 35274287_The prognostic factors in acute myeloid leukaemia with double-mutated CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha (CEBPAdm). 35941213_Alternatively spliced CSF3R isoforms in SRSF2 P95H mutated myeloid neoplasms. |
ENSMUSG00000028859 |
Csf3r |
42.343659 |
0.3600220468 |
-1.473843 |
0.387094027 |
13.656041 |
0.00021953384939286639944248935574222514333087019622325897216796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000570780274271394773635823760571383900241926312446594238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.6229575 |
6.3674042 |
71.1513553 |
11.6458861 |
| ENSG00000119547 |
9480 |
ONECUT2 |
protein_coding |
O95948 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator. Activates the transcription of a number of liver genes such as HNF3B. |
Activator;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the onecut family of transcription factors, which are characterized by a cut domain and an atypical homeodomain. The protein binds to specific DNA sequences and stimulates expression of target genes, including genes involved in melanocyte and hepatocyte differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9480; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; endocrine pancreas development [GO:0031018]; epithelial cell development [GO:0002064]; liver development [GO:0001889]; mesenchymal stem cell migration [GO:1905319]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; peripheral nervous system neuron development [GO:0048935]; positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell migration [GO:1905322]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001952]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
18288132_A CpG island proximal to ONECUT2 is frequently methylated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). 18418398_OC2 transcription factor is a direct target of T-bet in type-1 T-helper cells. 23472758_Mutations at the -5/-6 site of the F9 promotor account for the majority of hemophilia B Leyden cases and disrupt the binding of ONECUT1 and ONECUT2. 24402783_our data showed that transcript factor Onecut2 is involved in the EMT, migration and invasion of CRC cells; miR-429 inhibits the initiation of EMT and regulated expression of EMT-related markers 26547929_Data show that ONECUT2, IGF2BP1, and ANXA2 proteins were confirmed to be microRNA-9 (miR-9) targets and aberrantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 27756894_Bioinformatics-based prediction, combined with qRT-PCR analysis and Western blotting, identified Onecut2 and SIRT1 as the 2 prominent miR-9 target genes under the conditions tested. In this study, Onecut2 and SIRT1 were confirmed as miR-9 target genes, which will help future investigations to probe in greater detail the role of miR-9 in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. 29737581_These data indicated that OC-2 was an upstream regulator of VEGFA and silencing OC-2 could inhibit ovarian cancer angiogenesis and tumor growth. 30478421_Here we identify the transcription factor ONECUT2 (OC2) as a master regulator of AR networks in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). OC2 acts as a survival factor in mCRPC models, suppresses the AR transcriptional program by direct regulation of AR target genes and the AR licensing factor FOXA1, and activates genes associated with neural differentiation and progression to lethal disease. 30655535_ONECUT2 activates SMAD3, which regulates hypoxia signaling through modulating HIF1alpha chromatin-binding, leading neuroendocrine prostate cancers to exhibit higher degrees of hypoxia compared to prostate adenocarcinomas. 31049588_Data show that chromatin regions that contain the ONECUT motif were in- or lowly accessible in fibroblasts and became accessible after the overexpression of ONECUT1, ONECUT2 or ONECUT3. 31118200_Chemotherapy induced breast cancer cells to secrete multiple EV miRNAs, including miR-9-5p, miR-195-5p, and miR-203a-3p, which simultaneously targeted the transcription factor One Cut Homeobox 2 (ONECUT2), leading to induction of CSC traits and expression of stemness-associated genes. 31882655_ONECUT2 overexpression promotes RAS-driven lung adenocarcinoma progression. 32129880_ONECUT2 upregulation is associated with CpG hypomethylation at promoter-proximal DNA in gastric cancer and triggers ACSL5. 33015779_Up-regulated ONECUT2 and down-regulated SST promote gastric cell migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor growth in gastric cancer. 34365839_ONECUT2 which is targeted by hsa-miR-15a-5p enhances stemness maintenance of gastric cancer stem cells. 36178080_LncRNA TM1-3P Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis and Inflammation of Fibroblasts in Osteoarthritis through miR-144-3p/ONECUT2 Axis. |
ENSMUSG00000045991 |
Onecut2 |
171.707330 |
3.5328377267 |
1.820827 |
0.285741322 |
38.679167 |
0.00000000049951225886310714783348564229704426298273034490193822421133518218994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002449435528511448693457859101456179640177168721493217162787914276123046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
267.4261196 |
51.6186926 |
76.4388045 |
10.9142386 |
| ENSG00000119630 |
5228 |
PGF |
protein_coding |
P49763 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor active in angiogenesis and endothelial cell growth, stimulating their proliferation and migration. It binds to the receptor FLT1/VEGFR-1. Isoform PlGF-2 binds NRP1/neuropilin-1 and NRP2/neuropilin-2 in a heparin-dependent manner. Also promotes cell tumor growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21215706}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Heparin-binding;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a growth factor found in placenta which is homologous to vascular endothelial growth factor. Alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:5228; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005172]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to hormone stimulus [GO:0032870]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of mast cell chemotaxis [GO:0060754]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084] |
11810642_Maternal serum placenta growth factor concentration was elevated in Down syndrome pregnancies 11811792_Effect of placenta growth factor-1 on proliferation and release of nitric oxide, cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in human epithelial cells expressing the FLT-1 receptor 12091880_Placental growth factor promotes recruitment of VEGFR1(+) hematopoietic stem cells from a quiescent to a proliferative bone marrow microenvironment, favoring differentiation, mobilization and reconstitution of hematopoiesis. 12393422_increased inflammatory response, associated with more pronounced vascular enlargement, edema, and inflammatory cell infiltration in transgenic mice 12453985_Vitreous levels are altered in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy 12543719_This protein and its receptor VEGR-1 are novel therapeutic targets for angiogenic disorders (REVIEW) 12548207_placenta growth factor-to-human chorionic gonadotropin ratios were increased significantly in patients with persistent gestational trophoblastic disease 12548214_postulate that decreased placental growth factor production results in abnormalities of placental angiogenesis through direct and indirect effects on other vasculotropic growth factors 12673673_findings point to a role for PlGF in rapid restoration of tumor blood supply after treatment and thus, to enhanced likelihood of tumor regrowth 12714517_Placenta growth factor contributes to the inflammation observed in sickle cell disease and increases the incidence of vaso-occlusive events. 12808329_alteration of PlGF-2 and PlGFR-1 mRNA expressions in the placenta are related to the pathogenesis of pregnancy induced hypertension 13678785_paracrine role for mesenchynmal stem cell-derived PlGF in the angiogenesis and hematopoiesis that accompany BMP-2-induced bone formation. 14568550_Ang2, PIGF and VEGF-C play a role in promote endothelial survival and vascular remodeling by human cytotrophoblast. 14645176_findings suggest that production of placental growth factor is sensitive to the cyclic changes in ovarian steroids and may contribute to the pathogenesis of endometriosis 14684734_crystal structure of placental growth factor in complex with domain 2 of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 14741347_VEGF and PlGF induced expression of both full-length FosB mRNA and an alternatively spliced variant. 15126502_vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor-2 effects in dorsal root ganglion neurons are mediated via neuropilin-1 and cyclooxygenase-derived prostanoid production 15272021_a basis for understanding molecular recognition between PlGF-1 and VEGFR1 15516835_effect of VEGFA and PLGF on gene expression profiles obtained for HUVEC, dose effect, and variability between cells obtained from different individuals 15710418_vascular endothelial growth factor induced the production of PlGF protein 15886253_In contrast to preeclampsia, sFlt-1 does not appear to contribute substantially to decreased circulating free PlGF in small for gestational age pregnancies in the absence of a maternal syndrome 15938782_Altered expression of Fas, FasL and PGF in trophoblasts of placenta influence the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 16005848_These findings are consistent with the idea that the chemotactic effect of VEGF-A on mesenchymal progenitor cells (MPC) is mediated via VEGFR-1, and that VEGF-A and PlGF-1, have a functional role for recruitment of osteoprogenitor cells. 16146532_growth stimulation of ALL cells by PlGF was confirmed by the increase of S phase cells; the growth promoting effect of PlGF was cancelled by simultaneous addition of VEGFR1/Fc), but was not cancelled by VEGFR2/Fc 16635470_Correlation of placenta growth factor expression and placental perfusion suggests that placenta growth factor may contribute to assuring adequate vascular development/function of the placenta early in gestation. 16702473_Therapeutically administered human PIGF-1 demonstrates a desirable biological activity for promoting the growth of functionally relevant vasculature in mice. 16702604_Overexpression of VEGF but not PIGF exacerbated the lipopolysaccharide-mediated toxic effects, supporting a pathophysiological role for VEGF in mediating the sepsis phenotype. 16794222_Neither the hyperpermeability in response to simultaneous stimulation of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 nor VEGFR-1-mediated severe inflammation was associated with VEGF-E(NZ7)/PIGF-induced angiogenesis. 16839256_iodide at high concentration decreases the expression of the angiogenic factors VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and PG 16843105_The strong positivity for both PlGF and VEGF observed, implies that the t(10;14)(p13;q24) most likely involves PlGF, which may be one of the genes driving oncogenesis in these tumors. 16864484_The expression and localization of placenta growth factor (PlGF) within middle ear cholesteatoma were defined 17028267_These data suggest that mechanical stretch of bronchial airway epithelial cells induces iNOS expression and induces PIGF release in an erk1/2 activation-dependent manner. 17157858_placental growth factor-expression within human atherosclerotic lesions is associated with plaque inflammation and microvascular density 17187248_May be a potential regulation target for the control of diabetic retinal and macular oedema. 17593833_The plasma PIGF level in coronary artery disease group was significantly higher than that in the control group 17696935_PGF and VEGFR1 may have an important role in the pathogenesis of the neovascular response in cirrhosis. 17704140_Promoter is methylated, and methylation may be one of the mechanisms that contributes to the low PGF expression level in human lung and colorectal tumor tissues and cell lines. 17956952_Preeclampsia trophoblast cells produce more sEng, sFlt-1, and PlGF than normal TCs. Lowered oxygen conditions promote sEng and sFlt-1, but reduce PlGF, productions by PE TCs. 17964973_anlalysis of levels of circulating PIGF, SDF-1 and sVCAM-1 in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 17982238_sFlt-1 and PlGF and their ratio relative to one another may play a role in the development of preeclampsia 18006829_the ratio between the expression levels of two members of the VEGF family of angiogenic factors, PlGF-1 and VEGF-A, determines the overall angiogenic activity and, thus, the extent of tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth 18079407_Both placenta growth factor (PlGF-1) and VEGF-A (vascular endothelial growth factor-A ) can activate VEGFR-1-(vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1)dependent signaling pathways in primary human monocytes 18160678_a functional role for GCM1 contributing to constitutively high trophoblast PGF expression and is the first direct evidence of an oxygen-responsive, trophoblast-specific transcription factor contributing to the regulation of PGF expression. 18175241_patients destined to develop preeclampsia and those who delivered a small for gestational age neonate had lower plasma concentrations of placental grwoth factor (PlGF) than those with a normal pregnancy throughout gestation 18192038_Augmented release of PlGF is involved in the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy derived from chronic myocardial ischemia. 18258238_in angiogenesis,FGF-2(fibroblast growth factor 2)-mediated enhancement of Placental growth factor (PGF) expression was dependent on Vascular endothelial growth factor function 18264952_PlGF and sFlt-1 are present in the maternal and fetal fluid compartments in very early pregnancy, and their distribution is consistent with their site of production and the local conditions of transport 18293205_PlGF is related to mean arterial pressure in pregnant women 18306920_PIGF is involved in the pathomechanism of preeclampsia and its maternal serum concentration decreases significantly in the course of the disease. 18411415_PlGF-induced expression of ET-1 and its cognate ET-BR receptor occur via activation of HIF-1 alpha, independent of hypoxia. 18421240_The ARPE19 human junctions in culture are modulated by VEGF through VEGFR-1 but not through VEGFR-2. 18466718_Antibodies to PIGF may possibly be used as angiogenesis inhibitors. 18566591_PlGF concentrations were not different in preeclamptic smokers compared to nonsmokers 18615591_PlGF directly regulates the motility of human lung cancer cells and that this regulation critically dependent on ROCK-1 18805052_Gene expression revealed up-regulation of pro-angiogenic (PGF), anti-apoptotics (BAG-1, BCL-2), heart development (TNNT2, TNNC1) and extracellular matrix remodelling (MMP-2, MMP-7) genes in SM. 18927470_PlGF may be most strongly associated with long-term prediction of coronary disease in women, consistent with a potential role in early plaque formation and growth. 18945963_PlGF-mediated increased FLAP mRNA expression occurred via activation of phosphoinositide-3 (PI-3) kinase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, and hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha). 19010294_increased PlGF concentrations in the marrow of sickle cell patients may protect erythroid progenitors from cytokine-induced inhibition of colony formation 19022893_Findings suggest that MTF-1 is involved in hypoxia-dependent regulation of PlGF in trophoblast-derived cells. 19135290_In normotensive pregnancies, increasing maternal age was associated with a more antiangiogenic profile, including lower PlGF concentrations. 19165674_Women with gestational proteinuria showed a significantly lower sFlt1:PlGF ratio and higher PlGF level than those with preeclampsia. 19180491_Our data suggest that enhanced expression of PlGF and flt-1 may contribute to rheumatoid inflammation by triggering production of proinflammatory cytokines. 19201345_Human donor myocardium and biopsies from allografts without fibrin deposits express PIGF. 19293668_Increased circulating placental growth factor during percutaneous coronary intervention is associated with applied radiocontrast agent. 19505392_Placenta growth factor is a survival factor for human malignant mesothelioma cells. 19508152_Study suggests that AFS cells acquire endothelial cell characteristics when stimulated by growth factors and shear force, and produce angiogenic factors (VEGF, PGF, and hepatocyte growth factor [HGF]) in response to hypoxia. 19602778_Treatment with recombinant placental growth factor (PlGF) enhances both angiogenesis and arteriogenesis and improves survival after myocardial infarction. 19657001_There is increased expression of the PLGF isoforms in human colorectal cancer. 19658040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19712973_In contrast to the effects of hypoxia on PIGF expression in other cells, hypoxia suppresses transcription of PIGF in trophoblasts. Regulation of PIGF transcription under hypoxic conditions is independent of HIF-1. 19845534_PlGF may participate in both tumor-associated angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis of cervical carcinogenesis. 19956853_Loss of LI-cadherin results in up-regulation of MTF-1 and PlGF, thereby regulating angiogenesis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 20027339_A significant relationship between serum PlGF level and maximum tumor size (p=0.008) was detected in osteosarcoma. 20040765_Significantly higher levels of PlGF in sickle cell disease patients with pulmonary hypertension but observed no association of PlGF with the frequency of acute pain episodes or history of acute chest syndrome. 20043119_PLGF isoforms PLGF-1 and PGF-2 and indeed their receptor neuropilin, have an aberrant pattern of expression and high levels of the PLGF-1 and neuropilin are linked to a poor prognosis. 20091685_We found that the higher mean placenta growth factor (PlGF) labeling index was significantly associated with the progression and prognosis of 100 specimens of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 20097868_Data demonstrate that NFAT1 mediates PlGF-induced myelomonocytic cell recruitment via the induction of TNF-alpha. 20133349_Plasma levels of SDF-1 and PlGF were significantly elevated in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome than in controls, regardless of the arterial/venous nature of the thrombosis 20137369_Both IL-18 and PLGF are biomarkers for vulnerable plaques and helpful to predict vulnerable plaque. 20149032_plasma levels of PGF are decreased in pregnant women with gestational hypertension. 20301202_placental growth factor levels were significantly decreased in pregnancies with trisomy 21 20335221_Data suggest that strategies that block PlGF signaling may be therapeutically beneficial. 20351105_Placenta growth factor (PlGF) is a novel inducer of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in sickle cell disease 20451352_PLGF is involved in the development of skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20500895_contributes to atherosclerosis; inducable by Angiotensin II in vascular endothelium and smooth muscle cells 20509158_Low levels of first trimester PlGF provide a good indicator of small for gestational age complications and some hypertensive disorders. 20515481_FLT1 and its ligand PGF are expressed in myxoid liposarcomas as an indirect downstream effect of FUS-DDIT3. 20521248_high peritumoral PlGF expression is associated with tumor recurrence and survival after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20921624_Data identify the pro-proliferative VEGF family member placental growth factor (PGF) as an aldosterone-regulated vascular mineralocorticoid receptors target gene in mice and humans. 20948996_pattern of elevated concentrations of sFlt1 and sEng, and low PlGF in high-risk pregnant subjects who develop preeclampsia is similar to that reported in low-risk pregnant women 21062661_Eclampsia is associated with lower circulating concentrations of PlGF than normal pregnancy but with similar concentrations to severe preeclampsia. 21123739_Endothelial cell-released H2O2 acts as a positive regulator of placenta growth factor gene and protein expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. 21175428_PlGF-induced PAI-1 expression at early time points is post-transcriptionally regulated by two miRNAs, miR-30c and miR-301a. 21215706_Host-produced HRG inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by skewing tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) polarization away from the M2- to a tumor-inhibiting M1-like phenotype. Skewing of TAM polarization by HRG relies substantially on downregulation of PlGF. 21384313_Case Report: suggest that PlGF may play some role in the tumorigenesis of pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. 21401353_serum and urine levels increased in patients with decreased kidney function 21408222_This is the first demonstration that sustained intraocular PGF production induces vascular and retinal changes similar to those observed in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. 21448460_Maternal serum sFlt-1 and PlGF are markedly decreased in threatened miscarriage patients. 21501325_role of PlGF in placentation: Data suggest that in some women with habitual miscarriage, antagonism of beta2-GPI by autoantibodies against beta2-GPI suppresses PlGF production in trophoblasts and causes failure of placenta formation/function. 21534854_Women who developed preeclampsia had lower serum PlGF levels but normal sFlt-1 levels in the first trimester. 21568945_A longitudinal study demonstrates how placental growth factor fluctuates throughout normal pregnancy and postpartum. 21703189_Overexpression of miR-125b in HCC cells decreased PIGF expression, and altered the angiogenesis index. Furthermore, modulation of miR-125b also distorted expression of MMP-2 and -9, the mediators of enzymatic degradation of the extracellular matrix. 21709213_efficacy of anti-PlGF treatment strongly correlates with VEGFR-1 expression in tumor cells, but not with antiangiogenesis 21715541_Combined measurement of sFlt-1 and PlGF levels can differentiate normal from failed pregnancies, and sFlt-1/PlGF ratio can also discriminate ectopic pregnancy from missed abortion. 21717483_Serum PlGF is an acceptable marker in first trimester screening for early-onset pre-eclampsia but a poor marker in screening for intra-uterine growth restriction. 21827221_plasma concentration significantly lower in patients with mild preeclampsia who subsequently developed severe preeclampsia than in those who remained stable until term 21867402_Patients with late-onset preeclampsia (PE) and placental underperfusion had a lower median plasma concentration of PlGF, plasma PlGF/sVEGFR-1 ratio and plasma PlGF/sEng ratio than those with late-onset PE without placental underperfusion lesions. 21876459_There is no association between HIF1-a and PlGF in any melanoma type. Hypoxia, in the expression of HIF1-a, plays a key role in melanoma progression; it activates VEGF secretion, which induces angiogenesis and metastasis. Role of PlGF seems to be limited. 21939291_low serum level associated with medically-indicated preterm delivery 22000672_Preeclampsia patients had a significantly increased sFlt-1/placental growth factor ratio as compared with controls. Time to delivery was significantly reduced in women with preeclampsia in the highest quartile of the sFlt-1/placental growth factor ratio. 22055338_PlGF in maternal circulation may identify placental intrauterine growth restriction antenatally. 22079325_augmentation of brain Placental growth factor is associated with development of epilepsy. 22103490_Novel hypotheses involving altered bioavailability of VEGF isoforms resulting from reduced or bound PlGF, or increased sVEGFR1 increasing biological activity of circulating plasma, could be tested. 22170453_PlGF-1 functions similarly in inflamed synovium and in the placenta. It is related to vessel formation and, in osteoarthritis patients, to androgen/estrogen conversion. 22270936_PlGF, but not VEGF-A was associated with axillary lymph node status and tumor grade was only associated with VEGF-A. 22286035_In trisomy-21 pregnancies the median serum PLGF, adjusted for gestational age, maternal weight, racial origin, smoking status and method of conception, was significantly reduced, and this did not change significantly with gestational age. 22385934_Letter: Changes in VEGF/PlGF plasma levels differ in sepsis and organ failure. 22386962_PGF mRNA was reduced in placentae from late pre-term births, from pre-eclamptic pregnancies, and pregnancies complicated by gestational hypertension. 22418953_Although we have found no significant change in the second trimester levels of PlGF in trisomy 21 pregnancies, there remains wide disagreement within the literature on the behaviour of this marker during pregnancies of this syndrome. 22446996_Higher concentration of PlGF after ACS is associated with long-term risk of recurrent cardiovascular events independent of traditional risk factors. 22498340_CD105 and placental growth factor--potent prognostic factors in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. 22647886_Data suggest that identifying women with consistently low plasma placental growth factor (PGF) during pregnancy may provide a greater understanding of preeclampsia pathophysiology and may provide more focused research and clinical activities. 22675957_statistically significant decrease compared to physiological gestation in spontaneous and threatened abortions (p |
ENSMUSG00000004791 |
Pgf |
11.335233 |
0.1438699319 |
-2.797163 |
0.613981478 |
21.260728 |
0.00000400860591098584606969046015279012351584242423996329307556152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013198086827158396505156601197228383171022869646549224853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9143730 |
1.3072124 |
20.3278932 |
5.4487535 |
| ENSG00000119636 |
80127 |
BBOF1 |
protein_coding |
Q8ND07 |
FUNCTION: Basal body protein required in multiciliate cells to align and maintain cilia orientation in response to flow. May act by mediating a maturation step that stabilizes and aligns cilia orientation. Not required to respond to planar cell polarity (PCP) or flow-based orientation cues (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in motile cilium assembly. Predicted to be located in ciliary basal body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80127; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; motile cilium assembly [GO:0044458] |
|
ENSMUSG00000057265 |
Bbof1 |
10.922618 |
0.1836748863 |
-2.444774 |
0.554440620 |
20.051406 |
0.00000753880992019247057580244239516353843555407365784049034118652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024017447533356545136392842798578328711300855502486228942871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1198613 |
1.2620364 |
17.1735280 |
4.3707965 |
| ENSG00000119638 |
91754 |
NEK9 |
protein_coding |
Q8TD19 |
FUNCTION: Pleiotropic regulator of mitotic progression, participating in the control of spindle dynamics and chromosome separation. Phosphorylates different histones, myelin basic protein, beta-casein, and BICD2. Phosphorylates histone H3 on serine and threonine residues and beta-casein on serine residues. Important for G1/S transition and S phase progression. Phosphorylates NEK6 and NEK7 and stimulates their activity by releasing the autoinhibitory functions of Tyr-108 and Tyr-97 respectively. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12840024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14660563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19941817}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Mitosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the NimA (never in mitosis A) family of serine/threonine protein kinases. The encoded protein is activated in mitosis and, in turn, activates other family members during mitosis. This protein also mediates cellular processes that are essential for interphase progression. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:91754; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
12101123_binds the Ran GTPase and regulates mitotic progression 12840024_Activated in mitosis, and activates nek6 and nek7 kinase. 14660563_mediates certain cellular processes, which are ultimately essential for interphase progression 17443675_The disruption of a nuclear function of NEK9 by adenovirus E1A-associated cellular proteins is reported. 19941817_The activity of Nek6 and Nek7, but not the tyrosine mutant, is increased by interaction with the Nek9 noncatalytic C-terminal domain, suggesting a mechanism in which the tyrosine is released from its autoinhibitory position. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21454704_DYNLL/LC8 protein controls signal transduction through the Nek9/Nek6 signaling module by regulating Nek6 binding to Nek9. 21642957_Nek9 is a Plk1-activated kinase that controls early centrosome separation through Nek6/7 and Eg5. 21735226_The interaction between the human NimA-like protein kinase Nek9 and the Helicobacter HcpC has been validated by ELISA and surface plasmon resonance. 22818914_Nek9 phosphorylates NEDD1 on Ser377 driving its recruitment and thereby that of gamma-tubulin to the centrosome in mitotic cells. 23482567_Structural analysis of LC8 with both Nek9 peptides, together with different biophysical experiments, explains the observed diminished binding affinity of Nek9 to LC8 upon phosphorylation on Ser(944) within the Nek9 sequence 23665325_NEK9 inhibition represents a novel anti-cancer strategy by induction of mitotic catastrophe via impairment of spindle dynamics, cytokinesis and mitotic checkpoint control. 25131192_The findings demonstrate that a novel NEK9 network regulates the growth of cancer cells lacking functional p53. 26522158_The C-terminal domain of Nek9 activates Nek7 through promoting back-to-back dimerization. 26676776_Overall, these results highlight the complexity of virus-host interactions and identify a new role for the cellular protein Nek9 during human adenovirus infection, suggesting a role for Nek9 in regulating p53 target gene expression. 26908619_Recessive NEK9 mutation is associated with lethal skeletal dysplasia. 26956052_High expression level of NEK9 is associated with recurrence in glioblastoma. 27153399_Somatic Mutations in NEK9 Cause Nevus Comedonicus. 28630147_Signaling cascade of the NIMA-related kinases (Neks) Nek6, Nek7, and Nek9 is required for the localization and function of two kinesins essential for cytokinesis, Mklp2 and Kif14 to properly coordinate cytokinesis. 29276125_Eg5 localization and centrosome separation in prophase depend on the nuclear microtubule-associated protein TPX2, a pool of which localizes to the centrosomes before nuclear envelope breakdown. This localization involves the kinase Nek9, which phosphorylates TPX2 nuclear localization signal preventing its interaction with importin and nuclear import. 29472518_This study supports a role for NEK9 and MAP2K4 in mediating buparlisib resistance and demonstrates the value of unbiased omic analyses in uncovering resistance mechanisms to targeted therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. 31857374_NIMA-related kinase 9-mediated phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated LC3B protein at Thr-50 suppresses selective autophagy of p62/sequestosome 1. 32098687_Decreased Nek9 expression correlates with aggressive behaviour and predicts unfavourable prognosis in breast cancer. 32184261_EML4-ALK V3 oncogenic fusion proteins promote microtubule stabilization and accelerated migration through NEK9 and NEK7. 33500736_NEK9, a novel effector of IL-6/STAT3, regulates metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting ARHGEF2 phosphorylation. 33664869_The short isoform of PRLR suppresses the pentose phosphate pathway and nucleotide synthesis through the NEK9-Hippo axis in pancreatic cancer. 33819539_Three novel pathogenic NEK9 variants in patients with nevus comedonicus: A case series. 35935324_Study on the Expression of lncRNA ATB and Nek9 in Breast Cancer Patients Based on Q-PCR Technology and Its Relationship with the Disease. 36266340_NIMA-related kinase 9 regulates the phosphorylation of the essential myosin light chain in the heart. |
ENSMUSG00000034290 |
Nek9 |
701.785064 |
0.4997380393 |
-1.000756 |
0.182011340 |
29.707607 |
0.00000005023729914401420380918117185829741000446801990619860589504241943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000203485876884097070828102547974947089670649802428670227527618408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
466.5127880 |
59.2928341 |
941.3112776 |
86.2932187 |
| ENSG00000119669 |
64207 |
IRF2BPL |
protein_coding |
Q9H1B7 |
FUNCTION: Probable E3 ubiquitin protein ligase involved in the proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent degradation of target proteins (PubMed:29374064). Through the degradation of CTNNB1, functions downstream of FOXF2 to negatively regulate the Wnt signaling pathway (PubMed:29374064). Probably plays a role in the development of the central nervous system and in neuronal maintenance (Probable). Also acts as a transcriptional regulator of genes controlling female reproductive function. May play a role in gene transcription by transactivating GNRH1 promoter and repressing PENK promoter (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5EIC4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374064, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17334524, ECO:0000305|PubMed:29374064, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30057031}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Triplet repeat expansion;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:29374064}. |
This gene encodes a transcription factor that may play a role in regulating female reproductive function. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:64207; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; development of secondary female sexual characteristics [GO:0046543]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
17627301_C14orf4 encodes a transcriptional regulator that, acting within the neuroendocrine brain, contributes to controlling female reproductive function 30166628_These data support the causative role of truncating IRF2BPL variants in pediatric neurodegeneration and expand the spectrum of transcriptional regulators identified as molecular factors implicated in genetic developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. 31729144_IRF2BPL gene variants: One new case. 34102826_[Clinical features of epilepsy in children with IRF2BPL gene variation]. 34864472_Adult onset familiar dystonia-plus syndrome: A novel presentation of IRF2BPL-associated neurodegeneration. |
ENSMUSG00000034168 |
Irf2bpl |
420.809702 |
6.0335239119 |
2.593001 |
0.095674520 |
795.024379 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000065141078347370003109705445485136149432765412060308391448377103308088236992305674117419128586992556539869283708761697015036500878000720108284244939620557092 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000050339388293569697849816325056177902490289474066156722472073202671595827284762279078202391493187271741542270483600571500889884195489034765177687982650838909 |
Yes |
No |
734.1868275 |
42.0264795 |
122.5964404 |
6.1555129 |
| ENSG00000119686 |
55640 |
FLVCR2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPI3 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an importer of heme. Also acts as a transporter for a calcium-chelator complex, important for growth and calcium metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20823265}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the major facilitator superfamily. The encoded transmembrane protein is a calcium transporter. Unlike the related protein feline leukemia virus subgroup C receptor 1, the protein encoded by this locus does not bind to feline leukemia virus subgroup C envelope protein. The encoded protein may play a role in development of brain vascular endothelial cells, as mutations at this locus have been associated with proliferative vasculopathy and hydranencephaly-hydrocephaly syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:55640; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; heme transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015232]; heme export [GO:0097037] |
20206334_Direct sequencing of candidate genes within the target interval in chromosome 14q24.3 revealed five different germline mutations in FLVCR2 in five families with Fowler syndrome. 20690116_High-throughput sequence data identified mutations and a large deletion in the FLVCR2 gene casuing lethal cerebral vasculopathy. 20823265_Results report the cellular function of FLVCR2 as an importer of heme. 25131804_FLVCR2 mutation is associated with Hydranencephaly. 25677735_Mutations in FLVCR2 associated with Fowler syndrome and survival beyond infancy 25906927_Mutations in FLVCR2 gene are responsible for Proliferative vasculopathy and Hydranencephaly-hydrocephaly syndrome. FLVCR2 transporter is gatekeeper for the controlled entry of calcium into cell, and involves the regulation of calcium metabolism. 32333401_Expanding the clinical spectrum of Fowler syndrome: Three siblings with survival into adulthood and systematic review of the literature. 32901920_Variability of non-lethal Fowler syndrome phenotype associated with FLVCR2 variants. 32973183_MFSD7C switches mitochondrial ATP synthesis to thermogenesis in response to heme. |
ENSMUSG00000034258 |
Flvcr2 |
37.310844 |
0.4000281724 |
-1.321826 |
0.391535711 |
11.157844 |
0.00083677118839164499157490251235458345036022365093231201171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001978017735531819362021499486559150682296603918075561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.6127955 |
4.9714733 |
49.1055893 |
8.7178102 |
| ENSG00000119699 |
7043 |
TGFB3 |
protein_coding |
P10600 |
FUNCTION: Transforming growth factor beta-3 proprotein: Precursor of the Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-3 (TGF-beta-3) chains, which constitute the regulatory and active subunit of TGF-beta-3, respectively. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202}.; FUNCTION: [Latency-associated peptide]: Required to maintain the Transforming growth factor beta-3 (TGF-beta-3) chain in a latent state during storage in extracellular matrix (By similarity). Associates non-covalently with TGF-beta-3 and regulates its activation via interaction with 'milieu molecules', such as LTBP1 and LRRC32/GARP, that control activation of TGF-beta-3 (By similarity). Interaction with integrins results in distortion of the Latency-associated peptide chain and subsequent release of the active TGF-beta-3 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17125}.; FUNCTION: Transforming growth factor beta-3: Multifunctional protein that regulates embryogenesis and cell differentiation and is required in various processes such as secondary palate development (By similarity). Activation into mature form follows different steps: following cleavage of the proprotein in the Golgi apparatus, Latency-associated peptide (LAP) and Transforming growth factor beta-3 (TGF-beta-3) chains remain non-covalently linked rendering TGF-beta-3 inactive during storage in extracellular matrix (By similarity). At the same time, LAP chain interacts with 'milieu molecules', such as LTBP1 and LRRC32/GARP that control activation of TGF-beta-3 and maintain it in a latent state during storage in extracellular milieus (By similarity). TGF-beta-3 is released from LAP by integrins: integrin-binding results in distortion of the LAP chain and subsequent release of the active TGF-beta-3 (By similarity). Once activated following release of LAP, TGF-beta-3 acts by binding to TGF-beta receptors (TGFBR1 and TGFBR2), which transduce signal (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01137, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04202, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17125}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Methylation;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate a latency-associated peptide (LAP) and a mature peptide, and is found in either a latent form composed of a mature peptide homodimer, a LAP homodimer, and a latent TGF-beta binding protein, or in an active form consisting solely of the mature peptide homodimer. The mature peptide may also form heterodimers with other TGF-beta family members. This protein is involved in embryogenesis and cell differentiation, and may play a role in wound healing. Mutations in this gene are a cause of aortic aneurysms and dissections, as well as familial arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia 1. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:7043; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; transforming growth factor beta complex [GO:0099126]; transforming growth factor beta ligand-receptor complex [GO:0070021]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transforming growth factor beta binding [GO:0050431]; type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034713]; type II transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005114]; type III transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034714]; aging [GO:0007568]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; detection of hypoxia [GO:0070483]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; embryonic neurocranium morphogenesis [GO:0048702]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; frontal suture morphogenesis [GO:0060364]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904706]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; ossification involved in bone remodeling [GO:0043932]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of tight junction disassembly [GO:1905075]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to laminar fluid shear stress [GO:0034616]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; salivary gland morphogenesis [GO:0007435]; secondary palate development [GO:0062009]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; uterine wall breakdown [GO:0042704]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11384957_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11754469_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11776328_PAI-1 gene activation by TNF-alpha apparently is yet to be defined for the location of the response element and/or the signaling pathway, while TGF-beta is the most important cytokine for PAI-1 transcriptional activation through its 5' proximal promoter. 11850637_crystal structure of the human TbetaR2 ectodomain--TGF-beta3 complex 11969342_downregulation of TGF-beta 3 expression found in pre-eclamptic umbilical cord may contribute to the abnormal structure and mechanical properties seen in these pathological umbilical cords 12021923_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 isoforms are produced by chondrosarcomas and could have a potential role as autocrine growth stimulators in these neoplasms 12060054_present in diabetic foot ulcer 12168782_TGFbeta3 may have a role in mediating progesterone- and progestogen-induced endometrial differentiation 12171249_TGFbeta3 regulates GM-CSF induced human myelopoiesis 12221089_determination of the importance of conformational entropy in the interaction of TGF-beta3 with the receptors 12410804_children with active celiac disease have an altered expression of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3 in the small intestine 12432546_The role of TGF-beta1 and -beta3 in generating a high TIFP was investigated in xenografted experimental anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) derived from the human ATC cell line 12489185_investigated TGF-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 latency-associated peptides (LAP)expression in sound and carious human teeth 12607775_TGF-beta3 expression in peritoneal fibroblasts was not affected by hypoxia or TGF-beta1 stimulation 12651933_mutations make a contribution to clefts in South American populations 12652527_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12733956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12733956_positively associated with cleft lip and/or palate with hypodontia outside the cleft region 12772773_Glucocorticoids significantly inhibited TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 production and reduced expression of the up-regulated TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 mRNA induced by exogenous TGF-beta1, -beta2, or -beta3 12911534_All three TGF-beta isoforms have fibrogenic effects on renal cells. TGF-beta2 and TGF-beta3 effects may be partially mediated by TGF-beta1. Blockade of all isoforms together may yield best therapeutic effect in reducing renal fibrosis. 14659070_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15017149_NMR analysis of the extracellular domain of the human TGFbeta type II receptor in complex with monomeric TGFbeta3 15155569_regulation of TGF-beta3 promoter activity by HIF-1 represents a mechanism for trophoblast differentiation during hypoxia. 15639475_We identified TGFbeta3 as the disease gene involved in ARVD1. 15896309_Human TGF-beta2 but not human TGF-beta1, or -beta3 promotes cardiac myocyte differentiation from mouse ES cells. 15924806_No association was found between TGF-beta3 gene polymorphisms essential hypertension in Chinese. 15924806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16210002_TGF-beta 3 may promote endometrial tissue repair through the inhibition of the proliferation, expansion, and migration of endometrial stromal cells, and through stimulation of contraction of the collagen gel matrix by these cells. 16247549_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16549496_Depletion of TGFbeta3 from serum converts serum to a plasmalike reagent. 16778279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16781676_Hunchback sequence binding protein may function as a TGF-beta3 gene transcriptional regulator and may be expressed in a cell type-specific manner. 16930538_CD24 regulates E-cadherin and TGF-beta3 expression in cultured oral epithelial cells 17225872_Altered crosstalk between RA, GABAergic, and TGF-beta signaling systems could be involved in human cleft palate fibroblast phenotype. 17272867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17401695_BMP-2, TGF-beta2, and TGF-beta3 are involved in bone formation in heterotopic ossifications. 17671384_TGF-beta3 may play a role as regulator of variety of cellular events during HELLP syndrome. High local expression may be responsible for remodeling of the placental structure resulting in dysfunction of maternal-fetal circulation. 17673689_collagen I induces EMT in lung cancer cells by activating autocrine TGF-beta3 signaling. Epidermal growth factor also seems to initiate EMT via a TGF-dependent mechanism. 18039789_TGF-beta2 and -beta3 are differentially expressed during the menstrual cycle and regulated by progesterone in epithelial vs stromal cells. 18049952_There is a significantly elevated concentration of TGF-beta3 in PE eyes 18078367_TGF-beta 3 is closely related to mineral maturation matrix in human developing teeth 18080134_TGF-beta 3 was detected from the canalisation stage of the salivary gland, being weakly expressed on ductal cells, and it was the only factor detected on myoepithelial cells. 18156205_oxygen regulates the placental expression of endoglin via TGF-beta 3 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18243111_TGF-beta complexes assemble cooperatively through recruitment of the low-affinity (type I) receptor by the ligand-bound high-affinity (type II) pair. 18293167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18480962_Data support the involvement of TGFB3 in the development of oral clefts in patients among 204 triads of central European origin. 18480962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498721_study found different expression of the TGF-beta1, -2 and -3 isoforms in the human corneal epithelium; such differential expression of TGF-betas suggests that each of them may play a specific role in corneal tissue 18505915_the TGF-beta1-2-3/Smad3 pathway has a role in mediating ovarian oncogenesis by enhancing metastatic potential 18698632_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18799618_Snail and Slug promote formation of beta-catenin-T-cell factor (TCF)-4 transcription complexes that bind to the promoter of the TGF-beta3 gene to increase its transcription. 18950289_BMP-2 enhances TGF-beta3-mediated chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stromal cells. 19062040_TGF-beta cytokines may be involved in postsurgical adhesion formation 19107876_the combination of daily loading and TGFbeta(3) administration produced superior osteocyte survival at the core centres when compared to loading or TGFbeta alone. 19161338_High-affinity binding of TGF-beta1/3 to TGF-betaRII is primarily due to hydrogen bonding between Arg25 and 94 of TGF-beta1/3, and Glu119 and Asp32 of TbetaR-II. Arg25 and 94 are substituted by Lys in TGF-beta2, which binds with low affinity to TbetaR-II. 19212830_Report expression of decorin in esophageal cancer in relation to the expression of three isoforms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1, -beta2, and -beta3) and matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. 19231643_Overexpression of TGF-beta3 and extracellular matrix proteins may represent antecedent tissue repair and therefore may be considered a significant event in the resolution of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis lesions 19328471_TGF-beta3 induced a molecular phenotype in myometrial cells that was similar to leiomyoma cells, with elevated production of extracellular matrix (ECM)-related genes and decreased production of ECM degradation-related genes. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19396528_6 breast cancer studies show a negative correlation between TGF-beta3 mRNA levels & increasing tumor grade. High expression of TGF-beta3 mRNA is associated with good outcomem suggesting a protective role. Review. 19432813_TGF-beta type I receptor inhibitor LY364947 blocked the up-regulation on TGF-beta(1) and TGF-beta(3) production stimulated by mechanical load, and also blocked the chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19628198_A fetal TGF-beta3 polymorphism (rs1146414) is associated with pregnancy-induced hypertension in a predominantly Hispanic population. 19628198_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19651533_Studies indicate that TNFalpha and TGFbeta3 are present at high levels in the microenvironment of the seminiferous epithelium during spermatogenesis. 19656717_Studies indicated that TGF-beta3 may actually play a protective role against tumourigenesis in a range of tissues including the skin, breast, oral and gastric mucosa. 19700613_Aberrant production of excessive and disorganized extracellular matrix in uterine leiomyoma involves the activation of the TGF-beta3 signaling pathway and excessive production of GAG-rich versican variants. 19787410_TGF-beta3 may regulate taste epithelial cell homeostasis through controlling cell proliferation. 19897194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937272_Our data provide evidence that TGF-beta signaling patterns vary by age and pathologic features of prognostic significance including ER expression. 20082468_MTHFR, TGFB3, and TGFA polymorphisms have roles in non-syndromic cleft lip and cleft palate in different regions of China 20082468_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20083094_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20142847_TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, and TGF-beta3 mRNAs were detected in both normal and pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (PBK) corneas. 20170386_Allelic and haplotypic associations implicate a possible role of TGFB3 in nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Chilean population. 20170386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237132_CYR61 and NOV are regulated by HIF-1alpha and TGF-beta3 in the trophoblast cell line JEG3, and their enhanced secretion could be implicated in appropriate placental invasion. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20407224_TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3 similarly enhance terminal differentiation in an in vitro hypertrophy model of chondrogenically differentiating mesenchymal stem cells. 20408761_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497023_Results indicate that that levels of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3 mRNAs were significantly higher in lungs of chemical gas-injured patients. 20572854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20613589_TGF-B3 was upregulated in early and late osteogenesis in microarray and qRT analyses and demonstrated the largest increase in expression when compared with day 1. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736064_Mesenchymal stem cells and bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells can generate tendon-like tissue in 7 days mediated by transforming growth factor beta3. 20945347_TGFbeta1 and TGFbeta3 play separate yet complimentary roles in achieving cell cycle arrest and EMT/apoptosis and cell cycle arrest is a prerequisite for later cellular changes in palate development. 21041550_A susceptibility locus was identified on chromosome 14q24.3-31.2. The candidate functional gene is TGFB3. A suggestive linkage for mandibular prognathism in a Han Chinese pedigree. 21084396_Leiomyoma-secreted TGF-beta3 induces bone morphogenetic protein 2 resistance in endometrium by down-regulation of bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2, likely causing defective endometrial decidualization 21177256_MSX1 and TGF-beta3 are direct targets of FOXE1. 21305699_TGFbeta subtypes (1, 2 and 3) affect terminal differentiation of in vitro cultured hBMSCs differently 21352603_The restoration of the expression of TbetaRII and TbetaRIII in oral cancerous tissues may represent a novel strategy for the treatment of oral carcinoma. 21411746_Data show that TGF-beta pathways operate during ovarian fetal development, and fibrillin 3 is highly expressed at a critical stage early in developing human and bovine fetal ovaries. 21423151_These results provide evidence that the two TbetaRI:TbetaRII heterodimers bind and mediate TGF-beta3 signalling. 21611961_TGF-beta, besides acting as an inhibitor, also can, by dampening the noggin-mediated negative-feedback loop, enhance BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation. 21666950_study suggests that both combination medium, but better with the addition of TGF-ss3 could enhance BMSCs chondrogenesis in vivo, and promotes themaintenance of the chondrocyte phenotype 21823016_TGF-beta3 could be stably expressed in pcDNA3.1(+)-hTGF-beta3-transfected PSCs. 22143699_This study confirms the crucial role of TGF-beta3 in the fusion of palatal shelves during development and further, provides novel evidence of TGF-beta3 gene polymorphism in the etiology of nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate in Indian subpopulation 22191848_Significant statistical differences were found for genotype frequencies between tooth agenesis and TGFB3 control samples, as well as for allele and genotype frequencies between unilateral tooth agenesis and TGFB3 control samples. 22266274_We observed significant downregulation of Transforming Growth Factor beta 3 in women with recurrent miscarriage compared with controls. 22369552_involved in the modulation of epithelial barrier function by regulating assembly of tight junctions 22409215_analysis of genetic variants hints at the contribution of TGFB3 and MN1 in the aetiology of submucous cleft palate 22464821_The aim of the study was to determine temporal TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 gene expression profiles in the anterior lens capsule of paediatric patients with posttraumatic cataract. 22674391_Hypoxia may inhibit the invasion of human extravillous trophoblast cells through inducing the integrin switch from alpha1 integrin to alpha5 integrin and promoting TGFB3 expression. 22706080_TGF-beta3 isoform is a key agent in seminal plasma that signals induction of proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in cervical cells. 22795539_SOX9 gene plus heparinized TGF-beta 3 coated dexamethasone loaded PLGA microspheres induce chondrogenesis of hMSCs 22796605_IL-1B & TGFB3 synergistically activated MMP)-1, MMP-3,& MMP-10 gene expression in NSCLC cells via MAPK-dependent pathways. 22880017_These results highlight TGFbeta/5-HT signaling as a potent mechanism for control of biomechanical remodeling of atrioventricular cushions during development. 23023602_The GG genotype and G allele of TGF-beta 3 were significantly different in the patient group compared with the control. 23122986_These findings suggest human serum, FGF-2 and TGF-beta3 as possible candidates to support biological treatment strategies of AF defects. 23824657_Mutation in TGFB3 is associated with a syndrome of low muscle mass, growth retardation, distal arthrogryposis and clinical features overlapping with Marfan and Loeys-Dietz syndrome. 23968981_Shear stress of vascular endothelial cells induces TGF-beta3 signaling and subsequent activation of Kruppel-like factor 2 and NO, and represents a novel role for TGF-beta3 in the maintenance of homeostasis in a hemodynamic environment. 24053560_meta-analysis suggests that TGF-beta3 gene polymorphisms may contribute to NSCLP susceptibility, especially among Asian populations. 24056369_Transforming growth factor-beta3 (TGF-beta3) knock-in ameliorates inflammation due to TGF-beta1 deficiency while promoting glucose tolerance. 24306208_This study provides a comprehensive list of genes differentially expressed in the healing corneal epithelial cells of diabetic corneas and suggests the therapeutic potential of TGF-beta3 for treating corneal and skin wounds in diabetic patients. 24402195_Compared to controls, plasma levels of TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta2 were significantly lower in patients with recurrent VTE (p |
ENSMUSG00000021253 |
Tgfb3 |
152.038683 |
24.0639812231 |
4.588803 |
0.297295707 |
230.743593 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000041037265290714684883872397115873152969108653898655365452758793191801532911523581840548654287993484531527838363455186340203248028697669003150849675876088440418243408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009233384690410804543976027433562025705857678512914198830978501919090265199457492984233208026274057099271213558562429430906401102777114608954889263259246945381164550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
272.6883483 |
54.2982742 |
11.4154751 |
1.9023418 |
| ENSG00000119714 |
8111 |
GPR68 |
protein_coding |
Q15743 |
FUNCTION: Proton-sensing receptor involved in pH homeostasis. May represents an osteoblastic pH sensor regulating cell-mediated responses to acidosis in bone. Mediates its action by association with G proteins that stimulates inositol phosphate (IP) production or Ca(2+) mobilization. The receptor is almost silent at pH 7.8 but fully activated at pH 6.8. Also functions as a metastasis suppressor gene in prostate cancer (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12955148}. |
Amelogenesis imperfecta;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tumor suppressor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosylphosphorylcholine. The encoded protein is a proton-sensing receptor, inactive at pH 7.8 but active at pH 6.8. Mutations in this gene are a cause of amelogenesis imperfecta. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:8111; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; cellular response to pH [GO:0071467]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; negative regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045656]; osteoclast development [GO:0036035]; positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0035774]; positive regulation of osteoclast development [GO:2001206] |
12955148_ovarian cancer G-protein-coupled receptor 1 (OGR1), previously described as a receptor for sphingosylphosphorylcholine, acts as a proton-sensing receptor stimulating inositol phosphate formation 15665078_OGR1 was found to evoke strong pH-dependent responses as measured by inositol phosphate accumulation. 16087674_cAMP accumulation may occur through OGR1-mediated stimulation of the phospholipase C/cyclooxygenase/PGI(2) pathway 17728215_OGR1 is a novel metastasis suppressor gene for prostate cancer. OGR1's constitutive activity via G alpha(i) contributes to its inhibitory effect on cell migration in vitro. 18302504_OGR1/G(q/11)/phospholipase C/protein kinase C pathway regulates osteoblastic COX-2 induction and subsequent PGE(2) production in response to acidic circumstances 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20622109_acidic pH-induced vascular actions of aortic smooth muscle cells can be dissected to OGR1-dependent and -independent pathways: COX-2 expression, PGI(2) production, and MKP-1 expression are mediated by OGR1, but PAI-1 expression is not. 21740742_It indicated that OGR1 may be a tumor suppressor gene for ovarian cancer. 21907704_extracellular acidification induces CTGF production through the OGR1/G(q/11) protein and inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca(2+) mobilization in human airway smooth muscle cells. 22508039_OGR1 activation increased intracellular calcium in transfected HEK293 cells. 22835475_The involvement of ovarian cancer G-protein-coupled receptor 1 in acidic extracellular environment may be an underlying mechanism responsible for bone pain in osteoporosis or bone metastasis without clinically proved fractures. 23222714_the expression of OGR1 in myeloid-derived cells, especially in double positive cells, was required for prostate tumor cell-induced immunosuppression. 24375028_Provide evidence for the roles of OGR1 and ASIC1a in the regulation of intestinal passive Mg(2+) absorption. 26206859_The deconstruction of OGR1-dependent signaling may aid our understanding of mucosal inflammation mechanisms 27019624_Proton-sensing GPCR-YAP Signalling Promotes Cancer-associated Fibroblast Activation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells 27049592_coexpression of OGR1- and G2A-enhanced proton sensitivity and proton-induced calcium signals. This alteration is attributed to oligomerization of OGR1 and G2A. The oligomeric potential locates receptors at a specific site, which leads to enhanced 27166427_Blocking of GPR68 or NF-small ka, CyrillicB activity severely attenuated acidification induced IL-8 production. 27693231_data identify a role for GPR68 as a proton sensor that is required for proper enamel formation 28270026_These results suggest that zOGR1, but not GPR4, is also a metal-sensing G-protein-coupled receptor in addition to a proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptor, although not all metals that activate hOGR1 activated zOGR1. 28627017_Our results suggest that OGR1-dependent increases in TRPC4 expression may favour formation of highly Ca(2+) -permeable TRPC4-containing channels that promote transformed granule cell migration. Increased motility of cancer cells is a prerequisite for cancer invasion and metastasis, and our findings may point towards a key role for TRPC4 in progression of certain types of medullablastoma. 29042451_different benzodiazepines exhibit a range of biases for OGR1, with sulazepam selectively activating the canonical Gs of the G protein signaling pathway, in heterologous expression systems, as well as in several primary cell types. 29092903_High GPR68 expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 29677517_GPR68 is an essential flow sensor in arteriolar endothelium and is a critical signaling component in cardiovascular pathophysiology 30165600_OGR1 expression was correlated with increased expression levels of pro-fibrotic genes and collagen deposition. 30471999_Ovarian cancer G protein coupled receptor 1 (OGR1) (aka GPR68) acts as coincidence detector of membrane stretch and its physiological ligand, extracellular H(+). OGR1 only responds to extracellular acidification under conditions of membrane stretch and vice versa. 32279993_A missense mutation of Leu74Pro of OGR1 found in familial amelogenesis imperfecta actually causes the loss of the pH-sensing mechanism. 32358068_CRISPR-addressable yeast strains with applications in human G protein-coupled receptor profiling and synthetic biology. 32948783_Expression profiles of proton-sensing G-protein coupled receptors in common skin tumors. 33059544_GPR68 Is a Neuroprotective Proton Receptor in Brain Ischemia. 33478938_The evolution and mechanism of GPCR proton sensing. 35163345_pH-Sensing G Protein-Coupled Receptor OGR1 (GPR68) Expression and Activation Increases in Intestinal Inflammation and Fibrosis. 35623913_GPR-68 in human lacrimal gland. Detection and possible role in the pathogenesis of dry eye disease. |
ENSMUSG00000047415 |
Gpr68 |
471.956442 |
5.4832322441 |
2.455027 |
0.136882021 |
308.976995 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000364821595041577502286945839275074139598882629918844187914161010049088939020188132494548268633282520899398952263273484054984649429235754562822697552753819302409337780717388591278371734460961306467652320861816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000108732640454111671692776286936472277982602633584462092888566305546550073553770275983288663845793808272793132088464192771001647257395583813926666662862586589399290653863011657520587505132425576448440551757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
824.1536035 |
65.2764961 |
151.2600571 |
9.5499206 |
| ENSG00000119771 |
114818 |
KLHL29 |
protein_coding |
Q96CT2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:114818; |
|
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28081303_The fusion transcript NR5A2-KLHL29FT was identified in normal and cancerous colonic epithelia. It is due to an uncharacterized polymorphic germline insertion of the NR5A2 sequence from chromosome 1 into the KLHL29 locus at chromosome 2, rather than a chromosomal rearrangement. NR5A2-KLH29FT expression levels were significantly lower in colon cancers than in matched normal colonic epithelia. 28100790_Brazilian Amerindian ancestry compared to Asian, European, and African Genomes.SNPs within or proximal to CIITA (rs6498115), SMC6 (rs1834619), and KLHL29 (rs2288697) were most differentiated in the Amerindian-specific branch. SNPs in ADAMTS9 (rs7631391), DOCK2 (rs77594147), SLC28A1 (rs28649017), ARHGAP5 (rs7151991), and CIITA (rs45601437) in the Asian comparison. |
ENSMUSG00000020627 |
Klhl29 |
18.708558 |
0.2934133742 |
-1.768993 |
0.384784755 |
22.290435 |
0.00000234371149099508929632704537504572783745970809832215309143066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007957943778948128719539709119423775973700685426592826843261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1658375 |
2.3269313 |
31.5167690 |
4.6017825 |
| ENSG00000119812 |
25940 |
FAM98A |
protein_coding |
Q8NCA5 |
FUNCTION: Positively stimulates PRMT1-induced protein arginine methylation (PubMed:28040436). Involved in skeletal homeostasis (By similarity). Positively regulates lysosome peripheral distribution and ruffled border formation in osteoclasts (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TJZ6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28040436}. |
Reference proteome |
|
Enables protein methyltransferase activity. Involved in positive regulation of cell population proliferation; positive regulation of gene expression; and protein methylation. Predicted to be part of tRNA-splicing ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25940; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; tRNA-splicing ligase complex [GO:0072669]; protein methyltransferase activity [GO:0008276]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; lysosome localization [GO:0032418]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900029]; protein methylation [GO:0006479]; tRNA splicing, via endonucleolytic cleavage and ligation [GO:0006388] |
26503212_FAM98A is expressed in numerous ovarian cancer cell lines and is important for the malignant characteristics of ovarian cancer cells. 28040436_the two structural homologs FAM98A and FAM98B included in a novel complex with DDX1 and C14orf166 are required for PRMT1 expression in colorectal cancer cell lines 31114934_Mechanistically, it was demonstrated that miR-142-3p directly targeted FAM98A, and modulated its expression. 34783205_Circular RNA intraflagellar transport 80 facilitates endometrial cancer progression through modulating miR-545-3p/FAM98A signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000002017 |
Fam98a |
194.573365 |
2.4170238680 |
1.273232 |
0.129961237 |
96.505147 |
0.00000000000000000000008901213906046192656386421236548153771631526835209812812410861034007059089390168082900345325469970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000871810997035446473766740206057254240275451402894402242377052889010791147939016809687018394470214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
281.2688172 |
20.4985112 |
117.0598580 |
6.7715745 |
| ENSG00000119862 |
29094 |
LGALSL |
protein_coding |
Q3ZCW2 |
FUNCTION: Does not bind lactose, and may not bind carbohydrates. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18320588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18433051}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Lectin;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable carbohydrate binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:29094; |
carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246] |
16682780_Galectin-related protein named GRP comprises only one conserved carbohydrate-recognition domain with 38 additional N-terminal residues. The crystals belong to the monoclinic space group C2. 18219197_CCL13 and HSPC159 mRNA expressions in PBMC are up-regulated specifically in MCNS patients during the nephrosis phase. 18320588_Galectin-related protein is a novel protein that has a close similarity to galectin sequences but is not a member of the galectin family because of its lack of lactose-binding activity. The crystal structure has been solved. 29737572_our findings showed that HSPC159 contributed to breast cancer progression through the PI3K/Akt pathway |
ENSMUSG00000048398+ENSMUSG00000042363 |
Gm5065+Lgalsl |
24.228102 |
0.1904347501 |
-2.392631 |
0.366089184 |
47.946802 |
0.00000000000437941777297899365548281162562228733051150619814961828524246811866760253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000024957608621301137825810583194357215614661571478904988907743245363235473632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.9151561 |
2.0139061 |
41.9802701 |
5.8200094 |
| ENSG00000119865 |
25927 |
CNRIP1 |
protein_coding |
Q96F85 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Suppresses cannabinoid receptor CNR1-mediated tonic inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17895407}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Does not suppress cannabinoid receptor CNR1-mediated tonic inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17895407}. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein that interacts with the C-terminal tail of cannabinoid receptor 1. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:25927; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; type 1 cannabinoid receptor binding [GO:0031718]; negative regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:2000272]; regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:0010469] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27895162_CRIP1a can compete with beta-arrestins for interaction with C-terminal CB1R domains that could affect agonist-driven, beta-arrestin-mediated internalization of the CB1R. 28918320_The Arg82 and Cys126 of CRIP1b are involved in the majority of hydrogen bond interactions with the CB1 receptor and are possible key residues required for interactions between the CB1 receptor and CRIP1b 28940471_CNRIP1 and RUNX3 as potential DNA methylation biomarkers for CRC diagnosis and treatment 31614728_Through investigations of the function and structure of CRIP1a, new pharmacotherapies based upon the CRIP-CB1 receptor interaction can be designed to treat diseases such as epilepsy, motor dysfunctions and schizophrenia 32337552_A rare genomic duplication in 2p14 underlies autosomal dominant hearing loss DFNA58. 32756411_Tat-Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein Reduces Ischemia-Induced Neuronal Damage and Its Possible Relationship with 14-3-3eta. 32955740_DNA Methylation of Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein 1 Promotes Pathogenesis of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Through Suppressing Parkin-Dependent Pyruvate Kinase M2 Ubiquitination. 33261012_Cannabinoid Receptor Interacting Protein 1a (CRIP1a) in Health and Disease. 34638827_Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 Regulates Drug Reward Behavior via Glutamate Decarboxylase 67 Transcription. |
ENSMUSG00000044629 |
Cnrip1 |
80.606804 |
0.3586717242 |
-1.479264 |
0.187781033 |
63.602576 |
0.00000000000000152230006329032906832281291600651016613489710255918696546473256603349000215530395507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000010802475449117911113334375408065945573757738601416988899472926277667284011840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.0350986 |
5.5147494 |
115.5044447 |
9.9527184 |
| ENSG00000119899 |
26503 |
SLC17A5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRA2 |
FUNCTION: Transports glucuronic acid and free sialic acid out of the lysosome after it is cleaved from sialoglycoconjugates undergoing degradation, this is required for normal CNS myelination. Mediates aspartate and glutamate membrane potential-dependent uptake into synaptic vesicles and synaptic-like microvesicles. Also functions as an electrogenic 2NO(3)(-)/H(+) cotransporter in the plasma membrane of salivary gland acinar cells, mediating the physiological nitrate efflux, 25% of the circulating nitrate ions is typically removed and secreted in saliva. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10581036, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751519, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15510212, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21781115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22778404}. |
Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Symport;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a membrane transporter that exports free sialic acids that have been cleaved off of cell surface lipids and proteins from lysosomes. Mutations in this gene cause sialic acid storage diseases, including infantile sialic acid storage disorder and and Salla disease, an adult form. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:26503; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; carbohydrate:proton symporter activity [GO:0005351]; D-glucuronate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042880]; sialic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015136]; sialic acid:proton symporter activity [GO:0015538]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; anion transport [GO:0006820]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; sialic acid transport [GO:0015739] |
12359136_expression, localization, and targeting of the wild-type sialin, as well as two mutant polypeptides in sialic acid storage disorders 15006695_In primary neuronal cultures sialin was not targeted into lysosomes but rather revealed a punctate staining along the neuronal processes and was also seen in the plasma membrane. 15172005_Molecular studies showed that all four affected individuals were homozygous for the same novel 983G > A mutation in exon 8 of the SLC17A5 gene, replacing glycine with glutamic acid at position 328 of the sialin protein 15510212_Two missense mutations and one small, in-frame deletion in sialin are associated with ISSD abolished transport, the mutation causing Salla disease (R39C) slowed down, but did not stop the transport cycle. 15516337_there is a direct correlation between sialin function and the disease state of sialic acid storage disorders 16170568_a SLC17A5 p.K136E mutation may have a role in a case of Italian severe Salla disease 17933575_study assessed the effect of missense mutations in the sialin gene (G328E and G409E) and found complete loss of measurable transport activity with both and impaired trafficking of the G409E protein 18399798_The lysosomal localization of human sialin was not or only partially affected by pathogenic missense mutations; in contrast, all pathogenic mutations abolished transport of sialic acid. 18695252_sialin possesses dual physiological functions and acts as a vesicular aspartate/glutamate transporter 19557856_Mutations in the SLC17A5 gene must be considered in two siblings with hypomyelination, even in the absence of sialuria. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424173_analysis of crucial residues and substrate-induced conformational changes in SLC17 transporter sialin 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21781115_Human SLC17A5 carrying mutations that causes both phenotypes of Salla disease and mutations that cause infantile sialic acid storage disease showed no transport activity 22334707_the substrate-binding site of sialin (SLC17A5) 22778404_These data demonstrate that sialin mediates nitrate influx into salivary gland and other cell types. 27872510_Elevated levels of AST are Associated with Cardiovascular disease. 28187749_study describes a novel pathogenic variant in SLC17A5, namely an intronic transposal insertion, in a patient with mild biochemical and clinical phenotypes. The presence of a small fraction of normal transcript may explain the mild phenotype. This case illustrates the importance of including lysosomal sialic acid storage disease in the differential diagnosis of developmental delay with postnatal onset and hypomyelination. |
ENSMUSG00000049624 |
Slc17a5 |
472.682284 |
2.0313405392 |
1.022432 |
0.075707122 |
183.639098 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000777858162768294404816564933711308076513060910107429467711966370593794438338125732780865107915184561249253170772677279387607995886355638504028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000136356133995962289426355147073632312819391357357841475800004111999176761230618751686974517005439453239601030332117659327195724472403526306152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
645.0509312 |
28.9628953 |
319.6353275 |
11.2531434 |
| ENSG00000119938 |
5507 |
PPP1R3C |
protein_coding |
Q9UQK1 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a glycogen-targeting subunit for PP1 and regulates its activity. Activates glycogen synthase, reduces glycogen phosphorylase activity and limits glycogen breakdown. Dramatically increases basal and insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis upon overexpression in a variety of cell types. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TMB3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8985175}. |
Carbohydrate metabolism;Glycogen metabolism;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a carbohydrate binding protein that is a subunit of the protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) complex. PP1 catalyzes reversible protein phosphorylation, which is important in a wide range of cellular activities. The encoded protein affects glycogen biosynthesis by activating glycogen synthase and limiting glycogen breakdown by reducing glycogen phosphorylase activity. DNA hypermethylation of this gene has been found in colorectal cancer patients. The encoded protein also interacts with the laforin protein, which is a protein tyrosine phosphatase implicated in Lafora disease. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:5507; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; protein phosphatase type 1 complex [GO:0000164]; glycogen binding [GO:2001069]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004722]; glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005978]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005979] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19171932_phosphorylation of R5/PTG at Ser-8 by AMPK accelerates its laforin/malin-dependent ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation, which results in a decrease of its glycogenic activity. 20888814_Results demonstrated that HIF1 promotes glycogen accumulation through regulating PPP1R3C expression under hypoxia, which revealed a novel metabolic adaptation of cells to hypoxia. 21738631_Findings suggest that variations in PTG may condition the course of Lafora disease and establish PTG as a potential target for pharmacogenetic and therapeutic approaches. 24861485_detection of methylation of PPP1R3C alone or in combination with EFHD1 in plasma DNA showed high sensitivity and specificity in CRC detection, and may be useful detection method for CRC, especially for early-stage CRCs. 25846879_PPP1R3C, a novel hypermethylated gene in colorectal cancer, may play a critical role in cancer cell growth in association with glucose levels. 32915648_MiR-4461 Inhibits Tumorigenesis of Renal Cell Carcinoma by Targeting PPP1R3C. |
ENSMUSG00000067279 |
Ppp1r3c |
12.697813 |
0.1846584720 |
-2.437069 |
0.656079729 |
13.798387 |
0.00020351086424136649523537745398726883649942465126514434814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000532686709736224423862582799671372413286007940769195556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8853039 |
1.5970788 |
20.7868146 |
5.0960647 |
| ENSG00000119943 |
84795 |
PYROXD2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N2H3 |
FUNCTION: Probable oxidoreductase that may play a role as regulator of mitochondrial function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31170524}. |
FAD;Flavoprotein;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable oxidoreductase activity. Involved in mitochondrion organization. Located in mitochondrial matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84795; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29048625_MZF1 gene expression was not significantly correlated with PYROXD2 protein expression in the samples of resected tumor tissues, which revealed that the PYROXD2 promoter transcription activity was determined by the aggregated effect of numerous transcription factors. This finding may be helpful in understanding the underlying mechanism which regulates the PYROXD2 expression. 31170524_data illustrated that PYROXD2 localizes to the mitochondrial inner membrane/matrix, and it plays important roles in regulating mitochondrial function. |
ENSMUSG00000060224 |
Pyroxd2 |
31.384889 |
3.0634980259 |
1.615180 |
0.316125272 |
26.355027 |
0.00000028407857965519276334921770083008496499132888857275247573852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001066107255456558597521746732661451773083172156475484371185302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.4973560 |
9.1811419 |
15.6746748 |
2.3861876 |
| ENSG00000119979 |
404636 |
DENND10 |
protein_coding |
Q8TCE6 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) regulating homeostasis of late endocytic pathway, including endosomal positioning, maturation and secretion, possibly through activating Rab proteins such as RAB27A and RAB27B. Seems to promote the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound RAB27A and RAB27B into their active GTP-bound form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30771381}. |
Alternative splicing;Endosome;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Reference proteome |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and small GTPase binding activity. Involved in endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway; protein transport; and regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport. Located in late endosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:404636; |
late endosome [GO:0005770]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0032509]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:2000641] |
30771381_FAM45A defines a novel regulatory step in the homeostasis of late endocytic pathway, including endosomal positioning, maturation and secretion, possibly through activating Rab proteins such as Rab27a/b. |
ENSMUSG00000024993 |
Dennd10 |
116.369513 |
0.4035924610 |
-1.309029 |
0.181369470 |
52.222364 |
0.00000000000049558513490799929039538529528494328207661318019816576452285517007112503051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003011460103434363663742970856456808686606868574742179589520674198865890502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.3860253 |
9.9901186 |
170.8746139 |
17.2074390 |
| ENSG00000120049 |
30819 |
KCNIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NS61 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of Kv4/D (Shal)-type voltage-gated rapidly inactivating A-type potassium channels. Modulates channel density, inactivation kinetics and rate of recovery from inactivation in a calcium-dependent and isoform-specific manner. In vitro, modulates KCND2/Kv4.2 and KCND3/Kv4.3 currents. Involved in KCND2 and KCND3 trafficking to the cell surface. May be required for the expression of I(To) currents in the heart (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JJ69, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10676964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11287421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11684073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12829703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14623880}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Ion channel;Ion transport;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a member of the family of voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel-interacting proteins (KCNIPs), which belongs to the recoverin branch of the EF-hand superfamily. Members of the KCNIP family are small calcium binding proteins. They all have EF-hand-like domains, and differ from each other in the N-terminus. They are integral subunit components of native Kv4 channel complexes. They may regulate A-type currents, and hence neuronal excitability, in response to changes in intracellular calcium. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified from this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:30819; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; potassium channel complex [GO:0034705]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; ER retention sequence binding [GO:0046923]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; voltage-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005244]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; clustering of voltage-gated potassium channels [GO:0045163]; detection of calcium ion [GO:0005513]; membrane repolarization [GO:0086009]; membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086013]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; positive regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1903766]; positive regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:1903818]; potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0097623]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901379]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12135940_Regulation of Kv4.3 current by KChIP2 splice variants 12928444_Analysis with chimeric proteins between KChIP2 and NCS-1 reveals that the three regions of KChIP2 are necessary and sufficient for its effective binding to Kv4.3 protein 14623880_Kv4.2 and K+ channel-interacting protein 2 make up a complex of Ito channels 15358149_Data show that KChIP1, KChIP2.1, and KChIP2.2 could form homo- as well as hetero-oligomers, and that this oligomerization did not perturb their interaction with Kv4.2 potassium channel. 15498806_Both Kv4.3 and KChIP2 may contribute to epicardial-endocardial gradients in the transient outward current in normal and failing hearts. 15578212_Co-expression of SGK1, but not of SGK2 or SGK3, increased Kv 4.3/KChIP2b channel currents. [KChIP2b; AH010566] 16177826_KChIP-2 is a Ca2+-dependent repressor of the immune response. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16820361_the C-terminal domain of Kv4.2 plays a critical role in voltage-dependent activation and functional expression that is mediated by direct interaction between the Kv4.2 C terminus and KChIP2 16951992_The conformational change with metal-bound KChIP4.1 is crucial for its interaction with Kv channel but not for KChIP2.2, and that the Mg2+- and Ca2+-binding properties of KChIP2.2 and KChIP4.1 have different effects on their molecular structure. 18393943_These results reveal a new role for KChIP3 in the regulation of calcium regulated secretion and also suggest that the functions of each of the KChIPs may be more specialized than previously appreciated. 18501111_KChIP2c and KCNE2 simultaneously participate in recapitulation of the electrophysiological properties of transient outward current in cardiac myocytes 18957440_KChIP4a, KChIP2x, and KChIP3x comprise a novel class of KChIP isoforms characterized by an unusual transmembrane domain at their N termini that modulates Kv4 channel gating and trafficking. 19927631_Down-regulated atrial KChIP2 and Kv4.3 mRNA expressions in rheumatic heart disease patients with chronic atrial fibrillation might be one of the molecular bases responsible for the down-regulation of the I(to) current density of AF. 20354865_N-linked glycosylation of DPP10 plays an important role in modulating Kv4.3 channel/KCHIP2 complex activities. 20498229_The cytoplasmic accessory subunit KChIP2 also assembles with Kv4.2 to increase peak current, shift V1/2 ~5mV, slow time to peak ~10%, slow inactivation ~100%, and speed recovery from inactivation ~250% without overshoot. 20649599_The I(to) activator NS5806 modified Kv4.3/KChIP2 gating in several ways that inhibit current. 20709747_KChIP2 differentially regulates total and cell surface Kv4.2 protein expression and Kv4 current densities. 21422811_The 'structurally minimal' isoform KChIP2d modulates recovery of K(v)4.3 N-terminal deletion mutant Delta2-39. 24096004_A novel KCNQ1-G229D mutation identified in a juvenile-onset AF patient altered the IKs activity and kinetics, thereby increasing the arrhythmogenicity to AF. 26016905_mutations cause a gainoffunction of KV4.3/KChIP2encoded channels by increasing membrane protein expression and slowing channel inactivation. 27349185_although there is a baseline presence of KChIP2 in the nucleus both in vivo and in vitro, KChIP2 does not directly regulate transcriptional activity. Moreover, the nuclear transport of KChIP2 is not dependent on Ca(2+). Thus, KChIP2 does not function as a conventional transcription factor in the heart. 28263709_Results identify the KChIP2/miR-34 axis as a central regulator in developing cardiac electrical dysfunction. 28735419_Binding of Ca(2+) to KChIP2 EF-hands can acutely modulate Kv4.3/KChIP2 channel inactivation gating. 29385176_Our results do not support the notion that accessory KChIP2 binding is a prerequisite for dendritic trafficking and functional surface expression of Kv4.2 channels, however, accessory KChIP2 binding may play a potential role in Kv4.2 modulation during intrinsic plasticity processes. 30622142_polybasic motif in alternatively spliced KChIP2 isoforms prevents Ca(2+) regulation of Kv4 channels 31362018_The palmitoylation status of KChIP2 determines its subcellular distribution in cardiac myocytes. Stress promotes nuclear entry of KChIP2, diverting it from ion channel modulation at the plasma membrane to other functions in the nuclear compartment. |
ENSMUSG00000025221 |
Kcnip2 |
120.836885 |
0.1843560152 |
-2.439434 |
0.228904919 |
113.697370 |
0.00000000000000000000000001517942729821094208083827413185206548186626031187630287290613100310691409300378751368043594993650913238525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000171290785108251928177998445975164387876882642017064083208871173941915781735456647538740071468055248260498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.8575713 |
6.0530853 |
188.9312371 |
20.8985546 |
| ENSG00000120053 |
2805 |
GOT1 |
protein_coding |
P17174 |
FUNCTION: Biosynthesis of L-glutamate from L-aspartate or L-cysteine (PubMed:21900944). Important regulator of levels of glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter of the vertebrate central nervous system. Acts as a scavenger of glutamate in brain neuroprotection. The aspartate aminotransferase activity is involved in hepatic glucose synthesis during development and in adipocyte glyceroneogenesis. Using L-cysteine as substrate, regulates levels of mercaptopyruvate, an important source of hydrogen sulfide. Mercaptopyruvate is converted into H(2)S via the action of 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3MST). Hydrogen sulfide is an important synaptic modulator and neuroprotectant in the brain. In addition, catalyzes (2S)-2-aminobutanoate, a by-product in the cysteine biosynthesis pathway (PubMed:27827456). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16039064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21900944, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27827456}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Aminotransferase;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme which exists in cytoplasmic and mitochondrial forms, GOT1 and GOT2, respectively. GOT plays a role in amino acid metabolism and the urea and tricarboxylic acid cycles. The two enzymes are homodimeric and show close homology. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2805; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; L-aspartate:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity [GO:0004069]; L-cysteine transaminase activity [GO:0047801]; phosphatidylserine decarboxylase activity [GO:0004609]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; 2-oxoglutarate metabolic process [GO:0006103]; aspartate biosynthetic process [GO:0006532]; aspartate catabolic process [GO:0006533]; aspartate metabolic process [GO:0006531]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; fatty acid homeostasis [GO:0055089]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; glutamate catabolic process to 2-oxoglutarate [GO:0019551]; glutamate catabolic process to aspartate [GO:0019550]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536]; glycerol biosynthetic process [GO:0006114]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; oxaloacetate metabolic process [GO:0006107]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384] |
12480555_Glucose intolerance is associated with elevated serum aminotransferase independent of obesity. 15306699_mildly elevated in severe acute respiratory syndrome patients during second week after onset of fever. 16681433_saliva AST and ALP may have roles in development of periodontal diseases 17877759_PTLP activity is positively associated with serum ALT1, GOT1 and GOT2 in type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. 17907318_Abnormal serum aminotransferase values are uncommon in severely obese children in France. 18242760_Data revealed higher aspartate aminotransferase for women with a family history of diabetes, when adjusted for age and BMI. 18752324_Serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and aspartate aminotransferase are an efficient set of biochemistries to identify UDCA-treated patients with primary biliary cirrhosis at risk of death or liver transplantation (LT). 19012630_Neither ALT nor GGT concentrations were correlated with ALP concentration, but AST concentration was moderately correlated with ALP concentration. 19370784_Results suggest that alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels and AST/ALT ratio do not seem to be reliable predictors for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. 19393479_the management of patients with pyelonephritis should take into account that moderate and self-limited abnormalities in aminotransferase levels are frequent during the acute phase of the disease 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20205615_The association of coffee and green tea consumption with serum activities of liver enzymes in free-living Japanese men and women was examined, focusing on sex difference and effect modifications of alcohol and obesity. 20499337_Elevated serum LDH isoenzymes and AST indicate a disturbance (of uncertain clinical significance) within multiple extraosseous tissues when there is CLCN7 deficiency. 20972737_liver enzymes, including AST, were significantly associated with IR according to direct clamp assessment, which were independent of the traditional risk factors in diabetic patients 21750724_Data indicate that the percentages of CD4(+)CXCR5(+) TFH in IA patients were positively correlated with AST. 21900944_we discovered a rare in-frame deletion in GOT1 gene, which inactivates cAST enzyme in the Old Order Amish. 22132177_The patterns of interaction between smoking and alcohol consumption or BMI with respect to AST and ALT resembled those observed for gamma-GT. 22242166_This study highlights the necessity of intensive follow-up for those with elevated AST and ALT levels and comorbid alcohol use disorder for preventing excessive natural deaths. 22352690_APRI and AST/ALT are independent predictors for significant fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. 23667618_Alcohol consumption, smoking status, and metabolic syndrome impact on serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), was determined. 24849491_Significantly higher GOT levels were found in the 1-20 year age group of type 1 25272068_The aim of this study was to establish the reference intervals (RIs) of total bilirubin (TBIL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and creatinine (CREA) for apparently healthy elderly (Han ethnicity) in Shuyang, China. 25595905_We propose the GOT1 expression status as a simple and reliable prognostic biomarker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 26003525_Human GOT1 was expressed in E coli, purified by affinity chromatography and preliminary crystallographic studies were done. 26290281_The serum hepcidin, ferritin, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, gamma-glutamyltransferase and bilirubin were examined in two independent Chinese cohorts consisted of 3455 individuals. 26333544_High AST1 expression is associated with high mortality in hemodialysis patients. 26791191_Data suggest that, in context of abnormal hepatic lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, circulating GOT1 rises due to up-regulation of hepatic expression of GOT1 associated with greater gluconeogenesis and insulin resistance. 26881519_Elevated aspartate aminotransferase level was associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 27872510_Elevated levels of ALT are Associated with Cardiovascular disease. 28351330_Elevated preoperative aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index may be independently associated with poor overall survival and disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients following curative resection 28415934_Early abnormal liver enzyme levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase may increase the prevalence of human cytomegalovirus antigenemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 28455244_GOT1 plays an important role in energy metabolism and ROS balance in chronic acidosis stress in pancreatic tumor cells. 28544376_HIF-2a regulates non-canonical glutamine metabolism via activation of PI3K/mTORC2 pathway and GOT1 expression in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 28628604_ALT is a more suitable index than AST for developing a regression model. 28716744_Missense variant (p.Gln208Glu, rs374966349) in glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase 1 (GOT1) was found, as a putative causal variant predisposing to Familial Macro-aspartate aminotransferase . 29553104_high transaminase elevations do not predict severe complications or reflect remnant ischemic area. 29751795_Study suggests an important role of GOT1 to coordinate the glycolytic and the oxidative phosphorylation pathways in KRAS mutated cancer cells. High levels of GOT1 were further linked to poor survival as analysed by the GEPIA web tool, in thyroid and breast carcinoma and in lung adenocarcinoma. 30035324_findings demonstrate that miR-9 regulates ferroptosis by targeting GOT1 in melanoma cells, illustrating the important role of miRNA in ferroptosis. 30208107_we assessed the stability of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) bound to hGOT1 for the three variant and wildtype (WT) proteins. Conformational transition was associated with the rearrangement of the P15-R32 small domain loop providing substrate access to the R387/R293 binding motif. The amino acid substitutions at positions 266, 267, and 300 reduced the structural correlation between PLP and the protein active site 30566759_Association between serum liver enzymes and all-cause mortality: The Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. 30591220_This study suggested that miR-9-5p regulates GOT1 expression in pancreatic cancer, thereby stunting proliferation, invasion, glutamine metabolism and redox homeostasis, and that miR-9-5p may serve as a prognostic or therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. 32157800_Clinical implications of aminotransferase elevation in hospitalised infants aged 8-90 days with respiratory virus detection. 32488888_Elevated serum aspartate aminotransferase level identifies patients with coronavirus disease 2019 and predicts the length of hospital stay. 33273639_Moderate to severe liver siderosis and raised AST are independent risk factors for vitamin D insufficiency in beta-thalassemia patients. 33357229_Ambulatory end-stage liver disease in Ghana; patient profile and utility of alpha fetoprotein and aspartate aminotransferase: platelet ratio index. 34099767_Aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase ratio is associated with frailty and mortality in older patients with heart failure. 34315874_GWAS of serum ALT and AST reveals an association of SLC30A10 Thr95Ile with hypermanganesemia symptoms. 34325031_Glutamate-Oxaloacetate Transaminase 1 Impairs Glycolysis by Interacting with Pyruvate Carboxylase and Further Inhibits the Malignant Phenotypes of Glioblastoma Cells. 34352456_Structural and functional analysis of disease-associated mutations in GOT1 gene: An in silico study. 34381026_GOT1 inhibition promotes pancreatic cancer cell death by ferroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000025190 |
Got1 |
31.621226 |
2.3638514198 |
1.241139 |
0.278262244 |
20.278822 |
0.00000669374103579172662493567552699502698487776797264814376831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000021473509604061266745110916898120478890632512047886848449707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.6494480 |
7.4314841 |
19.4238200 |
2.5746658 |
| ENSG00000120093 |
3213 |
HOXB3 |
protein_coding |
P14651 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene is a member of the Antp homeobox family and encodes a nuclear protein with a homeobox DNA-binding domain. It is included in a cluster of homeobox B genes located on chromosome 17. The encoded protein functions as a sequence-specific transcription factor that is involved in development. Increased expression of this gene is associated with a distinct biologic subset of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3213; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; definitive hemopoiesis [GO:0060216]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; face development [GO:0060324]; glossopharyngeal nerve morphogenesis [GO:0021615]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; rhombomere development [GO:0021546]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878] |
14966272_Data report novel nucleoporin 98 fusions with homeobox (HOX)A10, HOXB3 and HOXB4, and describe the results of coexpression of these proteins with the Hox cofactor Meis1 in leukemic induction. 15674412_The HOXb3 was only weakly expressed in the inv(7) positive patients. 17972163_HOXA7, HOXB3, HOXA3, and HOXB13 expression levels changed during angiogenesis, sugessting these proteins might be involved in the angiogenesis of hMSCs. 19477923_Data show that inducible Hox genes are selectively sensitive to the inhibition of actin polymerization and that actin polymerization is required for the assembly of a transcription complex on the regulatory region of the Hox genes. 19854132_RASSF1A silencing strongly correlates with overexpression of HOXB3 and DNMT3B. 23219899_HoxB3 promote prostate cancer progression by upregulating CDCA3 expression. 24127533_describe familial cases of TH in two generations (proband and his father), in addition to other two sporadic cases. We have found polymorphisms in the HOXB3, HOXD3, and a new synonymous variant, and PITX2 genes 25996682_decreased methylation at HOXB3 and HOXB4 was associated with increased gene expression of both HOXB genes specific to the mid-risk AML, while increased DNA methylation at DCC distinctive to the high-risk AML was associated with increased gene expression 26482852_HOXB2 and HOXB3 act as tumor suppressors in acute myeloid leukemia patients carrying the FLT3 protein mutations. 27447302_miR-10b might control cell apoptosis, proliferation, migration, and invasion in endometrial cancer via regulation of HOXB3 expression. 28075453_HOXB3 is degraded by miR-375 in breast cancer cells.HOXB3 plays role in tamoxifen resistance. 29402501_HOXA4/HOXB3 gene expression-based risk score may be useful for prognostic risk stratification and warrants prospective validation in HGSOC patients. 29439669_Data indicate a miR-375-HOXB3-CDCA3/DNMT3B regulatory circuitry which contributes to leukemogenesis and suggest a therapeutic strategy of restoring miR-375 expression in Acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 31702491_miR-7 Reduces High Glucose Induced-damage Via HoxB3 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. 32748508_Levels of serum Hoxb3 and sFlt-1 in pre-eclamptic patients and their effects on pregnancy outcomes. 33352356_CSF levels of HoxB3 and YKL-40 may predict conversion from clinically isolated syndrome to relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. 35127344_Extracellular Vesicle-Encapsulated MicroRNA-375 from Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Regulating HOXB3-Mediated Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000048763 |
Hoxb3 |
22.805973 |
0.2848928663 |
-1.811509 |
0.346573159 |
28.396514 |
0.00000009884315725658889234958923283511089685759998246794566512107849121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000389670139184629302672962895826014317890439997427165508270263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.5192227 |
1.9199709 |
30.0970553 |
4.1058006 |
| ENSG00000120129 |
1843 |
DUSP1 |
protein_coding |
P28562 |
FUNCTION: Dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase MAPK1/ERK2 on both 'Thr-183' and 'Tyr-185', regulating its activity during the meiotic cell cycle. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28563}. |
3D-structure;Cell cycle;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Stress response |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a phosphatase with dual specificity for tyrosine and threonine. The encoded protein can dephosphorylate MAP kinase MAPK1/ERK2, which results in its involvement in several cellular processes. This protein appears to play an important role in the human cellular response to environmental stress as well as in the negative regulation of cellular proliferation. Finally, the encoded protein can make some solid tumors resistant to both chemotherapy and radiotherapy, making it a target for cancer therapy. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:1843; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0017017]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004722]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008138]; protein tyrosine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008330]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; endoderm formation [GO:0001706]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; negative regulation of meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051447]; negative regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090027]; negative regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1903753]; peptidyl-serine dephosphorylation [GO:0070262]; peptidyl-threonine dephosphorylation [GO:0035970]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint [GO:0090266] |
12080474_CL100 down regulation is associated with advanced stages of epithelial ovarian neoplasms 12356755_glucocorticoids synergistically enhance NTHi-induced TLR2 expression via specific up-regulation of the MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) that, in turn, leads to dephosphorylation and inactivation of p38 MAPK 12391149_Data suggest that mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) participates in a negative-feedback loop which regulates p38 function and that dexamethasone may inhibit proinflammatory gene expression in part by inducing MKP-1 expression. 12432554_Expression of MKP-1 may be associated with shorter progression-free survival times 12506119_role of activation on cAMP-dependent protein kinase enhancement of CYP17 transcription 12765304_our data suggest that deletion of the hv3005 and the 3-30.3 genes may predispose individual SLE patients to the development of lupus nephritis 12890671_MKP1 is a transcriptional target of p53 involved in cell cycle regulation 12947325_Cardiopulmonary bypass reduces ERK1/2 and p38 activity in peripheral tissue, potentially by MKP-1. 12960255_requirement of MAPK phosphatase-1 induction and therefore, inhibition of p38 MAPK in the ANP-mediated inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced expression of MCP-1 14551204_Jak2 is required for Ang II-induced ERK2 inactivation via induction of MKP-1 gene expression. 14680833_Here we found that hypoxia induces MKP-1 expression in human hepatoma cells HepG2 in a time-dependent manner. 14724291_the molecular mechanisms underlying the survival function of NGF in CESS B cell line predominantly consist in maintaining elevated levels of MKP-1 protein, which controls p38 MAPK activation. 15059515_The expression of MKP-1 in gastric cancer cell line was elevated under hypoxia, which could downregulate the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 trans-activition activity thereby repressing the expression of downstream target vascular endothelial growth factor. 15173070_CL100/MKP-1 has a role in progression of non-small cell lung cancer 15247770_Prevalent MKP-1 expression in renal cell carcinoma contributes to cancer cell survival by attenuating an apoptosis inducing signal cascade via JNK. 15339908_expression of the CL-100 phosphatase and its subsequent regulation of ERK activity play a key regulatory role in the thrombin signaling pathway 15448190_MKP-1 induction may be antiapoptotic om breast epithelial cells and a breast cancer cell line. 15569826_Rat ANP induces MKP-1 via endothelial Rac1 and Nox/Nox2. 15590693_Glucocorticoid receptor-induced MPK-1 expression inhibits paclitaxel-associated MAPK activation and contributes to breast cancer cell survival 15614136_MKP-1 is an important mediator of endotoxin tolerance via p38 regulation 15677475_preheating accelerates MAP kinase inactivation after a second heat shock, which is related to a HSP70-mediated increase in p-MKP-1 16044158_DNA damage in transcribed genes induces apoptosis via the JNK pathway and MKP-1. 16081065_Hypoxia-induced MKP-1 protects overactivation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation through inhibiting ERK kinase activity. 16224818_A molecular target of macrophage migration inhibitory factor - glucocorticoid crosstalk. 16286470_MKP-1 proteolysis can be achieved via ERK and SCF(Skp2) cooperation, thereby sustaining ERK activation 16289033_data suggest that MKP-1, a negative regulator of ERK1/2, plays a proapoptotic role in oxidative stress-induced cell death in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line 16293973_The MKP-1 expression in HCC (hepatocellular carcinoma) was an independent prognostic factor for outcome in HCC patients. 16387640_Anandamide-induced rapid MKP-1 expression switches off MAPK signal transduction in microglial cells activated by stimulation of pattern recognition receptors. 16951204_MKP-1 is required for cisplatin resistance in tumor cells. 17073741_DUSP1 is a central regulator of innate immunity, and its expression can profoundly affect the outcome of inflammatory challenges.[review] 17131384_These results suggest the existence of an ERK1/2-driven negative feed-back regulation of ERK5 signaling in epidermal growth factor-stimulated HK-2 cells, which is mediated by MKP-3, DUSP5 and/or MKP-1. 17489738_In human mesangial cells, connective tissue growth factor induces the rapid transcriptional activation and synthesis of MKP-1 (MAPK phosphatase-1), a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates p38 MAPK. 17638884_E2F-1 is a transcriptional activator of DUSP1 and DUSP1 is a link between E2F-1 and MAP kinases 17681939_The transcription factor ATF2, which is phosphorylated and activated by JNK, is a critical mediator for inducible expression of DUSP1 and DUSP10 in this signaling pathway. 17690186_Data suggest that JNK activation and decreased expression of MKP-1 may play important roles in progression of urothelial carcinoma. 17761948_Regulation of ERK by MKP-1 provides a novel mechanism for control of osteoblast proliferation by glucocorticoids 17848570_Ethanol-induced oxidative stress enhanced the tyrosine phosphorylation of PKCdelta, which in turn caused the proteasomal degradation of MKP-1, leading to sustained JNK activation and increased apoptosis in VL-17A cells. 18003751_Distinct MAPK signaling pathways for thrombin versus VEGF induction of MKP-1 in endothelial cells. MKP-1 induction important in VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell migration. 18089824_MKP-1 plays a critical role in ERK-mediated cisplatin resistance in ovarian carcinoma cells. 18095520_in patients with rheumatic heart disease and heart failure MKP-1 activity was depressed in class IV patients compared to those in classes II and III 18178562_a novel, stimulus-specific, and phosphatase-specific mechanism of ERK2 regulation in the nucleus by DUSP1, -2, and -4. 18314542_corticosteroid-induced MKP-1 contributes to the repression of IL-6 secretion in ASM cells. 18367666_overexpression of MKP-1 has no significant effect on Ton EBP/OREBP activity. This paradox is explained by opposing effects of p38alpha and p38delta, both of which are activated by high NaCl and inhibited by MKP-1. 18403641_These findings indicate that p53 is a transcriptional regulator of DUSP1 in stress responses. 18434324_distinct phosphorylation of PKCdelta on tyrosines 64 and 187 specifically activates the Erk1/2 pathway by the down-regulation of MKP-1, resulting in the persistent phosphorylation of Erk1/2 and cell apoptosis 18441094_Glucocorticoid regulation of CD38 expression in human airway smooth muscle cells: role of dual specificity phosphatase 1 18477563_phosphorylated heat shock protein 27 up-regulated the levels of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1, an inhibitory protein of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 18490444_MKP-1 upregulation by oxidative stress is potently influenced by increased mRNA stability and translation, mediated at least in part by the RNA-binding proteins HuR and NF90. 18519678_DUSP1 reactivation led to suppression of ERK, CKS1, and SKP2 activity, inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human hepatoma cell lines 18723442_whether MAP kinase phosphatase (MKP)-1, a negative regulator of p38 and JNK, mediates the antiinflammatory effects of shear stress. 18726921_High level of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 expression is associated with cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma 18782768_pneumolysin selectively induced expression of MKP1 via a TLR4-dependent MyD88-TRAF6-ERK pathway, which inhibited the PAK4-JNK signaling pathway,leading to up-regulation of MUC5AC mucin production 19020052_Histone H3 as a novel substrate for MAP kinase phosphatase-1. 19032224_The MAP kinase phosphatase-1 MKP-1/DUSP1 is a regulator of human liver response to transplantation. 19262425_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19411256_KLF5 promotes breast cell survival partially through fibroblast growth factor-binding protein 1-pERK-mediated dual specificity MKP-1 protein phosphorylation and stabilization. 19417026_Data show that MKP-1 is overexpressed during the malignant transformation of the breast and independently predicts poor prognosis. 19553005_Data show that inhibition of NF-kappaB or PI3K potently enhanced cisplatin cytotoxicity in cells with endogenous or genetically induced low MKP1 levels. 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19648110_Data reveal an important and novel role for transcriptional activation (transactivation) of MKP-1 in the repression of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription by glucocorticoids. 19697705_The abnormal expression of MKP-1 and p-ERK(1/2) probably assists in promoting the development and progression of ovarian carcinoma. 19724859_CTGF and DUSP1 overexpression in residual breast cancer samples may be a reflection of resistance to further administration of doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide regimen 19755862_The expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1)is associated with cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. 19793766_hypothermia protects against TNF-alpha-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction and apoptosis through an MKP-1-dependent mechanism. 19797979_These data strongly suggest that MKP-1 is a major effector in altering ERK1/2 phosphorylation status. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940143_a novel glucocorticoid-responsive region of the human DUSP1 gene contains a highly unusual element, in which three closely spaced GR half-sites are required for potent transcriptional activation 20043958_Results demonstrate that MG-132 upregulates MKP-1 and represses cytokine secretion from ASM and highlight the potential of the proteasome as a therapeutic target in asthma. 20089808_MKP-1 is an important negative regulator of inflammatory gene expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells. 20100830_VCP/p97-mediated inducible nitric-oxide synthase-dependent Tyr nitration of PP2A increases the levels of phosphatases PP2A and DUSP1 to contribute to the refractory response of conditioned cells 20145951_molecular cross-talk between the MKP-1, p38 MAPK and PI3K pathways promotes resistance to PI3K inhibitors in hilar cholangiocarcinoma cells. 20228065_generation of ROS by Nox4 mediates TGF-beta1-induced PAI-1 gene expression at least in part through oxidative modification and inhibition of MKP-1 leading to a sustained activation of JNK and p38 MAPKs. 20353815_Ritonavir (at 100 mg once daily and 100 mg twice daily significantly down-regulated dual specificity phosphatase 1 in 20 healthy individuals. 20375469_player in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis in skeletal muscle and mitochondrial dysfunction caused by overnutrition 20555314_NF-kB-mediated induction contributes to establishment of tolerance to TLR ligands in enterocytes 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673984_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673984_The DUSP1 polymorphisms rs881152 and rs34507926 localized to different haplotype blocks and appeared to significantly modify the relationship between Inhaled corticosteroid use and bronchodilator response among GALA study participants 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20708668_We propose DUSP1 as a novel target gene of DON, which is essential for the prevention of DON induced apoptosis in the epithelial cell line HepG2. 20803086_regulates the induction of Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1 by Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumolysin in epithelial cells 20805296_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20829434_Results propose a MIF-NURR1 signaling axis as a regulator of the glucocorticoid sensitivity of MKP1. 20868379_study reveals novel roles of pneumolysin in mediating MKP1 expression for the regulation of proinflammatory cytokine expression in a time-dependent manner 20890299_these results provide evidence for a role of DUSP1 in angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. 20953200_MKP-1 is identified as a key factor in major depressive disorder pathophysiology. 21060794_transcriptional activation of DUSP1 by glucocorticoids requires p300 and a rapid modification of the chromatin structure surrounding the GRE 21454676_Down-regulation of cytokine-induced interleukin-8 requires inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) via MAPK phosphatase 1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. 21507959_CK2 enhances the protein level and activity of TTP via the modulation of the MKP-1-p38 MAPK signaling pathway; TGF-beta1 enhances the activity of CK2 21547253_Results indicate that DUSP1 suppresses iNOS expression by limiting p38 MAPK activity in human and mouse cells. 21715333_T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase (TOPK) phosphorylation of MKP1 protein prevents solar ultraviolet light-induced inflammation through inhibition of the p38 protein signaling pathway. 21733716_work provides new mechanistic insight of MKP-1 signaling and regulation of cytokine mRNA stability through RNA binding proteins in response to inflammatory stimuli 21803700_Dexamethasone treatment inhibits cisplatin-induced cell apoptosis by up-regulation of cellular mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1. 21840882_Tauroursodeoxycholate inhibits neointimal hyperplasia by reducing proliferation and inducing apoptosis of smooth muscle cells by suppression of ERK via PKCalpha-mediated MKP-1 induction. 21959016_infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) infection of cultured cells activated p38 MAPK pathway and induced expression of IL6 and IL8; IBV has developed a strategy to counteract induction of IL6 and IL8 by inducing expression of dual-specificity phosphatase 1 21960346_The imbalanced expression of MKP-1 and p-ERK(1/2) may play a role in the development of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and these two molecules may be new targets for the therapy and prognosis of SCC. 22014408_S-nitrosylation of MKP-1 presents a novel mechanism underlying the enhanced MKP-1 expression levels and MKP-1-mediated radio-resistance in head and neck cancer. 22020934_Findings suggest that MKP-1 is a critical mediator of anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory actions of PR in the breast. 22200679_MKP-1: a negative feedback effector that represses MAPK-mediated pro-inflammatory signaling pathways and cytokine secretion in human airway smooth muscle cells. 22301548_Upon vitamin D treatment, the expression of MKP-1 phosphatase mRNA and protein is significantly upregulated in both human monocytes and murine bone marrow-derived macrophages. 22610099_PDE4B mediates ERK-dependent up-regulation of mucin MUC5AC by S. pneumoniae by inhibiting cAMP-PKA-dependent MKP-1 pathway. 22743041_By increasing MKP-1 expression via parallel p38 MAPK- and CREB-mediated pathways, S1P temporally regulates MAPK signaling pathways by upregulating the negative feedback controller MKP-1. 22924482_In lesional psoriatic skin, the p38 MAPK negative feedback mechanism provided by DUSP1 seems to be inhibited and downregulation of DUSP1 may contribute to the sustained inflammatory response seen in psoriasis. 22991462_Data indicate that knockdown of MKP-1 mimicked the priming effects of metabolic stress. 23030431_MKP-1 suppressed Tristetraprolin expression by inhibiting p38 MAPK pathway. 23097457_These data reveal an indirect role for miR-K12-11 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in the regulation of DUSP1 and downstream pathogenesis. 23149933_DJ-1 downregulates DUSP1 expression under conditions of oxidative stress. 23169297_Downregulation of DUSP1 mRNA is associated with prostate cancer. 23625220_Pneumolysin produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae is required for inducing hos beta-defensin 2 whose expression is under the control of p38 MAP and MKP1. 23825193_Authors showed that phosphorylation-dependent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and translation disruption of TNF-alpha and IL-6 follow increased MAPK phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) expression. 24080497_DUSP1 promotes apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through the inhibition of p38 MAPK. 24086554_Activating MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1). 24155659_Our approaches revealed signature candidates of differentially hypermethylated genes of DDAH2 and DUSP1 which can be further developed as potential biomarkers for OSCC as diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets in the future. 24267255_DUSP1 expression is increased in obstructive sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia 24308939_DUSP1, DUSP4, and DUSP5 differentially modulate endothelial MAPK signaling pathways downstream of Tie-2 receptors. 24339725_Keratoconic corneas are distinguished with high expression of TGF-beta1 and DUSP1. 24578378_MKP-1 promoted angiogenic and arteriogenic neovascular growth, potentially through dephosphorylation of histone H3 serine 10 on coding-region DNA to control transcription of angiogenic genes, such as fractalkine. 24658355_Data suggest that MKP-2 rather than MKP-1 is tamoxifen-regulated and that the elevated expression of MKP-2 in MCF7-TAMR cells potentially functions to restore tamoxifen sensitivity. 24692548_DUSP1 plays a transient, often partial, role in the dexamethasone-dependent repression of certain inflammatory genes. 25044272_Knockdown of MKP-1 abolished the miR-210-inhibition prevention of cell proliferation under hypoxia. 25204653_MKP-1 and MKP-2 stability is regulated by ERK-mediated phosphorylation through a degradation pathway independent of polyubiquitination 25296132_PDE4 inhibitors augment antiinflammatory effects of beta2-agonists via increased MKP-1 expression in airway smooth muscle cells. 25312268_Together, our results clearly establish the role of Dusp1 as a tumor suppressor gene that regulates cancer-associated inflammation. 25370852_DUSP1 upregulation is strongly linked to adiposity and that physical exercise modulates its expression. 25377473_Combined inhibition of MKP1 and HER2 enhanced cell killing in breast cancer. Together, our findings identify a new mechanism of resistance in breast tumors and reveal MKP1 as a novel therapeutic target for radiosensitization. 25389768_CYLD negatively regulates nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced IL-8 expression via MKP-1-dependent inhibition of ERK. 25593344_Decreased DUSP1 might be a mechanism responsible for gefitinib resistance. 25617504_Wild-type but not mutant p53 transcriptionally upregulated DUSP1 via its DNA-binding domain. DUSP1 and p53 might collaborate to suppress tumors in hepatocarcinogenesis via a positive regulatory loop. 25638726_Deregulation of EGR-1 and/or DUSP-1 in nasal epithelium could be responsible for the prolonged activated transcriptional state observed in vivo in allergic disease. 25724669_MKP-1 is a MAPK deactivator; thus, by controlling p38 MAPK phosphorylation status in a temporally distinct manner, MKP-1 ensures that TTP is expressed and made functional at precisely the correct time to repress cytokine expression. 25798824_DUSP1 is involved in the antiviral host defense mechanism against a HCV infection 25858560_Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest AMPK activation (AMPKa1 or AMPKa2) suppresses inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells by down-regulation of STAT1 signaling and up-regulation of MKP-1 (dual specificity phosphatase 1). 25872469_The proliferation of human cervical cancer cells was also inhibited by DUSP1 26111828_MKP1 recruits to the chromatin in response to DNA damage and correlates with the decrease of H3S10P, whereas MKP1 is released from chromatin during recovery phase of DNA damage response. 26158762_Data show that sorafenib inhibited microRNA miR-101 expression and enhanced dual specificity phosphatase 1 (DUSP1) expression and lowered transforming growth factor beta I (TGF-beta) release in M2 macrophage, slowing macrophage-driven hepatocarcinoma. 26176177_evidence of association between depressive symptom severity and increasing serum MKP-1 levels in women, and decreasing T levels in perimenopausal women. 26280733_Progesterone acts via GR to drive MKP-1 expression, which in turn inhibits IL-1beta-dependent c-Jun activation and COX-2 expression. 26329166_MKP-1 can attenuate tamoxifen-induced cell death through inhibiting the JNK signal pathway. 26457672_LPS tolerance interferes with TLR4 signaling by inhibiting Lyn and c-Src phosphorylation and their recruitment to TLR4, while increasing the phosphatase activity and expression of PP2A, PTPN22, PTP1B and MKP1. 26546680_DUSP1 overexpression and inhibition of MAPKs prevented IL1B-induced expression of ZFP36, this was associated with increased TNF mRNA expression at 6 h, an effect that was predominantly due to elevated transcription. 26689986_In E1a expressing non-small cell lung carcinoma cells, upregulation of MKP1 and the subsequent p38MAPK inhibition is required for the induction of chemosensitivity to cisplatin. 26769965_The heparin effects on TNFalpha-induced stress fiber formation and Map kinase signaling depend on increased DUSP1 expression. 26825339_dexamethasone-induced DUSP1 acts via p38 MAPK to switch on the mRNA destabilizing function of protein-tristetraprolin to repress pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion from ASM cells 26829212_This study shows that RIG-I activation results in MKP-1-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation in melanoma cells via controlling the p38-HSP27, c-Jun and rpS6 pathways 27314954_we show that IL-1 induces robust p38a activation both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm/membrane.Following stimulation, p38a activity returns to a basal level in absence of receptor degradation. While nuclear pulse is controlled by MKP1 through a negative feedback to pp38, its basal activity is controlled by both TAB1 and MKP1 through a positive feedback loop. 27422607_Collectively, these data indicated that DUSP1 may induce the resistance against paclitaxel through the p38 MAPK-mediated overexpression of p-glycoprotein in human ovarian cancer cells. 27538525_Curcumin suppressed CXCL5 expression by direct inhibition of IKKbeta phosphorylation, and inhibition of p38 MAPK via induction of negative regulator MKP-1. 27551049_silencing of IL1B plus dexamethasone-induced DUSP1 significantly reduced IRF1 expression. IL1B-induced expression of CXCL10 was largely insensitive to dexamethasone, whereas other DUSP1-enhanced, IRF1-dependent mRNAs showed various degrees of repression. 27572311_We propose a signaling cascade involving ARID1A, GADD45B and DUSP1 as mediators of the romidepsin effects in GCC cells. 27599524_Our results emphasize the importance of MKP-1 as a potential predictive biomarker for a subset of breast cancer patients with worse outcome and less susceptibility to treatment. 28112450_Increased MAP2K6, MAP4K3, and DUSP1 gene expressions in post-chemotherapy samples indicate a poor clinical outcome in osteosarcoma patients. 28129656_Dual-specific phosphatase (DUSP1) was found to inhibit gallbladder cancer (GBC) cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 28299397_The results presented here emphasize the importance of MKP-1 as a mediator of therapeutic effects of glucocorticoids in inflammatory lung diseases as well as its potential as a novel anti-inflammatory drug target. 28330703_MKP-1 is a redox-regulated master controller of monocyte function and macrophage phenotype. (Review) 28384165_Mean morning and evening DUSP1 mRNA levels showed significant increase during Ramadan compared to Shabaan, however, its diurnal rhythm was maintained. Morning IL-1alpha mRNA expression remained significantly higher than in the evening during Ramadan, but was markedly decreased compared to Shabaan. 28413926_Methylation-mediated silencing of the DUSP-1 promoter does not appear to be associated with reduced expression, indicating the involvement of other factors in specific suppression of DUSP-1 in diabetes-associated cardiac hypertrophy. 28650468_this work indicates that suppression of JNK1/2 activity by MKP-1 maintains PARP-1 levels and suggests that MKP-1-mediated cisplatin resistance can be bypassed by PARP-1 inhibition. 28801478_The aim of this review is to shed light on the role of four different phosphatases (PTEN, PP2A, CDC25 and DUSP1) in five different solid tumors (breast cancer, lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer and ovarian cancer), in order to better understand the most frequent and aggressive primary cancer of the central nervous system, glioblastoma. 28983624_the expression of DUSP1 was lower in OA FLSs than in normal FLSs, and DUSP1 may inhibit the expression of OA-associated mediators, MMP-13 and COX-2, by suppressing the activation of p38 MAPK and JNK pathways in OA FLSs. 29052270_Study reports the crystal structure of the human DUSP1 catalytic domain at 2.49 A resolution. The protein was crystallized as a (maltose-binding protein) MBP fusion protein in complex with a monobody that binds to MBP. Sulfate ions occupy the phosphotyrosine and putative phosphothreonine binding sites in the DUSP1 catalytic domain. 29234123_DUSP1 promotes Sendai virus-induced apoptosis and suppresses cell migration in Respiratory Syncytial Virus-infected cells. 29257221_Downregulation of the expression of DUSP1 or protein phosphatase 1 led to a decline in the beta2adrenergic receptormediated dephosphorylation of ERK1/2. 29434446_miR-202-3p is upregulated in type 1 gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms (g-NENs) lesions and might play important roles in the pathogenesis of type 1 g-NENs by targeting DUSP1. 29472726_we identified two modules with the AURKA gene and the DUSP1 gene as their cores. Interestingly, simultaneous activation of those genes was associated with the poorest prognosis in clinical samples. 29956792_High DUSP1 expression is associated with apatinib resistance by activating the MAPK pathway in gastric cancer. 30061089_Our results revealed a novel link between Mkp-1 and Nrf2 signaling pathways in protecting against colonic inflammation 30157211_A2B adenosine receptor in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells diminishes ERK1/2 phosphorylation by activation of MAPK-phosphatase-1 30191967_finding strategies to regulate the balance of the DUSP1-JNK-Mff signaling pathway and mitochondrial homeostasis may be a therapeutic target for treating diabetic nephropathy in clinical practice. 30198887_The molecular structure of DUSP1 crystallized as MBP fusion protein has been reported. 30262569_NRF2 expression levels are elevated in high-risk MDS patients and serve as a statistically significant prognostic variable for OS in MDS patients. Pharmacological inhibition of NRF2 re-sensitizes MDS cells to Ara-C treatment while activation of NRF2 by agonist resulted in the reduced sensitivity to Ara-C. NRF2 mediates Ara-C resistance partly through its direct target gene DUSP1. 30536303_DUSP1 plasmid transfection significantly enhanced DUSP expression, triggered SO-Rb5 cell senescence, and inhibited Akt signaling activation 30647800_Data suggest that high circulating DUSP1 levels reflect a chronic subclinical inflammation and underlying residual cardiovascular disease risks even in the treated population. 30967632_results indicate that the JAK2V617F(+) PV progenitors utilize DUSP1 activity as a protection mechanism against DNA damage accumulation, promoting their proliferation and survival in the inflammatory microenvironment, identifying DUSP1 as a potential therapeutic target in polycythemia vera 31061093_Data show that DUSP1 physically interacts with GP78 promoting its ubiquitination and its subsequent degradation. Further results suggest that K280 and K289 are responsible for DUSP1 polyubiquitination and that K280 is a priming site for DUSP1 ubiquitination, including its monoubiquitination. 31246497_This study suggested that miR-101 that regulated DUSP1, IRF1 TF that regulated CXCR4, as well as the differentially expressed genes as TYROBP and CTSS might contribute to the Rheumatoid Arthritis pathogenesis. 31316508_Role of Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 1 in Glucocorticoid-Driven Anti-inflammatory Responses. 31323199_In this pilot study, the expression of GR isoforms and MKP-1 corresponded with patients' clinical response to systemic CS treatment and disease activity, respectively. 31328390_Glucocorticoid receptor inhibits Muller glial galectin-1 expression via DUSP1-dependent and -independent deactivation of AP-1 signalling. 31330530_Dual-specificity phosphatase (DUSP) genetic variants predict pulmonary hypertension in patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 31918570_Clostridium difficile toxin B induces colonic inflammation through the TRIM46/DUSP1/MAPKs and NF-kappaB signalling pathway. 32866608_Lnc-FAM84B-4 acts as an oncogenic lncRNA by interacting with protein hnRNPK to restrain MAPK phosphatases-DUSP1 expression. 33056982_Long non-coding RNA CASC9 promotes gefitinib resistance in NSCLC by epigenetic repression of DUSP1. 33448324_Inhibition of miR1013p protects against sepsisinduced myocardial injury by inhibiting MAPK and NFkappaB pathway activation via the upregulation of DUSP1. 33780908_TORC2/3-mediated DUSP1 upregulation is essential for human decidualization. 33940385_DUSP1 overexpression attenuates renal tubular mitochondrial dysfunction by restoring Parkin-mediated mitophagy in diabetic nephropathy. 34024253_Parathyroid hormone-related protein inhibits nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate-induced apoptosis of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts by activating MKP1 phosphatase. 34303662_SARS-CoV-2 attenuates corticosteroid sensitivity by suppressing DUSP1 expression and activating p38 MAPK pathway. 34431063_Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes block malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through a lncRNA C5orf66-AS1/microRNA-127-3p/DUSP1/ERK axis. 34436551_CDKN2B antisense RNA 1 suppresses tumor growth in human colorectal cancer by targeting MAPK inactivator dual-specificity phosphatase 1. 34512872_MKP-1 Overexpression Reduces Postischemic Myocardial Damage through Attenuation of ER Stress and Mitochondrial Damage. 34578413_The MAPK/ERK Pathway and the Role of DUSP1 in JCPyV Infection of Primary Astrocytes. 34778900_MiR-34a-3p suppresses pulmonary vascular proliferation in acute pulmonary embolism rat by targeting DUSP1. 34785669_Rare variant analysis in eczema identifies exonic variants in DUSP1, NOTCH4 and SLC9A4. 35008797_DUSP-1 Induced by PGE2 and PGE1 Attenuates IL-1beta-Activated MAPK Signaling, Leading to Suppression of NGF Expression in Human Intervertebral Disc Cells. 35236965_STAMBPL1 promotes breast cancer cell resistance to cisplatin partially by stabilizing MKP-1 expression. 35332432_UBR3 promotes inflammation and apoptosis via DUSP1/p38 pathway in the nucleus pulposus cells of patients with intervertebral disc degeneration. 35500847_CircHIPK3 alleviates inflammatory response and neuronal apoptosis via regulating miR-382-5p/DUSP1 axis in spinal cord injury. 35689852_DNTTIP1 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis via recruiting HDAC1 to DUSP2 promoter and activating ERK signaling pathway. 35809838_LINC00702-mediated DUSP1 transcription in the prevention of bladder cancer progression: Implications in cancer cell proliferation and tumor inflammatory microenvironment. 35911442_Downregulated Dual-Specificity Protein Phosphatase 1 in Ovarian Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Study With Multiple Methods. |
ENSMUSG00000024190 |
Dusp1 |
213.259306 |
2.9669976462 |
1.569004 |
0.111212271 |
205.474192 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000013345016907351309350824568308113045759465944397711578927536850438333172404889857856348467325563386600012098300048669517400834472198312141699716448783874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002598581128661020273579346231445450474477146067895605664738169829709868225103531278825324793552289757988437054653826745187483737709044362418353557586669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
320.8167317 |
21.2567499 |
108.9169375 |
5.9747990 |
| ENSG00000120137 |
79646 |
PANK3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H999 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of pantothenate to generate 4'-phosphopantothenate in the first and rate-determining step of coenzyme A (CoA) synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17631502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20797618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27555321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30927326}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Coenzyme A biosynthesis;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; coenzyme A biosynthesis; CoA from (R)-pantothenate: step 1/5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17631502, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20797618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27555321, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30927326}. |
This gene encodes a protein belonging to the pantothenate kinase family. Pantothenate kinase is a key regulatory enzyme in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A (CoA) in bacteria and mammalian cells. It catalyzes the first committed step in the universal biosynthetic pathway leading to CoA and is itself subject to regulation through feedback inhibition by CoA. This family member is expressed most abundantly in the liver. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:79646; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; acetyl-CoA binding [GO:1905502]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; pantothenate kinase activity [GO:0004594]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; vitamin binding [GO:0019842]; coenzyme A biosynthetic process [GO:0015937]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] |
17631502_analysis of the homodimeric structures of the catalytic cores of PanK1alpha and PanK3 in complex with acetyl-CoA and the the structural effects of the PanK2 mutations that have been implicated in neurodegeneration 27555321_Biochemical analyses showed that the transition between the inactive and active conformations, as assessed by the binding of either ATP.Mg(2+) or acyl-CoA to PANK3, is highly cooperative indicating that both protomers move in concert. |
ENSMUSG00000018846 |
Pank3 |
723.759185 |
2.1086867624 |
1.076345 |
0.069144134 |
242.856323 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000093737787291016881403867833570883586769441446030261195674331282725112946666724198227000561517669727755073818955040133733256076891087442025038423132343723409576341509819030761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000021891926272395714592066291366145267208189904228397784117258490108279526213946653775103481403283779764856509571441072191506209618092537380618090026018762728199362754821777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
894.3668530 |
91.7560965 |
427.9633002 |
32.2068834 |
| ENSG00000120217 |
29126 |
CD274 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZQ7 |
FUNCTION: Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:28813410). As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:28813410). Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10) (PubMed:10581077). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10581077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11015443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417}.; FUNCTION: The PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway is exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and escape destruction by the immune system, thereby facilitating tumor survival (PubMed:28813417, PubMed:28813410). The interaction with PDCD1/PD-1 inhibits cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) effector function (By similarity). The blockage of the PDCD1-mediated pathway results in the reversal of the exhausted T-cell phenotype and the normalization of the anti-tumor response, providing a rationale for cancer immunotherapy (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EP73, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813410, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28813417}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes an immune inhibitory receptor ligand that is expressed by hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells, such as T cells and B cells and various types of tumor cells. The encoded protein is a type I transmembrane protein that has immunoglobulin V-like and C-like domains. Interaction of this ligand with its receptor inhibits T-cell activation and cytokine production. During infection or inflammation of normal tissue, this interaction is important for preventing autoimmunity by maintaining homeostasis of the immune response. In tumor microenvironments, this interaction provides an immune escape for tumor cells through cytotoxic T-cell inactivation. Expression of this gene in tumor cells is considered to be prognostic in many types of human malignancies, including colon cancer and renal cell carcinoma. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:29126; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0046007]; negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:2000562]; negative regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:2001186]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production [GO:1903556]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; positive regulation of activated CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell apoptotic process [GO:1905404]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of tolerance induction to tumor cell [GO:0002845]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
12091876_Cancer cell-associated B7-H1 increases apoptosis of antigen-specific human T-cell clones in vitro 12244148_B7-H1 is inducible on human endothelial cells by IFN-gamma both in vitro and in vivo; blocking its interaction with its receptor (PD-1) on T cells augments T cell cytokine synthesis. 12468426_up-regulation in HIV infection, relation to disease progression, and possible role in AIDS progression 12538684_Blockade of PD-L1 during T cell responses initiated by allogenic dendritic cells increases T cell proliferation and cytokine production, showing that PD-L1 functions to inhibit T cell activation. 12646628_Monoclonal antibody DF272-defined surface molecule B7-H1 represents a unique receptor structure on dendritic cells that may play a role in the induction and maintenance of T cell anergy. 12893276_binding properties of B7-H1 to programmed death-1. 12923066_B7-H1 is expressed in muscle cells and may have a negative immune regulatory function in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. 14617032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14686489_review of the negative immunoregulatory role of B7-H1 documented in human diseases, including cancer and auotimmune diseases 15131796_Inflammatory bowel disease intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) surface expressed B7h and B7-H1. Proliferation of IEC-stimulated T cells was inhibited only by B7h immunoglobulin. Interferon gamma was inhibited by both anti-B7h mAb and B7h Ig. 15297412_B7-H1 may have a role in antitumor immune responses in non-small cell lung cancer 15342209_IFN-beta up-regulates B7-H1 in vitro and in MS patients in vivo and might represent a novel mechanism how IFN-beta acts as a negative modulator on APC T-cell interactions in the periphery. 15837746_Data suggest that PD-L1 status may be a new predictor of prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer. 15973152_B7 homolog 1 (B7H1) may be involved in the immune evasion of human glioma 16002716_Inhibitory signals delivered from human rhinovirus HRV14-treated dendritic cells to T cells via B7-H1 are critical for induction of T-cell anergy. 16085391_dermal fibroblasts express the B7-H1 mRNA in the process of skin inflammation, suggesting the involvement of NF-kappaB and MAPK and PI3K 16221208_Interaction of tubular epithelial cells and kidney infiltrating T cells via ICOS-L and B7-H1 may change the balance of positive and negative signals to the T cells 16265694_dysfunction of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway may be related to tolerance for lymphocytes, which causes Sjogren syndrome 16282703_B7-H1 is inducible renal tubular epithelial antigen that inhibits T cell activation. B7-H1/PD-1 pathway might play role in protecting tubular epithelium from immune-mediated damage. B7-H1 may be therapeutic strategy in autoimmune renal diseases. 16482562_Our data suggest that PD-L1/PD-1 interactions negatively regulate T cell effector functions predominantly in the absence of exogenous cytokine support, indicating an important role for this pathway in tumor evasion. 16493058_B7-H1 is involved in suppression of T cell proliferation and IL-2 synthesis, roles suggested for B7-H1 on the gastric epithelium that contribute to the chronicity of Helicobacter pylori infection. 16530813_Multivariate analysis demonstrated that PD-L1 immunodetection could be used as an independent factor to evaluate the prognosis of gastric carcinoma. 16876901_a novel bidirectional interaction between hepatocytes and lymphocytes modulated by PD-L1 expression in hepatocytes may contribute to the unique immunological properties of the liver 16916652_Overexpression reduces accessory immune functions of endothelial cells. 17136123_data do not support an association between systemic lupus erythematosus and SNP's within the genes of the PDCD1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 17186290_The aberrant expression of B7-H1 in urothelial cancer is associated with aggressive tumors, suggesting a regulatory role of tumor-associated B7-H1 in antitumor immunity. 17203303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17311651_Modulation of PD-L1 system may play a role in the development of autoimmune liver diseases. 17360651_Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer. 17363736_Inhibition of the MyD88 and TRAF6 adaptor proteins of the TLR pathway blocked not only B7-H1 expression induced by TLR ligands but also that mediated by IFN-gamma 17366897_Data show that sPD-Ll and its antibodies provide the basis for detection of the potential anti-PD-L1 antibodies and soluble PD-L1 in humans as well as for further investigation of its in vivo bioactivities and characterization of its potential receptors. 17415709_B7-H1 was downregulated in quiescent cells and upregulated in cells stimulated with a mitogen confirming the association of proliferation with the induction of B7-H1. 17475895_Elevated B7-H1 expression is closely associated with the suppression of T cell immune function in chronic hepatitis B patients. 17562772_Induction of cells of the T regulatory (Treg) phenotype by B7-H1 may play an important role in the T-cell suppression associated with Helicobacter pylori infection, as well as other infections that result in an up-regulation of B7-H1. 17597384_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17597384_PD-L1 polymorphisms are not associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis, but 6777 G is associated with the prevalence of rheumatoid nodule in Taiwanese patients. 17603844_results indicate Hepatitis C virus core can upregulate a key negative T cell signaling pathway, PD-1/PDL-1, associated with viral persistence & expressed on T cells of infected individuals 17920123_chemopreventive agents were able to induce PD-L1 surface expression in human breast cancer cells, which then promoted PD-L1-mediated T cell apoptosis, a potential link between chemotherapy and cancer immunoresistance 17938288_PD-L1-deficient transgenic mice reconstituted with bone marrow from wild-type mice remain susceptible to severe myocarditis, demonstrating the protective effect of PD-L1 on non-bone marrow-derived cells. 17942371_results suggest that the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway may play a regulatory role in memory T cell subsets in addition to its association with T-cell exhaustion 17963598_B7-H1 and PD-1 expressions in patients with chronic hepatitis B are closely associated with their disease status. 18024277_There is no significant difference in B7-H1 expression on T cells and B cells between chronic hepatitis B patients and healthy subjects. 18086898_Blockade of the B7-H1 pathway may represent an attractive approach in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. 18173375_Induction and maintenance of T cell tolerance requires PD-1, and its ligand PD-L1 on nonhematopoietic cells can limit effector T cell responses and protect tissues from immune-mediated tissue damage. 18203952_deficient cellular immunity observed in Hodgkin lymphoma patients can be explained by 'T-cell exhaustion,' which is led by the activation of PD-1-PD-L signaling pathway 18294387_B7-H1, PD-1 and FOXP3 may have roles in progression of breast neoplasms 18301333_possible functional relationship between the enhanced incidence of precursor plasmacytoid dendritic cells, their comparatively high relative expression of the coinhibitory molecule PD-L1 18322304_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18322304_PD-L1 polymorphism plays a role in Graves' disease (GD) development, and GD patients with the C allele at position 8923 in PD-L1 gene had difficulty in achieving remission. 18347814_up-regulated B7-H1 expression in human pancreatic carcinoma tissues, which might play a role in tumor progression and invasiveness. 18378285_HRV-16 infection or exposure to dsRNA induces epithelial B7-H1 and B7-DC. 18476597_B7-H1 expression in newly diagnosed leukemia patients is lower than that in normal controls, and is higher in patients in remission than in newly diagnosed patients. Gene expression level and responsiveness to therapy are correlated. 18490751_data provide evidence that neurons can express the B7-H1 molecule after viral stress or exposure to a particular cytokine environment 18549878_Hepatitis c virus-specific CD8 T-cell dysfunction and responsiveness to PD-1/PD-L blockade are defined by their PD-1 expression and compartmentalization. 18550794_The PDCD1:CD274 pathway functions in modification of maternal decidual lymphocyte cytokine secretion during pregnancy. 18566376_PD-1 has a key regulatory role during the immune response of the host to the pathogen 18572307_Triptolide inhibits interferon-gamma-induced programmed death-1-ligand 1 surface expression in breast cancer cells. 18578991_B7-H1 expressions by mDCs, CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells were all significantly upregulated at 4 weeks after starting PEG-IFN alpha-2a therapy for chronic hepatitis B. 18585785_PD-L1 may play an important and undervalued role on human T cells. 18608206_Activation of TLR4 signaling in bladder cancer cells up-regulated B7-H1 expression. This regulation was significantly attenuated by ERK or JNK inhibitor. 18650129_findings show monocytes & CCR5(+) T cells of HIV-uninfected donors upregulate PDL-1 on in vitro exposure to HIV; HIV-induced PDL-1 required interferon alpha; in setting of HIV infection, IFN-alpha may negatively affect T cell responses by inducing PDL-1 18652314_Expression of PD-L1 was elevated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and significantly correlated with clinical TNM stage and lymphatic metastasis. 18676751_B7-H3 is highly expressed in urothelial cell carcinoma across tumor stages, whereas B7-H1 and PD-1 expression are associated with advanced disease 18684942_PD-L1 expression is central to autoimmune heart and lung disease in lupus-susceptible (MRL) mice, since PD-L1-null MRL mice succumb to autoimmune myocarditis and pneumonitis before developing renal or systemic illness. 18705009_High expression of PD-L1 on circulating DCs may be associated with T cell exhaustion and persistent high levels of HBV DNA replication in chronic hepatitis B patients. 18756622_B7-H1 is highly expressed on leukemia cells of acute monocyte leukemia (M5) patients 18756934_B7-H1 and PD-1 expressions are increased in gastric carcinoma. 18760278_stromal myofibroblasts and fibroblasts may limit T-helper cell proliferative activity in the gut and, thus, might play a prominent role in mucosal intestinal tolerance via PD-L1 18830259_PD-1/PD-L1 expression on cells from asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers and ATLL patients in comparison with cells from healthy donors. 18850006_Expression of B7-H1 correlates with PI(3) kinase activation in breast & prostate cancer patients. B7-H1-mediated immunoresistance can be attenuated by PI(3) kinase pathway inhibitors & is dependent on S6K1-mediated translational B7-H1 regulation. 18924219_B7-H1 inhibitory signaling may reversely mediate functional impairment of mDC in HIV-1 infection, which further supports the notion that B7-H1 blockade represents a novel therapeutic approach to this disease. 18928614_Blocking PD-L1 in dendritic cells could enhance T lymphocyte proliferation, increase the secretion of IL-2 and IFN-gamma, and inhibit the production of IL-10. 18941206_B7-H1 stimulation activates phosphorylation of JNK and c-jun and down-regulates mitogen-activated protein kinases 1/2 and akt proto-oncogene protein. 18981087_PD-1/PD-L1 interaction is essential for the induction and maintenance of Invariant NKT cell anergy. 19010538_These results highlight a novel mechanism for regulation of B7 family proteins in the placenta. 19056397_Data concluded that PD-1/PD-L1 pathway plays a key role in the regulation of proatherogenic T cell immunity by intervening antigen presenting cell (APC)-dependent T cell activation. 19081139_B7-H1 gene transcription and protein synthesis was enhanced by C5b-9. 19088198_Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1).( 19116915_The expression of PD-1/PDL-1 in renal tissue and during mixed lymphocyte reactions suggests an important role in regulating peripheral T cell tolerance 19224168_expression of B7-H1 is strongly associated with neoplastic progression and prognosis of bladder cancer 19229109_PD-L1 negatively regulates regulatory T cells at sites of chronic hepatitis c infection by controlling stat-5 phosphorylation. 19264916_B7-H1 was significantly upregulated at the growing edge of the gliomas. 19297851_Expression of PD-L1 was significantly higher in poorly and moderately differentiated larynx squamous carcinoma than in well differentiated carcinoma, and was significantly correlated with lymphatic metastasis. 19442732_high level of expression in keratinocytes is associated with induction of regulatory T cells 19451266_Results suggest that expression of PD-L1 on activated monocytes/macrophages may represent a novel mechanism that links the proinflammatory response to immune tolerance in the tumor milieu. 19535643_Activation of PPARgamma in dendritic cells of transgenic mice up-regulates coinhibitory molecule B7H1 which, despite enhanced cross-presentation, impairs the activation of naive ovalbumin-specific CD8-positive T cells and T cell tolerance induction. 19570392_Over-expression of B7-H1 may be responsible for the increasing IL-10 production in pancreatic cancer. 19597183_the first evidence implicating B7-H1 in the suppression of host immunity in T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders and suggest that the targeting of B7-H1 may represent a novel therapeutic approach. 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19664385_Blockade of B7-H1 greatly promoted the proliferation of CD3AK cells and extended the survival time of CD3AK cells in vitro. 19688742_Treg induced by Vitamin D3-modulated dendritic cells, but not Dexamethasone, expressed significant high levels of programmed death-1 ligand upon activation 19698245_Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells highly expressed B7-H1 which inhibited the proliferation of T lymphocytes in a dose-dependent manner. 19703193_B7-H1 expression is controlled by common ERK signaling pathways in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) and Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). 19729380_Isolated decidual stromal cells constitutively express B7H1 and B7DC; B7H1 and B7DC expression can be up-regulated (by IFN-gamma or TNF-alpha); B7H1 and B7DC appear to function in cell-to-cell communication. 19739236_All forms of chronic necroinflammatory liver disease examined correlate with increased B7-H1 and B7-DC expression on Kupffer cells, liver sinusoidal epithelial cells, and leukocytes. 19759858_There were no significant differences of the enhancing effects on cytokine production by blockage of PD-1/PDL pathway between SLE patients and normal subjects. 19794071_The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway plays an important role in modulating immune functions in multiple sclerosis patients. 19811426_Data suggest that the intrahepatic interaction of PD-1 and PD-L1 might play an important role in balancing the immune response to HBV and immune-mediated liver damage in chronic HBV infection. 19826049_Increased B7H1 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 19830728_investigated signaling mechanisms leading to protein expression of B7-H1 and demonstrated that ERK/p38-MAPK and PI3K pathways are differentially involved in the regulation of B7-H1 expression in DC subtypes. 19850680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19850680_We confirm the role of PD-L1 variants in Graves' disease susceptibility and extend these findings to demonstrate association in two Northern European patient cohorts with autoimmune Addison's disease 19916867_Cryptosporidium parvum induces B7-H1(programmed cell death 1 ligand 1) expression in cholangiocytes by down-regulating microRNA-513 19950173_Data show that the combinatorial signal delivered by R-DC to T cells via B7-H1 and sialoadhesin is crucial for the induction of IL-35(+) Treg. 19958630_B7-H1 protein was expressed in human pancreatic carcinoma tissues, and was associated with the prognosis. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20126379_Human Tregs can promote immune suppression via DC modulation through PD-L1 up-regulation. 20145927_B7-H1 and B7-1 significantly correlated with the pathological grade and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, respectively in pancreaticx cancer. 20349059_reduction of expression by siRNA improves tumor-specific T-cell immune functions 20363965_Keratinocyte-associated B7-H1 transgene, under the control of human keratin 14 promoter, directly downregulates the effector function of CD8-positive T cells by associating with programmed death (PD)-1 at local inflammatory sites. 20367936_B7-H1/PD-1 is up-regulated in sinus mucosa of chronic rhinosinusitis. 20373055_the expression rate of PD-L1 in non-small cell lung cancer was associated with histological types and overall survival 20386557_mediates immunosuppressive properties of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells 20445553_the PD-1 pathway is active in immature Langerhans cells and inhibits iLC activities, but expression of receptor and ligands reverses upon maturation and PD-L1 and PD-L2 on mLC function to inhibit T-cell responses 20450779_The expression of B7-H1 on myeloid dendritic cells is significantly up-regulated in HIV/AIDS patients. 20473887_PD-L1 upregulation promotes CD8 positive T-cell apoptosis and postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. 20506224_The negative costimulatory PD-1/PDL-1 pathway regulates peripheral T cell responses in both human and murine rheumatoid arthritis. 20513078_Costimulatory PD-L1 expression on denrtic cells down regulated dendritic cells-T lymphocytes activation in HCV-infected patients. 20522597_Human B7-H1 overexpression can lead to accelerated autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes, when expressed in NOD mice. 20587542_PD-L1 and PD-L2 bound PD-1 with comparable affinities, but striking differences were observed at the level of the association and dissociation characteristics 20601920_Growing tumors that were surgically removed after failed stereotactic radiation therapy were significantly more likely to strongly express B7-H1 protein 20617899_The authors described a novel inhibitory role played by PD-1:PD-L interactions in innate immunity in tuberculosis. 20626886_Results suggest the use of dual combinatorial agents to inhibit B7-H1 beside chemotherapy, in breast cancer patients. 20628145_The study reveals association between 9p24.1 copy number, increased PDL1 expression, and further induction by JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 20636820_Stduies indicate that Regulatory T cells and the PD-1: PD-ligand (PD-L) pathway are both critical to terminating immune responses. 20646001_Data show that PD-L1 expression in primary human gastric epithelial cells was strongly enhanced by H. pylori infection and activated T cells. 20661763_Results suggest that over-expression of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 within liver may participate in local immune dysfunction, which could be one of the mechanisms involved in the chronicity of HBV infection and chronic inflammation seen in CHB patients. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682852_PD-L1 and PD-L2 knockdown dendritic cells showed superior potential to expand minor histocompatibility antigen-specific CD8(+) effector and memory T cells from leukemia patients early after donor lymphocyte infusion and later during relapse. 20722638_REVIEW: role of PD-L1 and PD-L2 and ligands in allergic disease and asthma. 20814675_In acute myeloid leukemia, B7-H1 expression by blasts represents a possible immune escape mechanism. 20817864_the B7h-ICOS interaction may modulate spreading of cancer metastases and recruitment of polymorphonuclear cells in inflammatory sites 20943073_Direct suppression of HBV replication by telbivudine can decrease PD-1 and PD-L1 expressions and restore HBV-specific CD8+T cells. 21076061_Immunological effects of sublingual immunotherapy: clinical efficacy is associated with modulation of programmed cell death ligand 1, IL-10, and IgG4. 21203985_hPDL1 dimer, which may be either a functional unit in immunological synapse formation or a revolution relics of B7 family. 21268011_During dendritic cell differentiation toll-like receptor agonists induce a STAT-3-mediated expression of PD-L1 and favor the development of tolerogenic antigen presenting cells. 21269571_The results support a major role for PD-1/PD-L1 polymorphisms in disease susceptibility of ankylosing spondylitis. 21355078_sB7-H1 may systemically impair host immunity, thereby fostering cancer progression and subsequent poor clinical outcome 21442435_Increased PD-L1 is associated with actinic cheilitis and oral squamous cell carcinoma. 21461580_Uveal melanoma -related B7H1 expression negatively regulated T-cell immune response through the inhibition of T-cell activation, and not through the promotion of T-cell apoptosis. 21478111_The expression of B7-H1 molecules on immature myeloid and lymphoid dendritic cells in cord blood of healthy neonates 21503939_Human livers up-regulated B7-H1 expression after liver transplantation. 21509782_expression of the programmed death ligand 1, is increased in whole blood from active TB patients compared with whole blood from healthy controls or Mtb-exposed individuals, and expression by neutrophils is largely responsible for this increase 21514692_Alteration of the PD-L1/PD1 pathway is present in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. 21540239_PD-L1 may thwart effective antitumor immune responses and represents an attractive target for lymphoma immunotherapy. 21555531_the costimulatory molecule CD80 prevents PDL1-mediated immune suppression by tumor cells and restores T cell activation 21645441_PD-1/PD-L1 expressions were significantly higher in the patients in immune tolerant phase as compared to that in immune active phase of chronic HBV infection. 21659460_Immature leukemic progenitor cells seemed to evade the immune system by inhibiting T-cell function via the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. 21674477_Results show a positive correlation between IL-17-producing cells and B7-H1-expressing Mphis in the same area from HCC tissues. 21697455_PDL1 interaction with B7.1 plays an important role in inhibiting alloimmune responses in vivo and suggests a dominant direction for PDL1 and B7.1 interaction. 21730022_Review discusses the diverse functions of B7-H1 in carcinogenesis and cancer progression. 21733718_data demonstrate that the existence of circulating sPD-L1 in human serum might play an important role in immunoregulation 21791547_Our results suggest that PD-1 G-536A, PD-L1 A8923C and PD-L2 C47103T polymorphisms are associated with the presence of ankylosing spondylitis. 21830424_role of B7-H1 in promoting IL-10 production in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue. 21844574_human muscle cells express B7-H1 in polymyositis, but not in normal muscle fibers 21851845_decreased expression in patients with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis compared with asymptomatic carriers 21876620_Data suggest that PD-L1 may contribute to negative regulation of the immune response in chronic hepatitis B, and that PD-1 and PD-L1 and 2 may play a role in immune evasion of tumors. 21911310_PD-L1 expressed by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells correlates with a decreased number of intratumoral tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes 21912640_Upregulation of circulating PD-L1/PD-1 is associated with poor post-cryoablation prognosis in patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma 21949023_PDL1 transgene blockade inhibits antigen-specific alloreactive T cell apoptosis and induces apoptosis of regulatory T cells and a shift toward higher frequency of T helper (Th)17 cells, breaking fetomaternal tolerance. 22067141_Data suggest that brain endothelial cells contribute to control T cell transmigration into the CNS and immune responses via PD-L2 but not PD-L1 expression. 22133721_Either blocking PD1 expression on T(H)1 cells by small interfering RNA targeting or abrogation of PD1 signaling by SHP1/2 pharmacologic inhibition stabilized T(H)1 cell differentiation during PDL1 challenge. 22174448_Human CD8+ T cells take up functionally active PD-L1 from antigen-presenting cells in an antigen-specific fashion, leading to fratricide of programmed death 1-expressing, neighboring T cells. 22190470_Findings suggest a novel regulatory mechanism for CD274 overexpression in gastric cancer mediated by miR-570 and a somatic mutation in CD274 3'-UTR, and provide a new insight to gastric carcinogenesis. 22204817_interferon-gamma-induced expression on oral squamous carcinoma occurs through PKD2 signal pathway 22271878_AP-1 signaling and EBV infection represent alternative mechanisms of PD-L1 induction 22285902_Virus modulation of inhibitory molecule PD-L1 on epithelial cells may be important in limiting anti-viral effector CD8+ T cell responses and, consequently, worsening acute virus-induced lung tissue damage. 22322668_Data show that PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CCL17, and CCL22 mRNA was identified in papillomas. 22389764_PD-L1 expression in monocytes is regulated by opposing actions of TNF-alpha and TGF-beta. As PD-L1 functions to fine tune lymphocyte activation, dysregulation of cytokines resulting in reduced expression could lead to loss of peripheral T cell tolerance 22397822_study demonstrates, in primary monocytic cells, that peptidoglycan specifically stimulates PD-L1 expression and, using Crohn's disease derived mutants, that this occurs through both NOD2 dependent and NOD2 independent mechanisms 22408358_Data suggest that B7-H1 expression in tumor cells can inhibit the conventional T cell proliferation in tumor microenvironment through the PD-1 expression on conventional T cells. 22430646_PD-1/B7-H1 pathway may play an important role in negatively modulating T cell-mediated immune response in oral lichen planus, and provide the rationale to employ B7-H1 expression on peripheral blood T cells as a marker of severity of Oral lichen planus 22441249_data suggest that PD-1/PD-L1 molecules, rather than markers of T-cell exhaustion, may act as modulators of T-cell immune activation, contributing to the slower course of HIV-2 infection 22461641_Induction of the B7-H1/PD-1 pathway may represent an adaptive immune resistance mechanism exerted by tumor cells. 22462616_PD-L1 is highly expressed in various kinds of lymphomas, either in tumor tissues or lymphoma cell lines. 22482418_Data show that proportions of CD14(+) PD-L1(+) monocyte were correlated with disease activity and production of antibody. 22503210_Cell surface expressed PD1:CD28 retains the capacity to bind PD-L1 resulting in T cell costimulation. 22661084_B7-H1 suppresses killing of Epstein-Barr virus-immortalized B cells by their autologous T and natural killer (NK) cells. 22711893_Transgenic PDL-1 blockade initiated prior to induction of listeriosis infection blunts pathogen-specific CD8-positive T cell expansion in mice with targeted interferon-gamma defects. 22739151_A correlation exists between the expression level of B7-H1 gene in leukemia cells and response of patients to therapy. 22828443_High B7-H1 expression is associated with multiple myeloma. 22851860_HBsAg regulate immune response by tipping the balance between B7-H1 and CD40 22886978_When the miR-513a-5p inhibitor was added, B7-H1 expression was increased. 22894700_The levels of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression were significantly up-regulated in the inflammation ascending phase, initial and climax period and in parallel with hepatitis B virus-specific clonal expansion. 22895698_expression of PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, in liver biopsies from HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) and chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients were analyzed; results showed all 3 molecules were observed in the HBV-ACLF samples and levels were significantly higher than in CHB 23066977_The expression of B7-H1 molecule on immature BDCA-1(+) myeloid dendritic cells were significantly lower in umbilical cord blood of healthy neonates when compared with those cells in peripheral blood of healthy adults. 23107341_Data suggest that the immunomodulatory proteins B7-H1, B7-H3, and HLA-G5 are secreted from early and term placenta via exosomes and have important implications in mechanisms by which trophoblast immunomodulators modify maternal immunological milieu. 23179191_B7-H1 is expressed in the majority of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas with transcriptionally-active HPV suggesting that B7-H1 expression by tumor cells may play a role in harboring persistent HPV infection. 23193072_Elevated levels of B7H1 protein were associated with differentiated thyroid carcinomas. 23243206_Human cardiac progenitor cells in allogeneic settings have a PD-L1-dependent tolerogenic immune behavior. 23261407_Data indicate that PD-L1 and FasL molecules play significant roles in immunomodulation mediated by placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 23275603_B7h stimulation modulates dendritic cell function with effects on their maturation and recruitment into tissues. 23288508_Our findings support the role of the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction in creating an 'immune-privileged' site for initial viral infection and subsequent adaptive immune resistance once tumors are established 23300177_The PD-1/PD-L1 axis contributes to T-cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 23340297_PD-L1 expression in tumor cell promotes peritoneal dissemination by repressing CTL function. PD-L1-targeted therapy is a promising strategy for preventing and treating peritoneal dissemination. 23359812_Splenic dendritic cells had a higher PDL1 expression (p = 0.007), while CD33(+)CD14(+)HLA-DR(-) IMCs had a lower CTLA4 expression (p = 0.029) in PDAC patients 23381841_Sinomenine was observed to have a significant effect in decreasing the PDL1 expression in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells 23383287_Increased level of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, programmed death receptor ligand 1/programmed death receptor 1, and soluble CD25 in Sokal high risk chronic myeloid leukemia. 23388330_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expressed on hPMSCs could inhibit the hPMSCs-mediated up-regulation on the expression of IL-17 secreted by peripheral blood T cells 23398844_sPD-L1 may contribute to the continuous T cell activation and development of diabetic macrovascular diseases. 23403048_Gain-of-function STAT1 mutations are associated with PD-L1 overexpression and a defect in B-cell survival. 23430453_genetic polymorphisms influencing B7-H1 expression modify cancer susceptibility. 23478000_PD-L1 expression is paradoxically associated with improved survival in mismatch repair-proficient colorectal cancer. 23508008_B7-H1 expressed on mantle cell lymphoma cells was able to inhibit T-cell proliferation induced by the tumor cells. 23521696_Suggest that up-regulation of the inhibitory PD-1/PD-L1 pathway may negatively regulate cervical cell-mediated immunity to HPV and contribute to the progression of HR-HPV-related cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. 23585913_NF-kappaB plays a key role in inducing CD274 expression in human monocytes lipopolysaccharide treatment inflammation cell model. 23613317_Gliomas can upregulate B7-H1 expression in circulating monocytes and tumor-infiltrative macrophages through modulation of autocrine/paracrine IL-10 signaling, resulting in an immunosuppressive phenotype 23660190_These results suggest that PI3Kdelta mediates dsRNA-induced upregulation of B7-H1 without affecting the activation of NF-kappaB. 23676558_high levels of programmed death ligand-1 is associated with sarcomatoid lung carcinomas. 23756770_Human hepatic stellate cells demonstrate potent immunoregulatory activity via B7-H1-mediated induction of apoptosis in activated T cells. 23792703_[review] The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway regulates lymphocyte activation, promotion of T regulatory cell development and function, breakdown of tolerance and development of autoimmunity. 23824147_In recurrent genital papilloma lesions, proliferation, and cytokine production by CD4(+) T cells are impaired and the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction is responsible for the functional impairment of CD4(+) T cells. 23873101_High B7-H1 and B7-H4 expressions were closely correlated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. 23907003_Studies indicate that PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, consider |
ENSMUSG00000016496 |
Cd274 |
20.039586 |
6.2551844468 |
2.645052 |
0.471425322 |
33.162064 |
0.00000000847887017694880004932804777768862170006514134001918137073516845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000037191121489380181475456710283797323590704309026477858424186706542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.4107536 |
10.8384279 |
5.7191097 |
1.4750447 |
| ENSG00000120256 |
84918 |
LRP11 |
protein_coding |
Q86VZ4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables phosphoprotein binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including response to cold; response to immobilization stress; and response to water deprivation. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84918; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; multicellular organismal response to stress [GO:0033555]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to immobilization stress [GO:0035902]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to starvation [GO:0042594]; response to water deprivation [GO:0009414] |
|
ENSMUSG00000019796 |
Lrp11 |
87.181718 |
2.1306211559 |
1.091274 |
0.196102888 |
30.807570 |
0.00000002849242357490705326128540978477404754798385511094238609075546264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000118832487133548476645468038991743098264919353823643177747726440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
125.3066544 |
14.6511914 |
59.0524907 |
5.3448712 |
| ENSG00000120262 |
80129 |
CCDC170 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYT3 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in Golgi-associated microtubules organization and stabilization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28687497}. |
Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome |
|
The function of this gene and its encoded protein is not known. Several genome-wide association studies have implicated the region around this gene to be involved in breast cancer and bone mineral density, but no link to this specific gene has been found. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:80129; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226] |
20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20661439_SNPs associated with breast cancer differ for Asian, European, and African ancestry groups 24481879_Our findings suggest that ESR1 and C6orf97 gene polymorphism is associated with fracture and vertebral fracture risk in Chinese postmenopausal women. 25099679_ESR1-CCDC170 rearrangements are found in an aggressive subset of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers 25338983_Variation in rs3757318 of C6orf97 is associated with breast cancer risk. 25370037_Data suggest that rs2046210 SNPs located in the region of C6ORF97 (CCDC170)-estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) might have substantial roles not only in carcinogenesis but also in progression toward a more aggressive phenotype in breast cancer patients. 26911590_Genetic variation at the WLS and CCDC170/ESR1 loci were found to be significantly associated with bone mineral density 26928228_Expression of ESR1, RMND1 and CCDC170 associated with variants in separate enhancer elements predisposing breast cancer. [meta-analysis] 28687497_Findings demonstrate that CCDC170 plays an essential role in Golgi-associated microtubules organization and stabilization, and implicate a mechanism for how perturbations in the CCDC170 gene may contribute to the hallmark changes in cell polarity and motility seen in breast cancer. 30601066_The study shows that an association of theRMND1/CCDC170-ESR1 single nucleotide polymorphisms can exist with osteopenia, osteoporosis, or fragility fracture. 31246104_COL1A1, CCDC170, and ESR1 single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with distal radius fracture in postmenopausal Mexican women. 32771039_Therapeutic role of recurrent ESR1-CCDC170 gene fusions in breast cancer endocrine resistance. 33291081_CCDC170 affects breast cancer apoptosis through IRE1 pathway. 33785515_Three functional polymorphisms in CCDC170 were associated with osteoporosis phenotype. 35414641_Relationship between rs7586085, GALNT3 and CCDC170 gene polymorphisms and the risk of osteoporosis among the Chinese Han population. |
ENSMUSG00000019767 |
Ccdc170 |
192.777181 |
0.1092113861 |
-3.194805 |
1.150258376 |
5.581474 |
0.01815144202661717748314984532953531015664339065551757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032848857811779000326346533711330266669392585754394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.0780525 |
35.9558236 |
469.9884922 |
236.8447028 |
| ENSG00000120265 |
5110 |
PCMT1 |
protein_coding |
P22061 |
FUNCTION: Initiates the repair of damaged proteins by catalyzing methyl esterification of L-isoaspartyl and D-aspartyl residues produced by spontaneous isomerization and racemization of L-aspartyl and L-asparaginyl residues in aging peptides and proteins (PubMed:3167043, PubMed:6469980). Acts on EIF4EBP2, microtubule-associated protein 2, calreticulin, clathrin light chains a and b, Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1, phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1, stathmin, beta-synuclein and alpha-synuclein (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23506, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3167043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6469980}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the type II class of protein carboxyl methyltransferase enzymes. The encoded enzyme plays a role in protein repair by recognizing and converting D-aspartyl and L-isoaspartyl residues resulting from spontaneous deamidation back to the normal L-aspartyl form. The encoded protein may play a protective role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease, and single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene have been associated with spina bifida and premature ovarian failure. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:5110; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0004719]; protein methylation [GO:0006479]; protein repair [GO:0030091] |
11792715_Protein L-Isoaspartyl Methyltransferase 11847284_crystal structure complexed with adenosyl homocysteine (AdoHcy) to 1.6-A resolution 16256389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16256389_Our results showed that the Ile120Val polymorphism of PCMT1 gene is a genetic modifier for the risk of spina bifida. Val/Val genotype was associated with a reduction in risk for spina bifida. 17167531_A potential role for PIMT in biological processes such as wound healing, cell migration, and tumor metastasis dissemination. 18381200_These results suggest that PIMT repair of abnormal proteins is necessary to maintain normal MAPK signaling. 18582870_Four polymorphisms in the protein L-isoaspartyl-O-methyltransferase (PCMT1) gene, encoding a protein repair enzyme, are associated with premature ovarian failure (POF). 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21372823_study demonstrates a novel role for PIMT as a negative regulator of Abeta peptide formation and a potential protective factor in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease 21839816_Data show six differentially expressed proteins were identified as HSP70, PPIA and alpha-Enolase (up-regulated) S100-A9, PIMT and beta-5 tubulin (down-regulated), most of which had been shown to play a potential role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 21841813_A tight cross-regulation exists between ERK and PIMT in regards to their activation and expression during the epithelial mesenchymal transition. 22382029_PIMT may act as a co-activator in ERalpha-mediated transcription of TFF1 through its recruitment to the promoter via interacting with ERalpha. 22647835_The results implied that maternal polymorphisms in PCMT1 might be a potential genetic risk factor for isolated anencephaly in the Chinese population of Lvliang. 22735455_Study provides new insight into the molecular mechanisms by which PIMT suppresses the p53 activity through carboxyl methylation, and suggests a therapeutic target for cancers. 23647599_Overexpression of PCMT1 attentuates Mst1 kinase activation and its apoptotic effects in response to hypoxia-induced injury in cardiomyocytes. 23903319_Data indicate that human PROTEIN ISOASPARTYL METHYLTRANSFERASE (PIMT) can initiate isoAsp conversion to Asp, and is able to restore Arabidopsis PRH75's complex biochemical activity provided isoAsp formation has not led to conformational alterations. 24358311_ERK2-mediated phosphorylation of transcriptional coactivator binding protein PIMT/NCoA6IP at Ser298 augments hepatic gluconeogenesis. 25800307_The data of this study indicated that DA-associated PIMT downregulation is an important event contributing to neuronal cell death 26997432_Strong PIMT expression was a predictive marker of poor prognosis for surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma. 27327778_decrease of PCMT1 significantly increased the proportion of D-Asp residues in PHB1 and had significant and fatal impacts on morphology and functions of the mitochondria, such as ATP production and the mitochondrial fusion-fission system 28100787_PIMT heterozygosity for R36C, G175R, R17H, or R17S would be detrimental to successful aging, whereas homozygosity (should it ever occur) would produce devastating neuropathology 29517839_High expression of PCMT1 is associated with pancreatic cancer. 29856810_The new findings reported here extend the list of human PIMT variants that may contribute to neurological diseases in the young and the decline of CNS function in the aged. 33198416_PIMT Binding to C-Terminal Ala459 of CAIX Is Involved in Inside-Out Signaling Necessary for Its Catalytic Activity. 34082401_The enzyme L-isoaspartyl (D-aspartyl) methyltransferase promotes migration and invasion in human U-87 MG and U-251 MG glioblastoma cell lines. 35033172_Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library screen identifies PCMT1 as a critical driver of ovarian cancer metastasis. 35462043_PIMT/TGS1: An evolving metabolic molecular switch with conserved methyl transferase activity. 35535040_PCMT1 Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Is Correlated with Immune Infiltrates in Breast Cancer. 35628507_The Protein L-Isoaspartyl (D-Aspartyl) Methyltransferase Regulates Glial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Migration Induced by TGF-beta1 in Human U-87 MG Glioma Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000019795 |
Pcmt1 |
544.201526 |
2.1597729960 |
1.110880 |
0.068006325 |
270.321497 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000096569624476817528749124712711504110461515751608182738011540945992507445009425145133534913191205809121178574776621610722975972466385263914386298785886598994299134801622130908071994781494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000025006450127681171126029461158389496416617623360964177733811256532301725525983058510063659481255186929440801679002861144989066692662100574869418105963814191738947556586936116218566894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
760.3966675 |
31.2179733 |
354.8025200 |
11.5358440 |
| ENSG00000120278 |
57480 |
PLEKHG1 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULL1 |
|
Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57480; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] |
19165232_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20641033_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29967039_PLEKHG1 rs9478812 variant substantially increases risk of preeclampsia. 30659137_Genetic variation in PLEKHG1 is associated with white matter hyperintensities and ischemic stroke, most strongly with the small vessel subtype, suggesting it acts by promoting small vessel arteriopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000040624 |
Plekhg1 |
52.707653 |
0.4394653879 |
-1.186179 |
0.297704726 |
15.615417 |
0.00007761915929871976709171488284511042365920729935169219970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000217227681313823242290061976689230505144223570823669433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.8512676 |
7.1317267 |
79.4953185 |
11.3248980 |
| ENSG00000120280 |
80231 |
TASL |
protein_coding |
Q9HAI6 |
FUNCTION: Innate immune adapter that mediates the recruitment and activation of IRF5 downstream of endolysosomal toll-like receptors TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 (PubMed:32433612). Following recruitment to endolysosome by SLC15A4 downstream of TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9, specifically recruits IRF5 transcription factor via its pLxIS motif, leading to IRF5 activation and subsequent expression of type I interferons (PubMed:32433612). Plays a role in the regulation of endolysosomal pH in immune cells such as B-cells, dendritic cells and monocytes (PubMed:31001245). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31001245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32433612}. |
Cytoplasm;Endosome;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in positive regulation of innate immune response; positive regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway; and regulation of lysosomal lumen pH. Located in endolysosome membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80231; |
endolysosome membrane [GO:0036020]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway [GO:0034157]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 8 signaling pathway [GO:0034161]; regulation of lysosomal lumen pH [GO:0035751]; regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034121] |
31092820_Through combined genetic, in silico, in vitro, and ex vivo approaches, study defines CXorf21, a gene of hitherto unknown function, which escapes X-chromosome inactivation, as a candidate underlying the Xp21.2 systemic lupus erythematosus association and demonstrates that CXorf21 is an IFN-response gene and that the sexual dimorphism in expression is magnified by immunological challenge. 31695690_Characterization of cxorf21 Provides Molecular Insight Into Female-Bias Immune Response in SLE Pathogenesis. 32433612_identification of TASL as the component that links endolysosomal TLRs to the IRF5 transcription factor via SLC15A4 provides a mechanistic explanation for the involvement of these proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus |
ENSMUSG00000025058 |
Tasl |
175.716036 |
0.3244008050 |
-1.624151 |
0.141823387 |
133.220355 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000080913551290761627628381129084017643590773897269676164643499191563603500287478703482946240654882785747759044170379638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000010653737886276910139139182818284875657870489654596364430852559779052802923794132303192405686331767356023192405700683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.9737024 |
7.8923007 |
270.0072654 |
15.5340463 |
| ENSG00000120306 |
84418 |
CYSTM1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H1C7 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84418; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821] |
|
ENSMUSG00000046727 |
Cystm1 |
68.678269 |
2.3389021087 |
1.225831 |
0.193342691 |
40.807861 |
0.00000000016795611826442482873656259810351241978931824405663064680993556976318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000854544055699038339668078153286718406933530900460027623921632766723632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
96.8906396 |
11.7473947 |
41.7214877 |
4.0105370 |
| ENSG00000120318 |
64411 |
ARAP3 |
protein_coding |
Q8WWN8 |
FUNCTION: Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent GTPase-activating protein that modulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling by regulating ARF and RHO family members. Is activated by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) binding. Can be activated by phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P2) binding, albeit with lower efficiency. Acts on ARF6, RAC1, RHOA and CDC42. Plays a role in the internalization of anthrax toxin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11804589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15569923}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;GTPase activation;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a phosphoinositide binding protein containing ARF-GAP, RHO-GAP, RAS-associating, and pleckstrin homology domains. The ARF-GAP and RHO-GAP domains cooperate in mediating rearrangements in the cell cytoskeleton and cell shape. It is a specific PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/PtdIns(3,4)P2-stimulated Arf6-GAP protein. An alternatively spliced transcript has been found for this gene, but its biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:64411; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035021]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
12832619_The catalytic domain of ARF-GAP alone is sufficient to initiate uncoating of liposome-derived COPI-coated vesicles. ARF-GAP activity is not required for COPI coat assembly & does not seem to be an essential coat component of COPI vesicles. 15546919_ARAP3 has a role in integrin-mediated tyrosine kinase signalling pathways controlling Rho GTPases and cell spreading 15569923_ARAP3 deficiency produced by antisense expression of an ARAP3 EST impaired entry of anthrax PA and its bound toxigenic moieties into both human and mouse cells, resulting in reduced toxin sensitivity 17314030_In a yeast two-hybrid screen for new interaction partners of Arap3, the PI 5'-phosphatase SHIP2 was identified as an interaction partner of Arap3. 19786092_None of the individual PH domains can bind to PtdIns(3,4,5)P3; rather, a fragment comprising two PH domains and an N-terminal linker is minimally required for binding. 21076469_ARAP3 is a unique Src substrate that suppresses peritoneal dissemination of scirrhous gastric carcinoma cells. 22750419_The structural basis for the interaction between Arap3 and Vav2, hydrophobic pockets and binding specificity. 23180820_Phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase (PI3K) is input into the regulation of beta2 integrin activity, and processes dependent on its responses, by signaling through its effector ARAP3. 23239578_structural and binding affinity between odin and arap3 27311713_Structural Basis for the Specific Recognition of RhoA by the Dual GTPase-activating Protein ARAP3. |
ENSMUSG00000024451 |
Arap3 |
443.475185 |
0.4098483539 |
-1.286838 |
0.083121980 |
241.410479 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000193714395102184564423484283451280309744561046900360776418333519701782551798793468972031288983997064046787802218313692941095225475869434205583585750787278811912983655929565429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000044815430591038315081020413119298117319675965505060800902433104288456416475505369147392872456029683241034848729762753687693342372381447719087432801643444690853357315063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
264.1596187 |
19.9242775 |
649.7433098 |
34.0433804 |
| ENSG00000120327 |
56122 |
PCDHB14 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5E9 |
FUNCTION: Potential calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. May be involved in the establishment and maintenance of specific neuronal connections in the brain. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the protocadherin beta gene cluster, one of three related gene clusters tandemly linked on chromosome five. The gene clusters demonstrate an unusual genomic organization similar to that of B-cell and T-cell receptor gene clusters. The beta cluster contains 16 genes and 3 pseudogenes, each encoding 6 extracellular cadherin domains and a cytoplasmic tail that deviates from others in the cadherin superfamily. The extracellular domains interact in a homophilic manner to specify differential cell-cell connections. Unlike the alpha and gamma clusters, the transcripts from these genes are made up of only one large exon, not sharing common 3' exons as expected. These neural cadherin-like cell adhesion proteins are integral plasma membrane proteins. Their specific functions are unknown but they most likely play a critical role in the establishment and function of specific cell-cell neural connections. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56122; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] |
25566775_PCDHB14- and GABRB1-like nervous system developmental genes are altered during early neuronal differentiation of NCCIT cells treated with ethanol 35688944_PCDHB14 promotes ferroptosis and is a novel tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000046191 |
Pcdhb20 |
30.393118 |
0.4988955989 |
-1.003190 |
0.271809114 |
13.851838 |
0.00019780321189370560154736911062656190551933832466602325439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000518574672744421746872767187142017064616084098815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.8294676 |
3.5275119 |
39.9955042 |
4.6250277 |
| ENSG00000120332 |
63923 |
TNN |
protein_coding |
Q9UQP3 |
FUNCTION: Extracellular matrix protein that seems to be a ligand for ITGA8:ITGB1, ITGAV:ITGB1 and ITGA4:ITGB1 (By similarity) (PubMed:17909022). Involved in neurite outgrowth and cell migration in hippocampal explants (By similarity). During endochondral bone formation, inhibits proliferation and differentiation of proteoblasts mediated by canonical WNT signaling (By similarity). In tumors, stimulates angiogenesis by elongation, migration and sprouting of endothelial cells (PubMed:19884327). Expressed in most mammary tumors, may facilitate tumorigenesis by supporting the migratory behavior of breast cancer cells (PubMed:17909022). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80YX1, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80Z71, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17909022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19884327}. |
Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable integrin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including generation of neurons; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in osteoblast differentiation; and negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation. Predicted to act upstream of or within axonogenesis. Predicted to be located in extracellular matrix and neuron projection. Predicted to be active in collagen-containing extracellular matrix and extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:63923; |
CA3 pyramidal cell dendrite [GO:0097442]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; hippocampal mossy fiber expansion [GO:1990026]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; tenascin complex [GO:0090733]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; dendrite self-avoidance [GO:0070593]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in osteoblast differentiation [GO:1905240]; negative regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001223]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033689]; neuron projection extension [GO:1990138]; osteoblast development [GO:0002076]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; regulation of bone development [GO:1903010]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of smooth muscle tissue development [GO:1905899] |
15592496_The expression of tenascin-W is dependent on p38MAPK and JNK signaling pathways in mammary tumors. (tenascin-W) 17909022_data imply that tenascin-W expression in the activated tumor stroma facilitates tumorigenesis by supporting the migratory behavior of breast cancer cells 18306355_results reveal a clear association between elevated levels of tenascin-W and the presence of colorectal cancer and breast cancer 25868708_Results show that tenascin-W acts as a niche component for breast cancer metastasis to bone by supporting cell migration and cell proliferation of the cancer cells. 26627873_This study demonstrated that the genetic defect was totally or partly clarified in 21 patients with nine of them having potential disease-causing mutations in TTN. 28629900_specific association of NR1I3, C6 and TNN with low hip BMD risk 33603752_Tenascin-W: Discovery, Evolution, and Future Prospects. 33692777_Tenascin-W Is a Novel Stromal Marker in Biliary Tract Cancers. 35371015_Tenascin-C can Serve as an Indicator for the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment of Diffuse Low-Grade Gliomas. 36206596_TNN is first linked to auditory neuropathy. |
ENSMUSG00000026725 |
Tnn |
46.839803 |
0.1954384362 |
-2.355214 |
0.299231133 |
62.578664 |
0.00000000000000256012013447959659700240929559048047112353695131670150431091315113008022308349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000017849491348568185328430169391842196586854801115817892309678427409380674362182617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.6524586 |
3.3541247 |
75.2217093 |
11.3085249 |
| ENSG00000120337 |
8995 |
TNFSF18 |
protein_coding |
Q9UNG2 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF18/AITR/GITR. Regulates T-cell responses. Can function as costimulator and lower the threshold for T-cell activation and T-cell proliferation. Important for interactions between activated T-lymphocytes and endothelial cells. Mediates activation of NF-kappa-B. Triggers increased phosphorylation of STAT1 and up-regulates expression of VCAM1 and ICAM1 (PubMed:23892569). Promotes leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells (PubMed:23892569). Regulates migration of monocytes from the splenic reservoir to sites of inflammation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TS55, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17449724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18040044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23892569}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This cytokine is a ligand for receptor TNFRSF18/AITR/GITR. It has been shown to modulate T lymphocyte survival in peripheral tissues. This cytokine is also found to be expressed in endothelial cells, and is thought to be important for interaction between T lymphocytes and endothelial cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8995; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily binding [GO:0032813]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell lineage commitment [GO:2000329]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002687]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000508]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042129]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell proliferation involved in immune response [GO:0002309]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
15326137_Upregulation by proinflammatory cytokines suggests GITRL may play important role in ocular immunity. High level of constitutive GITRL expression on photoreceptor inner segments suggests photoreceptors participate in regulation of ocular inflammation. 16179414_Regulates ossteoclasst genersation and substantiate the major role played by the endothelium in bone physiology. 16397134_Using a GITRL-transfected cell line, we demonstrate that GITRL promotes NK cell cytotoxicity and IFN-gamma production. 16874737_GITRL could be a potential candidate for regulation of the ocular immune privilege and the balance between immune privilege and inflammation 16955181_Since regulatory T-cells are localized in the vicinity of GITRL-expressing cells in atopic dermatitis skin, the GITR/GITRL interaction may serve to perpetuate the inflammation locally. 17360848_Constitutive expression of GITRL by tumor cells diminishes natural killer cell antitumor immunity. 17449724_although huGITRL is not capable of alleviating Treg suppression of responder T cells, huGITRL overexpression on monocyte-derived DC enhances their capacity to induce antigen-specific T cell responses 17602748_These observations raise the possibility that the GITRL-mediated inflammatory activation of macrophages is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. 17914571_Levels of AITRL were significantly increased in serum of breast cancer patients 18040044_hGITRL ectodomain displays considerable self-association/dissociation in solution with a dynamic equilibrium between trimeric and monomeric forms over the range of protein concentrations studied. 18378892_identify multiple oligomeric species of hGITRL that possess distinct kinetics of ERK activation. 18689545_The strong correlation of tumor incidence and elevated soluble GITRL levels indicates that soluble GITRL is released from cancers in vivo, leading to impaired NK cell immunosurveillance of tumors 18924213_mechanism of IgG4 induction by regulatory cells involves GITR-GITR-L interactions, IL-10 and TGF-beta. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20228835_The incorporation of an isoleucine zipper motif could markedly improve the costimulation of hsGITRL. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21693309_GITRL expression on Kupffer cells may mediate acute rejection in liver transplantation 21705620_Although GITR transgene costimulation can therapeutically enhance T helper (Th) type 2 cell responses, GITR-GITR ligand interactions are not required for development of Th2-mediated resistance or pathology. 22112394_GITRL upregulation induced by IFN-beta on dendritic cells downregulates CTLA-4 on regulatory T (Treg) cells, facilitating proliferation of anergic Treg cells in multiple sclerosis treatment of multiple sclerosis patients. 22417213_observation suggests a link between cytokine-regulated keratinocyte GITRL expression and its role in inflammatory responses in AD 22649191_Glucocorticoid-induced TNF-related ligand (GITRL) confers pseudoexpression to tumor cells by platelets, which results in GITRL expression by megakaryocytes and their platelet progeny. 23251213_Serum GITRL levels were higher in SLE patients. 23935647_Our findings indicate the possible involvement of GITR-GITRL pathway in the pathogenesis of pSS. 25429429_An increase in GITRL may impair the balance of Th17/Treg, and contribute to the pathopoiesis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 26657118_GITRL modulates the activities of p38 MAPK and STAT3 to promote Th17 cell differentiation in autoimmune arthritis. 27098050_GITRL levels are significantly elevated in rheumatoid arthritis serum and synovial fluid and are positively correlated with autoantibody production in rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting a role of GITRL in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. 28524007_Cultured HCN-2 neurons were incubated at different times with GITRL and/or TRAIL, and thereafter nucleic acid and protein expression were measured. HCN-2 cells do not express GITRL mRNA, but the latter is induced after treatment with TRAIL. Cells did not express the GITRL receptor GITR mRNA, neither in control cultures, nor after treatment with TRAIL. TRAIL, when associated to GITRL, exerted additive toxic effects. 30760623_our studies have demonstrated a critical role of GITRL in modulating the suppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells 33188059_Type I interferons drive the maturation of human DC3s with a distinct costimulatory profile characterized by high GITRL. 33654081_Structures of mouse and human GITR-GITRL complexes reveal unique TNF superfamily interactions. |
ENSMUSG00000066755 |
Tnfsf18 |
254.059829 |
0.0900367676 |
-3.473342 |
0.142158919 |
752.552705 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000111777105507592147229874625912393837297006677012796964419573573847065049884837520792594620331137886997837721930308699525316418917023194384141279167125423046775686961 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000082906034034776898033599936103299777038268397643394087737880974604661032085584327745330089601027604838912533754028775123749831466757450653353021453259436463432869575 |
Yes |
No |
40.8516178 |
4.1306634 |
457.1871792 |
23.1729619 |
| ENSG00000120341 |
89866 |
SEC16B |
protein_coding |
Q96JE7 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the organization of the endoplasmic reticulum exit sites (ERES), also known as transitional endoplasmic reticulum (tER). Required for secretory cargo traffic from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus (PubMed:17192411, PubMed:21768384, PubMed:22355596). Involved in peroxisome biogenesis. Regulates the transport of peroxisomal biogenesis factors PEX3 and PEX16 from the ER to peroxisomes (PubMed:21768384). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17192411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21768384, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22355596}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Peroxisome biogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
SEC16B is a mammalian homolog of S. cerevisiae Sec16 that is required for organization of transitional endoplasmic reticulum (ER) sites and protein export (Bhattacharyya and Glick, 2007 [PubMed 17192411]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:89866; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070971]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; COPII vesicle coating [GO:0048208]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; peroxisome fission [GO:0016559]; peroxisome organization [GO:0007031]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0070863]; protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070973]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
17192411_Mammalian cells contain two distinct Sec16 homologues: a large protein Sec16L of 2154 aa and a smaller protein Sec16S of 1060 aa. 19812171_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19851340_Data show that SNPs in SEC16B and TMEM18 were significantly associated with obesity, and the SNPs in GNPDA2, BDNF, FAIM2 and MC4R were marginally associated with obesity in Japanese. 19851340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20215397_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20616199_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20724581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21768384_Data show that knockdown of Sec16B but not Sec16A by RNAi affected the morphology of peroxisomes, inhibited the transport of Pex16 from the ER to peroxisomes, and suppressed expression of Pex3. 22355596_describe characterization of the localization and dynamics of Sec16B relative to Sec16A, provide evidence that Sec16B is likely a minor or perhaps specialized form of Sec16, and that it is not functionally redundant with S 23121087_Data show the synthetic effect of SNPs on the indices of adiposity and risk of obesity in Chinese girls, but failed to replicate the effect of five separate variants of SEC16B rs10913469, SH2B1 rs4788102, PCSK1 rs6235, KCTD15 rs29941 and BAT2 rs2844479. 25637721_SEC16B, MC4R, MAP2K5 and KCTD15 (rs17782313, rs543874, rs2241423 and rs11084753) polymorphisms are associated with the risk for children obesity in China. 27005443_Significant associations were identified at 3.5 years for SEC16B rs10913469 with dietary parameters 30026463_SNPs in several gene loci, including SEC16B were similarly associated (albeit not at array-wide signficance (P = 6.7 x 10(-7)) with various phenotypes including fat mass, percentage fat mass, waist-to-hip ratio linked to body composition in this African cohort 33958541_Female-Specific Susceptibility Locus in BOC and SEC16B are Associated with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. 35295960_Associations between Gene-Gene Interaction and Overweight/Obesity of 12-Month-Old Chinese Infants. |
ENSMUSG00000026589 |
Sec16b |
44.868316 |
0.1606808026 |
-2.637731 |
0.882290685 |
5.650422 |
0.01745116947470668616881894763537275139242410659790039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031713772647952560845840963565933634527027606964111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.8802143 |
18.0875008 |
122.5842139 |
88.8415968 |
| ENSG00000120437 |
39 |
ACAT2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BWD1 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the biosynthetic pathway of cholesterol. {ECO:0000303|PubMed:15733928}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7911016}. |
The product of this gene is an enzyme involved in lipid metabolism, and it encodes cytosolic acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase. This gene shows complementary overlapping with the 3-prime region of the TCP1 gene in both mouse and human. These genes are encoded on opposite strands of DNA, as well as in opposite transcriptional orientation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. |
hsa:39; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0003985]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] |
14557872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15733928_Data describe the high resolution structure of human cytosolic acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase (CT), both unliganded (at 2.3 angstroms resolution) and in complex with CoA (at 1.6 angstroms resolution). 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19071091_The increased NPC1L1 and ACAT2 mRNA levels in gallstone patients might indicate an upregulated absorption and esterification of cholesterol in the small intestine. 19282863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21987487_Reduced ACAT2 is associated with impaired butyrate oxidation in ulcerative colitis. 25042803_Results show that DLAT and ACAT2 as upstream acetyltransferases of K76 and K294 in 6PGD protein. 27688151_results demonstrate that the low-level expression of human ACAT2 gene with specific CpG-hypomethylated promoter is regulated by the C/EBP transcription factors in monocytic cells, and imply that the lowly expressed ACAT2 catalyzes the synthesis of certain CE/SE that are assembled into lipoproteins for the secretion 34036483_Circ_RPL23A acts as a miR-1233 sponge to suppress the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by promoting ACAT2. |
ENSMUSG00000062480+ENSMUSG00000023832 |
Acat3+Acat2 |
187.158752 |
2.9222752006 |
1.547092 |
0.142602110 |
118.201536 |
0.00000000000000000000000000156636010825956763521508759792422932594846136424860282146578711197894637078067980873186115786666050553321838378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000018510388469104255783241085440032411577146335658201750753467712049316388177311321072693317546509206295013427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
279.0705910 |
24.3693778 |
96.2227436 |
6.6477883 |
| ENSG00000120498 |
56159 |
TEX11 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYF3 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of crossing-over during meiosis. Involved in initiation and/or maintenance of chromosome synapsis and formation of crossovers. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q14AT2}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Disease variant;Meiosis;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is X-linked and is expressed in only male germ cells. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56159; |
central element [GO:0000801]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; chiasma assembly [GO:0051026]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; male meiosis chromosome segregation [GO:0007060]; meiotic gene conversion [GO:0006311]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of developmental process [GO:0051093]; negative regulation of reproductive process [GO:2000242]; reciprocal meiotic recombination [GO:0007131]; resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates [GO:0000712]; synaptonemal complex assembly [GO:0007130] |
11279525_TEX11 was specifically expressed in human testis. 20378615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25970010_hemizygous TEX11 mutations were a common cause of meiotic arrest and azoospermia in infertile men 26136358_Genetic screening of a large cohort of idiopathic infertile men reveals that TEX11 mutations, including frameshift and splicing acceptor site mutations, cause infertility in 1% of azoospermic men. 26136358_TEX11 mutations, including frameshift and splicing acceptor site mutations, cause infertility in 1% of non-obstructive azoospermic men. 28364521_Through the translational regulation of novel RNA targets SMC1B and TEX11, DAZL may have a key role in regulating chromosome cohesion and DNA recombination; two processes fundamental in determining oocyte quality and whose establishment in foetal life may support lifelong fertility. 29661171_Data identified one novel TEX11 mutation in two brothers. The missense mutation is associated with male infertility, especially azoospermia. 29932616_This result suggests that regular expression of TEX11, TEX12, TEX14 and TEX15 is essential for the early stages of spermatogenesis. 33728612_Targeted next-generation sequencing panel screening of 668 Chinese patients with non-obstructive azoospermia. 33762476_A new TEX11 mutation causes azoospermia and testicular meiotic arrest. 33837739_Zinc transporter mutations linked to acrodermatitis enteropathica disrupt function and cause mistrafficking. 35248021_Association of CATSPER1, SPATA16 and TEX11 genes polymorphism with idiopathic azoospermia and oligospermia risk in Iranian population. 36258021_Downregulation of TEX11 promotes S-Phase progression and proliferation in colorectal cancer cells through the FOXO3a/COP1/c-Jun/p21 axis. 36319719_Testis-expressed gene 11 inhibits cisplatin-induced DNA damage and contributes to chemoresistance in testicular germ cell tumor. |
ENSMUSG00000009670 |
Tex11 |
18.880698 |
0.1472617479 |
-2.763545 |
0.439616409 |
44.494847 |
0.00000000002550276108626212632784537190431243701069230489508754544658586382865905761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000137630988531345149147636954317847936268837116813301690854132175445556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7714757 |
1.4650857 |
32.6121239 |
5.5065445 |
| ENSG00000120519 |
84068 |
SLC10A7 |
protein_coding |
Q0GE19 |
FUNCTION: Involved in teeth and skeletal development. Has an essential role in the biosynthesis and trafficking of glycosaminoglycans and glycoproteins, to produce a proper functioning extracellular matrix. Required for extracellular matrix mineralization (PubMed:30082715, PubMed:29878199). Also involved in the regulation of cellular calcium homeostasis (PubMed:30082715, PubMed:31191616). Does not show transport activity towards bile acids or steroid sulfates (including taurocholate, cholate, chenodeoxycholate, estrone-3-sulfate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) and pregnenolone sulfate). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17628207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29878199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30082715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31191616}. |
Alternative splicing;Amelogenesis imperfecta;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables bile acid transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular calcium ion homeostasis; glycoprotein transport; and heparin biosynthetic process. Located in Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum. Is intrinsic component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84068; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi medial cisterna [GO:0005797]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; bile acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015125]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; glycoprotein transport [GO:0034436]; Golgi vesicle transport [GO:0048193]; heparin biosynthetic process [GO:0030210]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814] |
15932064_cloning and characterization; mapped to chromosome 4q31.2 and contains 12 exons; widely expressed in human tissues 17628207_Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a novel member of the SLC10 family, SLC10A7, previously known as C4orf13, is reported 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29878199_Mutation in SLC10A7 gene is associated with anxiety defective bone mineralization. 30082715_SLC10A7 is involved in glycosaminoglycan synthesis and specifically in skeletal development. SLC10A7 mutations cause a skeletal dysplasia with amelogenesis imperfecta. 32350310_The orphan solute carrier SLC10A7 is a novel negative regulator of intracellular calcium signaling. 33561315_Circular RNA circHECTD1 facilitates glioma progression by regulating the miR-296-3p/SLC10A7 axis. 34999954_SLC10A7, an orphan member of the SLC10 family involved in congenital disorders of glycosylation. |
ENSMUSG00000031684 |
Slc10a7 |
91.304340 |
5.5356112061 |
2.468743 |
0.876269533 |
7.138073 |
0.00754642288989932144560590643322939286008477210998535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014841465936697400065935603663547226460650563240051269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
177.3137454 |
81.0853717 |
32.7305062 |
10.7670923 |
| ENSG00000120526 |
84955 |
NUDCD1 |
protein_coding |
Q96RS6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor antigen |
|
Predicted to be involved in immune system process. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84955; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; immune system process [GO:0002376] |
14688378_An alternative promoter (CML66-S short isoform) has been identified in combination with alternative splicing as a novel mechanism for regulation of the epitope generation of a self-tumor antigen. 18534745_CML66 may play an oncogenic role in ways of favoring tumor cells proliferation, invasion and metastasis-associated with multiple pathways. 18754882_study identified a novel gene, OVA66, which was expressed significantly higher in cancer patients than normal controls; IgG level against OVA66 was significantly elevated in the serum of cancer patients from different histological types of cancer [OVA66] 29021621_the different NudCD1 isoforms have unique interacting partners, with the first isoform binding to a putative RNA helicase named DHX15 involved in mRNA splicing. 29461594_NudCD1 significantly increased in renal cell carcinoma and was positively correlated with cell proliferation, migration, and invasion 30833190_OVA66 overexpression in the cancer cell lines promoted VEGF secretion, tumour growth and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo 32634806_NudCD1 Promotes the Proliferation and Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells through the Activation of IGF1R-ERK1/2. 33336728_Analysis of NudCD1 and NF-kappaBeta in the early detection and course evaluation of renal cancer. 36104662_NudCD1 as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer and its role in the upregulation of cellular spindle assembly checkpoint genes and LIS1 pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000038736 |
Nudcd1 |
203.356614 |
2.6628140992 |
1.412952 |
0.133720096 |
111.972157 |
0.00000000000000000000000003623635915687979088609646262575117750525280174551716644742916459967984818546504754976922413334250450134277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000402747485809898882637058115164030508448192824478903419105398058398369992572085607207554858177900314331054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
295.6202532 |
23.3225156 |
111.8524611 |
6.9501210 |
| ENSG00000120539 |
84930 |
MASTL |
protein_coding |
Q96GX5 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase that plays a key role in M phase by acting as a regulator of mitosis entry and maintenance. Acts by promoting the inactivation of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) during M phase: does not directly inhibit PP2A but acts by mediating phosphorylation and subsequent activation of ARPP19 and ENSA at 'Ser-62' and 'Ser-67', respectively. ARPP19 and ENSA are phosphatase inhibitors that specifically inhibit the PPP2R2D (PR55-delta) subunit of PP2A. Inactivation of PP2A during M phase is essential to keep cyclin-B1-CDK1 activity high. Following DNA damage, it is also involved in checkpoint recovery by being inhibited. Phosphorylates histone protein in vitro; however such activity is unsure in vivo. May be involved in megakaryocyte differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19680222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19793917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20538976, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20818157}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Kinase;Mitosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase. Mutations at this locus have been associated with autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia, also known as thrombocytopenia-2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this locus. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:84930; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; protein phosphatase 2A binding [GO:0051721]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; female meiosis II [GO:0007147]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; negative regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032515]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:1904668]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] |
12890928_A novel missense mutation in the human gene FLJ14813 is associated with autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia 12890928_A paper that narrows the identity of the gene for autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia (THC2) to FLJ14813. The mutation is present in all affected people across three generations while is absent in unaffected family members & 94 random blood donors. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20818157_MASTL enhances cyclin B1-Cdk1-dependent mitotic phosphorylation events, directing mitotic entry, anaphase and cytokinesis in human cells. 21444715_results identify Gwl as a member of the AGC family of kinases that appears to be regulated by unique mechanisms and that differs from the other members of this family 22102272_Studies indicate that mutations in three different genes within the THC2 locus have been associated with congenital thrombocytopenia, including a mutation in MASTL. 24391510_Taken together our results suggest a hierarchy of phosphatases coordinating Greatwall, Ensa/ARPP19 and Cdk substrate dephosphorylation during mitotic exit. 25373736_Mastl upregulation is involved in cancer progression and tumor recurrence after initial cancer therapy 25472593_data demonstrate that GWL acts in a pathway with PP2A which is essential for prophase I exit and metaphase I microtubule assembly in mouse oocytes. 25808837_Data show that siRNA knockdown of Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) or microtubule-associated serine/threonine kinase-like (MASTL) induces radiosensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 26613407_Thus, GWL is a human oncoprotein that promotes the hyperactivation of AKT via the degradation of its phosphatase, PHLPP, in human malignancies. 26616283_Boolean modeling identifies Greatwall/MASTL as an important regulator in the AURKA network of neuroblastoma. 26653855_Thus, Fcp1 coordinates Cdk1 and Gwl inactivation to derepress PP2A-B55, generating a dephosphorylation switch that drives mitosis progression. 26872783_Using mathematical modelling, this paper confirms that deactivation of MASTL is essential for mitotic exit. 26923777_these results established that precise control of MASTL is essential to couple DNA damage to mitosis through the rate of mitotic entry and APC/C activation. 28605876_E2F8 can shorten cisplatin induced G2/M arrest by promoting MASTL mediated mitotic progression in ER+ breast cancer cells, conferring drug resistance. 29229993_The proliferative function of MASTL in these tumor cells requires its kinase activity and the presence of PP2A-B55 complexes. 29743597_MASTL overexpression contributes to chromosome instability and metastasis, thereby decreasing breast cancer patient survival. 30068336_Data show that MASTL expression increases in colon cancer (CC) across all cancer stages. Also, increased levels of MASTL associated with high-risk disease and poor prognosis. Further, its silencing induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in vitro and inhibited xenograft-tumor growth. Functional analysis revealed that MASTL expression facilitates CC progression and chemoresistance by promoting the beta-catenin/Wnt signa... 30445205_MASTL depletion impaired thyroid tumor cell proliferation and increased the percentage of cells presenting nuclear anomalies, which are indicative of mitotic catastrophe. 32123010_AKT Regulates Mitotic Progression of Mammalian Cells by Phosphorylating MASTL, Leading to Protein Phosphatase 2A Inactivation. 32311005_MASTL promotes cell contractility and motility through kinase-independent signaling. 32692487_MASTL: A novel therapeutic target for Cancer Malignancy. 33582914_Knockdown of Microtubule Associated Serine/threonine Kinase Like Expression Inhibits Gastric Cancer Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis by Activation of ERK1/2 and Inactivation of NF-kappaB Signaling. 33627787_Mass-spectrometry-based proteomic correlates of grade and stage reveal pathways and kinases associated with aggressive human cancers. 34331012_MASTL regulates EGFR signaling to impact pancreatic cancer progression. 35732702_SILAC kinase screen identifies potential MASTL substrates. |
ENSMUSG00000026779 |
Mastl |
80.195303 |
2.0623608122 |
1.044297 |
0.185406430 |
31.672333 |
0.00000001825037171640316261114296493995451386993522646662313491106033325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000077406749004054788694152038942830618140078513533808290958404541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
102.7955029 |
13.6476545 |
50.2518714 |
4.9875960 |
| ENSG00000120659 |
8600 |
TNFSF11 |
protein_coding |
O14788 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF11B/OPG and to TNFRSF11A/RANK. Osteoclast differentiation and activation factor. Augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T-cell proliferation. May be an important regulator of interactions between T-cells and dendritic cells and may play a role in the regulation of the T-cell-dependent immune response. May also play an important role in enhanced bone-resorption in humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy (PubMed:22664871). Induces osteoclastogenesis by activating multiple signaling pathways in osteoclast precursor cells, chief among which is induction of long lasting oscillations in the intracellular concentration of Ca (2+) resulting in the activation of NFATC1, which translocates to the nucleus and induces osteoclast-specific gene transcription to allow differentiation of osteoclasts. During osteoclast differentiation, in a TMEM64 and ATP2A2-dependent manner induces activation of CREB1 and mitochondrial ROS generation necessary for proper osteoclast generation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22664871}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Osteopetrosis;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. This protein was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. This protein was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis. Targeted disruption of the related gene in mice led to severe osteopetrosis and a lack of osteoclasts. The deficient mice exhibited defects in early differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and failed to form lobulo-alveolar mammary structures during pregnancy. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8600; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily binding [GO:0032813]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; immune response [GO:0006955]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033598]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoclast development [GO:0036035]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; osteoclast proliferation [GO:0002158]; paracrine signaling [GO:0038001]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone secretion [GO:0051466]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade via TNFSF11-mediated signaling [GO:0071848]; positive regulation of fever generation by positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0071812]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034112]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction [GO:1902533]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of osteoclast development [GO:2001206]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of actin binding [GO:1904616]; TNFSF11-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0071847]; tooth eruption [GO:0044691]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
11606048_RANKL induces formation of avian osteoclasts from macrophages but not from macrophage polykaryons. 11741951_TRANCE stimulated DNA synthesis, chemotactic motility, and capillary-like tube formation in primary cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) 11792569_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor and receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand fail to rescue osteoclast-poor human malignant infantile osteopetrosis in vitro. 12043011_immunohistochemical localization of RANK and its ligand (this protein) in human deciduous teeth 12364326_stimulation by parathyroid hormone 12393586_Long-lived immature dendritic cells mediated by TRANCE-RANK interaction 12393684_Human myeloma cell lines increased the expression & secretion of RANKL in activated T-celes & MM cells stimulated RANKL production in autologous T-cells. This confirms the critical role of RANKL in MM bone disease. 12469211_compared the gene expression of RANKL and osteoprogerin in periodontitis and healthy subjects; data suggest up regulation of RANKL in inflammatory cells and epithelium may be associated with activation of osteoclastic bone destruction in periodontitis 12564836_REVIEW: role of these molecules in immunology and skeletal remodelling and assess their involvement in diseases of bones and joints, including rheumatoid arthritis, Paget's disease, post-menopausal osteoporosis and malignant bone diseases 12574344_RANKL can induce maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells and elicit sustained antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses, either alone or cooperatively with TNF-alpha or CD40L. 12619938_examination as indices of bone turnover in different bone diseases 12698202_RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and matrix metalloproteinase dependent matrix degradation are associated with osteolysis because of bone metastasis of breast cancer. 12702561_Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand plays a nonredundant role in doxorubicin-induced apoptosis. 12756027_the first case of Follicular Lymphoma with bone involvement displaying an aberrant expression of RANKL in malignant cells 12817763_Vitamin D upregulated the expression of RANKL mRNA preferentially in cultured osteoblasts. 12824189_endothelial nitric-oxide synthase and receptor activator of nuclear kappa B ligand expression are regulated via ERK1/2 MAPK after mechanical stress 12923331_osteoprotegerin and RANK ligand have roles in breast cancer bone metastasis 12954625_ICAM1 and RANKL are induced by Beta1 integrin/focal adhesion kinase on osteoblasts and in osteoclast maturation 12975380_RANKL has a role in regulation of osteoclastogenesis mediated by HIV gp120 14699143_RANKL gene expression in the bone microenvironment is regulated by HSF2 14734048_RANKL-OPG pathway may regulate valvular calcification in calcific aortic stenosis 14751235_induces osteoclastogenesis by binding with the receptor, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB in the presence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor 15044512_specimens of ameloblastomas, dentigerous cysts, odontogenic keratocysts, and radicular cysts were subjected to immunohistochemical analysis for RANKL and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP). 15205949_RANKL mRNA could be detected in bone marrow plasma cells from myeloma patients with osteolytic myeloma bone disease 15221493_in-situ involvement of RANKL in both osteoclastogenesis and osteoclastic bone resorptive events occurring in prosthetic joint loosening 15290725_Since RANK-L and OPG mRNA levels are elevated in peripheral blood monocytes in rheumatoid arthritis(RA) and CD4+ T cells are major contributors to RANK-L mRNA expression, monocytes in RA may be involved in pathways regulating bone metabolism. 15292354_Enhanced apoptosis adjacent to vascular calcification and concurrent expression of regulators of apoptosis and osteoclastic differentiation, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and OPG. May be involved in pathogenesis of vascular calcification. 15304486_RANKL-induced cathepsin K gene expression is cooperatively regulated by the combination of the transcription factors and p38 MAP kinase in a gradual manner. 15313187_Thus, the RANKL/OPG ratio was markedly increased, suggesting a potential mechanism of ATRA-induced bone resorption. 15322748_(RANK-L)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) signalling pathway is central to the processes regulating bone turnover in a wide variety of medical conditions, including diabetic neuropathy (review) 15377473_RANKL treatment induced a significant increase of IL-6 & IL-11 secretion by both bone marrow stromal & endothelial cells. 15476205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15554353_Parathyroid hormone [PTH (1-34)] induced RANKL messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression in cultured normal human osteoblast-like cells (hOB). 15564564_Review. The RANKL/RANK/OPG system may mediate links between the vascular, skeletal, & immune systems and play a central role in regulating the vascular calcification coincident with declines in skeletal mineralization with age, osteoporosis, or disease. 15613999_may play a role in apical periodontitis-induced bone resorption 15615493_Activating mutations in TNFRSF11A encoding RANK and deactivating mutations in TNFRSF11B encoding OPG cause systemic bone disease 15615497_disruption of the RANKL-RANK axis with OPG inhibited tumor-induced osteoclastogenesis and decreased bone cancer pain 15671541_RANKL has a role in breast carcinoma metastasis 15710592_human myeloma cells do not express significant levels of RANKL mRNA or produce RANKL able to stimulate osteoclast formation 15722361_When RANKL signaling through NFATc1 was blocked with cyclosporin A, both MCP-1 and RANTES expression was down-regulated 15731115_reactive oxygen species stimulate RANKL expression via ERKs and the PKA-CREB pathway 15732858_significantly increased in periodontal disease, supporting its role in the alveolar bone loss developed in this disease 15794927_megakaryocytes have direct effects on osteoblastic production of factors (RANKL) affecting both bone formation and resorption 15972386_simultaneous inhibition of RANKL and TNF-alpha is necessary to reduce acid-induced, cell-mediated net Ca efflux from bone 16052586_Involvement of RANK/RANKL in dendritic cell-T cell interactions during inflammatory process. RANK expression appears to be limited to sites of immune reaction, both in synovium and in lymph nodes. 16109714_analysis of a positive feedback circuit of TRANCE-induced activation of NFATc1, involving NFATc1-mediated OSCAR expression and its subsequent activation of NFATc1, necessary for efficient differentiation of osteoclasts 16133687_biological responses of OPG and sRANKL synthesis in osteoblasts to the application of cyclic tensile strain are regulated via the p38 MAPK pathway 16143421_CLD (chronic liver disease) is associated with alterations in RANKL/OPG serum levels, which could modulate bone loss in CLD. 16144909_Coexpression of RANKL and VEGF is associated with osteoclastic bone destruction and tumor expansion in bone 16191370_Active vascular epithelial cells contribute to the formation of multinucleated giant cells through regulating RANKL. 16215261_OPG dimer formation is required for the mechanism of inhibition of the RANK-L/RANK receptor interaction 16220542_Expression of RANKL in interferon-gamma-producing human T cells induces osteoclastogenesis from monocytes. 16234249_deltaCAPRI regulates RANKL shedding by modulating MMP14 expression through Ras signaling cascades other than the Erk pathway 16240334_we review the etiology of inflammatory bone loss, the RANK/RANK-ligand/OPG pathway, and the clinical development of anti-RANK-ligand therapy. 16249885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16270354_By upregulating IL-8, the RANKL/RANK system may contribute to the pathogenesis of B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 16317958_Osteoclastogenesis induced by Leukotriene B4 were dose-dependently increased and weaker than that of RANKL 16522681_Wnt signalling in osteoblasts regulates expression of RANKL and inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. 16533764_Up-regulation of RANK ligand is associated with osteosarcome 16572175_the cytokine RANKL (receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand) triggers migration of human epithelial cancer cells and melanoma cells that express the receptor RANK 16583245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16612568_Data show that substance P stimulates production of prostaglandin E2 and receptor activator of nuclear factor- B ligand, and promotes bone resorption. 16681444_RANKL in mast cells may play a role in atherosclerosis 16700737_involved in bone loss associated with periapical lesions 16704959_Sickle cell/beta-thalassemiapatients may develop osteopenia/osteoporosis mainly due to marrow expansion, in which RANKL may be involved. 16730419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16730419_Our results of preliminary clinical evaluation suggest that the -290C>T polymorphism in the TNFSF11 gene promoter could contribute to the genetic regulation of BMD. 16861684_IL-10 significantly decreased RANKL+ Th1-associated alveolar bone loss. Thus, there are critical cytokine interactions linking hIFN-gamma+ Th1 cells to RANKL-RANK/OPG signaling for periodontal osteoclastogenesis in vivo. 16925460_In periprosthetic osteolysis RANKL is present only in tissues with a large amount of wear debris and predominantly in cases involving loosened cemented implants. 16953816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16969487_RANKL expressed in gastric cancer may play a critical role in the promotion of osteoclast format 17018528_RANKL shedding is an important process that down-regulates local osteoclastogenesis 17042716_RGS12 is essential for the terminal differentiation of osteoclasts induced by RANKL. 17053039_activation of RankL gene expression by PKA- and gp130-inducers is mediated via common regulatory domains that also served to facilitate the activity of 1,25-(OH)2D3 17133360_Our results add new insight to the important role of the CCL20/CCR6, RANKL system in the bone tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. 17151927_analysis of RANKL-dependent and RANKL-independent mechanisms of macrophage-osteoclast differentiation in breast cancer 17195907_High receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma with bone metastasis 17197168_RANKL gene is regulated via multiple enhancers 17288531_This review describes the most recent knowledge on the OPG-receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK)-RANK ligand (RANKL) triad and its involvement in bone oncology. 17328065_Kinin B1 and B2 receptors synergistically potentiate IL-1- and TNFalpha-induced PG biosynthesis in osteoblasts by a mechanism involving increased levels of COX-2, resulting in increased RANKL. 17328075_Children with juvenile DM have an elevated RANKL:OPG ratio at the time of diagnosis, resulting in expansion of the number of osteoclasts and activation of the bone resorptive function. 17331078_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17448630_P. gingivalis up-regulates the RANKL/OPG expression ratio in GF and PDL cells, denoting an enhanced osteoclastogenic potential by the cells. 17506059_RNKL modulates expression of genes controlling survival/apoptosis/proliferation in differentiating osteoclasts. 17520299_These findings mean that the imbalance and the disturbed interaction of RANKL and osteoprotegerin may be an important cause and pathogenesis in reduced bone mineral density in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. 17558893_The OPG/RANKL ratio was significantly decreased in anorectic girls; it was due to an increase in serum RANKL values. The decrease in the OPG/RANKL ratio in girls with AN could partly explain the increase in bone loss that occurs in these patients. 17560137_no correlations between expression in any cell type and the severity of arthroscopic features [of temporomandibular joint disease] 17572386_These data establish a signaling cascade in which regulated Lys63-linked TRAF6 auto-ubiquitination is the critical upstream mediator of osteoclast differentiation. 17580719_The expression levels of RANKL and RANK were markedly increased in the perimatrix of cholesteatoma. 17593489_Dual opposing functions for RANKL signaling are highlighted in this review: the negative regulatory mechanism(s) for osteoclastogenesis, and the induction of bone resorption upon stimulation of the RANKL signaling cascade. 17606458_expression of OPG and RANKL were significantly increased in advanced clinical stages and high grade myeloma bone disease 17620507_Baseline serum level of RANKL is a highly significant predictor of risk for cardiovascular disease. 17632511_Study reports mutations in the gene encoding RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor-KB ligand) in six individuals with autosomal recessive osteopetrosis whose bone biopsy specimens lacked osteoclasts. 17634140_Review highlights the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin (OPG) system and its role in the regulation of bone resorption. 17634142_Review highlights the discovery of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) as a pivotal regulator of osteoclast activity and how its inhibition provides a new therapeutic target in osteoporosis. 17667143_OPG gene G1181C polymorphism, alone and in combination with the RANKL rs2277438 polymorphism, was identified as a genetic factor associated with bone mineral density of the lumbar spine in Korean women 17702740_Data suggest that OPG can bind both to RANKL and TRAIL and that the affinity of OPG for these two ligands is of a similar order of magnitude. 17703334_The median level of RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand) was elevated in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) patients as compared to controls; there was no diference in levels among different types of JLA 17852826_Reference intervals were established with a high analytic performance for OPN and an acceptable analytic performance for OPG and total sRANKL. The study revealed low biological variation for OPN and total sRANKL and high biological variation for hsCRP. 17876645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17876645_SNPs in RANKL and IL-17 may be associated with radiographic progression in Japanese patients with early RA. 17881498_Results demonstrate the specificity of RGS10A as a key component in the RANKL-evoked signaling pathway for osteoclast differentiation. 17891780_DACH1 plays an important role in negative regulation of RANKL gene expression in marrow stromal/preosteoblast cells in the bone microenvironment. 17895323_RANK/RANKL/OPG system mediates the effects of calciotropic hormones and, consequently, alterations in their ratio are key in the development of several clinical conditions--REVIEW 17966895_The OPG/RANKL/RANK system constitutes the important element of controlling the number of active osteoclasts by the osteoblasts. 17970704_OPG-RANKL system is involved in the pathogenesis and regulation of bone turnover in CRF. Circulating levels of OPG and RANKL may be useful markers to assess turnover renal osteopathies 17982618_Involvement of this protein in osteosarcoma biology and capability to identify novel therapeutic approaches targeting RANK-positive osteosarcomas. 17990294_cAMP/PKA signaling activates the canonical Wnt pathway through the inactivation of GSK-3beta, whereas Wnt signaling might inhibit bone resorption through a negative impact on RANKL expression in osteoblasts. 17993768_Lower values of sRANKL/OPG ratio in hemodialysis (HD) patients cannot be explained by the elimination of renal clearance only. Alterations in sRANKL/OPG ratio might reflect a compensatory mechanism to modulate bone remodeling. 18061491_differences in the RANK, RANKL, and OPG expression in odontogenic epithelial tumors...could contribute to the differential bone/tooth resorption activity in these lesions 18064531_One mechanism by which RANKL inhibition reduced tumor burden appears to be indirect through inhibition of the 'vicious cycle' and involved an increase in tumor cell apoptosis. 18072013_Study showed that serum levels of free RANKL and total RANKL decrease with age, and also reveals some gender-related differences. 18073309_circulating sRANKL did not correlate with PTH but did correlate with markers of bone resorption suggests that skeletal responsiveness to PTH may differ in this disease. 18172654_The aim of this study was to investigate sRANKL and OPG levels in serum and synovial fluid (SF) and to evaluate their relations in patients with RA in comparison to those with non-erosive arthritis (NEA). 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18208894_increased RANKL and osteoprotegerin in multiple sclerosis may compensate for negative balance of bone remodeling 18253488_the ratio of RANKL/OPG gene expression - a key factor of osteoclastogenesis- is mediated by the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway by suppressing leptin 18271850_Testosterone association with serum RANKL levels in male Hhemodialysis patients suggests that RANKL may mediate the effect of testosterone on bone metabolism in these patients. 18298349_serum OPG, RANKL, MMP-1 and TIMP-1 may have roles in mediating myocardial healing after myocardial infarct 18301383_human monocyte-derived multipotential cells derived from circulating monocytes can express RANKL and differentiate into functional osteoclasts without RANKL-expressing accessory cells 18305214_bone marrow sera from 21 multiple myeloma patients significantly suppressed Wnt3a-induced OPG expression and enhanced RANKL expression in osteoblasts in a DKK1-dependent manner 18311801_The relative protection against bone erosions in spondylarthritis cannot be explained by qualitative or quantitative differences in the synovial expression of RANKL, OPG, and RANK. 18319315_Serum OPG and RANKL do not account for the observed association between bone and coronary artery calcification among postmenopausal women using hormone therapy. 18361931_no significant associations were observed with disease stages, disease status, osteolytic lesions, and survival of patients with multiple myeloma 18362509_The increase in circulating free sRANKL may reflect directly or indirectly the conditions coexistent with bone loss in post-menopausal women. 18367263_Data reveals for the first time that OPG/RANK/RANKL are expressed in the pathological thyroid gland by follicular cells, by malignant parafollicular cells as well as in metastatic lymph node microenvironment. 18369625_surface and intracellular RANKL production is differentially regulated on T cells of patients with ankylosing spondylitis 18381203_These results suggest that E2F1 plays an important role in regulating RANKL transcription through binding to the E2F consensus binding site. 18389210_RANKL-mediated osteoclastic resorption occurs in acute Charcot's osteoarthropathy. However, the incomplete inhibition of RANKL after addition of osteoprogegerin may suggests existence of a RANKL-independent pathway. 18399769_serum osteoprotegerin and RANKL levels are affected by recombinant TSH 18406448_expression of RANKL promotes osteoclastogenesis in the breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cell line 18435789_Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from periodontitis patients did not require supplementation of M-CSF or M-CSF/RANKL for the formation of osteoclast-like cells; in controls, addition of these cytokines was needed. 18445777_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18445777_We have discovered common sequence variants that are consistently associated with bone mineral density and with low-trauma fractures in three populations of European descent. 18480302_A higher expression of RANKL in bone tissue suggests that increased bone resorption in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria is mediated by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand. 18502820_In postmenopausal osteoporosis, TNFSF11 gene promoter polymorphisms -290C>T, -643C>T and -693G>C play a functional role in the genetic regulation of bone mineral density. 18502820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18528653_increases in IL-6, MMP-13, and RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand)expression in osteoarthritis (OA) subchondral bone osteocytes suggest that in subchondral bone OA progression involves abnormal osseous tissue remodeling. 18539107_The level of membranous RANKL, comparing L- and H-OA {level of PGE2 [low (L) or high (H)]}, subchondral bone osteoblasts, as well as its modulation by osteotropic factors, was investigated. 18556224_This study thus investigated the effects of PRL on the osteoblast functions and the RANKL/OPG ratio in human fetal osteoblast (hFOB) cells which strongly expressed PRL receptors. 18565244_The high RANKL:OPG ratio, together with close fibroblast-to-monocyte contacts in pannus tissue, probably favor local generation of bone resorbing osteoclasts at the site of erosion in rheumatoid arthritis 18565252_OPG and RANKL levels, and consequently the OPG/RANKL ratio, differed according to human osteoarthritis subchondral bone osteoblast classification 18586671_TSG-6 has dual roles in bone remodeling: it inhibits RANKL-induced bone erosion in inflammatory diseases, and its interactions with BMP-2 and RANKL help to balance mineralization by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts 18589796_The overexpression of RANKL and the increased ratio of RANKL/OPG in cholesteatoma are associated with the destruction of bone. 18606662_These data indicate a key role for the RANKL system in the regulation of Langerhans cells (LC) survival within the skin and suggest a regulatory role for keratinocytes in the maintenance of epidermal LC homeostasis 18617513_The RING domain and first zinc finger of TRAF6 coordinate signaling by interleukin-1, lipopolysaccharide, and RANKL 18634923_mRNA expression was higher in periapical granulomas when compared with healthy periodontal ligament 18645583_Our results indicate that RANKL is a novel marker for EMT during prostate cancer progression. RANKL may function as a link between EMT, bone turnover, and prostate cancer skeletal metastasis. 18668542_Synovial fibroblasts may significantly contribute to bone resorption through modulation of RANKL and OPG production in a cytokine-rich milieu of inflamed joints. 18710934_These results show a new molecular cross talk between Notch and NF-kappaB pathways that is relevant in osteoclastogenesis. 18727653_RANKL levels appeared to be greater in the smokers with chronic periodontitis than in non-smokers with chronic periodontitis. 18754324_Cytolethal distending toxin enhances RANKL expression in T-cells, denoting that these cells are a potential target for the toxin and strengthening the potential link between this virulence factor and mechanisms associated with localized bone resorption. 18767923_lamin A/C is essential for proper RANKL-dependent osteoblastogenesis 18802807_Active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis with bone erosions is associated with high serum levels of RANKL and a low OPG/RANKL ratio. 18928898_might locally modulate [odontogenic tumor-associated bone resorption 19008470_Based on their role in atherogenesis, this enhanced expression of RANKL and RANK could contribute to the increased risk of cardiovascular disease in hyperhomocystinemia. 19058084_Basal expression of RANKL on the cell surface, and in co-culture with human osteoblast-like cells the number of cells expressing RANKL was increased between 2.5 and 4 times. 19058836_breast cancer cell produce a sufficient amount of osteoprotegerin to bind TRAIL, resulting in an upregulation of receptor activator factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) expression 19073256_The greater bone loss that characterizes OP patients can be mediated due to differences in the secretion and expression of the RANKL/OPG system in response to different stimuli. 19085839_RANKL/RANK have roles in bone-associated tumors (review) 19105036_OPG is a positive regulator of microvessel formation, while RANKL is an angiogenic inhibitor due to effects on regulation of endothelial cell proliferation, apoptosis, and signaling. 19112497_analysis of TRAF6 autoubiquitination-independent activation of the NFkappaB and MAPK pathways in response to IL-1 and RANKL 19131500_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19131500_results support the involvement of gene-gene interactions between the vitamin D receptor, osteoprotegerin and TNFSF11 genes in the BMD regulation, particularly in osteoporotic and non-osteoporotic post-menopausal women 19134349_Calcitriol can increase RANKL mRNA expression level in human periodontal ligament cells. 19158438_The OPG level provides a good predictor of osteoporosis as well as NTx in elderly women; additionally, the findings suggest that OPG might protect elderly women from bone loss or fractures. 19170075_Prostate cancer cells secrete factors, including IL-6 and IL-8, that play an important role in osteoclast fusion by a RANKL-independent mechanism 19185505_Key role of RANKL in the pathophysiology of several bone diseases. 19298221_Interleukin-1alpha and Porphyromonas endodontalis may be involved in developing apical periodontitis through the stimulation of RANKL production 19299182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19299513_Trolox prevents osteoclast formation and bone loss by inhibiting both RANKL induction in osteoblasts and c-Fos expression in osteoclast precursors. 19325145_Osteoprotegerin and soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and risk for coronary events: a nested case-control approach in the prospective EPIC-Norfolk population study 1993-2003. 19352306_Examine contributions of osteoprotegerin and RANKL to the pathogenesis of osteoporosis in patients with thalassaemia major. 19379170_PTH favors RANKL and inhibits OPG production in the serum of hemodialysis patients in a low turnover state; positive correlation between serum OPG and iPTH in normal or high turnover rates implies a homeostatic mechanism to limit bone resorption 19401376_21-hydroxylase deficiency patients had higher soluble RANKL and lower OPG serum levels compared with controls. 19415676_S100 treatment increased expression of RAGE by the MC3T3-E1 cells. 19416721_The binding affinity of RANKL for RANK was measured with surface plasmon resonance technology and K(D) value is about 1.09 x 10(-10) M. 19446344_TLR-3 enhances osteoclastogenesis through upregulation of RANKL expression in synoviocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis 19449178_analysis of competitive regulation of osteoprotegerin synthesis and RANKL expression in normal human osteoblasts stimulated by the application of cyclic tensile strain 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19458885_In summary, our findings suggest that the RANKL gene may play an important role in variation in fCSI, independent of fBMD and non-fBMD components. 19473572_Human annulus fibrosus in a herniated disc contained RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand) 19502537_Regarding the SNPs of osteoprotegerin G1181C, we found a significant linkage between the G allele and Charcot neuroarthropathy 19546479_Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a toll-like receptor 4 ligand, up-regulated the expression of membrane RANKL in human blood neutrophils and murine air pouch-derived neutrophils. 19548455_A more extensive analysis of genetic variants of RANKL/RANK/OPG signal pathways, joint with an investigation of modulated influence of estrogens, TNF-alpha or several interleukin influencing the development of osteoporosis is necessary. 19554506_The expression of RANKL gene of nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in multiple myeloma using bone marrow aspirates obtained at diagnosis is reported. 19556344_analysis of FGF-2 stimulation of RANK ligand expression in Paget's disease of bone 19633200_ADA-deficient SCID is associated with a specific microenvironment and bone phenotype characterized by RANKL/OPG imbalance and osteoblast insufficiency. 19662974_The expression level of RANKL in glucocorticoid-induced necrosis of the femoral head patients was significantly higher than in the control group. 19671684_NFATc3 is a downstream target of the CXCL13/CXCR5 axis to stimulate RANKL expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas cells. 19699688_Results suggest a novel pathway by which T lymphocytes contribute to bone changes, namely, via oxidized lipid enhancement of RANKL production. 19705167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19716455_Review. mechanisms that control RANKL gene expression in different osteoclast-support cells and how the study of such mechanisms may lead to a better understanding of the cellular interactions that drive normal and pathological bone resorption. 19781765_suggest that UHMWPE particles induce over-expression of RANKL, IL-6, IL-8, IP-10, MCP-1, and MIG in human periprosthetic microenvironment 19793762_Patients with Cushing's syndrome show increased levels of osteoprotegerin serum levels that remain unchanged after recovery, despite a restoration of bone formation. 19810098_Titanium influences phenotype and function of T-lymphocytes, resulting in activation of a CD69+ and CCR4+ T-lymphocyte population and secretion of RANK-L. 19847430_In rheumatoid arthritis elevated synovial tissue RANKL expression is associated with progressive joint erosion, and may be independent of the clinical response to targeted therapy. 19877052_SOFAT (secreted osteoclastogenic factor of activated T cells) can induce osteoblastic IL-6 production and osteoclast formation in the absence of osteoblasts or RANKL. It is insensitive to RANKL inhibitor osteoprotegerin 19896533_Results suggest that gene-gene interactions between RANK and OPG, and RANK and RANKL influence BMD in postmenopausal women. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934266_We have demonstrated associations between RANKL and OPG haplotypes and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women 19967657_Elevated OPG levels are associated with surrogate markers of inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease patients. 20033478_possible involvement of RANKL and OPG in the activation of pathways, which regulate the repair of the periodontal tissues in periodontitides 20066901_modulation of RANKL by VEGF165 may be one of the mechanisms responsible for the osteolytic process induced by Ewing's sarcoma cells. 20084381_and of osteocalcin, and significantly decreased levels of osteoprotegerin tahn controls. 20157786_Disturbances in the RANKL/OPG system are more profound in the bone marrow stromal cells of multiple myeloma patients than in those of control subjects after direct contact with myeloma cell lines. 20167120_IL-17A upregulates the receptor activator for NF-kappaB receptor on human osteoclast precursors in vitro 20205168_Genetic variation in the RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling pathway influences bone turnover and bone mineral density in European men. 20205168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20225273_study has shown that C/EBPbeta is a RANKL promoter activator in stromal cells of GCT of bone 20231205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20333869_There were no significant differences in OPG and RANKL serum levels or bone density results between GH-deficient and GH-sufficient children 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20412401_expression of RANKL in ameloblastoma was confirmed. Ameloblastoma cells found to induce bone marrow cells from neonatal rabbit to differentiate into osteoclasts with bone-resorption activity. 20416172_The sRANKL/OPG ratio in serum of multiple myeloma bone disease patients is significantly elevated. 20431232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20431232_subjects with CT/CC genotypes of the rs9594782 polymorphism had a 3.9 times higher risk of aortic calcification compared with TT genotype. 20506157_Results indicate that RANKL expression involves the MEK/ERK pathway in multiple myeloma mesenchy |
ENSMUSG00000022015 |
Tnfsf11 |
64.951498 |
5.1809477549 |
2.373216 |
0.242109038 |
101.552148 |
0.00000000000000000000000696066582243335263751575510420502824778403010408428064090209435796352543945886282017454504966735839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000071645346958937438025618398310180944954953662693845588308754379798515277144588253577239811420440673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
110.3094676 |
15.1360920 |
21.3777510 |
2.5732462 |
| ENSG00000120694 |
10808 |
HSPH1 |
protein_coding |
Q92598 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a nucleotide-exchange factor (NEF) for chaperone proteins HSPA1A and HSPA1B, promoting the release of ADP from HSPA1A/B thereby triggering client/substrate protein release (PubMed:24318877). Prevents the aggregation of denatured proteins in cells under severe stress, on which the ATP levels decrease markedly. Inhibits HSPA8/HSC70 ATPase and chaperone activities (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60446, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24318877}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Stress response |
|
This gene encodes a member of the heat shock protein 70 family of proteins. The encoded protein functions as a nucleotide exchange factor for the molecular chaperone heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein (Hsc70). In addition, this protein plays a distinct but related role as a holdase that inhibits the aggregation of misfolded proteins, including the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein. Elevated expression of this protein has been observed in numerous human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:10808; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle lumen [GO:0071682]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; adenyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0000774]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding [GO:0051085]; positive regulation of MHC class I biosynthetic process [GO:0045345]; positive regulation of NK T cell activation [GO:0051135]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
14534695_Heat shock protein 105 is overexpressed in a variety of human tumors 18083346_HSP105 appears to chaperone the responses to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through its interactions with GRP78 and GSK3, and without HSP105 cell death following ER stress proceeds by a non-caspase-3-dependent process. 18477890_HSP105 analysis may be a helpful tool as a poor prognostic indicator and as a diagnostic aid in problematic lesions. 19476517_HSP 105 is thought to be a more relevant tumor-associated antigen in malignant melanoma than is HSP 70. 20542028_Hsp105alpha and Hsp105beta suppressed the expanded polyQ tract-induced protein aggregation and apoptosis through the induction of Hsp70. 21860023_A direct correlation between HSP105 expression and lymphoma aggressiveness was also apparent. 22505710_The Hsp105-mediated multilevel regulation of DeltaF508 CFTR folding and quality control provides new opportunities to understand how chaperone machinery regulates the homeostasis and functional expression of misfolded proteins in the cell. 22712230_It restricts aggregation of denaturated proteins,plays a role in protein folding in cytoplasms,and enhance expression of hsp70 in cell nucleus.(review) 22901192_High HSP105 expression is associated with Barrett's esophagus. 23737532_HSPH1 and HSPH2 are bona fide chaperones on their own that collaborate with DNAJA1 and DNAJB1 to hydrolyze ATP and unfold polypeptides and HSPA1A and HSPH1 formed a powerful molecular machinery. 24157810_A receiver operating characteristic curve constructed with HSP105 and TIM gave a sensitivity of 54.3% and 95% (38/40) specificity in discriminating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from matched controls. 24318877_we measured the binding of human Hsp72 (HSPA1A) to BAG1, BAG2, BAG3, and the unrelated NEF Hsp105. These studies revealed a clear hierarchy of affinities: BAG3 > BAG1 > Hsp105 >> BAG2. 24512910_About 25% of patients with stages II-III colorectal tumors with microsatellite instability have an excellent response to chemotherapy, due to large, biallelic deletions in the T(17) intron repeat of HSP110 in tumor DNA. 25645927_HSP105 depletion disrupts the integration of protein phosphatase 2A into the beta-catenin degradation complex, favoring the hyperphosphorylation and degradation of beta-catenin. 26831756_HSP110 HT17 alone correctly classified samples judged to be uncertain with the pentaplex panel. 27819670_the expression of HSP110 in colon cancer contributes to STAT3-dependent tumor growth 28185835_Hsp105alpha localizes to the nucleus, interacts with HIF-1alpha and induces HIF-1a accumulation in CoCl2-treated cells. 28811251_deletion of the HSP110 T17 repeat was frequently observed in microsatellite-unstable advanced gastric cancers. 28971530_Established heat shock protein 110 (HSP110) as a prognostic biomarker of colorectal carcinomas (CRCs) with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) by considering the intratumoral heterogeneity of HSP110 expression. The HSP110wt-low MSI-H CRCs were significantly correlated with larger deletions in the HSP110 T17 mononucleotide repeat (>/=4 bp; p |
ENSMUSG00000029657 |
Hsph1 |
1771.465795 |
2.3025777646 |
1.203250 |
0.048984958 |
602.606487 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000045380522282059899947644597881051593625959021379905800314813532849936213662549757058936812626849176818104159409760507626279554553621440020400577272150548769962079876065338550454122360675564790589231 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000025181071762526472966626069349151011543104479950644309999324524732573349031211754625129825929433059233759351362754478234512282272832182939452301013483539855646696770962785004162720968337050158554540 |
Yes |
No |
2601.8876445 |
82.9815358 |
1137.7978881 |
27.9376761 |
| ENSG00000120738 |
1958 |
EGR1 |
protein_coding |
P18146 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator (PubMed:20121949). Recognizes and binds to the DNA sequence 5'-GCG(T/G)GGGCG-3'(EGR-site) in the promoter region of target genes (By similarity). Binds double-stranded target DNA, irrespective of the cytosine methylation status (PubMed:25258363, PubMed:25999311). Regulates the transcription of numerous target genes, and thereby plays an important role in regulating the response to growth factors, DNA damage, and ischemia. Plays a role in the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and cell death. Activates expression of p53/TP53 and TGFB1, and thereby helps prevent tumor formation. Required for normal progress through mitosis and normal proliferation of hepatocytes after partial hepatectomy. Mediates responses to ischemia and hypoxia; regulates the expression of proteins such as IL1B and CXCL2 that are involved in inflammatory processes and development of tissue damage after ischemia. Regulates biosynthesis of luteinizing hormone (LHB) in the pituitary (By similarity). Regulates the amplitude of the expression rhythms of clock genes: BMAL1, PER2 and NR1D1 in the liver via the activation of PER1 (clock repressor) transcription. Regulates the rhythmic expression of core-clock gene BMAL1 in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20121949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25258363, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25999311}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the EGR family of C2H2-type zinc-finger proteins. It is a nuclear protein and functions as a transcriptional regulator. The products of target genes it activates are required for differentitation and mitogenesis. Studies suggest this is a cancer suppressor gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. |
hsa:1958; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; double-stranded methylated DNA binding [GO:0010385]; hemi-methylated DNA-binding [GO:0044729]; histone acetyltransferase binding [GO:0035035]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cellular response to gamma radiation [GO:0071480]; cellular response to heparin [GO:0071504]; cellular response to interleukin-8 [GO:0098759]; cellular response to mycophenolic acid [GO:0071506]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; circadian temperature homeostasis [GO:0060086]; estrous cycle [GO:0044849]; glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072110]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; locomotor rhythm [GO:0045475]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glomerular metanephric mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072303]; positive regulation of hormone biosynthetic process [GO:0046886]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; positive regulation of post-translational protein modification [GO:1901875]; positive regulation of tau-protein kinase activity [GO:1902949]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of progesterone biosynthetic process [GO:2000182]; regulation of protein sumoylation [GO:0033233]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia [GO:0061418]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217] |
11819815_Egr-1 in the cancer tissue shows down-regulated expression that supports the inhibited function of Egr-1 in cancer growth and suggests Egr-1 may have an important role in gene therapy of esophageal carcinoma. 11830539_Early Growth Response-1 gene mediates up-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression during hypoxia 11909874_HIV Tat binds Egr proteins and enhances Egr-dependent transactivation of the Fas ligand promoter 11925592_Egr-1 gene of transfected HHCC and ECa109 cells showed obvious suppression of the cell growth and malignant phenotypes, but no suppression in SMMC7721 (HCC cell line) cells. 11956220_Activation of human monoamine oxidase B gene expression by a protein kinase C MAPK signal transduction pathway involves c-Jun and Egr-1. 11978801_role in mediating tissue factor expression in endothelial cells induced by CD40 ligand 12011097_Egr-1 is necessary and sufficient to activate human PPARgamma1 gene expression in VSMC 12065847_Egr1 has multiple roles in prostate tumor cell growth and survival, cell differentiation, tumor progression, angiogenesis, and apoptosis. 12165491_Egr1 translates developmental signals into appropriate changes in gene expression at multiple stages of thymocyte development. 12235180_Egr1 is the oncostatin M-induced transcription factor that binds to the SIRE sequence of the LDL receptor promoter 12384223_transactivation of the EGF receptor as well as stimulation of the mitogen activated/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) are essential for substance P/NK-1 receptor-induced activation of Egr-1 biosynthesis 12393577_The proximal serum response element in the Egr-1 promoter mediates response to thrombin in primary human endothelial cells. Thrombin does this by a MAPK-dependent mechanism that involves an interaction between SRF & SRE-1. 12439908_Egr-1 expression and cell apoptosis may have an important biological significance in esophageal carcinogenesis. 12456801_studies for the first time identify Egr-1 as a nuclear target of gastrin and show that functional interplay of Egr-1, Sp1, and CREB is indispensable for gastrin-dependent CgA transactivation in gastric epithelial cells 12457461_Data demonstrate that Egr-1, AP1 and Smad are part components of the transforming growth factor beta signal transduction pathway that regulates PPAR gamma expression. 12507899_Keratinocytes of chronic psoriatic plaques were characterized by enhanced p16, p14(ARF), and p12 expression accompanied by elevated Egr-1 levels 12517959_Overexpression of EGR1 via generation of superoxide anions inhibits the basolateral Na+/K+-ATPase activity of kidney proximal tubule cells. 12543866_role of Egr-1 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induction of TF and inflammatory mediators in vivo was evaluated using Egr-1(+/+) and Egr-1(-/-) mice 12553019_Egr-1 has a significant role in carcinogenesis and in cancer progression, especially metastasis. 12553721_upregulation of Egr-1 might contribute to fibrosis observed in rheumatoid arthritis synovium by activation of genes encoding the alpha1 and alpha2 chains of type I collagen 12566441_PI3K/ERK signaling by the EP(4) receptors induces the functional expression of early growth response factor-1 (EGR-1) 12571843_The enhanced expression of Egr-1 may regulate the activity of matrix metalloproteinases in synovial fibroblasts by enhancing the expression of the TIMP-1, -2, and -3 genes. 12618431_data demonstrates that eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 is a new target for early growth response-1 12637574_Egr-1 represses COL2A1 by preventing interactions between Sp1 and the general transcriptional machinery 12690110_Egr1 controls p21Cip1 expression by directly interacting with a specific sequence on its gene promoter. 12706485_These results suggest that induction of egr-1 may be needed to regulate genes involved in DNA repair, cell survival, and apoptosis. 12729460_stimulation by ATP via a protein kinase C-dependent pathway in the human osteoblastic HOBIT cell line 12872165_study provides the first evidence of the crucial role of Egr-1 in microvascular endothelial cell growth, neovascularization, tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth 12890669_EGR1 binds to the androgen receptor (AR) in prostate carcinoma cells, and an EGR1-AR complex can be detected 12947119_study provides strong evidence that early growth response 1 regulates low density lipoprotein receptor transcription via a novel mechanism of protein-protein interaction with CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta 12958075_activation of JNK and expression of Egr-1 gene in B lymphoblasts mediate a cellular response to genotoxic agents that may be induced by Fanconi anemia proteins 14522979_early growth response 1 regulates inducible heparanase gene transcription in activated T cells 14662774_EGR-1 is required for expression of NAG-1 by troglitazone 14966901_expression of Egr-1, c-fos and cyclin D1 varies in esophageal precancerous lesions and cancer tissues, suggesting an involvement of these genes in the development of esophageal carcinoma. 14985468_microtubules regulate EGR-1 localization in benign prostate cells but not in malignant prostate cells 15003938_Although EGR-1 is induced by PDGF in human airway smooth muscle cells in cell culture, the role of EGR-1 in airway remodeling and asthma remains to be established. 15023995_mPGES-1 and Egr-1 are novel targets of PPARgamma 15155664_Helicobacter pylori induced expression of Egr-1 in gastric epithelial cell lines in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting a role, in part, in Helicobacter pathology 15211096_Review examines emerging evidence that ERG-1 orchestrates transcriptional response to vascular injury. 15225550_Cells induced with serum to increase endogenous Egr1 increase the transcription of p300/CBP only when Egr1 binding sites in the promoter are not mutated, causing the expression of downstream targets of Egr1. 15231681_Egr-1 may display tumor-suppressing activity and offers a potential target for uterine leiomyoma management. 15449318_Deletion analyses of the Egr-1 promoter identify a minimal estradiol-responsive region of the promoter containing a serum response element which binds Elk-1 and serum response factor. 15486985_Findings suggest that EGR-1 expression and activity is differentially regulated in prostate cancer cell line PC-3 and BPH-1 cell line. 15517593_EGR-1 regulates PTEN expression in the initial steps of the apoptotic pathway 15523672_results show that there are genuine Sp1/Sp3 or Egr-1 controlled genes showing no cross-regulation of Sp1/Sp3 and Egr-1 through the same DNA-binding site 15545275_Egr-1 has roles in regulating both the basal and LPS-induced activity of the SOCS-1 promoter 15611055_the MEK1/ERK1/2 pathway couples the CCK2 receptor to nuclearization and DNA binding of Egr-1 15640148_IL-17-stimulated TNF-alpha mRNA expression and promoter activity was dependent on Egr-1 expression. 15689620_Data show that ionizing radiation causes stress-induced activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-Src-Mek-Erk-Egr-1 signaling that regulates the clusterin pro-survival cascade. 15709168_Up-regulation of EGR1 contributed significantly more to heparanase expression than did promoter CpG hypomethylation in prostate cancer samples. 15875316_finding of FGF2 and EGR1 upregulation in endothelial cell microvascular channels within organising thrombus 15910736_results show that distal serum response elements within the Egr-1 promoter are of major importance for the inducibility of Egr-1 gene transcription by tetradecanoylphorbol acetate 15923644_TNF-alpha-induced CD44 expression was regulated by AP-1 through the activation of the CaMK-II pathway, whereas LPS-induced CD44 transcription was regulated specifically by Egr-1 through JNK activation. 15999367_The EGR1 gene appeared to be deleted in ER-negative human breast carcinomas. Egr-1 may contribute to the pathogenesis of ER-negative breast carcinomas versus ER-positive breast carcinomas. 16007175_EGR1 expression in combination with promotor CpG methylation regulates heparanase expression 16079301_this is a novel first report demonstrating that the expression of ATF3 occurs via early growth response gene-1 downstream of extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 16091742_c-Abl promotes the induction of EGR1 through the MEK/ERK pathway in regulating apoptotic response to oxidative stress. 16093249_EGR1 regulates heparanase transcription in tumor cells and importantly, can have a repressive or activating role depending on the tumor type 16260776_Egr-1 induces the expression of its corepressor nab2 by activation of the nab2 promoter in a negative feedback loop 16382041_Nkx3.1 and Egr1 regulate gene programs involved in distinct aspects of prostate tumorigenesis [review] 16393964_Overexpression of Egr-1, but not Egr-3, is capable of augmenting transcription of an intact CD154 promoter. 16464174_Transcriptional stimulation of the human NHE3 promoter activity by PMA: PKC independence and involvement of the transcription factor EGR-1. 16552541_The IGFBP3, hRas, JunB, Egr-1, Id1 and MIDA1 genes were up-regulated in psoriatic involved skin compared with uninvolved skin. 16702209_EGR-1 is induced by transforming growth factor-beta and mediates stimulation of collagen gene expression 16741963_Expression of Tat decreased NGF-induced Egr-1 levels in neuroblastoma cells. 16831524_EGR1 regulates TOPBP1 gene transcription. 16858414_These findings indicate that Snail upregulation by HGF is mediated via the MAPK/Egr-1 signaling pathway and that both Snail and Egr-1 play a critical role in HGF-induced cell scattering, migration, and invasion. 16995904_GTP-Binding Protein alpha Subunits, Gq-G11, gene is regulated during megakaryocytic differentiation by EGR-1. 17099140_The identification that induction of MMP-2 and MT1-MMP by CSE from lung fibroblasts is EGR-1-dependent reveals a molecular mechanism for matrix remodeling in cigarette smoke-related emphysema. 17257596_cDNA microarray analysis revealed that expression of early growth response gene-1 (Egr-1) was increased by LMP1 expression in MCF7 and Jurkat cells. 17420284_Haploinsufficiency for Egr1plays a role in the development of acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes characterized by abnormalities of chromosome 5. 17448597_EGR1 is upregulated after radical prostatectomy for prostatic neoplasms. 17494953_The MAPK-EGR-1-HSP70 pathway regulates the cigarette smoke-induced inflammatory process. 17502875_Can repress herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 immediate-early gene expression, and thus may play a critical role in HSV-1 gene silencing during latency and reactivation. 17516844_reveal a novel role for protein phosphatase 1 inhibitor in the regulation of the tumor suppressor gene EGR1 via activation of the MEK-ERK MAPK pathway 17559061_Radiofrequency radiation (900 MHz) induces EGR1 gene expression and affects cell-cycle control in human neuroblastoma. 17581316_STI571 influence through inducing urokinase-type plasminogen activator and interleukin-8, in which the induction of early growth response-1 expression and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation might be involved. 17599039_Constitutive expression of Egr-1 transgene abrogates E2F-1 oncogene-mediated block in differentiation of murine myeloblastic leukemia cells, allowing the cells to differentiate into functionally mature macrophages that subsequently undergo apoptosis. 17631285_Our data demonstrate that IL-1beta-induced Id2 expression in VSMC is mediated by the transcription factor Egr-1 in VSMC. 17631291_Results reveal that egr-1 is a target gene of PGE(2) in HCA-7 cells and is regulated via the newly identified EP4/ERK/CREB pathway. 17671831_Calcipotriol affects proliferation of keratinocytes by decreasing the expression of EGR1 and PLK2. 17932312_Activated protein C may provide cytoprotective activity by activating the ERK pathway, which upregulates EGR-1 thereby suppressing the expression of TRAIL by PAR-1/S1p1 dependent but EPCR independent mechanism. 17967787_Hemin increased Egr-1 expression (mRNA, protein) within 30 minutes and ERK-1/2 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation within 5 minutes 17975260_These results indicate that EGR1 is a key player in coordinated down-regulation of genes in leiomyoma. 17986608_defect in upregulation of p57Kip2 transcription is due to reduced levels of EGR1 caused by direct, destabilizing interaction with PAX3-FOXO1 18027854_Egr-1 negatively regulates survivin expression and sensitizes cell lines to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 18067864_These results suggest that elevated expression and activity of PLD attenuate phorbol myristate acetate-induced Egr-1 expression via PI3K pathway. 18068676_Intact SP1-binding sites are essential for promoter activity, whereas EGR-1 suppresses the transcription of the human SREBP-1a promoter 18088351_Antithrombin might inhibit LPS-induced production of TNF-alpha by inhibiting the increase in Egr-1 expression in monocytes via interaction with heparin-like substances expressed on the cell surface 18171299_The greatest reduction in the number of C. pneumoniae inclusions was due to the silencing of the gene coding for the transcription factor early growth response 1, which decreased the number of inclusions by 38.6% 18174470_Prolonged exposure to heme, as may be observed after plaque rupture in atherosclerotic disease, leads to dysregulation and prolonged elevated Egr-1 expression that contributes to atherosclerotic progression 18204200_These results suggest that Egr-1 may be an important breast cancer marker and that an as yet uncharacterized pathway involved in Egr-1 and gelsolin expression exists which leads to breast cancer cell development. 18215136_Hepatocyte growth factor stimulates 5alpha-R1 expression through up-regulation of the transcription factor early growth response 1 18247371_Data demonstrate that a decrease in the level of Egr-1, one of the targets for MAPK, by Tat has a negative impact on the level of p35 expression in NGF-treated neural cells. 18281687_Transcriptional activation of the EGR-1 promoter by JNK-MKK7 or by IL-1 required a single upstream AP-1 site and three distal serum-response elements (SRE). 18303024_CAR requires early growth response 1 to activate the human cytochrome P450 2B6 gene 18316600_ERK and JNK MAPK/Elk-1/Egr-1 signal cascade is required for p53-independent transcriptional activation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) in response to curcumin in U-87MG human glioblastoma cells 18324520_APE1 regulated PTEN expression is mediated by Egr-1. 18434015_the early growth response 1 gene is repressed by Elk1 in normally cycling SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell line 18434089_ATP activated MAPKs through the P2Y2 purinoceptor/PLC/PKC/ERK signaling pathway and induced translocation of ERK1/2 into the nucleus. 18435749_EGR1 gene is implicated in idiopathic absence epilepsy. 18460021_Egr-1 plays an important regulatory role in the transcriptional activation of hTERT. 18469860_Activation of BAG3 by Egr-1 in response to FGF-2 in neuroblastoma. 18489490_findings show EGR-1 was mainly restricted to tumor cells expressing NMDA-R & significantly upregulated in astrocytic tumors compared to normal brain; EGR-1 expression was significantly associated with enhanced patient survival in high grade astrocytomas 18507785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18507785_association of Egr-1 polymorphisms with plasma total IgE and atopy in asthmatic children 18515748_After high glucose stimulation, AhR was found in complex with Egr-1 & activator protein-2. 18525291_Sp1/Egr1-repeat polymorphism in the ALOX5 promoter is not a genetic marker for the risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer disease 18583706_EGR1 is an important transcriptional stimulator of the human PCYT2 and that conditions that modify EGR1 also affect the function of ECT and consequently PE synthesis 18604866_the basal activity of the human PRDM1 promoter, through which several factors, including SP1, SP3 and early growth response 1, modulate its expression through a conserved GC-box. 18636116_No pathological mutations were detected upon sequencing of the coding regions and the adjacent intronic regions of EGR1 in 96 unrelated Chinese subjects with high myopia. 18636116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18675783_The role of the Early Growth Response-1 transcription factor in TNFalpha autoregulation in HaCaT human keratinocytes was investigated. 18682391_Histamine-induced Egr-1 expression is dependent on the activation of the H1 receptor, and rapidly and transiently activates PKCdelta, ERK1/2, p38 kinase, and JNK prior to Egr-1 induction. 18704310_The expression of EGR-1 mediated by p38MAPK pathway plays a critical role in paclitaxel resistance of ovarian carcinoma cells. 18711316_DIDS-sensitive Cl- channels play a key role in the Low-density lipoprotein-induced cell proliferation of human aortic smooth muscle cells via the activation of Erk1/2 and PI3K/Akt and the upregulation of Egr-1. 18772333_These findings define a Smad-independent TGF-beta signal transduction mechanism that underlies the stimulation of Egr-1. 18780286_growth factors and serum induce expression of Egr-1 and SRF, respectively, which in turn induces E2-EPF UCP expression that positively regulates cancer cell growth 18830406_demonstrate a critical role for Egr-1 in promoting autophagy and apoptosis in response to cigarette smoke exposure in vitro and in vivo 18989526_Report phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate responsive sequence in Galphaq promoter during megakaryocytic differentiation. Regulation by EGR-1 and MAP kinase pathway. 19032775_Results indicate that M12 cells undergo Egr1-dependent apoptotic response upon UV stimulation and led to the identification of downstream targets of Egr1, which mediate epidermal growth factor receptor function. 19074480_we show a strong association between endoglin and EGR-1, increased collagen and Ssmooth muscle cells expression, decreased levels of intraplaque thrombosis 19074849_activation of ESE-1 via enhanced nuclear translocation mediates tolfenamic acid-induced EGR-1 expression, which plays a critical role in the activation of apoptosis 19112164_Early growth response-1 regulates angiopoietin-1-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. 19115247_HDAC4 contributes to transcriptional induction of mPGES-1 by IL-1 through a mechanism involving up-regulation of Egr-1 transcriptional activity 19131339_Mutation of Sp1 and Egr1 binding sites within the essential region diminished Fyn promoter activity and identified Egr1 as conferring redox sensitivity. 19152168_thalidomide could suppress leukemia cell invasion and migration by upregulation of Egr-1 19245972_The present study demonstrates the differential up-regulation of Egr-1 in the thrombus-covered wall of human Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) and also suggests its possible contribution to the thrombogenic and inflammatory pathogenesis in human AAA. 19261809_TNF-alpha abrogated TGFbeta1-induced SMalphaA gene expression at the level of transcription without disrupting phosphorylation of regulatory Smads. 19276347_E2F1 activated the expression of transcription factor EGR1 for promoting cell survivalin prostate cancer. 19307156_these findings provide molecular insight into T-bet transcription and suggest that EGR1 is an upstream regulator of T-bet induction. 19307576_IL-10 expression may be regulated by miR-106a, which is in turn transcriptionally regulated by Egr1 and Sp1 19374776_Observations of in vivo occupancy changes of EGR-1 and SP1 suggest that several types of interplay between EGR-1 and other proteins result in multiple responses to EGR-1 downstream genes. 19426596_Data suggest that Flt3 Ligand(FL) gene regulated by Egr-1 promoter can protect hematopoiesis from 5-Fu injury. 19432968_Thrombin induced a robust and transient biosynthesis of Egr-1. 19435811_Results indicate that EGR-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB mediate GRO/CXCR2 proliferative signaling in esophageal cancer and may represent potential target molecules for therapeutic intervention. 19446747_Fluorescence in situ hybridization using a probe of EGR1 is able to detect a cryptic deletion in a patient with myelodysplastic syndrome. 19467232_ERG1 may loop the distal enhancer PB responsive enhancer module towards the proximal OA response element KI so that together, CAR and HNF4alpha synergistically activate the CYP2B6 promoter. 19526316_Egr-1 might play an important role in the up-regulation of VEGF and IL-8 induced by HGF and contribute to HGF-mediated angiogenesis, which might be promising targets for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. 19724854_pcDNA3.1-Egr-1-TRAIL recombinant plasmid can sensitize SW480 cells to radiation 19747485_Regulated WT1 followed by sequential Egr1 and Sp1 binding to elements within Prm1 mediate repression and subsequent induction of TPalpha during differentiation into the megakaryocytic phenotype. 19765320_Flt3 ligand transcriptional control is targeted by fluorouracil-induced Egr-1 promoter in hematopoietic damage 19781349_The activation of EGR-1 mediated by p38MAPK pathway plays a critical role in epirubicin resistance of human breast carcinoma cells. 19786090_Egr1 is a novel regulator of stathmin expression and p53 mediates the transcriptional repression of stathmin by Egr1 in human lung cancer cells. 19822898_Data show that VEGFR1 promoter binding sites for ELF-1, CREB and EGR-1/3 play a positive role in gene transcription in endothelial cells. 19833116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19833116_We showed high levels of Egr-1 mRNA expression and demonstrated a significant association of polymorphism with increased plasma total IgE and atopy in AR patients 19837667_Data show that EGR-1 knockdown inhibited gene transcription and production of IL-8 by a human prostate cancer cell line, and that silencing EGR-1 suppressed a synergistically functional interaction between EGR-1 and NF-kappaB. 19837979_JUN overexpression in multiple myeloma cells induced cell death and growth inhibition and up-regulated expression of early growth response protein 1. 19878561_Egr-1 protein expression is associated with disease progression in human bladder cancer. 19885607_Egr-1 downregulation by siRNA inhibits growth of human prostate carcinoma cell line PC-3 19888474_Nab2 is a novel endogenous negative regulator of Egr-1-dependent TGF-beta signaling responsible for setting the intensity of fibrotic responses 19913601_Knockdown of Egr-1 by expression of small interfering RNA attenuated EGF-induced Klotho promoter activity. 19915002_the first evidence that Egr-1 protein is differentially expressed in Th1 and Th2 cells and is involved in the acute phase of the IL-4 transcription in response to T cell receptor stimulation 20009530_Studies demonstrated that EGR1 is involved in regulating homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) by coordinating proliferation and migration. 20016208_P. gingivalis antigens and IL-6/sIL-6R stimulated Egr-1 and MCP-1 expression in coronary artery endothelial cells. 20018936_IL-1beta induction of EGR-1 transcription involves histone H3 phosphorylation, acetylation, and autoregulation by EGR-1. 20053757_15(S)-HETE-induced angiogenesis requires Src-mediated Egr-1-dependent rapid induction of FGF-2. 20087343_Egr-1 drives c-FLIP expression and the short splice variant of c-FLIP (c-FLIP(S)) specifically inhibits DR5 activation. 20121949_Snail associates with EGR-1 and SP-1 to mediate TPA-induced transcriptional upregulation of p15(INK4b) in HepG2 20144677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20190820_Overexpression of Egr-1 is caused by mutation of p53 and appears to be initiated through activation of the MEK/ERK1/2 signaling cascade by mutant p53. 20204305_Human SK-BR3 and MCF-7 breast carcinoma cell growth and capacity of anchorage transfected with siRNA-Egr-1 or treated with camptothecin was slower than that of the control group 20348948_EGR1 is required for the ability of TBX2 to repress NDRG1 and drive cell proliferationin breast cancer. 20363028_Data show that neutrophils constitutively express EGR-1 protein. 20372793_thymidine phosphorylase has a role in the induction of early growth response protein-1 and thrombospondin-1 by 5-fluorouracil in human cancer carcinoma cells 20403028_results indicate that aberrant expression of EGR1 in gastric cancer is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis, and heparanase transcription 20414733_these results reveal that Tat directly transactivates Egr-1 expression 20448047_Study provides a new therapeutic target, Egr-1, for attenuation of elevated leukotriene levels in patients with sickle cell disease and other inflammatory diseases. 20489156_Data suggest that EGR-1 plays important roles on VEGF-A expression in lung cancer cells, and epigenetic silencing of transactivator(s) associated with NAB-2 expression might also contribute to upregulate VEGF-A expression. 20506119_Results suggest that in many cells of neuroectodermal and epithelial origin EGR1, EGR2, and EGR3 activate NAB2 transcription which is in turn repressed by NAB2, thus establishing a negative feedback loop. 20507991_a novel mechanism by which an extracellular signal initiated by RAGE ligand AGEs regulates Egr-1 in a manner requiring mDia-1 20585888_Data show that co-expression of ZNF300 and Egr1 lead to enhanced IL-2Rbeta promoter activity, and suggest that ZNF300 is another regulator of the human IL-2Rbeta promoter. 20621662_Downregulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor-II expression by cigarette smoke-induced Egr-1 may contribute to smoking-induced premature skin aging. 20690147_In vivo EGR1 binding sites were identified in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-treated K562 cells. 20811575_Performed ChIP-Seq to find the targeting microRNA genes of Egr1, in K562 cells. Found Egr1 binding sites near the promoters of 124 distinct microRNA genes, accounting for about 42% of the miRNAs which have high-confidence predicted promoters. 20864524_Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded glycoprotein B promotes virus latency by regulating expression of cellular Egr-1. 20945384_CXCL5/ENA78 increased cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of hormone-independent prostate cancer by early growth response-1/snail signaling pathway. 21118966_Data show that miR-183 has a potential oncogenic role through the regulation of 2 tumor suppressor genes, EGR1 and PTEN, and the deregulation of this fundamental miRNA regulatory network may be central to many tumor types. 21160498_SAMD9, an IFN-gamma-responsive protein, interacts with RGL2 to diminish the expression of EGR1, a protein of direct relevance to the pathogenesis of ectopic calcification and inflammation. 21189327_results reveal that miR-199a and Brm form a double-negative feedback loop through Egr1, leading to the generation of two distinct cell types during carcinogenesis. 21212994_Glucose and TNF-alpha increased Egr-1 expressionvia ERK1/2 activation in endothelial cells. 21224049_these results reveal a new EGR-1/GGPPS/MAPK signaling pathway that controls cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation. 21297666_found that E-cadherin negatively regulates tumor cell growth, in part, by positively regulating PTEN expression via beta-catenin-mediated Egr1 regulation, thus influencing PI3K/Akt signaling 21321112_the Egr-1/GGPPS/Erk1/2 pathway is responsible for insulin resistance during hyperinsulinism 21336263_The absence of ERG rearrangement in bladder or lung small cell carcinomas highlights the utility of detecting ERG rearrangement in small cell carcinomas of unknown primary for establishing prostatic origin. 21354100_Chlorination of high-density lipoprotein induced phosphorylation of p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase, expression of transcription factor early growth response 1 and enhanced expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human endothelial cells. 21365018_The HMGB1/RAGE/OPN/Egr-1 pathway may be involved in inflammatory, angiogenic and fibrotic responses in proliferative vitreoretinal disorders. 21368226_Egr-1 expression is upregulated in rat and human astrocytes exposed to HIV-1 Tat protein in vitro. 21419860_nuclear translocation involves importin-7 21436631_The study suggests a connection between CD133 and EGR1 and emphasises the importance of the EGR1/TCF4/CD133/LGR5 network in colorectal cancer. 21479245_These data define serum response factor as a host cell transcription factor that regulates immediate early gene expression in Toxoplasma-infected cells. 21489990_Egr-1 is an in vivo regulator of tau phosphorylation and suggest that in AD brain increased levels of Egr-1 aberrantly activate an Egr-1/Cdk5/PP1 pathway, leading to accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau, thus destabilizing the microtubule cytoskeleton. 21506108_Induction of Id-1 by FGF-2 involves activity of EGR-1 and sensitizes neuroblastoma cells to cell death. 21551235_Removal of regions upstream of the SRE 1 or 2 sites led to a dramatic reduction in Egr-1 promoter activity & response to IGFBP-3 expression. Loss of all 5 SRE sites & 2 CRE sites led to a total elimination of Egr-1 promoter activity. 21596316_p53 and EGR1 play the role in two phases of mitogenic signaling in mammary epithelial cells exposed to EGF. 21617851_overexpression of EGR-1 selectively increased AP-1 and NF-kappaB activation. 21688838_Findings on the function of the arginine residue in the third zinc finger domain of Zif268 may be useful for the design of novel artificial zinc finger proteins. 21725089_control network for Egr-1 expression through a feedback loop between SHP and HNF4alpha. 21743491_Data show a crosstalk between mPGES-1/PGE(2) and EGR1/beta-catenin signaling that is critical for hepatocarcinogenesis. 21743958_The results suggest that Egr-1 may promote prostate cancer development by modulating the activity of factors NF-kappaB and AP-1, which are involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis. 21791614_Our study illustrates a central role of p300-acetylated ATF5 in ATF5-dependent Egr-1 activation 21931594_Egr-1 induces a distinct profibrotic/wound healing gene expression program in fibroblasts 21968973_NKX2-3 may play different roles in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease pathogenesis by differential regulation of EGR1. 21995436_Egr-1-dependent induction of Cyr61 may contribute to premature skin ageing by smoking. 21998680_SUMO-1 modification improving EGR1 ubiquitination is involved in the modulation of its stability upon EGF mediated induction 22053691_acquired knowledge on transcriptional regulation of Egr-1 is not entirely understood. In this review, we highlight upstream and downstream signaling in vitro and in vivo associated with Egr-1 22095683_tumor promoter induces RON expression via Egr-1, which, in turn, stimulates cell invasiveness in AGS cells 22115966_Results suggest that EGR-1 may stimulate prostate cancer cell growth through up-regulation of IGF-1R and indicate that down-regulation of EGR-1 could be an effective therapeutic approach against prostate cancer. 22127986_EGR-1 is deregulated in tumor and structurally intact adjacent prostate tissues and defines field cancerization. 22140445_Chronic hypoxia induces Egr-1 via activation of ERK1/2 and contributes to pulmonary vascular remodeling. 22198386_Data demonstrate that induction of EGR1 involves ERK-mediated down-regulation of microRNA-191 and phosphorylation of the ETS2 repressor factor (ERF) repressor, which subsequently leaves the nucleus. 22316125_EGR1 knockdown decreases the gene expression of growth factors and cytokines in mesenchymal stem cells. 22344601_Intracoronary delivery of DNAzymes targeting human EGR-1 reduces infarct size following myocardial ischaemia reperfusion. 22354777_When the histone H3 nonphosphorylatable mutant of serine 10 (S10A) was overexpressed in cells, arsenite induction of FOS, EGR1 and IL8 expression was significantly decreased as compared with wild-type cells. 22428032_Elevated Egr-1 expression activates lytic genes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-infected cells 22431919_p130Cas signaling induces the expression of EGR1 and NAB2 22433566_EGF activates TTP expression by activation of ELK-1 and EGR-1 transcription factors. 22455954_Down-regulation of PPARgamma expression by IL-1 requires de novo protein synthesis and is concomitant with induction of Egr-1. 22508482_Results provide evidence that Egr-1 is a mediator that is involved in the EGF-induced downregulation of E-cadherin and increased cell invasion in ovaria |
ENSMUSG00000038418 |
Egr1 |
182.034666 |
4.5322671378 |
2.180233 |
0.155124086 |
201.025535 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000124749827046606351874626042412539272815635328370319928783141488621263326735730103502474031818994925275624649119881638681395230605630786158144474029541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023913083729972852553683345542823926024426957425036171567361442468126909263378838354723334600516492320835959262950373704903483940142905339598655700683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
304.8218568 |
25.1609003 |
67.8616134 |
4.7628122 |
| ENSG00000120756 |
5357 |
PLS1 |
protein_coding |
Q14651 |
FUNCTION: Actin-bundling protein. In the inner ear, it is required for stereocilia formation. Mediates liquid packing of actin filaments that is necessary for stereocilia to grow to their proper dimensions. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3V0K9}. |
Acetylation;Actin-binding;Calcium;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Disease variant;Metal-binding;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Plastins are a family of actin-binding proteins that are conserved throughout eukaryote evolution and expressed in most tissues of higher eukaryotes. In humans, two ubiquitous plastin isoforms (L and T) have been identified. The protein encoded by this gene is a third distinct plastin isoform, which is specifically expressed at high levels in the small intestine. Alternatively spliced transcript variants varying in the 5' UTR, but encoding the same protein, have been found for this gene. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 11.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:5357; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; actin filament bundle [GO:0032432]; brush border [GO:0005903]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; terminal web [GO:1990357]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; actin filament network formation [GO:0051639]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; intestinal D-glucose absorption [GO:0001951]; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040018]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; regulation of microvillus length [GO:0032532]; terminal web assembly [GO:1902896]; vestibular receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060121] |
27304220_upregulated in eosinophils from atopic dermatitis patients 28694070_In this study, the authors found that the actin filament bundling abilities of PLS1 and PLS2 were similarly sensitive to Ca(2+) (pCa50 ~6.4), whereas PLS3 was less sensitive (pCa50 ~5.9). 30479022_Increased expression of L-plastin by eosinophils may contribute to abnormal fibrin deposition through TF translocation to the eosinophil cell surface in NERD nasal polyp tissue, which in turn may contribute to the pathogenesis of NERD. 30872814_a diverse genetic hearing impairment (HI) etiology in the Hungarian Roma and identify a new gene PLS1, for autosomal dominant human non-syndromic HI. 31397523_Findings identified missense variants in PLS1 gene in three unrelated autosomal dominant nonsyndromic hearing loss (NSHL) families. In silico protein modeling suggests that all variants destabilize the structure of the actin-binding domain 1. These results clearly support that PLS1 is required for normal hearing and is a novel gene for autosomal dominant HL. 31432506_Novel variant p.E269K confirms causative role of PLS1 mutations in autosomal dominant hearing loss. 32318696_Plastin 1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by regulating intracellular Ca2. 32350953_Plastin 1 drives metastasis of colorectal cancer through the IQGAP1/Rac1/ERK pathway. 33618712_L-plastin Ser5 phosphorylation is modulated by the PI3K/SGK pathway and promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness. 33771880_L-Plastin Promotes Gastric Cancer Growth and Metastasis in a Helicobacter pylori cagA-ERK-SP1-Dependent Manner. |
ENSMUSG00000049493 |
Pls1 |
12.387836 |
0.1635742372 |
-2.611983 |
0.521831605 |
28.537142 |
0.00000009191821933682111946733794350175572596128859004238620400428771972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000364007090617338014109093417489115829255297285271808505058288574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3236784 |
1.3925168 |
20.4659093 |
5.0067503 |
| ENSG00000120798 |
7181 |
NR2C1 |
protein_coding |
P13056 |
FUNCTION: Orphan nuclear receptor. Binds the IR7 element in the promoter of its own gene in an autoregulatory negative feedback mechanism. Primarily repressor of a broad range of genes. Binds to hormone response elements (HREs) consisting of two 5'-AGGTCA-3' half site direct repeat consensus sequences. Together with NR2C2, forms the core of the DRED (direct repeat erythroid-definitive) complex that represses embryonic and fetal globin transcription. Also activator of OCT4 gene expression. May be involved in stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Mediator of retinoic acid-regulated preadipocyte proliferation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12093804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17010934}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear hormone receptor characterized by a highly conserved DNA binding domain (DBD), a variable hinge region, and a carboxy-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD) that is typical for all members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. This protein also belongs to a large family of ligand-inducible transcription factors that regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences within promoters of target genes. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7181; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; PML body [GO:0016605]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048386]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12093744_DRED is a 540 kDa complex containing the nuclear orphan receptors TR2 and TR4, which form a heterodimer that binds to the epsilon and gamma globin promoter DR1 sites. TR2 & 4 mRNAs are expressed at all stages of murine and human erythropoiesis. 12093804_TR2 that may exert an important repressor in regulating ER activity in mammary glands. 12615366_TR2 and TR4 can have distinct functions. Existence of differential and bi-directional regulation between PPAR alpha and TR2/TR4. Possible roles in PPAR alpha signaling pathway in human keratinocytes. 12949936_TR2 may function as a negative modulator to suppress androgen receptor function in prostate cancer. Further studies on how to control TR2 function may result in the ability to modulate AR function in prostate cancer. 17010934_The NF1-A transcription factor plays an important role in the transcriptional activation of the TR2 gene expression via a promoter activating cis-element. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000005897 |
Nr2c1 |
187.151500 |
0.4810890675 |
-1.055624 |
0.186309001 |
31.708107 |
0.00000001791727459998489808052263326867969972511218657018616795539855957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000076103301610295573097400144858132309266807169478852301836013793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
115.6198509 |
14.8170128 |
241.5754715 |
21.6959650 |
| ENSG00000120800 |
27340 |
UTP20 |
protein_coding |
O75691 |
FUNCTION: Involved in 18S pre-rRNA processing. Associates with U3 snoRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17498821}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;rRNA processing |
|
UTP20 is a component of the U3 small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) (SNORD3A; MIM 180710) protein complex (U3 snoRNP) and is involved in 18S rRNA processing (Wang et al., 2007 [PubMed 17498821]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:27340; |
90S preribosome [GO:0030686]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; preribosome, small subunit precursor [GO:0030688]; small-subunit processome [GO:0032040]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; endonucleolytic cleavage in 5'-ETS of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000480]; endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000447]; endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 5'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000472]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] |
14503924_Analysis of the relationship between DRIM gene expression and the metastatic phenotype of breast neoplasms. 16458307_a single region located between amino acids 2744 and 2761 at the C-terminus is capable of nucleolar accumulation. Two basic amino acid clusters within this region are essential for nucleolar accumulation. 17498821_DRIM is involved in 18S rRNA processing 21151873_1A6/DRIM activates Pol I transcription most likely by associating with both hALP and UBF and thereby affecting the acetylation of UBF |
ENSMUSG00000004356 |
Utp20 |
165.657220 |
2.0964088274 |
1.067920 |
0.148948486 |
51.394617 |
0.00000000000075545408218682365548066636254535571209142025272953446801693644374608993530273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004527203513226762525669521171833923874408545096059697243617847561836242675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
229.5612490 |
19.2351226 |
110.0711055 |
7.2104868 |
| ENSG00000120889 |
8795 |
TNFRSF10B |
protein_coding |
O14763 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TNFSF10/TRAIL (PubMed:10549288). The adapter molecule FADD recruits caspase-8 to the activated receptor. The resulting death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs caspase-8 proteolytic activation which initiates the subsequent cascade of caspases (aspartate-specific cysteine proteases) mediating apoptosis. Promotes the activation of NF-kappa-B. Essential for ER stress-induced apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10542098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10549288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15322075}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily, and contains an intracellular death domain. This receptor can be activated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TNFSF10/TRAIL/APO-2L), and transduces an apoptosis signal. Studies with FADD-deficient mice suggested that FADD, a death domain containing adaptor protein, is required for the apoptosis mediated by this protein. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms and one non-coding transcript have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:8795; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; TRAIL binding [GO:0045569]; TRAIL receptor activity [GO:0036463]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; defense response to tumor cell [GO:0002357]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; TRAIL-activated apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0036462] |
10542098_crystal structure at 2.2 A resolution of a complex between TRAIL and the extracellular region of DR5 11844843_TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is not constitutively expressed in the human brain, whereas both apoptosis-mediating and apoptosis-blocking TRAIL receptors are found on neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes 11862476_highly expressed in metastatic gastric carcinoma and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes 12196516_examined whether TRAIL receptors use different intermediates to convey the apoptotic signal to mitochondria 12388624_cholestasis increased both liver TRAIL-R2/DR5 mRNA and protein expression (>10-fold) 12388693_Tyrosine-based sorting signal in adenovirus RID plays a role in RID's ability to down-regulate TRAIL receptor 2 and inhibit TRAIL induced apoptosis 12421985_Decreased expression of DR5 may contribute to prolonged survival of eosinophils in the airways of allergic asthmatics following segmental antigen challenge. 12488957_Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by TRAIL to beta-cell lines CM were inhibited competitively by soluble TRAIL receptors, R1, R2, R3 or R4. 12642868_role of upregulation in interferon-alpha sensitized hepatoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis 12808117_likely to be involved in chronic pancreatitis; pancreatic stellate cells may directly contribute to acinar regression by inducing apoptosis of parenchymal cells in a TRAIL-dependent manner 12847280_Like malignantly transformed cells, synovial cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients express high levels of DR5 and are highly susceptible to DR5-mediated apoptosis. 12915532_Respiratory syncytial virus infection strongly up-regulated the expression of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its functional receptors death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5. 12920112_results show that protein kinase C activation specifically inhibits the recruitment of TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 complexes, thereby modulating tumor necrosis-related apoptosis-inducing ligand(TRAIL)-induced apoptosis 14506242_Infection of primary cells with adenoviruses carrying the relevant point mutations confirmed the crucial role of putative YXX Phi and dileucine (LL) transport motifs within Ad2 10.4-14.5 for down-regulation of Fas, TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2, and EGFR. 14534720_Fas, DR4, and DR5 are activated in drug-sensitive cells in response to anticancer drugs depending on the cytotoxic effect of each drug 14561739_Sp1 is a bile acid-responsive transcription factor that mediates DR5/TRAIL-R2 gene expression downstream of JNK. 14576771_All of mAbs to TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 induced cell death in several cancer cell lines susceptible to TRAIL but not in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro 14688276_TRAIL-R2 expression is post-transcriptionally regulated by cytosolic proteins induced by TRAIL that bind to the 3'-UTR region of TRAIL-R2 mRNA 14691451_MG132 upregulates death receptor 5 and cooperates with APO2L to induce apoptosis in Bax-proficient and -deficient cells. 15173180_binding of Fas-associated death domain (FADD) to the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor DR5 is regulated by the death effector domain of FADD 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15334061_Malignant mesothelioma cells develop anintrinsic resistance to apoptosis induced by death receptor-4 upregulating the expression of the antiapoptotic protein c-FLIP. 15356269_DR4 and DR5 are differentially regulated by the signal recognition particle 15452120_in addition to the death domain, the C-terminal tails of DR4 and DR5 positively regulate FADD binding, caspase activation and apoptosis 15480430_CD95, DR4 and DR5 localization in rafts have roles in the toxicity of resveratrol and death receptor ligands in colon carcinoma cells 15485835_c-FLIPL is recruited to death receptor 5 independent of Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) 15502938_Although ischemic liver injury was not serious, due to the short ischemia time, TNFR1 and TRAIL are associated with liver ischemic injury in live-donor liver transplantation but Fas is not. 15507617_Adenovirus E3-6.7K protein is required in conjunction with the E3-RID protein complex for the internalization and degradation of TRAIL receptor 2. 15520016_DR5 may contribute more than DR4 to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells that express both death receptors 15538968_The death receptor 5 was widely expressed on both normal and maliganat cells 15608691_The TRAILR2 is expressed by humans thymocytes, which appear to be functional since considerable cell death was observed upon receptor ligation. 15655781_in patients infected with cagA+/vacAs1+ H. pylori strains, expression of TRAIL and TRAIL-R1 and -R2 was down-regulated; down-regulation may limit apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells & destruction of tissue and may enable H. pylori to maintain its niche 15685228_In colorectal carcinogenesis, there is a marked increase in sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis with progression from benign to malignant tumor, but alterations in cell surface TRAIL receptor expression may not be the primary reason for this change. 15757891_RAS-MEK-ERK1/2 signaling pathway can sensitize cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulating DR4 and DR5 15828026_addition in culture of TRAIL-R2-Fc chimera, which blocked the interaction between endogenous TRAIL and TRAIL-R2 on the surface of cultured megakaryocytic cells, increased the total megakaryocytic cell count 15921376_TRAIL-R2 downmodulation results in resistance to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia. 16003390_Extensive regions of the FADD death domain are required for binding to the TRAIL receptor DR5. 16007131_Luteolin induces apoptosis via DR5 up-regulation in malignant tumor cells. 16051735_TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 act as dosage-dependent tumor suppressor genes whose monoallelic deletion can impair TRAIL-induced apoptosis in B-cell lymphoma 16226105_TRAIL-R2 apoptotic pathway plays an important role in hepatic cell death during viral infection. 16463784_The expression level of TRAIL receptor DR5 in the fibroblasts of hypertrophic burn scar is much lower than the control. 16529749_Alpha-tocopheryl succinate activates expression of DR4/DR5 in a p53-dependent manner and re-establishes sensitivity of resistant MM cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. 16541419_TRAIL sensitivity was correlated with tumor progression and DR5 expression levels and apoptosis was exclusively mediated by DR5. Caspase 8 expression levels were as DR5 directly correlated to TRAIL sensitivity in prostate tumor cells. 16544055_The antigenic load of TRAIL-R2 was positively correlated with survival of patients with glioblastoma multiforme tumor. 16571651_DR5 expression is upregulated in human osteosarcoma cells after administration of sulforaphane 16632604_Data show that HIV-1 induces interferon-alpha and the TRAIL/DR5 apoptotic pathway in tonsillar tissue, suggesting a role for these cytokines in HIV-1 immunopathogenesis. 16729023_Upregulation of TRAIL-R2 is not involved in HDACi mediated sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 16731632_DR5-selective TRAIL variants do not induce apoptosis in DR4-responsive cell lines but show a large increase in biological activity in DR5-responsive cancer cell lines. 16778114_TRAIL receptor 1 expression may be important in analysis of clinical trials involving TRAIL receptor agonists in melanoma 16980044_Hepatocytes exposed to hypoxia showed decreased expression of mRNA. 16980609_The specificity of DcR1- and DcR2-mediated TRAIL inhibition reveals an additional level of complexity for the regulation of TRAIL signaling. 17027647_In addition, we show the possible involvement of co-factors CBP and p300 in ESE-3-mediated DR-5 up-regulation. 17070520_Arsenite treatment upregulated surface levels of death receptors, TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2, through increased translocation of these proteins from cytoplasm to the cell surface. 17273769_DR5/TRAIL-R2 expression is upregulated by fenretinide via the induction of the transcription factor CHOP 17548900_Quercetin increases expression of death receptor (DR) 5, but has no effect on that of other components of the death-inducing signaling complex in lung in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 17627287_HIPK2-induced p53Ser46 phosphorylation activates the KILLER/DR5-mediated caspase-8 extrinsic apoptotic pathway. 17666396_mutations in the TRAIL receptor DR5 inhibit TRAIL signaling through the DR4 receptor by competing for ligand binding 17689858_caspase-3 is a key regulator of apoptosis in response to combined genistein and TRAIL in human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells through the activation of DR5 and mitochondrial dysfunction 17690453_tryptophol induces apoptosis through DR5 and the resistance of PBL to tryptophol-induced apoptosis might be due to competition from DcR1 17881637_TP53 DNA-binding mutations were the most significant predictor of poor OS; TRAILreceptor-2 (DR5) was the most differentially underexpressed gene in the TP53 mutated cases 17922852_Doxorubicin may sensitize solid cancer cells to TRAIL-R2-mediated apoptosis by inducing TRAIL-R2 expression. 17968315_Celecoxib and a novel COX-2 inhibitor ON09310 upregulate death receptor 5 expression via GADD153/CHOP 17983809_Human hepatoma cells mount an intact innate antiviral defense through induction of interferon, Trail, death receptor 4 and 5, and triggering apoptosis of infected cells. 18022315_RRR-gamma-tocopherol is a potent pro-apoptotic agent for human breast cancer cells inducing apoptosis via activation of DR5-mediated apoptotic pathway. 18079962_Thus TRAIL-R may function as an inflammation and tumor suppressor in multiple tissues in vivo. 18190241_The findings revealed reduced concentrations of sTRAIL both before and after treatment and elevated levels of sTRAIL-R2 and OPG in patients before treatment 18203008_REVIEW: mechanism of DR4- and DR5-induced apoptosis and the regulation of DR4 and DR5 expression; regulation of DR4,5 signaling in hematological malignancies; sensitization of leukemia and lymphoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by chemotherapy 18219321_Results provide structural and functional insight into the interaction of Apomab with DR5 and support further investigation of this antibody for cancer therapy. 18314443_tumor cell-restricted loss of TRAIL-receptor 2 were observed in 16 of 16 SzS PBLs. 18341587_Novel therapeutic approaches using TRAIL or agonistic TRAIL receptor antibodies in combination with proteasome inhibitors may represent a promising approach to reactivate apoptosis in therapy-resistant high-grade gliomas 18424742_proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 inhibits the transcription repressor Yin Yang 1 (YY1) which regulates TRAIL resistance and negatively regulates DR5 transcription. 18511705_TRAILR2 (TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand receptor 2) levels were significantly higher in lung parenchyma in subjects with emphysema 18519235_The altered ability of neutrophils to secrete sTRAIL may have different implications for the immune response of patients with oral cavity cancer cells at different stages of disease. 18534188_Oxidative stress sensitizes human astroglial cells to TRAIL-induced cell death through up-regulation of DR5 expression. 18593935_CHOP-dependent DR5 up-regulation is a key event mediating SHetA2-induced apoptosis. 18599488_FADD protein, human; Humans; MCL1 protein, human; Mutagenesis; NF-kappa B 18625509_Report bioassay for BAFF based on expression of a mouse BAFF-receptor ectodomain-human tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor-2 endodomain fusion receptor in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. 18829683_SNP rs1047266 in the tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b, gene was associated with risk of asthma 18840411_an apoptotic inhibitory complex comprised of DR5, FADD, caspase-8, and c-FLIP(L) exists in MCF-7 cells, and the absence of c-FLIP(L) from this complex induces DR5- and FADD-mediated caspase-8 activation in the death inducing signaling complex 19037087_DR5-mediated apoptosis, which is induced by rottlerin alone or by the combined treatment with rottlerin and TRAIL, may offer a new therapeutic strategy against cancer. 19074831_TRAIL death receptors (DR4 and DR5) undergo constitutive endocytosis in some breast cancer cells 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19212626_expression of TRAIL and its receptors were lower in gastric cancer than those of normal tissue 19219602_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19230044_Progress from adhesion to detachment of esophageal carcinoma cells causes DR5 relocalization, and promotes cytoplasmic translocation of DR5 to cell surfaces via a Golgi-dependent pathway. 19243385_inhibition of c-FLIP(L) expression might be a potential strategy for lung cancer therapy, especially for those lung cancers resistant to the agonistic antibody against death receptors 19305384_This is the first study that shows that intervertebral disk cells express TRAIL, DR4 and DR5, which correlate to the degenerative state of the disk. 19379558_Sodium butyrate upregulates TRAIL and DR5 which causes apoptosis of leukemic cell lines. 19412666_The novel highly selective and effective DR5-A and DR5-B TRAIL variants will be useful in studies on the role of different receptors in TRAIL-induced apoptosis in sensitive and resistant cell lines. 19424623_Report efficacy of triple antineoplastic therapies including ionising radiation, agonistic TRAIL receptor antibodies and cisplatin. 19432816_This study indicates that the death-inducing signalling complex modification by RIP, c-FLIP and PED/PEA-15 is the most upstream event in TRAIL resistance in glioblastomas. 19434100_Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10b overexpression dramatically activates the release of the inflammatory cytokines IL-8, TNF-alpha, CCL20, MIP-2 and MIP-1beta in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. 19519609_TRAIL, DR5 and caspase-3 overexpression and enhanced Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase Mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) positivity were found in chronically bitumen-exposed skin 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19584075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19637313_DR4 and DR5 were significantly upregulated in 37 and 47% of the tumor samples respectively, while both DR4 and DR5 were coinstantaneously upregulated in 31% of the samples analyzed. 19643115_hypoxia/reoxygenation up-regulated the expression of DR4 and DR5, and enhanced TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in normal human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells 19661294_Low DR5 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 19674787_Findings highlight a mechanism by which TRAIL and DR5 serve to protect trophoblasts in normal development, but may be activated in conditions of excessive TNFalpha. 19730199_Results indicate that disc cells, after herniation, undergo apoptotic cell death via the DR5/TRAIL pathway. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19854829_Data demonstrate that XIAP antagonists in combination with Fas ligand (FasL) or the death receptor 5 (DR5) agonist antibody synergistically stimulate death in cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth. 19890662_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19939880_Treatment of various gliomas with capsaicin significantly upregulated DR5. The induction of DR5 was mediated by CHOP/GADD153. 20007968_CHM-1 exhibits vascular targeting activity associated with the induction of DR5-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis through p53 up-regulation, which suggests its potential as an antivascular and antitumor therapeutic agent. 20087343_Egr-1 drives c-FLIP expression and the short splice variant of c-FLIP (c-FLIP(S)) specifically inhibits DR5 activation. 20106985_the N-terminal epitope of death receptor 5 has a role in tumor cell death 20123409_results suggest a possible pivotal role of the TRAIL/DR5 system in temporomandibular joint disc degeneration 20156289_analysis of how DR5 binds and is inhibited by synthetic constrained peptides 20157774_Results suggest that upregulation of DR5 by tocotrienol treatment in breast cancer cells is dependent on JNK and p38 MAPK activation which is mediated by endoplasmic reticular stress. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20339295_Androgen ablation therapy alters expression of TRAIL death ligand and TRAIL-R2 in patients with prostate cancer. 20354842_Results analyze cell viability, DISC formation as well as IL-8 and NF-kappaB activation side by side in responses to TRAIL and agonistic antibodies against DR4 (mapatumumab) and against DR5 (lexatumumab) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. 20398055_DNMT1 and DNMT3b silencing sensitizes human hepatoma cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis via up-regulation of TRAIL-R2/DR5 and caspase-8. 20410100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20410100_SNFs in TNFRSF10B show strong statistical evidence of a funtional effect on plasma fatty acid distribution. 20422457_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in TNFRSF10B gene is associated with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. 20430723_Data suggest that cytotoxic agents capable of up-regulating the expression of TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 can sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis. 20450916_Inhibition of tissue transglutaminase 2 sensitizes TRAIL-resistant lung cancer cells through upregulation of death receptor 5. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20666744_Fas, TRAILR1 and TRAILR2 genes may not be mutated in prostate carcinomas. 20666744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673328_Similarly CRC subset with TRAIL-R2 expression was associated with a well-differentiated tumors, histology subtype of adenocarcinomas and tumors in left colon 20714870_Plumbagin alone could markedly up-regulate DR5 mRNA and protein expression, and slightly increase DR4 mRNA and protein expression in A375 cells. 20714918_A new single-chain fragment variable (scFv) to TRAIL-R2 receptor produced as minibody (MB2.23) significantly increase the median survival time of lymphoma-bearing animals. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802294_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20808443_DR5 and caspase-8 are involved in regulation of HNSCC metastasis. 20839416_TRAIL, its death receptor DR5 and caspase 3 were detected in the intima and media layers of newly formed vessels affected in affected temporomandibular joint discs. 20875141_ANT2 shRNA treatment sensitized MCF7, T47 D, and BT474 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulating the expression of TRAIL death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4 and DR5) and down-regulating the TRAIL decoy receptor 2 (DcR2). 21044953_small molecules such as celecoxib induce DR5 expression through activating ERK/RSK signaling and subsequent Elk1 activation and ATF4-dependent CHOP induction 21059290_Alpha-fetoprotein interacted with RAR-beta and suppressed the expression of DR5 in hepatoma cells. 21152876_The apoptosis of HCC cells only partially depended on the upregulation of DR5 and the status of p53. 21152878_gamma-humulene induced apoptotic cell death in HT29 cells through a DR5-mediated caspase-8 and -3-dependent signaling pathway. 21167276_Our results suggest that PIC sensitizes TRAIL-induced-apoptosis via Sp1- and ERK-dependent DR5 up-regulation. 21172010_Perifosine induces DR5 expression through a JNK-dependent mechanism independent of reactive oxygen species. 21272366_Critical difference between DR4- and DR5-mediated apoptotic signaling modulation. 21279373_increased expression in plaque psoriasis 21519792_lupulone-triggered enhanced expression of p38 plays a major role in the activation of p53 and of the TRAIL-death receptor apoptotic pathway in SW620 human colon cancer-derived metastatic cells 21538027_Inhibition of PI3K reduced rhTRAIL sensitivity independently of the cell line preference for either DR4- or DR5-mediated apoptosis signaling. 21697087_Modulation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein (CHOP)-dependent DR5 expression by nelfinavir sensitizes glioblastoma multiforme cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). 21769428_TRAIL-induced redistribution of DR4 and DR5 in lipid rafts contributed to the sensitivity to TRAIL in TRAIL-sensitive NSCLC H460 cell line. 21785270_Data show that TRAIL sensitive cancer cells have higher DR4 and DR5 expression on the cell surface. 21801305_DR5 is modulated by the ATF4-ATF3-CHOP axis in human NSCLC cells after Sirt1/2 inhibition or salermide treatment. 21803611_Data indicate that isoflavone biochanin-A sensitized the TRAIL-resistant LNCaP cells through the inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB(p65) activity and increased the expression of the death receptor TRAIL-R2 (DR5). 21805040_p53 and DR5 expression decreased progressively with colorectal caner stage, suggesting that these proteins are important markers of advanced tumor stages. 22020938_Findings suggest that the importin beta1-mediated nuclear localization of DR5 limits the DR5/TRAIL-induced cell death of human tumor cells and thus can be a novel target to improve cancer therapy with recombinant TRAIL and anti-DR5 antibodies. 22065586_Ras induces DR5 expression through co-activation of ERK/RSK and JNK signaling pathways 22072062_Endoplasmic reticulum stress alters the cellular levels of different apoptosis-related proteins including a decline in the levels of FLIP and Mcl-1 and the up-regulation of TRAIL-R2. 22158615_DR4 and DR5 have a capability to activate Nox1 by recruiting RFK, resulting in ROS-mediated apoptotic cell death in tumor cells. 22183068_Data show that a higher expression of FAS receptor, FAS ligand, TrailR1 and TrailR2 on T cells or blasts of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients is associated with a better prognosis. 22392486_Endometriosis is not associated with DR5 gene polymorphism. 22412938_membrane DR5 expression leading to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis may represent one of the pathways responsible for eradication of over-activated CD4(+) T cells during immune responses. 22419388_hDR5 reactive immune serum prevented growth of SUM159 TNBC cells in severe combined immune-deficient mice. 22447040_Data show that bufalin-induced down-regulation of Cbl-b contributed to the up-regulation of TRAIL Receptors DR4 and DR5. 22496450_Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces death receptor 5 networks that are highly organized. 22537456_Data indicate taht decreased serum death receptor 5 (sDR5) is associated with high level of liver damage and inhibited HBV antigen expression. 22665066_BCR-ABL is critically involved in the leukemia-specific expression of DR4 and DR5 and in the susceptibility of Ph(+) leukemia to TRAIL-mediated anti-leukemic activity. 22695614_Upregulation of DR4 and DR5 and colocalization with Abeta at the cell membrane suggests their involvement as initiators of the apoptotic machinery 22789540_Vascular disruption and antitumor activity required DR5 expression on tumor ECs but not malignant cells. These results establish a therapeutic paradigm for proapoptotic receptor agonists as selective tumor vascular disruption agents 22791814_these results identify the expression of MAGE-D2 suppresses TRAIL receptor 2 and protects againstas TRAIL-induced apoptosis 22824792_Up-regulation of DR4 and DR5 overcomes TRAIL resistance in glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. 22842544_TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human renal cancer cells by upregulation of DR5 as well as downregulation of c-FLIP and Bcl-2. 22895172_Gene silencing of DR5 by short hairpin RNA reduced the apoptosis induced by combination treatment of mitomycin C and TRAIL in colon cancer cells. 22948392_Suppression of HSP70 expression sensitizes NSCLC cell lines to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by upregulating DR4 and DR5 and downregulating c-FLIP-L expressions 23053497_DR5 upregulation in this case is mediated by C/EBP homology protein (CHOP), an important endoplasmic reticulum stress responsive protein. 23065795_pJNK2, CHOP, and DR5 are upregulated by gamma-tocopherol in breast cancer cell lines. 23091198_Studies suggest that TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) plays broader roles in regulating immune processes. 23247197_SIRT1 inhibition increases Ku70 acetylation, and the acetylated Ku70 with a decreased function mediates the induction of DR5 and the down-regulation of c-FLIP by up-regulating c-Myc/ATF4/CHOP pathway,promotes the TRAIL-induced apoptosis 23254287_Increased TRAIL-R2 expression on T cells in chronic hepatitis B. 23284732_Loss of membrane TRAIL-R2 expression is associated with early stage colorectal cancer. 23292651_analysis of small-molecule activation of the TRAIL receptor DR5 in human cancer cells 23306613_used a stable cell line with downregulated c-Cbl, infection with the c-Cbl shRNA-expressing adenovirus led to an increase in the death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5 levels, which is known to be a cause for the increase of TRAIL-induced apoptosis 23322903_Studies indicate that the anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP is an important regulator of death receptor signaling, including TNFR1, Fas, DR4, and DR5. 23423784_Deletion of TRAIL-R2 is relevant to the loss of 8p21.3 and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. 23428290_CBX enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis through upregulation of death receptor 5, blockade of GJ intercellular communication, and downregulation of connexin 43 23460812_The fraction of pancreatic cancer samples with positive membrane staining for TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 was lower than that of cells from surrounding non-tumor tissues. 23498957_Human cytomegalovirus UL141 binds to cellular TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 and protects virus infected cells from NK cell-mediated killing. 23579274_BNIP3 acts as transcriptional repressor of death receptor-5 expression and prevents TRAIL-induced cell death in gliomas. 23584885_The membrane expression of the TRAIL receptors DR4, DR5, DcR1 and DcR2 is greater in normal endometrium than endometrioid adenocarcinoma (EAC). The level of the receptors in EAC is not dependent on grading and staging and does not predict survival. 23608376_Assessed if casticin induces caspase-mediated apoptosis via activation of mitochondrial pathway and upregulation of DR5 in human lung cancer cells. 23615398_CHOP-mediated DR5 upregulation and proteasome-mediated downregulation of c-FLIP. 23686163_vThe antiproliferative GSI-I/TRAIL synergism was stronger in ER-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells compared with ER-positive MCF-7 cells. In MDA-MB-231 cells, GSI-I treatment induced upregulation of DR4 and DR5 TRAIL receptors 23724937_research may provide a backbone for understanding structural and functional insights of TNFRSF10B protein. The designed novel inhibitors and predicted interactions might serve to inhibit the disease 23806100_Human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells express TRAIL-1 and TRAIL-2 receptors and can be sensitized to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 23839018_TNFRSF10B polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with increased risk of non-small cell lung cancer. 23857473_these results indicate that CAPE potentiated TRAIL-induced apoptosis in SK-Hep1 cells, through upregulation of TRAIL receptors(DR4 and DR5) via modulation of p38 and JNK signaling pathways. 23908588_Data suggest that doxorubicin (DOX)-induced recruitment of death receptor 5 (DR5) to the cell surface impacts the enhanced apoptotic effect that can be longitudinally monitored by apoptosis imaging. 24002210_As detected by western blot analysis and real-time RT-PCR, ibuprofen upregulated the expression of death receptor 5 (DR5), a TRAIL receptor. 24078627_azadirone can sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL through ROS-ERK-CHOP-mediated up-regulation of DR5 and DR4 signaling, down-regulation of cell survival proteins, and up-regulation of proapoptotic proteins. 24085293_Ack1 acts in a kinase-independent manner to promote TRAIL-R1/2 accumulation in lipid rafts. These findings identify Ack1 as an essential player in the spatial regulation of TRAIL-R1/2. 24120475_Nuclear TRAIL-R2 inhibits maturation of the microRNA let-7 in pancreatic cancer cell lines and increases their proliferation. Pancreatic tumor samples have increased levels of nuclear TRAIL-R2, which correlate with poor outcome of patients. 24190693_Primary EOC is associated with lower TRAIL-R2 and BCL2 expression levels, while metastatic EOC is associated with higher expression of these genes. 24212133_was statistically significant association between DR5 expression and tumor site of asal cell and squamous cell carcinoma skin cancers 24213373_Our results indicate that indomethacin can potentiate TRAIL-induced apoptosis through upregulation of death receptors and downregulation of survivin. 24270523_Cotreatment with MESC and an ERK inhibitor (PD98059) significantly increased the expression of DR5 to induce apoptosis...MESC may induce apoptosis via the ERK pathway and may be a potential anticancer drug candidate against human oral MEC. 24387758_Parthenolide triggers extrinsic apoptosis by up-regulating TNFRSF10B and intrinsic apoptosis through increasing the expression of PMAIP1. 24551275_Report RR5 up-regulation in alveolar epithelial cells from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. 24662747_Low doses of triptolide sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL mediated death via death receptor 5. 24690311_These findings indicate that MUC16 protects EOC cells against TRAIL-induced apoptosis through multiple mechanisms including the blockade of TRAIL R2 expression and the regulation of cFLIP expression at both the transcriptional and the protein level. 24895135_Further analysis demonstrated that PARP inhibitor treatment results in activation of the FAS and TNFRSF10B (death receptor 5 (DR5)) promoters, increased Fas and DR5 mRNA, and elevated cell surface expression of these receptors in sensitized cells 24939851_results provide novel insights into the role of ATF3 as an essential transcription factor for p53-independent DR5 induction upon both ZER and CCB treatment, and this may be a useful biomarker for TRAIL-based anticancer therapy 24994655_DR5 integrates opposing UPR signals to couple the endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptotic cell fate. 25026275_Data suggest that H-Ras inhibits TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis through downregulation of surface death receptors DR4/DR5. 25110157_This study demonstrated lower apoptosis correlated with a deficiency of DR5 cell surface expression by CD4 T cells upon HIV-1 stimulation. 25144704_Studied the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells induced by SEA; found it could be reduced in hepatic stellate cells that were treated with p53-specific siRNA and in hepatic stellate cells that were treated with DR5-specific shRNA. 25174820_DR5 expression is dramatically reduced as a function of higher prostate tumor grade. 25230899_Over-expression of TRAIL-R2 is associated with breast cancer. 25293521_the present study demonstrated that the XIAP inhibitor Embelin could enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells by DR4 and DR5 upregulation and caspase activation 25724522_Methionine Deprivation Induces a Targetable Vulnerability in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Enhancing TRAIL Receptor-2 Expression 25770212_findings highlight novel mechanisms underlying endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced TNFRSF10A and TNFRSF10B expressions and apoptosis. 25795228_The expression of two proapoptotic genes, FAS and DR5, was significantly lower in tumor samples than in adjacent normal tissues 25843953_FTY720 ehances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through up-regulation of DR5 and down-regulation of Mcl-1 in human kidney cancer cells. 25845236_The results show that both TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 are highly expressed on human oligodendrocyte progenitors. 25882551_TRAIL signaling almost exclusively depends on DR5 despite these cells expressing high amounts of DR4 25909161_In an osteotropic variant of MDA |
ENSMUSG00000045362+ENSMUSG00000037613+ENSMUSG00000010751 |
Tnfrsf26+Tnfrsf23+Tnfrsf22 |
315.628258 |
3.3212265493 |
1.731716 |
0.102470523 |
291.259088 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002643713241207766217674469065957250232540836819762374587981765122225311843056082369169578920736668860163186244614130373608475673915841491011029276695238957435802121254120322646485874429345130920410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000747532709582885641109008547273365159631473354317398843639456883678399724053069850807574424479270247136543053232108103228551107989605118894970964262071748374863938702006294079183135181665420532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
473.7204480 |
30.0620537 |
143.8377939 |
7.4099305 |
| ENSG00000120896 |
10174 |
SORBS3 |
protein_coding |
O60504 |
FUNCTION: Vinexin alpha isoform promotes up-regulation of actin stress fiber formation. Vinexin beta isoform plays a role in cell spreading and enhances the activation of JNK/SAPK in response to EGF stimulation by using its third SH3 domain. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes an SH3 domain-containing adaptor protein. The presence of SH3 domains play a role in this protein's ability to bind other cytoplasmic molecules and contribute to cystoskeletal organization, cell adhesion and migration, signaling, and gene expression. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:10174; |
cell-substrate junction [GO:0030055]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; vinculin binding [GO:0017166]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of cytoskeleton organization [GO:0051495]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496] |
12510380_regulates cytoskeletal organization and signal transduction--review 15184391_vinexin is a novel substrate of ERK2 and may play roles in ERK-dependent cell regulation 15734736_phosphorylation of the AF-1 domain controls RARgamma-mediated transcription through triggering the dissociation of vinexin beta 16923119_These results suggest that vinexin beta plays a role in maintaining the phosphorylation of EGFR on the plasma membrane through the regulation of c-Cbl. 17486060_Vinexin is enriched at the leading edge of migrating cells, lamellipodia and and focal adhesions in well-spread cells. 19294487_Rhotekin forms a complex with vinexin and may play a role at focal adhesions. 20361963_Vinexin knockdown using siRNA delayed migration of both HaCaT human keratinocytes and A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells in scratch assay but did not affect cell proliferation. 25824575_Our findings revealed that Vinexin-beta acts as a novel modulator of ischaemic injury 25972535_Taken together, the findings suggest that vinexin beta modulates NS5A phosphorylation via its interaction with NS5A, thereby regulating hepatitis C virus replication, implicating vinexin beta in the viral life cycle. 27311882_The chromosome 8p tumor suppressor genes SORBS3 and SH2D4A are physically and functionally linked and provide a molecular mechanism of inhibiting STAT3-mediated IL-6 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 27437034_Study identified possible epigenetic influence on differential gene expression in SORBS3 under obese conditions. 28209562_Vinexin beta deficiency attenuates atherogenesis primarily by suppressing vascular inflammation and inactivating Akt-nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Our data suggest that vinexin beta could be a therapeutic target for the treatment of atherosclerosis. 34848853_Vinexin contributes to autophagic decline in brain ageing across species. |
ENSMUSG00000022091 |
Sorbs3 |
163.737248 |
0.2153810280 |
-2.215037 |
0.236299356 |
82.704338 |
0.00000000000000000009529187928489239755325381486811752992167539907675063060206455123335445023258216679096221923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000833239418391594692959578348979062105781109233188126694802377869564224965870380401611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.2264612 |
13.2498050 |
276.6647872 |
43.4597737 |
| ENSG00000121005 |
83690 |
CRISPLD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H336 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Involved in face morphogenesis. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83690; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis [GO:0061484] |
21254358_These novel findings suggest that CRISPLD1 plays a role in Nonsyndromic cleft lip and palate (NSCLP) through the interaction with CRISPLD2 and folate pathway genes. 32146539_CRISPLD1: a novel conserved target in the transition to human heart failure; findings provide new pathophysiological data on Ca(2+) regulation in the transition to failure and novel candidate genes with promising potential for therapeutic interventions |
ENSMUSG00000025776 |
Crispld1 |
57.329911 |
0.1416403855 |
-2.819695 |
0.263002552 |
131.918094 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000155921418050666242912034343772531424816651829389033504362217294397031041951586297078513609903893666341900825500488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000020223199740139135090528782908567904401228367080671648534008442907416884072385136056348997612985840532928705215454101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.3756695 |
3.2212208 |
88.4064648 |
14.6286110 |
| ENSG00000121068 |
6909 |
TBX2 |
protein_coding |
Q13207 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor which acts as a transcriptional repressor (PubMed:11111039, PubMed:11062467, PubMed:12000749, PubMed:22844464, PubMed:30599067). May also function as a transcriptional activator (By similarity). Binds to the palindromic T site 5'-TTCACACCTAGGTGTGAA-3' DNA sequence, or a half-site, which are present in the regulatory region of several genes (PubMed:11111039, PubMed:12000749, PubMed:22844464, PubMed:30599067). Required for cardiac atrioventricular canal formation (PubMed:29726930). May cooperate with NKX2.5 to negatively modulate expression of NPPA/ANF in the atrioventricular canal (By similarity). May play a role as a positive regulator of TGFB2 expression, perhaps acting in concert with GATA4 in the developing outflow tract myocardium (By similarity). Plays a role in limb pattern formation (PubMed:29726930). Acts as a transcriptional repressor of ADAM10 gene expression, perhaps in concert with histone deacetylase HDAC1 as cofactor (PubMed:30599067). Involved in branching morphogenesis in both developing lungs and adult mammary glands, via negative modulation of target genes; acting redundantly with TBX3 (By similarity). Required, together with TBX3, to maintain cell proliferation in the embryonic lung mesenchyme; perhaps acting downstream of SHH, BMP and TGFbeta signaling (By similarity). Involved in modulating early inner ear development, acting independently of, and also redundantly with TBX3, in different subregions of the developing ear (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of PML function in cellular senescence (PubMed:22002537). Acts as a negative regulator of expression of CDKN1A/p21, IL33 and CCN4; repression of CDKN1A is enhanced in response to UV-induced stress, perhaps as a result of phosphorylation by p38 MAPK (By similarity). Negatively modulates expression of CDKN2A/p14ARF and CDH1/E-cadherin (PubMed:11062467, PubMed:12000749, PubMed:22844464). Plays a role in induction of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (PubMed:22844464). Plays a role in melanocyte proliferation, perhaps via regulation of cyclin CCND1 (By similarity). Involved in melanogenesis, acting via negative modulation of expression of DHICA oxidase/TYRP1 and P protein/OCA2 (By similarity). Involved in regulating retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell proliferation, perhaps via negatively modulating transcription of the transcription factor CEBPD (PubMed:28910203). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11062467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11111039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12000749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22002537, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22844464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28910203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29726930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30599067}. |
Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. T-box genes encode transcription factors involved in the regulation of developmental processes. This gene product is the human homolog of mouse Tbx2, and shares strong sequence similarity with Drosophila omb protein. Expression studies indicate that this gene may have a potential role in tumorigenesis as an immortalizing agent. Transcript heterogeneity due to alternative polyadenylation has been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6909; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035909]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; atrioventricular canal development [GO:0036302]; atrioventricular canal morphogenesis [GO:1905222]; cardiac jelly development [GO:1905072]; cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation [GO:0060379]; cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0048738]; cell fate specification [GO:0001708]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; cochlea morphogenesis [GO:0090103]; developmental growth involved in morphogenesis [GO:0060560]; embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048596]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003272]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060441]; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008543]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; mammary placode formation [GO:0060596]; melanocyte proliferation [GO:0097325]; mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in lung development [GO:0060916]; muscle cell fate determination [GO:0007521]; negative regulation of cardiac chamber formation [GO:1901211]; negative regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000773]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of heart looping [GO:1901208]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; pharynx development [GO:0060465]; pigment metabolic process involved in pigmentation [GO:0043474]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902808]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051145]; ureteric peristalsis [GO:0072105] |
12000749_identification of a variant T-site as the essential TBX2/TBX3-binding element in the human p14(ARF) promoter 14595187_upregulation of Tbx2 gene in response to tension downregulates CX43 in cranial sutures 15781639_In human melanoma cells, expression of dnTbx2 leads to severely reduced growth and induction of senescence-associated heterochromatin foci. 16730707_Results are consistent with Tbx2 playing a role in cell cycle progression and organization of subnuclear compartments. 17407139_Tbx2 in fibroblasts reduces expression of the COL1A2 gene 18025091_the ability of Tbx2 to repress the p21 gene is enhanced in response to a stress-induced senescence pathway, which leads to a better understanding of the regulation of the anti-senescence function of Tbx2. 18640248_identify a Sp1 element and a reverse CCAAT box to be essential for basal Tbx2 promoter activity 18829543_Tbx2 and Tbx3 may play a dual role during the radial to vertical growth phase transition by both inhibiting senescence via repression of p21(CIP1) expression, and enhancing melanoma invasiveness by decreasing E-cadherin levels. 19216023_TBX2 is a cell type-dependent survival factor under a p53-negative background. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19469638_Tbx2 protein might play an important role in the process of the development and metastasis of pancreatic cancers 19633291_Data reveal that TPA activates transcription of TBX2 through activating MSK1, which leads to an increase in phosphorylated histone H3 and the recruitment of Sp1 to the TBX2 gene. 19960541_This review presents a state of the art overview of the role and regulation of Tbx2 in early embryonic development and in cancer[review] 20348948_Data identify a novel mechanism for TBX2-driven oncogenesis and highlight the importance of NDRG1 as a growth control gene in breast tissue. 20502058_We report the first analysis of PSCA, PIWIL1, and TBX2 expression in EAC. Our findings suggest that PSCA and TBX2 might be candidate targets for cancer therapy. 20534814_Rb1 is an important determinant of Tbx2 functional specificity. 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635360_TBX2 gene duplication is associated with complex heart defect and skeletal malformations. 21271665_Microdeletion of 17q22q23.2 encompassing TBX2 and TBX4 in a patient with congenital microcephaly, thyroid duct cyst, sensorineural hearing loss, and pulmonary hypertension. 22002537_PML and TBX2 act in an autoregulatory loop to control the effective execution of the senescence program. 22284968_TBX2 CPG island methylation predicts progression in bladder cancer. 22844464_an unanticipated link between TBX2 deregulation in cancer and the acquisition of EMT and invasive features of epithelial tumor cells 23020925_The identification of TBX2 as a target for PAX3 provides a key insight into how PAX3 may contribute to melanoma evolution. 23388722_Coimmunoprecipitations and immunofluorescence analyses confirmed the L2-TBX2 interaction and revealed that human papillomavirus 16 L2 also interacts with human TBX3, another member of the T-box family. 23727221_DNA sequence variants within TBX2 gene promoter may contribute to ventricular septal defects ethiology 23959449_TBX2 was a significantly prognostic factor for decreased survival. 24113180_Knocking down TBX2 sensitises the cells to cisplatin by disrupting the ATM-CHK2-p53 signalling pathway. 24309999_The data suggested that the DNA sequence variants within the TBX2 gene promoter was implicated in the indirect inguinal hernia development as a rare cause. 24470334_deregulated TBX2 serves as an oncogene in rhabdomyosarcoma 24742492_High TBX2 expression is associated with breast cancer. 25027744_High TBX2 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 25344916_Our results suggest a conserved role of Tbx2-related proteins in cell invasion and metastasis-related processes 25371204_Data show that the down-regulation of T-box transcription factor TBX2 by transforming growth factor beta I (TGF-beta1) is mediated by T-box transcription factor TBX3. 25394776_this new molecular-grade based on the combination of TBX2 and TBX3 methylation is an excellent marker for predicting progression to muscle-invasive bladder cancer in patients with primary pTaG1/2 bladder cancer. 26686089_TBX2 is a central component of the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway deregulation in RMS cells and that targeting TBX2 in RMS tumors may offer a novel therapeutic approach for RMS 28849151_The results indicated that the expression rates of TBX2 were significantly increased in the prostate cancerous tissues, compared with the healthy tumor adjacent tissue, and TBX2 increased staining was associated with the clinical stage and pathological grade. 29726930_We report four individuals with an overlapping spectrum of craniofacial dysmorphisms, cardiac anomalies, skeletal malformations, immune deficiency, endocrine abnormalities and developmental impairments, reminiscent of DiGeorge syndrome, who are heterozygotes for TBX2 variants. 30223900_Our results indicate that the R608W and R616Q variants of TBX2 as well as the A192T and A562V variants of TBX3 contribute to Conotruncal heart defects (CTDs)etiology; this was the first association of variants of TBX2 and TBX3 to CTDs based on a large population. 30262811_T allele of rs59382073 in TBX2 3'UTR contributes to greater congenital heart defects risk in the Han Chinese population 30451831_TBX2 is a neuroblastoma core regulatory circuitry component enhancing MYCN/FOXM1 reactivation of DREAM targets. 30525309_The minor C allele of rs4455026 in TBX2 promoter region was related with lower congenital heart disease susceptibility in the Han Chinese population via repressing its transcriptional activity. 30599067_transcription factor TBX2 is able to restrain ADAM10 gene expression and that this mechanism might play a role in regulating cellular processes in health, development and disease. 31253870_data demonstrate that TBX2 promotes suppression of normal growth control mechanisms through recruitment of a large repression complex to EGR1-responsive promoters leading to the uncontrolled proliferation of breast cancer cells 32271423_Clinical significance of TBX2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas and its role in cell migration and invasion. 32861705_MicroRNA-7 targets T-Box 2 to inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasiveness in glioblastoma multiforme. 34064060_TBX2, a Novel Regulator of Labour. 35891763_Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Preeclampsia. 36017860_T-Box Transcription Factor 2 Enhances Chemoresistance of Endometrial Cancer by Mediating NRF2 Expression. |
ENSMUSG00000000093 |
Tbx2 |
35.818830 |
3.1459508241 |
1.653496 |
0.268606664 |
39.242463 |
0.00000000037431050089016961697797910238883888761618479179560381453484296798706054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001853345519335425429445210909089932632687336422350199427455663681030273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.6216005 |
8.1915620 |
17.1727592 |
2.2037852 |
| ENSG00000121310 |
55268 |
ECHDC2 |
protein_coding |
Q86YB7 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Predicted to enable enoyl-CoA hydratase activity. Predicted to be involved in fatty acid beta-oxidation. Predicted to be active in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55268; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; enoyl-CoA hydratase activity [GO:0004300]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635] |
|
ENSMUSG00000028601 |
Echdc2 |
376.339419 |
0.3355070250 |
-1.575585 |
0.196606060 |
61.739459 |
0.00000000000000392044717979035838941503953731360234932664917198441578705114807235077023506164550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000027002240025060983618049017250969586470603312974847476368722709594294428825378417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
197.7910498 |
27.8566873 |
596.0963356 |
58.8887637 |
| ENSG00000121316 |
79887 |
PLBD1 |
protein_coding |
Q6P4A8 |
FUNCTION: In view of the small size of the putative binding pocket, it has been proposed that it may act as an amidase or a peptidase (By similarity). Exhibits a weak phospholipase activity, acting on various phospholipids, including phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylethanolamine and lysophospholipids. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19019078}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Lysosome;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable phospholipase activity. Predicted to be involved in phospholipid catabolic process. Located in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79887; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; phospholipase activity [GO:0004620]; phospholipid catabolic process [GO:0009395] |
31756302_Peripheral Blood RNA Levels of QSOX1 and PLBD1 Are New Independent Predictors of Left Ventricular Dysfunction After Acute Myocardial Infarction. |
ENSMUSG00000030214 |
Plbd1 |
35.050707 |
0.3153958560 |
-1.664764 |
0.275297947 |
38.271062 |
0.00000000061568938874080388395021095907975149097435263456645770929753780364990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002993272522336714921236628118828525246808425208655535243451595306396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.3534789 |
3.3291289 |
55.6055894 |
6.5667046 |
| ENSG00000121454 |
89884 |
LHX4 |
protein_coding |
Q969G2 |
FUNCTION: May play a critical role in the development of respiratory control mechanisms and in the normal growth and maturation of the lung. Binds preferentially to methylated DNA (PubMed:28473536). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28473536}. |
3D-structure;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Dwarfism;Homeobox;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of a large protein family which contains the LIM domain, a unique cysteine-rich zinc-binding domain. The encoded protein is a transcription factor involved in the control of differentiation and development of the pituitary gland. Mutations in this gene cause combined pituitary hormone deficiency 4. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:89884; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; medial motor column neuron differentiation [GO:0021526]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
7913017_In mice, a similar protein plays a critical role in the development of respiratory control mechanisms and in the normal growth and maturation of the lung. 11567216_germline mutations; phenotype characterized by short stature and by pituitary, hindbrain, and skull abnormalities 14714741_Heterozygous splice site mutations within LHX4 are associated with combined pituitary hormone deficiency and isolated growth hormone deficiency... small sella turcica...persistent craniopharyngeal canal...ectopic posterior pituitary... P. 207 15567726_LHX4 expression is transient, and, at 6 weeks of development, is stronger at the caudal than at the cervical level. 15998782_Findings are consistent with the existence of LHX4-driven pathway leading to expression of GH through transcriptional activation of POU1F1. They argue against dominant-negative effect of mutant LHX4 proteins over normal LHX4. 17667940_endogenous LHX4 binds to the CGA promoter and that LHX4-mediated CGA activation is enhanced by the SS18-SSX protein 18053794_We conclude Sp1 directly regulates Lhx4 gene expression. 18073311_LHX4 mutations are a relatively rare cause of combined pituitary hormone deficiency. 18445675_three new exonic LHX4 allelic variants with at least one being responsible for congenital hypopituitarism. 20534763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21270112_A novel HESX1 causative mutation was found in a consanguineous family, and two LHX4 mutations were present in familial Pituitary stalk interruption syndrome. 21965270_data indicate that LHX4 may act as a potential tumor suppressor in hepatocarcinogenesis, suggesting that targeting LHX4 to downregulate AFP might have therapeutic implications 22232309_Variably penetrant pituitary insufficiency, including this severe and atypical presentation, can be correlated with LHX4 insufficiency and highlights the role of LHX4 for pituitary development. 23029363_This study is the first to describe, a gradual loss of ACTH in a patient carrying an LHX4 mutation. 23199197_Data indicate that HESX1, LHX4 and SOX3 polymorphisms may be associated with pituitary stalk interruption syndrome (PSIS). 25034524_we found that LHX4 upregulated beta-catenin levels in human colorectal cancer cell lines 25871839_A novel homozygous mutation in LHX4 associated with a lethal phenotype, implying that recessive mutations in LHX4 may be incompatible with life. 25955177_The study identified 4 new LHX4 heterozygous allelic variants in patients with congenital hypopituitarism: W204X, delK242, N271S and Q346R. 27820671_LHX4 Mutation is associated with Pituitary Deficits. |
ENSMUSG00000026468 |
Lhx4 |
11.155736 |
0.2540494860 |
-1.976819 |
0.497124105 |
16.915627 |
0.00003907855133956640277317906573273376125143840909004211425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000113991979796837969419152913896908785318373702466487884521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7394849 |
1.8130668 |
18.5221970 |
4.2593945 |
| ENSG00000121552 |
1475 |
CSTA |
protein_coding |
P01040 |
FUNCTION: This is an intracellular thiol proteinase inhibitor. Has an important role in desmosome-mediated cell-cell adhesion in the lower levels of the epidermis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21944047}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell adhesion;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Ichthyosis;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Thiol protease inhibitor |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins, and kininogens. This gene encodes a stefin that functions as a cysteine protease inhibitor, forming tight complexes with papain and the cathepsins B, H, and L. The protein is one of the precursor proteins of cornified cell envelope in keratinocytes and plays a role in epidermal development and maintenance. Stefins have been proposed as prognostic and diagnostic tools for cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1475; |
cornified envelope [GO:0001533]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; peptidase inhibitor complex [GO:1904090]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004869]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; peptide cross-linking [GO:0018149] |
11451947_expression of cystatin A is regulated via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways positively by Ras/MEKK1/MKK7/JNK and negatively by Ras/Raf/MEK1/ERK. 12581647_crystal structure in complex with cathepsin H 12682854_The 1,25(OH)(2)D3-responsive element in cystatin A gene is identical to TRE, T2 (-272 to -278). Suppression of Raf-1/MEK1/ERK1,2 signaling pathway increases cystatin A expression of normal human keratinocytes. 14747998_backbone dynamics of the monomeric and domain-swapped dimeric forms of stefin A by (15)N relaxation using a model-free approach 15048832_By using ThT fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, and atomic force microscopy (AFM), it has been shown that human stefins A and B (subfamily A of cystatins) form amyloid fibrils 15175029_No association with psoriasis susceptibility 15175029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16342276_Chimeras of stefinA and B have been prepared and guanidine denaturation curves and folding rates have been examined. 16969475_only stefins A and B, i.e. type I cystatins, are up-regulated in lung tumours and thus able to counteract harmful tumour-associated proteolytic activity 17412564_Cystatin A suppresses UVB-induced apoptosis of keratinocytes by the inhibition of caspase 3 activation. 17441792_+344C allele associated with unstable mRNA could result in failing to protect the skin barrier in atopic dermatitis patients from both exogenous and endogenous proteases. 17985332_We conclude that Stefin A expression reduces distant metastasis in breast cancer and propose that this may be due to the inhibition of cysteine cathepsins, such as cathepsin B. 18364739_CSTA TCC haplotype is only associated with psoriasis in those individuals carrying the risk allele at the HLA-Cw6 locus 18364739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933866_Cystatin A binds reduced forms of mite group 1 allergens Der f 1 and Der p 1, in which the cysteine residue at the catalytic center of the protease activity is reduced by treatment with L-cysteine but does not bind oxidized forms. 20461718_A higher pretreated serum level of cystatin A was found to be associated with a higher nodal stage and poorer prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. 21038029_Up-regulation of stefin A, an endogenous inhibitor of cathepsin S, was found in inverted papilloma tissues as compared with its expression level in normal sinus mucosa tissues. 21325429_Findings establish that genetic variability, smoking, and COPD all influence CSTA expression, as does SCC, supporting the concept that CSTA may make pivotal contributions to NSCLC pathogenesis in early and late stages of disease development. 21412248_CSTA significantly increases the risk of developing psoriasis in HLA-Cw6 individuals 21944047_study identified loss-of-function mutations in the gene for protease inhibitor cystatin A as the underlying genetic cause of exfoliative ichthyosis 22615763_findings provide a new molecular understanding of the mechanisms of MYOC-causative glaucoma and reveal CSTA, a serum biomarker for cancer, as a potential biomarker and drug for the treatment of MYOC-induced glaucoma 22787201_Imiquimod suppresses propagation of herpes simplex virus 1 by upregulation of cystatin A via the adenosine receptor A1 pathway 23534700_We identified a homozygous nonsense mutation (p.Lys22X) in the CSTA gene in acral peeling skin syndrome. 23546957_Data indicate that desmoplakin (DSP) and cystatin A (CSTA) interaction and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), IGF-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) and syndecan 1 (SDC1) interaction were observed in protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. 23656633_High levels of bioactive recombinant stefins A and B can be produced by fermentation in P. pastoris. 25785582_a novel pathway of CSTA regulation involving Dsg2 26634210_Both MIP-3alpha and cystatin A overexpressions in NPC tumor tissues were strong independent factors of poor prognosis in NPC patients. 26676054_CSTA/TYROBP gene interaction might play pivotal roles in the occurrence and development of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis . 26753874_High expression of stefin A may be an important factor contributing to the development and metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 26967115_The results suggest that C12orf39, CSTA, and CALCB are novel ATF4 target genes, and that C12orf39 promoter activity is activated by ATF4 through amino acid response element. 28119996_UV phototoxicity-induced pre-elafin inside keratinocytes prior to cornified envelope formation could be involved in UV-induced keratinocyte apoptosis via cystatin-A downregulation resulting in pro-caspase-3 activation. 28898495_Expression of CSTA was detected in some tumor tissues and many tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cathepsin B expression was also observed in most tumor tissues and tumor-infiltrating immune cells 29086922_Identify myoepithelial cell stefin A as a suppressor of early tumor invasion and a candidate marker to distinguish patients who are at low risk of developing invasive breast cancer. 29246862_role of cystatin A in breast cancer and its functional link with ERalpha 29642180_High levels of CSTA expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma were correlated with tumor progression and advanced cancer stage, including lymph node metastasis. 30854931_Low CSTA expression is associated with brain metastasis in lung cancer. 31926189_Interplay of ERalpha binding and DNA methylation in the intron-2 determines the expression and estrogen regulation of cystatin A in breast cancer cells. 33831734_Decreased CSTA expression promotes lymphatic metastasis and predicts poor survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 35563761_In Silico, In Vitro, and Clinical Investigations of Cathepsin B and Stefin A mRNA Expression and a Correlation Analysis in Kidney Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000071561+ENSMUSG00000022902+ENSMUSG00000059657+ENSMUSG00000071562+ENSMUSG00000095620+ENSMUSG00000034362+ENSMUSG00000079597+ENSMUSG00000079594+ENSMUSG00000054905+ENSMUSG00000094733 |
Cstdc5+Stfa2+Stfa2l1+Stfa1+Csta2+Csta1+Cstdc4+Cstdc6+Stfa3+Csta3 |
36.328332 |
2.3534490074 |
1.234777 |
0.266266920 |
21.813872 |
0.00000300420258109351065065831948297514486512227449566125869750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010043494925694272854846574027920524940782343037426471710205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.6774610 |
8.1853032 |
21.7108390 |
2.8074946 |
| ENSG00000121577 |
64091 |
POPDC2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBU9 |
FUNCTION: Important for the maintenance of cardiac function. Plays a regulatory function in heart rate dynamics mediated, at least in part, through cAMP-binding and, probably, by increasing cell surface expression of the potassium channel KCNK2 and enhancing current density. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6JWV8, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ES82}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the POP family of proteins which contain three putative transmembrane domains. This membrane associated protein is predominantly expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscle, and may have an important function in these tissues. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:64091; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; cAMP binding [GO:0030552]; heart development [GO:0007507]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051146] |
28939104_recently a novel family of cAMP effector proteins emerged and was termed the Popeye domain containing (POPDC) family, which consists of three members POPDC1, POPDC2 and POPDC3. POPDC proteins are transmembrane proteins, which are abundantly present in striated and smooth muscle cells. POPDC proteins bind cAMP with high affinity comparable to PKA 32535041_POPDC2 a novel susceptibility gene for conduction disorders. 33261556_An interaction of heart disease-associated proteins POPDC1/2 with XIRP1 in transverse tubules and intercalated discs. |
ENSMUSG00000022803 |
Popdc2 |
11.021377 |
0.4311751527 |
-1.213654 |
0.489648337 |
6.257857 |
0.01236436618592167725749764173315270454622805118560791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.023254083193705907262049947803461691364645957946777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3886478 |
3.7196799 |
12.5202848 |
5.9111840 |
| ENSG00000121579 |
80218 |
NAA50 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZZ1 |
FUNCTION: N-alpha-acetyltransferase that acetylates the N-terminus of proteins that retain their initiating methionine (PubMed:19744929, PubMed:22311970, PubMed:21900231, PubMed:27484799). Has a broad substrate specificity: able to acetylate the initiator methionine of most peptides, except for those with a proline in second position (PubMed:27484799). Also displays N-epsilon-acetyltransferase activity by mediating acetylation of the side chain of specific lysines on proteins (PubMed:19744929). Autoacetylates in vivo (PubMed:19744929). The relevance of N-epsilon-acetyltransferase activity is however unclear: able to acetylate H4 in vitro, but this result has not been confirmed in vivo (PubMed:19744929). Component of N-alpha-acetyltransferase complexes containing NAA10 and NAA15, which has N-alpha-acetyltransferase activity (PubMed:16507339, PubMed:29754825, PubMed:27484799, PubMed:32042062). Does not influence the acetyltransferase activity of NAA10 (PubMed:16507339, PubMed:27484799). However, it negatively regulates the N-alpha-acetyltransferase activity of the N-terminal acetyltransferase A complex (also called the NatA complex) (PubMed:32042062). The multiprotein complexes probably constitute the major contributor for N-terminal acetylation at the ribosome exit tunnel, with NAA10 acetylating all amino termini that are devoid of methionine and NAA50 acetylating other peptides (PubMed:16507339, PubMed:27484799). Required for sister chromatid cohesion during mitosis by promoting binding of CDCA5/sororin to cohesin: may act by counteracting the function of NAA10 (PubMed:17502424, PubMed:27422821). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16507339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17502424, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19744929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21900231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22311970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27422821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27484799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29754825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32042062}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
Enables H4 histone acetyltransferase activity; peptide alpha-N-acetyltransferase activity; and peptidyl-lysine acetyltransferase activity. Involved in N-terminal protein amino acid acetylation; establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion; and mitotic sister chromatid cohesion, centromeric. Located in cytosol and nucleus. Part of NatA complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80218; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; NatA complex [GO:0031415]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; histone H4 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0010485]; N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0008080]; peptide alpha-N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0004596]; peptidyl-lysine acetyltransferase activity [GO:0052858]; establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0034087]; histone acetylation [GO:0016573]; mitotic sister chromatid cohesion [GO:0007064]; mitotic sister chromatid cohesion, centromeric [GO:0071962]; N-terminal protein amino acid acetylation [GO:0006474] |
16507339_The first description of the human homologue of Nat5p/San, hNAT5, the third component of the human NatA N-alpha-acetyltransferase complex 17502424_May be specifically required for the maintenance of centromeric cohesion in mitosis. 19398576_Data show that with MAK3 knockdown, p53 is stabilized and phosphorylated and there is a significant transcriptional activation of proapoptotic genes downstream of p53, and that localization of Arl8b is altered, suggesting that Arl8b is a Mak3 substrate. 19744929_Nat5 displays both protein N alpha- and N epsilon-acetyltransferase activity. 21900231_Naa50p can accommodate only an alpha-amino substrate and not a side chain lysine substrate that is acetylated by lysine acetyltransferase enzymes such as Gcn5. 22311970_Human protein N-terminal acetyltransferase hNaa50p (hNAT5/hSAN) follows ordered sequential catalytic mechanism: combined kinetic and NMR study. 23557624_Development of the first N-terminal acetyltransferase (NAT) inhibitors, including a specific Naa50 inhibitor. 25886145_The study quantitatively compared the Nt-acetylomes of wild-type yeast S. cerevisiae expressing the endogenous yeast Naa50 (yNaa50), the congenic strain lacking yNaa50, and an otherwise identical strain expressing human Naa50 (hNaa50). 27422821_co-depletion of NatA, a heterodimeric NAT complex that physically interacts with Naa50, rescues the sister-chromatid cohesion defects and the resulting mitotic arrest caused by Naa50 depletion, indicating that NatA and Naa50 play antagonistic roles in cohesion. 27484799_Because Naa10 is reported to acetylate all amino termini that are devoid of methionine and Naa50 acetylates all other peptides that are followed by methionine |
ENSMUSG00000022698 |
Naa50 |
938.239862 |
2.4609553630 |
1.299218 |
0.076606985 |
283.702828 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000117139756142090706555213390119184574877216584962548637765342190233815190253441460719363372207912885508414262205271130092982240122044109183531751157459103399732791572773749066982418298721313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031841303879507527547840359286417972771247493759914954156590188384213828948678501778993039842163801723346638615392908014570236506783320092408392213526881729668271958644254482351243495941162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1246.8186820 |
60.0269375 |
510.2024002 |
18.4998811 |
| ENSG00000121594 |
941 |
CD80 |
protein_coding |
P33681 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the costimulatory signal essential for T-lymphocyte activation. T-cell proliferation and cytokine production is induced by the binding of CD28, binding to CTLA-4 has opposite effects and inhibits T-cell activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10583602}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for adenovirus subgroup B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16920215}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane receptor that is activated by the binding of CD28 or CTLA-4. The activated protein induces T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. This protein can act as a receptor for adenovirus subgroup B and may play a role in lupus neuropathy. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:941; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein complex involved in cell adhesion [GO:0098636]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; immune response [GO:0006955]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009967]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045627]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] |
11196673_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11726649_Thus, this study is the first demonstration of a distinct signaling event induced by CD80 and CD86 molecules in B cell lymphoma. 11741888_specific small molecule inhibitors of human B7.1 were identified and characterized. These compounds inhibit the binding of B7.1 to both CD28 and CTLA4. 11826754_The B7-CD28/CTLA-4 costimulatory pathway has a dominant role in regulating T-cell activation. Antagonists enable graft survival and suppress autoimmunity. 11936473_colocalization of ICAM-1 and B7.1 molecules was demonstrated in Hashomoto's thyroiditis whereas no B7.1 expression was observed in Graves' disease 12015893_CD80 and CD86 molecules can substitute for each other in the initial activation of resting CD4(+) T cells and in the maintenance of their proliferative response 12097397_Leishmania major infection of macrophages cocultured with neutrophils results in a neutrophil-macrophage interaction via CD80 leading to IFN-gamma secretion and restriction of Leishmania growth. 12100477_expansion of CD5- B cells in multiple sclerosis correlates with CD80 (B7-1) expression 12149421_CD40 and CD80 molecules were observed to play a specific role in the induction of cytotoxic function but not in IFN-gamma production of IL-2-activated NK effectors. 12352894_with ctla4 pathway, is essential for generating regulatory cells after intratracheal delivery of alloantigen in mice 12355442_CD80 and CD86 differ in their interactions with CTLA-4 and that CD80 appears to be the preferential inhibitory ligand for CTLA-4 working via a population of CD4(+) CD25(+) CTLA-4(+) regulatory T cells. 12372936_After B7-1 and B7-2 induction, proximal tubular epithelial cells costimulate CD28 on T lymphocytes resulting in cytokine production. 12444120_data suggest that CD80 acquisition by human T cells might play a role in the immunoregulation of T cell responses 12513711_The identical effects of B7-1 and B7-2 on regulation of human IL-2 gene transcription factors NF-kappa B and AP-1. 12569387_On the biological relevance of MHC class II and B7 expression by tumour cells in melanoma metastases. 12798307_combined use of a vector driving the expression of OX40L with three other costimulatory molecules (B7-1, ICAM-1, and LFA-3) both enhances initial activation and then further potentiates sustained activation of nai;ve and effector T cells. 12800259_ICOS-B7H costimulatory pathway may be involved in the negative regulation of cell-mediated immune responses. 12829914_expression profiles and relative contribution in the porcine-human xenogeneic response 12829919_effect of PGE2 on the expression of ICAM-1 and B7 in the human mixed leukocyte reaction (MLR) in the presence or absence of IL-18 12860928_results show that BCL6 prevents CD40-induced expression of CD80 by binding its promoter region in vivo and suppressing its transcriptional activation by NF-kappaB 12878356_results demonstrate that herpes simplex virus-2 infection effects the expression of B7 isoforms (B7-1 and B7-2) on monocytes in two ways with opposing outcomes 12905492_Immature dendritic cells engulfed apoptotic and necrotic neutrophils, resulting in up-regulation of CD83 and class II major histocompatibility complex molecules, but down-regulation of CD40, CD80, and CD86 14530356_The CD80 immunoglobulin constant-like (C)-domain has a negative/regulatory effect on the immune response to a plasmid DNA vaccine; loss of the CD80 C-domain prevents modulation of the immune activation signal. 14692664_results confirm that both the CD80 and CD86 molecules play an important role in the maintenance and amplification of the inflammatory process 14871408_CD80 and CD86 activate T cells in IgA nephropathy, CD80/CD86 expressions correlated with renal function at the time of renal biopsy, and monocyte/macrophages and tubular epithelial cells act as antigen presenting cells 14975605_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14978077_CD80 and CD86 have opposite roles in the functioning of human regulatory T cells via CD28 and CTLA-4, an observation that has significant implications for manipulation of immune responses and tolerance in vivo. 15034022_Engagement of B7-1/B7-2 molecules on human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-positive dendritic cells delivers a signal that is obligately required for the triggering of IDO activity during antigen presentation. 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15110532_utilized as cellular attachment receptor by Adenovirus serotype 3 and thus may achieve both goals of cellular entry and evasion of the immune system 15163715_insertion of CD80 and CD86 antigens into HIV-1 virions increases virus infectivity by facilitating the attachment and entry process due to interactions with their two natural ligands, CD28 and CTLA-4 15201958_B7-1 gene transduction might be effective against peritoneal metastases of gastric cancer. 15254713_CD80 has a role in activating cytotoxic T lymphocytes in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 15254772_CD80 driven by NF-kappaB is regulated by the enzymatic actions of caspases, which allows monocytes to participate in massive T-cell activation 15272203_data demonstrated a correlation between HIV infection and impairment of CD80 by circulating monocytes 15377288_There is a potential role of B7 co-stimulatory molecules in facilitating hepatocellular carcinoma escape from immune surveillance without the involvement of IL-10. 15598660_CD80 binding polyproline helical peptide has a role inhibiting T cell activation 15628695_Upregulation in the colonic mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis. 15942292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15942292_There was no relationship between the B7 gene polymorphisms studied and disease susceptibility or BAL fluid cell profiles in Japanese sarcoidosis patients. 16002699_B7.1/B7.2 binding ultimately determines the formation of dimer-dependent CTLA-4 lattices that may be necessary for triggering B7-dependent T cell inactivation. 16237059_LPS-induced B7.1 transcription in human monocytic cells may be regulated by JNK-mediated activation of the IRF-7 transcription factor. 16237760_Th2 cytokine predominant in tumor microenvironment might be related to the expression of B(7)H(1),B(7)H(2) co-signal molecules in tumor cells and TIL 16521215_CD80 transfection can lower malignant phenotype of hepatocarcinoma cells and has a down-regulatory effect to activated T cells in vitro. 16621031_CD80-CD24 molecule spontaneously incorporated onto cell membrane through its glycolipid anchor suggesting that this hybrid costimulatory molecule can be used in protein transfer to develop effective cancer vaccines 16690948_While purified CD123+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells from adults up-regulated co-stimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 with IL-3 alone those from neonates required the addition of CpG-DNA to reach adult levels. 17201120_CD80 expression during early oral squamous cell carcinoma formation may contribute to the escape of tumors from immune elimination 17309825_Transduction of HMCLs with B7-1 retroviruses induced a high expression of B7-1 molecule and a strong T-cell activation ability. 17323353_These results define elevated populations of memory T-lymphocytes expressing B7 molecules in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fluid that either stimulate T cells through ICOS, or down-regulate RA synovial tissue T-lymphocytes through B7H1 and B7H2. 17524139_Expression of CD80 and CD86 costimulatory molecules appears to be a marker of better clinical outcome and survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 17605869_The expression of CD80 and CD86 on peripheral lymphocytes from idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura patients were higher than that of the normal control. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925605_CD40, CD80 and CD86 are upregulated in cultured monocyte-derived dendritic cells of patients with coronary artery disease 17953528_sCD80 in human serum adds a new member to the family of soluble receptors, implying a network of soluble costimulatory factors with functional relevance 17977894_T cells that had become non-responsive to anti-CD3 could be reactivated to proliferate when costimulated with 4-1BBL, either alone or combined with CD80/CD86. 17989345_CD80 expression was up-regulated on the circulating monocytes in septic subjects on Day 1 18005680_Results describe a two-pronged mechanism by which Nef removes CD80 and CD86 from the cell surface. 18026115_CD80 and 4-1BBL induce auto- and transcostimulation in tumor cells 18546634_this review focuses on inhibitory B7 family memberys in human ovarian carcinoma 18577795_During infection when the expression of B7.1 is downregulated, other co-stimulatory molecules may take over its crucial role to confer protective immune response against M. tuberculosis 18585785_Interaction of human PD-L1 and B7-1. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18802089_In the T cell-dendritic cell synapse, transgenic murine CD80 clusters are colocalized with CD28 and protein kinase C theta, a characteristic of the central supramolecular activation cluster. 18928583_Efficiency of GHA priming chemotherapy on refractory acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome may be correlated with B7.1 expression. 18929847_CD80 antigen may prevent monocyte activation and may be required for successful allograft transplantation. 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19056875_urinary soluble CD80 is elevated in idiopathic minimal-change disease, which could be relevant to both diagnosis and pathogenesis 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19433065_siRNA against IRF-1 prevents IFN-gamma-mediated CD80 activation 19550123_Data showed there was no significant differences between MoDCs from ovarian cancer women and healthy women in CD86 and CD80. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19811307_B cells with reduced B7 expression reduce the antigen (Ag) specific t-cell proliferation in vitro. 19817957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20034904_Thalidomide can up-regulate the expression of B7-1 molecules on myeloma cells. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20118277_Data show that pollen grains triggered the production of IL-8, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and strongly upregulated the membrane expression of CD80, CD86, CD83, HLA-DR and caused only a slight increase in the expression of CD40. 20140740_results suggest that B7/CD28 family peripheral blood transcripts may serve as valuable markers reflecting the pathological features of colon cancer 20145927_B7-H1 and B7-1 significantly correlated with the pathological grade and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, respectively in pancreatic cancer. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20601595_B7-1 costimulation is required for induction and maintenance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV)-specific CD8+ T cell memory, in T cell receptor (TCR)transgenic mice. 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802378_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20884055_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20884055_These results suggest that the polymorphisms of the CD86 gene may be used as genetic markers for making the diagnosis and prognosis of Graves' ophthalmopathy. 20979791_increased CD80 and CD86 expression with the progression of tubulointerstitial lesion might play an important role in the development of lupus nephropathy 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21288140_the expression of the co-stimulatory molecule CD80 was decreased in intestines of celiac disease children after gluten-free diet. 21414970_mRNA expression analysis of B7-1 and NPHS1 in urinary sediment may be useful to differentiate between different histologic subtypes of glomerular kidney disease, particularly between minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. 21469977_The low expression of CD80 and CD86 in thyroid papillary carcinoma may help them evade the immune system. 21474713_study shows CTLA-4 can capture its ligands (CD80, CD86)from opposing cells by trans-endocytosis; data reveal mechanism of immune regulation in which CTLA-4 acts as an effector molecule to inhibit CD28 costimulation by cell-extrinsic depletion of ligands 21555531_the costimulatory molecule CD80 prevents PDL1-mediated immune suppression by tumor cells and restores T cell activation 21697455_The interaction between PDL1 on antigen prresenting cells and B7.1 on T cells plays a dominant role in bidirectional interactions between these two molecules during alloimmune responses. 22074996_Data show that CD80 promoter and CD86 exon 8 allele frequencies vary significantly among populations of different ancestries. 22142817_Data suggest that expression of CD80, CD86, and CD40 on dendritic cells in normal endometrium is higher than on tumor infiltrating dendritic cells in endometrioid adenocarcinoma; this may reflect roles in antigen presentation/tumor escape. 22704122_he aim of this work was to analyse the interaction between early events in colonic ulcerative colitis-related and non-inflammatory carcinogenesis and CD80 expression to clarify what stimuli induce its up-regulation in these patients. 22917707_Results showed that serum sCTLA-4, sCD28, and CD80 but not CD86 concentrations in all RA patients were significantly higher than concentrations in healthy control subjects. 23246582_Data indicate that the frequencies of CD11c, CD11c/CD86, HLA-DR/CD86, CD83 and CD80 were significantly high, while CD11c/HLA-DR was low in Hepatitis E infection. 23289444_Lower expression of B7-1 and B7-2 proteins on peripheral monocytes in pre-eclampsia might indicate a secondary regulatory mechanism in response to the ongoing systemic maternal inflammation. 23470321_Studies indicate co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors B7-1, B7-2, CD28 and TNFRSF14 have a pivotal role in T cell biology, as they determine the functional outcome of T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. 23671644_Data indicate that low-dose decitabine (DAC) treatment can induce CD80 gene expression in a variety of cancer cells. 23689904_No role in CD80 expression by podocytes was found for cytokines released by peripheral blood mononuclear cells 23773232_lower expression on CD1c+ myeloid and CD303+ plasmacytoid DCs in pre-eclampsia 23918985_These studies identify CD80-Fc as an alternative and potentially more efficacious therapeutic agent for overcoming PDL1-induced immune suppression and facilitating tumor-specific immunity 24080446_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CD80 gene is associated with breast cancer risk after menopausal hormone replacement therapy. 24415757_NOTCH1 protein regulates CD80/CD86-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in interleukin-6 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase production by dendritic cells 24523507_Data indicate that STAT5A and STAT5B transcription activator complex induces expression of CD80 gene. 24845157_These findings reveal the distinct but complementary roles of CD80 and CD86 IgV and IgC domains in T cell activation. 24951814_Expression of costimulatory molecules CD80/86 is an absolute requirement for efficient CD8 T cell priming by adenoviral vectors. 24981235_SNP rs1599795 in CD80 3'-UTR, through disrupting the regulatory role of miR-132-3p, miR-212-3p, and miR-361-5p in CD80 expression, contributed to the occurrence of gastric cancer. 24981893_Meningococcal capsular polysaccharide-loaded vaccine nanoparticles induce expression of CD80. 25497975_Five functional polymorphisms of B7/CD28 co-signaling molecules alter susceptibility to colorectal cancer. 25862617_Genetic interaction of CD80 and ALOX5AP was observed in systemic lupus erythematosus in Asian populations. 25963805_In the present study, we investigated the prognostic significance of the expression of three genes in the PD-L1 pathway, including PD-L1, B7.1 and PD-1, in three independent bladder cancer datasets in the Gene Expression Omnibus database. 26409459_analysis of CTLA4-Ig in B7-1-positive diabetic and non-diabetic kidney disease [review] 26561569_Triple costimulation via CD80, 4-1BB, and CD83 ligand elicits the long-term growth of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells in low levels of IL-2. 26697986_B7-1 is not induced in podocytes from patients with minimal change disease or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. 26979751_CTLA-4(+) microvesicles can competitively bind B7 costimulatory molecules on bystander dendritic cells, resulting in downregulation of B7 surface expression. 27065104_Inhibitory Profile of Liver CD68+ Cells during HCV Infection as Observed by an Increased CD80 and PD-L1 but Not CD86 Expression 27198457_B7-1 is not expressed by podocytes in LN. A renoprotective effect of B7-1 blockade in LN patients cannot be ruled out but, if confirmed, cannot be the result of an effect on podocyte B7-1 27377375_Results show that CD80 down-regulation is associated to aberrant DNA methylation in dysplasia of sporadic colonic carcinogenesis. This study indicates that the failure of immune surveillance mechanisms in non-inflammatory colon carcinogenesis may be linked to genomic methylation directly or indirectly affecting CD80 expression. 27421624_this study shows that dendritic cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients have low expression levels of CD80 27609569_The expression of B7-H6 is up-regulated in U87-derived glioma stem like cells. 27733175_Fabry disease is characterized by early occurrence of increased uCD80 excretion that appears to be a consequence of glycolipid accumulation. 28210837_Increased expressions of TLR-3, TLR-4 and CD80 mRNA and the level of urinary CD80/creatinine could be useful markers to differentiate patients of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in relapse from those with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 28270509_PD-1 receptor has a role in interacting with programmed cell death ligands and B7-1 28337449_CD80-QPAR platform provides a useful predictive model for unknown RA extract's bioactivities using the chemical fingerprint inputs 28466138_Results showed novel genetic associations with bone phenotypes and points to the CD80 gene as relevant in postmenopausal bone loss. 28856392_Tregs were observed to regulate CD4(+), but not CD8(+), T cell infiltration into tumors through a CTLA-4/CD80 dependent mechanism. Disrupting CTLA-4 interaction with CD80 was sufficient to induce CD4 T cell infiltration into tumors. 29022109_Addition of TNFalpha to podocytes causes CD80 upregulation, actin reorganization and podocyte injury. 29069644_The rs1915087 (C>T), rs6804441 (A>G) and rs41271391 (G>T) of B7 antigens were suspected as the factors associated with reduced risk of recurrent spontaneous abortion. 29277562_Examining the mRNA expression levels of CD80 and CD86 genes between colon polyps with the rectal polyps shows that the enhanced level of CD86 in adenoma samples could be considered as a valuable biomarker for distinguishing the adenoma from hyperplastic polyps and the masses located in the colon from the rectum. 29507273_Urinary CD80 levels were significantly higher in the children with minimal change disease than in the controls and patients with other causes of nephrotic syndrome. 29569191_Urinary CD80 (uCD80) predicts progression and remission in children with nephrotic syndrome. The use of uCD80 as a prognostic marker facilitates the identification of high-risk patients at an early stage and may lead to better treatment selection. 30243953_Knockdown of LncRNA MALAT1 contributes to cell apoptosis via regulating NF-kappaB/CD80 axis in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome 30251665_Per-residue energy decomposition of the binding affinities of the two complexes revealed the unique fingerprint hot-spot sites in CTLA-4/B7-1 and CD28/B7-1 complexes 30411299_The Overexpression of CD80 and ISG15 Are Associated with the Progression and Metastasis of Breast Cancer by a Meta-Analysis Integrating Three Microarray Datasets. 30470792_High CD80 urine levels were associated with renal diseases. 30628844_Our data suggest that reduced CD80 expression independently predicts a poor prognosis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. 31072360_This study provide evidence for a major role of CD80 in orchestrating immune surveillance of colon preneoplastic lesions and might help to develop novel approaches that exploit anti-tumor immunity to prevent and control colon cancer. 31114583_Staphylococcal and Streptococcal Superantigens Trigger B7/CD28 Costimulatory Receptor Engagement to Hyperinduce Inflammatory Cytokines. 31235485_Investigation of ICOS, CD28 and CD80 polymorphisms with the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-control study in eastern Chinese population. 31575740_The secreted M2 protein encoded by cowpox virus (CPXV) specifically interacts with human and murine B7.1 (CD80) and B7.2 (CD86). 31755324_the expressions of CD80 on Bcells and of CD86 on monocytes were increased in peripheral blood from patients with autoimmune thyroid diseases, especially in severe cases, and their gene polymorphisms are associated with the susceptibility and the severity of Hashimoto's disease 32399663_Glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes can express CD80 in patients with minimal change disease during relapse. 32580776_Discovery of CD80 and CD86 as recent activation markers on regulatory T cells by protein-RNA single-cell analysis. 33358455_Predicting the functional consequences of genetic variants in co-stimulatory ligand B7-1 using in-silico approaches. 33488578_CD80 on Human T Cells Is Associated With FoxP3 Expression and Supports Treg Homeostasis. 33506028_CD80 Insights as Therapeutic Target in the Current and Future Treatment Options of Frequent-Relapse Minimal Change Disease. 33868791_CD80 expression is upregulated by TP53 activation in human cancer epithelial cells. 34191384_Cryptic association of B7-2 molecules and its implication for clustering. 34738707_Clinicopathological significance of CD28 overexpression in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. 36064421_The role of soluble CD80 in patients with soft tissue tumors. 36107635_Human immunomodulatory ligand B7-1 mediates synaptic remodeling via the p75 neurotrophin receptor. |
ENSMUSG00000075122 |
Cd80 |
46.303170 |
78.8313914331 |
6.300698 |
0.685673066 |
203.999306 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000027998563252456841851002407520653285743722691811514273158229351372647860110100887723504747898278830585897973516180351361698486201134983275551348924636840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005430470349622378464162396159148071258329900975607860279583959840278200652435646838415698991014054617320861055649976190107253160022082738578319549560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
93.9580253 |
44.6679369 |
1.1958787 |
0.5589029 |
| ENSG00000121691 |
847 |
CAT |
protein_coding |
P04040 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the degradation of hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) generated by peroxisomal oxidases to water and oxygen, thereby protecting cells from the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide (PubMed:7882369). Promotes growth of cells including T-cells, B-cells, myeloid leukemia cells, melanoma cells, mastocytoma cells and normal and transformed fibroblast cells (PubMed:7882369). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7882369}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Heme;Hydrogen peroxide;Iron;Metal-binding;Mitogen;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Peroxidase;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes catalase, a key antioxidant enzyme in the bodies defense against oxidative stress. Catalase is a heme enzyme that is present in the peroxisome of nearly all aerobic cells. Catalase converts the reactive oxygen species hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen and thereby mitigates the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide. Oxidative stress is hypothesized to play a role in the development of many chronic or late-onset diseases such as diabetes, asthma, Alzheimer's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancers. Polymorphisms in this gene have been associated with decreases in catalase activity but, to date, acatalasemia is the only disease known to be caused by this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:847; |
catalase complex [GO:0062151]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; aminoacylase activity [GO:0004046]; antioxidant activity [GO:0016209]; catalase activity [GO:0004096]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; NADP binding [GO:0050661]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on peroxide as acceptor [GO:0016684]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; aging [GO:0007568]; cellular detoxification of hydrogen peroxide [GO:0061692]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; hemoglobin metabolic process [GO:0020027]; hydrogen peroxide catabolic process [GO:0042744]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to fatty acid [GO:0070542]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to hyperoxia [GO:0055093]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to inactivity [GO:0014854]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to L-ascorbic acid [GO:0033591]; response to lead ion [GO:0010288]; response to light intensity [GO:0009642]; response to ozone [GO:0010193]; response to phenylpropanoid [GO:0080184]; response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0000302]; response to vitamin A [GO:0033189]; response to vitamin E [GO:0033197]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; UV protection [GO:0009650] |
11182520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11479740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11837458_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11907164_expression of catalase either in the cytosol or mitochondrial compartments was able to abolish the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential or damage to mitochondria observed in HepG2 cells overexpressing CYP2E1 12032677_results suggest that IGF-1/PI-3 kinase inhibited C2-ceramide-induced apoptosis due to relieving oxidative damage, which resulted from the inhibition of catalase by activated caspase-3 12110367_catalase in livers enhances drug oxidation activities catalyzed by P450 in human liver microsomes. 12165738_The results confirm the involvement of antioxidant enzymes, including catalase, in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. 12231449_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372460_Abnormal expression of catalase in the eutopic and ectopic endometrium strongly suggests pathologic involvement of free radicals in endometriosis and adenomyosis 12447480_Malignant lung tumors (squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma) had significantly decreased levels of this enzyme. 12468545_the level of catalase may play a critical role in cell-induced resistance to the effects of anti-cancer drugs which up-regulate p53 12469627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12487379_cell signaling molecules regulate catalase to control cell mitogenesis 12516882_activities of catalase (CAT), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were decreased during intense physical exercise 12603857_conclude that sun exposure results in a disturbed catalase to superoxide dismutase ratio in the stratum corneum 12606529_results suggest that high glucose flux through aldose reductase inhibits the expression of catalase, CuZn superoxide-dismutase and glutathione peroxidase 12730222_data indicate that catalase plays a direct role in generating oxidants in response to UVB light 12824748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12838770_Catalase activity in pulmonary diseases was suppressed by 38-45%. 12950161_findings indicate that, in addition to stimulating catalase activity, c-Abl and Arg promote catalase degradation in the oxidative stress response 14580687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14710363_effect of IGFBP-2 overexpression on the activity of catalas in two malignant cell lines 14962975_High catalase activity in human alveolar macrophages limits the effectiveness of H2O2 to act as a mediator of inflammatory gene expression. 15125229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15133753_findings support evidence of a new putative type 1 diabetes susceptibility locus for the catalase gene on chromosome 11p13 15182856_catalase (447)Tyr-Val-Asn-Val binds Grb2 upon phosphorylation in tumor cells when stimulated with serum or ligands for integrin receptors 15203188_catalase and hepatocyte growth factor have roles in ceramide-induced apoptosis 15472150_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528999_overexpression of human catalase in DF-1 cells endowed cells resistant to the oxidative stress by antimycin A treatment 15556604_SHP2 binds CAT and acquires a hydrogen peroxide-resistant phosphatase activity via integrin-signaling. 15705913_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15733034_catalase activates the growth of HL60 cells through dismutation of H(2)O(2), leading to activation of the ERK1/2 pathway; H(2)O(2) is an important regulator of growth in HL60 cells 15735318_Genetic variations in the promoter region of catalase gene influence the susceptibility to essential hypertension. 15735318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15774926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15800961_The novel G-->A mutation in exon 9 changes the essential amino acid Arg 354 to Cys 354 and may be responsible for the decreased catalase activity causing diabetes mellitus. 15870505_Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of superoxide dismutase and catalase reduced oxidative stress, restenosis, collagen accumulation, and inflammation and improved endothelial function after angioplasty. 15934434_Genetic polymorphisms of CAT and PPARy2 do not play a significant role in the development of SLE in a Korean population. 15988600_genetic polymorphisms of CAT do not play a significant role in the susceptibility to RA in Koreans 16026777_catalase activities in healthy persons 16047490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16076760_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16098030_the accumulation of reactive oxygen species due to catalase attenuation may be a critical aspect of the MAP kinase signaling changes that may lead to skin aging and photoaging in human skin in vivo 16192345_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16192345_The high-activity catalase CC genotype was associated with an overall 17% reduction in risk of breast cancer compared with having at least one variant T allele. 16204228_catalase has a critical role in CSF-independent survival of human macrophages via regulation of the expression of BCL-2 and BCL-XL 16298864_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16385446_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16387755_Cells were exposed to 250 microM hydrogen peroxide and and cell survival, mitochondria transfection with catalase function, were examined. 16424062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16453382_No evidence for a major effect of C1167T or C(-262)T sinsgle nucleotide polymorphism on type 1 diabetes mellitus susceptibility in two large sample collections. 16453382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16467073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16504657_Catalase activity may correlate with the concentration of hypoxanthine in the graft renal vein and other mediators of oxidative stress. 16523188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16523188_protective role of the -262T allele of the CAT gene against the rapid development of diabetic nepheropathy. 16586065_Catalase in human enzyme transfected mice rescues insulin-resistance-induced cardiac dysfunction related to ROS production and protein oxidation but probably does not improve insulin sensitivity. 16600249_overexpression of Cu, Zn-SOD and/or catalase in smooth muscle cells attenuates the cell proliferation caused by oxLDL stimulation 16630078_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16644728_catalase overexpression has a protective role against Ultraviolet B irradiation by preventing DNA damage mediated by the late reactive oxygen species increase. 16729966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16729966_The C/T genotype was significantly over-represented in the vitiligo patient group compared with the control cohort. 16773213_A statistically significant higher malondialdehyde concentration in erythrocytes and blood plasma and a higher activity of SOD or CAT in erythrocytes was shown in patients with a brain tumour. 16775184_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16868544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16956821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17005595_Mean relative levels of catalase & its mRNA were significantly decreased in women > or =38 years, which may account for granulosa-cell changes associated with reproductive aging. 17145829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17171548_Systemic activity of the enzymatic antioxidants (CuZn/SOD, MnSOD, GSH-Px, and CAT) as well as level of lipid peroxidation determined by MDA may not be increased in the course of immune-inflammatory processes associated with chronic idiopathic urticaria. 17209132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17209132_findings show that the +22348CT polymorphism and HT4 haplotype of the CAT gene were associated with bone mineral density and bone turnover markers in postmenopausal Korean women 17213227_The muscle of patients undergoing haemodialysis undergoes some adaptive responses in total glutathione content, heat shock protein content and catalase activity that are potentially related to chronic oxidative stress. 17264407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17548672_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17549373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17549373_Polymorphisms in catalase is associated with precancerous changes in the gastric mucosa 17566139_The increase in oxidative stress induced by various fatty acids in Jurkat and Raji cells partially occurs due to a reduction in catalase activity. 17567676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17567676_analysis of superoxide dismutase and catalase polymorphisms in smokers with COPD 17567781_Catalase is a Noise-induced hearing loss susceptibility gene, but that the effect of CAT polymorphisms can only be detected when noise exposure levels are taken into account. 17567781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17577741_C111T polymorphism may implicate a very weak effect on blood catalase activity in different types of diabetes mellitus. 17577741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17634480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17646900_Significant positive correlations were found between CAT(catalase) and MDA (malondialdehyde) and between CAT and C-reactive protein in children in the active stage of Henoch-Schonlein purpura; CAT levels were lower in patients 17693525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17696155_We have developed a novel AAV vector to enhance catalase expression. Lack of apparent toxicity in normal muscle strongly supports further exploration of this vector to reduce oxidative stress-induced muscle damage. 17850515_study shows the well-documented CAT exon 9 T/C & GPX 1 codon 200 polymorphisms may not be associated with Gujarat vitiligo patients; results suggest presence of novel SNPs in Gujarat vitiligo population 17879952_TNF-alpha mediated downregulation of catalase expression and accordingly sufficient H(2)O(2) is required for appropriate function of the NF-kappaB dependent survival pathway. 17937824_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18048809_Functional promoter variants in CAT and HMOX-1 showed ethnicity-specific associations with new-onset asthma. 18171680_catalase, CK2, and ARC constitute an anti-hypertrophic pathway in the heart. 18248894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18248894_This data do not support a role of two gene polymorphisms of the CAT rs1001179 as a possible susceptibility factors for sporadic AD. 18353692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18368408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18368408_the CAT -330CC genotype may contribute to some clinical manifestations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 18415766_The primary factor causing the oxidative stress observed in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus is excessive free radical production rather than impaired catalase or superoxide dismutase activity due to autoantibody inhibition. 18423055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18469277_Among the SNPs studied, the G-844A, A-89T and C-20T catalase mutant alleles were associated with a lower efficiency of renutrition in malnourished elderly subjects. 18469277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18483329_CAT genotype modifies the effect of HRT use on breast cancer risk and HRT may affect risk by affecting oxidative stress. 18483329_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18485895_Sirt1 overexpression rescued H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis through the upregulation of catalase. 18606005_An oxidatively modified catalase could be one of the reasons for lower enzymatic activity among SLE subjects, which in turn could favor the accumulation of deleterious hydrogen peroxide 18606005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18634817_By chronically reducing catalase activity to approximately 38% of normal, cells respond in a dramatic manner, displaying a cascade of accelerated aging reactions. 18682580_SOD2, SOD3, and CAT genes may influence brain tumor risk. 18930811_Increased catalase expression is associated with multiple sclerosis lesions. 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18949620_In AML and APL cell lines, but not primary patient samples, basal catalase levels matched sensitivity to As2O3. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19050255_Enhanced expression of the antioxidant enzyme catalase in human T cells can protect them against reactive oxygen species. 19064360_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19064360_the CAT -262 TT genotype may be slightly associated with an increased risk of asbestosis 19092850_catalase inhibits monocytic differentiation by TPA; the decrease in catalase level and the accumulation of H(2)O(2) are significant events for monocyte/macrophage differentiation by TPA 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19172437_Erythrocyte catalase activity was significantly lower in eclamptic pregnant women when compared with healthy pregnant women and non-pregnant women. 19242068_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19254215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19255063_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19274593_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19341793_The catalase is an H2O2 scavenger, suggest that endogenously produced H2O2 mediates MAEC proliferation by fostering the transition from G0/G1 to S phase. 19373626_Cigarette smoking, fruit and vegetable intakes have potentially inverse modifying influences on the asthma risk in individuals with -21AA CAT genotype. Gene-environment interactions support plausibility of CAT gene for the development of bronchial asthma. 19373626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19399816_Enhanced oxidative stress and a decrease in the number of anti-oxidant enzymes may be associated with pre-eclampsia. 19409565_Overexpression of catalase/SOD1 in ApoE-deficient mice suppresses benzo(a)pyrene-accelerated atherosclerosis. 19424819_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19424819_The aim of this study was to assess the distribution of CAT C-262T and GPX1 Pro198Leu genotypic variants in a Turkish population. 19497990_oxidative damage induced by decreased catalase is involved in Granular corneal dystrophy type II pathogenesis 19505917_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19538885_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19584075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19622717_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19622717_We observed no effect modification either by smoking on the association between genetic polymorphisms in CAT, MnSOD, MPO, or eNOS and colorectal cancer 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19688952_Serum levels of catalase were lower in patients with complete hydatidiform mole when compared with the Healthy pregnant and non-pregnant controls 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19705749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19731237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19787204_The present study is the first to evaluate the expression and activity of MnSOD, Cu/ZnSOD and catalase in human gastric samples. 19855359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19855359_The obtained results indicate no correlation between -262C>T polymorphism of the CAT gene (both with respect to genotype distribution and allele frequency) and the risk of depression. 19863340_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19896490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19897513_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19897742_Shear stress decreases PKCdelta activity, altering the phosphorylation pattern catalase, leading to decreased catalase activity and increased hydrogen peroxide signaling. 19902075_The increase in activities of catalase was maximum in patients with the most severe burns. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19929244_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19929244_The CAT TT genotypes were more frequent in hepatocellular carcinoma than in control. 19949914_The expression of catalase was decreased following exposure of tumor cells to cigarette smoke condensate. 20020532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20049130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20078877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20082261_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20097730_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20105444_enzyme activity is reduced in systemic lupus erythematosus patients 20109103_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20109103_the influences of the haptoglobin, MnSOD, CAT, GPX1, ACE, glutathione S-transferases M1 (GSTM1) and T1 (GSTT1) genes' polymorphisms on the oxidative stress and damage suffered by human runners was studied 20110814_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20194081_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20301895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444272_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20494887_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20613769_CAT -89A>T variant genotypes were associated with a significant decrease in catalase enzyme activity and a genetic predisposition for vitiligo in Chinese people 20613769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20643115_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20649881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20649881_Suggest that -262C/T polymorphism in the catalase gene is associated with delayed graft function in kidney allograft recipients. 20727719_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20727719_The association between the catalase C-262T polymorphism and melanoma risk was significantly modified by the history of severe sunburns and total carotenoid intake. 20732340_Chronic arsenic exposure causes higher serum catalase activity that correlates with induction of genetic damage. 20851292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20878976_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20923778_catalase-amyloid interactions have a role in Abeta-induced oxidative stress 21053180_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21054578_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21054578_we concluded that CAT TC exon 9 polymorphism may play an important role in vitiligo disease development and may serve as a genetic marker of vitiligo risk. 21054877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21069346_Prenatal treatment with drugs which can upregulate SOD2 and CAT transcripts may have a therapeutic potential in preventing omphalocele phenotype. 21083503_Whole-body cryotherapy of multiple sclerosis patients resulted in the significant increase of total antioxidative status level in plasma but had no effects on activities of CAT. 21109199_Targeted expression of human catalase to mitochondria prevents age-associated reductions in mitochondrial function and insulin resistance in a mouse model. 21131394_TGF-beta induced the expression of Nox4 while at the same time inhibiting the expression of MnSOD and catalase in airway smooth muscle cells. 21179281_No association was found between clinical outcome of acute paraquat intoxication and the genetic polymorphism of GPX1 (C593T) or the genetic polymorphisms or enzyme activity of superoxide dismutase (V16A) or catalase (C262T). 21180245_Data does not suggest an effect of 21A/T (rs7943316) polymorphism of catalase gene in the susceptibility for diabetic nephropathy in Romanian patients with type 1 diabetes 21191398_catalase expression/activity is an important effector in the responses of melanocytes to aging 21295602_The embryonic catalase transgene, although expressed at about 5% of maternal activity, may protect the embryo by detoxifying reactive oxygen species. Transgenic embryonic catalase activity may be a determinant of teratological risk. 21417634_Up-regulation of CAT and GR activity resulted in an increase in total antioxidant activity in A549 after exposure to B(a)P. 21689642_This study assessed the influence of catalase overexpression on the sensitivity of breast cancer cells towards various anticancer treatments. 21799178_Hydrogen peroxide derived from myeloid cells overexpressing catalase promotes neovascularization in response to ischemia and is a necessary factor for the development of ischemia-induced inflammation. 21827848_genetic polymorophism affects the efficiency of renutrition in malnourished elderly patients 21829032_The levels of SOD and CAT activity were significantly related to adult asthma. 21921984_In CAT-21A/T and GPX1-198C/T polymorphisms, there were no significant differences in the variant homozygous frequencies in patients compared to controls. 21947853_The -262 C>T polymorphism has a reverse effect on blood catalase in vitiligo patients and in controls. 21964540_The catalase-like oxygen production by human methemoglobin in the presence of H(2)O(2) was kinetically characterized with a Clark-type electrode. 21968610_Histone H4 deacetylation down-regulates catalase gene expression in doxorubicin-resistant AML subline. 21976670_interaction of PEX5 with catalase and PEX14 21985133_blood catalase activity and the relationship of blood catalase and beta-thalassemia gene mutations 21985966_Oct-1 is downregulated by reactive oxygen species via CpG island methylation in its promoter 22058000_no association between CAT (Asp-389) gene polymorphism and vitiligo susceptibility in Turkish vitiligo patients. 22089180_There was no evidence for CATint10(T9C) gene polymorphism association with bone mineral density. 22108257_Mitochondrial (mt)DNA haplogroups show an influence on serum levels of catalase among osteoarthritis patients. Carriers of mtDNA haplogroup J show higher serum levels than non-J carriers. 22167619_The common MnSOD, GPX1, and CAT TT+CC+CC genotype may contribute to hypertriglyceridemia in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes or diabetic cardiovascular disease. 22242279_increased activity correlates with disease progression in pneumoconiosis patients 22286031_analysis of polymorphisms of catalase exon 9: rs769217 in Hungarian microcytic anemia and beta-thalassemia patients 22465269_Results indicate that increased myeloperoxidase activity and decreased catalase activity is associated with increased oxidative stress, which may have a role in atherosclerotic processes in brucellosis patients. 22645453_coenzyme Q10, superoxide dismutase, and oxidative stress have roles in coronary artery disease, but the effect of malondialdehyde, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase is not significant 22736749_the study supports the notion of in vivo oxidative stress in systemic lupus erythematosus as indicated by the decrease in CAT activity; allelic variations in the CAT gene -262 are more likely to affect the expression or function of the enzyme 22880027_The post-transcriptional control of gene expression via miRNA modulation regulates human catalase. 22907559_Data suggest that serum catalase activity is higher in patients with either pemphigus vulgaris or pemphigus foliaceus than in control subjects, with patients with pemphigus vulgaris exhibiting the highest catalase levels. 22958044_Genetic polymorphisms of antioxidant enzymes in preterm infants. 22959522_SNP was shown to have limited association with the risk of PCa (rs554518; P = .09443) in all SNPs of CAT. 22970972_Data show that T allele of catalase (CAT) and C allele of superoxide dismutase (SOD1) were significant risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). 22998821_low CAT activity was associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer(CRC); however, no evidence was found to support an association between CAT-21A > T polymorphism and CRC risk 23066387_Five SNPs from two genes (CAT (rs11032703, rs2300181, rs511895) and NQO1 (rs1800566, rs1437135)) were associated with asthma in an industrial rural area of Quebec. 23098659_Genotype-dependent response of catalase activity to oxidative stress might be related to the predisposition of catalase mutant allele carriers to disorders mediated by oxidative stress 23212700_A CATc.66+78C>T polymorphism is associated with noradrenaline plasma concentration in schizophrenic patients. 23325794_SNPs in CYP1B1 and catalase are linked to ex vivo benzo(a)pyrene related DNA adduct formation. Expression of catalase strongly correlated with expression of CYP1B1. 23340375_The present study highlights the roles of CAT haplotypes in arterial aging and underlines the beneficial impact of the CAT1 haplotype on mean internal diameter of the CCA and atheromatous plaque number as well as on potential associated diseases. 23383735_Catalase over-expression might be sufficient to enhance cognition and reduce measures of anxiety 23390647_This study is the first to show that the polymorphism -21A>T CAT is associated with increased risk of cerebral stroke in hypertensive men, however, the relationship between the polymorphism and risk of cerebrovascular disease depends on whether the patients have environmental risk factors or not. 23425094_CAT C-262T polymorphism may be associated with UC, and that the -262C/T genotype may be a risk factor for the disease 23461612_These findings support an association between oxidized CAT and systemic lupus erythematosus. 23641975_This study shows that catalase activity and its SNPs seem to play a role in various aspects of the metabolic alterations which take place in obesity. 23701472_failed to demonstrate an association between either the -262C/T of the catalase gene promoter (rs1001179) or the C242T polymorphism of the P22phox gene (rs4673) or the 594C/T polymorphism of the glutathione peroxidase gene (rs1050450) and hypertension 23746122_Serum catalase activity was decreased in patients with adult nephrotic syndrome. 23771908_Data indicate a vital role for antioxidant enzymes, including catalase and superoxide dismutase, in facilitating the survival of breast cancer cells after extracellular matrix (ECM)-detachment. 23773345_TT genotype in the CAT C-262T polymorphism may be associated with increased prostate cancer risk 23781296_Serum samples were obtained to detect the antioxidative enzymes of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase in Sixty patients with age-related cataract. 23827365_The TT genotype of catalase was more frequent among the asthmatic patients than in healthy Slovak children. The -262 C/T promoter polymorphism may contribute to asthma and oxidative damage. 23828460_siRNAmediated knockdown of their expression sensitized the cells to nickel-induced apoptosis, suggesting that Bcl-2, Bcl-xl and catalase protein expression plays a critical role in apoptosis resistance 23868633_We found no association between CAT gene -89A>T and 389C>T polymorphism and vitiligo susceptibility in Turkish vitiligo patients 23911407_Data indicate that transgenic mice over-expressing human SOD1 or catalase were protected from loss of plasma membrane integrity (LPMI) at early but not late periods of reperfusion. 23961996_The catalase promoter variant rs1001179 SNP is not a risk factor for primary angle closure glaucoma in Saudi patients. 24057136_CAT variants were associated with the prevalence and incidence of diabetic nephropathy and ESRD in type 1 diabetic patients. Our results confirm the protective role of catalase against oxidative stress in the kidney. 24215654_This mutation is possibly associated with various clinical indices important for POAG and thus may be used as a parameter for assessing POAG severity, at least in this population. 24305782_Serum catalase activity in patients with chronic tonsillitis was significantly higher than in healthy controls. 24456074_The catalase C-262T polymorphism indicates that CAT-262T/T genotype confers less susceptibility to male infertility. 24517502_Variability within the CAT gene may be an important modifier of the clinical course of Wilson Disease. 24583396_catalase may regulate cathepsin activity by controlling the production of ROS (H2O2), leading to variation in migration and invasion ability of lung cancer cells. 24602691_Study provides evidence that microglial catalase activity is elevated in multiple sclerosis (MS) grey matter and may be an important endogenous anti-oxidant defence mechanism in MS 24630930_Catalase expression is increased in MCF-7 breast cancer cells but not in resistance to oxidatively stressed cells. 24817970_Six tag single nucleotide polymorphisms of the catalase gene may not be associated with post-traumatic stress disorder. 24824229_The catalase -262CT+TT genotype was significantly associated with adult-onset asthma in smokers. 24825136_After pooling all studies, the results indicated that the 389 C/T polymorphisms in CAT were not associated with the risk of vitiligo in Asians and Turks. 24915010_This st |
ENSMUSG00000027187 |
Cat |
417.310880 |
0.3881283313 |
-1.365394 |
0.094419023 |
210.137319 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001282055436018934129012621657812933438193113602460533656975611872702026092317954129769160272344282231049304146116754572022264357933352130203275009989738464355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000258160139640374708062228156331666650818566747216963431051794924122083342948150025409112650168256013542323319782394890932464281974034747690893709659576416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
239.1378123 |
14.6826555 |
620.6449873 |
25.3770516 |
| ENSG00000121716 |
29990 |
PILRB |
protein_coding |
Q9UKJ0 |
FUNCTION: Paired receptors consist of highly related activating and inhibitory receptors and are widely involved in the regulation of the immune system. PILRB is thought to act as a cellular signaling activating receptor that associates with ITAM-bearing adapter molecules on the cell surface. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The paired immunoglobin-like type 2 receptors consist of highly related activating and inhibitory receptors that are involved in the regulation of many aspects of the immune system. The paired immunoglobulin-like receptor genes are located in a tandem head-to-tail orientation on chromosome 7. This gene encodes the activating member of the receptor pair and contains a truncated cytoplasmic tail relative to its inhibitory counterpart (PILRA), that has a long cytoplasmic tail with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory (ITIM) motifs. This gene is thought to have arisen from a duplication of the inhibitory PILRA gene and evolved to acquire its activating function. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:29990; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; MHC class I protein binding [GO:0042288]; activation of transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0007171]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
10903717_Characterization of paired counterpart PILRA. 24843130_PILRbeta differs from PILRalpha in one of the three residues (Y2, R95 and W108) on the surface of PILRalpha (L108), explaining its inability to engage gB. 33188360_HACS1 signaling adaptor protein recognizes a motif in the paired immunoglobulin receptor B cytoplasmic domain. |
|
|
98.311543 |
0.3981811485 |
-1.328503 |
0.169057537 |
62.575125 |
0.00000000000000256472397706078637261022269486515509983874292442018738569231572910211980342864990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000017872582347122138566980342454661401452108799789431081705970427719876170158386230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.8861357 |
10.2281477 |
143.7584519 |
17.9920927 |
| ENSG00000121716_ENSG00000085514 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.594402 |
0.1526449561 |
-2.711748 |
0.927363565 |
7.748829 |
0.00537473934702979543043266374979793909005820751190185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010910624778181788815945019166520069120451807975769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8349764 |
1.9114465 |
15.1281288 |
10.0389213 |
| ENSG00000121797 |
9034 |
CCRL2 |
protein_coding |
O00421 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for CCL19 and chemerin/RARRES2. Does not appear to be a signaling receptor, but may have a role in modulating chemokine-triggered immune responses by capturing and internalizing CCL19 or by presenting RARRES2 ligand to CMKLR1, a functional signaling receptors. Plays a critical role for the development of Th2 responses. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a chemokine receptor like protein, which is predicted to be a seven transmembrane protein and most closely related to CCR1. Chemokines and their receptors mediated signal transduction are critical for the recruitment of effector immune cells to the site of inflammation. This gene is expressed at high levels in primary neutrophils and primary monocytes, and is further upregulated on neutrophil activation and during monocyte to macrophage differentiation. The function of this gene is unknown. This gene is mapped to the region where the chemokine receptor gene cluster is located. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9034; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; chemokine receptor activity [GO:0004950]; chemokine receptor binding [GO:0042379]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204] |
15188357_CCRL2 expression is up-regulated on synovial neutrophils of rheumatoid arthritis patients 18794339_Results identify chemerin as a natural nonsignaling protein ligand for both human and mouse CCRL2. 20002784_demonstration that the homeostatic chemokine CCL19 is a specific ligand for CRAM 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22046140_Considering the newly defined role of CCRL2 in lung dendritic cell trafficking, this atypical chemokine receptor may affect pneumocystis pneumonia through immune regulation and inducing inflammation. 23142225_these results suggest for the first time that elevated CCRL2 in glioma promotes cell migration and invasion. 26487662_CCRL2 inhibited the growth of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. 26563945_in breast cancer, CRAM-A becomes specifically upregulated under inflammatory stimuli and may serve as a potential marker of immune response. 28600126_CCRL2 mRNA was not significantly changed in murine and human non-alcoholic steatohepatitis liver. CCRL2 mRNA levels were positively correlated with inflammation, fibrosis and NASH scores in the patients. 31484658_The Atypical Receptor CCRL2 Is Essential for Lung Cancer Immune Surveillance. 33253374_C-C Chemokine receptor-like 2 (CCRL2) acts as coreceptor for human immunodeficiency virus-2. 33373444_Genomics Links Inflammation With Neurocognitive Impairment in Children Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1. |
ENSMUSG00000043953 |
Ccrl2 |
37.676277 |
2.4986691828 |
1.321160 |
0.265448174 |
25.358474 |
0.00000047605636554447858717770960743087549360552657162770628929138183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001749649391293950146500954349881862270876808906905353069305419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.5869878 |
8.4683887 |
22.3164119 |
2.8221826 |
| ENSG00000121807 |
729230 |
CCR2 |
protein_coding |
P41597 |
FUNCTION: Key functional receptor for CCL2 but can also bind CCL7 and CCL12 (PubMed:8146186, PubMed:8048929, PubMed:23408426). Its binding with CCL2 on monocytes and macrophages mediates chemotaxis and migration induction through the activation of the PI3K cascade, the small G protein Rac and lamellipodium protrusion (Probable). Also acts as a receptor for the beta-defensin DEFB106A/DEFB106B (PubMed:23938203). Regulates the expression of T-cell inflammatory cytokines and T-cell differentiation, promoting the differentiation of T-cells into T-helper 17 cells (Th17) during inflammation (By similarity). Facilitates the export of mature thymocytes by enhancing directional movement of thymocytes to sphingosine-1-phosphate stimulation and up-regulation of S1P1R expression; signals through the JAK-STAT pathway to regulate FOXO1 activity leading to an increased expression of S1P1R (By similarity). Plays an important role in mediating peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain (By similarity). Increases NMDA-mediated synaptic transmission in both dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-containing neurons, which may be caused by MAPK/ERK-dependent phosphorylation of GRIN2B/NMDAR2B (By similarity). Mediates the recruitment of macrophages and monocytes to the injury site following brain injury (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P51683, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23408426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23938203, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8048929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8146186, ECO:0000305|PubMed:15995708}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Alternative coreceptor with CD4 for HIV-1 infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9789057}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sulfation;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, a chemokine which specifically mediates monocyte chemotaxis. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is involved in monocyte infiltration in inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis as well as in the inflammatory response against tumors. The encoded protein mediates agonist-dependent calcium mobilization and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. This protein can also be a coreceptor with CD4 for HIV-1 infection. This gene is located in the chemokine receptor gene cluster region of chromosome 3. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:729230; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; CCR2 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031727]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 12 binding [GO:0035716]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 binding [GO:0035715]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 binding [GO:0035717]; chemokine receptor activity [GO:0004950]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inflammatory response to wounding [GO:0090594]; leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell [GO:0061756]; macrophage migration [GO:1905517]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; monocyte extravasation [GO:0035696]; negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007194]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of eosinophil degranulation [GO:0043310]; negative regulation of type 2 immune response [GO:0002829]; neutrophil clearance [GO:0097350]; positive regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046641]; positive regulation of astrocyte chemotaxis [GO:2000464]; positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell extravasation [GO:2000451]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of hematopoietic stem cell migration [GO:2000473]; positive regulation of immune complex clearance by monocytes and macrophages [GO:0090265]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; positive regulation of monocyte extravasation [GO:2000439]; positive regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor activity [GO:1904783]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010820]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002827]; positive regulation of thymocyte migration [GO:2000412]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of macrophage migration [GO:1905521]; regulation of T cell cytokine production [GO:0002724]; regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045580]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010574]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; T-helper 17 cell chemotaxis [GO:0035705] |
8995400_There are two splicing variants for human CCR2. One is NM_000647/NP_000638 (CCR2A) and the other is NM_000648/NP_000639 (CCR2B). See OMIM 601267 for details. 11023492_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11175286_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11377705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11385319_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11468722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11477473_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11485615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11500196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11596075_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11694103_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11696224_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11709782_Association of CCR2 genotype with disease progression of HIV infection 11709782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11729511_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11752157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11752157_genotypes and their relative contribution to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) seroconversion, early HIV-1 RNA concentration in plasma, and later disease progression 11756347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11856781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11860793_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11860823_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11873083_CCR2 641 allele homozygosity implicated in natural resistance to HIV-1 transmission through heterosexual contact 11898620_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11898620_The frequencies of CCR2 mutation associated with the development of clinical symptoms upon infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) were determined in a cohort of individuals from Moscow. 11958683_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11964548_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11988632_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12001056_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12010355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12032878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12070001_Most natural killer t-cells express receptors for extralymphoid tissue or inflammation-related chemokines (CCR2, CCR5, and CXCR3), while few NKT cells express lymphoid tissue-homing chemokine receptors (CCR7 and CXCR5). 12078856_expression of CCR2B in aiway epithelial cells after injury enhances cell migration and proliferation 12079277_May be a new candidate for a susceptibility locus for bone mass in middle-aged men and postmenopausal women 12079277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12192431_Electrostatic potential maps of human and primate CCR2b all display the dipolar characteristics of CCR2b with the negative pole located in the extracellular part and a strong positive pole in the cytoplasmic part. 12201365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12215924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12239249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12374865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12399623_Results show that high ambient glucose does not affect mesangial monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 release and decreases its chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) receptor expression. 12403355_C-C chemokine receptor 2 and C-C chemokine receptor 5 genotypes in patients treated for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. 12403355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12426226_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12426226_Val64Ile polymorphism in the C-C chemokine receptor 2 is associated with reduced coronary artery calcification. 12436194_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12447757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12469616_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12469616_Polymorphism is associated with myocardial infarct. 12556692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12557141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12571520_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12584049_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12651900_The specific distribution and regulation of chemokine receptors CXCR1, CXCR4, CCR5, and CCR2b in endometrial epithelium and blastocyst suggest a role for these receptors in the apposition and adhesion phases of human implantation. 12654703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12680626_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12719858_CCR2 genotype seems to predispose patients for myocardial infarction before the age of 65 years; the higher prevalence of heart failure in gene carriers with the rare alle might be a consequence of myocardial infarction 12719858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12837756_activation of CCR5 and CCR2 is induced by conformational changes in the conserved TXP motif in transmembrane helix 2 12853162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12853162_females with the VI genotype were seven times more prone to suffer from myocardial infarction before 50 years than those with the VV genotype 12853745_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12882757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12884524_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12884524_The calculation of the congruence revealed that 92.0% of individuals exhibited the same genotype for both CCR2-64I and CCR5-59653T polymorphisms. Our results confirm that linkage between CCR5-59653T and CCR2-64I alleles is not absolute. 12889997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12913933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12913933_Polymorphisms of CCR2 and CCR5 do not seem to be involved in susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosis 13678532_Angiotensin II significantly stimulated superoxide formation in monocytes, as well as the chemotactic response to MCP-1 with the increased expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 receptor determined by RT-PCR and western blotting analysis 14533004_A PCR-based genotyping method was used to determine the genetic variation at the CCR5 gene and an automated real-time Pyrosequencing technology was employed for the analysis of G right curved arrow A point mutation at the CCR2 gene 14533004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14533983_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14624371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14644039_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14644039_The presence of the CCR2-64I allele in a Japanese population seems to provide protection against the development of multiple sclerosis. 14647058_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14742283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14981141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15076247_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15086346_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15086398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15135805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15140377_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15192276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15230854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15236615_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15257681_Our findings suggest a limited role for CCL2/CCR2 in early active multiple sclerosis 15319853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15362666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15458467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15465089_A decreased frequency and an absence of homozygous for the polymorphism CCR2-64I were found. 15465089_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15466648_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15472820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15488313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15575507_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15579296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15579296_The impact of CCR2 on neuropathogenesis may involve alterations in inflammatory responses within the CNS rather than a direct impact on viral entry or replication. 15585333_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15602133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15611878_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15639953_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15721423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15750046_Did not support previous findings of an association between CCR2 gene variability and the risk of sarcoidosis; however, linkage disequilibrium showed positive results and suggests susceptibility gene in surrounding chromosomal region. 15750046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15754978_Frequency distribution of CCR2-64I mutations in Brazilian Amazon region 15754978_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15769362_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15863470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15929697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15976001_subclinical clotting activation may cause an increased CCR2 gene and protein expression on uremic peripheral blood mononuclear cells, contributing to hemodialysis-related chronic microinflammation 15980693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16033640_These data suggest that the regulation of the CCL2 and CXCL10 expression exhibit significant differences in their mechanisms, and also demonstrate that the alveolar epithelium contributes to the cytokine milieu of the lung. 16055130_Genetic variation in CC-chemokine receptor-2 (CCR2) and -5 (CCR5), and their common haplotypes, acting through inflammatory responses, may affect atherosclerosis and risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). 16055130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16095529_The results indicate that pulmonary CCR2+ T cells and MCP-1 contribute to the pathogenesis of pediatric ILD and might provide a novel target for therapeutic strategies. 16123688_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16140745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16196460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16206074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16207551_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16261210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16286054_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16286055_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16305685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16314800_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16320328_potential autocrine regulation of key profibrotic properties via a CCL2/CCR2 loop in early-stage diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis 16323127_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16356504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16415174_These data suggest that fibrogenic processes in Mo regulated by MCP-1/CCR2 may be novel, therapeutic targets for combating organ fibrosis. 16426243_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16461193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16461193_results of the present study provide no evidence that either CCR5-Delta32 or CCR2-64I is associated with hypertension 16478397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16480760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16485782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16524739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16529059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16598837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16598837_the risk of acute rejection in renal transplantation may be associated with genetic variation in the chemokine receptor genes CCR5-59029 and CCR2V641 in Turkey 16631114_Our data suggest that elevated serum MCP-1 levels and increased monocyte CCR2, CD36, CD68 expression correlate with poor blood glucose control and potentially contribute to increased recruitment of monocytes to the vessel wall in diabetes mellitus. 16733654_Double immunofluorescense staining demonstrated that cellular sources of MCP-1/CCL2 and IP-10/CXCL10 were hypertrophic astrocytes and that both astrocytes and microglia/macrophages expressed CCR2 and CXCR3. 16781696_The mRNA expressions of CCR2 of all post-kidney transplant patients were significantly higher than controls. 16858645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16865553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16903979_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16908772_In atherogenesis, oxidized lipid-driven activation of macrophage PPARgamma in the intima may result in a proadhesive chemokine receptor switch-CCR2 off. 16950632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17060059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17060059_evaluated the possible relation between CCR2 and CCR5 alleles and blood pressure (BP) levels in hypertensive 17091019_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17094383_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17135764_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17216598_Results suggest that CCR2 may contribute to prostate cancer development. 17240189_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17295203_Mesenchymal stem cells express chemokine receptor CCR2 and migrate upon stimulation with IL-8. 17298432_the CCR2-64*I allele is more common in asthmatic patients, especially among atopic subjects 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17361671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17364026_CCR2 is critical for monocyte mobilization and suggests new roles for monocyte chemoattractants in leukocyte homeostasis 17395051_The expression of FOUNT-mediated CCL2/CCR2 may have important implications in the pathogenesis of CHF. The CCL2/CCR2 pathway via FROUNT may influence the clinical severity of CHF. 17413295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17417600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17426779_In this review we focus on the known polymorphisms of two chemokines: CCL2, CCL5 and their corresponding receptors (CCR2, CCR5) and we also discuss their associations with susceptibility and progression to selected immune-mediated diseases. [REVIEW] 17428349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17464174_These results demonstrate that 9-cis-Retinoic acid transduces the signal through p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 for CCR1 and CCR2 up-regulation. 17465499_Mutations studied in the gene pair CCL2/CCR2 do not play a major role in the outcome and response to treatment for HCV infection in the Spanish population. 17465499_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17482150_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17482150_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP) CCR2 gene showed highly significant signals with the number of coronary arteries with stenosis Korean male patients; most significant signal was detected at the SNP located at exon 2. 17499741_Resveratrol inhibits monocyte CCR2 binding activity in an NO-, MAPK- and PI3K-dependent manner, whereas it inhibits CCR2 mRNA in an NO- and MAPK-independent, PI3K-dependent manner 17504503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17504503_no significant difference in allele or genotype distribution of CCR2 V64I polymorphism was observed in HIV-infected & healthy subjects indicating no association between CCR2 V64I polymorphism and susceptibility to HIV infection in North Indian population 17560067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17560067_neither CCR5 nor CCR2 polymorphisms showed peculiar segregation with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and/or non-determined leukoencephalopathy 17596666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17596666_RANTES, MCP-1, CCR2, CCR5, CXCR1 and CXCR4 gene polymorphisms do not have a role in progression of hepatitis B virus infection 17604544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17604544_the effect of CCR2b-64I polymorphisms on disease progression may differ according to the stage of HIV infection and interactions with other gene variants 17615573_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17653321_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17664883_The frequency of A carrier genotypes was higher in HSIL patients than in the controls suggesting that CCR2-64I polymorphism might contribute to the establishment of HSIL through the disruption of the naturally fragile immune response towards HPV infection 17672867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17688234_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17688234_The CCR-2 64I variant was associated with decreased risk of cervical cancer; homozygote carriers of the 64I variant had an odds ratio of 0.31 (0.12-0.77). 17703277_Overexpression of CC chemokine receptor-2A (CCR2A) was seen in glioblastoma specimens localized in the cytoplasm, and pronounced CCR2A immunoreactivity in tumor-infiltrating area was associated with prior chemo/radiation therapy. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17704101_CCR2 and CCL2 are co-expressed by human first-trimester decidual stromal cells and decidual tissue. 17715128_analysis of allosteric inhibition by CCR2/CXCR4 heterodimers 17786209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17845302_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17917677_preliminary evidence linking genetic variation in CCR2 to circulating levels of MCP-1 17934338_the relatively higher expression of CCR2A on the cell surface suggests that this isoform of MCP-1 receptor functions as the principal mediator of inflammatory signals in RA FLS. 17989610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18055544_MCP-1/CCR2 system is functionally active in podocytes and may be implicated in the migratory events triggered by podocyte injury in crescentic GN and other glomerular diseases 18060801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18093816_Data show that MCP-1 has a synergistic effect on COX-2 and CCR2 protein expression in CD40L-stimulated HUVECs and stimulates VEGF production in these cells. 18096169_The functionally relevant CCR2 promoter polymorphism T-960A (rs3918359) is associated with elevated vascular function. 18164016_AGE-LDL can increase CCR2 expression in macrophages and stimulate the chemotactic response elicited by MCP-1. 18172114_No evidence was found of an association between TLR4, CCR2, and CCL2 and AMD (age-related macular degeneration) 18172114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18186797_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18186797_There was no difference in the incidence of rejection among renal transplant recipients stratified by the CCR2-V64I genotype. 18197127_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18197127_Results showed that the combination of 2 non-synonymous substitutions, CCR2 V64I and CCR5 G316A, tended to occur more frequently in ESN(exposed to HIV but seronegative) females than in HIV-1 infected females. 18306985_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18332000_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18332000_The frequency of CCR2-64 I allele of 12 ethnic populations in China were lower than that of Han. The frequency of CCR2-64 I allele between Southern and South-east group showed significant variations. 18391751_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18513341_CCR2 haplotype 2 and HLA-DRB1*0301 are independent genetic risk factors for Lofgren's syndrome. 18513341_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18615095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18763111_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18829011_Protein expression of CCR2 are identified in the four ovulatory phases. 18845960_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18846510_The direct interaction of CCR2 with transportin1 (TRN1) is followed by CCR2 receptor internalization. TRN1-binding to CCR2 promotes its nuclear translocation in a TRN1-dependent manner. 18855658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18928397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977759_Role of CC chemokine receptor 2 in bone marrow cells in the recruitment of macrophages into obese adipose tissue. 18996288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19002595_activation of MCP-1/CCR2 axis promotes PCa growth in bone. 19017998_infiltrated neutrophils from patients with chronic inflammatory lung diseases and rheumatoid arthritis highly express CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, CCR5, CXCR3, and CXCR4 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19032065_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19037908_CCR2-64I allele to be associated with reduced risk for allograft rejection in North Indian transplant recipients influencing allograft outcome. 19055601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19055601_The results suggest that MCP-1, but not CCR2 gene variants, may participate in the pathogenesis of allergic phenotypes at least in the Caucasian population. 19064579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19082218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19082218_The CCR2V641 G - A polymorphism was transmitted preferentially from parents to asymptomatic non-asthmatic children, suggesting an important role for the CCR2 receptor in modulating airway inflammation independent of atopy. 19098363_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19098363_The chemokine receptors CCR2-V64I (A) and CCR5- 59029 A alleles may influence renal allograft survival. 19124913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19196047_No risk for End-stage renal disease was seen for CCR2 and CCR5 haplotypes. 19196047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19411748_The serum MCP-1 concentrations and protein expression of CCR2 in acute coronary syndrome patients are significantly higher than those in healthy controls. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19433914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19433914_Sequence variants of chemokine receptor CCR2 genes and susceptibility to HIV-1 infection 19465829_The effects of multiple CCR2 mutations on HIV viral load and vertical disease transmission is reported among pregnant women in Nairobi, Kenya. 19479237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506371_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19506371_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and its receptor act synergistically to increase the risk of carotid atherosclerosis. 19520154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19520154_rs3918356 and rs743660 polymorphisms in CCR2 were found to be associated with increased serum IgE levels in asthma. 19527467_C-C chemokine receptor 2 expression by circulating monocytes influences atherosclerosis in patients on chronic hemodialysis 19535619_A recombinant form of the CCL2 receptor selectively binds CCL2 and neutralizes its biological activity, including chemotaxis of human monocytes; it inhibits proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells expressing CCL2 and its receptor. 19559392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19643177_Knockdown of clathrin by RNA interference impairs CCR2 internalization, as does treatment with the dynamin inhibitor, dynasore. 19669591_A potentially important role of CCR2-64I allele in AIDS progression in the northern Chinese population, was identified. 19669591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19693089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720836_CCL2-expressing breast tumor cells engage CCR2(+) stromal cells of monocytic origin, including macrophages and preosteoclasts, to facilitate colonization in lung and bone 19841162_FROUNT binds to the C-terminal domain of CCR5 in addition to that of CCR2. 19904283_The chemokine system CC ligand 2 (CCL2) with its receptor CC receptor 2 (CCR2) have been implicated in a wide range of neuropathologies, including trauma, ischemic injury and multiple sclerosis--REVIEW 19942750_Data show that genotype frequencies of CCR2, MCP-1 and DC-SIGN polymorphisms did not differ significantly between the study groups, but a significantly increased frequency of SDF-1alpha polymorphism was observed among HIV+PTB+ patients. 19942750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19950235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19958843_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965779_Selective CCR2 antagonist decreased macrophage infiltration in ApoE deficient atherosclerotic mice. 20017911_Our data show that Haptoglobin is a novel monocyte chemoattractant and that its chemotactic potential is mediated, at least in part. by its interaction with CCR2. 20038229_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20066125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153665_The genetic variation at the CCR2/CCR5 genes did not contribute to the risk for psoriasis, but CCR2 polymorphisms could modulate the risk for arthritis in patients with psoriasis. 20181074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20182805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20182805_The effect of genetic variants of CCR2-V64I and CCR5-delta32 chemokine receptors on the development of myocardial infarction, was investigated. 20220260_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20231199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20339010_In summary, we found that SNPs in CCL2 and CCR2 are associated with exercise-induced muscle damage and that the presence of certain variants may result in an exaggerated damage response to strenuous exercise. 20339010_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20364004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364004_there appears to be an association between polymorphism of CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 and endometrial cancer 20411675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20442634_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20449800_CCR2-64I is a new risk factor for bladder cancer. 20449800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20483750_human beta-defensin (hBD)2 and 3 are chemotactic for a broad spectrum of leukocytes in a CCR6- and CCR2-dependent manner 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20531015_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20537184_CCR2 is important in invasive cancer of the cervix but not in HPV infection or in the development of pre-cancers. 20537184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20603037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605053_crucial for the recruitment of blood monocytes into tumor fibroblastic areas 20628649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20637631_Neither the MCP-1 -2518G (p=0.43) nor the CCR2 64Ile (p=0.52) variant contributed to the risk of multiple sclerosis in Tunisians. 20637631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational s |
ENSMUSG00000049103 |
Ccr2 |
4.937682 |
0.2356426513 |
-2.085327 |
0.823378787 |
7.044505 |
0.00795087991141225046420881739095420925877988338470458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015560194576033520644231522567224601516500115394592285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0176871 |
1.1417330 |
8.7022873 |
2.2777635 |
| ENSG00000121895 |
80008 |
TMEM156 |
protein_coding |
Q8N614 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80008; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000037913 |
Tmem156 |
52.705201 |
2.7386033775 |
1.453440 |
0.362095125 |
15.479434 |
0.00008340782533403265331609782728961022257863078266382217407226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000232020260446724860313796878763525910471798852086067199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
75.5660990 |
15.6699594 |
27.4011365 |
4.3579920 |
| ENSG00000121964 |
79712 |
GTDC1 |
protein_coding |
Q4AE62 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable glycosyltransferase activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79712; |
glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757] |
15068588_relatively high expression level in the adult lung, spleen, testis, and peripheral blood leukocyte. 19826048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21821951_The elevated expression of the Hmat-Xa gene (GTDC1) might serve as a candidate marker for colon adenocarcinoma. 28365779_By deriving iPSCs from this patient and differentiating them into neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and neurons we dissected the disease process at the cellular level and observed defects in both NPCs and neuronal cells. We also showed that disruption of GTDC1 expression in wild type human NPCs and neurons showed a similar phenotype as patient's iPSCs 30100616_Genomewide linkage scan by a targeted, high-density association scan for genetic variants enhancing persistently negative tuberculin skin test (PTST) in two independent Ugandan tuberculosis household cohorts. Association found with SNPs in neighboring genes ZEB2 and GTDC1 supported by both samples. Bioinformatic analysis suggests these variants may affect PTST- by regulating the histone deacetylase pathway. 31646584_MicroRNA-132 promotes neurons cell apoptosis and activates Tau phosphorylation by targeting GTDC-1 in Alzheimer's disease. |
ENSMUSG00000036890 |
Gtdc1 |
89.534929 |
2.1962773596 |
1.135060 |
0.248550183 |
20.658257 |
0.00000548999299049507396376429077533565248359082033857703208923339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017758557207913061695746595458622607566212536767125129699707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
119.2905434 |
18.3888709 |
54.7392217 |
6.3575182 |
| ENSG00000121989 |
92 |
ACVR2A |
protein_coding |
P27037 |
FUNCTION: On ligand binding, forms a receptor complex consisting of two type II and two type I transmembrane serine/threonine kinases. Type II receptors phosphorylate and activate type I receptors which autophosphorylate, then bind and activate SMAD transcriptional regulators. Receptor for activin A, activin B and inhibin A (PubMed:17911401). Mediates induction of adipogenesis by GDF6 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P27038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1314589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17911401}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Magnesium;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a receptor that mediates the functions of activins, which are members of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily involved in diverse biological processes. The encoded protein is a transmembrane serine-threonine kinase receptor which mediates signaling by forming heterodimeric complexes with various combinations of type I and type II receptors and ligands in a cell-specific manner. The encoded type II receptor is primarily involved in ligand-binding and includes an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic serine-threonine kinase domain. This gene may be associated with susceptibility to preeclampsia, a pregnancy-related disease which can result in maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:92; |
activin receptor complex [GO:0048179]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; inhibin-betaglycan-ActRII complex [GO:0034673]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; activin binding [GO:0048185]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; BMP receptor activity [GO:0098821]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; inhibin binding [GO:0034711]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004675]; activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032924]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; gastrulation with mouth forming second [GO:0001702]; mesoderm development [GO:0007498]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; penile erection [GO:0043084]; positive regulation of activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032927]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045648]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; Sertoli cell proliferation [GO:0060011]; sperm ejaculation [GO:0042713]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007178] |
11969340_distribution in gestational tissues across human pregnancy and during labour 12667445_crystal structure of BMP7 in complex with the extracellular domain (ECD) of the activin type II receptor 14691305_Activin type II receptor gene (ACTRII) is probably involved in both non-microsattelite unstable and microsattelite-unstable colorectal carcinogenesis, but more frequently in the latter subgroup. 14738881_Data indicate that activin A and activin receptors IIA and IIB may be involved in the regulation of germ cell proliferation in the human ovary during the period leading up to primordial follicle formation. 14988818_Mutations highly frequent in microsatellite unstable(MSI-H) colon cancers and cause loss of ACVR2, indicating biallelic gene nactivation. Loss of activin signaling through mutation of ACVR2 may have role in genesis of MSI-H colorectal cancer. 16337854_demonstrates that truncating mutations of the ACVR2 gene result in a significant reduction in activin mediated cell signaling. Inactivation of ACVR2 is a common event in prostate cancer and may play an important role in the development of prostate cancer 16380996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16672363_structure of the ternary complex representing the signaling competent complex of BMP-2 bound to the entire extracellular domains of both its type I receptor, BMPR-Ia, & its type II receptor, ActRII, at a resolution of 2.2 angstroms 17258738_Activin is growth suppressive and enhances migration in colon cancer. 17472960_RGMa facilitates the use of ActRIIA by endogenous BMP2 and BMP4 ligands that otherwise prefer signaling via BMPRII and that increased utilization of ActRIIA leads to generation of an enhanced BMP signal 18001154_Inhibin/activin BA subunit, follistatin, and activin receptor proteins and mRNAs are present in the human fetal palate. 18781190_Populations with different ancestors (Iceland/Norway-Australia/New Zealand) demonstrate a common maternal pre-eclampsia susceptibility locus on chromosome 2q22-23, may suggests a general role of this locus, and possibly the ACVR2A gene, in pre-eclampsia. 18941508_The -1 bp frameshift mutation rates of TGFBR2 and ACVR2 microsatellite sequences are dependent upon the human DNA Mismatch 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126782_It remains unclear what role, if any, ACVR2A polymorphisms play in pre-eclampsia risk, at least in these Australian families. 19126782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19308291_ActRII signaling is required for prostatic cancer cell and neuroblastoma cell viability, with ActRII mediating cell fate via the regulation of cell adhesion 19503063_The four most frequently mutated genes in colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability were ACVR2 (92%), TAF1B (84%), ASTE1/HT001 (80%) and TGFBR2 (77%). 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20011542_Of 51 microsatellite stable colon tumors, 7 (14%) lost ACVR2, 2 (4%) ACVR1, and 5 (10%) pSMAD2 expression. 20197483_Mutation in activin type II receptor is associated with colorectal cancer. 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22001236_Exonic selectivity for frameshift mutation within ACVR2 is specifically controlled by individual nucleotides flanking each coding ACVR2 microsatellite. 22296042_Activin type IIA receptors are clearly demonstrable throughout the adult human hypothalamus and basal forebrain. 22723898_This is the first report on the function of miR-195 in human placental trophoblast cells which reveals an invasion-promoting effect of the small RNA via repressing ActRIIA. 22848350_ACVR2A showed statistically significant differential dose-expression relationship. 22949641_ACVR2A interaction with Nodal and ADMP regulates head development from the 'organizer', a restricted group of cells in the embryo. 23263486_ACVR2A was identified as a subnetwork component in functional association network analysis. 23633461_For ACVR2A SNPs (rs10497025, rs1128919, rs13430086), no statistically significant difference was found between preeclampsia and control groups in terms of genotype and allele frequencies. 25499008_The gene ACVR2A was associated with the more severe early onset preeclampsia. 25659497_Data suggest that an SNP in promoter region of ACVR2A (rs1424954, the pre-eclampsia susceptibility allele) down-regulates 1) expression of ACVR2A in trophoblasts and 2) signal transduction in response to excess activin-A (as seen in pre-eclampsia). 26047946_Activin A inhibited signaling by BMP-6 and BMP-9 by competing for type 2 receptors ACVR2A and ACVR2B. 26086422_Adenomyotic tissues express high levels of myostatin, follistatin, and activin type II receptors. 26677222_Data suggest ALK1 and ACVR2A/ACVR2B, acting as BMP9 co-receptors, rearrange pro-domains of BMP9--pro-domain dimer complex leading to displacement of pro-domains after receptor binding, release of mature non-dimer BPM9, and activation of signaling. 27696331_TGF-beta receptor mediated telomerase inhibition, telomere shortening and breast cancer cell senescence.( 27832070_This locus harbors an evolutionary conserved gene-desert region with non-coding intergenic sequences likely involved in regulation of protein-coding flanking genes ZEB2 and ACVR2A. This region is intensively studied for mutations causing severe developmental/genetic disorders. Our analyses indicate a promising target region for interventions aimed to reduce risks of many major human diseases and mortality. 29203340_Altered decidual ACVR2A expression impairs the ability of stromal cells to properly decidualise and regulate trophoblast function at the maternalfetal interface, which may result in abnormal placentation that can lead to poor pregnancy outcomes such as pre-eclampsia. 29506428_A case-control study targeting next generation sequencing of ACVR2A gene by Ion Torrent Personal Genome Sequencing suggested that some variants in the ACVR2A gene are associated with pre-eclampsia. 29593124_Results showed no association between genotypes and preeclampsia for polymorphisms rs5186, rs4606 in 3'UTR of genes ACVR2A, AGTR1 and RGS2 in women with preeclampsia 30621627_The multifactor dimensionality reduction algorithm identified an interaction between age, body mass index and ACVR2A rs1014064, indicating that context among genetic variants and demographic/clinical factors may be crucial to understanding the pathogenesis of preeclampsia among Filipino women. 31273315_Synovial chondromatosis and soft tissue chondroma: extraosseous cartilaginous tumor defined by FN1 gene rearrangement. 31315975_the structure of an activin class member, GDF11, in complex with the type II receptor ActRIIB and the type I receptor Alk5, is reported. 31790936_Association between ACVR2A gene polymorphisms and risk of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in the northern Chinese population. 33420656_Activin a Receptor Type 2A Mutation Affects the Tumor Biology of Microsatellite Instability-High Gastric Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000052155 |
Acvr2a |
505.670028 |
3.1254432819 |
1.644061 |
0.113251341 |
205.965751 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010424721889295431918620412252779704474442025199394139841143381176027265856699054216427815029095882181007404940120057539043596506189715000800788402557373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002043411621328028786868777575267707695483232767688026764236038561656864333645924335814554435418261508246155500203395868896727449737227289006114006042480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
769.8440110 |
53.3901042 |
248.2308849 |
13.2943719 |
| ENSG00000122025 |
2322 |
FLT3 |
protein_coding |
P36888 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for the cytokine FLT3LG and regulates differentiation, proliferation and survival of hematopoietic progenitor cells and of dendritic cells. Promotes phosphorylation of SHC1 and AKT1, and activation of the downstream effector MTOR. Promotes activation of RAS signaling and phosphorylation of downstream kinases, including MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes phosphorylation of FES, FER, PTPN6/SHP, PTPN11/SHP-2, PLCG1, and STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Activation of wild-type FLT3 causes only marginal activation of STAT5A or STAT5B. Mutations that cause constitutive kinase activity promote cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis via the activation of multiple signaling pathways. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10080542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11090077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14504097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16266983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16627759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18490735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20111072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21067588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21262971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21516120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7507245}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a class III receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates hematopoiesis. This receptor is activated by binding of the fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand to the extracellular domain, which induces homodimer formation in the plasma membrane leading to autophosphorylation of the receptor. The activated receptor kinase subsequently phosphorylates and activates multiple cytoplasmic effector molecules in pathways involved in apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation of hematopoietic cells in bone marrow. Mutations that result in the constitutive activation of this receptor result in acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:2322; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005021]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus [GO:0071385]; common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation [GO:0035726]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097028]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; leukocyte homeostasis [GO:0001776]; lymphocyte proliferation [GO:0046651]; myeloid progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002318]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; pro-B cell differentiation [GO:0002328]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11290608_First report of D835X mutations in human. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. 11983110_Flt3/Flk-2-ligand in synergy with thrombopoietin may slow down megakaryocyte development by causing increased proliferation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells. 12060771_induces acute promyelocytic leukemia in a mouse model 12070009_Analysis of FLT3 length mutations in 1003 patients with acute myeloid leukemia 12239146_duplicated in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia 12239147_mutations occur in paired presentation and relapse samples from patients with acute myeloid leukemia 12468433_767 of 6586 genes differed in expression between FLT3-WT- and FLT-ITD(internal tandem duplication)-expressing cell lines. ITD mutations of Flt3 activate transcriptional programs that partially mimic IL-3 activity. 12468438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12481903_Internal tandem duplication of the Flt3 gene appearing or altering at time of AML relapse suggests Flt3-gene abnormalities are very important in the pathogenesis of chemotherapy-resistant AML 12676789_The striking difference in flt3 and c-kit expression on hematopoietic stem cells translated into a corresponding difference in flt3 and c-kit function because FL was more efficient than SCF at supporting the survival of HSCs 12681969_Intracellular signaling initiated by Flt3 ligation modulates the functional phenotype for native human AML blasts both with and without genetic Flt3 abnormalities. 12691136_FLT3 mutations that lead to constitutive receptor activation and confer a poor prognosis in AML 12816873_FLT3/ITD is less common in pediatric than in adult acute myeloid leukemia and FLT3/ITD is a strong and independent adverse prognostic factor, and high ratios between mutant and WT-FLT3 further compromise prognosis. 12842996_antiapoptotic pathways from FLT3 with internal tandem duplication are more divergent than those from WtFLT3 12854887_Mutations in the FLT3 gene are common in AML, including tandem repeats or a mutation in the kinase domain. 12926083_No significant correlation was found between FLT3 mutations and high levels of MDR1 in acute myeloid leukemia. 12935959_REVIEW: The role of FLT3 mutations in APL and other AML 12969963_wtFLT3 is often constitutively activated by FLT3 ligand in AML and thus, like its mutated form, might contribute to the altered signaling that characterizes leukemogenesis. 14504097_FLT3-D835/I836 mutations are one of the second genetic events in infant ALL with MLL rearrangements or pediatric ALL with hyperdiploidy 14562119_reduced AML1 activities predispose cells to the acquisition of the activating FLT3 mutation as a secondary event leading to full transformation in acute myeloblastic leukemia M0 14604974_distinct activating FLT3-TKD mutations at position D835 mediate primary resistance to FLT3 PTK inhibitors in FLT3-transformed cell lines 14630076_FLT3 mutations are associated with molecular lesions in acute myeloid leukemias 14654525_Phosphorylation is inhibited by SU11248 in acute myeloid leukemia. 14670924_search for the presence of FLT3 mutations in leukemic blasts from 71 patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia discovered three novel in-frame deletions within a 7-amino acid region of the receptor juxtamembrane domain. 14759363_FLT3 analysis shows the autoinhibitory conformation of its complete juxtamembrane domain 14977832_FLT3 Asp(835) mutations may have a role in relapse of acute myeloid leukemia 14981546_FLT3 can negatively regulate Foxo transcription factors, thereby promoting cell survival and proliferation. 14982881_Mutations of Flt3 may disrupt transcriptional repressor function resulting in aberrant gene regulation and abnormal leukemia cell growth. 15044257_Activating mutations in the FLT3 RTK gene were found in each of 3 CD117/KIT(+) cases that were analyzed, but not in 52 other adult T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia 15054042_CXCR-4 expression was significantly higher in fetal liver tyrosine kinase-3 (Flt3)/internal tandem duplication (ITD) acute myeloid leukemia 15059064_Internal tandem duplication of the juxtamembrane domain or by activating point mutations in the second tyrosine kinase domain in FLT3 are associated with leukocytosis and the monocytic FAB subtypes M4 and M5. 15061200_Flt3 mutations identify patients at high risk of relapse 15166029_FLT3/internal tandem duplication(ITD) mutations confer a particularly poor prognosis in pediatric acute myelogenous leukemia patients 15167911_high frequency of FLT3 mutations in adult acute myelocytic leukemia without recurrent cytogenetic translocations. 15178581_FLT3 autoinhibited structure showed that N841 is the key residue in a hydrogen-bonding network that likely stabilizes the activation loop 15242879_Wild-type Flt3-overexpressing CD34+ cells exposed to high levels of its physiologic ligand did not produce early cobblestone areas 15253381_FLT3 has roles in different signal transduction pathways that control proliferation, survival and other processes in hematopoietic cells [review] 15289019_The loss of a clone with a mutation in the FLT3 gene at relapse did not improve the prognosis. 15345593_Inspection of the FLT3 structure revealed that Y842 is the key residue in regulating the switch from the closed to the open (= active) conformation of the FLT3 activation loop 15363457_mutations of specific residues located in the activation loop (D835X and 836-deletion in Flt-3; D816V in c-Kit) as well as a 6-base pair (6-bp) insertion at residue 840 in Flt-3 operate in a similar way 15574429_transformation of TF-1 cells with FLT3/ITD mutations suppressed the activity of SHP-1 by approximately 3-fold 15583855_FLT3 mutations cause autoactivation and uncontrolled signaling in leukemia [review] 15604885_The FLT3 is widely expressed in AML and some cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia. 15604894_The FLT3 gene, partial tandem duplication of the MLL gene, mutations of the CEBPA gene, and overexpression of the BAALC gene-have been found to predict outcome in patients with AML and normal cytogenetics. 15645287_Potential impact of Flt3 based residual cancer status not only after but also prior to allogeneic peripheral blood cell transplantation. 15650056_Flt3-ITD and Wnt-dependent signaling pathways synergize in myeloid transformation 15674343_FLT3 gene expression might lead to the identification of further pathogenetic relevant candidate genes particularly in AML with normal karyotype. 15710585_MLL and FLT3 gene duplications could have roles in myeloid malignancies 15769897_Flt3-ITD and Flt3-TKD mutations display differences in their signaling properties 15770067_Circulating FLT-3 levels didn't increase in early neonatal life 15778081_FLT-3 is primarily expressed by hematopoietic cells & plays an important role in hematopoiesis. FLT-3 is also expressed in the majority of acute leukemias, in which the presence of FLT-3 activating mutations is associated with poor prognosis [review] 15781338_involvement of Src kinases in Flt3 signaling, with activation of Lyn by constitutively active Flt3 mutants as well as ligand-stimulated wild-type receptor; cell proliferation resulting from mutant Flt3 expression did depend on the activity of Src kinases 15797998_Internal tandem duplication mutations of the FLT3 gene are present in leukemia stem cells. 15831474_The maturation of wild-type FLT-3 is impaired by general protein-tyrosine phosphatases inhibition or by suppression of endogenous PTP1B. 15863200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15902284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15921740_Determination of minimal residual disease based on patient specific Flt3 internal tandem duplication and internal tandem triplication mutation in acute myeloid leukemia. 15959528_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15973451_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15978940_The Activating mutations or over-expression of the Flt3 is prevalent in acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML), associated with activation of NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 15996732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16015387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16029447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16046528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16076867_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16116483_FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutation is capable of inducing myeloproliferative as well as lymphoid disease 16185475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16213360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16234090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16263569_FLT3 is a therapeutic target and inhibition of FLT3 tyrosine kinase activity may provide a new approach in the treatment of leukemia carrying these mutations. (review) 16263793_Langerhans cells are derived mainly from myeloid progenitors and are dependent on Flt3-ligand for their development. 16320249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16320249_Our data suggest that the FLT3 D324N variant might be associated with a predisposition to different subtypes of leukemia. 16326981_confirmation of FLT3 mutations in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias 16368883_FLT3 internal tandem duplications in the juxtamembrane domain are found in approximately 25% of acute myeloid leukemia patients, ranging in size from 3 to hundreds of nucleotides, and may have prognostic significance. 16410449_characterized a new class of activating point mutations that cluster in a 16-amino acid stretch of the juxtamembrane domain of FLT3 16502586_methods for detecting internal tandem duplication and D835 missense mutations in the FLT3 gene in acute myeloid leukemia. 16517725_Flt3L reconstitutes a crucial afferent component of the immune response 16533526_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16598313_FLT3 mutations were significantly associated with a shorter EFS and survival (P |
ENSMUSG00000042817 |
Flt3 |
328.771158 |
0.0942781709 |
-3.406932 |
0.127084207 |
830.375226 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001343049865481638414710845018495369274998597243310740366795679529293238773221751174106449984871119946675337519195143458336464118666413768959522332672 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001119967006469434038384187047114738323801413176039940938806403676238695835158553317582225734141997897274171287551008790557881995533252167171147053820 |
Yes |
Yes |
58.8881853 |
5.2369622 |
628.8087533 |
30.0275519 |
| ENSG00000122432 |
100505741 |
SPATA1 |
protein_coding |
Q5VX52 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:100505741; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669] |
Mouse_homologues 31816150_Mouse spermatogenesis-associated protein 1 (SPATA1), an IFT20 binding partner, is an acrosomal protein. |
ENSMUSG00000028188 |
Spata1 |
12.814762 |
0.4088634116 |
-1.290309 |
0.463082792 |
7.813415 |
0.00518598191060455192963329906774561095517128705978393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010568147590849535921719848374777939170598983764648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
6.5254950 |
2.0393838 |
16.1706379 |
3.2375584 |
| ENSG00000122477 |
127495 |
LRRC39 |
protein_coding |
Q96DD0 |
FUNCTION: Component of the sarcomeric M-band which plays a role in myocyte response to biomechanical stress. May regulate expression of other M-band proteins via an SRF-dependent pathway. Important for normal contractile function in heart. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZXS4}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Leucine-rich repeat;Muscle protein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity. Predicted to be involved in signal transduction. Predicted to be located in M band. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and intracellular membrane-bounded organelle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:127495; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; M band [GO:0031430]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004722]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20847312_Reveal myomasp/LRRC39 as a previously unrecognized component of an M-band-associated signaling pathway that regulates cardiomyocyte gene expression in response to biomechanical stress. |
ENSMUSG00000027961 |
Lrrc39 |
40.442252 |
0.0583248636 |
-4.099745 |
1.370702672 |
6.930091 |
0.00847573629969758726709905261031963163986802101135253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016471608661426780095826671868053381331264972686767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5845970 |
4.6375397 |
52.7428635 |
45.0443626 |
| ENSG00000122592 |
3204 |
HOXA7 |
protein_coding |
P31268 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. |
Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor which may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. For example, the encoded protein represses the transcription of differentiation-specific genes during keratinocyte proliferation, but this repression is then overcome by differentiation signals. This gene is highly similar to the antennapedia (Antp) gene of Drosophila. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3204; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; negative regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001953]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045617]; negative regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002686]; negative regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045656]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863] |
14562113_B-lineage development can proceed in t(4;11) leukemic blasts in the absence of HOX-A gene expression. 14704364_Hox A7-sustained expression disturbs the regulation of cell adhesive and migratory capacities on fibronectin during early differentiation. 16597639_Study reveals the preferential expression of HOXA7 by germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes. 17959889_HOXA7 staining of tumor cell nuclei is correlated significantly with improved disease-specific survival, which is suggestive of the biological and potentially clinical importance of subcellular HOXA7 localization. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888898_found evidence for association of bone geometry variation with an SNP in ENPP1, a gene in the mineralization pathway. The alteration of a binding site of the deregulator of extracellular matrix HOXA7 warrants further investigation 20336696_The homeodomain and N- and C-termini are critical to transcriptional activation by Hoxa1 protein. The N-terminus also modulates interaction with Pbx1a protein during DNA-binding. 20540809_A novel mechanistic role for HOXA7 in modulating granulosa cell proliferation via upregulation of EGFR. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21323949_HOXA7, PIXT1 and PRRX1 homeobox genes have different patterns of expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas depending on its histological features. 21518888_Several targets of MLL fusions, MEIS1, HOXA7, HOXA9, and HOXA10 are functionally related and have been implicated in leukemias. Each of the four genes was knocked down separately in the precursor B-cell leukemic line RS4;11 expressing MLL-AF4. 22085718_Taken together, these results support the notion that down-regulation of PCGF2 is sufficient to induce granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells via de-repression of HOXA7 gene expression. 22251480_Data show that up-regulation of the HOXA7, HOXA9, HOXA11, and PBX3 resulting from the down-regulation of miR-181 family members probably contribute to the poor prognosis of patients with nonfavorable cytogenetically abnormal AML (CA-AML). 23660297_Hoxa7, Hoxa9 and Hox cofactor Meis1 were identified as AP-2alpha target genes, which are involved in myeloid leukemogenesis. 24099775_This finding contributes to our understanding of the role HOXA7 plays in regulating the proliferation of ER-positive cancer cells. 25246116_variants in the HOXA7 and HOXA9 genes are not common in Chinese women with Mullerian duct abnormalities 25501982_HOXA7 promotes cell proliferation, and these changes were mediated by cyclin E1/CDK2 26828989_HOXA7 might be a new gene candidate that influences the maturation of acute myeloid leukemia. 27600149_Results showed that HOXA7 was highly expressed in liver cancer cells which related with poorer prognosis. Its overexpression significantly promoted invasion and metastasis of liver cancer cells by activating Snail expression. 28529281_data suggest that HOXA7 could serve as a diagnostic marker for OSCC or a treatment target 29455183_Silencing of HOTAIR and HOXA7 could effectively inhibit tumor growth and increase chemosensitivity of ovarian tumors in nude mice. 30720179_Study found the miR-144-3p expression was reduced in neuroblastoma (NB) tissues and cell lines and resulted in the stimulation of cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and cell migration in vitro. Homeobox protein A7 (HOXA7) was validated as a direct target of miR-144-3p. Results demonstrated the tumor suppressive role of miR-144-3p in NB. 31670914_Correlation of miR-181a and three HOXA genes as useful biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. 32305054_MiR-193a-5p suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis by regulating HOXA7 in human ovarian cancer. 34978042_CircPAPPA Regulates the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis, and Cell Cycle of Trophoblast Cells Through the miR-3127-5p/HOXA7 Axis. |
ENSMUSG00000038236 |
Hoxa7 |
10.385088 |
0.3654399707 |
-1.452294 |
0.527198074 |
7.668782 |
0.00561843582413735619790484676627784210722893476486206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011367801612648028089513907445962104247882962226867675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4363614 |
2.0057385 |
15.1712672 |
3.4774557 |
| ENSG00000122641 |
3624 |
INHBA |
protein_coding |
P08476 |
FUNCTION: Inhibins and activins inhibit and activate, respectively, the secretion of follitropin by the pituitary gland. Inhibins/activins are involved in regulating a number of diverse functions such as hypothalamic and pituitary hormone secretion, gonadal hormone secretion, germ cell development and maturation, erythroid differentiation, insulin secretion, nerve cell survival, embryonic axial development or bone growth, depending on their subunit composition. Inhibins appear to oppose the functions of activins. |
3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Hormone;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate a subunit of the dimeric activin and inhibin protein complexes. These complexes activate and inhibit, respectively, follicle stimulating hormone secretion from the pituitary gland. The encoded protein also plays a role in eye, tooth and testis development. Elevated expression of this gene may be associated with cancer cachexia in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:3624; |
activin A complex [GO:0043509]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; inhibin A complex [GO:0043512]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; type II activin receptor binding [GO:0070699]; activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032924]; cardiac fibroblast cell development [GO:0060936]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to angiotensin [GO:1904385]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; defense response [GO:0006952]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; eyelid development in camera-type eye [GO:0061029]; GABAergic neuron differentiation [GO:0097154]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; hemoglobin biosynthetic process [GO:0042541]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048333]; multicellular organism aging [GO:0010259]; negative regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045578]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion [GO:0046882]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of macrophage differentiation [GO:0045650]; negative regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042326]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045648]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001241]; positive regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion [GO:0046881]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of ovulation [GO:0060279]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051247]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0045945]; progesterone secretion [GO:0042701]; regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion [GO:0046880]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; striatal medium spiny neuron differentiation [GO:0021773]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
11969340_distribution in gestational tissues across human pregnancy and during labour 12088879_Activin was secreted by both endometrial adenocarcinoma cell lines. Activin showed a weak, but significant, mitogenic effect on HEC-50 cells without modifications in Bax and Bcl-2. Activin is a regulator of endometrial cancer cell growth. 12149426_Activin A is potently induced in the bone marrow and may play a role in the suppression of inflammatory or immune processes. 12161551_Activin A promotes human endometrial stromal cell decidualization in vitro. 12399529_Seminal inhibin B levels were higher in normal men than in men after vasectomy and in men with azoospermia. 12414903_synthesis by the endosalpinx 12524226_Activin A induces cardiac ankyrin repeat protein (CARP) in cultured intimal smooth muscle cells in a dose-dependent way. 12587530_data suggest that the increased placental expression of inhibin subunit mRNAs is part of the mechanism leading to increased serum activin A and inhibin A levels 12651901_Results quantify the relative expression of inhibin alpha, inhibin/activin beta(A), beta(B), beta(C), follistatin, activin receptors and beta-glycan genes in placental tissue of term pre-eclamptic patients. 12665510_Activin A promotes Smad2 phosphorylation and its nuclear translocation. As an immediate response to activin A, Smad2 was modified by phosphorylation within 2 hours. 12702211_Activin-A modulates ActRI mRNA levels in human trophoblast cells. 12721183_Proportions of precursor inhibin B and alpha-subunit forms in the circulation are unchanged in men with spermatogenic disorders indicating there is no alteration of the Sertoli cell inhibin secretory pattern. 12877256_Serum inhibin B is an effective marker of follicular development in infertile women undergoing induction of superovulation, and may represent a further marker for ovarian follicular capacity. 14613548_activin promoted ovine preantral follicle & oocyte growth in vitro, but did not accelerate follicle differentiation; these results support a paracrine role for activin A during early oocyte & follicular development 14671202_Peripheral blood monoCYTES and endothelium, activated by TNFalpha, could be extraplacental sources of activin A in preeclampsia. May have role in mechanisms underlying endothelium dysfunction. 14671321_DLX1 blocks multiple signals from TGF-beta superfamily cytokines such as activin A, TGF-beta1, and BMP-4, including differentiation of a hematopoietic cell line by activin A 14738881_Data indicate that activin A and activin receptors IIA and IIB may be involved in the regulation of germ cell proliferation in the human ovary during the period leading up to primordial follicle formation. 14993131_Activin A markedly increased gene expression of mediators involved in infarction healing and myocardial remodeling in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. 15031321_the smad pathway and the tumor suppressor menin are key regulators of activin effects on PRL and Pit-1 expression, as well as on cell growth inhibition 15070957_Testosterone secretion is impaired in infants with Klinefelter syndrome. 15123352_Activin A increased the expression of VEGF receptors in cultured sinusoidal endothelial cells. 15123686_activin signaling via type II receptors requires a specific sequence for ALK4 binding 15188178_activin A is a novel stimulus of vascular endothelial growth factor gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma 15205401_Mutations in INHbetaB and INHbetaA genes are not associated with ovarian failure. 15205401_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15292256_may be an anabolic factor in cartilage 15374731_Women with POF showed low levels of inhibin A and inhibin B, but not of activin A, whereas the levels of pro-alphaC were significantly higher than in postmenopausal women 15451571_review article of gene expression of inhibin beta A in normal breast carcinoma, fibroadenoma, and normal mammary tissue 15580313_enhanced activin A expression suppresses proliferation and colony formation of human neuroblastoma cell 15737465_activin A inhibits adipogenesis via affecting the transcriptional factor cascade upstream of PPARgamma expression 15950648_Activin A and inhibin A may be used as markers to predict pregnancies that are likely to miscarry. 16081641_Activation of TAK1 (and probably p38-MAPK), but not Smad3, is necessary for triggering induction of oFSHbeta by activin. 16423381_Hyperplastic tissue labelled more intensely than endometrium for the presence of INH-betaA and -betaB. 16643884_When cultured with the mesonephros, Wolffian ducts formed ectopic buds in response to GDNF; inhibition of GDNF-induced budding by activin A led to inhibition of cell proliferation, & decrease of both Pax2 expression and PI3- & MAP kinase phosphorylation 16820918_Activin has autocrine roles in tumor growth of ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma cells. 16988001_Activin A has opposite effects on glucagon and arx gene expression in alpha-cells compared with beta-cells, a finding that may have relevance during pancreatic endocrine lineage specification and physiological function of the adult islets 17204604_Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase antagonizes the ability of human embryonic stem cells to differentiate in response to transforming growth factor beta family members such as Activin A 17384470_FGF-2 and activin A enhance their signals each other in bovine aortic endothelial cells, and endogenous activin A is critical for FGF-2-induced capillary formation. 17436000_Activin A suppresses interleukin-1-induced matrix metalloproteinase 3 secretion in human chondrosarcoma cells 17462637_Serum AMH and inhibin B are significantly lower in the men with nonobstructive azoospermia compared to the controls. 17478557_Activin-A is an excellent candidate for an effector molecule in human luteolysis whose paracrine action is inhibited during maternal recognition of pregnancy 17681301_Ovarian follicle size did influence rates of local hormone production. 17909904_Overexpression of Activin a causes cancer cell aggressiveness in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 17929017_bFGF does not directly act on p38 nor on the mRNA expression levels of activin receptors but inhibit activin A activation of p38 upstream of p38 in K562 cells. 17954979_A peptide corresponding to the N-terminal region of human follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)-binding inhibitor (FSHBI/ovarian follicular fluid peptide) shows FSHBI inhibitory activity in rat ovarian granulosa cell cultures. 17968943_Activin A is potentially an anticatabolic molecule in articular cartilage 18001154_Inhibin/activin BA subunit, follistatin, and activin receptor proteins and mRNAs are present in the human fetal palate. 18077449_new hypoxia-inducible and SOX9-regulated genes, Gdf10 and Chm-I. In addition, Mig6 and InhbA were induced by hypoxia, predominantly via HIF-2alpha 18089557_Cripto facilitates Nodal signaling and inhibits activin signaling by forming receptor complexes with these ligands that are structurally and functionally similar. 18156495_These findings establish an immune-regulatory role for activin-A in dendritic cells, highlighting the potential of antagonizing activin-A signaling in vivo to enhance vaccine immunogenicity. 18166170_The effects of activin on germ cells are indirect and include mediation by the kit ligand/c-Kit pathway, rather than being an autocrine germ cell effect. 18299275_analysis of the production and function of activin A in human dendritic cells 18319260_These results reveal a key role of GLI2 in activation of the activin/BMP antagonist FST in response to hedgehog (HH) signaling. 18353928_A dual role of activin A in regulating immunoglobulin production of B cells. 18359784_Activin A increases invasiveness of endometrial cells in an in vitro model of human peritoneum. 18381582_Concentration of anti-Mullerian hormone and inhibin-B in relation to steroids and age in follicular fluid from small antral human follicles. 18413775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18423626_Women with polycystic ovary syndrome have high serum concentration of total inhibin but not of inhibin A or inhibin B. 18450971_Activin A may mediate ovarian oncogenesis by activating Akt and repressing GSK to stimulate cellular proliferation. 18460206_ActA interferes with selected aspects of DC maturation & may help prevent activation of allogenic T-cells by the embryo. This may promote the generation of tolerance-inducing DCs. 18535106_Differential antagonism of activin, myostatin and growth and differentiation factor 11 by wild-type and mutant follistatin. 18600473_TGF-beta1 or activin A but not BMP-2 significantly decreased significantly decreased melanin content and expression of Tyrosinase and Tyrp-1 in the absence of alpha-MSH in melanoma cells 18608101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18695873_activin A may modulate the expression of MMP-7 via AP-1 18719101_synergistic effect of Wnt3a and ActivinA on hESCs differentiation into hepatic-like cells 18768470_analysis of the structure of the FSTL3.activin A complex 18854336_Adenoviral activin A expression prevents vein graft intimal hyperplasia in a rat model. 19027859_Synthesis, purification and bioactivity of recombinant human activin A expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris 19028479_The serum activin A level increased in acute myocardial infarction positively correlated with peak creatine kinase and CK-MB levels which are measures of infarction size. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19091310_Data suggest that activin A can down-regulate inflammatory mediator production and phagocytosis of LPS-activated macrophages via suppressing CD14 expression, and may influence the presentation of exogenous antigens via inhibiting MHC II expression. 19095948_activin-beta(C) is an antagonist of activin A 19128983_Results indicate that adiponectin upregulates monocytic activin A release via the p38 MAPK pathway. 19141859_A novel immune regulatory role of activin-A during DC-mediated NK-cell regulation. 19158274_Activin B is a key mediator of VHL/HIF-induced transformation in renal cell carcinomas. 19196915_Our findings in both clinical and experimental studies suggest a role for activin A in the development of various types of pulmonary hypertension 19200970_Activin A is secreted into uterine lumen; the levels in endometrial washing fluids were higher in women who subsequently became pregnant after IUI, so its measurement may be useful in predicting successful implantation. 19240652_INHBA overexpression promotes cell proliferation and may be epigenetically regulated in esophageal adenocarcinoma. 19257827_activation of the AR through Smads is required for activin A-promoted prostate cancer cell migration to bone matrix, thereby promoting the bone metastatic phenotype 19308293_INHBA is overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma relative to controls. 19324968_A novel role for FOXL2 in activin A-regulated Fshb transcription. 19383344_up-regulation in human colorectal cancer is correlated with upregulation of the TIMP-1 transcript 19386982_Activin A, activin receptor type II, nodal, and cripto mRNA are expressed by eutopic and ectopic endometrium in women with ovarian endometriosis. 19539911_Bone morphogenetic protein-6 stimulates gene expression of inhibin/activin beta subunits in human granulosa cells. 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19615428_The gonadally derived Inhibins are important regulators of locally produced osteotrophic factors. 19641514_Activin A is not a clinically useful marker of intrauterine infection in women with preterm prelabour rupture of membranes 19661148_Synthesis of activin and TGFB-signaling modulators may be affected by spermatogenic disruption and altered hormone levels in the testis. 19733294_Both TGF-beta and activin signaling pathways are activated on allergen provocation in asthma. Activin-A may contribute to resolution of inflammation. 19885849_roles of activin A in Human embryonic stem cell proliferation and differentiation were found. 20028875_in ductal carcinoma in situ lesions, high COX-2 expression is associated with high gammaH2AX, TRF2, activin A, and telomere malfunction 20036850_Activin A increased in asphyxiated full-term newborns with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy before the appearance of related signs. 20043075_down-regulated KLF4, CHGA, GPX3, SST and LIPF, together with up-regulated SERPINH1, THY1 and INHBA is an 8-gene signature for gastric cancer 20194748_Activin A, a TGF-beta family member, is a therapeutically amenable target exploited by multiple myeloma (MM) to alter its microenvironmental niche favoring osteolysis. 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20203128_results are consistent with a role for activin in maintaining oocyte granulosa cell interactions due to increased peripheral granulosa cell adhesion to the basement membrane and retention of adhesion at the surface of the zona pellucida. 20226172_activin A signal is transduced through the activin A type 1 receptor, ALK4, and transactivates several TGF-beta target genes in a SMAD-independent manner. 20309641_Overexpression of activin A is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20610541_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20660033_GDF9 attenuates the suppressive effects of activin A on StAR expression and progesterone production by increasing the expression of inhibin B, which acts as an activin A competitor. 20704626_Report serum/synovial fluid activin A and inhibin A levels in rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and knee ostoearthritis. 20720391_Elevated plasma activin A levels are associated with the presence of carcinoid heart disease. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926007_Protein levels of activin A and follistatin were assessed in glioblastoma and normal brain tissues in this study 21132402_INHBA may be a poor survival indicator of gastric cancer 21222045_analysis of candidate genes revealed four genes that influence fertility: CGB/LHB gene cluster (p = 0.0036), FSHR (p = 0.023), FST (p = 0.023), and INHB; none of the independent SNPs in these genes predicted mortality 21464440_Study found a significant association between activin A and newly detected abnormal glucose regulation in patients with acute myocardial infarction. 21475087_High inhibin beta A is associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 compared to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades 1 and 2. 21529351_Data show that inhibin A levels were significantly lower in the PCOS group compared to the control group, and inhibin B levels were comparable in the two groups. 21576276_results indicate that the coding regions of INHBA, SFRP4 and HOXA10 do not harbour mutations responsible for linkage to endometriosis in the families studied 21640344_Activin-A appears to promote endometriosis by stimulating interleukin-6 and protease-activated receptor-2 mRNA expression and increasing the proliferation of endometrioma stromal cells. 21767104_Activin A in maternal and fetal biological fluids is increased after SSRI administration in the third trimester of pregnancy. 21846490_Activin A in the follicular fluid is biologically inactivated by a more than ten times surplus of follistatin. 21952245_Activin-A was identified as strongly secreted by mesenchymal cells from control and T21 mesenchymal cells. Recombinant activin-A stimulated T21 trophoblast fusion 21992678_Human amniotic fluid activin-A and inhibin-A are involved in biological processes linked to intra-amniotic infection/inflammation-induced preterm birth. 22161160_High Activin-A levels were found in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) samples from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). 22234949_In patients with T2DM, increased activin A may reflect chronic underlying pathophysiological processes involved in development of cardiovascular disease. 22296042_Inhibin and activin beta subunits aree clearly demonstrable throughout the adult human hypothalamus and basal forebrain. 22416010_The present study demonstrated that serum activin A is not significantly altered in peritoneal or deep infiltrating endometriosis and has limited diagnostic accuracy in the diagnosis of ovarian endometrioma. 22425195_The pathological expression of activin beta A, iNOS and MUC1 by fallopian tubes bearing an ectopic pregnancy is not involved in the determination of implantation site. 22439617_Activin A levels were significantly higher in hypoxic than nonhypoxic newborns and in male newborns. 22548442_Activin A promotes the induction of mesoderm, as indicated by the upregulation of Brachyury expression. 22549017_The activin A signals via SMAD proteins, but not TAK1 or p38, to regulate murine and ovine Fshb transcription in gonadotrope-like cells. 22579070_The overarching hypothesis is that insensitivity to the growth inhibitory effects of activin A is an acquired capability in prostate cancer progression. 22685232_Plasma and placental productions of Activin A were significantly higher in preeclamptic patients when compared with normal pregnant subjects in a Chinese Han population 22845186_The study shows the involvement of activin A pathway in preterm premature rupture of the membranes associated with acute chorioamnionitis. 23024260_Activin A stimulates AKR1C3 expression and growth in human prostate cancer 23205865_Screening by maternal characteristics and activin-A at 30-33 weeks identifies half of the pregnancies that will subsequently develop preeclampsia. 23589129_Mineralization induction by 1alpha,25(OH)2 D3 may actually be controlled via interplay with activin A and osteocalcin. 23781072_Activin A suppresses osteoblast mineralization capacity by altering extracellular matrix composition and impairing matrix vesicle production. 23808611_Urine Activin A in preterm infants who developed intraventricular hemorrhage was significantly higher than in controls at all monitoring time-points, increasing progressively from first urination to 24 h when it reached the highest peak. 23812417_Activin A released from EAT-T2D inhibits insulin action via the induction of miR-143 in cardiomyocytes 23831638_retinoid signalling can potently suppress activin-induced proliferation by antagonising G1 phase progression and entry into the cell cycle. 24085226_The present study suggests that INHBA is useful as a predictive marker for prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. 24107149_Maternal serum inhibin-A levels were significantly higher in pregnancies with fetal Hb Bart's disease. 24134550_Circulating activin A levels are associated with impaired myocardial glucose metabolism and high left ventricular mass/volume ratio in men with uncomplicated type 2 diabetes, reflecting a potential detrimental role in early human diabetic cardiomyopathy. 24139759_the Activin/ALK4 pathway directly recruits PTP1B and stimulates its release from the endoplasmic reticulum through ALK4-mediated cleavage. 24168163_expression of erythroid differentiation regulator 1 was negatively correlated with the malignant potential in various skin tumors. 24204752_Follistatin, by its ability to neutralize the actions of activin A may be of value as an antifibrotic for radiation induced fibrosis. 24227781_Recombinant human activin A increases mature mast cell numbers in vivo in mouse skin via attraction of mast cell progenitors from bone marrow. 24302632_We identified an unreported germline mutation of the INHA gene encoding the alpha-subunit, the partner of the betaA-subunit. This mutation also alters the secreted activin/inhibin ratio, by disrupting both inhibin A and inhibin B biosynthesis. 24336657_IFN-gamma modulates NF-kappaB/c-Jun to antagonize activin A-mediated NF-E2 transcriptional activity on erythroid cell globin gene expression 24378873_Data show that expression of activin A and B was increased in many cancer cell lines. 24395917_Activin A, produced during NK-DC interactions, represents a relevant negative feedback mechanism that might function to prevent excessive immune activation by DCs. 24599287_Serum inhibin levels correlate with clinical characteristics and mortality in epithelial ovarian cancer patients. 24778035_Overexpression of the INHBA gene is considered a useful independent predictor of outcomes in patients with gastric cancer after curative surgery. 24916766_overexpression of INHBA in mesenchymal cells increases colony formation potential of epithelial cells, suggesting that it contributes to the dynamic reciprocity between breast mesenchymal and epithelial cells. 24928494_Activin A promoted chemotaxis, migration and proliferation of human periodontal ligament cells, and caused an increase in fibroblastic differentiation of these cells while down-regulating their osteoblastic differentiation. 25062451_Activin A, B, and AB have similar effects on steroidogenesis in human granulosa cells; in contrast, activin AC is not biologically active and does not act as a competitive antagonist. 25084052_Activin A is an anti-lymphangiogenic factor, but because of its pleiotropic effects on cell mobility it appears not suitable as a pharmacological target. 25114097_Endothelial cells initiate a smooth muscle cell differentiation program in adjacent adipose stromal cells via induction activin A expression. 25200295_Data suggest that activin A (dimer of INHBA), especially in lateral hypothalamus, plays role in neuronal sensing of free amino acids, appetite regulation, and neuronal plasticity. [REVIEW] 25449777_High activin A signal promotes cancer progression and is involved in cachexia in a subset of pancreatic cancer. 25488476_INHBA overexpression implies adverse clinical outcomes for urothelial carcinoma, justifying it is a potential prognostic biomarker and a novel therapeutic target in UC 25557874_Activin-A and -B are abundantly expressed in mesothelioma tumor tissue. 25565002_changes in Follistatin levels during pregnancy contribute to the control of the activin A system 25634576_Data suggest that activin A [plus bone morphogenic protein 4 (BMP4)] strongly stimulates germ cell differentiation potential of human embryonic stem cells; this stimulation appear to depend on gene expression regulation by activin A. 25659497_Data suggest that an SNP in promoter region of ACVR2A (activin A receptor type IIA; rs1424954, the pre-eclampsia susceptibility allele) down-regulates signal transduction in trophoblasts in response to excess activin-A (as seen in pre-eclampsia). 25729977_Increased serum level of activin A indicates its role in the pathogenesis of asthma, particularly in underweight and overweight patients. 25751105_our study suggests that increased circulating concentrations of ActA may contribute to the development of cachexia in cancer patients. 25796148_Low activin-A expression was correlated with the occurrence, development, metastasis and malignant degree of lung adenocarcinoma. 25833251_able to restore glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in islets from type 2 diabetic donors 26047946_Activin A inhibited signaling by BMP-6 and BMP-9 by competing for type 2 receptors ACVR2A and ACVR2B. 26096938_Inhibin betaA is translationally regulated by TGFbeta via hnRNP E1. 26215835_binding of SMAD2/3, the intracellular effectors of activin signaling, was significantly enriched at the Pmepa1 gene, which encodes a negative feedback regulator of TGF-beta signaling in cancer cells, and at the Kdm6b gene, which encodes an epigenetic regulator promoting transcriptional plasticity. 26298390_Our study uncovers the PITX2-induced expression of TGFB1/2/3 as well as INHBA genes (p |
ENSMUSG00000041324 |
Inhba |
37.362501 |
6.4658378967 |
2.692837 |
0.351968894 |
61.809857 |
0.00000000000000378275958083442081347986602032951860540439239719012753937477100407704710960388183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000026090435239773855335561643569650415515906666588663576078488404164090752601623535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
66.5076771 |
12.8299945 |
10.1814139 |
1.7684631 |
| ENSG00000122691 |
7291 |
TWIST1 |
protein_coding |
Q15672 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional regulator. Inhibits myogenesis by sequestrating E proteins, inhibiting trans-activation by MEF2, and inhibiting DNA-binding by MYOD1 through physical interaction. This interaction probably involves the basic domains of both proteins. Also represses expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNFA and IL1B. Regulates cranial suture patterning and fusion. Activates transcription as a heterodimer with E proteins. Regulates gene expression differentially, depending on dimer composition. Homodimers induce expression of FGFR2 and POSTN while heterodimers repress FGFR2 and POSTN expression and induce THBS1 expression. Heterodimerization is also required for osteoblast differentiation. Represses the activity of the circadian transcriptional activator: NPAS2-BMAL1 heterodimer (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P26687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12553906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25981568}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Biological rhythms;Craniosynostosis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Myogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor that plays an important role in embryonic development. The encoded protein forms both homodimers and heterodimers that bind to DNA E box sequences and regulate the transcription of genes involved in cranial suture closure during skull development. This protein may also regulate neural tube closure, limb development and brown fat metabolism. This gene is hypermethylated and overexpressed in multiple human cancers, and the encoded protein promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis, as well as metastatic recurrence. Mutations in this gene cause Saethre-Chotzen syndrome in human patients, which is characterized by craniosynostosis, ptosis and hypertelorism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:7291; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; cardiac neural crest cell migration involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003253]; cell proliferation involved in heart valve development [GO:2000793]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cranial suture morphogenesis [GO:0060363]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; embryonic camera-type eye formation [GO:0060900]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; eyelid development in camera-type eye [GO:0061029]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; mitral valve morphogenesis [GO:0003183]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000773]; negative regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043518]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000780]; negative regulation of histone acetylation [GO:0035067]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation uncoupler activity [GO:2000276]; negative regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035359]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0048642]; negative regulation of striated muscle tissue development [GO:0045843]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; outer ear morphogenesis [GO:0042473]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation [GO:2000144]; positive regulation of endocardial cushion to mesenchymal transition involved in heart valve formation [GO:2000802]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0032000]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production [GO:0071639]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000679]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021] |
10485844_Twist1 and Twist2 antagonize the ARF/p53 pathway. This is the first report suggesting a role for Twist genes as oncogenes 11474656_new TWIST mutation (7p21) with variable eyelid manifestations supports locus homogeneity of BPES at 3q22 11748846_Deletion of 18 nucleotides or insertion of three, 15, or 21 nucleotides was not consistently associated with clinical disease and was conclude that they are at most weakly pathogenic. 11754069_Identified direct paternal transmission of a novel missense TWIST mutation in the highly conserved Helix II domain of this bHLH-family gene. 11854168_Deficience causes skull osteoblast apoptosis due to increased TNFalpha expression and caspase-2 activation. 11948912_Cooperative E-box regulation of human GLI1 by this protein and USF 12015302_Characterization of a dominant negative C. elegans Twist mutant protein with implications for human Saethre-Chotzen syndrome 12218784_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12270142_inactivation reduces CBFA1/RUNX2 expression and DNA binding to the osteocalcin promoter in osteoblasts 12791045_One variant is associated with Robinow-Sorauf syndrome. 14513358_The risk for developmental delay in patients with deletions involving the TWIST gene is approximately 90%. 14724576_novel role for TWIST, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, which plays a central role in cell type determination and differentiation, during generation of acquired resistance to taxol in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line, HNE1-T3 15210113_TWIST1 plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. 15313894_Twist was highly and selectively expressed in T cells of patients with Sezary Syndrome. 15545268_loss of HOXA5 expression could lead to the functional activation of Twist resulting in aberrant cell cycle regulation and promoting breast carcinogenesis 15555546_A reporter assay with the p21 promoter demonstrated that Snail inhibited expression of p21 induced by E2A. Co-expression of Snail with Twist showed additive inhibitory effects. 15607966_H-Twist overexpression in neuroblastomas is responsible for the inhibition of the ARF/p53 pathway involved in the Myc-dependent apoptotic response. 15735646_Misregulation of Twist1 dimerization by post-translational mechanisms underlies phenotypes of individuals with Saethre-Chotzen syndrome 15880747_This analysis further dissects the structure-function relationships of TWIST and corroborates with phenotypic observations of disease expressivity. 15900593_TWIST gene is involved in high-grade pediatric osteosarcomas and is a new marker with a possible initial predictive value. 15958559_Results have identified TWIST as a critical regulator of prostate cancer cell growth and suggest a potential therapeutic approach to inhibit the growth and metastasis of androgen-independent prostate cancer through inactivation of the TWIST gene. 16229805_Overexpression of TWIST protein in a human glioma cell line significantly enhanced tumor cell invasion, a hallmark of high-grade gliomas. 16293629_Twist1 is induced by canonical Wnt signaling and expression of Twist1 strongly inhibited chondrocyte gene expression. 16322226_Twist over-expression induces angiogenesis in a mouse breast cancer model 16412561_Twist may play an important role in the invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 16502419_Dimer partner selection is an important mediator of Twist1 function in transgenic mice, providing a mechanistic understanding of craniosynostosis due to TWIST haploinsufficiency. 16540516_This provides genetic evidence that Twist1, Msx2 and Efna4 function together in boundary formation and the pathogenesis of coronal synostosis. 16737925_Twist overexpression plays a role in destabilizing the genome, thus promoting chromosomal instability. 16831897_These results implicate Twist proteins in regulation of TNFalpha production by antiinflammatory factors and pathways, and provide a mechanism by which type I IFNs and Axl receptors suppress inflammatory cytokine production. 16888803_Twist may act as a negative regulator of osteoblastic differentiation in periodontal ligament cells 17003487_Twist haploinsufficiency results in decreased Cbl-mediated PI3K degradation in osteoblasts. 17070479_Patients with TWIST gene mutations may have more ophthalmic abnormalities, including more strabismus, ptosis, NLDO, astigmatism, vertical deviations, and amblyopia compared with patients with FGFR3 gene mutations. 17157810_suggest critical implication of the CCT repeats in association with Sp1 and Sp3 factors in sustaining expression of the TWIST1 gene in mesenchymal cells 17236203_Twist, a novel oncogene, is upregulated in pancreatic cancer 17332324_Induction of Twist by a human viral oncoprotein LMP1 directly contributes to the metastatic nature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 17332325_Twist is a positive transcriptional regulator of AKT2 expression;Twist-AKT2 signaling is involved in promoting invasive ability and survival of breast cancer cells. 17343269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17343269_Some TWIST1 mutations in the RUNX2 binding site are associated with craniosynostosis. 17394502_TWIST may serve as a prognostic marker for high-grade prostatic cancer in humans; up-regulation of TWIST with aberrant expression of E-cadherin may predict development of metastatic disease. 17403902_Data suggest that Twist-1 and -2 play an important role in NF-kappaB-dependent chemoresistance. 17414280_no evidence that mosaicism for mutations, normally associated with syndromal forms of craniosynostosis, occur in single suture craniosynostosis 17487558_findings suggest that reduced expression of TWIST suppresses the multistep process of peritoneal dissemination (detachment from the primary lesion, adhesion to MCs and invasion of MCs. 17512904_Twist regulates cell motility and invasion in gastric cancer cell lines, probably through the N-cadherin and fibronectin production 17690110_TWIST plays a key role in the continuous proliferation of immortalized cells. Over-expression of TWIST results in down-regulation of p14(ARF), which leads to the impairment of DNA damage checkpoint in response to genotoxic stress. 17785550_TWIST1 was frequently observed in the bone marrow of breast cancer patients before chemotherapy; expression of TWIST1 correlated with the rapid occurrence of distant metastasis or local progression, within 1 year from initial diagnosis 17886095_TWIST may be a useful prognostic marker and target for gastric cancer therapy. 17893140_analysis of transcriptional activation by the proto-oncogene Twist1 17925286_Twist was found in cell membrane and cytoplasm of cervical cancers.High expression predicted poor survival; it was a significant prognostic factor in radiation-sensitive squamous cell carcinomas but not in radiation-resistant adenocarcinomas. 17967182_Results identified TWIST1 loci showing significant differential DNA methylation levels between tumor and non-tumor lung and highly significant hypermethylation in adenocarcinoma. 17987801_Twist may play an important role in the angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 18062917_Using transient promoter assays, we show that Twist can down-regulate E-cadherin promoter activity by up to two folds. 18172301_Both YB-1 and Twist expression could induce tumor progression, promoting cell growth and driving oncogenesis in various cancers. 18231738_Twist was up-regulated in primary liver cancer. 18255367_TWIST microdeletion is associated with Saethre-Chotzen phenotype and a complex rearrangement involving chromosomes 2 and 7 18297062_a key signalling pathway involving HIF-1alpha and TWIST promotes metastasis in response to intratumoural hypoxia 18349132_These data indicate that MSX2 plays a crucial role in pancreatic cancer development by inducing changes consistent with epithelial to mesenchymal transition through enhanced expression of Twist 1. 18353781_STAT3, Twist, and AKT2 form a functional signaling axis to regulate pivotal oncogenic properties of cancer cells 18391499_summary of the effects of FGFR2 and Twist genetic mutations resulting in altered osteoblast phenotype and premature cranial fusion based on analysis in human syndromic craniosynostosis [review] 18440840_Positive Twist expression may be a useful prognostic marker for patients with bladder cancer, and its expression seems to be correlated to the tobacco status of the patients. 18480983_high expression level of Twist is closely associated with more aggressive behaviors of human hepatocellular carcinoma 18504427_p53 interacted with the N-terminal domain of Twist and repressed Twist-dependent YB-1 promoter activity. 18519689_thrombin up-regulates Twist, which is required for thrombin-induced angiogenesis as measured by endothelial cell migration, Matrigel tubule formation, and tumor angiogenesis 18549475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18598946_Twist proteins promote malignant conversion and metastatic dissemination. 18663125_Th lymphocytes from the inflamed joint or gut tissue of patients with rheumatic diseases, Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis expressed high levels of twist1. 18974133_In human melanoma cells, MFG-E8 knockdown attenuated Akt and Twist signaling and thereby compromised tumor cell survival, EMT, and invasive ability 19051271_TWIST regulates the expression of several genes involved in the differentiation, adhesion, and proliferation of gastric cancer cells. 19064546_TWIST1 promoter methylation is significantly more prevalent in malignant compared with healthy breast tissue. 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19276370_using gene expression profiling, several genes differentially expressed in human choroid plexus papillomas could be identified. TWIST1 is highly expressed in choroid plexus papillomas and promotes proliferation and invasion. 19345188_The nuclear receptor PPARdelta not only mediates the actions of PGC-1alpha but also regulates twist-1 expression, suggesting a negative-feedback regulatory mechanism. 19373776_Studied TWIST1 mutation confirmed Saethre-Chotzen syndrome patients and possible increased risk of cancer. Found breast cancer risk not increased in individuals with TWIST1 mutation confirmed Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. 19381684_We found upregulation of mRNA for transcription factors Snail, Slug, Twist, and SIP1 in spindle cell carcinoma when compared to squamous cell carcinoma. 19412634_We describe for the first time that EMT markers Snail and Twist are expressed in PCC and that their expression is associated with malignancy 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19470737_Results show that cumulative RASSF1A, TWIST1, and HIN1 gene methylation accurately distinguished ducts with cancerous versus benign lesions. 19513566_Negative regulation of TIMP1 is mediated by transcription factor TWIST1. 19534813_Results demonstrates the presence of two putative putative nuclear localization signals (NLS) motifs in H-TWIST and suggests that these NLS sequences are functional. 19597909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19597909_results suggest that TWIST1 may be a useful genetic marker for osteoporosis and may have a role on bone metabolism in humans. 19609939_These findings implicate the TWIST gene family members as potential mediators of MSC self-renewal and lineage commitment in postnatal skeletal tissues by exerting their effects on genes involved in the early stages of bone development. 19644484_hypoxic TWIST1 induction is regulated by both HIF-1 and HIF-2 proteins through distinct regulatory elements in a tissue-specific manner 19802001_Data suggest that modulation of castration-induced oxidative stress or Twist1/AR signaling might be a useful strategy for developing a novel therapeutics in prostate cancer. 19816777_upregulated Twist expression in the primary ESCC significantly correlates with the high risk of subsequent development of distant metastasis and low postoperative survival rates. 19821482_Coexpression of Snail and Twist correlated with the worst prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 19851501_Twist contributes to EMT in the model of virus-induced pulmonary fibrosis 19860490_Girl with clinical features of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome who has a previously undescribed sequence variant in the TWIST1 gene, corresponding to p.R191M. 19863427_We have analysed women with BRCA1/2-negative hereditary breast cancer to study whether these families might have mutations in Saethre-Chotzen-associated genes. 19893041_Twist1 represents one of the factors that promotes pathogenic accumulation of fibroblasts in fibrotic lung disease. 19954024_Down-regulation of Twist1 could increase drug sensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line HNE1 to taxol by inducing apoptosis. 20007935_Twist1 may play a role in inflammation of human white adipocytes because it can regulate the expression and secretion of inflammatory adipokines via direct transcriptional effects in white adipocytes 20019840_Data demonstrate that the overexpression of Twist in breast cells can promote the generation of a cancer stem cell phenotype characterized by the high expression of CD44, little or no expression of CD24, and increased aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 activity. 20019840_Twist promotes breast cancer stem cell formation via down-regulation of CD24 20025748_Evaluation of Twist and E-cadherin expressions should be useful for determining tumor properties, including prognosis, in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 20079104_TWIST1 may play a pivotal role in paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of Hep-2 cells. 20140954_The TWIST1 methylation level was higher in colorectal adenoma and cancer than in normal colorectal mucosa. Elevated TWIST1 mRNA expression in normal colorectal mucosa in patients with CRC as well as in primary CRC specimens was assoc'd with poor outcomes. 20219012_Findings indicate that Twist1 induces HCC invasion via increased activity in MMPs, specifically in MMP2 and MMP9, leading to poor clinical prognoses. 20388391_The positive expression of Twist was correlated to lymph node metastasis in invasive lobular carcinoma. 20400975_Twist1 as a regulator of miRNA cluster responsible for the regulation of the IKKbeta/NF-kappaB and PTEN/AKT pathways and its association of ovarian cancer stem cell differentiation 20400976_PKB phosphorylates one of the anti-apoptotic proteins--transcription factor Twist-1 at Ser42. 20496080_HIN-1, RAR-beta, RASSF1A, and Twist had the ability to distinguish high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions/squamous cell carcinomas from low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions/negative cervical scrapings 20505321_The methylation levels and frequencies of HIN1, RASSF1A and TWIST, and average MR were significantly lower in basal-like subtype compared to luminal or human epithelial growth factor receptor-2 subtype. 20562331_role for dysregulation of TWIST in the pathophysiology of myelodysplastic syndromes 20564230_Studies indicate that understanding of the mechanistic insights in the role of Twist in lineage specification/differentiation and tumorigenesis is vital to the success of future clinical applications for the therapeutic use of MSCs. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20643727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20646316_studies demonstrated that TWIST1 enhances glioblastoma multiforma invasion in concert with mesenchymal change not involving the canonical cadherin switch of carcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition 20696219_This article summarizes the recent knowledge on the role and mechanisms of action of Twist1 in the control of skeletal cell fate with specific emphasize on postnatal bone biology and pathology. 20804746_These data implicate Twist1 as a critical regulator of valve development and suggest that Twist1 influences extracellular matrix production and cell proliferation during disease. 20818389_The results suggest that Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumour-initiating capability in cancer cells occurs through chromatin remodelling, which leads to unfavourable clinical outcomes. 20838384_ILK regulates the expression of Her2/neu through TWIST and YB-1, lending support to the use of ILK inhibitors in the treatment of aggressive Her2/neu-positive tumors. 20857420_Thrombin upregulates Twist via HIF-1alpha to make tumor cells malignant and also establish a link between the coagulation disorder and cancer metastasis. 20920982_Results showed the prognostic relevance of bone marrow disseminated tumor cells assessed by a multimarker mRNA panel consisting of TWIST1, cytokeratin 19 (gene name: KRT19), and mammaglobin A (gene name: SCGB2A2) mRNA in operable breast cancer patients. 20943789_Low twist1 expression in human white adipose tissue correlates with obesity and an insulin-resistant phenotype, which may be mediated by an increased sensitivity to the proinflammatory effect of TNFalpha. 20970163_Our data indicate that deregulation of TWIST is somehow important in the aggressiveness of triple-negative carcinomas and poor patient outcome 21083641_The present study showed that Twist1 regulates YB-1 expression and that both Twist1 and YB-1 promote malignant potentials, including tumour growth, invasion and anti-cancer-drug resistance in bladder cancer cells 21123820_Deregulation of TWIST-1 in the CD34+ compartment is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia. 21138866_Foxo3a suppression of urothelial cancer invasiveness through Twist1, Y-box-binding protein 1, and E-cadherin regulation. 21199805_results show that Twist1 needs to induce Snail2 to suppress the epithelial branch of the EMT program and that Twist1 and Snail2 act together to promote EMT and tumor metastasis 21208645_Twist1 is related to metastasis by tumor cells un hepatocellular carcinoma angiogenesis. 21316706_activated STAT3 signal may associate with Twist and E-cadherin expression and mediate HCC invasiveness and metastasis. 21317430_The results indicate that Snail1 controls Zeb1 expression at multiple levels and acts cooperatively with Twist in the ZEB1 gene transcription induction. 21324165_Expression of transcriptional factors zeb1 and twist mainly occur in the stromal compartment of breast carcinomas. 21333765_Data show that three patients carrying small deletions containing TWIST1 who present with significant postnatal microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, and short stature. 21389145_TWIST1 plays a key role in determining malignant features of the anaplastic phenotype in vitro 21397860_Data show that induction of PDGFRalpha and invadopodia is essential for Twist1 to promote tumor metastasis. 21461979_TWIST1 hypermethylation was detected in colorectal specimens of 46 patients with cancer, but in none of the tissues from the nonmalignant control group. 21464926_TWIST1 expression levels could be a tumor indicator in stage II patients. 21478681_Loss of p27(Kip)(1) causes an elongated/scatter cell-like phenotype involving up-regulation of Brachyury and Twist gene expression. 21502402_Twist1, a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, promotes breast tumor cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasiveness, and metastasis. 21503964_the TWIST mutation (R154S) may be an essential underlying factor in the development and pathophysiology of giant cell tumor of bone 21539816_These results suggest that the overexpression of Twist correlates to hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 21559372_Twist expression can be regulated at the post-translational level through phosphorylation by CK2, which increases Twist stability in response to IL-6 stimulation 21559426_Phosphorylation of the Twist1-family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors is involved in pathological cardiac remodeling and can be regulated by Akt signaling 21594904_analysis of twist expression in lung cancer provide clues to comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms, by which metastasis often develops in lung cancer 21677079_Twist1 overexpression in DPSCs enhanced expression of DSPP, gene that marks odontoblast terminal differentiation. Twist1 stimulates Dspp promoter activity by antagonizing Runx2 function in 293FT cells. 21732143_High TWIST1 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and associated with its epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 21740802_Twist expression correlates with lymph node metastasis. The mechanism involved in such a correlation may be related to lymphangiogenesis. 21748764_We report functional and structural interactions between Bcl-2 and the transcription factor Twist1 in the relationship with metastasis and vascular mimicry in hepatocellular carcinoma. 21796367_SNAIL and TWIST play a crucial role in epithelial to mesenchymal transition through regulation of E- and N-cadherin expression, exclusively in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients. 21822911_confirmed that down-regulation of TWIST expression decreased the motion, invasion, and migration ability of the Hep-2 cells 21834956_TWIST and SNAI1 expression in stromal cells is associated with clinical and histopathological characteristics that indicate progressive disease. Negative expression of these EMT-promoting transcription factors predicts a better outcome. 21854747_Cancer-associated fibroblasts in gastric cancer frequently have altered Twist1 expression. 21864967_expression was positively associated with lymph node metastasis, pathologic grade, and tumor stage [in oral squamous cell carcinoma] 21866569_Twist1 and Twist2 modulate ATF4-dependent transcriptional activity in response to Parathyroid hormone. 21883379_Twist1 directly activates Bmi1 expression and that these two molecules function together to mediate cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition--{REVIEW} 21914771_these findings strongly implicate an essential role for TWIST1 in the initiation of human decidualization and uterine stromal cell apoptosis that occurs upstream of the induction of forkhead box protein O1 and v-ets-erythroblastosis virus E26 mRNA. 21919891_Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness: the Twist1-Bmi1 connection 21931630_the important role of hypoxia-mediated signalling in osteogenic differentiation in MSCs through direct regulation of RUNX2 by TWIST 21983900_SET8 and TWIST are functionally interdependent in promoting EMT and enhancing the invasive potential of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo 21994965_Twist is an upstream regulator of the E-cadherin-mediated terminal differentiation and fusion in a human trophoblastic cell line in vitro. 22002117_down-regulation of the Twist gene suppressed the proliferation of MKN45 gastric cancer cells by negatively regulating the AP-1 activity 22006115_in both nontumorigenic and tumorigenic epithelial cancer cells, that Snail1 is uniquely required for EMT initiation, whereas Twist1 is required to maintain late EMT 22006371_Overexpression of MAML-1 and Twist1 were significantly associated with lymph node metastasis and the surgical staging of tumor 22007485_Overexpression of TWIST may correlate to tumor invasion in gastric adenocarcinoma. 22020939_CCN5-induced inhibition of TWIST1 expression is mediated through the translational inhibition/modification of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha via impeding JNK signaling pathway. 22050045_nucleostemin expression level correlated with TWIST expression level in esophageal cancer cell lines; identified that high nucleostemin proportion, TWIST intensity, and advanced pathological N stage were correlated with poor relapse-free survival 22056872_Twist recruits DNA methyltransferase 3B (DNMT3B) and histone acetylase 1 (HDAC1) to the estrogen receptor promoter, which reduces the estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer. 22056872_Twist transcriptionally regulates estrogen receptor alpha expression. 22056872_regulation of ER by Twist could be an underlying mechanism for the loss of ER activity observed in breast tumors, and may contribute to the generation of hormone-resistant, ER-negative breast cancer 22060274_ARTN and TWIST1 synergize to produce a worse outcome in ER-MC and combined inhibition of ARTN and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) may therefore provide a novel therapeutic strategy in this subtype of mammary carcinoma. 22102471_Human TWIST was found to be endogenously expressed in human fetal myoblasts, and its expression decreased during late stages of development. 22110753_bladder cancer T24 cells may undergo the telomerase-to-ALT-like conversion and promote cancer progression 22155737_Twist1 expression, owing to the abnormal NPM-ALK/STAT3 signaling, contributes to its invasiveness in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 22166980_Twist is an upstream regulator of N-cadherin-mediated invasion of human trophoblastic cells. 22178381_Increased expression of Twist was observed in 38.0% of primary NSCLC tumors. Overexpression of Twist in stage I NSCLC was associated with a worse overall survival and correlated with a shorter recurrence-free survival. 22184289_Glioblastoma multiforme tissue grade IV specimens showed significant expression of Twist1 and Sox2, known mesenchymal and stemness related markers, respectively, indicating their association with glial tumor genesis and metastasis. 22241470_Regulation of transcription factor Twist expression by the DNA architectural protein high mobility group A2 during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 22245869_*uggest that Twist1-mediated modulation of MDR1/P-gp expression plays an important role in sensitization of cervical cancer cells to cisplatin. 22253230_our results establish a signaling axis through which the tumor microenvironment elicits Twist1 expression to promote cancer metastasis. We 22266852_miR-580 is able to target the promoter region of TWIST1 and to control TWIST1 expression. 22272264_Results suggest that TWIST1 is an important driver of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in EGFR mutated cells and could be a potential marker in clinics to predict outcome in patients with EGFR mutated tumors. 22288519_None of 20 ordinary glioblastomas showed TWIST1 expression in >10% neoplastic cells. 22290439_These studies for the first time link Twist-1 to histone methylation of the Ink4A/Arf locus by controlling the expression of histone methyltransferases as well as the expression of other basic helix-loop-helix factors. 22331730_TWIST may act upstream of E-cadherin, which can indirectly regulate the expression levels of beta-catenin in bladder cancer. 22349827_TWIST-1 is constitutively degraded in EOC stem cells, and that the acquisition of TWIST-1 requires additional signals that will trigger the differentiation process 22360285_A potential role of TWIST as the promoter of tumor invasion and metastasis associated with down-regulation of E-cadherin. 22407364_The results uncover an essential mechanism to explain how Twist1 induces the motile stem-like cancer cell phenotype beyond simply suppressing E-cadherin. 22441818_our study indicates that nuclear twist plays an important role in ESCC lymphatic metastasis by increasing the expression of VEGF-C. 22457607_TWIST expression was inversely correlated with ERalpha expression in both breast cancer cell lines and human breast ductal carcinomas. 22515221_Increased Twist protein expression in advanced MF/SS lesions suggests that Twist expression may correlate with MF/SS stages. 22532563_identify Twist1 as an inhibitor of Sox9 and further suggest that the balance between Twist1 and Sox9 may determine the earliest steps of chondrogenesis. 22544111_Three novel TWIST1 mutations were detected, and p.P250R was the only mutation in FGFR3 associated with craniosynostosis. 22576709_Twist was expressed significantly more and E-cadherin significantly less in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) with metastasis, and expression of both was closely related to metastasis of GISTs. 22581441_Twist may be associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer and the tumorigenesis, invasion, and metastasis of gastric cancer. 22581828_results suggest that Notch1/STAT3/Twist signaling axis is involved in progression of human gastric cancer and modulation of this cascade has potential for the targeted combination therapy 22654667_The suppression of TWIST1 in human lung cancer cells also induced cellular senescence 22668877_these results indicate that Twist1 induces the repression of claudin-4 expression during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal carcinoma. 22797064_Depletion of TWIST1 in MMSET-overexpressing cells blocked cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, indicating that TWIST1 is a critical target of MMSET, responsible for the acquisition of an invasive phenotype. 22820497_Dysregulated expression of TWIST1, TGF-beta1 and SMAD3 mRNA observed in osteoarthritis bone is reflected in the functionality of the osteoblast when these cells are cultured ex vivo. 22847601_Our results suggest that Twist was expressed significantly more and E-cadherin significantly less in osteosarcoma with metastasis 22896337_findings indicate that CLU is an important mediator of TGF-beta-induced EMT, and suggest that CLU suppression may represent a promising therapeutic option for suppressing prostate cancer metastatic progression 22899291_we have demonstrated strong diffuse expression of SNAI2 and TWIST1 in the majority of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas but not in normal thyroids, thyroid adenomas or well-differentiated thyroid carcinomas 22961111_These results indicated that moscatilin inhibited MDA-MB-231 cell migration via Akt- and Twist-dependent pathways; this finding was consistent with moscatilin's antimetastatic activity in vivo. 22965800_Letter/Case Report: Twist1 may be a feasible biomarker for highly invasive and/or metastatic basal cell carcinoma. 22967435_TWIST1 mRNA expression is an independent prognostic factor for poor prognosis in LNN/ER-positive breast cancer. 22974478_Ectopic expression of Snail and Twist contributed to lymph node and disseminated metastasis, respectively, by reducing E-cadherin expression, providing a novel role for Snail and Twist in the progression of colorectal cancer. 22974479_The assessment of the Twist immunoreactivity and lymphovascular space involvement may distinguish high- from low-risk patients with locally invasive cervical carcinoma. 22975381_study found that Twist1 acts to inactivate p53 in mesenchymal tumors; evidence provided that Twist1 binds p53 C terminus through the Twist box; this interaction hinders key posttranslational modifications of p53 and facilitates its MDM2-mediated degradation 22982861_PROX1 directly binds to proximal promoter of TWIST1 gene to repress its transcription 22983574_TWIST-1 and miR10a/b expression are dysregulated in MDS. Expression of miRs10a/b is controlled by TWIST-1. 23029385_The overexpression of SLUG and TWIST with down-regulation of E-cadherin was characteristic findings in hemangiopericytomas and solitary fibrous tumors, but not in meningiomas. 23052737_It might play an important role in the implantation of metastatic foci. 23056278_Methylation levels of EOMES, HOXA9, POU4F2, TWIST1, VIM, and ZNF154 in urine specimens are promising diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer recurrence surveillance 23095743_ARTN promotion of the cancer stem cell-like cell phenotype was mediated by TWIST1 regulation of BCL-2 expression. 23135750_This study study showed that HMGA2 was able to elicit EMT and regulate several genes which are closely related to the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by directly binding to their promoter. 23150175_high expression of TWIST1 and TWIST1 promoter methylation were significantly more frequent in borderline/malignant phyllodes tumors (PT) than in benign PT; results suggest a high expression of TWIST1 and related proteins plays a pivotal role in the malignant progression of PT 23158991_The expression of Twist1 has a close relationship with MMP-2 in endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Twist1 may be closely correlated with the tumor invasion, metastasis and prognosis. 23161342_HBx activates the Twist promoter by activating STAT3 and promotes epithelium-mesenchymal transition occurrence in liver cells. 23167357_Twist is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis of ovarian cancer. 23222305_A previously unrecognized interplay between ERK1/2, TWIST1, and MMP-1 that is likely sign |
ENSMUSG00000035799 |
Twist1 |
56.955755 |
0.4855490271 |
-1.042311 |
0.220344182 |
22.650611 |
0.00000194298437974247440753177568195653179827786516398191452026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006661660730545626177094824943436535136243037413805723190307617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.8212670 |
5.3555716 |
76.3506397 |
7.3475834 |
| ENSG00000122707 |
8434 |
RECK |
protein_coding |
O95980 |
FUNCTION: Functions together with ADGRA2 to enable brain endothelial cells to selectively respond to Wnt7 signals (WNT7A or WNT7B) (PubMed:28289266, PubMed:30026314). Plays a key role in Wnt7-specific responses: required for central nervous system (CNS) angiogenesis and blood-brain barrier regulation (By similarity). Acts as a Wnt7-specific coactivator of canonical Wnt signaling by decoding Wnt ligands: acts by interacting specifically with the disordered linker region of Wnt7, thereby conferring ligand selectivity for Wnt7 (PubMed:30026314). ADGRA2 is then required to deliver RECK-bound Wnt7 to frizzled by assembling a higher-order RECK-ADGRA2-Fzd-LRP5-LRP6 complex (PubMed:30026314). Also acts as a serine protease inhibitor: negatively regulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) by suppressing MMP9 secretion and by direct inhibition of its enzymatic activity (PubMed:9789069, PubMed:18194466). Also inhibits metalloproteinase activity of MMP2 and MMP14 (MT1-MMP) (PubMed:9789069). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0J1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18194466, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28289266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30026314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9789069}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal;Tumor suppressor;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cysteine-rich, extracellular protein with protease inhibitor-like domains whose expression is suppressed strongly in many tumors and cells transformed by various kinds of oncogenes. In normal cells, this membrane-anchored glycoprotein may serve as a negative regulator for matrix metalloproteinase-9, a key enzyme involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. |
hsa:8434; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; coreceptor activity involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:1904928]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; metalloendopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0008191]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; blood vessel maturation [GO:0001955]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:1904684]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of establishment of blood-brain barrier [GO:0090210]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040] |
12438739_Four SNPs were identified in the coding region of the gene (exons 1, 9, 13 and 15), and the remaining nine in introns 5, 8, 10, 12, 15 and 17. 12738734_High RECK protein is associated with invasiveness of pancreatic cancer by MMP-2 activation 12810630_Histone deacetylase inhibition increases RECK expression which inhibits MMP activation and cancer cell invasion. Trichostatin A up-regulated RECK via transcriptional activation in CL-1 human lung cancer cells. This attenuated MMP-2 activity. 15328199_RECK suppresses tumor angiogenesis/ 16103099_Findings indicate that glycosylation mediates RECK suppression of tumor cell invasion by multiple mechanisms such as suppressing MMP-9 secretion and inhibiting MMP-2 activation. 16377629_HER-2/neu induces the binding of Sp proteins and HDAC1 to the RECK promoter to inhibit RECK expression and to promote cell invasion 16463672_RECK gene could inhibit the expression of MMP-9 in hilar cholangiocarcinomas. 16791855_RECK downregulation is critical for the invasiveness process in glioma 16951151_RAS oncogene induces RECK gene silencing through DNMT3b-mediated promoter methylation which may be useful in treatment of cancer metastasis 17033924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17033924_The TC heterozygotes of the RECK-420 T/C SNP showed a better survival compared to the TT homozygotes (P=0.02 in all cases and P=0.03 in lymph node negative cases) 17233834_downregulation of the metastasis suppressor RECK is caused by promoter methylation in non-small cell lung cancer 17262820_RECK plays an important role in the invasiveness of osteosarcoma 17328864_Tgat oncoprotein is the functional inhibitor of RECK 17329256_RECK protein interacts with MT1-MMP and CD13/aminopeptidase N and modulates their endocytic pathways 17443689_epigenetic down-regulation of the metastasis suppressor RECK in colon cancer is associated with promoter methylation 17583418_The expression of RECK at RNA and protein levels appears to decrease in prostate cancer specimens. 17628776_Decreased RECK expression in tumor compared with non-malignant prostate tissue. 17714826_suppression of RECK expression is involved in the progression of adenocarcinoma of the lung 18194466_The K23 motifs of RECK protein can inhibit MMP-9 secretion and activity and attenuate metastasis of lung cancer cells. 18319621_Data suggest that radiation post-transciptionally enhances RECK protein levels in Panc-1 cells, at least in part, via TGF-beta signaling, and that irradiation increases Panc-1 invasiveness via a mechanism that may not be linked to MMP-2 activity. 18425389_in colorectal neoplasms, MMP-2 expression correlates with the depth of invasion, venous invasion and liver metastasis; MMP-9 and RECK expression correlate with venous invasion 18652766_Data suggest that RECK protein is inversely correlated with tissue damage and MMP-9 secretion in systemic lupus erythematosus. 19022775_RECK is cleaved by MMP-2 and MMP-7 and competitively inhibits MMP-7-catalyzed cleavage of fibronectin 19197139_Motility, adhesion, homing, and mobilization of human hematopoietic progenitor cells are regulated in a cell-autonomous manner by dynamic and opposite changes in MT1-MMP and RECK expression. 19208844_RECK is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored glycoprotein that inhibits the enzymatic activities of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), thereby suppressing fibrosarcoma metastasis. 19827606_It regulates Notch signaling and its polarity mediated by ectodomain shedding of ADM10-activity-dependent DSL ligand. (review) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19995435_Low or no RECK expression and increased MMP-2 expression may be associated with negative clinical findings in ameloblastoma 20032402_There are differences in expression between histological types of NSCLC (SCC, adenocarcinoma). There is a higher expression of RECK in stage IA in comparison with stages IB-IIIA. 20127710_This work has associated RECK tumor-suppressing activity with the inhibition of motility and invasion in this glioblastoma multiforme model. 20143471_Aberrant methylation of RECK gene may provide useful information for the early diagnosis and treatment of peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. 20154725_Hypoxia and RAS-signaling pathways converge on, and cooperatively downregulate, the RECK tumor-suppressor protein through microRNAs. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20395433_Data show that RECK is up-regulated in human osteoarthritic cartilage and suggest that RECK plays a role in chondrocyte cloning through suppression and promotion of chondrocyte migration and proliferation, respectively. 20407016_RECK has a role in the development of vascular endothelial cells under physiologic and pathologic (tumor angiogenesis) conditions, mainly by use of RNA interference techniques. 20480266_miR-21 expression has a key role in regulating cellular processes in osteosarcoma, likely through regulating RECK 20510080_The abnormal expression levels of RECK and MMP-2 may play an important role in carcinogenesis of esophageal squamous carcinoma. 20579139_RECK and MMP-14 proteins may serve as markers in the estimation of the extent of metastasis and dissemination of the neuroblastoma. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20878580_RECK expression is low in colorectal cancer, while MMP-9 and VEGF-C expressions are high. 20973064_multivariate analysis confirmed that reduced RECK expression was an independent and significant factor to predict a poor prognosis in osteosarcoma. 21076843_RECK functions as a metastasis suppressor in cholangiocarcinoma 21254649_The expressions of RECK and RAGE in nasopharyngeal carcinoma were down-regulated. 21432940_Knockdown of ADRM1 in amplified ovarian cell-line OAW42 results in downregulation of growth factor GIPC1 and upregulation of tumor-suppressor RECK RNA and protein. 21468925_the ERK1/2, JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways are involved in RECK downregulation under hypoxic conditions 21565829_results support that gene-environment interactions between the RECK polymorphisms, smoking and betel quid may alter oral cancer susceptibility and metastasis 21613799_Decreased RECK and increased EMMPRIN expression are associated with increasing stage and grade of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. 21949998_Aberrant expression of MTA1 and RECK gene may be involved in the invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 22025325_RECK is expressed in cell lines and tissue with a significant decrease in malignant tissue in prostate cancer. RECK overexpression causes an up to 80% decrease in invasion for DU-145 tumor cell line. 22098593_RECK intensity expression could show linear correlation with grades of glioma by the digital method, which was superior compared to the manual method 22139647_TIMP-1 and RECK, are expressed in a reproducible, specific pattern and if the profiles are related to prognosis and clinical outcome in prostate cancer. 22158033_These findings reveal a novel molecular pathway linking cell-cycle progression to RECK downregulation, extracellular matrix degradation and SKP2 upregulation. 22178867_RECK and MMP9 are involved in middle ear squamous cell carcinoma and may serve as markers to evaluate progression and metastasis. 22183444_RECK was identified in endothelial cells of glioma and tended to increase toward higher grades. 22292753_This review addresses the potential value of RECK as a prognostic marker and as a molecular target for cancer therapy. [review] 22321642_Data suggest that H. pylori may function as an initiator in the process of carcinogenesis by up-regulating miR-222, which further participates in the progression of cancer by promoting proliferation and inhibiting RECK. 22338226_The well-differentiated samples showed higher expression of RECK than poorly and moderately differentiated gastric carcinoma samples. 22397871_decreased RECK expression was an independent prognostic factor of poor survival in colorectal cancer patients. 22404079_RECK expression was reduced in breast carcinoma; low levels of RECK protein correlated with shorter survival in patients with breast carcinoma; low RECK expression was associated with lymph node metastasis; RECK expression is a significant prognostic factor correlated with long-term survival for patients with invasive breast cancer 22419890_The results suggested that the hypermethylation may lead to promoter silencing of RECK mRNA and associated with poor survival in HCC. 22428065_RECK gene polymorphisms might be a risk factor increasing HCC susceptibility and distant metastasis in Taiwan. 22438955_effect of HPV16 oncoproteins on the expression and activity of MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP, and their inhibitors TIMP-2 and RECK in cultures of keratinocytes 22630347_Knockdown of miR-21 inhibits tumor cell invasion by increasing RECK expression and decreasing tumor growth. 22761427_Keratinization-associated miR-7 and miR-21 regulate tumor suppressor reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) in oral cancer 22844865_The conversely abnormal expression levels of MTA1 and RECK may be collectively involved in progression of malignancies and may serve as molecular predictors for metastasis, recurrence, and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 23176145_Findings indicate thet the miR-15a-RECK-matrix metalloproteinase-9 axis in neuroblastoma (NB) progression, especially in NB migration and invasion. 23189844_The level of HER-2/neu mRNA was higher and RECK mRNA was lower in breast carcinoma than homologous paraneoplastic breast tissue. 23226455_miR-182-5p plays an important role as an oncogene by knocking down RECK and Smad4, resulting in activation of the Wnt-beta-catenin signaling pathway in bladder cancer. 23333633_inverse association between miR-182 and RECK was demonstrated in breast tumor tissues 23383207_MicroRNA-182-5p promotes cell invasion and proliferation by down regulating FOXF2, RECK and MTSS1 genes in human prostate cancer. 23504349_In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma miR-21 expression is increased. miR-21 down-regulation inhibits cell growth, invasion and induces cells to apoptosis by targeting FASL, TIMP3 and RECK genes. 23679328_Down-regulation of RECK expression is associated with metastasis and invasion of cervical carcinoma. 23749490_Data indicate that reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) methylation was associated with clinical stage, histological differentiation and lymph node metastasis, but was not associated with gender, age, and tumor location. 23820254_The STAT3-induced miR-92a promotes cancer invasion by suppressing RECK. 23881612_These results indicate that RECK represses stemness gene expression and stem-like properties by inhibiting ADAM-mediated Notch1 shedding and activation. 24078004_miR-25 might promote gastric cancer cell growth and motility partially by targeting RECK. 24131772_propose RECK down regulation in renal cell carcinoma to be an early event that facilitates tumor formation and progression 24162673_MiR-92b may promote nonsmall cell lung cancer cell growth and motility partially by inhibiting RECK. 24227542_There was weaker immunohistochemical expression of RECK protein in placental membranes of women with histologic chorioamnionitis compared to control subjects (P=0.0498). 24269686_Data show that miR-221 is an oncogenic miRNA which may regulate colorectal cancer (CRC) migration and invasion through targeting RECK. 24335752_Data indicate a consistent correlation between RECK, MT1MMP, and TIMP2 across different models of clinical samples and cell lines and suggest evidence of the potential use of this subset of genes as a gene signature for diagnosing melanoma. 24366472_miR-96 promotes cellular proliferation, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells, at least in part, by targeting RECK. 24469470_Our data suggest that miR-96 might promote the growth and motility of NSCLC cells partially by targeting RECK. 24510537_no association between the RECK polymorphism and chemotherapy response status in non-small-cell lung cancer in Chinese cohort 24532189_demonstrate that RECK contributes to GA's anti-invasive activity and provide new evidence for GA being served as a therapeutic candidate for cancer metastasis 24647918_the data show that miR-200c expression sensitizes H460 cells to resveratrol and this is likely due to RECK expression. 24691523_The loss of E-cadherin expression is uncoupled from RECK-upregulation in carcinoma-derived cell lines. 24931164_RECK controls this angiogenic rheostat through a novel complex with cell surface receptors to regulate STAT3 activation 25031745_these findings suggest that dysregulations of RECK and RAGE expressions may be collectively involved in tumor progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating MMP9 expression 25278269_the aim of this study was to analyze the effect of RECK gene rs 11788747 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) susceptibility. 25412941_Association between RECK single nucleotide polymorphism and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Han Chinese population 25465153_RECK was identified as a target of miR-96 and RECK overexpression abrogates the growth of esophageal cancer cells. 25516656_Suggest that upregulation of miR-374b-5p contributes to gastric cancer cell metastasis and invasion through inhibition of RECK expression. 25537516_Data show that heat shock transcription factor 1/miR-135b/reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs and ecotropic viral integration site 5 axis provides novel insight into the mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. 25575057_MiR-25 promotes cell proliferation by targeting RECK in human cervical carcinoma. 25826661_microRNA-200b and microRNA-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting RECK. 25845681_Notably, miR-21 regulated the potential anticancer effects of icariin on cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in the ovarian cancer A2780 cells 25877754_D90 significantly inhibited the invasion and metastasis of OSCC cells by decreasing the expression of sp1 and increasing the expression of RECK to suppress the expression and activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9. 25885317_RECK promoter activity is suppressed when RbAp46 binds to it and is involved in experimental lung metastasis. 25987077_Loss of RECK expression is associated with metastasis in Hepatoblastoma and Neuroblastoma. 26004948_Expression of RECK is associated with the incidence of restenosis after vascular angioplasty. RECK may be induced as a part of the intrinsic defense mechanism against restenosis. 26026078_These findings suggest that immunohistochemical staining for RECK could be useful in the differential diagnosis between CMM and BMN. 26026961_A decrease in SPRY2 and RECK expression by nickel-induced miR-21 may promote invasiveness in lung cancer cells. 26130413_This downregulation of RECK in advanced grades of osteosarcoma and metastatic grades was also associated with the increased expression of invadosome-specific markers like MMP9 26141647_present data indicate that there is a significant association between mutant G of rs11788747 in RECK and WT risk 26261088_MMP-9/RECK imbalance in cervical smears is significantly associated with high-grade cervical diseases and infection by alpha-9 HPV and C. trachomatis. 26284486_miR-21 has a role in upregulating PTEN, RECK and PDCD4 in glioma 26364844_miR-221/miR-222-RECK axis might be an important path modulating H. pylori infection-related gastric cancer development 26431549_Findings suggest that RECK transcript variants might have opposite roles in GBM biology and the ratio of their expression levels may be informative for the prognostic outcome of GBM patients. 26449734_RECK is not an independent prognostic marker for breast cancer 26459448_RECK is a regulator of hMSC functions suggesting that modulation of RECK may improve the development of hMSC-based therapeutical approaches in regenerative medicine. 26921475_the RECK gene polymorphism influences molecular carcinogenesis and clinic pathological features of hepatocellular carcinoma within the Egyptian population 26993249_Reversion-inducing, cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) was identified as the direct and functional target of miR-92b in osteosarcoma 27058625_RECK CpG methylation pattern may predict prognosis and drug-sensitivity of breast cancers. 27268601_RECK Gene Promoter rs10814325 Polymorphism is associated with metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma 27272560_RECK could regulate the expressions of MMP-2, 9 and MT1-MMP as a cell surface-signaling molecule. Authors propose that RECK may play an important role in regulating MMPs in the ECM degradation of periodontal diseases. 27530410_RECK expression in uterine leiomyoma is negatively regulated by miR-15b. 27696293_Low expression of RECK is associated with oral cancer. 28043014_The expression of RECK in human healthy and diseased gingiva may contribute to periodontal physiological and pathological processes; low RECK expression may be associated with the enhanced MMP-2 and MMP-9 production in inflamed gingiva. 28340422_RECK gene polymorphisms were closely associated with active proliferation, capsular invasion, and clinical recurrence of ameloblastoma. 28561419_Results suggested that some paracrine substances produced by 786-0 cells may reduce RECK expression of adjacent HMEC-1 cells and enhance their proliferation and in vitro angiogenic capacity. 28740544_Collectively, these results demonstrated that IL-32alpha upregulates the atheroprotective genes Timp3 and Reck by downregulating microRNA-205 through regulation of the Rprd2-Dgcr8/Ddx5-Dicer1 biogenesis pathway. 29064588_Results report that the expression of RECK is significantly lower in cervical cancer cells than in normal cells. The relative protein expression levels of p53 signaling (p21 and Bax) were significantly elevated when RECK was upregulated, suggesting that the overexpression of RECK could promote the activation of p53 signaling pathway. 29108633_overexpressed in trophoblasts from preeclampsia 29363862_miR-15b promotes the progression of prostate cancers by targeting RECK. 29599320_The expression of RECK was inhibited by the transfection of miR-96 mimics. RECK mRNA level was reduced by miR-96 mimics and increased by miR-96 inhibitor. In the invasion assay, miR-96 mimics were shown to promote tumor invasion. 29874120_a shorter isoform of RECK is more highly expressed in proliferating fibroblasts, in TGF-beta-treated fibroblasts, and in tumors compared with differentiated tissue. 30704758_MMP9 released from long RECK by competition with short RECK digests ECM proteins and reduces integrin-ECM interaction 30733959_GAS5 positively regulates expression of RECK, also a target of miR-135b, which further inhibits MMP-2 expression and contributes to invasion repression. 30841433_Curcumin could inhibit RECK methylation. 31074012_increased MMP-13 and decreased RECK contribute to IL-17A-induced TRAF3IP2-dependent smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. 31210300_MicroRNA-375 accelerates the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer through targeting RECK. 31270250_Down-regulated microRNA-30b-3p inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration of glioma cells via inactivation of the AKT signaling pathway by up-regulating RECK. 31558368_RECK and TIMP-3 expression levels may be up-regulated by inhibiting the expression of miR-21, resulting in a decrease in ability of metastasis and invasion. 31764436_The alternatively spliced RECK transcript variant 3 is a predictor of poor survival for melanoma patients being upregulated in aggressive cell lines and modulating MMP gene expression in vitro. 31866421_Elevation of long non-coding RNA GAS5 and knockdown of microRNA-21 up-regulate RECK expression to enhance esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell radio-sensitivity after radiotherapy. 31933392_Activation of STAT-3 signalling by RECK downregulation via ROS is involved in the 27-hydroxycholesterol-induced invasion in breast cancer cells. 32081769_The role of miR-21/RECK in the inhibition of osteosarcoma by curcumin. 32138716_LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and may be a sponge of miR-25. 32206004_Exosomal miR-182 regulates the effect of RECK on gallbladder cancer. 32255303_MicroRNA-182 Suppresses Malignant Melanoma Proliferation by Targeting RECK. 32286475_Analysis of the inhibiting activity of reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK) on matrix metalloproteinases. 32522890_LINC01419 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis through targeting EZH2-regulated RECK. 32525042_miR-544a Stimulates endometrial carcinoma growth via targeted inhibition of reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs. 32661216_RECK and TIMP-2 mediate inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by Annona muricata. 32730638_Reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs and MT1-MMP promote the formation of robust fibrillin fibers. 33447989_MiR-590-5p regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting RECK. 33731436_GDE2-RECK controls ADAM10 alpha-secretase-mediated cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. 33781845_Reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with Kazal motifs and cardiovascular diseases: The RECKlessness of adverse remodeling. 34205376_Two RECK Splice Variants (Long and Short) Are Differentially Expressed in Patients with Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery Disease: A Pilot Study. 34392581_Methylation degree of metalloproteinase inhibitor RECK gene: Links to RECK protein level and hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic HCV infection patients. 35444107_RECK Variants are Associated with Clinicopathological Features and Decreased Susceptibility in Mexican Patients with Colorectal Cancer. 35892136_Mycoplasma pneumoniae downregulates RECK to promote matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion by bronchial epithelial cells. 35941073_RECK gene polymorphisms in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-control study. |
ENSMUSG00000028476 |
Reck |
551.679431 |
0.2722516633 |
-1.876987 |
0.110316590 |
283.270993 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000145480413695529977770153667740336766847643423215750753463038147307109568532448900077836833873438358306950742587121440606672443753440720236820006921242270784330047339594216282421257346868515014648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000039327672273736675060174041420762278272668731552268347923200411726479744507813421238705853076760577881052539242070668617612148018967020339380879511287098914545934391640003013890236616134643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
244.8209852 |
18.6053268 |
905.9796423 |
47.0161635 |
| ENSG00000122861 |
5328 |
PLAU |
protein_coding |
P00749 |
FUNCTION: Specifically cleaves the zymogen plasminogen to form the active enzyme plasmin. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood coagulation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Fibrinolysis;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Hydrolase;Kringle;Pharmaceutical;Phosphoprotein;Plasminogen activation;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a secreted serine protease that converts plasminogen to plasmin. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate A and B polypeptide chains. These chains associate via a single disulfide bond to form the catalytically inactive high molecular weight urokinase-type plasminogen activator (HMW-uPA). HMW-uPA can be further processed into the catalytically active low molecular weight urokinase-type plasminogen activator (LMW-uPA). This low molecular weight form does not bind to the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Quebec platelet disorder and late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:5328; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein complex involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098637]; serine protease inhibitor complex [GO:0097180]; serine-type endopeptidase complex [GO:1905370]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; fibrinolysis [GO:0042730]; negative regulation of fibrinolysis [GO:0051918]; negative regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010757]; plasminogen activation [GO:0031639]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033628]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of fibrinolysis [GO:0051917]; regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010755]; regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:0010469]; regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014910]; regulation of smooth muscle cell-matrix adhesion [GO:2000097]; regulation of wound healing [GO:0061041]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014909]; urokinase plasminogen activator signaling pathway [GO:0038195] |
11751384_Pleiotrophic inhibition of pericellular urokinase-type plasminogen activator system by endogenous tumor suppressive maspin. 11805108_Cooperativity between the Ras-ERK and Rho-Rho kinase pathways in urokinase-type plasminogen activator-stimulated cell migration 11827968_Exposure of cryptic domains in the alpha 1-chain of laminin-1 by elastase stimulates macrophages urokinase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. 11858184_TPA & urokinase progressed to maximum levels in late pregnancy, but decreased in labor, favoring a coagulation state despite elevated D-dimer levels suggesting enhanced fibrinolysis. 11876553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11880102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11906036_significant decresase in PBM uPA activity in HIV infected and immunosuppresed patients independent from the presence of P. carinii lung infections 11928806_Substitution of the two relevant serines with glutamic acid residues impairs the ability of urokinase to mobilize a variety of human and mouse cell lines as well as human primary T lymphocytes. 11928807_bFGF up-regulated UPA in both normal and dystrophic myoblasts and weakly upregulated UPA receptor in normal satellite cells. 11928809_Random peptide bacteriophage display used as a probe to identify urokinase receptor binding sites other than the binding site of UPA residues 1-48. 11928812_In a study of the differential role of UPA and TPA as inducers of fibronectin mRNA, UPA led to an increase of FN mRNA expression in early G1, did not lead to FN assembly in the ECM, induced monomric FN 11928816_Coculture of monocytes and vascular smooth muscle results in 5-fold increase in UPA expression in monocytes, resulting in VSMC migration. 11928818_Osteopontin modulates prostate carcinoma invasive capacity through RGD-dependent upregulation of UPA. 11930938_Protease activity, growth factor-like and kringle domains of uPA differentially contribute to activation of p42/p44erk1,2 and p38 MAP-kinases. 11956327_Endogenous UPA is not only overexpressed in smooth muscle cells upon stimulation with PDGF/bFGF, but also mediates the mitogenic activity of the growth factors in a catalytic-domain-dependent manner. 12008951_possible role of fibroblast growth factors in expression of genes of the plasminogen activator system in breast fibroblasts 12023847_Structural analysis of the interaction between urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor: a potential target for anti-invasive cancer therapy. Review. 12041678_Diagnostic significance of measurement of the receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator on granulocytes and in plasma from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. 12084931_interaction with urokinase receptor mediates inhibitory signal for HIV-1 replication 12115506_expression of uPA and uPAR is associated with the clinical behaviour of bladder neoplasms 12149463_Increased expression of urokinase during atherosclerotic lesion development causes arterial constriction and lumen loss, and accelerates lesion growth. 12152683_Characterization of the binding of human urokinase-type plasminogen activator to the asialoglycoprotein receptor of rat liver 12161038_Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor could be associated with BBB disruption and with promotion of CNS invasion by chemotactically active cells, macromolecules, and microbes. 12167592_upregulation of PAI-1, uPA, and tPA after long-term LDL exposure seems to be mediated by a delayed PKC activation associated with an increased PA inhibitory activity 12174885_the circluating level and its soluble receptor (suPAR) are not up-regulated by the circulating P105 fraction of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene: in vivo evidence from patients with advanced NSCLC 12183060_the role of urokinase in the regulation of monocyte/macrophage functions, such as that occurring in inflammatory reactions 12218297_There was a positive correlation between uPA and PAI-1 antigen levels and clinicopathological parameters such as grade (p /=7) & more than 90% lymph node metastases but not in normal prostate, benign prostate hyperplasia or prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia 16967469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16967469_distribution of four tagSNPs (rs2227562 in intron 5, rs2227564 in exon 6, rs2227571 in intron 9, and rs4065 in 3'UTR) in the PLAU gene in a large case-control study of Alzheimer's disease 17013094_autotaxin induces uPA expression via the Gi-PI3K-Akt-NF-kappaB signaling pathway that might be critical for autotaxin-induced tumor cell invasion and metastasis 17029796_uPA gene regulation by c-phycocyanin (c-pc) is transcriptionally controlled through cAMP mediated PKA pathway. 17080225_plasmin-mediated apoptosis of VSMC occurs via plasminogen activation by either t-PA or u-PA and is impaired by PAI-1. 17083312_The blood concentrations of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPAR) and mannan-binding lectin (MBL) are related to the risk of postoperative infectious complications. 17159381_Our results showed that the subcutaneous injection of small interfering RNAs (siRNA) u-PA SKHep1C3 stable transfected cells (pS siRNA u-PA) led to a growth delay in xenograft development. 17174555_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17174555_role for PLAU_1 as an independent genetic risk factor for Alzheimer disease in the Italian population for those subjects who do not have the APOE-epsilon4 allele 17187779_This study suggests that ILK serves as a key mediator in TGFbeta1 regulation of uPA/PAI-1 system critical for the invasiveness of human ovarian cancer cells. And ILK is a potential target for cancer therapy. 17192053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17192053_Urokinase gene 3'-UTR polymorphism associated with prostate cancer. 17203175_LRP is expressed in colorectal cancer and forms complexes with u-PA and its inhibitor 17203182_alpha2-antiplasmin induction inhibits E-cadherin processing mediated by the plasminogen activator/plasmin system, leading to suppression of progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via upregulation of cell-cell adhesion 17222367_The expression of p-p38 and uPA was negatively correlated to prognosis of breast cancer. 17233842_recombinant kringle domain inhibits the malignant glioma growth by suppression of angiogenesis 17240317_uPA may play a critical role in ligation-induced vessel remodeling 17258797_PAI-3, but not PAI-1 or uPA, may have a role in breast cancer survival by suppression of tumor invasion through protease inhibition in stroma 17264329_Elevation of plasma uPA and uPAR levels in CaP patients are partly caused by local release from the prostate. Plasma levels of uPA and uPAR are associated with biologically aggressive CaP, disease progression after radical prostatectomy, and metastasis 17299802_The production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), tissue inhibitors of MMPs, and plasminogen activators by gingival fibroblasts stimulated with lipopolysaccharides produced by periodontopathogens, are reported. 17299841_Upregulation of urokinase type plasminogen activator (UroPA) expression during early development of knee osteoarthritis (OA) occurs via MAPK ERK, JNK, and p38 signaling pathways and the PI3K signaling pathway in cultured cells debrided from OA knees. 17327908_uPA and uPAR are involved in generation of drug-resistant small-cell lung cancer cell phenotype. 17331567_The association between tissue factor and uPA/suPAR system is significantly related to the presence of cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients 17344041_PLAUR and the somatomedin B region of VTN direct the localization of UPA to focal adhesions in microvessel endothelial cells. 17355798_Both uPA and PAI-1 are up-regulated in epithelial ovarian cancer. 17363771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17363771_The PLAU gene codes for this enzyme, and is located on 10q24. This region has demonstrated evidence for linkage in a genome scan for asthma in a sample from northeastern Quebec. 17458906_In thyroid cells, plasminogen activators are regulated via MAPK and protein kinase c-beta pathways. 17523079_Altered expression of PLAU was observed in high-risk soft tssue sarcomas. 17532189_pemphigus vulagris-IgG-dependent uPA activation is not related to anti-Dsg3 antibody activity 17545513_stromal fibroblasts play a role in promoting pancreatic cancer metastasis via activation of the uPA-plasminogen-MMP-2 cascade 17548050_suggest a novel function for tyrosine kinase 2 as an important modulator of the urokinase-directed vascular smooth muscle cell functional behaviour at the place of injury 17549401_Simultaneous down-regulation of uPAR and uPA induced caspase-8 mediated apoptosis. 17559626_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17559626_The urokinase plasminogen activator (BamHI) and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (HindIII) genotypes may serve as useful markers for heritability of bone loss associated with periodontal disease. 17581316_STI571 influence through inducing urokinase-type plasminogen activator and interleukin-8, in which the induction of early growth response-1 expression and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation might be involved. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17611702_the p38(MAPK) signaling pathway is required for optimal LPA-dependent uPA secretion from ovarian cancer cells 17634019_There was a significant positive linear association between ERK1/2 activity and uPA protein expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 17649957_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17654528_we demonstrated that tyrosine phosphorylation of EGFR and the autocrine expression of uPA and HB-EGF depend on the activity of c-jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) in human prostatic DU-145 cells. 17661167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17681345_Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) stimulates cholesterol biosynthesis in macrophages through activation of SREBP-1 in a PI3-kinase and MEK-dependent manner 17709546_uPA plays a major role in inducing MMP-1 production in activated human monocytes, which is mediated by a plasmin-dependent mechanism involving signaling through the annexin A2 heterotetramer. 17877801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17880283_review of uPA - uPAR interactions with membrane proteins to modify signal transduction pathways and their role in oral squamous cell carcinoma 17921261_data of study population indicate a higher ETS2 RNA concentration compared with uPA in the case of bladder cancer, resulting in an increased ETS2:uPA RNA ratio in urine 17934860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17949787_Elevated expression of MMP-1 and urokinase plasminogen activator can be used to identify patients with a worse prognosis in skull base chordoma. 17974965_In xenograft glioblastoma mouse model and in vitro invasion assay, LRP-deficient cells, which secreted high levels of uPA, invaded the surrounding normal brain tissue, whereas the LRP-overexpressing and uPA-deficient cells did not invade normal brain. 17986506_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17994220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17994220_The urokinse haplotype CGCCCC is a genetic risk fctor for higher mortality and more severe clinical outcome with infection-associated acute lung injury. 18048089_The carotid atherosclerosis is independently related to uPA/its soluble receptor system in dialysis patients 18053985_Myeloma-osteoclast interactions stimulated the production of TRAP, cathepsin K, MMP-1, -9, and uPA 18076013_The multimarker phenotype of the absence of CD8+ TILs, loss of p27, and positive uPA expression was predictive of an adverse prognosis in patients with lymph node-negative, MMR-proficient colorectal cancer. 18177545_protein kinase C synergistically enhances the secretion of uPA in TNF-alpha-stimulated human dental pulp cells 18193533_In human renal tissues, protein C inhibitor and urinary plasminogen activator colocalized in the cytoplasm of renal proximal tubular epithelial cells 18196271_Data show that fibroblastic inflammatory reaction around the biopsy channel affects stromal uPA and PAI-1 expression, which possibly leads to falsely increased enzyme levels in ELISA. 18202522_IL-1beta stimulates uPA production via activation of NFkappaB and tyrosine phosphorylation, and also secretion of the enzyme, and that the uPA/plasmin system appears to be involved in inflammation in human dental pulp. 18208536_Each additional copy of the minor allele PLAU-3995 (Pro41Leu,(rs2227564) was associated with higher log(D-dimer) levels. 18237545_Together, the data indicate that SAA enhances plasminogen activation and suggest its possible role in plasmin(ogen)-mediated colon cancer progression. 18239069_Inactivation of FOXO3a after GR activation is an important mechanism contributing to GC-mediated repression of uPA gene expression in breast epithelial and cancer cells. 18240004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18240004_Urokinase 3'-UTR T/C gene polymorphism seems to appear more commonly in children with recurrenct calcium oxalate stone disease than in healthy children and in those with stones for the first time. 18257282_The plasma uPAR and uPA levels in nosebleed patients before treatment is higher than that in normal group. 18321763_TSP-1 promotes human follicular thyroid carcinoma cell invasion mainly through up-regulation of the urokinase-dependent activity 18331597_SAK reduces tPA/uPA-mediated Plg activation by means of SAK.Plg complex formation, consequently downregulating tPA/uPA-induced fibrinolysis. 18337556_upon cell binding and internalization, single-chain uPA (scuPA) translocates to the nucleus within minutes. Nuclear translocation does not involve proteolytic activation or degradation of scuPA. 18355442_uPA-mediated direct activation of MMP-9 may promote glioblastoma cell invasion. 18362146_A composite role of vitronectin and urokinase in the modulation of cell morphology upon expression of the urokinase receptor. 18376307_UPA expression was significantly up-regulated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 18376415_reports the crystal structures of uPAR in complex with both urokinase (uPA) and vitronectin and reveal that uPA occupies the central cavity of the receptor, whereas vitronectin binds at the outer side of the receptor 18390474_observations confirm a new role for p53 as a uPA mRNA binding protein that down-regulates uPA mRNA stability and decreases cellular uPA expression 18436804_Urokinase plasminogen activator upregulates paraoxonase 2 expression in macrophages via an NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanism. 18439850_the uPA system may be involved in the progression of prostate cancer 18466392_The expressions of both uPA mRNAs in the gastric cancer cells increased obviously (12-fold and 3-fold, respectively) with H. pylori stimulation. 18478929_NF-kappaB-mediated up-regulation of uPA expression is responsible for EGF-induced invasiveness in pancreatic cancer cells. 18491991_The pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is complex & the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA)/plasminogen system participates in the repair |
ENSMUSG00000021822 |
Plau |
639.929639 |
2.5554852561 |
1.353597 |
0.079780572 |
287.494833 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000017475012327216229989166541180962397908649652548092801333887988095818005760868727944643963380867766830248466302734687454987811033083307476227458964212637533531483763349356763683317694813013076782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004839234182921417929901894449137779138021935977759333088624767194537453315150104308716896253755002019959773759732000719867775038432789975010360943911304882313062503129685865133069455623626708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
922.7444373 |
48.7570031 |
363.8108748 |
14.7889527 |
| ENSG00000122873 |
55847 |
CISD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZ45 |
FUNCTION: Plays a key role in regulating maximal capacity for electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation (By similarity). May be involved in Fe-S cluster shuttling and/or in redox reactions. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17584744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17766440}. |
2Fe-2S;3D-structure;Acetylation;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein with a CDGSH iron-sulfur domain and has been shown to bind a redox-active [2Fe-2S] cluster. The encoded protein has been localized to the outer membrane of mitochondria and is thought to play a role in regulation of oxidation. Genes encoding similar proteins are located on chromosomes 4 and 17, and a pseudogene of this gene is located on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:55847; |
mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051537]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of cellular respiration [GO:0043457] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17376863_mito- NEET is an important iron-containing protein involved in the control of maximal mitochondrial respiratory rates 17584744_Spectroscopic studies show that the 2Fe-2S cluster is coordinated by Cys-3 and His-1. The His ligand is shown to be involved in the observed pH lability of the cluster, indicating that loss of this ligand via protonation triggered release of the cluster. 17766439_Crystal structure of mitoNEET reveals distinct groups of iron sulfur proteins. 17766440_biophysical properties of mitoNEET suggest that it may participate in a redox-sensitive signaling and/or in Fe-S cluster transfer 17905743_X-ray crystallographic studies show that mitoNEET dimer may interact with other proteins via the surface residues in close proximity to the [2Fe-2S] cluster 18047834_A CISD1-GFP chimera was found to be located into mitochondria. 19388667_The physiologically relevant acid ionization constant (pKa) of histidine residues makes histidine87 a likely candidate for modulating the lability of the metal cluster in mitoNEET. 19574633_There is considerable flexibility in the position of the cytoplasmic tethering arms, resulting in two different conformations in the crystal structure of mitoNEET. 20099820_We use electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate the [2Fe-2S]cluster in mitoNEET. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20932062_Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) can bind to homodimeric mitoNEET, influencing the stability of the [2Fe-2S] cluster that is bound within a loop region (Y71-H87) in each subunit. 21402934_Results describe the folding landscape of mitoNEET, and uncover communication between distal regions of the protein. 21531159_Results describe the discovery of potential mitoNEET ligand binding sites and novel ligands, and suggests the possibility for detailed structural studies of mitoNEET-ligand complexes. 21591687_The iron-sulfur cluster-containing protein mitoNEET interacts with two potentially redox active substances at the surface of mitochondria; mitoNEET forms complexes with resveratrol-3-sulfate, a primary metabolite of the natural product resveratrol. 21636891_crystal structure of H87C mitoNEET was determined to 1.7 A resolution (R factor = 18%) to investigate the structural basis of the changes in the properties of the 2Fe-2S cluster 21788481_These findings suggest a likely role for mNT in [2Fe-2S] and/or iron transfer to acceptor proteins. 22351774_NADPH can regulate both mitoNEET [2Fe-2S] cluster levels in the cell as well as the ability of the protein to transfer [2Fe-2S] clusters to cytosolic or mitochondrial acceptors. 23271805_a loop (L2) 20 A away from the metal center exerts allosteric control over the cluster binding domain and regulates multiple properties of the metal center. Mutagenesis of L2 results in significant shifts in the redox potential of the [2Fe-2S] cluster. 23959881_Data show that the protein levels of NAF-1 (CISD2) and mNT (CISD1) are elevated in human epithelial breast cancer cells. 24295216_The MitoNEET forms a covalent complex with GDH1 through disulfide bond formation and acts as an activator. 24403080_pioglitazone may modulate the function of mitoNEET by blocking the thiol-mediated reduction of [2Fe-2S] clusters in the protein. 24814435_In this review, we evaluate the current understanding regarding how mitoNEET regulates cellular bioenergetics as well as the structural requirements for drug compound association with mitoNEET 25012650_MitoNEET governs a novel trafficking pathway to rebuild an Fe-S cluster into cytosolic aconitase/IRP1. 25168891_SNPs in three genes CYP26B1 rs2241057, CISD1 rs2251039, rs2590370, and TBX1 rs4819522 were involved in six potential pathways to influence serum prostate-specific antigen levels. 25448035_Studies indicate that NEET proteins are associated with diseases including cancer and diabetes. 25645953_Glutathione reductase reduces mitochondrial protein mitoNEET [2Fe-2S] clusters. 26692580_A possible role of CISD1 in obesity-associated dysfunctional adipogenesis in human visceral adipose tissue. 26778000_Our results confirm the observation that mitoNEET is important in transferring the iron sulfur clusters to the cytosolic aconitase in living cells and the His-87 ligand in mitoNEET plays important role in this process. 26887944_the redox-sensing function of mNT is a key component of the cellular adaptive response to help stress-sensitive Fe-S proteins recover from oxidative injury. 27510639_CISD1 inhibits ferroptosis by protecting the cells against mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. 27923678_The results suggest that flavin nucleotides may act as electron shuttles to reduce the mitoNEET [2Fe-2S] clusters and regulate mitochondrial functions in human cells. 28461337_Data suggest that, compared with oxygen, ubiquinone-2 is more efficient in oxidizing mitoNEET [2Fe-2S] clusters, suggesting that ubiquinone could be an intrinsic electron acceptor of reduced mitoNEET [2Fe-2S] clusters in mitochondrial outer membrane. 28648056_The [2Fe-2S] clusters of mitoNEET are reduced via the formation of a transient complex that brings the [2Fe-2S] clusters of mitoNEET close to the redox-active [2Fe-2S] cluster of anamorsin. 31527235_mitoNEET regulates VDAC in a redox-dependent manner in cells, closing the pore and likely disrupting VDAC's flow of metabolites 32200954_Defects in CISD-1, a mitochondrial iron-sulfur protein, lower glucose level and ATP production in Caenorhabditis elegans. 32445867_Exploring the FMN binding site in the mitochondrial outer membrane protein mitoNEET. |
ENSMUSG00000037710 |
Cisd1 |
36.080798 |
2.0386084293 |
1.027585 |
0.261614563 |
15.608273 |
0.00007791296715613993319627522682324638481077272444963455200195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000217884690266128357204536425406615762767614796757698059082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.5954398 |
7.8581640 |
24.4547088 |
3.0631977 |
| ENSG00000122884 |
5033 |
P4HA1 |
protein_coding |
P13674 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in -Xaa-Pro-Gly- sequences in collagens and other proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9211872}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Dioxygenase;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Signal;TPR repeat;Vitamin C |
|
This gene encodes a component of prolyl 4-hydroxylase, a key enzyme in collagen synthesis composed of two identical alpha subunits and two beta subunits. The encoded protein is one of several different types of alpha subunits and provides the major part of the catalytic site of the active enzyme. In collagen and related proteins, prolyl 4-hydroxylase catalyzes the formation of 4-hydroxyproline that is essential to the proper three-dimensional folding of newly synthesized procollagen chains. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5033; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; procollagen-proline 4-dioxygenase complex [GO:0016222]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; L-ascorbic acid binding [GO:0031418]; procollagen-proline 4-dioxygenase activity [GO:0004656]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; peptidyl-proline hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-L-proline [GO:0018401] |
15369792_These in vivo data demonstrated that smokers had thinner atherosclerotic cap thickness and lower levels of P4Halpha and collagen. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16464861_Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase-alpha (I)mRNA is stabilized by interation of RNA-binding proteins hnRNP-A2/B1 with a U(16) element within the 3'-UTR 16488890_positive (transforming growth factor beta1) and negative (cigarette smoking extract) regulators appear to influence the USF-E-box interaction and affect P4Halpha(I) expression 16837461_Results suggest that the alteration of translational efficiency by nucleolin, which occurs through a hypoxia inducible factor independent pathway, is an important step in collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase-alpha(I) regulation under hypoxia. 16877351_In comparison with healthy cartilage, Osteoarthritis articular chondrocytes exhibit increased in vivo synthesis of collagen prolyl-4-hydroxylase type II, a pivotal enzyme in collagen triple helix formation. 16885164_HIF-P4H, HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha are effective oxygen sensors 19890397_analysis of the 2-His-1-Asp active-site motif in prolyl 4-hydroxylase 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23022409_IL-6 significantly downregulated P4Halpha1 expression in aortic smooth muscle cells 23178710_Overexpression of miR-122 markedly attenuated the expression of P4HA1 via targeting a binding site located at 3'-UTR of P4HA1 mRNA 23423382_Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) promotes extracellular matrix remodeling under hypoxic conditions by inducing P4HA1, P4HA2, and PLOD2 expression in fibroblasts. 25115393_Studies indicate P4HA1 copy number gain in a subset of metastatic prostate tumors and its expression is also regulated by microRNA-124. 26966067_Thus, we conclude that miR-30e suppresses proliferation of hepatoma cells through targeting P4HA1 mRNA. 28001367_Findings suggest that the catalytic domain of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases (CP4Hs) recognizes the cis conformation of the prolyl peptide bond. 28415787_Our study indicates that P4HA1 plays a pivotal role in the process of GSC-EC transdifferentiation and the structural formation of vascular BMs. 28419360_we report compound heterozygous frameshift and splice site mutations in P4HA1 that impair but not abolish C-P4H alpha(I) activity. The maternal P4HA1 exon 12 splice donor site mutation causes an internally deleted C-P4H alpha(I) predicted to completely lack catalytic activity. two nucleic acid insertion in exon 9 results in a premature stop in the exon 9 P4HA1 splice form. 28964577_High expression of P4HA1 was correlated with the malignancy of gliomas and could serve as a prognostic indicator for patients with high-grade gliomas 30136751_miR-122 inhibited migration, invasion, epithelial mesenchymal transition, and metastasis in peritoneal cavity of ovarian cancer cells by targeting P4HA1. 30367042_Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase alpha 1 subunit (P4HA1) protein expression is induced in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and HER2 positive breast cancer. Inhibition of P4HA1 sensitizes TNBC to the chemotherapeutic agent docetaxel and doxorubicin in xenografts and patient-derived models. Increased P4HA1 expression correlates with short relapse-free survival in TNBC patients who received chemotherapy. 31239153_Findings show that prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha 1 (P4HA1) can enhance hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF1alpha) stability, indicating a positive feedback loop between HIF1alpha and P4HA1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). 31782831_High P4HA1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for poor overall survival and recurrent-free survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 32053263_Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha 1 (P4HA1) is a biomarker of poor prognosis in primary melanomas, and its depletion inhibits melanoma cell invasion and disrupts tumor blood vessel walls. 32150689_Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of P4HA1 Expression in Lung Cancer, Breast Cancer, and Head and Neck Cancer 33299876_Overexpression of P4HA1 Is Correlated with Poor Survival and Immune Infiltrates in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 33415167_Systematic Analysis of the Expression and Prognostic Significance of P4HA1 in Pancreatic Cancer and Construction of a lncRNA-miRNA-P4HA1 Regulatory Axis. 34387118_Prognostic and diagnostic roles of prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha members in breast cancer. 34520234_Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles Identifies a P4HA1-Related Gene Panel as a Prognostic Model in Colorectal Cancer Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000019916 |
P4ha1 |
194.700793 |
2.0740107946 |
1.052423 |
0.175056719 |
35.736043 |
0.00000000225944858937391714207575854807003717938940212661691475659608840942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000010480660332859528736095917564059148974209279003844130784273147583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
269.3978712 |
27.6875500 |
130.3567007 |
10.2023911 |
| ENSG00000122986 |
84329 |
HVCN1 |
protein_coding |
Q96D96 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the voltage-dependent proton permeability of excitable membranes. Forms a proton-selective channel through which protons may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. Proton efflux, accompanied by membrane depolarization, facilitates acute production of reactive oxygen species in phagocytosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16554753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20037153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22020278}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Hydrogen ion transport;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a voltage-gated protein channel protein expressed more highly in certain cells of the immune system. Phagocytic cells produce superoxide anions which require this channel protein, and in B cells this same process facilitates antibody production. This same channel protein, however, can also regulate functions in other cells including spermatozoa. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:84329; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; voltage-gated cation channel activity [GO:0022843]; voltage-gated proton channel activity [GO:0030171]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular response to pH [GO:0071467]; cellular response to zinc ion [GO:0071294]; positive regulation of superoxide anion generation [GO:0032930]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; response to pH [GO:0009268]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043] |
16554753_data presented here identify H(v)1 as a long-sought voltage-gated H+ channel and establish H(v)1 as the founding member of a family of mammalian VSD proteins 17948262_We cloned a new B cell-specific tetraspanning (BTS) membrane molecule 18509058_Hv1 forms a dimer in the membrane;its regions that are close to the dimer interface were defined. 19233200_The Hv1 channel voltage sensor domain by itself supports H(+) flux. 19255483_The C-terminal domain of the human voltage-gated proton channel Hv1 (C-Hv1) was overexpressed in Escherichia coli, purified and crystallized using the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method. 20018719_Hv1 channels truncated just downstream of R2 in the S4 segment retain most channel properties. 20037153_Identification of Thr29 as a critical phosphorylation site that activates the human proton channel Hvcn1 in leukocytes 20144758_Since Hv1 specifically mediates proton efflux, it is likely to be the long-sought molecule that controls male fertility by mediating intracellular alkalinization of human sperm 20147290_In the 2.0 A structure of the C-terminal domain, the two monomers form a dimer via a parallel alpha-helical coiled-coil, in which one chloride ion binds with the Neta atom of Arg(264). 20543828_Molecular dynamics simulations revealed water molecules in the central crevice of Hv1 model structures but not in homologous voltage-sensor domain (VSD) structures. 20548053_The HVCN1 H(+) channel mediates pH-regulated acid secretion by the airway epithelium. Apical HVCN1 represents a mechanism to acidify an alkaline airway surface liquid. 20676047_Report on the interaction of HV1 proton channel protomers during ion channel gating. 20961760_HVCN1 not only modulates signaling from the B-cell receptor following B-cell activation and histamine release from basophils, but also mediates pH-dependent activation of spermatozoa, as well as acid secretion by tracheal epithelium. [Review] 21124855_Data demonstrated that a massive reduction in H(v)1 expression can limit the Nox2 mediated superoxide production of PLB-985 granulocytes. 21821008_these results strongly suggest that Hv1 regulates breast cancer intracellular pH and exacerbates the migratory ability of metastatic cells. 21843503_Interactions with two of the S4 arginines and the formation of a well defined hydrophobic gap in the center of the Hv1 are key to the formation of a robust water wire. 22020278_identification of aspartate 112 as a crucial component of the selectivity filter of H(V)1 22056415_Hv1 channels maintain a physiological membrane potential during the respiratory burst of neutrophils by providing a compensating charge for the electrons transferred by NOX2 from NADPH to superoxide. 22367212_inhibition of Hv1 function via knockdown of Hv1 expression can effectively retard cancer growth 22388960_Hv1-dependent reactive oxygen species production is responsible for a substantial fraction of brain damage at early time points after ischemic stroke. 23352164_In the Hv1 voltage-gated channel a highly conserved phenylalanine is found in the charge transfer center. 23352165_Two conformational changes are detected in Hv1 channels that are involved in channel opening. 23891691_inhibition of Hv1 activity via Zn(2+) ions can effectively retard the cancer growth and suppress the cancer metastasis by the decrease of proton extrusion and the down-regulation of gelatinase activity 23940591_Results suggest that Hv1 may be used as a potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal carcinoma, and a potential target for anticancer drugs in colorectal cancer therapy. 24379371_Salt bridge networks and the hydrophobic plug function as the gate in Hv1 channels; outward movement of the fourth transmembrane segment leads to the opening of this gate. 24867409_Divalent metal binding causes a conformational change in human the Hv1 c-terminal domain. 25296308_Hv1 activity displays hysteresis 25425665_A shorter isoform of HVCN1 with enhanced gating is specifically enriched in malignant B cells. 25446125_analysis of of the C-terminal domain of voltage-gated proton channel HV1 and the thermodynamic characteristics of Zn(2) binding to this domain 25964989_The main properties of the voltage-gated proton channel (HV1) are described in this review, along with what is known about how the channel protein structure accomplishes its functions. [review] 26458876_Trp207 is crucial for slow channel opening, highly temperature-dependent gating kinetics, proton selectivity, and DeltapH-dependent gating. 26559003_Our data demonstrated that the expression of Hv1 in pancreatic islet beta-cells regulates insulin secretion through regulating Ca(2+) homeostasis. 27572256_The authors now report that R1H mutation is sufficient to reconstitute resting-state H(+) 'shuttle' conductance in Hv1 without abrogating the intrinsic 'aqueous' H(+) conductance. 27859356_We suggest that cleavage and heterodimerization of Hv1 represents an adaptation to the specific requirements of pH control in sperm. 28013412_Inhibition of Hv1 channels by Zn(2+). 28064239_CREBBP mutations were associated with inferior progression-free survival (PFS), whereas mutations in previously unreported HVCN1, a voltage-gated proton channel-encoding gene and B-cell receptor signaling modulator, were associated with improved PFS. 29743300_His168 is essential for DeltapH-dependent gating of NV1. 29925021_Gating Currents in the Hv1 Proton Channel 30478045_A voltage-gated proton channel (Hv1) is the main pathway for H(+) efflux that allows capacitation in sperm and permits sustained reactive oxygen species production in white blood cells. A designed peptide inhibitor C6 was identified by a phage-display strategy whereby approximately 1 million novel peptides were fabricated on an inhibitor cysteine knot scaffold and sorted on purified Hv1 protein. 31462498_The hydrophobic gasket (HG) of the human voltage-gated proton channel, hHV1 plays a critical and exclusive role in preventing H(+) influx through closed channels. Mutation of HG residues produces gating pore currents reminiscent of several channelopathies. 31633762_Voltage-gated proton channels exist in the plasma membrane of human oocytes. 32346069_The voltage-gated proton channel hHv1 is functionally expressed in human chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 32374759_The limited growth thus appears to be independent of oxidant production by NADPH oxidase molecules and to be mediated by cell adhesion molecules. Although HV1 KO and KD affect certain cellular mechanisms differently, both implicate HV1-mediated pathways for control of tumor growth in the MDA-MB-231 cell line 32788354_Dimer interaction in the Hv1 proton channel. 32788614_Insights on small molecule binding to the Hv1 proton channel from free energy calculations with molecular dynamics simulations. 33807711_Regulation of Neutrophil Functions by Hv1/VSOP Voltage-Gated Proton Channels. 33875847_Genetic variation of staphylococcal LukAB toxin determines receptor tropism. 34158477_Direct activation of the proton channel by albumin leads to human sperm capacitation and sustained release of inflammatory mediators by neutrophils. |
ENSMUSG00000064267 |
Hvcn1 |
627.309809 |
2.1442444226 |
1.100469 |
0.066538173 |
276.336373 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004720438145617793272126636745886794976828886078232252857453299394051327213447881043500965782310475298911320655085370514181846394527763046839719550196108653963844581369357911171391606330871582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001248632025615029142422799299380090330536618075556094960261064363344217290528556627388995603106705159475664477491766743882625297676100392070274325300891990475626869283587438985705375671386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
860.7081412 |
34.0858104 |
404.0712052 |
12.7218180 |
| ENSG00000123080 |
1031 |
CDKN2C |
protein_coding |
P42773 |
FUNCTION: Interacts strongly with CDK6, weakly with CDK4. Inhibits cell growth and proliferation with a correlated dependence on endogenous retinoblastoma protein RB. |
3D-structure;ANK repeat;Cell cycle;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the INK4 family of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. This protein has been shown to interact with CDK4 or CDK6, and prevent the activation of the CDK kinases, thus function as a cell growth regulator that controls cell cycle G1 progression. Ectopic expression of this gene was shown to suppress the growth of human cells in a manner that appears to correlate with the presence of a wild-type RB1 function. Studies in the knockout mice suggested the roles of this gene in regulating spermatogenesis, as well as in suppressing tumorigenesis. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode an identical protein, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1031; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004861]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042326]; negative regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000647]; oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048709]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089] |
11668523_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12077144_conclude that E2F proteins and Sp1 play an important role in the control of p18 expression 12203782_Deletions in the CDKN2C locus and hypermethylation in the CDKN2C promoter region play a role in ovarian granulosa cell tumorogenesis. 12698196_Inhibitor shows antitumor effect on glioma cells. 14645011_p18INK4c may function as a tumor suppressor in Hodgkin lymphoma, and inactivation may contribute to cell cycle deregulation and defective terminal differentiation of the Reed-Sternberg cells. 15107819_protein kinase C promotes human cancer cell growth through downregulation of p18(INK4c) 16260494_p18(INK4C) loss may contribute to medulloblastoma formation in children 16802342_Transfer of the p16(INK4a) and p18(INK4c) genes and CDK4I suppressed the production of MMP-3 and MCP-1. 17409409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17710155_data suggest that p27 and p18 are unlikely to present classic tumor-suppressor genes in sporadic pancreatic endocrine tumors 17803708_Expression of p15, p18 and p27 was not generally related to the MEN1 gene mutational status of the investigated 18 pancreatic endocrine tumours. 18174243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18281541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18316595_oncogenic RET and loss of p18 cooperate in the multistep tumorigenesis of medullary thyroid carcinoma 18394558_These findings uncover a feedback regulatory circuit in the astrocytic lineage and demonstrate tumor suppressor role for p18(INK4C) in human glioblastoma wherein it functions cooperatively with other INK4 family. 18507837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18642058_NaBu-mediated p18( INK4C ) regulation played a role in cell cycle arrest and erythroid differentiation in K562 cells. 18829482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18829482_deletions of CDKN2C are important in the progression and clinical outcome of myeloma 18942719_P18 is a tumor suppressor gene involved in human medullary thyroid carcinoma and pheochromocytoma 18973139_Purpose was to investigate genetic alterations of CDKN2C gene in 38 pituitary adenomas. The absence of CDKN2C protein was correlated with LOH of the CDKN2C locus on chromosome 1 and with methylation of the CDKN2C promoter. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19141585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401813_The down-regulation of p18(INK4C) expression may contribute to the tumorigenesis of pituitary adenomas. 19411068_p18(INK4C) is a downstream target of GATA3, constrains luminal progenitor cell expansion, and suppresses luminal tumorigenesis in the mammary gland 19509251_Results identified a molecular basis for CDK inhibitors to exert an antitumor effect in p18-deficient cancers and support the clinical use of CDK inhibitors. 19738611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20507346_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20833334_review presents the recent advances in MEN-4 and other multiple endocrine neoplasias and summarises the current knowledge of how P27KIP1 and p18-INK4C may be implicated in endocrine neoplasia [review] 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21112821_results demonstrate for the first time that N-Myc is a downstream target of RET2A signaling, and propose that induction of N-Myc by RET2A is a key step leading to lower p18 levels during MEN2A tumorigenesis 21994415_Data indicate that the role of CDKN2C in the adverse outcome of cases with hemizygous deletion was less certain. 22080569_propose that the contrasting behavior of the two very similar INK4 proteins could reflect their respective roles in senescence versus differentiation 22685290_up-regulated HULC promotes proliferation of hepatoma cells through suppressing p18 22896639_Analysis of B1a lymphocyte phenotypes of p18-deficient C57BL/6 mice finds that p18 is a key regulator of the size of the B1a cell pool. 23715670_in 85 sporadic parathyroid adenomas, study identified alterations in 5 adenomas: 2 contained heterozygous changes in CDKN1A, 1 germline and 1 of undetermined germline status; 1 had a CDKN2B germline alteration, accompanied by loss of the normal allele in the tumor (LOH); 2 had variants of CDKN2C, 1 somatic and 1 germline with LOH 23896637_this studydemonstrated abundant levels of the critical negative cell-cycle regulators, p27(Kip1), its phosphorylated form, p-p27(S10), p18Ink4c, and GSK-3, in beta-cells of both adult human and mouse pancreatic islets, which contribute to maintenance of beta-cell quiescence. 24127162_Mutations in CDKN2C is associated with sporadic parathyroid adenoma. 26350239_DNA methyltransferase 3A promotes cell proliferation by silencing CDK inhibitor p18INK4C in gastric carcinogenesis 26740620_Data suggest that cell cycle-dependent kinase inhibitors CDKN2C/p18 and CDKN1A/p21 facilitate cell cycle entry/cell proliferation of quiescent adult human pancreatic beta cells in primary culture (from tissues obtained from organ donors). 26985855_The differences in p18(INK4c)and p57(Kip2)activities in chronic myeloid leukemia and normal stem cells suggest a different cell cycle regulation. 27287689_Our study suggests that p18 is a limiting factor for the noncanonical HSC differentiation path in lymphoid lineages. 27610696_genetic association studies in population in Houston TX: Data suggest that CDKN2C copy number variations are associated with sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma; these associations include presence of distant metastasis at presentation and decreased overall survival. 27750397_CDKN2C gene deletion is associated with plasma cell post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. 27888400_CDKN2C inactivation contributes to the leukemogenesis in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 28055967_Cycling hypoxia could induce significant changes in CLDN1 and CLDN7 expression in nasopharyngeal cancer cells, indirectly regulation P18 expression and affecting cell invasion/proliferation. 29134609_Low P18 expression is associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1-related pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 29694893_an oncogenic role for the protein lysine methyltransferase SETDB2 in leukemia pathogenesis. It is overexpressed in pre-BCR(+) ALL and required for their maintenance in vitro and in vivo. SETDB2 expression is maintained as a direct target gene of the chimeric transcription factor E2A-PBX1 in a subset of ALL and suppresses expression of the cell-cycle inhibitor CDKN2C through histone H3K9 tri-methylation. 32090490_miR-21-5p promotes cell proliferation and G1/S transition in melanoma by targeting CDKN2C. 32111816_MCL1 binding to the reverse BH3 motif of P18INK4C couples cell survival to cell proliferation. 32483149_A genome-wide gain-of-function screen identifies CDKN2C as a HBV host factor. 32945431_PRMT6 serves an oncogenic role in lung adenocarcinoma via regulating p18. 34076987_Downregulated miRNA-22-3p promotes the progression and leads to poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting CDKN2C. 34896253_CDKN2C expression in adipose tissue is reduced in type II diabetes and central obesity: impact on adipocyte differentiation and lipid storage? 34907231_The distinct effects of P18 overexpression on different stages of hematopoiesis involve TGF-beta and NF-kappaB signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000028551 |
Cdkn2c |
656.970691 |
0.4670293833 |
-1.098415 |
0.068533372 |
258.610637 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034464124858178749690353208672025675765216237130290833785822413430675955888672068112780209538125984872070815504695742645258337438390231191985969665114719617804439621977508068084716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008592744643694566096999403120072100605669361553769251579056725488388831989681905535490285681265332560535407988840742899543221023869773623365432568821375980405719019472599029541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
432.1815768 |
19.4320162 |
932.8102012 |
28.1336016 |
| ENSG00000123146 |
976 |
ADGRE5 |
protein_coding |
P48960 |
FUNCTION: Receptor potentially involved in both adhesion and signaling processes early after leukocyte activation. Plays an essential role in leukocyte migration. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0M6}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the EGF-TM7 subfamily of adhesion G protein-coupled receptors, which mediate cell-cell interactions. These proteins are cleaved by self-catalytic proteolysis into a large extracellular subunit and seven-span transmembrane subunit, which associate at the cell surface as a receptor complex. The encoded protein may play a role in cell adhesion as well as leukocyte recruitment, activation and migration, and contains multiple extracellular EGF-like repeats which mediate binding to chondroitin sulfate and the cell surface complement regulatory protein CD55. Expression of this gene may play a role in the progression of several types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms with 3 to 5 EGF-like repeats have been observed for this gene. This gene is found in a cluster with other EGF-TM7 genes on the short arm of chromosome 19. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:976; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954] |
11380941_CD97 is expressed in all types of macrophages and dendritic cells except for microglia, in most T cells but only a few B cells, in smooth muscle cells, and in a restricted set of thyroid and gastrointestinal carcinomas. 12414513_CD97 expression correlates with dedifferentiation, migration, and invasion in colorectal tumor cell lines 15576472_coengagement of alpha5beta1 and chondroitotin sulfate proteoglycan by CD97 synergistically initiates endothelial cell invasion 16273233_Findings suggest that CD97(EGF) may play a role in the development and invasion of gastric carcinomas. 16818763_CD55 engagement with its natural ligand CD97 can act as a potent costimulator of human CD4+ T cells, resulting in cellular activation and promoting enhanced proliferation and cytokine secretion. 16929497_enhanced CD97 expression in colorectal cancer cells is regulated independent of beta-catenin/Tcf-4, and is thus not a direct target of the canonical Wnt pathway 17449467_CD55 may simultaneously regulate both the innate and adaptive immune responses and can also regulate complement when bound to CD97. 18267122_EGF-TM7 pre-mRNAs also undergo the rare trans-splicing, leading to the generation of functional chimeric receptors. 18329191_Sp1 and Sp3 over-expression activates CD97 promoter activity in HEK293 cells. 19428565_CD97 is present on all lymphocytes in blood and lymphoid tissue. Expression of CD97 on B cells was lower compared to T and NK cells and did not differ between B-cell subsets. 19737555_CD97-mFc can adopt two different conformations; one capable of auto-proteolysis and the other not. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167235_complex cellular expression programmes rather than activation modes regulate the expression of EGF-TM7 receptors in macrophages 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20339853_Elevated expression of CD97 and its ligand CD55 at the invasion front correlate with tumor recurrence and metastasis, and CD95 may be a poor prognostic factor for rectal adenocarcinoma. 20428763_the tumor promoting role of CD97 small isoform in cancer progression 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21156175_expression of the wild type - but not the GPS cleavage-deficient CD97 up-regulates the expression of N-cadherin, leading to Ca(++)-dependent cell-cell aggregation. 21978933_CD97 functioned to mediate invasion in prostate cancer cells, by associating with lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPAR1), leading to enhanced LPA-dependent RHO and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. 22210915_binding of leukocytes to activated endothelium mediated by the interaction of CD97 with Thy-1 is involved in firm adhesion of polymorphonuclear cells during inflammation and may play a role in the regulation of leukocyte trafficking to inflammatory sites. 22313360_we conclude that the possible upregulation of CD97 mediated by WT1 promotes cellular invasiveness-one of the most characteristic and challenging aspects of glial tumor cells. 22547928_CD97 and CD55 showed high expression at the invasive front of gallbladder carcinoma. CD97 and CD55 expression was associated with high histologic grade, advanced pathologic T stage, clinical stage and positive venous/lymphatic invasion. 22768192_CD97 small isoform not only supported gastric cancer local growth, but also promoted metastatic spread in orthotopically implanted mouse model. 22797060_CD97 expression in human thyroid cancers correlated with LPA receptor and markers of aggressiveness including Ki67 and pAKT. 23658650_CD97 expression promotes invasion and migration in glioblastoma multiforme, but has no effect on tumor proliferation. 23771909_study reports gene expression in skeletal muscle tissue of women with metabolic syndrome is enriched in inflammatory response-related genes; IL6R, HDAC9 and CD97 expression correlated negatively with insulin sensitivity; suggests a role for these 3 inflammatory genes in development of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in women 23838008_Lysophosphatidylethanolamine utilizes LPA(1) and CD97 in a breast cancer cell line. 24274104_These results provide the first experimental evidence that cd97 is a direct target of miR-126. 24949957_We conclude that CD97 is located in the SR and at the peripheral sarcolemma of human and murine skeletal muscle, where its absence affects the structure of the SR without impairing skeletal muscle function 25174588_CD97 enhanced TIMP-2 secretion, leading to reduced MT-MMP-1 and -2 activities, impairing cell migration/invasion in vitro and lung macrometastasis in vivo and upregulating integrins. Both the NTF and the CTF of CD97 were required. 25714433_we identify the specific isoforms of CD97, a novel pro-invasive glioma antigen, across histologic grades of glioma and within BTICs. We also demonstrate a trend towards increased CD97 expression among the classical and mesenchymal GBM subtypes. 26034356_CD97 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion in vitro through exosome-mediated MAPK signaling pathway, and exosomal miRNAs are probably involved in activation of the CD97-associated pathway. 26107567_present study suggested that the expressions of CD97 antigen and decay accelerating factor(DAF) were both upregulated in human cervical squamous cell carcinoma 26233326_High expression of CD97 is associated with lymphatic metastasis in gastric cancer. 26462154_Knock down of CD97 led to an altered mechanical phenotype, reduced adhesion to a stromal layer and lower wildtype FLT3 expression. 27641734_Biochemical features of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor CD97 related to its auto-proteolysis and HeLa cell attachment activities 28345461_This study indicated that the CD97 and CD55 proteins might be reliable biomarkers to predict the metastasis status and prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients. 28373465_High CD97 expression Correlates with Breast, Colorectal and Pancreatic Cancer. 29669286_CD97 coordinates the coincidence of tumor cell migration and endothelial barrier retraction as a result of rapid bidirectional signaling between tumor cells and platelets. 29704239_CD97 as an effective potential prognosticator and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 29952218_High CD97 expression is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 30883974_Decreased migration and invasion was found in CD97 small isoform RNAi cervical carcinoma cells, with no change in cell proliferation. 30953469_Study identified ADREG5 as a MYC target gene able to discriminate between Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large cell lymphoma (DLBCL) irrespectively of the presence of MYC breaks in DLBCL. 31260716_CD97 expression is associated with poor overall survival in acute myeloid leukemia. 31371381_High levels of CD97 correlate with poor prognosis, and silencing of CD97 reduces disease aggressiveness in vivo. These phenotypes are due to CD97's ability to promote proliferation, survival, and the maintenance of the undifferentiated state in leukemic blasts. 31397926_findings suggest that CD97 on retinal pigment epithelium cells serves to control leukocyte activation and trafficking in uveoretinal inflammation while at the same time regulating second messenger-mediated gene expression, cell growth, and survival 31594642_CD97 stimulates tumor angiogenesis through RGD motif-independent mechanism.CD97 promotes tumor angiogenesis by overexpressing MMP-9. 31969668_G Protein-Coupling of Adhesion GPCRs ADGRE2/EMR2 and ADGRE5/CD97, and Activation of G Protein Signalling by an Anti-EMR2 Antibody. 32430705_CD97 Is Decreased in Preeclamptic Placentas and Promotes Human Trophoblast Invasion Through PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. 33497605_Tethered agonist exposure in intact adhesion/class B2 GPCRs through intrinsic structural flexibility of the GAIN domain. 33992645_Structural basis for CD97 recognition of the decay-accelerating factor CD55 suggests mechanosensitive activation of adhesion GPCRs. 34028660_Genetic manipulation of adhesion GPCR CD97/ADGRE5 modulates invasion in patient-derived glioma stem cells. 35087132_CD97 is associated with mitogenic pathway activation, metabolic reprogramming, and immune microenvironment changes in glioblastoma. 35563846_To Detach, Migrate, Adhere, and Metastasize: CD97/ADGRE5 in Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000002885 |
Adgre5 |
667.288455 |
0.2854342760 |
-1.808770 |
0.084938341 |
452.419927 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000021452382896234517431209457665881226928321445095819743051921639750405887610717012323335275785498766628784809673496745199927375642296124388234564551285435395623311510905672395811975559135191918952300088560469744642811812865243868638 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009124990534536640904848871691654043355256079543975370042172369290433315818988894133415577074999978345184025643690609058054612368016870973264162875417134496261950818258723712670074909071497889490248369804524204103923877629288329871 |
Yes |
Yes |
290.3244257 |
15.1330472 |
1024.9502733 |
34.5501341 |
| ENSG00000123213 |
57486 |
NLN |
protein_coding |
Q9BYT8 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes oligopeptides such as neurotensin, bradykinin and dynorphin A (By similarity). Acts as a regulator of cannabinoid signaling pathway by mediating degradation of hemopressin, an antagonist peptide of the cannabinoid receptor CNR1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P42676}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Mitochondrion;Protease;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the metallopeptidase M3 protein family that cleaves neurotensin at the Pro10-Tyr11 bond, leading to the formation of neurotensin(1-10) and neurotensin(11-13). The encoded protein is likely involved in the termination of the neurotensinergic signal in the central nervous system and in the gastrointestinal tract.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:57486; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; peptide metabolic process [GO:0006518]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; regulation of skeletal muscle fiber differentiation [GO:1902809] |
17251185_Mutations at only two residues (Arg-470 and Arg-498) are required to swap specificity with thimet oligopeptidase, a result that is confirmed by testing the two-mutant constructs. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29183787_The crystal structure of human neurolysin(E475Q) in complex with the products of neurotensin cleavage at 2.7A revealed a closed conformation with an internal cavity that restricts substrate length and highlighted the mechanism of enzyme opening/closing that is necessary for substrate binding and catalytic activity. 32269163_The mitochondrial peptidase, neurolysin, regulates respiratory chain supercomplex formation and is necessary for AML viability. |
ENSMUSG00000021710 |
Nln |
437.643848 |
2.5662613027 |
1.359668 |
0.142847181 |
88.141306 |
0.00000000000000000000609416406676230054266819300836270580089642677680000696467058768357460962761251721531152725219726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000055834799270894823270613360638623959422707790444725939587450325163331399380695074796676635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
620.9622182 |
82.4018881 |
245.0053778 |
23.8295393 |
| ENSG00000123329 |
64333 |
ARHGAP9 |
protein_coding |
Q9BRR9 |
FUNCTION: GTPase activator for the Rho-type GTPases by converting them to an inactive GDP-bound state. Has a substantial GAP activity toward CDC42 and RAC1 and less toward RHOA. Has a role in regulating adhesion of hematopoietic cells to the extracellular matrix. Binds phosphoinositides, and has the highest affinity for phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate, followed by phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11396949}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;GTPase activation;Lipid-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Rho-GAP family of GTPase activating proteins. The protein has substantial GAP activity towards several Rho-family GTPases in vitro, converting them to an inactive GDP-bound state. It is implicated in regulating adhesion of hematopoietic cells to the extracellular matrix. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:64333; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19911011_The Ala370Ser polymorphism in the ARHGAP9 gene is associated with coronary artery spasm. 30206221_The data clearly show that ARHGAP9/FOXJ2 inhibit cell migration and invasion during hepatocellular carcinoma development via inducing the transcription of CDH1. 33579308_The role of ARHGAP9: clinical implication and potential function in acute myeloid leukemia. 34159626_SOX4-induced upregulation of ARHGAP9 promotes the progression of acute myeloid leukemia. 35040754_GATA binding protein 5 (GATA5) induces Rho GTPase activating protein 9 (ARHGAP9) to inhibit the malignant process of lung adenocarcinoma cells. 35679685_ARHGAP9 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation, invasion and EMT via targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000040345 |
Arhgap9 |
784.891549 |
0.4268075266 |
-1.228342 |
0.058594806 |
446.278477 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000465617610812369172585759469134305191464475041485997134203482415984846233647378845570094858377840161245675314357743986318236957130023952224980581202738735000860591777065547623622399847749831359550058717559863135492166485625964383427 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000194138868237021717466081769823608477090223680824326147928561882276935422635882544337811978070499072596540785451429238731414805418105728752888290164569020162778272141470135427968813485550202575267466530132262408063298178366660860139 |
Yes |
Yes |
482.0439483 |
19.7754924 |
1137.5672535 |
30.9757593 |
| ENSG00000123342 |
4327 |
MMP19 |
protein_coding |
Q99542 |
FUNCTION: Endopeptidase that degrades various components of the extracellular matrix, such as aggrecan and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (comp), during development, haemostasis and pathological conditions (arthritic disease). May also play a role in neovascularization or angiogenesis. Hydrolyzes collagen type IV, laminin, nidogen, nascin-C isoform, fibronectin, and type I gelatin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10809722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10922468}. |
Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins that are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded protein is secreted as an inactive proprotein, which is activated upon cleavage by extracellular proteases. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:4327; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; luteolysis [GO:0001554]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; ovulation from ovarian follicle [GO:0001542]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to cAMP [GO:0051591]; response to hormone [GO:0009725] |
11801661_MMP-19 is expressed by myeloid cells in an adhesion-dependent manner and associates with the cell surface by an interaction with the hemopexin-like domain. 12516088_Downregulation of MMP-19 expression in the epidermis is associated with transformation and histologic dedifferentiation in skin neoplasms 12937269_MMP-19 is a likely candidate to be the major IGFBP-3 degrading MMP 15239678_the importance of MMP19 as a predictor of secondary Extramammary Paget's disease or the putative origin of Paget's cells from the dermal adenocarcinoma cells of apocrine duct origin 15868410_MMP-19 actively participates in the early stages of SCC invasion. 17195013_Our results suggest that Tst-1 and Skn-1a regulate expression of MMPs in keratinocytes and effect both the expression and activation of these proteolytic enzymes. 17980449_Therefore, MMP-1, MMP-11 and MMP-19 might be of importance for the development of high-grade astrocytic tumors and may be promising targets for therapy. 18161657_MMP-19 may have a role in tumor invasiveness in patients with oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20098411_the increase of MMP19 expression hallmarks the progression of cutaneous melanoma 20142769_Taken together, these results indicate that MMP19 is highly expressed in proliferating astrocytoma/glioma cells, and that its expression may facilitate their invasion through brain extracellular matrix components. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21261556_vascular MMP-19 expression significantly associated with Cerebral amyloid angiopathy--associated intracerebral haemorrhage 21787393_MMP-19 processes human plasminogen in a characteristic cleavage pattern to generate three angiostatin-like fragments 22576687_MMP-15 and MMP-19 are upregulated during colorectal tumorigenesis 22855183_These findings indicated for the first time that the co-expression of MMP-14 and MMP-19 is significantly correlated with prognosis in glioma patients 22859522_Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-19 (MMP19) induced by lung injury may play a protective role in the development of fibrosis through the induction of prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2). 23956056_ASNS and MMP19, along with eIF3a, are the sensitivity factors for cisplatin treatment and may serve as potential candidate molecular markers for predicting cisplatin sensitivity of advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 25056434_The expression of MMP-19 in the main forms of gastrointestinal diseases, was analysed. 25250855_Matrix metalloproteinase-19 in lung epithelial cells stimulates proliferation and cell migration. Read More: http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201310-1903OC 25581579_Triplication of an enhancer may lead to overexpression of MMP19 in the optic nerve that causes cavitary optic disc anomaly. 25840998_the intima+media of IPAH vessels, collagens (COL4A5, COL14A1, and COL18A1), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 19, and a disintegrin and metalloprotease (ADAM) 33 were higher expressed, whereas MMP10, ADAM17, TIMP1, and TIMP3 were less abundant. 26292259_Loss of NDRG2 induced the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-19 (MMP-19), which regulated the expression of Slug at the transcriptional level in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gallbladder carcinoma cells. 26548962_the downregulation of MMP19 following respiratory syncytial virus infection may be associated with the development of airway hyperresponsiveness. 26692439_Levels of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-19 and MMP-20 expression are significantly increased in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). 26700939_transcriptional target of ligand-bound activated estrogen receptor beta acting on a specificity protein-1 binding site 29323744_MiR-193b-3p is an important regulator of MMP-19 in human chondrocytes and may relieve the inflammatory response in OA. 31088409_Study found that the expression of MMP19 was upregulated in colorectal cancer (CRC). High expression of MMP19 was determined to be an independent and poor prognostic factor in CRC. These results suggest that MMP19 may be a good biomarker for CRC. 31298377_MicroRNA-16 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells by down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-19 expression. 33151424_Long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 affects paclitaxel and cisplatin resistance by regulating MMP19 in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000025355 |
Mmp19 |
156.610838 |
4.1775309230 |
2.062651 |
0.210611990 |
92.600032 |
0.00000000000000000000064006401748619400165470214099320557816107083801528987736153414322970434113813098520040512084960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000006087206764237257724249746927409447089723845817901284353996539666642462407253333367407321929931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
228.5342290 |
89.7965583 |
56.3620489 |
16.0349829 |
| ENSG00000123353 |
29095 |
ORMDL2 |
protein_coding |
Q53FV1 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of sphingolipid synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20182505}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in ceramide metabolic process. Acts upstream of or within negative regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:29095; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; SPOTS complex [GO:0035339]; cellular sphingolipid homeostasis [GO:0090156]; ceramide metabolic process [GO:0006672]; negative regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:1900060] |
23066021_ORMDL1, ORMDL2 and ORMDL3 mediate the feedback response in ceramide biosynthesis. 25395622_Expression of the ORMDLS, modulators of serine palmitoyltransferase, is regulated by sphingolipids in mammalian cells. |
ENSMUSG00000025353 |
Ormdl2 |
187.164126 |
2.0670233868 |
1.047555 |
0.118115393 |
79.343971 |
0.00000000000000000052185244277375721563346424566637352775023039847551871960040781317502478486858308315277099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000004414064215094932174939110688075144066324222597583540328436413346935296431183815002441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
250.2868027 |
17.4579721 |
122.0167970 |
6.6794674 |
| ENSG00000123360 |
5153 |
PDE1B |
protein_coding |
Q01064 |
FUNCTION: Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase with a dual specificity for the second messengers cAMP and cGMP, which are key regulators of many important physiological processes (PubMed:8855339, PubMed:9419816, PubMed:15260978). Has a preference for cGMP as a substrate (PubMed:9419816). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15260978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8855339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9419816}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calmodulin-binding;cAMP;cGMP;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) family, and PDE1 subfamily. Members of the PDE1 family are calmodulin-dependent PDEs that are stimulated by a calcium-calmodulin complex. This PDE has dual-specificity for the second messengers, cAMP and cGMP, with a preference for cGMP as a substrate. cAMP and cGMP function as key regulators of many important physiological processes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:5153; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0047555]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-activated 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0048101]; calmodulin-activated dual specificity 3',5'-cyclic-GMP, 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004117]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0036006]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; regulation of dopamine metabolic process [GO:0042053]; regulation of neurotransmitter levels [GO:0001505]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; serotonin metabolic process [GO:0042428]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
15625104_Selective up-regulation of PDE1B2 upon monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation. 16407168_PDE1B2 regulates a subset of phenotypic changes that occur upon phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced differentiation and likely also plays a role in differentiated macrophages by regulating agonist-stimulated cGMP levels 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28282490_The c.1618G>A, p.Gly540Ser substitution in CNGA3 was identified as the causative mutation for a novel form of ACHM in Awassi sheep. Gene augmentation therapy restored vision in the affected sheep. This novel mutation provides a large-animal model that is valid for most human CNGA3 ACHM patients; the majority of them carry missense rather than premature-termination mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000022489 |
Pde1b |
222.922512 |
0.4227767379 |
-1.242032 |
0.133005787 |
87.195457 |
0.00000000000000000000983093790949043078897024761342363064135026055570474445973946919785646514355903491377830505371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000089240248182090261121834288135576303740627022012089702377585220816058608761522918939590454101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
130.2594893 |
11.7157085 |
310.4030543 |
18.9695199 |
| ENSG00000123610 |
7130 |
TNFAIP6 |
protein_coding |
P98066 |
FUNCTION: Major regulator of extracellular matrix organization during tissue remodeling (PubMed:18042364, PubMed:26823460, PubMed:15917224). Catalyzes the transfer of a heavy chain (HC) from inter-alpha-inhibitor (I-alpha-I) complex to hyaluronan. Cleaves the ester bond between the C-terminus of the HC and GalNAc residue of the chondroitin sulfate chain in I-alpha-I complex followed by transesterification of the HC to hyaluronan. In the process, potentiates the antiprotease function of I-alpha-I complex through release of free bikunin (PubMed:20463016, PubMed:15917224, PubMed:16873769). Acts as a catalyst in the formation of hyaluronan-HC oligomers and hyaluronan-rich matrix surrounding the cumulus cell-oocyte complex, a necessary step for oocyte fertilization (PubMed:26468290). Assembles hyaluronan in pericellular matrices that serve as platforms for receptor clustering and signaling. Enables binding of hyaluronan deposited on the surface of macrophages to LYVE1 on lymphatic endothelium and facilitates macrophage extravasation. Alters hyaluronan binding to functionally latent CD44 on vascular endothelium, switching CD44 into an active state that supports leukocyte rolling (PubMed:26823460, PubMed:15060082). Modulates the interaction of chemokines with extracellular matrix components and proteoglycans on endothelial cell surface, likely preventing chemokine gradient formation (PubMed:27044744). In a negative feedback mechanism, may limit excessive neutrophil recruitment at inflammatory sites by antagonizing the association of CXCL8 with glycosaminoglycans on vascular endothelium (PubMed:24501198). Has a role in osteogenesis and bone remodeling. Inhibits BMP2-dependent differentiation of mesenchymal stem cell to osteoblasts (PubMed:18586671, PubMed:16771708). Protects against bone erosion during inflammation by inhibiting TNFSF11/RANKL-dependent osteoclast activation (PubMed:18586671). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15917224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16771708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16873769, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18586671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20463016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24501198, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26468290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26823460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27044744}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a secretory protein that contains a hyaluronan-binding domain, and thus is a member of the hyaluronan-binding protein family. The hyaluronan-binding domain is known to be involved in extracellular matrix stability and cell migration. This protein has been shown to form a stable complex with inter-alpha-inhibitor (I alpha I), and thus enhance the serine protease inhibitory activity of I alpha I, which is important in the protease network associated with inflammation. This gene can be induced by proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1. Enhanced levels of this protein are found in the synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:7130; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; carboxylic ester hydrolase activity [GO:0052689]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; hyaluronic acid binding [GO:0005540]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; fibronectin fibril organization [GO:1905590]; hyaluronan metabolic process [GO:0030212]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090024]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; ovarian cumulus expansion [GO:0001550]; ovulation [GO:0030728]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of receptor clustering [GO:1903911]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11854277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11854277_polymorphism in osteoarthritis; chromosome location given here (chromosome 2) 12692188_TSG-6 is a multifunctional protein associated with inflammation [review] 14515153_Tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6 activates an anti-inflammatory agent- inter-alpha-inhibitor[review]. 15653696_The TSG-6 and I alpha I interaction promotes a transesterification cleaving the protein-glycosaminoglycan-protein (PGP) cross-link. 15718240_This TSG-6 model reveals the residues most likely to be involved in stabilizing the inter-Link module interface, which are highly conserved across the Link protein/ chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan subfamily. 15809059_TSG-6 treatment also resulted in a rapid increase in cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA levels, suggesting that TSG-6 up-regulates COX-2 gene expression 15840581_TSG-6 acts as cofactor and catalyst in the production of IalphaI heavy chain x hyaluronan complexes 15917224_heparin with the Link module significantly increases the anti-plasmin activity of the TSG-6.IalphaI complex; TSG-6 is likely to contribute to matrix remodeling, at least in part, through down-regulation of the protease network 16006654_Results suggest a physiological function of thrombospondin-1 binding to TSG-6 in regulation of hyaluronan metabolism at sites of inflammation. 16453284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16467113_The tumor necrosis factor alpha induced protein 6 is a potential marker that could be used for early diagnosis and prognosis of cancerous or precancerous lesions. 16687630_hyaluronan synthase 2 and TSG-6 have roles in hyaluronan distribution and function in proximal tubular epithelial cells 16709183_Evidence is cited in this review that TSG-6 can regulate the expression of various molecules that have important roles in the control of inflammation. 16771708_TSG-6 is down-regulated during osteoblastic differentiation, and suppressed osteoblastic differentiation induced by both BMP-2 and osteogenic differentiation medium. 16873769_TSG-6 may play an important protective role in bronchial epithelium by increasing the antiprotease screen on the airway lumen. 17585936_Crystallography data on the free protein, and (15)N NMR relaxation data for the uncomplexed and HA(8)-bound forms of Link_TSG6, is presented. 18042364_TSG-6 is a high affinity ligand that can mediate fibronectin interactions with other matrix components and modulate some interactions of fibronectin with cells 18260761_3 genes were upregulated in patients with chronic EBV infection: guanylate binding protein 1, tumor necrosis factor-induced protein 6, and guanylate binding protein 5; they may be associated with the inflammatory reaction or with cell proliferation. 18448433_The transfer of heavy chains from bikunin proteins to hyaluronan requires both TSG-6 and HC2. 18586671_TSG-6 has dual roles in bone remodeling: it inhibits RANKL-induced bone erosion in inflammatory diseases, and its interactions with BMP-2 and RANKL help to balance mineralization by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts 18820257_TSG-6 transfers proteins between glycosaminoglycans via a Ser28-mediated covalent catalytic mechanism 19344623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19383344_up-regulation in human colorectal cancer is correlated with upregulation of the TIMP-1 transcript 19389798_myelomonocytic cells and MoDC are a major source of TSG-6 and that PTX3 and TSG-6 are coregulated 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463016_TSG-6/HC2 link heavy chains randomly on the chondroitin sulfate chain of bikunin, in contrast to the ordered attachment observed during the biosynthesis. 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21239672_negative correlation between TSG-6 expression levels and severity of capsular contracture (CC) suggests a possible protective role for TSG-6 in the context of CC formation, and this may have a clinically relevant role in prevention of breast CC 21566135_TSG-6 protein, a negative regulator of inflammatory arthritis, forms a ternary complex with murine mast cell tryptases and heparin. 21569482_TSG-6 expression by hMSCs was induced 12 h after oropharyngeal delivery to LPS-exposed lungs. Knockdown of TSG-6 expression in hMSCs by RNA interference abrogated most of their anti-inflammatory effects. 21596748_TSG-6 is a potent HA cross-linking agent 21864707_TSG-6 was central to EMT through effects on HA macromolecular structure and through CD44-dependent triggering of cell responses. 22267482_TSG-6 reverts the inhibitory effects exerted by PTX3 on FGF2-mediated angiogenesis through competition of FGF2/PTX3 interaction. 22922154_This review discusses TSG-6 as a potential molecular marker of oocyte maturation. 23017666_The protein product of tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulated gene-6 strongly correlated with ossification markers and hyaluronidase in calcified human aortic valves. 23129777_TSG-6 increases the accumulation of HA in the cell-associated matrix, partially by preventing its dissolution from the cell-associated matrix into the conditioned medium, but primarily by inducing HA synthesis 23166324_analysis of irreversible heavy chain transfer to hyaluronan oligosaccharides by tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6 23921952_This study provides insight into what we believe to be a previously undescribed multifaceted role of mesenchymal stem cell-released TSG-6 in wound healing. 24005673_Data indicate that TSG-6-mediated cross-linking of hyaluronan (HA) films is impaired in the presence of inter-alpha-inhibitor (IalphaI) and that this effect suppresses the TSG-6-mediated enhancement of HA binding to CD44-positive cells. 24213015_data suggest that TSG-6 expression might be essential in endometrial matrix organization and feto-maternal communication during the implantation process. 24403066_the HA-binding site defined here may not play a role in TSG-6-mediated transfer of heavy chains from inter-alpha-inhibitor onto HA, a process known to be essential for ovulation. 24501198_TSG-6 suppresses CXCL8-mediated chemotaxis of neutrophils; this lower potency effect might be important at sites where there is high local expression of TSG-6. 25325979_TSG-6 activity in tissues, was examined. 25329668_results suggest that systemic administration of hASC or TSG-6 may be novel approaches to reverse CS-induced myelosuppression. 25561734_Heavy chain transfer by tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene 6 to the bikunin proteoglycan. 25661977_TSG-6 exhibited anti-inflammatory effects during the wound healing process and cicatrization and significantly diminished hypertrophic scar formation in a rabbit ear model 26468290_the well characterized hyaluronan-binding site in the TSG-6 Link module is not used for recognition during transfer of HCs onto HA. 26685054_Data postulate that the molecular cross-linking enhanced by the multiple binding modes of the Link module might be critical for remodeling the ECM during inflammation/ovulation and might contribute to other functions of TSG-6. 26807758_This review will focus on the potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells for treatment of fibrotic diseases, with emphasis on the role of TSG-6 as a mediator of anti-inflammatory effects 27044744_Data show that TNF-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6) interacts with chemokines through their glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)-binding sites and inhibits their binding to GAGs and endothelial cell surfaces. 27143355_The current study describes a novel mechanism linking the TSG-6 transfer of the newly described HC5 to the HA-dependent control of cell phenotype. The interaction of HC5 with cell surface HA was essential for TGFbeta1-dependent differentiation of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts, highlighting its importance as a novel potential therapeutic target. 27444207_TSG-6 from MSCs attenuated severe burn-induced excessive inflammation via inhibiting activation of P38 and JNK signaling. 28005267_TNFAIP6 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28246883_Single nucleotide polymorphism in TNFAIP6 gene is associated with Systemic lupus erythematosus. 28247086_TSG-6 secreted by human mesenchymal stem cells suppresses inflammatory reactions through p38 and ERK in the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 28701721_We demonstrated that hAT-MSC-secreted TSG-6 induced macrophages that infiltrated into the colon to switch to the M2 phenotype, thus regulating the expression of inflammatory cytokines and the alleviation of DSS-induced colitis symptoms in mice. 29180197_abnormally elevated in both the plasma and aortic wall of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms 29238069_study has uncovered a novel link between IDO and TSG-6, and demonstrates that a metabolite of IDO controls the TSG-6-mediated anti-inflammatory therapeutic effects of human MSCs. 29301108_the results suggest that MSCs inhibit inflammatory neovascularization in the cornea by suppressing pro-angiogenic monocyte/macrophage recruitment in a TSG-6-dependent manner. 29362135_TSG-6 is constitutively expressed in some tissues, which are either highly active or subject to challenges. The diversity of its functions depend on its binding to ligands such as glycosaminoglycans, immune regulators and growth factors that themselves interact with these linear polysaccharides. TSG-6 can directly affect matrix structure and modulate its interaction with the extracellular signaling molecules. [review] 29401724_TSG-6 up-regulation counteracts the progression of atherosclerosis. (Review) 30257717_TSG-6 secreted by human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAT-MSCs) protects pancreatic acinar cells in severe acute pancreatitis model mice via the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress, as well as inflammatory responses. This study has revealed a new area for ER stress-targeted therapy in SAP patients 30507579_TSG-6 protein levels were significantly increased in high Alzheimer's Disease and was present in vasculature 30569148_Findings indicate that TSG6 is a novel regulator of keloid fibrogenesis. 30938674_The expression levels of Fas, FasL, FADD, caspase-3 and caspase- 8 were significantly raised in the TSG-6 overexpressing hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. 31310658_Keratocyte lineage induction was achieved in all MSCs as indicated by the upregulated expression of keratocyte markers, including keratocan, lumican, and carbohydrate sulfotransferase. TNFAIP6 response to inflammatory stimulation was observed only in CSSCs; increasing by 3-fold compared with the control 31558705_Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote healing via TNF-alpha-stimulated gene-6 in inflammatory bowel disease models. 31986937_TSG-6 Inhibits the Growth of Keloid Fibroblasts Via Mediating the TGF-beta1/Smad Signaling Pathway. 32317078_Tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6 interacts with CD44, which is involved in fate-change of hepatic stellate cells. 32450526_Inhibitory effect of the TSG-6 on the BMP-4/Smad signaling pathway and odonto/osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. 32829938_Detection of TSG-6-like protein in human corneal epithelium. Simultaneous presence with CD44 and hyaluronic acid. 33221562_TNFAIP6 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer and indicates poor prognosis of patients. 33471224_The Anti-inflammatory Protein TSG-6 Induced by S. aureus Regulates the Chemokine Function of Endothelial Cells In Vitro by Inhibiting the Chemokine-Glycosaminoglycan Interaction. 33670243_HGF and TSG-6 Released by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Colon Radiation-Induced Fibrosis. 34382584_Correlation of plasma TSG-6 with cardiac function, myocardial fibrosis, and prognosis in dilated cardiomyopathy patients with heart failure.', trans 'TSG-6. 35222359_Plasma Concentration of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Stimulated Gene-6 as a Novel Diagnostic and 3-Month Prognostic Indicator in Non-Cardioembolic Acute Ischemic Stroke. 35278816_Tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6-a new serum identification marker to identify severe and symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. 35353944_Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulated gene-6: A biomarker reflecting disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. 35718975_Identification of Neural Progenitor Cell-associated Chemoradiotherapy Resistance Gene Set (ARL4C, MSN, TNFAIP6) for Prognosis of Glioma. 35766985_Identification of TNFAIP6 as a hub gene associated with the progression of glioblastoma by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. 35773961_Bone Marrow Stem Cell-Exo-Derived TSG-6 Attenuates 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium+-Induced Neurotoxicity via the STAT3/miR-7/NEDD4/LRRK2 Axis. 35854776_TNFAIP6 Promotes Gastric Carcinoma Cell Invasion via Upregulating PTX3 and Activating the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. 36110074_[Expression of TNFAIP6 in oral verrucous carcinoma and oral squamous cell carcinoma and its relationship with clinicopathology]. 36379130_An update on the role of tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulating gene-6 in inflammatory diseases. |
ENSMUSG00000053475 |
Tnfaip6 |
44.024158 |
52.1225699171 |
5.703836 |
0.596385991 |
182.767804 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000001205372328643953467364573767672917830104361783458219326414452683411148029892022908767141157598475860115863969590499493733659619465470314025878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000210299002018732302299620506541886076621051204652416515944063630486184867359818291385506828920615170046021918937029226981394458562135696411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.6852994 |
36.5708134 |
1.7155139 |
0.6839905 |
| ENSG00000123643 |
206358 |
SLC36A1 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z2H8 |
FUNCTION: Electrogenic proton/amino acid symporter with selectivity for small apolar L-amino acids, their D-enantiomers and selected amino acid derivatives such as 4-aminobutanoate/GABA (PubMed:12809675, PubMed:12527723, PubMed:19549785). May be involved in the efflux from the lysosomal compartment of neutral amino acids resulting from proteolysis (By similarity). May play a role in specifying sites for exocytosis in neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q924A5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12527723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12809675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19549785}. |
Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the eukaryote-specific amino acid/auxin permease (AAAP) 1 transporter family. The encoded protein functions as a proton-dependent, small amino acid transporter. This gene is clustered with related family members on chromosome 5q33.1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:206358; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022858]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; amino acid:proton symporter activity [GO:0005280]; glycine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015187]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; L-proline transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015193]; proline:proton symporter activity [GO:0005297]; taurine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005368]; alanine transport [GO:0032328]; amino acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0089718]; amino acid transmembrane transport [GO:0003333]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; glycine transport [GO:0015816]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; L-alanine transport [GO:0015808]; proline transmembrane transport [GO:0035524]; proline transport [GO:0015824]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; taurine transport [GO:0015734] |
12527723_PAT1 expressed exclusively in apical membrane of Caco-2 cells. hPAT1 may be responsible for H(+)-coupled amino acid transport expressed in apical membrane of Caco-2 cells. 15521011_A high-capacity imino acid carrier localized at the small intestinal luminal membrane that transports nutrients and amino acids and imino acids. 15754324_Amino acid uptake via hPAT1 is inhibited by activators of the cAMP pathway indirectly through inhibition of NHE3 activity. 17050537_PAT1a, which is 99.0% identical to protein interacting with APP tail 1 (PAT1), is a functional link between the transport and processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein APP and its two paralogs APLP1 and APLP2 in vivo. 18230330_His-55 might be responsible for binding and translocation of H+ in the course of cellular amino acid uptake by PAT1. 19074966_This study is the first to demonstrate both taurine uptake via PAT1 and functional expression of PAT1 at the apical membrane of the intestinal epithelium. 19358571_Data conclude that hPAT1 might be responsible for the intestinal absorption of beta-GPA thereby allowing its oral administration. 19409386_The role of N-glycosylation in transport function and surface targeting of the human solute carrier PAT1 19549785_a disulfide bridge is essential for the transport function of the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter hPAT1 20498635_In human cells, SLC36A1 localized on intracellular membranes is required for amino acid-dependent mTORC1 activation and cell proliferation. SLC36A1 also has similar in vivo growth regulatory activity to fly SLC36 AAAPs when expressed in Drosophila. 22574197_PATs function as part of an amino acid-sensing engine that drives mTORC1 activation from endosomal and lysosomal membranes 22853447_In hPAT1 expressing oocytes Gly-Tyr, Gly-Pro, and Gly-Phe inhibited currents induced by drug substances. 22975709_estrogen attenuates the activity of PAT1 by directly closing PAT1 23488788_Data suggest that PAT1 in enterocytes is responsible for intestinal absorption of some of the alkaloids from areca nut (i.e., arecaidine, guvacine, isoguvacine). 23962042_Sertraline is an apparent non-competitive inhibitor of PAT1-mediated transport. 28117901_Data indicate that the glycosylation-deficient mutant of amino acid transporter PAT1 (PAT1(3)(NQ) ) is unstable and is degraded mainly via the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation pathway in HEK293 cells. 28670736_A mechanism through which amino acids may suppress the expression of PAT1 on lysosomes by inducing protein cleavage to remove a targeting signal. 30253187_Increasing the PAT1 level does not readily increase the mTORC1 activity. The lysosomal PAT1 was increased by starvation and decreased by nutrient replenishment. The lysosomal PAT1 plays a negative role on the mTORC1 activity. 31555743_SLC36A1-mTORC1 signaling drives acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000020261 |
Slc36a1 |
452.134682 |
2.8837643966 |
1.527953 |
0.080067182 |
373.135236 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003886544530514670565953043706258895922410147744540140648885143012623967778424301136727969865764950914965092944250182152578191669405746115387395515220756777593389201123913244224005890983711738478815318157538749588297832815442234277725219726562500000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001359369603563899125622118611721239845840173841989199320541406808944004603532509421863957774345503794941880626567802824693669453522785211742671389745439893714311934849546949368456404452581347308524092713788444797273768926970660686492919921875000000 |
Yes |
No |
659.4170847 |
32.9126216 |
230.0171278 |
9.3732847 |
| ENSG00000123689 |
50486 |
G0S2 |
protein_coding |
P27469 |
FUNCTION: Promotes apoptosis by binding to BCL2, hence preventing the formation of protective BCL2-BAX heterodimers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19706769}. |
Apoptosis;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway and positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:50486; |
lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238] |
16086669_A novel putative target gene of PPARalpha, G0S2 (G0/G1 switch gene 2) was identified and characterized. 18636162_G0S2 is an all-trans-retinoic acid target gene 19706769_G0S2 encodes a mitochondrial protein that specifically interacts with Bcl-2 and promotes apoptosis by preventing the formation of protective Bcl-2/Bax heterodimers 19816938_DNA methylation of G0S2 can be an important biomarker for squamous lung cancer. 19878646_mRNA expression of G0S2 was regulated mainly by DNA methylation in squamous lung cancer cell lines. 21613358_findings are compatible with the notion that the ATGL-G0S2 complex is an important long-term regulator of lipolysis under physiological conditions such as fasting in humans 22535977_Reduced mRNA and protein content of Plin and G0S2 and borderline increased ATGL protein in sc adipose tissue from poorly controlled type 2 diabetic subjects. 22716248_Gene expression profiles showed that G0/G1 switch 2 was up-regulated in epidermolysis bullosa subtypes. 22891293_Data indicate that downregulation of G0S2 in adipose tissue could represent one of the underlying causes leading to increased lipolysis in the insulin-resistant state. 23546556_This linked G0S2 subcellular localization to G0S2 transcriptional repression. The potential mechanisms responsible for this G0S2 repression are examined. 23951308_reelin expression is altered by Abeta leading to impaired reelin signaling. 24183236_A new mechanism that controls proliferation in K562 cells, suggesting a possible tumor suppressor function for G0S2 in leukemia cells. 25258314_Data indicate that the peptide corresponding to residues Lys-20 to Ala-52 from G0S2 Inhibits ATGL in the nanomolar range. 25588877_Results indicate that G0S2 acts as a prosurvival molecule in endothelial cells. 26318046_Data indicate that a tumor suppressor mechanism by which G0/G1 switch gene 2 product (G0S2) directly inhibits activity of a key intracellular adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL). 26707160_differences in G0S2 expression may explain depot-specific and obesity-associated differences in lipolysis on the molecular level 27605212_PML/RARalpha synergizes with C/EBPepsilon to reactivate the C/EBPepsilon target G0S2, thereby contributing to All-trans retinoic acid -mediated acute promyelocytic leukemia differentiation and potentially, clinical remission. 28645852_G0S2 functions as a master regulator of tissue-specific balance of TG storage vs. mobilization, partitioning of metabolic fuels between adipose and liver, and the whole-body adaptive energy response. 28910567_ER+ breast cancer cells with restored G0S2 expression had a relative increased sensitivity to tamoxifen 29209111_Palmitate can induce lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells by activating C/EBPbeta-mediated G0S2 expression. 30770352_G0S2 hypermethylation is a hallmark of rapidly recurrent or fatal ACC, amenable to targeted assessment using routine molecular diagnostics. Assessing G0S2 methylation is straightforward, feasible for clinical decision-making, and will enable the direction of efficacious adjuvant therapies for patients with aggressive ACC. 30802154_In addition to its role as a lipolytic inhibitor, G0S2 is capable of directly promoting TG synthesis by acting as a lipid-synthesizing enzyme. 31371451_We conclude that the RNF126/BAG6 complex contributes to G0S2 degradation and that interventions to prevent G0S2 degradation may offer a therapeutic strategy for managing ischemic diseases. 32171335_An epigenome-wide association study of posttraumatic stress disorder in US veterans implicates several new DNA methylation loci. 33545927_Low G0S2 gene expression levels in peripheral blood may be a genetic marker of acute myocardial infarction in patients with stable coronary atherosclerotic disease: A retrospective clinical study. |
ENSMUSG00000009633 |
G0s2 |
19.447364 |
5.6814561308 |
2.506261 |
0.447670276 |
33.376306 |
0.00000000759435905546141815118217296715769082382507804140914231538772583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000033436506990664944433013487266534435882192610733909532427787780761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.6919175 |
8.4039487 |
5.9729682 |
1.3217512 |
| ENSG00000123983 |
2181 |
ACSL3 |
protein_coding |
O95573 |
FUNCTION: Acyl-CoA synthetases (ACSL) activates long-chain fatty acids for both synthesis of cellular lipids, and degradation via beta-oxidation (PubMed:22633490). Required for the incorporation of fatty acids into phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid located on the surface of VLDL (very low density lipoproteins) (PubMed:18003621). Has mainly an anabolic role in energy metabolism. Mediates hepatic lipogenesis. Preferentially uses myristate, laurate, arachidonate and eicosapentaenoate as substrates. Both isoforms exhibit the same level of activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18003621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22633490}. |
ATP-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Membrane;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of the long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme is highly expressed in brain, and preferentially utilizes myristate, arachidonate, and eicosapentaenoate as substrates. The amino acid sequence of this isozyme is 92% identical to that of rat homolog. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2181; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; medium-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031956]; palmitoyl-CoA ligase activity [GO:0090433]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; long-chain fatty acid import into cell [GO:0044539]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0035338]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0035336]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0042998]; positive regulation of phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:2001247]; positive regulation of secretion [GO:0051047]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034379] |
11707336_Sequence analysis of genomic clones demonstrates that the human ACS3 gene spans at least 80.6 kb and contains 17 exons. 15556626_Repression of FAS mRNA expression is the consequence of feedback inhibition of FAS expression by long chain fatty acyl-CoAs, which are formed by FACL3 during its upregulation by vitamin D3in prostate cancer cells. 17761945_Oncostatin M directly lowers the plasma triglycerides in hyperlipidemia by stimulating the transcription of ACSL3/5 in the liver. 17901542_Data suggest that endogenous FATP4 does not function to translocate fatty acids across the plasma membrane, but functions more as a very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. 18003621_Small interfering RNA targeting ACSL3 inhibits secretion of hepatitis c virus from human hepatoma-derived cells 19221603_Data suggest that methylated ACSL3 5'CpG islands in umbilical cord white blood cell DNA may be a surrogate endpoint for transplacental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure and/or a potential biomarker for environmentally-related asthma. 20219900_Results suggest that liver X receptors play a regulatory role in fatty acid metabolism by direct regulation of ACSL3 in human placental trophoblast cells. 20308079_ACSL3 is a novel molecular target of PPARdelta in HepG2 cells; there is a regulatory mechanism for ACSL3 transcription in liver tissue 20605918_Results suggest that initiation of Golgi export of Lyn involves association of ACSL3 with the Lyn C-lobe, which is exposed to the molecular surface in an open conformation. 21328461_expression of ACSL3 was induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress 22357706_role of N-terminal region of acyl-CoA synthetase 3 in its function and localization on lipid droplets 23762027_activation of fatty acid import is linked to the up-regulation of cellular long chain acyl-CoA synthetase activity and identify the long chain acyl-CoA syntheatse3 (Acsl3) as a novel host factor required for polio replication. 23840832_The prominent expression of ACSL3 in VSMC. 27477280_ACSL3 is essential for mutant KRAS lung cancer tumorigenesis in vivo and is highly expressed in human lung cancer 28193492_ACLS4 and ACLS3 have roles in insulin secretion 28771887_Study shows that ACSL3 contributes to intratumoral steroidogenesis by modulating the steroidogenic genes and plays an important role in the growth of castration-resistant prostate cancer. 29450800_ACSL3 distribution closely overlapped with proteins involved in trafficking from the trans-Golgi network and endosomes. In contrast, the ACSL4 localisation pattern more closely followed that of calnexin which is an endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone. 29526665_Subcellular fractionation showed that at least 68% of ACSL3 remain at the ER even during extensive fatty acid supplementation. High resolution single molecule microscopy confirmed the abundance of cytoplasmic ACSL3 outside of LDs. 32034305_The ACSL3-LPIAT1 signaling drives prostaglandin synthesis in non-small cell lung cancer. 32286604_Immunohistochemical staining reveals differential expression of ACSL3 and ACSL4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic gastrointestinal metastases. 33030783_Metabolic enzyme ACSL3 is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with anticancer effectiveness of statins in non-small cell lung cancer. 35182729_Activation of MAT2A-ACSL3 pathway protects cells from ferroptosis in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000032883 |
Acsl3 |
1089.928096 |
2.4481749861 |
1.291707 |
0.129808224 |
96.170360 |
0.00000000000000000000010541125682219900607609176937273505887511468047667393051777893347997760997714067343622446060180664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001029014649930990445185899947249986100326807988783178342734369106747926991829444887116551399230957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1440.7708750 |
122.7344017 |
592.1429455 |
37.0366282 |
| ENSG00000124006 |
23363 |
OBSL1 |
protein_coding |
O75147 |
FUNCTION: Core component of the 3M complex, a complex required to regulate microtubule dynamics and genome integrity. It is unclear how the 3M complex regulates microtubules, it could act by controlling the level of a microtubule stabilizer (PubMed:24793695, PubMed:24793696). Acts as a regulator of the Cul7-RING(FBXW8) ubiquitin-protein ligase, playing a critical role in the ubiquitin ligase pathway that regulates Golgi morphogenesis and dendrite patterning in brain. Required to localize CUL7 to the Golgi apparatus in neurons. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21572988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24793695, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24793696}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Golgi apparatus;Immunoglobulin domain;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Cytoskeletal adaptor proteins function in linking the internal cytoskeleton of cells to the cell membrane. This gene encodes a cytoskeletal adaptor protein, which is a member of the Unc-89/obscurin family. The protein contains multiple N- and C-terminal immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains and a central fibronectin type 3 domain. Mutations in this gene cause 3M syndrome type 2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found in this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:23363; |
3M complex [GO:1990393]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; M band [GO:0031430]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; synapse [GO:0045202]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; cytoskeletal anchor activity [GO:0008093]; cardiac myofibril assembly [GO:0055003]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050775]; protein localization to Golgi apparatus [GO:0034067]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088]; retina layer formation [GO:0010842]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] |
17289344_report the cloning and characterization of OBSL1; OBSL1 is located on human chromosome 2q35 within 100 kb of SPEG, another gene related to obscurin 18477606_N-terminal Ig-domains of Obsl1 and Obscurin (Obsc) bind to titin-M10 and myomesin. Titin mutations, linked to limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2J (LGMD2J) or Salih myopathy, weaken or abrogate titin-Obsc and titin-Obsl1 binding. 19481195_Loss of OBSL1 leads to downregulation of CUL7 and results in primordial growth disorder 3-M syndrome. 19877176_OBSL1 modulates the expression of IGFBP2 and IGFBP5 proteins in 3-M syndrome. 21737058_We propose that CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 are members of a pathway controlling mammalian growth. 22156540_discussion of roles of OBSL1, CUL7 (cullin 7), and CCDC8 (coiled-coil domain containing protein 8) in growth and development using findings from patients with Miller-McKusick-Malvaux syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome [REVIEW] 23018678_Mutations in CUL7, OBSL1 and CCDC8 in 3-M syndrome lead to disordered growth factor signalling. 24711643_CUL7, OBSL1 and CCDC8 modulate the alternative splicing of the INSR 24793695_The CUL7, OBSL1, and CCDC8 proteins form a 3M complex that functions in maintaining microtubule and genome integrity and normal development. 24989974_High-quality solution NMR structures of immunoglobulin-like domains 7 and 12 from human obscurin-like protein 1 were solved. The two domains share 30% sequence identity and their structures are, as expected, rather similar. 27654294_The cytoskeletal adaptor OBSL1 was discovered as a previously unrecognized interaction partner of the minor capsid protein L2 and was identified as a proviral host factor required for HPV16 endocytosis into target cells. 27796265_Data indicate that the patient has a homozygous mutation in obscurin like 1 obscurin-like protein 1 (OBSL1) gene, and that both of the parents had heterozygous mutations on OBSL1. 27989621_Crystal structure of the obscurin(-like-1):myomesin complex reveals a trans-complementation mechanism whereby an incomplete immunoglobulin-like domain assimilates an isoform-specific myomesin interdomain sequence. 30980518_The mutational spectrum of CUL7, OBSL1, and investigation of genotype-phenotype correlation in 3M syndrome has been reported. 33135300_Three M syndrome 2 in two Indian patients. 33258289_A rare cause of syndromic short stature: 3M syndrome in three families. 34597859_Natural history of facial and skeletal features from neonatal period to adulthood in a 3M syndrome cohort with biallelic CUL7 or OBSL1 variants. |
ENSMUSG00000026211 |
Obsl1 |
331.472110 |
0.1569245036 |
-2.671857 |
0.110735985 |
637.304428 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001288811902718050024029508573538837358844402743761844712584843897204906600264717154202601288580160963750635540369405281651675700346899488237034303577893266179546470555718020104890347675382856 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000757883015303522675332805561795032241547965415282590242935881762603101887784534154015960662377621708242870522952115138088450079070945827750216535656374727801474262986508088349155622361302026 |
Yes |
Yes |
92.4829414 |
6.7900211 |
593.5743391 |
24.1688163 |
| ENSG00000124098 |
116151 |
FAM210B |
protein_coding |
Q96KR6 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in erythroid differentiation (PubMed:26968549). Involved in cell proliferation and tumor cell growth suppression (PubMed:28594398). Involved in the metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells in a PDK4-dependent manner (PubMed:28594398). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26968549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28594398}. |
Differentiation;Erythrocyte maturation;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tumor suppressor |
|
Involved in cellular response to estradiol stimulus and positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation. Located in mitochondrial outer membrane. Is intrinsic component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:116151; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; erythrocyte maturation [GO:0043249]; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045648] |
19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26968549_Both human and murine FAM210B are abundantly expressed in the later stages of erythroblast development. Moreover, the deduced amino acid sequence predicted that FAM210B is a membrane protein, and Western blot analysis demonstrated its mitochondrial localization. Loss-of-function analysis in erythroid cells suggested that FAM210B may be involved in erythroid differentiation. 28594398_it was found that low expression of FAM210B was significantly correlated with decreased survival and enhanced metastasis in vivo and in vitro, and the loss of FAM210B led to an increased mitochondrial respiratory capacity and reduced glycolysis through the downregulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4). 30366982_FAM210B is an erythropoietin target and regulates erythroid heme synthesis by controlling mitochondrial iron import and ferrochelatase activity |
ENSMUSG00000027495 |
Fam210b |
115.675375 |
0.3702959508 |
-1.433249 |
0.193805883 |
54.662934 |
0.00000000000014307956582599404309446564403898384095696443008005616093214484862983226776123046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000896753457151453158452513936227923059627681334760040954279247671365737915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
62.6214571 |
7.4634320 |
170.0466653 |
13.3187657 |
| ENSG00000124181 |
5335 |
PLCG1 |
protein_coding |
P19174 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the production of the second messenger molecules diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3). Plays an important role in the regulation of intracellular signaling cascades. Becomes activated in response to ligand-mediated activation of receptor-type tyrosine kinases, such as PDGFRA, PDGFRB, EGFR, FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4 (By similarity). Plays a role in actin reorganization and cell migration (PubMed:17229814). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10686, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17229814}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell projection;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transducer;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. This reaction uses calcium as a cofactor and plays an important role in the intracellular transduction of receptor-mediated tyrosine kinase activators. For example, when activated by SRC, the encoded protein causes the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor RasGRP1 to translocate to the Golgi, where it activates Ras. Also, this protein has been shown to be a major substrate for heparin-binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor)-activated tyrosine kinase. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5335; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; COP9 signalosome [GO:0008180]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipase C activity [GO:0050429]; neurotrophin TRKA receptor binding [GO:0005168]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; phospholipase C activity [GO:0004629]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038095]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; phosphatidylinositol metabolic process [GO:0046488]; phospholipid catabolic process [GO:0009395]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000353]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905564]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
10473113_Pharmacological and molecular inhibition of phospholipase C-gamma1 inhibits growth factor receptor-mediated invasion of breast and prostate tumor cells through Matrigel in vitro. 11353454_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11409699_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11886851_Interaction of elongation factor-1alpha and pleckstrin homology domain of phospholipase C-gamma 1 with activating its activity 11956228_Translocation of PKC[theta] in T cells is mediated by a nonconventional, PI3-K- and Vav-dependent pathway, but does not absolutely require phospholipase C 12071848_Leukotriene D4 induces association of active RhoA with phospholipase C-gamma1 in intestinal epithelial cells. 12496421_Phospholipase C gamma 1 is essential for NF-kappa B activation and lipid raft translocation of protein kinase C theta and the I kappa B kinase complex. 12771140_activation of Src kinase by depletion of glucosylceramide-based glycosphingolipids in cultured ECV304 cells is a critical up-stream event in the activation of phospholipase C-gamma1. 12788694_Stabilizes F-actin, preventing oxidative stress disruption of intestinal barrier. Essential for cellular prevention of oxidative stress of iNOS. Ability to suppress iNOS-driven reactions and cytoskeletal oxidation and disassembly. 12845332_in response to Src-dependent activation of phospholipase Cgamma1, the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor RasGRP1 translocated to the Golgi where it activated Ras 13129935_PLC gamma-dependent component of Fc epsilon RI-mediated calcium flux leading to degranulation of mast cells is independent of PI 3-kinase 14523024_PLCgamma function and activation are mediated by GIT1 through c-Src, which integrates signal transduction by GPCRs and TKRs 14647465_tr-kit promotes the formation of a multimolecular complex composed of Fyn, PLCgamma1 and Sam68, which allows phosphorylation of PLCgamma1 by Fyn, and may modulate RNA metabolism. 14702343_T-cell receptor activation of Rap1 depends on phospholipase C-gamma1 14989173_Treatment of cells of a carcinoma cell line with cysteine proteinase inhibitors results in increasing PLC1 intracellular level. Iyt is concluded that PLC1 is ubiquitinated and degraded by proteasomes. 15123640_Data suggest that hyaluronan-CD44 interaction with Rac1-protein kinase N gamma plays a pivotal role in phospholipase C gamma1-regulated calcium signaling and cortactin-cytoskeleton function required for keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion and differentiation. 15153499_LAB resembled a LAT molecule unable to bind phospholipase C-gamma1. 15161916_Tyr-783 phosphorylation of of phospholipase C-gamma 1 is not sufficient for enzyme activation 15563458_SHP-2 has a role in regulating IL-1-induced Ca2+ flux and ERK activation via phosphorylation of PLCgamma1 15623534_SLP-76 need not interact with SH3(PLC) to activate PLC-gamma1, and the P-I region of SLP-76 serves a structural role that is sequence-independent and is not directly related to protein-protein interactions 15654973_activation of store operated channels in keratinocytes depends, at least partly, on the interaction of TRPC with PLCgamma1 and IP3R 15872086_calcium activates PLC-gamma1 via increased PIP3 formation mediated by c-src- and fyn-activated PI3K 15944397_PLCgamma1 in cell motility, functioning as a mediator of both growth factor and integrin-initiated signals 15972651_PLC-gamma1 and PLC-gamma2 both regulate the functions of ITAM-containing receptors, whereas only PLC-gamma2 regulates the function of DAP10-coupled receptors. 15996687_PLCgamma1 plays a pivotal role in the migration of human colorectal cancer cells, and the upregulation of NF-kappaB binding activity and downregulation of Hsp70 expression in LoVo cells. 16341594_Data show that membrane transport of p42(IP4) induced by epidermal growth factor is inhibited by stimulation of phospholipase C-coupled thrombin receptor. 16764945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16921170_phospholipase C-gamma1 interaction with villin regulates epithelial cell migration 17023658_observations suggest a model in which TFII-I suppresses agonist-induced calcium entry by competing with TRPC3 for binding to phospholipase C-gamma 17111345_High phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C expression on the cell membrane surface is apparently involved in the ability of natural killer (NK) cytolytic cells to lyse sensitive target cells. 17130290_We show that Fas-mediated apoptosis requires endoplasmic reticulum-mediated calcium release in a mechanism dependent on phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1) activation and Ca2+ release from inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) channels. 17148460_Phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1) activation depends on a heterotrimeric complex of adaptor proteins such as SLP76. 17242406_the recruitment of PI3K to the E-cadherin/beta-catenin/p120-catenin complex via beta-catenin at the plasma membrane is required for calcium-induced phospholipase C-gamma1 activation and, ultimately, keratinocyte differentiation 17336371_Review discusses how the interaction between PLC-gamma1 and effector proteins plays a key role in on- or off-regulating PLC-gamma1-mediated cellular proliferation independent of its enzymatic activity. 17372230_corecruitment of c-Cbl and PLCgamma1 to VEGFR-2 serves as a mechanism to fine-tune the angiogenic signal relay of VEGFR-2 17419608_Results demonstrate that the gamma 1 isoform of phospholipase C associates with nuclear promyelocytic leukemia protein. 17561374_Cellular knockdown of protein kinase Cepsilon (PKCepsilon) leads to decreased activation of PLCgamma1 by epidermal growth factor (EGF). EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of PKCepsilon as well as its association with EGF receptor and PLCgamma1. 17561467_Results suggest that a PLCgamma-STAT1 pathway mediates apoptotic signaling by FGFR3 in genetic dwarfism and chondrogenic cell lines. 17562871_The association of PLCgamma1 with complexes containing GIT1 and beta-Pix is essential for its role in integrin-mediated cell spreading and motility. As a component of this complex, PLCgamma1 is also involved in the activation of Cdc42 and Rac1. 17991733_PLCgamma-mediated activation of PKCepsilon and PKCbetaI and intracellular calcium is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions from acetaldehyde-induced insult 18037957_Controls tumor cell adhesion by controlling the RAP guanine nucleotide exchange factor (RAPGEF) molecular switch. 18256683_HDAC8-selective inhibitors have a unique mechanism of action involving PLCgamma1 activation and calcium-induced apoptosis 18467332_tau interactions with Src homology 3 domains of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, phospholipase Cgamma1, Grb2, and Src family kinases are regulated by phosphorylation 18579528_PLSCR1 is a novel amplifier of FcepsilonRI signaling that acts selectively on the Lyn-initiated LAT/phospholipase Cgamma1/calcium axis, resulting in potentiation of a selected set of mast cell responses 18594017_PLCgamma-1 and c-Src activation contribute to HNSCC invasion downstream of EGF receptor 18671761_parkin interacts with PLCgamma1, affecting PLCgamma1 steady state protein levels in human and murine models with manipulated parkin function and expression levels 19018007_while Vav-1 and LAT preferentially bound to Syk, phospholipase C-gamma1 bound to both Syk and ZAP-70 19074886_Data show a critical role of PLCgamma1 in the metastatic potential of cancer cells. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19179337_Nephrin Tyr-1204 phosphorylation triggers the Ca(2+) response in a PLC-gamma1-dependent fashion. 19223396_Memo was detected in complexes with cofilin, ErbB2 and PLCgamma1. 19570985_VEGFR2-initiated PLCgamma1/calcium signaling is important but insufficient for full vWF release. 19586919_CD244 inhibition and activation depends on CD2 and phospholipase C-gamma1 19663908_parkin is an important factor for maintaining Ca2+ homeostasis and that parkin deficiency leads to a phospholipase C-dependent increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels. 19681907_YadA and invasin of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis both trigger signal transduction pathways during integrin-mediated phagocytosis into epithelial cells, which lead to the activation of Akt, PLC-gamma1, PKCalpha and -beta downstream of PI3 kinase. 19711039_Results suggest that bFGF increases the [Mg(2+)](i) from the intracellular Mg(2+) stores through the tyrosine kinase/PI3K/PLCgamma-dependent signaling pathways. 19712589_SH2D4A inhibited cell proliferation by suppression of the ERalpha/PLC-gamma/PKC signaling pathway. 19881535_We provide evidence for a previously unrecognized phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1)-controlled mechanism of mTOR/p70S6-kinase activation 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19952372_by regulating the localization of PLC-gamma1, RIAM plays a central role in TCR signaling and the transcription of target genes. 20011604_These data elucidate the role of PLCgamma1 in FGF-2 signalling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells demonstrating its key role in FGF-2-dependent tubulogenesis. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20080774_TonEBP/OREBP becomes phosphorylated at Y143, resulting in binding of PLC-gamma1 to that site, which contributes to TonEBP/OREBP transcriptional activity. 20232348_PC-PLC activity increased greatly in serum of Thromboangitis obliterans patients. 20379146_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20510673_These data suggest that PLC-gamma1 is required for EGFR-induced SCC cell mitogenesis and the mitogenic function of PLC-gamma1 is independent of its lipase activity. 20514023_miR-200bc/429 cluster targets PLCgamma1 and differentially regulates proliferation and EGF-driven invasion than miR-200a/141 in breast cancer. 20621058_These data suggest that the SH3 domain, but not the catalytic domain, is required for PLC-gamma1 to mediate EGF-induced SCC4 cell mitogenesis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20674545_These data indicate that EGF-induced cell migration is mediated by the lipase domain of PLC-gamma1 and the subsequent IP(3) generation and intracellular calcium mobilization. 20872577_over expression of SH3BP2 in RAW 264.7 cells potentiates sRANKL-stimulated phosphorylation of PLCgamma1 and PLCgamma2. 20889506_the CCR7/CCL21 signaling pathway leading to T lymphocyte migration on fibronectin is a beta1 integrin-dependent pathway involving transient ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which is modulated by PLCgamma1 21087080_Calcium-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells is delayed by HER1 receptor activation involving the Akt and PLCgamma signalling pathways. 21209106_These studies suggest that Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus has evolved to exploit ANG for its advantage via a so-far-unexplored PLC-gamma pathway for maintaining its latency. 21242968_propose c-Cbl as an angiogenic suppressor protein where upon activation it uniquely modulates PLCgamma1 activation by ubiquitination and subsequently inhibits VEGF-driven angiogenesis 21285289_In cultured vascular smooth muscle cells, phospholipase Cgamma1 expression was required for platelet-derived growth factor-induced ERK1/2 nuclear translocation, Elk-1 phosphorylation, and subsequent repression of SM alpha-actin gene expression. 21360263_The Epo/EpoR complex plays a critical role in the adhesion and migration of rat fibroblasts, and its functional inactivation is associated with PLC-gammal-dependent reduction of cell-matrix adhesion and this also affects cell migration. 21705626_PLC-gamma1, but not phospholipase C-beta3,is required for the migration of T cells in response to stromal cell-derived factor-1 21798286_Translocation of PLC-gamma 1 to the cell membrane and the associated calcium signal were enhanced only in mast cells responding to EP3 prostaglandin E2 receptor agonist sulprostone. 21986528_PLCgamma plays a key role in RhoGDI2-mediated cisplatin resistance and cell invasion in gastric cancer cells. 22022282_our approach, which is applicable to any set of interval scale traits that is heritable and exhibits evidence of phenotypic clustering, identified three new loci in or near APOC1, BRAP, and PLCG1, which were associated with multiple phenotype domains. 22262199_Report the interplay of HER2/HER3/PI3K and EGFR/HER2/PLC-gamma1 signalling in breast cancer cell migration and dissemination. 22454520_PDK1 and PLCgamma1 act on the same signalling cascade, and the PDK1/PLCgamma1 pathway is required for regulation of cell invasion. 22474331_The oncogenic truncation of this region elicits conformational changes that interfere with the Vav1-mediated activation of PLCgamma1 and that inhibit calcium mobilization. 22554284_Data indicate that Akt expression was up-regulated with high glucose and insulin in both cell lines, whereas PLCgamma expression was enhanced in colon cancer cells only. 22749651_analysis of two distinct mechanisms by which phospholipase C-gamma1 mediates epidermal growth factor-induced keratinocyte migration and proliferation 22837484_T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated proliferation is impaired in PLCgamma1/PLCgamma2 double-deficient T cells compared with PLCgamma1 single-deficient T cells. 22847294_High expression of PLCgamma1, and of its activated forms, is associated with a worse clinical outcome. 23063561_The role of four domains of human PLCG1 defined by structural and biochemical investigation. 23063587_PLC-gamma1 is highly expressed in brain and participates in neuronal cell functions mediated by neurotrophins. (Review) 23629676_The degradation of zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), and claudin-2 exhibited a great dependence on the activation of the transient receptor potential melastatin (TRPM) 2 channel, phospholipase Cgamma1 (PLCgamma1) and the protein kinase Calpha (PKCalpha) signaling cascade. 23703528_study showed that PLC-gamma directly binds c-Src through its SH2 domains, and this interaction is necessary for carbachol mediated inhibition of NHE3 activity in Caco-2/BBe/NHE3 cells 23925006_Phospholipase C gamma1 plays a key role in cell migration and invasion. [review] 24412752_A portion of PLC-gamma1 phosphorylated on tyrosine 783 is not found at LAT-containing clusters but instead is located at TCR-containing clusters. 24440983_Metastatic outcome can be dictated by the constitutive competition between Grb2 and Plcgamma1 for the phosphorylation-independent binding site on FGFR2. 24497536_Increased proliferative and survival mechanisms in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma may partially depend on the acquisition of somatic mutations in PLCG1 and other genes that are essential for normal T-cell differentiation. 24502564_PLCgamma1 signaling is the dominant pathway in promoting limbic epileptogenesis. 24633157_PLCG1, a signal transducer of tyrosine kinases, encoded a recurrent, likely activating p.Arg707Gln missense variant in 3 of 34 cases of angiosarcoma. 24706664_Results reveal that PLCG1 is genetically altered in a significant portion of Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. 24785188_Extracellular K(+) concentration regulated the levels of activated PLC-gamma1, chromosome X, and carbachol-stimulated intracellular Ca(2+) mobilization in human endothelial cells 24795022_Results provide evidence that PTPRB and PLCG1 mutations are driving events in a subset of secondary angiosarcomas. 24866019_The activation of the gamma1 isoform of phospholipase C (PLCgamma1) is critical for pressure sensing in cerebral arteries and subsequent vasoconstriction. 25162020_This SOCS7 knockdown-attributed effect could be due to a precise anti-PLCg-1 role. 25252913_these findings indicate that the PLCgamma1-R707Q mutation causes constitutive activation of PLCgamma1 and may represent an alternative way of activation of KDR/PLCg1 signaling besides KDR activation in angiosarcomas 25304611_Recurrent presence of the PLCG1 S345F mutation is associated with nodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas. 25456276_Data from structural, genetic, and mechanistic studies on the role of PLCG1 in cell biology suggest that dysfunctional forms of PLCG1 are linked to immune disorders and cancer. [REVIEW] 25491205_PLCgamma1 is part of the molecular mechanism. 25910029_PLLG1 protein mutations are uncommon in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. 25964059_hsa-miR-665 and hsa-miR-95 were downregulated in GSRCC but upregulated in intestinal gastric adenocarcinoma, and the relatively differential expression of the miRNAs negatively controlling their target genes, GLI2 and PLCG1 26212011_We show that the decrease in PI(4,5)P2 level under non-stimulated conditions inhibits PTEN activity leading to the aberrant activation of the oncoprotein Akt. As well as defining a novel mechanism of Akt phosphorylation with important therapeutic consequences, we also demonstrate that differential expression levels of FGFR2, Plc11 and Grb2 correlate with patient survival 26464646_expression of PLC-gamma1 and PIKE positively correlated with the tumor differentiation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 26481038_In a transgenic mouse model, PLCgamma1 is the dominant signaling effector by which activation of TrkB promotes epilepsy. 26482290_FGFR1 dimers forms a complex with its effector PLCgamma1. 26639088_Dysregulation of primary PLC signaling is linked to several brain disorders including epilepsy, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, Huntington's disease, depression and Alzheimer's disease. (Review) 26735859_Report PLCG1 genetic alterations in angiosarcomas. 26811493_High PLC gamma1 expression is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. 26896280_High FLC gamma expression is associated with Radioresistance in Glioblastoma. 27025961_These results suggest that immobilized EGF increases collective keratinocyte displacement via an increase in single-cell migration persistence resulting from altered EGFR trafficking and PLCgamma1 activation. 27221712_LAT and phospholipase C-gamma dephosphorylation by SHP-1 inhibits natural killer cell cytototoxicity 27310357_the PLCgamma-1 signaling plays an important role in the H1N1-induced inflammatory responses. Our study suggests that targeting the PLCgamma-1 signaling is a potential antiviral therapy against H1N1 by inhibiting both viral replication and excessive inflammation. 27340655_These results indicate that PP1 is recruited to the extracellular calcium-dependent E-cadherin-catenin-PIP5K1a complex in the plasma membrane to activate PIP5K1a, which is required for PLC-g1 activation leading to keratinocyte differentiation. 27464494_PLCG1, along with ITGA4 are regulated by miR-30b in clinical samples of coronary artery cells from coronary atherosclerosis patients. 27519475_the central biological role of the novel IL-2-R/Lck/PLCgamma/PKCtheta;/alphaPIX/Rac1/PYGM signalling pathway is directly related to the control of fundamental cellular processes such as T cell migration and proliferation. 27707630_The products of PLC-gamma activity mediate the innate immune response by regulating respiratory burst, phagocytosis, cell adhesion, and cell migration. (Review) 28112359_High PLC gamma expression is associated with breast cancer. 28574619_Results show that PLCgamma-1 activation enhanced skin cell transformation. 28644030_a previously unappreciated role for PLC-gamma1 in the positive regulation of Zap-70 and T-cell receptor tyrosine phosphorylation. Conversely, PLC-gamma1 negatively regulated the phosphorylation of SLP-76-associated proteins, including previously established Lck substrate phosphorylation sites within this complex. 28786489_Syk-induced signals in bone marrow stromal cell lines are mediated by phospholipase C gamma1 (PLCgamma1) in osteogenesis and PLCgamma2 in adipogenesis. 28926770_1,25(OH)2D3 indirectly modulates the differentiation of Treg/Th17 cells by a ff ;ecting the VDR/PLC-gamma1/TGF-beta1pathway. These results indicate that administration 1,25(OH)2D3 supplements may be a beneficial treatment for organ transplantation recipients. 28994193_the forced expression of FGFR2b signalling mutants and the use of specific inhibitors of FGFR2b substrates showed that the receptor-triggered autophagy requires PLCgamma signaling. 29066806_novel insight into autophagy regulation by PLCgamma1 in colon cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma cells 29174396_PLCgamma1: Potential arbitrator of cancer progression. 29242050_Data suggest that FGFR3 with mutation found in SADDAN (but not FGFR3 with mutation found in TDII) affects cytoskeleton organization in chondrocytes by inducing tyrosine hyperphosphorylation of paxillin; binding of FGFR3 to PLCG1 appears to be involved. (FGFR3 = fibroblast growth factor receptor 3; SADDAN = Severe Achondroplasia with Developmental Delay and Acanthosis Nigricans; TDII = Thanatophoric Dysplasia type II) 30005593_PLCgamma2 plays a critical role for Ca(2+) Flux in HCECs stimulated by A. fumigatus hyphae. Syk acts upstream of PLCgamma2 in the Dectin-1 signaling pathway. 30649922_Induced miR-222 represses expression of ZBP1 and PLCgamma1 at the posttranscriptional level. 30720116_In pancreatic cancer (PC) tissue samples expression of TSPAN1 was markedly increased compared to normal samples. siRNA knockdown of TSPAN1 in PC cell lines suppressed PC cell migration and invasion and downregulated MMP2 expression. Transfection with siRNA targeted to PLCgamma revealed that TSPAN1 siRNA suppressed PC cell migration and invasion, and MMP2 expression by blocking the translocation and phosphorylation of P... 31298409_BDNF activates TrkB/PLCgamma1 signaling pathway to promote proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells through inhibition of apoptosis. 31362705_PLCgamma1 overexpression is a strong predictive surrogate marker of development of metastases in early Luminal-A and -B breast cancer patients, being able to discriminate patients with high and low risk of metastases. 31376383_Frequent and Persistent PLCG1 Mutations in Sezary Cells Directly Enhance PLCgamma1 Activity and Stimulate NFkappaB, AP-1, and NFAT Signaling. 31548507_a combination of various biophysical methods has been employed to shed light on the atomistic interactions between PLCgamma1 and its known binding partners. Indeed, molecular modeling of PLCgamma1 with SLP76 peptide and with previously reported inhibitors 31755660_Reduced PLCG1 expression is associated with inferior survival for myelodysplastic syndromes. 31889510_we describe the 2.5 A-resolution crystal structure of essentially full-length PLC-gamma1. The structure highlights a regulatory array exquisitely positioned to prevent membrane engagement of the catalytic core while simultaneously arranged to scaffold tyrosine kinases and additional regulatory proteins into a signaling nexus. 31918402_Structural insights and activating mutations in diverse pathologies define mechanisms of deregulation for phospholipase C gamma enzymes. 32945365_PLCgamma1dependent invasion and migration of cells expressing NSCLCassociated EGFR mutants. 32973083_FGFR1 Is Critical for RBL2 Loss-Driven Tumor Development and Requires PLCG1 Activation for Continued Growth of Small Cell Lung Cancer. 33077911_PLCgamma1 suppression promotes the adaptation of KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinomas to hypoxia. 33236921_Phospholipase C controls chloride-dependent short-circuit current in human bronchial epithelial cells. 33397809_Prediction of Alzheimer's disease-specific phospholipase c gamma-1 SNV by deep learning-based approach for high-throughput screening. 34695195_PLCG1 is required for AML1-ETO leukemia stem cell self-renewal. 34697421_Phospholipase Cgamma1 (PLCG1) overexpression is associated with tumor growth and poor survival in IDH wild-type lower-grade gliomas in adult patients. 34793541_A computational in silico approach to predict high-risk coding and non-coding SNPs of human PLCG1 gene. 35848503_Methylation-mediated silencing of PTPRD induces pulmonary hypertension by promoting pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell migration via the PDGFRB/PLCgamma1 axis. 36153805_Loss of phospholipase Cgamma1 suppresses hepatocellular carcinogenesis through blockade of STAT3-mediated cancer development. |
ENSMUSG00000016933 |
Plcg1 |
241.286994 |
0.4853575816 |
-1.042880 |
0.277117231 |
13.856605 |
0.00019730200038485848877678474622143767192028462886810302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000517444478621270696587497450735781967523507773876190185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
152.1295601 |
31.7071217 |
316.4145832 |
47.2826230 |
| ENSG00000124191 |
84969 |
TOX2 |
protein_coding |
Q96NM4 |
FUNCTION: Putative transcriptional activator involved in the hypothalamo-pituitary-gonadal system. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables transcription coactivator activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84969; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
14764631_Identification and functional analysis of the rat Gcx1 ortholog. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22496870_A novel aberrantly hypermethylated CpG island in cancer was discovered within the TOX2 promoter. TOX2 was unmethylated in normal cells. Expression of two novel TOX2 transcripts was significantly reduced in primary lung tumors. 25352127_TOX2 plays a crucial role in controlling normal NK cell development by acting upstream of TBX21 transcriptional regulation 28153336_A haplotype block across a 24-kb region within the TOX2 gene reached genome-wide significance in haplotype-block-based regional heritability mapping. Single-SNP- and haplotype-based association tests demonstrated that five of nine genotyped SNPs and two haplotypes within this block were significantly associated with major depressive disorder. 35111387_CD4+ T cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma express exhaustion associated transcription factors TOX and TOX2: Characterizing CD4+ T cells in Hodgkin lymphoma. |
ENSMUSG00000074607 |
Tox2 |
84.979458 |
2.3554762267 |
1.236019 |
0.221203779 |
30.961063 |
0.00000002632572206077217644091314281869220526033359419670887291431427001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000110169452117095922961206736021694263527592738682869821786880493164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
120.7816789 |
15.1778593 |
51.4994566 |
5.0522421 |
| ENSG00000124222 |
8675 |
STX16 |
protein_coding |
O14662 |
FUNCTION: SNARE involved in vesicular transport from the late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18195106}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the syntaxin or t-SNARE (target-SNAP receptor) family. These proteins are found on cell membranes and serve as the targets for V-SNARES (vesicle-SNAP receptors) permitting specific synaptic vesicle docking and fusion. A microdeletion in the region of chromosome 20 where this gene is located has been associated with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ib. Multiple transcript variants have been found for this gene. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the neighboring downstream aminopeptidase-like 1 (NPEPL1) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:8675; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cisterna [GO:0031985]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
15800843_the region of overlap between the two microdeletions likely harbors a cis-acting imprinting control element that is necessary for establishing and methylation at GNAS exon A/B, thus allowing normal G alpha(s) expression in the proximal renal tubules. I 17389686_function of syntaxin 16 was specifically required for, and restricted to, the retrograde pathway 17852734_Syntaxin 16 may thus play a role in neurite outgrowth and perhaps other specific dendritic anterograde/retrograde traffic. 19887622_phosphorylation of RASSF1A by Aurora B is required for the recruitment of Syntaxin16 20826815_Results suggest that STX16 mediates recycling of CFTR and constitutes an important component of CFTR trafficking machinery in intestinal epithelial cells. 23087324_De novo 3-kb STX16 deletions, reported only once previously, are infrequent but should be excluded in all cases of Pseudohypoparathyroidism-Ib, even when the family history is negative for an inherited form of this disorder. 23095209_A patient with familial pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ib and his asymptomatic brother were found to have methylation defect at GNAS (guanine nucleotide-binding protein G) and microdeletion involving exons 4-6 of neighboring gene STX16. [CASE REPORT] 23677696_Data indicate that depletion of VAMP4, syntaxin 6, syntaxin 16, and Vti1a disrupted the Golgi ribbon structure. 24109596_syntaxin 16 is a key regulator of cytokinesis. 25843330_STX16 microdeletion was identified in male monozygotic twins (with pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1B leading to growth hormone deficiency) and mother/grandmother (not father/grandfather or sister [their triplet with separate placenta]). [CASE STUDY] 27338644_we here present a patient with PHP1b caused by a recurrent STX16 deletion, presenting with macrosomia, early onset obesity, and macrocephaly without other AHO symptoms. we reemphasize STX16 deletions and PHP1b as a rare cause for early onset obesity and macrosomia. 33247854_Preferential Maternal Transmission of STX16-GNAS Mutations Responsible for Autosomal Dominant Pseudohypoparathyroidism Type Ib (PHP1B): Another Example of Transmission Ratio Distortion. 33269569_Analysis of defects in GNAS and STX16 genes in a Chinese family with pseudohypoparathyroidism. 34477200_Progression of PTH Resistance in Autosomal Dominant Pseudohypoparathyroidism Type Ib Due to Maternal STX16 Deletions. |
ENSMUSG00000027522 |
Stx16 |
1226.543450 |
0.4809018316 |
-1.056186 |
0.055470302 |
363.352624 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000524286878089699794408998302684044638353118518119137081104961618065616761060040149884918991320197491583652349891983491043238571477311324185683999140166415200897526866128786939092623141989616554996386441067635075796715682372450828552246093750000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000178305859921750448194057318406782791565793374712521620670167211590702741052912786662755847044106879688177355135551056786288178206722810698448453110433703793829159764576836382721431370674503523975074070762047995231114327907562255859375000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
791.5731769 |
60.7084596 |
1657.3249831 |
90.9475094 |
| ENSG00000124222_ENSG00000215440 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53.406382 |
0.1857090887 |
-2.428884 |
0.630277647 |
13.589703 |
0.00022742964192619727738578494502519333764212206006050109863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000590165526517347433302362880169766867766156792640686035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.4183545 |
17.9873824 |
101.7818519 |
67.5064601 |
| ENSG00000124225 |
56937 |
PMEPA1 |
protein_coding |
Q969W9 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a negative regulator of TGF-beta signaling and thereby probably plays a role in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, motility, extracellular matrix production and immunosuppression. In the canonical TGF-beta pathway, ZFYVE9/SARA recruits the intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulators SMAD2 and SMAD3 to the TGF-beta receptor. Phosphorylated by the receptor, SMAD2 and SMAD3 then form a heteromeric complex with SMAD4 that translocates to the nucleus to regulate transcription. Through interaction with SMAD2 and SMAD3, LDLRAD4 may compete with ZFYVE9 and SMAD4 and prevent propagation of the intracellular signal (PubMed:20129061, PubMed:24627487). Also involved in down-regulation of the androgen receptor (AR), enhancing ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of AR, probably by recruiting NEDD4 (PubMed:18703514). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18703514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20129061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24627487}. |
Alternative splicing;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal transduction inhibitor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that contains a Smad interacting motif (SIM). Expression of this gene is induced by androgens and transforming growth factor beta, and the encoded protein suppresses the androgen receptor and transforming growth factor beta signaling pathways though interactions with Smad proteins. Overexpression of this gene may play a role in multiple types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:56937; |
early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; WW domain binding [GO:0050699]; androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030521]; negative regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060394]; negative regulation of SMAD protein complex assembly [GO:0010991]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512] |
12670906_Expression of PMEPA1 was well maintained both in colon cancer primary tumors and in colon cancer liver metastases. 12907594_PMEPA1 negatively regulates growth of androgen responsive or refractory prostate cancer cells, and these functions may be mediated through the interaction of PMEPA1 with the NEDD4 protein. 17318295_Differentially expressed genes were identified, including E-cadherin, IL-8 and STAG1/PMEPA1 in an androgen-independent prostate cancer PC3 subclone. 18174752_DNA methylation within the PMEPA1 promoter downstream sequences suggests that methylation of SP1 binding sites may also contribute to the repression of PMEPA1 gene 18703514_decreased PMEPA1 expression frequently noted in prostate cancers may lead to increased AR functions and strengthen the biological role of the NEDD4-binding protein PMEPA1 in prostate cancers 20610632_Results suggest that TMEPAI functions in breast cancer as a molecular switch that converts TGF-beta from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter. 23615405_The levels of TMEPAI in lung tumor tissues are very high. 24438557_TMEPAI promotes tumorigenic activities in lung cancer cells. 24694733_Downregulation of PMEPA1 may result in increased androgen receptor protein levels and function in cancer of the prostate cells, contributing to prostate tumorigenesis. 24933703_TMEPAI is translocated on the lysosome and late endosome, and that association with Nedd4 is required for the transport of TMEPAI to the lysosome. 25482449_EGF signaling collaboratively regulates TGF-beta-induced TMEPAI expression. 25883222_Data show that silencing of PMEPA1 protein facilitates the growth of prostate cancer cells and modulates androgen receptor (AR) through NEDD4 ubiquitin protein ligase and PTEN protein. 26215835_binding of SMAD2/3, the intracellular effectors of activin signaling, was significantly enriched at the Pmepa1 gene, which encodes a negative feedback regulator of TGF-beta signaling in cancer cells, and at the Kdm6b gene, which encodes an epigenetic regulator promoting transcriptional plasticity. 26590303_these data elaborated on the diverse activity among TCF/LEF family members with respect to the transcriptional regulation of the TMEPAI gene. 26758191_PMEPA1 was upregulated in breast cancer cell lines as well as in a set of clinical invasive breast ductal carcinomas. Interestingly, depletion of PMEPA1 decreased breast cancer stem cell (CSC)-enriched populations, while ectopic overexpression of PMEPA1 increased breast CSC-enriched populations. 26927372_Data show that over-expressed transmembrane prostate androgen-induced protein 1 (PMEPA1) can promote cell migration and maintain the mesenchymal-like morphology of breast cancer cells. 27035427_the present study suggest that the upregulation of miR19a3p expression levels contributes to tumor progression and that one of its underlying mechanisms involves inhibition of PMEPA1 expression. 27163528_study showed that the inhibition of autophagy induced by the depletion of TMEPAI is involved in regulation of Beclin-1. 27625141_Sp1 up-regulated TMEPAI protein expression, as well as Sp1 promoting TMEPAI-induced cell proliferation. 27697531_these findings indicated that PMEPA1 participates in TGF-beta- and hypoxia-regulated gene expression networks in solid tumors and thereby may contribute to tumor progression. 29467225_This study highlights that TMEPAI decreases c-Maf stability by recruiting the ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 to c-Maf for proteasomal degradation in myeloma cells. 29945215_describe recent progresses in the understanding of how the TMEPAI family physiologically contributes to cellular functions and diseases 30069967_JHY-A007-50 mediates the downregulation of TMEPAI expression. 30873542_observed that knockout (KO) of PMEPA1 in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 using a CRISPR-Cas9 system resulted in reduction of in vivo tumour growth and lung metastasis but not of in vitro monolayer growth capacity of these KO cell lines 30887697_Prostate transmembrane protein androgen induced 1 (PMEPA1) promotes colorectal cancer metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vivo and in vitro. 30890370_These data suggest that TMEPAI suppresses Wnt signaling by interfering with beta-catenin stability and nuclear translocation in a TGF-beta signaling-independent manner. 31605013_PMEPA1 isoform a drives progression of glioblastoma by promoting protein degradation of the Hippo pathway kinase LATS1. 32181976_PMEPA1/TMEPAI isoforms function via its PY and Smad-interaction motifs for tumorigenic activities of breast cancer cells. 32842649_PMEPA1 Gene Isoforms: A Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. 33831430_Diagnostic and therapeutic values of PMEPA1 and its correlation with tumor immunity in pan-cancer. 33857498_PMEPA1 Stimulates the Proliferation, Colony Formation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via the MAPK Signaling Pathway. 33896822_PMEPA1 facilitates non-small cell lung cancer progression via activating the JNK signaling pathway. 34254950_Linc00941 regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via functioning as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-877-3p to modulate PMEPA1 expression. 34777336_PMEPA1 Is a Prognostic Biomarker That Correlates With Cell Malignancy and the Tumor Microenvironment in Bladder Cancer. 35497877_PMEPA1 Serves as a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlates with Immune Infiltrates in Cervical Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000038400 |
Pmepa1 |
15.591499 |
3.4881778338 |
1.802474 |
0.729826472 |
5.663300 |
0.01732349973611622614977356704457633895799517631530761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031516683853700912243400722445585415698587894439697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.0396945 |
10.3695543 |
6.1797402 |
2.2685826 |
| ENSG00000124257 |
140825 |
NEURL2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BR09 |
FUNCTION: Plays an important role in the process of myofiber differentiation and maturation. Probable substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex, which mediates the ubiquitination of proteins. Probably contributes to catalysis through recognition and positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. During myogenesis, controls the ubiquitination and degradation of the specific pool of CTNNB1/beta-catenin located at the sarcolemma (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a protein that is involved in the regulation of myofibril organization. This protein is likely the adaptor component of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex in striated muscle, and it regulates the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of beta-catenin during myogenesis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:140825; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556] |
19472918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000039873 |
Neurl2 |
13.131063 |
0.2504510747 |
-1.997399 |
0.492183451 |
17.342616 |
0.00003121085697698919666663239236292781697557074949145317077636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000092356104446744284640694044874464907479705289006233215332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5635275 |
1.7632153 |
18.1605948 |
4.3921789 |
| ENSG00000124406 |
10396 |
ATP8A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2Q0 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic component of a P4-ATPase flippase complex which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of aminophospholipids from the outer to the inner leaflet of various membranes and ensures the maintenance of asymmetric distribution of phospholipids (PubMed:31416931). Phospholipid translocation seems also to be implicated in vesicle formation and in uptake of lipid signaling molecules. In vitro, its ATPase activity is selectively and stereospecifically stimulated by phosphatidylserine (PS) (PubMed:31416931). The flippase complex ATP8A1:TMEM30A seems to play a role in regulation of cell migration probably involving flippase-mediated translocation of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) at the plasma membrane (By similarity). Acts as aminophospholipid translocase at the plasma membrane in neuronal cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70704, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31416931}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The P-type adenosinetriphosphatases (P-type ATPases) are a family of proteins which use the free energy of ATP hydrolysis to drive uphill transport of ions across membranes. Several subfamilies of P-type ATPases have been identified. One subfamily catalyzes transport of heavy metal ions. Another subfamily transports non-heavy metal ions (NMHI). The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the third subfamily of P-type ATPases and acts to transport amphipaths, such as phosphatidylserine. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10396; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; chromaffin granule membrane [GO:0042584]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; organelle membrane [GO:0031090]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; synapse [GO:0045202]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019829]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylserine flippase activity [GO:0140346]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; aminophospholipid translocation [GO:0140331]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; learning [GO:0007612]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of phospholipid translocation [GO:0061092]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
17229723_APLT has a role in macrophage-induced nitrosylation/oxidation plays an important role in cell clearance 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23269685_the phospholipid flippase complex of ATP8A1 and CDC50A proteins has a role in cell migration 25595798_Depletion of ATP8A1 impaired the asymmetric transbilayer distribution of phosphatidylserine in recycling endosomes, dissociated EHD1 from recycling endosomes, and generated aberrant endosomal tubules that appear resistant to fission. 26415732_The increased level of intracellular ATP8A1 protein attenuated the inhibitor role of miR-140-3p in the growth and mobility of NSCLC cell. 27287255_A pronounced induction of the flippase Atp8a1 was observed in post-mortem tissue homogenates from the hippocampus and temporal lobe of juvenile autistic subjects compared to age-matched controls. 29093443_Knockdown of ATP8A1 (a recycling endosome phosphatidlyserine-flippase) suppresses nuclear localization of YAP and YAP-dependent transcription. ATP8A1 knockdown increases the phosphorylated (activated) form of Lats1 that phosphorylates and inactivates YAP. 30282721_Single-nucleotide polymorphism, rs17448506, located in ATP8A1 intron, reached the significance threshold for interaction with tobacco smoke expose and bronchial hyperresponsiveness (p=10-5). 30457983_Over-expression of ATP8A1 alleviated ethanol-induced hepatocyte injury. Moreover, the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway appears to participate in inhibition of ethanol-induced hepatocyte apoptosis. 30674456_ATP8A1 is cleaved by the cysteine protease calpain during apoptosis, and the cleavage is prevented indirectly by caspase inhibition, involving blockage of calcium influx into platelets and subsequent calpain activation. 31416931_cryo-electron microscopy structure of six intermediates of the human flippase ATP8A1 bound to the partner protein CDC50a; ATP binding and autophosphorylation of ATP8A1 drive a cycle of conformations in which lipids bind differently, powering translocation. 33990468_AP-3-dependent targeting of flippase ATP8A1 to lamellar bodies suppresses activation of YAP in alveolar epithelial type 2 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000037685 |
Atp8a1 |
214.514784 |
0.4879639292 |
-1.035154 |
0.195921145 |
27.241104 |
0.00000017959961210546369068329867080963113679104026232380419969558715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000690156280832242679311818757403873547673356370069086551666259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
154.7426039 |
21.0616800 |
320.5694195 |
30.9905677 |
| ENSG00000124459 |
7596 |
ZNF45 |
protein_coding |
Q02386 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7596; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19195718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 32363570_our study discovered 3 novel population-specific functional genetic variants (rs6913677, rs2078267, rs8100011) in 2 novel (SLC22A11 and ZNF45) and 1 earlier reported gene (BAI3) for BMI in Indians. Our study decodes key genomic loci underlying obesity phenotype in Indians that may serve as prospective drug targets in future |
ENSMUSG00000074282 |
Zfp94 |
123.292606 |
0.2387567821 |
-2.066386 |
0.848110611 |
5.462229 |
0.01943184742227665670610825543462851783260703086853027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034947492135104597787975677647409611381590366363525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
49.2658029 |
34.9754520 |
200.5565810 |
100.0228451 |
| ENSG00000124523 |
23408 |
SIRT5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NXA8 |
FUNCTION: NAD-dependent lysine demalonylase, desuccinylase and deglutarylase that specifically removes malonyl, succinyl and glutaryl groups on target proteins (PubMed:21908771, PubMed:22076378, PubMed:24703693, PubMed:29180469). Activates CPS1 and contributes to the regulation of blood ammonia levels during prolonged fasting: acts by mediating desuccinylation and deglutarylation of CPS1, thereby increasing CPS1 activity in response to elevated NAD levels during fasting (PubMed:22076378, PubMed:24703693). Activates SOD1 by mediating its desuccinylation, leading to reduced reactive oxygen species (PubMed:24140062). Activates SHMT2 by mediating its desuccinylation (PubMed:29180469). Modulates ketogenesis through the desuccinylation and activation of HMGCS2 (By similarity). Has weak NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity; however this activity may not be physiologically relevant in vivo. Can deacetylate cytochrome c (CYCS) and a number of other proteins in vitro such as UOX. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K2C6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18680753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21908771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22076378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24140062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29180469}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;NAD;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sirtuin family of proteins, homologs to the yeast Sir2 protein. Members of the sirtuin family are characterized by a sirtuin core domain and grouped into four classes. The functions of human sirtuins have not yet been determined; however, yeast sirtuin proteins are known to regulate epigenetic gene silencing and suppress recombination of rDNA. Studies suggest that the human sirtuins may function as intracellular regulatory proteins with mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. The protein encoded by this gene is included in class III of the sirtuin family. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:23408; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; NAD+ binding [GO:0070403]; NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity [GO:0034979]; protein-glutaryllysine deglutarylase activity [GO:0061697]; protein-malonyllysine demalonylase activity [GO:0036054]; protein-succinyllysine desuccinylase activity [GO:0036055]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; peptidyl-lysine demalonylation [GO:0036047]; peptidyl-lysine desuccinylation [GO:0036049]; protein deacetylation [GO:0006476]; protein deglutarylation [GO:0061698]; protein demalonylation [GO:0036046]; protein desuccinylation [GO:0036048]; regulation of ketone biosynthetic process [GO:0010566]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667] |
16484774_SIRT5 consists of eight exons and is found in two isoforms, which encode a 310 aa and a 299 aa protein, respectively. 16827919_Analyses did not yield convincing evidence for associations of schizophrenia with SIRT5. 16827919_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18680753_Results describe the substrates and regulation mechanisms for the human mitochondrial sirtuins Sirt3 and Sirt5. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20887790_SIRT5 represents a risk factor for mitochondrial dysfunction-related diseases, including Parkinson's, through accelerated molecular aging of disease-related genes. 21143562_these results indicate that human SIRT5 potentially controls various primate-specific functions via two isoforms with different intracellular localizations or stabilities. 21908771_we demonstrate that Sirt5, a member of the class III lysine deacetylases, can catalyze lysine demalonylation and lysine desuccinylation reactions both in vitro and in vivo 22076378_study found that Sirt5 is an efficient protein lysine desuccinylase and demalonylase in vitro; protein lysine succinylation may represent a posttranslational modification that can be reversed by Sirt5 in vivo 22585829_NAD(+)-dependent SIRT deacetylase has a role in regulating the expression of mitochondrial steroidogenic P450 22767592_The bicyclic intermediate structure provides insights into the desuccinylation mechanism of human sirtuin 5 (SIRT5). 23028781_Analysis of Sirt5 structures and activity data suggest that an Arg/succinate interaction is the molecular basis of the differential nicotinamide sensitivities of the two Sirt5 activities. 23475622_Downregulation of SIRT5 is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 23978077_Results suggest a role for SIRT5 in influencing oocyte quality and in vitro fertilization outcomes. 24140062_These results reveal a novel post-translational regulation of SOD1 by means of succinylation and SIRT5-dependent desuccinylation, which is important for the growth of lung tumor cells. 24464653_Expression of SIRT5 in the entorhinal cortex, hippocampus, and white matter increases during the progression of Alzheimer disease. It is seen in activated microglia. 25032863_SIRT1/SIRT5-mediated PML deacetylation plays a role in the regulation of cancer cell survival. 25070488_High SIRT5 expression facilitates cancer cell growth and drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. 25111069_The results reveal the Sirt5 substrate acyl selectivity and its molecular basis and enable the design of inhibitors for Sirt5. 25165814_Results show that mitochondrial sirtuins SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5 can promote increased mitochondrial respiration and cellular metabolism and respond to excess glucose by inducing a coordinated increase of glycolysis and respiration. 25361925_This study demonstrated that SIRT15 downregulation in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. 25717114_Data showed that SIRT5 was involved in protein post-translational modifications through its potent demalonylase, desuccinylase, and deglutarylase activities. Also, the protein was found in the mitochondrial, cytoplasmic, and nuclear compartments. [review] 26001219_Use of a pan-sirtuin inhibitor and shRNA-mediated protein knockdown led us to uncover a role for the NAD(+)-dependent family of sirtuins, and in particular for SIRT2 and SIRT5, in the regulation of the necroptotic cell death program 26701732_Data indicate that compared to non-neoplastic endometria (NNE), endometrial cancer (EC) showed SIRT7 mRNA overexpression, whereas SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT4 and SIRT5 were underexpressed, and no significant differences were observed for SIRT3 and SIRT6. 27023330_mutual cooperation between Y102 and R105 residues in promoting the desuccinylation versus deacetylation reaction in SIRT5. 27113762_Our study uncovers a SIRT5-dependent mechanism that regulates cellular NADPH homeostasis and redox potential by promoting IDH2 desuccinylation and G6PD deglutarylation. 27164052_The function of the three mitochondrial sirtuins (SIRT3, SIRT4, SIRT5) and their role in disease are reviewed. 27577743_Results demonstrated presence of endogenous SIRT5 in mitochondria of cultured SH-EP cells, identified down-regulation of cellular oxidative stress by SIRT5 as one of the possible mechanisms mediating the anti-apoptotic effect of SIRT5 in SH-EP cells. 27626398_a side chain-to-side chain cyclic pentapeptide harboring a central N(epsilon)-carboxyethyl-thiocarbamoyl-lysine residue behaved as a strong and selective (versus human SIRT1/2/3/6) inhibitor against human SIRT5-catalyzed deacylation reaction. 28036303_Results show that SIRT5 binds to, desuccinylates and inhibits PKM2 activity. Increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) decreases succinylation and activity of PKM2 by increasing its binding to SIRT5. Moreover, inhibition of SIRT5 suppresses tumor cell proliferation through desuccinylation of PKM2 K498. 28458255_Data (including data from studies using knockout mice) suggest that SIRT5 is targeted to protein complexes on the inner mitochondrial membrane via affinity for cardiolipin to promote respiratory chain function, particularly Complex I and Complex II; SIRT5 expression is observed in inner mitochondrial membrane of periportal hepatocytes. 28707979_In this study, we summarize biological functions of SIRT5 reported in normal tissues and in cancer and discuss potential mechanisms whereby SIRT5 may impact tumorigenesis, particularly focusing on its reported roles in metabolic reprogramming. Finally, we review current efforts to target SIRT5 pharmacologically 29115436_SIRT5 gene has an important regulatory role in liver carcinogenesis, and may function as a novel potential therapeutic target for HCC. 29180469_High SIRT5 expression is associated with Cancer Cell Proliferation. 29416026_This study showed that SIRT5 supports the anaplerotic entry of glutamine into the TCA cycle in malignant phenotypes of CRC via activating GLUD1. 29491006_Our study reveals a novel role of SIRT5 in inhibiting peroxisome-induced oxidative stress, in liver protection, and in suppressing hepatocellular carcinoma development. 29514096_Sirt5 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapeutic agents and/or cetuximab may represent a therapeutic strategy for colorectal cancer patients harboring wild-type Kras. 29637793_SIRT5 plays pivotal roles in cardiac physiology and stress responses and is involved in the regulation of numerous aspects of myocardial energy metabolism. SIRT5 is implicated in neoplasia, as both a tumor promoter and suppressor in a context-specific manner, and may serve a protective function in the setting of neurodegenerative disorders. 29896817_The roles of the CDK2/SIRT5 axis in gastric cancer. 29932920_In human beings, SIRT5 gene encodes for four SIRT5 protein isoforms, namely SIRT5iso1, SIRT5iso2, SIRT5iso3, and SIRT5iso4. SIRT5(iso1-3) were mitochondria-localized, while SIRT5(iso4) localized mainly in cytoplasm. SIRT5(iso2-4) had little deacylase activity comparing with SIRT5(iso1). 29981421_The DNA variants and SNPs identified in acute Myocardial infection (AMI) patients may change SIRT5 level by affecting activity of SIRT5 gene promoter, contributing to the AMI development as a risk factor. 30170358_miR-299-3p suppresses migration, invasion and proliferation of Hepatocellular carcinoma cells via directly targeting SIRT5 30279144_Hepatic overexpression of SIRT5 ameliorated the metabolic abnormalities of ob/ob mice, probably through demalonylating and desuccinylating proteins in the main metabolic pathways. SIRT5 and related acylation might be potential targets for metabolic disorders. 30443978_SIRT5-induced deacetylation of LDHB triggers hyperactivation of autophagy, a key event in tumorigenesis. 30523058_findings illustrate the molecular mechanism underlying the sequence-selective desuccinylase activity of Sirt5 and provide insights for further studies of the biological functions associated with histone succinylation and Sirt5. 30703481_High SIRT5 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. 30759120_study thus uncovers an important role of SIRT5 in regulating cellular energy metabolism and AMPK activation in response to energy stress. 30904607_mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated the fall in angiogenic capacity due to deficient CXCR4/JAK2/SIRT5 signaling of late EPCs is, at least in part, related to the capillary rarefaction in hypertension, providing the novel insight into the potential of late EPC mitochondria as a novel target for the treatment of hypertension-related loss of microvascular density 31247190_there is the direct interaction between SIRT5 and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH), and desuccinylation of OGDH by SIRT5 inhibits the activity of OGDH complex. 31970975_SIRT5-mediated protein desuccinylation played an important role in promoting the migration of hypoxic gastric cancer cells. 32284438_Citrate synthase desuccinylation by SIRT5 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and migration. 32596968_Hypoxia-induced miR-3677-3p promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing SIRT5. 32607966_LncRNA SNHG14 aggravates invasion and migration as ceRNA via regulating miR-656-3p/SIRT5 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32931562_Sirtuin 5 promotes arterial thrombosis by blunting the fibrinolytic system. 32953892_SIRT5 Contributes to Colorectal Cancer Growth by Regulating T Cell Activity. 32991157_Desuccinylation-Triggered Peptide Self-Assembly: Live Cell Imaging of SIRT5 Activity and Mitochondrial Activity Modulation. 33103371_Sirtuin 5 regulates the proliferation, invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells through acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1. 33455080_Dysregulation of the Sirt5/IDH2 axis contributes to sunitinib resistance in human renal cancer cells. 33479498_Pharmacological and genetic perturbation establish SIRT5 as a promising target in breast cancer. 33530803_SIRT5 regulates autophagy and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. 33945506_The deacylase SIRT5 supports melanoma viability by influencing chromatin dynamics. 34027418_SIRT5 IS A DRUGGABLE METABOLIC VULNERABILITY IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA. 34245764_Metabolic Rewiring by Loss of Sirt5 Promotes Kras-Induced Pancreatic Cancer Progression. 34279763_The role of SIRT5 and p53 proteins in the sensitivity of colon cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agent 5-Fluorouracil. 34500051_Mitochondrial sirtuins genetic variations and gastric cancer risk: Evidence from retrospective observational study. 34664305_Dysregulation of mitochondrial sirtuin genes is associated with human male infertility. 34768083_Role of mitochondrial sirtuins in rheumatoid arthritis. 34930316_SIRT5 functions as a tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma by reversing the Warburg effect. 34949659_SIRT5 Directly Inhibits the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. 35230909_LINC01234 regulates microRNA-27b-5p to induce the migration, invasion and self-renewal of ovarian cancer stem cells through targeting SIRT5. 35292350_Loss of SIRT5 promotes bile acid-induced immunosuppressive microenvironment and hepatocarcinogenesis. 35576836_SIRT5 is involved in the proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer by promoting aerobic glycolysis. 35946561_Knockdown of circLRWD1 weakens DDP resistance via reduction of SIRT5 expression through releasing miR-507 in non-small cell lung cancer. 36095012_SIRT5 is a proviral factor that interacts with SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 protein. 36253417_Sirtuin5 protects colorectal cancer from DNA damage by keeping nucleotide availability. |
ENSMUSG00000054021 |
Sirt5 |
56.625267 |
0.3140382225 |
-1.670988 |
0.321569256 |
26.066280 |
0.00000032989539422261733505882226949457169951074320124462246894836425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001230231434746294034244867496297182185571728041395545005798339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.3739333 |
7.2723639 |
94.1026481 |
16.0838944 |
| ENSG00000124532 |
57380 |
MRS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HD23 |
FUNCTION: Magnesium transporter that mediates the influx of magnesium into the mitochondrial matrix (PubMed:11401429, PubMed:18384665). Required for normal expression of the mitochondrial respiratory complex I subunits (PubMed:18384665). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11401429, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18384665}. |
Alternative splicing;Ion transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables magnesium ion transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in mitochondrial magnesium ion transmembrane transport. Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57380; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; magnesium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015095]; magnesium ion transport [GO:0015693]; mitochondrial magnesium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0045016]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
18384665_hMrs2 is the major transport protein for Mg (+) uptake into mitochondria and that expression of hMrs2 is essential for the maintenance of respiratory complex I and cell viability. 19242098_By enhanced hsaMrs2p expression, p27 was downregulated whereas cyclinD1 was upregulatedin gastric cancer. 19270501_Multidrug resistance phenotypes is related to MRS2 mitochondrial magnesium channel. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27458051_The results indicate regulation of mitochondrial Mg(2+) via MRS2 critically decides cellular energy status and cell vulnerability via regulation of mitochondrial Mg(2+) level in response to physiological stimuli. |
ENSMUSG00000021339 |
Mrs2 |
118.838085 |
2.1327398694 |
1.092708 |
0.159715025 |
47.031935 |
0.00000000000698394237521967378993561005183503167647457443578673519368749111890792846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000039180155628370349863274113195546499190113909349975074292160570621490478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
156.1542423 |
15.3506519 |
73.7202021 |
5.5905725 |
| ENSG00000124593 |
29964 |
|
protein_coding |
Q2TBC4 |
|
Alternative splicing;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc |
|
|
hsa:29964; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; filamentous actin [GO:0031941]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; muscle alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051371]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; heart development [GO:0007507]; muscle structure development [GO:0061061] |
|
|
|
112.547793 |
0.2079821433 |
-2.265468 |
0.268997837 |
68.419059 |
0.00000000000000013219371849064563847266453242182422316551220029413188372657828040246386080980300903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000991956931836263094212635292636180237709915530862347932128386673866771161556243896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.2196220 |
6.5716643 |
190.0143161 |
20.9268294 |
| ENSG00000124702 |
116138 |
KLHDC3 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQ90 |
FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of a Cul2-RING (CRL2) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex of the DesCEND (destruction via C-end degrons) pathway, which recognizes a C-degron located at the extreme C terminus of target proteins, leading to their ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:29779948, PubMed:29775578). The C-degron recognized by the DesCEND pathway is usually a motif of less than ten residues and can be present in full-length proteins, truncated proteins or proteolytically cleaved forms (PubMed:29779948, PubMed:29775578). The CRL2(KLHDC3) complex specifically recognizes proteins with a glycine (Gly) at the C-terminus, leading to their ubiquitination and degradation: recognizes the C-terminal -Arg-(Xaa)n-Arg-Gly, -Arg-(Xaa)n-Lys-Gly, and -Arg-(Xaa)n-Gln-Gly degrons (PubMed:29779948, PubMed:29775578). The CRL2(KLHDC3) complex mediates ubiquitination and degradation of truncated SELENOV and SEPHS2 selenoproteins produced by failed UGA/Sec decoding, which end with a glycine (PubMed:26138980). May be involved in meiotic recombination process (PubMed:12606021). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12606021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26138980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29775578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29779948}. |
Cytoplasm;Kelch repeat;Meiosis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29775578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29779948}. |
The protein encoded by this gene contains six repeated kelch motifs that are structurally similar to recombination activating gene 2, a protein involved in the activation of the V(D)J recombination. In mouse, this gene is found to be expressed specifically in testis. Its expression in pachytene spermatocytes is localized to cytoplasma and meiotic chromatin, suggesting that this gene may be involved in meiotic recombination. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:116138; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031462]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity [GO:1990756]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; reciprocal meiotic recombination [GO:0007131]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway [GO:0140627] |
12606021_cloned human and mouse Peas cDNAs (hPEAS/mPeas) and analyzed their tissue and stage-specific expressions; may be involved in meiotic recombination process 35468939_CRL2(KLHDC3) mediates p14ARF N-terminal ubiquitylation degradation to promote non-small cell lung carcinoma progression. |
ENSMUSG00000063576 |
Klhdc3 |
1371.369374 |
0.4036613486 |
-1.308783 |
0.050993360 |
662.852382 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003581072332482241926330351037191473722522282888087413576993968453861127554009733235535353612833487330561986506836806470466176446844894554078477509139759237717964690559988884293088276836 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002239687611332114044703747083252874894423247941691824217454993711405272240363941770666567365784133370214165615862377693458624082082235265172923772046465024937814896903211769755067989947 |
Yes |
No |
797.9076149 |
25.1234484 |
1991.0441906 |
40.9379435 |
| ENSG00000124713 |
27232 |
GNMT |
protein_coding |
Q14749 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the methylation of glycine by using S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) to form N-methylglycine (sarcosine) with the concomitant production of S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy), a reaction regulated by the binding of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. Plays an important role in the regulation of methyl group metabolism by regulating the ratio between S-adenosyl-L-methionine and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14651980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14739680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17660255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8281755}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Folate-binding;Methyltransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (along with glycine) to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine and sarcosine. This protein is found in the cytoplasm and acts as a homotetramer. Defects in this gene are a cause of GNMT deficiency (hypermethioninemia). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Naturally occurring readthrough transcription occurs between the upstream CNPY3 (canopy FGF signaling regulator 3) gene and this gene and is represented with GeneID:107080644. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:27232; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; folic acid binding [GO:0005542]; glycine binding [GO:0016594]; glycine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0017174]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding [GO:1904047]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; methionine metabolic process [GO:0006555]; methylation [GO:0032259]; one-carbon metabolic process [GO:0006730]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; S-adenosylhomocysteine metabolic process [GO:0046498]; S-adenosylmethionine metabolic process [GO:0046500]; sarcosine metabolic process [GO:1901052] |
11810299_compound heterzygotes in the gene that encodes GNMT have evidence of mild liver disease 12566309_Results suggest that GNMT alteration may be an early event in hepatocellular carcinoma development and that GNMT could be a new tumor susceptibility gene for hepatocellular carcinoma. 16317120_GNMT 1289 C-->T polymorphism influences plasma homocysteine and is responsive to folate intake. 16317120_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17332283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660255_GNMT is destabilized by a mutation. 18624901_Glycine N-methyltransferase is a favorable prognostic marker for human cholangiocarcinoma. 19035462_GNMT is a tumor suppressor gene for liver cancer, and it is associated with gender disparity in liver cancer susceptibility as shown in humans and in mouse models 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19146867_A transgenic mouse model is used together with in vitro methods to study the ability of the GNMT transgene to block the cytotoxic or carcinogenic activity of aflatoxin B1, a known causal agent of human hepatocellular carcinoma. 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19439180_Study identified a GNMT transcriptional start site at the 14th position upstream of the ATG codon; results indicate binding of the nuclear factor-Y (NF-Y) transcription factor to the CCAAT box (-71/-67) of the GNMT gene. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21411609_investigation of role of GNMT in methyl group homeostasis in liver: GNMT affects transmethylation kinetics, SAM synthesis, and conservation of methyl groups by limiting homocysteine remethylation flux; possible role of GNMT inactivation in hepatoma 21572396_GNMT may represent a novel marker of malignant progression and poor prognosis in prostate cancer 21691217_This study suggests that the glycine N-methyltransferase STRP1 phenotype could modulate urinary 1-hydroxypyrene and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine levels in coke-oven workers exposed to PAHs. 22160218_In conclusion, GNMT regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth in part through interacting with DEPDC6/DEPTOR and modulating mTOR/raptor signaling pathway 22183894_This is the first report demonstrating that GNMT plays an important role in regulating cholesterol homeostasis via interaction with NPC2 22264868_GNMT plays important role in maintaining normal function of brain; lack of GNMT causes dysfunction of important signaling pathways and results in alterations of neurotransmitter secretion as well as changes in neuropsychological behavior. 22415010_GNMT is a crucial regulator in cholesterol metabolism and in inflammation, and contributes to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 22807109_Report SNPs that are highly associated with hepatic GNMT protein expression and the coordinate regulation of MAT1A levels. 22850906_single-nucleotide polymorphisms in VEGF, IL-10 and GNMT genes might have a synergistic role in the development of Prostate cancer 23475283_DNA hypermethylation plays an important role in the repression of GNMT in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and loss of GNMT in human HCC could promote the establishment of aberrant DNA methylation patterns at specific gene promoters 23883094_GNMT is an androgen receptor-targeted gene with its functional androgen response element located at +19/+33 of the first exon. 23997240_The studies identify GNMT as a direct transcriptional target of the AR. 24800880_In men of European descent, the GNMT rs10948059 and short tandem repeat polymorphism 1 were associated with prostate cancer risk. 28205209_Elevated GNMT protein expression is associated with pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 30115977_miR-224 can target the glycine N-methyltransferase (GNMT) mRNA coding sequence and plays an important role in GNMT suppression during liver tumorigenesis 30318092_Common glycine N-methyltransferase variant genotypes increase the risk of cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 31057302_Exosomal miR-224 can decrease the expression of GNMT by directly targeting the 3'-UTR of GNMT mRNA to promote the proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. In addition, serum exosomal miR-224 may be used as a biomarker for the diagnosis of HCC and a prognostic factor for patients with HCC. 31199045_Total liver phosphatidylcholine content associates with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and glycine N-methyltransferase expression. 33714108_Polymorphisms in GNMT and DNMT3b are associated with methotrexate treatment outcome in plaque psoriasis. 35008908_Downregulation of Methionine Cycle Genes MAT1A and GNMT Enriches Protein-Associated Translation Process and Worsens Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognosis. |
ENSMUSG00000002769 |
Gnmt |
10.105229 |
0.1457483377 |
-2.778449 |
0.597691665 |
24.415746 |
0.00000077631582748848941544477647580535517590760719031095504760742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002778472748237173447122304661971448069834877969697117805480957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1112352 |
0.9900144 |
14.3167806 |
3.6271871 |
| ENSG00000124731 |
54210 |
TREM1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NP99 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Cell surface receptor that plays important roles in innate and adaptive immunity by amplifying inflammatory responses (PubMed:10799849, PubMed:21393102). Upon activation by various ligands such as PGLYRP1, HMGB1 or HSP70, multimerizes and forms a complex with transmembrane adapter TYROBP/DAP12 (PubMed:25595774, PubMed:17568691, PubMed:29568119). In turn, initiates a SYK-mediated cascade of tyrosine phosphorylation, activating multiple downstream mediators such as BTK, MAPK1, MAPK3 or phospholipase C-gamma (PubMed:21659545, PubMed:14656437). This cascade promotes the neutrophil- and macrophage-mediated release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and/or chemokines, as well as their migration and thereby amplifies inflammatory responses that are triggered by bacterial and fungal infections (PubMed:17568691, PubMed:17098818). By also promoting the amplification of inflammatory signals that are initially triggered by Toll-like receptor (TLR) and NOD-like receptor engagement, plays a major role in the pathophysiology of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of different etiologies including septic shock and atherosclerosis (PubMed:21393102, PubMed:11323674). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10799849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11323674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14656437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17098818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17568691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21393102, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21659545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25595774, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29568119}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Acts as a decoy receptor, counterbalancing TREM1 pro-inflammatory activity through the neutralization of its lignad. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26561551}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a receptor belonging to the Ig superfamily that is expressed on myeloid cells. This protein amplifies neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses triggered by bacterial and fungal infections by stimulating release of pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:54210; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; acute inflammatory response [GO:0002526]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; neutrophil-mediated killing of gram-negative bacterium [GO:0070945] |
12645956_The human TREM gene cluster at 6p21.1 encodes both activating and inhibitory single IgV domain receptors and includes TREM1. 12646648_Activation of TREM-1 on monocytes participates during the early-induced and adaptive immune responses involved in host defense against microbial challenges. 14656437_Crystal structure of the human myeloid cell activating receptor TREM-1 15067076_A new regulatory role is described for TREM-1-mediated signals in the resolution of acute inflammation and the control of neutrophil activity. 15309732_TREM-1 may play an important role in the occurrence and development of acute pancreatitis 15351648_monomeric state of this extracellular ectodomain in solution and, presumably, of the TREM family in general 15585833_TREM-1 is upregulated on monocytes during human endotoxemia together with an increase in soluble TREM-1. 16437719_TREM-1 may play an important role in establishing and amplifying the systemic inflammatory response 16733861_Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) seems to behave as a novel mediator in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in correlation with the degree of the inflammatory reaction of the intestinal mucosa. 17008237_Monocytes contribute to the production of sTREM-1 in the event of septic syndrome. 17202378_Regulation of TREM-1 and the soluble form of TREM-1 expression by prostaglandin E2 may modulate the inflammatory response to microbial pathogens 17277102_NTAL acts as a negative regulator of TNF-alpha and IL-8 production after stimulation via TREM-1 17336301_the effects of aging on TREM-1 engagement in human PMN; respiratory burst, PMN survival, recruitment of TREM-1 in the lipid-rafts, phosphorylation 17505044_sTREM-1 is detectable in exhaled ventilator condensate and may be useful in establishing or excluding the diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia. 17558349_Results show that sTREM-1 and procalcitonin are not specific for infection and can increase markedly in acute inflammation without infection. 17634956_We examined the transcriptional regulation of TREM-1 in macrophages. NF-kappaB and PU.1 are involved in the expression of TREM-1 17659879_prognostic value of serum sTREM-1 levels in patients hospitalized with community acquired pneumonia 17729416_Soluble TREM-1 secreted by the gastric mucosa is an independent mechanism connected to the pathogenesis of peptic ulcer. 17785845_Conclusive evidence favors proteolytic cleavage over alternative splicing as the mechanism responsible for the release of soluble TREM-1 from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated monocytes. 18008257_During melioidosis, TREM-1 expression is differentially regulated on granulocytes and monocytes; measurement of TREM-1 expression on blood granulocytes may not provide adequate information on granulocyte TREM-1 expression at the infection site. 18317529_serum concentrations of sTREM-1 are increased in patients with COPD. Prospective studies are warranted to evaluate the relevance of sTREM-1 as a potential marker of the disease in patients with COPD. 18396215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18396215_The present findings suggest that the three studied polymorphisms within the TREM-1 gene may not play a major role in the predisposition to severe sepsis in a Chinese Han cohort 18628981_down-regulation of TREM-1 expression in cystic fibrosis patients is at least partly responsible for the endotoxin tolerance state in which their monocytes are locked 18634145_sTREM-1 seems to be a new mediator involved in patients with AS, particularly in the early stages of disease. 18656898_Increased TREM-1 expression on monocytes is associated with both infectious and noninfectious inflammatory processes. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19109693_Results suggest that TREM-1 and sTREM-1 contribute to the development of shock in patients suffering from sepsis. 19230638_upregulation of expression on lamina propria macrophages in patients with inflammatory bowel disease; plasma levels is a prognostic factor for sepsis 19251433_sTREM-1 may not have a role in infection in patients with secondary peritonitis 19396532_TREM-1 protein expression levels were up-regulated in sepsis patients with acute cholangitis 19479878_TREM-1 ligation contributes to the pathology of autoimmune arthritis. 19484952_Serum sTREM-1 correlates closely with injury severity score, TNF-alpha and onset of sepsis. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19591072_propose that triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1(sTREM-1) play a role in the innate immune response against intra-amniotic infection 19596984_TREM-1 was up-regulation in infected lungs and human plasma together with augmented alveolar macrophage responsiveness toward Streptococcus pneumoniae 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917159_Serum sTREM-1 (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 ) levels were significantly higher in the infection group than in the flare group of febrile systemic lupus erythematosus patients 19923060_The expression of human TREM-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is up-regulated in the early stage of acute obstructive suppurative cholangitis. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20156945_Serum sTREM-1 levels were elevated in diffuse systemic sclerosis patients and correlated with severity of pulmonary fibrosis, suggesting that serum sTREM-1 is a novel serological marker for the disease severity of systemic sclerosis. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20375613_we provide new insights into the mechanisms how TREM-1 and TLR interact creating synergistic activation in polymorphonuclear neutrophils 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20640189_Trem1 expression is increased in the inner zone of amyloid plaques using a transgenic animal model of Alzheimer's disease. 21148811_TREM-1 is expressed on mature dendritic cells infiltrating the inflamed hypoxic joints of children affected by juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 21306476_sTREM-1 concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid fluid are of potential prognostic value in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia. 21393102_These data are in line with the TLR4-TREM1 co-localization in human neutrophils. 21421043_TREM-1 gene expression was increased in the monocytes of schizophrenic and bipolar patients & tended to be increased in the monocytes of major depressive disorder patients. 21555403_this study provides the fi rst evidence that TREM-1 functions as an in fl ammatory ampli fi er in P. aeruginosa keratitis by modulating TLR signaling and Th1/Th2 responses. 21701149_study shows an increase in sTREM-1 in patients with COPD compared to smokers but not in acute exacerbation-COPD compared to stable COPD. Viral exacerbations showed significantly lower sTREM-1 levels than non-viral exacerbations. 21763322_TREM-1 SNPs may play a significant role in the development of intestinal Behcet's disease and may have modest effects on disease severity. 21855288_Although serum levels of sTREM-1 are increased early upon advent of severe sepsis/shock, gene expression of TREM-1 on monocytes in severe sepsis/shock is not increased. 21910175_High sTREM-1 is associated with intestinal Behcet's disease. 21942576_Data show that kinetics of sTREM-1 differs among patients undergoing hemiarthroplasty of the hip and those undergoing total hip arthroplasty. 21967868_the putative periodontal pathogen P. gingivalis can positively regulate the expression of the TREM-1/DAP12 pathway in monocytic cells. 21976106_Data demonstrate that sTREM-1 is elevated in high-risk patients with febrile neutropenia and is potentially useful to predict their clinical course, either together with, or as an alternative to procalcitonin. 22179409_Serum and amniotic fluid sTREM-1 levels may emerge as early biological indicators for predicting PROM complicated with subclinical chorioamnionitis. 22417086_levels of sTREM-1 were significantly higher in patients with epatocellular carcinoma (HCC) than those with benign liver tumors; peritumoral density of TREM-1 was shown to be an independent prognosis predictor; observations suggest that TREM-1 is related to the aggressive tumor behavior and has potential value as a prognostic factor for HCC 22422501_Patients with rheumatoid arthritis had higher plasma sTREM-1 levels than controls, and plasma sTREM-1 levels were correlated with disease activity, suggesting that plasma sTREM-1 could play a role in the inflammatory process associated with TNF-alpha. 22459945_the sustained TREM-1 expression at the cell surface suffices to block the progress of a refractory state in human monocytes 22642593_Our finding that TREM-1 controls the production of interleukin-8 and TNF-alpha in U937 foam cells defines a potentially critical role of TREM-1 in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis 22721842_In ulcerative colitis, sTREM-1 level was correlated most closely with the endoscopic disease activity among serum biomarkers, but was not superior to the clinical activity index. 22798017_dynamic change in serum sTREM- 1 may be a more accurate parameter for the assessment of sepsis prognosis; there is no association between variations rs2234246 and rs2234237 in the TREM-1 gene and susceptibility to sepsis; TREM-1 rs2234237 polymorphism is associated with increased 28-day mortality in sepsis 22829716_Elevated plasma levels of sTREM-1 reflect the severity, state of exacerbation, presence of respiratory tract obstruction in allergic asthma bronchiale patients. 22996209_Gene expression in 23 patients (12 with pneumonia and 11 w/sepsis) were analyzed using quantitative real time pcr. The mRNA levels of TLR2 (20/23 cases) and CD14 (18/23 cases) were upregulated in the PMNs of patients when compared with healthy subjects. 23046618_Patients with sepsis had increased soluble TREM-1 and decreased TREM-1 expression on neutrophils compared to systemic inflammatory response syndrome patients. 23364598_Activation of TREM-1 protected monocytic cells from apoptosis through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homologue pathways and MCL1 23414215_Patients with E. coli sepsis are characterized by an association of Trem-1 expression on blood neutrophils with cytokine inducibility. 23436478_TREM-1 induction by the hypoxic microenvironment represents a mechanism of regulation of Th1-cell trafficking and activation by iDCs differentiated at pathologic sites. 23468854_sTREM-1 concentrations in maternal serum were elevated during spontaneous term and preterm labor and sTREM-1 levels were significantly higher in preterm labor. 23571837_Data indicate a positive correlation between serum levels of soluble TREM-1 (sTREM-1) and disease severity in infected patients as well as in experimentally infected mice. 23734253_Studies indicate that bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) sTREM-1 is a useful biomarker of bacterial lung infections in in intensive care unit (ICU) patients. 23861562_Serum sTREM-1 may have a role in myocardial dysfunction in patients with severe sepsis 23880194_We found an increased oxidative stress as well as an increased expression of TREM-1 and serum levels of sTREM-1 in patients with critical limb ischemia. 24012914_Studied sTREM-1, procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in postmortem serum in a series of sepsis-related fatalities and control individuals who underwent medico-legal investigations. 24012964_upregulated by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human monocytes/macrophages 24026310_Knockdown of TREM-1 by RNA interference inhibits cell differention but has no effect on cell-cell fusion. 24261769_The serum level of sTREM-1 may be a useful marker of disease activity in relapsing polychondritis. 24281714_signaling contributes to the regulation of innate inflammatory responses 24289157_Soluble TREM-1 levels in serum were useful for the diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia after cardiac surgery. 24290866_Elevated sTREM-1 could be considered an early marker for neonatal sepsis that reflects sepsis severity and poor prognosis. 24447863_gene expression is modulated in the process of dengue infection 24465168_The gene expression levels of TREM1 in PMNs isolated from patients with bacterial infections may be used as a surrogate biomarker for determining the severity. 24605677_Level of sTREM-1 in blood sera of patients with severe thermic injury could be proposed as an additional laboratory marker of burn wound mixed microbial infection. 24661408_Soluble TREM-1 is an accurate marker of Lower respiratory tract infections. The overall diagnostic value of sTREM-1 for community acquired and hospital-acquired Lower respiratory tract infections is similar. 24672147_sTREM-1 and procalcitonin have roles in sepsis and may predict sepsis mortality 24702227_elevated in cholesteatoma 24842612_TREM-1 is induced in tumor associated macrophages by cyclo-oxygenase pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer 24924298_Biofilm-challenged MM6 cells exhibited higher TREM-1 expression. 24954324_Unlike CRP levels and ESR, serum sTREM-1 levels were not correlated with endoscopic activity in patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. 25128583_Data indicate that single nucleotide polymorphisms of Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 (TREM-1) were significantly associated with elevated risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). 25213166_study found no association between the other investigated SNPs within TREM-1 gene and infective endocarditis risk 25242387_plays critical roles in fungal infection of corneal epithelial cells 25294884_Soluble TREM-1, a member of the immunoglobulin super-family, is upregulated when neutrophils are exposed to bacteria. 25319790_Soluble TREM-1 can serve as a biomarker for diagnosing sepsis and assessing disease severity. 25448705_25(OH)2D3-induced expression of TREM-1 was inhibited by rapamycin, a specific inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway, indicating the involvement of mTOR. 25461656_In neonates with late-onset neonatal sepsis, soluble TREM-1 has the potential to provide an excellent predictive value for septic shock/death. 25465376_High TREM-1 expression correlated significantly with increased recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25532536_A reciprocal decrease of the pro-inflammatory surface receptor TREM-1 linked with sepsis-induced immunosuppression may be part of the explanation 25545807_Variants within the TREM locus are associated with pathological features of AD and aging-related cognitive decline. 25595774_The role for PGLYRP1 as a TREM-1 activator provides a new mechanism by which bacteria can trigger myeloid cells, linking two known, but previously unrelated, pathways in innate immunity. 25642940_isolated PMNs have an increased proportion of both TREM1 and DAP12 compared to normal healthy control 25840803_Data indicate that plasma concentration of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) predicts death at 2 years after myocardial infarction. 25944130_Plasma and urine TREM-1 levels can be used as diagnostic biomarkers for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with sepsis. 26184544_Report altered TREM-1/TREM-2 ratio in cutaneous melanoma. 26281323_TREM-1 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily released from phagocytic cells in the presence of bacterial and fungal infections. 26320130_TREM-1 is induced by MSU and is associated with the inflammation of human acute gouty arthritis. 26384438_study to determine soluble TREM-1 and TREM-2 levels in serum, and membrane-bound TREM-1 and TREM-2 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with pulmonary TB 26397033_LPS-induced TREM-1 transcription. 26495896_Soluble TREM-1 level is significantly increased in hemodialysis patients as are other pro-inflammatory markers. 26506490_This study shows increased expression of TREM-1 in monocytes from patients with advanced cervical cancer. 26852644_TREM-1 expression is decreased during the generation of human osteoclast precursors 26877157_study found that soluble TREM-1 is increased and correlates with the clinical and laboratory findings in Crimean Congo Haemorrhagic Fever, a viral infection characterized by activation of inflammation. 26963514_TREM-1 and Dectin-1 function concurrently in the corneal innate immune response by regulating inflammatory cytokine expression in fungal keratitis. 27017522_Increased expression of TREM-1 in S compared to AS patients involving TNFa, MMP-1 and MMP-9 suggest a potential role of TREM-1 in plaque destabilization 27096761_The study simultaneously evaluated both PCT and soluble TREM-1 along with CRP in febrile patients with autoimmune diseases. 27238916_sTREM1 was increased in septic patients with myocardial depression compared to those without myocardial depression. 27244892_low expression level of TREM-1 might be a characteristic for tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer 27319606_Plasma levels of sTREM-1 were found to identify patients with septic shock more effectively than procalcitonin and C-reactive protein. Moreover, sTREM-1 was identified to be an early predictor for survival in patients with septic shock. 27324541_TREM-1 activation may be involved in the development of Kawasaki disease. 27409178_TREM-1 may have a role in pathology of craniopharyngioma and Rathke's cleft cyst 27448788_The results demonstrate that both commensal and pathogenic oral bacteria activate the TREM-1 pathway, resulting in a proinflammatory TREM-1 activity-dependent increase in proinflammatory cytokine production. 27521929_In the premature rupture of membranes group,the NF-kappaB p65 and sTREM-1 levels in maternal blood were significantly higher in women with chorioamnionitis than women without chorioamnionitis (P<.05 findings suggest that there are no differences in soluble trem-1 levels gingival crevicular fluid between healthy and periodontally diseased elderly adults serum level significantly associated with the presence severity of coronary artery disease restrains inflammatory reaction endothelial cells study shows higher plasma systemic lupus erythematosus egyptian patients provided evidence rs6910730g an intronic variant trem1 reduced ability human monocytes for abeta phagocytosis this reduction was likely attributed to a decreased monocytic expression. rs2234237t allele appears be risk factor development severe malaria. may play important role cascade after subarachnoid hemorrhage act as monitoring biomarker core temperature saps ii value were only independent predictors death adjustment potential confounders sepsis admitted intensive care. provides new insights into possible mechanism hif-1alpha psoriasis. links dyslipidemia inflammation lipid deposition atherosclerosis. hmgb1 rage shoulder tendon: dual mechanisms based on coincidence glenohumeral arthritis indicates children community-acquired pneumonia strem-1 midregional-proanp midregional-proadm blood have poor abilities differentiate bacterial from viral diseases or identify cases. seem newly diagnosed type diabetes than their siblings statistically significant concluded both released during response periodontal tissues they can promote process which leads tissue destruction. interventions by means lp17 lr12 fusion protein did not ameliorate ir-induced injury. renal transplant cohort donor recipient gene p.thr25ser dgf nor biopsy-proven rejection death-censored graft failure. we conclude does major experimental ir kidney transplantation plays critical osteoarthritis il1b induced chondrocyte injury through regulation nf-kappab signaling novel modulatory pathogenesis sle. production is useful diagnostic marker molecular target combination therapy lupus. found biopsies subjects obesity. greater expression activity underlying pathophysiology obesity comorbidities. data show macrophages infected immunodeficiency virus-1 increased trem-1. parallel direct exposure virus-1-related proteins tat gp120 induces confers anti-apoptotic attributes. showed detectable samples urinary tract infection non-uti groups detected uti but tend neutrophils cytokine bacteria minor t rs2234246 term1 discovery population explaining its variance mrna. bronchoalveolar lavage triggering receptor expressed myeloid cells-1 do discriminate mild-to-moderate asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary contrast interleukin ratio measured balf effectively differentiated these two diseases. mediating platelet activation. il-8 pct crp febrile neutropenia autologous stem cell predictive in-stent restenosis mediator cellular migration proliferation vascular smooth muscle murine colorectal tumors. review summarizes studies association trem-2 malignant tumors medical field provide ideas correlation periodontitis oral cavity cancer strem1 cytokines gcf decrease introduction treatment underlines importance periodontitis. present highlights urine late-onset sepsis. diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome positively correlates abdominal pain initiated trem-1-associated macrophage activation indicating existence subclinical d-ibs. tlr4 surface observed maternal cord monocyte confirming proinflammatory profiles preterm birth chorioamnionitis. might infection-related birth. become prediction neonatal however variation used threshold values ranged pg methodological across limit our clinical practice. circulating independently predict all-cause mortality adverse cardiac events acute myocardial infarction. neutrophilic pathway suppressed eosinophilic rhinosinusitis nasal polyps showing mrna dna hypomethylation ad methylation rates promoter. support liver hepatic fibrogenesis master regulator kupffer escalates responses activates stellate reveals promotion fibrosis. pro-inflammatory via regulating nf-small ka cyrillicb nuclear translocation mycoplasma pneumoniae-infected a549 lung epithelial cells. expressions behcet those group difference reach statistical significance. has been realized tnf-alpha macrophages. inhibit transition m1 phenotype stat-1 pathway. elevated thrombotic primary anti-phospholipid syndrome. concentrations correlated total tau alzheimer patients. subsequent subgroup analysis indicated more pronounced dementia. identified low specific anti-tnf endoscopic remission. results aid selection biologic-naive tumor-associated hepatocellular carcinoma advanced stages slamf7 up-regulation occur metastatic stage iv tissues. hiv hcv-mediated due enhanced erk1 indicate rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts upregulating suggesting therapy. modulation axis peri-implant familial mediterranean fever case amyloidosis demonstrated positive state progress diabetic nephropathy played high-glucose- transformation. here discussed trems especially bridging processes intestinal neurodegenerative disorders. biomarkers: pentraxin-3 pro-adrenomedullin early diagnosis onset impairs thrombin generation. influencing brain amyloid mild cognitive impairment disease. suggested could accelerate monosodium urate inflammation. inhibition strategy alleviating gouty receptors salmonella typhi cirp endogenous ligand fuel key driving enterovirus a71 infection. presepsin prognostic markers related aa-amyloidosis. non-bacterial infections. overweight patients: cells-1. other biomarkers cholangitis. cd14 sarcoidosis hypersensitivity pneumonitis context immune response. score il-6 sirs children. help survival high-grade glioma post-stroke depressive symptoms peripheral glial cell-derived neurotrophic proadrenomedullin andtriggering pyelonephritis. exacerbates neuroinflammatory nlrp3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis hemorrhage. signalling promotes trem-1-mediated prostate line invasion. integrating immune-related signature improve prognosis carcinoma. trem2 liver-related upregulated participated progression nf-kb promoted apoptosis inhibited autophagy lps-treated hk-2 effect idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. regulates antifungal invasive aspergillosis. arthritis. inhibits invasion polarization. organ injuries cardiogenic shock: cardshock study. outcome. maxillary sinusitis. outcomes covid-19. relationship course covid-19 pneumonia. genetic determinants cardiovascular prospective infarction fast-mi amplifies trophoblastic activating preeclampsia. modulate subtype microglia formation neutrophil extracellular traps interaction syk mediate immunogenic cells: focus microsatellite stability. fosters immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment papillary thyroid cancer.> | ENSMUSG00000042265 |
Trem1 |
42.591233 |
16.5116816537 |
4.045415 |
0.373103653 |
134.988941 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000033201294920001834402892438381159030913701416938099846928263079769475606279675286743036100034487390075810253620147705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000004446924800537451138325217158786119813319238848556989617899963815815392825889652145265884541913692373782396316528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
66.2827335 |
15.3231631 |
4.0755916 |
0.8447238 |
| ENSG00000124762 |
1026 |
CDKN1A |
protein_coding |
P38936 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in p53/TP53 mediated inhibition of cellular proliferation in response to DNA damage. Binds to and inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase activity, preventing phosphorylation of critical cyclin-dependent kinase substrates and blocking cell cycle progression. Functions in the nuclear localization and assembly of cyclin D-CDK4 complex and promotes its kinase activity towards RB1. At higher stoichiometric ratios, inhibits the kinase activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. Inhibits DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase delta by competing with POLD3 for PCNA binding (PubMed:11595739). Plays an important role in controlling cell cycle progression and DNA damage-induced G2 arrest (PubMed:9106657). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11595739, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8242751, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9106657}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein kinase inhibitor;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a potent cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. The encoded protein binds to and inhibits the activity of cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinase2 or -cyclin-dependent kinase4 complexes, and thus functions as a regulator of cell cycle progression at G1. The expression of this gene is tightly controlled by the tumor suppressor protein p53, through which this protein mediates the p53-dependent cell cycle G1 phase arrest in response to a variety of stress stimuli. This protein can interact with proliferating cell nuclear antigen, a DNA polymerase accessory factor, and plays a regulatory role in S phase DNA replication and DNA damage repair. This protein was reported to be specifically cleaved by CASP3-like caspases, which thus leads to a dramatic activation of cyclin-dependent kinase2, and may be instrumental in the execution of apoptosis following caspase activation. Mice that lack this gene have the ability to regenerate damaged or missing tissue. Multiple alternatively spliced variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:1026; |
cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PCNA-p21 complex [GO:0070557]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cyclin binding [GO:0030332]; cyclin-dependent protein kinase activating kinase activity [GO:0019912]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004861]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; protein sequestering activity [GO:0140311]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cellular response to amino acid starvation [GO:0034198]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; cellular response to gamma radiation [GO:0071480]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; cellular response to UV-B [GO:0071493]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest [GO:0006977]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator [GO:0006978]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; heart development [GO:0007507]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle tissue regeneration [GO:1905179]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:1904030]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045736]; negative regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000279]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042326]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904706]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043068]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902806]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0010389]; replicative senescence [GO:0090399]; stress-induced premature senescence [GO:0090400]; tissue regeneration [GO:0042246]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11084299_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11179504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11642719_expression is related to apoptosis in thymus 11695244_p21CIP1/WAF1 was able to repress the immortal phenotype. CDKIs mediate growth arrest in human osteosarcoma cell lines and provides further evidence of the existence of molecular links between cellular mortality and immortality. 11700040_tested for inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum cyclin dependent protein kinases 11733969_In the ovarian cancer cell lines studied, cell growth was inhibited after transfection with p16(INK4a), p21(WAF1/Cip-1), and p53. 11741909_Cdk4 activity does correlate with changes in the level of the Cdk inhibitor p21(WAF1/Cip1 11748297_induced after DNA damage and plays a role in cell survival 11751405_Overexpression of p21(WAF1/CIP1) is an early event in the development of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. 11751903_The ability of p21(Cip1) to inhibit cyclin D1 nuclear export correlates with its ability to bind to Thr-286-phosphorylated cyclin D1 and thereby prevents cyclin D1.CRM1 association 11756412_phosphorylation by AKT/PKB enhances protein stability and promotes cell survival 11762751_expression inhibited by Hepatitis C virus core protein 11781193_expression in normal, hyperplastic and carcinomatous human prostate 11809712_Loss of the p21(Cip1/Waf1) cyclin kinase inhibitor results in propagation of horizontally transferred DNA. 11815410_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11842244_hinge region of the human papillomavirus type 8 E2 protein activates the human p21(WAF1/CIP1) promoter via interaction with Sp1 11860939_The expression of p21(WAF1/CIP1) was higher in the skin of arsenic intoxication than in controls. 11872638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872638_We investigated three common sequence variants in TP53 and p21 for possible associations with the risk of breast cancer and with various phenotypic features of this disease 11877274_Inhibition of bone marrow stem cell proliferation by retinol was mediated by the up-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1). 11877298_The onset of ATRA-induced G(0)/G(1) arrest of U-937 cells is linked to an increase in p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. 11877436_Role of p21 in apoptosis and senescence of human colon cancer cells treated with camptothecin 11882322_Specific inhibition of p21(Waf1/Cip1) protein with the antisense oligodeoxynucleotide markedly reduces the production and secretion of the matrix proteins fibronectin and laminin, both in the presence and absence of TGF-beta stimulation. 11893252_Early induction of CDKN1A (p21) and GADD45 mRNA by a low dose of ionizing radiation is due to their dose-dependent post-transcriptional regulation 11908736_REVIEW: gene expression regulation and role of CDK inhibitor P21 in cell survival and cell cycle control in early hematopoiesis. 11911463_Expression of p21WAF1 is dependent on the activation of ERK during vitamin E-succinate-induced monocytic differentiation. 11943869_Negative regulation of cell growth and differentiation by TSG101 through association with p21(Cip1/WAF1). 11953864_cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in NA cells by upregulation of p21 11956602_expression in pelvic lymph nodes and primary tumors in early stage cervical carcinomas 11968052_Correlation of p21 gene codon 31 polymorphism and TNF-alpha gene polymorphism with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 11989975_Results suggest that p21(Cip/WAF1) and cyclin D1 induction may result from the activation of the ERK and PI-3 kinase pathways. 12015083_A strong inhibition of cell proliferation was observed in K562-p21(WAF1) cell as compared with that of the control, and the cell number in G(0)/G(1) phase was remarkably increased. 12025230_interferon-alpha exerts antitumor effects by increased p21 expression in neuroendocrine tumors 12046058_Review of the influence of histone acetylation and DNA methylation on p21(WAF1) transcription, and affection of pathways or factors associated such as p 53, E2A, Sp1 as well as several histone deacetylation inhibitors. 12052868_Cell attachment to the extracellular matrix induces proteasomal degradation of p21(CIP1) via Cdc42/Rac1 signaling (P21CIP1) 12054510_H(2)O(2)-induced AP-1 activation and its effect on p21(WAF1/CIP1)-mediated G2/M arrest in a p53-deficient human lung cancer cell. 12054572_Identification of the regulatory region required for ubiquitination of the cyclin kinase inhibitor, p21. 12054658_Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(waf1) and the tumor suppressor Rb. 12055678_results suggested that p21 is up-regulated by the stress of inflammation and fibrosis in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-associated chronic liver diseases and that high p21 expression might be related to hepatocarcinogenesis in cirrhotic patients 12058028_stabilization by phosphorylation influenzed by protein kinase p38 alpha and JNK1 12111504_p21/WAF1 expression associated with endocrine activity in pituitary adenomas; tumors expressing cytoplasmic p21/WAF1 may have resistance to DNA-damaging agents such as ionizing radiation 12123335_P27Kip1 immunoreactivity is higher in male breast cancers compared with female breast cancers. 12138103_transcriptional regulation of p21 CIP1 WAF1 controls p53 independent ovarian cancer apoptosis 12145325_C/EBPalpha is essential for p21-mediated inhibition of G1 to S-phase progression by RAP in KSHV-infected host cells 12151346_role in modulating threshold of apoptosis induced by DNA-damage and growth factor withdrawal in prostate cancer cells 12151347_Sp1-mediated activation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression is accompanied by G(1) cell cycle arrest induced by 3,3'-diindolylmethane in human breast cancer cells 12151395_inactivation sensitizes cells to apoptosis via an increase of both p14ARF and p53 levels and an alteration of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio 12168821_Mutations of the cell cycle arrest gene p21WAF1, but not the metastasis-inducing gene S100A4, are frequent in oral squamous cell carcinomas from Sudanese toombak dippers and non-snuff-dippers from the Sudan, Scandinavia, USA and UK. 12204872_p21(CIP1/WAF1) protein expression was increased in AMs and biopsies isolated from smokers and was found predominantly within the cytoplasm. 12205674_Msx2 and p21(CIP1/WAF1) mediate the proapoptotic effects of bone morphogenetic protein-4 on ventricular zone progenitor cells. 12354776_Cleavage of p21waf1 by proteinase-3, a myeloid-specific serine protease, potentiates cell proliferation 12359245_relationship of Mcl-1 isoforms, ratio to cyclin A and Jun kinase phosphorylation to apoptosis in human breast carcinomas 12370305_p21(cip1) induction is interrupted by ROCK-mediated signal transduction in preapoptotic cells 12379120_The proximal p21(WAF-1/Cip1) promoter region has been characterized and the contribution of individual Sp1 binding sites to both constitutive and inducible promoter activity in hepatocytes is analyzed in detail. 12384701_By inhibiting p21(Cip1) expression Myc favours the initiation of apoptosis, thereby influencing the outcome of a p53 response in favour of cell death 12388558_role of PIN1 in transactivation 12392301_insulin inhibits TNF-alpha-dependent cell killing, induction of p53, p21 and apoptosis in a human cervical carcinoma cell line 12393707_Forced expression of STAT5a in human cord blood-derived CD34+ cells enhanced expression Bcl-2 and p21(WAF/Cip1), suggesting they may be important in STAT5a-mediated eosinophil differentiation. 12396717_Oxidative stress induces rapid, but reversible, downregulation of functional p21 by accelerating its protein turnover. 12400017_In conclusion, no polymorphism exists in codon 149 of P21(Waf1/Cip1). 12400017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12412576_Lack of p21(CIP1) DNA methylation was found in 31 patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia. 12429910_promoter elements responsible for transcriptional inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 and topoisomerase IIalpha genes by p21(WAF1/CIP1/SDI1) 12431987_The 3'-untranslated region of this protein's mRNA is a composite cis-acting sequence bound by RNA-binding proteins from breast cancer cells, including HuR and poly(C)-binding protein. 12434183_cyclin kinase inhibitors p21 are associated with laryngeal papillomas. 12441075_LMP1 inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1-mediated induction of MAPK/p21 in Epstein-barr virus infected gastric epithelial cell line GT38 12457968_Hepatitis C virus NS4A and NS4B proteins at inhibited p21/Waf1 expression post-transcriptionally 12459877_p21(waf1) has a role in aortal endothelial cell aging 12474524_Codon 31 polymorphism is associated with bladder cancer 12474524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12485998_WAF1 degradation is regulated by atypical PKC and PDK1 12513833_p21(WAF1) transfection decreases sensitivity of K562 cells to VP-16 12517948_A direct role is demonstrated for p21 in suppressing spontaneous IL-6 and MMP-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts, whereas p21 overexpression has no effect on IL-6 or MMP-1 production in normal and osteoarthritic synovium. 12519780_p21 expression is regulated via a mechanism that is suppressed by PP5 12527941_p21 expression correlates positively with proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Up-regulation of p21 is associated with early progression. 12531694_Downregulation of waf1 mediates apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in response to interferon-gamma. 12545156_repression of p21 promoter/reporters as well as the endogenous p21 gene by Myc depends on interaction with Miz-1. Expression of Miz-1 increases during hematopoietic differentiation and Miz-1 activates the p21 promoter under conditions of low Myc levels 12599217_CDK2 activity was reduced dose-dependently after 24 h of ZD1839 treatment and this effect correlated with increased amount of p27(KIP1) and p21(CIP1/WAF1) associated with CDK2-cyclin-E and CDK2-cyclin-A complexes in head/neck squamous carcinoma cell lines 12612054_TNFalpha mediates cellular growth arrest through activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. The cdk inhibitor p21(Cip1/Waf1) is activated through NF-kappaB and is an important mediator of this growth arrest response 12642873_activation by insulin-like growth factor 1 inhibits UV-induced cell death 12644083_Gene expression is increased in chronic allograft nephropathy and coorelates with the number of acute rejection episodes. 12651158_Upon prolonged exposure, progestins activate p53, in human breast and endometrial tumor cells, which up-regulates the p21(Cip1,Waf1) promoter. 12665570_deacetylase HDAC1 acts as an antagonist of the tumor suppressor p53 in the regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 12665584_Abolition of p21(Cip1/Waf1) and p16(Ink4a) functions prevented oncogenically activated Ras from inducing growth arrest and was sufficient for limited anchorage-independent growth but not tumorigenesis. 12680256_The growth inhibitory action of ATR is associated with the activation of p21WAF1. 12681289_These results suggest that the delay of senescence in cultures grown in the presence of dexamethasone is due to a suppression of the senescence related increase in p21(Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1). 12690110_Egr1 controls p21Cip1 expression by directly interacting with a specific sequence on its gene promoter. 12698196_Inhibitor shows antitumor effect on glioma cells. 12699883_Investigations confirmed the rarity of mutations in this gene, arguing against a role for TP21 mutations in skin, head, and neck cancers. 12705898_p21waf1/cip1 is down-regulated in the lymphocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patients. 12706118_Mutant p53 can delay growth arrest in senescing fibroblasts without reducing p21(WAF1) expression. 12716906_laminar flow caused an increase of p21Waf1 level in the wild-type HCT116 (p53+/+) cells but not in the p53-null HCT116 cells 12727210_Data show that tetradecanoylphorbol acetate activated p21(WAF-1) expression by a protein kinase c-dependent mechanism and that one specific Sp1 binding site in the p21(WAF-1) promoter was critically essential for this activation. 12727815_CDKN1A and CDKN1B variants are associated with advanced prostate cancer. 12727815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12748190_expression of p21/CDKN1A is necessary and sufficient for the negative regulation of gene expression by p53 12771291_Reduced expression of p21 and p27, being VDR dependent, is major pathogenic factor for nodular parathyroid gland growth in advanced secondary hyperparathyroidism. Review. 12781424_Presence of p53 Pro allele and/or p21 Arg allele is associated with lower downstream target gene expression of p21 12782595_Histone deacetylase inhibitors activate p21(WAF1) expression via ATM. 12809883_In carcinoma in situ without muscle-invasive disease, positive p21 expression is independently associated with bladder cancer recurrence and progression. 12810668_The TGF-beta-1-induced decrease in CDK2 kinase activity was the result of increased p21 association with cyclin A-CDK2 and cyclin E-CDK2. , p21 induction in early G(1) is critical for TGF-beta 1 inhibition of CDK2 kinase activity. 12825853_ErbB positive status was associated with p21 overexpression in human ductal carcinoma in situ. 12839982_The dysfunction of p21 in NB cells represents a novel mechanism by which the G(0)-G(1) cell cycle checkpoint can be inactivated. 12841870_p21 is highly correlated with p73 expression irrespective of the p53 mutation status in human esophageal cancers 12847090_p21WAF1 binding to HDAC1 is disrupted by Che-1 protein in human colonic carcinoma 12853982_p53RFP, a p53-inducible RING-finger protein, regulates the stability of p21WAF1. 12855666_p21(WAF1) has a role in drug-induced senescence in colorectal cancer cells 12867429_p21CIP/WAF is a positive regulator in the cell proliferation induced by IGF-I in MCF-7 cells. 12884030_The differences in apoptotic activity and p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression between serrated adenomas (SA) and traditional adenomas or hyperplastic polyps indicate that SA should be considered as a distinct subtype of colorectal neoplasm 12885947_High expression of p21 Waf1 is associated with sarcoid granulomas 12890637_Hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein potentially modulates hepatocyte cell cycle differentially in the early stages of infection through biphasic regulation of p21 cdk kinase inhibitor 12930830_p21 is required for the G1/S arrest of HCT116 colon cancer cells but its mode of action is more complicated than the simple formation of a physical complex with cyclin-Cdk2 12930846_PARP-1 and p21 could cooperate in regulating the functions of PCNA during DNA replication/repair. 12931225_p21 has an antiapoptotic role in monocytic leukemia. 12936910_exposure in vitro to hyperoxia exerts G(1) arrest through p53-dependent induction of p21 that suppresses Cdk and PCNA activity. 12963997_p21WAF1/CIP1, pRB, Bax and NF-kappaB have roles in induction of growth arrest and apoptosis by resveratrol in tumor cell lines 12970742_p21 is a transcriptional target of CDX2. Our results may thus provide a new mechanism underlying the functions of CDX2. 13678583_UV-induced p21 degradation is essential for optimal DNA repair 14504476_These results suggest that in vivo p21CDKN1A does not interfere with loading of PCNA at DNA replication sites, but prevents, or displaces subsequent binding of DNA polymerase delta to PCNA at the G1/S phase transition. 14572899_the association of p21 and cyclin A in response to gamma-irradiation requires the CDK2 binding region 14580260_Cytoplasmic p21WAFI/CIPI may be a surrogate marker of functional HER-2 in vivo. 14592451_Resveratrol caused a dose-dependent increase in intracellular p53 and p21(WAF1/CIP1) levels. 14597617_p21 down-regulation is multiply determined and is required for the reversibility of the arrest in S phase 14607331_Codon 31 polymorphism in p21 may be associated with the development of esophageal cancer 14607337_Low p21 protein level is associated with advanced TNM stage and positive nodal status of squamous cell carcinoma of hypopharyngeal cancer 14628083_In adenocarcinomas, no statistically significant correlation was found between K-ras mutational status and p21WAF1/CIP1 and p53 expression. 14633995_MDM2 directly inhibits p21waf1/cip1 function by reducing p21waf1/cip1 stability in a ubiquitin-independent fashion 14637149_We conclude, therefore, that two major components of cell-cell interaction synergistically regulate cell cycle progression in HEK293 cells by regulating p21 expression in a beta-catenin/TCF-dependent manner. 14642618_in hepatocellular carcinoma, PCNA participates both in DNA synthesis and repair and that highly proliferating cancers may display a sustained DNA-repair. 14647439_how HO-1 and WAF1/Cip1 were regulated in two gastric cancer cell lines 14677632_cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21) levels rise abruptly in individual aging cells and remain elevated for extended periods of time. 14702288_Promoter is hypermethylated in various lymphomas and carcinomas. 14712207_NaB-induced apoptosis required P21(waf1/cip1) and its interaction with PCNA. 14715257_We present evidence that p21(WAF1) is required for 9-HSA mediated growth arrest in human colon carcinoma cells 14719078_Assessment of p21, p27, Bax, and cyclin E expression in tumor tissues have been reported to be useful as prognostic factors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 14738489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14744793_Perifosine increases Sp1 binding and enhanced p21(waf1/cip1) transcription. 14751560_Abnormally high amounts of Stat1, Stat5 and p21Cip1 proteins were found in prehypertrophic-hypertrophic chondrocytes, the extent of overexpression being directly related to the severity of the disease 14759525_Overexpression of integrin beta1 imposed a growth inhibitory effect on a liver neoplastic cell line which is mainly attributed to CIP1. 14761977_by reducing p21 protein stability via proteasome-mediated degradation, MDM2 functions as a negative regulator of p21 14762439_TGF-beta-Smad signaling pathway inhibits the growth of human epithelial cells and plays a role in tumor development. 14764039_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14981901_Loss of p21 and/or p53 might not predict for prognosis in oropharnyggeal squamous cell carcinoma. 15003515_Transactivation of the CIP1 promotor by fetal liver kinase-3 mutations involves stat5 binding site. 15014036_Flavopiridol abrogates depsipeptide mediated induction of p21 expression via inhibition of protein kinase C signaling in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells. 15016552_simultaneous expression of HPV-16 E7 protein and p21 proteins induces apoptosis and activates cathepsin B 15024057_Results suggest that basic helix-loop-helix proteins provide a direct transcriptional link between a cell cycle inhibitor, p21(Cip1), and a neurotrophic receptor, Trk. 15033443_p21WAF1 in vascular smooth muscle cells is regulated by transcription factor Sp1 and p38MAPK 15036662_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15059516_In human colon cancer cell lines, HDAC inhibitors stimulate the p21(WAF1) gene expression by selectively increasing the degree of acetylation of the gene-associated histones. 15060836_The expression patterns of cyclin D1, cyclin E, p21/waf1 and p27/kip1 in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) may indicate their contribution in epithelial cell turnover and their possible implication in IBD-related dysplasia-carcinoma. 15069711_The expression of p21 protein depends on p53 protein largely in normal gastric mucosa and dysplasia, but not in gastric carcinoma. 15081425_role of pathway in regulating G1-S transition and apoptosis along with RFT 15082782_Results suggest that p150(Sal2), acting in part as a p53-independent regulator of p21 and BAX, can function in some cell types as a regulator of cell growth and survival. 15094066_p21(Waf1) can activate the transcription of p16(INK4); this effect is GC-box dependent; and the transcription factor Sp1 plays a key role in this event 15107488_hepatitis B virus X protein natural variants have differential effects on p21 expression 15111320_activation of the p53-p21WAF1 pathway and overexpression of cyclin D1 are induced during tumor cell differentiation by beta-catenin 15122333_Low p21 protein levels are caused by reduced p21 gene transcription and sensitize cisplatin-treated TGCT cells to the Fas death pathway 15161699_p21 or p21B do not have a role in causing resistance to doxorubicin or mitomycin/5-fluorouracil in breast cancer 15169570_p21/waf1 could potentially function as an assembly factor in HTLV-1 infected cells. 15171713_Data suggest that dihydrotestosterone reverses titration of p21(Cip1/Waf1) and p27(Kip1) away from Cdk2 complexes, and increased association of p21 with Cdk2 complexes mediates the androgen-induced growth inhibition of breast cancer cells. 15173090_p21Cip1/WAF1 and HER2/neu togehter have a role in progression of breast neoplasms 15181148_in normal cells, p21 exerts a dual role in mediating DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest and exit before mitosis 15184045_Data show that ERK1/2-mediated phosphorylation of hepatitis B viral X-gene (HBx) regulates HBx function and localization, and that HBx repressed transcription from the p21(WAF1/Cip1) promoter. 15184659_hRAD9 and p53 co-regulate p21 to direct cell cycle progression by similar molecular mechanisms. 15190207_P21 expression stimulates promoters of six p21-responsive human genes and the cytomegalovirus promoter, as well as an artificial promoter containing NFkappaB response elements. 15201954_Disruption of p53-p21/WAF1 cell cycle pathways contributes to tumor progression and worse clinical outcome of hepataocellular hepatoma. 15201979_Relation between expression, DNA ploidy and human papillomavirus infection in cervical carcinoma. 15226418_Data show that extracellular signal-regulated kinase 3 (ERK3) is conjugated to ubiquitin via its free NH(2) terminus, and that N-terminal tags stabilize expression of p21 but not that of substrates ubiquitinated on internal lysine residues. 15240512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15240512_p53 and/or p21(WAF1/CIP1) genotype may influence the progression during gastric tumorigenesis. 15251435_p21WAF1 gene expression is regulated by histone deacetylase inhibitors at the post-transcriptional level in HepG2 cells 15286705_Stat3 mediates expression of p21waf1. 15291355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15297421_Cyclin D1, p53, and p21Waf1/Cip1 have roles in progression of serous epithelial ovarian cancer 15302882_physical interaction of Vpr with Sp1 and p53 could modulate transcriptional activity of p21. 15309711_Histone acetylation regulates p21WAF1 expression in human colon cancer cell lines, Colo-320 and SW1116. 15317660_pdcd4 represses the transcription of the mitosis-promoting factor cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)1/cdc2 via upregulation of p21(Waf1/Cip1) 15340083_Monocytic differentiation of the promyelomonocytic cell lines U937 and HL60 is associated with the upregulation of Brap2 expression concomitantly with the upregulation and cytoplasmic relocalization of p21. 15342418_P21Cip1 positively regulates the cytotoxic action of thymidylate synthase inhibitors, negatively regulates the cytotoxic action of IFN-gamma, and enhances S-phase exit after thymineless stress in colorectal carcinoma cells. 15347670_Cystathionine gamma-lyase has a role in regulating cell proliferation via a H2S-dependent modulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation and p21Cip/WAK-1 15367606_Tax1 markedly activated transcription from the cdk inhibitor p21(cip1/waf1) promoter in comparison to Tax2, suggesting that upregulation of p21(cip1/waf1) may account for the differential inhibition of cellular replication kinetics 15371422_repression of hTERT by endogenous p53 is mediated by p21 and E2F 15371446_PGA2 stabilizes the p21 mRNA through an ERK-independent increase in cytoplasmic HuR levels and an ERK-dependent association of HuR with the p21 mRNA 15378017_absence of p21 produced no overt alteration of the lifespan of the INK4a/ARF-null mice 15386430_We conclude that overexpression of PKCdelta in human colon cancer cells induces multiple antineoplastic effects that depend on the activities of p21(Waf1/Cip1) and p53. 15389598_p21(WAF1), acting through the phosphorylation of pRb, regulates whether 2BS cells cease to proliferate and become senescent but resistant to apoptosis, or whether they accelerate proliferation while becoming more susceptible to apoptotic stimuli 15456784_survivin can reduce the cell growth inhibition and apoptosis, and p53 elevates the p21 level, which may attenuate the cell death in the quercetin-treated human lung carcinoma cells 15474507_c-myc downregulation and release from the endogenous p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter contributes to transcriptional activation of the p21WAF1/CIP1 in HeLa cells 15475071_p21CIP1 mRNA is absent in human T-LBL biopsies and T-ALL cell lines at a high frequency. However, unlike p15INK4B, reduced p21CIP1 expression in T-LBL/ALL is independent of dense promoter-associated CpG methylation 15492264_Nuclear clusterin function is proapoptotic in colon cancer when induced by APC or chemotherapy in the context of p21 expression. 15497017_A significant increase in p21, p53, and fas mRNA expression were reported in the proximal incompetent veins; negative correlation between media apoptotic index and p21 mRNA expression was found. 15509808_IRF-1-p300 interface as an allosteric modifier of DNA-dependent acetylation of p53 at the p21 promoter 15510615_P21waf1/cip1 system alteration may be an early and frequent event in tongue carcinogenesis. 15528212_c-Myc antagonized the induction of p21Cip1 mediated by oncogenic H-, K-, and N-Ras and by constitutively activated Raf and ERK2 15555546_Deletion mutants of p21 promoter reveal that sequences between -270 and -264, forming a complex with unidentified nuclear factor(s), were critical for E2A and Snail function. E2A-dependent expression of endogenous p21 gene was also inhibited by Snail. 15582998_in tumor cells lacking functional p53 and/or p21, p14(ARF) impaired mitotic entry and enforced a primarily cytoplasmic localization of p34(cdc2) that was associated with a decrease in p34(cdc2) kinase activity and reduced p34(cdc2) protein expression 15592362_The cytoplasmic localization of p21,Cip1 may be the molecular mechanism whereby breast cancer cells circumvent TNF-alpha-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis. 15598783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15606307_We conclude that (1) clinically achievable doses of ionizing radiation can trigger CDKN1A-dependent accelerated senescence in some human tumor cell lines that express wild-type TP53. 15609309_p21WAF expression is induced by 5-Aza-CdR by demethylation of p73 leading to p53-independent apoptosis in myeloid leukemia 15645120_differentiation-inducing agents, particularly sodium butyrate, suppress growth of oral squamous carcinoma cells through apoptosis and induce cell differentiation possibly through mechanisms involving COX-2, p27Kip1 and/or p21WAF1/Cip1 in vitro and in vivo 15647383_Rb, p21Cip1, and PCNA have roles in cAMP-mediated inhibition of DNA replication and S phase progression 15664193_Results demonstrate the importance of posttranslational stabilization of p21 protein by WISp39 in regulating cellular p21 activity. 15665589_p21Cip/WAF1 induction is a determinant in the regulation of colonic proliferation by the ERK pathway. 15665816_increased expression leads to increase in apoptosis independent of p53 15671036_the mutually antagonistic action of two RNA-binding proteins, Hu and hnRNP K, control the timing of the switch from proliferation to neuronal differentiation through the post-transcriptional regulation of p21 mRNA 15690394_p21 is a common target of all TGF-beta superfamily pathways 15694358_Among cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p21 was induced and up-regulated by 15d-PGJ(2), but p16 and p27 were not changed, suggesting that the involvement of p21 in inhibition of cell proliferation. 15694838_results suggest that p21 and FasL gene activation is required for myeloid leukemia cell survival or maturation but not for cell death via Sp1 and NFkappaB as regulators of these genes 15708847_low molecular weight forms of cyclin E may contribute to tumorigenesis through their resistance to the inhibitory activities of p21 and p27 while sequestering these CKIs from the full-length cyclin E 15709169_Results showed a significant, progressive loss of expression of p21(Cip1/WAF1) with advancing papillary thyroid carcinomas. 15716956_Mitf-mediated activation of p21Cip1 expression and consequent hypophosphorylation of Rb1 will contribute to cell cycle exit and activation of the differentiation programme 15735102_Quercetin and ellagic acid combined increase the activation of p53 and p21(cip1/waf1. 15736438_Expression of CDKN1A and Gadd45 proteins acting on cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair in PCa relative to the presence of oxidative DNA damage was measured. 15738655_pioglitazone generally does not modulate p21 transcription in human cancer cell lines 15743033_P21 and Bax have roles in progression of cutaneous malignant melanoma 15743834_p21WAF1/CIP1 behaves as a transcriptional coactivator in a gene-specific manner implicated in cell differentiation. 15746092_Temporal ectopic expression of p21(Cip1) arrested cell proliferation, inhibited Cdk2 and Cdk4 activities, suppressed retinoblastoma phosphorylation and arrested cells in both G1 and G2 cell cycle phases. 15750619_Lack of functional p21 resulted in the accumulation of cells in G2/M phase of the cell cycle and markedly enhanced p14 ARF-induced apoptosis. 15752352_Dehydroepiandrosterone increased the expression of p53 and p21 mRNAs. 15753078_galectin-8 is a modulator of cellular growth through up-regulation of p21 15756520_Glioblastoma cells show different and independent responses in their p53 and p21 pathways to ionizing radiation 15763542_In the abscence of this this gene in colorectal carcinoma cells, toxicity of histone deacetylase inhibitors was reduced. 15764647_demonstrated that epigallocatechin-3-gallate activates growth arrest and apoptosis primarily via tumor suppressor p53-dependent pathway that involves the function of both p21 protein and Bax protein 15767448_These data implicate p21 as a pivotal macrophage facilitator of HIV-1 life cycle; regulators of p21, such as CDDO, may provide an interventional approach to modulate HIV-1 replication. 15776189_unable to arrest tumor progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma 15798220_Hyperphosphorylated p21 activates the Cdc2 kinase in the G2/M transition. 15807891_This study suggests that the p21 codon 31 polymorphism does not contribute to the risk of POAG (primary open-angle glaucoma) in the Caucasian population. 15817070_expression was found to be associated with poorer prognosis and tumor aggressivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma 15819981_TP53, CDKN1A, CDKN2A, and CDKN2B have roles in tumorigenesis in skin melanomas, but none of them is a main mutation target for melanoma tumorigenesis 15839202_Data show a coordinating inhibition of the proliferation of MCF-7 by enhancing expression of p53,p21 and decreasing expression of c-myc 15840769_the mechanism of p21 protection is by direct inhibition of cdk2 activity and that cisplatin-induced apoptosis in kidney failure is caused by a cdk2-dependent pathway 15866118_expression of p53, MDM2, and p21Waf1 suggests a role for these oncoproteins in the regulation of endometrioma cell growth, but not in adenomyosis 15878916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15878916_Significant increase in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in the presence of two p21 polymorphisms may be a marker of genetic susceptibility. 15880444_physiological concentrations of conjugated linoleic acid inhibit growth of colon cancer cells with either wild-type or mutant p53 15880942_In cholesteatoma, co-expression of p21 and pERK1/2 was prominent, whereas in retro-auricular skin there was hardly any co-expression. 15905168_mitochondrial stress causes resistance to |
ENSMUSG00000023067 |
Cdkn1a |
3931.041564 |
2.4566678437 |
1.296703 |
0.024792832 |
2798.763915 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5630.1997222 |
82.4803182 |
2308.1397752 |
27.5522089 |
| ENSG00000124767 |
2739 |
GLO1 |
protein_coding |
Q04760 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of hemimercaptal, formed from methylglyoxal and glutathione, to S-lactoylglutathione (PubMed:20454679, PubMed:9705294, PubMed:23122816). Involved in the regulation of TNF-induced transcriptional activity of NF-kappa-B (PubMed:19199007). Required for normal osteoclastogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CPU0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19199007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20454679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23122816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9705294}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glutathionylation;Lyase;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Secondary metabolite metabolism; methylglyoxal degradation; (R)-lactate from methylglyoxal: step 1/2. |
The enzyme encoded by this gene is responsible for the catalysis and formation of S-lactoyl-glutathione from methylglyoxal condensation and reduced glutatione. Glyoxalase I is linked to HLA and is localized to 6p21.3-p21.1, between HLA and the centromere. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2739; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; lactoylglutathione lyase activity [GO:0004462]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; methylglyoxal metabolic process [GO:0009438]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11436564_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11785295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11963573_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12942785_The analysis involved the data on nine polymorphic codominant loci: HP, GC, TF, PI, PGM1, GLO1, C3, ACP1, and ESD. The loci were selected by significance of differences in genotype frequencies between tuberculosis patients and healthy controls 15950319_the increase in glyoxalase I expression up to the age of 55 and progressively decreases thereafter. 16305054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16352396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16352396_The present study tested the hypothesis that this common genetic variant could confer susceptibility to panic disorder using an Italian population sample of 162 panic disorder patients and 288 matched controls. 16555297_In summary, our data suggest that a reduced glyoxalase I activity mimics some changes associated with neurodegeneration, such as neurite retraction and apoptotic cell death. 16803681_Overexpression of glyoxalase 1 is associated with kidney tumor 17346350_GLO1 gene variants do not confer autism vulnerability in this sample, but allele A419 apparently carries a protective effect, spurring interest into functional correlates of the C419A SNP 17346350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463067_Polymorphism in this enzyme and paraoxonase I increase susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. 17722011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17722011_Therefore, we suggest that common variants in glyoxalase 1 are not significant susceptibility factors forautism spectrum disorders in the Finnish population. 18079478_Association of A419C polymorphism of the glyoxalase I gene with age receptor levels and show the genetic predisposition to vascular complications in hemodialysis patients. 18079478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18344682_In androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells, testosterone upregulates GLO1 mRNA levels. 18413187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18413187_There was an association (odds ratio=2.9; 95% confidence interval=1.3-7.2) between the Glo1 A allele and T2DM in Zuni Indians. 18448827_Increased protection against dicarbonyl glycation of endothelial cell protein by transfected glyoxalase I protects hyperglycemia-induced angiogenesis deficit. 18455873_These results suggest that the aberrant expression of Glo1 might be involved in the pathophysiology of mood disorders. 18721844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18721844_the GLO1 gene is unlikely a major susceptible gene for autism in an ethnic Chinese population from Taiwan. 19211689_Glyoxalase I overexpression ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. 19238574_In the human lens, GLOI activity and immunoreactivity both decreased with age. 19379515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19379515_Results show that genetic polymorphisms in biotransformation enzymes CYP17, GSTP1, PON1 and GLO1 could be associated with the risk for breast cancer. 19412133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19452310_Report glyoxalase I Glu111Ala polymorphism in patients with breast cancer. 19470168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20093988_our data suggest a function of GLO1 in the regulation of detoxification and target adduction by the glycolytic byproduct methylglyoxal in malignant melanoma. 20180986_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185929_study shows for the first time a link between RAGE and GLO polymorphisms in the prognosis of hemodialysis patients 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20398646_It did not show any difference in allelic and genotype frequencies in all glyoxalase I genes polymorphisms among the studied groups. 20398646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20454679_that Glo1 activity directly can be regulated by an oxidative posttranslational modification that was found in the native enzyme, i.e., glutathionylation 20542521_This study suggested that GLO1 is not involved into the acute panic response to CCK-4 in healthy volunteers. 20544845_GLO1-A is an amplified gene in cancer. 20554694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20712647_Glyoxalase I Ala111Glu gene polymorphism is not associated with breast cancer risk but correlates with the absence of progesterone receptor. 20712647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21029593_The expression and enzyme activity of GLO-I is significantly increased in endometrial cancer, which could promote abnormal proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. 21056979_in an in vivo model of diabetes that GLO-I overexpression reduces hyperglycemia-induced levels of carbonyl stress, AGEs, and oxidative stress 21253391_These findings suggest that deglycating enzymes Glyoxalase I and fructosamine-3-kinase may be involved in the malignant transformation of colon mucosa. 21294693_This study shows that only the GLO1 C-7T polymorphism, and not the GLO1 A419C and ALR C-106T polymorphisms, is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. 21370249_The expression of GLO-1 was increased in mononuclear leukocytes from diabetic patients. 21386123_Our findings suggest that GLO1 deficits and carbonyl stress are linked to the development of a certain subtype of schizophrenia.[review] 21491613_A non-conservative, non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism in the glyoxalase I gene may be an autism susceptibility factor. 21738003_GLO1 C-7T polymorphism alters promoter activity and confers susceptibility to nephropathy and retinopathy to Type 2 diabetic patients. 22188542_We conclude that dicarbonyl stress is countered by up-regulation of Glo1 in the Nrf2 stress-responsive system. 22479608_GLO1 expression was higher in gastric cancer tissues, compared with that in adjacent noncancerous tissues. 22614840_GLO1 is overexpressed in 79 percent of tumors and GLO1 up-regulation correlates with advanced tumor grade. 22653787_GLOI may be involved in prostate cancer progression via the control of key molecules in the mitochondrial apoptotic mechanism through the nuclear factor (NF)-kB signaling pathway. 22771726_No evidence of an association of RAGE or glyoxalase I single nucleotide polymorphisms with pathological pregnancy. 23201419_We showed for the first time an association between genetic variants with GLO1 enzyme activity in humans. SNPs in GLO1 can be used to predict enzyme activity and detoxifying capabilities. 23351995_Data suggest that GLO1 activity is lower in blood (in whole blood assay) in type 1 or type 2 diabetes with painful peripheral diabetic neuropathy as compared to control subjects; Glo1 activity negatively correlates with duration of type 1 diabetes. 23360186_The Ala111Glu glyoxalase gene polymorphism did not have an effect on glyoxalase 1 activity in either the type 1 diabetes mellitus or healthy control group. 23775136_data suggest a possible association of C332C-genotype of the glyoxalase 1 gene with diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes, supporting the hypothesis that methylglyoxal might be an important mediator of diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. 23982595_GLO1 was the only protein which consistently varied according to the metastatic potentials of SN12C clones. GLO1 was increased in high metastatic cell lines by western blot analysis. 24002659_level by differently inhibiting GI via NF-kappaB.Superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide induced a diverse apoptosis. 24040147_we provided evidence of the biological plausibility of Glyoxalase 1 polymorphism, either alone or in combination with other ones, all related to oxidative stress control that represents a key event in PCa development and progression. 24105621_GLO1 expression level in prostate cancer tissues correlates with pathological grade and proliferation rate. 24158671_Overall, thus Glo1 might be essential for hepatocellular carcinoma progression and can be designated as a potential therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma in the future. 24259499_Overexpression of GLO1 in bone marrow cells is sufficient to overcome the defective neovascularization that is characteristic of diabetes. 24494193_Data show that GlxI is a novel substrate of TG2 and TG2 catalyzes either polyamine conjugation or deamidation depending the presence of polyamines. 24612481_GLO1 lessened inhibitory phosphorylation of eNOS (Thr495) by reducing glycative stress. Study demonstrates that blunting glycative stress prevents the long-term impact of endothelial dysfunction on vascular aging. 24662817_Study demonstrates that GLO1 is a novel metabolic oncogene of the 6p21 amplicon, which promotes tumor growth and aberrant transcriptional signals via regulating cellular metabolic activities for energy production. 24671236_Weak association of glyoxalase 1 (GLO1) variants with autism spectrum disorder 24767709_GLO1 activity affects the overall burden of carotid artery atherosclerosis. 24908234_Report association of GLO1 (rs4746) polymorphism with markers of endothelial activation in diabetes mellitus. 24966916_Suggest Glo1 pathway activation is required for cell proliferation and cell survival of hepatocellular carcinoma cells carrying Glo1 genetic amplification. 24995521_results suggested involvement of accumulated dicarbonyls and/or pentosidine in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia patients carrying Glyoxalase-1 mutations. 25139743_In ApoE(-/-) mice with or without diabetes, GLO1 overexpression did not lead to decreased atherosclerotic lesion size or systemic inflammation. 25184957_GLO1 is prevailingly expressed in cutaneous neoplasms of higher malignancy and contributes to the progression of squamous cell carcinoma 25201284_This study demonstrated that the GLO1 C332 (Ala111) allele confers autism vulnerability by reducing brain glyoxalase activity and enhancing advanced glycation end-products. formation 25342507_This review describes the role of GLO1 in tumor cell proliferation and survival, and the potential of GLO1 as a biomarker for tumor diagnosis and as a target for anticancer drug development. [review] 25407489_Significant differences in the allelic and genotype frequencies of GLO1. 25557363_Two classes of the metalloenzyme GlxI exist and vary in their metal dependencies 25841781_Glo1 is involved in the Min-U-Sil 5 crystalline silica-induced BEAS-2B cell mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. 26122242_individuals with the GLO1 A /E genotype, PON192/QR-RR genotypes and PON55/LM-MM genotypes had a significantly higher risk of cerebral cavernous malformations compared with the other genotypes. 26298793_The GLO1 variations were not the source of association of the BTBD9 locus with restless legs syndrome. 26552067_Studies indicate that the most extensively investigated The most extensively investigated glyoxalase enzymes are glyoxalase I and glyoxalase II (Glo1 and Glo2). 26618552_MMP-9 and Bcl-2 expression levels were dramatically decreased by addition of methylglyoxal or inhibition of GLOI. These findings may provide a new approach for the treatment of breast cancer. 26711908_Data suggest Glo1's effects on anxiety-like behavior are centrally mediated as overexpression of Glo1 in neurons was sufficient to increase anxiety-like behavior 26784015_MS5 induced hydrogen peroxide-mediated c-Jun-dependent Glo1 up-regulation which resulted in a decrease in the Argpyrimidine-modified Hsp70 protein level which triggered EMT in a novel mechanism involving miR-21 and SMAD signalling 26914966_expressed in basal epidermis; significantly higher expression in older individuals 27000251_GLO1 SNPs are significantly associated with late-onset and drug-resistant epilepsy. 27270765_The lowering of glycative stress via modulation of RAGE-AGE axis or glyoxalase 1 activity is beneficial for tubular homeostasis and the subsequent prevention and treatment of kidney disease, suggesting the possibility of novel therapeutic approaches which target glycative stress. 27406712_Glo-1 responds to dicarbonyl stress to enhance cytoprotection at the transcriptional level through stress-responsive increase of Glo-1 expression. 27478003_Reduction of GLO1 activity in atherosclerotic lesions of nondiabetic patients with increased HbA1c is associated with a functional involvement of this protective enzyme in atherogenesis. 27696457_Glo1, together with Glo2, represents a novel mechanism in prostate cancer progression driven by a PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. 27898103_GLO1-knockdown provoked collagen expression, endothelial inflammation and dysfunction and apoptosis which might contribute to vascular damage 27999356_GLO1 on one hand is crucial to maintaining tumor characteristics of malignant cells, and, on the other hand, supports malignant transformation of cells in a hypoxic environment when overexpressed. 28034013_The active sites of human and staphylococcus glyoxalases I are also different: the former contains one Zn-ion per chain; the latter incorporates two of these ions.. We suggest that only single Zn1-ion plays the role of catalytic center. The newly found differences between the two subfamilies could guide the design of new drugs against S. aureus, an important pathogenic micro-organism. 28106734_Studies suggest that the enhancement of glyoxalase I (GLO-1) is a promising strategy aimed at halting the vicious cycle between chronic kidney disease and increases in glycative stress. 28549423_Induced Glyoxalase 1 expression is a common feature in the pathogenesis of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma 28695773_Gly82Ser and 2184 A/G RAGE polymorphisms were related to the mortality due to the breast cancer and -419 A/C glyoxalase I polymorphism was related to the overall mortality of the patients suggesting their role not only in the risk of breast cancer but also in the outcome of patients with breast cancer. 29156655_current research highlighted the Glo-I/AGE/RAGE system as an interesting therapeutic target in chronic liver diseases. These findings need further elucidation in preclinical and clinical studies. 29225125_Interdependence of GLO I and PKM2 in the Metabolic shift to escape apoptosis in GLO I-dependent cancer cells. 29307109_The expression of glyoxalase system member glyoxalase 1 (GLO1) in melanoma cells is downregulated by miR-137. siRNA targeting of GLO1 mimicks inhibition of melanoma cell proliferation caused by miR-137 overexpression. Re-expression of GLO1 restores miR-137-mediated suppression of melanoma cell proliferation. 29385039_The critical role of glyoxalases as regulators of tumorigenesis in the prostate through modulation of various critical signaling pathways, and an overview of the current knowledge on glyoxalases in bladder, kidney and testis cancers is reviewed.(GLO1, GLO2) 29385725_Inhibition of GLO1 in Glioblastoma Multiforme Increases DNA-AGEs, Stimulates RAGE Expression, and Inhibits Brain Tumor Growth in Orthotopic Mouse Models 29504694_Glo1, together with miR-101, might be potential therapeutic targets for metastatic prostate cancer. 29975244_There was no statistically significant association between p.P122fs in GLO1 and schizophrenia (P=0.25) in the Japanese population. 30099685_GLO1 SNPs, rs1130534 (c.372A>T, p.G124G), rs2736654 (c.A332C, p.E111A) and rs1049346 (c.-7C>T, 5'-UTR) were genotyped. While c.A332C polymorphism was not associated with retinitis pigmentosa (RP), c.372A>T showed an allelic association. Conversely, c.-7C>T showed both genotypic and allelic associations. RP susceptibility may be associated with two of the analyzed GLO1 polymorphisms (rs1130534 and rs1049346). 30470837_GLO1 may be of functional importance target downstream of MMSET I. 30755587_The schizophrenia case with the highest neurite curvature carried a frame shift mutation in the GLO1 gene, suggesting that oxidative stress due to the GLO1 mutation caused the structural alteration of the neurites. 31534514_Glyoxalase 1 Prevents Chronic Hyperglycemia Induced Heart-Explant Derived Cell Dysfunction. 31591136_Results indicate that the GLO1 loss of function (GLO1 (fs) mutation derived from the schizophrenia patient and the engineered GLO1 (-/-) mutation) impaired the cellular development of iPS cells because of the enhanced carbonyl stress. 31630312_The most active compound (ST018515) showed an IC50 of 0.34 +/- 0.03 muM, which, compared to reported GLO-I inhibitors, can be considered a potent inhibitor, making it a good candidate for further optimization towards designing more potent GLO-I inhibitors. 31661534_Common GLO1 variants do not increase chronic pancreatitis risk. 31738028_High expression of GLO1 indicates unfavorable clinical outcomes in glioma patients. 32265040_The three genes associated with chronic kidney disease (AGT, GLO1, and SHROOM3) showed associations with both the high levels of oxidatively damaged DNA and genomic instability. 32368974_The Role of Glyoxalase in Glycation and Carbonyl Stress Induced Metabolic Disorders. 32721999_Resveratrol, Curcumin and Piperine Alter Human Glyoxalase 1 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. 32916503_LncRNA OIP5-AS1 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Regulating miR-216a-5p/GLO1. 33142109_Glyoxalase 1 expression analysis by immunohistochemistry in breast cancer. 33360689_Genomic GLO1 deletion modulates TXNIP expression, glucose metabolism, and redox homeostasis while accelerating human A375 malignant melanoma tumor growth. 33966051_Glyoxalase I disruption and external carbonyl stress impair mitochondrial function in human induced pluripotent stem cells and derived neurons. 34156474_Systemic inflammation down-regulates glyoxalase-1 expression: an experimental study in healthy males. 34838714_The activity of glyoxylase 1 is regulated by glucose-responsive phosphorylation on Tyr136. 34848450_GLO 1 and PKClambda Regulate ALDH1-positive Breast Cancer Stem Cell Survival. 35269594_Emerging Glycation-Based Therapeutics-Glyoxalase 1 Inducers and Glyoxalase 1 Inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000024026 |
Glo1 |
1711.423548 |
2.4593430494 |
1.298273 |
0.042169459 |
956.806621 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000439700817073414330038556070621446657073570606798590126263799281342630345091789920405733244151374851932022239379448438058 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000438512436486729425859724599102657133714347072959113038614641568603704137066094146080920835382157392034505446049673222001 |
Yes |
No |
2449.8139765 |
58.6814216 |
1003.3364394 |
19.2879111 |
| ENSG00000124772 |
57699 |
CPNE5 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCH3 |
FUNCTION: Probable calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein that may play a role in calcium-mediated intracellular processes (By similarity). Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell projection;Differentiation;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Calcium-dependent membrane-binding proteins may regulate molecular events at the interface of the cell membrane and cytoplasm. This gene is one of several genes that encode a calcium-dependent protein containing two N-terminal type II C2 domains and an integrin A domain-like sequence in the C-terminus. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. More variants may exist, but their full-length natures could not be determined. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:57699; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26522866_Results provide the first evidence of genetic variants in the CPNE5 gene influencing both alcohol dependence and obesity 30272363_Data revealed that CPNE5 mRNA expression was significantly lower in ESCC tissues and cell lines and correlated with significantly shorter overall survival. Multivariable analysis identified low CPNE5 expression to be an independent prognostic factor of OS. Analysis of recurrence patterns revealed that significantly more patients with local recurrence expressed lower levels of CPNE5 mRNA. 33780365_High expression of CPNE5 and CPNE9 predicts positive prognosis in multiple myeloma. |
ENSMUSG00000024008 |
Cpne5 |
86.754130 |
0.0305141055 |
-5.034380 |
0.877627608 |
23.160600 |
0.00000149019490260153598461831479099481967409701610449701547622680664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005166849133755854567523566750475438880130241159349679946899414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
7.4198052 |
3.5511554 |
239.0369312 |
79.0193811 |
| ENSG00000124802 |
9521 |
EEF1E1 |
protein_coding |
O43324 |
FUNCTION: Positive modulator of ATM response to DNA damage. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D1M4}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a multifunctional protein that localizes to both the cytoplasm and nucleus. In the cytoplasm, the encoded protein is an auxiliary component of the macromolecular aminoacyl-tRNA synthase complex. However, its mouse homolog has been shown to translocate to the nucleus in response to DNA damage, and it plays a positive role in ATM/ATR-mediated p53 activation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the neighboring downstream MUTED (muted homolog) gene. An EEF1E1-related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:9521; |
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex [GO:0017101]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001235]; positive regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000774]; positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043517]; translation [GO:0006412] |
15680327_p18 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor and a key factor for ATM/ATR-mediated p53 activation. 18343821_analysis of the three-dimensional structure and residues of the novel tumor suppressor AIMP3/p18 required for the interaction with 19024604_No EEF1E1 mutations were detected in human cancer specimens. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21789020_Decreased expression of AIMP3 in gastric and colorectal cancer tissues suggests that down-regulation of this protein may be related to inactivation of the tumor suppressor functions of AIMP proteins and might play a role in the development of GC and CRC. 22106287_Data show that aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multifunctional protein-3 (AIMP3)/p18 is released from aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multifunctional protein-3 (AIMP3) by UV irradiation-induced stress. 22867704_AIMP3 is a critical mediator of Met-tRNA(i)(Met) transfer from methionyl-tRNA synthetase to eIF2 complex for the accurate and efficient translation initiation 23306449_AIMP3 stabilizes and protects methionyl-tRNA synthetase and eIF2gamma through the binding interactions. 24104880_Identification of EEf1E1 and OBFC2B as novel BRCA1-partner genes in the DNA double-strand break repair pathway. 25465621_AIMP3 was shown to be involved in the cellular aging of human mesenchymal stem cells. 26472928_analysis of the heterotetrameric complex structure of the glutathione transferase (GST) domains shared among the four MSC components, methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MRS), glutaminyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS), AIMP2 and AIMP3 28797100_LmnA binds AIMP3 via its extreme C-terminus. Together these findings provide a structural insight for understanding the interaction between AIMP3 and LmnA in AIMP3 degradation. 30706629_The AIMP3 enhanced mitochondrial respiration and suppressed autophagic activity, indicating that the AIMP3-associated modulation of metabolism and autophagy is a key mechanism in the senescence of stem cells and further suggesting a novel target for interventions against aging. 33538115_AIMP3 inhibits cell growth and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma through activating a miR-96-5p-AIMP3-p53 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000001707 |
Eef1e1 |
36.118600 |
2.1303806971 |
1.091111 |
0.277351035 |
15.630417 |
0.00007700588152876682468839925066461660208005923777818679809570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000215715849566255131637693143176193188992328941822052001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.4217911 |
8.7184379 |
23.8272591 |
3.2205659 |
| ENSG00000124813 |
860 |
RUNX2 |
protein_coding |
Q13950 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in osteoblastic differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis (PubMed:28505335, PubMed:28738062, PubMed:28703881). Essential for the maturation of osteoblasts and both intramembranous and endochondral ossification. CBF binds to the core site, 5'-PYGPYGGT-3', of a number of enhancers and promoters, including murine leukemia virus, polyomavirus enhancer, T-cell receptor enhancers, osteocalcin, osteopontin, bone sialoprotein, alpha 1(I) collagen, LCK, IL-3 and GM-CSF promoters. In osteoblasts, supports transcription activation: synergizes with SPEN/MINT to enhance FGFR2-mediated activation of the osteocalcin FGF-responsive element (OCFRE) (By similarity). Inhibits KAT6B-dependent transcriptional activation. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11965546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28505335, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28703881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28738062}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the RUNX family of transcription factors and encodes a nuclear protein with an Runt DNA-binding domain. This protein is essential for osteoblastic differentiation and skeletal morphogenesis and acts as a scaffold for nucleic acids and regulatory factors involved in skeletal gene expression. The protein can bind DNA both as a monomer or, with more affinity, as a subunit of a heterodimeric complex. Two regions of potential trinucleotide repeat expansions are present in the N-terminal region of the encoded protein, and these and other mutations in this gene have been associated with the bone development disorder cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD). Transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms result from the use of alternate promoters as well as alternate splicing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:860; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; chondrocyte development [GO:0002063]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; ligamentous ossification [GO:0036076]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoblast development [GO:0002076]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; osteoblast fate commitment [GO:0002051]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in cellular response to chemical stimulus [GO:1901522]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040036]; regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042487]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to L-ascorbic acid [GO:0033591]; response to sodium phosphate [GO:1904383]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217] |
11768584_clavicular dysplasia was more pronounced with the R19OW mutation, while the bone density was markedly reduced in individuals with either R19OW or deletion of nucleotide C821 11857736_Analysis of the three-dimensional structure of the DNA binding runt domain of the RUNX2 protein and its interaction with DNA provide insight into how missense mutations affect RUNX2 function and cause cleidocranial dysplasia. 11968014_RT-PCR analysis of human bone marrow stromal cells during osteogenesis in vitro: the mRNA levels of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), bone sialoprotein-II (BSP), osteopontin (OP) and cbfa-1 increased with culture time in osteogenic medium. 11979975_is an essential transcription factor for the regulation of osteoblast differentiation 12060751_regulatory signals are active at transcriptional subnuclear sites 12088880_Runx2 expression in osteoblasts is reduced by hypoxia, and may be a mechanism of osteoporosis by decreased vascular supply. 12112004_Differential regulation of Cbfa1/Runx2 and osteocalcin gene expression by vitamin-D3, dexamethasone, and local growth factors in primary human osteoblasts 12162506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12162506_variants may be related to genetic effects on bone mineral density and osteoporosis 12196916_Cleidocranial dysplasia could result from much smaller losses in the RUNX2 function than has been envisioned on the basis of the conventional haploinsufficiency model. 12231506_RUNX2 is negatively regulated by the phosphorylation of two conserved serines 12270142_TWIST inactivation reduces expression and DNA binding to the osteocalcin promoter in osteoblasts. 12393937_This protein is regulated by human basic fibroblast growth factor. 12554794_Cbfa1 is required in mediating the bone anabolic effects of parathyroid hormone. 12568398_Runx2/Cbfa1 activity increases through a posttranslational mechanism involving phosphorylation of key residues and has a role in osteoblastic differentiation 12631081_Cbfa1 is a key regulatory factor in the vascular calcification observed in dialysis patients and is up-regulated in response to many uremic toxins. 12674332_Telomerase accelerates osteogenesis of bone marrow stromal stem cells by upregulation of CBFA1, osterix, and osteocalcin. 12732182_Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is an inherited autosomal-dominant skeletal disease caused by heterozygous mutations in the RUNX2 protein. 12746842_Expression of Runx2 in prostate cancer may be the molecular switch that is associated with expression of various bone-specific factors in prostate cancer. 12750290_Runx2 is ectopically expressed in breast cancer cells and that one isoform of Runx2 can activate bsp expression in these cells. 12815605_six novel mutations causing 2 amino acid substitutions and four frameshift mutations were identified in the RUNX2 gene of Italian cleidocranial dysplasia patients. 14523023_Runx2 has a role in parathyroid hormone-induced anti-apoptotic signaling in osteoblasts, which is shortened by proteasomal degradation 14639470_mechanical stress plays a key role in the progression of OPLL through an increase in Cbfa1 expression 14739291_The regulation of SOST expression by Cbfa1 suggests a potential role for the sclerosteosis gene in homeostatic regulation of osteoblast differentiation and function. 15051730_RUNX1 and RUNX2 regulate TIMP1 gene expression 15150273_Runx2 has a role in menin-induced bone morphogenetic protein 2- and transforming growth factor beta-regulated osteoblastic differentiation 15193550_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15231660_Runx2 expression in breast cancer cells provides a molecular phenotype that enables the interactions between tumor cells and the bone microenvironment that lead to osteolytic disease. 15273700_As a target gene of endostatin, cbfa1/osf2 was found to be specifically expressed in granulocytes in human breast neoplasms. 15304489_RUNX2 DNA binding is regulated by IGF-1 through sequential activation of the PI3K/Pak1 and ERK1/2 signaling cascade 15389579_Osteocalcin mRNA was down-regulated in Apert osteoblasts carrying the FGFR2 P253R mutation, Runt-related transcription factor-2 (RUNX2) mRNA was differentially spliced, and FGF2 secretion was greater. 15476590_Growth hormone attenuates the transcriptional activity of Runx2 by facilitating its physical association with Stat3beta 15583032_Physiologic coupling of osteoblast differentiation to cell cycle withdrawal is mediated through runx2 and p27KIP1, and these processes are disrupted in osteosarcoma. 15623533_PLZF plays important roles in early osteoblastic differentiation as an upstream regulator of CBFA1 15665096_Fidelity of Runx2 intranuclear organization is necessary for expression of target genes that mediate the osteolytic activity of metastatic breast cancer cells. 15725473_Capability of Imatinib to induce an anti-leukemic effect in Core Binding Factor (CBF)-leukemia patients. 15750689_4 new genes may be under the control of Cbfa1; 3 of them, SelM, elF-4AI, & RPS24, seemed to be linked to a global change in cellular metabolism & cell growth; the CD99/MIC2 gene was strongly overexpressed in cells presenting high levels of Deltacbfa1 15798204_Runx2 collaborates with Oct-1 and contributes to the expression of a mammary gland-specific gene. 15933061_RUNX2/CBFA1 has a critical role in the decreased bone formation in multiple myeloma 16110492_We propose that nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of RUNX2 may modulate its transcriptional activity, as well as its ability to interface with signal transduction pathways that are integrated at RUNX2 containing subnuclear sites. 16166639_Runx2-regulated MMP9 levels are functionally related to the invasion properties of cancer cells 16187316_Runx2 has a role in organizing gene transcription in developing and maturing osteoblasts [review] 16198163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16198163_The results of the present research contribute to the deeper understanding of the genetic architecture of femoral size and introduce the issues of site and sex dependency of the extent of RUNX2 effect. 16208410_silencing Runx2 with siRNA in myeloma cells suppressed OPN mRNA and protein expression, critical for the proangiogenic effect of myeloma cells 16237704_RUNX factors participate in prostate epithelial cell function and cooperate with an Ets transcription factor to regulate PSA gene expression 16244783_A novel RUNX2 missense mutation has been found in members of a family clinically diagnosed with cleidocranial dysplasia. 16270353_The cleidocranial dysplasia phenotype can be caused by a splice site mutation, which results in the deletion of N-terminus amino acids containing the QA stretch in RUNX2 that contains a previously unidentified second nuclear localization signal. 16299379_Smad6 interacts with Runx2 and mediates Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-induced Runx2 degradation 16407259_RUNX2 phosphorylation by cdc2 may facilitate cell cycle progression possibly through regulation of G(2) and M phases, thus promoting endothelial cell proliferation required for tumor angiogenesis 16418782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16418782_Of 16 SNPs in RUNX2 and its two promoters (P1 and P2), only SNPs in the P2 promoter were significantly associated with bone density. 16442859_Regulation of Gsalpha protein by Runx2 seems to be of particular interest considering the increasing evidences on bone metabolism regulation by G proteins 16463420_A severe calvarial phenotype is described that is associated with novel mutations in the C-terminal region of RUNX2 distal to the DNA-binding runt domain. 16467978_In dental follicle cells, gene expression of runx2, DLX-5, and MSX-2 was unaffected during osteogenic differentiation in vitro. 16476422_An unexpected interaction is found between transgenic Runx2 and mouse parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) in controlling the rate of chondrocyte proliferation. 16598384_autocrine BMP production is necessary for the RUNX2 transcription factor to be active and that BMPs and RUNX2 cooperatively interact to stimulate osteoblast gene expression. 16613856_BMP-2 stimulates Runx2 acetylation 17000892_The transcription axis of Cbfa-1 (Runx-2) is crucial in maintaining equilibrium of bone formation and resorption. Heparin affects expression in osteoblast culture. 17042739_Runx2 directly binds to the osteoblast specific binding elements 2 elements and transactivates the human NELL-1 promoter. 17171635_Results show that RUNX2 is hyper-phosphorylated by CDK1/cyclin B during mitosis in osteoblastic cells. 17251981_Runx2 is a critical mechanistic link between cell fate, proliferation and growth control 17350616_F promoter of ERalpha activity may be tightly regulated by a dynamic interplay between these two Runx2 sites, with a predominance of negative effect of the Runx2 (a) site. 17352650_Cbfa1 may act as a repressor of early stem cell markers such as human TERT as one possible mechanism for facilitating cellular differentiation. 17360627_Runx2 protein is stable during cell division and is bound to chromosomes during mitosis through sequence-specific DNA binding and thus has an active role in retaining phenotype during cell division to support control of gene expression in progeny cells. 17379770_Cbfb enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by stabilizing Cbfa-1 proteins. 17387386_findings demonstrate that Runx2 expression is active in variable chondrosarcomas compared to enchondromas, suggesting its importance in growth and differentiation of neoplastic cartilage 17434448_Thus, our results suggest that Cbfalpha1 upregulates DMP1 gene expression differentially that may contribute to the spatial-temporal expression pattern of DMP1 during odontoblast differentiation. 17438369_the RUNX2 and YAP65 interaction has a novel role in oncogenic transformation that may be mediated by modulation of p21(CIP1) protein expression 17522365_In this study of a 14-yr-old boy with typical cleidocranial dysplasia phenotype, the authors found a novel CBFA1/RUNX2 gene mutation. 17702747_STAT3, Runx2, and steroid receptor coactivator-1 are critical molecules in mediating leptin-stimulated cell osteogenesis in TOLF (thoracic ossification of ligament flavum) 17878995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17878995_The results highlight the importance of the RUNX2 promoter 2 polymorphism in femur neck bone density determination. 17956871_Runx2 and HDAC3 repress BSP gene expression and that this repression is suspended upon osteoblastic cell differentiation. 17973689_A novel missense mutation in the RUNT-domain (P210S) of RUNX2 was identified in 3 Japanese cleidocranial dysplasia siblings; they showed a wide variation in the number and position of supernumerary teeth 17981598_Runx2 regulates bone development, bone maturation, and bone maintenance through the regulation of osteoblast differentiation and function [review] 17997710_Histone deacetylase 7 associates with Runx2 and represses its activity during osteoblast maturation in a deacetylation-independent manner 18082140_Runx2 phosphorylation results from addition of hNELL1 protein 18166138_novel mutation of RUNX2 disrupts the protein-DNA interaction 18171674_TFIIA gamma together with ATF4 and Runx2 stimulates osteocalcin promoter activity and endogenous mRNA expression. 18223689_Runx2-mediated activation of the Bax gene increases osteosarcoma cell sensitivity to apoptosis 18316777_RUNX2 influences joint formation by affecting the differentiation pathways of chondrocytes and osteoblasts. 18319563_angiopoietin-1 is downstream of Runx2 in both OPLL primary cells and osteoblasts. Angiopoietin-1 may play an important role in ectopic ossification. 18321663_In cotransfection experiments with an osteocalcin (OC) promoter construct, we confirmed that only RUNX2wt and RUNX2Delta7 could upregulate the OC promoter activity in the osteosarcoma cell line. 18357615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18357615_RUNX2 appears to influence risk of CL/P through a parent-of-origin effect with excess maternal transmission 18373722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18373722_Polymorphisms in the RUNX2 promoter is significantly associated with the hand bone length and bone mineral density. 18381576_Cbfa-1 may play a role in calcification processes in human thyroid papillary carcinoma tissues. 18438928_These data suggest a functional contribution of Runx-2-regulated galectin-3 expression to glial tumor malignancy. 18442887_the region between -3 kb and -1 kb is required for the minimal skeletal tissue-specific expression of Runx2, and that the region between -155 bp and -75 bp is important for its basal transcription, which may be in part mediated by HIF2A in bone tissues. 18482578_This is the first report demonstrating significant upregulation in expression of Runx2 and Osterix by TGF-beta3 induction of human adipose-derived stromal cells during in vitro chondrogenesis. 18553107_Dats suggest that sparse neovascularization into areas underlying the atherosclerotic plaques' necrotic cores, where Cbfa1-expressing cells reside, might explain the rarity of ectopic bone formation in the arterial wall. 18653765_FHL2-beta-catenin interaction potentiates beta-catenin nuclear translocation and TCF/LEF transcription, resulting in increased Runx2 and alkaline phosphatase expression, which was inhibited by the Wnt inhibitor DKK1. 18688176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18688176_These data on a variant of RUNX2 suggest that lipid metabolism might be affected by genetic polymorphisms in the promoter region. 18759297_Runx2 contributes to the pathogenesis of intervertebral disk degeneration. 18777095_the RUNX2 gene was analyzed within a CCD family from China, and a novel missense mutation (c. 475G --> C [p.G159R]) was identified. 18829486_E4BP4 has a role as osteoblast transcriptional repressor in inhibiting both Runx2 and Osterix in myeloma bone disease 18829534_A novel role of Runx2 in up-regulating the vicious cycle of metastatic bone disease, in addition to Runx2 regulation of genes related to progression of tumor metastasis. 18931939_study showed Runx2 is expressed at higher levels in osteosarcoma cell line (OS1) than in fetal osteoblasts; high level of Runx2 suggest osteosarcomas may form from committed osteoblasts that have bypassed growth restrictions normally imposed by Runx2 18986983_Hey1 and Runx2 were shown to act synergistically in BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation, and Runx2 expression significantly decreased in the absence of Hey1, suggesting that Runx2 may function downstream of Hey1 19017541_This study identifies RUNX2 as a target for heavy metal-induced osteotoxicity. 19020999_Galectin-3 is regulated by RUNX1 and RUNX2 in human pituitary tumor cells by direct binding to the promoter region of LGALS3 and thus may contribute to pituitary tumor progression. 19116917_the HY(hypertrophy) box is the core element responsive to RUNX-2 in human COL10A1 promoter 19147956_This review validates that Runx2 is required for fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) responsiveness and that RUNX2 mediates plasma cell membrane glycoprotein PC-1 gene expression by binding to the PC-1 gene promoter. 19259136_Found evidence of Mendelian Transmission Distortion in the region harboring RUNX2 in one of the HapMap populations. 19259136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19342447_Runx2 regulates enzymes involved in sterol/steroid-related metabolic pathways and that activation of Cyp11a1 by Runx2 may contribute to attenuation of osteoblast growth. 19383984_euglycemia supports RUNX2 activity and promotes normal microvascular cell migration and wound healing, which are repressed under hyperglycemic conditions through the aldose reductase polyol pathway 19389811_androgen receptor binds Runx2 and abrogates its recruitment to DNA in osteoblasts and prostate cancer cells 19422937_Runx2 may play a crucial role in cytokine-mediated MMP-13 expression in Giant Cell Tumor of bone stromal cells. 19424741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19424741_the RUNX2 P2 polymorphism (-1025 T > C) may be a useful genetic marker for bone metabolism and may play an important role in BMD in postmenopausal Korean women. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453496_roxithromycin suppresses matrix metalloproteinase 13 via the downregulation of Runx2 in human gingival epithelial cell cultures 19509141_FTY720 treatment down-regulated Runx2 expression and its transcriptional activity, as well as inhibited its regulated downstream events. 19509297_reduced expression of HDAC4 in chondrosarcoma cells increases expression of Runx2 leading to increased expression of VEGF and in vitro angiogenesis 19515746_These results confirm that loss of function RUNX2 mutation (c.577C>T) in Case 1 family is responsible for its cleidocranial dysplasia phenotype. 19595020_strain enhance expression of osteocalcin, type I collagen gene and Cbfa1/Runx2 in human osteoblas 19631773_Immunolocalization of RUNX2 positive cells in delayed unions of the fibula reveals that delayed clinical fracture healing does not result in impairment of osteogenic cell proliferation and/or differentiation at the tissue level. 19632824_results show nuclear presence of Runx2 is significantly & positively correlated with ER-PR positive breast cancer tissues in Grade 2 & Grade 3 tumours 19649655_Regulation of bone development and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2. 19690135_direct mechanistic evidence for the biological activity of Runx2, dependent on its subnuclear localization, in promoting early events of breast cancer progression 19734454_We discuss expression of Runx2 during development as well as the post-translational regulation of Runx2 through modification by phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation. 19739101_Cell cycle control of Runx2 gene expression is impaired in osteosarcomas due to deregulated proteasomal degradation. This deregulation may contribute to the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. 19744171_Mutations have been identified in cleidocranial dysplasia patients 19767586_3 novel mutations in coding region of RUNX2: 2 missense; 1 frameshift. 1 missense converts threonine to isoleucine at codon200. Other 1 substitutes leucine for arginine codon225. Frameshift mutation in exon3 leads to translational stop codon at codon221. 19801668_Runx2 phosphorylation plays an important role in the control of osteoblast gene expression 19880526_TFII-I plays an inhibitory role in regulating genes that are essential in osteogenesis and intersects with the bone-specific transcription factor Runx2 and the retinoblastoma protein, pRb. 19915614_Runx2 is a key regulator of events associated with prostate cancer metastatic bone disease. 19949374_Runx2 (runt-related transcription factor 2) regulates survivin expression in prostate cancer cells 20007706_Data show that the FGF2-induced ERK MAP kinase strongly increased the Runx2 protein level through an increase in acetylation and a decrease in ubiquitination. 20053387_RUNX2 represents a critical link between cell fate, proliferation and growth control.RUNX2 might control osteoblastic growth depending on the differentiation stage of the cells by regulating expression of elements involved in hormone sensitivity. 20073986_The total expression of Runx2 in the concave side growth plates in the upper and lower end vertebrae were higher than that in the concave side growth plates of apex. 20082269_A novel missense mutation (c.1259C-->T[p.T420I]) in RUNX2 gene exon 7 was identified in patients with cleidocranial dysplasia 20082326_Runx2 is mechanistically linked to TGFbeta and androgen responsive pathways that support prostate cancer cell growth 20196777_there is an association among RUNX-2, SOX-9 and FGF-23 in relation to MMP-13 expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes 20200969_This study also suggested that, depending on the osteoblasts' differentiation stage, RUNX2 may control cell growth by regulating the expression of elements involved in hormone and cytokine sensitivity. 20225274_Loss of DNA binding, but not nuclear localization or CBF-beta heterodimerization, causes RUNX2 haploinsufficiency in patients with the RUNX2(R131G) mutation. 20306685_Studies show that FISH technic for the detection of CBF chromosomal aberrations was significantly higher than conventional cytogenetics. 20376792_Two novel RUNX2 mutations were found in two unrelated Chinese families with cleidocranial dysplasia. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20407796_Genetic association studies in a population of Spanish women confirm association between femur neck bone mineral density (BMD) and a RUNX2 SNP (-1025 T>C; promoter region). There is some association with another RUNX2 SNP (+198 G>A; exon 2). 20407796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20433876_The expression of Cbfalpha1 which were the key factors in osteogenic differentiation was also up-regulated. 20465837_Suggest RUNX2 expression as a potential biomarker of chemotherapy failure in osteosarcoma. 20525800_may play an important role in periodontal ligament-mediated bone remodelling in response to mechanical stimulation 20530675_WWOX reconstitution in osteosarcoma cells was associated with downregulation of RUNX2 levels and RUNX2 target genes, consistent with the ability of WWOX to suppress RUNX2 transactivation activity. 20560987_Identification of large chromosome aberrations in or near the RUNX2 locus in 3 of the 19 cases of Cleidocranial dysplasia 20564243_The stimulation of p38 MAPK by DDR2 was required for DDR2-induced activation of Runx2 and OCN promoters. 20593410_The mechanisms by which SOX9 regulates RUNX2 function may underlie broader signaling pathways that can influence osteochondrogenesis and mesenchymal fate. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20648631_135 unrelated patients with the clinical diagnosis of Cleidocranial Dysplasia were screened for RUNX2 mutations by sequencing analysis and demonstrated 82 mutations 48 of which were novel. 20648631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20665663_These results demonstrate that EWS-FLI blocks the ability of Runx2 to induce osteoblast specification of a mesenchymal progenitor cell. 20683987_identified a 1.1 Mb duplication encompassing RUNX2 in two affected cousins with metopic synostosis and hypodontia. 20702542_New genetic evidence that mutations involved in RUNX2 contribute to cleidocranial dysplasia. 20721706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20721706_Suggest RUNX2 could be responsible for ectopic bone formation in the spinal ligament in the Chinese Han population. 20738756_RT-PCR demonstrated that melatonin significantly suppressed PPARgamma expression but promoted Runx2 expression in the early stages of adipogenesis and osteogenesis of hMSCs. 20740684_Runx2 is an inhibitor of the Notch1 signaling pathway during normal osteoblast differentiation 20863401_Data highlight multiple mechanisms by which Runx2 promotes the metastatic phenotype of PCa cells, including tissue invasion, homing to bone and induction of high bone turnover. 20872798_Study suggests that the truncated RUNX2 mutant protein may be responsible for the alterations of RUNX2(+/m) dental pulp cells, and RUNX2 gene may be involved in dental development by affecting the cell growth and differentiation. 20946121_Runx2 plays very important roles in the progression of breast cancer 21040462_4 different mutations including 1 novel mutation were identified. 4 had R225Q mutation, 3 had P224S mutation, 2 others had different frame-shift mutations. Identical gene mutations showed wide variation in supernumerary tooth formation. 21078438_Sox9, Runx2, and Osterix-were play an essential role in determining the skeletal progenitor cells' fate in benign cartilage and bone forming tumors. 21088106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21121067_high glucose levels can evoke the calcification of human aortic smooth muscle cells by inducing osteoblastic trans-differentiation and intracellular calcium deposition via the BMP-2/Cbfalpha-1 pathway. 21131390_The molecular characterization of the novel RUNX2 gene mutation c.580 + 1G > A in an Italian family affected by cleidocranial dysplasia was proven to alter splicing of the RUNX2 messenger RNA. 21215027_Two novel mutations in CBFA1 were identified that contributes to cleidocranial dysplasia. 21236710_TGF-beta1 down-regulates Runx-2 and ALP in human dental pulp cells via ALK5/Smad2/3 signaling. These events may play important roles at specific stages of pulpal repair and dentinogenesis. 21302301_these studies reveal how the C/EBPbeta factor, known to have a key role during osteogenesis, contributes to regulating the expression of Runx2, the master regulator of osteoblast differentiation. 21505104_Inactivation of FOXO1 due to frequent loss of PTEN in prostate cancer cells may leave the oncogenic activities of Runx2 unchecked. 21520068_the inhibition of Runx2 expression after continuous cyclic mechanical tension stimulation is mediated by RhoA-ERK1/2 pathway. 21542013_This is the first time that the direct action of RUNX2 on LRP5 has been described. 21558934_RT-PCR showed that RUNX2 from osteoblasts from Pfeiffer syndrome grown on PLPG acid plates were downregulated after 30 days. 21559363_TIEG1 has a role in regulating the expression and activity of Runx2 in osteoblasts 21604327_RUNX2 knockdown impaired the repressive activity of RBP2 in osteogenic differentiation of hASCs. Study demonstrates the roles of H3K4 demethylase RBP2 in osteogenic differentiation of hASCs and to link RBP2 to the transcriptional regulation of RUNX2. 21649908_LGD1069 may impair angiogenic and metastatic potential induced by tumor cells through suppressing expression of Runx2 directly on human endothelial cells. 21674037_ox-PAPCs enhanced PPARgamma2 and adipogenic gene expression and reduced Runx2 and osteoblast differentiation marker gene expression in differentiating mesenchymal stem cells 21713451_The mRNA expression of type I collagen, ALP, osteocalcin and RUNX2 increased markedly in human adipose stem cells as a result of lactoferrin treatment. 21777514_Runx2 plus BMP2 mediated efficient conversion of fibroblast-like ligamentum flavum cells into osteoblast- like cells. 21809344_Data suggest that Runx2 controls a positive feedback loop between androgen signaling and PIP, and pharmacological inhibition of PIP may be useful to treat PIP positive tumors. 21885439_novel evidence that inhibition of BMP-2 or BMP-2-mediated MAPK/Runx2/Snail signaling is an attractive therapeutic target for osteolytic bone metastases in lung cancer patients. 21907184_BMP-2-mediated NADPH oxidase activation increased ER stress leading to an increase in Runx2 expression thus promoting vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. 21913213_Inhibition of RUNX2 expression or DNA binding may be a useful strategy to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation in tumor angiogenesis. 21931630_the important role of hypoxia-mediated signalling in osteogenic differentiation in MSCs through direct regulation of RUNX2 by TWIST 22023169_current findings suggest a correlation between dental alterations and mutations in the runt domain of RUNX2 in cleidocranial dysplasia patients 22032690_Runx2 and CBFbeta are required for the expression of genes that mediate the ability of metastatic breast cancer cells to directly modulate both osteoclast and osteoblast function. 22095611_Runx2 overexpression restored osteoblastic differentiation of PlxnA2-knockdown cells 22095691_findings show that C/EBPbeta and RUNX2, with MMP-13 as the target and HIF-2alpha as the inducer, control cartilage degradation 22102412_BMP2 induces osteoblast differentiation through Runx2-dependent ATF6 expression, which directly regulates Oc transcription. 22139789_The role of the Runx2 gene in bone regeneration and osteogenic differentiation. [Review] 22147940_This work provides clinical evidence for the importance of antagonism between Runx2 and E2 signaling in breast cancer 22158061_Data show that the mRNA expression levels of beta-catenin, Runx2, Sox9 and osteopontin were significantly higher in ossification of ligamentum flavum (OLF) cells than in non-OLF cells. 22158627_RUNX2 binding to diverse gene loci may support the biological properties of osteosarcoma cells. 22173721_LF and OSF-2 gene polymorphisms may have deep impact on the risk of rhinosinusitis nasal polyps' formation. 22189971_Cholecalciferol modulated RUNX2:DNA binding at nanomolar concentrations even in cells with low VDR. 22194205_Demonstratation that a novel mutation (c.549delC) of RUNX2 is associated with cleidocranial dysplasia in a Chinese family. 22241686_Our results suggest genetic variation in RUNX2 may influence susceptibility to cleft lip with or without cleft palate/P through interacting with environmental tobacco smoke. 22260235_In cells challenged with ethanol the expression of CBF-alpha1, a transcription factor involved in the regulation of osteoblastic transformation of Human vascular smooth muscle cells, was elevated. 22351759_Runx2 stabilizes HIF-1alpha by binding to ODDD to block the interaction between von Hippel-Lindau protein and HIF-1alpha. 22389001_study concludes that a subset of cancer-related Runx2 target genes require recruitment of G9a for their expression, but do not depend on its histone methyltransferase activity. 22393235_Downregulation of RUNX2 expression reduces the localization of HDAC1 to the nucleolar periphery and also decreases the association between HDAC1 and UBF. 22396198_RUNX2 is a potent prognostic factor in human colon carcinoma patients through the promotion of cell proliferation and invasion properties, and is at least partly upregulated by estrogen signals through ERbeta of carcinoma cells. 22407027_identified a significant excess of genes with pivotal roles in bone homeostasis, such as PPPT3B and the height associated SUPT3H-RUNX2 22493443_COUP-TFII negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation via interaction with Runx2, and during the differentiation state, BMP2-induced Runx2 represses COUP-TFII expression and promotes osteoblast differentiation. 22511796_Thyroid papillary carcinoma patients with microcalcifications expressed significantly higher levels of Runx2 mRNA in serum with respect to patients without microcalcifications. 22634173_IFITM1 knockdown in human alveolar-derived bone marrow stromal cells was associated with inhibition of Runx2 mRNA and protein expression. 22641097_Studied the potential molecular mechanism of thyroid cancer invasion.Data suggest enhanced Runx2 is functionally linked to tumor invasion and metastasis of thyroid carcinoma by regulating EMT-related molecules, MMPs and angiogenic/lymphangiogenic factors. 22750373_Runx2 P2 promotor is unmethylated in normal dental tissue and hypomethylated in pulp tissue. this study provides no evidence that differential promoter methylation may be responsible for the etiology of ectopic eruption. 22821892_We showed that Id1 controls the expression of the Runx2 isoform I and that this transcription factor plays a central role in mediating the Id1 proinvasive function in thyroid tumor cells. 22869368_Osterix regulates calcification and degradation of chondrogenic matrices through matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) expression in association with transcription factor Runx2 during endochondral ossification 22890388_RUNX2 mRNA expression was negatively correlated with CaP aggressiveness. Moreover, the nuclear location of RUNX2 may be a prognostic marker of metastasis in CaP. 22903460_Runx-2 gene expression highly correlated with bone mineral density in both genders; mesenchymal stem cells and peripheral mononuclear cells showed the same gene expression profile of Runx-2 22912713_novel Q-repeat mutations in RUNX2 alter BMD and display impaired transactivation function 22949168_Runx2 protein levels are cell cycle-regulated with respect to the G(1)/S phase transition in U2OS, HOS, G292, and 143B cells. 22966907_CD44 signaling regulates phosphorylation of RUNX2. Localization of RUNX2 in the nucleus requires phosph |
ENSMUSG00000039153 |
Runx2 |
384.302995 |
0.2345849414 |
-2.091818 |
0.108253808 |
377.326368 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000475398964427460462470035260497537739446647451321674073303005473930689044313814533509458822081145114586127983096343327474435903841438917018990234275920700792689855515144813271835849354152724312703858988650613970339264824360725469887256622314453125 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000167868151075342506543681516620939034158629547041424904194569359362386681901199972626792668171438119058072910908955132221873743160893373152998574929351694833550696760770095249995535831330720818231567797659820051592305389931425452232360839843750000 |
Yes |
No |
149.5659460 |
23.9149177 |
646.1037119 |
72.9062469 |
| ENSG00000124839 |
64284 |
RAB17 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0T7 |
FUNCTION: The small GTPases Rab are key regulators of intracellular membrane trafficking, from the formation of transport vesicles to their fusion with membranes. Rabs cycle between an inactive GDP-bound form and an active GTP-bound form that is able to recruit to membranes different set of downstream effectors directly responsible for vesicle formation, movement, tethering and fusion. That Rab is involved in transcytosis, the directed movement of endocytosed material through the cell and its exocytosis from the plasma membrane at the opposite side. Mainly observed in epithelial cells, transcytosis mediates for instance, the transcellular transport of immunoglobulins from the basolateral surface to the apical surface. Most probably controls membrane trafficking through apical recycling endosomes in a post-endocytic step of transcytosis. Required for melanosome transport and release from melanocytes, it also regulates dendrite and dendritic spine development (By similarity). May also play a role in cell migration. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22328529}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Endosome;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The Rab subfamily of small GTPases plays an important role in the regulation of membrane trafficking. RAB17 is an epithelial cell-specific GTPase (Lutcke et al., 1993 [PubMed 8486736]).[supplied by OMIM, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:64284; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; establishment of melanosome localization [GO:0032401]; filopodium assembly [GO:0046847]; immunoglobulin transcytosis in epithelial cells mediated by polymeric immunoglobulin receptor [GO:0002415]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051489]; regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051963]; transcytosis [GO:0045056] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21291502_Data reveal new functions for recycling endosomes and Rab17 in pigmentation through a distal step in the process of melanosome release via filopodia. 22328529_Knockdown of either Rab17 or liprin-beta2 restores invasiveness of ERK2-depleted cells, indicating that ERK2 drives invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells by suppressing expression of these genes. 25052408_These results suggest that Rab17 and Rab17-mediated REs are involved in Streptococcus pyogenes-containing autophagosome-like vacuole formation. 25707355_Rab17 might act as a tumour suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma , and the anti-tumour effects of Rab17 might be partially mediated by the Erk pathway. 26191189_Down-regulation of Rab17 promotes tumourigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Erk MAPK signaling. 28005073_Mass spectrometry and immunofluorescence microscopy of efferosomes and phagosomes in macrophages demonstrated that efferosomes lacked the proteins required for antigen presentation and instead recruited the recycling regulator Rab17. 28471261_Rab17 is rapidly recruited to efferosomes, followed by migration of the efferosome to the cell center where it intermixes with lysosomes and undergoes Rab17-dependent vesiculation. 31841274_Downregulation of Rab17 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer through STAT3/HIF-1alpha/VEGF signaling. 31959474_ALS2, the small GTPase Rab17-interacting protein, regulates maturation and sorting of Rab17-associated endosomes. |
ENSMUSG00000026304 |
Rab17 |
12.838779 |
3.7372612914 |
1.901981 |
0.603984182 |
8.710747 |
0.00316339607626936730050415391701790213119238615036010742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006737622811794495743253907704684024793095886707305908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
19.3556403 |
6.8564338 |
4.6690536 |
1.3697993 |
| ENSG00000124882 |
2069 |
EREG |
protein_coding |
O14944 |
FUNCTION: Ligand of the EGF receptor/EGFR and ERBB4. Stimulates EGFR and ERBB4 tyrosine phosphorylation (PubMed:9419975). Contributes to inflammation, wound healing, tissue repair, and oocyte maturation by regulating angiogenesis and vascular remodeling and by stimulating cell proliferation (PubMed:24631357). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9419975, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24631357}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Membrane;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a secreted peptide hormone and member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family of proteins. The encoded protein is a ligand of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the structurally related erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 4 (ERBB4). The encoded protein may be involved in a wide range of biological processes including inflammation, wound healing, oocyte maturation, and cell proliferation. Additionally, the encoded protein may promote the progression of cancers of various human tissues. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:2069; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030297]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; ERBB2-EGFR signaling pathway [GO:0038134]; ERBB2-ERBB4 signaling pathway [GO:0038135]; ERBB4-ERBB4 signaling pathway [GO:0038138]; female meiotic nuclear division [GO:0007143]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0043616]; luteinizing hormone signaling pathway [GO:0042700]; mRNA transcription [GO:0009299]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051151]; oocyte maturation [GO:0001556]; ovarian cumulus expansion [GO:0001550]; ovulation [GO:0030728]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0045741]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; primary follicle stage [GO:0048160]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
12702554_Blockade of epiregulin reduced the growth of hTERT-BJ cells and colony formation of hTERT-transformed fibroblasts. Moreover, inhibition of epiregulin function in immortal hTERT-BJ cells triggered a senescence program. 15274392_Epiregulin might be a more important tumor growth regulator of malignant fibrous histiocytoma through autocrine or paracrine pathways, when compared with betacellulin. 15474502_upregulation of the epiregulin and amphiregulin expression is part of the signal transduction pathway which leads to ovulation and luteinization in the human ovary 16888076_findings demonstrated that PGE2 may mimic LH action at least in part by the activation of amphiregulin and epiregulin biosynthesis in human granulosa cells 17429393_epiregulin, COX2, and MMP1 and 2 collectively facilitate the assembly of new tumour blood vessels, the release of tumour cells into the circulation, and the breaching of lung capillaries by circulating tumour cells to seed pulmonary metastasis 17962208_1st report of EREG expression in breast cancer (45.5% of breast cancers studied). It is preferentially expressed in breast tumors co-expressing HER2/HER4. 18079685_Epiregulin played an autocrine role in the proliferation of corneal epithelial cells presumably through cross-induction with other EGF family members. 18292222_hamartomatous TSC skin tumors are induced by paracrine factors released by two-hit cells in the dermis, and proliferation with mTOR activation of the overlying epidermis is an effect of epiregulin 18497965_Increased epiregulin is associated with oral squamous cell carcinomas 18835871_Epiregulin has a protective effect against apoptosis in the human corpus luteum. 18948081_The regulatory mechanism of epiregulin expression in Ki-ras-transformed 267B1 prostate epithelial cells was studied. 19138957_Epiregulin expression correlates with advanced disease, is EGFR dependent, and confers invasive properties on non-small cell lung cancer cells. 21161326_Data suggest that expression status of AR and EPI mRNAs might be evaluated as dynamic predictors of response in KRAS WT patients receiving any cetuximab-based therapy. 21769422_It is suggested that follow-up of the expression of Ep can serve as a reliable early indication of the development of ovarian cancer. 22170233_Epiregulin (EREG) variation is associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis. 22508389_EREG gene expression was low in 7 out of 11 gastric cancer cells and this downregulation was mediated by aberrant CpG methylation of the EREG promoter. 22964644_Data indicate that epiregulin (EREG) expression significantly correlated with KRAS expression or KRAS copy number in KRAS-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines. 23074094_FBXL11 inhibited osteo/dentinogenic differentiation potential in MSC cells by associating with BCOR, then increasing histone K4/36 methylation in Epiregulin promoter to repress Epiregulin transcription. 23625463_EREG-AREG and NRG1, which are members of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, seem to modulate Bhecet's Disease susceptibility through main effects and gene-gene interactions 23671122_Apical mistrafficking of EREG crystallizes an apical EGFR signaling complex that may be uncoupled from basolateral regulatory restraints leading to cell transformation. 23826119_keratinocyte hyperproliferation in cholesteatoma is promoted through overexpression of epiregulin by subepithelial fibroblasts via epithelial-mesenchymal interactions, which may play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of middle ear cholesteatoma 23829318_Depletion of Epiregulin with shRNA inhibited SCAP proliferation. 23885463_we did not find a correlation between the presence of a K-ras mutation and the presence of Epiregulin and Amphiregulin in colon cancer tissue. 24092824_Data suggest that EREG (epiregulin), AREG (amphiregulin), and BTC (betacellulin) induced prostaglandin E2 production by induction of COX-2 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2) through MAP kinase signaling in granulosa cells. 24330607_EREG may contribute to glioma progression under the control of IRE1a. 24335920_In pre-treated K-ras wild-type status colorectal cancer, patients with high EREG gene expression appear to benefit more from cetuximab therapy compared with low expression. 24470554_These results suggested that EREG is one of the molecules involved in glioma malignancy 24748662_Epiregulin is a transcriptional target of TSC2 (tuberin). 24800946_Plasma HGF and EREG levels are associated with resistance to treatment with anti-EGFR antibodies in KRAS wild-type patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. 24812054_Epiregulin promotes the proliferation of liver progenitor cells and DNA synthesis by hepatocytes and is upregulated in the serum of patients with liver injury. 24898387_Data indicate that the effects of epiregulin (EREG) and V-ATPase (TCIRG1) single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) on pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility, to the extent that they exist, are dependent on gene-gene interactions in West African populations. 25203737_Patients homozygous for the minor allele A of EREG rs12641042 had a significantly higher 3-year survival rate than patients with allele C (HR 0.48; P=0.034), but significance was lost in multivariable analysis 26215578_Together, these studies lead to identification of a novel pathway involving EREG and MMP-1 that contributes to the formation of early stage breast cancer 26627827_three-dimensional structure of the EPR antibody (the 9E5(Fab) fragment) in the presence and absence of EPR 26958807_we showed that epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) were constitutively activated in metastatic lung subtypes of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma cells, and that this activation was induced by autocrine expression of epiregulin 27270421_upregulation of EREG expression through promoter demethylation might be an important means of activating the EGFR pathway during the genesis of colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC) and potentially other cancers. 27272216_EREG and AREG are strongly regulated by methylation, and their expression is associated with CIMP status and primary tumour site. 28398769_EREG and MMP-1 were found to be elevated in nasal polyp and uncinate tissues in patients with Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. 28733611_Whole genome bisulfite sequencing revealed that integrin alpha6beta4 signaling promotes an overall hypomethylated state and site specific DNA demethylation of enhancer elements within the proximal promoters of AREG and EREG in pancreatic neoplasm cells as well as their expression. Additionally, base excision repair (BER) pathway is required to maintain the expression of AREG and EREG. 28988771_Study shows how the EGFR ligands epiregulin (EREG) and epigen (EPGN) stabilize different dimeric conformations of the EGFR extracellular region. Results reveal how responses to different EGFR ligands are defined by receptor dimerization strength and signaling dynamics. These findings have broad implications for understanding receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling specificity. 29091309_in Caco-2 CFTR-shRNA cells, the EGFR ligand EREG is overexpressed due to an active IL-1beta autocrine loop that indirectly activates EGFR, constituting new signaling effectors for the CFTR signaling pathway, downstream of CFTR, Cl(-) , and IL-1beta. 30011072_These results indicated that EREG improved the migration and chemotaxis ability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and depended on the activation of MAPK signaling pathways, including p38 MAPK, JNK, and Erk1/2. 30252132_In colorectal, AREG and EREG genes undergo a complex regulation involving both intragenic methylation and promoter-dependent control. 30607582_E2F7, EREG, miR-451a and miR-106b-5p were likely to be related to the cervical cancer development. 30634928_Epiregulin (EREG) belongs to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, which binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to regulate the immune response of the host during infections. EREG levels in tuberculosis (TB) patients and healthy controls and assess whether polymorphisms in EREG increase the risk of TB. 30738695_finding demonstrate that EREG is an independent prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer 30967627_results reveal a novel molecular mechanism of resistance to hormone therapies in which the miR-186-3p/EREG axis orchestrates tamoxifen resistance and aerobic glycolysis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer 31234944_High EREG expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts correlated with higher T stage, deeper invasion and inferior worst pattern of invasion (WPOI) in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients and predicted shorter overall survival. Overexpression of EREG in NFs activated the cancer-associated fibroblasts phenotype. 31519572_AREG and EREG mRNA expression levels in left-sided CRC were higher than in right-sided tumors. This may help explain why left-sided CRC is more responsive to anti-EGFR antibodies. 31930610_Epiregulin promotes osteogenic differentiation and inhibits neurogenic trans-differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via MAPKs pathway. 31964549_Platelet-derived growth factor-AA-inducible epiregulin promotes elongation of human hair shafts by enhancing proliferation and differentiation of follicular keratinocytes. 32408308_High EREG Expression Is Predictive of Better Outcomes in Rectal Cancer Patients Receiving Neoadjuvant Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. 32929368_EREG-driven oncogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma exhibits higher sensitivity to Erlotinib therapy. 33007298_Human papillomavirus-positivity is associated with EREG down-regulation and promoter hypermethylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 33640382_Role of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) in cancer metastasis to bone: Identifying a potential therapeutic target. 33775193_Immunohistochemical evaluation of the prognostic and predictive power of epidermal growth factor receptor ligand levels in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. 34128258_Possible role of epiregulin from dermal fibroblasts in the keratinocyte hyperproliferation of psoriasis. 34154572_Depletion of EREG enhances the osteo/dentinogenic differentiation ability of dental pulp stem cells via the p38 MAPK and Erk pathways in an inflammatory microenvironment. 34406412_Induction of apically mistrafficked epiregulin disrupts epithelial polarity via aberrant EGFR signaling. 34715618_MiR-192-5p suppresses M1 macrophage polarization via epiregulin (EREG) downregulation in gouty arthritis. 34830244_p130Cas Is Correlated with EREG Expression and a Prognostic Factor Depending on Colorectal Cancer Stage and Localization Reducing FOLFIRI Efficacy. 35491469_Differentially expressed EREG and SPP1 are independent prognostic markers in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 35551652_Epiregulin increases stemness-associated genes expression and promotes chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer via ERK signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000029377 |
Ereg |
17.267085 |
5.1498447380 |
2.364529 |
0.506282420 |
23.223777 |
0.00000144203372224138538925546949853728762036553234793245792388916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005011638631275277726642453784977604414052620995789766311645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.1410401 |
9.7394249 |
6.0448127 |
1.6577766 |
| ENSG00000124920 |
745 |
MYRF |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2G1 |
FUNCTION: [Myelin regulatory factor]: Constitutes a precursor of the transcription factor. Mediates the autocatalytic cleavage that releases the Myelin regulatory factor, N-terminal component that specifically activates transcription of central nervous system (CNS) myelin genes (PubMed:23966832). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23966832}.; FUNCTION: [Myelin regulatory factor, C-terminal]: Membrane-bound part that has no transcription factor activity and remains attached to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane following cleavage. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23966832}.; FUNCTION: [Myelin regulatory factor, N-terminal]: Transcription factor that specifically activates expression of myelin genes such as MBP, MOG, MAG, DUSP15 and PLP1 during oligodendrocyte (OL) maturation, thereby playing a central role in oligodendrocyte maturation and CNS myelination. Specifically recognizes and binds DNA sequence 5'-CTGGYAC-3' in the regulatory regions of myelin-specific genes and directly activates their expression. Not only required during oligodendrocyte differentiation but is also required on an ongoing basis for the maintenance of expression of myelin genes and for the maintenance of a mature, viable oligodendrocyte phenotype (PubMed:23966832). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23966832}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Autocatalytic cleavage;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor that is required for central nervous system myelination and may regulate oligodendrocyte differentiation. It is thought to act by increasing the expression of genes that effect myelin production but may also directly promote myelin gene expression. Loss of a similar gene in mouse models results in severe demyelination. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:745; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; central nervous system myelin maintenance [GO:0032286]; central nervous system myelination [GO:0022010]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048709]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of myelination [GO:0031643]; protein autoprocessing [GO:0016540] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23966832_A Bacteriophage tailspike domain promotes self-cleavage of a human membrane-bound transcription factor, the myelin regulatory factor MYRF. 28160598_molecular mechanisms underlying the homo-trimerization of Myrf N-terminal fragments and the homo-trimeric DNA binding of Myrf N-terminal fragments 28631093_The relative scarcity of oligodendrocyte lineage cells expressing MYRF in demyelinated MS lesions demonstrates, for the first time, that chronic lesions lack oligodendrocytes that express this necessary transcription factor for remyelination and supports the notion that a failure to fully differentiate underlies remyelination failure. 29265453_Functional defects of MYRF are likely to be causally associated with encephalopathy with extensive myelin vacuolization 29446546_Heterozygous variants in MYRF should be considered in patients with variants of Scimitar syndrome and urogenital anomalies. 30532227_We identified four unrelated individuals with congenital diaphragmatic hernia with damaging de novo variants in MYRF (P = 5.3x10(-8)), including one likely gene-disrupting (LGD) and three deleterious missense (D-mis) variants. Eight additional individuals with de novo LGD or missense variants were identified from our other genetic studies or from the literature. 30985895_The results suggest that MYRF is a novel causative gene of 46,XY and 46,XX disorders of sex development and MYRF is a transcription factor regulating coelomic epithelium and/or coelomic epithelium derived cells proliferation and migration, which is essential for development of multiple organs. 31048900_Identified a canonical splice site alteration upstream of the last exon of the gene encoding myelin regulatory factor (MYRF c.3376-1G>A), which produced a stable RNA transcript, leading to a frameshift mutation p.Gly1126Valfs*31 in the C-terminus of the protein. 31069960_results underline the importance of including SLC18A3 sequencing in the differential diagnostics of fetuses with arthrogryposis, FADS, or LMPS of unknown etiology 31172260_These evidence all support that truncation mutations in the C-terminal region of MYRF are responsible for autosomal dominant high hyperopia in these families. 31266062_This is the first trio-based whole-genome sequencing (WGS), study for nanophthalmos, revealing the potential role of de novo mutations (DNMs) in MYRF and rare inherited genetic variants in PRSS56 and MFRP. 31700225_C-terminal variants in MYRF, which are expected to escape nonsense-mediated decay, represent a rare cause of autosomal dominant nanophthalmos with or without dextrocardia or congenital diaphragmatic hernia. 31964908_Functional mechanism and pathogenic potential of MYRF ICA domain mutations implicated in birth defects. 32052405_The genetic and clinical landscape of nanophthalmos and posterior microphthalmos in an Australian cohort. 32997974_Pancreatic Cancer Cells Require the Transcription Factor MYRF to Maintain ER Homeostasis. 33670313_Common Myelin Regulatory Factor Gene Variants Predisposing to Excellence in Sports. 33798553_Functional mechanisms of MYRF DNA-binding domain mutations implicated in birth defects. 33864620_MYRF: A Mysterious Membrane-Bound Transcription Factor Involved in Myelin Development and Human Diseases. 35136345_Evaluation of MYRF as a candidate gene for primary angle closure glaucoma. |
ENSMUSG00000036098 |
Myrf |
102.250090 |
0.4846573419 |
-1.044963 |
0.208031369 |
24.777321 |
0.00000064350159277392650269077577218634900191318592987954616546630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002329103361781058060885974195231007399797817924991250038146972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
70.0721502 |
10.3747502 |
144.7628444 |
14.8711646 |
| ENSG00000125122 |
26231 |
LRRC29 |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbls class and, in addition to an F-box, contains 9 tandem leucine-rich repeats. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. Other variants may occur, but their full-length natures have not been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
|
|
|
15.213348 |
0.3810349308 |
-1.392005 |
0.401984248 |
12.378166 |
0.00043438361257821102127951728988364266115240752696990966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001079922877152500459985162706288974732160568237304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.1527509 |
2.1694296 |
21.4878516 |
3.5067761 |
| ENSG00000125124 |
583 |
BBS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXC9 |
FUNCTION: The BBSome complex is thought to function as a coat complex required for sorting of specific membrane proteins to the primary cilia. The BBSome complex is required for ciliogenesis but is dispensable for centriolar satellite function. This ciliogenic function is mediated in part by the Rab8 GDP/GTP exchange factor, which localizes to the basal body and contacts the BBSome. Rab8(GTP) enters the primary cilium and promotes extension of the ciliary membrane. Firstly the BBSome associates with the ciliary membrane and binds to RAB3IP/Rabin8, the guanosyl exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8 and then the Rab8-GTP localizes to the cilium and promotes docking and fusion of carrier vesicles to the base of the ciliary membrane. The BBSome complex, together with the LTZL1, controls SMO ciliary trafficking and contributes to the sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway regulation. Required for proper BBSome complex assembly and its ciliary localization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17574030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22072986}. |
Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Obesity;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Transport;Vision |
|
This gene is a member of the Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) gene family. Bardet-Biedl syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by severe pigmentary retinopathy, obesity, polydactyly, renal malformation and cognitive disability. The proteins encoded by BBS gene family members are structurally diverse and the similar phenotypes exhibited by mutations in BBS gene family members is likely due to their shared roles in cilia formation and function. Many BBS proteins localize to the basal bodies, ciliary axonemes, and pericentriolar regions of cells. BBS proteins may also be involved in intracellular trafficking via microtubule-related transport. The protein encoded by this gene forms a multiprotein BBSome complex with seven other BBS proteins.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:583; |
BBSome [GO:0034464]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; brain morphogenesis [GO:0048854]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0043001]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; negative regulation of appetite by leptin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038108]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040015]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040018]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein localization to organelle [GO:0033365]; regulation of cilium beat frequency involved in ciliary motility [GO:0060296]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288]; striatum development [GO:0021756]; vasodilation [GO:0042311]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11567139_Unaffected individuals in 2 pedigrees had 2 but not all 3 mutations that affecteds had which suggests that Bardet-Biedle syndrome might not be a single-gene recessive disease but a complex trait requiring three mutant alleles to manifest the phenotype. 12567324_Identification of a novel Bardet-Biedl syndrome protein, BBS7, that shares structural features with this protein. 12837689_The presence of three mutant alleles in the BBS family correlates with a more severe Bardet-Biedl phenotype. 12872256_A novel missense mutation found in BBS2 exon 4 and a novel intronic point mutation found in Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients. 17003356_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18299575_BBS2 and BBS4 localized to cellular structures associated with motile cilia. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19666486_RET and BBS mutations modulate enteric innervation and cause syndromic Hirschsprung disease 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20618352_Sequence analysis and subsequent RNA studies identified and confirmed a novel splice site mutation, c.472-2A>G, in BBS2. This mutation was also found in homozygous form in three subsequently studied Hutterite BBS patients from two different leuts. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 23432027_Novel mutation (c.115+5G>A) in BBS2 found in Tunisian families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 23829372_Carrier frequency has been determined for two BBS2 mutations present in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. 24400638_we report here, for the first time, in Indian population, a novel, different profile of mutations in BBS genes (BBS3, BBS9, BBS10 and BBS2) compared to worldwide (BBS1 and 10) reports. 25541840_Our study shows that BBS2 mutations can cause nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa and highlights yet another candidate for this genetically heterogeneous condition. 26078953_A pair of heterozygous nonsense mutations in BBS2 gene was identified in the proband, one being novel and the other recurrent. The novel mutation, p.Y644X, resides in exon 16 and was also found in the heterozygous state in the mother 31530639_Authors found that within this structure, BBS2 and BBS7 form a tight dimer through a coiled-coil interaction and that BBS9 associates with the dimer via an interaction with the alpha-helical domain of BBS2. Interestingly, a BBS-associated mutation of BBS2 is located in its alpha-helical domain at the interface between BBS2 and BBS9, and binding experiments indicated that this mutation disrupts the BBS2-BBS9 interaction. 32620959_Correction of cilia structure and function alleviates multi-organ pathology in Bardet-Biedl syndrome mice. 33688495_Identification of a Novel Homozygous Missense (c.443A>T:p.N148I) Mutation in BBS2 in a Kashmiri Family with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000031755 |
Bbs2 |
64.424462 |
0.4589530112 |
-1.123582 |
0.213986197 |
27.963217 |
0.00000012364351814038476953696958637873848374510998837649822235107421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000483181977164966695232934008885639087793606449849903583526611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.8044359 |
5.5417038 |
87.3915598 |
7.9266569 |
| ENSG00000125170 |
55715 |
DOK4 |
protein_coding |
Q8TEW6 |
FUNCTION: DOK proteins are enzymatically inert adaptor or scaffolding proteins. They provide a docking platform for the assembly of multimolecular signaling complexes. DOK4 functions in RET-mediated neurite outgrowth and plays a positive role in activation of the MAP kinase pathway (By similarity). Putative link with downstream effectors of RET in neuronal differentiation. May be involved in the regulation of the immune response induced by T-cells. {ECO:0000250}. |
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of MAPK cascade and transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within nervous system development. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55715; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
12595900_DOK4 expression in human T cells has been demonstrated, and its genomic structure has been predicted. 12730241_IRS5/DOK4 and IRS6/DOK5 represent two new signaling proteins with potential roles in insulin and IGF-1 action 16820412_Results suggest that Dok-4, through activation of the Rap1-ERK1/2 pathway, regulates GDNF-mediated neurite outgrowth during neuronal development. 17443497_IRS-5 (DOK4) is significantly upregulated in 90% of examined clear cell RCCs. Studies on this gene has shown that it is regulated through chromatin remodeling in kidney cells 19073520_Epigenetic regulation of DOK4 expression is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer. 19494292_Dok-4 represents a novel negative regulator of T cells 22982678_the current study have explored in more detail the structure and function of the Dok-4 PTB domain. 32386480_Study of DOK4 gene expression and promoter methylation in sporadic breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000040631 |
Dok4 |
8.480753 |
0.1026855309 |
-3.283695 |
0.766518028 |
22.699918 |
0.00000189375999592118498431655287950192700918705668300390243530273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006500441288324812048481007170641632342267257627099752426147460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6306076 |
0.9332263 |
15.7653651 |
4.4248689 |
| ENSG00000125245 |
2841 |
GPR18 |
protein_coding |
Q14330 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for endocannabinoid N-arachidonyl glycine (NAGly) (PubMed:16844083, PubMed:24762058, PubMed:27572937). However, conflicting results about the role of NAGly as an agonist are reported (PubMed:27018161). Can also be activated by plant-derived and synthetic cannabinoid agonists (PubMed:24762058). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase (PubMed:16844083). May contribute to regulation of the immune system. Is required for normal homeostasis of CD8+ subsets of intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) (CD8alphaalpha and CD8alphabeta IELs)in small intstine by supporting preferential migration of CD8alphaalpha T-cells to intraepithelial compartment over lamina propria compartment, and by mediating their reconstitution into small intestine after bone marrow transplant (By similarity). Plays a role in hypotensive responses, mediating reduction in intraocular and blood pressure (By similarity). Mediates NAGly-induced process of reorganization of actin filaments and induction of acrosomal exocytosis (PubMed:27572937). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K1Z6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16844083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24762058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27572937}. |
Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable G protein-coupled receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction and positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within T cell differentiation; negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis; and negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2841; |
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; CD8-positive, alpha-beta intraepithelial T cell differentiation [GO:0002300]; CD8-positive, gamma-delta intraepithelial T cell differentiation [GO:0002305]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002689]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025] |
16844083_N-arachidonylglycine is a natural ligand for GPR18 20880198_GPR18, the most abundantly overexpressed orphan G-protein-coupled receptor in all melanoma metastases, is constitutively active and inhibits apoptosis, indicating an important role for GPR18 in tumor cell survival. 21261596_REVIEW: functional properties and in vivo biology 24762058_the results presented herein provide further evidence for GPR18 as a candidate cannabinoid receptor 26195725_A novel RvD2-GPR18 resolution axis stimulates human and mouse phagocyte functions to control bacterial infections and promote organ protection. 27572937_Results indicate that G protein-coupled receptor 18 (GPR18) might be involved in physiological processes of spermatozoa, suggesting GPR18 to be a potential player in sperm physiology. 29870711_GPR18 interacts with cannabinoid CB2 but not with CB1 receptors. 30503722_Lipopolysaccharides-Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 signaling mediated the GPR18 expression on polymorphonuclear neutrophils. These results indicate that decreased percentage GPR18-positive polymorphonuclear neutrophils is associated with increased severity and poorer outcome of sepsis. 31075933_molecular dynamics simulations of wild-type (WT) GPR18 and the A3.39N mutant in fully hydrated (POPC) phophatidylcholine lipid bilayers, are reported. 33058313_Novel selective agonist of GPR18, PSB-KK-1415 exerts potent anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activities in animal models of intestinal inflammation and inflammatory pain. 35525326_The resolvin D2 - GPR18 axis is expressed in human coronary atherosclerosis and transduces atheroprotection in apolipoprotein E deficient mice. |
ENSMUSG00000050350 |
Gpr18 |
78.130466 |
3.2736545645 |
1.710902 |
0.210981400 |
66.512583 |
0.00000000000000034766711155323854081725423354578546368822772544629473578936540434369817376136779785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002547947649714896149507315080572757559573094732555120778272339521208778023719787597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
119.4237617 |
14.2193672 |
36.8302241 |
3.6097468 |
| ENSG00000125257 |
10257 |
ABCC4 |
protein_coding |
O15439 |
FUNCTION: ATP-dependent transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family that actively extrudes physiological compounds and xenobiotics from cells. Transports a range of endogenous molecules that have a key role in cellular communication and signaling, including cyclic nucleotides such as cyclic AMP (cAMP) and cyclic GMP (cGMP), bile acids, steroid conjugates, urate, and prostaglandins (PubMed:11856762, PubMed:12883481, PubMed:12523936, PubMed:12835412, PubMed:15364914, PubMed:15454390, PubMed:16282361, PubMed:17959747, PubMed:18300232, PubMed:26721430). Mediates the ATP-dependent efflux of glutathione conjugates such as leukotriene C4 (LTC4) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) too. The presence of GSH is necessary for the ATP-dependent transport of LTB4, whereas GSH is not required for the transport of LTC4 (PubMed:17959747). Mediates the cotransport of bile acids with reduced glutathione (GSH) (PubMed:12883481, PubMed:12523936, PubMed:16282361). Transports a wide range of drugs and their metabolites, including anticancer, antiviral and antibiotics molecules (PubMed:11856762, PubMed:12105214, PubMed:15454390, PubMed:18300232, PubMed:17344354). Confers resistance to anticancer agents such as methotrexate (PubMed:11106685). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11106685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11856762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12105214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12523936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12835412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12883481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15364914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16282361, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17344354, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17959747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18300232, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26721430}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Lipid transport;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MRP subfamily which is involved in multi-drug resistance. This family member plays a role in cellular detoxification as a pump for its substrate, organic anions. It may also function in prostaglandin-mediated cAMP signaling in ciliogenesis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:10257; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; external side of apical plasma membrane [GO:0098591]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet dense granule membrane [GO:0031088]; 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0016404]; ABC-type bile acid transporter activity [GO:0015432]; ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity [GO:0015431]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity [GO:0008559]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase-coupled inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0043225]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; efflux transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015562]; glutathione transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034634]; guanine nucleotide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0001409]; prostaglandin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015132]; purine nucleotide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015216]; urate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015143]; xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042910]; bile acid and bile salt transport [GO:0015721]; cAMP transport [GO:0070730]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; export across plasma membrane [GO:0140115]; leukotriene transport [GO:0071716]; platelet degranulation [GO:0002576]; prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032310]; prostaglandin transport [GO:0015732]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; urate transport [GO:0015747]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855] |
11856762_The MRP4/ABCC4 gene encodes a novel apical organic anion transporter in human kidney proximal tubules: putative efflux pump for urinary cAMP and cGMP. 12105214_These findings indicate that a nucleotide transporter, such as MRP4, modulates the cellular response to ganciclovir and thus may influence not only the efficacy of antiviral therapy, but also prodrug-based gene therapy. 12133003_Impaired 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine accumulation in T-lymphoblastoid cells as a mechanism of acquired resistance independent of multidrug resistant protein 4 with a possible role for ATP-binding cassette C11. 12523936_Steroid and bile acid conjugates are substrates of this protein. 12637526_MRP4 and MRP5 are low affinity cyclic nucleotide transporters that may at best function as overflow pumps, decreasing steep increases in cGMP levels under conditions where cGMP synthesis is strongly induced and phosphodiesterase activity is limiting 12695538_the affinity of MRP4 and MRP5 for nucleotide-based substrates is low. 12792791_MRP4 is not solely responsible for cisplatin resistance in small cell lung cancer 12835412_MRP4 functions as a prostaglandin efflux transporter and is inhibited by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs 12883481_MRP4 can mediate the efflux of reduced glutathione from hepatocytes into blood by cotransport with monoanionic bile salts. 14643890_ABCC4 may play a role in the cellular extrusion of Phase II detoxification metabolites 15297306_ATP-dependent cGMP transport codistributed with MRP4 detection in platelet subcellular fractions, with highest activities in the dense granule and plasma membrane fractions; altered distribution of MRP4 was observed in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome platelets 15364914_MRP4 exhibits substrate-stimulated ATP hydrolysis 15827327_MRP4 may have a role in MYCN oncogene amplification and in drug resistance in neuroblastoma 16156793_Plant flavonoids were able to reverse drug resistance in human cells transfected with ABCC4; direct inhibition of MRP4-mediated [3H]cGMP transport in inside-out vesicles prepared from human erythrocytes was observed. 16282361_In cholestatic conditions, ABCC4 may become a key pathway for efflux of bile acids from hepatocytes into blood. 16791115_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17003774_Induction of MRP4 mediates resistance of Prostate cancer cells to nucleotide-based chemotherapeutic drugs. 17083032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17229149_ABCC4/Abcc4 and ABCG2/Abcg2 have roles in cGMP transport 17404579_cholestasis is one major determinant of human hepatic MRP4 expression 17578901_Inhibition of renal uptake (via OAT3) and efflux processes (via MRP2 and MRP4) explains the possible sites of drug-drug interaction for methotrexate with probenecid and some NSAIDs, including their glucuronides. 17682070_Results suggest that Bcrp and Mrp4 are partly involved in the luminal efflux of edaravone sulfate and edaravone glucuronide, respectively. 17696930_MRP4 protein levels were induced three-fold in primary biliary cirrhosis, whereas mRNA levels remained unchanged. 17878487_MRP-4 is induced by celecoxib in lung cancer cells 17939016_New comprehensive substrate-screening method for ABC transporters allowed the identification of 18 new substrates for MRP4. 17959747_The role of ABCC4 in the ATP-dependent efflux transport of leukotrienes B4 and C4 is shown in a number of different cell types. 18045536_Mrp4 knockout mice are more prone to CFTR-mediated secretory diarrhea. 18364470_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of ABCC4 were identified and selected nonsynonymous variants were functionally characterized. 18612080_Functional role of arginine 375 in transmembrane helix 6 of multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) is reported. 18615486_MRP4/ABCC4 is an androgen-regulated gene important in the progression to prostate cancer and may be a potential drug target. 18625884_contributes to human DC migration toward the draining lymph nodes 18636120_ABCC4 regulates cAMP-dependent signaling pathways and controls human SMC proliferation. 18662272_The hepatic expression of multidrug-resistance protein 4 was enhanced in patients with untreated primary biliary cirrhosis at all stages. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18690847_Celecoxib upregulates MRP4 in colon cancer and results in lack of synergy with standard chemotherapy. 19073137_These data establish NHERF1 as a major determinant of MRP4 trafficking to apical membranes of mammalian kidney cells. 19077464_MRP3, MRP4, and MRP5 are upregulated in 5-fluorouracil-resistant cells, and MRP5 contributes to 5-FU resistance in pancreatic carcinoma cells. 19082692_Gaboxadol could be taken up into the kidney by hOAT1 followed by glucuronidation and efflux of the conjugate into urine via MRP4. 19138942_The existing model to explain increased PGE(2) in colorectal neoplasia should be modified to include the novel mechanism of coordinated up- and down-regulation of genes involved in PGE(2) transport. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19399588_mPGES-1 may be coupled to COX-1. ABCC4 up-regulation further supports the assumption of its involvement in prostanoid transport 19400747_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19480556_Application of multivariate statistical procedures to identify transcription factors that correlate with MRP2, 3, and 4 mRNA in adult human livers. 19515727_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19515727_Polymorphisms in multidrug resistance-associated protein gene 4 is associated with outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19696793_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19696793_The SNPs in ABCC4 might be applicable in predicting the risk of adverse drug reactions in patients receiving cyclophosphamide combination chemotherapy. 19735648_MRP4, among MRPs, plays a predominant role in the basolateral egress of adefovir in Caco-2 cells and in renal secretion of adefovir. 19903828_Sodium influx is not directly coupled to MRP4/5-mediated cyclic nucleotide efflux, is independent of the status of transporter activity, and determines the baseline membrane potential, which in turns modulates MRP4/5-mediated cyclic nucleotide efflux. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940267_Results identify key membrane transporters OATP2B1, MRP1, MRP4, and MRP5 as modulators of skeletal muscle statin exposure and toxicity. 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20018925_we did not find any important MRD-predisposing MRP4 genotype in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia 20032540_We show that cell activation induces MRP4 expression in T-lymphocytes and that multitreated HIV-1 patients with detectable viral load present higher levels of MRP4 than responders, suggesting a new mechanism of resistance of NRTIs. 20133816_Defective expression of platelet MRP4 is associated with selective defect in adenine nucleotide storage. 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200426_We observed suggestive associations between survival and GSTT1 copy number and GSTA5, GSTM4, and ABCC4 single nucleotide polymorphisms 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20393862_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20395535_Findings indicate that AhR and Nrf2 play important roles in regulating hepatocyte MRP4 expression. 20530583_Blocking multidrug resistance-associated protein-4 may be a useful therapeutic strategy to deplete COX-deficient pancreatic cancers of prostaglandins. 20547088_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20727860_this study demonistrated that reveal higher than normal expression in the Alzheimer Disease brains of MRP4, probably due to gliosis, MRP4 being present also in glial cells. 20804728_These results suggest that MRP4 is uniquely involved in retinal angiogenesis. 20922799_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21156465_Studies show that ABCC4 and SLC29A2 expression were predictive of achieving CR, and the high expression of GSTP1 suggests that this may be a therapeutic target for relapsed AML. 21205825_intracellular cAMP levels not only in U937 cells but also in other acute myeloid leukemia cell lines are also regulated by multidrug resistance-associated proteins (MRPs), particularly MRP4 21296199_FXR activation in obstructive cholestasis might worsen liver injury by hijacking a protective mechanism regulated by CAR and provides a new molecular explanation to the pathophysiology of cholestasis. 21359593_We found that patients with obstructive cholestasis diseases caused by stones originating from common bile duct had significantly higher levels of hepatic MRP4 expression than controls. 21571869_These genetic data suggest that ABCC4 could play a fundamental role in KD pathogenesis 21741706_Correlation of CYP2B6, CYP2C19, ABCC4 and SOD2 genotype with outcomes in allogeneic blood and marrow transplant patients. 21799180_Suppression of ABCC4 enhanced morphological differentiation and inhibited cell growth. 21866459_The expression of P53 and MRP4 protein were independently associated with the sensitivity of rectal cancer to radiation. 21897051_Higher-molecular-weight anionic beta-lactam antibiotics showed greater MRP4-mediated transport activity than lower-molecular-weight ones. 21922333_These results indicate that, besides their possible therapy-modulating effects, xenobiotic transporters, ABCC4 and ABCG2, may contribute significantly to other keratinocyte functions, such as cell proliferation. 22272278_Findings show that the gene expression of ATP-dependent efflux transporters MRP1, -3, -4, -5, and p-gp fluctuated during stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelial cells (hESC-RPE) maturation. 22411990_SNX27 interacts with MRP4 near the plasma membrane and promotes endocytosis of MRP4 and thereby negatively regulates its cell surface expression and transport function. 22542979_Substitution of Trp995 in MRP4 with Ala completely disrupts transport activity, whereas substitution with more conservative amino acids (Phe and Tyr) leads to decreased transport activity for all substrates tested. 23087145_The most spectacular increases in expression were observed with ABCC4 (MRP4) - at the mRNA level, and CYP1B1 - at both the mRNA and protein levels. 23126166_The presence of ITPase SNP suggests interference with the entry of thiopurine metabolites and eventual reductions in the 6-thioguanine nucleotide level. 23222202_Polymorphisms in ABCC4 is associated with response to methotrexate in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 23472950_MRP4 is expressed in human endometrium, elevated in peritoneal endometriosis, and modulated by lipoxin A(4) in endometriotic epithelial cells. 23503867_lower levels of MRP4 expression were associated with shorter prostate-specific antigen relapse-free survival times in the androgen-dependent group 23575399_Downregulated ABCC4 was significantly associated with tumor regression grading and response to neoadjuvant radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced rectal adenocarcinoma. 23665398_postulate that elevated uric acid levels hamper MRP4 and BCRP functioning, thereby promoting the retention of other potentially toxic substrates, including kynurenic acid, which could contribute to the development of CKD 23742099_EP1 and EP4 agonists mimicked H2O2 in both control and MRP4 knockdown cells. 23766510_studies provide the first evidence for a conserved domain in CL3 of ABCC4 that is crucial in ensuring its proper plasma membrane localization 23794731_Abcc4 in the stomach facilitates the oral absorption of dasatinib, and it possibly plays a similar role for other orally administered substrates, such as acetylsalicylic acid. 24024181_These results suggest that in epithelial ovarian cancer, ABCC1/MRP1 may be a marker for aggressiveness because its expression was associated with tumor grade and support that ABCC4/MRP4 may play an unfavourable role in disease outcome. 24184504_Regulation of ABCC4 by miRNAs represents a novel mechanism for regulation of MRP4 function. 24436471_NHERF3 is a key regulator of organic transport in the kidney, particularly MRP4-mediated clearance of drug molecules. 24454870_study suggests that ABCC4 serves as a novel predictive biomarker that is responsible for the radioresistance and predicts a poor prognosis for locally advanced rectal carcinoma after neoadjuvant radiotherapy 24510239_ABCC4 activates oncogenic pathways in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and facilitates cancer cell development and progression. 24606721_Knockdown of ABCC4 blocked the cell cycle progression in MGC80-3 gastric cancer cells. 24694755_Genetic variability in key genes in prostaglandin E2 pathway (COX-2, HPGD, ABCC4 and SLCO2A1) and their involvement in colorectal cancer development. 24836986_role of MRP4 in thrombus formation 24870404_Human MRP4 could be a major player in the elimination of arsenic. 24909729_Upregulation of COX-2 in lung cancer promotes overexpression of MRP4 via PGE2-dependent pathway 24958844_Hepatically derived enalaprilat is excreted across the hepatic basolateral membrane by MRP4. 25028266_The blockade of ABC transporter MRP4 could help to improve drug effectiveness, reduce tumour growth and prevent recurrence in glioblastoma multiforme. 25275481_These results suggest that eicosapentaenoic acid-derived prostaglandin PGE3, PGF(3alpha), and thromboxane B3 are substrates of ABCC4 and ABCC4 partially contributes to the release of PGE3 and PGF(3alpha). 25301721_MRP4/ABCC4 has a relevant role in tumor growth and apoptosis and in the eradication of leukemic stem cells, providing the basis for a novel promising target in acute myeloid leukemia therapy. 25339146_Influence of PTGS1, PTGFR, and MRP4 genetic variants on intraocular pressure response to latanoprost in Chinese primary open-angle glaucoma patients 25403995_MRP4 genotyping may be useful for personalizing the therapeutic dose of 6-mercaptopurine during the acute lymphoblastic leukemia maintenance therapy in Japanese 25433169_Multiple drug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4), prostaglandin transporter (PGT), and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) as determinants of PGE2 levels in cancer. 25461681_Multi-walled carbon nanotubes may act on c-Myc to down-regulate ABCB1/ABCC4 expression. 25572969_inhibition of ABCC4 gene expression can inhibit the proliferation of multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cells and can enhance gastric cancer cell sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs. 25586538_SNPs most associated with Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy were in glutathione peroxidase 7 (GPX7) gene. 25677905_Our result indicates that GSTP1rs1695 polymorphism was strongly associated with the response of chemotherapy, whereas ABCC4rs9561778 polymorphism was significantly related with chemotherapy-induced toxicities. 25735837_Similar molecular features between MRP4 and BSEP inhibitors may partially explain why various drugs have affinity for both transporters. 25790437_cAMP regulates MRP4 promoter activity 25801567_Data show the influence of ABCC2 and ABCC4 polymorphisms on tenofovir plasma concentrations in Thai HIV-infected patients 25879330_The overexpression of MRP4 is related to multidrug resistance in osteosarcoma cells 26122863_Genetic variability in ABCC4 may contribute to misoprostol-induced fever in pregnant women 26141932_Osteoarthritis patient platelets presented a higher expression of MRP4. 26291395_This study aimed to establish SULT1A3 stably transfected HEK293 cells, and to determine the contributions of BCRP and MRP transporters to excretion of chrysin and apigenin sulfates. 26405223_These findings have important clinical implications because they directly highlight an important relationship between ABCC4 transporter function and phosphodiesterases in accounting for the cAMP-directed activity of antithrombotic agents. 26491233_MRP4 overexpression is important to reduce aspirin-selective cell death 26497925_Results demonstrated the capacity of MRP4 to confer resistance to arsenite (AsIII), as evidenced by cell survival assays when treated with AsIII in the presence or absence of its two differential inhibitors. 26499190_ABCC4 levels were significantly upregulated both in human NK/T-cell lymphoma YTS and SNK-6 cells. ABCC4 overexpression induced chemotherapy resistance to epirubicin and cisplatin in YTS cells, and inhibited apoptosis. 26600514_the specific COX-2 inhibitor meloxicam can increase the intracellular accumulation of doxorubicin and enhance doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in A549 cancer cells by reducing the expression of MRP1 and MRP4. 26611713_Sulfate metabolites R-6-S and R-4'-S were generated from raloxifene in SULT293 expression HEK293 cells. Cellular excretion of the raloxifene sulfates was mainly mediated by BCRP and MRP4. 26807589_Approximately 20% of HIV-infected patients receiving tenofovir showed beta2-microglobulinuria. The C allele at position 4976 of the ABCC4 gene was associated with beta2-microglobulinuria in this population. 26842729_ABCC4 plays a protective role against cytarabine-mediated insults in leukemic and host myeloid cells. 26931636_Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) is a critical protein associated with the antiviral efficacy of nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA)s, and combination therapy of NA and MRP inhibitors could reduce the dosage for long-term NA use. MRP4 expression is an important factor predicting treatment failure in chronic hepatitis B patients and will provide a potential therapeutic target against hepatitis B virus. 27402191_This study provides direct evidence that ganciclovir (GCV) is a substrate of the efflux transporter MRP4 and suggests that the intracellular fate of GCV is significantly influenced by ABCC4 rs11568658 variant in renal transplant recipients receiving GCV 27659809_Data suggest that common SNPs in MRP4/ABCC4 (evaluated here via site-directed mutagenesis in recombinant proteins expressed in kidney cell lines) are responsible for variations in transport of methylated arsenic metabolites (major urinary arsenic metabolites in humans), prostaglandin E2, and estradiol-17 beta-glucuronide. 27665700_Analysis of gene-gene interactions with CYP2B6 was particularly useful to reinforce the role of MRP4 and to reveal unknown associations, such as that of DRD3. 27761583_MRP4 localisation and function are regulated by interactions with SNX27, PSD95, and AP3B1. 28011504_The tagSNP ABCC4 rs17268122 appears to be a prognostic factor in locally advanced rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) and surgery, independently of response to nCRT 28029661_MRP4 exports prostaglandin E2 PGE2 and contributes to cell migration/metastasis in basal/triple negative breast cancer cells. 28042832_Data indicate that R-flurbiprofen inhibits multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4, ABCC4)-mediated prostaglandins (PG) transport. 28371506_ABCC4 variant (rs4148500) was significantly associated with hyperuricemia and gout. The gout risk allele was associated with fractional excretion of uric acid in male individuals. 28418010_ABCC4 and (NUDT15) variants are major factors for 6-mercaptopurine intolerability in Japanese childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. 28550450_ABCC4 functional SNP in the 3' splice acceptor site of exon 8 (G912T) is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia 28659663_A functional polymorphism in the ABCC4 promoter, -1508A>G, may increase extracellular 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and periostin levels, contributing to airway inflammation in asthmatics. 28883280_All patients with both NUDT15 rs116855232 heterozygous variants and ABCC4 rs3765534 variants suffered from severe leukopenia and required 6-mercaptopurine dose reduction to less than 35 mg/m(2)/da 29103996_Inhibition of ABCC4 potentiates combination beta agonist and glucocorticoid responses in human airway epithelial cells. 29146910_Data suggest that targeting the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 4 (ABCC4)-membrane palmitoylated protein 1 (MPP1) protein complex can lead to new therapies to improve treatment outcome of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 29304533_release of S1P from platelets depends on MRP4; statins can interfere with this transport process 29530601_Proposed is a novel full molecular model of the human MRP4, which is available to the pharmacology community to decipher the impact of any other clinically observed polymorphism and mutation on drug transport, giving rise to in silico predictive pharmacogenetics. 29568871_MRP4 is mainly responsible for the efflux of lamivudine and entecavir in hepatocyte cultures. 29788724_miR-506 has an important role in suppressing cervical cancer cell proliferation and suppresses the expression of ABCC4 by directly targeting its 3'-UTR 30060118_Data show that forkhead box protein M1 (FoxM1) enhanced carboplatin resistance in Y-79CR cells through directly up-regulating the transcription of ATP-binding cassette transporter C4 (ABCC4). 30098863_HIF1A-induced MDR1 and MRP4 promote Th17 responses in Crohn's disease. 30363999_Specific SNPs in the ABCC4 gene may increase susceptibility to Kawasaki disease in a Southern Chinese population. 30634695_These results indicate that the substitution of Gly at position 187 of ABCC4 to Trp resulted in reduced SN-38 resistance. 30643796_findings concluded that IL-13 inhibited chemotherapy sensitivity of NK/T-cell lymphoma cells by regulating ABCC4, disrupting which may effectively improve the therapy protocols against resistant NK/T-cell lymphoma. 31043460_Study shows that MRP4 expression may influence pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patient outcome and identify an association between higher MRP4 expression levels and more undifferentiated and malignant in vitro models of PDAC. These results provide direct evidence of the involvement of MRP4 in cell proliferation of PDAC cell lines through its involvement in cAMP signaling pathway. 31410201_MRP4 sustains Wnt/beta-catenin signaling for pregnancy, endometriosis and endometrial cancer. 31637886_TNFalpha induces hepatic MRP4 expression through activation of the p38-E2F1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. 31826245_ABCC4 encoding the multidrug resistance protein 4 specifies the novel PEL human blood group system. The rare PEL-negative phenotype is associated with impaired platelet aggregation. 31948942_An ABC Transporter Drives Medulloblastoma Pathogenesis by Regulating Sonic Hedgehog Signaling. 31960988_Circular RNA circABCC4 regulates lung adenocarcinoma progression via miR-3186-3p/TNRC6B axis. 32277480_ABCC4/MRP4 contributes to the aggressiveness of Myc-associated epithelial ovarian cancer. 32333821_MRP4/ABCC4 expression is regulated by histamine in acute myeloid leukemia cells, determining cAMP efflux. 32544819_ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter C4 is a Prostaglandin D2 Exporter in HMC-1 cells. 32553977_Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) is overexpressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and is essential to regulate cell proliferation. 32848164_Multidrug transporter MRP4/ABCC4 as a key determinant of pancreatic cancer aggressiveness. 33023375_Circular RNA circABCC4 acts as a ceRNA of miR-154-5p to improve cell viability, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. 33081264_Roles of ABCC1 and ABCC4 in Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. 33788417_Novel risk factors for glucarpidase use in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Hispanic ethnicity, age, and the ABCC4 gene. 33850298_ABCC4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms as markers of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-induced kidney impairment. 33851387_Role of Membrane Lipid Rafts in MRP4 (ABCC4) Dependent Regulation of the cAMP Pathway in Blood Platelets. 33964863_Multidrug Resistance Protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4): A Suspected Efflux Transporter for Human's Platelet Activation. 34050721_Polymorphisms in the CYP2A6 and ABCC4 genes are associated with a protective effect on chronic myeloid leukemia in the Brazilian Amazon population. 34331561_Influence of FPGS, ABCC4, SLC29A1, and MTHFR genes on the pharmacogenomics of fluoropyrimidines in patients with gastrointestinal cancer from the Brazilian Amazon. 34693929_In-vitro characterization of coding variants with predicted functional implications in the efflux transporter multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4, ABCC4). 34951141_Founder genetic variants of ABCC4 and ABCC11 in the Japanese population are not associated with the development of subacute myelo-optico-neuropathy (SMON). 35226228_IL-10 contributes to gemcitabine resistance in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma cells via ABCC4. 35269592_The Daily Expression of ABCC4 at the BCSFB Affects the Transport of Its Substrate Methotrexate. 35295075_Specific inhibition of the transporter MRP4/ABCC4 affects multiple signaling pathways and thrombus formation in human platelets. 35381563_Drug resistance biomarker ABCC4 of selinexor and immune feature in multiple myeloma. |
ENSMUSG00000032849 |
Abcc4 |
116.041714 |
2.7991594232 |
1.484994 |
0.167728056 |
79.058808 |
0.00000000000000000060288350790642192961962222721639752289704297011078862160438074369039895827881991863250732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000005084891758113592703153152621200478755920866099406998581122785196839686250314116477966308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
170.7072154 |
16.7878294 |
61.4523192 |
4.8624989 |
| ENSG00000125355 |
55026 |
TMEM255A |
protein_coding |
Q5JRV8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to act upstream of or within response to bacterium. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55026; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
Mouse_homologues 17660561_Transcripts highly enriched in ovary; gene identified as candidate female fertility factor. 32391621_Fam70A regulates meiosis and quality of mouse oocytes through both canonical and non-canonical Wnt5a signalling pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000036502 |
Tmem255a |
673.369793 |
3.9505430853 |
1.982051 |
0.067176306 |
914.691539 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000628181721343926688934807899174050405137247024784406500802728713364443176218470736518306110659504779112223346880721362537862959178 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000579497637939772382870911246391182302479127660635813810430004889274157643351060654363187068829695748327745950939913758044534255179 |
Yes |
No |
1088.4705334 |
44.5032149 |
277.4395762 |
9.6114589 |
| ENSG00000125378 |
652 |
BMP4 |
protein_coding |
P12644 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor of the TGF-beta superfamily that plays essential roles in many developmental processes, including neurogenesis, vascular development, angiogenesis and osteogenesis (PubMed:31363885). Acts in concert with PTHLH/PTHRP to stimulate ductal outgrowth during embryonic mammary development and to inhibit hair follicle induction (By similarity). Initiates the canonical BMP signaling cascade by associating with type I receptor BMPR1A and type II receptor BMPR2 (PubMed:25868050, PubMed:8006002). Once all three components are bound together in a complex at the cell surface, BMPR2 phosphorylates and activates BMPR1A. In turn, BMPR1A propagates signal by phosphorylating SMAD1/5/8 that travel to the nucleus and act as activators and repressors of transcription of target genes (PubMed:25868050, PubMed:29212066). Can also signal through non-canonical BMP pathways such as ERK/MAP kinase, PI3K/Akt, or SRC cascades (PubMed:31363885). For example, induces SRC phosphorylation which, in turn, activates VEGFR2, leading to an angiogenic response (PubMed:31363885). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25868050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29212066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31363885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8006002}. |
Chondrogenesis;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytokine;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Microphthalmia;Osteogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. This protein regulates heart development and adipogenesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with orofacial cleft and microphthalmia in human patients. The encoded protein may also be involved in the pathology of multiple cardiovascular diseases and human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:652; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; co-receptor binding [GO:0039706]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; ameloblast differentiation [GO:0036305]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002043]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; BMP signaling pathway involved in heart development [GO:0061312]; BMP signaling pathway involved in heart induction [GO:0003130]; BMP signaling pathway involved in nephric duct formation [GO:0071893]; BMP signaling pathway involved in renal system segmentation [GO:0061151]; BMP signaling pathway involved in ureter morphogenesis [GO:0061149]; branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis [GO:0060442]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; bronchus development [GO:0060433]; bud dilation involved in lung branching [GO:0060503]; bud elongation involved in lung branching [GO:0060449]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; cardiac septum development [GO:0003279]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; cloacal septation [GO:0060197]; common-partner SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0007182]; coronary vasculature development [GO:0060976]; cranial suture morphogenesis [GO:0060363]; deltoid tuberosity development [GO:0035993]; dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning [GO:0021904]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; embryonic skeletal joint morphogenesis [GO:0060272]; endocardial cushion development [GO:0003197]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; endoderm development [GO:0007492]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060502]; epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060441]; epithelial-mesenchymal cell signaling [GO:0060684]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; germ cell development [GO:0007281]; glomerular capillary formation [GO:0072104]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; intermediate mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048392]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lens induction in camera-type eye [GO:0060235]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lung morphogenesis [GO:0060425]; lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002320]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; mammary gland formation [GO:0060592]; membranous septum morphogenesis [GO:0003149]; mesenchymal cell differentiation involved in kidney development [GO:0072161]; mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureter development [GO:0072198]; mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureteric bud development [GO:0072138]; mesenchymal to epithelial transition involved in metanephros morphogenesis [GO:0003337]; mesodermal cell fate determination [GO:0007500]; mesonephros development [GO:0001823]; metanephric collecting duct development [GO:0072205]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of branch elongation involved in ureteric bud branching by BMP signaling pathway [GO:0072097]; negative regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090191]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cell proliferation involved in heart morphogenesis [GO:2000137]; negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032331]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072125]; negative regulation of glomerulus development [GO:0090194]; negative regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033088]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureter development [GO:0072200]; negative regulation of metanephric comma-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:2000007]; negative regulation of metanephric S-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:2000005]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045839]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042326]; negative regulation of prostatic bud formation [GO:0060686]; negative regulation of striated muscle tissue development [GO:0045843]; negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033085]; negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070244]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904753]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904706]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neuron fate commitment [GO:0048663]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; pericyte cell differentiation [GO:1904238]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; pituitary gland development [GO:0021983]; podocyte development [GO:0072015]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0061047]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle fiber development [GO:0055020]; positive regulation of cardiac neural crest cell migration involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:1905312]; positive regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061036]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell proliferation involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:1901964]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045603]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epidermal cell differentiation [GO:0045606]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of kidney development [GO:0090184]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of miRNA maturation [GO:1903800]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of ossification [GO:0045778]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; prostatic bud formation [GO:0060513]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504]; pulmonary artery endothelial tube morphogenesis [GO:0061155]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of branching involved in prostate gland morphogenesis [GO:0060687]; regulation of cell fate commitment [GO:0010453]; regulation of mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:1905770]; regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042487]; regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060393]; regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042306]; regulation of smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051150]; renal system process [GO:0003014]; secondary heart field specification [GO:0003139]; sinoatrial node development [GO:0003163]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; smooth muscle tissue development [GO:0048745]; specification of animal organ position [GO:0010159]; specification of ureteric bud anterior/posterior symmetry by BMP signaling pathway [GO:0072101]; steroid hormone mediated signaling pathway [GO:0043401]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537]; telencephalon regionalization [GO:0021978]; tendon cell differentiation [GO:0035990]; trachea development [GO:0060438]; trachea formation [GO:0060440]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; type B pancreatic cell development [GO:0003323]; ureter epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0072192]; ureter smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0072193]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657] |
11642720_The expression signals of BMP-4 mRNA in malignant schwannoma were relatively lower than in benign lesions 11771659_BMP4 reached criteria of suggestive evidence of linkage in candidate genes of ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine. 11867524_Bmp-4 only activates Dkk-1 when it concomitantly induces apoptosis. Implanted recombinant human Bmp-4 beads abolish Dkk-1 transcription in chick limb buds and mouse embryo cells. 12019147_Oncogenic beta-catenin is required for bone morphogenetic protein 4 expression in human cancer cells. 12054672_Dissection of promoter control modules that direct Bmp4 expression in the epithelium-derived components of hair follicles. 12064918_directs Smad5 activation in human hematopoietic cells, resulting in significantly increased proliferation of erythroid progenitors and formation of glycophorin-A+ cells. 12163415_Transgenic expression of human Bmp4 driven by the mouse Msx1 promoter in the Msx1(-/-) palatal mesenchyme rescued the cleft palate phenotype and neonatal lethality 12235106_Data show that VEGF plays a role in bone formation elicited by bone morphogenetic protein 4, and can significantly enhance BMP4-elicited bone formation and regeneration. 12404109_Mutations act together with other gene variants in unlinked loci as susceptibility factors in spina bifida. 12404109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12445813_demonstrated that the enhancement of expression of mRNA of BMP-4 by phosphate depletion mediates alkaline phosphatase induction in cultured mouse marrow stromal cell line ST2 12531697_BMP2 and BMP4 differently affect activin A induction of erythropoiesis 12606287_trans-activation by GATA-4 and GATA-6 12702499_evidence for the role of cytokines and BMP-4 in promoting hematopoietic differentiation of embryonic stem cells 12766166_BMP4 is a mechanosensitive, inflammatory factor playing a critical role in early steps of atherogenesis in the lesion-prone areas. 12865307_data demonstrate the existence and putative function of bone morphogenetic protein 4 signaling in normal ovarian surface epithelium and ovarian cancer cells 14672349_Deletion mutants of BMP folding variants are a new form of BMP antagonists and act through competition with osteoinductive BMP for BMP receptor binding. 15102076_BMP2 or 4 in pilomatricoma is responsible for induction of proalpha(1)(II) collagen mRNA in overlying epidermal cells resulting in deposition of type II collagen in dermo-epidermal junction. 15173106_biglycan modulates BMP-4-induced signaling to control osteoblast differentiation 15186723_results revealed a novel potent effect of PTH and vitamin D(3) plus BMPs in inducing bone development by human mesenchymal stem cells 15388638_BMP4 produced in ECs by oscillatory shear sress stimulates ROS release from the nox1-dependent NADPH oxidase leading to inflammation, a critical early atherogenic step. 15516325_BMP-4 increases the levels of osteopontin, BMP-2, alkaline phosphatase and core binding factor alpha 1 mRNAs in human periodontal (HPL) ligament cells. 15516492_Antiproliferative and prodifferentiation effects of BMP4 were Smad1 dependent with JNK also contributing to differentiation. 15591037_the role of BMP family members in the control of ovarian folliculogenesis 15777683_A polymorphism found in the BMP4 gene, affecting amino acid sequence, is associated with hip bone density in postmenopausal women, presumably via regulation of anabolic effects on the skeleton. 15861517_To analyze the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in prostate and breast cancers with established metastasis in bone 16126463_BMPs influence the formation of the osteolytic prostate cancer metastases, and treatment modalities that inhibit BMP activity may limit the progression of the lytic component of prostate cancer metastases. 16195406_Retinoic acid induces both BMP-4 transcription and expression and its antiproliferative action in pituitary adenoma 16373339_OAZ can alter the intensity and duration of the BMP4 stimulus through Smad6 16514669_BMP-4 may play a role in the regulation of ocular angiogenesis associated with diabetic retinopathy (DR) by stimulating vascular endothelial growth factor release from retinal pigment epithelial cells 16542506_BMP-4 is expressed in normal synovial tissue and was decreased in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. 16604289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16719933_Topical and differential expression of BMP-2/4 and BMP-7 mRNA and protein was found in bursa tissue. 16769910_Recombinant human BMP4 infusion caused hypertension in mice in a vascular NADPH-oxidase-dependent manner. BMP4 is a novel mediator of endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. 17003113_GREMLIN 1 was expressed in the stroma of human basal cell carcinoma (BCC) tumors but not in normal skin in vivo. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 2 and 4 are expressed by BCC cells. 17003840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17015616_BMP4 and Gremlin are regulators of myogenic progenitor proliferation. 17189614_The finding that BMP-4 subverts the ability of mammary epithelial cells to form polarized lumen-containing structures and endows them with invasive properties supports the involvement of this cytokine in the progression of breast cancer. 17253944_BMP4 is a key growth factor for maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells and contributes to the properties of stromal culture. 17255107_the BMP1 prodomain specifically binds and regulates signaling by BMP2 and BMP4 17262821_strong BMP staining is seen in maturing chondrocytes, and thus may play a role in chondrocyte differentiation and/or apoptosis; BMP release by osteoclasts may promote osteoblastic differentiation at sites of bone remodeling 17272306_A link between autocrine BMP4 signalling mediated through the Rho GTPase family may collectively contribute to aggressive ovarian cancer behavior. 17275810_These results indicate that BMP-4 confers invasive phenotype during progression of colon cancer. 17343268_Association with autosomal recessive DOOR syndrome not found. 17350185_These data support a model in which TNF-alpha-induced RelA interacts with SP1 to bring about transcriptional repression of Bmp4 gene. 17429723_treatment of normal human colonocytes with lambdaCGN activated the Wnt/beta-Catenin cascade and suppressed the expression and secretion of BMP4 17472960_RGMa facilitates the use of ActRIIA by endogenous BMP2 and BMP4 ligands that otherwise prefer signaling via BMPRII and that increased utilization of ActRIIA leads to generation of an enhanced BMP signal 17516553_BMP4 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through MSX2 induction on pancreatic cancer cell line. 17556598_Distinct roles for bone morphogenetic protein 4, vascular endothelial growth factor, stem cell factor, and fibroblast growth factor 2 in hematopoiesis. 17570215_BMP pathway could play a role in the transformation of normal esophageal squamous cells into columnar cells. 17624341_Expression of BMP-4 and BMP-7 and their receptors in human ovaries from fetuses as well as adults. 17640799_BMP-4 can protect colon cancer cells from heat-induced apoptosis through enhancing the activation of ERK as well as inhibiting the activation of JNK. 17696196_Expression analysis of additional genes, AKT1, NOG and its antagonist BMP4, which interact downstream to FGFR1, demonstrated expression differences between primary rhabdomyosarcoma tumors and normal skeletal muscles 17708801_Human aorta-gonad-mesonephros derived stromal cells in vitro express BMP-4. 17785623_Endothelial cells coexpress BMP4 antagonists along with BMP4 to minimize the inflammatory response to oscillatory shear stress. 17847004_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17847004_interactive effect on serum ferritin level of rs235756 in BMP2 and a SNP in HJV, with a small additive effect of a SNP in BMP4 17850776_ERK1/2 functions as an alternative pathway in BMP-4 signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Capillary sprouting induced by BMP-4 is dependent on ERK phosphorylation. 17967130_SHED cells transmitted BMP signals through both the SMAD and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and responded to BMP4 treatment by inducing BMP responsive genes 17989347_A BMP4/growth differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) selective binding protein exists in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 18021008_polymorphisms in the BMP2 and BMP4 genes, both members of the TGF-beta superfamily, contribute to the susceptibility to otosclerosis and further strengthen the results from the recently reported association of TGFB1 with this disease 18029192_BMP-7 but not BMP-2 and BMP-4 prevents the loss of primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells cultured in SFM plus SF3. 18076106_Mutations in BMP4,are infrequently found in patients with congenital cardiac septal defects 18252212_Mutations in BMP4 cause eye, brain, and digit developmental anomalies: overlap between the BMP4 and hedgehog signaling pathways. 18292231_neural precursor cell ultrasensitivity is evident at the population and single-cell levels based on Msx1 induction when exposed to Bmp4 18305125_Defects in these proteins could affect kidney development at multiple stages, leading to the congenital anomalies observed in patients with renal hypodysplasia 18317771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18319260_These results reveal a key role of GLI2 in activation of the activin/BMP antagonist FST in response to hedgehog (HH) signaling. 18326817_BMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-6 are endogenous ligands for Hemojuvelin in hepatoma-derived cell lines, and all 3 of these ligands are expressed in human liver 18365875_the activity of BMP4 in EMT during development is recapitulated in adult airway epithelial cells and may contribute to inflammation and fibrosis in vivo 18369157_Suggest that BMP-4 and calcium binding in MGP are independent but functionally intertwined processes and that the BMP binding is essential for prevention of vascular calcification. 18385288_Demonstrate the impairment of BMP-4 signaling by glycosaminoglycans in multipotent stem cells in human Hurler syndrome. 18400943_These results support a model in which the angular gradient in gap junction-mediated intercellular coupling in the lens, and thus proper lens function, is dependent on signaling between the FGF and BMP pathways. 18436533_BMP-2/4 and BMP-6/7 differentially utilize cell surface receptors to induce osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells 18537141_The numbers of tyrosine hydroxylase- and calcitonin gene-related peptide (TrkC)-expressing neurons are increased by overexpression of transgenic BMP4. 18551993_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18587495_Hypoxia-induced upregulation of CHL-1 alters the homeostatic balance between BMP-4 and VEGF to synergize with VEGF in driving retinal angiogenesis. 18596037_the trophoblast induction effect of BMP4 correlates with and depends on the inhibition of Activin/Nodal signaling 18632632_Wnt3a and Wnt5a have roles in inducing BMP-4 and 6 expression in prostate cancer osteoblast differentiation 18643848_BMP-4 signalling activates AHF transcription in hair follicles. 18643848_In human keratinocytes, we found BMP-4 facilitates trichohyalin (THH) transcription, and lamin C plays a key role in the posttranslational stabilization of THH. 18664625_BMP4 plays an important role in the control of human megakaryopoiesis 18683889_BMP signaling plays a role in the induction of an osteoblastic phenotype in human dermal fibroblasts in response to vitamin D(3) stimulation 18720384_These results in the present study indicate that oversulfated chondroitin sulfate, which possesses 4,6-disulfates in N-acetyl-galactosamine, binds to BMP-4 and promotes osteoblast differentiation and subsequent mineralization. 18771417_Genotypes of 184 patients with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate and 205 controls showed significant differences in the genotype and allele distribution of 538T/C polymorphisms of the BMP4 gene among the cases and controls. 18771417_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18787191_BMPER is an endothelial cell regulator and controls bone morphogenetic protein-4-dependent angiogenesis. 18818419_BMP2/4 were selectively expressed by endothelial colony-forming cells but not by early colonies in culture (CFU-Hill). 19011631_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19158083_bone morphogenetic protein-4 may represent a novel therapeutic target to inhibit the progressive effects of oxidative stress and senescence in dry age-related macular degeneration 19213939_Ihh (Indian hedgehog homolog) signals via the BMP(bone morphogenetic protein) pathway, and specifically through BMP4, to promote endothelial cell differentiation from pluripotent cells 19240369_Osteoblasts exposed in dose-dependent manner to rhBMP-2, -4 and -7 had significantly lower rates of proliferation and higher rate of apoptosis. 19249007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19249007_There are missense and nonsense mutations in the BMP4 gene in 1 of 30 cases of microform clefts, 2 of 87 cases with subepithelial defects in the orbicularis oris muscle (OOM), 5 of 968 cases of overt CL/P, and 0 of 529 controls 19269967_increases of p16(INK4a) and p21(WAF1/cip1) expression in response to BMP4 were mediated by the Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. 19321257_Smad4 is dispensable for enhanced invasiveness of human colorectal cancer cells due to BMP-4 overexpression. 19407504_BMP-4 and RSUME may be interesting targets for inhibiting steps involved in pituitary tumorigenesis. 19450561_BMP-4 induced by NDRG2 expression inhibits the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells, especially via suppression of MMP-9 activity. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473100_Findings demonstrate for the first time an endogenous survival pathway of hMSCs driven by a BMP signal. 19488929_BMP4 may play an important role in the development of BE. 19557432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19557432_The predicted functional SNP 6007 C/T affects BMP4 gene expression and the risk to development of cutaneous melanoma. 19661459_Heat shock protein 70 enhances vascular bone morphogenetic protein-4 signaling by binding matrix Gla protein. 19685083_Functional analysis of BMP4 mutations identified in pediatric CAKUT patients. 19763374_Cox-2 ex vivo gene-transfer strategy not only lacks bone-regeneration effects but also suppresses the bone-regeneration action of BMP4 in healing of calvarial defects. 19799789_BMP-2 and BMP-4 were equally effective in provoking chondrogenesis by primary human mesenchymal stem cells 19814781_The purpose of this study is to examine the molecular mechanisms by which retinoic acid enhances skeletal myogenesis and interacts with Wnt and BMP4 signalling during P19 or mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. 19816200_Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP-)4 and BMP type II receptors may play autocrine/paracrine roles and interact with other transforming growth factor-beta superfamily members in regulating meningioma growth and differentiation. 19819988_analysis of BMP-4 induction of arrest and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells via p21 CIP1 and p27 KIP1 regulation 19839778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19839778_This study was directed to the association of the BMP4 gene (its polymorphisms) and cleft palate and/or cleft lip. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914800_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19923894_BMP4 counteracts the IL-7-induced proliferation and differentiation of CD34(+) cells. 19950207_BMP4 promoted human embryonic stem cells differentiation into CD34+CD31+ cells at an early stage 20001220_The delivery of BMP-4 protein in a bilayer collagen scaffold stimulates the formation of cartilage tissue. 20054823_LL-37 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation through activation of BMP4 signaling via a proteasome-dependent mechanism. 20057906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20144598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20144598_The T538C polymorphism in BMP4 is not associated with sickle-cell disease with orthopedic complications, but is significantly associated with increased blood uric acid and LDH levels. 20146882_Expression of SHH, GLI family zinc finger 2 (GLI2) and BMP4 mRNA and protein in the posterior wall of the terminal rectum in 40 patients with orectal malformations, were assessed. 20157553_BMP4 may be involved in the molecular switch determining which phenotypic pathway is taken in the progression of age-related macular degeneration. 20182795_Results suggest that BMP4 is an important regulator of key phenotypic characteristics of cancer cells, cell growth, cell migration, and invasion. 20437058_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20480203_Strongly reduced expression of the microRNA miR-196a in melanoma cells compared to healthy melanocytes leads to enhanced HOX-B7 mRNA and protein levels, which subsequently raise Ets-1 activity by inducing basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). 20486775_Bone morphogenetic protein 4 mediates human embryonic germ cell derivation 20505824_Agrin binds BMP2, BMP4 and TGFbeta1 with relatively high affinity. 20506112_Data find developmentally regulated and reciprocal patterns of expression of BMP2 and BMP4 and identify germ cells to be the exclusive targets of ovarian BMP signaling. 20546278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20573231_BMP-4 modulates the profibrotic effects of TGF-beta1 on normal lung fibroblasts. 20619754_We found a significant association between BMP4 expression with a mucosal appearance by magnified narrow band imaging observation and a high concentration of deoxycholic acid in gastric juice. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20659471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20668459_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682677_Results indicate that bone morphogenetic proteins 2, 4, and7 may play a role in the process of spinal ankylosis. 20705941_Gremlin-mediated BMP inhibition results in activation of epithelial cells and transient fibrosis, but also induction of epithelium-protective FGF10 20730570_BMP4 is associated with inhibition of proliferation of brain glioma cell line U251 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20844743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20858598_work establishes a link between Tbx5, Shox2 and Bmp4 in the pacemaker region of the developing heart 20931521_BMP4 inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis in U87 glioma stem cells. 20949628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20949628_mutation of BMP4is a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC). 21034624_Chinese Han male patients with CT and TT 6007C>T genotypes have a genetic susceptibility to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and more extensive OPLL in the cervical spine. 21034624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21050181_found that activation of the p38 MAPK pathway by BMP4 was essential for the full activation of transcription potential of Smad1/5 21054789_data indicate that WFIKKN proteins are antagonists of GDF8 and GDF11, but in the case of TGFbeta1, BMP2 and BMP4 they function as growth factor binding proteins 21072679_Inhibition of the acetylation of histone H3 associated with the StAR promoter region by BMP-4 may be one of the inhibitory molecular mechanisms of progesterone synthesis in granulosa cells. 21092609_In osteonecrosis the formation of sclerosis rim is positively related to the expression of BMP4. 21128211_conclude that genetic variations in BMP-2 and -4 do not substantially contribute to lumbar spine bone mineral density in postmenopausal Turkish women 21152263_Significantly lower levels of endogenous BMP4 were detected in retinoblastoma cell lines compared to the normal human retina. 21186333_serum BMP-4 levels were positively correlated with body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, fasting plasma insulin, homeostasis model assessment index, and triglycerides and were negatively correlated with HDL-cholesterol. 21228692_Data suggest that the genetic effect of promoter polymorphisms of BMP4, IL6, leptin, MMP3, and MTNR1B can be synergistic for susceptibility to AIS. 21340693_BMP4 loss-of-function mutations is associated with developmental eye disorders including SHORT syndrome. 21362572_FGF2 signaling switches the outcome of BMP4-induced differentiation of human embryonic stem cells by maintaining NANOG levels through the MEK-ERK pathway. 21456062_BMP-4 induces PTEN in E6 and BPH-1 prostate cells and reduces cell proliferation. Knockdown of PTEN attenuated the growth-inhibiting effects of BMP-4. BMP-4 also increased PTEN protein stability. 21565626_BMP-4 protein may contribute to the malignant metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck, which presents as a novel prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target for patients 21655089_Multiple common susceptibility variants near BMP pathway loci GREM1, BMP4, and BMP2 explain part of the missing heritability of colorectal cancer 21670081_The osteogenic MDA-PCa-118b xenograft expressed higher levels of bone morphogenetic protein BMP4. BMP4 secreted from MDA-PCa-118b contributed to about a third of the osteogenic differentiation seen in MDA-PCa-118b tumors. 21673106_down-regulation of Kruppel-like factor-4 (KLF4) by microRNA-143/145 is critical for modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype by transforming growth factor-beta and bone morphogenetic protein 4. 21674241_in serous ovarian carcinoma, BMP-4 has prognostic significance, which is not angiogenesis-related. 21704030_Bone morphogenetic protein -4 and -5 in pancreatic cancer--novel bidirectional players 21855631_Activin, BMP and FGF pathways cooperate to promote endoderm and pancreatic lineage cell differentiation from human embryonic stem cells. 21868759_BMP-4 is a negative regulator of VEGF-D-driven metastasis that induces vascular remodeling in lymph nodes. 21927809_The mutation c.485G> A in BMP4 might be one of the causes of human ureteropelvic junction obstruction. 22019704_BMP4 acts in part by activating HMGA2 making this architectural transcription factor one of the major downstream players. 22052794_Novel mutations in the BMP4 gene and a specific haplotype TGGGCTT appear to contribute to the risk of developing ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. 22064324_BMP4 causes endothelial cells (ECs) apoptosis through activation of caspase-3 in a ROS/p38MAPK/JNK-dependent signaling cascade. 22076569_BMP4 activation in non-specialized columnar metaplasia and early expression of CDX2 are involved in the columnar epithelial differentiation of Barrett's esophagus. 22103619_Serum BMP-4 levels are inversely associated with surrogate markers of arterial stiffness and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with Type 2 diabetes 22105615_Characterize bone morphogenetic protein 4 as a cellular regulator of mitral valve interstitial cell activation in myxomatous mitral valve prolapse. 22118688_components of the common cellular transcriptional response to BMP4 and BMP7 22158048_rs4444235 acts as a cis-regulator of BMP4, thus providing a basis for colorectal cancer (CRC) risk through differential expression and further emphasizes the importance of genetic variation in the BMP pathway genes as determinants of CRC risk. 22158624_Bone morphogenetic protein 4 promotes vascular smooth muscle contractility by activating microRNA-21 (miR-21), which down-regulates expression of family of dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK) proteins. 22167620_Suggest that BMP4 may promote the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells, at least in part by up-regulating the expressions of MMP-1 and CXCR4. 22170598_BMP4-rs4444235 polymorphism is probably associated with colorectal cancer risk. 22191848_BMP4 genotype distribution had a statistically significant difference between groups: the GG genotype of BMP4 was more frequent in individuals with three or more missing teeth than in the control group. 22209843_these data show that BMP-4 and BMP-7 are associated with granulosa cell survival via several non-Smad specific pathways: BMP-4 via the PI3K/PDK-1/PKC and BMP-7 via the PI3K/PDK-1/Akt. 22210872_Results suggest that BMPRIA expression identifies thymic NK cell precursors and that BMP signaling is relevant for NK cell differentiation in the thymus. 22241220_The induction of CDK1, cyclin B1 mRNA and protein were shown to be dependent on the activation of MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling. 22350792_Upregulation of bone morphogenetic protein 4 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 22383492_Oncogenic KRAS can downregulate Bmp4 through a transcriptional pathway that depends on ERK. These findings point to a unique link between two pathways that are frequently altered in colon cancer. 22392094_an anti-angiogenic role for BMP4 in laser-induced CNV, mediated by direct inhibition of MMP-9 and indirect inhibition of VEGF. 22396540_Combining BMP4/WNT3A induction and OCT4/EpCAM selection can significantly increase the putative germ cell population with meiotic competency. 22447857_Human adipose cells can promote adipogenesis via endogenous BMP4 activation, and the impaired adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity is mainly due to an inability to suppress canonical WNT and to induce DKK1. 22504665_Results imply that miRNA-145 indirectly targets BMP4 via GATA6 and is potentially involved in the development of Barrett Esophagus (BE). 22514733_Results provided further evidence of association between BMP4 and nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 22535375_Epigenomic analysis identified bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) as an epigenetically regulated gene highly expressed in cisplatin-resistant gastric cander cell lines. 22546285_Studies idicate that NOTCH, BMP4 and WNT pathways are involved in the regulation of intestinal cancer stem cells. 22641693_BMP4 and BMP6, from two different BMP subclasses, and their antagonists noggin and sclerostin were variably expressed in melanocytes and keratinocytes in human skin 22698853_This review focuses on the role of BMP4 in the control of the stem and precursor cells in the adult hippocampus during alzheimer disease--REVIEW 22700770_BMP-4 transcript and protein are differentially expressed and show increase in the majority of prolactinomas relative to normal pituitary. 22736943_No significant associations were identified between FOXC1, TGFbeta2, and BMP4 alleles and haplotypes and primary open-angle glaucoma. 22886282_Results suggest that BMP4 polymorphisms are not associated with variation in kidney size at birth. 22899288_aken together, BMP4 is expressed in a subset of normal adult tissues and is likely to contribute to tissue homeostasis. 22971142_A significant association was observed between the 455C allele of BMP4 and increased left ventricular internal diameter systolic 22988237_the negative regulatory loop of BMP4-miR-302-BMPRII is a potential mechanism for the maintenance and fine-tuning of the BMP4 signaling pathway in various systems 23010644_These findings suggest that BMP-4, while promoting osteoinduction, may also act on MPCs to promote formation of a fibrotic osteoinductive matrix. 23079991_This was the first time that BMP2 and BMP4 single nucleotide polymorphisms were observed in Mexican oligodontia families. 23161572_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in BMP4 gene is associiated with colorectal cancer. 23208015_Suggest role for BMP4 in increased coronary artery disease seen in chronic kidney disease patients. 23232839_Evidence suggests that expression and activity of BMP4 and COX2 (prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2) are up-regulated in endothelium of arteries of hypertensive and diabetic patients. [REVIEW] 23243277_In HSPCs, BMP4 directly regulates Integrin-alpha4 expression through SMAD-independent p38 MAPK-mediated signaling. 23386650_Theca cell-derived BMP4 and BMP7 down-regulate Cx43 expression and decrease gap junction cell communication activity in human granulosa cells. 23388637_These findings provide a genetic and metabolic basis for BMP4's role in altering insulin sensitivity by affecting white adipose tissue development. 23454123_In the HNSCC cell line OECM-1, knockdown of BMP4 reduced mesenchymal-mode migration and invasion in 3D culture. In clinical HNSCC samples, let-7i expression was inversely correlated with BMP4 expression. 23468018_Data indicate that BMP4 signaling regulates the phenotype of pancreatic progenitors. 23493551_Complete and unidirectional conversion of human embryonic stem cells to trophoblast by BMP4. 23590708_BMP4 has a role in grade and prognosis in grade III and grade IV gliomas 23643939_Bone morphogenetic protein activity plays a transient but essential role in inducing expression of preplacodal ectoderm competence factors and eventually preplacodal ectoderm cells. 23651239_Data show expression of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, BMP-4, and BMP-7 was increased in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) cocultured with pancreatic cancer cells, and vasohibin-1, VEGF-A, and vVEGF-C expression in pancreatic cancer cells was upregulated by TAMs. 23652531_BMP-4 may exert a certain influence on ectopic bone formation after total hip arthroplasty. 23673366_BMP4 activates intracellular signaling, in particular through enhancing phosphorylation of Smad1/5. 23702483_Our data clearly suggest a link between FAK and BMP4 induction of MSC adipogenesis, and may indicate a potential therapeutic approach targeting FAK for dealing with obesity. 23841782_Our finding suggests that in vivo, BMP4 prodomain behavior might also be altered by the mutation and could influence storage or transport of mature BMP4 in the extracellular matrix of the developing tooth. 23899883_6007C>T polymorphism of the BMP-4 gene not only was associated with occurrence of CSM, but also affect the clinical outcome after ACF treatment, implying this 6007C>T polymorphism might be a predictor for CSM prognosis. 23937428_TGF-beta1 reduces BMP4 signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, a response that is exacerbated on the background of reduced BMP responsiveness due to BMPR-II mutations. 23939983_A significant association of haplotype GTAA in BMP4 (p = 0.01) and FGFR1 rs13317 (p = 0.005) with NU could be observed. 23941573_Our results demonstrated that the optimized DNA sequence could significantly enhance hBMP4 protein expression in Pichia pastoris compared with the native sequence and produce biologically active recombinant hBMP4 23993924_BMP4-mediated signaling in adult mouse ovary-derived oogonial stem cells cultured in vitro drives differentiation of these cells into oocytes through Smad1/5/8 activation and transcriptional up-regulation of key meiosis-initiating genes. 24013228_BMP4/Thrombospondin-1 loop paracrinically inhibits tumor angiogenesis and suppresses the growth of solid tumors. 24044460_BMP4 plays a crucial role in the chemoresistance of leukemia cells through the activation of autophagy and subsequent inhibition of apoptosis. 24072698_We demonstrate a cross-talk between BMPs and CRYAB and a major effect of this regulatory interaction on resistance to apoptosis. 24099560_Low BMP4 expression is associated with glioma. 24100446_Using primary cells and a cell line mimicking CP-CML, we found that myeloid progenitor expansion is driven by the exposure of immature cells overexpressing BMP receptor Ib to BMP2 and BMP4. 24131739_The present data suggest that Brazilian individuals with polymorphisms of the BMP4 gene have a higher risk to develop CAKUT, especially the |
ENSMUSG00000021835 |
Bmp4 |
141.961478 |
0.0749086172 |
-3.738724 |
0.199009251 |
468.514015 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006747313522240701640500086492133549270502760263915680164212990126029868047177790653132173251003982853089068051908963729668143001223005951728699243045257184391663595683675518810442787601375032573142984682918800237292632357591757 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003027062236725615593660794671043021378774343108997049998920377234109011269091796819484598752950284754590786978926954087985909561308316370892468763164499764326362753525414995663653911367768513322834545351560529045008381387261505 |
Yes |
No |
16.2969489 |
2.6382839 |
220.5150354 |
19.3992290 |
| ENSG00000125384 |
5732 |
PTGER2 |
protein_coding |
P43116 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G(s) proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. The subsequent raise in intracellular cAMP is responsible for the relaxing effect of this receptor on smooth muscle. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a receptor for prostaglandin E2, a metabolite of arachidonic acid which has different biologic activities in a wide range of tissues. Mutations in this gene are associated with aspirin-induced susceptibility to asthma. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:5732; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; prostaglandin E receptor activity [GO:0004957]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to nematode [GO:0009624]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570] |
12051958_PGE(2) receptors and synthesis in human gastric mucosa: perturbation in cancer 12149218_effects of PGE2 on monocyte-derived dendritic cells were mediated through increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate by 2 of the known PGE2 receptors, EP2 and EP4 12228765_Activation of prostaglandin E2-receptor EP2 and EP4 pathways induces growth inhibition in human gastric carcinoma cell lines. 12466123_Data show that down-regulation of prostaglandin E(2) receptor subtype EP(2) receptors represents a potential mechanism for neoplastic progression to an invasive phenotype. 12743126_shear activates cyclooxygenase-2, via a c-Jun N-terminal kinase2/c-Jun-dependent pathway, which in turn elicits downstream prostaglandin EP2 and EP3a1 receptor mRNA synthesis 12788892_Agonists of EP(1) and EP(2) significantly increased aromatase activity levels, which were decreased by the corresponding antagonists. Generally reflective of changes in aromatase protein expression and the pattern of mRNA expression. 12933667_increased histone H3 acetylation involving the EP2 receptor, protein kinase A, CREB, and CREB binding protein is responsible for PGE(2)-induced StAR gene activation in endometriotic stromal cells. 14517215_COX-2 induction by bradykinin in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells is mediated by the cyclic AMP response element through a novel autocrine loop involving endogenous prostaglandin E2, EP2 receptor, and EP4 receptor 14562138_Human corpus cavernosum and cultured smooth muscle cells express EP1, EP2 and EP3 receptors. 14699136_role of araomatic amino acids in i2 loop in Gs coupling 15044590_elevated EP2 receptor expression may facilitate the PGE(2)-induced release of proangiogenic factors in reproductive tumor cells via intracellular cAMP-mediated transactivation of the EGFR and ERK1/2 pathways 15347673_Endothelin-1-induced prostaglandin E2-EP2 and EP4 signaling regulates vascular endothelial growth factor production and ovarian carcinoma cell invasion 15539459_PGE2, via EP2 receptor, enhances PTEN function in lung fibroblasts to inhibit directional migration 15970595_PGE2 increases VEGF transcriptionally and involves the Sp-1 binding site via a cAMP-dependent mechanism involving EP2 and EP4 receptors 16267225_a novel proinflammatory and proamyloidogenic function for the PGE2 EP2 receptor is demonstrated in a model of familial Alzheimer's disease. 16461132_significantly reduced expression of PGE(2) receptors on nasal mucosa inflammatory leukocytes in the aspirin-sensitive compared with nonaspirin-sensitive rhinosinusitis patients 16607275_Together, the results suggest that the overexpression of the human EP2 receptor plays a significant role in the protumorigenic action of PGE2 in mouse skin. 16879213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16879213_prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 polymorphisms, prostaglandin-E receptor 2 polymorphisms, and C-reactive protein concentrations may have a role in atherothrombosis 17028262_These data indicate that PGE(2) inhibits fibroblast activation in primary lung fibroblasts via binding of EP2 receptor and production of cyclic AMP; inhibition of collagen I proceeds via activation of PKA. 17078003_These results suggest that the COX-2-PGE(2) pathway may be involved in IL-8 production in gastric epithelial cells. 17290397_EP2 mRNA was significantly higher in normal colon tissue compared with tumor tissue. 17384145_Selective stimulation of the EP2 receptor subtype, leading to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation via protein kinase A 17496729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17525067_participates in placentation through EVT invasion by up-regulating PGE2 production and PGE2 receptor expression in first trimester extravillous trophoblasts 17533365_NB cells may lose responsiveness to PTGER2-mediated growth inhibition/apoptosis through epigenetic silencing of PTGER2 and/or disruption of downstream cAMP-dependent pathway during the neuroblastomagenesis. 17555711_treatment of LS174T cells with indomethacin causes a down regulation of EP2 prostanoid receptors 17611676_Results show co-expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptors EP1, 2 and 4 in non-small cell lung cancer cells concomitant with the synthesis of PGE2. 17728378_Role of EP2 receptor in mediating the PGE2 effect on stimulating cyst formation may have direct pharmacological implications for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. 17877755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18005048_Expression of prostaglandin E(2) receptors (EP(2), EP(3), EP(4)), prostaglandin D(2) receptor (DP(2)), prostanoid thromboxane A(2) receptor (TP) and to a lesser extent EP(1) were observed in several hair follicle compartments. 18086382_herpes simplex virus type 1 infected mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells demonstrated a dramatic down-regulation of the expression of the EP2 and EP4 receptors 18254372_PGE2 receptors were expressed in both NCI-H292 and human nasal epithelial cells. 18296611_results showed that EP2 is expressed in trigeminal neurons (58% of total neurons) and is co-expressed in TRPV(1)-positive neurons (64% of TRPV(1)-positive neurons. 18319253_CCR7 and the EP2/EP4 receptor signaling pathway are down-stream targets for COX-2 to enhance the migration of breast cancer cells toward LECs and to promote lymphatic invasion 18537828_Prostaglandin E(2), via the prostanoid receptor EP2 and subsequent cAMP elevation, downregulates mRNA and protein levels of protease-activated receptor-1 in human lung fibroblasts. 18666211_PTGER2 methylation was present with greater frequency in nonsmall cell lung cancer with EGFR mutation. 18790761_A new approach for blocking E-prostanoid receptor-mediated cell signaling using a soluble chimeric EP2 fragment, is described. 18792407_findings show the G(s)-coupled EP(2) receptor closes K(Ca)3.1 in lung mast cells and attenuates both chemokine- and PGE(2)-dependent lung mast cell migration 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18829529_PGE(2) induces angiogenesis in prostate cancer through EP2 and EP4. 18989535_Common polymorphisms of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptor and increased risk for acute coronary syndrome in coronary artery disease. 18989535_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19050969_Overexpression of EP2 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19169646_Results suggest that prostaglandin E2 mainly induces the activation of beta(1)-integrins via the EP(2) receptor in human coronary arterial endothelial cells. 19273625_PGE2 acts via prostaglandin receptor EP2- and EP4-mediated signaling and cyclic AMP pathways to up-regulate IL-23 and IL-1 receptor expression. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407222_EP2 and EP4 receptor inhibition induces apoptosis of human endometriotic cells through suppression of ERK1/2, AKT, NFkappaB, and beta-catenin pathways and activation of intrinsic apoptotic mechanisms 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19542367_opposite regulation of proinflammatory IL-6 and prodestructive MMP-1 by PGE(2) via EP2 in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblasts 19582788_Prostaglandin E2 inhibits the proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts via the EP2 receptor and Epac 19782748_demonstrates that co-activation of the FP and EP2 receptors results in enhanced release of cAMP via FP receptor-G alpha(q)-Ca(2+)-calmodulin pathway by activating calcium sensitive adenylyl cyclase 3 isoform. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19808686_Phosphatase and tensin homologue on chromosome 10 (PTEN) directs prostaglandin E2-mediated fibroblast responses via regulation of E prostanoid 2 receptor expression 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20018632_PGE2 potently inhibits secretion of IFN-alpha by TLR-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells, an effect mainly mediated by PG receptors E-prostanoid 2 and E-prostanoid 4 20086108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200425_Our data imply potential roles of inflammatory reaction by PTGER2 upregulation in carcinogenic process to microsatellite instability -high colorectal cancer. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304053_analysis of expression of serum vitamin D receptor, cyclooxygenase-2, and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in benign and malignant ovarian tissue and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and prostaglandin E2 in ovarian cancer patients 20347274_EP2 is a novel transcriptional target of Wnt3a in dermal papilla cells of human scalp hair follicles 20357748_Observed induction of the PG receptors EP2 and IP in atherosclerotic femoral arteries in the arterial intima, medial layer, as well as the associated atherosclerotic plaque. 20382140_The mRNA levels of EP2 implicated pathways differed significantly in gliomas according to the histological type. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484658_EP1 and EP4 subtypes of prostaglandin E receptors (but not EP2 and EP3 receptors) may be involved in regulation of paracellular permeability in differentiated Caco-2 cell cultures. 20516073_E prostanoid (EP) 2 and EP3 have roles in cAMP/protein kinase A- and PI3-K/Akt-dependent NF-kappaB activation during shear-induced interleukin-6 synthesis in chondrocytes 20551148_Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP2 and EP4 regulated gene expression profiling in ciliary smooth muscle cells. 20587336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20705717_Data suggest that early embryonic signals may regulate fetal-maternal crosstalk in the human endometrium by inducing CXCR4 expression via the PGE-PTGER2-mediated induction of the EGFR, PI3K and ERK1/2 pathways. 20889571_Data demonstrate that down-regulation of PTGER2 and consequent PGE2 resistance are both mediated by DNA hypermethylation; increased Akt signal transduction is a novel mechanism that promotes DNA hypermethylation during fibrogenesis. 21052031_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21081469_miR-16 and miR-21 are directly regulated by the transcription factor NF-kappaB and yet nicotine-promoted cell proliferation is mediated via EP2/4 receptors. 21111772_Data show that inhibition of PGE2 receptors EP2 and EP4 suppresses expression and/or activity of MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP7 and MMP9 proteins and increases expression of TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4 proteins. 21209948_PGE2 induces IL-6 in orbital fibroblasts through EP2 receptors and increased gene promoter activity 21419570_EP2 receptor FuEP2/Ex2 may have a role in suppressing endometrial cancer cell growth 22099390_This study suggested that antipsychotics showing association with PGE2-mediated respons. 22244821_morin inhibited the production of NO and PGE(2). 22276108_Neuroblastoma express all four forms of PGE(2) receptors. 22329897_Indomethacin has a potential antagonizing effect on human EP(2) receptors. 22551900_Single nucleotide polymorphism in PTGER2 associated with multiple adenomas. 22580611_Targeted interference of EP2/EP4 signal to RalA.GTP may provide benefit to patients diagnosed with advanced kidney cancer. 22706114_This review article presents a short overview of experimental approaches aimed at manipulation of signaling via EP2 and EP4 receptors that could have therapeutic utility. 22929011_Although EP2 methylation status is inversely correlated to expression levels in established breast cancer cell lines, we could not identify that such a correlation existed in tumour-associated stroma cells. 23048027_HB9 binds to the prostaglandin E receptor 2 promoter and inhibits intracellular cAMP mobilization in leukemic cells. 23069790_The expression of the EP2 receptor and Bcl-2 was significantly increased. 23242524_Loss of function of EP2- and EP4-mediated PGE2 signaling inhibits adhesion of human endometriotic epithelial and stromal cells through integrin-mediated mechanisms. 23337716_PGE(2) coordinates control of IL-23 release in a dose-dependent manner by differential use of EP(2) and EP(4) receptors in LPS-activated MoDCs. 23786281_Although human lung mast cells may express both EP2 and EP4 receptors, the principal mechanism by which PGE2 inhibits mediator release in mast cells is by activating EP2 receptors. 23861370_Data suggest that elevated PGE2 (prostaglandin E2) in peri-implantation uterine lumen stimulates conceptus PTGER2 expression, which in turn promotes trophoblast adhesion via integrins and synthesis/secretion of embryonic signal estradiol-17. 24146253_Elastogenesis is spatially regulated by PGE-EP4 signaling in the ductus arteriosus. 24471568_The 15-PGDH gene is a MiTF-CX target gene in cervical stromal cells and is down-regulated by PGE2 through EP2 receptors. 24561081_cyclic tensile force activates ERK1/2 and p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways, and induces COX-2 expression, which is responsible for the sequential PGE2 biosynthesis and release, and mediates the increase in BMP-2 expression at the transcriptional level. 24626807_PGE2 markedly enhanced Huh-7 cell invasion and migration ability by upregulating the expression level of Snail protein, and EP2 receptor played an important role in this process. 24728410_human albumin solution infusions may be used to reduce circulating PGE2 levels, attenuating immune suppression and reducing the risk of infection in patients with acutely decompensated cirrhosis or ESLD. 24812667_In Th17 cells, RORC repressed EP2 by directly silencing PTGER2 transcription, and knock down of RORC restored EP2 expression in Th17 cells. 24827772_In adjusted models, gestations were 3.3 days longer (95%CI 0.6, 6.0) for each interquartile range of PTGER2 DNA methylation. 24883443_Overexpression of EP2 was more observed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma than in the control group. Overexpression of EP2 ESCC tissues might play an important role in carcinogenesis and the progression of ESCC. 24980222_mediates inhibitory effect of Prostaglandin E2 on nasal fibroblast migration 25059824_EP2/cAMP/protein kinase A pathway mediates the stimulatory effect of PGEs on angiogenesis essential for tissue injury healing via the induction of CREB activity and VEGF expression. 25329458_data show a protective role for the PGE2 receptors EP(2) and EP(4) following osmotic changes, through the reduction of human mast cell activity caused by calcium influx impairment and MAP kinase inhibition. 25634217_Overall, our results demonstrate that p53 is a negative regulator of aromatase in the breast and its inhibition by PGE2 provides a novel mechanism for aromatase regulation in obesity and breast cancer. 25681680_EP2 receptors exhibit more constraints to mutations than DP receptors. 25828575_Intracellular EP2 prostanoid receptor promotes cancer-related phenotypes in PC3 prostate cancer cells. 26051534_Reduced EP2 receptor expression results in resistance to the antiproliferative effects of EP2 signaling in nasal polyp fibroblasts from subjects with AERD and support a role for EP2 signaling in the aberrant growth of nasal polyp tissue. 26538827_mPGES-1 is downregulated via EGR1 and has a role in caffeine inhibition on PGE2 synthesis of HBx hepatocytes 26560040_Altered expression of EP2 in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease contributes to deficient induction of IL-1RI, reducing the capacity of IL-1beta to increase COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression, which results in low PGE2 production 27012192_that the expression of ERG in prostate cancer is linked to the expression of IL-6 mediated by the prostanoid receptor EP2 27230257_PGE2 produced by mesenchymal stem cells contributes to maintenance of self-renewal capacity through EP2 in an autocrine manner, and PGE2 secretion is down-regulated by cell-to-cell contact. 27321910_EP2 receptor activation protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis through down-regulation of p53. 27377703_This is the first report that PGE2 -induced uPAR expression, which stimulates invasiveness of human gastric cancer AGS cells, is mediated by the EP2 receptor-dependent Src/EGFR/JNK1/2, Erk1/2/AP-1, and Src/EGFR/JNK1/2, Erk1/2/NF-kappaB cascades. 27616330_in breast cancer cells overexpression of S1P3 and its activation by S1P has pro-inflammatory and pro-metastatic potential by inducing COX-2 expression and PGE2 signaling via EP2 and EP4. 27636113_EP2 receptors seem to be able to distinguish endogenous ligands PGD2, PGE2 or prostaglandin F2alpha better than DP receptors. 28336329_These results indicate that the ICL2 region of the EP2 receptor is its potential interaction site with Galphas, and that the aromatic side chain moiety at position 143 is a determinant for the accessibility of the ICL2 to the Galphas protein. 28630103_EP2 and EP3 receptors are involved in tolerance induction through IL-10 production by tol-DCs. 28963072_this study shows that prostaglandin E2 restrains human Treg cell differentiation via E prostanoid receptor 2-protein kinase A signaling 29401596_Prostaglandin E2 suppresses hCAP18/LL-37 expression in human macrophages via EP2/EP4: implications for treatment of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. 29491476_COLEC12 integrates H. pylori, PGE2-EP2/4 axis and innate immunity in gastric diseases 30012671_a signaling circuit involving RIPK3 and PGE2 receptors enhances accumulation and immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells 30053598_Data indicates that PGE2 suppression of TNF-alpha by human monocytic cells occurs via EP2R and EP4R expression. However EP4Rs also control their own expression and that of EP2 whereas the EP2R does not affect EP4R expression. 30103548_EP receptor levels were enhanced in human PASMCs and in lung sections from PAH patients compared to controls. Thus, EP receptors represent a novel therapeutic target for treprostinil, highlighting key pharmacological differences between prostacyclin mimetics used in pulmonary arterial hypertension. 30835912_These results suggest that PGE2 regulates human brain endothelial cell migration via cooperation of EP2, EP3, and EP4 receptors. 30890164_Altered Prostaglandin E2-EP2 augmented the excessive inflammation of innate and adaptive immune cells in response to lipopolysaccharides or E. coli in chronic hepatitis B-acute-on-chronic liver failure. 30917001_EP2 and EP4 receptors play different roles in the regulation of COX-2 expression in human amnion fibroblasts. 31217077_a role for EP2/EP4 signaling in regulating IGF-1-induced cell proliferation, in which EP2/EP4 signaling represses IGF-1-induced GGCT expression, is reported. 31980713_The prostaglandin receptor EP2 determines prognosis in EP3-negative and galectin-3-high cervical cancer cases. 32313117_Prostaglandin EP2 receptor downstream of Notch signaling inhibits differentiation of human skeletal muscle progenitors in differentiation conditions. 32438662_Concerted EP2 and EP4 Receptor Signaling Stimulates Autocrine Prostaglandin E2 Activation in Human Podocytes. 32595209_Syntenin-1 promotes colorectal cancer stem cell expansion and chemoresistance by regulating prostaglandin E2 receptor. 32851536_The role of EP-2 receptor expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. 33011635_Expression of trophoblast derived prostaglandin E2 receptor 2 (EP2) is reduced in patients with recurrent miscarriage and EP2 regulates cell proliferation and expression of inflammatory cytokines. 33545665_Polymorphisms rs2745557 in PTGS2 and rs2075797 in PTGER2 are associated with the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease development in a Tunisian cohort. 33786738_The differential functional coupling of phosphodiesterase 4 to human DP and EP2 prostanoid receptors stimulated with PGD2 or PGE2. 34529833_Prostaglandin E2 directly inhibits the conversion of inducible regulatory T cells through EP2 and EP4 receptors via antagonizing TGF-beta signalling. 34742290_Alpha-Synuclein, cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins-EP2 receptors as neuroinflammatory biomarkers of autism spectrum disorders: Use of combined ROC curves to increase their diagnostic values. 34822808_Prostaglandin E2 EP receptors in cardiovascular disease: An update. 34886911_Identification of ACOT13 and PTGER2 as novel candidate genes of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease through whole exome sequencing. 34914140_The EP2 agonist, omidenepag, alters the physical stiffness of 3D spheroids prepared from human corneal stroma fibroblasts differently depending on the osmotic pressure. 35543087_Increased COX-2 after ureter obstruction attenuates fibrosis and is associated with EP2 receptor upregulation in mouse and human kidney. |
ENSMUSG00000037759 |
Ptger2 |
22.768872 |
4.1665341929 |
2.058848 |
0.366792212 |
33.683218 |
0.00000000648578175722724084796062165095276164095139392884448170661926269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000028756424973467727924385955486086263732659062952734529972076416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.2424047 |
8.0788961 |
8.4557153 |
1.6775208 |
| ENSG00000125430 |
9953 |
HS3ST3B1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y662 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) to catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group to an N-unsubstituted glucosamine linked to a 2-O-sulfo iduronic acid unit on heparan sulfate (PubMed:10520990, PubMed:9988768). Catalyzes the O-sulfation of glucosamine in IdoUA2S-GlcNS and also in IdoUA2S-GlcNH2 (PubMed:10520990, PubMed:9988768). The substrate-specific O-sulfation generates an enzyme-modified heparan sulfate which acts as a binding receptor to Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) and permits its entry (PubMed:10520990). Unlike HS3ST1/3-OST-1, does not convert non-anticoagulant heparan sulfate to anticoagulant heparan sulfate (PubMed:9988768). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10520990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9988768}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a type II integral membrane protein that belongs to the 3-O-sulfotransferases family. These proteins catalyze the addition of sulfate groups at the 3-OH position of glucosamine in heparan sulfate. The substrate specificity of individual members of the family is based on prior modification of the heparan sulfate chain, thus allowing different members of the family to generate binding sites for different proteins on the same heparan sulfate chain. Following treatment with a histone deacetylase inhibitor, expression of this gene is activated in a pancreatic cell line. The increased expression results in promotion of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In addition, the modification catalyzed by this protein allows herpes simplex virus membrane fusion and penetration. A very closely related homolog with an almost identical sulfotransferase domain maps less than 1 Mb away. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. |
hsa:9953; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 1 activity [GO:0008467]; [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 3 activity [GO:0033872]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0006024]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process, enzymatic modification [GO:0015015]; protein sulfation [GO:0006477] |
20705311_HS3ST3B1 showed potent inhibitory effect on HBV replication. 20797317_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21709440_the results from this study unveiled a distinct function for 3-OST-3B1 as an Epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer in cancer and provided a link between histone modification and Epithelial-mesenchymal transition modulation. 22475533_Genetic variants of HS3ST3A1 and HS3ST3B1 are associated with Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia. 24127555_A genome-wide high-throughput siRNA screen revealed that KIR2DL4 recognition of cell-surface ligand(s) is directly regulated by heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 3B1 (HS3ST3B1). 29516954_These findings indicate that HS3ST3B1 is a novel regulator of TGF-beta-mediated EMT and is regulated by miR-218 in NSCLC. 29718295_The SNP rs28470223 results in decreased promoter activity of HS3ST3A1 and slightly higher HS3ST3A1 catalytic activity in vitro. |
ENSMUSG00000070407 |
Hs3st3b1 |
115.126137 |
8.8464203558 |
3.145094 |
0.293892839 |
109.035332 |
0.00000000000000000000000015941870647082370458609331118356851315540110041502783031155682512717761123433035663765622302889823913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000001740399487802779412584853577781337958359739791953225396978811336228670780812421980954241007566452026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
206.9300309 |
28.9502702 |
23.0626894 |
2.8192287 |
| ENSG00000125434 |
399512 |
SLC25A35 |
protein_coding |
Q3KQZ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
SLC25A35 belongs to the SLC25 family of mitochondrial carrier proteins (Haitina et al., 2006 [PubMed 16949250]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:399512; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23266187_Compares and contrasts all the known human SLC25A* genes and includes functional information. |
ENSMUSG00000018740 |
Slc25a35 |
20.026034 |
0.2776898402 |
-1.848454 |
0.403930886 |
21.464517 |
0.00000360436903878358370006485325576228717636695364490151405334472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011925686395975273633093816094685735151870176196098327636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6232771 |
2.3244121 |
31.2500086 |
5.2453848 |
| ENSG00000125457 |
57409 |
MIF4GD |
protein_coding |
A9UHW6 |
FUNCTION: Functions in replication-dependent translation of histone mRNAs which differ from other eukaryotic mRNAs in that they do not end with a poly-A tail but a stem-loop. May participate in circularizing those mRNAs specifically enhancing their translation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18025107}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Translation regulation |
|
This gene encodes a protein which interacts with the N-terminus of the stem-loop binding protein (SLBP) and the 3' end of histone mRNA. This interaction facilitates the activation of histone mRNA translation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:57409; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; histone mRNA stem-loop binding complex [GO:0062073]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation activator activity [GO:0008494]; cap-dependent translational initiation [GO:0002191]; regulation of translational initiation [GO:0006446] |
18025107_downregulation of endogenous SLIP1 reduces the rate of translation of endogenous histone mRNA and also reduces cell viability. 22532700_INT6 and MIF4GD were observed to colocalize in cytoplasmic foci. It was concluded that INT6, by establishing interactions with MIF4GD and SLBP, plays an important role in translation of poly(A) minus histone mRNAs. 23286197_Data suggest that oligomerization and SLBP phosphorylation regulate SLBP-SLIP1-histone-mRNA complex formation/disassociation; sequential and ordered assembly is required. 23286197_This paper describes the oligomeric state of SLIP1 and the SLIP1-SLBP complex and how it is regulated by SLBP phosphorylation. Using alanine scanning mutagenesis, the authors demonstrate that the binding site on SLIP1 for SLBP lies close to the dimer interface. A single-point mutant near the SLIP1 homodimer interface abolished interaction with SLBP in vitro and reduced the abundance of histone mRNA in vivo. 24336329_Results suggest that MIF4GD is a potential regulator of p27-dependent cell proliferation in HCC. |
ENSMUSG00000020743 |
Mif4gd |
67.673709 |
0.3719813219 |
-1.426698 |
0.241277355 |
35.107770 |
0.00000000311953518151952313123339336723306020049406583893869537860155105590820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014255213399141847555515748605884512878461123364104423671960830688476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.2204896 |
7.7723013 |
97.9821981 |
14.5109065 |
| ENSG00000125538 |
3553 |
IL1B |
protein_coding |
P01584 |
FUNCTION: Potent pro-inflammatory cytokine (PubMed:3920526, PubMed:10653850, PubMed:12794819, PubMed:28331908). Initially discovered as the major endogenous pyrogen, induces prostaglandin synthesis, neutrophil influx and activation, T-cell activation and cytokine production, B-cell activation and antibody production, and fibroblast proliferation and collagen production (PubMed:3920526). Promotes Th17 differentiation of T-cells. Synergizes with IL12/interleukin-12 to induce IFNG synthesis from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells (PubMed:10653850). Plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing VEGF production synergistically with TNF and IL6 (PubMed:12794819). Involved in transduction of inflammation downstream of pyroptosis: its mature form is specifically released in the extracellular milieu by passing through the gasdermin-D (GSDMD) pore (PubMed:33377178, PubMed:33883744). Acts as a sensor of S.pyogenes infection in skin: cleaved and activated by pyogenes SpeB protease, leading to an inflammatory response that prevents bacterial growth during invasive skin infection (PubMed:28331908). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10653850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12794819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28331908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33377178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33883744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3920526}. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Inflammatory response;Lysosome;Mitogen;Pyrogen;Reference proteome;Secreted |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This cytokine is produced by activated macrophages as a proprotein, which is proteolytically processed to its active form by caspase 1 (CASP1/ICE). This cytokine is an important mediator of the inflammatory response, and is involved in a variety of cellular activities, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. The induction of cyclooxygenase-2 (PTGS2/COX2) by this cytokine in the central nervous system (CNS) is found to contribute to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Similarly, IL-1B has been implicated in human osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Patients with severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) present elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1B in bronchial alveolar lavage fluid samples. The lung damage induced by the Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is to a large extent, a result of the inflammatory response promoted by cytokines such as IL-1B. This gene and eight other interleukin 1 family genes form a cytokine gene cluster on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:3553; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to interleukin-17 [GO:0097398]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; cellular response to organic substance [GO:0071310]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; fever generation [GO:0001660]; hyaluronan biosynthetic process [GO:0030213]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; monocyte aggregation [GO:0070487]; negative regulation of adiponectin secretion [GO:0070164]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; negative regulation of gap junction assembly [GO:1903597]; negative regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010829]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050995]; negative regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0045833]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050768]; negative regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050805]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0060559]; positive regulation of cell adhesion molecule production [GO:0060355]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of complement activation [GO:0045917]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of fever generation [GO:0031622]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034116]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033092]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050996]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production [GO:0071639]; positive regulation of myosin light chain kinase activity [GO:0035505]; positive regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150078]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of prostaglandin biosynthetic process [GO:0031394]; positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0032308]; positive regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046827]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of RNA biosynthetic process [GO:1902680]; positive regulation of T cell mediated immunity [GO:0002711]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell cytokine production [GO:2000556]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030949]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0050691]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903140]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to carbohydrate [GO:0009743]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0030730]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle adaptation [GO:0014805]; vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010573] |
11023482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11076651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11079552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11083263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11127488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11138328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11171832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11211945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11241561_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11264025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350506_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11380940_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11422336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11427627_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11448121_The level of IL-1 beta is significantly higher in sera of cicatricial pemphigoid patients with active disease before intravenous immunoglobulin therapy compared to the post-treatment level. 11476790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11481169_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11498264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11506478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11527622_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11531943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11578018_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11579484_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11600466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11606496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11641511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11665666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11669478_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11686217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11686217_There were no significant differences in the distributions of the IL-1RN and IL-1B genotypes, allel frequencies or halotypes. 11686480_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11703512_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737511_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11751881_These studies demonstrate that PEIPC and PECPC isomers are potent activators of endothelial cells increasing synthesis of IL-8 and MCP-1. 11756575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11756575_data fall short of showing significant association between a variant of the promoter of interleukin-1beta, polymorphism of angiotensinogen, and the missense variant of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and occurrence of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage 11762793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11770040_Repressed transcription of IL-1beta and rapid decay of IL-1beta mRNA in septic shock neutrophils correlated with reductions in levels of IL-1beta after stimulation with LPS 11774564_Interleukin-1 alpha and beta system in testis--quantitative analysis. Expression of immunomodulatory genes in male gonad. 11777965_IL-1 beta increases CD40 ligand-induced cytokine secretion by monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DC), CD34+-derived DC, and peripheral blood DC independently of T cell-derived cytokines. 11784248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11790645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11801594_Heat shock factor 1 represses transcription of the IL-1beta gene through physical interaction with the nuclear factor of interleukin 6 11806247_role in upregulating VEGF in vascular smooth muscle cells via the P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 11838837_Genotype A2A2 of IL-1beta is associated with severe forms of rheumatoid arthritis. The allelic combination A1 IL-1beta/A2 IL-1Ra is less often present in rheumatoid arthritis patients with severe disease. 11838837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Test found no evidence of an association of mutations with hypertension. 11847219_Up-regulation of prostaglandin E2 synthesis by interleukin-1beta in human orbital fibroblasts 11849463_Carriage of IL1beta2 and IL1RN*2 together with non-carriage of TNF2 is associated with increased susceptibility, but not with a prognosis of IgAN. 11849463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11851889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11853544_differentiated articular chondrocytes are highly responsive to IL-1beta and that p38 MAPK mediates this response by inducing COX-2 gene expression. 11857060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11857060_T helper 1-type immunity to trophoblast antigens in women with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss is associated with polymorphism of the IL1B promoter region 11858158_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11858187_In dengue shock syndrome pts, IL-1beta was significantly associated with t-PA (p |
ENSMUSG00000027398 |
Il1b |
4475.360439 |
30.0663893279 |
4.910080 |
0.048453925 |
15977.173598 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8749.8596437 |
264.3832178 |
293.0856488 |
8.6323053 |
| ENSG00000125551 |
5342 |
PLGLB2 |
protein_coding |
Q02325 |
FUNCTION: May bind noncovalently to lysine binding sites present in the kringle structures of plasminogen. This may interfere with the binding of fibrin or alpha-2-antiplasmin to plasminogen and may result in the localization of activity at sites necessary for extracellular matrix destruction. |
Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable serine-type endopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5342;hsa:5343; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit binding [GO:0036313]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043553]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
8.539468 |
0.1141293473 |
-3.131258 |
0.969891923 |
9.851883 |
0.00169658052539809422153138651623294208548031747341156005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003801659109590993165794792219003284117206931114196777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3744536 |
2.1411453 |
21.4575904 |
11.9829628 |
| ENSG00000125630 |
84172 |
POLR1B |
protein_coding |
Q9H9Y6 |
FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Second largest core component of RNA polymerase I which synthesizes ribosomal RNA precursors. Proposed to contribute to the polymerase catalytic activity and forms the polymerase active center together with the largest subunit. Pol I is composed of mobile elements and RPA2 is part of the core element with the central large cleft and probably a clamp element that moves to open and close the cleft. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:16809778}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Disease variant;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Metal-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Eukaryotic RNA polymerase I (pol I) is responsible for the transcription of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes and production of rRNA, the primary component of ribosomes. Pol I is a multisubunit enzyme composed of 6 to 14 polypeptides, depending on the species. Most of the mass of the pol I complex derives from the 2 largest subunits, Rpa1 and Rpa2 in yeast. POLR1B is homologous to Rpa2 (Seither and Grummt, 1996 [PubMed 8921381]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:84172; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA polymerase I complex [GO:0005736]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity [GO:0003899]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ribonucleoside binding [GO:0032549]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; neural crest formation [GO:0014029]; nucleologenesis [GO:0017126]; rRNA transcription [GO:0009303] |
16055704_PTEN represses RNA Pol I transcription through a novel mechanism that involves disruption of the SL1 complex 16880508_CK2 has the potential to regulate Pol I transcription at multiple levels, in preinitiation complex (PIC) formation, activation, and reinitiation of transcription. 17499043_Human Maf1 protein negatively regulates transcription by all three nuclear Pols. Changes in Maf1 expression affect Pol I-dependent transcription in human glioblastoma lines. 18194663_The average FIX expression level of the rDNA recombinants was additionally enhanced to that from a strong Pol II promoter as a result of elimination of position effects. 31649276_POLR1B and neural crest cell anomalies in Treacher Collins syndrome type 4. |
ENSMUSG00000027395 |
Polr1b |
182.885312 |
2.5109582401 |
1.328238 |
0.196205965 |
45.014647 |
0.00000000001955662254590346413518955481243956698311770026066369609907269477844238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000106593703389045468642700952915317990504773248972014698665589094161987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
246.9053874 |
41.5157595 |
99.2813982 |
12.3156331 |
| ENSG00000125753 |
7408 |
VASP |
protein_coding |
P50552 |
FUNCTION: Ena/VASP proteins are actin-associated proteins involved in a range of processes dependent on cytoskeleton remodeling and cell polarity such as axon guidance, lamellipodial and filopodial dynamics, platelet activation and cell migration. VASP promotes actin filament elongation. It protects the barbed end of growing actin filaments against capping and increases the rate of actin polymerization in the presence of capping protein. VASP stimulates actin filament elongation by promoting the transfer of profilin-bound actin monomers onto the barbed end of growing actin filaments. Plays a role in actin-based mobility of Listeria monocytogenes in host cells. Regulates actin dynamics in platelets and plays an important role in regulating platelet aggregation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10087267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10438535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15939738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17082196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18559661}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3-binding;Tight junction |
|
Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is a member of the Ena-VASP protein family. Ena-VASP family members contain an EHV1 N-terminal domain that binds proteins containing E/DFPPPPXD/E motifs and targets Ena-VASP proteins to focal adhesions. In the mid-region of the protein, family members have a proline-rich domain that binds SH3 and WW domain-containing proteins. Their C-terminal EVH2 domain mediates tetramerization and binds both G and F actin. VASP is associated with filamentous actin formation and likely plays a widespread role in cell adhesion and motility. VASP may also be involved in the intracellular signaling pathways that regulate integrin-extracellular matrix interactions. VASP is regulated by the cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases PKA and PKG. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7408; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; profilin binding [GO:0005522]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008154]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289] |
11756574_Results show that VASP is expressed in a cell-specific and trimester-specific manner in the human placenta, and may be important for blastocyst implantation and placental develpoment. 12087107_Data show that phosphorylation of VASP is dynamically regulated by cellular adhesion to extracellular matrix. 12220179_The C-terminal fragment of VASP (336-380) forms a tetramer in solution via a coiled coil arrangement and is solely responsible for tetramerization of full-length VASP. 12397215_These results suggest that VASP may participate in vasculogenesis and endothelial sprouting during placental vasculogenesis 12566781_The platelet VASP shift is modified during coronary perfusion, and this modification correlates with mononuclear infiltration in the graft. 12576312_Phosphorylation of VASP induced by either cGMP analogs or a nitric oxide donor is inhibited by PKA; PKA plays a predominant role in the cGMP-induced phosphorylation of VASP and platelet inhibition in human platelets. 12652017_laminar shear stress can induce VASP translocation and phosphorylation in HUVECs, leading to actin filaments rearrangement, aligning cells along the flow direction. 12805219_These findings show that vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein and diaphanous 1 function cooperatively downstream of Rho to control F-actin assembly and serum response factor activity. 14679200_VASP, an important component of the cellular microfilament system, plays a major role in regulating serum response element-dependent transcription 15158464_M10 carries Mena/VASP from the root to the tip of the filopodia where extension of actin filament takes place 15178555_VASP phosphorylation at serine157 is required for the growth-stimulatory effect of transfected human VASP in rodent SMCs, whereas VASP phosphorylation at serine239 is involved in the growth inhibitory effects of NO on SMCs. 15569942_The basis for the right-handed geometry of VASP TD is a 15-residue repeat in its amino acid sequence, which reveals a characteristic pattern of hydrophobic residues 15634270_VASP is phosphorylated in patients with ischemic cardiovascular diseases and clopidogrel resistance 16046415_Galpha13-induced VASP phosphorylation that involves activation of RhoA and MEKK1, phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB, release of PKA catalytic subunit from the complex with IkappaB and NF-kappaB, and subsequent phosphorylation of VASP 16197368_Rho kinase and PKC were identified as the major kinases that phosphorylate VASP Ser157 in response to thrombin in human platelets. 16531412_Migfilin has a role in interacting with vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) and regulates VASP localization to cell-matrix adhesions and migration 17082196_VASP is a new AMP-activated protein kinase substrate 17167837_VASP may play a role in assembling and stabilizing the mitotic spindle of cells, and phosphorylation of the protein is the precondition for it to exert this function. 17351763_RSV resistance in a minority of clones was due to mono-allelic disruption of the cellular gene for VASP. 17488353_VASP phosphorylation may have a role in the individual response to clopidogrel loading dose prior to percutaneous coronary intervention 17684063_Data show that phosphorylation of Ser239 of VASP results in loss of lamellipodial protrusions and cell rounding, and is a powerful means of controlling directed actin polymerization within lamellipodia. 17914456_analysis of the structural basis of profilin-actin complexes during filament elongation by Ena/VASP 17938817_VASP has a role in increased impaired platelet responsiveness in patients with subacute stent thrombosis 18064332_Determination of VASP phosphorylation is superior to conventional platelet aggregometry and angiographic parameters for assessing the risk of stent thrombosis. 18217157_VASP phosphorylation demonstrated concordance across the response range of P2Y(12) receptor blockade following thienopyridine administration. 18278200_Examine prothrombotic status in low responder patients to clopidogrel indentified by VASP analysis. 18559661_Vasoactive gases CO and NO promote cytoskeletal changes through site- and cell type-specific VASP phosphorylation, and in diabetes, blunted responses to these agents may lead to reduced vascular repair and tissue perfusion 18569864_H2O2 in the absence of NO or exogenous haem- containing proteins induces nitration of platelet VASP 18680720_These results indicate that force-mediated adhesion strengthening occurs in endothelial adherens junctions and that dynamic VASP activity is necessary for this process. 18813837_Positive regulation of migration and invasion by vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein via Rac1 pathway in human breast cancer cells. 18832777_The antiplatelet effects of cilostazol intake could be evaluated by measuring VASP phosphorylation levels and maximal aggregation rates in platelets by ex vivo treatment with a low concentration of PGE(1). 18845790_VASP associated with nucleophosmin-ALK, and its phosphorylation required ALK activity. 18923426_Data show that both human and Dictyostelium VASP are directly involved in accelerating actin filament elongation by delivering monomeric actin to the growing barbed end. 19059569_Assessment of VASP index in acute coronary syndrome patients identifies low responders to clopidogrel who are at increased risk of recurrent cardiovascular events. 19081821_LPA receptor-induced VASP phosphorylation is a critical mediator of tumor cell migration initiation 19115233_Data demonstrate that profilin-1 downregulation results in a hyper-motile phenotype of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in an Ena/VASP-dependent mechanism. 19435808_Data provide the first demonstration that direct interaction of VASP with CXCR2 is essential for proper CXCR2 function and demonstrate a crucial role for VASP in mediating chemotaxis in leukocytes. 19463377_Results from the VASP-02 (Vasodilator-Stimulated Phosphoprotein-02) randomized study which used guided switching to clopidogrel 150 mg/day after 2 weeks in low responders. 19690214_These results identify tissue-specific VASP as a central protein in the control of the alveolar-capillary barrier properties during acute lung injury. 19798690_VASP phosphorylation at serine239 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling. 19825941_VASP phosphorylation controls remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. 19885626_Rab13,VASP,and ZO-1 were found in apical tight junctions in normal epithelium but were dislocated to the basolateral position in patients with inactive Crohn's disease. In patients with ulcerative colitis,these tight junction proteins were not dislocated. 19902490_Compared clopidogrel effectiveness in unstable ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients on mechanical ventilation with stable STEMI patients using the VASP index. 19943879_Platelet hyperreactivity in multiple electrode aggregometry might be a better risk predictor for stent thrombosis than the assessment of the specific clopidogrel effect with the VASP phosphorylation assay. 20044140_IRAK-1 forms a close complex with PKCepsilon as well as VASP, and participates in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced phosphorylation of VASP. 20110575_Combination of experimental and computational interactome research was used for the analysis of protein-protein interactions between Abi-1 and VASP in human platelets. 20589315_Letter: Report vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) ELISA to evaluate P2Y12-ADP receptor activity in coronary artery disease patients taking antiplatelet agents. 20624010_peroxynitrite may inhibit platelet function by inducing the phosphorylation of VASP through a mechanism that requires the activation of PKC. 20695985_vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is phosphorylated in patients with genetic defects of the platelet P2Y(12) receptor for ADP 20802179_High VASP expression is associated with focal adhesion assembly in myofibroblasts fostering a microenvironment that promotes tumor growth. 20822337_Results describe the impact of smoking on platelet reactivity and phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) in a group of 20 young smokers. 20826790_Results suggest that actin polymerization and bundling by VASP are critical for spine formation, expansion, and modulating synaptic strength. 20945373_VASP deficiency leads to a more profound endothelial barrier disruption and delayed recovery after activation of thrombin PAR-1 receptor. 21041447_presentation of a model for how VASP promotes actin filament assembly 21158099_VASP participates in the regulation of cell cytoskeleton reorganization and morphology modification induced by shear flow via a cAMP/cAK pathway. 21163344_Data show that VASP has different immunostaining patterns between cerebral cortical plates in prenatal and adult human brain samples, and suggest that VASP may play a crucial role in the regulation of human neonatal cerebral cortical development. 21398369_ENA/VASP-family proteins are functionally redundant in homologous recombination, and MENA, VASP and EVL may be involved in the DSB repair pathway in humans 21423205_Data show that VASP and Mena interact with RSK1. 21702043_Membrane organelle disassembly reflected specific phosphorylation of VASP Ser239, the cGMP/PKG preferred site, and rapid VASP removal from tumor cell protrusions 21814501_Studied generation of filopodia with regards to the dynamic interaction established by Eps8, IRSp53 and VASP with actin filaments. 21827504_The Ser-239 phosphorylation level of VASP might be a useful protein marker for riboflavin and UV light-mediated PLT compromise. 21874265_VASP protein regulates osteosarcoma cell migration and metastasis 22014333_The phosphorylation and dephosphorylation cycle of VASP by the Abi-1-bridged mechanism regulates association of VASP with focal adhesions, which may regulate adhesion of Bcr-Abl-transformed leukaemic cells. 22210825_Prolonged treatment with albuterol prevents the agonist-induced phosphorylation of VASP at Ser157. 22212857_Letter: In High on-treatment platelet reactivity assessed by various platelet function tests the consensus-defined cut-off of VASP-P platelet reactivity index too low. 22320863_a novel TNF-alpha/HIF-1alpha/VASP axis in which HIF-1alpha acts downstream of TNF-alpha to inhibit VASP expression and modulate the adhesion and proliferation of breast cancer cells 23436459_Active proteases in nephrotic plasma lead to a podocin-dependent phosphorylation of VASP in podocytes via protease activated receptor-1. 23469931_Results show that NPs, possibly through the clearance receptor (natriuretic peptide receptor-C) expressed on platelet membranes, increase VASP phosphorylation but only following PDE inhibition, indicating a small, localised cGMP synthesis. 23685951_Matrine modulates the structure, subcellular distribution, expression and phosphorylation of VASP in human gastric cancer cells, thus inhibiting cancer cell adhesion and migration. 23846685_PKD1 directly phosphorylates VASP at two serine residues, Ser-157 and Ser-322. These phosphorylations occur in response to RhoA activation and mediate VASP re-localization from focal contacts to the leading edge region. 24496446_palladin functions as a dynamic scaffolding protein that promotes the assembly of dorsal stress fibers by recruiting VASP to these structures. 24732788_low serum concentration of vaspin is a risk factor for the progression of T2DM 24857403_Binding of tetrameric VASP to interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)1 is regulated by assembly of IRAK1 onto signaling complexes. 24963131_PKA regulates VASP phosphorylation in Ras-transformed cells in a non-cell-autonomous manner. 25051011_Data show that tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) increased A549 lung adenocarcinoma cell permeability by repressing vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) expression through the activation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit (HIF-1alpha). 25117404_Overexpression of VASP in endothelial cells blocked inflammation and insulin resistance induced by palmitate. 25246528_VASP reconstitution of actin-based motility depends on the recruitment of F-actin seeds from the solution produced by cofilin 25298072_The authors demonstrate that vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), which is critical for regulation of actin assembly, cell adhesion and motility, is a direct substrate of Yersinia pestis YpkA kinase activity. 25355952_Ena/VASP's ability to bind F-actin and profilin-complexed G-actin are important for its effect, whereas Ena/VASP tetramerization is not necessary. 25457586_In clinical practice,LCR and CYP2C19 gene polymorphism should be assessed in NCIS patients receiving clopidogrel treatment. 25543053_Serine phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) regulates colon cancer cell survival and apoptosis. 25759389_VASP phosphorylation at Ser(157) mediates its localization at the membrane, but that VASP Ser(157) phosphorylation and membrane localization are not sufficient to activate its actin catalytic activity 26295568_The authors propose that Lpd delivers Ena/VASP proteins to growing barbed ends and increases their actin polymerase activity by tethering them to actin filaments. 26336132_Data show that the phosphorylation status of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) at serine S322 can be predictive for breast cancer progression to an aggressive phenotype. 26576037_VASP phosphorylation assay could be useful in studies aimed at investigating relations between clopidogrel active metabolite bioavailability and clinical events. 26611125_VASP, zyxin and TES are tension-dependent members of focal adherens junctions independent of the alpha-catenin-vinculin module. 27711191_This study provides the first evidence of VASP manipulation by an intravacuolar bacterial pathogen 28209486_VASP silencing downregulated Migfilin, beta-catenin and uPA and impaired spheroid invasion. 28376489_findings have uncovered a PKG/VASP signaling pathway in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells as a key molecular mechanism underlying T3-induced vascular relaxation. 28526707_Our results reveal a dual role of VASP in endothelial permeability. In addition to its well-documented function in barrier integrity, we show that S-nitrosylation of VASP contributes to the onset of endothelial permeability. 28667124_VASP role in the actin filament elongation 29460479_Silencing of stathmin-1 altered the expression, subcellular localization and phosphorylation status of VASP, which suggested that it might be associated with remodeling of the cell cytoskeleton in colorectal cancer metastasis. 30279729_Taken together, these results defined VASP as an oncogene of hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis and metastasis with the potential to serve as a prognostic biomarker. 30282752_Our results demonstrate a novel requirement for VASP and actin polymerization in maintaining lytic granule convergence during NK cell-mediated killing. 30463566_VASP may be involved in the pathophysiology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia via dysregulation of actin binding proteins 30814249_We found that VASP's interaction with Pfn1 is promoted by cell-substrate adhesion and requires down-regulation of PKA activity 30816548_Study results demonstrated that TNFalpha decreased VASP expression by upregulating the expression of HIF1alpha to inhibit A549 cell proliferation and adhesion. Inhibition of transplanted tumor growth was associated with downregulation of VASP expression in nude mice. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that expression levels of VASP or HIF1alpha lead to differential outcomes of overall survival in lung carcinoma. 31093978_this study highlights the important roles of BLACAT1/miR-605-3p/VASP axis in glioma progression. 31257464_these results indicated that SSb2 may be a potential antitumor drug for the treatment of breast cancer, which acts by suppressing proliferation and migration by downregulating the STAT3 signalling pathway and inhibiting the expression of VASP, MMP2 and MMP9 expression. 31270029_ANGPTL3 inhibits renal cell carcinoma metastasis by inhibiting VASP phosphorylation. 31987909_findings indicate that integrin alpha3 interacts with VASP and regulates its expression 32141559_Up-regulation of SNHG15 facilitates cell proliferation, migration, invasion and suppresses cell apoptosis in breast cancer by regulating miR-411-5p/VASP axis. 32200035_Depletion of LAMP3 enhances PKA-mediated VASP phosphorylation to suppress invasion and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32397169_RIAM-VASP Module Relays Integrin Complement Receptors in Outside-In Signaling Driving Particle Engulfment. 32470361_Arp2/3 and Mena/VASP Require Profilin 1 for Actin Network Assembly at the Leading Edge. 32997728_Transfer of HTLV-1 p8 and Gag to target T-cells depends on VASP, a novel interaction partner of p8. 33184177_Designed nanomolar small-molecule inhibitors of Ena/VASP EVH1 interaction impair invasion and extravasation of breast cancer cells. 36238292_Expression of the phagocytic receptors alphaMbeta2 and alphaXbeta2 is controlled by RIAM, VASP and Vinculin in neutrophil-differentiated HL-60 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000030403 |
Vasp |
4321.077575 |
2.4945946489 |
1.318805 |
0.054521973 |
571.245866 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000300820866279479081560941968328454017438480931555677674969405471671598695544016734421381268409488644230075881530069621468678997628943037369311502113147038221280070175758024142183116562481943604336492969450 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000162048028696536907513961110601550776065915488631559680709904109617983011833460024924484293236085796756943623797214371534217828583922671722267068998481131046245463965223493547225799365665757096465970546974 |
Yes |
Yes |
6067.3666936 |
208.9835056 |
2450.3282583 |
62.3549591 |
| ENSG00000125772 |
56261 |
GPCPD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPB8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the negative regulation of skeletal muscle differentiation, independently of its glycerophosphocholine phosphodiesterase activity. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable glycerophosphocholine phosphodiesterase activity. Predicted to be involved in glycerophospholipid catabolic process. Predicted to act upstream of or within skeletal muscle tissue development. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56261; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; glycerophosphocholine phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0047389]; starch binding [GO:2001070]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] |
22343285_common genetic variants in GPCPD1 are associated with scaling of visual cortical surface area in humans 22570503_We have identified EDI3, a key enzyme controlling GPC and choline metabolism; Because inhibition of it corrects the GPC/PC ratio and decreases the migration capacity of tumor cells, it represents a possible target for therapeutic intervention. 25482527_EDI3 links choline metabolism to integrin expression, cell adhesion and spreading 34626691_Circular RNA circSNX6 promotes sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma through the miR-1184/GPCPD1/ lysophosphatidic acid axis. |
ENSMUSG00000027346 |
Gpcpd1 |
113.959811 |
0.4371027535 |
-1.193956 |
0.314606512 |
13.853498 |
0.00019762856476674984509619981132289012748515233397483825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000518208849876927984262620086042261391412466764450073242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.7129446 |
14.5050969 |
144.6772434 |
23.1548142 |
| ENSG00000125780 |
7053 |
TGM3 |
protein_coding |
Q08188 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the calcium-dependent formation of isopeptide cross-links between glutamine and lysine residues in various proteins, as well as the conjugation of polyamines to proteins. Involved in the formation of the cornified envelope (CE), a specialized component consisting of covalent cross-links of proteins beneath the plasma membrane of terminally differentiated keratinocytes. Catalyzes small proline-rich proteins (SPRR1 and SPRR2) and LOR cross-linking to form small interchain oligomers, which are further cross-linked by TGM1 onto the growing CE scaffold (By similarity). In hair follicles, involved in cross-linking structural proteins to hardening the inner root sheath. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Acyltransferase;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Keratinization;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Zymogen |
|
Transglutaminases are enzymes that catalyze the crosslinking of proteins by epsilon-gamma glutamyl lysine isopeptide bonds. While the primary structure of transglutaminases is not conserved, they all have the same amino acid sequence at their active sites and their activity is calcium-dependent. The protein encoded by this gene consists of two polypeptide chains activated from a single precursor protein by proteolysis. The encoded protein is involved the later stages of cell envelope formation in the epidermis and hair follicle. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7053; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; acyltransferase activity [GO:0016746]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase activity [GO:0003810]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cell envelope organization [GO:0043163]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; keratinization [GO:0031424]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; peptide cross-linking [GO:0018149]; protein modification process [GO:0036211] |
11901200_epidermal transglutaminase (type 3) is the dominant autoantigen in dermatitis herpetiformis 12679341_x-ray crystallography in the presence of Ca2+ and/or Mg+2 shows Ca2+ binding in both sites two and three cooperate in opening the channel 12850301_Expression in upper layers of epidermis. Diffuse cytoplasmic distribution in vitro consistent with its proposed role in early phase of cornified cell envelope assembly in cytoplasm. 14645372_transglutaminase 3 is regulated by guanine nucleotides and calcium/magnesium 15084592_Crystal structure of transglutaminase 3 in complex with GMP 15304086_LEKTI deficiency in the epidermis and in hair roots at the protein level and an aberrant expression of other proteins, especially transglutaminase1 and 3, which may account for the impaired epidermal barrier in Netherton syndrome 15335352_upstream sequence of Ets core motif is critical for the expression of TGM3 in cells cultured in vitro. 15715085_In HEK 293T cell culture, transglutaminase 3 cross-links the N-terminal fragments of mutant huntingtin protein, therefore it could be involved in the cross-linking of huntingtin into intranuclear inclusions in Huntington disease. 16257432_We conclude from these in vitro experiments that the E1--E4 protein is cross-linked by transglutaminase 3, and that E1--E4 expression in differentiated keratinocytes induces morphologic abnormalities of the cornified cell envelope. 16786148_BCSG-1 significantly correlates with levels of transglutaminase-3 and may have a role in progression of breast cancer 16804985_Reduced expression of transglutaminase 3 (TGM3) may play an important role in esophageal carcinogenesis. 17205060_Using a new antibody raised in goat with specificity confirmed using a separately cloned recombinant protein, we have confirmed findings of Sardy et al. suggesting TG3 is the autoantigen of dermatitis herpetiformis 17380116_detected two splicing variants for TG3, as the transcription of these mRNAs appears to be not regulated during differentiation and in pathologies involving tranglutaminase activity 18719606_TGase 3-driven specific isopeptide bonds between intermediate filaments and keratin associated proteins participate to the progressive scaffolding of the hair shaft 19005484_Cathepsin L and transglutaminase 3 could be involved in the pathway that leads to terminal differentiation, not only in the epidermis but also in the human hair follicle and nail unit. 19142970_Reduced TGM3 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19522851_Lack of TGM3 expression is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 19590514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20300788_findings lend credence to the notion that TG3 and TG6 are involved in the gluten-induced autoimmune responses of dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten ataxia 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20716179_new information on the specific distribution of TGase 3 21335491_TGM3 in immunoglobulin A (IgA) and TGM3 immune complexes is responsible for cross-linking and tight binding of IgA to connective tissue in the dermis and explains the IgA deposits in dermatitis herpetiformis skin long after signs of disease are resolved. 22506423_The low expression of TGM3 may contribute to the carcinogenesis and development of laryngeal carcinoma. 23189155_Genetic variation in the epidermal transglutaminase genes is not associated with atopic dermatitis. 24112124_mRNA expression of transglutaminase 1 and transglutaminase 3 was significantly decreased in patients with chronic periodontitis compared with a healthy control group. 24289313_TGM3, a candidate tumor suppressor, contributes to the carcinogenesis and development of human head and neck cancer. 24403052_New basal cell carcinoma susceptibility loci were identified at TGM3 (rs214782) and RGS22(rs7006527). 24885370_IgA-anti-TG1 antibodies were found in 2% and IgA-anti-TG3 antibodies in 3% of patients with active atopic dermatitis (AD). Two out of the 5 patients with AD and concomitant celiac disease had IgA-anti-TG1 and IgA-anti-TG2 antibodies. 25178107_Transglutaminase 3 present in the IgA aggregates in dermatitis herpetiformis skin is enzymatically active and binds soluble fibrinogen. 27106676_Levels of TG3-IgA IC significantly elevated in plasma as well as in serum samples of untreated patients with dermatitis herpetiformis compared with healthy controls. 27430245_Our data collectively demonstrate that TGM3 can be a candidate tumor suppressor that is able to induce esophageal cancer cell proliferation and migration 27649154_Data indicate a decrease in transglutaminases TG1 and TG3 transcripts by about 70% in foreskins from patients with balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO) BXO in comparison with patients without BXO and an increase in transglutaminase TG2 mRNA levels by 2.9 fold. 27866708_The two enzymes PADI3 and TGM3, responsible for posttranslational protein modifications, and their target structural protein TCHH are all involved in hair shaft formation. 28161375_studies demonstrate that TGase-catalyzed transamidation and activation of rac1 and cdc42 results from stimulation of multiple types of receptors and this novel signaling pathway can regulate dendritic spine morphology and plasticity. 29182792_Cultured duodenal biopsies from patients with dermatitis herpetiformis produce transglutaminase-3 antibodies. 29953521_Patents having higher level of TGM-3 expression have good response to chemo-radiotherapy and also have better overall survival. TGM-3 may serve as a candidate biomarker for responsiveness to chemo-radiotherapy treatment in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients 30172723_TGM3 played an important role in OL malignant transformation 30213231_aberrant TGase 1 and TGase 3 localization and distribution are closely related to hyper-keratinization in Oral lichen planus. 31425706_Transglutaminase 3 Promotes Skin Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis by Activating Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells via DC-SIGN. 31822388_TGM3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and hepatocellular carcinogenesis and predicts poor prognosis for patients after curative resection. 32020212_TGM3 functions as a tumor suppressor by repressing epithelialtomesenchymal transition and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. 33899115_Downregulation of miR106b3p increases sensitivity to cisplatin in esophageal cancer cells by targeting TGM3. 33959126_T Cell Response Toward Tissue-and Epidermal-Transglutaminases in Coeliac Disease Patients Developing Dermatitis Herpetiformis. 34597849_Transglutaminase 3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: Correlation with tumor features and survival profile. 36356335_Circular RNA ciRS-7 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma development by inducing TGM3 hypermethylation via miR-432-5p/DNMT3B axis. |
ENSMUSG00000027401 |
Tgm3 |
24.972046 |
16.1643777646 |
4.014746 |
0.499545158 |
89.085509 |
0.00000000000000000000378110530166008761469567123810909348665089203142252932752891136924944248676183633506298065185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000034924351847623836634529089469279296998618864823318353775294387020267095067538321018218994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.8843804 |
18.0860751 |
2.8632834 |
0.9892853 |
| ENSG00000125816 |
644524 |
NKX2-4 |
protein_coding |
Q9H2Z4 |
FUNCTION: Probable transcription factor. |
Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:644524; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
34768865_NKL Homeobox Genes NKX2-3 and NKX2-4 Deregulate Megakaryocytic-Erythroid Cell Differentiation in AML. |
ENSMUSG00000054160 |
Nkx2-4 |
29.189074 |
0.1829721061 |
-2.450304 |
0.328486305 |
63.144411 |
0.00000000000000192093772978121339714555247132472482567879380581377102288342939573340117931365966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000013507880367589665912843762515084378670742219427647334839548420859500765800476074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1523234 |
1.9872925 |
50.2975300 |
5.6638943 |
| ENSG00000125844 |
6238 |
RRBP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2E9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a ribosome receptor and mediates interaction between the ribosome and the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translocation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a ribosome-binding protein of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Studies suggest that this gene plays a role in ER proliferation, secretory pathways and secretory cell differentiation, and mediation of ER-microtubule interactions. Alternative splicing has been observed and protein isoforms are characterized by regions of N-terminal decapeptide and C-terminal heptad repeats. Splicing of the tandem repeats results in variations in ribosome-binding affinity and secretory function. The full-length nature of variants which differ in repeat length has not been determined. Pseudogenes of this gene have been identified on chromosomes 3 and 7, and RRBP1 has been excluded as a candidate gene in the cause of Alagille syndrome, the result of a mutation in a nearby gene on chromosome 20p12. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:6238; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ribosome [GO:0005840]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; translation [GO:0006412] |
15184079_Results identify the ribosome receptor, p180, as a binding partner of the kinesin heavy chain isoform KIF5B. 17634287_These data suggest that p180 mediates interactions between the endoplasmic reticulum and microtubules mainly through the novel microtubule-binding and -bundling domain MTB-1. 18083570_over-expression of p180R failed to increase secretory pathway proteins calnexin, SEC61beta, and calreticulin, or ribosome biogenesis 19037105_results obtained demonstrate that p180 is both necessary & sufficient to induce a secretory phenotype in mammalian cells; findings support a central role for p180 in the terminal differentiation of secretory cells & tissues 19425502_the discovery overexpression of GPD1 and RRBP1 proteins and lack of expression for HNRNPH1 and SERPINB6 proteins which are new candidate biomarkers of colon cancer. 19932094_A novel function of p180-abundant endoplasmic reticulum on the trans-Golgi network expansion, both of which are highly developed in various professional secretory cells. 20647306_p180 plays crucial roles in enhancing collagen biosynthesis at the entry site of the secretory compartments by a novel mechanism that mainly involves facilitating ribosome association on the ER. 21111237_p180 is concentrated in ER sheets by interacting with polysomes and may play a role in ER morphology. 22679391_p180 promotes the ribosome-independent localization of a subset of mRNA to the endoplasmic reticulum. 23318453_RRBP1 could alleviate ER stress and help cancer cell survive 24019514_Data indicate that p180 is required for the efficient targeting of placental alkaline phosphatase (ALPP) mRNA to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 26196185_High RRBP1 expression facilitates colorectal cancer progression and predicts an unfavourable post-operative prognosis. 30684972_RRBP1 expression was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with endometrial carcinoma (EC) (both P |
ENSMUSG00000027422 |
Rrbp1 |
326.855563 |
2.1058696584 |
1.074416 |
0.125249982 |
72.931155 |
0.00000000000000001342521036851653033434539296577838595682397957728005169486529268851882079616189002990722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000106478293949115523886947499252544158755082497806818825347718870943936053663492202758789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
451.0772159 |
31.1408012 |
215.5960760 |
11.3906655 |
| ENSG00000125869 |
24141 |
LAMP5 |
protein_coding |
Q9UJQ1 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in short-term synaptic plasticity in a subset of GABAergic neurons in the brain. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D387}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in establishment of protein localization to organelle. Located in endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane; endosome membrane; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:24141; |
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; dendrite membrane [GO:0032590]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; growth cone membrane [GO:0032584]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; establishment of protein localization to organelle [GO:0072594] |
29030552_BAD-LAMP (LAMP5)-silencing enhances TLR9 retention in endolysosome compartment and consequent downstream signalling events. 30651276_High LAMP5 expression is associated with Leukemia. 35226222_Lysosomal-associated membrane protein family member 5 promotes the metastatic potential of gastric cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000027270 |
Lamp5 |
8.951423 |
0.3321676595 |
-1.590016 |
0.606369004 |
6.989131 |
0.00820061504538050455026532148394835530780255794525146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015993799956371068660132550576236099004745483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0856784 |
1.6698168 |
12.4091077 |
3.1922642 |
| ENSG00000125912 |
56926 |
NCLN |
protein_coding |
Q969V3 |
FUNCTION: Component of a ribosome-associated translocon complex involved in multi-pass membrane protein transport into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane and biogenesis (PubMed:32820719). May antagonize Nodal signaling and subsequent organization of axial structures during mesodermal patterning, via its interaction with NOMO (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NZ07, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32820719}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables ribosome binding activity. Involved in protein stabilization; regulation of protein complex stability; and regulation of protein-containing complex assembly. Located in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56926; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of protein complex stability [GO:0061635]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966] |
32914261_Identification of the soluble EphA7-interacting protein Nicalin as a regulator of EphA7 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000020238 |
Ncln |
689.130037 |
2.2752965942 |
1.186055 |
0.091825031 |
165.123963 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000008594697281383305156690649173156530651977011932679570453171101885680815752637351122772058864372887385107979696385882562026381492614746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001361134462158987014401981249221861288698343670216300076644998847144931980592898556169047493747716048861917670365073718130588531494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
958.0960621 |
55.4197150 |
423.6797273 |
18.5393023 |
| ENSG00000125968 |
3397 |
ID1 |
protein_coding |
P41134 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator (lacking a basic DNA binding domain) which negatively regulates the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors by forming heterodimers and inhibiting their DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Implicated in regulating a variety of cellular processes, including cellular growth, senescence, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and neoplastic transformation. Inhibits skeletal muscle and cardiac myocyte differentiation. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing the transcriptional activator activity of the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a helix-loop-helix (HLH) protein that can form heterodimers with members of the basic HLH family of transcription factors. The encoded protein has no DNA binding activity and therefore can inhibit the DNA binding and transcriptional activation ability of basic HLH proteins with which it interacts. This protein may play a role in cell growth, senescence, and differentiation. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3397; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; proteasome binding [GO:0070628]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043534]; blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048514]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell-abiotic substrate adhesion [GO:0036164]; cellular response to dopamine [GO:1903351]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to peptide [GO:1901653]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0050774]; negative regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043392]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045602]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transcription by transcription factor localization [GO:0010621]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0032233]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of vasculature development [GO:1901342]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
11729207_Id1, a dominant negative inhibitor of basic helix-loop-helix proteins, is a direct target gene for BMP 11896613_Id-1 expression is linked with the loss of NF-1/Rb/HDAC-1 transcription repressor complex in metastatic breast cancer 12016143_role in stimulating serum-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation through inactivation of p16(INK4a)/pRB pathway 12020803_TGF beta 1 may be one of the upstream regulators of Id-1 12203366_immunohistochemical studies on NPC samples showed that expression of Id-1 was present in NPC cells but absent in normal tissues. This study demonstrates that Id-1 plays an important role in cell proliferation in NPC cells 12296825_Data suggest that signalling of BMP-2 to stimulate the expression of Id1 would be transduced by BMPR-IA and mediated by Smad1 and Smad4. 12576450_Level of protein expression correlates with poor differentiation, enhanced malignant potential, and more aggressive clinical behavior of epithelial ovarian tumors. 12719589_expression in human endothelial cells induced by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus LANA protein, expression in Kaposi sarcoma tumor cells and in vivo 12787042_expression may relate to the metastatic behaviour in human oral squamous cell carcinoma 12823438_dysregulated Id-1 may not only contribute to delaying the senescence program in keratinocytes, it may also contribute to the escape of the relatively undifferentiated tumor cells in BCC from immune surveillance. 12881706_Our results strongly suggest that Id-1 may be one of the upstream regulators of NF-kappaB and activation of NF-kappaB signalling pathway may be essential for Id-1 induced cell proliferation through protection against apoptosis. 12947323_Significantly overexpressed in papillary thyroid cancer. Primarily localized to cytoplasm of thyroid follicular cells. Activation of the mitogen intracellular protein kinase A and protein kinase C signaling pathways up-regulated Id-1 mRNA expression. 12949053_over-expression of Id-1 induces cell proliferation in HCC through inactivation of p16INK4a/retinoblastoma pathway 14688027_Expression of Id-1 was able to reduce androgen-stimulated growth and S phase fraction of the cell cycle in prostatic cancer cells. 14690332_Id1 protein is involved in the process of differentiation of keratinocytes seeen in normal skin and Id1 pathway is activated in psoriasis. 14742319_Id-1 may be an upstream regulator of the Raf/MEK signalling pathway, which plays an essential role in protection against taxol-induced apoptosis 14755252_ID1 may contribute to oncogenesis not only by inhibiting transcriptional activity of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors and abrogate differentiation but also by subverting centrosome duplication. 15026801_ID-1 expression significantly associated with intratumoral microvessel density in pancreatic cancer 15041724_Id-1 and Id-2 proteins control prostate cancer cell phenotypes and could serve as molecular markers of aggressive human prostate cancer. 15064751_Id1 induction by LMP1 depends on its NF-kappaB activation domain at the COOH-terminal region, CTAR1 and CTAR2. This may facilitate clonal expansion of premalignant nasopharyngeal epithelial cells infected with EBV & promote malignant transformation. 15138269_silencing Id1 expression in young cells by RNA interference induced an increased p16(INK4a) level and premature cellular senescence 15163661_MyoD modulates the rate of Id1 degradation and suggest a dynamic interplay of these factors 15322112_induction of Id1 not only blocks transcriptional activity but also induces myogenin degradation by blocking formation of myogenin-E47 protein complexes. 15370294_Id1 can be up-regulated and p53 down-regulated by a statin in endothelial cells. Regulation of these proteins in endothelial cells may account for the proangiogenic effect of statins. 15489884_Id1 has cell cycle regulatory functions that are similar to those of c-Myc. 15494533_Overexpression of Id1 enhances expression of ICAM-1 and E-selectin, and induces angiogenic processes such as transmigration, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 expression, and tube formation in cultured vascular endothelial cells. 15575081_Idl protein may play an important role in the process of gastric carcinogenesis, and high-level Id I expression may be related to the malignant potential of tumor cells 15579766_Id1 is overexpressed in hyperplastic and neoplastic thyroid tissue and directly regulates the growth of thyroid cancer cells of follicular cell origin, but is not a marker of aggressive phenotype in differentiated thyroid cancer. 15645115_Id1, 2 and 3 might play a role in the early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis, but not in the development of advanced carcinoma, and might consequently be related to HCC dedifferentiation 15694377_Thus, we speculate that the regulation of cell growth mediated by CASK may be involved in Id1. 15701714_constitutive expression of Id1 inhibits eosinophil development, whereas in contrast neutrophil differentiation was modestly enhanced 15744343_These results indicate ID1 and ID2 are important retinoic acid responsive genes in acute promyelocytic leukemia [APL], and suggest that inhibition of specific bHLH transcription factor complexes may play a role in the therapeutic effect of ATRA in APL 15877825_In mature human B cells, BMP-6 inhibited cell growth, and rapidly induced an upregulation of Id1. 15905202_Downregulation of Id-1 may be a novel target to inhibit the growth of metastatic cancers through the suppression of angiogenesis. 16002046_Furthermore, by using DCs derived from Id1(-/-) mice that are defective in Flt-1 signaling, we demonstrated that the inhibitory function of VEGF on DC function is most likely mediated by Flt-1. 16007194_degradation is modulated by E12 and E47 16029118_Id1 gene expression may be associated with thyroid cancer cell growth and differentiation. 16115231_Expression of Id1 in HM was significantly higher than that in normal placenta. 16123120_Id-1 protein may be regulated by TNFalpha through the ubiquitin/proteasome degradation pathway and the stability of the Id-1 protein appears to correlate with the sensitivity of TNFalpha-induced apoptosis 16189525_study supports a significant role of the ID1 protein in melanoma progression and patient prognosis; inverse relation between ID1 and TSP-1 expression support an important role of ID1 in regulation of this complex multitarget protein. 16271072_Id1, 3 double-knockdown significantly impaired the ability of gastric cancer cells to form peritoneal metastasis 16287090_results indicate that increased Id-1 expression in prostate cancer cells may play a protective role against apoptosis, and downregulation of Id-1 may be a potential target to increase sensitivity of taxol-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells 16469432_Id-1 overexpression is associated with breast tumor angiogenesis 16506209_Study provides evidence for the first time that Id-1 plays a role in both proliferation and survival of esophageal cancer cells. 16525633_Up-regulation of Id-1 was associated with increased EGFR expression, clinical staging and the invasion ability of bladder cancer cells, and inactivation of Id-1 may be a potential therapeutic target to inhibit the invasion by bladder cancer cells. 16552541_The IGFBP3, hRas, JunB, Egr-1, Id1 and MIDA1 genes were up-regulated in psoriatic involved skin compared with uninvolved skin. 16682435_ID proteins (ID1, ID2, ID3 and ID4) were significantly increased in Mecp2-deficient Rett syndrome brain, ID genes are ideal targets for MeCP2 regulation of neuronal maturation that may explain the molecular pathogenesis of Rett syndrome 16894355_Interferon-alpha downregulates ID1 ID in cultured human vascular endothelial cells 17072841_Expression of ID1 decreased significantly in chondrocytes while the opposite was seen in mesenchymal stem cells. 17102133_expression of ATF-3 in hypoxic cells represses Id-1 and prevents their loss 17145808_Id-1 is a novel angiogenic factor for HCC metastasis and down-regulation of Id-1 may be a novel target to inhibit HCC metastasis through suppression of angiogenesis. 17202424_Id1 transcriptional inhibitor is a crucial player in mediating cell dedifferentiation of renal tubular epithelium and suggest that epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a multistep process. 17426247_In conclusion, we provide the molecular mechanism of the cross talk between HIF-1alpha and Id-1, which may play a critical role in tumor angiogenesis. 17537403_PLZF upregulates apoptosis-inducer TP53INP1, ID1, and ID3 genes, and downregulates the apoptosis-inhibitor TERT gene 17565736_Id1 expression is primarily regulated at the transcriptional level in radial growth phase melanomas and expect that therapies that target Id1 gene expression may be useful in the treatment of Id-associated malignancies. 17599389_significantly enhanced expression of Id-1 has been detected in malignant prostate cell lines and in primary carcinomas; the increase in Id-1 expression was significantly associated with the increasing Gleason score of carcinomas 17855368_caveolin-1 is a novel Id-1 binding partner that mediates the function of Id-1 in promoting prostate cancer progression through activation of the Akt pathway leading to cancer cell invasion and resistance to anticancer drug-induced apoptosis 17891176_Dysregulates centrosome homeostasis at least in part by interfering with S5A/Rpn10 activities at the centrosome. 17916352_a novel tumorigenic role of Id-1 through reorganization of actin cytoskeleton and disassembly of cell-cell adhesion in response to TGF-beta1 in human prostate epithelial cells 18000500_The Id-1 may promote distant metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma(ESCC), and both Id-1 may be used for prognostication for ESCC patients. 18072288_These data demonstrate that BMP-6 promotes migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells, potentially through activation of Id-1 and MMP activation. 18158619_Id-1 regulates Bcl-2 and Bax expression through p53 and NF-kappaB in MCF-7 breast cancer cells 18202790_Id-1 overexpression plays an important role in colorectal cancer progression. 18240291_Id1 may contribute to the malignant conversion of primary human melanocytes through extension of cellular lifespan. 18353975_The association of Id1 and Cdh1 is dependent on the canonical destruction box motif of Id1, the increased binding of which may compete with the interaction between Cdh1 and Aurora A, leading to stabilization of Aurora A in Id1-overexpressing cells. 18372912_a novel function of Id-1 in promoting chromosomal instability through modification of APC/C activity during mitosis and provide a novel molecular mechanism accounted for the function of Id-1 as an oncogene. 18413773_Id1 may contribute to early breast cancer by promoting excessive proliferation through cyclin D1. 18436795_The integration of signals at the level of Id gene expression may contribute to the pathogenesis of familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. 18542061_Id1 immortalizes hematopoietic progenitors in vitro and promotes a myeloproliferative disease in vivo. 18556654_ID1 is an effector of the p53-dependent DNA damage response pathway. 18559972_Id1 is an important target of constitutively activated tyrosine kinases and may be a therapeutic target for leukemias associated with oncogenic tyrosine kinases. 18583319_Id1 inhibited DNA binding by Dril1, and the two proteins co-localized in vitro and in vivo, providing a potential mechanism for suppression of fibrosis by Id1 through inhibition of the profibrotic function of Dril1. 18648363_study reports that the expression of the E6 onco-protein of the high-risk human papillomaviruses is correlated with Id-1 overexpression in the majority of invasive breast cancer tissue samples studied 18674781_These results demonstrated a novel function of Id-1 in regulating HBX protein stability through interaction with the proteasome. 18752043_Inhibitor of DNA binding-1 overexpression is associated with prostate cancer. 18922905_both ATF3 and Smad were crucially and synergistically involved in down-regulation of Id-1, which regulated JNK phosphorylation in REIC/Dkk-3-induced apoptosis. 19002177_In uterine cervical cancer, ID-1 might work on tumour advancement through angiogenic activity. ID-1 expression correlated with microvessel counts and with histoscore. 19014499_Id-1, took part in development and progression of colorectal carcinomas and that Id-1 was associated with regulations of EGFR and VEGF. 19031736_The expression of ID1 gene was up-regulated in ATRA-induced NB4 cells and APL cells from two patients and was independent of other protein synthesis. 19079342_Id-1 is a novel PTEN inhibitor that could activate the Akt pathway and its downstream effectors, the Wnt/TCF pathway and p27(Kip1) phosphorylation 19079362_Id1 can be strongly up-regulated by Transforming Growth Factor beta1 in the human mammary gland epithelial cell line MCF10A. 19201527_Id-1 expression in androgen-dependent prostate cancer was negatively regulated by androgen in a receptor-dependent way. 19217708_ERbeta1 inhibits breast cancer cell growth through binding with Id1 and upregulating p21 gene expression. 19288008_up-regulation of Id-1 in bladder cancer cells lead to increased cell viability in response to epirubicin by its improved anti-apoptotic role. 19330020_Targeting Id dimerization may therefore be effective for triggering differentiation and restraining neuroblastoma cell tumorigenicity. 19423615_Neuroblastoma cell adaptation to hypoxia involves the modulation of HIF1alpha and VEGF expression, nuclear translocation of ID1 and ID2 transcription factors, and activation of a gene expression program consistent with pro-metastatic events. 19438642_These data suggest that high-risk human papillomaviruses can enhance the progression of human cervical cancer through Id-1 regulation. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19491902_High ID1 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis and peritoneal dissemination in gastric cancer. 19515385_role in the development of peritoneal metastasis of pancreatic cancer 19551863_Id-1 overexpression is associated with esophageal cancer. 19567783_Examined regulatory mechanisms of p16 expression. Exogenously expressed Id1 suppressed up-regulation of p16 by Hepatocyte growth factor and the antiproliferative effect of HGF. Knockdown of Id1 sig. enhanced activity of the p16 promoter with ERK. 19571317_ID1 promotes expansion and survival of primary erythroid cells and is a target of JAK2V617F-STAT5 signaling 19643984_High Id1 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 19644139_data suggest that targeting the ID1 and C/EBPalpha transcriptional regulators may be of benefit in the design of novel therapies for low-risk myelodysplasia. 19710505_These results implicate Id1 and TSP1 as downstream mediators of Epac/Rap1, inhibitory regulators of the angiogenic process 19766362_may have important roles in the development of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma 19843640_Abl interactor 1 regulates Src-Id1-matrix metalloproteinase 9 axis and is required for invadopodia formation, extracellular matrix degradation and tumor growth of human breast cancer cells 19906510_Positive Id-1 expression is associated with high malignancy/poor prognosis. Protein expression status may help assess tumor malignancy and patient prognosis. 19926394_Anti-proliferative and chemosensitization effect of gamma-tocotrienol on breast cancer cells cells may be mediated through downregulation of Id1 protein. 19951400_KLF17 has a role in transcriptional regulation of metastasis by Id1 [review] 20003244_ID-1 increased in ovarian cancer cells during tumor progression 20010941_In prostate cancer cells, Id-1 has the ability to modulate bone cell differentiation favouring metastatic bone disease. 20070914_shows that not only ectopic expression in tissue culture but endogenous levels of ID1 modulate centrosome numbers. 20080245_The level of Id-1 protein expression was associated with the malignant potential of gastric tumors 20186495_Id1 promotes cancer/tumor morphology, cell cycle and epithelial to mesenchymal transition by influencing AP1, tnf, tgfbeta, PdgfBB and estradiol pathways. 20191379_Id1/3 peptide aptamer could represent a nontoxic exogenous agent that can significantly provoke antiproliferative and apoptotic effects in breast cancer cells, which are associated with deregulated expression of Id1 and Id3. 20388787_ID1 enhances docetaxel cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells through inhibition of p21 20484992_Id1 activation may need to occur at discrete stages in cooperation with additional gene dysregulation to repress and induce epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes during melanoma progression. 20515335_Supratentorial PNETs expressed significantly higher levels of SOX2, NOTCH1, ID1, and ASCL-1 transcripts. 20522807_Prostacyclin analogues inhibited smooth muscle cell proliferation and prevented progression of pulmonary hypertension while enhancing Smad1/5 phosphorylation and Id1 gene expression. 20574154_Id-1 expression is at least partially regulated by HBx and may serve as a potential prognostic marker for HBV-related HCC. 20697353_Id1 may contribute to tumor development through Polycomb group -mediated epigenetic regulation. 20709421_ID1 was expressed in the nucleus in 70% of squamous cell carcinomas and 50% of non-squamous cell carcinomas and in vascular endothelium of non-tumor tissue 20863724_in human liver, not only HAMP, but also SMAD7 and Id1 mRNA significantly correlate with the extent of hepatic iron burden. However, this correlation is lost in patients with HFE-HC, but maintained in subjects with non-hemochromatotic iron overload. 20881502_Silencing of the Id1 gene has an in-vivo preventive effect against the development of prostate cancer in a mouse model. 20887552_Id1 contributed to hyperproliferation of keratinocytes via enhancement of cell cycle progression, removal of cell cycle inhibition, and simultaneously increased keratin production. 21106423_Id-1 proteins were overexpressed in human mammary invasive ductal carcinoma and were increased from benign to premalignant and malignant lesions. 21106425_significant role of Id-1 protein in the gastric tumorigenesis 21467165_MUC18 is involved in cell signaling regulating the expression of Id-1 and ATF-3, thus contributing to melanoma metastasis 21486943_Study uniquely identifies ID1 and ID3 as negative regulators of the hPSC-hematopoietic transition from a hemogenic to a committed hematopoietic fate, and demonstrates that this is conserved between hESCs and hiPSCs. 21506108_Induction of Id-1 by FGF-2 involves activity of EGR-1 and sensitizes neuroblastoma cells to cell death. 21536374_Nude mice study further confirmed an increased tumor growth in Id1-overexpressing cells and a decreased tumor growth in Id1-knockdowned cells. In conclusion, inactivation of Id1 may provide a novel strategy for treatment of lung cancer patients 21606196_Data show that ID1 is induced by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in a panel of NSCLC cell lines and primary cells from the lung. 21630092_These results demonstrate that Id1-induced beta1-integrin expression in endothelial cells and the function of Id1 in cell migration and tubulogenesis are dependent on p53. 21670698_Inhibitor of differentiation 1 expression is correlated to human papillomavirus infection in cervical carcinoma. 21688151_ID-1 is implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of gastric cancer. 21701587_Study revealed that Id1 interacts with LMP1 by binding to the CTAR1 domain of LMP1. N-terminal region of Id1 is required for the interaction with LMP1. 21732357_Results suggest that IL-3 plays an inhibitory role in osteoclast differentiation by regulating c-Fos and Id1, and also exerts anti-bone erosion effects. 21896993_Id1 could be considered as a prognostic predictor for stage III esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 21921026_Bone morphogenetic proteins and ID1 exerted an anti-apoptotic effect in mesangial cells by inhibition of USF2 transcriptional activity. 21921784_Malignant rhabdoid tumors express many stem cell-associated transcription factors, which may be regulated by the expression of EZH2 and the Id family of proteins. 21955753_These results indicate that increased migration of MDA-MB-231 cells following cyclin D1 silencing can be mediated by Id1 and is linked to an increase in EMT markers. 21993163_Older muscle contained significantly more transcript for Forkhead Box O 1 (FoxO1, p=0.001), Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1, p=0.009), and Inhibitor of DNA Binding 3 (ID3, p=0.043) than young muscle. 22076920_Silencing of Id-1 protein inhibited the growth of A375 cells. 22139627_Acheron regulates vascular endothelial proliferation and angiogenesis together with Id1 during wound healing. 22226665_Results suggest that inhibitor of differentiation or DNA binding -1 (Id-1) may play roles in tumor progression and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) activation in bladder cancer. 22278018_Id1 shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm, and promotes peritubular inflammation and tubular epithelial dedifferentiation, suggesting that these two events are intrinsically coupled during renal fibrogenesis. 22301282_combined analysis of Id-1 and NF-kappaB/p65 can be useful for identifying patients at risk for unfavorable clinical outcomes. Id-1 or/and NF-kappaB/p65 enhanced tumor cell migration, which is associated with the secretion of MMP-9 22393458_Notch activation provides Id1-expressing tumor cells with selective advantages in growth and survival 22480390_High level of ID-1 expression suggested poor prognosis for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22580608_using Bcl-3 knockdown in prostate cancer cells, identified the inhibitor of DNA-binding (Id) family of helix-loop-helix proteins as potential Bcl-3-regulated genes 22592405_It was shown that the ID1-p65 interaction modulates activation of the NF-kappa B signaling pathway. By affecting p65 nuclear translocation, ID1 was essential in regulating p65 recruitment to the promoter of cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2. 22684559_These results indicate that Id1 may down-regulate the ability of PC3 cells to form osteolytic lesions in vivo and the signal pathway needs to be further investigated. 22698403_Data show that regulation of p21 by ID1 and ID3 is a central mechanism preventing the accumulation of excess DNA damage and subsequent functional exhaustion of cancer-initiating cells (C-ICs). 22781717_High expression level of ID1 gene was mostly seen in acute myeloid leukemia patients with adverse cytogenetics and older age (age >/= 60 years), and might be associated with poor prognosis. 22819717_shRNA knockdown of ID1 attenuates androgen-stimulated hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion. 23060149_These findings suggest an essential role of Id1 and Id3 in TGFbeta1 effects on proliferation and migration in prostate cancer cells. 23243024_Our results suggest that Id-1 regulates multiple tumor-promoting pathways in glioblastoma 23308043_Results suggests a definite role for Id1 in mediating nicotine-induced proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. 23311395_Id1 and Id3 co-expression seems associated with a poor clinical outcome in patients with locally advanced NSCLC treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy 23342268_increased Id1 and Id3 expression attenuates all three cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKN2B, -1A, and -1B) resulting in a more aggressive PCa phenotype. 23377983_these results suggest that ID1 may be a new prognostic marker for Glioblastoma multiforme 23555842_E47 interacts with Id1 in E47 overexpressing MDCK cells that underwent a full epithelial-mesenchymal transition as well as in mesenchymal breast carcinoma and melanoma cell lines 23558671_inhibitor of differentiation-1 is expressed during fetal embryogenesis and in different mouse and human cancer types 23645773_Higher ID1 expression was associated with advanced breast cancer. 23714001_Id1 can enhance EPC angiogenesis in ovarian cancer, which is mainly mediated by the PI3K/Akt and NF-kappaB/MMP-2 signaling pathways 23723304_This study revealed that there was a positive correlation between Id-1 expression and the expression of p-Akt, p-GSK3beta and p-HSF1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23771884_Id proteins, and particularly Id1 and Id3, are critical downstream effectors of BMP signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell. 23872946_Ectopic expression of ID proteins partially rescues the senescence-like phenotype induced by loss of DPY30. 23900621_EGCG induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of poorly differentiated AGS gastric cancer cells, and Id1 may be one of the target genes regulated by EGCG in cancer inhibition. 24129125_Higher Id1 mRNA expression levels might predict a higher hazard ratio for progression and a shorter disease-free survival in prostate cancer. 24133588_Id-1 is considered to be a candidate for new therapeutic target and a prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer. 24295493_The results demonstrate that Id-1B decreases the malignancy of lung and prostate cancer cells and counteracts the protumorigenic role of the classical form of Id-1. 24332369_Id1 induces mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and pulmonary metastatic colonization by antagonizing Twist1 activity. 24378760_ID1 is a synthetic sick/lethal gene that interacts with the R175H TP53 mutant. 24403496_High ID-1 expression is associated with high microvessel density in ovarian cancer. 24434151_Investigated the effect of Id1 on TGF-beta-induced collagen expression in dermal fibroblasts. When Id1-b isoform was overexpressed, TGF-beta-induced collagen expression was markedly inhibited. 24480377_ID1 expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma was associated with angiogenesis as measured by microvessel density. 24572994_Results show that Id1 and NF-kappaB regulate the expression of CD133 and BMI-1 in an additive or synergistic manner in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24599583_Inhibitor of differentiation 1 is a prognostic marker for multicentric Castleman's disease. 24599933_Data indicate that the inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (Id1)-IGF-II-IGF-IR-AKT signaling cascade plays an important role in esophageal cancer progression. 24620998_We conclude that Id1 is potently angiogenic and can be up-regulated in endothelial progenitor cells 24628854_Id-1 cooperates with HPV E6E7 proteins, which involves inactivation of p53 and pRb in host cells, to promote cervical carcinogenesis. 24662327_Id-1, a protein repressed by miR-29b, facilitates TGFbeta1-induced EMT in human ovarian cancer cells and represents a promising therapeutic target for treating ovarian cancer. 24695670_Id1 as an important modulator of molecular events during DPSC commitment and differentiation, which should be considered in dental research on tissue engineering. 24804700_Studies demostrated the regulatory role of ID1 in the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 24861919_Id-1 and TGF-beta1 played important roles in the progression of gastric cancer, in which Id-1 might act as a downstream mediator of TGF-beta1 signaling through a regulatory mechanism involving N-cadherin and beta-catenin. 24948111_Our results suggest that Id1 promotes breast cancer metastasis by the suppression of S100A9 expression 24970809_Data indicate that grap2 and cyclin D1 interacting protein (GCIP) and inhibitor of of DNA binding/differentiation 1 (Id1) are inversely expressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines and specimens. 25010525_Smad1 as a novel binding protein of KSHV latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA). LANA interacted with and sustained BMP-activated p-Smad1 in the nucleus and enhanced its loading on the Id promoters. 25028095_Overexpression of ID1 in two different cell lines induced STMN3 and GSPT1 at the transcriptional level, while depletion of ID1 reduced their expression. 25031707_This study elucidated the potential mechanism underlying Id1 participation in the progression of prostate cancer 25323535_LIF has a role in negatively regulating tumour-suppressor p53 through Stat3/ID1/MDM2 in colorectal cancers 25344919_NSCLC cells with high Id1 protein expression were vulnerable to the treatment of paclitaxel and cisplatin 25449776_High Id1b, generated by alternative splicing, maintains cell quiescence and confers self-renewal and cancer stem cell-like properties. 25496992_berberine's anti-proliferative and anti-invasive activities could be partially rescued by Id-1 overexpression in HCC models, revealing a novel anti-cancer/anti-invasive mechanism of berberine via Id-1 suppression. 25514034_ERbeta1 inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells and upregulated E-cadherin expression in a Id1-dependent manner. 25549282_Downregulation of ID1 by gene silencing can lead to acceleration of TGF-beta1-induced hESC differentiation into ECs and inhibition of proliferation and migration of ECs. 25778840_Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) acts as an inhibitor of ID-1, -2 and -3 and promotes basic helix loop helix (bHLH) E47 DNA binding and transcriptional activity. 25924227_Advanced melanoma patients, relative to healthy controls, express much higher levels of ID1 in myeloid peripheral blood cells. 25938540_these findings provide in vivo genetic evidence of Id1 functions as an oncogene in breast cancer 26072160_Four more genes (BMP4, BMPR1B, SMAD1 and SMAD4) of the ID1 pathway were investigated and only one (BMPR1B) shows the same down regulation 26191235_ID1 overexpression may be associated with higher risk karyotype classification and act as an independent risk factor in young non-M3 acute myeloid leukemia patients. 26475334_Our findings define an intricate E2F1-dependent mechanism by which Id1 increases thymidylate synthase and IGF2 expressions to promote cancer chemoresistance. The Id1-E2F1-IGF2 regulatory axis has important implications for cancer prognosis and treatment. 26577912_Peritoneal VEGF-A expression is regulated by TGF-beta1 through an ID1 pathway in women with endometriosis 26797271_Therefore, we identified a tumorigenic role of Id-1 in OS and suggested a potential therapeutic target for OS patients. 26858249_Simultaneous high expression of ID1 and c-Jun or c-Fos was correlated with poor survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 27044543_Results show that ID1, ID3 and IGJ genes are highly expressed in adult B-ALL and correlate with poor prognosis in Hispanic patients. 27087608_Reducing ID1 gene expression reduces metastatic spread of salivary gland neoplasms. 27466488_ID1 down-regulation induced parallel changes in the IGF and AKT pathways. The crosstalk of these pathways may enhance malignant phenotypes in salivary gland cancer. 27477274_a loss of CULLIN3 represents a common signaling node for controlling the activity of intracellular WNT and SHH signaling pathways mediated by ID1 27546618_High ID1 expression is associated with breast cancer. 27610466_MVD was determined by immunohistochemistry, and the expressions of mRNA and protein of inhibitor of differentiation-1 (ID1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were detected in gastric cancer. 27633352_High ID-1 expression is associated with colorectal carcinoma. 27978873_ID1 expression was positively related to drug resistance of EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer. 28510612_ID1 expression impacts the sensitivity of colon cancer cells to 5-FU and may be considered as a potential predictive marker in colorectal carcinoma treatment. 28549790_Id1 enables lung cancer liver colonization by activating an epithelial mesenchymal transformation program in tumor cells and establishing the pre-metastatic niche. 29039489_ID1 expression was associated with the proliferation, invasion and migration of SACC cells. The observed inhibition of SACC cell growth, invasion and migration following knockdown of ID1 expression in the present study, may have been due to restoration of the balance between oncogenic and tumor-suppressive effects resulting from changes in the expression of downstream genes or associated proteins. 29079782_CaMKII can directly phosphorylate Beclin 1 at Ser90 to promote K63-linked ubiquitination of Beclin 1 and activation of autophagy; it also promotes K63-linked ubiquitination of inhibitor of differentiation 1/2 (Id-1/2) by catalyzing phosphorylation of Id proteins and recruiting TRAF-6 29159326_The mutual correlation between the expression level of TWIST1 and ID |
ENSMUSG00000042745 |
Id1 |
82.156495 |
0.2014156467 |
-2.311752 |
0.208437444 |
132.106421 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000141809647914439036153932843108097467537588267369698607933950919120490399475922231944946538817475811811164021492004394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000018457763696800002487588623483389417198866601172982892541423191071082531131055531892215526568179484456777572631835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.0322700 |
3.7132601 |
135.2351637 |
10.5602370 |
| ENSG00000126215 |
7517 |
XRCC3 |
protein_coding |
O43542 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the homologous recombination repair (HRR) pathway of double-stranded DNA, thought to repair chromosomal fragmentation, translocations and deletions. Part of the RAD51 paralog protein complex CX3 which acts in the BRCA1-BRCA2-dependent HR pathway. Upon DNA damage, CX3 acts downstream of RAD51 recruitment; the complex binds predominantly to the intersection of the four duplex arms of the Holliday junction (HJ) and to junctions of replication forks. Involved in HJ resolution and thus in processing HR intermediates late in the DNA repair process; the function may be linked to the CX3 complex and seems to involve GEN1 during mitotic cell cycle progression. Part of a PALB2-scaffolded HR complex containing BRCA2 and RAD51C and which is thought to play a role in DNA repair by HR. Plays a role in regulating mitochondrial DNA copy number under conditions of oxidative stress in the presence of RAD51 and RAD51C. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14716019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20413593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23108668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23149936}. |
Acetylation;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the RecA/Rad51-related protein family that participates in homologous recombination to maintain chromosome stability and repair DNA damage. This gene functionally complements Chinese hamster irs1SF, a repair-deficient mutant that exhibits hypersensitivity to a number of different DNA-damaging agents and is chromosomally unstable. A rare microsatellite polymorphism in this gene is associated with cancer in patients of varying radiosensitivity. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7517; |
chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; Rad51C-XRCC3 complex [GO:0033065]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity [GO:0140664]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; double-strand break repair via synthesis-dependent strand annealing [GO:0045003]; interstrand cross-link repair [GO:0036297]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint [GO:0090267]; regulation of centrosome duplication [GO:0010824]; resolution of mitotic recombination intermediates [GO:0071140]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; t-circle formation [GO:0090656]; telomere maintenance via recombination [GO:0000722]; telomere maintenance via telomere trimming [GO:0090737]; telomeric loop disassembly [GO:0090657] |
10541549_XRCC3 promotes homology-directed repair of DNA double-strand breaks in mammalian cells 11059748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11285194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11304692_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11532866_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12023982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082022_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12115490_Mutation in XRCC3 gene may be associated with increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck neoplasms 12115490_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12223443_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12376526_no evidence seen that XRCC3 241Met variant significantly associated with increased risk of cutaneous malignant melanoma in case-control study 12393447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12393447_The genotype distribution of the XRCC3 gene does not indicate a role for base excision repair in the development of therapy-related acute myeloblastic leukemia 12565173_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12565173_Polymorphisms of XRCC1 and XRCC3 genes and susceptibility to breast cancer. 12815008_The XRCC3 T241M polymorphism is associated with risk of breast cancer. XRCC3 participates in the repair of DNA damage. 12869411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12917199_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14511439_frequency of flat or raised moles is associated with polymorphism at or near this DNA repair gene and certain alleles are associated with less efficient DNA repair and greater nevus density 14534887_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14578164_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14643949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14652281_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14652287_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14688016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14729591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009726_no evidence therefore that the T allele of this XRCC3 polymorphism is indicative of susceptibility to melanoma but there was a marginal relationship with nevus phenotype 15010895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15019159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15066914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15066923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15102670_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15126335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15184273_Finds no association between XRCC3 T241M and two intronic XRCC3 polymorphisms and risk of colorectal adenoma. 15199549_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15292210_The level of XRCC3 protein was sharply reduced in Rad51C-depleted HeLa cells, suggesting that XRCC3 is dependent for its stability upon heterodimerization with Rad51C 15312685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15313891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15333465_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15354414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15354414_Polymorphism of XRCC3 is associated with colorectal cancer 15372620_Xrcc3 forms distinct foci in human cells and that nuclear Xrcc3 begins to localize at sites of DNA damage within 10 min after radiation treatment. 15386379_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15450429_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15459223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15468052_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15491645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15679883_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15679883_The role of a genetic polymorphism of the XRCC3 gene in risk for colorectal cancer was investigated. 15680411_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15734952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15737490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15746160_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15767338_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15824172_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15843498_Xrcc3 overexpression is associated with increased Rad51C protein levels consistent with the known interaction of these two proteins 15878096_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15878910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15887211_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15887293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15914210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15914277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15933498_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15971256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15971256_the XRCC1 280His and XRCC3 241Met alleles affect individual chromosomal aberration levels, most probably via influencing the DNA repair phenotype 15990020_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15992842_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16002061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16030112_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16037119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16137195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16195237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16214912_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16234265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16271954_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16271954_XRCC3 T241M polymorphism and family history of cancer may be risk factors for colorectal cancer, and the XRCC3 241Met allele may be an effective biomarker for genetic susceptibility. 16284380_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16284386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16308313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16343742_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16357593_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16369171_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16373199_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16407418_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16425350_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16475125_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16485136_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16492913_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16492913_polymorphic variation in the XRCC3 gene, but not in ERCC2 or XRCC1, may be of importance for susceptibility to follicular lymphoma, perhaps primarily in current smokers 16501254_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16505003_Mitotic defects in XRCC3 variants T241M and D213N and their relation to cancer susceptibility 16510122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16540687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16542436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551674_XRCC1, XRCC3, GSTM1 and GSTT1 polymorphisms and chromosome damage are higher in welders than in a control group 16564556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16571649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16609022_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16621732_FANCG was found to interact with XRCC3, and this interaction was disrupted by the FA-G patient derived mutation L71P. 16622263_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16638864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16652373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16707649_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16728435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791138_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791138_Our meta-analysis results support that the XRCC3 might represent a low-penetrance susceptible gene especially for cancer of breast, bladder, head and neck, and non-melanoma skin cancer. 16824555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16940014_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16963196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16966185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16981340_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16981340_XRCC3 variated genotype was one of the risk factors of cardia cancer while different risks of factors might exsit between cardia and non-cardia gastric cancer. 16997330_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17018785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17034901_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17034901_Our results show that the genetic variation in XRCC1, XRCC3 and NBS1 influence lung cancer susceptibility among women, and that combinations of risk alleles in the two HR genes can enhance the effects. 17063276_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17063279_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17063279_Polymorphism of XRCC3 codon 241 Thr/Met is unlikely to have a substantial overall association with increased breast cancer risk in Korean women 17078101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17114795_the RAD51C-XRCC3-associated Holliday junction resolvase complex associates with crossovers and may play an essential role in the resolution of recombination intermediates prior to chromosome segregation 17116943_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17116943_XRCC1-01, XRCC3-01, and CCND1-01 may be predictive of survival outcome in patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with DNA-damaging chemotherapy 17131345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17158087_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17159780_Increased susceptibility to genotoxic agents with polymorphisms in DNA repair genes XRCC3. 17159780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17164360_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17177211_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17191090_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17197435_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17351336_A decrease in the expression of XRCC3 leads to accumulation of DNA breaks and induction of cell death. 17374967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17401013_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17410042_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17476281_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17535647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17535647_Patients with XRCC3 18067T variant allele are tolerant to benzene poisoning. 17549067_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17557904_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17605237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17614221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17617021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17627014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17630853_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17685459_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17701750_Fndings suggest that the XRCC3 Thr241Met polymorphism is likely to play a modifying role in the individual susceptibility to breast cancer among Thai women as already shown for women of European ancestry. 17701750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17705814_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17712032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17898541_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17901044_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17901044_Variation in DNA repair genes XRCC3, XRCC4, XRCC5 and susceptibility to myeloma. 17953974_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17971348_Evidence that the combination of different DNA repair genes (hOGG1, XRCC1 and XRCC3) and their interaction with environmental genotoxic agents may modulate micronuclei induction. 17971348_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17986315_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17986315_polymorphism may be one of the genetic modifiers for smoking-related pancreatic cancer 18033323_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18033323_patients heterozygous for the XRCC3 Thr241Met allele had improved post-induction disease-free survival compared to children homozygous for the major or minor allele 18046624_investigated the possible association of three SNPs, XRCC2 C41657T, XRCC2 G4234C and XRCC3 A17893G with susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma in a population of northern China 18067130_Multiplicative interaction of risk due to the MC1R variants and the common allele (high risk) of the T241M polymorphism in the XRCC3 gene. 18086758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18095557_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18095557_There could be a correlation between polymorphisms of XRCC3 and DNA repair capacity of DNA damage induced by benzene. 18188695_genetic variation in SNPs in XRCC1 and XRCC2 genes, but not XRCC3, may influence breast cancer susceptibility 18204928_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18212739_FANCG promotes formation of a newly identified protein complex containing BRCA2, FANCD2 and XRCC3. 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18300452_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18300452_XRCC3 Thr 241 Met plays an important role in the development of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma. 18330515_No significant association XRCC3 with brain tumors was found for any of the polymorphisms, but indicated possible associations between combinations of XRCC1 and XRCC3 SNPs and the risk of brain tumors. 18330515_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18335219_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18336773_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18365755_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18365755_The aim of the study was to investigate NAT1, NAT2, GSTM1, GSTT1, GSTP1, SULT1A1, XRCC1, XRCC3 and XPD genetic polymorphisms, coffee consumption and risk of bladder cancer (BC) through a hospital-based case-control study. 18410587_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18410587_combined XRCCs 1-4 polymorphisms associated with oral cancer risk 18448328_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18495522_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18504145_Findings support the hypothesis that the XRCC3 Thr241Met polymorphism may be associated with the risk of AFB1-related hepatocellular carcinoma among the Guangxi population. 18543213_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18543213_The results suggested that XRCC3 polymorphism may be associated with the risk of AFB1- related HCC among the Guangxi population, and interacts with AFB1 exposure in the development of HCC induced by AFB1. 18551366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18551366_Single nucleotide polymorphism in XRCC3 is associated with breast cancer. 18559563_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18559563_SMoking, XPD and XRCC# variants were the most important single-factor determinanats of risk for pancreatic cancer. 18579371_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18581889_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18582155_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18582155_single nucleotide polymorphisms in the SOD2, XRCC1 and XRCC3 genes are associated with the development of late radiation injury in patients treated with radiation therapy for prostate adenocarcinoma 18627000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18627000_Significant effects of XRCC3 241Met polymorphisms was seen on the initial repair of MMS-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes. 18630471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18701435_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18708406_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18712175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18752184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18756535_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18768166_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18824251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18829510_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18830263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18852222_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18852222_these results indicated that SLE leucocytes repair less efficiently the radiation-induced DNA damage, and DNA repair polymorphic sites may predispose to the development of particular clinical and laboratory features 18977234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18990748_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19027952_Frequencies of polymorphic variants of RAD51, XRCC3, NQO1, GSTA1, GSTM1, GSTT1, CYP3A4 and XPD enzymes were similar in patients and controls. 19027952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19031937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19031937_XRCC3 241Met allele was associated with an increased risk of lung and colorectal cancer. 19064565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19092295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19096231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116388_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19127255_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19177501_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19237606_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19251090_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19280628_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19286843_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19330829_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19330829_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the XRCC3 gene are associated with gliomas. 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19367277_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19393248_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19414392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19414392_XRCC3 T carriers had a protective role against bladder cancer. 19426727_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19426727_Results suggest that the variability of the DNA homologous recombination repair genes RAD51 and XRCC3 may play a role in breast cancer occurrence and progression, but this role may be underlined by a mutual interaction between these genes. 19429237_Evidence of gene-environment interaction betweenthe XRCC3 variant genotype and high toenail arsenic levels on bladder cancer risk was found. 19429237_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19481674_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19536092_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19549356_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19549356_The combined effect of NQO1C(609T), RAD51(G135C) and XRCC3(C241T) genotypes may promote occurrence of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19656722_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19661089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724896_results indicate that SNPs in DNA repair genes (XRCC3241 and XPD751) influence the ICS and together with the expression of EGFR, Hsp70, Bax, and Bcl-2, they could predict the cisplatin sensitivity of head and neck cancer cell lines. 19733688_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19733688_Polymorphisms in XRCC3 might contribute to the increased genetic damage in individuals occupationally exposed to chronic ionizing radiation. 19772428_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19789975_the XRCC3 Thr241Met T allele seems associated with elevated breast cancer risk in non-Chinese subjects 19815090_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19886181_Arg194Trp and Arg399Gln polymorphism of the XRCC1 gene as well as Trp241 Met polymorphism in XRCC3 may not be linked with appearance and development of breast cancer. 19886181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914098_There was no association between the XRCC3 single nucleotide polymorphism alleles and prostate cancer risk. 19915856_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915856_Meta-analysis: XRCC1 R194W and XRCC3 T241M polymorphisms had no association with colorectal cancer risk, whereas there was association between XRCC1 399QQ genotype and decreased risk. 19962393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20004634_may influence the repair capacity of breast cancer patients and, in turn, confer genetic predisposition to disease 20049524_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20049524_This meta-analysis suggests that the variant G allele of XRCC3 5'-UTR polymorphism is a low-penetrant risk factor for developing breast cancer, while the variant G allele of XRCC3 IVS5-14 polymorphism has a protective effect on breast cancer development. 20054644_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20054644_Polymorphisms in XRCC3 gene is associated with breast cancer. 20061190_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20140625_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in XRCC3is not associated with and breast cancer risk in Caucasian women 20150366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20199546_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20229274_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20229274_the XRCC3 241Met allele showed a protective tendency against rectal cancer (OR = 0.68, 95% CI 0.46-1.02) for both men and women. 20306073_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20331623_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20334523_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20429839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20462983_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20500515_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20500515_XRCC3 Thr241Met polymorphism may be weakly associated with the risk of bladder cancer. 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530453_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20549576_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20549576_the XRCC3 T241M polymorphism might influence gastric cancer risk oppositely in Asians and Caucasians. 20590474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20590474_homologous recombination (XRCC3) and nonhomologous end-joining (XRCC7) genes and conferring predisposition to prostate cancer 20601096_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20644561_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20687897_These results suggest that hINO80 assists double-strand break repair by positively regulating the expression of the Rad54B and XRCC3 genes. 20708344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20731661_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20804747_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20804747_our data showed that the C722T and the G135C polymorphisms of the XRCC3 and the RAD51 genes might be associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 20813000_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20817763_Observational study of gene-disease associati |
ENSMUSG00000021287 |
Xrcc3 |
181.571788 |
0.3508195888 |
-1.511199 |
0.189547618 |
62.250106 |
0.00000000000000302492690185686122313035775561849232639675196139539270490104172495193779468536376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000021000903608375951810830525223067416249958386589846703884632006520405411720275878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.1125537 |
18.7925774 |
287.1829546 |
38.5567097 |
| ENSG00000126262 |
2867 |
FFAR2 |
protein_coding |
O15552 |
FUNCTION: G protein-coupled receptor that is activated by a major product of dietary fiber digestion, the short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and that plays a role in the regulation of whole-body energy homeostasis and in intestinal immunity. In omnivorous mammals, the short chain fatty acids acetate, propionate and butyrate are produced primarily by the gut microbiome that metabolizes dietary fibers. SCFAs serve as a source of energy but also act as signaling molecules. That G protein-coupled receptor is probably coupled to the pertussis toxin-sensitive, G(i/o)-alpha family of G proteins but also to the Gq family (PubMed:12496283, PubMed:12711604, PubMed:23589301). Its activation results in the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, the mobilization of intracellular calcium, the phosphorylation of the MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2 kinases and the inhibition of intracellular cAMP accumulation. May play a role in glucose homeostasis by regulating the secretion of GLP-1, in response to short-chain fatty acids accumulating in the intestine. May also regulate the production of LEP/Leptin, a hormone acting on the central nervous system to inhibit food intake. Finally, may also regulate whole-body energy homeostasis through adipogenesis regulating both differentiation and lipid storage of adipocytes. In parallel to its role in energy homeostasis, may also mediate the activation of the inflammatory and immune responses by SCFA in the intestine, regulating the rapid production of chemokines and cytokines. May also play a role in the resolution of the inflammatory response and control chemotaxis in neutrophils. In addition to SCFAs, may also be activated by the extracellular lectin FCN1 in a process leading to activation of monocytes and inducing the secretion of interleukin-8/IL-8 in response to the presence of microbes (PubMed:21037097). Among SCFAs, the fatty acids containing less than 6 carbons, the most potent activators are probably acetate, propionate and butyrate (PubMed:12496283, PubMed:12711604). Exhibits a SCFA-independent constitutive G protein-coupled receptor activity (PubMed:23066016). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12496283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12684041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12711604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18801738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21037097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23066016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23589301}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the GP40 family of G protein-coupled receptors that are clustered together on chromosome 19. The encoded protein is a receptor for short chain free fatty acids and may be involved in the inflammatory response and in regulating lipid plasma levels. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:2867; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; cell surface pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002752]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; leukocyte chemotaxis involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002232]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; mucosal immune response [GO:0002385]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response to non-antigenic stimulus [GO:0002879]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002673]; regulation of peptide hormone secretion [GO:0090276] |
12393494_might play pivotal role in differentiation and immune response of monocytes and granulocytes 12684041_FFA2R is expressed on leukocytes and activated by short-chain fatty acids. 12711604_the highly selective expression of GPR43 in leukocytes, particularly polymorphonuclear cells, suggests a role in the recruitment of these cell populations toward sites of bacterial infection 16887331_GPR41 and 43 mediate SCFA signaling in mammary epithelial cells and thereby play an important role in their stress management. 17899402_Results indicate that the short chain fatty acid receptor, GPR43 is expressed by enteroendocrine L cells containing peptide YY in the human large intestine. 18801738_analysis of conserved polar residues in transmembrane domains V, VI, and VII of free fatty acid receptor 2 and free fatty acid receptor 3 are required for the binding and function of short chain fatty acids 19009545_In this review, the mechanism of receptor activation, pharmacology, and the physiological functions of the fatty acid binding receptors GPR40, GPR41, GPR43, and GPR119 are discussed. 19780758_upregulation of FFAR2 expression may contribute to malignant transformation. 20837008_Mutational analysis revealed several important residues located in transmembrane domains 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 for acetate binding. 20979106_Reduction of GPR43 expression is associated with colon cancers. 21037097_Collaboration among C-reactive protein, M-ficolin, and GPR43 under acidosis curtails interleukin (IL)-8 production, thus preventing immune overactivation during bacterial infection. 21216233_They report the results of mutagenesis studies on the receptor, and the identification of previous unknown residues that may affect receptor activation as well as residues important for allosteric interactions on FFA2. 21220428_Selective orthosteric free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) agonists: identification of the structural and chemical requirements for selective activation of FFA2 versus FFA3. 22712802_Propionate-stimulated GPR41 strongly coupled to ERK1/2 activation, while the coupling of linoleic acid-activated GPR40 and acetate-activated GPR43 was weaker. 22919070_Data indicate that a single mutation in human FFA2 of C4.57G resulted in a human FFA2 receptor with ligand selectivity similar to the bovine receptor. 23066016_Extracellular ionic locks determine variation in constitutive activity and ligand potency between species orthologs of the free fatty acid receptors FFA2 and FFA3 23985900_GPR43 modulates NF-kappaB activity via beta-arrestin 2. 24458110_[review] In vivo and in vitro studies suggest that short-chain fatty acid receptors (SCFAs) stimulate gut hormone secretion; therefore, the SCFA-FFA signal is likely to be important for gut physiological functions. 25298143_FFAR2 is a potential therapeutic target of T1 diabetes, representing a link between immune response and glucose homeostasis. 25581519_FFAR2 is expressed in pancreatic beta cells and mediates an inhibition of insulin secretion by coupling to Gi-type G proteins. 25633224_GPR43 expression is reduced in monocytes upon siRNA-knockdown of XBP1, while A549 cells overexpressing XBP1 displayed elevated GPR43 levels. 26023106_GPR3 agonism potentiates insulin secretion in isolated islets. 26075576_FFAR2 signaling occurs by divergent G protein pathways. 26518871_Although both agonist and antagonist ligands contain negatively charged carboxylates that interact with two key positively charged arginine residues in transmembrane domains V and VII of FFA2, there are clear differences in how these interactions occur. 26808470_the results of mutagenesis studies based on the crystal structure of hFFA1 bound to TAK-875 at 2.3 A resolution to identify important residues for orthosteric agonist 6e inducing FFA2 activation. 26921846_Compared with the control group, the densitometric quantification and mean density of GPR43 and ChAT proteins, and expression of GPR43 and CHAT genes, were significantly decreased in the patients with mixed refractory constipation. 27385588_FFA2 processes mediated by Gi signaling, whereas, in concert with blockade by the Gq/G11 inhibitor FR900359, the inability of AZ1729 to mimic or regulate propionate-mediated release of GLP-1 from mouse colonic preparations defined this physiological response as an end point transduced via activation of Gq/G11. 28075383_a single dose of soluble fibre was able to significantly reduce airway inflammation in stable asthma by downregulating GPR43 and GPR41 28322790_Short-chain fatty acids lowered TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression by reducing phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK in a GPR41/GRP43-dependent manner in renal cortical epithelial cells. 28883043_FFAR2 and FFAR3 interact to form a heteromer in primary monocytes and macrophages via proximity ligation assay, and during heterologous expression in HEK293 cells via bimolecular fluorescence complementation and fluorescence resonance energy transfer. FFAR2 and FFAR3 may interact to form a receptor heteromer with signaling that is distinct from the parent homomers. 29061999_single extracellular amino acid in Free Fatty Acid Receptor 2 defines antagonist species selectivity and G protein selection bias 29338778_Data suggest that the free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2/GPR43 receptor) plays an integral role in survival during and after sepsis. 29477577_we show functional similarities but also some important differences between GPR84 and FFA2R in human phagocytes, thus providing some mechanistic insights into GPR84 regulation in blood neutrophils and cells recruited to an aseptic inflammatory site in vivo. 30203438_FFAR2 directly mediates both the stimulatory effects of Sodium acetate and Sodium propionate on insulin secretion and their protection against islet apoptosis. We have also shown that Short chain fatty acids coupling in islets occurs via Gq-coupled intracellular signaling. 30546040_This study characterises enantiomers of functionally selective ligands for FFA2 in cells stably expressing hFFA2. It highlights the novel roles of selective FFA2 enantiomers 4CMTB and 2CTAP on Ca(2+), pERK1/2 and cAMP and their roles as allosteric modulators which, may assist in efforts to design novel therapeutic agents for FFA2-driven inflammatory diseases. 30836015_Increased expression of FFAR2 is associated with uterine cervical neoplasia. 31487233_Metabolic and physiological role of FFAR1 (GPR40), FFAR4 (GPR120), FFAR3 (GPR41) and FFAR2 (GPR43) is REVIEWED. 31628054_Our findings suggest that Ffar2 regulates colonic ILC3 proliferation and function, and they identify an ILC3-receptor signaling pathway modulating gut homeostasis and pathogen defense. 31694949_findings demonstrate that the FFAR2 signaling cascade is important for the efficient endocytosis of IAV into host cells. 31734354_C. butyricum decreased the fecal secondary BA contents, increased the cecal SCFA quantities, and activated G-protein coupled receptors (GPRs), such as GPR43 and GPR109A. The analysis of clinical specimens revealed that the expression of GPR43 and GPR109A gradually decreased from human normal colonic tissue to adenoma to carcinoma 32803826_Allosteric targeting of the FFA2 receptor (GPR43) restores responsiveness of desensitized human neutrophils. 32958255_Microbiota-derived short chain fatty acid promotion of Amphiregulin expression by dendritic cells is regulated by GPR43 and Blimp-1. 33020504_FFA2-, but not FFA3-agonists inhibit GSIS of human pseudoislets: a comparative study with mouse islets and rat INS-1E cells. 33754024_GPR43 deficiency protects against podocyte insulin resistance in diabetic nephropathy through the restoration of AMPKalpha activity. 34777363_GPR Expression in Intestinal Biopsies From SCT Patients Is Upregulated in GvHD and Is Suppressed by Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics. |
ENSMUSG00000051314 |
Ffar2 |
38.192208 |
2.0492936481 |
1.035127 |
0.242075285 |
18.600537 |
0.00001611751088725881309103409033678389050692203454673290252685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000049263711057349359161844359888959843374323099851608276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.0545910 |
7.6592356 |
25.6018969 |
3.0040201 |
| ENSG00000126353 |
1236 |
CCR7 |
protein_coding |
P32248 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the MIP-3-beta chemokine. Probable mediator of EBV effects on B-lymphocytes or of normal lymphocyte functions. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. This receptor was identified as a gene induced by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and is thought to be a mediator of EBV effects on B lymphocytes. This receptor is expressed in various lymphoid tissues and activates B and T lymphocytes. It has been shown to control the migration of memory T cells to inflamed tissues, as well as stimulate dendritic cell maturation. The chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 (CCL19/ECL) has been reported to be a specific ligand of this receptor. Signals mediated by this receptor regulate T cell homeostasis in lymph nodes, and may also function in the activation and polarization of T cells, and in chronic inflammation pathogenesis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:1236; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; C-C motif chemokine 19 receptor activity [GO:0038117]; C-C motif chemokine 21 receptor activity [GO:0038121]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 binding [GO:0035757]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 binding [GO:0035758]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; establishment of T cell polarity [GO:0001768]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; homeostasis of number of cells [GO:0048872]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lymphocyte migration into lymph node [GO:0097022]; mature conventional dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097029]; myeloid dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002408]; negative regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process [GO:2000669]; negative regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032695]; negative thymic T cell selection [GO:0045060]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002606]; positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000510]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process involved in immunological synapse formation [GO:2000526]; positive regulation of humoral immune response [GO:0002922]; positive regulation of hypersensitivity [GO:0002885]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immunological synapse formation [GO:2000522]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly [GO:0031274]; positive regulation of T cell costimulation [GO:2000525]; positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050862]; regulation of dendritic cell dendrite assembly [GO:2000547]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032649]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to nitric oxide [GO:0071731]; response to prostaglandin E [GO:0034695]; ruffle organization [GO:0031529] |
11830455_Up-regulation OF CCR7 in classical but not in lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin disease correlates with distinct dissemination of neoplastic cells in lymphoid organs 11929789_important for migration of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells into lymph nodes 12070001_Few NKT cells express lymphoid tissue-homing chemokine receptors (CCR7 and CXCR5). A population with homing potential for lymph nodes (L selectin(+) CCR7(+)) exists only within a small subset of CD4 NKT cells. 12149218_PGE2 enhanced the expression of the CCL19/CCL21 receptor CCR7 on the cell surface of monocyte-derived dendritic cells 12486098_Data show that interaction between iC3b-opsonized apoptotic cells and immature dendritic cells down-regulated the expression of CD86 and up-regulated expression of CC chemokine receptor 7. 12642342_Coincident expression of CCR6 and CCR7 by pathologic Langerhans cells in Langerhans cell histiocytosis may contribute to their accumulation in nonlymphoid organs such as skin and bone 12673677_Overexpression of CCR7 mRNA in nonsmall cell lung cancer is associated with development of lymph node metastasis 12799021_A striking pattern of early inducible CCR7 expression was seen preferentially on primary T(H)1 cell lines, as compared to T(H)2 cells, and was dependent on the strength and duration of the T cell receptor signal. 14990723_cytomegalovirus infection inhibits dendritic cell migration by impairment of the chemokine receptor switch at the level of the expression of CCR7 molecules 15034011_Premature expression of CCR7 repositions CD4+CD8+ double-positive cells into the thymic medulla of transgenic mice. This repositioning of the thymocytes is accompanied by impairment of their development. 15040017_The expression of VEGF-C and CCR7 is related to lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma and both of them may become new targets for the treatment of gastric carcinoma. 15059845_CCR7 induces antiapoptotic signaling in mature DCs 15073111_CCR7 has a role in cell migration induced by CCL21 chemokine in malignant melanoma 15122702_Study of expression of CCR7 and its ligands on dendritic and T cell populations in inflamed central nervous system lesions of multiple sclerosis patients gives insight into pathways for immune cell trafficking and surveillance. 15247147_IL-6 led to inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) binding activity, regulating CCR7 transcription 15265234_A dose-dependent, mesangioproliferative and antiapoptotic effect of SLC/CCL21 was seen via activation of the chemokine receptor CCR7, constitutively expressed on MC. This suggests involvement in renal inflammation, regeneration and glomerular homeostasis. 15284247_specific CC chemokine receptor 7 residues have roles in receptor activation 15304089_MAPK are necessary for haptens to induce CCR7 expression. 15569314_Activation of CCR7 on mesangial cells by SLC/CCL21 enhances the degree and firmness of cell adhesion and increases cell spreading and the formation of cell-cell contacts 15674360_The CC chemokine receptor 7 consists with the known defect in adhesion and migration of CML cells. 15743472_CCR7 may have a role in the synovial recruitment of memory T cells in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, irrespective of the pattern of lymphoid organisation. 15753377_Epigenetic up-regulation of C-C chemokine receptor 7 expression is associated with melanoma 15778365_CCR7 activates two independent signaling modules, one involving G(i) and a hierarchy of MAPK family members and another involving Rho/Pyk2/cofilin, which control, respectively, chemotaxis and the migratory speed of DCs. 15867478_High expressions of CCR7 is associated with differentiated and intestinal-type gastric cancers 15950936_The selective expression of CCR7 in JDM may open new perspectives in the understanding of the pathogenesis of inflammatory myopathies, offering a new tool for the differential diagnosis of these disorders. 16115904_Results suggest that the chemokine receptor CCR7 is a novel biomarker that can predict lymph node metastases in breast cancer. 16223574_we investigated the expression of CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas 16225771_Data show that CXCL13 and CCL19 together by means of activation of CXCR5 and CCR7 up-regulated PEG10 expression and function in leukemic B cells. 16272303_functional and lineage relationships of three distinct memory CD4 subpopulations distinguished by their expression of the cysteine chemokine receptor CCR7 and the TNFR family member CD27 16278374_Chemokine receptor 7 is a new player in regulating apoptosis of CD8+ T cells in cancer patients [editorial] 16278415_CCR7 absence on the majority of CD8(+) T cells in the peripheral circulation of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck contributes to apoptosis 16494043_CXCR4 and CCR7 are highly expressed in laryngeal carcinoma. Expression was associated with tumor grade, clinical stage and neck lymph node metastasis. 16500130_The maturation, in vitro migration and cytokine production of human DC after stimulation with live H. pylori is reported. 16690519_CD62L and CCR7, as well as dendritic cells, are reduced in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma 16786131_expression of CCR7 promotes intrahepatic and lymphatic human hepatocellular carcinoma dissemination 16802356_In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, significant increases of CCR7-, CD27- and CCR7-, CD27+ and a reduction of CCR7+, CD27+ CD4 memory T cells were found. 16857986_CD45RA+ CCR7- CD8+ T cells are resting memory cells that, upon antigenic stimulation and then proliferate, lose CD45RA, and transiently acquire CCR7. 16887149_The CCL19,CCL21/CCR7 chemokine system is expressed in inflamed muscles of polymyositis and may be involved in the pathomechanism of polymyositis. 17006331_Rapamycin selectively up-regulates CCR7 and enhances the migration of differentiated dendritic cells to regional lymph nodes. 17032700_Significantly higher CCR7 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in human cervical cancer 17178876_CCR7 may be regulated by the breast tumor microenvironment and further support the use of endothelin receptor antagonists in the treatment of invasive and metastatic breast cancer. 17440035_Borrelia garinii blocks the up-regulation of CCR7 and CD38, important molecules in DC migration to lymph nodes, thus affecting further immune responses in Lyme borreliosis infection. 17587445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17587445_variants of CCR7 gene occur at an extremely low frequency in the German population and that neither Sjogren's syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, nor systemic sclerosis are associated with these variants 17687340_High levels of CCR7 expression predicted a poor prognosis. 17890452_role for MMP-9 and CCR7 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression 18065728_We have identified a new three-gene classifier that is independent of and improves on stage to stratify early-stage NSCLC patients with significantly different prognoses. 18166500_This study showed that memory Tregs contain high proportions of inflammatory chemokine-expressing cells and comprise two populations that differ in the expression of the lymphoid chemokine receptor CCR7. 18235009_CXCR4 and CCR7 provide directional migration of uveal melanoma cells toward the liver, the most common site for the formation of uveal melanoma metastases. 18319253_CCR7 and the EP2/EP4 receptor signaling pathway are down-stream targets for COX-2 to enhance the migration of breast cancer cells toward LECs and to promote lymphatic invasion 18437055_CCR7 plays a critical role in mediating chemotactic and invasive responses in colon cancer 18497951_Expression of CCR7 was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 18544997_The survival impact of CCR7 expression on resectable pancreatic cancer may be associated with lymphatic spread. 18623114_results indicate in CRC frequent alternative splicing or post-transcriptional mRNA modification resulting in a CCR7 molecule lacking an intact signal peptide prohibiting membrane translocation 18664492_A CCR7 mutant lacking virtually the complete C-terminus readily bound CCL19 and was internalized, but was unable to activate the G protein and to transmit signals required for cell migration. 18696160_High CCR7 expression is associated with extrathyroidal extension, angiolymphatic invasion, and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 18802075_Independent of arrestin 2 or arrestin 3 expression, CCR7/CCL21 internalize. 19068542_Patients with psoriasis vulgaris have a skewed distribution of T lymphocytes, with an increased level of CCR7-positive T lymphocytes compared to healthy controls. No CCR7 expression is observed in the skin of healthy individuals. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19087620_CCR7 may play an important role in the development and lymph node metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 19136936_A novel property of the chemokine receptors CCR7 in inhibiting detachment-induced cell death-anoikis, which is believed to be one of the major blocks in the metastatic spread of various neoplasms. 19196101_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19287948_CCR7 expression might play an important role in establishing LN metastases in patients with esophageal SCC 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19513547_CCR7 and CXCR4 expression predicts lymph node status including micrometastasis in gastric cancer. 19536265_Ccr7 gene expression is controlled by the activity of the T-ALL oncogene Notch1 and is expressed in human tumours carrying Notch1-activating mutations 19536742_Low-expression frequency for the chemokine receptor CCR7 is associated with mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 19540558_macrophages may participate in lymphangiogenesis in diffuse alveolar damage, which is facilitated by CCL19 and CCR7. 19585516_Alloimmune-induced APOBEC3G was found to be significantly increased in CD45RA(-), CCR5(+) and CD45RA(-)CCR7(-) subsets of effector memory T cells. 19615795_Results show interaction between CCR7 and its ligand CCL19 induces phosphorylation of mTOR and its target p70s6k. This phosphorylation is abolished by inhibition of CCR7 and PI3K/Akt, indicating that mTOR is involved in the CCR7-PI3K cascade. 19731977_Our data support the notion that CCR3, CCR7, and CXCR4 are increasingly expressed in tumor cells from PTC and that CXCR4 expression in PTC could be a potential marker for enhanced tumor aggressiveness. 19749090_Analysis of NK-cell clones revealed that alloreactive (KIR-ligand mismatched) but not autologous NK cells acquire CCR7. 19862774_Data revealed that DV infection enhances DC migration by inducing CCR7 expression, and that blocking COX-2 or MAPK activity suppresses DV-induced DC migration. 20029460_demonstrated that hypoxia induces T-cell apoptosis by the A(2)R signaling pathway partly by suppressing CCR7. 20036791_CCR7 gene plays role in lymph nodes and distant metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20150960_SSTR5 and CCR7 have a role in Crohn's disease pathogenesis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20439195_We studied a unique cohort of 21 primary lung cancers with matched adrenal metastases for the expression of CX3CR1, CXCR4, CCR6, and CCR7 20651394_VEGF-C and -D and CCR7 may play critical roles in lymphatic invasion in primary tumors. 20811680_our data indicate that CCR7 regulate cell adhesion and migration via beta1 integrin in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 20855251_The expressions of CCR5 and CCR7 on dendritic cells may correlate to the disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. 20889506_the CCR7/CCL21 signaling pathway leading to T lymphocyte migration on fibronectin is a beta1 integrin-dependent pathway involving transient ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which is modulated by PLCgamma1 20889923_Studies indicate that improved prevention of graft-versus-host disease might be achieved by redirecting to lymph nodes adoptively transferred, alloreactive NK cells by inducing CCR7-uptake in vitro. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21071608_Human beta-defensin 3 represents a novel NF-kappaB-regulated mediator of CCR7 expression and anti-apoptotic pathways. 21081040_CCR7 induces lymph node metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via upregulating MMP-9 expression. 21092675_The relative expression levels of CCR6 and CCR7 mRNA in tumor tissues with lymphatic metastases were significantly lower than those without lymph node metastases. 21165563_NF-kappaB is activated by CCR7 via PI3K/Akt/mTOR; this signal pathway plays an important role in regulating the cell survival and prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 21165582_CCL19-induced chemokine receptor 7 activates the phosphoinositide-3 kinase-mediated invasive pathway through Cdc42 in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 21261017_CCR6 and CCR7 are expressed in metastatic lymph nodes and PBMC, and might play a role in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma development. 21347514_chemokine receptor 7 regulates cell adhesion and migration via integrin alpha v beta 3 in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 21464944_These results suggest a new combinatorial guiding mechanism by CCL19 and CCL21 for the migration and trafficking of CCR7 expressing leukocytes. 21548969_High CCR7 expression in T-NHL cells is significantly associated with lymphatic and distant dissemination as well as with tumor cell migration and invasion in vitro. 21594558_The chemotactic interaction between CCR7 and its ligand, CCL21, may be a critical event during progression in pancreatic cancer 21624121_In our series, unlike what was previously published, CCR7 was exclusively expressed on stromal cells and was not associated with survival. 21680174_RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. 21698152_results suggest that CCL21/CCR7 contributes to the time-dependent proliferation of human NSCLC cells by upregulating cyclin A, cyclin B1, and CDK1 potentially via the ERK pathway 21731495_in contrast to HPIV3 and IAV, HMPV and HRSV did not efficiently decrease CCR1, 2, and 5 expression, and did not efficiently increase CCR7 expression. 21735098_PKCalpha is involved in the CCR7/NF-kappaB autocrine signaling loop in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. 21739164_A(2A) adenosine receptor activation not only modulates CCR7 expression in both normal and inflammatory environments but also regulates macrophage migration to CCR7-specific chemoattractants. 21739671_Studies indicate that the mechanisms that regulate the retention of tissue-resident memory T cells include TGF-beta-mediated induction of CD103 and downregulation of CCR7. 21953548_The autoantigen DNA topoisomerase I interacts with chemokine receptor 7 and exerts cytokine-like effects on dermal fibroblasts. 22020953_Moderate-to-strong immunohistochemical CCR7 expression, found in 58 of 121 well-characterized human PDACs, correlated with high rates of lymph vessel invasion 22043010_we characterize a cross-talk between the TCR and CCR7 and provide mechanistic evidence that the activation status of T cells controls lymphocyte motility 22158872_an important biological role for inflammatory NF-kappaB and AP1 in the regulation of CCR7 expression in metastatic SCCHN. 22163030_Statins promote the beneficial remodeling of plaques in diseased mouse arteries through the stimulation of the CCR7 / CD68 emigration pathway in macrophages 22221265_Chemical shift mapping indicates that the CCR7 N-terminus binds to the N-loop and third beta-strand of CCL21's chemokine domain. 22251626_let-7a suppressed breast cancer cell migration and invasion by downregulating CCR7 expression. 22334704_the first report to link the two signaling events that control migration through the lymph nodes: CCR7 mediates entry into the lymph nodes and EDG-1 signaling controls their subsequent exit. 22350183_CCR7 overexpression correlated with expression of metallothionein, while CCR10 was associated with cerebral metastases. CCR7 and CCR10 overexpressions were associated with a worse outcome independent of Breslow's tumor thickness and Clark level. 22438908_CCL21/CCR7 prevents apoptosis by upregulating the expression of bcl-2 and by downregulating the expression of bax and caspase-3 potentially via the ERK pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines 22498742_the use of trogocytosis as a tool to transiently express the chemokine receptor CCR7 on expanded human NK cells with the aim to enhance their homing to lymph nodes. 22533989_CCR7 seems to influence distinct immunological events during inflammatory responses in the central nervous system, including immune-cell entry and migration, and neuroglial interactions. 22619482_oxLDL induces an in vitro downregulation of CCR7 and CCL21, which may play a role in the reduction of dendritic cell migration from the plaques 22634622_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) constitutively migrate into the splenic white pulp in a manner dependent on chemokine receptors CCR7 and CXCR4. 22659045_RhoA/ROCK pathway is essential for PGE2-mediated CCR7-dependent monocyte migration. 22718198_The results demonstrated that COX-2 up-regulates CCR7 expression via AKT-mediated phosphorylation and activation of Sp1 and that this pathway is highly activated in metastatic breast cancer. 22797918_The lack of CCR7 ubiquitylation profoundly impairs immune cell migration. 22821963_In a series of experiments, the yield of cultured CD8+CCR7+ T cells by the end of a 6-day induction period varies widely; loss of CD8+CCR7+ regulatory T (Treg) cells in the elderly may be of relevance in the aging immune system. 22923218_data suggest that CCR7 via Pyk2 and cofilin regulates the chemotaxis and migration ability of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck cells 22990666_A combination of Leishmania-reactive CCR7- T(effector memory) cells and Leishmania-reactive CCR7+ T(central memory) cells are identified in patients with a history of cutaneous leishmaniasis which may play a protective role against Leishmania infection. 23028633_a rise of CD56(bright) NK cells in HIV-infected individuals, which lack CCR7-expression and strongly correlate with HIV viral load 23290307_beta-arrestin 2 and CCR7 and PI3K phosphorylation have a role in bisoprolol reversed epinephrine-mediated inhibition of cell migration, in dendritic cells loaded with cholesterol 23363813_The CD8(+)CCR7(+) T-cell frequency in HNSCC patients' blood tested at diagnosis can discriminate them from normal controls and predicts disease recurrence 23449735_Human eosinophils express CCR7 and have multipotent responses to the known ligands of CCR7. 23469143_ChemR23 forms homomers, and provide data suggesting that ChemR23 also forms heteromers with the chemokine receptors CCR7 and CXCR4. 23498789_Results suggest that the CCL21/CCR7 signaling pathway is involved in renal fibrosis in kidney transplant patients. 23519840_Overexpression of CCR7 protein is associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. 23747721_The CCR7+CD45RA-CD27+CD28+ central memory subset is significantly decreased in the peripheral blood CD4+ T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 23888080_In the cord blood of children with respiratory syncytial virus disease there was downregulation of interleukin 7 receptor and chemokine receptor 7, and in the severe disease subcategory, downregulation of Toll-like receptor 4. 23922113_High CCR7 mRNA expressions indicated better prognoses than those of the groups with low CCR7 mRNA expressions. 23939705_Transwell assays revealed that VEGF-C receptor, VEGFR-3, as well as chemokine CCL21 receptor, CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7), were responsible for the migration of PC3 cells toward hypoxia preconditioned MSCs 24040244_High CCR7 expression in gastric cancer cells was significantly associated with poor overall survival and lymph node metastasis. 24052640_data suggest that CCR7 plays a role in uveal melanoma metastasis and is associated with poor survival. 24111618_CCR7 ligands CCL19 and CCL21 contribute to the accumulation of dendritic cells and alveolar macrophages in the inflamed lungs of patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. 24136650_This is the first report demonstrating the dissociation of CCR7 and MMP-9 expression in phenotypically mature CD83(+) dendritic cells by cervical cancer cells 24138884_Circulating precursor cd4+ T cells expressing CCR7(low)PD-1(high) CXCR5+ indicate T-helper cell activity and promote antibody responses upon antigen re-exposure. 24311382_In human histological sections of chronic thrombosed femoral veins, CCR7(+) cells were present in the fibrotic areas. 24411580_CCR7 is more likely to be expressed in mycosis fungoides skin lesions with subcutaneous involvement. Activation of CCR7 promotes migration of MyLa cells (MF cell line) through the mTOR pathway. 24595810_results indicate a regulatory influence of MR signaling on human T-cell migration and suggest a role for endogenous aldosterone in the redistribution of T-cell subsets to lymph nodes, involving CD62L, CCR7, and CXCR4. 24673602_The TRIMEL induces a phenotypic maturation and increases the expression of surface CCR7 on melanoma patient-derived DCs, and also on the monocytic/macrophage cell line THP-1. 24725321_The involvement of dendritic cells and their expression of CCR7 in corneal and ocular surface diseases such as in ocular allergy, dry eye disease, immune rejection and more, are also reviewed here. 24766770_These results demonstrated the significant clinicopathological relationship and functional causality between CCR7 expression and lymph node metastasis in ESCC patients. 24856897_Except for an increase in the number of C-C chemokine receptor 7-expressing DC from MS patients, no major differences were found between groups in the expression of maturation-associated membrane markers 24910430_Downmodulation of CCR7 did not involve degradation or endocytosis and was strictly dependent on Vpu expression. 24912620_Data indicated that CCR7 regulates cell chemotaxis and migration via MMP-9 in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. 24990231_Monocyte adhesion to HUVEC cells was induced by CCR7. CCR7 rs588019 was associated with coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population. 25142946_Studied expression of CCR7 and EMT markers in the primary breast carcinoma tissues from patients who underwent radical mastectomy. and investigated whether CCL21/CCR7 induces EMT process during mediating cancer cell invasion or migration in vitro. 25168373_CCR7 can constitutively express in epithelial ovarian carcinomas and be induced rapidly in response to hypoxia, which indeed participates in EMT development and prompts the cell migration and invasion. 25255875_Suggest that CCRL1 impairs chemotactic events associated with CCR7 in the progression and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 25270024_Therefore, our study demonstrates that MAPK members (ERK1/2 and JNK) play a key role in CCR7 regulating SCCHN metastasis. 25318003_High expression of CCR-7 is associated with atherosclerotic arteries. 25327843_Our findings show that the molecular cues secreted by TALs alone or in combination with CCR7 may emerge as future therapeutic targets for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. 25405202_JAk2/STAT3 plays a key role in CCR7 regulatingSquamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck metastasis. 25425646_CCR7 can also promote survival of mDCs through a novel MEK1/2-ERK1/2-AMPK signaling axis. 25434638_CCR7 via RhoA/ROCK-Pyk2 cofilin pathway promotes invasion and migration of metastatic SCCHN cells 25556164_CCL21/CCR7 pathway activates signallings to up-regulate Slug pathway, leading to the occurrence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in human chondrosarcoma 25557171_Data indicate that inhibition of TGF-beta-activated protein kinase 1 (TAK1) reduces chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 7 (CCR7) expression. 25572817_our study suggested that CCR7 promotes Snail expression to induce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, resulting in cell cycle progression, migration, and invasion in gastric cancer 25614627_Data indicate that coupling selectivity of chemokine receptors CCR2, CCR5, and CCR7 with G protein subtypes was measured and compared. 25636509_CrkL regulates CCL19 and CCR7-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via ERK signaling pathway in epithelial ovarian carcinoma patients. 25733353_Data show the effect of C-terminus mutation of CC chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) on lymphocyte migration. 25744065_These results reveal that CCR7 and VEGF-C display a significant crosstalk and suggest a novel role of the CCL21/CCR7 chemokine axis in the promotion of breast cancer-induced lymphangiogenesis. 25961063_in given donor/recipient pairs, KIR2DS4 expression may contribute to potentiating natural killer cell function by increasing both the cytotoxicity and the expression of CCR7 on their surface. 25961925_Blockade of CCR7, or treatment with a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor, reduced lymphatic dissemination of epithelial-mesenchymal transition cells. 26115234_The solution structure of CCL19 is reported. It contains a canonical chemokine domain. Chemical shift mapping shows the N-termini of PSGL-1 and CCR7 have overlapping binding sites for CCL19 and binding is competitive. 26176983_the CCR7 axis mediates TGF-beta1-induced EMT via crosstalk with NF-kappaB signaling, facilitating lymph node metastasis and poorer overall survival in patients with gastric cancer 26179425_High CCR7 expression was associated with colorectal cancer metastasis. 26219899_CCR7 pathway up-regulates Twist expression via ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling to manage the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 26231034_findings indicated that circulating memory Tfh cells, especially CCR7+ICOS+ memory Tfh cells, may be associated with the relapse of MS and may serve as a new therapeutic target 26282174_Recycling accounts, to a major extent, for the high levels of surface CXCR4/CCR7 on CLL cells. Increased CCR4/CCR7 is detectable not only in circulating leukemic cells, but also in secondary lymphoid organs of CLL patients with lymphoadenopathy. 26352169_Pyk2 is a key downstream signaling molecules of CCR7 in SCCHN, which promotes SCCHN tumorigenesis and progression. 26352871_Membrane associated PGES1dependent release of PGE2 is ccompanied by elevated CCR7 expression in colon cancer cells. 26616645_This study showed that CCR7 are overexpressed in CD4(-) CD8(-) thymocytes of myasthenia gravis patients. 26667143_Our findings suggested that MUC1 plays an important role in CCL21-CCR7-induced lymphatic metastasis and may serve as a therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . 26722441_The present study demonstrated that down-regulation of CCR7 reduced proliferation, cell cycle, cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells 26819318_leukocyte subsets express distinct patterns of CCR7 sialylation that contribute to receptor signaling and fine-tuning chemotactic responses. 26884842_CCL21/CCR7 induce VEGF-D up-regulation and promote lymphangiogenesis via ERK/Akt pathway in lung cancer. 26923638_Constitutively expressed Siglec-9 inhibits LPS-induced CCR7, but enhances IL-4-induced CD200R expression in human macrophages. 26936935_tumor microenvironment stimulation down-regulated the migration of CCR7-expressing tumor cells toward CCL21 and inhibited the formation of directional protrusions toward CCL21 in a novel 3-dimensional hydrogel system. 26984468_High CCR7 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 27009073_Results indicated that CCR7 is overexpressed in gallbladder cancer tissues and its expression correlates with staging and lymph node metastasis. 27317472_we conclude that CCR7 gene locus harbours a polymorphism that modifies risk of MI in patients with Coronary artery disease (CAD). Replication of this association could be sought in a prospective cohort of initially healthy individuals 27421624_this study shows that plasmacytoid dendritic cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients have high expression levels of CCR7 27424807_CCR7 expression levels in human tumors correlate with signatures of CD141(+) DC, intratumoral T cells, and better clinical outcomes. 27505247_specific role for CCL21/CCR7 in promoting EMT and metastasis in CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cells 27574129_CCL21/CCR7 interaction contributes to the time-dependent proliferation of PTC cells by upregulating cyclin A, cyclin B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway associated with iodine. 27666723_This study suggests that NRP1 expression and LVD are independent factors that are likely to predict the risk of LN metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)of the tongue, whereas the expression of VEGFC, VEGFR3, CCR7, and SEMA3E are nonindependent predictive factors 27916085_Down-regulating CCR7 expression in MG63 cells could apparently inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities of MG63 cells, and also induce cell apoptosis. 28011488_High CXCR4 expression in primary breast tumors (PTs) was found to be associated with luminal A type tumor, suggesting more favorable outcome. In contrast, CCR7 and FOXP3 expressions in PTs represented luminal B tumors, pointing to more aggressive tumor behavior. Maspin expression did not differ between luminal types. 28035134_These results suggest that upregulation of rat CCR7 expression does not change the phenotype, differentiation, or proliferation capacity of human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs), but does enable efficient migration of hASCs to rat secondary lymphoid organs. 28112745_the acute GvHD (aGvHD) patients received higher percentage of CD4+CCR7+ T-cells in donor T-cells, whereas chronic GvHD (cGvHD) patients were transplanted with higher percentages of CD8+CCR7+ T-cells. Functional experiments demonstrated that CCR7+ T-cells exhibited higher potential for activation than CCR7- T-cells did. 28114889_High tumoral CCR7 expression correlated with potential lymphatic involvement and poor prognosis of metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 28339080_Results show that upregulation of CCR7 promotes cell proliferation and inflammation in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells. However, silencing of CCR7 via siRNA treatment promotes cell apoptosis and suppresses the inflammatory response and TGF-beta1-induced EMT, which may be associated with NF-kappaB signaling. 28378417_Study provide evidence that CCR7 mediates EMT progress via AKT pathway, which indicates that CCR7 has a key role in breast cancer progression. 28416768_CCL21/CCR7 interaction was shown to allow NK cell adhesion to endothelial cells (ECs) and its reduction by hypoxia. 28421995_Report an increased percentage of peripheral CCR7 T cells accompanied by endothelial dysfunction in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. 28487957_these results demonstrated that CCL21/CCR7 may activate EMT in lung cancer cells via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 28534984_High CCR7 expression is associated with urinary bladder cancer metastasis. 28535405_CXCR4, CCR7, VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression might have synergistic effects on the lymph node metastasis in patients with cervical cancer. 28729639_The research findings demonstrate for the first time that the chemokines CCL19, CCL21 and CCR7 play important roles in bone destruction by increasing osteoclast migration and resorption activity, and that has been linked to rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 28767178_protein expression elevated in synovial tissue from osteoarthritis patients 28817313_that CCR7 mediates TGF-beta1-induced MMP2/9 expression through NF-kappaB signaling 28819198_Study indicates that chemokine receptor CCR7 (CCR7) homodimerization critically regulates CCR7 ligand-dependent cell migration and intracellular signalin |
ENSMUSG00000037944 |
Ccr7 |
74.503546 |
71.6100105520 |
6.162089 |
0.538480982 |
336.255264 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000417273292318202380902935708801977664592481699374142810169071502465624905392559284451149673810617235770963089315084967786604720399147328589963636072194995986716275675975026076437718455455772037510087102418765425682067871093750000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000133022760142908585319541906912296320588608028478639714677477735817547815855999970377325455074321798861947231482816271332043176122752406615736384670457573043472322041995277718458041017052240206908209074754267930984497070312500000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
150.5930039 |
55.3494476 |
2.1155376 |
0.7688153 |
| ENSG00000126457 |
3276 |
PRMT1 |
protein_coding |
Q99873 |
FUNCTION: Arginine methyltransferase that methylates (mono and asymmetric dimethylation) the guanidino nitrogens of arginyl residues present in proteins such as ESR1, histone H2, H3 and H4, ILF3, HNRNPA1, HNRNPD, NFATC2IP, SUPT5H, TAF15, EWS, HABP4, SERBP1, RBM15, FOXO1, CHTOP and MAP3K5/ASK1 (PubMed:10749851, PubMed:16879614, PubMed:26876602, PubMed:22095282, PubMed:26575292, PubMed:18951090, PubMed:25284789). Constitutes the main enzyme that mediates monomethylation and asymmetric dimethylation of histone H4 'Arg-4' (H4R3me1 and H4R3me2a, respectively), a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation. May be involved in the regulation of TAF15 transcriptional activity, act as an activator of estrogen receptor (ER)-mediated transactivation, play a key role in neurite outgrowth and act as a negative regulator of megakaryocytic differentiation, by modulating p38 MAPK pathway. Methylates RBM15, promoting ubiquitination and degradation of RBM15 (PubMed:26575292). Methylates FOXO1 and retains it in the nucleus increasing its transcriptional activity (PubMed:18951090). Methylates CHTOP and this methylation is critical for its 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC)-binding activity (PubMed:25284789). Methylates MAP3K5/ASK1 at 'Arg-78' and 'Arg-80' which promotes association of MAP3K5 with thioredoxin and negatively regulates MAP3K5 association with TRAF2, inhibiting MAP3K5 stimulation and MAP3K5-induced activation of JNK (PubMed:22095282). Methylates H4R3 in genes involved in glioblastomagenesis in a CHTOP- and/or TET1-dependent manner (PubMed:25284789). Plays a role in regulating alternative splicing in the heart (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JIF0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10749851, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11387442, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12718890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16879614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18320585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18657504, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18773938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19124016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20442406, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22095282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25284789, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26575292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26876602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28040436}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Isopeptide bond;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the protein arginine N-methyltransferase (PRMT) family. Post-translational modification of target proteins by PRMTs plays an important regulatory role in many biological processes, whereby PRMTs methylate arginine residues by transferring methyl groups from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to terminal guanidino nitrogen atoms. The encoded protein is a type I PRMT and is responsible for the majority of cellular arginine methylation activity. Increased expression of this gene may play a role in many types of cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene, and a pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:3276; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; methylosome [GO:0034709]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; histone H4R3 methyltransferase activity [GO:0044020]; histone methyltransferase activity [GO:0042054]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 binding [GO:0048273]; N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008170]; protein methyltransferase activity [GO:0008276]; protein-arginine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016274]; protein-arginine omega-N asymmetric methyltransferase activity [GO:0035242]; protein-arginine omega-N monomethyltransferase activity [GO:0035241]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding [GO:1904047]; cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0048738]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; histone H4-R3 methylation [GO:0043985]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0045653]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; peptidyl-arginine methylation [GO:0018216]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045648]; positive regulation of hemoglobin biosynthetic process [GO:0046985]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; protein methylation [GO:0006479]; regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0045652]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
12183049_several proteins extracted from HeLa cells were methylated by PRMT1 15364944_SAF-A is arginine methylated by PRMT1 15737635_These results suggest that PRMT1 plays a post-translationally important role in regulating the transcriptional activity. 15741314_PRMT1 arginine-methylates MRE11 and thus regulates the activity of MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex during the intra-S-phase DNA damage checkpoint response. 16159886_A fraction of PRMT1 is located in the nucleus, but the protein is predominantly cytoplasmic. 16294045_GAR (Glycine Arginine rich) motif is a region required for 53BP1 DNA binding activity and as the site of methylation by PRMT1. 16294047_a glycine-arginine rich (GAR) stretch of 53BP1 lying upstream of the Tudor motifs is methylated by PRMT1 16492668_arginine dimethylation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K by protein-arginine methyltransferase 1 inhibits its interaction with c-Src 16861234_SET-mediated promoter hypoacetylation is a prerequisite for coactivation of the estrogen-responsive pS2 gene by PRMT1 16879614_Methylates Ki-1/57 and CGI-55 (PAI-1 mRNA-binding protein) at a conserved Gly/Arg-rich motif cluster. 17052457_PRMT1 is a coactivator for HNF4, an orphan nuclear receptor that regulates the expression of genes involved in diverse metabolic pathways 17264152_CAF1 is a new regulator of PRMT1-dependent arginine methylation. 17550233_Our results suggest that PRMT1 might be involved in the previously reported methylation of Arg25 in HMGA1a in vivo. 17848568_relative balance of PRMT1 isoforms is altered in breast cancer 17891136_Study uncovers an essential function of PRMTs in oncogenesis and reveals their potential as novel therapeutic targets in human cancer. 17971302_Our results suggest that PRMT1-mediated methylation serves as a positive modulator of IR/IRS-1/PI3-K pathway and subsequent glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells. 18316480_PRMT1- dependent methylation of RUNX1 at arginine residues 206 and 210 abrogates its association with SIN3A. 18495660_C-terminal domain containing the methylated arginine residues is known to promote PAPBN1 self-association, and arginine methylation has been reported to inhibit self-association of an orthologous protein 18657504_These data indicate that the methylation of estrogen receptor alpha is a physiological process occurring in the cytoplasm of normal and malignant epithelial breast cells and that ERalpha is hypermethylated in a subset of breast cancers. 18700728_PRMT1 selectively recognizes a set of amino acid sequences in substrates that extend beyond the 'RGG' paradigm. 19078953_examined the expression pattern of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 gene in colon cancer patients 19124016_Data demonstrate that arginine methylation of TAF15 by PRMT1 is a crucial event determining its proper localization and gene regulatory function. 19144646_demonstrated mutual interactions and functional interplays between PXR and PRMT1, and this interaction may be important for the epigenetics of PXR-regulated gene expression 19158082_Type I Arginine Methyltransferases PRMT1 and PRMT-3 Act Distributively 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170758_Study shows that enzymatic activity is required for nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of PRMT1v2, as a catalytically inactive mutant highly accumulates in the nucleus. 19183483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19414388_High PRMT1 variant v2 expression is associated with colon cancer. 19641605_results suggest that the pathological mutation in the PABPN1 gene alters the protein conformation and induces a preferential interaction with type I PRMTs and Hsp70 chaperones 19643181_In this review, protein arginine methylation is a covalent modification that results in the addition of methyl groups to the nitrogen atoms of the arginine side chains and is catalyzed by a family of protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs). 19682581_In this review, the pathology previously attributed to elevated asymmetric dimethylarginine may be manifested, at least in part, through altered enzyme activity involved in ADMA regulation, specifically dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 and PRMT. 19913501_these data thus suggest that the PRMT1 plays a key role as a cellular regulator of HSV-1 replication through ICP27 RGG-box methylation. 20064924_we show that PRMT1 methylates FMRP in cells, suggesting a model where methylation of the RGG box modulates either the quantity or the identity of the RNAs bound by FMRP. 20442406_Modulation of the p38 MAPK pathway by PRMT1 is a novel mechanism regulating megakaryocytic differentiation. 20473859_PRMT1 may be involved in human carcinogenesis and may thus be a therapeutic target for various types of cancer. 20497508_PRMT1 was detected in colonic muscosa, enteric nervous system and endothelial cells of colon from patients with Hirschsprung disease. 20812326_In this study, we use Forster resonance energy transfer (FRET) to determine dissociation constant (K(D)) values for dimerization of PRMT1 and PRMT6. 21172665_The PRMT1 is transcriptional coactivators that deposit H3R17me2a and H4R3me2a marks, respectively. 21184736_these results identify preferred PRMT1 methylation sequences of hnRNP K by direct methylation assay and implicate a role of arginine methylation in regulating intracellular distribution of hnRNP K. 21187067_These results revealed a cooperative role of TLS and PRMT1 in transcriptional regulation of survivin. 21229402_Survival curves revealed that PRMT1-v1 status-low expression relates to longer disease-free survival (DFS; p = 0.036). 21242974_methylation of Axin by PRMT1 may serve as a finely tuned regulation mechanism for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 21285357_Protein-arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) methylates Ash2L, a shared component of mammalian histone H3K4 methyltransferase complexes. 21444773_PRMT1-mediated methylation of BAD inhibits phosphorylation by Akt. 21697082_Investigation of the molecular origins of protein-arginine methyltransferase I (PRMT1) product specificity reveals a role for two conserved methionine residues. 21851090_the SH3 domain may mediate an interaction between PRMT1 and -2 in a methylation-dependent fashion 21965298_Depletion of PRMT1 diminished the ability of ALS-linked FUS mutants to localize to the cytoplasm. 22095282_Results indicate that arginine methylation of ASK1 by PRMT1 contributes to the regulation of stress-induced signaling that controls a variety of cellular events including apoptosis. 22179613_LANA is subject to arginine methylation by protein arginine methyltransferase 1 in vitro and in vivo 22442049_The RG-rich and RGG box of SERBP1 is asymmetrically dimethylated by PRMT1 and the modification affects protein interaction and intracellular localization of the protein. 22482410_Results idicate that pcDNA3.1(+)-PRMT1 recombinant was successfully constructed. 22498736_PRMT1 interacts with AML1-ETO to promote its transcriptional activation and progenitor cell proliferative potential. 22614839_RAP55 is important for the assembly of cytoplasmic mRNP granules and that PRMT1 is required for RAP55A to localize to P-bodies. 22697391_protein arginine methyltransferase I 22749861_proteinuria might enhance asymmetric dimethylarginine generation in tubular cells, at least in part via the overexpression of PRMT-1 triggered by oxidative stress 22839530_Results indicate that SRSF1 serves as an anti-apoptotic factor and potentially contributes to leukemogenesis in pediatric ALL patients by cooperating with PRMT1. 22917032_The knock-down of PRMT1 resulted in an arrest in the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction in four glioma cell lines 23152885_PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation could be implicated in the nucleus-cytoplasmic shuttling of FUS/TLS. 23187807_Results provide insight into the redox-sensitive signaling mechanism that mediates cell survival involving p53 and its novel target NCF2/p67phox. 23388725_These results support the notion that the binding of HBx to PRMT1 might benefit hepatitis B virus replication by relieving the inhibitory activity of PRMT1 on hepatitis B virus transcription. 23419748_Loss of the major Type I arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 causes substrate scavenging by other PRMTs. 23483889_These findings unveil a link between PRMT1 and p38alpha in regulating the erythroid differentiation program. 23620769_wild type FUS (FUS-WT) specifically interacts with protein arginine methyltransferases 1 and 8 (PRMT1 and PRMT8) and undergoes asymmetric dimethylation 23624934_Arginine methylation of RACO-1 is required for efficient transcriptional activation by c-Jun/AP-1 and thus identify PRMT1 as an important regulator of c-Jun/AP-1 function. 23635657_Mutational defects in PRMT1 is not the cause of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 23699174_Data show the transcriptional regulation of the human ferritin gene by coordinated regulation of Nrf2 and protein arginine methyltransferases PRMT1 and PRMT4. 24121109_These results demonstrate that PRMT1 and PRMT5 are involved in hypoxia and ischemia-induced apoptosis via p-p38 MAPK and p-JNK in in vitro and in vivo models. 24211191_CARM1 and PRMT1 are dysregulated in lung cancer; only CARM1 expression was found to be correlated with tumor differentiation and neither CARM1 nor PRMT1 expression was correlated with survival. 24296620_In this review, we present the recent developments in the regulation of non-histone proteins by PRMTs. 24447537_PELP1 oncogenic functions involve alternative splicing via PRMT6. 24451260_PRMT1 is a novel regulator of HIF-1- and HIF-2-mediated responses. 24998928_PRMT1 concentrates in cytoplasmic bodies, which respond to DNA injury in the cell nucleus 25053681_increased levels of asymmetric dimethyl arginine in hemodialysis patients might be caused by PRMT-1 gene polymorphism. 25274782_Study provides evidence for loss of PRMT1 function as a consequence of cytoplasmic accumulation of FUS in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, including changes in the histone code regulating gene transcription. 25733715_GSK3- and PRMT-1-dependent modifications of desmoplakin control desmoplakin-cytoskeleton dynamics. 25748791_The ATXN2L associates with the protein arginine-N-methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1). 25847239_High PRMT1 expression is associated with Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition and metastasis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 25874535_PRMT1 regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through enhanced methylation-induced nuclear localization of FOXO1, which subsequently suppresses the nuclear localization of PDX-1 25911106_results challenge the unilateral view that increased PRMT1 expression necessarily results in increased ADMA synthesis and demonstrate that enzymatic activity can be regulated in a redox-sensitive manner 26020839_we define the arginines within the RGG/RG motifs as the site of methylation by PRMT1 both in vitro and in vivo. The arginines within the human hnRNPUL1 RGG/RG motifs were substituted with lysines to generate hnRNPUL1(RK). 26126536_Methylation by PRMT1 may regulate Smurf2 stability and control TGF-beta signaling. 26143443_Upon HBV infection, cellular mechanisms involving SETDB1-mediated H3K9me3 and HP1 induce silencing of HBV cccDNA transcription through modulation of chromatin structure. 26163260_miR-503-mediated PRMT1 could emerge as a potential important biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis 26392112_The oncogenic roles of PRMT1 in the progression of ESCC. 26460953_Data unveils a novel mechanism of PRMT1-mediated CPC regulation through methylation of INCENP. 26472729_Low expression of PRMT1 is associated with low chemosensitivity in gastric cancer. 26503212_FAM98A, whose physiological function is unknown, was arginine-methylated by PRMT1. 26527496_there is an imbalance in the vasoconstriction-vasodilation status toward constriction. It is our hypothesis that, in hypoxic stress, a key player in initiating this imbalance is the enzyme, protein arginine methyltransferase-1 (PRMT1). 26571401_PRMT1-mediated methylation of the EGF receptor regulates signaling and cetuximab response. 26575292_The authors demonstrate that RBM15 is methylated by protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) at residue R578, leading to its degradation via ubiquitylation by an E3 ligase (CNOT4). 26725954_IFNgamma induced PPAR gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1alpha) positively regulated RIG-I; with PRMT-1 and G9a affecting PGC-1alpha in a counter-regulatory manner. 26762411_PRMT1 promoted the methylation of Gli1. 26766589_Pharmacological inhibition of KDM4C/PRMT1 suppresses transcription and transformation ability of MLL fusions 26795953_findings suggest that PRMT1 is a central regulator of tissue remodeling and that the signaling sequence controlling its expression in primary human lung fibroblast is PDGF-ERK-STAT1. 26813495_we unraveled a dual function of PRMT1 in modulation of both EMT and senescence via regulating ZEB1. 26895297_This study demonstrated that Loss of PRMT1 not only results in an increase of UMA FUS and a decrease of ADMA FUS, but also in a significant increase of MMA FUS. 26911452_Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 is regulated by the Interleukin-4/STAT6 signal pathway in epithelial cells, while in fibroblasts PRMT1 is activated by Interleukin-1 beta through NF-kappa B. 26934120_High PRMT1 expression is associated with multidrug resistance in breast cancer. 27175582_PRMT1 is overexpressed in human melanoma, and may regulate tumor growth and metastasis via targeting ALCAM. 27183873_PRMT1 methylates Nrf2 protein at a single residue of arginine 437, both in vitro and in vivo. This leads to a moderate increase of its DNA-binding activity and transactivation, which subsequently protects cells against the tBHP-induced glutathione depletion and cell death. 27521225_Increase in HLAB expression was concomitant with increase in HIF-1alpha and decrease in PRMT1 levels. 27545444_The PRMT1 active site residues, Met48 and His293, have been determined to play a key role in dictating product specificity, as: (1) the single mutation of Met48 to Phe enabled PRMT1 to generate MMA, ADMA, and a limited amount of SDMA; (2) the single mutation of His293 to Ser formed the expected MMA and ADMA products only; (3) the double mutant H293S-M48F-PRMT1 produced SMDA as the major product with limit amount of SDMA. 27571165_PRMT1 has a role in regulating MYCN in neuroblastoma 27642082_Mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake is controlled by protein arginine methyl transferase 1 that asymmetrically methylates MICU1, resulting in decreased Ca(2+) sensitivity. UCP2/3 normalize Ca(2+) sensitivity of methylated MICU1 and, thus, re-establish mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake activity. 28040436_the two structural homologs FAM98A and FAM98B included in a novel complex with DDX1 and C14orf166 are required for PRMT1 expression in colorectal cancer cell lines 28081849_Our data suggest that miR-19a and PRMT1 might be novel indicators of asthma and present new disease-specific therapeutic targets to reduce airway wall remodeling and inflammation in asthmatic patients 28094300_the abnormal stable complex of FUS-R521C/PRMT1/Nd1-L mRNA could contribute to neurodegeneration upon oxidative stress. 28126510_This article reviews the current literature from research showing interdependent association between cav1-PRMT1-SIRT1 to the outcomes of experimental and clinical research aiming to preserve endothelial function with gene- or pharmaco-therapy. [review] 28231732_Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 expression was found to be significantly upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and clinical tissues. 28267599_Analysis of deletion constructs of SERBP1 showed that the C-terminal third of the SERBP1 protein, which contains one of its two substrate sites for protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1), is necessary and sufficient for it to interact with RACK1 28643125_High-PRMT1 expression is associated with resistance to cetuximab in triple-negative breast cancer. 28656289_High PRMT1 expression is associated with head and neck and oral cancer. 28733251_RALY promotes Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1 alternatively spliced isoform v2 relative expression and metastatic potential in breast cancer cells 28744817_data collectively suggest that silencing of PRMT1 exerts anti-catabolic and anti-inflammatory effects on IL-1beta-induced chondrocytes via suppressing the Gli-1 mediated Hedgehog signaling pathway, indicating that PRMT1 plays a critical role in OA development and serves as a promising therapeutic target for OA. 28857308_Study characterizes a novel splicing isoform of PRMT1 that correlates with cellular malignancy. This isoform lacks the dimerization arm of the enzyme, and is catalytically inactive, but able to bind substrates, and blocks cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. 28883095_Deacetylation on both K200 and K205 by Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) and acetylation of p300 (EP300) on K205 collaboratively prepare the motif for SCF(Fbxl17) binding thereby triggering PRMT1 protein degradation. 28943242_Maintenance of the progenitors thus requires cooperation by PRMT1 and CSNK1a1 to sustain proliferation gene expression and suppress premature differentiation driven by GRHL3 28987382_PRMT1 inhibition prevents gastric cancer progression by downregulating eIF4E and targeting type II PRMT5. 29026071_PRMT1 is an arginine methyltransferase involved in a variety of cell functions. Here the authors delete PRMT1 specifically in mature B cells to show the importance of arginine methylation for B cell proliferation, differentiation and survival, and thereby for humoral immunity. 29097184_Important roles of PRMT1 in progression of gastric cancer. Given the dual functions of PRMT1, it is as a potential drug target of gastric cancer with extreme caution. 29186683_TRIM48 Promotes ASK1 Activation and Cell Death through Ubiquitination-Dependent Degradation of the ASK1-Negative Regulator PRMT1 29193371_Study reports the interaction of PRMT1 with an extensive panel of polyRGG-box substrates showing that substrate aromatics (Phe or Tyr) are either neutral or promote binding to PRMT1, while sufficient numbers of substrate Asp residues impairs binding/methylation. 29540535_Target identification reveals protein arginine methyltransferase 1 is a potential target of phenyl vinyl sulfone and its derivatives. 29651020_GFI1 facilitates efficient DNA repair by regulating PRMT1 dependent methylation of MRE11 and 53BP1. 29945155_a significant role for PRMT1 in HCC progression and metastasis in vitro and in vivo via STAT3 signalling pathway activation. PRMT1 may be a potential novel prognostic biomarker and new therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 30194893_overexpressing ZEB1 reversed the antitumor effects of PRMT1 downregulation in Pancreatic cancer (PC) cells. PRMT1 was aberrantly upregulated in PC. PRMT1 inhibition, possibly inversely acting through ZEB1, might be an effective molecular intervention to inhibit PC growth and invasion. 30354839_RALY regulates PRMT1 expression and interacts with the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked protein FUS. 30569144_Study was the first to demonstrate that PRMT1 levels were reduced by propionate treatment in HCT116 colon cancer cells and that downregulation of PRMT1 induced cell apoptosis. Downregulation of PRMT1 expression by propionate, induced apoptosis by inhibiting p70 S6 kinase phosphorylation. 30679275_Methionine is required for Wnt-induced endolysosomal activitythrough the generation of SAM, which fosters the sequestration ofPRMT1 and GSK3 inside late endosomes/MVBs. 30826432_CBX7 and PRMT1 contribute to regulate E-cadherin expression through several mechanisms. 30849541_58 novel PRMT1 transcripts were identified. 31015230_The role of the arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 in breast cancer pathogenesis.Elevated PRMT1 expression correlates with malignancy of breast cancer. CEBPA is methylated by PRMT1 in breast cancer. 31043582_PRMT1 regulates the tumor-initiating properties of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through histone H4 arginine methylation coupled with transcriptional activation. 31114027_UBAP2L arginine methylation by PRMT1 modulates stress granule assembly. 31199999_Protein arginine methyltranferase-1 induces ER stress and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells and contributes to diabetic nephropathy. 31217189_Our study demonstrates that PRMT1-mediated FLT3 methylation promotes AML maintenance and suggests that combining PRMT1 inhibition with FLT3 TKI treatment could be a promising approach to eliminate FLT3-ITD(+) AML cells. 31395602_The study revealed that PRMT1 methylates Fms-like receptor tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) at arginine (R) residues 972 and 973 (R972/973), and its oncogenic function in MLL - rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells is FLT3 methylation dependent. 31467116_Bronchial thermoplasty decreases airway remodelling by blocking epithelium-derived heat shock protein-60 secretion and protein arginine methyltransferase-1 in fibroblasts. 31478263_Data indicate protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) as a positive regulator of Yes-associated protein (YAP) activity in chondrosarcoma. 31520395_PRMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and predicts poor prognosis. 31541584_This study uncovers a novel regulatory mechanism for PRMT1 by Ca(2+) and identifies the PRMT1/p38a axis as an intracellular mediator of Ca(2+) signaling during erythroid differentiation. 31555811_plays a regulatory role in thermogenic fat function 31607134_PRMT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatic carcinoma cells probably via TGF-beta1/Smad pathway 31634638_PRMT1 promotes MyoD-mediated myogenin expression, for which the enzymatic activity of PRMT1 is needed. The arginine methylation of MyoD by PRMT1 enhances its DNA binding activity and transactivation. 31655611_expression of PRMT1 may be characteristic for low grade and low stage clear cell renal cell carcinomas 31777917_PRMT1 down-regulation impairs global miRNA expression. 31995759_PRMT1 Is Recruited via DNA-PK to Chromatin Where It Sustains the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype in Response to Cisplatin. 32420808_LncRNA NNT-AS1 promote glioma cell proliferation and metastases through miR-494-3p/PRMT1 axis. 32429593_The MKK-Dependent Phosphorylation of p38alpha Is Augmented by Arginine Methylation on Arg49/Arg149 during Erythroid Differentiation. 32583741_SCYL1 arginine methylation by PRMT1 is essential for neurite outgrowth via Golgi morphogenesis. 32699135_Methylation of HSP70 Orchestrates Its Binding to and Stabilization of BCL2 mRNA and Renders Pancreatic Cancer Cells Resistant to Therapeutics. 32764667_PRMT1-dependent methylation of BRCA1 contributes to the epigenetic defense of breast cancer cells against ionizing radiation. 32767856_TC-E 5003, a protein methyltransferase 1 inhibitor, activates the PKA-dependent thermogenic pathway in primary murine and human subcutaneous adipocytes. 32861926_PRMT1 is critical to FEN1 expression and drug resistance in lung cancer cells. 32895488_Methylation of EZH2 by PRMT1 regulates its stability and promotes breast cancer metastasis. 33092789_Macrophages-stimulated PRMT1-mediated EZH2 methylation promotes breast cancer metastasis. 33127433_Roles of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) in brain development and disease. 33420374_PRMT1 enhances oncogenic arginine methylation of NONO in colorectal cancer. 33476674_Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 contributes to the development of allergic rhinitis by promoting the production of epithelial-derived cytokines. 33587951_The methyltransferase PRMT1 regulates gamma-globin translation. 33741434_mTOR regulates PRMT1 expression and mitochondrial mass through STAT1 phosphorylation in hepatic cell. 33849119_Abnormalities of the PRMT1-ADMA-DDAH1 metabolism axis and probucol treatment in diabetic patients and diabetic rats. 33853662_PRMT1-mediated H4R3me2a recruits SMARCA4 to promote colorectal cancer progression by enhancing EGFR signaling. 33859753_PRMT1 is a novel molecular therapeutic target for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 33999432_PRMT1 promotes the tumor suppressor function of p14(ARF) and is indicative for pancreatic cancer prognosis. 34147561_TSLP-induced collagen type-I synthesis through STAT3 and PRMT1 is sensitive to calcitriol in human lung fibroblasts. 34201091_A Pan-Inhibitor for Protein Arginine Methyltransferase Family Enzymes. 34330913_PRMT1-dependent regulation of RNA metabolism and DNA damage response sustains pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 34443661_Photoregulation of PRMT-1 Using a Photolabile Non-Canonical Amino Acid. 34619150_Coordinated regulation of the ribosome and proteasome by PRMT1 in the maintenance of neural stemness in cancer cells and neural stem cells. 34635781_Inducible Prmt1 ablation in adult vascular smooth muscle leads to contractile dysfunction and aortic dissection. 34688662_Naturally occurring cancer-associated mutations disrupt oligomerization and activity of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1). 35040433_Wnt activation promotes memory T cell polyfunctionality via epigenetic regulator PRMT1. 35196489_A genome-scale CRISPR screen reveals PRMT1 as a critical regulator of androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. 35764172_A peptoid-based inhibitor of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) induces apoptosis and autophagy in cancer cells. 35863589_PRMT1 suppresses doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. 36076907_PRMT1, a Key Modulator of Unliganded Progesterone Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer. 36151091_TIPE1 inhibits osteosarcoma tumorigenesis and progression by regulating PRMT1 mediated STAT3 arginine methylation. 36152748_Protein arginine methyltransferase 1 in the generation of immune megakaryocytes: A perspective review. |
ENSMUSG00000109324 |
Prmt1 |
680.649305 |
2.2776078531 |
1.187519 |
0.092200818 |
163.904235 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000015873843130502382600062772429919560502835981459549374646515303722467882098290827708660793061453244193192979594186908798292279243469238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000002489882301872637149850921612494208226739646631556365813766037853310440160151712709586998829814838418705846834200201556086540222167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
959.7443778 |
52.5876346 |
424.1388585 |
17.6453393 |
| ENSG00000126759 |
5199 |
CFP |
protein_coding |
P27918 |
FUNCTION: A positive regulator of the alternate pathway (AP) of complement (PubMed:20382442, PubMed:28264884). It binds to and stabilizes the C3- and C5-convertase enzyme complexes (PubMed:20382442, PubMed:28264884). Inhibits CFI-CFH mediated degradation of Complement C3 beta chain (C3b) (PubMed:31507604). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20382442, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28264884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31507604}. |
3D-structure;Complement alternate pathway;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a plasma glycoprotein that positively regulates the alternative complement pathway of the innate immune system. This protein binds to many microbial surfaces and apoptotic cells and stabilizes the C3- and C5-convertase enzyme complexes in a feedback loop that ultimately leads to formation of the membrane attack complex and lysis of the target cell. Mutations in this gene result in two forms of properdin deficiency, which results in high susceptibility to meningococcal infections. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009]. |
hsa:5199; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; complement activation [GO:0006956]; complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0006957]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; immune response [GO:0006955]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of opsonization [GO:1903028] |
16337490_A splice site mutation in exon 10 (c.1487-2A>G) was found in the properdin gene and co segregated with biochemically measured properdin deficiency. 18490764_study reports properdin binds predominantly to late apoptotic & necrotic cells but not to early apoptotic cells; binding occurs independently of C3b 18579773_The human complement protein properdin binds to early apoptotic T cells and initiates complement activation, leading to C3b opsonization and ingestion by phagocytic cells. 18753294_The contribution of properdin is pivotal in proteinuria-induced tubular complement activation and subsequent damage. Interference with properdin binding to tubular cells may provide an option for the treatment of proteinuric renal disease. 18791942_Properdin induces the formation of platelet-leukocyte aggregates via leukocyte activation, linking the complement system & platelet-leukocyte aggregates with potential significance in atherosclerotic vascular disease. 19005416_Significantly more transcripts encoding alternative pathway components factor B, C3 and properdin, and C3a receptor and C5a receptor were detected in grade 3 versus grade 0 or 1 biopsies of human cardiac allografts. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19584655_Factor P was expressed in 50% of choroidal neovascular membranes of patients with age-related macular degeneration(AMD). Additional studies need to investigate role of Factor P in development of AMD for potential therapeutic intervention. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934084_Properdin presence is associated with increased SC5b-9 excretion and worse renal function. 20122735_CFP does not seem to confer any risk for age-related macular degeneration. 20337960_levels of properdin are not associated with childhood wheezing and atopy 20382442_Human properdin can selectively recognize surfaces and enhance or promote alternative pathway of complement activation. 20530262_The conventional mechanism of properdin function is to bind to and stabilize alternative pathway C3 convertases on the surface of Neisseria meningitidis and N. gonorrhoeae. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21135110_tubular HS as a novel docking platform for alternative pathway activation via properdin, which might play a role in proteinuric renal damage. 22229731_report a large Finnish family with a novel mutation in the properdin gene. The mutation is located in exon 9 and changes guanine to adenine at nucleotide 1164 (c.1164G>A) that causes tryptophan to change to a premature stop codon (W388X). 22338105_Properdin and SC5b-9 may be novel biomarkers for future risk of type 2 diabetes in this high-risk population and warrant further investigation. 22368277_Immune human serum that contained bactericidal Abs directed against the 2C7 lipooligosaccharide epitope required functional properdin to kill C4BP-binding strains, but not C4BP-nonbinding strains. 22815489_Factor h and properdin recognize different epitopes on renal tubular epithelial heparan sulfate. 22851705_Properdin released from human polymorphonuclear cells does not bind to zymosan or E. coli, but when incubated in properdin-depleted serum this form of properdin binds efficiently to both substrates in a strictly complement C3-dependent manner. 23677468_Our data show that physiological forms of human properdin bind directly to human platelets after activation by strong agonists in the absence of C3 24355864_can directly interact with neutrophil myeloperoxidase resulting in activation of alternative pathway of complement 24885016_In the pathogenesis of renal tubular damage, P can directly bind to PTECs and may accelerate AP activation by surpassing fH regulation 26660535_P serum level expression could be a reliable clinical biomarker to identify patients with underlying surface alternative pathway C5 convertase dysregulation. 27183616_data indicate that properdin enhances platelet/granulocyte aggregates (PGAs) formation via increased production of C5a, and that inhibition of properdin function has therapeutic potential to limit thromboinflammation in diseases characterized by increased PGA formation 28069958_In conclusion, we challenge the view of properdin as a pattern recognition molecule by providing evidence that it binds to different exogenous and endogenous molecular patterns in only a C3-dependent manner. 28105653_this study shows that RNA interference of properdin in dendritic cells decreased alloantigen-specific T-cell proliferation 28264884_studies demonstrate an essential role of properdin oligomerization in vivo while our monomers enable detailed structural insight paving the way for novel modulators of complement. 28784323_Study identified 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms, 1 in the mannose-binding lectin 2 gene (p.Gly54Asp-MBL2) and 1 in the complement factor properdin gene (p.Asn428(p=)-CFP), that showed significant association with the absence and development of antibody-mediated cardiac allograft rejection, respectively. 30199474_Compound heterozygous mutations in IL10RA combined with a complement factor properdin mutation in infantile-onset inflammatory bowel disease. 30755730_TES-mediated upregulation of the transcription factor DDIT3 is involved in CFP suppression of breast cancer cell growth 32793201_Properdin Is a Key Player in Lysis of Red Blood Cells and Complement Activation on Endothelial Cells in Hemolytic Anemias Caused by Complement Dysregulation. 32909942_Soluble collectin-12 mediates C3-independent docking of properdin that activates the alternative pathway of complement. 33240263_The Role of Properdin in Killing of Non-Pathogenic Leptospira biflexa. 33494138_Properdin Is a Modulator of Tumour Immunity in a Syngeneic Mouse Melanoma Model. 35031611_Structure and function of a family of tick-derived complement inhibitors targeting properdin. 35843030_Properdin produced by dendritic cells contributes to the activation of T cells. |
ENSMUSG00000001128 |
Cfp |
300.513862 |
0.1397318719 |
-2.839267 |
0.130330129 |
507.711200 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000019961549973115938613865954580517689023089255367383427070776914619306464890085369213938031860041760076863014691068576499602892411714908568171319715343806759102753903015271965147438448695172946944432340514186250856391823 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009628512339973569999173895456147958108405985000872001572315813025742608636768183184950195544113915493061796117756198415924900509169758547430528436821871312375340606297365749955593923484620477608821197689376887854187731 |
Yes |
No |
75.0664031 |
6.8746754 |
541.1116935 |
29.0169276 |
| ENSG00000126861 |
4974 |
OMG |
protein_coding |
P23515 |
FUNCTION: Cell adhesion molecule contributing to the interactive process required for myelination in the central nervous system. |
Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Leucine-rich repeat;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in neuron projection regeneration. Predicted to act upstream of or within regulation of collateral sprouting of intact axon in response to injury. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4974; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; neuron projection regeneration [GO:0031102] |
12566166_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16425041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16425041_novel mutations and novel polymorphisms in coding regions and 5'UTR were detected in patients with with non-syndromic mental retardation 19034380_Data show that oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein is downregulated in schizophrenia anterior temporal lobe revealed by shotgun proteome analysis. 21534343_The results do not support a relationship between the OMGP gene and the learning disability phenotype observed in neurofibromatosis type 1. |
ENSMUSG00000049612 |
Omg |
31.010879 |
0.3725205585 |
-1.424608 |
0.295830655 |
23.272981 |
0.00000140560836338633012821091976263243594758023391477763652801513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004890801377553567429981758174495354296595905907452106475830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
17.9680592 |
3.8191853 |
48.6143753 |
7.0861633 |
| ENSG00000127152 |
64919 |
BCL11B |
protein_coding |
Q9C0K0 |
FUNCTION: Key regulator of both differentiation and survival of T-lymphocytes during thymocyte development in mammals. Essential in controlling the responsiveness of hematopoietic stem cells to chemotactic signals by modulating the expression of the receptors CCR7 and CCR9, which direct the movement of progenitor cells from the bone marrow to the thymus (PubMed:27959755). Is a regulator of IL2 promoter and enhances IL2 expression in activated CD4(+) T-lymphocytes (PubMed:16809611). Tumor-suppressor that represses transcription through direct, TFCOUP2-independent binding to a GC-rich response element (By similarity). May also function in the P53-signaling pathway (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99PV8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16809611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27959755}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;SCID;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a C2H2-type zinc finger protein and is closely related to BCL11A, a gene whose translocation may be associated with B-cell malignancies. Although the specific function of this gene has not been determined, the encoded protein is known to be a transcriptional repressor, and is regulated by the NURD nucleosome remodeling and histone deacetylase complex. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:64919; |
neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; alpha-beta T cell differentiation [GO:0046632]; commitment of neuronal cell to specific neuron type in forebrain [GO:0021902]; epithelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0003382]; hematopoietic stem cell migration [GO:0035701]; keratinocyte development [GO:0003334]; lymphoid lineage cell migration into thymus [GO:0097535]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070244]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; olfactory bulb axon guidance [GO:0071678]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive T cell selection [GO:0043368]; post-embryonic camera-type eye development [GO:0031077]; regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010837]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; striatal medium spiny neuron differentiation [GO:0021773]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; T cell receptor V(D)J recombination [GO:0033153]; thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070242]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
12930829_CTIP2 mediates transcriptional repression with SIRT1 in mammmalian cells 15104287_To our knowledge, this is the first report implicating BCL11B in hematological malignancies. 15325104_BCL11B is involved in hematological neoplasms of T-cells but not acute myeloid leukemia. 15668700_BCL11B appears to play a key role in T-cell differentiation, BCL11B disruption and disturbed expression may contribute to the development of T-cell malignancies in man. 16091750_transcriptional repression fuction is mediated by NuRD complex 17245431_CTIP2 recruits histone deacetylase (HDAC)1 and HDAC2 to promote local histone H3 deacetylation at the HIV-1 promoter region. 17308084_Data document homeobox gene dysregulation by a novel regulatory region at 3'-BCL11B responsive to histone deacetylase inhibition and highlight a novel class of potential therapeutic target amid noncoding DNA. 17369851_Bcl11b has a role in response to DNA replication stress and damages 18595722_We propose that sequestration and/or decreased expression of Bcl11b in HD is responsible, at least in part, for the dysregulation of striatal gene expression observed in HD and may contribute to the specificity of pathology observed in this disease. 18768194_The authors provide evidence that the transcription factor BCL11B represses expression from the HIV-1 long terminal repeat (LTR) in T lymphocytes through direct association with the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. 19366371_CTIP2 expression could be linked to disease progression and/or maintenance in human atopic dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis 19399189_A statistically significant increase in the expression of CTIP2 was detected in poorly differentiated samples of head and neck tumors. 19581932_CTIP2 is a constitutive p21 gene suppressor that cooperates with SUV39H1 and histone methylation to silence the p21 gene transcription. 20824091_Increased expression of bcl11b leads to chemoresistance and G1 arrest. 21060114_This study proposed that the expression of CTIP2 in the anterior neocortex may mark the early location of the human motor cortex, including its corticospinal projection neurons, allowing further study of their early differentiation. 21080944_BCL11B might play a role in anti-apoptosis in T-ALL cells through up-regulation of its downstream genes BCL2L1 and CREBBP. 21878675_BCL11B is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor that collaborates with all major T-ALL oncogenic lesions in human thymocyte transformation. 22068335_Common genetic variation in a locus in the BCL11B gene desert that is thought to harbor 1 or more gene enhancers is associated with higher CFPWV and increased risk for cardiovascular disease. 22245141_BCL11B directly interacts with P2 promoter region of HDM2 and inhibits HDM2 promoter activity in a p53-dependent manner. 22450536_REVIEW: describes phenotypes given by loss of Bcl11b and roles of Bcl11b in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, taking tissue development and lymphomagenesis into consideration 22700985_Bcl11b phospho-deSUMO switch was identified, the basis of which was phosphorylation-dependent recruitment of the SUMO hydrolase SENP1 to phospho-Bcl11b, coupled to hydrolysis of SUMO-Bcl11b 23040356_BLC11B is an oncogene in T-ALL pathogenesis. 23168072_BCL11B gene silencing alone does not affect hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in vitro. 23383087_a reduction in the level of the BCL11B protein is a key event in the multistep progression of ATLL leukemogenesis 23527175_BCL11B is up-regulated by EWS/FLI and contributes to the transformed phenotype in Ewing sarcoma. 23682716_overexpressed in mycosis fungoides lesions 23852730_CTIP2 controls P-TEFb function in physiological and pathological conditions. 24441149_Integrated genome-wide genotyping and gene expression profiling reveals BCL11B as a putative oncogene in acute myeloid leukemia with 14q32 aberrations. 25023966_low BCL11b expression was associated with poor prognosis; particularly in the standard risk group of thymic T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 25128552_a comprehensive review of the roles of Bcl11b in progenitors, effector T cells, regulatory T cells, and invariant NKT cells, as well as its impact on immune diseases. 25613934_Tax is responsible for suppressing BCL11B protein expression in HTLV-1-infected T-cells; Tax-mediated repression of BCL11B is another mechanism that Tax uses to promote oncogenesis of HTLV-1-infected T-cells. 25827435_BCL11B introduction in human cell lines downregulated transcription of beta-catenin target genes, whereas Bcl11b attenuation in Lgr5(+) crypt base columnar cells increased expression of beta-catenin targets including c-Myc and cyclin D1. 26096706_this is the first study to show that the inhibition of Bcl11b suppresses glioma cell growth by regulating the expression of the cell cycle regulator p21 and stemness-associated genes (Sox-2/Bmi-1). 27161321_Findings identify BCL11B Ser2 phosphorylation as a new mandatory step in the interconnected posttranslational modifications converting BCL11B from a transcriptional repressor to an activator. 27725726_In this present work, the authors identify and characterize a transcription factor i.e. HIC1, which physically interacts with both Bcl11b/CTIP2 and HMGA1 to co-regulate specific subsets of cellular genes and the HIV-1 tat gene. 28232744_studies show BCL11B is a key regulator of the initial stages of human T-cell differentiation and delineate the BCL11B transcriptional program, enabling the dissection of the underpinnings of normal T-cell differentiation and providing a resource for understanding dysregulations in T-ALL 28288848_BCL11B showed increased but varied expression in advanced tumor stage. Analysis of four patients receiving SAHA treatment suggested a positive correlation between BCL11B expression and favorable response to SAHA treatment. In conclusion, BCL11B may serve as a therapeutic target and a useful marker for improving HDACi efficacy in advanced CTCL. 28669733_Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax directly binds to BCL11B. Tax enhances BCL11B degradation through proteasome pathway. Loss of BCL11B enhances cell growth in HTLV-1-infected cells. 28794504_Decreased transcript and increased promoter methylation levels of BCL11B gene were identified in ankylosing spondylitis patients. 29039465_These results suggest that the upregulation of miR-650 contributes to the development of acute renal allograft rejection by suppression of BCL11B, which leads to apoptosis and inflammatory responses. Thus, miR-650 and BCL11B may represent potential therapeutic targets for the prevention of acute renal allograft rejection. 29203643_Results confirm the BCL11B dimerization hypothesis and prove its importance for BCL11B function. By mapping the relevant regions to the CCHC domain, authors describe a previously unidentified mechanism of transcription factor homodimerization. 29503088_BCL11B regulates mammary cell differentiation. 30242241_An interaction between a novel 3'-BCL11B gene desert locus and daily sodium consumption. 31067316_A de novo substitution in BCL11B leads to loss of interaction with transcriptional complexes and craniosynostosis. 31347296_This is the first report of neurodevelopmental disorder caused by a BCL11B variant in a Chinese population. The mutation identified in this report broadens the knowledge of mutation spectrum of BCL11B and might help in genetic counseling and reducing reproductive risk. 31447328_CTIP2-deficient medium spiny neurons implicates CTIP2 target genes at the heart of cAMP-Ca(2+) signal integration in the PKA pathway. 31479431_BCL11B suppression is induced by chimeric antigen receptor and propagates NK-like cell development 31511615_HIV-1 Vpr mediates the depletion of the cellular repressor CTIP2 to counteract viral gene silencing. 31673069_BCL11B regulates MICA/B-mediated immune response by acting as a competitive endogenous RNA. 31828511_The alteration of BCL11B levels might lead to abnormal transcription and inflammation. 32255245_Distinct Notch1 and BCL11B requirements mediate human gammadelta/alphabeta T cell development. 32588101_Role of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1, BCL11B, BMI-1, and CD44 in the prognosis of advanced HNSCC. 32729240_Genes regulated by BCL11B during T-cell development are enriched for de novo mutations found in schizophrenia patients. 33093445_BCL11B suppresses tumor progression and stem cell traits in hepatocellular carcinoma by restoring p53 signaling activity. 33168583_Endocannabinoid signalling in stem cells and cerebral organoids drives differentiation to deep layer projection neurons via CB1 receptors. 33712472_The transcription factor Bcl11b promotes both canonical and adaptive NK cell differentiation. 33876209_14q32 rearrangements deregulating BCL11B mark a distinct subgroup of T-lymphoid and myeloid immature acute leukemia. 34103329_Enhancer Hijacking Drives Oncogenic BCL11B Expression in Lineage-Ambiguous Stem Cell Leukemia. 34344074_[Expression of GATA3 and bcl-11b in peripheral T-cell lymphoma and their clinical significance]. 34402058_B-cell lymphoma/leukaemia 11B (BCL11B) expression status helps distinguish early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma (ETP-ALL/LBL) from other subtypes of T-cell ALL/LBL. 34559552_Human cytomegalovirus expands a CD8(+) T cell population with loss of BCL11B expression and gain of NK cell identity. 34738838_Diagnostic challenge of identifying cases with recurrent t(8;14)(q24.21;q32.2) Involving BCL11B in acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage: an analysis of eight patients. 34865701_Redefining the biological basis of lineage-ambiguous leukemia through genomics: BCL11B deregulation in acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. 35421541_Oncogenic isoform switch of tumor suppressor BCL11B in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. 35864006_Expression pattern and diagnostic utility of BCL11B in mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms. 36202297_A de novo BCL11B variant case manifesting with dystonic movement disorder regarding the article ''BCL11B-related disorder in two canadian children: Expanding the clinical phenotype (Prasad et al., 2020).'' 36211334_Decreased TCF1 and BCL11B expression predicts poor prognosis for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 36376973_Epigenome-wide analysis of T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia identifies BCL11B as a potential biomarker. |
ENSMUSG00000048251 |
Bcl11b |
8.713063 |
2.3335680304 |
1.222538 |
0.552376542 |
4.973935 |
0.02573204578826228036692036482691037235781550407409667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044963300086983688796937741471992922015488147735595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8935461 |
3.8686409 |
5.1714527 |
1.3462527 |
| ENSG00000127311 |
92797 |
HELB |
protein_coding |
Q8NG08 |
FUNCTION: 5'-3' DNA helicase involved in DNA damage response by acting as an inhibitor of DNA end resection (PubMed:25617833, PubMed:26774285). Recruitment to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) following DNA damage leads to inhibit the nucleases catalyzing resection, such as EXO1, BLM and DNA2, possibly via the 5'-3' ssDNA translocase activity of HELB (PubMed:26774285). As cells approach S phase, DNA end resection is promoted by the nuclear export of HELB following phosphorylation (PubMed:26774285). Acts independently of TP53BP1 (PubMed:26774285). Unwinds duplex DNA with 5'-3' polarity. Has single-strand DNA-dependent ATPase and DNA helicase activities. Prefers ATP and dATP as substrates (PubMed:12181327). During S phase, may facilitate cellular recovery from replication stress (PubMed:22194613). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12181327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22194613, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25617833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26774285}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA repair;Helicase;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a DNA-dependent ATPase which catalyzes the unwinding of DNA necessary for DNA replication, repair, recombination, and transcription. This gene is thought to function specifically during the S phase entry of the cell cycle. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:92797; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; 5'-3' DNA helicase activity [GO:0043139]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; single-stranded DNA helicase activity [GO:0017116]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; DNA replication, synthesis of RNA primer [GO:0006269]; maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000462]; negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:2000042]; regulation of DNA double-strand break processing [GO:1903775] |
12181327_role of dominant-negative mutant in blocking onset of chromosomal DNA replication 22194613_Replication stress-induced recruitment of HDHB to chromatin is independent of checkpoint signaling but correlates with the level of replication protein A (RPA) recruited to chromatin. 25617833_HDHB promotes homologous recombination in vivo and stimulates 5'-3' heteroduplex extension during Rad51-mediated strand exchange in vitro 25933514_The depletion of HDHB from human cells diminishes Cdc45 association with chromatin, suggesting that HDHB may facilitate Cdc45 recruitment at G1/S in human cells. 26774285_Conclude that mammalian DNA end resection triggers its own inhibition via the recruitment of HELB. 32455610_Genome Maintenance by DNA Helicase B. 32478505_The Expression of Human DNA Helicase B Is Affected by G-Quadruplexes in the Promoter. 35385349_Human HELB is a processive motor protein that catalyzes RPA clearance from single-stranded DNA. |
ENSMUSG00000020228 |
Helb |
19.311616 |
0.3185456277 |
-1.650428 |
0.505365501 |
10.563405 |
0.00115348517965355710536423661238814020180143415927886962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002661888876123593219991114722233760403469204902648925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7528885 |
3.0169317 |
30.7032321 |
6.2438913 |
| ENSG00000127314 |
5908 |
RAP1B |
protein_coding |
P61224 |
FUNCTION: GTP-binding protein that possesses intrinsic GTPase activity. Contributes to the polarizing activity of KRIT1 and CDH5 in the establishment and maintenance of correct endothelial cell polarity and vascular lumen. Required for the localization of phosphorylated PRKCZ, PARD3 and TIAM1 to the cell junction. Plays a role in the establishment of basal endothelial barrier function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18660803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20332120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21840392}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the RAS-like small GTP-binding protein superfamily. Members of this family regulate multiple cellular processes including cell adhesion and growth and differentiation. This protein localizes to cellular membranes and has been shown to regulate integrin-mediated cell signaling. This protein also plays a role in regulating outside-in signaling in platelets. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 3, 5, 6 and 9. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:5908; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein activity [GO:0003925]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; modification of postsynaptic structure [GO:0099010]; negative regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0045955]; negative regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:2000301]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of integrin activation [GO:0033625]; Rap protein signal transduction [GO:0032486]; regulation of cell junction assembly [GO:1901888]; regulation of establishment of cell polarity [GO:2000114] |
11994301_Relationships between Rap1b, affinity modulation of integrin alpha IIbbeta 3, and the actin cytoskeleton (integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3)) 12407113_Data show that stimulation of a G(i)-dependent signaling pathway causes activation of Rap1B through the action of the PI3K product PtdIns(3,4,5)P(3) and that this process may contribute to potentiation of platelet aggregation. 13679863_RAP1B is prominently expressed in the nucleus of squamous carcinomas. 15078882_PAR-1 and PAR-4 signal Rap1B activation, the ability of thrombin to activate this GTPase independently of secreted ADP involves costimulation of both receptors as well as binding to GPIb-IX-V. 15863506_TPO integrates G(i), but not G(q), stimulation, supports integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) activation platelet aggregation independently of phospholipase C but requires PI3-kinase and Rap1B 16118622_The RAP1B gene mutation is a rare event in myelodysplastic syndromes(MDS) bone marrow cells, in detecting RAP1B mutations, random mutagenesis was performed in RAP1B exons 2 and 3. 16357324_Rap1b is an important element in integrin-dependent outside-in signaling during platelet adhesion and regulates the cross talk between adhesive receptors. 18582561_These results demonstrate that Rap2b, but not the more abundant Rap1b, is associated to lipid rafts in human platelets. 18625726_Results suggest that Rap1a is a key regulator of fibroblast growth factor 2-induced angiogenesis and together with Rap1b controls endothelial cell functions. 18660803_structure of Epac2 in complex with a cAMP analogue (Sp-cAMPS) and RAP1B by X-ray crystallography and single particle electron microscopy 18805968_Rap1a and Rap1b are essential for the conformational activation of beta1-integrins in endothelial cells 18842593_Inhibition of PI3K or mTOR reduced the level of Rap1B, which acts downstream of Rheb and mTOR. The ubiquitin E3 ligase Smurf2 mediates the restriction of Rap1B by initiating its degradation. 18948674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18948674_RAP1 mutation does not play an important role in papillary thyroid carcinoma pathogenesis. 19651783_a mechanistic explanation for the differential effects of Rap1 phosphorylation by PKA on effector protein interaction 19864456_The PTEN-mediated down-regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity may be involved in the regulation of Rap1B-dependent inhibition of Rac1 activity. 22642900_miR-139 decreases proliferation by directly targeting RAP1B 22958893_miR-518b was down-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues and correlated with metastasis and survival. Furthermore, Rap1b was revealed to be directly regulated by miR-518b 23611601_phosphorylation of CalDAG-GEFI is a critical mechanism by which PKA controls Rap1b-dependent platelet aggregation 23716715_Adenosine signaling reduces prenylation and plasma membrane localization of Rap1B, resulting in enhanced tumor cell scattering and invasiveness. 23716716_High concentrations of extracellular adenosine in the tumor microenvironment can chronically activate A2B receptors to suppress Rap1B prenylation and signaling at the cell membrane, resulting in reduced cell-cell contact and promoting cell scattering. 23946483_optimal cell migration is associated with cycles of Rap1 activation, membrane egress, and inactivation, and requires the regulated phosphorylation of Rap1 by PKA 24353183_findings show Rap1b expression decreased significantly in tubules of renal biopsies from patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN); findings indicate Rap1b ameliorates tubular injury and slows progression of DN by modulation of mitochondrial dysfunction via C/EBP-beta-PGC-1alpha signaling 24573637_TMZ as a standard chemotherapeutic agent for GBM inhibits the Rap1B expression and actin cytoskeleton remodeling to exert its cell killing by upregulating miR-181a/b/c/d subunits 24697700_Hepatitis B virus down-regulated miR-101-3p expression, which resulted in up-regulation of Rap1b, and down-regulation of miR-101-3p or up-regulation of Rap1b promoted proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells 24790136_Rap1b in both smooth muscle and endothelium plays a key role in maintaining blood pressure by controlling normal vascular tone. 25569036_Glucocorticoids mediate induction of microRNA-708 to suppress ovarian cancer metastasis through targeting Rap1B. 26209110_Cholera toxin and beta-adrenergic receptor activation phosphorylate Rap1B and inhibit its prenylation and membrane localization. 26329876_The protein expression of RAP1B and HIF-1 alpha contributed to gastric cancer malignant behavior and poor prognosis. 27729617_In RCC tissues and renal carcinoma cells, miR-28-5p is expressed at a low level and RAP1B is expressed at a high level. miR-28-5p inhibits the tumorigenesis of RCC by directly downregulating RAP1B and influencing the activation of two MAP kinases in the MAPK signaling pathway, p38 and Erk1/2. 27760305_Unlike Rap1B, phosphorylation in the polybasic region of Rap1A does not detectably inhibit its prenylation or its binding to SmgGDS-607. 27787845_describe the methods for expression and purification of the plexin cytoplasmic region in E. coli, and characterization of its GAP activity using a photometric assay. We also provide a protocol for measuring GAP activity of single-chain constructs with Rap covalently linked to the plexin cytoplasmic region 28119087_Data show that RAP1B expression was up-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) clinical samples and RAP1B interacted with DVL2 and activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 28924375_Aberrant expression of lncRNA AFAP1-AS, a competing endogenous RNA of miR-181a, may involve in the onset and progression of Hirschsprung disease by augmenting the miR-181a target gene, RAP1B. 29170462_Talin-F0 domain binds to Rap1b like canonical Rap1 effectors despite little sequence homology, and disruption of the binding strongly impairs integrin activation, cell adhesion, and cell spreading. 29559227_Rap1b increased Twist 1 expression by targeting its promoter activity to induce proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 29618512_findings indicate that CAP1 is a geranylgeranyl-binding partner of Rap1 30796637_The authors demonstrate for the first time that RAP1 plays both telomeric and nontelomeric roles in regulating human stem cell homeostasis. 31245877_miR-206 inhibits thyroid cancer proliferation and invasion by targeting RAP1B. 31738148_MiR-181a Reduces Platelet Activation via the Inhibition of Endogenous RAP1B. 31877303_miR-200b/c-RAP1B axis represses tumorigenesis and malignant progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma through inhibiting the NF-kappaB/Twist1 pathway. 32112903_MicroRNA-30b-5p functions as a metastasis suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting Rap1b. 32184389_When amino acids are limited, the Rap1-GTPases confine lysosomes to the perinuclear region and reduce lysosome abundance, which suppresses mTORC1 signaling. 32191497_Long Noncoding RNA LUADT1 Is Upregulated in Melanoma and May Sponge miR-28-5p to Upregulate RAP1B. 32432747_MicroRNA-149 inhibits the progression of lung adenocarcinoma through targeting RAP1B and inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 32539601_Large Extracellular Vesicle-Associated Rap1 Accumulates in Atherosclerotic Plaques, Correlates With Vascular Risks and Is Involved in Atherosclerosis. 32627184_De novo missense variants in the RAP1B gene identified in two patients with syndromic thrombocytopenia. 34306997_LINC00665 Facilitates the Malignant Processes of Osteosarcoma by Increasing the RAP1B Expression via Sponging miR-708 and miR-142-5p. 36056690_SNORA70E promotes the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer through pseudouridylation modification of RAP1B and alternative splicing of PARPBP. |
ENSMUSG00000052681 |
Rap1b |
444.652087 |
2.1444674584 |
1.100619 |
0.090732155 |
146.744463 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000089246894362688382137453894126090167472165581046053583906496744264800317884585024704249822669055447477148845791816711425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000012839026908316575856933105531042362239522211623868684858884320622476635231287525222088410914444978061510482802987098693847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
604.9155498 |
33.0002858 |
284.0529403 |
11.8250440 |
| ENSG00000127415 |
3425 |
IDUA |
protein_coding |
P35475 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Mucopolysaccharidosis;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme that hydrolyzes the terminal alpha-L-iduronic acid residues of two glycosaminoglycans, dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate. This hydrolysis is required for the lysosomal degradation of these glycosaminoglycans. Mutations in this gene that result in enzymatic deficiency lead to the autosomal recessive disease mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3425; |
coated vesicle [GO:0030135]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds [GO:0004553]; L-iduronidase activity [GO:0003940]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; chondroitin sulfate catabolic process [GO:0030207]; dermatan sulfate catabolic process [GO:0030209]; disaccharide metabolic process [GO:0005984]; glycosaminoglycan catabolic process [GO:0006027]; heparin catabolic process [GO:0030211] |
11825626_Results show that leukocyte IDUA from mucopolysaccharidosis I heterozygotes differs from the normal enzyme in terms of optimum pH, Km, Vmax and thermostability at 50 degrees C. 12559846_Ninety percent of the MPS I patients in this study were genotyped and revealed 10 recurrent and thirteen novel IDUA gene mutations. 12818523_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15300847_6 new mutations, c.1087C>T (p.R363C), c.1804T>A (p.F602I), c.793G>C, c.712T>A (p.L238Q), c.1727+2T>A, & c.1269C>G (p.S423R), in a total of 14 different mutations, & 13 polymorphisms , including the new c.246C>G (p.H82Q), were found in 10 MPS I pts. 15862278_Model provides insights into why certain point mutations produce misfolded proteins and lead to severe mucopolysaccharidosis I, while other mutations produce proteins with minor structural perturbations and therefore the attenuated form of the disease. 16435195_analysis of Alpha-L-Iduronidase mutations in Mucopolysaccharidosis I in Tunisia 17570076_Describe a cohort of 14 Hurler-Scheie patients homozygous for the p.Leu490Pro missense mutation in the alpha-L-iduronidase gene. 18340403_Analysis of the structural change in alpha-L-iduronidase of the severe mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) group and that of the attenuated disease, except for a couple of mutations, can help to predict the clinical outcome of MPS I. 19396826_Mutations in the 130 C-terminal amino acids lead to clinical manifestations of Mucopolysaccharidosis type I , which indicates a functional importance of the C-terminus of the IDUA protein. 19751987_Studies show that mouse Idua-W392X mutation is analogous to the human IDUA-W402X mutation commonly found in MPS I-H patients. 19839758_This is the first report of IDUA mutations in Egyptian patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type I. 21176924_study describes monozygotic twins with an attenuated form of mucopolysaccharidosis type I associated with a novel mutation of IDUA, who both showed cervical myelopathy as the initial and cardinal manifestation 21364962_This study reports a novel mutation in IDUA, expanding the mutational spectrum for mucopolysaccharidosis type I. 21394825_this study characterized the underlying IDUA mutations in a group of 102 newly studied European patients, including 37 Italians, whose condition has been clinically and biochemically diagnosed as MPS I. 21397026_Transfer of a high level of human alpha-L-iduronidase gene into the central nervous system (CNS) of MPS I mutant mice susceptible to mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) improves the outcome for MPS when a high level of CNS gene expression is achieved. 21521498_This paper, showed a heterogeneous pattern of mutations and polymorphisms in the IDUA gene among Tunisian patients. 21639919_The identification of two novel alpha-L-iduronidase mutations should facilitate prenatal diagnosis and counseling for MPS I in Tunisia. 21831683_A previously unreported IDUA splice site mutation (NG_008103.1:g.21632G>C; NM_000203.3:c.1727+3G>C) causing a Hurler phenotype in a patient heterozygous for the common p.Q70X (NG_008103.1:g.5862C>T) mutation. 23143250_X-ray diffraction analysis of human alpha-L-iduronidase 23786846_We conclude that this procedure for determining residual IDUA activity in fibroblasts of MPS I patients may be helpful to predict MPS I phenotype. 23959878_Data show that alpha-l-iduronidase (hIDUA) enzyme activity was highly correlated with the N-glycan attached to N372. 24036510_The IDUA structures and biochemical analysis of the disease-relevant P533R mutation have enabled us to correlate the effects of mutations in IDUA to clinical phenotypes. 24368159_The alpha-L-iduronidase missense mutation causing L238Q substitution, when paired with a nonsense mutation, is associated with significant, late-onset brain disease. 24480078_Amino acid substitutions in alpha-L-iduronidase determine the severity of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. 25256405_A new IDUA variant that alters the structure of the signal peptide associated with mucopolysaccharidosis type I is reported. 27146977_Functional characterization of all the novel sequence variants identified in the study would be helpful to confirm the clinical significance and to determine the effect of these variations on the function of respective proteins (IDUA and IDS) 27196898_Molecular studies results unveiled the predominance of(Pro533Arg) IDUA variation in a series of 13 Algerian patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I presented mainly with an attenuated phenotype. 27238910_Enzyme activities (acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), galactocerebrosidase (GALC), glucocerebrosidase (GBA), alpha-galactosidase A (GLA), alpha-iduronidase (IDUA) and sphingomyeline phosphodiesterase-1 (SMPD-1)) were measured on ~43,000 de-identified dried blood spot (DBS) punches, and screen positive samples were submitted for DNA sequencing to obtain genotype confirmation of disease risk 27386755_Using lysosomal storage disease mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I) dogs tolerized to human IDUA as neonates, we evaluated intrathecal delivery of an adeno-associated virus serotype 9 vector expressing human IDUA as a therapy for the central nervous system manifestations of MPS 27520059_10 unrelated Korean patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis I, p.L346R and c.704ins5 were most commonly found in Korean patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis I. 28604952_IDUA deletion mutation is associate with with mucopolysaccharidosis type I . 29282708_the p.X654R mutation is an intermediate IDUA allele yielding residual IDUA activity in Thai patients with intermediate mucopolysaccharidosis type I 31275456_IDUA rs6831280 is associated with bone mineral density in the elderly Chinese population may serve as a marker for the genetic susceptibility to osteoporotic fractures. 31298590_pathogenic sequence variations in IDUA gene, which cause the development of mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 in Iranian patients 31319022_Missing mutations in MPS I: Identification of two novel copy number variations by an IDUA-specific in house MLPA assay. 31386236_Missense mutations in IUDA gene are associated with mucopolysaccharidosis type I. 31400021_IDUA gene mutations in mucopolysaccharidosis type-1 patients from two Pakistani inbred families. 31473686_IDUA gene mutation is associated with mucopolysaccharidosis type 1. 31758674_Identification of a novel compound heterozygous IDUA mutation underlies Mucopolysaccharidoses type I in a Chinese pedigree. 31926052_Estimated birth prevalence of mucopolysaccharidoses in Brazil. 31943709_Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I Phenotypically Corrected with Edited Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Instead of altering the IDUA gene, a protein was inserted in a repurposable place in the genome known as a ''safe harbor locus''. 34189746_Mucopolysaccharidoses type I gene therapy. 34783964_Why SNP rs3755955 is associated with human bone mineral density? A molecular and cellular study in bone cells. |
ENSMUSG00000033540 |
Idua |
314.057068 |
0.3495070125 |
-1.516607 |
0.527005182 |
7.445522 |
0.00635944738068890645654729354419032461009919643402099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012715281064058394158711173815845540957525372505187988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
194.0534667 |
70.3888650 |
565.5017344 |
146.9421828 |
| ENSG00000127507 |
30817 |
ADGRE2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHX3 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor that binds to the chondroitin sulfate moiety of glycosaminoglycan chains and promotes cell attachment. Promotes granulocyte chemotaxis, degranulation and adhesion. In macrophages, promotes the release of inflammatory cytokines, including IL8 and TNF. Signals probably through G-proteins. Is a regulator of mast cell degranulation (PubMed:26841242). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12829604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17928360, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22310662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22575658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26841242}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Autocatalytic cleavage;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the class B seven-span transmembrane (TM7) subfamily of G-protein coupled receptors. These proteins are characterized by an extended extracellular region with a variable number of N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like domains coupled to a TM7 domain via a mucin-like spacer domain. The encoded protein is expressed mainly in myeloid cells where it promotes cell-cell adhesion through interaction with chondroitin sulfate chains. This gene is situated in a cluster of related genes on chromosome 19. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:30817; |
leading edge membrane [GO:0031256]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; chondroitin sulfate binding [GO:0035374]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; granulocyte chemotaxis [GO:0071621]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043304] |
12829604_epidermal growth factor-like domains of the human EMR2 receptor mediate cell attachment through chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans 12860403_role of the extracellular stalk and the G protein-coupled receptor proteolysis site motif in EMR2 processing 15150276_Site-directed mutagenesis of the P(+1) cleavage site (Ser(518)) shows an absolute requirement of a Ser, Thr, or Cys residue for efficient proteolysis. 17174274_The results presented here further support the idea that EMR2 plays a role in the migration and adhesion of myeloid cells during cell differentiation, maturation, and activation. 17928360_Here we demonstrate how the human-restricted adhesion-GPCR EMR2 regulates neutrophil responses by potentiating the effects of a number of proinflammatory mediators and show that the transmembrane region is critical for adhesion-GPCR function. 18267122_EGF-TM7 pre-mRNAs also undergo the rare trans-splicing, leading to the generation of functional chimeric receptors. 20167235_complex cellular expression programmes rather than activation modes regulate the expression of EGF-TM7 receptors in macrophages 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21174063_The association of improved patient survival with higher nuclear expression levels identifies EMR2 as a potential biomarker in patients with invasive breast cancer. 21503828_High EMR2 is associated with invasive phenotype in glioblastoma. 22035891_a functional role for EMR2 in the modulation of neutrophil activation during inflammation. 22310662_Using the myeloid cell-restricted EMR2 receptor as a paradigm, we exam the mechanistic relevance of the subunit interaction and demonstrate a critical role for autoproteolysis in mediating receptor signaling and cell activation 26153037_Data suggest that blood neutrophils expressing CD11c antigen and EMR2 protein be considered as potential biomarkers for sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), respectively. 26841242_We identified a previously unknown missense substitution in ADGRE2 which was predicted to result in the replacement of cysteine with tyrosine as the only nonsynonymous variant cosegregating with vibratory urticaria in two large kindreds. 27905560_EMR2 expression levels correlated with CTP scores and increased further in cirrhotic patients with infections. These high EMR2-expressed neutrophils had activated phenotype but with deranged functions. Higher levels of these EMR2-expressed neutrophils correlated with infectious complications and predict mortality. 29072692_miR-99a reveals two novel targets E2F2 and EMR2 that play a key role in lung tumourigenesis. By inhibiting E2F2 and EMR2, miR-99a represses in vivo the transition of epithelial cells through an EMT process concomitantly with the inhibition of stemness features and consequently decreasing the CSC population. 29540735_Results show that the membrane-associated EMR2-NTF displays a distinct N-glycosylation pattern. Moreover, its membrane-association ability is found to be regulated by site-specific N-glycosylation in the GAIN domain. The membrane-association of EMR2-NTF takes place in post-ER compartments and identify a unique amphipathic alpha-helix at the GAIN sub-domain A as a putative in-plane membrane anchor. 30445064_The ADGRE2 mutation causing familiar vibratory angioedema is not responsible for the frequent nonfamilial form. 31594642_EMR2 stimulates tumor angiogenesis through RGD motif-dependent mechanism.EMR2 promotes tumor angiogenesis by overexpressing MMP-9. 31969668_G Protein-Coupling of Adhesion GPCRs ADGRE2/EMR2 and ADGRE5/CD97, and Activation of G Protein Signalling by an Anti-EMR2 Antibody. 32222457_Critical Signaling Events in the Mechanoactivation of Human Mast Cells through p.C492Y-ADGRE2. 33488598_Stimulation of Vibratory Urticaria-Associated Adhesion-GPCR, EMR2/ADGRE2, Triggers the NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation Signal in Human Monocytes. 33497605_Tethered agonist exposure in intact adhesion/class B2 GPCRs through intrinsic structural flexibility of the GAIN domain. |
|
|
1104.467031 |
3.3017365268 |
1.723225 |
0.061523609 |
787.649061 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002614590475319174917724011040904139309542472878174983117674557912130445030457724647513697844625545044284052988278355843421143749781777420112741685950226475594 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001999552094078291364906228426271941020533012983022389398711353909910649531473401091667607223641574818616924522928688718814034292314018007469440865362302411510 |
Yes |
Yes |
1703.6322105 |
65.9636185 |
519.9446851 |
16.0323255 |
| ENSG00000127526 |
79939 |
SLC35E1 |
protein_coding |
Q96K37 |
FUNCTION: Putative transporter. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable antiporter activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane transport. Located in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79939; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; antiporter activity [GO:0015297] |
35475666_Role of the Orphan Transporter SLC35E1 in the Nuclear Egress of Herpes Simplex Virus 1. |
ENSMUSG00000019731 |
Slc35e1 |
830.159624 |
2.0405631114 |
1.028967 |
0.070688672 |
211.313261 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000710155851978824783936889183267481748362712123052166333782084029346806563376130437224050137345517808979069382151061841194905621676980445045046508312225341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000143784641635218856666879929441456256108124529445360048920543251721761698821432486283077127873753188208005695507832799248659760849022859474644064903259277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1147.6185987 |
51.2752077 |
566.6188948 |
19.3492147 |
| ENSG00000127533 |
9002 |
F2RL3 |
protein_coding |
Q96RI0 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for activated thrombin or trypsin coupled to G proteins that stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis (PubMed:10079109). May play a role in platelets activation (PubMed:10079109). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10079109}. |
3D-structure;Blood coagulation;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the protease-activated receptor subfamily, part of the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family of proteins. The encoded receptor is proteolytically processed to reveal an extracellular N-terminal tethered ligand that binds to and activates the receptor. This receptor plays a role in blood coagulation, inflammation and response to pain. Hypomethylation at this gene may be associated with lung cancer in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:9002; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; thrombin-activated receptor activity [GO:0015057]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; platelet dense granule organization [GO:0060155]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11907122_When expressed in respiratory epithelial cells and cell lines, protease-activated receptor 4 (PAR4)induces the release of IL-6, IL-8, and PGE2. 12006403_Activation of platelets via the PAR4 pathway, by treatment with PAR4 agonist peptide AYPGKF, results in thrombin-induced thromboxane production by platelets. 12008957_The signal from PAR4 stabilizes platelet-platelet aggregate formation in the absence of P2Y12 activation by ADP. 12871418_PAR4 is activated independently of GPIbalpha and ADP 12888878_Important role in regulation of thromboxane formation in platelets responding to thrombin through prolonged elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) and activation of phospholipase A(2). Can be activated by relatively low concentrations of thrombin in human platelets. 13678420_Protease-activated receptor-4 exodomains utilize dual prolines and an anionic retention motif for thrombin recognition and cleavage. 14521606_PAR-1 and PAR-4 have roles in activating GPIb translocation into the cytoskeleton in platelets 14973136_plasmin induces platelet aggregation primarily through slow cleavage of PAR-4; prolonged incubation with plasmin desensitized platelets to further stimulation by thrombin. 15045135_evidence that only one of the thrombin platelet receptors, PAR1 or PAR4, is sufficient to induce intracellular signaling leading to the cleavage of the beta3 cytoplasmic domain 15078882_PAR-1 and PAR-4 signal Rap1B activation, the ability of thrombin to activate this GTPase independently of secreted ADP involves costimulation of both receptors as well as binding to GPIb-IX-V. 15099288_results suggest stimulation of both the PAR1 & PAR4 receptors are necessary for thrombin-induced procoagulant activity, & the P2Y(12) receptor, but not the P2Y(1) receptor, is responsible for potentiation of agonist-induced platelet procoagulant activity 15203717_beta- and gamma-thrombin selectively activate PAR-4; physiological roles are demonstrated 16837456_Data show that at relatively high concentration of agonist, inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor and of calcium mobilization result in complete inhibition of PAR4-induced aggregation, with no effect on either thrombin or PAR1-mediated platelet aggregation. 16952995_new class of cell-penetrating inhibitors, termed pepducins, that provide insight into previously unidentified roles of PAR1 and PAR4 in protease signaling. 17323377_cooperative PAR(1)/PAR(4) signaling network that contributes to thrombin-mediated tumor cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma 17373694_PARs (PAR-1, PAR-2, and PAR-4) are overexpressed in prostate cancer and may serve as potential predictors of recurrence. The data suggest potential role of PARs in autocrine and paracrine mechanisms of prostate cancer. 18179608_similar to the guinea-pig gallbladder, both PAR(1) and PAR(2) but not PAR(4) mediate muscle contraction in the human gallbladder 18427961_Results show the induction of Par-4 by the chemopreventive agent 3,3' diindolylmethane in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. 18480058_PAR4-pretreated platelets, epinephrine caused dense granule secretion, and subsequent signaling from the ATP-gated P2X(1)-receptor and the alpha(2A)-adrenergic receptor induced aggregation. 18682394_Coordinate activation of human platelet protease-activated receptor-1 and -4 in response to subnanomolar alpha-thrombin 19053259_PAR4 uses its anionic cluster to interact with alpha-thrombin. This interaction is important even in the presence of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1). 19058300_These data highlight the role of PAR4 as a new important player in the control of colon tumors and underline the critical role of ErbB-2 transactivation. 19437337_murine platelets are more sensitive to plasmin than human platelets due to differences in the primary sequence of PAR4. In contrast to thrombin-dependent activation of platelets,, mPAR3 inhibits plasmin-induced PAR4 activation. 19528350_both Cat-G and PAR(4) play key roles in generating and/or amplifying relapses in ulcerative colitis 19667088_Complement protease MASP-1 activates human endothelial cells through PAR4 cleavage 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20155436_Human cytomegalovirus induces PARs expression through transcriptional activation in endothelial cells, increasing sensitivity to thrombin. 20175118_Thrombin enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-2 and MMP-13 expression through the PAR/PLC/PKCalpha/c-Src/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 20230207_Data show that PAR1 and PAR4-activating peptides were as effective as thrombin in inducing annexin V binding in combination with collagen-related peptide in diluted whole blood and platelet rich plasma, but not in washed platelets. 20561531_SPSB1 and SPSB4 bind strongly to both Par-4 and VASA peptides. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20807173_Results suggest that lower levels of protease-activated receptors 1 and 4 contribute to the poor thrombin induced aggregation observed with newborn platelets, which can not be compensated by higher levels of GPIbalpha. 20930172_Low concentrations of alpha-thrombin accelerate tissue factor-induced thrombin generation on the surface of vascular smooth muscle cells, and this effect is mediated by PAR-3 and PAR-4. 21127289_Protease-activated receptor signaling in platelets activates cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha differently for cyclooxygenase-1 and 12-lipoxygenase catalysis. 21164077_High glucose enhances smooth muscle cell responsiveness to thrombin through transcriptional upregulation of PAR-4, mediated via PKC and NFkappaB. 21391917_The present study elucidates further differences in human platelet PAR signalling regulation and provides evidence for a cross-talk in which PAR4 signalling counteracts mechanisms involved in PAR1 signalling down-regulation. 21461878_Data show that frog TFF2 activates protease-activated receptor (PAR) 1 to induce human platelet aggregation, and suggest that human TFF2 promotes cell migration via PAR4. 21635966_down-regulation of PAR4 expression occurs frequently in gastric cancers and exhibits association with more aggressive gastric cancer 21649850_PKC inhibition markedly enhances Ca2+ signaling and phosphatidylserine exposure downstream of protease-activated receptor-1 but not protease-activated receptor-4 in human platelets. 22151913_PAR4 is down-regulated in the colonic mast cells of post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome. 22228373_The F2RL3 rs773857 risk allele homozygotes are associated with risk for increased platelet count and hyperactivity. 22318735_mutations that disrupted dimer formation had reduced calcium mobilization in response to the PAR4 agonist peptide. 22411985_Novel role for proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) in membrane trafficking of proteinase-activated receptor 4 (PAR4). 22511653_The results seem to indicate methylation in F2RL3 to be a potential mediator of the detrimental impact of smoking and mortality in coronary heart disease 23307185_Stimulation of PAR4 on platelets leads to faster and more robust thrombin generation, compared to PAR-1 stimulation. 23784669_PAR4 and GPVI-mediated platelet reactivity involves 12-lipoxygenase 24097976_PAR1 and PAR4 require allosteric changes induced via receptor cleavage by alpha-thrombin to mediate heterodimer formation 24216752_Phosphatidylcholine transfer protein contributes to the racial difference in PAR4-mediated platelet activation. 24510982_Lower F2RL3 methylation is a strong predictor of mortality, including all-cause, cardiovascular, cancer and other mortality. Systemic adverse effects of smoking may be mediated by pathways associated with F2RL3 methylation. 24723492_PAR4-P2Y12 association supports arrestin-mediated sustained signaling to Akt. 24776597_provide evidence against the hypothesis that PAR-1 and PAR-4 stimulation of platelets trigger differential release of alpha-granules 24990072_exosite II is critical for activation of PAR4. 25120239_This review summarizes the roles of PAR4 in coagulation and other extracellular protease pathways. 25239438_PAR-4 appears to play a hitherto unsuspected role in diabetic vasculopathy. 25278289_Washed platelets from black volunteers were hyperaggregable in response to PAR4-mediated platelet stimulation compared with whites. 25293779_Quantitative trait locus analysis identified 3 common single nucleotide polymorphisms in the PAR4 gene (F2RL3) associated with PAR4-induced platelet aggregation. Thr120 was more common in blacks than whites. 25664811_The PAR4 expression and activation via intracellular signaling pathways and the role of PAR4 signaling pathways in the development and maintenance of pain. 25821117_Findings suggested that F2RL3 methylation is a very strong predictor of lung cancer risk and mortality, particularly at older age. 25876034_protease-activated receptor 4 and Trefoil factor 2 are expressed in human colorectal cancer 26020638_Bladder PAR activation elicits urothelial MIF release and urothelial MIF receptor signaling at least partly through CXCR4 to result in abdominal hypersensitivity without overt bladder inflammation 26569550_Both GPIbalpha and PAR4 are required for thrombin-induced reactive oxygen species formation in human platelets. 26878340_PAR4 is required for platelet procoagulant function during thrombus formation in human blood 26966273_F2RL3 variants have the potential to markedly alter platelet PAR4 reactivity particularly after exposure to therapeutic PAR1 antagonists. 27126938_Suppression of PAR4 expression has no significant effect on the proliferation of SW620 cells, but can inhibit the migration of the cells. 27402844_these findings are the first to show that internalization of activated PAR4 is linked to proper ERK1/2 and Akt activation. 27784794_the contribution of PAR1 and PAR4 to thrombin-mediated activation of the platelet fibrin receptor (GPIIbIIIa), is reported. 28053157_PAR4 has a role in mediating platelet aggregation; its blockade provides antithrombotic activity 28126849_an intracellular PAR4 C-terminal motif that regulates calcium signaling and beta-arrestin interactions, was identified. 28448853_Thrombin binding to extra-cellular loop II (ECLII) of PAR4 is important for its cleavage and activation of PAR4. 28453567_Prospective study demonstrated that AHRR and F2RL3 methylation levels had inverse relationships with self-reported smoking status and accurately discriminated for both current- and former- smoking. Moreover, methylation markers distinguished former smokers from never-smokers with high accuracy and significantly associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. 29289806_Data suggested that PAR4-AP-induced platelet reactivity between PAR4 rs773902 was associated with altered intensity of Ca(2+) mobilization and ERK activation. 29357418_Endogenous H2S generated by CBS or CSE caused referred hyperalgesia mediated through MIF in mice with PAR4-induced bladder pain, without causing bladder injury or altering micturition behavior. 29677491_Allergen Der p3 from house dust mites activates store-operated calcium channels and protease-activated 4 receptors, stimulating mast cell migration. 29722794_Creosote-exposed workers (73.3%), but not chimney sweeps (76.6%) had lower methylation of F2RL3 cg03636183 than controls (76.7%). 29748334_The signaling difference by the PAR4-120 variant results in the enhancement of both Gq and G13 activation and an increase in thrombus formation resulting in a potential resistance to traditional antiplatelet therapies targeting COX-1 and the P2Y12 receptor. 30055940_lower major bleeding rates were observed in the overall TRACER cohort with the hyperreactive PAR4 Thr120 variant 30143503_This study found divergent and inverse allele frequencies of the PAR4 rs773902 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the Somali population compared with data previously reported for blacks in the United States. The A allele frequency of the PAR4 rs773902 SNP in Somalis was 38% compared with the previously reported 63% for blacks. 30314721_Increased expression of PAR-1 and -4 could be a contributing component in the mechanisms leading to endofibrosis in high performance athletes. 30574762_methylation of F2RL3 can affect the prognosis of different types of acute coronary syndrome and is closely related to mortality 31217499_PAR-4 overcomes chemo-resistance in breast cancer cells by antagonizing cIAP1. 31892516_Molecular basis for activation and biased signaling at the thrombin-activated GPCR proteinase activated receptor-4 (PAR4). 33812377_PAR-4/Ca(2+)-calpain pathway activation stimulates platelet-derived microparticles in hyperglycemic type 2 diabetes. 34469011_Disruption of the biological activity of protease-activated receptors2/4 in adults rather than children in SARS CoV-2 virus-mediated mortality in COVID-19 infection. 34852379_The PAR4 Platelet Thrombin Receptor Variant rs773902 does not Impact the Incidence of Thrombotic or Bleeding Events in a Healthy Older Population. 35012325_Epigenetic Regulation of F2RL3 Associates With Myocardial Infarction and Platelet Function. 35152546_Human and mouse PAR4 are functionally distinct receptors: Studies in novel humanized mice. 35343875_An optimized agonist peptide of protease-activated receptor 4 and its use in a validated platelet-aggregation assay. |
ENSMUSG00000050147 |
F2rl3 |
58.623868 |
5.1755458409 |
2.371711 |
0.238040065 |
107.787645 |
0.00000000000000000000000029917561676340370975087074868474275521312621621433375546515151237477424250865709609570330940186977386474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000003244549671879381667837604005995654775043360107022585028283804978264243112917597500199917703866958618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
97.9930404 |
13.6735656 |
19.1155583 |
2.3596152 |
| ENSG00000127586 |
63922 |
CHTF18 |
protein_coding |
Q8WVB6 |
FUNCTION: Chromosome cohesion factor involved in sister chromatid cohesion and fidelity of chromosome transmission. Component of one of the cell nuclear antigen loader complexes, CTF18-replication factor C (CTF18-RFC), which consists of CTF18, CTF8, DCC1, RFC2, RFC3, RFC4 and RFC5. The CTF18-RFC complex binds to single-stranded and primed DNAs and has weak ATPase activity that is stimulated by the presence of primed DNA, replication protein A (RPA) and by proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). The CTF18-RFC complex catalyzes the ATP-dependent loading of PCNA onto primed and gapped DNA. Interacts with and stimulates DNA polymerase POLH. During DNA repair synthesis, involved in loading DNA polymerase POLE at the sites of local damage (PubMed:20227374). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12766176, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12930902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17545166, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20227374}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;DNA replication;DNA-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein which is a component of a replication factor C (RFC) complex, which loads proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) on to DNA during the S phase of cell cycle. The encoded protein may interact with other proteins, including RFC complex 3, to form a clamp loader complex that plays a role in sister chromatid cohesion during metaphase-anaphase transition. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:63922; |
Ctf18 RFC-like complex [GO:0031390]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; DNA duplex unwinding [GO:0032508]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity [GO:1900264] |
12171929_identification as proliferating cell nuclear antigen-binding protein 12766176_hCTF18, hCTF8, and hDCC1 interact with each other as well as with the p38 subunit of RFC 12930902_The alternative Ctf18-Dcc1-Ctf8-replication factor C complex required for sister chromatid cohesion loads proliferating cell nuclear antigen onto DNA. 17545166_Ctf18-RFC interacts physically with pol eta, which allows DNA replication forks to overcome interference by various template structures, including damaged DNA and DNA-protein complexes that maintain chromosome cohesion 18499658_hChlR1 has a role in the establishment of sister chromatid cohesion, with Ctf18-RFC and Fen1 20826785_Stable interaction between the human proliferating cell nuclear antigen loader complex Ctf18-replication factor C (RFC) and DNA polymerase {epsilon} is mediated by the cohesion-specific subunits, Ctf18, Dcc1, and Ctf8. 23755103_This is the first report of somatic mutations within ESCO1 and CHTF18 in endometrial tumors and of MRE11A mutations in microsatellite-stable endometrial tumors. 27175616_CTF18 forms a complex with RPA when replication stress is elicited by hydroxyurea treatment or UV exposure during S phase. The interaction kinetics between CTF18 and RPA is positively associated with the phosphorylation status of Chk1. 28199690_Human CTF18-RFC clamp-loader complexed with non-synthesising POLE efficiently loads the PCNA sliding clamp. |
ENSMUSG00000019214 |
Chtf18 |
210.751343 |
0.3936578421 |
-1.344986 |
0.242562536 |
29.936100 |
0.00000004465215263324290063671451168035575474135612239479087293148040771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000181811247687355916154538083666369896462811084347777068614959716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
105.0880223 |
20.1720883 |
268.5022199 |
36.8796419 |
| ENSG00000127863 |
55504 |
TNFRSF19 |
protein_coding |
Q9NS68 |
FUNCTION: Can mediate activation of JNK and NF-kappa-B. May promote caspase-independent cell death. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor is highly expressed during embryonic development. It has been shown to interact with TRAF family members, and to activate JNK signaling pathway when overexpressed in cells. This receptor is capable of inducing apoptosis by a caspase-independent mechanism, and it is thought to play an essential role in embryonic development. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55504; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; tumor necrosis factor receptor activity [GO:0005031]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330] |
15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17187358_TROY regulates melanoma growth. 17239012_the ternary complex of NgR/TROY/LINGO-1 expressed on astrocytes, macrophages/microglia and neurones, by interacting with Nogo-A on oligodendrocytes, might modulate glial-neuronal interactions in demyelinating lesions of multiple sclerosis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20512145_Findings provide new insights into the pathogenesis of NPC by highlighting the involvement of pathways related to TNFRSF19 and MDS1-EVI1 in addition to HLA molecules. 20512145_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881009_TNFRSF19 overexpression in glioma cells activates Rac1 signaling in a Pyk2-dependent manner to drive glioma cell invasion and migration 21127458_The FAM134B and TNFRSF19 showed a dramatically strong synergistic epistasis in explaining the genetic dissection of the susceptibility to complex vascular dementia. 22057614_study demonstrated that TNFR2 and TROY mRNA levels are enhanced in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells compared to healthy ones in a Tunisian population 23142137_TROY is up-regulated in human colorectal cancer cell lines and in intestinal tumors in mice. It functions as a negative modulator of the Wnt pathway in LGR5-positive stem cells. 23699535_Results show aberrant expression and/or signaling by TROY as a contributor to the dispersion of glioblastoma cells and therapeutic resistance. 24129566_the association of RhoGDIalpha with TROY contributed to TROY-dependent RhoA activation and neurite outgrowth inhibition after Nogo-66 stimulation. 24623448_TNFRSF19 may contribute to the development of colorectal tumors with deregulated beta-catenin activity. 29117939_Glioblastoma tumors (GB) with elevated TROY expression have a statistically positive correlation with increased EGFR expression. TROY expression significantly increases the capacity of EGF to stimulate GB cell invasion, whereas depletion of TROY expression blocks EGF stimulation of glioblastoma cell invasion. TROY expression modulates EGFR signaling by facilitating EGFR activation and delaying its internalization. 29735548_Study showed that TNFRSF19 is highly expressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and is required for cell proliferation and NPC development. TNFRSF19 was not involved in NFkappaB activation or associated with TRAF proteins. TbetaRI was identified as a specific binding partner for TNFRSF19. TNFRSF19 bound the kinase domain of TbetaRI in the cytoplasm, thereby blocking Smad2/3 association with TbetaRI and subsequent sign... 30219706_TROY signaling role in the glioblastoma cell invasion and survival.PDZ-RhoGEF is an effector of TROY signaling. 30337686_isruption of the TROY/RKIP interaction using the TAT-TROY (234-371 aa) protein reduced the glioma development in xenografted mice. This suggests the TROY/RKIP interaction is a potential target for therapy of gliomas. 30475756_TROY may therefore be a new molecular marker to aid in identifying and selecting patients undergoing radical cystectomy who could potentially benefit from multimodal treatment. 30501144_An inverse trend was found between TROY down-regulation and LGR5 up-regulation in gastric cancer tissue. 31126313_three inherited variations at rs17336602 (G>C), rs4770489 (A>G), and rs34354770 (A>C) in 13q12.12 contribute to lung cancer risk and development by declining p53-responsive enhancer-mediated TNFRSF19 activation 31376183_tumor marker tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 19 as part of a four gene transcript score has prognostic value for metastatic-lethal progression in men treated for localized prostate cancer 32102752_Downregulation of TNFRSF19 and RAB43 by a novel miRNA, miR-HCC3, promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 32629176_TROY signals through JAK1-STAT3 to promote glioblastoma cell migration and resistance. 34358453_Troy/Tnfrsf19 marks epidermal cells that govern interfollicular epidermal renewal and cornification. 35351523_Unique molecular characteristics of NAFLD-associated liver cancer accentuate beta-catenin/TNFRSF19-mediated immune evasion. 35354542_Long noncoding RNA SNHG8 promotes chemoresistance in gastric cancer via binding with hnRNPA1 and stabilizing TROY expression. |
ENSMUSG00000060548 |
Tnfrsf19 |
15.921680 |
0.0836881115 |
-3.578833 |
0.637013267 |
35.820092 |
0.00000000216404596457845087578935739226846518556968135271745268255472183227539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000010057090188028316862166854919139608037781385974085424095392227172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1735396 |
0.9824653 |
25.8032012 |
6.0807951 |
| ENSG00000127920 |
2791 |
GNG11 |
protein_coding |
P61952 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction. |
Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
This gene is a member of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) gamma family and encodes a lipid-anchored, cell membrane protein. As a member of the heterotrimeric G protein complex, this protein plays a role in this transmembrane signaling system. This protein is also subject to carboxyl-terminal processing. Decreased expression of this gene is associated with splenic marginal zone lymphomas. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2791; |
heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
17092487_Collectively, these results suggest a novel senescence pathway mediated by GNG11 in response to environmental cues. 28380310_expression of GNG11 induced the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and abnormal nuclear morphology in SUSM-1 cells but not in HeLa cells |
ENSMUSG00000032766 |
Gng11 |
168.609281 |
8.8797589336 |
3.150521 |
0.203851095 |
242.520730 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000110939337124764375898311962729297963971443053389739045116395603404231021184417206031891970342390147486935596354337322171069463001933931263834343106111646193312481045722961425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000025868319367480601911166308633823909403137505446124107535347399780445187143900831056499045389074253127988459014368409628246604786564258326997389758616918697953224182128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
308.2834158 |
32.3134328 |
34.9857981 |
3.2756028 |
| ENSG00000127946 |
3092 |
HIP1 |
protein_coding |
O00291 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and trafficking (PubMed:11532990, PubMed:11577110, PubMed:11889126). Involved in regulating AMPA receptor trafficking in the central nervous system in an NMDA-dependent manner (By similarity). Regulates presynaptic nerve terminal activity (By similarity). Enhances androgen receptor (AR)-mediated transcription (PubMed:16027218). May act as a proapoptotic protein that induces cell death by acting through the intrinsic apoptosis pathway (PubMed:11007801). Binds 3-phosphoinositides (via ENTH domain) (PubMed:14732715). May act through the ENTH domain to promote cell survival by stabilizing receptor tyrosine kinases following ligand-induced endocytosis (PubMed:14732715). May play a functional role in the cell filament networks (PubMed:18790740). May be required for differentiation, proliferation, and/or survival of somatic and germline progenitors (PubMed:11007801, PubMed:12163454). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VD75, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11007801, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11532990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11577110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11889126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12163454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14732715, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16027218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18790740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9147654}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Activator;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Differentiation;Endocytosis;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The product of this gene is a membrane-associated protein that functions in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and protein trafficking within the cell. The encoded protein binds to the huntingtin protein in the brain; this interaction is lost in Huntington's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:3092; |
clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; extrinsic component of postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098890]; extrinsic component of presynaptic membrane [GO:0098888]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; AP-2 adaptor complex binding [GO:0035612]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; clathrin light chain binding [GO:0032051]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035254]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0080025]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; clathrin coat assembly [GO:0048268]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; neurotransmitter receptor transport [GO:0099637]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway [GO:2000588]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0048260]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization [GO:0099149] |
11788820_Results show that pro-apoptotic Hippi-Hip-1 heterodimers can recruit procaspase-8 into a complex of Hippi, Hip-1 and procaspase-8, and launch apoptosis through components of the 'extrinsic' cell-death pathway. 11889126_HIP1 and HIP12 display differential binding to F-actin, AP2, and clathrin. Identification of a novel interaction with clathrin light chain. 12163454_huntingtin-interacting protein 1 is overexpressed in prostate and colon cancer and is critical for cellular survival 14732715_both HIP1r and HIP1 bind inositol lipids via their epsin N-terminal homology (ENTH) domains. 15059611_HIP1 has roles in endocytosis and receptor trafficking and in tumorigenesis 15533940_roles of Hip1 and Hip1R in affecting clathrin assembly and actin distribution are mediated by their interaction with the conserved sequence of clathrin light chain 15581353_The F-actin binding capacity of Hip1 is regulated by intrasteric occlusion of primary actin-binding determinants within the Hip1 I/LWEQ module. 16027218_HIP1 is a nucleocytoplasmic protein capable of associating with membranes and DNA response elements and regulating transcription. 16847693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16979168_neurotoxic signals of Hip1 transmit through the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathwaysand the formation of apoptosome complex 17452370_Human HIP1 transgenic Hip1/Hip1r knockout mice are completely free from dwarfism and spinal defects. 18155047_Crystal structure at 2.8 A of HIP1 coiled-coil domain reveals a charged surface suitable for HIP1 protein interactor (HIPPI). 18790740_Actin binding by Hip1 (huntingtin-interacting protein 1) and Hip1R (Hip1-related protein) is regulated by clathrin light chain 19626275_Data demonstrate HIP1's role in pits maturation and formation of the coated vesicle, and its strong dependence on clathrin for membranal localization. 20179344_hydrogen-bond network and changes in coiled-coil monomer interaction suggest that the HIP1 coiled-coil domain is uniquely suited to allow conformational flexibility. 21109226_data characterize a neurodevelopmental and epilepsy syndrome that is likely caused by recurrent and nonrecurrent deletions, including HIP1 21697888_Huntingtin-interacting protein 1 is a Merkel cell carcinoma marker that interacts with c-Kit 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22835334_flexibility of the HIP1 coiled-coil domain is important for normal function and may lead to new insights into Huntington's disease 22913984_Three neuronal proteins (Huntingtin interacting protein 1, neurofascin, and olfactomedin-like 2a) are novel components of podocyte major processes and their expression in glomerular crescents supports their role in crescent formation. 23836884_Identified a four-tyrosine 'HIP1 phosphorylation motif' in the N-terminal region of HIP1 that is required for phosphorylation mediated by both EGFR and PDGFbetaR but not by the oncoproteins HIP1/PDGFbetaR (H/P), and TEL/PDGFbetaR (T/P). 24296488_SHON is a novel human oncogene with predictive utility in ER(+) breast cancer, perhaps offering a simple biomarker to predict the therapeutic efficacy of antiestrogen therapy in patients with breast cancer. 24496003_HIP1-ALK-rearranged tumor is sensitive to treatment with crizotinib, implicating HIP1-ALKas an oncogenic driver of lung tumorigenesis 24518094_HIP1-ALK, a novel fusion protein is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 25082541_SHON plays an important role in EMT and contributes to breast cancer progression. 26437767_HIP1 deletion is not involved in Williams-Beuren syndrome. 26595459_Huntingtin-interacting protein-1 (HIP1) is known to play a role in tumorigenesis. metastasis. Read More: http://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201412-2226OC#.V8DF69LrtNs 28452374_HIP1 gene expression might serve as a reliable predictor for overall survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients. 29039605_After HIP1 expression was blocked by siRNAs, EGFR endocytosis was accelerated and this effect was dependent on the EGF concentration. This endocytosis was colocalized with clathrin expression. These findings indicate that the inhibition of HIP1 can accelerate the endocytosis and degradation of EGFR 29284659_Data suggest that GLP1R signaling in pancreatic beta-cells leading to insulin secretion involves interactions of GLP1R with HIP1, SNX1, and SNX27; HIP1 appears to regulate coupling of cell surface GLP1R activation with endocytosis; SNX1 and SNX27 appear to control balance between GLP1R plasma membrane recycling and lysosomal degradation. 30049830_HIP1 is a new arthritis severity gene and a potential novel prognostic biomarker and target for therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. 30224518_Gdpd3 compensates for Hip1 loss. 31535203_White matter DNA methylation profiling reveals deregulation of HIP1, LMAN2, MOBP, and other loci in multiple system atrophy. 32069895_miR-1272 Exerts Tumor-Suppressive Functions in Prostate Cancer via HIP1 Suppression. 33368549_MOBP and HIP1 in multiple system atrophy: New alpha-synuclein partners in glial cytoplasmic inclusions implicated in the disease pathogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000039959 |
Hip1 |
58.417593 |
0.4281206375 |
-1.223911 |
0.237006382 |
26.560148 |
0.00000025545925995890048062610740327305069996555175748653709888458251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000965082845403985383164573164105348723751376383006572723388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.9139394 |
6.4588534 |
82.2174943 |
10.4534847 |
| ENSG00000127951 |
10875 |
FGL2 |
protein_coding |
Q14314 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in physiologic lymphocyte functions at mucosal sites. |
Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted protein that is similar to the beta- and gamma-chains of fibrinogen. The carboxyl-terminus of the encoded protein consists of the fibrinogen-related domains (FRED). The encoded protein forms a tetrameric complex which is stabilized by interchain disulfide bonds. This protein may play a role in physiologic functions at mucosal sites. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10875; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; fibrinogen complex [GO:0005577]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; negative regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050687]; negative regulation of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002605]; negative regulation of macrophage antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002617]; negative regulation of memory T cell differentiation [GO:0043381]; T cell activation via T cell receptor contact with antigen bound to MHC molecule on antigen presenting cell [GO:0002291] |
15490304_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905589_FGL2 expression may be critical to the pathogenesis of renal allograft rejection; these data provide a rationale for targeting the fgl2 gene in an attempt to modulate allograft rejection. 16437596_Results suggest that virus-induced fibrinogen-like protein 2 prothrombinase/fibroleukin expression and associated coagulation activity play a pivotal role in initiating severe hepatitis. 18390877_fgl2 gene transcription induced by the N protein of SARS-CoV was dependent on transcription factor C/EBP alpha binding with its cognate cis-element in fgl2 promoter. 18801734_Hepatitis B virus-induced hFGL2 transcription is dependent on c-Ets-2 and MAPK signal pathway 18932275_Human fg12 contributes to the hypercoagulability in cancer and may induce tumor angiogenesis and metastasis via cytokine induction. 19423547_SARS-CoV N protein specifically modulates transcription of the FGL2 gene to cause fibrosis and vascular thrombosis. 19590927_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20438701_FGL2 plays an important role in macrophage activation in the lungs of COPD patients through MAPK pathway modulation. 22082274_HBV surface antigen-induced transcription of hfgl2 prothrombinase gene. 22886967_The proliferation index of CD8(+)T cells after blocking FGL2 was higher. 22925132_FGL2 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma tumour growth and angiogenesis in a thrombin-dependent manner, and downregulation of its expression might be of therapeutic significance in HCC. 22983266_Circulating fibrinogen-like protein 2 is increased in patients with systemic sclerosis. 23195010_Serum fgl2 levels were increased among renal allograft recipients with acute rejection episodes to an extent dependent upon the pathological type and severity of the response. 24287641_immunomodulatory activity of FGL2 may be involved in the immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease 24728278_The selected peptide sequence NPG-12 may be a critical domain for hfgl2 prothrombinase activity. 25129313_Studied fibrinogen-like protein 2 expression and its role in CRC metastasis and underlying molecular mechanisms; results suggest that FGL2 plays an important oncogenic role in CRC aggressiveness by inducing EMT. 25303152_FGL-2 prothrombinase activity in PBMC of lymphoma patients is increased in active disease and normalizes during remission, thus being a potential marker for follow up of lymphoma patients. 25496996_these results suggest that FGL-2 mediates angiogenesis and tumorigenesis not by thrombin-mediated mechanism but rather through FGF-2/ERK signaling pathway. 25971300_Results show that FGL2 functions as a key immune-suppressive modulator and has potential as an immunotherapeutic target for treating glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). 27163335_Data suggest that fibrinogen-like protein 2 (hFGL2) gene silencing via miRNA may be an alternative strategy for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 27535237_Report increased expression of FGL-2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from mycosis fungoides patients. 28336906_Our results identified FGL2, GAL, SEMA4D, SEMA7A, and IDO1 as new candidate genes that could be involved in MSCs-mediated immunomodulation. FGL2, GAL, SEMA4D, SEMA7A, and IDO1 genes appeared to be differentially transcribed in the different MSC populations. Moreover, these genes were not similarly modulated following MSCs-exposure to inflammatory signals 28609212_serum levels of soluble FAS ligand (sFASL) and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) were analyzed and correlated with sFGL2 levels in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. 28978925_FGL2 expression is a novel, independent, and an adverse prognostic factor of clinical outcomes in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 29756667_The increase in intrahepatic and plasma sFGL2 by Tregs may restrict AIH progression by inhibiting conventional CD8+ T cells and Tc17 cell function. The high correlation between sFGL2 and disease severity may predict AIH outcome. 29947810_High FGL2 expression is associated with glioma. 30503273_Serum FGL2 is a promising biomarker for assessing the severity and prognosis in severe TBI 30683885_FGL2 promotes tumor progression in the brain by suppressing CD103-expressing dendritic cell differentiation. 30884164_Elevation of serum sFGL2 concentrations is strongly associated with the acute pancreatitis severity and has the potential to distinguish delirium after acute pancreatitis. 30916506_The presence of infectious/autoimmune diseases does not significantly alter FGL2 activity in the peripheral blood 31580221_The FGL2 prothrombinase contributes to the pathological process of experimental pulmonary hypertension. 31763448_Data show that RvDp5 enhances fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2) secretion via ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 (ADAM17) and synergistically accelerates resolution of inflammation. 32133407_Blood-stage malaria parasites manipulate host innate immune responses through the induction of sFGL2. 32350910_Soluble Fibrinogen-like protein 2 plays a role in varicocele induced male infertility. 32679128_Predictive value of soluble fibrinogen-like protein 2 for survival in traumatic patients with sepsis. 32683349_Soluble fibrinogen-like protein 2 in condyloma acuminatum lesions. 32716910_Fibrinogen-Like Protein 2 (FGL2) is a Novel Biomarker for Clinical Prediction of Human Breast Cancer. 32858440_Identification of integrative molecular and clinical profiles of Fibrinogen-like protein 2 in gliomas using 1323 samples. 32863955_Fibrinogen-like protein 2 aggravates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via interaction with TLR4, eliciting inflammation in macrophages and inducing hepatic lipid metabolism disorder. 33323552_Tumor-associated macrophage polarization promotes the progression of esophageal carcinoma. 33754059_Dabigatran activates inflammation resolution by promoting fibrinogen-like protein 2 shedding and RvD5n-3 DPA production. 33893391_Regulatory T cells induce polarization of pro-repair macrophages by secreting sFGL2 into the endometriotic milieu. 34109427_Soluble fibrinogenlike protein 2 levels are decreased in patients with ischemic heart failure and associated with cardiac function. 34154648_Identifying novel genetic variants for brain amyloid deposition: a genome-wide association study in the Korean population. 35029030_Fibrinogen-like protein 2 in gastrointestinal stromal tumour. |
ENSMUSG00000039899 |
Fgl2 |
12.934027 |
2.6841408323 |
1.424460 |
0.463530163 |
9.484725 |
0.00207189722479082924153082068130515835946425795555114746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004559594906502555458627234941104688914492726325988769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.9539334 |
5.1376067 |
7.1328432 |
1.5726267 |
| ENSG00000127955 |
2770 |
GNAI1 |
protein_coding |
P63096 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in numerous signaling cascades. The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and alternates between an active, GTP-bound state and an inactive, GDP-bound state. Signaling by an activated GPCR promotes GDP release and GTP binding. The alpha subunit has a low GTPase activity that converts bound GTP to GDP, thereby terminating the signal. Both GDP release and GTP hydrolysis are modulated by numerous regulatory proteins (PubMed:8774883, PubMed:18434541). Signaling is mediated via effector proteins, such as adenylate cyclase. Inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, leading to decreased intracellular cAMP levels (By similarity). The inactive GDP-bound form prevents the association of RGS14 with centrosomes and is required for the translocation of RGS14 from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. Required for normal cytokinesis during mitosis (PubMed:17635935). Required for cortical dynein-dynactin complex recruitment during metaphase (PubMed:22327364). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17635935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18434541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8774883}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;GTP-binding;Host-virus interaction;Intellectual disability;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitosis;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transport |
|
Guanine nucleotide binding proteins are heterotrimeric signal-transducing molecules consisting of alpha, beta, and gamma subunits. The alpha subunit binds guanine nucleotide, can hydrolyze GTP, and can interact with other proteins. The protein encoded by this gene represents the alpha subunit of an inhibitory complex. The encoded protein is part of a complex that responds to beta-adrenergic signals by inhibiting adenylate cyclase. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:2770; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell cortex region [GO:0099738]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; midbody [GO:0030496]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding [GO:0031821]; G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding [GO:0031683]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to forskolin [GO:1904322]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex [GO:1904778]; regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043949]; regulation of mitotic spindle organization [GO:0060236]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434] |
11976690_Structural determinants for GoLoco-induced inhibition of nucleotide release by Galpha subunits 12297512_co-stimulation of G(12/13) and G(i) pathways is sufficient to activate GPIIb/IIIa in human platelets in a mechanism that involves intracellular calcium 14576516_An age-induced increase in G alpha i may have a role in depressing cardiac function in aged human atria. 14581469_region of the third cytoplasmic loop of Dopamine D2 receptor is crucial for determining G(i) protein coupling specificity. 14602724_Gi has a role in insulin attenuation of platelet functions by interfering with cAMP suppression along with IRS-1 14623889_Gi, but not Gq or G12/13, signaling pathways are required for activation of Akt in platelets 14625285_Gi has a role in CXCL16 signaling that induces cell-cell adhesion and aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation 15657046_the G(alpha)o/i-coupled cannabinoid receptor, by regulating the proteasomal degradation of Rap1GAPII, activates Rap1 to induce neurite outgrowth. 15837785_G12, Rho, filamin-A, and the actin cytoskeleton are required for amino acid-stimulated Ca2+ oscillations produced by the Ca2+-sensing receptor 15863506_TPO integrates G(i), but not G(q), stimulation, supports integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) activation platelet aggregation independently of phospholipase C but requires PI3-kinase and Rap1B 16371464_Gialpha and Gbeta subunits both define selectivity of G protein activation by alpha2-adrenergic receptors. 16775006_Nef protein of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) reduces cell surface levels of eight different members of the CC- and CXC-family of Chemokine receptors (CKRs) by up to 92%. 17013094_autotaxin induces uPA expression via the Gi-PI3K-Akt-NF-kappaB signaling pathway that might be critical for autotaxin-induced tumor cell invasion and metastasis 17267663_These data revealed that PAR1 can be part of a preassembled complex with Galpha(i1) protein, resulting either from a direct interaction between these partners or from their colocalization in specific microdomains. 17416965_Data show that Gi and RGS proteins provide biochemical control of androgen receptor exclusion from the cell nucleus. 17646583_Selective induction of G alpha inhibiting subunit 1 (Gi alpha1) expression is a novel downstream event in hypertrophic signaling that may be a critical factor leading to cellular electrophysiological remodeling of the Ras transgenic mouse heart. 18037379_Heretotrimeric G protein subunit Galphai is associated with mitochondria. 18083345_The potency and efficacy of LPA-mediated inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity was enhanced in cells expressing RGSi G(i) (mutant) proteins as compared to RGSwt G(i). 18378672_MUPP1 binds to the G protein-coupled MT(1) melatonin receptor and directly regulates its G(i)-dependent signal transduction 18519563_analysis of structural determinants underlying the temperature-sensitive nature of a Galpha mutant 18984596_Galpha.GoLoco complexes have roles in mitotic spindle dynamics 19369247_Galpha(i1)(GDP) can bind a second Gbetagamma subunit with an affinity only 10-fold weaker than the primary site and close to the affinity between activated Galpha(i1) and Gbetagamma subunits. 19494521_differentialy expressed in dendritic cells upon stimulation of with with the major house dust mite allergen Der p 1 19666700_A switch in G-protein coupling, in which glutamate775lysine loses G(o) subunit coupling but retains coupling to G(i), may explain the highly specialized metabotropic glutamate receptor mGlu6 phenotype. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951712_The chemotaxis signal pathway induced by chemokines CKbeta8 and CKbeta8-1 is mediated via the Gi/Go protein, phospholipase C (PLC) and protein kinase C delta (PKC delta). 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20586915_analysis of a novel Gi, P2Y-independent signaling pathway mediating Akt phosphorylation in response to thrombin receptors 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20679342_Nucleobindin 1 is a calcium-regulated guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor of G{alpha}i1. 20696855_The RET combination analysis revealed that stimulation of the alpha(2A)-adrenergic receptor (alpha(2A)AR) leads to the recruitment of GRK2 at a receptor still associated with the Galpha(i1)beta(1)gamma(2) complex. 20716524_AGS3 receptor coupling to both Galphabetagamma and GPR-Galpha(i) offer additional flexibility for systems to respond and adapt to challenges and orchestrate complex behaviors 20829352_Data reveal a change in the repertoire of Galpha(i/o) subunits during T cell differentiation and suggest functional equivalence among Galpha(i/o) subunits irrespective of their relative abundance. 21654736_Galpha(o) protein contributes to maximally efficient mu-opioid receptor signaling and antinociception in Galpha(o) null transgenic mice. 21880739_RGS14 can form complexes with GPCRs in cells that are dependent on Galpha(i/o) and these RGS14.Galpha(i1).GPCR complexes may be substrates for other signaling partners such as Ric-8A 22070874_CXCL12 signaling via CXCR7 is Gialpha independent. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 23086480_resistin contributes to the pro-inflammatory state of SMC by the up-regulation of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 expression via a mechanism involving NF-kB, AP-1, and STAT1/3 transcription factors, (2) resistin employs TLR4 and Gi-protein signaling. 23179791_Data indicate that focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation and cell migration require Src, Gi/Go, COX-2 and LOXs activities. 23341447_Data suggest that chemokine binding to CCX-CKR (a) recruits Gi proteins and beta-arrestin (beta-arr) with high affinity. 23404499_leucine can directly facilitate insulin signaling through a Galphai protein-dependent intracellular signaling pathway 23467353_This study support a role for RGS proteins as negative regulators of opioid supraspinal antinociception and also reveal a potential novel function of RGS proteins as positive regulators of opioid spinal antinociceptive pathways. 23841650_AC5, by binding active Galphai1, interferes with G-protein deactivation and reassembly and thereby might sensitize its own regulation. 24914133_Data indicate that hydroxyurea (HU) induces SAR1 protein expression, which in turn activates gamma-globin expression, predominantly through the Gialpha/JNK/Jun pathway. 25078664_We observed increased expression of Galphai1/3 in wounded human skin and keloid skin tissues, suggesting the possible involvement of Galphai1/3 in wound healing and keloid formation. 25242222_Gi alpha subunit was found to be a key modulator of GABAB-receptors signaling in analgesia. 25291362_The loss-of-function mutations of GNAI loci are rare or nonexistent in familial pituitary adenomas. 25979337_Employed time-resolved FTIR difference spectroscopy to investigate the molecular reaction mechanisms of Galphai1. Mutants of the intrinsic arginine finger (Galphai1-R178S) affected exclusively the hydrolysis reaction. 26258638_In activation cluster I, helices alpha1 and alpha5 pack against strands beta1-beta3 to stabilize the nucleotide-bound states. 27109834_The authors demonstrate that Glu53, Glu60, and Glu118 of human Ngb are crucial for both the neuroprotective activity and interaction with Gi. Moreover, they show that Lys46, Lys70, Arg208, Lys209, and Lys210 residues of Gi are important for binding to human Ngb. 27298341_GTP analogs leads to a rigid and closed arrangement of the Galphai1, whereas the apo and GDP-bound forms are considerably more open and dynamic. 27462082_biochemical and computational data indicate that the interactions between alpha5, alpha1, and beta2-beta3 are not only vital for GDP release during G protein activation, but they are also necessary for proper GTP binding (or GDP rebinding). 27494760_complex between M2R and holo-Gi1 is an octamer comprising four copies of each, and that activation is accompanied by a decrease in the oligomeric size of Gi1 27566546_CGRP family of receptors displays both ligand- and RAMP-dependent signaling bias among the Galphas, Galphai, and Galphaq/11 pathways. 27621449_GIV is a bifunctional modulator of G proteins; it serves as a guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI) for Galphas using the same motif that allows it to serve as a guanine-nucleotide exchange factor for Galphai 27908592_Silencing of Galphai1 expression blocked the inhibitory effects of G-1 on prostate cancer cell growth 28145731_These data indicate that, unlike in taste cells, TAS2Rs couple to the prevalent G proteins, Galphai1, Galphai2, and Galphai3, with no evidence for functional coupling to Galphagust. 28219737_The results show ZIP9 is a specific Gi coupled-membrane AR mediating testosterone-induced MAP kinase and zinc signaling in PC3-ZIP9 cells. 28223151_testosterone rapidly increased whole-cell HCAEC SKCa and BKCa currents via a surface androgen receptor, Gi/o protein, and protein kinase A 28438833_These findings suggest that Gi1 interacts only with active GPCRs and that the well known high speed of GPCR signal transduction does not require preassembly between G proteins and GPCRs. 29259127_HL-60 neutrophil-like cells expressing Rap1a(G12V) or Radil have an elongated phenotype because of enhanced uropod adhesion as they attempt to migrate on fibronectin. This elongated phenotype driven by Rap1a(G12V) or Radil is reversed by Galphai1(Q204L), but not by WT Galphai1 expression, suggesting that Galphai-GTP also regulates adhesion in immune cells at the level of, or downstream of, Radil. 29520106_Galphai1 mRNA and protein expression were significantly upregulated in human glioma tissues and correlates with Akt hyperactivation and microRNA-200a downregulation. Galphai1 is the primary target of microRNA-200a in mediating its anti-glioma cell activity. 29740092_The conjugated bile acids were found to be partial agonists of the muscarinic M2, but not sphingosin-1-phosphate-2, receptors, and act partially through the Gi pathway. Furthermore, the contraction slowing effect of unconjugated bile acids may also relate to cytotoxicity at higher concentrations 29899450_using cryo-electron microscopy, it is shown that the major interactions between activated rhodopsin and Gi are mediated by the C-terminal helix of the Gi alpha-subunit, which is wedged into the cytoplasmic cavity of the transmembrane helix bundle and directly contacts the amino terminus of helix 8 of rhodopsin 29899455_3.5 A resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the mu-opioid receptor (muOR) bound to the agonist peptide DAMGO and nucleotide-free Gi; these results shed light on the structural features that contribute to the Gi protein-coupling specificity of the microOR 29925530_Interplay between negative and positive design elements in Galpha helical domains of G proteins determines interaction specificity toward RGS2. 30279732_These results provide mechanistic insights into the critical role played by Galphai1/3 proteins in VEGF-induced VEGFR2 endocytosis, signaling and angiogenesis. 31168089_24,25-epoxycholesterol, an endogenous ligand of PTCH1, can stimulate Hedgehog signalling in cells and can trigger Gi-protein signalling via human SMO in vitro 31233841_Orexin-A protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced cell damage by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis via the Gi and PI3K signaling pathways. 31243364_cryoelectron structures of human NTSR1 in complex with the agonist JMV449 and the heterotrimeric Gi1 protein, at a resolution of 3 A 31363053_Here, we present a 2.0-A crystal structure of Galpha i in complex with the GEM motif of GIV/Girdin. Nucleotide exchange assays, molecular dynamics simulations, and hydrogen-deuterium exchange experiments demonstrate that GEM binding to the conformational switch II causes structural changes that allosterically propagate to the hydrophobic core of the Galpha i GTPase domain 31936673_Preferential Coupling of Dopamine D2S and D2L Receptor Isoforms with Gi1 and Gi2 Proteins-In Silico Study. 32126208_Structures of Galpha Proteins in Complex with Their Chaperone Reveal Quality Control Mechanisms. 32193322_the structures of the glucagon receptor (GCGR) bound to glucagon and distinct classes of heterotrimeric G proteins, Gs or Gi1 was determined using cryo-electron microscopy 33308256_The Galphai protein subclass selectivity to the dopamine D2 receptor is also decided by their location at the cell membrane. 33493164_Galphai1 inhibition mechanism of ATP-bound adenylyl cyclase type 5. 33785921_Feeling at home: Structure of the NTSR1-Gi complex in a lipid environment. 33958720_LncRNA PINK1-AS promotes Galphai1-driven gastric cancer tumorigenesis by sponging microRNA-200a. |
ENSMUSG00000057614 |
Gnai1 |
119.431628 |
0.2275394637 |
-2.135811 |
0.214942282 |
96.953679 |
0.00000000000000000000007096832122384832394616042963773379287303162780511778019223447736690824072525174415204674005508422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000698794143605070934269750648257287025170217673177988417044311127146460904668856528587639331817626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.0718508 |
7.4419447 |
190.9339674 |
22.2728469 |
| ENSG00000127995 |
64921 |
CASD1 |
protein_coding |
Q96PB1 |
FUNCTION: O-acetyltransferase that catalyzes 9-O-acetylation of sialic acids (PubMed:20947662, PubMed:26169044). Sialic acids are sugars at the reducing end of glycoproteins and glycolipids, and are involved in various processes such as cell-cell interactions, host-pathogen recognition (PubMed:20947662, PubMed:26169044). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26169044, ECO:0000305|PubMed:20947662}. |
Acyltransferase;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables N-acetylneuraminate 7-O(or 9-O)-acetyltransferase activity. Involved in carbohydrate metabolic process. Is integral component of Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64921; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; N-acetylneuraminate 7-O(or 9-O)-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0047186]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975] |
20947662_human Cas1 protein is directly involved in O-acetylation of alpha2-8-linked sialic acids 26169044_CASD1 is a sialate O-acetyltransferase and serves as key enzyme in the biosynthesis of 9-O-acetylated sialoglycans. |
ENSMUSG00000015189 |
Casd1 |
164.120736 |
3.8982394109 |
1.962823 |
0.839345131 |
5.027144 |
0.02495301578151212090750377115000446792691946029663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043757456687076021206728171364375157281756401062011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
230.1694518 |
98.1045547 |
59.8212439 |
18.3237286 |
| ENSG00000128011 |
57622 |
LRFN1 |
protein_coding |
Q9P244 |
FUNCTION: Promotes neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neurons. Involved in the regulation and maintenance of excitatory synapses. Induces the clustering of excitatory postsynaptic proteins, including DLG4, DLGAP1, GRIA1 and GRIN1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in regulation of postsynaptic density assembly. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in cell surface. Predicted to be integral component of postsynaptic density membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57622; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839] |
33110456_Identification of a Set of Genes Improving Survival Prediction in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma through Integrative Reanalysis of Transcriptomic Data. |
ENSMUSG00000030600 |
Lrfn1 |
51.882353 |
0.4141653580 |
-1.271721 |
0.229826473 |
31.218440 |
0.00000002305654610242445495945848299434999262302881106734275817871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000096955732328143864595648964560536953172231733333319425582885742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.6810563 |
4.2549229 |
71.9628156 |
6.5647762 |
| ENSG00000128050 |
10606 |
PAICS |
protein_coding |
P22234 |
FUNCTION: Bifunctional phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase and phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinocarboxamide synthetase catalyzing two reactions of the de novo purine biosynthetic pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17224163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2183217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31600779}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Decarboxylase;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ligase;Lyase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Purine biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamide from 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate: step 1/2. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:31600779}.; PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxylate from 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole (carboxylase route): step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:31600779}. |
This gene encodes a bifunctional enzyme containing phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity in its N-terminal region and phosphoribosylaminoimidazole succinocarboxamide synthetase in its C-terminal region. It catalyzes steps 6 and 7 of purine biosynthesis. The gene is closely linked and divergently transcribed with a locus that encodes an enzyme in the same pathway, and transcription of the two genes is coordinately regulated. The human genome contains several pseudogenes of this gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10606; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; 5-amino-4-imidazole carboxylate lyase activity [GO:0043727]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase activity [GO:0004638]; phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase activity [GO:0004639]; 'de novo' AMP biosynthetic process [GO:0044208]; 'de novo' IMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006189]; 'de novo' XMP biosynthetic process [GO:0097294]; GMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006177]; purine nucleobase biosynthetic process [GO:0009113] |
19850283_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26140362_purine biosynthetic pathway enzymes PPAT and PAICS, as well as pyruvate kinase activity are increased in lung cancer 30121007_we show that PAICS, which catalyzes a critical step in purine biosynthetic pathway, is overexpressed and plays a role in BLCA cell proliferation, colony formation, and 3D spheroid invasion, suggesting a role in oncogenesis. 30641222_PAICS is hypomethylated in the lung adenocarcinoma tissues.PAICS is highly expressed in the lung adenocarcinoma tissues. 31624245_Combinatorial targeting of MTHFD2 and PAICS in purine synthesis as a novel therapeutic strategy. 32571877_Crystal structures of human PAICS reveal substrate and product binding of an emerging cancer target. 32632107_PAICS contributes to gastric carcinogenesis and participates in DNA damage response by interacting with histone deacetylase 1/2. 34173716_PAICS is related to glioma grade and can promote glioma growth and migration. 34323174_Regulating COX10-AS1 / miR-142-5p / PAICS axis inhibits the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer. 35285625_Evidence Supporting Substrate Channeling between Domains of Human PAICS: A Time-Course Analysis of (13)C-Bicarbonate Incorporation. 35331738_Multienzyme interactions of the de novo purine biosynthetic protein PAICS facilitate purinosome formation and metabolic channeling. |
ENSMUSG00000029247 |
Paics |
833.403106 |
3.0230813062 |
1.596020 |
0.076450908 |
432.050294 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000581626366642923996342543470853087391805810178954167642168871140298986248644375740752695618982803558662608437448233352175387061954744334954199056460188830306364769396258532758974471382893143999892284879374199578510221568170643566546459 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000232650546657169585230892888315763957003406208308826906096933661398714496566968759281050657763270997574303113331303022282370933617036717165446554784204690555070998009970123666809010591022976647699159674044557741393793868698685852261510 |
Yes |
Yes |
1171.1239000 |
72.0950604 |
390.2713625 |
18.1794511 |
| ENSG00000128052 |
3791 |
KDR |
protein_coding |
P35968 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for VEGFA, VEGFC and VEGFD. Plays an essential role in the regulation of angiogenesis, vascular development, vascular permeability, and embryonic hematopoiesis. Promotes proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation of endothelial cells. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. Isoforms lacking a transmembrane domain, such as isoform 2 and isoform 3, may function as decoy receptors for VEGFA, VEGFC and/or VEGFD. Isoform 2 plays an important role as negative regulator of VEGFA- and VEGFC-mediated lymphangiogenesis by limiting the amount of free VEGFA and/or VEGFC and preventing their binding to FLT4. Modulates FLT1 and FLT4 signaling by forming heterodimers. Binding of vascular growth factors to isoform 1 leads to the activation of several signaling cascades. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and the activation of protein kinase C. Mediates activation of MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1 and the MAP kinase signaling pathway, as well as of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Mediates phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and activation of PTK2/FAK1. Required for VEGFA-mediated induction of NOS2 and NOS3, leading to the production of the signaling molecule nitric oxide (NO) by endothelial cells. Phosphorylates PLCG1. Promotes phosphorylation of FYN, NCK1, NOS3, PIK3R1, PTK2/FAK1 and SRC. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10102632, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10368301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10600473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11387210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12649282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1417831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15026417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215251, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15962004, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16966330, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17303569, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18529047, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19668192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19834490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20224550, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20705758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21893193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25825981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7929439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9160888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9837777}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major growth factor for endothelial cells. This gene encodes one of the two receptors of the VEGF. This receptor, known as kinase insert domain receptor, is a type III receptor tyrosine kinase. It functions as the main mediator of VEGF-induced endothelial proliferation, survival, migration, tubular morphogenesis and sprouting. The signalling and trafficking of this receptor are regulated by multiple factors, including Rab GTPase, P2Y purine nucleotide receptor, integrin alphaVbeta3, T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase, etc.. Mutations of this gene are implicated in infantile capillary hemangiomas. [provided by RefSeq, May 2009]. |
hsa:3791; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome [GO:0005768]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; sorting endosome [GO:0097443]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; Hsp90 protein binding [GO:0051879]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; vascular endothelial growth factor binding [GO:0038085]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005021]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060837]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to hydrogen sulfide [GO:1904881]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; embryonic hemopoiesis [GO:0035162]; endocardium development [GO:0003157]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; endothelium development [GO:0003158]; epithelial cell maturation [GO:0002070]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lymph vessel development [GO:0001945]; mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0010463]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000352]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:0038083]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038033]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0002053]; positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051901]; positive regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090141]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; positive regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001214]; post-embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048597]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of bone development [GO:1903010]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:1901532]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling pathway [GO:0036324]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084]; vascular wound healing [GO:0061042]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
11693202_vitronectin increased the presence of all four growth factor receptors and most notably, VEGFR-1; in contrast, fibrin decreased all four receptors, especially FGFR-1 and FGFR-2 11807987_A potential mechanism involved in hemangioma formation is the alteration of the FLK1 signaling pathway in endothelial and/or pericytic cells. 11809684_green tea catechins are novel inhibitors of VEGFR-2 activity. 11824379_Involvement of VEGFR-2 (kdr/flk-1) but not VEGFR-1 (flt-1) in VEGF-A and VEGF-C-induced tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells in fibrin matrices in vitro. 11852061_In this study we give evidence of Flt-1 and KDR receptors in platelets. 11908876_VEGF, Flt1, and Flk1 can be considered as indicators of the malignancy potential of diffusely infiltrating astrocytomas. The expression of VEGF and the two receptors may be affected by the proliferative activity of tumor cells. 11960378_Constitutive activation of Stat3alpha in brain tumors: localization to tumor endothelial cells and activation by the endothelial tyrosine kinase receptor (VEGFR-2) 11986954_CLL B cells consistently express VEGFR2 mRNA; co-expression of angiogenic molecules and receptors suggest autocrine pathways of stimulation. 12067897_Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flk1/KDR is induced by shear stress through the CT-rich Sp1 binding site. 12174363_KDR plays a key role in regulating the proliferation of HGCC and HVEC. 12213878_findings implicate altered VEGF and KDR signaling in pituitary tumorigenesis; PTTG stimulation of FGF-2 and VEGF expression in the presence of up-regulated growth factor receptors may account for angiogenic growth and progression of human pituitary tumors 12426207_The binding of VEGF to its receptor, KDR, is necessary and sufficient to induce the gene expression profile induced by VEGF. 12439912_The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors KDR and Flt-1 by gastric carcinoma tissues and cell lines was detected to elucidate the molecular mechanism of this growth factor in promoting tumor growth. 12456025_VEGFR-2 has a role in regulating angiogenesis-related functions [review] 12464608_transcriptional activation of Flk-1 in endothelial cells requires the interaction between HIF-2alpha and Ets-1 12551914_A set of loop-1 and -3 structures in the novel vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family member, VEGF-ENZ-7, is essential for the activation of this protein's signaling. 12560084_Fluid shear stress induced upregulation requires Sp1 transcription factor binding to specific response elements in the 5' regulatory region 12607599_Staining for the receptors VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 was positive in large lymphoid cells in stage IV non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 12670961_Gq/11 proteins mediate KDR tyrosine phosphorylation and KDR-mediated HUVEC proliferation through interaction with KDR. 12810080_These data indicate that activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 prevents endothelial cell apoptosis by inhibiting p38 MAP kinase phosphorylation and reducing caspase-3 activity. 12949011_in humans: 1) VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA are increased by acute systemic exercise; 2) the time course of the VEGF, KDR, and Flt-1 mRNA responses are different from those previously reported in rats 14532277_TNF induces transactivation between Etk and VEGFR2, and Etk directly activates PI3K-Akt angiogenic signaling independent of VEGF-induced VEGFR2-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. 14635716_Altered expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and FLK-1 receptor in chronically hypoxic carotid body. 14654077_VEGF, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 are concomitantly expressed in pre-B ALL cells. Expression of the receptors is limited to the intra-cytoplasmic compartment and may suggest either internalization or a block in trafficking of the receptor to the surface. 14674128_changing of transcriptional activity of VEGF gene and its receptor FLK-1 indicates an autocrine mechanism of regulation of angiogenic gene activity in the first step of carcinogenesis--low-grade intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix 14687619_Specific VEGFR2 expression, examined in 27 B-CLL samples, was positive in 26 of them. The VEGF transduction pathway may be very active in CLL cells. Both its paracrine & autocrine pathways may contribute to their enhanced survival. 14691147_The expression of VEGF and KDR correlates highly with the normal ocular vascularization in humans 14704231_Intact caveolae are required for the VEGF/VEGFR-2-mediated MEK/ERK signaling cascade. 14724572_phosphorylation of Y1214 on VEGFR2 is required to trigger the sequential activation of Cdc42 and SAPK2/p38 and to drive the SAPK2/p38-mediated actin remodeling in stress fibers in endothelial cells exposed to VEGF 14726393_KDR is constitutively phosphorylated and located at the nucleus of VEGF-producing leukemias; a KDR-specific intracellular inhibitor failed to block KDR nuclear IMPORT, but inhibited the constitutive activation of MAPK/Erk and PI3-kinase/AKT pathways 14760936_the level of sVEGFR-2 is lower in active systemic lupus erythematosus than in inactive disease 14764537_maximal P-selectin translocation and subsequent neutrophil adhesion was mediated by VEGF-A(165) on the activation of VEGFR-2/NRP-1 complex and required PAF synthesis. 14967383_Our data support a role for KDR in oviduct angiogenesis. 14996703_VEGF receotor signaling regulates survival signals in CLL cells and that interruption of this autocrine pathway results in caspase activation and subsequent leukemic cell death. 15016828_Tgf-beta mediated repression of flk-1/KDR and mediated repression of flk-1/KDR and VEGF signaling involves the inducible formation of inhibitory Hex-GATA signaling Hex-GATA involves the formation of Hex-GATA complexes. 15026417_Shb binds to tyrosine 1175 in the VEGFR-2, which regulates VEGF-induced formation of focal adhesions and cell migration, of which the latter occurs in a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent manner 15060076_Nedd4-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 degradation is prevented by Grb10 15082792_Data suggest that periostin-mediated angiogenesis derives in part from the up-regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flk-1/KDR by endothelial cells through an integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway. 15111490_PPARgamma1 has bifunctional properties in the regulation of KDR gene expression mediated via interaction with both Sp1 and Sp3 15135240_vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is strongly expressed in villous cytotrophoblast cells and subsequently in Hofbauer cells while its receptors Flt-1 and Flk-1 are found on vasculogenic and angiogenic precursor cells 15135259_In chronic lower limb ischemia, growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and IGF-2, were upregulated in atrophic and regenerating myocytes together with attenuated HIF, VEGF, and VEGFR-2 expression in the same cells. 15166498_Increased expression of KDR is associated with an aggressive angiogenic phenotype in melanoma. 15175347_activation of the P2Y(2)R induced rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-2 in human coronary artery endothelial cells 15183893_VEGFR2 initiates a clonogenic response in myeloid leukemia cells that is PI3-kinase dependent. 15247219_VEGFR2 mediated phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase is regulated by heat shock protein 90 and Src kinase activities 15284224_Inhibition by flk-1 kinase inhibitor SU1498 and failure of placental growth factor (PlGF) to up-regulate DAF confirmed the role of VEGF-R2 in VEGF-mediated DAF up-regulation. 15291808_VEGF(165)-induced phosphorylation of KDR and PLCgamma was partially inhibited by PF-4 15470196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15470196_VEGF and its receptor, KDR, genes contributed to the development of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease patients. 15474514_VEGFR-3 needs to be associated to VEGFR-2 to induce ligand-dependent cellular responses 15492987_there was no significant correlation between VEGF and VEGF-R2 expression. VEGF-R2 expression was significantly increased on endothelial cell ( 15500293_The VEGFR2, through interaction with VEGF, regulated adhesive and migratory properties of the cancer cells. 15507525_Axl stimulation by GAS6 results in inhibition of the ligand-dependent activation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2 and the consequent activation of an angiogenic program in vascular endothelial cells 15522955_NRP-1 modulates VEGFR-2 signaling-dependent mitogenic functions of VEGF and regulates endothelial cell adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins independently of VEGFR-2. 15610528_These data support the involvement in melanoma growth and survival of a VEGF-dependent internal autocrine loop mechanism, at least in vitro. 15625130_The majority of embryonic stem cells with the potential to differentiate into osteoclasts expressed Flk-1. 15637071_the activation of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 heterodimer (VEGFR-1/R-2) is essential for PGI(2) synthesis mediated by VEGF-A(165) and VEGF-A(121), which cannot be reproduced by parallel activation of VEGFR-1 or -2 homodimers with corresponding agonists [VEGFR2] 15638384_Blood levels correlate with lymph node involvement in colorectal cancer. 15673613_regulatory mechanisms involved in the attenuation of VEGFR-2 activation is mediated by nonclassical Protein Kinase C and the presence of serine sites in the carboxyl terminal of VEGFR-2 15693894_VEGFR2 may be involved in the transcriptional regulation of T-cell lymphoma. 15714119_VEGFR-2 expression, co-localized in the cytoplasmic and nuclear membrane, is associated with progression towards invasive melanoma 15806151_Phosphorylated ERK1/2 was further associated with the presence of VEGFR2 (cohorts II and III) and the degree of phosphorylated Ets-2, indicating in vivo, a signalling cascade from VEGFR2 via ERK1/2 to Ets-2 phosphorylation 15845615_Targeting the release of VEGF from tumor epithelial cells as well as blocking interactions between VEGF and VEGFR-2 on both endothelial and tumor epithelial cells may facilitate the development of antiangiogenic therapies for breast tumors. 15941713_human VEGFR-2 promoter is functionally counter-regulated by TFII-I and TFII-IRD1. 15962006_key role of KDR in megakaryopoiesis 15975559_decrease in expression is caused by C-reactive protein 15980434_KLF2 is a regulator of VEGFR2/KDR and has a role in regulating angiogenesis 16007196_role in modulating tumor neovascularization in conjunction with interleukin-3 receptor 16049137_dynamin-2 regulates KDR expression and function and hence plays an important role in VPF/VEGF mediated angiogenesis 16105658_assessed the role of VEGF and its receptors in osteoclastogenesis, in vitro, by culturing osteoclast precursors in the presence of VEGF, VEGF receptor-specific ligands, and blocking antibodies to VEGF receptors 16169405_Up-regulation of VEGF-A receptor VEGFR-2 in capillaries in menorrhagia could be involved in abnormal endometrial vascular structure and permeability. 16226108_An immunohistochemical analysis of VEGFR2 in pituitary adenomas was made. 16260429_Blockade of either VEGF or its receptors with neutralizing antibodies significantly reduced cell viability and increased apoptosis levels of the VEGFR-positive thyroid tumour cell line. 16308314_vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 phosphorylation is inhibited by delphinidin 16322069_LPC-induced Flk-1/KDR transactivation via c-Src may have important implications for the progression of atherosclerosis 16339483_Type I collagen limits VEGFR-2 signaling by a SHP2 protein-tyrosine phosphatase-dependent mechanism 1. 16361360_Regulation of VEGF(165) signaling through the VEGFR-2 complex in response to cigarette smoke exposure in vivo, and in smokers with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 16375118_VEGF and its receptors many play key roles in the growth, invasion and metastasis of human laryngeal carcinoma cells. 16439688_New VEGFR2 containing cell subpopulation,which is apparently a precursor classical endothelial progenitor cells more potent with respect too homing and vasscular repair. 16467880_We conclude that neoplastic cells show a variable expression of total and phosphorylated KDR in the nucleus. 16513643_This study describes the first specific antagonist of VEGF-A165 binding to NP-1 and demonstrate that NP-1 is essential for optimum KDR activation and intracellular signaling. 16516857_We conclude that IL-6 triggers VEGF-induced angiogenic activity through increasing VEGF release, up-regulates KDR expression and phosphorylation through activating ERK1/2 signaling, and stimulates MMP-9 overexpression. 16557278_Phosphorylated KDR expression was significantly associated with poor prognosis. 16574784_Sp3 and Sp4 cooperatively interact with ERalpha to activate VEGFR2 16617095_In conclusion, EC death induced by high shear stress and VEGFR blockade leads to the production of factors, in particular TGF-beta1, that activate VSMC proliferation. 16630933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16630933_haplotype analysis showed that atopy prevalence was strongly associated with a haplotype (AGAG) of VEGFR2 16648151_Immunohistochemical staining showed that VEGF-R2 were expressed in epithelial, stromal and endothelial cells. 16678129_These results suggest that VEGFR2 cannot only be targeted by receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors but also by drugs that downregulate Sp proteins or block Sp-dependent transactivation. 16682007_In this study, we demonstrate that 1121B Fab is able to strongly block KDR/VEGF interaction, resulting in potent inhibition of an array of biological activities of VEGF, including activation of the receptor and its signaling pathway. 16684957_Vascular endothelial growth factor165 (VEGF165) and semaphorin3A (SEMA3A) elicit pro- and antiangiogenic signals respectively in endothelial cells (ECs) by binding to their receptors VEGFR-2, neuropilin-1 and plexin-a. 16761623_VEGF and VEGFR-2 may have a role in progression of gastric cancer 16763549_NRP1 expression and its GAG modification post-transcriptionally regulate VEGFR2 protein expression. 16782059_illuminate an important mechanism for notch/HESR1 regulation of VEGF-induced angiogenesis 16786116_VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 have roles in differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma 16787925_Gab1 thus appears as a primary actor in coupling VEGFR-2 to PI3K/Akt, recruited through an amplification loop involving PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 and its PH domain 16807673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16835467_REVIEW: The binding of VEGF-A to VEGFR-2 causes receptor dimerization, kinase activation and autophosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues within the dimeric complex. 16835828_overexpression of VEGF, its receptors flt-1, KDR/flk-1 and TGF-beta interaction may play an important role in the ovarian cancer biology, with potential effects on tumor growth and angiogenesis 16870555_VEGF receptors are found on plasma cells from all groups of patients with multiple myeloma with the lowest expression on plasma cells from normal individuals 16893970_Thus, vascular endothelial cadherin limits cell proliferation by retaining VEGFR-2 at the membrane and preventing its internalization into signaling compartments. 16909199_Taken together these data show that VEGF-A(165)b has attenuated signaling potential through VEGF receptor 2 defining this new member of the VEGF family as a partial receptor agonist. 16914140_Endothelial cell tissue transglutaminase (tTG) might be involved in modulation of the cellular response to VEGF by forming an intracellular complex with VEGFR-2, and mediating its translocation into the nucleus upon VEGF stimulation. 16914267_perlecan secreted by VEGF165-stimulated endothelial cells may be involved in the regulation of cellular behavior during angiogenesis 16930552_VEGFR-2 expressed on HaCaT cells plays a crucial role in VEGF-mediated regulation of cell activity 16951193_SCID mice bearing xenografts of transfected cell lines were used to assess the effect of VEGF overexpression and the effect of VEGF receptor (VEGFR) 2 inhibition on soft tissue sarcoma growth. 17013089_VEGF regulation of angiogenesis may in part be due to enhanced proliferation of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 17018613_Signaling via VEGFR-2 is involved in prostate lymphatic endothelial cell tube formation, migration, & proliferation in vitro. Blockade of VEGFR-2 significantly reduced tumor-induced activation of LECs. 17088944_These results suggest that the expression of VEGFRs and NRPs on keratinocytes may constitute important regulators for its activity and may possibly be responsible for the autocrine signaling in the epidermis. 17242158_in binding VEGFR-2, furin and PC5 promote cleavage of N-and C-terminal VEGF-D propeptides, whereas PC7 promotes cleavage of the C-terminal propeptide only 17293873_Binding of VEGF to membrane-distal immunoglobulin-like domains causes receptor dimerization and promotes further interaction between receptor monomers through the membrane-proximal immunoglobulin-like domain 7. 17336974_Endometrial blood vessels possess a discrete morphology that is characterized by endothelial gaps, and these gaps are more pronounced in women with menorrhagia and overexpression of VEGFR2. 17372230_corecruitment of c-Cbl and PLCgamma1 to VEGFR-2 serves as a mechanism to fine-tune the angiogenic signal relay of VEGFR-2 17456229_Mechanisms other than genetic variation may downregulate expression or function of the VEGFR2 receptor in patients with ALS. 17462601_Taken together, these results lend great support to use PDGFRbeta antagonists in combinations with other antitumor and/or anti-angiogenic agents in the treatment of a variety of cancers. 17470361_VEGF receptor KDR was expressed in ovarian cancer cells, and CDDP-inhibited VEGF expression was linked with cellular apoptosis, which was rescued by VEGF treatment. 17490619_These findings provide evidence for a novel cooperative interaction between VEGFR2 and RET that mediates VEGF-A functions in ureteric bud cells. 17575273_VEGFR2 enhances VEGF(165), but not VEGF(121) binding to NRP1. 17577783_Leukemia patients showing parallel activation of the studied proteins trended to exhibit higher incidence of fatal outcome. 17584927_High levels of VEGFR-3 and -2 seem to contribute to the etiology of lymphangiomas. 17599955_determined the expression pattern of VEGF splice variants in NSCLC and its correlation with the clinicopathological characteristics of tumors 17631646_ZD6474 treatment inhibited EGFR phosphorylation and led to a dose- and time-dependent decrease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell 17640715_Increased expression of Flk-1 may be involved in sinusoidal capillarization and the increased numbers of unpaired arteries in capillarized areas with increased numbers of unpaired arteries in dysplastic liver nodules. 17641225_c-Src controls functional association between integrin alphav-beta3 and VEGFR-2 via integrin beta3 phosphorylation. 17646929_PKA and VEGFR2 converge at the MEK/ERK1/2 pathway to protect serum starved neuronal cells from a caspase-dependent cell death. 17651148_increase in VEGF in AR with and without asthma despite a higher Flk-1 in AR patients with asthma may be a possible explanation for the presence of angiogenesis in the airway wall in patients with asthma but not in those with pure AR. 17702744_myoferlin forms a complex with dynamin-2 and VEGFR-2, which prevents CBL-dependent VEGFR-2 polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. 17707181_KDR polymorphisms may serve as novel genetic markers for the risk of coronary heart disease. 17707181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17721629_studied circulating CD31- and/or CD34-positive cell populations with a low to moderate VEGFR2 expression in human volunteers and cancer patients. 17765237_Vascularization and VEGF and Flk-1 expression are significantly higher in deeply infiltrating endometriosis affecting the rectum. 17850794_VEGF receptor Flk-1 is involved in c-kit up regulation via ERK-mediated pathway 17881084_HARP negatively affects diverse biological activities in C6 glioma cells, mainly due to binding of HARP to VEGF, which may sequester secreted VEGF from signalling through VEGFR2. 17891484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17927494_isolation and purification of Flk-1cells with mesenchymal stem cell characteristics from bone marrow of myeloma patients. 17928406_points to VEGFR2 transactivation as an important signaling pathway used by chemokines such as IL-8/CXCL8 17961532_Expression profile of total VEGF, VEGF splice variants and VEGF receptors in the myocardium and arterial vasculature of diabetic patients. 17979890_VEGFR2 up-regulation had no effect on VEGF-induced cell proliferation, but significantly enhanced endothelial progenitor cells migration and pseudotubes formation dependent on integrin alpha(6) subunit overexpression. 17999592_Within mdx mice, an animal model of DMD, adipose tissue-derived Flk-1(+) MSCs (AD-MSCs) homed to and differentiated into cells that repaired injured muscle tissue. 18006432_Activation of fractalkine/CX3CR1 by vascular endothelial cells induces angiogenesis through VEGF-A/KDR. 18035072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18037047_expressed in the microvascular endothelial cells of both primary and young permanent teeth 18162457_Increased levels of Factor VIII occurred in the precursors of cardiac myocytes, smooth muscle and endothelial cells in normal and post-ischemic hearts. 18164591_Support a role for NP-1 in mediating synergistic effects between VEGF-A(165) and FGF-2, which may occur in part through a contribution of NP-1 to KDR stability. 18175243_Preeclampsia and SGA are associated with low maternal plasma concentrations of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (sVEGFR-2) 18194650_These proteins have an essential molecule required for promoting the disruption of endothelial cell-cell contacts and paracellular permeability. 18211808_Overall, these results indicate that HDAC6 and HDAC10 play important roles in Hsp-mediated VEGFR regulation. 18218912_a maximal bout of exercise induces a significant shift in CD34+ cells toward CD34+/KDR+ cells 18223683_Gal-1 can directly bind to NRP1 on endothelial cells, and can promote the NRP1/VEGFR-2-mediated signaling pathway as well as NRP1-mediated biological activities. 18261985_The expression of VEGF-C and VEGF receptors is regulated specifically in HL-60 cells during macrophage differentiation. 18317954_Surveillance of VEGFR-2 levels to predict chemotherapy response is not useful. 18337563_the temporal expression of TNF is critical: it delays angiogenesis initially by blocking signaling through VEGFR2, and by inducing a tip cell phenotype through an NFkappaB-dependent pathway, it concomitantly primes ECs for sprouting 18356031_Found in normal and neoplastic thymus tissue. 18379357_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18396391_Intensity of VEGFR-2 in odontoblasts increases from cap stage to late bell stage. 18421240_VEGF is considered as an important factor in the pathogenesis of macular edema. VEGF induces the rupture of the blood retinal barrier and may also influence the retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) outer retinal barrier. 18509004_complex interaction between sphingosine-1-phosphate and VEGFR-2 in ML-1 thyroid follicular cancer cells, particularly in regulating migratory responses 18564921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18594014_the 167-181 region of VEGFR-2 has an important role in the stimulation of CD4(+) T cell responses to VEGFR-2 protein 18609713_VEGFR-2 levels were associated with poor tumor differentiation in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma 18628209_binding of Neuropilin-1 to VEGFR-2 requires the PDZ-binding domain of neuropilin-1 18645275_vascular endothelial growth factor, receptor KDR and p53 protein are expressed in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder 18651620_PTHrP (107-139) interacts with VEGFR-2 to promote human osteoblastic cell survival by a mechanism involving Runx2 activation. 18656381_sVEGFR-2 levels were not significantly increased in patients with liver cirrhosis. 18692535_in vascular endothelial cells the binding of adrenomedullin to its AM1 receptor could trigger a transactivation of the VEGFR-2 receptor, leading to a signaling cascade inducing proangiogenic events in the cells. 18719373_These results are consistent with a potential autocrine role of the VEGF-VEGFR2 (KDR) interplay as a factor contributing to malignant astrocytoma growth and radioresistance. 18784964_The tumor uptake of 64Cu-DOTA-VEGF measured by small-animal PET imaging reflects tumor VEGFR-2 expression level in vivo. 18785001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18818406_VEGF-A stimulates ADAM17-dependent shedding of VEGFR2 and crosstalk between VEGFR2 and ERK signaling. 18824714_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18840653_matrix-controlled TCPTP phosphatase activity can inhibit VEGFR2 signalling, and the growth, migration and differentiation of human endothelial cells 18922344_VEGF-R2 expression is significantly increased in port-wine stains, suggesting that VEGF-R2 could contribute to the pathogenesis of PWS by inducing vessel proliferation, vasodilation, or both. 18931684_Normalization of the constitutive VEGFR2 signaling in hemangioma endothelial cells with soluble VEGFR1 or antibodies that neutralize VEGF or stimulate beta1 integrin 18975312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987662_correlation between expression of VEGF and p27(Kip1) was observed in bone marrows from patients with acute myeloid leukemia 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19014781_Achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes, the scheduling of radiotherapy and antiangiogenic therapy requires patient-specific post-treatment monitoring of the VEGFR2 pathway. 19020728_glioma cells enhance EPC angiogenesis via VEGFR-2, not VEGFR-1, mediated by the MMP-9, Akt and ERK signal pathways 19021062_LDH5 is highly upregulated in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas and is in direct relation to factor HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha expression. LDH5 expression is linked with activated VEGFR2/KDR expression 19023980_Results show a significant positive correlation between the concentrations of tissue VEGF and its receptor VEGFR2 in primary breast neoplasms during neoadjuvant therapy, and suggest that VEGFR2 levels may indicate the level of lymphatic metastasis. 19058181_a distinct VEGFR-2-mediated pathway promoting tumor growth through autocrine mechanisms. 19066962_The expression of VEGF-A, VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3 in was higher in peritumoral liver tissue, while VEGF-C expression was higher in tumor. 19068081_High VEGFR-2 in stromal vessels is associated with gastric cancer. 19082506_VEGFR2 was significantly decreased in human colonic microvascular endothelial cells under hypoxia. In contrast, the responses of VEGFR2 levels to hypoxia in human umbilical vein endothelial cells were variable, that is, either unchanged or up-regulated. 19110567_No significant correlations between the levels of VEGFR2 in the blood and renal cancer tissue were found. 19136612_VE-PTP, regulates VEGFR2 activity thereby modulating the VEGF-response during angiogenesis. 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19160077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19160077_no activating mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the VEGFR-2 were identified in 66 hepatocellular carcinoma samples 19176370_In malignant pleural mesothelioma cells, plexin-A1 and VEGF-receptor 2 (VEGF-R2) are associated in a complex which are involved in survival pathways. 19177438_VEGFr2 up-regulation is a feature of poor differentiation and tumor progression. 19179362_Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) expression was significantly suppressed in Fut8(-/-) mice, suggesting that Fut8 was required for VEGFR-2 expression. 19199116_secretion and the regulation of the secretion of sVEGFR-2 by microvascular endothelial cells derived from the tissue of benign prostatic hyperplasia 19200976_A local defect of both VEGF transmembranous receptors (KDR and Flt-1) in the endometrium covering the septal area may be responsible for the clinical comportment of this mullerian anomaly. 19218116_In breast cancer patients, Flk-1/KDR was strongly expressed in vascular endothelial cells. 19244479_chronic hypoxia attenuates VEGF-stimulated signaling in coronary artery endothelial cells by specific downregulation of KDR expression 19246491_extracellular RNA serves an important cofactor function to engage VEGF for VEGF-R2-dependent signal transduction 19261502_Soluble VEGFR-2 was lower in Dengue Fever and Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever patients compared to study controls. 19265684_these findings suggest that CCL23 results in up-regulation of KDR/flk-1 receptor gene transcription and protein expression and that KDR/Flk-1 up-regulation induced by CCL23 may contribute to potentiation of VEGF action in angiogenesis. 19267251_REVIEW: possible mechanisms which mediate formation of the complex between VEGFR-2 and alphavbeta3 on endothelial cells 19287991_In contrast to sVEGFR-1, sVEGFR-2 was significantly decreased in both normal colonic tissue and human colon cancer tissue under hypoxic conditions. 19324448_expressionin cancer tissue has no prognostic impact in non-small cell lung cancer patients 19372376_Includes the study of a polymorphic upstream ORF in this gene, and shows that it functions to reduce protein levels by ~50%. 19372461_Rab GTPase regulation of VEGFR2 trafficking and signaling in endothelial cells; Endothelial cell migration was increased by Rab5a depletion but decreased by Rab7a depletion 19372622_KDR/CD34 and IL-10 are major independent predictors of 30-day major adverse clinical outcome in ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing primary coronary angioplasty. 19375500_We have identified a VEGFR2/NOX4 regulatory pathway by which Ox-PAPC controls important endothelial functions. 19409555_The presence of the VEGF-A receptors, particularly in the granulosa cells, suggests that VEGF-A might be involved in proliferation initiation of primordial follicles or play an as yet unknown role in human preantral follicles. 19419943_The aim of the study was to assess the usefulness of soluble angiogenesis markers such as endoglin and VEGFR2 in gastric cancer patients and to compare these results with those of VEGF levels. 19435508_271 G>A polymorphism of the KDR gene is related to transcriptional regulation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19469899_Repression of the small Rho GTPase Rac1 in human endothelial cellsseems to be an additional critical molecular mechanism in the regulation of VEGFR2 expression. 19520980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19520980_VEGF-2 gene variants may serve as novel genetic markers for the risk of stroke and its recurrence. 19521715_In conclusion, we have shown for the first time that variation in the VEGFR2 gene is associated with elite athlete status, endurance performance of female rowers and muscle fibre type composition. 19521715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19558547_(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate can exert, at least in part, its growth-inhibitive effect on HCC cells by inhibiting the VEGF-VEGFR axis 19563658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19563658_analysis of the experssion of EGFR, PDGFRA and VEGFR2 in cervical adenosquamous carcinoma 19570985_VEGFR2, but not VEGFR1, is responsible for the release of von Willebrand factor. 19595210_Abnormal expression of VEGF and Flk-1/KDR may be the initiating factor of angiogenesis in the process of breast hyperplasia-atypical hyperplasia-breast cancer. 19605404_Study provides novel insights for angiogenesis mechanisms in pediatric solid malignancies for which antiangiogenic targeting of VEGFR2+-BMD progenitors could be of interest. 19633424_The present study evaluated the epigenetic gene silencing |
ENSMUSG00000062960 |
Kdr |
5.815863 |
0.1245749654 |
-3.004914 |
0.849227031 |
14.752051 |
0.00012261409284254268367217455271145354345208033919334411621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000333232187507996688996536605031906219664961099624633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3333643 |
0.8667330 |
10.9029729 |
3.6321841 |
| ENSG00000128271 |
135 |
ADORA2A |
protein_coding |
P29274 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for adenosine (By similarity). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P11617}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, which is subdivided into classes and subtypes. The receptors are seven-pass transmembrane proteins that respond to extracellular cues and activate intracellular signal transduction pathways. This protein, an adenosine receptor of A2A subtype, uses adenosine as the preferred endogenous agonist and preferentially interacts with the G(s) and G(olf) family of G proteins to increase intracellular cAMP levels. It plays an important role in many biological functions, such as cardiac rhythm and circulation, cerebral and renal blood flow, immune function, pain regulation, and sleep. It has been implicated in pathophysiological conditions such as inflammatory diseases and neurodegenerative disorders. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A read-through transcript composed of the upstream SPECC1L (sperm antigen with calponin homology and coiled-coil domains 1-like) and ADORA2A (adenosine A2a receptor) gene sequence has been identified, but it is thought to be non-coding. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:135; |
axolemma [GO:0030673]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051393]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; G protein-coupled adenosine receptor activity [GO:0001609]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031802]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; biomineralization [GO:0110148]; blood circulation [GO:0008015]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; eating behavior [GO:0042755]; excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060079]; G protein-coupled adenosine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0001973]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inhibitory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060080]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; membrane depolarization [GO:0051899]; negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:0046636]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of locomotion [GO:0040013]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of acetylcholine secretion, neurotransmission [GO:0014057]; positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001235]; positive regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep [GO:0045938]; positive regulation of glutamate secretion [GO:0014049]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of renal sodium excretion [GO:0035815]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0032230]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; positive regulation of urine volume [GO:0035810]; prepulse inhibition [GO:0060134]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881]; regulation of norepinephrine secretion [GO:0014061]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to caffeine [GO:0031000]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035]; response to purine-containing compound [GO:0014074]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sensory perception [GO:0007600]; synaptic transmission, cholinergic [GO:0007271]; synaptic transmission, dopaminergic [GO:0001963]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11515749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11934694_A(1)- and A(2a)-adenosine receptor activation protects HK-2 proximal kidney tubule cells against H(2)O(2)-induced injury 12237741_Removal of the entire carboxy terminus of human A2aRT blunts the ability of the receptor to constitutively elevate cyclic AMP in intact cells; in contrast, MAP kinase stimulation is not affected by the truncation. 12406340_adenosine triggers a survival signal via A3 receptor activation and it kills the cell through A2A receptor inducing a signaling pathway that involves protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinases. 12429726_The A2A receptor mediates a negative feedback pathway to modulate cytokine expression in THP-1 cells 12634474_No evidence for genetically determined reduction of adenosine A 2(A) receptors in schizophrenia. Role of adenosine A (2A) receptors in the molecular effects of antipsychotic drugs. 12784121_The human D2 dopamine receptor synergizes with the A2A adenosine receptor to stimulate adenylyl cyclase in PC12 cells. 12804599_adenosine A2A Receptor, either homomeric or heteromeric with dopamine D2 receptors, exists as an oligomer in living cells 12825092_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12837758_an alpha-actinin-dependent association between the actin cytoskeleton and A2AR trafficking 12856413_Molecular modeling of the human A2a adenosine receptor. 12933819_In the most probable of two possible modes of interaction between D2R and A2AR, helix 5 and/or helix 6 and the N-terminal portion of I3 from D2R approached helix 4 and the C-terminal portion of the C-tail from the A2AR, respectively 14525968_Adenosine binding to A(2A)AR counteracts stimulation of neutrophil CD49d integrin expression 14666117_Evidence is found for a susceptibility locus for panic disorder, possibly including agoraphobia, either within the ADORA2A gene or in a nearby region of chromosome 22. 14715520_Most damage after hepatic ischemia occurs during reperfusion and can be blocked by adenosine A2a receptor activation. 15257174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15257174_adenosine-related gene variants do not appear to alter susceptibility to the disease in this group of essential hypertensives 15351206_A2A receptor activation increases protein phosphatase activity, which blocks IP3 receptor-regulated calcium release and reduction of intracellular calcium inhibits TNF-alpha production in monocytes 15461468_The tendency of some peptides of adenosine A2a receptor to self-associate, especially in aqueous environments, underscores the need to prevent improper interactions during folding and refolding of membrane proteins in vivo and in vitro 15539641_Adenosine A2A and dopamine D3 receptors seem to form A2A/D3 heteromeric receptor complexes in which A2A receptors antagonistically modulate both the affinity and the signaling of the D3 receptors when they are colocalized in the plasma membrane. 15704067_PBMC from CHF patients how an upregulation of A2AR-mediated inhibition of TNF-alpha, which may represent a mechanism of protection against inappropriate cytokine production. 15719154_Our findings suggest that it is unlikely that the A2aAR 1976T > C polymorphism plays a major role in the pathogenesis of PD, schizophrenia, or antipsychotic-induced tardive dyskinesia in the Chinese population. 15734651_Modeled pairs of A(2A)AR-derived neoceptor-neoligand, which are pharmacologically orthogonal with respect to the native species. 15774265_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15774265_The 1976C > T polymorphism of ADORA2A receptor may be in linkage disequilibrium with a functional variant that affects panic disorder, and the extent of this linkage disequilibrium is not similar for all ethnic populations. 15987888_Evidence of an individual adenosine A2A receptor transmembrane domain self-association. 16022683_Regulation of adenosine receptor expression, especially up-regulation of the A(2A)AR, is part of a delayed feedback mechanism initiated through NF-kappaB to terminate the activation of human and mouse macrophages. 16118787_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16184606_An increased platelet A2A receptor maximum receptor binding may belong in a cascade of toxic events leading to earlier onset of Huntington's disease. 16280366_Modulation by A2AR in the production of inflammatory signals by neutrophils may influence the evolution of an inflammatory response by reducing the activation status of inflammatory cells. 16339780_Activation of the A(2A) receptor might have a beneficial effect by inhibiting inflammatory cell influx and downregulating inflammatory cell activation in asthma and COPD, respectively. 16361356_Adenosine A2a receptor is involved in bronchial epithelial cell adenosine-stimulated wound healing. 16818375_Galpha(olf) variant XLGalpha(olf) interacts with the human adenosine A2A receptor 16824773_A2A upregulation in prefrontal cortex may contribute to memory dysfunction in depression 16917093_adenosine inhibits MMP-9 secretion by neutrophils; this effect involves the A2a receptor and is mediated through the cAMP/PKA/Ca(2+) pathway 16969271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17132707_The changes in peripheral A(2A) receptor expression suggest a significant inflammatory response to HD and heart or kidney failure. 17257240_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17329997_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17329997_a common variation in ADORA2A contributes to subjective and objective responses to caffeine on sleep 17474152_The G(alphas)-coupled adenosine A2A receptor closes KCa3.1, providing a clearly defined mechanism by which adenosine inhibits human lung mast cell migration and degranulation. 17512749_A(2A) receptor B(max) values are robustly increased at all Huntingon disease stages as well as in 32 pre-symptomatic subjects 17558310_the 1976C>T polymorphism does not affect the vasodilator response to adenosine and caffeine in vivo 17591446_Results describe the isolation and spectroscopic characterization of functional human adenosine A2a receptor. 17599669_an increased number and an up-regulation of adenosine A2A receptors in patients with spontaneous syncope and a positive head-up tilt, which in the context of high APLs may play a role in the recurrence of syncopal episodes 17616786_Findings show that the probability of having the ADORA2A 1083TT genotype decreases as habitual caffeine consumption increases. This observation provides a biologic basis for caffeine consumption behavior 17616786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17872970_Adenosine A2A receptors signal for increased collagen production by multiple signaling pathways, promoting the hypothesis that adenosine receptors promote hepatic fibrosis. 18057956_A2A receptors open Cl- channels in pancreatic ducts cells with functional cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR). 18197085_although there is a protein-protein interaction in the brain, there is no genetic association of the ADORA2A, either alone or in epistasis with DRD2, and the risk of schizophrenia 18215030_linear and nonlinear 3D-QSAR methods and LBHM computational techniques has been used to depict the hypothetical antagonist binding site of the human adenosine A2A receptor 18218631_A(2A) receptor is the first example of a G protein-coupled receptor documented to select signaling pathways in a manner dependent on the lipid microenvironment of the membrane. 18246094_adenosine A2a receptor may function as a coincidence detector and a signal integrator--REVIEW 18305461_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18305461_These findings provide support for an association between an ADORA2A polymorphism and self-reported anxiety after a moderate dose of caffeine. It is likely that other ADORA2A and DRD2 polymorphisms also contribute to responses to caffeine. 18331682_D2 and A2A receptors may play an important role in the maintenance of the function of human retinal pigment epithelium. 18434504_results identify stabilizing contacts that are likely related to the stability of the receptor and that are consistent with what is known about the three-dimensional structure and stability of rhodopsin and the beta(2) adrenergic receptor 18442791_stimulation with IL-4, IL-13 & subsequent stimulation with AMP/NECA decreased A2AR expression accompanied by increased histamine secretion; results suggest role for decreased A(2A)R expression in enhanced adenosine responsiveness as observed in asthma 18508500_Pharmacological data do not advocate for a clear implication of the A2A receptor in axiety. [REVIEW] 18524886_These observations support the hypothesis that long-term drug exposure differentially alters A(2A)/D(2) receptor oligomerization. 18539621_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18541693_In resting human PMNs, mainly A(2A)R transcripts with long 5'-UTRs are expressed, whereas in stimulated PMNs and PMNs of septic patients, short 5'-UTRs predominate. 18629431_This study...supports a role of the A(2A)R gene in the pathogenesis of anxiety disorders. 18759349_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18772204_The adaptations in the heart of highly trained endurance athletes lead to relative myocardial 'overperfusion' at rest. On the other hand hyperaemic perfusion is reduced, but is not explained by A2AR density. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19013155_At least three A(2A) receptors assemble into higher-order oligomers at the plasma membrane in differentiated neuronal cells. 19019012_A(2a) receptors operate through inhibitory nitrergic nerve pathways on human colonic motility. 19019667_Genetic polymorphisms of ADORA1 and ADORA2A were significantly associated with aspirin-intolerant-asthma in a Korean population. 19019667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19159073_Extracellular adenosine induces apoptosis in Caco-2 cells by activating caspase-9 and the downstream effector caspase caspase-3 in association with mitochondrial damage via A(2a) adenosine receptors 19262506_A(2A)AR limits the pro-inflammatory effects of Th cells and favor chronic Helicobacter infection. 19287996_cross-talk between A2AAR and ERalpha that is involved in ethanol action. This could open new perspectives for the therapy of estrogen-dependent breast cancer. 19303140_all four known adenosine receptors are expressed in the human placenta and adenosine receptor expression is significantly higher in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. 19386617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19386617_results clearly identify a subset of patients with unexplained syncope, high basal APLs and with high incidence of the CC variant in the A2A adenosine receptor gene. 19508402_The growing evidence that tonic adenosine A2A receptor activity is a crucial step to allow actions of neurotrophic factors in neurons is reviewed and discussed in light of therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases. [review] 19525944_identified a molecular pathway in microglia that converted ATP-driven process extension into process retraction during inflammation: reversal was driven by upregulation of the A(2A) adenosine receptor coincident with P2Y(12) downregulation. 19538256_A(2A)R function obviously is highly dependent upon the cellular environment and thus, further functional characterization of A(2A)R responses in sepsis may be a promising approach to develop new adenosine or A(2A)R agonists based therapeutic strategies. 19541651_Analysis of the A(2A) receptor gene promoter revealed a hypoxia-responsive element in the region between -704 and -595 upstream of the transcription start site, and by using a ChIP assay, we demonstrate that HIF-2alpha binding to this region is specific. 19565319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19565319_The adenosine A2A receptor gene (ADORA2A) is associated with panic disorder. 19591938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19591938_the 1976C/T single-nucleotide polymorphism in the ADORA2A gene significantly influences the variability in age at onset of Huntington's disease: our data thus strengthens the pathophysiological role of A(2A) receptors in Huntington's disease 19632986_Data suggest that calmodulin bind to the A(2A) receptor, induces conformational changes in the CaM-A(2A)-D(2) receptor oligomer and selectively modulates A(2A) and D(2) receptor-mediated MAPK signaling in the A(2A)-D(2) receptor heteromer. 19776336_An increase in A(2A)AR density in putamen was found. The presence and functionality of ARs in human lymphocyte and neutrophil membranes from patients with Parkinson disease revealed a specific A(2A)AR alteration compared with healthy subjects 19794965_Data suggest that adenosine receptor modulation may be useful for refining the use of chemotherapeutic drugs to treat human cancer more effectively. 19801629_analysis of inhibition of the equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 and activation of A2A adenosine receptors by 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-modified cAMP analogs and their hydrolytic products 19883624_Studies indicate that adenosine mediates its actions by means of activation of specifiic G protein-coupled receptors, for which 4 subbtypes: A1R, A2AR, A2BR and A3R have 19902562_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20021407_Homology modeling was used to construct the 3-D structure of A2A. Effective antagonist drugs were selected and active amino acid residues in A2A were targeted on the basis of robust binding affinity between protein-drug interactions in molecular docking. 20029460_demonstrated that hypoxia-induced apoptosis of T cells was mediated by A(2a )and A(2b) receptors. 20045081_Our results suggest, for the first time, that adenosine regulates the endothelial cell barrier function via A2A receptors followed by Galphas engagement and is associated with cytoskeletal activation. 20085598_Findings suggest that the adenosine A1 (and possibly coordinated with A2a) receptors contribute to dendritic cell differentiation and survival. 20089670_A2AR occupancy diminishes foam cell formation by stimulating increased reverse cholesterol transport via ABCA1. 20197060_These results point to a key role of serine 374 in the A(2A)R-D(2)R interface. 20334879_Data provide further support for an important role of ADORA2A variants in the pathogenesis of anxiety disorders and anxious personality reflecting their potential as basic susceptibility factors. 20334879_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354569_results suggest that adenosine-mediated signaling in the heart requires a balance between A(1)- and A(2A)-receptors 20371613_A(2A) receptor activation suppresses the activation-induced cell death of peripheral T cells. 20386734_several significant allelic associations with enhanced risk to severe malaria disease were identified in ADORA2A 20392501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20396431_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20413899_These data suggest that expression of A2AR in mononuclear cellss may be a valuable means of differentiating multiple cognitive domain and amnestic mild cognitive impairment 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20512606_ADORA2A, but not HAP1 or OGG1, may have a role in age at onset in Huntington's disease 20512606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20520601_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20520601_The present results confirm that the ADORA2A rs5751876 SNP is associated with variation in the anxiogenic response to caffeine. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20666933_increased Yin Yang-1 levels and DNA methylation percentage in the 5' untranslated region of Adenosine A(2A) receptors were found in the cerebellum with respect to the putamen of human brains 20691427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20799992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20799992_results suggest that the ADORA2A gene could be a vulnerability factor for METH dependence/psychosis, especially in females and/or in patients using only METH 20842321_Studies indicate that a joint impairment of BDNF and A(2A)Rs seems to play a pathogenetic role in Huntington's disease. 20926384_Adenosine A2A receptor is involved in cell surface expression of A2B receptor 21040702_The findings of this paper provide further evidence that D2R TM domains IV and V play a major role in the A2AR-D2R interface. 21062422_A(2A) receptor activation causes relaxation of human and mouse arteries. 21062644_Knockout of adenosine A2A receptors moderately but significantly worsens motor performances and survival of transgenic mice and leads to a decrease in striatal enkephalin expression. 21088442_Genetic variants of ADORA(2A) offer statistically significant protection against PDR development in patients with type I diabetes. 21088442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21256133_The antagonistic A(2A)R-D(2)R allosteric receptor-receptor interaction in A(2A)R-D(2)R heteromers favors beta-arrestin2 recruitment to the D(2L)R protomer with subsequent cointernalization associated with a reduced time onset of Akt phosphorylation. 21258856_study found that adenosine A2A receptor stimulation inhibited foam cell formation by a mechanism dependent on the expression of CYP27A1 21281405_Two ADORA2A polymorphisms are inversely associated with risk of Parkinson's; there is weak evidence of interaction with coffee consumption. 21335481_This review summarizes current knowledge of the cardioprotective effects of ADORA2A receptor subtype, as well as the proposed mechanisms of adenosine receptor-mediated cardioprotection. 21393508_study reports the crystal structure of the A(2A) adenosine receptor bound to an agonist UK-432097 at 2.7 angstrom resolution 21480628_The 'ionic lock' absent in the crystal structure of the inactive A(2A)AR is rapidly formed in two simulated receptors, and a complex network of interacting residues is presented that further stabilizes this structural element. 21486776_The A2A receptor reduces the desensitization of alpha3beta4 nAChR through the action of protein kinase A. Mutations disrupting the sequence 385RAES388 abolish PKA-induced changes in nAChR function. 21501622_The adenosine A2a receptor receptor was thermostabilised by systematic mutagenesis in the presence of a bound agonist. Four thermostabilizing mutations were identified. None of the thermostabilising mutations are in the ZM241385 binding pocket. 21542986_ADORA1 was expressed in nucleus of retinal pigment epithelium. 21550361_Suppression of A2A-receptor-mediated central sympathoexcitation contributes, at least partly, to the depressant effect of nicotine on reflex chronotropic responses to baroreceptor unloading. 21590734_Adenosine receptor expression and activation during the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cell to osteoblasts and adipocytes, was investigated. 21593763_crystal structures of the thermostabilized human adenosine A(2A) receptor (A(2A)R-GL31) bound to its endogenous agonist adenosine and the synthetic agonist NECA 21606452_Patients with Parkinson disease with levodopa-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) show increased adenosine A2A receptor availability in the striatum, suggesting that altered adenosine transmission plays a role in LIDs. 21633321_These data demonstrate that A2(A) 1976C>T polymorphism is associated with a blunted coronary vasodilatory response in patients with DCM, and support a direct consequences of this single nucleotide polymorphism for protein expression. 21638125_the ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 and ADORA2A appear as possible targets for novel treatments in ovarian cancer 21646447_The uropathogenic Escherichia coli-evoked neutrophil transmigration decreased in response to A(2A) receptor activation, possibly through inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 21658325_Letter: suggest that the role of ADORA2A in systemic sclerosis may not be genetically related in Korean patients. 21739164_results suggest that A(2A) adenosine receptor activation not only modulates CCR7 expression in both normal and inflammatory environments but also regulates macrophage migration to CCR7-specific chemoattractants 21840298_A2aR, adenosine, and HIF-2alpha are key contributors to the potentiation of catecholamine secretion in developing chromaffin cells during chronic hypoxia. 21885291_The structure of the ligand bound A(2A) receptor provides new insight into the features that define the ligand binding pocket as well as the cytoplasmic regions that interact with signal transduction proteins 21950736_These findings demonstrate a role for adenosine A(2A) receptors in the effects of prolonged wakefulness on vigilant attention and the sleep EEG 21966389_IL-4 amplifies the pro-inflammatory effect of adenosine in human mast cells by increasing expression levels of adenosine receptors A2B and decreasing A2A 22012471_In ADORA2A 1976TT risk genotype carriers, highest startle magnitudes were observed after caffeine administration in response to unpleasant pictures, with this effect arising particularly from the female subgroup. 22033526_A2Ar stimulation induces a pro-fibrotic phenotype in Sclerodermic dermal fibroblasts, either directly, and indirectly, by activating the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. 22079667_functional interaction of A2A and P2Y12 receptors on P2Y1 receptor 22119961_Neuroendocrine tumors predominantly express A2A receptors during cellular stress, damage and hypoxia, increasing cell proliferation. 22130015_Structure of the adenosine-bound conformation of the human adenosine A(2A) receptor. 22146575_Data show that A2A and A3 adenosine receptor density inversely correlated with Disease Activity Score in 28 or 44 joints (DAS28 or DAS) suggesting a direct role of the endogenous activation of these receptors in the control of RA joint inflammation. 22170367_Variability in the acute blood pressure response to coffee may be partly explained by genetic polymorphisms of the adenosine A2A receptors and alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors. 22213163_adenosine downregulates Bcl-X(L and upregulates Bid, disrupting mitochondrial membrane potentials to allow cytochrome c efflux, and then causing activation of caspase-9 and the effector caspase-3, as mediated via A(2a) adenosine receptors 22217884_adenosine stimulates human endothelial progenitor cells migration by activating AA and A receptors and provides evidence to support a role of adenosine in modulating angiogenic capacity of hEPC 22238572_The authors use rapid amplification of cDNA ends, tiling arrays, and deep RNA sequencing to identify chimeric transcripts on human chromosomes 21 and 22. They found that for 492 protein coding genes studied, 85% of these genes had boundaries that extended beyond the current annotated termini. 22240468_genetic association studies in population in Germany: Data suggest that two SNPs in ADORA2A (rs5751876; rs2298383) are differentially associated with efficiency of pre-attentive sensory memory sub-processes. 22249219_Adenosine A2A receptor upregulation in human PMNs is controlled by miRNA-214, miRNA-15, and miRNA-16 22333316_ADORA2A genotype did not moderate the effects of caffeine on wake after sleep onset, but did independently alter it such that those with the CC genotype had nearly three-times as much as those with CT or TT. 22336631_Caffeine intake increases tear volume and polymorphisms within ADORA2A, and CYP1A2 is associated with the tear increase after caffeine intake. 22356216_A1/A2 adenosine receptor activation does not directly contribute to cutaneous active vasodilatation. 22367999_Adenosine A2A receptor gene disruption protects in an alpha-synuclein model of Parkinson's disease. 22403020_confirmed at protein level the previously reported increased expression of DRD5 and the variably aberrant expression of ADORA2A, in Lesch-Nyhan disease lymphocytes 22462821_Results indicate a role for adenosine receptor A1 and A2A gene polymorphisms in susceptibility to apnoea of prematurity and bronchopulmonary dysplasia and in interindividual variability to caffeine response. 22585593_The results of this study suggested that the interaction between the ADORA2A and the dopamine D2 receptor is probably not relevant for the development of tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenic patients. 22740769_The reduced frequency of the heterozygote rs5751876 genotype in subjects suggests a possible association of A2AR with high myopia in a Chinese population. 22754043_SNP association with caffeine-induced insomnia 22792196_A(2A)-adenosine receptor over-expression is protective against pressure-induced heart failure secondary to transverse aortic constriction (TAC). 22798613_structure of reengineered receptor at 1.8 A;57 ordered water molecules inside the receptor comprising 3 clusters identified; central cluster harbors a putative sodium ion bound to conserved aspartate residue Asp(2.50); 2 cholesterols stabilize conformation of helix VI and one of 23 ordered lipids intercalates inside the ligand-binding pocket 22844517_insulin modulation of hCAT-1 expression and activity requires functional A(2A)AR in HUVECs 22923002_that A(2A)R and TNF-alpha regulate the intrinsic circadian clock in immune cells provides an explanation for both the pathologic changes in circadian rhythms in rheumatoid arthritis and for the adverse circadian effects of methotrexate, such as fatigue. 22940476_The present results point to an impaired ability to selectively process very early information and to gate irrelevant sensory information, respectively, in female ADORA2A 1976TT homozygotes in response to caffeine. 22963436_The most recent evidence concerning the role of ADORA2A and its potential therapeutic relevance is discussed. [Review Article] 23005256_Molecular dynamics simulations of the A(2A) adenosine receptor totaling 1.4 mus show clear evidence for specific sites mediating interactions between adenosine-bound A(2A) and cholesterol. 23071116_Reengineering the collision coupling and diffusion mode of the A2A-adenosine receptor: palmitoylation in helix 8 relieves confinement. 23171222_polymorphisms more behaviorally salient with increasing severity and/or duration of sleep restriction 23193172_ADA open form, but not the closed one, that is responsible for the functional interaction with AR and AAR. 23241554_Central adenosine A2A receptor upregulation is prevented in an animal model of sporadic dementia following caffeine consumption. 23332182_ADORA2A SNPs, rs35320474, showe significant asssociation worth ADHD traits. 23377438_High adenosine A2a receptor expression is associated with sickle cell vaso-occlusion. 23385980_Increased 5mC & reduced 5hmC were found in the 5'UTR region of ADORA2A in the putamen of HD patients with respect to age-matched controls. Altered A2AR DNA methylation may play a role in the pathologically decreased A2AR expression levels found in HD. 23454349_cholesterol interactions with the human A(2A) adenosine receptor 23478188_Although activation of the ADORA2A receptor is thought to be anti-inflammatory, the authors found that it has a proinflammatory effect in a mouse model of neurogenic acute lung injury induced by severe traumatic brain injury. The proinflammatory effect was also seen in white blood cells isolated from patients. 23489072_Loss of constitutive activity is correlated with increased thermostability of the human adenosine A2A receptor 23535492_diplotype of ADORA2A is associated with Acute encephalopathy with biphasic seizures and late reduced diffusion 23583199_These studies underscore the importance of adenosine A2A receptor in activation of survival and proliferative pathways in pulmonary endothelial cells that are mediated through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways 23594931_The function of A2AR of patients with VVS was preserved since their stimulation by Adonis led to cAMP production with an EC50 comparable with those in controls. 23657626_regulation of GABA uptake occurs via modulation of the GABA transporters by the adenosine A1 (A1R) and A2A (A2AR) receptors 23679925_Upregulation of A2AARs was observed in ALS patients, and A2AAR density values correlated with the functional rating scale scores. Stimulation of A2AARs mediated a significant increase in cyclic AMP levels in lymphocytes from ALS patients. 23682121_Adenosine regulates bone metabolism via A1, A2A, and A2B receptors. 23685887_Data indicate that furan-2-carboxylic-acid [4-phenyl-5-(pyridine-2-carbonyl)-thiazol-2-yl]-amide showed moderate selectivity for A2A adenosine receptors. 23695433_A2ARs are increased in the brain of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis patients 23749290_A2AR activation downstream signaling for Col1 and Col3 expression proceeds via two distinct pathways with varying sensitivity to cAMP activation. 23789814_Data indicate that the metabolites behaved in vitro as antagonist ligands of cloned A2A receptor with affinities (Ki 7.5-53 nM) comparable to that of ST1535 (Ki 10.7 nM). 23856527_This is a review of the role played by A2aR and A3AR in regulating cancer pathogenesis, with a focus on melanoma, and the therapeutic potential of adenosine receptors pharmacological modulation. [review] 23965991_Molecular chaperones (heat-shock proteins HSP90alpha and HSP70-1A) that interact with and retain partially folded A2A receptor prior to endoplasmic reticulum exit, were identified. 24166702_maps of information flow were calculated in A2 A adenosine receptor (A2 A AR) and bovine rhodopsin and identified key residues for signal transductions and their pathways. 24321892_This study demonistrated that statistically significant lower levels of A2AR mRNA in vascular dementia compared to Alzheimer's disease subjects. 24359090_novel approach consisting in the integration of molecular docking and membrane molecular dynamics simulations of the A(2A) adenosine receptor and ligands 24433848_This study demonistrated that a2a receptor lever change in putamin in patient with schizophrenia. 24509856_the contribution of the hydrophobic core and of the extended C terminus of A2A adenosine receptor in hippocampal neuronsvariants in dissociated hippocampal neurons 24517244_study reveals that the GEC express functional A2a receptor and P. gingivalis may use the A2a receptor coupled DS adenosine signaling as a means to establish successful persistence in the oral mucosa. 24589267_Studies indicate that adenosine signaling through the adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) and A2B receptor (A2BR) were involved in sickle cell disease (SCD). 24652540_The effects of extracellular cAMP on monocytes are mediated by CD73 ecto-5'-nucleotidase and A2A and A2B adenosine receptors, as selective antagonists could reverse its effects. 24892887_Findings reveal that increased A2AR protein levels occur in asymptomatic Parkinson's disease patients and provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying A2AR expression levels along the progression of this neurodegenerative disease 24943643_A1AR availability associated with ADORA1 and particularly ADORA2A SNPs, several of which had previously been shown to be associated with increased anxiety and |
ENSMUSG00000020178 |
Adora2a |
65.297516 |
12.9478836381 |
3.694644 |
0.557829366 |
38.275478 |
0.00000000061429775084354322188165037262877130053162488820817088708281517028808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002988449504396117333202504559521058002946602982774493284523487091064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
120.3475689 |
29.9322677 |
9.5156372 |
2.0008837 |
| ENSG00000128298 |
80115 |
BAIAP2L2 |
protein_coding |
Q6UXY1 |
FUNCTION: Phosphoinositides-binding protein that induces the formation of planar or gently curved membrane structures. Binds to phosphoinositides, including to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2) headgroups. There seems to be no clear preference for a specific phosphoinositide (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
The protein encoded by this gene binds phosphoinositides and promotes the formation of planar or curved membrane structures. The encoded protein is found in RAB13-positive vesicles and at intercellular contacts with the plasma membrane. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. |
hsa:80115; |
cell-cell contact zone [GO:0044291]; clathrin complex [GO:0071439]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838] |
30483805_these findings revealed BAIAP2L2 as a novel biomarker and potential therapeutic target for lung cancer 32570120_BAIAP2L2 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via AKT/mTOR and Wnt3a/beta-catenin signaling pathways. 33646530_BAIAP2L2 facilitates the malignancy of prostate cancer (PCa) via VEGF and apoptosis signaling pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000018126 |
Baiap2l2 |
53.289055 |
0.1060324998 |
-3.237422 |
0.335573852 |
96.930514 |
0.00000000000000000000007180353330456566875772824523758489219442346178542962481497935640917251731707438011653721332550048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000706546767716926152364181513402935147943449970634731240531423504536157054189970949664711952209472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.0403094 |
2.4387768 |
105.7384105 |
12.6389757 |
| ENSG00000128309 |
4357 |
MPST |
protein_coding |
P25325 |
FUNCTION: Transfer of a sulfur ion to cyanide or to other thiol compounds. Also has weak rhodanese activity. Detoxifies cyanide and is required for thiosulfate biosynthesis. Acts as an antioxidant. In combination with cysteine aminotransferase (CAT), contributes to the catabolism of cysteine and is an important producer of hydrogen sulfide in the brain, retina and vascular endothelial cells. Hydrogen sulfide H(2)S is an important synaptic modulator, signaling molecule, smooth muscle contractor and neuroprotectant. Its production by the 3MST/CAT pathway is regulated by calcium ions. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97532}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transferase |
|
This protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the transfer of a sulfur ion from 3-mercaptopyruvate to cyanide or other thiol compounds. It may be involved in cysteine degradation and cyanide detoxification. There is confusion in literature between this protein (mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase, MPST), which appears to be cytoplasmic, and thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (rhodanese, TST, GeneID:7263), which is a mitochondrial protein. Deficiency in MPST activity has been implicated in a rare inheritable disorder known as mercaptolactate-cysteine disulfiduria (MCDU). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding same or different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4357; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; synapse [GO:0045202]; 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase activity [GO:0016784]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity [GO:0004792]; cyanate catabolic process [GO:0009440]; hydrogen sulfide biosynthetic process [GO:0070814]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; liver development [GO:0001889]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510]; sulfur amino acid catabolic process [GO:0000098]; transsulfuration [GO:0019346] |
16545926_This work is the first report of a functional genetic polymorphism affecting MPST and should help in investigation of disorders such as mercaptolactate-cysteine disulfiduria. 19695240_Data suggest that impaired rhodanese expression is associated with increased whole cell reactive oxygen species as well as higher mitochondrial superoxide production and predicts mortality in hemodialysis patients. 20446008_In all the investigated cell lines, the activity of MPST was higher than that of CST, which suggests that in these cells, the main pathway of sulfane sulfur formation is the MPST-catalyzed reaction. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23698001_The crystal structure analysis allows us to propose a detailed mechanism for MST in which an Asp-His-Ser catalytic triad is positioned to activate the nucleophilic cysteine residue and participate in general acid-base chemistry 25336638_distinct roles of each TUM1 isoform in the sulfur transfer processes in the cell 25487919_In this review, we discuss the roles of non-canonical Hippo/Mst signaling pathways in lymphocyte development and functions. [review] 26519030_3-Mercaptopyruvate sulphurtransferase and not cystathionine gamma-lyase is the primary regulator of coronary artery hydrogen sulfide production and function. 30644090_3-Mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase supports endothelial cell angiogenesis and bioenergetics. 31634482_MPST inactivation or silencing enhances the plasticity of dermal fibroblasts in a TET1 and glycolysis dependent manner and promotes adipogenic transdifferentiation. 32179647_Thioredoxin regulates human mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase at physiologically-relevant concentrations. 35243746_3-Mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase represses tumour progression and predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 36126419_MPST deficiency promotes intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and aggravates inflammatory bowel disease via AKT. |
ENSMUSG00000071711 |
Mpst |
121.018180 |
0.4529180494 |
-1.142678 |
0.167801218 |
46.633137 |
0.00000000000856004210788240029621050315348325041031607440800144104287028312683105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000047767947641718044447740438411756781593442422462203467148356139659881591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.4768892 |
8.0788411 |
170.4410585 |
11.8123211 |
| ENSG00000128311 |
7263 |
TST |
protein_coding |
Q16762 |
FUNCTION: Formation of iron-sulfur complexes, cyanide detoxification or modification of sulfur-containing enzymes. Other thiol compounds, besides cyanide, can act as sulfur ion acceptors. Also has weak mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MST) activity (By similarity). Together with MRPL18, acts as a mitochondrial import factor for the cytosolic 5S rRNA. Only the nascent unfolded cytoplasmic form is able to bind to the 5S rRNA. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20663881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21685364}. |
Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Transferase |
|
This is one of two neighboring genes encoding similar proteins that each contain two rhodanese domains. The encoded protein is localized to the mitochondria and catalyzes the conversion of thiosulfate and cyanide to thiocyanate and sulfite. In addition, the protein interacts with 5S ribosomal RNA and facilitates its import into the mitochondria. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:7263; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 5S rRNA binding [GO:0008097]; thiosulfate sulfurtransferase activity [GO:0004792]; cyanate catabolic process [GO:0009440]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; rRNA import into mitochondrion [GO:0035928]; rRNA transport [GO:0051029]; sulfur amino acid catabolic process [GO:0000098]; transsulfuration [GO:0019346] |
17035239_The USP8 recognition domain of NRDP1 has a novel protein fold that interacts with a conserved peptide loop of the rhodanese domain. 20099848_Proteomics was used to study colonic epithelial aging, for differential proteins in the human normal colonic epithelial tissues from young and old people. Rack1, EF-Tu and Rhodanese, three validated differential proteins, were further investigated. 20663881_silencing of the rhodanese gene caused not only a proportional decrease of 5 S rRNA import but also a general inhibition of mitochondrial translation, indicating the functional importance of the imported 5 S rRNA inside the organelle. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23399736_Loss of Thiosulfate Sulfurtransferase is associated with decreased mucosal sulfide detoxification capacity in patients with Crohn's disease 26269602_show that polymorphic variations that are distant from the active site differentially modulate the sulfurtransferase activity of human rhodanese to cyanide versus sulfite 27270587_TST mRNA expression in adipose tissue correlated positively with insulin sensitivity in adipose tissue and negatively with fat mass. 32061776_Unraveling the role of thiosulfate sulfurtransferase in metabolic diseases. |
ENSMUSG00000044986 |
Tst |
93.829940 |
0.3194050068 |
-1.646541 |
0.183092738 |
82.765391 |
0.00000000000000000009239361508136048621792349579468228591976461911133828132716705461291439860360696911811828613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000809335168309128039313444613549285373616660642356526863747112621183532610302790999412536621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.5676326 |
5.6157448 |
146.9777237 |
11.0755790 |
| ENSG00000128342 |
3976 |
LIF |
protein_coding |
P15018 |
FUNCTION: LIF has the capacity to induce terminal differentiation in leukemic cells. Its activities include the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, the induction of neuronal cell differentiation, and the stimulation of acute-phase protein synthesis in hepatocytes. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a pleiotropic cytokine with roles in several different systems. It is involved in the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, induction of neuronal cell differentiation, regulator of mesenchymal to epithelial conversion during kidney development, and may also have a role in immune tolerance at the maternal-fetal interface. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:3976; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; leukemia inhibitory factor receptor binding [GO:0005146]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; immune response [GO:0006955]; leukemia inhibitory factor signaling pathway [GO:0048861]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; lung lobe morphogenesis [GO:0060463]; lung vasculature development [GO:0060426]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; meiotic nuclear division [GO:0140013]; muscle organ morphogenesis [GO:0048644]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of hormone secretion [GO:0046888]; negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045835]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of histone H3-K27 acetylation [GO:1901676]; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation [GO:0045651]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mesenchymal to epithelial transition involved in metanephros morphogenesis [GO:0072108]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0033141]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of metanephric nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0072307]; regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:1903025]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; spongiotrophoblast differentiation [GO:0060708]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863]; trophoblast giant cell differentiation [GO:0060707]; tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0007260] |
11448119_LIF stimulates proliferation of rat pituitary tumor cells in culture, inhibits secretion of prolactin and growth hormone and induces tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in the cells. 11587067_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11587067_The entire structure of the LIF gene of 48 alleles in the Japanese population was sequenced. 11811789_Oncostatin M and leukemia inhibitory factor regulate the growth of normal human breast epithelial cells 11855863_LIF does not activate STAT3, ERK, or gp130 receptor in human N tera-2/D1 EC cells. The suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1) is constitutively expressed, suggesting that LIF signal transduction is inhibited by elevated levels of SOCS-1 expression. 12153570_experimental N-Myc overexpression results in down-regulation of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), a modulator of endothelial cell proliferation 12218157_LIF stimulates (45)Ca release and enhances expression of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin in neonatal mouse calvarial cultures, but has no effect on the expression of RANK. 12574225_role for LIF in loss of autocrine prolactin suppression contributing to unrestrained prolactinomas prolactin secretion. 12579339_LIF regulates cell survival of normal human endometrial stromal cells dose-dependently. 12707269_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), cardiotrophin-1, and oncostatin M share structural binding determinants in the immunoglobulin-like domain of LIF receptor 12764151_LIF has a role in src family kinase-independent signal transduction and gene induction 12807438_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) increased overall expansion of human neural precursor cells grown in culture; Following LIF withdrawal, 200 genes showed significant decreases 14557674_binding of ETS transcription factors to the ETS binding sites in the human LIF promoter is critical for its inducibility in response to T cell activators and play an important functional role within the endocrine-immune network. 14647442_role in hepatocyte growth factor expression 14687743_Decreased concentartion of LIF in infertile women do not seem to have a genetic basis due to the low frequency of LIF gene alterations. 14715713_Constitutive expression of cytokines in brain induces changes in gene expression characteristic of chronic inflammation leading to either temporal weight reduction (CNTF) or severe cachexia (leukemia inhibitory factor). 15044601_immunocytochemical staining and mRNA expression of LIF and its receptor are consistent with the concept that LIF might be involved in growth initiation of primordial follicles through its receptor 15180980_At early human post-implantation stage, LIF is produced from decidua and chorionic villi and may exert its action on trophoblasts. Anembryonic pregnancy cannot be accounted for by defective expression of either LIF or LIF-Rbeta in most circumstances. 15341921_Both IL-6 and LIF can be very efficiently induced by IL-1beta in articular chondrocytes in vitro, more so in osteosarthritis than in normal cells. 15342941_LIFRbeta and the signaling subunit gp130 are expressed in hESCs and human LIF can induce STAT3 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation in hESCs. 15543003_LCH represents a cytokine-driven condition partially mediated by TNF, IL-11, and LIF. These three cytokines are all osteoclastogenic, suggesting a pathogenetic pathway for the osteolytic lesions in LCH. 15670782_These results indicated that LIF induced multi-lineage differentiation of adult stem-like cells in kidney via cadherin 16. 15731310_role of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and its receptors in human embryo implantation 15837065_demonstrate using RNAi that Stat3 activation is necessary in the invasive phenotype of trophoblast cells and can be controlled via Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) 15905624_different members of the TGF-beta superfamily may also contribute in the reproductive process by enhancing endometrial proimplantatory LIF secretion and reducing proinflammatory IL-6 release by endometrial epithelium 16263181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16295654_LIF plays an essential role in the preimplantation embryo development and the blastocyst implantation and its gene mutations in women contribute to the implantation failure and subsequent infertility. 16341766_Leukemia inhibitory factor concentration in follicular fluid is not a useful marker for the prediction of number and quality of embryos, or implantation and pregnancy rates. 16489116_Data show that increased leukemia inhibitory factor secretion enhances airway reactivity and intracellular calcium signaling. 16545901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16545901_results suggest that the LIF gene mutations affect fertility 16648972_Since we demonstrated that not only SDF-1, but also HGF and LIF are upregulated in damaged tissues, we postulate that CXCR4+ c-Met+ LIF-R+ TCSC could be mobilized from the BM into the PB, where they play a role in tissue repair/regeneration. 16759928_Down-regulation of PRB in the endometrium is concomitant with the presence of glycodelin in the endometrium, suggesting interaction. 16949591_Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 may prevent leukemia inhibitory factor signaling in human embryonic stem cells. 17000646_There is no receptivity defect with regard to LIF and IL-11 secretions by eutopic endometrium in infertile women with endometriosis. 17054938_Ciliary neurotrophic factor/LIF signaling pathway acts via regulation of nitric oxide production to modulate developmental programmed cell death of postmitotic rod precursor cells. 17332938_The regulation of LIF and its receptor (LIFR) expression in pancreatic carcinoma cells were studied. 17652170_provides a structural template to understand the formation and orientation of the high-affinity signaling complex between LIF, LIF receptor, and gp130 17671691_interleukin-8 (CXCL-8) is induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and leukemia inhibitory factor in pancreatic carcinoma cells 17681328_Endometrial integrin beta3 and LIF expressions in the peri-implantation phase were significantly lower in stimulated cycles (including both moderate and high responders) compared to natural controls. 17702963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17848619_LIF and IL6 skew monocyte differentiation into tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-like cells by enabling monocytes to consume monocyte-CSF. Depletion of LIF, IL-6, and M-CSF in ovarian cancer ascites suppressed TAM-like cell induction 17966612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17966612_the LIF gene mutation, the heterozygote G to A transition on the position 3400, affects fertility but the infertility treatment can succeed. 17979974_Increased expression of some IL-6 cytokine family members (oncostatin M, gp130, CT-1, LIF) in cutaneous inflammation might contribute to the promotion of hair loss. 18042242_Increased LIF expression in peri-infarcted regions and sequestration from the peripheral circulation in acute stroke patients are characteristic of the pathobiological response to ischaemia and tissue damage. 18047677_Present predominantly in glandular epithelium. 18048043_higher levels found in the placentas of pre-eclamptic compared with normotensive women 18258286_Immunohistochemical labeling of LIF in the fallopian tube was found to be increased in ectopic pregnancies compared to non-pregnant and healthy pregnant controls 18298054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18298054_The antiphospolipid antibodies (aPLs) are elevated in infertile women with LIF gene mutations. 18317962_secretion of OSM and LIF by both epithelial and stromal (paracrine manner) cells seems to promote tumor growth in human breast carcinoma 18468598_Leukemia inhibitory factor may be one of the reasons that cause patients with salpingitis to be more susceptible to tubal pregnancy and might be involved in the implantation process of tubal pregnancy. 18492704_LIF can regulate extravillous trophoblast invasion, suggesting an important role in early placental development. 18540977_Overexpression may be a potential molecular marker for predicting poor prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma. 18637760_LIF secretion is a predictor and indicator of early progenitor status in adult bone marrow stromal cells. 18639869_Results describe the role of leukemia inhibitory factor in human mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression. 18684446_Unexplained infertility in some women might be explained by disturbances in the LIF pathway in midsecretory-phase endometrium. 18953658_A potential role for LIF in the melanoma-induced bone metastasis possibly through the stimulation of osteoclastogenesis is suggested. 19011087_In silico models predicted that five of the up-regulated miRNAs targeted leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) expression 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19213836_IL-11 and LIF regulated endometrial epithelial cell adhesion, suggesting that targeting IL-11 and LIF may be useful in regulating fertility by either enhancing or blocking implantation. 19251277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19251277_results indicate that LIF 3' UTR StuI polymorphism is not associated with multiple sclerosis, however we cannot exclude the hypothesis that other polymorphic alleles of LIF could be implicated in MS susceptibility 19255255_hCG-mediated LIF expression in the endometrium is dependent on prior induction of PROK1. 19342253_Results indicate that leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and Oncostatin M increase the expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, and TIMP-1 several fold, and that their expression is reduced to basal levels in the presence of the LIF antagonist MH35-BD. 19361790_Leukemia inhibitory factor is dysregulated in the endometrium and uterine flushing fluid of women with adenomyosis during the implantation window. 19374770_LIF has a role in the optimization of the endometrium for embryo implantation. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19470478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19495417_N-Myc regulates expression of pluripotency genes in neuroblastoma including lif, klf2, klf4, and lin28b 19541590_The key features of leukaemia inhibitory factor cytokine, its numerous physiological effects the most recent data are presented. Review. 19545488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19545488_The results suggest that in LIF gene mutation-positive women the idiopathic infertility and endometriosis have a negative impact on the outcome of IVF treatment. 19548631_The levels of E-selectin, ICAM-1, IL-11, IRF-1, IL-6, IL-1beta and LIF genes expression in the B. pseudomallei-infected cells were 1.5-5 times lower than in the B. thailandensis-infected cells. 19550366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19647472_Studies indicate potential of LIF/IL11 as contraceptive targets and therapeutic agents for infertility. 19704963_The expression of mRNA isoforms for leukemia-inhibitory factor changes with embryonic and neonatal development, changes reflect a decrease in stimulatory influences on the expression and number of LIF-producing circulating cells 19751193_Studies indicate that leptin, CNTF, LIF and IL-6 present similar three-dimensional fold structure, interact with related class-I receptors and activate similar intracellular pathways. 19879916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20074285_LIF protein is expressed in Alzheimer's and Parkinson diseases. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20396801_Results describe the effects of 6-h marathon ultra-race on the levels of IL-6, leukemia inhibiting factor (LIF), and stem cell growth factor (SCF) in athletes. 20570039_Suggest that growth inhibition and activation of the autocrine/paracrine signaling through LIF/JAK/STAT may be a common response to Ras/Raf activation in different medullary thyroid carcinoma types. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20597819_Wharton's jelly - and adipose tissue-mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCc) were more potent than BMbone marrow-MSCs in suppressing lymphocyte responses, and they mediated this effect by secreting high levels of leukemia inhibitory factor. 20618183_Patients with recurrent spontaneous abortion not only displayed a decrease in LIF expression but also had a reduced frequency of endometrial infiltrated CD4+ LIF+ cells in comparison with fertile women. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20851233_OPN, IL-6 and LIF may have critical roles in human pregnancy maintenance. 21129244_TGFbeta1, TNFalpha and LIF expressions showed increased level in the untreated patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. 21155043_Serum concentrations of IL-6 family cytokines, including IL-6, IL-11, and LIF, were significantly elevated in patients with RA compared to those of healthy controls. 21178106_The cytokine LIF promotes trafficking of T-type calcium channel subunits in human HEK293 cells via transient activation of JAK- and ERK-kinase signaling pathways. 21191816_The epigenetic up-regulation of the LIF gene likely play an important role in the development of breast cancer. 21527666_LIF is a contraction-induced myokine, potentially acting in an autocrine or paracrine fashion to promote skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation. 21570299_LIF could be significantly involved in the pathophysiology of Multiple sclerosis 21613225_Extensive mannose phosphorylation on leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) controls its extracellular levels by multiple mechanisms. 21726338_MiR-141 has been significantly downregulated by more than 50% after leukemia inhibitory factor stimulation 21745467_stimulation with alpha(1)-adrenoceptor may enhance DNA synthesis and proliferation of mouse iPS cells cultured with LIF via augmentation of both the MEK/MAPK and the PI3K/Akt pathways 21966484_Study demonstrated that LIF was an important regulator of decidualization in humans and mice. 21987111_Endometrial HOXA11 and LIF mRNA expression levels (normalized to beta-actin expression) were significantly decreased in endometrium of infertile patients with endometriosis compared with healthy fertile controls 22142941_Addition of IL-4 or IL-13 had no effect on IL-6 expression, but significantly inhibited LIF and IL-11 mRNA and protein stimulated by IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. 22252755_No correlation was found between pinopodes development stage and LIF expressions in endometrium. 22285730_LIF expression might be regulated by microRNA-199a 22323722_LIF delivery can be harnessed to enhance the generation of oligodendrocytes that express myelin proteins and reform the nodes of Ranvier in the context of chronic demyelination in the adult mouse hippocampus. 22341639_LIF mRNA expression was significantly decreased in abnormal uterine cavities during the midsecretory phase, indicating that endometrial cavity defects are a possible cause of poor reproductive outcomes. 22436290_plasma concentrations is a predictive marker of in vitro fertilization outcome 22520363_LIF was expressed in endometrium of fertile women but significantly decreased in infertile women. Infertile women secreted significantly less LIF molecules in uterine flushing compared with fertile women. 22537815_there is an altered expression of LIF and IL-15 in the endometrium of women with recurrent implantation failure 22649064_Although leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and LIF receptors were increased in muscle tissue and myoblasts from diabetic patients, LIF signaling and LIF-induced cell proliferation were impaired in diabetic myoblasts. 22698642_Expression of LIF and integrin-beta3 (ITGB3) in the peri-implantation endometrium does not change in women with unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss. 22712053_Data show that LIF through STAT3 negatively regulates Th2 differentiation. 22720020_findings suggest that our LIF-dependent human iPSCs could provide a novel model to investigate the role of cytokine signaling in cellular reprogramming 22835519_LIF combined with VEGF can maintain the preliminary, progenitor phenotype of EPCs and alleviate cell differentiation by upregulating KLF4, which may provide new insights into transcriptional regulation in endothelial progenitor cells 22905257_Acyloxy nitroso compounds inhibit LIF signaling in endothelial cells and cardiac myocytes, showing that STAT3 signaling is redox-sensitive 23122949_Identification of novel molecules associated with a LIF-mediated increase in trophoblastic cell invasion may facilitate our understanding of implantation biology. 23541977_study found lower expression of LIF in the edndometrium in unexplained infertile women with multiple implantation failures compared to fertile women; data suggest that the initial lower expression of LIF in proliferative phase may be one of the causes for multiple failure of implantation 23628981_novel expression and purification protocol for the production of recombinant hLIF 23687977_Data show that the expressions of ER-alpha, PR, LIF, VEGF, iNOS and CB1 in fallopian tube and chorionic villi of tubal pregnancy were not altered by exposure to levonorgestrel emergency contraception. 23729555_Data from 3-year-old girl and other reported cases support model in which abundance of LIF in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia results in leukemic infiltration of central nervous system and development of Cushing syndrome. [CASE STUDY; REVIEW] 23831429_In summary, we can show that LIF is an important factor in melanoma progression. 23876532_Polyethylene glycated leukemia inhibitory factor antagonist inhibits human blastocyst implantation and triggers apoptosis by down-regulating embryonic AKT1. 23963683_Results show that endogenous levels of Pkig reciprocally regulate osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation and that this reciprocal regulation is mediated in part by LIF. 24074901_Data suggest LIF/LIF receptor (alpha subunit) signal transduction facilitates blastocyst implantation or development of tubal pregnancy by stimulating blastocyst adhesion and outgrowth/proliferation of placenta or Fallopian tube epithelial cells. 24270418_NPC patients had increased serum levels of LIF. Higher LIF levels correlated with local tumor recurrence. Xenograft mouse studies showed that LIF critically contributes to NPC tumor growth & radioresistance. 24310780_Addition of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) neutralizing antibodies inhibited oligodendrocyte differentiation, indicating a crucial role of TNFR2-induced astrocyte derived LIF for oligodendrocyte maturation 24664722_This mini review will summarize the findings that are related to LIF signaling and discuss the neuroprotective effects of LIF in different models. 24690239_The use of LIF in combination with alphanubeta3 integrin as biomarkers appears to be superior to integrin testing alone when evaluating endometrial receptivity, primarily because of its earlier pattern of expression during the secretory phase. 24857661_LIF mediates fibroblast activation to promote invasive tumor microenvironment. 25128195_An increased mRNA expression of PROK1 and LIF could be one of the several abnormalities characterizing the endometrium in women recurrent pregnancy loss. 25179300_Data indicate that NanoLuc-fusion strategy provided an efficient approach for preparation of recombinant leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) protein 25277705_Expression of LIF protects the lung from lung injury and enhanced pathology during respiratory syncytial virus infection. 25323535_LIF has a role in negatively regulating tumour-suppressor p53 through Stat3/ID1/MDM2 in colorectal cancers 25514345_LIF downregulates the autoimmune response by enhancing Treg numbers. 25790555_Studied the association of tubal pregnancy with leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) expression in oviduct tissues. 25879318_LIF structure, signaling pathway, and primary roles in the development and function of an organism are reviewed--{REVIEW} 25885043_LIF/p21 signaling cascade as a novel tumor suppressive-like pathway in melanoma, acting downstream of TGFbeta to regulate cell cycle arrest and cell death, further highlight new potential therapeutic strategies for the treatment of cutaneous melanoma 26187859_Despite common signal transduction mechanisms (JAK/STAT, MAPK and PI3K) LIF can have paradoxically opposite effects in different cell types including stimulating or inhibiting each of cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. 26271643_LIF was frequently overexpressed in osteosarcoma, which could promote the growth and invasion through activating the STAT3 pathway. 26296968_Data show that leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) signaling promote chemoresistance in cholangiocarcinoma by up-regulating myeloid cell factor-1 (Mcl-1) via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/c-akt protein (AKT)-dependent pathway. 26615902_LIF SNP T/G (rs929271) seems to be a susceptibility biomarker capable of predicting implantation efficiency and pregnancy outcomes. 26716902_Overexpression of LIF promotes Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and results in cancer. 26723254_Taken together, we firstly demonstrate that LIF enhances the adhesion of trophoblastic cells to endometrial cells by up-regulating expression of integrin heterodimer alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta5. 26776907_Women with dormant genital tuberculosis were found to have decreased endometrial LIF-STAT3 signaling. 26817395_Cytokines of the LIF/CNTF family and metabolism 26817565_This review discusses the role of LIF and the recent analysis of its action on the uterine LE in regulating endometrial receptivity and implantation. 26984928_Although further studies would be required to deconvolute the targets involved in LIF induction and to confirm activity of hits in more disease-relevant assays, our results have demonstrated the potential of the phenotypic approach to identify specific and chemically tractable small molecules that trigger the production of LIF in relevant cell lines 27082016_Endometrial expression of LIF and LIFR is significantly reduced in the epithelial cells of infertile women. 27304912_Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) - STAT3 transcription factor (STAT3) signaling pathway is systemically dysregulated in in the endometrium of patients with recurrent/repeated implantation failure (RIFE). 28064096_In summary, this study has shown that LIF is implicated in the HG-mediated inhibition of osteoblast differentiation, via promoting STAT3/SOCS3 signaling. This study may provide insights into the signal pathway of HG-induced bone loss or delayed injured joint healing. 28246407_These findings implicate ZEB1 as a stem cell regulator in glioma via LIF repression which when deleted leads to increased stemness, tumorigenicity and shortened patient survival. 28247842_The expression of LIF was associated with tumor size and a poorer overall survival. Microarray and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction assessments suggest that LIF can facilitate tumor-promoting inflammation. Results indicate that LIF plays a role in maintaining cancer stem cells in chordomas. 28391028_findings illustrate that DeltaNp63alpha can inhibit the levels of LIF mRNA by direct transcription regulation and decrease LIF mRNA stability by suppressing the expression of Lnc-LIF-AS. An inverse interaction of LIF and DeltaNp63alpha expression was as well validated in clinical samples of cervical cancer, and high level of LIF in cervical cancers was related with poor patient survival. 28432985_study indicated impaired LIF expression levels only in women with unexplained infertility, while LIF-R expression was impaired in all sub-groups of infertile women. 28466814_SNP 3951C/T of LIF may not be associated with in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer outcome in Iranian population. 28512205_Data suggest a 216-nucleotide proximal cis-element in LIF mRNA exhibits mRNA destabilizing potential; on exposure to carcinogen PMA (phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate), this cis-element exhibits mRNA stabilizing activity. PMA induces nucleo-cytoplasmic translocation of both nucleolin and PCBP1, 2 trans-acting factors that bind to and stabilize LIF mRNA. [LIF = leukemia inhibitory factor; PCBP1 = poly(rC) binding protein 1] 28577574_ATF3 plays a significant role in regulating human endometrial receptivity and embryo attachment in vitro via up-regulation of leukemia inhibitory factor. 28729093_These results demonstrate the involvement of PIM kinases in LIF-induced regulation in different trophoblastic cell lines which may indicate similar functions in primary cells. 28755912_This report describes the involvement of proteins responsible for cell growth and progression and defines the LIF-mediated novel autocrine-paracrine signaling loop for cell growth arrest. 29038846_Decreased serum LIF levels may be associated with vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and that Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the inhibition of LIF-dependent biological effects on SSc endothelial cells by suppressing the expression of LIF, LIF receptor, and gp130. 29063331_The endometrial expression of LIF and CD34 in the pathogenesis of non-developing pregnancy can be used for evaluating the pregnancy prognosis in women of young and old reproductive age. 29269518_In serum from human PDAC patients, authors found that LIF titers positively correlated with intratumoral nerve density. 29393372_This study uses LIF to activate the PI3K/ AKT signal and induce the anti-inflammatory effect during the neuron differentiation from human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural precursor cells. 29397316_The findings indicate that low LIF concentrations in serum and follicular fluid may contribute to disordered folliculogenesis in polycystic ovary syndrome. 29605252_miR-181c-3p and -5p promotes high-glucose-induced dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating leukemia inhibitory factor 30213486_Differential expression of LIF and IGF-1 in molar trophoblasts and chorionic villi might have a role in regulation of trophoblasts in complete moles. Decreased expression of glandular IGF-1 and decidual LIF might be related to the decidual changes during trophoblastic proliferation and invasion of decidua in complete HMs. 30242886_Low LIF expression is associated with myoma uteri. 30305729_Ruxolitinib-treated tumors in both the immunocompromised and immunocompetent animal models demonstrate decreased phospho-STAT3, indicating on-target activity. In conclusion, CA-MSC activate ovarian cancer cell STAT3 signaling via IL6 and LIF and increase tumor cell stemness. 30383471_Interplay Between Helicobacter pylori Infection, Interleukin-11, and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in Gastric Cancer Among Egyptian Patients 30565675_Leukemia inhibitory factor inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inducing G1-phase arrest. 30611552_The association between ESR1 and LIF polymorphisms can help in the prediction of recurrent implantation failure. 30664218_Although rhLIF had no effect on proliferation, it inhibited apoptosis of degenerated nucleus pulposus cells in a concentrationdependent manner. LIF was upregulated during the process of intervertebral disc degeneration, and may promote the expression of extracellular matrix components. 30996350_findings reveal a function of LIF in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis, and suggest its translational potential as an attractive therapeutic target and circulating marker; studies underscore how a better understanding of cell-cell communication within the tumour microenvironment can suggest novel strategies for cancer therapy 31296870_Study shows that LIF expression is induced specifically by oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas (PDAC) and that LIF depletion by genetic means or by neutralizing antibodies prevents engraftment in pancreatic xenograft models. The related cytokine IL-6 cannot substitute for LIF, suggesting that LIF mediates KRAS-driven malignancies through a non-STAT-signaling pathway. 31586768_Identification of miRNAs and associated pathways regulated by Leukemia Inhibitory Factor in trophoblastic cell lines. 31615908_Epigenetic Profiling Identifies LIF as a Super-enhancer-Controlled Regulator of Stem Cell-like Properties in Osteosarcoma. 31854204_Study in eight datasets from four public databases revealed that LIF was highly expressed while LIFR was lowly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) tissues compared with adjacent or normal tissues. High LIF expression was associated with shorter overall survival whereas high LIFR expression was associated with longer overall survival confirming significance LIF and LIFR as biomarkers in PAAD. 31916327_EC yes-associated protein (YAP) is not only a critical coactivator of Hippo signalling in retinal vessel development but also plays an essential role in retinal astrocyte maturation by regulating LIF production. 32045772_Examined whether and how LIF regulates the behavior of macrophages and trophoblast cells in response to pro-inflammatory stress factors. We found that LIF modulated the activating effects of interferon-gamma and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in macrophages and trophoblast cells. 32324266_Impact of IFN-beta and LIF overexpression on human adipose-derived stem cells properties. 32504404_Polymorphism in the 3'-UTR of LIF but Not in the ATF6B Gene Associates with Schizophrenia Susceptibility: a Case-Control Study and In Silico Analyses. 32540613_LIF in embryo culture medium is a predictive marker for clinical pregnancy following IVF-ET of patients with fallopian tube obstruction. 32827446_Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via the LIFR-Hippo-YAP pathway. 32914874_Leukemia inhibitory factor is a novel biomarker to predict lymph node and distant metastasis in pancreatic cancer. 33004621_Autocrine Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via Src Family Kinase-Dependent Yes-Associated Protein Activation. 33410420_Leukemia inhibitory factor: A main controller of breast cancer. 33555431_The expression and significance of leukemia inhibitory factor, interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor in Chinese patients with endometriosis. 33914392_Association of novel stop-gained leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene (rs121912501) variant, leukaemia inhibitory factor and ovarian steroids with unexplained infertility among Pakistani women. 33931487_Mutant KRAS Downregulates the Receptor for Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) to Enhance a Signature of Glycolysis in Pancreatic Cancer and Lung Cancer. 34074039_Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium Promotes Endogenous Leukemia Inhibitory Factor to Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury. 34265288_Tumor-derived LIF promotes chemoresistance via activating tumor-associated macrophages in gastric cancers. 34392367_Myeloid cell-mediated targeting of LIF to dystrophic muscle causes transient increases in muscle fiber lesions by disrupting the recruitment and dispersion of macrophages in muscle. 34416362_Plasma proteomics identifies leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) as a novel predictive biomarker of immune-checkpoint blockade resistance. 34815524_PCK1 regulates neuroendocrine differentiation in a positive feedback loop of LIF/ZBTB46 signalling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. 35012573_Endometrial injury concurrent with hysteroscopy increases the expression of Leukaemia inhibitory factor: a preliminary study. 35680099_The Pleiotropic role, functions and targeted therapies of LIF/LIFR axis in cancer: Old spectacles with new insights. |
ENSMUSG00000034394 |
Lif |
10.313124 |
3.4913579805 |
1.803788 |
0.493241594 |
14.169281 |
0.00016707605930210857715992323058173951721983030438423156738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000444171944398256957325238358791352766274940222501754760742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0215424 |
4.6582985 |
4.6191617 |
1.1515708 |
| ENSG00000128512 |
9732 |
DOCK4 |
protein_coding |
Q8N1I0 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that promotes the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound small GTPases into their active GTP-bound form (PubMed:12628187, PubMed:16464467). Involved in regulation of adherens junction between cells (PubMed:12628187). Plays a role in cell migration (PubMed:20679435). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12628187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16464467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20679435}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Has a higher guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity compared to other isoforms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16464467}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;SH3-binding |
|
This gene is a member of the dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK) family and encodes a protein with a DHR-1 (CZH-1) domain, a DHR-2 (CZH-2) domain and an SH3 domain. This membrane-associated, cytoplasmic protein functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor and is involved in regulation of adherens junctions between cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with ovarian, prostate, glioma, and colorectal cancers. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described, but only one has been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9732; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium bundle [GO:0032421]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction [GO:1904694]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904754]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
17027967_Taken together, these results suggest that Dock4 plays an important role in the regulation of cell migration through activation of Rac1, and that RhoG is a key upstream regulator for Dock4. 18459162_DOCK4 may be regulated by PIP(3) to exert its function 18641688_DOCK4 interacts with the beta-catenin degradation complex, consisting of the proteins adenomatosis polyposis coli, Axin and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. 19383911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401682_Evidence for the involvement of DOCK4 in autism susceptibility was supported by independent replication of association at rs2217262 and the finding of a deletion segregating in a sib-pair family 19401682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19528233_Cell migration is regulated by platelet-derived growth factor receptor endocytosis, which involves DOCK4. 20346443_Data suggest that exonic deletions of DOCK4 may act as a risk factor for reading impairment. Genomic disruption of both DOCK4 and CNTNAP5 genes may have an additive effect and may result in a more severe autism spectrum phenotype. 20346443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21532034_novel epigenetic alterations in myelodysplastic leukocytes and implicate DOCK4 as a pathogenic gene located on the 7q chromosomal region. 21682944_This study revealed ROCK4 as novel schizophrenia candidate genes in the Jewish population. 23720743_The Atypical guanine nucleotide exchange factor Dock4 regulates neurite differentiation through modulation of Rac1 GTPase and actin dynamics. 24599690_The study found significant associations between autism and a SNP of the DOCK4 gene. 25644601_activator DOCK4 as a key component of the TGF-beta/Smad pathway that promotes lung ADC cell extravasation and metastasis. 26129894_DOCK4 signalling is necessary for lateral filopodial protrusions and tubule remodelling prior to vascular lumen formation 26578796_These data identify DOCK4 as a putative 7q gene whose reduced expression can lead to erythroid dysplasia 28925399_DOCK4 over expression suppresses selfrenewal and tumorigenicity of glioblastoma (GBM) stem-like cells. Accordingly in the frame of GBM median of survival, increased level of DOCK4 predicts improved patient survival. 31019307_SR-B1 drives endothelial cell LDL transcytosis via DOCK4 to promote atherosclerosis 32576693_Up-regulated cytotrophoblast DOCK4 contributes to over-invasion in placenta accreta spectrum. 33559155_DOCK4 stimulates MUC2 production through its effect on goblet cell differentiation. 35302184_DOCK4 regulates ghrelin production in gastric X/A-like cells. |
ENSMUSG00000035954 |
Dock4 |
133.707581 |
2.5948804685 |
1.375668 |
0.202339646 |
45.521579 |
0.00000000001509664001887578718290418583011683155425952662653799052350223064422607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000082773553743910335287398710113563595966446051477305445587262511253356933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
207.0024183 |
25.8438567 |
80.2130671 |
7.6726762 |
| ENSG00000128524 |
9296 |
ATP6V1F |
protein_coding |
Q16864 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of the V1 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons (PubMed:33065002). V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q28029, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33065002}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c', and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This encoded protein is the V1 domain F subunit protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9296; |
ATPase complex [GO:1904949]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0033176]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; transmembrane transporter complex [GO:1902495]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0016471]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain [GO:0000221]; ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042625]; proton transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015078]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961]; endosomal lumen acidification [GO:0048388]; Golgi lumen acidification [GO:0061795]; intracellular pH reduction [GO:0051452]; lysosomal lumen acidification [GO:0007042]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; synaptic vesicle lumen acidification [GO:0097401]; vacuolar acidification [GO:0007035] |
19723111_Results show that NiK-12192, by affecting vacuolar- H(+)-ATPase activity (and intracellular pH), causes a modification of structures crucial for cell adhesion and induces cell death, likely by a modality involving an anoikis-mediated apoptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000004285 |
Atp6v1f |
553.492028 |
2.0333495729 |
1.023858 |
0.079236838 |
167.080636 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000003212301958716485872621006156251453481724109628246468615498722268337708820522881641568991210784224637347916697649452544283121824264526367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000516487765911278075249100067611490326718455516543046095334038786946515579694509028980784930341245766993729660043754847720265388488769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
746.8433636 |
36.3374149 |
370.2329932 |
13.8578057 |
| ENSG00000128590 |
4189 |
DNAJB9 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBS3 |
FUNCTION: Co-chaperone for Hsp70 protein HSPA5/BiP that acts as a key repressor of the ERN1/IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response (UPR) (By similarity). J domain-containing co-chaperones stimulate the ATPase activity of Hsp70 proteins and are required for efficient substrate recognition by Hsp70 proteins (PubMed:18400946). In the unstressed endoplasmic reticulum, interacts with the luminal region of ERN1/IRE1 and selectively recruits HSPA5/BiP: HSPA5/BiP disrupts the dimerization of the active ERN1/IRE1 luminal region, thereby inactivating ERN1/IRE1 (By similarity). Also involved in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) of misfolded proteins. Required for survival of B-cell progenitors and normal antibody production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:G3H0N9, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QYI6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18400946}. |
3D-structure;Chaperone;Endoplasmic reticulum;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Unfolded protein response |
|
This gene is a member of the J protein family. J proteins function in many cellular processes by regulating the ATPase activity of 70 kDa heat shock proteins. This gene is a member of the type 2 subgroup of DnaJ proteins. The encoded protein is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum. This protein is induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress and plays a role in protecting stressed cells from apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:4189; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; Hsp70 protein binding [GO:0030544]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; negative regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903895]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002639]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
18400946_ERdj4 and ERdj5 promote turnover of misfolded SP-C and this activity is dependent on their ability to stimulate BiP ATPase activity. 25146923_these results demonstrate that DNAJB9 is a downstream target of p53 that belongs to the group of negative feedback regulators of p53. 29198525_Study reports that the endoplasmic reticulum luminal co-chaperone ERdj4/DNAJB9 is a selective IRE1 repressor that promotes a complex between the luminal Hsp70 BiP and the luminal stress-sensing domain of IRE1alpha. 31010480_Study detected a 4-fold higher abundance of serum DNAJB9 in fibrillary glomerulonephritis (FGN) patients when compared to controls, including patients with other glomerular diseases. Serum DNAJB9 levels were also negatively associated with estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with FGN. 31227146_New developments in the diagnosis of fibrillary glomerulonephritis. 31285458_Targeting DNAJB9, a novel ER luminal co-chaperone, to rescue DeltaF508-CFTR. 31873072_these observations support a competition model whereby waning ER stress passively partitions ERdj4 and BiP to IRE1(LD) to initiate active repression of UPR signalling. 31884339_Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 regulates chemotherapy resistance through the miR-32/DNAJB9 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. 32049014_Hepatic DNAJB9 Drives Anabolic Biasing to Reduce Steatosis and Obesity. 32557205_Clinicopathological characteristics and outcome of patients with fibrillary glomerulonephritis: DNAJB9 is a valuable histologic marker. 32622524_DNAJB9-positive monotypic fibrillary glomerulonephritis is not associated with monoclonal gammopathy in the vast majority of patients. 33966034_DNAJB9 suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by promoting FBXO45-mediated degradation of ZEB1. |
ENSMUSG00000014905 |
Dnajb9 |
118.072876 |
2.4210170121 |
1.275613 |
0.166872426 |
58.425438 |
0.00000000000002111432206605586343102384553523539431504852867393928761430288432165980339050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000139314883189532654810457900375581044718304932206187629617488710209727287292480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
162.9414964 |
16.6364319 |
67.9968792 |
5.4058570 |
| ENSG00000128594 |
64101 |
LRRC4 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBW1 |
FUNCTION: Synaptic adhesion protein. Regulates the formation of exitatory synapses through the recruitment of pre-and-postsynaptic proteins. Organize the lamina/pathway-specific differentiation of dendrites. Plays an important role for auditory synaptic responses. Involved in the suppression of glioma (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is significantly downregulated in primary brain tumors. The exact function of the protein encoded by this gene is unknown. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:64101; |
dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; excitatory synapse assembly [GO:1904861]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; postsynaptic density protein 95 clustering [GO:0097119]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560] |
15967442_LRRC4 may play an important role in maintaining normal function and suppressing tumorigenesis in the central nervous system. 16188120_LRRC4 gene might be involved in tumor suppression by restraining DNA synthesis and nucleoli organizer regions-associated proteins. 16215635_these studies represent the first cDNA array analysis of the effects of LRRC4 on the involvement of different neurobiological genes in U251MG glioblastoma cells and provide new insights into the function of LRRC4 in glioma 16723503_LRRC4 plays a major role in suppressing U251 cell proliferation by regulating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/Akt/NF-kappaBp65, STAT3, and JNK2/c-Jun pathways. 16941076_LRRC4 may be a negative regulator of the RPTP-zeta receptor, and contribute to suppressing the invasion ability of gliomas cells 17541939_LRRC4 inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis by downgrading pleiotropic cytokine responses. 18976507_Methylation-mediated inactivation of LRRC4 is a frequent and glioma-specific event. 21435336_As a glioma suppressor, LRRC4 inhibits the endogenous expression of small regulatory microRNA hsa-miR-381 and decreases cell proliferation and tumor growth in cultured glioma cells. 21809374_Potentially, modulation of LRRC4 or STMN1 expression may be useful for design of new therapies for the intervention of glioma 22834685_LRRC4 inhibited the miR-185 pathway function in glioma 24404152_Disturbing miR-182 and -381 inhibits BRD7 transcription and glioma growth by directly targeting LRRC4. 24563334_polymorphisms and haplotypes in the LRRC4 may have a role in pituitary adenoma in a Chinese population 27612424_Results show a strong negative correlation between the expression of miR-381 and LRRC4 in osteosarcoma (OS) tissues, indicating LRRC4 as a direct target gene of miR-381. 27884160_Following EGF stimuli, the D domain of LRRC4 anchors ERK1/2 in the cytoplasm and abrogates ERK1/2 activation and nuclear translocation. 30790560_High LRRC4 expression is associated with Liposarcoma . 32372061_Leucine-rich repeat containing 4 act as an autophagy inhibitor that restores sensitivity of glioblastoma to temozolomide. |
ENSMUSG00000049939 |
Lrrc4 |
185.814687 |
0.2287458537 |
-2.128183 |
0.185575593 |
127.940365 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001156667018316019872271462977489121510584927545347453975266580253188886265932212166207548875718202907592058181762695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000147049140313044386688614088384686198750489445046973543363470737071887460567249511500520497975230682641267776489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
70.2886586 |
9.5257598 |
310.2933910 |
28.6204959 |
| ENSG00000128595 |
813 |
CALU |
protein_coding |
O43852 |
FUNCTION: Involved in regulation of vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of multiple N-terminal glutamate residues. Seems to inhibit gamma-carboxylase GGCX. Binds 7 calcium ions with a low affinity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Secreted;Signal |
|
The product of this gene is a calcium-binding protein localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and it is involved in such ER functions as protein folding and sorting. This protein belongs to a family of multiple EF-hand proteins (CERC) that include reticulocalbin, ERC-55, and Cab45 and the product of this gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:813; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0033018]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] |
17048007_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17049586_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17189218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17596133_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18688696_Data show that calumenin in the presence of calcium binds specifically to thrombospondin-1, but closely-related reticulocalbin does not form a similar complex. 19794411_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19958090_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20020283_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20149073_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20200517_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20499136_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20553802_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673165_associated with arterial calcification and short-term prognosis of the outcome of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome 21057703_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22188360_Quantitative PCR assays for VKORC1, CYP4F2, GGCX and CALU identified two copies in all populations. 22514732_Study found the secretion of calu-1/2-EGFP required microtubule integrity, and that calu-1/2-EGFP-containing vesicles were transported by the motor proteins Kif5b and cytoplasmic dynein. 22768251_Calumenin is a new CFTR chaperone. 24136234_Calu-15, a novel isoform of Calu with phosphorylation-dependent nuclear localization, has a critical role in promoting filopodia formation and cell migration by upregulating the GDF-15 transcription. 25120007_Calumenin is characterized as a charged protein exhibiting close similarity with intrinsically disordered proteins and is hypothesized to regulate F508del-CFTR folding by electrostatic effects. 25823396_CALU polymorphism A29809G affects calumenin availability involving vascular calcification 25963840_Results show that OSBPL5 and CALU were expressed at higher levels in the lung tissues of metastasis-positive cases than that in the metastasis-negative cases suggesting they can promote invasiveness of lung cancer cells. 26124285_Results provide direct evidence for the involvement of CALU and LGALS3BP as potential negative regulators in the virus-triggered induction of the typeI interferons. 27790916_irradiated tumor cells were observed to significantly up-regulate the expression of calcium-binding proteins CALM1, CALU, and RCN1, suggesting important roles for these mediators in promoting irradiated tumor cell survival during hypoxia 28189267_The Calumenin modulates Sarco/Endoplasmic reticulumCa2+ATPase (SERCA) pump activity without drastically affecting ER-Ca(2+) concentration. 29319298_Replacing Leu with Gly (L150G) in Calu1 enables the protein to adopt a structural fold even in the Ca(2+) free form. The fourth (of seven) EF-hand of HsCalu1 nucleates the structural fold of the protein depending on the switch residue (Gly or Leu). 32469983_Establishment of a CALU, AURKA, and MCM2 gene panel for discrimination of metastasis from primary colon and lung cancers. |
ENSMUSG00000029767 |
Calu |
1408.933237 |
2.4760898072 |
1.308064 |
0.050764843 |
665.321950 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001039795502421249515549643965550291079331934438262749901816393147921626039332109760988135129405160014263600770517932631582511259190779435214579302966369657759104236904949906834012099948 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000658685906254834532691668734905224257696246658474602291118430694965755322503543100847677995220917437253649881630352223880335042410090033653249001551128183646899787552799484518901963287 |
Yes |
No |
2019.3175686 |
56.0930867 |
821.6544440 |
18.1765282 |
| ENSG00000128596 |
64753 |
CCDC136 |
protein_coding |
Q96JN2 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in acrosome formation in spermatogenesis and in fertilization. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TVA9}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Differentiation;Fertilization;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in acrosome assembly and single fertilization. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in acrosomal membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64753; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; acrosome assembly [GO:0001675]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
15112360_Data suggest that NAG6 may represent a candidate tumor suppressor gene at 7q31-32 loci associated with gastric carcinoma. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25065397_CCDC136 locus showed association with a comparable reading/language measure. 28866788_Missense variant in CCDC136 gene is associated with reading disability. |
ENSMUSG00000029769 |
Ccdc136 |
22.120777 |
0.1938576873 |
-2.366930 |
0.432722206 |
30.151530 |
0.00000003995718507605132413267173536845777714887617548811249434947967529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000163733495758611201131214841694716533027076366124674677848815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7714717 |
2.2048167 |
40.5745575 |
6.7713600 |
| ENSG00000128849 |
84952 |
CGNL1 |
protein_coding |
Q0VF96 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in anchoring the apical junctional complex, especially tight junctions, to actin-based cytoskeletons. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22891260}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction |
|
This gene encodes a member of the cingulin family. The encoded protein localizes to both adherens and tight cell-cell junctions and mediates junction assembly and maintenance by regulating the activity of the small GTPases RhoA and Rac1. Heterozygous chromosomal rearrangements resulting in association of the promoter for this gene with the aromatase gene are a cause of aromatase excess syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:84952; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; myosin complex [GO:0016459]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051058]; negative regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051497]; protein localization to cell-cell junction [GO:0150105] |
15292197_This paper studied the mouse JACOP protein and found that the JACOP protein has structural and functional similarities to cingulin. 18653465_Paracingulin regulates the activity of Rac1 and RhoA GTPases by recruiting Tiam1 and GEF-H1 to epithelial junctions 21454477_ZO-1 and PLEKHA7 are paracingulin-interacting proteins that are involved in its recruitment to epithelial tight and adherens junctions, respectively 24163246_Results indentify plausible candidates include non-recurrent deletions at the glutamate transporter gene SLC1A1, a CNV locus recently suggested to be involved in schizophrenia through linkage analysis, and duplications at 1p36.33 and CGNL1. 24807907_MgcRacGAP colocalizes with CGN and CGNL1 at TJs and forms a complex and interacts directly in vitro with CGN and CGNL1. 29016873_demonstrate in a postnatal retinal vascular development model in mice that Cgnl1 function is crucial for sustaining neovascular growth and stability |
ENSMUSG00000032232 |
Cgnl1 |
7.727684 |
0.3055366614 |
-1.710583 |
0.595337742 |
8.658500 |
0.00325539254321513234560758753843856538878753781318664550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006914100920315591376763553199680245597846806049346923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5601324 |
1.3856206 |
11.7255967 |
2.6822082 |
| ENSG00000128881 |
146057 |
TTBK2 |
protein_coding |
Q6IQ55 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase that acts as a key regulator of ciliogenesis: controls the initiation of ciliogenesis by binding to the distal end of the basal body and promoting the removal of CCP110, which caps the mother centriole, leading to the recruitment of IFT proteins, which build the ciliary axoneme. Has some substrate preference for proteins that are already phosphorylated on a Tyr residue at the +2 position relative to the phosphorylation site. Able to phosphorylate tau on serines in vitro (PubMed:23141541). Phosphorylates MPHOSPH9 which promotes its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, loss of MPHOSPH9 facilitates the removal of the CP110-CEP97 complex (a negative regulator of ciliogenesis) from the mother centrioles, promoting the initiation of ciliogenesis (PubMed:30375385). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21548880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23141541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30375385}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinase;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Spinocerebellar ataxia;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a serine-threonine kinase that putatively phosphorylates tau and tubulin proteins. Mutations in this gene cause spinocerebellar ataxia type 11 (SCA11); a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive ataxia and atrophy of the cerebellum and brainstem. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:146057; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; microtubule plus-end binding [GO:0051010]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; tau-protein kinase activity [GO:0050321]; cerebellar granular layer development [GO:0021681]; cerebellar granule cell precursor tangential migration [GO:0021935]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; negative regulation of microtubule binding [GO:1904527]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; negative regulation of protein localization to microtubule [GO:1902817]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
15148151_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18037885_These data suggest that TTBK2 is important in the tau cascade and in spinocerebellar degeneration. 19533200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19533200_that SCA11 is an extremely rare cause for dominantly inherited ataxias (TTBK2) in the German population. 19768375_Examination the TTBK2 gene in 68 unrelated spinocerebellar ataxia patients displayed the normal elution profile, which denoted that no disease-related mutation was identified. We provided the evidence that SCA11 is a rare form of ataxia in China. 19768375_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20667868_two-basepair deletion (c.1306_1307delGA, p.D435fs448X in exon 12) lead to a premature stop codon in the TTBK2 gene; spinocerebellar ataxia patients had phenotypic of slowly progressive almost pure cerebellar ataxia with normal life expectancy 22020623_findings reveals a major role of PRKX, TTBK2 and RSK4 in triggering Sunitinib resistance formation; data suggest transcriptional regulation of these kinases together with other proteins might play an important role in formation of Sunitinib resistance by affecting transcription factors 22814243_TTBK2 is a completely novel regulator of Na(+)-coupled glucose transport. 23141541_Dominant truncating mutations in human TTBK2 cause spinocerebellar ataxia type 11 (SCA11); these mutant proteins do not promote ciliogenesis and inhibit ciliogenesis in wild-type cells. 24982133_data suggest that TTBK2 also acts upstream of Cep164, contributing to the assembly of distal appendages 25297623_TTBK2 bound EB1 and Cep164 through its SxIP motifs and a proline-rich motif, respectively. 25473830_TTBK1/2 kinases may represent attractive targets for therapeutic intervention for TDP-43 proteinopathies such as Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Frontotemporal lobar degeneration-TDP. 25950000_TTBK2 is a multifunctional kinase involved in important cellular processes and demands augmented efforts in investigating its functions 26323690_TTBK2 phosphorylates KIF2A and antagonizes KIF2A-induced depolymerization at microtubules plus ends for cell migration. 27607061_TTBK2 down-regulates GluK2 activity by decreasing the receptor protein abundance in the cell membrane via RAB5-dependent endocytosis. 28219405_Enhanced expression of circ-TTBK2 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while inhibited apoptosis in glioma cells. 29409526_Our findings suggest a possible etiology for the two most common frontotemporal lobar degeneration subtypes through a TTBK1/2 activation driven mechanism of neurodegeneration 30532139_Spinocerebellar ataxia type 11 (SCA11)-associated mutations are dominant negative alleles and the resulting truncated protein (TTBK2SCA11) interferes with the function of full length TTBK2 in mediating ciliogenesis. 31455668_The TTBK2-dependent CEP83 phosphorylation is important for early ciliogenesis steps, including ciliary vesicle docking and CP110 removal. 31858557_Circular RNA TTBK2 promotes the development of human glioma cells via miR-520b/EZH2 axis. 32129703_Phosphorylation of multiple proteins involved in ciliogenesis by Tau Tubulin kinase 2. 32196629_Circular RNA TTBK2 regulates cell proliferation, invasion and ferroptosis via miR-761/ITGB8 axis in glioma. 33846249_A complex of distal appendage-associated kinases linked to human disease regulates ciliary trafficking and stability. 34499853_Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of the centriolar CEP164-TTBK2 complex in ciliopathies. |
ENSMUSG00000090100 |
Ttbk2 |
436.266216 |
0.0812665481 |
-3.621195 |
1.300199506 |
6.011781 |
0.01421067654153765867641734388371332897804677486419677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026353761245520270634079551541617547627538442611694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.0438722 |
60.5559367 |
916.3792531 |
520.9379160 |
| ENSG00000128917 |
54567 |
DLL4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR61 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the Notch signaling pathway as Notch ligand (PubMed:11134954). Activates NOTCH1 and NOTCH4. Involved in angiogenesis; negatively regulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration and angiogenic sprouting (PubMed:20616313). Essential for retinal progenitor proliferation. Required for suppressing rod fates in late retinal progenitors as well as for proper generation of other retinal cell types (By similarity). During spinal cord neurogenesis, inhibits V2a interneuron fate (PubMed:17728344). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JI71, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11134954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17728344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20616313}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Notch signaling pathway;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sensory transduction;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Vision |
|
This gene is a homolog of the Drosophila delta gene. The delta gene family encodes Notch ligands that are characterized by a DSL domain, EGF repeats, and a transmembrane domain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:54567; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; blood circulation [GO:0008015]; blood vessel lumenization [GO:0072554]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; cardiac atrium morphogenesis [GO:0003209]; cardiac ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003208]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; dorsal aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035912]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903588]; negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090051]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; Notch signaling involved in heart development [GO:0061314]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; pericardium morphogenesis [GO:0003344]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000179]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; regulation of neural retina development [GO:0061074]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; ventral spinal cord interneuron fate commitment [GO:0060579]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12200365_Ectopic expression of human Delta4 in mice by retroviral gene delivery impairs hematopoietic development and leads to lymphoproliferative disease. 12482957_We show here that vascular endothelial growth factor but not basic fibroblast growth factor can induce gene expression of Notch1 and Dll4, in human arterial endothelial cells. The VEGF-induced specific signaling is mediated through VEGF receptors 1 and 2 12684674_suppresses the self-renewal capacity and long-term growth of two myeloblastic leukemia cell lines 14990974_upon transduction into cord blood CD34+ stem cells, DLL4 induced a 25-fold reduction in nucleated cell production by maintaining a higher proportion of cells in G0/G1 phase; specific retention of CD34+ cells throughout the culture was observed. 15820317_DLL4 not associated with susceptibility to periodic catatonia in German patients from 15q15 linked families 16204037_DLL4 expression is essential for tumor angiogenesis. 16914569_DLL4 expression is associated with vascular differentiation in bladder cancer. 17157169_CD34+ cord blood progenitors were exposed for 4 days to either immobilized Notch ligand Delta-4. Delta-4 priming led to an acceleration of T-cell development, including a completion of the TCR rearrangement. 17533181_Dll4-triggered Notch signaling may mediate inflammatory responses in macrophages and promote inflammation. 17664272_Notch1 ligand, Delta-like ligand-4, stimulates R-Ras-dependent alpha 5 beta 1 integrin-mediated adhesion, demonstrating the physiological relevance of this pathway. 17692341_Dll4 expression acts as a switch from the proliferative phase of angiogenesis to the maturation and stabilisation phase by blocking endothelial cell proliferation and allowing induction of a more mature, differentiated phenotype. 17822320_Overexpression of DLL4 is associated with breast cancer 17916635_Endometrial Dll4 may enhance the development of the endometrial microvascular system and facilitate the implantation of blastocyst in a fertile cycle. 17998388_integrated role of dll4 with interleukin-12 demonstrated that, together, both of these instructive signals direct the immune response toward a more competent, less pathogenic antiviral response. 18055448_The effects of a soluble form of Delta4 (solD4) by exposing CD34+CD38(low) cells to S17 feeders engineered to express solD4 (solD4/S17), were assessed. 18056450_Overexpression of Delta-like 4 Notch ligand regulates tumor angiogenesis, improves tumor vascular function, and promotes tumor growth 18339870_Dll4 may contribute to vascular differentiation and inhibition of the angiogenic response by regulating multiple receptor pathways. 18435556_Global intrinsic (conformational) disorder, in concert with local preorganization, may play a role in Notch signaling mediated by Delta-4. 18577711_retrovirus-induced over-expression of Dll4 in tumor cells activates Notch signaling in cocultured endothelial cells and limits vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell growth 19208840_Escape of human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells from dormancy is associated with increased Notch3 signaling in tumor cells 19263417_dynamic changes in neurite morphology were rapidly reversible and dependent on the activation of the Notch signaling pathway 19816565_possible complementary role for JAG1 and DLL4 in the context of Kaposi sarcoma. 20036815_Studies indicate that the imbalance of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors VEGFA, Notch, Dll4, PDGF and angiopoietin-1 promotes tumor angiogenesis. 20167561_This review focuses on negative regulators of angiogenesis delta-like 4 and vasohibin 1 produced by endothelial cells. 20167860_vascular notch ligand delta-like 4 is expressed with inflammatory markers in breast cancer 20182391_Results suggests that cell-to-cell interaction via DLL4-Notch signaling pathway has been implicated in tumor angiogenesis, and control of this pathway can be a new therapeutic approach to solid tumor. 20193271_Inhibiting the Dll4/Notch signal transduction pathway stimulates the proliferation of HUVEC and facilitates angiogenesis. 20508179_Dll4/Notch interaction is essential for proper reparative angiogenesis. Moreover, Dll4/Notch signaling regulates sprouting angiogenesis and coordinates the interaction between inflammation and angiogenesis under ischemic conditions. 20558614_exosomes can transfer the Dll4 protein to other endothelial cells and incorporate it into their cell membrane, which results in an inhibition of Notch signaling and a loss of Notch receptor 20959466_DLL4 could propagate its own expression and enable synchronization of NOTCH expression and signaling between ECs. 21045140_Studies indicate that different receptors and ligands expression in breast cancer and various ways in which the pathway can be inhibited. 21212269_the Ang1/Tie2 signal potentiates basal Notch signal controlling vascular quiescence by up-regulating Dll4 through AKT-mediated activation of beta-catenin. 21362319_DLL4 signaling appears to play an essential role in the biological behavior of choroid vascular endothelial cells under hypoxia. 21362320_Through activating the Dll4-Notch-Hey2 signaling pathway, HGF indirectly promotes the proliferation and migration ability of cells, so that offspring artery branches are formed. 21372153_we have investigated their influence on early human hematopoiesis and show that Jagged2 affects hematopoietic lineage decisions very similarly as Delta-like-1 and -4, but very different from Jagged1 21474814_SiRNA-mediated knockdown of alpha2beta1 and alpha6beta1 integrins abolishes Dll4 induction, which discloses a selective integrin signaling acting upstream of Notch pathway 21517260_Expression of DLL4, VEGF and HIF-1alpha was very strong in gliomas. 21526177_Dll4 play an important role in choroidal neovascularization (CNV) angiogenesis, which appears to be regulated by HIF-1alpha and VEGF during the progression of CNV under hypoxic conditions. 21726900_The receptors Notch2, -3, -4 and their ligands Jagged1, -2 and Delta1, -4 were detected at both the mRNA and protein level in early and late placenta 21832157_we show that Tis11b silencing in endothelial cells leads to up-regulation of Dll4 protein and mRNA expressions, indicating that Dll4 is a physiological target of Tis11b 22010178_In DLL4-expressing CR carcinoma xngrft model, Notch blockade combined with ionizing radiation caused tumor growth delay. The DLL4 monoclnl antibody in combination with ionizing radiation also delayed tumor growth in the non-DLL4-expressing xngrft model 22020917_DLL4 and Jagged1 siRNA gene therapy mediated by adenovirus may be useful for inhibiting growth and invasion of SGC7901 through a Notch/VEGF pathway. 22066479_Detection of Notch1, Notch4, and DLL4 in thyroid glands and their regulation in various pathologies suggest that this pathway may play a role in thyroid carcinogenesis and angiogenesis. 22296176_Dll4 and Jag1 are expressed in glioblastoma vasculature. 22699504_Dll4 skewed macrophages toward a proinflammatory phenotype ('M1'). These results suggest that Dll4-Notch signaling plays a central role in the shared mechanism for the pathogenesis of cardiometabolic disorders. 23086751_miR-30b and miR-30c regulate DLL4. 23108591_expression of DLL4 is associated with reduced radio-resistance, presumably by reducing hypoxia and improving chemotherapy accessibility 23207622_DLL4 may be an important regulator for vessel proliferation and maturation in human high-grade malignant gliomas. 23239744_Upregulation of Dll4 expression in acute myeloid leukemia cells suppressed VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation. 23275120_These findings provide evidence that high expression of DLL4 serves as an independent predictor of poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. 23300864_Overexpresion of DLL4 in endothelial cells inhibited cell proliferation, but did not affect cell migration, sprouting angiogenesis or cell adhesion. 23787764_High Dll4 expression is associated with glioblastoma multiforme. 23817492_Our data suggest that miR-30a stimulates arteriolar branching by downregulating endothelial Dll4 expression, thereby controlling endothelial tip cell behavior. 23839946_direct measurement of the binding affinity of Notch1 EGF repeats 6-15 for Dll1 and Dll4 revealed that Dll4 binds with at least an order of magnitude higher affinity than Dll1 23898884_and stromal DLL4 expression was found in 48% and 22% in gastric cancer, and significantly affected postoperative clinical outcomes. 23901223_Activation of DLL4-mediated Notch signaling promotes the expression and secretion of MMP-2 proenzyme and influences the progress of gastric cancer. 23950980_Aberrant DLL4 expression and HIF-1alpha/VEGF angiogenesis signaling may have a role in missed abortion. 24025398_the role of macrophages and Dll4/Notch signaling in the development of inflammation in both the cardiovascular system and metabolic organs. [review] 24025447_Synaptojanin-2 binding protein stabilizes the Notch ligands DLL1 and DLL4 and inhibits sprouting angiogenesis. 24394305_These findings indicate a potential role for the Notch-1-Dll4 signaling pathway in foreign body-induced granulomatous reactions 24504253_Dll4-containing exosomes increase endothelial cell motility while suppressing their proliferation. 24615277_Demonstrate that the action of IFNgamma on endothelial cellss, but not other cells, is highly effective for tumour angiostasis, which involves down-regulating Dll4. 24696220_High expression of DLL4 is associated with metastasis in breast cancer. 24931473_Our data suggest that renal cell carcinoma progression is caused in part by activated DLL4/Notch signaling, interaction of endothelium and cells 24949865_expression of VEGF and Dll4/Notch pathway molecules in ovarian cancer 24966922_Dll4 expression is up-regulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients, and predicts poor prognosis. 25041739_Dengue virus up-regulates expression of notch ligands Dll1 and Dll4 through interferon-beta signalling pathway. 25130545_findings suggest that ADAM10/Dll4 signaling is a major signaling pathway in ECs driving inflammatory events involved in inflammation and immune cell recruitment 25139440_Inhibition of ADAM10/17 or knockdown of DLL4 reduced the proangiogenic effects of fibulin-3 in culture 25260720_these results suggest that high expression of DLL4 is associated with axillary lymph node metastasis and a poor prognosis in breast cancer, suggesting its value as a diagnostic marker for breast cancer. 25348865_Dormant Dbf4 mRNA in immature GV oocytes is recruited by cytoplasmic polyadenylation during oocyte maturation and is dependent on MPF activity via its cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE) 25355291_High DLL4 expression is associated with T acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 25833803_Among all the Notch ligands, Delta-like4 (Dll4) is specifically involved in angiogenesis. hD4R could suppress angiogenesis in vitro as manifested by network formation assay and sprouting assay. 25986715_The expression of DLL4 was positively correlated with CD105-labeled MVD. 26062426_IL-23 could promote migration of human ESCC cells by activating DLL4/Notch1 signaling pathway 26070613_The detection of Notch1 and Delta-like 4 expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes of renal transplant recipients can serve as a positive indicator for evaluating the diagnosis and treatment efficacy of the AR reaction. 26111775_DLL4 and VEGFA expression was closely related to tumour diameter, clinical stage, histological grade and lymph node metastasis. 26212082_Activation of Dll4/Notch signaling led to increased expression of ephrin-B2 and subsequent inhibition of endothelial progenitor cells activity. 26241546_Overexpression of DLL4 is associated with thyroid tumor invasion and metastasis. 26299364_Heterozygous Loss-of-Function Mutations in DLL4 Cause Adams-Oliver Syndrome. 26404485_Macrophage Dll4 promotes lesion development in vein grafts via macrophage activation and crosstalk between macrophages and smooth muscle cells. 26471266_DLL4/Notch1 and BMP9 interdependent signaling induces endothelial cell quiescence via P27KIP1/thrombospondin pathway. 26472724_Data suggest that the vascular DLL4-Notch4 signaling and VEGF signaling complementing each other plays an important role in the progression of tumor angiogenesis in primary glioblastoma. 26546434_our data indicate that high DLL4 expression predicts pelvic lymph node metastasis and poor survival in cervical cancer. Therefore, DLL4 may be a potential clinical diagnostic marker for patients with early-stage cervical cancer. 26546995_DLL4 and JAG1 may have opposing effects on tumor angiogenesis in glioblastoma. 26712946_DLL4 is a unique functional molecule of human circulating dendritic cells critical for directing Th1 and Th17 differentiation 26739060_Antagonism of the DLL4-Notch signaling pathway might provide a potential therapeutic approach for breast cancer treatment by preventing angiogenesis. 26808710_Data indicate the role for altered forkhead box C2 (FoxC2)-Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4)signaling in structural alterations of saphenous veins in patients with varicose veins. 26870802_Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein Mediates Pathological Retinal Neovascularization via Modulating DLL4-NOTCH1 Signaling 26957058_Angiogenesis in Infantile haemangioma (IH) appears to be controlled by DLL4 within the endothelium in a VEGF-A isoform-dependent manner, and in perivascular cells in a VEGF-independent manner. The contribution of VEGF-A isoforms to disease progression also indicates that IH may be associated with altered splicing. 27073072_In gastric epithelial cells co-cultured with Helicobacter pylori, the expression level of the ligand DLL4 was found to be significantly increased. 27117596_Data show that the IgA/delta-like protein 4 (Delta-4)/Notch receptor (Notch) axis is not observed in IgG-dendritic cells (DCs). 27171900_Dll4 modulates liver inflammatory response by down-regulating chemokine expression 27174628_Positive Jagged1 and DLL4 expression is closely correlated with severe clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in patients with gallbladder cancers. 27334972_Overexpression of DLL4 could significantly attenuate the cytotoxic effects of docetaxel in MCF-7 cells by increasing Bcl-2 expression, while decreasing Bax expression, apoptosis rate and DNA damage 27440153_Results show that DLL4 is involved in SYNJ2BP-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development though activating its pathway. 27487663_Expression of D114 in the vessels of dermal microvasculature was shown to increase from 20 weeks of gestation to 20 years. 27542210_epigenetic silencing and TP53 mutation have an effect on the expression of DLL4 in human cancer stem disorder 27755532_Low DLL4 abundance in tumour cells may predict the benefit from adjuvant gemcitabine therapy after PDAC resection. 27891816_Results provide evidence that DLL4 is associated with gastric cancer stem/progenitor cells (GCSPCs), and its expression impacts CSPC stemness characteristics associated with the Notch-1 pathway including self-renewal, differentiation, proliferation, and tumor formation. 27919854_Positive Jagged1 and DLL4 expression is closely correlated with severe clinicopathological characteristics and poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal carcinoma. 27926858_We show that GIT1, which also contains an ANK domain, inhibits the Notch1-Dll4 signaling pathway by competing with Notch1 ANK domain for binding to RBP-J in stalk cells 28445154_Data show that Delta-like 4 (DLL4) and Jagged1 (JAG1) displayed equal potency in stimulating Notch target genes in HMEC-1 dermal microvascular endothelial cells but had opposing effects on sprouting angiogenesis in vitro. 28472949_the Notch signaling and atherosclerosis relevant markers in lesions from femoral arteries of symptomatic peripheral artery disease patients, were characterized. 28572448_The authors present novel structures of human ligands Jagged2 and Delta-like4 and human Notch2, together with functional assays, which suggest that ligand-mediated coupling of membrane recognition and Notch binding is likely to be critical in establishing the optimal context for Notch signalling. 28946938_The regulation of DLL4 by the LDB2 complex provides a novel mechanism of DLL4 transcriptional control that may be exploited to develop therapeutics for aberrant vascular remodeling. 29042443_Data suggest that Numb acts as a Notch antagonist by controlling intracellular destination and stability of the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 (DLL4) through a post-endocytic sorting process; Numb negatively controls DLL4 plasma membrane recycling through well-documented recycling regulator protein AP1. 29686270_data demonstrates a surface-based method to spatially pattern Dll4 to gain control over endothelial sprout location and direction 29749499_this study revealed that DLL4 has pathophysiological roles on the progression of esophagus cancer cells, including migration, invasion and apoptosis, which indicated that DLL4 may be considered as a potent therapeutic target for the treatment of malignant esophageal cancer. 30205087_The results demonstrate that ephrin-B2 and Dll4 mediated co-dependence of hepatocellular carcinoma and endothelial progenitor cells intercellular crosstalk in the initial stages of hepatocellular carcinoma establishment and development. 30226615_These data indicate that DLL4 represents a new prognostic biomarker for nonsmall cell lung cancer , and DLL4 overexpression inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro. 30228780_Study demonstrates that DLL4 is important in regulating the tumour growth of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma as well as the neovascularization and suppression of HBV replication. 30607695_A regulatory role of KLF4 in developmental angiogenesis through regulation of DLL4 transcription. 30660174_The expression profile of Jagged1 and Delta-like 4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30886104_Notch1 inactivation in keratinocytes is sufficient to cancel the repressive effects of the Dll4-Notch1 loop on wound healing in diabetes, thus making Notch1 signaling an attractive locally therapeutic target for the treatment of Diabetic foot ulcerations. 30930165_TR3/Nur77 regulated the expression of DLL4 and Jagged1 in culture endothelial cells. DLL4 and Jagged1 play important roles in the angiogenic responses induced by TR3/Nur77. 31578584_Histological samples from 51 primary tumors that originated from patients treated with bevacizumabbased firstline chemotherapy were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for NICD, DLL4 and CD44 expression, and CD31 for microvessel count. 31676012_DLL4 stimulates Notch1 signaling in NOTCH1-mutated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and is expressed by the microenvironment in MCL lymph nodes. 31984546_Serum delta-like 4 levels: A possible association with interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. 31996265_Long non-coding RNA UCA1 promotes malignant phenotypes of renal cancer cells by modulating the miR-182-5p/DLL4 axis as a ceRNA. 32506201_RHOQ is induced by DLL4 and regulates angiogenesis by determining the intracellular route of the Notch intracellular domain. 32580836_Synergistic antitumor activity of a DLL4/VEGF bispecific therapeutic antibody in combination with irinotecan in gastric cancer. 32801053_NOTCH1 and DLL4 are involved in the human tuberculosis progression and immune response activation. 32990541_Anti-Cancer Effect of Melatonin via Downregulation of Delta-like Ligand 4 in Estrogen-Responsive Breast Cancer Cells. 33351914_O-Fucose and Fringe-modified NOTCH1 extracellular domain fragments as decoys to release niche-lodged hematopoietic progenitor cells. 33469672_Dll4/Notch1 signalling pathway is required in collective invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. 33628824_Analysis of Molecular Mechanism of YiqiChutan Formula Regulating DLL4-Notch Signaling to Inhibit Angiogenesis in Lung Cancer. 33830085_Delta-like 4 is required for pulmonary vascular arborization and alveolarization in the developing lung. 34362349_Correlation of serum delta-like ligand-4 level with the severity of diabetic retinopathy. 34408144_DL4-mubeads induce T cell lineage differentiation from stem cells in a stromal cell-free system. 34487019_Delta-like ligand 4 level in colorectal cancer is associated with tumor aggressiveness and clinical outcome. 35289275_Potential biomarkers and the molecular mechanism associated with DLL4 during renal cell carcinoma progression. 35725756_Probing Notch1-Dll4 signaling in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells using single cell nanobiosensor. |
ENSMUSG00000027314 |
Dll4 |
124.862602 |
6.0568526893 |
2.598568 |
0.175184439 |
239.552016 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000492477544646201213358519753114752056855226288529428653267378677683619873891360606709802712089997538947759385321790451889957756510441300341895942693781762500293552875518798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000113223809329874294465759540488000568079769995730229575511518704884532715395836517635592159776897122432119937184310933811605818827446257035518328848411329090595245361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
217.8628066 |
22.1957502 |
36.2219460 |
3.2851006 |
| ENSG00000128923 |
54629 |
MINDY2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NBR6 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolase that can remove 'Lys-48'-linked conjugated ubiquitin from proteins (PubMed:27292798). Binds to polyubiquitin chains of different linkage types, including 'Lys-6', 'Lys-11', 'Lys-29', 'Lys-33', 'Lys-48' and 'Lys-63' (PubMed:28082312). May play a regulatory role at the level of protein turnover (PubMed:27292798). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27292798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28082312}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
Enables cysteine-type peptidase activity and polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in protein K48-linked deubiquitination. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54629; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cysteine-type carboxypeptidase activity [GO:0016807]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; K11-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0071795]; K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0036435]; K6-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0071796]; K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0070530]; Lys48-specific deubiquitinase activity [GO:1990380]; protein K48-linked deubiquitination [GO:0071108] |
27175219_Results identified FAM63B hypomethylation in bipolar disorder patients and data support that FAM63B is a shared epigenetic risk gene for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. 34529927_Mechanism of activation and regulation of deubiquitinase activity in MINDY1 and MINDY2. |
ENSMUSG00000042444 |
Mindy2 |
511.749259 |
0.4630478022 |
-1.110767 |
0.125785413 |
76.321739 |
0.00000000000000000241016002026797979969832136970436604540770014090092683567423392787532065995037555694580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000019785295828228802158448173128491573009561086649260412684281362771798740141093730926513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
346.7176199 |
26.3045231 |
754.2031712 |
39.7411860 |
| ENSG00000128965 |
79094 |
CHAC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BUX1 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of glutathione into 5-oxo-L-proline and a Cys-Gly dipeptide. Acts specifically on glutathione, but not on other gamma-glutamyl peptides (PubMed:27913623). Glutathione depletion is an important factor for apoptosis initiation and execution. Acts as a pro-apoptotic component of the unfolded protein response pathway by mediating the pro-apoptotic effects of the ATF4-ATF3-DDIT3/CHOP cascade (PubMed:19109178). Negative regulator of Notch signaling pathway involved in embryonic neurogenesis: acts by inhibiting Notch cleavage by furin, maintaining Notch in an immature inactive form, thereby promoting neurogenesis in embryos (PubMed:22445366). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19109178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22445366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27913623}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Lyase;Neurogenesis;Notch signaling pathway;Reference proteome;Unfolded protein response |
|
This gene encodes a member of the gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase family of proteins. The encoded protein has been shown to promote neuronal differentiation by deglycination of the Notch receptor, which prevents receptor maturation and inhibits Notch signaling. This protein may also play a role in the unfolded protein response, and in regulation of glutathione levels and oxidative balance in the cell. Elevated expression of this gene may indicate increased risk of cancer recurrence among breast and ovarian cancer patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:79094; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase activity [GO:0003839]; glutathione specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase activity [GO:0061928]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; glutathione catabolic process [GO:0006751]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of protein processing [GO:0010955]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
22108517_High CHAC1 mRNA expression could be an independent indicator for elevated risk of cancer recurrence in breast and ovarian cancer 23342279_nisin exerts these effects on HNSCC, in part, through CHAC1, a proapoptotic cation transport regulator, and through a concomitant CHAC1-independent influx of extracellular calcium 24767995_Botch regulates Notch signaling through deglycination and identify a posttranslational modification of Notch that plays an important role in neurogenesis. 25931127_Human CHAC1 Protein Degrades Glutathione, and mRNA Induction Is Regulated by the Transcription Factors ATF4 and ATF3 and a Bipartite ATF/CRE Regulatory Element. 27986595_Temozolomide (TMZ)-mediated gene expression profiles and networks are involved in inducing glioblastoma cell death. Increased CHAC1 and reduced Notch3 levels are both also significantly involved in TMZ-mediated cytotoxicity. The TMZ-regulated CHAC1 pathway inhibits Notch3 activation, resulting in attenuation of Notch3-mediated signaling pathways. 29054545_The data revealed that CHAC2 prevented CHAC1-mediated GSH degradation, which suggests that CHAC2 competes with CHAC1 to maintain GSH homeostasis. 30555487_results suggest that CHAC1 is involved in the regulation of inflammation in bronchial cells during Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and may explain the excessive inflammation present in the respiratory tracts of patients with cystic fibrosis. 31111570_Significant CHAC1 overexpression was detected in H. pylori-infected parietal cells that expressed the human proton pump/H,K-ATPase alpha subunit. 32949369_Transcriptomic analysis of the effect of (E)-3-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(2-methoxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one (DPP23) on reactive oxygen species generation in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. 33728749_Ferroptosis-related gene CHAC1 is a valid indicator for the poor prognosis of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. 35930144_High levels of unfolded protein response component CHAC1 associates with cancer progression signatures in malignant breast cancer tissues. |
ENSMUSG00000027313 |
Chac1 |
10.654901 |
2.3582816014 |
1.237736 |
0.480107798 |
6.748526 |
0.00938251454312422419890005187426140764728188514709472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018081461634222945056293951893167104572057723999023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.7183583 |
4.3330005 |
6.2574054 |
1.4631909 |
| ENSG00000128973 |
54982 |
CLN6 |
protein_coding |
Q9NWW5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is one of eight which have been associated with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCL). Also referred to as Batten disease, NCL comprises a class of autosomal recessive, neurodegenerative disorders affecting children. The genes responsible likely encode proteins involved in the degradation of post-translationally modified proteins in lysosomes. The primary defect in NCL disorders is thought to be associated with lysosomal storage function. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:54982; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; lysophosphatidic acid binding [GO:0035727]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; sulfatide binding [GO:0120146]; cellular macromolecule catabolic process [GO:0044265]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; ganglioside metabolic process [GO:0001573]; glycosaminoglycan metabolic process [GO:0030203]; locomotion involved in locomotory behavior [GO:0031987]; lysosomal lumen acidification [GO:0007042]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; positive regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045862]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11727201_gene mutated in variant late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CLN6) and in nclf mutant mice encodes a novel predicted transmembrane protein 11791207_novel approximately 36-kD CLN6-gene product augments an intriguing set of unrelated membrane-spanning proteins, whose deficiency causes neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis in mouse and man 12815591_Eight novel mutations identified in CLN6 in 26 families with late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 15010453_ER-resident CLN6 protein lead to lysosomal dysfunctions, which may result in lysosomal accumulation of storage material 15265688_CLN6 is an ER resident protein, the activity of which, despite this location, must contribute to lysosomal function. 15996215_These data indicate that CLN6 mutations, in addition to those of CLN8, should be considered a diagnostic alternative in Turkish variant late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis patients. 16857350_Cholesterol accumulation in lysosomes suggests a homeostasis block as a result of CLN6p deficiency, while dysfunctional endosomal/lysosomal vesicles may act as one of the triggers for apoptosis and cell death. 17453415_CLN6 maintains its endoplasmic reticulum localization by expressing retention signals present in both the N-terminal cytosolic domain and in the carboxy-proximal transmembrane domains 6 and 7. 18811591_knockdown of SEL1L [sel-1 suppressor of lin-12-like (Caenorhabditis elegans)], a member of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex involved in ER protein extraction, rescued significant amounts of Cln6(G123D) and Cln6(M241T) polypeptides. 19135028_11 mutations in patients with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses, eight of which are novel, were detected in CLN6, all predicting a direct impairing of the putative gene function. 19201763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19520283_three families with CLN6-associated variant late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis from Saudi Arabia are described; one had a novel mutation in the CLN6 gene 20020536_Expression studies of three mutations found in CLN6 patients predicted to affect transmembrane domain 3, cytoplasmic loop 2 or result in a truncated membrane protein respectively, is reported. 21359198_CLN6 and CLN3 mutations trigger distinct processes that converge on a shared pathway, which is responsible for proper subunit c protein turnover and neuronal cell survival. 21549341_Sequencing of CLN6 will provide a simple diagnostic strategy in this disorder, in which definitive identification usually requires invasive biopsy. 22883287_our results add CLN6 to the genetic mutations causing teenage-onset progressive myoclonus epilepsy 23180398_The study describes the first report in the North of Morocco of the CLN6 p.I154del mutation in 3 patients belonging to a large consanguineous family. 24581221_study demonstrates the central role of the metal transporter, Zip7, in the aberrant biometal metabolism of CLN6 variants of Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. 26115733_describe the spectrum of clinical and neurophysiologic features associated with mutations of CLN6. 28476624_The CLN6 is not only a molecular entity of the anti-aggregate activity conferred by the ER manipulation using TMalphaBC, but also serves as a potential target of therapeutic interventions. 30528883_Novel mutations in CLN6 cause late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis without visual impairment 30561534_Clinical distinction of type A (progressive myoclonus epilepsy) and type B (dementia with motor disturbance) Kufs disease was supported by molecular diagnoses. Type A is usually caused by recessive pathogenic variants in CLN6 or dominant variants in DNAJC5. Type B Kufs is usually associated with recessive CTSF pathogenic variants. 31901039_compound heterozygous mutations of CLN6:c.486+2T>C and c.486+4A>T are possibly the genetic causes of the autosomal recessive neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses 32171521_Implications of graded reductions in CLN6's anti-aggregate activity for the development of the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. 32597833_The CLN6 protein associates with the CLN8 protein to form the EGRESS complex (ER-to-Golgi Relaying of Enzymes of the lySosomal System), which mediates ER exit and Golgi transfer of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes. The second luminal loop of CLN6 is required for the interaction of CLN6 with the enzymes. Loss-of-function mutations in CLN6 affect enzyme trafficking and result in lower levels of enzymes at the lysosome. 34380921_CLN6's luminal tail-mediated functional interference between CLN6 mutants as a novel pathomechanism for the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. 34597687_p.Asn77Lys homozygous CLN6 mutation in two unrelated Japanese patients with Kufs disease, an adult onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 35012600_Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis Type 6 (CLN6) clinical findings and molecular diagnosis: Costa Rica's experience. |
ENSMUSG00000032245 |
Cln6 |
425.617407 |
2.0422305053 |
1.030146 |
0.120590437 |
72.422216 |
0.00000000000000001737469712962894925791720352744066579024756367879023938316507269519206602126359939575195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000136555127600278651275424368825869618428597997801185459643136255181161686778068542480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
573.9396567 |
38.9127755 |
283.0121101 |
14.4672070 |
| ENSG00000129007 |
91860 |
CALML4 |
protein_coding |
Q96GE6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity and enzyme regulator activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:91860; |
calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; enzyme regulator activity [GO:0030234] |
32209652_The small EF-hand protein CALML4 functions as a critical myosin light chain within the intermicrovillar adhesion complex. |
ENSMUSG00000032246 |
Calml4 |
55.504424 |
0.3573356814 |
-1.484648 |
0.217511936 |
48.322436 |
0.00000000000361591397578733696291587880716587318592411537387931730336276814341545104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000020766883378451787124609979104198091617167198918991743994411081075668334960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.9982543 |
4.0769134 |
82.2874395 |
6.8364592 |
| ENSG00000129128 |
60559 |
SPCS3 |
protein_coding |
P61009 |
FUNCTION: Essential component of the signal peptidase complex (SPC) which catalyzes the cleavage of N-terminal signal sequences from nascent proteins as they are translocated into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:27499293, PubMed:34388369). Essential for the SPC catalytic activity, possibly by stabilizing and positioning the active center of the complex close to the lumenal surface (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q12133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27499293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34388369}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays an important role in virion production of flaviviruses such as West Nile virus, Japanese enchephalitis virus, Dengue virus type 2 and Yellow Fever virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27383988}. |
3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable peptidase activity. Involved in proteolysis and viral protein processing. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:60559; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; signal peptidase complex [GO:0005787]; protein targeting to ER [GO:0045047]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; signal peptide processing [GO:0006465]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
ENSMUSG00000048040+ENSMUSG00000048355 |
Arxes2+Arxes1 |
1366.964806 |
2.0773886388 |
1.054771 |
0.086416246 |
146.671579 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000092581933489742607134216102554356571329097871818297848655219354332544087749214431545677957829942883449803048279136419296264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000013305835816052587903689833827312047336359454523798257003701177332861064070987798573170515781249889641912886872887611389160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1754.9748561 |
131.6873090 |
851.4812470 |
46.6407495 |
| ENSG00000129151 |
8424 |
BBOX1 |
protein_coding |
O75936 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the formation of L-carnitine from gamma-butyrobetaine. |
3D-structure;Carnitine biosynthesis;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Amine and polyamine biosynthesis; carnitine biosynthesis. |
This gene encodes gamma butyrobetaine hydroxylase which catalyzes the formation of L-carnitine from gamma-butyrobetaine, the last step in the L-carnitine biosynthetic pathway. Carnitine is essential for the transport of activated fatty acids across the mitochondrial membrane during mitochondrial beta-oxidation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8424; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase activity [GO:0008336]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; carnitine biosynthetic process [GO:0045329] |
17110165_the use of 3 different promoters is responsible for the 5'-end heterogeneity 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20599753_the three-dimensional structure of recombinant human GBBH at 2.0A resolution was solved. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29065368_BBOX 1 might be one of several genes that play a role in polygenic susceptibility to schizophrenia. 30819181_urinary BBOX1 might serve as a promising biomarker of diabetic kidney disease. 32515533_BBOX1 antisense RNA 1 facilitates CC progression by upregulating HOXC6 expression via miR-361-3p and HuR. 35506252_Long non-coding RNA BBOX1-antisense RNA 1 enhances cell proliferation and migration and suppresses apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-3940-3p/laminin subunit gamma 2 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000041660 |
Bbox1 |
68.697055 |
0.0266525643 |
-5.229582 |
0.435891166 |
243.454968 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000069404915272632519797834845538041737516676624962728497738693669773882657121240361555589279121276632749049251981822317421716908058532390654940535945627289038384333252906799316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016286431628363370299973040437433231968740807689662661720904759425341257752456841411557623357648296454212542949068308650644034805642893122545888928698332165367901325225830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2614387 |
1.0155282 |
123.6617574 |
14.5963597 |
| ENSG00000129355 |
1032 |
CDKN2D |
protein_coding |
P55273 |
FUNCTION: Interacts strongly with CDK4 and CDK6 and inhibits them. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7739548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8741839}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ANK repeat;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tumor suppressor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the INK4 family of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. This protein has been shown to form a stable complex with CDK4 or CDK6, and prevent the activation of the CDK kinases, thus function as a cell growth regulator that controls cell cycle G1 progression. The abundance of the transcript of this gene was found to oscillate in a cell-cycle dependent manner with the lowest expression at mid G1 and a maximal expression during S phase. The negative regulation of the cell cycle involved in this protein was shown to participate in repressing neuronal proliferation, as well as spermatogenesis. Two alternatively spliced variants of this gene, which encode an identical protein, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1032; |
cyclin D2-CDK4 complex [GO:0097129]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004861]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; autophagic cell death [GO:0048102]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair [GO:0000731]; negative regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902807]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:1902230]; negative regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042326]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; response to UV [GO:0009411]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
11786024_protein folding and stability 12062451_The human p19(INK4d) gene is under the control of TATA-less promoter and the Sp1 binding site is involved in the transcription. 12203782_Deletions in the CDKN2D locus and hypermethylation in the CDKN2D promoter region plays a role in ovarian granulosa cell tumorogenesis. 12698196_Inhibitor shows antitumor effect on glioma cells. 15107822_p19(INK4d) in addition to p21(WAF1/Cip1) is an important molecular target of HDAC inhibitors inducing growth arrest 15750620_In addition to its role as cell cycle inhibitor, p19INK4d is involved in maintenance of DNA integrity and, therefore, would contribute to cancer prevention. 17409409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804013_Data suggest that the graded stability and the facile unfolding of repeats 1 and 2 is a prerequisite for the down-regulation of the inhibitory activity of p19(INK4d) during the cell-cycle. 18174243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18276842_p19(INK4D) knockdown led to a moderate increase (31.7% +/- 5%) in the mean ploidy of megakaryocytes suggesting a role of p19(INK4D) in the endomitotic arrest. 18281541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18507837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18950845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19063602_The study shows that mimicking the phosphorylation site of p19INK4d by a glutamate substitution at position 76 dramatically decreases the stability of the native but not an intermediate state. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19141585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19430707_Results show that overexpression of CDK4, cyclin D1, and Rb proteins, and loss of expression of proteins p16, p27, and p19 were statistically significant in NPC tissues compared with non-cancerous NPE (PCdk8 and Cdkn2d as New Prame-Target Genes in 2C-like Embryonic Stem Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000096472 |
Cdkn2d |
23.284653 |
2.0657983331 |
1.046699 |
0.330558568 |
10.112650 |
0.00147255081754215332023871809496995410881936550140380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003339850148349300402311756741369208612013608217239379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.8764376 |
6.3405882 |
15.0418940 |
2.3978650 |
| ENSG00000129422 |
57509 |
MTUS1 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULD2 |
FUNCTION: Cooperates with AGTR2 to inhibit ERK2 activation and cell proliferation. May be required for AGTR2 cell surface expression. Together with PTPN6, induces UBE2V2 expression upon angiotensin-II stimulation. Isoform 1 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation, delays the progression of mitosis by prolonging metaphase and reduces tumor growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12692079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19794912}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Microtubule;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene encodes a protein which contains a C-terminal domain able to interact with the angiotension II (AT2) receptor and a large coiled-coil region allowing dimerization. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. One of the transcript variants has been shown to encode a mitochondrial protein that acts as a tumor suppressor and partcipates in AT2 signaling pathways. Other variants may encode nuclear or transmembrane proteins but it has not been determined whether they also participate in AT2 signaling pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57509; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; spindle [GO:0005819]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010758] |
12692079_identified a tumor suppressor gene named MTSG1 at chromosome 8p21.3-22, encoding a mitochondrial protein, controlling cellular proliferation 15123706_Results identify ATIP1 (angiotensin II AT2 receptor-interacting protein) as a novel early component of growth inhibitory signaling cascade 16650523_Nucleotide variations result in amino-acid substitution or deletion of conserved structural motifs and also exonic splicing enhancer motifs and physiological splice sites, suggesting deleterious effects on ATIP function and/or expression. [REVIEW] 16887298_MTUS1 encodes a family of proteins(ATIP1, ATIP3 and ATIP4), with potential important biological roles in tumor suppression and/or brain function. 17301065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301065_There is an association of the deletion variant of MTUS1 with a decreased risk for both familial and high-risk familial BC supporting its role in human cancer. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19344625_two transcriptional start sites in the ATIP1 promoter were identified; PARP-1 activates the ATIP1 gene 19794912_ATIP3 is a novel microtubule-associated protein isoform of MTUS1, with a role in invasiveness and progression of breast neoplasms. 19794912_ATIP3 is a novel microtubule-associated protein related to MTUS1, with a role in invasiveness and progression of breast neoplasms 19956880_MTUS1 could be involved in the loss of proliferative control in human colon cancer 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20687230_Results in human prostate cancer cell lines demonstrate the presence of ATIP in both cell lines examined. 22153618_MTUS1 plays major roles in the progression of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 23396587_analysis of a functional ATIP3 domain that associates with microtubules and recapitulates the effects of ATIP3 on microtubule dynamics, cell proliferation, and migration in breast cancer 24299308_The present data suggested MTUS1 as a potential tumor suppressor in gastric cancer and might lead to a better understanding of gastric carcinogenesis. 24650297_Data identifies MTUS1 as a tumour suppressor gene in cultured bladder cancer cells and in advanced bladder tumours. 25885343_Our studies confirm that MTUS1 plays an important role in the progression of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma , and may serve as a biomarker or therapeutic target for patients with salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma 26498358_We propose a novel mechanism by which ATIP3-EB1 interaction indirectly reduces the kinetics of EB1 exchange on its recognition site, thereby accounting for negative regulation of microtubule dynamic instability 26643896_Deregulated microRNA (miRNA) expression has been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of several types of cancers including colorectal cancer (CRC). MTUS1 targeting miRNAs may play key roles in the development of CRC by downregulating tumor suppressor MTUS1. 26643896_MTUS1 targeting miRNAs may play key roles in the development of CRC by downregulating tumor suppressor MTUS1. 27155522_Study reports differential expression of MTUS1 and its regulatory miRNAs in breast cancer and fibroadenoma tissues; among MTUS1 targeting miRNAs, miR-183-5p was overexpressed in breast cancer and down-regulated in fibroadenoma tissues; expression levels of MTUS1 and miR-183-5p correlated with clinical parameters. In particular, MTUS1 was found to be diminished and miR-183-5p was elevated with advancing stage. 27789289_Our findings showed that MTUS1 regulates the p38 MAPK-mediated cytokine production in ECs. MTUS1 gene probably plays a protective role against pro-inflammatory response of ECs. 28364280_findings have provided the first clues regarding the roles of miR-19a/b, which appear to function as oncomirs in lung cancer by downregulating MTUS1. 28499941_MTUS1 is not only involved in the formation and progression of human cancers but also involved in the complex pathological conditions such as cardiac hypertrophy, atherosclerosis, and SLE-like lymphoproliferative diseases. Several molecular mechanisms such as proliferation, differentiation, DNA repair, inflammation, vascular remodeling and senescence appear to be tightly regulated by the MTUS1-encoded proteins. 28651497_angiotensin II type 2 receptor-interacting protein 3a presents potential in suppressing the proliferation and aggressiveness of ovarian carcinoma cells through the high mobility group AT-hook 2-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition signal pathway. 29558204_The N-terminal coiled-coil domain of MTUS1 interacted with the mitochondrial membrane proteins. 30368744_studies emphasize the importance of studying combinatorial expression of EB1 and ATIP3 genes and proteins rather than each biomarker alone. A population of highly aggressive breast tumors expressing high-EB1/low-ATIP3 may be considered for the development of new molecular therapies. 30528566_Low expression of MTUS1 correlates to DNA methylation and histone deacetylation in human NSCLC. 31210288_MicroRNA-765 targets MTUS1 to promote the progression of osteosarcoma via mediating ERK/EMT pathway. 31685623_ATIP3 is an important regulator of mitotic integrity. 31882471_MTUS1 may act as tumor suppressor and might be a potential biomarker for predicting prognosis in GBC. 32373949_Reduced long non-coding RNA PTENP1 contributed to proliferation and invasion via miR-19b/MTUS1 axis in patients with cervical cancer. 32789689_Reciprocal regulation of Aurora kinase A and ATIP3 in the control of metaphase spindle length. 33311452_RNA-binding protein SORBS2 suppresses clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis by enhancing MTUS1 mRNA stability. 34062782_Microtubule-Associated Protein ATIP3, an Emerging Target for Personalized Medicine in Breast Cancer. 34125870_In silico analysis of deleterious SNPs of human MTUS1 gene and their impacts on subsequent protein structure and function. 35962436_MTUS1 is a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000045636 |
Mtus1 |
237.610150 |
0.4878835619 |
-1.035391 |
0.142141532 |
52.772045 |
0.00000000000037459522526993644773498288259813455026298045780208667565602809190750122070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002298015596419061438379935409797432137226497195214847124589141458272933959960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
156.4195253 |
25.3914838 |
319.6691583 |
36.8699980 |
| ENSG00000129450 |
27180 |
SIGLEC9 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y336 |
FUNCTION: Putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3- or alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable monosaccharide binding activity and sialic acid binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell adhesion. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of inflammatory response and negative regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment. Predicted to be located in external side of plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:27180; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; sialic acid binding [GO:0033691]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166] |
14693915_Binding studies on recombinant human Siglec-9 show recognition of both Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc; in striking contrast, chimpanzee and gorilla Siglec-9 strongly prefer binding Neu5Gc. 15292262_Siglec-7 and Siglec-9 are capable of negative regulation of TCR signaling and ligand binding is required for optimal activity 15557178_Siglec-9 can inhibit Fc epsilon receptor I-mediated serotonin release from rat basophilic leukemia cells and recruit the tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2. 15827126_data suggest that apoptotic (ROS- and caspase-dependent) and nonapoptotic (ROS-dependent) death pathways are initiated in neutrophils via Siglec-9 16732727_Siglecs-9 did not interact with sulfate derivatives of LacNAc and sulfated oligosaccharides containing sialic acid. 16828866_The Siglec-9 provides not only a useful marker for certain subsets of AML, but also a potential therapeutic target. 18325328_These results demonstrate that Siglec-9 enhances the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in macrophages. 18558361_A review of the cytotoxic effects of natural anti-Siglec9 autoantibodies on both neutrophils and eosinophils. 19196661_Increased bacterial survival are also facilitated by group b Streptococcus sialylated capsular polysaccharide interactions with Siglec-9. 19295491_Septic shock patients exhibit different ex vivo death responses of blood neutrophils after Siglec-9 ligation early in shock. 19542910_Data suggest that age-specific interactions between Siglec-9 and SHP-1 may influence the altered inflammatory responsiveness and longevity of neonatal polymorphonuclear neutrophils. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497550_MUC16-Siglec-9 binding likely mediates inhibition of anti-tumor immune responses. 20733319_Siglec-9 A391C was the only polymorphism related to TCR-mediated signaling in human Siglec-9, resulting in less inhibition compared to the wild type. 20971061_These results suggest that Siglec-9 expressed on DCs is involved in immunoregulation through ligation with mucins in an epithelial cancer patient. 21821708_The Siglec-9 peptide binding to the enzymatic groove of VAP-1 can be used for imaging conditions, such as inflammation and cancer. 24045940_Siglec-9 expressed on immune cells may play a role as a potential counterreceptor for MUC1 and that this signaling may be another MUC1-mediated pathway and function in parallel with a growth factor-dependent pathway. 24145038_Protein degradation of focal adhesion kinase and related molecules was induced by Siglec-9 binding to its counterreceptors via sialylglycoconjugates, leading to the modulation of adhesion kinetics of cancer cells. 24569453_Expression of Siglec-7 and -9 ligands was associated with susceptibility of NK cell-sensitive tumor cells and, unexpectedly, of presumably NK cell-resistant tumor cells to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. 24882272_Dasatinib enhances migration of monocyte-derived dendritic cells by reducing phosphorylation of inhibitory immune receptors Siglec-9 and Siglec-3. 25225409_a polymorphism that reduced Siglec-9 binding to carcinomas was associated with improved early survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients 25747723_Inflammation results in up-regulation of immuneinhibitory Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 sialoglycan ligands on human airways. 26694037_Ligands for Siglec-8 and Siglec-9 may regulate the function of eosinophils, mast cells, neutrophils, and other cells in sinus mucosa. 26923638_Constitutively expressed Siglec-9 inhibits LPS-induced CCR7, but enhances IL-4-induced CD200R expression in human macrophages. 27595232_This work defines a critical role for aberrantly glycosylated MUC1 and identifies an activating pathway that follows engagement of Siglec-9. 27878892_The SIGLEC9 rs2075803 G/rs2258983 A haplotype, which corresponds to a Siglec-9 variant that is less effective at suppressing inflammatory response, may be a risk factor for the development of emphysema. 27893774_The mechanism of the Siglec-9 and AOC3 interaction is mediated both by protein-sugar interactions via the V domain and by the protein-protein interactions via the C22 Siglec9 domain. 28273363_Data suggest that sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin-9 (Siglec-9)may serve as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 28416510_Glycophorin A, the most abundant sialoglycoprotein on erythrocytes, engaged neutrophil Siglec-9, a sialic acid-recognizing receptor known to dampen innate immune cell activation. These studies demonstrate a previously unsuspected role for erythrocytes in suppressing neutrophils ex vivo and in vitro and help explain why neutrophils become easily activated after separation from whole blood. 28860481_Siglec-9 expression is upregulated in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 29899741_These findings identify Siglec-9 as a negative regulator for NK cells contributing to HBV persistence and the intervention of Siglec-9 signaling might be of potentially translational significance. 30130255_Targeting of the sialoglycan-SAMP/Siglec pathway in vitro and in vivo resulted in increased anticancer immunity. T cell expression of Siglec-9 in NSCLC patients correlated with reduced survival, and Siglec-9 polymorphisms showed association with the risk of developing lung and colorectal cancer. 30988027_Expression of cognate Siglec-9 ligands was observed on the majority of tumor cells in primary and metastatic melanoma specimens. Targeting the tumor-restricted, glycosylation-dependent Siglec-9 axis may unleash this intratumoral T-cell subset, while confining T-cell activation to the tumor microenvironment. 31901888_SS erythrocytes are deficient in binding to neutrophil Siglec-9 which may contribute to the increased oxidative stress in SCD. 32322597_The Roles of Siglec7 and Siglec9 on Natural Killer Cells in Virus Infection and Tumour Progression. 32391973_Targeting glycosylated antigens on cancer cells using siglec-7/9-based CAR T-cells. 33431669_Modulation of immune cell reactivity with cis-binding Siglec agonists. 35854240_Identification and validation of a siglec-based and aging-related 9-gene signature for predicting prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia patients. |
ENSMUSG00000030474 |
Siglece |
277.665522 |
7.3120792852 |
2.870282 |
0.116934582 |
683.086529 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000142466755172386909516884677900537751945807728508661887174409982320624586412003720865176484465802313648187654836127975839674994179061460623355237583803050520265564621396633138001596 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000095582241197474138258762024506973788171650594531078183848593522051724541758578089481416223792873988851604178314169735378232700791159966517451320147113787531203554479376660615753213 |
Yes |
No |
481.0181406 |
49.9239365 |
66.4331925 |
5.5931465 |
| ENSG00000129450_ENSG00000268581 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.666450 |
20.0825710986 |
4.327872 |
0.798777932 |
24.623967 |
0.00000069679704115668172494888485749009454650604311609640717506408691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002510306157547625560412215064975960387982922839000821113586425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.3052199 |
33.8295134 |
4.0858061 |
1.5199097 |
| ENSG00000129465 |
11035 |
RIPK3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y572 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that activates necroptosis and apoptosis, two parallel forms of cell death (PubMed:19524512, PubMed:19524513, PubMed:22265413, PubMed:22265414, PubMed:22421439, PubMed:29883609, PubMed:32657447). Necroptosis, a programmed cell death process in response to death-inducing TNF-alpha family members, is triggered by RIPK3 following activation by ZBP1 (PubMed:19524512, PubMed:19524513, PubMed:22265413, PubMed:22265414, PubMed:22421439, PubMed:29883609, PubMed:32298652). Activated RIPK3 forms a necrosis-inducing complex and mediates phosphorylation of MLKL, promoting MLKL localization to the plasma membrane and execution of programmed necrosis characterized by calcium influx and plasma membrane damage (PubMed:19524512, PubMed:19524513, PubMed:22265413, PubMed:22265414, PubMed:22421439, PubMed:25316792, PubMed:29883609). In addition to TNF-induced necroptosis, necroptosis can also take place in the nucleus in response to orthomyxoviruses infection: following ZBP1 activation, which senses double-stranded Z-RNA structures, nuclear RIPK3 catalyzes phosphorylation and activation of MLKL, promoting disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol (By similarity). Also regulates apoptosis: apoptosis depends on RIPK1, FADD and CASP8, and is independent of MLKL and RIPK3 kinase activity (By similarity). Phosphorylates RIPK1: RIPK1 and RIPK3 undergo reciprocal auto- and trans-phosphorylation (PubMed:19524513). In some cell types, also able to restrict viral replication by promoting cell death-independent responses (By similarity). In response to Zika virus infection in neurons, promotes a cell death-independent pathway that restricts viral replication: together with ZBP1, promotes a death-independent transcriptional program that modifies the cellular metabolism via up-regulation expression of the enzyme ACOD1/IRG1 and production of the metabolite itaconate (By similarity). Itaconate inhibits the activity of succinate dehydrogenase, generating a metabolic state in neurons that suppresses replication of viral genomes (By similarity). RIPK3 binds to and enhances the activity of three metabolic enzymes: GLUL, GLUD1, and PYGL (PubMed:19498109). These metabolic enzymes may eventually stimulate the tricarboxylic acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, which could result in enhanced ROS production (PubMed:19498109). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZL0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19498109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19524512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19524513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22265413, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22265414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22421439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25316792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29883609, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32298652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32657447}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of herpes simplex virus 1/HHV-1 infection, forms heteromeric amyloid structures with HHV-1 protein RIR1/ICP6 which may inhibit RIPK3-mediated necroptosis, thereby preventing host cell death pathway and allowing viral evasion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33348174}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Necrosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
The product of this gene is a member of the receptor-interacting protein (RIP) family of serine/threonine protein kinases, and contains a C-terminal domain unique from other RIP family members. The encoded protein is predominantly localized to the cytoplasm, and can undergo nucleocytoplasmic shuttling dependent on novel nuclear localization and export signals. It is a component of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-I signaling complex, and can induce apoptosis and weakly activate the NF-kappaB transcription factor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11035; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0004704]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; amyloid fibril formation [GO:1990000]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; execution phase of necroptosis [GO:0097528]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; necroptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097527]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of ligase activity [GO:0051351]; positive regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060545]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of oxidoreductase activity [GO:0051353]; positive regulation of phosphatase activity [GO:0010922]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; programmed necrotic cell death [GO:0097300]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0046006]; regulation of activation-induced cell death of T cells [GO:0070235]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta cytotoxic T cell extravasation [GO:2000452]; regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001914]; regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032649]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spleen development [GO:0048536]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; thymus development [GO:0048538] |
15208320_RIP3 acts a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein with nuclear export and import signals 15896315_Real-time PCR analysis reveals that the ratio of RIP3 gamma to RIP3 is significantly increased in colon and lung cancers relative to their matched normal tissues, indicating that RIP3 gamma might be a splice form associated with tumorigenesis. 16429275_Evidence is found for an association between overexpression of RIP3 and homocysteine-induced congenital cardiovascular malformations. 16844082_tRIP3 may function upstream of Fas (TNFRSF6)-associated via death domain to induce apoptosis in TNFR-1 signaling pathway 17114179_the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway is inhibed by gamma-tocopherol through inhibition of receptor-interacting protein and TAK1 leading to suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and potentiation of apoptosis 17827388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18025550_analysis of human receptor-interacting protein 3 truncation expressed in Escherichia coli 18533105_NLS of RIPK3 exhibits several other roles besides apoptotic function. 19524512_The expression of RIP3 in different cell lines correlates with their responsiveness to necrosis induction. 19690434_Gene expression of RIPK3 and RNF216 in PBMC could identify those obese subjects, who will regain more weight after a successful initial weight loss. The mRNA levels of these genes could be nutrigenomic biomarkers for predicting obesity treatment outcome. 20354226_RIP1 and RIP3 have roles in TNF-induced necrosis 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21153365_RIP3 is an essential inducer of TNF-induced programmed necrosis 21894190_FADD: an endogenous inhibitor of RIP3-driven regulated necrosis 22421439_study suggests that MLKL is a key RIP3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrotic cell death 22817896_Study shows that RIP1 and RIP3 form an amyloid structure through their RIP homotypic interaction motifs and that this heterodimeric amyloid structure is a functional signaling complex that mediates programmed necrosis. 23071110_procaspase-8 activity is essential for cell survival by inhibiting both apoptotic and nonapoptotic cell death dependent on receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3 23612963_the importance of the RIP3-MLKL interaction in the formation of functional necrosomes and suggest that translocation of necrosomes to mitochondria-associated membranes is essential for necroptosis signaling. 24059293_an alanine residue substitution for Ser(89) enhanced RIP1 kinase activity and TNF-induced programmed necrosis without affecting RIP1-RIP3 necrosome formation. 24095729_RIP3-mediated MLKL phosphorylation, though important for downstream signaling, is dispensable for stable complex formation between RIP3 and MLKL. 24314238_The protein levels of crucial modulators of necroptosis, RIP1 and RIP3, are increased by shikonin treatment in primary tumor tissues. 24322838_RIP3 protein expression is significantly increased in the inflamed tissue of inflammatory boowel disease pediatric patients. 24413151_targeting the RIP kinase signalling pathway could be an effective therapeutic intervention in retinal degeneration patients. 24703947_Report role of MLKL/RIP3 pathway in necrotic membrane disruption. 24746856_The results of this study showed that cerebral ischemia activates transcriptional changes that lead to an increase in the endogenous RIP3 protein level. 24963148_RIP3-dependent necroptosis mediates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-induced liver fibrosis via activation of JNK, MCP-1-mediated recruitment of monocytes, and an expansion of intrahepatic biliary/progenitor cells. 25144719_RIP3 silencing in leukemia cells results in suppression of the complex regulation of the apoptosis/necroptosis switch and NF-kappaB activity. 25326752_our results reveal a specific role for the RIP1-RIP3-DRP1 pathway in RNA virus-induced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome 25423287_although JNK activation and RIP3 expression are induced by FS, neither contributes to the liver injury. 25450619_RIPK3 serves as a negative regulator of selective autophagy by regulating regulates p62-LC3 complex formation via the caspase-8-dependent cleavage of p62 25459880_RIP3 holds both necroptosis and apoptosis in balance through a Ripoptosome-like platform. 25563840_Enhanced RIP3 signaling in aneurysmal tissues contributes to abdominal aortic aneursym progression by causing smooth muscle cell necroptosis, as well as stimulating vascular inflammation. 25575821_Data suggest that neoalbaconol-induced necroptosis include receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 1-dependent expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha and receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 3-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. 25674983_Herpes simplex virus 1- and 2 ICP6 and ICP10 proteins prevent necroptosis in human cells by inhibiting the interaction between receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3, a key step in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced necroptosis. 25748555_High expression of RIP3 in keratinocytes from toxic epidermal necrolysis patients potentiates MLKL phosphorylation/activation and necrotic cell death. 25778401_Suppression of RIP3-dependent necroptosis by human cytomegalovirus 25852146_RIP3 activation following the induction of necroptosis requires the activity of an HSP90 and CDC37 cochaperone complex. 25888634_PolyIC stimulation of cervical cancer cells induced necroptotic cell death, which was strictly dependent on the expression of the receptor-interacting protein kinase RIPK3. 25906154_Data implicate the infiltrating macrophages as a source of damaging inflammasomes after photoreceptor detachment in a RIP3-dependent manner and suggest a novel therapeutic target for treatment of retinal diseases. 25952668_The RIP3 expression is reduced in tumors compared to normal tissue in 85% of breast cancer patients, suggesting that RIP3 deficiency is positively selected during tumor growth/development. 26269957_Additionally, later in infection, RIP3 is cleaved by the coxsackievirus B3-encoded cysteine protease 3C(pro), which serves to abrogate RIP3-mediated necrotic signaling and induce a nonnecrotic form of cell death. 26355347_RIPK3 expression may allow unmasking the necroptotic signalling machinery in melanoma and points to reactivation of this pathway as a treatment option for metastatic melanoma. 26381214_Results identify a crucial role for RIPK3-PGAM5-Drp1/NFAT signalling in NKT cell activation, and further suggest that RIPK3-PGAM5 signalling may mediate crosstalk between mitochondrial function and immune signalling. 26437789_CNOT3 suppression promotes necroptosis by stabilizing mRNAs for cell death-inducing proteins, Ripk1 and Ripk3. 26496737_The main route of cell death induced by shikonin is RIP1K-RIP3K-mediated necroptosis. 26749282_The expression level of RIP3K was significantly lower in the malignant tumors. 26769846_Results suggest that impaired hepatic proteasome function by alcohol exposure may contribute to hepatic accumulation of RIP3 resulting in necroptosis and steatosis while RIP1 kinase activity is important for alcohol-induced inflammation. 26865533_Necroptosis signaling is modulated by the kinase RIPK1 and requires the kinase RIPK3 and the pseudokinase MLKL. (Review) 26900751_CHIP is a bona fide negative regulator of the RIPK1-RIPK3 necrosome formation leading to desensitization of TNF-mediated necroptosis 26925809_In critically ill trauma patients, plasma levels of the necroptosis mediator RIP3 at 48 h were associated with AKI stage and RBC transfusions. 27323669_The necroptosis-inducing kinase RIPK3 reduces adipose tissue inflammation and glucose intolerance. 27344176_our results reveal that the necroptosis adaptor RIPK3 has key anti-inflammatory and anti-tumoral functions in the intestine, and define RIPK3 as a novel colon tumor suppressor 27362805_Renal clear cell carcinoma cells cells express increased amounts of RIPK1 and RIPK3 and are poised to undergo necroptosis in response to TNFR1 signaling. 27411587_Data identify RIPK3 and the inflammasome as key tumor suppressors in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 27411587_Results demonstrate that RIPK3 restricts malignant myeloproliferation by activating the inflammasome, which promotes differentiation and cell death, and that loss of RIPK3 increases leukemic burden in mice. Reduced RIPK3 expression is observed across several human acute myeloid leukemia subtypes. 27517160_RIPK3-dependent cell death and inflammasome activation in FLT3-internal-tandem-duplication-expressing leukemia-initiating cells 27748372_inactivation of RIP1/RIP3 resulted in reduction of SOCS1 protein levels and partial differentiation of AML cells. AML cells with inactivated RIP1/RIP3 signaling show increased sensitivity to IFN-gamma-induced differentiation. 27756058_results reveal a pathway for MLKL-dependent programmed necrosis that is executed in the absence of RIPK3 and potentially drives the pathogenesis of severe liver diseases. 27932417_the in vivo effects were diametrically reversed with RIP3 deletion or RIP1 blockade, resulting in marked tumor protection. The dichotomy between the in vivo and in vitro results suggests that the microenvironmental milieu resulting from RIP1/RIP3 signaling is likely responsible for its protumorigenic effects 27984090_The results highlight a new role of TSC2 in protecting glioblastoma against photodynamic therapy-induced cell death, and TSC2 and YWHAZ as new RIP3 partners. 28176780_The major function of RIP1 kinase activity in TNF-induced necroptosis is to autophosphorylate serine 161. This specific phosphorylation then enables RIP1 to recruit RIP3 and form a functional necrosome, a central controller of necroptosis. 28412393_adhesion-induced eosinophil cytolysis takes place through RIPK3-MLKL-dependent necroptosis, which can be counterregulated by autophagy 28564603_2-hydroxyglutarate bound to DNMT1 and stimulated its association with the RIP3 promoter, inducing hypermethylation that reduces RIP3 protein and consequently impaired RIP3-dependent necroptosis. 28816233_Shikonin induces glioma cell necroptosis in vitro by reactive oxygen species overproduction and promoting RIP1/RIP3 necrosome formation. 28844856_We showed that RIP3 spontaneously drives a necroptosis-induced inflammation in established intestinal cell lines and in ileal/colonic samples from IBD patients. 28978351_These data demonstrate that caspase-8 functions in synovial antigen-presenting cells to regulate the response to inflammatory stimuli by controlling RIPK3 action, and this delicate balance maintains homeostasis within the joint. 28981102_The induced expression of RIP3 by UHRF1 RNAi depends on the presence of Sp1. Remarkably, the ectopic expression of RIP3 in RIP3-null cancer cells results in a decrease in tumor growth in mice. Therefore, our findings offer insights into RIP3 expression control in cancer cells and suggest an inhibitory effect of RIP3 on tumorigenesis. 29331417_Data indicate that receptor-interacting protein 3 (RIP3) is down-regulated in multiple cancers. 29358703_Our data uncover a regulation mechanism of PDC activity, show that pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activation by RIP3 is most likely the major mechanism activated by TNF to increase aerobic respiration and its by-product ROS, and suggest that RIP3-dependent induction of aerobic respiration contributes to pathologies related to oxidative stress 29413844_Ripk3 was involved in microvascular ischemia reperfusion injury via regulation of IP3R-mediated calcium overload, xanthine oxidase-dependent oxidative damage and filopodia-related cellular migration, ultimately leading to endothelial apoptosis and migratory inhibition. 29415885_Study revealed increased kidney expression of RIPK3 in mouse models of progressive kidney fibrosis and in human chronic kidney disease kidney and demonstrate a pathway by which RIPK3 promotes fibrogenesis through the AKT-dependent activation of ATP citrate lyase independently of mixed-lineage kinase domain-like protein-dependent necroptosis. 29720570_We demonstrate that the necroptosis-related molecule RIPK3, but not RIPK1 or MLKL, may be important in the development of experimental VILI and that impaired FAO may be involved. 29875323_Study revealed that in kidney tubular epithelial cells RIPK3 promotes oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction by upregulation of NOX4 and inhibition of mitochondrial complex I and -III, and that RIPK3 and NOX4 are critical for kidney tubular injury in vivo. Elevated urinary and plasma RIPK3 levels in human patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury represent potential markers of this condition. 29883609_PELI1 may function to control inadvertent activation of RIP3, thus preventing aberrant cell death and maintaining cellular homeostasis. 30012671_a signaling circuit involving RIPK3 and PGE2 enhances accumulation and immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells 30158627_Necroinflammation driven by RIPK3-MLKL-dependent necroptosis plays a crucial role in the progression of IRI to CKD. 30355688_Activation of necroptosis by Infleunza A virus leads to the phosphorylation of MLKL by RIPK3 and results in MLKL oligomerization and membrane translocation, leading to membrane disruption and a loss of cellular ion homeostasis. 30509860_REVIEW: recent structural studies of the core machinery of the pathway, the protein kinases receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK)1 and RIPK3, and the terminal effector, the pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), in shaping our mechanistic understanding of necroptotic signaling 30548986_human polymorphonuclear neutrophils secreted IL-1beta through a previously unrecognized mechanism dependent on RIPK3 and serine proteases but independent of canonical NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase-1 activation. 30770249_OGT-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of the serine-threonine kinase RIPK3 on threonine 467 (T467) prevented RIPK3-RIPK1 hetero- and RIPK3-RIPK3 homo-interaction. 30786994_specific role of RIPK3 in intestinal tumors and myeloid-derived suppressor cells function sheds light on a key inflammatory mechanism driving tumorigenesis and allows for possible therapeutic intervention 30904034_Study of 74 colon cancer patients showed that those with higher expression of RIPK3 had longer progression-free survival and longer overall survival compared with those who expressed low levels of RIPK3. 30944411_Dectin-1-induced RIPK1 and RIPK3 activation protects host against Candida albicans infection. 30996211_elevated RIPK3 mRNA levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells are associated with poor prognosis of acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. 31003931_The alongside RIPK3 and caspase-8, exerts regulatory functions on RIPK1-mediated inflammation. 31129968_Ectopic expression of RIP3 promoted cisplatin-induced HepG2/DDP cells death, HMGB1 and LDH release 31131045_LMP1-induced metabolic reprogramming inhibits necroptosis through the hypermethylation of the RIP3 promoter. 31148336_A common variant of RIP3 promoter region is associated with poor prognosis in heart failure patients by influencing SOX17 binding. 31177396_Expression level of receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) in cisplatin-resistant A549 (A549/DDP) cells is lower. RIPK3 expression level which influences cisplatin sensitivity of lung cancer cells is regulated by CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 3 (CNOT3). CNOT3 depletion up-regulates the expression level of RIPK3 and enhances apoptosis by elevating RIPK3 to further trigger Caspase 8 activation. 31205096_Plasma RIP3 levels were independently associated with CAD. Plasma RIP3 levels could potentially supplement clinical assessment to screen CAD and determine CAD severity. 31247189_inhibiting UCHL1 to downregulate the RIPK1/RIPK3 pathway may be a novel strategy to protect the podocytes in diabetic nephropathy patients. 31295018_that RIP3 plays a crucial proinflammatory role in liver fibrosis by regulating the ROCK1-TLR4-NF-kappaB signaling pathway in macrophages 31719524_Current translational potential and underlying molecular mechanisms of necroptosis. 31902237_SNO-MLP (S-Nitrosylation of Muscle LIM Protein) Facilitates Myocardial Hypertrophy Through TLR3 (Toll-Like Receptor 3)-Mediated RIP3 (Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3) and NLRP3 (NOD-Like Receptor Pyrin Domain Containing 3) Inflammasome Activation. 31968247_Constitutive Interferon Attenuates RIPK1/3-Mediated Cytokine Translation. 31997355_Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 3 (RIPK3) inhibits autophagic flux during necroptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. 32004572_ID1 overexpression increases gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by activating RIP3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis. 32122992_RIPK3 Orchestrates Fatty Acid Metabolism in Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Hepatocarcinogenesis. 32162861_The Trend of ripk1/ripk3 and mlkl Mediated Necroptosis Pathway in Patients with Different Stages of Prostate Cancer as Promising Progression Biomarkers. 32221312_New insights in acetaminophen toxicity: HMGB1 contributes by itself to amplify hepatocyte necrosis in vitro through the TLR4-TRIF-RIPK3 axis. 32222932_RIPK3 is a novel prognostic marker for lower grade glioma and further enriches IDH mutational status subgrouping. 32616439_Regulatory mechanisms of RIPK1 in cell death and inflammation. 32737444_RIP3-mediated necroptosis is regulated by inter-filament assembly of RIP homotypic interaction motif. 32753382_Identification of MYC as an antinecroptotic protein that stifles RIPK1-RIPK3 complex formation. 32853963_RIPK3 mRNA level acts as a diagnostic biomarker in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. 32895234_TRIM24-RIP3 axis perturbation accelerates osteoarthritis pathogenesis. 33051424_Changes in plasma levels of RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL in patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease and its clinical predictive value.', trans 'RIPK1RIPK3MLKL. 33119828_Expression of Protein Kinases RIPK-1 and RIPK-3 in Mouse and Human Hair Follicle. 33203643_Somatic Epigenetic Silencing of RIPK3 Inactivates Necroptosis and Contributes to Chemoresistance in Malignant Mesothelioma. 33329521_The Role of RIPK1/3 in Adult Onset Still's Disease Patients With Liver Damage: A Preliminary Study. 33361348_RIPK3 acts as a lipid metabolism regulator contributing to inflammation and carcinogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 33369872_USP22 controls necroptosis by regulating receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 ubiquitination. 33531383_Location, location, location: A compartmentalized view of TNF-induced necroptotic signaling. 33625952_RIPK3 Activates MLKL-mediated Necroptosis and Inflammasome Signaling during Streptococcus Infection. 33790016_The structure of a minimum amyloid fibril core formed by necroptosis-mediating RHIM of human RIPK3. 33796483_RIPK3-Dependent Necroptosis Is Induced and Restricts Viral Replication in Human Astrocytes Infected With Zika Virus. 33841405_Leaky Gut Driven by Dysbiosis Augments Activation and Accumulation of Liver Macrophages via RIP3 Signaling Pathway in Autoimmune Hepatitis. 33850121_Conformational interconversion of MLKL and disengagement from RIPK3 precede cell death by necroptosis. 33924766_Targeting RIP Kinases in Chronic Inflammatory Disease. 34029184_A phosphorylation of RIPK3 kinase initiates an intracellular apoptotic pathway that promotes prostaglandin2alpha-induced corpus luteum regression. 34156033_RIP3-dependent necroptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 34173165_The expression of RIPK3 is associated with cell turnover of gastric mucosa in the mouse and human stomach. 34419074_RIPK3 activation induces TRIM28 derepression in cancer cells and enhances the anti-tumor microenvironment. 34488677_The potential value of plasma receptor interacting protein 3 in neonates with culture-positive late-onset sepsis. 34498705_Upregulation of RIP3 promotes necroptosis via a ROSdependent NFkappaB pathway to induce chronic inflammation in HK2 cells. 34654937_RIPK3 signaling and its role in the pathogenesis of cancers. 34811356_Human RIPK3 maintains MLKL in an inactive conformation prior to cell death by necroptosis. 35094251_MiR-325-3p Alleviates Acute Pancreatitis via Targeting RIPK3. 35256774_Mosaic composition of RIP1-RIP3 signalling hub and its role in regulating cell death. 35264437_Necroptosis-driving genes RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL-p are associated with intratumoral CD3(+) and CD8(+) T cell density and predict prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35346043_RIP3 knockdown inhibits necroptosis of human intestinal epithelial cells via TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling and ameliorates murine colitis. 35438255_Phosphoproteomics identifies pathways underlying the role of receptor-interaction protein kinase 3 in alcohol-associated liver disease and uncovers apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 as a target. 35464769_RIP3 Contributes to Cardiac Hypertrophy by Influencing MLKL-Mediated Calcium Influx. 35739084_Human RIPK3 C-lobe phosphorylation is essential for necroptotic signaling. 35805993_Ca(2+)/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Regulation by Inhibitor of Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase 3 Alleviates Necroptosis in Glycation End Products-Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury. 36030035_RIPK1 and RIPK3 regulate TNFalpha-induced beta-cell death in concert with caspase activity. 36037995_Epigenetic Silencing of RIPK3 in Hepatocytes Prevents MLKL-mediated Necroptosis From Contributing to Liver Pathologies. 36169895_Feedback loop between fatty acid transport protein 2 and receptor interacting protein 3 pathways promotes polymorphonuclear neutrophil myeloid-derived suppressor cells-potentiated suppressive immunity in bladder cancer. 36240069_Mechanisms of TNF-independent RIPK3-mediated cell death. |
ENSMUSG00000022221 |
Ripk3 |
55.857994 |
0.3205356821 |
-1.641443 |
0.229414009 |
52.321728 |
0.00000000000047113273649601417419280257963931890204459240756307281117187812924385070800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002868778544010383357901559443999716303083657997774480463704094290733337402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.4550324 |
4.0708144 |
83.1436174 |
8.2186638 |
| ENSG00000129467 |
196883 |
ADCY4 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFM4 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the formation of the signaling molecule cAMP in response to G-protein signaling. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P26770}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;cAMP biosynthesis;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;Lyase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the family of adenylate cyclases, which are membrane-associated enzymes that catalyze the formation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Mouse studies show that adenylate cyclase 4, along with adenylate cyclases 2 and 3, is expressed in olfactory cilia, suggesting that several different adenylate cyclases may couple to olfactory receptors and that there may be multiple receptor-mediated mechanisms for the generation of cAMP signals. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:196883; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0004016]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; cAMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006171]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556] |
11055432_This paper reports the presence of adenylyl cyclases 2, 3, and 4 in mouse olfactory cilia. 11299302_The HIV-1 regulatory protein Tat was shown to inhibit the activity of adenylyl cyclase in rat microglial cells. 21228062_AC4 and AC2, both isoforms stimulated by Gbetagamma, are expressed in bronchial nonlipid raft membrane fractions where they colocalize with and couple to prostanoid EP2 receptors. 31584294_ADCY4 may be used as an epigenetic biomarker for breast cancer, as well as a possible target for therapy. |
ENSMUSG00000022220 |
Adcy4 |
27.223129 |
0.3222593969 |
-1.633706 |
0.350348089 |
22.458785 |
0.00000214701312064005504177065762616560817832578322850167751312255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007313619584732797477394893037594414408886223100125789642333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.8895034 |
8.9984986 |
47.3846298 |
18.3842312 |
| ENSG00000129595 |
64097 |
EPB41L4A |
protein_coding |
Q9HCS5 |
|
Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the band 4.1 protein superfamily. Members of this superfamily are thought to play an important role in regulating interactions between the cytoskeleton and plasma membrane, and contain an amino terminal conserved domain that binds glycophorin C. This gene product is thought to be involved in the beta-catenin signaling pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:64097; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; actomyosin structure organization [GO:0031032] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000024376 |
Epb41l4a |
26.109572 |
3.5955088154 |
1.846196 |
0.514976488 |
12.054193 |
0.00051676015299636894346352322671123147301841527223587036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001265115252649926403522018247826963488478213548660278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
36.8546527 |
14.5934396 |
10.0426493 |
2.8780488 |
| ENSG00000129625 |
7905 |
REEP5 |
protein_coding |
Q00765 |
FUNCTION: Plays an essential role in heart function and development by regulating the organization and function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in cardiomyocytes. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60870}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in endoplasmic reticulum organization and regulation of intracellular transport. Located in endoplasmic reticulum tubular network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7905; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network [GO:0071782]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane organization [GO:0090158]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; regulation of intracellular transport [GO:0032386] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22795047_To determine the pathogenesis and treatment response of major depressive disorder. REEP5 gene polymorphisms may influence antidepressant treatment response in MDD. 27966653_Depletion of receptor accessory proteins REEP5 and REEP6 causes a decrease in CXC Chemokine Receptor 1 (CXCR1) signaling. 32075961_The sarco-endoplasmic reticulum (SR/ER) plays an important role in the development and progression of many heart diseases. Receptor accessory protein 5 (REEP5), a cardiac enriched, sarco-endoplasmic reticulum (SR/ER) membrane protein,is centrally involved in regulating SR/ER organization and cellular stress responses in cardiac myocytes. |
ENSMUSG00000005873 |
Reep5 |
818.288032 |
2.4330954736 |
1.282793 |
0.074033064 |
297.438625 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000119073878365278277419304410672741598641169089527389453381994977658791775116309264330497702817630348627298600029582363255262890174209438883652257857146324986318393314085883893937989341793581843376159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034193199312675241577598615434170610074414853064781026126698261232785349261271052576904399674837694680650512172060495129992528294968334469383676472873331922893726762813226827120161033235490322113037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1083.1899524 |
46.9288908 |
448.6868804 |
14.7211094 |
| ENSG00000129675 |
9459 |
ARHGEF6 |
protein_coding |
Q15052 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a RAC1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Rho GTPases play a fundamental role in numerous cellular processes that are initiated by extracellular stimuli that work through G protein coupled receptors. The encoded protein belongs to a family of cytoplasmic proteins that activate the Ras-like family of Rho proteins by exchanging bound GDP for GTP. It may form a complex with G proteins and stimulate Rho-dependent signals. This protein is activated by PI3-kinase. Mutations in this gene can cause X-chromosomal non-specific cognitive disability. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9459; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032] |
11937491_The plexin-B1/Rac interaction inhibits PAK activation and enhances Sema4D ligand binding 12935897_Expression of Cbl-b effectively blocks the ability of Cool-2 to stimulate PAK, providing an additional mechanism, aside from catalyzing receptor ubiquitination, by which Cbl-b acts as a negative regulator for signaling activities requiring PAK activation. 15242552_Data suggest that Rac-dependent activation of the NFkappaB pathway may be a critical element promoting thrombin-induced tissue factor expression and activity, and thus a prothrombotic state in pulmonary hypertension. 15611136_Whereas alphaPIX guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity contributes to enhanced formation of cellular protrusions, the GEF-independent association with calpain 4 leads to induction of a yet unknown signaling cascade resulting in cell spreading. 16320026_Semi-quantitative RT-PCR experiments with 6 of those genes confirmed higher expression of DNCH2, ARHGEF6, NPM1 and SRI and lower expression of NRGN and TM4SF2 in GBM tumors. 16897755_PAK4 and alphaPIX can induce highly localized changes in actin dynamics and thereby regulate size and number of podosomes in primary human macrophages. 17405911_phosphorylation of CagA induces the dephosphorylation of alpha-Pix, which may modulate cytoskeletal changes of gastric epithelial cells through PAK 19672789_The interaction of alphaPix with CagA activates PAK1, ERK and NF-kappaB, which induces IL-8 expression in H. pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19918261_results suggest that low doses of chlorambucil and very low doses of chronic oxidative stress together kill Cbl-resistant ovarian carcinoma cells and ARHGEF6 signaling may have an instrumental role in induction of apoptosis in Cbl(cos) cells. 19969308_These findings suggest that alpha Pix plays an important role in mutant huntingtin aggregation. 25450678_c-Cbl negatively regulates alphaPix-mediated cell migration and invasion; the lack of c-Cbl in C6 and A172 glioma cells is responsible for their malignant behavior 26177020_The novel recycling regulator alpha-PIX and the degradation factor c-Cbl closely cooperate in the regulation of EGFR trafficking. 26507661_show that ARHGEF6 is constitutively linked to GIT1, a GAP of Arf family small G proteins, and that ARHGEF6 phosphorylation enables binding of the 14-3-3 adaptor protein to the ARHGEF6/GIT1 complex 27182061_we discuss recent findings in key physiological systems that exemplify current understanding of the function of this important regulatory complex. Further, we draw attention to gaps in crucial information that remain to be filled to allow a better understanding of the many roles of the GIT-PIX complex in health and disease 28333213_In this first X chromosome-wide association study of adult patients with IBD, we identified an IBD susceptibility locus with genome-wide significance at rs2427870 on chrXq26.3, located 66 kbp upstream of CD40LG and 83.4 kbp upstream of ARHGEF6 [OR, 1.22; combined p = 3.79 x 10-15]. |
ENSMUSG00000031133 |
Arhgef6 |
339.620603 |
0.4582571791 |
-1.125771 |
0.099546442 |
128.052823 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001092950836592494106059208618654966752728113984427878008034341533722960481574680048633130269308821880258619785308837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000139068571966424249418675854021179496398560552405860694586321207415276522212713161685826435132184997200965881347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
216.3659721 |
13.2420850 |
475.0218508 |
19.3311943 |
| ENSG00000129757 |
1028 |
CDKN1C |
protein_coding |
P49918 |
FUNCTION: Potent tight-binding inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/CDK complexes (cyclin E-CDK2, cyclin D2-CDK4, and cyclin A-CDK2) and, to lesser extent, of the mitotic cyclin B-CDC2. Negative regulator of cell proliferation. May play a role in maintenance of the non-proliferative state throughout life. |
Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Disease variant;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein kinase inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene is imprinted, with preferential expression of the maternal allele. The encoded protein is a tight-binding, strong inhibitor of several G1 cyclin/Cdk complexes and a negative regulator of cell proliferation. Mutations in this gene are implicated in sporadic cancers and Beckwith-Wiedemann syndorome, suggesting that this gene is a tumor suppressor candidate. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:1028; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004861]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; adrenal gland development [GO:0030325]; aging [GO:0007568]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; digestive system development [GO:0055123]; embryonic placenta morphogenesis [GO:0060669]; genomic imprinting [GO:0071514]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:1904030]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045736]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033673]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045930]; negative regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042326]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron maturation [GO:0042551]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; regulation of exit from mitosis [GO:0007096]; regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:1902746]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; uterus development [GO:0060065] |
8610162_CDKN1C gene is imprinted, with preferential expression from the maternal allele. 11815601_Identification and functional characterization of an intragenic DNA binding site for the spumaretroviral trans-activator in the human p57Kip2 gene 11891335_Induction of p57(KIP2) expression by p73beta 11891530_Down-regulation of p57 may play a role in the dedifferentiation of thyroid carcinoma. 11965547_DNA methylation and histone deacetylation of p57KIP2 promoter results in gene silencing of p57KIP2 in human tumors 12239171_aberrant DNA methylation of the gene occurs in the promoter region in lymphoid malignancies of B-cell phenotype 12514787_findings support the hypothesis that misexpression of p57 is involved in the abnormal development of androgenetic complete moles 12532471_Expression of p57kip2, Rb protein and PCNA and their relationships with clinicopathology in human pancreatic cancer. 12553041_P57/KIP2 is a determinant pro-survival factor for cell protection from green tea polyphenol-induced apoptosis. 12586619_frequently methylated in adult patients with ALL, and that inactivation of a pathway composed of p73, p15, and p57KIP2 predicts for poor prognosis in Ph-negative patients 12790805_identified a functional glucocorticoid response element, located 5 kilo bases upstream of the transcription start site in the human p57(Kip2) promoter 12925736_SCFSkp2 complex plays an important role in cell-cycle progression by determining the abundance of p57Kip2 and that of the related CDK inhibitor p27Kip1. 12947099_it is evident that B-Myb protein may promote cell proliferation by a non-transcriptional mechanism that involves release of active cyclin/cyclin dependent kinase 2 from cyclin-dependent inhibitor 1C p57(KIP2) 12963725_p57KIP2 modulates stress-activated signaling by functioning as an endogenous inhibitor of JNK/SAPK 14530263_p57 may act as a key regulator in embryogenesis by regulating cell cycle through binding to Cdks and the regulating actin dynamics through binding to LIMK-1 14612924_loss of p57KIP2 expression appears associated with colorectal carcinogenesis 14627666_An epimutation at KvDMR1, the absence of maternal methylation, causes the aberrant silencing of CDKN1C, some 180 kb away on the maternal chromosome. 15007390_Diminished CDKN1C expression is associated with loss of methylation of CpG & H3K9 at DMR-LIT1, & is involved in esophageal cancer. DMR-LIT1 epigenetically regulates CDKN1C expression through histone modifications at DMR-LIT1 promoter. 15332324_p57KIP2 was weakly expressed in 4/6 glioblastoma (GBM) specimens by western blot. p57KIP2 immunoreactivity was positive in 8/40 GBMs, and was primarily nuclear in location. The motility of glioma cells was significantly reduced after p57KIP2 induction. 15492797_Aberrant methylation of p57KIP2 gene is associated with lung and breast cancers and malignant mesotheliomas 15749785_p57 is up-regulated in the process of decidualization. 15821902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15821902_Variants in CDKN1C may contribute to the inter-individual variation in birth weight. 15888726_p57KIP2 is part of an imprinted gene network that may play a role in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. 15900410_endothelial cells of infantile hemangiomas not associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome normally express p57(KIP2) while chorioangiomas do not 15936816_The Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p57 plays key roles in cell cycle regulation, and was methylation-negative in myeloid neoplasia. 15952111_Transcripts of P57KIP2, imprinted genes related to BWS, were detected in human oocytes and at all stages of preimplantation embryos. 15978938_The P57 was methylated in 2 (10%) pediatric patients , compared to 20 (37%)respectively in adult patients. 15985436_identification of a novel p73-Kip2/p57 pathway that coordinates mitotic exit and transition to G1 16061564_The absence of methylation and repressive chromatin structure at the CDKN1C promoter in Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome patients with loss of methylation at KvDMR1 suggests a direct role of this epimutation in silencing CDKN1C. 16124066_The decreased expression of p57(kip2) and/or overexpression of cyclinE protein and PCNA may contribute to the occurrence and progression of pancreatic cancer. 16357845_Methylation of p57(KIP2) may contribute to the malignant progression of gastric MALT lymphomas. 16575194_Recent advances in epigenetic control of the CDKN1C/KCNQ1OT1 imprinted domain in both humans and mice, causing Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and cancer. (review) 16705184_Global gene expression analysis in neuroblastoma cells engineered to acutely express the E protein E47 and Id2, showed that p57Kip2 is a target of E47. 16936778_These results suggest that the tumor suppressive properties of p57KIP2 in leukemia may depend on the intrinsic promoter DNA methylation status of the gene. 16943770_TGF-beta1 and/or TGF-beta2 inhibit proliferation of primary cultured human limbal epithelial cells, and p57 and p15 play roles in this process. 16950772_CTIP2 associates with the NuRD complex on the promoter of p57KIP2, a newly identified CTIP2 target gene. 17050328_findings suggest p57kip2 may play a role in the regulation of meiotic progression of early spermatocytes & cell cycle arrest & differentiation of spermatids 17112701_These data demonstrate the role of BMP2 compared to BMP6 in the inhibition of growth and induction of differentiation of keratinocytes; p57(Kip2) and p21(Cip1) have a BMP2/6-induced expression. 17351341_Genetic evidence links the association between DNA-variants in the CDKN1C gene with a risk of atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. 17351341_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17464323_mechanism whereby p57(Kip2) influences the mitochondrial apoptotic cell death pathway in cancer cells 17572845_In this study, P57kip2 immunostaining was absent in the trophoblastic layers of CHM and was positive in the trophoblast layer of nonmolar villi and MD. 17885492_We did not find p16, p14, and p57 to be useful as prognostic markers in stage III ovarian cancer 17986608_demonstrate that these myoblasts are unable to complete myogenic differentiation because of an inability to up-regulate p57Kip2 transcription 18325103_The expression of CDKN1C decreases in the large majority of breast cancers and does not appear to be mediated by AI/LOH at the gene. CDKN1C may be a breast cancer tumor suppressor. 18430730_cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57(Kip2) and vascular endothelial growth factor mRNAs are selectively translated by an IRES-independent mechanism under hypoxic stress 18521080_miR-221 has an oncogenic function in hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting CDKN1B/p27 and CDKN1C/p57, hence promoting proliferation by controlling cell-cycle inhibitors. 18647205_The difference in expression patterns of p27(KIP1) and p57(KIP2) in proliferating and senescent melanocytes suggests the interplay between these proteins may play a functional role in melanocytic tumorigenesis 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18822693_p57(Kip2) down-regulation is a well-established feature of urothelial carcinoma. Probably, this down-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors supports the proliferation phase of oncogenesis. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19109226_Detection of epigenetic alterations allows the identification of patients with ALL with standard risk but with poor prognosis. 19116812_The loss of p57 expression in placental mesenchymal dysplasia could be of diagnostic value in helping to distinguish this rare placental lesion from its mimickers. 19141585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19145201_This study validates p57 immunostaining as a prospectively applicable triage assay for the diagnosis of complete hydatidiform mole 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19221586_Results show that the imprinted cell cycle inhibitor CDKN1C is a downstream target for SMARCB1 and is transcriptionally activated by increased histone H3 and H4 acetylation at the promoter. 19340297_study reveals a novel epigenetic mechanism governing CDKN1C repression in breast cancer. As a newly identified EZH2 target with prognostic value, it has implications in patient stratification for cancer therapeutic targeting EZH2-mediated gene repression 19386358_CDKN1C mutations in children born to women with preeclampsia/HELLP syndrome; suggesting the involvement of an imprinted gene in the pathophysiology of preeclampsia 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19542869_We recommend use of p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping to evaluate all products of conception specimens for which there is any consideration of a diagnosis of hydatidiform mole. 19544095_KLF4 binds to the p57(Kip2) promoter and transcriptionally upregulates its expression, which in turn inhibits the stress activated protein kinase cascade and c-Jun phosphorylation. 19544458_Data show that the miRNA miR-92b directly downregulates protein levels of the G(1)/S checkpoint gene p57. 19571260_Conservation of maternal allele-specific expression of CDKN1C in humans, mice and swine is supported by expression profiling between swine parthenotes and biparental control fetuses. 19590511_Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor p57 repressed Mash1 transcriptional activity, and the interaction with Mash1 as well as the repression of transcriptional activity turned out to be independent of cyclin dependent kinase interactions. 19616848_methylation of the p57KIP2 gene was analyzed in 63 cases of DLBCL by methylation-specific real-time quantitative PCR. Methylation of the p57KIP2 gene was detected in 53 (84.1%) of these 63 cases of DLBCL 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19734939_the p57(Kip2) control of LIMK-1 ultimately affects cell mobility negatively. 20056082_The degradation of cholesterol didn't affect the level of p57 in cell membrane. 20106982_CDKN1C negatively regulates RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation in an E2F1-dependent manner 20484977_Gene expression pattern of CDKN1C imprinted genes in spontaneous miscarriages or fetal deaths. 20503313_these findings suggest that Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome patients with CDKN1C mutations have a different pattern of clinical malformations than those with other molecular defects. 20565244_High levels of CDKN1C expression are common in human retinoblastoma tumors (RB). 20626178_The androgenetic/biparental chimeric Complete Hydatidiform moles demonstrated a negative p57(KIP2)(cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C) staining pattern for the androgenetic cells and positive staining for the biparental cells 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21205084_EZH2 gene acts as an oncogene in tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer with the possible mechanism to suppress the anti-oncogene p57. 21278784_MiR-221 binds to the target site in the 3'-UTR of the CDKN1C/p57 mRNA to inhibit CDKN1C/p57 expression by post-transcriptional gene silencing to promote colorectal carcinoma occurrence and progress 21360479_expression levels of p57(KIP2) and TGF-beta 1 associated with histological type of lung cancer; expression levels of decorin and p57(KIP2)associated with lymphatic invasion; increased expression of decorin and p57(KIP2) correlated with increased survival 21371741_reduced immunostaining of PCNA and Ki67 and increased immunostaining of p27 and p57 in the dexamethasone-induced intrauterine growth restriction placental development compared to control placental development 21538272_miR-221 inhibits CDKN1C/P57 expression by post-transcriptional gene silencing to promote colorectal carcinoma development and progression. 21575583_The different LH subdomains, despite their sequence and thermodynamic differences, play similar roles in binding and inhibiting Cdk2/cyclin A. 21767919_We confirm that for distinguishing complete hydatidiform mole from its mimics, p57(KIP2) immunohistochemistry can be used as successfully as DNA microsatellite genotyping 21769918_Through MEK/ERK pathway, S1P stimulates GAP43 transcription with increased binding of C/EBPbeta to the 5'-promoter tumor cell for metastais 21816904_We particularly focus our attention on p57(Kip2) changes in cancers and pharmacological approaches for modulating p57(Kip2) levels. 22002319_downregulation of p57 accelerates the growth and invasion of HCC, indicating that p57 is an important tumor suppressor in HCC. Based on these findings, p57 may be a potential target for HCC prevention and therapy 22064387_Upregulation of p57(kip2) may play an important role in the decidual differentiation by progesterone and growth inhibition of malignant cells in human endometrium. 22079941_Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome patients that inherited a maternal translocation or inversion of chromosome 11 also demonstrated reduced expression of the growth suppressing imprinted gene, CDKN1C. 22126772_MIR221 can interact with the target site on the 3'-UTR of CDKN1C/p57 mRNA to inhibit CDKN1C/p57 expression by post-transcriptional gene silencing to promote colon carcinoma cell proliferation. 22197173_Case Report: Combination of p57(kip2) immunostaining and HER2 fluorescent in situ hybridization was useful in diagnosing complete hydatidiform mole in a perimenopausal woman. 22205991_deletion of enhancer elements required for CDKN1C expression lying within or close to the imprinting centre 22233925_Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57(Kip2) is a candidate biomarker of platinum sensitivity/resistance in EOC and such cases may show preferential response to the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor seliciclib. 22245958_Report role of p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping to improve diagnostic reproducibility of hydatidiform moles. 22292406_The decreased expression of P57(kip2) and Maspin in abnormal scar shows that they are cicatrix-related genes. There is a positive relationship between the two genes. 22394561_Signaling through the PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase)-Akt-mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) pathway was necessary and sufficient for the increase in p57Kip2 22541097_Low expression of p57kip2 gene may play a role in the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome. 22569127_A novel function was uncovered for p57 that integrates external signals transduced by p38 stress-activated protein kinase to control the cell-cycle, establishing a checkpoint in G1 which is critical to permit cellular adaptation to stress. 22592318_The p57(KIP2-)mediated stabilization of the actin cytoskeleton was associated with the displacement of hexokinase-1 from the mitochondria, providing a possible mechanism for the promotion of the mitochondrial apoptotic cell death pathway. 22634751_All IMAGe-associated mutations clustered in the PCNA-binding domain of CDKN1C and resulted in loss of PCNA binding. 22705236_Down-regulation of Notch1 and Notch3 in two hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines resulted in Hes1 down-regulation, CDKN1C/P57 up-regulation, and reduced cell growth. 22980580_Co-culture of CB CD34(+) cells with mesenchymal stromal cells, especially in the absence of cytokines, maintained mRNA expression of p21 and p57 genes in ex vivo expanded CD34(+) cells. 22992698_Report reproducibility of p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping in the diagnosis of hydatidiform moles. 23008285_Cdkn1c (p57/KIP2) is a novel regulator of early epidermal differentiation and controls proliferation in primary keratinocytes and HaCaT cells. 23153226_Based on these findings we conclude that the imprinted gene expression of KCNQ1OT1, CDKN1C, H19, and PLAGL1 are conserved between human and bovine 23171462_Downregulation of CDKN1C is associated with poor disease outcome in patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, while upregulation of AHI1 shows a weak association with aggressive disease course. 23187808_Data suggest that CSN6 is an important negative regulator of p57 (Kip2) , and that overexpression of CSN6 in many types of cancer could lead to decreased expression of p57 (Kip2) and result in promoted cancer cell growth. 23197429_A novel mutation in CDKN1C was found in a family with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and cleft palate, sensorineural hearing loss, and supernumerary flexion creases. 23244105_High p57 KIP2 is asociated with breast cancer. 23421998_These data suggest that HER2/Akt is an important negative regulator of p57 (Kip2), and that p57 restoration in HER2-overexpressing cells can reduce breast tumor growth. 23438793_The co-expression of p27 and p57 by extravillous cytotrophoblasts and their positive correlation in non-molar gestations may indicate its suppressive role on the proliferation of these cells to provide them the capacity for differentiation and invasion. 23580324_p15(INK4b) and p57(KIP2) may be involved in the progression of vulvar carcinomas and the combined p14(ARF)/p15(INK4b)/p16(INK4a) status was a statistically independent prognostic factor. 23828667_p57kip2 appears to be widely expressed in the human oligodendroglial lineage, and potential beneficial effects on remyelination in the mulltiple sclerosis brain are not based on subcellular p57kip2 localization shifts. 23842948_This study indicates that the abnormal expression of p57 and RhoA contributes to progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and poor survival of patients. 23887308_p57 expression is highly correlated with genotyping, serves as a reliable marker for diagnosis of complete hydatidiform moles 23963898_cell cycle related proteins PCNA, Ki67, cyclin D3, p27 and p57 were expressed in both normal and diabetic human term placentas. 24065356_A report of a novel mutation of CDKN1C affecting the PCNA-binding domain in a family with a history of Russell Silver syndrome. 24098681_Increased protein stability of CDKN1C causes a gain-of-function phenotype in patients with IMAGe syndrome. 24613849_In conclusion, combined p57 immunostaining and FISH with a set of 3 CEP probes for chromosomes X, Y, and 17 could be useful in the classification of hydatidiform moles. 24652995_p57 regulates T-cell development and prevents lymphomagenesis by balancing p53 activity and pre-TCR signaling. 24848107_p57 and p21 serve nonredundant functions in trophoblast giant cells; the role of p21 in suppressing apoptosis is restricted to terminally differentiated cells. 24852133_Staining intensities of cell cycle inhibitors p27 and p57 significantly increased in all parts of preeclamptic placentas compared to control 24986528_The gene expression pattern of CDKN1C, H19, IGF2, KCNQ1 and PHLDA2 genes was evaluated using RT-PCR. 25057881_We report a novel CDKN1C mutation associated with features of IMAGe syndrome, but without adrenal insufficiency or metaphyseal dysplasia, and characterized by early-adulthood-onset diabetes. 25195859_p57Kip2 has a role in DNA damage response, suppresses tumorigenesis and causes chemoresistance. 25216674_This report shows that p57(Kip2) is a novel target of miR-21 in prostate cancer and revealing a novel oncogenic function of this microRNA. 25262539_opposed functional mutations in CDKN1C cause opposite clinical features; loss-of-function mutations cause overgrowth; gain-of-function mutations in the PCNA domain result in growth restriction; only maternally inherited mutations in CDKN1C are associated with disturbed growth [review] 25339094_Lefty1 could regulates the cell cycle via modulating the expressions of P57 and cyclin D1 and then inhibit the decidualization in vitro. 25427884_Data show the presence of maternally derived extra copies of the distal chromosome 11p involving the wild-type cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C protein (CDKN1C). 25588980_Up-regulation of miR-199a-5p in ADPKD tissues might promote cell proliferation through suppressing CDKN1C 25960208_downregulation of CDKN1 by siRNA blocked the activity of miR-25 on promoting glioma cell proliferation. 26077438_CDKN1C sequencing should be performed for BWS patients presenting with abdominal wall defects or cleft palate without 11p15 methylation defects or body asymmetry, or in familial cases of BWS. 26091021_Using human placental samples, we show that the expression of the imprinted gene CDKN1C associates with birth weight 26161420_Polymer-based immunohistochemical staining of p57(kip2) (paternally imprinted gene, expressed from maternal allele) is a very effective method that can be used to differentiate androgenetic complete mole from partial mole and hydropic abortion. 26271467_Our data indicated that reduced cytoplasmic p57 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. 26362858_These results indicate that the inhibitory effect of rapamycin may be due mainly to increased p14, p15, and p57 expression via promoter demethylation and decreased mTOR and p70S6K expression in ALL cell lines. 26606000_Jab1/Csn5 expression with concurrent low p57 expression associated with poor overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma 26857110_The data has been provided on fetal growth patterns and on the molecular subtypes of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, including gain or loss of DNA methylation, 11p15.5 paternal uniparental disomy, and CDKN1C mutation. 26985855_The differences in p18(INK4c)and p57(Kip2)activities in chronic myeloid leukemia and normal stem cells suggest a different cell cycle regulation. 27170453_CDKN1C protein expression in the BM of newly diagnosed, treatment-naive MDS and secondary AML patients was identified as a prognostic factor for poor survival in patients treated with antiproliferative chemotherapy. 27221896_Low P57KIP2 Expression is associated with Hydatidiform Moles. 27402879_Data provide evidence that SLC22A18 and/or CDKN1C are tumor modifier genes involved in the tumorigenesis of SDHD-mutated paraganglioma. 27436784_The mean Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS)score was 5.6 for 19 subjects with 'IC2 hypomethylation'(KCNQ1OT1-associated ), compared with 3.8 for 2 subjects with pUPD. The BWS score of one subject with CDKN1C mutation and one with IC1( H19-associated imprinting center) hypermethylation was 6 and 7, respectively 27611768_Analysis of the chromatin status of Cdkn1c promoter and KvDMR1 in unresponsive compared to responsive cell types showed that their differential responsiveness to the MyoD-dependent induction of the gene does not involve just their methylation status but, rather, the differential H3 lysine 9 dimethylation at KvDMR1. 28106536_Our findings show that the overexpression of p21;{Waf1/Cip1}, down-expression of p57;{Kip2} and gene promoter methylation of p57;Kip2 could be considered as promising diagnostic markers for breast cancer 28413121_Expression of CIP/KIP proteins was found abundantly within the proliferative hair matrix, concomitant with a role in cell cycle checkpoint control. p21(CIP1), p27(KIP1) and cyclin E persisted within post-mitotic keratinocytes of the pre-cortex, whereas p57(KIP2) protein decreased but became nuclear. 28508599_Gain-of-function mutations in the PCNA domain of CDKN1C have been reported as the genetic basis of various growth-retarded syndromes including IMAGe syndrome, Russell Silver syndrome as well as a novel undergrowth syndrome that additionally exhibited early adulthood onset diabetes. {review] 28574027_This study showed that negative p57KIP2 immunostaining reliably identified complete mole (CM)and could be used in association with the histological findings to distinguish CM from its mimics. 28803575_findings showed that pathogenesis of selective intrauterine growth restriction may be related to the co-effect of the up-regulated protein expression of CDKN1C and down-regulated mRNA expression of KCNQ1OT1 in the placenta. 28930539_Studies indicate that misregulation of p57(kip2) expression has been associated, to growth disorders and the onset of several types of cancers [Review]. 28933484_SNHG17 exerted oncogenic effects partly through epigenetically silencing P57 expression through interaction with EZH2. 29207083_expression of the nearby cyclindependent kinase inhibitor 1C (CDKN1C) gene was revealed to be upregulated after SP3 knockdown in cells that possessed non-risk alleles. This suggests that CDKN1C is potentially one of the functional targets of SNP rs163184, which modulates the binding activity of the locus for Sp3 and Lsd1/Kdm1a 29277274_Data suggest that expression of CDKN1C and IGF2 is significantly up-regulated in placenta after assisted reproductive technology; DNA methylation was significantly down-regulated in DMR of CDKN1C and up-regulated in DMR of IGF2. (CDKN1C = cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor-1C; IGF2 = insulin like growth factor 2; DMR = differential methylation regions) 29295723_Low p57 expression is associated with Spinal Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation. 29325014_P57 is one of the key determinants of endometrial stromal cell differentiation due to its effect on the cell cycle distribution, but its association with the decidua-specific transcription factor needs further investigation. 29428729_conclusion, our data suggested an essential role of CDKN1C in the tumorgenesis of breast cancer. Targeting CDKN1C may be a promising strategy for anticancer therapeutics. 29511350_Data identified p57KIP2 as a novel downstream target of TBX3 in PTC and showed that TBX3 represses expression of p57KIP2 through recruiting PRC2 and HDAC1/2 chromatin modification complex. 29614816_review provides an appraisal of the published data on the p57Kip2 protein; mainly focused on the regulation of CDKN1C (the p57Kip2 encoding gene) expression and its relevance in human diseases, including overgrowth and undergrowth syndromes 29661169_If, as expected, the consequences of the deregulation of the CDKN1C-E2F1-TP53 axis were the same as those experimentally demonstrated in mouse models, the disruption of this axis might be useful to predict tumor aggressiveness, and to provide the basis towards the development of potential therapeutic strategies in human Precursor T-cell lymphoblastic lymphomas 29734178_The expression of SH3PXD2A-AS1 was inversely correlated with the expression of P57 and KLF2 in Colorectal Cancer tissue samples. 30077532_CDKN1C is a novel female-specific biomarker of LV function after AMI. 30119259_HOXD-AS1 could interact with EZH2, and then repress p57 expression, to aggravate osteosarcoma oncogenesis. 30178471_Through activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway, p57 can reverse Er/C-225-induced autophagy, and thereby increase the therapeutic efficiency of Er/C-225 treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30544064_MIRN-92b inhibits p57kip2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues, thus enhancing the radio-resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to ionizing radiation-based radiotherapy. 30686519_Studied splicing factor 1 (SF1), insulin like growth factor 2(IGF2), and cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (p57) as possible prognostic tumor markers in pediatric adrenal cortical tumors. Found SF1 and IGF2 to be highly sensitive in diagnosis and prognosis of pediatric adrenal cortical tumors. 30792202_this study identified KLF4 as a target gene and a binding partner of RUNX1. KLF4 mediated proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction of t(8;21) leukemia cells through transactivating P57 30941985_Cyclin D1 expression in >10% of positive cells was observed mostly in the clear cell RCC, while p57 expression in =5% of positive cells was found in 86% of chromophobe RCC specimens. The higher expression of cyclin D1 and lower expression of p57 were more frequent in grade I-II tumors. 31059007_These results may provide a novel molecular mechanism to understand the involvement of p57KIP2 in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 31194812_Increased CDKN1C and PHLDA2 and reduced IGF-2 abundances in placental tissue were related to BW and early period catch-up growth in full-term SGA infants. 31367252_CDYL promotes the chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer by regulating H3K27 trimethylation at the CDKN1C promoter. 31497289_CDKN1C is a key negative regulator of fetal growth. Variants in a very localised 'hot-spot' cause growth restriction, with or without adrenal insufficiency. However, pathogenic variants in this region are not a common cause of isolated fetal growth restriction phenotypes or loss-of-pregnancy/recurrent miscarriages. 31708464_ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and CDKN1C gene expression in the prediction of lymph nodes metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 31804259_Rare clinical findings in three sporadic cases of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome due to novel mutations in the CDKN1C gene. 31833013_Identification of a hydatidiform mole in twin pregnancy following assisted reproduction. 31961825_Steroid resistance in Diamond Blackfan anemia associates with p57Kip2 dysregulation in erythroid progenitors. 32055942_the atypical features of hydatidiform moles from patients with recessive NLRP7 mutations and the important relationship between NLRP7 defects in the oocyte and p57 expression that appear to be the main contributor to the molar phenotype regardless of the zygote genotype 32346031_The CDK inhibitor p57(Kip2) enhances the activity of the transcriptional coactivator FHL2. 32364515_Protein and genetic expression of CDKN1C and IGF2 and clinical features related to human umbilical cord length. 32430359_Improved molecular detection of mosaicism in Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. 32686837_Androgenetic Complete Hydatidiform Moles With p57KIP2-Positive Immunostaining. 32933137_Regulation of p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) Functions by Natural Polyphenols. 32966862_USP7 promotes proliferation of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells through TBX3-mediated p57(KIP2) repression. 33046535_Dephosphorylation of the Proneural Transcription Factor ASCL1 Re-Engages a Latent Post-Mitotic Differentiation Program in Neuroblastoma. 33076988_Novel mutation points to a hot spot in CDKN1C causing Silver-Russell syndrome. 33360007_Expression of p57(KIP2) reduces growth and invasion, and induces syncytialization in a human placental choriocarcinoma cell line, BeWo. 33704912_Investigation of (epi)genotype causes and follow-up manifestations in the patients with classical and atypical phenotype of Beckwith-Wiedemann spectrum. 33792119_CDKN1C-mediated growth inhibition by an EZH1/2 dual inhibitor overcomes resistance of mantle cell lymphoma to ibrutinib. 33974722_Prenatal molecular testing and diagnosis of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. 34018382_Complementary role of p57kip2 immunostaining in diagnosing hydatidiform mole subtypes. 34065128_Variable Expressivity of the Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome in Four Pedigrees Segregating Loss-of-Function Variants of CDKN1C. 34074808_Loss of p57 Expression in Conceptions Other Than Complete Hydatidiform Mole: A Case Series With Emphasis on the Etiology, Genetics, and Clinical Significance. 34272384_Glucocorticoid receptor triggers a reversible drug-tolerant dormancy state with acquired therapeutic vulnerabilities in lung cancer. 34299047_A Beckwith-Wiedemann-Associated CDKN1C Mutation Allows the Identification of a Novel Nuclear Localization Signal in Human p57(Kip2). 34464504_CDKN1C as a prognostic biomarker correlated with immune infiltrates and therapeutic responses in breast cancer patients. 34580843_High Maternal Serum Estradiol in First Trimester of Multiple Pregnancy Contributes to Small for Gestational Age via DNMT1-Mediated CDKN1C Upregulation. 36037042_Identification and targeting of a HES1-YAP1-CDKN1C functional interaction in fusion-negative rhabdomyosarcoma. |
ENSMUSG00000037664 |
Cdkn1c |
7.774134 |
0.1828542731 |
-2.451234 |
0.738601345 |
11.656649 |
0.00063973485200047026759395674133656939375214278697967529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001543142084577045405197059935176184808369725942611694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0870050 |
1.0904674 |
11.5080892 |
3.4728143 |
| ENSG00000129932 |
83475 |
DOHH |
protein_coding |
Q9BU89 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydroxylation of the N(6)-(4-aminobutyl)-L-lysine intermediate produced by deoxyhypusine synthase/DHPS on a critical lysine of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A/eIF-5A. This is the second step of the post-translational modification of that lysine into an unusual amino acid residue named hypusine (PubMed:16533814, PubMed:16371467, PubMed:19706422). Hypusination is unique to mature eIF-5A factor and is essential for its function (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99LN9, ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16371467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16533814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19706422}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Hypusine biosynthesis;Iron;Metal-binding;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Repeat |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; eIF5A hypusination. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16371467, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16533814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19706422}. |
This gene encodes a metalloenzyme that catalyzes the last step in the conversion of lysine to the unique amino acid hypusine in eukaryotic initiation factor 5A. The encoded protein hydroxylates deoxyhypusine to form hypusine in the mature eukaryotic initiation factor 5A protein. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009]. |
hsa:83475; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; deoxyhypusine monooxygenase activity [GO:0019135]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; peptidyl-lysine modification to peptidyl-hypusine [GO:0008612] |
16533814_The structure and function of DOHH are reported. 17213197_analysis of the deoxyhypusine hydroxylase-eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF5A) interaction 19706422_Resonance Raman experiments show that its blue chromophore arises from a (mu-1,2-peroxo)diiron(III) center that forms in the reaction of the reduced enzyme with O2, so the peroxo form of hDOHH is unusually stable. 22908221_a novel role for miR-331-3p and miR-642-5p in the control of prostate cancer cell growth via the regulation of DOHH expression and eIF5A activity. 22927971_eIF-5A as well as the hypusine-forming enzymes deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS) and deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH) are highly overexpressed in glioblastoma patient sample 24843120_Here, we show that PCBP1 and PCBP2 also deliver iron to deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH), the dinuclear iron enzyme required for hypusine modification of the translation factor eukaryotic initiation factor 5A. 25865244_Data describes 3-D structure of hDOHH in two states, hDOHHperoxo (POX) and a complex of the diiron core with glycerol (GLC) providing an explanation for the extreme longevity of POX and illustrate its substrate specificity for deoxyhypusine-eIF-5A. 35007708_Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase as a novel pharmacological target for ischemic stroke via inducing a unique post-translational hypusination modification. 35858628_Bi-allelic variants in DOHH, catalyzing the last step of hypusine biosynthesis, are associated with a neurodevelopmental disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000078440 |
Dohh |
67.756335 |
2.5366333339 |
1.342915 |
0.214432868 |
39.605041 |
0.00000000031087974042981953362247597385690719984374652540282113477587699890136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001552820632400722915026783272653392725670684626493311952799558639526367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
97.9059605 |
13.4244375 |
38.8916862 |
4.1804951 |
| ENSG00000129946 |
25759 |
SHC2 |
protein_coding |
P98077 |
FUNCTION: Signaling adapter that couples activated growth factor receptors to signaling pathway in neurons. Involved in the signal transduction pathways of neurotrophin-activated Trk receptors in cortical neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
Predicted to enable receptor tyrosine kinase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25759; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
21658278_Data show that copy number loss of SHC2 strongly indicates a causal link to multiple system atrophy. 24170347_SHC2 gene deletions underlie few, if any, cases of well-characterized multiple system atrophy in the US population. 25613377_Sck was identified as a novel molecule indispensable for CD95's activation of the PI3K and MAPK pathways and induction of cell cycle progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. |
|
|
95.816006 |
0.3077836214 |
-1.700012 |
0.180509861 |
90.773933 |
0.00000000000000000000161061254892520481051901649895520698863886134390490424085000224774244514946985873393714427947998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000015141809695628041015952862992463225851779397138328196899519778595433194823272060602903366088867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.9422071 |
5.1819891 |
150.2289237 |
10.5441360 |
| ENSG00000129951 |
79948 |
PLPPR3 |
protein_coding |
Q6T4P5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The proteins in the lipid phosphate phosphatase (LPP) family, including PRG2, are integral membrane proteins that modulate bioactive lipid phosphates including phosphatidate, lysophosphatidate, and sphingosine-1-phosphate in the context of cell migration, neurite retraction, and mitogenesis (Brauer et al., 2003 [PubMed 12730698]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:79948; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; lipid phosphatase activity [GO:0042577]; phosphatidate phosphatase activity [GO:0008195]; phospholipid dephosphorylation [GO:0046839]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
Mouse_homologues 27744421_PRG3 emerges as a developmental RasGRF1-dependent conductor of filopodia formation and axonal growth enhancer. PRG3-induced neurites resist brain injury-associated outgrowth inhibitors and contribute to functional recovery after spinal cord lesions. |
ENSMUSG00000035835 |
Plppr3 |
29.786270 |
0.0607857339 |
-4.040123 |
0.509959018 |
75.019298 |
0.00000000000000000466135502670934431101557271667137358230216154139071912942959841075207805261015892028808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000037823859370109911961280454803626157720876450256224099444324338037404231727123260498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6568337 |
0.9302809 |
43.9628498 |
7.4461072 |
| ENSG00000130024 |
55274 |
PHF10 |
protein_coding |
Q8WUB8 |
FUNCTION: Involved in transcription activity regulation by chromatin remodeling. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and is required for the proliferation of neural progenitors. During neural development a switch from a stem/progenitor to a post-mitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to post-mitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene contains a predicted ORF that encodes a protein with two zinc finger domains. The function of the encoded protein is not known. Sequence analysis suggests that multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants are derived from this gene but the full-length nature of only two of them is known. These two splice variants encode different isoforms. A pseudogene for this gene is located on Xq28. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55274; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; npBAF complex [GO:0071564]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RSC-type complex [GO:0016586]; SWI/SNF complex [GO:0016514]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000781]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of G0 to G1 transition [GO:0070316]; regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000045]; regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition [GO:0030071]; regulation of nucleotide-excision repair [GO:2000819]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20068294_Data show that that PHF10 is required for cell growth. 20530714_PHF10 repressed caspase-3 expression and impaired the programmed cell death pathway in human gastric cancer at the transcriptional level. 24763304_The study demonstrates the existence of functionally different PBAF complexes in mammalian cell. It also provides an insight into the molecular structure and role of human PHF10/BAF45a and characterizes it as an essential PBAF subunit. 27193724_We studied the expression of S100A4 and the total PHF10 protein in some human cancer cell lines. We have found that, in the cell lines studied, the PHF10 expression is correlated with the S100A4 expression. 27239853_Phosphorylation of PHF10 isoforms occurs while they are incorporated as a subunit of the PBAF complex, and therefore phosphorylation of PHF10 isoforms may play an essential role in regulation of PBAF complex's function and mechanism of action. 28717195_Data show that PHF10 subunit of the PBAF signature module is the most unstable PBAF subunit, and demonstrate an important role of beta-TrCP ubiquitin ligase in regulation of PHF10 level and PBAF in general. Also, PHF10 isoforms contained two non-canonical beta-TrCP degrons and are degraded by beta-TrCP in a phospho-dependent manner. 31012017_PHF10 expression in cells of different lines is activated by the c-MYC oncogene. Since PHF10 stimulates cell proliferation, its c-MYC-dependent activation in cancer cells should lead to an increase in their proliferation rate. 31911482_The sequential phosphorylation of PHF10 subunit of the PBAF chromatin-remodeling complex determines different properties of the PHF10 isoforms. 34465901_PHF10 subunit of PBAF complex mediates transcriptional activation by MYC. 35033590_ZC3H13-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of PHF10 is impaired by fisetin which inhibits the DNA damage response in pancreatic cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000023883 |
Phf10 |
457.221615 |
0.3760238158 |
-1.411104 |
0.089411986 |
250.407963 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002115925831141958130722844140633961445002987120438240534072983514341381308028687286065665222308800168656844063668049254056386989351873843367545652283112644909124355763196945190429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000508649271460184043321042043753036506929678223096857626303781908651421659269417387732742083536485575271946935845004921422942356525681779130104720465510581561829894781112670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
256.5391533 |
15.9805744 |
687.4309673 |
28.5140365 |
| ENSG00000130054 |
27112 |
NALF2 |
protein_coding |
O75949 |
FUNCTION: Probable component of the NALCN channel complex, a channel that regulates the resting membrane potential and controls neuronal excitability. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:32494638}. |
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a product belonging to a family of proteins with unknown function. The presence of two transmembrane domains suggests that this protein is a multi-pass membrane protein. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:27112; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098703] |
|
ENSMUSG00000071719 |
Nalf2 |
12.096440 |
0.1909436926 |
-2.388781 |
0.506852290 |
25.014808 |
0.00000056891712702386668419819075806498354097584524424746632575988769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002067770695610015366770490646830538139511190820485353469848632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8516400 |
1.3389738 |
20.3005408 |
3.7834874 |
| ENSG00000130158 |
57572 |
DOCK6 |
protein_coding |
Q96HP0 |
FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for CDC42 and RAC1 small GTPases. Through its activation of CDC42 and RAC1, may regulate neurite outgrowth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17196961}. |
Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the dedicator of cytokinesis (DOCK) family of atypical guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors interact with small GTPases and are components of intracellular signaling networks. The encoded protein is a group C DOCK protein and plays a role in actin cytoskeletal reorganization by activating the Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1. Mutations in this gene are associated with Adams-Oliver syndrome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:57572; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
21820096_A homozygous truncating mutation in dedicator of cytokinesis 6 gene (DOCK6) which encodes an atypical guanidine exchange factor (GEF) known to activate two members of the Rho GTPase family: Cdc42 and Rac1, was identified. 25824905_DOCK6 mutations are responsible for a distinct autosomal-recessive variant of Adams-Oliver syndrome associated with brain and eye anomalies 25832008_this study demonstrates that miR-142-3p is a key regulator of the TGFbeta-mediated contractile phenotype of VSMCs that acts through inhibiting cell migration through targeting DOCK6. 27693507_acute knockdown of the Adams-Oliver syndrome (AOS) gene DOCK6, coding for a RAC1/CDC42 guanine nucleotide exchange factor, results in strikingly different phenotypes to those generated by genomic DOCK6 disruption. 28287327_DOCK6 localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in dependence of its DHR-1 domain. 29587866_Dock6 was over-expressed in GC tissues, and its positive expression was associated with GC metastasis and indicated poor prognosis of GC patients. 30898718_Results identified c.4106rC and c.3063 C>G mutations in the DOCK6 gene in a 5-year-old Chinese girl with the phenotype of Adams-Oliver syndrome (AOS). When caused by mutations in the DOCK6 gene, the AOS inheritance pattern is autosomal recessive. The two mutations carried by the patient were inherited from the father and mother respectively, generating compound heterozygosity in the patient. 31654484_Expanding the phenotype in Adams-Oliver syndrome correlating with the genotype. 34742001_Overexpression of DOCK6 in oral squamous cell cancer promotes cellular migration and invasion and is associated with poor prognosis. 35241069_Attenuated clinical and osteoclastic phenotypes of Paget's disease of bone linked to the p.Pro392Leu/SQSTM1 mutation by a rare variant in the DOCK6 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000032198 |
Dock6 |
125.674568 |
0.2338642753 |
-2.096257 |
0.178379300 |
138.364047 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000006066991766259262780303736189703026913620338974434777726546240521317778820435306019135529576047360933443997055292129516601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000826858711634226396270601890842914473541052560689890135072366060251195083573039776650426269100080389762297272682189941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.2782389 |
9.9319990 |
196.5128974 |
29.6090939 |
| ENSG00000130164 |
3949 |
LDLR |
protein_coding |
P01130 |
FUNCTION: Binds LDL, the major cholesterol-carrying lipoprotein of plasma, and transports it into cells by endocytosis. In order to be internalized, the receptor-ligand complexes must first cluster into clathrin-coated pits. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:3005267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6091915}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for hepatitis C virus in hepatocytes, but not through a direct interaction with viral proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10535997, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12615904}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Vesicular stomatitis virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23589850}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, may function as a receptor for extracellular Tat in neurons, mediating its internalization in uninfected cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11100124}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cholesterol metabolism;Coated pit;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Endocytosis;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;LDL;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
The low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene family consists of cell surface proteins involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands. The encoded protein is normally bound at the cell membrane, where it binds low density lipoprotein/cholesterol and is taken into the cell. Lysosomes release the cholesterol, which is made available for repression of microsomal enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase, the rate-limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. At the same time, a reciprocal stimulation of cholesterol ester synthesis takes place. Mutations in this gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. |
hsa:3949; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endolysosome membrane [GO:0036020]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034362]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; PCSK9-LDLR complex [GO:1990666]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; somatodendritic compartment [GO:0036477]; sorting endosome [GO:0097443]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; clathrin heavy chain binding [GO:0032050]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0071813]; low-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0030169]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0005041]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0030229]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; amyloid-beta clearance [GO:0097242]; amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process [GO:0150094]; artery morphogenesis [GO:0048844]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0071404]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol import [GO:0070508]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; cholesterol transport [GO:0030301]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; high-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034384]; intestinal cholesterol absorption [GO:0030299]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipoprotein catabolic process [GO:0042159]; long-term memory [GO:0007616]; low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034383]; negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905907]; negative regulation of astrocyte activation [GO:0061889]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0010989]; negative regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903979]; negative regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051248]; negative regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001920]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; phospholipid transport [GO:0015914]; plasma lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:0034381]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process [GO:1905167]; positive regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0010867]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:0090118]; regulation of cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0090181]; regulation of phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0010899]; regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051246]; response to caloric restriction [GO:0061771] |
11050659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11173876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11194026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317361_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11332639_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11453971_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11462246_mutations in German patients with familial hypercholesterolemia 11524740_Nineteen mutations were novel: two nonsense, five missense, six nucleotide(s) insertions and six nucleotide(s) deletions. 11668627_mutations in Canadian subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia, but not of French descent 11668640_novel mutations in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia in Spain 11702052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11848618_HDL cholesterol levels in patients with molecularly defined familial hypercholesterolemia. LDL receptor gene mutation (81T>G, 858C>A, 1285G>A, 1646G>A, and 1775G>A,) did not significantly influence HDL cholesterol levels. 11849659_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11851376_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11857755_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11860839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11860839_These results suggested that polymorphisms of LDL-Rgene might play an independent role of risk factor for hyperlipidemia. 11916007_Eight novel mutations and functional impairments are identified in familial hypercholesterolemia in the north of Japan. 11923121_Review. The proposed association between apoB secretion and FH may, however, be a function of the class of LDL receptor defect. 11923123_LDLR mutations in 350 cases of FH revealed 34 missense, 10 nonsense, 18 frameshift, 2 inframe, 10 splice, and 2 promoter mutations and 10 rearrangements. 11933210_Molecular basis of familial hypercholesterolemia in Brazil: Identification of seven novel LDLR gene mutations 11947895_Defective LDL receptors give rise to a phenotype of elevated LDL cholesterol. Disturbances in IDL metabolism provide the basis for understanding why FDB is less severe than FH. An apoB-LDL receptor interaction is important in the IDL to LDL conversion. 11997513_Critical role of diacylglycerol- and phospholipid-regulated protein kinase C epsilon in induction of low-density lipoprotein receptor transcription in response to depletion of cholesterol. 12002911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12031600_Influence of an asparagine to lysine mutation at amino acid 3516 of apolipoprotein B on low-density lipoprotein receptor binding. 12036962_apoE binds to the LDL receptor by interacting with more than one of the receptor ligand-binding repeats. 12042130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12048680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12052488_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12055704_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12072496_human rhinovirus serotype 1A (HRV1A)does not bind to the LDL receptor 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12113284_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12121347_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12149270_bile acids affect gene expression via a MAPK cascade-mediated stabilization of mRNA 12165956_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12189808_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12209363_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12221107_ARH functions as an adaptor protein that couples LDLR to the endocytic machinery 12235180_Egr1 is the oncostatin M-induced transcription factor that binds to the SIRE sequence of the LDLR promoter 12414836_Two novel missense mutations in the LDL-R gene causing FH were found in two unrelated families from central and southern Tunisia. 12417285_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12442279_Double mutant allele was founded in 10 out of 458 unrelated patients and not all carriers of the double mutant allele develop hypercholesterolemia. 12442279_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12459547_crystal structure of the extracellular portion of LDL-R at pH = 5.3 and at 3.7 A resolution; this structure should represent the conformation of LDL-R adopted in endosomes 12464675_restoration of function in cells from patients with autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia by retroviral expression of ARH1 12473254_Observational study of genetic testing and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 12473547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12485531_A novel mutation of LDLR gene was reported. This mutation may severely affect the function of LDLR. 12492446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12493918_productive LDL-R folding in a cell is not vectorial but is mostly posttranslational, and involves transient long-range non-native disulfide bonds that are isomerized into native short-range cysteine pairs 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12551936_fatty acids and rosiglitazone directly stimulate transcription of the LRP gene through activation of PPARgamma and increase functional LRP expression. 12562867_pp90RSK- and protein kinase C-dependent pathway regulates p42/44MAPK-induced LDL receptor transcription in HepG2 cells. 12705331_Deletion in low-density lipoprotein receptor gene is associated with severe familial hypercholesterolemia 12716819_Insulin plays an important role in the in vivo expression of LDL receptors on monocyte cell surface. 12730724_mutation spectrum of the LDLR gene among patients with familial hypercholesterolemia in Morocco 12810610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12820708_a new mutation is found, in which a serine residue was replaced by a cysteine at amino acid position 305 (S305C) 12873747_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12873747_The allelic distribution of the (TA)n polymorphism was significantly different between migraine without aura (MO) and both controls and migraine with aura (MA). 12898587_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12901493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12944120_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12944120_data presented raise the possibility that the -175g-->t polymorphism in the promoter region of the LDLR gene may have subtle effects that become clinically important within certain genetic and/or environmental contexts 12947119_study provides strong evidence that early growth response 1 regulates low density lipoprotein receptor transcription via a novel mechanism of protein-protein interaction with CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta 12969990_Doubling transfected human Ldlr expression caused severe atherosclerosis with marked accumulation of cholesterol-rich, apoE-poor remnants in mice with human apoE4, but not apoE3, suggesting that the receptor can trap apoE4. 12975003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14508510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14550622_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14557872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14568562_data provide an alternative mechanism of LDL receptor gene expression by non-classical estradiol- and tamoxifen-stimulated induction through an ER-alpha/Sp1 complex 14615367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14624402_The mean of carotid artery intima-media maximum thicknesses was significantly higher in the 2312-3 C-->A group than in patients with other LDLr mutations 14746139_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14756670_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14967814_patients with familial hypercholesterolemia carrying the null LDL receptor have elevation of plasma LDL-cholesterol attributable to both decreased clearance of LDL and increased hepatic production of apoB-100-containing lipoproteins 14993243_cell surface levels of the LDLR mutants were significantly increased upon inhibition of the proteasome degradation pathway 15015036_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15015036_Point mutations in low density lipoprotein receptor is associated with severe hypercholesterolemia 15068387_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15068387_a rapid diagnostic assay capable of simultaneously analyzing seven point mutations in the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene, which occur at high frequency in South African familial hypercholesterolemia patients. 15100232_low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) has a role in hypercholesterolemia mutations resulting in misfolding of the LDLR epidermal growth factor-AB pair 15133863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15135251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15144588_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15166224_findings indicate that low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor adaptor protein(ARH) is required not only for internalization of the LDL.LDL Receptor complex but also for efficient binding of LDL to the receptor 15172466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15241806_A total of 39 Novel missense mutations, nonsense mutations, and frameshift mutations were identified in a spanish familial hypercholesterolemia cohort. 15241806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15286151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15321837_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15321838_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15321839_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15359125_Results identify 16 different mutations of the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) gene in 25 unrelated Korean patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and show effects on LDL receptor metabolism. 15477777_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15526154_Low-density lipoprotein receptor structure and folding [review] 15546598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15556092_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15585340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15585340_low density lipoprotein receptor variants appear significantly associated with Alzheimer's disease. 15630635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15637307_LDL receptor contributes significantly to the clearance of LDL from plasma but plays a lesser role in the clearance of larger apoB-containing lipoproteins 15665085_Atherosclerosis was significantly reduced in T-bet protein-deficient Ldlr-/- mice. 15677715_Results indicate that overexpression of proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 induces the degradation of the low-density lipoprotein receptor by a nonproteasomal mechanism in a post-endoplasmic reticulum compartment. 15689450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15701167_Analysis of all 34 low density lipoprotein receptor gene mutations found in St.-Petersburg argues against strong founder effect in Russian familial hypercholesterolemia. 15701167_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15741231_LDL receptor intracellular fate depends on the cooperation between its ligand-binding and EGF domains 15754974_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15795426_Increased expression after weight loss may contribute to lower plasma ldl cholesterol and triglycerides in obese premenopausal women. 15797858_apolipoprotein B mutation may have a role in hypobetalipoproteinemia, despite decreased binding to the low density lipoprotein receptor 15823276_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15823276_Ten novel (including three frame shift small deletions or insertions) and seven known mutations were detected 15823280_75 different LDL receptor mutations in 645 children with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia; in these children, null alleles were clearly associated with more elevated LDL cholesterol levels compared to receptor-defective mutations 15823280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15823288_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15842735_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15863833_like the LDL receptor, LRP prefers lipid-bound forms of apoE, but in contrast to the LDL receptor, both LRP and the VLDL receptor recognize all apoE isoforms 15864114_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15888448_central nervous system levels of both human and murine apoE are directly regulated by LDLR 15890894_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15899484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15899484_The genotype of the mutant LDL receptor allele was independently associated with variations in LDL-PPD and could partly explain why negative-receptor FH heterozygotes may be at greater risk of cardiovascular disease than defective-receptor FH subjects. 15931608_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15936313_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16015283_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16020744_significance of tendon xanthomas (TX) in heterozygous subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia with LDL receptor mutation 16092059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16092059_we identified 5 missense mutations and 1 large deletion in LDLR gene, including 1 novel mutation in Han Chinese with FH in Taiwan 16129683_ARH is an endocytic sorting adaptor that actively participates in the internalization of the LDL-LDLR complex, possibly enhancing the efficiency of its packaging into the endocytic vesicles 16159606_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16179341_results demonstrate that the modular adaptor protein autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia (ARH) must bind the LDLR tail and either clathrin or AP-2 to promote receptor clustering and internalization of LDL 16183066_Combined mutations in LDLR and proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 are associated with a severe phenotype for premature coronary disease. 16205024_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16259478_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16286607_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16286607_In familial hypercholesterolemia children, the null allele genotype was associated with a greater carotid intima-media thickness, higher HDL cholestserol levels and attenuated response to cholesterol lowering agents. 16289238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16378661_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16389549_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16459141_No relationship was found between LDL-R polymorphism and coronary disease in the Chinese Han population. 16459141_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16465405_The mutation identified in the South American patient represents the first description of a variant in South American patients other than Brazilian Familial hypercholesterolemia patients. 16596945_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16608402_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16627557_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16650578_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16741934_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16741934_Study does not demonstrate an association between LDLR genotypes or haplotypes and Alzheimer's disease. 16750665_PAF enhances its own receptor expression and then increases lipid accumulation by dysregulating LDL receptor regulation and inducing scavenger receptor expression in mesangial cells 16770077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16792510_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16796766_Five genomic deletions in the LDLR gene were characterized by amplification of mutated alleles and sequencing to identify genomic breakpoints in Danish familial hypercholesterolemic patients. 16806138_It's identified three novel mutations (C25X, IVS3+5G>T, D558A) and two mutations previously described (D151N, A480E) in the low-density lipoprotein receptor(LDLR)gene. 16809787_Amino acid sequences in the LDL receptor binding region of apolipoprotein B-100 was frequently recognized by autoantibodies that have been generated in response to breakdown products of LDL oxidation. 16825289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16828076_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16837242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16907851_findings support a role for LDLR in the natural infection by hepatitis C virus in humans 16920108_Data show that liver X receptor alpha regulates the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene, which mediates the endocytic uptake of LDL cholesterol in the liver. 16927291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17044844_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17044844_data confirm the absence of a significant impact of the A370T polymorphism on LDL receptor function, at least as measured by the effect on plasma lipid levels and CHD risk. 17079229_analysis of the LDLR recognition properties of apoE 17090611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17090611_Results of the study indicate that LDL-C levels are a more important risk factor of event-free survival than the type of LDLR mutation. 17094996_LDLR mutations included 85 different point mutations (7 not previously described) and 13 different large rearrangements in familial hypercholesterolemia 17142622_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17156886_LDLR is involved at an early stage in infection of normal human hepatocytes by serum-derived HCV virions. 17196209_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17196209_three new mutations of LDL receptor: G266C, T368M, and D451Y were identified in a cohort screening program in Italy 17223614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17234631_apoE4, but not apoE3, in macrophages enhances atherosclerotic plaque development in an LDLr-dependent manner 17239995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17273844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17273844_Thus our data shows that 3'UTR sequences that cause higher reporter gene expression in vitro are associated in Caucasians with plasma lipid profiles indicative of higher cardiovascular risk. 17277381_replacing monounsaturated with polyunsaturated fat can benefit coronary heart disease by reducing the availability of oleoyl-CoA in the substrate pool of hepatic ACAT2 17328821_PCSK9-mediated degradation of the LDLR appears to take place intracellularly and occurs even when endocytosis through clathrin-coated pits is blocked by hypertonic medium. 17335829_analysis of rare polymorphism in the low density lipoprotein (LDL) gene that affects mRNA splicing 17347910_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17399720_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17399720_two new large deletions in familial hypercholesterolemia patients of French Canadian descent 17445538_two novel mutations were identified in exon 4 of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene in a Chinese family with clinically diagnosed autosomal genetic hypercholesterolemia 17452316_proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 binding to epidermal growth factor-like repeat A of low density lipoprotein receptor decreases receptor recycling and increases degradation 17473053_LDL-R may be one of the receptors implicated in Hepatitis C virus replication. 17517690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17517690_the low-density lipoprotein receptor exon 12 polymorphism decreases splicing efficiency and associates with increased cholesterol 17531953_Our data suggest that the LDLr plays a role in regulating cholesterol delivered to the baby from the placenta. 17539906_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17566095_Functional LDLR mutations occurred in 31 (60%) subjects, who received a diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). 17566095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17607901_mutations in the familial hypercholesterolaemia (Review) 17625505_A novel sequence change in repeat 3 of the promoter of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene has been identified in a female patient with familial hypercholesterolemia. 17706090_APOE epsilon 4 allele may be a latent risk factor in the development of primary glaucoma, but APOE epsilon 2 allele may play a protective role in primary open-angle glaucoma. 17709443_study provided novel evidence of an early decrease in LDLR mRNA in men and a later decrease in LRP mRNA in circulating mononuclear cells during the postprandial period 17766366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17784865_Reduced expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma with paraneoplastic hypercholesterolemia. 17855807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17889283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17898945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17898945_phlegm-dampness constitution is related with the P- and A+ allelic frequency of higher LDL-R genes at Pvu II and Ava II 17905649_scavenger receptor class B, type I and the low-density lipoprotein receptor have roles in High-density lipoprotein-associated 17beta-estradiol fatty acyl ester uptake 17935672_2 novel mutations were identified in the LDLR gene of a family with a member suffering from severe Familial hypercholesterolemia; 1 was W165X, G > A substitution and IVS5-1G > A, was also a G > A substitution at the acceptor splice site of intron 5. 17964958_results reveal a characteristic mutation pattern of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia in Taiwan, mainly in the LDLR and APOB genes 17988659_The importance of allele drop-out in LDLR genotyping. 18006500_In the setting of low density lipoprotein receptor deficiency, apoM-Tg mice with approximately 2-fold increased plasma apoM concentrations developed smaller atherosclerotic lesions than controls. 18028451_REVIEW: overview of mutations reported for the LDLR gene, the APOB gene, the PCSK9 gene, resulting in ADH. 18065781_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18065781_The rs688T allele is associated with decreased LDLR exon 12 splicing efficiency in aged males, but not females. 18097620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193043_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18206115_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18210030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18243212_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18243212_a low-density lipoprotein receptor mutation has a role in cardiovascular disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia 18247305_It is possible that the W462X mutation of LDLR gene is the main cause for familial hypercholesterolemia the family studied. 18261733_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18288382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18288382_These findings suggest that the 3'UTR LDLR polymorphisms in the Chinese population do not cause a predisposition to the development of coronary heart disease, nor do they affect the plasma lipid levels or the cholesterol-lowering effect of berberine. 18296645_Male and female carriers of the T allele of LDLR IVS9-30C>T had a 1.5-fold risk of bile duct cancer. 18296645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18307033_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18317771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18331356_stability upon EDTA treatment is confined to LDLR type A (LA) ligand-binding repeats 1-7 18343813_analysis of oxidative folding of ligand binding module 5 of the low density lipoprotein receptor 18354102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18355452_study identified a novel splice mutation c.1186+1 G>A in the LDL receptor gene in a Tunisian family; it causes the utilization of a new cryptic donor splice site 51 bp downstream from the normal site 18369154_The high affinity of apoE4 to the LDLR enhances VLDL sequestration on the hepatocyte surface but delays their internalization. 18376126_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18400033_Two variants, G186G and R385R, were found to be associated with altered splicing that cause familial hypercholesterolemia. 18513389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18622260_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18635818_Report effects of six APOA5 variants, identified in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia, on in vitro lipoprotein lipase activity and receptor binding. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18669884_PECAM-1 influences initiation and progression of atherosclerosis in LDL receptor deficient mice both positively and negatively, and that it does so in a site-specific manner. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18677035_The epidermal growth factor homology domain of the LDL receptor drives lipoprotein release through an allosteric mechanism involving H190, H562, and H586 18685438_Interaction of the A2 domain of F8 with LDLR follows the general mode, requires dissociation of factor VIII from von Willebrand factor, and is activation sensitive. 18701038_The LDL-R synthesis dysfunction of familial hypercholesteremia patients leads to arterial stenosis and calcification, which are the major phenotype of the clinical disorder. 18714375_A common variant at the LDLR gene locus affects LDL-cholesterol levels and, thereby, the risk for coronary artery disease. 18714375_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18718593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18718593_analysis of eight common LDLR mutations in the Japanese population 18757057_LDLR gene mutations enrich the spectrum of mutations causing familial hypercholesterolemia in the Tunisian population 18799458_identification of the minimal inhibitory sequence of AnxA2 should pave the way toward the development of PCSK9 inhibitory lead molecules for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia 18847225_Whereas the sedimentation coefficient for WT sLDLR increased when the pH was reduced from 7 to 5, no such change occurred in the case of the triple Lys mutant receptor or a His562Lys/His586Lys double mutant receptor. 18851860_No statistical differences were found for LDLR C1773T distributions 18851860_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18936517_JNK may play an important role in posttranscriptional control of LDL receptor expression, thus constituting a novel mechanism to enhance plasma LDL clearance by liver cells. 18940289_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19007590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020990_A heterozygous p.W483X mutation of LDLR gene was identified in family A which caused a premature stop codon, while a homozygous mutation p.A627T was found in family B. The predicted secondary structures of the mutant LDLR were altered. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19060911_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19062533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19062533_The spectrum of mutations in the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene in the Russian population 19073363_Report mutations in the LDL receptor gene in four Chinese homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia phenotype patients. 19081415_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19081568_PCSK9-mediated LDLR degradation is not entirely dependent on ARH function 19087220_polymorphisms in the 3' regulatory region of the LDLR gene are associated with CHD among African American individuals recruited from the general US population but not among white individuals in the same cohort. 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19141871_Data demonstrate that LDL receptor mRNA stability is controlled by a group of ARE binding proteins, including hnRNP D, hnRNP I, and KSRP. 19148283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148831_Nonsense mutations in the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) induces nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19196236_These data indicate that antibodies targeting PCSK9 can reverse the PCSK9-mediated modulation of cell-surface LDLRs. 19198609_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19208450_18 intronic mutations in the LDLR gene were selected for comprehensive studies of their effects on pre-mRNA splicing. 19222187_The data suggest the existence of distinct conformational states in free and receptor-bound PCSK9. 19224862_Results support the concept that pharmacological inhibition of the PCSK9-LDLR interaction extracellularly will increase hepatic LDLR expression and lower plasma low density lipoprotein levels. 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19318025_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19319977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19319977_impact of PCSK9 polymorphism on LDL-cholesterol levels of FH patients carrying a same LDLR mutation 19322023_Overexpression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha in HepG2 cells represses the gene expression of LDL receptor and does not affect the estrogen receptor alpha -induced LDL receptor expression. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336475_Observational study o |
ENSMUSG00000032193 |
Ldlr |
312.870035 |
4.7307068718 |
2.242056 |
0.122227707 |
341.296075 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000033312711318454421380380975313916728604257003741668375991390249162089840806830239280654403655196463084856325106347492181452018876009526605673040860336220135518247093251492453009807510791017576279315903775568585842847824096679687500000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010735712206558673778044168437787357933587302623985478360385291948853855854728033381918720959198931242835558762567302835103528509557556900945100699812574020107871189208297873944910857165607742658153256343211978673934936523437500000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
522.3204219 |
46.1224885 |
110.8498390 |
7.8384629 |
| ENSG00000130204 |
10452 |
TOMM40 |
protein_coding |
O96008 |
FUNCTION: Channel-forming protein essential for import of protein precursors into mitochondria (PubMed:15644312, PubMed:31206022). Plays a role in the assembly of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I) by forming a complex with BCAP31 and mediating the translocation of Complex I components from the cytosol to the mitochondria (PubMed:31206022). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15644312, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31206022}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Ion transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Porin;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane beta strand;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is localized in the outer membrane of the mitochondria. It is the channel-forming subunit of the translocase of the mitochondrial outer membrane (TOM) complex that is essential for import of protein precursors into mitochondria. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:10452; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0044233]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrial outer membrane translocase complex [GO:0005742]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; pore complex [GO:0046930]; porin activity [GO:0015288]; protein transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008320]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; protein import into mitochondrial matrix [GO:0030150]; protein insertion into mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0045040]; protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:0006626] |
16495475_examined by immunohistochemical and molecular methods the expression of Haymaker in gynecologic organs with and without tumor; significant differences in Haymaker expression between malignant and normal gynecologic tissues were not observed 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 1 18095154_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18430993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19668339_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20029386_In two independent clinical cohorts, longer lengths of rs10524523 of TOMM40 are associated with a higher risk for LOAD. 20029386_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20100581_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20370913_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21717124_Analysis revealed a dominant beta-sheet structure and a short alpha-helical part for both proteins together with a high thermal stability. Two secondary structure elements can be denatured independently 21720235_Poly-T variants of TOMM40 may modulate the negative effects of lorazepam on memory in healthy, cognitively intact, elderly individuals, in the absence of APOEepsilon4. 21784354_This study demonistrated taht among APOE epsilon3/epsilon3 late middle-aged adults suggest that a subgroup with VL TOMM40 poly-T lengths may be experiencing incipient LOAD-related cognitive and brain changes. 21803501_increase in CSF cortisol associated with the presence of the APOE e4 allele was only detected when a short TOMM40 poly-T variant, shown to associate with later age of onset of AD in e4 carriers, was not present. 21820212_There is no association of TOMM40 poly-T repeat length with age of onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD) nor with risk of psychosis in AD. 21825236_No association is found between polyT polymorphisms and TOMM40 gene expression 21835183_The authors propose that the identified weakly stable beta-strands 1, 2 and 9 of human Tom40A play an important role in quaternary protein-protein interactions within the mammalian TOM machinery. 21943158_variants in LPL, OASL and TOMM40/APOE-C1-C2-C4 genes are associated with multiple cardiovascular-related traits 21983493_Subjects with APOE epsilon4 have higher CSF NFL levels than non-epsilon4 carriers, only when they do not carry a short poly-T variant of TOMM40, which is associated with later age of onset of AD 22008263_This study identi fi ed TOMM40alleles, genotypes,as well asTOMM40-E4haplotypes that in fl uencelongevity. 22089642_The main novel finding of this investigation was that multiple APOE locus cis-elements influence both APOE and TOMM40 promoter activity according to haplotype and cell type. 22359560_the poly-T, rs10524523 allele frequencies in different ethnicities. 22472643_This study demonistrated that Downregulation of TOMM40 expression in the blood of Alzheimer disease. 22596268_Expression levels of TOMM40 protein in mitochondria do not reveal any differences related to the very long or short poly-T variant associated with the risk of late onset Alzheimer's disease. 22710912_Three SNPs of TOMM40 and APOC1 representating linkage disequilibrium at the 19q13-q13.2 chromosomal region suggest the presence of a different genetic background underlying primary progressive aphasia and the behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia. 22863908_The results of this study suggested important APOE-independent associations between the TOMM40 '523' polymorphism and specific cognitive domains of memory and executive control that are preferentially affected in early-stage Alzheimer's disease. 22898894_In chronic hepatitis C, genetic heterogeneity in the APOE/TOMM40 genomic region is significantly associated with variation in serum ApoE and ApoB levels, and also with fibrosis suggesting a pleiotropic attribute of this genomic region. 23102119_Both TOMM40 and APOE significantly influence age-related memory performance, but they appear to do so independently of each other 23183136_TOMM40 intron 6 poly-T length may explain some of the variation in age at onset in PSEN2 familial mouseclick Alzheimer's disease 23234877_TOMM40 gene expression remains significantly lower in Alzheimer's disease patients compared to controls. 23288655_3 SNPs (rs157580, rs2075650, and rs11556505)were studied in late-onset Alzheimer disease after adjustment for risk factors. Haplotypes derived from SNPs in rs2075650, rs11556505, and rs1160985 were associated with either risk or protective effects. 23435269_we report data from two independent Caucasian samples (242 U.S. women and men; 466 Danish men) showing that chronic family stress moderates the association between TOMM40 SNP rs157580 and triglyceride levels. 23522842_TOMM40 and APOE common genetic variants are not Parkinson's disease risk factors. 23546992_This study demonstrated that the TOMM40 gene does not have an APOE-independent role in the risk of developing LOAD and FTLD. 23626796_the interaction of alpha-Syn with the mitochondrial protein import machinery, in particular Tom40, might be an upstream event in alpha-Syn-induced neurotoxicity. 23792692_This study associating theTOMM40rs10524523 genotype with clinical characteristics ofpatients carrying thePSEN1M146L mutation belong-ing to the same kindred. 24103330_The results of this study suggested that Polymorphism in the TOMM40 gene modifies the risk of developing sporadic inclusion body myositis and the age of onset of symptoms. 24146538_These data provide no evidence to support an association of rs2075650 in TOMM40 with neovascular age-related macular degeneration or polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. 24149440_Blockade of mitochondrial protein import triggers the recruitment of PARK2, by PINK1, to the TOMM machinery. 24260406_in a large community-dwelling sample of older adults, we found no effects of APOE epsilon or TOMM40 523 genotypes on hippocampal volumes. 24439168_Elevated levels of TOMM40 and APOE transcripts found in the brains of late-onset Alzheimer's disease-affected individuals compared with unaffected control brains 24508314_It is an Alzheimer-disease susceptibility gene. 24549102_This study development of depression characterized by reduced extraversion, impaired executive function, and decreased positive emotional recall, and reduced top-down cortical control during sad emotion processing. 24838536_The present study shows for the first time that TOMM40 rs157581 polymorphism may modulate regional spontaneous brain activity and related to the progression of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. 24924924_PVRL2, TOMM40 and APOE might be associated with human longevity. 25044051_The results of this study suggested that previous findings of an association of the TOMM40 short allele with better cognitive performance, independently from the APOE variant status, are pertinent to elderly with diabetes. 25140902_Influenza A virus protein PB1-F2 translocates into mitochondria via Tom40 channels and impairs innate immunity. 25201778_The findings of this study consistently lower TOMM40 expression on longitudinal 2-year sampling support its potential role as a diagnostic blood AD biomarker. 25247594_Two genetic risk factors for late onset Alzheimer's disease are in the apolipoprotein-e and translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 40 (TOMM40) gene poly-T repeat loci. 25304313_study did not confirm the impact of rs2075650 on advanced AMD risk, indicating that rs2075650 is unlikely a superior marker for APOE/TOMM40 susceptible region with advanced AMD in Han Chinese population. 25644384_This study show genome-wide significant SNP-based associations within three genomic regions 6q16.1 (MIR2113), 14q12 (AKAP6/NPAS3 region) and 19q13.32 (TOMM40/APOE region) with cognition. 25670332_TOMM40 VL polyT repeat, although not influencing disease susceptibility, has a disease-modifying effect on sIBM, which can be enhanced by the APOE genotype epsilon3/epsilon3. 25703783_Epilepsy, impaired fine motor function and gastrostomy tube feeding were less common in cerebral palsy children with single nucleotide polymorphisms in the APOE or TOMM40 genes 25711031_It was discovered that polymorphic variants of TOMM40 rs741780, rs1160985, and rs8106922 are associated with serum triglyceride concentrations. 25862420_Its variants are related to impairment in allocentric spatial navigation and reduced cortical thickness of specific brain regions among aMCI individuals with (LOAD neutral) APOE epsilon3/epsilon3 genotype. 26310205_No significant effects of APOE epsilon or TOMM40 523 genotypes on white matter hyperintensities or cerebral microbleed burden were found amongst 624 participants 26572157_rs2075650 polymorphism in TOMM40 gene may increase the risk of Alzheimer disease. 26576771_rs2075650 at intron region TOMM40 is associated with the A beta-42 levels in CSF. 26657933_These findings indicated that variants in TOMM40/APOE/APOC1 region might be associated with human longevity. Further studies are needed to identify the causal genetic variants influencing human longevity. 26742953_investigate the influence of the TOMM40 intron 6 poly-T variant (rs10524523) on TOMM40 gene expression and cognitive abilities and decline in a cohort of 1613 community-dwelling elderly volunteers 26756745_Our results do not support the notion that TOMM40 poly-T repeat variants have independent effects on Parkinson's disease with dementia and Dementia with Lewy bodies pathology 27023435_Survival analyses suggest that AD patients with TOMM40 allele rs2075650-G have an average age of disease onset of 6 years earlier compared with carriers of the A allele. The age of disease onset is earlier if APOE4/4 is present in the Colombian population studied. 27328316_meta-analysis to investigate the association between rs2075650 polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease (AD) in Asian, Caucasian, and mixed populations; analysis shows TOMM40 rs2075650 polymorphism is associated with AD susceptibility in Asian, Caucasian, and mixed populations 27707806_Among white women, three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (rs2075650 [TOMM40], rs4420638 [APOC1], and rs429358 [APOE]) were significantly associated with survival to 90 years after correction for multiple testing (p |
ENSMUSG00000002984 |
Tomm40 |
348.917126 |
2.1081624321 |
1.075986 |
0.093636153 |
132.873304 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000096369714495584675863729520724894413294478763135247715040642131323266957191721955762464535411027100053615868091583251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000012632477672778239507325839059974300622529481234512279305995119157130006926612920958863384157666587270796298980712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
483.0020999 |
25.3049816 |
230.7298088 |
9.5140774 |
| ENSG00000130222 |
10912 |
GADD45G |
protein_coding |
O95257 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the regulation of growth and apoptosis. Mediates activation of stress-responsive MTK1/MEKK4 MAPKKK. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is a member of a group of genes whose transcript levels are increased following stressful growth arrest conditions and treatment with DNA-damaging agents. The protein encoded by this gene responds to environmental stresses by mediating activation of the p38/JNK pathway via MTK1/MEKK4 kinase. The GADD45G is highly expressed in placenta. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10912; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] |
11889197_a powerful growth suppressor controlling pituitary cell proliferation and the first identified gene whose expression is lost in the majority of human pituitary tumors. 12716909_results suggest that CRIF1 is a novel nuclear protein that interacts with Gadd45 and may play a role in negative regulation of cell cycle progression and cell growth 14672412_Data show that GADD45 gamma mRNA expression is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, and that GADD45 gamma causes cell cycle arrest at G2/M transition when transfected into Hep-G2 cells. 15062559_GADD45g induction by androgens requires new protein synthesis; overexpression of GADD45g inhibited cell growth and caused morphological changes in prostate cell lines, arguing that GADD45g is involved in differentiation induced by androgens 15353598_Inhibition of GADD45alpha and gamma in cancer cells by small interfering RNA abrogates apoptosis induction by the inhibitor of NF-kappaB 16166418_Results show that GADD45G can act as a functional new-age tumor suppressor but being frequently inactivated epigenetically in multiple tumors. 17178890_Establish MDA-7/IL-24 and GADD45alpha and GADD45gamma as critical mediators of apoptosis and growth arrest in response to NSAIDs in cancer cells. 18997345_Human Gadd45gamma and its selenomethionine derivative were expressed in an Escherichia coli expression system and purified; they were then crystallized using the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method. 19048389_Flow cytometric analysis revealed significant G2/M arrest in cells transfected with either Gadd45alpha or Gadd45gamma. Importantly, we found that expression of either Gadd45alpha or Gadd45gamma activated P38 and JNK kinase pathways to induce G2/M arrest. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19293565_urinary GADD45gamma expression is associated with progression of renal disease 20111973_Epigenetic regulation of GADD45G is associated with carcinogenesis in stomach, colorectal and pancreateic cancers. 20739400_The induction of GADD45gamma gene expression by 1,25-(OH)2D3 may mark therapeutic response in prostate cancer. 21850407_clinically non-functioning adenomas had a significant decrease (P |
ENSMUSG00000021453 |
Gadd45g |
14.008060 |
5.4521792722 |
2.446833 |
0.497572366 |
26.158471 |
0.00000031451428875682342778063679301914223884750754223205149173736572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001174356413369773186091272847153543779086248832754790782928466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.5173304 |
6.7461875 |
4.3653919 |
1.1142544 |
| ENSG00000130244 |
147965 |
FAM98C |
protein_coding |
Q17RN3 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be part of tRNA-splicing ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:147965; |
tRNA-splicing ligase complex [GO:0072669] |
|
ENSMUSG00000030590 |
Fam98c |
67.812588 |
0.4551049708 |
-1.135729 |
0.194367109 |
34.663592 |
0.00000000391892756618932528916381103191793333628822892933385446667671203613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000017737924218630617464298172792844243694787564891157671809196472167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
43.3605725 |
5.8541832 |
95.8440106 |
8.6510049 |
| ENSG00000130270 |
148229 |
ATP8B3 |
protein_coding |
O60423 |
FUNCTION: P4-ATPase flippase which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of aminophospholipids from the outer to the inner leaflet of various membranes and ensures the maintenance of asymmetric distribution of phospholipids. Phospholipid translocation seems also to be implicated in vesicle formation and in uptake of lipid signaling molecules. May be responsible for the maintenance of asymmetric distribution of phosphatidylserine (PS) in spermatozoa membranes. Involved in acrosome reactions and binding of spermatozoa to zona pellucida. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6UQ17}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of aminophospholipid-transporting ATPases. The aminophospholipid translocases transport phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from one side of a bilayer to the other. This gene encodes member 3 of phospholipid-transporting ATPase 8B; other members of this protein family are located on chromosomes 1, 15 and 18. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:148229; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332] |
35997042_Association of ATP8B3 gene polymorphisms with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease in asthmatics. |
ENSMUSG00000003341 |
Atp8b3 |
61.032025 |
0.2660271623 |
-1.910355 |
0.257913657 |
55.581603 |
0.00000000000008965880405417268828792885077134030831318145526864782368647865951061248779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000569433712495520229789739895619522276485127698641974802740151062607765197753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
24.5683474 |
4.2422056 |
93.0641728 |
10.3287458 |
| ENSG00000130340 |
51429 |
SNX9 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5X1 |
FUNCTION: Involved in endocytosis and intracellular vesicle trafficking, both during interphase and at the end of mitosis. Required for efficient progress through mitosis and cytokinesis. Required for normal formation of the cleavage furrow at the end of mitosis. Plays a role in endocytosis via clathrin-coated pits, but also clathrin-independent, actin-dependent fluid-phase endocytosis. Plays a role in macropinocytosis. Promotes internalization of TNFR. Promotes degradation of EGFR after EGF signaling. Stimulates the GTPase activity of DNM1. Promotes DNM1 oligomerization. Promotes activation of the Arp2/3 complex by WASL, and thereby plays a role in the reorganization of the F-actin cytoskeleton. Binds to membranes enriched in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and promotes membrane tubulation. Has lower affinity for membranes enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11799118, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12952949, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15703209, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17609109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17948057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18388313, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20427313, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21048941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22718350}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endocytosis;Golgi apparatus;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Mitosis;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sorting nexin family. Members of this family contain a phosphoinositide binding domain, and are involved in intracellular trafficking. The encoded protein does not contain a coiled coil region, like some family members, but does contain a SRC homology domain near its N-terminus. The encoded protein is reported to have a variety of interaction partners, including of adaptor protein 2 , dynamin, tyrosine kinase non-receptor 2, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome-like, and ARP3 actin-related protein 3. The encoded protein is implicated in several stages of intracellular trafficking, including endocytosis, macropinocytosis, and F-actin nucleation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:51429; |
clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cuticular plate [GO:0032437]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; 1-phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0005545]; Arp2/3 complex binding [GO:0071933]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cleavage furrow formation [GO:0036089]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; lipid tube assembly [GO:0060988]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; plasma membrane tubulation [GO:0097320]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898] |
11799118_The Cdc42 target ACK2 interacts with sorting nexin 9 (SH3PX1) to regulate epidermal growth factor receptor degradation 11879186_SNX9 may function to assist AP-2 in its role at the plasma membrane. 12952949_SNX9 may be recruited together with dynamin-2 and become co-assembled with AP-2 and clathrin at the plasma membrane 15299020_SNX9-dependent recruitment of Dyn2 to the membrane is regulated by an interaction between SNX9 and aldolase 15703209_SNX9 is required for efficient clathrin-mediated endocytosis and suggest that it functions to regulate dynamin activity 16137687_Data show that in the presence of SNX9, synaptojanin-1 is able to colocalize with distinct ACK1 containing vesicles. 16316319_Dimerization, which is mediated by the BAR domain, is essential for the intracellular function of SH3PX1. 16585770_identified sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) as a host cell enteropathogenic E. coli EspF binding partner protein, which binds EspF via its amino-terminal SH3 region 17242350_the WASp/SNX9/p85/CD28 complex enables a unique interface of endocytic, actin polymerizing, and signal transduction pathways required for CD28-mediated T cell costimulation 17609109_SNX9 is directly involved in coupling actin dynamics to achieve membrane remodeling during multiple modes of endocytosis 17948057_SNX9 PX and BAR domains work in concert in targeting and tubulation of phosphoinositide-containing membranes. 18065239_crystallization and x-ray diffraction of SNX9 18388313_SNX9 functions in the coordination of membrane remodeling and fission via interactions with actin-regulating proteins, endocytic proteins and PtdIns(4,5)P2-metabolizing enzymes 18682798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18940612_Tip-to-tip interactions between the BAR domains in a trigonal crystal form of Snx9(PX-BAR) reminiscent of functionally important interactions described for F-BAR domains. 20088948_Findings suggest that EspF promotes EPEC invasion of intestinal epithelial cells by harnessing the membrane-deforming activity of SNX9. 20129922_SNX9 binding to aldolase is structurally precluded by the binding of substrate to the active site. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20491914_The interaction with SNX9 is mediated by the proline-rich domain (PRD) of Itch, a domain distinct from the conventional WW recognition domain, and the SH3 domain of SNX9. 20964629_study identifies critical amino acids within the BAR domains of SNX9 and SNX33 as determinants for the specificity of BAR domain-mediated interactions and suggests that SNX9 and SNX33 have distinct molecular functions. 22718350_The sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) subfamily members - SNX9, SNX18 and SNX33 - are required for progression and completion of mitosis. 23861900_SNX9 and CHC function in the same molecular pathway for chromosome alignment and segregation, which is dependent on their direct association. 25256216_this study shows that SNX9 uses a unique mechanism to induce the tubulation of the plasma membrane which mediates proper membrane deformation during clathrin-mediated endocytosis. 26608909_reduced levels of SNX9 were observed in blood samples from colorectal cancer patients, emphasizing the feasibility of its use as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker sensing the host's immune status and inflammatory stage. 27278018_The diversified changes associated with SNX9 expression in cancer highlight its importance as a central regulator of cancer cell behavior. 28266622_In conclusion, the authors identified SNX9 as a facilitator of podocin endocytosis in severe podocyte injury and demonstrated the expression of SNX9 in the podocytes of both nephropathy model mice and human patients with irreversible glomerular disease. 28627515_SNX9 assembles into ring-like structures around the endocytic vesicles 29622675_SNX9 knockdown revealed a nonredundant effect on overall ADAM9 protein levels, resulting in increased ADAM9 levels at the cell surface 30784076_SNX9 depletion significantly delayed the recycling of integrin beta1 31430451_NECAP recruits drivers of late stages of clathrin-coated pit (CCP) formation, including SNX9, via a site distinct from where NECAP binds AP2. 35050850_SNX9-induced membrane tubulation regulates CD28 cluster stability and signalling. |
ENSMUSG00000002365 |
Snx9 |
1355.568504 |
3.0729744414 |
1.619636 |
0.049741217 |
1075.740586 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006188469120275499548296836339881086840037173454953558321438661271724992030551727813600313499116 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006972656810325676882400052201209646365033456236624967877894109409581071820835807747163261753029 |
Yes |
Yes |
2066.2059202 |
59.2309103 |
677.4913972 |
15.8565543 |
| ENSG00000130368 |
4142 |
MAS1 |
protein_coding |
P04201 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for angiotensin 1-7 (By similarity). Acts specifically as a functional antagonist of AGTR1 (angiotensin-2 type 1 receptor), although it up-regulates AGTR1 receptor levels. Positive regulation of AGTR1 levels occurs through activation of the G-proteins GNA11 and GNAQ, and stimulation of the protein kinase C signaling cascade. The antagonist effect on AGTR1 function is probably due to AGTR1 being physically altered by MAS1. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15809376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16611642}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a class I seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor. The encoded protein is a receptor for angiotensin-(1-7) and preferentially couples to the Gq protein, activating the phospholipase C signaling pathway. The encoded protein may play a role in multiple processes including hypotension, smooth muscle relaxation and cardioprotection by mediating the effects of angiotensin-(1-7). [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:4142; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; angiotensin receptor activity [GO:0001595]; angiotensin type II receptor activity [GO:0004945]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0060732]; protein kinase C signaling [GO:0070528]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to gonadotropin [GO:0034698]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
16611642_the ability of MAS to up-regulate AT(1) receptor levels reflects the constitutive capacity of MAS to activate Galpha(q)/Galpha(11) and hence stimulate PKC-dependent phosphorylation of the AT(1) receptor 18636314_Mas, MrgD, and MRG mediated Ang IV-stimulated AA release that was highest for Mas. While Ang III activated Mas and MrgX2, Ang II stimulated AA release via Mas and MRG. 19164480_The vasoactive peptide angiotensin-(1-7), its receptor Mas and the angiotensin-converting enzyme type 2 are expressed in the human endometrium. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19461648_the Mas oncogene acts as a receptor for Angiotensin (1-7)--REVIEW 20361351_The immunolocalization of Ang-(1-7) and its receptor Mas in testes of fertile and infertile men suggests that this system may be altered when spermatogenesis is severely impaired. 20592051_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20674894_Angiotensin-(1-7), its receptor Mas, and ACE2 are expressed in the human ovary 21316680_Report expression (pro)renin receptors and angiotensin converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis in human aortic valve stenosis. 22003054_Activation of Mas during myocardial infarction contributes to ischemia-reperfusion injury and suggest that inhibition of Mas-G(q) signaling may provide a new therapeutic strategy directed at cardioprotection. 22048948_MasR was significantly upregulated in colon adenocarcinoma compared with non-neoplastic colon mucosa, which showed little or no expression of it. ACE gene expression and enzymatic activity were also increased in the tumors. 23459756_Mas appears to be a critical component required for NO-mediated vasodilatation induced by renin angiotensin system-dependent and RAS-independent agonists and therefore arises as a key pharmacological target to modulate endothelial function 23488800_Data suggest that angiotensin converting enzyme 2/angiotensin II-(1-7)/MAS1 axis regulates leukocyte recruitment/activation, cell proliferation, and inflammation/fibrosis; main topic here is kidney/inflammatory renal disease. [REVIEW] 23592774_Control of adipogenesis by the autocrine interplays between angiotensin 1-7/Mas receptor and angiotensin II/AT1 receptor signaling pathways. 24128372_A proximal promoter construct for the MAS gene was repressed by the SOX [SRY (sex-determining region on the Y chromosome) box] proteins SRY, SOX2, SOX3 and SOX14, of which SRY is known to interact with the KRAB domain. 24168260_Up-regulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis protected against pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway. 25068582_Data show that MAS receptor exhibited constitutive activity that was inhibited by the non-peptide inverse agonist. 26080617_MAS1 might act as an inhibitory regulator of breast cancer. 26225830_Ang-(1-7) downregulated AT1R mRNA, upregulated mRNA levels of Ang II type 2 receptor (AT2R) and Mas receptor (MasR) and p38-MAPK phosphorylation and suppressed H22 cell-endothelial cell communication 26883384_These results indicated that angiotensin-(1-7)/ACE2/Mas axis may reduce liver lipid accumulation partly by regulating lipid-metabolizing genes through ATP/P2 receptor/CaM signaling pathway. 26995300_Here, we review the role and effects of ACE2, ACE2 activators, Ang-(1-7) and synthetic Mas receptor agonists in the control of inflammation and fibrosis in cardiovascular and renal diseases and as counter-regulators of the ACE-Ang II-AT1 axis. 27063099_Downregulation of ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis stimulates breast cancer metastasis through the activation of store-operated calcium entry and PAK1/NF-kappaB/Snail1 pathways. 28599664_High levels of MAS is associated with angiogenesis in bladder cancer. 28747140_These findings suggest that mitochondrial assembly receptor signaling may be a promising novel target for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 29052864_These findings suggest a critical role for MasR in cardiomyocyte survival. 29351514_ANG-(1-7) acts on the receptor MAS to influence a range of mechanisms in the heart, kidney, brain, and other tissues. [review] 29982252_High MAS1 expression in the endometrium might promote the initiation of endometriosis via migration of proliferative tissue. 30055537_We have hypothesized the mechanism that reverses the downregulation of the ACE2-angiotensin 1-7/Mas receptor axis path and the upregulation of angiotensin receptor type 1-mediated signaling. Thus, we posit that ACE2, Ang-(1-7), and the Mas receptor could be novel therapeutic targets for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia . 30581499_MAS1 expression in the left atrium in mitral regurgitation patients significantly differed from those in aortic valve disease patients and normal controls. 31642813_The production of ANG 1-7 was significantly lower in breast cancer cells, whereas the expression of MAS receptor was higher than that in the control breast tissue cells. This finding suggests that substances with MAS receptor agonist activity could be useful in the treatment of breast cancer. 31843339_Ang-(1-7) stimulates beige markers and thermogenesis via the Mas receptor. 32599080_Angiotensin- and angiotensin-(1-7) imbalance affects comorbidity of depression and coronary heart disease. 32764118_Oestrogen-mediated upregulation of the Mas receptor contributes to sex differences in acute lung injury and lung vascular barrier regulation. 32777324_Impact of angiotensin II type 1 and G-protein-coupled Mas receptor expression on the pulmonary performance of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 32875393_Localization of angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas receptor in the rat ovary throughout the estrous cycle. 33511992_ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas1 axis and the vascular system: vasoprotection to COVID-19-associated vascular disease. 34124808_Human placenta mesenchymal stem cell protection in ischemic stroke is angiotensin converting enzyme-2 and masR receptor-dependent. 35328506_Neuroinflammation and COVID-19 Ischemic Stroke Recovery-Evolving Evidence for the Mediating Roles of the ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas Receptor Axis and NLRP3 Inflammasome. 35363333_The function of the ACE2/Ang(1-7)/Mas receptor axis of the renin-angiotensin system in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. 36148474_Sex Difference in MasR Expression and Functions in the Renal System. |
ENSMUSG00000068037 |
Mas1 |
38.286850 |
12.1053337570 |
3.597571 |
0.370899910 |
118.511611 |
0.00000000000000000000000000133967626730649957405970360481887585500679467071478431381792822328931206500579609297574279480613768100738525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000015882427072645730547012942059627177170010259047717641749089084988140539549117402629008211079053580760955810546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.9949064 |
15.9320450 |
5.9878721 |
1.2565405 |
| ENSG00000130513 |
9518 |
GDF15 |
protein_coding |
Q99988 |
FUNCTION: Regulates food intake, energy expenditure and body weight in response to metabolic and toxin-induced stresses (PubMed:28953886, PubMed:28846097, PubMed:28846098, PubMed:28846099, PubMed:23468844, PubMed:29046435). Binds to its receptor, GFRAL, and activates GFRAL-expressing neurons localized in the area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarius of the brainstem (PubMed:28953886, PubMed:28846097, PubMed:28846098, PubMed:28846099). It then triggers the activation of neurons localized within the parabrachial nucleus and central amygdala, which constitutes part of the 'emergency circuit' that shapes feeding responses to stressful conditions (PubMed:28953886). On hepatocytes, inhibits growth hormone signaling (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0J7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23468844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28846097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28846098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28846099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28953886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29046435}. |
3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. The protein is expressed in a broad range of cell types, acts as a pleiotropic cytokine and is involved in the stress response program of cells after cellular injury. Increased protein levels are associated with disease states such as tissue hypoxia, inflammation, acute injury and oxidative stress. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:9518; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035860]; negative regulation of growth hormone receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060400]; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040015]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; reduction of food intake in response to dietary excess [GO:0002023]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
9326641_MIC-1, a divergent TGF-b superfamily cytokine, was cloned from a U937 subtracted cDNA library enriched for activation-associated sequences. It is induced in macrophages by many activation-associated stimuli but not LPS or IFN-g 10811612_Unlike other TGF-b cytokines, MIC-1 is able to be expressed correctly folded without its propeptide. A 28 aa propeptide epitope contains a quality control signal which can signal misfolding of MIC-1, leading to proteasomal degradation. 11134143_MIC-1 is present in large amounts in placenta and amniotic fluid. Very high levels of MIC-1 are present in the sera of pregnant women and rise substantially with progress of gestation 11141057_At least five immunogenic regions on the MIC-1 surface can be detected by MAbs. One MAb is directed against the amino terminus of the protein and can distinguish between the two allelic forms of MIC-1 11259636_NAG-1 is an antitumorigenic and proapoptotic protein, and its regulation by COX inhibitors may provide new clues for explaining their proapoptotic and antitumorigenic activities. 11278594_Propeptide deletion mutants of MIC-1 enabled identification of a region between residues 56 and 78, which is important for the interaction between the propeptide and the mature peptide during folding 11445565_the level of expression of the NAG-1 gene will depend on the availability of Sp proteins and on co-factors such as chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor 1 11895857_Resveratrol enhances the expression of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1) by increasing the expression of p53 11994274_report that autocrine hGH production by mammary carcinoma cells specifically results in the transcriptional repression of the p53-regulated placental transforming growth factor-beta gene (Placental growth factor-beta; TGF-beta) 12011055_placental transforming growth factor-beta as an important downstream mediator of DNA damage signaling and a transcriptional target of p53 (PTGF-beta) 12082608_Anoxia induces macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) in glioblastoma cells independently of p53 and HIF-1. MIC-1 is an important downstream mediator of p53 function and intercessor of cellular stress signaling and exerting antitumorigenic activities. 12082608_In the experimental model MIC-1 may exert anti-tumorigenic properties via a paracrine mechanism mediated by host cells in vivo. MIC-1 is an important downstream mediator of p53 function 12090982_MIC-1 serum levels were higher at baseline in women who later had cardiovascular events. Levels > 90th percentile were associated with a 2.7x greater risk and independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and at least additive to that of CRP 12139236_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12139236_There are at least two alleles of MIC-1 that are due to a G-->C point substitution at position 6 of the mature protein, which alters a his to an asp (MIC-1 H and MIC-1 D). The frequency of the 3 common MIC-1 genotypes was: HH 54%; HD 39%; DD 7% 12514175_GDF-15 prevents apoptosis in cerebellar granule neurons by activating Akt and inhibiting endogenously active ERK 12624183_Microarray analysis identifies MIC-1 as being upregulated in cancer of breast, prostate, and colon. Tissues from these patients show increased MIC-1 by IHC and their serum shows elevated levels 12855642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12855642_There is a strong association between MIC-1 serum levels and neoplastic progression (polyps to cancer) within the large bowel and significant differences in time to relapse and overall survival between subjects with different MIC-1 levels and genotypes 12894347_Decreased NAG-1 expression in higher grade cancer is consistent with its known antitumorigenic, proapoptotic activities. 12900512_amniotic fluid MIC-1 is derived from the fetal membranes and decidua, but that MIC-1 is unlikely to be involved in the pathophysiology of preterm birth or premature rupture of membranes 12941831_Treating DU145 prostate cancer cells with MIC-1 causes loss of adhesion and consequently induces cell detachment and apoptosis. This is mediated at least in part by reduction in metallothionein 1E, RhoE and catenin delta 1. 14575402_NAG-1 may be involved in differentiation and apoptotic processes of nasal epithelial cells. It is still unclear whether NAG-1 is an inducer or a byproduct of differentiation or apoptosis 14662774_expression of NAG-1 by troglitazone requires the early growth response gene EGR-1 14726168_Serum MIC-1 levels are markedly depressed in women, some weeks before miscarriage and at a time when the fetus is still viable. This suggests possible predictive and causative roles, as well as therapeutic potential 15073115_MIC-1 has a role in progression of primary pancreatic cancers, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms, and pancreatic cancer 15073115_The combination of serum levels of MIC-1 and CA19-9 significantly improved diagnostic accuracy of pancreatic cancer (sensitivity, 70%; specificity, 85%) 15316060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15316060_This study shows an association between a nonsynonymous change (H6D) in the MIC-1 gene and prostate cancer. This finding supports the hypothesis that genetic variation in the inflammatory process contributes to prostate cancer susceptibility 15342369_Findings suggest that early prostate carcinogenesis is associated with expression of mature GDF15 protein. 15670751_The results suggest that I3C represses cell proliferation through up-regulation of NAG-1 and that ATF3 may play a pivotal role in DIM-induced NAG-1 expression in human colorectal cancer cells. 15677629_expression levels may serve as a surrogate marker for the AKT activation in tumors 15757899_NAG-1 expression is up-regulated by TPA in LNCaP cells through a PKC-dependent pathway involving the activation of NF-kappa B 16154591_GDF-15 induction is an immediate early response to liver injury that can occur through TNF and p53 independent pathways 16286461_t10,c12-CLA stimulates ATF3/NAG-1 expression and subsequently induces apoptosis in an isomer specific manner 16388506_An additional serum marker for the detection of prostatic cancer. 16397141_GDF-15 expression increased within 12 hours of symptom onset and remained upregulated for at least 2 weeks after myocardial infarct. 16484622_highly expressed in the placenta and the prostate, but not normally in many other organs, including the heart 16699947_Study suggests that proapoptotic activity of NAG-1 is cell type specific and not related to COX-2 expression. 16741990_Induction of message and protein in prostate cancer cells requires 1alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. 16775185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16775185_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 is associated with prostate cancer 17050687_Stimulation of macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1-dependent S phase arrest in normal gut epithelial cells might help to revitalize the clinical use of N-phosphonacetyl-l-aspartate, which has been limited by gut toxicity 17328047_Serum levels of MIC-1 and MIC-1 genotype may be clinically useful in the management of rheumatoid arthritis as well as in selection of patients for hemopoietic stem cell transplantation, since they predict disease course and response to therapy. 17548705_study does not support the role of common genetic variation at MIC1 and IL1RN in prostate cancer susceptibility 17637746_TAp63-dependent induction of growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) plays a critical role in the regulation of keratinocyte differentiation. 17721544_GDF15 overexpression arising from an expanded erythroid compartment contributes to iron overload in thalassemia syndromes by inhibiting hepcidin expression. 17908975_growth differentiation factor 15 has a role in molecular alterations in prostate carcinomas resulting from exposure to chemotherapy 17909264_The induction of GDF15 and STC2 is likely specific to MK-4, vitamin K2 analog. 17982462_Transgenic mice overexpressing MIC-1 show hypophagia and weight loss; sera from subjects with advanced prostate cancer show a direct correlation between MIC-1 abundance and cancer-associated weight loss, defining MIC-1 as a central regulator of appetite. 18264720_The NAG-1 was expressed strongly in intestinal metaplasia and adenoma, and inversely correlated to tumor stages 18359786_There is a possible role for macrophage-inhibiting cytokine-1 (MIC-1) in coronary artery cardiovascular events. 18398830_Microarray studies show that our in vitro model system reflects many cellular and molecular alterations characteristic of cervical cancer, and identified SIX1 and GDF15 as 2 novel potential biomarkers of cervical cancer progression. 18550273_GDF-15 does not decrease proliferation of glioblastoma cell lines, while its effects on invasiveness are not consistent. 18657084_GDF15 is normal in most superdonors, indicating that GDF15 overexpression arising from the expanded erythroid pool necessary to replace donated red cells is not the biochemical mechanism for the decreased serum hepcidin 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18754039_MIC-1 may function to promote development of more aggressive melanoma tumors 18801729_trichostatin A-induced NAG-1 expression involves multiple mechanisms at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. 18824595_CDA I patients express very high levels of serum GDF15, and GDF15 contributes to the inappropriate suppression of hepcidin with subsequent secondary hemochromatosis. 19047680_GDF15 can be induced by pathophysiologic changes in iron availability, raising important questions about the mechanism of regulation and its role in iron homeostasis 19074584_Data conclude that MIC-1 is expressed in adipose tissue and secreted from adipocytes and is therefore a new adipokine. MIC-1 may have a paracrine role in the modulation of adipose tissue function and body fat mass. 19100681_Increased PDF mRNA stability in response to hypoxia and cobalt chloride, but not doxorubicin, indicates that p53-dependent induction of PDF expression occurs via diverse mechanisms. 19125423_This is the first report of the induction of the proapoptotic protein NAG-1 in pancreatic cancer cells. 19133249_MIC-1 was obviously overexpressed in gastric cancers and MIC-1 secretion into blood may be useful for the prediction of gastric cancer progression. 19152406_Osteoclast formation at the tumor-bone interface are significantly higher MIC-1 prostatic tumors, whereas bone formation is higher in control mice. 19168526_GDF-15 can provide long-term prognostic value in post-acute myocardial infarction patients 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19302795_human dermis is a site for macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) production and that visible light activates a dermal transcription cascade 19341722_Data show that MIC-1 is a new diagnostic marker in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea. 19357976_GDF15 may be PPARalpha-independent master-regulator of fenofibrate action in human endothelial cells. 19375854_a possible inverse relationship exists between the expression of NAG-1 and COX-2 in tumor formation of colon tissue. 19401523_the NAG-1 protein inhibits urethane-induced tumor formation 19470878_Study is the first to show that GDF-15 is dysregulated, both in preeclampsia and in diabetic pregnancies. 19505289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19505289_results show that a promoter haplotype containing the -3148G variant increases GDF15 transcription activity and is associated with favourable left ventricular remodelling in human essential hypertension. 19505919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19515791_In contrast to patients with cancer cachexia, increased MIC-1 levels in obese patients and diabetic patients do not induce weight loss. 19521960_Elevated levels of MIC-1/GDF15 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients are associated with glioblastoma. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19695766_GDF-15 inhibits differentiation into osteoclasts--a novel factor involved in control of osteoclast differentiation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19946339_a progressive increase in secretory MIC-1 production correlated with the increase in the metastatic potential of PC-3 and LNPCa prostate cancer metastatic variants. 20024638_The prognostic information provided by GDF-15 in cardiovascular disease may inform patient management, e.g., by identifying patients with non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. 20031597_This study identifies GDF-15 as a strong and independent predictor of coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality across the broad spectrum of patients with stable and unstable CHD. 20067113_Celecoxib can enhance apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells by induction of NAG-1 gene transcription in human. 20104227_There is no independent link between plasma MIC-1 levels and depleted nutritional status or survival in oesophago-gastric cancer. 20130018_The integrated stress response-associated signals modulates intestinal tumor cell growth by NSAID-activated gene 1. 20160200_GDF-15 is independently related to adverse events in non-ST-segment-elevation acute coronary syndrome both in the acute setting and for at least 6 months after clinical stabilization. 20167682_Baseline MIC-1 concentrations were increased, not decreased, in individuals before type 2 diabetes manifestation, but not independently associated with incident type 2 diabetes in multivariable analyses. 20193126_Inhibition of c-Src activity resulted in the complete abolition of MIC-1-induced phosphorylation of the EGFR, ErbB2, and ErbB3, as well as invasiveness and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in SK-BR-3 cells. 20215826_NAG-1 may have a role in malignancy in prostate cancer 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20357380_Higher levels of GDF-15 are a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in patients with diabetic nephropathy;higher levels of GDF-15 are associated with faster deterioration of kidney function 20385121_NAG-1 promoter activity in human colorectal cancers is controlled by Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4). 20431030_Data show that MIC-1 is secreted from melanoma cells together with VEGF to promote vascular development mediated by (V600E)B-Raf signaling. 20534737_GDF-15 at endogenous levels contributes to proliferation and immune escape of malignant gliomas in an immunocompetent host. 20576287_Median plasma GDF-15 concentration was elevated in ovarian cancer as compared to healthy controls and women with benign ovarian tumors or borderline ovarian tumors. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20854422_Serum MIC-1/GDF15 is a novel predictor of all-cause mortality 20855664_GDF-15 provides independent prognostic information in heart failure and disease severity. 20860541_findings indicate that GDF-15 concentration was elevated with the progressing stages of heart failure (HF) and might have potential screening implications for stage B HF 20884666_GDF-15 is present in the active form in semen. In vitro cultivation of sperm cells with GDF-15 did not affect their viability or rates of apoptosis; however, it did inhibit proliferation of PBMCs and induce expression of FOXP3 in CD4+CD25+ cells. 20937742_NAG-1 may be important in maintaining homeostasis in the normal endometrium and alterations in NAG-1 expression may be associated with the establishment of endometriosis. 20966402_Finding supports GDF-15 as a prognostic marker in acute coronary syndrome. 20975101_GDF15, HSPA2, TMEFF2, and VIM were identified as epigenetic biomarkers for Bladder cancer. 21097678_Nag-1 induction following NSAID treatment is mediated by the p38 MAPK pathway 21245963_AREG and GDF15 produced in response to UVB exposure can affect the growth and protein synthesis of lens epithelial cells 21312063_These data do not support an association of rs4808793 with coronary artery disease or its severity in a Chinese population. 21336029_Growth differentiation factor-15 emerges as a potential prognostic biomarker in ovarian carcinoma. 21437897_Data indicate that methylation of specific promoter sequences causes transcriptional silencing of the NAG-1 locus in glioma and may ultimately contribute to tumor progression. 21475976_GDF15 is among the erythroid factors down-regulating hepcidin and contributing to iron overload in conditions of dyserythropoiesis. 21487066_Data suggest that plasma markers: CEACAM, ICAM-1, osteopontin, MIA, TIMP-1 and S100B particularly when assessed in combination, can be used to monitor patients for disease recurrenc. 21503121_GDF-15 protein expression increases in acute coronary syndrome, and the level of GDF-15 rapidly increases and remains elevated in the early period of acute myocardial infarction. 21504622_Data indicate that isochaihulactone induces G2/M cell cycle arrest via downregulation of cyclin B1 and cdc2, and induces cellular death by upregulation of NAG-1 via JNK activation in LNCaP cells. 21535154_GDF15 levels were significantly elevated when comparing anaemia of unknown cause with controls and were markedly elevated in patients with renal disease. 21548946_GDF-15 expression is increased in pulmonary arterial hypertension lungs and appears predominantly located in vascular endothelial cells, where if affects proliferation and apoptosis. 21586550_GDF-15 mediates the functions of p53 by autocrine/paracrine action. 21616994_we report for the first time plasma GDF-15 as a biomarker for endometrial cancer phenotype. 21645023_Hyperinsulinemia resulted in a significant increase in serum MIC-1 in different states of adiposity. 21773947_GDF-15 promoted angiogenesis in hypoxic HUVECs possibly through inhibiting p53 signal, which subsequently enhanced and stabolized HIF-1alpha expression, and up-regulated the related downstream angiogenic signaling. 21803025_These results support GDF15-mediated activation of TGF beta receptor-Src-HER2 signaling crosstalk as a novel mechanism of trastuzumab resistance. 21809352_Our data suggest that the H6D variant of NAG-1 inhibits prostate tumorigenesis by suppressing IGF-1 and cyclin D1 expression but likely additional mechanisms are operative. 21865063_Levels of growth differentiation factor-15 are high and correlate with clinical severity in transfusion-independent patients with beta thalassemia intermedia. 21881845_Our data suggest that GDF-15 can be used as a serum marker for the diagnosis of metastases in UM patients 22023041_In the elderly, GDF-15 reflects endothelial activation and vascular inflammation and thus, multiple pathways involved in the development and progression of atherosclerosis. 22064648_MIC-1 is a novel factor (secreted by decidual cells in early pregnancy) that could promote the increase of a tolerogenic subtype of DC in decidua 22144502_Serum MIC-1/GDF15 levels vary with the development of adnenomatous colonic polyps. 22160844_GDF-15 may play a role in the development of cutaneous and pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. 22180562_This highlights a novel role of GDF15 in regulating airway mucosal immunity (e.g. mucin) in cigarette smoke-exposed lungs. 22231869_As an acute stroke biomarker, GDF-15 independently predicts unfavorable functional 90-day stroke outcome. 22301101_The findings suggested that tumor microenvironment-derived GDF15 is a key survival and chemoprotective factor for multiple myeloma cells, which is pathophysiologically linked to both initial parameters of the disease as well as patient survival. 22341306_Growth differentiation factor 15 has an anti-apoptotic effect in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines, with significant elevated serum GDF 15 levels having a prognostic value in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 22365732_Our findings suggest that hepcidin expression is controlled by body iron stores where soluble HJV and EPO may act as suppressors of hepcidin. 22384099_analysis of expression of EGFR, pAkt, NF-kappaB and MIC-1 in prostate cancer stem cells and their progenies 22484283_The results suggest that MIC-1 secreted from cancer cells stimulates endothelial cell proliferation by enhancing AP-1- and E2F-dependent expression of G(1) cyclins via PI3K/Akt, JNK, and ERK signaling pathways 22505696_The GDF15/MIC-1 gene polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and suggests a common etiology for that disease and atherothrombotic manifestations. 22511768_Two in-and-out modulation strategies for endoplasmic reticulum stress-linked gene expression of pro-apoptotic macrophage-inhibitory cytokine 1. 22723347_DEC1 controls the response of p53-dependent cell survival vs. cell death to a stress signal through MIC-1 22815297_Data identified GDF-15 as a clinically valuable marker for predicting transition in albuminuria stage in T2DM beyond conventional risk markers. These findings were confirmed in nondiabetic HT subjects. 22872134_the expression of GDF15 is upregulated by IL-6 in prostate carcinoma cells 22975449_growth-differentiation factor-15 is a new player in histamine-induced melanogenesis. 23071585_Cross-sectional data on a hospital-based sample indicate that plasma GDF-15 levels are associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in hypertensive patients. 23146921_Data show that neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, MIC-1, and CA19-9 were significantly elevated in the pancreatic juice of chronic pancreatitis (CP) and pancreatic cancer (PC) as compared with nonpancreatic nonhealthy controls. 23154866_High levels of GDF15 were seen in related hereditary hemochromatosis cases. Hepcidin mRNA was upregulated in HepG2 cells treated with these patients' serum. 23262134_GDF15 impairs aortic contractile and relaxing function through an endothelium-dependent mechanism involving altered caveolar endothelial NO synthase signaling. 23280549_A novel signaling pathway for GDF-15 through interaction with the matricellular signaling molecule CCN2. 23328263_Growth and differentiation factor-15 is a potential novel factor associated with muscle atrophy, which may become a therapeutic target in patients with ICU acquired paresis and other forms of acute muscle wasting. 23335088_Our study suggests that GDF15 induction helps suppress further activation of macrophages in stressful physiologic states as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis...resulting in enhanced ferroportin-mediated iron efflux. 23468844_MIC-1/GDF15 is involved in the physiological regulation of appetite and energy storage. 23503457_Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli enhances MIC-1 gene expression in the human intestinal cancer cells 23525862_Suggest that GDF-15 might be a useful biomarker for discriminating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy from left ventricular hypertrophy. 23758647_MIC-1/GDF15 levels are associated with cognitive performance and cognitive decline. 23799024_High glucose can promote GDF15 expression and secretion in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, which in turn attenuates high glucose-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. 23824055_Serum MIC-1 levels in PUL were not able to categorically diagnose EP, however, MIC-1 could distinguish women with an EP that required medical intervention and those women whose PULs spontaneously resolved 23836903_knockdown of MIC-1 can decrease RNPC1-induced cell growth suppression. 23850849_Growth-differentiation factor-15 level may be used as a biomarker of anthracycline-induced cardiovascular disease severity in the CCS. 23996089_Results indicate a possible relationship between serum GDF15 levels and circulating tumor cells may exist. 24069146_MIC-1 and PAPP-A levels are significantly depressed in women presenting to EPAU with ultrasound evidence of fetal viability, but later miscarry. 24136234_Calu-15, a novel isoform of Calu with phosphorylation-dependent nuclear localization, has a critical role in promoting filopodia formation and cell migration by upregulating the GDF-15 transcription. 24216602_Serum GDF 15 levels were measured in 35 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients and 27 healthy controls. GDF 15 level did not have an impact on survival. 24236027_GDF-15 may be one of the critical molecules that inhibit dendritic cell maturation and function and are involved in tumor immune escape. 24312445_in elderly men, GDF-15 improves prognostication of both cardiovascular, cancer mortality and morbidity beyond established risk factors and biomarkers of cardiac, renal dysfunction and inflammation. 24345755_GDF15 is produced by bone marrow stromal cells after direct contact with plasma cells and enhances the tumor-initiating potential and self-renewal of multiple myeloma cells in a protein kinase B- and SRY (sex-determining region Y)-box-dependent manner. 24383865_The expression of MIC1 was upregulated in 37.5% (3/8) ESCC cell lines. 24384540_The tumor progression results in increased GDF-15 secretion, which may down-regulate hepcidin expression, resulting in iron overload in cancer patients; this phenomenon has also been found in some patients with sideropenic anemia. 24401984_GDF15 may be a promising novel biomarker for the preoperative identification of malignant pelvic disease. 24430093_GDF-9 and GDF-15 levels may influence bone parameters in polycystic ovary syndrome 24447735_Circulating levels of GDF-15 were associated with paroxysmal non-valvular atrial fibrillation. 24462860_results suggest that GDF-15 has an overall protective effect on the progression of atherosclerosis, likely through inducing ABCA1 expression via the PI3K/PKCzeta/SP1 signaling pathway and enhancing cholesterol efflux 24504814_Growth differentiation factor 15, a marker of lung involvement in systemic sclerosis, is involved in fibrosis development but is not indispensable for fibrosis development. 24521768_High GDF-15 level is a strong predictor of death and heart failure in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. 24554716_NE induces myocardial hypertrophy and up-regulates GDF-15, and this up-regulation of GDF-15 negatively regulates NE-induced myocardial hypertrophy by inhibiting EGF receptor transactivation following NE stimulation. 24565956_Results support an association between higher levels of circulating MIC-1 (GDF15) and colorectal cancer (CRC). 24597762_GDF15 mediates KV2.1 through the TGFbetaRII-activated Akt/mTOR pathway in cerebellar granule cells. 24669014_GDF15 promotes tumorigenesis and progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma 24681016_Takotsubo cardiomyopathy patients showed markedly high, but transient elevation of GDF-15 levels. 24759784_Study demonstrates that NAG-1 can induce apoptosis in a restricted set of glioblastoma cell lines via the mitochondrial pathway. 24780757_GDF15 was found upregulated in situ and in primary cultures of cancer-associated fibroblasts from prostate cancer. 24839357_Change in growth differentiation factor 15, but not C-reactive protein, independently predicts major cardiac events in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome 24867648_8 GDF-15 polymorphisms (3 coding, 5 regulatory) were found in Indian beta-thalassemia patients. The G allele in rs4808793 was associated with increased GDF15 levels in controls and patients. A novel TCG insertion was found at codon 167 in 4 patients. 25016703_Studied serum levels of GDF-15, IMA and PAPP-A in 348 patients with CAD and 205 controls. PAPP-A had the lowest sensitivity and negative predictive value compared with other markers. GDF-15 seemed to be associated with severity of CAD. 25052873_HAMP mRNA and GDF15 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of multiple myeloma patients is up-regulated. 25065856_GDF-15 levels are related to hemolysis and iron overload and may provide utility for identifying patients at increased risk of thrombotic events. 25093616_The binding of MMP-26 to GDF15 was responsible for the processing and maturation of pro-GDF15, and the process was dependent on enzymatic activity of MMP-26. In human placental trophoblast cells, MMP-26 could facilitate the pro-apoptotic effect of GDF15. 25117302_The relationship between serum GDF-15, mortality, and carotid artery thickening suggests that GDF-15 may be a novel marker of atherosclerosis, inflammation, and malnutrition in HD patients. 25124572_High MIC-1 expression is associated with weight loss and poor response to chemotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 25171167_Data indicate that plasma growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) levels increased gradually during and after surgery. 25179833_Growth Differentiation Factor 15 expression and regulation during erythroid differentiation in non-transfusion dependent thalassemia. 25180886_Counterbalance between MIC-1 and ATF3 is critical for deciding the fate of enterocytes under the food chemical stress. 25294786_GDF-15 is a risk factor for major bleeding, mortality, and stroke in atrial fibrillation. 25327758_The inverse relationship between GDF-15 and inflammation demonstrates a novel expression pattern for GDF-15 in the human prostate and suppression of NFkappaB activity may shed light on a potential mechanism for this inverse correlation. 25347430_Data suggest that growth differentiation factor 15 protein (GDF15) may have beneficial effects on erythropoiesis in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). 25380934_GDF15, by affecting iron status, might be involved in the pathogenesis of anemia in patients with cardiovascular pathology. 25464937_Results demonstrate that the circulating levels of ADH, MIC-1 and CA19-9 in blood of PC were significantly higher than in healthy controls. 25490861_Data identi fi ed GDF15 as potential resistance-related factor acting by maintaining a low proliferative and undifferentiated tumor phenotype through upregulation of p27 Kip1 during carboplatin treatment. 25516419_GDF-15 may increase sensitivity to transforming growth factor-beta signalling by suppressing the expression of muscle microRNAs, thereby promoting muscle atrophy in intensive care unit-acquired weakness. 25590623_The increases in plasma GDF-15 levels in testicular cancer patients during chemotherapy and its association with vWF and hsCRP suggest that GDF-15 is a potentially useful biomarker related to endothelial damage. 25730371_Studied contribution to tumor progression of GDF15 in tumor-associated macrophages and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 25767870_MIC-1 and PDGF-A expression is elevated in both prostate tumors and structurally intact adjacent tissues. 25820390_GDF-15 is a novel blood biomarker of acute exacerbation chronic obstructive pulmonary disease that is more sensitive than C-reactive protein. 25823874_tumour markers DcR3 and growth/differentiation factor (GDF)15 from 100 mul human serum, were quantified. 25853582_The analysis based on correlation of MIC-1 and PSA concentrations in serum with the patient PCa status improved the specificity of Prostate cancer diagnosis 25867265_Data show that plasma and tissue levels of MIC-1/GDF15 are significantly elevated in patients with Barrett's oesophagus, low-grade dysplasia and oesophageal adenocarcinoma. 25867369_Data show that plasma growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) levels and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) are associated with chronic heart failure (CHF) in coronary atherosclerosis patients and can be used as biomarkers. 25867953_MIC-1/GDF15 serum levels were inversely associated with gray matter volumes both cross-sectionally and longitudinally 25880686_Study describes for the first time the vital role of GDF15 both in tumorigenesis and in radioresistance of OSCC cells. With its anti-apoptotic effects, GDF15 possibly promotes tumor progression and might protect carcinoma cells against irradiation effects. 25893289_our study indicates that NAG-1 is localized in the nucleus and provides new evidence that NAG-1 controls transcriptional regulation in the Smad pathway 26004619_Role of GDF15 in pulmonary oxygen toxicity 26018318_Twist promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasion and cisplatin chemoresistance through inducing GDF15 expression via a p38 MAPKdependent mechanism. 26026393_High plasma levels of |
ENSMUSG00000038508 |
Gdf15 |
448.220195 |
3.1867954701 |
1.672106 |
0.090978220 |
340.418539 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000051727362917131742804753033706356261804193354276861137665998598985153097960565068832555178850399320612742106712608996002860043352311807892607854591675411202483526898775418520756959539974237372028653680899878963828086853027343750000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016633897094920796264487708989245321390688116824777769772227135163792713160351807551013614893885444200500366680310715043120249249855924884559003127879513128950037728527981550451598569736327837276235186436679214239120483398437500000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
685.7715001 |
37.1465445 |
216.8875894 |
9.4640496 |
| ENSG00000130518 |
80726 |
IQCN |
protein_coding |
Q9H0B3 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80726; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000110622 |
Iqcn |
33.479575 |
0.2480326734 |
-2.011398 |
0.403020515 |
24.510865 |
0.00000073891983676980227233624344204687695025768334744498133659362792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002651703571777846334600256539282270296098431572318077087402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8452296 |
3.1972003 |
48.4784131 |
8.0301415 |
| ENSG00000130589 |
85441 |
HELZ2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYK8 |
FUNCTION: Helicase that acts as a transcriptional coactivator for a number of nuclear receptors including PPARA, PPARG, THRA, THRB and RXRA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16239304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23525231}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;DNA-binding;Helicase;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear transcriptional co-activator for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha. The encoded protein contains a zinc finger and is a helicase that appears to be part of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha interacting complex. This gene is a member of the DNA2/NAM7 helicase gene family. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:85441; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay [GO:0000184]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944] |
22446964_Genetic polymorphisms in PRIC285 gene is associated with autoimmune disease. 23525231_Thrap3 could play indispensable roles in terminal differentiation of adipocytes by enhancing PPARgamma-mediated gene activation cooperatively with Helz2. 34761308_HELZ2 promotes K63-linked polyubiquitination of c-Myc to induce retinoblastoma tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000027580 |
Helz2 |
308.604649 |
2.3048356696 |
1.204664 |
0.118324065 |
103.583291 |
0.00000000000000000000000249674058109905463210510176636763434702585111490009977192541467901944207685716037303791381418704986572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000026191820168459168344768673783781223617092450608383181062584096855314075291687458957312628626823425292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
478.1066289 |
35.4909508 |
208.8136608 |
12.0662822 |
| ENSG00000130590 |
140700 |
SAMD10 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYL1 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to be active in cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:140700; |
cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
|
ENSMUSG00000038605 |
Samd10 |
12.060016 |
0.4694139968 |
-1.091067 |
0.465332211 |
5.430034 |
0.01979329455503262696902666561982186976820230484008789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.035528277712791142550763368035404710099101066589355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8595496 |
2.3885612 |
16.7104240 |
3.3659377 |
| ENSG00000130592 |
4046 |
LSP1 |
protein_coding |
P33241 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in mediating neutrophil activation and chemotaxis. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes an intracellular F-actin binding protein. The protein is expressed in lymphocytes, neutrophils, macrophages, and endothelium and may regulate neutrophil motility, adhesion to fibrinogen matrix proteins, and transendothelial migration. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4046; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to interleukin-7 [GO:0098761]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12972289_LSP1 interacts with F-actin and the cytoskeleton through residues downstream of amino acid residue 230. The cytoskeleton binding site of mouse LSP1 maps to the 300-330 interval. 15090600_Leukocyte-specific protein 1 is a cytoskeletal targeting protein for the ERK/MAP kinase pathway 17296787_LSP1 protein facilitates virus transport into the proteasome after its interaction with DC-SIGN through its interaction with cytoskeletal proteins. 17481585_MK2-regulated LSP1 phosphorylation is involved in stabilization of F-actin polarization during neutrophil chemotaxis. 17827388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17997823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18437204_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18973230_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19232126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19656774_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19656774_The LSP1 and 2q35 SNPs appear to interact multiplicatively on breast cancer risk for BRCA2 mutation carriers. 19718030_DC-SIGN was constitutively associated with a signalosome complex consisting of the scaffold proteins LSP1, KSR1 and CNK and the kinase Raf-1 19789366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19843670_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19856316_Low-risk variants of LSP1 is associated with familial breast cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20054709_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20095854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20145138_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20417875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453838_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605201_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21127985_The LSP1 rs3817198T>C polymorphism is a low-penetrant risk factor for developing breast cancer but may not be in Africans. 22454379_Single nucleotide polymorphism in LSP1 is associated with breast cancer. 23119100_Data indicate that slit2N alters the localization and binding of Robo1 to WASp and LSP1 in HIV-1-gp120-treated immature dendritic cells (iDCs). 24681604_The breast cancer SNP LSP1 rs3817198 was associated with an increased risk of lung cancer (odds ratio: 1.10) This association was strongest for women with adenocarcinoma (P = 1.2x10(-4)). 26191300_LSP1 rs569550 and rs592373 polymorphisms are both risk factors for breast cancer. 26554018_the importance of LSP1 Copy number variations and LSP1 insufficiency in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, is reported. 27165221_Underexpression of LSP1 is associated with Breast Cancer Recurrence. 27590509_LSP1 rs3817198 T > C polymorphism is associated with increased risk of breast cancer, especially in Caucasian and Asian populations [meta-analysis] 29080679_Differential gene expression by SFRP2(+), FMO1(+), and COL11A1(+) fibroblasts suggests roles in matrix deposition, inflammatory cell retention, and connective tissue cell differentiation, respectively. 29410425_These results show that LSP1 is critical regulator of actomyosin contractility in primary macrophages. 32279313_Lymphocyte-specific protein 1 (LSP1) regulates bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (BST-2)-mediated intracellular trafficking of HIV-1 in dendritic cells. 32738313_Predictive and prognostic value of LSP1 rs3817198 in sporadic breast cancer in northeastern population of Iran. 32770294_MiR-920 and LSP1 co-regulate the growth and migration of glioblastoma cells by modulation of JAK2/STAT5 pathway. 34691030_Identification of Diagnostic Signatures and Immune Cell Infiltration Characteristics in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Integrating Bioinformatic Analysis and Machine-Learning Strategies. 36397430_The correlation of leukocyte-specific protein 1 (LSP1) rs3817198(T>C) polymorphism with breast cancer: A meta-analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000018819 |
Lsp1 |
325.889043 |
3.1901925003 |
1.673643 |
0.693638080 |
5.463997 |
0.01941219704927990563625428421801188960671424865722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034920661602360923703169959253500564955174922943115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
424.7551987 |
180.2645693 |
131.6541592 |
40.2184802 |
| ENSG00000130653 |
375775 |
PNPLA7 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZV29 |
FUNCTION: Lysophospholipase which preferentially deacylates unsaturated lysophosphatidylcholine (C18:1), generating glycerophosphocholine. Also can deacylate, to a lesser extent, lysophosphatidylethanolamine (C18:1), lysophosphatidyl-L-serine (C18:1) and lysophosphatidic acid (C16:0). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2AJ88}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Human patatin-like phospholipases, such as PNPLA7, have been implicated in regulation of adipocyte differentiation and have been induced by metabolic stimuli (Wilson et al., 2006 [PubMed 16799181]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2008]. |
hsa:375775; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; phosphatidyl phospholipase B activity [GO:0102545]; phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0034638] |
25867316_We explored Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in the PNPLA7 gene on chromosome 9 and investigated their correlation with the susceptibility to menstrual disorder. 28887301_PNPLA7 acts as an endoplasmic reticulum -anchored lysophosphatidylcholine hydrolase that is composed of specific functional domains mediating catalytic activity, subcellular positioning, and interactions with cellular organelles. 32103509_The Patatin-Like Phospholipase Domain Containing Protein 7 Facilitates VLDL Secretion by Modulating ApoE Stability. |
ENSMUSG00000036833 |
Pnpla7 |
97.073067 |
0.0866867169 |
-3.528045 |
0.451312851 |
52.873741 |
0.00000000000035569328985352332049567680370502800155140324389613226685469271615147590637207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002185692322330559601690368841101882644260834265281800981028936803340911865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7391148 |
6.8674125 |
173.0534480 |
51.6304475 |
| ENSG00000130684 |
26152 |
ZNF337 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3M9 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a zinc finger domain containing protein. The function of this protein has yet to be determined. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:26152; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000055150 |
Zfp78 |
113.379482 |
0.4148789971 |
-1.269237 |
0.282915890 |
19.724317 |
0.00000894557970987851836560788426622181646052922587841749191284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000028182872255668500239590701372804915081360377371311187744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.5968600 |
11.6589894 |
164.4304322 |
19.7578230 |
| ENSG00000130707 |
445 |
ASS1 |
protein_coding |
P00966 |
FUNCTION: One of the enzymes of the urea cycle, the metabolic pathway transforming neurotoxic amonia produced by protein catabolism into inocuous urea in the liver of ureotelic animals. Catalyzes the formation of arginosuccinate from aspartate, citrulline and ATP and together with ASL it is responsible for the biosynthesis of arginine in most body tissues. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:18473344, ECO:0000305|PubMed:27287393, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8792870}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Arginine biosynthesis;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Urea cycle |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-arginine biosynthesis; L-arginine from L-ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate: step 2/3. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:18473344, ECO:0000305|PubMed:27287393, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8792870}.; PATHWAY: Nitrogen metabolism; urea cycle; (N(omega)-L-arginino)succinate from L-aspartate and L-citrulline: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:18473344, ECO:0000305|PubMed:27287393, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8792870}. |
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the penultimate step of the arginine biosynthetic pathway. There are approximately 10 to 14 copies of this gene including the pseudogenes scattered across the human genome, among which the one located on chromosome 9 appears to be the only functional gene for argininosuccinate synthetase. Mutations in the chromosome 9 copy of this gene cause citrullinemia. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:445; |
cell body fiber [GO:0070852]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; amino acid binding [GO:0016597]; argininosuccinate synthase activity [GO:0004055]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; toxic substance binding [GO:0015643]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; aging [GO:0007568]; arginine biosynthetic process [GO:0006526]; argininosuccinate metabolic process [GO:0000053]; aspartate metabolic process [GO:0006531]; cellular response to amine stimulus [GO:0071418]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to ammonium ion [GO:0071242]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to glucagon stimulus [GO:0071377]; cellular response to laminar fluid shear stress [GO:0071499]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to oleic acid [GO:0071400]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; citrulline metabolic process [GO:0000052]; diaphragm development [GO:0060539]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; liver development [GO:0001889]; midgut development [GO:0007494]; negative regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:1903038]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to growth hormone [GO:0060416]; response to mycotoxin [GO:0010046]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043]; urea cycle [GO:0000050] |
11708871_Mutational analysis revealed three alleles with a common mutation and five new mutations. 11941481_structure and use in diagnosing citrullinemia 12815590_Sixteen novel mutations have been identified in the argininosuccinate synthetase gene in citrullinemia patients. 14570901_argininosuccinate synthetase gene expression is stimulated by glutamine through cytosolic O-glycosylation of Sp1 in tumor cells 15192091_Argininosuccinate synthetase has a role in preventing autotoxicity from nitric oxide overproduction 16124451_Extensive mutation study by direct genomic sequencing of ASS demonstrated a homozygous G117S mutation in one patient and homozygous R363W mutations in the other two families 16380201_IL-1beta induces nitric oxide which has antagonistic effects on argininosuccinate synthetase gene and on the activity of argininosuccinate synthetase 16703398_ASS, the c-myc-regulated gene is involved in genotype-C-HBV-related HCC, suggesting that c-myc is related to the hepatocarcinogenic activity of genotype-C HBV. 17096330_Low argininosuccinate synthetase is associated with renal cell carcinoma 17354225_high levels of AS expression, which may be required for several arginine-dependent processes in cancer, including the production of nitric oxide, proline, pyrimidines and polyamines, is regulated by TNF-alpha 18263583_HSCARG regulation of argininosuccinate synthetase activity is crucial for maintaining the intracellular balance between redox state and nitric oxide levels 18840401_These results show that liver-specific enhancement of ASS gene expression is mediated in part by the cAMP signaling pathway through a distal CRE site. 19000307_argininosuccinate synthetase behaves as a typical suckling enzyme because its expression all but disappears in the putative weaning period of human infants. 19006241_a survey of the correlation between mutations in the ASS1 gene and the respective clinical courses of citrullinemia type I as described so far (Review) 19358837_The studied families showed the same mutation: ASS~p.G390R, associated with the early-onset/severe phenotype. 19409979_changes in gene expression are induced by laminar shear stress as well as by cellular senescence 19533750_Epigenetic silencing of argininosuccinate synthetase confers resistance to platinum-induced cell death but collateral sensitivity to arginine auxotrophy in ovarian cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934275_Studies indicate that the proximal region of the AS promoter contains an E-box that is recognized by c-Myc and HIF-1alpha and a GC-box by Sp4. 20159990_In patients with osteosarcoma, reduced expression of ASS is not only a novel predictive biomarker for the development of metastasis, but also a potential target for pharmacologic intervention. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20739017_Analysis of five SNPs of the ASS1 gene revealed that the G allele of rs7860909 is associated with increased CL/P risk. 20739017_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21106532_the expression of ASS1 harmonized with that of NOS3 may be important for the optimized endothelial NO production and the prevention of the inflammatory monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. 21481813_The ASS release represents a potential counteracting liver reaction to LPS. 22430140_The present study demonstrated a key regulatory role of KLF4 in the endothelial ASS1 expression and NO production in response to laminar shear stress. 23099195_Mutations are identified only in exons of ASS1 gene from the Korean patients with citrullinemia type I. 23339388_ASS expression is decreased significantly in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 23549872_Our findings highlight ASS1 as a novel tumor suppressor in myxofibrosarcomas, with loss of expression linked to promoter methylation, clinical aggressiveness, and sensitivity to ADI-PEG20. 23897555_Aberrant loss of ASS1 strongly links to DNA methylation in neck nodal metastases of NPC and significantly correlates with advanced T classification, and independently predicts worse DSS and DMFS in independent NPC tissue specimens. 24192130_Argininosuccinate synthetase gene is silenced by CpG methylation in children with phenylketonuria.The promoter of argininosuccinate synthetase was methylated which silence the transcription of argininosuccinate synthetase. 24297925_Together with the observation that AS1 protein and mRNA levels decrease during wild-type infection, this work suggests that reduced AS1 activity is partially responsible for the metabolic program induced by infection. 24508627_we reviewed the English literature on mutations in the ASS and SLC25A13 genes, and their genotype-phenotype correlations to provide valuable insights into the molecular genetic background of citrullinemia--{REVIEW} 24692592_Data indicate that argininosuccinate synthetase 1 (ASS1) abundance is a prognostic factor for overall breast cancer survival. 24927999_Point mutation of ASS1, ASL and SLC25A13 is associated with citrullinemia. 25179242_Three novel splicing and missense mutations have been identified in the ASS1 gene in classical citrullinemia patients. 25333458_ASS expression in gastric cancer was associated with a poor prognosis. 25548129_More than 50 % of the high-grade pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas tested lack immunohistochemically detectable ASS, suggesting that they are auxotrophic for arginine and potential candidates for arginine deprivation therapy. 26560030_results demonstrate that ASS1 downregulation is a novel mechanism supporting cancerous proliferation, and they provide a metabolic link between the urea cycle enzymes and pyrimidine synthesis 26895070_ASS1 genomic variants (rs10901080 and rs10793902) can serve as pharmacogenomic biomarkers to predict hydroxyurea treatment efficacy in sickle cell disease/beta-thalassemia compound heterozygous patients. 26972697_combining hypoxia and ADI-PEG20 synergistically inhibited ASS1. 26982031_results show that ASS1 is elevated at the mRNA and protein levels in mesothelioma 3D spheroids and in human pleural mesotheliomas. We also have uncovered a survival role for ASS1 27287393_Of 21 ASS potential kinetic mutations, 13 were totally inactive while 8 exhibited decreased affinity for aspartate and citrulline. 27431689_Low expression of ASS1 is associated with glioblastoma. 27584578_In this trial, arginine deprivation with ADI-PEG20 improved PFS in patients with ASS1-deficient mesothelioma. Targeting arginine is safe and warrants further clinical investigation in arginine-dependent cancers. 27683125_Results indicate that the reduced ASS1 expression in Dox-resistant sarcomas may contribute to drug resistance in association with the expression of P-glycoprotein. 27765932_Cisplatin-induced synthetic lethality to arginine-starvation therapy by transcriptional suppression of ASS1 is regulated by DEC1, HIF-1alpha, and c-Myc transcription network and is independent of ASS1 promoter DNA methylation. 28111830_update reports 137 mutations in the ASS1 gene (64 of which are novel), consisting of 89 missense mutations, 19 nonsense mutations, 17 mutations that affect splicing, and 12 deletions; the change p.Gly390Arg is by far the most common mutation and is widely spread throughout the world 28132756_Identification of three novel CTLN1 mutations in fourteen patients with citrullinemia type 1 has been reported. 28187218_Low ASS1 expression was associated with higher recurrence , shorter disease-free survival and shorter overall survival in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 28358054_In ASS1-knockout cells, DEPTOR, an inhibitor of mTORC1 signal, was downregulated and mTORC1 signaling was more activated in response to arginine. 28560349_findings uncover a new function of p53 in the regulation of Akt signaling and reveal how p53, ASS1, and Akt are interrelated to each other. 28587924_The authors showed that ASS1 mutations linked to type I citrullinemia disrupt the ASS1-PRMT7 interaction, which might explain the molecular pathogenesis of the disease. 28646562_defined a new hepatocellular adenoma subgroup at a high risk of bleeding 28883660_Arginine starvation induces p300 dissociation, allowing histone HDAC2 and cofactor Sin3A to deacetylate these histones at the ASS1 promoter, thereby facilitating HIF-1alpha-proteasomal complex, driven by PHD2, to degrade HIF-1alpha in situ. 28981931_The remaining five patients were diagnosed with neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis due to citrin deficiency, and have respectively carried mutations of the SLC25A13 gene including [c.851-854delGTAT+c.851-854delGTAT], [c.851-854delGTAT+IVS6+5G>A], [c.851-854delGTAT+IVS16ins3kb], [c.851-854delGTAT+IVS6-11A>G] and [c.851-854delGTAT+c.1638-1660dup23] 28985504_ASS1 acetylation by CLOCK exhibits circadian oscillation in human cells and mouse liver, possibly caused by rhythmic interaction between CLOCK and ASS1, leading to the circadian regulation of ASS1 and ureagenesis. 29401583_results propose that ASS1 might contribute to gastric cancer (GC) metastasis and support its utility as a prognostic predictor of GC. 29572896_associated with sonic hedgehog activation as part of a periportal program expressed in hepatocellular adenomas 30546006_The combination of ADI-PEG20 with temozolomide (TMZ) demonstrates enhanced effects in both ASS1 negative and ASS1 positive backgrounds.Our data provide proof of principle for a therapeutic strategy for GBM using peripheral blood arginine depletion that does not require BBB passage of drug and is well tolerated 30883650_Overexpression of ASS1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inactivating the pSTAT3Ser727 pathway, which subsequently decreases the expression of ID1. 31135443_Does Argininosuccinate Synthase 1 (ASS1) Immunohistochemistry Predict an Increased Risk of Hemorrhage for Hepatocellular Adenomas? 31208364_Citrullinemia type I (CTLN1) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of the urea cycle caused by a deficiency in the argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS1) enzyme due to mutations in the ASS1 gene. 31903153_Histone deacetylase inhibition is synthetically lethal with arginine deprivation in pancreatic cancers with low argininosuccinate synthetase 1 expression. 32273051_Neonatal factors related to survival and intellectual and developmental outcome of patients with early-onset urea cycle disorders. 32409304_Arginine Depletion Therapy with ADI-PEG20 Limits Tumor Growth in Argininosuccinate Synthase-Deficient Ovarian Cancer, Including Small-Cell Carcinoma of the Ovary, Hypercalcemic Type. 33508432_Therapeutic targeting of argininosuccinate synthase 1 (ASS1)-deficient pulmonary fibrosis. 33838671_Argininosuccinate synthase 1 suppresses tumor progression through activation of PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33851512_Variants associated with urea cycle disorders in Japanese patients: Nationwide study and literature review. 35012429_N(6)-adenosine-methyltransferase-14 promotes glioma tumorigenesis by repressing argininosuccinate synthase 1 expression in an m6A-dependent manner. 35674458_PGAM1 regulation of ASS1 contributes to the progression of breast cancer through the cAMP/AMPK/CEBPB pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000076441 |
Ass1 |
140.625222 |
0.1602820048 |
-2.641316 |
0.159854040 |
304.285928 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003837369230812688696079517809196237959864180736395069395756849405924650283309211511963302115978379368448501154253564825549903857537702236492719189152990894306861503868129326111358068374102003872394561767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001123800989023715907038523886602743459203829830205307996349130877653219245412178074901711593312635168782041913246234367921785589644881591123321093134006034407613560527350315965122717898339033126831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.3010662 |
4.1583982 |
247.7135246 |
14.1760540 |
| ENSG00000130720 |
84929 |
FIBCD1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N539 |
FUNCTION: Acetyl group-binding receptor which shows a high-affinity and calcium-dependent binding to acetylated structures such as chitin, some N-acetylated carbohydrates, and amino acids, but not to their non-acetylated counterparts. Can facilitate the endocytosis of acetylated components. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19710473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19892701}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Chitin-binding;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
FIBCD1 is a conserved type II transmembrane endocytic receptor that binds chitin and is located primarily in the intestinal brush border (Schlosser et al., 2009 [PubMed 19710473]).[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:84929; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; chitin binding [GO:0008061]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155] |
19710473_FIBCD1 is a high-affinity receptor for chitin and chitin fragments, and may play an important role in controlling the exposure of intestine to chitin and chitin fragments 19892701_The recognition unit of FIBCD1 organizes into a noncovalently linked tetrameric structure and uses a hydrophobic funnel (S1) for acetyl group recognition. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24293368_The high affinity ligand N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) binds FIBCD1 in the S1 site, predominantly via the acetyl group with the oxygen and acetamide nitrogen hydrogen-bonded to the protein and the methyl group inserted into a hydrophobic pocket. 29220632_FIBCD1 is expressed in epithelial cells derived from all three germ layers. Endodermal-derived epithelial cells throughout the gastrointestinal tract and the respiratory system showed high expression of FIBCD1 and also mesodermal-derived cells in the genitourinary system and ectodermal-derived epidermis and sebaceous glands cells expressed FIBCD1. 29659669_FIBCD1 may be a novel biomarker to evaluate the prognosis of gastric cancer. 30279687_thses findings support FIBCD1 as a lung epithelial pattern recognition receptor that recognizes the complex Aspergillus fumigatus cell wall polysaccharides and modulates the lung epithelial inflammatory response by suppressing inflammatory mediators and mucins 35501350_The myokine Fibcd1 is an endogenous determinant of myofiber size and mitigates cancer-induced myofiber atrophy. 35916241_FIBCD1 is an endocytic GAG receptor associated with a novel neurodevelopmental disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000026841 |
Fibcd1 |
7.251128 |
0.1014161414 |
-3.301641 |
0.859177919 |
15.695645 |
0.00007439526331597290278573736399536642238672357052564620971679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000208799027675177787050433964033402389759430661797523498535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2031297 |
0.9014058 |
10.7975506 |
4.2178555 |
| ENSG00000130749 |
23211 |
ZC3H4 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPT8 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein that suppresses transcription of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) (PubMed:33913806, PubMed:33767452). LncRNAs are defined as transcripts more than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into protein (PubMed:33913806, PubMed:33767452). Together with WDR82, part of a transcription termination checkpoint that promotes transcription termination of lncRNAs and their subsequent degradation by the exosome (PubMed:33913806, PubMed:33767452). The transcription termination checkpoint is activated by the inefficiently spliced first exon of lncRNAs (PubMed:33767452). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33767452, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33913806}. |
3D-structure;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Metal-binding;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transcription termination;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of CCCH (C-x8-C-x5-C-x3-H type) zinc finger domain-containing proteins. These zinc finger domains, which coordinate zinc finger binding and are characterized by three cysteine residues and one histidine residue, are nucleic acid-binding. Other family members are known to function in post-transcriptional regulation. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:23211; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; DNA-templated transcription termination [GO:0006353]; lncRNA catabolic process [GO:0110064]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation [GO:0032785]; negative regulation of lncRNA transcription [GO:0140744]; nuclear RNA surveillance [GO:0071027] |
33767452_A first exon termination checkpoint preferentially suppresses extragenic transcription. 33767452_ZC3H4 controls termination of extragenic transcription in human and mouse cells. Cells depleted of ZC3H4 show greatly enhanced synthesis of long and spliced extragenic transcripts. 33913806_ZC3H4 restricts non-coding transcription in human cells. 35325203_ZWC complex-mediated SPT5 phosphorylation suppresses divergent antisense RNA transcription at active gene promoters. |
ENSMUSG00000059273 |
Zc3h4 |
538.923978 |
3.1625469151 |
1.661087 |
0.612603291 |
6.616115 |
0.01010600216775299833860124465445551322773098945617675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019354429998187913652962777177890529856085777282714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
573.0552323 |
317.3777837 |
172.6992322 |
67.9686558 |
| ENSG00000130762 |
27237 |
ARHGEF16 |
protein_coding |
Q5VV41 |
FUNCTION: Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor of the RHOG GTPase stimulating the exchange of RHOG-associated GDP for GTP. May play a role in chemotactic cell migration by mediating the activation of RAC1 by EPHA2. May also activate CDC42 and mediate activation of CDC42 by the viral protein HPV16 E6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20679435}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Although the specific function of this protein is not known yet, it is thought to be involved in protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27237; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078] |
19707205_Sixty-four novel structural analogues of Y27632 were synthesized and tested for their ability to persistently inhibit the transformation of NIH3T3 cells by Rho guanidine exchange factor 16 (ARHGEF16) or Ras. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20679435_The ephexin4 protein mediates cell migration through a RhoG-dependent mechanism. 21139582_These data suggest that HPV16 E6, Tip-1 and ARHGEF16 may cooperate to activate Cdc42 and support a potential link between the expression of HPV16 E6 and Cdc42 activation 30305138_Authors found that ARHGEF16 mRNA level was upregulated in U87 cells overexpressing GLI2A relative to control cells. GLI2 binds to the ARHGEF16 promoter and activates gene transcription. Glioma cells U87 and U118 overexpressing ARHGEF16 showed enhanced migration and proliferation. 32811808_FYN is required for ARHGEF16 to promote proliferation and migration in colon cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000029032 |
Arhgef16 |
9.897952 |
0.2146552253 |
-2.219907 |
0.561503652 |
17.283757 |
0.00003219270120393213045891997459158062611095374450087547302246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000095108941106893164795822726009788539158762432634830474853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4261969 |
1.3375874 |
15.9923506 |
3.4325139 |
| ENSG00000130787 |
9026 |
HIP1R |
protein_coding |
O75146 |
FUNCTION: Component of clathrin-coated pits and vesicles, that may link the endocytic machinery to the actin cytoskeleton. Binds 3-phosphoinositides (via ENTH domain). May act through the ENTH domain to promote cell survival by stabilizing receptor tyrosine kinases following ligand-induced endocytosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11889126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14732715}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Endocytosis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables several functions, including phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding activity; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding activity; and protein homodimerization activity. Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of signal transduction; protein stabilization; and regulation of organelle organization. Located in clathrin-coated vesicle; cytosol; and ruffle membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9026; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; clathrin light chain binding [GO:0032051]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0080025]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; clathrin coat assembly [GO:0048268]; digestive system development [GO:0055123]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030837]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of Arp2/3 complex-mediated actin nucleation [GO:0034316]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of clathrin coat assembly [GO:1905445]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901030]; positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway [GO:2000588]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; postsynapse organization [GO:0099173]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:2000369]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of gastric acid secretion [GO:0060453] |
11889126_HIP1 and HIP12 display differential binding to F-actin, AP2, and clathrin. Identification of a novel interaction with clathrin light chain. (HIP12) 14732715_both HIP1r and HIP1 bind inositol lipids via their epsin N-terminal homology (ENTH) domains 14742709_Hip1R has a role in making the interaction between actin and the endocytic machinery functional and transient 15581353_The F-actin binding capacity of Hip12 is regulated by intrasteric occlusion of primary actin-binding determinants within the Hip12 I/LWEQ module. 15588756_the stability of intergenerational transmission of a variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) polymorphism, found in the Huntingtin interacting protein-1 related gene (HIP12/HIP1R) that is mapped to the chromosome 12q24.31 region. 16415883_characterize the F-actin-binding region of HIP1R, termed the talin-HIP1/R/Sla2p actin-tethering C-terminal homology (THATCH) domain 17452370_Human HIP1 transgenic Hip1/Hip1r knockout mice are completely free from dwarfism and spinal defects. 17928447_Neuronal dysfunction in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans expressing mutant N-terminal huntingtin is specifically enhanced by hipr-1 loss of function. 18165318_in mammalian cells CLCs function in intracellular membrane trafficking by acting as recruitment proteins for HIP1R, enabling HIP1R to regulate actin assembly on clathrin-coated structures 18790740_Actin binding by Hip1 (huntingtin-interacting protein 1) and Hip1R (Hip1-related protein) is regulated by clathrin light chain 19255499_This study provided the previously unknown function of HIP1R involved in the intrinsic cell death pathway and further explored possible mechanisms by which HIP1R induces cell death. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21189155_HIP1r plays an important role in regulating the attachment of spindle microtubules to chromosomes during mitosis, an event that is required for accurate congression and segregation of chromosomes. 24312176_STK39 (rs2102808) and CCDC62/HIP1R (rs12817488) do not appear to influence PD risk. 25818163_our findings support the conclusion that the rs12817488 in CCDC62/HIP1R polymorphism may increase the risk of Parkinson's disease in the Chinese Han population. 26341140_We conclude that HIP1R expression is strongly indicative of survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 26898757_HIP1R rescued miR-23b/-27b-mediated repression of migration in prostate cancer cells. HIP1R mRNA levels were decreased in seminal vesicle tissue from mice bearing miR-23b/-27b-transduced prostate cancer cell xenografts compared with scrambled controls, suggesting HIP1R is a key functional target of miR-23b/-27b. 30397328_HIP1R is a natural regulator of PD-L1 lysosomal degradation, and the functions of HIP1R relied on two sequence stretches- one involved in the interaction with PD-L1 and for the sorting to the lysosome. 31672988_There is coordinated action of myosin VI and CLCa at the apical surface where these proteins are essential for fission of clathrin-coated pits. Myosin VI and Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related protein (Hip1R) are mutually exclusive interactors with CLCa, and suggest a model for the sequential function of myosin VI and Hip1R in actin-mediated clathrin-coated vesicle budding. 32548851_HIP1R acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer by promoting cancer cell apoptosis and inhibiting migration and invasion through modulating Akt. 35209947_Flurbiprofen inhibits cell proliferation in thyroid cancer through interrupting HIP1R-induced endocytosis of PTEN. |
ENSMUSG00000000915 |
Hip1r |
337.193799 |
0.2055310159 |
-2.282572 |
0.116549995 |
388.269056 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001971097200233975688636938976237230618344715927349989737983395125341094889777784164022323207066859982051369822810842468848499649504977499195728763299052848488700243101890273988543905738008100557413307731369174003246969029135016171494498848915100 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000718355424085271162083550368495137590659198799460292693852198345012061883457572735869881266984276109370210760483296498492234818024086793111176120224508791609999355413439701780709884873497943389421713478545277256626100381708965869620442390441895 |
Yes |
No |
114.6801204 |
11.9094290 |
559.2958832 |
39.0783209 |
| ENSG00000130810 |
56342 |
PPAN |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ55 |
FUNCTION: May have a role in cell growth. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an evolutionarily conserved protein similar to yeast SSF1 as well as to the gene product of the Drosophila gene peter pan (ppan). SSF1 is known to be involved in the second step of mRNA splicing. Both SSF1 and ppan are essential for cell growth and proliferation. Exogenous expression of this gene was reported to reduce the anchorage-independent growth of some tumor cells. Read-through transcription of this gene with P2RY11/P2Y(11), an adjacent downstream gene that encodes an ATP receptor, has been found. These read-through transcripts are ubiquitously present and up-regulated during granulocyte differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:56342;hsa:692312; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; preribosome, large subunit precursor [GO:0030687]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA binding [GO:0019843]; ribosomal large subunit assembly [GO:0000027]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] |
10359593_The functional analysis of the Drosophila homolog. [LH] 25759387_a novel nucleolar stress-response pathway involving PPAN, NPM, and BAX to guarantee cell survival in a p53-independent manner. 30716409_data underline the notion that the PPAN-mediated, p53-independent nucleolar stress response has multiple facets. 31416196_The study uncovers that PPAN knockdown is linked to mitochondrial damage and stimulates autophagy. 34741342_An SNP reducing SNORD105 and PPAN expression decreases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000004100 |
Ppan |
59.036065 |
2.7970125005 |
1.483887 |
0.379626912 |
14.996580 |
0.00010770616857757126991462087728379515283450018614530563354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000294997782186853232597179008678267564391717314720153808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
89.5714036 |
19.0271034 |
32.8966683 |
5.3859056 |
| ENSG00000130822 |
139728 |
PNCK |
protein_coding |
Q6P2M8 |
FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase belonging to a proposed calcium-triggered signaling cascade. In vitro phosphorylates CREB1 and SYN1/synapsin I. Phosphorylates and activates CAMK1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calcium;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
PNCK is a member of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase family of protein serine/threonine kinases (see CAMK1; MIM 604998) (Gardner et al., 2000 [PubMed 10673339]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:139728; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0004683]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105] |
18562482_Pnck induces ligand-independent EGFR degradation, and it may represent an attractive therapeutic target in EGFR-regulated oncogenesis. 21325639_Pnck induces epidermal growth factor receptor degradation, most likely through perturbation of Hsp90 chaperone activity due to Hsp90 phosphorylation. Epidermal growth factor receptor degradation is coupled to proteasomal degradation of Pnck. 23634203_the relationship between PNCK and prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 25773930_Pnck may be a marker of Trastuzumab resistance and possibly a therapeutic target in breast cancer. 33099476_Expression of Pregnancy Up-regulated Non-ubiquitous Calmodulin Kinase (PNCK) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000002012 |
Pnck |
8.054663 |
0.1540806295 |
-2.698243 |
0.664346759 |
19.889863 |
0.00000820341510739452417532487776830052439436258282512426376342773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000026028032455963710220308779397235809938138118013739585876464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.2411641 |
1.0735163 |
14.2853073 |
3.3471794 |
| ENSG00000130962 |
5638 |
PRRG1 |
protein_coding |
O14668 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a vitamin K-dependent, gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla)-containing, single-pass transmembrane protein. This protein contains a Gla domain at the N-terminus, preceded by a propeptide sequence required for post-translational gamma-carboxylation of specific glutamic acid residues by a vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase. The C-terminus is proline-rich containing PPXY and PXXP motifs found in a variety of signaling and cytoskeletal proteins. This gene is highly expressed in the spinal cord. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:5638; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] |
|
ENSMUSG00000047996 |
Prrg1 |
85.796351 |
2.1908500877 |
1.131491 |
0.160019195 |
50.991603 |
0.00000000000092761925087711842171296655618451616667069492550012910214718431234359741210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000005529749653855520480228505269714976981705600866945360394311137497425079345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
117.4666502 |
12.2470543 |
54.0003254 |
4.4676911 |
| ENSG00000131002 |
|
TXLNGY |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
81.126910 |
0.3918849954 |
-1.351498 |
0.396306227 |
10.530958 |
0.00117391366337593269775219084749551257118582725524902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002703536537904316881808508554740910767577588558197021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.8661389 |
11.9413778 |
117.5942202 |
22.1088414 |
| ENSG00000131037 |
54869 |
EPS8L1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TE68 |
FUNCTION: Stimulates guanine exchange activity of SOS1. May play a role in membrane ruffling and remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14565974}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is related to epidermal growth factor receptor pathway substrate 8 (EPS8), a substrate for the epidermal growth factor receptor. The function of this protein is unknown. At least two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:54869; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; T cell receptor binding [GO:0042608]; positive regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900029]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790]; regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035023]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
|
ENSMUSG00000006154 |
Eps8l1 |
70.096432 |
0.3273765428 |
-1.610977 |
0.335843182 |
22.164639 |
0.00000250240504081044920340649861945081511294119991362094879150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008450125463821146279950503876765566246831440366804599761962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.5445306 |
7.3881474 |
113.4376676 |
16.0881973 |
| ENSG00000131149 |
23199 |
GSE1 |
protein_coding |
Q14687 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a proline-rich protein with coiled coil domains that may be a subunit of a BRAF35-HDAC (BHC) histone deacetylase complex. This gene may function as an oncogene in breast cancer and enhanced expression of the encoded protein has been observed in breast cancer patients. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:23199; |
|
26828271_In this study, we reported that GSE1 is overexpression in breast cancer and silencing of GSE1 significantly suppressed breast cancer cells proliferation, migration and invasion. 29367342_High GSE1 expression is associated with gastric cancer growth and metastasis. 33623790_Overexpression of GSE1 Related to Trastuzumab Resistance in Gastric Cancer Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000031822 |
Gse1 |
158.956062 |
0.2815370200 |
-1.828603 |
0.190167852 |
90.539827 |
0.00000000000000000000181290715209119327961700514719908953018625058555483832244516542719914298231742577627301216125488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000017000323738796705115223721534379288782933354122016959440386041357839985721511766314506530761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.4734870 |
9.9929615 |
244.1388831 |
24.4801930 |
| ENSG00000131203 |
3620 |
IDO1 |
protein_coding |
P14902 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first and rate limiting step of the catabolism of the essential amino acid tryptophan along the kynurenine pathway (PubMed:17671174). Involved in the peripheral immune tolerance, contributing to maintain homeostasis by preventing autoimmunity or immunopathology that would result from uncontrolled and overreacting immune responses (PubMed:25691885). Tryptophan shortage inhibits T lymphocytes division and accumulation of tryptophan catabolites induces T-cell apoptosis and differentiation of regulatory T-cells (PubMed:25691885). Acts as a suppressor of anti-tumor immunity (PubMed:23103127, PubMed:25157255, PubMed:14502282, PubMed:25691885). Limits the growth of intracellular pathogens by depriving tryptophan (PubMed:25691885). Protects the fetus from maternal immune rejection (PubMed:25691885). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14502282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17671174, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23103127, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25157255, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25691885}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Direct protein sequencing;Heme;Immunity;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Tryptophan catabolism |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-tryptophan degradation via kynurenine pathway; L-kynurenine from L-tryptophan: step 1/2. |
This gene encodes indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) - a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in tryptophan catabolism to N-formyl-kynurenine. This enzyme acts on multiple tryptophan substrates including D-tryptophan, L-tryptophan, 5-hydroxy-tryptophan, tryptamine, and serotonin. This enzyme is thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation, and antioxidant activity. Through its expression in dendritic cells, monocytes, and macrophages this enzyme modulates T-cell behavior by its peri-cellular catabolization of the essential amino acid tryptophan.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:3620; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; smooth muscle contractile fiber [GO:0030485]; stereocilium bundle [GO:0032421]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0033754]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0004833]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process from tryptophan [GO:0034354]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; kynurenic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0034276]; multicellular organismal response to stress [GO:0033555]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070233]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; positive regulation of chronic inflammatory response [GO:0002678]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070234]; positive regulation of T cell tolerance induction [GO:0002666]; positive regulation of type 2 immune response [GO:0002830]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; swimming behavior [GO:0036269]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; tryptophan catabolic process [GO:0006569]; tryptophan catabolic process to kynurenine [GO:0019441] |
11867636_heme environment--structural properties and substrate-ligand interactions 11987129_Data show that overexpression of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase is present in Crohn's disease as well as in ulcerative colitis, but nit in diverticulitis, as compared to normal mucosa. 12186837_inhibition of allogeneic T cell proliferation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing dendritic cells: mediation of suppression by tryptophan metabolites 12228717_describe a subset of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells that use IDO to inhibit T cell proliferation in vitro 12471139_Induction of IDO in airway epithelial-like tumor cells by exposure to IFN-gamma for 24 hr markedly amplifies IL-6 and IL-8 responses via depletion of tryptophan from the culture medium. 12766158_Asp274 and his346 are essential for heme binding and catalytic function of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 12938169_Data show that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing fibroblasts embedded within collagen gel suppress the proliferation of allogenic immune cells, while they still remain viable in a tryptophan-deficient culture environment. 12963490_one important consequence of increasing IDO activity in astroglial cells during inflammation is to maintain NAD levels through de novo synthesis from tryptophan. 13678429_characterization of regulatory sequences involved in the synergistic transcriptional activation of the indoleamine dioxygenase gene by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. 14502282_Data show that most human tumors constitutively express indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), and that expression of IDO by immunogenic mouse tumor cells prevents their rejection by preimmunized mice. 14871294_indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is necessary for cytolytic activity of natural killer cells. 14969766_Downregulation of MHC class I expression by Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase(IDO) might be one of the mechanisms through which IDO mediates local immunosuppression. 15001472_Bone marrow stromal cells express IDO protein and exhibit functional IDO activity upon stimulation with IFN-gamma. 15070879_despite suppression by progesterone, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in endometrial stromal cells may increase during decidualization due to stimulation by interferon-gamma secreted by infiltrating leukocytes. 15102781_RT4 cells were able to inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in an IDO-mediated fashion, and this bacteriostatic effect was abolished by endogenously produced NO. 15245429_stimulation with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) induces the expression of functionally active IDO in highly purified human epidermal Langerhans cells 15254595_Data suggest that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated suppression by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes creates a local microenvironment that is potently suppressive of host antitumor T cell responses. 15374002_HSV-2 antiviral effect of type II interferon and TNF-alpha is dependent on IDO activation. 15528322_IDO induction in eosinophils is a potential mechanism in the regulation of T helper type 2 (Th2) cell polarization. 15711557_Findings indicate that attenuated Bin1 causes elevation of IDO and immune escape of cancers in mice. Additionally, small molecule inhibitors of IDO reverse the effects of Bin1 loss and leverage the efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs in cancer. 15919929_IFN-gamma-induced enzyme IDO plays an important antiviral role in Measles Virus infections of epithelial, endothelial, and astroglial cells. 15947091_indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) activity is induced in a two-step process during dendritic cell maturation 15950064_the function of IDO and kynurenine hydroxylase may change from a role in immunosuppression at the maternal-fetal interface in early pregnancy, to one associated with regulation of fetoplacental blood flow or placental metabolism in late gestation 15967116_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is expressed not by tumor cells, but by normal cells infiltrating the peritumoral stroma 16135011_A high T-helper type 1 (Th1)/Th2 cell ratio is more likely to cause loss of an allogeneic embryo in early pregnancy than is the loss of putative protection by reduced uterine levels of IDO. 16176799_In this review, the unique catalytic properties of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase are described, and the recent findings regarding the dioxygenase-initiated tryptophan metabolism are summarized. 16319139_HO-1/IDO cross-regulation modulates apoptosis and proliferation in rat and human breast cancer cells 16406698_examine the arguments for and against a function of IDO-expressing human dendritic cells (DCs) and conclude that proof for an immunoregulatory role in vivo is still lacking 16421220_CTLA-4 on regulatory T cells up-regulates IDO expression on decidual and peripheral blood dendritic cells and monocytes by the induction of IFN-gamma production. 16477023_X-ray crystal structure of human IDO, complexed with the ligand inhibitor 4-phenylimidazole and cyanide was reported. 16489067_IDO significantly contributes to disease progression and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer. 16511306_purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray study of human IDO 16513157_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase may have a role in the decline of T cell responses in immunosenescence 16686756_The variable expression of IDO in different endothelial cells is important not only in understanding the role of endothelial cells in the regulation of graft rejection, but also as a potential therapeutic strategy. 16834326_These data provide the first glimpse of the possible regulatory mechanism of hIDO by NO and suggest that the NO-dependent regulation can be modulated by cellular factors, such as the NO abundance, pH, redox environment, and L-Trp availability. 16842443_reduced IDO activity found in the macrophages of patients with hepatitis C virus infection suggest the infection may hamper macrophage functions 17015408_Sleeping beuaty-bsed human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase represents a new strategy for treating lung transplantation-associated chronic complications in rats. 17038913_Recombinant antithymocyte globulin inhibits maturation of immature dendritic cells and llows the generation of dendritic cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. 17170728_Acute myelocytic leukemia cells expresse INDO mRNA, but not IDO protein when exposed to optimal concentrations of IFN-gamma. 17182891_hCG can upregulate human trophoblast indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase, which probably plays a key role at maternal fetal interface in preventing fetal rejection. 17192467_IDO activation may protect islet cells from cytotoxic damage by interferon gamma. 17202379_TNF-alpha enhanced TLR ligand-induced IL-8 production in human gingival fibroblasts 17229698_Induction of IDO may dampen T-cell reactivity to viral antigens in chronic hepatitis C virus infection 17294609_change in the clinical course of multiple sclerosis observed in pregnancy may be related to the estrogen-dendritic cell-IDO axis 17318080_CD123/CCR6 dendritic cells (DCs) do not constitutively express IDO and 'induced' IDO DCs 17321596_From the expression pattern we conclude that IDO may play a central role in human pregnancies for the establishment of maternal tolerance of fetal antigens 17393386_Review discusses the immunoregulatory pathway of tryptophan catabolism initiated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) as a bidirectional feedback loop that could be part of an integrated response for preventing excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. 17433037_IDO expression at the invasive front of cancer cells and APC, and the localization of Foxp3(+) Treg cells in front of cancer tissues, may create a network between IDO and Treg for the 17535808_NO inhibits rhIDO activity reversibly by binding to the active site heme to trap the enzyme as an inactive nitrosyl-Fe(II) enzyme adduct with Trp bound and O2 displaced 17605849_Human acute monocyte leukemia and acute lymphocyte leukemia express indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase. 17626075_poly(I:C)induction of IDO was mediated in part by IFN-beta but not IFN-gamma, and both NF-kappaB and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) were required. 17674321_The levels of intralesional expression of mRNA of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon, interleukin-10, RANTES, and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in Mediterranean spotted fever are reported; levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase are also reported. 17711549_Transfected into rats, reduces vascular permeability and leukocyte extravasation, and consequently improves graft function and histologic appearance. 17911610_Interferon gamma-inducible expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase by human vascular smooth muscle cells inhibits allogeneic T cell activation, proliferation, and accumulation in vitro and in vivo. 17951526_indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2 represent key mediators of the Mesenchymal stem cells-induced inhibition of NK cells 18008147_The finding of this study revealed that the proliferation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells are suppressed in response to tryptophan deficient environment caused by IDO expression and it is more so for CD8+ T than CD4+ T cells. 18036645_The present study has demonstrated for the first time that baseline IDO enzymatic activity in induced sputum from asthmatic patients is very low compared with that seen in nonasthmatic control subjects and is inversely related to sputum eosinophilia. 18045970_Any possible antitumor effects of dextro-1-methyl tryptophan cannot be attributed to abrogation of IDO activity in dendritic cells. 18055547_Type I IFN-mediated skin disorders, such as lichen planus , strongly express IDO in lesional skin. 18176870_We submit that an impaired IDO induction characterizes PBC (primary biliary cirrhosis)and might represent a contributing factor in disease pathogenesis in association with several specific defects in the target tissue 18205804_it is suggested that tryptophan depletion via IFN-gamma-mediated IDO induction is a major antibacterial, antiparasitic, antiviral and immunoregulatory mechanism in human lung cells. 18274832_are differences and similarities between biochemical behaviour and structural features of recombinant human IDO and recombinant mouse IDO 18299324_Cytochrome b(5) rather than O(2)(*-) plays a major role in the activation of IDO in human cells. 18332894_transgenic expression of IDO in xenografts contributes to prolonged graft survival 18370410_reveal significant differences between the IDO and tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO) enzymes, and the implications of these results are discussed in terms of our current understanding of IDO and TDO catalysis 18438685_IDO may be a novel favorable prognostic indicator and candidate adjuvant therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 18622801_IDO is a sensitive marker of atherosclerosis--or the inflammatory response associated with it--but does not have an independent role in the pathogenesis of this disease. 18639339_In patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the serum kynurenine/tryptophan ratio (Kyn/Trp) was raised, suggesting a higher IDO activity than in healthy people 18660700_considerable potential for immunoregulation and antigen-specific tolerance induction in transplantation 18776940_differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into Tregs with suppressive function was primarily dependent on plasmacytoid dendritic cell expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 18802343_increased activity is associated with asymptomatic atopy during seasonal allergen exposure 18832696_IDO pathway is essential for PDC-driven Treg generation from CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells and implicate the generation of kynurenine pathway metabolites as the critical mediator of this process. 19004406_Hydatidiform moles express IDO, but the majority of gestational trophoblastic tumors do not express this enzyme, suggesting that IDO-mediated immunoregulation is unlikely to be a major component of the malignant phenotype in these tumors. 19010841_IDO overexpression in human cancer cells contributes to tumor progression in vivo with suppression of NK cells 19050070_determined INDO mRNA expression in leukemic blasts of 286 patients with acute myeloid leukemia by gene-expression profiling; high INDO expression is a strong negative independent predicting variable for overall and relapse-free survival 19058839_House dust mite-sensitive DCs exposed to Der p 1 downregulated IDO activity and tipped the T(H)1/T(H)2 cytokine balance toward IL-4, resulting in sustainable IDO suppression. 19074858_IDO is critically involved in tumor resistance to repeated treatments with IFNgamma-NGR, likely causing excessive stimulation of tryptophan catabolism and inhibiting antitumor immune mechanisms 19106591_significance of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in recurrent breast cancer patients during chemotherapy 19155537_IDO activity and serum levels of tryptophan catabolites of the kynurenine pathway increase with chronic kidney disease (CKD) severity. In CKD, induction of IDO may primarily be a consequence of chronic inflammation. 19168733_Role in the suppressive activity of intralesional Treg cells during acute and chronic cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania guyanensis. 19264674_Our results demonstrate that IDO plays an important role in the antiviral effect of IFN-gamma against DENV infection in vitro and suggest that it has a role in the immune response to DENV infections in vivo. 19306922_Elevation of intracellular iron levels during stimulation with IFNgamma impeded IFNgamma-induced IDO mRNA and protein expression. 19353519_Induction of IDO1 by TLR involved an autocrine interferon (IFN)-beta signaling loop, which was dependent on protein kinase R 19363598_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-expression in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) may control autoimmune responses by depleting the available tryptophan, whereas tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (TTS) may counteract this effect 19434461_Imaging correlates of differential expression of IDO1 in brain neoplasms are reported. 19448397_These data support the notion that metastatic malignant melanoma cells select for expression of IDO to evade immunologic detection. 19465693_priming of resting T cells with autologous, IDO-expressing, mature moDCs results in up to 10-fold expansion of CD4(+)CD25(bright)Foxp3(+)CD127(neg) Tregs. 19487045_These results suggest that increased IDO activity is involved in disease progression of lung cancer, possibly through its immunosuppressive effect. 19489917_INDO showed significant associations with Aspirin-intolerant asthma. 19514129_Identification of genetic variants in the human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) gene, which have altered enzyme activity 19564344_impaired cytotoxic function seen in the IDO-treated CD8(+) T cells was accompanied by defects in production of granule cytotoxic proteins, including perforin and granzyme A and B 19597340_rhIDO significantly inhibited IL-2 expression in CHO cells. It decreased proliferative response & increased apoptosis in human T cells. IDO suppressed Vav1 mRNA & protein production in T cells. IDO inhibited TCR-activation-induced Vav1 phosphorylation. 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19604349_Foxp3 and IDO expression is associated with sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer 19693771_These results suggest that the activation of NF-kappaB through the PI3K-PKC-reactive oxygen species and PI3K-Akt pathways is required for the Hb-induced IDO expression in bone marrow dendritic cells. 19695096_Data show that high density indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)+ cells exist in tumor-draining lymph nodes and that IDO is down-regulated in lymph nodes with metastases, implying that IDO in tumor and immune cells functions differently. 19737010_Presented is evidence supporting the presence of an inhibitory substrate binding site in IDO that is capable of binding the substrates (L-Trp and 1-methyl-L-tryptophan), an effector (3-indole ethanol), and an uncompetitive inhibitor (Mitomycin C). 19740345_Inhibition of IDO expression with both classes of siRNAs inhibited dendritic cells immunosuppressive function on T-cell proliferation 19783182_Plasma IDO activity does not reflect the degree of lung graft acceptance, but instead is correlated with the degree of chronic inflammation. 19815714_Results suggest that functional thymic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-positive eosinophils during human infant life may have an immunomodulatory role in Th2 immune responses. 19828629_IDO1-mediated tryptophan depletion induces transcriptional repressor B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1 (BLIMP-1) in U937 cells. 19829303_IDO positive plasmacytoid dendritic cells are the classical BDCA2 positive cells in melanoma lymph nodes 19844741_increased IDO expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas is from a mixed cellular source (both cancer cells and noncancerous cells) 19929471_Dendritic cells polarizing culture conditions increased expression of IDO protein and IDO enzyme activity. 19933867_Activated T cells can induce functional IDO expression in breast and kidney tumor cell lines. IDO is expressed in the majority of breast and kidney carcinoma samples, with infiltration of activated T helper type 1-polarized T cells in human tumors. 20128646_The expression of IDO may in part explain retinal pigment epithelial mediated immune suppression effects. 20192952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20192952_Variation 'c.-147_150delGAAA' in the 5'-untranslated region of the IDO1 gene does not appear to be a primary cause of pre-eclampsia. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20361220_subtle differences between the TDO and IDO reactions 20386557_mediates immunosuppressive properties of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells 20484731_Postulate that induction of IDO may represent a critical initiating event that results in inversion of the T(H)17/T(reg) balance and in the consequent maintenance of a chronic inflammatory state in progressive HIV disease. 20522587_Human IDO transfected into composite three-dimensional islet grafts in mice, prolongs the islet allograft. 20570568_In human chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)IDO metabolic activity is intact. Reactive oxygen intermediates apparently are dispensable for IDO activity. Thus, hyperinflammation in human CGD cannot be attributed to disabled IDO activation. 20635895_Studies suggest that increased IDO activity may play an activating role in the autoimmune response. 20648630_Data suggest that high expression of protein IMPACT homolog in non-immune cells acts as a protective mechanism against indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-induced GCN2 activation, making them resistant to the amino acid-deprived environment caused by IDO. 20663292_Data show elevated levels of 3-HK modifications and the upstream, rate-limiting enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO-1) in Alzheimer's diseased brains when compared to controls. 20689575_Psychological stress stimulates cytokine-driven IDO1 activation and Trp depletion which seems to have a central role for developing stress-induced immunosuppression and behavioral alteration. 20801903_Data identify indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated catabolism as a tolerogenic mechanism exerted by leukemic dendritic cells and have clinical implications for the use of these cells for active immunotherapy of leukemia. 20938662_Data suggest that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity might play a role in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and cells that express IDO appear important for determining outcomes after R-CHOP treatment. 21028817_Binding of CO to l-Trp-bound IDO causes a significant change in the electronic and RR spectra of the heme, indicating that the pi* orbitals of the carbon atom of CO interact with pi orbitals of Fe and the porphyrin 21030093_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21030093_study concludes that there is no association between INDO polymorphisms and susceptibility of Iranian women to recurrent spontaneous abortion 21094802_Patients receiving belatacept showed greater amounts of peripheral blood CD16+/IDO+ cells and Tregs on graft biopsies than those under cyclosporine treatment. 21118329_[review] Induction of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and quinolinic acid mediates seizure activity in multiple sclerosis at least in part via an increase in interferon (IFN)gamma. 21176371_Thymosin alpha1 can up-regulate the expression of ido mRNA in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from children with aplastic anemia. 21292009_Compared to healthy volunteers, IDO concentration was twice as high in hemodialysis patients, which contributed to inadequate immune response to HBV vaccination. 21324164_Data suggest an inflammatory response characterized by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation may be relevant to the development of post-stroke cognitive impairment. 21328335_Loss of indoleamine 23-dioxygenase is associated with basal-like breast carcinoma. 21355883_High IDO Dioxygenase is associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. 21359206_IFN-gamma inhibited proliferation and altered human and mouse MSC neural, adipocytic and osteocytic differentiation via the activation of IDO. 21361337_Studies indicate that the heme dioxygenases are differentiated by their ability to catalyze the oxidation of l-tryptophan to N-formylkynurenine. 21461563_The intensity of IDO immunostaining was lower in the preeclamptic placentae than in the normal controls, and was related to the clinical severity of the preeclampsia. 21461581_IDO plays a key role in gastric cancer immune suppression, possibly by inhibiting T cell-mediated cytotoxicity and proliferation in vitro. 21487895_These results suggest that the activity of IDO enzyme is insufficient in immune thrombocytopenia patients. 21501890_in infectious, but also in noninfectious human cutaneous granulomas the large myeloid CD11c(+)S100(+)CD68(-) dendritic cells and the CD68(+) macrophages express IDO. 21502325_analysis of ferryl derivatives of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 21517752_This article reviews the interplay between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in chronic inflammation and cancer. 21517753_This review offers a survey of preclinical literature suggesting that IDO functions as a modifier of inflammatory states rather than simply as a suppressor of immune function. 21517755_The paper suggests that IDO may represent an important regulatory checkpoint influencing Regulatory T cells activity: both by stabilizing and augmenting the suppressive phenotype, and by preventing reprogramming into non-suppressive helper-like cells. 21517756_IDO is widely expressed in human tissues and cell subsets, including dendritic cells, where it modulates their function by increasing tolerogenic capacities. 21517757_As it is comprehensively reviewed, IDO competence in human dendritic cells, in general, is induced by molecules such as interferon-gamma, which otherwise initiate immunity. 21575365_Treatment with thymosin alpha1 downregulated TLR9 expression but upregulated IDO expression in a concentration- and time-dependent manner in aplastic anemia mesenchymal stem cells. 21592112_data suggest that M. leprae chronic infection activates the suppressive molecule IDO which, in turn, contributes to the specific immunosuppression observed in lepromatous leprosy 21600662_In women, IDO activity moderated the association between depressive symptoms and carotid intimamedia thickness (IMT), so that a longitudinal association between depressive symptoms and IMT was found only in combination with high IDO activity 21616522_indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression seems to be an independent prognostic factor in patients with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma . 21617756_It is possible that the substitution c.422+90G-->A; rs4613984 in an intron downstream to exon 4 of indoleamine 2, 3- dioxygenase (IDO) may be related with cataract formation among the aged. 21690092_trace amounts of peroxide previously proposed to occur in NADH solutions as well as solid NADH activate IDO and lead to aerobic formation of superoxide and the reactive dioxygen adduct of the enzyme. 21691274_The findings in Caucasians further support the notion that IDO has an important role in cytokine-induced behavioral changes. 21692032_IDO expression in lower lip squamous cell carcinoma may aid immune escape and chronic inflammation to promote cancer progression. 21693183_Our results suggest no influence of the variants in the IDO gene and the diagnosis of interferon-alpha-related depression in the Brazilian population. 21712776_Somatization is characterized by increased IDO activity 21742973_the ability of IDO-expressing tumor cells to thrive in a tryptophan-depleted microenvironment by expressing a novel, highly tryptophan-specific transporter, which is resistant to inhibition by most other amino acids 21755000_A gradient of vascular endothelial IDO1 expression is present at both sides of the feto-maternal interface. 21823214_High Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase-1 is associated with Crohn's disease. 21835147_The proportion of CD4(+)IDO(+) T cells was significantly higher in patients with moderate GVHD. 21835273_Purification and kinetic characterization of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases 1 and 2 (IDO1 and IDO2) and discovery of selective IDO1 inhibitors. 21892828_The data suggest that IDO uses a ring-opening mechanism during N-formylkynurenine formation, rather than Criegee or dioxetane mechanisms as previously proposed. 21952237_ligation of TLR-3 by poly(I:C) induces IDO expression in human first-trimester trophoblasts via an IFN-beta-dependent pathway 21980470_identification of a variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism in IDO1 promoter and characterization of LEF-1 response elements 22013481_high expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with impaired overall survival time 22039265_Data suggest a strong association of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity with the severity and outcome of clinical graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). 22069308_a novel role for interleukin-27 (IL-27) as mediator of intestinal epithelial barrier protection mediated via DMBT1 and IDO1 22093628_Expression of IDO is associated with clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, and microvessel density in breast cancer. 22110525_upregulated expression in primary breast cancer correlates with increase of infiltrated regulatory T cells and lymph node metastasis 22112045_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression and serum kynurenine concentrations in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 22184722_T cells isolated from the hepatocellular carcinoma tissues expressed significantly more CD69 molecules than did those on paired circulating and nontumor-infiltrating T cells; these tumor-derived CD69(+) T cells could induce considerable IDO in monocytes 22202241_expression of IDO did not correlate to histologic classification, tumor size, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion and lymph nodes metastasis, but it was correlated to clinical stage 22301793_although IDO is not required by MDM for the clearance of established viral infection, the spread of flavivirus infection is limited by IDO expressed in uninfected, neighboring cells. 22424783_zebularine plus interferon gamma induce IDO1 gene expression related to demethylation events in the IDO1 promoter region and to up-regulation of expression of transcription factors 22519828_results show that cholera toxin per se does not induce the expression of functional IDO protein 22526360_The expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells of immune thrombocytopenia patients was significantly decreased. 22592557_IDO1 activation represents a local compensatory mechanism to limit obesity-induced inflammation and hypertension. 22638210_IDO1 is possibly involved in endometriosis pathogenesis via promoting COX-2 and MMP-9 expression and regulation of endometrial stromal cells biological characteristics 22690871_The cystine/glutamate antiporter regulates the functional expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in human dendritic cells. 22722711_Data indicate that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is expressed in primary MMCs to a low degree and is unlikely to play a direct major role in vivo in dampening antitumor immunity. 22751107_observed elevated plasma IDO activity in patients with both pain and depression 22828446_High IDO expression is associated with acute graft-versus-host disease. 22860140_Activation of IDO1 appeared to be a defensive mechanism downstream of IFN-gamma that limited intracellular expansion of Orientia tsutsugamushi via tryptophan depletion. 22891315_IDO inserts oxygen into indole in a reaction that is mechanistically analogous to the 'peroxide shunt' pathway of cytochrome P450. 22913669_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E-2 are key modulators involved in the mesoangioblast suppression of T-cell proliferation. 22923135_IDO downregulation enhanced the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to natural killer cells in vitro and promoted NK cell accumulation in the tumor stroma in vivo. 22929065_Data suggest that IDO activity may be a risk factor for future depression especially in women. IDO-induced alterations in serotonergic function may offer one biologic explanation to the well-established associations between inflammation and depression. 22932670_A critical role for IDO-mediated immunosuppression in glioma. 22936460_The upregulation of IDO1 in peripheral blood dendritic cells after maturation was significantly reduced in immune thrombocytopenia. 23090116_Systemic delivery of Salmonella typhimurium transformed with IDO shRNA enhances intratumoral vector colonization and suppresses tumor growth. 23109825_Downregulation of CD4 expression by IDO was significantly attenuated by the addition of tryptophan or IDO inhibitor in the infected C8166 cells. 23179760_Tumoral indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase express-ion predicts poor outcome in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 23200754_Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase gene polymorphisms correlate with CD8+ Treg impairment in systemic sclerosis. 23209301_IDO has a novel function of catalyzing physiological peroxidase reactions. 23232072_These data suggest that IDO1 expression may contribute to immune suppression in patients with multiple myeloma and possibly other hepatocyte growth factor-producing cancers. 23289444_IDO plays an important role in the pregnancy-specific immune tolerance, and might be a contributing factor in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 23344392_Indoleamine 2-3 dioxygenase (IDO1) is expressed in breast cancer tissue, as shown by immunohistochemistry. Expression is lower in ER- breast tumors with greater neoangiogenesis. 23358471_Freshly-resected meningiomas expressed both LAT1, the tryptophan transporter system and IDO, demonstrating an active kynurenine pathway. Dissociated meningioma cells lost IDO expression. 23411497_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 (IDO1) enhances survival and invasiveness of endometrial stromal cells via the activation of JNK signaling pathway. 23413147_decrease in activity could constitute a relevant biomarker for the restoration of the immune response during visceral leishmaniasis 23426156_IDO is expressed more strongly in both primary and secondary glioblastoma tissue than low-grade glioma and may affect clinical outcome 23440412_Myeloid-derived suppressor cells suppress antitumor immune responses through IDO expression and correlate with lymph node metastasis in patients with breast cancer. 23620105_the data provide proof-of-principle that immunisation with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase -silenced DC vaccine is safe and effective in inducing antitumour immunity. 23651343_Indoleamine2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase may play critical roles in the immune pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. 23669411_In human colon cancer cells, blockade of IDO1 activity reduced nuclear and activated b-catenin, transcription of its target genes (cyclin D1 and Axin2), and, ultimately, proliferation. 23682557_Results show that expressions of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) mRNA and protein were coincidentally higher in non-Hodgkin lymphoma tissues. 23751345_study reports on the contribution of all the individual cysteine residues towards the overall catalytic properties, secondary structure, heme environment and stability of IDO1 23752227_The immunosuppressive role of IDO is to target immune checkpoints |
ENSMUSG00000031551 |
Ido1 |
14.640450 |
2.3351467153 |
1.223513 |
0.457838381 |
7.193337 |
0.00731747698924336761883147062235366320237517356872558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014435439770279619164927709107359987683594226837158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.3150616 |
5.5724097 |
9.6697128 |
2.0026799 |
| ENSG00000131242 |
84440 |
RAB11FIP4 |
protein_coding |
Q86YS3 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of endocytic traffic by participating in membrane delivery. Required for the abcission step in cytokinesis, possibly by acting as an 'address tag' delivering recycling endosome membranes to the cleavage furrow during late cytokinesis. In case of infection by HCMV (human cytomegalovirus), may participate in egress of the virus out of nucleus; this function is independent of ARF6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12470645}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene interacts with RAB11 and is thought to be involved in bringing recycling endosome membranes to the cleavage furrow in late cytokinesis. Hypoxic conditions can lead to an upregulation of the encoded protein and enhance the metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:84440; |
cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; midbody [GO:0030496]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; spindle [GO:0005819]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465] |
12470645_Rab11-FIP4 interacts with Rab11 in a GTP-dependent manner and its overexpression condenses the Rab11 positive compartment in HeLa cells. 12857874_Rab11 FIP4 was also discovered through a yeast two-hybrid screen for Arf5 effectors and named Arfophilin-2, as described here. Rab11 FIP4/Arfophilin-2 was shown to localize to a perinuclear compartment, the centrosome, and focal adhesions in HeLa cells. Rab11 FIP4/Arfophilin-2 over-expression was shown to cluster the Rab11-positive endosomal recycling compartment around the centrosome. 16148947_FIP3 and FIP4 serve to couple Rab11-positive vesicle traffic from recycling endosomes to the cleavage furrow/midbody where they are tethered prior to fusion events via interactions with Arf6 and the Exocyst. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25745995_Results show the expression of Rab11-FIP4 upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and correlated with poor prognosis. Rab11-FIP4 dramatically contributed to HCC metastasis via phosphorylation of PRAS40. 28035375_Our findings suggest that overexpression of Rab11-FIP4 predicts poor clinical outcomes for pancreatic cancer and contributes to pancreatic tumor progression. 29257314_Rab11-FIP4 expression promotes migration and invasion of colon cancer cells and correlates with poor prognosis. |
ENSMUSG00000017639 |
Rab11fip4 |
219.504178 |
2.0721351106 |
1.051118 |
0.203412793 |
26.314175 |
0.00000029015122799500975352851128534481528475907907704822719097137451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001087514506146862452447927546717032498690969077870249748229980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
285.3180039 |
36.8587959 |
138.7116357 |
13.1874344 |
| ENSG00000131323 |
7187 |
TRAF3 |
protein_coding |
Q13114 |
FUNCTION: Cytoplasmic E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates various signaling pathways, such as the NF-kappa-B, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and interferon regulatory factor (IRF) pathways, and thus controls a lot of biological processes in both immune and non-immune cell types (PubMed:33148796, PubMed:33608556). In TLR and RLR signaling pathways, acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase promoting the synthesis of 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains on several substrates such as ASC that lead to the activation of the type I interferon response or the inflammasome (PubMed:25847972, PubMed:27980081). Following the activation of certain TLRs such as TLR4, acts as a negative NF-kappa-B regulator, possibly to avoid unregulated inflammatory response, and its degradation via 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination is required for MAPK activation and production of inflammatory cytokines. Alternatively, when TLR4 orchestrates bacterial expulsion, TRAF3 undergoes 'Lys-33'-linked polyubiquitination and subsequently binds to RALGDS, mobilizing the exocyst complex to rapidly expel intracellular bacteria back for clearance (PubMed:27438768). Acts also as a constitutive negative regulator of the alternative NF-kappa-B pathway, which controls B-cell survival and lymphoid organ development. Required for normal antibody isotype switching from IgM to IgG. Plays a role T-cell dependent immune responses. Down-regulates proteolytic processing of NFKB2, and thereby inhibits non-canonical activation of NF-kappa-B. Promotes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of MAP3K14. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15084608, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15383523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17991829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19937093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20097753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20185819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25847972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27980081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32562145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33148796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33608556, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34011520}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Endosome;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Thioester bond;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) protein family. TRAF proteins associate with, and mediate the signal transduction from, members of the TNF receptor (TNFR) superfamily. This protein participates in the signal transduction of CD40, a TNFR family member important for the activation of the immune response. This protein is found to be a critical component of the lymphotoxin-beta receptor (LTbetaR) signaling complex, which induces NF-kappaB activation and cell death initiated by LTbeta ligation. Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent infection membrane protein-1 (LMP1) can interact with this and several other members of the TRAF family, which may be essential for the oncogenic effects of LMP1. The protein also plays a role in the regulation of antiviral response. Mutations in this are associated with Encephalopathy, acute, infection-induced, herpes-specific 5. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:7187; |
CD40 receptor complex [GO:0035631]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; serine/threonine protein kinase complex [GO:1902554]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; thioesterase binding [GO:0031996]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070534]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050688]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032648]; regulation of proteolysis [GO:0030162]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; Toll signaling pathway [GO:0008063]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224]; TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035666]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] |
12136149_The TRAF domain from TRAF3 has been crystallized. 12220533_results suggest that in DG75 cells, TRAF3-induced MEK1 activation may be involved in CD40-mediated upregulation of IL-4-driven germline C epsilon transcription 12270937_Results establish a major role of TRAF3 and -6 in X-linked ectodermal dysplasia receptor (XEDAR) signaling and in the process of ectodermal differentiation. 12471121_TRAF3 interacts with BAFFR in yeast two-hybrid assays and in TALL-1-treated B lymphoma cells and is a negative regulator of BAFFR-mediated NF-kappa B activation and IL-10 production. 12571250_TRAF2, TRAF3, cIAP1, Smac, and lymphotoxin beta receptor associate and are involved in apoptosis 12860972_EBV LMP1 blocks p16INK4 pathway by promoting nuclear export of E2F-4 and E2F-5. 14517219_the TRAF3-binding crevice has hot spots that promote molecular interactions driving specific signaling after contact with LTbetaR, CD40, or the downstream regulator TANK 14716302_LMP1 associated protein induces micronucleus formation, represses DNA repair and enhances sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents in human epithelial cells. 15084608_induction of noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling may involve the rescue of NIK from TRAF3-mediated negative regulation 15383523_there is a novel association between TRAF2 and TRAF3 that is mediated by unique portions of each protein and that specifically regulates activation of NF-kappaB, but not AP-1 15514968_LMP-1 proteins are required for in vitro growth of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells. 15585864_This study of the crystal structure of TRAF3 bound in complex with BAFF-R reveals the dynamic conformational adjustment of Tyr377 in TRAF3 that occurs forming a new intermolecular contact with BAFF-R that stabilizes the complex. 15708970_TRAF3 specifically blocked the NF-kappaB activation via TRAF2/5. 16009714_LMP1 from the Epstein-Barr virus is a structural CD40 decoy in B lymphocytes for binding to TRAF3. 16280329_LMP1 utilizes two distinct pathways to activate NF-kappaB: a major one through CTAR2/TRAF6/TAK1/IKKbeta (canonical pathway) and a minor one through CTAR1/TRAF3/NIK/IKKalpha (noncanonical pathway) 16311516_These data indicate that vFLIP uses TRAF2 and TRAF3 for signalling to NF-kappaB, which is crucial for KSHV-associated lymphomagenesis 16429118_TRAF3 stabilization, JNK activation and caspase-9 induction define a novel pathway of CD40-mediated apoptosis in carcinoma cells. 16582590_TRAF3 has a role in innate antiviral immunity [review] 16858409_TRAF3, like Cardif, is required for type I interferon production in response to intracellular double-stranded RNA. 17586463_The current data support the notion that LMP1 modifies stress-induced apoptosis in epithelial cells through molecular interactions downstream of its C-terminal signaling domain. 17608743_Results show that decrease in the ubiquitination of TRAF3 is YopJ-dependent and to prevent or is to remove the K63-polymerized ubiquitin conjugates required for signal transduction. 17626074_Dominant-negative forms of TRAF2 and TRAF3 inhibited but did not fully block LMP1-mediated transformation. 17692805_Inactivation of TRAF3 is associated with multiple myeloma 18042799_LMP1's activation of the unfolded protein response is a normal event in a continuum of LMP1's expression that leads both to stimulatory and inhibitory functions and regulates the physiology of epstein barr virus-infected B cells. 18275617_The researchers found an association between LMP1 30-bp deletion or XhoI-loss with Chinese race and type III nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 18607851_Somatic mutation of TRAF3 gene is rare in common human cancers and acute leukemias. 18614628_These findings indicate that the NY-1V Hantavirus Gn cytoplasmic tail forms a complex with TRAF3 which disrupts the formation of TBK1-TRAF3 complexes and downstream signaling responses required for IFN-beta transcription. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19419966_c-Src enhances RIG-I-mediated signaling, acting at the level of TRAF3 19667091_TRAF2/3 binding affinity and TRAF2/3 binding site sequence dictate a distinct subset of CD40 antigen versus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) signaling properties. 19693093_biallelic inactivation of TRAF3 and lower expression of its mRNA occures with del(14) due to breaks in IGH and ZEP36L1 regions 19893624_Triad3A represents a versatile E3 ubiquitin ligase that negatively regulates RIG-like receptor signaling by targeting TRAF3 for degradation following RNA virus infection. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19954665_Lack of TRAF3 expression might be one of the reasons for the aberrant expression of the unclassical NF-kappaB activity in Hodgkin's lymphoma cells. 19996094_Findings suggest that OTUB1 and OTUB2 negatively regulate virus-triggered type I IFN induction and cellular antiviral response by deubiquitinating TRAF3 and -6. 20008286_CD40L induces apoptosis by influencing the balance between apoptotic and survival signals, by stabilizing TRAF3 to induce apoptosis and by suppressing TRAF6 survival signals 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20097753_virus-triggered ubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6 by cIAP1 and cIAP2 is essential for type I IFN induction and cellular antiviral response 20138174_Data found that BS69 directly interacted with TRAF3, a negative regulator of NF-kappaB activation. Results revealed that TRAF3 was involved in the BS69-mediated suppression of LMP1/CTAR1-induced NF-kappaB activation. 20185819_Modulation of cellular TRAF3 levels may thus contribute to regulation of NFkappaB-dependent gene expression by LTBR by affecting the balance of LTBR-dependent activation of canonical and non-canonical NFkappaB pathways. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20348096_the LTbetaR modifies the ubiquitin:NIK E3 ligase, and also acts as an allosteric regulator of the ubiquitin:TRAF E3 ligase 20504251_An association was found between MGP -7A>G and CD40 -1C>T polymorphisms, and reocclusion risk. 20585848_Taken together, LMP1 activates alternative NF-kappaB pathway through functional NIK and IKKalpha that is regulated by TRAF2 or TRAF3. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20832341_Toll-like receptor 3-mediated immunity against primary infection by Herpes Simplex Virus 1 in the central nervous system is critically dependent on TRAF3. 21041727_Although located outside of any known TRAF binding sites, the Pro227Ala polymorphism can alter TRAF binding and dramatically changes the role played by TRAF3 in CD40 signaling. 21084666_In contrast to TRAF3 transgenic mice lacking TRAF3 in B cells, T cell TRAF3-deficient mice exhibit defective IgG1 responses to T-dependent antigen, as well as impaired T cell-mediated immunity to infection with Listeria monocytogenes. 21228035_Data show that IKBalpha, NFKB2, and TRAF3 gene polymorphisms play a role in the development of multiple myeloma and in the response to bortezomib therapy. 21660053_Studies indicate that TRAF3 plays a highly versatile role of in immunity-related signal transduction. 21864338_Interaction was observed between LMP1 and TRAF2 or TRAF3 and mutation of the LMP1 signaling domains reduced the interaction. 22017431_TRAF3 participates in a number of the regulatory post-translational modifications involving ubiquitin that are important in various signaling pathways. 22079989_MIP-T3 is unique among cellular inhibitors of innate immunity because it appears to affect TRAF3 ubiquitination only slightly, but is capable of preventing TRAF3 from engaging downstream transducers and effectors. 22469134_Genetic lesions of the TRAF3 and MAP3K14 genes in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 22709905_A novel microRNA-32 mediated mechanism regulates TRAF3 in human microglial cells exposed to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 Tat protein. 22715070_TRAF3 functioned as ubiquitin E3 ligase for calcineurin and promoted its degradation. 22792062_model proposed where dsDNA and dsRNA sensing induces the formation of membrane-bound compartments originating from the Golgi, which mediate the dynamic association of TRAF3 with MAVS leading to an optimal induction of innate immune responses 22901541_Ubiquitination of NEMO negatively regulates the interferon antiviral response through disruption of the MAVS-TRAF3 complex. 23303668_Levels of TRAF3 degradation correlate with number of cells infected with Chlamydia pneumoniae, because more TRAF3 is detected at a lower multiplicity of C. pneumoniae infection. 23329887_TRAF3 and TRAF5 are overexpressed in inflammatory bowel disease. Although the endoscopic appearance can be normal, TRAF3 and TRAF5 pre-activation can be detected in non-inflamed colonic segments 23333941_In an attempt to explore TRAF3 binding partners that may be involved in TRAF3-regulated signaling, a yeast two-hybrid screen of a human spleen cDNA library was undertaken. RIP2 was identified as a TRAF3 binding partner. 23612708_noncanonical NF-kappaB activation by Tio depends on a distinct sequence motif that directly recruits tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3). 23986588_These findings demonstrate that herpes simplex virus 1 ubiquitin-specific protease UL36 removes polyubiquitin chains on TRAF3 and counteracts the IFN-beta pathway. 24260396_SUMOylation is required for optimal TRAF3 signaling capacity. 24433987_It has become increasingly evident that the roles and functions of TRAF3 are highly context-dependent. TRAF3 can serve distinct roles for different receptors in the same cell, and also has highly cell-type-dependent functions. 24671418_a mechanistic basis for Traf3 alternative splicing and ncNFkappaB activation in contributing to T cell-dependent adaptive immunity. 24739416_The role of TRAF3 and NIK in T cell malignancies is clarified. Results indicate that TRAF3 differentially governs the growth of B and T cell cancers. 24763515_After viral infection, HSCARG interacted with tumor necrosis receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) and inhibited its ubiquitination by promoting the recruitment of OTUB1 to TRAF3. 25051892_preventing CD40-TRAF2,3 or CD40-TRAF6 interaction inhibits pro-inflammatory responses in human non-haematopoietic cells. 25468570_Focal genetic loss of TRAF3 is recurrent in human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 25723057_TRAF3 regulates signaling to T cells not only through costimulatory members of the TNFR superfamily, but also through the T cell receptor complex, and cytokine receptors. 26034202_Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) is a positive regulator of pathological cardiac hypertrophy in mice and humans. 26186972_ESR1 directly interacts with TRAF3 and promotes K48-linked proteasomal degradation of TRAF3. 26329582_findings identify TRAF3 and PTPN22 as inhibitors of IL-6R signaling in B cells and reveal a previously uncharacterized role for TRAF3 in the regulation of plasma cell differentiation 26454171_RIG-I-like receptor mediated antiviral innate immune responses in the lower respiratory tract involves TRAF3 and TRAF5 signaling. 26456228_These findings suggest that RNF166 positively regulates RNA virus-triggered IFN-beta production by enhancing the ubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6. 26519536_these findings demonstrate that WDR82 is a negative regulator of virus-triggered type I IFNs pathway through mediating TRAF3 polyubiquitination status and stability on mitochondria. 26755589_TRAF3 regulates B-cell survival via inhibition of CREB stability 26779844_Study presents the characterization of the peptide binding preferences of TRAFs 2, 3, and 5 using deep mutational scanning. The three TRAF proteins demonstrated different preferences for binding to members of the CD40 library, and three peptides from that library individually showed striking differences in affinity for the three TRAFs. 26928339_Findings establish CK1varepsilon as a regulator of antiviral innate immune responses and indicate a novel mechanism of immunoregulation that involves CK1varepsilon-mediated phosphorylation of TRAF3. 27003818_PLK1 overexpression in prostate epithelial cells triggers oncogenic transformation. The signaling mechanisms underlying the observed cellular effects of PLK1 involve direct PLK1-dependent phosphorylation of CRAF with subsequent stimulation of the MEK1/2-ERK1/2-Fra1-ZEB1/2 signaling pathway. 27026194_OPN acts as a positive regulator in innate antiviral immunity through stabilization of TRAF3. 27026631_TRAF3 epigenetics may significantly contribute to the variability of clopidogrel response and recurrence of ischemic events in patients with stroke. 27154354_An important B cell-specific role for TNFR-associated factor 3 is the inhibition of homeostatic survival, directly relevant to the common occurrence of TNFR-associated factor 3 mutations in human B cell malignancies. Review. 27208423_Viral proteins aim to subvert TRAF3 antiviral action. 27213432_Mechanistic studies showed that HACE1 exerts its inhibitory role on virus-induced signaling by disrupting the MAVS-TRAF3 complex. 27387501_The NleB effector limited host IFN-beta production by inhibiting Lys(63)-linked ubiquitination of TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3). Inhibition was dependent on the glycosyltransferase activity of NleB. 27493095_Taken all together, Helicobacter pylori toxin Tip-alpha might activate NF-kappaB to promote inflammation and carcinogenesis by inhibiting miR-3178 expression, which directly targets TRAF3, during Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric mucosal epithelial cells. 27752131_These results indicate that TRAF3 deficiency suffices to metabolically reprogram B cells, a finding that improves our understanding of the role of TRAF3 as a tumor suppressor, and suggests potential therapeutic strategies. 27980081_DDX3 directly regulates TRAF3 ubiquitination and acts as a scaffold to co-ordinate assembly of signaling complexes downstream from MAVS. 28031331_These data suggest an interplay between CELF2 and hnRNP C as the mechanistic basis for activation-dependent alternative splicing of TRAF3 exon 8. 28181356_Association between the rs1883832 and rs3765459 CD40 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to cervical cancer in a subset of Malaysian population. 28219902_NDR1 interacts with TRAF3 and interferes with the association of TRAF3 and IL-17R, resulting in increased formation of the activation complex IL-17R-Act1, which is required for the downstream signaling and production of pro-inflammatory factors 28295222_The current investigations identified a subset of HPV-positive HNSCCs with mutations in the genes TRAF3 (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3) and CYLD (cylindromatosis lysine 63 deubiquitinase). Defects in TRAF3 and CYLD correlated with the activation of transcriptional factor nuclear factor kappaB, episomal HPV status of tumors, and improved patient survival. 28479387_The GA genotype and GA+AA genotype of TRAF3 rs12147254 were found to increase the risk of coronary heart disease among T2DM patients. the GACGAC haplotype in TRAF3 had a protective effect on T2DM micro-macrovascular complications. 28559278_Data suggest that UBR5 down-regulates levels of TRAF3, a key component of Toll-like receptor signaling, via the miRNA pathway; p90RSK is an upstream regulator of UBR5; p90RSK phosphorylates UBR5 as required for translational repression of TRAF3 mRNA. (UBR5 = ubiquitin protein ligase E3 component n-recognin 5 protein; TRAF3 = TNF receptor-associated factor 3; p90RSK = 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase) 28627449_MicroRNA-214 regulates immunity-related genes in bovine mammary epithelial cells by targeting NFATc3 and TRA 29146913_Data show that TNF receptor-associated factor 3 (TRAF3) autophagy is driven by RAS and results in activation of transcription factor RelB (RELB). 29693188_Study demonstrated that TRAF3, as a novel RIP2 binding partner, was downregulated in glioma tissues and functionally was a negative regulator involved in RIP2induced glioma cell growth. 29765142_The present study confirms that genes involved in activation of NF-kappaB-signaling pathways are a major driver in oncogenesis of H. pylori eradication-resistant gastric marginal zone lymphoma and revealed that TRAF3 mutation is a major contributor in MALT1 rearrangement-negative gastric marginal zone lymphoma. 29875129_The authors found that tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), as well as TRAF1 and 3, directly binds to the active caspase-2 dimer. 29903906_The findings suggest that Parkin plays a novel role in innate immune signaling by targeting TRAF3 for degradation and maintaining the balance of innate antiviral immunity. 29921694_Overexpression of TRAF3 in HPV(+) cell lines with decreased endogenous TRAF3 inhibited NF-kappaB2/RELB expression, nuclear localization, and NF-kappaB reporter activity, while increasing the expression of IFNA1 mRNA and protein and sensitizing cells to its growth inhibition. Overexpression of TRAF3 also enhanced TP53 and RB tumor suppressor proteins and decreased HPV E6 oncoprotein in HPV(+) cells 30018345_A TRAF3-NIK axis differentially regulates viral DNA vs RNA pathways in innate immune signaling. 30226589_Study identified that TRAF3 was a direct and functional target of the miR-17-92 cluster in MGC-803 gastric cancer cells. The loss-of-function of TRAF3 led to the acquirement of phenotypes, like what had been observed in the MGC-803 cells overexpressing the miR-17-92 cluster. Survival analyses revealed that TRAF3 served as an important prognostic indicator in patients with gastric cancer. 30319624_TRAF3 is also now known to function as a resident nuclear protein, and to impact B cell metabolism. Through these and additional mechanisms TRAF3 exerts powerful restraint upon B cell survival and activation. It is thus perhaps not surprising that TRAF3 has been revealed as an important tumor suppressor in B cells. 30323820_TRAF3 protein levels decrease in bone and bone marrow during aging in mice and humans. Development of drugs to prevent TRAF3 degradation in immune and bone cells could be a novel therapeutic approach to prevent or reduce bone loss and the incidence of several common diseases associated with aging. 30463990_TRAF3 rs12435483 confer genetic susceptibility to cervical precancerous lesions. 30687320_Study results indicate that TRAF3, perhaps by promoting exacerbated B cell responses to certain antigens, and BCL2, presumably by supporting survival of these clones, cooperate to induce mature B cell neoplasms in transgenic mice expressing human proteins. TRAF3 upregulation favors the production of V(H)DJ(H) rearrangements producing HCDR3 sequences similar to those recognizing PAMPs and DAMPs. 30692554_Results identify TRAF3 as a novel candidate gene for gallstone disease (GSD) and gallbladder cancer (GBC) in the high-risk Chilean admixed population. Gene expression analyses indicated that TRAF3 was significantly decreased in gallbladder and duodenal mucosa of GSD individuals compared to healthy controls. 31016787_Construction of Traf3 knockout liver cancer cell line using CRISPR/Cas9 system. 31322228_TRAF3 as a functional target of miR-671-3p. 31390091_Results found that TRAF3IP3 mediates TRAF3 recruitment to MAVS upon virus infection. 31501481_TRAF3 regulates the oncogenic proteins Pim2 and c-Myc to restrain survival in normal and malignant B cells. 31539122_Long non-coding RNA MEG3 represses cholangiocarcinoma by regulating miR-361-5p/TRAF3 axis. 31666375_data identify a new molecular determinant of USP7 recognition, TRAF3/6-specific targeting by the deubiquitinase, associated activation of these TRAFs by vIRF-2, and activities of vIRF-2 and vIRF-2-USP7 interaction in HHV-8 latent and lytic biology 31826940_these findings suggest that TRAF3-regulated choline metabolism has diagnostic and therapeutic value for B cell malignancies with TRAF3 deletions or relevant mutations 31922244_SMAC mimetic birinapant inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by activating the cIAP1/TRAF3 signaling pathway. 32647955_MicroRNA MiR-27a-5p Alleviates the Cerulein-Induced Cell Apoptosis and Inflammatory Injury of AR42J Cells by Targeting Traf3 in Acute Pancreatitis. 32656094_Results demonstrate that PDCoV NS7a inhibits IFN-beta production by disrupting the association of IKKepsilon with both TRAF3 and IRF3, revealing a new mechanism utilized by a PDCoV accessory protein to evade the host antiviral innate immune response. 32744342_Identification of putative phenotype-modifying genetic factors associated with phenotypic diversity in Brooke-Spiegler syndrome. 32779804_SHP-1 suppresses the antiviral innate immune response by targeting TRAF3. 32802180_Lentinan-functionalized Selenium Nanoparticles target Tumor Cell Mitochondria via TLR4/TRAF3/MFN1 pathway. 33414375_TRAF3 mediates neuronal apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage via targeting TAK1-dependent MAPKs and NF-kappaB pathways. 33692778_Swine Acute Diarrhea Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein Antagonizes Interferon-beta Production via Blocking the Interaction Between TRAF3 and TBK1. 33718275_Rv3722c Promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Survival in Macrophages by Interacting With TRAF3. 33784010_Hypoxic colorectal cancer-derived extracellular vesicles deliver microRNA-361-3p to facilitate cell proliferation by targeting TRAF3 via the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathways. 34011520_Inducible ATP1B1 Upregulates Antiviral Innate Immune Responses by the Ubiquitination of TRAF3 and TRAF6. 34075889_Mechanism of inflammasome activation by SARS coronavirus 3a protein: abridged secondary publication. 34257589_Brief Research Report Regional Difference in TRAF2 and TRAF3 Gene Mutations in Colon Cancers. 34587513_RIP2 knockdown inhibits cartilage degradation and oxidative stress in IL-1beta-treated chondrocytes via regulating TRAF3 and inhibiting p38 MAPK pathway. 34745083_Mitochondrial Fission Factor Is a Novel Interacting Protein of the Critical B Cell Survival Regulator TRAF3 in B Lymphocytes. 35413678_Circ_0050908 up-regulates TRAF3 by sponging miR-324-5p to aggravate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. 35472012_TRAF3 alterations are frequent in del-3'IGH chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients and define a specific subgroup with adverse clinical features. 35960817_Immunodeficiency, autoimmunity, and increased risk of B cell malignancy in humans with TRAF3 mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000021277 |
Traf3 |
452.469226 |
2.0812733737 |
1.057466 |
0.103102745 |
104.331875 |
0.00000000000000000000000171113937233264259327588215518783136637033617465920950430867736508956655772095700740464963018894195556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000018040297954021289841984267504619235491654761131303753741853598130395752718868607189506292343139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
623.4091253 |
41.4682941 |
301.6794045 |
14.9870344 |
| ENSG00000131370 |
9467 |
SH3BP5 |
protein_coding |
O60239 |
FUNCTION: Functions as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) with specificity for RAB11A and RAB25 (PubMed:26506309, PubMed:30217979). Inhibits the auto- and transphosphorylation activity of BTK. Plays a negative regulatory role in BTK-related cytoplasmic signaling in B-cells. May be involved in BCR-induced apoptotic cell death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10339589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26506309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30217979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9571151}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3-binding |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and protein kinase inhibitor activity. Acts upstream of or within intracellular signal transduction. Located in cytoplasmic vesicle membrane and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9467; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061099]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15158451_mitochondrial protein Sab is phosphorylated by stress-activated protein kinase 3 23861391_SH3BP5 binds to JNK and directly inhibits JNK through its two putative mitogen-activated protein kinase interaction motifs (KIMs). 25666017_The interplay of p-JNK with mitochondrial Sab leads to impaired respiration, ROS production, sustained JNK activation, and apoptosis. 26745340_REI/SH3BP5 protein family is conserved in evolution and is a group of new guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rab11. 27184832_SH3BP5, LMO3, and SNAP25 were expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells and associated with clinical features. 30322886_SH3 domain binding protein 5 (Sab) expression is reduced in ovarian cancer (OC), suggesting that Sab may be a prognostic biomarker to discern personalized treatments for OC patients. 31546831_Study found that expression of SH3BP5 was enhanced in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and was negatively correlated with patients survival. Elevated expression of SH3BP5 was an independent prognostic factor for AML patients. Furthermore, SH3BP5-mediated activation of JNK-BAD signaling contributes to the survival of AML cells. 32066809_trans-Fatty acids facilitate DNA damage-induced apoptosis through the mitochondrial JNK-Sab-ROS positive feedback loop. 34128958_Tankyrase regulates epithelial lumen formation via suppression of Rab11 GEFs. 34783986_Novel blood-based hypomethylation of SH3BP5 is associated with very early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000021892 |
Sh3bp5 |
128.393539 |
2.5980145625 |
1.377410 |
0.207878945 |
43.342108 |
0.00000000004595861516563324741938371400477164607778490790224168449640274047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000243223076315793007175841350530503572058282912848881096579134464263916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
186.3106225 |
20.6306491 |
72.2067993 |
6.1874108 |
| ENSG00000131378 |
23180 |
RFTN1 |
protein_coding |
Q14699 |
FUNCTION: Involved in protein trafficking via association with clathrin and AP2 complex (PubMed:27022195, PubMed:21266579). Upon bacterial lipopolysaccharide stimulation, mediates internalization of TLR4 to endosomes in dendritic cells and macrophages; and internalization of poly(I:C) to TLR3-positive endosomes in myeloid dendritic cells and epithelial cells; resulting in activation of TICAM1-mediated signaling and subsequent IFNB1 production (PubMed:27022195, PubMed:21266579). Involved in T-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling by regulating tyrosine kinase LCK localization, T-cell dependent antibody production and cytokine secretion (By similarity). May regulate B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling (PubMed:12805216). May play a pivotal role in the formation and/or maintenance of lipid rafts (PubMed:12805216). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6A0D4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12805216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21266579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27022195}. |
Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables double-stranded RNA binding activity. Involved in B cell receptor signaling pathway; membrane raft assembly; and positive regulation of growth rate. Acts upstream of or within dsRNA transport; response to exogenous dsRNA; and toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway. Located in endosome; membrane raft; and plasma membrane. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23180; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; dsRNA transport [GO:0033227]; membrane raft assembly [GO:0001765]; positive regulation of growth rate [GO:0040010]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; protein localization to membrane raft [GO:1903044]; protein transport into membrane raft [GO:0032596]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; T cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002457]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852]; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway [GO:0034138] |
12805216_These data suggest that Raftlin plays a pivotal role in the formation and/or maintenance of lipid rafts, therefore regulating B-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21266579_Raftlin cooperates with the uptake receptor to mediate cell entry of poly(I:C), which is critical for activation of TLR3. 22222511_combination of ATOH7 and RFTN1 SNPs increased risk to POAG, indicating their diversified effects in the complex genetics of glaucoma. 23645746_Mitogen-inducible Gene-2 expression is reduced in breast cancer. 27022195_this study shows that raftlin appears to modulate cargo selection as an accessary protein of clathrin-associated adaptor protein-2 in clathrin-mediated endocytosis of TLR3/4 ligands 32274611_Raftlin is recruited by neuropilin-1 to the activated VEGFR2 complex to control proangiogenic signaling. 35490655_RFTN1 facilitates gastric cancer progression by modulating AKT/p38 signaling pathways. 36139155_Expression of Major Lipid Raft Protein Raftlin in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps in Smoking and Non-Smoking Patients Correlated with Interleukin-17 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Levels. 36341844_Serum NOX1 and Raftlin as new potential biomarkers of Major Depressive Disorder: A study in treatment-naive first episode patients. |
ENSMUSG00000039316 |
Rftn1 |
803.868056 |
6.0984165352 |
2.608435 |
0.067176800 |
1670.495669 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1402.4948525 |
60.8285868 |
231.7793748 |
8.7441064 |
| ENSG00000131389 |
6533 |
SLC6A6 |
protein_coding |
P31641 |
FUNCTION: Mediates sodium- and chloride-dependent transport of taurine (PubMed:8382624, PubMed:8010975, PubMed:8654117, PubMed:31345061, PubMed:31903486). Mediates transport of beta-alanine (PubMed:8010975). Can also mediate transport of hypotaurine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31345061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31903486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8010975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8382624, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8654117}.; FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent taurine and beta-alanine transporter. Chloride ions are necessary for optimal uptake. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31345061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31903486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8382624}. |
Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Neurotransmitter transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a multi-pass membrane protein that is a member of a family of sodium and chloride-ion dependent transporters. The encoded protein transports taurine and beta-alanine. There is a pseudogene for this gene on chromosome 21. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:6533; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane protein complex [GO:0098797]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022858]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; amino acid:sodium symporter activity [GO:0005283]; gamma-aminobutyric acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015185]; gamma-aminobutyric acid:sodium:chloride symporter activity [GO:0005332]; taurine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005368]; taurine:sodium symporter activity [GO:0005369]; alanine transport [GO:0032328]; amino acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0089718]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; gamma-aminobutyric acid import [GO:0051939]; import across plasma membrane [GO:0098739]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; neurotransmitter transport [GO:0006836]; nitrogen compound transport [GO:0071705]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of necrotic cell death [GO:0010940]; sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0035725]; taurine transport [GO:0015734]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
12062416_TNF-alpha-treated cells showed a higher mRNA level of the TAUT (taurine transporter) than did the control cells. 12163498_TauT is involved with p53 in renal development and apoptosis. 12681485_regulation by WT1 15166008_nitric oxide plays an important role in downregulating microvillous plasma membrane taurine transporter activity in intrauterine growth restriction 15225620_The increased expression level of TAUT mRNA by hypertonicity was repressed by the specific Ca(2+)/CaM kinase II inhibitor. 15630186_TAUT activity in TNF-alpha-treated Caco-2 cells suggests that up-regulation was associated with an increase in the amount of TAUT. 15907840_reporter assay revealed that TNF-alpha-induced TAUT transcriptional activity through the NF-kappaB consensus-like sequence in the human TAUT promoter region 16356117_taurine cotransporter is regulated by oxidative stress and overexpression of aldose reductase and high glucose impair this response 16956961_Greater system beta activity in fetal platelets compared with T lymphocytes is the result of relatively greater TAUT mRNA and protein expression. 18703994_Report taurine transporter activity in fetal T lymphocytes in intrauterine growth restriction and with tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment. 19074966_This study demonstrates the functional coexpression of TauT along with the PAT1 transporter (SLC36A1) at the apical membrane of the intestinal epithelium. 19423693_critical role in protecting against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity, possibly by attenuating a p53-dependent pathway 19602579_Glucose reduced taurine transporter (TauT) mRNA and protein in a dose-dependent manner. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21739148_TauT gene is overexpressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 2 diabetic patients. 23180277_Taurine transporter is a novel pathological marker for stressed motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 23392873_Syncytiotrophoblast TauT activity is reduced in maternal obesity and pre-eclampsia compared to normal pregnancy. 23392891_Expression of TauT is differentially regulated by Vitamin D(3) and retinoic acid via formation of VDR and RXR complexes in the nuclei in a cell type-dependent manner. 23392892_Knockdown of TauT impairs kidney development, possibly through regulation of cell cycle-related genes. 23519128_Taurine transporter deficiency results in aberrant trophoblast turnover and fetal growth restriction. 24842606_Neurotransmitter transporters including SLC6A6 and SLC6A13 mediate the uptake of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) and can play roles in the enhancement of ALA-induced accumulation of protoporphyrin in cancerous cells. 24866236_Immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry analyses revealed that these mAbs recognized the native form of the extracellular domain of SLC6A6 on the cell surface. 25501278_This is the first study to present information on the transcriptional regulation of taurine transporter gene and the localization of the taurine transporter protein in chondrocytic cells. 26206726_CNDP1 and CARNS are expressed in glomeruli and tubular cells; TauT is expressed in renal epithelial cells; CDNP1 may have a role in diabetic neuropathy 26955642_TauT gene expression is significantly upregulated in mononuclear leukocytes of type 1 diabetes patients and is related to HbA1c levels and inversely to plasma homocysteine. 30767502_Elevated SLC6A6 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 31345061_TAUT(SLC6A6) p.A78E still localized in the plasma membrane but is predicted to impact structural stabilization. 32114438_Protein kinases as regulators of osmolyte accumulation under stress conditions: An overview. 32705197_Significance of taurine transporter (TauT) in homeostasis and its layers of regulation (Review). |
ENSMUSG00000030096 |
Slc6a6 |
971.588274 |
2.1687157181 |
1.116841 |
0.067552783 |
272.759097 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000028417590619600151708567350613929777853899240704467977319324103432841848328460023071916637795210369964307938789087850545792331596334789501162272177482086103761371731479812297038733959197998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007436943928108125671719701005847834647175936348417712914647323055675151457688718716942164947486064144578444327907363268969697255447590023740104945475584696801263362431200221180915832519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1331.4816155 |
50.4688882 |
618.2797311 |
18.2481127 |
| ENSG00000131400 |
9476 |
NAPSA |
protein_coding |
O96009 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in processing of pneumocyte surfactant precursors. |
Aspartyl protease;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase A1 family of aspartic proteases. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate an activation peptide and the mature protease. The activation peptides of aspartic proteinases function as inhibitors of the protease active site. These peptide segments, or pro-parts, are deemed important for correct folding, targeting, and control of the activation of aspartic proteinase zymogens. The encoded protease may play a role in the proteolytic processing of pulmonary surfactant protein B in the lung and may function in protein catabolism in the renal proximal tubules. This gene has been described as a marker for lung adenocarcinoma and renal cell carcinoma. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:9476; |
alveolar lamellar body [GO:0097208]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; multivesicular body lumen [GO:0097486]; aspartic-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004190]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; membrane protein proteolysis [GO:0033619]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129] |
12151090_Pronapsin A gene expression in normal and malignant human lung and mononuclear blood cells 12698189_Napsin is a promising marker for the diagnosis of primary lung adenocarcinoma. 13129928_role in the N- and C-terminal processing of pro-surfactant protein-B in type-II pneumocytes 18195689_NAPSA suppresses tumor growth independent of its catalytic activity. 18216060_A general defect in napsin A or cathepsin H expression or activity was not the specific cause for abnormal surfactant accumulation in juvenile pulmonary alveolar proteinosis 19740516_The combined use of napsin A and thyroid transcription factor-1 results in improved sensitivity and specificity for identifying pulmonary adenocarcinoma in primary lung tumors and in a metastatic setting. 20830690_Although TTF-1 had a higher sensitivity, napsin-A was useful as a surrogate marker when encountering a poorly differentiated lung adenocarcinoma. 21164283_Immunohistochemical staining using a combination of TTF-1, napsin A, p63, and CK5/6 allows subclassification of poorly differentiated non-small cell carcinomas on small lung biopsies in most cases. 21464700_in combination with thyroid transcription factor-1-positive immunostaining helps in differentiating primary lung adenocarcinoma from metastatic carcinoma in the lung 21717589_Data suggest that the panels of Napsin A, TTF-1, and p63 were effective in identifying histologic type in NSCLC, and that a combination of either Napsin A and p63 or TTF-1 and p63 should be chosen, depending on morphology. 21838611_Diagnostic utility of PAX8, TTF-1 and napsin A for discriminating metastatic carcinoma from primary adenocarcinoma of the lung. 22156835_napsin A is a useful marker that can assist in the diagnosis of both lung adenocarcinomas and renal cell carcinomas[review] 22198009_None of the 90 squamous cell carcinomas of the lung exhibited napsin A positivity in the neoplastic cells; however, strong napsin A reactivity was observed in hyperplastic type II pneumocytes and in intra-alveolar macrophages entrapped within the tumor. 22288963_Nap-A was more specific than thyroid transcription factor 1 for primary lung adenocarcinoma versus all tumors, excluding kidney, independent of tumor type 22418245_absence of napsin A was an independent prognostic factor for reduced survival time in lung adenocarcinoma 22495379_a useful immunohistochemical marker for differentiation of lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma from other subtypes 22914608_Napsin-A seems to be a useful marker in classifying primary pulmonary neoplasm as adenocarcinomas. 23194051_investigation of expression of NAPSA (a potential diagnostic marker) in lungs/respiratory mucosa of subjects with pulmonary sclerosing hemangioma 23333608_Napsin B was duplicated from napsin A during the early stages of primate evolution, and the subsequent loss of napsin B function during primate evolution reflected ongoing human-specific napsin B pseudogenization 23355200_Mucin-producing neoplasms of the lung infrequently express napsin A, suggesting that immunohistochemical assessment of napsin A may have limited diagnostic usefulness for distinguishing primary and metastatic mucinous adenocarcinomas involving the lung. 23503645_PAX2 and napsin A have high specificity but low sensitivity and only have limited value in the differential diagnosis of mesotheliomas and renal cell carcinomas 23681073_A minority of anaplastic and poorly differentiated micropapillary pattern thyroid carcinomas are napsin A positive. 23899066_24 cases each of pulmonary and esophageal adenocarcinoma were stained with TTF-1, napsin A, CDX2, 34betaE12, N-cadherin, and IMP3 in an attempt to find an optimal panel for differentiation. IMP3, CDX2, and N-cadherin are superior to either TTF-1 or napsin A. 24145649_Napsin A is a sensitive and specific biomarker of the clear cell histotype in endometrial carcinomas and accordingly may have diagnostic utility in their histotyping. 24191930_Napsin A as a marker of clear cell ovarian carcinoma. 24331839_TTF-1 is more sensitive than napsin for detection of lung sarcomatoid carcinoma, and no cases were positive for napsin but negative for TTF-1 24479710_These data suggest that napsin A may be a useful marker for identifying metastatic adenocarcinomas of pulmonary origin 24721826_napsin A is another sensitive and specific marker for distinguishing ovarian clear cell tumors (especially adenocarcinomas) from other ovarian tumors 25389337_Our study showed that napsin A is an extremely sensitive (100%) marker of ovarian clear cell carcinomas 25521803_Data indicate that polyclonal but not monoclonal napsin A antibody has a virtually universal nonspecific labeling in mucinous adenocarcinomas of various sites. 25551297_In diagnosis of ovarian clear cell carcinoma, Napsin A is specific but of intermediate sensitivity. 25889632_Napsin A is expressed in a broad spectrum of renal neoplasms. 25971546_Napsin A is frequently expressed in ovarian and endometrial clear cell carcinomas. 25982999_Low expression levels of NAPSA is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 26339401_Combining HNF-1beta and napsin A may distinguish clear cell carcinoma from high-grade serous carcinoma, endometrioid adenocarcinoma and metastatic Krukenberg tumors. 26400099_napsin A is aberrantly expressed in a subset of lymphomas 26447895_it may be useful to combine NAPA and TTF-1 for increased sensitivity in lung cancer diagnostics. There is no substantial difference between monoclonal and polyclonal p40 and between different NAPA clones, whereas there is a difference between the TTF-1 clones 8G7G3/1 and SPT24 26469326_CK7, TTF-1 and napsin A are predominantly expressed in primary lung adenocarcinoma patients, with CDX-2 being inconsistently expressed. 26696549_The immunocytochemical expressions of napsin A and p40 in imprint cytology seem to be of great utility for the accurate histological differentiation of lung cancers. 26710975_Napsin-A, and Desmocollin-3 were sensitive and specific markers for the diagnosis of AC and SCC, respectively. Both markers allowed classification of 54/60 cases into either AC or SCC. 26808134_To the best of our knowledge, expression of monoclonal Napsin A in lymphomas has never been reported. ALK-DLBCL should be considered in the differential diagnosis when evaluating a Napsin A-positive tumor of poorly differentiated morphology and of unknown primary 26842346_It is important for pathologists to be aware that breast carcinomas with apocrine features can express napsin A. 26945446_Although napsin A is infrequently expressed in endometrial carcinomas, positive results of napsin A immunostaining in endometrial neoplasms might support the diagnosis of clear cell carcinoma when the pathologic differential diagnosis includes other histologic subtypes 27045515_Immunohistochemical detection of thyroid transcription factor 1, Napsin A, and P40 fragment of TP63 can be used in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas. 27412420_High Napsin A expression is associated with adenocarcinoma in non-small cell lung carcinoma. 29845258_These data indicated that napsin A expression may inhibit TGFbetalinduced EMT and was negatively associated with EMTmediated erlotinib resistance, suggesting that napsin A expression may improve the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to EGFRTKI through the inhibition of EMT. 29901522_Napsin A is of value in resolving diagnostic confusion between gastric-type adenocarcinoma (GAS) and clear cell carcinoma (CCC), whereas HNF1beta lacks specificity and its use in this setting is discouraged. 29956857_Raspberry bodies and hyaline globules with positive napsin A immunoexpression are useful features in diagnosing clear cell carcinoma. 31130231_Data indicate that lung napsin A aspartic peptidase (napsin A) in many mammals is a heterogeneous enzyme. 31361605_Napsin-A and AMACR are Superior to HNF-1beta in Distinguishing Between Mesonephric Carcinomas and Clear Cell Carcinomas of the Gynecologic Tract. 31953311_Surfactant Expression Defines an Inflamed Subtype of Lung Adenocarcinoma Brain Metastases that Correlates with Prolonged Survival. 32270298_Immunohistochemical expression of Napsin A in normal human fetal lungs at different gestational ages and in acquired and congenital pathological pulmonary conditions. 32561332_Napsin A is a highly sensitive marker for nephrogenic adenoma: an immunohistochemical study with a specificity test in genitourinary tumors. 33247694_Role of Napsin A and Survivin Immunohistochemical Expression in Bronchogenic Adenocarcinoma. 33876717_A study on the immunohistochemical expression of napsin A in oral squamous cell carcinomas, intraepithelial neoplasia, and normal oral mucosa. 35696768_P504S/alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase, HNF1beta and napsin A in morular metaplasia and clear cell carcinoma of the endometrium: An immunohistochemical analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000002204 |
Napsa |
8.031532 |
0.3121562758 |
-1.679660 |
0.699345439 |
5.953641 |
0.01468692263399163332182606467313235043548047542572021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027127891137243960451019830770746921189129352569580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1400646 |
2.0260928 |
13.3308204 |
3.9177331 |
| ENSG00000131409 |
94030 |
LRRC4B |
protein_coding |
Q9NT99 |
FUNCTION: Synaptic adhesion protein. Regulates the formation of excitatory synapses. The trans-synaptic adhesion between LRRC4B and PTPRF regulates the formation of excitatory synapses in a bidirectional manner (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of synapse assembly and synaptic membrane adhesion. Predicted to be located in cerebellar mossy fiber and presynaptic membrane. Predicted to be active in glutamatergic synapse and plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of postsynaptic density membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:94030; |
cerebellar mossy fiber [GO:0044300]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of postsynaptic density assembly [GO:0099151]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560] |
Mouse_homologues 28695613_NGL-3 induced differentiation of hippocampal mossy fibers. This activity of NGL-3 was dependent on afadin, but not the afadin-binding presynaptic nectin-1. |
ENSMUSG00000047085 |
Lrrc4b |
47.672810 |
0.2179883557 |
-2.197677 |
0.338095011 |
41.515442 |
0.00000000011694356201985870668093799282406678244350395345918514067307114601135253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000601633661698541136075091942300155020695306973266269778832793235778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.2854973 |
3.9214290 |
79.8023480 |
11.9271000 |
| ENSG00000131435 |
8572 |
PDLIM4 |
protein_coding |
P50479 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Suppresses SRC activation by recognizing and binding to active SRC and facilitating PTPN13-mediated dephosphorylation of SRC 'Tyr-419' leading to its inactivation. Inactivated SRC dissociates from this protein allowing the initiation of a new SRC inactivation cycle (PubMed:19307596). Involved in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton (PubMed:21636573). In nonmuscle cells, binds to ACTN1 (alpha-actinin-1), increases the affinity of ACTN1 to F-actin (filamentous actin), and promotes formation of actin stress fibers. Involved in regulation of the synaptic AMPA receptor transport in dendritic spines of hippocampal pyramidal neurons directing the receptors toward an insertion at the postsynaptic membrane. Links endosomal surface-internalized GRIA1-containing AMPA receptors to the alpha-actinin/actin cytoskeleton. Increases AMPA receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents in neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P36202, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19307596, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21636573}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Involved in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and in regulation of cell migration. In response to oxidative stress, binds to NQO1, which stabilizes it and protects it from ubiquitin-independent degradation by the core 20S proteasome. Stabilized protein is able to heterodimerize with isoform 1 changing the subcellular location of it from cytoskeleton and nuclei to cytosol, leading to loss of isoforms 1 ability to induce formation of actin stress fibers. Counteracts the effects produced by isoform 1 on organization of actin cytoskeleton and cell motility to fine-tune actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and to attenuate cell migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21636573}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;LIM domain;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Synaptosome;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a protein which may be involved in bone development. Mutations in this gene are associated with susceptibility to osteoporosis. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:8572; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; early endosome lumen [GO:0031905]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; filamentous actin [GO:0031941]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; recycling endosome lumen [GO:0034777]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051393]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; muscle alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051371]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; excitatory chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0098976]; heart development [GO:0007507]; muscle structure development [GO:0061061] |
12908099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12908099_RIL and its variant sequences may be an important determinant of osteoporosis 14729062_Ril modulates actin stress fiber turnover and enhances the association with actinin and actins. 16489065_Results showed that the hypermethylation of PDLIM4 gene could be used as a sensitive molecular tool in detection of prostate. 17332327_RIL methylation is a marker of adverse prognosis independent of chromosome 5 and 7 deletions. 19011242_several genes that are known to be regulated by DNA methylation were up-regulated dramatically by integrin alpha6beta4 expression, including S100A4, FST, PDLIM4, CAPG, and Nkx2.2. 19131452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19212833_PDLIM4 may function as a tumor suppressor, involved in the control of cell proliferation by associating with actin in prostate cancer cells. 19307596_Reversion-induced LIM interaction with Src reveals a novel Src inactivation cycle. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21636573_Actin cytoskeleton remodeling by the alternatively spliced isoform of PDLIM4/RIL protein. 22695491_Methylation of HIN-1, RASSF1A, RIL and CDH13 in breast cancers was associated with clinical characteristics, but only RASSF1A methylation was associated with time to first recurrence and overall survival. 24039914_The levels of the EDNRB, HJURP and p60/CAF-1 proteins were strongly associated with overall survival in high-grade gliomas patients (p |
ENSMUSG00000020388 |
Pdlim4 |
24.077276 |
0.4836921966 |
-1.047839 |
0.359912718 |
8.438455 |
0.00367368316246509483274929053209234552923589944839477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007725254805240745585581674248487615841440856456756591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.2322355 |
4.9685412 |
39.8855997 |
7.1937569 |
| ENSG00000131459 |
9945 |
GFPT2 |
protein_coding |
O94808 |
FUNCTION: Controls the flux of glucose into the hexosamine pathway. Most likely involved in regulating the availability of precursors for N- and O-linked glycosylation of proteins. |
Aminotransferase;Glutamine amidotransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Nucleotide-sugar biosynthesis; UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine biosynthesis; alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate from D-fructose 6-phosphate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P82808}. |
Predicted to enable glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing) activity. Predicted to be involved in UDP-N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process; fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process; and protein N-linked glycosylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Implicated in type 2 diabetes mellitus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9945; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; carbohydrate derivative binding [GO:0097367]; glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing) activity [GO:0004360]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; energy reserve metabolic process [GO:0006112]; fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0006002]; glutamine metabolic process [GO:0006541]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006048]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process [GO:0006047] |
14764791_GFPT2 mRNA levels in transformed lymphocytes significantly increased among African-Americans. Associated allele of 3' UTR SNP approximately 2-fold overexpressed. 3' UTR variant results in increased GFPT2 mRNA with resultant increased hexosamine flux. 14764791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17574229_Increased GFAT activity appears to be associated with insulin resistance, postprandial hyperglycaemia and oxidative stress in T2DM and may point towards a potential pathway amenable for therapeutic intervention. 20353610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353610_association of nine single nucleotide polymorphisms in ADPRT1, AKR1B1), RAGE, GFPT2 and PAI-1 genes with chronic renal insufficiency among Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes 26887390_GNPDA1 siRNA induced GFAT2 which was hardly measurable in these cells under standard culture conditions, GNPDA2 siRNA increased GFAT1, and GFAT1 siRNA increased the expression of hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2). Silencing of GFAT1 stimulated GNPDA1 and GDPDA2, and inhibited cell migration. 29760045_Transcriptome analysis of human primary non-small cell lung cancer specimens showed that glucose uptake associated with GFPT2-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts was prognostic for adenocarcinoma. GFPT2 was predictive of glucose uptake independent of GLUT1, the primary glucose transporter, and was prognostically significant at both gene and protein level. 29943541_PPP2R2A interacts with GFPT1/2, and leads to the phosphorylation of GFPT2, which can regulate the cellular O-GlcNAcylation in breast cancer 30849544_Homozygosity of the GFPT2 p.Arg366Gln mutation was associated with increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in spermatozoa and decreased sperm motility. 30885209_Elevated GFPT2 expression correlates with poor clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer. 31685298_Glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 (GFPT2) activates the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway to increase the nuclear location of beta-catenin and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of serous ovarian cancer. 33303629_Enzymatic and structural properties of human glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 2 (hGFAT2). 33846782_Stomatinlike protein 2 induces metastasis by regulating the expression of a ratelimiting enzyme of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway in pancreatic cancer. 34735873_Cardiomyocyte protein O-GlcNAcylation is regulated by GFAT1 not GFAT2. 34923141_Glutamine-Fructose-6-Phosphate Transaminase 2 (GFPT2) Is Upregulated in Breast Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Responds to Oxidative Stress. 36195245_VCAM-1 and GFPT-2: Predictive markers of osteoblast differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells. |
ENSMUSG00000020363 |
Gfpt2 |
10.350496 |
18.1118205739 |
4.178860 |
0.831241295 |
32.047745 |
0.00000001504296369571128138720809952998125336165458065806888043880462646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000064283191704892452904873440151789498742118666996248066425323486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.9879694 |
9.6701406 |
1.0552633 |
0.5266926 |
| ENSG00000131471 |
8639 |
AOC3 |
protein_coding |
Q16853 |
FUNCTION: Cell adhesion protein that participates in lymphocyte extravasation and recirculation by mediating the binding of lymphocytes to peripheral lymph node vascular endothelial cells in an L-selectin-independent fashion. Has semicarbazide-sensitive (SSAO) monoamine oxidase activity. May play a role in adipogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17400359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19588076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23349812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9653080}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Copper;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;TPQ;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase family. Copper amine oxidases catalyze the oxidative conversion of amines to aldehydes in the presence of copper and quinone cofactor. The encoded protein is localized to the cell surface, has adhesive properties as well as monoamine oxidase activity, and may be involved in leukocyte trafficking. Alterations in levels of the encoded protein may be associated with many diseases, including diabetes mellitus. A pseudogene of this gene has been described and is located approximately 9-kb downstream on the same chromosome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2013]. |
hsa:8639; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; primary amine oxidase activity [GO:0008131]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; quinone binding [GO:0048038]; tryptamine:oxygen oxidoreductase (deaminating) activity [GO:0052593]; amine metabolic process [GO:0009308]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of primary amine oxidase activity [GO:1902283]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677] |
12097405_VAP-1 is expressed on hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells in vitro and supports adhesion and transmigration of lymphocytes across these cells under physiological shear stress. 12466139_Data show that increases in vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) due to absolute or relative insulin deficiency may be directly involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic angiopathy. 12700900_normal mice and human lungs revealed vascular adhesion protein-1 expression in the endothelium of large and mid-sized pulmonary vessels 14715500_may convert endogenous amines, like methylamine, to vasoactive metabolites. 14726375_the oxidase activity of VAP-1 controls PMN exit from the blood during the relatively poorly understood transmigration step 14755492_Semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase is a source of oxidative stress in diseased human skeletal muscle; it contributes to oxidative stress-induced damage in various inflammatory and other myopathies. 15057044_VAP-1 protein expression is significantly decreased in intratumoral vessels compared with peritumoral ones; this difference was independent of the skin melanoma thickness 15830186_Plasma semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (SSAO) is elevated in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes and has been implicated in the pathophysiology of diabetic late complications. 15919838_results suggest that vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) levels are correlated with fasting glucose and insulin in morbidly obese subjects, and after surgery VAP-1 levels were associated with changes in visceral adiposity and diastolic blood pressure 16046623_The dimer structure reveals intriguing features that may have fundamental roles in the adhesive and enzymatic functions of hVAP-1. 16361866_This study indicates the important role of VAP-1 in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory cutaneous disorders, including AE. 16507887_A role for AOC3-mediated deamination in pulmonary inflammation was shown. 16511016_Tetragonal crystals were obtained and a data set extending to 2.5 A was collected. The crystals are merohedrally twinned and the estimate of the twinning fraction was complicated by pseudo-symmetry of the crystals. 16556889_VAP-1 may contribute critically to the oxidase activities in utero, and prove important for lymphocyte trafficking during human ontogeny. 16806498_We propose that VAP-1 might participate in controlling leukocyte entry into inflamed brain. 17006978_Expression of VAP-1, Stabilin-1, L-SIGN can be used to identify sinusoidal endothelium and to permit discrimination from vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. 17256751_We propose that as well as directly promoting adhesion via interactions with the as yet unknown ligand, binding of enzyme substrate to VAP-1 can indirectly promote inflammatory cell recruitment via upregulation of adhesion molecules and chemokines. 17393059_Taken together, these results allow us to postulate that SSAO may contribute to the vascular damage associated to AD. 17393062_VAP-1 was located solely in the membrane fraction of the vascular smooth muscle cell. However it was also shown to be released into the cell-culture medium. 17400359_semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase expression during in vitro differentiation of human preadipocytes and in adipose and stroma-vascular fractions of human fat depots 17431736_The elevated serum SSAO activity measured through the detection of the enzyme-generated hydrogen peroxide in HD patients might indicate its contribution to the accelerated atherosclerotic disease observed in uremia. 17490641_Data suggest atherosclerotic inflammation may be a trigger for sclerosis in calcified stenotic aortic valves through upregulation TGF-beta, VAP-1, MIG and Eotaxin3, which is only partially inhibited by previous statin therapy. 18005095_VAP-1 may aggravate ischaemic vascular changes and thhe subsequent release of VAP-1 into circulation could be further examined as a potential marker of early ischaemic vasculopathy. 18644360_Serum levels of VAP-1 are associated with the severity of kidney damage or stages of kidney disease. 18853098_Increase in the SSAO activity and nitrite and nitrite levels observed in type 2 diabetic patients could be parameters to take in account and play relevant role in diabetes development. 18991279_VAP-1 regulates the inflammatory response in ischemia-reperfusion injury and suggest that blockade of VAP-1 may have therapeutic value. 19336232_Serum VAP-1 is increased in both acute and chronic hyperglycemia. 19361461_acute change of serum SSAO/VAP-1 is a novel marker for hyperglycemia-induced atherosclerosis 19761765_immunohistochemistry reveals constitutive expression of VAP-1 in human ocular tissues. 19789505_Inflammation of the dental pulp was accompanied by a significant decrease in MAO labeling, MAO B (but not MAO A) activity and the increase in SSAO activity. 19861682_the Siglec-10-VAP-1 interaction seems to mediate lymphocyte adhesion to endothelium 20063021_The SSAO activity in the serum of patients with type 2 diabetes is higher when compared with control group and may be a useful marker for diabetes. 20512991_A novel combination of surface molecules, including VAP-1 and CX(3)CL1 promotes the recruitment of CD16(+) monocytes to the liver, allowing them to localize at sites of chronic inflammation and fibrosis. 21114364_These remarks suggest that MAO-A and SSAO may play an important role in vascular tissue as well as in the vascular pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. 21139198_The structure of VAP-1 was refined to a resolution of 2.9A. 21282368_Serum VAP-1 can predict 10-year all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and cancer mortality independently in type 2 diabetic subjects. 21512782_This review examines the biological functions of VAP-1, especially the role that this molecule might play in the establishment and progression of chronic liver disease. 21585208_Met211 and Leu469 were shown to be key residues for substrate specificity. 21819380_using an endothelial cell model, a description for the first time the involvement of the leucocyte-adhesion activity of SSAO/VAP-1 in the Abeta (amyloid beta-peptide)-mediated pro-inflammatory effect 21821708_The Siglec-9 peptide binding to the enzymatic groove of VAP-1 can be used for imaging conditions, such as inflammation and cancer. 22133888_Plasma VAP-1/SSAO activity is increased in intracranial hemorrhage and predicts neurological outcome, suggesting a possible contribution of the soluble protein in secondary brain damage. 22150439_We found increased VAP-1 activity and anchor protein syndecan-1 content in critically ill patients with septic shock 22354146_The immunolocalization of VAP-1 varied in the histopathology of the conjunctiva, involving the pathology of inflammatory conjunctival disorders. 22618595_Protein level of sVAP-1 was increased and correlated with HEL in the vitreous fluid of patients with PDR. 22714978_high vascular SSAO/VAP-1 levels in human hippocampus may contribute to vascular degeneration 22753196_In psoriatic patients, VAP-1 elevation correlated with elevation of Lp (a). This may be responsible for a higher prevalence of cardiovascular accidents in psoriatic patients. 23062326_Data suggest that subjects with diabetic retinopathy have higher serum levels of soluble VAP1 than subjects with non-angiogenic ocular diseases (i.e., epiretinal membrane [ERM], idiopathic macular hole [MH], age-related macular degeneration [AMD]). 23120772_The pathogenetic link between the increase in SSAO activity and severity of neurological deficitin ischemic stroke patients was shown. 23349812_Data suggest that the down-regulation of both the expression and enzymatic activity of VAP-1 may result from a dominant-negative effect caused by heterodimerization between VAP-1 and alternatively spliced VAP-1Delta3. 23769096_VAP-1 elevations in heart transplant recipients were predominantly dependent on left ventricular diameter and use of tacrolimus 24211727_Serum VAP-1 predicts mortality independently and improves risk stratification in colorectal cancer subjects. 24379274_We concluded that VAP-1, elevated in patients on Peritoneal Dialysis, was predominantly dependent on residual kidney function and glucose level, factors both linked to endothelial damage and cardiovascular complications. 24503888_SSAO expression in endothelial cells increases oxygen-glucose-deprivation-associated cell damage. It mediates some tissue damage during the reoxygenation process by oxidizing its known enzymatic substrate, methylamine. 24781952_Higher serum VAP-1 and Chronic kidney disease can independently predict future development of cancers in type II diabetic subjects 24903765_This study demonstrated that low serum VAP-1 levels are associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients. 25279492_These findings suggest that vaspin and VAP-1 may play a role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and can be used as markers of the disease 25342050_the semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase activity of VAP-1 modifies hepatic glucose homeostasis and may contribute to patterns of GLUT expression in chronic disease. 25420878_Complexes of human ORP2 and VAPs at endoplasmic reticulum-lipid droplet interfaces regulate the hydrolysis of triglycerides and lipid droplet turnover. 25457560_It stimulates amyloid beta proteins on the vascular walls, and is contributing to cerebral amyloid angiopathies and Alzheimer disease. 25562318_these results link the amine oxidase activity of VAP-1 with hepatic inflammation and fibrosis and suggest that targeting VAP-1 has therapeutic potential for NAFLD and other chronic fibrotic liver diseases. 26287391_In this article, we will review the general characteristics and biological functions of VAP-1, focusing on its important role as a prognostic biomarker in human pathologies. [review] 26395033_psoriatic patients with the dominant AT1R-A1166C polymorphism had significantly higher serum levels of VAP-1 and MDA but lower total bilirubine, uric acid, ARE, SOD and CAT activities compared to the corresponding control group 26845338_serum VAP-1 can predict ESRD and is a useful biomarker to improve risk stratification in type 2 diabetic subjects. 27036009_Our results show that colorectal myofibroblasts, as defined by the expression of AOC3, NKX2-3, and other markers, are a distinctly different cell type from TGFbeta-activated fibroblasts 27300745_Correlation among soluble receptors for advanced glycation end-products, soluble vascular adhesion protein-1/semicarbazide-sensitive amine oxidase (sVAP-1) and cardiometabolic risk markers in apparently healthy adolescents: a cross-sectional study 27731409_immunohistochemistry revealed that VAP-1 localized to endothelial cells of intra-plaque neovessels in carotid endarterectomy samples from patients with recent ischemic symptoms 27766585_Adipose tissue SSAO activity did not vary according to anatomical location and/or metabolic status in severely obese women. 27893774_The mechanism of the Siglec-9 and AOC3 interaction 28251930_This study showed that the oxidase activity of AOC3 contributes to the development of lung fibrosis mainly by regulating the accumulation of pathogenic leukocyte subtypes, which drive the fibrotic response. 28428344_VAP-1 expression is increased in primary sclerosing cholangitis, facilitates adhesion of gut-tropic lymphocytes to liver endothelium in a substrate-dependent manner, and elevated levels of its circulating form predict clinical outcome in patients. 29229088_The study showed that serum VAP-1 level increased with an increasing severity of obstruction in patients with stable COPD. This increase was associated with a reduced quality of life and increased severity of hypoxia. 29392528_proangiogenic factor VEGF induces sVAP-1 release from retinal capillary endothelial cells and facilitates hydrogen peroxide generation via enzymatic property of sVAP-1, followed by the increase of oxidative stress, one of the crucial factors in the pathogenesis of DR. 30022055_Studied association of serum vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) and hyperglycemia; findings support the hypothesis that up-regulation of VAP-1 occurs in response to hyperglycemia in subjects with prediabetes. 30787099_Soluble VAP-1 activity and levels were lower than in aorta membranes. 31638437_Elevated VAP-1 levels in gestational diabetes correlated with clinical follow-up and inflammatory markers; may suggest the pathogenetic role of VAP-1 in gestational diabetes. 32001775_Amine oxidase 3 is a novel pro-inflammatory marker of oxidative stress in peritoneal endometriosis lesions. 32315567_Zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein as an inhibitor of amine oxidase copper-containing 3. 32410850_Comparison of Inhibitor and Substrate Selectivity between Rodent and Human Vascular Adhesion Protein-1. 32411328_Semicarbazide-Sensitive Amine Oxidase Increases in Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis and Contributes to Valvular Interstitial Cell Calcification. 33727640_NG2/CSPG4, CD146/MCAM and VAP1/AOC3 are regulated by myocardin-related transcription factors in smooth muscle cells. 33805974_SSAO/VAP-1 in Cerebrovascular Disorders: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Stroke and Alzheimer's Disease. 35174543_Downregulation of VAP-1 in OSCC suppresses tumor growth and metastasis via NF-kappaB/IL-8 signaling and reduces neutrophil infiltration. |
ENSMUSG00000019326 |
Aoc3 |
13.540097 |
0.1002259767 |
-3.318672 |
0.712092179 |
23.410546 |
0.00000130859142856778554601438792348577777602258720435202121734619140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004567228537635496363915939971311885869909019675105810165405273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3576552 |
1.2136080 |
23.6940934 |
6.6701587 |
| ENSG00000131477 |
10266 |
RAMP2 |
protein_coding |
O60895 |
FUNCTION: Transports the calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor (CALCRL) to the plasma membrane. Acts as a receptor for adrenomedullin (AM) together with CALCRL. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22102369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9620797}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAMP family of single-transmembrane-domain proteins, called receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are type I transmembrane proteins with an extracellular N terminus and a cytoplasmic C terminus. RAMPs are required to transport calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CRLR) to the plasma membrane. CRLR, a receptor with seven transmembrane domains, can function as either a calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor or an adrenomedullin receptor, depending on which members of the RAMP family are expressed. In the presence of this (RAMP2) protein, CRLR functions as an adrenomedullin receptor. The RAMP2 protein is involved in core glycosylation and transportation of adrenomedullin receptor to the cell surface. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10266; |
adrenomedullin receptor complex [GO:1903143]; amylin receptor complex 2 [GO:0150057]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; adrenomedullin binding [GO:1990409]; adrenomedullin receptor activity [GO:0001605]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adherens junction assembly [GO:0034333]; adrenomedullin receptor signaling pathway [GO:1990410]; amylin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0097647]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; basement membrane assembly [GO:0070831]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cellular response to hormone stimulus [GO:0032870]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; heart development [GO:0007507]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000352]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001214]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
11973435_results show the presence of calcitonin receptor-like receptor and receptor activity-modifying proteins in middle meningeal, middle cerebral, pial, and superficial temporal vessels 12565884_Co-expression of calcitonin receptors (CT) lacking a portion of domain 1 with receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) 1, 2, or 3 appears to produce functional CT-(8-32)-sensitive adrenomedullin receptors. 15245870_TNF-alpha induced time- and dose-dependent decreases in the expression of RAMP2 mRNA in cultured human coronary artery smooth muscle cells , thereby diminishing AM-evoked cAMP production 15300632_Data found that expressions of RAMP1, RAMP2 and RAMP3 mRNAs increased with the worsening of heart function, but the expressions of RAMP1 and RAMP2 mRNA decreased at level IV of heart failure. 15613468_adrenomedullin receptors are comprised of RAMP2 and calcitonin receptor-like receptor. 16410241_the respective C-tails of hRAMP2 and -3 differentially affect hCRLR surface delivery and internalization 16912219_This study reveals important functionality of the RAMP C-terminal domain and identifies key differences in the role of the RAMP C terminus for calcitonin receptor versus calcitonin receptor-like receptor-based receptors. 17671114_RAMP2 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in lung cancer 18593822_Identification of RAMP2 residues for adrenomedullin receptors are reported. 18835256_The His residues of hRAMP2 and -3 differentially govern adrenomedullin receptor function. 19210874_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19210874_findings provided no significant linkage or association of adrenomedullin and CRLR-RAMP-2 genes with rheumatoid arthritis in the studied trio families 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20074556_the hCRLR C-tail is crucial for adrenomedullin-evoked cAMP production and internalization of the CRLR/RAMP2, while the receptor internalization is dependent on the aforementioned GPCR kinases, but not Gs coupling. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22102369_The CRLR-RAMP2 interactions were confirmed for the full-length proteins on the cell surface by site-specific photo-crosslinking. 24169318_RAMP2 gene expression increases with gestational age development in the fetal lung. 24199627_Data suggest isoforms of RAMP modulate accessibility of peptides to residues situated on CALCRL (calcitonin receptor-like receptor) N-terminal domain; RAMP3/RAMP2/RAMP1 appear to alter accessibility of specific residues at CALCRL-RAMP interface. 24505304_Adrenomedullin-RAMP2 system suppresses ER stress-induced tubule cell death and is involved in kidney protection. 24831942_the AM system is widely expressed in human thymus from newborns; both AM1 receptor components CLR and RAMP2, but not RAMP3, are not associated with the plasma membrane of TECs and thymocytes but are located intracellularly, notably in the nucleus 25982113_Data suggest that ligand binding of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) may inform drug development targeting calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR):receptor activity-modifying proteins RAMP1/2 complexes. 26198634_This study reveals the glucagon receptor as a previously unidentified target for GLP-1 receptor agonists and highlights a role for RAMP2 in regulating its pharmacology. 27013657_interaction of RAMP2 or RAMP3 with CLR induces conformational variation in the juxtamembrane region, yielding distinct binding pockets, probably via an allosteric mechanism. 28586439_This work suggests that RAMP2 may modify the agonist activity and trafficking of the GCGR, with potential relevance to production of new peptide analogs with selective agonist activities. 28614667_Data suggest that a single GlcNAc residue at CTR N130 (asparagine 130) is responsible for enhanced affinity of calcitonin for CTR ECD; the same appears to apply for enhanced affinity of amylin for RAMP2-CTR ECD. [GlcNAc = N-acetylglucosamine; CTR = calcitonin receptor; ECD = extracellular domain; RAMP2 = receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying protein 2]. 28904253_Single nucleotide polymorphism of RAMP2 is associated with Stroke. 30826286_Interactions between RAMP2 and CRF receptors: The effect of receptor subtypes, splice variants and cell context 31150417_Based on the finding that an acylated chimeric ADM/ADM2 analog potently stimulates CLR/RAMP1 and 2 signaling, we hypothesized that the binding domain of this analog could have potent inhibitory activity on CLR/RAMP receptors. 33385343_Adrenomedullin-Receptor Activity-Modifying Protein 2 System Ameliorates Subretinal Fibrosis by Suppressing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. 34271220_Receptor Activity-Modifying Protein 2 (RAMP2) alters glucagon receptor trafficking in hepatocytes with functional effects on receptor signalling. |
ENSMUSG00000001240 |
Ramp2 |
7.395275 |
0.0213769155 |
-5.547802 |
1.126888502 |
37.401155 |
0.00000000096165139741188246989842294246055715012388986906444188207387924194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000004606937561116320875671687878069940347280919468175852671265602111816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3080382 |
0.2650482 |
14.4686319 |
3.9336422 |
| ENSG00000131584 |
116983 |
ACAP3 |
protein_coding |
Q96P50 |
FUNCTION: GTPase-activating protein for the ADP ribosylation factor family. {ECO:0000305}. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;GTPase activation;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity and metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within neuron migration and regulation of neuron projection development. Predicted to be located in growth cone. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:116983; |
growth cone [GO:0030426]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975] |
19548526_minisatellite locus UPS29 can regulate an activity of CENTB5, SCNN1D and ACOT7 in nervous system cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 33276684_Length Polymorphism and Methylation Status of UPS29 Minisatellite of the ACAP3 Gene as Molecular Biomarker of Epilepsy. Sex Differences in Seizure Types and Symptoms. |
ENSMUSG00000029033 |
Acap3 |
280.794758 |
0.4189388366 |
-1.255188 |
0.183255317 |
45.643641 |
0.00000000001418458002689626121107770236403030944712100325233450348605401813983917236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000077859576495719160317200367168950824250939213300171104492619633674621582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
158.5996012 |
21.6995038 |
378.5312842 |
36.6965588 |
| ENSG00000131668 |
56033 |
BARX1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBU1 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor, which is involved in craniofacial development, in odontogenesis and in stomach organogenesis. May have a role in the differentiation of molars from incisors. Plays a role in suppressing endodermal Wnt activity (By similarity). Binds to a regulatory module of the NCAM promoter. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804553}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Bar subclass of homeobox transcription factors. Studies of the mouse and chick homolog suggest the encoded protein may play a role in developing teeth and craniofacial mesenchyme of neural crest origin. The protein may also be associated with differentiation of stomach epithelia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56033; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; digestive system development [GO:0055123]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spleen development [GO:0048536]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
17486624_PITX2, BARX1, and FOXC1 mutations were absent in De Hauwere syndrome and suggest that De Hauwere syndrome is caused by a different gene. 18708738_Regional expression of barx1 was observed in epithelium before mixed dentition, while during mixed dentition gene appeared in hyaline cartilage. Expression of barx1 appears in cleft lip palate affected structures mainly in mixed dentition. 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26383589_we provide supportive evidence that genetic variants at FOXP1, BARX1, and FOXF1 confer risk for the development of EAC. 29454095_results suggest that genetic variants at 9q22 are associated with the risk of both esophageal adenocarcinoma/Barrett esophagus and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, possibly by regulating the function of BARX1 30281099_associated with Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis risk 33026187_Congenital hiatal hernia segregating with a duplication in 9q22.31q22.32 in two families. 33451979_HAND1 and BARX1 Act as Transcriptional and Anatomic Determinants of Malignancy in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. |
ENSMUSG00000021381 |
Barx1 |
148.024292 |
0.1568265883 |
-2.672758 |
0.159834502 |
317.134269 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006097168360360020360987174180731488390562560984657839345062028372935368647071120013016748559389401797180052698451317371257699298453749194916743435437805729164977759522178019872123977407341044454369693994522094726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001840372290366337411218341824096124313895323157534915297766727604621586427765358910983583567055380810682321985250711702468734821774550061491605481843727773557975114030322823580054780734371888684108853340148925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.9647404 |
4.5719111 |
263.3709241 |
16.0220353 |
| ENSG00000131669 |
4814 |
NINJ1 |
protein_coding |
Q92982 |
FUNCTION: [Ninjurin-1]: Homophilic transmembrane adhesion molecule involved in various processes such as inflammation, cell death, axonal growth, cell chemotaxis and angiogenesis (PubMed:8780658, PubMed:9261151, PubMed:33472215). Promotes cell adhesion by mediating homophilic interactions via its extracellular N-terminal adhesion motif (N-NAM) (PubMed:33028854). Involved in the progression of the inflammatory stress by promoting cell-to-cell interactions between immune cells and endothelial cells (PubMed:22162058, PubMed:26677008, PubMed:32147432). Involved in leukocyte migration during inflammation by promoting transendothelial migration of macrophages via homotypic binding (By similarity). Promotes the migration of monocytes across the brain endothelium to central nervous system inflammatory lesions (PubMed:22162058). Acts as a regulator of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling triggered by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) during systemic inflammation; directly binds LPS (PubMed:26677008). Acts as a mediator of both programmed and necrotic cell death (PubMed:33472215). Plays a key role in the induction of plasma membrane rupture during programmed and necrotic cell death: oligomerizes in response to death stimuli to mediate plasma membrane rupture (cytolysis), leading to release intracellular molecules named damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that propagate the inflammatory response (PubMed:33472215). Plays a role in nerve regeneration by promoting maturation of Schwann cells (PubMed:8780658, PubMed:9261151). Acts as a regulator of angiogenesis (PubMed:33028854). Promotes the formation of new vessels by mediating the interaction between capillary pericyte cells and endothelial cells (By similarity). Promotes osteoclasts development by enhancing the survival of prefusion osteoclasts (By similarity). Also involved in striated muscle growth and differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22162058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26677008, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32147432, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33028854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33472215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8780658, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9261151}.; FUNCTION: [Secreted ninjurin-1]: Secreted form generated by cleavage, which has chemotactic activity (By similarity). Acts as an anti-inflammatory mediator by promoting monocyte recruitment, thereby ameliorating atherosclerosis (PubMed:32883094). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32883094}. |
Acetylation;Angiogenesis;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cytolysis;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The ninjurin protein is upregulated after nerve injury both in dorsal root ganglion neurons and in Schwann cells (Araki and Milbrandt, 1996 [PubMed 8780658]). It demonstrates properties of a homophilic adhesion molecule and promotes neurite outgrowth from primary cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons.[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:4814; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098631]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cytolysis [GO:0019835]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; leukocyte chemotaxis involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002232]; muscle cell differentiation [GO:0042692]; necrotic cell death [GO:0070265]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034145]; programmed cell death [GO:0012501]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090025]; tissue regeneration [GO:0042246] |
15464245_Ninjurin1 is able to induce the senescence program. Ninjurin1 may be involved in the regulation of cellular senescence in the liver during carcinogenesis. 17825431_Our data suggests that Ninjurin 1 asp110ala SNP could be a valuable genetic marker of nerve damage in leprosy. 17893696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18504448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22162058_Data show an important cell-specific role for Ninjurin-1 in the transmigration of inflammatory APCs across the BBB. 22326538_The NINJ1 gene polymorphism plays an important role in nerve degeneration in leprosy patients. 25766274_Ninj1 expression was detected in both HSMCs and HUVECs, and was higher in the former. Ninj1 expression was enhanced by hypoxia in HUVECs. 25860173_Ninj1 modulates TLR4 signaling, which itself plays a major role in systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis. 26815582_Ninj1 suppresses migration, invasion and metastasis of lung cancer via inhibition of the IL-6 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. 28067406_Data show that Ninj1 assembles into a homomeric protein complex and that N-glycosylation is a prerequisite for Ninj1 homomer assembly. 28373430_High ninjurin 1 expression is associated with Prostate Cancer. 30326781_Our study demonstrates that Ninj1 is expressed in endometriosis and adenomyosis and is induced by the inflammatory stimuli 31091274_We analyzed cardiac biopsies from aortic-stenosis patients and control patients undergoing elective heart surgery..We conclude that Ninjurin1 contributes to myocyte growth and differentiation, and that these effects are mainly mediated by N-glycosylated Ninjurin1-24. 32353975_Radiation Potentiates Monocyte Infiltration into Tumors by Ninjurin1 Expression in Endothelial Cells. 32385864_Ninjurin1 deficiency aggravates colitis development by promoting M1 macrophage polarization and inducing microbial imbalance. 33472215_NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. 35392805_Elevated plasma Ninjurin-1 levels in atrial fibrillation is associated with atrial remodeling and thromboembolic risk. 35395804_Ninjurin1 drives lung tumor formation and progression by potentiating Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling through Frizzled2-LRP6 assembly. 36166142_NINJ1 triggers extravillous trophoblast cell dysfunction through blocking the STAT3 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000037966 |
Ninj1 |
286.715812 |
2.3564980891 |
1.236645 |
0.106962557 |
133.855581 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000058757812187958843374008741611389908737657100902358433544009511241018231815441761733270764622716342273633927106857299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000007792141131125539051760636201500524676957266377378347759313992833911472338709108473309150610930373659357428550720214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
407.5323439 |
24.0284722 |
174.1302506 |
8.1370507 |
| ENSG00000131711 |
4131 |
MAP1B |
protein_coding |
P46821 |
FUNCTION: Facilitates tyrosination of alpha-tubulin in neuronal microtubules (By similarity). Phosphorylated MAP1B is required for proper microtubule dynamics and plays a role in the cytoskeletal changes that accompany neuronal differentiation and neurite extension (PubMed:33268592). Possibly MAP1B binds to at least two tubulin subunits in the polymer, and this bridging of subunits might be involved in nucleating microtubule polymerization and in stabilizing microtubules. Acts as a positive cofactor in DAPK1-mediated autophagic vesicle formation and membrane blebbing. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18195017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33268592}. |
Acetylation;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Microtubule;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-nitrosylation;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the microtubule-associated protein family. The proteins of this family are thought to be involved in microtubule assembly, which is an essential step in neurogenesis. The product of this gene is a precursor polypeptide that presumably undergoes proteolytic processing to generate the final MAP1B heavy chain and LC1 light chain. Gene knockout studies of the mouse microtubule-associated protein 1B gene suggested an important role in development and function of the nervous system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4131; |
apical dendrite [GO:0097440]; axon [GO:0030424]; basal dendrite [GO:0097441]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; hippocampal mossy fiber [GO:0097457]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; somatodendritic compartment [GO:0036477]; synapse [GO:0045202]; varicosity [GO:0043196]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus [GO:0071375]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; developmental maturation [GO:0021700]; establishment of monopolar cell polarity [GO:0061162]; induction of synaptic plasticity by chemical substance [GO:0051915]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitochondrion transport along microtubule [GO:0047497]; negative regulation of intracellular transport [GO:0032387]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; odontoblast differentiation [GO:0071895]; peripheral nervous system axon regeneration [GO:0014012]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031116]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0031114]; response to carbohydrate [GO:0009743]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035]; response to insecticide [GO:0017085]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to vitamin A [GO:0033189]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] |
12807913_MAP1B action is modulated by mapmodulin/leucine-rich acidic nuclear protein 16996626_Complexes (MAP1B heavy chain-MAP1A light chain) form through interaction of homologous domains conserved in heavy and light chains of MAP1A and MAP1B. Conserved domains of the MAP1A and MAP1B light chains account for formation of light chain heterodimers. 18063656_The light chain (LC1) of microtubule-associated protein 1B (MAP1B)-5-HT(3A) receptor interaction contributes to a mechanism that regulates receptor desensitization kinetics. 18079022_Amyloid-beta 1-42 binds to a peptide comprising the microtubule binding domain of the heavy chain of microtubule-associated protein 1B by the screening of a human brain cDNA library expressed on M13 phage. 18195017_a role for MAP1B in DAPK-1-dependent signaling in autophagy and membrane blebbing. 18656471_MAP1B light chain can interact with the tumor suppressor p53. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19567321_a new protein involved in the terminal differentiation of odontoblasts 20719958_These observations define a new and crucial function of MAP1B that is required for efficient cross-talk between microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton during neuronal polarization. 21508097_We suggest a role for Stau2 in the generation and regulation of Map1b mRNA containing granules that are required for mGluR-long-term depression 24566975_An interaction between MAP1B LC1 and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2L3. 24614691_signal transduction pathways downstream of 5-HT6R are regulated by MAP1B, which might play a role in 5-HT6R-mediated signaling in the brain. 24754922_Yeast-two-hybrid screening using human LRRK2 kinase domain as bait identified microtubule associated protein 1B (MAP1B) as a LRRK2 interactor. 25429138_Localization of MAP1B is altered in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cords in a transgenic animal model. 25483588_The the MAP1B-LC1-mediated regulation most likely involves an internalization of the channels via a dynamin and clathrin-dependent pathway. 25902260_KIRREL3 interacting proteins MAP1B and MYO16 are potential candidates for intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder. 26233433_The found of this study suggested that possible roles of MAP1B genes in working memory performance in ADHD patients 28864773_These results suggest that a change in the intracellular calcium level plays a role in regulation of the secretory pathway via interaction of ALG-2 with MISSL and MAP1B. 29136244_High MAP1B expression is associated with resistance to mTOR inhibition in glioblastoma. 29432744_MAP1B heavy chain has a unique binding site for a calcium-binding protein ALG-2. 29738522_All of the patients with a microtubule associated protein 1B (MAP1B) variant had a similar brain abnormality, and at least one of the parents who transmitted the variant to their child was also similarly affected. 29925525_MAP1B-LC1 links microtubules and Stx17 in fed cells, and starvation causes the dephosphorylation of MAP1B-LC1 at Thr217, allowing Stx17 to dissociate from MAP1B-LC1 and bind to Atg14L. 30425305_Calpain-10 regulates actin dynamics by proteolysis of microtubule-associated protein 1B 31235589_These neuritic defects result from impaired Nrf2 activity on antioxidant response elements (AREs) localized to a microtubule-associated protein (Map1b) gene enhancer and are rescued by forced expression of Map1b as well as by both Nrf2 overexpression and pharmaceutical activation in Parkinson's disease (PD) neurons 31492158_Knockdown of microtubule-associated protein 1B light chain (MAP 1B-LC1) represses E-cadherin downregulation, vimentin upregulation and actin filament remodeling, decreases cell migration and invasion during TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in A549 cells. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) promotes the EMT of lung cancer cells induced by TGF-beta1 through interacting with MAP... 33268592_Mutations of MAP1B encoding a microtubule-associated phosphoprotein cause sensorineural hearing loss. 33772511_Epilepsy phenotypes associated with MAP1B-related brain malformations. 33839256_The miR-223-3p/MAP1B axis aggravates TGF-beta-induced proliferation and migration of BPH-1 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000052727 |
Map1b |
63.173463 |
2.0048778832 |
1.003514 |
0.186571059 |
29.365031 |
0.00000005994971477394709218681866222042109448864266596501693129539489746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000241018164822159805543998244495296212619450670899823307991027832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.3647103 |
10.0518067 |
41.3850396 |
3.9585280 |
| ENSG00000131759 |
5914 |
RARA |
protein_coding |
P10276 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for retinoic acid (PubMed:19850744, PubMed:16417524, PubMed:20215566). Retinoic acid receptors bind as heterodimers to their target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, and regulate gene expression in various biological processes (PubMed:28167758). The RXR/RAR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5 (PubMed:28167758, PubMed:19398580). In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone deacetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression (PubMed:16417524). On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and associate with the coactivators leading to transcriptional activation (PubMed:9267036, PubMed:19850744, PubMed:20215566). Formation of a complex with histone deacetylases might lead to inhibition of RARE DNA element binding and to transcriptional repression (PubMed:28167758). Transcriptional activation and RARE DNA element binding might be supported by the transcription factor KLF2 (PubMed:28167758). RARA plays an essential role in the regulation of retinoic acid-induced germ cell development during spermatogenesis (By similarity). Has a role in the survival of early spermatocytes at the beginning prophase of meiosis (By similarity). In Sertoli cells, may promote the survival and development of early meiotic prophase spermatocytes (By similarity). In concert with RARG, required for skeletal growth, matrix homeostasis and growth plate function (By similarity). Together with RXRA, positively regulates microRNA-10a expression, thereby inhibiting the GATA6/VCAM1 signaling response to pulsatile shear stress in vascular endothelial cells (PubMed:28167758). In association with HDAC3, HDAC5 and HDAC7 corepressors, plays a role in the repression of microRNA-10a and thereby promotes the inflammatory response (PubMed:28167758). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P11416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16417524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19398580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19850744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20215566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28167758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9267036}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene represents a nuclear retinoic acid receptor. The encoded protein, retinoic acid receptor alpha, regulates transcription in a ligand-dependent manner. This gene has been implicated in regulation of development, differentiation, apoptosis, granulopoeisis, and transcription of clock genes. Translocations between this locus and several other loci have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this locus.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:5914; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; alpha-actinin binding [GO:0051393]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity [GO:0001217]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; mRNA 5'-UTR binding [GO:0048027]; mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity [GO:0000900]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase A binding [GO:0051018]; protein kinase B binding [GO:0043422]; retinoic acid binding [GO:0001972]; retinoic acid-responsive element binding [GO:0044323]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; chondroblast differentiation [GO:0060591]; embryonic camera-type eye development [GO:0031076]; face development [GO:0060324]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; germ cell development [GO:0007281]; glandular epithelial cell development [GO:0002068]; growth plate cartilage development [GO:0003417]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; limb development [GO:0060173]; liver development [GO:0001889]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061037]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030853]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive regulation of binding [GO:0051099]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of interleukin-13 production [GO:0032736]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of interleukin-5 production [GO:0032754]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of T-helper 2 cell differentiation [GO:0045630]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; prostate gland development [GO:0030850]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:1901532]; regulation of myelination [GO:0031641]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; response to vitamin A [GO:0033189]; retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048384]; Sertoli cell fate commitment [GO:0060010]; trachea cartilage development [GO:0060534]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055012] |
11106752_two critical hits for promyelocytic leukemia 11891284_UBE1L is a retinoid target that triggers PML/RARalpha degradation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia 11929748_Interactions of STAT5b-RARalpha, a novel acute promyelocytic leukemia fusion protein, with retinoic acid receptor and STAT3 signaling pathways. 12009305_Results show that both RARalpha and RARbeta are mediators in the anticancer function of All-trans retinoic acid via AP-1 activity inhibition. 12060771_induces acute promyelocytic leukemia in a mouse model 12080444_obesity is associated with an inverse relationship between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and RARalpha expressions in subcutaneous adipose tissue 12193472_the silencing of the RAR alpha2 promoter by hypermethylation may play a contributory role in the dysregulation of RA signaling in mammary tumorigenesis. 12213824_Retinoid-induced G1 arrest and differentiation activation are associated with a switch to cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase hypophosphorylation of the receptor. 12393611_IL-3-induced enhancement of retinoic acid receptor activity is mediated through Stat5, which physically associates with recombinant human retinoic acid receptors in an IL-3-dependent manner. 12399530_In normal epithelium, both RAR-alpha and -gamma present with minimal nuclear accumulation. Increased in luminal epithelial nuclei in prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia 12420222_RAR pan-agonists and the RARalpha-selective agonist Am580, but not RXR agonists, stimulate the expression of SOX9 in a wide variety of retinoid-inhibited breast cancer cell lines. 12468549_mutational analysis of human retinoic acid receptor alpha ligand binding domain 12505266_Cryptic translocation of PML/RARA on 17q. A rare event in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 12810556_endocrine molecule retinoic acid, and its receptor RARs play a critical role in alveolarization during the neonatal period of the lung. 12835288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12935958_REVIEW the biology of RARalpha, and the RARalpha fusion proteins created in APL and the normal forms of the partner proteins 14559998_data suggest that Sp110b is a transcriptional cofactor negatively regulating retinoic acid receptor alpha-mediated transcription 14592536_RARA has a distinct role and functional mode in mediating tretinoin-induced signalling. 14691372_In a 9-cis retinoic acid-dependent fashion in cells in vitro, retinoic acid receptor alpha isoform stimulates the expression of reporter constructs containing the site that binds aldehyde dehydrogenase-2. 14705796_depletion of vitamin A and retinoid receptors by UV irradiation, together with unchanged or even increased c-Jun levels, might seriously interfere with retinoid signaling and thus promote future tumor development, especially in keratinocytes. 14737102_role in development of myelodi leukemia with promyelocytic features 15171703_Results show an increased DNA binding of the retinoic acid receptor alpha/retinoid X receptor alpha heterodimer and the stability of nuclear localization of this heterodimer, which facilitates signal transduction. 15246741_intrinsic ageing of human skin is accompanied by significant elevation in the content of RAR alpha 15255287_Increase in expression of RARalpha is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinomas 15337793_retinoic acid receptor-alpha is synthesized by activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes 15601827_PML-retinoic acid receptor alpha activities are regulated by neutrophil elastase in early myeloid cells 15635645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15746941_CDDO-Im downregulates RARA expression in acute promyelocytic leukemic cells. 15809060_inhibition of monocyte differentiation all contribute to the oncogenic activity of PML-RARalpha 15831516_analysis of estrogen activation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha1 gene in breast cancer cells 15870697_Transient transfection of either all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) receptor alpha or estrogen receptor alpha expression vectors increased cellular retinoic acid binding protein II expression in MDA-MB-231 cells 16085646_all-trans-retinoic acid, an RARalpha ligand, regulates IFNgamma-induced IRF-1 by affecting multiple components of the IFNgamma signaling pathway, from the plasma membrane to the nuclear transcription factors 16113082_loss of one copy of PU.1 through deletion, plus down-regulation of the residual allele caused by PML-RARalpha expression, synergizes to expand myeloid progenitors susceptible to transformation, increasing the penetrance of acute promyelocytic leukemia 16203797_p16INK4a, RARbeta, and MGMT expression is activated by genistein and related soy isoflavones partially through a direct inhibition of DNA methyltransferase 16239915_RARA is the first myeloid-specific transcription factor shown to be dysregulated by both translocation and aberrant methylation 16289102_All trans retinoic acid suppresses 24-hydroxylase expression through RARalpha-dependent signaling pathway and can enhance vitamin D action in suppression of cell growth. 16311697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16417524_protein kinase b interacts with RARalpha and phosphorylates the Ser96 residue of its DNA-binding domain. 16424870_Ski seems to be involved in the blocking of differentiation in AML via inhibition of RARalpha signaling 16432238_PML-RARalpha functions by recruiting an HDAC3-MBD1 complex that contributes to the establishment and maintenance of the silenced chromatin state 16449642_permanent transcriptional silencing is mediated by the association of PML-RAR with chromatin-modifying enzymes and by recruitment of the histone methyltransferase SUV39H1, responsible for trimethylation of lysine 9 of histone H3 16480812_The aryl hydrocarbon receptor activates the retinoic acid receptoralpha through SMRT antagonism 16504291_The NPM-RAR localizes diffusely throughout the nucleoplasm. NPM-RAR does not alter the localization of PML in transfected HeLa cells, and does not associate with PML in vitro. 16540467_analysis of cytoplasmic function of mutant promyelocytic leukemia (PML) and PML-retinoic acid receptor-alpha 16606617_ASXL1 is a novel coactivator of RAR that cooperates with SRC-1 16630218_frequencies of the PML-RARalpha transcripts and subtypes in a series of 32 APL patients from Northeast Brazil 16728697_prevalence of anti-RARalpha antibodies in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia 16769902_providing an explanation for how cAMP synergizes with retinoic acid for transcription 16797070_The PML-RARA fusions can be identified by molecular analyses such as reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). 17005281_liganded RXRalpha is a potent activator of endogenous SOX3 protein expression 17244680_AML1/ETO participates in a protein complex with the RA receptor alpha (RARalpha) at RA regulatory regions on RARbeta2. 17252005_Selection of the RARalpha locus in leukemia patients occursas the consequence of the nuclear architecture of the different RAR loci. 17272513_our results indicate that activator Sp1 and repressor RXRalpha:RARalpha act in concert to regulate MRP3 expression. 17272867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17451432_RARalpha/RXRalpha heterodimer is involved in the differential regulation of the GnRH II gene in neuronal and placental cells 17456381_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17475621_the hormone-independent association between PML-RARalpha and coactivators contributes to its ability to regulate gene expression 17595318_Ligand binding to RAR would play a major role in the assembly and intracellular location of a signaling complex involving RAR and the subunits of PI3K. 17611697_Am-80-induced cell-type non-specific growth inhibition is mediated by TGF-beta2, where the total mass of RARalpha could be an important regulatory factor in hematologic malignant cells 17628022_Retinoic-acid-induced RAR-CAK signaling events appear to proceed intrinsically during granulocytic development of normal primitive hematopoietic cells. ALDH-governed RA availability may mediate this process by initiating RAR-CAK signaling. 17656367_p21WAF1/CIP1 is a common transcriptional target of retinoid receptors RAR and RXR 17761950_demonstrate the distinct regulatory mechanisms of p300 and TR3 on RXRalpha acetylation 17943164_PML/RAR gene cytogenetic abnormalities in APL 17960617_Promoter hypermethylation of RAR alpha is associated with prostate cancer progression 17991421_These results would shed new insights for the molecular mechanisms of PML-RARalpha-associated leukemogenesis. 17993618_Mechanisms responsible for deregulation of gene expression in acute myeloid leukemia support the notion that diminished RARA expression contributes to leukemogenesis. 18000064_supports an active role for PLZF and RARalpha-PLZF in leukemogenesis, identifies up-regulation of CRABPI 18024792_The transcription factor PML-RARalpha regulates key cancer-related genes and pathways by inducing a repressed chromatin formation on its direct genomic target genes. 18180299_CCR4 plays a role in the regulation of certain endogenous RARalpha target genes and RCD1 and CCR4 might mediate their function through their interaction with NIF-1 18212063_Topoisomerase II beta associates with & negatively modulates RARalpha transcriptional activity. Increased levels of and association with TopoIIbeta cause resistance to retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia cell lines. 18305945_IN COLONIC SERRATED ADENOMAS Three genes (TNFRSF10A, BENE, RARA) with strongly significant expression intensities in the oligonucleotide microarray 18416830_a role for RAR-alpha engagement in the regulation of genes and proteins involved with human T cell activation and type 2 cytokine production 18636556_PML/RARalpha fusion protein mediates the unique sensitivity to arsenic cytotoxicity in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19029980_whereas transcriptional activation of PML-RARA is likely to control differentiation, its catabolism triggers leukemia-initiating cell eradication and long-term remission of mouse acute promyelocytic leukemia 19100514_Acute promyelocytic leukemia with insertion of PML exon 7 a and partial deletion of exon 3 of RARA is reported. 19106195_These data indicate that the RAR/RXR heterodimer is a critical regulator of human hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) differentiation, and pharmacological modulation of RXR signaling prevents the loss of human HSCs that otherwise occurs in short-term culture. 19128831_First documented case of acute promyelocytic leukemia with an RARalpha submicroscopic deletion which is not associated with X-RARalpha fusion. 19144697_Data show that retinoids induce gene expression of ADAM10 and alpha-secretase activity by nonpermissive retinoid acid receptor/retinoid X receptor (RAR/RXR) heterodimers, whereby alpha- and beta-isotypes of RAR play a major role. 19173001_Derangement/lack of a critical factor necessary for RARalpha function induces epigenetic repression of a RA-regulated gene network downstream of RARalpha, with major pleiotropic biological outcomes. 19224461_Identification of PML/RARalpha fusion gene transcripts that showed no t(15;17) with conventional karyotyping and fluorescent in situ hybridization 19322209_Knock-in human PML-RARalpha alone can confer properties of self-renewal to committed murine hematopoietic progenitors before the onset of disease. 19341714_Ski can stabilize RARalpha and HDAC3 thus Ski represses retinoic acid signaling by stabilizing corepressor complex. 19458357_Knockdown of RARalpha2 but not RARalpha1 induced significant MM cell death and growth inhibition; and overexpressing RARalpha2 activated STAT3 and MEK and ERK signaling pathways. 19465599_RARalpha-deficient germ-cell stem cells were able to repopulate germ-cell-depleted wild-type testes and initiate spermatogenesis; however, improper cellular associations and abnormal sperm formation were observed. 19563758_Study found that RARalpha/RARgamma exhibit extensive colocalization of their genomic binding regions with ERalpha in the vicinity of genes that are antagonistically regulated by estrogen and RA. 19626135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19626135_Variations in the nucleotide sequence of RARA are not associated with myopia, hypermetropia, or ocular biometric measures. 19628791_Induction of transglutaminase 2 by a liver X receptor/retinoic acid receptor alpha pathway increases the clearance of apoptotic cells by human macrophages. 19732752_TNIP1 interacts with liganded RARalpha and RARgamma but acts as a corepressor of their activity. 19799861_redox regulation function of thioredoxin glutathione reductase protects the DNA-binding activity of RAR against cellular ROS damage. 19828696_Data show that induction of CCL2 and CCL24 was directly mediated by ligand-activated retinoic acid receptors. 19855079_Data show that PLZF-RARalpha binds to a region of the c-MYC promoter, suggesting that PLZF-RARalpha may act as a dominant-negative version of PLZF by affecting the regulation of shared targets. 19863682_alternative splicing of PML/RARalpha transcripts might be involved in nonsense-mediated decay 19884280_Retinoic acid receptor alpha is the major isoform responsible for CYP26A1 induction. 19902255_Data show significant associations between SNPs in RARA, RARB, TOP2B and RARG, RXRA, TLR3, TRIM5 and RIG-I genes and rubella virus-specific cytokine immune responses. 19902255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965660_Leukemic transformation by acute promyelocytic leuckemia fusion protein PRKAR1A-RARalpha is critically dependent on RXRalpha. 20080953_RAR alpha as an essential component of the estrogen receptor-alpha (ER)- complex, potentially by maintaining ER-cofactor interactions, and suggest that different nuclear receptors can cooperate for effective transcriptional activity in breast cancer cells 20133705_PML/RARalpha transactivates the TF promoter through an indirect interaction with an element composed of a GAGC motif and the flanking nucleotides, independent of AP-1 binding. 20155840_We studied 21 PML-RARA positive/RARA-PML negative cases by bubble PCR and multiplex long template PCR to identify the genomic breakpoints. 20159609_PML-RARalpha/RXR functions as a local chromatin modulator and that specific recruitment of histone deacetylase activities to genes important for hematopoietic differentiation, RAR signaling, and epigenetic control is crucial to its transforming potential. 20159610_Selective targeting of PU.1-regulated genes by PML/RARalpha is a critical mechanism for the pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia(APL). 20185965_Role of RARA in differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells is reported. 20190807_Retinoic acid-suppressed phosphorylation of RARalpha induces FGF8f expression to mediate differentiation response pathway in U2OS osteosarcoma cells. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354914_RAR, RXR and VDR are expressed in human fetal pancreatic progenitor cells. 20543827_The basal repressive activity of RAR is conferred by an extended beta-strand that forms an antiparallel beta-sheet with specific corepressor residues. 20544846_RARA breakpoints are associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. 20572854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574048_autophagic degradation contributes significantly both to the basal turnover as well as the therapy-induced proteolysis of PML/RARA 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736163_CART1 might be a cytoplasmic, testis-specific derepressor of RAR 20804918_RARA amplification in hematologic malignancies may serve as an independent prognostic factor. 20807888_BCOR is a fusion partner of RARA in a t(X;17)(p11;q12) variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia. BCOR-RARA possesses common features with other RARA fusion proteins. 21053424_Tribles homolog 1 (Trib1) functions as a negative regulator of Retinoic acid receptor-alpha. 21150871_RARa-mediated signaling acts as an endogenous protective pathway to slow the progression of kidney disease, and selective activation of the RARa receptor may be a promising treatment option for patients with HIV-associated nephropathy. 21187718_Autophagy regulates myeloid cell differentiation by p62/SQSTM1-mediated degradation of PML-RARalpha oncoprotein 21190992_Rara haploinsufficiency (like Pml haploinsufficiency and RARA-PML) can cooperate with PML-RARA to influence the pathogenesis of APL in mice, but that PML-RARA is the t(15;17) disease-initiating mutation. 21245861_New insights that arose from these studies, in particular focussing on newly identified PML-RARalpha target genes, its interplay with RXR and deregulation of epigenetic modifications. 21254357_One variant in the RARA gene (rs12051734), three variants in the RARB gene (rs6799734, rs12630816, rs17016462), and one variant in the RARG gene (rs3741434) were found to be statistically significant at p |
ENSMUSG00000037992 |
Rara |
184.146722 |
2.9457656719 |
1.558643 |
0.219586439 |
48.872561 |
0.00000000000273145320372729994061223637300439055384734809983626746543450281023979187011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000015828916092271279686941647601387123112104404754063580185174942016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
265.3872786 |
36.7547526 |
90.7554539 |
9.3778220 |
| ENSG00000131781 |
2330 |
FMO5 |
protein_coding |
P49326 |
FUNCTION: Acts as Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase on a broad range of substrates. Catalyzes the insertion of an oxygen atom into a carbon-carbon bond adjacent to a carbonyl, which converts ketones to esters (PubMed:28783300, PubMed:26771671, PubMed:20947616). Active on diverse carbonyl compounds, whereas soft nucleophiles are mostly non- or poorly reactive (PubMed:26771671, PubMed:7872795). In contrast with other forms of FMO it is non- or poorly active on 'classical' substrates such as drugs, pesticides, and dietary components containing soft nucleophilic heteroatoms (Probable) (PubMed:7872795). Able to oxidize drug molecules bearing a carbonyl group on an aliphatic chain, such as nabumetone and pentoxifylline (PubMed:28783300). Also, in the absence of substrates, shows slow but yet significant NADPH oxidase activity (PubMed:26771671). Acts as a positive modulator of cholesterol biosynthesis as well as glucose homeostasis, promoting metabolic aging via pleiotropic effects (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20947616, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26771671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28783300, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7872795, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26771671}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;FAD;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Methylation;Microsome;Monooxygenase;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Metabolic N-oxidation of the diet-derived amino-trimethylamine (TMA) is mediated by flavin-containing monooxygenase and is subject to an inherited FMO3 polymorphism in man resulting in a small subpopulation with reduced TMA N-oxidation capacity resulting in fish odor syndrome Trimethylaminuria. Three forms of the enzyme, FMO1 found in fetal liver, FMO2 found in adult liver, and FMO3 are encoded by genes clustered in the 1q23-q25 region. Flavin-containing monooxygenases are NADPH-dependent flavoenzymes that catalyzes the oxidation of soft nucleophilic heteroatom centers in drugs, pesticides, and xenobiotics. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:2330; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; aldehyde oxidase activity [GO:0004031]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; monooxygenase activity [GO:0004497]; N,N-dimethylaniline monooxygenase activity [GO:0004499]; NADP binding [GO:0050661]; NADPH oxidase H202-forming activity [GO:0106294]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; NADPH oxidation [GO:0070995]; regulation of cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0090181]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
16183778_fmo5 displayed a significant, dominant liver-specific mRNA profile. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26771671_absence of the typical characteristic sequence motifs sets human FMO5 apart from all characterized Baeyer-Villiger mono-oxygenases so far. These findings open new perspectives in human oxidative metabolism 26839369_Report relatively stable FMO5 expression throughout development. 28783300_Nabumetone and pentoxifylline, two widely used pharmaceuticals, were thereby demonstrated to be efficiently oxidized in vitro by FMO5 to the corresponding acetate esters with high selectivity. |
ENSMUSG00000028088 |
Fmo5 |
25.412555 |
0.4980321966 |
-1.005689 |
0.329626346 |
9.377957 |
0.00219610151287077471141118145681048190454021096229553222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004810694320269016943658613172374316491186618804931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.0351917 |
3.4794442 |
34.4211344 |
4.7058851 |
| ENSG00000131871 |
55829 |
SELENOS |
protein_coding |
Q9BQE4 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the degradation process of misfolded endoplasmic reticulum (ER) luminal proteins. Participates in the transfer of misfolded proteins from the ER to the cytosol, where they are destroyed by the proteasome in a ubiquitin-dependent manner. Probably acts by serving as a linker between DERL1, which mediates the retrotranslocation of misfolded proteins into the cytosol, and the ATPase complex VCP, which mediates the translocation and ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215856}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Selenocysteine;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It is involved in the degradation process of misfolded proteins in the ER, and may also have a role in inflammation control. This protein is a selenoprotein, containing the rare amino acid selenocysteine (Sec). Sec is encoded by the UGA codon, which normally signals translation termination. The 3' UTRs of selenoprotein mRNAs contain a conserved stem-loop structure, designated the Sec insertion sequence (SECIS) element, that is necessary for the recognition of UGA as a Sec codon, rather than as a stop signal. Two additional phylogenetically conserved stem-loop structures (Stem-loop 1 and Stem-loop 2) in the 3' UTR of this mRNA have been shown to function as modulators of Sec insertion. An alternatively spliced transcript variant, lacking the SECIS element and encoding a non-Sec containing shorter isoform, has been described for this gene (PMID:23614019). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:55829; |
cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex [GO:0036513]; Derlin-1-VIMP complex [GO:0036502]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034362]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034361]; antioxidant activity [GO:0016209]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; ubiquitin-specific protease binding [GO:1990381]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; ER overload response [GO:0006983]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; negative regulation of acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002865]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902236]; negative regulation of glucose import [GO:0046325]; negative regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045719]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of macrophage apoptotic process [GO:2000110]; negative regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051771]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; regulation of nitric oxide metabolic process [GO:0080164]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to redox state [GO:0051775]; retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol [GO:0030970]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
15063746_SELS is regulated by glucose deprivation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. It is a glucose-regulated protein. 15161744_Positive relationship between Tanis mRNA and the acute-phase protein serum amyloid A suggests an interaction between innate immune system responses and Tanis expression in muscle and adipose tissue. 15215856_Derlin-1 interacts with US11, a virally encoded ER protein that specifically targets MHC class I heavy chains for export from the ER, as well as with VIMP, a novel membrane protein that recruits the p97 ATPase and its cofactor 16227999_Regulatory variant in SELS influences inflammatory response to ER stress 16574427_SEPS1 may regulate cytokine production in macrophage cells and there may be a regulatory loop between TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and SEPS1 that plays a key role in control of the inflammatory response 17374524_SEPS1 protein is secreted from hepatoma cells. Fractionation of human serum indicated that SEPS1 was associated with LDL and possibly with VLDL. 17641917_significant association with increased CHD risk in females carrying the minor allele of rs8025174. Another variant, rs7178239, increased the risk for ischemic stroke significantly in females. 17661913_-105G>A polymorphism is not associated with IBD susceptibility and does not contribute to a certain disease phenotype or increased TNF-alpha levels in IBD patients. 17880573_Selenoprotein S -105(adenosine) allele is a non-significant risk factor in young stroke patients from Italy and Germany. 18068137_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18625033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18625033_Six polymorphisms were studied in this gene, and none are associated with type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel diseases. 18675776_SelS has a role in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in hepatoma HepG2 cells 18710632_SelS protein may be involved in insulin resistance in Chinese with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) by acting as the SAA receptor, thus playing an important role in the development of T2DM and atherosclerosis 18728048_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18974842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19144102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19144102_The -105G>A promoter polymorphism of SEPS1 was associated with the intestinal type of gastric cancer. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19398551_Selenoprotein S/SEPS1 modifies endoplasmic reticulum stress in Z variant alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20114070_beta-ME, also an ER stress agent, could induce cell apoptosis, and SelS may play an important role in protecting cells from apoptosis induced by ER stress in HepG2 cells. 20378690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20619427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20619427_a role for SELS in the development of metabolic disease, especially in the context of insulin resistance. 21052528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21456042_Upregulation of SelS expression in reactive astrocytes reveals a new protective role for SelS against inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress that can be relevant to astrocyte function. 22700979_the redox properties observed for recombinant VIMP are compatible with a function as a reductase 23161441_These results suggest a potential role for the SELS region in the development subclinical cardiovascular disease in this sample enriched for type 2 diabetes mellitus. 23776519_Findings suggest that the SEPS1 G-105A polymorphism contributes to the risk of developing SPTB in a Chinese population. 23829426_Our results indicated that the rs12910524 in the Tanis gene was associated with triglyceride concentrations in subjects without diabetes in China. 23914919_Data suggest that selenocysteine allows selenoprotein S (SelS, VIMP) to sustain activity under oxidative stress. 24275540_Selenoprotein S is a marker but not a regulator of endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. 24471570_Existence of a link between SEPS1 promoter genetic variation and Hashimoto thyroiditis risk. 24573439_that SEPS1 may protect mice against LPS-induced sepsis and organ damage. Therefore, SEPS1 may be a new target to resolve LPS-induced sepsis. 24700463_Pro(178) and Pro(183) of SelS play important roles in the translocation of p97(VCP) to the ER membrane and protect cells from ER stress 25008318_Although VIMP can interact with CLIMP-63 and Syn5L, it does not interact with MT-binding ER proteins (such as Reep1) that shape the tubular smooth ER 25390504_SNP rs4965814 of SELS may affect the susceptibility to ischemic stroke. 25433273_The SEPS1 -105G>A is associated with an increased risk of Kashin-Beck disease and influences the expression of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in Kashin-Beck disease patients 26016409_Potential roles of the SEPS1 gene in the pathogenesis and etiology of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 26382012_SEPS1 may be a potential gene marker for disease diagnosis and prognosis. 26504085_interaction between SelK and p97(VCP) is SelS-dependent, and the resulting ERAD complex (SelS-p97(VCP)-SelK) plays an important role in ERAD and ER stress 27121097_regulating liver and serum Selenoprotein S levels might become a new strategy for the prevention and treatment of DM and its macrovascular complications 27802219_In these studies found that SelS increases in negative correlation with tau phosphorylation in brain. 28315680_The results suggest that SelS is required for C99 degradation through endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation, resulting in inhibition of amyloid beta production. 29555962_the Role of VIMP in Endoplasmic Reticulum-Associated Degradation of CFTRDeltaF508 30082770_The levels of SelS and SelK were decreased during adipocyte differentiation and were inversely related to the levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), a central regulator of adipogenesis. 30413610_The present study suggested that genetic polymorphisms of SelS were associated with Type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population 31265177_SEPS1 gene polymorphism is associated with diabetic nephropathy. 31426718_Interaction of Genetic Variations in NFE2L2 and SELENOS Modulates the Risk of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis. 31542866_Studied association of selenoprotein S (SEPS1) and selenoprotein P (SEPP1) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with expression of SEPS1 and SEPP1 in patients with metabolic syndrome and history of cardiovascular disease. 31846435_Selenoprotein S regulates adipogenesis through IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway. 31880214_significantly down-regulated in mesangial cells exposed to high glucose or TGF-beta1 33290140_The SELS rs34713741 Polymorphism Is Associated with Susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer and Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. 35569765_Selenoprotein S regulates tumorigenesis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through AKT/ GSK3beta/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000075701 |
Selenos |
296.921878 |
2.2712849157 |
1.183509 |
0.104917348 |
127.785817 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001250335370754860390679076935724443525625999468521181599583330008076934946906698907509447593611184856854379177093505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000158684007500788835004044242252732861392222755135514081867264202640028348352194131898329487739829346537590026855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
413.0099026 |
25.2631442 |
183.0769541 |
8.7621181 |
| ENSG00000131979 |
2643 |
GCH1 |
protein_coding |
P30793 |
FUNCTION: Positively regulates nitric oxide synthesis in umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). May be involved in dopamine synthesis. May modify pain sensitivity and persistence. Isoform GCH-1 is the functional enzyme, the potential function of the enzymatically inactive isoforms remains unknown. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12176133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16338639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17057711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8068008, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9445252}. |
3D-structure;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Dystonia;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Parkinsonism;Phenylketonuria;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate biosynthesis; 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate from GTP: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:16778797, ECO:0000305|PubMed:2463916, ECO:0000305|PubMed:3753653}. |
This gene encodes a member of the GTP cyclohydrolase family. The encoded protein is the first and rate-limiting enzyme in tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) biosynthesis, catalyzing the conversion of GTP into 7,8-dihydroneopterin triphosphate. BH4 is an essential cofactor required by aromatic amino acid hydroxylases as well as nitric oxide synthases. Mutations in this gene are associated with malignant hyperphenylalaninemia and dopa-responsive dystonia. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described; however, not all variants give rise to a functional enzyme. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2643; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuron projection terminus [GO:0044306]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTP cyclohydrolase I activity [GO:0003934]; GTP-dependent protein binding [GO:0030742]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; translation initiation factor binding [GO:0031369]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0035998]; dopamine biosynthetic process [GO:0042416]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; neuromuscular process controlling posture [GO:0050884]; nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0006809]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; pteridine-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0042559]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of lung blood pressure [GO:0014916]; regulation of removal of superoxide radicals [GO:2000121]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to pain [GO:0048265]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthetic process [GO:0006729]; tetrahydrofolate biosynthetic process [GO:0046654]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11580249_kinetic studies with GFRP 12391354_A kindred is reported in which GTP-CH deficiency presents as a dopa-responsive myoclonus-dystonia syndrome, documented as a missense mutation in exon 6 of GTP-CH1 gene (K224R). 12821132_GTP cyclohydrolase I is alternatively spliced in mononuclear cells 12925450_Gene transfer of human GTPCH I restored arterial GTPCH I activity and BH4 levels, resulting in reduced O2- and improved endothelium-dependent relaxation and basal NO release in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats 14551046_Genetic transfer into rabbit vascular endothelium in vivo increases intracellular concentration of tetrahydrobiopterin. 15604419_GTPCH1 induction in endothelial cells is stimulated by cytokines and mediated by Stat1/3, Jak2 and NF-kappaB. 15679701_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15753436_We tested 23 individuals with dopamine-resistant dystonia for the different GCH1 mutation types by conventional and quantitative PCR analyses and found mutations, including two large exon deletions, in 87%. 15852365_A new mutation (Thr106Ile) of the GTP cyclohydrolase 1 gene associated with DYT5 dystonia (Segawa disease). 15909293_Results suggest that variants within GCHI may contribute to bipolar disorder in the Irish population. 16149046_GTP cyclohydrolase I gene transcription is regulated by basic region leucine zipper transcription factors 16267845_Dopa-responsive dystonia and early-onset Parkinson's disease in a patient revealed a mutation in the GTP cyclohydrolase I gene (GCH1). 16643317_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16696853_Aha1 may recruit GCH1 into the endothelial nitric oxide synthase/heat shock protein (eNOS/Hsp90) complex to support changes in endothelial nitric oxide production through the local synthesis of BH4. 17044972_Data show that the detection of GCH I mutations is helpful in early diagnosis of non-typical cases of dopa-responsive dystonia. 17111153_Utility of multiple ligation-dependent probe amplificatino for deletion analysis of GCH1 in dopa-responsive dystnoia. 17343757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17363416_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17407085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17410324_A novel mutation(H210Q) in GCH-1 gene in a case of dopa-responsive dystonia. 17557242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17557242_a new heterozygotic point mutation 151(G-->A) in GCH1 gene in Chinese sporadic patients with DRD 17655760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17717598_NO secretion traits are heritable, displaying joint genetic determination with autonomic activity by functional polymorphism at GCH1 17717598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804835_A large genomic deletion in GCH1 is sufficient to explain neurologic symptoms in the majority of Swiss family members with dopa-responsive dystonia. 17804835_This study rules out the previously reported DYT14 locus as a cause of dopa-responsive dystonia, since a novel multiexonic deletion has been identified in GTP cyclohydrolase I (GCH1). 17898029_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17898029_We found a GCH1 point mutation in 27 patients of group 1 (54%) and in four patients of group 2 (5%). Of these, nine single and one double mutation have not been described before. GCH1 deletions were detected in four patients. 18044725_This study identified three mutations; two affected siblings carried a novel T209P mutation and two siblings from another family were compound heterozygous carriers of Met211Val and Lys224Arg mutations. 18202219_Sequencing of exons 1-6 of the GCH1 gene revealed a heterozygous deletion of two guanines at positions 64 and 65 and an insertion of 4 bases (AACC). 18276179_a unique presentation of autosomal recessive (AR) GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH) deficiency, with severe CNS involvement but without hyperphenylalaninemia 18358407_male toddler with dopa-responsive dystonia caused by an autosomal-dominant GCH1 mutation found in three other family members 18374612_This study verifies previous results that decreased GCH1 function or inducibility as a result of genetic polymorphisms protects against pain, supporting specific functions of BH4 in relation to particular aspects of pain. 18410856_This study reports two Korean children affected with dopa-responsive dystonia caused by a novel missense mutation of the guanosine triphosphate cyclohydrolase I gene. One child exhibits a novel sporadic mutation(THR186ILE) 18515178_there is a common clinically relevant GCH1 genetics that is so far known to be related to unfavorable changes of endothelial function and a reduced risk for chronic pain. 18554280_identified novel mutations in dopa-responsive dystonia are Leu91Val, Pro95Leu, Val204Gly and 628delC in GCH-1 gene 18598896_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18598896_haplotype has a striking effect on enzymatic coupling of eNOS as well as vascular O2 production and nitric oxide bioavailability in patients with coronary artery disease 18752196_Study identified the mutation at the GCH1 gene, IVS5+3insT, as the cause of Dopa-responsive dystonia in a Brazilian family 18824773_These findings highlight the importance of MCP-1/CCR2 signaling in the response to vascular injury and identify novel pathways linking endothelial BH4 to inflammation and vascular remodeling. 19011239_Quantitative analysis of cellular tetrahydrobiopterin versus superoxide production between GCH/eNOS-LOW and GCH/eNOS-HIGH cells revealed a striking linear relationship between eNOS protein and cellular BH4 stoichiometry 19014702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19014702_The GCH1 pain-protective haplotype does not have a significant effect on pain patterns or severity in recurrent acute pancreatitis or chronic pancreatitis 19081190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19081190_We conclude that SNPs of the GCH1 gene may profoundly affect the ratings of pain induced by capsaicin. 19101819_6BH(4) de novo synthesis is controlled by H(2)O(2) in a concentration-dependent manner, but H(2)O(2)-mediated oxidation does not affect the functionality of the GTPCHI/GFRP complex. 19104007_GTPCH I is targeted to caveolae microdomains in vascular endothelial cells, and tetrahydrobiopterin production occurs in proximity to endothelial NO synthase. The regulation of GTPCH I activity involves the caveolar coat protein, caveolin-1. 19195260_genetic confirmation of the diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia,GCH-I mutation in dopa-responsive dystonia can be successfully managed using low doses of levodopa over a long period of time 19292934_Autosomal dominant GTP cyclohydrolase I (AD GCH 1) deficiency (Segawa disease) is an autosomal dominant dopa responsive dystonia caused by heterozygous mutation of the GCH 1 gene located on 14q22.1-q22.2. 19294699_In this study, using MALDI-TOF/MS,etc. several proteins were identified by coimmunoprecipitation with GTP cyclohydrolase 1. Findings provide a first glimpse into the mechanisms regulating GCH1 activation by cytokines in normal adult human astrocytes. 19332422_A detailed clinical evaluation of 34 patients with confirmed mutations in the GCH1 gene is presented 19442649_this study is the first to provide a comprehensive analysis of the GCH-1 interactome. 19491146_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19515581_In the Chinese type 2 diabetes population, C59038T polymorphism of GTP cyclohydrase 1 was associated with an increased risk of cerebrovascular, cerebrovascular, and peripheral vascular disease. 19515581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19533203_This study report the founder effect of Q89X mutation in Cordoba community and also describe the diverse phenotypic spectrum of clinical variability occurring in this population of patients affected with the same mutation. 19566901_A novel non-sense mutation in the GCH1 gene can be associated with Dopa-responsive dystonia and reduced penetrance in South African patients. 19573577_The present study did not identify gender-specific differences in GCH1 expression; however, other mechanisms may explain the skewed gender distribution of dopa-responsive dystonia among GCH1 mutation carriers 19674121_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19735094_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19735094_This study does not support a significant role for genetic variation at the GCH1 locus in early-onset Parkinson's disease 19775452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851158_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19851158_This study further strengthens the support for a modest yet reproducible and consistent pain-protective effect associated with a GCH1 haplotype known to reduce GCH1 and thus BH4 up-regulation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19926872_Studies provide a new mechanism for regulation of endothelial GTPCH-1 by its phosphorylation and interplay with GFRP. 19959292_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19959292_The study of this study showed the interval between cancer diagnosis and opioid therapy initiation was significantly longer in homozygous carriers of these genetic variants than in heterozygous and non-carriers . 20108370_GCH1 mutation is noted in Chinese patient with dopa responsive dystonia. 20187889_We propose that GCH-1 mutations should be considered a genetic cause of familial paroxysmal exercise-induced dystonia, especially if additional clinical features of monoaminergic deficiency are present in affected individuals 20418482_Cardiac myocyte-specific overexpression of human GTP cyclohydrolase I protects against acute cardiac allograft rejection. 20437540_The data presented here do not provide sufficient evidence to establish a genotype-phenotype correlation of dopa-responsive dystonia. 20491893_A novel missense mutation in the GCH1 gene can be associated with Dopa-responsive dystonia 20581851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20581851_Single-locus analysis revealed that the C+640T polymorphism (rs1049255) in the 3'-UTR of CYBA and the G+243A polymorphism (rs841) in the 3'-UTR of GCH1 were independently associated with an elevated risk of CHD in a Chinese Han population 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20633294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20633294_The pain-protective SNP combination of GCH1 may be of importance in the limited number of homozygous carriers during the initial dilation of cervix but upon arrival at the delivery unit these women are more inclined to use second line labor analgesia. 20838263_Genetic association analysis shows that a common GCH1 haplotype is highly associated with improvement in absolute disability index scores in patients undergoing surgery for lumbar degenerative disc disease. 20838263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20842020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20937667_Sympathetic, cardiac, and endothelial functions are preserved in patients with GCH1 mutations despite a neurological phenotype, reduced plasma biopterin, and norepinepherine and epinephrine concentrations 21037510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21181356_The GCH1 3'-UTR C+243T variant was an independent predictor of worsening long-term outcomes in patients with first-onset ischemic stroke. 21422102_Increased BH(4) by cardiomyocyte-specific overexpression of GTPCH-1 preserves the ability of ischemic preconditioning to elicit myocardial and mitochondrial protection impaired by hyperglycemia. 21674621_This study demonistrated that -22C>T mutation in the GCHI gene segregates with affected status in multiple generations of a single Dystonia, Dopa-responsive family 21733738_We report here a novel splicing mutation in intron 3 of GCH1 gene in Segawa disease with parkinsonism. 21834904_In all four patients with Dopa-responsive dystonia , a new frameshift mutation (c.729delG; p.A190fsX191) was identified in the exon 5 of GCH1 21896313_the C+243T polymorphism of the GCH1 gene affects the personality trait of novelty seeking in males 21969008_Increased vascular GCH1 expression and endogenous tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis in response to inflammation preserves endothelial function in inflammatory states. 22068827_this study reported that 2 children with dopa-responsive dystonia with GTP-cyclohydrolase 1 mutations. 22172551_This study found that Modest genotypic associations (P G, p.(Glu2Gly), within the GCH1 gene in affected family members displaying a range of phenotypes; variant is pathogenic in studied family and may underlie Parkinson's disease and Dopa-responsive dystonia 25783971_No association was seen between the pain protective GCH-1 haplotype and the development of hypersensitivity following injury. An increase in baseline pain thresholds was seen between visits in protective haplotype carriers who sensitized to injury. 26215833_The risk of orofacial clefts is associated with variants of the GCH1 gene related to BH4 metabolism. 26392364_No association between the GCH1 pain-protective haplotype and cervical dilation was found, but a previously demonstrated association with increased use of second-line analgesia was confirmed. 26400349_Exonic deletion in the GCH1 gene only accounted for the etiology in a small percentage of patients with sporadic dopa-responsive dystonia in our Han Chinese cohort. 26804608_suggest that the GCH1 and MIR4697 but not SIPA1L2 and VPS13C are genetic loci influencing risk of Parkinson's disease in Taiwan 26814432_GTPCH/Ang-1 interaction in stromal fibroblasts and activation of Tie2 on breast tumor cells could play an important role in supporting breast cancer growth. GTPCH may be an important mechanism of paracrine tumor growth and hence a target for therapy in breast cancer. 27185167_This study indicates that mutations in GCH1 are rare in late-onset Parkinson disease. 27269966_This study shown GCH1 genetic variants for Parkinson's disease are associated with the risk of incident Parkinson's disease in the general population and with impairment in daily functioning in individuals without clinical parkinsonism. 27653855_This study found that rs11158026 (GCH1) is associated with Parkinson disease in Iran population. 27666935_This study demonstrated that whole-exome sequencing show reveled GCH1 mutation with early-onset generalized dystonia. 27667361_Dopa-responsive dystonia phenotype may have heterogeneous genetic background and may be caused by point mutations or rearrangements in the GCH1 gene as well as in the PARK2 gene. 27826622_High GCH1 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 27871051_GCH1 variants affect early PD risk through altered dopamine uptake, and aging alters how genetic factors contribute to disease development. 28380328_Our results suggest that rs329648 is associated with risk of developing PD in the Han Chinese population. Our findings should be verified in further studies, and they highlight the need for functional studies of MIR4697. 28397219_c.550C>T mutation is associated with dopa-responsive dystonia. 28558098_Deletion of GCH1 likely contributes to dopa-responsive dystonia. 28582483_In a Chinese population, GCH1 rare variants were associated with a risk factor for Parkinson's disease. 28585439_Association analysis indicated that the Tibetan version of GCH1 was significantly associated with multiple physiological traits in Tibetans, including blood nitric oxide concentration, blood oxygen saturation, and hemoglobin concentration. 28596578_the pivotal role of GCH1 overexpression in post-infarction cardiac remodeling is attributable to preservation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) handling proteins, and identify a new therapeutic target for cardiac remodeling after infarction. 28958832_Our data expand the genotypic spectrum of GCH1 and confirm the broad phenotypic spectrum of GTP cyclohydrolase 1-deficient DOPA-responsive dystonia in the Serbian population 29289916_Her 2 uncles and probably her 2 grandaunts also have limbs tremor. Genetic analysis by using PCR-direct sequencing revealed a novel point mutation (c.263G>T: p. Arg88Leu) in GCH1 29405179_One novel mutation of c.679A>G (p.T227A) in GCH1 and 3 known mutations of c.457C>T (p.R153X), c.739G>A (p.G247S), and c.698G>A (p.R227H) in tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) have been found and predicted to be damaging or deleterious. 29409010_High GCH1 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 29470312_The results of this study showed that no effect on pain perception was observed for this combined GTP-cyclohydrolase-1 haplotype. 29724574_It is a genetic risk for Parkinson's disease. 29948246_Study identified 15 patients with GCH1 mutations (15 patients from seven families and five sporadic cases). The patients presented two distinctive phenotypes of juvenile or young-onset dopa-responsive dystonia and Parkinson's disease, which clinically and radiologically shared characteristic features. GCH1 mutations induce the distinctive symptoms among young or middle age at onset. 30031848_The study indicates potential contribution of GCH1 polymorphisms to the variability of pain in African Americans with sickle cell disease. 30091833_Mechanistically, human antigen R (HuR) bound with the adenylateuridylate-rich elements of the GTPCH1 3' untranslated region and increased its stability; nicotine inhibited HuR translocation from the nucleus to cytosol, which downregulated GTPCH1. 30314816_Common and rare GCH1 genetic variants are associated with Parkinson's disease. 30911941_Dopa-responsive dystonia proband was found to be a compound heterozygote for GCH1 variants. Pedigree analysis demonstrates reduced penetrance of GCH1 mutations. 31230962_A tetrahydrobiopterin deficit finding in schizophrenia: A confirmation study. 31486149_the rs3783641 single-nucleotide polymorphism in the GCH1 gene is associated with post-herpetic neuralgia, and the AA genotype showed a protective effect in post-herpetic neuralgia. 31676569_CTRP13 preserves endothelial function in diabetic mice by regulating GCH1/BH4 axis-dependent eNOS coupling, suggesting the therapeutic potential of CTRP13 against diabetic vasculopathy. 31819149_GCH1 (rs841) polymorphism in the nitric oxide-forming pathway has protective effects on obstructive sleep apnea. 32278297_Autosomal dominant GCH1 mutations causing spastic paraplegia at disease onset. 32363908_Oxidative Stress, GTPCH1, and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Uncoupling in Hypertension. 32662044_Association of TOR1A and GCH1 Polymorphisms with Isolated Dystonia in India. 32746945_GCH1 variants contribute to the risk and earlier age-at-onset of Parkinson's disease: a two-cohort case-control study. 33087420_Brain structural alterations in patients with GCH1 mutations associated DOPA-responsive dystonia. 33221620_Increased superoxide in GCH1 mutant fibroblasts points to a dopamine-independent toxicity mechanism. 33229582_A hybrid approach reveals the allosteric regulation of GTP cyclohydrolase I. 33387654_Biophysical and structural investigation of the regulation of human GTP cyclohydrolase I by its regulatory protein GFRP. 33713342_GCH1 mutations in hereditary spastic paraplegia. 33781891_Epigenetic silencing of GCH1promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by activating superoxide anion-mediated ASK1/p38 signaling via inhibiting tetrahydrobiopterin de novo biosynthesis. 33903016_Molecular and metabolic bases of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiencies. 34418703_Polymorphisms of Nav1.6 sodium channel, Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor, Catechol-O-methyltransferase and Guanosine Triphosphate Cyclohydrolase 1 genes in trigeminal neuralgia. 34450011_GTP Cyclohydrolase I as a Potential Drug Target: New Insights into Its Allosteric Modulation via Normal Mode Analysis. 34674384_Association analysis of SYT11, FGF20, GCH1 rare variants in Parkinson's disease. 36266731_CircLRFN5 inhibits the progression of glioblastoma via PRRX2/GCH1 mediated ferroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000037580 |
Gch1 |
59.832981 |
0.4691262264 |
-1.091952 |
0.195093703 |
31.971161 |
0.00000001564784511129002355546328362299185466000039923528674989938735961914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000066825486084240596931699870519166806204225395049434155225753784179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.7059748 |
4.6657696 |
80.8880984 |
6.4522948 |
| ENSG00000131981 |
3958 |
LGALS3 |
protein_coding |
P17931 |
FUNCTION: Galactose-specific lectin which binds IgE. May mediate with the alpha-3, beta-1 integrin the stimulation by CSPG4 of endothelial cells migration. Together with DMBT1, required for terminal differentiation of columnar epithelial cells during early embryogenesis (By similarity). In the nucleus: acts as a pre-mRNA splicing factor. Involved in acute inflammatory responses including neutrophil activation and adhesion, chemoattraction of monocytes macrophages, opsonization of apoptotic neutrophils, and activation of mast cells. Together with TRIM16, coordinates the recognition of membrane damage with mobilization of the core autophagy regulators ATG16L1 and BECN1 in response to damaged endomembranes. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15181153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19594635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19616076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27693506}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;IgE-binding protein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lectin;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Spliceosome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the galectin family of carbohydrate binding proteins. Members of this protein family have an affinity for beta-galactosides. The encoded protein is characterized by an N-terminal proline-rich tandem repeat domain and a single C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain. This protein can self-associate through the N-terminal domain allowing it to bind to multivalent saccharide ligands. This protein localizes to the extracellular matrix, the cytoplasm and the nucleus. This protein plays a role in numerous cellular functions including apoptosis, innate immunity, cell adhesion and T-cell regulation. The protein exhibits antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:3958; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; IgE binding [GO:0019863]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; molecular condensate scaffold activity [GO:0140693]; oligosaccharide binding [GO:0070492]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071674]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; negative regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045806]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of immunological synapse formation [GO:2000521]; negative regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:1903614]; negative regulation of T cell activation via T cell receptor contact with antigen bound to MHC molecule on antigen presenting cell [GO:2001189]; negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050860]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090280]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071677]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902041]; regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070232]; regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042129]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
11724777_These results demonstrate that galectin-3 phosphorylation regulates its anti-apoptotic signaling activity 11839755_translocates to the perinuclear membranes and inhibits cytochrome c release from the mitochondria. A role for synexin in galectin-3 translocation. 12112826_galectin-3 and CD26/DPPIV as preoperative diagnostic markers for thyroid nodules 12213909_not a universal marker of malignancy in thyroid nodular disease in children and adolescents 12366402_conclude that because of its location and affinity for gonococcal lipooligosaccharides (LOS) galectin-3 could play a role in gonococcal infection 12375039_Galectin-3 expression is significantly stronger in metastatic lymph nodes and in poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of stomach 12438311_role in mediating MDA-MB-435 human breast carcinoma cell homo- and heterotypic adhesion under flow conditions 12439750_role of galectin-3 on cyclin D(1) gene expression 12615069_galectin 3 controls proliferation in thyroid cells 12673672_downregulation of galectin-3 is associated with epithelial skin cancer 12696064_Non-small-cell lung cancers examined were found to overexpress LGALS3 gene at levels three times higher than those of normal epithelial cells. 12714580_Changes in the expressions of galectin-3 are potentially important for myeloid cell differentiation into specific lineages. 12767519_Stable thyroid galectin- 3 transfectants acquired serum-independent growth, clonogenicity in soft agar, & loss of contact inhibition, indicating transformation of thyroid follicular cells by galectin-3 & possible involvement of galectin-3 in cell cycle. 12878156_mechanism by which galectin-3 overexpression promoted cell death and PARP cleavage as well as caspase (-8, -9, and -3) activation during TRAIL treatment 12963125_results demonstrate that galectin-3 mRNA may not be a suitable target for molecular-based diagnosis of thyroid carcinomas 14558920_an additional marker of malignant potential of thyroid nodular lesions 15205467_Galectin-3 has a role in activating Ras 15279903_nuclear galectin-3 and TTF-1 have roles in progression of non-small cell lung carcinoma 15326483_exerts opposite biological activities according to its cellular localization: nuclear galectin-3 plays antitumor functions and cytoplasmic galectin-3 promotes tumor progression 15362030_A major circulating ligand for galectin-3, which is elevated in the sera of patients with colon cancer, is a cancer-associated glycoform of haptoglobin. 15386597_The aim of this study was to investigate the potential of galectin-3 as a marker of malignancy in follicular patterned thyroid lesions 15501810_expression is required for T. cruzi adhesion to human coronary artery smooth muscle cells and exogenous galectin-3 enhances this process, leading to parasite entry. 15555581_Cultured galectin-3 deficient glioblastoma cells showed increased motility potential and modifications in cytoskeleton reorganization. Galectin-3 deficient cells have increased expression of proteins implicated in cell adhesion regulation. 15561101_GALIG encodes a mitochondrial protein promoting cytochrome c release. 15579437_Alterations in galectin-3 expression and distribution correlate with breast cancer progression 15604089_Gal-3 and sFbg are two physiological mediators present at inflammatory sites that activate different components of the MAPK pathway and could be acting in concert to modulate the functionality and life span of neutrophils. 15643504_Elevated expression of galectin-3 in the nuclei but not the cytoplasm may be an important biological parameter related to histological differentiation and vascular invasion in patients with ESCC. 15645276_Expression of Gal-3 was higher in thin primary melanoma lesions than in benign pigmented skin lesions or metastases and seemed to correlate inversely with the aggressiveness. 15843888_galectin-3 has a role in cancer apoptosis [review] 15867344_Data give credence to the suggestion that gal-3 is a key regulator in the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and highlight the functional similarities between gal-3 and beta-catenin. 15887854_Cytoplasmic-perinuclear gal-3 in majority of thyroid carcinomas and follicular adenomas(FA). Suggests involvement in thyroid tumorigenesis throughout antiapoptosis. In FA might anticipate evolution towards malignancy. 16045783_The presence of galectin-3 in clinically silent microcarcinomas may indicate that galectin-3 is not related to growth or aggressiveness of papillary thyroid microcarcinomas but rather plays some other role in thyroid tumour biology. 16112008_Gal-3 immunostaining is a valuable tool to support a diagnosis of PC in highly proliferating (Ki67 >6%) tumors affecting a single parathyroid gland. 16184379_galectin-3 expression in adenoid cystic carcinoma; galectin-3 reactivity was significantly associated with regional and distant metastasis (P=0.045 and P75% of cells) showed a significant association with stage III/IV, >or=2 extranodal involvements and risk of high/high-intermediate international prognostic index (p |
ENSMUSG00000050335 |
Lgals3 |
322.408182 |
2.1961716641 |
1.134991 |
0.090110528 |
160.311665 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000096728309438941298693099097708875370798959974376258821992359593566952565813488472141017816407094348507555992000561673194169998168945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000014841058703937354914597972913603978226917312790272411518709125405709433484161082898602454808664741214840887550963088870048522949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
447.3917839 |
23.5228969 |
205.1439744 |
8.5776493 |
| ENSG00000132185 |
84824 |
FCRLA |
protein_coding |
Q7L513 |
FUNCTION: May be implicated in B-cell differentiation and lymphomagenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11754007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11891275}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a protein similar to receptors for the Fc fragment of gamma immunoglobulin (IgG). These receptors, referred to as FCGRs, mediate the destruction of IgG-coated antigens and of cells induced by antibodies. This encoded protein is selectively expressed in B cells, and may be involved in their development. This protein may also be involved in the development of lymphomas. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:84824; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166] |
12966588_The concentration of FREB FCRL in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is three times higher than in healthy adults. 15551350_FCRL/FREB may function in melanocytes and melanoma and may be useful for development of diagnostic methods for various pigment disorders and immunotherapy of melanoma. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20668221_Analysis of human cell lines has confirmed that FcRLA is not secreted but is maintained as an intracellular protein in B cells where it interacts with immunoglobulins. 21149418_The studies reported here demonstrate that FCRLA is more broadly expressed among human B lineage cells than originally reported; it is found at significant levels in resting blood B cells and at varying levels in all B-cell subsets in tonsil. 23742757_alternative splicing of FCRLA mRNA results in the production of isoforms differing by their domain composition and possessing either the short or long signal peptide. 26980576_This first genome-wide association approach for cyclophosphamide response in lupus nephritis patients yielded a robust profile of genetic associations including large-effect SNP in the FCGR2B-FCRLA locus, which may provide better insights to cyclophosphamide metabolism and efficacy. 27015273_FCGR2C SNPs that associated with vaccine efficacy in RV144 also strongly associated with the expression of FCGR2A/C and one of them also associated with the expression of Fc receptor-like A (FCRLA), another Fc-gamma receptor (FcgammaR) gene 28879521_FCRLA-A Resident Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein that Associates with Multiple Immunoglobulin Isotypes in B Lineage Cells 29236355_FCRLA has long been viewed as a B cell specific protein, and this is the first time its expression has also been shown in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells 32908921_Development and Validation of the B Cell-Associated Fc Receptor-like Molecule-Based Prognostic Signature in Skin Cutaneous Melanoma. |
ENSMUSG00000038421 |
Fcrla |
11.945455 |
4.1629313426 |
2.057600 |
0.550762507 |
14.392290 |
0.00014840871518735109283425310788828710428788326680660247802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000397407952860178196544810313994844364060554653406143188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.5828273 |
6.2602703 |
4.7755325 |
1.3085207 |
| ENSG00000132205 |
84034 |
EMILIN2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXX0 |
FUNCTION: May be responsible for anchoring smooth muscle cells to elastic fibers, and may be involved not only in the formation of the elastic fiber, but also in the processes that regulate vessel assembly. Has cell adhesive capacity. |
Cell adhesion;Coiled coil;Collagen;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable extracellular matrix constituent conferring elasticity. Predicted to be involved in cell adhesion. Located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84034; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; EMILIN complex [GO:1990971]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular matrix constituent conferring elasticity [GO:0030023]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030194]; positive regulation of defense response to bacterium [GO:1900426]; positive regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:1901731]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127] |
17698584_Results suggest that the expression of EMILIN2 triggers the apoptosis of different cell lines by activation of death receptors. 17988845_EMILIN1 interacts with anthrax protective antigen and inhibits toxin action in vitro. EMILIN1 may be a potential target and/or a protein useful for countermeasures against B. anthracis toxin lethality. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360940_The possibility of using EMILIN2 fragments as potent antineoplastic tools for cancer treatment. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23593459_Apoptosis plays a fundamental role in maintaining epidermal homeostasis, balancing keratinocytes proliferation, and forming the stratum corneum. EMILIN2 is known to trigger the apoptosis of different cell lines 24374807_Identify emilin2 as a key extracellular regulator of the Wnt signalling pathway suppressing breast cancer cell growth and migration. 25445627_Data suggested mechanisms for homo- and hetero-typic EMILINs multimers formation: EMILIN1 or EMILIN2 alone can form trimers and multimers in the absence of each other or they can co-polymerize in a head-to-tail fashion to form hetero-typic multimers. 29483644_High EMILIN2 expression is associated with angiogenesis in B16 melanoma. 30544909_Loss of Multimerin-2 and EMILIN-2 Expression in Gastric Cancer Associate with Altered Angiogenesis 34280481_Expression, methylation and prognostic feature of EMILIN2 in Low-Grade-Glioma. 35588228_Decreased EMILIN2 correlates to metabolism phenotype and poor prognosis of ovarian cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024053 |
Emilin2 |
4210.138517 |
6.6536944563 |
2.734156 |
0.032736892 |
7484.111640 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
7476.8434073 |
141.4726248 |
1131.5704059 |
18.9810081 |
| ENSG00000132329 |
10267 |
RAMP1 |
protein_coding |
O60894 |
FUNCTION: Transports the calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor (CALCRL) to the plasma membrane. Acts as a receptor for calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP) together with CALCRL. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9620797}. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAMP family of single-transmembrane-domain proteins, called receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are type I transmembrane proteins with an extracellular N terminus and a cytoplasmic C terminus. RAMPs are required to transport calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CRLR) to the plasma membrane. CRLR, a receptor with seven transmembrane domains, can function as either a calcitonin-gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor or an adrenomedullin receptor, depending on which members of the RAMP family are expressed. In the presence of this (RAMP1) protein, CRLR functions as a CGRP receptor. The RAMP1 protein is involved in the terminal glycosylation, maturation, and presentation of the CGRP receptor to the cell surface. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:10267; |
amylin receptor complex 1 [GO:0150056]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; CGRP receptor complex [GO:1990406]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; amylin receptor activity [GO:0097643]; calcitonin gene-related peptide binding [GO:1990407]; calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor activity [GO:0001635]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; amylin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0097647]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor signaling pathway [GO:1990408]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cellular response to hormone stimulus [GO:0032870]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; positive regulation of protein glycosylation [GO:0060050]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277] |
11693189_Receptor activity modifying proteins interaction with human and porcine calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CRLR) in HEK-293 cells 11733510_Co-expression of RAMP1 and CRLR reconstituted a CGRP receptor that was able to activate the pheromone-signaling pathway with pharmacological properties similar to those observed previously in mammalian cells. 11847213_Receptor activity-modifying protein 1 determines the species selectivity of non-peptide CGRP receptor antagonists. 11937264_The CGRP receptor components, RAMP1 and CRLR, are down-regulated during myeloid differentiation of CD34+ cells, and CGRP receptor selectively promotes the development of CFU-GM. 11973435_results show the presence of calcitonin receptor-like receptor and receptor activity-modifying proteins in middle meningeal, middle cerebral, pial, and superficial temporal vessels 12565884_Co-expression of calcitonin receptors (CT) lacking a portion of domain 1 with receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) 1, 2, or 3 appears to produce functional CT-(8-32)-sensitive adrenomedullin receptors. 12574158_The extracellular domain of receptor activity-modifying protein 1 is sufficient for calcitonin receptor-like receptor function 12684503_identification of domains responsible for agonist binding specificity 15245870_TNF-alpha induced time- and dose-dependent decreases in the expression of RAMP1 mRNA in cultured human coronary artery smooth muscle cells, thereby diminishing AM-evoked cAMP production 15300632_Data found that expressions of RAMP1, RAMP2 and RAMP3 mRNAs increased with the worsening of heart function, but the expressions of RAMP1 and RAMP2 mRNA decreased at level IV of heart failure. 15613468_calcitonin receptor-like receptor heterodimer with RAMP1 yields a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor 16912219_This study reveals important functionality of the RAMP C-terminal domain and identifies key differences in the role of the RAMP C terminus for calcitonin receptor versus calcitonin receptor-like receptor-based receptors. 17310067_CLR and RAMP1 traffic from endosomes to lysosomes by ubiquitin-independent mechanisms, where they are degraded at different rates 17493758_RAMP1 interacts with tubulin. 17785463_Functional calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors are formed by the asymmetric assembly of a calcitonin receptor-like receptor and RAMP1. 18198792_We did not observe any difference in mRNA for CL-R and RAMPs in arteries from patients with hemorrhagic stroke, arteriosclerosis and acute myocardial infarction when compared to patients without these diagnoses 18240900_RAMP1 may be strongly considered as a candidate gene for migraine. 18593822_Identification of RAMP1 residues important for calcitonin gene-related peptide are reported. 18725456_the crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human RAMP1 at 2.4 A resolution was determined. 19710695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19710695_The T-A-C haplotype is a genetic marker for cerebral infarction, and RAMP1 is associated with increased susceptibility to cerebral infarction. 20100989_RAMP1 overexpression attenuates Ang-II-induced hypertension and induces a protective change in cardiovascular autonomic regulation 20188075_These data for the first time pinpoint a specific RAMP1 residue important for both antagonist and agonist potency and are consistent with the N-terminal domain of RAMP1 forming the binding pocket interface with calcitonin receptor-like receptor. 20933260_lower expression in bronchial biopsies from subjects with asthma 22208649_The present finding demonstrated that RAMP1 immunoreactivity was localized in many neurons and phenopalatine ganglion. 22484227_CLR and RAMP1 co-localize in the enteric nervous system of human stomach, ileum, and colon, and are in close proximity to their ligands CGRP and IMD 22949393_RAMP1 overexpression enhances the promoting effect that exogenous CGRP has on osteogenic differentiation 23237777_No significant association of the tested SNPs of the RAMP1 gene were found with migraine susceptibility. 23867798_multiple NKX3.1 binding sites were found in the RAMP1 locus in human prostate cancer cells and in the normal mouse prostate. 24454825_A novel functional role for RAMP1 in regulation of CaSR signalling in addition to its known role in receptor trafficking, is reported. 25881990_RAMP1 rs7590387 has a role in the transformation of episodic migraine into medication overuse headache. 25982113_Data suggest that ligand binding of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) may inform drug development targeting calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR):receptor activity-modifying proteins RAMP1/2 complexes. 26501962_Evidence that DNA methylation at RAMP1 gene promoter plays a role in migraine was described. 28181496_T-A-T RAMP1 gene haplotype might have utility as a genetic marker for Essential Hypertension and that the RAMP1 gene may be associated with increased susceptibility to Essential Hypertension in a Japanese population. 28691801_Data suggest CGRP receptor (CGRPR) ECL2 (extracellular loop 2 domain) enables interaction with N-terminal residues of CGRP; this provides evidence for dual involvement of ECL2 in two-domain binding model of CGRP/CGRPR interaction; CGRPR is obligate heterodimer of CLR/RAMP1. (CGRP = calcitonin gene-related peptide; CLR = calcitonin receptor-like receptor; RAMP1 = receptor [calcitonin] activity modifying protein 1) 29297736_in nestin/hRAMP1 transgenic mice, hypertension caused by Ang II or phenylephrine was greatly attenuated, and associated autonomic dysregulation and increased sympathetic vasomotor tone were diminished or abolished. 30209400_structure of the human CGRP receptor in complex with CGRP and the Gs-protein heterotrimer at 3.3 A global resolution, determined by Volta phase-plate cryo-electron microscopy 31150417_Based on the finding that an acylated chimeric ADM/ADM2 analog potently stimulates CLR/RAMP1 and 2 signaling, we hypothesized that the binding domain of this analog could have potent inhibitory activity on CLR/RAMP receptors. 33602864_Structure and dynamics of the CGRP receptor in apo and peptide-bound forms. 35007660_Peptide ligand interaction with maltose-binding protein tagged to the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor: The inhibitory role of receptor N-glycosylation. |
ENSMUSG00000034353 |
Ramp1 |
125.921079 |
0.3730832779 |
-1.422430 |
0.143880642 |
100.647241 |
0.00000000000000000000001099146563581566558797653683879417441951648698484851965118327011151216909823347123165149241685867309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000112350438216509144818427842781928331645666899239294575371460966836667516588477155892178416252136230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.1257962 |
6.2540907 |
183.8700900 |
10.5184219 |
| ENSG00000132359 |
23108 |
RAP1GAP2 |
protein_coding |
Q684P5 |
FUNCTION: GTPase activator for the nuclear Ras-related regulatory protein RAP-1A (KREV-1), converting it to the putatively inactive GDP-bound state. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632203}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a GTPase-activating protein that activates the small guanine-nucleotide-binding protein Rap1 in platelets. The protein interacts with synaptotagmin-like protein 1 and Rab27 and regulates secretion of dense granules from platelets at sites of endothelial damage. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:23108; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] |
15632203_Rap1GAP2 is the first GTPase-activating protein of Rap1 found in platelets and is likely to have an important regulatory role in platelet aggregation 18039662_Platelet activation by ADP and thrombin enhances serine 9 phosphorylation and increases 14-3-3 binding to endogenous Rap1GAP2. 19528539_Slp1 inhibits dense granule secretion in platelets and that Rap1GAP2 modulates secretion by binding to Slp1. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000038807 |
Rap1gap2 |
223.894553 |
0.1263748936 |
-2.984218 |
0.235643635 |
146.093851 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000123829446753593013395775118612179464843496705274287682993954852946685734912034349130692707785517114871254307217895984649658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000017727668613802453594340309188460491445081486515078139189115627131892086991170680266519804613167821116803679615259170532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.5650194 |
8.5321009 |
435.2536004 |
46.0628291 |
| ENSG00000132386 |
5176 |
SERPINF1 |
protein_coding |
P36955 |
FUNCTION: Neurotrophic protein; induces extensive neuronal differentiation in retinoblastoma cells. Potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. As it does not undergo the S (stressed) to R (relaxed) conformational transition characteristic of active serpins, it exhibits no serine protease inhibitory activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7592790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8226833}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Dwarfism;Glycoprotein;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Phosphoprotein;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serpin family that does not display the serine protease inhibitory activity shown by many of the other serpin proteins. The encoded protein is secreted and strongly inhibits angiogenesis. In addition, this protein is a neurotrophic factor involved in neuronal differentiation in retinoblastoma cells. Mutations in this gene were found in individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta, type VI. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:5176; |
axon hillock [GO:0043203]; basement membrane [GO:0005604]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; aging [GO:0007568]; cellular response to cobalt ion [GO:0071279]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development [GO:0060767]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development [GO:0060770]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; ovulation cycle [GO:0042698]; positive regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050769]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; response to acidic pH [GO:0010447]; response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0046685]; response to peptide [GO:1901652]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; short-term memory [GO:0007614] |
12200129_role of PEDF in protecting retinal pericytes from oxidant injury 12237317_Results describe the first collagen-binding site described for a serpin, pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), which is distinct from its heparin-binding region, neurotrophic active site, and its serpin exposed loop. 12599204_EPC-1 may play a role in the entry of early passage fibroblasts into a G(0) state or the maintenance of such a state once reached 12603315_reactive center loop, specifically Gly376 and Leu377, is involved in the interaction of PEDF with components of the quality control system in the endoplasmic reticulum, thus ensuring its efficient secretion 12670505_VEGF secreted by retinal pigment epithelial cells upregulates pigment epithelium-derived factor expression via VEGFR-1 in an autocrine manner. 12687338_pigment epithelium-derived factor content in the aqueous humor of diabetic patients strongly predicts who among them will develop progression of retinopathy 12711260_PEDF may block the angiogenic effects of leptin through its anti-oxidative properties 12737624_Present in plasma at approx. 100 nM (5 microg/ml) or twice the level required to inhibit aberrant blood-vessel growth in the eye 12827055_Pterygia exhibit significantly lower PEDF but higher VEGF levels than those in normal corneas and conjunctivae. The decreased PEDF level in pterygia may play a role in the formation and progression of pterygia. 12837042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12860293_human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells produce VEGF, which in turn regulates PEDF production, and this balance may be contributing to neovascularization in tumors. 12878936_Gene transfer of pigment epithelium-derived factor suppresses tumor vascularization and growth, while prolonging survival in syngeneic murine models of thoracic malignancies. 12920663_level of the natural ocular anti-angiogenic agent pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is inversely associated with proliferative retinopathy 14991838_Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) Schwann cells lose the ability to downregulate PEDF upon axonal contact. 15096582_effectively abates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced vascular permeability 15140209_potential role of the age-associated decline in EPC-1 expression in tissue remodeling and in the development of skin diseases with excessive angiogenesis 15150108_PEDF expression suggests a more favorable prognosis than in patients with ductal pancreatic adenocarcinomas. 15239109_Role in angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC). Reduction of serum PEDF concentration associated with development of chronic liver diseases may contribute to progression of HCC. Gene therapy using PEDF may be efficient treatment for HCC. 15374885_novel role of extracellular phosphorylation is shown here to completely change the nature of PEDF from a neutrophic to an antiangiogenic factor. 15377265_PEDF-6 affects different second messenger biosynthesis systems in HL-60 cells. and inhibits phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C stimulated by aluminum tetrafluoride anions 15713745_PEDF downregulates Fyn through Fes, resulting in inhibition of FGF-2-induced capillary morphogenesis of endothelial cells 15846509_PEDF inhibits Ang-II-induced EC activation by suppressing NADPH-oxidase-mediated ROS generation and that PEDF may play a protective role in the development 15856012_PEDF gene contains a response element specific for p63 and p73 in its promoter region 15994443_PEDF may play a significant role in determining the balance of angiogenesis/ antiangiogenesis during atherogenesis 16102727_In tumor xenografts, the overexpression of wild-type PEDF significantly suppressed tumor growth, whereas a mutant of the collagen I-binding site of PEDF (Col-mut PEDF) did not inhibit tumor growth 16196102_In painless neuropathies, there is decreased level of PEDF in cerebrospinl fluid, compared with patients with painful neuropathies. 16322471_Phosphorylation induces variable effects of PEDF, and therefore contributes to the complexity of PEDF action, shich might be used to generate effective antiangiogenic or neurotrophic drugs. 16409998_REVIEW: this paper describes the unbalanced expressions of VEGF and PEDF as a cause of CNV 16596284_Results show that low levels of PEDF in lung tumor tissues was associated with a significantly shorter survival. 16707486_Central mechanism for PEDF inhibition of the AGE signaling to vascular permeability is by suppression of NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species generation and subsequent VEGF expression. 16740777_These observations collectively support the hypothesis that a lack of PEDF expression is a potent factor for the enhancement of tumor growth and angiogenesis in breast cancer. 16777976_study is the first to demonstrate a role of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in ovarian surface epithelium biology and ovarian cancer and suggests that the loss of PEDF may be of relevance in carcinogenesis 16797605_PEDF may play a protective role against early diabetic retinopathy by attenuating the deleterious effect of AGE 16896539_The analysis of the promoter region of the EPC-1/PEDF gene in this paper suggests the age- and cell cycle-dependent expression of specific transcriptional factor(s). 17188371_Increase in serum PEDF during ulcerative colitis, especially in severe forms of disease suggests its involvement in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis. 17202143_heparin induces a conformational change in the vicinity of Lys(178) 17213275_High levels of PEDF in the plasma may be related to the progression of diabetic retinopathy. 17479108_PEDF-overexpressing tumors exhibited reduced intratumoral angiogenesis, and PEDF may be a new and promising approach for the treatment of osteosarcoma. 17525281_These results demonstrate that PEDF could inhibit neointimal formation via suppression of NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species generation. 17593873_hepatic PEDF levels may be elevated to counteract the effects of oxidative stress 17604022_The correlation between PEDF and VEGF striatal levels in PD patients suggests that concerted neurotrophic functions of these factors or structural changes in blood vessel walls play an important role in the pathophysiology of PD. 17651710_PEDF induces human umbilical vein endothelial cells apoptosis through the sequential induction of PPARgamma and p53 overexpression. 17658465_These results demonstrate that the PEDF gene, in cooperation with the VEGF gene, may contribute to the development of diabetic retinopathy. 17870167_PEDF induces macrophage apoptosis and necrosis through the signaling of PPARgamma. 18084848_Results demonstrate that the aqueous humour level of asymmetric dimethylarginine is correlated with pigment epithelium-derived factor in humans and suggest that both ADMA and PEDF may be elevated in response to inflammation in uveitis. 18180304_GPR39 protects from cell death by increasing secretion of pigment epithelium-derived growth factor 18191271_There is a novel role for PEDF in hepatic triglyceride homeostasis through binding to ATGL. Both localize to adiposomes in hepatocytes. 18226801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18226801_Our data suggest that the PEDF Met72Thr T allele may be a risk factor for wet AMD in the Taiwan Chinese population. PEDF may play a role in the pathogenesis of wet AMD. 18312852_These results give the first direct demonstration that PEDF might represent a target for PARP inhibition treatment and the effects of PEDF on endothelial cells growth are context dependent. 18455830_PEDF levels are significantly higher in type 1 diabetic patients with retinopathy compared to the patients without it. 18523656_The levels of plasma PEDF increases with advances in both diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy. 18625531_serum level of PEDF was one of the independent determinants of resting heart rate in Japanese outpatients 18676622_In moderate hypoxia, PEDF is downregulated such that the VEGF-to-PEDF ratio increases (and angiogenesis is facilitated). 18677713_Serum levels of PEDF were positively associated with metabolic components and TNF-alpha in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. 18704312_HIF-1alpha-specific shRNA can effectively silence the HIF-1alpha gene, and consequently down-regulate VEGF and up-regulate PEDF expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells under hypoxic conditions. 18715664_Data show that serum PEDF levels (mean (S.D.)) were increased in 96 Type 2 diabetic vs. 54 non-diabetic subjects. 18787046_Plasma SERPINF1 level is strongly associated with body adiposity, especially with the visceral fat depot in the non-diabetic general population. 18787502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18792873_PEDF could improve the Advanced glycation end products-elicited insulin resistance in Hep3B cells by inhibiting JNK- and IkappaB kinase-dependent serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 via suppression of Rac-1 activation. 18805795_The HA-binding activity of PEDF may contribute to deposition in the extracellular matrix and to its reported antitumor/antimetastatic effects. 18845835_An apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF)-related pathway is an essential target of PEDF-mediated neuroprotection. 19091957_Cytosolic phospholipase A2-alpha is an early apoptotic activator in PEDF-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. 19180572_review summarizes the current knowledge on the biochemical properties of PEDF and its receptors and the therapeutic potential of PEDF 19182495_study found a difference in protein levels of expression of VEGF and PEDF between diabetic and non-diabetic epiretinal membranes 19223990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19223990_data suggest that none of the investigated PEDF polymorphisms is likely a major risk factor for exudative age-related macular degeneration in a white European population 19224861_Results suggest that the laminin receptor is a pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)receptor that mediates PEDF angiogenesis inhibition. 19247457_Transduced PEDF reduces retinal ganglion cell(RGC) loss and vision decline in DBA/2J mice, possibly via reduction of TNF and IL-18, and downregulation of GFAP. Novel approach to prevention of glaucomatous RGC death. 19253105_The reduction in PEDF expression levels may be, in part, responsible for tumor malignancy in VEGF-low ovarian tumors 19298519_Data suggest a role for PEDF in the regulation of angiogenesis in the heart and propose PEDF as a possible therapeutic target in heart disease. 19342598_Late outgrowth endothelial cells derived from Wharton jelly in human umbilical cord reduce neointimal formation after vascular injury: involvement of pigment epithelium-derived factor. 19503741_Genotyped the Met72Thr variant (rs1136287) and report a lack of association between the PEDF Met72Thr variant and either neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) in a Japanese population. 19503741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19513563_Showed that reduced PEDF levels in lung cancer tissues significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis and an overall poor prognosis in the lung cancer patients. 19583952_The pigment epithelium-derived factor is a negative regulator of insulin action in obesity. 19608741_NCoR1 expression is required to maintain IEC in a proliferative state, and PEDF is a novel transcriptional target for NCoR1 repressive action 19635565_Serum PEDF levels may be elevated in response to circulating advanced glycation end products(AGEs) as a counter-system against the AGE-elicited tissue damage. 19637042_Decreased PEDF expression contributes to tumor progression, possibly through increased tumor cell proliferation and increased angiogenesis. 19661223_Lentivirus-mediated gene transfer of PEDF decreased the growth of ocular melanoma and its hepatic micrometastasis in a mouse ocular melanoma model. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948828_PEDF may exert anti-apoptotic effects through inhibition of lysosomal degradation of Bcl-xL in camptothecin-treated HepG2 cells. 20087951_Data suggests serum pigment epithelium derived factor (PEDF) is an independent marker of metabolic syndrome in a Caucasian population. 20104255_Decreased expression of PEDF in primary human lens epithelial cells resulted in a decrease in the expression of vimentin and the increase of alphaB-crystallin expression, two proteins critical for maintaining lens clarity. 20132989_Gene variants in both CFH and HTRA1 contribute significantly to the AMD (age-related macular degeneration) phenotype in a Japanese population. 20141354_Our results suggest lack of association of PRKCB1 gene promoter polymorphisms and moderate protective association of PEDF gene polymorphism with diabetic retinopathy in the south Indian population. 20228934_polarity is an important determinant of the level of PEDF and VEGF secretion in pigment epithelial cells 20229034_PEDF expression is a potentially useful prognostic marker for breast cancer survival. 20237999_The results suggest a molecular pathway by which PEDF ligand/receptor interactions on the cell surface could generate a cellular signal. 20381502_Our present study suggests that substitution of PEDF proteins may be a promising strategy for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. 20412062_Size-exclusion ultrafiltration assays showed that recombinant human PEDF formed a complex with recombinant yeast F(1)-ATP synthase. 20504225_55% lower plasma level of PEDF in colorectal cancer patients than in a healthy control group. 20504225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631025_PEDF concentrations decrease significantly after weight loss in association with blood pressure. PEDF seems to be involved in human adipocyte biology. 20664971_PEDF gene loaded in PLGA nanoparticles could effectively inhibit the growth of mouse colonic carcinoma. 20678803_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20685859_Plasma PEDF was significantly associated with the presence of the metabolic syndrome and predicted the development of the metabolic syndrome in Chinese men. 20709803_Reduced pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with liver cirrhosis and fibrosis. 20857208_These results indicate that PEDF may play an inhibitory role on growth and migration of HaCaT cells through dephosphorylation of ERK1/2. 21058962_Three-step serum proteome analysis reveals that excessive alcohol drinking increases the PEDF level 21067572_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21122834_Significantly lower levels of peritoneal fluid PEDF in patients with endometriosis compared with patients without endometriosis, suggest that peritoneal fluid PEDF plays a role in the pathogenesis of this disorder. 21152082_Studies indicate that preferred codon usage is advantageous to translational efficiency of biologically active PEDF in E coli. 21174599_Detection of SNPs in the PEDF gene was not found to be significantly associated with exudative age-related macular degeneration. 21209034_The serum PEDF level is elevated in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and is associated with insulin resistance 21211310_The expression of PEDF and the incidence of prostate cancer have a negative correlation. 21236558_Data indicate that bone marrow stem cells play an important role in regulating neovascularization, and that the ratio of VEGF and PEDF may be an indicator of the pro- or anti-angiogenic activities of BMSCs. 21275514_VEGF and PEDF may independently influence retinal vascular permeability in CRVO patients with macular edema. 21281801_Overexpression of PEDF inhibits retinal inflammation and neovascularization. 21292512_Expressional change of PEDF and TNF-alpha is in relation to angiogenesis of bladder tumor 21323605_The combined assessment of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), Haptoglobin and Tau protein levels, using Iterative Marginal Optimization, improved the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease and other dementias. 21330424_PEDF may be a useful biomarker for assessing the effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers independent of a reduction in blood pressure. 21336718_PEDF expression had a negative correlation with IL-8 in papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential. 21353196_These data provide genetic evidence for SERPINF1 involvement in human bone homeostasis. 21570865_Data show that PEDF inhibits the production of IL8 in human hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells, through PEDF receptor/phospholipase A2 regulation of NFkappaB and PPARgamma, and delays the growth of these cells in vitro. 21652703_Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) shares binding sites in collagen with heparin/heparan sulfate proteoglycans. 21673604_PEDF modulated diverse categories of genes known to be involved in angiogenesis and migration in human melanoma cells. 21697716_may be involved in cross talk between adipose tissue and skeletal muscle [review] 21777264_Data suggest that plasma PEDF concentration is significantly associated with BP, and incident hypertension. 21826736_Loss of pigment epithelium-derived factor function constitutes a novel mechanism for osteogenesis imperfecta and shows its involvement in bone. mineralization. 21846721_a novel mechanism for the tumoricidal activity of PEDF, which involves tumor cell killing via PPARgamma-mediated TRAIL induction in macrophages. 21851923_We found that ficolin-3 levels were elevated in the vitreous fluid of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR); and may be used as a new therapeutic target for treatment of PDR. 21947986_PEDF may play a role in renal dysfunction in coronary artery disease patients. 22028839_a novel nuclear localization signal and mechanism for serpinF1 nuclear import 22029535_No evidence was found to support a role for the Met72Thr variant in susceptibility to either PCV or nAMD in a Han Chinese cohort. 22051848_Lower levels of serum PEDF were found in women with endometriosis than in those without endometriosis. 22113968_the patients are homozygous for a frameshift mutation in exon 4 of the SERPINF1 gene, which leads to lack of the transcription/translation product, likely a key factor in bone deposition and remodeling 22115973_MITF acts through PEDF to inhibit RPE cell migration and to play a significant role in regulating RPE cellular function. 22120651_elevated sera levels in psoriasis patients 22215693_findings establish PEDF as both a metastatic suppressor and a neuroprotectant in the brain, highlighting its role as a double agent in limiting brain metastasis and its local consequences 22218393_Results indicate that adeno-associated virus-mediated PEDF gene expression may offer an active approach to inhibit Lewis lung carcinoma growth. 22234980_In patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, both tissue and serum levels of PEDF were decreased, stromal TIP47 expression was higher and the tissue VEGF to PEDF ratio was increased. 22315956_PEDF processing is associated with coronary plaque rupture. 22457728_findings show that hypoxic conditions encountered during primary melanoma growth downregulate antiangiogenic and antimetastasic PEDF by a posttranslational mechanism involving degradation by autophagy 22457810_functional common genetic variant in the gene locus encoding PEDF contributes to overall body adiposity, obesity-related insulin resistance, and circulating leptin levels 22547925_Show that long-term survival and neurotrophic potential of hRPE cells can be enhanced by FDA-approved plastic-based microcarriers. Growth of hRPE cells on microcarriers led to sustained levels of PEDF and VEGF-A in conditioned media for two months. 22570532_This paper highlights the current understanding of probable mechanism of how PEDF blocks deterioration of diabetic retinopathy through its antioxidative properties and application prospects of PEDF as a novel therapeutic target in diabetic retinopathy. 22669302_results suggest that lack of circulating PEDF is a common characteristic of osteogenesis imperfecta type VI, regardless of the nature of the underlying SERPINF1 mutation 22701300_The differential effects exhibited by StVOrth-2 and StVOrth-3 in this orthotopic model of osteosarcoma may be related to the functional epitopes on the PEDF glycoprotein that they represent. 22792709_PEDF (44-77) suppressed proliferation of endothelial cells by 53% and inhibited endothelial cell tube formation at the concentration of 1 nM. 22819570_Data suggest that down-regulation of PEDF expression and increased microvascular density in ovarian endometriotic lesions play roles in pathogenesis of ovarian endometriosis; lesions were compared to endometrium from patients and control subjects. 22827961_Serum levels of PEDF are independently associated with fasting apoB48 levels in carotid atherosclerosis. 22837306_Data suggest that patients exhibit elevated circulating PEDF in obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance compared with subjects with normal glucose tolerance. Plasma PEDF might be useful biomarker for atherosclerosis. 22884488_The present study reveals that serum levels of PEDF are independently associated with P-III-P levels, suggesting that PEDF level is a novel biomarker of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 22915824_Adenoviral E4 region stimulated expression and secretion of PEDF by human renal epithelial cells that acted as a survival factor for glomerulus-derived endothelial cells. 22917444_these data validate that MSCs-PEDF can migrate and deliver PEDF to target glioma cells, which may be a novel and promising therapeutic approach for refractory brain tumour. 22930782_Plasma PEDF is elevated in overweight youth and is positively associated with insulin resistance. These findings suggest that PEDF may play a role in the development of cardiometabolic dysfunction in youth. 23038613_PEDF acts directly on monocytes/macrophages by inducing their migration and differentiation into M1-type cells in prostate. 23055574_Increased levels of PEDF may be a response to counterbalance the activity of angiogenic and fibrogenic factors in proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR). 23075882_the dynamic expression of PEDF that inversely portrays VEGF expression may imply its putative role as a physiological negative regulator of follicular angiogenesis. 23123582_Adenovirus mediated PEDF is potent in retarding the growth and invasiveness of endometrial cancer cells. 23151593_PEDF silencing confers resistance to tamoxifen in breast cancer cells and its stable expression sensitizes resistant cells to endocrine therapy 23218576_Circulating levels of PEDF were independently associated with asymmetrical dimethylarginine levels. 23318725_Liver, but not adipose tissue, might be the source of increased circulating PEDF linked to insulin resistance. 23346798_Dry form of age related retinal degeneration was associated with lower plasma PEDF levels. A strong positive correlation between VEGF and PEDF concentrations was seen in patients with wet form and in patients with bilateral disease. 23359450_PEDF suppression of oxidative stress delays cellular senescence and allows greater expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. 23393224_Our data showed that the elevated AZGP1 and decreased PEDF and PRDX2 expressions in CRC serum and tissues were correlated with liver metastases. 23547472_Only full length PEDF was shown to form amyloid like fibril structures, but not the truncated form. Accumulation of fibrils results in fibroblasts destruction and might be the cause of changes in structure of Tenon's capsule observed in myopia 23547730_Serum PEDF levels are positively associated with coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. 23553951_PEDF stimulated limbal stem cell proliferation. 23569025_PEDF may be involved in the pathogenesis of condyloma acuminatum. 23600479_Data suggest that serum PEDF (pigment epithelium-derived factor) is positively associated with insulin resistance and negatively associated with HDL level in prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose), diabetes type 2, and control subjects. 23722394_We demonstrated a marginal association of the PEDF SNP, rs12603825, with myopic CNV in extremely myopic patients 23818523_PEDF-R is required for the survival and antiapoptotic effects of PEDF on retina cells. 23844817_This review discusses the role of PEDF in cardiometabolic disorders and the utility of measuring its levels. 23924722_Here, PEDF was purified from human plasma by use of a dermatan sulfate affinity column, and then hydroxyapatite, gel filtration and ion exchange columns 23939834_PEDF activated ERK and AKT signaling pathways in MSCs to induce expression of osteoblastic-related genes. These data suggest that PEDF is involved in MSCs osteoblastic differentiation. 24078214_Loss of PEDF expression is associated with malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours. 24105071_serum PEDF levels are closely associated with hs-CRP in women with PCOS. PEDF may play a role in the development of chronic inflammation in PCOS 24161393_the present study suggests that atheroprotective effects of PEDF might be partly ascribed to its caveolin-1-interacting properties. 24255038_iPS-RPE possesses the machinery to process retinoids for support of visual pigment regeneration. Inhibition of all-trans retinyl ester accumulation by NEM confirms LRAT is active in iPS-RPE. 24342618_PEDF causes anti-angiogenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombogenic reactions in myeloma cells through the interaction with LR. 24361362_PEDF is emerging as an ovarian factor, which has unexpected reactive oxygen species (ROS)-augmenting activities in the human ovary; it may be involved in ovarian ROS homeostasis and may contribute to oxidative stress 24698153_PEDF may play a pivotal role in skin homoeostasis and the response of keratinocytes to injury or inflammatory insults. 24760990_Data (including data from transgenic mice expressing human PEDF) suggest white adipose tissue exhibits near-normal angiogenesis/growth (adiposity)/lipid metabolism/insulin sensitivity in response to mild PEDF overexpression (as seen in obesity). 24766673_TFAP2B overexpression contributes to tumor growth and a poor prognosis of human lung adenocarcinoma through modulation of ERK and VEGF/PEDF signaling. 24769282_The expression levels of PEDF are inversely correlated to that of vascular endothelial growth factor during the menstrual cycle. 24810046_Suggest that PEDF/low-dose chemotherapy may represent a new therapeutic alternative for castration-refractory prostate cancer. 25030625_these results identify PEDF as a novel transcriptional target of MITF and support a relevant functional role for the MITF-PEDF axis in the biology of melanoma. 25064413_PEDF represents a novel intrinsic antioxidant of granulosa cells. 25127091_Heterozygous SERPINF1 mutation carriers had no detectable abnormalities in fat and bone, despite decreased PEDF expression. 25159325_Data suggest that healthy adult stem cells exposed to vitreous/aqueous humors of subjects with proliferative diabetic retinopathy results in increased expression of serpin F1, CXCL4 (platelet factor 4), and endothelin-1 (aqueous only). 25166721_Elevated PEDF levels may represent a compensatory change in type 2 diabetic patients with renal disease and appear to be a useful marker for evaluating the progression of diabetic nephropathies. 25172543_study supports the possible influence of sICAM-1 and PEDF on the pathophysiology of retinal neovascularization in SCD patients. 25284724_PEDF inhibited breast cancer cell migration and invasion by down-regulating fibronectin 25293868_plasma PEDF similar in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obese groups of children 25363869_pigment epithelium derived factor may regulate Sost expression by osteocytes leading to enhanced osteoblastic differentiation and increased matrix mineralization 25447045_MITF-regulated PEDF has a role in melanoma progression 25450390_PEDF is anti-angiogenic and is associated with the growth inhibition of hemangioma-derived endothelial cells. 25462587_The review discuss the evolving role of PEDF as a novel metabolic regulatory protein that plays a causal role in insulin resistance probably through proposed mechanism as inflammation, lipolytic free fatty acid mobilization or mitochondrial dysfunction. 25562624_PEDF inhibits retinal microvascular dysfunction induced by 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. 25678686_PEDF peptide derivative may be an innovative strategy for tissue engineering and repair therapy in partial LSC deficiency diseases. 25700221_Data suggest that pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) and adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) may serve as therapeutic targets for managing vascular hyperpermeability in sepsis. 25705004_Serum PEDF levels were one of the independent correlates of circulating DPP-4 levels in cardiovascular disease patients. 25820866_the results suggest that PEDF is not a major susceptibility gene for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) in the overall population. 25821324_Retinal pigment epithelial cells exposed to adiponectin showed decreased expression of VEGF mRNA, protein whereas PEDF protein is unaltered and PEDF mRNA was increased. 25844034_Elevated PEDF levels may be involved in promoting the development of COPD by performing proinflammatory functions. 25868797_MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts stably overexpressing SERPINF1 with the p.Ala91_Ser93dup mutation had decreased collagen type I deposition and mineralization 25881671_Studies indicate that role of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in diabetic and hypoxia-induced angiogenesis, and the pathways mediating PEDF's effects under these conditions. 25948043_PEDF binds VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in vascular endothelial cells. 25992628_PEDF sustained glioma stem cell self-renewal by Notch1 cleavage. 26304116_region composed of positions 98-114 of PEDF contains critical residues for PEDF-R interaction that mediates survival effects, the findings reveal distinct small PEDF fragments with neurotrophic effects on photoreceptors 26308290_Data suggest differences in regulation of expression of PEDF (up-regulation) vs. VEGF (down-regulation) in granulosa cells explain reduced risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome due to ovulation induction using GnRH/GNRHR agonists rather than hCG. 26333415_Thus PEDF could be involved in the establishment of the avascular nature of seminiferous tubules and after puberty androgens may further reinforce this feature. 26427478_Studies indicate that pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is a natural protein of the retina . 26450919_We demonstrate that rPEDF may serve as a useful intervention to alleviate the risk of tamoxifen-induced endometrial pathologies 26612427_hCG-induced PEDF downregulation and VEGF upregulation are mediated by similar signaling cascades emphasizes the delicate regulation of ovarian angiogenesis. 26693895_We confirmed that expression of SERPINF1 in the liver restored the serum level of PEDF. We also demonstrated that PEDF secreted from the liver was biologically active by showing the expected metabolic effects of increased adiposity and impaired glucose tolerance in Serpinf1(-/-) mice. 26697494_We showed that transplantation of pigment epithelial cells overexpressing PEDF can restore a permissive subretinal environment for RPE and photoreceptor maintenance, while inhibiting choroidal blood vessel growth. 26700654_Study demonstrated the inhibitory effect of PEDF on insulin-dependent molecular mechanisms of glucose homeostasis, and suggests that PEDF could be a specific target in the management of metabolic disorders. 26746675_Study discuss the anti-tumor activities of PEDF and focus on its dual role as an inhibitor (e.g., angiogenesis) and as an inducer of various vital biological processes that lead to the therapeutic effect via different mechanisms of action. [review] 26815784_we report on two apparently unrelated children with OI type VI who had the same unusual homozygous variant in intron 6 of SERPINF1 26921338_results demonstrate that PEDF maintains tumor-suppressive functions in fibroblasts to prevent CAF conversion and illustrat |
ENSMUSG00000000753 |
Serpinf1 |
288.526462 |
0.3788595008 |
-1.400265 |
0.121291233 |
134.096086 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000052054285923255787966651225297944638353132932609003854707818897095638383279799952726984990647451922995969653129577636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000006909363850964527828842102081603279769775692445926759965138523912554360464780348061175629936769837513566017150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
154.0015912 |
13.8483813 |
408.2572290 |
24.2026672 |
| ENSG00000132424 |
25957 |
PNISR |
protein_coding |
Q8TF01 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Located in cytosol; nuclear speck; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25957; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; RNA binding [GO:0003723] |
28589370_results indicate that LUC7L3, PPIG, and SFRS18 are not only implicated in EDA+ fibronectin formation, but also that they could possess multiple roles in psoriasis-associated molecular abnormalities. 29512856_In our present RNA-Seq experiment, we demonstrated that the LUC7L3 and SFRS18 splicing factors contribute to the regulation of several well-known psoriasis-associated pathways, including the IFN signalling pathway, antiviral immunity and ubiquitination. |
ENSMUSG00000028248 |
Pnisr |
1448.399805 |
0.4931255878 |
-1.019973 |
0.060626698 |
281.201523 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000410927614739647741613020452351555813726405107080720109219824365995577065062012792441944170275664523708611983715566090782840286311822160474008965678668407165048670481866111003910191357135772705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000110077887360384771807416766112640095571692341995344389859020301812134323752812494410637728105553251683848713417989937037299882730288701380141099213505061389650752090574314934201538562774658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
973.5563059 |
36.1439953 |
1988.7921043 |
50.4376394 |
| ENSG00000132429 |
64208 |
POPDC3 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBV1 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in the maintenance of heart function mediated, at least in part, through cAMP-binding. May play a role in the regulation of KCNK2/TREK-1-mediated current amplitude (PubMed:31610034). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ES81, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10882522, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31610034}. |
cAMP;cAMP-binding;Glycoprotein;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the POP family of proteins containing three putative transmembrane domains. This gene is expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle and may play an important role in these tissues during development. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:64208; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; cAMP binding [GO:0030552]; heart development [GO:0007507]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051146] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627872_Frequent silencing of POPDC3 is associated with promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22654436_Reduced expression of Popdc3 may play a significant role in the carcinogenesis and progression of gastric cancer. Popdc3 may be an independent prognostic factor. 28939104_recently a novel family of cAMP effector proteins emerged and was termed the Popeye domain containing (POPDC) family, which consists of three members POPDC1, POPDC2 and POPDC3. POPDC proteins are transmembrane proteins, which are abundantly present in striated and smooth muscle cells. POPDC proteins bind cAMP with high affinity comparable to PKA 31610034_Pathogenic variants in POPDC3 are responsible for a novel type of autosomal recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophy. 34069715_The Transition from Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia to Gastric Cancer Involves POPDC1 and POPDC3 Downregulation. 35075722_Homozygous missense variant in POPDC3 causes recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 26. |
ENSMUSG00000019848 |
Popdc3 |
16.241145 |
18.0761216076 |
4.176013 |
0.601104996 |
63.266543 |
0.00000000000000180545019283894843189145290665243356382062430397217323019276591367088258266448974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000012732176228525026564585841973754435247365504602079511187184834852814674377441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.6636754 |
11.1316128 |
1.6621924 |
0.5830731 |
| ENSG00000132481 |
91107 |
TRIM47 |
protein_coding |
Q96LD4 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of CYLD. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29291351}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29291351}. |
Enables ubiquitin-protein transferase activity. Involved in protein ubiquitination. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:91107; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
26873435_Study shows that protein and gene expression level of TRIM47 are up-regulated in prostate neoplasm. 27583843_These results suggest that rs1055129 in TRIM47 is not associated with leukoaraiosis (LA) risk in the Chinese population. However, the association of rs1055129 (TRIM47) with LA before Bonferroni correction and Sidak correction is worth highlighting. 28186994_High TRIM47 expression is associated with non-small cell lung carcinoma. 30979374_our study has shown the biological and clinical significance of TRIM47 in colorectal cancer. TRIM47 exerts an inhibitory effect on SMAD4 by ubiquitylating and degrading SMAD4, thereby promoting tumor growth and progression. 32603762_Knockdown of TRIM47 inhibits glioma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through the inactivation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 33350849_Trim47 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. 33529753_TRIM47 accelerates aerobic glycolysis and tumor progression through regulating ubiquitination of FBP1 in pancreatic cancer. 33833824_Upregulated Tripartite Motif 47 Could Facilitate Glioma Cell Proliferation and Metastasis as a Tumorigenesis Promoter. 34433666_TRIM47 activates NF-kappaB signaling via PKC-epsilon/PKD3 stabilization and contributes to endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. 36203070_TRIM47 promotes glioma angiogenesis by suppressing Smad4. 36288633_TRIM47 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by activating STAT3 signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000020773 |
Trim47 |
18.942736 |
2.9332671622 |
1.552508 |
0.665347273 |
4.968255 |
0.02581668333875865306570318580270395614206790924072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.045079172610916568020300587704696226865053176879882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.0265517 |
11.7847803 |
9.6524887 |
2.9774326 |
| ENSG00000132507 |
1984 |
EIF5A |
protein_coding |
P63241 |
FUNCTION: mRNA-binding protein involved in translation elongation (PubMed:16987817, PubMed:17187778, PubMed:33547280). Has an important function at the level of mRNA turnover, probably acting downstream of decapping (PubMed:16987817, PubMed:17187778, PubMed:33547280). Critical for the efficient synthesis of peptide bonds between consecutive proline residues (PubMed:16987817, PubMed:17187778, PubMed:33547280). Can resolve ribosomal stalling caused by consecutive prolines during translation (PubMed:16987817, PubMed:17187778, PubMed:33547280). Involved in actin dynamics and cell cycle progression, mRNA decay and probably in a pathway involved in stress response and maintenance of cell wall integrity (PubMed:16987817, PubMed:17187778, PubMed:33547280). With syntenin SDCBP, functions as a regulator of p53/TP53 and p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis (PubMed:15371445). Regulates also TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis (PubMed:15452064). Mediates effects of polyamines on neuronal process extension and survival (PubMed:17360499). May play an important role in brain development and function, and in skeletal muscle stem cell differentiation (By similarity). Also described as a cellular cofactor of human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1) Rex protein and of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) Rev protein, essential for mRNA export of retroviral transcripts (PubMed:8253832). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3T1J1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15371445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15452064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16987817, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17187778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17360499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33547280, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8253832}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Elongation factor;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hypusine;Membrane;Nucleus;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
Enables U6 snRNA binding activity and protein N-terminus binding activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to virus; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator; and tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway. Located in annulate lamellae; cytoplasm; and nucleus. Part of nuclear pore. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1984; |
annulate lamellae [GO:0005642]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation elongation factor activity [GO:0003746]; U6 snRNA binding [GO:0017070]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:1902255]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of translational elongation [GO:0045901]; positive regulation of translational termination [GO:0045905]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
11161802_Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) (eIF-4D, eIF-5A) stimulates ribosomal peptidyltransferase activity, transport of HIV-1-mRNAs and binds exportins 1 and 4. Contains hypusine at lys 50. Human EIF5A1 and EIF5A2 encode two isoforms: eIF5AI and eIF5AII. 11870779_Heat stress-induced loss of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF-5A) in a human pancreatic cancer cell line 12210765_Subcellular distribution of eIF-5A by indirect immunofluorescent staining and by direct visualization of green fluorescent protein tagged eIF-5A (GFP-eIF5A) 12687616_Patients having a higher eIF-5A protein expression showed a relatively poorer survival suggesting the use of eIF-5A as prognostic marker in lung adenocarcinoma. 12894223_EIF-5A expression inhibition by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides significantly enhanced the stimulating effect of GM-CSF on cell growth. Therefore, the eIF-5A accumulation played important roles in the apoptosis induced by UP inhibitors. 15371445_eIF5A may be a regulator of p53, and syntenin might regulate p53 by balancing the regulation of eIF5A signaling to p53 for apoptosis 16519677_These findings suggest that the failure to detect eIF5A-2 protein even in eIF5A-2 mRNA positive cells is, at least in part, due to inefficient translation. 16522190_Recombinant human eIF-5A was crystallized by the hanging-drop vapor diffusion method 16842744_molecular model for the human eIF5A protein based on the crystal structure of the eIF5A from Leishmania brasiliensis 16987817_data suggest that eIF5A mediates important cellular processes like cell viability and senescence through its effects on the stability of certain mRNAs 17008552_analysis of differences in global protein expression in BCR-ABL-positive K562 cells treated with or without imatinib revealed down-regulation of eIF5A; hypusination inhibitors exerted an antiproliferative effect 17187778_These findings collectively indicate that unhypusinated eIF5A may have pro-apoptotic functions and that eIF5A is rapidly translocated to the nucleus following the induction of apoptotic cell death 17213197_analysis of the deoxyhypusine hydroxylase-eukaryotic translation initiation factor (eIF5A) interaction 18067580_Mutational analyses of human eIF5A-1--identification of amino acid residues critical for eIF5A activity and hypusine modification 19160416_Results suggest that the stability of eIF5A may have an important role in determining the fate of the particular cell type after severe heat stress. 19379712_These findings provide strong evidence that the hypusine modification of eIF5A dictates its localization in the cytoplasmic compartment where it is required for protein synthesis. 19825182_These data support the importance of eIF5A and hypusine formation in HIV-1 gene expression. 19998337_High eIF5A expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 20232312_These observations collectively indicate that unhypusinated eIF5A1 plays a central role in the regulation of apoptosis. 20830705_findings suggested that overexpression of eIF5A-2 correlates with local invasion of NSCLC, and might serve as an adverse prognostic marker of survival for stage I NSCLC patients 20942800_loss of eIF5A activity by this SSAT1-mediated acetylation confirms the strict structural requirement for the hypusine side chain and suggests a possible regulation of eIF5A by hypusine acetylation/deacetylation 21224998_EGF-induced upregulation of eIF5A stimulates corneal epithelial cell proliferation in vitro 21360055_HIV-1 Rev cofactors Sam68, eIF5A, hRIP, and DDX3 also function in the translation of HIV-1 RNA. 21778671_hybrid exercise increases expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (EIFSA), peroxisomal biogenesis factor 6 (PEX6) and histone cluster 1 H4 (HIST1H4), compared with electrical stimulation alone 22771473_identified PCAF as the major cellular acetyltransferase of eIF5A, and HDAC6 and SIRT2 as its major deacetylases. Inhibition of the deacetylases or impaired hypusination increased acetylation of eIF5A, leading to nuclear accumulation. 22908221_a novel role for miR-331-3p and miR-642-5p in the control of prostate cancer cell growth via the regulation of DOHH expression and eIF5A activity. 22927971_eIF-5A as well as the hypusine-forming enzymes deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS) and deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH) are highly overexpressed in glioblastoma patient sample 23132580_acetylation regulates the subcellular localization of eIF5A2 23322277_Overexpression of EIF5A is associated with early-onset colorectal cancer. 23539416_Altered expression of Hsc70 and eIF5A-1 may cause defects in nucleocytoplasmic transport and play a role in esophageal carcinogenesis. 23733422_The expression of eIF5A-2 was up-regulated following EMT phenotype changes in A549 cells, which correlated with enhanced tumor invasion and metastatic capabilities. 23991020_Data indicate that the signal of EIF5A2, MYCN, and MCL1 genes is decreased in hydroxyurea (HU) and gemcitabine (GEM) treated UACC-1598 ovarian cancer cell line. 24220243_mature eIF5A controls a translational network of cancer-driving genes, termed the eIF5A regulon, at the levels of mRNA abundance and translation 24402910_The findings that eIF5A and EF-P are important for specific cellular processes and play a role in the relief of ribosome stalling caused by specific amino acid sequences 24491565_Data suggest a regulatory mechanism for the pro-apoptotic protein eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A1 (eIF5A1) in which its level is possibly modulated by NF-kappaB in lung cells. 25218134_Mature eIF5A (hypusinated form) is not involved in the autophagic pathway. 25261239_eIF5A proteins utilize PEAK1 as a downstream effector to drive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) pathogenesis. 25979826_eIF5A has been shown to regulate a number of gene products specifically, termed the eIF5A regulon, and its role in translating proline-rich sequences has recently been identified. 26282002_eIF5A-2 protein was highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues 26403856_Upregulation of translation initiation factor 5a observed in thalassemia is a novel finding and plays a protective role toward cell survival under oxidative stress. 26483550_findings also implicate the eIF5A/RhoA/ROCK module as a potential new therapeutic target to treat metastatic PDAC cells 26773503_Our results suggest that functional, hypusinated eIF5A is necessary for HIF-1alpha expression during hypoxia and that eIF5A is an attractive target for cancer therapy. 27115996_These results suggest that binding of eEF2 to the ribosome alters its conformation, resulting in a weakened affinity of eIF5A and impairment of this interplay compromises cell growth due to translation elongation defects. 27180817_the depletion of eIF5A leads to endoplasmic reticulum stress, an unfolded protein response and up-regulation of chaperone expression in HeLa cells. 27306458_Molecular structure of the exportin Xpo4 in complex with RanGTP and the hypusine-containing translation factor eIF5A has been reported. 27414022_eIF5A1 isoform A has a role in mitochondrial function. 28381547_Findings indicate that eIF5A-PEAK1-YAP signaling contributes to PDAC development by regulating an STF program associated with increased tumorigenicity. 29321164_EIF5A protein level is increased during pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression with the highest levels of expression observed in metastatic cell populations.Kras protein expression is controlled by a self-regulating feedforward mechanism mediated by eIF5A-PEAK1. 29428664_EIF5A1 is a vital regulator of epithelial ovarian cancer proliferation and progression. 29533498_Cross-talk between eIF5A and CAMK1D enhances proliferation. 29712776_The study identifies eIF5A as a key requirement for autophagosome formation and demonstrates the importance of translation in mediating efficient autophagy. eIF5A is required for lipidation of LC3B and its paralogs and promotes autophagosome formation. 30170728_Silencing of the eIF5A-1 gene could induce the apoptosis of HPV 16 E6-infected cervical carcinoma cells. 30206208_EIF5A1 may be a regulator of trophoblast function at the maternal-fetal interface and low levels of EIF5A1 and ARAF may be associated with recurrent miscarriage. 30761741_The results revealed that EIF5A regulated the proliferation of pancreatic cancer through the SHH signaling pathway while decreasing the gemcitabine sensitivity. 31558321_DHPS-dependent hypusination of eIF5A1/2 is necessary for TGFbeta/fibronectin-induced breast cancer metastasis and associates with prognostically unfavorable genomic alterations in TP53 31801078_Suppression of Ribosomal Pausing by eIF5A Is Necessary to Maintain the Fidelity of Start Codon Selection. 32605139_Inhibition of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5A (eIF5A) Hypusination Suppress p53 Translation and Alters the Association of eIF5A to the Ribosomes. 32817651_Klf5 down-regulation induces vascular senescence through eIF5a depletion and mitochondrial fission. 32882370_Hypusination of Eif5a regulates cytoplasmic TDP-43 aggregation and accumulation in a stress-induced cellular model. 33188200_A translational program that suppresses metabolism to shield the genome. 33303756_Blockade of EIF5A hypusination limits colorectal cancer growth by inhibiting MYC elongation. 33547280_Impaired eIF5A function causes a Mendelian disorder that is partially rescued in model systems by spermidine. 34273022_Post-translational formation of hypusine in eIF5A: implications in human neurodevelopment. 34921595_LncRNA FOXP4-AS promotes the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the miR-3184-5p/EIF5A axis. 34947982_eIF5A-Independent Role of DHPS in p21(CIP1) and Cell Fate Regulation. |
ENSMUSG00000078812 |
Eif5a |
1157.582729 |
2.1865967353 |
1.128687 |
0.068470296 |
269.641118 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000135870805358620585929282450711442962710835347613257827175934252268012196988388429945045763903395973787967011421315071727609336039300804446761397639123654379478267628655885346233844757080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000035121770351895619497354069503994878142374227661658168273925664058093429389582883090938315996539291881092294126501678467493257650919467959502375681030833520779310674697626382112503051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1578.2381037 |
61.6889216 |
726.8703260 |
21.6674222 |
| ENSG00000132510 |
23135 |
KDM6B |
protein_coding |
O15054 |
FUNCTION: Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code (PubMed:17825402, PubMed:17851529, PubMed:17713478, PubMed:18003914). Demethylates trimethylated and dimethylated H3 'Lys-27' (PubMed:17825402, PubMed:17851529, PubMed:17713478, PubMed:18003914). Plays a central role in regulation of posterior development, by regulating HOX gene expression (PubMed:17851529). Involved in inflammatory response by participating in macrophage differentiation in case of inflammation by regulating gene expression and macrophage differentiation (PubMed:17825402). Plays a demethylase-independent role in chromatin remodeling to regulate T-box family member-dependent gene expression by acting as a link between T-box factors and the SMARCA4-containing SWI/SNF remodeling complex (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5NCY0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17713478, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17825402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17851529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18003914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28262558}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Dioxygenase;Disease variant;Inflammatory response;Intellectual disability;Iron;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a lysine-specific demethylase that specifically demethylates di- or tri-methylated lysine 27 of histone H3 (H3K27me2 or H3K27me3). H3K27 trimethylation is a repressive epigenetic mark controlling chromatin organization and gene silencing. This protein can also demethylate non-histone proteins such as retinoblastoma protein. Through its demethylation actvity this gene influences cellular differentiation and development, tumorigenesis, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. This protein has two classical nuclear localization signals at its N-terminus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:23135; |
MLL3/4 complex [GO:0044666]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; histone demethylase activity [GO:0032452]; histone H3K27me2/H3K27me3 demethylase activity [GO:0071558]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; heart development [GO:0007507]; histone H3-K27 demethylation [GO:0071557]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048333]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] |
17713478_the human JmjC-domain-containing proteins UTX and JMJD3 demethylate tri-methylated Lys 27 on histone H3 17923864_JMJD3 was identified as a demethylase capable of removing the trimethyl group from histone H3 lysine 27 and upregulated in prostate cancer. 18003914_JMJD3 demethylates di- and trimethylated lysine 27 of histone H3 in vitro and in cells. 18628393_These results indicate that epigenetic derepression by JMJD3 controls mammalian epidermal differentiation. 19451217_JMJD3 expression is induced upon activation of the RAS-RAF signaling pathway 21209387_The role of the H3K27 demethylases Jmjd3 and UTX in gene expression, is discussed. 21242977_KDM6B may have a role in antigen-driven B-cell differentiation. 21245294_KDM6A- and KDM6B-responsive Homeobox genes are expressed at significantly higher levels, suggesting that HPV16 E7 results in reprogramming of host epithelial cells 21841772_H3K27 demethylation by JMJD3 at a poised enhancer of anti-apoptotic gene BCL2 determines ERalpha ligand dependency 21890490_An epigenetic gene coding for a histone demethylase such as JMJD3 is a VDR co-target that partially mediates the effects of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) on human colon. 22020331_loss of BTG3 in normal cells induced cellular senescence, which was correlated with enhanced ERK-AP1 signaling and elevated expression of the histone H3K27me3 demethylase JMJD3/KDM6B 22252741_Knockdown of JMJD3 in THP-1 cells affected expression of key genes in NF-kappaB, chemokine and CD40 signalling. 22589717_PAN RNA interacts with demethylases JMJD3 and UTX, and the histone methyltransferase MLL2 22713873_JMJD3 activates bivalent gene transcription by demethylating H3K27me3 and promoting transcriptional elongation. 22770241_The histone demethylases KDM4B and KDM6B play critical roles in osteogenic commitment of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. 22782721_neurogenesis is promoted by an interplay between the TGFbeta pathway, Smad3, and the H3K27me3 histone demethylase (HDM) JMJD3 22907667_KDM6B contributes to the activation of WNT3 and DKK1 at different differentiation stages when WNT3 and DKK1 are required for mesendoderm and definitive endoderm differentiation. 22915621_These data demonstrate a novel role of H3 Lys27 histone methylation in fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. 22955275_ATF4-dependent regulation of the JMJD3 gene during amino acid deprivation can be rescued in Atf4-deficient cells by inhibition of deacetylation. 23152497_Overexpression of KDM6B induced the expression of mesenchymal genes and promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 23236496_Deregulation of JMJD3 may contribute to gliomagenesis via inhibition of the p53 pathway resulting in a block to terminal differentiation. 23538751_Overexpression of JMJD3 is associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. 23711388_Data suggest that the suppression of different key inflammatory regulators through JMJD3-attenuation would evaluate potential therapeutic targets and to elucidate the molecular mechanism of JMJD3-knockdown (KD) dependent effects in THP-1 cells. 24158144_results demonstrated critical role of histone demethylase in epigenetic regulation of odontogenic differentiation of dental MSCs. KDM6B may present potential therapeutic target in regeneration of tooth structures and repair of craniofacial defects. 24212761_Studies indicate that Jmjd3 is able to enhance the polarization of M2 microglia by modifying histone H3K27me3, and it has a pivotal role in the switch of microglia phenotypes that may contribute to the immune pathogenesis of PD. 24572572_Histone demethylase Jmjd3 is required for the development of subsets of retinal bipolar cells. 24646476_Subcellular localization of Jmjd3 is dynamically regulated and has pivotal roles for H3K27me3 status. 24726732_JMJD3 promotes osteogenesis in differentiating human mesenchymal stem cells, with MIR146A regulating JMJD3. 24797517_JMJD3 is recruited to p53 responsive elements via its interaction with p53 and therefore could act as a fail-safe mechanism to remove low levels of H3K27me3 and H3K27me2 to allow for efficient acetylation of H3K27. 24925089_JMJD3 at the nexus of epigenetic regulation of inflammation and the aging process 24947179_our results propose a significant role for the KDM6B-C/EBPalpha axis in the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma phenotype. 25049231_demonstrated that miR-941 and KDM6B regulated the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process and affected cell migratory/invasive properties 25427687_Incubation of nickel chloride upregulated the expression of H3K27me3 demethylase jumonji domain-containing protein 3 (JMJD3) in kidney cancer cells, which was accompanied by the reduction in the protein level of H3K27me3. Enhanced demethylation of H3K27me3 may represent a novel mechanism underlying the carcinogenicity of nickel compounds. 25520177_KDM6B is a new hypoxia response gene regulated by HIF-2alpha 25652587_Results show that JMJD3 protein is overexpressed in high-grade glioma cells and correlated with dysfunctional activation of senescence-related processes, including proinflammatory cytokines and stem cell tropism toward tumors. 25698448_JMJD3 promotes SAHF formation by demethylating RB at K810, which reduce the level of phosphorylation of RB protein at S807/811, and this interplay promotes the formation of senescence-associated heterochromatin foci in senescent WI38 cells. 25791244_Data indicate a reverse correlation between the mRNA levels of histone H3 lysine-27 demethylase (JMJD3) and global histone h3 lysine 27 methylation (H3K27me3). 25827480_Demethylation of IGFBP5 by Histone Demethylase KDM6B Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Periodontal Tissue Regeneration by Enhancing Osteogenic Differentiation and Anti-Inflammation Potentials. 26193001_JMJD3 is an epigenetic regulator in development and disease. (Review) 26215835_binding of SMAD2/3, the intracellular effectors of activin signaling, was significantly enriched at the Pmepa1 gene, which encodes a negative feedback regulator of TGF-beta signaling in cancer cells, and at the Kdm6b gene, which encodes an epigenetic regulator promoting transcriptional plasticity. 26261509_We demonstrate that KDM6B plays a key role in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 26303949_KDM6B may act in a pro-apoptotic role in NSCLC. 26416711_Low JMJD3 expression is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 26729791_Findings reveal a novel epigenetic mechanism by which JMJD3 promotes melanoma progression and metastasis. 26795455_Jmjd3 regulates osteoblast apoptosis through targeting Bcl-2 expression and Bim phosphorylation. 26802933_JMJD3 up-regulation and NF-kappaB activation occur in the region of the wound edge during keratinocyte wound healing 26871869_JMJD3 and EZH2 in prostate biopsies also demonstrated an increase of JMJD3 and EZH2 in adenocarcinoma with Gleason score 7 and 8 by comparison with a normal biopsy. 27102442_In this study, we showed that aberrantly upregulated JMJD3 exerts an anti-apoptotic effect in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 27151432_Here, we discuss the roles of lysine 27 demethylases, JMJD3 and UTX, in cancer and potential therapeutic avenues targeting these enzymes. Despite a high degree of sequence similarity in the catalytic domain between JMJD3 and UTX, numerous studies revealed surprisingly contrasting roles in cellular reprogramming and cancer, particularly leukemia 27529370_KDM6B expression strongly correlates with ERbeta level in human pleural mesothelioma tumors and cell lines. 27737800_Our data indicate that hypoxic inhibition of JMJD3 activity reduces demethylation of H3K27me3, nucleosome removal, and hence induction of the STAT6 target gene CCL18, while induction of other STAT6-inducible genes such as SPINT2 remained unaffected by JMJD3. 27779233_Taken together, the authors propose that the miR-939-Jmjd3 axis perturbs the accessibility of hepatitis B virus enhancer II/core promoter (En II) promoter to essential nuclear factors (C/EBPalpha and SWI/SNF complex) therefore leading to compromised viral RNA synthesis and hence restricted viral multiplication. 27802135_Transient and forced expression of JMJD3c followed by the forced expression of lineage-defining transcription factors enabled the hPSCs to activate tissue-specific genes directly. Study have also shown that the introduction of JMJD3c facilitates the differentiation of hPSCs into functional hepatic cells and skeletal muscle cells. 27983522_JMJD3 gene expression in renal cell carcinoma and bladder cancer. 28177890_Data show that histone demethylase JMJD3 was reduced and its target gene Snai1 expression was down-regulated after HOTAIR suppression. 28189690_Lipopolysaccharide treatment recruited Jmjd3 and NF-kappaB to the promoter region of target genes, suggesting Jmjd3 synergizes with NF-kappaB to activate the expression of target genes. 28197626_Kdm6a and Kdm6b were found to be significantly overexpressed in Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) at the mRNA level. However, tests examining if targeting therapeutically Kdm6a/b using a specific small molecule inhibitor was potentially useful for treating MPM, revealed that members of the Kdm6 family may not be suitable candidates for therapy 28314754_The number of Kdm6b-positive chondrocytes was lower in human osteoarthritis cartilage samples. 28384648_results demonstrate that the regulation of Jmjd3 by STAT3 maintains repression of differentiation specific genes and is therefore important for the maintenance of self-renewal of normal neural and glioblastoma stem cells 28423536_Low JMJD3 expression is associated with breast cancer. 28430662_These results demonstrated that histone demethylase JMJD3 regulates CD11a expression in lupus T cells by affecting the H3K27me3 levels in the ITGAL (CD11a) promoter region, and JMJD3 might thereby serve as a potential therapeutic target for SLE. 28487543_Our study therefore delineates KDM6B function that links NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathway mediating MM cell growth and survival, and validates KDM6B as a novel therapeutic target in MM. 28747631_The authors found that Notch1 is up-regulated in the wound edge and its expression is dependent on JMJD3 and NF-kappaB in wounded keratinocytes. 28947543_inhibition of the H3K27 demethylase JMJD3 in naive CD4 T cells demonstrates how critically important molecules required for T cell differentiation, such as JAK2 and IL12RB2, are regulated by H3K27me3. 29161520_The interaction of methyltransferase EZH2 or demethylase JMJD3 on RGMA, RARb2, AR, PGR, and ERa genes in the progression and aggressiveness of prostate cancer. 29220567_Computational methods identifyied H3(17-33)-derived peptides with improved binding affinity that would allow co-crystallization with the KDM6B catalytic core. A co-crystallized H3(17-33)A21M peptide had interactions between the KDM6B zinc binding domain and the H3(17-23) region. KDM6B uses the zinc binding domain to achieve H3K27me3/me2 specificity. A 1564 His-to-Gln substitution explains its higher affinity than KDM6A. 29301935_JMJD3 are key regulators of cytokine production in human NK cell subsets. 29477140_The KDM6B inhibitor GSK-J4 perturbed the PMA-mediated differentiation of THP-1 cells. The AURKA inhibitor alisertib accelerates the expression of the H3K27 demethylase KDM6B, dissociating AURKA and YY1 from the KDM6B promoter region and inducing differentiation. 29489027_We demonstrate that extraskeletal osteosarcoma (ESOS) may include at least two small subsets: an MDM2-amplified deep soft-tissue ESOS and an H3K27me3-deficient organ-based ESOS 29621735_Our results demonstrate that in the early stage of sepsis, JMJD3 contributes to high levels of neutrophil mPR3 expression and thereby to the production of the inflammatory cytokine IL-1beta 29757189_histone demethylase KDM6B is a direct CSL-negative target, with inverse roles of CSL in HKC and SCC proliferative capacity, tumorigenesis, and tumor-associated inflammatory reaction. CSL/KDM6B protein expression could be used as a biomarker of SCC development and indicator of cancer treatment. 29911994_JMJD3 was identified unexpectedly as a gene-specific transcriptional partner of SIRT1 and epigenetically activated mitochondrial beta-oxidation, but not gluconeogenic, genes during fasting. 30224337_We demonstrate that ubiquitin-specific protease 7 (USP7) interacts with NOTCH1 and controls leukemia growth by stabilizing the levels of NOTCH1 and JMJD3 histone demethylase. 30275007_These results indicate that overexpression of KDM6B mediates activation of innate immune signals and has a role in MDS and CMML pathogenesis, and that KDM6B targeting has therapeutic potential in these myeloid disorders. 30277596_KDM6B is elevated in epithelial ovarian cancer and its expression level is closely related with metastasis and invasion. KDM6B plays an oncogenic role in ovarian cancer by modulating the transforming growth factor-beta1. 30633952_KDM6B promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioblastoma cells. 30678869_Jumonji-domain containing 3 overexpression was independently associated with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. In vitro, Jumonji-domain containing 3 expression regulated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell growth. 31085554_H3K27me3 plays a crucial role in defining tumour-promoting capacities of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts, and multiple stem cell niche factors were secreted from CAFs due to loss of H3K27me3. 31124279_findings will allow for further investigation in to the role of the KDM6B gene in human neurodevelopmental disorders 31138771_data suggest a role for KDM6B as a regulator of podocyte differentiation, which is important for the understanding of podocyte function in kidney development and related diseases. 31155967_Down-regulation of KDM6B is significantly associated with aggressive progression of NSCLC 31210309_JMJD3 enhances invasiveness and migratory capacity of non-small cell lung cancer cell via activating EMT signaling pathway. 31251802_The findings revealed that enhancer-mediated enrichment of novel JMJD3-DDX21 interaction at ENPP2 locus is necessary for nascent transcript synthesis via the resolution of aberrant R-loops formation in response to inflammatory stimulus. 31285428_EZH2 methyltransferase and JMJD3/UTX demethylases were deregulated during hepatic differentiation of human HepaRG cells. 31959746_Knock-out of KDM6s (JMJD3 and/or UTX) in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) showed that KDM6s (JMJD3 and/or UTX)-deficient human ESCs exit pluripotency and commit to neural progenitor cells (NPC) differentiation normally, but the resulting NPCs fail to transit into neurons and glia due to a lack of accessibility at loci essential for neurogenesis. 32394143_Jumonji domain containing-3 (JMJD3) inhibition attenuates IL-1beta-induced chondrocytes damage in vitro and protects osteoarthritis cartilage in vivo. 32447376_Prognostic Value of Histopathological Features and Loss of H3K27me3 Immunolabeling in Anaplastic Meningioma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. 32825938_Four methods to analyze H3K27M mutation in diffuse midline gliomas. 32843613_JMJD3 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma pathogenesis through epigenetic regulation of MYC. 32929331_Targeted inhibition of KDM6 histone demethylases eradicates tumor-initiating cells via enhancer reprogramming in colorectal cancer. 32992420_[Function and mechanism of histone demethytransferase Jmjd3 mediated regulation of Th1/Th2 balance through epigenetic modification in pre-eclampsia]. 33318475_JmjC-KDMs KDM3A and KDM6B modulate radioresistance under hypoxic conditions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33391480_Histone H3K27 methyltransferase EZH2 and demethylase JMJD3 regulate hepatic stellate cells activation and liver fibrosis. 33414463_KDM6B is an androgen regulated gene and plays oncogenic roles by demethylating H3K27me3 at cyclin D1 promoter in prostate cancer. 33472090_Tumor-associated mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via a DNM3OS/KDM6B/TIAM1 axis. 33478063_The Functions of the Demethylase JMJD3 in Cancer. 33581195_KDM6B (JMJD3) and its dual role in cancer. 33664867_KDM6B-mediated histone demethylation of LDHA promotes lung metastasis of osteosarcoma. 33742970_JMJD3-regulated expression of IL-6 is involved in the proliferation and chemosensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells. 33749791_NTRK Fusions Can Co-Occur With H3K27M Mutations and May Define Druggable Subclones Within Diffuse Midline Gliomas. 33771881_An IFNgamma/STAT1/JMJD3 Axis Induces ZEB1 Expression and Promotes Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 33789369_[Role of histone demethylase KDM6B in HBx-mediated podocyte-macrophage transdifferentiation]. 33895173_The occurrence of lupus nephritis is regulated by USP7-mediated JMJD3 stabilization. 34001062_KDM6B promotes ESCC cell proliferation and metastasis by facilitating C/EBPbeta transcription. 34093857_Cancer-derived exosomal miR-138-5p modulates polarization of tumor-associated macrophages through inhibition of KDM6B. 34217316_JMJD3: a critical epigenetic regulator in stem cell fate. 34262032_SMARCA4 deficient tumours are vulnerable to KDM6A/UTX and KDM6B/JMJD3 blockade. 34432948_Pharmacological Inhibition of Core Regulatory Circuitry Liquid-liquid Phase Separation Suppresses Metastasis and Chemoresistance in Osteosarcoma. 34533398_Repetitive spikes of glucose and lipid induce senescence-like phenotypes of bone marrow stem cells through H3K27me3 demethylase-mediated epigenetic regulation. 34696686_Activation of epigenetic regulator KDM6B by Salmonella Typhimurium enables chronic infections. 34862309_Lysine Demethylase 6B Regulates Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation by Controlling c-MYC Expression. 34893606_KDM6B promotes activation of the oncogenic CDK4/6-pRB-E2F pathway by maintaining enhancer activity in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. 35132566_The Epigenetic Regulation of OLIG2 by Histone Demethylase KDM6B in Glioma Cells. 35396990_Jumonji Domain-containing Protein-3 (JMJD3/Kdm6b) Is Critical for Normal Ovarian Function and Female Fertility. 35697791_Cooperation between KDM6B overexpression and TET2 deficiency in the pathogenesis of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. 35790358_Histone Demethylase Jmjd3 Regulates the Osteogenic Differentiation and Cytokine Expressions of Periodontal Ligament Cells. 35831280_Histone demethylase JMJD3 downregulation protects against aberrant force-induced osteoarthritis through epigenetic control of NR4A1. 35867069_JMJD3 Promotes Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Th17-Cell Differentiation by Modulating the STAT3-RORc Signaling Pathway. 36213329_Decreased Jumonji Domain-Containing 3 at the Promoter Downregulates Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 Expression and Cytoactivity of T Follicular Helper Cells from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. 36233212_A Screening of Epigenetic Therapeutic Targets for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Reveals PADI4 and KDM6B as Promising Candidates. |
ENSMUSG00000018476 |
Kdm6b |
315.424730 |
2.5239942640 |
1.335709 |
0.343835604 |
14.485239 |
0.00014126214956787237330554374281632590282242745161056518554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000379855953292365850805512028642851873883046209812164306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
478.6473301 |
102.8580341 |
190.8209148 |
29.7704505 |
| ENSG00000132561 |
4147 |
MATN2 |
protein_coding |
O00339 |
FUNCTION: Involved in matrix assembly. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the von Willebrand factor A domain containing protein family. This family of proteins is thought to be involved in the formation of filamentous networks in the extracellular matrices of various tissues. This protein contains five von Willebrand factor A domains. The specific function of this gene has not yet been determined. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4147; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; matrilin complex [GO:0120216]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198] |
11852232_matrilin-2, a filament-forming protein widely distributed in extracellular matrices. 12164922_matrilin-2 is expressed in normal skin by keratinocytes and fibroblasts and may thus contribute to cutaneous homeostasis. 12180907_study of interactions by which matrilin-2 can be integrated into extracellular filamentous networks 16401863_These results suggest that matrilin-2 may be a specific and clinically useful biomarker for discriminating between indolent and clinically aggressive pilocytic astrocytoma. 18328806_DeltaNp63/BMP-7 signaling pathway modulates wound healing process through the regulation of matrilin-2. 18386166_data indicate matrilin-2 is a novel basement membrane component in the liver, synthesized during sinusoidal 'capillarization' in cirrhosis & in hepatocellular carcinoma 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26271809_Matrilin-2 induces post-burn inflammatory responses as an endogenous danger signal, partly through a TLR4-mediated mechanism 27105914_Taken together, our results showed that high-glucose-induced Matrilin-2 expression that was mediated by the TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling pathway might play a role in Diabetic nephropathy (DN) pathogenesis and our finding provided a potential diagnostic and/or therapeutic target for DN. 27923659_Data show that the mRNA and protein levels of matrilin-2 were increased after irradiation treatment in both mouse lung tissue and human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells (HPAEpiC). 28533472_findings showed that YopK binds to the cell surface-exposed endogenous MATN2 and that purified YopK protein strongly inhibits the bacterial adherence to HeLa cells 30408806_miR-202-5p could target MATN2 to induce M2 polarization involved in allergic rhinitis. 31493245_MiR-202-5p/MATN2 are associated with regulatory T-cells differentiation and function in allergic rhinitis. 32046115_Mechanistic Roles of Matrilin-2 and Klotho in Modulating the Inflammatory Activity of Human Aortic Valve Cells. 33633437_Extracellular matrix changes in corneal opacification vary depending on etiology. 35274748_Peritumoral matrilin-2 staining may be useful in distinguishing basal cell carcinoma from folliculocentric basaloid proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000022324 |
Matn2 |
128.578577 |
0.2440930095 |
-2.034497 |
0.252194799 |
62.087433 |
0.00000000000000328541400364528201089412950507004723961859173064770089922603801824152469635009765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000022745173871390415135206904605887719984634197031847513414959394140169024467468261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.2832360 |
8.8288422 |
220.3695003 |
24.5286742 |
| ENSG00000132589 |
2319 |
FLOT2 |
protein_coding |
Q14254 |
FUNCTION: May act as a scaffolding protein within caveolar membranes, functionally participating in formation of caveolae or caveolae-like vesicles. May be involved in epidermal cell adhesion and epidermal structure and function. |
Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Endosome;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Caveolae are small domains on the inner cell membrane involved in vesicular trafficking and signal transduction. This gene encodes a caveolae-associated, integral membrane protein, which is thought to function in neuronal signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2319; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; adherens junction [GO:0005912]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cell-cell contact zone [GO:0044291]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; flotillin complex [GO:0016600]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; uropod [GO:0001931]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; anterograde dendritic transport [GO:0098937]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; epidermis development [GO:0008544]; negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902992]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of establishment of T cell polarity [GO:1903905]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein localization to plasma membrane raft [GO:0044860]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045661]; regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels [GO:0099072] |
15492257_Flot-2 overexpression is associated with melanoma progression, with increased PAR-1 expression, and with transformation of SB2 melanoma cells to a highly metastatic line. 16521037_flotillin-2 identified and immunolocalized in the caveola-vesicle complexes (CVC )present in erythrocytes infected with P. vivax 17013097_flotillin-2 has a role in lymph node metastasis in melanoma 17113085_The results showed that flotillin-1 can interact with arginase1, and hence arginase activity was up-regulated by 26.8%. 17307333_These lines of evidence suggested that a Gq-coupled receptor activates specifically p38 MAPK through lipid rafts and Src kinase activation, in which flotillins positively modulate the Gq signaling. 17600709_Coassembly of flotillin1 and flotillin2 into microdomains induces membrane curvature, the formation of plasma-membrane invaginations morphologically similar to caveolae, and the accumulation of intracellular vesicles. 17854803_Reggie-1/flotillin-2 microdomains form independent of actin 18237819_deletion mutants of reggie-1/flotillin-2 accumulate in the Golgi complex in HeLa and Jurkat cells, suggesting Golgi-dependent trafficking of reggie-1/flotillin-2 18296650_Flotillin 2 is a direct transcriptional target of the p53 family member genes in human cancer cells. 18337418_The interaction of flotillin-2 with amyloid precursor protein (APP) promotes the clustering of APP at the cell surface. 19318123_Epidermal Growth Factor stimulation of cells, flotillin 2 is tyrosine phosphorylated by Src kinases and endocytosed into late endosomes. 19404397_Flotillin-1 and -2 associate with PSGL-1 in resting and in stimulated neutrophils are importantly involved in neutrophil uropod formation and/or stabilization 19542222_copper modulates flotillin-2 association with cholesterol-rich lipid raft domains, and consequently Abeta synthesis is attenuated via copper-mediated inhibition of APP endocytosis 19605558_These results show that basolateral endocytosis of GPI-anchored proteins in hepatic cells occurs via a clathrin-independent flotillin-2-dependent pathway. 20027317_In hematopoietic cells, flotillins provide intrinsic cues that govern segregation of certain microdomain-associated molecules during immune cell polarization. 20515742_Studies indicate that spatial link between PrP and the microdomain-forming protein flotillins may contribute to PrP signaling, leading to thelocal assembly of membrane protein complexes at sites involved in cellular communication. 21119006_Reggie-1 (flotillin-2) dynamically colocalizes with KIF9 in living cells 21187433_flotillins have a role in NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol uptake and NPC1L1-flotillins-postive cholesterol-enriched membrane microdomains are involved in the mechanism for efficient cholesterol absorption 22081607_potentially relevant protein substrates of DHHC5 22438585_by promoting EGFR internalization, reggie-1 restricts EGFR signaling involved in E-cadherin macropinocytosis and recycling and regulate adherens junction formation 22669515_Report role for flotillin 1/2 in interactions of lung epithelial cells with silica nanoparticles. 22869152_we describe how flotillin-1 and -2 contribute to the stabilization of ErbB2 at the cell surface in breast cancer tissue 23012365_results support predominant formation of flotillin-1 and -2 hetero-oligomers in resting and chemokine-stimulated human T-cells which may importantly contribute to structuring of the uropod. 23064789_The FLOT2 is abundantly expressed in term villous placental CTs and endothelial cells, and in comparison, expression of these proteins in the ST is reduced. 23146906_Flot2 is an important regulator of mammary tumor-derived lung metastasis 23658725_a positive correlation exists between flotillin2 and erbB2 expression levels 23825023_Results identify reggie-1 as a regulator of the Rab11a/SNX4-controlled sorting and recycling pathway. 23945257_High FLOT2 protein expression was associated with poor outcomes in patients with breast cancer. 23983584_By virtue of its abundant expression in enterocytes, flotillin-2 must have an essential function in intestinal physiology, especially in the colon. 24046456_We have identified flotillin 1 and 2 as new partners of the cadherin complexes 24391950_Flotillins directly interact with gamma-catenin and regulate epithelial cell-cell adhesion. 24747692_Depletion of either flotillin-1 or flotillin-2 resulted in downregulation of ErbB3 and a selective reduction of ErbB2-ErbB3 receptor complexes. 24854103_Study suggests the Flot2 protein expression is correlated with cancer progression and poor prognosis in gastric carcinomas, probably due to its role in the regulation of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in gastric carcinoma cells. 25014228_results suggest that the increased expression of Flot-2 protein is a novel higher sensitivity biomarker that can predict lymph node metastases in NPC. 25053596_Our data suggest that FLOT2 is a novel molecule involved in renal cell carcinoma progression 25105415_Flotillin-2 is plays a role in the initial steps of skeletal myogenesis. 25403318_Flotillin 2 (FLOT2) is a direct target of microRNA-34a and the miR-34a/FLOT2 pathway plays a key role in melanoma proliferation and metastasis. 25738752_Knockdown of FLOT2 decreases breast cancer cell proliferation. Silencing of FLOT2 enhanced the transcriptional activity of FOXO factors by decreasing its phosphorylation through inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 25755751_Our findings provided that high FLOT2 expression was associated with poor outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer patients 25755754_FLOT2 may serve as an oncogene in the development of cervical cancer 25909165_Flot2 is an indispensable member for TGF-beta signaling, which is essential for the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis 26161893_increased expression of Flot-2 and EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer patients is inversely proportional to the disease prognosis. 26206082_Flot-2 exerts a pro-neoplastic role in NPC and is involved in tumor progression and metastasis. Moreover, Flot-2 exerts its role through NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt3 signaling. 26339392_Positive expression of Flot-2 protein may be an independent biomarker for poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 26556629_There was a strong association between polymorphisms of flotillin-2 gene and CAD in the Chinese Han population 26576674_that miR-449a suppressed Flot2 expression results in decreased cell invasion through repressing TGF-beta-mediated-epithelial-mesenchymal transition 27221048_This study presents the endocytic pathways of internalization for muscarinic type 3 receptor and flotillin-1/2 in salivary gland epithelial cells. knockdown of flot-1 or -2 by flotillin-specific siRNA prevented internalization and reduced the endocytic efficiency of muscarinic type 3 receptor. 27262438_Ectopic Flot2 could significantly reverse miR-485-mediated inhibition of metastasis and EMT, demonstrating Flot2 downregulation is involved in function of miR-485 27664330_Western blot experiments designed to detect flotillin 2, TMEM256, Rab3B and LAMTOR1 showed that the level of these proteins was higher in urinary exosomes from prostate cancer patients compared to healthy males, and ELISA-based detection of flotillin 2 and PARK7 showed that the combination of these proteins was able to distinguish prostate cancer patients and healthy controls with 68% sensitivity and 93% specificity 27981826_Flot-2 protein expression was significantly elevated in cancerous tissues and Flot-2 played pivotal roles in the development and progression of cancers. Increased expression of Flot-2 was correlated to a poor prognosis in cancer patients. Review. 28188157_Data indicate miR-802 as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer (PCa) progression and elucidated a novel mechanism of the miR-802/Flotillin-2 (Flot2) axis in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which may be a potential therapeutic target. 28503944_miR-133 involves in lung adenocarcinoma cell metastasis by targeting FLOT2 28739689_We demonstrated that LXR stimulation decreases mRNA and protein expression of FLOT2 and DHHC5 in MCF-7 cells. LXR stimulation also reduces Akt phosphorylation and its localization at the plasma membrane 29115528_Results provide evidence that Flot2 plays an important role in the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, which may be partially related to its interaction with PLCD3. 30111578_In invasive cells, MT1-MMP endocytosis to the endolysosomal reservoir compartment requires flotillin 1 and flotillin 2. 30452906_the presence of Flotillin-1, in addition to Flotillin-2 in the cardiac intercalated disc, is reported. 30820716_Results showed that flotillin-1 and flotillin-2 expression were upregulated in HCCLM3 cells following 45 degrees C heat treatment and in residual HCCLM3 xenografts cells after insufficient RFA. 30836864_It has been concluded that miR-485-5p, as a tumor suppressor, inhibits the growth and metastasis in small cell lung cancer cells by targeting FLOT2. 30914515_Together, the data revealed that FLOT1 and FLOT2 are crucial for Anaplasma replication in host cells, likely by aiding vesicular traffic of low-density lipoprotein-derived free cholesterol to Anaplasma inclusions. 31138766_analysis of how flotillin-mediated endocytosis and ALIX-syntenin-1-mediated exocytosis protect the cell membrane from damage caused by necroptosis 31446795_miR-34c-5p can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells 32196611_Long non-coding RNA MIR4435-2HG recruits miR-802 from FLOT2 to promote melanoma progression. 33631676_FLOT2 upregulation promotes growth and invasion by interacting and stabilizing EphA2 in gliomas. 33744853_Flotillin-2 promotes cell proliferation via activating the c-Myc/BCAT1 axis by suppressing miR-33b-5p in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 34254281_N6-methyladenosine Demethylase FTO Induces the Dysfunctions of Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Upregulating Flotillin 2. 34544283_Anaplasma phagocytophilum Hijacks Flotillin and NPC1 Complex To Acquire Intracellular Cholesterol for Proliferation, Which Can Be Inhibited with Ezetimibe. 34930675_MicroRNA-486-3p promotes the proliferation and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing flotillin-2. 35298613_The differential role of the lipid raft-associated protein flotillin 2 for progression of myeloid leukemia. 35872627_FLOT2 Promotes the Proliferation and Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition of Cervical Cancer by Activating the MEK/ERK1/2 Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000061981 |
Flot2 |
526.914135 |
0.4740777938 |
-1.076804 |
0.278328719 |
14.579927 |
0.00013433793477436311051761985702057700109435245394706726074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000362292694549533941111851831351486907806247472763061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
342.0933355 |
78.7007661 |
730.4324992 |
121.3125424 |
| ENSG00000132613 |
92154 |
MTSS2 |
protein_coding |
Q765P7 |
FUNCTION: Involved in plasma membrane dynamics. Potentiated PDGF-mediated formation of membrane ruffles and lamellipodia in fibroblasts, acting via RAC1 activation (PubMed:14752106). May function in actin bundling (PubMed:14752106). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14752106}. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables GTPase activator activity and small GTPase binding activity. Involved in activation of GTPase activity and cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus. Located in ruffle membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92154; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin monomer binding [GO:0003785]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; cell projection assembly [GO:0030031]; cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus [GO:0036120]; lamellipodium organization [GO:0097581]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; ruffle assembly [GO:0097178] |
20875796_these data indicates that the interaction between full-length Abba and Rac1 is implicated in membrane deformation and subjected to a growth factor-mediated regulation through the C-terminal sequence. 25669885_The ABBA motif in cyclin A is required for its proper degradation in prometaphase through competing with BUBR1 for the same site on CDC20 36067766_The recurrent de novo c.2011C>T missense variant in MTSS2 causes syndromic intellectual disability. |
ENSMUSG00000033763 |
Mtss2 |
104.785298 |
0.3964814471 |
-1.334675 |
0.155263777 |
76.051490 |
0.00000000000000000276363740856917321476013009483584884050859280367354407076385669483897800091654062271118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000022636674889279132362572441745802054492594643358700616520007287135740625672042369842529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.3070897 |
6.7705294 |
145.0250305 |
11.2311085 |
| ENSG00000132635 |
64773 |
PCED1A |
protein_coding |
Q9H1Q7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the GDSL/SGNH superfamily. Members of this family are hydrolytic enzymes with esterase and lipase activity and broad substrate specificity. This protein belongs to the Pmr5-Cas1p-esterase subfamily in that it contains the catalytic triad comprised of serine, aspartate and histidine and lacks two conserved regions (glycine after strand S2 and GxND motif). A pseudogene of this gene has been identified on the long arm of chromosome 2. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2012]. |
hsa:64773; |
transferase activity [GO:0016740] |
|
ENSMUSG00000037773 |
Pced1a |
164.319084 |
0.4601659386 |
-1.119774 |
0.219733011 |
25.594309 |
0.00000042128000330365329987981708702304839420094140223227441310882568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001556079291481962558117116586509087738932066713459789752960205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.3653350 |
19.0836152 |
233.3741025 |
29.1831847 |
| ENSG00000132718 |
23208 |
SYT11 |
protein_coding |
Q9BT88 |
FUNCTION: Synaptotagmin family member involved in vesicular and membrane trafficking which does not bind Ca(2+). Inhibits clathrin-mediated and bulk endocytosis, functions to ensure precision in vesicle retrieval. Plays an important role in dopamine transmission by regulating endocytosis and the vesicle-recycling process. Essential component of a neuronal vesicular trafficking pathway that differs from the synaptic vesicle trafficking pathway but is crucial for development and synaptic plasticity. In macrophages and microglia, inhibits the conventional cytokine secretion, of at least IL6 and TNF, and phagocytosis. In astrocytes, regulates lysosome exocytosis, mechanism required for the repair of injured astrocyte cell membrane (By similarity). Required for the ATP13A2-mediated regulation of the autophagy-lysosome pathway (PubMed:27278822). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R0N3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27278822}. |
Calcium;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Lysosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the synaptotagmin gene family and encodes a protein similar to other family members that are known calcium sensors and mediate calcium-dependent regulation of membrane trafficking in synaptic transmission. The encoded protein is also a substrate for ubiquitin-E3-ligase parkin. The gene has previously been referred to as synaptotagmin XII but has been renamed synaptotagmin XI to be consistent with mouse and rat official nomenclature. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:23208; |
axon [GO:0030424]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; dopaminergic synapse [GO:0098691]; early phagosome [GO:0032009]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; inhibitory synapse [GO:0060077]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; synapse [GO:0045202]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; beta-tubulin binding [GO:0048487]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; translation initiation factor binding [GO:0031369]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; calcium ion regulated lysosome exocytosis [GO:1990927]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; establishment of vesicle localization [GO:0051650]; learning [GO:0007612]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0033602]; negative regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045806]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903979]; negative regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0046929]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; plasma membrane repair [GO:0001778]; positive regulation of protein localization to phagocytic vesicle [GO:1905171]; regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0017158]; regulation of defense response to bacterium [GO:1900424]; regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0014059]; regulation of phagosome maturation [GO:1905162]; regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:1900242]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
12925569_parkin interacts with and ubiquitinates synaptotagmin XI 15354386_Lack of disease-causing mutations in a detailed analysis of a large sample of familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease patients argues against a major role of mutations in the synaptotagmin XI gene in PD. 17192956_Excessive expression of Syt11 can be associated with schizophrenia. 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 24164654_The genetic variations of VAMP2, Synaptotagmin XI might be indication of the relationship between these genes and idiopathic generalized epilepsy 26944171_In summary, This study supports the existence of association between Parkinson disease and markers in or around SYT11 27278822_ATP13A2 and SYT11 form a functional network in the regulation of the autophagy-lysosome pathway, which may contribute to forms of Parkinson's Disease-associated neurodegeneration. 29311685_parkin deficiency induces synaptotagmin-11 accumulation and PD-like neurotoxicity in mouse models, which is reversed by SYT11 knockdown in the SNpc or knockout of SYT11 restricted to dopaminergic neuron 32253955_The rs3129882/rs4248166 in HLA-DRA and rs34372695 in SYT11 are not associated with sporadic Parkinson's disease in Central Chinese population. 33349842_Targeted sequencing of Parkinson's disease loci genes highlights SYT11, FGF20 and other associations. 34674384_Association analysis of SYT11, FGF20, GCH1 rare variants in Parkinson's disease. 34857756_Atlas of RNA editing events affecting protein expression in aged and Alzheimer's disease human brain tissue. 35753051_The highly expressed calcium-insensitive synaptotagmin-11 and synaptotagmin-13 modulate insulin secretion. 35768842_Synaptotagmin 11 scaffolds MKK7-JNK signaling process to promote stem-like molecular subtype gastric cancer oncogenesis. 36170810_Impad1 and Syt11 work in an epistatic pathway that regulates EMT-mediated vesicular trafficking to drive lung cancer invasion and metastasis. |
ENSMUSG00000068923 |
Syt11 |
176.027713 |
3.6248892515 |
1.857937 |
0.131671132 |
206.283965 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008884501189371185762350316642533637904369424699538564092790154836626490763769986109702185286359931871630074938670179694050199614707707951311022043228149414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001743819648339344543379984672334166727849642234830387339765281344862656325999286523141971961982431025413705573371575020813484258042080909945070743560791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
279.5475524 |
21.7387663 |
77.7505853 |
5.0739819 |
| ENSG00000132793 |
64900 |
LPIN3 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQK8 |
FUNCTION: Magnesium-dependent phosphatidate phosphatase enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of phosphatidic acid to diacylglycerol during triglyceride, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis therefore regulates fatty acid metabolism. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99PI4}. |
Alternative splicing;Fatty acid metabolism;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the lipin family of proteins, and all family members share strong homology in their C-terminal region. This protein is thought to form hetero-oligomers with other lipin family members, while one family member, lipin 1, can also form homo-oligomers. This protein contains conserved motifs for phosphatidate phosphatase 1 (PAP1) activity as well as a domain that interacts with a transcriptional co-activator. Lipin complexes act in the cytoplasm to catalyze the dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acid to produce diacylglycerol, which is the precursor of both triglycerides and phospholipids. Lipin complexes are also thought to regulate gene expression as transcriptional co-activators in the nucleus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:64900; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phosphatidate phosphatase activity [GO:0008195]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; cellular lipid metabolic process [GO:0044255]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0009062]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0019432] |
20735359_Data revealed that lipin 1 formed stable homo-oligomers with itself and hetero-oligomers with lipin 2/3. 22481384_LPIN1-related myolysis constitutes a major cause of early-onset rhabdomyolysis and occasionally in adults. Heterozygous LPIN1 mutations may cause mild muscular symptoms. No major defects of LPIN2 or LPIN3 genes were associated with muscle manifestations. 23263658_a newly identified novel cell-penetrating sequence (LPIN; RRKRRRRRK) from the nuclear localization sequence (NLS) of human nuclear phosphatase, LPIN3. 33596934_Identification of lipidomic profiles associated with drug-resistant prostate cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000027412 |
Lpin3 |
222.893105 |
0.2854731970 |
-1.808573 |
0.221113946 |
63.454100 |
0.00000000000000164147356968288282245803276539745339966695151633774285571121254179161041975021362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000011625791693147481269639762365237999641753331714344454894671798683702945709228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
102.3888412 |
13.8718801 |
361.1588297 |
33.7196769 |
| ENSG00000132958 |
93492 |
TPTE2 |
protein_coding |
Q6XPS3 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a lipid phosphatase, removing the phosphate in the D3 position of the inositol ring from phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11716755}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Shows no phosphoinositide phosphatase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11716755}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
TPIP is a member of a large class of membrane-associated phosphatases with substrate specificity for the 3-position phosphate of inositol phospholipids.[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2002]. |
hsa:93492; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase activity [GO:0016314]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase activity [GO:0051800]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051896] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22164291_the TPIP splice-variant (TPIP-C2) mRNA is expressed in human and mouse tissues and strongly inhibits cell growth in HeLa cells 22311048_findings suggest that C2-domain of TPIP-C2 may act as a dominant negative effector, which may bind to and arrest the cell proliferation signalling complex 22896666_TPTE2 was originally reported to be a phosphoinositide 3'-phosphatase, like the tumor suppressor PTEN. Later on, other homologous phosphatases, such as Ci-VSP and Dr-VSP, have been described. These proteins are 5'-phosphatases. More recently, using a chimeric construct, we have shown that the catalytic domain of TPTE2 behaves as a 5'-phosphatase as well. 25676706_The role of TPTE2 in gallbladder cancer cells |
ENSMUSG00000031481 |
Tpte |
31.276627 |
11.1368564932 |
3.477270 |
1.069383271 |
8.632797 |
0.00330164244075664128560965160374962579226121306419372558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007005785282571595946887743622255584341473877429962158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.8697157 |
31.1208092 |
2.6270527 |
1.7602155 |
| ENSG00000132965 |
241 |
ALOX5AP |
protein_coding |
P20292 |
FUNCTION: Required for leukotriene biosynthesis by ALOX5 (5-lipoxygenase). Anchors ALOX5 to the membrane. Binds arachidonic acid, and could play an essential role in the transfer of arachidonic acid to ALOX5. Binds to MK-886, a compound that blocks the biosynthesis of leukotrienes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2300173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8440384}. |
3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;Leukotriene biosynthesis;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein which, with 5-lipoxygenase, is required for leukotriene synthesis. Leukotrienes are arachidonic acid metabolites which have been implicated in various types of inflammatory responses, including asthma, arthritis and psoriasis. This protein localizes to the plasma membrane. Inhibitors of its function impede translocation of 5-lipoxygenase from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane and inhibit 5-lipoxygenase activation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:241; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0004051]; arachidonic acid binding [GO:0050544]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; glutathione transferase activity [GO:0004364]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; leukotriene-C4 synthase activity [GO:0004464]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; leukotriene biosynthetic process [GO:0019370]; leukotriene production involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002540]; lipoxygenase pathway [GO:0019372]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002675]; protein homotrimerization [GO:0070207] |
12571239_FLAP gene is transactivated by members of the C/EBP family of transcription factors in inflammatory cells and that these factors play an important role in FLAP gene induction by TNFalpha 12629151_LOX5 and FLAP pathway in monocytes and microglia yields products toxic toward neurons (neuroblastoma cell line) 12911785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14702425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14749922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14770184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14770184_We conclude that variants of ALOX5AP are involved in the pathogenesis of both myocardial infarction and stroke by increasing leukotriene production and inflammation in the arterial wall. 15593193_Both the eicosanoids PGE(2) and LTB(4) are important cofactors in regulating FLAP expression; the inhibition of PGE(2) down-regulates FLAP gene expression. 15640973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15640973_role for ALOX5AP variant in stroke patients 15731479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15731479_Variants in the ALOX5AP gene but not the PDE4D gene are associated with risk for stroke in individuals from central Europe 15784112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15861005_ALOX5AP (encoding 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein) associated with myocardial infarction and stroke 15876305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15886380_Observational study and clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16127181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16144515_FLAP is present as a monomer and a homodimer in human polymorphonuclear cells; leukotriene biosynthesis in intact cells not only requires the presence of FLAP but its further organization into a FLAP homodimer. 16282974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778124_No evidence for association of specific Icelandic ALOX5P gene variants/at-risk haplotypes tested with risk of incident myocardial infarction nor ischemic stroke in this prospective, non-Icelandic study. 16939001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17304054_No association of polymorphisms in the gene encoding 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein and myocardial infarction in a large central European population. 17304054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17387518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17387518_Study reports significant association of variants of ALOX5AP with ischemic stroke and ischemic stroke subtypes among whites; no significant association was identified among blacks. 17460547_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17505527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17505527_the role of variants of the gene encoding arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (ALOX5AP) as possible susceptibility factors for coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction in patients with or without angiographically proven CAD 17600184_x-ray crystal structures of FLAP in complex with two leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitors at 4.0 and 4.2 angstrom resolution, respectively; structures show that inhibitors bind in membrane-embedded pockets of FLAP 17627106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17627106_a significant correlation of FLAP gene promoter 17A allele carriers with higher plasma high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in patients with coronary artery disease. 17655870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17655870_This study did not confirm the association between ALOX5AP HapA haplotype and ICVD, but a non-significant risk was observed in the Large Artery Atherosclerosis subtype. 18084092_Diffraction-quality crystals of FLAP in complex with leukotriene-synthesis inhibitor MK-591 and with an iodinated analogue of MK-591 have been grown using the sitting-drop vapor-diffusion method 18318662_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18323512_Genetic variation in leukotriene pathway members and their receptors confer an increased risk of ischemic stroke in 2 independent populations 18323512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18366797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18369664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18369664_findings do not support a link between common allelic variation in or near ALOX5 or ALOX5AP and the risk of coronary artery disease 18374923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18398223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18398440_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18506375_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18547289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18547289_These data provide evidence for the role of SNPs spanning the ALOX5AP and LTA4H genes in asthma and atopy susceptibility 18775537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18775537_genetic variation in the ALOX5AP gene contributes to CHD risk in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia 18843019_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18843019_There was a significant interaction between the ALOX5AP -4900 A>G polymorphism and dietary linoleic acid intake. 18945963_PlGF-mediated increased FLAP mRNA expression occurred via activation of phosphoinositide-3 (PI-3) kinase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase, and hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha). 18977990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19046748_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19126581_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126581_meta-analysis of all studies with ALOX5AP genotyping showed significant heterogeneity among studies and a nonsignificant association between the HapA haplotype and stroke risk [review] 19130089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131661_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19166692_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19233132_LTC(4)S interacts in vitro with both FLAP and 5-LO and that these interactions involve distinct parts of LTC(4)S. 19288030_Results suggest that ALOX5AP, IRAK1, and FABP2 are susceptibility loci for CKD among Japanese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19361804_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19361804_Variants in the ALOX5AP gene are associated with the presence of xanthomas in familial hypercholesterolemia patients. This result supports our hypothesis that inflammation is a pathogenetic factor of xanthomas. 19373490_MTHFR C677T, ALOX5AP T2354A and NOTCH3 C381T were significant combinational contributors to thrombotic stroke. 19417766_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19417766_we found no evidence of association between PDE4D and ALOX5AP genes and the risk of IS in a genetically homogenous population from Sardinia. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19450127_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19524426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19596330_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19596330_Suggests a significant but modest contribution of the ALOX5AP gene variants to the susceptibility of premature coronary artery disease in an US Midwestern population of European-American ancestry. 19622707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20014490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014490_The polymorphism of SG13S114A/T in ALOX5AP is not related with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. 20067482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20067482_Our results support the role of LTA4H and ALOX5AP variants as risk factors for asthma in Latino populations. 20128419_no association between gene polymorphism and bronchial asthma in a Spanish population 20194722_hypoxia-mediated 5-lipoxygenase activating protein expression is regulated by hypoxia-response elements and NF-kappaB site in its promoter, and negatively regulated by miR-135a and miR-199a-5p 20357438_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20357438_The ALOX5AP SG13S114 variant is an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke in the Iberian population and is associated with ALOX5AP expression levels 20369037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20376802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20376802_The polymorphism of SG13S114 A/T in the ALOX5AP gene may be associated with the instability of atherosclerosis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20592751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20810156_LTA4H and ALOX5AP gene polymorphisms modify the augmentation of bronchodilator responsiveness by leukotriene modifiers in Puerto Ricans but not Mexicans with asthma. 20810156_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21153769_These results suggested that the genetic variants in ALOX5AP might modulate the risk of stroke in Eastern Chinese Han population. 21199733_Data show that the HapB haplotype and rs1722842 polymorphism in ALOX5AP gene were associated with coronary heart disease, and the HapA haplotype was associated with risk of MI. 21227888_Polymorphisms of the 5-lipo-oxygenase-activating protein may be associated with chronic spontaneous urticaria. 21675249_No statistically significant associations were found between acute stroke and the ALOX5AP gene polymorphisms examined 21816595_A Promoter polymorphism (rs17222919, -1316T/G) of ALOX5AP is associated with intracerebral hemorrhage in Korean population 21893978_Genetic variants in the promoter region of the ALOX5AP gene might be a novel genetic risk factor for ischemic stroke in a north Chinese Han population. 22051033_This study provides preliminary evidence suggesting that genetic polymorphisms of ALOX5AP are associated with atherothrombotic stroke. 22074807_Our data do not support the hypothesis that variants in ALOX5AP are associated with risk of MRI-defined brain infarcts. 22129473_ALOX5AP SNPs are unlikely to play a dominant role in the pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. 22206291_The polymorphisms spanning ALOX5AP is not major determinants of baseline lung function in smokers. 22537113_study is the first to demonstrate the association between lung function and ALOX5AP polymorphisms in a healthy and general population 22726381_SNP haplotypes with susceptibility to coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population 22849376_The ALOX5AP SNP A allele in rs4073259 and genotype rs9579646 GG, rs9551963 AC, and haplotype rs9315050 & rs9551963 AAAC were associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke. 23076369_Data indicate that single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (ALOX5AP), phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), and interleukin-1alpha (IL-1alpha) were associated with an increased risk of atherothrombotic stroke (ATS) in Chinese. 23404351_Genetic variability in FLAP and ALOX15 may modify the protective effect of NSAID use against colorectal neoplasia. 23546934_The two genetic polymorphisms of ALOX5AP, SG13S114 and SG13S32, are not associated with cerebral infarction. 23765972_the interaction between ALOX5AP-SG13S114AA and COX-2-765CC apparently increases susceptibility to cerebral infarction. 23828562_The results of our study failed to confirm whether the selected variants in ALOX5AP gene within the LT metabolism pathway contribute to platelet reactivity in a diabetic population treated with ASA. 24148560_ALOX5AP SG13S114 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Chinese population. [review] 24183033_This meta-analysis identifies three polymorphisms of ALOX5AP that are significantly associated with risk for the Chinese population to develop ischemic stroke. 24198186_A common genetic variant SG13S114/AA in ALOX5AP was associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese cohort. 24368493_This study showed that interactions between the ALOX5AP SG13S114 and CYP3A5 A6986G genes can engender a significantly higher risk of stroke than a single risk factor. 24411318_ALOX5AP polymorphisms are associated with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in a cigarette smoking Chinese population. 24485247_No association was found between single-nucleotide polymorphisms of ALOX5AP or PDE4D and the risk of overall ischemic stroke in a southeastern Chinese population. The ALOX5AP gene might be related to ischemic stroke incidence in females. 24635928_There was no statistically significant association of ALOX5AP rs4073259 SNP with ischemic stroke in this northeastern Chinese Han population living in Heilongjiang province, China. 24641614_BRP-7 potently suppresses leukotriene biosynthesis by interacting with FLAP in human neutrophils/monocytes. 24905297_The cellular biosynthesis of 5-LO products from endogenously derived substrate requires not only functional 5-LO/FLAP co-localization but also additional prerequisites which are dispensable when exogenous AA is supplied 25010723_a protective role of the three ALOX5AP SNPs for stroke 25025775_FLAP protein inhibition attenuates inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) or the lipid A fraction of LPS. 25034252_The roles of CLP and FLAP in in cellular leukotriene biosynthesis, were studied. 25210744_Rs10507391, rs4769874 and its haplotypes in ALOX5AP are unrelated to ACS risk in the Chinese Han population of Changwu, but elevated serum LTB4 level is strongly associated withacute coronary syndrome risk 25242267_results of the meta-analysis indicate that ALOX5AP rs10507391/SG13S114 A>T polymorphism is not associated with the risk of cerebral infarction in the Chinese population. 25534367_Genetic polymorphisms of ALOX5AP and CYP3A5 increase susceptibility to ischemic stroke and are associated with atherothrombotic events in stroke patients. 25721704_Report no association between ALOX5AP SNPs and atherosclerotic plaque phenotypes. 25815512_Our study provides evidence that the promoter single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs17222919 of the ALOX5AP is a potential genetic protective factor for IS in the Chinese Han population. 25862617_Genetic interaction of CD80 and ALOX5AP was observed in systemic lupus erythematosus in Asian populations. 26159646_The results of this study supported the association of the epistatic interactions of ALOX5AP, THBD, and KNG1 and present novel evidence for the main effect of KNG1 gene on IS susceptibility 26289316_findings show that several enzymes known to be involved in the biosynthesis of proinflammatory LTs, such as FLAP and cPLA2alpha, also contribute to LX and Rv formation 26327594_THE 5-LOX interface involving the four cysteines 159, 300, 416 and 418 is important for the translocation to the nuclear membrane and the colocalization with FLAP. 26842853_The observation that the coexpression of FLAP with a subset of the 5-LOX mutants restores 5-LOX-wild-type (wt)-like levels of products formed in intact cells suggests a physical protein-protein interaction, beyond colocalization, of 5-LOX and FLAP. 27129215_Data indicate that a single amino acid mutation was sufficient to reverse the speciation observed in wild type 5-Lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP). 27350673_Genetic polymorphisms of T-1131C APOA5 and ALOX5AP SG13S114 can be considered risk factors for the susceptibility to ischemic stroke in Morocco. 27416969_rs17222919 of ALOX5AP is a potential genetic protective factor against ischemic stroke in the Chinese population 28101761_Meta-analysis suggests that the A allele at the ALOX5AP SG13S114 polymorphism is a protective factor for the ischemic stroke in the European population 28160477_The results the study indicate that SNP genetic variants of ALOX5AP might play a role in the development of SSc-related pulmonary fibrosis and ventilatory dysfunction. 29041000_This study revealed that epistatic interaction among the ALOX5, ALOX5AP and MPO genes played a significant role in vulnerability to ischemic stroke. 29096760_No significant association was found between ALOX5AP rs10507391 polymorphism and ischemic stroke risk in males. Moreover, ALOX5AP rs10507391 polymorphism was not associated with cardioembolic ischemic stroke risk. 29392977_Indicate a potential protective role of ALOX5AP and 5-arachidonate lipoxygenase gene in diabetes type 2 pathogenesis. 30003372_Two-stage association study to screen the positive CpG-SNPs of ALOX5AP gene, then explored the relationship among CpG-SNPs, methylation levels, and mRNA expression levels. Findings showed that CpG-SNP rs4073259 associated with ischemic stroke affected DNA methylation and then regulated the mRNA expression via allele-specific DNA methylation. 30291962_Data support the conclusion that the presence of FLAP reduces triple K mutant-5-LOX product formation to wild type-5-LOX levels. 30313062_This meta-analysis indicates that ALOX5AP rs17222919-1316T/G may be a protective factor against stroke. 30678701_Our study showed that ALOX5AP rs10507391 was associated with total cholesterol (TC) levels but we didn't observe any association between rs10507391 and the risk of myocardial infarction 31992246_Key genes with prognostic values in suppression of osteosarcoma metastasis using comprehensive analysis. 32027251_genotype AA, AG and allele A, G of ALOX5 rs2029253, as well as ALOX5AP rs10507391 may be correlate with the susceptibility to myeloid leukemia 32165305_the study was designed to investigate the association between the polymorphism of the ALOX5 gene (rs12762303) and the ALOX5AP gene (rs3802278), and diabetic nephropathy (DN) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 33454679_ASSOCIATION BETWEEN SINGLE POLYMORPHISM IN THE LOCUS RS17216473 OF THE GENE THAT ENCODES 5-LIPOXYGENASE-ACTIVATING PROTEIN AND RISK OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION. |
ENSMUSG00000060063 |
Alox5ap |
1485.391431 |
10.0512033744 |
3.329296 |
0.060213391 |
3460.412020 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2735.2392997 |
95.5978296 |
274.0359769 |
8.7853698 |
| ENSG00000133019 |
1131 |
CHRM3 |
protein_coding |
P20309 |
FUNCTION: The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7565628}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The muscarinic cholinergic receptors belong to a larger family of G protein-coupled receptors. The functional diversity of these receptors is defined by the binding of acetylcholine and includes cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degeneration, and potassium channel mediation. Muscarinic receptors influence many effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. The muscarinic cholinergic receptor 3 controls smooth muscle contraction and its stimulation causes secretion of glandular tissue. Alternative promoter use and alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that have different tissue specificities. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:1131; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; synapse [GO:0045202]; acetylcholine binding [GO:0042166]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor activity [GO:0016907]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0004993]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0095500]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007197]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045987]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; regulation of ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0032412]; regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle contraction [GO:0003056]; saliva secretion [GO:0046541]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939] |
11856737_potential role of endogenous GRK6 in the regulation of M(3) mACh receptor 11877431_Stimulation of phospholipase C-epsilon by the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediated by cyclic AMP and the GTPase Rap2B 12126481_We show that activation of these receptors leads to divergent growth responses: M(2) AChR activation causes an increase in DNA synthesis, whereas M(3) AChR activation causes a dramatic decrease in DNA synthesis. 12194018_both G(q) and G(11) are involved in mediating the action of the M(3) receptor on cytosolic Ca(2+) in HT29 cells 12381439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12642833_Single nucleotide polymorphisms not more frequent in asthma. No nonrandom transmission of short tandem repeat polymorphism haplotypes in asthma. Nonrandom transmission of haplotypes in skin test reactivity to cockroach allergens. 12649280_the conserved poly-basic region in the C-terminal tail of the M3 muscarinic receptor contributes to the ability to mediate protection against apoptotic cell death 12799371_the M3 receptor displays a major ARF1-dependent route of phospholipase D1 activation with an additional ARF6-dependent pathway to PLD1 or PLD2 14573754_M3 mAChR desensitization is mediated by GRK6 in human SH-SY5Y cells, and receptor desensitization of phospholipase C signaling can be monitored in 'real-time' in single, living cells. 14977875_The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 is a mediator of bradycardia and bronchoconstriction due to vagal innervation. 15263021_M3 up-regulates 'sedentary' integrins alpha2beta1 and alpha3beta1. Inhibition of migration by M3 was mediated through Ca2+-dependent guanylyl cyclase-cyclic GMP-protein kinase G signaling pathway. 15280370_M1- and M3- but not M2- or M4-AchR signals activate HIF-1 by both stabilization and synthesis of HIF-1alpha and by inducing the transcriptional activity of HIF-1alpha. 15383626_(HEK) 293 cells expressing recombinant Galpha(q/11)-coupled muscarinic M3 receptors showed transient coexpression of RGS proteins 15725576_demonstration of the antigenicity of a novel peptide fragment of the human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 3 in primary Sjogren's syndrome 15769745_binding of beta-arrestin-1 to muscarinic M(3) receptors requires paired stimulation of two receptor components within the same receptor dimer 16113538_characterization of the muscarinic receptor in the spontaneously immortalized human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT and its role in cell migration 16368694_Data demonstrate that M(1), M(2), and M(3) muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR)can form homo- and heterodimers in living cells, and suggest that heterodimerization plays a role in the mechanism of mAChR long term regulation. 17005862_The muscarinic Ca2+ signaling pathway is not necessarily affected by depolarization and suggest that the M3 receptor itself is not sensitive to voltage. 17130513_C allele as associated with a reduced acute insulin response and modestly associated with increased risk of early-onset type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 17130513_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17192665_affects endocrine and exocrine hormone and salivary secretion 17335853_Resuts show that urothelium carries multiple cholinergic receptor subtypes, with predominant expression of M2R, M3R and alpha7-nAChR and suggest that this layer-specific distribution serves to stratify cholinergic regulation of urothelial function. 17373692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17513382_alphaM3 belongs to a complex and diverse set of synchronously moving parts that change structure relatively late in the channel-opening process. 17637176_M3R was involved in the up-regulation of H1R by activating H1R gene transcription through a PKC-dependent process 17851256_Poly I:C caused increased M3R in airway smooth muscle cells by interacting with TLR3. 17890325_These results indicate caveolae and caveolin-1 facilitate [Ca(2+)](i) mobilization leading to ASM contraction induced by submaximal concentrations of acetylcholine. 17951979_the M(3)/M(5) subtypes appear to be the major contributor, leading to intracellular calcium mobilization from the internal store via an IP(3)-dependent pathway in the undifferentiated retinoblastoma cells. 18070938_M3 employs two distinct mechanisms of chemical imitation to potently sequester chemokines, thereby inhibiting chemokine receptor binding events as well as the formation of chemotactic gradients necessary for directed leukocyte trafficking 18249005_Neither the linear M3R peptide nor M3R transfectants represent suitable tools for discrimination of pathogenic from natural autoantibodies in Sjogren's syndrome. 18272392_The observed effect of tau protein on neurons (in neuroblastomas and primary cultures of hippocampal and cortical neurons) is through M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors. 18348264_The results demonstrate that multiple muscarinic receptor subtypes regulate mTOR, and that both MAPK-dependent and -independent mechanisms may mediate the response in a cell context-specific manner. 18385290_Results demonstrate that the actions of pilocarpine and carbachol in salivary cells are mediated through two distinct signaling mechanisms via M3/M1 receptors. 18422974_Muscarinic receptor M3 expression is associated with invasive migration of melanomas. 18524769_airway M(2)Rs inhibit BK channels by a dual, Gbetagamma-mediated mechanism, a direct membrane-delimited interaction, and the activation of the phospholipase C/protein kinase C pathway 18563417_M2 and M3 receptors are upregulated in a time-dependent and pressure-dependent fashion after as little as a 24 h exposure to increased hydrostatic pressure in bladder 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19033440_the beta2 adrenergic and M3 muscarinic receptors, enter cells constitutively by clathrin-independent endocytosis and colocalize with markers of this endosomal pathway on recycling tubular endosomes subsequently recycle back to the plasma membrane 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19182865_The DEP domain of RGS7 can directly bind to the third intracellular loop of the M3R and attenuate receptor-induced Ca2+ mobilization in a M3 subtype-selective manner. 19183167_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19460789_muscarinic M3 receptor stimulation augments cigarette smoke extract-induced IL-8 (but not IL-6) production by airway smooth muscle 19575010_Data show that NALCN and M3R belong to the same protein complex, involving the intracellular I-II loop of NALCN and the intracellular i3 loop of M3R. 19626040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19648965_M(3)-muscarinic receptor can regulate the apoptotic properties of a chemotherapeutic DNA-damaging agent by regulating the expression, subcellular trafficking and modification of p53 in a manner that is, in part, dependent on the cell type. 19668880_The protein and gene expression of the M3 receptor in the prostatic carcinoma group were higher than that of benign prostatic hyperplasia group and normal prostate group. 19669628_Data show that exon-acquisition and alternative splicing events of CHRM3 genes were occurred through the continuous integration of transposable elements following conservation. 19751772_m3 receptor-expressing HeLa cells are a valuable system for studying IP(3) receptor ERAD, and suggest that the SPFH1/2 complex is a factor that selectively mediates the ERAD of activated IP(3) receptors. 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19927300_Muscarinic cholinoceptor activation by pilocarpine triggers apoptosis in human skin fibroblast cells. 19951374_The results showed that microbial products up regulate the expression of M3 receptor in nasal mucosal immune cells that further increases the production of OX40L in nasal DCs and drives the production of TNF-alpha in nasal mucosa. 20146726_Distribution of M3 receptors in human colon. 20332620_The results of co-immunoprecipitation of different scaffold and kinase proteins, provide experimental evidence for the role for the third cytoplasmic loop of the human M(3) muscarinic receptor in G-protein activation and multiprotein complex formation. 20395537_Use muscarinic antagonists to demonstrate that muscarinic M3 receptors mediate the excitatory effects of acetylcholine on small intestinal and colonic transit in humans. 20489201_the capacity of the human M(3) muscarinic acetylcholine receptor to exist as dimeric/oligomeric complexes at the surface of cells 20519144_M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype as being primarily responsible for these transcription factor responses after stimulation with carbachol through activation of the ERK1/2 pathway 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20613776_skin of patients with cholinergic urticaria CHRM3 lack of expression is divided into anhidrotic and wheal occuring hypohidrotic areas 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21118716_WNK4 kinase negatively regulates the anterograde trafficking of MR through kinase-independent mechanism. 21224444_Data show that the crosstalk between ORs and the M3-R suggests that the functional coupling of ORs and the M3-R is required for robust OR activation. 21245133_Complex regulation of the TRPM8 cold receptor channel: role of arachidonic acid release following M3 muscarinic receptor stimulation. 21450750_In contrast to other genes reported to be associated with primary SJogren syndrome, like STAT4 and IRF5, CHRM3 has not been reported to be associated with other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis. 21685385_Structural basis of M3 muscarinic receptor dimer/oligomer formation. 21798865_The data provide experimental evidence of the critical role that N-glycan chains play in determining muscarinic receptor distribution, localization, as well as 21873996_The M3R C terminus is sufficient, and a six-amino-acid polybasic sequence distal to helix 8 ((565)KKKRRK(570)) is necessary for preassembly with G(q). 21877253_Autoantibodies against the second extra-cellular loop of M3R could be involved in salivary dysfunction in patients with Sjogren's syndrome. 21940308_CHRM3 polymorphisms are likely associated with disease duration in IBS. CHRM3 polymorphisms could be associated with IBS. 22077972_Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3(1q41-q44) homozygous frameshift mutation in familial congenital bladder malformation associated with a prune-belly-like syndrome, defining an isolated gene defect underlying this sometimes devastating disease. 22137887_Incubation of hSMG cells with pSS IgG (1mg/ml) significantly decreased M3R expression levels at the membrane. 22178951_The Asn-7.49 is important for the interaction between M(3)R and ARF1 and also for the formation of the ARF/Rho/beta gamma signaling complex, a complex that might determine the rapid activation and desensitization of PLD.(muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3) 22192964_The results of the study suggest that the differential expression of the ADRB2 and CHRM3 genes in bronchial mucosa is associated with asthma and COPD clinical subtypes. 22410194_Data suggest that M3 muscarinic receptor and Kir6.1 colocalize to detrusor caveolae; studies include tissue from both male and female subjects. 22466417_Mutation of this region in the M3-MR altered receptor coupling to G protein. 22500107_The study reports the results of a combined computational and site mutagenesis study designed to provide new insights into the orthosteric binding site of the human M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. 22510450_The anti-M3RP205-220 antibody was detected in most patients with Sjogren syndrome. 22511543_Its cytoprotective effect was decreased by a M3R antagonist. 22564786_The Asn-514-Tyr point mutation produces constitutive activation of muscarinic M3-AChR by decreasing the rate of receptor deactivation, while having minimal effect on receptor activation. 22610841_Exposure to the cholinergic agonist carbachol induced a concentration-dependent increase in cell proliferation rate. This effect was mainly mediated by the receptor subtypes M3 and M2. 22691178_The acetylcholine M3 receptor was slightly decreased as compared to control in overactive bladder. 22893470_The expression of mAChR M3 is influenced by the extent of differentiation, distant metastasis and the site of cholangiocarcinoma. It also plays a key role in the proliferation and metastasis of cholangiocarcinoma. 22899762_CHRM3 and M(3) were suggested to play important roles in the pathogenesis of myopia and in the arrested progression of myopia by atropine. 22949513_Generalized epilepsies implicates susceptibility genes: CHRM3 at 1q43, VRK2 at 2p16.1, ZEB2 at 2q22.3, SCN1A at 2q24.3 and PNPO at 17q21.32. 23142559_Overall, the results of the present study suggest that TNF--alpha causes (1) the release of ACh from A549 cells, (2) the decrease in cholinesterase activity, and (3) the upregulation of M3R expression facilitating the autocrine effects of ACh on M3R. 23227858_Results suggest a major role of M(3) muscarinic receptors mediating the human gallbladder contraction through voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels and Rho kinase. 23382834_Our findings clearly indicate that binding of anti-M3R autoantibodies to the receptor, which was verified by immunoprecipitation, suppresses AQP5 trafficking to the membrane and contribute to impaired fluid secretion in SjS. 23521066_CHMR3 at the plasma membrane exists as stable dimeric complexes, a large fraction of which interact dynamically to form tetramers without the presence of trimers, pentamers or higher-order oligomers 23760269_Data indicate that carbachol (Cch) activates cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) through the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 (M3R). 23786223_M3-mediated contractions in the M2KO strain were decreased 54% by the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor chelerythrine. 23838802_Data indicate that high M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M3 receptor) expression correlates with poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, indicating that M3 receptor may be a novel antineoplastic target. 24334576_The presence of muscarinic M3 receptor (HM3) autoantibodies may be related to the underlying disease mechanism in idiopathic generalized anhidrosis patients. 24393526_M3R preserves the endothelial barrier function through a mechanism potentially maintaining PTP1B activity, keeping the adherens junction proteins (AJPs) dephosphorylation. 24419413_Overexpression of muscarinic receptor 3 promotes metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer. 24430298_CHRM2 but not CHRM1 or CHRM3 polymorphisms are associated with asthma susceptibility in Mexican patients. 24522860_HM3-mediated IL8 expression through PKC-NFkappaB signaling pathways 24596086_the M3 muscarinic receptor maximizes the efficiency of PLCbeta3 signaling beyond its canonical role as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Galpha. 24697698_The M3 receptor facilitates interaction of the VE-cadherin-based adherens junctional complex and the actin-based cytoskeleton by maintaining Rac1 activity, which regulates the interaction between IQGAP1/Rac1 and IQGAP1/beta-catenin. 24821386_changes in membrane cholesterol concentration differentially impact preferential and non-preferential M1 and M3 receptor signaling 25316767_Results uncovered that Gaq binding to GRK2 enhances the recruitment of GRK2 to M3-ACh receptors. 25375131_Cigarette smoking may contribute to this imbalance by affecting the polarization and survival of Th/Tregs through the up-regulation of MR3 and MR5. 25769304_an incorrect organizational structure of many mutants of hM3R provides the molecular basis for why they are poorly expressed and fail to be effectively trafficked to the cell surface. 25916507_Suggest Gbeta4gamma1 as a modulator of M3 muscarinic receptor signaling. 25964092_ACh-induced activation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway and subsequent IL-8 upregulation may be one of the important mechanisms of M3R function 26066647_M3 AChR or AMP-activated protein kinase Small Interfering RNA abrogated the ACh-elicited the attenuation of Endoplasmic reticulum stress in endothelial cells, indicating that the salutary effects of ACh were likely mediated by M3 AChR-AMPK signaling. 26071486_Blockading CHRM3 by shRNA or treatment with darifenacin inhibited prostate cancer growth. 26346168_our findings support an oncogenic role for the M3 receptor in gastric cancer 26692031_Report using biosensing techniques to monitor dynamic changes of inositol lipid pools in living cells reveals a PKC-dependent PtdIns4P increase upon EGF and M3 receptor activation. 26901532_results suggest that the autoantibodies against peptides of the second extracellular loop of M3R are not pathogenic in vivo and they are not suitable as biomarkers for pSS diagnosis 26956674_These findings indicate that M3 mAChR may be important therapeutic target for obstructive airway diseases, as it regulates the effects of the epithelial-derived chemokines on ASM cell migration, which results in lung remodeling. 26959877_The CHRM3 gene plays a role in abnormal thalamo-orbital frontal cortex functional connectivity in first-episode treatment-naive patients with schizophrenia. 27221048_This study presents the endocytic pathways of internalization for muscarinic type 3 receptor and flotillin-1/2 in salivary gland epithelial cells. knockdown of flot-1 or -2 by flotillin-specific siRNA prevented internalization and reduced the endocytic efficiency of muscarinic type 3 receptor. 27460476_this study shows that anti-M3R is significantly elevated in Sjogren's syndrome plasma in comparison with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and healthy controls 27803431_M3-mAChR activation leads to enhancement of hsp expression via PKC-dependent phosphorylation of HSF1, thereby stabilizing the mutant hERG-FLAG protein. Thus, M3-mAChR activators may have a therapeutic value for patients with LQT2. 27923235_There were no significant associations between CHRM3 SNPs and autonomic nervous system activity in patients with schizophrenia on high-dose antipsychotics. 28008134_Interacting post-muscarinic receptor signaling pathways potentiate MMP1 expression and invasion of human colon cancer cells. 28053981_To our knowledge, this is the first genetic association study that reveals the genetic contribution of CHRM3 gene in bladder cancer etiology. 28276525_Regulation of molecular clock oscillations and phagocytic activity via muscarinic Ca(2+) signaling in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. 28411124_Morphine-induced MOP receptor endocytosis is facilitated by concurrent M3 activation.M3 and MOP assemble in receptor heterocomplexes mainly located at the plasma membrane.M3-MOP receptor pharmacological interaction is independent of heterocomplex formation.M3 and MOP receptor heteromers disrupt upon both receptor endocytosis. 28412413_These results indicate that not H1 but M3 receptor-induced activation of p38 MAPK might contribute to the maintenance of epithelial barrier function through down-regulation of TNF-alpha signalling and activation of EGFR. 28416748_M3R expression plays an important role in early progression and invasion of colon neoplasia but is less important once tumors have spread. 29864421_M3R activation-induced GRK2 recruitment is Ggamma subtype dependent in which Gbetagamma dimers with low cell membrane-affinity Ggamma9 exhibited a two-fold higher GRK2-recruitment compared to high affinity Ggamma3 expressing cells. 29935595_The CHRM3 polymorphism and the Apfel score independently predict PONV susceptibility. Dexamethasone/acustimulation should be considered in patients with low Apfel score but at high genetic risk 29959237_Genetic M3R ablation in human cells results in improved remyelination and is mediated by acceleration of oligodendrocyte commitment from oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. 29959979_the M3 receptor is the dominant muscarinic receptor in the human adrenal cortex. 30483762_The findings of the present study suggest that miR30e inhibited the adhesion, migration, invasion and cell cycle entry of Prostate cancer (PCa) cells by suppressing the activation of the MAPK signaling pathway and inhibiting CHRM3 expression. Thus, miR30e may serve as a candidate target for the treatment of PCa. 31441039_A homozygous missense variant in CHRM3 associated with familial urinary bladder disease. 31445019_M3R has protective effects against hepatocyte lipid accumulation by activating AMPK pathway. 31584702_Muscarinic receptor M3 contributes to vascular and neural growth factor up-regulation in severe asthma. 31740666_A regulatory variant of CHRM3 is associated with cannabis-induced hallucinations in European Americans. 32205868_Muscarinic receptors promote castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer through a FAK-YAP signaling axis. 32614803_M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-reactive Th17 cells in primary Sjogren's syndrome. 34935917_Methylation-reprogrammed CHRM3 results in vascular dysfunction in the human umbilical vein following IVF-ETdagger. 35673819_Expression of M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in gastric cancer. 35967390_Impaired sweating in patients with cholinergic urticaria is linked to low expression of acetylcholine receptor CHRM3 and acetylcholine esterase in sweat glands. |
ENSMUSG00000046159 |
Chrm3 |
847.603300 |
0.3389185186 |
-1.560990 |
0.134015876 |
130.956080 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000253145681898196584728987912385937406034097319644370397961571483840271199464215480176565442604896816192194819450378417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000032718303544810697315933402759683349241063062054486345806381878484271326793853852665794335052851238287985324859619140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
441.3464228 |
39.6414543 |
1312.5858284 |
83.7409548 |
| ENSG00000133055 |
4608 |
MYBPH |
protein_coding |
Q13203 |
FUNCTION: Binds to myosin; probably involved in interaction with thick myofilaments in the A-band. |
Cell adhesion;Immunoglobulin domain;Muscle protein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Thick filament |
|
Predicted to be a structural constituent of muscle. Predicted to be involved in regulation of striated muscle contraction. Predicted to be located in myosin filament. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4608; |
myosin filament [GO:0032982]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; regulation of striated muscle contraction [GO:0006942] |
19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22085929_MYBPH inhibited assembly competence-conferring phosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chain (RLC) as well as activating phosphorylation of LIM domain kinase, unexpectedly through its direct physical interaction with Rho kinase 1 23068101_These results suggest that MYBPH inhibits RLC and NMHC IIA, independent components of NM IIA, and negatively regulates actomyosin organization at 2 distinct steps, resulting in firm inhibition of NM IIA assembly. 24184715_MyBP-H expression signals the onset of dysregulation in actin-myosin interaction; this in turn might contribute to the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 26969327_variation in MYBPH can modulate the severity of hypertrophy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients. |
ENSMUSG00000042451 |
Mybph |
261.456790 |
0.2646332086 |
-1.917934 |
0.121947897 |
252.058578 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000923970827186257014447573319526749684496760881322196341336193617485017853663084856086390864940320705527242781985870236881509743669954185977350943903552149549796013161540031433105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000223937757130856409566024008962101089843911739371041309991657654881423215084952175450710880482259237086050698914792659561096571232918130546322987850516028629499487578868865966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.6738403 |
8.9637620 |
409.9325120 |
21.6108586 |
| ENSG00000133059 |
25778 |
DSTYK |
protein_coding |
Q6XUX3 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a positive regulator of ERK phosphorylation downstream of fibroblast growth factor-receptor activation (PubMed:23862974, PubMed:28157540). Involved in the regulation of both caspase-dependent apoptosis and caspase-independent cell death (PubMed:15178406). In the skin, it plays a predominant role in suppressing caspase-dependent apoptosis in response to UV stress in a range of dermal cell types (PubMed:28157540). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15178406, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23862974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28157540}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Kinase;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
This gene encodes a dual serine/threonine and tyrosine protein kinase which is expressed in multiple tissues. It is thought to function as a regulator of cell death. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:25778; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004712]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045743]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674] |
17123648_Confocal imaging of transiently expressed human Dusty-GFP fusion proteins showed a cytoplasmic distribution. 23862974_We detected independent DSTYK mutations in 2.3% of patients with congenital abnormalities of the kidney or urinary tract, a finding that suggests that DSTYK is a major determinant of human urinary tract development, downstream of FGF signaling. 28157540_we identified a complex homozygous 4-kb deletion/20-bp insertion in DSTYK in all four affected family members with Autosomal-Recessive Complicated Spastic Paraparesis, SPG23 29238045_RIPK3 promotes adenovirus type 5 oncolytic activity. 35011659_DSTYK Enhances Chemoresistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. 36169652_DSTYK inhibition increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. |
ENSMUSG00000042046 |
Dstyk |
101.308725 |
0.3694256983 |
-1.436644 |
0.175986718 |
67.448422 |
0.00000000000000021627147546140653571625671351626076573485995592233815942861951953091192990541458129882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001603298331396464200312548317072627913592973306414202205871788464719429612159729003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.0772258 |
6.2027107 |
152.8547759 |
10.7560744 |
| ENSG00000133106 |
94240 |
EPSTI1 |
protein_coding |
Q96J88 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in M1 macrophage polarization and is required for the proper regulation of gene expression during M1 versus M2 macrophage differentiation (By similarity). Might play a role in RELA/p65 and STAT1 phosphorylation and nuclear localization upon activation of macrophages (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDI1}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has been shown to promote tumor invasion and metastasis in some invasive cancer cells when overexpressed. Expression of this gene has been shown to be upregulated by direct binding of the Kruppel like factor 8 protein to promoter sequences. The translated protein interacts with the amino terminal region of the valosin containing protein gene product, resulting in the nuclear translocation of the nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 gene product, and activation of target genes. Overexpression of this gene has been observed in some breast cancers and in some individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:94240; |
|
20133812_These observations implicate EPSTI1 as a hitherto unappreciated regulator of tumor cell properties. 24096480_A novel KLF8 to EPSTI1 to VCP to NF-kappaB signaling mechanism potentially critical for breast cancer invasion and metastasis. 30083277_circEPSTI1,a significantly upregulated circRNA, which is derived from the EPSTI1 (epithelial stromal interaction 1) gene locus, is an independent prognostic marker for triple-negative breast cancer patient survival. 30887698_Data show that showed that circular RNAs (circEPSTI1) and EPSTI1 (epithelial stromal interaction 1) could directly bind to miR-942. 31702512_circEPSTI1 Acts as a ceRNA to Regulate the Progression of Osteosarcoma. 32114510_Elevated EPSTI1 expression in primary Sjogren's syndrome B cells promoted TLR9 signalling activation and contributed to the abnormal B cell activation, which was promoted by facilitating p65 phosphorylation and activation of NF-kappaB signalling via promoting IkappaBalpha degradation. 32769326_Role of epithelial - Stromal interaction protein-1 expression in breast cancer. 32826876_The circEPSTI1/mir-942-5p/LTBP2 axis regulates the progression of OSCC in the background of OSF via EMT and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. 34738627_Contrasting functions of the epithelialstromal interaction 1 gene, in human oral and lung squamous cell cancers. 35527663_Knockdown of EPSTI1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury through regulation of NF-kappaB signaling in a cellular pneumonia model. 36330510_EPSTI1 as an immune biomarker predicts the prognosis of patients with stage III colon cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000022014 |
Epsti1 |
22.034420 |
3.4684975128 |
1.794311 |
0.333565045 |
29.648532 |
0.00000005179184374142240883408439986942961574811761238379403948783874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000209437702362573885804761263974838048085302943945862352848052978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.2509769 |
6.5841980 |
9.6508856 |
1.5285528 |
| ENSG00000133195 |
201266 |
SLC39A11 |
protein_coding |
Q8N1S5 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a cellular zinc transporter. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BWY7}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Ion transport;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
Predicted to enable zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in zinc ion transmembrane transport. Predicted to be located in Golgi apparatus; nucleus; and plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201266; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577] |
11707075_This paper describes the genomic region surrounding the SOX9 gene which includes SLC39A11 (C17orf26). 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 25900876_Polymorphisms within ZIP11 gene were significantly associated with bladder cancer risk. 25921144_In glioma tumors, low ZIP11 expression was significantly associated with higher grade. Higher ZIP11 expression was weakly correlated with IDH1 mutation status. 30122198_We found 8 different single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are significantly different between subjects without gastritis and those with gastritis... In conclusion, we found that zinc transporter gene ZIP11 is associated with chronic gastritis in the Korean population and it may interact with spicy food, which suggests ZIP11 as a therapeutic target for precision nutrition. 33631610_Increased expression of zinc transporter ZIP4, ZIP11, ZnT1, and ZnT6 predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000041654 |
Slc39a11 |
198.129273 |
2.0463912975 |
1.033082 |
0.127783941 |
65.586047 |
0.00000000000000055631237852184360485827263998878666575363888605054718539122404763475060462951660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004042920092064210569607421003353213487150838185285595116624790534842759370803833007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
261.5057402 |
23.1544834 |
128.6977821 |
8.7178503 |
| ENSG00000133246 |
84106 |
PRAM1 |
protein_coding |
Q96QH2 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in myeloid differentiation. May be involved in integrin signaling in neutrophils. Binds to PtdIns(4)P. |
Lipid-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is similar to FYN binding protein (FYB/SLAP-130), an adaptor protein involved in T cell receptor mediated signaling. This gene is expressed and regulated during normal myelopoiesis. The expression of this gene is induced by retinoic acid and is inhibited by the expression of PML-RARalpha, a fusion protein of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RARalpha). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:84106; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043313]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
15572693_PRAM-1 is required for optimal integrin-dependent neutrophil function. 15637062_Caspase 3-cleaved SH3 domain of HIP-55 is likely involved in PRAM-1-mediated JNK activation upon arsenic trioxide-induced differentiation of NB4 cells. 16502581_The use of reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction for the detection of the PML-RARA and RARA-PML fusion genes that allow for monitoring of acute myelocytic leukemia. 16502582_PML-RARalpha fusion transcripts have been shown to be useful markers for establishing the diagnosis and for monitoring the response to treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. 16831444_Interaction of PRAM-1 and hSH3 domains of adhesion and degranulation promoting adapter protein (ADAP) with phosphatidylcholine-containing liposomes is observed upon incorporation of phosphatidylserine or phosphoinositides into the membrane bilayer. 19109227_hidden abnormalities and novel disease-related genomic changes occur in t(15;17)translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia formation of PML-RARA gene 19623654_We conclude that our sp-RQ-PCR is specific enough to identify various forms of PML-RARalpha and yields no false-positive results. 21673516_autophagy contributes to the anti-apoptotic function of the PML-RARalpha protein through inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway 25126724_The MIR125B1-mediated blockade of PML-RARA proteolysis was regulated via an autophagy-lysosomal pathway, contributing to the inhibition of acute promyelocytic leukemia differentiation. 25815789_The 3-plex RT-qPCR assay is a specific, sensitive, stable, and cost-effective method that can be used for the rapid diagnosis and treatment monitoring of acute promyelocytic leukemia with PML-RARa 25944686_Our results show that the pretreatment PML-RARA molecular burden could therefore be used to improve risk stratification in order to develop more individualized treatment regimens for high-risk APL cases. 28317833_This study establishes PML as an important regulator of NF-kappaB and demonstrates that PML-RARalpha dysregulates NF-kappaB. 28431836_we diagnosed a spinal promyelocytic sarcoma as a manifestation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia with M3 morphology according to the French-American-British classification with t(15;17)(q22;q21) and PML-RARA fusion gene 34047481_NRF2 activation induced by PML-RARalpha promotes microRNA 125b-1 expression and confers resistance to chemotherapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 34448811_KDM5A suppresses PML-RARalpha target gene expression and APL differentiation through repressing H3K4me2. |
ENSMUSG00000032739 |
Pram1 |
311.441202 |
0.0967558303 |
-3.369508 |
0.161014899 |
455.492477 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004600620911057418678626604154680414386639916661310779011311071204356494288673427906576156086178779021033783906901262551977437776113382577523619510912569379896559961338927775134888044013442874518110044881109457770339012645669432154 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001997210724917867577670464385217854279260155285241377214112357138776895135291498108737880545343123660741430380314040100622313612313391212014733711579123129941789790577790245307517269554485406579775018167761709210265648136283777725 |
Yes |
No |
54.9223960 |
6.2539811 |
571.5291353 |
37.9584686 |
| ENSG00000133247 |
84787 |
KMT5C |
protein_coding |
Q86Y97 |
FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase that specifically methylates monomethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me1) and dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) of histone H4 to produce respectively dimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me2) and trimethylated 'Lys-20' (H4K20me3) and thus regulates transcription and maintenance of genome integrity (PubMed:24396869, PubMed:28114273). In vitro also methylates unmodified 'Lys-20' (H4K20me0) of histone H4 and nucleosomes (PubMed:24396869). H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression. Mainly functions in pericentric heterochromatin regions, thereby playing a central role in the establishment of constitutive heterochromatin in these regions. KMT5C is targeted to histone H3 via its interaction with RB1 family proteins (RB1, RBL1 and RBL2) (By similarity). Facilitates TP53BP1 foci formation upon DNA damage and proficient non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ)-directed DNA repair by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4 (PubMed:28114273). May play a role in class switch reconbination by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation of 'Lys-20' of histone H4 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6Q783, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24396869, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28114273}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Chromosome;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Zinc |
|
SUV420H2 and the related enzyme SUV420H1 (MIM 610881) function as histone methyltransferases that specifically trimethylate nucleosomal histone H4 (see MIM 602822) on lysine-20 (K20) (Schotta et al., 2004 [PubMed 15145825]).[supplied by OMIM, Dec 2009]. |
hsa:84787; |
condensed chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000779]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; pericentric heterochromatin [GO:0005721]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; histone H4K20 methyltransferase activity [GO:0042799]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding [GO:1904047]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; histone H4-K20 dimethylation [GO:0034772]; histone H4-K20 trimethylation [GO:0034773]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:2001034]; positive regulation of isotype switching [GO:0045830] |
16322686_The decrease in trimethylation of lysine 20 of histone H4 in breast cancer cells was accompanied by diminished expression of Suv4-20h2 histone methyltransferase. 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 5 18296440_The data indicate that Suv4-20 generates nearly ubiquitous dimethylation that facilitates the DNA damage response and selective trimethylation that is involved in heterochromatin formation.[Suv4-20] 21206904_SUV420H1 and SUV420H2 isoforms have different in their cellular localization and effects on myogenic differentiation 21321083_data indicate that H4K20me3 invokes gene repression by antagonizing hMOF-mediated H4K16Ac 24396869_The crystal structure of SUV420H2 was used to characterize substrate selectivity and product specificity. 25814362_One of the most downregulated genes in response to SUV420H2 expression was the Src substrate, tensin-3, a focal adhesion protein that contributes to cancer cell migration. 26904956_Upregulation of long non-coding RNA PAPAS in response to hypoosmotic stress does not increase H4K20me3 because of Nedd4-dependent ubiquitinylation and proteasomal degradation of Suv4-20h2. 27105552_The sequences surrounding both methylation sites do not fit to the specificity profile of SUV4-20H1. 27862226_Study provides evidence that Suv420h2 controls the H4K20 methylome of osteoblasts and is critical for normal progression of osteoblastogenesis. 28778956_Altogether, these results reveal Suv4-20h-mediated histone H4K20 tri-methylation as a critical determinant in the selection of active replication initiation sites in heterochromatin regions of mammalian genomes. 29229751_The analysis of human pancreatic cancer biopsies was concordant with these findings, because high levels of SUV420H2 correlated with a loss of epithelial characteristics in progressively invasive cancer. Together, these data indicate that SUV420H2 is an upstream epigenetic regulator of epithelial/mesenchymal state control. 33144397_H4K20me3 methyltransferase SUV420H2 shapes the chromatin landscape of pluripotent embryonic stem cells. 35404406_Loss of KMT5C Promotes EGFR Inhibitor Resistance in NSCLC via LINC01510-Mediated Upregulation of MET. |
ENSMUSG00000059851 |
Kmt5c |
73.642650 |
0.3511849013 |
-1.509697 |
0.197951451 |
59.164655 |
0.00000000000001450152931357764090828756579738959114200943720240921663844346767291426658630371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000096328790579840667277766998872366442413679721301633662733365781605243682861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.6398187 |
5.5544237 |
105.0454282 |
10.6375686 |
| ENSG00000133315 |
28992 |
MACROD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQ69 |
FUNCTION: Removes ADP-ribose from aspartate and glutamate residues in proteins bearing a single ADP-ribose moiety (PubMed:23474714, PubMed:23474712). Inactive towards proteins bearing poly-ADP-ribose (PubMed:23474714, PubMed:23474712). Deacetylates O-acetyl-ADP ribose, a signaling molecule generated by the deacetylation of acetylated lysine residues in histones and other proteins (PubMed:21257746). Plays a role in estrogen signaling (PubMed:17893710, PubMed:17914104, PubMed:19403568). Binds to androgen receptor (AR) and amplifies the transactivation function of AR in response to androgen (PubMed:19022849). May play an important role in carcinogenesis and/or progression of hormone-dependent cancers by feed-forward mechanism that activates ESR1 transactivation (PubMed:17893710, PubMed:17914104). Could be an ESR1 coactivator, providing a positive feedback regulatory loop for ESR1 signal transduction (PubMed:17914104). Could be involved in invasive growth by down-regulating CDH1 in endometrial cancer cells (PubMed:17893710). Enhances ESR1-mediated transcription activity (PubMed:17914104). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17893710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17914104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19022849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19403568, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21257746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23474712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23474714}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA damage;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables ADP-ribosylglutamate hydrolase activity and deacetylase activity. Involved in cellular response to DNA damage stimulus; peptidyl-glutamate ADP-deribosylation; and purine nucleoside metabolic process. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:28992; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ADP-ribosylglutamate hydrolase activity [GO:0140293]; deacetylase activity [GO:0019213]; hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds [GO:0016798]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; peptidyl-glutamate ADP-deribosylation [GO:0140291]; protein de-ADP-ribosylation [GO:0051725]; purine nucleoside metabolic process [GO:0042278] |
15691879_ERalpha and Sp1 play a role in activation of the promoter 16831279_LRP16 overexpression is closely correlated to the positive rates of estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor, Ki-67 level, tumor diameter, and axillary lymph node metastasis of breast cancer. 17532767_identified a novel RUNX1 fusion partner, LRP16 on 11q13 involving t(11;21)(q13;q22) 17914104_A role for estrogenically regulated LRP16 as an ERalpha coactivator, providing a positive feedback regulatory loop for ERalpha signal transduction. 19022849_the single macro domain in LRP16 can serve as the androgen receptor coactivator 19403568_The unliganded ERalpha upregulated LRP16 expression and enhanced LRP16 promoter activity in SKOV3 cells; however, this induction was blocked by estrogen stimulation. 19698216_lrp16 is a leukemic oncogene and closely relates to genesis and progression of leukemia. 19824120_LRP16 may have a role in invasion, metastasis and prognosis of gastric cancer 19840441_LRP16 gene overexpression shows a promotive effect on proliferation of K562 cells. 19958623_LRP16 may play an important role in leukemia progression by promoting cell proliferation, regulating cell cycle, and antagonizing radiation-induced DNA damage. 20035625_K18 attenuates estrogen receptor alpha-mediated signaling by sequestering LRP16 in cytoplasm. 20355243_LRP16 expression is related to the degree of differentiation, invasiveness, metastasis and prognosis of colorectal carcinoma. 21483817_Findings not only indicate that LRP16 is a crucial regulator for NF-kappaB activation inside the nucleus, but also suggest that LRP16 may be an important contributor to the aberrant activation of NF-kappaB in tumors. 25735744_LRP16, through its constitutive interactions with PARP1 and IKKgamma, functions to facilitate the lesion-specific recruitment of PARP1 and IKKgamma and, ultimately, the concomitant recruitment of PIASy to IKKgamma in response to DNA damage. 26261536_The results indicate that abnormal LRP16 expression is noted in neuroendocrine lung tumors and the expression can give insight into the pathogenesis of the disease. 28820388_Here, the authors report that LRP16 selectively interacts and activates double-stranded RNA-dependent kinase (PKR), and also acts as scaffolds to assist the formation of a ternary complex of PKR and IKKbeta, prolonging the polymers of ADP-ribose (PAR)-dependent nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) transactivation caused by DNA-damaging agents and confers acquired chemoresistance. 29748698_We demonstrated that LRP16 positively regulates the Wnt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which elucidates an important mechanism of HCC cell growth, metastasis, and prognosis. 30562745_These findings revealed the functions of LRP16 in promoting the inflammatory response through activating the Rac1-MAPK1/ERK pathway in human adipocytes. 32427867_Comparative analysis of MACROD1, MACROD2 and TARG1 expression, localisation and interactome. 32683309_Molecular basis for the MacroD1-mediated hydrolysis of ADP-ribosylation. |
ENSMUSG00000036278 |
Macrod1 |
16.868511 |
0.2052658067 |
-2.284435 |
0.565022317 |
14.948302 |
0.00011049747594194198139355700405417337606195360422134399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000302362392455147132013654198701146924577187746763229370117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
5.6842042 |
3.4754756 |
30.0024551 |
12.5620573 |
| ENSG00000133317 |
85329 |
LGALS12 |
protein_coding |
Q96DT0 |
FUNCTION: Binds lactose. May participate in the apoptosis of adipocytes. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Lectin;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the galectin superfamily, a group of beta-galactoside-binding proteins with conserved carbohydrate recognition domains. The related mouse protein is a primary regulator of the early stages of adipose tissue development. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:85329; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; lactose binding [GO:0030395]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; lymphatic endothelial cell migration [GO:1904977]; regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045598]; regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050994] |
15131127_results suggest that mouse galectin-12 is a major regulator of adipose tissue development 25953264_Lower LGALS12 gene expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 27256573_Overexpression of galectin-12 contributes to a differentiation block in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells, and suppression of galectin-12 facilitates granulocytic differentiation. 29098769_Galectin-12 is silenced in colorectal cancer via hypermethylation of its promoter. 30935948_that binding of galectin-12 to SLC1A5 significantly reduced glutamine uptake 32752134_Ablation of Galectin-12 Inhibits Atherosclerosis through Enhancement of M2 Macrophage Polarization. 34860822_Galectin-12 in Pancreatic Cancer: A New Player in the Microenvironment? |
ENSMUSG00000024972 |
Lgals12 |
64.943458 |
10.7066732408 |
3.420438 |
0.332412256 |
110.979818 |
0.00000000000000000000000005977615661967935480581578630752947264465717569410077713432352210703784808898397784560074796900153160095214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000660895933862522302755637543939624471485703111708081770123683736041422104312559326899645384401082992553710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
117.0663507 |
21.3092392 |
10.9518768 |
1.8063361 |
| ENSG00000133460 |
66035 |
SLC2A11 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYW1 |
FUNCTION: Facilitative glucose transporter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12175779}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene belongs to a family of proteins that mediate the transport of sugars across the cell membrane. The encoded protein transports glucose and fructose. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:66035; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; fructose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005353]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; hexose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015149]; sugar transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0051119]; fructose transmembrane transport [GO:0015755]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659]; hexose transmembrane transport [GO:0008645]; monosaccharide transmembrane transport [GO:0015749] |
12175779_a novel sugar transporter that is alternatively spliced in various tissues 16154905_Different promoters and splicing generate three SLC2A11 isoforms which are expressed in a tissue specific manner but do not appear to differ in their functional characteristics. 17710649_GLUT11 can also transport fructose, but it has the motif DSV at the same position, which appears to function in the same manner as NXI and when all three residues are replaced with NAV fructose transport lost. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22452979_Critical roles for novel GLUT family members highlight a therapeutic strategy entailing selective GLUT inhibition to specifically target aberrant glucose metabolism in cancer. |
|
|
42.533746 |
0.4529511062 |
-1.142573 |
0.430836861 |
6.600212 |
0.01019666012649456457439534062814345816150307655334472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019502747630822828833752069499496428761631250381469726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.0352959 |
9.0171522 |
58.3488692 |
13.9981537 |
| ENSG00000133466 |
114904 |
C1QTNF6 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXI9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Collagen;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be located in extracellular space. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114904; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802] |
19073967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20410501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21508531_C1qTNF6 is overexpressed and possibly contributes to tumor angiogenesis by activating the Akt pathway in many hepatocellular carcinomas. 25962701_AMPK and Akt activation are responsible for the CTRP6-mediated anti-fibrotic effect by targeting RhoA/MRTF-A pathway 26404464_CTRP6 is expressed in human synoviocytes, and CTRP6 levels are increased in RA patients. 26648301_CTRP6 inhibits the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells via blocking IL-8/VEGF pathway. 27155158_CTRP6 expression was decreased in scar tissues and TGF-beta1-treated dermal fibroblasts. CTRP6 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced the proliferation of dermal fibroblasts. 28665696_We found both the rs229527 allele within C1QTNF6 (odds ratio [OR] = 1.23, confidence interval [95% CI]: 1.12-1.33, pAllelic = 4.60 . 10-6) and the rs2284038 allele within RAC2 (OR = 1.10, 95% CI: 1.01-0.19, pAllelic = 3.00 . 10-2) showed significant associations with Graves' Disease susceptibility. 28726640_The results establish CTRP6 as a novel metabolic/immune regulator linking obesity to adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. 30083983_CTRP6 may be a metabolism- and nutrition-related adipokine and may be related to insulin resistance and T2 Diabetes mellitus. 30431096_C1QTNF6 is involved in promoting the proliferation and migration, and in reducing the apoptosis of gastric carcinoma cells. 31111552_Inhibition of CTRP6 prevented survival and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma through inactivating the AKT signaling pathway. 31292940_aberrant C1QTNF6 expression was implicated in terrible prognosis accompanying with the damage of relevant cell potential in lung adenocarcinoma. 32041782_C1q/TNF-Related Protein 6 Is a Pattern Recognition Molecule That Recruits Collectin-11 from the Complement System to Ligands. 32077518_Knockdown of CTRP6 inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress, inflammation and extracellular matrix accumulation in mesangial cells through regulating the Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. 32170998_Circulating levels of C1q/TNF-alpha-related protein 6 (CTRP6) in polycystic ovary syndrome. 32282241_C1QTNF6 as a Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma 33123583_C1QTNF6 Overexpression Acts as a Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Bladder Cancer Patients. 33245899_Role of the CTRP6/AMPK pathway in kidney fibrosis through the promotion of fatty acid oxidation. 33269376_C1QTNF6 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo. 34469206_Adipocyte factor CTRP6 inhibits homocysteine-induced proliferation, migration, and dedifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells through PPARgamma/NLRP3. 34632797_CTRP6 rapidly responds to acute nutritional changes, regulating adipose tissue expansion and inflammation in mice. 34964705_C1q/tumor necrosis factor related protein 6 (CTRP6) regulates the phenotypes of high glucose-induced gestational trophoblast cells via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) signaling. 35397057_Potential participation of CTRP6, a complement regulator, in the pathology of age related macular degeneration. |
ENSMUSG00000022440 |
C1qtnf6 |
61.265907 |
0.1118129134 |
-3.160841 |
0.465370616 |
40.313993 |
0.00000000021625450148485221013041311655111798017969704233109951019287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001092373867870095221384638180402680551761562810497707687318325042724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8987005 |
4.5042978 |
112.2393591 |
26.0073640 |
| ENSG00000133561 |
474344 |
GIMAP6 |
protein_coding |
Q6P9H5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the GTPases of immunity-associated proteins (GIMAP) family. GIMAP proteins contain GTP-binding and coiled-coil motifs, and may play roles in the regulation of cell survival. Decreased expression of this gene may play a role in non-small cell lung cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene, which is found in a cluster with seven additional GIMAP genes on the long arm of chromosome 7. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:474344; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTP binding [GO:0005525] |
20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27667392_These data,demonstrating the downregulation of the mRNA and protein expression levels of GIMAP5 and GIMAP6 in the tumor tissues and blood of patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) , suggested the involvement of GIMAP5 and GIMAP6 in the pathogenesis of HCC, and indicate their possible use as diagnostic markers for HCC. 28381553_GIMAP6 plays a role in modulating immune function and that it does this by controlling cell death and the activation of T cells. 33328581_A human case of GIMAP6 deficiency: a novel primary immune deficiency. 35551368_GIMAP6 regulates autophagy, immune competence, and inflammation in mice and humans. |
ENSMUSG00000047867 |
Gimap6 |
303.156934 |
0.4590480672 |
-1.123283 |
0.107234613 |
110.295638 |
0.00000000000000000000000008441415697821410922136175847943103633122868303688184785777310943785060187716240420741087291389703750610351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000929122264726651877555789770410492083606347377118899230666152643963104362789806600630981847643852233886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
194.0885589 |
13.9426734 |
425.6413875 |
20.5606732 |
| ENSG00000133574 |
55303 |
GIMAP4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NUV9 |
FUNCTION: During thymocyte development, may play a role in the regulation of apoptosis (By similarity). GTPase which exhibits a higher affinity for GDP than for GTP. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99JY3}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein belonging to the GTP-binding superfamily and to the immuno-associated nucleotide (IAN) subfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins. The encoded protein of this gene may be negatively regulated by T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia 1 (TAL1). In humans, the IAN subfamily genes are located in a cluster at 7q36.1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55303; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; GTP binding [GO:0005525] |
11964296_molecular and genetic properties; expression in resting T- and B-cells and decreased expression during lymphocyte activation 18701445_GIMAP1 and GIMAP4 genes are up-regulated by IL-12 and other Th1 differentiation-inducing cytokines in cells induced to differentiate toward Th1 lineage and down-regulated by IL-4 in cells induced to Th2. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23041938_Genome-wide association study identifies GIMAP as a novel susceptibility locus for Behcet's disease 25287446_GIMAP4 regulates secretion of cytokines in early differentiating human CD4(+) T helper lymphocytes and in particular the secretion of interferon-gamma also affecting its downstream targets. 36246963_Prognostic Value of GIMAP4 and Its Role in Promoting Immune Cell Infiltration into Tumor Microenvironment of Lung Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000054435 |
Gimap4 |
59.059619 |
0.3120124073 |
-1.680325 |
0.216821548 |
62.630498 |
0.00000000000000249361938238500714692020902862297167453133452455493745958392537431791424751281738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000017414741782124497007176974062607720318313249407982112870740820653736591339111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.7131697 |
4.1540739 |
92.3831488 |
8.1312782 |
| ENSG00000133612 |
116988 |
AGAP3 |
protein_coding |
Q96P47 |
FUNCTION: GTPase-activating protein for the ADP ribosylation factor family (Potential). GTPase which may be involved in the degradation of expanded polyglutamine proteins through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16461359, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;GTPase activation;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes an essential component of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor signaling complex which mediates long-term potentiation in synapses by linking activation of NMDA receptor to alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor trafficking. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal GTPase-like domain, a pleckstrin homology domain, an ArfGAP domain and several C-terminal ankryn repeat domains. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2017]. |
hsa:116988; |
cell periphery [GO:0071944]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding [GO:0031593]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161] |
14506264_M-RIP can assemble a complex containing both RhoA and Myosin phosphatase myosin binding subunit, suggesting that M-RIP may play a role in myosin phosphatase regulation by RhoA 23904596_AGAP3 is an essential signaling component of the NMDA receptor complex that links NMDA receptor activation to AMPA receptor trafficking. 30591445_AGAP3 expression was significantly increased in colorectal cancer (CRC)and colorectal adenoma compared to normal tissue. CRAG overexpression up-regulated c-Jun expression, and significantly increased cell proliferation and colony formation capability. AGAP3 expression did not have a concordant association with patient prognosis among datasets 34398495_Gastrointestinal stromal tumors with BRAF gene fusions. A report of two cases showing low or absent KIT expression resulting in diagnostic pitfalls. |
ENSMUSG00000023353 |
Agap3 |
867.823426 |
2.0918404183 |
1.064773 |
0.059135324 |
325.986628 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000071931818706411990969530566330043560811670402371607307016563295526562678846920630174097977610355393847319298357362668118775928658178551433425878017736618708181726933391058364158704083179962651684036245569586753845214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022165211776756596776708780441945117321478906742914732248747759735202278533449242510433717698228339562486471658428869294866989394415918780081826531048768506437115085538136830239225316674378518655430525541305541992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1162.0381501 |
45.5105319 |
559.0626924 |
16.9403687 |
| ENSG00000133627 |
57180 |
ACTR3B |
protein_coding |
Q9P1U1 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. May function as ATP-binding component of the Arp2/3 complex which is involved in regulation of actin polymerization and together with an activating nucleation-promoting factor (NPF) mediates the formation of branched actin networks. May decrease the metastatic potential of tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14651955}. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the actin-related proteins (ARP), which form multiprotein complexes and share 35-55% amino acid identity with conventional actin. The protein encoded by this gene may have a regulatory role in the actin cytoskeleton and induce cell-shape change and motility. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on chromosomes 2, 4, 10, 16, 22 and Y. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants and protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:57180; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ATP binding [GO:0005524] |
14651955_Thus, overexpression of Arp11 may suppress tumorigenicity in nude mice. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000056367 |
Actr3b |
34.036407 |
2.1083299589 |
1.076101 |
0.349934447 |
9.254926 |
0.00234862763740853984495426942658014013431966304779052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005118225886335456102649299481299749459140002727508544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.1123940 |
11.6263460 |
24.4486987 |
4.0684645 |
| ENSG00000133636 |
4922 |
NTS |
protein_coding |
P30990 |
FUNCTION: Neurotensin may play an endocrine or paracrine role in the regulation of fat metabolism. It causes contraction of smooth muscle. |
3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Vasoactive |
|
This gene encodes a common precursor for two peptides, neuromedin N and neurotensin. Neurotensin is a secreted tridecapeptide, which is widely distributed throughout the central nervous system, and may function as a neurotransmitter or a neuromodulator. It may be involved in dopamine-associated pathophysiological events, in the maintenance of gut structure and function, and in the regulation of fat metabolism. Neurotensin also exhibits antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi. Tissue-specific processing may lead to the formation in some tissues of larger forms of neuromedin N and neurotensin. The large forms may represent more stable peptides that are also biologically active. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:4922; |
axon terminus [GO:0043679]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; neuropeptide hormone activity [GO:0005184]; neuropeptide receptor binding [GO:0071855]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11906607_topography of its binding site to NT 1 receptor 11912133_Neurotensin induces protein kinase C-dependent protein kinase D activation and DNA synthesis in human pancreatic carcinoma cell line PANC-1. 12074933_The antimicrobial peptide neurotensin has activity against invasive microbes. 12150975_role in counteracting apoptosis in breast cancer cells 12531461_Neurotensin expressing neurons develop earlier than vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, vasopressin, and neuropeptide Y expressing neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. (neurotensin) 14699144_neurotensin has a role in chronic mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and cancer progression 14743366_Analysis of the NTS genomic sequence revealed 2 intronic polymorphisms and 1 variant located in the 5' untranslated region (UTR). None of the observed variants co-segregated with RLS and no disease-associated polymorphisms were detected 15123666_neurotensin secretion is mediated by protein kinase C-alpha/-delta and Rho/Rho kinase, and protein kinase D 15358593_Transcription of NT in the mitochrondria of BON cells in response to pharmacologic manipulation. 15623535_MARCKS-mediated neurotensin release occurs via protein kinase C-delta downstream of the Rho/ROK pathway 16087676_Ca2+ mobilization elicited by R-NT is via NTR1 16519961_Proneurotensin 1-117 is a stable neurotensin precursor fragment identified in human circulation 16984735_NT uses PKC-dependent pathways to modulate GSK-3, which may play a role in the NT regulation of intestinal cell growth 17068197_Rap1 mediates cyclic AMP-stimulated neurotensin secretion downstream of both Epac and protein kinase A signaling pathways 17289170_NTS-induced growth signaling in a prostatic neoplasm cell line is sensitive to metabolic stress. 17570131_Neurotensin induces a striking increase in Hsp27 phosphorylation on Ser-82 in PANC-1 cells through convergent p38 MAPK, PKD, and PKD2 signaling. 17644423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17644423_The purpose of the current study is to further explore the NTS gene for potential functional variant(s) in its entire genomic and potential regulatory regions and their possible association with RLS symptoms. 17870207_study suggests two pathways of NTS1 overexpression during IBD-related oncogenesis: one triggered by NT overexpression, and a second associated with an activation of the APC/beta-catenin pathway 18048355_endogenous PKD1, PKD2, and Kidins220 co-exist with neurotensin-containing vesicles 18624930_NT autocrine and/or paracrine stimulation mediated by NTR3 may be a mechanism associated with the tumourigenesis of functioning adenomas. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19393580_Neurotensin signaling induces intracellular alkalinization and interleukin-8 expression in human pancreatic cancer cells. 19878995_The aim of this study was to provide an up-to-date review of the literature concerning the regulatory role of NT on the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary axons--REVIEW 19932148_The expression of NTS is identified as a prognostic marker in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. 20138826_neurotensin /NTR1 signaling in pancreatic cancer cells seems to promote the induction of a metastatic phenotype, in contrast to its varying effects on tumor cell proliferation. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20731814_Neurotensin is increased in serum of young children with autistic disorder. 20810387_Data show that neurotensin- and NTSR1-positive mmunohistochemistry staining in 60.4% and 59.7% of lung adenocarcinomas, respectively. 20858966_Expression of neurotensin and ghrelin systems are markedly altered in the temporal lobe of Alzheimer's disease patients, which may contribute to the severe cognitive deficit observed in this pathology. 21030593_key regulatory elements in the promoter region that are involved in human NT/N (hNT/N) gene expression 21212273_IGF-1R activation represents a previously unrecognized key pathway involved in the mechanisms by which NT and NTR1 modulate colonic inflammation and inflammatory bowel disease. 21233215_NT acutely regulates D2 autoreceptor function and DA neuron excitability through PKC-mediated phosphorylation of the D2R, leading to heterologous receptor desensitization. 21272935_Results indicate that the counteraction of neurotensin and neurotensin receptor subtype-1 regulates the genesis and development of pancreatic carcinomas. 21508335_study found that inhibition of mTORC1 signaling by rapamycin, torin1, and shRNA-mediated knockdown enhances NT secretion by increasing NT gene expression in the endocrine cell line BON 21542591_Human, pig, and frog NT and [Gln(4)]NT and [D-Tyr(11)]NT adsorbed to the silver surface via the tyrosine ring, the oxygen atom of the deprotonated phenol group of Tyr(11), and the -CH(2)- unit(s), most probably of Tyr(11), Arg(9), and/or Leu(13). 21623207_determined the status of ERalpha and ERbeta in the myometrium and leiomyomas, atypical leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas, concomitantly with the expression of NTS/NTS receptor 1 in these tumors 21806946_Neurotensin signaling activates microRNAs-21 and -155 and Akt, promotes tumor growth in mice, and is increased in human colon tumors. 21994122_CD133(+) liver tumor-initiating cells promote tumor angiogenesis, growth, and self-renewal through neurotensin/interleukin-8/CXCL1 signaling. 22416137_Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1) degrades NT in acidic conditions, and its activity is crucial for NTR1 recycling. 22700584_Neurotensin secretion is regulated by PI3 kinase p110 alpha and protein kinase B signaling pathways. 22825476_Proneurotensin expression in the tumor tissues indicated that this precursor was produced by small cell lung carcinoma tumors and secreted into plasma as the tumors grew. 22849656_Results showed that NT, NPY, and PGP 9.5 neurofibers are almost equally present in pseudocapsule of uterine fibroids as in normal myometrium of a no pregnant uterus. As all of these neuropeptides are present in the uterine muscle and can affect muscle contractility, uterine peristalsis and muscular healing. 23064014_a lineage of mature enteroendocrine cells have the ability to coexpress members of a group of functionally related peptides: CCK, secretin, GIP, GLP-1, PYY, and neurotensin 23109725_NTSR2 was overexpressed, NTSR1 decreased, and neurotensin was not expressed in B cell leukemia patient's B-cells, as compared with healthy B cells. 23140271_Results show that both the neurotensin (NT) and the neurotensin 1 receptor hNTS1(321-344)fragment present a 3D structure in complex. 23418512_Data indicate synchronous increase of neurotensin (NTS) and IL-8 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) correlated with worse prognosis and shorten survival after surgery. 23436714_Nanoparticles exposing neurotensin tumor-specific drivers. 23962427_Neurotensin-mediated calcium signaling appears more sensitive to differentiation than ATP-mediated Ca(2+) signaling 24000330_These findings provide new insights into the potential therapeutic role of NT in chronic wounds, such as in DFU, characterized by a deficit in the migratory properties of cells and a chronic proinflammatory status. 24198343_NT production by keratinocytes may exert a paracrine effect on other skin cells, namely fibroblasts, macrophages, and dendritic cells for correct wound healing. 25098665_indicate that neurotensin is a direct target of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and may be a mediator for neuroendocrine tumor cell growth 25200966_NTS/IL-8/CXCR1/STAT3 signaling is crucial for the maintenance of stem-like traits in glioblastoma stem cells . 25249538_NTS/NTSR1 complex enhances breast tumor aggressiveness via EGFR/HER2/HER3 pathway. 25249545_Neurotensin and its receptor NTSR1 causes EGFR, HER2 and HER3 over-expression and their autocrine/paracrine activation in lung adenocarcinomas, confirming responsiveness to erlotinib. 25724188_pretreatment of gastric cancer cells with NTR1 inhibitor SR48692 was shown to significantly inhibit the NT-mediated MMP-9 activity, cell invasion, and migration 25847417_Although no measures for pain threshold, thermal instability or gastric motility were performed in our study participants, higher plasma NT levels were found in PWS children 27193687_findings directly link NT with increased fat absorption and obesity and suggest that NT may provide a prognostic marker of future obesity and a potential target for prevention and treatment 27312221_Higher concentrations of proneurotensin are associated with a greater risk of incident cardiovascular events in the community. This association did not vary according to sex, baseline low-density lipoprotein, or sortilin receptor 1 genotype. 27611941_NTS may be an important stimulus to promote hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. 27612962_children with untreated coeliac disease have elevated peripheral pro-NT levels compared with disease controls. Pro-NT levels also seem to reflect more severe forms of active coeliac disease, indicating a potential role of NT in small intestinal inflammation. 27666481_sortilin is a PIP3 binding protein with binding likely to occur at the C-terminal neurotensin binding site, and is a competitor of neurotensin 28560510_Neurotensin plasma values differentiate healthy people from patients suffering from colonic pathologies such as adenomatous polyps and adenocarcinoma. 29417469_Higher pro-neurotensin levels are associated with circulating leptin, independent of diabetes, obesity and metabolic syndrome. 29546332_In the elderly population, proneurotensin independently predicts development of cardiovascular diseases in both genders, whereas it only predicts diabetes in women. 29590379_Increased plasma pro-NT levels identify the presence/severity of NAFLD; in dysmetabolic individuals, NT may specifically promote hepatic fat accumulation through mechanisms likely related to increased insulin resistance. 29795470_Studied levels of neurotensin in obese patients before and after metabolic surgery. Results show proneurotensin positively correlates with insulin sensitivity after weight loss induced by metabolic surgery, and found biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch leads to a stronger increase in the proneurotensin compared to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. 30213686_The authors demonstrate that neuromedin N and neurotensin induce a unique dephosphorylation signaling in the MEK/ERK pathway that is regulated by endocytosis. 30359740_High NTS expression is associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis. 30527352_Circulating Pro-NT is not independently associated with gestational diabetes, but is with HOMA-IR, creatinine, and free fatty acids even after adjustment for pregnancy status. 30770901_A novel role of NTS in the development of Castration-resistant prostate cancer with Neuroendocrine differentiation (NED), and a possible strategy to prevent the onset of NED by targeting the NTS signaling pathway. 30991633_Real-time RT-PCR revealed that Intermittent Hypoxia significantly increased the mRNA levels of peptide YY (PYY), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and neurotensin (NTS) in Caco-2 cells. 31093954_Neurotensin has the potential to be a non-invasive biomarker for colorectal neoplasia 31541684_Patients with gastric cancers presented with lower plasma concentrations of CCK than healthy controls and individuals from colorectal cancers (p = 0.02). The highest plasma concentrations of neurotensin was found in colorectal cancer patients in comparison to gastric (p = 0.02). 31926821_Identification of U-shaped curve relation between proneurotensin and risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with premature CAD. 32121246_Upregulation of Thr/Tyr kinase Increases the Cancer Progression by Neurotensin and Dihydropyrimidinase-Like 3 in Lung Cancer. 32336282_The role of Neurotensin and its receptors in non-gastrointestinal cancers: a review. 32663609_Neurotensin up-regulation is associated with advanced fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with MAFLD. 32764278_Characterisation of the Expression of Neurotensin and Its Receptors in Human Colorectal Cancer and Its Clinical Implications. 33089749_Pro-neurotensin/neuromedin N and risk of ischemic stroke: The REasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) study. 33196849_Generation of onco-enhancer enhances chromosomal remodeling and accelerates tumorigenesis. 33493519_Suppression of the NTS-CPS1 regulatory axis by AFF1 in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 33549442_Circulating pro-neurotensin levels predict bodyweight gain and metabolic alterations in children. 33599716_The Role of Central Neurotensin in Regulating Feeding and Body Weight. 33682882_Neurotensin: a neuropeptide induced by hCG in the human and rat ovary during the periovulatory perioddagger. 34013344_Pro-Neurotensin/Neuromedin N and Risk of Incident Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus in the REGARDS Cohort. 34596798_Expression of neurotensin receptor-1 (NTS1) in primary breast tumors, cellular distribution, and association with clinical and biological factors. 35611414_Elevated neurotensin levels among obese adolescents may be related to emotion dysregulation and impulsivity: a cross-sectional, case-control study. |
ENSMUSG00000019890 |
Nts |
5.916683 |
0.0731068638 |
-3.773849 |
0.951120445 |
24.347441 |
0.00000080433509869328897020019156216541489357041427865624427795410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002873877041082775622341362667389041973819985287263989448547363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
0.8349861 |
0.5916743 |
11.5821936 |
2.9268672 |
| ENSG00000133657 |
79572 |
ATP13A3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H7F0 |
FUNCTION: ATP-driven pump involved in endocytosis-dependent polyamine transport. Uses ATP as an energy source to transfer polyamine precursor putrescine from the endosomal compartment to the cytosol. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27429841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33310703}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Endosome;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
ATP13A3 is a member of the P-type ATPase family of proteins that transport a variety of cations across membranes. Other P-type ATPases include ATP7B (MIM 606882) and ATP7A (MIM 300011).[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:79572; |
early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; membrane [GO:0016020]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; ABC-type polyamine transporter activity [GO:0015417]; ABC-type putrescine transporter activity [GO:0015594]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019829]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; P-type transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0140358]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; polyamine transmembrane transport [GO:1902047]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 29650961_Case-control analyses reveal significant overrepresentation of rare variants in ATP13A3, AQP1 and SOX17, and provide independent validation of a critical role for GDF2 in heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension. 30679663_In addition to EIF2AK4, which has been already suggested to be associated with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease, we identified the novel candidate genes ATP13A3, CD248, EFCAB4B, involved in lung vascular remodeling that represent reliable drivers contributing to the disease according to their biological functions/inheritance patterns 33091845_Pairing a prognostic target with potential therapeutic strategy for head and neck cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000022533 |
Atp13a3 |
1710.691209 |
2.8770710169 |
1.524601 |
0.041784229 |
1360.146247 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000096122224617580920297575335904860 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000140471686668860846476579311598612 |
Yes |
No |
2590.2524182 |
63.7843429 |
906.5296035 |
18.3066405 |
| ENSG00000133687 |
83857 |
TMTC1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IUR5 |
FUNCTION: Transfers mannosyl residues to the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine residues. The 4 members of the TMTC family are O-mannosyl-transferases dedicated primarily to the cadherin superfamily, each member seems to have a distinct role in decorating the cadherin domains with O-linked mannose glycans at specific regions. Also acts as O-mannosyl-transferase on other proteins such as PDIA3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28973932}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28973932}. |
Enables mannosyltransferase activity. Involved in protein O-linked mannosylation. Predicted to be located in endoplasmic reticulum. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83857; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0004169]; mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0000030]; protein O-linked mannosylation [GO:0035269]; RNA processing [GO:0006396] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24764305_findings provide an important link between aneuploidy and the stress pathways activated by Aurora B inhibition and also support the use of Aurora B inhibitors in combination therapy for treatment of cancer. 28973932_O-mannosylation pathway dedicated to cadherins/ protocadherins orchestrated by the four TMTC1-4 genes 33436046_Conserved sequence motifs in human TMTC1, TMTC2, TMTC3, and TMTC4, new O-mannosyltransferases from the GT-C/PMT clan, are rationalized as ligand binding sites. |
ENSMUSG00000030306 |
Tmtc1 |
2676.096953 |
3.6338629159 |
1.861504 |
0.048324383 |
1455.184444 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000214237733481 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000325994735344 |
Yes |
Yes |
4160.3666437 |
140.4806825 |
1152.6350183 |
29.8125135 |
| ENSG00000133805 |
272 |
AMPD3 |
protein_coding |
Q01432 |
FUNCTION: AMP deaminase plays a critical role in energy metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9291127}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Nucleotide metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; IMP biosynthesis via salvage pathway; IMP from AMP: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9291127}. |
This gene encodes a member of the AMP deaminase gene family. The encoded protein is a highly regulated enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine monophosphate to inosine monophosphate, a branch point in the adenylate catabolic pathway. This gene encodes the erythrocyte (E) isoforms, whereas other family members encode isoforms that predominate in muscle (M) and liver (L) cells. Mutations in this gene lead to the clinically asymptomatic, autosomal recessive condition erythrocyte AMP deaminase deficiency. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms of this gene have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:272; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; AMP deaminase activity [GO:0003876]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; AMP catabolic process [GO:0006196]; AMP metabolic process [GO:0046033]; IMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006188]; IMP salvage [GO:0032264] |
12213808_N-terminal sequence and distal histidine residues are responsible for pH-regulated cytoplasmic membrane binding 12604357_mtDNA deletion coordinately induces AMP deaminase to contribute to the loss of atrial adenine nucleotides through degrading AMP excessively. 16670071_The primary underlying mechanism for increased catabolic flow through the AMP deaminase reaction in circulating erythrocytes of individuals with familial phosphofructokinase deficiency is Ca2+-calmodulin activation of AMP deaminase isoform E. 18409530_may control the systemic metabolic status by changing AMPK activity through the AMP level. 18493842_This is a first report evidencing the pattern of AMPD genes expression in neoplastic human liver. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 35241525_Down-regulation of AMPD3 Is Associated With Poor Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000005686 |
Ampd3 |
2346.226542 |
2.0556341169 |
1.039584 |
0.074871460 |
189.012508 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000052225435095956896875981402685560259033642501312559578277294237929767680789096529441420598341098003698273674871160876520548299595247954130172729492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000009354944441945676851061435417599868604815380909119022213136874189039804540665072677762799022168939470540396062536725452218888676725327968597412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3189.2628974 |
141.0025388 |
1562.9565935 |
50.9499126 |
| ENSG00000133816 |
9645 |
MICAL2 |
protein_coding |
O94851 |
FUNCTION: Methionine monooxygenase that promotes depolymerization of F-actin by mediating oxidation of residues 'Met-44' and 'Met-47' on actin to form methionine-sulfoxide, resulting in actin filament disassembly and preventing repolymerization (PubMed:24440334, PubMed:29343822). Regulates the disassembly of branched actin networks also by oxidizing ARP3B-containing ARP2/3 complexes leading to ARP3B dissociation from the network (PubMed:34106209). Acts as a key regulator of the SRF signaling pathway elicited by nerve growth factor and serum: mediates oxidation and subsequent depolymerization of nuclear actin, leading to increase MKL1/MRTF-A presence in the nucleus and promote SRF:MKL1/MRTF-A-dependent gene transcription. Does not activate SRF:MKL1/MRTF-A through RhoA (PubMed:24440334). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24440334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34106209}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;FAD;Flavoprotein;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Monooxygenase;NADP;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a monooxygenase that enhances depolymerization of F-actin and is therefore involved in cytoskeletal dynamics. The encoded protein is a regulator of the SRF signaling pathway. Increased expression of this gene has been associated with cancer progression and metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:9645; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; NAD(P)H oxidase H2O2-forming activity [GO:0016174]; NADPH:sulfur oxidoreductase activity [GO:0043914]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, NAD(P)H as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen [GO:0016709]; actin filament depolymerization [GO:0030042]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; sulfur oxidation [GO:0019417] |
16675569_MICAL2-PV is likely to be involved in cancer progression of prostate cancer and could be a candidate as a novel molecular marker and/or target for treatment of prostate cancers. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22331357_although MICAL1 is auto-inhibited by its C-terminal coiled-coil region, MICAL2 remains constitutively active and affects stress fibers, suggesting differential but complementary roles for MICAL1 and MICAL2 in actin microfilament regulation 24440334_These data show that SRF/MRTF-A signaling is regulated by MICAL-2-dependent redox regulation of nuclear actin. 26689989_Data suggest that MICAL2 protein might be an important regulator of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and therefore a promising target for anti-metastatic therapy. 28719045_MICAL2 is a major regulator of breast cancer cell migration 30853343_In pulmonary artery hypertension miR-205-5p suppressed pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation by targeting MICAL2, which activated ERK1/2 signaling. 31004710_MICAL2 expression in endothelial cells participates to inflammation-induced neo-angiogenesis and that MICAL2 inhibition should be tested in cancer- and noncancer-associated neo-angiogenesis, where chronic inflammation represents a relevant pathophysiological mechanism. 32360180_MICAL2 is a novel nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein promoting cancer invasion and growth of lung adenocarcinoma. 34096155_MICAL2PV suppresses the formation of tunneling nanotubes and modulates mitochondrial trafficking. 34106209_MICAL2 enhances branched actin network disassembly by oxidizing Arp3B-containing Arp2/3 complexes. 34650666_MICAL2 Contributes to Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation by Promoting YAP Dephosphorylation and Nuclear Translocation. 36064550_MICAL2 contributes to gastric cancer cell migration via Cdc42-dependent activation of E-cadherin/beta-catenin signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000038244 |
Mical2 |
716.565702 |
0.3781521092 |
-1.402961 |
0.419496089 |
10.590215 |
0.00113687729974536059010525868018248729640617966651916503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002626437461925422520853112828831399383489042520523071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
322.5164845 |
94.1861937 |
860.6134866 |
181.2074851 |
| ENSG00000133874 |
79845 |
RNF122 |
protein_coding |
Q9H9V4 |
FUNCTION: May induce necrosis and apoptosis. May play a role in cell viability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16751333}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The encoded protein contains a RING finger, a motif present in a variety of functionally distinct proteins and known to be involved in protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions. The encoded protein is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus, and may be associated with cell viability. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:79845; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010917]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865] |
28710364_Findings indicate genetic association between E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF122 and Attention Deficit Disorders with Hyperactivity (ADHD). |
ENSMUSG00000039328 |
Rnf122 |
302.339599 |
0.3604665019 |
-1.472063 |
0.093250902 |
257.353983 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064758354322798683262566018729208570177635379248573660384680844202912650795468403139621696860433932172685642449979590150387066529557074886673051841712300813469482818618416786193847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016037471641015244876054084221486602339165501264538008540489579435246112359466063672476225906905580363100764894863028965292069474388210024334063680262474349547119345515966415405273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
160.9133774 |
11.2358131 |
449.8862050 |
20.3611931 |
| ENSG00000133985 |
23508 |
TTC9 |
protein_coding |
Q92623 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein that contains three tetratricopeptide repeats. The gene has been shown to be hormonally regulated in breast cancer cells and may play a role in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:23508; |
bone development [GO:0060348] |
18699990_TTC9A acts as a chaperone protein to facilitate the function of tropomyosins (including Tm5NM-1) in stabilizing microfilament and it may play a role in cancer cell invasion and metastasis 25798063_It is plausible therefore that TTC9A negatively regulates ERalpha activity through interacting with co-chaperone proteins such as FKBP38 and FKBP51. 30325323_In this study, we propose a molecular mechanism whereby TTC9 mutations function to generate ichthyosiform hyperkeratosis of the skin, either directly or indirectly through altered myofibroblasts and altered hormone regulation. |
ENSMUSG00000042734 |
Ttc9 |
19.580967 |
2.0224175549 |
1.016081 |
0.357885438 |
8.144444 |
0.00431932952160769129124062715163745451718568801879882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008949088116076576310264911739977833349257707595825195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.5542035 |
5.5595607 |
12.2890583 |
2.1871502 |
| ENSG00000134028 |
27299 |
ADAMDEC1 |
protein_coding |
O15204 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in the control of the immune response and during pregnancy. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This encoded protein is thought to be a secreted protein belonging to the disintegrin metalloproteinase family. Its expression is upregulated during dendritic cells maturation. This protein may play an important role in dendritic cell function and their interactions with germinal center T cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27299; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12037602_molecular evolution by duplication in a metalloprotease gene cluster on chromosome 8p12 18449420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18449420_The ADAMDEC 1 haplotype may indicate an underlying mechanism for high FVIII levels in venous thromboembolism. 19218196_Gene expression profiling performed on tissues obtained from pulmonary sarcoidosis patients identified ADAMDEC1 as a potential pathogenic mediator of lung damage and/or remodeling and may serve as a marker for this disease. 23754285_ADAMDEC1 functions as an active metalloprotease. 25564618_We hypothesize that these unique features of ADAMDEC1 may have evolved to escape from inhibition by endogenous metalloprotease inhibitors 28455445_Data suggest that activated platelets release ADAMDEC1, which hydrolyzes pro-EGF (epidermal growth factor) to soluble, active HMW-EGF; proteolytic cleavage of pro-EGF first occurs at the C-terminal arginyl residue of the EGF domain; proteolysis is the regulated, rate-limiting step in generating soluble EGF from activated platelets. 29941981_ADAMDEC1 is a positive regulator of Epithelial Defense Against Cancer (EDAC) that promotes apical extrusion of RasV12-transformed cells 30352365_Data show the critical pathways regulating the expression of ADAMDEC1 and the roles of enhancer RNAs and mechanistically links E1A binding protein p300 (p300) and enhancer RNAs, which is dependent on NF-kappa B (NFkappaB). 31434712_ADAMDEC1 Maintains a Growth Factor Signaling Loop in Cancer Stem Cells. 31627897_The ADAMDEC1 plays a pro-inflammatory role in rosacea via modulating the M1 polarization of macrophages. 32378728_Knockdown of ADAMDEC1 inhibits the progression of glioma in vitro. 35178875_Upregulation of ADAMDEC1 correlates with tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) via the PI3K/AKT pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000022057 |
Adamdec1 |
757.868541 |
6.8531800504 |
2.776774 |
0.094917823 |
843.554656 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001831488059994613992020612060420210587892534506292889915972515843892234275987035150065546819972144156769249244757861356774380714063190675522214307 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001544729358029742881825825794479183603094838074435905991493543257206208039555878809434540864214223619093821902918497284998939977238928718868003861 |
Yes |
No |
1341.9933197 |
74.2055387 |
197.3088283 |
9.0341262 |
| ENSG00000134046 |
8932 |
MBD2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBB5 |
FUNCTION: Binds CpG islands in promoters where the DNA is methylated at position 5 of cytosine within CpG dinucleotides. Binds hemimethylated DNA as well. Recruits histone deacetylases and DNA methyltransferases. Acts as transcriptional repressor and plays a role in gene silencing. Functions as a scaffold protein, targeting GATAD2A and GATAD2B to chromatin to promote repression. May enhance the activation of some unmethylated cAMP-responsive promoters. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10471499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10947852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12665568, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16415179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24307175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774669}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
DNA methylation is the major modification of eukaryotic genomes and plays an essential role in mammalian development. Human proteins MECP2, MBD1, MBD2, MBD3, and MBD4 comprise a family of nuclear proteins related by the presence in each of a methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD). Each of these proteins, with the exception of MBD3, is capable of binding specifically to methylated DNA. MECP2, MBD1 and MBD2 can also repress transcription from methylated gene promoters. The protein encoded by this gene may function as a mediator of the biological consequences of the methylation signal. It is also reported that the this protein functions as a demethylase to activate transcription, as DNA methylation causes gene silencing. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:8932; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; NuRD complex [GO:0016581]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; C2H2 zinc finger domain binding [GO:0070742]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; methyl-CpG binding [GO:0008327]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; satellite DNA binding [GO:0003696]; siRNA binding [GO:0035197]; aging [GO:0007568]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0006346]; embryonic organ development [GO:0048568]; heart development [GO:0007507]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; maternal behavior [GO:0042711]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of chromatin binding [GO:0035563]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of DNA methylation [GO:0044030]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11960994_Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 represses transcription from hypermethylated pi-class glutathione S-transferase gene promoters in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 12177048_MBD2 protein activates CpG sites within the promoter region of reporter genes 12183469_interaction with two highly related p66 proteins 12388720_interacts with latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)to tether KSHV to cell chromosomes 12588985_MBDin relieves MBD2 repression potential and reactivates transcription from methylated promoters 12646234_Results show that methyl-CpG binding domain protein 1 (MBD1) is expressed in tumor cells, but methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 (MBD2) and methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) are not. 12665568_MBD2a and RNA helicase A cooperatively enhanced CREB-dependent gene expression. 14610093_MBD2 has a role in the methylation-mediated inhibition of ribosomal RNA gene expression 14688029_Antisenses oligoDNA suppresses tumor growth in nude mice, a potential anticaner therapy approach. 15112265_MBD2 gene expression may be significant factor in tumorigenesis. 15456747_role of MBD3L1 as a methylation-dependent transcriptional repressor that may interchange with MBD3 as an MBD2-interacting component of the NuRD complex 15701600_MBD3L2 interacts with MBD3 and components of the NuRD complex and can oppose MBD2-MeCP1-mediated methylation silencing 16052033_MBD2 is associated with the methylated region of a CpG island containing the bidirectional promoter of the Breast cancer predisposition gene 1, BRCA1, and the Near BRCA1 2 (NBR2) gene. 16168120_Genetic variations in rhis methylation related genes may potentially serve as a biomarker in risk estimates for breast cancer. 16168120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16428440_MBD2 assembles into mutually exclusive distinct Mi-2/NuRD-like complex, called MBD2/NuRD. 16951344_A previously unrecognized intracellular factor required for the efficient generation of protective memory CD8 T cells. 16998846_Sex-specific time windows for concomitant upregulation of MBD2 are associated with prenatal remethylation of the human male and female germ line. 17353267_Results suggest that modulation of MBD2 during gut development establishes a region-specific gene expression pattern that is essential for establishing correct segmental character. 17360956_MBD2 and MBD4 transcript overexpression and inverse correlations with DNA methylation indices indicate that both enzymes may really have a direct and active role on the genome-wide DNA hypomethylation observed in CD4+ T cells from SLE patients. 17634428_These data show, for the first time, the involvement of methyl-CpG binding domain proteins in the regulation of the MAGE-A genes. 17688412_We found clinically relevant levels of Hcy (0-500 microM) induced elevation of SAH, declination of SAM and SAM/SAH ratio and reduced expression of SAHH and MBD2, but increased activity of DNMT3a and DNMT3b affecting DNA methylation 18414412_MBD2 may play an important role in modulating NSCLC patient survival and thus be useful for identifying NSCLC patients who would benefit most from aggressive therapy. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18830263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18931530_These findings implicate MBD2 in transcriptional repression of the methylated p14(ARF) tumor suppressor gene and suggest that repression by MBD2 selectively affects a subset of methylated promoters. 18952593_results indicate MBD2 is specifically & directly involved in transcriptional repression of hTERT in HeLa cells & breast, liver & neuroblastoma cancer cell lines; MBD2 seems to be a general repressor of hTERT in hTERT-methylated telomerase-positive cells 19019634_The ratio of MBD-2/DNMT-1 might be valuable in explanation of hypomethylation and evaluation of clinical activity of systemic luopus erythematosus. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19690890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20300195_MBD2 and ERalpha drive opposite effects on pS2 expression, which are associated with specific steady state levels of histone H3 acetylation and methylation marks 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20937307_The anti-TNFalpha biological agents do not seem to affect DNA methylation and mRNA expressions of DNMT1 and MBD2 in RA 21078759_This study demonstrated that patients with SLE had a significantly lower level of DNA methylation than the controls, and that expression of both DNMT1 and MBD2 mRNA was significantly increased in the SLE patients compared with controls. 21086164_In hilar cholangiocarcinoma, down-expression of miR-373 leads to increase of MBD2, which in turn suppresses the methylation-mediated gene such as RASSF1A. 21165562_miR-373 is a methylation-mediated gene and the implication of MBD2 in methylation-mediated suppression of miR-373 plays an important role in tumourigenesis and development in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. 21296012_human epsilon-globin gene is subject to multilayered silencing mediated in part by MBD2 21316665_Expression level of MBD2 is significantly lower in endometriotic lesions compared with disease-free controls. 21377502_decreased expression in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia 21693597_These results show a role for MBD2 in cancer progression and provide support for the prospect of targeting MBD2 therapeutically in aggressive breast cancers. 21724586_MBD2 overexpression during gliomagenesis may drive tumor growth by suppressing the antiangiogenic activity of a key tumor BAI1. 22048253_The association between MBD2 binding and transcriptional repression weakened as the distance between binding site and TSS increased, suggesting that MBD2 represses transcriptional initiation 22258532_A two-stage association study identifies methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2 gene polymorphisms as candidates for breast cancer susceptibility. 22876037_MiR-373 behaves as a direct transcriptional target and negative regulator of MBD2 activity through a feedback loop of CpG island methylation in hilar cholangiocarcinoma 23071088_repressive functions of MBD2-containing NuRD complexes are dependent on cooperative interactions between the major domains of CHD4 with histones and DNA and on binding of methylated DNA by MBD2 23127209_Abnormal expression levels of DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferase 1 and MBD2 mRNA may be important causes of the global hypomethylation observed in CD4+T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. 23239876_These factors lead to a binding affinity hierarchy of p66alpha for the different MBD2 homologues (MBD2 approximately MBD3 > MBD3L1 approximately MBD3L2). 23361464_MBD3 is enriched at active promoters, whereas MBD2 is bound at methylated promoters and enriched at exon sequences of active genes. 23770133_In metastatic colorectal cancer cells, reduced levels of miR-221* and miR-224 increase levels of MBD2, thereby decreasing expression of the metastasis suppressor maspin. 23820632_global DNA hypomethylation is one of the possible epigenetic variations associated with the complex etiology of TOF and significantly correlates with the aberrant expression of MBD2 mRNA in patients with TOF. 23888954_MBD2 seems to play a selective role in gene repression depending on the CpG content of the promoter region 23955541_MBD2 binds a significant fraction of the hypomethylated genes. 24204564_Methylated DNA binding domain protein 2 (MBD2) coordinately silences gene expression through activation of the microRNA hsa-mir-496 promoter in breast cancer cell line. 24338710_reduced mRNA expression of MBD2 and MBD3 is implicated in gastric carcinogenesis. 24813856_alternatively spliced isoforms support pluripotency of stem cells 24849540_This study investigates the genetic association between methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD) gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia. 24927503_Data suggest that MBD2 binds primarily at highly methylated regions, with a strong preference for CpG islands and highlights that MBD2 binding sites display increased methylation in primary breast cancer tissues as compared to normal mammary cells. 25135974_The methylated-DNA binding protein MBD2 enhances NGFI-A (egr-1)-mediated transcriptional activation of the glucocorticoid receptor. 25178277_These data point to a potential new approach in targeting the DNA methylation machinery by combination of MBD2 and DNMT inhibitors. 25753662_Biophysical analyses show that the MBD2IDR is an intrinsically disordered region (IDR). However, despite this inherent disorder, MBD2IDR increases the overall binding affinity of MBD2 for methylated DNA. 25798578_MBD2 targets short interspersed nuclear elements, but does not exclude RNA Polymerase III. 26007656_The dynamics of MBD2 deposition across methylated DNA regions was associated with the oncogenic transformation of human mammary cells. 26788506_downregulation of miR-221 inhibits cell migration and invasion at least partially through targeting MBD2 in the human OSCC cell line UM1. 26827827_Specifically, methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2 (MBD2) is revealed to be recruited to DNA damage sites after laser microirradiation, which was mediated through MBD domain and MBD2 C-terminus. 27315121_MBD2 expression was elevated in HCC tissue, which suggesting MBD2 as a candidate prognostic marker of HCC. 27388476_Results show that MBD2 mediates epigenetic silencing of Htra1. 27593931_MBD2 has a critical role in 'rewriting' the cancer methylome at specific regulatory regions. 28637186_CpG and methylation-dependent DNA binding and dynamics of the MBD2 protein at the single-molecule level have been reported. 29022913_knockdown of MBD2 by siRNA attenuated vancomycin-induced apoptosis, caspase activity, and the expression of BAX and cleaved caspase 3. 29330145_In Notch1-driven T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), MBD2 was required for the progression and maintenance of leukemia. The results define essential roles for MBD2 in lymphopoiesis and T-ALL and suggest MBD2 as a candidate therapeutic target in T-ALL. 29535511_Suggest that reduced MBD2 expression could contribute to chronic airway inflammation in COPD. 29565710_we conclude that disruption of MBD2 can inhibit the proliferation of CML-BP cells in vivo and in vitro. Given the striking effect in CML blast crisis cell lines, we believe that targeting MBD2 could be a candidate therapeutic strategy for CML-BP patients. 29741809_IL-6 treatment downregulated wild-type TP53 protein and induced mRNA and protein expression of the epigenetic reader methyl CpG binding domain protein 2 (MBD2), specifically the alternative mRNA splicing variant MBD2_v2. 30636104_MBD2_v2 expression is induced by obesity and drives triple-negative breast cancer cell tumorigenicity. 30735628_Low MBD2 expression is associated with metastasis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 30912130_LOC105369748 was shown to promote MBD2 expression through competitively binding to microRNA(miR)-5095 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30980593_our results demonstrate that mCG-binding arginine fingers embedded into a conserved structural fold are essential structural features for MBD2/3s binding to methylated DNA among metazoans. 31114989_Upregulated exosomal miR-221/222 promotes cervical cancer via repressing methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2. 31412880_The HERV-E clone 4-1 also takes part in disease pathogenesis of SLE through miR-302d/Methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 (MBD2)/DNA hypomethylation and IL-17 signaling via its 3'LTR. 33264408_The topology of chromatin-binding domains in the NuRD deacetylase complex. 33402389_Hypoxia-Induced Suppression of Alternative Splicing of MBD2 Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis via Activation of FZD1. 33997955_GATA zinc finger domain-containing protein 2A (GATAD2A) deficiency reactivates fetal haemoglobin in patients with beta-thalassaemia through impaired formation of methyl-binding domain protein 2 (MBD2)-containing nucleosome remodelling and deacetylation (NuRD) complex. 34617573_Silencing of MBD2 and EZH2 inhibits the proliferation of colorectal carcinoma cells by rescuing the expression of SFRP. 36037972_Densely methylated DNA traps Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 2 but permits free diffusion by Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein 3. 36090987_Blockade of Mbd2 by siRNA-loaded liposomes protects mice against OVA-induced allergic airway inflammation via repressing M2 macrophage production. |
ENSMUSG00000024513 |
Mbd2 |
468.035159 |
2.1093514633 |
1.076799 |
0.213148119 |
24.349663 |
0.00000080340818543700012583871385152267663443126366473734378814697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002871260246259109432152107840852117703889234689995646476745605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
579.7666268 |
193.1016157 |
267.8528608 |
64.2599461 |
| ENSG00000134061 |
4064 |
CD180 |
protein_coding |
Q99467 |
FUNCTION: May cooperate with MD-1 and TLR4 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in B-cells. Leads to NF-kappa-B activation. Also involved in the life/death decision of B-cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
CD180 is a cell surface molecule consisting of extracellular leucine-rich repeats (LRR) and a short cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular LRR is associated with a molecule called MD-1 and form the cell surface receptor complex, RP105/MD-1. It belongs to the family of pathogen receptors, Toll-like receptors (TLR). RP105/MD1, by working in concert with TLR4, controls B cell recognition and signaling of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a membrane constituent of Gram-negative bacteria. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4064; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; B cell proliferation involved in immune response [GO:0002322]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031666] |
15852007_RP105 regulated TLR4 signaling in dendritic cells 17448566_Expression of RP105 and TLR4 is altered on PBC monocytes, which appear to be hypersensitive to LPS, resulting in increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20133206_RP105 cross-linkaage enhanced B-lymphocyte proliferation, TLR9 expression, and growth. 20233331_Lower mRNA expression of LY64 was detected in gingival tissue of chronic periodontitis patients compared to healthy controls. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20430725_Data show that CD180, CD284 and CD14 expression is higher on normal B cells than on CD19+ B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21959264_Both mouse and human RP105/MD-1 exhibit dimerization of the 1:1 RP105/MD-1 complex, demonstrating a novel organization. 22484241_IL-4 failed to up-regulate expression of RP105 at the cell surface. In conclusion, the anti-inflammatory actions of IL-4 occur independently of IL-10, RP105, and the kinase activity of RIPK2 23103284_Data indicate that TLR9-signaling as a crucial factor for turning retinoic acid (RA) into a strong stimulator of RP105-mediated B-cell proliferation. 25802446_we address of monocytes functional status through assessment of the patterns of expression of Fcgamma receptors CD64, CD32, CD16 and CD180 receptor on monocytes from CLL patients and healthy individuals using specific mAbs and flow cytometry. 25879560_Since MEC1 cells are derived from a CLL patient with mutated IGVH genes (M-CLL) negative correlation between CD180 and CD32 expression on cycling MEC1 cells could be limited to M-CLL. 26277892_the close association between the increased proportion of CD180-negative B cells and the activation of IFN-alpha signaling in Systemic lupus erythematosus, is reported. 26555723_By associating with PIM-1L, CD180 can thus obtain autonomous signaling capabilities, and this complex is then channeling inflammatory signals into B cell survival programs 28005267_CD180 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28073847_Our data strongly support the use of CCR2 and CD180 mRNAs as whole blood pharmacodynamic (PD)biomarkers for BRD4 inhibitors, especially in situations where paired tumor biopsies are unavailable. In addition, they can be used as tumor-based PD biomarkers for hematologic tumors. 28982149_combination of signals via CD150 and CD180 leads to blocking of pro-survival pathways that may be a restraining factor for neoplastic CLL B cells propagation in more than 50% of CLL cases where these receptors are coexpressed 29089453_Calcitriol regulates immune genes CD14 and CD180 to modulate LPS responses in human trophoblasts. 29284783_CD150 and CD180 receptors may modulate transcriptional program in lymphocytic leukemia cells by regulating the transcription factor expression levels 29511161_Silencing Cd180 results in increased phagocytosis while tempering the production of the proinflammatory cytokine TNF during Borrelia burgdorferi infection. 33455071_The relative expression levels of CD148 and CD180 on clonal B cells and CD148/CD180 median fluorescence intensity ratios are useful in the characterization of mature B cell lymphoid neoplasms infiltrating blood and bone marrow - Results from a single centre pilot study. 33904315_CD150 and CD180 are negative regulators of IL-10 expression and secretion in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. 34124274_Toll-Like Receptor Homolog CD180 Expression Is Diminished on Natural Autoantibody-Producing B Cells of Patients with Autoimmune CNS Disorders. |
ENSMUSG00000021624 |
Cd180 |
407.758803 |
3.1666291743 |
1.662948 |
0.086715614 |
377.413843 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000455001895514338798865649107034209681209654275755826630626677124180097837299302697965667648125491829285918512783517129557579681919618132903561245386660658621500619761167205763903238148680951881647921238222866124889520733631798066198825836181640625 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000161051030642485375432639565306054266640118947596790411591078289900515303076089385075909092690934904352470258642088562459436018726407724299248338590997774118591819301875715796171987300586119424606907496455576733751513529568910598754882812500000000 |
Yes |
No |
626.7437111 |
33.4066662 |
199.1134429 |
8.7148059 |
| ENSG00000134070 |
3656 |
IRAK2 |
protein_coding |
O43187 |
FUNCTION: Binds to the IL-1 type I receptor following IL-1 engagement, triggering intracellular signaling cascades leading to transcriptional up-regulation and mRNA stabilization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10383454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9374458}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
IRAK2 encodes the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 2, one of two putative serine/threonine kinases that become associated with the interleukin-1 receptor (IL1R) upon stimulation. IRAK2 is reported to participate in the IL1-induced upregulation of NF-kappaB. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3656; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001959]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555] |
15670593_CTCF plays a major role in IRAK2 transcription; EMSA revealed a CTCF-binding site within the mouse Irak2 promoter 17878161_IRAK-2 plays a more central role than IRAK-1 in TLR signaling to NFkappaB through TRAF6 ubiquitination 18996842_TRAF6 and interleukin receptor-associated kinase 2 are novel binding partners for PS1, and IL-1R1 is a new substrate for presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase cleavage 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20200953_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332216_Our data show that interleukin-1R-associated kinase 2 is a novel and critical component of TGFbeta signaling. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485341_the crystal structure of the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 death domain (DD) complex, which surprisingly reveals a left-handed helical oligomer that consists of 6 MyD88, 4 IRAK4 and 4 IRAK2 DDs 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20937840_analysis of differential regulation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) and IRAK-2 by microRNA-146a and NF-kappaB in stressed human astroglial cells and in Alzheimer disease 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21606490_Human interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-2 is essential for Toll-like receptor-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha. 23724040_These findings demonstrate an unexpected linkage of the innate immunity machinery to unfolded protein response signaling, revealing IRAK2 as a novel amplifier of the IRE1 pathway. 24662294_Results suggest that D431E-IRAK2 (interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-2) increases NF-kappaB activation by promoting TRAF6 ubiquitination by enhancing TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 6 (TRAF6)-IRAK2 interaction. 24973222_This for the first time implicates human IRAK2 in a human disease and highlights the R214G IRAK2 variant as a potential novel and broadly applicable biomarker for disease or as a therapeutic intervention point. 25063738_Human miR-373 is silenced by histone modification in lung cancer cells and is a negative regulator of the mesenchymal phenotype through downstream IRAK2 and LAMP1 target genes. 26250868_IRAK2 L392V showed intact binding to, but impaired ubiquitination of, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6, a vital step in signal transduction 29129009_This study for the first time ever reports the association of IRAK2 rs3844283, IRAK2 rs708035, and the corresponding haplotypes with rheumatoid arthritis. 29753111_these findings demonstrate a novel mechanism of interplays for the different branches of ER stress signaling network and highlight IRAK2 as a potential tumor suppressor to counterbalance oncogenic Smurf1. 29978465_Authors identified IRAK2 rs779901 C > T as a predictor of NSCLC OS, with a variant-allele (T) attributed hazards ratio (HR) of 0.78 [95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.67-0.91, P = 0.001] in the PLCO dataset, 0.84 (0.72-0.98, 0.031) in the Harvard dataset, and 0.81 (0.73-0.90, 1.08x10(-4) ) in the meta-analysis of these two GWAS datasets. 31073143_Both IRAK2 and TLR10 play important roles in the onset and development of Hashimoto's disease. 31650390_IRAK2 is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus risk. 31995744_MyD88 Death-Domain Oligomerization Determines Myddosome Architecture: Implications for Toll-like Receptor Signaling. 33799071_The extreme C-terminus of IRAK2 assures full TRAF6 ubiquitination and optimal TLR signaling. 33864770_IRAK2 Has a Critical Role in Promoting Feed-Forward Amplification of Epidermal Inflammatory Responses. 35588430_Multi-locus SNP analyses of interleukin 1 receptor associated kinases 2 gene polymorphisms with the susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000060477 |
Irak2 |
222.904151 |
7.6724466546 |
2.939687 |
0.137895998 |
510.382625 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005235599633955385154296306684238914857904496869868171017841998035874604959229672673736173260516888529799028985075398336746704133111710251737890413656303598671985639036619437336688631355978232470199851875245835147649015 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002575915019906049703655801788824601177164954616153892492372071734921826429742277499545026525499492570668190587685438301242516218496472536126474528514132717867297924958204649574772637254074729300162853106899706002056488 |
Yes |
No |
396.8547447 |
32.6337539 |
52.0886352 |
3.8579173 |
| ENSG00000134072 |
8536 |
CAMK1 |
protein_coding |
Q14012 |
FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that operates in the calcium-triggered CaMKK-CaMK1 signaling cascade and, upon calcium influx, regulates transcription activators activity, cell cycle, hormone production, cell differentiation, actin filament organization and neurite outgrowth. Recognizes the substrate consensus sequence [MVLIF]-x-R-x(2)-[ST]-x(3)-[MVLIF]. Regulates axonal extension and growth cone motility in hippocampal and cerebellar nerve cells. Upon NMDA receptor-mediated Ca(2+) elevation, promotes dendritic growth in hippocampal neurons and is essential in synapses for full long-term potentiation (LTP) and ERK2-dependent translational activation. Downstream of NMDA receptors, promotes the formation of spines and synapses in hippocampal neurons by phosphorylating ARHGEF7/BETAPIX on 'Ser-694', which results in the enhancement of ARHGEF7 activity and activation of RAC1. Promotes neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth by activation and phosphorylation of MARK2 on 'Ser-91', 'Ser-92', 'Ser-93' and 'Ser-294'. Promotes nuclear export of HDAC5 and binding to 14-3-3 by phosphorylation of 'Ser-259' and 'Ser-498' in the regulation of muscle cell differentiation. Regulates NUMB-mediated endocytosis by phosphorylation of NUMB on 'Ser-276' and 'Ser-295'. Involved in the regulation of basal and estrogen-stimulated migration of medulloblastoma cells through ARHGEF7/BETAPIX phosphorylation (By similarity). Is required for proper activation of cyclin-D1/CDK4 complex during G1 progression in diploid fibroblasts. Plays a role in K(+) and ANG2-mediated regulation of the aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) to produce aldosterone in the adrenal cortex. Phosphorylates EIF4G3/eIF4GII. In vitro phosphorylates CREB1, ATF1, CFTR, MYL9 and SYN1/synapsin I. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11114197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12193581, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14507913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14754892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17056143, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17442826, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18184567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20181577}. |
3D-structure;Allosteric enzyme;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I is expressed in many tissues and is a component of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase cascade. Calcium/calmodulin directly activates calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I by binding to the enzyme and indirectly promotes the phosphorylation and synergistic activation of the enzyme by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I kinase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8536; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0004683]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; nucleocytoplasmic transport [GO:0006913]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060999]; positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051149]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein acetylation [GO:1901985]; positive regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046827]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of synapse structural plasticity [GO:0051835]; positive regulation of syncytium formation by plasma membrane fusion [GO:0060143]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051147]; regulation of protein binding [GO:0043393]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12193581_CaMKI is involved in angiotensin II and K(+) stimulation of CYP11B2 transcription and the capacity of the adrenal to produce aldosterone 12935886_we cloned a novel calmodulin-kinase (CaM-KIdelta) from HeLa cells and characterized its activation mechanism. CaM-KIdelta exhibits Ca(2+)/CaM-dependent activity that is enhanced in vitro by phosphorylation of its Thr180 by CaM-K kinase (CaM-KK)alpha 14754892_calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I regulates of cyclin D1/Cdk4 complexes 15251453_Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I inhibits neuronal nitric-oxide synthase activity through serine 741 phosphorylation 18089838_Dioxin-mediated up-regulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor target genes is dependent on the calcium/calmodulin/CaMKIalpha pathway. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19844571_variants in doublecortin- and calmodulin kinase like 1, a gene up-regulated by BDNF, have roles in memory and general cognitive abilities 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21249615_CaMKI was significantly upregulated in adrenal adenomas. 23028635_structures of three CaMKIalpha truncates in apo form and in complexes with ATP 23707388_Fbxl12-induced CaMKI degradation attenuates p27 phosphorylation at these sites in early G1 and iii) activation of CaMKI during G1 transition followed by p27 phosphorylation appears to be upstream to other p27 phosphorylation events 24461366_It is one of Ca(2+)-sensing proteins and substantial age- and Alzheimer disease(AD)-related alterations in Ca(2+)-sensing proteins most likely contribute to selective vulnerability of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons to degeneration in AD. 24825433_CAMK1 functional regulation subnetwork in hepatocellular carcinoma 24841198_this study suggests that the tightly linked regulatory loop comprised of the SIK2-PP2A and CaMKI and PME-1 networks may function in fine-tuning cell proliferation and stress response. 26466644_Barettin has inhibitory activity against two protein kinases related to inflammation, namely the receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (RIPK2) and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1alpha (CAMK1alpha). 27907007_The mRNA expressions of PPP3CB and MEF2C were significantly up-regulated, and CAMK1 and PPP3R1 were significantly down-regulated in mitral regurgitation(MR) patients compared to normal subjects. Moreover, MR patients had significantly increased mRNA levels of PPP3CB, MEF2C and PLCE1 compared to aortic valve disease patients 33342045_Expression of CAMK1 and its association with clinicopathologic characteristics in pancreatic cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000030272 |
Camk1 |
624.963890 |
2.3256518951 |
1.217635 |
0.068094044 |
322.428053 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000428573076478710876222938510408274801028399386506301220040853251198249316434654259642924925261499124948742031784007540050741220121103840080753823865762615407750816255522177667097033504362002531706821173429489135742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000130159230634275157682060162490444815917107033659159115755197574849538070447149021906154208561808376207322371092212735700537632513476300609850008013375265977659080884654184753768113580463250400498509407043457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
883.3043964 |
36.3903777 |
382.2967505 |
12.4191085 |
| ENSG00000134107 |
8553 |
BHLHE40 |
protein_coding |
O14503 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor involved in the regulation of the circadian rhythm by negatively regulating the activity of the clock genes and clock-controlled genes (PubMed:12397359, PubMed:18411297). Acts as the negative limb of a novel autoregulatory feedback loop (DEC loop) which differs from the one formed by the PER and CRY transcriptional repressors (PER/CRY loop) (PubMed:14672706). Both these loops are interlocked as it represses the expression of PER1/2 and in turn is repressed by PER1/2 and CRY1/2 (PubMed:15193144). Represses the activity of the circadian transcriptional activator: CLOCK-BMAL1|BMAL2 heterodimer by competing for the binding to E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') found within the promoters of its target genes (PubMed:15560782). Negatively regulates its own expression and the expression of DBP and BHLHE41/DEC2 (PubMed:14672706). Acts as a corepressor of RXR and the RXR-LXR heterodimers and represses the ligand-induced RXRA and NR1H3/LXRA transactivation activity (PubMed:19786558). May be involved in the regulation of chondrocyte differentiation via the cAMP pathway (PubMed:19786558). Represses the transcription of NR0B2 and attentuates the transactivation of NR0B2 by the CLOCK-BMAL1 complex (PubMed:28797635). Drives the circadian rhythm of blood pressure through transcriptional repression of ATP1B1 in the cardiovascular system (PubMed:30012868). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12397359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14672706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15193144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15560782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18411297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19786558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28797635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30012868}. |
Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix protein expressed in various tissues. The encoded protein can interact with ARNTL or compete for E-box binding sites in the promoter of PER1 and repress CLOCK/ARNTL's transactivation of PER1. This gene is believed to be involved in the control of circadian rhythm and cell differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:8553; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; MRF binding [GO:0043426]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11688991_hypoxia-induced gene in pancreatic cancer cell lines 12119049_DEC1-mediated anti-apoptosis is achieved by blocking apoptotic pathways initiated via the mitochondria. The results functionally distinguish DEC1 from other bHLH proteins and directly link this factor to oncogenesis. 12354771_DEC1 and DEC2 may play a crucial role in the adaptation to hypoxia 12384505_DEC1 is the first transcription factor that can promote both chondrogenic differentiation and terminal differentiation 12397359_Dec1 and Dec2 are regulators of the mammalian molecular clock, and form a fifth clock-gene family. 12624110_DEC1-mediated repression on the expression of DEC2 provides an important mechanism that these transcription factors regulate the cellular function of members within the same class 15560782_Findings suggest that the basic region of DEC1 participates in the transcriptional regulation through a protein-protein interaction with BMAL1 and DNA binding to the E-box. 15719173_STRA13 interacts with the cell cycle-associated transcription factor MSP58. 15994878_STRA13 was expressed in epithelial cells of normal and neoplastic tissues mostly in the nucleus. Intense cytoplasmic STRA13 immunoreactivity was characteristic of myoepithelial and differentiated squamous epithelial cells and their neoplastic counterparts 16136500_DEC1 expression is found in the majority of 1p-aberrant oligodendroglial neoplasms; its immunohistochemical detection does not correlate with tisue hypoxia in this type of primary brain tumor. 16462771_DEC1 selectively increases the expression of survivin among antiapoptotic proteins. 16487626_These findings suggest that Dec1 modulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inducing the expression of several, but not all, bone-related genes. 16878149_link between HIF-1 and STAT1 reveals a previously unknown role of STRA13 in hypoxia and carcinogenesis 17376295_differentiated embryo-chondrocyte expressed gene 1 downregulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha at both mRNA and protein levels at hypoxia in lung adenocarcinoma cells 18025081_DEC1 is induced by the p53 family and DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner. p53 family proteins bind to, and activate, the promoter of the DEC1 gene. 18228528_A multi-locus interaction between rs6442925 in the 5' upstream of BHLHB2, rs1534891 in CSNK1E, and rs534654 near the 3' end of the CLOCK gene, however, is significantly associated with bipolar disorder 18228528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18345027_MLH1 is transcriptionally repressed by the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, DEC1 and DEC2. 18411297_DEC1, along with DEC2, plays a role in the finer regulation and robustness of the molecular clock CLOCK/BMAL1 19590847_Identificaiton of BHLHB2 as a potential novel mediator of insulin transcriptional action in human skeletal muscle. 19624270_The hypoxia-regulated transcription factor DEC1 and its expression in gastric cancer are reported. 19693801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20174623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20863812_Hypoxia-inducible BHLHB2 expression is a novel independent prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer patients and indicates increased chemosensitivity towards gemcitabine. 21317427_Study conclude that DeltaNp63 is a novel target of DEC1 and HDAC2 and modulates the efficacy of HDAC inhibitors in growth suppression and keratinocyte differentiation. 21327324_DEC1 has pro-apoptotic effects on the paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. 21528084_DEC1 is expressed in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes and because nuclear DEC1 expression is decreased with decreasing differentiation status ofhepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), nuclear DEC1 might be a marker of HCC differentiation 21779800_DEC1 expression is correlated with HIF-1alpha protein in gastric cancer cell line. 21829689_findings suggested that posttranslational modification of DEC1 in the form of SUMOylation may serve as a key factor that regulates the function of DEC1 in vivo 21867633_Expression of BHLHB2 is inhibited by PML-RARalpha through binding to its promoter in acute promyeloid leukemia. 22644784_IL-1beta can induce DEC1 and HIF-1alpha protein levels in gingival epithelial cells. We also demonstrate that the increase in DEC1 protein subsequently is followed by Akt phosphorylation. 22678901_Marginal zone B cells activated by hepatitis C virus undergo functional exhaustion associated with BCR signaling defects and overexpression of a key antiproliferative gene, and may subsequently become terminally spent CD21(low) B cells. 22723347_DEC1 controls the response of p53-dependent cell survival vs. cell death to a stress signal through MIC-1 22728071_findings suggest that the repression of CYP3A4 by IL-6 is achieved through increasing the DEC1 expression in human hepatocytes, the increased DEC1 binds to the CCCTGC sequence in the promoter of CYP3A4 to form CCCTGC-DEC1 complex 22825629_These findings suggest that DEC1 plays an important role in the regulation of these EMT-related factors in pancreatic cancer. 22844531_DEC1 overexpression in precursor lesions of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is a protective mechanism 22905217_SUMO modification of Stra13 is required for repression of cyclin D1 expression and cellular growth arrest 23220548_Staircase-style fluctuations in the BHLHE40 mRNA accumulation relate to the short half-life of the gene's mRNA of 0.9h. 23423709_Loss of DEC1 may promote tumor progression in non-small-cell lung cancer through upregulation of cyclin D1 23426649_Studied DEC1 & claudin-1 in invasive breast ductal carcinomas;found DEC1 elevated in invasive breast ductal carcinoma. DEC1 knockdown led to the enhanced expression of claudin-1 at both the mRNA and protein levels in breast cancer cell lines. 23445622_DEC1 level was positively correlated with HIF-1alpha and Ki67 expression in gastric cancer. 23578198_Sunitinib treatment performance could be attributable to TIS, depending on p53/Dec1 activation. 24100543_The efficacy of inhibiting HIF-1alpha and DEC1 expression as a possible treatment for HCC should be assessed in clinical trials. 24397494_Study demonstrates that DEC1 is involved in osteogenesis. 24404147_DEC1 coordinates with HDAC8 to differentially regulate TAp73 and DeltaNp73 expression. 24758579_The expression of DEC1 was associated with the incidence of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and there was a negative correlation between the expression of DEC1 and the prognosis of OSCC. 25202122_USP17 binds and deubiquitylates DEC1, markedly extending its half-life. Subsequently, during checkpoint recovery, DEC1 proteolysis is reestablished through betaTrCP-dependent ubiquitylation. 25876658_DEC1 has a pro-apoptotic effect on human esophageal cancer TE 10 cells of well-differentiated type. 26340669_decreases of CES and CYP3A4 expression and enzymatic activities induced by Fluoxetine are through decreasing PXR and increasing DEC1 in HepG2 cells 26391953_BHLHE40/41 are promising markers to predict the aggressiveness of each Endometrial Neoplasm case and that molecular targeting strategies involving BHLHE40/41 and SP1 may effectively regulate Endometrial Neoplasm progression. 26967308_BHLHE40 was identified as a viable candidate for which a droplet digital PCR assay for demethylation was developed. The assay revealed high demethylation in activated NK cells and low demethylation in naive NK, T- and B-cells. We conclude the NK cell methylome is plastic with potential for remodeling. 26967585_STRA13 may be essential for the progression of atopic dermatitis by interacting with hsa-miR-148b and hsamiR- 152. 27591677_High BHLHE40 expression is associated with glioblastomas. 27765932_Cisplatin-induced synthetic lethality to arginine-starvation therapy by transcriptional suppression of ASS1 is regulated by DEC1, HIF-1alpha, and c-Myc transcription network and is independent of ASS1 promoter DNA methylation. 27840944_Dec1 is a prognostic factor for the clinical outcome and a predictive factor for the response to TMZ chemotherapy in patients with glioma 28794399_DEC1 is involved in hypoxia-induced EMT processes via negatively regulating E-cadherin expression in HepG2 cells. 28797635_This study was performed to test the hypothesis that the SHP gene is a target gene of DEC1. Cotransfection demonstrated that DEC1 repressed the SHP promoter and attenuated the transactivation of the classic circadian activator complex of Clock/Bmal1. 29601939_The expression of transcription factor BHLHE40 DEC1/STRA13) is induced in human naive and memory resting B cells by activation through the B-cell receptor (BCR) or Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). DEC1/STRA13 is upregulated in human anergic CD21(low) B cells clonally expanded in patients with HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia, which fail to proliferate in response to BCR or TLR9 ligation. 29704436_BHLHE40 suppressed CLDN1 transcription by preventing the interaction between SP1 and a specific motif within the promoter region of CLDN1. 30002194_Study reveals sCLU as a novel target of DEC1 (BHLHE40) which modulates the sensitivity of the DNA damage response. DEC1 and sCLU are frequently overexpressed in breast cancer. 30158530_DEC1 expression is a specific feature of tumor cells, that this transcription factor is significantly over-expressed in all major thyroid cancer histotypes and that its expression correlated with NOTCH1 in these tumors. 30285805_Gene expression analysis suggests a role of basic helix-loop-helix protein 40 (BHLHE40) in transcriptional activation of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HBEGF). 30442142_The involvement of DEC1 provides new insight into the positive or negative functional roles of p53 in the metformin-induced cytotoxicity in tumor cells. 31914631_BHLHE40 upregulation in gastric epithelial cells increases CXCL12 production through interaction with p-STAT3 in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis 32483833_LncRNA-ES3 inhibition by Bhlhe40 is involved in high glucose-induced calcification/senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells. 32522343_DEC1 directly interacts with estrogen receptor (ER) alpha to suppress proliferation of ER-positive breast cancer cells. 32579212_BHLHE40 plays a pathological role in pre-eclampsia through upregulating SNX16 by transcriptional inhibition of miR-196a-5p. 32885250_Systematic screening of CTCF binding partners identifies that BHLHE40 regulates CTCF genome-wide distribution and long-range chromatin interactions. 33176151_TFEB Transcriptional Responses Reveal Negative Feedback by BHLHE40 and BHLHE41. 33507476_Loss of Dec1 prevents autophagy in inflamed periodontal ligament fibroblast. 34045534_Identification of BHLHE40 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells as a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 34215553_Role of differentiated embryo-chondrocyte expressed gene 1 (DEC1) in immunity. 34481230_Hypoxia-induced DEC1 mediates trophoblast cell proliferation and migration via HIF1alpha signaling pathway. 34638690_The Potential Roles of Dec1 and Dec2 in Periodontal Inflammation. 34758708_DEC1 negatively regulates CYP2B6 expression by binding to the CYP2B6 promoter region ascribed to IL-6-induced downregulation of CYP2B6 expression in HeLa cells. 34758939_Differentiated embryo chondrocyte 1, induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, promotes cell migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. 35217585_REL and BHLHE40 Variants Are Associated with IL-12 and IL-10 Responses and Tuberculosis Risk. 35334277_Differentiated embryonic chondrocyte expressed gene-1 (DEC1) enhances the development of colorectal cancer with an involvement of the STAT3 signaling. 35689549_Upregulation of INHBA mediated by the transcription factor BHLHE40 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and migration. 36053880_Overexpression of DEC1 in the epithelium of OSF promotes mesenchymal transition via activating FAK/Akt signal axis. |
ENSMUSG00000030103 |
Bhlhe40 |
281.958577 |
10.0552771808 |
3.329881 |
0.161509841 |
438.490392 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023067278949307576205799555668001722293627111718657557729091784190015957112283640015654280341055795506598323130414523929291826233468023543582609209233336144171768144399369115221875537213807411374091183666154119090730939472090438009753 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009457584369216105412745036572288768657954749350097089245764206847851542235362446342666530575467224539534046130470559899273155557918076101854303038293740221143243079920410747442170347624268479147267742946553058201556262772958856186682 |
Yes |
No |
533.0089396 |
45.5742232 |
53.3507956 |
4.1196589 |
| ENSG00000134138 |
4212 |
MEIS2 |
protein_coding |
O14770 |
FUNCTION: Involved in transcriptional regulation. Binds to HOX or PBX proteins to form dimers, or to a DNA-bound dimer of PBX and HOX proteins and thought to have a role in stabilization of the homeoprotein-DNA complex. Isoform 3 is required for the activity of a PDX1:PBX1b:MEIS2b complex in pancreatic acinar cells involved in the transcriptional activation of the ELA1 enhancer; the complex binds to the enhancer B element and cooperates with the transcription factor 1 complex (PTF1) bound to the enhancer A element; MEIS2 is not involved in complex DNA-binding. Probably in complex with PBX1, is involved in transcriptional regulation by KLF4. Isoform 3 and isoform 4 can bind to a EPHA8 promoter sequence containing the DNA motif 5'-CGGTCA-3'; in cooperation with a PBX protein (such as PBX2) is proposed to be involved in the transcriptional activation of EPHA8 in the developing midbrain. May be involved in regulation of myeloid differentiation. Can bind to the DNA sequence 5'-TGACAG-3'in the activator ACT sequence of the D(1A) dopamine receptor (DRD1) promoter and activate DRD1 transcription; isoform 5 cannot activate DRD1 transcription. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10764806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11279116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21746878}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a homeobox protein belonging to the TALE ('three amino acid loop extension') family of homeodomain-containing proteins. TALE homeobox proteins are highly conserved transcription regulators, and several members have been shown to be essential contributors to developmental programs. Multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4212; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription factor binding [GO:0008134]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; brain development [GO:0007420]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; eye development [GO:0001654]; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045638]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; pancreas development [GO:0031016]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle myoblast proliferation [GO:0110024]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045931]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to growth factor [GO:0070848]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
18408019_Analysis of an Affymetrix data set in the public domain showed high expression of MEIS1 in human endometrium 18973687_co-expression of PBX1 and MEIS1/2 in granulosa cells in normal human ovaries suggested that MEIS1/2 might control PBX1 sublocalization, as seen in other systems 19559479_co-operation between TLX1 and MEIS proteins may have a significant role in T-cell leukemogenesis. 19584346_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20195266_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20195266_The Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in Meis homeobox 2 (MEIS2) mediated the effects of risperidone on hip circumference (q=0.004). 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20523026_Data demonstrate by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry that the two homeobox genes Pax6 and MEIS2 are expressed during early fetal brain development in humans. 20553494_This work suggests that the transcriptional activity of all members of the Meis/Prep Hth protein family is subject to autoinhibition by their Hth domains, and that the Meis3.2 splice variant encodes a protein that bypasses this autoinhibitory effect. 21368052_Transgenic mice lacking microRNAs miR-9-2 and miR-9-3 exhibit multiple defects of telencephalic structures which may be brought about by dysregulation of Foxg1, Nr2e1, Gsh2, and Meis2 expression. 21746878_Klf4 recruits a complex of Meis and Pbx proteins to DNA, resulting in Meis2 transcriptional activation domain-dependent activation of a subset of Klf4 target genes. 23541832_The data suggest existence of a complex regulatory pathway in the trabecular meshwork part of which includes interactions between FOXC1, miR-204, MEIS2, and ITGbeta1. 24678003_Our results show that MEIS2 is a gene needed for palate closure. In syndromic cases of cleft palate, MEIS2 should be considered among the candidate genes, for example, in cases without 22q11.2 deletions. 25210800_FOXM1 is a direct target gene of MEIS2 and is required for MEIS2 to upregulate mitotic genes. 25712757_This is the first report showing a de novo small intragenic mutation in MEIS2 and further confirms the important role of this gene in normal development. 26512644_Meis2 as the target of miR-134 in the regulation of cardiomyocyte progenitor cell proliferation. 27225850_we have identified a novel nonsense MEIS2 mutation in a female patient with cleft palate, cardiac septal defect, severe ID, developmental delay and feeding difficulty with gastro-esophageal reflux. Our findings strongly suggest neurocristopathy be included in the clinical features associated with MEIS2 alterations. 27346355_High expression of MEIS2 impairs repressive DNA binding of AML1-ETO, inducing increased expression of genes such as the druggable proto-oncogene YES1. 29337667_Mechanistic analyses integrate this unrecognized anti-atrial function of ISL1 with known and newly identified atrial inducers. In this revised view, ISL1 is antagonized by retinoic acid signaling via a novel player, MEIS2. 29382709_Moderate elevation of MEIS2A expression reduced proliferation of MYCN-amplified human neuroblastoma cells, induced neuronal differentiation and impaired the ability of these cells to form tumors in mice 29716922_These data implicate a functional role for MEIS proteins in regulating cancer progression, and support a hypothesis whereby tumor expression of MEIS1 and MEIS2 expression confers a more indolent prostate cancer phenotype, with a decreased propensity for metastatic progression 30055086_these are the first described de novo missense variants in MEIS2, expanding the known mutation spectrum of the newly recognized human disorder caused by aberrations in this gene. 30291340_Loss-of-function MEIS2 mutations were identified in nine patients with palatal defects, congenital heart defects, and intellectual disability. 30526668_TAL1 acts as a downstream gene mediating the function of MEIS2 during early hematopoiesis. 30594396_The present study indicated that Meis2 repress the osteoblastic transdifferentiation of aortic valve interstitial cells through the Notch1/Twist1 signaling pathway. 30742945_Study shows that MEIS2 expression is regulated in bladder neoplasm via alternative splicing by PTBP1. 30859572_MEIS2 might be involved in the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 31115559_Study demonstrated that MEIS2 acted as a promoter of metastasis in colorectal cancer (CRC). Knockdown of MEIS2 significantly suppressed CRC migration, invasion and EMT. MEIS2 was associated with a shorter overall survival time for patients with CRC. These results suggest that MEIS2 may serve as a novel biomarker for CRC. 31315484_Inhibition of Senescence-Associated Genes Rb1 and Meis2 in Adult Cardiomyocytes Results in Cell Cycle Reentry and Cardiac Repair Post-Myocardial Infarction. 31623651_MEISC/D promote hepatocellular carcinoma development via Wnt/beta-catenin and Hippo/YAP signaling pathways 31640805_Results strongly indicate that aberrant DNA hypermethylation is associated with epigenetic silencing of MEIS2 transcriptional expression in prostate cancer (PC) and validate MEIS2 as a potential prognostic biomarker for PC. 33091211_MEIS2 sequence variant in a child with intellectual disability and cardiac defects: Expansion of the phenotypic spectrum and documentation of low-level mosaicism in an unaffected parent. 33427397_Intellectual disability associated with craniofacial dysmorphism, cleft palate, and congenital heart defect due to a de novo MEIS2 mutation: A clinical longitudinal study. 33864110_Expression of ISL1 and its partners in prostate cancer progression and neuroendocrine differentiation. 33975520_Meis homeobox 2 (MEIS2) inhibits the proliferation and promotes apoptosis of thyroid cancer cell and through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000027210 |
Meis2 |
111.189571 |
0.4817466281 |
-1.053654 |
0.321564415 |
10.451801 |
0.00122529958113427417214225112473968692938797175884246826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002813537930544786694331271803548588650301098823547363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.9019957 |
15.5172835 |
149.5742733 |
22.9398889 |
| ENSG00000134207 |
148281 |
SYT6 |
protein_coding |
Q5T7P8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of secretory vesicles through Ca(2+) and phospholipid binding to the C2 domain or may serve as Ca(2+) sensors in the process of vesicular trafficking and exocytosis. May mediate Ca(2+)-regulation of exocytosis in acrosomal reaction in sperm (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R0N8}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the synaptotagmin family. Synaptotagmins share a common domain structure that includes a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic region composed of 2 C2 domains, and are involved in calcium-dependent exocytosis of synaptic vesicles. This protein has been shown to be a key component of the secretory machinery involved in acrosomal exocytosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:148281; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0097038]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; acrosomal vesicle exocytosis [GO:0060478]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0017158]; regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0014059]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
16111671_Acrosomal exocytosis is regulated through the PKC-mediated phosphorylation of conserved threonines in the polybasic regions of synaptotagmin VI. 18639284_SYT6 is hypermethylated in renal cell carcinoma. 20551332_synaptotagmin must be dephosphorylated at a specific window of time and phosphorylated synaptotagmin has an active role at early stages of the acrosomal exocytosis. |
ENSMUSG00000027849 |
Syt6 |
14.632598 |
0.0477349571 |
-4.388810 |
0.741614924 |
54.944932 |
0.00000000000012395462154391099796133322533507507368175787343389515626768115907907485961914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000779867951401588396838336572009552633672445354218183410921483300626277923583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1659875 |
0.6361427 |
24.6699011 |
5.2430077 |
| ENSG00000134250 |
4853 |
NOTCH2 |
protein_coding |
Q04721 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged-1 (JAG1), Jagged-2 (JAG2) and Delta-1 (DLL1) to regulate cell-fate determination. Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBPJ/RBPSUH and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus (PubMed:21378985, PubMed:21378989). Affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs (By similarity). Involved in bone remodeling and homeostasis. In collaboration with RELA/p65 enhances NFATc1 promoter activity and positively regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation (PubMed:29149593). Positively regulates self-renewal of liver cancer cells (PubMed:25985737). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21378985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21378989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25985737, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29149593}. |
3D-structure;Activator;ANK repeat;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Notch family. Members of this Type 1 transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple, different domain types. Notch family members play a role in a variety of developmental processes by controlling cell fate decisions. The Notch signaling network is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway which regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells. In Drosophilia, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signaling pathway that plays a key role in development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remain to be determined. This protein is cleaved in the trans-Golgi network, and presented on the cell surface as a heterodimer. This protein functions as a receptor for membrane bound ligands, and may play a role in vascular, renal and hepatic development. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:4853; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cilium [GO:0005929]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; atrial septum morphogenesis [GO:0060413]; atrioventricular node development [GO:0003162]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; bone remodeling [GO:0046849]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; cellular response to tumor cell [GO:0071228]; cholangiocyte proliferation [GO:1990705]; ciliary body morphogenesis [GO:0061073]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; glomerular capillary formation [GO:0072104]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; hepatocyte proliferation [GO:0072574]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002437]; intrahepatic bile duct development [GO:0035622]; left/right axis specification [GO:0070986]; marginal zone B cell differentiation [GO:0002315]; morphogenesis of an epithelial sheet [GO:0002011]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0043011]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; Notch signaling involved in heart development [GO:0061314]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; podocyte development [GO:0072015]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010838]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; proximal tubule development [GO:0072014]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; regulation of osteoclast development [GO:2001204]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11836628_expressed in human osteoblastic cells and that the expression is differentially regulated upon stimulation with osteogenic factors 11978185_Notch signalling involved in differentiation of normal adult human epidermis is altered under experimental conditions and pathologies which modify this program. 12531696_Notch2 protein distribution in human teeth under normal and pathological conditions, and in embryo and adult. 12931033_identified two proteins that interacted with the Tat protein of the caprine arthritis encephalitis virus: the EGF-like repeats 1-6 of the extracellular domain of the human Notch2 receptor and the epithelin/granulin growth factor precursor 14609630_EGF-like repeats1-6 of human Notch2 interact with Tat protein of Hiv-1 14726396_Notch receptors 1&2 and their ligand Jagged1 are highly expressed in cultured and primary MM cells, suggesting Notch signaling is involved in the tight interactions between neoplastic plasma cells and their bone marrow microenvironment 15492845_Notch-2 could play a tumour-suppressive role in human breast cancer. 15507668_c-jun, junD, junB, and c-fos and Notch2 are expressed in splenic marginal zone lymphoma 15565166_Loss of Notch2 activity is an early steps in PI-induced apoptosis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia lymphocytes and may be part of the full apoptotic response. 15621797_review of mechanisms leading to the upregulation of CD23 in the leukemic cells and review of the potential functions of CD23 as well as its regulation by Notch2 in B-CLL 15976178_density of Notch ligands in different organ systems may be an important determinant in regulating cell-fate outcomes 16773578_Alagille syndrome is a heterogeneous disorder and implicates NOTCH2 mutations in human disease 16899352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17401372_The X-ray structure of the human NOTCH2 negative regulatory region, which adopts an autoinhibited conformation, is presented. 17573339_NOTCHES N1, N2, and N3 all bound to FIH; results suggest the possibility that Notch ICDs are FIH substrates. 17593975_Loss of NOTCH2 positively predicts survival in subgroups of human glial brain tumors. 17652726_Notch family members and ligands are expressed in the human corneal epithelium and appear to play pivotal roles in corneal epithelial cell differentiation 17675579_Results demonstrate that Notch2 signaling is a potent inhibitory signal in human breast cancer xenografts. 17920003_Cytoplasmic expression of Notch 2 receptors was downregulated and Notch signaling might be involved in development of hepatocellular carcinoma. 18087195_support the role of Notch and Akt in breast cancer progression 18184405_NOTCH2, NOTCH3 and NOTCH4 genes are rarely mutated in common human cancers. 18239137_Present a novel mechanism by which a balance between Notch-1/-2/-4 signaling, via CBF-1, and HRT-1/-2 activity determines the expression of smooth muscle differentiation markers including actin. 18266235_The absence of mutations in NOTCH2 and Hey2 its downstream target in the heart does not exclude the possibility that other genes in this pathway might be implicated in the diverse phenotypes observed in Alagille syndrome 18311147_activation of the Notch pathway, which is critical in glomerular patterning, contributes to the development of glomerular disease 18372903_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18508802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18508802_analysis of potentially activating mutations of NOTCH2 in 5% of MZL cases, comprising a splenic and an extranodal MZL case 18567820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18591388_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18703315_Wnt (Wnt2), Stat3, and Notch-1 and -2 signaling are correlated in human epidermal tumors. 18714373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020323_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19020324_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19119320_Results suggest that the NOTCH2 gene is not physically rearranged by t(1;19) translocation of oligodendroglioma tumors, and that the t(1;19) translocation arises from complex intra and interchromosomal rearrangements. 19139842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19147558_In gliomas, the TNC gene is transactivated by Notch2 in an RBPJk-dependent manner mediated by an RBPJk binding element in the TNC promoter. 19247373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19276344_Notch-2 and its ligand, Jagged-1, are highly up-regulated in gemcitabine resistant pancreatic cancer cells, which is consistent with the role of the Notch signaling pathway in the acquisition of EMT and cancer stem-like cell phenotype. 19324937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19330030_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339697_Notch signaling in B cells and B-cell lymphomas is only compatible with proliferation if pathways leading to antiapototic signals are active. 19404845_The levels of expression of Notch2 and Notch3 were minimally detected in renal cell carcinoma tumours and non-neoplastic tissues 19445024_mutant Notch2 receptors show increased activity compared with wild-type Notch2 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19502414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19602701_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19603167_Notch2 decreased statistically in immune thrombocytopenic purpura patients. 19653042_Notch2 expression is decreased in colorectal cancer and related to tumor differentiation status. 19670153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19701457_S1 cleavage has distinct effects on the surface expression of Notch1 and Notch2, but is not generally required for physiologic or pathophysiologic activation of Notch proteins 19720844_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19794065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19833888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19862325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20011512_TNF signaling activates Notch2 that sensitizes endothelial cells to apoptosis via modulation of the key apoptosis regulator survivin. 20069356_The pattern of Notch gene expression mirrors the progression from immature cells to endothelial-lined vascular channels (i.e., endothelial differentiation) that characterizes the growth and involution of infantile hemangioma. 20075150_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20351182_Notch2- but not Notch1-deficient CD8-positive T cells fail to expand in response to tumor inoculation; Notch2 signaling directly controls cytotoxic T lymphocyte effector molecules. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20482849_expression of NOTCH2 differs in subgroups of breast tumors and by genotypes of the breast cancer-associated SNP rs11249433 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20643108_The implication of a dysregulated Notch pathway to endothelial and vascular dysfunction. 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20829885_Notch 2 contributes to stem cell factor-mediated delay of erythroid differentiation. 20879858_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21124806_Data show no detectable difference in the DNA binding site preferences of CSL before and after loading of four different Notch receptors and MAML1 proteins. 21238798_In this study, Notch 2 receptors were detected in the lining epithelium of human periapical cysts with limited inflammation, showing Notch pathway activation in those cells. 21378985_Hajdu-Cheney syndrome mutations are predicted to lead to the premature truncation of NOTCH2 with either disruption or loss of the C-terminal proline-glutamate-serine-threonine-rich proteolytic recognition sequence. 21378989_Mutations in NOTCH2 are a major cause of Hajdu-Cheney syndrome 21378989_sequenced the exomes of six unrelated individuals with Hajdu-Cheney syndrome and identified heterozygous nonsense and frameshift mutations in NOTCH2 in five of them 21437251_Notch-2 was identified as a novel target for beta-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling. 21443520_Down-regulating Notch signaling may be a useful approach to inhibit the progression of pancreatic cancer 21466361_This study demonstrated a close correlation of Notch2 expression with gastric cancer formation and the potential link of Notch1 upregulation with intestinal-like phenotypes of gastric lesions. 21471519_Data show that Notch1 to -3 may have potential use as a strong prognostic fact 21639801_NOTCH2 expression and activation, independent of JAGGED1 expression, may contribute to the pathogenesis of hepatoblastoma. 21681853_Our results support the suggestion that modulation of the Notch pathway, and specifically NOTCH2, may be a productive therapeutic mode for treatment of typical age-related osteoporosis. 21726900_The receptors Notch2, -3, -4 and their ligands Jagged1, -2 and Delta1, -4 were detected at both the mRNA and protein level in early and late placenta 21793104_Serpentine fibula-polycystic kidney syndrome and Hajdu-Cheney syndrome are both conditions caused by NOTCH2 mutations. 21976141_suppression of tumor progression by Notch2 knockdown in SC-M1 cells was reversed by exogenous COX-2 or its major enzymatic product PGE(2) 22006338_study describes a spectrum of inactivating somatic mutations of Notch receptors in lung and skin cancers, indicating that Notch loss of function plays a prominent role in multiple variants of squamous cell carcinomas 22161246_The expression of Notch2 gene in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients, was examined. 22190591_Paired upregulation of Notch2 and Six1 is a transcriptional aberration that contributes to preinvasive-to-invasive adenocarcinoma progression by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and nuclear atypia. 22209762_This work confirms the importance of NOTCH2 as a second disease gene in ALGS and expands the repertoire of the NOTCH2 related disease phenotype. 22526456_immunohistochemical analysis of NOTCH1-3, JAGGED1, cMET, and phospho-MAPK in 100 carcinomas of unknown primary 22695918_Inactivating mutations are found in Notch2 signaling pathways in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, while activating mutations are found in mature B cell lymphomas. (Review) 22717580_Notch2 signaling in NSCs produces features of GSCs and induces astrocytic lineage entry, consistent with a possible role in astrocytoma formation 22891273_Mutations in NOTCH2, a gene required for marginal-zone B cell development, represent the most frequent lesion in splenic marginal zone lymphoma 22891276_NOTCH2 mutations play a role in the pathogenesis and progression of the splenic marginal zone lymphoma and are associated with a poor prognosis. 22915591_Characterization of CSL (CBF-1, Su(H), Lag-1) mutants reveals differences in signaling mediated by Notch1 and Notch2. 22970250_Taken together, the GSK3B, CTNNB1 and NOTCH2 expression signature is a novel, promising prognostic parameter for gastric cancer 23011796_Data indicate that force applied to the Notch2 negative regulatory region (NRR) can indeed expose the S2 site and, crucially, allow cleavage by the metalloprotease TACE (TNF-alpha-converting enzyme). 23243020_Findings indicate a critical role for the midkine-Notch2 signaling axis in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis, which implicates new strategies to treat neuroblastoma. 23326131_Notch2 may negatively regulate cell invasion by inhibiting the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer 23331119_an imbalanced interaction of Jagged1 expression in periductal and periportal myofibroblasts and Notch2 expressed in cholangiocytes, may be involved in the formation of bile duct lesions in Polycystic kidney rats 23380742_These data indicate that Notch signaling controls human CD8(+) T cell priming and also influences effector T cell functions. 23389697_The findings confirm that heterozygous NOTCH2 mutations are the cause of Hajdu-Cheney Syndrome and expand the mutational spectrum of this disorder. 23401378_Clinical and molecular data (NOTCH2 mutations) suggest that Hajdu-Cheney syndrome and serpentine fibula polycystic kidney syndrome are a single disorder with variable degree of expression. [Case-report and review] 23444212_Data indicate that the expression of Notch-2 and Notch-4 receptors was higher in the GFP-bright population whereas Notch-1 and Notch-3 receptors were more expressed in GFP-dim population. 23536545_Pancreatic cancer stem cells expressing NOTCH2 are highly tumorigenic in mice. 23549787_netrin-1 forms a complex with both Notch2 and Jagged1. 23587900_This study supports the involvement of Notch2 and Notch4 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. Participation of Notch2 seems more evident in male patients, possibly early onset, while that of Notch4 is more evident in late onset female patients. 23589286_An increase in expression of selective NOTCH receptors (NOTCH1 and -2), ligand (JAGGED2), and target genes (HES1, HEY1, and HEY2) was observed in NP cells following cytokine treatment. 23752887_The role of NOTCH2 and JAG1 in formation of proximal nephron structures and podocytes might explain the observed phenotypes of renal dysplasia and proteinuria in patients with Alagille syndrome. 23965337_Propose a receptor-specific function for Notch2 in regulating Jag-1-induced p27(kip1) expression and growth arrest in vascular smooth muscle cells. 23967108_genetic variation in NOTCH2 increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes among people exposed to inorganic arsenic 23999936_A gene fusion involving MIR143 in band 5q32 was identified with NOTCH2 in 1p13 in glomus tumors 24122995_NOTCH1 and 2 knockdown reduces the level of mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein in the monoblastic leukemia cell line THP-1. 24151014_In the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and amygdala of suicide victims, NOTCH2 expression is decreased compared to control brain. 24336671_In the placentas from women with early-onset severe preeclampsia, Notch2 expression was significantly increased. 24489102_Knockdown of Notch1 and Notch2 genes in gammadelta T cells using small interfering RNA inhibited their antitumor cytotoxic potential 24574459_NOTCH2 and FLT3 mis-splicing is a common characteristic of AML and has the potential to generate transcripts encoding proteins with altered function. 24671051_Expression of Notch1, -2, and -3, CDK2, and CCNE1 was significantly decreased by upregulation of ALDH1A1 in A549 cells, but increased by its interruption in A549s cells. 24995648_All three syndromes result from mutations in the gene that encodes NOTCH2. 25038880_The present study indicates that Notch2 activation by ZER inhibits its proapoptotic and anti-migratory response at least in breast cancer cells. 25041344_Its signaling pathway determines pathological aggressiveness of intra ductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. 25141821_NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 mutations are uncommon in Follicular lymphoma but may occur in a subset of cases with distinctive, characteristic, clinicopathological features. 25257302_drives multiple myeloma associated osteoclast development and bone destruction 25311243_Intracellular NOTCH1 and NOTCH2, by inducing MYC, suppressed miR-30a in B- and T-cell malignancies. 25314575_The Notch2 receptor with PEST domain truncation enhances cell proliferation which may be associated with the activation of the Notch2 and the NF-kappaB signaling. 25323114_The cumulative survival rate was significantly longer in the Notch2shRNA group. 25338527_28 of 30 in: Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jan;11(1) Interference of Notch 2 inhibits the progression of gliomas and induces cell apoptosis by induction of the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase 25368376_a novel biological method that entails selection of human BMSCs based on NOTCH2 expression and activation of the NOTCH signaling pathway in cultured BMSCs via a tissue culture plate coated with recombinant human JAGGED1 (JAG1) ligand. 25381127_NOTCH2 mutations were associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with hepatitis C virus infection. 25381598_High NOTCH2 expression is associated with minimal deviation adenocarcinoma of uterine cervix. 25397403_Notch2 controls prolactin and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 expression in decidualizing human stromal cells of early pregnancy. 25491639_This review establishes that gain-of-function mutations of NOTCH2 are associate with Hajdu-Cheney syndrome. 25558064_Inhibition of Notch2 prevents goblet cell metaplasia induced by a broad range of stimuli. 25574842_results indicate that NOTCH serves as a tumor suppressor in the bladder and that loss of this pathway promotes mesenchymal and invasive features. 25659500_Data suggest that expression of NOTCH2 in first-trimester placenta is cell-type specific; NOTCH2 is expressed in differentiated cells of extravillous trophoblast lineage; inhibition of NOTCH2 by RNA interference promotes trophoblast motility. 25676721_AGS is caused by mutations in one of two genes, namely, JAG1 or NOTCH2. These genes are part of the Notch signaling pathway, which is involved in cell fate determination. JAG1 mutations have been identified in 70-94% of individuals with clinically diagnosed AGS 25696021_Hajdu-Cheney syndrome and serpentine fibula-polycystic kidney syndrome are a single disease entity with a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations associated with truncating mutations in exon 34 of NOTCH2. 25849484_High Notch2 expression is associated with chronic myeloid leukemia. 25918160_Human NOTCH2 but not mouse Notch2 is resistant to negative regulatory region perturbation and ligand-independent activation by Adam17. 25957400_NOTCH2 inhibits PDGF-B-dependent proliferation and its expression is decreased by PDGF-B. 25985737_C8orf4 negatively regulates the self-renewal of liver CSCs via suppression of NOTCH2 signalling 25992613_miR-191 represses proliferation in primary human fibroblasts via targeting multiple proto-oncogenes, including CDK9, NOTCH2, and RPS6KA3. 26018735_NOTCH2 inhibition triggers the Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle and cell apoptosis; and NOTCH2 inhibition may represent an appealing therapeutic strategy against Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies. 26041881_Results suggest that Notch2 pathway and miR-23b interplay in a reciprocal regulation loop in gastric cancer cells and this axis plays an important role in gastric carcinogenesis. 26041884_Notch signaling sustains chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival by promoting Mcl-1 expression and eIF4E activity, and given the oncogenic role of these factors, underscores the therapeutic potential of Notch inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 26165719_A functional polymorphism in the premiR146a gene influences the prognosis of glioblastoma multiforme by interfering with the balance between Notch1 and Notch2 26252838_These findings suggested that the NOTCH2 signaling may confer aggressive behavior and immature morphology in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 26427670_suggest that Notch2 has an essential role in the cell growth, invasion, and migration of SACC. Notch2 may therefore be a potential target gene for the treatment of SACC by interfering with cell growth and metastasis 26640406_Notch2 and Notch3 inhibited both cell proliferation and cell apoptosis in BeWo and JAR trophoblast cell lines. 26769750_NOTCH2 acts as an oncogene that promotes bladder cancer growth and metastasis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, cell-cycle progression, and maintenance of stemness. Inhibition of NOTCH2 is a rational novel treatment strategy for invasive bladder cancer. 26933171_Notch1 and Notch2 are the primary Notch receptors regulating epithelial cell homoeostasis in mouse and human stomach. 26983574_This is supported by the depletion of CTCF in glioblastoma cells affecting the expression levels of NOTCH2 as a target of miR-181c. CONCLUSION: Together, our results point to the epigenetic role of CTCF in the regulation of microRNAs implicated in tumorigenesis 27073072_In gastric epithelial cells co-cultured with Helicobacter pylori, there was a significant reduction in the mRNA expression level of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2, together with a reduced level of active forms of NOTCH1 (NICD1) and NOTCH2 (NICD2). 27118257_Low levels of Notch pathway genes Notch1, Notch2, Notch4 and Jagged1 correlated with poor prognostic factors such as larger tumor size, positive lymph-node status, tumor phenotype and infiltrating tumor Treg cells. 27158037_Notch2 is up-regulated in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues and could serve as a promising biomarker for identifying individuals with poor prognostic potential. 27221981_Notch2 may confer stemness properties in HCC. 27335277_Mutation in NOTCH2 gene is associated with nodal marginal zone lymphoma. 27460529_Findings indicate that niclosamide inhibits the progression of colon cancer by downregulating Notch1, Notch2 and Notch3 signaling and by upregulating the microRNA miR-200 family members (miR200a, miR-200b, miR-200c). 27502039_These data demonstrated fascin as a critical regulator of breast cancer stem cell pool at least partially via activation of the Notch self-renewal signaling pathway. 27564686_this study shows that Treg cells infiltrating uveitic eyes display elevated Notch2 expression 27566587_analysis of highly recurrent genetic lesions in components of the NF-kappaB pathway, of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 as well as KMT2D that may have a role in ocular adnexal MALT-type marginal zone lymphomas 27697639_Macrophage notch1 may play a more important role than notch2 and notch 3 in the regulation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway in atherosclerosis. 27717083_Mutations in NOTCH2 gene is associated with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 27800305_In conclusion, Notch siganling appears to be an important mediator of the liver inflammation by modulating hepatic IL-22-secreting NKp46(+) innate lymphoid cells. 27832663_miR-146a-5p functions as a tumour-suppressive miRNA targeting Notch2 and inhibits the EMT progression of ESCC 27966788_Intermittent compressive stress regulates Notch receptor and target gene expression via the TGF-beta signaling pathway. Notch signaling participates in TGF-beta-induced sclerostin expression in periodontal ligament cells. 28061457_Data indicate that mRNA high expression level of Notch1 was associated with better overall survival (OS) for all NSCLC, hazard ratio (HR), better OS in adenocarcinoma (Ade), HR, as well as in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), HR, and mRNA high expression levels of Notch2 and Notch3 were associated with worsen OS for all NSCLC, and mRNA high expression level of Notch4 was not found to be associated with to OS for all NSCLC. 28084316_TNFalpha regulates NOTCH2 and NOTCH3 expression in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via preferential ACTR-IIA signalling in BMPR-II-deficient cells. 28161537_High NOTCH2 expression is associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer. 28167435_Genetic variation in NOTCH2 was associated with troponin T levels in women with psychosis. 28389242_Together, these data show that miR-181a may play an essential role in GSC formation and GBM progression by targeting Notch2, suggesting that Notch2 and miR-181a have potential prognostic value as tumor biomarkers in GBM patients. 28522570_results confirm the association of the NOTCH2-mutation with shorter median treatment-free survival and suggest the possible usefulness of the identification of these changes for the diagnosis of splenic marginal zone lymphoma. 28572448_The authors present novel structures of human ligands Jagged2 and Delta-like4 and human Notch2, together with functional assays, which suggest that ligand-mediated coupling of membrane recognition and Notch binding is likely to be critical in establishing the optimal context for Notch signalling. 28592489_Transgenic mice harboring Notch2 mutation analogous to that in patients with Hajdu-Cheney syndrome (HCS) are severely osteopenic because of enhanced bone resorption; this model has now been validated. Data from further studies in transgenic mice suggest that the HCS mutation in osteoblasts, but not in osteoclasts, causes osteopenia in this model. 28666642_Notch2 is important in Club cell differentiation in normal lungs and adenocarcinoma. Notch2 is regulated mutually with Notch1, and the balance of the expression of Notch receptors could determine the biological behaviours of lung cancer cells. 28688656_Human biliary atresia and 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine (DDC)-induced experimental cholestasis in mice are associated with increased expression of Notch2. 28705113_our results indicated epidermal growth factor-like domain multiple 7 protein participates in growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma proliferation and invasion regulation via Notch2/DLL3 signaling pathway. These findings raised the possibility that epidermal growth factor-like domain multiple 7 protein might serve as a useful biomarker to assess growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma invasion and prognosis 28733035_The data showed that the overexpression of miR-18a-5p could downregulate Notch2 expression and subsequently suppress endothelial-mesenchymal transition and cardiac fibrosis. 28796347_ATRX, NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 expression varies in angiosarcomas and shows significant correlations with site of origin and poor clinical outcome 28820917_Major genomic mutation profiles in lacrimal gland adenoid cystic carcinoma (LGACC) were uncovered by exome-seq. Although preliminary in nature, the Notch pathway could be a potential therapeutic target for LGACC. 28849037_IRF4 is overexpressed in human non-small cell lung cancer and activates the Notch signaling pathway. 28851699_Examination of the molecular underpinnings of this 'NOTCH2-BCR axis' in cGVHD revealed imbalanced expression of the transcription factors IRF4 and IRF8, each critical to B-cell differentiation and fate. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) increased IRF4 expression, restored the IRF4-to-IRF8 ratio, abrogated BCR-NOTCH hyperactivation, and reduced NOTCH2 expression in cGVHD B cells without compromising viability. 28923203_miR-34a expression is silenced epigenetically by EZH2 and DNA methylation, which promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell growth through activation of the Notch pathway. 29075789_BANCR may promote melanoma cell growth through inhibition of miR204, leading to the activation of Notch2 pathway. Authors further demonstrated that BANCR knockdown inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Results suggest the BANCR/miR204/Notch2 axis mediates melanoma cell proliferation and tumor progression. 29229388_The SNHG12/miR-195-5p/Notch2-Notch signaling pathway axis might become a novel therapeutic target for osteosarcoma. SNHG12 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA, modulating the expression of Notch2 by sponging miR-195-5p in osteosarcoma. 29329397_MINAR1 physically interacts with Notch2 and its binding to Notch2 increases its stability and function. 29581534_Further studies verified that miR-1 regulates EMT signalling pathways directly through Notch2. Therefore, these results confirm that, as a tumor suppressor gene, miR-1 may be a potential tumor marker for the early diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and a new drug target 29626590_Altered expression of WFS1 and NOTCH2 genes may play a role in pathogenesis and development of DN in patients with T2DM. 29643502_Review of the roles of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 in urinary bladder cancer suggests that NOTCH1 acts as a tumor suppressor and NOTCH2 acts as an oncogene that promotes cell proliferation and metastasis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, cell cycle progression, and maintenance of stemness. 29702280_In conclusion, we demonstrated that EV71 infection induced elevated expressions of TLR3/4 and Notch1/2 in CD14+ monocytes. 29767458_This review focuses on the mutations described in NOTCH1, NOTCH2, and NOTCH3 and their associated cardiovascular phenotypes. 29875313_Reduced monocyte NOTCH2 expression in neutralizing antidrug antibodies (nADA)+ multiple sclerosis patients was associated with NOTCH2. NOTCH2 activation was T cell dependent and was only triggered in the presence of serum from nADA+ patients. Thus, nADA development was driven by a proinflammatory environment that triggered activation of the NOTCH2 signaling pathway prior to first IFN-beta administration. 29915190_Notch2 depletion significantly reduced the mesenchymal stem cell-mediated radio-protective effect in human- and mouse-derived hematopoietic progenitor/stem cell. 30226866_Jag1 and Notch2 play a key role in kidney fibrosis development by regulating Tfam expression and metabolic reprogramming. 30242258_Notch2 activation in the microenvironment is a pre-requisite for the activation of canonical Wnt signalling in tumour cells. 30296524_this study shows increased surface expression of NOTCH2 on memory T cells in peripheral blood from patients with asthma 30304577_NOTCH2 mutations contribute to primary ovarian insufficiency etiology. 30404578_High NOTCH2 expression is associated with bladder cancer. 30470250_ectopic miR-181b expression suppressed cancer stem cell properties and enhanced sensitivity to cisplatin (DDP) treatment by directly targeting Notch2. miR-181b could inactivate the Notch2/Hes1 signalling pathway. 30497876_that miR-1-5p acted as a suppressive miRNA and played vital roles in the growth, migration and invasion of gallbladder carcinoma cell through targeting Notch2 30523789_Notch2 expression is associated with neural stem cells differentiation status. 30580840_Increase in Notch2 expression in RANKL-predominant periapical lesions corroborates their joined involvement in extensive periapical bone resorption. 30808369_miR-195-5p may play a vital role in regulating NOTCH2-mediated tumor cell EMT, thereby affecting IL-4-related M2-like TAM polarization in CRC. 31239543_Notch2 represents a key determinant of breast cancer cellular dormancy and mobilisation in the bone microenvironment. 31316119_Notch Inhibition Prevents Differentiation of Human Limbal Stem/Progenitor Cells in vitro. 31343788_Study identified three novel NOTCH2 variants and along with previously published ones, these data present the most comprehensive pathogenic variants overview for Alagille syndrome. 31413119_The GGC repeated expansion in the 5'UTR of the NOTCH2NLC gene is associated with the pathogenesis of NIID. 31433517_A GGC expansion in NOTCH2NLC was found to be the most frequent cause of adult leukoencephalopathy. 31659254_ZNF774 is a potent suppressor of hepatocarcinogenesis through dampening the NOTCH2 signaling. 31699119_These findings reveal that loss of NOTCH2 activates the TRAF6/AKT axis and promotes metastasis in NPC, suggesting that NOTCH2 may represent a therapeutic target for the treatment of NPC. 31854042_The analysis of tissue samples from patients revealed that the expression of NOTCH2 was hig |
ENSMUSG00000027878 |
Notch2 |
907.439224 |
3.5160168667 |
1.813942 |
0.070606404 |
658.488109 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031851723196918482491187595886305900829479757825831863143480341010429185765804649204101995228383613413892808157988811795494647747337429960840160098499183120550012402977002964160629787149 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000019836769383397333295133534677438515218620910015931754264809387412093395066664563251418915250629274109623963746220679740790575382785375762626110460901592560691802824316177653990496952125 |
Yes |
No |
1414.4066251 |
54.8311937 |
405.1284496 |
12.7493186 |
| ENSG00000134253 |
80263 |
TRIM45 |
protein_coding |
Q9H8W5 |
FUNCTION: May act as a transcriptional repressor in mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15351693}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the tripartite motif family. The encoded protein may function as a transcriptional repressor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:80263; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; bone development [GO:0060348]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893] |
15351693_TRIM45 may act as a new transcriptional repressor in mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway 22634006_These findings suggest that TRIM45 acts as a repressor for the NF-kappaB signal and regulates cell growth. 24681954_The TRIM-FLMN protein TRIM45 directly interacts with RACK1 and negatively regulates PKC-mediated signaling pathway. 28542145_These findings suggest that TRIM45 is a novel tumor suppressor that stabilizes and activates p53 in glioma. 31663468_TRIM45 Suppresses the Development of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000033233 |
Trim45 |
18.536959 |
0.3219482487 |
-1.635099 |
0.407239560 |
16.484038 |
0.00004906136859953840736667252109270975779509171843528747558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000141379500298552710727678638491511264874134212732315063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6447982 |
2.7457297 |
27.2370296 |
5.6489388 |
| ENSG00000134333 |
3939 |
LDHA |
protein_coding |
P00338 |
FUNCTION: Interconverts simultaneously and stereospecifically pyruvate and lactate with concomitant interconversion of NADH and NAD(+). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11276087}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycogen storage disease;Isopeptide bond;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Fermentation; pyruvate fermentation to lactate; (S)-lactate from pyruvate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:11276087}. |
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the conversion of L-lactate and NAD to pyruvate and NADH in the final step of anaerobic glycolysis. The protein is found predominantly in muscle tissue and belongs to the lactate dehydrogenase family. Mutations in this gene have been linked to exertional myoglobinuria. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. The human genome contains several non-transcribed pseudogenes of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:3939; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; oxidoreductase complex [GO:1990204]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; L-lactate dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004459]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; lactate metabolic process [GO:0006089]; pyruvate metabolic process [GO:0006090]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] |
12555229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12555229_an LDHA exon5 haplotype confers increased risk for paradoxically decreased minute volume respiratory response to CO2 challenge but not to panic disorder 12629811_The study of this protein in a sportsman is significant for assessment of training efficiency. 12712614_The activity of this enzyme was studied in tissues, erythrocytes, and blood plasma of patients with peptic ulcer both in its uncomplicated course and in the development of complications. 15240094_These data indicate that LDH-A is induced through a non-genomic pathway of estrogen action. 16132575_Lactate dehydrogenase 5 content in tumor cells is directly related to an up-regulated hypoxia inducible factor pathway and is linked with an aggressive phenotype in colorectal adenocarcinomas. 16766262_Reduction in LDH-A activity resulted in stimulation of mitochondrial respiration and decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential.The tumorigenicity of the LDH-A-deficient cells was severely diminished. 17178662_LDH1 was decreased in essential thrombocythemia. This isoenzymatic pattern could be expression of a metabolic adaptation. 17178662_LDH5 was reduced in idiopathic myelofibrosis. This isoenzymatic pattern could be expression of a metabolic adaptation [LDH5] 17483170_biophysical study of ligand binding and protein dynamics in lactate dehydrogenase 18521687_The results of the current study show that LDH-5 expression may be a useful prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma. 18534967_LDL-M is released into blood fo patients exposed to myocardial ischemia reperfusion. 18814027_Modulation of LDH expression involves alpha6beta4 integrin-FAK-p38MAPK pathway. 18821170_The expression of LDH and its isoenzymes in pleural effusions reflects the host reaction in pleural space and, in non-small-cell lung cancer, may also feature the anaerobic phenotype of cancer cells. 19021062_LDH5 is highly upregulated in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas and is in direct relation to factor HIF1alpha and HIF2alpha expression. LDH5 expression is linked with activated VEGFR2/KDR expression in both lymphoid lesions. 19276158_LDH-A knockdown in the background of FH knockdown results in significant reduction in tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. 19668225_ErbB2 promotes glycolysis at least partially through the HSF1-mediated upregulation of LDH-A. 19838163_Correlation of LDH-5 expression with clinicopathological factors and with the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, Mcl-1 and GRP78 was examined in pigmented lesions, including nevi and melanoma at different stages of progression 19847924_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923867_LDH5 is highly expressed in squamous cell head and neck cancer and is linked with local relapse, survival and distant metastasis. 20385008_LDH5 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and could serve as a marker for malignancy. LDH5 correlates positively with the prognostic marker transketolase like 1 protein. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20828817_High lactate dehydrogenase is associated with acute adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20951115_Presented are QM/MM calculations that show differences in geometries of active sites of M(4) and H(4) isoforms of human LDH ligated with oxamate, pyruvate or L-lactate. 21249322_High LDH is associated with M1b prostate cancer. 21452021_LDH-A reduction resulted in an inhibited cancer cell proliferation, elevated intracellular oxidative stress, and induction of mitochondrial pathway apoptosis. 21632858_Serum LDH and tissue LDH5 levels are complementary features that help to characterize the activity of LDH in colorectal cancer and have a potent value in predicting response to chemotherapy. 21858537_Results show that S-100B, MIA and LDH levels were significantly higher in patients with advanced melanoma than in disease-free patients or healthy controls. 21969607_LDH-A is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated by FGFR1 in cancer cells. 22127970_Case Report: describe an elderly patient with physical therapy-induced rhabdomyolysis complicated by acute kidney injury associated with reduced skeletal muscle LDH-A activity. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22429998_We demonstrate that LDH-A reduction can suppress the tumorigenicity of intestinal-type gastric cancer (ITGC) cells by downregulating Oct4 both in vitro and in vivo. 22593701_Data suggest that serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) kinetics might reflect disease behaviour in extracranial metastatic and primary sites without need for comprehensive imaging studies and is a quite inexpensive diagnostic test. 22897481_Studies indicate the mechanisms by which lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) promotes tumor growth and metastasis. 22923663_Lactic acid induces myofibroblast differentiation via pH-dependent activation of transforming growth factor beta. 22948140_Cells expressing either PDK1 or LDHA maintained a lower mitochondrial membrane potential and decreased reactive oxygen species production with or without exposure to toxins. 22961700_LDHA plays an important role in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating cell growth 23166385_Elevated lactate dehydrogenase level is associated with recurrent or refractory aggressive lymphoma. 23184277_Increased LDH5 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23266049_Data indicate that serum lactic dehydrogenase (S-LDH) appears to be a significant independent prognostic index in patients with metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). 23318563_The result suggest that assessment of NGAL in peritoneal fluids, especially in combination with LDH, may be a reliable approach for screening of bacterial peritonitis in patients with new onset nonmalignant ascites. 23404405_Lactate dehydrogenase A is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer. 23467744_Human LDHA was introduced as a transgene to Ldhc-null mice and rescued sperm function. 23516535_the role played by ERRalpha in the regulation of lactate dehydrogenases A and B 23583676_It is shown that shRNA mediated knockdown of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), a key mediator of aerobic glycolysis, results in elevated mitochondrial ROS production and a concomitant decrease in cell proliferation and motility. 23703029_The PFK2 expression along with LDH-4 were observed to be increased ~2-fold (P 145% as well as baseline LDH were associated with impaired overall survival (OS) whereas increasing LDH of >25% was not (P = .64). S100B could serve as a strong baseline marker for OS in melanoma patients receiving anti-PD-1 therapy. 29970686_High LDH expression is associated with small cell lung cancer. 30015851_the results of the present study demonstrated that miR199a3p can inhibit LDHA expression by downregulating Sp1, and provided mechanistic evidence supporting the existence of a novel miR199a3p/Sp1/LDHA axis and its critical contribution to aerobic glycolysis in testicular cancer cells. 30138330_e evaluated the link between mTOR kinase activity and the level of LDH expression / function. Furthermore, we elaborated the metabolic changes produced in cells by the mTOR-directed LDH-A up-regulation. Interestingly, we observed that in the non-neoplastic MCF-10A culture, mTOR-directed up-regulation of LDH-A was followed by a reprogramming of cell metabolism, which showed an increased dependence on glycolysis rather tha 30158244_Knockout of both LDH-A and LDH-B leads to suppression of glycolysis. 30197328_This is the first study from this highly prevalent region of Head neck cancer showing that serum LDH could be regarded as a biomarker for malignant and premalignant conditions of the head and neck. 30209241_LDHA inhibition fails to impact human melanoma cell proliferation, survival, or tumor growth. Reduced intracellular serine and aspartate following LDHA inhibition engage GCN2-ATF4 signaling to initiate an expansive pro-survival response. 30213286_The study reveals that miR-33b plays a suppressive role in the regulation of osteosarcoma cell proliferation through direct targeting LDHA. 30417313_High LDH expression is associated with gastric cancer. 30509961_LDHA promotes malignant behavior via activation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma. 30521130_the present study reports that the combination of tumour stroma percentage and tumour cell expression of cytoplasmic MCT-2 or nuclear LDH-5 is associated with poor prognosis. 30587628_Oligometastatic disease is not always correctly diagnosed, because all radiological modalities are limited by certain thresholds for detection of small metastases. We hypothesize that LDH is associated with survival, because this biomarker may reflect the total burden of malignant disease. 30610122_LDHA and LDHB are dispensable for aerobic glycolysis in neuroblastoma cells while promoting their aggressiveness. 30618169_Repression of LDHA induced by wt-p53 blocks tumor growth and invasion through downregulation of aerobic glycolysis in breast cancer. 30688660_Chronic stress-induced epinephrine activated LDHA to generate lactate, and the adjusted pH directed USP28-mediated deubiquitination and stabilization of MYC. 30878502_Results indicate that LDHA modulates autophagy by interacting with Beclin-1 in tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells. Further data confirmed the association of LDHA in apoptosis resistance, increasing of EMT like phenomena and augmented pro-survival autophagy leading to the enhanced survivability of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. 30976022_Diagnostic value of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and lactate dehydrogenase in paediatric malignant solid tumour concurrent with infection and tumour progression. 31037905_Knockdown of LDHA by siRNA inhibits the migration and invasion via downregulation of glycolysis in ErbB2 over expressing breast cancer cell line 31100640_LDHA/PDHA1 changes in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) resulted in a broad metabolic reprogramming while intracellular molecules including polyunsaturated fatty acids and nitrogen metabolism related metabolites underlie the malignant changes. 31257519_the results of the present study demonstrated that chidamide reprogramed glucose metabolism, partially by targeting the miR33a5p/LDHA pathway, in Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). These findings indicate that chidamide may be a promising novel drug in the treatment of patients with TNBC. 31298387_MicroRNA 34b inhibits cell proliferation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia via regulating LDHA. 31366532_Serum LDH levels at baseline before nivolumab treatment were associated with the objective response and clinical outcome of nivolumab treatment 31471554_we demonstrate here that inhibition with siRNA against the glycolytic genes PFKFB3 or LDHA, respectively, prevents the proliferation of HUVECs and inhibits vessel formation in vitro as well as in vivo. 31570164_MTA1 coregulator has a role in regulating LDHA expression and function in breast cancer 31838771_The Warburg effect and tumour immune microenvironment in extramammary Paget's disease: overexpression of lactate dehydrogenase A correlates with immune resistance. 31886754_The Biochemical and Clinical Perspectives of Lactate Dehydrogenase: An Enzyme of Active Metabolism. 32319143_ARNT-dependent CCR8 reprogrammed LDH isoform expression correlates with poor clinical outcomes of prostate cancer. 32359394_Quantification analysis of lactate dehydrogenase and C-reactive protein in evaluation of the severity and prognosis of the acute pancreatitis. 32493992_Impact of hypoxia on chemoresistance of mesothelioma mediated by the proton-coupled folate transporter, and preclinical activity of new anti-LDH-A compounds. 32707073_ANXA2P2/miR-9/LDHA axis regulates Warburg effect and affects glioblastoma proliferation and apoptosis. 32719987_MiR-34a suppresses osteoblast differentiation through glycolysis inhibition by targeting lactate dehydrogenase-A (LDHA). 32777299_STIP1 down-regulation inhibits glycolysis by suppressing PKM2 and LDHA and inactivating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cervical carcinoma cells. 32859246_Lysine-222 succinylation reduces lysosomal degradation of lactate dehydrogenase a and is increased in gastric cancer. 32859627_Whole-transcriptome Analysis of Fully Viable Energy Efficient Glycolytic-null Cancer Cells Established by Double Genetic Knockout of Lactate Dehydrogenase A/B or Glucose-6-Phosphate Isomerase. 33110235_Metabolic programming of distinct cancer stem cells promotes metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 33452143_Prognostic value of elevated lactate dehydrogenase in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 33470415_High Expression of Lactate Dehydrogenase A is a Potential Promoter of Malignant Behaviour in Extramammary Paget's Disease. 33571038_E2F1-Induced FTH1P3 Promoted Cell Viability and Glycolysis Through miR-377-3p/LDHA Axis in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 33663300_Readily available biomarkers predict poor survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer. 33664867_KDM6B-mediated histone demethylation of LDHA promotes lung metastasis of osteosarcoma. 33677931_Lactate Dehydrogenase A as a Potential New Biomarker for Thyroid Cancer. 33714987_POU1F1 transcription factor induces metabolic reprogramming and breast cancer progression via LDHA regulation. 33756038_H19 promotes aerobic glycolysis, proliferation, and immune escape of gastric cancer cells through the microRNA-519d-3p/lactate dehydrogenase A axis. 33962616_Blocking circ-CNST suppresses malignant behaviors of osteosarcoma cells and inhibits glycolysis through circ-CNST-miR-578-LDHA/PDK1 ceRNA networks. 34022218_Excess exogenous pyruvate inhibits lactate dehydrogenase activity in live cells in an MCT1-dependent manner. 34051289_Redox-responsive nanoassembly restrained myeloid-derived suppressor cells recruitment through autophagy-involved lactate dehydrogenase A silencing for enhanced cancer immunochemotherapy. 34110068_LDH-A negatively regulates dMMR in colorectal cancer. 34168116_Novel circular RNA circSLIT2 facilitates the aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via miR-510-5p/c-Myc/LDHA axis. 34185423_Functional inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase suppresses pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression. 34217785_A feedback circuit comprising EHD1 and 14-3-3zeta sustains beta-catenin/c-Myc-mediated aerobic glycolysis and proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. 34217973_LDHA is enriched in human islet alpha cells and upregulated in type 2 diabetes. 34242184_Diagnostic and early prognostic value of serum CRP and LDH levels in patients with possible COVID-19 at the first admission. 34278456_Hypoxiainduced lactate dehydrogenase A protects cells from apoptosis in endometriosis. 34293399_Antitumor effect of dimethyl itaconate on thymic carcinoma by targeting LDHA-mTOR axis. 34404767_STAT3/LINC00671 axis regulates papillary thyroid tumor growth and metastasis via LDHA-mediated glycolysis. 34409524_Circ-DONSON Facilitates the Malignant Progression of Gastric Cancer Depending on the Regulation of miR-149-5p/LDHA Axis. 34463208_Long non-coding RNA LINC01207 promotes cell proliferation and migration but suppresses apoptosis and autophagy in oral squamous cell carcinoma by the microRNA-1301-3p/lactate dehydrogenase isoform A axis. 34478437_Association between serum lactate dehydrogenase and frailty among individuals with metabolic syndrome. 34482592_Downregulation of GTSE1 leads to the inhibition of proliferation, migration, and Warburg effect in cervical cancer by blocking LHDA expression. 34495869_Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, lactate dehydrogenase, D-dimer, and computed tomography score in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. 34635009_Novel circular RNA circATRNL1 accelerates the osteosarcoma aerobic glycolysis through targeting miR-409-3p/LDHA. 34708888_Association between serum lactate dehydrogenase and 60-day mortality in Chinese Hakka patients with acute myeloid leukemia: A cohort study. 35092510_ErbB2 promotes breast cancer metastatic potential via HSF1/LDHA axis-mediated glycolysis. 35102488_Hippocalcin-like 1 is a key regulator of LDHA activation that promotes the growth of non-small cell lung carcinoma. 35191522_Inhibition of LDHA suppresses cell proliferation and increases mitochondrial apoptosis via the JNK signaling pathway in cervical cancer cells. 35343073_Inhibition of KDM4C/c-Myc/LDHA signalling axis suppresses prostate cancer metastasis via interference of glycolytic metabolism. 35349377_Clinical Significance and Prognostic Value of Lactate Dehydrogenase Expression in Cervical Cancer. 35615882_GLUT1, LDHA, and MCT4 Expression Is Deregulated in Cervical Cancer and Precursor Lesions. 35794505_Lactate dehydrogenase as promising marker for prognosis of brain metastasis. 35832094_N(6)-methyladenosine-mediated LDHA induction potentiates chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells through metabolic reprogramming. 35858615_Capsaicin ameliorates inflammation in a TRPV1-independent mechanism by inhibiting PKM2-LDHA-mediated Warburg effect in sepsis. 36033372_MYC Promotes LDHA Expression through MicroRNA-122-5p to Potentiate Glycolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 36064857_Adipocyte-derived lactate is a signalling metabolite that potentiates adipose macrophage inflammation via targeting PHD2. 36096316_Lactate Dehydrogenase and its clinical significance in pancreatic and thoracic cancers. 36109751_Circ-CSNK1G1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion and glycolysis metabolism during triple-negative breast cancer progression by modulating the miR-28-5p/LDHA pathway. 36371026_Role of LDH in tumor glycolysis: Regulation of LDHA by small molecules for cancer therapeutics. |
ENSMUSG00000063229 |
Ldha |
2400.033030 |
4.1448071259 |
2.051305 |
0.251614006 |
61.276098 |
0.00000000000000496066163421092859830333541739115296132861749126008454879865894326940178871154785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000033929270491637306764556309568745901878621465397323220258840592578053474426269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4190.0608857 |
1201.8359246 |
1029.7427258 |
213.2860087 |
| ENSG00000134369 |
89796 |
NAV1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEY1 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in neuronal migration. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Methylation;Microtubule;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene belongs to the neuron navigator family and is expressed predominantly in the nervous system. The encoded protein contains coiled-coil domains and a conserved AAA domain characteristic for ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities. This gene is similar to unc-53, a Caenorhabditis elegans gene involved in axon guidance. The exact function of this gene is not known, but it is thought to play a role in in neuronal development and regeneration. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:89796; |
axon initial segment [GO:0043194]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron migration [GO:0001764] |
12079279_cloning of the gene neuron navigator-1 (NAV1), a human homolog of unc-53, a gene involved in axon guidance in Caenorhabditis elegans 25065758_NAV1 forms a complex with the RhoGEF TRIO and the +TIP EB1 on the plus ends of growing microtubules, and regulates TRIO-mediated Rac1 activation and neurite outgrowth. 25065758_The +TIP Navigator 1 (NAV1) is important for neurite outgrowth and interacts and colocalizes with TRIO, a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor that enables neurite outgrowth by activating the Rho GTPases Rac1 and RhoG. 32141789_Genetic Association Analyses Highlight IL6, ALPL, and NAV1 As 3 New Susceptibility Genes Underlying Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis. |
ENSMUSG00000009418 |
Nav1 |
355.108947 |
2.5559966817 |
1.353886 |
0.087621654 |
243.870164 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000056346179679528039958058614289369660070476698068565292794990805577304287474765886395411877058785963993197164491371057272955782664906461908692347773097708341083489358425140380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000013264268135085070822099581188110961838971257579036424443694355423596375626825044323895706688988990321534046668203313839263050937408955180785152805356119642965495586395263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
519.8441529 |
26.5595064 |
204.8195915 |
8.5693673 |
| ENSG00000134371 |
79577 |
CDC73 |
protein_coding |
Q6P1J9 |
FUNCTION: Tumor suppressor probably involved in transcriptional and post-transcriptional control pathways. May be involved in cell cycle progression through the regulation of cyclin D1/PRAD1 expression. Component of the PAF1 complex (PAF1C) which has multiple functions during transcription by RNA polymerase II and is implicated in regulation of development and maintenance of embryonic stem cell pluripotency. PAF1C associates with RNA polymerase II through interaction with POLR2A CTD non-phosphorylated and 'Ser-2'- and 'Ser-5'-phosphorylated forms and is involved in transcriptional elongation, acting both independently and synergistically with TCEA1 and in cooperation with the DSIF complex and HTATSF1. PAF1C is required for transcription of Hox and Wnt target genes. PAF1C is involved in hematopoiesis and stimulates transcriptional activity of KMT2A/MLL1; it promotes leukemogenesis through association with KMT2A/MLL1-rearranged oncoproteins, such as KMT2A/MLL1-MLLT3/AF9 and KMT2A/MLL1-MLLT1/ENL. PAF1C is involved in histone modifications such as ubiquitination of histone H2B and methylation on histone H3 'Lys-4' (H3K4me3). PAF1C recruits the RNF20/40 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex and the E2 enzyme UBE2A or UBE2B to chromatin which mediate monoubiquitination of 'Lys-120' of histone H2B (H2BK120ub1); UB2A/B-mediated H2B ubiquitination is proposed to be coupled to transcription. PAF1C is involved in mRNA 3' end formation probably through association with cleavage and poly(A) factors. In case of infection by influenza A strain H3N2, PAF1C associates with viral NS1 protein, thereby regulating gene transcription. Connects PAF1C with the cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) complex and the cleavage stimulation factor (CSTF) complex, and with Wnt signaling. Involved in polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15580289, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15923622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16630820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16989776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19136632, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19952111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20178742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20541477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21329879}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell cycle;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a tumor suppressor that is involved in transcriptional and post-transcriptional control pathways. The protein is a component of the the PAF protein complex, which associates with the RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2A and with a histone methyltransferase complex. This protein appears to facilitate the association of 3' mRNA processing factors with actively-transcribed chromatin. Mutations in this gene have been linked to hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome, familial isolated hyperparathyroidism, and parathyroid carcinoma. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009]. |
hsa:79577; |
Cdc73/Paf1 complex [GO:0016593]; chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II complex binding [GO:0000993]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; endodermal cell fate commitment [GO:0001711]; histone H2B ubiquitination [GO:0033523]; histone monoubiquitination [GO:0010390]; mRNA polyadenylation [GO:0006378]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045638]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902808]; positive regulation of mRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0031442]; positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0032968]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; protein destabilization [GO:0031648]; recruitment of 3'-end processing factors to RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex [GO:0034402]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; stem cell population maintenance [GO:0019827]; transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II promoter [GO:0006368]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12434154_This gene is now identified as associated with the hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome. 12960210_It is hypothesised that HRPT2 mutation is an early event that may lead to parathyroid malignancy and suggest intragenic mutation of HRPT2 as a marker of malignant potential in both familial and sporadic parathyroid tumours. 14715834_among 32 familial isolated hyperparathyroidism families, only a single one was found to have a mutation in parafibromin (HRPT2) gene 14985373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14985373_genotype phenotype analysis in familial isolated hyperparathyroidism 14985403_mutations in the HRPT2 gene are likely to be associated with parathyroid tumourigenesis; DNA mutational analysis in familial isolated hyperparathyroidism 15046050_Missense Mutation in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15046094_Mutations in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15046098_Mutations in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15046102_Mutations in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15046105_Mutations in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15046107_Mutations in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15046109_Mutations in HRPT2 is associated with Hyperparathyroidism Jaw-tumor syndrome. 15070940_Patients shared common haplotype of seven markers spannning approximately 12.5-cM region, flanked centromerically by D1S202 and telomerically by D1S306. A 2-bp (TG or GT) frameshift deletion in exon 8, which predicts a truncated parafibromin protein. 15580289_Human parafibromin is a nucleocytoplasmic tumor suppressor protein which regulates cyclin D1/PRAD1 expression. 15613436_Mutation of HRPT2 is associated with the formation of parathyroid tumors in hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome. 15632063_By purifying cellular parafibromin and characterizing its associated proteins, a human counterpart to the yeast Paf1 complex including homologs of Leo1, Paf1, and Ctr9, has been described. 15923622_findings link the tumor suppressor parafibromin to the transcription elongation and RNA processing pathway as a PAF1 complex- and RNA polymerase II-bound protein. 15956079_HRPT2 inactivation is not an important participant in the pathogenesis of typical parathyroid adenomas. 16061557_A non-consensus (non-canonical) donor splice site within exon 1 of the HRPT2 gene is associated with familial isolated primary hyperparathyroidism (FIHP). 16116486_specific HRPT2 mutations identified in HPT-JT or sporadic parathyroid carcinoma predicted to truncate parafibromin upstream of or within this NLS disrupt nuclear localization 16448924_mutation in exon 1 (nt 20AGGACG --> GGGAG) is predicted to inactivate the parafibromin protein through protein truncation and premature termination of translation 16630820_Data show that Drosophila Hyrax and its human ortholog, Parafibromin, are required for nuclear transduction of the Wnt/Wg signal and bind directly to the C-terminal region of beta-catenin/Armadillo. 16728578_The presented data suggest that in the majority of benign parathyroid tumours the expression of parafibromin remains unaltered, while the loss of parafibromin expression is strongly indicative of gene inactivation through mutation of the HRPT2 gene. 16989776_parafibromin has a critical role in cell growth, and mutations in HRPT2 can directly inhibit this role 17130827_renal cancer-associated mutations in parafibromin occur in the absence of von Hippel-Lindau mutation 17138574_The molecular basis for HPT has been further elucidated by teh detection of inactivating germline mutations in the CaSR gene in familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia syndrome and in the HRPT-2 genes in the familial forms of HPT. 17314275_These experiments identify for the first time a proapoptotic activity of endogenous parafibromin likely to be important in its role as a tumor suppressor and show a functional role for the NLS of parafibromin in this activity. 17404568_Acts as a positive regulator of cell growth similar to an oncoprotein in the presence of Simian virus 40 large T antigen. 17555500_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17555500_These results suggest that not only HRPT2 but also MEN1 mutations may play a role in sporadic parathyroid cancer formation. 17923126_Three identified NoLSs play only a minor role in nuclear localization, but are critical for the nucleolar localization of parafibromin. 18080135_Downregulated parafibromin expression possibly contributed to pathogenesis, growth, invasion and metastasis of gastric carcinomas. 18217513_loss of HRPT2 gene expression is strongly associated with parathyroid carcinomas. 18338208_inactivating mutations and/or allelic loss of the HRPT2 gene may not play a major role in parathyroid carcinogenesis in secondary HPT due to CKD 18436011_germline mutations with familial hyperparathyroidism associated with 80% recurrence/persistence rate, increasingly difficult re-operations and risk of parathyroid carcinoma 18687124_Parafibromin interacted with muscle alpha-actinins (actinin-2 and actinin-3). 18755853_CDC73 germline mutations are responsible for more than half of cases of hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome. 18987311_The parafibromin tumor suppressor protein HRPT2 inhibits cell proliferation by repression of the c-myc proto-oncogene 19017757_Positive staining for PGP9.5 has utility as a marker for parathyroid malignancy, with a slightly superior sensitivity (P = 0.03) and similar high specificity to that of parafibromin. 19058032_A variety of genetic abnormalities, including HRPT2 mutations, occur in parathyroid carcinomas. 19081034_parathyroid carcinoma may be a manifestation of HRPT2 germline mutations 19136632_Shows that this protein interacts with cleavage stimulation factor (CstF) complexes that are required for the maturation of mRNA 3' ends in the cell nucleus. 19169472_HRPT2 mutation is an early event that may lead to parathyroid malignancy and, moreover, it has been suggested that intragenic mutation of HRPT2 should be considered as a marker of malignant potential in both familial and sporadic parathyroid tumors. 19332451_Aberrant splicing caused by disruption of exonic splice enhancer sites does not appear to have a major role in HRPT2-associated disease. 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19474519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20026646_Alternative mechanisms such as mutation in intronic regions, additional epigenetic regulation, or other regulatory inactivation mechanisms may play a role in the loss of parafibromin expression. 20052758_analysis of the cell division cycle protein 73 homolog (CDC73) mutations in the hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome (HPT-JT) and parathyroid tumors 20304979_The simultaneous loss of nucleolar localization and acquisition of a growth stimulatory phenotype with the L95P mutation raise the possibility that parafibromin must interact with targets in the nucleolus to fully execute its tumor suppressor functions. 20480190_HRPT2 (replaced with this gene ID 79577) gene mutation may be associated with tumor recurrence. 20541447_The stability of the altered HRPT2 transcripts and translation products produced in the hyperparathyroidim-jaw tumors syndrome, was investigated. 21221636_The demonstrated absence of nucleolar parafibromin in three carcinomas with HRPT2 mutations suggests that parafibromin exhibits nucleolar tumour suppressor properties also in vivo. 21240254_Downregulation of CASR expression and global loss of parafibromin staining are strong negative determinants of prognosis in parathyroid carcinoma 21315421_It was suggested that parafibromin overexpression might suppress cell cycle progression and promote differentiation of DLD-1 cells. 21360064_The present data suggests that patients with apparently sporadic parathyroid carcinomas, or parathyroid tumors with atypical histological features, should undergo molecular genetic testing, as it may detect germline HRPT2 mutations. 21652691_Mutational analysis of the CDC73 gene identified 8 sequence changes, 3 of them have been reported previously, whereas 5 are novel: c.1346delG, c.88_94delTTCTCCT, non-coding variants, c.307+5G>T and c.424-5T>C and c.*12C>A of unknown significance. 21692036_Parafibromin expression could be employed to indicate the favorable prognosis of patients with adenocarcinoma. 21717873_Detected HRPT2 mutation in parathyroid carcinoma or atypical parathyroid adenoma in sporadic hyperparathyroidism in Thai patients. 21732217_identified one novel germline mutation CDC73 NM_024529.4: c.1475G > A; NP_078805.3: p.Trp492X and one novel somatic mutation CDC73 NM_024529.4: c.142G > T; NP_078805.3: p.Glu48X associated with parathyroid neoplasm 22187299_germ-line inactivating mutations in CDC73 gene are common in young patients with clinically non-familial primary hyperparathyroidism 22932087_Complete loss of parafibromin expression was seen in 9 of 15 (60%) carcinomas, and all normal parathyroid tissues and parathyroid benign tumors stained positive for parafibromin except for one (4%) adenoma. 22987117_CDC73 mutations and negative immunostaining were common in atypical parathyroid adenomas 23029104_we have firstly demonstrated the high prevalence of HRPT2/CDC mutations and loss of expression of its corresponding protein in clinically sporadic parathyroid carcinomas in Chinese population. 23029479_CDC73-mutated carcinomas displayed losses in chromosome 1p and loss of the entire chromosome 13 which are not seen in CDC73-mutated adenomas. 23060304_Twenty cases of CCPRCC were stained for parafibromin and showed diffuse and strong nuclear positivity for this marker 23166327_Oncogenic microRNA-155 down-regulates tumor suppressor CDC73 and promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation 23453027_The contribution of HRPT2 inactivation to the pathogenesis of OF, FD, and OS is marginal at best and may be limited to progression rather than tumor initiation. 23757631_Genetic analysis of a patient with hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor revealed a novel nonsense mutation in exon 1 of CDC73 23991985_High parafibromin expression is associated with colorectal carcinomas. 24081804_Negative parafibromin staining is associated with malignant behavior in atypical parathyroid adenomas. 24121387_We present three siblings with familial isolated hyperparathyroidism due to solitary parathyroid adenoma and favorable evolution post-parathyroidectomy. Genetic tests revealed HRPT2 mutation. 24257751_Data indicate that overexpression of Wilms tumor 1 gene (WT1) decreased CDC73 levels and promoted proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells. 24340015_Mutations within the nucleolar localisation signals of the CDC73 gene led to instability either of the corresponding mutated protein or mRNA or both. 24716902_3 unrelated Chinese families with familial isolated primary hyperparathyroidism and 1 with hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumour syndrome were described; genetic analysis revealed 4 germline mutations that were responsible for the 4 kindreds including 2 novel point mutations, 1 recurrent point mutation and 1 deletion mutation 24823466_A previously unreported intragenic deletion of exons 1 to 10 of CDC73 was detected in a three-generation family with familial primary hyperparathyroidism with parathyroid carcinoma. 24889687_gene expression profiling experiments suggest that upregulated FGFR1 expression appears to be associated with parathyroid carcinoma in HPT-JT syndrome due to an HRPT2 splicing mutation 25113791_Data report a novel mutation in the CDC73 gene that may underlie HPT-JT syndrome. 25388829_targets and destabilizes p53 mRNA to control p53-mediated apoptosis 26124004_These findings suggest that downregulated expression of parafibromin protein plays an important role in the pathogenesis, differentiation, and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas 26232434_Parafibromin interacted with JAK1/2, promoted the interactions of JAK1-JAK2 and JAK1/2-STAT1, and promoted tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT1 by JAKs after IFN-gamma stimulation. 26409451_parafibromin downregulation might promote the pathogenesis, dedifferentiation and metastasis of ovarian cancers possibly by suppressing aggressive phenotypes, such as proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration and invasion. 26832176_We suggest that parafibromin may be a possible prognostic and predictive parameter for breast carcinomas 27544721_Germline mutation of HRPT2 is associated with parathyroid carcinoma. 27864865_The HPT-JT syndrome - multiple Parathyroid Adenomas, Parathyroid Carcinomas in 15% of patients, as well as Fibro-osseous Jaw tumours (in 35% of patients) results from mutations of the CDC73 (HRPT2) gene (encoding parafibromin). 28223542_Data suggest that down-regulated parafibromin (HRPT2; CDC73) expression might be closely linked to colorectal carcinogenesis and cancer differentiation. 28394026_Recurrent Hyperparathyroidism Due to a Novel CDC73 Splice Mutation. 28674121_Each of these autosomal dominant syndromes results from a specific germline mutation in unique genes: MEN1 is due to pathogenic MEN1 variants (11q13), MEN2A and MEN2B are due to pathogenic RET variants (10q11.21), MEN4 is due to pathogenic CDKN1B variants (12p13.1), and the HPT-JT syndrome is due to pathogenic CDC73 variants (1q25). 28774260_A novel deletion of exons 4 to 10 of CDC73 was detected by CNV analysis in the three affecteds. A novel insertion in the 5'UTR (c.-4_-11insG) that co-segregated with the deletion was identified. 28881068_CDC73 mutations are major driver mutations in the etiology of parathyroid carcinomas (PCs). 29040582_Pathogenic germline CDC73 variants were identified in primary hyperparathyroidism patients, with (suspected) hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome familial isolated primary hyperparathyroidism and apparently sporadic parathyroid carcinoma 29142233_our results provide a solid structural basis for understanding the structure and function of CDC73 and its association with the hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor (HPT-JT) syndrome and other diseases 29621547_post-transcriptional down-regulation of CDC73 contributed to cellular senescence. 29982334_Somatic mutations in CDC73 were associated with sporadic parathyroid adenomas in a Chinese population. 30452964_Three members of a family presented with mixed epithelial tumor of the kidney and were found to possess a germline mutation in CDC73, a gene which is associated with hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome 30541148_Our results suggest a novel pathway involving RNAPII, CDC73 and PNUTS-PP1 in ATR signaling and give new insight into the diverse functions of ATR. 30923346_Parafibromin immunohistochemistry is a useful marker in the clinical routine when applied on a pre-selected material of cases, with positive immunoreactivity as a confident rule out marker of parathyroid malignancy. 30926677_Loss of parafibromin expression was significantly higher in the parathyroid carcinoma than in the atypical parathyroid adenoma, parathyroid adenoma and parathyroid hyperplasia.[meta-analysis] 31595586_Tumor predisposition in an individual with chromosomal rearrangements of 1q31.2-q41 encompassing cell division cycle protein 73. 32780442_The Oncosuppressors MEN1 and CDC73 Are Involved in lncRNA Deregulation in Human Parathyroid Tumors. 34424918_Cell-cell adhesion regulates Merlin/NF2 interaction with the PAF complex. 34729685_A novel long-range deletion spanning CDC73 and upper-stream genes discovered in a kindred of familial primary hyperparathyroidism. |
ENSMUSG00000026361 |
Cdc73 |
669.983157 |
2.7061203213 |
1.436226 |
0.443205487 |
9.725068 |
0.00181771615597547519377341629365218977909535169601440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004050345782336656728916945979790398268960416316986083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1027.6713848 |
269.2733862 |
380.4328487 |
72.0186998 |
| ENSG00000134463 |
79746 |
ECHDC3 |
protein_coding |
Q96DC8 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in fatty acid biosynthesis and insulin sensitivity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31010960}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Predicted to enable enoyl-CoA hydratase activity. Involved in positive regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus. Predicted to be active in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79746; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; enoyl-CoA hydratase activity [GO:0004300]; hydro-lyase activity [GO:0016836]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; positive regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:1900078] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27586541_Increased levels of monounsaturated fatty acids, especially oleic acid, and ECHDC3 upregulation in patients with coronary artery lesion suggests that these are independent factors associated with the initial progression of cardiovascular disease. 28183528_Genome-wide significant (GWS) associations in single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based tests (P |
ENSMUSG00000039063 |
Echdc3 |
13.841695 |
2.3769733437 |
1.249126 |
0.449608624 |
7.647938 |
0.00568372427189939299907450731552671641111373901367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011488875685186940994730875331697461660951375961303710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.1307441 |
5.4658288 |
8.4885906 |
1.8054397 |
| ENSG00000134531 |
2012 |
EMP1 |
protein_coding |
P54849 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in bleb assembly and cell death. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2012; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; bleb assembly [GO:0032060]; cell death [GO:0008219]; epidermis development [GO:0008544] |
12451984_EMP-1 gene has some relationship with carcinogenesis of esophagus. 12632483_Overexpression of human EMP-1 gene can inhibit the proliferation of EC9706 cell with S phase arrested and G1 phase prolonged. EMP-1 may be one of regulators involved in cell signaling, cell communication and adhesion regulators. 16087880_role of the adhesion molecule, EMP-1, as a biomarker of gefitinib clinical resistance, and further suggests a probable cross-talk between this molecule and the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway 19288191_We found expression of EMP-1 mRNA was higher in intractable epilepsy per the gene scanning, EMP-1 immunoreactivity was apparent in neurons of IE patients but not in the control group, and the expression of EMP-1 and EGFR occurred in the same neuron. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20980531_Decreased expression of EMP1 was significantly correlated with clinical stage (p=0.002) and lymph node metastasis (p=0.044) of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma and may be a tumor suppressor. 21146590_The EMP1 gene may be implicated in the pathophysiology of MDD in the Japanese population. 21538935_Overexpression of EMP1 in spinal chondrocytes promotes cell proliferation and survival, alters cell morphology and cell cycle, reduces cell condensation, and inhibits cell hypertrophy. 23271282_EMP-1 was significantly up-regulated in NSCLC patients. 24033346_EMP1 could be a biomarker for aberrant epithelial remodelling and metaplasia in chronic inflammatory upper airway mucosa 24292952_EMP1 may play important roles as a negative regulator to nasopharyngeal cancer cell. 24338711_EMP1 expression decreased in prostate cancer and correlated significantly T stages, lymph node metastasis, clinic stage, and Gleason score 24402572_EMP1 may play important roles as a negative regulator to breast cancer MCF-7 cell by regulating the expression of caspase 9 and VEGFC protein. 24625531_EMP1 as an independent predictor for poor outcome in precursor-B ALL (BCP-ALL) (P=0.004, hazard ratio: 2.36 (1.31-4.25). 24744589_Low EMP1 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with increased disease severity, suggesting that EMP1 may be a negative regulator of colorectal cancer 24920167_Results demonstrated that EMP1 protein levels were significantly reduced in gastric carcinoma and were associated with tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis, clinical stage and cell differentiation. 25394671_SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1.EMP1 localises to tight junctions and is essential for their formation and function. 27279240_The studies implicating GAS3 protein family (EMP1, EMP2, EMP3 and PMP22) in cancer pathogenesis as well as probe the structural similarities between the family members were highlighted. 27909719_Therefore, EMP1 is a tumor suppressor in laryngeal carcinoma. Boosting EMP1 expression in laryngeal carcinoma initiates multiple anticancer phenotypes and thus presents a promising therapeutic strategy for laryngeal cancer. 28779068_The abnormal expression of EMP-1 may be associated with progression of laryngeal carcinoma (LC) and the gene may act as a prognostic marker for LC. 29867202_upregulation of EMP1 significantly increases cancer cell migration that leads to tumor metastasis 31111534_EMP1 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and stemness in gliomas through PI3K-AKT signaling and CD44. 31233190_High EMP1 expression is associated with glioblastoma progression. 32633341_Circ100284 promotes invasion and migration of osteosarcoma cells by down-regulating PTEN and EMP1. 32716150_EMP1 promotes the malignant progression of osteosarcoma through the IRX2/MMP9 axis. 32819595_MIR31HG exhibits oncogenic property and acts as a sponge for miR-361-3p in cervical carcinoma. 33799364_Epithelial Membrane Protein 2 Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibition of MAPK Pathway. 34420253_Cell-to-cell contact-mediated regulation of tumor behavior in the tumor microenvironment. 34569869_Serum epithelial membrane protein 1 serves as a feasible biomarker in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 34617578_Expression of epithelial membrane protein (EMP) 1, EMP 2, and EMP 3 in thyroid cancer. 35432717_Epithelial Membrane Protein 1 Promotes Sensitivity to RSL3-Induced Ferroptosis and Intensifies Gefitinib Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer. 35850179_Loss of EMP1 promotes the metastasis of human bladder cancer cells by promoting migration and conferring resistance to ferroptosis through activation of PPAR gamma signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000030208 |
Emp1 |
3410.280470 |
2.1856309847 |
1.128050 |
0.029104990 |
1511.238904 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4629.0440258 |
86.9046206 |
2133.8467749 |
30.9258673 |
| ENSG00000134545 |
3821 |
KLRC1 |
protein_coding |
P26715 |
FUNCTION: Immune inhibitory receptor involved in self-nonself discrimination. In complex with KLRD1 on cytotoxic and regulatory lymphocyte subsets, recognizes non-classical major histocompatibility (MHC) class Ib molecule HLA-E loaded with self-peptides derived from the signal sequence of classical MHC class Ia molecules. Enables cytotoxic cells to monitor the expression of MHC class I molecules in healthy cells and to tolerate self (PubMed:9486650, PubMed:18083576, PubMed:9430220). Upon HLA-E-peptide binding, transmits intracellular signals through two immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) by recruiting INPP5D/SHP-1 and INPPL1/SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases to ITIMs, and ultimately opposing signals transmitted by activating receptors through dephosphorylation of proximal signaling molecules (PubMed:9485206, PubMed:12165520). Key inhibitory receptor on natural killer (NK) cells that regulates their activation and effector functions (PubMed:9486650, PubMed:9430220, PubMed:9485206, PubMed:30860984). Dominantly counteracts T cell receptor signaling on a subset of memory/effector CD8-positive T cells as part of an antigen-driven response to avoid autoimmunity (PubMed:12387742). On intraepithelial CD8-positive gamma-delta regulatory T cells triggers TGFB1 secretion, which in turn limits the cytotoxic programming of intraepithelial CD8-positive alpha-beta T cells, distinguishing harmless from pathogenic antigens (PubMed:18064301). In HLA-E-rich tumor microenvironment, acts as an immune inhibitory checkpoint and may contribute to progressive loss of effector functions of NK cells and tumor-specific T cells, a state known as cell exhaustion (PubMed:30503213, PubMed:30860984). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12165520, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12387742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18064301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18083576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30503213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30860984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9430220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9485206, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9486650}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Viruses like human cytomegalovirus have evolved an escape mechanism whereby virus-induced down-regulation of host MHC class I molecules is coupled to the binding of viral peptides to HLA-E, restoring HLA-E expression and inducing HLA-E-dependent NK cell immune tolerance to infected cells. Recognizes HLA-E in complex with human cytomegalovirus UL40-derived peptide (VMAPRTLIL) and inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10669413, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23335510}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May recognize HLA-E in complex with HIV-1 gag/Capsid protein p24-derived peptide (AISPRTLNA) on infected cells and may inhibit NK cell cytotoxicity, a mechanism that allows HIV-1 to escape immune recognition. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15751767}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Upon SARS-CoV-2 infection, may contribute to functional exhaustion of cytotoxic NK cells and CD8-positive T cells (PubMed:32203188, PubMed:32859121). On NK cells, may recognize HLA-E in complex with SARS-CoV-2 S/Spike protein S1-derived peptide (LQPRTFLL) expressed on the surface of lung epithelial cells, inducing NK cell exhaustion and dampening antiviral immune surveillance (PubMed:32859121). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32203188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32859121}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes that can mediate lysis of certain tumor cells and virus-infected cells without previous activation. They can also regulate specific humoral and cell-mediated immunity. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the killer cell lectin-like receptor family, also called NKG2 family, which is a group of transmembrane proteins preferentially expressed in NK cells. This family of proteins is characterized by the type II membrane orientation and the presence of a C-type lectin domain. This protein forms a complex with another family member, KLRD1/CD94, and has been implicated in the recognition of the MHC class I HLA-E molecules in NK cells. The genes of NKG2 family members form a killer cell lectin-like receptor gene cluster on chromosome 12. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:3821; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; HLA-E specific inhibitory MHC class Ib receptor activity [GO:0062082]; MHC class I protein complex binding [GO:0023024]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; CD8-positive, gamma-delta intraepithelial T cell differentiation [GO:0002305]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; natural killer cell inhibitory signaling pathway [GO:0002769]; negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045953]; negative regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001915]; regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032814] |
12165520_Role that each NKG2A immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif plays in mediating the human CD94/NKG2A inhibitory signal. 12387742_TCR antigenic specificity dictates NKG2A commitment, which critically regulates subsequent activation of CTL. 12444112_NK cell CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors are internalized and recycle independently of inhibitory signaling processes. 12461076_CD94/NKG2A+ NK cells can recognize stressed cells in a peptide-dependent manner. 12618865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528343_Aberrant expression of natural killer (NK) receptors NKG2A/CD94 may have an impact on the magnitude and direction of dendritic cell activation of T cells under pathological conditions, such as chronic hepatitis C virus infection. 15550116_reveal strict gene regulatory mechanisms for CD94 and NKG2 gene expression on CD4+ cells 15561299_Expression of the inhibitory NKR (CD94/NKG2A) of the G-CSF mobilized peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 15687235_immaturity of NK cells and inhibitory effect of NKG2A override graft versus leukemia effect 16434388_only a subpopulation of NK cells expressing high levels of the inhibitory receptor NKG2A are able to lyse autologous vaccinia-infected targets, and that this is due to selective down-regulation of HLA-E 16690409_identified co-induction of NKG2A and CD56 on activation of TH2 cells 16951318_Prevents actin-dependent recruitment of raft-associated activation receptors complexes to the activating immunologic synapse. 17545086_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17545086_Results sugges that KLRC1 can be a probable candidate gene for SLE on 12p12.3-13.2, but which is not associated with the disease activity. 17706207_Increased expression of CD94/NKG2A in peritoneal NK cells may mediate the resistance of endometriotic tissue to NK cell-mediated lysis, thus contributing to the progression of the disease. 17767552_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17767552_indicate that the SNPs of the inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A and its haplotypes, as well as its ligand HLA-E, are associated with Behcet's disease immune systems 17927829_We show that signalling through NKG2A suppresses TH2 effector function. This may provide a means to modulate Th1/Th2 balance in diseases where Th2 cytokines predominate. 17976318_The results indicated that the high expression of NKG2A/CD94 and low expression of granzyme B may be related with the reduced activity of cord blood NK cells. 18056444_High levels of NKG2A is associated with tongue cancer 18083576_the invariant CD94 chain plays a more dominant role in interacting with HLA-E in comparison to the variable NKG2 chain. 18172398_HIV-1 infection is associated with higher levels NKG2A in the cytotoxic NK subset in HIV-1-infected patients with more advanced disease. 18332182_crystal structure of CD94-NKG2A in complex with HLA-E bound to a peptide derived from the leader sequence of HLA-G 18448674_The evolution of the NKG2x/CD94 family of receptors has likely been shaped both by the need to bind the invariant HLA-E ligand and the need to avoid subversion by pathogen-derived decoys. 18500933_T cells were highly susceptible to NKG2A-mediated inhibition of cytotoxic activity and NKG2A(+) lymphocytes were preferentially attracted by CCR5 ligands induced by hepatitis C virus E2 antigen. 18700876_No significance was observed between the inhibitory (NKG2A) or activating (NKG2C and NKG2D) receptor genotypes and the presence of RF, ANA, or bony erosions in Rheumatoid arthritis. 18700876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18941190_NKG2A expression is inversely correlated with the number of coexpressed killer inhibitory receptors (KIR) and is more frequent on KIR3DL2-single positive natural killer cells. 18981088_MICA-NKG2D interaction constitutes a mechanism by which monocytes and NK cells as an early source of IFN-gamma may communicate directly during an innate immune response to infections in humans. 19002424_Data suggest that RNAi-mediated silencing of NKG2A in effector cells could improve the efficacy of cell-based immunotherapies but also show that indirect effects of NKG2A knockdown exist. 19124726_Under the influence of interleukin-12 stimulation, CD94/NKG2A is transiently inducible in natural killer (NK) cells bearing the homologous CD94/NKG2C-activating receptor,providing a potential negative regulatory feedback mechanism. 19395088_expression by Vdelta2+ T cells is higher in pregnant women 19615756_negatively controls decidual NK cell cytotoxicity 19694640_Although the percentages of both NKG2A- and NKG2C-positive NK cells were normal in preeclamptic women, the levels of NKG2A and NKG2C on NK cells were significantly up-regulated in these women 19782712_demonstrate that human cytomegalovirus induces an immediate proportional enlargement of a functionally active CD94/NKG2A expressing subset of natural killer cells. 20012119_increased CD8+ T-cell subsets as well as the abnormal expression of NKG2A and NKG2D on CD3+ T and CD3-CD56 + NK cells may play a role in the etiology of systemic lupus erythematosus 20139023_alloreactivity of a significant fraction of KIR(-) NK cells leads to killing of acute myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia blasts that is mediated by NKG2A and LIR-1. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20550548_NK cell NKG2A expression is dysregulated in chronic hepatitis C. NKG2A-positive NK cells are associated with a beneficial response to pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20648603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20654155_The differences of CD94 and NKG2 expression between nasal NK/T-cell lymphomas and B cell lymphoma or T cell lymphoma were statistically significant. 20696944_CD56(dim) NK cells continue to differentiate. During this process, they lose expression of NKG2A, sequentially acquire inhibitory killer cell inhibitory immunoglobulin-like receptors and CD57. 20700504_a new model in which the NK cell differentiation and functional fate are based on a stepwise decrease of NKG2A and acquisition of KIRs 20952657_NKG2A expression on gammadelta lymphoproliferative Disease of Large Granular Lymphocytes correlates with asymptomatic pathology, even in the presence of NKG2C coexpression. 21212510_These results suggested that these glycans can interact with NKG2D and CD94 to modulate NK cell-dependent cytotoxicity. 21518478_The positive expression rate of NKG2D and NKG2A on NK cells and CD3(+) T cells in ALL patients was no significantly different from that in AML patients. 21538351_The level of NKG2A expression on resting CD8-positive T cells inversely correlated with acquisition of regulatory function when activated. 22486170_Results suggested that the low expression level of CD94/NKG2A upon gammadelta T cell activation might lead to the over-activation of gammadelta T cells in patients with SLE. 24673109_Balance between activating NKG2D, DNAM-1, NKp44 and NKp46 and inhibitory CD94/NKG2A receptors determine natural killer degranulation towards rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. 25220367_The presence of TIM3+and/or NKG2A+ T cells is associated with the absence of recurrences and a longer recurrence-free survival. 26453102_CD94 and NKG2A polymorphisms may contribute to genetic susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis or affect the response to anti-TNF therapy in patients of Caucasian origin. 26453750_Coengagement of inhibitory receptors, either KIR2DL1 or CD94-NKG2A, did not inhibit phosphorylation of Stat5 but inhibited selectively phosphorylation of Akt and S6 ribosomal protein. 26856773_NK cell maturation to CD56(dim) subset associated with high levels of NCRs overrides the inhibitory effect of NKG2A and recovers impaired NK cell cytolytic potential after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 27465324_These results indicate NKG2A inhibitory receptor may play a key role in transfusion-induced immunodepression of NK cells in patients with b-thalassemia major 27801784_Collectively, these results provide evidence for the first time that CD94/NKG2C is involved in chronic graft-versus-host disease prevention 27828717_Compared with NKG2D, NKG2A expressed on both peripheral CD3-CD56+NK cells and CD3+CD8+T cells plays a more pivotal negative regulatory role in the progression of HBV-related ACLF. 29700172_NKp46(neg-low)/CD56(dim)/CD16(neg) cells displayed a markedly defective cytotoxicity that could be reversed by blocking the inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A. These data open new and important perspectives to better understand the ontogenesis/homeostasis of human natural killer cells and to develop a novel immune-therapeutic approach that targets the inhibitory NKG2A check-point. 30645023_Targeting NKG2A to elucidate natural killer cell ontogenesis and to develop novel immune-therapeutic strategies in cancer therapy. 30779432_Human liver-derived CXCR6(+) NK cells are predominantly educated through NKG2A and show reduced cytokine production. 30860984_NKG2A downregulation evades the HLA-E cancer immune-checkpoint, and increases the anti-tumor activity of NK cell infusions 31160572_Increased HLA-E expression contributes to persistence of senescent cells in tissues via interaction with the inhibitory receptor NKG2A expressed by NK and highly differentiated CD8(+) T cells to inhibit immune responses against senescent cells. 31409873_The inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A on CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer: a promising new druggable immune checkpoint in the context of HLAE/beta2m overexpression. 32010126_CD8(+) T Cells Form the Predominant Subset of NKG2A(+) Cells in Human Lung Cancer. 32409305_The NKG2A-HLA-E Axis as a Novel Checkpoint in the Tumor Microenvironment. 32575403_NKG2A/CD94 Is a New Immune Receptor for HLA-G and Distinguishes Amino Acid Differences in the HLA-G Heavy Chain. 32830898_Characterization of KIR + NKG2A + Eomes- NK-like CD8+ T cells and their decline with age in healthy individuals. 33203899_Epstein-Barr virus peptides derived from latent cycle proteins alter NKG2A + NK cell effector function. 33887202_The CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptor educates uterine NK cells to optimize pregnancy outcomes in humans and mice. 34049578_Potential prognostic value of PD-L1 and NKG2A expression in Indonesian patients with skin nodular melanoma. 34686325_NKG2A expression identifies a subset of human Vdelta2 T cells exerting the highest antitumor effector functions. 34716584_NKG2A is a late immune checkpoint on CD8 T cells and marks repeated stimulation and cell division. 35039632_Downregulated cytotoxic CD8(+) T-cell identifies with the NKG2A-soluble HLA-E axis as a predictive biomarker and potential therapeutic target in keloids. 35235832_SARS-CoV-2 Nsp13 encodes for an HLA-E-stabilizing peptide that abrogates inhibition of NKG2A-expressing NK cells. 35295095_Targeting NKG2A to boost anti-tumor CD8 T-cell responses in human colorectal cancer. 36032104_Implications of NKG2A in immunity and immune-mediated diseases. 36099881_NKG2A and HLA-E define an alternative immune checkpoint axis in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000052736+ENSMUSG00000033027+ENSMUSG00000030167+ENSMUSG00000071158+ENSMUSG00000047720+ENSMUSG00000067610+ENSMUSG00000043932+ENSMUSG00000050241 |
Klrc2+Klrc3+Klrc1+Klrh1+Clec2m+Klri1+Klri2+Klre1 |
8.815466 |
0.1279809787 |
-2.965999 |
0.653773443 |
25.097445 |
0.00000054505039860628240195716126548219904179859440773725509643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001988369719087673676813409276431521277572755934670567512512207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.9905591 |
0.9336444 |
15.6736053 |
3.5672628 |
| ENSG00000134627 |
143689 |
PIWIL4 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z3Z4 |
FUNCTION: Plays a central role during spermatogenesis by repressing transposable elements and preventing their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity (By similarity). Acts via the piRNA metabolic process, which mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of piRNAs and Piwi proteins and governs the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons (By similarity). Directly binds piRNAs, a class of 24 to 30 nucleotide RNAs that are generated by a Dicer-independent mechanism and are primarily derived from transposons and other repeated sequence elements (By similarity). Associates with secondary piRNAs antisense and PIWIL2/MILI is required for such association (By similarity). The piRNA process acts upstream of known mediators of DNA methylation (By similarity). Does not show endonuclease activity (By similarity). Plays a key role in the piRNA amplification loop, also named ping-pong amplification cycle, by acting as a 'slicer-incompetent' component that loads cleaved piRNAs from the 'slicer-competent' component PIWIL2 and target them on genomic transposon loci in the nucleus (By similarity). May be involved in the chromatin-modifying pathway by inducing 'Lys-9' methylation of histone H3 at some loci (PubMed:17544373). In addition to its role in germline, PIWIL4 also plays a role in the regulation of somatic cells activities. Plays a role in pancreatic beta cell function and insulin secretion (By similarity). Involved in maintaining cell morphology and functional integrity of retinal epithelial through Akt/GSK3alpha/beta signaling pathway (PubMed:28025795). When overexpressed, acts as an oncogene by inhibition of apoptosis and promotion of cells proliferation in tumors (PubMed:22483988). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CGT6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17544373, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22483988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28025795}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Meiosis;Methylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;RNA-mediated gene silencing;Spermatogenesis;Translation regulation |
|
PIWIL4 belongs to the Argonaute family of proteins, which function in development and maintenance of germline stem cells (Sasaki et al., 2003 [PubMed 12906857]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:143689; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P granule [GO:0043186]; piP-body [GO:0071547]; piRNA binding [GO:0034584]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; DNA methylation involved in gamete generation [GO:0043046]; epithelial structure maintenance [GO:0010669]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; negative regulation of transposition [GO:0010529]; piRNA processing [GO:0034587]; regulation of translation [GO:0006417]; RNA-mediated gene silencing [GO:0031047]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
17544373_PIWIL4 plays important roles in the chromatin-modifying pathway in human somatic cells 20146808_EIF2C2-4 and PIWIL4 appear increased in advanced tumors with distant metastasis, suggesting they may promote tumor invasion 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20721975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20940137_An SNP in the 3'untranslated region of HIWI2 and a non-synonymous SNP in HIWI3 were significantly associated with an altered risk of oligozoospermia. 20940137_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22483988_PIWIL4 might play an oncogenic role in cervical cancer 22748119_we identified a significant association between the expression of Piwi-like 2 and 4 mRNAs and the tumor-specific survival of soft tissue sarcoma patients. 24464225_Data suggest that MIWI2 and MIWI2-associated piRNAs have functions beyond TE suppression. 24509249_associations were determined between the Piwi-like family member expression levels and clinicopathological parameters of ccRCC, suggesting a potential role for these genes/proteins in ccRCC diagnostics and tumorigenesis 24969058_study to evaluate frequency of PIWIL4 genetic variants in order to better define the relationship between PIWIL4 SNPs and defective spermatogenesis and specific spermatogenic disorders; results suggest genetic and epigenetic alterations that affect the PIWI pathway contribute to unsuccessful sperm production 25038252_Immunoprecipitation of Hiwi2 from MDAMB231 cancer cells enriches for piRNAs that are predominantly derived from processed tRNAs and expressed genes. 26646899_Results show that three CpG loci within FYN were hypermethylated in obese individuals, while obesity was associated with lower methylation of CpG loci within PIWIL4 and TAOK3. 26957540_PIWIL4 is highly expressed in both breast cancer tissues and the cytoplasm of MDA-MB-231 cells derived from breast cancer. Reducing PIWIL4 expression drastically impairs the migration ability of MDA-MB-231 cells, significantly increases their apoptosis, and mildly affects their proliferation. 27893851_PIWIL2 and PIWIL4 genes expression in synovial fibroblasts of the rheumatoid arthritis patients.PIWIL4 does not regulate methylation or expression of LINE-1. 27894076_Results revealed that Piwil4 exhibits lower expression in the cell nucleus than in the cytoplasm. Along with nuclear location of PIWIL2, PIWIL4 expression is associated with worse prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 28025795_study demonstrates the presence of PIWI-like proteins in somatic cells and the possible role of HIWI2 in preserving the functional integrity of epithelial cells probably by modulating the phosphorylation status of Akt. 28861107_HIWI2 is aberrantly expressed in cells of the Retinoblastoma (RB) line (Y79) and silencing of HIWI2 downregulates OTX2, suggesting that HIWI2 might affects cell cycle and plays a role in the progression of RB. 28920925_data delineate MIWI2-dependent functions outside of the germline and demonstrate the presence of distinct subsets of airway multiciliated cells that can be discriminated by MIWI2 expression. 30226541_these findings revealed that Piwil4 is a novel regulator of ER signaling that could be targeted to inhibit breast cancer growth and migration. 32161174_PIWIL4 Maintains HIV-1 Latency by Enforcing Epigenetically Suppressive Modifications on the 5' Long Terminal Repeat. 32372724_Role of PIWI-like 4 in modulating neuronal differentiation from human embryonal carcinoma cells. 35074406_HIWI2 induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human fibrosarcoma via the ROS/DNA damage/p53 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000036912 |
Piwil4 |
112.422287 |
0.3874978417 |
-1.367740 |
0.160987597 |
72.642408 |
0.00000000000000001554035496689438876580768762069082514463343033187924663307555306346330326050519943237304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000122529721854359619019327557067965354823219252598624773309410329602542333304882049560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.1910548 |
10.0643547 |
169.9162028 |
18.3017156 |
| ENSG00000134775 |
80206 |
FHOD3 |
protein_coding |
Q2V2M9 |
FUNCTION: Actin-organizing protein that may cause stress fiber formation together with cell elongation (By similarity). Isoform 4 may play a role in actin filament polymerization in cardiomyocytes. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21149568}. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the diaphanous-related formins (DRF), and contains multiple domains, including GBD (GTPase-binding domain), DID (diaphanous inhibitory domain), FH1 (formin homology 1), FH2 (formin homology 2), and DAD (diaphanous auto-regulatory domain) domains. This protein is thought to play a role in actin filament polymerization in cardiomyocytes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), characterized by dilation of the ventricular chamber, leading to impairment of systolic pump function and subsequent heart failure. Increased levels of the protein encoded by this gene have been observed in individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. A muscle-specific isoform has been shown to possess a casein kinase 2 (CK2) phosphorylation site at the C-terminal end of the FH2 domain. Phosphorylation of this site alters its interaction with sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1), and targets this isoform to myofibrils, while other isoforms form cytoplasmic aggregates. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:80206; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin filament network formation [GO:0051639]; cardiac myofibril assembly [GO:0055003]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030837]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214] |
19066393_Single nucleotide polymorphism in FHOD3 gene is associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19706596_actin dynamics regulated by Fhod3 are critical for sarcomere organization in striated muscle cells. 20195266_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23052206_C-terminal phosphorylation by ROCK1 is sufficient for FHOD3 activation as evidenced by an increase in F-actin in HeLa cells. 23255317_FHOD variants is with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 24088304_DCM-associated FHOD3 variant may cause DCM by interfering with actin filament assembly. 26370503_Suggest alpha5beta1/Arp2/Arp3/FHOD3 pathway reprograms the actin cytoskeleton to promote invasive migration and local invasion in vivo. 26912794_FHOD3 played a role in glioma linear migration. 30442288_FHOD3 is a novel disease gene in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, accounting for approximately 2% of cases. 30468920_These results indicate that RBM20 and PTBP1 play a role in the actin filament functional organization mediated by FHOD3 isoforms and suggest their possible involvement in heart diseases. 31742804_Exome sequencing identifies a FHOD3 p.S527del mutation in a Chinese family with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 32335906_Deletions of specific exons of FHOD3 detected by next-generation sequencing are associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 32447646_FHOD3 promotes carcinogenesis by regulating RhoA/ROCK1/LIMK1 signaling pathway in medulloblastoma. 33586461_Variant Spectrum of Formin Homology 2 Domain-Containing 3 Gene in Chinese Patients With Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000034295 |
Fhod3 |
22.926942 |
0.1073978607 |
-3.218963 |
0.459371143 |
61.732821 |
0.00000000000000393368608655089910326282309456413604095107328789682199499111447948962450027465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000027080786677934361617022188277902411421505174740631538554680446395650506019592285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5734652 |
1.4924884 |
43.3686312 |
6.6104617 |
| ENSG00000134802 |
29015 |
SLC43A3 |
protein_coding |
Q8NBI5 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-independent purine-selective nucleobase transporter which mediates the equilibrative transport of extracellular purine nucleobases such as adenine, guanine and hypoxanthine (PubMed:26455426, PubMed:32339528). May regulate fatty acid (FA) transport in adipocytes, acting as a positive regulator of FA efflux and as a negative regulator of FA uptake (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2AVZ9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26455426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32339528}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Sodium-independent purine-selective nucleobase transporter which mediates the equilibrative transport of extracellular purine nucleobase adenine (PubMed:30910793). Mediates the influx and efflux of the purine nucleobase analog drug 6-mercaptopurine across the membrane (PubMed:30910793). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30910793}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Sodium-independent purine-selective nucleobase transporter which mediates the equilibrative transport of extracellular purine nucleobase adenine (PubMed:30910793). Mediates the influx and efflux of the purine nucleobase analog drug 6-mercaptopurine across the membrane (PubMed:30910793). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30910793}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Lipid transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:29015; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; adenine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015207]; fatty acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015245]; guanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015208]; xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042910]; hypoxanthine transport [GO:0035344] |
26455426_SLC43A3 is an equilibrative nucleobase transporter involved in purine salvage in mammals. 26527604_transcriptome sequencing of patient-derived angiosarcoma cells, identified a novel fusion gene NUP160-SLC43A3 found to be expressed in 9 of 25 human angiosarcoma specimens that were examined. 32217606_Slc43a3 is a regulator of free fatty acid flux. 32339528_Functional Analysis of the Role of Equilibrative Nucleobase Transporter 1 (ENBT1/SLC43A3) in Adenine Transport in HepG2 Cells. 35798387_Impact of SLC43A3/ENBT1 Expression and Function on 6-Mercaptopurine Transport and Cytotoxicity in Human Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000027074 |
Slc43a3 |
4225.859073 |
2.3365119530 |
1.224356 |
0.049727366 |
595.726225 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001423588734876156431336142785415434680088689451637349499054918327473377390347433356963335180570043070845785888341317697130904338568215998399618106305516900379520647888908265461621594019922911205181328 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000784036183834778639293717659152745241608871140715658118477553745922274946895605353899779109521725354876095000822656815534173910039326117244836708471908277316694606111390946593367694201131226096703062 |
Yes |
Yes |
5986.5680997 |
170.1666911 |
2579.9566982 |
54.9993373 |
| ENSG00000134815 |
9704 |
DHX34 |
protein_coding |
Q14147 |
FUNCTION: Probable ATP-binding RNA helicase required for nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) degradation of mRNA transcripts containing premature stop codons (PubMed:25220460, PubMed:33205750). Promotes the phosphorylation of UPF1 along with its interaction with key NMD pathway proteins UPF2 and EIF4A3 (PubMed:25220460). Interaction with the RUVBL1-RUVBL2 complex results in loss of nucleotide binding ability and ATP hydrolysis of the complex (PubMed:33205750). Negatively regulates the nucleotide binding ability and ATP hydrolysis of the RUVBL1-RUVBL2 complex via induction of N-terminus conformation changes of the RUVBL2 subunits (PubMed:33205750). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25220460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33205750}. |
ATP-binding;Helicase;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this DEAD box protein family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. This gene encodes a member of this family. It is mapped to the glioma 19q tumor suppressor region and is a tumor suppressor candidate gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9704; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; negative regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay [GO:2000623]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process [GO:0000956]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay [GO:0000184]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327] |
23828042_DHX34 and NBAS act in concert with core nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors to co-regulate a large number of endogenous RNA targets. 25220460_DHX34 promotes mRNP remodeling and triggers the conversion from the SURF complex to the DECID complex resulting in NMD activation. 26841701_DHX34 activates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by functioning as a scaffold for SMG1-mediated UPF1 phosphorylation via complex formation with SMG1 and UPF1. 31256877_Missense mutation in DHX34 gene is associated with neurodevelopmental disorder. 33205750_Regulation of RUVBL1-RUVBL2 AAA-ATPases by the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor DHX34, as evidenced by Cryo-EM. 35768279_A dual role for the RNA helicase DHX34 in NMD and pre-mRNA splicing and its function in hematopoietic differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000006019 |
Dhx34 |
109.184560 |
2.1474364764 |
1.102615 |
0.395130237 |
7.663690 |
0.00563431427768009297080142872005126264411956071853637695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011398366055175189123782608646706648869439959526062011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.8960582 |
37.6445625 |
67.4691715 |
12.9256926 |
| ENSG00000134815_ENSG00000134830 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73.146480 |
0.0421050607 |
-4.569863 |
1.341017726 |
6.677112 |
0.00976587193870242543936033285945086390711367130279541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018761456438272521712873341925842396449297666549682617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9825811 |
5.2805650 |
111.1572040 |
56.1287201 |
| ENSG00000134824 |
9415 |
FADS2 |
protein_coding |
O95864 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the biosynthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) from the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) linoleic acid (LA) (18:2n-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (18:3n-3) precursors, acting as a fatty acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) desaturase that introduces a cis double bond at carbon 6 of the fatty acyl chain. Catalyzes the first and rate limiting step in this pathway which is the desaturation of LA (18:2n-6) and ALA (18:3n-3) into gamma-linoleate (GLA) (18:3n-6) and stearidonate (18:4n-3), respectively (PubMed:12713571). Subsequently, in the biosynthetic pathway of HUFA n-3 series, it desaturates tetracosapentaenoate (24:5n-3) to tetracosahexaenoate (24:6n-3), which is then converted to docosahexaenoate (DHA)(22:6n-3), an important lipid for nervous system function (By similarity). Desaturates hexadecanate (palmitate) to produce 6Z-hexadecenoate (sapienate), a fatty acid unique to humans and major component of human sebum, that has been implicated in the development of acne and may have potent antibacterial activity (PubMed:12713571). It can also desaturate (11E)-octadecenoate (trans-vaccenoate, the predominant trans fatty acid in human milk) at carbon 6 generating (6Z,11E)-octadecadienoate (By similarity). In addition to Delta-6 activity, this enzyme exhibits Delta-8 activity with slight biases toward n-3 fatty acyl-CoA substrates (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B8R1K0, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z122, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12713571}. |
Alternative splicing;Electron transport;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9867867}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) gene family. Desaturase enzymes regulate unsaturation of fatty acids through the introduction of double bonds between defined carbons of the fatty acyl chain. FADS family members are considered fusion products composed of an N-terminal cytochrome b5-like domain and a C-terminal multiple membrane-spanning desaturase portion, both of which are characterized by conserved histidine motifs. This gene is clustered with family members at 11q12-q13.1; this cluster is thought to have arisen evolutionarily from gene duplication based on its similar exon/intron organization. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:9415; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; linoleoyl-CoA desaturase activity [GO:0016213]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with oxidation of a pair of donors resulting in the reduction of molecular oxygen to two molecules of water [GO:0016717]; stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase activity [GO:0004768]; alpha-linolenic acid metabolic process [GO:0036109]; linoleic acid metabolic process [GO:0043651]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; unsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006636] |
12147235_meication of suppression by highly unsaturated fatty acids mediated by E-box like sterol regulatory element 12562861_data indicate that the 5'-flanking region of the human D6D gene contains a DR-1 that functions in the regulation of human D6D gene transcription, and thereby plays a role in the synthesis of 20- and 22-carbon polyenoic fatty acids 12713571_Delta-6 desaturase/FADS2 is the major fatty acid desaturase in human sebaceous glands 12851727_It is concluded that aggressive breast tumours have a reduced level of delta-6-desaturase. This aberrant expression has clinical bearings to the outcome in patients with breast cancer. 12951357_6-fold decrease in promoter activity in the polymorphic variant FADS2 regulatory region compared with the normal gene, confirming the functional relevance of the insertion mutation to the decreased expression of the gene in the patient-derived cells 16670158_FADS1 FADS2 genetic varients and their reconstructed haplotypes are associated with the fatty acid composition in phospholipids 16670158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16893529_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16893529_These preliminary findings are suggestive of an association between FADS2 and ADHD. 16908951_FABP 2 may have a role in reducing delta 6 desaturase activity and plasma arachidonic acid in obese children 17284757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17284757_The realtionship of genetic polymorphisms of FADS2 to alpha-linolenic on the risk of myocardial infarction in Costa Rican patients is reported. 17852835_The results indicate that when the supply of FA to HL60 cells is limited, the intracellular content of n-3 and n-6 FA decreases and this leads to upregulation of the desaturases, particularly D5D and D6D. 17984066_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17984066_the association between breastfeeding and IQ is moderated by a genetic variant in FADS2, a gene involved in the genetic control of fatty acid pathways 18320251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18320251_strong association of FADS2 gene polymorphisms with the levels of arachidonic acid, which is a precursor of molecules involved in inflammation and immunity processes, cardiovascular disease 18479586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18626191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18842780_In populations following a Western diet, subjects carrying FADS haplotypes that are associated with higher desaturase activity may be prone to a proinflammatory response favoring atherosclerotic vascular damage. 18842780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936223_This study showed that genetic variants of FADS1 and FADS2 influence blood lipid and breast milk essential fatty acids in pregnancy and lactation. 18937842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19060906_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19060910_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19060911_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19144731_ALA concentrations in adipose tissue are associated with lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. Lack of association among homozygote carriers of the FADS2 deletion allele suggests that this association may be due to the conversion of ALA into EPA. 19144731_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19148276_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19352218_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19546342_polymorphism rs968567 influences FADS2 gene promoter activity and alters DNA binding affinity of the transcription factor ELK1. 19776639_Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the 2 desaturase encoding gene FADS2 is highly associated with the concentration of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. 19809313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19875987_Liver Delta-6D and Delta-5D activities in obese patients were 87% and 66% lower than controls (P |
ENSMUSG00000024665 |
Fads2 |
449.200704 |
2.9556533036 |
1.563477 |
0.214249326 |
50.635643 |
0.00000000000111207002136299260742818111664656084941298075374760401246021501719951629638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006597328583327078699722279930309866207913116475936021743109449744224548339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
685.4954357 |
87.2257959 |
233.3860699 |
22.0692181 |
| ENSG00000134830 |
27202 |
C5AR2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P296 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the chemotactic and inflammatory C3a, C4a and C5a anaphylatoxin peptides and also for their dearginated forms ASP/C3adesArg, C4adesArg and C5adesArg respectively. Couples weakly to G(i)-mediated signaling pathways. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15833747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19615750}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a G-protein coupled receptor 1 family member involved in the complement system of the innate immune response. Unlike classical G-protein coupled receptors, the encoded protein does not associate with intracellular G-proteins. It may instead modulate signal transduction through the beta-arrestin pathway, and may alternatively act as a decoy receptor. This gene may be involved in coronary artery disease and in the pathogenesis of sepsis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:27202; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; complement component C5a receptor activity [GO:0004878]; complement receptor activity [GO:0004875]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; complement receptor mediated signaling pathway [GO:0002430]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090024]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032677] |
11773063_C5L2 is a high affinity binding protein for C5a and C5a des Arg74, and has a moderate affinity for C3a. Unlike the original receptors for C5a (CD88) and C3a (C3aR), C5L2 couples weakly to Gi-mediated signalling pathways. 11773063_These results suggest that C5L2 is an anaphylatoxin-binding protein with unique ligand binding and signaling properties. 12540846_C3a des Arg77 binds to C5L2 but not to the C3a receptor (LocusID: 719). C3a and C3a des Arg77 both stimulate triglyceride synthesis (acylation stimulating protein, ASP) in adipocytes and fibroblasts and so C5L2 could be the receptor for ASP. 14570896_A8Delta71-73 is the first antagonist of c5a that blocks C5a and C5adesArg74 binding to C5L2 making it a valuable tool for studying C5L2 functions. 15634936_C5L2 on neutrophils diminishes during sepsis due to systemic generation of complement 5a (C5a), which is associated with a poor prognosis. 15833747_first demonstration that C5L2 is a functional receptor, mediating acylation-stimulating protein triglyceride stimulation 17068344_C5L2 is a highly regulated scavenger receptor for C5a and C5a-des-Arg(74) 17158873_C5L2 appears to bind complement factor C5a and C5a des Arg by different mechanisms, and, unlike C5a receptor (C5aR), C5L2 uses critical residues in its N-terminal domain for binding only to C5a des Arg. 19100624_a major function of human C5L2 is to remove active complement fragments from the extracellular environment. 19615750_C5L2 is a functional metabolic receptor, and serine 323 is important for ASP induced functionality. 19767107_Recombinant C3adesArg/acylation stimulating protein (ASP) is highly bioactive: a critical evaluation of C5L2 binding and 3T3-L1 adipocyte activation. 20044484_Data show that C5L2 is predominantly intracellular, while C5aR is expressed on the plasma membrane, and that internalized C5aR following ligand binding is co-localized with both C5L2 and beta-arrestin. 21630250_negatively modulated during TLR-mediated enhancement of C5a-induced proinflammatory responses 21698200_698CT genotype of C5L2 may be a genetic maker of CAD in the Han and Uygur population in western China 22180093_genetic association studies in the Chinese Han population: Data suggest that an SNP in C5L2 (C698T) is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus; 698CT heterozygotes exhibited increased serum triglyceride levels. 22187344_The aim of this study was to investigate the genetic alterations and mRNA expression pattern of C5aR and C5L2 genes in neutrophils from attack-free familial Mediterranean fever patients. 22194190_Neither the familial combined hyperlipidemia subjects nor the type 2 diabetes patients were found to have the S323I variant of the C5L2 gene. 22960554_C5L2 was expressed in the kidney and localized to the distal convoluted tubule and connecting tubule. 23239822_C5L2 has been recently demonstrated to physically interact with both C5aR and beta-arrestin to negatively regulate C5aR signaling toward an anti-inflammatory manner 23394121_C5L2 receptors are abundant in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease brain compared to controls. 23460866_The results suggest that insulin sensitivity may be permissive for coupling of C5L2 levels to lipid storage and utilization. 23785491_C5L2 may be implicated in the pro-inflammatory role in C5a-primed neutrophils for ANCA-induced activation. 24073849_A novel polymorphism (901G > a) of C5L2 gene is associated with coronary artery disease in Chinese Han and Uyghur population. 24078164_our study indicates that 698C>T polymorphism of C5L2 gene is associated with the T2DM in individuals of Saudi population which was found to be similar with other studies. 24523571_C5aR and C5L2 may have roles in adiposity in women 24777312_C5a2 can modulate ERK1/2 signaling in macrophages via heteromer formation with C5a1 and beta-arrestin recruitment. 24819959_prominent C5L2 expression in advanced atherosclerotic stages directly correlates with high levels of proinflammatory cytokines 24885523_The present study has extended the mutation spectrum of C5L2, and Thr196Asn mutations in C5L2 were associated with retinitis pigmentosa and serum lipid levels. 25726869_C5AR and C5L2-mediated neutrophil dysfunction is associated with a poor outcome in sepsis. 25935173_All the C698T genotypes and allele frequencies in C5L2 were almost similar in both the cases and controls. 26283482_this study reveals a novel role for C5aR2 in C5a-mediated activation of mast cells and demonstrates that C5aR2 ligation initiates a beta-arrestin-2-, PI3K-, and ERK-dependent signaling pathway in these cells. 28033061_negative regulator of BDNF secretion by pulp fibroblasts under carious teeth 28052000_Both rs2972607 and rs8112962 SNPs of C5L2 are associated with coronary artery disease in a Han population of China. 28576324_Studies indicate that the complement response lie the active fragments, C3a and C5a, acting through their specific receptors, C3aR, C5aR1 and C5aR2 to direct the cellular response to inflammation. 30258440_Expression of C5aR1 and C5aR2 in whole blood was significantly attenuated by IL-6R-inhibition in non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients. 32611725_C5aR2 Activation Broadly Modulates the Signaling and Function of Primary Human Macrophages. 36466856_Differential expression of C5aR1 and C5aR2 in innate and adaptive immune cells located in early skin lesions of bullous pemphigoid patients. |
ENSMUSG00000074361 |
C5ar2 |
2451.615707 |
5.9357195324 |
2.569423 |
0.052357075 |
2355.015732 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4135.3516712 |
128.1447235 |
701.6276500 |
17.6026248 |
| ENSG00000134852 |
9575 |
CLOCK |
protein_coding |
O15516 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator which forms a core component of the circadian clock. The circadian clock, an internal time-keeping system, regulates various physiological processes through the generation of approximately 24 hour circadian rhythms in gene expression, which are translated into rhythms in metabolism and behavior. It is derived from the Latin roots 'circa' (about) and 'diem' (day) and acts as an important regulator of a wide array of physiological functions including metabolism, sleep, body temperature, blood pressure, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, and renal function. Consists of two major components: the central clock, residing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain, and the peripheral clocks that are present in nearly every tissue and organ system. Both the central and peripheral clocks can be reset by environmental cues, also known as Zeitgebers (German for 'timegivers'). The predominant Zeitgeber for the central clock is light, which is sensed by retina and signals directly to the SCN. The central clock entrains the peripheral clocks through neuronal and hormonal signals, body temperature and feeding-related cues, aligning all clocks with the external light/dark cycle. Circadian rhythms allow an organism to achieve temporal homeostasis with its environment at the molecular level by regulating gene expression to create a peak of protein expression once every 24 hours to control when a particular physiological process is most active with respect to the solar day. Transcription and translation of core clock components (CLOCK, NPAS2, BMAL1, BMAL2, PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1 and CRY2) plays a critical role in rhythm generation, whereas delays imposed by post-translational modifications (PTMs) are important for determining the period (tau) of the rhythms (tau refers to the period of a rhythm and is the length, in time, of one complete cycle). A diurnal rhythm is synchronized with the day/night cycle, while the ultradian and infradian rhythms have a period shorter and longer than 24 hours, respectively. Disruptions in the circadian rhythms contribute to the pathology of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, metabolic syndromes and aging. A transcription/translation feedback loop (TTFL) forms the core of the molecular circadian clock mechanism. Transcription factors, CLOCK or NPAS2 and BMAL1 or BMAL2, form the positive limb of the feedback loop, act in the form of a heterodimer and activate the transcription of core clock genes and clock-controlled genes (involved in key metabolic processes), harboring E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') within their promoters. The core clock genes: PER1/2/3 and CRY1/2 which are transcriptional repressors form the negative limb of the feedback loop and interact with the CLOCK|NPAS2-BMAL1|BMAL2 heterodimer inhibiting its activity and thereby negatively regulating their own expression. This heterodimer also activates nuclear receptors NR1D1/2 and RORA/B/G, which form a second feedback loop and which activate and repress BMAL1 transcription, respectively. Regulates the circadian expression of ICAM1, VCAM1, CCL2, THPO and MPL and also acts as an enhancer of the transactivation potential of NF-kappaB. Plays an important role in the homeostatic regulation of sleep. The CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer regulates the circadian expression of SERPINE1/PAI1, VWF, B3, CCRN4L/NOC, NAMPT, DBP, MYOD1, PPARGC1A, PPARGC1B, SIRT1, GYS2, F7, NGFR, GNRHR, BHLHE40/DEC1, ATF4, MTA1, KLF10 and also genes implicated in glucose and lipid metabolism. Promotes rhythmic chromatin opening, regulating the DNA accessibility of other transcription factors. The CLOCK-BMAL2 heterodimer activates the transcription of SERPINE1/PAI1 and BHLHE40/DEC1. The preferred binding motif for the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer is 5'-CACGTGA-3', which contains a flanking Ala residue in addition to the canonical 6-nucleotide E-box sequence (PubMed:23229515). CLOCK specifically binds to the half-site 5'-CAC-3', while BMAL1 binds to the half-site 5'-GTGA-3' (PubMed:23229515). The CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer also recognizes the non-canonical E-box motifs 5'-AACGTGA-3' and 5'-CATGTGA-3' (PubMed:23229515). CLOCK has an intrinsic acetyltransferase activity, which enables circadian chromatin remodeling by acetylating histones and nonhistone proteins, including its own partner BMAL1. Represses glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1/GR-induced transcriptional activity by reducing the association of NR3C1/GR to glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) via the acetylation of multiple lysine residues located in its hinge region (PubMed:21980503). The acetyltransferase activity of CLOCK is as important as its transcription activity in circadian control. Acetylates metabolic enzymes IMPDH2 and NDUFA9 in a circadian manner. Facilitated by BMAL1, rhythmically interacts and acetylates argininosuccinate synthase 1 (ASS1) leading to enzymatic inhibition of ASS1 as well as the circadian oscillation of arginine biosynthesis and subsequent ureagenesis (PubMed:28985504). Drives the circadian rhythm of blood pressure through transcriptional activation of ATP1B1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14645221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18587630, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21659603, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21980503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22284746, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23229515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23785138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24005054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28985504}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Acyltransferase;Biological rhythms;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene plays a central role in the regulation of circadian rhythms. The protein encodes a transcription factor of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family and contains DNA binding histone acetyltransferase activity. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with ARNTL (BMAL1) that binds E-box enhancer elements upstream of Period (PER1, PER2, PER3) and Cryptochrome (CRY1, CRY2) genes and activates transcription of these genes. PER and CRY proteins heterodimerize and repress their own transcription by interacting in a feedback loop with CLOCK/ARNTL complexes. Polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with behavioral changes in certain populations and with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:9575; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; chromatoid body [GO:0033391]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; CLOCK-BMAL transcription complex [GO:1990513]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; histone acetyltransferase activity [GO:0004402]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0000077]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway [GO:2000323]; photoperiodism [GO:0009648]; positive regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042753]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein acetylation [GO:0006473]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of hair cycle [GO:0042634]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of type B pancreatic cell development [GO:2000074]; response to redox state [GO:0051775]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
10198158_essential regulator of circadian rhythms 11927173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12464098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12841365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12897057_BMAL1 and CLOCK have roles in circadian system control 12898572_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14582141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14582141_a role for the CLOCK gene polymorphism in the regulation of long-term illness recurrence in bipolar disorder 14750904_CLOCK was cloned & sequenced and its circadian expression studied. 15331141_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15475734_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15572273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15578592_Findings suggest the significance of the association of the 3111C/C allele of hClock with evening preference in a Japanese population sample. 15578592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905809_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15917222_RNA interference against beta-TRCP greatly decreases Clock-dependent gene expression in tissue culture cells, indicating that beta-TRCP controls endogenous Per1 activity and the circadian clock by directly targeting Per1 for degradation 15952199_Findings may suggest that CLOCK genotype influences the time course of insomnia during antidepressant treatment. 15952199_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16024980_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in the 3'-untranslated region of clock gene is associated with Sleep Disorders 16125818_Single nucleotide polymorphism is not associated with narcolepsy. 16232160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16474406_a molecular genetic screen in mammalian cells to identify mutants of the circadian transcriptional activators CLOCK and BMAL1. 16528748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17106427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17116390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17116390_The results of this study suggests that the T3111C polymorphism of the CLOCK gene is associated with schizophrenia. 17221848_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17221848_compared to T/T homozygotes, bipolar depressed carriers of the C allele had a similar degree of severity of depression, but showed higher activity levels in the evening, a delayed sleep onset and a reduced amount of sleep during the night 17239050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17264841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17364575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17364575_These results show that there is no association between either polymorphism T3111C or T257G in the Clock gene with diurnal preference or delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS). 17428266_CLOCK 3111 T/C SNP was associated with activity levels in the second part of the day, neuropsychological performance and BOLD fMRI correlates (interaction of genotype and moral valence of the stimuli). 17428266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17469042_The difference between the mean value for the lowest expression individual (DeltaCT 8.8) and the highest expression individual (DeltaCT 3.7) revealed an approximately 34-fold difference in relative clock gene expression levels. 17516548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17516548_polymorphism of the CLOCK gene confers a predisposition to a lifetime lower body weight in patients with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa 17551301_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17696255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17696255_Our study suggests a potential role of the CLOCK polymorphisms and their haplotypes in susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and disease severity. 17701674_Allelic variants interaction of CLOCK gene and GNB3 subunit gene with diurnal preference. 17701674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17848551_peripheral clock in vascular endothelial cells regulates TM gene expression and that the oscillation of TM expression may contribute to the circadian variation of cardiovascular events 17948273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17948273_This is the first study suggesting that a polymorphism of a gene within the circadian 'clock' mechanism is a direct or linked contributing factor in adult ADHD 17994337_CLOCK/BMAL1-mediated activation of PER1 by AP1 and E-Box elements is distinct from peripheral transcriptional modulation via cAMP-induced CREB and C/EBP. 18071340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18071340_the Clock gene CGC haplotype may be protective for the development of obesity and support the hypothesis that genetic variation in the Clock gene may play a role in the development of the metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. 18228528_A multi-locus interaction between rs6442925 in the 5' upstream of BHLHB2, rs1534891 in CSNK1E, and rs534654 near the 3' end of the CLOCK gene, however, is significantly associated with bipolar disorder 18228528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18283403_study does not support the hypothesis that the T3111C CLOCK polymorphism is associated with cluster headache 18314271_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18314271_Present findings show for the first time that the 3111T/C SNP of the CLOCK gene is not associated to human obesity and/or BED, but it seems to predispose obese individuals to a higher BMI. 18379422_No relationship between hCLOCK T3111C polymorphism and endometriosis, nor any effect of the polymorphism on the relationship of shift work to endometriosis. 18379422_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18411297_DEC1, along with DEC2, plays a role in the finer regulation and robustness of the molecular clock CLOCK/BMAL1 18419323_Evidence linking circadian rhythms, the Clock gene, and bipolar disorder is discussed, along with the possible biology that underlies this connection. Review. 18430226_The regulators of clock-controlled transcription PER2, CRY1 and CRY2 differ in their capacity to interact with each single component of the BMAL1-CLOCK heterodimer and, in the case of BMAL1, also in their interaction sites. 18458078_HAT gene expression is required for cisplatin resistance and Clock and Tip60 regulate not only transcription, but also DNA repair, through periodic histone acetylation 18541547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18541547_Putative role of the CLOCK polymorphism and related haplotypes in susceptibility to obesity. 18587630_The transcription of human nocturnin gene displayed circadian oscillations in Huh7 cells (a human hepatoma cell line) and was regulated by CLOCK/BMAL1 heterodimer via the E-box of nocturnin promoter. 18957941_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18974966_Impairment of the circadian clock protein appears to be closely associated with the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes in humans. 19224106_Data show that there are not significant association between CLOCK gene and pathophysiology of Japanese schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. 19224106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19296127_expression of CLOCK in breast cancer is associated significantly with 3-year survival 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19347611_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19347611_Results indicate that CLOCK genotype may be a predictor of fluvoxamine treatment response in Japanese major depressive disorder. 19470168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605937_PER2 is inhibited by BMAL2-CLOCK, which reemphasizes its negative role and a positive role of BMAL2 in circadian transcription 19693801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714310_Evidence suggests metabolic processes feed back into the circadian clock, affecting clock and per2 gene expression and timing of behaviour. 19839995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19846548_CLOCK polymorphisms interact with fatty acids to modulate metabolic syndrome X traits. 19846548_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888304_A novel association of genetic variation at CLOCK with total energy intake, which was particularly relevant for single nucleotide polymorphism rs3749474. 19888304_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934327_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19946213_This investigation begins the characterization of a complex phospho-regulatory site that controls the activity and degradation of CLOCK, a core transcription factor that is essential for circadian behavior. 19967263_The frequencies of the shorter allele (4 repeats) in the PER3 gene and the T allele in the CLOCK gene among Asians (0.86 and 0.84, respectively) were significantly higher than among Caucasians (0.69 and 0.71, respectively). 20065968_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20065968_The genetic variation in the rs1801260 CLOCK was associated with obesity at baseline and also affected weight loss and patients with the variant allele (G) lost significantly less weight i(P=0.008) compared with wild type. 20072116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20081528_We show that endotoxin causes profound suppression of circadian clock gene expression, clearly manifested in human peripheral blood leukocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes. 20124474_Circadian genes influence tumorigenesis, and identify a set of circadian gene variants as candidate breast cancer susceptibility biomarkers. 20149345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20149345_We report an association between variants of the human CLOCK gene and sleep duration in two independent populations. This adds another putative function for CLOCK besides its possible involvement in circadian timing, depression, obesity, and personality. 20174623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20180986_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364331_The T3111C (RS1801260) polymorphism of hClock gene is associated with schizophrenia, but it seems that the length polymorphism of 18 exon of hPer3 may not be associated with schizophrenia. 20368993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20370469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20370469_Results do not support the hypothesis of an effect of the T3111C CLOCK variant on sleep disturbances in major depressive disorder. 20396431_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551151_Clock genes have been implicated in cancer-related functions; in this work, we investigated CLOCK as a possible target of somatic mutations in microsatellite unstable colorectal cancers. 20554694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20560707_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20560707_meta-analysis shows no association between rs1801260 and mood disorders or depression severity and points out necessity of further research to better understand underlying biological machinery of circadian dysfunction in subjects with mood disorders 20600471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20600471_This study suggested that CLOCK 3111T/C is significant allelic and genotypic associations with bipolar disorder 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20653450_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20704703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20704703_This study provides evidence for the possible involvement of CLOCK in susceptibility to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder 20861012_ID2 can interact with the canonical clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 and mediate inhibitory effects on mPer1 expression 20876123_Circadian CLOCK histone acetyl transferase localizes at ND10 nuclear bodies and enables herpes simplex virus gene expression. 20886252_Clock T3111C SNPs do not influence circadian rhythmicity in healthy Italian population. 20886252_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20961464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20961464_the Clock 3111 T/C SNP might be associated with the existence of sdLDL small dense low-density lipoprotein 20978934_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21050724_Variations in genes implicated in circadian regulation or its related downstream pathways may be important in the regulation of antropomorphic parameters in patients with schizophrenia during long-term treatment with SGA. 21123577_Disruption of transgenic Clock gene function promotes alterations in nucleus accumbens microcircuits. 21164265_Circadian CLOCK-mediated regulation of target-tissue sensitivity to glucocorticoids: implications for cardiometabolic diseases. 21386998_Influence of the CLOCK gene may extend to a broad range of variables linked with human behaviors. 21463335_SiRNA specific inhibition of either Clock or Per2 protein significantly inhibited alcohol-induced monolayer hyperpermeability in intestinal cells. 21479263_REV-ERBalpha plays a dual role in regulation of the activity of the BMAL1/CLOCK heterodimer by regulation of expression of both the BMAL1 and CLOCK genes. 21628555_did not find a significant association between the CLOCK 3111C/T polymorphism and morningness/eveningness or any circadian marker 21714069_Failure to replicate previous research in relation to PERIOD3 and CLOCK concurs with previous research suggesting that the effects of these genes are small and may be related to population composition. 21734043_The authors report that CLOCK is a component of the transcriptional complex that includes TFIID, ICP4, ICP27, and ICP22. 21773969_CLOCK gene polymorphisms may serve as an independent prognostic marker for colorectal cancer patients. 21898035_We conclude that menopause transition induces several changes in the genotype of the adipose tissue chronobiological machinery related to an increased risk of developing MetS. 21980503_CLOCK-mediated circadian acetylation of the human GR may function as a target-tissue, gene-specific counter regulatory mechanism to the actions of diurnally fluctuating cortisol 22003994_Our study did not provide evidence for the association between the CLOCK gene 3111C/T polymorphism and personality traits in the Japanese population. 22080789_association between the three tagging SNPs (rs3736544, rs1801260, and rs3749474) in CLOCK and risk of bipolar disorder (n=867) and major depressive disorder (n=139) compared to controls (n=889) in the Japanese population 22193177_results suggest that altered promoter methylation may contribute to the abnormal expression of clock genes in Parkinson's disease 22232930_The genotype frequency distributions of the polymorphism of the CLOCK gene examined in the EAH and CAD patients were statistically significantly different from that in the individuals without clinical signs of these diseases. 22284746_Findings establish that Clock regulates Thpo and Mpl expression in vivo, and demonstrate an important link between the body's circadian timing mechanisms and megakaryopoiesis. 22537959_There is an association between CLOCK gene T3111C polymorphism and both attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and related sleep disturbances in children. 22578325_RAI1 is a positive transcriptional regulator of CLOCK, pinpointing a novel and important role for this gene in the circadian oscillator 22709985_No significant differences were found in breakfast frequency, energy intake, or HRV between CLOCK 3111T/C minor C allele (T/C or C/C) and T/T subjects. 22806005_Borderline personality disorder may be associated with circadian typology, and perhaps to CLOCK genotypes. 22823872_The combination of a sensitive genotype (3111C/C) and environmental stress increases vulnerability to circadian rhythm sleep pattern disruption in females. 22905804_disturbances in clock expression may result in the disruption of the control of normal circadian rhythm, thus benefiting the survival of glioma cells and promoting carcinogenesis. 22999556_Genetic variation in the CLOCK gene is associated with semen quality in idiopathic male infertility. 23003921_DNA methylation levels at different CpG sites of CLOCK, BMAL1 and PER2 genes were analyzed in sixty normal-weight, overweight and obese women following a 16-week weight reduction program. 23033538_Data indicate that Clock-Bmal1 regulates the response to glucocorticoids in peripheral tissues through acetylation of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), possibly antagonizing the biologic actions of diurnally fluctuating circulating cortisol. 23129285_Expression of the CLOCK, BMAL1, and PER1 circadian genes in human oral mucosa cells as dependent on CLOCK gene polymorphic variants. 23131019_A significant interaction was observed between the 3111T/C SNP of CLOCK gene and sex for overweight/obesity risk 23160374_enhancement of ERalpha transcriptional activity exerted by wild-type but not mutant (2K/2R) CLOCK in response to estrogen indicated that sumoylation of CLOCK may have an important role in estrogen-dependent signaling 23183326_C genetic variants in CLOCK 3111T/C display a less robust circadian rhythm than TT and a delayed acrophase that characterizes 'evening-type' subjects. 23221812_findings suggest that the CLOCK C3111T polymorphism may affect personality traits in healthy Japanese subjects. 23229515_CLOCK His84 and BMAL1 Leu125 are the key residues for the mutual recognition between CLOCK and BMAL1 bHLH domains. 23242607_Loss of Clock expression is associated with skin tumors. 23357097_among APOEepsilon4 noncarriers, C carriers in CLOCK gene rs 4580704 were associated with a high susceptibility of Alzheimer's disease 23395176_O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) promotes expression of BMAL1/CLOCK target genes and affects circadian oscillation of clock genes in vitro and in vivo. 23496259_TNF -alpha modulates expression of the clock gene in rheumatoid arthritis. 23527142_Genetic variability in the CLOCK gene might be associated with male infertility. 23546644_Studies indicate that in the cytoplasm, PER3 protein heterodimerizes with PER1, PER2, CRY1, and CRY2 proteins and enters into the nucleus, resulting in repression of CLOCK-BMAL1-mediated transcription. 23584858_Data suggest that clock genes Per1, Cry1, Clock, and Bmal1 and their protein products may be directly involved in the daytime-dependent regulation and adaptation of hormone synthesis. 23768840_Selected genetic polymorphisms in the AHR-signaling pathway (i.e., AHRR) and CLOCK may play a role in decreasing the risk for experiencing insomnia during the menopausal transition. 23781009_the CLOCK rs1554483 G allele was associated with increased susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease. 23792158_we suggest that as a target of glioma suppressor miR-124, CLOCK positively regulates glioma proliferation and migration by reinforcing NF-kappaB activity 23871470_Common variants in CLOCK are not associated with measures of sleep duration in people of european ancestry . 23912676_Among APOE epsilon4 noncarriers, C carriers in CLOCK gene 3111T/C were associated with a high susceptibility of Alzheimer's disease in a Chinese population. 23970287_CLOCK may interact with HIF-1alpha/ARNT and activate VEGF to stimulate tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. 24037774_The 311T>C polymorphism in the CLOCK1 gene significantly increases the risk for CRC development while it does not affect the outcome of CRC patients. 24068320_This study failed to show a mediating role of evening preference, ongoing efforts are needed to identify the mechanisms by which the CLOCK gene determines ADHD-related traits. 24235147_The Cdk5-dependent regulation of CLOCK function is mediated by alterations of its stability and subcellular distribution. 24328727_data support the notion that a chronic consumption of a healthy diet may play a contributing role in triggering glucose metabolism by interacting with the rs1801260 SNP at CLOCK gene locus in metabolic syndrome patients 24332565_Sleep disruptions may contribute to increases in depressive symptoms via their impact on cognitive control and variation in the CLOCK gene may be associated with sleep quality. 24510388_A population specific variation of MTHFR and hCLOCK genes also highlights ethnicity specific risk management. 24597447_In an arousal model, prolonged wakefulness has a negative effect on subjective sleepiness and mood in three clock gene PERIOD3 polymorphisms analyzed. 24636202_No association with SNPs or haplotypes of the CLOCK gene was observed in prophylactic lithium response. 24789043_E2 promoted the binding of ERalpha to the EREs (estrogen-response elements) of CLOCK promoter, thereby up-regulating the transcription of CLOCK 24818524_The CLOCK 3111T/C polymorphism was not significantly associated with overweight or sleep duration. 24821610_SNP (rs6855837) in the CLOCK gene is significant correlation with genotype and allele frequency in lung cancer. 24824748_CLOCK polymorphisms are associated with increased susceptibility of schizophrenic patients to restless legs syndrome 24892753_The results of this study present no evidence for an association of CLOCK polymorphisms with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. 24905098_CLOCK 3111 T/C SNP interacts with emotional eating behavior to modulate total weight loss. 24919398_Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in RORA were associated with breast cancer in the whole sample and among postmenopausal women, and we also reported an association with CLOCK, RORA, and NPAS2 in the analyses at the gene level 25070164_There is not a significant difference in the expression of CLOCK, BMAL1, and PER1 in buccal epithelial cells of patients with essential arterial hypertension regardless of patient genotype. 25309987_The observed interaction effects provide converging evidence that the clock gene and OXT/AVP systems are intertwined and contribute to human prosociality. 25527757_Data suggest that influence of obesity-associated CLOCK SNPs (rs12649507, rs6858749) on sleep duration and macronutrient intake can be ameliorated via habitual longer sleep duration and favorable dietary profile (lower protein; higher PUFA). 25625359_the circadian gene hClock promoted CRC progression and inhibit tumor cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo, while silencing hClock was able to reverse this effect. 25775462_minor polymorphisms of CLOCK may be associated with poor morning gastric motility, and may have a combinatorial effect with PER3. 25936801_PASD1 is a circadian bHLH-PAS paralog repressor of CLOCK protein expression. 25976934_Our results suggest that the circadian gene human Clock may play an important role in carcinogenesis by inhibiting apoptotic cell death via attenuating proapoptotic signaling 26134245_CLOCK, ARNTL, and NPAS2 gene polymorphisms may have a role in seasonal variations in mood and behavior 26164627_these findings suggest that sumoylation plays a critical role in the spatiotemporal co-activation of CLOCK-BMAL1 by CBP for immediate-early Per induction and the resetting of the circadian clock. 26181468_Variants of the CLOCK gene are associated with idiopathic male infertility and therefore may be applied as a risk factor of male infertility. 26204460_CLOCK rs1801260 modulated the relationship between early stress, adult history of attempted suicide and current suicide ideation 26247999_possible circadian rhythm in full-term placental expression 26299356_Upregulation of CLOCK is associated with the expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in varicose veins. 26370682_found that overexpression of both Clock and Bmal1 suppressed cell growth 26374515_Clock circadian regulator (CLOCK) gene single nucleotide polymorphism rs1801260 minor allele C showed a significantly higher association with the prevalence of diabetes in the Japanese population independent of body mass index (BMI). 26390085_Findings indicate that CLOCK protein plays an important role in fertility and its knockdown leads to reduction in reproduction and increased miscarriage risk. 26453284_The CLOCK 3111T > C polymorphism could be an independent risk factor for irregular menstrual cycles, irrespective of psychological distress and endocrine or metabolic conditions in Korean adolescents. 26553137_Clock gene variants associated with obesity and sleep duration. [review] 26690565_The possession of CLOCK rs3749474 may influence the effect of reducing the percentage intake of dietary fat on obesity-associated variables and carrying this SNP might benefit more than others from weight loss treatment involving dietary fat restriction. 26739996_CLOCK gene variation is associated with incidence of type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in type-2 diabetic subjects. Suggest diet-gene interaction. 26850841_when overexpressed, c-MYC is able to repress Per1 transactivation by BMAL1/CLOCK via targeting selective E-box sequences. Importantly, upon serum stimulation, MYC was detected in BMAL1 protein complexes 26923944_Our findings suggest that CLOCK and CRY1 polymorphisms might be involved in individual susceptibility to abdominal obesity in Chinese Han population. 27335043_This study showed that Lack of Association between Genetic Polymorphism of clock gene with Late Onset Depression and Alzheimer's Disease in a Sample of a Brazilian Population This study showed that Lack of Association between Genetic Polymorphism of PER2 gene with Late Onset Depression and Alzheimer's Disease in a Sample of a Brazilian Population 27339606_Evening chronotype is associated with higher obesity in severely obese subjects and with lower weight loss effectiveness after bariatric surgery. In addition, circadian preferences interact with CLOCK 3111T/C for obesity. The circadian and genetic assessment could provide tailored weight loss recommendations in subjects who underwent bariatric surgery. 27373683_TFEB regulates PER3 expression via glucose-dependent effects on CLOCK/BMAL1 27492458_Low Clock gene expression is associated with colorectal liver metastases. 27614897_Immunostaining of CLOCK and PER2 protein was detected in the granulosa cells of dominant antral follicles but was absent in the primordial, primary, or preantral follicles of human ovaries.Oscillating expression of the circadian gene PER2 can be induced by testosterone in human granulosa cells in vitro. Expression of STAR also displayed an oscillating pattern after testosterone stimulation 27996307_CLOCK rs1801260*C and PER3(4/4) influence myelination processes by regulating sleep quality and quantity. 28058089_a novel mechanism of action of CLOCK in human umbilical vein endothelial cells, is reported. 28290876_the CLOCK gene polymorphism is one of factors determining elastic properties of vascular wall 28384165_CLOCK gene expression mean was significantly higher in morning than in evening during Shabaan 28466652_We found a significant association with CLOCK rs12649507 and cluster headache 28498393_These findings suggest that upregulation of the circadian gene hClock plays an important role in metastasis of colorectal cancer. 28514207_Results indicated that inhibiting the circadian gene Clock expression can reverse the cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer SKOV3/DDP cell lines by affecting the protein expression of drug resistance genes during which autophagy plays an important role. 28645331_CLOCK SNP rs2070062 is associated with shorter sleep duration. 28780642_The present study confirmed that circadian dysfunction is associated with the risk of PD in a Chinese population at the genetic level and provided a potential genetic locus related to PD and CLOCK rs1801260 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to Parkinson's Disease. 28853078_No association between 3111T/C Clock gene polymorphism and complaints of patients with insomnia was detected. 28899534_Study found three gene variants (CLOCK-rs4864548, PEMT-rs936108, and GHRELIN-rs696217) that exhibited uncorrected gene-by-sleep duration interactions in relation to BMI z-scores in a cohort of New Zealand European children. However, no interactions were identified in percentage body fat differences. Notably, these interactions are evident without detectable effects on sleep duration. 28985504_ASS1 acetylation by CLOCK exhibits circadian oscillation in human cells and mouse liver, possibly caused by rhythmic interaction between CLOCK and ASS1, leading to the circadian regulation of ASS1 and ureagenesis. 29064730_The CLOCK SNP may affect daytime gastric motility less than food stimulation. 29180440_As a novel CLOCK-dependent diurnal gene, TIMP3 inhibits the expression of inflammatory cytokines that are up-regulated by UV irradiation in human keratinocytes. 29196536_CLOCK regulates the expression of genes involved in neuronal migration, and a functional assay showed that CLOCK knockdown increased neuronal migratory distance. 29271044_Low expression of CLOCK protein is associated with kidney tumor. 29316898_Rhythmic luciferase activity from clock gene luciferase reporter cells lines was used to test the effect of p38 MAPK inhibition on clock properties as determined using the damped sine fit and Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm.Glioma treatment with p38 MAPK inhibitors may be more effective and less toxic if administered at the appropriate time of the day. 29318394_Association between HCRTR2, ADH4,CLOCK gene polymorphisms and cluster headache was not significant in the present study. 29324865_results of this study suggest that genetic variability in the ARNTL and CLOCK genes might be associated with risk for multiple sclerosis 29621412_The frequency of the TT-genotype and 3111T-allele of the Clock 3111T/C gene polymorphic marker in the Caucasian women with insomnia is higher as compared to control. 29658882_Basal and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake were significantly reduced upon CLOCK depletion. The findings suggest an essential role for the circadian coordination of skeletal muscle glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism in humans. 29673458_The proliferation of cells significantly decreased after the expression of CLOCK was knocked down in HepG2 cells. 29768442_data suggest that SNP variability in the CLOCK gene for rs6850524 and rs11932595 is associated with idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion in pregnancies from Slovenia and Serbia 29860109_Loss of protective endothelial CLOCK expression aggravates TGF-beta/ROCK1-modulated endothelial to mesenchymal transition progression, which contributes to the vulnerability of human carotid plaque. 29943823_the messenger RNA expression of brain and muscle ARNT-like 1 (BMAL1) and circadian locomotor output cycles kaput (CLOCK) genes is altered by low doses (5 mJ/cm(2) ) of ultraviolet B in the immortalized HaCat human keratinocyte cell line. 30003419_In patients wit |
ENSMUSG00000029238 |
Clock |
164.573815 |
2.1751706681 |
1.121129 |
0.227554867 |
23.672906 |
0.00000114178729555940405375718659647388264488654385786503553390502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004014478437936351599101252735080080924490175675600767135620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
225.6259455 |
35.6971984 |
103.8904199 |
11.9803766 |
| ENSG00000134853 |
5156 |
PDGFRA |
protein_coding |
P16234 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as a cell-surface receptor for PDGFA, PDGFB and PDGFC and plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, survival and chemotaxis. Depending on the context, promotes or inhibits cell proliferation and cell migration. Plays an important role in the differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Required for normal skeleton development and cephalic closure during embryonic development. Required for normal development of the mucosa lining the gastrointestinal tract, and for recruitment of mesenchymal cells and normal development of intestinal villi. Plays a role in cell migration and chemotaxis in wound healing. Plays a role in platelet activation, secretion of agonists from platelet granules, and in thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. Binding of its cognate ligands - homodimeric PDGFA, homodimeric PDGFB, heterodimers formed by PDGFA and PDGFB or homodimeric PDGFC -leads to the activation of several signaling cascades; the response depends on the nature of the bound ligand and is modulated by the formation of heterodimers between PDGFRA and PDGFRB. Phosphorylates PIK3R1, PLCG1, and PTPN11. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, mobilization of cytosolic Ca(2+) and the activation of protein kinase C. Phosphorylates PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and thereby mediates activation of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Mediates activation of HRAS and of the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes activation of STAT family members STAT1, STAT3 and STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Receptor signaling is down-regulated by protein phosphatases that dephosphorylate the receptor and its down-stream effectors, and by rapid internalization of the activated receptor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10734113, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10947961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11297552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12522257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1646396, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17087943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1709159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17141222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20972453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21224473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21596750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2554309, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8188664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8760137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8943348}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chemotaxis;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a cell surface tyrosine kinase receptor for members of the platelet-derived growth factor family. These growth factors are mitogens for cells of mesenchymal origin. The identity of the growth factor bound to a receptor monomer determines whether the functional receptor is a homodimer or a heterodimer, composed of both platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and beta polypeptides. Studies suggest that this gene plays a role in organ development, wound healing, and tumor progression. Mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome, somatic and familial gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and a variety of other cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:5156; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; BBSome binding [GO:0062063]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptor activity [GO:0005018]; platelet-derived growth factor binding [GO:0048407]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; vascular endothelial growth factor binding [GO:0038085]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005021]; adrenal gland development [GO:0030325]; cardiac myofibril assembly [GO:0055003]; cell activation [GO:0001775]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis [GO:0048557]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; estrogen metabolic process [GO:0008210]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; Leydig cell differentiation [GO:0033327]; lung development [GO:0030324]; luteinization [GO:0001553]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; metanephric glomerular capillary formation [GO:0072277]; negative regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010544]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor-alpha signaling pathway [GO:0035790]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038091]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050920]; regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [GO:2000739]; retina vasculature development in camera-type eye [GO:0061298]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; signal transduction involved in regulation of gene expression [GO:0023019]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; white fat cell differentiation [GO:0050872]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11175793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12023424_high expression associated with long survival in patients with grade 2 astrocytomas and oligoastrocytomas 12176024_PDGFRA is endogenenously activated in medulloblastoma tumor cell lines 12522257_KIT and PDGFRA mutations appear to be alternative and mutually exclusive oncogenic mechanisms in gastrointestinal stromal tumors 12660384_The hypereosinophilic syndrome may result from a novel fusion tyrosine kinase - FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha - that is a consequence of an interstitial chromosomal deletion. 12842979_observations suggest that the FIP1L1-PDGFRA rearrangement occurs in an early hematopoietic progenitor and suggests that the molecular pathogenesis for a subset of SMCD patients is similar to that of HES 14630792_results indicate that the fusion of FIP1L1 to PDGFRA occurs rarely in leukemia cell lines 14741194_Result from our case-control study demonstrated that the frequencies of haplotypes with low transcription activity were significantly higher in NTD mothers than that observed in control mothers (odds ratio=2.2, 95% CI=1.0-4.6). 14745431_results confirm the high frequency of BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations in patients with secondary resistance to imatinib and exclude mutations of the activation loops of KIT, PDGFRA and PDGFRB as causes of resistance in patients without ABL mutations 14766209_PDGFRa expression is regulated by C-EBP 15154005_PDGFRA mutations were found in 7 (25.0%)gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) , carrying either D842 V mutations or exon 18 deletions. 15284118_FIP1L1-PDGFRA is a relatively infrequent but treatment-relevant mutation in primary eosinophilia that is indicative of an underlying systemic mastocytosis. 15326474_gene expression profiling of 26 gastrointesstinsal stromsal tumors with known KIT and PDGFRA mutational status 15380338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15492989_These results suggest that myxoid epithelioid GISTs are a distinct subtype of GISTs that are closely correlated with the PDGFRA gene mutation 15635072_link between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the PDGFRalpha gene promoter and the occurrence of brain tumours 15674355_The Receptor, PDGF alpha (PDGFRA)is implicated in the pathogenesis of AML, and the mechanisms of cytogenetic progression and oncoprotein-driven function may be similar in AML expressing oncogenic forms of PDGFRA. 15685537_High sensitivity of the imatinib-resistant KIT -T670I and KIT -V654A and of PDGFRA -D842V mutants to PKC412 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 15791568_study demonstrates that platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and beta, and c-kit protein are expressed in a high percentage of epithelial ovarian cancers 15862965_Western blot showed a high amount of PDGFRalpha and beta proteins in primary stromal cells that could not be detected in prostatic cancer cells. 15871904_In human ASMCs, IFNgamma again stimulated a transient STAT1-binding to the PDGF-Ralpha promoter. 15894928_single example of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor with activating mutation and immunoreactivity without CD117 positivity 15897742_The point mutations of c-kit and platelet- derived growth factor receptor alpha genes may play a limited role in the tumorigenesis of type 1 neurofibromatosis-associated gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 15928335_PDGFRA mutations are associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors 16116920_The hypereosinophilic syndrome may result from a novel fusion tyrosine kinase - FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha - that is a consequence of an interstitial chromosomal deletion. 16126374_The current identification of cis-acting elements in the PDGFRA promoter and the transcription factors that bind them, provides a new strategy for the identification of genes that are potentially involved in neural tube defects. 16135486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16168125_An intronic insertion IVS17-50insA at exon 18 in all sequenced cases. None of these genetic alterations was correlated with PDGFR-alpha expression in breast cancer. 16186508_Two-basepair deletion in the C terminus of PDGFRA (exon 23) found in glioblastomas. 16283668_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16283668_PDGFRA P1 promoter region haplotypes do not have a major role in the development of spina bifida meningomyelocele . 16305343_data describe percentage of bone marrow cells expressing receptors for interleukin-1, platelet-derived growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, transforming growth factor-beta, epidermal growth factor and c-Fos and c-Myc in untreated lung & breast cancer 16331269_Specific PDGFR inhibition by siRNA or a neutralizing antibody to the receptor inhibited PDGF-stimulated receptor activation and cell proliferation, suggesting that receptor targeting has a role in ovarian cancer treatment 16357008_describes frequence mutation of PDGFRA in malignant periphaerl nerve sheath tumors often associated with coamplification of KIT 16373964_activating mutations of PDGFR-alpha, c-kit and B-RAF are absent in gliosarcomas 16498388_Demonstrates the utility of screening for PDGFRA kinase domain overexpression in patients with IHES and has identified KIF5B as a third PDGFRA fusion partner in chronic myeloproliferative disorders. 16502585_Fusion protein is detected in hypereosinophilic syndrome and chronic eosinophilic leukemia. 16675559_The most intense expression of PDGFRalpha was observed in fibroblasts in the lung carcinoma outer rim. 16685437_Six of the 20 gastrointestinal stomach tumors lacking KIT mutations had mutations in exon 18 of PDGFRA, and 1 had a mutation in exon 12 in this receptor. 16690743_FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha activation requires disruption of the juxtamembrane domain of PDGFRalpha and is FIP1L1-independent 16697720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16730575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16785193_Gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) with platelet-derived growth factor receptor mutations often have reduced expression of the KIT protein in immunohistochemistry (IHC), suggesting that IHC may be potentially useful in identification of such GISTs. 16804324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16850112_77% of the examined primary central nervous system lymphoma specimens showed expression of PDGFRalpha. Tumours expressing survivin frequently co-expressed PDGFRalpha. 16892550_PDGFRalpha mutations have been identified as alternative oncogenic mechanism in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 17047316_In midgut carcinoid tumor stroma PDGFRalpha was expressed in 35%, PDGFRbeta in 94% and EGFR in 9%. 17070723_Signaling through PDGFRA activates RhoA, which results in Rho-associated kinase-dependent cofilin phosphorylation, enhancing smooth muscle alpha-actin filament polymerization, and upregulates smooth muscle alpha-actin expression. 17079230_17-AAG promotes PDGFRalpha degradation selectively in transformed cells 17137731_The presence of the FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene is detected in chronic eosinophilic leukemia. 17145809_The PDGFRA was less expressed and phosphorylated with the absence of gain-of-function mutations and the presence of the cognate ligands, strongly support the hypothesis that the activation mechanism is the autocrine/paracrine loop in chordoma. 17193822_PDGFRA mutations usually occur in gastric GISTs, especially in the epithelioid variants; their overall frequency is approximately 30% to 40% of KIT mutation negative GISTs. Most common is exon 18 mutation leading Asp842Val at the protein level. 17214097_These cases demonstrate the first known linkage between F1P1L1-PDGFRalpha and hypereosinophilic syndrome 17261495_data and previous reports suggest that FIP1L1-PDGFRA - positive HES is a distinct clinical entity with myeloproliferative features and showing a poor response to corticosteroid treatment 17298867_no activating mutations in the PDGFRA were found, but pleomorphism was identified in exon 18 of the PDGFRA gene in children with Ewing sarcoma 17299092_FIP1L1 and PDGFRalpha have roles in response to imatinib mesylate in chronic eosinophilic leukemia 17344284_these observations indicate that an IE and/or E human cytomegalovirus protein(s) downregulates the expression of PDGFR-alpha and -beta in smooth muscle cells 17363728_Stimulatory antibodies to PDGFR-A&-B were found selectively in all patients with extensive cGVHD but in none of the patients without cGVHD. Higher levels were detected in patients with generalized skin involvement and/or lung fibrosis. 17377585_FIP1L1-PDGFRA-positive patients who presented with acute myeloid leukemia (AML, n=5) or lymphoblastic T-cell non-Hodgkin-lymphoma (n=2) in conjunction with AML or Eos-MPD. 17438095_Genomic alterations were present at disease onset in 1/3 of the examined cases. They therefore represent an early event possibly related to primary imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 17448020_PDGFRalpha was expressed in 24/37 endometrial stromal sarcomas(ESS)[65%; strongly by 19/37 & weakly by 5/37 ESS]; mutational analysis of PDGFRalpha & PDGFRbeta of metastatic ESS from 3 patients detected no mutations leading to amino acid changes 17532173_GISTs were commonly associated with KIT mutation, but rarely associated with PDGFRA mutation in Taiwan. 17532173_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17566086_Multiple gastrointestinal stromal and other tumors may be caused by germline PDGFRA gene mutations (V561D. 17568391_sequence variation in diaphragmatic hernia 17591942_Fluorescence in situ hybridization and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction protocols were developed for an accurate del(4)(q12q12) and FIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion gene detection. 17623951_No associations were found with exons 12 and 18 of the PDGFRA gene and GIST. 17673922_A significant correlation was found between a higher protein expression of PDGFRA and longer disease-free survival of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors of stomach and intestine. 17690840_A positive correlation was observed between PDGFR-alpha and proliferation index in pilocytic astrocytomas; expression of PDGFR-alpha was significantly related to progression-free survival. 17701174_A new fusion transcript skiping alphaPDGFR exon 12 forms by a previously unreported splicing mechanism. Exon skipping did not disrupt exonic splicing enhancers within the exon but lost most of FIP1L intron 8a (intronic splicing enhancers). 17762857_PDGFRA is not the relavant gene in melanoma that drives the selection of copy number increases of the locus 17827398_The incidence of both KIT and PDGFRA mutations in a Portuguese series was 63%. The great majority of mutations were located in KIT exon 11, statistically associated with worse prognosis and indicative of favourable response to imatinib-based therapy. 17881156_Transcriptional regulation of PDGFRA by E2F1. 18042065_one mixed cell-type GIST showed a somatic PDGFRalpha mutation...both epithelioid and spindle components showed identical mutations 18070887_Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent membrane recruitment of Rac-1 and p47phox is critical for alpha-platelet-derived growth factor receptor-induced production of reactive oxygen species. 18077793_PDGFR-alpha receptors contribute to the formation of the renal cortical interstitium 18084259_Silent mutations of KIT and PDGFRA were found in Merkel cell carcinoma that have the potential to lead to alternate protein function. 18157090_Expression status of PDGF receptor alpha was not significantly associated with progression-free survival in choroid plexus carcinomas. 18187489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18190445_Three out of nine (33.3%) Merkel cell carcinomas showed an identical novel single heterozygous base change in exon 10 of the PDGFRA gene 18197502_Phosphorylated protein induced by PDGFR-alpha mutation may be associated with the important alternative molecular mechanism and the biological behavior of gastrointestinal and extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumor development. 18265649_As a sensitive and specific marker of GIST, PDGFR-alpha oncogenic mutations are more likely seen in giant, CD-117-negative GISTs arising outside the gastrointestinal tract and have an unfavorable clinical course. 18284546_regularly expressed in variable levels in ameloblastomas, and somatic mutations of exon 12 and exon 18 are rare findings 18288404_PDGFRalpha expression in colorectal cancer significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis. 18312355_PDGFRA genotyping is important for gastrointestinal stromal tumours diagnosis and assessment of sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.(Review) 18314611_may be mutated in gastrointtestinal stromal tumors. 18326546_The proteins and mRNA transcripts for PDGFRA were detected in oocytes. PDGFR-alpha mRNA was expressed in granulosa cells of a minority of the samples from women/girls. 18331602_demonstrated the expression of PDGFalpha and PDGFbeta in the peripheral blood samples of transient myeloproliferative disorder, indicating that the PDGF pathway may play an important role in the fibrosis of several organs in patients with TMD 18360281_When critically applied, CD117/PDGFRA immunophenotyping is a useful diagnostic tool correctly predicting the presence of PDGFRA mutations in most cases. 18416137_Significant correlation between PDGFRA mutations, on the one hand, and tumor site and histological pattern of GastroIntestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST), on the other. 18464291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18464291_PDGFRA promoter haplotypes may predispose to gliomas 18492696_There is significant expression of PDGFR-beta in ovarian granulosa cell tumors, whereas normal ovarian tissues have a complete absence of staining. 18519768_high expression of p-PDGFR alpha and PDGFR beta was the only significant association with malignant histology in childhood glioma 18547963_PDGFRalpha mutations in GISTs were found to be rare in this Korean population 18548106_constitutively active PDGFRA mutation found in acute lymphoblastic leukemia that may be associated with leukemic cell growth 18615679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18618605_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18633616_Overall survival in mature T- and NK-cell lymphomas correlated with disease subtypes and prognostic index but not PDGFRA (platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha) expression. PDGFRA expression was different in mature T- and NK-cell lymphomas 18636362_Most gastrointestinal stromal tumors have a c-kit or PDGFRA gene mutation. 18679424_Proof-of-principal for PDGFR-A as a therapeutic target in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 18686281_the vast majority of IFPs harbour gain-of-function mutations in the PDGFRA gene. The presence of PDGFRA mutations questions the reactive nature of IFPs and raises the possibility of a neoplastic process. 18701889_data indicate that PDGFR-alpha is a critical receptor required for HCMV infection, and thus a target for novel anti-viral therapies 18706197_FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha emerges as a relatively homogeneous clinicobiological entity that co-exists with other abnormalities of tyrosine kinase family genes. It reflects the disease progression and there is a good response to imatinib. 18758297_High tumor cell PDGFR-alpha is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 18950958_VEGF, HIF-1alpha, and predominantly PDGFRalpha are expressed in neoplastic cells in the majority of Hodgkin lymphomas. 18955458_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987651_characterized FIP1L1-PDGFRA junction sequences from 113 patients at the mRNA (n=113) and genomic DNA (n=85) levels 18992915_We showed that Prx I, PDGF-A, and PDGFR-alpha follow the same expression pattern during carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma progression. 19035305_data showed that no pathogenic mutations in PDGFRA and PDGFRB were detected in the context of core-binding factor leukaemia (CBFL) without KIT and FLT3 mutations; thus, PDGFR genes do not seem to be involved in CBFL 19047372_PDGFRalpha signaling stimulates osteogenesis of neural crest cells-derived osteoblasts by activating the PLC-gamma pathway, suggesting an involvement of this pathway in the etiology of human craniosynostosis. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19115205_combined inhibition of PDGFRalpha and -beta results in markedly decreased tumor growth in vivo because of impaired recruitment of periendothelial cells. 19118897_studied a new FISH method to detect CHIC2 deletion, FIP1L1/PDGFRA fusion and PDGFRA translocation in patients with myeloid neoplasms associated with eosinophilia 19126548_a novel mechanism for activation of PDGFRalpha that appears capable of enhancing the responsiveness of cells to growth factors outside of the PDGF family. 19212337_FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha D842V mutation is associated with drug resistance in chronic eosinophilic leukemia. 19215021_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19215021_Results suggest that the child's PDGFRA promoter haplotype is differentially sensitive for periconceptional exposure to glucose, myo-inositol, and zinc in the risk of spina bifida. 19248967_REVIEW: role of c-kit and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumor 19291337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19291337_The authors conclude that KIT exon 11 deletions and somatic loss of the wild-type KIT identified post-surgical gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients with poor prognosis. 19302534_expression of c-kit, PDGFR-alpha and -beta is a common feature of KS, regardless of stage and clinical settings. 19307738_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19326424_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19333543_results suggest interstitial cells of Cajal adjacent to overt gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) did not have mutations in c-kit or PDGFRA genes; overt GISTs may develop after local & sporadic acquisition of these mutations with additional events 19333919_one-third of sera from scleroderma patients contained detectable autoantibodies to PDGFR, but these antibodies were not specific to scleroderma 19333949_Purified IgG samples from patients with systemic sclerosis were positive when tested for antinuclear autoantibodies, but did not specifically activate PDGFRalpha or PDGFRbeta in any of the tests 19335066_PDGFRA is involved in tumor angiogenesis & maintenance of the tumor microenvironment & is implicated in development & metastasis of HCC, as well as playing a role in normal angiogenesis and embryo development. Review. 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19393245_residues that compose the target motif of the PDGFRA form part of the alpha 3 helix of p190-A. 19411681_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19448595_This study showed consistent expression and common mutational activation of PDGFRA in small intestinal inflammatory fibroid polyps 19496203_Results provide the first report of esophageal malignant melanoma with an examination of the expression of KIT and PDGFRA and the mutational status of KIT and PDGFRA genes. 19563658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19563658_analysis of the experssion of EGFR, PDGFRA and VEGFR2 in cervical adenosquamous carcinoma 19614767_In the absence of RAS mutations, MAPK could be activated through SCF/KIT autocrine/paracrine mechanisms and/or mutated BRAF in a subset of KIT/PDGFRA wild-type GISTs. 19644140_Data show that chimeric receptor tyrosine kinases escape ubiquitination and down-regulation and that their stabilization is critical to efficient stimulation of cell proliferation. 19648886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19649203_PDGF-Ralpha strongly impairs melanoma growth 19675092_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19694830_Expression and mutational analysis of PDGFRA in renal cell carcinoma is reported. 19696981_Analysis of the hot spot regions of KIT and PDGFRalpha genes is important for therapy planning and also may have some prognostic significance, for which reason it is recommended to be performed in GIST regularly. 19707201_concurrent expression of PDGFA and PDGFRA in different subtypes of gliomas, reinforce the recognised significance of this signalling pathway in gliomas. 19717644_The proportion of phosphorylated PDGF receptor alpha was low in choroid plexus papillomas and choroid plexus carcinomas, whereas phosphorylated PDGF receptor beta was found to be significantly higher in choroid plexus carcinomas. 19755855_Observations implicate PDGFRA and KIT as potential oncogenes in NSCLC. 19756614_The majority of IFP reveal activating PDGFRA mutations. Our data indicate that IFP are true neoplasms (true benign tumors) and not reactive lesions. 19779861_KIT, PDGFRA, and VEGFR2 amplifications were all present in 4% of Medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal tumor and KIT amplification was associated with concurrent PDGFRA and VEGFR2 amplifications 19787330_Of the tumors 85% carry somatic activating mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinases KIT or PDGFRA. The detection of these molecular events has changed the treatment. 19839721_PDGF receptor signaling sustains proliferation without affecting osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. 19843560_for the in situ PLA reaction a PDGFRbeta-specific antibody was used 19846951_study found all the subtypes of thymomas and the thymic carcinomas showed staining for PDGFRA, but no mutations in the known mutational hotspots were identified 19861461_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19862822_PDGFRA may be amplified in fibrosarcoma of bone. 19900103_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19900103_PDGFRA-mutated GISTs have distinctive histological patterns that are differentiated from KIT-mutated GISTs. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19936766_VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and PDGFRalpha are over-expressed in K-ras mutated colorectal adenocarcinoma. 19943934_Fifteen and eleven gastrointestinal stromal tumours tumours possessed mutations in KIT and PDGFRA, respectively 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20001342_Genetic changes of therapeutically relevant exons of the PDGFRA gene and the c-kit gene are not seen in giant cell tumours of bone. 20023271_DHPLC is a cost-effective, rapid, and sensitive test for screening for mutations of c-KIT and PDGFRA in GISTs. 20023271_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20036812_Studies indicate communication between tumor cells and their microenvironment is through polypeptide growth factors EGF, FGF, PDGF and receptors for these growth factors. 20071345_these data from human genetics and animal models support a role for PDGF-signaling in normal PV development, and in the pathogenesis of TAPVR. 20107158_Clinically significant overexpression of PDGFRalpha is detected in eosinophilia-associated myeloproliferative neoplasm disorders, as a possible indicator of underlying fusion. 20129251_Aberrations and gene expression of EGFR, NF1, and PDGFRA/IDH1 each define the Classical, Mesenchymal, and Proneural subtypes, respectively of glioblastoma multiforme 20133985_There was no mutational correlation between GISTs and the coexistent tumors of different histogenesis regarding KIT and PDGFRA genes. 20169295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20169295_PDGFRA mutations are linked with familial vitiligo vulgaris in a Chinese population. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20393746_Six Vanek's tumors harbored activating mutations in PDGFRA exons 12 (n = 5) and 18 (n = 1) respectively: S566_E571delinsK (n = 1), S566_E571delinsR (n = 4), and D842 del (n = 1). 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20425130_PDGFRA gene mutations were not found in a Japanese melanoma population. 20442296_PDGFRalpha mutant lacking the extracellular ligand-binding domain is associated with bone-metastatic potential to prostate cancer. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20470368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20473908_PDGFRA mutations are associated with sensitivity to Imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 20479398_Single nucleotide polymorphism in PDGFRalpha is associated with pediatric high-grade gliomas. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20589679_High PDGFRalpha and phosphorylation is associated with recurrent glioblastoma. 20598160_Standard operating procedures were developed to identify potential pitfalls when performing PDGFRA mutational analysis in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 20615084_PDGFRA alternative transcripts resulting in PDGFRA gene fusions are associated with aematological malignancies and eosinophilia. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20651400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20651400_Prognostic relevance of KIT and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 20686603_Transcript and protein expression of PDGFRA matched well with its increased copy number suggesting a central role of PDGFRA within the amplicon in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. 20718716_PDGFRA mutations cn be found in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20823768_C-KIT and PDGFRA zygosity in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Correlation with tumor site, tumor size, exon, and CD117 immunohistochemistry. 20861712_Small gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) share with overt GIST KIT/PDGFRA mutation. 20889717_PDGFRA mutants behave as oncogenes in this subset of gliomas 21080877_PDGFRA expression is not a prognostic marker for osteosarcoma patients 21092857_PDGFalphaR transgenic mice provide an effective means to determine the fate of NG2-positive cells in vivo under both normal and pathological conditions. 21131919_Primary esophageal melanomas of Caucasian patients did not harbor mutations of PDGFRA. 21157293_Expression of PDGFR in the formalin-fixed vestibular schwannoma tumor tissue was observed in 23 (67.5%) of the 34 samples. 21210262_We found that hedgehog-interacting protein, PDGFRalpha, smoothened and Su(Fu) gene highly expressed in the primary esophageal squamous cell carcinomas 21224473_our data provide evidence that imatinib-sensitive PDGFRA point mutations play an important role in the pathogenesis of hypereosinophilic syndrome 21274753_PDGFR-alpha mutation in EGISTs was essentially similar to that in GISTs 21281241_Acquired PDGFRA mutation has resulted in decreased imatinib sensitivity in chronic eosinophilic leukemia with T-cell clonal evolution. 21310211_The Lnk is a negative regulator of PDGFRalpha signaling. 21357737_Chronically activated, monomeric PDGFRA induced prolonged activation of Akt and suppressed the level of p53. 21382095_amplification of PDGFRA, KIT and KDR may be implicated in the pathogenesis of a small fraction of both subtypes of glioblastoma 21387320_Mutational status of PDGFRA are not associated with primary gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 21396851_High expression of PDGFR-alpha is associated with poor response to sorafenib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. 21397860_Data show that induction of PDGFRalpha and invadopodia is essential for Twist1 to promote tumor metastasis. 21399396_FIP1L1/PDGFRA fusion gene-positive myeloproliferative disorders with eosinophilia are discussed. 21403518_mutational status of PDGFRA gene in ipsilateral testicular seminomas 21434524_The high rate of c-Kit/PDGFRA coexpression suggests that both receptors are involved in oncogenicity in gastrointestinal stromal tumors 21461555_Data confirm that the type of KIT mutation is associated with various clinicopathologic features of gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and indicate that PDGFRA mutations are associated with rather indolent tumors. 21478825_KIT and PDGFRA mutations do occur in ocular melanomas at a frequency (11%) that is similar to acral and mucosal melanomas 21496277_In addition to c-Met, the cross-talk with Axl and/or PDGFR-alpha also contributes to the progression of human bladder cancer 21527588_KIT/PDGFRA mutations are very frequent molecular event in GISTs and the type of mutation has a prognostic significance for patients' outcome. 21574155_this study demonstrated that coexpression of PDGFR-alpha, PDGFR-beta and VEGF is an independent prognostic factor for predicting early tumor recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 21590454_High PDGFRA is associated with recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. 21596750_specific inhibition of Cbl interaction with RTKs promotes the osteogenic differentiation program in hMSCs in part by decreased Cbl-mediated PDGFRalpha and FGFR2 ubiquitination 21605429_The aim of this paper is to review the clinical significance of tyrosine kinase mutational status of KIT or PDGFRA genes. 21642621_Even though retinal pigment epithelial cells express less PDGFRalpha than fibroblasts, it boosts proliferative vitreoretinopathy-related signaling events and cellular responses of ARPE19 cells. 21645144_PDGF and PDGFR-alpha may be involved in the pathophysiology of the human thymus. 21665993_Polymorphisms of FRAP1 and PDGFRA were associated with corneal curvature in Asian populations. 21725412_In one tumour, c-Kit mutation analysis demonstrated positivity of exon 11_c.1674_1676delGGT, thus confirming the diagnosis of a GIST. Mutational analysis of the second stomach lesion demonstrated negativity for all known c-KIT and PDGFRA exons. 21769672_Studies suggest that various isoforms of PDGF bind with differential affinities to two related tyrosine kinase receptors, denoted the PDGF alpha- and beta-receptors. 21818111_Treatment with imatinib is associated with an excellent prognosis in FIP1L1-PDGFRA-positive chronic eosinophilic leukemia in first chronic phase 21819482_the F-P fusion gene was not detected with increased frequency in EoE. 21947029_CD9(+)/CD140a(+) cells may constitute an even more highly enriched population of myelinogenic progenitor cells. 21953054_These data suggest that KIT and PDGFRA mutations and standardized mitotic count deserve to be investigated to evaluate the relapse risk of Gastrointestinal stromal tumors 21993628_human PDGFR-alpha activation in mouse beta-cells stimulated Erk1/2 phosphorylation, leading to Ezh2-dependent expansion of adult beta-cells 22076173_Case Report: rare case of esophageal small cell carcinoma with KIT and PDGFRA expressions but without KIT and PDGFRA mutations. 22080864_PDGFRalpha signaling in glioblastomas leads to Src-dependent phosphorylation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Dock180 at tyrosine 1811 (Dock180(Y1811)) that results in activation of the GTPase Rac1 and subsequent cell growth and invasion. 22137795_multiple receptor tyrosine kinases are amplified in a subset of glioblastoma subclones, epidermal growth factor receptor, MET and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha 22144915_This highlights the potential role of variants in PDGFRA in the genetic etiology of corneal astigmatism across diverse Asian populations [meta-analysis] 22160160_High expression of PDGFRA was significantly correlated with shorter patient survival and could serve as a prognostic mar |
ENSMUSG00000029231 |
Pdgfra |
42.653299 |
2.2296119565 |
1.156793 |
0.416063808 |
7.323988 |
0.00680402767454440018934924694349319906905293464660644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013518299700669719407009061740154720610007643699645996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
80.8284543 |
20.9927397 |
36.0158419 |
7.1262895 |
| ENSG00000134901 |
79070 |
POGLUT2 |
protein_coding |
Q6UW63 |
FUNCTION: Protein glucosyltransferase that catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to a serine residue within the consensus sequence peptide C-X-N-T-X-G-S-F-X-C (PubMed:30127001). Can also catalyze the transfer of xylose from UDP-xylose but less efficiently (PubMed:30127001). Specifically targets extracellular EGF repeats of proteins such as NOTCH1, NOTCH3, FBN1, FBN2 and LTBP1 (PubMed:30127001, PubMed:34411563). May regulate the transport of NOTCH1 and NOTCH3 to the plasma membrane and thereby the Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:30127001). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30127001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34411563}. |
3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30127001}. |
This gene encodes a protein product localized to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. As a member of the endoplasmic reticulum protein family the encoded protein contains a Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu or KDEL motif located at the extreme C-terminus which prevents all endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins from being secreted. Proteins carrying this motif are bound by a receptor in the Golgi apparatus so that the receptor-ligand complex returns to the endoplasmic reticulum. A processed non-transcribed pseudogene located in an intron of a sodium transporter gene on chromosome 5 has been defined for this gene. This gene has multiple transcript variants which are predicted to encode distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:79070; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; EGF-domain serine glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0140561]; EGF-domain serine xylosyltransferase activity [GO:0140562]; glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0046527]; UDP-glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0035251]; UDP-xylosyltransferase activity [GO:0035252]; protein O-linked glycosylation via serine [GO:0018242] |
11167020_This paper reports data on mouse Kdelc1 30249898_Our results suggest that GA733-2-Fc conjugated to ER-retention motif KDEL is a more efficient antigen to prevent tumor growth induced by colorectal carcinoma and minimize an allergic response. 34411563_POGLUT2 and POGLUT3 O-glucosylate multiple EGF repeats in fibrillin-1, -2, and LTBP1 and promote secretion of fibrillin-1. |
ENSMUSG00000026047 |
Poglut2 |
23.565543 |
2.1874603261 |
1.129257 |
0.479622833 |
5.378937 |
0.02038129791999243947686615285874722758308053016662597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036477259282052670874563204961305018514394760131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9145834 |
11.0213206 |
17.3340512 |
3.8303704 |
| ENSG00000134982 |
324 |
APC |
protein_coding |
P25054 |
FUNCTION: Tumor suppressor. Promotes rapid degradation of CTNNB1 and participates in Wnt signaling as a negative regulator. APC activity is correlated with its phosphorylation state. Activates the GEF activity of SPATA13 and ARHGEF4. Plays a role in hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced cell migration. Required for MMP9 up-regulation via the JNK signaling pathway in colorectal tumor cells. Acts as a mediator of ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. It is required for the localization of MACF1 to the cell membrane and this localization of MACF1 is critical for its function in microtubule stabilization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10947987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17599059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19151759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19893577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937854}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Membrane;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a tumor suppressor protein that acts as an antagonist of the Wnt signaling pathway. It is also involved in other processes including cell migration and adhesion, transcriptional activation, and apoptosis. Defects in this gene cause familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), an autosomal dominant pre-malignant disease that usually progresses to malignancy. Mutations in the APC gene have been found to occur in most colorectal cancers, where disease-associated mutations tend to be clustered in a small region designated the mutation cluster region (MCR) and result in a truncated protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2022]. |
hsa:324; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; beta-catenin destruction complex [GO:0030877]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; catenin complex [GO:0016342]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; dynein complex binding [GO:0070840]; gamma-catenin binding [GO:0045295]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule plus-end binding [GO:0051010]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein kinase regulator activity [GO:0019887]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell fate specification [GO:0001708]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling [GO:0007094]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902807]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045736]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of protein localization to centrosome [GO:1904781]; positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly [GO:0031274]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore [GO:0051988]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of microtubule-based process [GO:0032886]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11159880_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11221825_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11241320_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11354631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11466700_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11483640_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11487538_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11535846_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11584047_Asp1822Val variant is a common polymorphism without clinical implications 11606402_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11668620_Mutation analysis in northwest Spanish patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and sporadic colorectal cancer 11696170_Results suggest that mutations of the beta-catenin and APC genes are rare and that activation of the Wnt signaling pathway may not contribute to pathogenesis in human papillary and follicular thyroid carcinomas. 11720476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11741105_Mutations in APC coding region are not the sole cause of FAP or CHRP 11748858_Nine mutations were novel and eight families were shown to harbor two recurrent mutations. 11751382_APC regulates survivin expression: a possible mechanism contributing to the stem cell origin of colon cancer. 11754114_Maternal mosaicism for a second mutational event-a novel deletion-in a familial adenomatous polyposis family harboring a new germ-line mutation in the alternatively spliced-exon 9 region of APC. 11768389_novel 3' mutation in the APC gene in a family presenting with a desmoid tumour and minimal colonic phenotype 11768390_silent mutation in exon 14 of the APC gene is associated with exon skipping in a FAP family 11809680_Different combinations of biallelic APC mutation confer different growth advantages in colorectal tumours. 11809682_Quantitative adenomatous polyposis coli promoter methylation analysis in tumor tissue, serum, and plasma DNA of patients with lung cancer. 11856748_androgen receptor does not interact with adenomatous polyposis coli or glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and, therefore, conclude that androgen-mediated transport of beta-catenin occurs through a distinct pathway. 11868006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11868006_Older age and APC mutation in the central part of the gene are risk factors for the development of severe duodenojejunal polyposis. Location of the mutation affects severity of familial adenomatous polyposis. 11891193_Molecular alterations in the APC/beta-catenin pathway were detected in 23.5% (4 of 17) of the pancreatic acinar cell carcinomas 11912492_APC interacts with the kinesin superfamily 11920497_mutations rare in ulcerative colitis-related colorectal carcinomas; significant difference in frequency of APC mutations seen between right- and left-sided sporadic tumors suggests different molecular pathways 11921277_Three APC mutations have been identified in 22 tested samples, all of them in xenografts developed from metastatic prostate tumors. 11933206_APC germline mutations identified in Czech patients with familial adenomatous polyposis: includes 11 which were not previously reported 11956815_Dysfunction of APC may be a major cause of changes in beta-catenin function in colorectal tumors. 11972058_Association and regulation of casein kinase 2 activity by adenomatous polyposis coli protein 12034871_alleles produce functional protein from internal translation initiation 12045208_results indicate selection for APC genotypes that are likely to retain some activity in downregulating beta-catenin signaling 12057910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12070164_demonstration of the direct interaction of APC-(129-250) fragment with the nuclear export factor chromosome maintenance region 1 (Crm-1) 12093899_Mutations in APC, Kirsten-ras, and p53--alternative genetic pathways to colorectal cancer. The most common combination of mutations was p53 and APC (27.1%), whereas mutations in both p53 and K-ras were extremely rare. 12124804_Molecular genetic analysis of malignant melanomas for aberrations of the WNT signaling pathway genes CTNNB1, APC, ICAT and BTRC. 12136240_Different familial adenomatous polyposis phenotypes resulting from deletions of the entire APC exon 15 12163385_somatic mutation of the APC gene plays an important role in the pathogenesis of gastric adenoma and dysplasia 12173026_Pathogenic mutations and rare variants of the gene identified in 75 Belgian patients with familial adenomatous polyposis by fluorescent enzymatic mutation detection 12173321_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12374230_Alternations in the APC gene mutations are involved in tumor growth and in tumor progression. 12378616_APC mutation is involved in carcinogenesis of intestinal type of gastric cancer and is independent of MSI phenotype but related to the LOH pathway in gastric cancer. 12387883_role in mediating growth-suppressive effect of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor 12439748_implication of activation of the APC/beta-catenin signalling pathway due to beta-catenin mutations in the development of a subset of endometrial carcinomas 12485844_structure of the amino-terminal nuclear export domain 12504226_Partial loss of function of APC protein by truncation of its carboxy(C)-terminus is an early factor in the development of many colorectal neoplasms. 12508668_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12537656_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12538344_Human DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT1 is regulated by the APC pathway 12575848_In human pilomatricoma,loss of heterozygosity was observed in the APC gene, but no mutations in the mutation cluster region were found in seven tumours without beta-catenin mutations. 12581900_Novel mutations of the APC gene in familial adenomatous polyposis in Greek patients. 12584179_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12606575_Data indicate that the rate of nuclear export of adenomatous polyposis coli protein (APC), rather than its nuclear import or steady-state levels, determines the transcriptional activity of beta-catenin. 12647217_study verified reduced expressions of adenomatous polyposis coli and E-cadherin proteins in colorectal cancer cells and suggests that normal protein expressions in benign epithelium are progressively and independently lost in sporadic colorectal cancers 12655564_The APC I1307K mutation may contribute to colorectal cancers (CRC) in Israeli Arabs; inactivating mutations of MSH2 and MLH1 may not be a major cause for early onset CRC. 12737446_APC mutations were found in 37/56 adenomas. The lack of the proliferative stimulus resulting from a K-ras mutation may contribute to the process of adenoma regression. 12800081_Beta-catenin can increase sensitivity of the androgen receptor, it may be assumed that the increased beta-catenin-expression in angiofibromas is involved in the typical growth stimulus of this tumor in adolescent males. 12800196_APC inactivation due to mutations, LOH and methylation is associated with invasive and in situ lobular breast cancer. 12856637_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12901799_Arg283Ter mutation in the APC gene is causative of the adenomatous polyposis coli phenotype in a Chinese family. 12907646_APC mutation is associated with gain of 7p in colorectal adenocarcinoma. 12955080_nuclear targeting of APC is driven by cell cycle entry rather than altered cell-cell contact. The ability of truncated APC to accumulate in the nucleus suggests that nuclear import signals other than NLS1(APC) and NLS2(APC) are functionally important. 14514668_neither APC nor p150glued binding domain is necessary for EB1 or EBF3 to induce microtubule bundling 14520463_Decreased expression of adenomatosis polyposis coli protein is associated with ovarian epithelial cell transformation and in tumour progression 14573780_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14574158_Mutations in apc gene is associated with both familial adenomatous polyposis and thyroid carcinoma 14578136_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14578138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14579148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14624392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14662741_Data suggest that adenomatous polyposis coli modulates microtubule plus-end attachments during mitosis, and its mutation predisposes cells to increased mitotic abnormalities, which may contribute to tumor progression. 14672538_REVIEW: Role of APC and DNA mismatch repair genes in the development of colorectal cancers. 14679305_a role in cell adhesion in addition to its known role in beta-catenin transcriptional signalling 14691304_Familial adenomatous polyposis/attenuated adenomatous polyposis coli can result from APC constitutive haploinsufficiency, with gene deletion being a possible cause of reduced gene expression. 14729851_Novel germline mutations in APC exons 5 and 11 affected age of onset in Polish Adenomatous Polyposis Coli patients Complicated with brain cancer. 14871261_APC protein was expressed in the cytoplasm of a very small number of prospermatogonia and interstitial (Leydig) cells in testis fetal development 14961559_This study enlarges the spectrum of APC gene mutations and sheds light on the correlation between the site of APC germline mutations and clinical manifestations of familial adenomatous polyposis. 14991743_APC/GSK-3beta, through beta-catenin, may crossregulate NF-kappaB signaling pathway 15020226_Mucin 1 and adenomatous polyposis coli co-immunoprecipitate in breast cancer cells. 15040027_Mutations of APC gene were detected in more than half of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancers (HNPCC). Mutation was common molecular event and might play important role in tumorigenesis of HNPCC 15108288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15122587_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15133491_Genetic and epigenetic alterations of the APC gene were studied in malignant melanoma. 15190067_APC and CDX2 have roles in controlling retinoic acid biosynthesis and in promoting a retinoid-induced program of colonocyte differentiation 15251938_The tumor suppressor gene, APC, is an independent prognostic parameter with poor outcome in breast cancer patients. 15257316_Results conclude about important role of APC alterations for melanoma progression. 15266213_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15273719_All three APC isoforms showing a different effect on tumorigenesis may be nontranscriptional in origin. 15326380_APC promoter hypermethylation contributes to the loss of APC expression in colorectal cancers with allelic loss on 5q 15327769_Results describe the crystal structure of beta-catenin in complex with a phosphorylated adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) fragment containing two 20-amino-acid repeats, whose phosphorylation could be a critical switch for APC function. 15331612_APC forms complex with AP-2alpha and beta-catenin and sequesters beta-catenin away from TCF/LEF transcription factors. 15355978_APC is down-regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in a process facilitated by Axin 15375803_Review of APC mutation that leads to genetic unstability in carcinogenesis of colon cancer 15446460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15459959_first systematic evaluation of different single-base substitutions in APC at or close to splice sites at the transcript level, found in familial adenomatous polyposis patients 15507235_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15520370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15523694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15540296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15542524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15548520_identified a sequence in APC that binds POLB and blocks POLB-mediated strand-displacement synthesis in long patch BER without affecting short patch BER; APC gene expression is required for DNA methylation-induced sensitivity of colon cancer cells 15561772_Truncating APC mutations have dominant effects on cell proliferation, spindle checkpoint control, survival and chromosome stability. 15591320_identify selective beta-catenin binding hot spots of Tcf4, E-cadherin, and APC 15639864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15640937_Feeding of Apc1638N transgenic mice with enriched diet with probiotic components during 8 months have shown a minor therapeutic effect. 15689459_Large deletions in the APC gene are a common cause of typical familial adenomatous polyposis. 15733272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15754020_contribution of down-regulated APC expression to the development of human oral squamous cell carcinoma was about 30% 15755874_APC induces apoptosis and thus plays a role in tumor suppression. 15761860_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15768050_results indicate that the APC may be a candidate gene conferring susceptibility to schizophrenia and also may be associated with reduced vulnerability to cancer in schizophrenia. 15821699_This gene encodes a tumor suppressor protein that includes among its many intracellular functions one of nuclear export. Defects in this gene cause familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). 15824157_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15832580_The APC mutations associated wiht desmoid tumors and responsible for the behavior of the invasiveness of these neoplasms. 15833136_analysis of rare mutations predisposing to familial adenomatous polyposis 15929773_The I1307K mutation is associated with a moderate excess risk for CRC, but age of onset seems not to be earlier and this variant is not associated with a multiple colonic polyp phenotype. 15943410_The sequential accumulation of mutations in adenomatous polyposis coli (APC)drives the transition from normal epithelium through increasing adenomatous dysplasia to colorectal cancer. 15951963_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15952110_Thirteen APC germline mutations were identified in 22 FAP patients. All of the mutations were nonsense or framshift mutations. FAP patients with mutations in the 5'or 3'extreme parts of the APC gene showed mild clinical symptoms. 15959913_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15981102_No significant genetic alterations were found. 16030254_APC regulates mitotic spindle function and how errors in chromosome segregation are tolerated in tumor cells. 16088911_APC gene mutational analysis in Korean families with familial adenomatous polyposis 16142311_MUC5AC and MUC2, TFF1 and TFF3, APC and p21 in subsets of colorectal polyps and cancers suggests a distinct pathway of pathogenesis of mucinous carcinoma of the colorectum 16163548_The cytoplasmic accumulation of beta-catenin is a common characteristic of oral SCC, but is not closely associated with mutational alterations in the APC, beta-catenin and Axin1 genes. 16184469_Finds several types of meat may contribute differently to the aetiology of colon and rectal cancer, depending on APC mutation status. 16184469_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16188939_the interaction of APC with microtubules and the beta-catenin-targeting complex are mutually exclusive, and indicate that the distribution of endogenous APC between different pools is dynamic, which allows cells to distribute it as required 16201232_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16228836_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16322291_Hypermethylation of Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Protein is asspciated with prostate tumorigenesis 16329837_Wnt-1, beta-catenin and APC expressions were related to the differentiation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 16356174_APC and K-ras, but not CTNNB1 mutations have roles in regulation of expression of hMLH1 in sporadic colorectal carcinomas 16356174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16382042_sulindac sulfone can modulate the APC/beta-catenin pathway in vitro but its efficacy is dependent upon the mutational status of APC and beta-catenin 16407829_Promoter methylation of APC was found in all Barrett esophagus samples & 95% of esophageal adenocarcinomas. Full methylation of APC correlated with lack of expression. 16411234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16423286_the N-terminal region of the APC protein mediated its junctional localisation, consistent with the observation that truncated APC proteins in colon cancer cell lines are still capable of localising to the cell cortex 16426911_results of this study show that esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with genetic instability, that is, allelic imbalance/loss of heterozygosity and microsatellite instability of the APC gene 16433700_In this report, we analyze the first kindred clustering Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and multiple gynecolgic tumors. 16450383_decrease of APC levels achieved by RNA interference impairs cell proliferation and DNA replication, not only in 293 cells that express a wild-type protein, but also in SW480 colon cancer cells that express exclusively a truncated APC fragment. 16461775_Attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis (AFAP) is associated with germline mutations in the 5', 3', and exon 9 of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. 16525027_The association of endogenous APC with microtubule ends correlates directly with their increased growth stability, that this can occur independently of its association with EB1. 16537703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16545110_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16569251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16619216_Hypermethylation of adenomatosis polyposis coli protein is associated with primary adenocarcinomas of the small bowel 16650078_Novel mutations within the APC gene are associated with familial and sporadic adenomatous polyposis. 16680592_APC mutations are important in development of the cribiform-morula variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma(an extracolonic manifestations of familial adenomatous polyposis)occurring mostly in the 5' side of the APC gene between codons 308 and 935. 16699180_Mutations in the APC gene resultt in impaired retinoic acid biosynthesis and upegulation of cyclooxygenase-2. 16699861_The high frequency of methylation of the APC gene promoter suggests that the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes and of the genes related to the control of cellular proliferation through this mechanism is involved in gallbladder carcinogenesis. 16710723_case of the AAPC syndrome caused by a CCTT deletion at codon 173, with polyps diagnosed at the age of 17. The father and grandfather of the proband died of colorectal cancer (CRC), which developed from untreated polyps 16753179_the central region of APC is unstructured in the absence of beta-catenin and Axin; beta-catenin may interact with each of the APC 15aa and 20aa repeats independently 16763565_Impaired EB1 or APC function generates lesions invisible to the spindle checkpoint and thereby promotes low levels of chromosomal loss (CIN) expected to fuel aneuploidy and possibly tumorigenesis. 16798748_APC regulates beta-catenin phosphorylation and ubiquitination by distinct domains and by separate molecular mechanisms 16804979_Most adenomas expressed full-length APC protein, suggesting that protein expression is not a reliable marker for assessment of APC gene mutation. 16820884_analysis of APC gene deletion in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis 16843107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16843107_These data indicate that somatic mutations affecting APC and CTNNB1 do not play a major role in the pathogenesis of sporadic ependymomas. 16855398_genomic instability is an early event that occurs at precancerous stages prior to changes in tumor suppressor genes (p53 and APC) in Barrett's esophagus-associated tumorigenesis in patients 16951153_APC transgenic mice provide an alternative model to Apc mice to study familial adenomaatous polyposis and distal sporadic colorectal cancer. 16981189_APC methylation was associated with wildtype BRAF (p = 0.003) and with lower concentrations of methyl group carriers (p T transversion caused a splice site mutation which resulted in deletion of exon 4 of the APC gene in a family with attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis 17411426_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17411426_both novel and reported APC mutations were identified in Czech and Slovak FAP patients 17418091_The retained beta-catenin in cytoplasm by APC may be down-regulated by Axin 2, which is induced by beta-catenin/Tcf signaling. 17437043_APC protein and GSK3beta may synergistically play an important role in the repair of airway epithelial cells. 17454753_racial factor may not be related to the occurrence of mismatch repair defects and APC mutations in our multi-racial patient cohort. 17486639_APC mosaicism is a frequent cause of familial adenomatous polyposis 17489848_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17489848_the presence of germline mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) genes in attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis. 17505512_Hypermutation of APC does not cause multiple colorectal adenoma. 17506007_identified a novel frameshift mutation at exon 15, corresponding to codon 12 17556698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17556698_results suggest a significant interaction between the D1822V APC polymorphism and the dietary intakes of cholesterol, calcium, and fiber for colorectal cancer risk 17558858_there are somatic mutations of APC & beta-catenin genes in desmoid-type fibromatosis & abnormalities in Wnt signal pathway; these abnormalities may result in aberrant cell proliferation & apoptosis, which may be important in tumorigenesis & progression 17562260_APC gene is hypermethylated in HCI-H460 cells, and its transcription coud be activated by 5-aza-dC. 17562262_Abnormal methylation of APC gene occurs in the progression of breast cancer, which is the main cause for the absence of APC protein expression, and the major mechanism of inactivation of APC gene. 17569124_Familial adenomas polyp is caused by mutations in the APC tumor suppressor gene. 17572842_APC is highly expressed in the intestinal and colorectal epithelia and it is involved in homeostasis of the enterocyte renewal phenomena, in which proliferation, migration, differentiation, and apoptosis are highly regulated both temporally and spatially 17620292_The APC tumor suppressor mutation was ssessed in the ability of apigenin in induce cell cycle arrest in HT29-APC cells. 17653897_A nonsense mutation in Arg1114X in the APC gene was found in 5 of 43 colorectal cancer patients. The patients also had higher rates of metastasis. 17665205_FAP is associated with germline mutation in the APC gene inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. 17704924_Report genetic alterations of APC in Korean colorectal cancer patients. 17854661_Adenomatous polyposis coli gene variant is associated with colorectal cancer 17854661_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17882487_We identified two novel mutations: 1018T>C and 1309delGAAAA. This study helps in defining new biomarkers for the early diagnosis of Turkish patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. 17905526_This paper focuses on changes in E-cadherin (CDH1), adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and beta-catenin (CTNNB1) in 50 tumors of the central nervous system. 17910481_Chemical dissection of APC repeat 3 multistep phosphorylation by the concerted action of protein kinases CKI and GSK3. 17920230_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17920230_the E1317Q gene variant in the APC gene is not found in cancers outside of the colon 17927853_The positive rate of APC was significantly lower in colorectal carcinoma and colorectal adenoma with malignancy than in colorectal adenoma and normal colorectal mucosa. 17947477_hypermethylation of APC has a role in progression of prostate neoplasms 17952864_Desmoid tumors occurring in the background of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) usually contain inactivating germline mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene. 17954272_Two cancer-free dysmorphic patients with karyotypes that confer susceptibility to familial Adenomatous polyposis and von-Hippel-Lindau syndrome. 17960617_Promoter hypermethylation of APC is associated with prostate cancer progression 17963004_study detected 17 different truncating mutations APC in 21 of 24 Chilean familial adenomatous polyposis families; 9 of these were novel 17964080_Analyzed the phenotype, DNA ploidy patterns, and microsatellite regions linked to APC gene on chromosome 5q of low-grade gastric adenomas/dysplasias, Vienna Category 3, to investigate whether these lesions have the potential to become adenocarcinomas. 17968317_binding per se of beta-catenin by adenomatous polyposis coli does not require phosphorylation by GSK-3beta 17973119_Promoter methylation of the APC gene seems to be of significance in hepatocarcinogenesis 18026870_The researchers describe a family with de novo mutations of the mosaic form in a family with familial adenomatous polyposis. 18027849_investigate the possible role of germline hypermethylation of the APC promoter in FAP and AFAP families that were negative for APC and MUTYH mutations 18058812_No field effect, defined as absence of epigenetically transformed cells, for GSTP1 was observed, whereas APC, RARbeta2, and RASSF1A showed a field effect up to 3 mm from the malignant core in three prostatectomy samples. 18063416_Two large AFAP (attenuated form of familial adenomatous polyposis) kindreds with the identical APC disease-causing mutation (c.426_427delAT) were linked to a founding couple who came to America from England around 1630 18066497_genetic changes of APC gene play a role in meningioma formation. 18070451_APC gene methylation plays an important role in the carcinogenesis of cervical cells, and can re-express after treatment with Hydralazine. 18091433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18160396_cancer mutations induce APC mitochondrial localization and that APC regulation of Bcl-2 at mitochondria may contribute to tumor cell survival. 18166348_Findings strongly support a pathogenic role of the APC N1026S variant in the AFAP phenotype. 18199528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18199528_multiple rare nonsynonymous variants in APC play a significant role in predisposing to colorectal adenomas. 18224684_The number of beta-catenin downregulating 20-aa repeats in truncated APC gene associated with colorectal tumorigenesis is different in profuse, sparse and attenuated types of FAP, and is also different between colorectal and extracolonic tumors. 18265644_The data support that the frequencies and patterns of somatic mutation othe APC gene in colorectal cancer are variable among different populations. 18321998_The result of approximately 10(-5) mutations per allele per year, although higher than previous estimates, appears to be consistent with the mutational spectrum of adenomatous polyposis coli. 18337602_Methylation of the promoter region of the APC gene in patients with stage I NSCLC treated with curative intent by means of surgery is associated with early recurrence. 18343606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18343606_Variants of this protein found in this study are not involved in the colorectal carcinogenic process. 18369740_results suggest that the inactivation of the APC gene is very common in sporadic colorectal cancer, and the main inactivation mechanism of the APC gene is promoter hypermethylation 18375958_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18384130_Mutations in APC are associated with melanoma 18387968_Tumour-associated truncations of APC abolish the interaction with beta-catenin. 18393237_The mutation rate of the APC gene in this group of Chinese FAP families was about 48.39%, and 4 novel mutations were detected. Frameshift mutation was the major mutation type in Chinese FAP and mainly located in exon 15. 18393246_APC gene germline mutations can cause the development of familial adenomatous poly. 18403596_There is a conserved signature of 166 genes that were differentially expressed between adenomas and normal intestinal mucosa with APC mutation. 18406876_D |
ENSMUSG00000005871 |
Apc |
106.768735 |
2.5166280044 |
1.331492 |
0.350449118 |
14.015272 |
0.00018133186230888287036010220187876029740436933934688568115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000478965334230334847942511800056308857165277004241943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
152.8369327 |
39.1995033 |
61.3121008 |
11.5493708 |
| ENSG00000134986 |
9315 |
NREP |
protein_coding |
Q16612 |
FUNCTION: May have roles in neural function. Ectopic expression augments motility of gliomas. Promotes also axonal regeneration (By similarity). May also have functions in cellular differentiation (By similarity). Induces differentiation of fibroblast into myofibroblast and myofibroblast ameboid migration. Increases retinoic-acid regulation of lipid-droplet biogenesis (By similarity). Down-regulates the expression of TGFB1 and TGFB2 but not of TGFB3 (By similarity). May play a role in the regulation of alveolar generation. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11358844, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16229809}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in axon regeneration; regulation of neuron differentiation; and regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9315; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; axon regeneration [GO:0031103]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0017015] |
12417574_role for P311 in inducing TGF-beta1-independent myofibroblast transformation 16229809_These results suggest a role for levels of P311 in regulating glioma motility and invasion through the reorganization of actin cytoskeleton at the cell periphery. 16484684_P311 expression is tightly regulated during the critical periods of alveolar formation, and that under pathologic conditions, its relative absence may contribute to failure of alveolar regeneration and lead to the development of human emphysema. 20404911_P311 may be involved in the pathogenesis of hypertrophic scar via induction of a myofibrobla 21029697_P311 and ITGB4BP expression was elevated in non-small cell lung cancer, possibly indicative of a new signaling pathway. 22490543_Protein HYI may closely bind with protein P311 by an alpha helix in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. 22967977_P311 may promote the migration of ESCs both in micewith superficial partial-thickness burns and in an injured cell model in vitro, and it may play an important role in wound healing. 25336651_Novel RNA-binding protein P311 binds eIF3b to promote translation of TGF-beta1, TGF-beta2, TGF-beta3. 26616407_P311 plays a key role in renal fibrosis via TGFbeta1/Smad signaling, which could be a novel target for the management of renal fibrosis. 27906099_P311 is a novel TGFbeta1/Smad signaling-mediated regulator of transdifferentiation in epidermal stem cells during cutaneous wound healing. 27927130_P311 could accelerate skin wound reepithelialization by promoting the migration of Epidermal Stem Cell through RhoA and Rac1 activation. 27939132_These studies demonstrate that P311 is required for the production of normal cutaneous scars 30230348_P311 expression in the in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000042834 |
Nrep |
2024.770702 |
0.2146109547 |
-2.220204 |
0.038726242 |
3605.679865 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
718.4795570 |
18.6063248 |
3370.9845206 |
48.8920162 |
| ENSG00000135047 |
1514 |
CTSL |
protein_coding |
P07711 |
FUNCTION: Thiol protease important for the overall degradation of proteins in lysosomes (Probable). Plays a critical for normal cellular functions such as general protein turnover, antigen processing and bone remodeling. Involved in the solubilization of cross-linked TG/thyroglobulin and in the subsequent release of thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) by limited proteolysis of TG/thyroglobulin in the thyroid follicle lumen (By similarity). In neuroendocrine chromaffin cells secretory vesicles, catalyzes the prohormone proenkephalin processing to the active enkephalin peptide neurotransmitter (By similarity). In thymus, regulates CD4(+) T cell positive selection by generating the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) bound peptide ligands presented by cortical thymic epithelial cells. Also mediates invariant chain processing in cortical thymic epithelial cells (By similarity). Major elastin-degrading enzyme at neutral pH. Accumulates as a mature and active enzyme in the extracellular space of antigen presenting cells (APCs) to regulate degradation of the extracellular matrix in the course of inflammation (By similarity). Secreted form generates endostatin from COL18A1 (PubMed:10716919). Critical for cardiac morphology and function. Plays an important role in hair follicle morphogenesis and cycling, as well as epidermal differentiation (By similarity). Required for maximal stimulation of steroidogenesis by TIMP1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P06797, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07154, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P25975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10716919, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In cells lacking TMPRSS2 expression, facilitates human coronaviruses SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 infections via a slow acid-activated route with the proteolysis of coronavirus spike (S) glycoproteins in lysosome for entry into host cell (PubMed:32142651, PubMed:32221306, PubMed:16339146, PubMed:18562523). Proteolysis within lysosomes is sufficient to activate membrane fusion by coronaviruses SARS-CoV and EMC (HCoV-EMC) S as well as Zaire ebolavirus glycoproteins (PubMed:16081529, PubMed:26953343, PubMed:18562523). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16081529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16339146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18562523, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26953343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32142651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32221306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32855215}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Functions in the regulation of cell cycle progression through proteolytic processing of the CUX1 transcription factor (PubMed:15099520). Translation initiation at downstream start sites allows the synthesis of isoforms that are devoid of a signal peptide and localize to the nucleus where they cleave the CUX1 transcription factor and modify its DNA binding properties (PubMed:15099520). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15099520}. |
3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Membrane;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Thiol protease;Zymogen |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a lysosomal cysteine proteinase that plays a major role in intracellular protein catabolism. Its substrates include collagen and elastin, as well as alpha-1 protease inhibitor, a major controlling element of neutrophil elastase activity. The encoded protein has been implicated in several pathologic processes, including myofibril necrosis in myopathies and in myocardial ischemia, and in the renal tubular response to proteinuria. This protein, which is a member of the peptidase C1 family, is a dimer composed of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. Additionally, this protein cleaves the S1 subunit of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which is necessary for entry of the virus into the cell. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:1514; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; chromaffin granule [GO:0042583]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endocytic vesicle lumen [GO:0071682]; endolysosome lumen [GO:0036021]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; proteoglycan binding [GO:0043394]; serpin family protein binding [GO:0097655]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation [GO:0019882]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen [GO:0048002]; CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment [GO:0043373]; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0097067]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; elastin catabolic process [GO:0060309]; enkephalin processing [GO:0034230]; fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane [GO:0039654]; fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane [GO:0019064]; immune response [GO:0006955]; macrophage apoptotic process [GO:0071888]; protein autoprocessing [GO:0016540]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process [GO:0051603]; receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell [GO:0019065]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718]; zymogen activation [GO:0031638] |
11767948_cis-acting element on cathepsin L mRNA can be bound by a negative trans-acting regulator, thus leading to reduced expression rates 11771045_its activity resulted in extensive bone destruction in both cholesteatomas and noncholesteatomas of the middle ear 11978977_Characterization and comparative mapping of the porcine CTSL gene indicates a novel synteny between HSA9q21-->q22 and SSC10q11-->q12 12437117_the subcellular distribution of cathepsin B, L, and S ativities underwent a shift from endosome to lysosome localization during monocyte differentiation in cell culture 12437119_suppression of cathepsin L expression in A549 cells leads to a growth inhibition which is partially compensated by an upregulation of IL-8 production. 12492488_cathepsin K and L processed high-molecular weight kininogen under stoichiometric conditions, only cathepsin L generated significant amounts of immunoreactive kinins. Cathepsin L exhibited higher specificity constants (kcat/Km) than tissue kallikrein 12748383_lack of involvement in degrading MHC class II-associated invariant chain in nonprofessional antigen-presenting cells 12818188_These results show that cathepsin L is secreted from human fibroblasts in response to external stimuli and plays an important role in IL-8 processing in inflammatory sites. 12926111_The expression of cathepsin L in non-small cell lung cancer is not related to the patients' outcome at a statistically significant level. 12941783_insulin-stimulated cathepsin L expression in skeletal muscle is impaired in diabetic but not in nondiabetic monozygotic twins, suggesting that the changes may be secondary to impaired glucose metabolism. 15100281_Cathepsin L is released and catalytically active in T lymphocyte cytosol during supraoptimal activation-induced apoptosis of T cells in vitro and may participate in high dose tolerance in vivo. 15255544_endothelial cell-associated cathepsins B and L are not involved in the invasive growth of capillaries from existing blood vessels and the presence of collagen is necessary for MMP2 expression in endothelial cells 15318816_The function of cathepsin L (catL) in the proteolytic network of human lung epithelial cells and its role in the regulation of apoptosis. 15454886_serum level of cathepsin L can serve as a marker of bone resorption and bone density 15498563_Peptide fragment of p47 SEP is a reversible competitive inhibitor of cathepsin L. 15512772_Mechanical stress (compression and tension forces) causes an increase in secretion of cathepsins B and L in periodontal ligament cells in vitro. 15665831_Data suggest that cathepsin L has a critical role in the integration of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) into ischemic tissue and is required for EPC-mediated neovascularization. 15816632_cathepsins B and L have roles in atypical pituitary adenoma 15832773_cathepsin and inhibitor expression was not different between central and peripheral meningioma tissue or between histological subtypes of meningiomas with the exception of cathepsin L, the level of which was significantly lower in transitional meningiomas 15982660_cathepsin L is over-expressed in human AAA and atherosclerotic lesions and its expression in vascular cell types found in these lesions is regulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines. 16354158_The presence of active cathepsins L, K and S suggests that they contribute to the extracellular breakdown of the extracellular matrix. 16433682_highest expression of Cat L was found in psoriasis, atopic eczema and squamous cell carcinoma 16565075_Identification of CTSV & CTSL as targets for cystatin M/E, their (co)-expression in the stratum granulosum of skin, and activity of CTSL toward transglutaminase 3 strongly imply an important role for them in the differentiation process of human epidermis. 16740135_Results showed that the breast cancer cell line exhibiting the highest in vitro invasiveness also expressed the highest amount of cathepsin L splice variant L-A3. 16913838_CTSL is expressed in the brain of these compound mutants, predominantly in neurons of the cerebral cortex and in Purkinje cells of the cerebellum, where it appears to prevent neuronal cell death 16918298_the 32-kDa cathepsin L found in HT 1080 cell medium is involved in cancer invasion and metastasis 17227755_analysis of human cathepsins K, L, and S iunteractions with elastins 17519890_level of active cathepsin B and L is increased in tumors 17561110_Results describe the structure of chagasin in complex with the host cysteine protease, cathepsin L, at 1.75 A resolution. 17574778_over-expression of VEGF in human glioblastoma cells induces cathepsin L expression at the transcriptional level. This mechanism could be involved in the enhanced tumorogenic potential of these cells. 17643114_Results describe the participation of cathepsin L in adipogenesis and glucose intolerance. 17928356_Here we demonstrate a role for cathepsin L (CatL) cleavage of Ebola virus GP in the generation of a stable 18-kDa GP1 viral intermediate that exhibits increased binding to and infectivity for susceptible cell targets. 18163891_did not detect any plasminogen degradation by cathepsins B, K and L. 18221013_shortening the heavy-light chain loop does not change substrate affinity but does influence activity, in part via conformational change 18366346_These results indicated that in vivo a tumour hypoxic environment up-regulates cathepsin L expression which promotes tumour progression. 18450756_Cathepsin L has a role in processing and activation of proheparanase through multiple cleavages of a linker segment 18495127_cathepsin L is involved in death of macrophages, necrotic core formation and development of atherosclerotic plaque instability 18616803_blood levels are significantly elevated in patients with colorectal adenoma and colorectal carcinoma 18619973_Cathepsin L is required for invasion of endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) into ischemic tissue; thereby its reduction may limit the functional capacity of EPC to improve neovascularization in diabetics. 18658137_Caspase-3 activation triggers extracellular cathepsin L release and endorepellin proteolysis. 18971274_These findings suggest that 229E takes an endosomal pathway for cell entry and that proteases like CPL are involved in this mode of entry. 19005484_Cathepsin L and transglutaminase 3 could be involved in the pathway that leads to terminal differentiation, not only in the epidermis but also in the human hair follicle and nail unit. 19096818_Study indicates that CTSL improves cardiac function and inhibits cardiac hypertrophy, inflammation, and fibrosis through blocking Akt/GSK3beta signaling. 19270352_Serum Cathepsin L levels were significantly higher in coronary heart disease than in controls. 19291794_High nuclear cathepsin L expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 19550400_Cathepsin L is a potential biomarker for prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 19663777_unknown mRNA clone PP1959 identified as splice variant of cathepsin L mRNA which encodes truncated form of cathepsin L containing only 151 C-terminal amino acids; localization to nuclear, perinuclear & cytosolic region 19915865_Levels of CatB and CysC were higher in CF of malignant serous tumors compared to those found in benign serous tumors whereas levels of CatL were significantly higher in CF of malignant mucinous tumors compared to those found in benign mucinous tumors 19924101_Proteinuria can result from enzymatic cleavage of essential regulators of podocyte actin dynamics by cytosolic cathepsin L, resulting in a motile podocyte phenotype. 19958782_The combination of cathepsin L inhibition with conventional chemotherapy seems to be more promising and has yielded more consistent results. 19959474_Data show that SCCA-1 inhibition of cathepsin L-like proteolytic activity secreted from breast and melanoma cancer cell lines was significantly enhanced by heparin. 20075068_Stefin B interacts with histones and cathepsin L in the nucleus 20302512_arsenite toxicity involves a complex interplay between autophagy and apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells and is associated with inhibition of Cathepsin B, and that this toxicity is highly exacerbated by simultaneous Cathepsin L inhibition. 20347002_functions of CTSL and CTSV in the positive selection of CD4+ T cells 20497254_Granule-bound cathepsins are essential for processing perforin to its active form, and that CatL is an important, but not exclusive, participant in this process. 20524145_analysis of CTSL1 gene transcript demonstrated that cathepsin L protein and transcript correlate both in fibroblasts expressing Ras mutants and in pharmacologically treated cells, thus indicating a transcriptional up-regulation 20567828_Results suggest a potential utility of CTSL and CTSB as prognostic markers for this malignancy. 20837372_imbalance between catL and cystatin C in patients with coronary artery ectasia 20881085_These data indicate that cathepsins B, L and S may act as cell-death mediators in in monocytic cells infected with ICP4 and Us3 deletion mutant herpes simplex virus type 1. 20926012_Plasma cathepsin L and placenta growth factor, acting as important modulators of angiogenesis, could be used as biomarkers to predict coronary collateral formation in patients with coronary heart disease. 21029616_CTSL might increase the invasion and metastasis ability of ovarian cancer cells in vitro. 21134415_abnormal distribution of cathepsin L may be responsible for dopamine neuron death, involved in the pathogenic cascade event for the development of Parkinson's disease. 21226994_This study showed that cathepsin L provides significant prognostic information and that it might be a useful therapeutic target in the future. 21308479_Studies indicate that cathepsin L as the heparanase activating protease. 21395501_Data suggest that differential stability and translation initiation modes mediated by the 5'UTRs of human cathepsin L variants are involved in regulating its expression. 21484410_Cathepsin L is present in the nucleus and regulates the transcription of effector caspases 3 and 7, in a p53 dependent manner. 21496199_this is the first report demonstrating the phase-specific expression of CTSL in chronic myeloid leukaemia 21501115_Procathepsin L secretion, which triggers tumour progression, is regulated by Rab4a in human melanoma cells 21555518_CTSL1 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21562164_CTSL and CTSB are capable of directly processing both alpha- and beta-protryptases from human mast cells to their mature enzymatically active products. 21585286_The cathepsin L deserves further evaluation as therapeutic targets to develop disease modifying drugs to treat Alzheimer's disease. 21700710_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma induces apoptosis and inhibits autophagy of human monocyte-derived macrophages via induction of cathepsin L: potential role in atherosclerosis. 21715684_Cathepsin L- and K-cleaved chemerin trigger robust migration of human blood-derived plasmacytoid dendritic cells ex vivo 21742978_Processing of human protryptase in mast cells involves cathepsins L, B, and C. 21750527_Overexpression of human CTSL in wild-type murine fibroblasts leads to decreased 53BP1 protein levels and changes in its cellular distribution, resulting in defective repair of DNA DSBs. 21756348_Cathepsins K, L, and S activity are profiled in 10 mug human breast, lung, and cervical tumors. 21769426_cathepsin L is highly expressed in GISTs compared to its expression in other cancerous lesions; this identifies cathepsin-L as a new diagnostic marker for GISTs. 21775114_DHA supplementation significantly suppressed the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor and cathepsin L1, both of which were also up-regulated by LPS. 21880013_Data show that mRNA levels of the two main lysosomal enzymes (cathepsin B and L) were not changed but, conversely, genes related to calpain and caspase had a higher expression in the muscles of the patients. 21896479_Cysteine cathepsins S and L modulate anti-angiogenic activities of human endostatin. 21898833_high-resolution structures reveal that the backbone C=O group of Gly61 in most cathepsin L co-crystal structures maintains water solvation while engaging in halogen bonding 21925292_Recently discovered biological roles of cathepsins L and B indicate their significance in human health and disease. 21965756_Elevated serum CL, Hpa, and MMP-9 levels are correlated with malignant invasion and progression in ovarian cancer. 21967108_Cathepsin L has a strong preference for aromatic and, to a slightly lesser extent, aliphatic residues. 22031933_Cathepsin L cleavage potentiates the Ebola virus GP to undergo a fusion-relevant conformational change. 22222211_Cathepsins B and L activate Ebola but not Marburg virus glycoproteins for efficient entry into cell lines and macrophages independent of TMPRSS2 expression. 22281037_Report transient expression of progesterone receptor and cathepsin-l in human granulosa cells during the periovulatory period. 22365146_Regulation of cathepsins S and L by cystatin F during maturation of dendritic cells. 22451661_Cathepsins L and Z are critical in degrading polyglutamine-containing proteins within lysosomes. 22571763_Seminal plasma cathepsin B was approximately 70 times higher, while the cathepsin L values were approximately 500 times higher and the cathepsin S values approximately 40 times higher in seminal plasma than in a group of serum samples. 22674323_Cathepsin L has a significant impact on antigen-induced arthritis severity by influencing the selection of Th cell populations in the thymus, but seems not play any significant role in the direct joint destruction 22695494_The activity of cathepsin B and L in blood significantly increased with age. 22871890_conclude that common genetic variation in the proximal CTSL1 promoter, especially at position C-171A, is functional in cells, and alters transcription so as to explain the association of CTSL1 with BP in vivo 22963824_Cathepsin L expression is related to the invasive and metastatic potential of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23009386_In this study, various molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of pro- and mature human cathepsins L and O were performed. 23063511_Up-regulation of cysteine cathepsins B and L and TGF-beta production/signaling were required for the activation of fibroblasts and their promotion of the invasive growth of melanoma cells. 23229094_Oxidized low-density lipoprotein upregulated CATL protein levels and activation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (ECs) in a concentration-dependent manner and stimulated EC autophagy and apoptosis and increased EC monolayer permeability. 23337117_BRCA1 loss activates cathepsin L (CTSL)-mediated degradation of 53BP1. 23536651_TMPRSS2 and HAT activate HCoV-229E for cathepsin L-independent virus-cell fusion. 23603447_our data demonstrate that chronic UVA inhibits both cathepsin B and L enzymatic activity and that dual inactivation of both enzymes is a causative factor underlying UVA-induced impairment of lysosomal function in dermal fibroblasts. 23677785_Thus, cathepsin L and cathepsin B are not required for human papillomavirus type 16 infection but instead appear to restrict infection. 23900981_CTSL protein level was positively associated with forced expiratory volume in emphysema. The C allele of rs2274611 was associated with increased protein level. CTSL may be involved in the development of airflow limitation. 23915070_Both cathepsin L and matrix metalloprotease-2 showed correlation with some of the clinicopathological parameters in pancreatic cancer but only cathepsin L expression in tumor epithelium predicted a poor prognosis for the disease. 23958260_correlation of plasma CatL levels with aortic diameter and the lowest ankle-brachial index suggest that this cysteinyl protease plays a detrimental role in the pathogenesis of peripheral arterial diseases and abdominal aortic aneurysms 24108784_Data suggest that CTSL (cathepsin L) and CTSB (cathepsin B) of the autophagic-lysosomal proteolytic system are involved as the main proteolytic system in skeletal muscle during cancer cachexia development in patients with esophageal cancer. 24319737_The increase in cathepsins B and L activities in lymphosarcoma tissues is caused by cyclophosphamide induction of apoptosis. 24402045_Overexpression of CTSL is involved in tumor invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer. 24583396_catalase expression (or activity) was higher, while intracellular and extracellular Cat S, Cat L, and Cat K activities were lower in the non-invasive CL1-0 cells compared to the highly invasive CL1-5 cells. 25333746_the results suggested that CTSL contributes to the proliferation and metastasis of OC, and that CTSL may be a novel molecular target for OC treatment. 25384089_CTSL might involve in the development and progression of HCC as a oncogene. 25516668_study showed plasma cathepsin L may be used as an independent predictor of prognosis in pancreatic cancer; this protease may be one of the factors responsible for tumor invasion, as its level was found to be significantly higher in pancreatic tumor tissues compared to non-neoplastic adjacent tissue 25558848_Cathepsins in Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy: Identification in Human Chronic Tears and Temporal Induction in a Rat Model. 25626674_The study determined almost identical substrate specificities for cysteine cathepsins K, L and S. 25632968_TGFbetainduced epithelialmesenchymal transition was associated with increased cathepsin L in A549 and MCF7 cells. CATL may be involved in the regulation of EMT. CATL knockdown in A549 cells inhibited xenograft tumor growth and EMT in vivo 25633482_Cathepsins B and L activity correlates with the efficiency of reovirus-mediated tumor cell killing. 25957406_in vivo functional evidence for overexpressed CTSL as a promoter of lung metastasis, whereas high CTSL levels are maintained during tumor progression due to stress-resistant mRNA translation. 25991043_In addition, cathepsin L positively correlates with MMP2. PRACTICE: The cathepsin L may be used as a monitoring index in age-related diseases. 26081835_shedding of surface proteins by extracellular cathepsins impacts intracellular signaling as demonstrated for regulation of Ras GTPase activity. 26299995_Cathepsin L targeting in cancer treatment 26343556_Data suggest that nuclear cathepsin L accelerates cell cycle progression of HCT116 colorectal carcinoma cells. 26374357_The study results indicate the A-allele of rs3118869 [of the human cathepsin Lgene] is a protective factor in hypertension. 26474873_CTSL may contribute to gefitinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer 26661692_endothelial CTSL up-regulation partially due to Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the development of vasculopathy, while the decrease in dermal CTSL expression is likely associated with dermal fibrosis in systemic sclerosis 26706414_Knockdown of Cathepsin L promotes radiosensitivity of glioma stem cells both in vivo and in vitro. 26757339_cathepsin L activity was decreased in p53 positive cells after adriamycin treatment, but not in p53 negative cells. 26757413_these data indicate that the CTSL inhibitor KGP94 has the potential to alleviate metastatic disease progression and associated skeletal morbidities and hence may have utility in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer patients 26797274_Our findings highlight the potential role of CTSL in the cross talk between autophagy and apoptosis, which might be considered a therapeutic strategy for treatment of pathologic conditions associated with neurodegeneration. 26953343_Mechanistic studies showed that teicoplanin blocks Ebola virus entry by specifically inhibiting the activity of cathepsin L, opening a novel avenue for the development of additional glycopeptides as potential inhibitors of cathepsin L-dependent viruses. 26960148_p41 fragment is also shown to reduce the secretion of interleukin-12 (IL-12/p70) during the subsequent maturation of treated dendritic cells. 26975192_Kidney tubule/glomerulus cathepsin L expression did not change in cyclosporine A-treated nephrotic syndrome. 26992470_the crystal structure determined at 1.4 A revealed that the cathepsin L molecule is cleaved, with the cleaved region trapped in the active site cleft of the neighboring molecule. 27055649_Collectively, these data indicate that CTSL is an important contributor to tumor angiogenesis and that the CTSL inhibition may have therapeutic utility in the treatment of breast cancer patients. 27351223_these findings suggest that CTSL functions as a carcinogenic factor and may contribute to Paclitaxel resistance in human ovarian cancer 27373979_Cathepsin L knockdown induced by RNA interference significantly promoted curcumin-induced cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest. The knockdown also inhibited the migration and invasion of glioma cells. Cathepsin L may be a new target to enhance the efficacy of curcumin against cancers. 27718373_An association between higher serum cathepsin L and increased risk of cardiovascular mortality was found in two independent cohorts. Impaired kidney function appears to be an important moderator or mediator of these associations. 27729455_cathepsin L and cathepsin B as the lysosomal cysteine proteases that activate the PEDV spike. 27764212_interactions of human family 1 & 2 cystatins with cathepsin L1 27902765_CtsB/L as major regulators of lysosomal function and demonstrate that CtsB/L may play an important role in intracellular cholesterol trafficking and in degradation of the key AD proteins 27956696_a positive feedback loop between Snail-nuclear Cat L-CUX1 drives epithelial mesenchymal transition, is reprted. 27989700_CTSL is an important protein which mediates cell invasion and migration of human glioma U251 cells. 28074340_Results showed an increase level of CTSL, and CTSB in dilated cardiomyopathy patients which correlates with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. 28478025_these data suggest that oxidative stress prevents the protective autophagy by inhibition of CTSL processing 28614652_Data suggest substrate specificity of CTSL includes SNCA; CTSL truncates SNCA first at C-terminus before attacking internal beta-sheet-rich region between residues 30 and 100; three of four proteolysis sites contain glycine residues likely involved in beta-turn, where proteolysis leads to solvent exposure of internal residues and further proteolysis of amyloid. (CTSL = cathepsin L; SNCA = alpha-synuclein) 28698143_Therefore, we show for the first time that the nuclear localization of Cat L and its substrate Cux1can be positively regulated by Snail NLS and importin beta1, suggesting that Snail, Cat L and Cux1 all utilize importin beta1 for nuclear import. 28743268_identify Cat L as a key intracellular lysosomal gene encoding progranulin protease 28787468_The active CATL activity and the expression of the mature single-chain enzyme are lowest the umbilical cord arteries and highest in Wharton's jelly. 29149174_Findings from this community-based cohort of young children show that surrogate markers for cardiovascular disease such as total fat mass, percent body fat, abdominal fat, body fat distribution, maximal oxygen uptake and pulse pressure were all associated with cystatin B. This was not found for cathepsin L or cathepsin D 29154036_Cathepsin L (CTSL) has been shown to participate in the microglia-mediated neuroinflammation.Level of CTSL was positively correlated with expression of inflammatory mediators and NF-kappaB in Parkinson's disease patients. 29246726_the findings demonstrated that mutated K-ras promotes cathepsin L expression and plays a pivotal role in EMT of human lung cancer. The regulatory effect of IR-induced cathepsin L on lung cancer invasion and migration was partially attributed to the Cathepsin L /CUX1-mediated EMT signaling pathway 29278883_The key findings of this study provided evidence suggesting that miR-152 functions by means of binding to CTSL to induce GIST cell apoptosis and inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion. 29331585_This study revealed that ionizing radiation-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) as well as migration and invasion of glioma cells are mediated by cathepsin L through the proto-oncogene proteins c-akt (Akt)/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta)/EMT-related transcription factor snail and homeobox protein cut-like1 (CUX1) pathways. 29345177_Results suggest the potential utility of cathepsin L (CTSL) in predicting the outcome of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 30679571_the transcriptional induction of CatB and CatL depends on the binding of PPARgamma to PPRE sequences as a PPARgamma/Retinoid X Receptor-alpha heterodimer. 30999160_Low expression of CatL and DC-SIGN is a feature of filovirus-resistant epithelial cells. 31269957_Human omental microvascular endothelial cells Gal1 transcription and release in response to CathL secreted from metastasising high-grade serous carcinoma acts in an autocrine manner on the local microvasculature to induce pro-angiogenic changes. 32242285_Mechanisms of L-Serine-Mediated Neuroprotection Include Selective Activation of Lysosomal Cathepsins B and L. 32468052_Altered expression of TMPRSS2 and cathepsin L in neoplasms may facilitate cellular entry of SARSCoV2 leading to COVID-19. 32842606_In Silico Identification of Potential Natural Product Inhibitors of Human Proteases Key to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. 33293479_Tandem mass tag-based proteomic analysis reveals cathepsin-mediated anti-autophagic and pro-apoptotic effects under proliferative diabetic retinopathy. 33315943_Female reproductive tract has low concentration of SARS-CoV2 receptors. 33364201_Cathepsin L in COVID-19: From Pharmacological Evidences to Genetics. 33713388_The lysosomal endopeptidases Cathepsin D and L are selective and effective proteases for the middle-down characterization of antibodies. 33774649_Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development. 33933142_The lnc-CTSLP8 upregulates CTSL1 as a competitive endogenous RNA and promotes ovarian cancer metastasis. 33980181_Cancer-associated mutations reveal a novel role for EpCAM as an inhibitor of cathepsin-L and tumor cell invasion. 34407143_Genomics-guided identification of potential modulators of SARS-CoV-2 entry proteases, TMPRSS2 and Cathepsins B/L. 34686211_Upregulation of cathepsin L gene under mild cold conditions in young Japanese male adults. 34807310_Expressions and significances of CTSL, the target of COVID-19 on GBM. 34883264_XPA is susceptible to proteolytic cleavage by cathepsin L during lysis of quiescent cells. 35414771_COVID-19 receptor and malignant cancers: Association of CTSL expression with susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2. 35941174_A novel high-risk subpopulation identified by CTSL and ZBTB7B in gastric cancer. |
|
|
4855.383442 |
2.6046357990 |
1.381082 |
0.024532120 |
3215.123264 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7088.2295535 |
100.2877456 |
2741.0352803 |
31.3281851 |
| ENSG00000135048 |
23670 |
CEMIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHN6 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface hyaluronidase that mediates the initial cleavage of extracellular high-molecular-weight hyaluronan into intermediate-size hyaluronan of approximately 5 kDa fragments (PubMed:28246172). Acts as a regulator of angiogenesis and heart morphogenesis by mediating degradation of extracellular hyaluronan, thereby regulating VEGF signaling (By similarity). Is very specific to hyaluronan; not able to cleave chondroitin sulfate or dermatan sulfate (PubMed:28246172). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A3KPQ7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28246172}. |
Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a type II transmembrane protein that belongs to the interferon-induced transmembrane (IFITM) protein superfamily. The encoded protein functions as a cell surface hyaluronidase that cleaves extracellular high molecular weight hyaluronan into intermediate size fragments before internalization and degradation in the lysosome. It also has an interferon-mediated antiviral function in humans through activation of the JAK STAT signaling pathway. The activation of this gene by transcription factor SOX4 in breast cancer cells has been shown to mediate the pathological effects of SOX4 on cancer progression. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:23670; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; hyalurononglucosaminidase activity [GO:0004415]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; hyaluronan catabolic process [GO:0030214]; regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903670] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22610944_Results showed that missense mutations in transmembrane protein 2 p.Ser1254Asn, interferon alpha 2 p.Ala120Thr, its regulator NLR family member X1 p.Arg707Cys, and complement component 2 p.Glu318Asp were associated with chronic hepatitis B. 27253403_TMEM2 inhibits Hepatitis b virus infection in HepG2 and HepG2.2.15 by activating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. 27328729_our findings lead us to propose that TMEM2 may not only mediate the pathologic effects of SOX4 on cancer progression but also potentially its contributions to embryonic development 30241936_Findings indicate that hyaluronan-binding protein (HYBID) is indispensable for KIAA1199 (CEMIP)-mediated hyaluronan-B (HA) depolymerization in skin fibroblasts, but transmembrane protein 2 (TMEM2) is not involved in the HYBID-mediated process as a catalytic hyaluronidase. 31761535_ectopic expression of human TMEM2 in C. elegans protected animals from endoplasmic reticulum stress and increased both longevity and pathogen resistance. 32326855_Transcriptome alterations in HepG2 cells induced by shRNA knockdown and overexpression of TMEM2 gene. 33251982_miR-518a-3p Suppresses Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Invasion and Migration Through Regulation of TMEM2. 35525055_TMEM2 expression is downregulated as bladder cancer invades the muscle layer. 36241903_Expression and regulation of recently discovered hyaluronidases, HYBID and TMEM2, in chondrocytes from knee osteoarthritic cartilage. 36395406_Concurrent Overexpression of Two Hyaluronidases, KIAA1199 and TMEM2, Strongly Predicts Shorter Survival After Resection in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000024754 |
Cemip2 |
593.323713 |
0.4632421375 |
-1.110162 |
0.122415179 |
80.904744 |
0.00000000000000000023686436997895573533881044044012968693250077114909350403659793471433658851310610771179199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000002034993073858781184546849130949164098433025279190019575514813965355642721988260746002197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
385.1462374 |
34.1614006 |
838.2812195 |
53.1735727 |
| ENSG00000135063 |
9413 |
FAM189A2 |
protein_coding |
Q15884 |
FUNCTION: Functions as an activator of the E3 ubiquitin protein ligase ITCH in the ubiquitination of the CXCL12-activated CXCR4 receptor. Thereby, triggers CXCR4 endocytosis and desensitization, negatively regulating the CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34927784}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Endosome;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9413; |
early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; ubiquitin ligase activator activity [GO:1990757]; CXCL12-activated CXCR4 signaling pathway [GO:0038160]; negative adaptation of signaling pathway [GO:0022401]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623] |
34927784_ENTREP/FAM189A2 encodes a new ITCH ubiquitin ligase activator that is downregulated in breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000071604 |
Fam189a2 |
15.960560 |
0.3417957164 |
-1.548794 |
0.423391464 |
13.720242 |
0.00021215551434050408381552788039670076614129357039928436279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000552862886946652617829733866727792701567523181438446044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2526464 |
2.4562334 |
23.8866504 |
4.3150494 |
| ENSG00000135077 |
84868 |
HAVCR2 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDQ0 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor implicated in modulating innate and adaptive immune responses. Generally accepted to have an inhibiting function. Reports on stimulating functions suggest that the activity may be influenced by the cellular context and/or the respective ligand (PubMed:24825777). Regulates macrophage activation (PubMed:11823861). Inhibits T-helper type 1 lymphocyte (Th1)-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance (PubMed:14556005). In CD8+ cells attenuates TCR-induced signaling, specifically by blocking NF-kappaB and NFAT promoter activities resulting in the loss of IL-2 secretion. The function may implicate its association with LCK proposed to impair phosphorylation of TCR subunits, and/or LGALS9-dependent recruitment of PTPRC to the immunological synapse (PubMed:24337741, PubMed:26492563). In contrast, shown to activate TCR-induced signaling in T-cells probably implicating ZAP70, LCP2, LCK and FYN (By similarity). Expressed on Treg cells can inhibit Th17 cell responses (PubMed:24838857). Receptor for LGALS9 (PubMed:16286920, PubMed:24337741). Binding to LGALS9 is believed to result in suppression of T-cell responses; the resulting apoptosis of antigen-specific cells may implicate HAVCR2 phosphorylation and disruption of its association with BAG6. Binding to LGALS9 is proposed to be involved in innate immune response to intracellular pathogens. Expressed on Th1 cells interacts with LGALS9 expressed on Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages to stimulate antibactericidal activity including IL-1 beta secretion and to restrict intracellular bacterial growth (By similarity). However, the function as receptor for LGALS9 has been challenged (PubMed:23555261). Also reported to enhance CD8+ T-cell responses to an acute infection such as by Listeria monocytogenes (By similarity). Receptor for phosphatidylserine (PtSer); PtSer-binding is calcium-dependent. May recognize PtSer on apoptotic cells leading to their phagocytosis. Mediates the engulfment of apoptotic cells by dendritic cells. Expressed on T-cells, promotes conjugation but not engulfment of apoptotic cells. Expressed on dendritic cells (DCs) positively regulates innate immune response and in synergy with Toll-like receptors promotes secretion of TNF-alpha. In tumor-imfiltrating DCs suppresses nucleic acid-mediated innate immune repsonse by interaction with HMGB1 and interfering with nucleic acid-sensing and trafficking of nucleid acids to endosomes (By similarity). Expressed on natural killer (NK) cells acts as a coreceptor to enhance IFN-gamma production in response to LGALS9 (PubMed:22323453). In contrast, shown to suppress NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity (PubMed:22383801). Negatively regulates NK cell function in LPS-induced endotoxic shock (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VIM0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11823861, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14556005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16286920, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22323453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23555261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24838857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26492563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30374066, ECO:0000305|PubMed:24825777}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily, and TIM family of proteins. CD4-positive T helper lymphocytes can be divided into types 1 (Th1) and 2 (Th2) on the basis of their cytokine secretion patterns. Th1 cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity to intracellular pathogens and delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions, whereas, Th2 cells are involved in the control of extracellular helminthic infections and the promotion of atopic and allergic diseases. This protein is a Th1-specific cell surface protein that regulates macrophage activation, and inhibits Th1-mediated auto- and alloimmune responses, and promotes immunological tolerance. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:84868; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; macrophage activation involved in immune response [GO:0002281]; maternal process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060135]; natural killer cell tolerance induction [GO:0002519]; negative regulation of defense response to bacterium [GO:1900425]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0071656]; negative regulation of immunological synapse formation [GO:2000521]; negative regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032687]; negative regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032703]; negative regulation of interleukin-3 production [GO:0032712]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of myeloid dendritic cell activation [GO:0030886]; negative regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032815]; negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002859]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of T cell activation via T cell receptor contact with antigen bound to MHC molecule on antigen presenting cell [GO:2001189]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of T-helper 1 type immune response [GO:0002826]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of defense response to bacterium [GO:1900426]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 production [GO:0032732]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043032]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of tolerance induction dependent upon immune response [GO:0002652]; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway [GO:0034138]; toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway [GO:0034154]; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034162] |
15325803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15325803_Tim-3 gene associated with rheumatoid arthritis 15603868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15603868_the -574T > G polymorphism of Tim-3 might be associated with the susceptibility of atopic diseases 15867855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16159638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16456792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16685421_Human Tim-3 can promote HAV entry into target cells but itself may not function as a cellular receptor of HAV. 16754722_Failure to up-regulate T cell expression of TIM3 in inflammatory sites may represent a novel, intrinsic defect that contributes to the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and other human autoimmune diseases. 16940744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17069754_Stimulation of Tim-3 by its ligand galectin-9 results in increased phosphorylation of Y265, suggesting that this tyrosine residue plays an important role in downstream signalling events regulating T-cell fate. 17096021_Expressed in melanoma cell lines at higher level than in isolated epidermal melanocytes, which can contribute to lower adhering capacity of tumor cells. TIM-3 in TGF-beta-stimulated mast cells and melanoma cells may support survival of this tumor type. 17430399_High expressionof TIM-3 in in acute kidney transplant rejection makes it a promising noninvasive test for its diagnosis. 17665973_T-cell immunoglobulin- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3 (Tim-3) influences autoimmune diseases, and its role in other inflammatory diseases including allergies and cancer is becoming clear. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18006747_data show that Tim-3 is highly expressed by cells of the innate immune system and that its expression on antigen-presenting cells promotes the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines from monocytes and dendritic cells 18052965_Involved in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. 18294362_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18354161_multiple sclerosis may function in part by restoring TIM-3 immunoregulation of T cell function 18401547_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18401547_role of the rs10515746 (A/C), rs1036199 (A/C), and rs10053538 (A/C) SNPs within the TIM-3 gene in 186 German type 1 diabetes families and its interaction with human leukocyte antigen (HLA) high-risk haplotypes 18485114_increase of TIM-3 expression on PBMCs, overproduction of IFN-gamma in the sera, and increased galectin-9 in PBMCs was observed in acquired aplastic anemia patients 18785518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18785518_strong linkage disequilibrium between the two SNPs sites in the TIM-3 gene in a Han population from Hubei province 19001139_Data show that blockade of the Tim-3 pathway can enhance HIV-1 - specific T cell responses, and suggest that the Tim-3 pathway plays a critical role in suppressing the overall T cell response to HIV-1. 19005181_Nasopharyngeal carcinoma exosomes induce massive apoptosis in EBV-specific CD4(+) cells used as a model of target T cells. This effect is inhibited by both anti-Tim-3 and antigalectin-9 blocking antibodies. 19100864_The simultaneous expression of galectin-9 and Tim-3 may indicate an immunoregulatory function, during the ongoing cytotoxic response. 19104436_Tim-3 messenger RNA evaluation in renal transplant recipients is a noninvasive method to evaluate graft dysfunction. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19332093_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332093_The -1516G>T, -574T>G, and 4259G>T of TIM-3 gene polymorphisms might not play an important role as a genetic risk factor in the pathophysiology of ITP. 19395088_expression is increased on Vdelta T cells of pregnant women 19414817_Tim-3, by virtue of its up-regulation in innate immune cells in pregnant women, enhances both innate and adaptive immune responses 19480659_Reduced TIM-3 expression in the lungs of patients may result in a defective T cell ability to control the Th1 immune response and could thus contribute to the pathogenesis of sarcoidosis. 19494522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19494522_haplotypes including TIM-3 genetic variants confer susceptibility to asthma in a Chinese population 19566956_These data suggest that polymorphisms in the TIM3 promoter region are unlikely to play an important role in susceptibility to allergic diseases 19587053_Tim-3 expression correlates with a dysfunctional and senescent phenotype (CD127(low) CD57(high)), a central rather than effector memory profile (CD45RA(negative) CCR7(high)), and reduced Th1/Tc1 cytokine production. 19676072_These results suggest that TIM-3 is a negative regulator of human T cells and regulates Th1 and Th17 cytokine secretion. 19768575_The TIM-3 pathway and the therapeutic potential of modulating the pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus, is reviewed. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083673_Structural and biologic studies reveal that TIM-3 is a receptor for phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) and that TIM-3 polymorphic variants differ functionally in their recognition of PtdSer and clearance of apoptotic cells. 20133006_Hepatitis B virus infection can up-regulate Tim-3 expression in natural killer cells (NK), which may in turn suppress NK-cell functions in chronic hepatitis B patients. 20176801_Mucin domain-containing molecule 3 (Tim-3) is preferentially expressed in lymphoma-derived endothelial cells. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574007_The Tim-3/galectin-9 pathway regulates T helper cell type (Th)1 immune responses through at least two mechanisms: directly, by triggering cell death in Th1 cells and indirectly, through the expansion of suppressive CD11b+Ly6G+ cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20656318_Histiocytic and dendritic cell neoplasms consistently express TIM-3 and TIM-4 and that these molecules are new markers of neoplasms derived from histiocytic and dendritic cells. 20805041_Tim-3 might participate in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by its negative regulation on various T cell subsets. 20811886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20811886_three genetic variations within the TIM-3 gene promoter may be associated with the increased susceptibility to gastric cancer, especially among the haplotypes with the risk. 20819923_PD-1(+) NY-ESO-1-specific CD8(+) T cells in patients with advanced melanoma up-regulates Tim-3 expression 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21084749_Blockade of either PD-1 or Tim-3 enhanced in vitro proliferation of HCV-specific CTLs to a similar extent, whereas cytotoxicity against a hepatocyte cell line that expressed cognate HCV epitopes was increased exclusively by Tim-3 blockade. 21263071_Both TIM-3 and galectin-9 undergo rapid proteolytic degradation in the cystic fibrosis CF lung, primarily because of neutrophil elastase and proteinase-3 activity. 21367814_The findings suggest that the polymorphisms of TIM gene family might not contribute to systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in the Chinese population. 21382414_The elevated expression of Tim-3 on CD8 T cells correlates with functional defects of CD8 T cells and disease severity of pulmonary TB. 21392402_Tim-3 expression on peripheral T cell subsets correlates with disease progression in hepatitis B infection. 21402546_These data suggest that Tim-3 expression is reduced in human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) infection and that a high number of Tim-3(-) HTLV-I-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes preserves their cytolytic activity. 21446887_TIM-3 and its interaction with Gal-9 are closely associated with rheumatoid arthritis activity. 21519864_augmented expression of Tim-3 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke by regulation of proinflammatory cytokines. 21565238_T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 genetic polymorphisms are associated with rheumatoid arthritis independent of a shared epitope status. 21621846_results suggest the regulatory role of MEK in TIM-3 transcription by human CD4+ T cells and mast cells 21637332_Tim-3 is constitutively expressed on human resting CD14(+) monocyte/macrophages (M/M(O)) and functions as a cap to block IL-12. 21717191_data suggest that TIM-3 and its interaction with Gal-9 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of RA and may represent a potential therapeutic target 21807895_Data suggest that ectopic expression of Tim-3 in T cells leads to enhancement of T-cell receptor-dependent signaling pathways. 21844165_Blocking Tim-3 increases TLR-mediated IL-12 production & decreases activation-induced up-regulation of the immunoinhibitor, PD-1. TNF-alpha production is not altered significantly, but IL-10 production was increased. 21989170_Genetic variations of TIM-3 gene contribute to rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility among different populations. 22172823_TIM-3 mRNA quantification by RT-PCR in peripheral blood leukocytes may be a promising tool for a noninvasive diagnosis of acute rejection in renal graft recipients. 22177036_There is no correlation between allergic rhinitis susceptibility and Tim-3 gene polymorphism in Uigur and Han people in Xinjiang. 22294262_Impaired Tim-3 expression allows Th17, Th1 and Tc1 cells to escape from Tim-3-mediated negative regulatory systems and may contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriasis. 22323453_Tim-3 functions as a human NK-cell coreceptor to enhance IFN-gamma production, which has important implications for control of infectious disease and cancer. 22363469_This study reveals a new role of TIM-3 as an important immune regulator in the tumor microenvironment via its predominant expression in regulatory T cells. 22371007_Reduced levels of Tim-3 on CD4(pos) CD25(neg) effector cells and of Gal9 in T-regs contribute to impaired immunoregulation in autoimmune hepatitis by rendering effector cells less prone to T-reg control and T-regs less capable of suppressing. 22383801_Findings suggest that natural killer-cell responses may be negatively regulated when NK cells encounter target cells expressing cognate ligands of Tim-3. 22387059_data provide evidence that augmented Tim-3 expression on natural killer (NK) cells plays an important role in NK cell loss in atherosclerosis 22426209_Long-term exposure of CD4+ T cells to IL-12 caused T cell dysfunction & induced TIM-3. TIM-3 was required for this negative effect. TIM-3 was highly expressed on functionally impaired intratumoral T cells. 22469568_concluded that pro-apoptotic effects on Th1 population through galectin-9-Tim-3 pathway and the up-regulation of Tim-2 on Th2 cells might be critical to Th2-biased response of host with schistosomiasis japonica. 22472081_polymorphisms in the TIM-3 gene are new risk factors for RCC 22505239_The Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling pathway mediates T-cell senescence in Hepatitis B Virus-associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 22539292_It was shown that Tim-3 negatively regulates antiviral responses of CD8+ T cells isolated from chronic hepatitis B patients, and this response is reversed by blocking the Tim-3 pathway. 22587604_-1516G/T polymorphism in the promoter region of TIM3 gene may affect the disease susceptibility and hepatocellular carcinoma traits associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection infection. 22733499_the correlation of TIM-3 polymorphisms with susceptibility to pancreatic cancer in the Chinese population 22738814_Th17 cell differentiation, IL-17 levels, and TIM-3 regulation may be involved in the pathogenesis of GBS. 22792231_Tim-3 negatively regulates cytotoxicity in exhausted CD8+ T cells in HIV infection. 22842346_TIM-3 circumvents the stimulatory effects of nucleic acids in tumor immunity by interactding with HMGB1 to interfere with the recruitment of nucleic acids into dendritic cell endosomes 22875804_Mutation of Tim3 transgene results in decreased phosphorylation of the T cell receptor-CD3zeta-chain; mice with this Tim3 mutation infected with influenza are protected from morbidity and mortality without impairment in viral clearance. 22968087_The polymorphisms of TIM-3 gene may not contribute to Grave's disease susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 23029209_data suggest that Tim-3 upregulation was driven by both HIV-1 viral replication and increased age, whereas PD-1 expression is associated with immune activation 23117395_a dysregulated Tim-3/Gal-9 pathway may contribute to the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis 23144609_This study therefore uncovered a previously unknown mechanism for T-cell immune responses regulated by Tim-3, and findings may have implications for potential immune intervention in TB. 23161469_HCV-infected human hepatocytes express higher levels of Gal-9 and TGF-beta, and upregulate Tim-3 expression. 23180819_A potential pathway activated by Tim3/galectin 9 is the secretion of interleukin (IL)-1beta, which plays a crucial role in antimicrobial immunity by modulating innate inflammatory networks in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. 23291409_PD1 and TIM3 polymorphisms may differentially and interactively predispose cirrhosis and HCC in chronic HBV infection. 23314411_results demonstrate that, during HIV infection, Tim-3 expression on innate cells is dysregulated and that this dysregulation is only partially restored after 6 months of cART; findings suggest Tim-3 is differentially regulated on innate immune effector cells 23334427_These results suggest that the imbalanced expression of Tim-3 and T-bet may play a role in the pathogenesis and course of aplastic anaemia (AA), and the downregulation of T-bet/Tim-3 may represent a reasonable therapeutic strategy for AA treatment. 23335978_the expression of Tim-3 in tumor cells may be an independent prognostic factor for patients with cervical cancer. Moreover, Tim-3 expression may promote metastatic potential in cervical cancers. 23359271_Polymorphism in TIM-3 gene is associated with increased susceptibility to non-small-cell lung cancer 23365080_Tim-3 negatively regulates the TLR4 response in sepsis patients. 23385979_These results suggested polymorphisms in TIM-3 gene could be new risk factors for non-Hodgkin lymphoma as well as HIV-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma and suggested a possible role of the inflammatory factor in these diseases. 23388728_These findings suggest that Tim-3-mediated differential regulation of IL-12/IL-23 drives T(H)17 cell development, a milieu favoring viral persistence and autoimmune phenomenon during chronic hepatitis C. 23526963_Tim-3-expressing CD4 T cells in tumors could represent the functional regulatory T cells which contribute to the formation of the immune-suppressive tumor micromilieu. 23665438_Altered expression of Tim-3 might play an important role in the pathogenesis of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. 23773130_In patients with chronic hepatitis C, CD8+ T cells are positive for exhaustion markers (i.e., expressing both TIM-3 and PD-1) more frequently in the spleen and the liver, compared to the peripheral blood. 23791624_Mass spectrometry-based profiling of plasma from multiple subjects diagnosed with common diseases provided evidence for restricted release of soluble Tim-3 in the context of GVHD. 23837986_Tim-3 expression, which is up-regulated on PBMs of CHB patients, is negatively correlated to the level of ALT in sera of IA CHB patients. 23866914_Persistent Gal-9 production might impair Tim-3 activity and contribute to natural killer cell dysfunction in chronic HIV-1 infection. 23886204_High TIM-3 expression is associated with prostate cancer. 23922299_MCC-targeting T cells expand with tumor burden and express high levels of immune checkpoint receptors PD-1 and Tim-3. Reversal of these inhibitory pathways is therefore a promising therapeutic approach for this virus-driven cancer. 23936526_Reduced TIM3 expression is associated with preeclampsia. 23967307_a ligand (Gal-9) compartment-dependent regulatory effect on receptor (Tim-3) activities and inflammatory responses via TLR pathways 24007284_expression of Tim-3 was significantly increased in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in ovarian cancer cases, suggesting that Tim-3 may participate in the development and progression of ovarian cancer by its negative regulation on various T-cell subsets 24083425_Data indicate the expression of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), inducible T-cell Costimulator (ICOS), Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and T cell immunoglobulin and mucin protein 3 (Tim-3) in T-cells from geriatric and younger subjects. 24121505_we describe Tim-3 as novel target for ADAM-mediated ectodomain shedding and suggest a role of Tim-3 shedding in TLR-mediated immune responses of CD14(+) monocytes. 24195506_Knockdown of TIM-3 suppressed the proliferation and invasion capacity of Clear cell renal carcinoma (ccRCC) cell lines.TIM-3 expression was associated with poor prognosis in ccRCC. 24209883_Polymorphisms rs10053538 or rs10515746 in the Tim-3 promoter are not be associated with URSA in Han Chinese women. 24231118_The decreased levels of Tim-3 during active stages of disease suggest a possible role in the pathogenesis and course of ITP and restoration of Tim-3 may be a reasonable therapeutic strategy for ITP. 24253699_The results showed that there was the expression of TIM-3 in renal tissue from the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), but rarely expression in cases without SLE. Expression of TIM-3 was associated with the diseases' activity. 24337741_Tim-3 interacts with Lck. 24339967_The results suggest that expression of Gal-9 and Tim-3 in tumor cells may be a potential, independent prognostic factor for patients with gastric cancer. Gal-9 and TIM-3 may play an important part in the gastric carcinogenesis. 24412470_The ratio of Tim-3 to Tim-1 in patients with active disease was significantly decreased compared with the ratios in the normal group and in the immune thrombocytopenia patients in remission. 24477913_neutrophil TIM-3/Gal-9 signaling is perturbed in the CF airways due to proteolytic degradation of the receptor. 24498204_blocking Tim-3 signaling significantly improved the innate and adaptive immune responses in chronically HCV-infected patients 24512143_Tim-3 on peripheral CD4 and CD8 T cells is involved in the development of glioma. 24639110_Tim-3, which specifically expresses on LSCs, is beneficial for LSCs survival and AML progression by promoting expansion of MDSCs and differentiating into TAMs at the leukemia site 24642562_Increased frequency of Tim-3 expressing T cells is associated with symptomatic West Nile virus infection. 24651720_Galectin-9 expressing regulatory T cells, TIM-3+ cytotoxic T cells and NK cells could play an important role in the maintenance of healthy pregnancy. 24689929_The percentage of TIM-3 on both peripheral CD4+ and peripheral CD8+ T cells was negatively correlated with disease activity. 24702227_elevated in cholesteatoma 24825777_Tim-3 functions to inhibit T cell responses, particularly under conditions involving chronic stimulation. 24833097_revealed that patients with advanced tumor stages had elevated Tim-3 expression on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells compared to those with primary tumor stages 24838857_Enhanced suppressor function of TIM-3+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. 24845464_Expression of human Tim-3 on kidney tissue from immunoglobulin A nephropathy patients 24855276_Suggest RepSox may reduce Tim-3 expression by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta signaling and slow decay of CD34(+) AML cells by increasing CXCL12 and MYC, two factors that inhibit AML cell differentiation. 24867713_Results show that genetic variants of Tim-3 have an important impact on disease progression of HBV infection. With specific Tim-3 polymorphisms, patients infected with HBV could be potential candidates of hepatocellular carcinoma and HBsAg seroclearance. 24905803_TIM-3 polymorphism is associated with increased susceptibility to Ankylosing spondylitis possibly by downregulating gene expression. 25091272_Tim-3/Gal-9 interaction favors apoptosis of MBP-specific T lymphocytes in benign multiple sclerosis; this process is reduced in PPMS by the up-regulation of Bat3 25135732_It was suggested that the overexpression of Tim-3/Gal-9 pathway may be related to the pathogenesis of RSA. 25136083_Our study uncovers a novel ability of TIM-family proteins to block the release of HIV-1 and other viruses by interaction with virion- and cell-associated phosphatidylserine. 25180498_A positively selected polymorphism in the 3' UTR, which modulates HAVCR2 expression, is associated with the susceptibility to HIV-1 infection. 25220367_The presence of TIM3+and/or NKG2A+ T cells is associated with the absence of recurrences and a longer recurrence-free survival. 25342285_Tim-3 levels were significantly decreased in CD4+ T cells and CD8+ cells from intracranial aneurysm patients compared to controls. 25363763_CEACAM1 serves as a heterophilic ligand for TIM-3 that is required for its ability to mediate T-cell inhibition, and this interaction has a crucial role in regulating autoimmunity and anti-tumour immunity 25375372_Tumor-induced senescent T cells promote the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and angiogenic factors by human monocytes/macrophages through a mechanism that involves Tim-3 and CD40L. 25400771_Tim-3 is highly expressed on the peripheral blood T cells of AML patients, and Tim-3 expression significantly correlates with clinicopathological prognostic stratification. 25483439_Tim-3 triggers growth factor type responses in acute myeloid leukaemia cells by activating a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. 25520133_High Tim-3 expression is associated with lung cancer. 25578313_The Gal-9/Tim-3 signal is important for the regulation of decidua NK cells function, which is beneficial for the maintenance of a normal pregnancy. 25609823_Authors show that Tim-3 is shed from the surface of responding CD8(+) T cells by the matrix metalloproteinase ADAM10, producing a soluble form of the coinhibitory receptor. 25685816_The elevation of differential Tim-3 and PD-1 expression patterns on T cells represents a state of T cell exhaustion and can be induced by common gamma-chain cytokines 25772938_These data indicate that HCV-induced, miR-155-regulated Tim-3 expression regulates NK cell function, suggesting a novel mechanism for balancing immune clearance and immune injury during chronic viral infection. 25784621_Participation of TIM-3 and its ligand (galectin-9) in the pathogenesis of active generalized vitiligo 25797693_In chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected subjects, there was increased Tim-3 on NK cells, which was associated with an activated phenotype. 25876049_Study found that the prevalence of Tim-3 rs200181745TG genotype and G allele was significantly increased in knee osteoarthritis. Furthermore, patients and controls with rs200181745TG genotype had up-regulated IFN-gamma mRNA and protein levels in CD4 + T cells. 25937557_TIM-3 polymorphism is associated with increased susceptibility to osteoarthritis. 25950468_Findings underline the important roles of Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways in regulating decidual CD8+ T-cell function and maintaining normal pregnancy. 26008981_Results indicate that upregulation of the inhibitory receptor Tim-3 may restrict T cell responses in CRC patients. 26062425_TIM-3, as a key negative regulator in the anti-tumor immunity, contributes to the tumor immune evasion 26076826_Expression of Tim-3 and co-expression of Tim-3 and Fas on certain peripheral T subsets are associated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. 26125859_there was no significant differ-ence in TIM-1 mRNA expression between the patients and the healthy controls. Our results suggest that insufficient expression of TIM-3 mRNA may be involved in the pathogenesis of nephropathy 26141233_IL-15 induces strong but short-lived tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cell responses through the regulation of Tim-3 in breast cancer. 26214042_Our data indicate that Tim-3 expression on NK cells is regulated by T-bet, and that Tim-3 levels correlate with advanced stages of gastric cancer 26215444_The functional decline of invariant natural killer T cells was closely related to the decrease in CD28 expression and the increases of Tim-3 and PD-1. 26239720_Study found that LGALS9 was expressed in 68.4% of the human gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) and Tim-3 in the infiltrated NK cells of 68.4% of GISTs and suggest that Tim-3/LGALS9 pathway may be involved in the immune checkpoint mechanism of GISTs. 26253654_Tim-3 may be used as a novel target for increasing immune responses in RCC tumor microenvironment. 26265374_Tim-3 over-expression is associated with bladder urothelial carcinoma. 26279267_TIM-3 and its ligand, galectin-9 (Gal-9), constitute an autocrine loop critical for leukemic stem cells self-renewal and development of human acute myeloid leukemia. 26339368_Tim-3 might participate in the tumorgenesis of colon cancer and Tim-3 expression might be a potential independent prognostic factor for patients with colorectal cancer. 26342682_an abnormal Tim-3/Gal-9 pathway was able to facilitate the development of preeclampsia. 26373631_sTim-3 was involved in the development of sepsis. The homeostasis-promoting role of the Tim-3 on the monocytes was disrupted, while the inhibitory role of sTim-3 emerged during sepsis-induced immunosuppression. 26401029_Studied the effects of altered Tim-3 expression in vivo in mice and in vitro in human endothelial cells, on day 3 after Rickettsia heilongjiangensis infection. 26413815_Tim-3 in primary leukocytes, both healthy and malignant AML cells, displays moderate properties of an inflammatory receptor with additional growth factor (mTOR activation) and pro-angiogenic (VEGF release) activities 26428847_These data indicate that Tim-3 expression in NK cells can function as a prognostic biomarker in human lung adenocarcinoma and support that Tim-3 could be a new target for an immunotherapeutic strategy. 26463635_Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients have high expression level of PD-1 and TIM-3, which are related to DLBCL staging. PD-1 and TIM-3 expression levels are also related to the efficiency of chemotherapy. 26464703_Tim-3 played an important role in the development and progression of gastric cancer, and it could be used as an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer patients. 26482613_ovarian tumor-infiltrating Treg cells were more immunosuppressive than their peripheral blood counterparts in a TIM3-dependent fashion. 26492563_TIM-3 is a negative regulator of TCR-function by attenuating activation signals mediated by CD3/CD28 co-stimulation. 26715281_Increased Tim3 expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 26820685_Hepatitis B virus surface antigen stimulation of human, monocyte-derived dendritic cells increases expression of Tim-3. 26908841_Data suggest that PD-1/PDCD1 (programmed cell death protein 1) and Tim-3/HAVCR2 (hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2) operate within the functional immune-modulatory network to promote Th2-(type-2 helper T cell-)mediated immunity at the maternal-fetal interface. 26930930_Data show that T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain protein 3 (Tim-3) on peripheral blood CD4+ T cells is increased in advanced schistosomiasis patients. 27008699_Results indicate that T cell Ig and mucin domain 3 protein (TIM-3) polymorphisms (-1516G/T, -574G/T, and +4259T/G) were associated with the increased risk of cancer in Chinese Han population. 27034168_TIM-3 polymorphism is associated with response to therapy in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 27044824_Reduction of Tim-3(+) Treg cells (Tregs) in osteoarthritis patients resulted in less IL-10-producing Tregs. 27049082_decreased serum TIM-1 and TIM-3 levels and association of TIM-3 with nephritis suggest their possible role in the development and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. 27070448_findings support the use of Tim-3-Tim-3L blockade together with PD-1-PD-L1 blockade to reverse tumor-induced T-cell exhaustion/dysfunction in patients with colorectal cancer. 27091308_The results of our study showed that there is no significant association between TIM-1 5383-5397ins/del and Multiple sclerosis (MS) (P = 0.38); however, the frequency of CT genotype of TIM-3 -1541C>T in patient group was significantly higher than the control group, and there was a significant association between CT genotype and MS 27156907_We found a novel mechanism through which Tim-3 could suppress antitumor immunity by utilizing the suppression of CD4(+) follicular helper cells (Tfh) function and provide new insight in the regulation of Tfh cells in breast cancer patients 27182056_T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing molecule 3 might participate in the progression of type 2 diabetes by its negative regulation on immune cells, and Tim-3 on CD14(+) monocytes serves as a novel biological marker for diabetes duration in type 2 diabetes patients. 27185658_TLR2, Tim1, Tim3, TNF-alpha, IgE and EOS play a role in Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia-related wheezing in children. 27230511_Studied the associations of T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (Tim-3) polymorphisms and the alternate reading frame protein (F protein) with the outcomes of HCV infection; findings suggest that the rs12186731 CT and rs13170556 TC/CC genotypes of Tim-3 provide potential protective effects with the F protein in the outcomes of HCV infection and that these effects are related to sex and age. 27243212_The present study defines the minimal TIM-3 promoter region and demonstrates its interaction with c-Jun during TIM-3 transcription in CD4(+) T cells. 27248321_These findings suggested that rs10053538 in TIM-3 might increase susceptibility to and promote the progression of breast cancer in Chinese women 27329385_Tim-3 blockade in combination with TLR activation induces the expression of antiviral molecules without a significant increase in TNF-alpha or SOCS1. 27341144_miR-330-5p has a strong inhibitory effect on TIM-3 expression in acute myeloma leukaemia cell line 27363280_Data show there was a negative correlation between soluble T cell immunoglobulin mucin molecule 3 (sTim-3) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) as well as between IFN-gamma and interleukin-4 (IL-4), while sTim-3 and IL-4 were positively correlated. 27394439_this study shows that the levels of expression of TIM-3 on CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, CD56+ T cells and in serum in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus are significantly higher than those of healthy controls 27430162_these results suggest that TIM3 is a novel therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and promotes metastasis of ESCC by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via, at least partially, the Akt/GSK-3beta/Snail signaling pathway. 27506934_BMI-1, TIM-3 and CLL-1 have roles in acute myeloid leukemia prognosis and therapy 27565576_this study shows that TIM-3 expressed on myeloid leukaemia cells may facilitate functional exhaustion in T helper cells 27638944_In conclusion, Tim-3 on immune cells negatively regulates cell-mediated immunity against Plasmodium infection, and blocking Tim-3 signaling enhances sterile immunity and may play a protective role during malarial parasite infections. 27651303_serum levels may be increased in patients with early phase diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and associated with cardiac involvement and renal crisis 27706678_Tim-3 facilitates osteosarcoma proliferation and metastasis through the NF-kappaB pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 27809352_this study shows that the transcription factor T-bet controls Tim-3-mediated inhibition of monocyte/macrophage function duri |
ENSMUSG00000020399 |
Havcr2 |
1093.423208 |
2.1544889351 |
1.107346 |
0.048094295 |
536.825397 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009248355972983896009554059423984445360693440499171723765580875258013510591646595713173649354983960387956668743343805700926696733041287321627748788437386219591755080096760612352815018188869503838383090142319634084 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004739782436154246691138245186494630483687490729655443268499973905436441490414361593814330108201243916781536379027284436858370067818978462590411524591083749402085477774028223741740155879303305284091367392293588009 |
Yes |
No |
1508.7026514 |
48.0209023 |
705.7301727 |
17.5743924 |
| ENSG00000135083 |
79616 |
CCNJL |
protein_coding |
Q8IV13 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cyclin;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity. Predicted to be involved in mitotic cell cycle phase transition and regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Predicted to be part of cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex. Predicted to be active in centrosome; cytoplasm; and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79616; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity [GO:0016538]; mitotic cell cycle phase transition [GO:0044772]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079] |
|
ENSMUSG00000044707 |
Ccnjl |
16.425229 |
0.1399966741 |
-2.836536 |
0.521059255 |
30.340531 |
0.00000003624721555321788343667497233821506164019865536829456686973571777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000149527362092089450892393848700778757887519532232545316219329833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1696222 |
1.4758752 |
29.8118780 |
6.2038075 |
| ENSG00000135094 |
10993 |
SDS |
protein_coding |
P20132 |
|
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Gluconeogenesis;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate biosynthesis; gluconeogenesis. |
This gene encodes one of three enzymes that are involved in metabolizing serine and glycine. L-serine dehydratase converts L-serine to pyruvate and ammonia and requires pyridoxal phosphate as a cofactor. The encoded protein can also metabolize threonine to NH4+ and 2-ketobutyrate. The encoded protein is found predominantly in the liver. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10993; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; L-serine ammonia-lyase activity [GO:0003941]; L-threonine ammonia-lyase activity [GO:0004794]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; isoleucine biosynthetic process [GO:0009097]; L-serine catabolic process [GO:0006565]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; pyruvate biosynthetic process [GO:0042866]; threonine catabolic process [GO:0006567] |
18289528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23112234_S84A serine racemase mutant behaved like serine dehydratase, whereas A65S serine dehydratase mutant acquired an additional function of using D-serine as a substrate. 28005267_SDS expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing |
ENSMUSG00000029597 |
Sds |
40.551028 |
2.5286360902 |
1.338359 |
0.238934636 |
32.468574 |
0.00000001211356134930189110728716010050368123707187351101310923695564270019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000052356124601960741434940891161908815831793617689982056617736816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.6421775 |
8.5000920 |
22.9342897 |
2.7920734 |
| ENSG00000135127 |
92558 |
BICDL1 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZP65 |
FUNCTION: Component of secretory vesicle machinery in developing neurons that acts as a regulator of neurite outgrowth. Regulates the secretory vesicle transport by controlling the accumulation of Rab6-containing secretory vesicles in the pericentrosomal region restricting anterograde secretory transport during the early phase of neuronal differentiation, thereby inhibiting neuritogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable dynactin binding activity and small GTPase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in Golgi to secretory granule transport; neuron projection development; and vesicle transport along microtubule. Predicted to be located in centrosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92558; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dynactin binding [GO:0034452]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; Golgi to secretory granule transport [GO:0055107]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; vesicle transport along microtubule [GO:0047496] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21555518_CCDC64 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000041609 |
Bicdl1 |
158.298877 |
0.3820935226 |
-1.388002 |
0.152531812 |
82.723020 |
0.00000000000000000009439551047532074397595211266676992228522443882325536975048951848776823680964298546314239501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000825890773334756391979804357582200551798225028831107030063973795108722697477787733078002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
95.2277390 |
9.9658382 |
250.8628870 |
17.7661642 |
| ENSG00000135144 |
1840 |
DTX1 |
protein_coding |
Q86Y01 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a ubiquitin ligase protein in vivo, mediating ubiquitination and promoting degradation of MEKK1, suggesting that it may regulate the Notch pathway via some ubiquitin ligase activity (By similarity). Regulator of Notch signaling, a signaling pathway involved in cell-cell communications that regulates a broad spectrum of cell-fate determinations. Mainly acts as a positive regulator of Notch, but it also acts as a negative regulator, depending on the developmental and cell context. Mediates the antineural activity of Notch, possibly by inhibiting the transcriptional activation mediated by MATCH1. Involved in neurogenesis, lymphogenesis and myogenesis, and may also be involved in MZB (Marginal zone B) cell differentiation. Promotes B-cell development at the expense of T-cell development, suggesting that it can antagonize NOTCH1. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11869684, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9590294}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3-binding;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Studies in Drosophila have identified this gene as encoding a positive regulator of the Notch-signaling pathway. The human gene encodes a protein of unknown function; however, it may play a role in basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1840; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0008593]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
12617994_characterization of two genes expressed in centroblasts of human tonsils: deltex (Drosophila) homolog 1 (DTX1), which is related to the Notch pathway and a new Kelch-like protein, KLHL6 12670957_It is reported that BBAP and the human family of DTX proteins (DTX1, DTX2, and DTX3) function as E3 ligases based on their capacity for self-ubiquitination. 23395680_this study reports the identification of two new hGIP-interacting partners, DTX1 and STAU1. 26894927_Two SNPs (rs2384077 and rs10744794) in an intron of DTX1 and the linkage disequilibrium (LD) block are significantly associated with the immune response to HBV vaccination. 28146432_Data indicate that decreased expression of deltex E3 ubiquitin ligase 1 (DTX1) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors maybe associated with NOTCH pathway activation and increased migration potential. 28183850_Deltex-1 mutations predict poor survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 29374180_DTX1 is an E3 ligase for c-FLIP in gastric cancer cells. 29440432_PI5P4Kgamma positively regulates the DTX1-mediated Notch pathway by promoting receptor recycling 29704870_frameshift mutations in DTX1 and NLRC5, two genes involved in immune regulation, were identified in a family with familial pityriasis rubra pilaris. 31313037_DTX1 rs1732786 single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with lung Cancer. 32700476_Effect of genetic variation in Notch regulator DTX1 on SCLC prognosis compared with the effect on NSCLC prongosis. |
ENSMUSG00000029603 |
Dtx1 |
101.807122 |
4.6479582679 |
2.216597 |
0.430427982 |
24.517629 |
0.00000073633037942679653083149398165585530762200505705550312995910644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002643696521610196362882987466957906974585057469084858894348144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
179.2112159 |
45.7207821 |
38.1255859 |
7.4062301 |
| ENSG00000135299 |
22881 |
ANKRD6 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2G4 |
FUNCTION: Recruits CKI-epsilon to the beta-catenin degradation complex that consists of AXN1 or AXN2 and GSK3-beta and allows efficient phosphorylation of beta-catenin, thereby inhibiting beta-catenin/Tcf signals. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway and positive regulation of JNK cascade. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway. Located in intracellular membrane-bounded organelle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22881; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:2000096] |
19591803_Diversin, containing several nuclear localization signals, translocates to the nucleus, where it interacts with the transcription factor AF9. 22580979_ANKRD6 genetic variants were associated with the muscle size and strength response to resistance training and habitual physical activity levels. 24833088_diversin is overexpressed in human glioma and regulates glioma cell proliferation and invasion, possibly through MMP9 24858714_study demonstrated that diversin was overexpressed in human breast cancers. Diversin could contribute to breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion. 25200652_missense mutations in ANKRD6 are associated with neural tube defects. |
ENSMUSG00000040183 |
Ankrd6 |
148.583399 |
0.4161156830 |
-1.264943 |
0.265594892 |
22.144722 |
0.00000252850200119727351919613964059685429219825891777873039245605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008534344737633604936061226808874380367342382669448852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.2566169 |
17.2736183 |
199.2476702 |
29.7745159 |
| ENSG00000135318 |
4907 |
NT5E |
protein_coding |
P21589 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of nucleotide monophosphates, releasing inorganic phosphate and the corresponding nucleoside, with AMP being the preferred substrate (PubMed:21933152, PubMed:34403084, PubMed:24887587, PubMed:22997138, PubMed:23142347). Shows a preference for ribonucleotide monophosphates over their equivalent deoxyribose forms (PubMed:34403084). Other substrates include IMP, UMP, GMP, CMP, dAMP, dCMP, dTMP, NAD and NMN (PubMed:21933152, PubMed:34403084, PubMed:24887587, PubMed:22997138, PubMed:23142347). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21933152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22997138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23142347, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24887587, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34403084}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Signal;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a plasma membrane protein that catalyzes the conversion of extracellular nucleotides to membrane-permeable nucleosides. The encoded protein is used as a determinant of lymphocyte differentiation. Defects in this gene can lead to the calcification of joints and arteries. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:4907; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 5'-deoxynucleotidase activity [GO:0002953]; 5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0008253]; GMP 5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0050484]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; IMP 5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0050483]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; thymidylate 5'-phosphatase activity [GO:0050340]; XMP 5'-nucleosidase activity [GO:0106411]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; adenosine biosynthetic process [GO:0046086]; ADP catabolic process [GO:0046032]; AMP catabolic process [GO:0006196]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; biomineralization [GO:0110148]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; DNA metabolic process [GO:0006259]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035] |
12000134_Review: Ecto-5'-nucleotidase in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia 12030367_Regulation of ecto-5'-nucleotidase by TNF-alpha in human endothelial cells. 14578500_a critical enzyme responsible for the generation of adenosine 16709165_Review defines glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored 5'-nucleotidase as an extracellular, raft-associated enzyme responsible for conversion of extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into adenosine. 16718268_Expression of ecto-5'-nucleotidase in melanoma correlates with a number of metastasis-related markers and thus may have a function in this process. 16735966_Gliclazide inhibits the activity of lymphocyte ecto-5'-nucleotidase and decreases the concentration of adenosine at the cell surface. 17065075_CD73 is coexpressed with metastasis promoting antigens in human melanoma cells 17487388_CD73 may accelerate the growth of breast cancer by stimulating cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. 17671792_CD73 may facilitate the adhesion, migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells through its enzyme activity of generating adenosine 17911479_CD73 expression on central nervous system (CNS) microvasculature was confirmed with stainings of frozen tissue sections of multiple sclerosis brain samples taken at autopsy 18062933_eN is a novel and specific receptor for tenascin C 18566412_inhibition of TRAIL signaling works through interaction of CD73 with death receptor 5, as CD73 and death receptor 5 could be coimmunoprecipitated and were shown to be colocalized in the plasma membrane by confocal microscopy 18636315_Ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 may regulate the extracellular adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine levels. 18787389_Data show that in varicocele patients, 5'-nucleotidase activity is decreased in seminal plasma and spermatozoa. 18924612_PMNs facilitate translocation across human epithelium and alter fluid homeostasis via epithelial cell-expressed NT5E. 19008478_CD73 plays a critical role by suppressing transendothelial leukocyte trafficking through its enzymatic activity and mitigates inflammatory and immune sequelae of cardiac transplantation via the adenosine 2B receptor. 19536092_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20392501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20476579_CD73 expression can be modulated within minutes following exposure of HUVEC to lysophosphatidylcholine, and this response may be mediated by PKC 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20874842_CD73 plays an important role in breast cancer growth by affecting cell cycle progression and apoptosis. 21057730_Studies indicate that it remains unclear whether interruption of IFNalphaA and IL-10 signaling in the absence of CD73 activity results from a deficiency of its product adenosine or an accumulation of its substrate nucleotides. 21092450_Abnormal expression of CD(73) in Treg cells may participate in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. 21288095_We identified mutations in NT5E in members of three families with symptomatic arterial and joint calcifications. This gene encodes CD73, which converts AMP to adenosine. 21346249_CD73 is expressed on a subpopulation of afferent lymph vessels but is absent on efferent lymphatics, unlike LYVE-1 and podoplanin, which are expressed on both types of lymphatics. 21638125_the ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73 and ADORA2A appear as possible targets for novel treatments in ovarian cancer 21677139_Exosomes from diverse cancer cell types exhibit potent 5'AMP and ATP phosphohydrolytic activity, partly attributed to exosomally expressed CD73 and CD39, which contribute to extracellular adenosine production. 21732280_MSC migration is controlled by CD73 & CD29, which in turn are regulated by mechanical stimulation of cells 21933152_Sequence and structural analysis of H. influenzae NadN led to the discovery that human CD73 is capable of processing both NAD and NMN, therefore disclosing a possible novel function of human CD73 in systemic NAD metabolism. 21998208_CD73-generated extracellular adenosine activates type 1 purinergic A2A receptors that are constitutively expressed by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and that are further elevated in proliferating neoplastic cells. 22040959_The expression of CD73 is associated with leukemia subtype, differentiation and development. The higher differentiation of leukemia cells, the lower of CD73 expression in myeloid and B lymphoid leukemia. 22184407_Data show that the alterations in the CD39/CD73 adenosinergic machinery and loss of function in ADA-deficient Tregs provide insights into a predisposition to autoimmunity and the underlying mechanisms causing defective peripheral tolerance in ADA-SCID. 22287455_In multivariate Cox regression analysis, overexpression of CD73 was proven to be an independent prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. 22454080_deregulation of NT5E expression in melanoma occurs via epigenetic changes in the NT5E CpG island 22553809_Elevated CD73 expression in breast cancer can predict a good prognosis. However, the actual role of CD73 in cancerogenesis remains unclear and requires further analysis. 22833450_the activity of CD73 to trigger adenosine signaling sustains a chemoresistant phenotype in glioblastoma multiforme cells 23094051_The absence of ecto-5'NT/CD73 in the D283 cell line, a metastatic medulloblastoma phenotype, suggests that high expression levels of this ectonucleotidase could be correlated with a poor prognosis in patients with medulloblastoma. 23122642_Mutations in the underlying disease genes ENPP1, ABCC6, NT5E, and SLC20A2, respectively, lead to arterial media calcification. 23142347_Crystal structures of the dimeric human e5NT reveal an extensive conformational switch between the open and closed forms of the enzyme. 23192044_crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of an open structural conformation of human e5NT are described. 23288168_Coronary vasodilation to adenine nucleotides is associated with endothelial CD73-dependent production of extracellular adenosine that acts as an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. 23315321_SNPs at the 5'-nucleotidase and xanthine oxidase genes influence the risk of noncirrhotic portal hypertension in HIV patients treated with didanosine. 23423261_Isoflurane causes TGF-beta1-dependent induction of renal tubular CD73 and adenosine generation to protect against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury. 23508889_concluded that CD73 can promote endothelial cells forming new vessels in cancer condition, facilitating tumor growth and hematogenous metastasis 23569336_NT5E expression correlates closely with HIF-1alpha expression in gastric carcinoma 23584256_CD73 promotes the production of renal adenosine that is a prominent driver of renal hypertension by enhanced ADORA2B signaling-mediated endothelin-1 induction in a hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha-dependent manner. 23625284_This study demonstrated that the differential CD73 expression around intestinal tuberculosis granuloma indicates that Mycobacterium tuberculosis evades host immunity by recruiting mesenchymal cells with CD73 expression. 23653114_Analyzed the expression of CD73 in prostate cancer tissue using immunohistochemistry staining in 116 tissue specimens. 23729294_CD73 mRNA levels were also dramatically decreased in human liver biopsies from hepatitis C and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients 23737488_The data indicates that glioma-derived CD73 contributes to local adenosine-mediated immunosuppression in synergy with CD39 from infiltrating CD4(+)CD39(+) T lymphocytes in human malignant gliomas. 23880765_CD73 protein as a source of extracellular precursors for sustained NAD+ biosynthesis in FK866-treated tumor cells. 24043462_Our data suggests that human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells can effectively suppress immune responses of the Th17 cells via the CD39-CD73-mediated adenosine-producing pathway 24310606_Immunochemistry and clinicopathological results showed that the expression of NT5E and FcGBP in gallbladder adenocarcinoma is an independent marker for evaluation of the disease progression, clinical biological behaviors and prognosis. 24707115_ecto-nucleotidases CD39 and CD73 are expressed in human endometrial tumors 24798880_CD73 expression in triple negative breast cancer is associated with worse clinical outcomes and increased resistance to anthracycline chemotherapy. 24887587_novel genetic causes of human disease suggest that the syndrome of premature arterial calcification due to NT5E mutations may also involve a novel 'trafficking-opathy'. 25205101_we report that ATP-mediated suppression of IFNgamma production by Th17 cells can be overcome by genetic ablation of CD73 or by using IL1beta instead of TGFbeta to program Th17 cells ex vivo 25298403_Species-specific CD73 regulation, with potential significance to cancer, fibrosis, and other diseases characterized by changes in CD73 expression and function. 25402681_CD73 enhances endothelial barrier function and sprouting in blood but not lymphatic vasculature. 25486201_The Nt5e(-/-) targeted mutant mice recapitulate some, but not all, features of ACDC and serve as a model system to study pharmacologic interventions for ectopic mineralization. 25644539_Expression of NPP1 and 5'-nucleotidase by valve interstitial cells promotes the mineralization of the aortic valve through A2aR and a cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. 25675814_It decompose ATP and produce adenosine, which regulates immunity via adenosine receptor. 25677906_Although upregulated CD73 expression in tumor cells correlates with a poor prognosis in patients with rectal adenocarcinoma, the combination of CD73 expression in malignant epithelial cells and tumor stroma may have a better prognostic value 25770019_these data suggest a possible role for CD73 and A2A in inflammation observed in patients with T2D and obesity mediated via apoptosis. 26040919_rs9444348 heterozygosity is associated with increased risk of post-traumatic epilepsy development after brain injury. 26178434_report on a Chinese family with CALJA and novel compound heterozygous mutations (c.1360G>A (p.Gly454Arg) and c.1387C>T (p.Arg463X)) in NT5E 26226423_role of CD73 and CD39 ectonucleotidases in T cell differentiation 26253870_Our study revealed that CD73 is an independent prognostic factor in prostate cancer. 26258883_CD73 activity from any host cell type is not required for the monocyte/macrophage polarization in the peritoneum towards a pro- or an anti-inflammatory phenotype in vivo 26363007_This study highlights a role for CD73 as a prognostic marker of patient survival and also as a candidate therapeutic target in high-grade serous ovarian cancers. 26629888_The NT5E gene is involved in both intrinsic and acquired resistance to platinum-based drugs in ovarian cancer. [meta-analysis] 26642367_findings reveal that CD73-generated adenosine promotes epithelial integrity and suggest why loss of CD73 in endometrial cancer allows for tumor progression 26691441_CD73 expression was significantly correlated with the invasion into adjacent organs. 26708311_CD73 promotes the growth of human colorectal cancer cells through EGFR and the b-catenin/cyclin D1 signaling pathway. CD73 may be used as a valuable biomarker of colorectal cancer. 26854859_These results provide a finely mapped epitope that can be targeted for selective, potent, and non-competitive inhibition of CD73, as well as establish a strategy for inhibiting enzymes that function in both membrane-bound and soluble states. 26884147_Aim of the present study was to investigate the role of CD73 in glioma blood vessels; results found that the expression of CD73 in glioma vascular cells is significantly decreased, and this reduction may down-regulate the expression of brain microvascular endothelial tight junction-related proteins 27044834_This study aimed to investigate the activities of purinergic system ecto-enzymes present on the platelet surface as well as CD39 and CD73 expressions on platelets of sickle cell anemia treated patients. 27281619_Data show that MiR-422a and its target CD73 are involved in early loco(regional) recurrence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors and are targets for personalized medicine. 27557512_high levels of CD73 are significantly associated with reduced overall survival in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 27650530_Hippocampal astrogliosis observed in medial temporal lobe epilepsy patients was accompanied by a proportionate increase in A2A receptor and ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 immunoreactivities. 27670764_CD73 may play an important role in breast cancer stem cells. 27705752_Endogenous Plastic Somatic (ePS) cells in a latent state, i.e. lacking SOX2, OCT3/4 and NANOG (SON) expression, in non-diseased breast specimens through immunohistochemical analysis of previously identified ePS-specific biomarkers (CD73(+), EpCAM(+) and CD90(-)). 27718302_CD73 and CD86 are the most relevant markers to incorporate in the routine MRD evaluation of BCPALL. 27732656_This study found that in septic critically ill patients the soluble CD73 levels were generally low and showed a further decrease from 0h to 24h. Moreover, the sCD73 levels were higher in acute kidney injury (AKI) versus non-AKI patients and in non-survivors with severe sepsis than in survivors, but were not independently associated either with the development of AKI or 90-day mortal 27899277_concluded that CD39 and CD73 are molecular targets for the development of drugs for ALF patients care 27906615_Genetic polymorphism of NT5E may contribute to the pathogenesis of calcific aortic valve disease. 27906627_Oxidized low density lipoproteins modulate CD39 and CD73 activity in the endothelium. 28060732_Report prognostic impact of CD73 expression in non-small lung cancers. 28158983_CD73 expression is upregulated in NSCLC and is correlated with a decrease in miR-30a-5p expression. 28193736_Down-regulation of CD73 on B cells of patients with viremic HIV correlates with B cell activation and disease progression. 28202050_High CD73 expression is associated with cervical cancer. 28212442_CD73 polymorphisms play a role in calciphylaxis development in dialysis patients. 28389406_this paper shows that simultaneous overexpression of human E5NT and ENTPD1 protects porcine endothelial cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in vitro 28404888_we demonstrated the existence of CSCs in both cultured ccRCC cell line and tissues, and CD73 as a cell-surface biomarker for ccRCC CSC-like cells. 28464916_Studied role of miR-30a in colorectal cancer(CRC). Found miR-30a is downregulated in CRC, and it inhibits cell proliferation in CRC by reducing expression of CD73. 28652244_High CD73 expression is associated with Melanoma Metastasis. 28825389_Case Report: identify novel mutations in the NT5E gene in patient with calcification of joints and arteries. 28916770_While in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic auto-antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) patients (n = 29) CD26 was increased on CD4(+) lymphocytes, CD39 and CD73 were generally reduced on patients' T-cells. 28950987_HPV+ cervical cancer cells express higher levels of CD73 than HPV- cells, and this expression is associated with the production of larger amounts of adenosine, as well as a stronger inhibition of proliferation, activation, and cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells via interaction with A2A adenosine receptor 29047106_High CD73 expression is associated with breast cancer. 29103803_this paper shows that CD73 activity is protective in a mouse model of antiphospholipid antibody-induced miscarriages 29155108_NT5E-targeting miRNAs (miR-30b and miR-340) function as tumor suppressors 29202855_soluble CD73 might be used as serologic prognostic biomarker in patients with metastatic melanoma patients. 29273916_The Ecto-5'nucleotidase, together with alkaline phosphatase, also expressed apically in oviductal epithelium, complete the hydrolysis sequence by dephosphorylating AMP to adenosine. 29278640_Serum CD73 increases following infant cardiopulmonary bypass; low rewarming CD73 is independently associated with increased postoperative support requirements 29305710_Induction of ecto-5'-nucleotidase/CD73 by radiation contributes to the radiosensitivity of T24 urinary bladder cancer cell line. 29367423_High CD73 expression is associated with the increase in the ability of surviving breast cancer cells to evade innate and adaptive immunity. 29377887_analysis of how inhibitors block human CD73 and block efficiently its enzymatic function in the low micromolar range through a non-competitive inhibition mechanism 29514610_High CD73 expression is associated with neoplasms. 29551673_CD73 promotes the expression of stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated genes, implying a regulation of ovarian Cancer-initiating cells function at the transcriptional level. 29663369_High CD73 expression is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 29916747_High expression of NT5E is associated with Prostate Cancer. 30056298_Changes in the local expression and activity of CD39 and CD73 in calcified valves suggest their potential role in calcific aortic valve disease. 30097462_treatment of alpha,beta-methylene adenosine 5'-diphosphate, a potent CD73 specific inhibitor, significantly decreased sickling, hemolysis, multiorgan damage, and disease progression in the murine model of SCD. Taken together, both human and mouse studies reveal a novel molecular mechanism contributing to the pathophysiology of SCD and identify potential therapeutic strategies to treat SCD. 30100409_This study confirmed that the cell surface antigen CD73 is exclusively expressed in human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs)-derived photoreceptors by generating a fluorescent cone rod homeobox (Crx) reporter hiPSC line using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. 30117104_CD73 is an interesting target for glioblastoma treatment and its inhibition may provide new opportunities to improve the treatment of brain tumors. 30184475_NT5E have a role in papillary thyroid carcinoma microenvironment. 30211969_The minimal consensus definition criteria of ex vivo expanded MSCs requires them to be positive for CD73, CD90, and CD105 expression. 30281919_NT5E expression was upregulated in sunitinib-resistant RCC tissues and cells. NT5E downregulation repressed RCC cell proliferation, migration as well as invasion. EMT course and AKT/GSK-3beta signal pathway both in vitro and in vivo in sunitinib environment was suppressed to varying degrees via NT5E inhibition. 30295112_significantly more patients with intestinal tuberculosis express CD73 in their granulomas than those with Crohn's disease 30301599_The autocrine activity of TGF-beta1 and expression of CD73. 30409763_The NT5E and ecto-adenosine deaminase (E-ADA )perform key functions in the modulation of the immune and inflammatory response in Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). 30417547_Our results support that CD73 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis mediated by EGFR. 30548323_1alpha, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 alters ectonucleotidase expression and activity in human cutaneous melanoma cells. 30591485_Spindle-shaped gastric cancer stromal cells expressing CD73, CD90 or CD105 are involved in disease progression, and among them, CD105-positive cells are strongly associated with poor prognosis. 30663116_Physical fitness modulates the expression of CD39 and CD73 on CD4(+) CD25(-) and CD4(+) CD25(+) T cells following high intensity interval exercise. 30664812_Findings uncovered that patients with CD73(+) on tumor cells as well as A2aR(+) on TILs or low CD8(+) TILs exhibited inferior survival. 30676071_CD73-deficient humans present with the complex phenotype of vascular calcification, arteriomegaly and tortuosity, and calcification in small joints. There are differences between the mouse and human systems. Review. 30696359_These results suggest that the interaction of MSCs with CeCa tumor cells in the TME may condition higher TGF-beta1 production to maintain an immunosuppressive status not only through the activity of this cytokine per se but also through its ability to induce CD73 expression in tumor cells and generate an immunosuppressive microenvironment rich in Ado. 30927045_CD73 was upregulated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and correlated with poor prognosis. 30932882_The expression level of serum NT5E increased in patients with colorectal cancer, and closely correlated with the malignant evolution and clinical prognosis of colorectal cancer. NT5E might serve as a serological indicator for molecular diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer clinically. 30954629_The review summarizes available data regarding the complex regulation of CD73 at the neurovascular unit (NVU) during neuroinflammation. [review] 30957676_These evidences provide the basis for translational strategies of immune combination, while CD73 would serve as potential prognostic biomarker in metastatic melanoma. 30971294_Mechanistically, adenosine produced by CD73 binds to adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) and activates Rap1, which recruits P110beta to the plasma membrane and triggers PIP3 production, thereby promoting AKT phosphorylation in HCC cells. 30985656_Pilot study examined 3 candidate genes, ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (ENPP1), ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 6 (ABCC6), and 5'-Nucleotidase Ecto (NT5E) involved in pyrophosphate (PPi) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) metabolism, which may predispose to coronary arterial or valvular calcification; report 4 new genetic variants potentially related to coronary calcification. 30992388_Silencing of Ecto-5'-nucleotidase expression suppressed cell proliferation. 31014364_In contrast to the long recognized immune suppressive effect of CD73-adenosine signaling in tumor tissue, authors made a striking observation that in AML, CD73 expression on CD8 T cells associates with an increased immune response. 31309149_Increased expression of CD73, mediated by the CEBPA-p30 isoform, sustained leukemic growth via the CD73/A2AR axis 31404305_Generation and Function of Non-cell-bound CD73 in Inflammation. 31461341_Cell type- and tissue-specific functions of NT5E have been summarized. (Review) 31652269_Monitoring and characterizing soluble and membrane-bound ectonucleotidases CD73 and CD39. 31770109_CD73 immune checkpoint defines regulatory NK cells within the tumor microenvironment. 31868071_High-Throughput Screening Assays for Cancer Immunotherapy Targets: Ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73. 31873309_CD73 is a specific immunotherapeutic target to improve antitumor immune responses to immune checkpoint therapy in glioblastoma multiforme. 31879272_Upregulation of CD73 Confers Acquired Radioresistance and is Required for Maintaining Irradiation-selected Pancreatic Cancer Cells in a Mesenchymal State. 31980601_Cancer associated fibroblasts-CD73 expression is enhanced via an adenosine-A2B receptor-mediated feedforward circuit triggered by tumor cell death, which enforces the CD73-checkpoint. 32017200_Extracellular adenosine enhances the ability of PMNs to kill Streptococcus pneumoniae by inhibiting IL-10 production. 32024555_CD73 sustained cancer-stem-cell traits by promoting SOX9 expression and stability in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32067282_MicroRNA-30a suppresses self-renewal and tumorigenicity of glioma stem cells by blocking the NT5E-dependent Akt signaling pathway. 32205841_CD73 promotes tumor metastasis by modulating RICS/RhoA signaling and EMT in gastric cancer. 32266820_The expression of CD73 on pathological B-cells is associated with shorter overall survival of patients with CLL. 32289379_The TGF-beta profibrotic cascade targets ecto-5'-nucleotidase gene in proximal tubule epithelial cells and is a traceable marker of progressive diabetic kidney disease. 32345959_Breast cancer-derived exosomes transmit lncRNA SNHG16 to induce CD73+gammadelta1 Treg cells. 32362028_Identification of a regulatory Vdelta1 gamma delta T cell subpopulation expressing CD73 in human breast cancer. 32375544_Dysregulation of FOXO1 (Forkhead Box O1 Protein) Drives Calcification in Arterial Calcification due to Deficiency of CD73 and Is Present in Peripheral Artery Disease. 32401115_Genome-wide identification of lncRNAs and mRNAs differentially expressed in human vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by high phosphorus. 32419582_Host surface ectonucleotidase-CD73 and the opportunistic pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, cross-modulation underlies a new homeostatic mechanism for chronic bacterial survival in human epithelial cells. 32446352_Human platelets express functional ectonucleotidases that restrict platelet activation signaling. 32450615_HIF-1alpha and CD73 expression in cardiac leukocytes correlates with the severity of myocarditis in end-stage Chagas disease patients. 32473077_Highly expressed tumoral emmprin and stromal CD73 predict a poor prognosis for external auditory canal carcinoma. 32522903_NT5E Genetic Mutation Is a Rare But Important Cause of Intermittent Claudication and Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia. 32548862_CD8(+) CD73(+) T cells in the tumor microenvironment of head and neck cancer patients are linked to diminished T cell infiltration and activation in tumor tissue. 32585229_The therapeutic potential of targeting CD73 and CD73-derived adenosine in melanoma. 32590342_Genotype of CDC73 germline mutation determines risk of parathyroid cancer. 32643277_CD73 acts as a prognostic biomarker and promotes progression and immune escape in pancreatic cancer. 32676968_Prognostic impact of CD73 expression and its relationship to PD-L1 in patients with radically treated pancreatic cancer. 32707842_Defining the CD39/CD73 Axis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The CD73(-) Phenotype Identifies Polyfunctional Cytotoxic Lymphocytes. 32777746_Targeting CD73 to augment cancer immunotherapy. 32847938_An IL6-Adenosine Positive Feedback Loop between CD73(+) gammadeltaTregs and CAFs Promotes Tumor Progression in Human Breast Cancer. 32970317_Enhanced migration of breast and lung cancer cells deficient for cN-II and CD73 via COX-2/PGE2/AKT axis regulation. 32970335_CD73 contributes to anti-inflammatory properties of afferent lymphatic endothelial cells in humans and mice. 33037085_PCBP2 Posttranscriptional Modifications Induce Breast Cancer Progression via Upregulation of UFD1 and NT5E. 33177176_Prognostic significance and immune correlates of CD73 expression in renal cell carcinoma. 33222670_Targeting Tumor-derived Exosomes Expressing CD73: New Opportunities in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Cancer. 33268695_Involvement of CD73 and A2B Receptor in Radiation-Induced DNA Damage Response and Cell Migration in Human Glioblastoma A172 Cells. 33416944_CD73 expression defines immune, molecular, and clinicopathological subgroups of lung adenocarcinoma. 33433704_Loss of stromal CD73 expression plays a role in pathogenesis of polypoid endometriosis. 33434633_CD73 and cN-II regulate the cellular response to chemotherapeutic and hypoxic stress in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 33609609_Loss of CD73 shifts transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) from tumor suppressor to promoter in endometrial cancer. 33727591_CD73 facilitates EMT progression and promotes lung metastases in triple-negative breast cancer. 33744914_Multifocal calcific periarthritis with distinctive clinical and radiological features in patients with CD73 deficiency. 33788714_CD73 Is Regulated by the EGFR-ERK Signaling Pathway in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 34019179_CD73 expression in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic thyroid: a systematic evaluation revealing CD73 overexpression as a feature of papillary carcinomas. 34031899_A three-dimensional microenvironment alters CD73 expression in cervical cancer. 34097876_SIRT1-dependent restoration of NAD+ homeostasis after increased extracellular NAD+ exposure. 34265363_Regulation of immune responses through CD39 and CD73 in cancer: Novel checkpoints. 34299260_CD73 Overexpression in Podocytes: A Novel Marker of Podocyte Injury in Human Kidney Disease. 34302921_CD73 induces gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A promising target with non-canonical mechanisms. 34508993_Impact of intratumoural CD73 expression on prognosis and therapeutic response in patients with gastric cancer. 34526098_circHMGCS1-016 reshapes immune environment by sponging miR-1236-3p to regulate CD73 and GAL-8 expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 34610532_Modeling codelivery of CD73 inhibitor and dendritic cell-based vaccines in cancer immunotherapy. 34637682_A novel circular RNA circ_HN1/miR-628-5p/Ecto-5'-nucleotidase competing endogenous RNA network regulates gastric cancer development. 34650224_Therapeutically expanded human regulatory T-cells are super-suppressive due to HIF1A induced expression of CD73. 34741235_Is the regulation by miRNAs of NTPDase1 and ecto-5'-nucleotidase genes involved with the different profiles of breast cancer subtypes? 34831141_Transcriptional and Metabolic Investigation in 5'-Nucleotidase Deficient Cancer Cell Lines. 34961895_Mono-ADP-ribosylation sites of human CD73 inhibit its adenosine-generating enzymatic activity. 35163489_CD73 and PD-L1 as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Gallbladder Cancer. 35199627_Variability in CD39 and CD73 protein levels in uveal melanoma patients. 35235138_NT5E gene and CD38 protein as potential prognostic biomarkers for childhood B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 35273100_Exosomal CD73 from serum of patients with melanoma suppresses lymphocyte functions and is associated with therapy resistance to anti-PD-1 agents. 35325005_Elevated ATP via enhanced miRNA-30b, 30c, and 30e downregulates the expression of CD73 in CD8+ T cells of HIV-infected individuals. 35485681_The Prognostic Role of CD73/A2AR Expression and Tumor Immune Response in Periampullary Carcinoma Subtypes. 35598361_The regulation of CD73 in non-small cell lung cancer. 35622118_Functional expression of CD73 on human natural killer cells. 35657703_CD73 facilitates invadopodia formation and boosts malignancy of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via the MAPK signaling pathway. 35813221_CD73 (NT5E) Promotes the Proliferation and Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma through the EGFR/AKT/mTOR Pathway. 35997119_LncRNA ZFPM2-AS1 Enhances Retinoblastoma Development by Targeting the miR-3612/NT5E Signaling Axis. 36048381_Evaluation of CD39, CD73, HIF-1alpha, and their related miRNAs expression in decidua of preeclampsia cases compared to healthy pregnant women. 36091055_NT5E upregulation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A novel biomarker on cancer-associated fibroblasts for predicting immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. 36131912_Intratumoral CD73: An immune checkpoint shaping an inhibitory tumor microenvironment and implicating poor prognosis in Chinese melanoma cohorts. |
ENSMUSG00000032420 |
Nt5e |
339.674747 |
2.8778934923 |
1.525013 |
0.093331324 |
272.093230 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000039692210441122066898379999685667698441025320072668984596960950951682509462741282902317277935660904973227281611271987405561634433541313314371898566401556177063447705677390331402420997619628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010350830850016991499315987582147976478822838729868614213173514467350166405467556411970908889751560491263035639266112661722663944504043442640076500439044737689187059004325419664382934570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
513.2526156 |
26.9258137 |
179.8022639 |
7.7792266 |
| ENSG00000135338 |
167691 |
LCA5 |
protein_coding |
Q86VQ0 |
FUNCTION: Involved in intraflagellar protein (IFT) transport in photoreceptor cilia. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80ST9}. |
Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Leber congenital amaurosis;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is thought to be involved in centrosomal or ciliary functions. Mutations in this gene cause Leber congenital amaurosis type V. Alternatively spliced transcript variants are described. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:167691; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cilium [GO:0005929]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
16082399_Macular coloboma-type LCA shows genetic heterogeneity and it is not possible to establish a phenotype-genotype correlation with LCA5 and macular coloboma. 17546029_The LCA5 gene on chromosome 6q14 encodes the ciliary protein lebercilin associated with Leber congenital amaurosis type 5. 18000884_Data report the identification of three novel LCA5 mutations (3/3 homozygous) in three families confirming the modest implication of this gene in this series (3/179; 1.7%). 18334959_This is the second report of LCA5 mutations causing Leber congenital amaurosis. 19172513_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19172513_This result shows that mutation in LCA5 is likely to be a rare genetic cause in Koreans 19503738_Leber congenital amaurosis 2 patients with LCA5 mutation had evidence of retained photoreceptors mainly in the central retina; retinal remodeling was present in pericentral regions 19800048_OFD1 is mutated in X-linked Joubert syndrome and interacts with LCA5-encoded lebercilin 21850168_A novel LCA5 mutation is present in a Pakistani family with Leber congenital amaurosis and cataracts. 23946133_Identification of novel LCA5 mutations in patients with Leber congenital amaurosis and retinitis pigmentosa. 24144451_This work reveals a higher frequency of LCA5 mutations in a Spanish Leber congenital amaurosis cohort than in other populations. 27067258_The authors report novel biallelic LCA5 mutations, Ala212Pro and Tyr441Cys, as causing cone dystrophy. |
ENSMUSG00000032258 |
Lca5 |
23.250832 |
0.3540156203 |
-1.498115 |
0.390777277 |
14.891109 |
0.00011389851512939920563129148067815776812494732439517974853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000311149747049774619278572629355039680376648902893066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.2970064 |
3.1545436 |
34.9832032 |
5.7734815 |
| ENSG00000135362 |
79899 |
PRR5L |
protein_coding |
Q6MZQ0 |
FUNCTION: Associates with the mTORC2 complex that regulates cellular processes including survival and organization of the cytoskeleton (PubMed:17461779). Regulates the activity of the mTORC2 complex in a substrate-specific manner preventing for instance the specific phosphorylation of PKCs and thereby controlling cell migration (PubMed:22609986). Plays a role in the stimulation of ZFP36-mediated mRNA decay of several ZFP36-associated mRNAs, such as TNF-alpha and GM-CSF, in response to stress (PubMed:21964062). Required for ZFP36 localization to cytoplasmic stress granule (SG) and P-body (PB) in response to stress (PubMed:21964062). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17461779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21964062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22609986}. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal transduction inhibitor;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in several processes, including TORC2 signaling; positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process; and regulation of fibroblast migration. Part of TORC2 complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79899; |
TORC2 complex [GO:0031932]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; positive regulation of intracellular protein transport [GO:0090316]; positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process [GO:0061014]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010762]; TORC2 signaling [GO:0038203] |
17461779_It was demonstrated that immunoprecipitation of Protor-1 or Protor-2 results in the co-immunoprecipitation of other mTORC2 subunits, but not Raptor, a specific component of mTORC1. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21964062_Protor-2 associates with tristetraprolin (TTP) to accelerate TTP-mediated mRNA turnover and functionally links the control of TTP-regulated mRNA stability to mTORC2 activity |
ENSMUSG00000032841 |
Prr5l |
376.466530 |
0.3876992860 |
-1.366990 |
0.179475879 |
55.760301 |
0.00000000000008186818795023406643952085048790879253017595262864603000707575120031833648681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000522653310616546190036682937455698771999149099265480344911338761448860168457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
196.7922369 |
37.6640575 |
515.8159465 |
70.7417012 |
| ENSG00000135363 |
4005 |
LMO2 |
protein_coding |
P25791 |
FUNCTION: Acts with TAL1/SCL to regulate red blood cell development. Also acts with LDB1 to maintain erythroid precursors in an immature state. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc |
|
LMO2 encodes a cysteine-rich, two LIM-domain protein that is required for yolk sac erythropoiesis. The LMO2 protein has a central and crucial role in hematopoietic development and is highly conserved. The LMO2 transcription start site is located approximately 25 kb downstream from the 11p13 T-cell translocation cluster (11p13 ttc), where a number T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia-specific translocations occur. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:4005; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0097067]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944] |
15541480_Negative regulatory elements are present in the human LMO2 oncogene and may contribute to its expression in leukemia. 16793212_Therapies directed against LMO2 may be important for treatment of hemangioma because of hemangioma's limited localization and the fact that LMO2-associated protein complexes could regulate angiogenesis. 16873670_identification of a new recurrent and cryptic deletion on chromosome 11 (del(11)(p12p13)) in about 4% (6/138) of pediatric T-ALL patients that activates the LMO2 oncogene in 4 of 6 del(11)(p12p13)-positive T-ALL patients 17038524_LMO2 protein is expressed in normal germinal-center (GC) B cells and GC-derived B-cell lines and in a subset of GC-derived B-cell lymphomas, also in erythroid and myeloid precursors, megakaryocytes, and in lymphoblastic and acute myeloid leukemias. 17268520_LMO2 is most highly transcribed in CD34+ progenitor cells. Upon stimulation with growth factors typically used in gene therapy protocols transcription of LMO2. 17360939_critical role for the exact breakpoint location in determining LMO2 activation levels and the consequent pressure for T-ALL development. 17878155_the SCL-LMO2 interaction couples protein stabilization with higher order protein complex assembly, thus providing a powerful means of modulating the stoichiometry and spatiotemporal activity of SCL complexes 17910069_characterize the assembly of a five-component complex containing TAL1, LMO2, Ldb1, E12, and DNA. The bHLH domains of TAL1 and E12 alone primarily formed helical homodimers, but together formed heterodimers, to which LMO2 bound with high affinity 17964543_Both LMO2 and LMO4 interacted strongly to LDB1, which was required for their localization to the nucleus. 17972953_LMO2 associated with the endogenous human miR-142 promoter; LMO2 appeared to play a pivotal function in negatively regulating the expression of miR-142. 18079736_biallelic activation of LMO2 in immature T-ALL cases may reflect their early T-cell development stage rather than it represents a true oncogenic mechanism. 18187418_LMO2, TAL1, Ttg-1, and SIL support levels of V(D)J recombination above background levels in cell culture and are also cleaved by the RAG proteins, while Hox11 and SCL are nicked but not cleaved efficiently in vitro 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18844071_LMO2-C can bind endogenous GATA1 and LDB1 protein in K562 cells and downregulate the expression of hematopoietic specific gene glycoprotein. 19047678_GC-enriched hsa-miR-125b down-regulates the expression of IRF4 and PRDM1/BLIMP1, and memory B cell-enriched hsa-miR-223 down-regulates the expression of LMO2. 19141387_The restricted expression pattern, nuclear localization, and crisp staining of LMO2 in paraffin blocks make it an attractive candidate for the diagnostic immunohistochemistry laboratory. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19278969_decline of miR-223 is an important event for erythroid differentiation that leads to the expansion of erythroblast cells at least partially mediated by unblocking LMO2 protein expression 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336746_LMO2 is regulated at both a posttranscriptional and post-translational level in erythroid progenitors during erythropoiesis.[review] 19487290_Lmo2 is, therefore, required for sustained T-cell tumor growth, in addition to its preleukemic effect. 19568416_LMO2 is a promising marker for predicting a better prognosis in pancreatic cancer. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19635185_LMO2 protein expression is correlated with improved hematologic remission and overall survival in the CML patients treated with IM. 19671288_The abnormal expression and protein interaction of LMO2 and LYL1 may play a role in the abnormal proliferation and differentiation of myeloid hematopoietic cells. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20346173_Homo-binding character of LMO2 isoforms and their synergic and antagonistic functions regulate hematopoietic-related target genes. 20519628_E2A-HLF promotes cell survival of t(17;19)- acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by aberrantly up-regulating LMO2 expression 20557670_We report that LMO2 protein is expressed in a significant proportion of B-ALL and AML and the staining of LMO2 protein does not predict survival in acute leukemia. 20660332_The findings suggest LMO2 as a potential marker for the germinal center B-cell phenotype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 20676125_a self-sustaining triad of LMO2/ERG/FLI1 stabilizes the expression of important mediators of the leukaemic phenotype such as HHEX/PRH. 20686118_Overexpression of either KLF1 or LMO2 partially rescued the defect in erythropoiesis caused by c-myb silencing, whereas only KLF1 was also able to repress the megakaryocyte differentiation enhanced in Myb-silenced CD34+ cells. 20697248_Our results show that HGAL and LMO2 are sensitive markers for follicular lymphoma diagnosis. 20731704_ectopically expressed LMO2 impaired the function of DeltaEF1 in both transcriptional and protein levels and identified DeltaEF1 as a novel pathogenic target of LMO2 in T-cell leukemia. 20955387_LMO2 probably promotes angiogenesis by up-regulation of bFGF expression and thereby consequently influences progression of infantile haemangiomas 21045296_Multiple-wavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD) data have been collected at the zinc X-ray absorption edge to a resolution of 2.8 A and the data were used to solve the structure of the LMO2:Ldb1-LIM-interaction domain complex. 21059912_As LMO2 controls hematopoiesis, its dysregulation is leukemogenic 21072044_both Lmo2 and Bcl-2 are required for the action of E2A-HLF in leukemogenesis 21076045_first structural model of the DNA-binding complex containing LMO2, LDB1, SCL/TAL1, and GATA-1 21375434_SStudies suggest that the expression of LMO2 protein in lymphoma tissue biopsies predicts survival in patients with RA who have developed DLBCL 21459790_B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cases expressed variable levels of LMO2 depending on immunophenotypical and cytogenetic features 21502424_LMO2 is sensitive and specific marker for detecting follicular lymphoma in nodal and extranodal sites 21670469_The measurement of a single gene expressed by tumor cells (LMO2) and a single gene expressed by the immune microenvironment (TNFRSF9) powerfully predicts overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 21722313_Data suggest that both HGAL and LMO2 are directly regulated by the transcription repressor PRDM1--overexpression of PRDM1 down-regulates HGAL and LMO2; PRDM1 directly binds to promoters of both HGAL and LMO2 and represses genetic transcription. 22066713_Germline genetic variation in LMO2 was associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma prognosis and provided slightly stronger predictive ability relative to LMO2 immunohistochemistry status. 22394247_The new anti-LMO2 antibody can be applied confidently to routine sections, contributing to the differential diagnosis of several lymphoma subtypes, subtyping of DLBCLs and potential development of innovative therapies. 22517897_Overexpression of LMO2 in diffuse large B-cell (DLBCL) cell lines results in centrosome amplification. 22615488_evidence that the H3K9-me1/2 demethylase KDM3B might play a role in leukemogenesis via activation of lmo2 through interdependent actions with the histone acetyltransferase complex containing CBP 22776842_LMO2 expression is a special feature of germinal center diffuse large B cell lymphomas. 22914613_HGAL and LMO2 may be useful adjuncts in the identification of follicular lymphoma of the nongastric gastrointestinal tract. 23327922_Transcriptional regulators cooperate to establish or maintain primitive stem cell-like signatures in leukemic cells. 23708655_a regulatory hierarchy of HOX control of LMO2 in normal development 23812588_In t(8;21) leukemia cells, LMO2 functions as a component of the stable AML1-ETO-containing transcription factor complex (AETFC). The AETFC components cooperatively regulate gene expression and contribute to leukemogenesis. 23892628_GATA2 and Lmo2 cooperatively regulate VEGF-induced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis via NRP2. 23897248_Staining for LMO2 in addition to CD10 and BCL6 facilitates the detection of a germinal center phenotype in follicular lymphoma 24330148_LMO2 is expressed in a subset of acute myeloid leukaemia patients and is associated with normal karyotype, which is different from T lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukaemia, where specific translocation (11p13) mediates protein expression. 24465765_HHEX is a direct transcriptional target of LMO2 consistent with its concordant gene expression. 25203428_Diagnostic Utility of the Germinal Center-associated Markers GCET1, HGAL, and LMO2 in Hematolymphoid Neoplasms. 25499232_results suggest that E47 has diverse effects in T-ALL but that functional deficiency of E47 is not a universal feature of Lmo2-induced T-ALL. 25682596_Cryptic chromosomal rearrangements in the LMO2 gene were associated with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 25710580_that suppression of MIR223 expression, as compared with controls, is associated with lack of differentiation and adverse cytogenetic profile, but unrelated with LMO2 protein expression or overall survival. 25721045_LMO2 expression was elevated in GBM tissues and inversely correlated with prognosis of GBM patients. Taken together, our findings describe novel dual roles of LMO2 to induce tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. 26161748_Data show that the Lim domain only 2 (LMO2) regulatory element (element-25) region consists of transcription factor GATA2-binding myeloid ennhancer and RUNX protein-binding T-cell repressor. 26383528_LMO2 was associated with increased levels of cytosolic p27(Kip1) protein. 26598604_Alanine scanning mutagenesis of the LIM interaction domain of LDB1 revealed a discrete motif, R(320)LITR, required for LMO2 binding. 26686090_FOXP3 binds LMO2 in vitro, resulting in decreased interaction between LMO2 and TAL1, providing a molecular mechanism for FOXP3-mediated transcriptional modulation in T-ALL. 26764384_This article demonstrates a novel and unexpected function of the LMO2 oncogenic transcription factor in controlling DNA replication that we unravelled via an unbiased proteome-wide screen for LMO2-interacting partners. 26796495_LMO2 is a useful marker for immunophenotypic assessment of thymic neoplasms. 27028859_stromal LMO2 may be responsible for zonal characteristic of Prostate cancer 27302866_we demonstrate previously unrecognized mechanisms by which LMO2 alters human T-cell development in vivo; these mechanisms correlate with human T-ALL leukemogenesis. 27569286_this study revealed a novel function of LMO2 involving in the regulatory hierarchy of UBA6-USE1-FAT10ylation pathway by targeting the E1 enzyme UBA6. 27779255_the data in this study revealed a novel crosstalk between LMO2 and the Wnt signaling pathway during tumorigenesis and suggested that LMO2 might be a tumor suppressor in certain solid tumors. 27792641_The transcriptional factor LMO2 regulates endothelial proliferation and angiogenesis in vitro. 27880729_LMO2 has a predominantly cytoplasmic location in breast cancer cells. LMO2 interaction with cofilin1 regulates actin cytoskeleton dynamics, promoting tumor cell invasion and metastasis. 28170369_Data indicate a novel functional mechanism of LMO2 in facilitating the delivery of actin monomers to the branched microfilament and increasing lamellipodia/filopodia formation in basal-type breast cancer cells. 28270453_recurrent activating intronic mutations of LMO2, a prominent oncogene in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Heterozygous mutations were identified in PF-382 and DU.528 T-ALL cell lines in addition to 3.7% of pediatric (6 of 160) and 5.5% of adult (9 of 163) T-ALL patient samples. 28288039_Findings suggest that LMO2 loss may be a good predictor for the presence of MYC translocation in large B-cell lymphoma. 29278703_These data indicate that Lhx2 is capable of blocking proliferation of T-ALL-derived cells by both LMO2-dependent and -independent means. We propose Lhx2 as a new molecular tool for anti-T-ALL drug development. 30320491_Our findings reveal a previously unidentified mechanism, by which PML-RARalpha interferes with erythropoiesis through directly targeting and transrepressing LMO2 expression in the development of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). 30419549_these data helped drawing a roughly dynamic LMO2 regulatory procedure during hematopoiesis, suggested diversified transcriptional regulation patterns of LMO2 in different hematopoietic lineages and could partially explain the lineage-specific, differentially functional performance of LMO2 in hematopoietic system. 30679322_our data suggest that Zeb2 and Lmo2 drive malignant transformation of immature T-cell progenitors via distinct molecular mechanisms. 31304537_Study presents genetic evidence that the development of Wilms tumors in WAGR syndrome patients should be attributed to the deletion of WT1 and LMO2 rather than WT1 only. 31366618_Lysine deacetylation of LMO2 is essential for the LDB1 interaction and transcriptional activity of the TAL1 complex. 31447348_Study demonstrates that in diffuse large B cell lymphomas LMO2 controls DNA double-strand break (DSB) pathway choice, resulting in homologous recombination dysfunction and tumor cell sensitization to genotoxic agents that could be further enhanced with PARP1/2 inhibitors. Mechanistically, LMO2 inhibits BRCA1 recruitment to DSBs by interacting with 53BP1 during repair. 32713935_Biochemical Feature of LMO2 Interactome and LMO2 Function Prospect. 32910224_FGF primes angioblast formation by inducing ETV2 and LMO2 via FGFR1/BRAF/MEK/ERK. 33503448_LMO2 upregulation due to AR deactivation in cancer-associated fibroblasts induces non-cell-autonomous growth of prostate cancer after androgen deprivation. 33811533_Lack of expression of LMO2 clone SP51 identifies MYC rearrangements in aggressive large B-cell lymphomas. 33988072_Low LIM-domain only 2 (LMO2) expression in aggressive B cell lymphoma correlates with MYC and MYC/BCL2 rearrangements, especially in germinal center cell-type tumors. 34077008_MiR-223 Suppresses Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cells Through Lmo2 and MAPK Signaling Pathway. 35094691_Identification of LMO2 as a new marker for acinic cell carcinoma of salivary gland. 35286869_LMO2 plays differential roles in trophoblast subtypes and is associated with preeclampsia. 35322192_LMO2 expression is frequent in T-lymphoblastic leukemia and correlates with survival, regardless of T-cell stage. |
ENSMUSG00000032698 |
Lmo2 |
672.411394 |
0.2106290114 |
-2.247224 |
0.074325312 |
963.684061 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014066568211367637175566745533884873929991507221744739239700701583526208687245011616731175454412502507313939090594625079 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014220722383547009029922674450809862745449225460277919131711986938686791900509569838349623247244109988146225438788721753 |
Yes |
Yes |
234.4224026 |
11.9189598 |
1120.9437349 |
34.1894941 |
| ENSG00000135378 |
79056 |
PRRG4 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZD6 |
FUNCTION: May control axon guidance across the CNS (PubMed:28859078). Prevents the delivery of ROBO1 at the cell surface and down-regulates its expression (PubMed:28859078). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28859078}. |
Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Gamma-carboxyglutamic acid;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables WW domain binding activity. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79056; |
endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; WW domain binding [GO:0050699] |
23873930_Cellular localization and characterization of cytosolic binding partners for Gla domain-containing proteins PRRG4 and PRRG2. 24357251_the unique genotype identified in this study suggested that haploinsufficiencies of PAX6 or PRRG4 included in this region are candidate genes for severe developmental delay and autistic features characteristic of WAGR syndrome. 28859078_PRRG4 could re-localize hRobo1 from the cell surface, suggesting that PRRG4 is a functional homologue of Comm. Comm is required for axon guidance and synapse formation in the fly, so PRRG4 could contribute to the autistic symptoms of WAGR by disturbing either of these processes in the developing human brain. 33037408_PRRG4 promotes breast cancer metastasis through the recruitment of NEDD4 and downregulation of Robo1. |
ENSMUSG00000027171 |
Prrg4 |
45.397030 |
0.3887006234 |
-1.363269 |
0.372697146 |
13.133727 |
0.00029002729000710133436952142815812294429633766412734985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000741649826837286071067045778448800774640403687953948974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.7766081 |
6.5727688 |
61.4893903 |
11.9400963 |
| ENSG00000135404 |
967 |
CD63 |
protein_coding |
P08962 |
FUNCTION: Functions as cell surface receptor for TIMP1 and plays a role in the activation of cellular signaling cascades. Plays a role in the activation of ITGB1 and integrin signaling, leading to the activation of AKT, FAK/PTK2 and MAP kinases. Promotes cell survival, reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, spreading and migration, via its role in the activation of AKT and FAK/PTK2. Plays a role in VEGFA signaling via its role in regulating the internalization of KDR/VEGFR2. Plays a role in intracellular vesicular transport processes, and is required for normal trafficking of the PMEL luminal domain that is essential for the development and maturation of melanocytes. Plays a role in the adhesion of leukocytes onto endothelial cells via its role in the regulation of SELP trafficking. May play a role in mast cell degranulation in response to Ms4a2/FceRI stimulation, but not in mast cell degranulation in response to other stimuli. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16917503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21803846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21962903, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23632027, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24635319}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Palmitate;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Secreted;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. The encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein that is known to complex with integrins. It may function as a blood platelet activation marker. Deficiency of this protein is associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Also this gene has been associated with tumor progression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:967; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; endosome lumen [GO:0031904]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; multivesicular body membrane [GO:0032585]; multivesicular body, internal vesicle [GO:0097487]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet dense granule membrane [GO:0031088]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; endosome to melanosome transport [GO:0035646]; pigment granule maturation [GO:0048757]; positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2001046]; positive regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002092]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901379]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900746] |
11907283_Results show that AP-3 is absolutely required for the delivery of CD63 to lysosomes via the trans-Golgi network. 12036870_C-kit is physically associated with transmembrane 4 superfamily proteins CD9, CD63, and CD81, that may negatively modulate c-kit and thus regulate c-kit receptor sensitivity to SLF in hematopoietic progenitors. 12579280_downregulation of CD63 antigen is associated with breast tumor progression 12610138_possible role in HIV-1 infections specific for macrophages 12755696_Post-translational modification of CD63 may be involved in the functional and morphological changes of MHC class II compartments that occur during dendritic cell maturation 12826159_relationships between the expression levels of CD61, CD63, and PAC-1 on the platelet surface and the incidences of acute rejection and tubular necrosis as well as the recovery of graft function after renal transplantation 12871315_Upon platelet interaction with fibrinogen, cholesterol accumulated at the tips of filopodia and at the leading edge of spreading cells; cholesterol-rich raft aggregation was accompanied by concentration of c-Src and CD63 in these cell domains 12974720_The study on CD63 included its chemistry eg. if it had and O-linked carbohydrate that was digested with O-glycanase. 14660791_CD63 serves as an adaptor protein that links its interaction partners to the endocytic machinery of the cell. 15130945_results suggest that CD9, CD63, CD81, and CD82 could play a role in modulating the interactions between immature DCs and their environment, slowing their migratory ability. However, only CD63 would intervene in the internalization of complex antigens 15375577_Constitutive expression of CD63 may indicate that this factor does not play a direct role in thyroid carcinogenesis 15528334_CD63 represents an activation-induced reinforcing element, whose triggering promotes sustained and efficient T cell activation and expansion. 15711748_The linkage of CD63 with PI 4-kinase may result in the recruitment of this signaling enzyme to specific membrane locations in the platelet where it influences phosphoinositide-dependent signaling and platelet spreading. 16410552_This study identifies a trafficking pathway from CD63-positive multivesicular bodies to the bacterial inclusion, a novel interaction that provides essential lipids necessary for maintenance of a productive intracellular infection. 16683915_CD63 is recruited to already-budded Weibel-Palade bodies by an AP-3-dependent route 16908530_CD63-syntenin-1 complex is abundant on the plasma membrane 16917503_CD63 is a cell surface binding partner for TIMP-1, regulating cell survival and polarization via TIMP-1 modulation of tetraspanin/integrin signaling complex. 16918509_Chronic urticaria serum-induced CD63 expression assay performed on atopic whole blood by means of tricolor flow cytometry could be the most useful tool for identification of a subset of patients with autoimmune chronic urticaria. 17275019_In conclusion, using well-defined experimental conditions, the measurement of CD203c up-regulation on basophils in response to specific allergens is as reliable as CD63-BAT for the in vitro diagnosis of patients with IgE-mediated allergy. 17279322_positive correlation between CD63 and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in rheumatoid arthritis 17350713_Results suggest that CD63 can be a biomarker for predicting the prognosis in early stages of lung adenocarcinoma. 17390088_These results suggest that chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients have different patterns of CD63 expression and polymorphonuclear neutrophils mediator release than healthy individuals. 17522207_Data show that HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env) and core protein (Gag) colocalize strongly with CD63 and CD81 and less strongly with CD9, and suggest that HIV-1 promotes virus assembly and cell-cell transfer by targeting these plasma membrane proteins. 17624082_There is low expression of the proteins and mRNA of ME491/CD63 and integrin alpha5 in ovarian cancer. The lower the pathological differentiation is, the more significant the loss of expression is and the more likely metastasis is. 17827389_PrP(c) at the cell surface of cultured human erythroblasts is rapidly internalized through the endosomal pathway, where it colocalizes with the tetraspanin CD63. 18182005_Data show that an N-terminal deletion mutant of CD63 blocks entry of CXCR4-using, T-cell tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (X4 HIV-1) by suppressing CXCR4 surface expression. 18211905_CD63 plays a role in the regulation of ROMK channels through its association with RPTPalpha, which in turn interacts with and activates Src family PTK, thus reducing ROMK activity. 18321974_Together, our results indicate that at least in tissue culture, CD63 expression is not required for either the production or the infectivity of HIV-1. 18426873_These studies confirm CD63 as a constituent in multivesicular body-to-chlamydial inclusion transport but it is not required for this association. 18600034_Induction of hypercortisolism in healthy volunteers was associated with a trend toward higher expression of glycoprotein 53 on the platelet surface. 18669870_CD63 is involved in granule targeting of neutrophil elastase 18727065_Antigen-induced p38 MAPK phosphorylation in human basophils essentially contributes to CD63 upregulation 19079288_the activation-induced degranulation of Fas ligand has distinct requirements and involves different mechanisms than those of the granule markers CD63 and CD107a/Lamp-1 19381331_Exotest for CD63+ plasma exosomes had limited sensitivity but the Exotest for detection of caveolin-1+ plasma exosomes showed a higher sensitivity. Caveolin-1+ plasma exosomes were significantly increased with respect to CD63+ exosomes in patients group 19458002_CD9, CD81 and CD63 are negative regulators of HIV-1-induced cell-cell fusion. 19581020_Serum sCD163 is a homogenous protein covering more than 94% of the CD163 ectodomain including the haptoglobin-hemoglobin -binding region. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20337613_Surface expression of the novel CD63 variant is a distinguishing feature of mast cells, which are are stable, multiple-use cells capable of surviving and delivering several consecutive hits 20633031_CD63 expression results from only the anaphylactic degranulation form of histamine release. 20693981_this work provides the first evidence of a TIMP-4/CD63 association in astrocytoma tumor cells 21149578_ameloblastin is expressed in osteoblasts and functions as a promoting factor for osteogenic differentiation via a novel pathway through the interaction between CD63 and integrin beta1 21315401_These findings suggest that CD63 plays an early post-entry role prior to or at the reverse transcription step. 21521534_decreased levels of CD63 were associated with distant and lymph node metastasis status and does play a direct role in human gastric carcinogenesis. 21527913_C-terminal modifications that retain LMP1 in Golgi compartments preclude assembly within CD63-enriched domains and/or exosomal discharge leading to NF-kappaB overstimulation. 21660937_shRNA knockdown in B lymphoblastoid cell line results to increased CD4(+) T-cell recognition 21803846_Loss of CD63 has a similar phenotype to loss of P-selectin itself, thus CD63 is an essential cofactor to P-selectin. 23522389_Timp1 is assembled in a supramolecular complex containing CD63 and beta1-integrins along melanoma genesis and confers anoikis resistance by activating PI3-K signaling pathway. 24507450_Collectively, these findings indicate that CD63 may support Env-mediated fusion as well as a late (post-integration) step in the HIV-1 replication cycle. 24608085_CD9 and CD63 tetraspanins block HIV-1-induced cell-cell fusion at the transition from hemifusion to pore opening. 24635319_Data suggest that TIMP1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1) acts as chemoattractant for neural stem cells (NSC); TIMP1 enhances NSC adhesion, migration, and cytoskeletal reorganization; these effects are dependent on CD63/CD29 (integrin beta1). 24884960_these results indicated that high glycosylation of CD63 by RPN2 is implicated in clinical outcomes in breast cancer patients 24940653_CD63 tetraspanin is a negative driver of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human melanoma cells. 25033048_TM4SF5 interacted with CD151, and caused the internalization of CD63 from the cell surface. 25297946_Diesel exhaust exposure during exercise induces platelet activation as illustrated by a dose-response increase in the release of CD62P and CD63. 25354204_Data show that CD63 is a crucial player in the regulation of the tumor cell-intrinsic metastatic potential by affecting cell plasticity. 25658293_It was shown that treatment of macrophages with anti-CD63 inhibits CCR5-mediated virus infection in a cell type-specific manner, but that no inhibition of CXCR4-tropic viruses occurs. 26001794_Our findings reveal that elevated levels of TIMP-1 impact on neutrophil homeostasis via signaling through CD63. 26213230_These findings indicate that rhTIMP-1 promotes clonogenic expansion and survival in human progenitors via the activation of the CD63/PI3K/pAkt signaling pathway 26242181_CD163(+) TAMs in oral premalignant lesions coexpress CD163 and STAT1, suggesting that the TAMs in oral premalignant lesions possess an M1 phenotype in a Th1-dominated micromilieu. 26988336_Concentrations of Cd63 were elevated in gingival crevicular fluid of patients with pre-eclampsia. 27443953_CD63 and exosome expression is altered in scleroderma dermal fibroblasts 27506299_TIMP1 signaling via CD63 leads to activation of hepatic stellate cells, which create an environment in the liver that increases its susceptibility to pancreatic tumor cells. 27578500_our results identify the CD63-syntenin-1-ALIX complex as a key regulatory component in post-endocytic HPV trafficking. 27974566_CD63 is a critical player in LMP1 exosomal trafficking and LMP1-mediated enhancement of exosome production and may play further roles in limiting downstream LMP1 signaling. 28566689_Signaling focal contacts via CD63 were identified to facilitate cell adhesion, migration and mediate extracellular matrix-physical cues to modulate hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells function. 28609367_Exosomal markers CD63 and CD9 are elevated in pancreatic tumor tissues. 29208635_Human CD63-GFP expression was controlled under the rat Sox2 promoter (Sox2/human CD63-GFP), and it was expressed in undifferentiated fetal brains. 29330012_Basophil testing with CD63 in pollen-sensitized patients. 30288810_Updates on the surface antigens of basophils: CD16 on basophils of patients with respiratory or insect venom allergy and the rejection of CD203c and CD63 externalization decoupling by bisindolylmaleimides. 30352458_findings suggest that the CD63 gene may be involved in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, since they participate in mechanisms such as inhibition of apoptosis, angiogenesis and cell proliferation, which lead to the loss of cell homeostasis in the ectopic endometrium, thus contributing to the implantation and survival of the tissue in the extrauterine environment 30355691_Data indicate that CD63 negatively impacts HSV-1 infection and that the CD63-positive extracellular vesicles (EVs) could control the dissemination of the virus in the host. Perhaps EV release by HSV-1-infected cells is a mechanism that controls virus dissemination. 30367559_Our results offer a new transcriptome landscape of platinum-resistance that provides valuable insights into chemosensitivity and drug resistance in cancers, and we identify a novel platinum resistance gene, COX7B, and a surrogate marker, CD63. 31536880_Anti-CD63 mAb induces IL-10 secretion by monocytes, which later play a role in T-cell hypo-responsiveness. 31820861_Low CD63 expression might be an unfavourable prognostic factor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer 31957842_Occurrence and development of diabetic nephropathy caused by CD63 by inhibiting Wnt-beta-catenin signaling pathway. 32073129_Tetraspanin CD63 independently predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. 32311306_Generation of the Rat Monoclonal Antibody Against the Extracellular Domain of Human CD63 by DNA Immunization. 32463402_Sequential deletion of CD63 identifies topologically distinct scaffolds for surface engineering of exosomes in living human cells. 32535702_HPV caught in the tetraspanin web? 32871743_Prognostic Value of CD63 Expression in Solid Tumors: A Meta-analysis of the Literature. 33204025_A fusion of CD63-BCAR4 identified in lung adenocarcinoma promotes tumorigenicity and metastasis. 33277798_CD63 negatively regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development through suppression of inflammatory cytokine-induced STAT3 activation. 33345458_Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles are increased in sera of Alzheimer's disease patients, as revealed by Tim4-based assays. 33669497_Resistance Training Diminishes the Expression of Exosome CD63 Protein without Modification of Plasma miR-146a-5p and cfDNA in the Elderly. 33674191_Activated steady status and distinctive FcepsilonRI-mediated responsiveness in basophils of atopic dermatitis. 33920772_Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 Modulates the CD63 Interactome. 33976357_The large extracellular loop of CD63 interacts with gp41 of HIV-1 and is essential for establishing the virological synapse. 34051511_CD63 expression in metastatic melanoma and melanocytic nevi in lymph nodes. 34265052_CD63 is regulated by iron via the IRE-IRP system and is important for ferritin secretion by extracellular vesicles. 34282141_Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9. 34407412_CD63-mediated cloaking of VEGF in small extracellular vesicles contributes to anti-VEGF therapy resistance. 34685701_Regulation of Tumor Metabolism and Extracellular Acidosis by the TIMP-10-CD63 Axis in Breast Carcinoma. 35046480_A potential target gene CD63 for different degrees of intervertebral disc degeneration. 35350978_CD63-positive extracellular vesicles are potential diagnostic biomarkers of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 35787446_Aberrant TIMP-1 overexpression in tumor-associated fibroblasts drives tumor progression through CD63 in lung adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000025351 |
Cd63 |
4765.982774 |
2.0930226200 |
1.065588 |
0.023206086 |
2132.155718 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6548.4385723 |
147.1790555 |
3151.4959281 |
53.2522460 |
| ENSG00000135407 |
10677 |
AVIL |
protein_coding |
O75366 |
FUNCTION: Ca(2+)-regulated actin-binding protein which plays an important role in actin bundling (PubMed:29058690). May have a unique function in the morphogenesis of neuronal cells which form ganglia. Required for SREC1-mediated regulation of neurite-like outgrowth. Plays a role in regenerative sensory axon outgrowth and remodeling processes after peripheral injury in neonates. Involved in the formation of long fine actin-containing filopodia-like structures in fibroblast. Plays a role in ciliogenesis. In podocytes, controls lamellipodia formation through the regulation of EGF-induced diacylglycerol generation by PLCE1 and ARP2/3 complex assembly (PubMed:29058690). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20393563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29058690}. |
3D-structure;Actin capping;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell junction;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the gelsolin/villin family of actin regulatory proteins. This protein has structural similarity to villin. It binds actin and may play a role in the development of neuronal cells that form ganglia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10677; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; actin filament [GO:0005884]; axon [GO:0030424]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; Arp2/3 complex binding [GO:0071933]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; actin filament severing [GO:0051014]; actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008154]; barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:0051016]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly [GO:0010592]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of diacylglycerol biosynthetic process [GO:1900480] |
15096633_NMR structure of the C-terminal headpiece subdomains of advillin. Evaluation of F-actin-binding requirements. 18022635_Predicting the effect of a point mutation on a protein fold: the villin and advillin headpieces and their Pro62Ala mutants. 29058690_podocyte migration rate was increased by overexpression of WT Avil or PLCE1, or by EGF stimulation; however, this increased PMR was ameliorated by inhibition of the ARP2/3 complex, indicating that ARP-dependent lamellipodia formation occurs downstream of AVIL and PLCE1 function. 32651364_A cytoskeleton regulator AVIL drives tumorigenesis in glioblastoma. 34948433_Targeting AVIL, a New Cytoskeleton Regulator in Glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000025432 |
Avil |
23.791744 |
0.1459214562 |
-2.776736 |
0.382227864 |
58.342428 |
0.00000000000002202427436494386784756752213060792867598924708871788169517458300106227397918701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000145059477745011827559448646410987248691042833526054778303659986704587936401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1599454 |
1.5537872 |
42.4925779 |
5.9102564 |
| ENSG00000135424 |
3679 |
ITGA7 |
protein_coding |
Q13683 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-7/beta-1 is the primary laminin receptor on skeletal myoblasts and adult myofibers. During myogenic differentiation, it may induce changes in the shape and mobility of myoblasts, and facilitate their localization at laminin-rich sites of secondary fiber formation. It is involved in the maintenance of the myofibers cytoarchitecture as well as for their anchorage, viability and functional integrity. Isoform Alpha-7X2B and isoform Alpha-7X1B promote myoblast migration on laminin 1 and laminin 2/4, but isoform Alpha-7X1B is less active on laminin 1 (In vitro). Acts as Schwann cell receptor for laminin-2. Acts as a receptor of COMP and mediates its effect on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) maturation (By similarity). Required to promote contractile phenotype acquisition in differentiated airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10694445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17641293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9307969}. |
ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell shape;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the integrin alpha chain family. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. They mediate a wide spectrum of cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, and thus play a role in cell migration, morphologic development, differentiation, and metastasis. This protein functions as a receptor for the basement membrane protein laminin-1. It is mainly expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscles and may be involved in differentiation and migration processes during myogenesis. Defects in this gene are associated with congenital myopathy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009]. |
hsa:3679; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] |
12057917_conclude that secondary integrin alpha 7 deficiency is rather common in muscular dystrophy/myopathy of unknown etiology 15117962_FHL2 and FHL3, respectively, are colocalized with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin receptor at the periphery of Z-discs, suggesting a role in mechanical stabilization of muscle cells 17054947_alpha7-expressing fetal myoblasts are capable of differentiation to osteoblast lineage with a coordinated switch in integrin profiles and may represent a mechanism that promotes homing and recruitment of myogenic stem cells for tissue remodeling. 17551147_Integrin alpha7 mutations are associated with prostate cancer, liver cancer, glioblastoma multiforme, and leiomyosarcoma 17618648_analysis of how distinct acidic clusters and hydrophobic residues in the alternative splice domains X1 and X2 of alpha7 integrins define specificity for laminin isoforms 17641293_Alpha7B is a novel marker of the contractile phenotype, and alpha7 expression is essential for human airway smooth muscle cell maturation, which is a laminin-dependent process. 18940796_cleavage is a novel mechanism that regulates alpha7 integrin functions in skeletal muscle, and that the generation of such cleavage sites is another evolutionary mechanism for expanding and modifying protein functions. 19416897_laminin-111 (alpha(1), beta(1), gamma(1)), which is expressed during embryonic development but absent in normal or dystrophic skeletal muscle, increased alpha(7)-integrin expression in mouse and DMD patient myoblasts 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460506_ILK interaction with MCM7 and MCM7 phosphorylation may be a critical event in ITGA7 signaling pathway, leading to tumor suppression. 20651226_This report provides a novel insight into the mechanism, involving interaction with high temperature requirement A2, by which ITGA7 acts as a tumor suppressor. 23800289_Digenic mutational inheritance of the integrin alpha 7 and the myosin heavy chain 7B genes causes congenital myopathy with left ventricular non-compact cardiomyopathy. [ITGA7] 23830872_ITGA7 binds to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (TIMP3) in prostate cancer cells. 24091324_Alpha7beta1D integrin modifies Ca2+ regulatory pathways and offers a means to protect the myocardium from ischemic injury. 24227711_The absence of either alpha7beta1 integrin or alpha6beta1 integrin impairs the ability of Schwann cells to spread and to bind laminin. 26011651_Data suggest that ITGA7 is an epigenetically regulated tumour suppressor gene and a prognostic factor in human malignant pleural mesothelioma. 26076707_Taken together, these results further support the use of a7 integrin as a potential therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy 26320193_Data indicate that S100 calcium binding protein P (S100P) increased lung cancer cell migration by binding integrin alpha7. 27924820_As knockdown of Integrin alpha7 (ITGA7) can effectively reduce the stemness of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells, ITGA7 could be a potential therapeutic target in OSCC treatment. 28602620_targeting of ITGA7 by RNAi or blocking mAbs impaired laminin-induced signaling, and it led to a significant delay in tumor engraftment plus a strong reduction in tumor size and invasion. 29884889_we identified forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) as a novel regulator of colorectal cancer metastases. FOXC1 directly binds its target genes integrin alpha7 (ITGA7) and fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) and activates their expression 29943828_circITGA7 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by suppressing the Ras signalling pathway and promoting the transcription of ITGA7. 30089289_Speculate that the postnatal splicing of alpha7A to alpha7B and of beta1A to beta1D integrins is delayed, altering spontaneous descent of the testes in the first months of life. 31289310_Integrin alpha7 expression is increased in asthmatic patients and its inhibition reduces Kras protein abundance in airway smooth muscle cells. 31325216_Overexpression of ITGA7 is associated with breast cancer. 31418948_Overexpression of ITGA7 is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer. 31698037_Integrin alpha 7 correlates with poor clinical outcomes, and it regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and stemness via PTK2-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31713264_Integrin alpha7 is overexpressed and correlates with higher pathological grade, increased T stage, advanced TNM stage as well as worse survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients: A retrospective study. 31789398_Integrin alpha7 correlates with worse clinical features and prognosis, and its knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and stemness in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 31855276_Predictive value of integrin alpha7 for acute myeloid leukemia risk and its correlation with prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia patients. 31942970_Downregulating integrin subunit alpha 7 (ITGA7) promotes proliferation, invasion, and migration of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells through regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 32963582_Circular RNA CircITGA7 Promotes Tumorigenesis of Osteosarcoma via miR-370/PIM1 Axis. 34253873_Transcriptome profiles of stem-like cells from primary breast cancers allow identification of ITGA7 as a predictive marker of chemotherapy response. 34743543_ITGA7 relates to disease risk, pathological feature, treatment response and survival in Ph(-) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 34884422_Decrease in ITGA7 Levels Is Associated with an Increase in alpha-Synuclein Levels in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Disease Mouse Model and SH-SY5Y Cells. 35194895_ITGA7, CD133, ALDH1 are inter-correlated, and linked with poor differentiation, lymph node metastasis as well as worse survival in surgical cervical cancer. 35430343_The relationship among integrin alpha 7, CD133 and Nestin as well as their correlation with clinicopathological features and prognosis in astrocytoma patients. |
ENSMUSG00000025348 |
Itga7 |
206.306217 |
0.4727179765 |
-1.080948 |
0.257528594 |
16.697591 |
0.00004383663557566843489363139774184219277231022715568542480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000127342794941323774176450411843575238890480250120162963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
151.0695814 |
24.3638473 |
320.4779596 |
36.4246476 |
| ENSG00000135426 |
9840 |
TESPA1 |
protein_coding |
A2RU30 |
FUNCTION: Required for the development and maturation of T-cells, its function being essential for the late stages of thymocyte development (By similarity). Plays a role in T-cell antigen receptor (TCR)-mediated activation of the ERK and NFAT signaling pathways, possibly by serving as a scaffolding protein that promotes the assembly of the LAT signalosome in thymocytes. May play a role in the regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-mediated Ca(2+) release and mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake via the mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membrane (MAM) compartment. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22561606}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signalosome |
|
Predicted to enable phospholipase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including COP9 signalosome assembly; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus; and positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within TCR signalosome assembly. Part of COP9 signalosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9840; |
COP9 signalosome [GO:0008180]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; TCR signalosome [GO:0036398]; phospholipase binding [GO:0043274]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; COP9 signalosome assembly [GO:0010387]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033089]; positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050862]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; TCR signalosome assembly [GO:0036399] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23501103_Tespa1 is a novel component of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes and affects mitochondrial calcium flux. 23541577_Tespa1 is post-translationally modified upon intracellular divalent calcium-ion Ca2+ increase in thymocytes. 24893580_The TESPA1 gene was found to not be involved in ankylosing spondylitis in a Chinese population. 25736038_Tespa1 hay have a role in susceptibility but not severity of rheumatoid arthritis in the Zhejiang Han population in China 28598420_Tespa1 functions in T cell development and the regulation of TCR-induced Ca(2+) signalling through IP3R1 31316154_Thymic-specific regulation of TCR signaling by Tespa1. 35705636_Alcohol use disorder is associated with DNA methylation-based shortening of telomere length and regulated by TESPA1: implications for aging. |
ENSMUSG00000034833 |
Tespa1 |
22.006758 |
3.1833745984 |
1.670557 |
0.562190333 |
8.064726 |
0.00451352904250131199692663841460671392269432544708251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009312229335661078785668642865402944153174757957458496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.9223290 |
10.5037137 |
9.7009452 |
2.5480976 |
| ENSG00000135437 |
5959 |
RDH5 |
protein_coding |
Q92781 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxidation of cis-isomers of retinol, including 11-cis-, 9-cis-, and 13-cis-retinol in an NAD-dependent manner (PubMed:11675386, PubMed:10588954, PubMed:9931293, PubMed:9115228). Has no activity towards all-trans retinal (By similarity). Plays a significant role in 11-cis retinol oxidation in the retinal pigment epithelium cells (RPE). Also recognizes steroids (androsterone, androstanediol) as its substrates (PubMed:9931293, PubMed:29541409). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q27979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10588954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11675386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29541409, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9115228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9931293}. |
Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Steroid metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Vision |
PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; retinol metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9115228}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme belonging to the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR) family. This retinol dehydrogenase functions to catalyze the final step in the biosynthesis of 11-cis retinaldehyde, which is the universal chromophore of visual pigments. Mutations in this gene cause autosomal recessive fundus albipunctatus, a rare form of night blindness that is characterized by a delay in the regeneration of cone and rod photopigments. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the neighboring upstream BLOC1S1 (biogenesis of lysosomal organelles complex-1, subunit 1) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:5959; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; 11-cis-retinol dehydrogenase [GO:0106429]; androstan-3-alpha,17-beta-diol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047044]; androsterone dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047023]; NAD-retinol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004745]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; steroid dehydrogenase activity [GO:0016229]; response to stimulus [GO:0050896]; retinoid metabolic process [GO:0001523]; retinol metabolic process [GO:0042572]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11812441_Macular dystrophy is caused by the RDH5 mutation as a phenotype variation in fundus albipunctus. 12732844_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12788147_Macular dystrophy is caused by the RDH5 gene mutation as a phenotype variation in fundus albipunctatus. 12860821_Fundus changes due to Fundus albipunctatus associated with mutations in the RDH5 gene. 12906118_RDH5 gene mutations cause a progressive cone dystrophy or macular dystrophy as well as night blindness. The clinical phenotype including electrophysiological responses varied among patients with the RDH5 gene mutations. 12967826_A homozygous G490T (Val164Phe) missense RDH5 gene mutation was detected. 15007239_Homozygous Gly107Arg mutation in the RDH5 gene in two unrelated Japanese families with fundus albipunctatus. 15302662_Cone dystrophy can be present in patients with fundus albipunctatus, not only elderly men but also young women. 16637847_Our study indicates that different mutations in the RDH5 gene can cause phenotypic variations of either fundus albipunctatus or familial fleck retina with night blindness. 18363170_study describes an unusual family which included a mother with fundus albipunctatus and three children with typical retinitis pigmentosa; a novel RDH5 mutation was found 20382160_An amino acid important for steroid/retinoid discrimination was identified and its significance was highlighted by the results of molecular modeling studies. 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20829743_Mutations in RDH5 associated with fundus albipunctatus seem to prevent normal lipofuscin accumulation. 21529959_The clinical and electrophysiologic phenotype of patients with RDH5 retinopathy is variable. 22669287_The proband had a compound heterozygotic missense mutation of Cys59Ser (TGC --> AGC) and a nonsense mutation of Trp95ter (TGG --> TGA) in the RDH5 gene. 22736946_RDH5 sequence analysis revealed a novel five base pair deletion, c.913_917delGTGCT (p.Val305Hisfs*29), in family A, and a novel missense mutation, c.758T>G (p.Met253Arg), in family B with fundus albipunctatus. 22815624_Four novel RDH5 gene mutations were identified in fundus albipunctatus Israeli patients. Of them, the null mutations c.343C>T (p.R54X) and c. 242delTGCC were the most prevalent. 24246574_Macular cone density is lower and the regularity of the macular cone mosaic spatial arrangement is disrupted in eyes with fundus albipunctatus. 25170858_A novel c.832C>T (p.Arg278Ter) nonsense mutation in RDH5 was identified. Preserved rod function was observed in one young subject in this study. 26876013_We conclude that the expression of Rlbp1 and Rdh5 critically depends on functional Mitf in the RPE and suggest that MITF has an important role in controlling retinoid processing in the RPE. 29892959_a novel homozygous missense mutation, (c.602 C > T) in exon 4 of the RDH5 gene (MIM: 601617) was identified. This mutation resulted in substitution of phenyl alanine for serine at amino acid 201 (p.Ser201Phe) of the RDH5 gene. Identification of this mutation reveals the allelic heterogeneity of RDH5 in patients with retinitis pigmentosa phenotype. 31933420_A founder RDH5 splice site mutation leads to retinitis punctata albescens in two inbred Pakistani kindreds. 32232344_Multimodal imaging and electroretinography of RDH5-related fundus albipunctatus (FAP) revealed high frequencies of macular involvement in older patients and decreased cone responses. 32788868_Retinal dehydrogenase 5 (RHD5) attenuates metastasis via regulating HIPPO/YAP signaling pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 34115091_Shared Features in Retinal Disorders With Involvement of Retinal Pigment Epithelium. 35148716_Novel variants in the RDH5 Gene in a Chinese Han family with fundus albipunctatus. |
ENSMUSG00000025350 |
Rdh5 |
10.236816 |
0.1914870133 |
-2.384682 |
0.599860227 |
18.042800 |
0.00002159939434080286149481194002408557253147591836750507354736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000065262448407420718286472971492173655860824510455131530761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6870766 |
1.8212590 |
20.0175980 |
5.5331594 |
| ENSG00000135454 |
2583 |
B4GALNT1 |
protein_coding |
Q00973 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the biosynthesis of gangliosides GM2, GD2, GT2 and GA2 from GM3, GD3, GT3 and GA3, respectively. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1601877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7487055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7890749}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1601877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7487055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7890749}. |
GM2 and GD2 gangliosides are sialic acid-containing glycosphingolipids. GalNAc-T is the enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of G(M2) and G(D2) glycosphingolipids. GalNAc-T catalyzes the transfer of GalNAc into G(M3) and G(D3) by a beta-1,4 linkage, resulting in the synthesis of G(M2) and G(D2), respectively. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2013]. |
hsa:2583; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; (N-acetylneuraminyl)-galactosylglucosylceramide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0003947]; acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008376]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; ganglioside biosynthetic process [GO:0001574]; glycosphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006687]; lipid glycosylation [GO:0030259]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
17119850_The expression of three messengers coding for SAT-1, SAT-2 and GalNAcT-1 in human samples of intestinal cancer and some cell lines (breast cancer and melanomas), was evaluated. 19318031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19318031_Transmission disequilibrium test and case-control analysis did not detect an association of B4GALNT1 gene with T1DM. 19457569_GD2/GM2 is not a reliable biomarker in small cell lung carcinoma 21135695_Molecular upstaging of GalNAc-T using rt-pcr was correlated with prognosis in melanoma patients 23721779_Minimally disseminated disease in high risk retinoblastoma patients was detected using reverse transcriptase PCR for GD2 synthase mRNA in CSF. 24103911_The resukts of this study identified mutations in B4GALNT1 (GM2 synthase), encoding the enzyme that catalyzes the second step in complex ganglioside biosynthesis, as the cause of this neurodegenerative phenotype. 24283893_Novel B4GALNT1 mutations reported in two families with hereditary spastic paraplegia. 28698248_Data suggest that ganglioside glycosyltransferases ST3GAL5, ST8SIA1, and B4GALNT1 are S-acylated at conserved cysteine residues located close to cytoplasmic border of their transmembrane domains; ST3Gal-II is acylated at conserved cysteine residue in N-terminal cytoplasmic tail; for B4GALNT1 and ST3Gal-II, dimer formation controls their S-acylation status. 29983310_Since the nineties, mice lacking genes for single glycosyltransferases involved in ganglioside biosynthesis, including ST3GAL5 and B4GALNT1, were created and studied. The resulting phenotypes were frequently mild or very mild, so double knock-out animals were created to effectively study the function of gangliosides 30463940_Sp1 or HDAC1 knock down increased GM2-synthase transcription, and butyrate-mediated activation of GM2-synthase mRNA expression in SK-RC-45 cells was accompanied by Sp1 and HDAC1 loss from the +38/+187 region. Taken together, we have identified an epigenetic mechanism for the de-repression of the GM2-synthase gene in RCC. 30521973_Study analyzed enzyme activity and intracellular localization of the products of mutant cDNAs from eleven cases of hereditary spastic paraplegia with mutation in the coding region of B4GALNT1, and noted a lack of enzyme activity in a majority of them except two family cases. Then compared profiles of clinical findings of patients with hereditary spastic paraplegia and abnormal phenotypes of B4galnt-KO mice. 31075227_Data suggest that GD2 synthase (GD2) can well be considered as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in breast cancer. 31491435_High B4GALNT1 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis. 31988291_B4GALNT1 enhanced tumorigenesis via induction of angiogenesis,ganglioside GM2/GD2 and cell motility. 33367717_B4GALNT1 promotes progression and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma through JNK/c-Jun/Slug pathway. 34907737_Does GD2 synthase (GD2S) detect cancer stem cells in blood samples of breast carcinomas? 35775650_Functional validation of novel variants in B4GALNT1 associated with early-onset complex hereditary spastic paraplegia with impaired ganglioside synthesis. |
ENSMUSG00000006731 |
B4galnt1 |
24.768007 |
2.2575606711 |
1.174765 |
0.319698209 |
13.668208 |
0.00021811596356930169492323312585568828581017442047595977783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000567393659196843941176779946289343570242635905742645263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.7959192 |
6.8832002 |
15.0973738 |
2.4196614 |
| ENSG00000135473 |
9924 |
PAN2 |
protein_coding |
Q504Q3 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic subunit of the poly(A)-nuclease (PAN) deadenylation complex, one of two cytoplasmic mRNA deadenylases involved in general and miRNA-mediated mRNA turnover. PAN specifically shortens poly(A) tails of RNA and the activity is stimulated by poly(A)-binding protein (PABP). PAN deadenylation is followed by rapid degradation of the shortened mRNA tails by the CCR4-NOT complex. Deadenylated mRNAs are then degraded by two alternative mechanisms, namely exosome-mediated 3'-5' exonucleolytic degradation, or deadenlyation-dependent mRNA decaping and subsequent 5'-3' exonucleolytic degradation by XRN1. Also acts as an important regulator of the HIF1A-mediated hypoxic response. Required for HIF1A mRNA stability independent of poly(A) tail length regulation. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16284618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23398456}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a deadenylase that functions as the catalytic subunit of the polyadenylate binding protein dependent poly(A) nuclease complex. The encoded protein is a magnesium dependent 3' to 5' exoribonuclease that is involved in the degradation of cytoplasmic mRNAs. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:9924; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; PAN complex [GO:0031251]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; poly(A)-specific ribonuclease activity [GO:0004535]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening [GO:0000289]; positive regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA processing body assembly [GO:0010606] |
14583602_hPan2 and hPan3 have roles in mRNA decay and exhibit cytoplasmic co-localization 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23398456_USP52 is a key component of P-bodies required to prevent HIF1A mRNA degradation 29599486_USP52 is a bona fide ubiquitin-specific protease, and USP52 promotes ASF1A deubiquitination and stabilization. 33097710_USP52 regulates DNA end resection and chemosensitivity through removing inhibitory ubiquitination from CtIP. 34533198_USP52 inhibits cell proliferation by stabilizing PTEN protein in non-small cell lung cancer. 35304602_Biallelic PAN2 variants in individuals with a syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder and multiple congenital anomalies. |
ENSMUSG00000005682 |
Pan2 |
295.338483 |
0.1965227927 |
-2.347231 |
0.264088663 |
72.729380 |
0.00000000000000001487038407541899056604478988425841309992524066733998733269572767312638461589813232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000117561258143108895238797528920161374138380461608702209908017266570823267102241516113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
103.3150524 |
17.2994041 |
532.1010139 |
62.4578984 |
| ENSG00000135480 |
3855 |
KRT7 |
protein_coding |
P08729 |
FUNCTION: Blocks interferon-dependent interphase and stimulates DNA synthesis in cells. Involved in the translational regulation of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 mRNA (HPV16 E7). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10492017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12072504}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Intermediate filament;Isopeptide bond;Keratin;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. The type II cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral proteins which are arranged in pairs of heterotypic keratin chains coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. This type II cytokeratin is specifically expressed in the simple epithelia lining the cavities of the internal organs and in the gland ducts and blood vessels. The genes encoding the type II cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q12-q13. Alternative splicing may result in several transcript variants; however, not all variants have been fully described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3855; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; keratin filament [GO:0045095]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; structural constituent of skin epidermis [GO:0030280]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; keratinization [GO:0031424] |
11962749_Changing pattern of cytokeratin 7 and 20 expression from normal epithelium to intestinal metaplasia of the gastric mucosa and gastroesophageal junction 12072504_HPV16 E7 mRNA-cytokeratin 7 binding in squamous cervical cancer SiHa cells occurs through the 6-mer peptide SEQIKA present in human cytokeratin 7 protein 12359226_cloning and expression of the gene 14513050_altered expression and transcription of SCL in patients' hematopoietic cells emphasizes the possible contribution of this regulatory nuclear factor to the hematopoietic dysregulation, which is a feature of myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia 14631371_The combined expression of CK7 and CK20 has a low specificity in the distinction between esophageal and cardiac (stomach) adenocarcinomas. 15371952_Alteration of CK7 and CK20 expression profile that occurs early in small intestinal tumorigenesis. 15489654_Cytokeratin 7 and epithelial membrane antigen are essentially negative in yolk sac tumors but are diffusely positive in clear cell carcinomas and endometriod adenocarcinomas making them useful markers for differentiating YSTs from both CCCs and EACs. 15502805_Cytokeratin 7 was found in the majority of type 1 papillary renal cell carcinomas and chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. 15894926_expressed in sinonasal intestinal-type adenocarcinoma less frequently than in colonic adenocarcinoma 16483709_In peripheral blood mononuclear cells, sarcolectin induced CD4+ T cell growth and expression of inflammatory cytokine genes, including TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6 and IL-8 16879391_Results showed that 28% of hepatocellular carcinomas contained cells expressing CK7. 17593078_salivary gland neoplasms showed a CK7+/CK20- immunoprofile ranging from 5 to 100%; squamous carcinoma showed negative CK7/20 immunoexpression 17715023_CK7 is a possible marker for colorectal carcinogenesis. 18042078_an immunohistochemical panel including CK7,CD10 and mesothelin is optimal for distinguishing between ovarian and renal clear cell carcinoma. 18092953_Possible relationship between expression of CK7 and CK20 and neoplastic development of colorectal mucosa in patients with ulcerative colitis. 18317225_In ovarian metastases from undiagnosed colorectal adenocarcinomas, elevated CA-125 levels and frequent coexpression of cytokeratin 7 are features that can contribute to misclassification of these metastases as primary ovarian neoplasms. 18478571_The variability of CK expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) can be explained by genetic heterogeneity. The CK7/CK19 expressing subtype is associated with better outcome. 18602664_Distinct cytokeratin 7, cytokeratin 19, & neuronal cell adhesion molecule staining patterns are seen in hepatic adenoma & focal nodular hyperplasia possibly suggest activation of different subsets of hepatic progenitor/stem cell. 18604734_Clear cell renal cell carcinoma characterised by diffuse CK7 positivity represents a distinct type of CRCC with characteristic histopathological and immunohistochemical features 18936968_CK7, bax, CCND1, and HER2 represent marker proteins and frequently amplified genes in carcinomas of the ampulla of Vater. 18949396_CK7 expression was a useful biomarker for predicting the outcome of stage I/IIA/IIB Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus 19032382_Human eccrine sweat glands express CK7, CK8, CK14, CK18, CK19, CEA, EMA, Ki67, p63, EGF and EGFR. In skin, CEA can be used as a specific immunological marker of sweat glands. 19098678_It can be helpful in cases with metastatic rectal carcinoma, especially those with CK7+/CK20+ or CK20-/CK7- immunophenotype. 19157505_cytokeratins 7 and 19, are very helpful in distinguishing normal from lesional tissue, as well as hepatic adenoma from focal nodular hyperplasia 19302533_the combination of CK7, S100A1 and claudin 8 immunohistochemistry can be useful for classifying tumours of overlapping histology as chromophobe renal cell carcinoma or renal oncocytomas. 19396034_expression of KRT7 might help to explain the pathological, reflux-related nature of columnar-lined esophagus, as aberrant expression in a very early stage of the multistep Barrett esophagus progression 19419944_There was a significant difference between AP, CK 7 and CK 8 expressions in primary lung adenocarcinomas (P=0.02; Chi-squared test). 19601945_Unlike Paget's disease, breast Toker cells have small bland nuclei and are characterized by CK7 positivity. 19614771_The presence of microcystic, elongated and fragmented ('MELF') gland invasion was characterized by strong CK7 expression, sometimes in contrast to adjacent unstained tumour glands. 20001343_Toker cells and mammmary Paget cells share immunoreactivity to CK7. 20043065_FOXA1 induces not only KRT7 but also LOXL2 in a subset of poor prognostic esophageal squamous cell carcinomas with metastatic lymph nodes 20398190_the expression of Cytokeratins 7, 8, 18, and 19 may serve as differential diagnostic markers for pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and small cell lung carcinoma 20538416_Immunohistochemistry for cytokeratins 7 and 19, which mark biliary epithelium, is helpful in the diagnosis of biliary diseases. 20557372_Endometrial adenocarcinomas show micro-anatomical variations in Ki67 expression and this is often inversely correlated with CK7 immunoreactivity. 20574624_Case Report: CK7+/CK20- Merkel cell carcinoma presenting as inguinal subcutaneous nodules with subsequent epidermotropic metastasis. 20727680_Case Report: Primary pulmonary adenocarcinoma with enteric differentiation resembling metastatic colorectal carcinoma, negative for cytokeratin 7. 21228364_Hepatocyte CK7 expression is frequently noted in chronic allograft rejection, and it would appear to reflect ductopenia. 21282015_A considerable number of colorectal carcinomas showed immunoreactivity to CK7. 21358552_Our results reveal that menopause influences the adipose tissue expression of many genes, especially of neurexin 3, metallothionein 1E, and keratyn 7, which are associated with the alteration of several key biological processes. 21574103_Our results along with the data from the literature indicate that CK7/CK20 expression may be of clinical significance. 21681009_CK-7 expression grades correlated positively with histological stages of primary biliary cirrhosis (r=0.639, P |
ENSMUSG00000023039 |
Krt7 |
5.357546 |
12.5552528375 |
3.650219 |
0.962497388 |
19.344495 |
0.00001091333994998609643000114094446573176355741452425718307495117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000034069563803256084288332422582712410985550377517938613891601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.8703920 |
7.0781394 |
0.7933914 |
0.5153639 |
| ENSG00000135521 |
84946 |
LTV1 |
protein_coding |
Q96GA3 |
|
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in ribosomal small subunit biogenesis and ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84946; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; preribosome, small subunit precursor [GO:0030688]; ribosomal small subunit biogenesis [GO:0042274]; ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus [GO:0000056] |
30348748_Ribosome biogenesis factor Ltv1 chaperones the assembly of the small subunit head. 34999892_Mutations in the ribosome biogenesis factor gene LTV1 are linked to LIPHAK syndrome, a novel poikiloderma-like disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000019814 |
Ltv1 |
400.830970 |
2.1321480738 |
1.092308 |
0.082680012 |
176.150031 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000033579480273753864994277654822843136635674578569248887806120010746974257737172761032470432629173253779968078003292930588941089808940887451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000005619423229485340645877875019338955409601484130949619772856147683906032732512027538210467319178029296962428862372007642989046871662139892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
552.7877665 |
28.8749283 |
261.1522784 |
10.6571025 |
| ENSG00000135547 |
23493 |
HEY2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBP5 |
FUNCTION: Downstream effector of Notch signaling which may be required for cardiovascular development. Transcriptional repressor which binds preferentially to the canonical E box sequence 5'-CACGTG-3'. Represses transcription by the cardiac transcriptional activators GATA4 and GATA6. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10692439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11095750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15485867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16293227}. |
Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the hairy and enhancer of split-related (HESR) family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-type transcription factors. The encoded protein forms homo- or hetero-dimers that localize to the nucleus and interact with a histone deacetylase complex to repress transcription. Expression of this gene is induced by the Notch signal transduction pathway. Two similar and redundant genes in mouse are required for embryonic cardiovascular development, and are also implicated in neurogenesis and somitogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23493; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; arterial endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060842]; ascending aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035910]; atrial septum morphogenesis [GO:0060413]; cardiac conduction system development [GO:0003161]; cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0060317]; cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003214]; cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010659]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:0014898]; cardiac right ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003215]; cardiac septum morphogenesis [GO:0060411]; cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell development [GO:0060948]; cardiac ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003208]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; circulatory system development [GO:0072359]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; coronary vasculature morphogenesis [GO:0060977]; dorsal aorta morphogenesis [GO:0035912]; endocardial cushion to mesenchymal transition involved in heart valve formation [GO:0003199]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003198]; heart trabecula formation [GO:0060347]; labyrinthine layer blood vessel development [GO:0060716]; mesenchymal cell development [GO:0014031]; muscular septum morphogenesis [GO:0003150]; negative regulation of biomineral tissue development [GO:0070168]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:2000723]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transcription by transcription factor localization [GO:0010621]; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter involved in smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:2000820]; negative regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060633]; negative regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000678]; Notch signaling involved in heart development [GO:0061314]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein-DNA complex assembly [GO:0065004]; pulmonary artery morphogenesis [GO:0061156]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045607]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001212]; smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051145]; tricuspid valve formation [GO:0003195]; tricuspid valve morphogenesis [GO:0003186]; umbilical cord morphogenesis [GO:0036304]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055015]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222] |
12535671_These results indicate that the molecular association between HES1-, HEY2- and SIRT1-related proteins is conserved among metazoans, from Drosophila to human, and suggest that the Sir2-bHLH interaction also plays important roles in human cells. 15389319_To clarify the role of HEY2 in human CHD and AGS, we screened by direct sequencing 23 children with CHD and 38 patients diagnosed with AGS. Mutation of HEY2 is not a major contributing factor. 15643620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15680351_A similar gene in mouse regulates cardiovascular development 16151017_HERP1 may play a role in promoting the phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells during vascular injury and atherosclerotic process by interfering with SRF binding to CArG-box 16293227_CHF1/Hey2 may affect smooth-muscle cell phenotype through an important transcriptional mechanism 16329098_This result suggests a possible role of HEY2 in the regulation of ventricular septation in humans. 18239137_Present a novel mechanism by which a balance between Notch-1/-2/-4 signaling, via CBF-1, and HRT-1/-2 activity determines the expression of smooth muscle differentiation markers including actin. 18266235_The absence of mutations in NOTCH2 and Hey2 its downstream target in the heart does not exclude the possibility that other genes in this pathway might be implicated in the diverse phenotypes observed in Alagille syndrome 21290414_In this study, we analyzed the effects of HESR1, -2, and -3 on DAT1 expression in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells 21362320_Through activating the Dll4-Notch-Hey2 signaling pathway, HGF indirectly promotes the proliferation and migration ability of cells, so that offspring artery branches are formed. 22310065_Report down-regulation of Notch signaling components NOTCH3 and HEY2 in abdominal aortic aneurysms. 23744056_Hey2 and COUP-TFII have an important role in arteriovenous differentiation of human endothelial cells. 23872634_Common variants at SCN5A-SCN10A and HEY2 are associated with Brugada syndrome, a rare disease with high risk of sudden cardiac death 24108462_Data indicate that culture abrogated differential gene expression in part due to gradual loss of canonical Notch activity and HEY2 expression. 24366871_a new HRD1-associated membrane protein named HERP2, which is homologous to the previously identified HRD1 partner HERP1. Despite sequence homology, HERP2 is constitutively expressed in cells, whereas HERP1 is highly induced by ER stress. 25361534_Overexpression of HEY1 and HEY2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is correlated to different indices of poor prognosis, and it is extrapolated that such overexpression is important in progression and development of ESCC tumorigenesis. 25799559_bone morphogenic proteins within the serum of cell culture medium are potent inducers of endothelial Hey1 and Hey2 gene expression within the first few hours after medium change 25832314_Individuals with HEY2 duplications should be screened for congenital heart defects. 26729854_HEY2 CC genotype may be a favorable prognostic marker for BrS, protectively acting to prevent ventricular fibrillation presumably by regulating the repolarization current. 27191260_HEY2 as a promising biomarker for unfavorable outcomes and a novel therapeutic target for the clinical management of HCC 28637782_Genetic variation of HEY2 is associated with Brugada syndrome through alteration of ion channel expression in the cardiac ventricular wall. 28694461_We also highlighted that Hey2 is involved in radiation-induced EndoMT and that Hey2 invalidation reduces EndoMT and tissue damage. 29636455_The findings identify HEY2 as a novel component of the NKX2-5 cardiac transcriptional network. 30125982_These results provide evidence that miR-146a and Hey2 form a mutual negative feedback regulatory loop to regulate the inflammatory response in chronic apical periodontitis. 30257372_we confirmed that lncRNA PRNCR1 upregulates HEY2 to promote tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer by competitively binding miR-448. 31255287_Attenuation of PRRX2 and HEY2 enables efficient conversion of adult human skin fibroblasts to neurons. 31565805_microRNA-599 promotes apoptosis and represses proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via downregulation of Hey2-depentent Notch signaling pathway. 32712748_TWIST1 correlates with Notch signaling pathway to develop esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32820247_Germline variants in HEY2 functional domains lead to congenital heart defects and thoracic aortic aneurysms. 32997309_Notch-HEY2 signaling pathway contributes to the differentiation of CD34(+) hematopoietic-like stem cells from adult peripheral blood insulin-producing cells after the treatment with platelet-derived mitochondria. |
ENSMUSG00000019789 |
Hey2 |
121.292501 |
0.1924530333 |
-2.377422 |
0.183076352 |
177.616389 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000016064904176823658790350490265976506203298533526440730452972605541473813370486979075542947306617778307005761639913998806150630116462707519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000002716128128865031095191353671745206970599381978950937705937160910389264460097565973792704518905990562858271397672638158837798982858657836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.5361459 |
5.5881248 |
206.3869540 |
18.2498578 |
| ENSG00000135604 |
8676 |
STX11 |
protein_coding |
O75558 |
FUNCTION: SNARE that acts to regulate protein transport between late endosomes and the trans-Golgi network. |
Coiled coil;Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the syntaxin family. Syntaxins have been implicated in the targeting and fusion of intracellular transport vesicles. This family member may regulate protein transport among late endosomes and the trans-Golgi network. Mutations in this gene have been associated with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8676; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; membrane fusion [GO:0061025]; synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0031629]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
16278825_A large group of 63 unrelated patients with Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) was analysed for mutations in STX11, PRF1, and UNC13D. 17525286_Defective cytotoxic lymphocyte degranulation is associated with syntaxin-11 deficient familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 4 patients 17785771_Syntaxin 11 plays a role in natural killer (NK) cell granule exocytosis and in the generation of cell-mediated killing. 18710388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19169743_DNA methylation of Stx11 contribute to disease susceptibility at the 6q24 locus in humans. 19259622_These data indicate that human neutrophils express syntaxin 11 and call attention to the possible involvement of neutrophils in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis pathology 19804848_Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 5 (FHL-5) is caused by mutations in Munc18-2 and impaired binding to syntaxin 11 19967551_a novel homozygous deletion (c. 581_584delTGCC; p.Leu194ProfsX2) in the gene-encoding syntaxin 11 (STX11), causing a premature termination codon in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20486178_The mutations in STX11 are responsible for HLH in approximately 1% of North American patients and can cause variable defects in syntaxin 11 expression and function with resultant impact on clinical phenotype. 21298754_STX11 should be sequenced in HLH patients even when impaired NK cell degranulation is not found 21342435_Data suggest that syntaxin 11 promotes the fusion of Rab27a-expressing vesicles with cytotoxic granules and reveal additional complexity in spatial/temporal segregation of subcellular structures involved in granule-mediated cytotoxicity. 21674762_No detrimental mutations were identified in STX11 in Chinese children with Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 22767500_Platelets deficient in syntaxin-11 from a Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis type 4 had secretion defect. 23160464_Distinct severity of HLH in both human and murine mutants with complete loss of cytotoxic effector PRF1, RAB27A, and STX11. 24227526_Stx11 functions as a t-SNARE for the final fusion of LG at the IS. 24910990_a pivotal role for S-acylation in the function of syntaxin 11 in NK cells 26176172_The results suggest that STX11 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Peripheral T-cell lymphomas and they may contribute to the future development of new drugs for the treatment of Peripheral T-cell lymphomas. 29044293_Neonatal platelets exhibit low levels of the Stx11-Munc18b complex (essential component of the SNARE machinery) and of beta1-tubulin. These developmental deficiencies are associated with defects in platelet adhesion, spreading and secretion. 29352103_Data suggest that acylation of SNAP23 (synaptosome associated protein 23) and STX11 (syntaxin-11) regulates exocytosis in platelets; maintaining acylation states of SNAP23 and STX11 is important for platelet function. 31207086_STX11-deficient familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis type 4 is associated with self-resolving flares and a milder clinical course. 34339548_Spectrum mutations of PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, and STXBP2 genes in Vietnamese patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 35293882_Familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis With Heterozygous STX11 and Homozygous UNC13D Mutations Diagnosed in the Neonatal Period. |
ENSMUSG00000039232 |
Stx11 |
60.595830 |
2.2047016161 |
1.140583 |
0.218878447 |
27.395390 |
0.00000016582609586512889882589942471685651170787423325236886739730834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000639392156470559726340742272288064640406446414999663829803466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.8554078 |
10.7581685 |
37.8355991 |
3.8823911 |
| ENSG00000135624 |
10574 |
CCT7 |
protein_coding |
Q99832 |
FUNCTION: Component of the chaperonin-containing T-complex (TRiC), a molecular chaperone complex that assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis (PubMed:25467444). The TRiC complex mediates the folding of WRAP53/TCAB1, thereby regulating telomere maintenance (PubMed:25467444). The TRiC complex plays a role in the folding of actin and tubulin (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25467444, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a molecular chaperone that is a member of the chaperonin containing TCP1 complex (CCT), also known as the TCP1 ring complex (TRiC). This complex consists of two identical stacked rings, each containing eight different proteins. Unfolded polypeptides enter the central cavity of the complex and are folded in an ATP-dependent manner. The complex folds various proteins, including actin and tubulin. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 5 and 6. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:10574; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; chaperonin-containing T-complex [GO:0005832]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; positive regulation of establishment of protein localization to telomere [GO:1904851]; positive regulation of protein localization to Cajal body [GO:1904871]; positive regulation of telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body [GO:1904874]; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase [GO:0032212]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
11532003_Functional characterization of the CCT complex and its subunits in mouse. 15347653_A protein in mouse, that is highly similar to the one described in this record, was found to interact with a protein involved in the Nitric oxide (NO) signal transduction pathway, soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC). 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23292503_the increased expression of CCT-eta appears to be a marker for latent and active Dupuytren's contracture and to be essential for the increased contractility exhibited by these fibroblasts 35073517_Overexpression of chaperonin containing TCP1 subunit 7 has diagnostic and prognostic value for hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000030007 |
Cct7 |
1298.083639 |
2.0286362383 |
1.020510 |
0.064572758 |
247.806222 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007811085076432998266262280484443556190500975549384318060789785015198986955976439182141914001074988090221484901228253944350355851827443978826689963135265770688420161604881286621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001850587732394077809433630177240537561233767865717348013780634289544013216491571845544681356746461268212282723142871149817133202365103091316389516407525661634281277656555175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1736.6201658 |
90.0855500 |
862.7953500 |
33.1734808 |
| ENSG00000135636 |
8291 |
DYSF |
protein_coding |
O75923 |
FUNCTION: Key calcium ion sensor involved in the Ca(2+)-triggered synaptic vesicle-plasma membrane fusion. Plays a role in the sarcolemma repair mechanism of both skeletal muscle and cardiomyocytes that permits rapid resealing of membranes disrupted by mechanical stress (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ferlin family and is a skeletal muscle protein found associated with the sarcolemma. It is involved in muscle contraction and contains C2 domains that play a role in calcium-mediated membrane fusion events, suggesting that it may be involved in membrane regeneration and repair. In addition, the protein encoded by this gene binds caveolin-3, a skeletal muscle membrane protein which is important in the formation of caveolae. Specific mutations in this gene have been shown to cause autosomal recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B (LGMD2B) as well as Miyoshi myopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:8291; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; macrophage activation involved in immune response [GO:0002281]; membrane fusion [GO:0061025]; monocyte activation involved in immune response [GO:0002280]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; plasma membrane repair [GO:0001778]; T-tubule organization [GO:0033292]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
12836053_The dysferlin gene, a strong candidate gene responsible for two other distal myopathies in the same region, is located centromeric to PAC3-H52 and can thereby formally be excluded as cause for Welander distal myopathy 14506716_Isolated calf atrophy and weakness with onset after age 30, and associated with serum CK levels that are only moderately elevated, represents a distinct myopathy phenotype. 14512171_In muscular dystrophy with dysferlinopathy, the inflammatory response is triggered by altered expression of dysferlin and is involved in muscle degeneration. 14749532_the importance of dysferlin-caveolin 3 relationship for skeletal muscle integrity 15221058_If, in particular, a dysferlinopathy is supposed, the underlying mutation should be identified to confirm the diagnosis and as a basis for current and future therapeutic interventions. 15318348_Dysferlin and its differentially spliced isoforms play different roles in myogenic cell differentiation, hence dysferlin function in peripheral nerve might be accomplished by this novel spliced variant isoform. 15469449_This study identified 11 different mutations, including eight missense and three deletion mutations. Nine of them were novel mutations. 15477515_Miyoshi distal myopathy in these 2 Chinese families demonstrated a homogenous phenotype and compound heterozygous mutations. Among the 4 mutations, 3 were novel mutations that, to our knowledge, have not been reported previously. 15535137_Dysferlin expression when satellite cells are activated confirm the involvement of dysferlin in human muscle regeneration/repair and its possible role in fusion events during muscle development. 15835269_Data show that affixin is a dysferlin binding protein that colocalizes with dysferlin at the sarcolemma of normal skeletal muscle. 16010686_LGMD2B mutational analysis in Miyoshi myopathy, and atypical dysferlinopathies 16087766_The new R1905X dysferlin founder mutation produced the 3 possible dysferlinopathy phenotypes without intrafamilial heterogeneity. 16100712_annexin A1 and A2 may have roles in dysferlin deficiency and in muscular dystrophies 16606933_Two severely affected sisters sith limb-girdle muscular dystrophy were homozygous for a dysferlin null mutation. 16608842_there is a functional link between dysferlin and myogenin in the differentiation of skeletal muscle 16797397_dysferlin is present in glomeruli and may be associated with glomerular permeabi 16862423_membrane attack complex deposits and a pro-inflammatory milieu in the absence of interleukin-10 expression may contribute to progressive muscle damage in dysferlinopathies 16896923_DYSF_v1 retains phylogenic conservancy and shows similar expression pattern as the currently known human dysferlin. 16934466_While the quantity of beta-sarcoglycan was nearly normal in the limb girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD)2E carrier, the levels of dysferlin protein were reduced to 50% of controls in the carriers of LGMD2B. 16996541_Thus, alteration of structurally important residues in dysferlin could lead to improper folding and degradation of the mutant protein. 17287450_The diagnosis of symptomatic carriers of dysferlin mutations should be considered when a pathologic pattern of dysferlin protein is observed. 17363620_dysferlin is not expressed at the plasmalemma of myotubes but mostly localizes to the T-tubule network. However, dysferlin translocated to the site of injury and toward the plasma membrane in a Ca2+-dependent fashion in response to a wounding assay 17554076_A proteomics screen of human placental microvillous syncytiotrophoblasts (STBs) revealed the expression of dysferlin (DYSF), a plasma membrane repair protein associated with certain muscular dystrophies. 17698709_Phenotypic study in 40 patients with dysferlin gene mutations 17825554_Genomic analysis of the dysferlin coding sequence performed in patients from Caucasus Jews, who lacked muscle dysferlin, revealed a homozygous frameshift mutation predicting a truncated dysferlin and a complete loss of functional protein. 17828519_These data suggest that disturbances in dysferlin as well as Z-line proteins and transcription factors particularly under mechanical stress cause cardiomyopathy. 17868276_study reports a novel pair of heterozygous mutations in the 3'-splicing site of exon 26 and the translation site of exon 28 of the dysferlin gene in two siblings 17897828_Cytoplasmic localization of dysferlin correlates with fiber regeneration in a subset of muscular dystrophy patients. We also identified patients with forms of LGMD and with abnormal dysferlin localization that doesn't correlate with fiber regeneration. 18276788_Dysferlin deficiency enhances monocyte phagocytosis. 18294055_missense mutation c.4253G>A on the DYSF gene in a Mexican family from an endogamic population 18306167_Mutations located between exons 7 and 16, corresponding to the predicted second and third C2 domain of dysferlin, are amyloidogenic. 18396043_A case represents the eldest age of onset of dysferlinopathy reported so far and widens the clinical spectrum of this disease. 18495154_solution structure of the inner DysF domain of the dysferlin paralogue myoferlin, which has a unique fold held together by stacking of arginine and tryptophans, mutations that lead to clinical disease in dysferlin 18641458_AQP4 expression was analyzed in muscle biopsies from patients affected by Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophies. 18832576_Rab27A/Slp2a expression in limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B muscle provides a compensatory vesicular trafficking pathway that is able to repair membrane damage in the absence of dysferlin. 18853459_The mutational spectrum significantly shows a higher proportion of nonsense mutations in DYSf gene, but a lower proportion of deleterious missense changes as compared to previous series . 19084402_We report two patients with a new phenotype of dysferlinopathy presenting as congenital muscular disease. Muscle biopsy showed mild dystrophic features and the absence of dysferlin. 19221801_study identified alternative splicing involving novel dysferlin exons 5a & 40a, in addition to previously reported exon 17; differences in frequencies of dysferlin transcripts in skeletal muscle & blood were characterized 19228595_In trophoblastic cells, there was a positive correlation between cell fusion and increased dysferlin expression. 19253956_Dysferlin's C2A domain was able to bind to phosphoinositides in a Ca(2+)-dependent fashion. 19286669_dysferlin-deficient patients show an increase in immature muscle fibres. 19309282_In two Chilean patients with dysferlinopathy, two new mutations were found: homozygous c.1948delC (p.Leu650TyrfsX6) in a male patient; the heterozygous mutation c.1276G>A (p.Gly426Arg) in a female patient in association with c.2858dupT (p.Phe954ValfsX2). 19326120_All of the mutations associated with amyloid were located in the N-terminal region of dysferlin, and dysferlin clearly proved to be a component of the amyloid deposits. 19380584_Molecular complex formed by MG53, dysferlin, and Cav3 is essential for repair of muscle membrane damage in muscular dystrophy. 19493611_Mutation analysis of DYSF revealed novel compound heterozygous mutations in two related Miyoshi myopathy patients 19545895_role for DYSF in the stability of the apical syncytiotrophoblast plasma membrane may account for the increased shedding of microparticles from this membrane in preeclampsia 19594366_We report for the first time the characterization of disease-causing exonic rearrangements in the large-sized gene encoding dysferlin. 19834057_Data show that restoration of dysferlin in skeletal muscle fibers is sufficient to rescue Dysf-deficient mice, although its mild overexpression does not appear to functionally enhance membrane repair in other models of muscular dystrophy. 19929428_No disease-causing mutation was identified in alternative exons 1 of DYSF-v1, exon 5a, and exon 40a, demonstrating a low frequency of disease-causing mutations in these exons. 20082313_Dysferlin is necessary for correct T-tubule formation, and dysferlin-deficient skeletal muscle is characterized by abnormally configured T-tubules. 20373350_Expression levels of dysferlin are important for appropriate function without deleterious or cytotoxic effects. Future endeavors in gene replacement for correction of dysferlinopathy should be tailored to take account of this. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20413686_Data show that components of the inflammasome pathway are specifically up-regulated and activated in dysferlin-deficient but not in dystrophin-deficient and normal muscle, and suggest that muscle cells can actively participate in inflammasome formation. 20535123_Dysferlin exon skipping mutation (c.5492G>A) with a founder effect reveals further alternative splicing involving exons 49-51 in muscle disorders. 20544924_Six subjects had atypical calf enlargement, and 3 of these exhibited a paradoxical pattern of dysferlin expression 20558759_Nonsense suppression drug, ataluren (PTC124), is able to induce read-through of the premature stop codon in a patient with a R1905X mutation in dysferlin and produce sufficient functional dysferlin to rescue myotube membrane blebbing. 20574037_Splitting dysferlin myopathy into separate phenotypes does not reveal significant differences in terms of rate of progression, prognosis, genotype, or MRI pattern 20595382_dysferlin and syntaxin-4 similarly transit a common endosomal pathway in skeletal muscle cells. 20618995_B cell depletion with rituximab/dysferlin monoclonal antibody has been proved useful in the treatment of two patients affected by muscular dystrophy. There may be a possible role for B cells in the immune system involvement of this muscle disorder. 20724702_loss of dysferlin in endothelial cells resulted in deficient adhesion followed by growth arrest an impaired angiogenic response 21119217_Dysferlin function in intracellular vesicles and its implication in muscle membrane resealing. 21173544_A simple and rapid screening method to detect hot spot mutations in the dysferlin gene is essential for the diagnosis of dysferlinopathy. 21280221_A new computational method establishes an increase in the mean average prediction precision for dysferlin protein partners, which is important for new targeted therapies. 21412170_MG53, annexin A1, and dysferlin localize to the t-tubule network and show enriched labeling at longitudinal tubules of the t-system in overstretch 21522182_This study presents the first direct and conclusive evidence that an amount of Dysferlin =20% is pathogenic and always caused by primary dysferlin gene mutations. 21556485_Studies indicate that dysferlinopathies are autosomal recessive disorders caused by mutations in the dysferlin (DYSF) gene, encoding the dysferlin protein. 21658164_A novel mutation in exon 47 (c.5289G>C) of the dysferlin gene in the heterozygous state, causing an amino acid change (p.Glu1763Asp), was detected in 2 patients 22037454_these data further support the claims that dysferlin not only mediates membrane repair but also trafficking of client proteins, ultimately, help bridging dysferlinopathies to aberrant membrane signaling. 22043020_Data suggest dysferlin has an important function in the internal membrane systems of skeletal muscle, involved in calcium homeostasis and excitation-contraction coupling. 22110769_C2 domains mediate high affinity self-association of dysferlin in a parallel homodimer 22194990_The aim of the study was to determine whether dysferlin expression in peripheral blood monocytes correlates with that in skeletal muscle. 22297152_In Koreans with dysferlinopathy, DYSF mutations appeared to cluster in the N-terminal region. 22720081_provide proof of principle that AAV5 mediated delivery of dysferlin is a highly promising strategy for treatment of dysferlinopathies and has far-reaching implications for the therapeutic delivery of other large genes 23185377_Dysferlin-peptides reallocate mutated dysferlin thereby restoring function 23243261_we observed 40 Japanese patients in 36 families with limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B in whom dysferlin mutations were confirmed 23254335_We described 8 Chinese patients with dysferlinopathy 23516275_Dysferlin is subject to enzymatic cleavage releasing a synaptotagmin-like fragment with a specialized protein- or phospholipid-binding role for muscle membrane repair. 23519732_study reported 4 novel mutations and 2 cases of dysferlinopathy in which patients exhibited a reduction of sarcolemmal dysferlin in conjunction with cytoplasmic retention 23558685_dysferlin is involved in regulating cellular interactions and has a role in inflammatory cells 23792176_a direct interaction of dysferlin with Trim72/MG53, AHNAK, cytoplasmic dynein, myomesin-2 and calsequestrin-1, but not with caveolin-3 or dystrophin, is reported. 23859474_Data indicate that dysferlin, otoferlin, and myoferlin do not merely passively adsorb to membranes but actively sculpt lipid bilayers. 24091414_our results identify dysferlin as a newly identified binding partner of AbetaPP 24239457_Alternate splicing of the dysferlin C2A domain confers Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent binding for membrane repair. 24438169_The crystal structure of the human dysferlin inner DysF domain shows that most of the pathogenic mutations are part of aromatic/arginine stacks that hold the domain in a folded conformation. 24454878_distinct membrane protein signature specific to patients with Diamond-Blackfan Anemia 24461013_all dysferlin domains bind Ca(2+) albeit with varying affinity and stoichiometry 24488599_Our results suggest that dysferlin protein levels of =10% in PBMCs, are highly indicative of primary dysferlinopathies 24685690_These novel observations of conspicuous intermyofibrillar lipid and progressive adipocyte replacement in dysferlin-deficient muscles. 24687993_The tricomplex Fam65b-HDAC6-dysferlin is transient. 24838345_Dysferlin carrier frequency and the number of affected individuals at risk for dysferlinopathy could be higher than previously estimated. 24902367_These data suggest that although dysferlin is not an integral part of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex, its expression is altered in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 24967968_results provide the mechanism for dysferlin-mediated repair of skeletal muscle sarcolemma and identify ASM as a potential therapy for dysferlinopathy 25312915_minigene strategy is an efficient tool for the detection of splicing defects in dysferlinopathies, which could allow for a better comprehension of splicing defects due to mutations and could improve prediction tools evaluating splicing defects 25591676_Our study underlines clinical heterogeneity and a high proportion of novel mutations for dysferlin in Chinese patients affected with dysferlinopathy. 25904108_By targeting DYSF premRNA introns harbouring differentially defined 3' splice sites (3' SS), we found that target introns encoding weakly defined 3' SSs were trans-spliced successfully in vitro in human myoblasts also in vivo in skeletal muscle of mice. 26077327_We conclude that two independent mutations in ALMS1 and DYSF cause CRD and muscular dystrophy in the studied consanguineous Israeli Arab family. 26671124_This study demonstrated that novel mutation of DYSF in patient with Dysferlinopathy in Iran. 26806107_These differences in the structural dynamics of the predicted binding site suggest that mutation R959W alters recognition dynamics of the inner DysF domain. 26911292_This study showed that 4 patients with Inflammatory Myopathy associated with DYSF mutation. 27226605_results support a function for dysferlin as a calcium-sensing SNARE effector for membrane fusion events 27229680_Human deltoid muscle biopsies of 5 Chilean dysferlinopathy patients exhibited the presence of muscular connexins (Cx40.1, Cx43 and Cx45). 27349407_This review suggested that the functions of dysferlin in vesicle trafficking and membrane remodeling in skeletal muscle. 27641898_arginine-rich motif crucial for phosphatidylserine accumulation in sarcolemma repair 27647186_DYSF mutations in Chinese patients clustered in the N-terminal region of the gene. Exonic rearrangements were found in 23% of patients with only one pathogenic mutation identified by Sanger sequencing or NGS. The novel mutations found in this study greatly expanded the mutational spectrum of dysferlinopathy. 27666772_Immunofluorescence demonstrated that the percentage of complex I- and complex IV-deficient fibres was higher in patients with DYSF mutations than in age-matched controls. No clonally expanded mtDNA deletions were detected using long-range PCR in any of the analysed muscle fibres. Complex I and complex IV deficiency is higher in patients than age matched controls but patients do not have rearrangements of the mtDNA. 28005267_DYSF expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28104817_dysferlin has membrane tubulating capacity and that it shapes the T-tubule system. 28523511_As muscular biopsy showed inflammatory infiltrates, polymyositis was suspected and immunosuppressive treatment was initiated. However, clinical improvement could not be achieved. Gene sequencing of the DYSF-gene showed a previously unreported homozygous mutation. 28904177_Data suggest that dysferlin exhibits modular architecture of 4 tertiary domains: 1) C2A, readily removed as solo domain; 2) midregion C2B-C2C-Fer-DysF, excised as intact module with several dynamic folding options; 3) C-terminal four-C2 domain module; 4) calpain-2-cleaved mini-dysferlinC72, particularly resistant to proteolysis. Missense variant L344P in muscular dystrophy patient largely escapes proteasomal surveillance. 29209666_A novel duplication of 22 bases (c.897_918dup; p.Gly307Leufs5X) in the DYSF gene was identified in a family suffering from Miyoshi myopathy 29480214_This review detailed the different partners and function of dysferlin and positions the sarcolemma repair in normal and pathological conditions. [Review] 29484758_MiRNA target prediction software, TargetScan, revealed dysferlin (DYSF) and protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA), as target genes of miR-92a-1-5p. 29879922_DYSF mutation is associated with Neuromuscular Disease. 30026467_Results show that, in addition to clinically-defined dysferlin FerA mutations, is a novel four-helix bundle fold with its own Ca(2+)-dependent phospholipid-binding activity which interaction with the membrane is enhanced by the presence of Ca(2+). 30098242_two compound heterozygous mutations of the DYSF gene probably underlie the limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2B in the two pedigrees 31004665_The initial C2 domains of dysferlin and myoferlin are 57% similar (42% identical). Unlike dysferlin C2A, myoferlin binds two Ca2+ with equivalent affinity. Unlike dysferlin C2A, the membrane binding loop 1 of myoferlin C2A is relatively rigid. 31019989_Deep intronic mutations of dysferlin can be a common underlying cause of dysferlinopathy 31693312_In patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B, two new mutations were found in DYSF. A nonsense mutation c.2419C > T, which eliminates downstream part of the protein, and a novel one c. (1,053 + 1_1,054-1)_(1,397 + 1_1,398-1)del causing deletion of the DNA from exon 12 to exon 15. Two unrelated families are from the same ethnicity and share the same mutation and haplotype patterns, suggesting a founder mutation. 31770675_Radiological findings in siblings with dysferlin mutation with diverse phenotype. 31861684_Results support a role of dysferlin in actin cytoskeleton dynamics in muscle cells and suggest that this mechanism could be deregulated in dysferlinopathy. 31873062_Antisense-Mediated Skipping of Dysferlin Exons in Control and Dysferlinopathy Patient-Derived Cells. 32087766_AMPK Complex Activation Promotes Sarcolemmal Repair in Dysferlinopathy. 32400077_The genetic profile of dysferlinopathy in a cohort of 209 cases: Genotype-phenotype relationship and a hotspot on the inner DysF domain. 32666437_Novel splicing dysferlin mutation causing myopathy with intra-familial heterogeneity. 33215690_Null variants in DYSF result in earlier symptom onset. 33927379_Retrospective analysis and reclassification of DYSF variants in a large French series of dysferlinopathy patients. 33987686_Frequent DYSF rare variants/mutations in 152 Han Chinese samples with ovarian endometriosis. 34559919_Molecular landscape of DYSF mutations in dysferlinopathy: From a Chinese multicenter analysis to a worldwide perspective. 35460889_DYSF promotes monocyte activation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease as a DNA methylation-driven gene. 35962550_Identification of a novel heterozygous DYSF variant in a large family with a dominantly-inherited dysferlinopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000033788 |
Dysf |
376.187342 |
0.0781492672 |
-3.677624 |
0.166080365 |
478.353389 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000048757763429828277658858184311919915447515253164048168349769630054415790831940060170915509780688449053949068059878085366854642492913011721710310309161452661052600783472939939430491227488287818753566417783820257661590322493869 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022280637406324007666922412214975894764843160532284088956685066907662829170902390000453680565742848246921172842349910730872002629435669081051689425175416685179452849280762672528721511064242730336697908796795002984284118521176 |
Yes |
No |
45.9010764 |
5.5852179 |
590.2777128 |
45.1393032 |
| ENSG00000135643 |
27345 |
KCNMB4 |
protein_coding |
Q86W47 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the calcium activated potassium KCNMA1 (maxiK) channel. Modulates the calcium sensitivity and gating kinetics of KCNMA1, thereby contributing to KCNMA1 channel diversity. Decreases the gating kinetics and calcium sensitivity of the KCNMA1 channel, but with fast deactivation kinetics. May decrease KCNMA1 channel openings at low calcium concentrations but increases channel openings at high calcium concentrations. Makes KCNMA1 channel resistant to 100 nM charybdotoxin (CTX) toxin concentrations. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10692449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10792058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10828459}. |
3D-structure;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
MaxiK channels are large conductance, voltage and calcium-sensitive potassium channels which are fundamental to the control of smooth muscle tone and neuronal excitability. MaxiK channels can be formed by 2 subunits: the pore-forming alpha subunit and the modulatory beta subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is an auxiliary beta subunit which slows activation kinetics, leads to steeper calcium sensitivity, and shifts the voltage range of current activation to more negative potentials than does the beta 1 subunit. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27345; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calcium-activated potassium channel activity [GO:0015269]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; voltage-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential [GO:0099508]; action potential [GO:0001508]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; detection of calcium ion [GO:0005513]; neuronal action potential [GO:0019228]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0046928]; regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0019229] |
17913586_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18559348_Structural basis for toxin resistance of beta4-associated calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels 18981408_The beta4 subunit controls ethanol tolerance at the molecular, cellular, and behavioral levels, and could determine individual differences in alcohol abuse and alcoholism, as well as represent a therapeutic target for alcoholism. 19204046_Report beta subunit (KNMB1-4)-specific modulations of BK channel function by a Slo1 mutation associated with epilepsy and dyskinesia. 19578543_results argue that, for native mouse Slo3 channels, the beta4 subunit must be considered as a potential interaction partner and, furthermore, that KCNMB subunits may have functions unrelated to regulation of the Slo1 alpha subunit 21848922_These results suggest that fast-gating, type I BK channels lacking beta4 can increase neuronal excitability in response to reduced phosphatase activity and activation of calcium channels. 23623847_our data suggest that the rs398702 variant in the KCNMB4 gene is unlikely to influence significantly the risk of developing mesial temporal lobe epilepsy or its severity 24414257_IFN-gamma changed mRNA levels of the BK beta-modulatory proteins KCNMB2 (increased) and KCNMB4 (decreased) as well as leucine-rich repeat-containing protein (LRRC)26 (decreased). 24486049_Study shows that beta4 subunit of the MaxiK channel has no potential endocytic signal and 2 specific amino acids in the functional basic motif retention/retrieval trafficking signal at the C-terminus may play a role in controlling cellular excitability 24759175_Recombinant martentoxin selectively blocks KCNMA1/KCNMB4 channels. 25190810_BK channel beta4 subunit influences sensitivity and tolerance to alcohol by altering its response to kinases 25300797_Two recurrent fusion genes associated with the 12q locus, LRP1-SNRNP25 and KCNMB4-CCND3, were by RT-PCR, Sanger sequencing and FISH, and were found to be osteosarcoma specific in a validation cohort of 240 other sarcomas. 31815672_This study presents cryo-EM structures of Slo1 in complex with the auxiliary protein, beta4. Four beta4, each containing two transmembrane helices, encircle Slo1, contacting it through helical interactions inside the membrane. 34562210_Family-Based Cohort Association Study of PRKCB1, CBLN1 and KCNMB4 Gene Polymorphisms and Autism in Polish Population. |
ENSMUSG00000054934 |
Kcnmb4 |
8.933785 |
0.2330409944 |
-2.101344 |
0.610416698 |
12.572382 |
0.00039148928294258143831957363900642121734563261270523071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000980217441260814587034033706913760397583246231079101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4696158 |
1.4983705 |
15.0087321 |
3.7929654 |
| ENSG00000135722 |
55336 |
FBXL8 |
protein_coding |
Q96CD0 |
FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of the SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. {ECO:0000250}. |
Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of the ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbls class. It shares 78% sequence identity with the mouse protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55336; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 33122824_Fbxl8 suppresses lymphoma growth and hematopoietic transformation through degradation of cyclin D3. |
ENSMUSG00000033313 |
Fbxl8 |
51.222333 |
0.3791862246 |
-1.399022 |
0.239197679 |
34.990757 |
0.00000000331274111147795716375305820323125816084797179428278468549251556396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015091376174510694205530938788624439883534478212823159992694854736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
27.8621450 |
4.3344235 |
74.0077906 |
7.3388562 |
| ENSG00000135744 |
183 |
AGT |
protein_coding |
P01019 |
FUNCTION: Essential component of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), a potent regulator of blood pressure, body fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10619573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1132082, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17138938}.; FUNCTION: [Angiotensin-2]: Acts directly on vascular smooth muscle as a potent vasoconstrictor, affects cardiac contractility and heart rate through its action on the sympathetic nervous system, and alters renal sodium and water absorption through its ability to stimulate the zona glomerulosa cells of the adrenal cortex to synthesize and secrete aldosterone (PubMed:10619573, PubMed:17138938). Acts by binding to angiotensin receptors AGTR1 and AGTR2 (PubMed:1567413). Also binds the DEAR/FBXW7-AS1 receptor (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10619573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1567413, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17138938}.; FUNCTION: [Angiotensin-3]: Stimulates aldosterone release. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1132082}.; FUNCTION: [Angiotensin 1-7]: Is a ligand for the G-protein coupled receptor MAS1 (By similarity). Has vasodilator and antidiuretic effects. Has an antithrombotic effect that involves MAS1-mediated release of nitric oxide from platelets (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P11859}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Vasoactive;Vasoconstrictor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene, pre-angiotensinogen or angiotensinogen precursor, is expressed in the liver and is cleaved by the enzyme renin in response to lowered blood pressure. The resulting product, angiotensin I, is then cleaved by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) to generate the physiologically active enzyme angiotensin II. The protein is involved in maintaining blood pressure, body fluid and electrolyte homeostasis, and in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension and preeclampsia. Mutations in this gene are associated with susceptibility to essential hypertension, and can cause renal tubular dysgenesis, a severe disorder of renal tubular development. Defects in this gene have also been associated with non-familial structural atrial fibrillation, and inflammatory bowel disease. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2019]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:11606; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; sodium channel regulator activity [GO:0017080]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; type 1 angiotensin receptor binding [GO:0031702]; type 2 angiotensin receptor binding [GO:0031703]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; aging [GO:0007568]; angiotensin-activated signaling pathway [GO:0038166]; angiotensin-mediated drinking behavior [GO:0003051]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0061049]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to angiotensin [GO:1904385]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway coupled to cGMP nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007199]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034374]; maintenance of blood vessel diameter homeostasis by renin-angiotensin [GO:0002034]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0051387]; negative regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:2000650]; negative regulation of tissue remodeling [GO:0034104]; nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0007263]; operant conditioning [GO:0035106]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0010536]; positive regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045777]; positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090190]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010666]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010613]; positive regulation of CoA-transferase activity [GO:1905920]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0003331]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of gap junction assembly [GO:1903598]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046628]; positive regulation of L-arginine import across plasma membrane [GO:1905589]; positive regulation of L-lysine import across plasma membrane [GO:1905010]; positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010744]; positive regulation of membrane hyperpolarization [GO:1902632]; positive regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity [GO:0033864]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051247]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061098]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of renal sodium excretion [GO:0035815]; positive regulation of superoxide anion generation [GO:0032930]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904754]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of blood volume by renin-angiotensin [GO:0002016]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of cardiac conduction [GO:1903779]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of extracellular matrix assembly [GO:1901201]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048169]; regulation of norepinephrine secretion [GO:0014061]; regulation of renal output by angiotensin [GO:0002019]; regulation of renal sodium excretion [GO:0035813]; regulation of transmission of nerve impulse [GO:0051969]; regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0019229]; renal system process [GO:0003014]; renin-angiotensin regulation of aldosterone production [GO:0002018]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to muscle activity involved in regulation of muscle adaptation [GO:0014873]; smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048659]; stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0051403]; uterine smooth muscle contraction [GO:0070471]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11024214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11027844_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11053482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11082147_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11096141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11106322_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11114694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11136175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11142763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11157174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11181802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11191642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11200871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11208365_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11213892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11230286_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11234373_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11244011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11288810_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11300226_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11325075_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11330506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11330874_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11341749_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11345362_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11354780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11355019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11359462_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11372768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11393670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11422735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11422818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11431175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11447495_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11463770_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11484170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11507973_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11531970_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11544438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11575217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11577832_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11593098_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11668351_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11675943_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11677359_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11688760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11689223_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11707217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11707686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11711524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11714857_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11720807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11725160_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11731937_single nucleotide polymorphism and haplotype structure in two populations, Japanese and white 11737220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11751698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11754397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11756575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11756575_data fall short of showing significant association between a variant of the promoter of interleukin-1beta, polymorphism of angiotensinogen, and the missense variant of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and occurrence of idiopathic recurrent miscarriage 11776100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11849656_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11860821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11865575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11882570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11910300_Polymorphisms of genes encoding angiotensinogen as risk factors for orthostatic hypotension. 11910301_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11910301_angiotensinogen T174M and M235T and the AT1-receptor A1166C polymorphisms were related to the change in LVH during antihypertensive treatment with an AT1-receptor antagonist 11918988_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11923478_IL-6-inducible expression of the hAGT promoter is mediated by physical association of the COOH terminus of STAT3 with p300/CBP, the recruitment of which targets histone acetylation and results in chromatin remodeling. 11923700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11924723_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11926202_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11938025_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11963567_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11997278_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12006677_neuronal AGT may play an important role in regulating salt intake and salt appetite. 12015946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12031704_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12037699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12040348_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12051013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12081721_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12095411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12118911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12130713_autocrine/paracrine mechanism whereby angiotensin II, formed at adrenergic nerve endings in myocardial ischemia, elicits carrier-mediated norepinephrine release by activating adjacent AT(1) receptors 12145290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12145290_polymorphism in angiogensinogen is associated with hypertension in African Americans 12164881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12169209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12173461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12173461_T174M polymorphism associated with higher risk of essential hypertension in people aged over 45 12181363_determine whether the M235T angiotensinogen (AGT) polymorphism, either interacting with habitual physical activity (PA) levels or independently, was associated with cardiovascular (CV) hemodynamics during maximal and submaximal exercise 12181364_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12181364_role of the M235T polymorphism in the AGT gene in modifying the blood pressure response to regular exercise 12187393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12194787_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12205735_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12234952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12270765_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12352892_relationship to intragraft messenger RNA expression of angiotensinogen and to chronic allograft nephropathy in kidney transplant patients 12394950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12417054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12417054_study shows that the M235T variant in the gene encoding angiotensinogen could be a risk factor in mild and severe pre-eclampsia 12425365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12426159_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12431442_Review. Angiotensin exerts mitogenic and growth promoting effects on cardiac myocytes and non-myocytic elements; and both of these effects significantly contribute to the development and progression of hypertensive heart disease. 12446192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12446468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12449516_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12450315_Increased plasma Ang-(1-7) in normal pregnant subjects compared with nonpregnant subjects and decreased Ang-(1-7) in preeclamptic subjects compared with normal pregnant subjects, consistent with the development of hypertension 12454231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12469628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12476421_No association was noted between the haplotypes of AGT gene and hypertension in tested people, but T235 allele might play an important role in increased risk for essential hypertension. 12476421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12476891_No statistically significant differences between groups were found in the allele frequency and genotype distribution for ACE and AGT polymorphisms. 12476891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12479284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12479284_The M235T polymorphism of the AGT gene is associated with MVPS in the Chinese population of Taiwan. The association of the TT genotype with MVPS is more noteworthy than an overall increase in the frequency of the T allele at the M235T locus. 12482638_results suggest elevated glucose levels stimulate AII production via mechanisms dependent on glucose-induced PKC activation in mesangial cells and locally produced AII partly mediates the increase in mesangial matrix synthesis in high-glucose conditions 12511523_Angiotensinogen gene haplotypes are associated with hypertension and might act synergistically with I allele of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene. 12511525_Angiotensinogen 235T polymorphism is associated with blood pressure phenotypes. 12511525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12513040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12536339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12536339_The M235T variant of the angiotensinogen gene and the body mass index are useful markers for prevention of hypertension in pregnancy: a tree-based analysis of gene-environment interaction 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12548125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12556231_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12559679_leukocyte level strongly correlates with steady-state of plasma glucose concentration and significantly correlates with body mass index, plasma insulin, and leptin levels in essential hypertension; may be directly associated with insulin resistance 12569265_in hypertensive subjects with activated renin-angiotensin system, unopposed activity of angiotensin II is not involved in L-NAME-induced pressor and renal vasoconstrictor response 12575194_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12576245_Maternal and fetal angiotensinogen Thr235 genotypes are associated with an increased risk of intra-uterine growth retardation. 12576245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12597535_Polymorphism in essential arterial hypertension in childhood. 12611423_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12627873_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12661912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12661912_lack of a significant effect of AGT M235T polymorphism on blood pressure level, but the difference in pulse pressure in the older population suggests that further investigations of this polymorphism should be made in the Japanese population. 12663441_Ang II increased cytosolic Ca2+ release from Ca stores, enhanced calcineurin synthesis & activity, & stimulated NF-kappaB DNA-binding in cultured human neutrophils, demonstrating for the 1st time a stimulatory role of Ang II in phagocytic cell activation. 12663475_study indicates that the alteration in nephrin expression is an early event in proteinuric patients with diabetes and suggests that glycated albumin and angiotensin II contribute to nephrin downregulation 12669427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12669427_Polymorphism of the promoter region of the angiotensinogen gene (ATG) and an angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene (ACE) insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism were studied in Kazakhs with hypertension and cardiovascular disease 12670743_findings suggest that obstructive sleep apnea mediates hypertension, at least in part, via a stimulation of angiotensin II production 12675870_Polymorphism of the AGT M235T gene but not ACE I/D gene is associated with greater left ventricular mass index and relative wall thickness, indicating more concentric LVH, in Chinese peritoneal dialysis patients. 12695419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12716844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12716844_Polymorphism is associated with diabetic retinopathy in NIDDM in Chinese patients. 12728975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12743009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12743009_Relationship of angiotensinogen single nucleotide polymorphisms with elevated blood pressure and risk of cardiovascular disease. 12767551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12805070_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12811821_results indicate that the change of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) from contractile to synthetic phenotype sequentially increases expression of proteases, production of Ang II, and productions of growth factors, culminating in VSMC proliferation 12819040_Results suggest that connective tissue growth factor mediates angiotensin II-induced fibrosis in the heart and kidneys via blood pressure and calcineurin-dependent pathways. 12830507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12832734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12854169_In normal subjects the expression of local renin and angiotensinogen mRNA was organ specific, but with increase of the expression locally, the organ-specificity became lost in cirrhotic patients 12865608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12874613_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12888892_angiotensin II may act on the pre-existing pancreatic arteries around neoplasms, leading to formation of hypovascular or avascular regions 12898858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911327_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911556_M235T and A(-20)C genotype of angiotensinogen can influence therapeutic efficacy of renin-angiotensin system blockade on renal survival in IgA nephropathy. 12911556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12932862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12938141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12939534_Alcohol drinking might be specifically associated with the HNBP in M allele carriers of angiotensinogen gene T174M polymorphism. 12939534_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12950120_findings suggest that the AGT and angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms would not have an effect on hypertension or the end stage renal disease in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 12964504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14500990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14502296_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14508190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14508191_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14519430_angiotensin II and lipopolysaccharide regulate the human tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter in human cardiac fibroblasts 14521795_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14523024_EGF and angiotensin II activation of phospholipase Cgamma through src is mediated by GIT1 14530292_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14565954_angiotensin II-dependent activation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein transcription requires janus kinase 2 and calcium 14569094_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14597849_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14597849_Significant association between the -217A variant of the AGT gene and hypertension. This variant plays a functional role in basal transcription of AGT, and may confer a risk for hypertension in Taiwanese populations. 14610337_in patients with nephrotic syndrome due to biopsy proven focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, AGT-M235T polymorphism was associated with the severity of arterial hypertension 14625185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14638622_A role for AGT in genetic susceptibility to preeclampsia. 14638622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14642613_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14643573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14643574_In this hypertensive population, the association of ACE inhibitor use with risk of nonfatal stroke varied by AGT genotype. There is a protective association between ACE inhibitor use and nonfatal stroke risk among individuals with ThrThr genotype of AGT. 14643574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14644777_ANG II, via AT(1)R, modulates the secretion of TNF-alpha and MMP-2 from vascular endothelial cellsANG II, via AT(1)R, modulates the secretion of TNF-alpha and MMP-2 from endothelial cells and TNF-alpha mediates the effects of ANG II on MMP-2 release. 14648325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14648325_The AC/CC genotype of this polymorphism may be associated with an increased severity of proteinuria, suggesting that this polymorphism may play a significant role in the progression of IgA nephropathy in Japanese children. 14660489_The Cl- -dependent effects of ANG II on Ca2+ transients may be mediated, at least in part, by a Cl- -dependent Ins(1,4,5)P3 accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells. 14669517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14672953_results suggest that bile acids negatively regulate the human angiotensinogen gene through the inhibitory effect of small heterodimer partner on hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 14688807_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14700505_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14749533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14749533_gene polymorphisms in Turkish hypertensive patients 14765837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14767013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14767903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14767903_Results suggest that the polymorphism of A(-6)G in 5' upstream core promoter of the AGT gene may be involved in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension. 14961043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14961043_Significant association of AGT M235T with blood pressure and cholesterol metabolism in an Afro-Caribbean population in 'genetic context' of RH blood group system. 14970360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14970360_Relationship of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the angiotensinogen gene and susceptibility to hypertension. 14973087_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14997233_AGT M235T polymorphism does not confer any increased risk for MI in young South African Indians. 14997233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15013293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15013322_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15013333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15017542_M235 T polymorphism may be associated with persistent pulmonary hypertension in newborns with congenital diaphragmatic hernia 15017542_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15023884_The M235 allele in exon 2 of the AGT gene, the G-6 and G-217 alleles in its promoter, & the corresponding haplotypes were associated with non-familial structural atrial fibrillation. 15031629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15042429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15044674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15044674_angiotensinogen M235T polymorphism was associated with adipocyte size in cultured adipocytes from obese subjects 15045574_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15055256_AGT T174M polymorphism was associated with higher diastolic blood pressure levels in younger and non-overweight Japanese and was more evident among subjects with higher sodium intake. 15055256_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15062885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15067378_PPARalpha and HNF-4 competitively affect the human angiotensinogen promoter through the C region 15067738_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15075192_dual production of renin and angiotensinogen in the renal proximal tubule can result in a systemic increase in arterial pressure 15076187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15079791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15082899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15082899_a molecular variant of ACE, but not angiotensinogen, gene is associated with preeclampsia in Korean women. 15097234_No significant differences in the distribution of any of these polymorphisms were found between patients with pre-eclampsia or eclampsia and the normal control 15097234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15108186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15112434_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15112973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120696_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15123355_Low-glomerular filtration rate cirrhotic patients had worse survival rate associated with more severe contraction of effective arterial blood volume, higher active renin /angiotensin II ratio and lower angiotensin-converting enzyme levels. 15130920_Ang II stimulates IL-6 and IL-8 production and release from human adipocytes by a NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. This proinflammatory action of Ang II seems to be mediated by the AT1. 15131005_Locally generated Ang II amplifies the immunomediated inflammatory process of coronary microvessels occurring in unstable angina. 15149328_AGT expression in kidney proximal tubules adapts in the long-term to changes in glomerular filtration rate 15153556_Angiotensin II increases Pax-2 expression in fetal kidney cells via the AT2 receptor 15153745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15192838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201544_Our results designate the C-532T and G-6A as the best candidates for functional studies on the AGT gene 15201545_Patients homozygous for the T allele had a reduced carotid distensibility and an increased stiffness of the carotid wall material 15278435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15294367_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15317677_ANG II activates rapamycin-sensitive mTOR signaling pathway in human coronary smooth muscle cells and involves activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p70(S6k), and eukaryotic initiation factor-4E, leading to activation of protein synthesis. 15326089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15343353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15343353_Variants at two AGT sites together, in conjunction with age, may be significantly associated with elevated systolic blood pressure, whereas the single-site models are as good models of diastolic blood pressure. 15353577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15364762_The ACE-I/D polymorphism is not associated with HAPE susceptibility in Japanese subjects. The AT(1)R gene polymorphisms may likely associate with HAPE susceptibility. 15385810_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15385810_Polymorphism is not associated with increased risk of developing chronic kidney allograft dysfunction. 15386947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15387996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15388495_Localization of expression in the nucleus of human astrocytes of CCF-STTG1 line. 15448113_The prostate may be a source of the secreted angiotensin II found in seminal plasma. 15498133_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15504143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15505642_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15563875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15575510_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15599691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15599691_common haplotype of the angiotensinogen gene is linked to angiotensinogen levels 15614026_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15621215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15624175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15628301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15642127_AGT M235T TT genotype confers a significantly decreased risk for the development of hypertension. 15642127_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15649942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15649942_rare variants in the promoter and coding regions are associated with different blood AGT levels 15659127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15662219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15668245_CAML is an important signal transducer for the actions of Ang II in regulating the calcineurin-NFAT pathway and the interaction of CAML with ATRAP may mediate the Ang II actions in vascular physiology 15673342_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15673342_The AGT A-20C genotypes may influence resting blood pressure (BP) response to strength training(ST) 15676177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15676177_There are interactions between the angiotensin II type 1 receptor 1166 A/C as well as the angiotensinogen 235 M/T gene polymorphism and age with respect to the outcome after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. 15718424_studies indicate that the angiotensin-converting enzyme-Angiotensin II-Angiotensin II receptor type 1 system serves as a positive feedback loop and fosters pulmonary artery adventitial fibroblasts proliferation under hypoxic conditions 15718497_Angiotensin II activates mineralocorticoid-receptor-mediated gene transcription via the AT1 receptor. 15743363_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15754274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15789057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15798183_Dissection of DNA cis elements that are demonstrably indispensable for regulating both the level and cell type specificity of hAGT gene transcription. 15811183_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824464_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15860756_Angiotensin II mediates the inflammatory gene expression effects of IL-18 by inducing the expression of the IL-18 receptor alpha subunit in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) via STAT-3 activation. 15869758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15879922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15914614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15914769_human renin and human angiotensinogen have roles in development of hypertension in transgenic mice, and may predispose to spontaneous stroke 15915003_data show that Ang II promotes coronary inflammation and remodeling, in part independent of blood pressure but dependent upon endothelin signal 15922319_AngII stimulates platelet superoxide production through act |
ENSMUSG00000031980 |
Agt |
776.394454 |
0.4955421466 |
-1.012920 |
0.058349167 |
305.096303 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002555577864197850028193212310461571630632011333704256435919357902756792931567710892692616973732923430951487123441326118323407891242830122111401350729886841391270172970957147429160727369890082627534866333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000752900783943318599012157430211136998619664643450803812392821231985000553487359105429590607083517524480263672192371704780078723075974318743362580225470475141368069870936863274835104675730690360069274902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
520.8873160 |
18.4408082 |
1058.7751898 |
24.3600978 |
| ENSG00000135763 |
9816 |
URB2 |
protein_coding |
Q14146 |
FUNCTION: Essential for hematopietic stem cell development through the regulation of p53/TP53 pathway. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B0V0U5}. |
Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in ribosome biogenesis. Located in aggresome; midbody; and nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9816; |
aggresome [GO:0016235]; midbody [GO:0030496]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796]; ribosome biogenesis [GO:0042254] |
|
ENSMUSG00000031976 |
Urb2 |
207.030825 |
2.0708761884 |
1.050241 |
0.141235672 |
55.243069 |
0.00000000000010650919910348990899757180761260685913525622647846091695100767537951469421386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000673265858144544353268563404636076286189499962020477141777519136667251586914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
301.7121301 |
26.8771909 |
146.7394487 |
10.0883164 |
| ENSG00000135766 |
54583 |
EGLN1 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZT9 |
FUNCTION: Cellular oxygen sensor that catalyzes, under normoxic conditions, the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins. Hydroxylates a specific proline found in each of the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domains (N-terminal, NODD, and C-terminal, CODD) of HIF1A. Also hydroxylates HIF2A. Has a preference for the CODD site for both HIF1A and HIF1B. Hydroxylated HIFs are then targeted for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex. Under hypoxic conditions, the hydroxylation reaction is attenuated allowing HIFs to escape degradation resulting in their translocation to the nucleus, heterodimerization with HIF1B, and increased expression of hypoxy-inducible genes. EGLN1 is the most important isozyme under normoxia and, through regulating the stability of HIF1, involved in various hypoxia-influenced processes such as angiogenesis in retinal and cardiac functionality. Target proteins are preferentially recognized via a LXXLAP motif. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11595184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12181324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12351678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15897452, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19339211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21792862, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25129147}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Congenital erythrocytosis;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Disease variant;Iron;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Vitamin C;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins. HIF is a transcriptional complex that plays a central role in mammalian oxygen homeostasis. This protein functions as a cellular oxygen sensor, and under normal oxygen concentration, modification by prolyl hydroxylation is a key regulatory event that targets HIF subunits for proteasomal destruction via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex. Mutations in this gene are associated with erythrocytosis familial type 3 (ECYT3). [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:54583; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase activity [GO:0016706]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; ferrous iron binding [GO:0008198]; L-ascorbic acid binding [GO:0031418]; peptidyl-proline 4-dioxygenase activity [GO:0031545]; peptidyl-proline dioxygenase activity [GO:0031543]; cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055008]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; heart trabecula formation [GO:0060347]; labyrinthine layer development [GO:0060711]; negative regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0051344]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; oxygen homeostasis [GO:0032364]; peptidyl-proline hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-L-proline [GO:0018401]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of modification of postsynaptic structure [GO:0099159]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; regulation protein catabolic process at postsynapse [GO:0140252]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to nitric oxide [GO:0071731]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
12912907_PHD2 is the critical oxygen sensor setting the low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. It is upregulated by oxygen. 15156561_we demonstrate that PHD2 is not affected by overexpression or downregulation of HIF-2alpha 15247232_PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 have roles in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 15563275_The phd2 gene is transcribed exclusively from the downstream promoter that contains a functional hypoxia-responsive, cis-regulatory element. 16155211_the N-terminal region of PHD2 contains a Myeloid translocation protein 8, Nervy, and DEAF1 (MYND)-type zinc finger domain, whereas the catalytic domain is located in its C-terminal region; the MYND domain inhibits the catalytic activity of PHD2 16157596_Accumulated EGLN1 in hypoxia acts as a negative-feedback mechanism to modulate HIF-1alpha target gene expression. 16161047_EGLN1 can be considered as a candidate tumor suppressor on chromosome 1q, and our observation could open the new aspect in exploring the machinery of senescence induction associated with hypoxia-inducible factor 1, alpha signal transduction 16407130_Critical for normal regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. 16489060_PHD2 shows strongly elevated expression both at the mRNA and protein level in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 16782814_Crystal structures of the catalytic domain of human PHD2 were described. 16815840_a novel mechanism by which a growth factor controls hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 (HIF-1alpha)stability, and thereby drives the expression of specific genes, through the regulation of PHD2 levels 16880998_A recombinant form of a human prolyl-4-hydroxylase (PHD2) was characterised and shown to have an unexpectedly high affinity for, and to copurify with endogenous levels of, its Fe(ii) cofactor and 2-oxoglutarate cosubstrate. 17060326_PHD2 induction is an underlying mechanism of NO-induced degradation of HIF-1alpha 17353276_Data suggest that the peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase FKBP38 determines hypoxia-inducible transcription factor prolyl-4-hydroxylase PHD2 protein stability. 17579185_PHD2 mutation is associated with abnormal erythrocytosis 17932321_PHD inhibitors preferentially bind to the active site of PHD2 and stabilize HIF activity, induce angiogenesis and protect against cerebral ischemia. 17933562_Genetic defects are first frameshift and nonsense mutations reported in PHD2 gene and suggest that a decreased prolyl hydroxylase activity disturbing the oxygen-sensing pathway might be the cause of erythrocytosis. 18072750_PHD2 does not mediate the TCDD-mediated HIF-1 alpha destabilization nor control the interference of AhR and HIF-1 alpha pathways. 18347341_Chronic hypoxia not only increases the pool of PHDs but also overactivates the three PHD isoforms. 18505927_PHD2 has a role in modulating tumor-forming potential 18776187_suggest a role for PHD2 as a decisive oxygen sensor of the hypoxia-inducible factor degradation pathway within the cell nucleus 18834144_Biochemical characterization of PHD2 variants associated with polycythemia is reported. 19159641_These data suggest that the effects of Egln1 knockdown depend on the status of pVHL and can be correlated with effects on Rpb1. 19304911_Given the role of PHD2 as an oxygen sensor in mammalian cells, these results raise the possibility that PHD2 links vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation to O(2) availability 19339211_Results describe the localization signal of HIF-prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs) 1-3, and their intracellular localization in response to hypoxia. 19477431_PHD2 plays a critical role in regulating tumor angiogenesis. 19546213_Data indicate that PHD2 protein stability is regulated by a ubiquitin-independent proteasomal pathway involving FKBP38 as adaptor protein that mediates proteasomal interaction. 19563769_study on the reactivity of the cysteines in the catalytic domain of PHD2; results reveal that of the seven cysteinyl residues in the catalytic domain, Cys201 is the most nucleophilic 19631610_these findings provide new insights into the mechanisms of the regulation of the oxygen sensor cascade of PHD1 and PHD2 in different cellular compartments. 19639506_nuclear PHD2 expression may act as a surrogate marker for radiation resistance in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck 19724277_BRCA1 tumours correlate with a HIF-1alpha phenotype and have a poor prognosis through modulation of hydroxylase enzyme profile expression. 19737309_EGLN1 CPG-island methylation was not observed in various plasma cell dyscrasias. 19915370_Its mutation accelerates the transcription of EPO gene by stabilizing HIF-alpha protein. (review) 20026900_Regulation and expression of both PHD2 and HIF-1a are important to the biology of sarcomas, and loss of PHD2 function has an additional adverse effect in the prognosis of sarcomas in tumors expressing HIF-1a. 20028863_our findings recognize the PHD/HIF regulatory axis as a novel therapeutic target to disable a tumor's ability to adjust to hypoxic conditions and control cell survival 20156434_Nuclear PHD2 localization promotes malignant cancer phenotype. 20404338_Depletion of PHD2 results in greater HIF-2alpha levels and enhances SOX9-induced cartilage matrix production. 20466884_genome-wide scans reveal positive selection in regions with genes whose products likely involved in high-altitude adaptation; positively selected haplotypes of EGLN1 and PPARA associated with decreased hemoglobin unique to highland population of Tibet 20574527_the underlying mechanism by which ET-1, through the regulation of PHD2, controls HIF-1alpha stability and thereby regulates angiogenesis and melanoma cell invasion 20727020_Methylation-induced epigenetic silencing of PHD1, PHD2, PHD3 and FIH is unlikely to underlie up-regulated HIF-1alpha expression in human breast cancer but may play a role in other tumour types. 20801873_PHD2 affects cell migration and F-actin formation via RhoA/rho-associated kinase-dependent cofilin phosphorylation 20856199_Data suggest that PHD2/HIF-2/amphiregulin signaling has a critical role in the regulation of breast tumor progression and propose PHD2 as a potential tumor suppressor in breast cancer. 20956315_EGLN1 polymorphisms are associated with high-altitude adaptation 20956315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20959442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20961960_Observational study and genome-wide association study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20978146_Elevated PHD1 concomitant with decreased PHD2 are causatively related to Rpb1 hydroxylation and oncogenesis in human renal clear cell carcinomas with WT VHL gene. 21030426_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 21251613_The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate is a competitive inhibitor of multiple alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, including histone demethylases, prolyl hydroxylases, and the TET family of 5-methlycytosine hydroxylases. 21601578_The reaction of PHD2 with nitric oxide (NO) is potentially complex, consistent with proposals based on cellular studies that NO may regulate the hypoxic response by direct reaction with hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) hydroxylases. 21748337_The expression of PHD genes and their relationship with the tumor behavior and apoptosis-associated factors in non-small cell lung cancer, was investigated. 21792862_Prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) exerts tumor-suppressive activity in pancreatic cancer. 21828119_The investigation of 67 patients with isolated erythrocytosis, either sporadic or familial, allowed the identification of three novel mutations in the catalytic domain of the PHD2 protein. 21877141_In a cohort of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast patients there was a tendency for increased survival and longer disease-free survival among patients with high tumor PHD2 expression. 21887331_PHD1 and PHD2 are independent negative prognostic factors in NSCLC. 21933857_there are functional differences between the PHD2 mutants with regards to hypoxia inducible factor regulation. 22068265_Studies indicate that EPAS1, EGLN1 and PPARA genes subject to natural selection in native high-altitude Tibetans. 22236543_Cytoplasmic PHD2 is a strong prognostic biomarker for gastric adenocarcinoma that might be useful in identifying high-risk patients. 22286099_Data show that the tumour suppressor protein LIMD1 acts as a molecular scaffold, simultaneously binding the PHDs and VHL, thereby assembling a PHD-LIMD1-VHL protein complex and creating an enzymatic niche that enables efficient degradation of HIF-1alpha. 22308030_PHD2 modulated eEF2 activity and protein translation under acute hypoxia. 22343896_(R)-2HG, but not (S)-2HG, stimulates EGLN activity, leading to diminished HIF levels, which enhances the proliferation and soft agar growth of human astrocytes 22395314_Here, we outline specific functions of PHD enzymes in surgically relevant pathological conditions, and discuss how these functions might be exploited in order to support the treatment of surgically relevant diseases. 22488178_Our data suggest that PHD-2 is the major hydroxylase regulating HIF levels and the expression of angiogenic genes in arthritic cells. 22595196_Heart rate and oxygen saturation level of hemoglobin were found to be significantly associated with the EGLN1 (rs480902) SNP in the Han patients with acute mountain sickness. 22747465_The unusual kinetic pK(a) further suggested that PHD2 might function physiologically to sense both intracellular pO(2) as well as pH, which could provide for feedback between anaerobic metabolism and hypoxia sensing. 22802519_present study indicated that low expression of PHD2 in CRC predicts poor survival independent of HIF-1alpha, specifically for patients who have early stage tumors 22833384_PHD2 short interfering RNA supports bone regeneration in vivo. 22946054_PHD2-mediated hydroxylation of HIF-1alpha predominantly occurs in the cell nucleus and is dependent on very dynamic subcellular trafficking of PHD2. 22975349_PHD2 may directly interact with PDE4D to function as a novel regulator of the intracellular cAMP levels in cardiomyocytes. 23077544_The study scrutinizes the unfolding pathways of the PHD2 catalytic domain's possible species and demonstrates the properties of their unfolding states by computational approaches. 23088526_results demonstrate that HIF-1alpha transcription and protein synthesis are controlled by TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling, whereas HIF-1alpha protein stability is controlled by PHD2, which is regulated by TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling. 23130672_prevalence of the risk alleles in high altitude pulmonary edema and the protective alleles in healthy Lakakhi highland natives have provided us with allelic variants at the same locus that are involved in disease and adaptation 23225569_Knockdown of prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain 2 inhibits tumor growth of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by affecting TGF-beta1 processing. 23334958_HIF-specific hydroxylase PHD-2 may represent a relevant target for cartilage repair. 23413029_p23 recruits PHD2 to the HSP90 machinery to facilitate HIF-1alpha hydroxylation 23487784_a unique mechanism for the regulation of HIF-1alpha stability that involves ERbeta-mediated transcriptional regulation of PHD2 and they highlight an unexpected role for PHD2 in maintaining epithelial differentiation. 23666208_EGLN1 contributes to the adaptively low hemoglobin level of Tibetans compared with acclimatized lowlanders at high altitude. 23694817_PHD2 silencing promotes adipose-derived stem cell survival in infarcted myocardia. 23787140_PHD2 regulates and hydroxylates HIF-1alpha by binding to its C-terminal domain. 23836663_the N-terminal region of C16 is predicted to have a PHD2-like structural fold but lacks the catalytic active site residues of PHDs 24121508_These studies formally prove that a missense mutation in PHD2 is the cause of the erythrocytosis, show that this occurs through haploinsufficiency, and point to multifactorial control of red cell mass by PHD2. 24195777_The diminished expression of PHD1 and PHD2 and elevated level of FIH protein in cancerous tissue compared to histopathologically unchanged colonic mucosa was not associated with DNA methylation within the CpG islands of the PHD1, PHD2 and FIH genes. 24354513_higher expression in normal skin compared to seborrheic keratosis, Bowen's disease and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 24513612_striking enrichment of high-altitude ancestry in the Tibetan genome, indicating that migrants from low altitude acquired adaptive alleles from the highlanders 24711448_Data indicate that the Tibetan prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 (PHD2) haplotype (D4E/C127S) strikingly diminishes the interaction of PHD2 with heat shock protein 90 co-chaperone protein p23 (prostaglandin E synthase). 25010988_PHD2 inhibits the adaptation of glioblastoma cells to hypoxia by regulating the expression of HIF-alpha subunits. 25263965_Germ-line PHD1 and PHD2 mutations detected in patients with pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma-polycythemia 25420025_Data show that dimethyl-2-ketoglutarate (DKG) inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) proline hydroxylation and degradation mediated by prolyl-4-hydroxylase PHD2. 25431923_The association between EGLN1 and HIF-1AN single nucleotide polymorphisms and acute mountain sickness in a Han Chinese population, was examined. 25546659_Compared to those with high PHD2 expressions, patients with low PHD2 expression had significantly longer DFS and OS periods. 26047609_a genetic link between EGLN1 and VWF in a constitution specific manner which could modulate thrombosis/bleeding susceptibility and outcomes of hypoxia, is reported. 26082309_Sulfur mustard negatively affects hypoxia-stimulated HIF-1alpha signaling in keratinocytes and fibroblasts and thus possibly contributes to delayed wound healing in SM-injured patients, which could be treated with PHD-2 inhibitors. 26112411_The kinetic properties of PHD2 and FIH with respect to oxygen reflect their cellular hypoxia-sensing ability. 26205124_the levels of both miR-182 and HIF1alpha were elevated, while the expression PHD2 and FIH1 was downregulated in a mouse model of prostate cancer. 26267649_In this article, UTMD/PEI mediated gene transfection was investigated and the US parameters were optimized. Furthermore, the biological effects of PHD2 shRNA were investigated in H9C2 cells. 26323721_findings show hypoxia and loss of PHD2 revert cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) activation 26676934_The present study demonstrated that the antiapoptotic effect of TMP in CoCl2-induced HUVECs was, at least in part, via the regulation of the PHD2/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway. 26740011_Disulfide bond-mediated PHD2 dimerization and inactivation result in the activation of HIF-1alpha and aerobic glycolysis in response to oxidative stress. 26951539_The role of PHD-2 in breast cancer [review] 27030384_miR-21 contributes to the protection of delayed ischemic preconditioning against renal ischemia reperfusion injury in mice, which is at least in part mediated by targeting of PHD2 and subsequently up-regulating HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway. 27307407_prolyl hydroxylase 2 plays an important tumor suppressive role in liver cancer 27368101_The HIFalpha subunit is usually prolyl-hydroxylated by EglN family members under normoxic conditions, causing its rapid degradation. Study confirmed that triple-negative breast cancer cells secrete glutamate, which is both necessary and sufficient for the paracrine induction of HIF1alpha in such cells under normoxic conditions. 27502280_Tuning the Transcriptional Response to Hypoxia by Inhibiting Hypoxia-inducible Factor (HIF) Prolyl and Asparaginyl Hydroxylases. 27515179_Genetic variants in HIF-1alpha and PHD2 genes exist in Caucasians but do not appear to alter 30-day mortality in sepsis 27795296_Results identified a critical role of PHD2 for a reversible glycolytic reprogramming in macrophages with a direct impact on their function. 28038470_PHD2 is a direct binding partner of EGFR and show that PHD2 regulates EGFR stability as well as its subsequent signaling in breast carcinoma cells. 28199842_A mechanism of PHD2 regulation that involves the mTOR and PP2A pathways. 28233034_We genotyped 347 Tibetan individuals from varying altitudes for both the Tibetan-specific EGLN1 haplotype and 10 candidate SNPs in the EPAS1 haplotype and correlated their association with hemoglobin levels. 28329677_These data unravel B55alpha as a PHD2 substrate and highlight a role for PHD2-B55alpha in the response to nutrient deprivation. 28506759_In vitro studies showed that a complement C1q-A chain peptide is not a substrate for PHD2 but is a substrate for CP4H1. 28537846_the expression of prolyl hydroxylase domain 2 (PHD2) is selectively increased in CKD-AT-MSCs and its inhibition can restore the expression of HIF-1alpha and the wound healing function of CKD-AT-MSCs. These results indicate that more studies about the functions of MSCs from CKD patients are required before they can be applied in the clinical setting 28613249_Functionally active PHD2 SNP rs516651 [18], located in the key pathway for the hypoxic-inflammatory response, is associated with increased 30-day mortality in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) patients. In contrast, the PHD2 SNP rs480902 is not. Furthermore, the HIF-2alpha SNP [ch2: 46441523(hg18)] GG-genotype was neither present in our ARDS patients of Caucasian heritage nor in healthy Caucasian blood donors. 28805660_Phd2 is the dominant HIF-hydroxylase in neutrophils under normoxic conditions; intrinsic regulation of glycolysis and glycogen stores is linked to the resolution of neutrophil-mediated inflammatory responses 28839461_GPT2 reduced alpha-ketoglutarate level in cells leading to the inhibition of proline hydroxylase 2 (PHD2) activity involved in the regulation of HIF1alpha stability. Accumulation of HIF1alpha, resulting from GPT2-alpha-ketoglutarate-PHD2 axis, constitutively activates sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway. 28900510_This study elucidates the molecular basis of the c-Myc/EGLN1-mediated induction of LSH expression that inhibits ferroptosis 29625625_Studied the association between SNPs around the EGLN1 genomic region, possibly involved in high-altitude adaptation, and physiological changes to hypobaric hypoxia exposure in a cohort of Japanese lowlanders. 30144273_The overall results indicate how the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase 2 Catalytic Domain achieves selectivity for HIFalpha oxygen-dependent degradation domains. 30575721_During the transition of nevi to melanoma, the expression of PHD2 protein is significantly decreased, and lower expression of PHD2 in melanoma is associated with worse clinical outcome. Knockdown of PHD2 leads to elevated Akt phosphorylation in melanocytes. 30575913_Both lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) had elevated PHD2 (EGLN1) expression compared to normal tissues. High PHD2 expression LUAD, but not LUSC, patients had shorter overall (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) compared to the low expression group. High methylation level of these two CpG sites (cg07040244 and cg21875980) in PHD2 was associated with better OS in LUAD patients. 30677555_PHD2 silencing in endothelial progenitor cell elevated the expression of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha), which enhanced the migration and survival ability of endothelial progenitor cell respectively. 30719713_the high-altitude adaptative mutations in EGLN1 in Tibetans are absent or found at low frequency in highland Andeans 30898838_findings reveal a differential dependency of clear cell ovarian cancers on EGLN1, thus identifying EGLN1 as a potential therapeutic target in clear cell ovarian cancer patients 31009679_Results show that SNP rs479200 in EGLN1 gene is associated with the predisposition to preeclampsia and this association is modified by the severity. 31142511_An oxygen-independent mechanism of PHD2 regulation that has important implications in cancer cell survival.The three N-terminal SH3 domains of CIN85 bind to the N-terminus of PHD2. 31239290_PHD2 is the key regulatory enzyme of BRD4 proline hydroxylation and the modification significantly affects BRD4 interactions with key transcription factors as well as BRD4-mediated transcriptional activation. 31285371_ERK Regulates HIF1alpha-Mediated Platinum Resistance by Directly Targeting PHD2 in Ovarian Cancer. 31500697_The authors did not detect prolyl-hydroxylase activity on any reported non-HIF protein or peptide, using conditions supporting robust HIF-alpha hydroxylation. 31712437_An EGLN1 causal variant enhances O2 delivery or use during exercise at altitude in Peruvian Quechua. 31763849_Label-Free Interactome Analysis Revealed an Essential Role of CUL3-KEAP1 Complex in Mediating the Ubiquitination and Degradation of PHD2. 32414920_Tibetan PHD2, an allele with loss-of-function properties. 32464411_Hypoxia responsiveness linked variant in EGLN1 gene is enriched in oral cancer patients. 32755251_Isolated Erythrocytosis Associated With 3 Novel Missense Mutations in the EGLN1 Gene. 33282944_Effect of EGLN1 Genetic Polymorphisms on Hemoglobin Concentration in Andean Highlanders. 33319810_Use of cyclic peptides to induce crystallization: case study with prolyl hydroxylase domain 2. 33823854_An integrative functional genomics approach reveals EGLN1 as a novel therapeutic target in KRAS mutated lung adenocarcinoma. 33988258_Inhibiting PHD2 in human periodontal ligament cells via lentiviral vector-mediated RNA interference facilitates cell osteogenic differentiation and periodontal repair. 34007987_High-altitude pulmonary edema is aggravated by risk loci and associated transcription factors in HIF-prolyl hydroxylases. 34102396_Gain-of-function Tibetan PHD2(D4E;C127S) variant suppresses monocyte function: A lesson in inflammatory response to inspired hypoxia. 35538889_AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 phosphorylates PHD2 to maintain systemic iron homeostasis. 36064857_Adipocyte-derived lactate is a signalling metabolite that potentiates adipose macrophage inflammation via targeting PHD2. 36180894_Differential methylation in EGLN1 associates with blood oxygen saturation and plasma protein levels in high-altitude pulmonary edema. 36219563_The ribosomal chaperone NACA recruits PHD2 to cotranslationally modify HIF-alpha. |
ENSMUSG00000031987 |
Egln1 |
788.651225 |
0.2922776648 |
-1.774589 |
0.093322171 |
352.464977 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000123129245493738300516943262509126137089465366616414296167008516412287942766161291094167739889549377551642100215006342507592551919251656731868481016849763996901125093351752226227282456458560645079503004239995789248496294021606445312500000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040657442136187415843744959597492190508137396056924565654865012607475252990636226122127180136019505399050416887269464488966465417557540432683186095222517685035510053981042712022101298484236600594421418009005719795823097229003906250000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
375.2019708 |
22.5881874 |
1291.6794361 |
52.7148834 |
| ENSG00000135898 |
9290 |
GPR55 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2T6 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in hyperalgesia associated with inflammatory and neuropathic pain (By similarity). Receptor for L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI). LPI induces Ca(2+) release from intracellular stores via the heterotrimeric G protein GNA13 and RHOA. Putative cannabinoid receptor. May play a role in bone physiology by regulating osteoclast number and function. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19805329}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily. The encoded integral membrane protein is a likely cannabinoid receptor. It may be involved in several physiological and pathological processes by activating a variety of signal transduction pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:9290; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cannabinoid receptor activity [GO:0004949]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025] |
17765871_These results strongly suggest that GPR55 is a specific and functional receptor for lysophosphatidylinositol. 17876302_The GPR55 is a novel cannabinoid receptor, it binds to and is activated by the cannabinoid ligand CP55940 and couples to Galpha13 and can mediate activation of rhoA, cdc42 and rac1. 18263732_establish GPR55 as a cannabinoid receptor with signaling distinct from CB(1) and CB(2). 18445684_in endothelial cells, two receptors for anandamide were found, which were characterized as cannabinoid 1 receptor & and G-protein-coupled receptor 55; integrin clustering enables anandamide-induced Ca2+ signaling in endothelial cells via GPR55 18757503_Treatment with lysophosphatidylinositol induces marked GPR55 internalization and stimulates a sustained, oscillatory calcium release pathway, which is dependent on Galpha13 and requires RhoA activation. 19723626_GPR55 is an atypical cannabinoid responder. 19805329_Data reveal a role of GPR55 in bone physiology by regulating osteoclast number and function. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20051382_results suggest that GPR55 and its endogenous ligand LPI play essential roles in the homoeostatic responses to stress signals in several mammalian tissues and cells including certain types of immune cells 20506567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506567_this study demonistrated that low-functioning Val195 allele of GPR55 appears to be a risk factor for anorexia nervosa. 20549374_HIV-infected human cells injected into immunodeficient mice to observe expression levels of CB1R, CB2R and GPR55. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20818416_GPR55 expression in human tumors from different origins correlates with tumor aggressiveness. Moreover, GPR55 promotes cancer cell proliferation through the overactivation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade. 20838378_GPR55 is expressed in several prostate and ovarian cancer cell lines and has a critical role in regulating proliferation and anchorage-independent growth. GPR55 mediates the effects of lysophosphatidylinositol in prostate and ovarian cancer cells. 21367464_GPR55 is expressed in human tumours and drives proliferation and its expression correlates with tumour aggressiveness 21467997_GPR55 limits the tissue-injuring inflammatory responses mediated by CB(2)R, while it synergizes with CB(2)R in recruiting neutrophils to sites of inflammation. 21534610_The chemical diversity provided by three lead compounds combined with the identification of key GPR55 receptor interaction sites should provide a basis for the design of more efficacious second-generation GPR55 ligands that retain GPR55 selectivity. 21537344_New blood brothers: the GPR55 and CB2 partnership 21718301_GASP-1 is a key regulator of the trafficking and, by extension, functional expression of GPR55 22179809_alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol(LPI)/GPR55 system is positively associated with obesity in humans. 22285325_Studies suggest the lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI)/orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR55 axis plays an important role in different physiological and pathological contexts. 22751111_GPR55 drives skin carcinogenesis and is upregulated in human squamous cell carcinomas. 22820167_This review presents a summary of what is known about the G-protein coupled receptors GPR35 and GPR55 and their potential characterization as lysophospholipid or cannabinoid receptors, respectively--{REVIEW} 23151004_This article reviews current data about GPR55 pharmacology and signalling, highlighting its involvement in several pathophysiological conditions. [review] 23161546_CB1 modulates the signaling properties of the lysophosphatidylinositol receptor GPR55. 23603203_Data (including data from tissue bank samples) suggest that GPR55 is strongly expressed on myenteric neurons of the colon. 23639801_Data suggest that GPR55 is functionally expressed in vascular endothelium/platelets and is involved in regulation of calcium signaling; as suspected, lysophosphatidylinositol is a ligand/agonist for GPR55. 24274581_GPR55 antagonists occupies a horizontal binding pocket extending into the extracellular loop region, a central ligand portion that fits vertically in the receptor binding pocket. 24652077_GPR55 receptors were expressed in urothelial cell lines and interact with CB1 receptors. 24942731_CB2R and GPR55 form heteromers in cancer cells, these structures possess unique signaling properties, and modulation of these heteromers can modify the antitumoral activity of cannabinoids in vivo 24972076_This review summarizes our current knowledge of expression and function of GPR55 in tissues involved in metabolic regulation and the signaling cascades through which GPR55 is reported to act. 25048571_Heteromerization of GPR55 and cannabinoid CB2 receptors modulates signalling 25233417_Data suggest GPR55 (G-protein coupled receptor 55), ABCC1 (ATP-binding cassette sub-family C), and MPR1/ABCB1 (multidrug resistance protein 1) participate/cooperate in autocrine communication/tumorigenesis involving lysophosphatidylinositol. [REVIEW] 25344934_proinflammatory role in innate immunity 25545857_expression of CB1 and GPR55 in proximal tubules is altered in response to elevated levels of glucose and albumin 25869640_GPR55 is expressed in placenta,located solely at the placental endothelium; L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI), the endogenous ligand of GPR55, increases migratory activity of venous but not arterial placental endothelial cells suggesting a role of LPI-GPR55 axis in placental venous endothelium function 25889562_GPR55 was a direct target gene of miR-675-5p. 25970609_GPR55 could play deleterious role in ox-LDL-induced foam cells and could be a novel pharmacological target to manage atherosclerosis and other related cardiovascular diseases. 25989290_Inhibiting the pro-angiogenic L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol /GPR55 pathway appears a promising target against angiogenesis in ovarian carcinoma 26436760_GPR55 is involved in the migratory behaviour of colon carcinoma cells. 26588872_The signalling pathways activated by lysophosphatidylinositol through its receptor GPR55 play a pivotal role in different cancer. [review] 27423937_Inhibition of GPR55 activity produces antitumor effects via attenuation of the MEK/ERK and PI3K-AKT pathways leading to a reduction in the expression and function of MDR proteins. 27561953_GPR55 was highly expressed by beta-cells of both humans and mice. It was also present in a small proportion of mouse islet alpha-cells and in the majority of human islet alpha-cells, but it was absent or at very low levels in delta-cells of both species. GPR55 was preferentially expressed in the endocrine pancreas, with only faint immunoreactivity in the exocrine pancreas in mice and humans. 28005346_Crucial amino acid residues involved in agonist signaling at the GPR55 receptor have been identified. 28272905_We observed a significantly higher expression of GPR55 mRNA in Crohn's disease (CD) patients compared to ulcerative colitis (UC) and controls. CD patients manifested higher GPR55 mRNA expression in inflamed compared with non-inflamed colonic tissues. In contrast, the analysis of GPR55 mRNA expression in UC patients revealed no statistically significant differences between inflamed and non-inflamed colonic tissue. 28875496_our data suggest that GPR55 and CB1 play differential roles in colon carcinogenesis where the former seems to act as oncogene and the latter as tumor suppressor. 29188802_GPR55 is involved in the migratory behavior of human breast cancer cells. 29435814_The GPR55 gene expressions were significantly lower in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex of suicide cases. 29888782_Our findings support the hypothesis that neural stem cells (NSC) express functional GPR55 and that targeting GPR55 with selective agonists increases NSC proliferation and early neurogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. A better understanding of the role GPR55 plays during neurogenesis may provide new prospects for therapeutic treatments utilizing this receptor as a target. 30830860_Study found GPR55 expression downregulated in salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinomas and GPR55 reinstatement by antitumor irradiation, suggesting that GPR55 controls renegade proliferation. GPR55 antagonism increases cell proliferation and function determination in quasiphysiological systems. GPR55 signaling in epithelial cells ensures both the life-long renewal of ductal cells and the continuous availability of saliva 30890410_hypertension can be mitigated via CB1 agonism and impaired adrenoceptor responsiveness prevented by functional GPR55. 31149342_Results provide evidence that l-alpha-Lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via a GPR55/ROCK-dependent pathway. 31200545_The authors conclude that hepatitis C virus induces lncR 8 expression, while lncR 8 indirectly favors hepatitis C virus replication by stimulating expression of its neighboring gene GPR55, which in turn downregulates expression of ISGs. The latter fact is also consistent with an anti-inflammatory role of GPR55. 31925452_The cannabinoid ligands SR141716A and AM251 enhance human and mouse islet function via GPR55-independent signalling. 32121640_Ginseng Gintonin Contains Ligands for GPR40 and GPR55. 32329085_The L-alpha-Lysophosphatidylinositol/G Protein-Coupled Receptor 55 System Induces the Development of Nonalcoholic Steatosis and Steatohepatitis. 33902596_Peptide targeting of lysophosphatidylinositol-sensing GPR55 for osteoclastogenesis tuning. 33952459_Expression of Lysophosphatidylinositol Signaling-relevant Molecules in Colorectal Cancer. 33959968_BRET analysis reveals interaction between the lysophosphatidic acid receptor LPA2 and the lysophosphatidylinositol receptor GPR55 in live cells. 34237432_Lysophosphatidylglucoside is a GPR55 -mediated chemotactic molecule for human monocytes and macrophages. 34271437_Interactions between lysophosphatidylinositol receptor GPR55 and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P5 in live cells. 34324032_Expression of the putative cannabinoid receptor GPR55 is increased in endometrial carcinoma. 34948125_Gene Expression Data Mining Reveals the Involvement of GPR55 and Its Endogenous Ligands in Immune Response, Cancer, and Differentiation. 35562947_Prognostic Significance of GPR55 mRNA Expression in Colon Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000049608 |
Gpr55 |
10.683191 |
0.3057397990 |
-1.709624 |
0.559837789 |
9.281103 |
0.00231529953176072816195540937656005553435534238815307617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005052309445415190461425858359234553063288331031799316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2422765 |
1.9509297 |
17.4350068 |
3.9525750 |
| ENSG00000135929 |
1593 |
CYP27A1 |
protein_coding |
Q02318 |
FUNCTION: Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that catalyzes regio- and stereospecific hydroxylation of cholesterol and its derivatives. Hydroxylates (with R stereochemistry) the terminal methyl group of cholesterol side-chain in a three step reaction to yield at first a C26 alcohol, then a C26 aldehyde and finally a C26 acid (PubMed:9660774, PubMed:12077124, PubMed:21411718, PubMed:28190002). Regulates cholesterol homeostasis by catalyzing the conversion of excess cholesterol to bile acids via both the 'neutral' (classic) and the 'acid' (alternative) pathways (PubMed:9660774, PubMed:1708392, PubMed:11412116, PubMed:2019602, PubMed:7915755, PubMed:9186905, PubMed:9790667). May also regulate cholesterol homeostasis via generation of active oxysterols, which act as ligands for NR1H2 and NR1H3 nuclear receptors, modulating the transcription of genes involved in lipid metabolism (PubMed:9660774, PubMed:12077124). Plays a role in cholestanol metabolism in the cerebellum. Similarly to cholesterol, hydroxylates cholestanol and may facilitate sterol diffusion through the blood-brain barrier to the systemic circulation for further degradation (PubMed:28190002). Also hydroxylates retinal 7-ketocholesterol, a noxious oxysterol with pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic effects, and may play a role in its elimination from the retinal pigment epithelium (PubMed:21411718). May play a redundant role in vitamin D biosynthesis. Catalyzes 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D3 that is required for its conversion to a functionally active form (PubMed:15465040). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11412116, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12077124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15465040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1708392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2019602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21411718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28190002, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7915755, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9186905, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9660774, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9790667}. |
Acetylation;Cataract;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Heme;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Hormone biosynthesis; cholecalciferol biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:15465040}.; PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism; cholesterol degradation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12077124, ECO:0000305|PubMed:9660774}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; bile acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:11412116}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This mitochondrial protein oxidizes cholesterol intermediates as part of the bile synthesis pathway. Since the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids is the major route for removing cholesterol from the body, this protein is important for overall cholesterol homeostasis. Mutations in this gene cause cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, a rare autosomal recessive lipid storage disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1593; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 3-alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha-trihydroxycholestan-26-al 26-oxidoreductase activity [GO:0047103]; cholestanetetraol 26-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047748]; cholestanetriol 26-monooxygenase activity [GO:0047749]; cholesterol 26-hydroxylase activity [GO:0031073]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; steroid hydroxylase activity [GO:0008395]; vitamin D3 25-hydroxylase activity [GO:0030343]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699]; calcitriol biosynthetic process from calciol [GO:0036378]; cholesterol catabolic process [GO:0006707]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; sterol metabolic process [GO:0016125] |
11903362_A Japanese patient with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis has different mutations within two functional domains of CYP27. 12011083_regulation of CYP7A1 and CYP27A1 in human liver 12117727_Endogenous CYP27A1 is of importance for the normal efflux of both cholesterol and cholestanol from tendons. 12119285_levels of 27-hydroxycholesterol are not of critical importance for cholesterol homeostasis in mice. 12242561_A compound heterozygous mutation in CYP27A1 (one missense mutation and one intronic nucleotide change) occurs in a Taiwanese family with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. 12777473_The very high activity of CYP27A1 towards the cholestanol precursor 4-cholesten-3-one may be of importance in connection with the accumulation of cholestanol in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis 14672608_The pathogenesis of cholesterolosis may be multifactorial, but is not caused by reduced efflux of cholesterol due to a defect sterol 27-hydroxylase mechanism. 14741198_We reported a Hong Kong Chinese proband with Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis in which a novel acceptor splicing site mutation (IVS6-1G>T) was identified. 15340076_nuclear receptor-regulated CYP27 expression is likely to be a key integrator of retinoic acid receptor-PPARgamma-LXR signaling, relying on natural ligands and contributing to lipid metabolism in macrophages 15533057_stimulation of CYP27A1 by PPARgamma may represent a key previously unrecognized mechanism by which PPARgamma protects against atherosclerosis 15708352_Data suggest that induction of sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) by TGF-beta1 may be responsible for some of the anti-atherogenic properties of this cytokine. 16157755_In this study showed that the Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis( CTX) due to CYP27 mutation R362C. 16372260_Mutation in Cytochrome P-450 CYP27A1 is associated with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis 16584175_Mutation of the overlapping substrate-contact residues (W100, H103, T110, M301C, V367, I481, and V482) affected CYP27A1 binding and enzyme activity in a substrate-dependent manner and allowed identification of several important side chains. 16930540_Monocyte-derived cells express CYP27A1 and convert vitamin D3 into its active metabolite 17088262_there may be an intestine-specific PXR/CYP27A1/LXRalpha pathway that regulates intestine cholesterol efflux and HDL assembly. 17292862_Glutamine 85 cyp27A1 plays essential roles in both substrate-binding and protein folding. 17482558_human CYP27A1 gene is a target for estrogens and androgens 17697869_K226R, D321G, and P408S mutants showed 25-hydroxylation activity for 1alphaOHD(3) as well as wild type. 17875655_CYP27A1 and CYP24 expression is a function of malignant transformation in the colon 18227423_We found the first cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis family from Argentina with a new mutation in CYP27A1 gene. 18791760_Results describe the membrane topology of CYPs 27A1 and 11A1. 19255064_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19255064_Single nucleotide polymorphisms may be associated with risk of prostate cancer in men with low vitamin D status. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19671838_Overexpression of CYP27A1 in CHOP cells decreased progesterone conversion to 20alpha-DH-progesterone in a dose-dependent manner 19852851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20149624_down-regulation of genes involved in the cholesterol synthesis pathway results in down-regulation of CYP27A1 which diminishes oxysterol concentrations 20402754_Four novel mutations located in different exons, in particular in the region of exons 2-5 of the CYP27A1 gene, present as classical cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. 20450308_There needs to be a high level of suspicion of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CXT) for any child with cataracts and developmental delay 20558929_An Arg104Gln mutation in sterol 27-hydroxylase is identified in Japanese patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis; case 1 is a compound heterozygote for Arg104Gln in exon 2 and Arg441Gln in exon 8. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20654748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20809279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21049985_The average P450 concentrations/mg of total tissue protein were 345 fmol of CYP46A1 and 110 fmol of CYP27A1 in the temporal lobe, and 60 fmol of CYP46A1 and 490 fmol of CYP27A1 in the retina. 21134350_results indicate involvement of the JNK/c-jun pathway in AR-mediated upregulation of CYP27A1. The link to JNK signaling is interesting since inflammatory processes may upregulate CYP27A1 to clear cholesterol from peripheral tissues. 21258856_study found that adenosine A2A receptor stimulation inhibited foam cell formation by a mechanism dependent on the expression of CYP27A1 21411718_Sterol 27-hydroxylase cytochrome P450 27A1 (CYP27A1) is involved in elimination of 7-ketocholesterol from the retinal pigment epithelium. 21498512_the post-translational modifications identified in CYP27A1 exemplify a general mechanism whereby oxidative stress and inflammation deleteriously affect protein function 21958693_Mutations consisting of c.1146_1151deletion-insertion and c.1214G>A substitution of CYP27A1 are identified in patients having cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. 22018287_CYP27A1 mutations were found in the proband and a Chinese family with Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis 22185844_An alternative to elimination of brain cholesterol by the CYP46A1 mechanism is elimination by CYP27A1. 22227097_Features of the retinal environment which affect the activities and product profile of cholesterol-metabolizing cytochromes P450 CYP27A1 and CYP11A1. 22509407_This study has identified candidate genes for sporadic Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis( ALS), most notably CYP27A1. Mutations in CYP27A1 are causal to cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis which can present as a clinical mimic of ALS . 24029861_The increased cutaneous CYP27B1 levels in the CKD patients suggest that the loss of renal activity of this enzyme is at least partially compensated for by the skin. 24080357_Cyp27A1 mutations were identified in early onset CAD pedigree. 24096962_The expression of CYP27A1 modulates the concentrations of active glucocorticoids in both humans and mice and in vitro. 24280213_Data indicate that inhibition of CYP27A1 activity or knockdown and deletion of the Cyp27a1 gene induced adipocyte differentiation. 24584636_study describes two unrelated Sardinian families sharing the same CYP27A1 mutation, p.Arg479Cys; phenotype of the patients is characteristic of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis 24732451_Studied whether abnormal endometrial expression of CYP27A1 and/or CYP2R1 may impair VDR-antiproliferative properties in endometrial carcinoma. 25447658_In a patient with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, analysis of the CYP27A1 gene identified compound heterozygosity for p.A335V, a novel mutation. 25845986_The 25-hydroxylases CYP2R1 and CYP27A1 catalyze vitamin D to its circulating form 25-hydroxyvitamin D. 26374826_marinobufagenin is derived from bile acids and its biosynthesis is initiated by CYP27A1 enzyme 26638999_CYP27A1 belongs to the mitochondrial CYPs and plays a crucial role in the cholesterol homeostasis. 26643207_Analysis of ~60,000 human exomes points to underdiagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis due to CYP27A1 mutations. 26844446_A novel mutation (c.1183_1184insT) in several members of a Colombian cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis family is responsible for mental retardation, psychiatric disorders, behavioral changes, and multiple domains cognitive impairment with dysexecutive dominance that progressed to early dementia. 26891232_CYP27A1 catalyzes hydroxylation of beta-sitosterol and ergosterol 27259383_we demonstrated the rare missense variant of CYP27A1 is associated with atopic dermatitis with elevated levels of total serum IgE. 27792005_A significant decrease in the expression level of CYP27A1 in female patients could indicate their greater vulnerability to multiple sclerosis than the male patients. 28130224_CYP27A1 is a critical cellular cholesterol sensor in prostate cells and that dysregulation of the CYP27A1/27-hydroxycholesterol (27HC) axis contributes significantly to prostate cancer pathogenesis. 28190002_CYP46A1 is involved in cholestanol removal from the brain and that several factors contribute to the preferential increase in cholestanol in the cerebellum arising from CYP27A1 deficiency. 28229379_Molecular study identified a novel homozygous frameshift mutation in CYP27A1 gene in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis without cataract 28306719_The 32 kb deleted region harbors the CYP2A7 gene and was enriched with enhancer, repressor and insulator sites. The wildtype allele was lost in the polyps of the proband 28337550_This study suggests a shared genetic etiology between MS and the characterized single-gene disorders, and highlights cholesterol metabolism and the synthesis of oxysterols as important biological mechanisms for familial MS 28396342_Increased maternal and fetal cholesterol efflux capacity and placental CYP27A1 expression in preeclampsia 28590052_Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis .. is caused by mutations in the CYP27A1 gene that result in decreased production of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and elevated levels of cholestanol and bile alcohols. Sequencing of CYP27A1 showed a paternally inherited splice mutation, c.446 + 1G>T, and a maternally inherited nonsense mutation, c.808C>T, predicting p.(Arg270*). 28623566_Three novel mutations in CYP27A1 were found in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis patients in Chinese families 29116467_Vitamin D supplementation can decrease circulating 27HC of breast cancer patients, likely by CYP27A1 inhibition. This suggests a new and additional modality by which vitamin D can inhibit ER+ breast cancer growth, though a larger study is needed for verification. 29269672_Whole-exome sequencing assuming recessive inheritance determined his genetic diagnosis to be cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis caused by homozygous mutations (c.410G>A or p.Arg137Gln) in the cytochrome P450 subfamily 27 A1 (CYP27A1) gene 29935100_Donor/recipient CYP27A1 rs4674344 and graft VDR rs2228570 may be related to low serum 25(OH)D and may play a major role in the development of fatty liver disease in recipients after living donor liver transplantation. 30088172_CYP27A1 SNPs are not associated with vitamin D status and multiple sclerosis. 30563407_These findings all suggest that CYP27A1 is a critical cholesterol sensor in bladder cancer cells that may contribute significantly to bladder cancer proliferation. 30668811_analysis of the role of CYP27A1, CYP27B1, and CYP24A1 in non-melanoma skin cancer reveals that the expression of CYP27A1 and CYP24A1, but not CYP27B1 is changed in malignant cells 30867220_Low CYP27A1 expression is associated with higher cholesterol synthesis and a higher risk of Lethal Prostate Cancer. 31520221_Study found no statistically significant associations of HCV infection outcomes with CYP27A1 gene. 31774068_Relationship between rs4674344 CYP27A1 gene polymorphism and coronary artery disease in a Polish population. 31875301_A case of Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis with spinal cord involvement and without tendon xanthomas: identification of a new mutation of the CYP27A1 gene. 32344004_CYP2R1 and CYP27A1 genes: An in silico approach to identify the deleterious mutations, impact on structure and their differential expression in disease conditions. 33058307_Dysregulation of vitamin D synthesis pathway genes in colorectal cancer: A case-control study. 33107041_Extending the vitamin D pathway to vitamin D3 and CYP27A1 in periodontal ligament cells. 33176848_CYP27A1 expression is associated with risk of late lethal estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal patients. 33400472_Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Splicing Variant in CYP27A1 in an Iranian Family with Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis. 33794192_CYP27A1-dependent anti-melanoma activity of limonoid natural products targets mitochondrial metabolism. 34930075_Analysis of CYP27A1 mutations in Han Chinese women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. 35810773_CYP27A1 inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activation of LXRs/ABCA1. 35969149_The tumor-repressing effect of CYP27A1 on renal cell carcinoma by 27-HC arising from cholesterol metabolism. |
ENSMUSG00000026170 |
Cyp27a1 |
18.438279 |
0.4029784588 |
-1.311225 |
0.356345664 |
13.917117 |
0.00019105061550301970880669233388005068263737484812736511230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000502209632203841674878697087791579178883694112300872802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8049696 |
2.4376436 |
27.0096006 |
3.7856072 |
| ENSG00000135931 |
80210 |
ARMC9 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z3E5 |
FUNCTION: Involved in ciliogenesis (PubMed:32453716). It is required for appropriate acetylation and polyglutamylation of ciliary microtubules, and regulation of cilium length (PubMed:32453716). Acts as a positive regulator of hedgehog (Hh)signaling (By similarity). May participate in the trafficking and/or retention of GLI2 and GLI3 proteins at the ciliary tip (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E7F187, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D2I5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32453716}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Joubert syndrome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in cilium assembly and positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway. Located in centriole and ciliary basal body. Implicated in Joubert syndrome 30. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80210; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28625504_ARMC9 localizes to the basal body of the cilium and is upregulated during ciliogenesis. 29159890_Our report of variant in ARMC9 Leading to Joubert syndrome phenotype (JS30), elucidates the genetic heterogeneity of Joubert syndrome, and expands the gene list for ciliopathies. 30395750_Our study suggests that ARMC9 variants do not play a critical role in the development of Vogt-Koyanagi disease. |
ENSMUSG00000062590 |
Armc9 |
488.993375 |
0.3421047094 |
-1.547490 |
0.128322575 |
141.821034 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000001064175999309200401768871294400014639872353010808225190278589544309572890779494191450509771312837870027578901499509811401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000148742781721626858134391511682879932634876984792692972329589262175498249989798622014772200294885351468110457062721252441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
237.3474079 |
20.6358968 |
697.9083903 |
41.9466626 |
| ENSG00000135968 |
9648 |
GCC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWJ2 |
FUNCTION: Golgin which probably tethers transport vesicles to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and regulates vesicular transport between the endosomes and the Golgi. As a RAB9A effector it is involved in recycling of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor from the late endosomes to the TGN. May also play a role in transport between the recycling endosomes and the Golgi. Required for maintenance of the Golgi structure, it is involved in the biogenesis of noncentrosomal, Golgi-associated microtubules through recruitment of CLASP1 and CLASP2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16885419, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17543864}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a peripheral membrane protein localized to the trans-Golgi network. It is sensitive to brefeldin A. This encoded protein contains a GRIP domain which is thought to be used in targeting. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009]. |
hsa:9648; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090161]; late endosome to Golgi transport [GO:0034499]; microtubule anchoring [GO:0034453]; microtubule organizing center organization [GO:0031023]; protein localization to Golgi apparatus [GO:0034067]; protein targeting to lysosome [GO:0006622]; recycling endosome to Golgi transport [GO:0071955]; regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0070861]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] |
12446665_targeting to subcompartments of trans-Golgi network by GRIP domain 15654769_The ability of the four mammalian GRIP domain proteins, p230, golgin-97, GCC88, and GCC185 to interact is reported. 16885419_These data assign a specific pathway to an interesting, TGN-localized protein and suggest that GCC185 may participate in the docking of late endosome-derived, Rab9-bearing transport vesicles at the TGN. 17488291_GCC2 is required for endosome-to-Golgi transport and maintenance of Golgi structure. 18243103_Rab and Arl GTPase family members cooperate in the localization of GCC2. 18946081_Results show that GCC185 contains at least six binding sites for as many as 14 different Rab GTPases across its entire length. 19703403_Study demonstrates that Golgi recruitment of endogenous GCC185 does not involve Rab6A/A' and Arl1. 21875948_Two distinct domains of GCC185 are needed either for Golgi structure maintenance or transport vesicle tethering. The domain needed for vesicle tethering binds to the clathrin adaptor AP-1. 22159419_Deletion of the ARL4A-interacting region of GCC185 results in inability to maintain Golgi structure and modulate endosome-to-Golgi transport. 26653856_These unexpected features support a model in which GCC185 collapses onto the Golgi surface, perhaps by binding to Rab GTPases, to mediate vesicle tethering. 27105913_In light of existing report suggesting critical role of Nef-GCC185 interaction reveals valuable mechanistic insights affecting specific protein transport pathway in docking of late endosome derived Rab9 bearing transport vesicle at TGN elucidating role of Nef during viral pathogenesis. 31840180_The co-localization of M6PR and of GCC2 with ASOs is influenced by the PS modifications, which have been shown to enhance the affinity of ASOs for proteins, suggesting that localization of these proteins to LEs is mediated by ASO-protein interactions. Reduction of M6PR levels also decreased PS-ASO activity in mouse cells and in livers of mice treated subcutaneously with PS-ASO, indicating a conserved mechanism. |
ENSMUSG00000038039 |
Gcc2 |
587.251504 |
0.4876769723 |
-1.036002 |
0.082085810 |
158.930728 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000193765364600250211010010819284398886266237671668016860893897118563221206795845669079291035351818306420312865157029591500759124755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000029545214684914184211281546278715522013771049092189985780194402755543753878994006390888200528840878966718719311757013201713562011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
400.7714701 |
19.8758380 |
827.4296569 |
28.4671277 |
| ENSG00000136010 |
160428 |
ALDH1L2 |
protein_coding |
Q3SY69 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase that catalyzes the NADP(+)-dependent conversion of 10-formyltetrahydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate and carbon dioxide. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21238436}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Mitochondrion;NADP;One-carbon metabolism;Oxidoreductase;Phosphopantetheine;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
This gene encodes a member of both the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily and the formyl transferase superfamily. This member is the mitochondrial form of 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (FDH), which converts 10-formyltetrahydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate and CO2 in an NADP(+)-dependent reaction, and plays an essential role in the distribution of one-carbon groups between the cytosolic and mitochondrial compartments of the cell. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:160428; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004029]; formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase activity [GO:0016155]; hydroxymethyl-, formyl- and related transferase activity [GO:0016742]; 10-formyltetrahydrofolate catabolic process [GO:0009258]; biosynthetic process [GO:0009058]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; folic acid metabolic process [GO:0046655]; NADPH regeneration [GO:0006740]; one-carbon metabolic process [GO:0006730] |
19933275_Our study identifies human PPT as the FDH-modifying enzyme and supports the hypothesis that mammals utilize a single enzyme for all phosphopantetheinylation reactions. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20498374_a gene at chromosome locus 12q24.11 of the human genome, the product of which has 74% sequence similarity with cytosolic FDH 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21238436_ALDH1L2 has enzymatic properties similar to its cytosolic counterpart |
ENSMUSG00000020256 |
Aldh1l2 |
34.579261 |
2.9534391817 |
1.562396 |
0.512346417 |
8.778856 |
0.00304742311548367780099644264169000962283462285995483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006518835533991172194456797939210446202196180820465087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.4036897 |
16.8559318 |
17.6003613 |
4.3127224 |
| ENSG00000136040 |
10154 |
PLXNC1 |
protein_coding |
O60486 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for SEMA7A, for smallpox semaphorin A39R, vaccinia virus semaphorin A39R and for herpesvirus Sema protein. Binding of semaphorins triggers cellular responses leading to the rearrangement of the cytoskeleton and to secretion of IL6 and IL8 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20727575}. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the plexin family. Plexins are transmembrane receptors for semaphorins, a large family of proteins that regulate axon guidance, cell motility and migration, and the immune response. The encoded protein and its ligand regulate melanocyte adhesion, and viral semaphorins may modulate the immune response by binding to this receptor. The encoded protein may be a tumor suppressor protein for melanoma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:10154; |
cerebellar climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0150053]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; semaphorin receptor complex [GO:0002116]; semaphorin receptor activity [GO:0017154]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of synapse pruning [GO:1905806]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287] |
17671519_GTP-bound form of Rab7 promotes melanogenesis through the regulation of gp100 maturation in melanoma cells. 18628988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18987670_Plexin C1, a receptor for semaphorin 7a, inactivates cofilin and is a potential tumor suppressor for melanoma progression. 19318806_significant loss of Plexin C1 in metastatic melanoma compared with primary melanoma, suggesting the possibility that the Plexin C1 receptor is a tumor suppressor protein for melanoma 20727575_Study reports the structures of Sema7A and A39R complexed with the Semaphorin-binding module of PlexinC1; both structures show two PlexinC1 molecules symmetrically bridged by Semaphorin dimers. 23160370_loss of Plexin C1 in melanoma may promote early steps in melanoma progression through suppression of migration and proliferation 27609773_Plexin C1 deficiency permits synaptotagmin 7-mediated macrophage migration and enhances mammalian lung fibrosis 29514220_Results indicate that long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) CASC2 can promote PLXNC1 expression by sponging miR-181a, thereby inhibiting the proliferation and invasion of melanoma cells. 31317324_Results indicated that PLXNC1 was a direct target of miR-4500. Its knockdown inhibits proliferation and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) cells. On the contrary, its overexpression of impairs miR-4500-induced inhibition of PTC malignancy. 33656690_The Relationship Between Plexin C1 Overexpression and Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) Study. |
ENSMUSG00000074785 |
Plxnc1 |
609.867751 |
3.6645746351 |
1.873646 |
0.148199025 |
152.969619 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000003889668006500445660845669778267794164090343765610827888769874631229867784659479401690362269754241975050490509602241218090057373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000577580480643325775116895473042279831311498113508700930383026281426593710471756579124267064195841214768734062090516090393066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
981.1621820 |
83.9797671 |
269.4959171 |
17.5318360 |
| ENSG00000136052 |
84102 |
SLC41A2 |
protein_coding |
Q96JW4 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a plasma-membrane magnesium transporter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16984228}. |
Cell membrane;Ion transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in magnesium ion transmembrane transport. Predicted to act upstream of or within metal ion transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84102; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; magnesium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015095] |
Mouse_homologues 15809054_SLC41A2 is a Mg2+ transporter that might be involved in magnesium homeostasis in epithelial cells |
ENSMUSG00000034591 |
Slc41a2 |
94.723706 |
3.3476131934 |
1.743133 |
0.283528950 |
36.253563 |
0.00000000173242957299044168343327600986586087272733891495590796694159507751464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000008120247855617313738662351330771516089157557871658354997634887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
134.2941690 |
26.0113201 |
40.6012940 |
5.9737689 |
| ENSG00000136059 |
50853 |
VILL |
protein_coding |
O15195 |
FUNCTION: Possible tumor suppressor. |
Actin capping;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the villin/gelsolin family. It contains 6 gelsolin-like repeats and a headpiece domain. It may play a role in actin-bundling. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:50853; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; actin filament severing [GO:0051014]; actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008154]; barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:0051016] |
16921170_phospholipase C-gamma1 interaction with villin regulates epithelial cell migration 18006815_Brm is required for villin expression, a definitive marker of intestinal metaplasia and differentiation 18022635_Predicting the effect of a point mutation on a protein fold: the villin and advillin headpieces and their Pro62Ala mutants. |
ENSMUSG00000038775 |
Vill |
48.335068 |
0.4251545216 |
-1.233941 |
0.231306830 |
28.980148 |
0.00000007312385378568611917152598837776888984762990730814635753631591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000292099616204797596402442704313640042812494357349351048469543457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.2838920 |
4.7034380 |
69.5175745 |
7.3367152 |
| ENSG00000136153 |
4008 |
LMO7 |
protein_coding |
Q8WWI1 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing a calponin homology (CH) domain, a PDZ domain, and a LIM domain, and may be involved in protein-protein interactions. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, however, the full-length nature of some variants is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:4008; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of signaling [GO:0023051] |
17067998_Lmo7 positively regulates many EDMD-relevant genes (including emerin), and is feedback-regulated by binding to emerin. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21525034_functional interaction between emerin and Lmo7 is crucial for temporally regulating the expression of key myogenic differentiation genes. 21670154_show that LMO7 is upregulated in the stroma of invasive breast carcinoma in a manner that correlates with the increased expression of serum response factor target genes 26786059_Data suggest that Lmo7 is localized at the perinuclear region and in fibril-like structures along subsarcolemma of human skeletal myoblasts whereas in human myotubes Lmo7 is found diffuse throughout the cytoplasm. 27988857_study suggested that the LMO7 gene may play an important role in the pathogenesis of DCM in the Han Chinese population. 28026121_The miR-96-LMO7 axis may be a therapeutic target for lung cancer patients, and new diagnostic or therapeutic strategies could be developed by targeting the miR-96-LMO7 axis. 29158164_Data suggest that LMO7 interacts with MAD1 during spindle assembly phase of mitosis; LMO7 plays role in control of mitosis progression and exerts effect on spindle assembly checkpoint; LMO7 colocalizes with actin filaments; LMO7 does not colocalize with MAD1 at kinetochores in prometaphase nor at spindle poles in metaphase. (LMO7 = LIM domain only protein-7; MAD1 = mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD1) 29768105_the LMO7-BRAF fusion behaves as an oncogenic alteration in papillary thyroid carcinoma 30429017_LMO7 and LIMCH1 co-localized and co-immunoprecipitated. 34884689_New Findings on LMO7 Transcripts, Proteins and Regulatory Regions in Human and Vertebrate Model Organisms and the Intracellular Distribution in Skeletal Muscle Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000033060 |
Lmo7 |
192.316558 |
2.7070916711 |
1.436744 |
0.203361155 |
48.740537 |
0.00000000000292164847761323814351571054754571282003824950201931187621084973216056823730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000016878694826729268937079411581016663741749983529416567762382328510284423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
284.7486481 |
38.9662767 |
105.8823691 |
10.8618048 |
| ENSG00000136156 |
9445 |
ITM2B |
protein_coding |
Q9Y287 |
FUNCTION: Plays a regulatory role in the processing of the amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein (APP) and acts as an inhibitor of the amyloid-beta peptide aggregation and fibrils deposition. Plays a role in the induction of neurite outgrowth. Functions as a protease inhibitor by blocking access of secretases to APP cleavage sites.; FUNCTION: Mature BRI2 (mBRI2) functions as a modulator of the amyloid-beta A4 precursor protein (APP) processing leading to a strong reduction in the secretion of secretase-processed amyloid-beta protein 40 and amyloid-beta protein 42.; FUNCTION: Bri23 peptide prevents aggregation of APP amyloid-beta protein 42 into toxic oligomers. |
Alternative splicing;Amyloid;Amyloidosis;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Amyloid precursor proteins are processed by beta-secretase and gamma-secretase to produce beta-amyloid peptides which form the characteristic plaques of Alzheimer disease. This gene encodes a transmembrane protein which is processed at the C-terminus by furin or furin-like proteases to produce a small secreted peptide which inhibits the deposition of beta-amyloid. Mutations which result in extension of the C-terminal end of the encoded protein, thereby increasing the size of the secreted peptide, are associated with two neurogenerative diseases, familial British dementia and familial Danish dementia. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:9445; |
endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi-associated vesicle membrane [GO:0030660]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; organelle membrane [GO:0031090]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; negative regulation of amyloid precursor protein biosynthetic process [GO:0042985]; nervous system development [GO:0007399] |
12196136_oxidized form of ABri and reduced form of ADan are toxic to human neuronal cell lines in culture 12903036_Data show that the expression of BRI gene was up-regulated in the highly metastatic cell line and down-regulated in the low metastatic cell line and there was no relation between BRI gene differential expression and rearrangements of chromosome. 14586629_While a physiological role of BRI in brain remains to be determined, the behavior of BRI in diverse brain lesions appears to be somewhat analogous to that of amyloid precursor protein. 14656991_expression of wild-type British or Danish mutants of BRI2, in mouse neuroblastoma N2a cells that do not express endogenous BRI2, induces elongation of neurites, which suggests a role for this protein in differentiation of neuronal cells 15968464_Mutations at or near the stop codon of the chromosome 13 gene BRI2 that cause generation of longer-than-normal protein products. 15983050_BRI2 gene binds the Alzheimer gene amyloid-beta precursor protein and inhibits amyloid-beta production 16027166_BRI2 had a modulatory effect on amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing, increasing levels of cellular APP and COOH-terminal fragments while decreasing COOH-terminal fragments and secretion of total APP and Abeta peptides. 16612984_early-onset dementia is linked to specific mutations in the BRI2 {REVIEW} 17965014_SPPL2a and SPPL2b mediate the intramembrane cleavage, whereas neither SPP nor SPPL3 is capable of processing the Bri2 N-terminal fragment. 18282158_in familial British dementia the mutated precursor BRi2 protein may undergo furin cleavage within neurones to produce the amyloid peptide ABri 18440095_BRI2 dimerizes in cells and that dimers are held via non-covalent interactions and via disulfide bridges between the cysteines at position 89. Additionally, we showed that BRI2 dimers are formed in the ER and appear at the cell surface. 18524908_Expression of wild-type human ITM2B reduces cerebral amyloid beta deposition in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. 19366692_BRI3 inhibits the various processing of amyloid protein precursor by blocking the access of alpha- and beta-secretases in a manner unlike BRI2. 19748705_BRI2 is a specific inhibitor that reduces access of secretase to amyloid-betaprecursor protein (APP) in intracellular compartments where APP is normally processed. 20036644_These data suggest a model for how the processing of Bri2 and APP are interrelated. 20600910_Decreased cerebrospinal fluid levels of Bri2-23, a peptide cleaved from Bri2, significantly associates with multiple scleerosis patients with cerebellar dysfunction and cognition impairment. 21048150_The British mutation drastically reduces expression of mature BRI2 in both knock-in mice and the brains of familial British dementia patients. 21587206_Knock-in mice with familial Danish dementia, a mouse model congruous to human disease since they carry one mutant and one wild-type Bri2 allele, show that the Danish mutation causes loss of Bri2 protein, synaptic plasticity and memory impairment. 21752865_BRI2 is N-glycosylated at Asn170 and show that this post-translational modification is essential for its expression at the cell surface but not for its proteolytic processing. 21841249_Neurological effects of the Danish form of BRI2 dementia caused by toxic amyloid Abeta protein precursor metabolites suggest that familial Danish and Alzheimer's dementias share common pathogenic mechanisms. 21873424_BRI2 protein regulates beta-amyloid degradation by increasing levels of secreted insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE). 22194595_The alpha-helical content of the transmembrane domain of the British dementia protein-2 (Bri2) determines its processing by signal peptide peptidase-like 2b (SPPL2b). 23261769_Similarities of ABri and ADan to Abeta in Alzheimer's disease suggest that posttranslational pGlu-modification of amyloid peptides might represent general pathological mechanism leading to increased aggregation and toxicity forms of degenerative dementias. 23418567_Data indicate that double transgenic (Tg-FDD-Tau) mice showed a significant decrease in synaptophysin levels. 23701002_These results suggest that BRI2 may prevent access of BACE1 to APP and the BRI2/BACE1 interaction may mediate the reduction in BACE1 levels. 24026677_Findings highlight pathogenic mechanism(s) associated with ITM2B mutations underlying dementia or retinal disease and add a new candidate to the list of genes involved in inherited retinal dystrophies. 24099305_Structural modeling of transmembrane (BRICHOS) domains of BRI2/ITM2B and SFTPC (pulmonary surfactant protein C) precursor identifies conserved region structurally complementary to beta-sheet/amyloid-prone region in BRICHOS domain-containing proteins. 24473189_This review support the hypothesis that BRI2 change during disease devel-opment, and thus may have a role in Alzheimer disease. 24524963_It binds amyloid precursor protein to halt amyloid-b production and inhibits amyloid-b aggregation via its BRICHOS-domain suggesting a link between BRI2 and Alzheimer's disease (AD) 25261792_Data indicate that the mutation originates the highly amyloidogenic molecule integral membrane protein 2B ABri. 25557390_Data indicate integral membrane 2B (ITM2B) as a target of B-cell CLL/lymphoma 6 protein (BCL6) repression in lymphoma. 25957407_Cystine-linked oligomers of ABri are toxic to neurons and block long-term potentiation. 26459115_familial Danish dementia mutation and pE posttranslational modification are primary elements driving intact ADan into an amyloidogenic/neurotoxic pathway while truncations at the C-terminus eliminate the pro-amyloidogenic characteristics of the molecule 26515131_when BRI2 is phosphorylated a significant increase in neuronal outgrowth and differentiation is evident 26528887_Data depict roles for Bri2 and apolipoprotein E4 (ApoE4) proteins in a long-term memory regulation pathway. A single mutation in one Itm2b/Bri2 allele can affect both long-term and working memory, while ApoE4 seems to regulate short-term/working memory. 26862951_ITM2B is expressed in most cortical neurons, neurons of the hippocampus and dentate nucleus, cerebellar Purkinje and granule cells, and (newly described here) in focal neurons in the basal ganglia, many neurons of the thalamus and brainstem, many cells in the ependyma and choroid plexus, and in the smooth muscle of blood vessels. ITM2B expression is prominent in plaques in AD-containing dystrophic neurites 28131015_Familial British dementia (FBD) and familial Danish dementia (FDD) are caused by mutations in the BRI2 gene. 28176357_by modulating BRI2 processing using an ADAM10 inhibitor, a dual role for BRI2 in neurite outgrowth is suggested: phosphorylated full-length BRI2 appears to be important for the formation of neuritic processes, and BRI2 NTF promotes neurite elongation. 29234026_Bri2 BRICHOS monomers potently prevent neuronal network toxicity of amyloid-beta peptide (A-beta), while dimers strongly suppress A-beta fibril formation. 29480190_We found a novel possible pathogenic variant in the ITM2B gene in one amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient with a complex phenotype, associating movement disorders, psychiatric and cognitive features, deafness, and optic atrophy. 29507232_Bri2 BRICHOS domain is a potent inhibitor of IAPP fibril formation.Bri2 is highly expressed in human pancreatic islets and beta cells and colocalizes with IAPP both intracellularly and in islet amyloid deposits. 29687167_Analysis of knock-in mice harboring the disease mutation revealed the memory defect in the mice, attributable to loss of protective function of BRI2. (REVIEW) 30890756_The Familial dementia gene ITM2b/BRI2 facilitates glutamate transmission via both presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms. 32160551_NRBP1-Containing CRL2/CRL4A Regulates Amyloid beta Production by Targeting BRI2 and BRI3 for Degradation. 32826790_DEEP PHENOTYPING AND FURTHER INSIGHTS INTO ITM2B-RELATED RETINAL DYSTROPHY. 33172889_Danish and British dementia ITM2b/BRI2 mutations reduce BRI2 protein stability and impair glutamatergic synaptic transmission. 33690096_The synthesis and characterization of Bri2 BRICHOS coated magnetic particles and their application to protein fishing: Identification of novel binding proteins. 33814452_A Novel ITM2B Mutation Associated with Familial Chinese Dementia. 34298087_Association of clusterin with the BRI2-derived amyloid molecules ABri and ADan. 34446781_First identification of ITM2B interactome in the human retina. |
ENSMUSG00000022108 |
Itm2b |
6070.975272 |
0.4929477256 |
-1.020493 |
0.020954400 |
2399.550424 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3987.4031065 |
55.8145392 |
8147.4496425 |
75.4800852 |
| ENSG00000136160 |
1910 |
EDNRB |
protein_coding |
P24530 |
FUNCTION: Non-specific receptor for endothelin 1, 2, and 3. Mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7536888}. |
3D-structure;Albinism;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hirschsprung disease;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Waardenburg syndrome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a G protein-coupled receptor which activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Its ligand, endothelin, consists of a family of three potent vasoactive peptides: ET1, ET2, and ET3. Studies suggest that the multigenic disorder, Hirschsprung disease type 2, is due to mutations in the endothelin receptor type B gene. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:1910; |
membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endothelin receptor activity [GO:0004962]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; type 1 angiotensin receptor binding [GO:0031702]; aging [GO:0007568]; aldosterone metabolic process [GO:0032341]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; developmental pigmentation [GO:0048066]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; enteric nervous system development [GO:0048484]; enteric smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035645]; epithelial fluid transport [GO:0042045]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; heparin metabolic process [GO:0030202]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318]; negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007194]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of neuron maturation [GO:0014043]; negative regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051248]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; neuroblast migration [GO:0097402]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; pharynx development [GO:0060465]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; podocyte differentiation [GO:0072112]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of penile erection [GO:0060406]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of renal sodium excretion [GO:0035815]; positive regulation of urine volume [GO:0035810]; posterior midgut development [GO:0007497]; protein transmembrane transport [GO:0071806]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050678]; regulation of fever generation [GO:0031620]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of pH [GO:0006885]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; renal albumin absorption [GO:0097018]; renal sodium excretion [GO:0035812]; renal sodium ion absorption [GO:0070294]; renin secretion into blood stream [GO:0002001]; response to endothelin [GO:1990839]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to pain [GO:0048265]; response to sodium phosphate [GO:1904383]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; vasoconstriction [GO:0042310]; vasodilation [GO:0042311]; vein smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014826] |
11376172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11565556_novel mutation in a patient with Shah-Waardenburg syndrome and Down syndrome 11601839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11601839_The endothelin system plays a role in the complex pathophysiology of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 11829485_determination of the molecular basis of embryonic arrest from defects associated with mesoderm development 11854280_signal peptide is necessary for translocation of the N-terminal tail across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 11891690_A homozygous nonsense mutation in exon 3 (R201X) of the EDNRB gene, a gene known to be involved in Shah-Waardenburg syndrome, was found in ABCD syndrome. 11920632_Repression of endothelin receptor plays a role in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 11930911_The vasoconstrictor effect of endothelin-1 in small resistance arteries of normotensive subjects and, in part, also in hypertensive patients is mediated by ET(A) receptors, while ET(B) receptors play a minor role, if any 12117726_Augmented synthesis and altered expression of ET(B) receptors in the peripheral vasculature contribute to the increased incidence of hypertension and related complications in African American patient populations. 12226103_N-terminal proteolysis has a role in the regulation of cell surface expression of the ET(B) receptor 12355085_genetic interaction between mutations in RET and EDNRB is an underlying mechanism for Hirschsprung disease 12439722_Down-regulation of endothelin receptor B correlated with death from metastatic disease in uveal melanoma 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12628594_Detection of endothelin-B receptor gene polymorphisms in patients that have both Hirschsprung's disease and Down's syndrome. 12628594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12629276_autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney 12694195_a study of interactions with caveolin-1 in caveolae 12875994_Data show that in a human Kaposi sarcoma cell line, blockade of endothelin receptors A and B blocked the endothelin-1-induced increase in secretion and activation of matrix-metalloproteinases. 12972292_The ETB receptor shows remarkable stability in lysosomes, held together by disulfide bonds, and maintaining ligand binding for long periods of time 14519635_ET(B)R is more common in breast carcinomas of patients with lower disease-free survival time and overall survival. 14636059_It is clear from the present data for lung fibroblasts that for both stimulated and unstimulated states of ETB receptors, there exist multiple covalent forms differing in the number and location of sites of posttranslational modifications. 14669347_Mutations are found in Hirschsprung's disease in a Chinese population. 14729387_Endothelin ETB receptor mRNA levels are significantly higher in arteries from patients with ischemic heart disease as compared to congestive heart failure and controls. 15073116_increased ET-1, ET(A)R, and ET(B)R expression are associated with increased VEGF expression and higher vascularity of breast carcinomas and could be involved in the regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer 15213100_ET-1/ETA/ETB autocrine/paracrine loops on DCs appear to be essential for the normal maturation and function of human dendritic cells 15350137_Combined cleavage data strongly suggest that the binding domain of ETB receptor includes a portion of the fifth transmembrane domain, between residues Trp275 and Met296. 15598844_Within the second intracellular loop of ETB, a consensus sequence was identified, KXXXVPKXXXV, that is required for ET-1 stimulation of NHE3 activity. 15838263_Endothelin-B receptor blockade inhibits molecular effectors of melanoma cell progression. 15838285_Compared kidney endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptor distribution visualized by radioligand binding versus immunocytochemical localization using subtype selective antisera. 15950764_These data point to ET-1 as a possible survival factor for oligodendrogliomas via ET(B)-R activation and suggest that ET(B)-R-specific antagonists might constitute a potential therapeutic alternative for oligodendrogliomas. 15988412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16002759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16002759_Polymorphisms in the ET-1 gene (K198N), the ET receptor type A (ETA), (-231G>A and +1222C>T), and the ET type B (ETB) receptor (G57S and L277L) do not play a role in cerebral small-vessel disease 16145050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16328051_Inactivation of the EDNRB gene through its promoter methylation is highly prevalent in lung cancer in Taiwan. 16531800_Observations strongly suggest that the expression of ETB receptor is enhanced in neointimal smooth muscle cells at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervention injury in human coronary arteries. 16567585_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16816835_Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed mRNA the ETB receptor subtype in the human trigeminal ganglion. Immunocytochemistry revealed numerous cell bodies containing ETB proteins. 16944573_Data show that mutation of EDNRB gene can be detected in Chinese patients with sporadic Hirschsprung's disease and EDNRB gene might play an important role in the pathogenesis of Hirschsprung's disease . 16947775_Associations between endothelin receptors A and B in aystemic ssclerosis subsets supports the role of endothelin and its receptors in the pathogenesis of this disease. 16947775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16962346_ET receptors in pigment cells of vertebrate species were identified by RT-PCR assays, and the differential expression of the various subtypes in each species was compared by quantitative PCR. 17009072_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17011274_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17011274_This study identified additional sequence variants of the EDNRB gene, but the estimated EDNRB haplotypes did not show any disease risk. 17202412_Transfected into mice, implicating endothelin as a major modifying factor for cystic disease progression in human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. 17203161_analysis of Endothelin-1, ETAR and ETBR expression in different histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma 17353514_Endogenous endothelin, predominantly via ET(A) receptor stimulation, contributes to basal constrictor tone and endothelial dysfunction, whereas ET(B) activation mediates vasodilation in human coronaries. 17470272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17470272_The EDNRB-30G>A polymorphism could be a determinant of airway obstruction in humans with predisposing factors such as tobacco smoke exposure or asthma. 17525706_EDNRB-rs5351 was the most susceptible SNP associated with atherosclerosis in male hypertensives, and the genetic background may be involved in the progression of atherosclerosis in EHT patients. 17525706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17535295_transmembrane segment 1 of human endothelin B receptor is essential area for ET-1 binding and homodimer formation 17554617_a previously described polymorphism (G831A in exon 4) and a novel variant (G553A in exon 2) of EDNRB were identified in two Chinese Hirshprung disease patients 17611649_Results suggest that analysis of ETBR expression by means of simple immunohistochemical analysis might improve prediction of the prognosis for patients with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma. 17616673_Endothelin receptor type B counteracts tenascin-C-induced endothelin receptor type A-dependent focal adhesion and actin stress fiber disorganization 17618893_all investigated patients with anorectal malformations showed mobility shift aberrations and polymorphisms in the EDNRB gene 17855483_Reduction in fractional excretion of ET-1 after ETB blockade appears to indicate that renal excretion of ET-1 is at least partly facilitated by ETB receptor activation. 18060649_Endothelin receptor B might play an important proliferative role in malignant melanoma. 18157142_Endothelin B receptor mediates the endothelial barrier to T cell homing to tumors 18162831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162831_higher mutation rate for short-segment Hirschsprung disease(HSCR) suggests the important role that the Endothelin-B receptor(EDNRB) gene plays in the pathogenesis of short-segment HSCR in Taiwan 18187958_EDNRB expression may be affected by aberrant promoter methylation and gene deletion and may play a role in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 18310504_The changes of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and its receptor B in an experimental mouse model of PVR and in human proliferative vitreoretinopathy, were studied. 18411415_PlGF-induced expression of ET-1 and its cognate ET-BR receptor occur via activation of HIF-1 alpha, independent of hypoxia. 18535108_ET1, via ETB1, inhibited NADPH oxidase activity in vascular endothelial cells by suppressing the Pyk2-Rac1-Nox1 pathway 18551992_aberrant methylation of p16 and EDNRB was highly prevalent in leukemia patients in Taiwan. 18564167_Promoter hypermethylation of EDNRB gene, which is associated with the loss of EDNRB mRNA expression may play a role in the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18756291_review of heterodimerization involving the ETA receptor and renal endothelin ETB-dopamine D(3) receptor interactions at the cellular level that appear to have functional consequences in vivo 18758497_A possible synergistic effect to salt-sensitive hypertension was found by combining EDNRB with angiotensinogen genotypes 18758497_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18778461_Up-regulation of endothelin type B receptors in the human internal mammary artery in culture is dependent on protein kinase C and mitogen-activated kinase signaling pathways. 19040731_ETRB-specific antagonist, A-192621 reduces glioma and melanoma cells viability by activating stress/DNA damage response pathways 19136571_The adjacent amino-terminus tail sequences following the signal peptide of the type B endothelin receptor are necessary for efficient translocon gating. 19148482_Significant involvement of ETB receptor epigenetic deregulation in the pathogenesis of lung cancer makes thia gene a promising candidate biomarker for response to regimens modulating the endothelin axis. 19320733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536618_Expression of endothelin B receptor was closely associated with tumor cell differentiation of neuroblastic tumors. 19558538_No significant association was detected between migraine with aura end-diagnosis and three migraine trait components and 32 single nucleotide polymorphisms in endothelin-1 and its receptors EDNRA and EDNRB 19558538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19661472_In our study population, variants in EDN and EDNRB were associated with stroke susceptibility in white but not in black women. We found no evidence that these genes mediate the association between migraine and stroke. 19661472_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706169_Demonstrate upregulation of ETB and AT1 receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells in ischemic heart disease. 19757321_Distinct subcellular localisations of ET(B) receptor constructs and epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor ligands were analysed. In caveolae-free HEK293 cells, only ET(B) receptor constructs fused to caveolin-2 localised to membrane microdomains. 19853744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20009762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20009762_Truncating mutation found in an alternative isoform of EDNRB found in Hirschsprung disease. 20028935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20034471_these results suggest that the amount of Jab1 bound to ETR regulates the degradation rate of ET(A)R and ET(B)R by modulating ubiquitination of these receptors, leading to changes in ET(A)R and ET(B)R levels. 20043107_Both ET(A)R and ET(B)R are present in lung carcinomas but at different levels, according to the histological type of tumor. 20108069_The expression of arterial smooth muscle ET(B) and AT(1) receptors are increased in patients with suspected but ruled out acute coronary syndrome. 20162572_Promoter hypermethylation of KIF1A and EDNRB is a frequent event in primary HNSCC, and these genes are preferentially methylated in salivary rinses from HNSCC patients. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20401344_The results suggested that during the luteal phase, ET(A) and ET(B) receptors participate in contractile effects of endothelins on isthmic segment of fallopian tubes, probably regulating the length of time the oocyte remains in the ampulla 20427706_Endothelin B receptor stimulation inhibits suicidal erythrocyte death. 20495744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20595785_Activation of ETBR (with endothelin-1) leads to sustained Ca influx into cells; this process involves activation of Na/H exchanger by p38MAPK. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20698855_cigarette smoke extract induced ET(B) receptor overexpression by a feed forward mechanism mediated partly by ET release, promoting pulmonary artery endothelial cell dysfunction and attenuated by ET(B) receptor blockade, Rho kinase and ROS inhibition 20703215_The acid-activated pathway mediating stimulation of kidney NaDC-1 activity requires a functional ET(B) receptor in vivo and in vitro. 20798208_EDNRB methylation in salivary rinses was independently associated with histologic diagnosis of premalignancy and malignancy and may have potential in classifying patients at risk for oral premalignant and malignant lesions. 21057729_Studies indicate that understanding the mechanisms of how cigarette smoke causes up-regulation of endothelin receptors in the vasculature and airways may provide new strategies for treatment of cigarette smoke-associated cardiovascular and lung diseases. 21223556_Endothelin type B receptor-mediated contractions of the cerebrovasculature are significantly reduced following inhibition of B-raf kinase. 21264540_promoter hypermethylation of EDNRB gene is highly prevalent in gastric cancer 21356562_Expression of endothelin A and B receptors and endothelin-1 in the pulmonary arteries is significantly increased in failed Fontan patients. 21418087_Renal medullary endothelin-1/endothelin receptor second messenger signaling regulates sodium/water balance via control of natriuresis and renin-angiotensin system; both endothelin 1 receptor and endothelin 2 receptor are involved. [REVIEW] 21498912_Increased expression of ET-1, ETRA/B, and activation of signaling pathways were observed in the pulmonary arteries and arterioles of irreversible pulmonary arterial hypertension patients associated with congenital heart defects. 21507037_No association of S305N EDNRB polymorphism with sporadic melanoma risk in the French or Italian populations, but there was an indication that EDNRB might be a melanoma-predisposing gene in French patients with a hereditary predisposition to melanoma. 21547364_3 novel mutations in EDNRB gene associated with Waardenburg-Shah syndrome (WS4) in Pakistani patients. 21601190_Immunohistochemical evaluation of spermatic and control vein samples from 55 patients with varicocele showed overexpression of ET-1 and its receptors ETA and ETB in varicose veins. 21770857_Survival analysis shows that the ETB receptor high expression group had significantly shorter disease-free survival and overall survival rates than the low expression group. 21777246_Our results point to a regulatory function of ET-1, its type B receptor (ET(B)) and endothelin-converting enzyme-1 proteins in transendothelial passage of monocytes 21825025_Attenuated ET-B receptor mediated vasodilatation during local skin warming compared to Controls. 21858821_In transgenic Ednrb-deficient mice, sacral crest-derived cells diminish in number from fetal to postnatal stages. 22013079_These data suggest that autocrine EDN3/EDNRB signaling is essential for maintaining GSCs. Incorporating END3/EDNRB-targeted therapies into conventional cancer treatments may have clinical implication for the prevention of tumor recurrence. 22213152_Loss of EDNRB is associated with metastasis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. 22341591_PTEN overexpression attenuates angiogenic processes of endothelial cells by blockade of endothelin-1/endothelin B receptor signaling, contributing to thrombosis of arteriovenous grafts in hemodialysis patients. 22365955_ETB receptors predominated in normal human liver and displayed the highest ratio (ETB:ETA 63:47) compared with other peripheral tissues; liver ETB expression was upregulated in cirrhosis (ETB:ETA 83:17) 22504006_endothelin-1 activation of endothelin receptor type B leads to a reduction in cell number by end-point cell counting and a decrease in cell growth. 22535604_results obtained give evidence of a possible participation of receptor for endothelin B in the pathogenesis of the itch in the dermatitis herpetiformis 22580289_Early onset preeclampsia (PE)(=GW34) with or without fetal growth restriction is associated with increased mRNA expression of the ET/ETR system, while in late onset PE and gestational diabetes, the opposite effect was observed 22688668_Both endothelin A and B receptors were reduced in pulmonary arterial hypertension, particularly type B, and type B signaling through protein kinases was markedly reduced in vascular smooth cells with a mutation in bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2. 22787113_Our findings demonstrate that aldosterone modulates an ET(B) cysteinyl thiol redox switch to decrease pulmonary endothelium-derived NO(.) and promote pulmonary arterial hypertension. 22865454_Data indicate that endothelin receptor B (EDNRB) overexpression facilitates intracranial melanoma growth. 22965194_The expression of VEGFR-3 and its ligands, VEGF-C and VEGF-D, significantly increased after activating ET(B)R by ET-1 in primary and metastatic melanoma cell lines 22997346_These findings support the role of ET-1 and ETB in recovery following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. 23384184_There was no difference in EDNRB mRNA expression between reflux esophagitis, Barrett's esophagus, and controls. 23436727_C-terminus of ETA/ETB receptors regulate endothelin-1 signal transmission. 23515723_The presence ETr-A and ETr-B in rheumatic mitral valves suggests its interaction with the system of c endothelins, particularly ETr-B detected in a greater proportion, which could explain the lack of expression of endothelin in rheumatic mitral valve. 23518706_Endothelin receptor type B is a novel pathway and therapeutic target for enhancing remyelination in multiple sclerosis. 23579558_EDNRB is generally accepted as a major gene for Hirschsprung's disease. 23637120_EDNRB and/or DCC methylation in salivary rinses compares well to examination by an expert clinician in CRC of oral lesions. 23683481_The study demonstrated unexpected unaltered expression of ET-1 axis in keratinocytes in lesional vitiligo and perilesional normal epidermis. 24039914_The levels of the EDNRB, HJURP and p60/CAF-1 proteins were strongly associated with overall survival in high-grade gliomas patients (p |
ENSMUSG00000022122 |
Ednrb |
76.427944 |
0.1038406629 |
-3.267557 |
0.252983935 |
198.797540 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000382154901113103895660214978489675822017017532564657117121446494566139641778504695211248882168671250290128322705867844333305072268558433279395103454589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000072222872476689035533737302267315820821357522856627883018361732791092030483715405554365591129910183841513191579496860894593623925175052136182785034179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.2191256 |
2.4303881 |
137.8053428 |
11.6779817 |
| ENSG00000136169 |
83852 |
SETDB2 |
protein_coding |
Q96T68 |
FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase involved in left-right axis specification in early development and mitosis. Specifically trimethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (H3K9me3). H3K9me3 is a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional repression that recruits HP1 (CBX1, CBX3 and/or CBX5) proteins to methylated histones. Contributes to H3K9me3 in both the interspersed repetitive elements and centromere-associated repeats. Plays a role in chromosome condensation and segregation during mitosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20404330}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Chromatin regulator;Chromosome;Developmental protein;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Mitosis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins that contain a methyl-CpG-binding domain (MBD) and a SET domain and function as histone methyltransferases. This protein is recruited to heterochromatin and plays a role in the regulation of chromosome segregation. This region is commonly deleted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Naturally-occuring readthrough transcription occurs from this gene to the downstream PHF11 (PHD finger protein 11) gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:83852; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone H3K9 methyltransferase activity [GO:0046974]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell division [GO:0051301]; chromosome segregation [GO:0007059]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; heterochromatin organization [GO:0070828]; histone H3-K9 methylation [GO:0051567]; left/right axis specification [GO:0070986]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of DNA methylation-dependent heterochromatin formation [GO:0090309] |
20085599_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20404330_Results provide evidence that CLLD8/KMT1F is recruited to heterochromatin regions and contributes in vivo to the deposition of trimethyl marks in concert with SUV39H1/KMT1A.SUV39H1/KMT1A. 26378653_Results indicate that the IgE-associated AT/G polymorphism (rs386770867) regulates transcription of SETDB2. 26572639_the relation of genetic variation in SETDB2-and its paralogue SETDB1-with different handedness phenotypes in 950 healthy adult participants, was investigated. 26709698_these findings identify Setdb2 as a novel regulator of the immune system in acute respiratory viral infection. 27572307_our data indicated that SETDB2 is often over-expressed in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines and SETDB2 overexpression significantly accelerated cell proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells 29099276_SETDB2 transcripts were overexpressed in renal cell tumor subtypes and associated with prognosis. 29234167_Findings implicate SET domain bifurcated 2 (SETDB2) locus in the longstanding links of handedness with asthma and other atopic diseases. 29694893_an oncogenic role for the protein lysine methyltransferase SETDB2 in leukemia pathogenesis. It is overexpressed in pre-BCR(+) ALL and required for their maintenance in vitro and in vivo. SETDB2 expression is maintained as a direct target gene of the chimeric transcription factor E2A-PBX1 in a subset of ALL and suppresses expression of the cell-cycle inhibitor CDKN2C through histone H3K9 tri-methylation 30850015_A number of converging phenotypes outline a stress-responsive mechanism for SETDB1 and SETDB2 activation and subsequent increased tumor survival, providing novel insights into epigenetic biology. [review] 31350176_Setdb2 regulates macrophage plasticity during normal and pathologic wound repair 34479991_Coronavirus induces diabetic macrophage-mediated inflammation via SETDB2. |
ENSMUSG00000071350 |
Setdb2 |
446.600448 |
0.1130695515 |
-3.144718 |
0.499481898 |
33.777780 |
0.00000000617804748718534546548195333839220699800875991059001535177230834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000027457988831934869103111175971977664378442796078161336481571197509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
78.5382395 |
41.7280099 |
703.8740290 |
265.7840624 |
| ENSG00000136193 |
9805 |
SCRN1 |
protein_coding |
Q12765 |
FUNCTION: Regulates exocytosis in mast cells. Increases both the extent of secretion and the sensitivity of mast cells to stimulation with calcium (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Exocytosis;Reference proteome |
|
This gene likely encodes a member of the secernin family of proteins. A similar protein in rat functions in regulation of exocytosis in mast cells. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:9805; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; cysteine-type exopeptidase activity [GO:0070004]; dipeptidase activity [GO:0016805]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693] |
12221138_Purified and identified bovine secernin, in addition to bioinformatics analysis of similar proteins in mouse, rat and human. 20039278_SCRN1 expression is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer patients 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex from patients with schizophrenia 21385630_in synovial sarcoma, metastasis-free survival was significantly higher in the group with high secernin-1 expression compared to low expression; results indicate secernin-1 may be used as a biomarker to predict overall and metastasis-free survival 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 25399950_Luciferase report assay showed that the rs6976789 variant T allele influenced the binding ability of miR-148a. Our results suggested that the SCRN1 rs6976789 polymorphism may play an important role in the GC development and progression 26883194_Upregulation of SCRN1 is associated with acquired resistance to erlotinib in non-small cell lung cancer. 31796108_Secernin-1 is a novel phosphorylated tau binding protein that accumulates in Alzheimer's disease and not in other tauopathies. |
ENSMUSG00000019124 |
Scrn1 |
69.507649 |
0.3824014362 |
-1.386840 |
0.193132953 |
53.154762 |
0.00000000000030827715854415801373845642614931408396952011718994413058680947870016098022460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001899862572071721073811730094209679212471919562688071891898289322853088378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.1092201 |
4.9851938 |
100.4712420 |
8.3044295 |
| ENSG00000136250 |
313 |
AOAH |
protein_coding |
P28039 |
FUNCTION: Removes the secondary (acyloxyacyl-linked) fatty acyl chains from the lipid A region of bacterial lipopolysaccharides (PubMed:1883828, PubMed:8089145, PubMed:29343645). By breaking down LPS, terminates the host response to bacterial infection and prevents prolonged and damaging inflammatory responses (By similarity). In peritoneal macrophages, seems to be important for recovery from a state of immune tolerance following infection by Gram-negative bacteria (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1883828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29343645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8089145}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This locus encodes both the light and heavy subunits of acyloxyacyl hydrolase. The encoded enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of acyloxylacyl-linked fatty acyl chains from bacterial lipopolysaccharides, effectively detoxifying these molecules. The encoded protein may play a role in modulating host inflammatory response to gram-negative bacteria. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:313; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; acyloxyacyl hydrolase activity [GO:0050528]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; lipopolysaccharide catabolic process [GO:0009104]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728] |
16815140_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22723975_Polymorphisms in RYBP and AOAH genes are associated with chronic rhinosinusitis in a Chinese population. 26319989_AOAH rs60023210 variants may be associated with carotid intima-media thickness at bifurcation. 27888910_AOAH - Gene involved in innate immunity that have been associated with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. 29343645_analysis of AOAH function through its crystal structure and complex with lipopolysaccharide |
ENSMUSG00000021322 |
Aoah |
50.854101 |
0.0972302050 |
-3.362452 |
0.721266858 |
17.808179 |
0.00002443307574659971183089930690801594437289168126881122589111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000073120883621210819346483700265082461555721238255500793457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0208881 |
4.5017946 |
82.3416822 |
30.2340379 |
| ENSG00000136261 |
28969 |
BZW2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6E2 |
FUNCTION: Translation initiation regulator which represses non-AUG initiated translation and repeat-associated non-AUG (RAN) initiated translation by acting as a competitive inhibitor of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 (EIF5) function (PubMed:21745818, PubMed:28981728, PubMed:34260931, PubMed:29470543). Increases the accuracy of translation initiation by impeding EIF5-dependent translation from non-AUG codons by competing with it for interaction with EIF2S2 within the 43S pre-initiation complex (PIC) in an EIF3C-binding dependent manner (PubMed:21745818, PubMed:28981728, PubMed:34260931). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21745818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28981728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29470543, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34260931}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translation regulation |
|
Enables cadherin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation and nervous system development. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:28969; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; regulation of translational initiation [GO:0006446] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21745818_5MP1 (BZW2) acts as a partial mimic and competitor of eIF5, interfering with the key steps by which eIF5 regulates eIF2 function. 27325740_overexpression of eIF5 and 5MP induces translation of ATF4 28791373_These data demonstrated that the knockdown of BZW2 suppresses protein phosphorylation in the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. These observations suggest that BZW2 is upregulated and has a pro-tumor effect in osteosarcoma via activation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and thus is a potential target for gene therapy. 28981728_Data show that eIF5-mimic protein (5MP) represses non-AUG translation by competing with translation initiation factor 5 (eIF5) for the Met-tRNAi-binding factor eIF2. 29470543_results reveal a surprising role for BZW1 and BZW2 in maintaining homeostatic stringency of start codon selection, and taking into account recent biochemical, genetic and structural insights into eukaryotic initiation, suggest a model for BZW1 and BZW2 function 30932331_BZW2 has an oncogenic role in muscle-invasive bladder cancer and serves as a promising target for molecular diagnosis and gene therapy. 31175057_5MP1 is a novel oncogene that reprograms c-Myc translation in CRC. 5MP1 could be a potential therapeutic target to overcome therapeutic resistance conferred by tumor heterogeneity of CRC. 31643092_BZW2 promotes the malignant progression of colorectal cancer via activating the ERK/MAPK pathway. 34260931_Human oncoprotein 5MP suppresses general and repeat-associated non-AUG translation via eIF3 by a common mechanism. 35068373_miR-140-3p attenuated the tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma via attenuating BZW2. |
ENSMUSG00000020547 |
Bzw2 |
343.658442 |
2.2662740398 |
1.180322 |
0.087264351 |
185.299019 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000337691325519732533107862655083056309737059294989977021506692436925530846360520312830229043363204015095705313315166407051037822384387254714965820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000059621100055876225413712169776830680785147635065278532148251388937357859894620852934538148075341557855389568176818215761159081012010574340820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
488.5754387 |
25.2173560 |
217.1573230 |
8.9425337 |
| ENSG00000136383 |
57538 |
ALPK3 |
protein_coding |
Q96L96 |
FUNCTION: Involved in cardiomyocyte differentiation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:26846950, ECO:0000305|PubMed:27106955, ECO:0000305|PubMed:28630369, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30046096}. |
Cardiomyopathy;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable ATP binding activity; protein serine kinase activity; and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in cardiac muscle cell development. Predicted to be active in nucleus. Implicated in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57538; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; heart development [GO:0007507]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
26846950_Biallelic Truncating Mutations in ALPK3 Cause Severe Pediatric Cardiomyopathy. 28223422_ALPK3 variant segregated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in 3 affected members of the family. 30046096_ALPK3 should be included in the list of genes to be considered in genetic studies for patients affected with pediatric syndromic cardiomyopathy. 31074094_Phenotypic spectrum of ALPK3-related cardiomyopathy in a consanguineous family from Oman has been reported. 32480058_Expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum of ALPK3 variants: Phenotypes identified in pediatric cardiomyopathy patients and adults with heterozygous variants. 33076350_Two New Cases of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy and Skeletal Muscle Features Associated with ALPK3 Homozygous and Compound Heterozygous Variants. 33191771_A Pathogenic Variant in ALPK3 Is Associated With an Autosomal Dominant Adult-onset Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. 34263907_Alpha-protein kinase 3 (ALPK3) truncating variants are a cause of autosomal dominant hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 35510648_MicroRNA-384-5p protects against cardiac hypertrophy via the ALPK3 signaling pathway. 36321451_Pathogenesis of Cardiomyopathy Caused by Variants in ALPK3, an Essential Pseudokinase in the Cardiomyocyte Nucleus and Sarcomere. |
ENSMUSG00000038763 |
Alpk3 |
46.421848 |
0.3491498621 |
-1.518082 |
0.223509277 |
47.413451 |
0.00000000000574868695708355074528653026958970257212500065691074269125238060951232910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000032447655635393196224861236893737144980354170087366583175025880336761474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.4399578 |
3.6440987 |
70.3430150 |
6.7101662 |
| ENSG00000136404 |
53346 |
TM6SF1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BZW5 |
FUNCTION: May function as sterol isomerase. {ECO:0000303|PubMed:25566323}. |
Alternative splicing;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in lysosomal membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:53346; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765] |
25123395_Data conclude that AKR1B1 and TM6SF1 may serve as candidate methylation biomarkers for early breast cancer detection. |
ENSMUSG00000038623 |
Tm6sf1 |
70.937457 |
0.3744341815 |
-1.417216 |
0.205949967 |
48.366057 |
0.00000000000353636712443099522196297355798699210477006871222727113490691408514976501464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000020341690863835344992315629870676307790894332683251377602573484182357788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.3178582 |
5.5554013 |
105.8378337 |
9.6888034 |
| ENSG00000136514 |
64108 |
RTP4 |
protein_coding |
Q96DX8 |
FUNCTION: Probable chaperone protein which facilitates trafficking and functional cell surface expression of some G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Promotes functional expression of the bitter taste receptor TAS2R16 (PubMed:16720576). Also promotes functional expression of the opioid receptor heterodimer OPRD1-OPRM1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ER80, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16720576}. |
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable olfactory receptor binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus; detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of bitter taste; and protein targeting to membrane. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64108; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; olfactory receptor binding [GO:0031849]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of bitter taste [GO:0001580]; protein insertion into membrane [GO:0051205]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612] |
32709745_RTP4 inhibits IFN-I response and enhances experimental cerebral malaria and neuropathology. 34154655_RTP4 is a novel prognosis-related hub gene in cutaneous melanoma. |
ENSMUSG00000033355 |
Rtp4 |
15.919129 |
0.4544396669 |
-1.137839 |
0.370785244 |
9.677669 |
0.00186521083636833262184295811891843186458572745323181152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004143665253581666450821696656703352346085011959075927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3761014 |
2.4066487 |
22.9141744 |
3.2664156 |
| ENSG00000136636 |
51133 |
KCTD3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y597 |
FUNCTION: Accessory subunit of potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 3 (HCN3) up-regulating its cell-surface expression and current density without affecting its voltage dependence and kinetics. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BFX3}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel tetramerization-domain containing (KCTD) protein family. Members of this protein family regulate the biophysical characteristics of ion channels. In mouse, this protein interacts with hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel complex 3 and enhances its cell surface expression and current density. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:51133; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260] |
23382386_KCTD3 is an accessory subunit of native HCN3 complexes 29406573_this largest series to date on KCTD3-mutated patients, we show that biallelic loss of function mutations in KCTD3 lead to a consistent phenotype of developmental epileptic encephalopathy and abnormal cerebellum on brain imaging. |
ENSMUSG00000026608 |
Kctd3 |
211.386846 |
0.4885582521 |
-1.033398 |
0.132894831 |
60.423250 |
0.00000000000000765040018641647291788754863084164718371260952012313794057263294234871864318847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000051608732518970354974148201310303961901601241257786512051097815856337547302246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
140.7859396 |
13.4703489 |
290.2389297 |
19.3433427 |
| ENSG00000136643 |
26750 |
RPS6KC1 |
protein_coding |
Q96S38 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transmitting sphingosine-1 phosphate (SPP)-mediated signaling into the cell (PubMed:12077123). Plays a role in the recruitment of PRDX3 to early endosomes (PubMed:15750338). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12077123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15750338}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Kinase;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Sphingosine kinase catalyzes the formation of sphingosine 1 phosphate, a lipid cellular messenger. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to sphingosine kinase and to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, suggesting a role in sphingosine 1 phophate signaling. The encoded protein can also bind to peroxiredoxin-3 and may help transport it to mitochondria. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:26750; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12077123_cloning and characterization of RPK118 as a sphingosine kinase-1-binding protein 12471243_Identified as a pseudokinase and named RSKL1 15750338_findings indicate that RPK118 is a PRDX3-binding protein that may be involved in transporting PRDX3 from the cytoplasm to its mitochondrial site of function or to other membrane structures via endosome trafficking. |
ENSMUSG00000089872 |
Rps6kc1 |
165.064498 |
2.9118949111 |
1.541958 |
0.645009779 |
5.466574 |
0.01938359251880908407095205348014133051037788391113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034886212117744432037458324202816584147512912750244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
274.1901278 |
97.7210168 |
95.1511300 |
24.5242156 |
| ENSG00000136689 |
3557 |
IL1RN |
protein_coding |
P18510 |
FUNCTION: Anti-inflammatory antagonist of interleukin-1 family of proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1beta/IL1B and interleukin-1alpha/IL1A. Protects from immune dysregulation and uncontrolled systemic inflammation triggered by IL1 for a range of innate stimulatory agents such as pathogens. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P25085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7775431}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the interleukin 1 cytokine family. This protein inhibits the activities of interleukin 1, alpha (IL1A) and interleukin 1, beta (IL1B), and modulates a variety of interleukin 1 related immune and inflammatory responses, particularly in the acute phase of infection and inflammation. This gene and five other closely related cytokine genes form a gene cluster spanning approximately 400 kb on chromosome 2. A polymorphism of this gene is reported to be associated with increased risk of osteoporotic fractures and gastric cancer. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:3557; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-1 receptor antagonist activity [GO:0005152]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; interleukin-1 type I receptor antagonist activity [GO:0045352]; interleukin-1 type II receptor antagonist activity [GO:0045353]; interleukin-1, type I receptor binding [GO:0005150]; interleukin-1, type II receptor binding [GO:0005151]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002437]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034115]; negative regulation of interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2000660]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384] |
11023482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11027520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11033452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11045853_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11127488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11138328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11171832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11247888_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11264025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11448121_The serum level of IL-1Ra is higher in cicatricial pemphigoid patients in prolonged clinical remission and following intravenous immunogloglobulin therapy, when compared to the pre-IVIg treatment level. 11531943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11600466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11606494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11606496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11641511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11665981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11686217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11686217_There were no significant differences in the distributions of the IL-1RN and IL-1B genotpes, allele frequencies or halotypes. 11762793_There is an association between urolithiasis and polymorphism in the IL-1Ra gene. 11770040_Septic shock whole-blood leukocytes and neutrophils (PMNs) selectively maintained production of sIL-1RA after treatment with LPS. 11784248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11793861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803448_Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) gene VNTR polymorphism was studied in children with DSM-IV ADHD and their parents to determine the role of brain cytokine activity in the etiopathogenesis of ADHD. 11816697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840488_Slight association of mutations with hypertension. 11841485_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11841485_results suggest that polymorphisms within IL1RN and IL1L1 themselves or a gene in linkage disequilibrium with IL1RN and IL1L1 predispose to the more severe forms of alopecia areata 11841553_A borderline association was observed between il-1rn and patchy alopecia areata. 11846196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11858187_In dengue shock syndrome pts, IL-1Ra was significantly associated with F1+2, TATc (p T and IL1RA VNTR polymorphisms do not play a crucial role in susceptibility or resistance to cerebral malaria. 16098232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100774_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16106254_Association seen between common haplotype in the IL1RN gene and prostate cancer in Swedish population; supports role of inflammation in prostate cancer development 16106254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16109659_IL-1Ra gene polymorphism was found in patients diagnosed with crohn disease living in India. 16109659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16114018_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16115908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16126303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16126303_results indicate that individuals homozygous for the IL1RN*1 allele and carrying the IL1B-31T allele had increased risk of non-small cell lung cancer; findings support the significance of IL1 gene cluster polymorphisms and risk of lung cancer 16128937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142351_an IL-1Ra polymorphism has a role in colorectal carcinogenesis 16159520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16164697_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16172101_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16174285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16183821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16195370_IL-1Ra, Bcl-2, and iNOS are upregulated and counter the proinflammatory and proapoptotic effects of ischemia-reperfusion 16200608_IL1RN has a role in determining susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in the Spanish population. 16200608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16202742_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16217062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16226351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16244470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16246569_Exerts intracellular functions regulating effect of N-terminal IL-1alpha propiece on movement of ECV304 tumor cells. 16263000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16268484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284379_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16301842_Increased levels of cord IL-1ra levels are associated with neonatal morbidity and adverse outcome in preterm infants 16318998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16319982_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16361275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16361815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16362796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16389181_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16403098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16405550_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16409203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16414081_substance P, epinephrine, and norepinephrine are not involved in mediating peripheral inflammation following psychosocial stress, at least with respect to interleukin-1 receptor antagonist 16423338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16423338_results suggest that IL-1RN2 allele positivity is associated with periodontal disease in a Turkish population 16436009_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16454826_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16454826_The |
ENSMUSG00000026981 |
Il1rn |
410.912688 |
6.0114688349 |
2.587718 |
0.094498840 |
825.116496 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018680443944721321972886341434786621481421162091293218298811542182424918930779275121953328277395148577523395531005400153206209975942875396373061204481 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000015403539252742273889587405407605380138118410089550794339378156211450773790777893418827854886302182592880416398879490321927482057294136982567350934443 |
Yes |
No |
721.0261023 |
38.8087407 |
120.7904817 |
5.8581840 |
| ENSG00000136717 |
274 |
BIN1 |
protein_coding |
O00499 |
FUNCTION: Is a key player in the control of plasma membrane curvature, membrane shaping and membrane remodeling. Required in muscle cells for the formation of T-tubules, tubular invaginations of the plasma membrane that function in depolarization-contraction coupling (PubMed:24755653). Is a negative regulator of endocytosis (By similarity). Is also involved in the regulation of intracellular vesicles sorting, modulation of BACE1 trafficking and the control of amyloid-beta production (PubMed:27179792). In neuronal circuits, endocytosis regulation may influence the internalization of PHF-tau aggregates (By similarity). May be involved in the regulation of MYC activity and the control cell proliferation (PubMed:8782822). Has actin bundling activity and stabilizes actin filaments against depolymerization in vitro (PubMed:28893863). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24755653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27179792, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28893863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8782822}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Endocytosis;Endosome;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes several isoforms of a nucleocytoplasmic adaptor protein, one of which was initially identified as a MYC-interacting protein with features of a tumor suppressor. Isoforms that are expressed in the central nervous system may be involved in synaptic vesicle endocytosis and may interact with dynamin, synaptojanin, endophilin, and clathrin. Isoforms that are expressed in muscle and ubiquitously expressed isoforms localize to the cytoplasm and nucleus and activate a caspase-independent apoptotic process. Studies in mouse suggest that this gene plays an important role in cardiac muscle development. Alternate splicing of the gene results in several transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Aberrant splice variants expressed in tumor cell lines have also been described. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:274; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; axon [GO:0030424]; axon initial segment [GO:0043194]; axon terminus [GO:0043679]; cerebellar mossy fiber [GO:0044300]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0098850]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; I band [GO:0031674]; lipid tube [GO:0060987]; membrane [GO:0016020]; node of Ranvier [GO:0033268]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; RNA polymerase II transcription repressor complex [GO:0090571]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; varicosity [GO:0043196]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; aspartic-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0019828]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; RNA polymerase binding [GO:0070063]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; lipid tube assembly [GO:0060988]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; negative regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902960]; negative regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel [GO:1904878]; negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901380]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:1903946]; nucleus localization [GO:0051647]; nucleus organization [GO:0006997]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010564]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0048488]; T-tubule organization [GO:0033292] |
8782822_A nucleocytosolic myc-interacting isoform of Bin1 has properties of a tumor suppressor. 9395479_Several tissue-specific splice isoforms of the human Bin1 gene are found only in brain or muscle. 9418903_Bin1 plays a crucial role in terminal differentiation of myoblasts; associated with induction of a muscle-specific splice isoform and subcellular relocalization. 10449755_Missplicing of a brain-specific exon of Bin1 in human melanoma is sufficient to abolish tumor suppressor properties; ectopic WT Bin1 activates PCD in malignant but not normal melanocytes. 10652430_There is frequent downregulation of Bin1 in malignant breast cells; ectopic Bin1 activates PCD in cells lacking expression. 10738240_There is frequent loss or downregulation of Bin1 in metastatic prostate cancer. 12183633_findings support a role of the bilayer-deforming properties of amphiphysin at T-tubules and, more generally, a physiological role of amphiphysin in membrane deformation 12532338_Results document the extent of expression of nuclear Bin1 isoforms, which exhibit cancer suppression and proapoptotic activity in human cells. 12668730_Sorting nexin 4 and amphiphysin 2 have roles in endocytosis and intracellular trafficking 12773571_Studies in mouse indicate that Bin1 is dispensable for endocytosis but essential for appropriate cardiac development. 14704274_role in activating various target genes after induction with the microtubule disrupting agent T113242 15483625_Phosphoinositides regulate BIN1 SH3 domain binding. 15992821_tumor-specific isoforms of Bin1 are precluded from interaction with c-Myc through an intramolecular polyproline-SH3 domain interaction. Furthermore, c-Myc/Bin1 interaction can be inhibited by phosphorylation of c-Myc at Ser62. 16516635_combination of gene dosages of MYCN and Survivin and the expression level of BIN1 using the quantitative polymerase chain reaction method was significantly correlated with the clinical stage and the patients' outcome in neuroblastoma 17059209_Crystal structure shows that both the quaternary and tertiary architectures of the homodimeric Bin1 BAR domain are built upon 'knobs-into-holes' packing of side chains, and this packing governs the curvature of a putative membrane-engaging concave face. 17210688_Mammary specific deletion of the Bin1 gene cooperates with ras activation to drive mammary tumor progression. The findings establish a role for Bin1 as a negative modifier of oncogenicity and progression in breast cancer. 17218774_Bin1 gene encodes a protein that suppresses neoplastic cell transformation.Bin1 may be a clinical prognostic marker in breast cancer. 17218774_Immunohistochemical losses of nuclear Bin1 proteins in cases of human breast cancer were associated with increased progression status and poor prognosis. 17611416_hob1+, the fission yeast homolog of Bin1, supports a mechanism of Rad6/Set1-dependent transcriptional repression that may relate to cancer suppression by Bin1. 17671430_potential relevance of Bin1-Ku interaction to cancer are discussed in light of these findings 17676042_Mutations in amphiphysin 2 (BIN1) disrupt its membrane tubulation properties and its interaction with dynamin 2, and cause autosomal recessive centronuclear myopathy 17676042_Results suggest that mutations in BIN1 cause centronuclear myopathy by interfering with remodeling of T tubules and/or endocytic membranes, and that the interaction between BIN1 and DNM2 is necessary for normal muscle function and positioning of nuclei. 17699764_Mosaic knockout mice lacking Bin1 exhibit lung and liver cancer, increased inflammation or premalignant lesions in prostate, and more progressive colon cancer. Thus, Bin1 suppresses inflammation and cancer during aging. 18154705_Mutated in recessive centronuclear myopathies. 18348166_Results suggest that Bin1 gene suppression caused by oncogenic E1A via Rb/E2F1 inactivation is an essential step in cell cycle progression promoted by c-Myc, and subsequently, E1A transformation. 18658220_findings support models for membrane curving by BAR domains in which helix-0 increases the binding affinity to the membrane and enhances curvature generation 18817572_REVIEW : BIN1 mutations and centronuclear myopathy 19004523_Amphiphysin 2/BIN1 participates in the tubulation of traffic intermediates and intracellular organelles first via its intrinsic tubulating potential and second via its ability to bind CLIP-170 and microtubules. 19418541_Bin1 appears to function as a metastasis suppressor and chemosensitizer in neuroblastoma. 19629135_BIN1 is transcriptionally activated by E2F1 and mediates E2F1-induced apoptosis in response to DNA damage. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915558_show a requirement for human BIN1 (also known as Amphiphysin 2) in EHD1-regulated endocytic recycling. 20140253_Characterization of amphiphysin 2 membrane tubules in cultured cells with correlative light-electron microscopy 20142620_BIN1 sequencing revealed a homozygous missense mutation in a patient with recessive centronuclear myopathy 20169111_Data have identified that membrane-associated BIN1 not only induces membrane curvature but can direct specific antegrade delivery of microtubule-transported membrane proteins. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460622_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20558387_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20558387_This study shown that established and candidate AD genes have a role in 6 neuroimaging traits linked to AD. 2 promising genes from Alzheimer disease GWASs, CNTN5 and BIN1, are associated with these neuroimaging measures. 20927630_This study proposed that aberrant BIN1 localization and defects in triad structure are part of a common pathogenetic mechanism shared between the three forms of centronuclear myopathies. 21059989_BIN1 polymorphisms were associated with late-onset Alzheimer disease in an independent cohort from the National Institute on Aging Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease Family Study 21059989_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21129173_We present the first clinical description of intrafamilal variability in two first-degree cousins with a novel BIN1 stop mutation. 21220176_we confirmed that BIN1 is a genetic determinants of Alzheimer disease. 21321396_Logistic regression analysis successfully replicates the association of BIN1 (rs744373) with late-onset Alzheimer's disease, with an odds ratio comparable to that previously reported. 21347408_variants in BIN1, CLU, CR1 or PICALM are associated with changes in the CSF levels of biomarkers 21379329_There was evidence of association for recently-reported late-onset Alzheimer's disease risk loci, including BIN1 and CLU and CUGBP2 with APOE. 21447796_A model has been proposed in which increased abundance of c-MYC indirectly leads to decreased BIN1 expression, in turn leading to increased PARP activity and resistance to DNA-damaging agents. 21623381_alternative splicing associated with T tubule alterations and muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy 21678469_Results suggest that the coiled-coil BIN1 BAR peptide encodes a novel BIN1 MID domain, through which BIN1 acts as a MYC-independent cancer suppressor. 21984944_Study showing the importance of Bin1 in the maintenance of intact t-tubule structure and ([Ca(2)]i) homeostasis in adult skeletal muscle could provide insight on the potential role of Bin1 in skeletal muscle contractility and pathology of myopathy. 22281836_BIN1 expression is significantly decreased in surgically excised hepatocellular carcinoma patient specimens as well as in HCC cell lines and decreased BIN1 expression correlates with the degree of differentiation of HCC and predicts poor prognosis. 22539578_The SNP genotype pattern at the BIN1 gene is associated with episodic memory. 22544318_The re-expression of BIN1 specifically compromises the proliferation of SNF5-deficient rhabdoid tumors cell lines. 22976291_Findings suggest that RIN1 orchestrates RAB5 activation, ABL kinase activation and BIN1 recruitment to determine EGFR fate. 23202439_We identified rare small events overlapping CR1 and BIN1 in Alzheimer's disease and normal controls with opposite copy number variation dosage. 23399914_BIN1 expression is increased in Alzheimer Disease brains when compared with controls. 23570733_To our knowledge, this is the first study to show significant association between rs744373 polymorphism and AD in East Asian population. 23754947_Our data demonstrate that the alteration of the muscle-specific function of BIN1 is a common pathomechanism for centronuclear myopathy, myotonic dystrophy, and IMGD. 23803295_The resukts of this study highlight the possible use of plasma BIN1 as a biomarker for AD diagnosis. 23871436_REVIEW--BIN1: form, function, and Alzheimer's disease 24205320_BIN1 is decreased in sporadic but not familial Alzheimer's disease or in aging 24582639_It is the most important genetic susceptibility locus in late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 24590001_BIN1 downregulation is linked to cancer progression and also correlates with ventricular cardiomyopathy and arrhythmia preceding heart failure. Increased BIN1 expression is linked to increased susceptibility for late-onset Alzheimer's disease. [review] 24616074_The study compares the binding dynamics and affinities of the relevant regions for binding of c-Myc and NS5A to Bin1 SH3. The result gives further insights into the potential role of NS5A in Bin1-mediated apoptosis. 24660791_physical activity attenuated the effects of genetic risk (ie. the constellation of PICALM, BIN1, and CLU polymorphisms) on episodic memory 24755653_Two mutants of BIN1 showed impaired membrane tubulation both in vivo and in vitro, and displayed characteristically different behaviors. 25022885_BIN1 rs744373 polymorphism is significantly associated with late onset Alzheimer disease. 25024306_Results suggest that BIN1 is likely involved in Alzheimer's disease as a modulator of neurofibrillary tangle pathology, and that this role may extend to other human diseases that feature tau pathology 25051234_These findings suggest that an intracellular form CLU and BIN1 interaction might impact Tau function in neurons and uncover potential new mechanisms underlying the etiology of Tau pathology in in Alzheimer's disease. 25129075_Our analyses suggest that these DNA methylation changes may have a role in the onset of Alzheimer disease given that we observed them in presymptomatic subjects and that six of the validated genes connect to a known susceptibility gene network. 25257171_The release of BIN1 from hypo-poly(ADP-ribosyl)ated E2F1 is a mechanism by which serum starvation promotes E2F1-induced apoptosis. 25260562_specific amphiphysin 2 mutations can cause either recessive or dominant centronuclear myopathy and that both disorders involve different pathomechanisms 25262827_These results support a role for N-WASP in amphiphysin-2-dependent nuclear positioning and triad organization and in centronuclear myopathy and myotonic dystrophy pathophysiology. 25350771_These results suggest an autoinhibition model for BIN1 that involves a synergistic regulation by membrane composition and protein-protein interactions. 25365775_Brain DNA methylation in BIN1 was associated with pathological Alzheimer disease. 25461955_The study is the first to confirm the association of the variant rs7561528 adjacent to Bin1 with Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease in a Han Chinese Population. 25487648_BIN1/M-Amphiphysin2 has a role in inducing clustering of phosphoinositides to recruit its downstream partner dynamin 25578476_Reduced BIN1 expression is associated with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 25630570_This study findings demonstrate that rs744373 itself or a variation in linkage disequilibrium may provide a neurogenetic mechanism for BIN.1 25683635_Results show low expression of Bin1, along with high expression of IDO, are predictor for poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell cancer and thereby could be used to establish new therapeutic strategies. 25957634_This study demonistrated that BIN1 mutation releated to Centronuclear myopathy. 26194865_analysis of a novel deregulated mechanism in chronic myeloid leukemia patients, indicating BIN1 and RIN1 as players in the maintenance of the abnormal RTK signaling in this hematological disease 26195312_In vitro studies in human Caco-2 cells showed that Bin1 antibody altered the expression of tight junction proteins and improved barrier function. 26233692_Alterations in the BIN1 locus, previously associated with Alzheimer disease, may modify the age of onset of GBA-associated Parkinson. 26733302_no association was found for either polymorphism, suggesting that these genes are not implicated in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease in all populations. 26738348_The frequencies of BIN1 alleles were similar in both control and Alzheimer patients showing o no association. 26833786_Data demonstrate that EHBP1L1 links Rab8 and the Bin1-dynamin complex, which generates membrane curvature and excises the vesicle at the endocytic recycling compartment for apical transport. 26846281_the association between the rs744373 polymorphism of BIN1 protein and late-onset Alzheimer's disease in East Asian, American, and European populations (Meta-Analysis) 26947052_findings support a contribution of BIN1 to individual differences in episodic memory performance among Type 2 Diabetes patients. 27003210_This study supported that BIN1 contributes to the risk of Alzheimer's disease by altering neural degeneration (abnormal tau, brain atrophy and glucose metabolism) but not Abeta pathology 27179792_the depletion of BIN1 increases cellular BACE1 levels through impaired endosomal trafficking and reduces BACE1 lysosomal degradation, resulting in increased Ab production. Our findings provide a mechanistic role of BIN1 in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease (AD), as a novel genetic regulator of BACE1 levels and Ab production 27268056_data show that the previously described consensus sequence PXRPXR for amphiphysin SH3 ligands is inaccurate and instead define it as an extended Class II binding motif PXXPXRpXR, where additional positive charges between the two constant arginine residues can give rise to extraordinary high SH3 binding affinity. 27346750_BIN1 protein expression in cerebral cortex was related to disease progression in Alzheimer's Disease patients. 27538496_propose that efforts to define how genetic variants in BIN1 elevate the risk for Alzheimer's disease would behoove to consider BIN1 function in the context of its main expression in mature oligodendrocytes 27773727_BIN1 is involved with late onset Alzheimer's disease. [review] 27854204_Italian family with centronuclear myopathy, carrying a novel pathogenic mutation of BIN1 gene in heterozygous state, consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance. 28152502_Low Bin1 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 28302384_bridging integrator 1 Gene rs7561528 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer's disease susceptibility in East Asian and Caucasian populations 28714960_Findings indicated that BIN1 restoration in NSCLC could reverse PD-L1-mediated immune escape by inactivating the c-MYC and EGFR/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. 28755476_The results emphasize an additional level of complexity in the regulation of the interaction between BIN1 and Tau dependent on the BIN1 isoforms. 28806752_Data (including data from studies using transgenic mice) suggest that the process leading to microparticle release from cardiac myocytes involves recruitment of CHMP4B protein to the forming microparticle membrane which also contains cBIN1; plasma cBIN1 is reduced in patients with heart failure as compared to control subjects. (CHMP4B = charged multivesicular body protein 4B; cBIN1 = cardiac bridging integrator 1) 28893863_The findings reveal the ability of Bin1 to modify actin dynamics and provide a possible mechanistic connection between Bin1 and tau-induced pathobiological changes of the actin cytoskeleton. 29504051_Meta-analysis validated the association of late onset Alzheimer disease with BIN1 (rs744373) variants. 29764032_incidence of amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) in Tujia region of Enshi may be related to the rs744373 polymorphic site of BIN1 gene, ApoEepsilon2 is the protective factor and ApoEepsilon4 is the risk factor for aMCI in Tujia region of Enshi 29950440_A BIN1 founder Roma mutation associated with a highly specific phenotype, was identified as the cause of centronuclear myopathy in Spain. 30253944_propose that under conditions of oxidative stress given by the internalization of oxLDL, macrophages employ the formation of the amphiphysin 2(Bin1)/c-Myc complex as a control mechanism to initially avoid the process of cell death 30260023_the findings of the study indicated that miR-211 mediated BIN1 downregulation had crucial significances in Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), suggesting the miR-211 might be a novel potential therapeutic target for the OSCC treatment. 30353632_By studying the role of BIN1 during the differentiation of hESC-CMs, we show that BIN1 is also important for CaV 1.2 channel clustering, junctional SR organization, and the establishment of excitation-contraction coupling 30733337_study unveils an E2F1-specific signaling circuit that constitutively activates ATM and provokes cisplatin resistance in BIN1-deficient cancer cells and further reveals that gammaH2AX emergence may not always reflect DSBs if BIN1 is absent. 30885349_this study shows that high BIN1 expression has a favorable prognosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma and is associated with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes 30967682_A novel role for the late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD)-associated protein Bin1 in regulating postsynaptic trafficking and glutamatergic signaling. 30992433_BIN1 rs744373 SNP is associated with increased tau but not beta-amyloid pathology, suggesting that alterations in BIN1 may contribute to memory deficits via increased tau pathology 31263146_BIN1 favors the spreading of Tau via extracellular vesicles. 31335457_we found that hypomethylation levels at specific CpGs in BIN1, rather than in the whole open sea region, elevated the risk for late onset Alzheimer's Disease (LOAD). We also found that hypomethylation at specific CpGs (26, 44, and 87) increased the risks for LOAD. 31478261_SRSF1-dependent alternative splicing attenuates BIN1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. 31815296_Splicing Regulator p54(nrb) /Non-POU Domain-Containing Octamer-Binding Protein Enhances Carcinogenesis Through Oncogenic Isoform Switch of MYC Box-Dependent Interacting Protein 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 31874619_large-scale meta-analysis highlighted the significant association between BIN1 rs744373 polymorphism and AD risk in Caucasian populations but not in the East Asian populations[meta-analysis] 31884801_MiR-744 mediates the Oxaliplatin chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through inhibiting BIN1. 32568785_Alzheimer Gene BIN1 may Simultaneously Influence Dementia Risk and Androgen Deprivation Therapy Dosage in Prostate Cancer. 32719966_The Mechanistic Role of Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1) in Alzheimer's Disease. 32727516_BIN1 protein isoforms are differentially expressed in astrocytes, neurons, and microglia: neuronal and astrocyte BIN1 are implicated in tau pathology. 32842621_Microglia Implicated in Tauopathy in the Striatum of Neurodegenerative Disease Patients from Genotype to Phenotype. 33516273_Convergent lines of evidence support BIN1 as a risk gene of Alzheimer's disease. 33531457_Association between methylation of BIN1 promoter in peripheral blood and preclinical Alzheimer's disease. 34060233_The BIN1 rs744373 Alzheimer's disease risk SNP is associated with faster Abeta-associated tau accumulation and cognitive decline. 34072165_Genetic Predisposition to Alzheimer's Disease Is Associated with Enlargement of Perivascular Spaces in Centrum Semiovale Region. 34375641_Alzheimer's disease BIN1 coding variants increase intracellular Abeta levels by interfering with BACE1 recycling. 34982487_Enrichment of rare variants of BIN1 but not APOE genes in Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. 35217605_BIN1 modulation in vivo rescues dynamin-related myopathy. 35241726_The neuronal-specific isoform of BIN1 regulates beta-secretase cleavage of APP and Abeta generation in a RIN3-dependent manner. 35269588_Epigenetic Studies in the Male APP/BIN1/COPS5 Triple-Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. 35526014_BIN1 is a key regulator of proinflammatory and neurodegeneration-related activation in microglia. 35546756_Link of BIN1, CLU, and IDE Gene Polymorphisms with the Susceptibility of Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence from a Meta-analysis. 35871342_Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1, rs6733839) and Sex Are Moderators of Vascular Health Predictions of Memory Aging Trajectories. 36280690_Genetic polymorphism in BIN1 rather than APOE is associated with poor recognition memory among men without dementia. |
ENSMUSG00000024381 |
Bin1 |
189.579881 |
0.3079586085 |
-1.699192 |
0.134708293 |
163.004190 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000024963526918972458331286937294100621334767721182628782827946037820171441410922491823725312018141583164654306870033906307071447372436523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000003890830594762761179869498585462351473718832614551641664080833803348948811170220582830002470234656564151975999266142025589942932128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.8456545 |
8.6842754 |
303.2852028 |
18.0945942 |
| ENSG00000136810 |
7295 |
TXN |
protein_coding |
P10599 |
FUNCTION: Participates in various redox reactions through the reversible oxidation of its active center dithiol to a disulfide and catalyzes dithiol-disulfide exchange reactions (PubMed:2176490, PubMed:17182577, PubMed:19032234). Plays a role in the reversible S-nitrosylation of cysteine residues in target proteins, and thereby contributes to the response to intracellular nitric oxide. Nitrosylates the active site Cys of CASP3 in response to nitric oxide (NO), and thereby inhibits caspase-3 activity (PubMed:16408020, PubMed:17606900). Induces the FOS/JUN AP-1 DNA-binding activity in ionizing radiation (IR) cells through its oxidation/reduction status and stimulates AP-1 transcriptional activity (PubMed:9108029, PubMed:11118054). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11118054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16408020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17606900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19032234, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2176490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9108029}.; FUNCTION: ADF augments the expression of the interleukin-2 receptor TAC (IL2R/P55). |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Allergen;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Electron transport;Nucleus;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Secreted;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene acts as a homodimer and is involved in many redox reactions. The encoded protein is active in the reversible S-nitrosylation of cysteines in certain proteins, which is part of the response to intracellular nitric oxide. This protein is found in the cytoplasm. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:7295; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-disulfide reductase (NAD(P)) activity [GO:0047134]; protein-disulfide reductase activity [GO:0015035]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; thioredoxin-disulfide reductase activity [GO:0004791]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death [GO:1903206]; negative regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046826]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation [GO:2000170]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; response to nitric oxide [GO:0071731]; response to radiation [GO:0009314] |
11751890_The roles of thioredoxin in protection against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis 11841832_overexpressed TRX, induced by HTLV-I Tax, may play an important role in HTLV-I infection 11972307_serum levels may reflect the status of insulin resistance in Type 2 diabetic patients 12008049_Enhanced resistancy of thioredoxin-transgenic mice against influenza virus-induced pneumonia 12029072_Results suggest that glutaredoxin plays an important role during implantation, while Trx levels remained constant during the secretory phase. 12099690_C-propeptide region of human pro alpha 1 type 1 collagen interacts with thioredoxin 12119401_Glutathionylation; crossstalk between the glutathione and thioredoxin systems 12189205_decrease in mRNA levels in prostate cancer cells related to induction of thioredoxin-binding protein-2 12244325_Trx is essential for maintaining the content of S-nitrosylated molecules in endothelial cells. Trx can exert its complete redox regulatory and anti-apoptotic functions in endothelial cells only when cysteine 69 is S-nitrosylated 12529245_N-acetylcysteine does not block nonclassic pathway for Trx secretion. Mutations in active site or dimerization site of Trx do not alter its secretion. Nonclassic secretion of Trx is not dependent on redox status of cell or protein. 12660821_role in redox regulation of the antioxidant response element in electrophile response 12804587_Trx-1 may play a role in the redox regulation of SSAT expression and polyamine homeostasis that could contribute to the biological effects of Trx-1 12816947_human thioredoxin 1 redox potential and examination of dithiol/disulfide motifs 12870673_TRX is upregulated in myocarditis and cardiomyopathies with active necrotic stage associated with DNA damage 12878985_increased TXN-1 expression is a relatively late event in colorectal carcinogenesis and provides evidence in a small group of subjects with colorectal cancer of Dukes stages A through D; thioredoxin-1 expression may be an independent marker of prognosis 12882768_Human lens thioredoxin: molecular cloning and functional characterization. 14503974_Secreted Trx may participate in removing inhibitors of collagen-degrading metalloproteinases. 14644168_novel deregulatory effect of extracellular Trx upon morphological capillary differentiation that appears to depend upon the reduction of laminin and destabilisation of its interaction with galectin-3 14688353_A redox-active site in TRX is essential for its release from T lymphocytes in response to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2): extracellular TRX regulates its own H2O2-induced release. 14695120_Exposure to low Trx concentrations (1 microM) caused significant increases in the percentage of liquid phase of sputum in cystic fibrosis patients. 14703116_Prx I and Trx expression is increased in lung cancer cells following hypoxia and in human lung cancer tissues 14730345_Thioredoxin is a regulator of gene expression. 15096327_Data show that oxidant-injured and stressed airway epithelial cells upregulate thioredoxin, but produce little IL-8, which may be important in airway epithelial cell-mediated multistep navigation of neutrophils to sites of oxidant injury. 15128745_reduced thioredoxin activity through interaction with Txnip is an important mechanism for vascular oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus 15480426_Trx may regulate cell cycle and growth through a novel modulation of AP-1 activity and p27Kip1 degradation with Jab1 15494431_A truncated form of endogenous thioredoxin (Trx80) is an early signal in response to danger which can stimulate CD14+ monocytes to differentiate into a novel cell population that may play a major role in triggering innate immune responses. 15507528_Mitogenic cytokine truncated thioredoxin (Trx80) inhibits Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell transformation in cord blood mononuclear cells in vitro via T cells that are activated by IL-15 and IL-12 produced by monocytes. 15694802_Thioredoxin is elevated after angioplasty for peripheral artery disease. Thioredoxin impairs chemotaxis and attenuates ischemia reperfusion injury. It acts as both as a marker of oxidative stress and as a therapeutic agent. 15723974_AlphaAR-stimulated hypertrophic signaling in adult rat ventricular myocytes is mediated via a TRX1-sensitive posttranslational oxidative modification of thiols on Ras. 15894171_hepatopoietin association with thioredoxin constitutes a redox signal transduction in activation of AP-1/NF-kappaB 16115022_different redox-active cysteines are important for Trx chemotactic action, whereas its desensitizing action does not have these requirements, which suggests a redox-independent mechanism 16207716_thioredoxin-1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-1beta expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages 16263712_CatD induces apoptosis via degradation of Trx protein, which is an essential anti-apoptotic and reactive oxygen species scavenging protein in endothelial cells 16311508_Abeta neurotoxicity might be mediated by oxidation of GRX1 or TRX1 and subsequent activation of the ASK1 cascade. 16424062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16492688_Thioredoxin inhibited the binding of PPARalpha to the PPAR-response element 16712525_indicate an intrinsic form of control of promoter activity by the thioredoxin system itself 16766796_identified two Txnip cysteines that are important for thioredoxin binding and showed that this interaction is consistent with a disulfide exchange reaction between oxidized Txnip and reduced thioredoxin 16868544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16966583_Thioredoxin-1 nitration plays a causative role in postischemic cardiomyocyte apoptosis. 17007870_In this review, we will summarize the cardiac effects of thioredoxin and the mechanisms by which thioredoxin mediates inhibition of ventricular remodeling. 17045827_overexpression of hTRX-1 protects against hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in cells of the alveolar walls 17113580_The data indicate that the redox status of mitochondrial thioredoxin is a regulatory mechanism underlying the vulnerability of mitochondria to oxidative injury. 17115890_The stimulation of T-cell mitogenic response by the physiological levels of selenite is caused by increased TR activity, which may lead to reduction of Trx-1 dependent on the intracellular expression level and promotion of DNA binding of NF-kappaB. 17220299_Thioredoxin 1 and thioredoxin 2 have opposed regulatory functions on hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. 17316609_ver-expression of hTrx-1 in Drosophila melanogaster promotes cell growth and proliferation during eye development as measured by eye size and ommatidia size. Furthermore, hTrx-1 rescues the small eye phenotype induced by the over-expression of PTEN. 17360766_Overexpression in transgenic mice inhibits development of diabetic neuropathy. 17369362_analysis of complex protein dynamics in human thioredoxin 17557078_thioredoxin-1 affects CD30-dependent changes in lymphocyte effector function 17574940_analysis of structure and function of human thioredoxin 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17606900_A specific transnitrosation reaction between procaspase-3 and thioredoxin-1 (Trx) occurs in cultured human T cells and prevents apoptosis. 17634480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17651689_Nuclear Trx-1 is required to resist apoptosis of MCF-7 cells induced by cisplatin, probably through up-regulating the anti-apoptotic gene, p53. 17652454_These results indicate that Ask1 oxidation is required at a step subsequent to activation for signaling downstream of Ask1 after H(2)O(2) treatment. 17724081_These findings demonstrate that Trx, TRAF2, and TRAF6 regulate ASK1 activity by modulating N-terminal homophilic interaction of ASK1. 17823364_Thioredoxin-1-dependent induction of glutathione 3-transferase P1 (GST-P1) expression is required for apoptosis inhibition in human endothelial cells. 17896802_results suggest that oxidative stress induces thioredoxin in the salivary gland; suppression of IL-6 production and apoptosis by rTRX in HSG cells suggests TRX acts to protect the salivary glands of Sjogren's syndrome patients from tissue damage 17917077_Data suggest that thioredoxin could not only assist ABAD-inhibiting peptide expression, but rebalance the disturbed 'redox equilibrium' caused by intracellular amyloid beta in PC12 cells. 17949784_Expression of VEGF and Ref-1 is associated with Trx-1 overexpression and poor prognosis in patients with liver metastases from colorectal cancer. 17972886_investigatation of the catalytic mechanism of thioredoxin (human and E coli) 17982132_Chemical modification of Trx1 by common environmental and endogenously generated reactive aldehydes can contribute to atherosclerosis development by interfering with antioxidant and redox signaling functions of Trx1. 18209488_The results of the present study suggest that thioredoxin is a direct stimulator of IFN-gamma gene expression in human T cells and that there is a positive feed-back circuit by IFN-gamma and thioredoxin in the regulation of Th1 immune response. 18384140_These findings demonstrate that Trx1 is subject to changes in expression, redox state and subcellular localization with changing culture density. 18420212_TRX is up-regulated in response to increased oxidative stress and associated with intraplaque hemorrhage of coronary culprit lesions 18457020_Results describe the expression of genes for thioredoxin 1 and thioredoxin 2 in multidrug-resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. 18497292_in resting human lymphocytes, thioredoxin-1 actively denitrosylated cytosolic caspase-3 and thereby maintained a low steady-state amount of S-nitrosylation 18544525_The reversible inhibition of human Trx1 activity by H(2)O(2) and NO donors is suggested to act in cell signaling via temporal control of reduction for the transmission of oxidative and/or nitrosative signals in thiol redox control 18579387_The results of this study suggest that increasing the electrophilic character of these molecules might enhance the antiproliferative activity at the expense of the selectivity toward thioredoxin-1 and the G(0)/G(1) phase arrest. 18835792_The expressions of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor-A, thioredoxin, and thioredoxin interacting protein were related to macrophage infiltration rather than neovascularization in carotid atherosclerotic plaques 18848838_stimulation of PPARalpha in human macrophages might reduce arterial inflammation through differential regulation of the Trx-1 and VDUP-1 gene expression 18976655_The increase of Trx expression and activity inhibited Hcy-induced ROS production and MCP-1 secretion. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18983687_Identification of human TXN as a novel IFN-gamma-induced factor: mechanism of induction and its role in cytokine production are reported. 19120277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19120277_The frequency of the A allele of the G/A SNP in the 3' flanking region was highest in T1D (8.4%), followed by type 2 diabetes (6.8%), and the lowest in the controls (5.9%), suggesting the contribution of TXN polymorphism to susceptibility to T1D. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19135121_Report the effects of acrolein on peroxiredoxins, thioredoxins, and thioredoxin reductase in human bronchial epithelial cells. 19208085_the elicited TRX is beneficial to reduce allergic inflammation through negative regulation of eosinophil functions and has potential in the treatment of allergic diseases, such as asthma. 19328186_The results of this study indicated that Trx-1 overexpression protects neurons from apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion. 19337991_thioredoxin is upregulated in Human papillomavirus related oral squamous cell carcinoma 19385090_Review discusses the cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of Trx1, its anti-oxidant and anti-chemotaxis effects against neutrophils and as an inhibitor of complement activation, and its use in animal models of oxidative and inflammatory disorders. 19540723_thioredoxin is increased in first-episode schizophrenic patients 19558833_The high expressions of Prx1, Trx1 and HIF-1alpha were related to invasion and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 19566940_Overexpression of thioredoxin1 and is associated with breast carcinoma. 19592618_AICAR injection increases the expression of Trx and decreased reactive oxygen species production in the aortic wall of apolipoprotein-E mice fed a high-fat diet. 19601712_These results suggest that the cell surface TRX serves as one of the MIF binding molecules or MIF receptor component and inhibits MIF-mediated inflammatory signals. 19620238_Findings suggest that Trx and TrxR are multifunctional proteins that, in addition to modulating H(2)O(2) levels and transcription factor activity, aid ERalpha in regulating the expression of estrogen-responsive genes in target cells. 19671194_Lentivirally transduced human TRX prolonged transplanted mouse islet survival. The reactive oxygen species scavenger & antiapoptotic functions of TRX are critical to islet survival after transplantation. 19723146_The thioredoxin family of proteins is important for growth and differentiation of lung cancer cells. 19773351_p21(WAF1) can induce thioredoxin secretion and angiogenesis in cancer cells, by direct transcriptional repression of the thioredoxin-binding protein 2 promoter 19799607_the redox regulatory function of Trx plays an important role in bile duct cell transformation and tumor progression during cholangiocarcinogenesis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20074557_TRX1 has a role in suppressing senescence in normal cells in addition to its function as a redox-protective protein. 20103619_Findings indicate that mda-7/IL-24 induces PERK activation that triggers production of ceramide, ceramide synthase 6 and thioredoxin, which in turn promote glioma cell autophagy and cell death. 20172870_TBP-2 mRNA levels in the endometrium were lower, and the TRX to TBP-2 ratio was higher in patients with endometriosis than in the control group. 20218863_Actin is kept in a reduced state by Trx1 under oxidative stress via a direct interaction of the proteins. Cysteine 62 in Trx1 is the key site that interacts with actin, and is required to maintain cellular viability and anti-apoptotic function. 20298786_we have demonstrated that overexpression of Trx strongly delays inherited photoreceptor cell degeneration and preserves the visual function via activating survival signaling pathways in a phenotypic model for sensorineural deafness and retinal dystrophy 20347035_Nrf2-dependent Trx1 induction turned out to enhance HIF-1 alpha signaling in intermittent hypoxia. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20423474_Increased levels of CRP and TRX in subjects with mildly reduced glomerular filtration rate(GFR). The GFR-CRP link and the GFR-TRX link appeared to be mediated, at least partly, by alterations in blood pressure and plasma lipids. 20430109_Down-regulation of thioredoxin, increased intracellular reactive oxygen species, and activation of ASK1-ERK/p38 MAPK signaling all were associated with Japanese encephalitis virus-induced apoptosis. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536427_TR1 and Trx1 interaction play key role in redox homoeostasis. 20619274_Thioredoxin-1 mutated at T100 causes lower survival rate induced by H(2)O(2), and higher apoptosis rate induced by cis-platinum and adriamycin in HepG2 cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20661909_Determined is a novel human thioredoxin crystal structure that when compared to wild type has undergone a conformational change involving unraveling of a helix alpha 3 and exposure of residues Cys 62 and Cys 69 resulting in a more open conformation. 20662007_Presented are two crystal structures of the C69S/C73S mutant TRX1 under oxidizing (1.5 A) and reducing (1.1 A) conditions. 20847814_The plasma levels of MIF and TRX1 were significantly elevated in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20929309_calreticulin and thioredoxin were found in patterns of fibroadenoma, mucinous carcinoma, and NST carcinoma, but with different quantitative expression among them. 20955789_Thioredoxin 1 as a subcellular biomarker of redox imbalance in human prostate cancer progression 21030559_Results demonstrate that Tregs express and secrete higher levels of thioredoxin-1, a major antioxidative molecule. 21158569_TRX1 and TRX2 regulate the proliferation and survival of adipocyte derived stem cells; these processes are mediated by the activation of ERK1/2 21212402_Data demonstrate that the actin-Trx-1 complex protects Trx-1 from degradation and, thus, endothelial cells from apoptosis. Reciprocally, Trx-1 prevents stress fiber formation. 21250889_significant reduction in plasma levels found immediately following delivery only in normotensive group, not in women with preeclampsia 21324905_Knockdown of TRX1 increases the level of S-nitrosylated NSF, prolongs the inhibition of exocytosis, and suppresses leukocyte adhesion. 21353370_increased in pre-eclamptic endothelial cells 21526215_Increased Trx1 in cell nuclei can increase severity of disease responses by potentiation of redox-sensitive transcription factor activation. 21557999_knockdown of TRX-1 or TRX-2 sensitizes cells to CYP2E1-induced oxidant stress partially via ASK-1 and JNK1 signaling pathways. Both TRX-1 and TRX-2 are important for defense against CYP2E1-induced oxidative stress. 21620911_When genetically fused with human serum albumin, Trx retains the biological properties of Trx and thus has great potential in treating oxidative stress-related disease. 21636804_role for the TXNIP-TRX1 complex to enable inflammation by promoting endothelial cell survival and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling under conditions of physiological oxidative stress 21704743_Many nitrosylation sites are reversibly regulated by Trx1, suggesting a more prominent role for Trx1 in regulating S-nitrosylation. 21705327_thioredoxin regulates the intrinsic function of Txnip as an inhibitor of adipogenesis through protein stabilization. 21908620_Activation of extracellular transglutaminase 2 by thioredoxin. 21963718_Thioredoxin stimulates MMP-9 expression, de-regulates the MMP-9/TIMP-1 equilibrium and promotes MMP-9 dependent invasion in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. 22134635_Thioredoxin might play an important role in mild hyperthermia-induced G2/M arrest via p53 and Gadd45a activation. 22248473_Data show that lowering TRX1 expression through increased secretion leads cisplatin-resistant cells to higher reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and increased dependency on oxidative metabolism (OXMET). 22384152_S. zooepidemicus uses SzP to recruit TRX and regulated the alternative complement pathways to evade the host immune phagocytosis 22430737_This study adds a further role to the known anti-inflammatory properties of Trx1 and highlights the difference in function between the full-length and truncated forms. 22447839_Trx-1 plays a key role in cell growth and survival, as well as chemoresistance, and is a potential target to overcome drug resistance in relapsed/refractory Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 22492997_These findings provide a new mechanism to support the antioxidant function of DJ-1 by increasing Trx1 expression via Nrf2-mediated transcriptional induction. 22505815_MsrB1/Trx complex was studied in attempt to understand MsrB1 reduction mechanism. Using NMR data, molecular mechanics, protein docking & molecular dynamics simulations, found that intermediate MsrB1/Trx complex is stabilized by interprotein beta-layer. 22516068_The ability of Trx-1 to promote differentiation of macrophages into an alternative, anti-inflammatory phenotype may explain its protective effects in cardiovascular diseases. 22760822_A thioredoxin interacting protein mutant with all but one cysteine changed to serine (Cys247) showed an enhanced capacity to form complexes with TRX. 22867430_Trx-1 plays a role in different physiological situations, cardiac hypertrophy, ischemia reperfusion injury, heart failure, atherosclerosis, & diabetes mellitus type 2. It has a central rolein cardiovascular health & disease. Review. 22882193_TRX-1 nuclear expression in the tumour invasion front of patients with gallbladder carcinoma may be a useful prognostic marker for survival. 22933306_ADAM10 and 17, two alpha-secretases, are responsible for Trx80 generation and a deficit in Trx80 could participate in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. 22977247_Studies show that the glutaredoxin system with glutathione plays a backup role to keep oxidized thioredoxin 1 (Trx1) reduced in cells with loss of thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) activity. 23068965_The results indicate that TRX-1 may be adaptively induced by the effects of inflammation and oxidative stress, suggesting protective roles for TRX-1 against these effects in the placenta of PTD. 23105116_This study identifies Trx-1 as a novel interaction partner of the ADAM17 cytoplasmic domain. 23112551_TXN is overexpressed in 65% of the gastric cancer tissues 23133653_Polymorphisms in thioredoxin reductase and selenoprotein K genes and selenium status modulate risk of prostate cancer 23212077_thioredoxin 1 has a role in the regulation of apoptosis by S-nitrosylation [review] 23223577_By modifying Cys residues or regulating Cys redox states in TF extracellular domain, hTrx1/TrxR function as a safeguard against inappropriate TF activity. 23238053_The differential association of TRX and cognitive performance in schizophrenia and controls may be related to the impaired oxidative stress status of schizophrenia patients. 23319048_SCO2 increases the generation of reactive oxygen species and induces dissociation of the protein complex between apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and its cellular inhibitor, the redox-active protein thioredoxin (Trx). 23335265_The ability of truncated thioredoxin Trx-80 to promote differentiation of macrophages into the classical proinflammatory phenotype may explain its atherogenic effects in cardiovascular diseases. 23356570_Plasma thioredoxin levels were found to be elevated early following cardiac arrest. 23485938_We showed that overexpression of TRXs reduced cell death; TRX2 was expressed in the mitochondria, while TRX1 was expressed in the cytoplasm. 23571504_role in cell-mediated reduction of human beta-defensin 1 23606123_These results suggest that DON-induced accumulation of Trx-1 in HepG2 cells plays one of the key roles in protection against cytotoxicity caused by deoxynivalenol(DON) and that the mechanism may be mediated by the antioxidant properties of Trx-1. 23671274_Data suggest a pathway in which thioredoxin (Trx) acts as a tonic, endogenous regulator of Cav3.2 channels, while heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)-derived carbon dioxide (CO) disrupts this regulation, causing channel inhibition. 23743503_Glutathione acts in concert with human thioredoxin type 1 in the denitrosation of cytosolic S-nitrosoproteins (PSNOs) from HepG2 cells. 23850970_Our results indicate a close relationship between Trx1 and the 20S nuclear proteasome 24008424_MAP3K5 R256C mutation revealed attenuation of MKK4 activation through increased binding of the inhibitory protein thioredoxin (TXN/TRX-1/Trx), resulting in increased proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of melanoma cells. 24062305_Thioredoxin 1 is inactivated due to oxidation induced by peroxiredoxin under oxidative stress and reactivated by the glutaredoxin system. 24086714_Thioredoxin1 downregulates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced adhesion molecule expression via Smad3 protein. 24130091_The expression of TRX-1 was increased in leiomyomas compared with the matched adjacent myometrium. 24130874_In endothelial cells CD IgA mediate the constitutive activation of extracellular TG2 by a mechanism involving the redox sensor protein TRX. 24147004_The transient up-regulation of miR-525-3p, and the resultant repression of its direct targets ARRB1, TXN1 and HSPA9, is required for cell survival following irradiation. 24270206_In the early stages of Alzheimer's disease, thioredoxin is released into the cerebrospinal fluid as a promising early biomarker involved potentially in the pathogenesis of the disease. 24295294_The Grx2 system could help to keep Trx2/1 reduced during an oxidative stress, thereby contributing to the anti-apoptotic signaling. 24338024_Inhibition of Trx activity in the lung attenuates LPS-induced SNO-p65 denitrosylation, NF-kappaB activation, and airway inflammation, supporting a pathophysiological role for this mechanism in lung injury. 24376827_Changes in TRX-1 compartmentalization under nitrosative/oxidative stress conditions are dependent on the expression levels of TXNIP. 24389582_The inhibition of TRX by TXNIP is mediated by an intermolecular disulphide interaction resulting from a novel disulphide bond-switching mechanism. This bond dissociates in the presence of high concentrations of reactive oxygen species. 24459704_A role of TRx1 protein in the modulation of the base excision repair. 24632182_Loss of Trx-1 and upregulation of NOX4 contribute to the imbalance in the redox-status of senescent endothelial cells ex vivo and in vivo. 24689038_Level of TRX-1 in skeletal muscle tissue was lower while that of HSP90 was higher in type 2 diabetes than in impaired glucose tolerance subjects. 24720336_Data suggest that hyperglycemia, as exhibited in 85% of pancreatic cancer patients, up-regulates expression of TXNIP (thioredoxin interacting protein) and modulates activity of TRX and production of reactive oxygen species in pancreatic cancer cells. 24925443_Diabetes was associated with a 21 % reduction in thioredoxin activity. 24962940_Thioredoxin protein, human is higher in patients with breast cancer. It can be a useful marker in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. 24976139_TRX1 physically interacts with and reactivates PTP1B and PTEN through a direct thiol disulfide exchange. 25106706_hyperoxic impairment of Trx1 has a negative impact on HSP90-oxidative responses critical to cell survival, with potential implications for pathways implicated in lung development and the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 25174623_Combinational analysis of CA125 with Trx1 for the detection of ovarian cancer suggests that the diagnostic capacity of CA125 alone for the early detection of ovarian cancer is significantly improved by its combination with Trx1. 25184225_The Trx1 ubiquitination site was determined along with the 3D structure of the SlrP-Trx1 complex. 25197784_The unfolding kinetics of the model substrate thioredoxin, when pulled through an alpha-haemolysin pore, differ markedly depending on whether the process is initiated from the C terminus or the N terminus. 25218830_Data indicate in the fasting state the mRNA levels of antioxidant enzymes and thioredoxin (TXN), were significantly increased in the familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) group compared to the healthy controls. 25231459_LEDGF and 44 other novel putative nuclear targets of human thioredoxin 1 have been identified. 25297388_Plasma TRX levels of male patients in a manic episode were significantly lower than the controls. 25350977_Suggest that urinary TRX1 is an oxidative stress-specific biomarker useful for distinguishing AKI from chronic kidney disease and healthy kidneys. 25483711_Trx1 increased FOXO1-induced drug resistance, while Trx1 C69S mutant completely abolished the regulation of FOXO1-mediated drug resistance by Trx1. 25483731_Thioredoxin is inhibited by 1-methylpropyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide, which inhibits the growth, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cell lines 25520003_Serum TRX levels at admission were associated with stroke severity and lesion volumes. 25547896_Transient increase in TRX-1 protein expression during exercise was found. 25555670_Thioredoxin is a novel diagnostic and prognostic marker in patients with ischemic stroke. 25561728_Data show redox and non-redox interaction targets for thioredoxin-like proteins. 25576832_Se/S-palmitoylation acts as an important modulator of TrxR1/hTrx1 activities 25622749_thioredoxin is a remote ischemic preconditioning-induced factor in heart tissue of cardiosurgical patients. 25656992_the overexpression and nuclear translocation of thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) are closely associated with hypoxia-drug resistance through the regulation of the metabolism by the oxidative stress response to glycolysis. 25735211_Grx2 and Trx1 contribute significantly to neuronal integrity and could be clinically relevant in neuronal damage following perinatal asphyxia and other neuronal disorders. 25839660_S-palmitoylation alters conformation or secondary structure of Trx1, as well as decreases the ability of Trx1 to transfer electrons from thioredoxin reductase to S-nitrosylated protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B and S-nitroso-glutathione 25945832_Trx1 inhibition results in reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in Multiple myeloma cells, sensitizes Multiple myeloma cells to the NF-small ka, Cyrillicbeta inhibitors, and also induces apoptosis in bortezomib-resistant myeloma cells. 25979194_differential expression in children with allergic asthma 26021764_In Jurkat cells exposed to ionizing radiatin (4 Gy), constitutively active Trx systems respond to restore cellular redox balance. After 16 hrs, Trx increases and rescues cells against IR-mediated damage. 26028649_MKK4 is activated in vitro by reduced Trx but not oxidized Trx in the absence of an upstream kinase, suggesting that autophosphorylation of this protein occurs due to reduction of Cys-246 and Cys-266 by Trx. 26119781_identification of the novel interaction between Trx1 and AIF has provided opportunities to design and develop therapeutically relevant strategies that either promote or prevent this protein-protein interaction for the treatment of different disease 26210445_The results demonstrate that the antiproliferative effect of NO is hampered by Trx1 and Grx1 and support the strategy of weakening the thiolic antioxidant defenses when designing new antitumoral therapies. 26276860_Results indicate that reduced Trx1 plays important protective roles against methyl methanesulfonate-induced DNA damage and cell death, suggesting that cell protection is regulated by the intracellular redox state. 26325518_Thioredoxin 1 mediates TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. 26329592_genetic variants of TXN and COMT have roles in regulating abdominal obesity 26334622_Serum levels of thioredoxin and DJ-1 were significantly higher in non-small cell lung cancer patients; therefore, these may be utilized as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer 26453009_The crystal structure of fully oxidized thioredoxin shows a non-active Cys62-Cys69 disulfide bond in addition to the active Cys32-Cys35 disulfide. 26460805_Data show that the overexpression of thioredoxin1 (Trx1) attenuated apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in lung cancer cells. 26536897_Based on its collective anti-oxidative, cytoprotective, and cytokine-like properties of TRX, TRX is likely to be involved in the optimal growth and maturation of ovarian follicles and responsiveness to hyperstimulation. 26656445_change of serum levels of thioredoxin in patients with severe traumatic brain injury 26760912_Analysis of 25 independent cohorts with 5910 patients showed that Trx1 and TrxR1 were both associated with a poor patient prognosis in terms of overall survival, distant metastasis free survival and disease free survival. 26933812_High TRX1 expression is associated with myocardial infarction. 27000227_Elevated plasma thioredoxin levels are correlated with the severity and poor prognosis in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients. 27132507_our findings identify the TXN-FOXO1-p300 circuit as the sensor and effector of oxidative stress in DLBCL cells 27158980_Authors found that TXN was under expressed in both AML and ALL groups as compared to the control group. Also TXN expression level was nega |
ENSMUSG00000028367 |
Txn1 |
662.520170 |
2.0400782280 |
1.028624 |
0.068855476 |
224.044596 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001186286618988719753438053479500356033410973004817968773865841302214974927034498351384356161495888593612732727709047120783145677115621996478012079023756086826324462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000257873203185176787709780357325631402308259899412844680067994832555156815460937722426880389274401432704810051952398831015328059534930105201055994257330894470214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
896.6257418 |
34.9531976 |
442.6415583 |
13.5024057 |
| ENSG00000136830 |
64855 |
NIBAN2 |
protein_coding |
Q96TA1 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in apoptosis suppression. May promote melanoma cell invasion in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19362540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21148485}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables transcription coactivator activity. Involved in several processes, including gonadotropin secretion; positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding activity; and regulation of cellular macromolecule biosynthetic process. Located in several cellular components, including adherens junction; cytosol; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64855; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; gonadotropin secretion [GO:0032274]; hypomethylation of CpG island [GO:0044029]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000279]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030948]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of embryonic development [GO:0040019]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048743]; positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000679] |
19362540_Phosphorylation of FAM129B has a role in controlling melanoma cell invasion. 21148485_The rapid induction of apoptosis in FAM129B knockdown cells was reversed by co-transfection with recombinant FAM129B, indicating that its effect on apoptosis was specific. 26721396_activated EGFR phosphorylates the Y593 residue of the protein known as family with sequence similarity 129, member B (FAM129B), which is overexpressed in many types of human cancer. 31262713_We have demonstrated that FAM129B in cancer promotes Nrf2 activity by reducing its ubiquitination through competition with Nrf2 for Keap1 binding via its DLG and ETGE motifs. In addition, FAM129B reduces chemosensitivity by augmenting Nrf2 antioxidative signaling and confers poor prognosis in breast and lung cancer 33142954_Structural Insight on Functional Regulation of Human MINERVA Protein. |
ENSMUSG00000026796 |
Niban2 |
2373.781438 |
3.2145172115 |
1.684602 |
0.036302369 |
2204.797636 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3646.1520177 |
81.1423823 |
1142.3926038 |
20.7736902 |
| ENSG00000136840 |
27090 |
ST6GALNAC4 |
protein_coding |
Q9H4F1 |
FUNCTION: Transfers the sialyl group (N-acetyl-alpha-neuraminyl or NeuAc) from CMP-NeuAc to the GalNAc residue on the NeuAc-alpha-2,3-Gal-beta-1,3-GalNAc sequence of glycoproteins and glycolipids forming an alpha-2,6-linkage. Produces branched type disialyl structures by transfer of a sialyl group onto a GalNAc residue inside the backbone core chains. Prefers O-glycans to glycoproteins or glycolipids. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R2B6}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sialic acid;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R2B6}.; PATHWAY: Glycolipid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R2B6}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid from CMP-sialic acid to galactose-containing substrates. The encoded protein prefers glycoproteins rather than glycolipids as substrates and shows restricted substrate specificity, utilizing only the trisaccharide sequence Neu5Ac-alpha-2,3-Gal-beta-1,3-GalNAc. In addition, it is involved in the synthesis of ganglioside GD1A from GM1B. The encoded protein is normally found in the Golgi apparatus but can be proteolytically processed to a soluble form. This protein is a member of glycosyltransferase family 29. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Readthrough transcripts exist for this gene and the downstream ST6GALNAC6 gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2022]. |
hsa:27090; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; (alpha-N-acetylneuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1,3)-N-acetyl-galactosaminide 6-alpha-sialyltransferase activity [GO:0047290]; alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase activity [GO:0001665]; sialyltransferase activity [GO:0008373]; ganglioside biosynthetic process [GO:0001574]; glycolipid metabolic process [GO:0006664]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; oligosaccharide metabolic process [GO:0009311]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
15528990_Sp1 and MZF1 are involved in the transcriptional regulation of the hST6GalNAc IV gene in Jurkat T cells 18598683_Data show that serum from a patient with axonal Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) with IgG anti-GalNAc-GD1a antibody yielded positive immunostaining with X1, X2, and X3. 26715099_This study implies the potential therapeutic application of miR-4299 and ST6GALNAC4 in modulating the invasion and tumorigenicity of follicular thyroid carcinoma cell |
ENSMUSG00000079442 |
St6galnac4 |
184.447798 |
2.1933120823 |
1.133111 |
0.136236726 |
69.335781 |
0.00000000000000008304920645314765357380177898474870535686714418050283215144702353427419438958168029785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000629910733426751997209375386173079394674737538969283567880097507440950721502304077148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
254.4323555 |
21.4709885 |
116.9583456 |
7.6199944 |
| ENSG00000136867 |
1318 |
SLC31A2 |
protein_coding |
O15432 |
FUNCTION: Involved in low-affinity copper uptake. {ECO:0000305}. |
Copper;Copper transport;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable copper ion transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in cellular copper ion homeostasis. Predicted to act upstream of or within regulation of copper ion transmembrane transport. Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1318; |
late endosome [GO:0005770]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; copper ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005375]; cellular copper ion homeostasis [GO:0006878]; copper ion transport [GO:0006825]; regulation of copper ion transmembrane transport [GO:1902311] |
17617060_hCTR2 is as an oligomeric membrane protein localized in lysosomes, which stimulates copper delivery to the cytosol of human cells at relatively high copper concentrations. 17944601_Ctr2 promotes copper uptake at the plasma membrane and plays a role in regulating copper levels in COS-7 cells 19509135_CTR2 functions by limiting drug accumulation, and its expression correlates with the sensitivity of human ovarian carcinoma cell lines to cisplatin. 23564780_Increased CTR2 expression is associated with platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. 24522273_Over-expression of CTR2 increased exchangeable Cu(+) by 150% and rendered the human epithelial 2008 cancer cell model 2.5-fold resistant to cisplatin. 24703712_Data suggest that SLC31A1 and SLC31A2, despite being structurally closely related and sharing important amino acid motifs, play different roles in copper homeostasis and in platinum-based chemotherapy of neoplasms. [REVIEW] 26205368_Studied the interaction of CTR1 and CTR2 in fully malignant HEK293T and OVCAR8 human ovarian cancer cells using a CRISPR-Cas9 knock out system. 26411550_Decreased expression of CTR2 is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 28507097_Gene duplication and neo-functionalization in the evolutionary and functional divergence of the metazoan copper transporters Ctr1 and Ctr2 28737129_11 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in CTR1, CTR2, ATP7A, and ATP7B were genotyped in these patients. |
ENSMUSG00000066152 |
Slc31a2 |
332.995249 |
9.5763733733 |
3.259479 |
0.140076407 |
565.309178 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005884421821883474980748362020584730408234067597425578246970178643516378307182322614229702166950149140294165896987270802250191933179183327340156704555506046127328384924183450233443331412274574629787209940162 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003135525851660652914968140932281044927805787072737670001558390225619514016593645128809087840401884828558101722924433574344751170965494648585856066727868241316863911665116698792081325750313774700083466369488 |
Yes |
No |
609.8192124 |
49.0813654 |
64.1480951 |
4.5601665 |
| ENSG00000136868 |
1317 |
SLC31A1 |
protein_coding |
O15431 |
FUNCTION: High-affinity, saturable copper transporter involved in dietary copper uptake. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11734551}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Copper;Copper transport;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a high-affinity copper transporter found in the cell membrane. The encoded protein functions as a homotrimer to effect the uptake of dietary copper. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:1317; |
intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; copper ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005375]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cellular copper ion homeostasis [GO:0006878]; copper ion import [GO:0015677]; copper ion transport [GO:0006825]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649] |
11983704_fundamentally conserved mechanism for high affinity copper uptake through the Ctr proteins in yeast and humans 12023893_biochemical characterization and subcellular localization 12177073_observations demonstrate that, although Ctr1 is critical for both cellular copper uptake and embryonic development, mammals possess additional biochemically distinct functional copper transport activities 12466020_Results suggest that human copper transporter 1 (CTR1) spans the membrane at least six times, permitting formation of a channel, which is consistent with its proposed role as a copper transporter. 12501239_hCtr1-mediated copper uptake into mammalian cells is regulated by a post-translational mechanism involving copper-stimulated endocytosis and degradation of the transporter 14976198_there are common biochemical mechanisms regulate both transport and trafficking functions of hCtr1 15326162_there is a direct interaction between cisplatin and the hCtr1 protein; cisplatin and copper have distinct biochemical consequences on this transporter 15634665_Internalization of endogenous human Ctr1 in response to elevated extracellular copper levels does not play a significant regulatory role in copper homeostasis. 16356544_Hormones have a role in the formation of the active hCTR1 protein in human placental cells. 16501047_formation of a putative pore for metal ions at the interface of three identical subunits deviates from the structural design of typical primary and secondary active transporters 17627945_hCTR1 plays a key role in the physiologically important delivery of copper from blood to intracellular proteins, whereas its role in the initial apical uptake of dietary copper is indirect. 17959139_The results of NMR methods and site-directed mutagenesis of the two cysteine residues demonstrate that Cys-189 but not Cys-161 is essential for both dimer formation and proper folding of the protein. 19144690_Downregulation of Ctr1 suppresses cisplatin nephrotoxicity, including cell death by both apoptosis and necrosis. 19147760_Proteasomal inhibition prevents cisplatin-induced down-regulation of hCTR1 in ovarian cancer cells and enhanced drug uptake and cell killing in a synergistic manner 19240214_structure of the human CTR1 protein solved by electron crystallography to an in plane resolution of 7 A 19529937_Results demonstrate that co-exposure of tumor cells to emodin or DRB with cisplatin inhibits platinum drug uptake by impacting the hCtr1 transporter. 19669174_Results describe the interactions of a peptide corresponding to the N-terminal domain of the human copper transporter 1 with cisplatin and its analogues, at the molecular level. 19684018_Data indicate that human copper transporter 1 cleavage occurs in a late endosomal, Rab9-positive compartment prior to delivery of the transporter to the plasma membrane. 19740744_Copper-dependent internalization and recycling of hCTR1 provides an acute and reversible mechanism for the regulation of cellular copper entry. 19856191_findings reveal a high level of conservation between the mammalian and insect Ctr1-type copper importers 19929093_Sequence analysis demonstrated SLC31A1 on chromosome 9 was rearranged with breaks occurring within its intron. SLC31A1 lies close to BSPRY which is a candidate for cleft lip/palate involvement. 20534491_Identified as dominant hinge regions, CTR1's MxxxM and GxxxG motifs were shown to have significant roles in functional movements characterized by the two slowest modes of motion. 20569931_Ctr1 is an important transport protein in the accumulation of silver in mammalian cells. 20699218_Data show apical localization of Ctr1 in intestinal epithelia and suggest that increased Ctr1 apical localization in response to dietary copper limitation may represent an adaptive response to modulate Ctr1 availability at the site of copper absorption. 21072377_Compared the binding interactions between cisplatin, carboplatin and oxaliplatin with synthetic peptides corresponding to hCtr1 Mets motifs. 21602128_Cisplatin induces drug resistant phenotype by decreasing the protein level of CTR1 in human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell line EC109. 22068728_Data show that both shRNA-DMT1 and shRNA-hCTR1 cells had lower apical Fe uptake, Cu uptake, and Zn content compared to control cells. 22354499_There was little difference in rates/kinetics of uptake of copper in the Ctr1+/+ and -/- cells. Endocytosis was not involved. 22516052_CTR1 plays an essential role in cisplatin toxicity and could be considered as a predictor for pretreatment evaluation in lung cancer patients. 22552365_The cells expressing the hCTR1 mutants of histidine-rich motifs in the N-terminus (H22-24A, NHA) resulted in a higher basal copper level in the steady state compared to those expressing wild-type protein. 22569840_Structure of CTR1 confirms that two triads of methionine residues delineate the intramembranous region of the transporter, and further identifies two additional methionine triads that are located in the extracellular N-terminal part of the transporter. 22684009_basal expression of Ctr1 is regulated by HIF2alpha; however, the induction by hypoxia is a HIF2alpha-independent event 22725681_genetic association study in Han population in China: Data suggest that SNPs in SLC31A1 (rs7851395; rs12686377) are associated with resistance to platinum compounds as antineoplastics and survival outcomes in non-small cell lung carcinoma patients. 22962276_This review explains how modulating cellular copper availability could influence treatment efficacy in platinum-based cancer chemotherapy through hCtr1 regulation[review] 23010323_Our findings imply that reduced CTR1 expression accounts for decreased cisplatin accumulation and represents one of the determinants of cisplatin resistance in A2780cis cell line 23426973_Depletion of glutathione decreases cellular copper uptake mediated by human copper transporter 1. 23658018_Results show that hCTR1 elements on the intracellular side of the hCTR1 pore, including the carboxyl tail, are not essential for permeation, but serve to regulate the rate of copper entry. 23782748_The patients with tumors showing high expression levels of at least one of OATP1B3 and CTR1 had potentially longer disease-free survival. 23827522_This study demonistrated that Inhibition of human high-affinity copper importer Ctr1 orthologous in the nervous system of Drosophila ameliorates Abeta42-induced Alzheimer's disease-like symptoms. 23963605_Duodenal CTR1 mRNA and protein expression was decreased in Wilson's disease patients, while ATP7A mRNA and protein production was increased. This can be a defense mechanism against systemic copper overload resulting from functional impairment of ATP7B. 24039729_Knockdown of CTR1 expression in human umbilical cord endothelial cells increases cell proliferation and migration. 24132751_Cisplatin transcriptionally induces the expression of human Ctr1 in time- and concentration-dependent manners. 24485600_Extracellular copper concentrations regulate the levels of CTR1 through internalisation and degradation, the addition of prolactin, inhibits the degradation of CTR1, thus promoting copper uptake by mammary epithelial cells. 24614111_CTR1, ATP7A, and lysyl oxidase were upregulated in the lung tissues and pulmonary arteries of mice with hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. 24703712_Data suggest that SLC31A1 and SLC31A2, despite being structurally closely related and sharing important amino acid motifs, play different roles in copper homeostasis and in platinum-based chemotherapy of neoplasms. [REVIEW] 24792335_CTR1 expression may be necessary for therapeutic efficacy of platinum based drugs in non-small cell lung cancer treatment. 24800945_NSC73306 is a transport substrate of CTR1 24837030_The data collected here shows that the Atox1 keeps its dimer nature also in the presence of the CTR1 c-terminal domain; however, two geometrical states are assumed by the Atox1. 25823781_allele distribution of the SLC31A1 was not different between group N and O, and out of the 11 SNPs of the SLC22A2 gene only the allele distribution of the nonsynonymous SNP was significantly different between patients who experienced ototoxicity 26061257_Two methionine residues in the MXXXM motif of of the CTR1 second transmembrane domain are important for binding to silver. 26067577_Gene silencing of either CTR1 or DMT1 did not affect copper accumulation in cells, but deficiency in both CTR1 and DMT1 resulted in a complete inhibition of copper uptake. 26205368_Studied the interaction of CTR1 and CTR2 in fully malignant HEK293T and OVCAR8 human ovarian cancer cells using a CRISPR-Cas9 knock out system. 26745413_C-Terminus of Human Copper Importer Ctr1 Acts as a Binding Site and Transfers Copper to Atox1 26851002_High CTR1 Expression is associated with poor response to chemotherapy in Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer. 26945057_CTR1 recycling via clathrin-mediated and Rab11 pathways enable cells to dynamically modulate copper entry 27112899_It has been demonstrated in ovarian cancer cells that cisplatin resistance and uptake correlates with reduced CTR1 and LRRC8A protein expression/activity and a concomitant upregulation in cisplatin exporting transporters (ATP7A, ATP7B), which implies that the resistant cells have a reduced ability to accumulate cisplatin and activate proapoptotic transporters for osmolytes. 27270317_Study showed that NEAT1 could function as a competing endogenous lncRNA in lung cancer, mediating CTR1 by sponging hsa-mir-98-5p. 27384479_combination of desferal with oxaliplatin can overcome cervical cancer oxaliplatin resistance through the regulation of hCtr1 and TfR1 28507097_Gene duplication and neo-functionalization in the evolutionary and functional divergence of the metazoan copper transporters Ctr1 and Ctr2 28714373_we assessed the role of miR-21 in mediating renal cell carcinoma chemoresistance and further showed that miR-21 silencing significantly (1) increased chemosensitivity of paclitaxel, 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and dovitinib; (2) decreased expression of multi-drug resistance genes; and (4) increased SLC22A1/OCT1, SLC22A2/OCT2, and SLC31A1/CTR1 platinum influx transporter expression 28759062_This result indicates that the formation of copper-finger protein of Sp1 is the molecular basis of copper sensing for the transcriptional regulation of hCtr1 in mammalian cells. 30230404_Impaired copper transport in schizophrenia results in a copper-deficient brain state: A new side to the dysbindin story. 30706544_SLC31A1-dependent copper levels are correlated with the malignant degree of pancreatic cancer. Copper deprivation increased mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species level and decreased ATP level, which rendered cancer cells in a dormant state. 30728448_Human marrow stromal cells secrete microRNA-375-containing exosomes to regulate glioma progression. 30959888_The loss of CTR1 resulted in a decrease in the level of COMMD1, XIAP, and NF-kappaB. Differently, the DMT1 deficiency induced increase of the COMMD1, HIF1alpha, and XIAP levels. 32207235_PTBP1 modulates osteosarcoma chemoresistance to cisplatin by regulating the expression of the copper transporter SLC31A1. 33404748_Dual-mode imaging of copper transporter 1 in HepG2 cells by hyphenating confocal laser scanning microscopy with laser ablation ICPMS. 33411033_Effects of SLC31A1 and ATP7B polymorphisms on platinum resistance in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma receiving neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. 33434736_Abnormalities in the copper transporter CTR1 in postmortem hippocampus in schizophrenia: A subregion and laminar analysis. 35996075_High expression of cuproptosis-related SLC31A1 gene in relation to unfavorable outcome and deregulated immune cell infiltration in breast cancer: an analysis based on public databases. |
ENSMUSG00000066150 |
Slc31a1 |
612.465507 |
4.1730235921 |
2.061093 |
0.077478330 |
728.066983 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023578890445321776743298152090174515351031885844111205957060478616586329868327256826158570263010424571830746049695872096388523550998474818549172753786279955046048998537654 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016976801120631678497079429763889106059505545288148937130960309249890924792217036260053197944327182402088045060260759376305255877001829150451304942301282049590289089022864 |
Yes |
No |
987.5234604 |
44.8459996 |
238.2637839 |
9.0655417 |
| ENSG00000136875 |
9128 |
PRPF4 |
protein_coding |
O43172 |
FUNCTION: Plays role in pre-mRNA splicing as component of the U4/U6-U5 tri-snRNP complex that is involved in spliceosome assembly, and as component of the precatalytic spliceosome (spliceosome B complex). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25383878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28781166}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Spliceosome;WD repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a heteromeric complex that binds U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear RNAs and is involved in pre-mRNA splicing. The encoded protein also is a mitotic checkpoint protein and a regulator of chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:9128; |
Cajal body [GO:0015030]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; spliceosomal snRNP complex [GO:0097525]; U2-type precatalytic spliceosome [GO:0071005]; U4/U6 snRNP [GO:0071001]; U4/U6 x U5 tri-snRNP complex [GO:0046540]; U4 snRNA binding [GO:0030621]; U6 snRNA binding [GO:0017070]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380]; RNA splicing, via transesterification reactions [GO:0000375] |
11971898_interaction between Hprp3p and Hprp4p 17998396_PRP4 is a spindle assembly checkpoint protein required for MPS1, MAD1, and MAD2 localization to the kinetochores. 18687998_PRP-4 belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family, plays a role in pre-mRNA splicing and cell mitosis, and interacts with CLK1 24003220_the requirement of enzymatic activity of PRP4 in regulating cancer cell growth and identified an array of potential novel substrates through orthogonal proteomics approaches 24419317_PRPF4 missense mutations is associated with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. 25383878_The p.R192H variant of PRPF4 represents a functional null allele which compromises the function of the tri-snRNP, reinforcing the notion that this spliceosomal particle is of crucial importance in the physiology of the retina. 29787735_Possible molecular mechanism of PRP4-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, makes PRP4 an important target in colon cancer. 31445970_Results confirmed that the PRPF4 gene was overexpressed in various breast cancer cell lines. Its knockdown slows down breast cancer progression via suppression of p38 MAPK phosphorylation. In conclusion, the PRPF4 gene plays an important role in the growth of breast cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000066148 |
Prpf4 |
312.378768 |
2.0634726634 |
1.045074 |
0.095112443 |
121.720323 |
0.00000000000000000000000000026578395357688696388213173528745178378990195957788268798777865179029731689669402427966815594118088483810424804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000003228782843452553091865992137787652190793775893304714498570921589529870250265264353117800055770203471183776855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
426.3679016 |
23.0854451 |
208.1548882 |
8.8802747 |
| ENSG00000136940 |
5082 |
PDCL |
protein_coding |
Q13371 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a positive regulator of hedgehog signaling and regulates ciliary function. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DBX2}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Functions as a co-chaperone for CCT in the assembly of heterotrimeric G protein complexes, facilitates the assembly of both Gbeta-Ggamma and RGS-Gbeta5 heterodimers.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Acts as a negative regulator of heterotrimeric G proteins assembly by trapping the preloaded G beta subunits inside the CCT chaperonin. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Chaperone;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Vision |
|
Phosducin-like protein is a putative modulator of heterotrimeric G proteins. The protein shares extensive amino acid sequence homology with phosducin, a phosphoprotein expressed in retina and pineal gland. Both phosducin-like protein and phosphoducin have been shown to regulate G-protein signaling by binding to the beta-gamma subunits of G proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5082; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; cell projection organization [GO:0030030]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex assembly [GO:1902605]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12466282_physiological control of G-protein regulation by PhLP seems to involve phosphorylation by CK2 and alternative splicing of the regulator 15745879_the strong inhibitory action of PhLP(S) on Gbetagamma signaling is the result of a previously unrecognized mechanism of Gbetagamma-regulation, inhibition of Gbetagamma-folding by interference with TCP-1alpha 16717095_PhLP phosphorylation permits the release of a PhLP x Gbeta intermediate from cytosolic chaperonin complex, allowing Ggamma to associate with Gbeta in this intermediate complex. 19376773_cytosolic chaperonin complex-dependent mechanism exists for Gbeta5-RGS7 assembly that utilizes the co-chaperone activity of PhLP1 in a unique way 19403526_PhLP-M1-G149, a Gbetagamma-interacting construct derived from phosducin-like protein 1 (PhLP) is a differential inhibitor of Gbetagamma 23888055_evidence of a generic mechanism, whereby the splicing of the PhLP gene could potentially and efficiently regulate the cellular levels of heterotrimeric G proteins. 25675501_PhLP1 binding stabilizes the Gbeta fold, disrupting interactions with CCT and releasing a PhLP1-Gbeta dimer for assembly with Ggamma. |
ENSMUSG00000009030 |
Pdcl |
174.651033 |
0.4453633386 |
-1.166945 |
0.164228135 |
49.968824 |
0.00000000000156208299847818241096493693480622347974882957455378118538646958768367767333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000009163889132566761418242649309792751321709913803204017312964424490928649902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
108.8752650 |
11.4168925 |
246.7525135 |
17.7339907 |
| ENSG00000136986 |
79139 |
DERL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BUN8 |
FUNCTION: Functional component of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) for misfolded lumenal proteins (PubMed:15215856, PubMed:33658201). Forms homotetramers which encircle a large channel traversing the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane (PubMed:33658201). This allows the retrotranslocation of misfolded proteins from the ER into the cytosol where they are ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome (PubMed:33658201). The channel has a lateral gate within the membrane which provides direct access to membrane proteins with no need to reenter the ER lumen first (PubMed:33658201). May mediate the interaction between VCP and the misfolded protein (PubMed:15215856). Also involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control, a mechanism that selectively attenuates the translocation of newly synthesized proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum and reroutes them to the cytosol for proteasomal degradation (PubMed:26565908). By controlling the steady-state expression of the IGF1R receptor, indirectly regulates the insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway (PubMed:26692333). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26565908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26692333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33658201}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of infection by cytomegaloviruses, it plays a central role in the export from the ER and subsequent degradation of MHC class I heavy chains via its interaction with US11 viral protein, which recognizes and associates with MHC class I heavy chains. Also participates in the degradation process of misfolded cytomegalovirus US2 protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15215856}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Unfolded protein response |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the derlin family. Members of this family participate in the ER-associated degradation response and retrotranslocate misfolded or unfolded proteins from the ER lumen to the cytosol for proteasomal degradation. This protein recognizes substrate in the ER and works in a complex to retrotranslocate it across the ER membrane into the cytosol. This protein may select cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) for degradation as well as unfolded proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:79139; |
Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex [GO:0036513]; Derlin-1-VIMP complex [GO:0036502]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment [GO:0044322]; Hrd1p ubiquitin ligase ERAD-L complex [GO:0000839]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; MHC class I protein binding [GO:0042288]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; signal recognition particle binding [GO:0005047]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; ubiquitin-specific protease binding [GO:1990381]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; ER-associated misfolded protein catabolic process [GO:0071712]; ERAD pathway [GO:0036503]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; protein destabilization [GO:0031648]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol [GO:0030970]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
15215855_Derlin-1 is an important factor for the extraction of certain aberrantly folded proteins from the mammalian ER 15215856_Derlin-1 interacts with US11, a virally encoded ER protein that specifically targets MHC class I heavy chains for export from the ER, as well as with VIMP, a novel membrane protein that recruits the p97 ATPase and its cofactor 16055502_Derlin-1 interacts with the N-terminal domain of PNGase via its cytosolic C-terminus. PNGase distributed in two populations; ER-associated and free in the cytosol, which suggests the deglycosylation process can proceed at either site 16186510_Derlin-1 is part of a retrotranslocation channel that is associated with both the polyubiquitination and p97-ATPase machineries at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 16954204_Derlin-1 recognizes misfolded, nonubiquitylated CFTR to initiate its dislocation and degradation early in the course of CFTR biogenesis, perhaps by detecting structural instability within the first transmembrane domain 17453418_The pool of active Derlin-1 in the ER membrane can be modulated in response to ER stress. 17872946_SVIP is an endogenous inhibitor of ERAD that acts through regulating the assembly of the gp78-p97/VCP-Derlin1 complex. 18048502_DERL1-containing protein mediates the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of V2 vasopressin receptors. 18094046_These findings indicate that Derlin-1 facilitates the retro-translocation of Cholera toxin. 18205950_derlin-1 overexpression in breast cancer, together with its function in relieving ER stress-induced apoptosis, suggests that regulation of the ER stress response pathway may be critical in the development and progression of breast cancer. 18227067_KCa3.1 and KCa2.3 are translocated out of the endoplasmic reticulum associated with Derlin-1. 18927294_Overexpression of DERL1 is associated with neoplasms 19114714_Derlin-1 did not modify KCNQ1 expression level, and no interaction between endogenous KCNQ1 and Derlin-1 could be detected. 21184741_Derlin-1 is a negative regulator for both glycosylated and non-glycosylated BCRP expression and provide a novel posttranslational regulatory mechanism of BCRP by Derlin-1. 22238364_These results indicate that ApoB after lipidation is dislocated from the ER lumen to the LD surface for proteasomal degradation and that Derlin-1 and UBXD8 are engaged in the predislocation and postdislocation steps, respectively. 22311976_Derlin-1 expression levels may affect glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by altering surface expression of K(ATP) channels. 22627700_Upregulation of derlin-1 may be associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress in neuronal cells in Alzheimer's disease. 23306155_Derlin-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes invasion by EGFR-ERK-mediated up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. 24089527_Cav-1 may be a cofactor in the interaction of Derlin-1 and N-glycosylated COX-2 and may facilitate Derlin-1- and p97 complex-mediated COX-2 ubiquitination, retrotranslocation, and degradation. 25030448_TMEM129 contains an unusual cysteine-only RING with intrinsic E3 ligase activity and is recruited to US11 via Derlin-1. 26173415_Results showed that Derlin-1 is overexpressed in colon cancer and promotes proliferation of colon cancer cells. 27572270_data suggest that miR-181d is a tumor suppressor in ESCC inversely regulating its downstream target gene of DERL1. 27714797_insights into the interactions between other SHP-containing proteins and p97N 27977784_Derlin-1 was overexpressed in bladder cancer and was associated with the malignancy of bladder cancer. 28137758_The derlin-1 pathway therefore may represent a significant early checkpoint in the recognition and degradation of ENaC in mammalian cells. 28178653_Derlin-1 is overexpressed in bladder cancer and promotes malignant phenotype through ERK/MMP-2/9 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 28219405_ChIP assays were used to ascertain the correlations between HNF1beta and Derlin-1 in the miR-217/HNF1beta/Derlin-1 pathway in glioma cells 29530993_Overexpression of Derlin-1 is Associated with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 29743537_association of the degradation factor HRD1 with the translocon and the rerouting factor Derlin-1 may be necessary for the smooth and effective clearance of ERpQC substrates 29768262_These findings for the first time revealed that miR-598, as a tumor suppressor, negatively regulate DERL1 and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition to suppress the invasion and migration in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), thereby putatively serving as a novel therapeutic target for NSCLC clinical treatment. 31670413_Derlin-1 exhibits oncogenic activities and indicates an unfavorable prognosis in breast cancer. 31721721_Derlin-1 functions as a growth promoter in breast cancer. 33658201_The cryo-EM structure of an ERAD protein channel formed by tetrameric human Derlin-1. 35046954_Derlin-1, as a Potential Early Predictive Biomarker for Nonresponse to Infliximab Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Is Related to Autophagy. 35916080_Circular RNA circTTBK2 facilitates non-small-cell lung cancer malignancy through the miR-873-5p/TEAD1/DERL1 axis. 36122532_Regulation of Derlin-1-mediated degradation of NADPH oxidase partner p22(phox) by thiol modification. |
ENSMUSG00000022365 |
Derl1 |
1143.658826 |
2.6635295052 |
1.413339 |
0.118321263 |
138.511028 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000005634164655892642338330179284010417628959126777846859392113674776125363056837953748112041152396045617933850735425949096679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000769290197233814993523570268321946134975797248831766502877673977041105016315137828455950064210355776594951748847961425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1576.0879747 |
110.3507520 |
595.6070163 |
30.6262785 |
| ENSG00000136997 |
4609 |
MYC |
protein_coding |
P01106 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that binds DNA in a non-specific manner, yet also specifically recognizes the core sequence 5'-CAC[GA]TG-3' (PubMed:24940000, PubMed:25956029). Activates the transcription of growth-related genes (PubMed:24940000, PubMed:25956029). Binds to the VEGFA promoter, promoting VEGFA production and subsequent sprouting angiogenesis (PubMed:24940000, PubMed:25956029). Regulator of somatic reprogramming, controls self-renewal of embryonic stem cells (By similarity). Functions with TAF6L to activate target gene expression through RNA polymerase II pause release (By similarity). Positively regulates transcription of HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2 and PTBP1 which in turn regulate splicing of pyruvate kinase PKM by binding repressively to sequences flanking PKM exon 9, inhibiting exon 9 inclusion and resulting in exon 10 inclusion and production of the PKM M2 isoform (PubMed:20010808). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20010808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24940000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25956029}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA-binding;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene is a proto-oncogene and encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein that plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with the related transcription factor MAX. This complex binds to the E box DNA consensus sequence and regulates the transcription of specific target genes. Amplification of this gene is frequently observed in numerous human cancers. Translocations involving this gene are associated with Burkitt lymphoma and multiple myeloma in human patients. There is evidence to show that translation initiates both from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site, resulting in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:4609; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; Myc-Max complex [GO:0071943]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; RNA polymerase II transcription repressor complex [GO:0090571]; core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001046]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; transcription regulator activator activity [GO:0140537]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; chromosome organization [GO:0051276]; energy reserve metabolic process [GO:0006112]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; fibroblast apoptotic process [GO:0044346]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell division [GO:0051782]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045656]; negative regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032873]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; oxygen transport [GO:0015671]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of DNA methylation [GO:1905643]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:1902255]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0002053]; positive regulation of metanephric cap mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0090096]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:2001022]; positive regulation of telomerase activity [GO:0051973]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein-DNA complex disassembly [GO:0032986]; regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010564]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:1904672]; regulation of telomere maintenance [GO:0032204]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to growth factor [GO:0070848]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
3277717_Alternative translation initiation from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site results in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. 11182042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11443860_Review: EBV regulates c-MYC, apoptosis, and tumorigenicity in Burkitt's lymphoma 11777933_We have located a region in the c-myc promoter that is required for the complete activation by the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer 11795828_In Situ studies demonstrate enhanced mRNA expression of the proto-oncogene c-myc in stenotic venous bypass grafts. 11804592_c-Myc physically interacts with Smad2 and Smad3 involved in TGF-beta signaling.c-Myc promotes cell growth and cancer development partly by inhibiting the growth inhibitory functions of Smads 11817538_Uteroglobin promoter-targeted c-MYC expression in transgenic mice cause hyperplasia of Clara cells and malignant transformation of T-lymphoblasts and tubular epithelial cells 11840336_initiates illegitimate recombination of ribonucleotide reductase 2 gene 11848444_Acute hyperglycaemia induces an up-regulation of seven major genes, four of which were not previously reported in the literature. Northern blot analyses, performed on these 4 genes, confirm macroarrays results for alphav, beta4, c-myc, and MUC18. 11848471_Activation of c-MYC and c-MYB proto-oncogenes is associated with decreased apoptosis in tumor colon progression. 11850082_amplification in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia 11861398_Repression of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression under hypoxic conditions in human hepatoma cells: characterization of a negative hypoxia response element that mediates opposite effects of hypoxia inducible factor-1 and c-Myc. 11877042_The cytoplasmic domain of gp130 is involve the induction of c-myc expression and the cell proliferation in Meg-01 cell. 11877298_Retinoic acid-induced cell cycle arrest of human myeloid cell lines is associated with sequential down-regulation of c-Myc and cyclin E. 11909963_Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor stimulation of glioblastoma cell cycle progression through G(1) is c-Myc dependent and independent of p27 suppression, Cdk2 activation, or E2F1-dependent transcription. 11916966_complex with Nmi and BRCA1 inhibits c-Myc-induced human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene promoter activity in breast cancer 11956070_c-myc-induced apoptosis in polycystic kidney disease is independent of FasL/Fas interaction. 11960382_The N-myc and c-myc downstream pathways include the chromosome 17q genes nm23-H1 and nm23-H2 11968011_estrogen and Myc negatively regulate EphA2 expression in mammary epithelial cells 12027803_A novel form of the RelA nuclear factor kappaB subunit is induced by and forms a complex with this proto-oncogene protein 12031912_overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia while translocations associated with this gene are absent 12032779_The proto-oncogene c-myc in hematopoietic development and leukemogenesis 12049739_c-Myc can induce DNA damage, increase reactive oxygen species, and mitigate p53 function 12072203_Overexpression of c-myc mRNA was found in an Achilles tendon clear cell sarcoma and may have a role in its malignant progression. 12077335_TRRAP binding and the recruitment of histone H3 and H4 acetyltransferase activities are required for the transactivation of a silent TERT gene in exponentially growing human fibroblasts by c-Myc or N-Myc protein. 12082260_Effects of fluid shear stress on expression of proto-oncogenes c-fos and c-myc in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 12130502_the in vitro effects of iron on the proliferation of a primary, human synovial fibroblast cell line and the involvement of c-myc in this process as a model for c-myc proto-oncogene expression in hemophilic synovitis 12149248_role of c-Myc increasing susceptibility to tumor necrosis factor mediated apoptosis 12177005_Myc activates transcription by stimulating elongation and that P-TEFb is a key mediator of this process 12209953_dysregulated beta-catenin may cause a transcriptional upregulation of the c-myc gene; the c-Myc protein expression appears to be further regulated by posttranscriptional mechanism(s) during neoplastic progression in colorectal adenocarcinomas 12213716_C-Myc may be a downstream target of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)signaling and its expression a defining characteristic of ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphomas 12226097_c-myc induces programmed cell death in a process requiring glutathione in human tumor cells 12237776_Amplifications of c-myc and CCND1 are associated with detrusor-muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma 12356725_results reveal a novel cytoskeletal function for Myc and indicate the feasibility of quantitative whole-proteome analysis in mammalian cells 12360279_This review describes the role of MYC in tumor progression 12362975_c-myc and c-erbB2 amplification in breast cancer 12379776_Marked intratumoral heterogeneity of this and cyclinD1 but not of c-erbB2 amplification in breast cancer 12394763_Beta-catenin mutations correlate with over expression of C-myc and cyclin D1 Genes in bladder cancer. 12420224_CD19+ cells from transgenic mice with a lamba-humanMYC construct driven by B-cell elements overexpressed both C-MYC and protein kinase A-Cbeta. 12435808_c-Myc promotes cell survival under stressful conditions. 12452058_the mechanism of apoptosis induced by c-myc gene in oral squamous cell 12490316_Reduction in the c-myc protein was correlated with neck metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 12509468_c-myc translation is regulated by hnRNP C via internal ribosomal entry site binding 12529648_c-Myc binds to TFIIIB, a pol III-specific general transcription factor, and directly activates pol III transcription 12538578_examination of functionality of basic domains compared with Mad 12545156_repression of differentiation-induced p21 expression through Miz-1 may be an important mechanism by which Myc blocks differentiation 12562237_Expression of c-Myc in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma may be a prognostic marker for poor overall survival. 12637327_results show that Ser727/Tyr701-phosphorylated Stat1 plays a key role as a prerequisite for the ATRA-induced down-regulation of c-Myc; cyclins A, B, D2, D3, and E; and simultaneous up-regulation of p27Kip1, associated with arrest in the G0/G1 phase 12637527_results indicate that Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 gene (NBS1) is a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc and links the function of c-Myc to the regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway 12646176_c-myc binds to the hTERT promoter and is involved in the pathway for regulation of cellular immortalization through BRCA1 12673205_A detailed structure-function analysis of the Myc N-terminal domain in deletion & point mutants studied their ability to induce cell cycle progression, apoptosis & transformation as well as repress & activate endogenous target genes. 12688321_Up-regulation of c-Myc protein could disturb the signaling pathway of ceramide & sphingosine, endogenous modulators mediating apoptosis. c-Myc protein is a mediator of cytoprotective effect of PKC pathway in HL-60 cells. 12721301_Myc down-regulation might directly mediate the growth-inhibitory properties of 3'-5' RNA exonuclease 12729735_inverse correlation between TMEFF2 and c-Myc expression 12748187_findings suggest that Myc-mediated functions can be negatively regulated by KRAB box containing zinc finger protein (Krim-1) 12776177_MYC recruits the TIP60 histone acetyltransferase complex to chromatin 12783888_c-myc gene is regulated by nitric oxide via inactivating NF-kappa B complex 12808131_c-Myc together with its heterodimeric partner, Max, occupy >15% of gene promoters tested in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Overexpressed c-Myc plays a role in global transcriptional regulation in some cancer cells and functions in malignant transformation. 12818373_the PI3K/p70 S6K/c-Myc cascade plays an important role in neutrophilic proliferation in HL-60 cells. 12821782_Induction of hTERT by Myc/E6 was independent of Myc phosphorylation at Thr-58/Ser-62 within the transactivation domain. E6 associates with Myc complexes & activates a Myc-responsive gene, hTERT. 12824159_Inhibition of this oncoprotein limits the growth of human melanoma cells by inducing cellular crisis 12829833_expression of MYC oncogene is reduced at the mRNA level and MYC protein has an increased half-life in Adenovirus infected Hela cells resulting in constant steady state levels. 12842909_results demonstrate that MYC directly stimulates transcription of the Werner syndrome gene,WRN; propose that WRN up-regulation by MYC may promote MYC-driven tumorigenesis by preventing cellular senescence 12855588_hematopoietic growth factors induce cell cycle progression via internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation of c-myc though the PI3K pathway in human factor-dependent leukemic cells 12909717_overexpression of MYC disrupts the repair of double-strand DNA breaks, resulting in a several-magnitude increase in chromosomal breaks and translocations 12970749_the mutated version of the c-myc IRES that is prevalent in patients with multiple myeloma bound hnRNPK more efficiently in vitro and was stimulated by hnRNPK to a greater extent in vivo. 14532990_p53 and c-Myc expression may have a role in regulation of telomerase activity in ovarian tumours 14576301_c-Myc regulates cell growth and proliferation by the coordinated induction of cdk activity and rRNA processing 14625288_contribution of JNK to the regulation of c-Myc protein stability under normal growth conditions 14645543_identified an evolutionarily conserved boundary at which the c-myc transcription unit is separated from the flanking condensed chromatin enriched in lysine 9-methylated histone H3 14645547_PLZF expression maintains a cell in a quiescent state by repressing c-myc expression and preventing cell cycle progression. 14663479_we review Myc-induced pathways that contribute to the apoptotic response. 14663583_These data also suggest that location of intragenic PTEN mutations and their coexistence with the CMYC amplification may play a crucial part in the development of various subtypes of endometrial carcinoma. 14672406_Data suggest that cyclin dependent kinase 4 is involved in the development of tobacco-mediated oral carcinogenesis, and that c-myc expression is absent in normal and high in later stages of oral cancer development. 14697225_c-myc may have a role in the development of Burkitt's lymphoma, through an RNA-mediated gene silencing pathway 14724288_c-Myc may control the activity of multiple signal pathways involved in cellular transformation by induction of HSP90A 14744757_Aurora-A induces telomerase activity and hTERT by up-regulation of c-Myc 14760071_MYC has a role in tumor progression in BRCA1-associated breast cancers 14769798_c-Myc expression is regulated by cytosolic phospholipase A2 in a process that involves B-myb 14991929_c-Myc does not play a major role in gene regulation of the catalytic subunit of telomerase (hTERT) in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 15067010_c-Myc can support self-renewal of HSCs as a downstream mediator of Notch and HOXB4. 15071503_Myc is an integral part of a novel HIF-1alpha pathway, which regulates a distinct group of Myc target genes in response to hypoxia. 15077166_Levels of both c-myc and beta-catenin increased in Cyr61 stably transfected H520 cells. 15083194_Gene amplification of c-myc may play key role in regulating expression of its mRNA and protein in high-grade breast cancers 15108364_c-Myc can specifically recognize the HIV-1 initiator element surrounding the start site of transcription and linker scanning mutagenesis experiments confirmed a loss of c-Myc-mediated repression in the absence of this region 15126105_High nuclear expression of c-myc is correlated with locally advanced colorectal cancer 15160911_C-Myc over-expression was significantly associated with high sVEGF and normal sFlt-1 level in DLBCL patients, suggesting a complex interrelationship between c-Myc oncogene expression and angiogenic regulators 15190416_expression of c-Myc protein is increased not only in uterine cervix cancer but also in the premalignant lesions 15191563_Translocations involving the MYC locus were detected in six cases of B-cell lymphoma, five of them derived from a MYC/IGH juxtaposition and one from a translocation involving a non-IG gene partner. 15192039_c-myc transactivates rat and human adrenomedullin genes and accelerates the degradation rate of adrenomedullin mRNA. 15198123_c-myc mRNA was detected in 18 of 59 cases, and was associated with shorter patient survival times on both univariate and multivariate analyses. The presence of c-myc mRNA was also significantly associated with tumor anaplasia. 15199070_cMyc is a target of ARF tumor suppressor 15199147_Myc binds well to conserved canonical E boxes, but not nonconserved E boxes. Results show Myc is an important regulator of glycolytic genes, suggesting that MYC plays a role in a switch to glycolytic metabolism during cell proliferation or tumorigenesis. 15243561_c-myc oncogene has not shown to be a prognostic factor for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma of the supraglottic larynx. 15282543_c-MYC activated transcription from the upstream binding factor promoter 15286700_A prolactin signalling cascade in W53 cells involves Src kinases that mediate stimulation of c-Myc expression. 15287031_There is no obvious correlation between breakpoint locations within the immunoglobulin H locus and the amount of MYC mRNA. 15355849_polyamine-induced nuclear c-Myc interacts with Max, binds to the specific DNA sequence, and plays an important role in stimulation of normal intestinal epithelial cell proliferation. 15361884_p53-independent checkpoint to prevent c-Myc-mediated tumorigenesis 15457447_Inhibition of c-Myc (and c-Raf-1) significantly reduced the growth and invasiveness of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts in the SCID mouse model. 15459488_There was a significant positive correlation between the levels of c-myc mRNA expression and the occurrence of apoptosis in 59 hepatocellular carcinomas. 15468060_novel iron-dependent cell cycle regulatory mechanism involving modulation of translocated c-myc gene expression 15474507_c-myc downregulation and release from the endogenous p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter contributes to transcriptional activation of the p21WAF1/CIP1 in HeLa cells 15516975_Myc is essential for the regulation of a large number of growth-related genes in B cells, and cannot be replaced by other serum-induced factors. 15522869_CREB binding protein is essential for keeping c-myc in a repressed state in G(1) and thereby preventing inappropriate entry of cells into S phase. 15528212_c-Myc antagonized the induction of p21Cip1 mediated by oncogenic H-, K-, and N-Ras and by constitutively activated Raf and ERK2 15542830_chromosomal c-myc replicator activity can be altered by transcription factors that induce transcription 15580293_Myc stimulates VEGF production by a rapamycin- and LY294002-sensitive pathway. 15595642_LMP1 activates telomerase via c-myc 15601838_c-myc expression is regulated by TFIIH using an expanded proximal promoter 15629428_the increased affinity for the duplex state due to mutation in the nuclease hypersensitive element could play a functional role in the aberrant regulation of c-myc 15645079_c-myc and mad1 can regulate the hTERT transcript in a different manner in hTERT positive cells, but not in normal cells 15663936_the entire N and C-terminal regions of c-Myc transactivation domain act in concert to achieve high specificity and affinity to two structurally and functionally orthogonal target proteins 15688026_Tyrosine residues become phosphorylated following receptor engagement and, as such, form two Grb2 binding sites, which have been proposed to be differentially coupled to Myc-dependent survival. 15697230_This paper reports the first solution structure of a G-quadruplex found to form in the promoter region of an oncogene (c-MYC). 15716988_frequency and chromosomal features of this der(8)t(8;14;18) in a series of acute leukaemias and malignant lymphomas 15723053_c-Myc coordinates the activity of all three nuclear RNA polymerases, and thereby plays a key role in regulating ribosome biogenesis and cell growth 15723054_stimulation of rRNA synthesis by c-Myc is a key pathway driving cell growth and tumorigenesis 15739117_Stimulation of islet expression by 30 mmol/l glucose results from activation of a distinct, probably oxidative-stress-dependent signalling pathway. 15743499_c-Myc has a pivotal function in the development of breast cancer; data show that decreasing the c-Myc protein level in MCF-7 cells by RNAi could significantly inhibit tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo 15756435_c-MYC amplification is an early event in breast cancer progression, while ZNF217 and Her2/neu amplification may play a role in the later stage of tumor development 15763593_expression of ESRA, bcl-2 and c-myc gene expression in fibroadenomas and adjacent normal breast is related to nodule size, hormonal and reproductive features 15769738_observed, subsequent to knocking down CRD-BP/IMP1, decreased c-myc expression, increased IGF-II mRNA levels, and reduced cell proliferation rates 15800668_p16(INK4A) reconstitution in p16(INK4A)-deficient T-ALL cells induced cell cycle arrest in the presence of cyclin E and c-Myc expression, uncoupled growth from cell cycle progression and caused a sequential process of growth, differentiation and apoptosis 15839202_Data show a coordinating inhibition of the proliferation of MCF-7 by enhancing expression of p53,p21 and decreasing expression of c-myc 15856024_elevated levels of Myc counteract p53 activity in human tumor cells.This mechanism could contribute to explain the c-Myc deregulation frequently found in cancer 15878876_chromatin remodeling at the c-myc gene involves the local exchange of histone H2A.Z 15929079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15937962_the c-MYC gene is sufficient to induce carcinogenesis for prostate cancer 15944709_c-Myc activates expression of a cluster of six miRNAs on human chromosome 13 15965094_results are consistent with the possibility that IL-5 inhibits apoptosis in JYTF-1 cells via the upregulation of c-myc expression 15972952_The presence of activated beta-catenin and c-myc in the epidermis of chronic wounds may serve as a molecular marker of impaired healing 15986448_conclude that alterations of the CMYC gene, including copy number gains and amplifications, are linked to genetically unstable bladder cancers that are characterized by a high histologic grade and/or invasive growth 15988031_A pivotal role for Myc in regulating mitochondrial biogenesis was shown. 15991278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15992821_tumor-specific isoforms of Bin1 are precluded from interaction with c-Myc through an intramolecular polyproline-SH3 domain interaction. Furthermore, c-Myc/Bin1 interaction can be inhibited by phosphorylation of c-Myc at Ser62. 16007143_c-Myc overexpression showed an upregulation of beta4 promoter activity 16085756_Kinetic analysis of the interconversion between the duplex and the quadruplex forms of the human c-myc promoter. 16094360_mutant MYC proteins, by selectively disabling a p53-independent pathway, enable tumour cells to evade p53 action during lymphomagenesis 16107691_p53 represses c-myc transcription through a mechanism that involves histone deacetylation 16107734_17-beta-estradiol promotes survival signals in breast cancer cells through mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent increase in Myc expression 16116477_MYC family genes might affect oncogenesis through distinct sets of targets, in particular implicating the importance of transcriptional repression 16126174_p300 can acetylate DNA-bound Myc:Max complexes and that acetylated Myc:Max heterodimers efficiently interact with Miz-1 16139224_The MYC protein phosphorylation and turnover are thus linked to cell cycle exit in primary mouse CGNP cultures and the developing cerebellum. 16167342_replicative senescence-specific factors may block c-Myc inhibition of Miz-1 activation of hMad4 expression, and the continual presence of hMad4 protein may transcriptionally repress selected c-Myc target genes 16169462_Increased wild-type MYC expression occurs frequently in human cancers, except in Burkitt's lymphoma. 16172399_c-MYC binds to the genomic MTA1 locus and recruits transcriptional coactivators, which is essential for the transformation potential of c-MYC. 16173081_transcription activity is repressed by various MM-1 isoforms 16174239_expression of cyclin D1 and c-Myc in epithelial ovarian cancer reaffirms the notion that they are crucial components in the pathway of tumorigenesis 16201965_data demonstrate that the sphingosine-recycling pathway for the generation of endogenous long-chain ceramide in response to exogenous C6-cer is regulated by ROS, and plays an important biological role in controlling c-Myc function 16205115_Myc induces nuclear encoded mitochondrial gene expression and mitochondrial biogenesis, thereby directly linking Myc's transcriptional properties to mitochondrial ROS production, promotion of genomic oxidative damage, and genomic instability. 16210249_These results identify glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and FBW7 as potential cancer therapeutic targets and MYC as a critical substrate in the GSK3beta survival-signaling pathway. 16260605_c-Myc isoforms differentially regulate cell growth and apoptosis in a species-specific manner 16269333_Site-specific ubiquitination regulates the switch between an activating and a repressive state of the Myc protein, and they suggest a strategy to interfere with Myc function in vivo. 16287840_dual roles for p300-CBP-associated factor in Myc regulation: as a Myc coactivator that stabilizes Myc and as an inducer of Myc instability via direct Myc acetylation 16293596_decreased internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent Myc mRNA translation accounts for the phenotypic changes induced by inhibition of the BCR/ABL-ERK-dependent HNRPK translation-regulatory function. 16295419_C-myc expression shows a positive association with increasing grade of breast carcinoma. 16308474_We aimed to investigate the expression pattern of p53, Bcl-2 and C-Myc in colorectal cancer(CRC)tissues obtained from Egyptian colorectal cancer patients divided in two different groups, associated with and without Schistosoma mansoni. 16316993_up-regulation of mitochondrial CLIC4, together with a reduction in Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, sensitizes Myc-expressing cells to the proapoptotic action of Bax. 16328057_Down-regulation of MYC is not necessary to abolish malignant phenotypes by induction of terminal monocyte-macrophage differentiation in leukaemic cells carrying t(9;11)(p22;q23). 16352593_Miz-1 is essential for Myc-mediated apoptosis 16367922_interferon-gamma, which induces HLA-DR antigens on the cell surface, also suppresses c-myc expression in situ, and is a possible non-immunological mechanism involved in the better long-term survival of colorectal cancer patients 16376880_Data show that hepatitis B virus X protein blocks the ubiquitination of c-myc through a direct interaction with the F box region of Skp2 and destabilization of the SCF(Skp2) complex. 16378632_dominant-negative forms of c-Myc block transformation by activated Notch1, E6 and E7, suggesting that c-Myc is required for HPV16-mediated transformation 16410719_study shows that p14ARF directly associates with Myc and relocates Myc from the nucleoplasm to the nucleolus, in addition, p14ARF down regulates Myc activated transcription 16410805_overexpression of c-myc protects melanoma cells from IFN-beta-mediated growth inhibition 16423995_PEG10 is a direct target of c-MYC; findings link cancer genetics and epigenetics by showing that a classic proto-oncogene, MYC, acts directly upstream of a proliferation-positive imprinted gene, PEG10 16423996_c-myc seems to play a causal role in inducing anaplasia in medulloblastoma; it is proposed that c-myc dysregulation is involved in the progression of these malignant embryonal neoplasms 16432227_Myc overexpression causes DNA damage in vivo and the ATM-dependent response to this damage is critical for p53 activation, apoptosis, and the suppression of tumor development 16466700_Modifications in iron metabolism, resulting from the strong basal expression of c-Myc, and amplified by iron addition, could lead to a disruption in homeostasis and consequently to growth arrest in Burkitt's lymphoma. 16478988_abnormal expression of REST/NRSF and MYC in undifferentiated neural stem/progenitor cells causes cerebellum-specific tumors. Furthermore, these results suggest that such a mechanism plays a role in the formation of human medulloblastoma. 16490593_Positive C-MYC staining is detected mainly in the cytoplasm of esophageal cancer cells. 16494045_Inhibition of hTERT expression by RNAi could increase the expression of C-myc protein in Hep-2 cells. 16508012_These findings provide a molecular basis for increased TFRC1 expression in human tumors, illuminate the role of TFRC1 in the c-Myc target gene network 16537449_p16(INK4a) expression was regulated by the Polycomb group repressor Bmi-1, which is shown as a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc. 16537801_Doubling the hMYC level by breeding homozygous transgenic animals switched the phenotype from primarily monocytic tumors to exclusively T-cell tumors. Results imply that MYC level affects the spontaneous acquisition of synergistic oncogenic mutations. 16541139_In both Richter's transformation and prolymphocytic transformation, high-levels of AID mRNA expression and high-frequency mutations of c-MYC genes were detected. 16543245_there is an alternative mechanism for the hypoxic induction of VEGF in colon cancer that does not depend upon HIF-1alpha but instead requires the activation of PI3K/Rho/ROCK and c-Myc 16552729_Results showed that certain regulation involved in c-myc, c-fos, and c-jun was present in the apoptosis, and the c-Myc dependent-on and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway also play roles. 16554306_Bcl2, in addition to its survival function, may also suppress DNA repair in a novel mechanism involving c-Myc and APE1, which may lead to an accumulation of DNA damage in living cells, genetic instability, and tumorigenesis 16572399_Taken together, these findings suggest that Bax and caspase activation, together with PKCdelta signaling are involved in c-Myc-dependent etoposide-induced apoptosis. 16582589_Myc and E2F1 engage the ATM signaling pathway to activate p53 and induce apoptosis [review] 16596619_These data suggest that an increase in c-Myc phosphorylation in response to prolonged ERK phosphorylation negatively auto-regulates c-Myc gene expression, leading to the suppression of its target gene expression and cell cycle block. 16628215_Results describe the roles of the FarUpStream Element (FUSE), FUSE Binding Protein (FBP), FBP Interacting Repressor (FIR), and TFIIH in the regulation of c-myc expression. 16631470_APL-like case lacking t(15;17) and the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) breakpoint and also has the deletion MYC of 8q24 associated with the occurrence of MYC amplification on double-minute chromosomes (dmin). 16675879_Results show that the CT-element is not especially susceptible to the formation of breakpoints leading to chromosomal translocations in Burkitt's lymphoma. 16682952_MYC activation, triggered by the insertion of human papillomavirus DNA sequences, can be an important genetic event in cervical oncogenesis. 16690525_in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, molecular alterations in ice, bcl-2, c-myc and p53 are present in hematopoietic cells from bone marrow as well as in primitive hematopoietic progenitors 16706751_p21Cip1 is one of the direct mediators of induced c-Myc following increased polyamines and that p21Cip1 repression by c-Myc is implicated in stimulation of normal intestinal epithelial cell proliferation 16724113_This study provides the first evidence for regulation of global chromatin structure by an oncoprotein and may explain the broad effects of Myc on cell behavior and tumorigenesis. 16785237_TGFbeta suppresses TERT by Smad3 interactions with c-Myc and the hTERT gene 16788099_c-Myc is only required for pre-TCR-induced proliferation but is dispensable for developmental progression from the DN to the DP stage 16797278_Having an S allele in the L-myc gene may increase the risk of renal failure. 16797278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16809765_proteins implicated in replication initiation are selectively and differentially bound across the c-myc replicator, dependent on discrete structural elements in DNA or chromatin 16857742_Ras and c-Myc play important roles in the up-regulation of nucleophosmin/B23 during proliferation of cells associated with a high degree of malignancy, thus outlining a signaling cascade involving these factors in the cancer cells. 16874304_Together, these results demonstrate that ectopic activation of NFATc1 and the Ca2+/calcineurin signaling pathway is an important mechanism of oncogenic c-myc activation in pancreatic cancer. 16940161_Ketogenesis is an undesirable metabolic characteristic of the proliferating cell, which is down-regulated through c-Myc-mediated repression of the key metabolic gene HMGCS2. 16964280_Functional promoter analyses revealed that both the Myc-binding site cluster and the C/EBPalpha-binding site are essential for strong transcriptional activation, and that Myc and C/EBPalpha synergistically activate the WS5 promoter 16984727_c-myc and VEGFA may be involved in the regulation of angiogenesis in esophageal adenocarcinoma 16996503_provide a mechanism for elevated Myc expression in hormone-dependent and hormone-independent breast cancer 17001014_Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) acts as an antiapoptotic in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) by selecting among three transcriptional programs, all of which, unlike the full virus growth-transforming program, remain compatible with high c-myc expression. 17028906_Several genes in the MYCN amplicon, including the DEAD box polypeptide 1 (DDX1) gene, and neuroblastoma-amplified gene (NAG gene), have been found to be frequently co-amplified with MYCN in NB. 17046748_Nuclear arrangement of c-myc genes and transcripts was conserved during cell differentiation and, therefore, independent of the level of differentiation-specific c-myc gene expression. 17050536_NDRG2 expression is repressed by Myc via Miz-1-dependent interaction with the NDRG2 core promoter 17070983_Fluorescent protocol can successfully be applied to diagnostic needle biopsies to identify relative 8q gain in prostate carcinomas and that patients with a MYC/CEP18 ratio > or = 1.5 present a significantly higher risk of dying from the disease. 17082179_repression of BCL2 transcription is the single essential consequence of targeting the MIZ-1 pathway during apoptosis induction, which explains a copperative interaction between c-MYC and BCL2 17082780_Max as a novel co-activator of C/EBPalpha functions, thereby suggesting a possible link between C/EBPalpha and Myc-Max-Mad network. 17093053_Results provide a snapshot of genome-wide, unbiased characterization of direct Myc binding targets in a model of human B lymphoid tumor using ChIP coupled with pair-end ditag sequencing analysis (ChIP-PET). 17114293_identify c-MYC as an essential mediator of NOTCH1 signaling and integrate NOTCH1 activation with oncogenic signaling pathways upstream of c-MYC 17141659_FOXM1c transactivates the human c-myc P1 and P2 promoters synergistically with Sp1, a transcription factor known to bind and transactivate these two promoters 17145812_The c-Myc oncogene expression was very low in normal and cancer tissues but highly increased in papillomatosis. 17146437_E-cadherin repression is necessary for c-Myc-induced cell transformation. 17146439_establish PML-mediated destabilization of Myc and the derepression of cell cycle inhibitor genes as an important regulatory mechanism that allows cell differentiation 17151361_Our data suggest that Mel-18 regulates Bmi-1 expression during senescence via down-regulation of c-Myc. 17158641_MYC amplification is not associated with 'basal-like' phenotype and proved to be an independent prognostic factor for breast cancer patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. 17159920_c-MYC functions are cellular-context-dependent and |
ENSMUSG00000049086+ENSMUSG00000022346 |
Bmyc+Myc |
330.351511 |
5.7006738473 |
2.511132 |
0.154404356 |
254.528109 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000267488925112440129314665131025870799733794381551510817029180008792240534160582700551827770112937170734294137794330687449339721967763592202127400504485521537390013691037893295288085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000065366498918205559845979529535508168153118340294226126210573179988137119908585404208002995987206152831071867042616831482436237294693791608857572072999175816221395507454872131347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
556.6456817 |
53.9532214 |
98.1353299 |
7.5115488 |
| ENSG00000137070 |
3590 |
IL11RA |
protein_coding |
Q14626 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for interleukin-11 (IL11). The receptor systems for IL6, LIF, OSM, CNTF, IL11 and CT1 can utilize IL6ST for initiating signal transmission. The IL11/IL11RA/IL6ST complex may be involved in the control of proliferation and/or differentiation of skeletogenic progenitor or other mesenchymal cells (Probable). Essential for the normal development of craniofacial bones and teeth. Restricts suture fusion and tooth number. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21741611, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: [Soluble interleukin-11 receptor subunit alpha]: Soluble form of IL11 receptor (sIL11RA) that acts as an agonist of IL11 activity (PubMed:30279168, PubMed:26876177). The IL11:sIL11RA complex binds to IL6ST/gp130 on cell surfaces and induces signaling also on cells that do not express membrane-bound IL11RA in a process called IL11 trans-signaling (PubMed:30279168, PubMed:26876177). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26876177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30279168}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform HCR2]: Soluble form of IL11 receptor (sIL11RA) that acts as an agonist of IL11 activity (PubMed:30279168, PubMed:26876177). The IL11:sIL11RA complex binds to IL6ST/gp130 on cell surfaces and induces signaling also on cells that do not express membrane-bound IL11RA in a process called IL11 trans-signaling (PubMed:30279168, PubMed:26876177). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26876177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30279168}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Craniosynostosis;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Interleukin 11 is a stromal cell-derived cytokine that belongs to a family of pleiotropic and redundant cytokines that use the gp130 transducing subunit in their high affinity receptors. This gene encodes the IL-11 receptor, which is a member of the hematopoietic cytokine receptor family. This particular receptor is very similar to ciliary neurotrophic factor, since both contain an extracellular region with a 2-domain structure composed of an immunoglobulin-like domain and a cytokine receptor-like domain. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:3590; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-11 binding [GO:0019970]; interleukin-11 receptor activity [GO:0004921]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; head development [GO:0060322]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284] |
11241561_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11315919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11498264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12200462_IL-11Ralpha was expressed in both epithelial and stromal cells, with epithelial staining being more intense 12569176_expression and function in human endometrium 14701802_the interleukin-11 receptor alpha-chain has evidence of antiapoptotic effects in human colonic epithelial cells 14744752_IL-11Ralpha is a candidate target for translational clinical trials against advanced and metastatic prostate cancer. 15512823_interleukin-11 receptor is expressed in CD38-positive cells from patients with multiple myeloma 16291580_High expression of interleukin-11 receptor alpha is associated with Hodgkin's lymphoma 16614887_High interleukin 11 receptor is associated with breast cancer 16964382_IL-11/IL-11R pathway plays an important role in the progression of colorectal adenocarcinoma. 17332920_The objectives of this study were to clarify the role of IL-11 and IL-11Ralpha in human gastric carcinoma. 18941632_binding site of il-11 to IL-11R alpha is characterized 18987331_IL11 inhibits human extravillous trophoblast invasion via STAT3, indicating a likely role for IL11 in the decidual restraint of EVT invasion during normal pregnancy. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20553623_IL11 as well as IL11RA are likely to play a role in the progression of endometrial carcinoma. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21982075_IL11RA promoter polymorphism--rs1061758--may be associated with the risk of papillary thyroid cancer in the Korean population. 22075555_data suggest that IL-11Ralpha-CAR T cells may represent a new therapy for patients with osteosarcoma pulmonary metastases 22433466_Constructed a designer cytokine Hyper IL-11 (H11), which is exclusively composed of naturally existing components. It contains the full length sIL-11Ralpha connected with the mature IL-11 protein, and acts as an agonist on cells expressing the gp130 molec 25524575_These results indicate that IL-11Ralpha is a potential target for the development of molecular targeted therapy and noninvasive tumor imaging in human osteosarcoma. 26551279_Data suggest domains D1-D3, which contain cytokine binding module, determine which cytokine can activate interleukin-6 or interleukin-11 alpha-receptor subunits; stalk, transmembrane, or intracellular regions do not participate in ligand selectivity. 26876177_Proteolysis of the IL-11R represents a molecular switch that controls the IL-11 trans-signaling pathway which is the target in intestinal tumorigenesis, lung carcinomas, and asthma. 27920471_Report IL11RA and MELK amplification in gastric cancer cell lines and primary gastric adenocarcinomas. 27922075_Cancer-associated fibroblasts treated with cisplatin facilitate chemoresistance of lung adenocarcinoma through IL-11/IL-11R/STAT3 signaling pathway. 28186993_High IL11RA expression is associated with endometrioid tumours. 29237553_we show by molecular replacement that Arg-112 does not participate in binding of IL-11 to its receptors IL-11R and glycoprotein 130 (gp130). Recombinant IL-11 R112H expressed in E. coli displays a correct four-helix-bundle folding topology, and binds with similar affinity to IL-11R and the IL-11/IL-11R/gp130 complex. 29523682_The results presented here reveal an additional function in classic IL-11 signaling, highlighting the importance of the IL-11R stalk in IL-11 signaling 29533934_The D2 domain of the IL-11R contains two N-linked glycans, which are dispensable for its biological activity, but differentially control maturation and intracellular trafficking of the receptor. 29901200_The results indicate that miR-23b regulates IL-11 and IL-11Ralpha expression, and it might act as an anti-oncogenic agent in the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by directly downregulating IL-11 expression. 29926465_identified six missense mutations in IL11RA, a gene encoding the alpha subunit of interleukin 11 receptor, 4 of them being novel, including 2 in the Ig-like C2-type domain 30811827_IL11RA mutation is associated with craniosynostosis with dental anomalies syndrome. 32277509_Multiple craniosynostosis and facial dysmorphisms with homozygous IL11RA variant caused by maternal uniparental isodisomy of chromosome 9. 32332100_The structure of the extracellular domains of human interleukin 11alpha receptor reveals mechanisms of cytokine engagement. 33566379_Interleukin-11 (IL-11) receptor cleavage by the rhomboid protease RHBDL2 induces IL-11 trans-signaling. 33590875_IL11 is elevated in systemic sclerosis and IL11-dependent ERK signalling underlies TGFbeta-mediated activation of dermal fibroblasts. 34530329_Interleukin-11 receptor expression on monocytes is dispensable for their recruitment and pathogen uptake during Leishmania major infection. 35331937_The outcome of targeted NGS screening in patients with syndromic forms of sagittal and pansynostosis - IL11RA is an emerging core-gene for pansynostosis. 36376885_IL-11 system participates in pulmonary artery remodeling and hypertension in pulmonary fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000078735+ENSMUSG00000073876+ENSMUSG00000073889 |
Il11ra2+Gm13305+Il11ra1 |
79.239821 |
0.2669756241 |
-1.905220 |
0.222926013 |
75.035066 |
0.00000000000000000462427636752878685979879331925959419970125119351178795412682376309021492488682270050048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000037543629914590148698765549341397859367863272609657995793064344525191700085997581481933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.8596584 |
4.8041594 |
127.9302528 |
10.9638116 |
| ENSG00000137077 |
6366 |
CCL21 |
protein_coding |
O00585 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits hemopoiesis and stimulates chemotaxis. Chemotactic in vitro for thymocytes and activated T-cells, but not for B-cells, macrophages, or neutrophils. Shows preferential activity towards naive T-cells. May play a role in mediating homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs. Binds to atypical chemokine receptor ACKR4 and mediates the recruitment of beta-arrestin (ARRB1/2) to ACKR4. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This antimicrobial gene is one of several CC cytokine genes clustered on the p-arm of chromosome 9. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. Similar to other chemokines the protein encoded by this gene inhibits hemopoiesis and stimulates chemotaxis. This protein is chemotactic in vitro for thymocytes and activated T cells, but not for B cells, macrophages, or neutrophils. The cytokine encoded by this gene may also play a role in mediating homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs. It is a high affinity functional ligand for chemokine receptor 7 that is expressed on T and B lymphocytes and a known receptor for another member of the cytokine family (small inducible cytokine A19). [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:6366; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; CCR7 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031732]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; chemokine receptor binding [GO:0042379]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell maturation [GO:0048469]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 signaling pathway [GO:0038116]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; dendritic cell dendrite assembly [GO:0097026]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; establishment of T cell polarity [GO:0001768]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; immunological synapse formation [GO:0001771]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; mesangial cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0035759]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process [GO:2000669]; negative regulation of dendritic cell dendrite assembly [GO:2000548]; negative regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903237]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002606]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0010560]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000529]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly [GO:0031274]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0048260]; positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010820]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to prostaglandin E [GO:0034695]; ruffle organization [GO:0031529]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] |
11929789_located in high endothelial venules in an appropriate location to induce transendothelial migration of CLL cells into lymph nodes 12393410_the expression of CCL21 but not CCL19 or 20 was highly induced in endothelial cells of T-cell autoimmune diseases 12393730_CCL21 binding to CCR7 on primary lymphocytes brings about rapid Jak2 phosphorylation. 12651610_Cathepsin D specifically cleaves this protein that is expressed in human breast cancer. 12707342_Most blood vessels in tissue samples from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis express CCL21, and many perivascular CD45RA+ naive T cells are found in these tissues, but not in psoriasis, where CCL21+ vessels are rare. 12949249_CCL21 is an antimicrobial protein with bacteriocidal activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14517790_Expression of CCL21 during chronic hepatitis C is implicated in the recruitment of T lymphocytes and the organization of inflammatory lymphoid tissue and may promote fibrogenesis in the inflamed areas via activation of CCR7 on hepatic stellate cells 14592837_monocyte-derived dendritic cell migration to CCL19 and CCL21 is dependent on phospholipase C and intracellular calcium flux but not on phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase 14667884_6Ckine may be a potential chemoattractant for endometrial NK cells. 14709406_expression of CCL21, and TLRs 2 and 4 is predominantly induced in the peripheral lymphatic endothelium of the small intestinal microcirculation 14726633_CCL21, a constitutively expressed chemokine, is strongly upregulated in human lymphatic vessels during a Th1/Tc1 allergic inflammatory response. 14978072_Evidence is provided that human CCL21 is a functional ligand for endogenously expressed CXCR3 in human adult microglia. 15073111_CCL21 chemokine has a role in regulating chemokine receptor CCR7 in malignant melanoma 15569314_Activation of CCR7 on mesangial cells by SLC/CCL21 enhances the degree and firmness of cell adhesion and increases cell spreading and the formation of cell-cell contacts 15674360_The CCL-21 chemokine migrated poorly towards the (GFP)-transduced umbilical cord blood (UCB) CD34+ cells. 15863780_no CCL21 mRNA could be detected in high endothelial venules, whereas immunostaining revealed CCL21 protein 15934082_The acquisition of lymphoid features in periductal foci in Sjogrens syndrome is associated with the expression of CXCL13 and CCL21 within the infiltrate. 16887149_The CCL19,CCL21/CCR7 chemokine system is expressed in inflamed muscles of polymyositis and may be involved in the pathomechanism of polymyositis. 16904643_Despite sharing only 25% sequence identity with CCL19, the amino terminal hexapeptide of CCL21 is capable of performing an in vitro role similar to that of CCL19, resulting in G protein activation of the CCR7 receptor. 17331965_chemokine ligand 21 modulates the functional properties of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/usual interstitial pneumonia fibroblasts, but not normal fibroblasts 17460916_Results of electrophoresis of the purified SLC protein showed that the molecular weight was larger than the predicted molecular weight. 17469160_The abundance of CD83+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs) in perivascular areas and the overexpression of CCL19 and CCL21 in perivascular cellular foci suggest plasmacytoid DCs are central to the muscle inflammation in juvenile dermatomyositis. 17474076_prostate-associated lymphoid aggregates, frequently below the epithelia, arranged in B cell follicles expressed CXCL13, and parafollicular T cell areas showed CCL21 expression. 17495955_CXCL13 and CCL21 are expressed in ectopic lymphoid follicles in cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders. 17881634_after HIV-1 infection of CCL19- or CCL21-treated CD4(+) T-cells, low-level HIV-1 production but high concentrations of integrated HIV-1 DNA, approaching that seen in mitogen-stimulated T-cell blasts, was observed 17890452_CCL21 significantly increased B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia MMP-9 production 17949547_knee synovial fluid CCL 21 levels were found to be increased in Rheumatoid arthritis patients as compared to Behcets disease and osteoarthritis patients 17982129_the pattern of CCL21 production in SLOs is maintained during inflammation and that the phenotypic and functional properties of stromal cells, found in SLO T-cell areas, are reproduced at ectopic sites. 18354239_in salivary gland MALT lymphoma the lymphoid chemokines CXCL13 and CCL21 are directly implicated in the organization of ectopic reactive lymphoid tissue 18757429_experiments performed to investigate the survival, adhesion, and metalloproteases secretion indicate that CXCL13 combined with CCL19 and CCL21 mainly affects the chemotaxis of Sezary syndrome cells 18794853_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18802075_Independent of arrestin 2 or arrestin 3 expression, CCR7/CCL21 internalize. 19082456_Our study implied that lower level of CCL21 in colorectal cancer tissue supports the idea that cancer is related to immunodeficiency 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19624896_CCL21 enhances the invasive ability of SW480 cells, induces MMP-9 expression, and promotes the survival of SW480 cells. 19644859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19674979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19750015_prolonged TLR4 engagement is required for the generation of polySia-expressing DCs that facilitate CCL21 capture and subsequent CCL21-directed migration 19832038_Dendritic cell transfected with secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine and/or interleukin-2 gene-enhanced cytotoxicity of T-lymphocyte in human bladder tumor cell S in vitro. 19847900_Although CCL21 attracts both human T and B cells, it acts more strongly on naive pathogenic antibody-producing B cells. 20049410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20233754_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20439292_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20461788_In patients with inflammatory polyarthritis carriage of 1 or more risk alleles of the CCL21 gene was associated with increased cardiovascular disease mortality, whereas carriage of 2 copies was associated with increased all-cause mortality. 20461788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20488224_Analysis of migratory and prosurvival pathways induced by the homeostatic chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 20488940_Polysialyted NRP2 enhances dendritic cell migration of basic C-terminal ergion of CCL21. 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20739459_These results imply a direct role for CCL21 in lymphatic transmigration that involves the selective use of integrin activation in inflammation. 20797713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20797713_We found an association of CCL21 (rs2812378) and HLA-DRB1 (rs660895) with moderate to severe endometriosis 20889506_the CCR7/CCL21 signaling pathway leading to T lymphocyte migration on fibronectin is a beta1 integrin-dependent pathway involving transient ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which is modulated by PLCgamma1 21464944_These results suggest a new combinatorial guiding mechanism by CCL19 and CCL21 for the migration and trafficking of CCR7 expressing leukocytes. 21586211_The results obtained through a cohort of European Caucasian Systemic sclerosis patients do not support the implication of CCL21 gene in the pathogenesis of SSc but the gene were identified as Rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility gene. 21594558_The chemotactic interaction between CCR7 and its ligand, CCL21, may be a critical event during progression in pancreatic cancer 21666055_Overexpression of the chemokine CCL21 in the thyroids of CCL21 transgenic mice leads to formation of lymphoid aggregates containing topologically segregated T and B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and specialized vasculature. 21698152_results suggest that CCL21/CCR7 contributes to the time-dependent proliferation of human NSCLC cells by upregulating cyclin A, cyclin B1, and CDK1 potentially via the ERK pathway 21972019_CCL21 was more localized to chondrocytes and meniscal cells during the development of osteoarthritis in mice. 22221265_CCL21 structure solved by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) contains a conserved chemokine domain followed by an extended, unstructured C-terminus that is not typical of most other chemokines. 22392503_CCL21 is a mediator of rheumatoid arthritis angiogenesis. 22427939_High serum levels of CCL21 are independently associated with mortality in chronic and acute post-myocardial infarction heart failure. 22438908_CCL21/CCR7 prevents apoptosis by upregulating the expression of bcl-2 and by downregulating the expression of bax and caspase-3 potentially via the ERK pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines 22468089_These results suggest that overexpression of CCL21 and CCL7 is associated with tumor metastasis and serves as a prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. 22619482_oxLDL induces an in vitro downregulation of CCR7 and CCL21, which may play a role in the reduction of dendritic cell migration from the plaques 22884357_CCL21 attenuates HSV-induced inflammation through up-regulation of CD8+ memory cells. 22976543_Our findings would suggest that CCL19 and CCL21 may not be associated with cervical lymph node metastasis or other clinical and microscopic factors in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23498789_Results suggest that the CCL21/CCR7 signaling pathway is involved in renal fibrosis in kidney transplant patients. 23760102_CCL21 expression was found to be an independent prognostic biomarker for CRC. 23764550_Elevated serum CCL21 correlates with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome severity and duration in pediatric opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. 24035972_In amnion epithelial cells exposed to zinc ferrite nanoparticles there is an increase in CCL21 activation; in situ nanoparticles induce oxidative stress, alterations in cellular membrane and DNA strand breaks. 24111618_Although CCL21 levels are elevated, no CCL21-positive cells are observed in patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. 24383579_these data suggested an important role of the lymphoid-endothelium-associated chemokine, CCL21, on dendritic cells in the induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes responses. 24393484_overexpressed in myasthenia gravis thymus 24507453_Serum CCL19 and CCL21 were up-regulated during Rickettsia conorii infection. 24556356_CCL21 expression was increased in hyperplastic myasthenia gravis thymuses. 24841666_CCL21 was shown to be involved in the induction of ulcerative colitis. Suppression of CCL21 expression decreased damage induced from ulcerative colitis, indicating that CCL21 targeted therapy might be an effective treatment for this disease 24945611_Priming by CCL21 restricts lateral mobility of the adhesion receptor LFA-1 and restores adhesion to ICAM-1 nanoaggregates on human mature dendritic cells. 24990231_CCL21 rs2812377 was associated with coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population. 25142946_Studied expression of CCR7 and EMT markers in the primary breast carcinoma tissues from patients who underwent radical mastectomy. and investigated whether CCL21/CCR7 induces EMT process during mediating cancer cell invasion or migration in vitro. 25260647_CCL21 and CCL19 were significantly increased in serum from ankylosing spondylitis patients. 25398010_CCL21/CCR7 interactions might be involved in the response to pressure overload secondary to aortic stenosis. 25473269_Modulation of the chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 represents a potent immunoregulatory treatment approach, and thus represents a novel therapeutic target to stabilize atherosclerotic lesions. 25556164_CCL21/CCR7 pathway activates signallings to up-regulate Slug pathway, leading to the occurrence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in human chondrosarcoma 25575049_CCL21 promotes the metastasis of pancreatic cancer via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 25744065_These results reveal that CCR7 and VEGF-C display a significant crosstalk and suggest a novel role of the CCL21/CCR7 chemokine axis in the promotion of breast cancer-induced lymphangiogenesis. 25957582_increased expression in mononuclear inflammatory cells isolated from the brain during active stage of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis 25961925_TGF-beta1 promoted CCL21 expression in lymphatic endothelial cells. CCL21 acted in a paracrine fashion to mediate chemotactic migration of EMT cells toward lymphatic endothelial cells. 26146068_over-expression of CCL21 could increased the expressions of antigen presentation-related genes in CK8/18 TECs in MG patients 26320593_CCL21 gene SNP (rs951005) might confer genetic predisposition to polymyositis patients or such patients with interstitial lung disease in a Chinese Han population. 26667143_Our findings suggested that MUC1 plays an important role in CCL21-CCR7-induced lymphatic metastasis and may serve as a therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . 26884842_CCL21/CCR7 induce VEGF-D up-regulation and promote lymphangiogenesis via ERK/Akt pathway in lung cancer. 26965559_CCL21 correlated significantly with Bladder Pain Syndrome: gene expression in bladder biopsies of patients with Bladder Pain Syndrome was increased in the patients and correlated with clinical profiles. 27021907_the white pulp regions of ME7-infected spleens were smaller, and contained markedly diminished T zones, as compared to control spleens. Although lymphoid tissue inducer cells were not affected, the expression of both CCL19 and CCL21 was decreased. 27057280_CCL21 can facilitate chemoresistance and stem cell property of colorectal cancer cells via the upregulation of P-gp, Bmi-1, Nanog, and OCT-4 through AKT/GSK-3beta/Snail signals. 27157859_CCL21/IL21-armed oncolytic adenovirus enhances antitumor activity against TERT-positive tumor cells. 27301418_plasmin cleaves surface-bound CCL21 to release the C-terminal peptide responsible for CCL21 binding to glycosaminoglycans on the extracellular matrix and cell surfaces, thereby generating the soluble form. 27338641_Deletion of this extended C-terminus reduces CCL21's affinity for heparin and transferring the CCL21 C-terminus to CCL19 enhances heparin binding mainly through non-specific, electrostatic interactions 27538371_Taken together, these results suggest that SERCA2 contributes to the migration of CCL21-activated Dendritic Cells as an important feature of the adaptive immune response and provide novel insights regarding the role of SERCA2 in Dendritic Cells functions. 27574129_CCL21/CCR7 interaction contributes to the time-dependent proliferation of PTC cells by upregulating cyclin A, cyclin B1 and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) expression via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway associated with iodine. 27614982_Results provide evidence for an association between an increase level of CCL21 and IP-10 in the blood and pulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. 27782867_CCL21 and CXCL13 levels are increased in the minor salivary glands of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. 27783999_Low CCL21 expression was a potential independent adverse prognostic biomarker for overall survival and progression-free survival for metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with targeted therapy. 27815426_Gata1-KO(DC) DCs have reduced polysialic acid levels on their surface, which is a known determinant for the proper migration of DCs toward CCL21. 28112745_The migratory index to the CCR7 ligands, CCL19 and CCL21, was higher in T-cells from donors whose recipients will develop GvHD. 28275068_These data show that CCR7-CCL19/CCL21 axis facilitates retention CD4(+) T lymphocytes at the site of collateral artery remodeling, which is essential for effective arteriogenesis. 28416768_CCL21/CCR7 interaction was shown to allow NK cell adhesion to endothelial cells (ECs) and its reduction by hypoxia. 28487957_these results demonstrated that CCL21/CCR7 may activate EMT in lung cancer cells via the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 28534984_High CCL21 expression is associated with urinary bladder cancer metastasis. 28729639_The research findings demonstrate for the first time that the chemokines CCL19, CCL21 and CCR7 play important roles in bone destruction by increasing osteoclast migration and resorption activity, and that has been linked to rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 28799100_Significant associations between the CCL21 rs2812378 G;A polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis risk were observed in the total population, as well as in subgroup Caucasian population. 28935759_An expanded lymphatic network is capable of enhanced chemoattractant CCL21 production, and lymphangiogenesis will facilitate initial lymph formation favoring increased clearance of fluid in situations of augmented fluid filtration. 29687228_Gene Expression Profiles in Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 21-Overexpressing Pancreatic Cancer Cells. 29733244_The use of anti-CCL21 aptamers to mimic the chemotaxis mechanism thus represents a promising approach to achieve targeted delivery of drugs to the T cell-rich zones of the lymph node. This may be important for the treatment of HIV infection and the eradication of HIV reservoirs. 30785638_These data show that PSC is characterized by intrahepatic CCL21 expression and accumulation of CCR7(+) NK cells in the inflamed liver tissue. 31028199_CCL21 induced mTOR activation in MyLa cells, followed by expression of MALAT1, causing cell migration. MALAT1 and mTOR are potential therapeutic targets for MF. 31342120_the functional significance of CCL21/CCR7 signaling in different phases of rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis, was characterized. 31523177_Positive correlations of CD8(+) cell number and CCL21 mRNA expression with CDK12 level in gastric cancer were identified. 31572374_Biased Signaling of CCL21 and CCL19 Does Not Rely on N-Terminal Differences, but Markedly on the Chemokine Core Domains and Extracellular Loop 2 of CCR7. 31825941_this study shows increased expression of CCL21 in chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps 32017846_CCL21/CCR7 interaction promotes EMT and enhances the stemness of OSCC via a JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. 32044878_Clinical Significance of CBS and CCL21 in Gallbladder Adenocarcinomas and Squamous Cell/Adenosquamous Carcinomas. 32060847_REVIEW: CCL21 Programs Immune Activity in Tumor Microenvironment 32182428_Structural Features of an Extended C-Terminal Tail Modulate the Function of the Chemokine CCL21. 32712954_iNKT cells with high PLZF expression are recruited into the lung via CCL21-CCR7 signaling to facilitate the development of asthma tolerance in mice. 33158173_Lymphatic Metastasis of NSCLC Involves Chemotaxis Effects of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells through the CCR7-CCL21 Axis Modulated by TNF-alpha. 33376730_Serum CCL21 as a Potential Biomarker for Cognitive Impairment in Spinal Cord Injury. 33503170_Association of serum chemokine ligand 21 levels with asthma control in adults. 33572290_CD9 Upregulation-Decreased CCL21 Secretion in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduces Cancer Cell Migration. 33778831_[Effect of pulp revascularization on CCL21, IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 in chronic periapical periodontitis]. 34404433_Urinary small extracellular vesicles derived CCL21 mRNA as biomarker linked with pathogenesis for diabetic nephropathy. 34586443_The C-terminal peptide of CCL21 drastically augments CCL21 activity through the dendritic cell lymph node homing receptor CCR7 by interaction with the receptor N-terminus. 34595235_Crosstalk between Heart Failure and Cognitive Impairment via hsa-miR-933/RELB/CCL21 Pathway. 35380893_CCL21 and IP10 as serum biomarkers for pulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. 35690148_Plasminogen and plasmin can bind to human T cells and generate truncated CCL21 that increases dendritic cell chemotactic responses. 36211384_Target organ expression and biomarker characterization of chemokine CCL21 in systemic sclerosis associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. |
ENSMUSG00000094686+ENSMUSG00000095675+ENSMUSG00000096596+ENSMUSG00000073878+ENSMUSG00000094065 |
Ccl21a+Ccl21b+Gm10591+Gm13304+Ccl21d |
8.515956 |
0.0211194164 |
-5.565286 |
1.115338356 |
40.004947 |
0.00000000025332044279792374531700614004965307901606763607560424134135246276855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001270907456049406658557291957859728542823418706575466785579919815063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3290237 |
0.2755740 |
15.7480603 |
3.7368854 |
| ENSG00000137094 |
25822 |
DNAJB5 |
protein_coding |
O75953 |
|
Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the DNAJ heat shock protein 40 family of co-chaperone proteins. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal DNAJ domain and a C-terminal substrate binding domain but lacks the cysteine-rich domain found in other DNAJ family members. In mice, a multi-protein complex containing this protein, thioredoxin 1, and histone deacetylase 4, serves as a master negative regulator of cardiac hypertrophy. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:25822; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding [GO:0051085]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
33191150_Critical role of zebrafish dnajb5 in myocardial proliferation and regeneration. |
ENSMUSG00000036052 |
Dnajb5 |
57.875540 |
2.6085039250 |
1.383223 |
0.237937582 |
33.839038 |
0.00000000598654455203893950637723331623107902998981444397941231727600097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000026679165938434403027181059261073448052314915912575088441371917724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.7518218 |
12.9462681 |
33.2040552 |
3.8692929 |
| ENSG00000137161 |
10695 |
CNPY3 |
protein_coding |
Q9BT09 |
FUNCTION: Toll-like receptor (TLR)-specific co-chaperone for HSP90B1. Required for proper TLR folding, except that of TLR3, and hence controls TLR exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Consequently, required for both innate and adaptive immune responses (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a protein that binds members of the toll-like receptor protein family and functions as a chaperone to aid in folding and export of these proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Naturally occuring readthrough transcription occurs between this locus and the downstream GNMT (glycine N-methyltransferase) gene and is represented with GeneID:107080644. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:10695; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; innate immune response [GO:0045087] |
22447933_a mechanism for the differential trafficking of TLR1 I602S variants, and highlight the distinct roles for PRAT4A and PRAT4B in the regulation of TLR1 surface expression. 29394991_The data suggest that CNPY3 performs essential roles in brain function, in addition to known Toll-like receptor-dependent immune responses. 35334124_The TLR-chaperone CNPY3 is a critical regulator of NLRP3-inflammasome activation. |
ENSMUSG00000023973 |
Cnpy3 |
1306.519309 |
0.4519804784 |
-1.145668 |
0.053249706 |
464.140239 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000060382683322754074907068095951109762828089791084085931010870980918462388670650435956849842083021261751917965404438823672717653912798276226956296689842685629841359553327326709291297064274428220252950146871625763489745892820230693 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000026764216391707211816218698361371467983381945525581154345526321159737817188364851458190231328540963091192031621947437625595717727862444178237240160893784084329918237272433135696225941133569583906960056884912178574259675288803164 |
Yes |
No |
822.2303603 |
28.1530002 |
1831.9500976 |
42.0875158 |
| ENSG00000137171 |
89953 |
KLC4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NSK0 |
FUNCTION: Kinesin is a microtubule-associated force-producing protein that may play a role in organelle transport. The light chain may function in coupling of cargo to the heavy chain or in the modulation of its ATPase activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Motor protein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and microtubule. Predicted to be part of kinesin complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:89953; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
20818331_Data reveal aspects of the molecular mechanism of kinesin-8 motors that contribute to their unique dual motile and depolymerising functions, which are adapted to control microtubule length. 26423925_The association of a KLC4 mutation with spastic paraplegia identifies a new locus for the disease. 31235251_Findings indicate that SET domain protein 3 (SETD3) down-regulated the expression of kinesin light chain 4 (KLC4), contributing to the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells, suggesting targeting SETD3 might be a potential strategy for the clinical management of cervical cancer. 32457423_Kinesin light chain 4 as a new target for lung cancer chemoresistance via targeted inhibition of checkpoint kinases in the DNA repair network. |
ENSMUSG00000003546 |
Klc4 |
151.750676 |
0.3895409936 |
-1.360153 |
0.154310631 |
77.710645 |
0.00000000000000000119296693705337279121733427277892713364185754380814149730460904663686960702762007713317871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000009936902929406198017372284290530460963628568615206397562911178056310745887458324432373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.4356803 |
13.7605282 |
222.8507760 |
24.7854671 |
| ENSG00000137266 |
63027 |
SLC22A23 |
protein_coding |
A1A5C7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
SLC22A23 belongs to a large family of transmembrane proteins that function as uniporters, symporters, and antiporters to transport organic ions across cell membranes (Jacobsson et al., 2007 [PubMed 17714910]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:63027; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; ion transport [GO:0006811] |
19068216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19174780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20886065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20921969_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24740203_Genetic variations in the SLC22A23 locus contribute to the susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease in a small fraction of white patients. |
ENSMUSG00000038267 |
Slc22a23 |
12.944466 |
0.4167118770 |
-1.262878 |
0.552805481 |
5.083100 |
0.02416013858230499355972398234371212311089038848876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.042523687750396103879335640840508858673274517059326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6274293 |
2.8187753 |
18.4679879 |
4.7066234 |
| ENSG00000137267 |
7280 |
TUBB2A |
protein_coding |
Q13885 |
FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers. Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms. Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Isopeptide bond;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Microtubules, key participants in processes such as mitosis and intracellular transport, are composed of heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulins. The protein encoded by this gene is a beta-tubulin. Defects in this gene are associated with complex cortical dysplasia with other brain malformations-5. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:7280; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; neuron migration [GO:0001764] |
12064592_Data show that connexin 43 (cx43) binds alpha-tubulin equally well as beta-tubulin, and that ZO-1 binds directly to Cx43. 12209967_lack of mutations in early stage lung cancer 12861402_Mutations of the beta-tubulin gene, which might be a contraindication for chemotherapy based on taxans, were very rare events in gastric cancer. 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex from patients with schizophrenia 22180309_Data suggest that the increased betaII- and betaIII-tubulin contributed significantly to the resistance phenotype. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22449234_Class II beta-tubulin may be very useful for immunohistochemical diagnosis of classical Hodgkin's lymphoma. 22718863_This is the first study showing that paclitaxel neuropathy risk is influenced by polymorphisms regulating the expression of a beta-tubulin gene. 24702957_study associates mutations in TUBB2A with the spectrum of 'tubulinopathy' phenotypes 28840640_TUBB2A missense mutation is associated with arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, brain abnormalities, and severe developmental delay. 29547997_Consistent with the differential clinical and structural impact, TUBB2AA248V does not drastically affect TUBB2A binding to KIF1A, nor mitotic spindle bipolarity. Overall, our data demonstrate a pathogenic role of the p.D417N substitution that is different from previously reported TUBB2A mutations and expand the phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations in this gene. 30621030_The results suggest that betaII-tubulin may facilitate cancer growth and metastasis and, to accomplish this, may not need to be in microtubule form. 32203252_De novo mutations of TUBB2A cause infantile-onset epilepsy and developmental delay. 32571897_Defining the phenotypical spectrum associated with variants in TUBB2A. 33006960_Circular RNA circ_C16orf62 Suppresses Cell Growth in Gastric Cancer by miR-421/Tubulin beta-2A Chain (TUBB2A) Axis. 33547136_Using data from the 100,000 Genomes Project to resolve conflicting interpretations of a recurrent TUBB2A mutation. 35930870_Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line (DHMCi009-A) from an individual with TUBB2A tubulinopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000058672 |
Tubb2a |
14.715669 |
4.2792605506 |
2.097362 |
0.443258502 |
23.758095 |
0.00000109235001127556771461377463361408501896221423521637916564941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003849829552633089808553155941606149781364365480840206146240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.9912678 |
6.8632319 |
5.8533874 |
1.3570169 |
| ENSG00000137309 |
3159 |
HMGA1 |
protein_coding |
P17096 |
FUNCTION: HMG-I/Y bind preferentially to the minor groove of A+T rich regions in double-stranded DNA. It is suggested that these proteins could function in nucleosome phasing and in the 3'-end processing of mRNA transcripts. They are also involved in the transcription regulation of genes containing, or in close proximity to A+T-rich regions. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ADP-ribosylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Chromosome;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a chromatin-associated protein involved in the regulation of gene transcription, integration of retroviruses into chromosomes, and the metastatic progression of cancer cells. The encoded protein preferentially binds to the minor groove of AT-rich regions in double-stranded DNA. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Pseudogenes of this gene have been identified on multiple chromosomes. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:3159; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; senescence-associated heterochromatin focus [GO:0035985]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity [GO:0051575]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA binding, bending [GO:0008301]; DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity [GO:0003906]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding [GO:0003680]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding [GO:0042974]; nuclear retinoid X receptor binding [GO:0046965]; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding [GO:0042975]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; structural constituent of chromatin [GO:0030527]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; base-excision repair [GO:0006284]; DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication [GO:0006268]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; nucleosome disassembly [GO:0006337]; oncogene-induced cell senescence [GO:0090402]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
12002338_HMG-I/Y is an oncogene important in the pathogenesis of human breast cancer 12653562_during apoptosis of different types of tumor cells there is a monomethylation of the nuclear protein HMGA1a 12665574_HMGI-Y physically interacts with Sp1 and C/EBP beta and facilitates the binding of both factors to the insulin receptor promoter 12700639_HMGA1a is methylated in leukemia cells induced to undergo apoptosis 12761578_HMGA1a expression was induced by hypoxia and accumulated in nuclear speckles with the endogenous splicing factor SC35. Overexpression of HMGA1a generated Presenilin-2V. 13680222_expression and localization of HMGI(Y) in the subpopulations of placental tissue 14960313_HMGA1 cooperates with either the N- or the C-terminal transcriptional activation domain of the estrogen receptor to stimulate estrogen response element binding and promoter transcriptional activity 15213251_regulated dynamic properties of HMGA1a fusion proteins indicate that HMGA1 proteins are mechanistically involved in local and global changes in chromatin structure 15247513_HMG-I(Y) expression may have a role in intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma 15350136_Examination of HMGA1a posttranslational modification patterns in breast cancer cell lines supports the existence of a dynamic biochemical switching mechanism for HMGA1a expressed in different ways in normal and malignant cells. 15378028_HMGA1 positively regulates the human KL promoter in breast and ovarian cancer cells 15569996_HMGA1 expression might have a role in human breast cancer 15591590_study focuses on whether HMGA1a and HMGA1b proteins isolated from the same cell type have identical or different post-translational modifications patterns and whether these isoform patterns differ between non-malignant and malignant cells 15631895_These results suggest hypoxia-induced signals in SK-N-SH cells lead to expression of HMGA1a, which may induce expression of the transcription factor N-Myc. 15835918_sites of phosphorylation and the nature of methylation of HMGA1 15893306_HMGA1 is translocated from the nucleus into the cytoplasm and mitochondria and associates with the regulatory D-loop region of the mitochondrial genome. 15901130_HMGA1 as one of the first mediators in the development of human atherosclerotic plaques 16033759_HMGA1 directly influences both the formation and repair of UV-induced DNA lesions in intact cells 16166307_HMGA1 repression by RNA interference reduced neuroblastoma cell proliferation, indicating that HMGA1 is a novel MYCN target gene relevant for neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. 16256199_NF-Y and HMG-I(Y) may play an important role in regulating the IL-10 promoter activity in B cells. 17045586_mtDNA levels were reduced approximately 2-fold in HMGA1a over-expressing transgenic MCF-7 cells 17178855_HMGA1 may be a novel molecular determinant of invasiveness and metastasis, as well as a potential therapeutic target, in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 17434141_Since HMGA1 regulates IR promoter activity, expression of IR gene was impaired causing reduction of IR on cell surface and that compromises with insulin sensitivity. 17550233_Our results suggest that PRMT1 might be involved in the previously reported methylation of Arg25 in HMGA1a in vivo. 17616660_HMGA1 proteins are involved in inhibiting XPA expression, resulting in increased UV sensitivity in cells that overexpress these proteins 17654722_Fluorescence in situ hybridization was used to identify rearrangements of HMGA2 and its homologue HMGA1. HMGA1 rearrangement was not found in any of the cases 17723105_HMGA1 nonhistone chromatin proteins, the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes, and sequence-specific transcription factors act together to regulate the expression of the CRYAB gene. 17877762_HMGA1 disturbs retobblastoma protein (RB)-mediated cell arrest, suggesting a negative control of RB by HMGA1. 17903177_HMGA1a is a sequence-specific RNA-binding factor causing sporadic Alzheimer's disease-linked exon skipping of presenilin-2 pre-mRNA 17935122_the different profiles of HMGA1 protein expression in post-pubertal testicular tumours could represent a valuable diagnostic tool in some cases in which the histological differential diagnosis is problematic 18202751_HMGA proteins are overexpressed in different tumors and the HMGA genes are often involved in chromosomal rearrangements [review] 18279675_A previously unknown role for HMGA1 in the regulation of hNOS2, is demonstrated. 18316571_HMGA1 overexpression is associated with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and promoted chemoresistance to gemcitabine 18473350_HMGA1 promotes tumorigenicity through a PI3-K/Akt-dependent mechanism 18670638_HMGA1 expression is necessary for the full expression of HPV18 E6 and E7 oncoproteins thus establishing a positive autoregulatory loop between HPV E6/E7 and HMGA1 expression. 19060921_HMGA1 proteins bind directly to Hand1 promoter both in vitro and in vivo and inhibit Hand1 promoter activity 19074878_In primary human leukemia samples, there was a positive correlation between HMGA1a and STAT3 mRNA. Moreover, blocking STAT3 function in human leukemia or lymphoma cells led to decreased cellular motility and foci formation. 19250063_MiR-16 negatively regulate HMGA1 and caprin-1 which are involved in cell proliferation. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19609535_The HMGI-C and HMGI(Y) quantitations by real-time RT-PCR are associated with Dukes staging and metastasis; hence, the gene expression levels may be useful in clinical practice. 19687300_Increased ROS levels and reduced repair efficiency in HMGA1-overexpressing cells likely contribute to the increased occurrence of mutations in mtDNA frequently observed in cancer cells. 19729480_HMGA1 is involved in proliferation and gastric tumor formation via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 19739099_HMGA1a is a nuclear architectural protein that triggers receptor-mediated endocytosis 19820691_These results suggest that HMGA1 promotes tumor progression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 19848064_HMGA1 is a promising candidate biomarker and therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. 19903768_Forced overexpression of HMGA1 induces a transformed phenotype with anchorage-independent cell growth in cultured lung cells derived from normal tissue. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956671_analysis of HMGA1a recognition candidate DNA sequences in humans 20004941_The overexpressions of high-mobility group A1, high-mobility group A2, and down-regulation of let-7 may be associated with tumorigenesis and progression of retinoblastomas. 20189936_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20194618_The HMGA1a-induced aberrant exon skipping is caused by impaired dissociation of U1 snRNP from the 5' splice site, leading to a defect in exon definition. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20335021_HMGA1 protein is a positive regulator of IGF-IR expression and its overexpression may contribute to IGF-IR dysregulation in cancer cells. 20347905_present study is the first to report a significant upregulation of high-mobility group A protein 1a (HMGA1a) in schizophrenia 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20975707_Study report that this destabilization of HMGA1 mRNA is triggered by enhanced expression of RNA from an HMGA1 pseudogene, HMGA1-p. 21089648_It causes sporadic Alzheimer's disease-associated aberrant splicing. (review) 21138859_miR-296 regulates HMGA1 expression and is associated with prostate cancer growth and invasion 21156240_analysis of 6p21 rearrangements in uterine leiomyomas targeting HMGA1 21282977_HMGA1 transcription activity can dependent and independent of 7SK snRNA. 21300033_the expression of HMGA1 is related to malignant proliferation, invasion, and differentiation of glioblastoma and glioma from the prospective of tumor stem cells 21329653_HMGA1a is involved in specific splice site regulation of HIV-1. 21364139_Compared with healthy controls, the presence of functional HMGA1 gene variants in individuals of white European ancestry was associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus 21573994_knockdown of the HMGA1 gene could inhibit growth and metastasis potentials in tumor cells 21656127_These results suggested that HMGA1 is a positive regulator of miR-222, and HMGA1 overexpression might contribute to dysregulation of Akt signaling in NSCLC 21957495_7SK RNA thus establishes gene-dependent plasticity between HMGA1 chromatin remodeling and transcription initiation and P-TEFb transcription elongation. 21984063_These results indicated that expression of HMGA1 correlates significantly with malignancy, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis of gliomas. We conclude that HMGA1 may be a potential biomarker and rational therapeutic target for human tumors. 22106824_The data in the present study reveal a role of Hmga1 in transcriptional silencing in T cell lineages and leukemic cells. 22139073_Data indicate that miR-15a, miR-16, miR-26ab, miR-196ab and Let-7a as potential HMGA1 and HMGA2-targeting miRNAs. 22156211_results suggest a core promoter-specific regulation of Mediator and the basal transcription machinery by HMGA1.(HMGA1) 22199144_HMGA1B mediates PIT1 over expression in pituitary neoplasms. 22210315_demonstrates that HDAC6 is an essential regulator of hepatic glucocorticoid-stimulated gluconeogenesis and impairment of whole-body glucose metabolism through modification of glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation 22221703_These findings suggest that HMGA rearrangements likely contribute to the pathogenesis of endometriosis. 22249617_This study delineated the mechanisms underlying the deregulation and reveal the functional significance of HMGA1 in controlling medulloblastoma cell growth and migration/invasion. 22332738_knockdown of HMGA1 expression in OVCAR cells could change cell morphology, decrease cell proliferation, and reduce invasion in vitro 22392906_These results suggest that exposure to estrogens or estrogen-mimics, in some as of yet undefined manner, diminishes the ERbeta-mediated growth restraint in human testicular seminoma. 22411136_HMGA1 is an important susceptibility locus that confers a high cross-race risk of the development of type 2 diabetes. 22503056_HMGA1 knockdown induced inhibition of colony formation and apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma cells.HMGA1 has a role in the metastatic including the acquisition of invasion potential and anoikis resistance. 22564666_Down-regulation of miRNA targeting HMGA1, HMGA2, and E2F1 in human pituitary GH adenomas. 22745191_Data propose that, by affecting the expression of both IGFBP protein species, HMGA1 can serve as a modulator of IGF-I activity, thus representing an important novel mediator of glucose disposal. 22898640_studies identify for the first time an important role for the high-mobility group A1-cyclooxygenase-2 pathway in pancreatic cancer 22961697_The role of HMGA1 played in the proliferation, growth and survival of both traditional colon cancer cells and colon cancer stem cells using the beta-catenin/TCF-4 axis as a transcriptional switch. 23036517_Increased HMGA1 expression in human chondrocytes is associated with increased expression of IGFBP-3. 23149213_A synergism between Ionising Radiations and trabectedin treatment restricted to the HMGA-overexpressing cancer cells. 23166588_HMGA1 reprograms somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells by inducing stem cell transcriptional networks. 23201162_miR-137, induced by its upstream transcription factor HMGA1, can suppress colorectal cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting FMNL2. 23302499_results suggest that HMGA1 IVS5-13insC is not a functional variant and not associated with type 2 diabetes in an ethnically diverse, hypertensive, coronary artery disease population 23311322_Inactivation of the Cdkn2a locus cooperates with HMGA1 to drive T-cell leukemogenesis. 23392246_Results support a model in which the HMGA1/TAR interaction prevents the binding of transcription-activating cellular co-factors and Tat, subsequently leading to reduced HIV-1 transcription. 23394223_Expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with clinical stage, histological grade, and lymph node metastasis 23508853_HMGA1 gene rearrangement is associated with lipomas. 23512162_The rs146052672 variant of HMGA1 represents an early predictive marker of metabolic syndrome, as well as a predictive tool for therapy. 23530587_HMGA1 and HMGA2 might serve to discriminate between reactive atypia, adenoma and adenocarcinoma in ampulla and common bile duct biopsies. 23545254_Interfering with HMGA1 expression reduces the tumorigenic and metastatic potential of breast cancer cells in vivo. 23658826_HMGA1 is a master regulator of tumor progression in breast cancer 23796420_High mobility group AT-hook 1 (HMGA1), a gene that modulates cell cycle transition and cell motility, was verified as a novel target of miR-26a in bladder cancer 23798998_HMGA1, a non-histone protein, is a target of let-7b in prostate cancer. 23835740_High HMGA1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer metastasis. 23935884_high levels of HMGA1 are associated with adverse clinical outcomes in uveal melanoma patients. 24122990_An increase of HMGA1-positive cells correlating to the degree of dysplasia was registered in epithelium and in the connective tissue in oral leukoplakia patients. 24148075_HMGA1 gene variant may have a role in type 2 diabetes, body mass index, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in a Hispanic-American population 24367622_a differential control exerted by both Oct-1 and Oct-2 in the transcriptional regulation of the HMGA1 gene 24452592_The prognostic significance of the HMGA-1 antigen was not confirmed in pituitary adenomas with residual tumor growth. 24684280_HMGA1 is a key molecular switch required by cancer cells for tumor progression and a poorly differentiated, stem-like state. The HMGA1 gene and proteins are expressed at high levels in all aggressive tumors studied to date. Review. 24696416_High HMGA1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 24803022_results indicated that miR-142-3p may function as a tumor suppressor by targeting HMGA1 in osteosarcoma 24833610_our data indicate a critical role for HMGA1 in regulating both self-renewal and the symmetric/asymmetric division ratio in cancer stem cells 24976238_Somatic mutation of mtDNA was associated with better prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 25344216_HMGA1 plays an important role on NSCLC progression and prognosis and may act as a convictive biomarker for prognostic prediction 25455159_High expression of HMGA1 along with miR-26a downregulation indicated a worse prognosis for patients with urothelial bladder cancer. 25557289_Report epigenetic modification of miRNA targets HMGA transcripts on pituitary cells. 25586095_Our data indicates that measuring urine high mobility group AT-hook 1 may serve as a useful diagnostic tool for serous epithelial ovarian cancer. 25595895_CBX7/HMGA1b/NF-kappaB could take part in the same transcriptional mechanism that finally leads to the regulation of SPP1 gene expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 25755724_The results of the present study indicate that miR-26a may be associated with human breast carcinogenesis, which inhibits tumor cell proliferation by targeting HMGA1. 25772486_HMGA1 plays an important role on breast cancer aggressiveness and prognosis and may act as a promising target for prognostic prediction. 26009886_Results show that HMGA1 binds CRMP1 promoter and regulates its expression in medulloblastoma cells. 26251519_HMGA1 is overexpressed in human breast carcinomas and its levels are associated with a particular endocrine status. 26265440_In breast cancer patients, high levels of HMGA1 and CCNE2 expression are associated with the YAP/TAZ signature. 26296198_The HMGA1 rs146052672 genotype variant had an overall statistically significant effect on increasing the risk of development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Europeans. (Meta-analysis) 26527623_Data indicate that the high mobility group A1 (HMGA1) proteomic signature has prognostic value in breast cancer. 26657872_expression of HMGA1 was significantly associated with choroidal invasion and poor retinoblastoma differentiation 26708416_in splenic hemangioma with t(3;6)(q26;p21), the entire coding region of HMGA1 comes under the control of the TBL1XR1 promoter, bringing about dysregulation of HMGA1 26717491_SNP rs5498 in ICAM-1 gene and IVS5-13insC variant in HMGA1 gene were not associated with the susceptibility of DR in the Chinese T2DM cohort. 26895108_Studies indicate that pseudogenes of the HMGA1 gene, that codes for the HMGA1a and HMGA1b proteins having a critical role in development and cancer progression. 26898758_We show that the chromatin remodeling protein HMGA1 functions as a downstream effector of these biological responses to miR-296-5p and regulates Sox2 expression, a master driver of cell stemness, by modifying chromatin architecture at the Sox2 promoter 27001612_Studies define a novel HMGA1-MMP-2 pathway involved in a subset of human carcinosarcomas and tumor progression in murine models. 27008379_This is the first report for the association between HMGA1 and S100A13 expression in the modulation of thyroid cancer growth and invasion. 27045138_Increased HMGA1 in pulmonary arterial endothelial cells resulting from dysfunctional BMPr2 signaling can transition endothelium to smooth muscle-like cells associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. 27470368_HMGA1 may function as an oncogene and modulate endometrial cancer cell migration and invasion by activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 27486901_The results reported here indicate a critical role of HMGA1 in the development of glioblastoma multiforme; its suppression impairs proliferation and self-renewal of brain tumor stem cells 27537384_miR-214 expression was poor while that of HMGA1 was high in cervical and colorectal cancer tissues. miR-214-re-expression or HMGA1 downregulation inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of cancer cells while miR-214 inhibition had opposite effects. miR-214 was demonstrated to bind to the wild-type 3' untranslated region of HMGA1 but not with its mutant. 27561949_HMGA1 overexpression in adherent A2780 cells increased cancer stem cell properties, including proliferation, spheroid-forming efficiency and the expression of stemness-related genes. In addition, HMGA1 regulated ABCG2 promoter activity through HMGA1-binding sites. 27602961_IL-24 inhibits AKT via regulating the HMGA1/miR-222 signaling node in human lung cancer cells and acts as an effective tumor suppressor. 27725726_In this present work, the authors identify and characterize a transcription factor i.e. HIC1, which physically interacts with both Bcl11b/CTIP2 and HMGA1 to co-regulate specific subsets of cellular genes and the HIV-1 tat gene. 27839822_Findings demonstrate that a relationship exists between the HMGA1 rs146052672 variant and acute myocardial infarction, suggesting that defects at the HMGA1 locus may play a pathogenetic role. 27855356_HMGA1 is frequently expressed in cirrhotic tissues and HCCs and its expression is associated with high Edmondson grade and worse prognosis in HCC. 27882471_High HMGA1 expression is associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 27991577_The HMGA1 rs139876191 variant played a key role in a protective mechanism against proliferative diabetic retinopathy by downregulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), a major activator of neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy. 28255268_study revealed a subset of potential development-associated miRNAs and suggests a novel regulatory axis for myogenesis in which miR-195/497 promote myogenic differentiation by repressing the HMGA1-Id3 pathway. 28290473_Study reveals HMGA1, a CK2 Substrate, as a drug-resistant target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Results delineate the tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) resistance-associated kinase-substrate network, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming TKI-induced resistance in NSCLC. 28345487_Findings demonstrate that proper subcellular localization of High-mobility group A1 (HMGA1) is important for its function in trophoblast cells, and suggest that aberrant cytoplasmic expression of HMGA1 contributes to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia through impairment of trophoblast migration. 28389416_These data reveal an essential role for the molecular chaperone GRP78 in IGF-IR signaling and implicate the use of GRP78 inhibitors in blocking IGF-IR signaling in hepatoma cells. 28393241_tissue microarray revealed that HMGA1 was expressed in thyroid carcinoma more than that in normal thyroid tissues ; expression of HMGA1 and MMP-2 was identified to be positively correlated . The present study established the first link between HMGA1 and TGF-b1 in the regulation of thyroid cancer proliferation and invasion 28753127_IGF2BP2 protein is a tumor promoter that drives cancer proliferation through its client mRNAs IGF2 and HMGA1. 28777374_these results clearly indicate HMGA1 as a key regulator of the autophagic pathway in cancer cells. 28831670_Thrombocytosis was more prevalent in patients with inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)than in those with non-IBC and it was associated with poor prognosis. GRO and TGF-beta were associated with thrombocytosis in IBC. 28924209_The ability of HMGA1 to regulate the plasminogen activator system may constitute an important mechanism by which HMGA1 promotes cancer progression. 29052178_HMGA1 overexpression increased FoxO1 mRNA and protein expression in vitro, in cultured HepG2 and HEK-293 cells by binding FoxO1 gene promoter, thereby activating FoxO1 gene transcription. 29152644_results from Transwell and woundhealing experiments indicated that HMGA1 participates cell invasion and migration through the ILK/Akt/GSK3beta pathway 29316384_HMGA1 expression was closely correlated with the clinical stage, histological grade, and tumor size in breast cancer patients and breast cancer progression in transgenic MMTV-PyMT mice 29374701_HMGA1 and MMP-11 may play a key role in the proliferation and progression of skin tumors in humans. 29697014_Results provide evidence that epigenetic alteration through CpG methylation of HMGA1 may regulate its gene expression in various cancers. 29789601_HMGA1 participates in the migration and invasion process via the miR-221/222-TIMP3-MMP2/MMP9 axis in cervical cancer. 29867121_findings highlight a novel FoxO1/HMGA1-mediated mechanism by which insulin may regulate gene expression and metabolism. 29945308_Results indicate that miR-142-3p may serve as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by suppressing the expression of oncogene AT-Hook 1a Protein, High Mobility Group (HMGA1) and frizzled 7 protein (FZD7). 30308301_High HMGA1b levels in blood is associated with colorectal cancer. 30614613_In this paper, to characterize HMGA1 comprehensively, research on various types of tumours is discussed to further understanding of the function and mechanism of HMGA1.The findings provide a more reliable basis for classifying HMGA1 function according to the tumour location 30766549_This meta-analysis indicated that the HMGA1 variant IVS5-13insC can be a risk factor of T2D development, particularly among Caucasians. Significant risks were also found in Asians and Hispanic-Americans. 30776481_PD-L1 could crucially contribute to the maintenance of CSC self-renewal by activating HMGA1-dependent signaling pathways 30816441_Results provide evidence that HMGA1 expression is regulated by Let-7d through direct mechanism. HMGA1 silencing inhibit cell cycle progression in ovarian cancer (OC) cell lines. 30999005_pituitary neuroendocrine tumors displayed strong nuclear HMGA1 and strong cytoplasmic HMGA2 immunoreactivity. 31076808_RPSAP52 is overexpressed in pituitary adenomas. RPSAP52 increases HMGA protein levels. 31096664_Results reveal that HMGA1 and HMGA2 mRNA and protein are overexpressed in ECC, but only HMGA1 expression is associated with increased histological grade and tumor size. 31116627_HMGA1 knockdown-induced NUMB upregulation. 31167352_These data suggest that HMGA1 might promote chromatin relaxation through a histone H1-mediated mechanism strongly impacting on the invasiveness of cancer cells. 31229266_In gastric cancer patients, HMGA1 and c-Myc expression were closely associated with the glycolysis gene signature. 31300541_We demonstrate that Fra-1 bound to an intragenic enhancer region is required for RNA Pol II recruitement at the HMGA1 promoter. 31311575_HMGA1 regulates FOXM1 at a post-transcriptional level preventing its proteasomal degradation by stabilizing it in the nucleus. Also, their cooperative action supports breast cancer aggressiveness, by promoting tumor angiogenesis. 31340016_First structural model for AT-hook 1 of HMGA1a that can adopt a transient alpha-helical structure, which might serve as an additional regulatory mechanism in HMAG1a. The CK2-, cdc2- and cdc2/CK2-phosphorylated forms of HMGA1a each exhibit a different binding affinity towards the PRD2 element of the NFkappaB promoter. 31340839_Our findings suggest that KIFC1, activated by TCF-4 (TCF7L2), functions as an oncogene and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) pathogenesis through regulating HMGA1 transcriptional activity and that KIFC1 is a potential therapeutic target to enhance the paclitaxel sensitivity of HCC 31394192_HMGA1 exacerbates tumor progression by activating miR-222 through PI3K/Akt/MMP-9 signaling pathway in uveal melanoma. 31410930_These data suggest that BRCA1 is an important regulator of the oncofetal protein HMGA2 and promotes cell survival in human placental cells. 31531802_High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) protein and gene expression correlate with ER-negativity and poor outcomes in breast cancer. 31686521_HMGA1 was positively correlated with miR-671 expression; however, miR-671 was negatively correlated with APC in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 31779212_The secretion of HMGA1 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells increase their migratory and invasive phenotype and correlates with an increased incidence of distant metastasis in TNBC patients. TNBC tumors with nuclear HMGA1 show a decreased incidence of metastasis when they are compared to TNBC tumors with cytoplasmic HMGA1. [review] 32052688_Long noncoding RNA LINC00963 promotes breast cancer progression by functioning as a molecular sponge for microRNA-625 and thereby upregulating HMGA1. 32127525_MYC-regulated pseudogene HMGA1P6 promotes ovarian cancer malignancy via augmenting the oncogenic HMGA1/2. 32329839_HMGA1 accelerates the malignant progression of gastric cancer through stimulating EMT. 32572906_LncRNA LINC00467 contributes to osteosarcoma growth and metastasis through regulating HMGA1 by directly targeting miR-217. 32989212_HMGA1 Promotes Hepatic Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Inducing Expression of Glucose Transporter 3 (GLUT3). 33139812_Identification of HMGA2 inhibitors by AlphaScreen-based ultra-high-throughput screening assays. 33150374_Progression signature underlies clonal evolution and dissemination of multiple myeloma. 33169939_Circ_0067835 sponges miR-324-5p to induce HMGA1 expression in endometrial carcinoma cells. 33332531_ANP32A promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating the HMGA1/STAT3 pathway. 33526059_LINC00460/DHX9/IGF2BP2 complex promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis by mediating HMGA1 mRNA stability depending on m6A modification. 33545070_Phosphorylation-regulated HMGA1a-P53 interaction unveils the function of HMGA1a acidic tail phosphorylations via synthetic proteins. 33755320_GRP75-mediated upregulation of HMGA1 stimulates stage I lung adenocarcinoma progression by activating JNK/c-JUN signaling. 33835503_Gene network analysis using SWIM reveals interplay between the transcription factor-encoding genes HMGA1, FOXM1, and MYBL2 in triple-negative breast cancer. 33858292_NRF1-regulated CircNSUN2 promotes lymphoma progression through activating Wnt signaling pathway via stabilizing HMGA1. 33872661_Pancreatic cancer cells-derived exosomal long non-coding RNA CCAT1/microRNA-138-5p/HMGA1 axis promotes tumor angiogenesis. 34072941_HMGA1 Is a Potential Driver of Preeclampsia Pathogenesis by Interference with Extravillous Trophoblasts Invasion. 34167089_HMGA1 promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis by transactivating SUZ12 and CCDC43 expression. 34431162_Pseudogene HSPB1P1 contributes to renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by targeting miR-296-5p to regulate HMGA1 expression. 34483139_Knockdown of hsa_circ_0091994 constrains gastric cancer progression by suppressing the miR-324-5p/HMGA1 axis. 34560189_RNF144A-AS1 promotes the development of glioma cells by targeting miR-665/HMGA1 axis. 34887392_HMGA1 stimulates MYH9-dependent ubiquitination of GSK-3beta via PI3K/Akt/c-Jun signaling to promote malignant progression and chemoresistance in gliomas. 34970695_Long noncoding RNA LINC01748 exerts carcinogenic effects in nonsmall cell lung cancer cell lines by regulating the microRNA520a5p/HMGA1 axis. 34973275_miR-142-3p simultaneously targets HMGA1, HMGA2, HMGB1, and HMGB3 and inhibits tumorigenic properties and in-vivo metastatic potential of human cervical cancer cells. 35040749_lncRNA TMPO antisense RNA 1 promotes the malignancy of cholangiocarcinoma cells by regulating let-7g-5p/ high-mobility group A1 axis. 35114891_Upregulation of exosomal circPLK1 promotes the development of non-small cell lung cancer through the miR-1294/ high mobility group protein A1 axis. 35130798_Hsa_circ_0039569 facilitates the progression of endometrial carcinoma by targeting the miR-197/high mobility group protein A1 axis. 35282770_The role of HMGA1 protein in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 35459188_microRNA-4701-5p protects against interleukin-1beta induced human chondrocyte CHON-001 cells injury via modulating HMGA1. 35785026_HMGA1 Promotes Macrophage Recruitment via Activation of NF-kappaB-CCL2 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 35805937_Prognostic Significance of HMGA1 Expression in Lung Cancer Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. 35864955_High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1): Structure, Biological Function, and Therapeutic Potential. 35948739_HMGA1 gene expression level in cancer tissue and blood samples of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients: preliminary report. 36087034_Apelin-mediated deamidation of HMGA1 promotes tumorigenesis by enhancing SREBP1 activity and lipid synthesis. |
ENSMUSG00000046711 |
Hmga1 |
2982.798402 |
2.7875662897 |
1.479006 |
0.033275993 |
1998.581318 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4441.1317082 |
84.1388620 |
1604.3842893 |
24.6206310 |
| ENSG00000137331 |
8870 |
IER3 |
protein_coding |
P46695 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in the ERK signaling pathway by inhibiting the dephosphorylation of ERK by phosphatase PP2A-PPP2R5C holoenzyme. Acts also as an ERK downstream effector mediating survival. As a member of the NUPR1/RELB/IER3 survival pathway, may provide pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with remarkable resistance to cell stress, such as starvation or gemcitabine treatment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12356731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16456541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22565310}. |
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene functions in the protection of cells from Fas- or tumor necrosis factor type alpha-induced apoptosis. Partially degraded and unspliced transcripts are found after virus infection in vitro, but these transcripts are not found in vivo and do not generate a valid protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8870; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1901029]; negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003085]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; regulation of DNA repair [GO:0006282]; regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport [GO:0046822]; regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000377]; regulation of response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:2001020]; response to protozoan [GO:0001562] |
11782530_Impaired apoptosis, extended duration of immune responses, and a lupus-like autoimmune disease in IEX-1-transgenic mice. 11844788_regulation by p53 tumor suppressor and Sp1 11910304_mechanical strain increased IEX-1 gene expression in macrophages 12032839_Characterization of a novel hexameric repeat DNA sequence in the promoter of the immediate early gene, IEX-1, that mediates 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)-associated IEX-1 gene repression. 12356731_IEX-1 is a new type of ERK substrate that has a dual role in ERK signaling by acting both as an ERK downstream effector mediating survival and as a regulator of ERK activation 12510147_IEX-1 has roles in regulation of cell death and oncogenesis [review] 12682234_Overexpression of IEX-1S results in acceleration of TNF-alpha-induced hepatocyte apoptosis through blockade of the PI3K/Akt survival pathway. 12743274_failure of IEX-1 to express its protein reflects the numerous mechanisms by which HSV-1 thwarts the cells from expressing its genes after infection 12761504_IEX-1 attenuates NF-kappaB activation, a possible counter-regulatory process leading to apoptosis. 15120418_IEX-1 expression was stimulated by hydroxytamoxifen, that the degree of increase was greater in resistant cells (four-fold versus 1.5-fold) and that this hydroxytamoxifen regulation was estrogen receptor dependent 15451437_Our data suggest that IEX-1 may regulate apoptosis by directly interacting with various proteins involved in the control of apoptotic pathways. 15767410_concluded that IEX-1 mRNA is not preferentially degraded during HSV-1 infection and that HSV-1 instead inhibits the normal turnover of this mRNA 15781630_We found that p73beta targets the apoptotic program at multiple levels: facilitating caspase activation through p53-dependent signals and inducing p57KIP2, while down-regulating c-IPA1 and IEX1 through a p53-independent mechanism. 15855159_IEX-1 is organized in subnuclear structures and partially co-localizes with promyelocytic leukemia protein in HeLa cells 16567805_sequence-targeting mutagenesis reveals a transmembrane-like integrated region of the protein that is critical for both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic functions 16960879_IEX-1 plays an important role in astrocytic differentiation of human glioma cells and that IEX-1 functions at downstream of PKA. 16973576_ICP27 is essential for IEX-1 mRNA stabilization whereas virion host shut plays little if any role 17704804_Modulates NF-kappaB-dependent antiapoptotic protection and thereby exerts tumor-suppressive potential. 18026799_This study indicates that an evaulation of IEX-1 expression may be clinically useful for predicting patient prognosis in pancreatic cancer. 18564103_study showed that IEX-1 is involved in the radiation-induced apoptosis of human glioma cells and that its overexpression enhances the apoptotic sensitivity of these cells to gamma-radiation 19152102_down-regulation of IEX-1 gene was associated with short survival in myelodysplastic syndrome patients 19285955_This study demonstrated the physical association of the MCL-1 and IEX-1 proteins, the modulatory role of MCL-1 in IEX-1-induced apoptosis, and the role of BIM as an essential downstream molecule for IEX-1-induced cell death. 19690192_The small interfering RNA knockdown of BNIP3, IER3, and SEPW1 genes affected critical multiple myeloma endothelial cell functions correlated with the overangiogenic phenotype 19773435_Results suggest dysregulated expression of IER3 is common in MDS (61% >4-fold increase or decrease in expression with decreased expression primarily in early MDS and increased expression primarily in later MDS progressing toward leukemia). 19837266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20713914_Results suggest that hypertension in IEX-1 knockout mice may arise primarily from impaired cAMP signaling induced by overproduction of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in vascular smooth muscle cells. 20934684_IER3 is upregulated in human PDLCs subjected to tensile stress related to mechano-induced cell cycle arrest. 21112119_IER3 plays a complex and to some extent contradictory role in cell cycle control and apoptosis. Effects of IER3 relate to an interference with certain signalling pathways 21250941_IEX-1 plays a role in suppression of apoptosis and protects cells by controlling sensitivity to TNFalpha under both normal and inflammatory conditions. 21518511_Changes of methylation status of gene IEX-1 promoter CpG island correlates with hematologic malignancies. 22085302_Altered IEX-1 expression can potentially be a new predictor of the malignant transformation and a prognostic indicator for cancer therapy. 23403649_Studied the binding effect of hcmv-miR-UL148D to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of IEX-1.Results showed that only one binding site in the 3'UTR of IEX-1 was completely complementary to an 11nt sequence in the 5' terminus of hcmv-mir-UL148D. 23725081_IEX-1 expression levels correlate with the severity of preeclampsia 24311782_the interference of IER3 with the PI3K/Akt-Fyn pathway represents a novel mechanism of Nrf2 regulation that may get lost in tumors and by which IER3 exerts its stress-adaptive and tumor-suppressive activity. 25036043_In human samples removed from failed AVF, there was a significant increase in IEX-1 expression localized to the adventitia. 25066273_interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta)-induced IER3 expression is mediated by the ERK1/2 target, transcription factor Elk-1. 25666857_findings suggest that IER3 is a putative tumor suppressor in the cervix, and the c-Ab1/p73beta/IER3 axis is a novel and crucial signaling pathway that confers etoposide chemosensitivity. 25684507_High expression of IER3 is associated with hepatocarcinoma. 26973248_we determined the molecular mechanism responsible for IER3 degradation, involving a ternary complex of IER3, MDM2 and FHL2, which may contribute to cervical tumor growth. Furthermore, we demonstrated that FHL2 serves as a scaffold for E3 ligase and its substrate during the ubiquitination reaction, a function that has not been previously reported for this protein 27736946_Study characterized IEX-1's expression and function in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and showed that IEX-1 is highly expressed in RA-SFs and negatively regulates RA-SF activation. 27890615_Analysis of consensus EGR-binding elements (EBEs) showed that the immediate early response 3 gene (IER3) is a novel transcriptional target gene of EGR2 as confirmed by the luciferase assay, electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA), chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and western blot analysis. 30249226_Our findings suggest for the first time that the increased expression of IER3 protein may promote the aggressive progression of BCa. Importantly, IER3 may be a potential prognostic marker for BCa patients. 30579899_Overexpression of GAS5 enhanced the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to radiation treatment via up-regulating IER3 through miR-106b. 34729939_IER3 (IEX-1) dysregulation serves as a potential prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia patients. |
ENSMUSG00000003541 |
Ier3 |
283.135972 |
30.3573067219 |
4.923972 |
1.158956919 |
12.719318 |
0.00036189779661555446753362641487683504237793385982513427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000911849006153223604932700485647956156753934919834136962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
608.6562412 |
379.7295928 |
20.6548469 |
9.2563911 |
| ENSG00000137364 |
7172 |
TPMT |
protein_coding |
P51580 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the S-methylation of thiopurine drugs such as 6-mercaptopurine (also called mercaptopurine, 6-MP or its brand name Purinethol) and 6-thioguanine (also called tioguanine or 6-TG) using S-adenosyl-L-methionine as the methyl donor (PubMed:657528, PubMed:18484748). TPMT activity modulates the cytotoxic effects of thiopurine prodrugs. A natural substrate for this enzyme has yet to be identified. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18484748, ECO:0000269|PubMed:657528, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Methyltransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes the enzyme that metabolizes thiopurine drugs via S-adenosyl-L-methionine as the S-methyl donor and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine as a byproduct. Thiopurine drugs such as 6-mercaptopurine are used as chemotherapeutic agents. Genetic polymorphisms that affect this enzymatic activity are correlated with variations in sensitivity and toxicity to such drugs within individuals, causing thiopurine S-methyltransferase deficiency. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 3, 18 and X. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014]. |
hsa:7172; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; S-adenosyl-L-methionine binding [GO:1904047]; thiopurine S-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008119]; methylation [GO:0032259]; nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006139]; xenobiotic catabolic process [GO:0042178]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
10751626_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11007234_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11025471_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11422006_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11503013_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11927101_Defective methylation and subsequent hyperhomocysteinemia leading to impairment of thiopurine methyltransferase activity may serve as a MS susceptibility factor. 11927834_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12142782_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12142782_Polymorphisms in TPMT are associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Asians and whites 12172211_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12176518_Azathioprine toxicity is related to enzyme genotype (and mutation) in renal transplant patients. 12217596_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12492733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12509611_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12563179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12703994_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12732844_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12777968_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12777968_polymorphisms of thiopurine methyltransferase were studied in 306 healthy Brazilians who were classed, on the basis of self-declared colour and ancestry 12814450_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12815366_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12815366_This study is the first analysis of TPMT mutant allele frequency in a sample of the Brazilian population. 12880540_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12903038_Allele frequency of TPMT*3C is low among Jing Chinese (1.0%), and TPMT*3C appears to be the most prevalent deleterious allele in this population. 12903038_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12940924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12949626_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12972954_The pharmacogenetics of TPMT was studied in relation to drug toxicity and therapeutic efficacy. 14508387_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14576848_REVIEW: pharmacogenetics of TPMT in cancer therapy 14634700_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14656901_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14723818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14985890_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14985890_Thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) polymorphisms have been linked with severe and potentially fatal myelosuppression in deficient metabolizers and rejection of transplanted organs in high metabolizers. 14985891_Allelic variation at the TPMT (thiopurine S-methyltransferase) locus resulted in large inter-individual differences in the activity of enzyme TPMT, which the gene encodes and which are responsible for differences in toxicity/efficacy of thiopurine drugs. 14985891_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15022030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15206995_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15226671_Polymorphism affects pharmacogenetics. (review) 15226673_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15226673_Provides solid basis to predict TPMT phenotype in a Northern European Caucasian population by molecular diagnostics. 15247157_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15255798_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15349717_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15349717_When azathioprine is administered at an initial dose of 1.5 mg/kg per day, both coding and promoter TPMT polymorphisms influence the dose tolerated. 15385838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15476481_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15476481_TPMT genotype was an independent predictor for hemoglobin, hematocrit and red blood cell changes during azathioprine treatment after kidney transplantation. 15571264_thiopurine methyltransferase polymorphisms modify the metabolism of the thiopurine drugs [review] 15571267_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15571267_TPMT promoter Variable Number Tandem Repeats are unlikely to play a significant role in changes in TPMT activity in response to azathioprine therapy 15691505_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15709212_Specific genetic polymorphisms in drug metabolizing enzymes such as TPMT, drug transporters (MDR1), and drug target enzymes (TS) are associated with clinical outcomes in patients treated with chemotherapy drugs, such as 5-fluorouracil and irinotecan. 15784872_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15784872_TPMT genotype has a substantial impact on minimal residual disease after administration of mercaptopurine in the early course of childhood ALL, most likely through modulation of mercaptopurine dose intensity. 15792824_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15802809_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15931768_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15946151_Genotyping for the major TPMT variant alleles may be valuable tool in preventing azathioprine toxicity. 15967990_there is a unique pharmacogenetic mechanism by which common polymorphisms affect TPMT protein function and therapeutic response to thiopurine drugs 15973722_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15973722_TPMT, ITPA, and MTHFR genotypes do not predict adverse drug reactions, including bone marrow suppression, in liver transplant patients. Possible association between nodular regenerative hyperplasia and heterozygous TPMT genotype. 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16044099_Genotyping for the major TPMT variant alleles may be valuable tool in preventing azathioprine toxicity. 16044099_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16164497_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16166171_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16202677_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16214825_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16272700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16306100_polymorphisma in the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene may play an important role in determing the erythrocyte thiopurine methyltransferase phenotype 16396707_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16418693_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16431304_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16459728_Importance of performing surveillance testing for allelic characterization prior to treatment with azathioprine for multiple sclerosis. 16476125_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16595084_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16611274_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16643135_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16691038_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16724002_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16773681_The only discovery translated until now into daily practice is the relation between thiopurine S-methyltransferase (TPMT) gene polymorphisms and hematological toxicity of thiopurine treatment in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). 16789994_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16876902_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16917910_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16946561_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16946561_Three novel single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of thiopurine S-methyltransferase were identified-106G>A in exon 3 (Gly36Ser, *20 allele), 967A>G in 3'-untranslated region, and -87C>T in intron 8. 16952345_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17065060_TPMT does not appear to have a role in response to thiopurine treatment in inflammatory bowel disease 17113562_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17129980_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17152495_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17164697_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17176368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17206640_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17220558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17241387_Observational study of genotype prevalence and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17241387_The relationship of TPMT genotype to azathioprine side effects is reported in Japanese patients with autoimmune liver diseases. 17243178_Structure of TPMT shows that naturally occurring amino acid polymorphisms scatter throughout, & amino acids whose alteration have most influence on function are those that form intra-molecular stabilizing interactions (mainly van der Waals contacts). 17323057_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17617792_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17617792_study provides the first data on the frequency of common TPMT variants in the Turkish population, based on analysis of pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia 17690215_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17885628_The novel variant allele of TPMT affects enzyme activity, as the individuals carrying it had almost undetectable TPMT activity. 17909762_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17919375_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18021342_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18188716_Thiopurine S-methyltransferase gene (TMPT) polymorphisms in a Mexican population of healthy individuals and leukemic patients. 18193212_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18303966_A higher prevalence of TPMT deficiency was recorded than in previous studies. Afro-Caribbeans have lower activity than Caucasians and South Asians. TPMT enzyme activity was lower among females, especially in South Asians. 18385010_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18408566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18408566_Trinucleotide repeat variants in the promoter of the thiopurine S-methyltransferase gene of patients exhibiting ultra-high enzyme activity. 18467186_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18482735_The A80P polymorphism in TPMT*2 disrupts helix alpha3 bordering the active site, which breaks several salt-bridge interactions and opens up a large cleft in the protein. The A154T polymorphism is located within the co-substrate binding site. 18484748_Either Arg152 or Arg226 may participate in the TPMT reaction, with one residue compensating when the other is altered, and Arg152 may interact with substrate more directly than Arg226. 18600549_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18600549_the frequency of functional gene polymorphisms in 396 patients with inflammatory bowel disease and 300 healthy subjects 18602085_Identification and functional characterisation of four novel TPMT allelic variants. 18605963_detected in an Estonoian population were 3 novel mutations -30T>A exon 3, 10A>G intron 3 & 145A>G intron 10; 4 markers whose frequencies were significantly different in intermediate methylators; 1 haplotype associated with intermediate TPMT activity 18616518_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18693152_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18708949_analysis of thiopurine S-methyltransferase allelic variants 18775689_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18823306_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18827410_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18827410_TPMT mutations are not associated with myelosuppression in Japanese IBD patients. Even in IBD patients with a wild TPMT genotype, clinicians should pay attention for the possible development of myelosuppression. 18987654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987654_Risk of relapse was higher for the 526 TPMT wild type patients than for the remaining 75 patients. Despite this, patients with low TPMT did not have superior survival possibly due to an excess of secondary cancers among these patients. 18987660_Heterozygosity at the TPMT gene locus, augmented by mutated MTHFR gene, predisposes to 6-Mercaptopurine related toxicities in childhood ALL patients. 18987660_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19034904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19034904_found no significant association between TPMT SNPs and ALL treatment outcome; TPMT*3A is the most prevalent variant allele in the Russian Federation. 19048244_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19048245_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19057372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19057372_The frequency of allele variants of gene TPMT*2, *3A, *3B, and *3C was estimated in a population of 116 Brazilian children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19164342_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19177822_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19214663_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19229528_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19239109_(Heterozygosity, PD, PIC, PE) of TPMT minisatellite locus showed that this marker is informative and can be used for DNA typing and population studies besides being used in clinical investigation in checking thiopurine drug sensitivity of individuals. 19239109_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19252404_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19252404_We have demonstrated no significant association between TPMT variant alleles and adverse effects in Han Chinese IBD patients, so the prediction of AZA-related toxicity by TPMT genotyping remains imperfect. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19473575_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19474452_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19535798_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19543639_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19543639_The allele TPMT*3A, is the most prevalent in Chilean blood donors, as in Caucasian populations. 19546880_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19579612_Adverse reactions to thiopurines in IBD may be predisposed by thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) or inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPA) gene mutation. Allele frequencies of TPMT*2, TPMT*3A, TPMT*3B, and TPMT*3C were 0, 0, 0, and 0.010 (17/1624). 19650826_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19675376_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19682085_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19682195_Adverse reactions to azathioprine cannot be predicted by thiopurine S-methyltransferase genotype in Japanese patients with inflammatory bowel disease. 19682195_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19695401_In these kidney transplant recipients, patients who carried the TPMT*3C allele were at a higher risk for azathioprine-induced myelosuppression than noncarriers 19695401_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19748501_Data show that MTHFR and TYMS genotypes influence TPMT activity, and that males and females demonstrate differential modulation of TPMT activity. 19748501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19774638_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19830600_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19830600_TPMT polymorphisms are not associated with 6-mercaptopurine toxicity in precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19891552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898482_the strong associations of cisplatin-induced hearing loss with specific genetic variants in TPMT were identified 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20017316_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20017316_Two novel heterozygote mutations, 210C>T (C70C, silent) and 622T>C (F208L), were identified in the coding region of the TPMT in Chinese children with acute leukemia. 20037211_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20066544_TPMT testing before starting a regimen of azathioprine in combination with N-acetylcysteine and steroids in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis can predict likelihood of leukopenia. 20081263_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20081263_Thiopurines administration is related to the increase in hemato-oncological treatment toxicity in TPMT heterozygotes. 20136357_This meta-analysis suggests that individuals with both intermediate and absent TPMT activity have an increased risk of developing thiopurine-induced myelosuppression--REVIEW 20136364_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20153897_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20153897_Thiopurine S-methyltransferase gene polymorphism is associated with less 6-mercaptopurine dose intensity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 20173083_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20175804_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20175804_approximately 1 in 180 persons born in Mexico City might have low or undetectable TPMT enzyme activity. 20175817_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20308917_Data showed that it could be helpful to examine TPMT genotypes and to measure TPMT activity in Korean patients taking AZA/6-MP to predict the development of leukopenia. 20308917_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20349237_Case Report: invasive aspergillosis concomitant with azathioprine-induced leucopenia without carrying any TPMT mutant allele. 20350137_Both the number and type of VNTRs, as well as the upstream regulatory region of the TPMT gene promoter, determine the overall level of TPMT gene transcription. 20350137_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20393862_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20403997_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20408054_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20521035_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20593505_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20881512_Characterization of a novel sequence variant, TPMT*28, in the human thiopurine methyltransferase gene 20945351_novel mutation, TPMT c.349>A,resulting in the amino acid substitution p.117G>R, caused misdiagnosis of TPMT deficiency 20972624_A patient carrying TPMT*3C polymorphism is diagnosed with azathioprine-induced severe cholestatic hepatitis. 21254844_The distribution of NAT2, TPMT, and MTHFR gene polymorphisms in Baja California, Mexico exhibited allele and genotype frequencies that are highly similar to those observed in Caucasian populations. 21348397_Thioguanides family of drugs can cause life-threatening myelosuppression due to low activity of a critical metabolic enzyme, thiopurine S-methyl transferase 21819368_Frequency of thiopurine S-methyltransferase gene mutations is low among Iranian kidney transplant patients. The incidence of adverse reactions to azathioprine was also low. 21938428_Distributions of TPMT genotype and allele frequency in Iranian populations are different from the genetic profile found among Caucasian or Asian populations. 22225964_This study provides the first analysis of TPMT mutant allele frequency in individuals of Tunisian origin 22304581_6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) treatment results in a VNTR architecture-dependent decrease of TPMT gene transcription. 22318545_The distribution of TPMT, UGT1A1 and MDR1 gene polymorphisms of the South Indian population was significantly different from other populations. 22385887_Inflammatory bowel disease patients may have significantly higher prevalence of TPMT polymorphism and, even more, low activity. 22486532_High TPMT enzyme activity does not explain drug resistance Many of these patients preferentially produce the toxic 6-methylmercaptopurine metabolites (6-MMP) rather than the active 6-thioguanine nucleotides (6-TGN) 22594254_TPMT activity was measured in RBC by HPLC method. 22616585_aim of this study was to determine the frequency of the four most common allelic variants of TPMT gene in the population of Slovak IBD patients.TPMT genetic polymorphisms lead to dose-related hematopoetic toxicity 22747506_TPMT*2 allelic variant displays a protected region in the C-terminus, which differs from wild-type TPMT, whereas the protected regions in TPMT*5 allele are located mainly in the N-terminus close to the active site. 22846425_These data indicate that polymorphism in PACSIN2 significantly modulates TPMT activity and influences the risk of GI toxicity associated with mercaptopurine therapy. 22931646_Severe intolerance to 6-mercaptopurine in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia might be not related with the mutation of coding region in TPMT gene. 22972540_TPMT kd cells were more sensitive to 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) (10 mumol/L) and 6-thioguanine (6-TG) (8 mumol/L) than wild-type (wt) cells, (32% versus 20%) and (18% versus 9%), respectively. 23014567_observed influence of the TMPT-genotype on MRD in patients with precursor B-ALL before application of mercaptopurines suggests a direct connection to the physiological role of TPMT 23025308_The study focused on explaining how a locally occurred TPMT A167G substitution propagated through hydrogen bonds alteration to induce structural modification which affects both thiopurine and S-adenosylmethionine receptors. 23065291_The G238C and A719G single nucleotide polymorphisms in the human TPMT gene are not associated with increased risk of developing acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 23126166_SNP of TPMT (TPMT*3C) is recognized in only 1-2% of Japanese and its ill effect among them is difficult to surmise. 23192017_Letter/Case Report: TPMT monitoring is unable to predict azathiopurine-associated non-myelotoxicity. 23252704_Based on the HRMA and sequencing in the investigated group, two most frequent alleles for the Caucasian population were found: TPMT*1 with the frequency of 96.72% and TPMT*3A with the frequency of 3.28%.in this study of the polish population. 23252716_In childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, TPMT activity should not be used to predict heterozygosity particularly in blood samples obtained at disease diagnosis 23377985_this is the first study that assesses the TPMT variant allele frequencies in Guatemalan populations 23398787_identify the most common genetic polymorphisms of TPMT in healthy Jordanian volunteers and patients with rheumatoid arthritis 23400745_In a study of Italian myasthenia gravis patients treated with azathioprine, a new TPMT haplotype, TPMT* 3E, was observed only in association with intolerance. 23553048_TPMT*3A and the TPMT*3C, which cause the largest decrease in enzyme activity, were both variant alleles detected in the Tunisian population 23581716_distribution of the most frequent variants of TPMT gene was similar in a healthy population and patients with inflammatory bowel disease 23588304_A predictive model combining variants in TPMT, ABCC3, and COMT with clinical variables significantly improved the prediction of hearing-loss development as compared with using clinical risk factors alone 23731044_This study shows the prevalence of TPMT genetic polymorphisms in population of Slovak IBD patients 23811272_differential contribution of the enzyme TPMT to the cytotoxicity of the two thiopurines is probably due to its role in formation of the meTIMP, the cytotoxic methylated metabolite of 6-MP 23820299_our results indicated that TPMT or COMT genetic variation was not related to cisplatin ototoxicity in children with cancer and did not influence cisplatin-induced hearing damage in laboratory models 23844534_A high frequency and diversity of variant TPMT genotypes was found in this series with predominance of the TPMT*3B allele 23996738_plays a key role in the metabolism of azathioprine/6- mercaptopurine (6-MP). Mutations in the enzyme lead to generation of excess thioguanine, which causes neutropenia via suppression of neutrophils. 24121523_Heart transplantation recipients with TPMT genetic variant alleles who are treated with AZA develop acute rejection earlier, more frequently, and of greater severity. 24322830_TPMT*3c mutant allele was associated with azathioprine side effects (leukopenia, alopecia) in Chinese systemic lupus erythematosus patients. 24643197_Activity measurement performed at diagnosis provides clinicians with information on immediate pharmacokinetic-related adverse events and/or hypermetabolism 24696613_The prevalence of TPMT genotypes was high among Brazilian patients. Variants genes 2 and 3C may be associated with azathioprine pancreatic toxicity in a IBD southeastern Brazilian population 24710034_TPMT*37 introduces a premature stop codon at position 216, resulting in loss of the last 29 amino acid residues from the C terminal of the TPMT protein. 24737678_suggest that germline genetic variation in TPMT and MTHFR do not significantly alter SOS risk in patients exposed to thioguanine 24774509_TMPT genotyping appears an important tool to further optimize 6-MP treatment design in Chilean patients with ALL 25347948_Data suggest risk of myelotoxicity of high-dose methotrexate during methotrexate/6-mercaptopurine maintenance chemotherapy of childhood acute leukemia is not associated with heterozygosity in thiopurine methyltransferase in Nordic population studied. 25551397_this paper shows that the influence of TPMT and COMT on the development of cisplatin-induced hearing loss may be less important than previously suggested. 25564374_Results show complete sequence-based screening study evaluating all TPMT variants in Asian populations some of them may ne of relevance in Korean population. 25799415_association of TPMT polymorphisms with overall thiopurine-induced adverse drug reactions 25819542_We report on the presence of the TPMT*3C and *3A mutant alleles in the Libyan population. Therefore, monitoring the patients to be treated with doses of thiopurine drugs for TPMT variants is worthwhile to avoid the development of severe myelosuppression. 25940902_refinements in risk stratification and treatment have reduced the influence of TPMT genotype on treatment outcome in a contemporary protocol. 26072396_Identification of TPMT variants and subsequent dose reduction reduces hematologic events during thiopurine treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. 26410243_structure-function relationships of TPMT 26411491_The TPMT promoter region may serve as a pharmacogenomic biomarker when introducing thiopurine therapy 26633017_Association of TPMT polymorphisms with overall azathioprine-induced adverse drug reactions, bone marrow toxicity and gastric intolerance, but not with hepatotoxicity (meta-analysis). 26674571_The aim of the study was to investigate frequencies of TPMT and ITPA polymorphisms in Lithuanian inflammatory bowel disease patients and analyze their association with azathioprine-related adverse events. 26845729_With respect to TPMT, the variants TPMT*2 and TPMT*3A were not implicated in genetic susceptibility to childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia 26974142_A point mutation in the thiopurine S-methyltransferase gene that led to exon 5 deletion in the transcribed mRNA. 27217052_Review/Meta-analysis: thiopurine S-methyltransferase testing for averting drug toxicity. 27333713_The most frequently occurring no |
ENSMUSG00000021376 |
Tpmt |
93.335943 |
2.3542700746 |
1.235280 |
0.158273575 |
62.201006 |
0.00000000000000310129421585828774683613568977373507458582453134854350906834952183999121189117431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000021510856497212558488876752185387330132827331946598903300582605879753828048706054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
133.0855855 |
13.7872726 |
56.9988759 |
4.6960619 |
| ENSG00000137414 |
51439 |
FAM8A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBU6 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the assembly of the HRD1 complex, a complex involved in the ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent process of ER-associated degradation (ERAD). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28827405}. |
Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway. Part of Hrd1p ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51439; |
Hrd1p ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000836]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
|
ENSMUSG00000069237 |
Fam8a1 |
75.193142 |
0.3724736009 |
-1.424790 |
0.176724219 |
67.353840 |
0.00000000000000022689962071752684482917445003711853017980292802902031468192944885231554508209228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001681244177605771178253075301512666673303488299416608153791230506612919270992279052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.5715429 |
4.7005806 |
112.3684225 |
7.7931836 |
| ENSG00000137460 |
85462 |
FHDC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9C0D6 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated formin which regulates both actin and microtubule dynamics. Induces microtubule acetylation and stabilization and actin stress fiber formation (PubMed:18815276). Regulates Golgi ribbon formation (PubMed:26564798). Required for normal cilia assembly. Early in cilia assembly, may assist in the maturation and positioning of the centrosome/basal body, and once cilia assembly has initiated, may also promote cilia elongation by inhibiting disassembly (PubMed:29742020). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18815276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26564798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29742020}. |
Actin-binding;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Golgi apparatus;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable actin binding activity and microtubule binding activity. Involved in Golgi ribbon formation; cilium assembly; and stress fiber assembly. Located in cilium and microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:85462; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090161]; stress fiber assembly [GO:0043149] |
35524876_LncRNA LINC00665 Promotes Ovarian Cancer Cell Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis via Targeting miR-181a-5p/FHDC. |
ENSMUSG00000041842 |
Fhdc1 |
34.391904 |
2.6832858286 |
1.424001 |
0.279788539 |
26.460566 |
0.00000026897324638963211319544121744029574472278909524902701377868652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001012250157244000508237075780515468181874894071370363235473632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.0464063 |
8.4178980 |
19.1494223 |
2.5714614 |
| ENSG00000137462 |
7097 |
TLR2 |
protein_coding |
O60603 |
FUNCTION: Cooperates with LY96 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins and other microbial cell wall components. Cooperates with TLR1 or TLR6 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides (PubMed:21078852, PubMed:17889651). Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. May also activate immune cells and promote apoptosis in response to the lipid moiety of lipoproteins (PubMed:10426995, PubMed:10426996). Recognizes mycoplasmal macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2kD (MALP-2), soluble tuberculosis factor (STF), phenol-soluble modulin (PSM) and B.burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein (OspA-L) cooperatively with TLR6 (PubMed:11441107). Stimulation of monocytes in vitro with M.tuberculosis PstS1 induces p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 activation primarily via this receptor, but also partially via TLR4 (PubMed:16622205). MAPK activation in response to bacterial peptidoglycan also occurs via this receptor (PubMed:16622205). Acts as a receptor for M.tuberculosis lipoproteins LprA, LprG, LpqH and PstS1, some lipoproteins are dependent on other coreceptors (TLR1, CD14 and/or CD36); the lipoproteins act as agonists to modulate antigen presenting cell functions in response to the pathogen (PubMed:19362712). M.tuberculosis HSP70 (dnaK) but not HSP65 (groEL-2) acts via this protein to stimulate NF-kappa-B expression (PubMed:15809303). Recognizes M.tuberculosis major T-antigen EsxA (ESAT-6) which inhibits downstream MYD88-dependent signaling (shown in mouse) (By similarity). Forms activation clusters composed of several receptors depending on the ligand, these clusters trigger signaling from the cell surface and subsequently are targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway. Forms the cluster TLR2:TLR6:CD14:CD36 in response to diacylated lipopeptides and TLR2:TLR1:CD14 in response to triacylated lipopeptides (PubMed:16880211). Required for normal uptake of M.tuberculosis, a process that is inhibited by M.tuberculosis LppM (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QUN7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10426995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10426996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11441107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15809303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16622205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16880211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17889651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19362712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21078852}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;NAD;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. This protein is a cell-surface protein that can form heterodimers with other TLR family members to recognize conserved molecules derived from microorganisms known as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). Activation of TLRs by PAMPs leads to an up-regulation of signaling pathways to modulate the host's inflammatory response. This gene is also thought to promote apoptosis in response to bacterial lipoproteins. This gene has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:7097; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; Toll-like receptor 1-Toll-like receptor 2 protein complex [GO:0035354]; Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 protein complex [GO:0035355]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; lipopolysaccharide immune receptor activity [GO:0001875]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; peptidoglycan binding [GO:0042834]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; Toll-like receptor binding [GO:0035325]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; triacyl lipopeptide binding [GO:0042497]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell activation [GO:0001775]; cellular response to bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071221]; cellular response to diacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071726]; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid [GO:0071223]; cellular response to triacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071727]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; central nervous system myelin formation [GO:0032289]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; detection of diacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0042496]; detection of triacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0042495]; I-kappaB phosphorylation [GO:0007252]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; learning [GO:0007612]; leukotriene metabolic process [GO:0006691]; microglia development [GO:0014005]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; negative regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051964]; nitric oxide metabolic process [GO:0046209]; positive regulation of cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:1903974]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-18 production [GO:0032741]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of matrix metallopeptidase secretion [GO:1904466]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034123]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; response to fatty acid [GO:0070542]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway [GO:0034134]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224]; toll-like receptor TLR6:TLR2 signaling pathway [GO:0038124] |
11035751_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11477091_TLR2 stimulation resulted in the release of the IL-12 inhibitory p40 homodimer, producing conditions that are predicted to favor Th2 development, also resulted in preferential induction of IL-8 and p19/IL-23. 11724772_These results indicate that the direct interaction of SP-A with TLR2 alters PGN-induced cell signaling 11836257_identification of role in novel signal transduction pathway utilized by exracellular HSP70 11842086_stimulation of signal pathway by HSP70 11867630_Glucocorticoids synergistically enhance nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced Toll-like receptor 2 expression via a negative cross-talk with p38 MAP kinase. 11867688_TLR2 initiated the signaling pathway for p38 in response to bacterial products /LPS/ 11877429_signaling events by TLR2 and TLR4 agonists are similar but there are distinct differences in the responses elicited by two bacterial products 11932927_Non-LPS components of Chlamydia pneumoniae stimulate cytokine production through Toll-like receptor 2-dependent pathways. 12061629_mycoplasmal lipoproteins induce caspases-dependent necrotic and apoptotic cell death in lymphocytes and monocytes/macrophages, which is partially induced by TLR2-mediated signaling. 12089142_involvement in cell activation by mannuronic acid polymers 12163593_report that wild-type measles virus but not vaccine strains activate cells via the TLR2, and this is a property of the hemagglutinin (H) protein 12171914_TLR2 has a role in mediating signaling responses to Aspergillus fumigatus 12207338_Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae activate human peripheral blood monocytes utilizing TLR2, CD14 and CD11a/CD18 as cellular receptors. 12270725_Susceptibility of human dendritic cells (DCs) to measles virus (MV) depends on their activation stages in conjunction with the level of CDw150: role of Toll stimulators in DC maturation and MV amplification 12356755_glucocorticoids synergistically enhance NTHi-induced TLR2 expression via specific up-regulation of the MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) that, in turn, leads to dephosphorylation and inactivation of p38 MAPK 12397021_TLR4 was found to be involved in PM(2.5-10) and Pseudomonas-induced activation, whereas TLR2 activation was induced by both Gram+ and Gram- bacteria and by PM. 12437972_An extensively associated dimer is observed in the crystal structure of a mutant of the TIR domain of TLR2. 12438323_lipopolysaccharide may induce proliferation of periodontal epithelial cells by upregulating keratinocyte growth factor 1 expression via the CD14 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 12443841_On cell surface. LPS response inhibited with mAb specific for TLR2.LPS response of epidermal keratinocytes might be mediated by TLR2-dependent recognition of non-LPS bacterial components contaminating commercial LPS preparations. 12445799_innate immune response of monocytes against M. lepraeis is mediated by TLR2, the mutation in the intracellular domain of TLR2 gene is associated with IL-12 production in lepromatous leprosy 12525572_TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA were significantly up-regulated by IL-10 in monocyte cells that were adherent compared to those nonadherent. 12538701_The relative absence of TLR2 protein expression by intestinal epithelial cells may be important in preventing chronic proinflammatory cytokine secretion in response to commensal Gram-positive bacteria in the gut. 12540550_findings suggest that oral treponemes and their outer membrane extracts activate human gingival epithelial cells through TLR2 12588460_participates in the innate immune response to stimulation by bacterial products in periodontal tissues 12594207_innate immune recognition of LTA via LBP, CD14, and TLR-2 represents an important mechanism in the pathogenesis of systemic complications in the course of infectious diseases brought about by Gram-positive pathogens. while TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. 12630564_Review. Maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) and cytokine induction by the cell wall skeleton of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin are induced via both TLR2 and TLR4. 12646604_Expression of the Arg677Trp variant of human TLR2, which was identified in Korean patients with lepromous leprosy, was not able to mediate a response to either M. leprae or M. tuberculosis. 12651614_role in synovial fibroblast activation in rheumatoid arthritis 12663765_Human cytomegalovirus activates inflammatory cytokine responses via CD14 and Toll-like receptor 2 12734363_Costimulation with TLR2 (or TLR9) and TLR4 induces synergistic release of Th1 cytokines, IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, and additive HIV-LTR trans-activation and HIV replication, as measured by p24 antigen release from HIV-1 transgenic mouse spleen cells. 12734376_First comparative investigation in highly purified, monocyte-depleted neutrophil populations shows a distinct and separate role for TLR2, compared with TLR4, in neutrophil responses and neutrophil survival. 12810071_Data show that Toll-like receptors TLR2 and TLR4 were expressed on dendritic cells, whereas only TLR2 was weakly detected on Langerhans cells. 12816980_TLR2 is an endocytic receptor that channels ligands into the major histocompatibility complex class II presentation pathway for stimulation of specific CD4+ T cells. 12817025_Zymosan cosediments the soluble form of recombinant TLR2 possessing the putative extracellular domain (sTLR2); sTLR2 directly binds to zymosan with an apparent binding constant of 48 nM. 12860988_contains multiple binding domains for ligands that may contribute to the characterization of its promiscuous molecular pattern recognition 12874236_Human TLR2, but not TLR4, can mediate cellular activation by heat-killed Brucella abortus (HKBA); human embryonic kidney 293 cells, which do not respond to HKBA, are made responsive by transfecting TLR2, but not TLR4 or TLR9. 12942028_Results show that the surface receptors TLR2/4 and CD14 are essential for in vitro cellular activation induced by Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharide-containing outer membrane vesicles and purified lipopolysaccharides. 12946842_TLR-2 on human NK cells is upregulated and stimulated by Leishmania major lipophosphoglycan (LPG), a phosphoglycan belonging to a family of unique Leishmania glycoconjugates 12958190_Toll-like receptor 2 mediates beta-defensin 2 gene induction through NF-kappaB in lung epithelial cells. 12966099_In addition to TLR2, the activation of NF-kappaB by H.8/Lip in HEK cells was enhanced upon coexpression of TLR1 but not TLR6. 12975352_TLR1 and TLR2 are required for ara-lipoarabinomannan- and tripalmitoyl cysteinyl lipopeptide-stimulated cytokine secretion from mononuclear cells. Confocal microscopy revealed that TLR1 and TLR2 cotranslationally form heterodimeric complexes 14500665_Leu-107, Leu-112, and Leu-115 in a leucine-rich repeat motif of TLR2 are each critical for recognition of mycoplasmal diacylated lipoproteins and lipopeptides and are involved in the recognition of Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycans. 14551607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14607814_Data show that flagella signaling in airway cells can be initiated by interactions with asialoGM1 and toll-like receptor (TLR)2 as well as by activation of TLR5. 14651524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14662888_TLR2 is coexpressed with tracheobronchial epithelial cell markers; airway epithelial cells respond to bacterial lipopeptide in a TLR2-dependent manner with induction of mRNA and protein of the antimicrobial peptide beta defensin-2. 14673018_CD14 and TLR2 but not TLR4 play a major role in lipoteichoic acid -mediated effects on PMN and granulocytes 14694183_peptidoglycan signaling through TLR2 and bacterial CpG DNA signaling through TLR9 are functionally equivalent at synergizing with IFN-gamma in regulating Tap-1 expression in macrophages 14706103_downregulated by Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection in monocytes 14706104_stimulation by Mycoplasma fermentans lipoproteins mediates NF-kappa B activation as an early event and apoptosis as a later event in HEK293 cells 14707104_Direct activation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial fibroblasts via TLR-2 results in chemokine secretion and points to RA synovial fibroblasts at a very early stage of the disease as part of the innate immune system. 14709406_expression of CCL21, and TLRs 2 and 4 is predominantly induced in the peripheral lymphatic endothelium of the small intestinal microcirculation 14738464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14966134_Toll-like receptor 2 dimerized with Toll-like receptor 6 or 1 is activated by saturated fatty acid and inhibited by polyunsaturated fatty acid 14979495_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14979495_The present data suggest that the arginine to glutamine substitution at residue 753 polymorphism of the Toll-like receptor 2 gene influences the risk of developing tuberculosis. 14981245_TLR2 serves as a costimulatory receptor for antigen-specific T cell development and participates in the maintenance of T cell memory. 14987294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007351_genetic variation in TLR2 is a major determinant of the susceptibility to asthma and allergies in children of farmers 15007364_The toll-like receptor 2 R753Q polymorphism defines a subgroup of patients with atopic dermatitis having severe phenotype. 15041961_Expression of toll-like receptor 2 and immune response in innate immunity may be altered after surgical insults. 15044215_primary ATII cells express mRNA and protein for both TLR-2 and TLR-4, which can be modulated by incubation with lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor 15064239_Lipoteichoic acid-stimulated p42/p44 MAPK phosphorylation is mediated through a TLR2 receptor and involves tyrosine kinase, PLC, PKC, Ca(2+), MEK, and PI 3-kinase. 15138193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15138193_The frequency of a human TLR2 Arg677Trp polymorphism (C2029T nucleotide substitution) in tuberculosis patients in Tunisia is significantly higher than in healthy controls (P |
ENSMUSG00000027995 |
Tlr2 |
1094.804923 |
2.0148016982 |
1.010638 |
0.055687338 |
329.063499 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000015373024909904101695540625117383261860170925032556089733960986642430729040683100352048845630509369473064390688706595520504708893233636546408305295959492426869086404866258789701403356803277588937817199621349573135375976562500000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004787043199792922286269571660598730639049095774933786645333116116055743480240560745110203723849401410615349418846443175970338284652094653572316835557165909136674145115557106014599064724990284958039410412311553955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1466.0456679 |
54.5737007 |
732.8251063 |
20.6876632 |
| ENSG00000137473 |
83894 |
TTC29 |
protein_coding |
Q8NA56 |
FUNCTION: Axonemal protein which is implicated in axonemal and/or peri-axonemal structures assembly and regulates flagella assembly and beating and therefore sperm motility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31735292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31735294}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Flagellum;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Involved in cilium movement and cilium organization. Located in sperm flagellum. Implicated in spermatogenic failure 42. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83894; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; cilium organization [GO:0044782] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 28005267_TTC29 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 31735292_Mutations in TTC29 results in Asthenozoospermia and Male Infertility. |
ENSMUSG00000037101 |
Ttc29 |
16.242612 |
5.0262337435 |
2.329478 |
0.483771727 |
23.452544 |
0.00000128033298964198021419481215987801192568440455943346023559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004474950255059348214550524885924076556875661481171846389770507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.7232829 |
12.4732208 |
3.4377488 |
1.7449217 |
| ENSG00000137494 |
338699 |
ANKRD42 |
protein_coding |
Q8N9B4 |
|
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable NF-kappaB binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity and positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:338699; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092] |
17123353_the cloning and characterization of a new protein, termed SARP (several ankyrin repeat protein), which is shown to interact with all isoforms of PP1 by a variety of techniques. |
ENSMUSG00000041343 |
Ankrd42 |
70.005595 |
2.6697966123 |
1.416730 |
0.220936945 |
40.980048 |
0.00000000015379121818317923545068657229932833005459080766286206198856234550476074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000786268922890102433015323337990153812482319040100264828652143478393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
103.7957210 |
14.8353233 |
39.1377728 |
4.2799097 |
| ENSG00000137501 |
54843 |
SYTL2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCH5 |
FUNCTION: Isoform 1 acts as a RAB27A effector protein and plays a role in cytotoxic granule exocytosis in lymphocytes. It is required for cytotoxic granule docking at the immunologic synapse. Isoform 4 binds phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) and promotes the recruitment of glucagon-containing granules to the cell membrane in pancreatic alpha cells. Binding to PS is inhibited by Ca(2+) while binding to PIP2 is Ca(2+) insensitive. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18266782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18812475}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a synaptotagmin-like protein (SLP) that belongs to a C2 domain-containing protein family. The SLP homology domain (SHD) of this protein has been shown to specifically bind the GTP-bound form of Ras-related protein Rab-27A (RAB27A). This protein plays a role in RAB27A-dependent vesicle trafficking and controls melanosome distribution in the cell periphery. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:54843; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extrinsic component of plasma membrane [GO:0019897]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; neurexin family protein binding [GO:0042043]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
11773082_Synaptotagmin-like protein 2-a (Slp2-a) contains an N-terminal Slp homology domain (SHD) (PMID: 11327731). The SHD of Slp2-a specifically and directly binds the GTP-bound form of Rab27A. 17182843_Exophilin4/Slp2-a is specifically expressed in pancreatic alpha cells. 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 9 18266782_These results suggest that both Slp1 and Slp2-a may form part of a docking complex, capturing secretory lysosomes at the immunological synapse. 18812475_Rab27a recruits Slp2a-hem on vesicular structures in peripheral CTLs and following CTL-target cell conjugate formation, the Slp2a-hem/Rab27a complex colocalizes with perforin-containing granules at the immunologic synapse 18832576_Rab27A/Slp2a expression in limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2B muscle provides a compensatory vesicular trafficking pathway that is able to repair membrane damage in the absence of dysferlin. 20654157_A high expression level of SLP-2 may be associating with the development of invasion and metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and breast cancer. 20729199_Calmodulin suppresses synaptotagmin-2 transcription in cortical neurons 21223688_SLP2 may play an important role in tumorigenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 27220283_Overexpression of SYTL2 promoted metastatic potential. 33853352_Synaptotagmin-Like Protein 2a Regulates Angiogenic Lumen Formation via Weibel-Palade Body Apical Secretion of Angiopoietin-2. |
ENSMUSG00000030616 |
Sytl2 |
96.473390 |
0.0900959640 |
-3.472394 |
0.236834255 |
239.498507 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000505887492451702870500061450838879981836727756929437079174580886646063912758521338288280271000444128706832874950471440075571779623590535496235887080729298759251832962036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000116125962497467106315543515856257240262295438710222967867095257182549404784304058592923201160153145665654772798131405887640654666444380016532278432350722141563892364501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.5950857 |
2.1862131 |
151.9660399 |
13.3637438 |
| ENSG00000137558 |
51050 |
PI15 |
protein_coding |
O43692 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease inhibitor which displays weak inhibitory activity against trypsin (PubMed:8882727). May play a role in facial patterning during embryonic development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q98ST6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8882727}. |
Developmental protein;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a trypsin inhibitor. The protein shares similarity to insect venom allergens, mammalian testis-specific proteins and plant pathogenesis-related proteins. It is frequently expressed in human neuroblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines, and thus may play a role in the central nervous system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51050; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466] |
29900129_Human serine peptidase inhibitor PI15 as a potential host factor involved in the regulation of CPAF activation. Silencing expression as well as over expression of PI15 affected normal development of Chlamydia. 30638862_PI15 as a novel marker for predicting the diagnosis and follow-up of cholangiocarcinoma patients. |
ENSMUSG00000067780 |
Pi15 |
36.782297 |
0.2718431147 |
-1.879154 |
0.296989475 |
41.569207 |
0.00000000011377121992484293012049479834846233902712064889328757999464869499206542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000585925752299609719415708478286062763085162430343189043924212455749511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.3196593 |
2.9678583 |
56.6150772 |
6.6022064 |
| ENSG00000137673 |
4316 |
MMP7 |
protein_coding |
P09237 |
FUNCTION: Degrades casein, gelatins of types I, III, IV, and V, and fibronectin. Activates procollagenase. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2550050}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Extracellular matrix;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This secreted protease breaks down proteoglycans, fibronectin, elastin and casein and differs from most MMP family members in that it lacks a conserved C-terminal hemopexin domain. The enzyme is involved in wound healing, and studies in mice suggest that it regulates the activity of defensins in intestinal mucosa. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. This gene exhibits elevated expression levels in multiple human cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4316; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis [GO:0031293]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
11701474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11801551_MMP-7 activity is upregulated in colorectal cancer liver metastases 11925859_plays an important role not only in tumor metastasis but in micrometastasis to lymph node 11927011_Overexpression of MMP-7 is associated with invasiveness in gastric carcinoma 11983918_Gene expression analysis reveals matrilysin as a key regulator of pulmonary fibrosis in mice and humans. 12005165_Immunoelectron microscopy revealed that matrix metalloproteinase-7 was expressed within basal laminar deposits and amorphous materials around the retinal pigment epithelial cells in age-related macular degeneration. 12034345_destruction of the surrounding matrix by endometriosis might be caused by various MMPs, which are mainly produced in stromal cells. 12112311_study of expression in ulcerative colitis related tumorigenesis 12464266_Cleavage of FasL by MMP-7 occurs at the leucine residues in sequence 'ELAELR' within the region between the transmembrane and trimerization domains. When this site is unavailable, a 'SL,' is cleaved. MMP-7 differentially processes murine and human FasL 12579270_increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 is associated with high grade transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder may be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis 12684625_Increased expression of MMP-7 in high grade renal cell carcinoma might be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis 12759241_In alveolar-like epithelial cells, transfection of activated matrilysin resulted in shedding of E-cadherin and accelerated cell migration. In vivo, matrilysin co-localized with E-cadherin at the basolateral surfaces of migrating tracheal epithelium. 12759346_findings suggest that local pericellular production of hypochlorous acid by phagocytes is a physiological mechanism for governing matrix metalloproteinase-7 activity during inflammation 12808021_MMP-7 is induced in human gastric epithelial cells infected with Helicobacter pylori; it has a role in epithelial cell migration 12958188_src oncogene signaling involves synergistic cooperation between the AP-1 and LEF-1 transcription factors in activation of the matrilysin promoter in colon cancer cells. 12963695_Data show that matrilysin confers macrophages with their most potent matrix metalloproteinase-dependent elastolytic system. 14516315_Down-regulated PTEN expression and up-regulated MMP-7 expression were greatly implicated in tumorigenesis and progression of gastric carcinoma. 14744783_May contribute to the tumorigenesis of MMP-7-producing IGF-IR-expressing tumors in the primary site and to organ-specific metastasis in a paracrine manner 15040016_Heparanase, CD44v6 and nm23 may play important roles in the invasive infiltration and lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinomas. 15102692_matrix metalloproteinase-7 has a role in progression of pancreatic cancer 15149334_matrilysin may have a role in renal tubular injury and progression of tubulointerstitial fibrosis, and Wnt4 may regulate matrilysin expression in the kidney 15239678_the importance of MMP7 as a predictor of secondary Extramammary Paget's disease or the putative origin of Paget's cells from the dermal adenocarcinoma cells of apocrine duct origin 15375490_Overexpression of MMP-7 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 15523695_These results indicate MMP-7 is overexpressed in malignant ovarian epithelium and suggest MMP-7 may facilitate tumor cell invasion in vivo partly through the induction of progelatinase activation. 15618645_alcohols are considered to bind the hydrophobic S1' subsite most plausibly, and the size of the pocket was estimated to be large enough to accommodate the length of 1-butanol (4-carbon chain) and the bulk of tertiary alcohols 15652345_pattern of secretion in polarized MDCK cells expressing stably transfected human MMP-7 15696117_Results imply that MMP-7 is a major MMP associated with the tissue remodeling during the progression of liver fibrosis in biliary atresia. 15725655_We assessed mRNA expression of MMPs in six human colorectal cancer cell lines and found a considerable level of MMP-7 expression in HT-29 cells. 15800927_results suggest E1A-F is overexpressed in early stages of human CRC development and may be an important factor in the overexpression of COX-2 and MMP-7 15809719_Activation of MMP-7 protein closely involved in disruption of tight junction structure and consequent induction of cell dissociation as well as invasion in pancreatic cancer 15860507_Some green tea catechins induce pro-MMP-7 production via O2- production and the activation of JNK1/2. 15866216_expression up-regulated in Helicobacter species-infected colon and bile duct epithelial cells and hepatocytes. 15930031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15930031_Polymorphism might be a candidate marker for predicting individuals who are at higher risk to certain tumors but might not be used to predict potential of lymphatic metastasis in various cancers. 15979995_sFasL and matrilysin are expressed in seminal plasma and have a role in regulation of the function of the Fas system 16097959_MMP7 immunoreactivity was present in only polymyositis not dermatomyositis 16115946_Study suggests that targeting matrilysin may have important therapeutic implications. 16142384_Increased expression of MMP-7 in high grade uterine endometrial carcinoma (UEC) may be associated with tumor invasion and metastasis, and MMP-7 could serve as a prognostic maker in UEC. 16248458_In chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps tissues the expression of TGF-beta1, MMP-7, MMP-9, TIMP-1 protein was significant increased compared to controls. 16278009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16286510_shed syndecan-1 or MMP7-syndecan-1 complexes may have roles in tumor progression 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16405530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16455621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16455621_The 181A/G polymorphism in MMP7 has a potential to be a susceptibility factor for endometriosis and adenomyosis. 16474169_Fas downregulation and a consequential increased resistance to FasL-triggered apoptosis resulting from upregulated MMP-7 in colorectal cancer cells could be a key mechanism for their escape from the immune surveillance 16474379_Data suggest that tissue expression of MMP-7 could be a useful marker to predict the progression and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 16476739_it is likely that binding of matrilysin to cholesterol sulfate facilitates the matrilysin-catalyzed modulation of cell surface proteins, thus inducing the cancer cell aggregation 16494848_FGF-2-induced MMP7 expression in endothelium depends on AP-1 and FGF-2 signaling to AP-1 involves a Stat1/3-dependent pathway. 16804904_intense MMP-7 signal in tumor cells is an independent prognostic factor predicting better survival in epithelial ovarian cancer 16940985_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16956593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16956593_The present result, for the first time, suggested that the MMP-7-181A/G polymorphism might be associated with the susceptibility to adult astrocytoma. 17009118_Matrix metalloproteinase-7 overexpression is thought to be an early event in the colonic adenoma-carcinoma pathway. 17009258_These data demonstrate that CD151 is overexpressed in osteoarthritic cartilage and suggest that CD151 plays a role in the pericellular activation of proMMP-7, leading to cartilage destruction and/or chondrocyte cloning. 17029196_Data show that MMP7 may be relevant with carcinogenesis, development and metastasis of adenoid cystic carcinoma, and different metastasis potential may result from different subtype of MMPs gene family. 17038551_Estrogen modulates tight junctional resistance through estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated remodeling of occludin 17114341_MMP-7 secretion/activation may represent a new mechanism that facilitates ovarian cancer invasion. 17125518_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17129995_A significant increase in the proportion of MMP 7 immunopositive cells was seen in the nucleus pulposus of discs classified as showing intermediate levels of degeneration and a further increase was seen in discs with severe degeneration. 17145820_MMP-7 influences tumor progression by regulating invasion and angiogenesis. Multivariate analysis showed that MMP-7 status of cancer tissues was strong predictor of poor prognosis. MMP-7 targeting treatment may be a potential target against human RCC. 17145868_Data show that MMP7 and LN5 are coexpressed in colonic carcinoma cells HT29 cells. 17153464_Our results suggested the importance of MMP-7 and MT1-MMP in the peritoneal metastases of gastric cancer. 17209789_MMP-7 is associated with the innate host defense in periodontal tissues. 17219436_MMP-7 has a role in invasiveness of glioma 17310281_MMP-7-selective targeting to the plasma membrane of epithelial cells promotes its activity by conferring resistance to TIMP-2. 17373931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17396032_incubation with HGF mediated the release of MMP-7, resulting in extracellular cleavage of E-cadherin from stomach cancer cells 17487834_MMP-7 is an independent prognostic factor for survival in advanced colorectal cancer. In our sample, the risk of death associated to MMP-7 increase is much higher than the risk of death associated to lactate dehydrogenase elevation 17502620_reveal the MMP7-activated photodynamic therapy efficacy of this photodynamic molecular beacons 17507989_The expression of MMP7 was specifically enhanced at the bronchiolo-alveolar duct junction and suggests that MMP7 plays a key role during the bronchioalveolar remodeling. 17554258_Diminished expression of MMP-7 may play a role in fibronectin accumulation in the diabetic kidney in response to advanced glycation end products and/or TGF-beta. 17564313_Expression of MMP7 was evaluated in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-tumor tissue. 17607721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17671679_VEGF, MMP2, 7 and 9, and COX-2 expression is related to progression of advanced uterine cervical cancer in young women 17672933_MMP-7 -181A/G polymorphism may influence the susceptibility to astrocytoma. 17672933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17695544_MMP-7 gene expression is associated with increased risk only for early stages of oral cancer. 17718429_MMP-7 expression in human rectal cancer increases significantly and plays a key role in the invasion and metastasis of human rectal cancer. 17728005_Wnt1 may play a critical role in regulating the intratumoral MMP-7 expression 18006768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18023162_MMP-7 is involved in tumor angiogenesis, thereby contributing to malignant growth and hence associated with decreased survival 18036564_evidence that matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) interacts with anionic, cationic and neutral lipid membranes, although it interacts strongest with anionic membranes. 18179407_the significantly increased expression of MMP7 in primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL), suggest the involvement of this MMP in the characteristic infiltration pattern of PCNSL. 18202161_Circulating Pro-MMP-7 is associated with IgG specific to pro-MMP-7 in patients with renal cell carcinomas 18214300_Immunoassays showed significantly elevated content of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in tumors compared to adjacent histologically unchanged mucosa of patients with colorectal cancer. 18308831_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18329694_Expression of MMP-7 in cholangiocarcinoma is an unfavorable postoperative prognostic factor of cholangiocarcinoma arising from the large bile ducts. Underexpression of MMPs in papillary cholangiocarcinoma might be associated with a favorable prognosis. 18340552_matrilysin may be multiple, multifarious, and multifaceted functions contributing to early tumor growth 18364512_reduced extracellular proteolytic activity of certain matrix metalloproteinases-for example, MMP-7-is associated with accelerated aging and senescence in normal HMECs. 18385523_TIMP-1 interacts with matrix metalloproteinases and regulates matrilysin activity during airway epithelial repair. 18411043_HER2-dependent transcriptional upregulation and protein secretion of MMP-7 are mediated by activated STAT3. 18422740_Increased plasma MMP-7 is associated with metastatic disease in patients with renal cell carcinomas 18447576_MMP7 and MMP1, are overexpressed in the lung microenvironment and distinguish idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis from other chronic lung diseases. Additionally, increased MMP7 concentration may be indicative of asymptomatic ILD and reflect disease progression. 18448157_Individuals with MMP-7 -181GG genotype are at significantly higher risk of cervical cancer. 18448157_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18485588_HLE may be a natural inactivator of MMP-7 which can counteract MMP-7-induced apoptosis resistance. 18500535_MMP7 may contribute to the process by which intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas advances from adenoma to carcinoma and to subsequent invasion of tumor cells in IPMN. 18511876_E1AF mRNA overexpression correlated well with matrilysin expression in rectal cancers. 18548257_MMP7 may act as a downstream mediator of FVIIa/TF signal transduction to facilitate the development of metastasis in colon cancer. 18600430_HRG-beta-induced MMP-7 expression was regulated by HER2-mediated AP-1 activation in MCF-7 cells. 18636198_Higher matrix metallopeptidase 7 is associated with colorectal cancer. 18644839_MMP-7 cleaves the NR1 subunit of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor to generate an N-terminal fragment of approximately 65 kDa 18648013_Results from our study suggest that common MMP-7 genetic polymorphisms may contribute to breast cancer susceptibility 18653469_p120 and Kaiso regulate Helicobacter pylori-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 18674869_beta-catenin expression was significantly related to E-cadherin and MMP-7 expression 18695873_activin A may modulate the expression of MMP-7 via AP-1 18713744_MMP7 and MMP9-mediated cleavage of EphB2 is induced by receptor-ligand interactions at the cell surface and that this event triggers cell-repulsive responses 18715618_The matrix metalloproteinase-7 gene may be up-regulated by mutated or continuously elevated beta-catenin protein in sporadic desmoid tumors. 18721140_It is supposed that the cleavage of cell surface annexin II by matrilysin contributes to tumor invasion and metastasis by enhancing tPA-mediated pericellular proteolysis by cancer cells. 18768525_Functional polymorphisms in the promoter of MMP-7 do not significantly confer susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma in a southern Chinese population. 18768525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18798254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18798254_common MMP-7 genetic polymorphisms may have roles in survival among Chinese women with breast cancer 18805052_Gene expression revealed up-regulation of pro-angiogenic (PGF), anti-apoptotics (BAG-1, BCL-2), heart development (TNNT2, TNNC1) and extracellular matrix remodelling (MMP-2, MMP-7) genes in SM. 18823373_the expression level of MMP-7 in tumor cells is predictive of response to chemotherapy and outcome in patients with advanced NSCLC receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. 18931651_metalloproteinase-7 expression was associated with more aggressive buccal squamous cell carcinomas 18955490_Identification of amino acid residues of matrix metalloproteinase-7 essential for binding to cholesterol sulfate. 18958543_In Japan, carriage of the MMP-7-181 G allele and of the CMA/B A allele were each associated with an increased risk for H. pylori-related noncardia gastric cancer development. 18958543_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18974372_VEGF escapes the sequestration by endothelial sVEGFR-1 and promotes angiogenesis in the presence of MMP-7. 19000448_High concentration of tamoxifen can inhibit the proliferation of ERbeta-positive HT-29 cells, and effectively bind with ERbeta to down-regulate MMP-7 expression. 19016757_MMP7 gene expression was significantly higher in colorectal cancer patients than in healthy volunteers. 19020757_Serous and mucinous ovarian tumors express different profiles of MMP-7. 19022775_RECK is cleaved by MMP-2 and MMP-7 and competitively inhibits MMP-7-catalyzed cleavage of fibronectin 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19121849_metastasis and survival of patients with bladder cancer are mediated, at least in part, by matrix metalloproteinase-7 19132754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19173304_cleavage of CLEC3A by MMP-7 weakens the stable adhesion of 19181662_Differential Processing of {alpha}- and {beta}-Defensin Precursors by Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7). 19221016_These findings indicate that MMP7-catalyzed release of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor mediates acetylcholine induced transactivation of epithelial growth factor receptors and consequent proliferation of colon cancer cells 19231585_Hyaluronan synthase (HAS2 and HAS3) and hyaluronan may mediate cellular invasion via changes in MMP-7 expression in SW620 colon carcinoma cells. 19266094_MMP7 is related to the acquisition of oxaliplatin-resistance and its inhibition restores drug sensitivity by increasing Fas receptor. 19303106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19317620_Helicobacter pylori CagA-positive patients carrying MMP-7 -181 G allele had a higher risk for lymphoid follicle formation. 19317620_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19329997_MMP7 coordinates allergic lung inflammation by activating interleukin 25 while simultaneously inhibiting retinoid-dependent development of regulatory T cells. 19360357_Three-dimensional culture using a radial flow bioreactor induces matrix metalloprotease 7-mediated EMT-like process in tumor cells via TGFbeta1/Smad pathway. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19421758_Elevated expressions of MMP7, TROP2, and survivin are associated with survival, disease recurrence, and liver metastasis of colon cancer. 19435861_none of 30 haplotype tagging polymorphisms in MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-7 were found to be significantly associated with endometrial cancer risk. 19465902_Hepatocellular adenoma was characterized by the complete absence of matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression 19505922_The fecal RNA test using COX-2 and MMP-7 mRNAs improved the sensitivity to detect colorectal cancer without decreasing the specificity 19586554_SFRP5 is downregulated and inversely correlated with MMP-7 and MT1-MMP in gastric cancer 19596921_Significantly higher expression of MMP-7 and MMP-9 in tumor tissue than in the surrounding tissue or in benign lung disease tissue supports the notion of an important role of these metalloproteinases in the growth of lung carcinoma 19608871_matrilysin-1 may play an important role in the bronchiolization of alveoli by promoting proliferation, migration, and attenuation of apoptosis involving multiple genes in the MAP kinase pathway. 19634113_E-cadherin and metalloproteinase-1 and -7 polymorphisms have roles in colorectal cancer 19634113_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19643940_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19643940_SNPs in MMP1, MMP2, MMP7 and MMP12 have roles in response to chemotherapy in lung cancer 19654318_These observations demonstrate that sulfated GAGs regulate matrilysin activation from promatrilysin and its activity against specific substrates. 19676133_A novel nonsynonymous variant of matrix metalloproteinase-7 confers risk of liver cirrhosis. 19676133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19679556_The selective inhibition of MMP-7 in the tumor-bone microenvironment may be of benefit for the treatment of lytic breast-to-bone metastases. 19682489_Cellular senescence of human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) is associated with an altered MMP-7/HB-EGF signaling and increased formation of elastin-like structures. 19690403_increased expression in interstitial pneumonia 19690958_Concomitant elevations of MMP-3 and MMP-7 serum levels in the H. pylori-infected gastric cancer patients could serve as potential biomarkers to correlate with poor survival. 19701966_Results suggest that laminin (LN)gamma2 and LNbeta3, in conjunction with MMP7, play a key role in the progression of biliary tract cancer. 19724852_positive expression of both CD44v6 and MMP-7, and negative expression of nuclear Cdx2 may serve as powerful predictors of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer 19728912_MMP-7 and survivin are related to the generation of colon cancer, and are independent factors for prognosis of colon cancer. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19785773_endocrine therapy is an efficient therapy for inhibiting ERbeta-positive colon cancer cell proliferation and migration via down-regulation of MMP7. 19787626_Immunoexpression of metalloproteinase-7 does not correlate with recurrence, mortality, relapse-free survival, survival, degree of cell differentiation, or staging of colorectal cancer. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19929564_MMP-7 is associated with the prognosis of patients with acinic cell and mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 20007614_MMP-7 protein expression in epithelial cells was significantly higher in red peritoneal lesions compared with that of deep infiltrating endometriosis, ovarian endometriosis and black peritoneal lesions, in all phases of the menstrual cycle. 20040080_although the level of MMP7 secretion was the highest in the secretory phase the difference from the proliferative phase did not reach statistical significance 20096949_we have identified novel relationships between serum MMP-7 and diabetic complications specifically in renal disease and in diastolic dysfunction. 20113256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20113256_The MMP-7 -181 A/G genotype is a potential factor for susceptibility to endometrial cancer. 20132413_Data show that genes overexpressed in ovarian/peritoneal carcinoma including MMP7. 20139113_MMP-7 is involved in the cleavage of N-cadherin and modulates vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis, and may contribute to atherosclerotic plaque development and rupture. 20146992_Increased circulating MMP-7 might indicate enhanced adipocyte differentiation in subjects who had undergone bariatric surgery. 20156184_MMP-7 was used for the screening secretory metalloproteinase inhibitors in conditioned media of human cancer cell cultures. Human epidermoid carcinoma conditioned media demonstrated the most intense band in reverse-zymography and in Western blotting. 20180812_MMP-7 is a promising marker to detect present and to predict future metastasis in bladder cancer 20192597_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20219015_MMP-10 and -7 abundance increased, accompanied by decreased TIMP-4 in dilated cardiomyopathy failing hearts compared with non-failing hearts. 20230842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20300917_MMP-7 overexpression is associated with lymph node and distant metastases as well as with prognosis of gastric cancer 20347338_Genetic polymorphisms of MMP7 predispose to development of bronchiolitis obliterans (BOS). Patients carrying these risk alleles express lower levels of MMP-7, which may contribute to aberrant tissue repair and culminate in development of BOS. 20347338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20359117_The positive rates of Ang-2 and MMP-7 were significantly higher in laryngeal carcinoma tissue than those in adjacent non-cancerous tissue. Patients with positive expression of Ang-2 had worse overall survival. 20360147_MMP7 -181 AG and GG genotype carriers had an increased gastric cancer risk 20360147_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20372795_MMP-7 and SGCE are distinctive molecular factors in sporadic colorectal cancers from the mutator phenotype pathway 20375326_Increased expression of MMP7 was the only consistent differentially regulated gene in the conjunctival samples of trichiasis subjects. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20473942_Elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels are associated with metastatic prostate cancer. 20484597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20491537_role of these proteins in the process of invasion and metastasis cannot be ruled out since their presence is more marked along the tumor invasion front compared to more central areas of squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue 20584750_Enhanced expression of MMP-7 is associated with progression from non-dysplastic Barrett's oesophagus to adenocarcinoma. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605361_The A/G genotype had a significant association with recurrence-free survival in postprostatectomy patients & the frequency of the risk-reducing genotype A/A was 74% whereas that of the risk-enhancing genotypes A/G & G/G were 20% & 6% 20605794_Cholesterol sulfate alters substrate preference of matrix metalloproteinase-7 and promotes degradations of pericellular laminin-332 and fibronectin. 20624652_chronic disordered epithelial expression of MMP-7 in patients with asthma might increase mFasL cleavage and contribute to airway epithelial damage and inflammation. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20662554_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20662554_investigation of the association of single-nucleotide polymorphism at MMP-1 16071G/2G, MMP-7 181A/G, and MMP-9 279R/Q genes with colorectal cancer in the southwest Chinese Han population 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20680712_High MMP7 expression was confirmed to be an independent prognostic factor of colon cancer 20707923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20730428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736794_Tissue present at the site of hypertrophic nonunions commonly expresses significantly higher levels of MMP-7 and MMP-12 in relation to mineralized fracture callus. 20813660_PKD3 may contribute to the malignant progression of prostate cancer cells through negative regulation of MMP-7 expression. 20826916_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20826916_study provided new support for the association of MMP1-1607 and MMP7-181 in bladder cancer development, the tumorigenic effect of which was observed to be more enhanced in case of tobacco exposure 20827277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20853162_NGAL may be considered a novel stress protein, whereas MMP-7, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 may be regarded as indicators of stress response in the pediatric population on chronic dialysis 20872971_Serum values of MMP7 and CA19-9 appear to be useful biomarkers for differentiating cholangiocarcinoma from benign biliary tract obstructive diseases. 20939893_Up-regulation of MMP-7 expression through beta2-AR-mediated signaling pathway is involved in invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. 20979817_In the serum of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, the level of MMP-1 was lower but the level of MMP-7 higher than in patients with sarcoidosis. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21116502_The concentration of MMP-7 was maximum in the blood of patients with tumor invasion in lymph vessels. These data suggest MMP-7 as a possible serological marker of gastric cancer. 21165404_We revealed a positive correlation between serum levels of MMP-7 in patients with primary ovarian cancer and the size of the primary tumor 21255765_direct association observed between morphological scores of malignancy and MMP immunoreactivity, with the association being significant for MMP-7. present results demonstrate important role of MMPs in development of SCCs of lower lip and tongue. 21302026_There is marked relationship between matrix metalloproteinase 7 and brain atrophy in HIV infection. 21315773_These results suggest that the induction of MMP-7 by Tax is regulated by JunD and that MMP-7 could facilitate visceral invasion in adult T-cell leukemia . 21336735_There was significant difference in IL-8 -251TT and MMP-7 -181GG genotypes between the cervical cancer group and the lymph node metastasis group. Individuals with IL-8 T or MMP-7 G carriers were at significantly higher risk of cervical cancer. 21455340_MMP-7 may have a role in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 21481787_demonstrate that serum MMP7 level in human patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma correlated with metastatic disease and survival 21516345_The aim of this study was to evaluate serum concentrations of sFas, sFasL, and their potential regulators (MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, TIMP-1, TIMP-2), in children and young adults chronically dialyzed. 21517234_Homozygous variant GG genotype of MMP-7 (-181A>G) polymorphism was associated with a more than two fold increased risk of gastric cancer. 21593056_These results suggest thatactive-site tyrosyl residue, Tyr219 of the matrix metalloproteinase 7 is not critical for catalytic activity, but is involved in the broad pH-dependence of the activity. 21707759_The median MMP-7 serum level of systemic sclerosis patients with lung fibrosis (LF) was significantly higher compared with those without LF. 21722074_MMP7 -181A/G polymorphism is associated with the development of vulnerable carotid plaques 21764478_High levels of MMP-7 in tumor cells and high levels of MMP-9 in tumor associated stroma were independent positive prognostic factors in NSCLC patients. 21787888_Thermodynamic analysis of ionizable groups involved in the catalytic mechanism of human matrix metalloproteinase 7. 21814482_The increased MMP-7 expression due to H2O2 treatment of SW620 cells was mediated by activation of MAP kinases in an AP-1-dependent manner. Dimerumic acid inhibits AP-1-mediated MMP-7 gene transcription. 21858178_Data show that decidualization was associated with increased expression of 428 genes including SCARA5 (181-fold), DKK1 (71-fold) and PROK1 (32-fold), and decreased expression of 230 genes including MMP-7 (35-fold) and SFRP4 (21-fold). 21901248_fibulin-3 negatively modulates the invasiveness of lung cancer cells via regulation of MMP-7 and MMP-2 and its expression is regulated by hypermethylation of the promoter region 21912055_MMP-7 (-181A>G) GG carriers are at a higher risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Kashmir valley. 21935919_plasma HYP, collagen I and MMP-7 may be useful as novel predictive markers of opisthorchiasis-related BBD, and HYP may be used as a diagnostic marker for CCA 21981819_Antisense oligonucleotide targeting matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) changes the ultrastructure of human A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells, inhibiting proliferation and invasion. 21999204_correlation between MSLN and MMP-7 in the progression of ovarian cancer, and the mechanism of MSLN in enhancing ovarian cancer invasion 22024063_Overexpression of MMP-7 generally indicated a higher metastatic potential and inferior overall survival of adenocarcinoma of colon and rectum. 2204255 |
ENSMUSG00000018623 |
Mmp7 |
13.818144 |
5.6467648225 |
2.497425 |
0.491072174 |
28.756855 |
0.00000008205894466376712776952366936236704653140350274043157696723937988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000326466313541025040461074054401469091146736900554969906806945800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.3428779 |
7.2718449 |
4.3571864 |
1.1495590 |
| ENSG00000137693 |
10413 |
YAP1 |
protein_coding |
P46937 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator which can act both as a coactivator and a corepressor and is the critical downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway that plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis (PubMed:17974916, PubMed:18280240, PubMed:18579750, PubMed:21364637, PubMed:30447097). The core of this pathway is composed of a kinase cascade wherein STK3/MST2 and STK4/MST1, in complex with its regulatory protein SAV1, phosphorylates and activates LATS1/2 in complex with its regulatory protein MOB1, which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates YAP1 oncoprotein and WWTR1/TAZ (PubMed:18158288). Plays a key role in tissue tension and 3D tissue shape by regulating cortical actomyosin network formation. Acts via ARHGAP18, a Rho GTPase activating protein that suppresses F-actin polymerization (PubMed:25778702). Plays a key role in controlling cell proliferation in response to cell contact. Phosphorylation of YAP1 by LATS1/2 inhibits its translocation into the nucleus to regulate cellular genes important for cell proliferation, cell death, and cell migration (PubMed:18158288). The presence of TEAD transcription factors are required for it to stimulate gene expression, cell growth, anchorage-independent growth, and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) induction (PubMed:18579750). Suppresses ciliogenesis via acting as a transcriptional corepressor of the TEAD4 target genes AURKA and PLK1 (PubMed:25849865). In conjunction with WWTR1, involved in the regulation of TGFB1-dependent SMAD2 and SMAD3 nuclear accumulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P46938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17974916, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18158288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18280240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18579750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21364637, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25778702, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25849865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30447097}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Activates the C-terminal fragment (CTF) of ERBB4 (isoform 3). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12807903}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Activates the C-terminal fragment (CTF) of ERBB4 (isoform 3). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12807903}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a downstream nuclear effector of the Hippo signaling pathway which is involved in development, growth, repair, and homeostasis. This gene is known to play a role in the development and progression of multiple cancers as a transcriptional regulator of this signaling pathway and may function as a potential target for cancer treatment. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:10413; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; female germ cell nucleus [GO:0001674]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; TEAD-YAP complex [GO:0140552]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; bud elongation involved in lung branching [GO:0060449]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cardiac muscle tissue regeneration [GO:0061026]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to gamma radiation [GO:0071480]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; contact inhibition [GO:0060242]; embryonic heart tube morphogenesis [GO:0003143]; enterocyte differentiation [GO:1903703]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; glandular epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0002067]; heart process [GO:0003015]; hippo signaling [GO:0035329]; interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070102]; intestinal epithelial cell development [GO:0060576]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; lateral mesoderm development [GO:0048368]; lung epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060487]; negative regulation of cilium assembly [GO:1902018]; negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process [GO:1904036]; negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030857]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000737]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; notochord development [GO:0030903]; organ growth [GO:0035265]; paraxial mesoderm development [GO:0048339]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033148]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; progesterone receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050847]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010837]; regulation of metanephric nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0072307]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:0072091]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894]; trophectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0001829]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11743730_NMR structures of the YAP65 WW domain and the variant L30 K in complex with the peptides GTPPPPYTVG, N-(n-octyl)-GPPPY and PLPPY and the application of peptide libraries reveal a minimal binding epitope 12807903_YAP is a potential signaling partner of the full-length ErbB4 receptor at the membrane and of the COOH-terminal fragment of ErbB-4 that translocates to the nucleus to regulate transcription 15096513_Yap binds to HNRNPU and regulates its co-activation of Bax transcription 15800888_the minimum binding domain is larger than the latter two strands of the WW domain beta-sheet 16061658_WWOX antagonizes the function of YAP by competing for interaction with ErbB-4 and other targets and thus affect its transcriptional activity. 16596258_Results suggested that YAP65 plays a role in the normal and diseased pancreas. 16772533_WBP-2 and YAP are coactivators for estrogen and progesterone receptor transactivation pathways. 16894141_Results point to a potential oncogenic role for YAP in 11q22-amplified human cancers, and suggest that this signaling pathway regulates both cellular proliferation and apoptosis in mammalian epithelial cells. 17110958_The Yes-associated protein 1 stabilizes p73 by preventing Itch-mediated ubiquitination of p73. 17438369_the RUNX2 and YAP65 interaction has a novel role in oncogenic transformation that may be mediated by modulation of p21(CIP1) protein expression 17502622_Proline-rich Gla protein 2 may be involved in a signal transduction pathway, the impairment of which may be an unintended consequence of warfarin therapy 17823615_YAP identified as a novel and critical downstream effector of c-Jun-mediated apoptosis following cisplatin treatment 17889654_Delineate a mammalian Hippo signaling pathway that culminates in the phosphorylation of YAP, the mammalian homolog of Yki. Is a potent regulator of organ size, and its dysregulation leads to tumorigenesis. 17980593_findings report that YAP1 increases organ size and causes aberrant tissue expansion 18158288_LATS1 inactivates YAP oncogenic function by suppressing its transcription regulation of cellular genes via sequestration of YAP in the cytoplasm after phosphorylation of YAP. 18175224_Increased YAP protein is associated with esophageal and gastric epithelial tumorigenesis. 18280240_c-Abl directly phosphorylates Yap1 at position Y357 in response to DNA damage. Tyrosine-phosphorylated Yap1 is a more stable protein that displays higher affinity to p73 and selectively coactivates p73 proapoptotic target genes. 18413746_Expression profiling of genes induced by ectopic expression of YAP or by knockdown of LATS1 reveals a subset of the potential Drosophila Hippo pathway targets implicated in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 18617895_This is the first report indicating YAP as a tumor suppressor, revealing its decreased expression in breast cancer as well as demonstrating the functional implications of YAP loss in several aspects of cancer signaling. 18640976_Overexpression of YAP2 in cells promoted apoptosis, whereas the Mst2/Lats1-induced phosphorylation of YAP partially rescued the cells from apoptotic death. 18701449_The modified Yap1 does not co-activate Runx in supporting Itch transcription. The subsequent reduction in the Itch level gives rise to p73 accumulation. 18703216_findings suggest that activation of the Hippo signaling pathway may occur through YAP as part of cell proliferation in normal tissue homeostasis and also might be a frequently activated oncogenic pathway in 3 common malignant tumor types. 18725387_this is the first report of negative regulatory signaling from Merlin to YAP1 in mammalian cells and may shed light on mechanisms of malignant pleural mesothelioma development 18953429_results represent the first demonstration that merlin regulates cell growth in meningioma cells by suppressing YAP 19015275_YAP and TEAD gain of function causes marked expansion of the neural progenitor population, partly owing to their ability to promote cell cycle progression by inducing cyclin D1 and to inhibit differentiation by suppressing NeuroM. 19111660_The existence of a proapoptotic autoregulatory feedback loop between p73, YAP, and the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) tumor suppressor gene, is shown. 19371381_The PDZ-binding motif is necessary for YAP2 localization in the nucleus, for the stabilization of p73, and for promoting apoptosis of HEK293 cells maintained at low concentration of serum. 19705503_Yes-associated protein and survivin have roles in gastric carcinoma and precancerous lesions 19935651_show that YAP-expressing MCF10A breast epithelial cells enhance the proliferation of neighbouring untransfected cells, implicating a non-cell-autonomous mechanism. 19952108_findings implicate YAP1 as a new Shh effector that may be targeted by medulloblastoma therapies aimed at eliminating medulloblastoma recurrence. 20016275_Results strongly suggest that Yap1 plays a role in the regulation of endogenous DeltaNp63alpha levels and is likely to contribute to the regulation of DeltaNp63alpha, in physiological conditions. 20048001_identified CK1delta/epsilon as new regulators of YAP and uncovered an intricate mechanism of YAP regulation 20153295_This data suggests that the phosphorylation of Yap at Ser127 leads to a changed expression of myogenic regulatory factors and cell cycle regulators and is required for C2C12 myoblasts to differentiate into myotubes. 20219076_YAP plays an important role in NSCLC and might be a useful therapeutic target of NSCLC. 20226166_miR-375 is an important regulator of YAP oncogene playing the role in hepatocellular carcinoma development. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20677011_that YAP1 overexpression in primary human keratinocytes blocks clonal evolution and induces cell immortalization, but not malignant transformation. 20729916_YAP function as a tumor suppressor may alternatively be dysregulated by AKT phosphorylation at serine-127 and cytoplasmic sequestration, or by transcriptional repression by DeltaNp63, in different subsets of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs). 20823509_14-3-3sigma has been cloned, purified and crystallized in complex with a phosphopeptide from the YAP 14-3-3-binding domain, which led to a crystal that diffracted to 1.15 A resolution. 20842732_data suggest that the amplification and overexpression of YAP1 and VGLL3 could be involved in oncogenesis and progression of soft tissue sarcomas 20868367_translocation of YAP2 to nucleus requires complexation with ZO-2; PDZ domains on both proteins are involved in complex formation; YAP2/ZO-2 complex appears to be involved in cell detachment 20947521_Overexpression of Yap2 and phosphorylation-defective Yap2-5SA is associated with ovarian cancer. 21041411_Data show that ASPP1 enhances nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ and YAP/TAZ-dependent transcriptional regulation. 21076472_AXL is a mediator of YAP-dependent oncogenic activities 21112960_Overexpression of YAP protein was associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 21118971_Results suggest that YAP1 may play an important role in prognosis of small-cell lung cancer patients treated with platinum-based chemotherapy. 21170084_a previously unrecognized link between BMI-1, contact inhibition and the Hippo-YAP pathway 21187284_a new mechanism for YAP1 regulation, which is mediated via its direct interactions with angiomotin-like proteins. 21205866_a novel mechanism of YAP and TAZ inhibition by AMOT-mediated tight junction localization 21224387_novel mechanism to restrict the activity of TAZ and YAP through physical interaction with Amot and AmotL1 21278236_Data suggest that defective expression of LATS2 is attributable to FOXP3 defects and may be a major independent determinant of YAP protein elevation in cancer. 21317925_findings suggest that YAP derepression contributes to the genesis of ovarian clear cell carcinoma and that the SWH pathway is an attractive therapeutic target 21346147_Data suggest that YAP1 could be a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for gastric cancer. 21364637_JNK1 and JNK2 were identified as robust YAP kinases. 21399893_YAP may act as a tumor suppressor in invasive breast carcinomas and it can also be used as a molecular marker for ER and PR negative breast tumors. 21454516_AGR2 induction of AREG is mediated by activation of the Hippo signaling pathway co-activator, YAP1. 21610251_alphaE-catenin as a tumor suppressor that inhibits Yap1 activity and sequesters it in the cytoplasm. 21654799_findings identify YAP/TAZ as sensors and mediators of mechanical cues instructed by the cellular microenvironment 21666501_This study demonistrated taht the YAP1 overexpression promotes growth of glioblastoma cell lines in vitro. 21685940_AmotL1 and ZO-2 are two candidates that could be harnessed to control the oncogenic function of YAP. 21708480_study shows that YAP could promote cell proliferation by activating transcription factor Fra-1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 21800344_Expression of CTGF can be stimulated through the EGFR-signaling system in HCC cells in a novel cross-talk with the oncoprotein YAP 21856745_the transcriptional coactivator YAP1 was determined to be a direct target of miR-375 in lung cancer cells 21874045_Our results establish a central role for YAP in counteracting radiation-based therapies and driving genomic instability, and indicate the YAP/IGF2/Akt axis as a therapeutic target in medulloblastoma. 21909427_These findings define a novel molecular mechanism that YAP2 is positively regulated by PP1-mediated dephosphorylation in the cell survival. 21981024_The WW1 and WW2 domains of YAP2 recognize various PPXY motifs within WBP1 and WBP2 in a highly promiscuous and subtle manner. 22012126_liver regeneration alone elevated YAP protein levels without elevating YAP mRNA levels. YAP mRNA and protein levels were both elevated in liver cancer cells 22024089_results of the qRT-PCR and western blotting showed an obvious inhibition of YAP mRNA and protein expression in the YAP-shRNA group 22042863_Data show that Yap is overexpressed in 68 of 71 colon cancers and in at least 30 of 36 colon cancer-derived cell lines. 22056638_Breast cancer cell lines in which YAP was either overexpressed or depleted confirmed that YAP markedly promotes cell proliferation 22096589_YAP expression, in combination with p63 can facilitate identification of HNSCC tumors from hyperplastic and benign tissues and the metastatic function of YAP in HNSCC may not be a result of epithelia to mesenchymal transdifferentiation. 22098159_Yap induction mediated by inactivation of Lats is observed in hepatic malignancies. 22234184_The authors show that YAP and TAZ, the transcriptional co-activators in the Hippo pathway, suppress Wnt signalling without suppressing the stability of beta-catenin but through preventing its nuclear translocation. 22286761_YAP activation in the mesothelioma cells promotes cell cycle progression by upregulating transcription of cell cycle-promoting genes. 22308035_The coactivator activity of YAP correlated with its state of phosphorylation and sensitivity to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. 22337891_these results implicate YAP as an oncogene whose expression is driven by aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human colorectal carcinoma cells. 22396793_YAP1 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and potentially plays an important role in the clonogenicity and growth of pancreatic cancer cells 22436626_Our findings suggested that Yes-associated protein contributes to primary liver tumorigenesis and likely mediates its oncogenic effects through modulating Survivin expression. 22499345_Identification of a new susceptibility gene YAP1 on chromosome 11q13 for polycystic ovary syndrome. 22544757_analysis of a novel acetylation cycle of transcription co-activator Yes-associated protein that is downstream of Hippo pathway is triggered in response to SN2 alkylating agents 22558212_YAP1, excluded from the nucleus, contributes to the maintenance of tight junctions. 22609549_crosstalk between the insulin/IGF signaling pathway and Yorkie leads to coordinated regulation of these two oncogenic pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma 22618028_these findings suggest that in meningiomas, deregulation of the Hippo pathway is largely observed in primary tumors and that YAP1 functions as an oncogene promoting meningioma tumorigenesis. 22632819_YAP promotes breast cell proliferation and survival partially through stabilizing the KLF5 transcription factor. 22689061_YAP forms a protein complex with PTPN14 through the WW domains of YAP and the PPXY motifs of PTPN14. 22707013_YAP is a key driver gene in Hepatitis B virus X protein-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in a cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein-dependent manner. 22843909_YAP expression failed to produce any significant relationship with the overall survival rate. CONCLUSION: YAP expression is not an independent prognostic factor in patients with breast cancer. 22895435_Studies indicate that the transcriptional co-activators YAP and TAZ recently emerged as key mediators of the biological effects that are observed in response to extracellular matrix (ECM) elasticity and cell shape. 22948661_that PTPN14 acts to suppress cell proliferation by promoting cell density-dependent cytoplasmic translocation of YAP1 22993325_The nuclear overexpression of YAP1 is an independent biomarker for poor survival, especially for patients with intestinal-type gastric cancer. 23027127_LKB1 inhibited Yap independently of either AMPK or mTOR activation 23027379_In this review, we will discuss the points of intersection between the Wnt/beta-catenin and Hippo/YAP pathways and how these interactions contribute to homeostasis, organ repair, and tumorigenesis. 23058008_YAP is strongly expressed in gastric adenocarcinomas, and knockdown of YAP may inhibit gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. 23060277_study reveals that GPC3 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by increasing cell proliferation, enhancing metastasis as well as invasion; GPC3 may collaborate with YAP to regulate the HCC development 23158133_Over-expression of YAP was associated with non-small cell lung cancer, especially lung adenocarcinoma. 23178811_yes-associated protein 1 (YAP; also known as YAP1)--a protein known for its powerful growth-inducing and oncogenic properties--has an unexpected growth-suppressive function, restricting Wnt signals during intestinal regeneration 23232767_we provide evidence that YAP overexpression plays an important role in the chemoresistance of hepatocellullar carcinoma cells to doxorubicin. 23245941_beta-catenin forms a complex with YAP1 and TBX5, which promotes colon cancer cell survival and contributes to malignant transformation. These observations reveal hitherto unidentified components of the beta-catenin pathway that play key roles in survival of beta-catenin-active cells. 23258147_The expression of YAP/TAZ and ECM-related-genes is impacted on physiologically relevant substrates. YAP was upregulated in cells on softer substrates. 23298488_YAP1 is highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues compared with the dysplasia and chronic gastritis tissues and its expression level is elevated with the ascending order of tumor malignancy. 23298489_Spearman rank correlation analysis showed a positive correlation between YAP1 and Axl expression 23333314_MASK1 complexes with YAP and is required for the full activity of YAP. 23333315_Mask proteins are functionally conserved between Drosophila and humans and are coexpressed with YAP in a wide variety of human stem/progenitor cells and tumors. 23340296_we found that YAP1 expression was inversely correlated with miR-200a expression in breast cancer clinical specimens, and miR-200a expression was associated with distant metastasis in patients with breast cancer. 23422184_YAP1 is involved in the carcinogenesis and development of OSCC. There is a transformation between nucleus and cytoplasm. 23450633_F-Actin, assembled in response to Galpha12/13 induced RhoA-GTP, promotes dephosphorylation and activation of the YAP oncogene 23502453_YAP1 has oncogenic potential in cervical cancer with distinct functions in squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinoma. 23527718_YAP1 is highly expressed in osteosarcoma tissue, and knockdown of YAP1 resulted in downregulation of RUNX2, CyclinD1, and MMP-9 and inhibited the proliferation and invasion of MG-63 cells 23532963_Mutual interaction between YAP and CREB promotes tumorigenesis in liver cancer. 23542177_findings reveal a new regulatory mechanism of YAP2 by the SIRT1-mediated deacetylation that may be involved in HCC tumorigenesis and drug resistance 23544078_High Yap activity in muscle fibres does not induce fibre hypertrophy nor fibre type changes but instead results in a reversible atrophy and deterioration. 23558963_results indicated that YAP overexpression contributed to the tumorigenesis and played a pivotal role in the progression in colorectal cancer 23564455_Amot130 repurposes AIP4 from its previously described role in degrading large tumor suppressor 1 to the inhibition of YAP and cell growth. 23576552_Data indicate that knockdown of TEAD1/3/4 induces an almost identical cellular senescent phenotype as YAP silencing. 23594797_These findings provide mechanistic insight into the regulation of YAP and AREG by RASSF1A in human multistep hepatocarcinogenesis. 23613971_Data demonstrate that PTPN14 downregulation can phenocopy YAP activation in mammary epithelial cells and synergize with YAP to induce oncogenic transformation. 23667252_YAP binding to dendrin is a prosurvival mechanism in podocytes. 23673988_results suggest that the expression of YAP and phosphorylated YAP is a possible predictor of tumor cell proliferation and prognosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma 23685355_YAP1 was downregulated in medullary thyroid carcinoma. 23727052_In conclusion, substratum stiffness alters YAP/TAZ expression and YAP localization in trabecularmeshwork cells which then may modulate the expression of extracellular matrix proteins important in glaucoma. 23737213_In summary, we are reporting a novel subset of EHE occurring in young adults, showing a distinct phenotype and YAP1-TFE3 fusions. 23760493_YAP functions as a tumor suppressor that enhances apoptosis by modulating p53 during chemotherapy. 23762387_Overexpression of YAP is associated with metastasis in colorectal cancer. 23870412_YAP 1 is an independent biomarker for poor prognosis of patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder 23897276_Both YAP and TAZ contribute to the invasive and metastatic capacity of melanoma cells. 23949920_data indicate that nuclear YAP localization is more common in breast cancers lacking functional adherens junctions, it suggests that YAP-mediated transcription may be involved in the development and progression of invasive lobular breast cancer. 23954413_Study reports that physical and architectural features of a multicellular sheet inform cells about their proliferative capacity through mechanical regulation of YAP and TAZ, known mediators of Hippo signaling and organ growth. YAP/TAZ activity is confined to cells exposed to mechanical stresses. 23994529_identified an intronic region of the NAIP gene responding to TEAD1/YAP activity, suggesting that regulation of NAIP by TEAD1/YAP is at the transcriptional level 23994632_These results establish a new signaling mechanism by which the interaction between YAP and c-Myc promotes liver cancer growth. 24003252_Scaffold proteins angiomotin (Amot) and angiomotin-related AmotL1 and AmotL2 were recently identified as negative regulators of YAP and TAZ by preventing their nuclear translocation. 24003254_Within the nucleus, Amot-p130 was associated with the transcriptional complex containing Yap and Teads (TEA domain family members) and contributed to the regulation of a subset of Yap target genes, many of which are associated with tumorigenesis. 24023255_A molecular mechanism linking JNK activity to Yki regulation. JNK can promote YAP activity in mammalian cells. 24086533_Increased YAP1 expression was more frequently found in combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma with stemness than in HCCs without, and a YAP1 pathway may be involved in the stemness characteristics in HCCs and cHC-CCs. 24101154_A previously unrecognized mechanism for controlling the activity of YAP that is crucial for its oncogenic function mediated by mitotic dysregulation. 24101467_Data indicate that Yap1 is epigenetically regulated by menin and correlated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 24101513_Data indicate that the phosphorylation of Amot130 by LATS1/2 is found to be a key feature that enables it to inhibit Yes-associated protein (YAP) dependent signaling and cell growth. 24106282_combined genetic association studies in women from China/Netherlands/United States: Data suggest that an SNP in YAP1 (rs1894116) and SNPs in other proteins are associated with polycystic ovary syndrome across ethnic differences. [META-ANALYSIS] 24115727_Phosphorylation of Yes-associated protein-1 is associated with Wilms tumor. 24211253_MEK1-YAP interaction is critical for liver cancer cell proliferation and maintenance of transformed phenotypes both in vitro and in vivo. 24223879_Data indicate that when compared with level of yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) mRNA expression of the AA genotype, the mRNA expression level in CC genotype was statistically lower. 24242138_SiRNA targeting YAP1 significantly inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells 24268772_Patients with diverse biliary dysfunctions exhibit enhanced IQGAP1 and nuclear YAP expression. 24323901_YES1 and YAP transcript levels were higher in liver metastases of patients with colon cancer after 5FU-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. 24324261_post-transcriptional regulation of Dicer is controlled by the cell density-mediated localization of the Hippo pathway effectors TAZ (transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif) and YAP (Yes-associated protein) (TAZ/YAP). 24346160_Studies indicate that yes-associated protein (YAP)-1 plays a dual role as oncogene and tumor suppressor gene in oncogenesis, depending on the specific tissue type involved. 24362629_identification of a signalling axis that links YAP activation with LKB1 mutations, and implications for the treatment of LKB1-mutant human malignancies; in addition, findings provide insight into upstream signals of the Hippo-YAP signalling cascade 24367099_RHAMM transcription is regulated via YAP in a pathway involving mevalonate and Hippo that modulates breast cancer cell motility 24369055_results suggest that E2A suppresses CRC cell metastasis, at least partially if not all, by inhibiting YAP expression 24380865_The PDZ-binding motif of YAP is critical for YAP-mediated oncogenesis, and that this effect is mediated by YAP's co-activation of TEAD-mediated CTGF transcription. 24389730_YAP regulates cell proliferation, migration, and steroidogenesis in adult granulosa cell tumors 24462371_Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in YAP1 cause both isolated and syndromic optic fissure closure defects. 24468535_Overexpression of YAP induced the translocation of itself and SRSF1 and was independent of LATS. 24482231_this work summarizes a novel link between CD166 and YAP, explores the interplay among related important signaling pathways, and may lead to more effective therapeutic strategies for liver cancer. 24485923_we report that YAP and its downstream transcriptional targets CCN1 and CCN2 are markedly elevated in keratinocytes in human skin basal cell carcinoma 24511017_Activation of YAP1 is significantly associated with prognosis and the YAP1 signature can predict response to taxane-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with ovarian cancer. 24558021_Tumor cell proliferation in human schwannomas is linked to a signaling network controlled by the Hippo effector YAP. 24559095_Decreased YAP1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for recurrence in less aggressive luminal A breast cancer subgroup. 24606817_a role of YAP as a suppressor gene in breast cancer (BC); showed differences in YAP expression in different patterns of ductal BC. 24621512_nicotine activated nAChRs signaling pathway which further activates YAP1 plays an important role in the development of esophageal cancer 24622501_YAP promotes ovarian cancer cell growth and tumorigenesis 24643316_Overexpression of YAP1 is correlated with progression and metastasis in gastric carcinoma. 24648515_Nuclear TAZ/YAP also cooperate with TGFbeta signaling to promote phenotypic and transcriptional changes in nontumorigenic cells to overcome TGFbeta-repressive effects. 24682895_NSCLC cell lines in which LATS1 was either overexpressed or depleted confirmed that LATS1 markedly inhibited cell proliferation and invasion and could regulate the nuclear location of yes-associated protein (YAP). 24703331_In melanoma, Hippo signaling is affected by copy number alterations and YAP1 overexpression impairs patient survival. 24726915_ANKHD1 is a positive regulator of YAP1 and promotes cell growth and cell cycle progression through Cyclin A upregulation. 24728461_Mechanistic studies revealed a multi-targeted mechanotransductive process involving Smad phosphorylation and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling, regulated by rigidity-dependent Hippo/YAP activities and actomyosin cytoskeleton integrity and contractility. 24747426_knowledge of how YAP and TAZ function as mechanosensors and mechanotransducers 24779718_MIR31 significantly suppressed the luciferase activity of mRNA combined with the LATS2 3'-UTR and consequently promoted the translocation of YAP1, a key molecule in the Hippo pathway, into the nucleus 24803537_findings identified Yap as a critical oncogenic KRAS effector and a promising therapeutic target for PDAC and possibly other types of KRAS-mutant cancers 24806962_Human myoblasts with LMNA mutations have mechanosensing defects through a YAP-dependent pathway. 24810048_Report coordinated control of chaetocin treated glioma cell proliferation and metabolism by ROS through (i) ATM-YAP1-driven apoptotic pathway and (ii) JNK-regulated metabolic adaptation. 24810989_YAP1 acts as oncogenic target of 11q22 amplification in multiple cancer subtypes. 24813251_Low YAP1 levels prevent nuclear ABL1-induced apoptosis in hematologic malignancies. 24833660_Cardiac-specific YAP activation after myocardial infarction mitigated myocardial injury, improved cardiac function, and enhanced survival. 24837480_beta-catenin and the transcriptional regulator Yap1 interact physically and are activated in most human hepatoblastoma tissues; overexpression of activated forms of these proteins in livers of mice leads to rapid tumor development. 24860833_The expression of YAP was significantly correlated with Edmondson stage, serum AFP level, and hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. 24881775_Hippo and Yap regulated cardiomyocyte death and regeneration.[review] 24884509_Fbxw7 induces apoptosis and growth arrest by regulating YAP abundance in hepatocellular carcinoma. 24906622_Findings identify YAP1-driven SOX9 expression as a critical event in the acquisition of cancer stem cell properties in esophageal cancer. 24954536_Using a colon cancer cell line, study found 147 genes that promoted survival upon KRAS suppression. In particular, the transcriptional coactivator YAP1 rescued cell viability in KRAS-dependent cells upon suppression of KRAS and was required for KRAS-induced cell transformation. 24972085_Increased nuclear YAP expression was significantly associated with higher grade, stage and radiation sensitivity in endometrial cancer. YAP overexpression promoted cell proliferation in vitro. 24993351_Results show that YAP1 is highly expressed in human osteosarcoma suggesting an important regulator role in osteosarcoma tumorigenesis. 25031743_there was a significant difference in YAP and phosphorylated YAP expression status according to molecular subtypes and tumoral and cellular components of breast cancers. 25078107_TAZ and YAP are differentially regulated by hypoxia in cancer cells 25087979_YAP1 is a potent embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma oncogenic driver. 25087998_YAP mRNA might be one of the targets of miR-506. 25101858_data are presented showing that CD44 could act through RhoA signaling to regulate YAP expression 25115923_YAP inhibits squamous transdifferentiation of Lkb1-deficient lung adenocarcinoma through ZEB2-dependent DNp63 repression. 25122798_shows how this association of small t antigen with YAP is important for its effects on cell phenotype. It also suggests that PyST can be used to characterize cellular processes that are regulated by YAP 25127217_Cyclic stretch is associated with a JNK-dependent increase in binding of a LATS inhibitor, LIMD1, to the LATS1 kinase and that reduction of LIMD1 expression suppresses the activation of YAP by cyclic stretch. 25168380_Our findings define the alteration of the Hippo/YAP pathway in the development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 25175178_Expression of YAP mRNA and protein in clear cell renal carcinoma tissues was higher than in adjacent normal tissue. YAP knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. 25180228_the oncogenic activity of Ras(V12) depends on its ability to counteract Hippo pathway activity, creating a positive feedback loop, which depends on stabilization of YAP1. 25201954_Substratum-induced differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells reveals the coactivator YAP is a potent regulator of neuronal specification. 25218593_The activation of the AXL/MAPK pathway was involved in the oncogenic functions of YAP1 in GBC. 25261601_The close relationship between Runx2 and YAP plays a pro-carcinogenetic role in liver cancer cells through inhibiting tumor suppressor lncRNA, MT1DP in a FoxA1 dependent manner. 25270913_both LATS1 demethylation and overexpression of LATS1 downregulated the expression of Yes-associated protein (YAP), inhibited cell proliferation, induced cell apoptosis and cell cycle G1 arrest in 786-O cells 25283809_data show that the WW tandem domains of YAP2 negatively cooperate when binding to their cognate ligands 25288394_the regulation of YAP by mTOR and autophagy is a novel mechanism of growth control, matching YAP activity with nutrient availability under growth-permissive conditions. 25290150_YAP, TAZ and HSP90 take part in contact guidance and intercellular junction formation in corneal epithelial cells. 25304677_High expression of Yes-associated protein is associated with cervical squamous epithelium lesions. 25337244_Expression level of YAP in stromal component was increased along with histologic grade of breast phyllodes tumor and YAP expression in PT was related to tumor progression and poor prognosis. 25344213_the YAP expression in metaplastic carcinoma is higher than that in TNBC, representing the association of stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition features in metaplastic carcinoma. 25360797_ASPP2 directly induces the dephosphorylation and activation of junctional YAP 25384421_the YAP-TEAD interaction can be disrupted using cyclic YAP-like peptides, which targets the HIPPO pathway 25388162_Activation of YAP1 is highly associated with poor prognosis for colorectal cancer. 25393475_The control of LATS activation by angiotensin II and subsequent YAP localization is important for podocyte homeostasis and survival. 25404446_SIRT1 was overexpressed in HCC and the expression was positively related to P53 and YAP2 expression. 25425573_Conversely, increased expression of betaPIX in breast cancer cell lines re-couples the Hippo kinase cassette to Yap/Taz, promoting localization of Yap/Taz to the cytoplasm and inhibiting cell migration and proliferation. 25436413_these observations reveal that Itch and Yap1 have antagonistic roles in the regulation of ASPP2 protein stability through competing post-translational regulatory mechanism of ASPP2. 25438054_YAP complexes with HIF1alpha and is essential for HIF1alpha stability and function in tumours in vivo. 25473897_Data show that fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF8) can activate YAP1 (Yes-associated) protein signaling in colorectal cancer (CRC). 25492964_identifying neuregulin 1 and its cognate receptor ERBB4 [epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family member v-erb-b2 avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4] as a major receptor complex that activates YAP activity |
ENSMUSG00000053110 |
Yap1 |
46.430384 |
3.6741115836 |
1.877395 |
0.272815429 |
48.530122 |
0.00000000000325254394141326994907707321303250212838481525423617313208524137735366821289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000018752948662210883022912787736011664806862198062731295067351311445236206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.1930135 |
11.2432662 |
20.0763967 |
2.5711167 |
| ENSG00000137726 |
53826 |
FXYD6 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0Q3 |
|
Alternative splicing;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Schizophrenia;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the FXYD family of transmembrane proteins. This particular protein encodes phosphohippolin, which likely affects the activity of Na,K-ATPase. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 10 and X. Read-through transcripts have been observed between this locus and the downstream sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit gamma (FXYD2, GeneID 486) locus.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:53826; |
glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; ion channel regulator activity [GO:0099106]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; regulation of ion transport [GO:0043269] |
17357072_Base-pair changes in FXYD6 or in associated promoter/control regions are likely to cause abnormal function or expression of phosphohippolin and to increase genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. 17357072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18455306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18455306_Our findings suggest that FXYD6 is unlikely to be related to the development of schizophrenia in a Japanese population. 20149392_Data show that FXYD6 does not play a role in schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population. 20149392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468077_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21216238_these results support that FXYD6 is a susceptibility gene of schizophrenia. 21983730_FXYD6 gene might play an important role in schizophrenia susceptibility. 24715268_FXYD6 plays a critical role of in hepatocellular carcinoma disease progression. 26302771_FXYD6 was verified to be directly interacting with miR-137.. 33231612_FXYD protein isoforms differentially modulate human Na/K pump function. 34212047_FXYD6 Regulates Chemosensitivity by Mediating the Expression of Na+/K+-ATPase alpha1 and Affecting Cell Autophagy and Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000066705 |
Fxyd6 |
32.222401 |
0.3356227351 |
-1.575088 |
0.276449435 |
34.078639 |
0.00000000529291182490219192950151215417038674804217635028180666267871856689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000023709674821109669866476366917665274947069065092364326119422912597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.6796977 |
2.8063431 |
47.0449540 |
4.9965258 |
| ENSG00000137745 |
4322 |
MMP13 |
protein_coding |
P45452 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins including fibrillar collagen, fibronectin, TNC and ACAN. Cleaves triple helical collagens, including type I, type II and type III collagen, but has the highest activity with soluble type II collagen. Can also degrade collagen type IV, type XIV and type X. May also function by activating or degrading key regulatory proteins, such as TGFB1 and CCN2. Plays a role in wound healing, tissue remodeling, cartilage degradation, bone development, bone mineralization and ossification. Required for normal embryonic bone development and ossification. Plays a role in the healing of bone fractures via endochondral ossification. Plays a role in wound healing, probably by a mechanism that involves proteolytic activation of TGFB1 and degradation of CCN2. Plays a role in keratinocyte migration during wound healing. May play a role in cell migration and in tumor cell invasion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16167086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17623656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19422229, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19615667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20726512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22689580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23810497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8207000, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8576151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8603731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8663255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9065415}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This protease cleaves type II collagen more efficiently than types I and III. It may be involved in articular cartilage turnover and cartilage pathophysiology associated with osteoarthritis. Mutations in this gene are associated with metaphyseal anadysplasia. This gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4322; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; growth plate cartilage development [GO:0003417]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645] |
11883937_AGRE site plays a rate-limiting role in human collagenase-3 production. 11903048_Investigation of the role of Endo180/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor-associated protein as a collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase 13) receptor 12009331_involvement of MAPKs, AP-1 and NF-kappa B transcription factors in the IL-1 induction of MMPs in chondrocytes 12009332_Reduction of cytokine-induced expression and activity of MMP-1 and MMP-13 by mechanical strain in MH7A rheumatoid synovial cells 12139441_REVIEW: The structure, regulation, and function of human matrix metalloproteinase-13 12192005_Data show that keratinocytes use an alternative plasminogen and matrix metalloproteinase-13-dependent pathway for dissolution of collagen fibrils. 12270924_induction by transforming growth factor-beta via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 12392760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12392760_Two new MMP13 promoter polymorphisms. Genotype for one MMP13 polymorphism associated with fibrous plaque in black males. MMP13 expressed in all layers of aorta. Polymorphism a functional variant. Genetic risk factor for extent of fibrous plaque. 12426321_translational repression by an alternatively spliced form of T-cell-restricted intracellular antigen-related protein 12734180_MMP13 expression is regulated by IGF-1 and OP-1 12878172_induction of the MMP-13 gene by TNF-alpha is mediated by ERK, p38, and JNK MAP kinases as well as AP-1 and NF-kappaB transcription factors 12974393_Together with other prognostic markers, determination of MMP-13 in ascitic fluid may help to identify patients at risk for early death and help to individualize adjuvant therapy 14558091_catabolic role of ET-1 in osteoarthritis cartilage via MMP-1 and MMP-13 up-regulation. 15067375_MMP-13, uPA, and PAI-1 antigen levels were determined in the synovium of patients with osteoarthritis 15551360_MMP13 is upregulated in breast cancer 15640153_MMP-1 and MMP-3 secretion by gastric epithelial cells are differentially regulated by E prostaglandins and MAPKs 15654517_gene expression regulation in Lyme disease 15693018_regulation of the PLC pathway through the PTH1R is increased by elevating expression of G(11)alpha in osteoblastic cells leading to increased PTH stimulation of MMP-13 expression by increased stimulation of AP-1 factors c-jun and c-fos. 15763932_study showed a marked expression of MMP-13 in dental pulp tissue of both sound and carious teeth 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15947272_MMP-9 and MMP-13 are involved in stroke progression and the neuroinflammatory response 16024014_Down-regulated by integrin alphavbeta6, not essential for the degradation of type I collagen by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 16144844_GADD45beta plays an essential role during chondrocyte terminal differentiation and mediates MMP-13 gene expression 16331612_activation of MMP-13 as well as MMP-9 induced by H-Ras is involved in angiogenesis and with farnesyl transferase inhibitors, in part, exerts their anticancer effects 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16398406_MMP-13 appears to be a factor associated with tumor aggressiveness in cutaneous malignant melanoma 16507124_MMP-13 can degrade members from two classes of small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycans. Site at which biglycan is cleaved by MMP-13. MMP-13 induced SLRP degradation may represent early event affecting collagen network by exposing MMP-13 cleavage site. 16648633_the involvement of p38 MAP kinase in the hyaluronan oligosaccharide induction of MMP-13 16877349_The expression of matrix-modeling genes in chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (cIMF) is not influenced by the JAK2 mutation status but is predominantly related to the stage of disease. 16917496_a novel role for human MMP-13 in regulating dermal fibroblast survival, proliferation, and interaction in 3D collagen. 16948116_Since both S100A4 and RAGE are up-regulated in osteoarthritis cartilage, this signaling pathway could contribute to cartilage degradation in this disease. 16984617_TUNEL-positive cells and MMP-3- and -13-expressing cells were distributed in the degenerative articular cartilage and reparative fibrocartilage tissue in osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of the elbow. 17009260_Premature induction of hypertrophy-related molecules (type X collagen and matrix metalloproteinase 13) occurred before production of type II collagen and was followed by up-regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity. 17033924_No convincing evidence was found to support the association of MMP13 SNPs with increased breast cancer risk or survival. 17033924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17076612_activity in gingival crevicular fluid samples was significantly increased in active sites from progressive periodontal disease, supporting its role in the alveolar bone loss 17116693_These results identify an unexpectedly broad involvement for p8 in key cellular events linked to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and cardiac fibroblast matrix metalloproteases production, both of which occur in heart failure. 17138534_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17138534_Thus, in the region of Hebei Province where there is a high incidence of GCA and ESCC, the MMP-13 A-77G SNP may not be associated with cancer susceptibility. 17151781_nicotine stimulates bone matrix turnover by increasing production of tPA and MMP-1, 2, 3, and 13, thereby tipping the balance between bone matrix formation and resorption toward the latter process 17196980_We have solved the 2.0 A crystal structure of the complex between the catalytic domain of human MMP-13 (cdMMP-13) and bovine TIMP-2. 17208315_oncostatin M-stimulated ADAMTS-4 and MMP-13 expression is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinases, Janus kinase 3/STAT1/3 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and by cross talk between these pathways 17311929_deregulation of cross-talk between mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein kinase Cdelta signaling may contribute to the etiology of osteoarthritis in human patients 17373717_CpG-ODN-treatment also increased MMP-13 activity and neutralizing anti-MMP-13 antibody prevented CpG-ODN-induced invasion in TLR9(+) CaP cells. 17373931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17395008_Increased production of reactive oxygen species but not nitric oxide as secondary messengers in the chondrocyte fibronectin fragment signaling pathway leads to increased production of MMPs, including MMP-13. 17495113_MMP-13 is involved in osteogenic differentiation. 17607721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17623656_a matrix metalloprotease-13 inhibitor reduces cartilage damage in vivo without joint fibroplasia side effects 17626252_Nucleolin interacts with the AP-1 site within the promoter sequence of the metalloproteinase-13 gene. 17697361_TauCl differentially inhibits the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-13 in human synoviocytes 17724016_BFGF activates the MAPK and NFkappaB pathways that converge on ELK1 to control production of MMP13 by articular chondrocytes. 17786186_MMP-13 may serve as a marker for progression of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. 17822788_Y-box binding protein-1 (YB-1) as a new repressor of MMP-13 transactivation. 17853491_Fibroblasts of the interface from aseptically loosened endoprostheses selectively express MMP-13 17876296_ROCK-II is a critical mediator of colon cancer cell invasion through its modulation of MMP-2 and -13 at the site of invadopodia but regulates proliferation in non-malignant intestinal cells. 17905570_MyD88, IRAK1 and TRAF6 proteins are crucial early mediators for the IL-1-induced MMP-13 regulation through MAPK pathways and AP-1 activity. 18006768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18091353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18091353_the MMP-13 gene, at least in part, contributes to the development of coroonary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease 18225566_MMP-13 gene expression-related polymorphism is associated with risk for the highly aggressive form of oral cancer; the high expression A allele of the -77A/G polymorphism seems to be a prognostic factor for tumor progression 18225566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18262231_MMP-13 is involved in disc histopathology, and that disc cells actively participate in the synthesis of extracellular matrix-degrading proteinases 18289056_This review highlights MMP-13, expressed by chondrocytes and synovial cells in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis and thought to play a critical role in cartilage destruction. 18289383_Chondrocytes were found to express IL-7 receptors and to respond to IL-7 stimulation with increased production of matrix metalloproteinase-13. 18308831_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18308831_potential role for MMP12 -82 A/G and MMP13 -77 A/G combined polymorphisms in superficial endometriosis. As no association was found with deep infiltrating endometriosis, these polymorphisms might protect from a more in-depth penetration of tissues. 18366705_MMP8, but not MMP1 or MMP13, may affect the metastatic behaviour of breast cancer cells through protection against lymph node metastasis 18373849_MMP-13 may be particularly useful as a prognostic marker when evaluated along with Her-2/neu and lymph node status. 18487224_CXCL12 enhances Laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell invasiont through paracrine-activated CXCR4, triggering MMP-13 upregulation. 18528653_increases in IL-6, MMP-13, and RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand)expression in osteoarthritis (OA) subchondral bone osteocytes suggest that in subchondral bone OA progression involves abnormal osseous tissue remodeling 18593949_SRC-3/AIB1 directly regulates transcription of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-13 through its coactivation of AP-1 and PEA3. 18709334_MMP-13 is over-expressed in renal cell carcinoma bone metastasis and is induced by TGF-beta1. 18753468_MMP-13 and thioredoxin-like 2 in lungs increased in patients with COPD. MMP-13 was mainly expressed in the alveolar macrophages and type II pneumocytes 18755271_MMP-1 and -13 differentially regulate osteoblastic markers and their combined suppression is important for the elaboration of an osteoblastic phenotype in periodontal ligament cells 18971037_The structural changes in the venous wall in addition to the increased expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and MMP-13 in venous aneurysms suggests a possible causal role for these MMPs in their pathogenesis. 18985055_Nuclear extracts from cells confirmed upregulation of active MMP-13 after oxygen and glucose deprivation 18987329_Active MMP13 is suppressed in vivo and in vitro by estradiol and progesterone, suggesting a protective effect against vaginal supportive tissue deterioration. 19038372_BMP-2 enhanced the invasiveness of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the PI3K, Akt, c-Fos/c-Jun and AP-1 signal transduction pathway. 19094243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19185056_Data show that both AF-1 and AF-2 domains of estrogen receptor alpha are required for regulation of MMP-13 promoter activity. 19248099_C/EBPbeta directly binds to the MMP-13 promoter region and stimulates the expression of MMP-13 in chondrocytes in inflammatory arthritis. 19248107_Activated protein C resulted in MMP-13 activation in cartilage cultures, and it was associated with increased MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity. 19248116_IL-7 stimulates chondrocyte secretion of S100A4 via activation of JAK/STAT signaling, and then S100A4 acts in an autocrine manner to stimulate MMP-13 production via RAGE. 19258954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258954_the A/A genotype of MMP-13-77A/G polymorphism was associated with special pathological subtype and clinical stage in epithelial ovarian cancer at least in Chinese women. 19296842_15-lipoxygenases may have chondroprotective properties by reducing MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression. 19301259_Connective tissue growth factor enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the alphavbeta3 integrin, FAK, ERK, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 19333684_mRNA expression and protein production of IL-6, IL-8, and MMP-13, which are involved in the progression of osteoarthritis, were increased in the osteophytes 19415460_DDR2-mediated MMP-13 induction by collagen matrix in synovial fibroblasts of RA contributed to articular cartilage destruction 19422937_Runx2 may play a crucial role in cytokine-mediated MMP-13 expression in Giant Cell Tumor of bone stromal cells. 19442604_Primary cultures stromal cells from giant cell tumour of bone produce MMP-1 and MMP-13. Immunohistochemistry confirmed the presence of MMP-1 and MMP-13 in paraffin-embedded GCT tissue samples. 19453573_Data suggest that the -77A/G and 11A/12A polymorphisms of MMP-13 gene are not associated with susceptibility to severe, generalized CP in a Turkish population. It seems that -77G allele carriage may not influence the outcome of periodontal therapy. 19494318_age-related shift in ALK1/ALK5 ratio in murine cartilage and a strong correlation between ALK1 and MMP-13 expression in human cartilage 19551542_The migration of bone marrow (BM) mesenchymal stromal cells was the result of the variable level of MMP/TIMP in response to inflammatory stimuli. 19561643_Results indicate that Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling involves the activation of a SFK, leading to MMP-13 expression, and that constitutively active Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling confers invasive properties on osteosarcoma cells in a cell-autonomous manner. 19562509_Functional polymorphisms in matrix metalloproteinases might play roles in developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric cardia adenocarcinoma in high incidence region of North China. 19562509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19564415_FOXO3a promotes invasive migration by inducing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and MMP-13. 19615667_Mutation in MMP13 determines the mode of inheritance and the clinical spectrum of metaphyseal anadysplasia. 19779140_Nitric oxide may regulate the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms in part by inducing the expression of EMMPRIN and modulating the activity of MMP-13 in murine and human aneurysms. 19784544_Elevated HDAC7 expression in human osteoarthritis may contribute to cartilage degradation via promoting MMP-13 gene expression. 19787229_High MMP13 is associated with breast cancer. 19821768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19883500_Adiponectin may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by stimulating the production of VEGF and MMP-1 and MMP-13 19902888_Membrane type-1 metalloproteinase mediates nitric oxide-induced activation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 in chondrocytes (chondrocarcoma cell line sw1353) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948051_Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. 20043086_overexpression of ErbB2 promotes invasive and migratory abilities of H-Ras-activated MCF10A human breast epithelial cells through upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). 20067416_Taken together, these studies demonstrate a new level of transcriptional regulation of MMP-13 expression by the c-maf. 20097749_HDAC4 represses matrix metalloproteinase-13 transcription in osteoblastic cells, and parathyroid hormone controls this repression 20131257_miR-27b may play a role in regulating the expression of MMP-13 in human chondrocytes 20175118_Thrombin enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-2 and MMP-13 expression through the PAR/PLC/PKCalpha/c-Src/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 20196777_there is an association among RUNX-2, SOX-9 and FGF-23 in relation to MMP-13 expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes 20376807_Individuals with MMP-12 -82A/G and MMP-13 -77A/A might have higher risk of overall or special histological type of epithelial ovarian carcinoma development. 20376807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463008_These data identify atypical PKC isozymes as STAT and ERK activators that mediate c-fos and collagenase expression. 20484597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506238_MMP-13 loss leads to a breakdown in primary human articular chondrocyte differentiation by altering the expression of multiple regulatory factors. 20573369_Inhibition of MMP-13 reduces resorptive activity of the cells indicating that MMP-13 likely plays an important role giant cell tumor of bone. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20615395_These results indicate that Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) enhances migration of glioma cells through the increase of MMP-13 production and is mainly regulated by the MEK/ERK and JNK, c-Jun and AP-1 pathways. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20667128_data show for the first time that growth stimuli are mediated via MMP13 in melanocytes and melanoma, suggesting an autocrine MMP13-driven loop 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20683000_MMP-13 expression levels were higher in tumour tissue with liver metastasis than in that without liver metastasis. It is concluded that MMP-13 gene expression is a useful predictor of liver metastasis in patients with CRC. 20685652_Nuclear S100A4 was bound to the promoter region of MMP-13 in IL-1beta-treated cells. 20706991_Hyaluronan inhibits IL-1beta-induced MMP-13 and p-p38 in a concentration-dependent manner in arthritic chondrocytes, via CD44. 20827277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20857147_MMP-9 and -13 mRNA levels are significantly elevated in patients with chronic pain, indicating their possible synergistic effect in intervertebral disc herniation. 20878060_the highly invasive potential of cancer stem cells depends on MMP-13 enzymatic activity, thus MMP-13 might be a potential therapeutic target for glioblastomas. 20878116_that MMP13 is a secreted protein with a significant correlation to development of postoperative relapse; hence it could be a potential prognostic marker for colorectal cancer patients 20936527_RT-PCR performed on samples of whole umbilical cord confirmed the transcriptional expression for the genes encoding all the six matrix metalloproteinases investigated, while in HUVEC only the expression of MMP-2, 3, 9, 10 and 13 mRNAs was detected. 20948207_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21039987_over-expression of Nedd4L might lead to gallbladder cancer invasion by regulating the transcription of the MMP-1 and MMP-13 genes. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21107991_polymorphism of the -77 MMP-13 promoter region acts as a surrogate marker of anti-CCP antibody production in HLA-DRB1*SE allele-negative patients, which may reflect rheumatoid arthritis severity 21142220_Results describe the conserved water molecular dynamics of catalytic and structural Zn(+2) ions in matrix metalloproteinase 13 21187486_Cells expressed PTHrP and that this factor stimulated MMP-13 expression, metastatic bone destruction may result from a PTHrP autocrine loop involving a PKC-ERK1/2 signaling pathway. 21191416_Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 is controlled by IL-13 via PI3K/Akt3 and PKC-delta in normal human dermal fibroblasts. 21205837_These results strongly suggest the underlying mechanism of CXCR4 promoting Tca8113 migration and invasion by regulating MMP-9 and MMP-13 expression perhaps via activation of the ERK signaling pathway. 21211511_the implication of H-Ras and NADPH oxidase-generated superoxide production in MMP-13 gene regulation by IL-1beta and TNF-alpha 21278254_IL-6 and IL-6 receptor interaction enhances migration of chondrosarcoma through an increase in MMP-13 production. 21339746_findings indicate that MUC1 contributes to ESCC metastasis by stimulating MMP13 expression, suggesting MUC1 as a novel diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target in ESCC 21344378_CCN3 enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-13 expression through the alphavbeta3/alphavbeta5 integrin receptor, FAK, PI3K, Akt, p65, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 21344384_15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin-J2 and ciglitazone attenuated TNF-alpha-induced MMP-13 expression in synovial fibroblasts primarily through the modulation of NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 21437966_Autologous protein solution inhibits MMP-13 production by IL-1beta and TNFalpha-stimulated human articular chondrocytes. 21508380_Induction of MMP-13 expression is associated with bone-metastasizing breast cancer. 21539914_MMP-1 and MMP-13 differential regulation of osteoblastic markers in MG63 cells likely results from their modulation of divergent signaling pathways involved in osteoblastic differentiation 21720458_Short-term, high-dose rosuvastatin therapy has no effect on matrix metalloproteinase-13 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 levels in hypercholesterolemic patients. 21849805_Forced MMP-13 expression effectively accelerated recovery from liver cirrhosis 21881840_MMP-9, MMP-13 and TIMP-1 expression may serve as a prognostic marker for early tumor invasiveness. Moreover, up-regulation of TIMP-1 in tumor and/or surrounding stromal cells may indicate an increased risk for BCC recurrence. 21913037_MMP-9 and uPA might be involved in the activation of pro-MMP-13 through unknown mechanisms in arthritic diseases. 21938739_Oct-3/4 enhanced degradation of surrounding extracellular matrix by increasing MMP-13 expression and altering integrin signaling 21959927_ET-1 activated FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR, which in turn activated IKK and NF-kappaB, resulting in increased MMP-13 expression and migration in human chondrosarcoma cells. 22006368_The results suggest that the main proteolytic cascade, MMP-2/MMP-13/MT1-MMP is involved in osteoblast differentiation through mechanical forces. 22032644_within the inflammatory bone microenvironment MMP-13 production was up-regulated in breast tumour cells leading to increased pre-osteoclast differentiation and their subsequent activation 22084953_Nuclear expression of MMP-13, but not cytoplasmic expression of MMP-2, -8, and -9, was associated with invasion depth and tumor size. Furthermore, high nuclear MMP-13 expression was predictive of poor outcome 22095691_findings show that C/EBPbeta and RUNX2, with MMP-13 as the target and HIF-2alpha as the inducer, control cartilage degradation 22102411_a conserved region at 20 kb upstream from the MMP-13 TSS includes a distal transcriptional response element of MMP-13, which contributes to MMP-13 gene expression. 22128168_Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling might also be required for expression of MMP-13 gene during the development of the cartilaginous tissue. 22153941_analysis of non-zinc binding inhibitors of MMP13 22158614_a novel role for ELF3 as a procatabolic factor that may contribute to cartilage remodeling and degradation by regulating MMP13 gene transcription. 22273691_Expression of miRNA-140 and MMP-13 was induced by IL-1beta 22327326_Increased expression of MMP-13 and MT1-MMP in the tumor portion of hyperostosis of meningiomas might contribute to the initiation of osteolysis. 22488635_expression by tumor cells associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer 22505473_identified CREB as the regulating factor able to only bind to the MMP13 promoter when the -104 CpG is demethylated 22573319_The minimum collagen type III sequence necessary for cleavage by MMP1 and MMP13 was 5 GXY triplets, including 4 residues before and 11 residues after the cleavage site (P4-P11'). 22590832_Data show that angiotensin II through activation of AT1 receptors can stimulate the expression of MMP-2, MMP-13 and VEGF, but not MMP-13, in B16F10 melanoma cells. 22610965_demonstrate that beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation leads to MMP-13 transactivation of protease-activated receptor 1 in both cardiac fibroblasts and cardiomyocytes 22710194_Genetic variations in MMP13 may contribute to individual differences in caries susceptibility. Our findings reinforce that susceptibility to caries results from gene-environment interactions. 22710868_T allele of MMP-13 intron polymorphism rs640198 is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease. 22722466_MMP-13 is expressed by tumor epithelial cells, stromal and inflammatory cells of nonmelanoma skin cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum and non-xeroderma pigmentosum. 22782903_a novel molecular mechanism by which MMP13 is up-regulated in cSCCs and indicate that miR-125b plays a tumor suppressive role in cSCC. 22869368_Osterix regulates calcification and degradation of chondrogenic matrices through matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) expression in association with transcription factor Runx2 during endochondral ossification 22950625_MMP-13 was correlated with progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 22992737_MMP-13 may directly and indirectly promote tumor angiogenesis 23132541_Report elevated expression of MMP-13 in osteroarthritic cartilage. 23162804_The present results suggest that the S100A4 gene may control the invasive potential of human breast cancer cells by modulating MMP-13 levels, thus regulating metastasis and angiogenesis in breast tumors. 23334990_Our data add to the understanding of MMP13 regulation, which is essential before such mechanisms can be exploited to alleviate the cartilage destruction associated with osteoarthritis. 23417678_methylation of different CpG sites in the proximal promoters of the human MMP13 and IL1B genes modulates their transcription by distinct mechanisms 23465389_Decreases in the MMP-2 (-735) polymorphism GG genotype and increases in the MMP-13 (A77G) polymorphism AG and GG genotypes increase the risk for lung cancer. 23467939_MMP-13 is associated with thyroid tumour invasion and metastasis. 23665089_Nonmucinous carcinomas showed higher MMP-13 expression compared with mucinous carcinomas. 23732700_MicroRNA-143 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 13 in prostate cancer. 23762330_This is the first report elucidating a feedback regulation between miR-127 and the TGFbeta/c-Jun cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma migration via MMP13. 23847446_provide the first evidence to demonstrate that 1,25-(OH)2D3 activates MMP13 expression through p38 pathway in chondrocytes 23898086_The present study evaluated the association between these single nucleotide polymorphisms in MMP12 and MMp13 in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) patients and healthy controls. 23913860_Crystal structure of peptide-MMP-13 interactions have led authors to propose how triple helical collagen strands fit into the active site cleft of the collagenase. 24008762_MMP13 expression alone is sufficient to overcome the SENP2-induced inhibition of cell migration and invasion. 24023851_presence of MMP-13 seems to limit the overall extent of ECM deposition in lung fibrosis 24180431_activity in chondrocytes reduced by moderate fluid flow shear stress 24351915_genotype distribution of MMP13 differed significantly between the group with unilateral tooth agenesis and the controls 24360951_miR-126-5p was significantly downregulated in stromal cells of Giant cell tumor and affect osteoclast (OC) differentiation and bone resorption by repressing MMP-13 expression at the post-transcriptional level. 24398989_All these data proved the utility of CXCR4, MMP-13 and beta-catenin immunohistochemical investigation in basal cell carcinoma. 24563279_In colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence, MMP- 13 overexpression occurred early in the adenoma stage and persisted after malignant transformation. 24599080_Data indicate that osthole-directed migration activity involves down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 and cell motility dependent focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in migration-prone glioma cells. 24610617_Suggest elevated level of preoperative MMP-13 was found to associate with tumor progression and poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 24615104_The results showed that MMP7-181A/G and MMP13-77A/G variants were associated with Colorectal cancer 24648384_MMP13 mutations are the cause of recessive metaphyseal dysplasia, Spahr type. 24704999_These in vivo findings suggest a role for metalloproteinase-13 in the development and progression of adult human dental tissue disorders. 24781753_Nonsense mutation in exon 2 of MMP13 was described in two brothers who presented with short stature and mixed epiphyseal and metaphyseal dysplasia. 24974940_Collagenase-3 may play a role in the conversion of a periapical granuloma with epithelium to radicular cyst 25006778_Elevated levels of MMP-13 may play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic periodontitis. There is a direct correlation of increased expression of MMP-13 with various clinical and histologic parameters in disease severity 25166220_MMP-13 overexpression or exogenous MMP-13 reduces anoikis by more effectively shedding NG2. 25401159_High level of protein expression of MMP13 was significantly associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 25433723_in degenerative intervertebral discs, IL1b upregulates NFkB, MMP13 and ADAMTS4 25527274_Pit-1 regulates MMP-1 and MMP-13, and that inhibition of MMP-13 blocked invasiveness to lung in Pit-1-overexpressed breast cancer cells. 25562781_During the Barrett's pathogenesis process, MMP activity is increased early on in the inflamed esophagus and remains high in metaplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma. However, there is a switch of MMP13 to MMP9 expression once neoplasia develops. 25607396_The expression of MMP-7, -8, -9 and -13 in the gingiva of the young patients with aggressive periodontitis and type 1 diabetes mellitus was positive in all studied cases. 25609201_Clusterin is an independent predictive factor for prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and it facilitates metastasis through EIF3I/Akt/MMP13 signaling. 25726157_MMP13 expression positively related to the lymph node and distal metastasis, tumor stage and relapse of colorectal cancer 25742789_Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 13 is associated with colitis-associated cancer. 25749207_MMP-13 was associated with metastasis and poor survival in 79 patients with melanoma. MMP-13 expression was inversely correlated with vasculogenic mimicry. MMP-13 cleaves laminin-5 gamma 2 to accelerate metastasis. 25772251_Expression levels of miR-125b were negatively correlated with metastatic potential of NSCLC tumors, which may function through regulation of MMP-13. 25835975_Together, these data suggest that GRh2 may suppress GBM migration through inhibiting Akt-mediated MMP13 activation. 25846944_IL-32 stimulation promotes the invasion and motility of osteosarcoma cells, possibly via the activation of AKT and the upregulation of MMP-13 expression. 25863779_MMP-13 can be useful to confirm the diagnosis of alcoholic liver cirrhosis, but levels of MMP-1 are not significantly increased in patients with liver cirrhosis compared to controls. 25880591_This study demonstrates that stromal as well as tumor derived MMP13 contribute to tumor cell extravasation and establishment of metastases in the liver microenvironment. 25948792_High expression of matrix metalloproteinase-13 is associated with pancreatic cancer. 25966777_Both VEGF-C and MMP13 are significantly upregulated in Multiple Myeloma with lymph-node metastases. 25976617_our resu |
ENSMUSG00000050578 |
Mmp13 |
79.218457 |
7.4069701648 |
2.888884 |
0.269561264 |
118.245990 |
0.00000000000000000000000000153164525806100614510278317012977349554683527327128183823260360022823907107450414066818211722420528531074523925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000018114650648221515416518982285132381433480327417317239057639274695473449554306011322069025482051074504852294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
141.9939271 |
21.8766287 |
19.3349290 |
2.5769865 |
| ENSG00000137747 |
84000 |
TMPRSS13 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYE2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine protease;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the type II transmembrane serine protease family. The encoded protein contains a type II transmembrane domain, a receptor class A domain, a scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain and a protease domain. Transmembrane serine proteases are regulated by protease inhibitors and known to function in development, homeostasis, infection, and tumorigenesis. This protein facilitates entry of viruses into host cells by proteolytically cleaving and activating viral envelope glycoproteins. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2021]. |
hsa:84000; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; membrane [GO:0016020]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
17981585_cloning of MSPL/TMPRSS13, which may play roles in the proteolytic processing of prohormones, precursors of growth factors, and also play roles in the pathogenicity of many viruses and bacteria in vivo 20219906_The authors report that serine proteases, MSPL and its splice variant TMPRSS13, are novel candidates for proteases processing HA proteins of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses. 20977675_results suggest that TMPRSS13 functions as an HGF-converting protease, the activity of which may be regulated by HAI-1 25122802_study demonstrates that two cellular serine proteases, DESC1 and MSPL, activate influenza viruses and emerging coronaviruses in cell culture and, because of their expression in human lung tissue, might promote viral spread in the infected host 28710277_The data provide novel insight into the cellular properties of TMPRSS13 and highlight phosphorylation of TMPRSS13 as a novel post-translational modification of this TTSP family member and potentially other members of this family of proteases. 32807808_TMPRSS13 promotes cell survival, invasion, and resistance to drug-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer. 32868877_The cell-surface anchored serine protease TMPRSS13 promotes breast cancer progression and resistance to chemotherapy. 33671076_TMPRSS11D and TMPRSS13 Activate the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. 33820827_Crystal structure of inhibitor-bound human MSPL that can activate high pathogenic avian influenza. 34562451_Posttranslational modifications of serine protease TMPRSS13 regulate zymogen activation, proteolytic activity, and cell surface localization. 36131918_IL4I1 binds to TMPRSS13 and competes with SARS-CoV-2 spike. |
ENSMUSG00000037129 |
Tmprss13 |
10.414302 |
0.2671962332 |
-1.904028 |
0.498274537 |
15.967064 |
0.00006445414088929667887489793898225798329804092645645141601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000182774854856103543361209307072101637459127232432365417480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3709687 |
1.4635896 |
16.4909688 |
2.9971605 |
| ENSG00000137757 |
838 |
CASP5 |
protein_coding |
P51878 |
FUNCTION: Thiol protease that acts as a mediator of programmed cell death (PubMed:29898893, PubMed:28314590). Initiates pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway through cleavage of Gasdermin-D (GSDMD): cleavage releases the N-terminal gasdermin moiety (Gasdermin-D, N-terminal) that binds to membranes and forms pores, triggering pyroptosis (PubMed:29898893). During non-canonical inflammasome activation, cuts CGAS and may play a role in the regulation of antiviral innate immune activation (PubMed:28314590). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28314590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29898893}. |
Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce two subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. Overexpression of the active form of this enzyme induces apoptosis in fibroblasts. Max, a central component of the Myc/Max/Mad transcription regulation network important for cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, is cleaved by this protein; this process requires Fas-mediated dephosphorylation of Max. The expression of this gene is regulated by interferon-gamma and lipopolysaccharide. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:838; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; NLRP1 inflammasome complex [GO:0072558]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097199]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] |
12191486_inflammasome comprises caspase-1, caspase-5, Pycard/Asc, and NALP1; a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta 12479849_Identification of caspase-5 coding region microsatellite mutations in vivo implicates this gene in the pathogenesis of human T-LBL/ALL 12964016_Caspase-5 might be a suppressor gene of highly metastatic potential in lung cancer 15886296_CASPASE-5, an acknowledged frameshift target in MSI+ gastrointestinal tract tumors, was frequently mutated in Microsatellite instability+ cell lines 16886895_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16893518_novel exon was present in six alternatively spliced caspase-5 mRNA variants expressed in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and encoded the previously unknown amino-terminus of caspase-5. 17676485_Alterations in TGF-betaRII, BAX, IGFIIR, caspase-5, hMSH3 and hMSH6 genes of microsatellite instability are rare in urinary bladder carcinoma and they are not associated with microsatellite instability or the presence of p53 mutations. 18430458_Caspase-5 gene is commonly mutated in the cancers with microsatellite instability suggesting that inactivation of caspase-5 may play a role in their tumorigenesis. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19203830_Coding polymorphisms in Casp5, Casp8 and DR4 genes may play a role in predisposition to lung cancer. 19203830_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19269008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19270026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19270026_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in CASP5 and RBBP8 gene are associated with survival in ovarian cancer patients. 19414860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19604093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20402676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20434535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20434535_Unfavorable significance of CASP5 heterozygous genotype explained by its role in inflammation-related processes. 20635389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21051981_The changes of caspase-2 and caspase-5 activities could be indicative of their involvement in the cervical malignancy mechanisms. 21191419_Caspase-5 and the inflammasome may have an important role in the inflammatory response in psoriasis. 21454616_analysis of concerted antigen processing of a short viral antigen by human caspase-5 and -10 21668377_Data suggest a positive association of caspase-3 and diplotype analysis of caspase-5 to be associated with prostate cancer risk. 21700414_Association of death receptor 4, Caspase 3 and 5 gene polymorphism with increased risk to bladder cancer in North Indians. 21969293_Mutual activation between caspase-5 and -1 suggests caspase-5 may work predominantly in concert with caspase-1 in modulating retinal pigment epithelium inflammatory responses. 22906436_Data show that exposure of hepatocytes to direct hypoxia resulted in acid sphingomyelinase activation and ceramide elevation associated with activation of caspase 5 and the subsequent cleavage of HuR and apoptotic cell death. 25753570_The distribution of the other genotypes; rs507879, rs518604 and rs523104 of caspase-5) was not significantly different between patients with psoriasis vulgaris and the healthy controls. 25943872_this study has identified epithelial-expressed caspases-4 and -5 as biomarkers with diagnostic and therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer. 26173988_both caspase-4 and caspase-5 are functionally important for appropriate responses to intracellular Gram-negative bacteria. 26508369_Caspase-4 and caspase-5 mediate IL-1alpha and IL-1beta release from human monocytes after lipopolysaccharides stimulation. 26884849_CASP5 gene overexpression significantly promoted angiogenesis ability of HMEC-1 cells, which was probably achieved by inhibiting angpt-1/Tie2 and promoting VEGF-1 signal pathway. 28422993_Th17 micro-milieu via IL-17A regulates NLRP1-dependent CASP5 activity in psoriatic skin autoinflammation. 29158166_Study shows that CASP5 was positively correlated with inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and provides evidence that certain CASP5 SNPs were associated with an increased risk of RA. 29715460_Long non-coding RNA CASP5 promotes the malignant phenotypes of human glioblastoma multiforme. 30250284_Knockdown of caspase-4/5 preserved human tubular epithelial cells from cell death and reduced the release of mature IL-1beta. 30604868_The in vitro application of cyclic stretching induced programmed cell death by activation of caspase-3 and -5 in periodontal ligament cells, and these two caspases could interact with each other after mechanical stretch loading. 34747049_SNX10-mediated LPS sensing causes intestinal barrier dysfunction via a caspase-5-dependent signaling cascade. 34895171_CASP5 and CR1 as potential biomarkers for Kawasaki disease: an Integrated Bioinformatics-Experimental Study. 35030963_Inhibition of circular RNA circ_0138959 alleviates pyroptosis of human gingival fibroblasts via the microRNA-527/caspase-5 axis. |
|
|
11.632548 |
10.9479073611 |
3.452583 |
0.732310023 |
27.435787 |
0.00000016239802562104506723139531621652453807769234117586165666580200195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000626501531146530347168681351899266473992611281573772430419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.0581108 |
12.1285937 |
2.2734448 |
1.0305975 |
| ENSG00000137766 |
440279 |
UNC13C |
protein_coding |
Q8NB66 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in vesicle maturation during exocytosis as a target of the diacylglycerol second messenger pathway. May be involved in the regulation of synaptic transmission at parallel fiber - Purkinje cell synapses (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable calmodulin binding activity and syntaxin-1 binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including glutamatergic synaptic transmission; regulated exocytosis; and synaptic vesicle maturation. Predicted to be located in presynaptic active zone. Predicted to be active in several cellular components, including axon terminus; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse; and presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440279; |
calyx of Held [GO:0044305]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0098688]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component [GO:0098831]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; dense core granule priming [GO:0061789]; negative regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0031914]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; presynaptic dense core vesicle exocytosis [GO:0099525]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081]; synaptic vesicle maturation [GO:0016188]; synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0016082] |
18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33715625_Circ-KIAA0907 inhibits the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR-96-5p/UNC13C axis. |
ENSMUSG00000062151 |
Unc13c |
10.425503 |
8.0121965900 |
3.002198 |
0.839429127 |
12.847360 |
0.00033795562437106334112424388393947083386592566967010498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000856200654946257270691556406916333799017593264579772949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2673452 |
7.6263947 |
1.4836206 |
0.8134002 |
| ENSG00000137767 |
58472 |
SQOR |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6N5 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide with the help of a quinone, such as ubiquinone-10, giving rise to thiosulfate and ultimately to sulfane (molecular sulfur) atoms. Requires an additional electron acceptor; can use sulfite, sulfide or cyanide (in vitro) (PubMed:22852582). It is believed the in vivo electron acceptor is glutathione (PubMed:25225291,PubMed:29715001). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22852582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25225291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29715001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32160317}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;FAD;Flavoprotein;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Quinone;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
The protein encoded by this gene may function in mitochondria to catalyze the conversion of sulfide to persulfides, thereby decreasing toxic concencrations of sulfide. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2012]. |
hsa:58472; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; quinone binding [GO:0048038]; sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase activity [GO:0070224]; hydrogen sulfide metabolic process [GO:0070813]; sulfide oxidation, using sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase [GO:0070221] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22852582_Sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase catalyzes the first step in hydrogen sulfide metabolism and produces a sulfane sulfur metabolite. 25225291_SQR is part of the human mitochondrial hydrogen sulfide oxidation pathway 26258864_The I264T SQRDL polymorphism is associaated with osteoporosis in Korean postmenopausal women. 26318450_Hydrogen Sulfide Oxidation Catalyzed by Human Sulfide Quinone Oxidoreductase 27856619_Therefore, this study reveals the reduction in SQR activity as one of the pathomechanisms associated with Coenzyme Q deficiency syndrome. 28512131_Data, including data from studies using recombinant SQR immobilized by embedding in nanodiscs, suggest that immobilized SQR exhibits enhanced catalytic performance; pre-steady-state kinetic characterization of immobilized SQR catalytic cycle indicates that glutathione serves as physiologically relevant sulfur acceptor during hydrogen sulfide oxidation. 29855663_The evidence supported the significant role of SQRDL in the etiology of postmenopausal osteoporosis and suggest that it may be a genetic risk factor for BMD and osteoporosis in Han Chinese postmenopausal women. 30905673_human SQOR contains unique features: an electropositive surface depression implicated as a binding site for sulfane sulfur acceptors and postulated to funnel negatively charged substrates to a hydrophilic H2S-oxidizing active site, which is connected to a hydrophobic internal tunnel that binds coenzyme Q 32160317_Pathogenic variants in SQOR encoding sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase are a potentially treatable cause of Leigh disease. |
ENSMUSG00000005803 |
Sqor |
484.977153 |
2.2251150527 |
1.153880 |
0.089331856 |
166.597954 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000004094965831666434155496408335456076078950579476501815689954170195765214085083261203008034708721171127804305811537233239505439996719360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000654839606450667089551596746740358657444511700827429153801759088632361344948083663776051638550019032281035435971716651692986488342285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
679.8575970 |
38.4924284 |
307.8610985 |
13.3688529 |
| ENSG00000137809 |
22801 |
ITGA11 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKX5 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-11/beta-1 is a receptor for collagen. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an alpha integrin. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. This protein contains an I domain, is expressed in muscle tissue, dimerizes with beta 1 integrin in vitro, and appears to bind collagen in this form. Therefore, the protein may be involved in attaching muscle tissue to the extracellular matrix. Alternative transcriptional splice variants have been found for this gene, but their biological validity is not determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:22801; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; integrin alpha11-beta1 complex [GO:0034681]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; collagen binding involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098639]; collagen receptor activity [GO:0038064]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; collagen-activated signaling pathway [GO:0038065]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; substrate-dependent cell migration [GO:0006929] |
12392762_Major transcription start site mapped. A core promoter [nt (-)127-(+)25], a potential silencer region [nt (-)400-(-)127] and a potential enhancer region [nt (-)1519-(-)400] identified as important for alpha11 transcription in mesenchymal cells. 12496264_the GFOGER sequence in fibrillar collagens is a common recognition motif used by integrins, particularly alpha11beta1 16697656_A new interferon stimulated gene. (Integrin alpha 11) 17600088_Through interaction between matrix collagen and stromal fibroblasts, integrin alpha 11 stimulates cancer cell growth. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18990704_analysis of a prokaryotic Scl1 collagen sequence motif that mediates binding to human collagen receptors, integrins alpha2beta1 and alpha11beta1 19390575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19641149_is a major collagen receptor on human periodontal ligament cells [and plays] a role in collagen lattice remodeling [ITGA11B1] 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913614_Data show that the 3 kb alpha11 promoter contains most of the regulatory elements that direct ectomesenchymal and mesodermal fibroblast-specific expression. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21796158_The disturbance of alpha11beta1 mediated interactions to collagen I results in a tremendous reduction of hMSC numbers owing to mitochondrial leakage accompanied by Bcl-2-associated X protein upregulation. 22869616_Interactions between alpha11 integrins and the Smad-dependent TGF-beta2 signalling may contribute to the formation of pro-fibrotic myofibroblasts and the development of a fibrotic interstitium in diabetic cardiomyopathy. 24520080_Myometrium and uterine fibroids express ITGA11. 24962729_glycated collagen in the cardiac interstitium triggers an autocrine TGF-beta2 signaling pathway that stimulates alpha11 integrin expression through Smad2/3 binding elements in the alpha11 integrin promoter 26403263_FGF2 may be redirecting fibroblasts towards an anti-fibrotic phenotype during wound healing by overriding TGFb1 mediated ITGA11 expression. 27121382_Using MDR and RF, the overall best classifier of lung cancer status were SNPs rs1799732 (DRD2), rs5744256 (IL-18), rs2306022 (ITGA11) with training accuracy of 0.6592 and a testing accuracy of 0.6572 and a cross-validation consistency of 10/10 with permutation testing P |
ENSMUSG00000032243 |
Itga11 |
67.914181 |
5.0749813222 |
2.343403 |
0.333425725 |
47.508004 |
0.00000000000547798246491947891368646247237068425475770006016773550072684884071350097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000030955214847707311514786408519588067900230043960618786513805389404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
98.3837089 |
24.1098088 |
19.4769486 |
3.6408707 |
| ENSG00000137819 |
54852 |
PAQR5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NXK6 |
FUNCTION: Plasma membrane progesterone (P4) receptor coupled to G proteins (PubMed:23763432). Seems to act through a G(i) mediated pathway (PubMed:23763432). May be involved in oocyte maturation (PubMed:12601167). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12601167, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23763432}. |
Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Oogenesis;Receptor;Reference proteome;Steroid-binding;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in oogenesis. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54852; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; steroid binding [GO:0005496]; oogenesis [GO:0048477] |
18603275_Heterologous expression of MPRG in yeast confirms its ability to function as a membrane progesterone receptor. 21761364_Data show abundant mPRalpha (PAQR7), mPRbeta (PAQR8), and mPRgamma (PAQR5), but not classical nuclear PR (A or B isoforms) mRNA expression and mPRalpha protein expression in a panel of commonly used ovarian cancer cell lines. |
ENSMUSG00000032278 |
Paqr5 |
43.907811 |
7.4105362245 |
2.889578 |
0.518094596 |
27.779293 |
0.00000013597370911213784523090665565941970172048058884683996438980102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000529125216581902037130732269210042773011082317680120468139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.3988381 |
25.2138661 |
9.0838977 |
2.5636361 |
| ENSG00000137834 |
4091 |
SMAD6 |
protein_coding |
O43541 |
FUNCTION: Transforming growth factor-beta superfamily receptors signaling occurs through the Smad family of intracellular mediators. SMAD6 is an inhibitory Smad (i-Smad) that negatively regulates signaling downstream of type I transforming growth factor-beta (PubMed:9436979, PubMed:16951688, PubMed:22275001, PubMed:9759503, PubMed:10647776, PubMed:10708948, PubMed:10708949, PubMed:30848080). Acts as a mediator of TGF-beta and BMP anti-inflammatory activities. Suppresses IL1R-TLR signaling through its direct interaction with PEL1, preventing NF-kappa-B activation, nuclear transport and NF-kappa-B-mediated expression of pro-inflammatory genes (PubMed:16951688). Blocks the BMP-SMAD1 signaling pathway by competing with SMAD4 for receptor-activated SMAD1-binding (PubMed:9436979, PubMed:30848080). Binds to regulatory elements in target promoter regions (PubMed:16491121). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16491121, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16951688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22275001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30848080, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9436979, ECO:0000303|PubMed:10647776, ECO:0000303|PubMed:10708948, ECO:0000303|PubMed:10708949, ECO:0000303|PubMed:9759503}. |
Alternative splicing;Craniosynostosis;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD family of proteins, which are related to Drosophila 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and C. elegans Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein functions in the negative regulation of BMP and TGF-beta/activin-signalling. Multiple transcript variants have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:4091; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; heteromeric SMAD protein complex [GO:0071144]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; co-SMAD binding [GO:0070410]; I-SMAD binding [GO:0070411]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; R-SMAD binding [GO:0070412]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; type I activin receptor binding [GO:0070698]; type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034713]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; coronary vasculature development [GO:0060976]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; immune response [GO:0006955]; mitral valve morphogenesis [GO:0003183]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060394]; negative regulation of SMAD protein complex assembly [GO:0010991]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to laminar fluid shear stress [GO:0034616]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281]; zygotic specification of dorsal/ventral axis [GO:0007352] |
12397035_Smad6 has no role in TGF-beta response and injury in podocytes. In contrast, Smad6 is upregulated in the mesangium in human glomerular diseases and may be involved in functions independent of TGF-beta/Smad signaling. 12407115_Smad6 and Smad7 regulate thrombomodulin-dependent activation of protein C 14645520_Smad6 repressed bone morphogenetic protein-induced Id1 transcription through recruiting transcriptional corepressor C-terminal binding protein (CtBP). 15033458_tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate down-regulates Smad6 expression presumably via PKCmu-ERK-dependent pathway and up-regulates Smad7 expression via PKCmu-dependent mechanism(s) which need no MAPK and NF-kappaB activation 15529348_The regulation in chondrocytes of Smad6 and Smad7 expression by IL-1beta suggests a potentially important role of IL-1beta signaling in chondrocytes, via indirect influencing of the bone morphogenetic protein/TGFbeta signaling cascade. 15665522_Adrenomedullin can attenuate TGF-beta1-mediated renal tubulointerstitial extracellular matrix turnover via an antagonistic mechanism of inhibitory Smad 6 in TGF-beta1-elicited signaling. 15716278_the level of Smad6s can alter the level of TGF-beta and the subsequent induction of PAI-1 via a FoxD1 transcription site 15736400_Smad6 and Smad7 expression affects the progression of early lesions of esophageal SCC and indicates a poor prognosis. 16249187_appears that the anti-glucocorticoid actions of Smad6 may contribute to the neuroprotective, anticatabolic and pro-wound healing properties of the TGFbeta family of proteins 16299379_Smad6 interacts with Runx2 and mediates Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-induced Runx2 degradation 16373339_OAZ can alter the intensity and duration of the BMP4 stimulus through Smad6 16687405_Smad6 appears to functionally interact with Dlx3, altering the ability of Dlx3 to bind target gene promoters. 16886151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16951688_Smad6 bound to Pellino-1 promoted TGF-beta-mediated anti-inflammatory effects. 17359969_These data suggest autocrine TGF-beta1 antagonizes BMP signaling through modulation of inducible Smad6 and the activity of BMP specific Smad1/5. 17850776_Stimulation of Smad 6 inhibits ERK activation and thus results in a negative feedback loop to fine-tune BMP signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 17931948_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17934461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18445023_A case-control study in Afro-Caribbeans found SMAD6 SNPs were not strongly associated with increased risk of developing keloids. 18445023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19032685_Splice variant Smad6B, in human prostatic and rodent testicular cell lines, exhibits a truncated C-terminus lacking the entire MH-2 domain and most parts of the linker region. 19047146_Knockdown of SMAD6 led to the activation of TGF-beta signaling through up-regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and phosphorylation of SMAD2/3 in NSCLC. 19211612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19277452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19277452_Smad6 gene is a candidate for the genetic determinants of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. 19688145_Study data demonstrates downregulated SMAD6 expression in psoriatic skin. 19959123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20462450_Smad6 together with Smad2 may be prognostic factors, independent of nodal status in oral SCC after curative resection 20658468_Smad6 and Smad7, inhibitors of BMP signaling, were up-regulated in HFE-mutant hereditary hemochromatosis compared to controls, disruptin bone morphogenic protein signaling. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21576367_Data show that Runx1, in conjunction with Fli1, Gata2, and Scl, directly regulates the expression of Smad6 in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region in the developing embryo, where hematopoietic stem cells originate. 21897371_results suggest that MyD88 degradation driven by the Smad6-Smurf pathway is a novel mechanism for TGF-beta1-mediated negative regulation of MyD88-dependent pro-inflammatory signalling 21984931_Haplotype analysis further revealed that two haplotype blocks within SMAD6 were significantly associated with decreased ovarian cancer risk, as compared to the most common haplotype. 22223368_Loss of SMAD6 is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 22275001_Congenital cardiovascular malformation is related to genetic variation in SMAD6 22705548_Smad6 indirectly maintains stemness by preventing spontaneous erythropoiesis in hematopoietic stem cells. 23284751_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in SMAD6 gene is associated with brain metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer 23455153_monoubiquitinated SMAD6 impairs the binding affinity of non-modified SMAD6 to the BMP type I receptor. Moreover, UBE2O and SMAD6 cooperated in the regulation of BMP7-induced adipogenesis 27113436_Results show that high Smad6 expression is correlated with increased risk of metastasis in ER negative breast cancer and that Smad6 determines BMP-regulated invasive behavior of breast cancer cells in a zebrafish xenograft model. 27606499_This search revealed that rare mutations that disable one copy of a gene called SMAD6 in combination with a common DNA variant near another gene called BMP2 account for about 7% of infants with midline forms of craniosynostosis. 28847510_activation of AMPK upregulated Smad6 and Smurf1 and thereby enhanced their interactions, resulting in its proteosome-dependent degradation of ALK2. 28935696_evaluated the role of inherited genetic variation in Langerhans cell histiocytosis susceptibility and identified a novel risk variant in SMAD6 29344637_Overexpression of miR186 mimic induced HUVEC apoptosis through mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK) activation by targeting and inhibiting SMAD family member 6 (SMAD6). 29618840_SMAD6 overexpression leads to accelerated myogenic differentiation of LMNA mutated cells. 29950561_Study reports that SMAD6 is overexpressed in nuclei of glioma cells, which correlates with poor patient survival and regulates STAT3 activity via negatively regulating PIAS3. Mechanically, SMAD6 interacts directly with PIAS3, and this interaction is mediated through the Mad homology 2 domain of SMAD6 and the Ring domain of PIAS3. 30796334_data provide improved insights into the clinical spectrum of SMAD6-related bicuspid aortic valve/thoracic aortic aneurysm and has important implications for molecular diagnostics. 30848080_A novel SMAD6 variant was identified in a patient with severely calcified bicuspid aortic valve and thoracic aortic aneurysm. 30963242_Data indicate two individuals with biallelic missense variants in SMAD6 and a complex cardiac phenotype. 31138930_Exome sequencing identified 16 loss-of-function (LOF) and 6 missense variants (minor allele frequency [MAF] |
ENSMUSG00000036867 |
Smad6 |
32.466014 |
0.4394461291 |
-1.186242 |
0.419476944 |
7.911410 |
0.00491239741941899062810383824739801639225333929061889648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010059237778943437915946113037080067442730069160461425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5979167 |
4.8835268 |
42.5871080 |
7.6897499 |
| ENSG00000137936 |
8412 |
BCAR3 |
protein_coding |
O75815 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an adapter protein downstream of several growth factor receptors to promote cell proliferation, migration, and redistribution of actin fibers (PubMed:24216110). Specifically involved in INS/insulin signaling pathway by mediating MAPK1/ERK2-MAPK3/ERK1 activation and DNA synthesis (PubMed:24216110). Promotes insulin-mediated membrane ruffling (By similarity). In response to vasoconstrictor peptide EDN1, involved in the activation of RAP1 downstream of PTK2B via interaction with phosphorylated BCAR1 (PubMed:19086031). Inhibits cell migration and invasion via regulation of TGFB-mediated matrix digestion, actin filament rearrangement, and inhibition of invadopodia activity (By similarity). May inhibit TGFB-SMAD signaling, via facilitating BCAR1 and SMAD2 and/or SMAD3 interaction (By similarity). Regulates EGF-induced DNA synthesis (PubMed:18722344). Required for the maintenance of ocular lens morphology and structural integrity, potentially via regulation of focal adhesion complex signaling (By similarity). Acts upstream of PTPRA to regulate the localization of BCAR1 and PTPRA to focal adhesions, via regulation of SRC-mediated phosphorylation of PTPRA (By similarity). Positively regulates integrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of BCAR1 (By similarity). Acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for small GTPases RALA, RAP1A and RRAS (By similarity). However, in a contrasting study, lacks GEF activity towards RAP1 (PubMed:22081014). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZAZ5, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QZK2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18722344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19086031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22081014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24216110}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
Breast tumors are initially dependent on estrogens for growth and progression and can be inhibited by anti-estrogens such as tamoxifen. However, breast cancers progress to become anti-estrogen resistant. Breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance gene 3 was identified in the search for genes involved in the development of estrogen resistance. The gene encodes a component of intracellular signal transduction that causes estrogen-independent proliferation in human breast cancer cells. The protein contains a putative src homology 2 (SH2) domain, a hall mark of cellular tyrosine kinase signaling molecules, and is partly homologous to the cell division cycle protein CDC48. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:8412; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0002089]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045742]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
15671247_AND-34 activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and induces anti-estrogen resistance in a SH2 and GDP exchange factor-like domain-dependent manner 17270363_BCAR3 and NSP1 are more highly expressed than SH2D3C (SHEP1) in breast cancer cells, and the expression patterns suggest differential roles for the three genes during breast cancer progression. 17427198_BCAR3 induces anti-estrogen resistance in breast tumor cell lines by altering cell-cell/cell-matrix interactions and cyclin D1 promoter activity. 17616674_the spatial and temporal regulation of BCAR3/p130(Cas) interactions within the cell is important for controlling breast cancer cell motility 18722344_BCAR3 protein, through its SH2 domain, is involved in the signaling pathways of EGF leading to cell cycle progression; BCAR3 itself is part of a mitogenic signaling pathway. 19454314_The expression of breast cancer anti-estrogen resistance 3 results in basal serine phosphorylation of Crk-Associated Substrate Protein that normally occurs during adhesion of breast cancer cells to fibronectin. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940159_the c-Src/Cas/BCAR3 signaling axis is a prominent regulator of c-Src activity, which in turn controls cell behaviors that lead to aggressive and invasive breast tumor phenotypes 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21262352_BCAR3-p130Cas complex formation is not required for BCAR3-mediated anti-estrogen resistance, Rac activation or discohesion of epithelial breast cancer cells 22711540_BCAR3 expression may regulate Src signaling in a BCAR3-p130(cas) complex-dependent fashion by altering the ability of the Src SH3 domain to bind the p130(cas) SBD 23388341_The high expressions of Mig-7 and MMP-2 in gastric carcinoma tissues may have a synergistic promoting effect on VM formation. VM is closely associated with the invasion, metastasis and poor prognosis of gastric carcinoma. 23762409_BCAR3 promotes cell motility by regulating actin cytoskeletal and adhesion remodeling in invasive breast cancer cells. 24216110_Taken together, these results demonstrated that BCAR3 plays an important role in the signaling pathways of insulin leading to cell cycle progression and cytoskeleton reorganization, but not GLUT4 translocation. 24584939_BCAR1 and BCAR3 scaffolding proteins have roles in cell signaling and antiestrogen resistance 25499443_BCAR3 acts as a putative suppressor of breast cancer progression by inhibiting the prometastatic TGFbeta/Smad signaling pathway in invasive breast tumors. 25817040_BCAR3 is an essential interactor and mediator of HEF1-induced migration. 27050277_Inhibiting MIG-7 by RNA interference in grafted EOC cells retarded tumor growth, angiogenesis and improved host survival, and suppressing MIG-7 expression with a small molecule inhibitor D-39 identified from the mitigated EOC growth and invasion and specifically abrogated the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. 28616909_MIG7 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue is high and correlated positively with vasculogenic mimicry formation, invasion and metastasis. 29192416_MIG-7 mRNA expression may serve as an additional molecular marker of vasculogenic mimicry in ovarian malignancies. 29251318_Study provides evidence that MIG7 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissue is correlated positively with vasculogenic mimicry (VM) formation and MIG7 expression in different HCC cell lines is coincident with their VM formation, invasion and metastasis. 29750896_MIG-7 serves as an independent unfavorable prognostic indicator in osteosarcoma patients and MIG-7 is an important mediator of osteosarcoma Vascular Mimicry formation. 30563570_high expression level of BCAR3 predicted better prognosis of multiple myeloma patients. 31140421_Silencing of Mig-7 gene inhibits vasculogenic mimicry formation and invasion of U251 cells possibly by suppressing MEK/ERK signaling, suggesting the important role of Mig-7 gene in vasculogenic mimicry formation and invasion of human glioma cells 31233772_miR-126-5p negatively regulated BCAR3 expression in eutopic endometriosis, enhanced the migration and invasion of endometrial cells, and promoted the occurrence of endometriosis. 31688418_this study indicates that the expression of Mig-7 in gliomas is positively correlated with vasculogenic mimicry formation and is related to the glioma pathological grade 34169835_A Cas-BCAR3 co-regulatory circuit controls lamellipodia dynamics. 35031902_Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of RET, BCAR1, and BCAR3 expression in patients with Luminal A and B breast cancer subtypes. |
ENSMUSG00000028121 |
Bcar3 |
87.447558 |
0.1890986408 |
-2.402789 |
0.248107418 |
93.697266 |
0.00000000000000000000036766836116146421883014668166141174730624713025533909887117246448329233032836782513186335563659667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000003535364827845740662509927722614943132892292593784125219599431821926316388271516188979148864746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.5721248 |
3.7893875 |
114.9842184 |
13.0666908 |
| ENSG00000137959 |
10964 |
IFI44L |
protein_coding |
Q53G44 |
FUNCTION: Type I interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) that plays a critical role in antiviral and antibacterial activity (PubMed:34722780). During bacterial infection, promotes macrophage differentiation and facilitates inflammatory cytokine secretion (PubMed:34722780). Plays a role in the control of respiratory syncytial virus/RSV infection, reducing the ability of the virus to replicate (PubMed:32611756). Exhibits a low antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus (PubMed:21478870). Acts also as a feedback regulator of IFN responses by negatively regulating IKBKB and IKBKE kinase activities through interaction with FKBP5 (PubMed:31434731). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21478870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31434731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32611756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34722780}. |
Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10964; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955] |
20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24755989_LMKB is the first protein identified to date that interacts with this portion of Ge-1. LMKB was expressed in human B and T lymphocyte cell lines; depletion of LMKB increased expression of IFI44L. 28289848_study reveals common CD46 and IFI44L SNPs associated with measles-specific humoral immunity, and highlights the importance of alternative splicing/virus cellular receptor isoform usage as a mechanism explaining inter-individual variation in immune response after live measles vaccine 29848298_Study demonstrated for the first time that IFI44L is a novel tumor suppressor to affect cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance via regulating Met/Src signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma and can be serve as an important prognostic marker. 31018104_miR-628-5p promotes growth and migration of osteosarcoma by targeting IFI44L. 31409879_A qPCR expression assay of IFI44L gene differentiates viral from bacterial infections in febrile children. 32561935_Associations Between IFI44L Gene Variants and Rates of Respiratory Tract Infections During Early Childhood. 32611756_Interferon-Induced Protein 44 and Interferon-Induced Protein 44-Like Restrict Replication of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. 33159419_IFI44L expression is regulated by IRF-1 and HIV-1. 33494515_Targeted Profiling of Immunological Genes during Norovirus Replication in Human Intestinal Enteroids. 34516357_Integrated weighted gene co-expression network analysis uncovers STAT1(signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) and IFI44L (interferon-induced protein 44-like) as key genes in pulmonary arterial hypertension. 34722780_IFI44L as a Forward Regulator Enhancing Host Antituberculosis Responses. 34884921_Identified Three Interferon Induced Proteins as Novel Biomarkers of Human Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. 34903206_The prognostic and clinical significance of IFI44L aberrant downregulation in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 35059970_Differentially methylation of IFI44L gene promoter in Iranian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. 35592687_Epigenetic Regulation of IFI44L Expression in Monocytes Affects the Functions of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. |
ENSMUSG00000039146 |
Ifi44l |
9.153569 |
3.8262351935 |
1.935926 |
0.634954945 |
9.211629 |
0.00240482563972468444193908432282569265225902199745178222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005232968663177996193613950026701786555349826812744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.0443185 |
3.8928902 |
3.1554664 |
0.8655280 |
| ENSG00000137968 |
204962 |
SLC44A5 |
protein_coding |
Q8NCS7 |
Mouse_homologues |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane transport. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:204962; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; choline transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015220]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:0006656]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27082540_the present study indicated the important role of SLC44A5 as a tumor promoter in HCC through the inhibition of choline uptake, suggesting that SLC44A5 may be a potential target for HCC therapy. |
ENSMUSG00000028360 |
Slc44a5 |
95.980242 |
0.4033214589 |
-1.309998 |
0.166713865 |
63.194428 |
0.00000000000000187277430268283219505460851440515671187175480993936105278407922014594078063964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000013175476028407342679128169876365195146007518178787876195201533846557140350341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.7683154 |
6.8378224 |
139.0551183 |
11.2073828 |
| ENSG00000138018 |
85465 |
SELENOI |
protein_coding |
Q9C0D9 |
FUNCTION: Ethanolaminephosphotransferase that catalyzes the transfer of phosphoethanolamine/PE from CDP-ethanolamine to lipid acceptors, the final step in the synthesis of PE via the 'Kennedy' pathway (PubMed:17132865, PubMed:28052917, PubMed:29500230). PE is the second most abundant phospholipid of membranes in mammals and is involved in various membrane-related cellular processes (PubMed:17132865). The enzyme is critical for the synthesis of several PE species and could also catalyze the synthesis of ether-linked phospholipids like plasmanyl- and plasmenyl-PE which could explain it is required for proper myelination and neurodevelopment (PubMed:29500230). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17132865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28052917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29500230, ECO:0000303|PubMed:17132865}. |
Acetylation;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Phospholipid biosynthesis;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Selenocysteine;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis; phosphatidylethanolamine from ethanolamine: step 3/3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28052917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29500230}. |
The multi-pass transmembrane protein encoded by this gene belongs to the CDP-alcohol phosphatidyltransferase class-I family. It catalyzes the transfer of phosphoethanolamine from CDP-ethanolamine to diacylglycerol to produce phosphatidylethanolamine, which is involved in the formation and maintenance of vesicular membranes, regulation of lipid metabolism, and protein folding. This protein is a selenoprotein, containing the rare selenocysteine (Sec) amino acid at its active site. Sec is encoded by the UGA codon, which normally signals translation termination. The 3' UTRs of selenoprotein mRNAs contain a conserved stem-loop structure, designated the Sec insertion sequence (SECIS) element, that is necessary for the recognition of UGA as a Sec codon rather than as a stop signal. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:85465; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; ethanolaminephosphotransferase activity [GO:0004307]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006646] |
28052917_These studies define the first human disorder arising due to defective CDP-ethanolamine biosynthesis and provide new insight into the role of Kennedy pathway components in human neurological function 29101747_intracellular localization of human selenoprotein SelI and the degree of expression of its gene in different human tumor cell lines 29500230_the indispensable role of EPT1 in the myelination process and neurodevelopment, and in the maintenance of normal homeostasis of ether-linked phospholipids in humans 32142958_Accessing the transcriptional status of selenoproteins in skin cancer-derived cell lines. 34681834_Roles for Selenoprotein I and Ethanolamine Phospholipid Synthesis in T Cell Activation. 36007576_Selenoprotein I (selenoi) as a critical enzyme in the central nervous system. |
ENSMUSG00000075703 |
Selenoi |
338.324473 |
2.7855421612 |
1.477958 |
0.102999360 |
207.903057 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003938855278918036983131569726459927821297582656684146020868721546905106212452786405984865569072504254082076425647670342433670498394349124282598495483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000783524311547577202459005836733377824412649353942168920620292711698084801445565221241416950862767839294728106793830151033386499648258904926478862762451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
509.7839915 |
29.8586116 |
184.1192923 |
8.7567960 |
| ENSG00000138028 |
10669 |
CGREF1 |
protein_coding |
Q99674 |
FUNCTION: Mediates cell-cell adhesion in a calcium-dependent manner (By similarity). Able to inhibit growth in several cell lines. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell cycle;Growth arrest;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of cell population proliferation. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10669; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26022276_Results clearly indicated that CGREF1 is a novel secretory protein, and plays an important role in regulation of AP-1 transcriptional activity and cell proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000029161 |
Cgref1 |
13.592756 |
4.8227822766 |
2.269866 |
0.481724090 |
23.470514 |
0.00000126842974514575172338866348997754585070651955902576446533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004439654502810361872962123530594880094213294796645641326904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.4865311 |
6.7469397 |
4.7532227 |
1.2050196 |
| ENSG00000138061 |
1545 |
CYP1B1 |
protein_coding |
Q16678 |
FUNCTION: A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in the metabolism of various endogenous substrates, including fatty acids, steroid hormones and vitamins (PubMed:20972997, PubMed:11555828, PubMed:12865317, PubMed:10681376, PubMed:15258110). Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via cytochrome P450 reductase (NADPH--hemoprotein reductase) (PubMed:20972997, PubMed:11555828, PubMed:12865317, PubMed:10681376, PubMed:15258110). Exhibits catalytic activity for the formation of hydroxyestrogens from estrone (E1) and 17beta-estradiol (E2), namely 2- and 4-hydroxy E1 and E2. Displays a predominant hydroxylase activity toward E2 at the C-4 position (PubMed:11555828, PubMed:12865317). Metabolizes testosterone and progesterone to B or D ring hydroxylated metabolites (PubMed:10426814). May act as a major enzyme for all-trans retinoic acid biosynthesis in extrahepatic tissues. Catalyzes two successive oxidative transformation of all-trans retinol to all-trans retinal and then to the active form all-trans retinoic acid (PubMed:10681376, PubMed:15258110). Catalyzes the epoxidation of double bonds of certain PUFA. Converts arachidonic acid toward epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EpETrE) regioisomers, 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15- EpETrE, that function as lipid mediators in the vascular system (PubMed:20972997). Additionally, displays dehydratase activity toward oxygenated eicosanoids hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoates (HpETEs). This activity is independent of cytochrome P450 reductase, NADPH, and O2 (PubMed:21068195). Also involved in the oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics, particularly converting polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heterocyclic aryl amines procarcinogens to DNA-damaging products (PubMed:10426814). Plays an important role in retinal vascular development. Under hyperoxic O2 conditions, promotes retinal angiogenesis and capillary morphogenesis, likely by metabolizing the oxygenated products generated during the oxidative stress. Also, contributes to oxidative homeostasis and ultrastructural organization and function of trabecular meshwork tissue through modulation of POSTN expression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64429, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10426814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10681376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11555828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12865317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15258110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20972997, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21068195}. |
3D-structure;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Glaucoma;Heme;Iron;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Peters anomaly;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism |
PATHWAY: Steroid hormone biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11555828, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12865317}.; PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; retinol metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10681376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15258110}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; arachidonate metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20972997}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. The enzyme encoded by this gene localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and metabolizes procarcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and 17beta-estradiol. Mutations in this gene have been associated with primary congenital glaucoma; therefore it is thought that the enzyme also metabolizes a signaling molecule involved in eye development, possibly a steroid. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1545; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; aromatase activity [GO:0070330]; estrogen 16-alpha-hydroxylase activity [GO:0101020]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; hydroperoxy icosatetraenoate dehydratase activity [GO:0106256]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; monooxygenase activity [GO:0004497]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen [GO:0016712]; adrenal gland development [GO:0030325]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; benzene-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0042537]; blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043534]; blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048514]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to cortisol stimulus [GO:0071387]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to luteinizing hormone stimulus [GO:0071373]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; cellular response to progesterone stimulus [GO:0071393]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; DNA modification [GO:0006304]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542]; endothelial cell-cell adhesion [GO:0071603]; epoxygenase P450 pathway [GO:0019373]; estrogen metabolic process [GO:0008210]; estrous cycle [GO:0044849]; ganglion development [GO:0061548]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to oxidative stress [GO:0008631]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; membrane lipid catabolic process [GO:0046466]; negative regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033629]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0006809]; omega-hydroxylase P450 pathway [GO:0097267]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000377]; response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0046685]; response to dexamethasone [GO:0071548]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to follicle-stimulating hormone [GO:0032354]; response to indole-3-methanol [GO:0071680]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; retinal blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0061304]; retinal metabolic process [GO:0042574]; retinol metabolic process [GO:0042572]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; sterol metabolic process [GO:0016125]; toxin metabolic process [GO:0009404]; trabecular meshwork development [GO:0002930]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
9097971_'drug-metabolizing' enzymes might modulate the processes of growth and differentiation by controlling the steady-state-levels of oxygenated growth-effector molecules. 9097971_The first study describing mutations of human cytochrome P4501B1 gene (CYP1B1) in affected individuals of PCG families linked to locus GLC3A on 2p21. 9497261_This study presents three-dimensional homology model of the conserved C-terminal half of CYP1B1. 11221602_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11303589_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11389067_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11403040_mutations in a patient with Peters' anomaly 11558822_CYP1B1 mutations for congenital glaucoma 11749050_Investigators examining possible associations between early menarche and mutations in genes of estrogen metabolism found no such association for this gene. 11749050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11774072_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11774072_digenic inheritance of early-onset glaucoma: CYP1B1, a potential modifier gene 11854439_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11955671_airborne particulates generated during the frying of beef, fish and pork can induce carcinogen-metabolizing CYP1B1 in the human lung-derived cell line 12010864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12183407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12200121_CYP1B1 polymorphism in prostate neoplasms 12200121_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12385014_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12415427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12419832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12520071_CYP1B1 mRNA is expressed in human liver and the levels are increased in smokers, but the protein is undetectable. 12525557_CYP1B1 gene is a major gene associated with primary congenital glaucoma (GLC3A). 12567107_The phenotypic expression of 3 patients confirm the crucial role of CYP1B1 mutations for congenital glaucoma. 12598442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12602902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12618873_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12692107_High-activity CYP1A2 and CYP1B1 alleles, whose gene products metabolize estradiol, were not associated with pubertal stage. 12692107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12718576_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12770747_polymorphism and risk of endometrial cancer 12807732_Single amino acid mutations, but not common polymorphisms, decrease the activity of CYP1B1 against (-)benzo[a]pyrene-7R-trans-7,8-dihydrodiol. 12837283_CYP1B1 is a senescence-associated gene in normal human oral keratinocytes. 12844487_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12844487_the studied CYP1B1 gene polymorphisms do not influence breast cancer risk overall but may modify the risk after long-term menopausal hormone use. 14507861_Identification of R368H as a predominant CYP1B1 allele causing primary congenital glaucoma in Indian patients. 14520706_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14562027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14656940_Carriers of the CYP1B1 Ser allele had a statistically significant decreased risk of endometrial cancer. 14656940_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14729846_Four founder mutations were identified in congenital glaucoma patients in two ethnically heterogeneous populations. 14734460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14734460_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of CYP1B1 is associated with breast cancer 14744739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14961553_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15072827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15075793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15102677_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15122594_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15177664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15199113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15255109_Mutations in CYPIBI are not a major cause of PCG (primary congenital glaucoma) in this population and that at least one additional locus for this condition is responsible for most cases. 15255550_CYP1B1*3 does not have a role in ovarian cancer development in the Italian Caucasian population 15255550_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15285606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15297370_CYP1B1 is induced in tobacco smoke-induced carcinogenesis in the aerodigestive tract. 15299091_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15333708_Transcription factors with an affinity for Sp1 sites mediate transcriptional activation of the CYP1B1 gene in biotin-supplemented T cells, increasing the occurrence of single-stranded DNA breaks. 15342454_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15342693_CYP1B1 mutations might pose a significant risk for early-onset primary open-angle glaucoma and might also modify glaucoma phenotype in patients who do not carry a MYOCILIN mutation 15342693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15382051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15386537_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15475877_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15596250_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15636228_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15654505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15723004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15733270_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15734954_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15734958_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15774541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15774541_The number of full-term pregnancies and the CYP1B1-4 polymorphism are significant predictors of timing of natural menopause in Caucasian women. 15777990_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15808404_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15861043_cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) is inhibited by coumarins, regardles of the CYP1B1 polymorphism 15896461_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15905203_Methoxylated dietary flavonoids may be potent chemoprotectants by direct inhibition of CYP1B1/1A1 function and/or their protein expression in mouth mucosa and cancer. 15941966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15958554_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15987428_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16051642_CYP1B1 Leu(432)Val alone and in combination with Phase II enzyme polymorphisms was more strongly associated with increased lung cancer susceptibility among those with at least some household environmental tobacco smoke exposure 16051642_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16103451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16115918_Hypomethylation of the CYP1B1 gene may play an important role in prostate cancer. 16172228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16172230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16202920_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16207128_A common polymorphism in the CYP1B1 gene was associated with changes in urinary estrogen levels: both Caucasian and African-American women carrying the variant allele showed higher urinary metabolite ratios than women with the wild-type allele. 16260521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284375_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16319265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16319821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16319821_The common N453S coding variant of CYP1B1 is potentially a factor of severity in POAG patients. 16384942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16384942_The strong association of specific haplotypes with some predominant CYP1B1 mutations underlying primary congenital glaucoma (PCG) and the observed geographical clustering, may be useful for predictive testing. 16490498_The CYP1B1 mutation spectrum of Kuwaiti PCG (primary congenital glaucoma) patients is similar to that detected in the neighboring countries. 16569655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16598069_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16638984_The frequency of mutations in the FOXC1, GJA1, PITX2, and CYP1B1 genes in this study were 25%, 12.5%, 0% and 0%, respectively. 16688110_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16688110_On rare occasions CYP1B1 may be primarily responsible for juvenile primary open-angle glaucoma by possible monogenic association. 16716118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16730930_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16735991_This study supports the role of CYP1B1 as a causative gene in Peters anomaly. Furthermore, this emphasizes the broad range of phenotypic expression for CYP1B1 mutations, and its role in eye development. 16735994_Founder effects for most of CYP1B1 mutations. 16766147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16766147_The results from this study suggested that CYP1B1 genetic polymorphisms may be associated with the natural onset of menopause. 16808847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847423_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16847423_Strong evidence against the existence of a substantial overall association between common genetic variation in CYP1B1 and breast cancer risk. 16850246_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16862072_Heterozygous CYP1B1 mutations could confer increased susceptibility to the development of primary open angle glaucoma in the Spanish population. 16862072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16864595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16896040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16949388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16949388_The urinary levels of estradiola nd estrogen metabolites associated with polymorphisms of CYP1A1 AND CYP1B1 in premenopausal/perimenopausal women are reported. 16963504_Compared to the wild-type of CYP1B1 the core regions in the mutant structures are associated with subtle but significant changes, and the functionally important regions. 16977255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16978616_CYP1B1 Val432Leu polymorphism is associated with first-trimester miscarriage, and it may also modify the risk among coffee drinkers. 16978616_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16985026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16985250_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17035385_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17053044_No association between the CYP1B1 Val432Leu polymorphism and breast cancer was observed in Asians. An inverse association was observed in populations of mixed/African origin. 17053044_Observational study, meta-analysis, and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17063266_CYP1A1 but not CYP1B1 genetic polymorphisms may have roles in breast cancer risk in a Finnish Caucasian population along with smoking 17063266_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17077994_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17077994_SHBG, but not CYP17, CYP1B1, or COMT polymorphisms are associated with different sex hormone levels in post-menopausal breast cancer survivors 17157584_Most patients in our cohort had compound heterozygous CYP1B1 mutations. Specific CYP1B1 mutations may be associated with severe or moderate angle abnormalities. 17164573_while mutations that affect the conserved core structures of cytochrome P4501B1 result in primary congenital glaucoma (PCG), mutations in other regions hold the potential to define differences in estrogen metabolism. 17174438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17187946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17200336_AhR overexpression up-regulates the expression of CYP1B1 in the early stage of lung adenocarcinoma 17220347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17224759_This is the first report of molecular genetic analysis of PCG (primary congenital glaucoma) in the Egyptian population in which 2 novel mutations have been identified. 17224914_Breast cancer patients homozygous for the CYP1B1*3 allele had a significantly longer progression-free survival after paclitaxel treatment. 17224914_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17301257_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17311112_Proliferation of breast cancer cells is accompanied not only by expression of genes encoding cytochromes involved in estrogen metabolism, but also by changes in the expression of other genes. 17321191_glaucoma-associated genes (MYOC, CYP1B1) expressed in the ciliary body and their mutant proteins could influence intraocular pressure, contributing to the development of glaucoma. 17363580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17372239_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17372243_CYP1B1 Leu(432) carriers were at increased risk of ovarian cancer, with an adjusted OR of 1.5 17372243_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17403528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17429315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17449539_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17449559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17458695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17458695_The CYP1B1 gene appears to influence breast cancer susceptibility in Poland. 17496311_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17498780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17507616_These results support the hypothesis that the formation and accumulation of catechol estrogens in breast tissue through increased CYP1B1 expression and reduced COMT expression may play a significant role in breast cancer risk. 17507624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17548691_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17562158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17562158_Single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes of the genes encoding the CYP1B1 has no association with advanced endometriosis 17563717_3.59% of our primary open-angle glaucoma patients had mutations in the CYP1B1, MYOC, and OPTN genes; first report to document the involvement of the CYP1B1, MYOC, and OPTN genes in the etiology of POAG in the same set of Indian patients 17563717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17575219_CYP1B1 is frequently expressed in a variety of gliomas and could be used as a target for immunotherapy. 17588204_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17589376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17591938_CYP1B1 mutations were identified in 70% of primary congenital glaucoma patients. 17591938_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17603900_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17615053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17615053_This study provides some support for polymorphic variation in CYP1A2 and CYP1B1 playing a role in colorectal cancer susceptibility. 17627011_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17642299_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17687619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17704407_CYP1B1 AND CYP19 WERE ASSOCIATED WITH RISK OF PROSTATE CANCER 17704407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17718864_Mutations in CYP1B1 account for approximately one in five primary congenital glaucoma cases from Australia. 17893647_Two novel (p.R117W and p.G329V), as well as six previously reported mutations were identified. Two new mutant proteins showed considerably reduced enzyme activity as well as diminished localization in mitochondria. 17914928_it is speculated that diminished or absent metabolism of key endogenous CYP1B1 substrates adversely affects the development of the trabecular meshwork [review] 17919675_Benzo(k)fluoranthene and benzo(a)pyrene induced CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in T-47D human breast cancer cells. 17922187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17922187_the CYP1B1_1358_A>G polymorphism has an impact on ERalpha status in breast cancer 17925548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17980933_CYP1B1, CYP1A1, MPO, and GSTP1 polymorphisms and lung cancer risk in never-smoking Korean women. 17980933_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18055790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18055790_The results demonstrate an involvement of CYP1B1 in a proportion of POAG and PACG cases that should be explored further. 18059014_While increasing AhR binding to both CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induced CYP1A1 mRNA in both a malignant and non-malignant line but increased only CYP1B1 mRNA in the malignant line 18067928_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18067928_Several fold increase in risk in head and neck cancer with use of tobacco (cigarette smoking or tobacco chewing) or alcohol with the variant genotypes of CYP1B1 (CYP1B1*2 and CYP1B1*3). 18070520_A novel mutation in exon 3 of CYP1B1 was found in primary congenital glaucoma patients of Hubei Han nationality. 18070520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18187806_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18187806_This pilot study provides evidence that CYP1B1*3 may be an important marker for estimating docetaxel efficacy in patients with prostate cancer 18227148_study demonstrates that several genetic variants of CYP1B1 have significant changes in the protein expression level and 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhIP)metabolizing activity 18258609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18268125_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18268125_PAH-DNA adduct formation could be modulated by common genetic variants in CYP1B1 in African American, Dominican and Caucasian mothers and newborns. 18318428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18347981_In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, polymorphisms in CYP1B1 might be related with k-ras activation pathways. 18347981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18385784_MYOC and CYP1B1 contributed equally to the disease status of the Iranian juvenile open angle glaucoma patients studied. The contribution of the two genes appeared to be independent in that no patient carried mutations in both genes. 18414103_Mexican patients with PCG (primary congenital glaucoma) are rarely (less than 10%) due to CYP1B1 mutations. 18415014_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18425393_CYP1B1, GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1 polymorphisms may have a role in susceptibility to breast cancer 18425393_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18470941_CYP1B1 mutations causing primary congenital glaucoma can act by either reducing enzymatic activity (p.G61E and p.N203S), reducing the abundance of the enzyme (p.Y81N and p.E229 K), or both (p.L343del). 18483560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18483560_The potential of coding single nucleotide polymorphisms (cSNPs) in the gene for association with primary open-angle glaucoma, was examined. 18486761_CYP240 peptide from CYP1B1 protein is spontaneously recognized by HLA-A1 and HLA-B35 restricted CD8 T cells in cancer patients. 18497059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18510611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18537981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18537981_identified five different CYP1B1 mutations - four known and one novel and potentially pathogenic (F445I), which together accounted for approximately 30% of disease alleles in a Gypsy population with congenital glaucoma 18544568_CYP1B1 variants are associated with prostate cancer. 18544568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18569579_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18569591_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18573508_Genotype polymorphic combinations of CYP1B1Ala119Ser and CYP1B1Leu432Val with GSTM1 is associated with lung cancer. 18573508_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18575334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18616618_The exclusion of these genes as likely candidates supports the hypothesis that the ocular phenotype associated with peters' anomaly segregating in this family is a distinct, new, autosomal dominant entity in the anterior segment dysgenesis spectrum. 18622259_Primary congenital glaucoma-related mutations cause identifiable structural changes negatively impacting CYP1B1 biochemistry and stability. 18628428_Observational study of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18628428_Risk of breast cancer increased little with increasing years of E+P use among women with at least one CYP1B1 Val(432) allele; a large increase in risk was seen among women homozygous for CYP1B1 Leu(432). 18632753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18763031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18763031_the genotype of CYP1A1 Ile462Val, but not the CYP1B1 polymorphism, is associated with the increased risk of uterine leiomyomas in Chinese women 18779756_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18779756_results suggest that the L432V polymorphism in the cytochrome P450 1B1 gene could be used to predict the effect of hormone therapy on lumbar bone mineral density and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in Japanese women 18784359_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18794456_CYP1B1 mRNA is expressed in human skin, at higher levels in men than in women in hip or arm. No gender difference in face skin. CYP1B1 levels are not altered by topical 17beta-estradiol treatment. 18820009_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18829176_CYP1B1 is overexpressed in tumor tissues independent of oncogenic origin and may be able to generate compounds of interest in photodynamic therapy. 18841557_possible role of MYOC and CYP1B1 in the development of PACG 18852424_CYP1B1 mutations associated with primary congenital glaucoma in Chinese population. 18852424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18922394_This study found a significant association between CYP1B1 expression and decreased HDL cholesterol levels in incinerator workers. 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18977467_Data suggest that through its effect on the rate of estrogen catabolism, the Val432Leu polymorphism of the CYP1B1 gene may represent as a possible genetic risk factor for osteoporosis in American women. 18977467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18980759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18989382_These results strongly suggest that missense mutations in CYP1B1 are most likely to be responsible for primary congenital glaucoma in these families. 18990750_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19015200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19031960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064581_No association between CYP1b1 polymorphisms and risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. 19064581_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19083124_No differences between BRCA1 mutation carriers and 22 non-carriers were found in the expression of CYP1B1 and fatty acid synthase in breast cancer patients 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19096718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19096718_The results suggest that CYP1B1 is implicated in primary open angle glaucoma among Iranians, notably in the juvenile-onset form. 19116217_discusses CYP1B1 overexpression in tumor cells and tissues and its role in metabolism of photochemicals in fruits and vegetables in the context of cancer prevention and treatment [review] 19126602_Expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 in human endothelial cells: regulation by fluid shear stress. 19127255_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19138946_Resveratrol can prevent breast cancer initiation by blocking multiple sites in the estrogen genotoxicity pathway. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19174490_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19179758_The present study revealed essential differences in the interactions between ligand and protein in wild-type and disease mutants,and helped in understanding the deleterious nature of disease mutations at the level of molecular function. 19195637_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19195637_Our results indicate that only a minor proportion of German primary congenital glaucoma patients harbor mutations in the CYP1B1 gene and are in line with similar studies from other ethnic populations in which the rate of consanguinity is low. 19199255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19199255_The gene polymorphisms of CYP1B1 in exon 2 codon 119 may be a genetic risky factor for endometriosis. 19208203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19214745_CYP1B1 V432L significantly increased the dose-response relationship between personal diagnostic X-ray exposure & breast cancer risk, adjusted for cumulative occupational radiation dose & for the reverse. 19214745_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19229255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19234632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19234632_data indicate approximately one-third of Spanish patients with primary congenital glaucoma carry loss-of-function CYP1B1 & show that null alleles are associated with the most severe phenotypes 19247456_CYP1B1 is major gene for primary congenital glaucoma(PCG), appearing to be responsible for disease in roughly one in six Chinese PCG patients. R390H mutation was identified as predominant CYP1B1 allele among Chinese PCG patients in our study. 19247456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19274671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287966_CpG methylation of the CYP1B1 promoter region, but not CYP1A1, epigenetically regulates CYP1B1 expression during development of some colorectal cancers 19290787_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19293312_Genetic variation in CYP1B1 has at most a minor influence on breast cancer susceptibility. 19293312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19324859_TCDD potently induces CYP1B1 mRNA in human nonpigmented ciliary epithelial cells, suggesting the involvement of an AHR-mediated pathway in the regulation of ciliary CYP1B1 expression. 19331196_High levels of CYP1B1 expression were more prevalent in stage-IV disease than in earlier stages in NSCLC. 19338043_An decreased risk of DLBCL in nonsmokers was associated with the variant G allele for CYP1B1 (OR = 0.6, 95% CI 0.4-1.0). 19338043_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19349377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19357154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19383894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19383894 |
ENSMUSG00000024087 |
Cyp1b1 |
416.480724 |
4.6225061115 |
2.208675 |
0.092225554 |
601.378344 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000083945782428531236741211696381314238074931054047730773455914980503073369766036182868384866791232074713647495202171281945905023344084381591505216472167829394076658038779184656124023216384774659166448 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000046405983095322884382296659192387325379242969870961741262018956871061344090992268545468089004840597007826709875506662330300677177152129057888263442556262782563881100162913805012359806231025209003070 |
Yes |
No |
691.7837026 |
39.2513178 |
150.6454890 |
7.2344777 |
| ENSG00000138074 |
8884 |
SLC5A6 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y289 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter that transports pantothenate, biotin and lipoate (PubMed:10329687, PubMed:15561972, PubMed:21570947, PubMed:20980265, PubMed:22927035, PubMed:22015582, PubMed:25971966, PubMed:25809983, PubMed:28052864, PubMed:27904971, PubMed:31754459). Required for biotin and pantothenate uptake in the instestine (By similarity). Plays a role in the maintenance of intestinal mucosa integrity, by providing the gut mucosa with biotin (By similarity). May play a role in the transport of biotin and pantothenate into the brain across the blood-brain barrier (PubMed:25809983). May also be involved in the sodium-dependent transport of iodide ions (PubMed:20980265). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5U4D8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10329687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15561972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20980265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21570947, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22015582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22927035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25809983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25971966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27904971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28052864, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31754459}. |
Biotin;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables biotin transmembrane transporter activity and pantothenate transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in anion transmembrane transport and transport across blood-brain barrier. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8884; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle membrane [GO:0012506]; biotin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015225]; pantothenate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015233]; sodium-dependent multivitamin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008523]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; vitamin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0090482]; biotin import across plasma membrane [GO:1905135]; biotin transport [GO:0015878]; iodide transmembrane transport [GO:1904200]; pantothenate transmembrane transport [GO:0015887]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
12646417_in intestinal and liver epithelial cells, SMVT is the major (if not the only) biotin uptake system that operates. 15561972_biotin uptake by human renal epithelial cells occurs via the hSMVT system and that the process is regulated by intracellular PKC- and Ca(2+)/calmodulin-mediated pathways. 16749865_A sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter, SMVT, responsible for biotin uptake and transport, was identified and functionally characterized in MDCK-MDR1 cells. 16959947_Human intestinal biotin uptake is adaptively regulated but is not mediated via changes in hSMVT RNA stability. 17135299_KLF-4 and AP-2 is regulating the activity of the hSMVT promoter in the intestine and provide direct in vivo confirmation of hSMVT promoter activity. 17904341_findings from this study are consistent with the theory that HCS senses biotin, and that biotin regulates its own cellular uptake by participating in HCS-dependent chromatin remodeling events at the SMVT promoter 1 locus in Jurkat cells. 19211916_Conclude that the COOH tail of hSMVT contains several determinants important for polarized targeting and biotin transport in epithelial cells. 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20962270_These results show important role for His(1)(1) and His(2) residues in hSMVT function, which is most probably mediated via an effect on level of hSMVT expression at the cell membrane. 20980265_hSMVT may play an important role in the homeostasis of I(-) in the body 21183659_PDZD11 is an interacting partner with hSMVT in intestinal epithelial cells and that this interaction affects hSMVT function and cell biology. 21570947_Human SMVT protein is glycosylated, and that glycosylation is important for its function. The study also shows a role for the putative PKC-phosphorylation site Thr(286) of hSMVT in the PKC-mediated regulation of biotin uptake. 22015582_Cys(294) is essential for the function of the human sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter. 22304562_PCR analysis had confirmed the existence of FR-alpha, SMVT, and B ((0, +)) in Y-79 and ARPE-19 cells. 22732670_This study for the first time confirms the molecular expression of SMVT and demonstrates that SMVT, responsible for biotin uptake, is functionally active in PC-3 prostate cancer cells 22927035_This study shows for the first time the functional and molecular presence of SMVT in immortalized human corneal epithelial (HCEC) and retinal pigment epithelial (D407) cells 23142496_these studies demonstrated for the first time the functional and molecular expression of sodium dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT) in human derived breast cancer (T47D) cells 25809983_SLC5A6 is responsible for the supplies of biotin and pantothenic acid into the brain across the blood brain barrier. 25971966_SMVT-mediated transport is highly specific for R-(+)-alpha-lipoic acid. 25999427_S. typhimurium infection inhibits intestinal biotin uptake by SLC5A6, and that the inhibition is mediated via the action of proinflammatory cytokines. 28052864_This study shows for the first time that LPS inhibits colonic biotin uptake via decreasing membrane expression of its transporter and that these effects likely involve a CK2-mediated pathway. 31894266_Integrated profiling identifies SLC5A6 and MFAP2 as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer patients. 35013551_Novel biallelic variants expand the SLC5A6-related phenotypic spectrum. |
ENSMUSG00000006641 |
Slc5a6 |
446.399128 |
2.9514426592 |
1.561420 |
0.082201307 |
368.953206 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031631116314952263307230605843481944430969668516650833178670938355731811279211592908789200045354356197652776340668807335641542364788715384024274611372108910362604625317070300208889760687434389728516165654625957870393904158845543861389160156250000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010933847232053755347178311007968722947395315085442013931635091058654864806037945305784127287734760475384378751592755340277264157938604598593676040328267158235337497852519428521643088048969618138292654585530527810988132841885089874267578125000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
667.7520371 |
32.7225971 |
227.9441525 |
9.1514282 |
| ENSG00000138135 |
9023 |
CH25H |
protein_coding |
O95992 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the formation of 25-hydroxycholesterol from cholesterol, leading to repress cholesterol biosynthetic enzymes (PubMed:9852097). Plays a key role in cell positioning and movement in lymphoid tissues: 25-hydroxycholesterol is an intermediate in biosynthesis of 7-alpha,25-dihydroxycholesterol (7-alpha,25-OHC), an oxysterol that acts as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR183/EBI2, a chemotactic receptor for a number of lymphoid cells (By similarity). May play an important role in regulating lipid metabolism by synthesizing a corepressor that blocks sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) processing (PubMed:9852097). As an interferon-stimulated gene, has broad antiviral activities against a wide range of enveloped viruses, such as vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and SARS coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Its product, 25-hydroxycholesterol, activates the ER-localized enzyme ACAT to induce internalization of accessible cholesterol on the plasma membrane and restricts SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated fusion which inhibits virus replication (PubMed:33239446, PubMed:32944968). In testis, production of 25-hydroxycholesterol by macrophages plays a role in Leydig cell differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4QQV7, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0F5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32944968, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33239446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9852097}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This is an intronless gene that is involved in cholesterol and lipid metabolism. The encoded protein is a membrane protein and contains clusters of histidine residues essential for catalytic activity. Unlike most other sterol hydroxylases, this enzyme is a member of a small family of enzymes that utilize diiron cofactors to catalyze the hydroxylation of hydrophobic substrates. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9023; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; C-4 methylsterol oxidase activity [GO:0000254]; cholesterol 25-hydroxylase activity [GO:0001567]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; steroid hydroxylase activity [GO:0008395]; B cell chemotaxis [GO:0035754]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane [GO:1903914]; response to type I interferon [GO:0034340]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126] |
15465627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16157450_Based on the results of genome-wide screens, along with biological studies, we selected three genes as candidates for AD risk factors: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H) and cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CH24H). 16157450_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16909003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18830724_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20413850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20534741_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20535486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20699362_Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase production by dendritic cells and macrophages is regulated by type I interferons. 25903345_These results demonstrate that CH25H constitutes a primary innate response against hepatitis C virus infection through regulating host lipid metabolism. 25999047_Infection with HCV causes up-regulation of interferon-inducible CH25H in vivo. 26857497_Exome analysis in 212 multiple sclerosis and 14 neuromyelitis optica patients identified a rare CH25H p.Q17H mutation in two NMO patients of Asian ancestry. In addition, association analysis of common CH25H variants. 27912195_We detected Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase, the enzyme responsible for 25-HC production, in human spermatozoa at the level of the neck and the post acrosomal area. Upon incubation with spermatozoa, 25-HC induced calcium and cholesterol transients in connection with the acrosomal reaction. 29950420_We examined whether 25HC restricts infection by mammalian reovirus. Results suggest that 25HC inhibits the efficiency of cellular entry of reovirus virions, which may require specific endosomal membrane dynamics for efficient membrane penetration. 30645975_Limited analysis of leukocytes from melanoma patients is suggestive of an association between the loss of CH25H and poor disease outcome. CH25H acts to restrict tumor-derived extracellular vesicles uptake and limit the education of healthy cells to promote metastases. 30684189_The CH25H rs13500 polymorphism is associated with an increased Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk in the Turkish population and co-occurrence of CH25H 'T' and APOE epsilon4 alleles is a strong risk factor for AD. Based on our overall results, it can be concluded that CH25H might have a role in the pathogenesis of AD together with, and independently from APOE 31375561_we observed that cAMP-dependent transcription factor (ATF3) weakly binds to the CH25H promoter, suggesting cooperation with STAT1. However, ZIKV-induced CH25H was independent of type I interferon. These findings provide important information for understanding how the Zika virus induces innate inflammatory responses and promotes the expression of anti-viral CH25H protein. 31552533_Overexpression of both human and murine CH25H inhibited rabies virus (RABV) infection in HEK-293T cells. 32229247_Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H) as a promoter of adipose tissue inflammation in obesity and diabetes. 34227577_Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase expression following immune activation in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
ENSMUSG00000050370 |
Ch25h |
70.059874 |
8.6645596807 |
3.115126 |
0.246351033 |
188.212077 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000078091811874067865260624880973634817263398113947568330103136916625406227618702516394089451738406848914191005217588781306403689086437225341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000013920714290594705418610369203677824415828458231738267517867641886541522337944522976305259579975241868160388061803622861134499544277787208557128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
127.2501227 |
20.7933833 |
14.8111919 |
2.1499633 |
| ENSG00000138166 |
1847 |
DUSP5 |
protein_coding |
Q16690 |
FUNCTION: Dual specificity protein phosphatase; active with phosphotyrosine, phosphoserine and phosphothreonine residues. The highest relative activity is toward ERK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7961985}. |
3D-structure;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual specificity protein phosphatase subfamily. These phosphatases inactivate their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues. They negatively regulate members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase superfamily (MAPK/ERK, SAPK/JNK, p38), which are associated with cellular proliferation and differentiation. Different members of the family of dual specificity phosphatases show distinct substrate specificities for various MAP kinases, different tissue distribution and subcellular localization, and different modes of inducibility of their expression by extracellular stimuli. This gene product inactivates ERK1, is expressed in a variety of tissues with the highest levels in pancreas and brain, and is localized in the nucleus. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1847; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0017017]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008138]; protein tyrosine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008330]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; endoderm formation [GO:0001706]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; peptidyl-threonine dephosphorylation [GO:0035970]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
12944906_DUSP5 is a direct target of p53. 15713638_DUSP5 inactivates ERK2 and causes both nuclear translocation and sequestration of inactive ERK2. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17078075_the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of DUSP5 in an active conformation. 17131384_These results suggest the existence of an ERK1/2-driven negative feed-back regulation of ERK5 signaling in epidermal growth factor-stimulated HK-2 cells, which is mediated by MKP-3, DUSP5 and/or MKP-1. 18430737_proper regulation of DUSP5 activity is critical for normal immune system development, IL-2 actions, and tolerance 18927432_mutations in dusp-5 and snrk-1 have been identified in affected tissues of patients with vascular anomalies, implicating the Snrk-1-Dusp-5 signaling pathway in human disease. 19801501_In FD-Fms cells, overexpression of human DUSP5 increased M-CSF-dependent proliferation & decreased differentiation. Overexpression in multipotent EGER-Fms cells increased M-CSF-induced proliferation & caused granulocytic, not macrophage, differentiation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554528_the differential up-regulation of MKP3 by Ets2 and of DUSP5 by c-Jun may converge in similar functional roles for these MAP kinase phosphatases in the growth arrest versus proliferation decisions of breast cancer cells 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20806045_DUSP5 and DUSP6 selectively control ERK pathway activity and proliferation. 22812510_Studies indicate that dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) DUSP6/MKP-3 and DUSP5 are localized in the cytoplasm and nuclear compartments. 23402999_DUSP5 methylation may serve as a prognostic marker for gastric cancer (GC), but this requires validation in a larger set of GC samples. 24308939_DUSP1, DUSP4, and DUSP5 differentially modulate endothelial MAPK signaling pathways downstream of Tie-2 receptors. 24651368_Data indicate that cells from Burkitt's lymphoma, leukemia, neuroblastoma and Ewing sarcoma showed a higher dual-specificity phosphatase 5 pseudogene 1 (DUSP5P1)/dual specificity phosphatase 5 (DUSP5 ratio than normal cells. 25519881_The DUSP5 S147P protein is hypoactive compared to the DUSP5 wild-type protein. 26967242_Findings indicate that zinc-finger protein X-linked (ZFX) promotes colorectal cancer (CRC) progression by suppressing dual specificity phosphatase 5 (DUSP5) expression and suggest that ZFX is a prognostic biomarker and potentially useful therapeutic target in stage II/III CRC patients. 27739308_role of the secondary binding site in assembling the DUSP5-pERK pre-reactive complex was further demonstrated by molecular dynamics simulations that showed that the remote C197-C219 disulfide linkage controls the structure of the secondary binding pocket based on its redox state (i.e., disulfide/dithiol) and, in turn, the enzymatic activity of DUSP5 28910386_Results show that DUSP5 and DUSP6 mRNA are overexpressed in human PTCs, especially in BRAFV600E mutated papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs), and positively control cell migration and invasion. 28989118_DUSP5 expression in skeletal muscle was ninefold higher immediately after exercise and returned to pre-exercise level within 2 h. 29018280_DUSP5 functions in the feedback inhibition of ERK1/2 signaling in response to TNFalpha, which resulted in increased inflammatory gene expression. 29379130_Methylation the DUSP5 gene promoter can serve as an additional means of identifying CIMP-high colorectal cancers. 30387548_Data show that dual specificity phosphatase 5 (DUSP5) is a downstream target of p68 RNA helicase (p68). 30835471_Conserved Histidine and Serine in the HCXXXXXRS Motif of Human Dual-Specificity Phosphatase 5 31309567_microRNA-95 knockdown inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype in gastric cancer cells through MAPK pathway by upregulating DUSP5. 31330530_Dual-specificity phosphatase (DUSP) genetic variants predict pulmonary hypertension in patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. 31491992_DUSP5 expression is elevated in hepatocytes by ER stress through the PERK-CHOP pathway, contributing to hepatocyte death possibly through ERK inhibition. 31821724_Integrated analysis identifies DUSP5 as a novel prognostic indicator for thyroid follicular carcinoma. 32480039_Distinct intra-mitochondrial localizations of pro-survival kinases and regulation of their functions by DUSP5 and PHLPP-1. 32703413_The long noncoding RNA H19 attenuates force-driven cartilage degeneration via miR-483-5p/Dusp5. 32985327_Long non-coding RNA ARAP1-AS1 promotes the proliferation and migration in cervical cancer through epigenetic regulation of DUSP5. 33361528_DUSP5 suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte inflammation and ameliorates osteoarthritis in rats. 34142888_DUSP5-mediated inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation suppresses pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular hypertrophy. 34192359_Silencing of AFAP1-AS1 lncRNA impairs cell proliferation and migration by epigenetically promoting DUSP5 expression in pre-eclampsia. 34799724_METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of DUSP5 mRNA promotes gallbladder-cancer progression. 36183924_miR-203 suppresses pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration by modulating DUSP5 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000034765 |
Dusp5 |
175.604488 |
6.4375217306 |
2.686505 |
0.142347464 |
408.535146 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000076381652062269548082276480181596007744484897313043709670819670699830430478230143674580476337842265282331772934949847028606640475672312630468296739933970956762765178763037775189094669767577719049127512713202900097191928863171739294557482935 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000029131606833051640620741531715396504418738610784566789227862745639755689537427021706422847949775289071949174286971353543224108358483023498427554665836395836942782233448364930225944871788826214907483961860459285107675421466755238952828221954 |
Yes |
Yes |
310.8291197 |
28.0785763 |
48.6717834 |
3.9239792 |
| ENSG00000138190 |
54536 |
EXOC6 |
protein_coding |
Q8TAG9 |
FUNCTION: Component of the exocyst complex involved in the docking of exocytic vesicles with fusion sites on the plasma membrane. Together with RAB11A, RAB3IP, RAB8A, PARD3, PRKCI, ANXA2, CDC42 and DNMBP promotes transcytosis of PODXL to the apical membrane initiation sites (AMIS), apical surface formation and lumenogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC15 gene product, which is essential for vesicular traffic from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface in yeast. It is one of the components of a multiprotein complex required for exocytosis. The 5' portion of this gene and two neighboring cytochrome p450 genes are included in a deletion that results in an autosomal-dominant form of nonsyndromic optic nerve aplasia (ONA). Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants. A paralogous gene encoding a similar protein is present on chromosome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:54536; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; exocyst [GO:0000145]; Flemming body [GO:0090543]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; Golgi to plasma membrane transport [GO:0006893]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; membrane fission [GO:0090148]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904]; vesicle tethering involved in exocytosis [GO:0090522] |
15292201_Sec15 has a role as an effector for the Rab11 GTPase in mammalian cells 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16478783_The SEC15 protein plays a crucial role in integrating the signals between Sec4p and the components of the early-polarity-establishment machinery. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20944747_coordinated disruption of the Rab11/Sec15 exocyst by anthrax toxins may contribute to toxin-dependent barrier disruption and vascular dysfunction during B. anthracis infection 21044367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23435566_NDR2-mediated Rabin8 phosphorylation is crucial for ciliogenesis by triggering the switch in binding specificity of Rabin8 from PS to Sec15. |
ENSMUSG00000053799 |
Exoc6 |
51.324127 |
0.3086380302 |
-1.696012 |
0.605247167 |
6.625923 |
0.01005050587314987829701262711523668258450925350189208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019258141852225393875208681038202485069632530212402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.3943973 |
9.5303326 |
80.4073726 |
22.4828087 |
| ENSG00000138380 |
79800 |
CARF |
protein_coding |
Q8N187 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional activator that mediates the calcium- and neuron-selective induction of BDNF exon III transcription. Binds to the consensus calcium-response element CaRE1 5'-CTATTTCGAG-3' sequence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11832226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22174809}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables DNA binding activity and DNA-binding transcription factor activity. Involved in cellular response to potassium ion and positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to calcium ion. Predicted to be located in granular component. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79800; |
granular component [GO:0001652]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to calcium ion [GO:0061400]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11832226_Cloned as a calcium- and neural-selective transcriptional activator of the gene for Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). 29321561_Data demonstrate that CARF is a new target of miR-451 that mediates its tumor suppressor function in normal and stressed biological states. 29718136_Wi-A caused upregulation of CARF (collaborator of ARF) demonstrating an activation of DNA damage oxidative stress response in both cancer and normal cells. In line with this, upregulation of p21WAF1, p16INK4A, and hypophosphorylated pRB and induction of senescence were observed demonstrating that Wi-A-induced senescence is mediated by multiple pathways in which CARF-mediated DNA damage and oxidative stress play a major ro 32617772_Inhibition of MicroRNA-302c on Stemness of Colon Cancer Stem Cells via the CARF/Wnt/beta-Catenin Axis. |
ENSMUSG00000026017 |
Carf |
55.874505 |
0.4506841302 |
-1.149811 |
0.469915277 |
5.670096 |
0.01725650969899160738774135381845553638413548469543457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031410295123580726783796279732996481470763683319091796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.9137448 |
10.6061989 |
76.0183549 |
16.5931835 |
| ENSG00000138411 |
57520 |
HECW2 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2P5 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination of TP73. Acts to stabilize TP73 and enhance activation of transcription by TP73 (PubMed:12890487). Involved in the regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition (PubMed:24163370). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12890487, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24163370}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a member of a family of E3 ubiquitin ligases which plays an important role in the proliferation, migration and differentiation of neural crest cells as a regulator of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF)/Ret signaling. This gene also plays an important role in angiogenesis through stabilization of endothelial cell-to-cell junctions as a regulator of angiomotin-like 1 stability. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal calcium/lipid-binding (C2) domain involved in membrane targeting, two-four WW domains responsible for cellular localization and substrate recognition, and a C-terminal homologous with E6-associated protein C-terminus (HECT) catalytic domain. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with neurodevelopmental delay, hypotonia, and epilepsy. The decreased expression of this gene in the aganglionic colon is associated with Hirschsprung's disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:57520; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; negative regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:2000650]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814]; regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition [GO:0030071] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24163370_NEDL2 is a novel substrate of APC/C-Cdh1 as cells exit mitosis and functions as a regulator of the metaphase to anaphase transition 25156441_Low HECW2 expression is associated with cervical cancer. 27334371_This work lends further support to previously identified candidate gene HECW2 as a novel candidate gene in intellectual disability and epilepsy. In 39 patient-parent trios, 29 de novo mutations in coding sequence were identified. 27389779_HECW2 is an ubiquitin ligase that stabilises p73, a crucial mediator of neurodevelopment and neurogenesis. This study implicates pathogenic genetic variants in HECW2 as potential causes of neurodevelopmental disorders in humans. 27498087_HECW2, a novel EC ubiquitin E3 ligase, plays a critical role in stabilizing endothelial cell-to-cell junctions by regulating AMOT-like 1 (AMOTL1) stability. 29753763_Results show that HECW2 interacts with two lamin A-binding proteins: proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), via a canonical PCNA-interacting protein (PIP) motif, and lamin B1. HECW2 mediates their ubiquitination and targets them for proteasomal degradation. 30208514_Ectopic expression of HECW2 causes the ubiquitination of HP1alpha and beta, thereby targeting them for proteasomal degradation. 33205896_Association of HECW2 variants with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy and knockdown of zebrafish hecw2a. 34047014_HECW2-related disorder in four Japanese patients. 34321324_Delineating the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of HECW2-related neurodevelopmental disorders. 34327820_A novel likely pathogenic heterozygous HECW2 missense variant in a family with variable expressivity of neurodevelopmental delay, hypotonia, and epileptiform EEG patterns. 34767155_Circ_0057583 facilitates brain microvascular endothelial cell injury through modulating miR-204-5p/NR4A1 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000042807 |
Hecw2 |
21.696176 |
4.1829574394 |
2.064523 |
0.506721057 |
16.061812 |
0.00006130798951050298267826527132129399433324579149484634399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000174288506389642521314173317925622086477233096957206726074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.5577593 |
10.8207893 |
8.3546516 |
2.0890597 |
| ENSG00000138439 |
150864 |
FAM117B |
protein_coding |
Q6P1L5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:150864; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000041040 |
Fam117b |
48.050238 |
0.4599736553 |
-1.120377 |
0.257053438 |
19.052275 |
0.00001271860707805469728676802526612377164383360650390386581420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000039446656959883874505809475685680354217765852808952331542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.2178388 |
5.0483798 |
68.2168529 |
7.2710539 |
| ENSG00000138442 |
55759 |
WDR12 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZL7 |
FUNCTION: Component of the PeBoW complex, which is required for maturation of 28S and 5.8S ribosomal RNAs and formation of the 60S ribosome. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03029, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16043514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17353269}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ribosome biogenesis;rRNA processing;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. This protein is highly similar to the mouse WD repeat domain 12 protein at the amino acid level. The protein encoded by this gene is a component of a nucleolar protein complex that affects maturation of the large ribosomal subunit.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:55759; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; PeBoW complex [GO:0070545]; preribosome, large subunit precursor [GO:0030687]; ribonucleoprotein complex binding [GO:0043021]; maturation of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000466]; maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000463]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273] |
16043514_WDR12 triggers accumulation of p53 in a p19ARF-independent manner in proliferating cells but not in quiescent cells. 17353269_Results describe the role of PeBoW-specific proteins Pes1, Bop1, and WDR12 in complex assembly and stability, nucleolar transport, and pre-ribosome association. 19198609_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20971364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25825154_The DDX27 can interact specifically with the Pes1 and Bop1 but fulfils critical function(s) for proper 3' end formation of 47S rRNA independently of the PeBoW-complex. 25915632_MI associated WDR12 allele was associated significantly with diastolic dysfunction and left atrial size. 32180229_Integrative genomic analyses identify WDR12 as a novel oncogene involved in glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000026019 |
Wdr12 |
179.853804 |
2.7197305588 |
1.443464 |
0.216223158 |
42.695187 |
0.00000000006396948731458116294516974410750776228185010552351741353049874305725097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000334937790976664776198400346886416452385493158772078459151089191436767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
250.1020658 |
32.5339809 |
92.7459502 |
9.0070524 |
| ENSG00000138448 |
3685 |
ITGAV |
protein_coding |
P06756 |
FUNCTION: The alpha-V (ITGAV) integrins are receptors for vitronectin, cytotactin, fibronectin, fibrinogen, laminin, matrix metalloproteinase-2, osteopontin, osteomodulin, prothrombin, thrombospondin and vWF. They recognize the sequence R-G-D in a wide array of ligands. ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to fractalkine (CX3CL1) and may act as its coreceptor in CX3CR1-dependent fractalkine signaling (PubMed:23125415). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to NRG1 (via EGF domain) and this binding is essential for NRG1-ERBB signaling (PubMed:20682778). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to FGF1 and this binding is essential for FGF1 signaling (PubMed:18441324). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to FGF2 and this binding is essential for FGF2 signaling (PubMed:28302677). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to IGF1 and this binding is essential for IGF1 signaling (PubMed:19578119). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to IGF2 and this binding is essential for IGF2 signaling (PubMed:28873464). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to IL1B and this binding is essential for IL1B signaling (PubMed:29030430). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to PLA2G2A via a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and this induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1 (PubMed:18635536, PubMed:25398877). ITGAV:ITGB3 and ITGAV:ITGB6 act as receptors for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and mediate R-G-D-dependent cell adhesion to FBN1 (PubMed:12807887, PubMed:17158881). Integrin alpha-V/beta-6 or alpha-V/beta-8 (ITGAV:ITGB6 or ITGAV:ITGB8) mediates R-G-D-dependent release of transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-beta-1) from regulatory Latency-associated peptide (LAP), thereby playing a key role in TGF-beta-1 activation (PubMed:15184403, PubMed:22278742, PubMed:28117447). ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for CD40LG (PubMed:31331973). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12807887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15184403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17158881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18441324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18635536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19578119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22278742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23125415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25398877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28117447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28302677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28873464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29030430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31331973}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB5 acts as a receptor for Adenovirus type C. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20615244}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB5 and ITGAV:ITGB3 act as receptors for Coxsackievirus A9 and B1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15194773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7519807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9426447}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for Herpes virus 8/HHV-8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18045938}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB6 acts as a receptor for herpes simplex 1/HHV-1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24367260}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for Human parechovirus 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11160695}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for West nile virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23658209}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397733}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Integrin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the integrin alpha chain family. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha subunit and a beta subunit that function in cell surface adhesion and signaling. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate light and heavy chains that comprise the alpha V subunit. This subunit associates with beta 1, beta 3, beta 5, beta 6 and beta 8 subunits. The heterodimer consisting of alpha V and beta 3 subunits is also known as the vitronectin receptor. This integrin may regulate angiogenesis and cancer progression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Note that the integrin alpha 5 and integrin alpha V subunits are encoded by distinct genes. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. |
hsa:3685; |
alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex [GO:0035868]; alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex [GO:0035867]; alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex [GO:0035866]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; integrin alphav-beta3 complex [GO:0034683]; integrin alphav-beta5 complex [GO:0034684]; integrin alphav-beta6 complex [GO:0034685]; integrin alphav-beta8 complex [GO:0034686]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; extracellular matrix protein binding [GO:1990430]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; opsonin binding [GO:0001846]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; transforming growth factor beta binding [GO:0050431]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0005245]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038027]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; entry into host cell by a symbiont-containing vacuole [GO:0085017]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell [GO:2000536]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010888]; negative regulation of lipid transport [GO:0032369]; negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process [GO:0050748]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905598]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction [GO:1902533]; positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033690]; positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051057]; regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050764]; regulation of transforming growth factor beta activation [GO:1901388]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; transforming growth factor beta production [GO:0071604]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] |
10982404_integrin alphavbeta3 is shown to interact with PECAM-1 11724803_Processing of integrin alpha(v) subunit by membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase stimulates migration of breast carcinoma cells on vitronectin 11848444_Acute hyperglycaemia induces an up-regulation of seven major genes, four of which were not previously reported in the literature. Northern blot analyses, performed on these 4 genes, confirm macroarrays results for alphav, beta4, c-myc, and MUC18. 11858476_Review. Alpha(v)beta3 integrins are involved in vascular repair processes. The challenge is to develop a therapeutic agent that will prove effective in reducing restenosis in humans following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). 11872628_They analyzed the expression of these cell surface receptors in nine ovarian cancer cell lines and also in the primary human ovarian surface epithelial cell line (HOSE). 11928818_Chemotaxis and chemoinvasion analyses revealed a dose-dependent increase in prostate cancer cell movement induced by osteopontin and a strict dependence of cell invasion on alphavbeta3 integrin function. 11934894_Unique ability of integrin alpha(v)beta 3 to support tumor cell arrest under dynamic flow conditions (Integrin alpha-v beta-3) 11959660_Del1 mediates vascular smooth muscle cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation through interaction with integrin alpha(v)beta(3). 12031826_Factor XIII mediates adhesion of platelets to endothelial cells through alpha(v)beta(3) and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa integrins. 12099514_Acute cellular rejection following human heart transplantation is associated with increased expression 12143051_existence of an alpha V integrin/vitronectin connection in hepatocellular carcinoma and suggest that this connection may be an adverse prognostic factor. 12161360_Alpha(v)beta(3) integrin engagement enhances cell invasiveness in human multiple myeloma. 12168086_integrin alphaVbeta3 expression is reduced when ROR alpha is activated in prostate cancer cells 12198771_Integrin alphavbeta3. Expression of integrin alpha v beta 3 promotes the metastatic phenotype in human melanoma by supporting specific adhesive, invasive and migratory properties of the tumor cells 12210725_alpha v beta 3 integrin signaling through Shc recruitment in response to mechanical stimulation in human osteoblasts 12237112_phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2alpha was found to be differentially regulated by alpha(v)beta(3) engagement 12237321_promotion of integrin alpha Vbeta 3-dependent endothelial cell adhesion by PGE2 12270930_identification of a new alphavbeta5 integrin-interacting motif that is highly conserved in the fas-1 domains of many proteins suggesting that fas-1 domain-containing proteins may perform their biological functions by interacting with integrins 12324452_induced alpha(v)beta(8) integrin expression mediated Fas-stimulated migration 12324470_identification of functional segments within the beta2I-domain 12358597_Data show clearly that integrin alpha(v)beta(3) interacts with the latency-associated peptide (LAPbeta1 and 3) RGD motif. 12364323_role in mediating pro-angiogenic activity of CYR61 12370491_An autocrine loop of the integrin alpha(V)beta(3)/CD47 receptor complex and thrombospondin-1 is identified as the molecular coupling device between mechanical loading and apoptosis. 12372469_in patients with endometriosis a significant negative correlation was observed between luminal expression of eNOS and alpha(v)beta(3) integrin and between glandular expression of eNOS and luminal expression of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin 12372811_thrombin interacts with alphavbeta3 as demonstrated by direct binding of alphavbeta3 protein to immobilized thrombin. 12384999_Overexpression of integrin alphaV promotes human osteosarcoma cell populated collagen lattice contraction and cell movement. 12399420_activation state of alphaVbeta3 integrin is an important regulator of the duration of insulin-like growth factor I receptor phosphorylation and this regulation is mediated through changes in the subcellular localization of SHP-2 12427871_Data show a novel mechanism by which ECM regulates membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) association with beta1 or alphavbeta3 integrins, thus modulating its internalization, activity, and function on human endothelial cells. 12486108_integrin alpha5beta1-mediated control of the levels of integrin alphaVbeta3 is important for the distribution of focal contacts 12553378_has a role in the early phase of liver metastasis 12639965_thymidine phosphorylase and 2-deoxyribose-induced focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation was blocked by the antibodies to integrins alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3, directly linking their migration and signaling components 12642872_role in regulating cell proliferation through integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in ovarian cancer cells 12645863_decreased expression of endometrial integrin alphavbeta3 suggests that functional, but not morphological, endometrial defect may be one of the causes for the patients with unexplained infertility and recurrent IVF-ET failures 12660257_Alphavbeta3 integrin expression and pinopode formation in human endometrium are processes closely related to endometrial maturation; unlikely as targets for contraceptive approaches or fertility-promoting strategies 12682293_tumstatin binds to alpha v beta 3 integrin in a vitronectin/fibronectin/RGD cyclic peptide independent manner 12691260_Data suggest that this alphavbeta3 binding to alpha5-laminins is involved in the regulation of cellular responses to growth factors known to be involved in epithelial and endothelial development. 12750158_signaling through JAM-1 and alphavbeta3 is necessary for bFGF-induced angiogenesis. 12765524_Data provide the first evidence that alphavbeta3 integrin can generate apoptosis-stimulating signals. 12807887_alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 are both important but cell-specific fibrillin-1 receptors 12874388_integrin alphavbeta3 cooperates with metalloproteinase MMP-9 in regulating migration of metastatic breast cancer cells 12875973_These data provide evidence for a functional role for integrin alphavbeta8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta in control of human airway epithelial proliferation in vivo. 12893184_AlphaV- and beta1-integrin subunits are commonly expressed in malignant effusions from ovarian carcinoma patients. 14524530_integrin alpha(v)beta3 has an important role in bone metabolism and angiogenesis, and in controlling growth of metastatic prostate cancer cells in the bone 14596610_Disulfide bonding patterns of the integrin alpha V chain are described; the alpha chain displays differences in the disulfide patterns of those bonds near their C-terminal regions linking the heavy and light chains. 14666169_alpha3beta1, alpha4beta1 and alphaVbeta1 integrins may play an important role in the implantation process 14741360_alphav subunit cleavage is essential for integrin function and has a considerable impact on integrin-dependent events, especially those leading to cell migration 14766759_alpha(v)beta(1) supports fetal beta-cell migration and could play an important role in early motile processes required for islet neogenesis 14966135_CD47-alpha(v)beta(3) interactions that lead to integrin clustering are detergent resistant and do not require cholesterol or the transmembrane region of CD47 15044441_alphavbeta3 integrin has a role in regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells 15051489_Role of alpha4, alpha5, and alphav integrin receptors--which are central to mediating interactions with these domains of FN--in regulating ssquamous cell carcinoma migration. 15194773_integrin alpha(v)beta(6) is an RGD-dependent receptor for Coxsackievirus A9 and may be important in natural Coxsackievirus A9 infections 15269586_alpha-v integrin signals through JAB1 (Jun activation binding protein 1) to prolong MMP1 production 15299032_secondary structure analysis of integrin alphaVbeta3 15509546_CEACAM1 and alpha(v)beta(3) integrin are functionally interconnected with respect to the invasive growth of melanomas 15557124_Integrin alphav controls melanoma cell survival in 3D-collagen through a pathway involving p53 regulation of MEK1 signaling. 15609323_alphav integrins and MMP2 have roles in migration of human ovarian adenocarcinoma cells through endothelial extracellular matrix 15638730_The Integrin alphaV receptor is members of the group of the cellular adhesion molecules (CAM), are heterodimeric transmembrane glycoprotein receptors involved in processes such as cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion, cell migration and signaling. 15647827_BMP-2 upregulates the expression of alphavbeta integrins, and these integrins, in turn, play a critical role in BMP-2 function in osteoblasts 15695828_Pyk2 is a phosphorylated beta(3) binding partner, providing a potential structural and signaling platform to achieve alpha(V)beta(3) -mediated remodeling of the actin cytoskele 15795319_We conclude that the ectodomain of alphaVbeta3 manifests a bent conformation that is capable of stably binding a physiological ligand in solution. 15828940_We conclude that integrin alphavbeta6-dependent MMP-2 and -9 up-regulation is an important feature of increased migration in hypoxic human keratinocytes. 15834425_Epidermal growth factor receptor and alphavbeta3 work together as coreceptors for Human cytomegalovirus entry and signaling. 15866865_urokinase receptor-derived SRSRY peptide regulates cross-talk between fMLP and vitronectin receptors 15897908_new pair of adhesion molecules, Thy-1 and alphavbeta3, inditified that mediate the interaction of melanoma cells and activated endothelial cells 15914035_IGROV1 cells were shown to adhere rapidly on the HUVECs monolayer; adhesion was inhibited by anti-alphav integrin and anti-Vn blocking antibodies, but not by anti-beta1 integrin antibodies 15921657_Gal3ST-2 is involved in tumor metastasis process by regulation of adhesion ability to selectins and expression of integrin alphaV but not beta3 15925879_May contribute to the formation of arteriovenous malformaions in younger patients. 15998788_melanoma cells cross-present, in an alpha v beta3-dependent manner, an antigen derived from secreted matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) to human leukocyte antigen A*0201-restricted T cells 16005200_integrin alphavbeta6, alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, alpha5beta1 and alpha9beta1 binding to osteopontin is controlled by specific structural motifs that are recognized by extracellular proteases 16024014_Alphavbeta6 integrin down-regulates MMP-13 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 16100012_Increased transcripts of activators of TGFB1 (Itgav and Thbs1), and genes that are activated by TGFB1 (Spp1, Timp1, and Tnc) occurs during acute lung injury 16105876_Data show that alpha(v)beta3/Tat interaction triggers the activation of NF-kappaB in endothelial cells in a focal adhesion kinase-, RhoA- and pp60src-dependent manner, and this activation is required for motogenic activity of Tat in endothelial cells. 16150802_alphavbeta3 integrin is transiently up-regulated (and activated) in graft arteriopathy 16186116_the RGD-dependent interaction between the P2Y(2)R and alpha(v) integrins is necessary for the P2Y(2)R to activate G(o) and to initiate G(o)-mediated signaling events leading to chemotaxis 16385340_Expression of integrins alphavbeta1, alphavbeta3, and alphavbeta5 in cerebral arteriovenous malformations and cavernous malformations. (Integrins alphavbeta1, alphavbeta3, and alphavbeta5) 16400188_the signal interaction between IGF-1R and alpha(v)beta3 integrin plays an important role in promoting the development and progression of cervical cancer 16407244_cardiotoxin A5 binds to alpha(v)beta3 integrin and inhibits bone resorption 16448724_These results indicate that the alpha2beta1 and alphaVbeta1 integrin signaling pathway may be critical components of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. 16496302_thymosin beta10, but not thymosin beta4, have direct inhibitive effects on endothelial migration and tube formation that might be mediated via downregulation of VEGF, VEGFR-1 and integrin alphaV in HCAECs. 16614246_While tolerogenic DCs are not induced via alphavbeta5, coligation of CR3 and alphavbeta5 maintains the DC's tolerogenic profile. 16631740_Findings suggest that in melanoma cells the increase in MMP-2 activity, CD44 surface expression, and cell migration is integrin alpha V-dependent. 16631833_The effects of the EBV nuclear antigen 3C on the activities of Nm23-H1 via GATA-1 and Sp1 are reported. 16672769_Alphavbeta5 integrin may play a role in the adhesion and migration of VSMCs during the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 16675963_upregulated expression of alphavbeta5 contributes to autocrine TGF-beta signaling in localized scleroderma fibroblasts 16702213_periostin has an active role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and metastasis that requires cross-talk between integrin and EGFR signaling pathways 16731529_integrin alpha3beta1 is a receptor for the alpha3NC1 domain and transdominantly inhibits integrin alphavbeta3 activation 16790523_binding of resveratrol to integrin alphaVbeta3, principally to the beta3 monomer, is essential for transduction of the stilbene signal into p53-dependent apoptosis of breast cancer cells. 16818691_PET Molecular imaging of alpha(v)beta3 expression with [18F]Galacto-RGD in humans correlates with alpha(v)beta3 expression as determined by immunohistochemistry. 16835373_S 36578-2 is highly selective for alpha v beta3 and alpha v beta5 integrins and induces detachment, caspase-8 activation, and apoptosis in human umbilical endothelial cells 16877343_These findings elucidate the function and complex regulation of integrin-mediated activation of TGF-beta within the epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit (EMTU).[integrin alphavbt=eta6, integrin alphavbeta8] 16947382_Relevance of betaIG-H3 and alpha v beta3 integrin-interacting motifs as potential therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis. 16973584_integrin binding loop of Foot-and-mouth disease virus has most likely evolved for binding to alphavbeta6 with a higher affinity than to alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta8 17034033_The transition from a locally invasive phenotype to a metastatic phenotype may be primed by the elevated expression of alpha(v)beta(3) receptors in prostate cancer cells. 17158881_identifies integrin alphaVbeta6 as a novel cellular receptor for fibrillin-1 with a K(d) of approximately 0.45 mum 17175151_type I collagen induction of MT1-MMP-mediated MMP-2 activation is repressed by alphaVbeta3 integrin in human breast cancer cells 17275949_Mn(2+) promoted convergent changes in integrin alphavbeta6 conformation and Fb structure through activation of ERK/MAPK and MMP-9 17300927_integrins alpha5beta1 and alphaV are inhibited by lebectin and lebecetin snake venom lectins 17331499_Adhesion of breast cancer cells through the VLA integrins alpha2beta1 and alpha5beta1 was significantly reduced by an apoptosis-inducing natural triterpenoid, dehydrothyrsiferol (DT), when studied on low amounts of extracellular matrix. 17369840_Prostate cancer cells expressing fully functional but not dysregulated alphavbeta3 integrin are able to control their own adherence and migration to bone matrix, functions that facilitate tumor growth and control bone lesion development. 17408468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17446174_Necl-5 has a critical role in integrin alphavbeta3 clustering and focal complex formation 17483236_Endothelial cell integrin alphaV beta3 is involved in sickle cell red blood cell adhesion. 17550972_Results suggest that CTGF plays a crucial role in migratory/invasive processes in human breast cancer by a mechanism involving activation of the integrin-alphavbeta3-ERK1/2-S100A4 pathway. 17615072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17615072_The rs3738919-C allele of the ITGAV gene is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in the European Caucasian population, suggesting ITGAV as a new minor susceptibility gene for rheumatoid arthritis. 17621633_establishes alphavbeta3 integrin as one key component of the transendothelial migration process of tumor cells, and as a potential target for anti-metastatic therapy 17641225_c-Src controls functional association between integrin alphav-beta3 and VEGFR-2 via integrin beta3 phosphorylation. 17854909_macrophage migration inhibitory factor directly up-regulates alphavbeta3 integrin and VEGF expression in human endometrial Ishikawa cells 17879163_These findings provide evidence that mutations in fibronectin, induce anoikis in human squamous cell carcinoma cells by modulating integrin alpha v-mediated phosphorylation of FAK and ERK. 17965016_Results show that the tyrosine phosphatase protein-tyrosine phosphatase mu dephosphorylated PIPKIgamma and thus canceled the PIPKIgamma-dependent activation of integrin alpha(v)beta(3) by blocking the interaction of integrin alpha(v)beta(3) with talin. 18045938_the studies demonstrate that Vbeta3 is a cellular receptor mediating both the cell adhesion and entry of KSHV into target cells through binding the virion-associated gB(RGD). 18062611_Report observed that alphav-beta3 integrins and Focal Adhesion Protein-Tyrosine Kinases co-localize and that fibrillin filament attachment sites to endothelial cells merge with these molecules. 18064530_anti-tumor and anti-metastatic activities of CNTO 95 in breast cancer models and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms mediating its inhibitory effects on metastasis. 18079201_Signal transduction pathways underlying the enhanced cell migration reveal that the IGF-I-IGFBP-VN complex stimulates a transient activation of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway and a sustained activation of the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. 18084301_uPAR is required to activate alphavbeta3 integrin in podocytes, promoting cell motility and activation of the small GTPases Cdc42 and Rac1 18090124_Alpha v beta 5, alpha v beta 5 and their ligands Del-1 and L1 play an important role in the process of tumor cells moving from the original place. 18191107_TGF-beta1 acts through PI3K/Akt, which in turn activates IKKalpha/beta and NF-kappaB, resulting in the activations of alphavbeta3 integrins and contributing the migration of chondrosarcoma cells 18211678_We used suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) to study molecular signature of melanoma progression, by showing characteristics of early neoplastic lesions including expression of KISS1, lack of alphavbeta3-integrin and low levels of RHOC. 18221819_Integrin alphavbeta6 is induced de novo in rodent and human liver fibrosis, where it is expressed on activated bile duct epithelia and (transitional) hepatocytes during fibrosis progression. 18227168_The role of alpha(v)beta(3) and Fas as the mediators of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin (SPE) B-induced apoptosis is described. 18247041_Integrin alpha v beta 3 plays a critical role in the S1P-stimulated chemotactic response of ECs 18310319_The shear-induced G(2)/M arrest and corresponding changes in G(2)/M regulatory protein expression and activity were mediated by alpha(v)beta(3) and beta(1) integrins through bone morphogenetic protein receptor type IA-specific Smad1 and Smad5. 18310446_T(3) and T(4) hormones rapidly stimulate ERK activation in MG-63 cells via integrin alpha(V)beta(3) and that one functional effect of this ERK activation is increased DNA synthesis 18331351_Mn(2+) simultaneously modulates the thiol isomerase activity of protein disulfide isomerase that is bound to alpha(V)beta(3) and induces its transition to the ligand-competent state, suggesting an alternative mechanism of integrin regulation 18345483_Data show that in preeclamptic pregnancies, histamine does not stimulate expression of integrin alphaVbeta3, as it does in uncomplicated pergnancies. 18349127_These results suggest that activation of TGF-beta1 by integrin alphavbeta6 contributes to pathological changes and may impair endothelial cell functions in tissues that are chronically infected with cytomegalovirus. 18353318_Infertile women with isolated polycystic ovaries are deficient in endometrial expression of osteopontin but not alphavbeta3 integrin during the implantation window. 18353785_results demonstrate that TGFbeta1 induces alphavbeta3 integrin expression via a beta3 integrin-, c-Src-, and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway 18357713_There was significant relationship between integrin alpha-v subunit expression and lymphatic metastasis of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 18364349_ROCK-dependent actomyosin-driven contractility is a critical determinant for the regulation of the interaction between Necl-5 and integrin alpha(V)beta(3). 18394009_significant difference in the expression of the beta(3) integrin subunit between primary glioblastomas compared with low-grade gliomas 18427826_expression of ITGAV was significantly correlated with differentiation and metastasis of the laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinomas; down-regulation of ITGAV gene could inhibit proliferation of Hep-2 cells and induce to its apoptosis. 18441324_integrin alphavbeta3 binding to FGF1 plays a role in FGF1 signaling 18445685_data identify PAI1 as a novel regulator of fibronectin matrix assembly, and indicate that this regulation occurs through a previously undescribed crosstalk between the alphavbeta5 and alpha5beta1 integrins 18451156_Alpha vbeta 6 Integrin promotes the invasion of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma through stromal modulation. 18549690_osteopontin:alpha(v)beta(3)integrin complex untenable as marker of endometrial receptivity and implantation potential 18550570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18635536_integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 may serve as receptors for sPLA2-IIA and mediate pro-inflammatory action of sPLA2-IIA 18648521_human umbilical vein endothelial cells adhere to immobilized CXCL4 through alphavbeta3 integrin, and also through other integrins, such as alphavbeta5 and alpha5beta1 18694400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18695916_Integrin alphavbeta3 is not significantly implicated in the anti-migratory effect of anti-angiogenic urokinase kringle domain 18698261_overexpressed in endometrial carcinomas, especially with high grade and in lymph node metastases 18781095_ability of ovarian carcinoma cells to bind to peritoneal mesothelium in vitro and strongly suggest that vitronectin and its receptors contribute to this crucial event. 18814143_SDF-1alpha enhances the invasiveness of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing alphavbeta3 integrin expression through the CXCR4/ERK/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 18821851_The apo(a) component of Lp(a) signals through integrin alphaVbeta3 to activate endothelial cells. 18844213_urokinase-derived antagonists of alphavbeta5 integrin activation inhibit migration and invasion of carcinoma cells 18854176_These results demonstrate that integrin alphavbeta3-mediated transcriptional regulation of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 is critical for suppressing the ovarian cancer cell invasion. 18927433_VWF strings bind specifically to integrin alpha(v)beta(3) on human endothelial cells 19017937_Analogous to EAE, in subjects with MS, we found increased expression of Opn in DCs and increased expression of the Opn receptors CD44, beta(3), and alpha(v) on T cells. 19037107_M6P/IGF2R controls cell invasion by regulating alphaV integrin expression and by accelerating uPAR cleavage, leading to the loss of the urokinase/vitronectin/integrin-binding site on uPAR. 19061491_in cutaneous nodular melanomas, necrosis was associated with increased tumor thickness, tumor ulceration, vascular invasion, higher tumor proliferation and apoptotic index, increased expression of alphavbeta3 integrin & poor patient outcome 19074851_analysis of how the different antiangiogenic potential of resveratrol stereoisomers is related to their different capacity to affect alphavbeta3 integrin function 19088289_These data suggest that Coxsackievirus A9 binding to alphaVbeta6 is a high-affinity interaction, which may indicate its importance in clinical infections 19118218_pneumococci exploit the vitronectin-alphavbeta3-integrin complex as a cellular receptor for invasion and this integrin-mediated internalization requires the cooperation between the host signalling molecules ILK, PI3K and Akt. 19141530_data suggest that alpha(v)beta(3) is a key molecule that determines the stimulatory or inhibitory effect of pleiotrophin on cell migration 19164533_data suggest that alphavbeta1 integrin is a functional receptor for hMPV 19212436_Data show that cilengitide activated cell surface alphaVbeta3, stimulated phosphorylation of FAK, Src and VE-cadherin, increased cell permeability and decreased cell adhesion in endothelial cells. 19212638_In neuroendocrine tumors, gene-expression integrin alphaV was highly variable 19255147_The active site within the Sdc1 core protein was identified and a peptide inhibitor called synstatin (SSTN) that disrupts Sdc1's interaction with alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) integrins was derived. 19267182_Compound 4, having the DGR retro-sequence, is a low micromolar ligand for the alphavbeta5 integrin. 19334037_Data demonstrated significantly upregulated integrin-linked kinase as a function of alphavbeta3 in two ovarian cancer cell lines, and proved co-localization at the surface of alphavbeta3-overexpressing adherent cells. 19371633_These data strongly indicate that KAI1 may suppress ovarian cancer progression by inhibiting integrin alphavbeta3/vitronectin-provoked tumor cell motility and proliferation as important hallmarks of the oncogenic process. 19435649_Down-regulation of alphav integrin by retroviral delivery of siRNA significantly reduced drug resistance of colon tumor cells & xenografts, indicating that ITGAV plays an important role in MCR to oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells. 19448673_Results show that alphavbeta6- and alpha5beta1-integrin-dependent activation of Rac1 was mediated through Eps8. 19475568_OPN enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing MMP-9 expression through the alphavbeta3 integrin, FAK, MEK, ERK and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 19487690_PAI-1-mediated regulation of alphavbeta3 integrin is critical for the control of TGFbeta signaling and the prevention of fibrotic disease. 19541645_In metastatic brain lesions carrying activated alpha(v)beta(3), VEGF expression is controlled at the post-transcriptional level and involves phosphorylation and inhibition of translational respressor 4E-binding protein (4E-BP1). 19549907_Tumors express alpha(v)beta(6) suggest that this probe has significant potential for the in vivo detection of the malignancy. 19581046_VEGF is critical to the invasive process in human gastric cancer and that this occurs via up-regulation of integrin alphavbeta6 expression and activation of ERK. 19590686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19617625_Cell adhesion to tropoelastin is mediated via the C-terminal GRKRK motif and integrin alphaVbeta3 19695571_Periostin mediates vascular smooth muscle cell migration through the integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) pathway 19704023_These data are the first demonstration of conformational coupling of the integrin alphaVbeta3 leg and head domains, and suggest that inside-out activation may involve conformational changes other than the postulated switch to a genu-linear state. 19710103_upregulated expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells following bacterial infection 19751734_Smooth muscle cell hyperplasia in stricturing Crohn disease is regulated by increased endogenous IGF-I and alphaVbeta3 integrin ligands that regulate augmented proliferation and diminished apoptosis 19808093_Data show that leberagin-C can inhibit the adhesion of melanoma tumour cells on fibrinogen and fibronectin, by interfering with the function of alphavbeta3 and, to a lesser extent, with alphavbeta6 and alpha5beta1 integrins. 19808644_This study shows that alpha(v)beta(3)-integrin expression on tumor cells actually slows tumor progression and acts as a tumor suppressor. 19811096_Beta1 integrins are required for adhesion and proliferation of induced pluripotent stem cells on matrigel. On vitronectin, the integrin alphavbeta5 is required for initial attachment, but both alphavbeta5 and beta1 is required for proliferation. 19815712_Data show that under basal conditions, sphingosine kinase-1, integrin alpha(v)beta(3), and CD31 exist as a heterotrimeric complex which is required in SK-1-mediated endothelial cell survival. 19818132_Association of ITGAV SNP rs7378919 with rhuematoid arthritis was not replicated in New Zealand or Oxford case control sample sets 19818132_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19837659_alphav beta3 integrin may, in part, negatively regulate VEGF signaling by sequestering NRP1 and preventing it from interacting with VEGFR2 19882657_suggest that a divalent metal-ion coordination was a common driving force for the formation of both SDV/alpha v beta 3 and RGD/alpha v beta 3 complexes. 19888429_GPIIb/IIIa and alphavbeta3 integrins are important mediators in the pathology of cervical cancer. 19888537_VEGFR-2 was significantly upregulated by alpha-v suppression in HUVEC & downregulated in HMVEC at mRNA & protein levels. Suppression of alpha-v can either augment or inhibit VEGFR-2 levels & VEGF-induced proliferation in EC from different vascular beds. 19889638_Oscillatory shear stress induces osteoblast-like cell proliferation through activation of alpha(v)beta(3) and beta(1) integrins and synergistic interactions of FAK and Shc with PI3K, leading to the modulation of ERK and Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathways. 19910644_The angiogenic effects of leptin are mediated by circulating angiogenic cells and involve src kinase dependent phosphorylation of integrin alphavbeta5. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19998373_Blocking integrin alpha V beta 3 inhibits differentiation and subsequently tumor formation. 20019187_Reduced expression of integrin beta8 may be involved in the pathogenesis of sporadic brain arteriovenous malformations. 20026907_Definitive endoderm highly express the integrins alphaV and beta5, which have the ability to bind to vitronectin. 20033473_Data show that cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) promotes cell attachment via independent mechanisms involving cell surface CD47 and alphaVbeta3 integrin and that cell attachment to COMP induces formation of fascin-stabilized actin microspikes. 20037822_OPN and its receptor integrin alphanubeta3 may be involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 20121756_Mast cell-bronchial smooth muscle cell adhesion involved collagen, CD44, and CD51, particularly under inflammatory conditions. 20158572_Data show that PLT adhesion to HIMEC was ICAM-1, FKN and integrin alpha(v)beta(3) dependent. 20224109_Expression of integrin alphaVbeta3 on T lymphocytes does not predict its endometrial expression. 20306691_Results proved the importance of VEGF and integrin alphavbeta3 in the pathogenesis of AML. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20400979_Ovarian cancer ascites induces FAK and Akt activation in an alphavbeta5 integrin-dependent pathway, which confers protection from TRAIL-induced cell death and caspase activation. 20477989_These results suggest that PKD1-regulated alphavbeta3 trafficking contributes to the angiogenesis process by integrating VEGF-A signaling with extracellular matrix interactions. 20519501_the Tie2/alphavbeta3 integrin association-induced integrin internalization and degradation are mechanistic consequences of endothelial Ang-2 stimulation 20554778_Alpha(V)beta(6), but not alpha(V)beta(3), blocked human parechovirus 1 cellular infectivity. 20558745_Secreted heat shock protein 90alpha induces colorectal cancer cell invasion through CD91/LRP-1 and NF-kappaB-mediated integrin alphaV expression. 20600001_A fragment of vitronectin containing the RGD integrin binding site showed similar binding affinity as that of full vitronectin protein to purified integrin alphavbeta3 but had diminished cell adhesion and spreading function in vivo. 20605574_Integrin alphavbeta3 and Lewis Y, which is contained within it, are expressed in secretory-stage endometrial tissue. 20615244_Integrin alphavbeta5 is a prima |
ENSMUSG00000027087 |
Itgav |
1464.266678 |
2.3941589696 |
1.259519 |
0.048625039 |
673.382830 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018362967447411288406851949704179743535416689597190615691309812186710001773725792250834914526031101228344883036938099741133767089586274872945583576468958026586196472648411522244704711 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011887605242271520580311549474002971476256633531851919732179221507649919417489075549764646020518867563509917417855544730496510713833836977466550220998309802619847379974526367652835876 |
Yes |
No |
2091.4182682 |
57.2737186 |
879.6953406 |
19.0758696 |
| ENSG00000138449 |
30061 |
SLC40A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NP59 |
FUNCTION: Major iron transporter that plays a key role in balancing cellular and systemic iron levels (PubMed:29237594, PubMed:22682227, PubMed:15692071). Transports iron from intestinal, splenic, and hepatic cells into the blood to provide iron to other tissues (By similarity). Controls therefore dietary iron uptake, iron recycling by macrophages, and release of iron stores in hepatocytes (By similarity). When iron is in excess, hepcidin/HAMP levels increase resulting in a degradation of ferroportin/SLC40A1 limiting the iron efflux to plasma (PubMed:22682227, PubMed:29237594, PubMed:32814342). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JHI9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15692071, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22682227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29237594, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32814342}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Iron;Iron transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cell membrane protein that may be involved in iron export from duodenal epithelial cells. Defects in this gene are a cause of hemochromatosis type 4 (HFE4). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:30061; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; ferrous iron transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015093]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; iron ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005381]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; endothelium development [GO:0003158]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; iron ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1903988]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; iron ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034755]; lymphocyte homeostasis [GO:0002260]; multicellular organismal iron ion homeostasis [GO:0060586]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to iron [GO:0034395]; spleen trabecula formation [GO:0060345]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
11518736_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11774199_Hemochromatosis is caused by mutations in the iron-regulatory protein ferroportin. 11783942_gene coding and flanking regions were sequenced and examined for mutations that might modulate the iron burden of individuals harboring the common mutant hemochromatosis HFE genotype or cause hemochromatosis independent of mutations in the HFE gene 11897618_expression levels of human DCT1 mRNA, and to a lesser extent IREG1 mRNA, are regulated in an iron-dependent manner 12091367_A 3-base pair deletion in exon 5 of the ferroportin 1 gene predicting Val162 deletion was found in a family with autosomal dominant inheritance of increased body iron stores without hemochromatosis. 12376346_Iron increases expression of this iron-export protein in lung cells. 12730114_both L ferritin IRE and ferroportin mutations can account for isolated hyperferritinemia. 14636642_Q248H mutation is a common polymorphism in the ferroportin 1 gene in African populations that may be associated with mild anemia and a tendency to iron loading 14636643_variant is associated with increased ferritin levels in African-Americans and may play a role in their propensity to develop iron overload 14757427_review of a new inherited disorder of iron metabolism due to pathogenic mutations in the SLC40A1 gene 14768003_the presence of cirrhosis is an independent factor associated with increased expression of DMT1 but not Ireg1. 15075083_Neither HFE (C282Y and H63D) nor ferroportin(Val162del) mutations were determinants of total body iron status, as assessed by ferritin levels, in thalassemia intermedia and betas/betathal patients 15338274_In Africans with iron overload not related to the HFE gene, the possible involvement of the SLC40A1 and CYBRD1 genes was demonstrated for the first time. 15692071_ferroportin mutations A77D, V162delta, and G490D are associated with a typical pattern of hemochromatosis disease in vivo 15727899_Hereditary hemochromatosis associated with a previously unrecognized ferroportin mutation (Cys326Ser). 15831700_the Y64N and C326Y mutants of FPN are completely resistant to hepcidin inhibition and N144D and N144H are partially resistant. Hemochromatosis-associated FPN mutations, either reduce iron export or produce an FPN variant that is insensitive to hepcidin 15894659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15897636_Mutation in the ferroportin 1 may be related to hemochromatosis. 15935710_HFE4 mutations are heterogeneous in their effects on protein function; all mutants appear to be unresponsive to hepcidin and do not demonstrate the expected internalization on exposure to hepcidin. 15942076_ferroportin mutations A77D, V162delta, and G490D are associated with a typical pattern of hemochromatosis disease in vivo 15956209_The behavior of mutant ferroportin in cell culture and the ability of mutant Fpn to act as a dominant negative explain the dominant inheritance of hemochromaatois as well as the different patient phenotypes. 16280445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16330432_FPN1 is present in erythroid cells at all stages of differentiation. The existence of multiple FPN1 transcripts indicates a complex regulation of the FPN1 gene in erythroid cells. 16648237_Iron mobilization by alveolar macrophages can be affected by iron and LPS via several pathways, including HAMP-mediated degradation of FPN1, and that these cells may use unique regulatory mechanisms to cope with iron imbalance in the lung. 16885049_Fpn amino acid substitution represents a class of Fpn mutants whose behavior in vitro does not explain the phenotype of patients with iron overload. 17042772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17135308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17276706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17276706_findings conclude that the frequency of the FPN1 Q248H polymorphism is greater in African American men with elevated serum ferritin than in those with normal serum ferritin 17383046_the S338R mutation results in a mutated ferroportin associated with iron overload and is predicted insensitive to regulation by the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin 17475779_After binding of hepcidin, Fpn is tyrosine phosphorylated at the plasma membrane. 17486601_Results suggest the possibility that FPN-1 might associate and interact with Heph in the process of iron exit across the basolateral membrane of intestinal absorptive cell. 17490902_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17490902_frequency of SLC40A1 Q248H is significantly lower in African-Americans than Native Africans; OR estimates of iron overload in African-Americans & Native Africans with Q248H were greater than unity, increased OR were not statistically significant 17847004_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17997113_analysis of the SLC40A1 gene at the mRNA level in 2 patients with hyperferritinemia, normal transferrin saturation & iron accumulation predominantly in macrophages & Kupffer cells; first displayed V162 Delta; the second a novel mutation (R178G) 18160317_ferroportin was investigated as a candidate gene in 2 pedigrees with hyperferritinaemia and siderosis in mononuclear phagocytes; A77D mutation was detected in patient 1, his father & brother; V162del mutation was detected in patient 4 18160816_A new SLC40A1 exon 7 mutation c.1402G-->A results in aberrant splicing to a cryptic upstream splice site at nt 990 in the same exon. The truncated protein, missing its C-terminal 241 AAs, lacks all structural motifs beyond transmembrane region 7. 18177470_We identified two novel mutations (D157N and V72F) at the heterozygous state of SLC40A1 in two probands. Phenotype heterogeneity was observed in both families, suggesting variable penetrance and expression 18586377_No significant change in placental expression of either protein or mRNA ferroportin 1 (FP1) was observed in the maternal anemia groups 18646536_The expression of both protein and mRNA of FP1 of term placentas was not influenced by different degree of iron status of pregnant women. 18782341_Ther is a higher prevalence of ferroportin Q248H with greater alcohol consumption, and this higher prevalence raises the possibility that the allele might ameliorate the toxicity of alcohol. 18820912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19066423_Multi-organ iron overload in an African-American man with ALAS2 R452S and SLC40A1 R561G. 19150361_Hepcidin addition resulted in a redistribution of ferroportin to intracellular compartments that labeled with early endosomal and lysosomal, but not Golgi, markers and that trafficked along microtubules. 19234114_These results show that cooperativity between the ferroportin monomers is required for hepcidin-mediated Jak2 activation and ferroportin down-regulation. 19589941_These relatively high hepcidin levels are probably a consequence of patients' elevated transferrin saturation 19610021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19709084_the functional relevance of a novel ferroportin variant: the c.1502 A>G transition, which changes amino acid 501 from tyrosine to cysteine (p.Y501C);the p.Y501C mutant protein reached the plasma membrane and retained a full iron export ability 19759876_None of the individuals in this cohort of Brazilian patients with the classical phenotype of HH had any of the aforementioned non-C282Y mutations in the HFE gene or any mutations in the TfR2 and SCL40A1 genes. 19787796_identified mutations in HFE, SLC40A1, HAMP, HJV, TFR2, and FTL that could explain TRANSFERRIN SATURATION/SERUM FERRITIN heterogeneity in adults with previous HFE genotyping to detect C282Y and H63D; results were correlated with racial groups 19846751_Phenoypic clustering of mutations with gain-of-function variants associate with a hypothetical channel through the axis of ferroportin. 19937651_We report a novel pathological SLC40A1 variant associated with abnormal cell surface expression of ferroportin due to intracellular retention of the mutant protein 19958990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20007457_Suggest a novel mechanism of regulation of intestinal iron absorption based on inward and outward fluxes at both membrane domains, and repositioning of DMT1 and FPN between membrane and intracellular compartments as a function of iron supply. 20230395_study presents a family with a novel mutation in the SLC40A1 gene leading to a type 4a haemochromatosis phenotype, ferroportin disease 20460119_Ferroportin Q248H and low iron stores are both associated with lower circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha, while only ferroportin Q248H is associated with lower circulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor 20460119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564534_Intestinal FPN protein is upregulated in anemic Crohn's disease. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20655381_Findings supported the notion that under low levels of hepcidin, mutant ceruloplasmin cannot stabilize ferroportin because of a loss-of-function in the ferroxidase activity. 20686179_Ferroportin is a pivotal protein in breast biology and a strong and independent predictor of prognosis in breast cancer. 20688958_Zinc and cadmium can activate FPN1 transcription through the Metal Transcription Factor-1. 20691492_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20739079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21094556_Identified a G to A nucleotide change at position 238 in the ferroportin gene leading to the G80S substitution. The G80S mutation results in a mutated ferroportin associated with iron overload and is predicted to be defective in iron export. 21126372_Expression of ferroportin was associated with reduced HIV-1 transcription. 21199650_Members of families with ferroportin disease should be screened for biochemical parameters of iron metabolism as well as genotype to detect silent mutations that might cause disease with acquired or genetic cofactors 21231898_This study confirmed the presence of Q248H mutation at polymorphic frequencies in three native sub-Saharan populations. 21303654_Nrf2 regulates iron efflux from macrophages through Fpn1 gene transcription 21396368_Report mutations in SLC40A1 that affect ferroportin function and phenotype of human ferroportin iron overload. 21607294_Letter: Report Absence of functional mutations in the ferroportin-encoding SLC40A1 gene in porphyria cutanea tarda. 22137264_Data suggest that FPN-1 expression in enterocytes increases upon zinc supplementation and decreases with iron or zinc depletion; FPN-1 appears to be involved in efflux of excess sequestered iron and thus helps maintain cellular iron homeostasis. 22170436_Placental FPN1 expression is not dependent on the iron regular element/iron regular protein regulation. 22178646_Mn is a substrate for FPN1, and that this export process is inhibited by a low extracellular pH and by incubation in a high K(+) medium, indicating the involvement of transmembrane ion gradients in FPN1-mediated transport. 22246570_the present study demonstrated the presence of ferroportin 1 in cultured human osteoblast cells. Furthermore, the osteoblast ferroportin 1 is functionally regulated by hepcidin. 22249207_Ferroportin (SLC40A1) Q248H mutation is associated with lower circulating serum hepcidin levels in Rwandese HIV-positive women. 22357659_Four SLC40A1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were associated with an increased risk of tuberculosis and 1 SNP with reduced risk. 22682226_Hepcidin-induced ferroportin internalization did not require JAK2 or phosphorylation of ferroportin residues 302 and 303 22682227_human ferroportin mutation K240E, previously associated with clinical iron overload, caused hepcidin resistance in vitro by interfering with ferroportin ubiquitination 22776295_labeled hepcidin was also a suitable tool to visualize internalization of overexpressed or even endogenously expressed ferroportin without tags 22890139_Mutations in the SLC40A1 gene is associated with hemochromatosis. 23012398_Letter: report mutations in SLC40A1 promoter in and possible role in iron hemostasis in patients with porphyria cutanea tarda. 23065513_ferroportin Q248H protein is resistant to physiological concentrations of hepcidin and that this mutation has discernible effects on iron metabolism-related clinical complications of sickle cell anemia. 23178444_ferroportin polymorphism and iron homeostasis and infection [review] 23335088_Our study suggests that GDF15 induction helps suppress further activation of macrophages in stressful physiologic states as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis...resulting in enhanced ferroportin-mediated iron efflux. 23630227_Nitric oxide up-regulated the expression of ferroportin-1 (Fpn1), the major cellular iron exporter, in mouse and human cells. 23640881_Iron efflux from human brain microvasculature endothelial cells ferroportin requires the action of an exocytoplasmic ferroxidase which can be either endogenous hephaestin or extracellular ceruloplasmin. 23680252_The Q248H mutation in ferroportin was associated with hyperferritinemia and aytpical type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients from South Kivu. 23784628_Tryptophan residue 42, which is localized within the extracellular end of the ferroportin pore, is likely involved in the iron export function of SLC40A1. 23846698_A model is proposed that suggests that unlike proteases, which are irreversibly bound to activated alpha2M, hepcidin remains labile and available to down-regulate Fpn1. 23996061_Manganese (Mn) transport carriers DMT1 and FPN1 mediate the apical uptake and basolateral exit of Mn in colonic epithelial Caco-2 cells. 24252754_Results suggest that reduction in ferroportin levels in Alzheimer's disease brains are likely associated with cerebral ischaemia, inflammation, loss of neurons due to protein misfolding, senile plaque formation and possibly ageing process itself 24304836_Ferroportin is an iron-preferring cellular metal-efflux transporter with a narrow substrate profile that includes cobalt and zinc. 24644245_Findings and the iron overload phenotype of the patient suggest that the novel mutation c.386T>C (p.L129P) in the SLC40A1 gene has incomplete penetrance and causes the classical form of ferroportin disease. 24859227_D181V and A69T ferroportin mutation is associated with hemochromatosis. 25093806_combined data overall deciphered the machinery that altered the hepcidin-ferroportin signaling in breast cancers. 25176568_Chlorpyrifos elevates ferroportin expression through transcriptional regulation. 25284586_Data indicate that elevated miR-492 expression in prostate tumors that resulted in diminished myeloid zinc-finger 1 (MZF-1) and ferroportin (FPN). 25330009_The expression of duodenal Fpn1 is negatively correlated with mRNA levels of hepcidin, and positively correlated with serum iron parameters. 25441019_Several family members had hemochromatosis and hyperferritinemia associated with a SLC40A1 deletion in exon 5(485_487delTTG) resulting in the deletion of a valine residue (p.V162del). This is the 1st Spanish family reported with this European mutation. 25451081_The effects of abnormal FPN on tumor growth and the molecular mechanisms of diminished tumor FPN, were examined. 25744489_study of healthy adults provides further evidence that ferroportin Q248H mutation affects serum ferritin concentration in Africans 25745821_Low hepcidin and high ferroportin expression by erythroblasts and macrophages were seen in iron deficiency anemia, while the opposite was true in anemia of chronic disorders. 25805936_Decreased expression of hepcidin and ferroportin in hepatitis C patients indicates the importance of hepatocytic iron retention for viral response during pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin treatment. 25855377_we demonstrated that downregulation of FPN1 plays critical roles in promoting myeloma cell growth and bone resorption in multiple myeloma. 25976471_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in HAMP, BMP2, FTL and SLC40A1 genes have phenotype-modifying roles in hereditary hemochromatosis type 1. 26125411_TLR4 dependent macrophage signaling is controlled via hepcidin-ferroportin1 axis by influencing TLR4-lipid raft interactions 26437604_The concentration of functional membrane-associated ferroportin is controlled by its ligand, the iron-regulatory hormone hepcidin, and fine-tuned by regulatory mechanisms serving iron homeostasis, oxygen utilization, host defense, and erythropoiesis. 26474245_Of the 13 iron-overloaded patients showed that 10 were homozygous for the c.44-24G>C polymorphism located in intron 1, whereas the three remaining patients were heterozygous for this sequence variation. Several reports have suggested that this polymorphism could be linked to IO and/or to the severity of haemochromatosis. 26560875_Mir-20a controls expression of the iron exporter ferroportin (FPN1) by binding to highly conserved target sites in its 3'-untranslated region. Expression of miR-20a is inversely correlated to FPN1 in lung cancer. 26633544_Of the non-HFE forms of iron overload, TFR2-, HFE2-, and HAMP-related forms are predicted to be rare, with pathogenic allele frequencies in the range of 0.00007 to 0.0005. Significantly, SLC40A1 variants that have been previously associated with autosomal-dominant ferroportin disease were identified in several populations (pathogenic allele frequency 0.0004), being most prevalent among Africans 26666535_Erythroblasts from Beta-thalassemia patients showed a significantly reduced expression of total MTP1 protein. 27067485_All these findings suggest that in erythroid cells FPN1 could be part of the signaling pathway through which the erythron communicates iron needs to expand the erythroid compartment regardless of systemic iron level. 27302059_These results suggest that FPN1 exports iron received from the iron chaperone PCBP2. Therefore, it was found that PCBP2 modulates cellular iron export, which is an important physiological process. 27788496_Nrf2 suppresses prostate cancer cells viability, migration, and mitosis by upregulating ferroportin expression. 27842994_Reduced expression of ferroportin mRNA identifies a subset of infertile women and may constitute a target for therapy. 28027576_FPN1 cycles as a monomer within the endocytic/plasma membrane compartment and responds to its physiological inhibitor, Hepc, in both control and ferroportin disease (FD) cells. However, in FD, FPN1 fails to reach the cell surface when cells undergo high iron turnover. 28110135_In this study, we identified three domestic sporadic families of hereditary hemochromatosis in China and demonstrated mutations in HFE and SLC40A1 respectively. 28681497_study followed the dynamics of hepcidin-mediated ferroportin internalization; also showed that the novel p.D84E mutation, associated with the classical form of ferroportin disease, is both iron transport defective and hepcidin insensitive 28826751_The 1st 3D model of human ferroportin was used to study disease-associated mutations to determine the role of conserved residues in protein stability and iron transport. Molecular mechanisms critical for ferroportin endocytosis include at least 3 fundamental steps: hepcidin binding, structural reorganization of the N- and C-ter ferroportin lobes, and ferroportin ubiquitination. 29061069_Findings establish FPN as a key lever in regulating iron balance and proliferation in multiple prostate cancer cell types. 29082606_SLC40A1 expression is increased in the intestine of patients with type 2 diabetes in association with iron stores and serum hepcidin levels. 29154924_SLC40A1 mutation analysis in 7 Italian families with type 4 hereditary hemochromatosis 29599243_Ferroportin protects erythrocytes against oxidative stress and malaria infection. 29774528_Regarding the rs13015236 single nucleotide polymorphisms in SLC40A1, the presence of a C allele could protect against porphyria cutanea tarda patients of mixed ancestry. 30002125_p.Arg178Gln represents a new category of loss-of-function mutations and that the study of 'gating residues' is necessary in order to fully understand the action mechanism of FPN1. 30082682_Ca(2+) is required for human Fpn transport activity 30154413_IL-6 was also found to increase hepcidin transcription and release from human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (hPASMCs) suggesting a potential autocrine response. Hepcidin or IL-6 mediated iron accumulation contributes to proliferation in hPASMCs; ferroportin mediated cellular iron excretion limits proliferation. 30213870_The mean corpuscular volume (MCV) values of gain-of-function FPN1 mutation patients were positively associated with serum transferrin saturations, whereas MCVs of loss-of-function FPN1 mutation patients were not, supporting that erythroblasts donate iron to blood through FPN1 in response to serum iron levels. 30500107_The SLC40A1 p.Y333H mutation is associated with gain of function of ferroportin, representing one of the major aetiological factors of haemochromatosis in China. 30852438_High SLC40A1 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 31049138_These and other data suggest that iron handling and the HAMP-FPN axis regulation in FRDA cardiac cells are hampered and that FPN may have new, still not fully understood, functions. These findings underline the complexity of the cardiac iron homeostasis. 31423010_Ferroportin downregulation promotes cell proliferation by modulating the Nrf2-miR-17-5p axis in multiple myeloma. 31442954_Reduced expression of FPN1 and CP was identified as a potential signature for poor prognosis of adrenocortical carcinoma. 31554201_miR-20b is identified to regulate intestinal FPN expression in vitro and in vivo, which will provide a potential target for intestinal iron exportation. 31675496_Of the macrophages in tumors that exhibited distinct transcriptional states, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) were associated with poor prognosis, and we established the inflammatory role of SLC40A1 and GPNMB in these cells 31721611_Enhanced expression of apical membrane- and basolateral membrane-localized DMT1 and FPN1 in UC human colon. 31761321_Local hepcidin increased intracellular iron overload via the degradation of ferroportin in the kidney. 32301493_Evidence for dimerization of ferroportin in a human hepatic cell line using proximity ligation assays. 32360131_Ferroportin disease: A novel SLC40A1 mutation. 32534701_miR-194-5p inhibits SLC40A1 expression to induce cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. 32814342_Structure of hepcidin-bound ferroportin reveals iron homeostatic mechanisms. 33340587_The role of cellular iron deficiency in controlling iron export. 33341511_Splicing analysis of SLC40A1 missense variations and contribution to hemochromatosis type 4 phenotypes. 33628376_Ferroportin-Dependent Iron Homeostasis Protects against Oxidative Stress-Induced Nucleus Pulposus Cell Ferroptosis and Ameliorates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration In Vivo. 33664298_Knocking out alpha-synuclein in melanoma cells dysregulates cellular iron metabolism and suppresses tumor growth. 33714956_Downregulation of FPN1 acts as a prognostic biomarker associated with immune infiltration in lung cancer. 33735560_Ferroportin and FBXL5 as Prognostic Markers in Advanced Stage Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 33804198_Iron Availability in Tissue Microenvironment: The Key Role of Ferroportin. 34098197_Upregulation of miR-18a-5p promotes the proliferation of prostate cancer via inhibiting the expression of SLC40A1. 34183746_Decreased ferroportin in hepatocytes promotes macrophages polarize towards an M2-like phenotype and liver fibrosis. 34203920_Insights into the Role of the Discontinuous TM7 Helix of Human Ferroportin through the Prism of the Asp325 Residue. 34320783_UBA6 and NDFIP1 regulate the degradation of ferroportin. 34493724_Gene interfered-ferroptosis therapy for cancers. 35162984_Interplay of Ferritin Accumulation and Ferroportin Loss in Ageing Brain: Implication for Protein Aggregation in Down Syndrome Dementia, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's Diseases. 35225679_Estimates of West African Ancestry in African Americans Using Alleles of Iron-Related Genes HJV, SLC40A1, and TFR2. 35646516_MicroRNA-4735-3p Facilitates Ferroptosis in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by Targeting SLC40A1. 35705926_Assessment of iron overload in a cohort of Sri Lankan patients with transfusion dependent beta thalassaemia and its correlation with pathogenic variants in HBB, HFE, SLC40A1, and TFR2 genes. |
ENSMUSG00000025993 |
Slc40a1 |
12.298070 |
0.2365227917 |
-2.079949 |
0.570441154 |
13.436601 |
0.00024676224253462804856043555368216857459628954529762268066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000637307209065811038420368284107553336070850491523742675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3981215 |
1.8087501 |
18.6701949 |
4.5386897 |
| ENSG00000138468 |
57337 |
SENP7 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQF6 |
FUNCTION: Protease that acts as a positive regulator of the cGAS-STING pathway by catalyzing desumoylation of CGAS. Desumoylation of CGAS promotes DNA-binding activity of CGAS, subsequent oligomerization and activation (By similarity). Deconjugates SUMO2 and SUMO3 from targeted proteins, but not SUMO1 (PubMed:18799455). Catalyzes the deconjugation of poly-SUMO2 and poly-SUMO3 chains (PubMed:18799455). Has very low efficiency in processing full-length SUMO proteins to their mature forms (PubMed:18799455). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BUH8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799455}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
The reversible posttranslational modification of proteins by the addition of small ubiquitin-like SUMO proteins (see SUMO1; MIM 601912) is required for many cellular processes. SUMO-specific proteases, such as SENP7, process SUMO precursors to generate a C-terminal diglycine motif required for the conjugation reaction. They also display isopeptidase activity for deconjugation of SUMO-conjugated substrates (Lima and Reverter, 2008 [PubMed 18799455]).[supplied by OMIM, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:57337; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SUMO-specific endopeptidase activity [GO:0070139]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; protein desumoylation [GO:0016926] |
18799455_SENP6 and SENP7 exhibit lower rates for processing pre-SUMO1, pre-SUMO2, or pre-SUMO3 in comparison with SENP2 21878624_Loop 1 insertion in SENP6 and SENP7 as a platform to discriminate between SUMO1 and SUMO2/3 isoforms in this subclass of the SUMO protease family. 23045645_differential splicing of the SENP7 regulates either tumor suppression or progression 24018422_deSUMOylation by SENP7 is required to promote a permissive chromatin environment for DNA repair. 25895136_c-Myc is targeted to the proteasome for degradation in a SUMOylation-dependent manner, regulated by PIAS1, SENP7 and RNF4 28429743_non-tumorigenic MCF10-2A cells with reduced SENP7S exhibit greater cell proliferation and anchorage-dependent growth. SENP7S depletion directly potentiates tumorigenic properties of MCF10-2A cells with induction of anchorage-independent growth and self-renewal in 3D-spheroid conditions. Collectively, the results identify SENP7S as a novel mediator of beta-catenin signaling and normal mammary epithelial cell physiology. 29777712_SPOP inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell metastasis via ubiquitin-dependent SENP7 proteolysis and may thus serve as a new opinion for the prevention of HCC metastasis. 31825833_DeSUMOylase SENP7-Mediated Epithelial Signaling Triggers Intestinal Inflammation via Expansion of Gamma-Delta T Cells. 35143421_SENP7 senses oxidative stress to sustain metabolic fitness and antitumor functions of CD8+ T cells. |
ENSMUSG00000052917 |
Senp7 |
135.250006 |
0.4731915458 |
-1.079504 |
0.180000535 |
35.865268 |
0.00000000211444592168749176841956196573786563863706078336690552532672882080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000009832773095181909409972863906831963554111553094116970896720886230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.8832553 |
12.5036648 |
157.0499049 |
18.7647240 |
| ENSG00000138600 |
84888 |
SPPL2A |
protein_coding |
Q8TCT8 |
FUNCTION: Intramembrane-cleaving aspartic protease (I-CLiP) that cleaves type II membrane signal peptides in the hydrophobic plane of the membrane. Functions in FASLG, ITM2B and TNF processing (PubMed:16829952, PubMed:16829951, PubMed:17557115, PubMed:17965014). Catalyzes the intramembrane cleavage of the anchored fragment of shed TNF-alpha (TNF), which promotes the release of the intracellular domain (ICD) for signaling to the nucleus (PubMed:16829952). Also responsible for the intramembrane cleavage of Fas antigen ligand FASLG, which promotes the release of the intracellular FasL domain (FasL ICD) (PubMed:17557115). Essential for degradation of the invariant chain CD74 that plays a central role in the function of antigen-presenting cells in the immune system (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity (PubMed:16829952). Catalyzes the intramembrane cleavage of the simian foamy virus envelope glycoprotein gp130 independently of prior ectodomain shedding by furin or furin-like proprotein convertase (PC)-mediated cleavage proteolysis (PubMed:23132852). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JJF9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16829951, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16829952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17557115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17965014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23132852}. |
Endosome;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the GXGD family of aspartic proteases, which are transmembrane proteins with two conserved catalytic motifs localized within the membrane-spanning regions, as well as a member of the signal peptide peptidase-like protease (SPPL) family. This protein is expressed in all major adult human tissues and localizes to late endosomal compartments and lysosomal membranes. A pseudogene of this gene also lies on chromosome 15. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:84888; |
cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0098554]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi-associated vesicle membrane [GO:0030660]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0098553]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; aspartic endopeptidase activity, intramembrane cleaving [GO:0042500]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis [GO:0031293]; membrane protein proteolysis [GO:0033619]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010803] |
15385547_SPP, SPPL2a, -2b, -2c, and -3 probably cleave type II-oriented substrate peptides as shown by consensus analysis 17557115_ADAM10 and SPPL2a were identified as two proteases implicated in FasL processing and release of the FasL intracellular domain, which has been shown to be important for retrograde FasL signaling 17965014_SPPL2a and SPPL2b mediate the intramembrane cleavage, whereas neither SPP nor SPPL3 is capable of processing the Bri2 N-terminal fragment. 21896273_Data show that endogenous SPPL2a - in agreement with overexpression studies - is localised in membranes of lysosomes/late endosomes. 24872421_Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of the frontotemporal lobar degeneration risk factor, TMEM106B, by signal peptide peptidase-like 2a (SPPL2a). 25035924_In human B cells, SPPL2a is indispensable for turnover of CD74 N-terminal fragment. A human 15q21.2 microdeletion leads to loss of SPPL2a transcript and protein. 26987812_Study propose that elements within the transmembrane segment and the luminal juxtamembrane domain facilitate intramembrane proteolysis of CD74 by SPPL2a. 30127434_inherited SPPL2a deficiency in humans underlies mycobacterial disease by decreasing the numbers of dendritic cells and impairing IFN-gamma production by mycobacterium-specific memory TH1* cells 30819724_SPPL2a/b negatively regulates LOX-1 signaling and atherosclerosis. |
ENSMUSG00000027366 |
Sppl2a |
1348.916649 |
2.4154229030 |
1.272276 |
0.083380192 |
228.144894 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000151327297358340997752183171167878531636964386906638768026649883365737497676877690374522199754469596441090485334856921939057587526457349103026217562728561460971832275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000033537401036172867173656177777260584898825134954584370576520269681002829658584450106145235208322640692070616096223352944820741451670276234153789118863642215728759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1745.3381800 |
100.0895739 |
727.3484191 |
30.7838089 |
| ENSG00000138623 |
8482 |
SEMA7A |
protein_coding |
O75326 |
FUNCTION: Plays an important role in integrin-mediated signaling and functions both in regulating cell migration and immune responses. Promotes formation of focal adhesion complexes, activation of the protein kinase PTK2/FAK1 and subsequent phosphorylation of MAPK1 and MAPK3. Promotes production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by monocytes and macrophages. Plays an important role in modulating inflammation and T-cell-mediated immune responses. Promotes axon growth in the embryonic olfactory bulb. Promotes attachment, spreading and dendrite outgrowth in melanocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12879062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17377534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17671519}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Intrahepatic cholestasis;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the semaphorin family of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored membrane glycoprotein. The encoded protein is found on activated lymphocytes and erythrocytes and may be involved in immunomodulatory and neuronal processes. The encoded protein carries the John Milton Hagen (JMH) blood group antigens. Mutations in this gene may be associated with reduced bone mineral density (BMD). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:8482; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; olfactory lobe development [GO:0021988]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526] |
12193228_Sema7A is a potent stimulator of cytokine production, chemotaxis and superoxide release in monocytes 15907379_SEMA 7A might be a molecule involved in the terminal innervation of the dentin-pulp complex. 16372136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16372136_Polymorphisms in SEMA7A may play a role in decreased bone mineral density and increased risk of vertebral fracture. 17671519_beta1-integrins and Plexin C1 receptors are ligands for Semaphorin 7a, and that signaling by these receptors has opposing effects on Semaphorin 7a-induced dendrite formation. 19318806_Sema7A binds to human melanocytes through beta1-integrins and the Plexin C1 receptor 20727575_Study reports the structures of Sema7A and A39R complexed with the Semaphorin-binding module of PlexinC1; both structures show two PlexinC1 molecules symmetrically bridged by Semaphorin dimers. 20854351_A new SEMA7A variant was identified in Native American plasma samples, and an alloantibody that recognizes the wild-type protein 21524887_Sema7A on keratinocytes and beta1-integrin on monocytes contribute to monocyte activation by keratinocytes within skin inflammation, inducing IL-8 22448926_Sema7A markedly reduces the production rates of megakaryocytes and platelets from CD34(+) progenitor cells. 22845496_Semaphorin 7A protein variants differentially regulate T-cell activity. 22891341_We report here the expression and induction of semaphorin 7A (SEMA7A) on endothelium through hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha during hypoxia. 23166499_two MTRAP monomers interact via their tandem TSR domains with the Sema domains of a Semaphorin-7A homodimer 23850082_SEMA7A was expressed in the liver and was increased in the course of liver fibrosis, both in mice and in humans. 24333536_Semaphorin 7A is a potentially important modulator of eosinophil profibrotic functions in the airway remodeling of patients with chronic asthma. 24522099_heterozygous missense variants in SEMA3A and SEMA7A may modify the phenotype of Kallmann syndrome but most likely are not alone sufficient to cause the disorder 25406498_These results suggest that SEMA7a plays a role as a CSF biomarkers associated with the conversion to clinically definite multiple sclerosis in clinically isolated syndromes patients 26432853_Sema3A and sema7A expression correlated with the inflammatory activity of the multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions, suggesting their involvement in the immunological process that takes place in MS. 26597008_This study demonstrates that Sema7A controls the assembly of actin-based protrusions that drive Dendritic cell migration in response to CCL21. 26752048_SEMA7A has a role in the development of lung injury 27065336_short hairpin-mediated silencing of SEMA7A reveals roles for semaphorin 7a in the promotion of DCIS growth, motility and invasion as well as lymphangiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment. Our studies also uncover a relationship between COX-2 and semaphorin 7a expression and suggest that semaphorin 7a promotes tumor cell invasion on collagen and lymphangiogenesis via activation of b1-integrin receptor 28109308_These findings indicate that Sema7A as a potent activator of T cells and monocytes in the immune response contributes to the inflammation and progression of rheumatoid arthritis 28336906_Our results identified FGL2, GAL, SEMA4D, SEMA7A, and IDO1 as new candidate genes that could be involved in MSCs-mediated immunomodulation. FGL2, GAL, SEMA4D, SEMA7A, and IDO1 genes appeared to be differentially transcribed in the different MSC populations. Moreover, these genes were not similarly modulated following MSCs-exposure to inflammatory signals 29269512_Sema7A has a significant role in atherosclerosis by mediating endothelial dysfunction in a beta1 integrin-dependent manner. 29509252_Semaphorin-7A promoted growth and migration of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma by regulating transforming growth factor-beta induced epithelial mesenchymal transition. 30254150_SEMA7A, which is expressed on mammary cells during glandular involution, alters macrophage biology and lymphangiogenesis to drive breast cancer metastasis 30729666_High Serum semaphorin 7A level is associated with the risk of acute atherothrombotic stroke. 31016720_this study shows that semaphorin 7A modulates cytokine-induced memory-like responses by human natural killer cells 31179640_Sema7A, a brain immune regulator, regulates seizure activity in PTZ-kindled epileptic rats. 31394943_Sema3A and Sema7A gene polymorphisms are not related to systemic lupus erythematosus genetic susceptibility, but may link to several clinical features of systemic lupus erythematosus. 31732974_The LOXL1-AS1/miR-28-5p/SEMA7A axis facilitated pancreatic cancer progression, which may be regarded as an innovative therapeutic target for PC treatment. 32161256_Study reports that soluble SEMA7A is elevated in plasma of patients with acute Myocardial infarction (MI), and that Semaphorin 7A holds significant impact on the extent of MI reperfusion injury. In mouse model Sema7a promotes myocardial thrombo-inflammation and tissue damage by reinforcing platelet thrombotic activity and platelet-neutrophil complexes formation through a platelet GPIb-dependent mechanism. 32313230_Antibodies against a short region of PfRipr inhibit Plasmodium falciparum merozoite invasion and PfRipr interaction with Rh5 and SEMA7A. 32826874_Semaphorin 7A promotes endothelial to mesenchymal transition through ATF3 mediated TGF-beta2/Smad signaling. 33122307_Hormonal Regulation of Semaphorin 7a in ER(+) Breast Cancer Drives Therapeutic Resistance. 33637648_Sema7A is crucial for resolution of severe inflammation. 34126161_The Expression of Semaphorin 7A in Human Periapical Lesions. 34561423_Anoikis resistance in mammary epithelial cells is mediated by semaphorin 7a. 35955933_A Comprehensive Prognostic Analysis of Tumor-Related Blood Group Antigens in Pan-Cancers Suggests That SEMA7A as a Novel Biomarker in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000038264 |
Sema7a |
655.082511 |
9.2027172532 |
3.202060 |
0.086103951 |
1583.962039 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1191.3296344 |
60.3677059 |
130.3394069 |
6.0538787 |
| ENSG00000138670 |
153020 |
RASGEF1B |
protein_coding |
Q0VAM2 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) with specificity for RAP2A, it doesn't seems to activate other Ras family proteins (in vitro). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19645719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23894443}. |
Alternative splicing;Endosome;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Reference proteome |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity and small GTPase mediated signal transduction. Predicted to be located in early endosome; late endosome; and midbody. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:153020; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; midbody [GO:0030496]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265] |
19645719_Mutation of the Ser39 in Rap1 changed the specificity and allowed the nucleotide exchange of Rap1(S39F) to be stimulated by RasGEF1B 22303795_As an addition to PRKG2 and RASGEFIB genes, we propose to include BMP3 gene as the principal determinant of the observed common phenotype. 27362560_We show that knockdown of the expression of mcircRasGEF1B reduces LPS-induced ICAM-1 expression. Additionally, we demonstrate that mcircRasGEF1B regulates the stability of mature ICAM-1 mRNAs. 31044621_study provides evidence for two novel candidate genes, SPG7 and RASGEF1B, associating with white coat effect |
ENSMUSG00000089809 |
Rasgef1b |
161.100120 |
5.6843221122 |
2.506988 |
0.190961557 |
171.740314 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000308372443919784743115875036506691108214828562296022538582760029673019380428161373450924100665531161439419927106087015999946743249893188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000050685715726681762137035526579145924167595175735622156089043517539035639358432671176095218891873494734823246687938080867752432823181152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
284.5364187 |
33.4207182 |
50.2328282 |
4.8937894 |
| ENSG00000138678 |
84803 |
GPAT3 |
protein_coding |
Q53EU6 |
FUNCTION: Converts glycerol-3-phosphate to 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate (lysophosphatidic acid or LPA) by incorporating an acyl moiety at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone (PubMed:17170135). Also converts LPA into 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate (phosphatidic acid or PA) by incorporating an acyl moiety at the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone (PubMed:19318427). Protects cells against lipotoxicity (PubMed:30846318). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17170135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19318427, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30846318}. |
Acyltransferase;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phospholipid biosynthesis;Phospholipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Glycerolipid metabolism; triacylglycerol biosynthesis.; PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthesis; CDP-diacylglycerol from sn-glycerol 3-phosphate: step 1/3. |
This gene encodes a member of the lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase protein family. The encoded protein is an enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of glycerol-3-phosphate to lysophosphatidic acid in the synthesis of triacylglycerol. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:84803; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0003841]; glycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0004366]; sn-1-glycerol-3-phosphate C16:0-DCA-CoA acyl transferase activity [GO:0102420]; CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthetic process [GO:0016024]; glycerol-3-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0006072]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032006]; triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0019432] |
17002884_LPAAT-theta gene consisted of 12 exons and 11 introns, and mapped to chromosome 4q21.23, was ubiquitously expressed in 18 human tissues and overexpression of LPAAT-theta can induce mTOR-dependent p70S6K and 4EBP1 phosphorylation in HEK293T cells. 20181984_Results reveal a link between the lipogenic effects of insulin and microsomal GPAT3 and GPAT4, implying their importance in glycerolipid biosynthesis. 22985252_findings identified a direct role that mag-1 played in metastasis and implicated its function in cellular adaptation to tumour microenvironment 26110566_Data show that 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 9 (AGPAT9) inhibit cell growth by regulating expression of KLF4/LASS2/V-ATPase proteins in breast cancer. 32094408_Oligomers of the lipodystrophy protein seipin may co-ordinate GPAT3 and AGPAT2 enzymes to facilitate adipocyte differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000029314 |
Gpat3 |
56.894220 |
4.6420548265 |
2.214764 |
0.334341342 |
43.287275 |
0.00000000004726474458115400062473734987694988680939633951538780820555984973907470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000249777167926184427381382059050454400028762336205545580014586448669433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
105.7559631 |
19.2401405 |
21.7979437 |
3.4496325 |
| ENSG00000138685 |
2247 |
FGF2 |
protein_coding |
P09038 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a ligand for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4 (PubMed:8663044). Also acts as an integrin ligand which is required for FGF2 signaling (PubMed:28302677). Binds to integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 (PubMed:28302677). Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, cell differentiation and cell migration (PubMed:8663044, PubMed:28302677). Functions as a potent mitogen in vitro (PubMed:1721615, PubMed:3964259, PubMed:3732516). Can induce angiogenesis (PubMed:23469107, PubMed:28302677). Mediates phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and thereby promotes retinal lens fiber differentiation (PubMed:29501879). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1721615, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29501879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3732516, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3964259}. |
3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Angiogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Growth factor;Heparin-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Mitogen;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members bind heparin and possess broad mitogenic and angiogenic activities. This protein has been implicated in diverse biological processes, such as limb and nervous system development, wound healing, and tumor growth. The mRNA for this gene contains multiple polyadenylation sites, and is alternatively translated from non-AUG (CUG) and AUG initiation codons, resulting in five different isoforms with distinct properties. The CUG-initiated isoforms are localized in the nucleus and are responsible for the intracrine effect, whereas, the AUG-initiated form is mostly cytosolic and is responsible for the paracrine and autocrine effects of this FGF. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2247; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; chemokine binding [GO:0019956]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; fibroblast growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005104]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; receptor-receptor interaction [GO:0090722]; aging [GO:0007568]; angiogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis [GO:0060978]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation [GO:0021930]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; chondroblast differentiation [GO:0060591]; corticotropin hormone secreting cell differentiation [GO:0060128]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; embryonic morphogenesis [GO:0048598]; endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001935]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008543]; glial cell differentiation [GO:0010001]; growth factor dependent regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation [GO:0014843]; hyaluronan catabolic process [GO:0030214]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032958]; lung development [GO:0030324]; lymphatic endothelial cell migration [GO:1904977]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043537]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040037]; negative regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010764]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000647]; negative regulation of wound healing [GO:0061045]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007405]; organ induction [GO:0001759]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; paracrine signaling [GO:0038001]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell fate specification [GO:0042660]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation [GO:0021940]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:2001028]; positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor [GO:2000546]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of epithelial tube formation [GO:1905278]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045609]; positive regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:1902748]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:1902913]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000738]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905564]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903587]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090049]; regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor [GO:2000544]; regulation of retinal cell programmed cell death [GO:0046668]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; stem cell development [GO:0048864]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762]; thyroid-stimulating hormone-secreting cell differentiation [GO:0060129]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
2538817_Alternate protein isoforms arise through the use of AUG and non-AUG (CUG) translation initiation codons. 2726761_Four FGF2 isoforms result from alternative translation initiation from an AUG and 3 non-AUG (CUG) start codons. 9858574_A new FGF2 isoform results from the use of a non-AUG (CUG) translation initiation codon. 11742492_Significant association with poor survival by bFGF. 11864711_Snake venom disintegrin significantly suppresses basic fibroblast growth factor-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation, but has little effect on normal growth of the cell. 11891198_Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) was significantly associated with increased microvessel density in cutaneous melanomas 11891801_b-FGF serum levels were significantly higher in patients with chronic myeloproliferative disorders. 11928807_bFGF up-regulated UPA in both normal and dystrophic myoblasts. 11940567_Phosphorylation of STAT-3 in response to basic fibroblast growth factor occurs through a mechanism involving platelet-activating factor, JAK-2, and Src in human umbilical vein endothelial cells 11960370_Phorbol esters inhibit fibroblast growth factor-2-stimulated fibroblast proliferation by a p38 MAP kinase dependent pathway 11964307_HTLV-I-transformed T cells, but not HTLV-I-negative CD4(+) T cells, secrete biologically active forms of VEGF and bFGF and induce angiogenesis in vitro. 11976347_stress-induced release from endothelial cells mediated by integrin alpha v beta 3 11985797_plasma basic fibroblast growth factor may have a role in progression of multiple myleoma 11986954_level spontaneously secreted by patient CLL B-cells quantified; consistently secreted in all patient samples. 11999550_REVIEW: Association of expression of bFGF with clinical characteristics in human leukemia and lymphoma 12000311_FGF2 binds to heparin-derived oligosaccharides and stimulates phosphorylation of p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase and proliferation of rat mammary fibroblasts. 12006402_Basic fibroblast growth factor may control proteolysis and fibrinolysis in vessel walls by inducing plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in vascular endothelium. 12008951_possible role of fibroblast growth factors in expression of genes of the plasminogen activator system in breast fibroblasts 12020352_role for farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase in fibroblast growth factor-mediated signal transduction 12032827_Biological activity of substrate-bound basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2): recruitment of FGF receptor-1 in endothelial cell adhesion contacts 12054499_FGF-2 and TPA induce matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in MCF-7 cells through PKC activation of the Ras/ERK pathway. 12057924_bFGF and aFGF may suppress endothelial-dependent monocyte recruitment and thus have an anti-inflammatory action during angiogenesis in chronic inflammation but inhibit the immunoinflammatory tumor defense mechanism 12080186_Noninvasive dynamic fluorescence imaging of human melanomas reveals that targeted inhibition of bFGF or FGFR-1 in melanoma cells blocks tumor growth by apoptosis. 12087465_expression associated with poor outcome in non-Hodgkin lymphoma 12168799_FGF2 has a role in controlling normal and premature cranial ossification in humans [review] 12172783_results show that Hensen's node and FGFs induce ectopic expression of cardiac lineage markers, and that FGF and TGFbeta family members can modulate early development of the heart 12209593_Serum levels of angiogenin, basic fibroblast growth factor and endostatin in patients receiving intensive chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia. 12235165_FGF-2 is a novel modulator of Lef/Tcf-beta-catenin signaling in endothelial cells 12369790_BFGF may sensitively regulate local bone resorption and remodeling through direct and indirect mechanisms that promote angiogenesis and OC recruitment, formation, differentiation, and activated bone pit resorption. 12393937_This protein has a modulating control of the differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells. 12403780_Data show that FGF/FGFR signaling stimulates the DNA-binding and transcriptional activities of Runx2 as well as its expression, and these are largely regulated by the PKC pathway. 12428103_FGF2 and VEGF release by platelets support cell survival and cell growth of vascular endothelium cells in coculture. 12478660_FGF2 is inhibited by glypican 3 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 12496364_EphA2 does not inhibit endothelial cell survival, migration, sprouting, and corneal angiogenesis induced by this protein. 12509902_The determination of bFGF will be helpful in estimating the size of infarct lesion at acute stage of cerebral infarction. 12517814_Paracrine interactions of basic fibroblast growth factor and interleukin-6 in multiple myeloma 12538477_bFGF has a stimulating role in lymphangiogenesis 12545206_umbilical cords of 10 control and 10 pre-eclamptic newborns demonstrated that both the umbilical cord arterial wall and Wharton's jelly contain FGF mainly in complexes with the components of different molecular mass 12571252_Fibroblast growth factor-2-induced signaling is mediated through lipid raft-associated fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 12574959_IL-6r and TNF-alpha increase in parallel to VEGF and FGF-2 with increasing stage of multiple myeloma. 12590983_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12607599_VEGF, but not bFGF, was associated with higher tumor grading of NHL and high-grade transformation of low-grade lymphoma. 12623787_reduction of neointimal hyperplasia was observed in autologous vein grafts treated by Sendai virus human-fibroblast growth factor 2; these grafts demonstrated significant restoration of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation 12631070_IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, TGF-beta, and bFGF are involved in bone remodeling regulation, acting as local effectors, possibly under the control of PTH. 12651930_expression system is involved in angiogenesis in inflamed synovial tissue in the temporomandibular joint 12659634_focal sequences of cell surface heparin/heparan sulphate-like glycosaminoglycans from smooth muscle cells and bovine aortic endothelial cells govern, at least in part, the differential activity of FGF2 on these two cell types 12676798_FGF-2, but not VEGF, upregulated the mRNA levels for hTERT and for the hTERT gene transactivation factor Sp1. This restores telomerase activity and maintains the replicative capacity of endothelial cells. 12682649_FGF-2 was expressed in most human leukemia and lymphoma cell lines tested, but only a small amount was released into the media. It may play a role in apoptosis regulation and pathogenesis. 12727994_pituitary tumor transforming gene and fibroblast growth factor-2 expression are potential prognostic markers (and perhaps therapeutic targets) for differentiated thyroid cancer 12746216_TSH stimulates FGFR1 but not FGF-2 expression and PKC activation stimulates FGF-2 synthesis and secretion, and TSH synergizes with PKC activators so increases in FGFR1 or FGF-2 or in both may contribute to goitrogenesis. 12755687_Alpha-2 macroglobulin and this protein interact at specific binding sites, involving different FGF-2 sequences. 12799459_pancreatic precursor cells secrete FGF2 to stimulate clustering into hormone-expressing islet-like cell aggregates 12815619_FGF2-stimulated cranial suture closure requires the Erk pathway and activator protein 1 12823444_FGF-2-overexpressing melanocytes exhibited marked proliferation, upwards migration, cluster formation and type IV collagen expression within the epidermal compartment, simulating early radial growth phase melanoma 12857600_Serum levels of both bFGF and TGF-beta1 were found to be significantly higher in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Significantly higher in patients with progressive disease. 12857733_The determination of the FGF-2 5'-ATR RNA secondary structure by enzymatic and chemical probing experiments showed that the FGF-2 IRES contained two stem-loop regions and a G quartet motif that constitute novel structural determinants of IRES function. 12871330_plasmic degradation of fibrinogen modulates the activity and binding of FGF-2 that involves a site near the carboxyl terminus of the gamma chain 12871334_when FGF-2 was incorporated into fibrin, vascular endothelial cell proliferation was increased 6.5 -fold, equal to growth on a fibrin surface with FGF-2 continually present in the medium 12872165_role of Egr-1 (early growth response-1)in FGF-2 dependent neovascularization, tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth 13680247_FGF-2 clearly enhances cell survival of corneal endothelium after storage at 4 degrees C. Potential future application of FGF-2 as adjuvant to corneal preservation media in order to better maintain endothelial viability during corneal storage. 14523006_Addition of serum to serum-starved cells rapidly induced intracellular FGF-2 clustering under the plasma membrane and into granules that colocalized with patches of the cell membrane with typical features of shed vesicle membranes. 14630795_5 residues (Phe95, Ser100, Asn102, Arg107, and Arg109) from FGF-2 into the corresponding sites in the third cassette of FGF-1 imparted high-affinity binding with dissociation constants (Kd) of 5.3 nM and 8.6 nM, compared to 1.3 nM for wild-type FGF-2. 14669345_Plasma VEGF and bFGF are elevated in patients with liver cirrhosis depending on age and are predictors of outcome. 14672345_bFGF adds trabecular bone mass through increasing trabecular number and trabecular connectivity. 14680499_Data repropose bFGF as a noninvasive diagnostic tool for breast cancer. 14699503_Down-regulation of hSulf1 contributes to hepatocarcinogenesis by enhancing heparin-binding growth factor signaling and resistance to apoptosis. 14706681_increased fibroblast growth factor-2 expression and decreased stromal cell compartment turnover in the diabetic placenta might be a compensatory mechanism in response to the altered physiologic milieu of maternal diabetes on placental function 15033176_Recombinant human IGF-2 and IGF-1 synergistically increase the numbers of rat oligodendrocyte progenitor cells recruited into S phase; FGF-2 decreases the levels of cdk inhibitor p27(Kip1) associated with cyclin E-cyclin dependent kinase 2. 15096041_Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 2 dramatically enhances the association of FGF receptor (FGFR) 1 with heparin and leads to proposal of a model for the stepwise assembly of a ternary FGF-FGFR-heparan sulfate proteoglycan complex on the plasma membrane. 15117822_The proangiogenic action of thyroxine is MAPK dependent and mediated by FGF2. 15120936_Decreased levels of bfgf in circulating blood is associated with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or Hodgkin's lymphoma 15166228_lamellipodial protrusion in smooth muscle cells can be regulated by waves of Rac1 activation, corresponding to the sequential presentation of FGF-2 and remodeled collagen. 15208265_Pulsed electromagnetic field augment angiogenesis primarily by stimulating endothelial transcription and release of FGF-2, inducing paracrine and autocrine changes in the surrounding tissue. 15243127_Results confirmed basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) expression in human adult ovarian cortex, and in the isolated follicles a down-regulation of bFGF mRNA was evident as small follicles develop. 15247002_upregulation of telomerase activity by FGF-2 plays a functional role in preventing the early onset of senescence 15247275_A bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS) was uncovered near the C-terminus of FGF2. The NLS also contains signals controlling the nucleolar localization of FGF2. 15249224_These results suggest that bFGF can negatively modulate p38 and positively modulate ERK1/2 to antagonize activin A-mediated growth inhibition and Hb synthesis in K562 cells. 15293454_This study demonstrates that Chlamydia pneumoniae activates endothelial cells to produce bFGF, a growth factor which is linked to the development of atherosclerotic plaques. 15297314_fibrinogen binding of FGF-2 enhances EC proliferation through the coordinated effects of colocalized alpha(v)beta(3) and FGFR1. 15302993_No significantly elevated bFGF levels were found in veins draining tumours compared with arterial samples in a patient population, suggesting that serum bFGF levels might also be derived from other sources besides the tumour 15316024_fibroblast growth factor 2 signaling is regulated by IRS-4 and ShcA 15464234_Basic fibroblast growth factor has the ability to induce the trans-differentiation into hepatic lineage cells from bone marrow cells. 15481452_bFGF in plasma and bone marrow stromal cells in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura cases are decreased, whereas the production of bFGF remains unchanged. 15496150_Overexpression of caveolin-1 in mesangial cells suppresses MAP kinase activation and cell proliferation induced by bFGF and PDGF, two major cytokines in mesangioproliferative nephritis(MN). Caveolin-1 expression vector is potential therapy for MN. 15525641_HNRNPA1 is a novel internal ribosome entry site trans-acting factor that modulates alternative initiation of translation of the fibroblast growth factor 2 mRNA 15573376_These results provide new evidence for the possible involvement of FGF-2 in the regulation of HA production and its appreciable roles in not only homeostasis but also regeneration of periodontal tissues. 15603823_chitosan could potentiate FGF-2 activity by protecting it from inactivations by the interaction between FGF-2 and chitosan molecules 15610530_The IL-6-mediated bFGF upregulation is through activation of JAK/STAT3 and PI3-Kinase/Akt pathways. 15631865_The bFGF expression was evaluated in myomas obtained after surgery. 15680705_bFGF is endogenously positioned to be involved in ongoing neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. 15695515_Data show that Npn-1 can potentiate the growth-stimulatory activity of FGF-2 on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, indicating that Npn-1 may not just bind but also regulate the activity of heparin-binding proteins. 15703886_opposite effects of Noggin and bFGF for the neural tube development 15713745_PEDF downregulates Fyn through Fes, resulting in inhibition of FGF-2-induced capillary morphogenesis of endothelial cells 15725477_A role for FGF2 in cell survival and proliferation of lymphoid and myeloid tumor cells. 15726914_estrogen-dependent vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), especially VEGF165, and basic fibroblast growth factor(bFGF) might work on growth via angiogenesis in the human placenta throughout all trimesters of gestation 15731686_Authors show that recombinant human FGF-2 alters osteoblastic expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and Msx-2 in vitro to favor cellular differentiation and osteoinduction. 15737206_essential role for soluble factors, mainly IL-1alpha and bFGF, in the stimulation of dermal fibroblasts by human melanoma cells to secrete MMP-1. 15756443_bFGF, but not VEGF, may havea role in systemic hypoxia and anemia in solid tumor patients 15769511_analysis of complexes of FGF-2 and regioselectively desulfated heparin in aqueous solutions 15769981_Pituitary tumor-transforming gene-1 is up-regulated in human uterine leiomyomas and that the positive feedback loop between PTTG-1 and basic fibroblast growth factor may be pivotal in the growth of leiomyoma cells. 15780951_Recombinant human FGF-2 signaling enhances the intrinsic osteogenic potential by selectively expanding committed chick embryo osteogenic cell populations as well as inversely regulating bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) and noggin gene expression. 15809086_combination of noggin and basic fibroblast growth factor was sufficient to maintain the prolonged growth of human embryonic stem cells 15817123_High expression of Hsulf-1 occurs in the stromal elements as well as in the tumor cells in pancreatic cancer and interferes with heparin-binding growth factor signaling 15825079_hrbFGF significantly increased Ki-67-positive cells in colonic epithelium of normal mice and up-regulated gene expression of COX-2, TGF-beta, MUC2, ITF, and VEGF in colon. Rectal administration of bFGF might be treatment for inflammatory bowel disease. 15875316_finding of FGF2 and EGR1 upregulation in endothelial cell microvascular channels within organising thrombus 15875782_Hepatocyte growth factor released FGF-2 in the matrix but did not induce FGF-2 expression in external auditory canal cholesteatoma. 15906377_FGF2 regulates the expression of Foxc1, indicating that Foxc1 integrates Bmp and Fgf signalling pathways 15924676_bFGF and GLUT1 play important roles in the carcinogenesis and progression of ovarian epithelial carcinoma. 15942693_bFGF and vascular endothelial growth factor contribute to a significant proportion of the survival stimulating activity 15947088_abnormally sulfated heparan sulfate in Hurler multipotent progenitor cells perturb critical FGF-2-FGFR1-HS interactions, resulting in defective FGF-2-induced proliferation and survival of Hurler multipotent progenitor cells. 15985216_bFGF was found to bind more strongly to heparin-Sepharose than endostatin, the latter, but not the former, displaced protamine from heparin in solution, which supports the notion that endostatin can compete with bFGF for binding to heparan sulfate 15996482_the MAPK and two PLC pathways are required for FGF-2 to stimulate RGC neurite extension in vitro, but the response of axons to FGF-2 applied asymmetrically to the growth cone depended only on the PLC pathways 16077964_Expression of b-FGF may be associated with promotion of angiogenesis and a good prognostic factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. 16077988_Results suggest that the release of bFGF following cell death contributes to enhanced chemosensitivity in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC) cell lines. 16080018_Not the expression of bFGF in the primary tumour but in its invasion front reflects the aggressiveness of RCC, hereby indicating a different biological potential within both areas. 16095497_TGF-beta1/bFGF and ET-1 have different roles in graft fibrosis in heart failure patients 16103882_bFGF inhibited IR-induced p53 accumulation to some extent in most of these samples and by more than 50% in seven samples from seven patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia 16135988_Significantly higher expression of TGFbeta1 and bFGF, although lower expression of core protein on the concave side, suggesting possible etiological factor or secondary change in development of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. 16160009_Using a placental explant model in a fibrin matrix, wtFGF-2 resulted in 2.6-fold more growth over control, and FGF2 binding (to fibrin) mutants increased growth 3.3 -fold. Vessel outgrowth with a nonbinding FGF2 mutant was minimal, comparable to control. 16210019_The expression of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and its receptors FGFR-2, FGFR-3, and FGFR-4 in human ovaries suggests that bFGF might have a role in early folliculogenesis. 16222707_The reciprocal modulating effects of FGF2 and TGFbeta1 on each other's receptors make the GM-490 cell line a new model for investigating the relationship between these growth factors and their receptors in autocrine loops. 16227592_18-kDa FGF-2 directly regulates rRNA transcription. 16227592_Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) regulates rRNA transcription, in part, by localizing to rRNA genes and directly interacting with the upstream binding factor (UBF), an architectural transcription factor, in the nucleolus. 16278388_FGF-2 has a role in esophageal cancer recurrence and mortality 16304044_existence of an HIF-1alpha-bFGF amplification pathway that mediates survival and sprouting of endothelial cells under hypoxic conditions. 16320338_excessive release of bFGF from the cartilage matrix during injury, with loading, or in arthritis could contribute to increased proliferation and reduced anabolic activity in articular cartilage 16463783_Adrenaline can increase the production of bFGF and decrease production of TGF-beta1 and I procollagen in human normal dermal and hypertrophic scar fibroblasts cultured in vitro. 16490198_MM-LDL and HDL have opposite effects on aortic SMCs: MM-LDL increases both bFGF production and release and SMC proliferation, while HDL decreases both bFGF production and release and SMC proliferation. 16495214_Hsp90 is required for translocation of FGF-1 and FGF-2 across the endosomal membrane 16521228_Blood levels are usesful in the prognosis of antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis C. 16597610_These experiments show for the first time that overexpression of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in developing rodent kidneys can induce the formation of renal cysts in vivo. 16631837_could play an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic apical periodontitis and periapical cysts 16638370_Overexpression of bFGF in skin of patients with systemic sclerosis along with normal serum levels suggests that bFGF probably acts in an autocrine or paracrine manner in fibrogenesis. 16685268_bFGF expression upregulates CD13 expression in human melanoma cells and results in enhanced invasive capacity and metastatic behaviour of human melanoma cells. 16709186_A novel mechanotransduction model is proposed in this review that supports a key regulatory role for bFGF in articular cartilage turnover, and highlights its importance as a mechanotransducer. 16723715_altered HSPGs contribute to enhanced signaling of FGF-2 via FGFR1c in gliomas with glypican-1 playing a significant role in this mitogenic pathway 16739027_Study found that a dyad symmetry element (DSE) in the fibroblast growth factor-2 gene promoter exhibited different promoter activities; in HepG2 cells it did, while in U87MG cells it did not, exhibit repressive activity. 16769728_there is an FGF2-binding domain in the N-terminal extension of PTX3 spanning the PTX3-(97-110) region 16807244_analysis of heparan sulfate-related oligosaccharide binding to fibroblast growth factors 1 and 2 and their receptors 16816927_abnormal expression in cartilage of Kashin-Beck disease 16820871_VEGF, FGF2, TGFB1, EGF and IGF1 have roles in the development of both prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia 16822883_BFGF Is able to increase the migratory activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells through activation of the Akt/protein kinase B (PKB) pathway. 16840552_Clearly identify the key function of FGF2 in the maintenance of self-renewal of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. 16867222_heparanase modifies FGF2 binding, signaling, and angiogenesis in metastatic melanoma cells 16876430_Data suggest that the relative concentrations of Anosmin-1 and FGF-2 modulate the migration of oligodendrocyte precursors during development through their interaction with FGFR1. 16905765_Seminal plasma and PGE(2) can similarly activate FGF2 expression and EP2 receptor signalling in endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. 16949906_Immunohistochemical expression of bFGF in tumors was confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction. 16996573_Data suggest role for FGFF2 in ductal integrity during mammary carcinogenesis, with loss of expression corresponding to loss of ductal structure. 17157157_The mRNA levels of BFGF were significantly produced by the megakaryocytes may be associated with the etiology of bone marrow fibrosis in AMM. 17166351_The serum level of bFGF in patients with exacerbation of chronic cor pulmonale is significantly increased. 17169545_data show that growth plate perlecan binds to FGF-2 by its heparan sulfate chains but can only deliver FGF-2 to FGF receptors when its chondroitin sulfate chains are removed 17204151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17217840_The expression of collagen type II and TGF-beta1, bFGF in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis was similar to congenital scoliosis. 17234579_FGF-2 transgene plays an important role in the establishment of the proper number of dopaminergic neurons and a normal sized substantia nigra during development. 17285972_The bFGF expression in the endothelial cells of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma and hemangioma was positive. 17298206_Intracytoplasmic sperm injection patients with serum progesterone above 0.9 ng/ml have elevated serum concentrations of basic fibroblast growth factor. 17381064_Real-Time-PCR showed that TGFbeta1 expression is auto-inductive, whereas FGF2 is auto-repressive. The bioavailability of TGFbeta1 regulated by FGF2 may represent part of a negative feedback mechanism controlling stromal growth, differentiation and ECM. 17466952_Inhibition of BFGF with neutralizing antibodies reduced pro-inflammatory gene expression. 17478553_role for PGF(2alpha)-FP receptor interaction in modulating FGF2 expression and signaling using an endometrial adenocarcinoma cell line 17497037_Data Show bFGF was expressed in regenerative hepatocytes, but not in fibroblasts, suggesting its role in promoting oxidative stress produced by hepatocytes may contribute to the development of fibrous bands in hepatic cirrhosis. 17503459_Chromatin compaction and cell death by high molecular weight FGF2 depend on its nuclear localization, intracrine ERK activation, and engagement of mitochondria. 17505261_Overexpression of the 18 kDa basic fibroblast growth factor protein can promote autocrine melanoma cell growth and paracrine-driven angiogenesis. 17522998_In cartilage, FGF did not significantly affect ROS levels or antioxidant enzyme activity 17532297_These results suggest that FGF-2 suppresses the hMSCs cellular senescence dependent on the length of culture through down-regulation of TGF-beta2 expression. 17537644_study of cellular mechanisms underlying Apert phenotype, by analyzing effects of FGF2 in cultures of Apert periosteal fibroblasts carrying the FGFR2 Pro253Arg mutation 17537668_FGF2 has a role in tumor angiogenesis associated with haematological malignancies [review] 17543283_Fibroblast growth factor-2 stimulates adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells 17556598_Distinct roles for bone morphogenetic protein 4, vascular endothelial growth factor, stem cell factor, and fibroblast growth factor 2 in hematopoiesis. 17562265_The expression of hTERT, maspin and bFGF correlate to each other, and associate with the malignant degree of glioma. 17578349_expression not different in endometriosis 17605857_The secretion of VEGF and bFGF in myelodysplastic syndrome patients is elevated and the serum levels of VEGF and bFGF are related to the classification and prognosis in MDS. 17637743_TGF-beta signaling in reactive stroma is angiogenic and tumor promoting and is mediated in part through a TbetaRII/Smad3-dependent upregulation of FGF-2 expression and release. 17651425_FGF2 may contribute to the synaptic reorganization after noise damage; it may protect and/or aid recovery of synapses after overstimulation. 17653045_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17676480_bFGF augments hypoxia induced VEGF release in breast cancer cells mainly through the PI3K pathway and partly depending on HIF-1 activity. 17699594_FGF-2 release from the lens capsule by matrix metallopeptidase 2 is essential to lens epithelial cell viability and survival 17706726_Provide useful information for understanding mechanisms of angiogenesis induced by bFGF and important data for validating a mathematical model of angiogenesis. 17724016_BFGF activates the MAPK and NFkappaB pathways that converge on ELK1 to control production of MMP13 by articular chondrocytes. 17726742_bFGF may promote obviously the healing of orbital implant exposure, particularly it can be the first choice for the treatment of mild degree exposure. 17762899_Fibrin gel-immobiized VEGFA and BFGF efficiently stimulate angiogenesis in the AV loop model. 17825301_alpha-Tocopheryl succinate disrupts angiogenesis mediated by malignant mesothelioma cells by inhibiting FGF2 paracrine signalling 17929017_bFGF does not directly act on p38 nor on the mRNA expression levels of activin receptors but inhibit activin A activation of p38 upstream of p38 in K562 cells. 17942638_Exogenous human FGF-2 increased endogenous FGF-2 promoter activity and protein levels in ovine pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. 17949478_endogenously synthesized fibrinogen promotes the growth of lung and prostate cancer cells through interaction with FGF-2. 17968311_Thrombin cleaves the high molecular weight forms of basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2): a novel mechanism for the control of FGF-2 and thrombin activity. 17968943_activen A expression is induced by wounding in an FGF-2- and NF-kappaB-dependent manner 17996481_Study demonstrates that the fibroblast growth factor-2 binding site of thrombospondin-1 is located in the type III repeats. 17997184_Increased plasma level of the bFGF confirmed the importance of this candidate gene in the formation of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. 17997184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18006148_IGF-1 and EGF down-regulation and FGF2 up-regulation seem to comprise the main features of endometrial carcinogenesis. 18025790_We propose FGF-2 negative feedback as potentially important in microvascular remodelling. This is consistent with the absence of a secretory signal sequence in FGF-2, as well as canalicular fragmentation, which is unique to endothelial apoptosis. 18031768_Developed a mathematical model to numerically simulate angiogenesis induced by basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in the corneal pocket assay. 18036796_Basic fibroblast growth factor regulates expression of heparan sulfate in human periodontal ligament ce 18042549_the involvement of FGFR-1 through FGF2 in eliciting PGE(2) angiogenic responses 18051571_The expression levels of endostatin, VEGF and FGF-2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma are obviously higher than those in para-carcinoma and normal laryngeal tissues. 18052595_Local controlled release of bFGF from the stent-graft significantly accelerated the proliferation of new intimal tissue between the aorta and the stent-graft and within the graft materials. 18055262_REVIEW: FGF2 confers to ASM cells the ability to proliferate in response to different asthma mediators 18088275_bFGF is a mitogen for the rapidly dividing cells (olfactory neuronal precursors and olfactory ensheathing cells), and also a survival factor for both slowly and rapidly dividing cells of the olfactory mucosa. 18093228_FGF2 was among the genes differentially expressed in an in vivo-in vivo comparison between unfused and prematurely fused calvarial tissue. 18094712_In vitro, primary effusion lymphoma -induced angiogenesis is dependent on VEGF and VEGF receptors. However, although PEL cells produce VEGF and bFGF transcripts, they only secrete VEGF in vitro 18164591_Support a role for NP-1 in mediating synergistic effects between VEGF-A(165) and FGF-2, which may occur in part through a contribution of NP-1 to KDR stability. 18164704_Our data first suggest that JNK participates in bFGF-mediated surface cadherin downregulation. Loss of surface cadherins may affect the cell-cell interaction between endothelial cells and facilitate angiogenesis. 18171671_Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced neuronal differentiation of mouse bone marrow stromal cells requires FGFR-1, MAPK/ERK, and transcription factor AP-1 18179408_FGF-2 expression in malformations of cortical development reflects incomplete differentiation and maturation of dysplastic cells 18187129_Sox2-expressing MSCs showed consistent proliferation and osteogenic capability in culture media containing bFGF 18253936_bFGF differently changes intracellular signals in ECs depending whether it is applied under microgravity or normal gravity conditions 18258238_in angiogenesis,FGF-2(fibroblast growth factor 2)-mediated enhancement of Placental growth factor (PGF) expression was dependent on Vascular endothelial growth factor function 18279437_AT genotype of the 553 T/A polymorphism was associated with PDR in Caucasians with type 2 diabetes. 18279437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18281281_potent mitogenic signaling results from heparin-mediated trans-dimerization of FGF2, consistent with the asymmetric model of ternary complex formation 18298475_bFGF immunoreactivity was found to be increased in fibroblasts and in endothelial cells in early oral submucous fibrosis cases, while the expression of bFGF in stroma increased notably in advanced fibrosis. 18332228_identified activin-mediated transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling and fibroblast growth |
ENSMUSG00000037225 |
Fgf2 |
111.568081 |
3.6699017520 |
1.875741 |
0.161950300 |
140.360261 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000002220412172408204516116557559885982780666969856907426242746808075562086847102712954698557068500264222166151739656925201416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000306578893028485477938071462925646547582965344277671236640491728705661195433506977913590274553712333727162331342697143554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
176.6063853 |
19.7011426 |
48.5606385 |
4.4329939 |
| ENSG00000138686 |
55212 |
BBS7 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWZ6 |
FUNCTION: The BBSome complex is thought to function as a coat complex required for sorting of specific membrane proteins to the primary cilia. The BBSome complex is required for ciliogenesis but is dispensable for centriolar satellite function. This ciliogenic function is mediated in part by the Rab8 GDP/GTP exchange factor, which localizes to the basal body and contacts the BBSome. Rab8(GTP) enters the primary cilium and promotes extension of the ciliary membrane. Firstly the BBSome associates with the ciliary membrane and binds to RAB3IP/Rabin8, the guanosyl exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8 and then the Rab8-GTP localizes to the cilium and promotes docking and fusion of carrier vesicles to the base of the ciliary membrane. The BBSome complex, together with the LTZL1, controls SMO ciliary trafficking and contributes to the sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway regulation. Required for proper BBSome complex assembly and its ciliary localization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17574030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22072986}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Obesity;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transport;Vision |
|
This gene encodes one of eight proteins that form the BBSome complex containing BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BBS5, BBS7, BBS8, BBS9 and BBIP10. The BBSome complex is believed to recruit Rab8(GTP) to the primary cilium and promote ciliogenesis. The BBSome complex assembly is mediated by a complex composed of three chaperonin-like BBS proteins (BBS6, BBS10, and BBS12) and CCT/TRiC family chaperonins. Mutations in this gene are implicated in Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a genetic disorder whose symptoms include obesity, retinal degeneration, polydactyly and nephropathy; however, mutations in this gene and the BBS8 gene are thought to play a minor role and mutations in chaperonin-like BBS genes are found to be a major contributor to disease development in a multiethnic Bardet-Biedl syndrome patient population. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:55212; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; BBSome [GO:0034464]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; digestive tract morphogenesis [GO:0048546]; eye development [GO:0001654]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; intracellular transport [GO:0046907]; limb development [GO:0060173]; melanosome transport [GO:0032402]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; pigment granule aggregation in cell center [GO:0051877]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; primary palate development [GO:1903929]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12567324_A novel Bardet-Biedl syndrome protein is identified anad characterized. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19093007_This study describes a novel mutation in BBS7 causing Bardet-Biedl syndrome in a Chinese family. 19402160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19402160_small role of BBS7 and TTC8 in the overall mutational load of Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 25553308_BBS7 gene was a novel variant (c.103-1G>A) in the consensus splice acceptor site, which altered the splicing recognition site of 'AG' to 'AA' at the BBS7 gene intron 2 and exon 3 boundary. 27004616_Sequence variants in BBS7 were identified in families with CRB2-related syndrome. 28761321_Two novel mutations and three previously reported variants, identified in the present study, further extend the body of evidence implicating BBS6, BBS7, BBS8, and BBS10 in causing Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. 31469663_A novel missense variant in the BBS7 gene underlying Bardet-Biedl syndrome in a consanguineous Pakistani family. 31530639_Authors found that within this structure, BBS2 and BBS7 form a tight dimer through a coiled-coil interaction and that BBS9 associates with the dimer via an interaction with the alpha-helical domain of BBS2. Interestingly, a BBS-associated mutation of BBS2 is located in its alpha-helical domain at the interface between BBS2 and BBS9, and binding experiments indicated that this mutation disrupts the BBS2-BBS9 interaction. 33729075_Bardet-Biedl syndrome-7 (BBS7) shows treatment potential and a cone-rod dystrophy phenotype that recapitulates the non-human primate model. |
ENSMUSG00000037325 |
Bbs7 |
83.946890 |
0.2231675204 |
-2.163801 |
0.617991321 |
11.076822 |
0.00087413501512421368146860123360397665237542241811752319335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002059085991578901014831259885795589070767164230346679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.0210638 |
20.5749414 |
143.7186033 |
67.4934446 |
| ENSG00000138738 |
11107 |
PRDM5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQX1 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific DNA-binding transcription factor. Represses transcription at least in part by recruitment of the histone methyltransferase EHMT2/G9A and histone deacetylases such as HDAC1. Regulates hematopoiesis-associated protein-coding and microRNA (miRNA) genes. May regulate the expression of proteins involved in extracellular matrix development and maintenance, including fibrillar collagens, such as COL4A1 and COL11A1, connective tissue components, such as HAPLN1, and molecules regulating cell migration and adhesion, including EDIL3 and TGFB2. May cause G2/M arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15077163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17636019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21664999}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor of the PR-domain protein family. It contains a PR-domain and multiple zinc finger motifs. Transcription factors of the PR-domain family are known to be involved in cell differentiation and tumorigenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11107; |
nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; histone H3-K9 methylation [GO:0051567]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of extracellular matrix organization [GO:1903053]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] |
15077163_PRDM5 caused G2/M arrest and apoptosis upon infection of tumor cells. These results suggest that inactivation of PRDM5 may play a role in carcinogenesis. 17636019_Results identify PRDM5, which acts as a sequence-specific, DNA binding transcription factor that targets hematopoiesis-associated protein-coding and microRNA genes, some of which are targets of Gfi1. 17699856_Data suggest that epigenetic alteration of PRDM5 (e.g., methylation of its 5'-CpG island or trimethylation of Lys(27) of histone H3) likely plays a key role in the progression of gastrointestinal cancers and may be a useful molecular marker. 20213097_Data show that reduced expression of PRDM5 may play an important role in the pathogenesis and/or development of cervical cancer, and is considered to be caused in part by aberrant DNA methylation. 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21664999_ZNF469 and PRDM5, two genes that when mutated cause brittle cornea syndrome, participate in the same regulatory pathway. 22087297_Frequent epigenetic silencing of PRDM5 is involved in multiple tumorigeneses, which could serve as a tumor biomarker 23873026_Data provide the first causal link between Prdm5 loss and intestinal carcinogenesis, and uncover an extensive and novel PRDM5 target repertoire likely facilitating the tumor-suppressive functions of PRDM5. 24395656_Promoter methylation-mediated downregulation of PRDM5 contributes to the development of lung squamous cell carcinoma. 24966940_PRDM2, PRDM5, PRDM16 promoters are methylated and their expression is suppressed in lung cancer cells. 25613750_These data suggest that PRDM5 is a relevant tumour suppressor gene that is frequently targeted in colorectal tumourigenesis. 26395458_Defective interaction of PRDM5 with repressive complexes, and dysregulation of H3K9me2, play a role in PRDM5-associated disease. 26489929_Genetic variants in PRDM5 can lead to various syndromic and nonsyndromic disorders affecting the anterior segment of the eye. 26560304_Reduced expression of PRDM5 was observed in the cornea and retina of brittle cornea syndrome patients. 27032025_The current study revealed a novel mutation in the PRDM5 gene in a Brittle cornea syndrome (BCS) family and recurrent mutation in a sporadic BCS patient. 27295517_The miR-182 promoter is rarely methylated in epithelial ovarian cancers (EOCs), and its methylation status is associated with lower miR-182 expression. Deletion of the PRDM5 locus may play a supportive role in miR-182 overexpression in EOC. miR-182 is an unfavorable prognostic factor in EOC. 28228349_Both Prdm 4 and Prdm 5 are expressed in human corneal endothelium, primary hCECs and in HCECs-12 cells, characterised by expression of the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. 28476379_Inhibiting PRDM5 expression by siRNA attenuated the IFN-gamma-triggered accumulation of active caspase-3 and cleaved PARP in intestinal epithelial cells. Moreover, flow cytometry assay and CCK-8 analysis revealed that PRDM5 knockdown significantly alleviated the IFN-gamma-induced cellular apoptosis in HT29 cells. 29939776_Truncations may be the primary mutation type in PITX2. Glaucoma onset may be earlier in patients with mutations in PITX2 than in those without mutations in PITX2 and FOXC1. A block of the anterior chamber angle by the end of the iris might represent the main factor influencing the development of glaucoma in ARS patients with an asymmetric aniridia phenotype. 32083978_Silencing of PRDM5 increases cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in glioma. 33739556_More than meets the eye: Expanding and reviewing the clinical and mutational spectrum of brittle cornea syndrome. 34757658_PRDM5 suppresses oesophageal squamous carcinoma cells and modulates 14-3-3zeta/Akt signalling pathway. 35799142_Low expression of PRDM5 predicts poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000029913 |
Prdm5 |
11.828546 |
0.3773443189 |
-1.406047 |
0.548533268 |
6.523914 |
0.01064334952264732458981910667716874741017818450927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020301865980133691758080516365225776098668575286865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9503823 |
2.8472404 |
18.2572696 |
4.8148694 |
| ENSG00000138759 |
80144 |
FRAS1 |
protein_coding |
Q86XX4 |
FUNCTION: Involved in extracellular matrix organization (By similarity). Required for the regulation of epidermal-basement membrane adhesion responsible for proper organogenesis during embryonic development (By similarity). Involved in brain organization and function (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80T14}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an extracellular matrix protein that appears to function in the regulation of epidermal-basement membrane adhesion and organogenesis during development. Mutations in this gene cause Fraser syndrome, a multisystem malformation that can include craniofacial, urogenital and respiratory system abnormalities. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:80144; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell communication [GO:0007154]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; metanephros morphogenesis [GO:0003338]; morphogenesis of an epithelium [GO:0002009]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skin development [GO:0043588] |
12766769_Locus FS1 at chromosome 4q21 is associated with Fraser syndrome. Mutation analysis identified five frameshift mutations in FRAS1, which encodes one member of a family of novel proteins related to an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein found in sea urchin. 17654118_In this review, recent studies support direct interactions between Fras1 and Frem proteins and shed new light on their role in the regulation of epidermal-basement membrane adhesion and organogenesis during development. 18155042_Supramodular nature of GRIP1 revealed by the structure of its PDZ12 tandem in complex with the carboxhyl tail of Fras1. 18671281_11 new mutations in FRAS1 were identified in families with Fraser syndrome. 20602751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21900877_Heterozygous missense mutations in FRAS1 cause non-syndromic congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract in humans. 22029163_molecular, clinical findings of 4 fetuses with Fraser syndrome from 2 families; in family one, found nonsense mutation (c.3730C>T, p.R1244X) previously described; in family 2 found a novel nonsense mutation previously not known (c.370C>T, p.R124X) 22283518_Analysis of FRAS1 and STRA6 mutations in the same family with eye anomalies. 23473829_First case of a family with two patients affected by Fraser syndrome due to a deletion of 64 kb (deletion 4q21.21) and an additional novel frameshift mutation in exon 66 of the FRAS1 gene. 24700879_In 15 of 590 families, we identified recessive mutations in the genes FRAS1, FREM2, GRIP1, FREM1, ITGA8, and GREM1, all of which function in the interaction of the ureteric bud and the metanephric mesenchyme. 29618029_Based on these data, we conclude that deficiency of FREM2, and possibly FRAS1, are associated with an increased risk of developing Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) and that loss of the FREM1/FREM2/FRAS1 complex, or its function, leads to anterior sac CDH development through its effects on mesothelial fold progression 31597194_Fraser extracellular matrix complex subunit 1 promotes liver metastasis of gastric cancer. 31999076_Two unrelated families with variable expression of Fraser syndrome due to the same pathogenic variant in the FRAS1 gene. 32643034_Novel loss of function variants in FRAS1 AND FREM2 underlie renal agenesis in consanguineous families. 33956343_A polymorphism in the promoter of FRAS1 is a candidate SNP associated with metastatic prostate cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000034687 |
Fras1 |
61.250936 |
0.3895881201 |
-1.359978 |
0.197853380 |
48.835047 |
0.00000000000278420023219358702102888251574214976795385023677908975514583289623260498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000016128255662157512594590320273085846773664098208200812223367393016815185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.2019800 |
4.9676302 |
91.0752018 |
8.2095910 |
| ENSG00000138771 |
57619 |
SHROOM3 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF72 |
FUNCTION: Controls cell shape changes in the neuroepithelium during neural tube closure. Induces apical constriction in epithelial cells by promoting the apical accumulation of F-actin and myosin II, and probably by bundling stress fibers (By similarity). Induces apicobasal cell elongation by redistributing gamma-tubulin and directing the assembly of robust apicobasal microtubule arrays (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q27IV2, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QXN0}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell shape;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Membrane;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a PDZ-domain-containing protein that belongs to a family of Shroom-related proteins. This protein may be involved in regulating cell shape in certain tissues. A similar protein in mice is required for proper neurulation. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:57619; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical junction complex [GO:0043296]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; apical protein localization [GO:0045176]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cellular pigment accumulation [GO:0043482]; epithelial cell development [GO:0002064]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
19430482_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19740415_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20222955_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20636464_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20700443_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21936905_A recessive missense mutation in SHROOM3 is associated with heterotaxy syndrome. 23586973_RESULTS: rs1260326 in GCKR (beta=1.30, P = 3.23E-03), rs17319721 in SHROOM3 (beta = -1.28, P-value = 3.18E-03) and rs12917707 in UMOD (beta = 2.0, P-value = 8.84E-04) were significantly associated with baseline estimated GFR 25273069_variants disrupting the actin-binding domain of SHROOM3 may cause podocyte effacement and impairment of the glomerular filtration barrier 25437874_The SNP rs17319721 functions as a cis-acting expression quantitative trait locus of SHROOM3 that facilitates TGF-B1 signaling and contributes to allograft injury. 25805808_Two protein-truncating de novo mutations in two independent cases in SHROOM3 strongly implicates this protein in severe human neural tube defects. 29423651_Functional variants were further confirmed by western blot and the mammalian two-hybrid assays. Loss of function (LoF) variants were identified in SHROOM3. We observed 1.56 times as many rare [minor allele frequency (MAF) |
ENSMUSG00000029381 |
Shroom3 |
15.734756 |
0.4043262030 |
-1.306408 |
0.478764283 |
7.516187 |
0.00611469827880485681387279228715669887606054544448852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012264294957896409998809872377023566514253616333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1117909 |
3.1644440 |
22.6650191 |
5.2295261 |
| ENSG00000138772 |
306 |
ANXA3 |
protein_coding |
P12429 |
FUNCTION: Inhibitor of phospholipase A2, also possesses anti-coagulant properties. Also cleaves the cyclic bond of inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate to form inositol 1-phosphate. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Annexin;Calcium;Calcium/phospholipid-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Phospholipase A2 inhibitor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the annexin family. Members of this calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein family play a role in the regulation of cellular growth and in signal transduction pathways. This protein functions in the inhibition of phopholipase A2 and cleavage of inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate to form inositol 1-phosphate. This protein may also play a role in anti-coagulation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:306; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule [GO:0042581]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; phospholipase A2 inhibitor activity [GO:0019834]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043312]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of DNA metabolic process [GO:0051054]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to growth factor [GO:0070848] |
16236264_ANXA3 is a novel angiogenic factor that induces vascular endothelial growth factor production through the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 pathway 20103635_Annexin A3 could be a target for therapeutic intervention and may also serve as a biomarker for drug resistance in ovarian cancer patients. 20167856_two spliced isoforms of Annexin A3 are expressed differently in human renal cortex and renal-cell carcinoma 21055154_AnnexinA3 plays an important role in the initiation and progression of human gallbladder cancer. 21132403_results suggest that annexin-1, annexin-2, and annexin-3 are identified as potential biomarkers associated with lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 21137070_Decreased expression of ANXA3 in papillary thyroid cancer supports the idea that ANXA3 may be an effective marker of microcarcinoma, and a negative predictor of papillary thyroid cancer progression. 21435174_annexin A3 secretion may be associated with exocytosis and the release of exosomes 22189913_the association of multi-drug resistance with ANXA3, one of the highly expressed proteins in BEL7402/5-FU-resistant hepatoma cell line, was verified 23011854_The expression change of Anxa3 can be utilized as a potential indicator for the development, invasion, metastasis and drug resistance of tumors. 23464856_Low ANXA3 expression is associated with radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 23631820_Annexin A3 expression correlates with tumor size and lymph node metastasis.Annexin A3 might be regulated apoptosis by affecting Bcl-2/Bax balance.Annexin A3 was an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. 24375474_Findings reveal that ANXA3 might play an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma progression and chemoresistance. 24815437_Expression of annexin A3 was increased in gastric cancer compared with that in normal gastric tissues. Annexin A3 expression was significantly associated with tumor volume and TNM stage. 24824926_Annexin A3 was upregulated in gastric cancer cells. Deletion of endogenous Annexin A3 significantly inhibited gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. 24884814_Urinary calreticulin, annexin A2, and annexin A3 are very likely a panel of biomarkers with potential value for upper tract urothelial carcinoma diagnosis. 24954692_Two different antigenic variants of ANXA3 are present in post-DRE urines and their clinical significance for diagnosis of prostate cancer should be further investigated. 25267273_findings suggest that ANXA3 plays a role in HCC CSC/CIC maintenance, and that ANXA3 may represent a potential CSC/CIC-specific therapeutic target for improving the treatment of HCC. 26093083_ANX A3 has roles as a mammary biomarker, regulator and therapeutic target in breast cancer 26095609_Our results suggest that ANXA3 can serve as a novel diagnostic biomarker and that the inhibition of ANXA3 may be a viable therapeutic option for the treatment of CD133+ liver-CSC-driven HCC. 26475168_These results suggest that the iEA index or a combination of polymorphisms in EGFR and ANXA3 may serve as predictive factors of drug response, and therefore could be useful for optimal selection of chemotherapy regimens. 27475959_Results identified potential variant in ANXA3 gene [chr4, c.C820T(p.R274*)] in a large family with an unknown equinus deformity, which could lead to a three-dimensional conformational change. 27653686_we identified ANXA3 as a regulator of hepatitis C virus maturation and egress 27878264_ANXA3 role in the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells. 27894078_ANXA3 plays important roles in gastric cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis. 27995049_Anxa3 knockdown inhibited the growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. 28497041_The findings implicate the expression of ANXA3 with the natural progression of breast cancer and associate it with increased lymphatic metastasis. The study validates the use of ANXA3 as a potential prognosis biomarker for breast cancer. 28703915_ANXA3 levels in urine show clinically significant correlation with real tumor volumes. 29217453_Levels of Annexin A3 (ANXA3) expression are higher in the basal subtype of breast cancer cells. ANXA3 silencing inhibits cell proliferation, invasion across transwell membranes, and wound-healing and colony forming abilities. Expression of ANXA3 is closely correlated with tumor size, with higher ANXA3 expression associated with reduced disease-free survival in breast cancer patients. 29224019_The down-regulation of Annexin A3 by siRNA inhibited the invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells through the up-regulation of p53. 29374148_This study described the role and mechanisms of ANXA3 in regulating breast cancer stem cells and breast cancer growth and metastasis. 30003741_The expression of ANXA3 might play a crucial role in promoting the occurrence. 30070320_Down-regulation of ANXA3 or up-regulation of miR-340-5p inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. 30519762_High serum ANXA3 levels are associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 30868675_Results show that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) expressed higher level of ANXA3 than normal fibroblasts (NF), and CAF-conditioned medium incubation increased the ANXA3 level in lung cancer cells. CAF potentiated chemoresistance of lung cancer cells through a novel ANXA3/JNK pathway both in vitro and in vivo. 30998268_Annexin A3 depletion overcomes resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer via the MAPK signaling pathway. 31128000_Compared with CEF regimen, NAC with TEC regimen can improve the clinical and pathological effectiveness rate, inhibit the expression of ANXA3, and improve the prognosis of patients, thus having a certain application prospect in NAC 31524248_ANXA3 is highly expressed in the osteosarcoma cell lines HOS and U2OS. In addition, downregulation of ANXA3 expression in HOS and U2OS cells could increase apoptotic ability. 32329851_ANXA3 deletion inhibits the resistance of lung cancer cells to oxaliplatin. 32606294_The H2BG53D oncohistone directly upregulates ANXA3 transcription and enhances cell migration in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 32861643_36-kDa Annexin A3 Isoform Negatively Modulates Lipid Storage in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. 33118214_Microglial Annexin A3 promoted the development of melanoma via activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha/vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway. 33191179_Annexin A3 upregulates the infiltrated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio to remodel the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34109455_The calcimedin annexin A3 displays tumor-promoting effect in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating NF-kappaB signaling. 35464477_Upregulated of ANXA3, SORL1, and Neutrophils May Be Key Factors in the Progressionof Ankylosing Spondylitis. |
ENSMUSG00000029484 |
Anxa3 |
18.307097 |
0.1186867897 |
-3.074769 |
0.553624025 |
32.779166 |
0.00000001032454851783993312600942081824414997548444716812809929251670837402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000044926396262770460478097177704076559123791412275750190019607543945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8120118 |
1.4705412 |
32.3807630 |
7.2252107 |
| ENSG00000138795 |
51176 |
LEF1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UJU2 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that binds DNA in a sequence-specific manner (PubMed:2010090). Participates in the Wnt signaling pathway (By similarity). Activates transcription of target genes in the presence of CTNNB1 and EP300 (By similarity). PIAG antagonizes both Wnt-dependent and Wnt-independent activation by LEF1 (By similarity). TLE1, TLE2, TLE3 and TLE4 repress transactivation mediated by LEF1 and CTNNB1 (PubMed:11266540). Regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function (PubMed:19653274). Required for IL17A expressing gamma-delta T-cell maturation and development, via binding to regulator loci of BLK to modulate expression (By similarity). May play a role in hair cell differentiation and follicle morphogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P27782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11266540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19653274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2010090}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Transcriptionally activates MYC and CCND1 expression and enhances proliferation of pancreatic tumor cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19653274}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Lacks the CTNNB1 interaction domain and may therefore be an antagonist for Wnt signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11326276}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Transcriptionally activates the fibronectin promoter, binds to and represses transcription from the E-cadherin promoter in a CTNNB1-independent manner, and is involved in reducing cellular aggregation and increasing cell migration of pancreatic cancer cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19653274}. |
Activator;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor belonging to a family of proteins that share homology with the high mobility group protein-1. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to a functionally important site in the T-cell receptor-alpha enhancer, thereby conferring maximal enhancer activity. This transcription factor is involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, and it may function in hair cell differentiation and follicle morphogenesis. Mutations in this gene have been found in somatic sebaceous tumors. This gene has also been linked to other cancers, including androgen-independent prostate cancer. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:51176; |
beta-catenin-TCF complex [GO:1990907]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-DNA complex [GO:0032993]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; armadillo repeat domain binding [GO:0070016]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; C2H2 zinc finger domain binding [GO:0070742]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA binding, bending [GO:0008301]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; gamma-catenin binding [GO:0045295]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription corepressor binding [GO:0001222]; transcription regulator inhibitor activity [GO:0140416]; anatomical structure regression [GO:0060033]; apoptotic process involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:1902262]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; chorio-allantoic fusion [GO:0060710]; dentate gyrus development [GO:0021542]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; epithelial cell apoptotic process [GO:1904019]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; forebrain neuroblast division [GO:0021873]; forebrain radial glial cell differentiation [GO:0021861]; formation of radial glial scaffolds [GO:0021943]; histone H3 acetylation [GO:0043966]; histone H3-K56 acetylation [GO:0097043]; histone H4 acetylation [GO:0043967]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of apoptotic process in bone marrow cell [GO:0071866]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022408]; negative regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043392]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of interleukin-13 production [GO:0032696]; negative regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032713]; negative regulation of interleukin-5 production [GO:0032714]; negative regulation of striated muscle tissue development [GO:0045843]; neutrophil differentiation [GO:0030223]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; paraxial mesoderm formation [GO:0048341]; positive regulation by host of viral transcription [GO:0043923]; positive regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0090068]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell proliferation in bone marrow [GO:0071864]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022409]; positive regulation of chondrocyte proliferation [GO:1902732]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of gamma-delta T cell differentiation [GO:0045588]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030854]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; secondary palate development [GO:0062009]; sensory perception of taste [GO:0050909]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; T cell receptor V(D)J recombination [GO:0033153]; T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045063]; tongue development [GO:0043586]; trachea gland development [GO:0061153]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
12032083_Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor interacts with LEF-1, a mediator of Wnt signaling. 12048204_MITF-M transactivates its own promoter (M promoter) by interacting with LEF-1 12052822_wnt3a-beta catenin signaling regulates LEF-1 gene expression 12095232_direct evidence for a role of beta-catenin/LEF-1 signaling pathway in induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transformation 12161443_ZEB1 plays a role in repressing E-cadherin and MUC1 in epithelial cells [ZEB-1] 12183361_Nr-CAM is the gene most extensively induced by LEF1 12235165_induction of Lef/Tcf-dependent transcription in human endothelial cells by fibroblast growth factor-2 12556497_These results suggest that NLK phosphorylation on these sites contributes to the down-regulation of LEF-1/TCF transcriptional activity. 12589056_Tcf/LEF1 has a role in transcriptional induction of cyclin D1 12707037_loss of expression of this transcription factor in a subset of peripheral t-cell lymphomas 14990565_Beta-catenin, Lef-1, Ets transcription factors, and the AP-1 protein c-Jun each weakly enhanced luciferase expression from an OPN promoter. 15000148_Lymphoid enhancer factor/T cell factor has a role in development of colorectal cancer [review] 15194563_Wnt regulation of the Lef-1 promoter at the WRE may play an important role during airway submucosal glandular bud formation. 15245424_a 110 bp Wnt/beta-catenin-responsive element, contained within a minimal 2.5 kb Lef-1 promoter, plays an important role in regulating mesenchymal, and potentially epithelial, expression during follicle development in mouse embryos. 15728254_LEF-1 expression is regulated through PITX2, LEF-1 and beta-catenin direct physical interactions 15750622_Smad-binding peptide aptamer LEF1 can be developed to selectively inhibit TGF-beta-induced gene expression. 15756419_Taken together, these data suggest that LEF-1 is abundantly expressed in human tumors and the ratio of the oncogenic and the dominant negative short isoform altered not only in carcinomas but also in leukemia. 16120831_LEF1 5'-untranslated region (UTR) mediates cap-independent translation; the 5'-UTR of full-length LEF1 mRNA contains a bona fide internal ribosome entry site (IRES). 16142310_LEF1, a downstream component of the Wnt signaling pathway, mediates breast cancer cell invasion, and may be regulated in part by estradiol 16415175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424171_Involvement of LEF1 protein in the wingless type protein (WNT) signaling pathway not only regulates T cell development, but also peripheral T cell differentiation. 16474850_hAR is a direct target of LEF-1/TCF transcriptional regulation in PCa cells; expression of the hAR protein is suppressed by a degradation pathway regulated by cross-talk of Wnt, Akt, and PP2A 16565724_Sebaceous gland neoplasms harbor inactivating mutations in LEF1. 16714285_NARF functions as a novel ubiquitin-ligase to regulate ubiquitylation and degradation of T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor 16809766_the biological outcome of aberrant LEF1 activation in colon cancer is directed by differential promoter activation and repression 17063141_LEF-1 is an instructive factor regulating neutrophilic granulopoiesis whose absence plays a critical role in the defective maturation program of myeloid progenitors in individuals with congenital neutropenia 17132729_Cooperates with SMAD4 to activate c-myc expression. 17240357_Additional prolactin (PRL) regulatory elements corresponding to LEF-l and AP-1 transcription factor binding sites appear important for PRL expression. 17360796_LEF-1 is a decisive transcription factor in neutrophil granulopoiesis [review] 17466981_This study demonstrates that the two consensus Lef/Tcf binding elements (TBE)reported in neoplastic cells are dispensable for c-Myc regulation in normal keratinocytes, which instead use a novel TBE sequence variant. 17585052_Notch1 co-opts Lef1 during the process of transformation to maintain survival of T-cell lymphomas 17785436_Re-expression of E-cadherin in HT29(US) cells restored the ability of caveolin-1 to down-regulate beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription and survivin expression, as seen in HT29(ATCC) cells. 17785445_These data support a role for PITX2 in cell proliferation, migration, and cell division through differential Lef-1 isoform expression and interactions with Lef-1 and beta-catenin. 17947518_Marked upregulation of lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF-1), a transcription factor in the Wnt pathway, was found in HBsAg-expressing cells 18316418_role of Lef-1 in the biology of acute leukemia, pointing to the necessity of balanced Lef-1 expression for an ordered hematopoietic development 18579517_IL-4 stimulation possesses a negative effect on the expressions of LEF-1 and TCF-1 in primary T cells, suggesting a positive feedback effect of IL-4 on IL4 gene expression. 18615589_beta-catenin acts together with Lef-1 to influence DeltaNp63 promoter activity and protein expression 18936100_Dpr1 negatively modulates the basal activity of Wnt1/beta-catenin signaling in the nucleus by keeping LEF1 in the repressive state. 19079342_Id-1 is a novel PTEN inhibitor that could activate the Akt pathway and its downstream effectors, the Wnt/TCF pathway and p27(Kip1) phosphorylation 19131506_GnRH regulation of Jun transcription requires a functional interaction between TCF/LEF and beta-catenin. 19244345_By reducing COX-2 expression, caveolin-1 interrupts a feedback amplification loop involving PGE(2)-induced signaling events linked to beta-catenin/Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription of tumor survival genes including cox-2 itself and survivin. 19351848_LEF1 is a potential marker for androgen-independent disease and a key regulator of AR expression and prostate cancer growth and invasion. LEF1 is highly expressed in androgen-independent prostate cancer. 19402906_hepatitis B surface antigen could stimulate proliferation and functional modification of hepatocytes via LEF-1 through the Wnt pathway at the pre-malignant stage 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19576624_Two WNT target genes, LEF1 and HOXB9, are identified as promoters of lung adenocarcinoma metastasis and mediators of chemotactic invasion and colony outgrowth. 19590514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19653274_expression of alternatively spliced Lef-1 isoforms is involved in the determination of proliferative or migratory characteristics of pancreatic carcinoma cells. 19784072_Data show that elevated Snail expression by Pdcd4 knockdown leads to downregulation of E-cadherin resulting in activating beta-catenin/Tcf-dependent transcription. 20019092_EWS/FLI1 binds LEF1, interfering with the formation of beta-catenin-LEF1 complexes, and thus with their transcriptional activity. 20098615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20124220_LEF1 inactivation is an important step in the molecular pathogenesis of T-ALL in a subset of young children. 20219685_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20363964_LEF-1 binds specifically to the major histocompatibility complex class I-like protein CD1D promoter; enhanced expression of LEF1 in K562 or Jurkat cells suppresses CD1D promoter activity and downregulates endogenous CD1D transcripts. 20595513_This study identified aberrant protein expression of LEF-1 specifically in chronic lymphocytic leukemia but not in normal mature B-cell subsets or after B-cell activation. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20676368_LRP6-ICD interacts with AES exclusively in the nucleus and represses AES mediated TCF/LEF-1 reporter transcription. 21190562_PC3 tumors are sustained by a small number of tumor-initiating cells with stem-like characteristics, including strong self-renewal and pro-angiogenic capability and marked by the expression pattern FAM65Bhigh/MFI2low/LEF1low. 21270130_Lef1DeltaN binds beta-catenin, stimulates Lef/Tcf reporter activity, and promotes terminal osteoblast differentiation. 21285352_HIPK2-dependent phosphorylation caused the dissociation of LEF1, TCF4, and TCF3 from a target promoter in vivo. 21383983_Overexpression of LEF1 in primary colorectal carcinoma is a prognostic factor for poor survival and increased risk for liver metastasis. 21444716_Alternative splicing of LEF1 exon 6 is regulated during pre-TCR signaling in thymic development and in response to activation of the JSL1 T-cell line and this is driven by the activity of CELF2. 21471213_a novel interaction between the VDR and LEF1 that is mediated by the DNA-binding domain of the VDR and that is required for normal canonical Wnt signaling in keratinocytes. 21527502_lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 identifies androgen-independent epithelium in the developing prostate 21544627_A strong promoter activity of pre-B cell stage-specific Crlz1 gene is caused by one distal LEF-1 and multiple proximal Ets sites. 21599871_Melanoma cell phenotype switching behaviour is regulated by differential LEF1/TCF4 activity. 21685909_Report universal nuclear overexpression of LEF1 but lack of nuclear beta-catenin in the majority of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphomas. 21781440_An association between the maternal genotype and the occurrence of cleft lip or palate was observed at two polymorphic loci (rs10022956 and rs10025431), while a foetal-maternal effect modulating the risk of clefting was found at locus rs10025431. 21980470_identification of a variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism in IDO1 promoter and characterization of LEF-1 response elements 21998751_differentiation status of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells would result in loss of LEF-1 expression 22020335_The study demonstrated a novel b-catenin/ LEF1-miR-372&373-Dickkopf-1 regulatory feedback loop, which may have a critical role in regulating the activity of Wnt/b-catenin signaling in human cancer cells. 22111711_In this review we present mounting evidence for the interdependency of TCF7/LEF1 variant expression and functions with cell lineage and cell state. [Review] 22261717_nuclear IGF1R associates with the transcription factor LEF1 and increases promoter activity of LEF1 downstream target genes cyclin D1 and axin2. 22359570_a robust transcriptional CTNNAL1 up-regulation occurs during acute ozone-induced stress and is mediated at least in part by ozone-induced recruitments of LEF-1 and AP-2alpha to the human CTNNAL1 promoter. 22436613_findings suggest that transcriptional activation of LEF1 is a mechanism of cross talk between HGF/c-Met and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways and is essential for HGF-induced tumor invasion 22507326_results suggest that assessing intracellular beta-catenin and LEF1 expression might help in patient risk stratification and outcome prediction 22639890_LEF-1 might play an important role in colon carcinogenesis by acting as a regulator. 22686279_our results indicate a pivotal role of LEF-1 in the regulation of proliferation and MMP-7 transcription in breast cancer cells. 22766851_miR-218 is involved in the invasive behavior of glioblastoma cells by targeting LEF1 and blocking the invasive axis. 22769578_this study demonstrated that miR-449a directly targets LEF-1, which in turn affects the expression of Sox 9, ultimately leading to the proper regulation of the differentiation and chondrogenesis 22792274_Lef1 is overexpressed in human endometrial tumors, consistent with it playing a role in gland proliferation. 22815426_High LEF1 expression is associated with significantly better relapse-free survival, overall survival, and event-free survival of cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia patients. 22905168_n-Butyl benzyl phthalate promotes breast cancer progression by inducing expression of lymphoid enhancer factor 1 23001182_interaction of HCLS1 with LEF-1 is essential for G-CSF-triggered myeloid differentiation 23068607_Results suggest that NDRG2 and prenylated Rab acceptor-1 (PRA1) might act synergistically to prevent signaling of T-cell facto/beta-catenin. 23224985_Nuclear LEF1 correlate with cerebral metastasis of lung adenocarcinomas. 23325550_DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit is a novel interaction partner of lymphocyte enhancer factor 1. 23375451_This study supports a functionally important role for LEF1 and its target genes in Burkitt's lymphoma. 23572277_Studied the expression of TCF/LEF and SFRP family members (SFRP1 and SFRP3) to gain a better understanding of biological signaling pathways responsible for epidemiology and clinical parameters of clear cell RCC (cRCC). 23713453_Results indicate that lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1) contributes to the pathophysiology of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and could be a predictor of better treatment response. 23913826_High LEF1 expression is associated with prostate cancer. 24021930_Our study suggests LEF1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma may play an important role in tumor progression and can be served as a predictor of poor prognosis for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24098538_LEF1 protein was overexpressed in colon cancer tissues and knockdown of LEF1 expression inhibited colon cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. 24378360_LEF1 expression is an independent prognostic factor in APL, and could be used in patients risk stratification. 24419084_By beta-catenin's association with LEF1 and BCL9-2/B9L. 24577083_Selenite caused CYLD upregulation via LEF1 and cIAP downregulation, both of which contribute to the degradation of ubiquitin chains on RIP1 and subsequent caspase-8 activation and colorectal tumor cell apoptosis. 24658583_These results further implicate the CTNNB1/LEF1 transcriptional complex in the development of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas 24785257_miR26b may act as a potential therapeutic agent in reducing cancer cell proliferation through repressing LEF1 activation of c-Myc and cyclin D1 expression 24847765_Tcf1 and Lef1 cooperate with Runx factors to achieve stable silencing of the Cd4 gene in CD8(+) T cells. 24858819_Elevated TCF-1 and LEF-1 expression is characteristic of malignant gliomas 24897388_the expression of LEF1 is associated with the progression of human renal cell carcinoma and LEF1 maybe involved in the development of RCC 25343173_Increased expression of beta-catenin, lymphoid enhancer-binding protein-1, and heparanase-1 is significantly correlated with decreased survival and poor prognosis in acral melanoma. 25394300_LEF-1 expression is associated with the presence of KRAS mutations and may have prognostic value as a trend of worse overall survival is seen in patients with LEF-1-positive colorectal carcinoma. 25497834_LEF-1 expression in both basal cell adenomas and basal cell adenocarcinomas preferentially over other salivary gland tumors suggesting some utility as a diagnostic marker 25587085_Study found a negative correlation between miR-34a and LEF1 expression in prostate cancer cell lines and tumors and that miR-34a regulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition through direct binding to LEF1 mRNA 3' UTR region and silencing its translation. 25596247_Proper sample processing ensured sufficient separation of positive LEF1 staining in T cells from negative staining in normal B and natural killer (NK) cells 25639559_The results describe a novel mutation in LEF1 causing dysregulation of Wnt/B catenin signaling in eyelid sebaceous cancinoma 25646419_study identified TCF1 and LEF1 as Tax antagonistic factors in vivo, a fact which may critically influence the peripheral T-cell tropism of this virus 25808920_Authors found that the N-terminus of delta-catenin bound to the middle region of LEF-1 unlike beta-catenin. Overexpressed delta-catenin entered the nucleus and inhibited LEF-1-mediated transcriptional activity in Bosc23 and DLD-1 cell lines. 25942645_high LEF1 expression and mutation are associated with high-risk leukemia and our results also revealed that LEF1 high expression and/or gain-of-function mutations are involved in leukemogenesis of ALL. 25955539_Overexpression of LEF1 is a favorable prognostic factor in childhood ALL. 26339357_Methylprednisolone can suppress Wnt signaling pathway by down-regulating LEF-1 protein expression in chronic lymphocyte leukemia cells. 26580798_LEF-1 and MITF regulate tyrosinase gene transcription in vitro via binding to its promoter. 26950276_Results show that high enhancer-binding factor-1 (LEF1) expression is associated with poor survival for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients. 27067790_The results suggest a role for beta-catenin/LEF1-mediated transcription in both malignant transformation and metastasis of prostate cancer 27433921_Lef1 and Tcf1 showed oncogenic effect in colonic carcinogenesis. Cellular context of miRNAs might play important roles in carcinogenesis by altering the expression pattern of Lef/Tcfs members. 27811057_and CTU1/2, partner enzymes in U34 methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thio tRNA modification, are up-regulated in human breast cancers and sustain metastasis. 27908728_EVI1 transcription is directly regulated by LEF1/beta-catenin complex in myeloid blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Loss of p53 function as a key regulator for beta-catenin-EVI1 in myeloid blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia. 27965462_these data suggest that LEF1 rather has tumor suppressive functions and attenuates aggressiveness in a subset of RMS. 28027119_Comparison of beta-Catenin and LEF1 Immunohistochemical Stains in Desmoid-type Fibromatosis and its Selected Mimickers, With Unexpected Finding of LEF1 Positivity in Scars. 28038713_a frequency of 4-9% expression of LEF1 bymantle cell lymphoma 28122350_Data indicate that microRNA miR-27a directly targets GSK-3beta and increases expression of beta-catenin and LEF1 in all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)-induced Hep2 cells. 28395058_LEF1 is a sensitive and specific marker for chronic lymphocytic B-cell leukemia 28639890_MicroRNA-557 might work as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating the expression of lymphocyte enhancement factor 1 in lung cancer cells. 28664938_LEF1 was consistently expressed in the tubal-peritoneal junctions and all tubal intraepithelial lesions, independent of p53 status. 28677753_High LEF1 expression is associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma. 28943339_Knockdown of GATA6 completely eliminated the effect of TCF1, while forced expression of GATA6 induced hESC differentiation 28972308_Positive LEF-1 favors a benign neoplasm. 29369390_LEF-1 and CDX2 performed at least as well as beta-catenin, if not better, as a diagnostic marker for pilomatrical carcinomas 29736797_Sinonasal glomangiopericytomas (sinonasal-type hemangiopericytomas) with CTNNB1 exon 3 mutation and LEF1 expression in tumor cells. 29953980_study identifies a novel mechanism of hepatocellular carcinoma inhibition through beta-catenin-independent Wnt signalling, which is regulated by WT1-associated LEF1 repression. The study also highlights mangiferin as a promising Wnt inhibitor for HCC treatment. 29974668_the overexpression of both OCT4 and LEF1 is an important feature in ESCC progression, and OCT4 is closely correlated with LEF1 expression in the regulation of cancer cell EMT, invasion, and migration. 29991769_interaction between LEF1 andTAZ (WWTR1) is crucial for the osteoblastogenic activity of Wnt3a, and LEF1 and TAZ contribute to the cooperative effect of Wnt3a and BMP2 on osteoblast differentiation through association with Runx2. 30026867_These results provide new insight into the mechanisms underlying hyperactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma, as well the oncogenic ability of TFAP4 to enhance the tumor-forming ability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via its binding to the promoters of DVL1 (dishevelled segment polarity protein 1) and LEF1 (lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1). 30193961_Experimental analysis showed the importance of LEF1, ETV4 and FABP6 as three co-regulated prognostic markers in patients with colorectal cancer metastasis. 30270548_a concerted increase in ETS1 and LEF1 expression in salivary gland epithelial cells of primary Sjogren's syndrome patients 30446587_Disruption of the LEF1/DCLK1-B axis by niclosamide eradicates cancer stemness and elicits therapeutic effects on colorectal cancer initiation, progression, and resistance. These findings provide a preclinical rationale to broaden the clinical evaluation of niclosamide for the treatment of colorectal cancer. 30468298_TCF1 and LEF1 were both significantly upregulated. 30630973_LEF-1 overexpression promotes both nuclear-localization and beta-catenin-dependent transcriptional responses in myeloid leukemia. 30696957_LEF1 could enhance the self-renewal ability. 30706227_High LEF1 expression is associated with Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. 30886049_Loss of LEF1 expression is associated with sebaceous gland and skin cancer. 30918012_The expression of LEF1 associated positively with TCF1 (TCF7) and clinical progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, predicting poor prognosis. 30920079_Expression analysis of selected miR-206 targets from the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway in breast cancer. 30968150_Study revealed that miR300 expression was significantly decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines compared with normal liver cells. LEF1 which was verified as a direct target gene of miR300, promoted cell proliferation, migration and invasion and mediates the effects of miR300. Low expression of miR300 and high expression of LEF1 in HCC tissues is associated with poor prognosis of patients with HCC. 31253399_Data suggest that methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) silence decreased the m6A methylation and total mRNA level of lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1), followed by inhibited the activity of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 31289135_Lef1 contributed to drug resistance by inducing the expression of the other genes in the breast cancer. 31296250_Our results indicate that the overexpression of LEF1 promotes a CSC-like phenotype in and the tumorigenicity of ESCC by activating the TGF-beta signaling pathway. The inhibition of LEF1 might therefore be a novel therapeutic target to inactivate CSCs and inhibit tumor progression. 31513434_Downregulations of miR-449a and miR-145-5p Act as Prognostic Biomarkers for Endometrial Cancer. 31623618_MYC is a transcriptional regulator of LEF1 in colonic cells 31626715_LEF1 supports metastatic brain colonization by regulating glutathione metabolism and increasing ROS resistance in breast cancer. 31753039_Let-7i-3p, acting as a negative regulator of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by targeting LEF1, inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of hASCs under cyclic strain in vitro. 31758089_Differences in expression and function of LEF1 isoforms in normal versus leukemic hematopoiesis. 31848806_LEF1/integrin alphaMbeta2 expression was regulated by TGF-beta1, and LEF1/integrin alphaMbeta2 was involved in TGF-beta1's improvement effects on the proliferation and metastasis of Renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Blocking integrin alphaMbeta2 activity could be a therapeutic option for patients with advanced RCC. 31953940_LEF1 is not expressed in most CD5-positive marginal zone lymphomas and lymphoplasmacytic lymphomas; therefore, it is a reliable marker for distinguishing them from chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. 32022899_LEF1 haploinsufficiency causes ectodermal dysplasia. 32068261_Silencing of long noncoding RNA LEF1-AS1 prevents the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the crosstalk with microRNA-136-5p/WNK1. 32329830_m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the progression of prostate cancer via m6A-modified LEF1. 32401815_expression is a biomarker of early T-cell precursor, an aggressive subtype of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia 32403323_Diverse LEF/TCF Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer Correlates with Altered Wnt-Regulated Transcriptome in a Meta-Analysis of Patient Biopsies. 32534708_Concurrent Wnt pathway component expression in breast and colorectal cancer. 32586085_LEF1 Induces DHRS2 Gene Expression in Human Acute Leukemia Jurkat T-Cells 32633375_MicroRNA-381 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioblastoma cells through targeting LEF1. 32645172_Simultaneous bone marrow involvement by CLL/SLL and LEF1/cyclin D1-positive metastatic melanoma. 32703426_DOCK2 couples with LEF-1 to regulate B cell metabolism and memory response. 32732957_LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-small ka, CyrillicB signaling pathway. 32760207_LEF1/Id3/HRAS axis promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 32824603_2,4-Diamino-Quinazoline, a Wnt Signaling Inhibitor, Suppresses Gastric Cancer Progression and Metastasis. 32856045_High expression of LEF1 correlates with poor prognosis in solid tumors, but not blood tumors: a meta-analysis. 32933177_Cinobufagin Suppresses Melanoma Cell Growth by Inhibiting LEF1. 32977233_Lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF1) expression is significantly higher in Hodgkin lymphoma associated with Richter syndrome relative to de novo classic Hodgkin lymphoma. 32980885_Deciphering the role of Wnt signaling in acute myeloid leukemia prognosis: how alterations in DNA methylation come into play in patients' prognosis. 33165091_Striking Association of Lymphoid Enhancing Factor (LEF1) Overexpression and DUSP22 Rearrangements in Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. 33245988_Expression of lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 in breast fibroepithelial lesions. 33314668_Downregulation of Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF-1) expression (by immunohistochemistry and/ flow cytometry) in chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with atypical immunophenotypic and cytologic features. 33398088_Deficient LEF1 expression is associated with lithium resistance and hyperexcitability in neurons derived from bipolar disorder patients. 33523480_Human fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles promote hair growth in cultured human hair follicles. 33608451_Colorectal Cancer-Associated Smad4 R361 Hotspot Mutations Boost Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling through Enhanced Smad4-LEF1 Binding. 33677883_[A study of LEF1 protein expression in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of lymphoblastic lymphoma/acute lymphoblastic leukemia]. 33844466_Prognostic evidence of LEF1 isoforms in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 33887729_[Diagnostic Utility of LEF1 Immunostain in Cytology Specimens of Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of Pancreas]. 34021424_LncRNA LEF1-AS1/LEF1/FUT8 Axis Mediates Colorectal Cancer Progression by Regulating alpha1, 6-Fucosylationvia Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. 34048981_A limited panel of INSM1 and LEF1 immunostains accurately distinguishes between pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor and solid pseudopapillary neoplasm. 34096776_Circular RNA hsa_circ_0032463 Acts as the Tumor Promoter in Osteosarcoma by Regulating the MicroRNA 498/LEF1 Axis. 34269120_Downregulation of LEF1 Impairs Myeloma Cell Growth Through Modulating CYLD/NF-kappaB Signaling. 34337014_lncRNA OXCT1-AS1 Promotes Metastasis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Stabilizing LEF1, In Vitro and In Vivo. 34397171_Destruction of DNA-Binding Proteins by Programmable Oligonucleotide PROTAC (O'PROTAC): Effective Targeting of LEF1 and ERG. 34563944_LncRNA landscape analysis identified LncRNA LEF-AS1 as an oncogene that upregulates LEF1 and promotes survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 34639214_LEF1 Enhances the Progression of Colonic Adenocarcinoma via Remodeling the Cell Motility Associated Structures. 35066013_Immunohistochemistry for LEF1 and SOX11 adds diagnostic specificity in small B-cell lymphomas. 35139734_Interaction between CASP8AP2 and ZEB2-CtBP2 Regulates the Expression of LEF1. 35421421_Aberrant expression of lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 in Hodgkin lymphoma. 35583550_Monoallelic and biallelic variants in LEF1 are associated with a new syndrome combining ectodermal dysplasia and limb malformations caused by altered WNT signaling. 35594394_Lef1 ablation alleviates cartilage mineralization following posttraumatic osteoarthritis induction. 35628310_Impaired LEF1 Activation Accelerates iPSC-Derived Keratinocytes Differentiation in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome. 35871391_Loss of LEF-1 expression as a diagnostic indicator for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: An immunohistochemical study of 88 cases. 35950640_Lef1 is transcriptionally activated by Klf4 and suppresses hyperoxia-induced alveolar epithelial cell injury. 35960138_Increased Expression of LEF1 and beta-Catenin in Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast is Associated With Lymphovascular Invasion and Lymph Node Metastasis. 36153326_Recruitment of LEF1 by Pontin chromatin modifier amplifies TGFBR2 transcription and activates TGFbeta/SMAD signalling during gliomagenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000027985 |
Lef1 |
81.764764 |
3.8391850364 |
1.940800 |
0.386197716 |
23.676978 |
0.00000113937405357540097153746117691897055124172766227275133132934570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004006948065468886832857318275324942646875570062547922134399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
133.8485922 |
30.6018254 |
35.0155407 |
6.1643416 |
| ENSG00000138821 |
64116 |
SLC39A8 |
protein_coding |
Q9C0K1 |
FUNCTION: Electroneutral divalent metal cation:bicarbonate symporter of the plasma membrane mediating the cellular uptake of zinc and manganese, two divalent metal cations important for development, tissue homeostasis and immunity (PubMed:12504855, PubMed:22898811, PubMed:23403290, PubMed:29337306, PubMed:26637978, PubMed:29453449). Transports an electroneutral complex composed of a divalent metal cation and two bicarbonate anions or alternatively a bicarbonate and a selenite anion (PubMed:27166256, PubMed:31699897). Thereby, it also contributes to the cellular uptake of selenium, an essential trace metal and micronutrient (PubMed:27166256). Also imports cadmium a non-essential metal which is cytotoxic and carcinogenic (PubMed:27466201). May also transport iron and cobalt through membranes (PubMed:22898811). Through zinc import, indirectly regulates the metal-dependent transcription factor MTF1 and the expression of some metalloproteases involved in cartilage catabolism and also probably heart development (PubMed:29337306). Also indirectly regulates the expression of proteins involved in cell morphology and cytoskeleton organization (PubMed:29927450). Indirectly controls innate immune function and inflammatory response by regulating zinc cellular uptake which in turn modulates the expression of genes specific of these processes (PubMed:23403290, PubMed:28056086). Protects, for instance, cells from injury and death at the onset of inflammation (PubMed:18390834). By regulating zinc influx into monocytes also directly modulates their adhesion to endothelial cells and arteries (By similarity). Reclaims manganese from the bile at the apical membrane of hepatocytes, thereby regulating the activity of the manganese-dependent enzymes through the systemic levels of the nutrient (PubMed:28481222). Also participates in manganese reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the kidney (PubMed:26637978). By mediating the extracellular uptake of manganese by cells of the blood-brain barrier, may also play a role in the transport of the micronutrient to the brain (PubMed:26637978, PubMed:31699897). With manganese cellular uptake also participates in mitochondrial proper function (PubMed:29453449). Finally, also probably functions intracellularly, translocating zinc from lysosome to cytosol to indirectly enhance the expression of specific genes during TCR-mediated T cell activation (PubMed:19401385). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91W10, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12504855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18390834, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19401385, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22898811, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23403290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26637978, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27166256, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27466201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28056086, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28481222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29337306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29453449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29927450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31699897}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the SLC39 family of solute-carrier genes, which show structural characteristics of zinc transporters. The encoded protein is glycosylated and found in the plasma membrane and mitochondria, and functions in the cellular import of zinc at the onset of inflammation. It is also thought to be the primary transporter of the toxic cation cadmium, which is found in cigarette smoke. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Additional alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:64116; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; organelle membrane [GO:0031090]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; solute:bicarbonate symporter activity [GO:0140410]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; arginine metabolic process [GO:0006525]; bicarbonate transport [GO:0015701]; cadmium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070574]; cartilage homeostasis [GO:1990079]; cellular cadmium ion homeostasis [GO:0006876]; cellular manganese ion homeostasis [GO:0030026]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; cobalt ion transport [GO:0006824]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; iron ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098711]; leukocyte adhesion to arterial endothelial cell [GO:0061757]; manganese ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071421]; mercury ion transport [GO:0015694]; mitochondrial manganese ion transmembrane transport [GO:1990540]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; plasma membrane selenite transport [GO:0097080]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; zinc ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0071578]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577]; zinc ion transport [GO:0006829] |
18390834_These data are the first to characterize human SLC39A8 (Zip8) and remarkably demonstrate that upregulation of Zip8 is sufficient to protect lung epithelia against TNF-alpha-induced cytotoxicity. 18556457_These results demonstrate the importance of Sp1 in the regulation of ZIP8 expression. 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401385_ZIP8, through control of zinc transport from the lysosome, may provide a secondary level of IFN-gamma regulation in T cells. 20864672_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22078303_findings reveal a role for brain metal homeostasis in psychosis. 22898811_data identify ZIP8 as an iron transport protein that may function in iron metabolism. 23403290_The zinc transporter SLC39A8 (ZIP8) is a transcriptional target of NF-kappaB and functions to negatively regulate proinflammatory responses through zinc-mediated down-modulation of IkappaB kinase (IKK) activity in vitro. 23688035_MicroRNA-488 regulates zinc transporter SLC39A8/ZIP8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis 23921484_Data indicate that the average expression level of zinc transporter Zip2 was significantly higher and zinc transporters Zip6, Zip8 mRNA levels were significantly lower in short stature children than in health controls. 24514587_Polymorphisms in SLC39A14 and SLC39A8 seemed to affect blood cadmium concentrations, for SLC39A14 this effect may occur via differential gene expression. 26006263_data provide evidence of positive selection on a schizophrenia risk SNP rs13107325 in the SLC39A8 gene, and we propose a hypothesis about the relationship among positive selection of host alleles, schizophrenia, hypertension, energy intake, and the unique history of Europeans. 26025379_The lead single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the 4q24 locus was rs13107325 (P-value = 5.1 x 10(-11), beta = -0.77), located in an exon of SLC39A8, which encodes a protein involved in manganese and zinc transport. 26637978_Autosomal-recessive intellectual disability with cerebellar atrophy syndrome is caused by mutation of the manganese and zinc transporter gene SLC39A8. 26908625_SLC39A8 SNP (rs13107325) was associated with NT-proBNP levels in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). The SLC39A8 SNP was also associated with higher risk of cardiovascular death. 27466201_These results indicate that the ZIP8 Ala391-to-Thr391 substitution has an effect on intracellular cadmium accumulation and cell toxicity, providing a potential mechanistic explanation for the association of this genetic variant with blood pressure. 27492617_We identified an association between Crohn's Disease and a missense variant encoding alanine or threonine at position 391 in the zinc transporter solute carrier family 39, member 8 protein (SLC39A8 alanine 391 threonine, rs13107325) and replicated the association with Crohn's Disease in 2 replication cohorts. 27995398_SLC39A8 deficiency can cause both a type II CDG and Leigh-like syndrome. 28917719_The study indicates that common single nucleotide polymorphisms in manganese transporters (SLC30A10 and SLC39A8) influence manganese homeostasis in early development. 29120360_The expression, localization, and function of ZIP8 and other divalent cation transporters within macrophages have important implications for TB prevention and dissemination and warrant further study. [review] 29333637_Increased free Zn(2+) correlates with induction of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum stress via altered expression levels of Zn(2+) -transporters, Zip8, Zip14, and ZnT8, in heart failure. 29453449_a potential pathogenic mechanism of diseases that are associated with hSLC39A8 mutations 29749445_the results of the present study suggested that Zip8 was an important regulator of neuroblastoma cell proliferation and migration, indicating that Zip8 may be a potential anticancer therapeutic target and a promising diagnostic biomarker for human neuroblastoma. 30301978_a missense single nucleotide polymorphism in SLC39A8 (p.Ala391Thr, rs13107325) associated with severe idiopathic scoliosis. 30649180_results show that a missense mutation in gene SLC39A8 is associated with larger gray matter volume in the putamen and that this association is significantly weakened in schizophrenia. 30703110_Study confirms the genetic association of the missense variant [Thr]391 of SLC39A8 with Crohn's disease but could not replicate the association in gut microbiome composition. 31151823_results suggest a potential role for ZIP8 in intestinal inflammation, induced by IFNgamma in the intestinal epithelial compartment, and that perturbations in negative regulation of NF-kappaB by ZIP8 A391T may contribute to Crohn's disease pathogenesis 31261654_Both ZIP8 and ZIP14 have roles in manganese metabolism of alveolar epithelial cells. 31513097_A novel coding variant of SLC39A8 is found to be significantly associated with adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in a Chinese Han population. 31533672_SLC39A8 encodes a protein named ZIP8, which is responsible for the transport of the essential metals including ferrum (Fe2+), manganese (Mn2+) and zinc (Zn2+), and the nonessential neurotoxic metal cadmium (Cd2+). 31699897_solute carriers ZIP8 and ZIP14 regulate manganese accumulation in brain microvascular endothelial cells and control brain manganese levels 32247823_Genome-wide and Mendelian randomisation studies of liver MRI yield insights into the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. 32392784_The Functions of ZIP8, ZIP14, and ZnT10 in the Regulation of Systemic Manganese Homeostasis. 32753748_The schizophrenia risk locus in SLC39A8 alters brain metal transport and plasma glycosylation. 32788640_Genetic markers and continuity of healthy metabolic status: Tehran cardio-metabolic genetic study (TCGS). 32852845_N-glycome analysis detects dysglycosylation missed by conventional methods in SLC39A8 deficiency. 32897876_Pleiotropic ZIP8 A391T implicates abnormal manganese homeostasis in complex human disease. 33139556_A missense variant in SLC39A8 confers risk for Crohn's disease by disrupting manganese homeostasis and intestinal barrier integrity. 33608496_Schizophrenia-associated SLC39A8 polymorphism is a loss-of-function allele altering glutamate receptor and innate immune signaling. 33795795_ZIP8 exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis by increasing pathogenic T cell responses. 34198528_HIF-1alpha Dependent Upregulation of ZIP8, ZIP14, and TRPA1 Modify Intracellular Zn(2+) Accumulation in Inflammatory Synoviocytes. 34672770_C Deletion at the re74650330 Locus of the SLC39A8 Gene (rs74650330) Increases the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Individuals with Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels. 34768831_The Impact of ZIP8 Disease-Associated Variants G38R, C113S, G204C, and S335T on Selenium and Cadmium Accumulations: The First Characterization. 34924116_Manganese transport in mammals by zinc transporter family proteins, ZNT and ZIP. 35636252_Effects of individual amino acid mutations of zinc transporter ZIP8 on manganese- and cadmium-transporting activity. 35642632_Deficiency in the zinc transporter ZIP8 impairs epithelia renewal and enhances lung fibrosis. 35787370_Calcium and the Ca-ATPase SPCA1 modulate plasma membrane abundance of ZIP8 and ZIP14 to regulate Mn(II) uptake in brain microvascular endothelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000053897 |
Slc39a8 |
429.081553 |
2.9219565840 |
1.546935 |
0.161935663 |
88.189188 |
0.00000000000000000000594841566267393362245399553569778490968683471877491370026058009612413002287212293595075607299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000054567194021794438111026856900307834620686592816434017051349658622427796217380091547966003417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
622.7095267 |
133.5805562 |
213.7987725 |
33.3574266 |
| ENSG00000138834 |
23162 |
MAPK8IP3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPT6 |
FUNCTION: The JNK-interacting protein (JIP) group of scaffold proteins selectively mediates JNK signaling by aggregating specific components of the MAPK cascade to form a functional JNK signaling module (PubMed:12189133). May function as a regulator of vesicle transport, through interactions with the JNK-signaling components and motor proteins (By similarity). Promotes neuronal axon elongation in a kinesin- and JNK-dependent manner. Activates cofilin at axon tips via local activation of JNK, thereby regulating filopodial dynamics and enhancing axon elongation. Its binding to kinesin heavy chains (KHC), promotes kinesin-1 motility along microtubules and is essential for axon elongation and regeneration. Regulates cortical neuronal migration by mediating NTRK2/TRKB anterograde axonal transport during brain development (By similarity). Acts as an adapter that bridges the interaction between NTRK2/TRKB and KLC1 and drives NTRK2/TRKB axonal but not dendritic anterograde transport, which is essential for subsequent BDNF-triggered signaling and filopodia formation (PubMed:21775604). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ESN9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12189133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21775604}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene shares similarity with the product of Drosophila syd gene, required for the functional interaction of kinesin I with axonal cargo. Studies of the similar gene in mouse suggested that this protein may interact with, and regulate the activity of numerous protein kinases of the JNK signaling pathway, and thus function as a scaffold protein in neuronal cells. The C. elegans counterpart of this gene is found to regulate synaptic vesicle transport possibly by integrating JNK signaling and kinesin-1 transport. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23162; |
axon [GO:0030424]; axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; cell body [GO:0044297]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; JUN kinase binding [GO:0008432]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; MAP-kinase scaffold activity [GO:0005078]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; anterograde axonal protein transport [GO:0099641]; axon development [GO:0061564]; axon regeneration [GO:0031103]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046328]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
12189133_demonstration that JSAP1 bound ASK1 and enhanced ASK1- and H2O2-induced JNK activity 15532711_Pressure application of 160 mmHg for 3 h produced cell proliferation and activated ERK and c-JUN N-terminal kinase 15911620_JIP1 and JIP3, have a cross-talk that leads to the regulation of the ASK1-SEK1-JNK signal during glucose deprivation; cross-talk between JIP3 and JIP1 is mediated through SEK1-JNK2 and Akt1. 16141199_JSAP1.FAK complex functions cooperatively as a scaffold for the JNK signaling pathway and regulator of cell migration on FN 19036714_Upon UVB-induced stress in keratinocytes, ROCK1 was activated, bound to JIP-3, and activated the JNK pathway 19574423_Cyclic mechanical strain impairs signaling of cell migration after injury via a pathway that involves FAK-JIP3-JNK. 20018857_Expression of constitutively active PI3K stimulated translocation of Tiam1 to the membrane, increased Rac1 activity, and increased wound healing of airway epithelial cells. Increased Rac1 activity resulted in increased phosphorylation of JNK1. 21775604_This study demonistrated that JIP3 mediates TrkB axonal anterograde transport and enhances BDNF signaling by directly bridging TrkB with kinesin-1. 22072677_The results of this study finding suggested that a model by which the self-assembly of SYD-2/Liprin-alpha proteins mediated by the coiled-coil LH1 domain is one of the key steps to the accumulation of presynaptic components at nascent synaptic junctions 26002316_Results demonstrated the increased expression of JIP3 in the temporal neocortex of TLE patients and in the experimental model of epileptic seizures 26320416_JSAP1 and JLP play critical roles in kinesin-1-dependent axonal transport 26919523_The crystal structure of an N-terminally truncated form of LZII of JIP3 alone shows an unexpected antiparallel arrangement. 29604277_JIP3 was highly expressed in hearts with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The findings indicated that blockage of JIP3 could alleviate cardiac hypertrophy via inactivating JNK pathway, and thus might be a promising strategy to prevent pathological cardiac hypertrophy. 30612693_implication of de novo variants in MAPK8IP3 as a cause of a neurodevelopmental disorder with intellectual disability and variable brain anomalies 30945334_MAPK8IP3 variants cause a neurodevelopmental disease which includes spastic diplegia, intellectual disability, cerebral atrophy and corpus callosum hypoplasia. 30969891_in HT1080 cells, a human fibrosarcoma cell line, a requirement for microtubules, dynein, the JIP3 microtubule motor scaffold protein, and Arf6, a JIP3 interacting protein, for the formation and inward movement of the macropinosome, is reported. 31690808_Structural characterization of the RH1-LZI tandem of JIP3/4 highlights RH1 domains as a cytoskeletal motor-binding motif. 33788575_Overlapping roles of JIP3 and JIP4 in promoting axonal transport of lysosomes in human iPSC-derived neurons. 34014261_Sequential dynein effectors regulate axonal autophagosome motility in a maturation-dependent pathway. 35013510_JIP3 links lysosome transport to regulation of multiple components of the axonal cytoskeleton. 35829703_JIP3 interacts with dynein and kinesin-1 to regulate bidirectional organelle transport. |
ENSMUSG00000024163 |
Mapk8ip3 |
1019.893366 |
0.3286474102 |
-1.605387 |
0.122852259 |
164.993972 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000009175435362598271802434724561233819209476868358065992167742998756401255565237880511405080130666787018023367039631921215914189815521240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001451547973761527302159234511595395043024303441430228047570608318436877171983001392713370230496718049639781611404032446444034576416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
498.1792692 |
59.9245659 |
1526.5009648 |
131.6472590 |
| ENSG00000138835 |
5998 |
RGS3 |
protein_coding |
P49796 |
FUNCTION: Down-regulates signaling from heterotrimeric G-proteins by increasing the GTPase activity of the alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. Down-regulates G-protein-mediated release of inositol phosphates and activation of MAP kinases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10749886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11294858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8602223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9858594}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal transduction inhibitor;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS) family. This protein is a GTPase-activating protein that inhibits G-protein-mediated signal transduction. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Long isoforms are largely cytosolic and plasma membrane-associated with a function in Wnt signaling and in the epithelial mesenchymal transition, while shorter N-terminally-truncated isoforms can be nuclear. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:5998; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11985497_Data are consistent with the model wherein 14-3-3 serves as a scavenger of RGS3, regulating the amounts of RGS3 available for binding G-proteins. 12210723_C2PA is expressed in the cell nucleus and induces heat shock response element (HSE)-dependent gene transcription 15383626_RFS3 promoted the conversion of more stable Ca2+ elevations into oscillatory signals. 16821082_mRNA expression of CCT5, RGS3, and YKT6 was significantly up-regulated in p53-mutated tumors and associated with a low response rate to docetaxel. 16855219_Full-length RGS3, RGS3T, and the core domain of RGS3 were equally effective in antagonizing inhibition of Ca(V)2.3 through M(2)R. 17300916_RGS3L functions as a molecular switch, redirecting Gi-coupled receptors via Gbetagamma-dimers and PI3K from Rac1 to RhoA activation. 18287247_This study identifies a novel, noncanonical role of RGS3 in regulation of TGF-beta signaling through its interaction with Smads and interfering with Smad heteromerization. 19333232_in apoptosis-initiated cells, the ligand-dependent C5aR-mediated dual signal affects the fate of cells, either apoptosis execution or survival, through regulation of RGS3 gene expression and subsequent modulation of ERK signal. 19778949_Regulator of G-protein signalling 3 (RGS3) showed a difference between follicular cells from follicles leading to a pregnancy or developmental failure. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20347994_14-3-3 protein binding induces structural changes in both the N-terminal part and the C-terminal RGS domain of phosphorylated RGS3 molecule 20627871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22027839_Results suggest that the 14-3-3 protein binding affects the structure of the Galpha interaction portion of RGS3 as well as sterically blocks the interaction between the RGS domain and the Galpha subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins. 22859293_PDZ-RGS3 can enhance signals generated by the Wnt canonical pathway and plays a pivotal role in epithelial mesenchymal transition 24297163_ectopic expression of R4 subfamily members RGS2, RGS3, RGS4, and RGS5 reduced activated PAR1 wild-type signaling, whereas signaling by the PAR1 AKKAA mutant was minimally affected. 24375609_cardiac overexpression of RGS3 inhibits maladaptive hypertrophy and fibrosis and improves cardiac function by blocking MEK-ERK1/2 signaling 26416661_Our data provide a novel miR-25/RGS3 signal in the development of lung cancer. 27754994_Findings suggest that overexpressed RGS3 regulated by microRNA-126 through the post-transcriptional modulation is associated significantly with a poor prognosis of GC patients. 30006548_It has been reported that mitotic kinesin KIF20A interacts with RGS3 and plays a crucial role in controlling the division modes of neural progenitor cells during cortical neurogenesis. 30971721_A Multi-Trait Approach Identified Genetic Variants Including a Rare Mutation in RGS3 with Impact on Abnormalities of Cardiac Structure/Function. 31364749_The present study revealed that miR1263p plays a role as a tumor suppressor in regulating TNBC cell activities by targeting RGS3. 32928707_Regulator of G-protein signalling 3 and its regulator microRNA-133a mediate cell proliferation in gastric cancer. 34618566_The G protein signaling regulator RGS3 enhances the GTPase activity of KRAS. 36214767_Pseudogene UBE2MP1 derived transcript enhances in vitro cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through miR-145-5p/RGS3 axis. 36318984_RGS3 and IL1RAPL1 missense variants implicate defective neurotransmission in early-onset inherited schizophrenias. |
ENSMUSG00000059810 |
Rgs3 |
171.455152 |
6.5515102145 |
2.711828 |
0.170397637 |
263.789400 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002561769127372159840198388727112762625264240169011009756326193036949193128900730406403952884181801282729473358053355399105105400501234084560932350574033455892219990346347913146018981933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000646354056752360277211502568712292529599943106444447367555253907638783919593053605431113613138737295982928666475972828093593316121453567506716271495736947372279246337711811065673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
296.1674384 |
31.9555236 |
45.3877133 |
4.1481561 |
| ENSG00000138964 |
64098 |
PARVG |
protein_coding |
Q9HBI0 |
FUNCTION: Probably plays a role in the regulation of cell adhesion and cytoskeleton organization. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Members of the parvin family, including PARVG, are actin-binding proteins associated with focal contacts.[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2004]. |
hsa:64098; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; cell projection assembly [GO:0030031]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446] |
11722847_Mammalian parvins are likely to have arisen late in evolution from gene duplication as they share a remarkably similar exon/intron organization. 15993274_INI1hSNF5 and PARVG do not seem to be the tumor suppressor genes involved in oligodendroglioma development and progression 16517730_integrin-linked kinase-gamma-parvin complex is critically involved in the initial integrin signaling for leukocyte migration 23146538_Suggest role for PARVG gene polymorphisms in operational renal allograft tolerance. |
ENSMUSG00000022439 |
Parvg |
828.482678 |
0.3429147126 |
-1.544078 |
0.057078812 |
764.291732 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000313258806977301556101427738315336603970200360412469168242685766880898296444252045136528512961005251026654319286038098468761607363909747716312393271686241736826023 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000234705583298729482870148838711364342722963535134337696406028093829705855880361156608431457939884133530499474689323249891700513215615504149566108607347843601407281 |
Yes |
Yes |
427.6449534 |
18.0172906 |
1256.6818402 |
33.3042623 |
| ENSG00000139174 |
144165 |
PRICKLE1 |
protein_coding |
Q96MT3 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the planar cell polarity pathway that controls convergent extension during gastrulation and neural tube closure. Convergent extension is a complex morphogenetic process during which cells elongate, move mediolaterally, and intercalate between neighboring cells, leading to convergence toward the mediolateral axis and extension along the anteroposterior axis. Necessary for nuclear localization of REST. May serve as nuclear receptor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21901791}. |
Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;LIM domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear receptor that may be a negative regulator of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. The encoded protein localizes to the nuclear membrane and has been implicated in the nuclear trafficking of the transcription repressors REST/NRSF and REST4. Mutations in this gene have been linked to progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 3. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:144165; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anterior visceral endoderm cell migration [GO:1905070]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; coronary vasculature development [GO:0060976]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; embryonic brain development [GO:1990403]; establishment of bipolar cell polarity involved in cell morphogenesis [GO:0061159]; extracellular matrix assembly [GO:0085029]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation [GO:2000691]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; primitive streak formation [GO:0090009]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:0060071] |
12525887_PRICKLE1 and PRICKLE2 mRNAs were expressed together in brain, eye and testis. 12941693_A physical and functional interaction between Prickle and Strabismus was found in Drosophila and Xenopus, but is likely conserved in human, too. 14645515_appears to serve as a nuclear receptor for REST/NRSF, REST4, and possibly other transcription factors 16764822_NRSF/REST functions as a repressor of TH transcription in NSCs via a mechanism dependent on the TH NRSE/RE1 sites. 17030191_Prickle-1 is a negative regulator of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and is a putative tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma 18976727_A homozygous mutation in PRICKLE1 causes an autosomal-recessive progressive myoclonus epilepsy-ataxia syndrome. 19252133_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20842693_PRICKLE1 mutations are not a frequent cause of progressive myoclous epilepsies in Southern Italy. 21276947_Mutations in prickle1 causes seizures. 21901791_study demonstrates that PRICKLE1 could act as a predisposing factor to human neural tube defects 22037766_MINK1 interacts with and phosphorylates PRICKLE1 and PRICKLE2. 24312498_these findings suggest PRICKLE1 mutations contribute to ASD by disrupting the interaction with SYN1 and regulation of synaptic vesicles. 27036398_Our experimental data demonstrate that high expression of Prickle1 and Vangl2 reduce the growth of neuroblastoma cells and indicate different roles of PCP proteins in tumorigenic cells compared to normal cells. 27184734_upregulation of PRICKLE1 in basal breast cancers, a subtype characterized by high metastatic potential, is associated with poor metastasis-free survival. 27378169_Prickle1 localized to the membrane through its farnesyl moiety, and the membrane localization was necessary for Prickle1 to regulate migration, to bind to CLASPs and LL5beta, and to promote microtubule targeting of focal adhesions. 30345727_This clinical report highlights the fact that in the context of an epileptic encephalopathy with developmental arrest, early onset severe PME-ataxia syndrome can be a PRICKLE1-associated phenotype 30564977_showed that the patient's father (p.Asp760del) and mother (p.Asp201Asn) each had a mutation in prickle1 30971775_Authors used a proteomic approach to identify protein complexes associated with PRICKLE1. The mRNA expression levels of the corresponding genes were assessed in 8982 patients with invasive primary breast cancer. AUthors then characterised the molecular interaction between PRICKLE1 and the guanine nucleotide exchange factor ECT2. 34001134_PRICKLE1, a Wnt/PCP signaling component, is overexpressed and associated with inferior prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000036158 |
Prickle1 |
87.487026 |
0.0900368290 |
-3.473341 |
0.249605039 |
228.852809 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000106054364728700996590652037237120374512840113834410545249365029428580861061011211089027160155527818128419039977530719805135430854232947428528177624684758484363555908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023610292962226645131669395923782954119673276444744643145281257808705130050689443565975064031854435423394698230424457963457375141852478961368433374445885419845581054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.7582270 |
2.3236030 |
154.2289476 |
12.8936424 |
| ENSG00000139178 |
51279 |
C1RL |
protein_coding |
Q9NZP8 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the proteolytic cleavage of HP/haptoglobin in the endoplasmic reticulum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15358180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15385675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15527420}. |
Complement pathway;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Sushi |
|
Predicted to enable serine-type endopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in zymogen activation. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51279; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; zymogen activation [GO:0031638] |
15358180_CLSPa itself possesses little protease activity, but it plays an inhibitory role in other active protease catalytic processes 15385675_coexpression of the proform of Hp (proHp) and C1r-LP effected cleavage of proHp in the endoplasmic reticulum 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32993564_Immunological and clinicopathological characteristics of C1RL in 2120 glioma patients. |
ENSMUSG00000038527 |
C1rl |
49.022181 |
0.4831410607 |
-1.049484 |
0.247544443 |
18.110119 |
0.00002084905139424424413930811428308231825212715193629264831542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000063059835774394482846988418955902488960418850183486938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.3140239 |
5.1768428 |
63.1837111 |
7.0328713 |
| ENSG00000139190 |
6843 |
VAMP1 |
protein_coding |
P23763 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the targeting and/or fusion of transport vesicles to their target membrane. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Congenital myasthenic syndrome;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Synaptosome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Synapotobrevins, syntaxins, and the synaptosomal-associated protein SNAP25 are the main components of a protein complex involved in the docking and/or fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)/synaptobrevin family. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal dominant spastic ataxia 1. Multiple alternative splice variants have been described, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been defined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:6843; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; SNARE complex assembly [GO:0035493]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
18457912_The expression of the SNARE protein SNAP-25 and its cellular homologue SNAP-23, as well as syntaxin1 and VAMP (vesicle-associated membrane protein) in samples of normal parathyroid tissue, chief cell adenoma, and parathyroid carcinoma, was examined. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21330375_multiple domains outside the R-SNARE of tomosyn are critical to the efficacy of inhibition by tomosyn on exocytotic secretion 22958904_This report identifies vesicle-associated membrane protein 1 (VAMP1), which encodes a critical protein for synaptic exocytosis, as the responsible gene fora dominantly inherited spastic ataxia 25010769_residue 48 of VAMP1 varies frequently between M and I across seventeen closely related primate species, suggesting a potential selective pressure from members of BoNTs for resistance in vertebrates. 25881291_Genetically regulated VAMP1 expression in the brain may modify both Alzheimer's disease risk and may contribute to Alzheimer's pathophysiology 28253535_VAMP1 homozygous mutations causes of presynaptic congenital myasthenic syndrome. 33631708_Recessive VAMP1 mutations associated with severe congenital myasthenic syndromes - A recognizable clinical phenotype. 34454100_Prefrontal cortex VAMP1 gene network moderates the effect of the early environment on cognitive flexibility in children. |
ENSMUSG00000030337 |
Vamp1 |
20.864331 |
0.4240842912 |
-1.237577 |
0.508324620 |
5.638142 |
0.01757382509552111657380457643284898949787020683288574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031917024536716090410415347378147998824715614318847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.4565479 |
4.2039608 |
34.8275734 |
6.8050392 |
| ENSG00000139192 |
55080 |
TAPBPL |
protein_coding |
Q9BX59 |
FUNCTION: Component of the antigen processing and presentation pathway, which binds to MHC class I coupled with beta2-microglobulin/B2M. Association between TAPBPR and MHC class I occurs in the absence of a functional peptide-loading complex (PLC). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23401559, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26869717}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Microsome;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Tapasin, or TAPBP (MIM 601962), is a member of the variable-constant Ig superfamily that links major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules to the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP; see MIM 170260) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The TAPBP gene is located near the MHC complex on chromosome 6p21.3. TAPBPL is a member of the Ig superfamily that is localized on chromosome 12p13.3, a region somewhat paralogous to the MHC.[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:55080; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; MHC class I protein complex binding [GO:0023024]; negative regulation of antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I [GO:0002590]; peptide antigen assembly with MHC class I protein complex [GO:0002502]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776] |
18340469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21362330_HLA-I, TAP1, CNX, LMP7, Erp57, Tapasin and ERAP1 were down-regulated in 68%, 44%, 48%, 40%, 52%, 32% and 20% of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma lesions then, respectively. 23401559_The function of the tapasin-related protein, TAPBPR, was investigated. 24163410_the data indicate that TAPBPR and tapasin bind in a similar orientation to the same face of MHC class I. 24444341_The longer TAPBPR protein interacted with MHC class I but was attenuated in its ability to down-regulate surface expression of MHC class I. 25720504_TAPBPR is a new player in the MHC class I presentation pathway. (Review) 26439010_It is now clear there are two MHC class I specific peptide editors, tapasin and TAPBPR, intimately involved in controlling peptide presentation to the immune system. 26869717_These results support a role of TAPBPR in stabilizing peptide-receptive conformation(s) of MHC-I, permitting peptide editing. 28425917_The authors identify an interaction between TAPBPR and UDP-glucose:glycoprotein glucosyltransferase 1 (UGT1), a folding sensor in the calnexin/calreticulin quality control cycle that is known to regenerate the Glc1Man9GlcNAc2 moiety on glycoproteins. The results suggest the formation of a multimeric complex, dependent on a conserved cysteine at position 94 in TAPBPR, in which TAPBPR promotes the association of UGT1 with p 29025991_this study reports the crystal structure of MHC I in complex with the peptide editor TAPBPR (TAP-binding protein-related), a tapasin homolog. 29025996_this study presents the x-ray structure of the TAPBPR-MHC I complex, which delineates the central step of catalysis. 29988068_The results demonstrate an inverse relationship between MHC-I peptide occupancy and TAPBPR binding affinity, wherein the lifetime and structural features of transiently bound peptides control the regulation of a conformational switch located near the TAPBPR binding site, which triggers TAPBPR release. 30077416_The ability of TAPBPR to interact with MHC class I molecules outside of the ER. 30213851_soluble TAPBPR, consisting of the luminal domain alone, added to intact cells, also functions as an effective peptide editor on surface MHC I molecules. 30484775_Data suggest therapeutic potential of TAP binding protein like tapasin-related protein (TAPBPR) manipulation to increase tumour immunogenicity. 31693900_Distinct Polymorphisms in HLA Class I Molecules Govern Their Susceptibility to Peptide Editing by TAPBPR. 32167472_A loop structure allows TAPBPR to exert its dual function as MHC I chaperone and peptide editor. 32814254_The Ins and Outs of TAPBPR. 34039964_TAPBPR promotes antigen loading on MHC-I molecules using a peptide trap. 34052734_Why TAPBPR? Implications of an additional player in MHC class I peptide presentation. 34265495_The role of MHC I protein dynamics in tapasin and TAPBPR-assisted immunopeptidome editing. |
ENSMUSG00000038213 |
Tapbpl |
88.290177 |
0.3587350220 |
-1.479009 |
0.175388561 |
72.597346 |
0.00000000000000001589927111288675369788176166033843810369142782418054593573941701833973638713359832763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000125292707755583800297212627281071496937878481789038764837584949418669566512107849121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
46.9862382 |
5.2448716 |
131.8330091 |
9.4618105 |
| ENSG00000139220 |
8499 |
PPFIA2 |
protein_coding |
O75334 |
FUNCTION: Alters PTPRF cellular localization and induces PTPRF clustering. May regulate the disassembly of focal adhesions. May localize receptor-like tyrosine phosphatases type 2A at specific sites on the plasma membrane, possibly regulating their interaction with the extracellular environment and their association with substrates. In neuronal cells, is a scaffolding protein in the dendritic spines which acts as immobile postsynaptic post able to recruit KIF1A-driven dense core vesicles to dendritic spines (PubMed:30021165). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30021165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9624153}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the LAR protein-tyrosine phosphatase-interacting protein (liprin) family. Liprins interact with members of LAR family of transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatases, which are known to be important for axon guidance and mammary gland development. It has been proposed that liprins are multivalent proteins that form complex structures and act as scaffolds for the recruitment and anchoring of LAR family of tyrosine phosphatases. This protein has been shown to bind the calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (MAGUK family) protein (also known as CASK) and proposed to regulate higher-order brain functions in mammals. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:8499; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; dense core granule cytoskeletal transport [GO:0099519]; regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060998]; regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061001]; synapse organization [GO:0050808] |
12119554_Liprin-alpha2 expression is downregulated by androgens in prostate cancer cells. It might play a role in androgen-responsive human prostate cancer & the loss of this gene expression might be associated with the androgen-independence. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21855798_Liprins can mediate assembly of target proteins into large protein complexes capable of regulating numerous cellular activities. 23422819_3 genes identified by association study and supported by ocular expression and/or replication, UHRF1BP1L, PTPRR, and PPFIA2, are novel candidates for myopic development within the MYP3 locus that should be further studied. 26740234_mong the 22 cases, we identified PPFIA2 as a novel candidate gene forIntellect Analysis of copy-neutral loss of heterozygosity (CNLOH) detected one case in which the CNLOH regions seem to be significant. The SNP array detected a modest fraction of small causative CNVs, which is explained by the fact that the majority of causative CNVs have larger sizes, and those had been mostly identified in the two previous screenings. 30879928_Liprin alfa 2 gene expression is increased by cannabis use and associated with neuropsychological function. |
ENSMUSG00000053825 |
Ppfia2 |
158.030604 |
6.3573824784 |
2.668433 |
0.385534115 |
43.361184 |
0.00000000004551273532436762802024604731943133607147133901094093744177371263504028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000240949775246652138458887196112651399304560584369028219953179359436035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
222.0415076 |
102.2781499 |
35.7853735 |
11.9312416 |
| ENSG00000139324 |
160418 |
TMTC3 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZXV5 |
FUNCTION: Transfers mannosyl residues to the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine residues. The 4 members of the TMTC family are O-mannosyl-transferases dedicated primarily to the cadherin superfamily, each member seems to have a distinct role in decorating the cadherin domains with O-linked mannose glycans at specific regions. Also acts as O-mannosyl-transferase on other proteins such as PDIA3 (PubMed:28973932). Involved in the positive regulation of proteasomal protein degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and the control of ER stress response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21603654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28973932}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Lissencephaly;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28973932}. |
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the transmembrane and tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein family. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:160418; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0004169]; mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0000030]; positive regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901800]; protein O-linked mannosylation [GO:0035269]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
21603654_that SMILE is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response, by modulating proteasome activity and XBP-1 transcript expression. This function of SMILE may influence immune cell behavior in the context of transplantation. 21956870_SMILE is a novel transgene specifying both bronchial smooth muscle and lung alveolar myofibroblast lineages, contributing to the understanding of the biological control of the development of these cells. 28973932_O-mannosylation pathway dedicated to cadherins/ protocadherins orchestrated by the four TMTC1-4 genes 33436046_Conserved sequence motifs in human TMTC1, TMTC2, TMTC3, and TMTC4, new O-mannosyltransferases from the GT-C/PMT clan, are rationalized as ligand binding sites. 34794738_The deep infiltrating endometriosis tissue has lower T-cadherin, E-cadherin, progesterone receptor and oestrogen receptor than endometrioma tissue. 35982901_A Novel ER Stress Mediator TMTC3 Promotes Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression by Activating GRP78/PERK Signaling Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000036676 |
Tmtc3 |
91.995826 |
2.7553924392 |
1.462258 |
0.194861971 |
56.661494 |
0.00000000000005176737064608357222438607640109267159705475416786590869833162287250161170959472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000334246015195185297904126653072803246249250497257321512734051793813705444335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
136.7688097 |
15.4412208 |
50.0050029 |
4.5055275 |
| ENSG00000139428 |
326625 |
MMAB |
protein_coding |
Q96EY8 |
FUNCTION: Converts cob(I)alamin to adenosylcobalamin (adenosylcob(III)alamin), a coenzyme for methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, therefore participates in the final step of the vitamin B12 conversion (PubMed:12514191). Generates adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) and directly delivers the cofactor to MUT in a transfer that is stimulated by ATP-binding to MMAB and gated by MMAA (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12514191, ECO:0000305|PubMed:28497574}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide |
|
This gene encodes a protein that catalyzes the final step in the conversion of vitamin B(12) into adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), a vitamin B12-containing coenzyme for methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. Mutations in the gene are the cause of vitamin B12-dependent methylmalonic aciduria linked to the cblB complementation group. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]. |
hsa:326625; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase activity [GO:0008817]; cobalamin binding [GO:0031419]; transferase activity, transferring alkyl or aryl (other than methyl) groups [GO:0016765]; cobalamin metabolic process [GO:0009235] |
12514191_report the identification of ATR cDNA as well as the corresponding gene; ATR expression is altered in cell lines derived from cblB methylmalonyl aciduria patients; propose that inborn errors in the ATR gene identified here result in methylmalonyl aciduria 15347655_Results describe two common polymorphic variants of ATP:cob(I)alamin adenosyltransferase that are found in normal individuals, and their interactions with methionine synthase reductase. 17410422_Mutations in methylmalonic aciduria type B protein is associated with methylmalonic acidemia 17597648_Long-term outcome in methylmalonic acidurias is influenced by the underlying genetic defects in MCM/MMAA/MMAB. 17957493_Methylmalonic acidaemia: examination of genotype and biochemical data in 32 patients belonging to mut, cblA or cblB complementation group. 18193043_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18251506_Results functionally defined the hATR active site and tentatively implicated three amino acid residues in facilitating the reduction of cob(II)alamin to cob(I)alamin which is a prerequisite to adenosylation. 19487539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605566_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19605566_homozygotes for the major allele (G) at MMAB_3U3527G-->C had higher LDL-cholesterol concentrations than did carriers of the minor allele (P = 0.034). 19625202_Characterization of ligand-binding by MMAB provides insight into the mechanism of cobalamin adenosylation and the effect of patient mutations in the inherited disorder 20159775_These data suggest MMAB is the most likely gene influencing high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels at MMAB-MVK locus. 20160193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20430392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20556797_c.584G>A, c.349-1G>C, and c.290G>A mutations affect the splicing process of ATR. 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20972250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21604717_Pathogenicity of the human truncation mutant results from its inability to sequester AdoCbl for direct transfer to methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, resulting in holoenzyme formation. 23707710_MMAB mutations, including one novel nonsense mutation (c.12 C>A [p.C4X]), were identified in all members of the cblB cohort. 27716295_These findings suggest that rs11066782 in KCTD10, rs11613718 in KCTD10 and rs11067233 in MMAB may contribute to the susceptibility of coronary heart disease by altering plasma HDL-C levels in Han Chinese. 29190729_MMAB might be a target and potential biomarker of hepatotoxicity in EFV-induced liver toxicity 29197662_analysis of how molecular chaperones interact with ATR in methylmalonic aciduria cblB type 31203192_A genetic epidemiological study in British adults and older adults shows a high heritability of the combined indicator of vitamin B12 status (cB12) and connects B12 status with utilization of mitochondrial substrates and energy metabolism. 34750386_MMAB promotes negative feedback control of cholesterol homeostasis. |
ENSMUSG00000029575 |
Mmab |
86.942684 |
2.0789017301 |
1.055822 |
0.173941524 |
36.919805 |
0.00000000123089228071469966128014462589893712740618525458557996898889541625976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005836161279585277026229482068026693797335724411823321133852005004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
117.9977907 |
14.7493143 |
57.0972207 |
5.4010196 |
| ENSG00000139438 |
84915 |
FAM222A |
protein_coding |
Q5U5X8 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:84915; |
|
31964863_Study reports FAM222A as a putative brain atrophy susceptibility gene. The protein encoded by FAM222A is predominantly expressed in the CNS and is increased in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and in an AD mouse model. It accumulates within amyloid deposits, physically interacts with amyloid-beta (Abeta) via its N-terminal Abeta binding domain and facilitates Abeta aggregation. |
ENSMUSG00000041930 |
Fam222a |
54.862411 |
6.4403576072 |
2.687141 |
0.256377986 |
125.242354 |
0.00000000000000000000000000004504346578313862023977439073587885858841502388766575355182207519505361854438713065107435795653145760297775268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000561996242568999186330991596589366634774781532120528735826709009536687820362405032525998649362009018659591674804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.5909682 |
16.4854890 |
15.7167350 |
2.2889161 |
| ENSG00000139514 |
6541 |
SLC7A1 |
protein_coding |
P30825 |
FUNCTION: High-affinity, low capacity permease involved in the transport of the cationic amino acids (arginine, lysine and ornithine) in non-hepatic tissues. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10485994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9174363}. |
Amino-acid transport;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables L-arginine transmembrane transporter activity and L-histidine transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in amino acid transport. Located in membrane. Part of apical plasma membrane; basolateral plasma membrane; and protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:6541; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015171]; basic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015174]; L-arginine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0061459]; L-histidine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005290]; L-lysine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015189]; L-ornithine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0000064]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; amino acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0089718]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; L-amino acid transport [GO:0015807]; L-arginine import across plasma membrane [GO:0097638]; L-arginine transmembrane transport [GO:1903826]; L-histidine import across plasma membrane [GO:1903810]; L-ornithine transmembrane transport [GO:1903352]; lysine transport [GO:0015819]; ornithine transport [GO:0015822]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11665818_analysis of the genomic organization 11891586_Stable polarized expression of hCAT-1 in an epithelial cell line. 12787129_Keratinocytes express cationic amino acid transporters 1 and 2. Cationic amino acid transporter mediated L-arginine essential for inducible nitric oxide synthase and arginase enzyme, which modulate proliferation and differentiation of epidermal cells. 15064952_Insulin-mediated stimulation of the L-arginine/NO pathway is thus associated with increased hCAT-1 and hCAT-2B mRNA, and eNOS expression 15086470_Glomerular arginine uptake is elevated through modulation of CAT-1 expression, thus, contributing to the pathogenesis of hyperfiltration. Increased nitric oxide formation may play a role in this process. 15491978_protein kinase C(PKC) did not phosphorylate human cationic amino acid transporter hCAT-1 directly as evidenced by in vivo phosphorylation experiments and mutational analysis, indicating an indirect action of PKC on hCAT-1 15631944_The CAT-1 is thought to supply substrate to endothelial NOS by virtue of its co-localisation with this enzyme. 17325243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17325243_The present study identifies a key functionally active polymorphism in the 3'UTR of SLC7A1 [which] may account for the apparent link between altered endothelial function, L-arginine, and nitric oxide metabolism and predisposition to essential hypertension 17494634_Ornithine uptake in retinal pigment epithelium is depdendent on induction of SLC7A1 mRNA and spermine. 18172665_distribution of human cationic amino acid transporters 1 (hCAT1) and 2 (hCAT2) in healthy skin and compared it to psoriatic skin lesions by means of immunohistochemistry 18574322_CAT1 is directly involved in erythropoiesis through supplying arginine to the blood cells. 19067360_Data provide novel insights into the mechanism by which ss52051869 influences SLC7A1 gene expression. 21212261_PKC activation also resulted in ubiquitination of CAT-1 21302286_Insulin increased hCATs-L-arginine transport, maximal transport capacity, and hCAT-1 expression. Sp1 nuclear protein abundance and binding to DNA, and SLC7A1 promoter activity was increased by insulin. 21308737_Data show that the CAT-1 isoform plays a role in arginine uptake. 21722652_In acute congestive heart failure acute renal impairment function and the modulation of metabolism and extracellular transport by the DDAH-1/CAT-1 system determine high ADMA and SDMA levels after therapy for acute congestive heart failure. 21923750_In hypoxic human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells, overexpression of CAT-1 resulted in significantly greater L-arginine transport and NO production 22705145_The data demonstrates that CAT1 significantly (but most likely not exclusively) contributes to the cellular uptake of asymmetric dimethylarginine. 22870827_CAT1, CAT2, and CAT3 localized in adult brains but with uneven distribution. 23009292_mRNA levels for high-affinity CAT-1, expressed as a percentage of the wild-type value, are increased by an average 12% and 32% in mdx and transgenic mdx:utr mice respectively. 23841815_The rs41318021 polymorphism in the SLC7A1 gene was not associated with essential hypertension in 50-year-old subjects. 24040099_Overexpression of arginine transporter CAT-1 is associated with accumulation of L-arginine and cell growth in human colorectal cancer tissue. 26062636_Estradiol increases arginine transport and CAT-1 activity through modulation of constitutive signaling transduction pathways involving ERK. Progesterone inhibits arginine transport and CAT-1 via both PKCalpha and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. 28684763_L-homoarginine is a substrate of the cationic amino acid transporters CAT1, CAT2A and CAT2B. 32008093_Human cationic amino acid transporters are not affected by direct nitros(yl)ation. 34314821_High total cholesterol and triglycerides levels increase arginases metabolism, impairing nitric oxide signaling and worsening fetoplacental endothelial dysfunction in gestational diabetes mellitus pregnancies. |
ENSMUSG00000041313 |
Slc7a1 |
394.219285 |
4.2049139800 |
2.072076 |
0.086557195 |
609.695002 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001303427531597265322759493930691064546252176688433430261506189084782819164839331617384330587278619408287795087209034371235837192370412870570664403649914909933893245171263471360735039832638128235605 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000728734483574834606087739544935295464916262796944077114717078615211721469686769705652189134429203395309150035688494325863349577399891985137314956735145365479458265552602677695783567050192499955650 |
Yes |
No |
642.4406621 |
34.3851334 |
153.9811214 |
7.0246264 |
| ENSG00000139572 |
53831 |
GPR84 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQS5 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for medium-chain free fatty acid (FFA) with carbon chain lengths of C9 to C14. Capric acid (C10:0), undecanoic acid (C11:0) and lauric acid (C12:0) are the most potent agonists. Not activated by short-chain and long-chain saturated and unsaturated FFAs. Activation by medium-chain free fatty acid is coupled to a pertussis toxin sensitive G(i/o) protein pathway. May have important roles in processes from fatty acid metabolism to regulation of the immune system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16966319}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable urotensin II receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in neuropeptide signaling pathway. Part of receptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:53831; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; urotensin II receptor activity [GO:0001604]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218] |
23449982_Medium-chain fatty acid-sensing receptor, GPR84, is a proinflammatory receptor. 25293777_A previously unrecognized role of GPR84 in maintaining fully developed acute myeloid leukemia by sustaining aberrant beta-catenin signaling in leukemic stem cells. 25425658_concluded that diindolylmethane was a positive allosteric modulator for GPR84 28404994_GPR84 modulates TNFalpha mRNA expression in the LPS tolerant monocytes. 28835131_Data suggest that cytokines TNFalpha and interleukin-1b markedly reduce GPR120/FFAR4 expression in adipocytes; in contrast, these cytokines induce expression of GPR84 and GPR41/FFAR3 in adipocytes. These studies were conducted in adipocytes cultured from subcutaneous adipose tissue. (GPR = G-protein coupled receptor; FFAR = free fatty acid receptor) 29477577_we show functional similarities but also some important differences between GPR84 and FFA2R in human phagocytes, thus providing some mechanistic insights into GPR84 regulation in blood neutrophils and cells recruited to an aseptic inflammatory site in vivo. 29775920_Has a strong stimulatory effect on the expression of cytokine and chemokine genes, particularly CSF3, and on the expression of GPR84, a pro-inflammatory fatty acid receptor. 32102673_Natural biased signaling of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 and G protein-coupled receptor 84. 33001759_20 Years an Orphan: Is GPR84 a Plausible Medium-Chain Fatty Acid-Sensing Receptor? 33789297_The Two Formyl Peptide Receptors Differently Regulate GPR84-Mediated Neutrophil NADPH Oxidase Activity. 34497417_Inter-cellular CRISPR screens reveal regulators of cancer cell phagocytosis. 34968686_Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 and GPR84 - Two metabolite-sensing G protein-coupled receptors with opposing functions in innate immune cells. |
|
|
373.004475 |
8.8704053827 |
3.149000 |
0.108076186 |
996.154779 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001230495456746291126471565554198571827990289786929210823053697658610432235747284394086257005700731920936884016998 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001297293781541089872450507998174455277535466611693380885386430877921544051478357262534265631521433721155853054212 |
Yes |
No |
676.1499559 |
43.8797538 |
76.7951239 |
4.5783449 |
| ENSG00000139597 |
90634 |
N4BP2L1 |
protein_coding |
Q5TBK1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:90634; |
|
19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27184799_Cox proportional hazards analysis identified N4BP2L1 expression as an independent predictor of disease-free survival |
ENSMUSG00000041132 |
N4bp2l1 |
114.788272 |
0.2357593506 |
-2.084613 |
0.521573467 |
13.506212 |
0.00023777496238253298995596329845625405141618102788925170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000615280232252136526777119840403429407160729169845581054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.8890741 |
15.0208049 |
187.1429359 |
46.6557558 |
| ENSG00000139625 |
7786 |
MAP3K12 |
protein_coding |
Q12852 |
FUNCTION: Part of a non-canonical MAPK signaling pathway (PubMed:28111074). Activated by APOE, enhances the AP-1-mediated transcription of APP, via a MAP kinase signal transduction pathway composed of MAP2K7 and MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 (PubMed:28111074). May be an activator of the JNK/SAPK pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28111074}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Magnesium;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. This kinase contains a leucine-zipper domain and is predominately expressed in neuronal cells. The phosphorylation state of this kinase in synaptic terminals was shown to be regulated by membrane depolarization via calcineurin. This kinase forms heterodimers with leucine zipper containing transcription factors, such as cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) and MYC, and thus may play a regulatory role in PKA or retinoic acid induced neuronal differentiation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different proteins have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:7786; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; JUN kinase kinase kinase activity [GO:0004706]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; negative regulation of motor neuron apoptotic process [GO:2000672]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; post-translational protein modification [GO:0043687]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
14697235_for the selective expression of ZPK gene, cell-specific negative regulatory element(s) which locate outside of the core promoter region repress the potent basic promoter activity 15611134_ZIPK is positively regulated by phosphorylation within its kinase domain and contains an inhibitory C-terminal domain that controls enzyme activity. 15695824_DLK is a signaling molecule implicated in the regulation of keratinocyte terminal differentiation and cornification 18995835_DAPK-ZIPK-L13a axis forms a unique regulatory module that first represses, then repermits inflammatory gene expression. 19146952_Src-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation recombinant human DLK was important for regulation of its activity. DLK may have a role in PDGF signaling. 19675578_the DLK-ERK signaling pathway may act as a regulator of the interaction that occurs between Hsp27 and the cytoskeleton during the formation of the cornified cell envelope, a process conferring to the skin its crucial barrier function 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851984_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21526495_The results confirm the significance of apoptosis deregulation in CLL, and suggest a possible relationship between ZIPK expression and the clinical course of the disease. 21893036_these findings indicate that DLK participates in cell proliferation and/or survival, at least in part, by modulating the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins. 25341110_Data suggest that specific pharmacological inhibition of dual leucine zipper kinase (DLK, MAP3K12) may have therapeutic potential in multiple indications of neuronal degeneration. 25999017_miR-130a inhibited the JNK pathway by targeting MAP3K12, contributing to its anti-apoptotic effect and the maintenance of diabetic endothelial progenitor cell function. 27100796_REVIEW: Regulation of Beta-Cell Function and Mass by the Dual Leucine Zipper Kinase 28641113_LZK cooperates with DLK to promote retinal ganglion cell death in response to axon injury. 30009782_Aryl hydrocarbon receptor enhances the expression of miR-150-5p to suppress cell proliferation and invasion in prostate cancer by regulating MAP3K12 |
ENSMUSG00000023050 |
Map3k12 |
85.516991 |
0.2627523215 |
-1.928225 |
0.248318674 |
59.453325 |
0.00000000000001252293068832743582815196223271714092082338744271741148850196623243391513824462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000083599483021127515756040556877431585774897333795951936963319894857704639434814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.5023313 |
7.3621309 |
139.7984317 |
19.1802549 |
| ENSG00000139629 |
11226 |
GALNT6 |
protein_coding |
Q8NCL4 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the initial reaction in O-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis, the transfer of an N-acetyl-D-galactosamine residue to a serine or threonine residue on the protein receptor (PubMed:10464263, PubMed:31932717). May participate in synthesis of oncofetal fibronectin (PubMed:10464263). Has activity toward MUC1A, MUC2, EA2 and fibronectin peptides (PubMed:10464263). Glycosylates FGF23 (PubMed:31932717). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10464263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31932717}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lectin;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
This gene encodes a member of the UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T) family of enzymes. GalNAc-Ts initiate mucin-type O-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus by catalyzing the transfer of GalNAc to serine and threonine residues on target proteins. They are characterized by an N-terminal transmembrane domain, a stem region, a lumenal catalytic domain containing a GT1 motif and Gal/GalNAc transferase motif, and a C-terminal ricin/lectin-like domain. GalNAc-Ts have different, but overlapping, substrate specificities and patterns of expression. The encoded protein is capable of glycosylating fibronectin peptide in vitro and is expressed in a fibroblast cell line, indicating that it may be involved in the synthesis of oncofetal fibronectin. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11226; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0004653]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493]; protein O-linked glycosylation via threonine [GO:0018243] |
18854599_ppGalNAc-T6 is an IHC marker associated with venous invasion in gastric carcinoma and may contribute to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms that underlie aberrant glycosylation in gastric carcinogenesis and in gastric carcinoma. 19287074_Expression of ppGalNAc-T6 is significantly higher in breast cancer compared to 'normal'/benign breast tissue samples. ST6GalNAc-I expression in breast cancer is associated with better prognosis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21472136_GALNT6-fibronectin pathway should be a critical component for breast cancer development and progression. 27035742_Role of N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 6 in early tumorigenesis and formation of metastasis. 27237318_knockdown of GALNT6 caused drastic morphological changes of pancreatic cells, accompanied with the cadherin switching from P-cadherin to E-cadherin. 27659430_GalNAcT6 role in cancer [review] 28053144_These data suggest that excess O-glycosylation on APP by GalNAc-T6 inhibits Abeta production. 28110670_GALNT6-induced O-glycosylation is critical for the stability, subcellular localization, and anti-apoptotic function of GRP78 protein in cancer cells. We also suggest that GRP78 might enhance the activity of GALNT6 in carcinogenesis through driving Golgi-to-ER relocation of GALNT6. 28388560_GALNT6 knockdown decreased phosphorylation of EGFR, whereas GALNT6 overexpression increased the phosphorylation. Results suggest that GALNT6 expression is associated with poor prognosis of ovarian cancer and enhances the aggressive behavior of ovarian cancer cells by regulating EGFR activity. 28668893_Findings show that the expression of GalNAc-T6 in endometrial carcinoma is significantly related to E-cadherin expression, and better prognosis and overall survival. 28668894_Study showed that GalNAc-T6 expression in epithelial ovarian carcinoma was different according to pathological type. In low-grade serous carcinoma, GalNAc-T6 expression may contribute to improved long-term survival. 29187600_these data strongly suggest that aberrant GalNAc-T6 expression and site-specific glycosylation is involved in oncogenic transformation. 29844132_the 15-glycogene signature and the expression levels of GALNT6 mRNA and protein each serve as a novel prognostic biomarker, highlighting the role of dysregulated glycogenes in cancer-associated glycan synthesis and poor prognosis 30208353_O-glycosylation of ER-alpha by GALNT6 in breast cancer cells. 31071912_We confirmed that GALNT3 gene ablation leads to strong and rather compensatory GALNT6 upregulation in EOC cells. Moreover, double GALNT3/T6 suppression was significantly associated with stronger inhibitory effects on EOC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and accordingly displayed a significant increase in animal survival rates compared with GALNT3-ablated and control (Ctrl) EOC cells. 31894262_The GALNT6LGALS3BP axis promotes breast cancer cell growth. 32393740_GALNT6 promotes invasion and metastasis of human lung adenocarcinoma cells through O-glycosylating chaperone protein GRP78. 32559179_GALNT6 promotes breast cancer metastasis by increasing mucin-type O-glycosylation of alpha2M. 35909886_RUNX3-Regulated GALNT6 Promotes the Migration and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Mediating O-Glycosylation of MUC1. |
ENSMUSG00000037280 |
Galnt6 |
259.234560 |
3.3990867654 |
1.765147 |
0.100302202 |
323.499873 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000250360511929568743271186116459547842822951532440456337058283689571759126677085789456977501407985571341514479979915589712922449566663222854837560532917815542057478860584313651066641626119491093049873597919940948486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000076507684390899276048243268301250252327571985139244862827245734112221171291282046625967596826324737248708543902385386991983778618455239880620728929526423897833921599753032039004096986900549381971359252929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
401.8780467 |
27.8091171 |
119.2521431 |
6.7022719 |
| ENSG00000139631 |
51380 |
CSAD |
protein_coding |
Q9Y600 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-aspartate, 3-sulfino-L-alanine (cysteine sulfinic acid), and L-cysteate to beta-alanine, hypotaurine and taurine, respectively. The preferred substrate is 3-sulfino-L-alanine. Does not exhibit any decarboxylation activity toward glutamate. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DBE0}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Decarboxylase;Lyase;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Organosulfur biosynthesis; taurine biosynthesis; hypotaurine from L-cysteine: step 2/2. |
This gene encodes a member of the group 2 decarboxylase family. A similar protein in rodents plays a role in multiple biological processes as the rate-limiting enzyme in taurine biosynthesis, catalyzing the decarboxylation of cysteinesulfinate to hypotaurine. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:51380; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; aspartate 1-decarboxylase activity [GO:0004068]; carboxy-lyase activity [GO:0016831]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; sulfinoalanine decarboxylase activity [GO:0004782]; L-cysteine catabolic process to hypotaurine [GO:0019449]; L-cysteine catabolic process to taurine [GO:0019452]; taurine biosynthetic process [GO:0042412] |
22718265_The presence of cysteine inhibited ADC, CSAD and GDC activity. 26327310_taurine biosynthesis in vertebrates involves two structurally related PLP-dependent decarboxylases (cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase and glutamic acid decarboxylase like 1) |
ENSMUSG00000023044 |
Csad |
85.901344 |
0.3159593545 |
-1.662189 |
0.247868942 |
44.260693 |
0.00000000002874300633265530637817875785982685244920875611285282502649351954460144042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000154608882459909742544278893133184032970817156638076994568109512329101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.6218691 |
6.8860080 |
135.8044811 |
14.4915879 |
| ENSG00000139880 |
64403 |
CDH24 |
protein_coding |
Q86UP0 |
FUNCTION: Cadherins are calcium-dependent cell adhesion proteins. They preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells; cadherins may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types. Cadherin-24 mediate strong cell-cell adhesion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12734196}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables several functions, including alpha-catenin binding activity; beta-catenin binding activity; and delta-catenin binding activity. Acts upstream of or within cell-cell adhesion. Located in cell-cell junction. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64403; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; catenin complex [GO:0016342]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; alpha-catenin binding [GO:0045294]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; delta-catenin binding [GO:0070097]; adherens junction organization [GO:0034332]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; cell-cell junction assembly [GO:0007043]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156] |
12734196_cadherin-24 is a novel alternatively spliced type II cadherin 24898286_Unconventional CDH10, CDH24 and DCHS2 genes harbored frameshift mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000059674 |
Cdh24 |
908.511178 |
0.3159119439 |
-1.662406 |
0.060296951 |
775.173555 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001348600429205081267497397126433704258934722786023654947642516748329400787017869056593575564190362463816012337672108720110953485087031679742100170083339471405179 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001015578690564642830928474809116400851738979439672373010842622014994213820614830542692975596637017535214645016349588256194371704692442621518893330312106505006846 |
Yes |
Yes |
440.2155818 |
16.4477179 |
1403.4523809 |
32.6215924 |
| ENSG00000139899 |
643866 |
CBLN3 |
protein_coding |
Q6UW01 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in synaptic functions in the CNS. {ECO:0000250}. |
Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Synapse |
|
Members of the precerebellin family, such as CBLN3, contain a cerebellin motif (see CBLN1; MIM 600432) and a C-terminal C1q signature domain (see MIM 120550) that mediates trimeric assembly of atypical collagen complexes. However, precerebellins do not contain a collagen motif, suggesting that they are not conventional components of the extracellular matrix (Pang et al., 2000 [PubMed 10964938]).[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:643866; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; synapse [GO:0045202]; maintenance of synapse structure [GO:0099558] |
Mouse_homologues 17030622_Cbln3 is a secreted glycoprotein that participates in heteromeric complexes with Cbln1. 19250438_immunohistochemical localization suggests the basis for anatomical convergence of the Cbln-GluRdelta2 signaling pathway in parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses |
ENSMUSG00000040380 |
Cbln3 |
42.591175 |
0.4118464963 |
-1.279821 |
0.314075901 |
16.620441 |
0.00004565629501491466277207642576740909134969115257263183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000132264360043207154955802185014590577338822185993194580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.6523578 |
4.4607422 |
57.7804310 |
7.2065810 |
| ENSG00000139946 |
57161 |
PELI2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HAT8 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin ligase catalyzing the covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties onto substrate proteins. Involved in the TLR and IL-1 signaling pathways via interaction with the complex containing IRAK kinases and TRAF6. Mediates IL1B-induced IRAK1 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination and possibly 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitination. May be important for LPS- and IL1B-induced MAP3K7-dependent, but not MAP3K3-dependent, NF-kappa-B activation. Can activate the MAP (mitogen activated protein) kinase pathway leading to activation of ELK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12804775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12860405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17675297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17997719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22669975}. |
3D-structure;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Predicted to enable protein-macromolecule adaptor activity and ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of MAPK cascade and positive regulation of protein phosphorylation. Predicted to be located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57161; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity [GO:0034450]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; regulation of Toll signaling pathway [GO:0008592] |
12804775_interacts with TRAF6 (tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6) and TAK1 (transforming growth factor-beta activated kinase 1); can activate the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway 12860405_Pellino2 interacts with kinase-active as well as kinase-inactive IRAK1 and IRAK4 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22669975_Pellino 2 plays a critical role for TLR/IL-1R-mediated post-transcriptional control. 25027698_A high-affinity Pellino2 e3 ubiquitin ligase binding domain is specific for phosphothreonine motifs. 34387857_K(+) regulates relocation of Pellino-2 to the site of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. 34674267_Pellino-2 in nonimmune cells: novel interaction partners and intracellular localization. |
ENSMUSG00000021846 |
Peli2 |
26.010309 |
0.1807642684 |
-2.467819 |
0.384175923 |
44.294807 |
0.00000000002824645761075939653173704626389848562281748023394811752950772643089294433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000152048765257041837688612793837476203778757977147506608162075281143188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4731544 |
2.2572263 |
47.1107258 |
7.1491553 |
| ENSG00000139970 |
6252 |
RTN1 |
protein_coding |
Q16799 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits amyloid precursor protein processing, probably by blocking BACE1 activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15286784}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the family of reticulon encoding genes. Reticulons are associated with the endoplasmic reticulum, and are involved in neuroendocrine secretion or in membrane trafficking in neuroendocrine cells. This gene is considered to be a specific marker for neurological diseases and cancer, and is a potential molecular target for therapy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:6252; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902430]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182] |
14995077_RTN1-A and RTN1-B share N-terminal 168 amino acid region, suggesting that the 168 amino acid region might play a role in regulating the endocytic process 16602018_Data demonstrate that reticulon 1 interacts specifically with spastin. 17303085_analyzed the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) localization signal of human RTN1-A. Mutant proteins lacking the first (39 residues) or second (36 residues) hydrophobic segment showed ER localization 17596210_These data indicate that RTN-1C is able to modulate the cellular sensitivity to different apoptotic pathways representing a promising molecular target for new drug development. 19140693_Nucleic acid binding of the RTN1-C C terminal region is reported with a view towards the functional role of a reticulon protein. 19668229_RTN-1C protein binds to DNA and that its biological function is regulated by acetylation and is coupled to the inhibition of HDAC activity. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20708685_RTN-1C is able to specifically regulate gene expression, modulating transcript clusters which have been implicated in the onset of neurodegenerative disorders 22522967_In the present study a potential metal ion binding motif (HxE/D) at the C-terminal of the RTN1-C has been identified and its capability to bind metals investigated by UV-vis, CD, multidimensional NMR spectroscopy and biological assays. 23559015_RTN1-C induces PDI redistribution in endoplasmic reticulum vesicles, and concomitantly modulates its activity by decreasing the levels of its S-nitrosylated form. 25543119_MANF is a protein that interacts with RTN1-C 25573430_RTN-1C involvement in the regulation of Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria cross-talk, defines a role for RTN-1C in maintaining the function of contacts between the two organelles. 26227493_RTN1A contributes to progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress. 26496126_Results suggest evidence of genetic association between common variants in RTN1 and end-stage kidney disease in African-Americans and European-Americans. 26739891_RTN1A is a key mediator for proteinuria-induced tubular cell toxicity and renal fibrosis. 28733667_Results show that mice deficient in RTN1 are generally normal and that RTN1 is a predominantly expressed in the nervous system, mainly in neurons. In neurons, RTN1 is enriched in dendrites. Also, RTN1 deficiency shows no obvious effects on BACE1 activity due to compensation by RTN3, as RTN1 deficiency causes elevation of RTN3 expression suggesting that RTN1 does not have a prominent role in Alzheimer's pathogenesis. 28760823_Data suggest that reticulon 1A (RTN1A) functions not only as an endoplasmic reticulum-shaping protein but also as a protein that promotes contacts between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. 29369773_Study findings show that RTN1A is a marker for cells of the dendritic lineage, including Langerhans cells and dermal dendritic cells. 34702929_Prognostic efficacy of the RTN1 gene in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 35469894_Reticulon-1A mediates diabetic kidney disease progression through endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial contacts in tubular epithelial cells. 35747917_[The Expression of RTN1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Its Effect on Immune Microenvironment]. 35804263_CircRTN1 acts as a miR-431-5p sponge to promote thyroid cancer progression by upregulating TGFA. 36223176_Interoperability of RTN1A in dendrite dynamics and immune functions in human Langerhans cells. |
ENSMUSG00000021087 |
Rtn1 |
343.323519 |
2.4137193879 |
1.271258 |
0.088292575 |
211.809817 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000553379332466377615026025118083974964602194603723580387390757293022678627241497501290298773120242361867336384548429989525125671789851367066148668527603149414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000112350466949157260326565307197683320976175318828932364782110288349999162142052587299832163600275365739734943836327111989920046752899907005485147237777709960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
514.8008409 |
30.4842668 |
214.5232753 |
10.1435578 |
| ENSG00000139998 |
376267 |
RAB15 |
protein_coding |
P59190 |
FUNCTION: May act in concert with RAB3A in regulating aspects of synaptic vesicle membrane flow within the nerve terminal. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity and GTPase activity. Involved in positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway. Located in cilium; endosome membrane; and perinuclear region of cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:376267; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; insulin-responsive compartment [GO:0032593]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; positive regulation of regulated secretory pathway [GO:1903307]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; Rab protein signal transduction [GO:0032482]; regulation of exocytosis [GO:0017157]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904] |
16195351_Rab15 effector protein is a binding partner for Rab15-GTP. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21491086_Rab15 expression correlates with retinoic acid-induced differentiation of neuroblastoma cells 22427180_identified 4 Rab15 isoforms, Rab15CN, Rab15AN1, Rab15AN2 and Rab15AN3 in neuroblastoma cells and demonstrated that Rab15 isoform balance was significantly decreased in spheres of neuroblastoma cells; study suggests Rab15 alternative splicing may serve as a biomarker to discriminate tumor-initiating cells (TICs) from non-TICs in neuroblastoma |
ENSMUSG00000021062 |
Rab15 |
56.259908 |
0.3822471042 |
-1.387423 |
0.268426501 |
26.512960 |
0.00000026177605362931507396317292769849505162937930435873568058013916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000986673787428164043809548748587001654186678933911025524139404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.4822123 |
5.2147113 |
80.4107058 |
9.0092948 |
| ENSG00000140006 |
112840 |
WDR89 |
protein_coding |
Q96FK6 |
|
Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
|
hsa:112840; |
corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591] |
|
ENSMUSG00000045690 |
Wdr89 |
94.956037 |
2.4170371968 |
1.273240 |
0.163708817 |
61.413789 |
0.00000000000000462559672531949484172943351930459345677088250220476695062643557321280241012573242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000031755259379402674646678159349504634828120080980440320672641973942518234252929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
132.9374271 |
14.7110934 |
55.3570331 |
4.7996484 |
| ENSG00000140030 |
8477 |
GPR65 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYL9 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the glycosphingolipid psychosine (PSY) and several related glycosphingolipids (PubMed:11309421). Plays a role in immune response by maintaining lysosome function and supporting phagocytosis-mediated intracellular bacteria clearance (PubMed:27287411). May have a role in activation-induced cell death or differentiation of T-cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11309421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27287411}. |
Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables G protein-coupled receptor activity. Involved in several processes, including actin cytoskeleton reorganization; activation of GTPase activity; and positive regulation of stress fiber assembly. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8477; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; response to acidic pH [GO:0010447] |
15221007_GPR4 and TDAG8 overexpression in human tumors plays a role in driving or maintaining tumor formation 15326175_TDAG8 is one of the proton-sensing GPCRs coupling to adenylyl cyclase and psychosine, and its related lysosphingolipids behave as if they were antagonists against protein-sensing receptors, including TDAG8, GPR4, and OGR1. 15618224_TDAG8 may play biological roles in immune response and cellular transformation under conditions accompanying tissue acidosis. 15665078_Expression of TDAG8 by immune cells may regulate responses in acidic microenvironments. 19234222_At least partly, TDGA8 mediates extracellular acidification-induced inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production through the Gs protein/cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A signaling pathway in transgenic mouse macrophages. 20855608_These results support the hypothesis that TDAG8 enhances tumor development by promoting adaptation to the acidic environment to enhance cell survival/proliferation. 22445881_Data suggest that one physiological function of TDAG8 is negative regulation of inflammation by inhibiting production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in T-lymphocytes and macrophages. 22685289_Acidosis promotes Bcl-2 family-mediated evasion of apoptosis: involvement of acid-sensing G protein-coupled receptor Gpr65 signaling to Mek/Erk. 23707809_GPR65 is a regulator upstream of MMP3, which is regulated by proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors 24152439_TDAG8 expression is decreased by more than 50%. 27287411_this study establishes a role for GPR65 in inflammatory bowel disease susceptibility and identify lysosomal dysfunction as a potentially causative element in pathogenesis 28736033_Study results suggest greater T cell death associated gene-8 (TDAG8) expression in patients with panic disorder compared to healthy subjects, and directly link TDAG8 expression and the severity of the panic disorder symptoms 29017562_TDAG8 functions as a contextual tumor suppressor down-regulated in hematological malignancies. 29223793_GPR65 is overexpressed in glioblastoma and its high expression predicts unfavorable clinical outcome for patients. 30194289_Panic disorder (PD) patients appear to display polymorphisms in the ACCN gene and elevated levels of TDAG8 mRNA. [systematic review, meta-analysis ] 30529363_this study shows that genetic polymorphisms of G protein-coupled receptor 65 gene are associated with ankylosing spondylitis in a Chinese Han population 30616622_we confirmed a significant association between the rare homozygote rs8005161 TT genotype and a diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. Our study did not identify biochemical changes in individuals with various genotypes of rs8005161, however we identified a lower activation of RhoA upon an acidic pH shift in inflammatory bowel disease patients. 32078831_T-cell death-associated gene 8 accelerates atherosclerosis by promoting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. 32948783_Expression profiles of proton-sensing G-protein coupled receptors in common skin tumors. 33057165_The protective role of proton-sensing TDAG8 in the brain injury in a mouse ischemia reperfusion model. 33431967_Carbon dioxide inhibits UVB-induced inflammatory response by activating the proton-sensing receptor, GPR65, in human keratinocytes. 33478938_The evolution and mechanism of GPCR proton sensing. 34656742_Multilocus evaluation of genetic predictors of multiple sclerosis. 35218908_IBD-associated G protein-coupled receptor 65 variant compromises signalling and impairs key functions involved in inflammation. 35343079_GPR65 promotes intestinal mucosal Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation and gut inflammation through downregulating NUAK2. 36102304_MicroRNAs combined with the TLR4/TDAG8 mRNAs and proinflammatory cytokines are biomarkers for the rapid diagnosis of sepsis. |
ENSMUSG00000021886 |
Gpr65 |
152.775332 |
2.4049252123 |
1.265992 |
0.148336075 |
73.316055 |
0.00000000000000001104657145220837995215078497782693446183780298952038789739305002512992359697818756103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000088086112714530355773895108297971201080941809884866655622204234532546252012252807617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
218.9027729 |
18.8820747 |
91.7024442 |
6.2459327 |
| ENSG00000140105 |
7453 |
WARS1 |
protein_coding |
P23381 |
FUNCTION: Isoform 1, isoform 2 and T1-TrpRS have aminoacylation activity while T2-TrpRS lacks it. Isoform 2, T1-TrpRS and T2-TrpRS possess angiostatic activity whereas isoform 1 lacks it. T2-TrpRS inhibits fluid shear stress-activated responses of endothelial cells. Regulates ERK, Akt, and eNOS activation pathways that are associated with angiogenesis, cytoskeletal reorganization and shear stress-responsive gene expression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1373391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14630953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28369220}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Ligase;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Two forms of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase exist, a cytoplasmic form, named WARS, and a mitochondrial form, named WARS2. Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (WARS) catalyzes the aminoacylation of tRNA(trp) with tryptophan and is induced by interferon. Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase belongs to the class I tRNA synthetase family. Four transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7453; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0019210]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; tryptophan-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004830]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; translation [GO:0006412]; tryptophanyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006436] |
11773625_In this study, we show that a recombinant form of a COOH-terminal fragment of TrpRS is a potent antagonist of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis in a mouse model and of naturally occurring retinal angiogenesis in the neonatal mouse 11773626_Thus, protein synthesis may be linked to the regulation of angiogenesis by a natural fragment of TrpRS 11834741_Recognition by tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetases of discriminator base on tRNATrp from three biological domains 12416978_The recently discovered antiangiogenic and cell-signaling activities of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase bioactive fragments are discussed in this review. 14630953_TrpRS may have a role in the maintenance of vascular homeostasis 14660560_results suggest that mammalian and bacterial tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase might use different mechanisms to recognize the substrate and modeling studies indicate that transfer RNA binds with the dimeric enzyme 14671330_A crystal structure of human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase was solved at 2.1 A with a tryptophanyl-adenylate bound at the active site 15628863_May play an important role in the intracellular regulation of protein synthesis under conditions of oxidative stress. 15939065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16724112_These crystals captured two conformations of the human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase and tRNATrp complex, which are nearly identical with respect to the protein and a bound tryptophan. 16798914_The first crystal structure of human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (hTrpRS) in complex with tRNA(Trp) and Trp which, together with biochemical data, reveals the molecular basis of a novel tRNA binding and recognition mechanism. 17877375_Results provide the first evidence of the involvement of heme in regulation of TrpRS aminoacylation activity. 17999956_the annexin II-S100A10 complex, which regulates exocytosis, forms a ternary complex with TrpRS. 18180246_Analysis of the molecular basis of the mechanisms of the substrate recognition and the activation reaction by tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. 19363598_Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-expression in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) may control autoimmune responses by depleting the available tryptophan, whereas tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (TTS) may counteract this effect 19768679_Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase is a multidomain protein exhibiting excellent allosteric communication, and this research has provided valuable structural as well as functional insights into the protein. 19900940_Low tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase is associated with recurrence in colorectal cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20963594_Mini-tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase inhibited ischemic angiogenesis in rats. 21442253_Naturally occurring fragments of the two proteins involved in translation, TyrRS and TrpRS, have opposing activities on angiogenesis. 21926542_Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase down-regulation by hypoxia may be a factor responsible for low TrpRS in pancreatic tumors with high metastatic ability. 23651343_Indoleamine2,3-dioxygenase and tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase may play critical roles in the immune pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease. 23670221_Genes within recently identified loci associated with waist-hip ratio (WHR) exhibit fat depot-specific mRNA expression, which correlates with obesity-related traits. Adipose tissue (AT) mRNA expression of 6 genes (TBX15/WARS2, STAB1, PIGC, ZNRF3, GRB14) 24515434_Tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase expression is up-regulated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 26209610_Overexpression of WARS predicts no recurrence and good survival for triple-negative breast cancer patients. 27748732_Based on these results, secretion of full-length tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase appears to work as a primary defence system against infection, acting before full activation of innate immunity. 28369220_findings establish WARS as a gene whose mutations may cause distal hereditary motor neuropathy and alter canonical and non-canonical functions of tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. 29666190_Inhibition of human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase (TrpRS) expression by TrpRS-specific siRNAs decreased and overexpression of TrpRS increased Trp uptake into the cells 30153112_Human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase is an IFN-gamma-inducible entry factor for Enterovirus. 30355684_Data report a novel noncanonical function of WARS in antiviral defense. WARS is rapidly secreted in response to viral infection and primes the innate immune response by inducing the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and type I IFNs, resulting in the inhibition of virus replication both in vitro and in vivo. These results suggest that WARS is a member of the antiviral innate immune response. 31033497_Expression of Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase (WARS) in Gastric Cancer Molecular Subtypes. 31786502_Mini tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase is required for a synthetic phenotype in vascular smooth muscle cells induced by IFN-gamma-mediated beta2-adrenoceptor signaling. 32899943_Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase 1 Signals Activate TREM-1 via TLR2 and TLR4. 33754909_Identification of Prognostic RBPs in Osteosarcoma. 35790048_WARS1 and SARS1: Two tRNA synthetases implicated in autosomal recessive microcephaly. 35815345_Biallelic variants in WARS1 cause a highly variable neurodevelopmental syndrome and implicate a critical exon for normal auditory function. |
ENSMUSG00000021266 |
Wars |
504.028027 |
2.3110020087 |
1.208519 |
0.081286335 |
222.000539 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003311492157356987129880152468210737922422026369050263742146928895366060755267751674267011653813216419774482737503326074898237201676876040323804772924631834030151367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000709399481024515692297366364467196784117183788121414347035339456178292026420857555727891138479070540225328337509000254236350702097269049772876314818859100341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
700.1393815 |
34.0652676 |
304.8372259 |
11.6387940 |
| ENSG00000140157 |
81614 |
NIPA2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N8Q9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a selective Mg(2+) transporter. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Endosome;Ion transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a possible magnesium transporter. This gene is located adjacent to the imprinted domain in the Prader-Willi syndrome deletion region of chromosome 15. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 3, 7 and 21.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:81614; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; magnesium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015095]; magnesium ion transport [GO:0015693] |
14508708_located in the genomic domain between break points 1 and 2 on chromosome 15, of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes 15067324_Altered mRNA expression is associated with prostate cancer recurrence. 16982806_quantitated mRNA levels of NIPA2, NIPA2,l CYFIP1, and GCP5 in Prader-Willi syndrome and correlated levels with psychological and behavior scales 22367439_mutations in NIPA2 gene were associated with childhood absence epilepsy (CAE), which indicated that the haploinsufficiency of NIPA2 might be a candidate mechanism underlying the IGE/CAE phenotypes caused by 15q11.2 microdeletions or rare mutations in NIPA2 25347071_This study primarily reveals that a selective magnesium transporter NIPA2 may play a role in the pathogenesis of CAE. 31003774_AGEs dose-dependently down-regulated the expression of NIPA2 in osteoblasts. NIPA2 also regulated osteoblast apoptosis by affecting the intracellular magnesium level and further affecting the osteogenic capacity of osteoblasts. |
ENSMUSG00000030452 |
Nipa2 |
573.927499 |
2.1069170187 |
1.075133 |
0.092775941 |
133.396617 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000074039510746756256306215324747302325849249253001243449282922778552775855862091720482193180075114469218533486127853393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000009766069514049350256335722304024848788860153380954510132142151566503938141982276918695582423879386624321341514587402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
766.9892923 |
50.5773925 |
366.6328805 |
18.0624025 |
| ENSG00000140262 |
6938 |
TCF12 |
protein_coding |
Q99081 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator. Involved in the initiation of neuronal differentiation. Activates transcription by binding to the E box (5'-CANNTG-3') (By similarity). May be involved in the functional network that regulates the development of the GnRH axis (PubMed:32620954). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32620954}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Craniosynostosis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism;Isopeptide bond;Kallmann syndrome;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) E-protein family that recognizes the consensus binding site (E-box) CANNTG. This encoded protein is expressed in many tissues, among them skeletal muscle, thymus, B- and T-cells, and may participate in regulating lineage-specific gene expression through the formation of heterodimers with other bHLH E-proteins. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6938; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; HMG box domain binding [GO:0071837]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; immune response [GO:0006955]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to gonadotropin-releasing hormone [GO:0097210] |
12826747_two alternative acceptor sites for mRNA splicing yield two distinguishable transcripts (HTF4a and HTF4b) which differ in their 5' untranslated region but share identical coding sequences. 15333839_study identifes E proteins(HEB, E2A) as AML1-ETO targets whose dysregulation may be important for t(8;21) leukemogenesis, as well as an E protein silencing mechanism that is distinct from that associated with differentiation-inhibitory proteins 15351717_dHAND/E-protein (E2A, ME2, and ALF1) heterodimers have distinct DNA binding specificities 18456661_CBFA2T3 interacts with ZNF652 to repress HEB expression, and in addition CBFA2T3 interacts with the HEB protein to inhibit its activator function. 19043539_The DNA binding profile of the E-protein HEB was grossly rearranged upon expression of AML1/ETO, and the fusion protein was found to co-localize with both AML1 and HEB on many of its regulated targets 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20483740_T cell development is impaired by Id2, most likely by sequestering HEB, whereas NK cell development is promoted by increasing a pool of CD1a-CD5+ NK cell progenitors, which together with IL-15 differentiate into mature NK cells 20798984_As a first exploitation of this unique cohort, we identify three novel candidate dyslexia genes, ZNF280D and TCF12 at 15q21, and PDE7B at 6q23.3, by molecular mapping of the familial translocation with the 15q21 breakpoint. 21828274_HEB and E2A-bind the SCA motif at regions overlapping SMAD2/3 and FOXH1 22130667_TCF12 functioned as a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and its overexpression was significantly correlated with the occurrence of CRC metastasis. 23354436_haploinsufficiency of TCF12 causes coronal synostosis in humans and that severe bilateral coronal synostosis occurs in mice with 50% of the wild-type dosage of both the Tcf12 and Twist1 genes highlights the key role of TCF12 acting with TWIST1. 23386606_the CD91/IKK/NF-kappaB signaling cascade is involved in secreted HSP90alpha-induced TCF12 expression, leading to E-cadherin down-regulation and enhanced CRC cell migration/invasion 23812588_In t(8;21) leukemia cells, the two E proteins, HEB and E2A, function as components of the stable AML1-ETO-containing transcription factor complex (AETFC). The AETFC components cooperatively regulate gene expression and contribute to leukemogenesis. 23812588_Within the AETFC complex, AML1-ETO oligomerization is required for a specific interaction between the oligomerized NHR2 domain and a novel NHR2-binding (N2B) motif in E proteins, including HEB and E2A. Disruption of this interaction by point mutations abrogates AML1-ETO-induced hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell self-renewal and leukemogenesis. 24736737_several familial cases of coronal synostosis associated with mutations in TCF12 25271085_Studies suggest that transcription factor 12 (TCF12) should be included in level 2 genetic testing. 26068201_show that these mutations compromise TCF12 transcriptional activity and are associated with a more aggressive tumour type 26671595_Two novel translocations leading to the inactivation of RUNX1 and its partners SIN3A and TCF12 in myeloid leukemia. 27092878_HDAC1 promoted migration and invasion of gallbladder tumor cells by binding with TCF12 to promote epithelial mesenchymal transformation. 27158814_Study describes the identification of three large inherited intragenic exon deletions in TCF12 using whole-genome sequencing and one large inherited duplication using targeted TCF12 sequencing in patients with craniosynostosis. 27572702_Heb expression is regulated by Med19 in breast cancer cells. 27779678_HEB may be involved in GBM cell proliferation, as HEB silencing reduced proliferation in cells cultured as monolayers or neurospheres. Furthermore, the results suggested a potential role for HEB in the maintenance of GBM stem cells, as HEB silencing affected the differentiation capacity of cells. 28651494_enforced expression of transcription factor 12 suppressed cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and inhibited tumor growth in vivo. In conclusion, transcription factor 12 protein may be a novel molecule which plays a critical role in prostate cancer progression and patients' prognosis, suggesting it might be a promising therapeutic target for prostate cancer therapy 28803914_These results identify HEB as a critical regulator of human mesodermal and hematopoietic specification. 29215649_Pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in non-FGFR genes were identified in 43 individuals, with diagnostic yields of 14% and 15% in retrospective and prospective cohorts, respectively. Variants were identified most frequently in TCF12 (N = 22) and EFNB1 (N = 8), typically in individuals with nonsyndromic coronal craniosynostosis or TWIST1-negative clinically suspected Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. 30593567_directly interacts with AML1-ETO, confers new DNA-binding capacity to the AML1-ETO-containing transcription factor complex, and is essential for leukemogenesis 31311684_The results suggest that TCF12 is a poor prognostic factor of ovarian cancer 31692066_SNHG1/miR-556-5p/TCF12 feedback loop enhances the tumorigenesis of meningioma through Wnt signaling pathway. 31789414_Study demonstrates that TCF12 is a direct target of miR26a, and upregulation of miR26a resulted in TCF12 inhibition in epithelial ovarian cancer (OC) cells. Furthermore, the proliferation, migration and invasion were inhibited and apoptosis was induced by miR26a upregulation in OC cells. These results indicated that miR26a may act as a tumor suppressor in OC, and TCF12 targeting by miR26a. 32119786_Circ_0000388 Exerts Oncogenic Function in Cervical Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-337-3p/TCF12 Axis. 32572916_Proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma are accelerated by LINC01287 via the miR-559/TCF12 axis. 32620954_TCF12 haploinsufficiency causes autosomal dominant Kallmann syndrome and reveals network-level interactions between causal loci. 33904513_Neurodevelopmental, Cognitive, and Psychosocial Outcomes for Individuals With Pathogenic Variants in the TCF12 Gene and Associated Craniosynostosis. 34121515_miR-218-5p inhibits the malignant progression of glioma via targeting TCF12. 34369267_Long non-coding RNA GLIDR accelerates the tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma by miR-1270/TCF12 axis. 34424951_Evaluation of dental maturity in Muenke syndrome, Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, and TCF12-related craniosynostosis. 34904178_Craniofacial morphology and growth in Muenke syndrome, Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, and TCF12-related craniosynostosis. |
ENSMUSG00000032228 |
Tcf12 |
1292.266490 |
0.4845744591 |
-1.045210 |
0.289858592 |
12.727841 |
0.00036025221621717787561650636618537646427284926176071166992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000908322977684582308528782323975292456452734768390655517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
786.6139495 |
308.6312955 |
1642.3415647 |
462.4466203 |
| ENSG00000140284 |
11001 |
SLC27A2 |
protein_coding |
O14975 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the import of long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) into the cell by facilitating their transport across cell membranes, playing an important role in hepatic fatty acid uptake (PubMed:20530735, PubMed:22022213, PubMed:24269233, PubMed:10198260, PubMed:10749848, PubMed:11980911). Also functions as an acyl-CoA ligase catalyzing the ATP-dependent formation of fatty acyl-CoA using LCFA and very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) as substrates, which prevents fatty acid efflux from cells and might drive more fatty acid uptake (PubMed:20530735, PubMed:22022213, PubMed:24269233, PubMed:10198260, PubMed:10749848, PubMed:11980911). Plays a pivotal role in regulating available LCFA substrates from exogenous sources in tissues undergoing high levels of beta-oxidation or triglyceride synthesis (PubMed:20530735). Can also activate branched-chain fatty acids such as phytanic acid and pristanic acid (PubMed:10198260). May contribute to the synthesis of sphingosine-1-phosphate (PubMed:24269233). Does not activate C24 bile acids, cholate and chenodeoxycholate (PubMed:11980911). In vitro, activates 3-alpha,7-alpha,12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholestanate (THCA), the C27 precursor of cholic acid deriving from the de novo synthesis from cholesterol (PubMed:11980911). However, it is not critical for THCA activation and bile synthesis in vivo (PubMed:20530735). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10198260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10749848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11980911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20530735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22022213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269233}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Exhibits both long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) transport activity and acyl CoA synthetase towards very long-chain fatty acids (PubMed:21768100, PubMed:10198260). Shows a preference for generating CoA derivatives of n-3 fatty acids, which are preferentially trafficked into phosphatidylinositol (PubMed:21768100). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10198260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21768100}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Exhibits long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) transport activity but lacks acyl CoA synthetase towards very long-chain fatty acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21768100}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Membrane;Microsome;Nucleotide-binding;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme activates long-chain, branched-chain and very-long-chain fatty acids containing 22 or more carbons to their CoA derivatives. It is expressed primarily in liver and kidney, and is present in both endoplasmic reticulum and peroxisomes, but not in mitochondria. Its decreased peroxisomal enzyme activity is in part responsible for the biochemical pathology in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:11001; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cholate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047747]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; fatty acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015245]; long-chain fatty acid transporter activity [GO:0005324]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; oleate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901480]; phytanate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0050197]; pristanate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0070251]; very long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031957]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699]; fatty acid alpha-oxidation [GO:0001561]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0046949]; long-chain fatty acid import into cell [GO:0044539]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; methyl-branched fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0097089]; very long-chain fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0042760] |
17998437_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20965718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21768100_FATP2a functions in fatty acid transport and activation and provides specificity toward n-3 fatty acids in which the corresponding n-3 acyl-CoAs are preferentially trafficked into acyl-CoA pools destined for phosphatidylinositol incorporation 22028793_even though hypoxia regulates the expression of FATP2 and FATP4 in human trophoblasts, mouse Fatp2 and Fatp4 are not essential for intrauterine fetal growth. 24113382_these data support the conclusion that FATP2 has a dual function in the pathways linking the transport and activation of exogenous fatty acids. 24277691_Protective effects of breastfeeding are reflected in higher expression levels of SLC27A2, FASN, PPARalpha and INSR in blood cells. 26284975_In mice Grassofermata decreased absorption of (13)C-oleate demonstrating its potential as a therapeutic agent. 27016784_In overweight/obese pregnancies, the increased FATP2 placental expression could contribute to increased fatty acid delivery to the fetus. 30996346_mouse and human polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSCs) exclusively upregulate fatty acid transport protein 2 (FATP2); FATP2 mediates the acquisition of immunosuppressive activity by PMN-MDSCs and represents a target to inhibit the functions of PMN-MDSCs selectively and to improve the efficiency of cancer therapy 33219209_Involvement of FATP2-mediated tubular lipid metabolic reprogramming in renal fibrogenesis. 34854499_Upregulated SLC27A2/FATP2 in differentiated thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor proliferation and migration. 36169895_Feedback loop between fatty acid transport protein 2 and receptor interacting protein 3 pathways promotes polymorphonuclear neutrophil myeloid-derived suppressor cells-potentiated suppressive immunity in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000027359 |
Slc27a2 |
15.560594 |
0.3081542404 |
-1.698275 |
0.670145864 |
5.992907 |
0.01436350897696354010635300113563062041066586971282958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026610442136310009930699749247651197947561740875244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.8170731 |
2.9192449 |
21.5530367 |
6.3126961 |
| ENSG00000140332 |
7090 |
TLE3 |
protein_coding |
Q04726 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional corepressor that binds to a number of transcription factors. Inhibits the transcriptional activation mediated by CTNNB1 and TCF family members in Wnt signaling. The effects of full-length TLE family members may be modulated by association with dominant-negative AES (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;WD repeat;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a transcriptional co-repressor protein that belongs to the transducin-like enhancer family of proteins. The members of this family function in the Notch signaling pathway that regulates determination of cell fate during development. Expression of this gene has been associated with a favorable outcome to chemotherapy with taxanes for ovarian carcinoma. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Additional alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:7090; |
beta-catenin-TCF complex [GO:1990907]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
18273443_results demonstrate that different isoforms of TLE genes are commonly transcribed in human tissues and suggest that TLE3 could be involved in prostate cancer development 20181723_Studies suggest that TLE1 and TLE3 might also play roles independent of HESX1 by interacting with other transcription factors like PROP1. 22050093_A lack of TLE3 expression in cutaneous angiosarcoma may reflect differing pathogenesis. 22194527_High TLE3 expression predicts a favorable response to taxane containing chemotherapy regimens in ovarian carcinoma. 24444608_induction of TLE3 by Wnt signaling is part of a negative feedback loop active during osteoblast differentiation 25249007_Increased adipose tissue (AT) TLE3 in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in AT from high fat diet and PPARgamma knockout mice suggest that TLE3 may play an adaptive regulatory role that improves AT function under decreased PPARgamma expression 28107193_Data indicate that microRNA miR-744 activated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by targeting multiple negative regulators of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, including SFRP1, GSK3beta, TLE3 and NKD1, and that NKD1 is a major functional target of miR-744. 28689657_Wnt signaling pathway inactivates the TLE3 co-repressor via HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase Hyd/UBR5 ubiquitination. 28859615_Patients with TLE3-negative tumors displayed poorer outcomes regarding progression-free survival than patients with TLE3-positive tumors when prognosis within the group of patients with triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) lesions was analyzed. In contrast, no such difference in prognosis was found in a comparison of TLE-3 positive/negative patients in the group of all patients. 29374067_RNF6-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of TLE3 activates the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in colorectal carcinogenesis 31855178_vour findings reveal a mechanistic link between TLE3 and GR-mediated resistance to AR inhibitors in human prostate cancer 33571907_Differential functions of TLE1 and TLE3 depending on a specific phosphorylation site. 34551306_Enhancer recruitment of transcription repressors RUNX1 and TLE3 by mis-expressed FOXC1 blocks differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000032280 |
Tle3 |
268.325509 |
3.2341025185 |
1.693365 |
0.224224986 |
54.502792 |
0.00000000000015522712707178955280923053622695868380542555398093895746569614857435226440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000972062959516170399424344840846908661312342214699810938327573239803314208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
416.1649668 |
78.5651681 |
129.6468440 |
17.9047204 |
| ENSG00000140379 |
597 |
BCL2A1 |
protein_coding |
Q16548 |
FUNCTION: Retards apoptosis induced by IL-3 deprivation. May function in the response of hemopoietic cells to external signals and in maintaining endothelial survival during infection (By similarity). Can inhibit apoptosis induced by serum starvation in the mammary epithelial cell line HC11 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07440}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the BCL-2 protein family. The proteins of this family form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- and pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities such as embryonic development, homeostasis and tumorigenesis. The protein encoded by this gene is able to reduce the release of pro-apoptotic cytochrome c from mitochondria and block caspase activation. This gene is a direct transcription target of NF-kappa B in response to inflammatory mediators, and is up-regulated by different extracellular signals, such as granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), CD40, phorbol ester and inflammatory cytokine TNF and IL-1, which suggests a cytoprotective function that is essential for lymphocyte activation as well as cell survival. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:597; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066] |
11929871_Bcl-2 family member Bfl-1/A1 sequesters truncated bid to inhibit is collaboration with pro-apoptotic Bak or Bax. 12665576_role for NF-kappa B in bfl-1 transcription 12692420_the level of Bfl-1 gene expression was higher in more advanced breast cancers than in early cancers; it seems that the increased expression of the Bfl-1 gene serves as a contributory factor in breast cancer in the same way that another group of genes 12771180_identification of two novel minor histocompatibility antigens, encoded by two separate single nucleotide polymorphisms on a single gene, BCL2A1, and restricted by HLA-A*2402 and B*4403 14747545_Epstein Barr virus LMP1 drives bfl-1 promoter activity through interactions with components of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)/CD40 signaling pathway; evidence presented that this process is NF-kappa B dependent 14966372_confers protection from hydrogen peroxide- and peroxynitrite- induced apoptosis in neutrophils and HL-60 cells 14981542_The expression of BCL2A1 was compared in two inbred strains of mice. 15499630_High expression of bfl-1 contributes to the apoptosis resistant phenotype in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia 15501771_expression in urethral epithelium upregulated by Neisseria gonorrhoeae PorB IB and upregulation dependent on NF-kappaB activation 15592513_Oxidative stress induces the expression of Bfl-1 via NF-kappaB activation, and this early-response gene protects cells from Fas-mediated apoptosis. 15617521_results suggest that Anaplasma phagocytophilum inhibits human neutrophil apoptosis via transcriptional upregulation of bfl-1 and inhibition of mitochondria-mediated activation of caspase 3 15696550_performed a Bfl-1 deletion study in order to elucidate the underlying mechanism of GFP-Bfl-1-induced cell death 16164629_A1 and A20 are both required for optimal protection from apoptosis (A1) and inflammation (A20) in conditions leading to renal damage 16551634_The C terminus of A1 did not function as a membrane anchor; it serves a dual function by controlling the stability of A1 and by amplifying the capacity of the protein to protect cells against apoptosis. 16572199_Bfl-1/A1 mRNA is not expressed in these cell lines, however, its expression is markedly induced by ATRA treatment in NB4 and HL-60 cells, but not in R4 or HL-60/Res cells, which correlates with inhibition of apoptosis. 16873269_EBNA2 trans-activates bfl-1, which requires CBF1 (or RBP-J kappa). 17121585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17121585_the known polymorphisms of exon 1 and a novel polymorphism in the promoter region provide evidence for an association between bfl-1 polymorphisms and genetic predisposition to atopic dermatitis 17666431_Amphipathic tail-anchoring peptide (ATAP) targets specifically to mitochondria, and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis that does not require Bax or Bak. 17724464_Bfl-1 associates with tBid to prevent activation of proapoptotic Bax and Bak, and it also interacts directly with Bak to antagonize Bak-mediated cell death, similar to myeloid cell factor (Mcl)-1. 17726463_Specific downregulation of bfl-1 using siRNA induced apoptosis in resistant cells. Our data suggest that bfl-1 contributes to chemoresistance and might be a therapeutic target in B-CLL. 17942758_While TNFalpha had no effect on MCL-1 transcription, it induced expression of another antiapoptotic molecule, BFL-1. 18093280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18206119_Results clearly indicated that differential expression of bfl-1/A1 in M. tuberculosis H37Rv and M. tuberculosis H37Ra infected THP-1 cells probably account for the difference in infection outcome. 18414982_targeting mHags encoded not only by HMHA1, whose aberrant expression in solid tumors has been reported, but also BCL2A1 may bring about beneficial selective graft-versus-tumor effects 18512730_C/EBP beta overexpression significantly upregulated promoter activities of IL-8, COX-2, and anti-apoptotic Bfl-1 genes in prostate cancer cells. 18812174_The crystal structure of Bfl-1, the last anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member to be structurally characterized, in complex with a peptide corresponding to the BH3 region of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim is presented. 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19759007_the amphipathic character of Bfl-1 C-terminal helix alpha9 is required for the anchorage of Bfl-1 to the mitochondria and regulation the antiapoptotic function Bfl-1 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185581_Defective ubiquitin-mediated degradation of antiapoptotic Bfl-1 predisposes to lymphoma. 20353833_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21167304_Bfl-1/A1 negatively regulates autophagy and expression of Bfl-1/A1 in H37Rv infected macrophages 21491422_These findings are the first indication that Bfl-1 plays a crucial role in setting the elevated threshold of resistance of this malignant cell type to apoptosis 21843371_Bfl-1 importantly regulates lung cancer cell sensitivity to gemcitabine. 22231730_neutrophils from patients with sepsis express reduced levels of antiapoptotic Mcl1 and A1 22292048_Inhibition of Mcl-1 and A1 strongly induced cell death in some melanoma cell lines. 22510878_The transcription factor Spi-B regulates human plasmacytoid dendritic cell survival through direct induction of the antiapoptotic gene BCL2-A1. 22553204_results directly implicate Bfl-1 and Bcl-x(L) in HTLV-1-infected T-cell survival and suggest that both Bfl-1 and Bcl-x(L) represent potential therapeutic targets for ATLL treatment. 22720045_results highlight Bfl-1 as a major effector in activation-induced human mast cell survival 22745672_Data demonstrate that calpain-mediated cleavage of full-length Bfl-1 induces the release of C-terminal membrane active alpha-helices that are responsible for its conversion into a pro-apoptotic factor. 22865454_Data indicate that BCL2a1 expression enhances tumor cell survival in nervous system (CNS) leading to intracranial tumor growth. 23118966_Bcl2a1 should be considered as a proto-oncogene with a potential role in both lymphoid and myeloid leukemogenesis 23152563_Mitochondrial antiapoptotic factor Bfl-1 is significantly reduced by suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)1. 23447565_MITF-BCL2A1 as a lineage-specific oncogenic pathway in melanoma and underscore its role for improved response to BRAF-directed therapy. 23480177_Results indicate that mismatches in minor H antigens HA-8 (KIAA0020) and ACC-1 (BCL2A1) predisposed to chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD). 23841872_BCL2A1 is a novel marker associated with seizure prognosis following surgery for low-grade brain neoplasms. 24810636_Bcl2a1 overexpressing granulocytic MDSCs demonstrated prolonged survival. 25486183_Bfl-1 was mitochondrially resident in both resting and apoptotic cells and experienced regulation by the proteasome and NFkappaB pathways. 27386628_Demonstrate immunohistochemical expression of Wnt11 and BCL2A1 in complete moles and normal villi. 29276033_Crystal structures of anti-apoptotic BFL-1 and its complex with a covalent stapled BH3 peptide inhibitor have been presented. 30042493_overexpression of TRIM28 or knock-out of TRIM17 reduced BCLA1 protein levels and restored sensitivity of melanoma cells to BRAF-targeted therapy. Therefore, our data describe a molecular rheostat in which two proteins of the TRIM family antagonistically regulate BCL2A1 stability and modulate cell death. 30560933_BFL1 inhibits apoptosis through three distinct mechanisms which are similar but not identical to those of BCLXL, the paradigmatic antiapoptotic BCL2 family protein. 30773399_Molecular characterization of anti-apoptotic BFL1 and MCL1 enabled facile prediction and design of peptides that bind to them. 30816537_the results of present study indicated that overexpression of ACC1 is significantly associated with the survival time of patients with liver cancer, and may provide insight into the association between ACC1 and cell proliferation in BRL 3A cells. 31003775_prenylated Rab acceptor 1 (RABAC1 or PRA1) inhibits the anti-apoptotic activity of BCL2A1 and induces apoptosis in AGS gastric cancer cells. 31300747_Comparative transcriptome analysisuncovered BCL2A1 as a potential mediator of ABT-199 resistance in acute myeloid leukemias 31719651_Characterization of a novel human BFL-1-specific monoclonal antibody. 32487689_Snail augments fatty acid oxidation by suppression of mitochondrial ACC2 during cancer progression. 32618200_LncRNA HORAS5 promotes taxane resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer via a BCL2A1-dependent mechanism. 32661419_A redox switch regulates the structure and function of anti-apoptotic BFL-1. 33391539_Molecular stratification by BCL2A1 and AIM2 provides additional prognostic value in penile squamous cell carcinoma. 34423048_lncRNA PANTR1 Upregulates BCL2A1 Expression to Promote Tumorigenesis and Warburg Effect of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Restraining miR-587. 35603962_Construction of three-gene-based prognostic signature and analysis of immune cells infiltration in children and young adults with B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 35832273_Bulk RNA Sequencing With Integrated Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies BCL2A1 as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Sepsis. |
ENSMUSG00000099974+ENSMUSG00000102037+ENSMUSG00000089929+ENSMUSG00000053820 |
Bcl2a1d+Bcl2a1a+Bcl2a1b+Bcl2a1c |
151.864154 |
12.1189102856 |
3.599188 |
0.183332793 |
492.991995 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031826740524829213123521136759969987008491406275628225310217268793623834748402501039090085285383401904399304483820849495735289641438327054339287204815521120486807198939428069973619986734765219674446654199328379661146225002 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014865907916027822771597496586976081564150068499933940760216904652591091785990191481626561515472357083341325393041312516533367691633013874829039687586928513093151332711013449922339377344025227448277856123764101949507797018 |
Yes |
No |
282.9304243 |
32.4156237 |
23.5150085 |
2.5158420 |
| ENSG00000140398 |
79661 |
NEIL1 |
protein_coding |
Q96FI4 |
FUNCTION: Involved in base excision repair of DNA damaged by oxidation or by mutagenic agents. Acts as DNA glycosylase that recognizes and removes damaged bases. Has a preference for oxidized pyrimidines, such as thymine glycol, formamidopyrimidine (Fapy) and 5-hydroxyuracil. Has marginal activity towards 8-oxoguanine. Has AP (apurinic/apyrimidinic) lyase activity and introduces nicks in the DNA strand. Cleaves the DNA backbone by beta-delta elimination to generate a single-strand break at the site of the removed base with both 3'- and 5'-phosphates. Has DNA glycosylase/lyase activity towards mismatched uracil and thymine, in particular in U:C and T:C mismatches. Specifically binds 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), suggesting that it acts as a specific reader of 5hmC. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11904416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12200441, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12509226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14522990}. |
3D-structure;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Lyase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA editing |
|
This gene is a member of the Nei endonuclease VIII-like gene family which encodes DNA glycosylases. The encoded enzyme participates in the DNA repair pathway by initiating base excision repair by removing damaged bases, primarily oxidized pyrimidines. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:79661; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; class I DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity [GO:0140078]; damaged DNA binding [GO:0003684]; DNA N-glycosylase activity [GO:0019104]; DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease activity [GO:0003906]; hydrolase activity, acting on glycosyl bonds [GO:0016798]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; base-excision repair [GO:0006284]; base-excision repair, gap-filling [GO:0006287]; depyrimidination [GO:0045008]; negative regulation of nuclease activity [GO:0032074]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
12433996_hFPG1 and hFPG2 repair 8-oxoguanine and other DNA oxidation products. (hFPG1 and hFPG2) 12509226_Pyrimidine dimer repair enzyme located on the long arm of chromosome 15 that is frequently deleted in human cancers. 14522990_NEIL1 and NEIL2 are preferentially involved in repair of lesions in DNA bubbles generated during transcription and/or replication 14734554_hNEIL1 has a significant role in the repair of 5S-Tg in human cells. 15159582_Overproduction, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of NEIL1 15232006_zincless finger appears to be required for NEIL1 activity, because mutating a very highly conserved arginine within this motif greatly reduces the glycosylase activity of the enzyme. 15319300_Reduced expression of NEIL1 is associated with the pathogenesis of gastric cancers 15350146_NEIL1 and OGG1, two DNA glycosylases which do not stably interact with each other, stimulate 8-oxoguanine repair by a collaboration that is possible because of higher abasic (AP) site affinity and stronger AP lyase activity of NEIL1 relative to OGG1. 15533839_NEIL1 is a DNA glycosylase that excise 5-formyluracil, 5-hydroxymethyluracil and Thymine glycol in human cells. 16118226_Oxidative stress-induced activation of NEIL1 appears to be involved in the feedback regulation of cellular repair activity needed to handle an increase in the level of oxidative base damage 16446124_Nth1 released 5R,6S 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diastereoisomer (Tg2) much more rapidly than cis 5S,6R-deoxyribonucleoside diastereoisomer (Tg1) regardless of the opposing purine. Neil1 released Thymine glycol non-stereoselectively. 17029639_A T434+2C mutation was found in familial colorectal cancer DNA suggesting a limited role for this gene in the devlopment of CRC. 17150535_The damage specificity of human homologues of Endo III (hNTHl) and Endo VIII (hNEIL1 and hNEIL2) is compared to elucidate the repair role in cells. 17348689_we found that although both SMUG1 and NEIL1 are able to excise 5-OHU lesions located in the proximity of the proximity of the 3'-end of a DNA SSB, NEIL1 is more efficient in the repair of these DNA lesions. 17395641_Human NEIL1 DNA glycosylase activity is significantly stimulated by hHus1, hRad1, hRad9 separately and by the 9-1-1 complex. 17432829_The ability of Neil1 to recognize a variety of pyrimidine lesions is connected to the flexible binding pocket of the enzyme and the common chemical features of lesions that contain a pyrimidine ring. 17556049_Centrosomal localization of hNEIL1 was observed when mitotic HeLa cells were immunostained with hNEIL1 antibodies 17611195_WRN participates in the same DNA repair pathway as NEIL1. 18032376_human DNA glycosylase NEIL1 interacts with proliferating cell nuclear antigen and may have a role in replication-associated repair of oxidized bases 18155253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515411_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18543945_These results indicate that the hydantoin lesions are the best substrates identified thus far for hNEIL1 and suggest that repair of these lesions may be a critical function of the hNEIL1 enzyme in vivo. 18594018_NEIL2, but not NEIL1, polymorphisms may have a role in risk and progression of squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and oropharynx 18594018_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18662981_NEIL1 could also participate in strand displacement repair synthesis (long patch repair (LP-BER)) mediated by FEN-1 and stimulated by PCNA. 19047128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19179336_Cockayne syndrome group B protein plays a role in repair of formamidopyrimidines, possibly by interacting with and stimulating NEIL1 19258314_a model for the mechanism of ICL repair in mammalian cells that implicates the DNA glycosylase activity of NEIL1 downstream of XPF/ERCC1 and translesion DNA synthesis repair steps. 19443904_The NEIL1 G83D mutant was dysfunctional for the major oxidation products 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine (8oxoG), thymine glycol and dihydrothymine in duplex DNA, and the ability to perform delta-elimination at abasic sites was significantly reduced. 19840299_enzymological activity in peripheral leukocytes is increased in children with asthma bronchiale 20005182_These results suggest that, in vivo, NEIL1 functions either at nucleosome-free regions (such as those near replication forks) or with cofactors that limit its non-specific binding to DNA. 20099873_The results indicate that NEIL1 does not require a base opposite to identify and remove hydantoin lesions. 20338831_Modulation of NEIL1's activity on single-stranded DNA substrate by RPA and PCNA support NEIL1's involvement in repairing the replicating genome. 20346739_WRN is the only human RecQ helicase that stimulates NEIL1 DNA glycosylase activity, and that this stimulation requires a double-stranded DNA substrate. 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21068368_NEIL1 recoding site is a preferred editing site for the RNA editing adenosine deaminase ADAR1. 21131780_These data suggest Neil1 may be a critical mediator of base excision repair of incorporated dUMP following thymidylate synthetase pathway inhibition. 21697813_Homozygosity mapping and exome sequencing in a consanguineous kindred identified MYO1E and NEIL1 as novel candidate genes for human autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 21985917_NEIL1 gene mutation may have a causative role in the development of type 2 diabetes in the Turkish population. 22170059_Structural characterization of viral ortholog of human DNA glycosylase NEIL1 bound to thymine glycol or 5-hydroxyuracil-containing DNA. 22286769_aberrant promoter methylation of NEIL1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 22465744_we demonstrated that hNEIL1 and hNTH1 cleave Oz sites as efficiently as 5-hydroxyuracil sites. Thus, hNEIL1 and hNTH1 can repair Oz lesions 22639086_the binding of these modified DNAs with the unedited and edited forms of human NEIL1 along with E. coli Endo III 22858590_Pro2 and Lys54 are involved in the AP lyase activity; Met81, Arg119 and Phe120 are essential for removal of 8-oxoG in duplex DNA 22902625_the hnRNP-U protection of cells after oxidative stress is largely due to enhancement of NEIL1-mediated repair. 23104860_binds to the BRCT domain of PARP-1 23508956_NEIL1 recognizes specifically and distinctly interstrand crosslinks in DNA, and can obstruct the efficient removal of lethal crosslink adducts. 23542007_Authors show that the intrinsically disordered C-terminal domain interacts with the folded domain in native NEIL1 containing 389 residues. 23898192_Prereplicative repair of oxidized bases in the human genome is mediated by NEIL1 DNA glycosylase together with replication proteins. 23926102_one role for Neil3 and NEIL1 is to repair DNA base damages in telomeres in vivo and that Neil3 and Neil1 may function in quadruplex-mediated cellular events, such as gene regulation via removal of damaged bases from quadruplex DNA. 24022861_The NEIL1 rs4462560 SNP may serve as a predictor of acute RIET and RP risk but not of overall survival. 24382305_genome and cancer single nucleotide polymorphisms of the human NEIL1 DNA glycosylase 25605055_Results show that YB-1 interferes negatively with the AP site DNA cleavage activity of both APE1 and NEIL1 for ssDNA and bubble structures. 25873625_Rad9 regulates base excision repair by controlling NEIL1 transcription. 26074017_first study to show that SNPs of genes involved in DNA repair, may modulate the risk of Depressive Disorder. 26095805_Findings suggesting that DNA glycosylase NEIL1 c.C844T is a defective allele. 26134572_NEIL1 forms a multiprotein complex with DNA replication proteins via its C-terminal domain, allowing recruitment at the replication fork. 26662719_NEIL1 (rs5745908) is associated with Behcet's disease. The genetic association in NEIL1 is a predicted splice donor variant that may introduce a deleterious intron retention and result in a noncoding transcript variant. 26751644_NEIL1 and NEIL2 cooperate with TDG during base excision: TDG occupies the abasic site and is displaced by NEILs, which further process the baseless sugar, thereby stimulating TDG-substrate turnover. 27042257_The abnormal expressions of NEIL1, NEIL2, and NEIL3 are involved in cancer through their association with the somatic mutation load. 27518429_identified the c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) as the kinase involved in the phosphorylation of NEIL1 27924031_cellular NEIL1 is regulated by the UPP mediated by the E3 ubiquitin ligases Mule and TRIM26, which plays a vital role in co-ordinating the cellular response to DNA damage. 28093361_Nei Like DNA Glycosylase 1 (NEIL1) as a likely candidate gene due to its crucial role in B-cell activation and terminal differentiation. 28575236_Data indicate that DNA glycosylases MYH, UNG2, MPG, NTH1, NEIL1, 2 and 3 on nascent DNA. 28827588_The authors confirm direct NEIL1 TDG binding and NEIL1 mediated 2'-deoxyribose excision downstream of TDG glycosylase activity. NEIL1 acts not only downstream of TDG, but also enhances TDG activity on 5-formylcytosine or 5-carboxylcytosine containing DNA. 29234069_NEIL3 cleaves psoralen-induced DNA-DNA cross-links in three-stranded and four-stranded DNA substrates to generate unhooked DNA fragments containing either an abasic site or a psoralen-thymine monoadduct. Nei and NEIL1 also cleave a psoralen-induced four-stranded DNA substrate to generate 2 unhooked DNA duplexes with a nick; NEIL3 targets both DNA strands in interstrand cross-links without generating single-strand breaks. 29522991_NEIL1 and homotetrameric mtSSB form a larger ternary complex in presence of DNA, however, the tetrameric form of mtSSB gets disrupted by NEIL1 in the absence of DNA as revealed by the formation of a smaller NEIL1-mtSSBmonomer complex. 29626765_The level of OGG1 expression was significantly reduced in bipolar patients compared to healthy individuals, whereas the two groups exhibited similar levels of NEIL1 expression. 29698889_The major role of acetylable Lys residues in NEIL1 is to stabilize the formation of chromatin-bound repair complexes which protect cells from oxidative stress. 30448017_NEIL1 and NEIL3 may protect cells against cytotoxic and mutagenic effects of NM-Fapy-dG, but NEIL1 may have a unique role in initiation of base excision repair of AFB1-Fapy-dG 30716333_NEIL1 as an enzyme that actively destabilizes damaged DNA and uses multiple checkpoints along the reaction coordinate to drive substrate lesions into the active site while rejecting normal bases and non-substrate lesions. 31018584_Results indicate that whilst specificity for 5-hydroxyuracil and thymine glycol was observed, NEIL1 acts preferentially on double-stranded DNA, including the damage upstream to the replication fork. 31100703_P68H allelic variant had a modest reduction in catalytic activity on the release of FapyGua, FapyAde, and AFB1-FapyGua. A51V variant was unstable at physiological temperature. 31733589_Recognition of DNA adducts by edited and unedited forms of DNA glycosylase NEIL1. 31784740_Requirements for DNA bubble structure for efficient cleavage by helix-two-turn-helix DNA glycosylases. 32198476_Cervical carcinoma risk associate with genetic polymorphisms of NEIL2 gene in Chinese population and its significance as predictive biomarker. 32302101_Inhibition of Excision of Oxidatively Generated Hydantoin DNA Lesions by NEIL1 by the Competitive Binding of the Nucleotide Excision Repair Factor XPC-RAD23B. 32685496_Nei Endonuclease VIII-Like1 (NEIL1) Inhibits Apoptosis of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. 33087268_Fine-tuning of DNA base excision/strand break repair via acetylation. 33300026_Heritable pattern of oxidized DNA base repair coincides with pre-targeting of repair complexes to open chromatin. 33498912_Effect of DNA Glycosylases OGG1 and Neil1 on Oxidized G-Rich Motif in the KRAS Promoter. 33595290_DNA Sequence Modulates the Efficiency of NEIL1-Catalyzed Excision of the Aflatoxin B1-Induced Formamidopyrimidine Guanine Adduct. 33925271_NEIL1 and NEIL2 Are Recruited as Potential Backup for OGG1 upon OGG1 Depletion or Inhibition by TH5487. 33929180_RNA Editing of the Human DNA Glycosylase NEIL1 Alters Its Removal of 5-Hydroxyuracil Lesions in DNA. 34105905_Genetic variations in DNA repair gene NEIL1 associated with radiation pneumonitis risk in lung cancer patients. 34226550_DNA repair glycosylase hNEIL1 triages damaged bases via competing interaction modes. 35190641_p53-NEIL1 co-abnormalities induce genomic instability and promote synthetic lethality with Chk1 inhibition in multiple myeloma having concomitant 17p13(del) and 1q21(gain). 35917336_NEIL1 Recoding due to RNA Editing Impacts Lesion-Specific Recognition and Excision. |
ENSMUSG00000032298 |
Neil1 |
53.995770 |
0.3907579631 |
-1.355653 |
0.291347183 |
21.883296 |
0.00000289745115713776732444570231883584909837736631743609905242919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009706395614923614374247931579908765797881642356514930725097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.9182793 |
8.2836600 |
87.8335579 |
14.2986187 |
| ENSG00000140400 |
4123 |
MAN2C1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NTJ4 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves alpha 1,2-, alpha 1,3-, and alpha 1,6-linked mannose residues on cytoplasmatic free oligosaccharides generated by N-glycoprotein degradation pathways. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16848760}. |
Alternative splicing;Cobalt;Cytoplasm;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable alpha-mannosidase activity. Predicted to be involved in oligosaccharide catabolic process. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4123; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; alpha-mannosidase activity [GO:0004559]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mannose metabolic process [GO:0006013]; oligosaccharide catabolic process [GO:0009313] |
12643454_plays an important role in preventing oncosis-like death in BJAB cells 16721356_Results suggest that inhibition of alpha-mannosidase Man2c1 gene expression enhances adhesion of Jurkat T cells. 19018777_Inhibition of MAN2C1 gene expression suppresses growth of esophageal carcinoma cells through mitotic arrest and apoptosis. 19572206_Reduced antibody response to BSA was observed in transgenic mice, suggesting that specific antibody response to tumor antigens might be suppressed by hMan2c1 transgene. 20978011_regulation of Man2C1 expression is essential for maintaining efficient protein N-glycosylation 21508515_MAN2C1 methylation levels modify cumulative traumatic burden on risk of post traumatic stress disorder 21556061_MAN2C1 binds PTEN thereby inhibiting its phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5 triphosphate phosphatase activity 23486476_Man2C1 has dual functions: one in glycan catabolism and another in apoptotic signaling. 27355585_MAN2C1 may contribute to the verbal difficulties observed in microduplications and to the intellectual disability of microdeletion syndromes 35045343_Impaired catabolism of free oligosaccharides due to MAN2C1 variants causes a neurodevelopmental disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000032295 |
Man2c1 |
1201.034964 |
0.3570288931 |
-1.485887 |
0.078361783 |
351.651999 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000185095510516787247334128528225035710659724689981827764041945347666837711369335351174132375390946838992507899225867811844427674618618594411719984700515078836235981905135820311183744886569850713123330798737242730567231774330139160156250000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000060982360161334364495888750188737348015973609344516211588842936108130822193117666217803564798237881354239263611647174898499520779642895891871534011477686635927847316212615527839214594002189596955165740155280218459665775299072265625000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
621.2791687 |
35.1637781 |
1751.3863079 |
69.7297825 |
| ENSG00000140470 |
170691 |
ADAMTS17 |
protein_coding |
Q8TE56 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Deafness;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. ADAMTS family members share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protein, which may promote breast cancer cell growth and survival. Mutations in this gene are associated with a Weill-Marchesani-like syndrome, which is characterized by lenticular myopia, ectopia lentis, glaucoma, spherophakia, and short stature. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]. |
hsa:170691; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19836009_Homozygous mutation in ADAMTS17 causes lenticular myopia, ectopia lentis, glaucoma, spheropakia, and short stature. 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21037509_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21555518_ADAMTS17 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 22486325_Recessive ADAMTS17 mutations are a recurrent cause of isolated spherophakia with short stature. 23661674_Endothelial protease nexin-1 is a novel regulator of A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 maturation and endothelial protein C receptor shedding via furin inhibition. 24906090_higher Adamts17 expression is found in several human cancer cell subtypes, especially in breast ductal carcinoma and there is an inverse correlation between higher Adamts17 expression and patients' survival. 24940034_A mutation in WMS-like gene ADAMTS17 also causes WMS. 24940034_The mutation in the Weill-Marchesani syndrome (WMS)- gene ADAMTS17 also causes WMS in an Indian family. 28176809_Secretion of ADAMTS17 requires O-fucosylation. ADAMTS17 binds fibrillin-2 but not fibrillin-1 and does not cleave either. ADAMTS17 regulates fibrillin isoform composition of microfibrils in the eye. 31019231_A novel nonsense mutation c.1051 A > T in ADAMTS17 had been identified caused autosomal recessive WMS in the Chinese family. 31726086_A novel ADAMTS17 variant that causes Weill-Marchesani syndrome 4 alters fibrillin-1 and collagen type I deposition in the extracellular matrix. 32616716_A novel pathogenic missense ADAMTS17 variant that impairs secretion causes Weill-Marchesani Syndrome with variably dysmorphic hand features. |
ENSMUSG00000058145 |
Adamts17 |
128.284764 |
0.3919761280 |
-1.351162 |
0.196864241 |
46.676300 |
0.00000000000837355854623333946483010441315175198875864204239860555389896035194396972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000046763670497609368346878530171400458956276757760406326269730925559997558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.0754771 |
10.6999402 |
190.9834850 |
18.7996371 |
| ENSG00000140479 |
5046 |
PCSK6 |
protein_coding |
P29122 |
FUNCTION: Serine endoprotease that processes various proproteins by cleavage at paired basic amino acids, recognizing the RXXX[KR]R consensus motif. Likely functions in the constitutive secretory pathway, with unique restricted distribution in both neuroendocrine and non-neuroendocrine tissues. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family, which includes proteases that process protein and peptide precursors trafficking through regulated or constitutive branches of the secretory pathway. The encoded protein undergoes an initial autocatalytic processing event in the ER to generate a heterodimer which exits the ER and sorts to the trans-Golgi network where a second autocatalytic event takes place and the catalytic activity is acquired. The encoded protease is constitutively secreted into the extracellular matrix and expressed in many tissues, including neuroendocrine, liver, gut, and brain. This gene encodes one of the seven basic amino acid-specific members which cleave their substrates at single or paired basic residues. Some of its substrates include transforming growth factor beta related proteins, proalbumin, and von Willebrand factor. This gene is thought to play a role in tumor progression and left-right patterning. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:5046; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; nerve growth factor binding [GO:0048406]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; glycoprotein metabolic process [GO:0009100]; nerve growth factor production [GO:0032902]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030510]; regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0051004]; secretion by cell [GO:0032940]; zygotic determination of anterior/posterior axis, embryo [GO:0007354] |
12535616_a unique SPC family protease that anchors heparan sulfate proteoglycans at the extracellular matrix; distribution in human placenta 12805404_reduction of PACE4 expression in ovarian cancer cells is caused, in part, by DNA hypermethylation and histone deacetylation 14561729_These results suggest that PACE4 expression is down-regulated by Hash-2/Mash-2 in both human and rat placenta and that many bioactive proteins might be regulated by PACE4 activity. 15043778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17707572_RB1CC1 and PACE4 genes might be the DNA targets of sodium arsenite treatment in human lymphoblastoid cells. 17825503_upregulation of the expression of PACE4 by E2F 17909005_Overexpression in a stable manner of the prosegment ppPACE4 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells resulted in increased matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 (but not MMP-2) activity and a reduced secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP-1). 18671934_PACE4 is a proprotein convertase responsible for activation of aggrecanases in osteoarthritic and cytokine-stimulated cartilage; posttranslational activation of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 in the extracellular milieu of cartilage results in aggrecan degradation 18772886_Data show that Cripto binds the proprotein convertases Furin and PACE4 and localizes Nodal processing at the cell surface. 19339735_PC1 and PC2 were primarily expressed in neurons, whereas PACE4 appeared to be largely restricted to glia. Thus, elevated PACE4 may modulate the bioactivity of proteins secreted in the ONH and retina. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21051773_In a genome-wide association study of handedness in patients with dyslexia, PCSK6 was the most highly associated marker. 21051773_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21722156_PCSK6 as a novel glioma invasion-associated candidate gene that likely contribute to the invasive phenotype of malignant gliomas. 22440827_A variant in PCSK6 is strongly associated with protection against pain in knee osteoarthritis. 23226097_PACE4 has a distinct role in maintaining proliferation and tumor progression in prostate cancer. 23826248_Results provide evidence for the role of PCSK6 as candidate for involvement in the biological mechanisms that underlie the establishment of normal brain lateralization and thus handedness and support the assumption that the degree of handedness, instead the direction, may be the more appropriate indicator of cerebral organization. 23908247_PCSK6 was detected at increased levels in the fibrous cap of symptomatic carotid plaques, possibly associated with key processes in plaque rupture such as inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. 24860148_PCSK6 regulated by LH inhibits the apoptosis of human granulosa cells via activin A and TGFbeta2. 24913567_miR-124 exhibits antiproliferative and antiaggressive effects on prostate cancer cells through PACE4 pathway. 25433529_PCSK6 is upregulated in the synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and has a genetic effect on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Inhibition of PCSK6 may play a protective role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. 26114115_PACE4-knockdown associated growth deficiencies were established on the knockdown HepG2, Huh7, and HT1080 cells as well as the antiproliferative effects of the multi-Leu peptide supporting the growth capabilities of PACE4 in cancer cells. 26259032_identified a PCSK6 mutation that impaired corin activation activity in a hypertensive patient 26604689_PACE4 regulates apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial signaling pathways 26744331_In summary, our study implicated a gene network involving Tbx5, Osr1 and Pcsk6 interaction in second heart field for atrial septation, providing a molecular framework for understanding the role of Tbx5 in congenital heart disease ontogeny. 26908617_Variants in non-coding sequences of PCSK6 gene is associated with handedness. 26921480_These results implicate PCSK6 in mediation of brain developmental pathways that jointly impact upon handedness, autism and aspects of schizotypy 28347547_Our results suggest that PACE4 is a promising target for estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. 28993410_PACE4 pre-mRNA undergoes DNA methylation-sensitive alternative splicing of its terminal exon 3' untranslated region, generating an oncogenic, C-terminally modified isoform (PACE4-altCT). 29180304_Data suggest that soluble corin lacking transmembrane domain is activated by PCSK6 in conditioned medium or in cell-free system but not intracellularly; cell membrane association is unnecessary for PCSK6 to activate corin; soluble corin and PCSK6 are secreted by cardiomyocytes (or HEK293 cells) via different intracellular pathways. (PCSK6 = proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-6) 31115778_PCSK6, a gene that has been implicated in the ontogenesis of bodily asymmetries by regulating the nodal cascade, is also relevant for structural asymmetries in the human brain. 31893970_PCSK6 Is a Key Protease in the Control of Smooth Muscle Cell Function in Vascular Remodeling. 32119574_Upregulation of PACE4 in prostate cancer is not dependent on E2F transcription factors. 32449780_Paired Basic Amino Acid-cleaving Enzyme 4 (PCSK6): An Emerging New Target Molecule in Human Melanoma. 33359561_Up-regulation of PCSK6 by lipid oxidation products: A possible role in atherosclerosis. 34301174_Up-regulation of microRNA-135 or silencing of PCSK6 attenuates inflammatory response in preeclampsia by restricting NLRP3 inflammasome. 35410344_PACE4-altCT isoform of proprotein convertase PACE4 as tissue and plasmatic biomarker for prostate cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000030513 |
Pcsk6 |
2084.925974 |
0.2609750629 |
-1.938016 |
0.064097289 |
885.163461 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001648677171537946908481515476293796176328823055578347137684605462753297875815276630435259045367721866058115412951224643338104521931679166 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001448480657851196286322603744498616925788850882707840088115041675647136965774125562155599847497704120545173855423311192519919147825276313 |
Yes |
Yes |
874.1051255 |
40.4335223 |
3373.1319601 |
107.5509843 |
| ENSG00000140479_ENSG00000279970 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
216.727825 |
0.0867094244 |
-3.527667 |
1.109059311 |
7.702381 |
0.00551480340337720705001789411880963598378002643585205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011173438329972213561847027563089795876294374465942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.7103712 |
23.5842738 |
438.5288625 |
187.1636342 |
| ENSG00000140488 |
60677 |
CELF6 |
protein_coding |
Q96J87 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein implicated in the regulation of pre-mRNA alternative splicing. Mediates exon inclusion and/or exclusion in pre-mRNA that are subject to tissue-specific and developmentally regulated alternative splicing. Specifically activates exon 5 inclusion of TNNT2 in a muscle-specific splicing enhancer (MSE)-dependent manner. Promotes also exon exclusion of INSR pre-mRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14761971}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;mRNA processing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
Members of the CELF/BRUNOL protein family contain two N-terminal RNA recognition motif (RRM) domains, one C-terminal RRM domain, and a divergent segment of 160-230 aa between the second and third RRM domains. Members of this protein family regulate pre-mRNA alternative splicing and may also be involved in mRNA editing, and translation. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified in this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:60677; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; mRNA splice site selection [GO:0006376]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381] |
14761971_CELF6 is a member of the CELF family of RNA-binding proteins that regulates muscle-specific splicing enhancer-dependent alternative splicing 23407934_Analysis of common variants near the corresponding genes implicated the RNA binding protein CELF6 in autism risk 31534127_RNA-binding protein CELF6 is cell cycle regulated and controls cancer cell proliferation by stabilizing p21. 32601971_CELF6 modulates triple-negative breast cancer progression by regulating the stability of FBP1 mRNA. 33357440_CLIP and Massively Parallel Functional Analysis of CELF6 Reveal a Role in Destabilizing Synaptic Gene mRNAs through Interaction with 3' UTR Elements. 35088780_The natural compound neobractatin inhibits cell proliferation mainly by regulating the RNA binding protein CELF6. |
ENSMUSG00000032297 |
Celf6 |
15.313090 |
0.0520574659 |
-4.263751 |
0.824419488 |
27.314703 |
0.00000017289175288430391659226872686644371768238670483697205781936645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000665766311654663741878871444784815381012776924762874841690063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.9489051 |
1.1187277 |
39.3913774 |
10.5890712 |
| ENSG00000140526 |
11057 |
ABHD2 |
protein_coding |
P08910 |
FUNCTION: Progesterone-dependent acylglycerol lipase that catalyzes hydrolysis of endocannabinoid arachidonoylglycerol (AG) from cell membrane (PubMed:26989199). Acts as a progesterone receptor: progesterone-binding activates the acylglycerol lipase activity, mediating degradation of 1-arachidonoylglycerol (1AG) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2AG) to glycerol and arachidonic acid (AA) (PubMed:26989199). Also displays an ester hydrolase activity against acetyl ester, butanoate ester and hexadecanoate ester (PubMed:27247428). Plays a key role in sperm capacitation in response to progesterone by mediating degradation of 2AG, an inhibitor of the sperm calcium channel CatSper, leading to calcium influx via CatSper and sperm activation (PubMed:26989199). May also play a role in smooth muscle cells migration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QXM0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26989199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27247428}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Flagellum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Serine esterase;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing an alpha/beta hydrolase fold, which is a catalytic domain found in a wide range of enzymes. The encoded protein is an acylglycerol lipase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of endocannabinoid arachidonoylglycerol from the cell membrane. This leads to activation of the sperm calcium channel CatSper, which results in sperm activation. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:11057; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; sperm plasma membrane [GO:0097524]; acetylesterase activity [GO:0008126]; acylglycerol lipase activity [GO:0047372]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; hormone-sensitive lipase activity [GO:0033878]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; short-chain carboxylesterase activity [GO:0034338]; triglyceride lipase activity [GO:0004806]; acrosome reaction [GO:0007340]; acylglycerol catabolic process [GO:0046464]; cellular lipid metabolic process [GO:0044255]; medium-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0051792]; medium-chain fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0051793]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014912]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014909]; sperm capacitation [GO:0048240]; steroid hormone mediated signaling pathway [GO:0043401] |
17980156_Our results showed that the ABHD2 was expressed in atherosclerotic lesions, and that the ABHD2 expression was significantly higher in the patients with UA than with SA. 20007591_Patients with selective immunoglobulin (Ig)A deficiency have a highly significant increase of homozygousity of HS1.2 allele *1, with an increase of 2.6-fold; the HS1.2 polymorphism influences Ig seric production, but not IgG switch. 25880496_ABHD2 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms, such as rs12442260 contribute to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 26989199_ABHD2 is highly expressed in spermatozoa, binds progesterone, and acts as a progesterone-dependent lipid hydrolase by depleting the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2AG) from plasma membrane. 27247428_A mutant ABHD2 developed with alanine in place of Ser(207). 27323405_Suppression of ABHD2 in OVCA420 cells increased phosphorylated p38 and ERK, platinum resistance, and side population cells (p |
ENSMUSG00000039202 |
Abhd2 |
976.359234 |
2.5140624019 |
1.330020 |
0.072773856 |
331.829381 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003840156636557801979624920876297575562217628145704917244323969959718954536846294989061036093802234306476080723818156615168074406294669046740288225596029969936411252542069050868660078090766063496630522422492504119873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001205972594799854505180518505373127800667992024382047044514476870743499748311808094429299904171368333557726838560874869330492718964571369523876765982230282916783739349356593796125207418423741501101176254451274871826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1442.4549467 |
67.8102941 |
577.8009132 |
20.8820273 |
| ENSG00000140538 |
4916 |
NTRK3 |
protein_coding |
Q16288 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase involved in nervous system and probably heart development. Upon binding of its ligand NTF3/neurotrophin-3, NTRK3 autophosphorylates and activates different signaling pathways, including the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT and the MAPK pathways, that control cell survival and differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25196463}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) family. This kinase is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself and members of the MAPK pathway. Signalling through this kinase leads to cell differentiation and may play a role in the development of proprioceptive neurons that sense body position. Mutations in this gene have been associated with medulloblastomas, secretory breast carcinomas and other cancers. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:4916; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; GPI-linked ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005004]; neurotrophin binding [GO:0043121]; neurotrophin receptor activity [GO:0005030]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; heart development [GO:0007507]; negative regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048712]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; neuron fate specification [GO:0048665]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; postsynaptic density assembly [GO:0097107]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051896]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; response to corticosterone [GO:0051412]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11877382_Although TrkB and TrkC signals mediating survival are largely similar, TrkB and TrkC signals required for maintenance of target innervation in vivo are regulated by distinct mechanisms. 12399943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12450792_Expression of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion is a primary event in human secretory breast carcinoma. 14668342_ETV6-NTRK3.IRS-1 complex formation through the NTRK3 C terminus is essential for ETV6-NTRK3 transformation 15167446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15198123_While survival rates were higher for patients with high TrkC expression, these differences were not statistically significant. 15932601_truncated trkC is prevalent in the human prefrontal cortex and that neurons and glia may be responsive to NT-3 throughout life 16648236_These novel data demonstrate that neurotrophins influence ASM [Ca(2+)](i) and force regulation and suggest a potential role for neurotrophins in airway diseases 16786155_Light and electron microscopy immunohistochemistry showed that tonsillar samples were positive for TrkC. 16826429_TrkC was significantly present in 100% of medulloblastoma female patients 16862449_Human lung adenocarcinomas express TrkA and TrkB, but not TrkC; A549 cells, express mRNA transcripts encoding nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), TrkA, TrkB, and p75, and high protein levels of TrkA and TrkB. 16941478_NTRK3 gene was implicated in the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancers and it may be useful targets for diagnostic and therapeutic intervention in selected patients. 17971243_in astrocytomas, Trk receptors (TrkA, TrkB, TrkC) expression, but not p75NTR may promote tumor growth independently of grade 18068631_Using a conditional knock-in mouse model, the authors showed that ETV6(mouse)-NTRK3(human) fusion protein targeted committed alveolar bipotent or CD61(+) luminal progenitors for tumorigenesis via AP1 activation. 18179783_NTRK3 might be involved in the molecular basis of the age-dependent changes in ADHD symptoms throughout life span. 18203754_A strong significant association was found between eating disorders and NTRK3 gene. 18203754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18293376_somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of NTRK3 gene are frequent in large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas. Such mutational events could represent an important step in the cancerogenesis of these tumors 18319596_A potential role of all neurotrophins, through their different receptors, in pituitary functions. 18336001_protein levels of translational, splicing, processing, chaperone, protein handling, and metabolism machineries were shown to depend on neurotrophin-3-induced TrkC activation in the medulloblastoma cell line DAOY 18347002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18347002_childhood-onset mood disorders are linked to NTRK3 gene on chromosome 15q25.3-q26.2. 18367154_Here we present initial linkage-disequilibrium (LD) fine mapping of this signal and sequence analysis of NTRK3 (neurotrophic receptor kinase-3), a biologically plausible candidate gene. 18367154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18428117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18616610_NTRK3 may contribute to the genetic susceptibility to hoarding in obsessive-compulsive disorder 18616610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18639687_novel sequence variant, G76R, is present in 2 different patients and absent in controls could generate a lack of mature functional NTF-3 proteins in neural crest cell precursors altering NTF-3/TrkC signaling pathway and influencing ENS development. 18713973_Stress conditions induced the membranous expression of p75 neurotrophin receptor and tyrosine protein kinase receptor B, maximal in mature B cells 19011601_Secretory breast carcinomas with ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene belong to the basal-like carcinoma spectrum. 19040714_Novel R645C mutation was detected in NTRK3 in 2 affected siblings with Hirschsprung disease. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156760_A proteomic approach identified thirteen proteins from several pathways that were differentially expressed following NP-3-induced TrkC receptor activation. 19179422_TrkC is a new neurotrophic receptor that Trypanosoma cruzi engages to promote the survival of neuronal and glial cells. 19187638_Insufficient expression of NTRK3 is associated with the outflow tract defect of human tetralogy of Fallot and may contribute to the progression of this defect. 19344762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344762_The present results, although not robust, suggest that the NTRK-3 gene influences hippocampal function and may modify the risk for schizophrenia. 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19370765_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19370765_miRNAs are implicated as key posttranscriptional regulators of NTRK3 and provide a framework for allele-specific miRNA regulation of NTRK3 in anxiety disorders. 19417027_Trk signaling pathways were found to be targeted therapy with Trk-selective inhibitors to treat neuroblastomas and other tumors with activated Trk expression. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19556619_Findings suggest that mutations in RET and NTRK3 acting together are necessary and sufficient for the appearance of Hirschsprung disease and the EDN3 mutation acts as a phenotype modifier. 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19680743_Mesenchymal stem cells modified by adenovirus carrying the TrkC gene are further promoted to differentiate into neuron-like cells with the potency of forming synapses by overexpressing the NT-3 gene in Schwann cells. 19893451_Study identified the previously reported pathogenic mutation of NTRK3 in a KRAS/BRAF wild-type tumor and 2 somatic mutations in the Src family of kinases (YES1 and LYN) that would be expected to cause structural changes. 20078941_ShcD binds to TrkC in a kinase-activity-dependent manner through its PTB and SH2 domains. 20160348_TrkC ligand neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) is upregulated in a large fraction of aggressive human neuroblastomas (NBs) and that it blocks TrkC-induced apoptosis of human NB cell lines, consistent with the idea that TrkC is a dependence receptor. 20219210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20554328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554328_This study demonistrated that Intron 12 in NTRK3 is associated with bipolar disorder. 20802235_Overexpression of TrkC is associated with breast tumor growth and metastasis. 21070662_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21139137_Studies indicate that insulin, IGF-1, TrkA, and TrkC receptors as trophic and as dependence receptors. 21295543_These results suggest that TrkA, TrkB, TrkC may contribute to growth and metastasis of liver cancer. 21392742_NT3 and its receptor may be involved in early folliculogenesis, particularly in the activation of primordial follicles. 21401966_We have characterized a novel ETV6-NTRK3 fusion transcript which has not been previously described in AML FAB M0 by FISH and RACE PCR. 21552290_Data indicate that the CYLD mutant tumours showed dysregulated tropomyosin kinase (TRK) signalling, with overexpression of TRKB and TRKC in tumours. 21617231_Low TRKC is associated with low vincristine and lomustine response in medulloblastoma. 21728718_The significant expression of Trk isoforms among advanced neuroblastoma cases support their role as possible risk assessment tools alongside N-Myc amplification status. 21788388_TrkC is implicated as a functional PDNF receptor in cell entry, independently of sialic acid recognition, mediating broad T. cruzi infection both in vitro and in vivo. 22265740_SOX2 utilizes a specific binding motif to directly interact with the TRKC regulatory region. 22343487_expression of neurotrophin receptors Pan-Trk, p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR) and ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor-alpha in ulveal melanoma does not show a role in growth. 23027130_NT-3 promoted motility, migration, invasion, soft-agar colony growth and cytoskeleton restructuring in TrkC-expressing U2OS cells 23332094_These results suggest that TrkB and TrkC have a tumor progressive function and may be a useful diagnostic and therapeutic target in colorectal cancer 23341610_provide evidence that a mutation of TrkC detected in a sporadic cancer is a loss-of-proapoptotic function mutation 23416450_Genetic evidence shows that TrkC and TrkB activation in early cortical neurons depends on transactivation by epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. 23727532_NTRK3 genetic variants may influence white matter integrity in brain regions implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders. 23832765_Results show that TrkC plays physiological role in the pathogenesis of leukemia and have important implications for understanding various hematological malignancies. 23869086_Patients with mastocytosis featured elevated serum levels of NGF, NT-3, and NT-4. TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC expression was also elevated. 23874207_our findings suggest NTRK3 is a conditional tumor suppressor gene that is commonly inactivated in colorectal cancer by both epigenetic and genetic mechanisms 24145651_Report ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion in mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary glands with high-grade transformation. 24327398_ETV6-NTRK3 rearrangement can be directly induced in thyroid cells by ionizing radiation in vitro and, thus, may represent a novel mechanism of radiation-induced carcinogenesis. 24603864_Data indicate how the neurotrophins function through tyrosine kinase receptors TrkC and TrkA. 25196463_findings suggest a novel pathophysiological mechanism involving NTRK3 in the development of VSDs 25456394_Report molecular genetic tests for ETV6-NTRK3 for differential diagnosis of mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of the salivary gland. 25772499_Experimental verification of a conserved intronic microRNA located in the human TrkC gene with a cell type-dependent apoptotic function. 26055783_SNPs in the NTRK3 gene, pain, physical activity, and fear of falling were directly associated with depressive symptoms in older adults. 26216473_TNS1, MET, and TRKC tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins are upregulated during epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced with TGF-beta, and predict the outcome in lung adenocarcinoma patients. 26291510_Spectrum of secretory breast carcinoma with ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion ranging from low-grade to high-grade histology, with occasional low hormonal receptor expression, simplex genomic profiles, and possible unfavorable course. 26410934_The role of NTRK3 in in paranoid schizophrenia development in Russians. 26459250_High expression of TrkA, TrkB, or TrkC was significantly associated with histopathology 26492182_Molecular analysis of ETV6 gene rearranged mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary glands tumors with lack of classical ETV6-NTRK3 fusion. 26606880_the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion might identify a subset of gastrointestinal stromal tumours with peculiar clinicopathological characteristics 26647767_A subset of ALK-negative inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (IMT) have rearrangement of ROS1, ETV6 or NTRK3 as a possible oncogenic mechanism. 26884591_We report the case of a patient with an initial diagnosis of salivary acinic cell carcinoma later reclassified as Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma after next-generation sequencing revealed an ETV6-NTRK3 fusion. 27259007_we demonstrate the expression of the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion oncogene in a small subset of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors 27282352_Case Reports: mammary analog secretory carcinoma of the thyroid gland with ETV6 rearrangement and ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion. 27351280_LINC00052 could regulate NTRK3 expression by forming complementary base pairing with miR-128 and miR-485-3p to reduce the luciferase activity of NTRK3 3'UTR. 27477320_ETV6-NTRK3, MYO5A-NTRK3 and MYH9-NTRK3 fusions are identified in Spitz tumours and demonstrated that NTRK3 fusions constitutively activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase and phospholipase Cgamma1 pathways in melanocytes. 27631515_We report 6 cases of secretory carcinomas of the skin harboring the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion 27763904_Case Report: ETV6-NTRK3 translocation in primary cutaneous mammary analog secretory carcinoma. 27826991_Pilot study usee targeted exome sequencing in an attempt to discover novel candidate genes related to Internet Gaming Disorder. Despite a relatively small sample, the targeted exome sequencing was feasible and valuable and revealed that rs2229910 of NTRK3 may be a protective SNP against Internet Gaming Disorder. 27974047_5 gastrointestinal stromal tumors cases lacking alterations in the KIT/PDGFRA/SDHx/RAS pathways, including two additional cases with FGFR1-TACC1 and ETV6-NTRK3 fusions, are reported. 28097808_NTRK fusions occur in a subset of young patients with mesenchymal or sarcoma-like tumors at a low frequency 28100780_TrkC-miR2 as a novel regulator of Wnt signaling, which might be a candidate oncogenic colorectal cancer biomarker. 28125451_ETV6-NTRK3 translocated papillary thyroid carcinomas are locoregionally aggressive and can metastasize distantly. 28181547_The authors found a significant association between the localization of RET mutations and the expression of three genes: NNAT (suggested to be a tumour suppressor gene), CDC14B (involved in cell cycle control) and NTRK3 (tyrosine receptor kinase that undergoes rearrangement in papillary thyroid cancer) in patients with medullary thyroid cancer. 28215291_Data suggest that kinase domains of neurotrophin receptor isoforms, TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC, exhibit a bulky phenylalanine gatekeeper, leading to a small and unattractive back pocket/binding site for antineoplastic kinase inhibitors. [REVIEW] 28402394_High expression of TrkC is associated with glioblastoma. 28455963_Data show that neurotrophin 3 receptor TrkC acts as an activator in tumorigenicity and metastasis of colorectal cancer, and was frequently overexpressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, patients' tumor samples. 28683589_6 patients with mesenchymal tumors composed of infiltrative fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumor cells were studied. Using next-generation DNA sequencing, TMP3-NTRK1 fusions were identified in 4 cases, an LMNA-NTRK1 fusion in one case, and a variant EML4-NTRK3 fusion in one case. 28695340_High TrkC mRNA expression appears to be frequent in the sonic hedgehog subgroup and seems not to have a major effect on therapy responsiveness in medulloblastoma patients. 28719467_Pan-Trk immunohistochemistry is a time-efficient and tissue-efficient screen for NTRK fusions, particularly in driver-negative advanced malignancies and potential cases of secretory carcinoma and congenital fibrosarcoma. 28746220_Study found that copy number variations of NTRK3 were associated with platinum-sensitive and platinum-resistant recurrences. Amplification of NTRK3 perfectly predicted platinum-sensitive relapse of ovarian cancer. 29046324_The prevalence of ETV6-NTRK3 kinase fusions were determined in papillary thyroid cancer of adult population 29391602_STAT1 as a significant ETV6-NTRK3 (EN) fusion-regulated transcription factor and a crucial mediator of EN-induced tumorigenesis. 29553955_Report a novel subset of high-grade uterine sarcomas with features reminiscent of soft tissue fibrosarcoma and characterized by oncogenic activation of Trk through recurrent NTRK gene fusions. 30187166_Case Report: congenital CD34-positive dermohypodermal spindle-cell neoplasm occurring in a female infant and harboring a novel KHDRBS1-NTRK3 fusion. 30366959_Trk receptors Trk-A, Trk-B, and Trk-C have a propensity to interact laterally and to form dimers even in the absence of ligand. 30520818_we detected novel and related STRN-NTRK3 and STRN3-NTRK3 fusions in 2 fibrosarcomas that occurred in the bone and soft tissue of young adult patients 31127997_Overexpression of circ-10021 promotes the proliferative and migratory capacities of breast cancer cells by sponging microRNA-485-3p to upregulate the NTRK3 expression. 31268127_Experts from several Institutions were recruited by the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Translational Research and Precision Medicine Working Group (TR and PM WG) to review the available methods for the detection of NTRK gene fusions, their potential applications, and strategies for the implementation of a rational approach for the detection of NTRK1/2/3 fusion genes in human malignancies. 31479159_Morphological, immunophenotypical and molecular features of hypermutation in colorectal carcinomas with mutations in DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE). 31569361_Results found that half of the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors expressed TrkC. However, HNSSCC that also expressed CD271 had a reduced correlation with distant metastases and better survival rates. HNSCC cell lines expressing both CD271 and TrkC have low proliferative rate. 31871300_TRK Fusions Are Enriched in Cancers with Uncommon Histologies and the Absence of Canonical Driver Mutations. 32034283_NTRK3 overexpression in undifferentiated sarcomas with YWHAE and BCOR genetic alterations. 32278476_NTRK-rearranged mesenchymal tumours: diagnostic challenges, morphological patterns and proposed testing algorithm. 32315394_Discovery and characterization of targetable NTRK point mutations in hematologic neoplasms. 32880785_Detection of NTRK1/3 Rearrangements in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Immunohistochemistry, Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization, and Next-Generation Sequencing. 32931153_Fine-needle aspiration cytomorphology of papillary thyroid carcinoma with NTRK gene rearrangement from a case series with predominantly indeterminate cytology. 32968185_Fusion partners of NTRK3 affect subcellular localization of the fusion kinase and cytomorphology of melanocytes. 33046021_KANK1-NTRK3 fusions define a subset of BRAF mutation negative renal metanephric adenomas. 33074583_Cytomorphologic features of NTRK-rearranged thyroid carcinoma. 33290352_S100 and Pan-Trk Staining to Report NTRK Fusion-Positive Uterine Sarcoma: Proceedings of the ISGyP Companion Society Session at the 2020 USCAP Annual Meeting. 33301751_Pan-tropomyosin receptor kinase immunoreactivity, ETV6-NTRK3 fusion subtypes, and RET rearrangement in salivary secretory carcinoma. 33524004_NTRK fusion analysis reveals enrichment in Middle Eastern BRAF wild-type PTC. 33593392_Genome-wide analysis identifies critical DNA methylations within NTRKs genes in colorectal cancer. 33627781_Nerve growth factor receptor increases the tumor growth and metastatic potential of triple-negative breast cancer cells. 33758144_Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization Must be Preferred to pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry to Diagnose NTRK3-rearranged Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST). 33894748_Identification of NTRK3 as a potential prognostic biomarker associated with tumor mutation burden and immune infiltration in bladder cancer. 33899788_Pan-TRK Immunohistochemistry Is Highly Correlated With NTRK3 Gene Rearrangements in Salivary Gland Tumors. 34378283_An unusual fusion gene EML4-ALK in a patient with congenital mesoblastic nephroma. 34445205_The Role of the Second Extracellular Loop of Norepinephrine Transporter, Neurotrophin-3 and Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase C in T Cells: A Peripheral Biomarker in the Etiology of Schizophrenia. 35152631_[Clinicopathological features of NTRK3 gene rearrangement papillary thyroid carcinoma]. 35536742_Selective activation and down-regulation of Trk receptors by neurotrophins in human neurons co-expressing TrkB and TrkC. 35737155_Prediction of EVT6-NTRK3-Dependent Papillary Thyroid Cancer Using Minor Expression Profile. 36171207_TrkC, a novel prognostic marker, induces and maintains cell survival and metastatic dissemination of Ewing sarcoma by inhibiting EWSR1-FLI1 degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000059146 |
Ntrk3 |
114.389072 |
4.5040950835 |
2.171237 |
0.571285996 |
13.239795 |
0.00027406784127089579101640981484422354697016999125480651855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000703275614944092884901760687199612220865674316883087158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
177.8657787 |
64.2341651 |
39.7073406 |
10.5478030 |
| ENSG00000140543 |
55070 |
DET1 |
protein_coding |
Q7L5Y6 |
FUNCTION: Component of the E3 ubiquitin ligase DCX DET1-COP1 complex, which is required for ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of target proteins. The complex is involved in JUN ubiquitination and degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14739464}. |
Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
Enables ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity and ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process; protein ubiquitination; and protein-containing complex assembly. Part of Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55070; |
Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0080008]; Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031464]; cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031461]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity [GO:1990756]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003] |
14739464_promotes ubiquitination and degradation of c-Jun by assembling a multisubunit ubiquitin ligase containing DNA Damage Binding Protein-1 (DDB1), cullin 4A (CUL4A), Regulator of Cullins-1 (ROC1), and constitutively photomorphogenic-1 17452440_These findings demonstrate that the conserved DET1 complex modulates Cul4A functions by a novel mechanism. 29360641_COP1/DET1/ETS axis regulates ERK transcriptome and sensitivity to MAPK inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000030610 |
Det1 |
26.597818 |
0.4204246653 |
-1.250081 |
0.469435197 |
6.978321 |
0.00825029545747877832151395693927042884752154350280761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016075823228037855461280969393556006252765655517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.9774933 |
4.7394799 |
38.3045948 |
7.7737369 |
| ENSG00000140545 |
4240 |
MFGE8 |
protein_coding |
Q08431 |
FUNCTION: Plays an important role in the maintenance of intestinal epithelial homeostasis and the promotion of mucosal healing. Promotes VEGF-dependent neovascularization (By similarity). Contributes to phagocytic removal of apoptotic cells in many tissues. Specific ligand for the alpha-v/beta-3 and alpha-v/beta-5 receptors. Also binds to phosphatidylserine-enriched cell surfaces in a receptor-independent manner. Zona pellucida-binding protein which may play a role in gamete interaction. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19204935}.; FUNCTION: [Medin]: Main constituent of aortic medial amyloid. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19204935}. |
Alternative splicing;Amyloid;Angiogenesis;Cell adhesion;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Fertilization;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to form multiple protein products. The major encoded protein product, lactadherin, is a membrane glycoprotein that promotes phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. This protein has also been implicated in wound healing, autoimmune disease, and cancer. Lactadherin can be further processed to form a smaller cleavage product, medin, which comprises the major protein component of aortic medial amyloid (AMA). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:4240; |
acrosomal membrane [GO:0002080]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; membrane [GO:0016020]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; single fertilization [GO:0007338] |
15478463_Truncated fragment of medin, the hexapeptide, NFGSVQ can form typical amyloid fibrils. 16115445_Might prove useful in the treatment of prolonged ischemia. 17420351_Lactadherin) is expressed in normal and atherosclerotic human arteries. 17637751_The trans-activator (TA) isoforms of p63 activate MFGE8 transcription though a p53/p63 motif at -370, which was confirmed by a chromatin immunoprecipitation experiment. 17679143_Identification of the last 18-19 amino acid residues as constituting the amyloid-promoting region of medin. 17906662_aggregated medin induced death of aortic smooth muscle cells in vitro. Cells incubated together with medin increased the production of matrix metalloproteinase-2, a protease that degrades elastin and collagen and subsequently weakens the vessel wall. 18160406_analysis of membrane-interactive loops of Lact-C2 18303131_Some childhood-onset and adult SLE patients carried a significant level of MFG-E8 in their blood samples. 18647368_Lactadherin promoted phagocytosis of phosphatidylserine-expressing RBCs by macrophages in a concentration-dependent manner. 18974133_findings delineate pleiotropic roles for MFG-E8 in the tumor microenvironment and raise the possibility that systemic MFG-E8 blockade might prove therapeutic for melanoma patients 18990388_SED1 is expressed on the surface of acrosome-intact human sperm and in the anterior caput of the human epididymis, similar to that seen in mouse 19196164_molecular architecture of fibrils formed by the peptide AMed42-49 representing residues 42-49 of the 50 amino acid polypeptide medin 19443842_arterial MFG-E8 significantly increases with aging and is a pivotal relay element within the angiotensin II/MCP-1/VSMC invasion signaling cascade. 19502262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19502262_Results suggest that the impairment of phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells through phosphotidylserine-dependent MFG-E8 system may lead to the development of human systemic lupus erythematosus. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20213738_intronic mutation in the human MFG-E8 gene can lead to the development of SLE. 20956946_overexpression of MFGE8 during bladder tumor development, correlated with expression of genes involved in cell adhesion or migration and in immune responses. 21127199_MFG-E8 is expressed in triple-negative breast cancers as a target gene of the p63 pathway, but may serve a suppressive function in ER(+) and erbB2(+) breast cancers. 21177637_Prolactin has a modulatory role for as a stromal/epithelial paracrine factor controlling MFG-E8. This is the first report on MFG-E8 protein localization to the human endometrial epithelium and its up-regulation during the window of implantation. 21841820_We conclude that MFG-E8-dependent signaling stimulates cell proliferation and the acquisition of mesenchymal properties and contributes to mammary carcinoma development. 22018779_serum lactadherin is correlated with poor blood glucose control and diabetic vascular complications. 22070546_in vitro studies showed that medin amyloid-like fibrils promote the aggregation of protein amyloid A into fibrils 22204000_Decreased colonic MFGE8 expression in patients with ulcerative colitis may be associated with mucosal inflammatory activity and clinical disease activity through basal cell apoptosis and preventing tissue healing in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis 22438901_The distribution of the SNP (rs4945 and rs1878326) of MFGE8 was analyzed in two groups of patients with 'wet' age-related macular Degeneration and their age-matched controls. 22558449_a key role of MFG-E8 release from apoptotic endothelial cells in macrophage reprogramming 22770563_MFG-E8 expression in the endometrial epithelium as well as in chorionic villi suggests its possible role in endometrial reorganization during the receptive phase and in events related to normal pregnancy in mammals 22921913_Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 has proapoptotic activity, suggesting participation in endometrial remodeling via an epithelial-stromal cell paracrine effect. 23194669_our data argue that MFGE8 is not likely involved in the phagocytic clearance of neuronal debris associated with nigrostriatal pathway injury. 23262193_NMR solution structure of C2 domain of MFG-E8 and insights into its molecular recognition with phosphatidylserine 23832117_MFG-E8-dependent promotion of apoptotic cell clearance is a novel anti-inflammatory facet of glucocorticoid treatment 24122204_Our results strongly suggested that MFG-E8 is a promising biomarker for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy target of opisthorchiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma 24194865_Lactadherin may decrease inflammation by inhibiting secretory phospholipase A2 activity on pre-apoptotic leukemia cells. 24262600_TNF-alpha up-regulates endometrial epithelial cell migration and MFG-E8 production. 24424369_Blockage of MFG-E8 in endometrial tumor cells diminishes trophoblaast cell attachment. 24554711_MFG-E8 could be used as a biomarker for diagnosis and monitoring of disease activity in certain systemic lupus erythematosus patients 24561551_MFG-E8 had a negative association with hs-CRP and a positive association with LDL-c. The serum level of MFG-E8 was negatively associated with the severity of coronary artery stenosis and the risk of clinical events. 24602872_medin adopts a predominantly beta-sheet conformation with some unstructured elements. 24838098_MFG-E8 promotes cutaneous wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis. 24958900_Exogenously added MFG-E8 inhibits receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand-induced osteoclastogenesis of human osteoclast precursors. 25264705_promotes tumor progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma 25751740_Studied the therapeutic effect of rhMFG-E8 in mouse models of IBD. Treatment with rhMFG-E8 significantly attenuated colitis in both models in a dose-dependent way. 26391522_MFG-E8 is a protective factor in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and subsequent bone loss. 26819373_After myocardial infarction, Mfge8 (and Mertk)-expressing macrophages synergistically engage the clearance of injured cardiomyocytes. 27102803_an efficient purification method for production of non-aggregated, full-length MFG-E8. 27956229_Levels of MFGE8 were reduced in cirrhotic liver tissue from patients compared with controls. 28035763_Circulating MFG-E8 levels are dramatically elevated in pregnancy, and are significantly higher in gestational diabetes mellitus than in normal pregnancy. 28067023_MFG-E8 levels are elevated in T2D but suppressed by increased adipose tissues, thereby allowing inflammatory factors to rise to high levels. MFG-E8 may serve as a potential biomarker for obesity and T2D in the clinical setting 28089751_Reduced serum milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) concentrations are associated with an increased risk of microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. 28266034_Elevated serum MFG-E8 levels may be associated with cerebrovascular diseases or neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. 28653875_These findings provide a better understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying colorectal cancer progression and suggest a predictive role for MFG-E8 in colorectal cancer metastasis and prognosis 28923329_MFG-E8 could be a potential novel prognostic marker for colorectal cancer (CRC) and overexpression of MFG-E8 might be involved in lymph node metastasis and angiogenesis of CRC. 28967712_This study showed for the first time that MFG-E8 expression is impaired in the endometrium of patients with endometriosis and infertility during the window of implantation. 29152651_Our findings suggest that both MFGE8 and TGFbeta1 are agerelated inflammatory factors and are related to the degree of Atherosclerosis (AS). In conclusion, both MFGE8 and TGFbeta1 may serve as potential markers of the severity of AS 30053459_MFGE8 polymorphisms were not associated with MetS but were related to DBP, HDL-C level, and WC in Chinese adults. 30156356_Esophageal cancer patients with high MFG-E8 expression had worse overall survival and relapse-free survival in the subgroup with preoperative chemotherapy. The abundant MFG-E8 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma might have a negative influence on the long-term survival of patients after chemotherapy by affecting T-cell regulation in the tumor microenvironment. 30175895_Vasculopathy-induced dysfunction of pericytes and endothelial cells, the main cells secreting MFG-E8, may be associated with the decreased expression of MFG-E8 in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and that the deficient inhibitory regulation of latent TGFbeta-induced skin fibrosis by MFG-E8 may be involved in the pathogenesis of SSc and may be a therapeutic target for fibrosis in SSc patients. 30612778_Our findings indicate that MFG-E8 may be a potential marker for poor prognosis and survival in breast cancer. 30857759_Lactadherin (milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 [MFG-E8]) is an endogenous secreted glycoprotein bridging the integrin-expressing phagocytes and PS-presenting apoptotic cells. 30861420_The intergenic locus CARMA (CAD Associated Region between MFGE8 and ABHD2) regulates MFGE8 in a haplotype dependent manner. Individuals genetically susceptible to increased MFGE8 expression exhibit greater coronary artery disease risk. These data support an atherogenic contribution of CARMA/MFGE8 that may be linked to cell proliferation and/or improved survival of coronary artery disease relevant cell types 31256324_Immunological and Clinicopathological Significance of MFG-E8 Expression in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 31342838_he levels of MFG-E8 in synovial fluid and plasma are inversely correlated with the radiographic severity of knee osteoarthritis. 31358619_In chicken, we confirmed the presence of EDIL3 and MFGE8 proteins in eggshell, uterine fluid, and uterus. We observed that only edil3 is overexpressed in tissues in which eggshell mineralization takes place and that this overexpression occurs only at the onset of shell calcification. 31447183_The expressions of MFG-E8 in murine and human angiosarcoma (AS) cells were significantly higher than those in melanoma cells, macrophages and endothelial cells. Depletion of MFG-E8 in murine AS cells by siRNA significantly inhibited the formation of capillary-like structures and migration. AS-derived MFG-E8 might enhance tumor growth via angiogenesis and the induction of TAMs in autocrine/paracrine manner. 31673081_Serum milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MFG-E8) as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 31793433_Central for portal function is the bridging glycoprotein MFG-E8. Using a phosphatidylserine binding domain and an RGD motif, MFG-E8 helps target HIV-1 VLPs to alpha V integrin bearing sinus lining macrophage. Lack of MFG-E8 or integrin blockade severely limits HIV-1 VLP spread onto FDC networks. 31811237_Polymorphisms of MFGE8 are associated with susceptibility and clinical manifestations through gene expression modulation in Koreans with systemic lupus erythematosus. 31899997_The expression levels and clinical significance of MFG-E8 and CD133 in epithelial ovarian cancer. 31958465_MFGE8 attenuates Ang-II-induced atrial fibrosis and vulnerability to atrial fibrillation through inhibition of TGF-beta1/Smad2/3 pathway. 32025861_A rare missense variant in the milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MFGE8) increases T2DM susceptibility and cardiovascular disease risk with population-specific effects. 32324268_Knockdown of milk-fat globule EGF factor-8 suppresses glioma progression in GL261 glioma cells by repressing microglial M2 polarization. 32592231_Absence of the MFG-E8 gene prevents hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. 32900929_Medin aggregation causes cerebrovascular dysfunction in aging wild-type mice. 33115371_Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) on monocytes is a novel biomarker of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. 33588911_Identification of MFGE8 and KLK5/7 as mediators of breast tumorigenesis and resistance to COX-2 inhibition. 34031369_MFG-E8 regulated by miR-99b-5p protects against osteoarthritis by targeting chondrocyte senescence and macrophage reprogramming via the NF-kappaB pathway. 34085177_Mfge8 attenuates human gastric antrum smooth muscle contractions. 34928287_Identification of mitochondria-related hub genes in sarcopenia and functional regulation of MFG-E8 on ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and cell cycle arrest. 34939829_Maternal Variants in the MFGE8 Gene are Associated with Perceived Breast Milk Supply. 35005020_DCI after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Is Related to the Expression of MFG-E8. |
ENSMUSG00000030605 |
Mfge8 |
389.299147 |
0.4241086736 |
-1.237494 |
0.143565023 |
73.234943 |
0.00000000000000001150998825826916775940164149630886640135224360657244593864056980692112119868397712707519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000091731871863959457094341504535322326026427497967005025847342380984628107398748397827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
232.9452374 |
21.2537630 |
553.5914924 |
35.0989972 |
| ENSG00000140563 |
55784 |
MCTP2 |
protein_coding |
Q6DN12 |
FUNCTION: Might play a role in the development of cardiac outflow tract. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23773997}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Developmental protein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of neurotransmitter secretion. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. Is integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55784; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0046928] |
15528213_MCTPs are evolutionarily conserved C2 domain proteins that are unusual in that the C2 domains are anchored in the membrane by two closely spaced transmembrane regions and represent Ca(2+)-binding but not phospholipid-binding modules 18367154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19223264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19223264_The present study suggested that MCPT2 gene as aputative susceptibility gene for schizophrenia of Scandinavian origin. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23773997_Results identify MCTP2 as a novel genetic cause of coarctation of the aorta and related cardiac malformations. 33198772_Circular RNA MCTP2 inhibits cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by miR-99a-5p-mediated induction of MTMR3 expression. 33826368_Multiple C2 domain-containing transmembrane proteins promote lipid droplet biogenesis and growth at specialized endoplasmic reticulum subdomains. |
ENSMUSG00000032776 |
Mctp2 |
16.088730 |
7.0565346122 |
2.818960 |
0.602521692 |
23.680250 |
0.00000113743823523553360737507311045701996476964268367737531661987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004001093506214603058579459826660240651108324527740478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.0755325 |
10.4693675 |
3.8594493 |
1.2703312 |
| ENSG00000140749 |
10261 |
IGSF6 |
protein_coding |
O95976 |
|
Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane signaling receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in cell surface receptor signaling pathway and immune response. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10261; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; immune response [GO:0006955] |
12786995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12786995_There was no evidence for association of the common IGSF6 single nucleotide polymorphisms with disease in a large cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease |
ENSMUSG00000035004 |
Igsf6 |
121.034123 |
3.9669328362 |
1.988024 |
0.367186659 |
27.492310 |
0.00000015772035356967711287759590504942153188494557980448007583618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000609252137840469555999398185847093500910887087229639291763305664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
197.3856964 |
46.1557649 |
49.9160835 |
8.6899955 |
| ENSG00000140848 |
221184 |
CPNE2 |
protein_coding |
Q96FN4 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein that plays a role in calcium-mediated intracellular processes. Exhibits calcium-dependent cell membrane binding properties. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P59108}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Calcium-dependent membrane-binding proteins may regulate molecular events at the interface of the cell membrane and cytoplasm. This gene is one of several genes that encode a calcium-dependent protein containing two N-terminal type II C2 domains and an integrin A domain-like sequence in the C-terminus. Sequence analysis identified multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants but their full-length natures could not be determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:221184; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277] |
20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex in women patients with schizophrenia. |
ENSMUSG00000034361 |
Cpne2 |
2029.571574 |
0.1751541495 |
-2.513303 |
0.042749115 |
3767.744729 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
618.8405622 |
18.7341119 |
3559.6063190 |
62.8936585 |
| ENSG00000140853 |
84166 |
NLRC5 |
protein_coding |
Q86WI3 |
FUNCTION: Probable regulator of the NF-kappa-B and type I interferon signaling pathways. May also regulate the type II interferon signaling pathway. Plays a role in homeostatic control of innate immunity and in antiviral defense mechanisms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20061403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20434986}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the caspase recruitment domain-containing NLR family. This gene plays a role in cytokine response and antiviral immunity through its inhibition of NF-kappa-B activation and negative regulation of type I interferon signaling pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:84166; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060339]; positive regulation of MHC class I biosynthetic process [GO:0045345]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060340]; positive regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060335]; regulation of kinase activity [GO:0043549] |
20061403_NLRC5 may represent a molecular switch of interferon (IFN)-gamma activation sequence and IFN-specific response element signaling pathways contributing to antiviral defense mechanisms. 20434986_Study identifies NLRC5 as a negative regulator that blocks two central components of the NF-kappaB and type I interferon signaling pathways and suggest an important role for NLRC5 in homeostatic control of innate immunity. 20538593_function for NLRC5 in anti-viral innate immune responses 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20610642_NLRC5 is identified and characterized as a key regulator of proinflammatory pathways in immune cells. 20639463_suggest that NLRC5 is a transcriptional regulator, orchestrating the concerted expression of critical components in the MHC class I pathway. 21191067_NLRC5 is a critical component of inflammasome-dependent interleukin (IL)-1beta secretion in response to a repertoire of stimuli that also activate NLRP3. 22024701_NLRC5 was proposed to function as a positive and as a negative regulator of IFN, NF-kappaB, AP-1 signaling and antiviral immunity. (Review) 22310711_NLRC5-mediated MHC class I gene induction requires an intact nuclear localization signal and nuclear distribution of NLRC5. 22412192_NLRC5 acts as a key transcriptional regulator of MHC I in lymphocytes and support an essential role for NLRs in directing not only innate but also adaptive immune responses. 22490867_Expression of NLRC5 positively correlates with histocompatibility class I expression in human tissues. 22490869_NLRC5 can cooperate with X1 box-binding transcription factor RFX and X2 box-binding transcription factor ATF1 in activation of histocompatibility class I promoter region. 23815151_rhinovirus ion channel protein 2B triggers NLRP3 and NLRC5 inflammasome activation and IL-1beta secretion in bronchial cells 24044430_A model for full-length human NLRC5 was prepared and, besides the closed conformation of monomeric NLRC5, a heptameric platform was also modeled for the opened conformational NLRC5 monomers. 24815518_Unusual structural features revealed by the solution NMR structure of the NLRC5 caspase recruitment domain. 25127861_This study presents a detailed functional study of the domains of NLRC5 revealing that the N-terminal domain of human NLRC5 has intrinsic transcriptional activity. 25404059_a novel role for NLRC5 in RIG-I-mediated antiviral host responses against influenza virus infection, distinguished from the role of NLRC5 in MHC class I gene regulation. 25820389_In a transformed cell line, NLRC5 plays a significant role in IL-6 and IL-1Beta secretion. 25972545_RSV infection of lung epithelial cells induces expression of RIG-I, NLRC5, and subsequent upregulation of HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C. 26592197_NLRC5 regulates TGFB1-induced proliferation and activation of hepatic stellate cells during hepatic fibrosis. 26620909_NLRC5 function is shaped by reversible ubiquitination, which modulates the NF-kappaB activation switch 26975630_NLRC5 not only positively correlates with the increase of beta-catenin but also coordinates the activation of downstream Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, regulating cell proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. 27087581_CITA/NLRC5 and CIITA are transcriptional regulators that orchestrate the concerted expression of critical components in the MHC class I and class II pathways, respectively. [review] 27162338_NLRC5 expression was significantly associated with the activation of CD8(+) cytotoxic T cells and patient survival in multiple cancer types. Thus, NLRC5 constitutes a novel prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target of cancers. 27338800_These results demonstrate that NLRC5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the AKT/VEGF-A signaling pathway 27423514_NLRC5 interacts with miR-34a.NLRC5 role in HPV16 persistence. 27525969_silencing NLRC5 reduced extracellular matrix expression in keloid fibroblasts through inhibiting the TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathway. 28122660_Our study, for the first time, identified the possible involvement of a polymorphism within NLRC5 gene as a possible biomarker for periodontitis condition susceptibility among Italian individuals from genetic isolates. 28780973_NLRC5 performed a crucial role in the process of cardiac fibrosis 29394898_the methylation profile combination of HKR1, ROD1, and NLRC5 could be a promising biomarker for aging in Hainan centenarians 29408916_obtained 18 pair-wise interactions within and between the NLRC5 ad PD-L1 genes and 6 more when IFNGR variants were added 29608899_NLRC5 may act as a key mediator in renal fibroblast activation and fibrogenesis 29655162_knockdown of NLRC5 attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in vitro through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 29704870_frameshift mutations in DTX1 and NLRC5, two genes involved in immune regulation, were identified in a family with familial pityriasis rubra pilaris. 29762254_Genetic polymorphisms in NLRC5 may be used as prognostic markers of survival of colorectal cancer patients, as well as for survival in response to 5-FU treatment. 30316442_The expression of NLRC5 in the ectopic and eutopic endometrium of endometriosis groups was significantly higher than that in the endometrium of leiomyoma group. 30453994_NLRC5 could potentially be a diagnostic index and represents a prognostic factor in IgA nephritis patients. 30543814_High NLRC5 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 30559222_This study evaluated the effect of Orientia tsutsugamushi on the internal immunological systems of HeLa and aortic endothelial cells. 30867141_present an overview on NLRC5, addressing its underlying molecular mechanisms and implications in host defense, inflammatory response, and associated cancers 31186034_The expression of NOD2 and NLRC5 was associated with the severity of renal lesions in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. 31207033_Knockdown of LncRNA SCAMP1 suppressed malignant biological behaviours of glioma cells via modulating miR-499a-5p/LMX1A/NLRC5 pathway. 31293340_Study in human hepatic stellate cell line LX-2 revealed that NLRC5 may participate in the process of hepatic stellate cells activation and extracellular matrix synthesis through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway and may play a key role in the development and reversal of hepatic fibrosis. 31694750_Long noncoding RNA FER1L4 regulates rheumatoid arthritis via targeting NLRC5. 31746301_miR-4319 Suppresses the Growth of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via Targeting NLRC5. 31900803_Promotion of NLRC5 by IFN-gamma with upregulation of MHC class I (HLA-ABC) in SKBR3 breast cancer cells. 32169428_Innate Immune Molecule NLRC5 Protects Mice From Helicobacter-induced Formation of Gastric Lymphoid Tissue. 32431202_NLRC5 promotes cell migration and invasion by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in endometrial cancer. 32505342_NLRC5 deficiency ameliorates cardiac fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating EndMT through Smad2/3 signaling pathway. 32790491_NLRC5 alleviated OGD/R-induced PC12-cell injury by inhibiting activation of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathway. 33754073_The subcellular redistribution of NLRC5 promotes angiogenesis via interacting with STAT3 in endothelial cells. 34220868_NLRC5: A Potential Target for Central Nervous System Disorders. 34438368_NLRC5 attenuates inflammatory response in IL-1beta-stimulated human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 34782775_Dysregulation of long noncoding RNA MEG3 and NLRC5 expressions in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: is there any correlation? 34974132_LC3 and NLRC5 interaction inhibits NLRC5-mediated MHC class I antigen presentation pathway in endometrial cancer. 35174769_Selective autophagy of NLRC5 promotes immune evasion of endometrial cancer. 35734971_NLRC5 modulates bone metabolism and plays a role in periodontitis. 35835172_NLRC5 modulates phenotypic transition and inflammation of human venous smooth muscle cells by activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway via TLR4 in varicose veins. 35880269_NLRC5 Might Promote Endometrial Cancer Progression by Inducing PD-L1 Expression. 36103539_Transcription and splicing regulation by NLRC5 shape the interferon response in human pancreatic beta cells. |
ENSMUSG00000074151 |
Nlrc5 |
190.932212 |
0.4638894494 |
-1.108147 |
0.221968317 |
24.519289 |
0.00000073569650559287153079922414594671309373552503529936075210571289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002642706357398584268768391286608121504286827985197305679321289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
112.5089547 |
17.2117630 |
244.2781117 |
26.4330403 |
| ENSG00000140939 |
8996 |
NOL3 |
protein_coding |
O60936 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: May be involved in RNA splicing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10196175}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Functions as an apoptosis repressor that blocks multiple modes of cell death. Inhibits extrinsic apoptotic pathways through two different ways. Firstly by interacting with FAS and FADD upon FAS activation blocking death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) assembly (By similarity). Secondly by interacting with CASP8 in a mitochondria localization- and phosphorylation-dependent manner, limiting the amount of soluble CASP8 available for DISC-mediated activation (By similarity). Inhibits intrinsic apoptotic pathway in response to a wide range of stresses, through its interaction with BAX resulting in BAX inactivation, preventing mitochondrial dysfunction and release of pro-apoptotic factors (PubMed:15004034). Inhibits calcium-mediated cell death by functioning as a cytosolic calcium buffer, dissociating its interaction with CASP8 and maintaining calcium homeostasis (PubMed:15509781). Negatively regulates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by phosphorylation-dependent suppression of the mitochondria-mediated intrinsic pathway, by blocking CASP2 activation and BAX translocation (By similarity). Negatively regulates hypoxia-induced apoptosis in part by inhibiting the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria in a caspase-independent manner (By similarity). Also inhibits TNF-induced necrosis by preventing TNF-signaling pathway through TNFRSF1A interaction abrogating the recruitment of RIPK1 to complex I (By similarity). Finally through its role as apoptosis repressor, promotes vascular remodeling through inhibition of apoptosis and stimulation of proliferation, in response to hypoxia (By similarity). Inhibits too myoblast differentiation through caspase inhibition (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62881, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D1X0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15004034, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15509781}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes an anti-apoptotic protein that has been shown to down-regulate the enzyme activities of caspase 2, caspase 8 and tumor protein p53. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:8996; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; caspase binding [GO:0089720]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043027]; death effector domain binding [GO:0035877]; death receptor binding [GO:0005123]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010659]; inhibition of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:1990001]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; mRNA splice site selection [GO:0006376]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1903298]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process [GO:1902109]; negative regulation of muscle atrophy [GO:0014736]; negative regulation of necrotic cell death [GO:0060547]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902176]; negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090201]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010804]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901222]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0014808]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to injury involved in regulation of muscle adaptation [GO:0014876]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
12734105_These results suggest that the antiapoptotic effect of apoptotic repressor with caspase recruitment domain is, in part, due to inhibition of voltage-gated potassium channels in cardiomyocytes. 15383280_ARC holds multiple death pathways in check by non-homotypic death-fold interactions. Loss of ARC disinhibits these, leading to accelerated DISC assembly and Bax activation and may be an apoptotic trigger in heart failure and ischemia-reperfusion. 15383280_ARC is recruited to the Fas DISC. By interacting with Fas and FADD through CARD-DD and CARD-DED interactions, ARC prevents DISC assembly and procaspase-8 activation. 15383280_The CARD of ARC binds the Bax C-terminus, preventing Bax activation and activation of the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway 15509781_calcium binding mediates regulation of caspase 8 and cell death by ARC 15848180_Unexpectedly, ARC was localized almost exclusively to the nuclei of cancer cells, which was unlike the cytoplasmic localization of ARC in non-cancer cells 15861191_ARC was present in the cytoplasm and nuclei of epithelial cells in invasive ductal carcinoma 16505176_is downregulated in human failing myocardium 17142452_ARC undergoes poly-ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome-dependent degradation. Mutation of ARC's lysine residues prevents this and enhances its pro-survival effects. 18087040_nuclear apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC)is induced in cancer cells and negatively regulates p53 18172857_the high level of ARC protein and the constitutive phosphorylation of ARC in cancer cells may play an important role in the protection of cancer cells against oxidative stress 18245485_Transfection of cDNA encoding ARC into Me1007 cells inhibited both caspase-8 activation and apoptosis induced by thapsigargin or tunicamycin. 18469522_ARC is a novel marker of human colon cancer and suggest that it may be a general feature of epithelial cancers. 18516683_the balance between antiapoptotic ARC and proapoptotic caspase-8 is the only one to be disturbed during carcinogenesis and tumour progression of renal cell carcinomas 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20392691_Ras induces ARC in epithelial cancers, and ARC plays a role in the oncogenic actions of Ras 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21041716_Results suggest that ARC expression levels are highly prognostic in AML and that ARC is a potential therapeutic target in AML. 22037876_Data show that ARC promotes breast carcinogenesis by driving primary tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis as well as by promoting chemoresistance in invasive cells. 22082675_ARC, previously unlinked to pulmonary hypertension, is a critical determinant of vascular remodeling in this syndrome. 22475487_HIF-1alpha directly bound to hypoxia-responsive element located at -419 to -414 of ARC gene, which is essential for HIF-1-induced expression. 22926851_This study utilized unbiased, genome-wide approaches to identify a NOL3 mutation that likely causes Familial cortical myoclonus. 22933109_ARC is a previously unrecognized inhibitor of apoptosis in beta-cells and that its protective effects are mediated through suppression of the ER stress response pathway. 23877130_high expression of ARC plays an important role in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and leads to X-radiation and cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 24763054_RUNX3, miR-185 and ARC regulate the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to chemotherapy. 25079338_ARC is regulated via BIRC2/MAP3K14 signalling and its overexpression in AML or MSCs can function as a resistant factor to birinapant-induced leukaemia cell death. 25344068_Results show that in response to DNA damage, p53 total levels increase proportionally to the strength of the damage; however, p53 tetramers are formed at a constant rate under the control of ARC protein. 26721253_Increased ARC expression is associated with liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. 28232469_a novel genetic primary myelofibrosis-like mouse model and identify a tumor suppressor role for NOL3 in the pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies. 28464919_role of apoptosis repressor with a CARD domain (ARC) in the therapeutic resistance of renal cell carcinoma 32771410_Apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain promotes cell proliferation and phenotypic modulation through 14-3-3epsilon/YAP signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. 32816906_ARC Is a Critical Protector against Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and IBD-Associated Colorectal Tumorigenesis. 33579312_Expression of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC) in familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) adenomas and its correlation with DNA mismatch repair proteins, p53, Bcl-2, COX-2 and beta-catenin. |
ENSMUSG00000014776 |
Nol3 |
20.910081 |
0.4215799357 |
-1.246122 |
0.505104054 |
5.722757 |
0.01674641335240430531361432997528027044609189033508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.030579866520040521749024264863692224025726318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8662392 |
4.4479620 |
30.2004623 |
6.9500484 |
| ENSG00000140968 |
3394 |
IRF8 |
protein_coding |
Q02556 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that specifically binds to the upstream regulatory region of type I interferon (IFN) and IFN-inducible MHC class I genes (the interferon consensus sequence (ICS)) (PubMed:25122610). Can both act as a transcriptional activator or repressor (By similarity). Plays a negative regulatory role in cells of the immune system (By similarity). Involved in CD8(+) dendritic cell differentiation by forming a complex with the BATF-JUNB heterodimer in immune cells, leading to recognition of AICE sequence (5'-TGAnTCA/GAAA-3'), an immune-specific regulatory element, followed by cooperative binding of BATF and IRF8 and activation of genes (By similarity). Required for the development of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), which produce most of the type I IFN in response to viral infection (By similarity). Positively regulates macroautophagy in dendritic cells (PubMed:29434592). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25122610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29434592}. |
Activator;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP) is a transcription factor of the interferon (IFN) regulatory factor (IRF) family. Proteins of this family are composed of a conserved DNA-binding domain in the N-terminal region and a divergent C-terminal region that serves as the regulatory domain. The IRF family proteins bind to the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE) and regulate expression of genes stimulated by type I IFNs, namely IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. IRF family proteins also control expression of IFN-alpha and IFN-beta-regulated genes that are induced by viral infection. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3394; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097028]; follicular B cell differentiation [GO:0002316]; germinal center B cell differentiation [GO:0002314]; immune response [GO:0006955]; immune system process [GO:0002376]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; plasmacytoid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0002273]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032479] |
15371411_ICSBP1 activates transcription of the gene encoding neurofibromin 1 15489234_interleukin-12 p35 gene transcription is activated by interferon regulatory factor-1 and interferon consensus sequence-binding protein 15837792_proteasomal degradation of IRF-8 mediated by the ubiquitin E3 ligase Cbl down-regulates IL-12 expression 16484229_the interaction of IRF-8 with TRAF6 modulates TLR signaling and may contribute to the cross-talk between IFN-gamma and TLR signal pathways 16504056_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16886895_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16914719_ICSBP tyrosine phosphorylation is necessary for the activation of NF1 transcription. ICSBP is a substrate for SHP2 protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP2-PTP). 16918696_Our data suggest that ATRA-induced regulation of Stat2, ICSBP and C/EBPepsilon is dependent on active Stat1, and that a failure to correctly regulate these transcription factors is associated with the inhibition of monocytic differentiation. 17200120_IRF8 cooperates with PU.1 and IRF-2 to activate a composite ets/IRF-cis element in the NF1 promoter. The conserved IRF domain tyrosine in ICSBP/IRF8 is required for interaction with the DNA-bound PU.1-IRF2 heterodimer. 17386941_IRF8 is involved in a cooperative interaction with transcription factors Spi-1/PU.1 and non-tyrosine phosphorylated Stat1 in the formation of a pre-associated, poised complex for interleukin 1-beta gene induction. 17687331_this CHRNA1 variant prevents binding of interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) and abrogates CHRNA1 promoter activity in thymic epithelial cells in vitro 18195016_The interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP/IRF8) represses PTPN13 gene transcription in differentiating myeloid cells 18246201_activation of SHP2 protein tyrosine phosphatase synergized with ICSBP haploinsufficiency to facilitate cytokine-induced myeloproliferation, apoptosis resistance, and rapid progression to AML in a murine bone marrow transplantation model. 18316378_Dendritic cell priming by L. major infection results in the early activation of NF-kappaB transcription factors and the up-regulation and nuclear translocation of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-8. 18469857_IRF8 was identified as a functional tumor suppressor, which is frequently silenced by epigenetic mechanism in multiple carcinomas 18580679_Suggest role for IRF8 during germinal center B-cell development and in related lymphomas, and provide a new diagnostic marker helpful in distinguishing B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. 18596738_Age-associated expression changes of IRF8 protein and mRNA levels in PB CD34+ cells 18701018_Pint mutations in patients with type 2 diabetes and their families were studied. mitochondrial genes including np3316, np3394 and np3426 in the ND1 region and np3243 in the tRNA(Leu(UUR))were screened. 18922617_silencing of ICSBP/IRF8 expression, by DNA methylation or other epigenetic mechanisms, may be associated with the malignant phenotype of MM. 19074829_colon carcinoma cells silence IFN-gamma-activated IRF8 expression through MBD1-dependent and PIAS1-mediated inhibition of pSTAT1 function at the methylated IRF8 promoter 19525953_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19525953_Replication in an independent set of 2,215 subjects with multiple sclerosis (MS) and 2,116 control subjects validates new MS susceptibility loci at TNFRSF1A, IRF8 and CD6; TNFRSF1A harbors two independent susceptibility alleles. 19542426_Increased expression of IRF-8 in tumor-induced CD11b-positive/Gr-1-positive cells exerts an antitumor rather than protumorigenic effect in tumor-bearing IRF-8-transgenic hybrid mice. 19801548_Data identify the gene encoding Fanconi F (FANCF) as an ICSBP target gene. 19865102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20430450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20435892_IL-27 p28 gene transcription is activated by interferon regulatory factor 8 in cooperation with interferon regulatory factor 1 20573402_IRF8 and PU.1 can have both combined, and independent actions on different promoters in myeloid cells. 20634887_The chromatin modifications were determined at five PRC2 targets commonly underexpressed in multiple myeloma (CIITA, CXCL12, GATA2, CDH6 and ICSBP/IRF8). The selected genes were confirmed to be underexpressed in MM compared to normal plasma cells. 20679491_Studies have identified a Gas2/calpain-dependent mechanism by which ICSBP influences beta-catenin activity in myeloid leukemia. 20980339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21131588_independent association of 4 SNPs that met genome-wide statistical significance within the IRF8 gene in familial chronic lymphocytic leukemia 21178004_IRF8 is required for normal development of marginal zone (MZ) and follicular B cells. Mice with a conventional knockout of Irf8 or a point mutation in the IRF association domain of IRF8 have increased numbers of MZ B cells. 21216962_Positive regulatory domain I (PRDM1) and IRF8/PU.1 counter-regulate MHC class II transactivator (CIITA) expression during dendritic cell maturation. 21220691_IRF-8 is a key player in the control of intracellular viral dsRNA-induced responses by a mechanism that negatively regulates Toll-like receptor (TLR)3 expression and can be exploited to block excessive TLR activation. 21228327_we propose a model for the rapid induction of IFN-beta in monocytes, whereby IRF8 and PU.1 form a scaffold complex on the IFN-beta promoter to facilitate the recruitment of IRF3 21475251_The promoter was methylated in many MDS or AML patients. This may be the main mechanism of ICSBP inactivation in myeloid malignancies & may be functionally important for accumulation of chromosome aberrations during leukemic progression. 21487040_Findings determine the mechanism of IRF8 downregulation in CML cells. 21524210_We detected two distinct disease-causing mutations affecting interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8). Both mutations impair IRF8 transcriptional activity. 21552549_association of single nucleotide polymorphisms to multiple sclerosis 21625229_study identifies a novel role for ICSBP in regulating cell growth via TGF-beta receptor upregulation and subsequent activation of the TGF-beta receptor/TAK-1/p38 pathway 22003407_IRF4 has activities similar to IRF8 in regulating myeloid cell development 22046141_Association analysis identified five SLE susceptibility genes reaching genome-wide levels of significance : NCF2 ,IKZF1 ,IRF8 ,IFIH1 , and TYK2 22082370_[review] Induction of transcriptional repressors such as IRF8 is one of the mechanisms that inhibits osteoclastogenesis. 22096565_Data showed that IRF8 target genes contributes to multiple aspects of the biology of mature B cells including critical components of the molecular crosstalk among GC B cells, T follicular helper cells, and follicular dendritic cells. 22262849_interaction between Tel and Tel-PdgfRbeta decreases Tel/Icsbp/Hdac3 binding to the PTPN13 cis element, resulting in increased transcription. 22464253_Four additional susceptibility loci (IRF8, TMEM39A, IKZF3, and ZPBP2) for systemic lupus erythematosus were robustly established a multiethnic population (European, African American, Asian, Hispanic, Gullah, and Amerindian). 22879909_The association of IRF1 and IRF8 variants with tuberculosis susceptibility was investigated. 22942423_In resting macrophages, some IRF8 is conjugated to small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMO) 2/3 through the lysine residue 310. Macrophage activation prompts a reduction in SUMOylated IRF8. 22994200_In a Korean population, there was no association of IRF8 polymorphisms, with inflammatory demyelinating diseases. 23307532_A 3'UTR variant in IRF8 gene is associated with risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 23308054_these results underscore a key role of IRF-8 in the cross talk between melanoma and immune cells, thus revealing its critical function within the tumor microenvironment in regulating melanoma progression and invasiveness. 23468103_IRF8 is required for ontogeny of the myeloid lineage and for host response to mycobacteria. The K108E & T80A mustations cause distinct forms of a novel primary immunodeficiency & associated susceptibility to mycobacteria. Review. 23573829_IRF8 is associated with germinal center B-cell-like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and exceptionally involved in translocation t(14;16)(q32.33;q24.1). 23658517_novel insights into the contribution of EBNA3C to EBV-mediated B-cell transformation through regulation of IRF4 and IRF8 and add another molecular link to the mechanisms by which EBV dysregulates cellular activities 23661672_Coronary heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with IRF8 gene variants. 23775715_Using a capture sequencing strategy, we discovered the B-cell relevant genes IRF8, EBF1, and TNFSF13 as novel targets for IGH deregulation. 23967110_the prognostic significance of IRF8 transcripts in other populations of AML patients 24034601_The IRF8 gene polymorphisms might be associated with susceptibility to SLE. 24435047_Mutations in linker histone genes HIST1H1 B, C, D, and E; OCT2 (POU2F2); IRF8; and ARID1A underlying the pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma. 24753251_These data reveal a previously unrecognized BCR-ABL-STAT5-IRF-8 network, which widens the repertoire of potentially new anti-chronic myeloid leukemia targets. 24832596_Data demonstrate a novel function for ICSBP in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell motility, and invasion through the TGF-beta and Snail signaling pathways. 24943672_gene variants in IRF5, IRF8 and GPC5 were not associated with risk of relapse or disease progression in multiple sclerosis 24957708_MN1 prevents activation of the immune response pathway, and suggest restoration of IRF8 signaling as therapeutic target in AML 25109451_Data demonstrate that IRF8 as a functional tumor suppressor is frequently methylated in RCC, and IRF8-mediated interferon signaling is involved in RCC pathogenesis. 25387409_Expression of WT1and IRF8 showed a moderate inverse correlation in acute myeloid leukemia patients. WT1 can be used as an minimal residual disease marker, especially in patients without recurrent genetic abnormalities. 25453760_Irf8 forms a negative feedback loop with Cebpb, a monocyte-derived DC epigenetic fate-determining transcription factor. 25749660_This article provides an overview of recent advances in our understanding of the role of IRF8 in myelopoiesis and related diseases. [review] 25880423_The IRF8 gene variant influenced the interaction between IRF8 and NF-kappaB and thus susceptibility to systemic sclerosis. 25903733_This study demonstrated that the Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide of IRF8 is associated with multiple sclerosis in woman in Russia. 25989711_Results show that IRF8 is a possible genetic variant associated with the development of HT and production of thyroid antibody 26563595_cytarabine-induced upregulation of the IRF8 in leukemic cells involves increased levels of ZNF224, which can counteract the repressive activity of WT1 on the IRF8-promoter 26613957_IRF5 and IRF8, two transcription factors with opposing functions, control TLR9 signaling in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. 26794091_IRF8 may contribute to the genetic susceptibility of Behcet's disease by regulating IRF8 expression and cytokine production. 27183582_It findings provide evidence for an additional mechanism of epigenetic IRF8 silencing during osteoclastogenesis that likely works cooperatively with DNA methylation, further emphasizing the importance of IRF8 as a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis. 27582125_Total cellular protein presence of the transcription factor IRF8 does not necessarily correlate with its nuclear presence. 27658717_TP(thymidine phosphorylase ) curbed the expression of three proteins-IRF8, RUNX2, and osterix. This downregulation was epigenetically driven: High levels of 2DDR, a product of TP secreted by myeloma cells, activated PI3K/AKT signaling and increased the methyltransferase DNMT3A's expression 27709315_down-regulation of IRF8 in the wound leads to impaired wound healing possibly through the regulation of macrophage function and apoptosis in skin wound. 27893462_these data indicate that human NK cells require IRF8 for development and functional maturation and that dysregulation of this function results in severe human disease, thereby emphasizing a critical role for NK cells in human antiviral defense. 28090699_IRF8 is dispensable for induced pluripotent stem cell and embryonic stem cell differentiation into hemogenic endothelium and for endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition. 28388578_These findings identify IRF8 as a novel tumor suppressor regulating IFN-gamma/STAT1 signaling and beta-catenin signaling in breast cancer. 28432342_Study shows that hypermethylation of IRF8 associated with decreased mRNA expression in dendritic cells confers risk to VKH disease. 28477415_Data suggest that ubiquitin specific protease 4 (USP4) interacts with interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) and, by its Lys48-specific deubiquitinase/endopeptidase activity, stabilizes IRF8 protein levels in regulatory T-lymphocytes; USP4 and IRF8 are also expressed in helper T-lymphocytes. 28492552_Irf8 induction, but not its knockdown, decreased APL leukemogenic potential through driving monocytic maturation. 28537908_IRF8 upregulation in tumor cells inhibited the generation of Th17 cells in vitro, and this may be mediated by the downregulation of RORgammat. we found that a high level of IRF8 in the DLBCL tumor microenvironment was a predictor of poor survival in DLBCL patients. 29247272_These findings identified a novel function of IRF-8 in regulating articular cartilage matrix destruction by promoting the expression of MMP-13. 29569949_This paper suggests that IRF4 and IRF8 are important in the counter-balancing mechanisms controlling differentiation of plasma cells in myasthenia gravis. 30241692_this study shows that IRF8-regulated T follicular helper cells can directly cause colon inflammation 30266821_Our work complements existing data to indicate an important role for IRF8 suppression in APL pathogenesis. 30285234_data supports a role for regulation of these genes in mononuclear phagocytic cells by vitamin D as contributing to autoimmunity 30466106_Exogenous expression of IRF8 in the silenced or downregulated lung cancer cell lines restored the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to apoptosis, and arrested cells at the G0/G1 phase. IRF8 bound to the T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF /LEF) promoter, thus repressing beta-catenin nuclear translocation and its activation. 30710564_interferon consensus sequence-binding protein upregulates transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor (TGF-beta RI) expression by binding to nucleotides -216/-211 (GGXXTC) in the TGF-beta RI promoter, which resulted in increased tumorigenicity and tumor progression in human osteosarcoma cells. 30840779_Inactivating Mutation in IRF8 Promotes Osteoclast Transcriptional Programs and Increases Susceptibility to Tooth Root Resorption. 30900036_We found a significant hypermethylation of the IRF8 gene promoter and a downregulation of the mRNA levels of the IRF8 gene in ankylosing spondylitis patients. 31221219_Evaluation of protein expression within histologic sections of primary clear cell renal cell carcinoma patient samples showed intensity of IRF8 by CD68(+) macrophages correlated inversely with stage. 31594449_IRF8 induces senescence of lung cancer cells to exert its tumor suppressive function. 31794020_Genome-Wide Analysis Identifies Two Susceptibility Loci for Positive Thyroid Peroxidase and Thyroglobulin Antibodies. 32039830_Single-cell RNA sequencing of immune cells in gastric cancer patients. 32049023_SENP3 Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis by De-conjugating SUMO2/3 from IRF8 in Bone Marrow-Derived Monocytes. 32341037_Loss of a Negative Feedback Loop between IRF8 and AR Promotes Prostate Cancer Growth and Enzalutamide Resistance. 32735845_Differential IRF8 Transcription Factor Requirement Defines Two Pathways of Dendritic Cell Development in Humans. 33705797_Downregulated IRF8 in Monocytes and Macrophages of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis May Aggravate the Fibrotic Phenotype. 33766090_High IRF8 expression correlates with CD8 T cell infiltration and is a predictive biomarker of therapy response in ER-negative breast cancer. 33839155_Interferon regulatory factor 8 regulates expression of acid ceramidase and infection susceptibility in cystic fibrosis. 33897697_PU.1 and IRF8 Modulate Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome via Regulating Its Expression in Human Macrophages. 34172624_IRF8 is a Reliable Monoblast Marker for Acute Monocytic Leukemias. 34331664_IRF4 and IRF8 expression are associated with clinical phenotype and clinico-hematological response to hydroxyurea in essential thrombocythemia. 34358447_ZMYND8-regulated IRF8 transcription axis is an acute myeloid leukemia dependency. 34478526_Frequent mutated B2M, EZH2, IRF8, and TNFRSF14 in primary bone diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reflect a GCB phenotype. 34991467_Predicting the targets of IRF8 and NFATc1 during osteoclast differentiation using the machine learning method framework cTAP. 35085599_Global assessment of IRF8 as a novel cancer biomarker. 35086136_IRF8 is a transcriptional activator of CD37 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 35388006_Lupus enhancer risk variant causes dysregulation of IRF8 through cooperative lncRNA and DNA methylation machinery. 35460405_IRF8 as a Novel Marker to Differentiate Between CD30-Positive Large Cell Lymphomas. 36288724_Tumor-associated macrophages expressing the transcription factor IRF8 promote T cell exhaustion in cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000041515 |
Irf8 |
164.985228 |
0.2443272645 |
-2.033113 |
0.136604464 |
233.632392 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009620660171635008513987123466912135543435112223193959456768409479612071103289129912121285119920383986925604011257605438533922096540264984332324615934339817613363265991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002171268258919460739870512040018817608058204133618740669784848670155832812376977557516323495769193672020663747715840138969523113446000173176742009673034772276878356933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
65.3052584 |
5.6033721 |
269.3569148 |
13.3403869 |
| ENSG00000141027 |
9611 |
NCOR1 |
protein_coding |
O75376 |
FUNCTION: Mediates transcriptional repression by certain nuclear receptors (PubMed:20812024). Part of a complex which promotes histone deacetylation and the formation of repressive chromatin structures which may impede the access of basal transcription factors. Participates in the transcriptional repressor activity produced by BCL6. Recruited by ZBTB7A to the androgen response elements/ARE on target genes, negatively regulates androgen receptor signaling and androgen-induced cell proliferation (PubMed:20812024). Mediates the NR1D1-dependent repression and circadian regulation of TSHB expression (By similarity). The NCOR1-HDAC3 complex regulates the circadian expression of the core clock gene ARTNL/BMAL1 and the genes involved in lipid metabolism in the liver (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14527417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20812024}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that mediates ligand-independent transcription repression of thyroid-hormone and retinoic-acid receptors by promoting chromatin condensation and preventing access of the transcription machinery. It is part of a complex which also includes histone deacetylases and transcriptional regulators similar to the yeast protein Sin3p. This gene is located between the Charcot-Marie-Tooth and Smith-Magenis syndrome critical regions on chromosome 17. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 17 and 20.[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:9611; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; nuclear receptor binding [GO:0016922]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; locomotor rhythm [GO:0045475]; negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060766]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0045922]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225] |
9724795_This paper describes the cloning of the full-length human NCOR1 cDNA. 11903058_Nuclear receptor corepressor-dependent repression of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor delta-mediated transactivation 11931768_Results show that the N-CoR-HDAC3 complex inhibits JNK activation through the associated GPS2 subunit and thus could potentially provide an alternative mechanism for hormone-mediated antagonism of AP-1 function. 12077342_Mammalian PRP4 kinase copurifies and interacts with components of both the U5 snRNP and the N-CoR deacetylase complexes. 12089345_These results demonstrate that AR, in contrast to other SHRs, is regulated by NCoR 12150997_Exchange of N-CoR corepressor and Tip60 coactivator complexes links gene expression by NF-kappaB and beta-amyloid precursor protein. 12466959_recruited by prohibitin for transcriptional repression 12648520_N-CoR functions not merely as a repressor of basal transcription, but rather as a modulator of both basal and ligand-activated transcription of genes controlled by RAR/RXR heterodimers in a dose-dependent manner 12861000_N-CoR/histone deacetylase 3 complex is required for repression by thyroid hormone receptor 12890497_associates with CHD1 and histone deacetylase as well as with RNA splicing proteins 15377655_N-CoR utilizes repression domains I and III for interaction and co-repression with ETO 15561719_THAP7 coimmunoprecipitates with histone deacetylase 3 and the nuclear hormone receptor corepressor and represses transcription 15598662_NCoR is a physiological regulator of the AR; the N-terminal surface of the AR-mediating NCoR recruitment was distinct from tau5 and from the FXXLF motif that mediates agonist-induced N-C-terminal interaction 15695367_the DAD domain of N-CoR is singularly essential for repression by the thyroid hormone receptor 15761026_the N-CoR/HDAC3 complex has a role in regulating the expression of genes involved in circadian rhythm by functioning as corepressor for Rev-erbalpha 15802375_N-CoR and SMRT play an active role in preventing tamoxifen from stimulating proliferation in breast cancer cells through repression of a subset of target genes involved in ERalpha function and cell proliferation 16024779_N-CoR together with JMJD2A could play a role in repressing achaete scute-like homologue 2 (ASCL2) expression in various tissues. 16141343_mechanism by which the estrogen-ER complex markedly reduces the level of N-CoR through a process involving the up-regulation of Siah2 and the subsequent targeting of N-CoR for proteasomal degradation 16195251_SAFB1 was shown to interact directly with the nuclear receptor corepressor N-CoR. 16216492_N-CoR and TRbeta cooperate in the regulation of the TSHbeta gene and this ligand-dependent repression is mediated by the LXXLL motif in N-CoR 16373395_SMRT and N-CoR corepressors are involved in transcriptional regulation by both agonist- and antagonist-bound AR and regulate the magnitude of hormone response, at least in part, by competing with coactivators. 16730330_Results provide evidence to show that the N-CoR/HDAC3 co-repressor complex is involved in the aberrant transcription regulation in PML-RARalpha-expressing cells. 16849648_RB7 and butyrate induce dissociation of HDAC3 (but not HDAC1 or HDAC2) and its adaptor protein NCoR. 16914745_The repression mechanisms by the nuclear receptor corepressor (N-CoR) of steroid hormone receptor (SHR)-mediated transactivation were examined. 17073437_first report of a direct interaction between N-CoR and CBP, and suggests that the role of N-CoR in mediating transcriptional events may be more complex than previously anticipated 17630505_Data show that IKKalpha phosphorylates the homologous N-CoR corepressor in serines 2345 and 2348 creating a functional 14-3-3 binding domain (RK(p)S(2348)KSP). 17768398_Data support a role for N-CoR in erythroid differentiation and suggest that N-CoR is required for the induction of a key enzyme involved in heme synthesis. 18052923_both SMRT and N-CoR are limited in cells and knocking down either of them results in co-repressor-free TR and consequently de-repression of TR target genes 18362166_Vitamin D receptor (VDR) with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) recruits NCoR and SMRT strictly in a VDR agonist-dependent manner. 18586123_ETO family member-mediated oligomerization and repression can be distinct events and that interaction between ETO family members and hSIN3B or N-CoR may not necessarily strengthen transcriptional repression. 18632669_SMRT and NCoR have important roles in the regulation of beta-catenin-TCF4-mediated gene transcription 18637017_A point mutation (S296R) in the amino-terminal domain of the androgen receptor (AR) can decrease the ligand specificity of the AR and alter the interaction between serine296arginine and the nuclear receptor co-repressor 1 (N-coR). 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18669643_Data show that, at sufficiently high concentration, the NR corepressor (NCoR) influences the activity of the liver X receptor (LXR) even in the presence of a potent full agonist that destabilizes NCoR binding. 18832723_apoptotic cells induce PPARgamma sumoylation to attenuate the removal of NCoR, thereby blocking transactivation of NF-kappaB. 18852122_These findings show that AR antagonists can enhance corepressor recruitment by stabilizing a distinct antagonist conformation of the AR coactivator/corepressor binding site. 19048289_NCoR was expressed in the cytoplasm of colorectal carcinoma-associated myofibroblasts, but was rarely noted in myofibroblasts of normal mucosa or adenomas. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126649_NCOR1 is a selective regulator of nuclear receptors, notably PPARgamma and VDR, and contributes to their loss of sensitivity. 19183483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19414341_Up-regulation of nuclear receptor corepressor is associated with progestin-induced growth suppression of endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma 19608741_NCoR1 expression is required to maintain IEC in a proliferative state, and PEDF is a novel transcriptional target for NCoR1 repressive action 19781322_NCOR1 protein expression level predicts response to endocrine therapy as first-line treatment for breast cancer patients on relapse. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955185_hPPARalpha SUMOylation on lysine 185 down-regulates its trans-activity through the selective recruitment of NCoR 20003447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20181716_The authors established an interaction of E8;E2C with an NCoR1/HDAC3 complex and demonstrated that this interaction requires the wild-type E8 open reading frame. 20466759_Elevated NCOR1 disrupts PPARalpha/gamma signaling and is associated with prostate cancer. 20581824_Study reports the crystal structure of a nuclear receptor-co-repressor (N-CoR) interaction domain 1 (ID1) peptide bound to truncated human Rev-erbalpha ligand-binding domain. 20587609_Amino-terminal A/B domain deletion facilitated the in vitro binding of nuclear receptor CoR with wild-type PPARG2. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20974212_These data support the hypothesis that NCoR might control a cell cycle dependent regulation of expression androgen receptor target genes in prostate cells. 21131350_Aberrant corepressor interactions implicated in PML-RAR(alpha) and PLZF-RAR(alpha) leukemogenesis reflect an altered recruitment and release of specific NCoR and SMRT splice variants. 21143702_We immunohistochemically analyzed the expression of NCOR1 and 2 as well as HDAC1, 2, and 3 on a tissue microarray comprising tumor samples from 283 astrocytic gliomas 21389087_Differential interaction of NCoR1 with TR isoforms accounted for the TR isoformdependent regulation of adipogenesis and that aberrant interaction of NCoR1 with TR could underlie the pathogenesis of lipid disorders in hypothyroidism. 21518914_data strongly support a model in which EBNA2 association with NCoR-deficient RBPJ enhances transcription and EBNALP dismisses NCoR and RBPJ repressive complexes from enhancers 21525722_ERbeta and its co-regulators p300 and NCoR are expressed in human transitional cell bladder cancer 21966475_Data suggest a possible role of misfolded N-CoR protein in the activation of oncogenic survival pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 21987803_the aberrant recruitment of NCOR1 by TRbeta mutants leads to clinical resistance to thyroid hormone (RTH) 22337871_Regulated HDAC3 degradation serves as a buffering mechanism to protect independent formation of N-CoR and SMRT corepressor complexes. 22349439_PCOS rat models also showed alterations of PPARG1, NCOR1, and HDAC3 mRNA expression and methylation changes of PPARG1 and NCOR1, consistent with the results from humans. 22514634_Findings suggest that N-CoR-induced repression of Flt3 might be crucial for limiting the contribution of the Flt3 signaling pathway on the growth potential of leukemic cells. 22622808_A novel mechanism by which overexpression of estrogen receptor (ER) beta through NCoR is able to down regulate ER alpha gene expression, thus blocking ER alpha's driving role on breast cancer cell growth. 22651256_analysis of regulation of small ubiquitin-like modifier-1, nuclear receptor coreceptor, histone deacetylase 3, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in human adipose tissue 22675025_CK2alpha-NCoR cascade selectively represses the transcription of IP-10 and promotes oncogenic signaling in human esophageal cancer cells. 22944139_Corepressor molecules NCoR and SMRT are present at 1,25(OH)2D3 activated gene enhancers 23129261_These results uncover a regulatory mechanism by which PKA positively modulates NCoR function in transcriptional regulation in prostate cancer. 23295231_The aberrant cytoplasmic expression of NCoR1 in retinoblastoma appears to be associated with the proliferative and/or dedifferentiated properties of retinoblastoma. 23428870_NCOR1 and HDAC3 are instrumental in the repression of glucocorticoid receptor gene transcription. 23940660_Site directed mutagenic analysis of N-CoR identified serine 1450 as the crucial residue whose phosphorylation by Akt was essential for the misfolding and loss of N-CoR protein. 24315104_Study shows that NCoR1 is a key target of proteolysis and physically interacts with the transcription factor CREB, the genome-wide map described here ties proteolysis in mammalian cells to active enhancers and to promoters of specific gene families. 24335696_Low NCoR expression is associated with glioblastoma. 24840043_Data suggest that direct interactions of HLCS (holocarboxylase synthetase) with NCOR1 (nuclear receptor corepressor 1) and HDAC1 (histone deacetylase 1) contribute toward transcriptional repression of repeats, presumably increasing genome stability. 25823659_loss of nuclear NCoR results in upregulation of a specific cancer-related genetic signature, and is significantly associated with malignant melanoma progression. 25928846_The co-localization of AML1-ETO with the N-CoR co-repressor to be primarily on genomic regions distal to transcriptional start sites. (NcoR1) 26589942_PDCD2 and NCoR1 may act as tumor suppressors in Gastrointestinal stromal tumors cells through the Smad signaling pathway. 26663086_Data suggest that complexes of HDAC3-H1.3 with NCOR1 and NCOR2/SMRT accumulate on chromatin in synchronized HeLa cells in late G2 phase and mitosis; deacetylation activity of HDAC3 is activated via phosphorylation of Ser-424 by CK2 only in mitosis. 26729869_NCoR depletion enhances cancer cell invasion and increases tumor growth and metastatic potential. 26968201_NCOR1 function declines with prostate cancer progression. Reduction in NCOR1 levels causes bicalutamide resistance in LNCaP cells and compromises response to bicalutamide in mouse prostate in vivo 27149915_Nuclear Receptor Corepressor 1 is an important transcriptional regulator that interacts with nuclear receptors and other transcription factors. Recent results have shown the presence of inactivating mutations or deletions of the nuclear receptor corepressor 1 gene in human tumors. 27375289_verexpression of COPS5, through its isopeptidase activity, leads to ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of NCoR, a key corepressor for ERalpha and tamoxifen-mediated suppression of ERalpha target genes. 27806339_Authors previously shown that Nuclear Receptor Corepressor 1 (NCoR) and the thyroid hormone receptor beta1 (TRbeta) inhibit tumor invasion. Here they show that these molecules repress VEGF-C and VEGF-D gene transcription in breast cancer cells, reducing lymphatic vessel density and sentinel lymph node invasion in tumor xenografts. 27880911_USP44 contributes to N-CoR functions in regulating gene expression and is required for efficient invasiveness of triple-negative breast cancer cells. 27956629_the NCOR/HDAC3 complex is a major suppressor of differentiation in rhabdomyosarcoma 29483668_19 patients with neurodevelopmental disorders harboring a rare deletion inherited from a healthy parent were investigated by whole-exome sequencing to search for SNV on the contralateral segment. This strategy allowed us to identify a candidate variant in two patients in the NUP214 and NCOR1 genes. 30117609_Survival of developing thymocytes is regulated by NCOR1. NCOR1 controls positive and negative selection of thymocytes during T cell development. HDAC3 interacts with NCOR1 corepressor complexes. Review. 30138371_Microarray analysis revealed differential expression of three vitamin D associated genes in the aortic adventitia in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and non-RA patients with coronary artery disease: while the expression of GADD45A and NCOR1 was higher, the expression of PON2 was lower in RA patients. 30485330_the presence and prognostic role of mutations in the NCOR1 gene in hormone receptor negative breast and lung adenocarcinomas 30982983_vitamin E and PIAS1-shRNA partially decreased ROS production and IKK activation induced by high glucose and PA exposure. These data indicate that ROS-IKK-PIAS1 pathway mediates PPARgamma sumoylation, leading to endothelium insulin resistance (IR) via stabilizing PPARgamma-NcoR complex. 31208445_Data suggest that the nuclear receptor co-repressor 1/2 protein NCoR-1/NCoR-2 paralogs have been subject to a mix of shared and distinct selective pressures, resulting in the pattern of divergent and convergent alternative-splicing observed in extant species. 31661545_Abnormally localized DLK1 interacts with NCOR1 in non-small cell lung cancer cell nuclear. 32034166_Exome sequencing revealed DNA variants in NCOR1, IGF2BP1, SGLT2 and NEK11 as potential novel causes of ketotic hypoglycemia in children. 33058520_NCOR1 may be a potential biomarker of a novel molecular subtype of prostate cancer. 33199837_Leukemic cells expressing NCOR1-LYN are sensitive to dasatinib in vivo in a patient-derived xenograft mouse model. 33722704_BCOR modulates transcriptional activity of a subset of glucocorticoid receptor target genes involved in cell growth and mobility. 33761934_Discovery of LAMP-2A as potential biomarkers for glioblastoma development by modulating apoptosis through N-CoR degradation. 33861372_Nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR) is a positive prognosticator for cervical cancer. 35395674_Aberrant Nuclear Export of circNCOR1 Underlies SMAD7-Mediated Lymph Node Metastasis of Bladder Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000018501 |
Ncor1 |
494.498594 |
0.4027877057 |
-1.311908 |
0.194716483 |
44.049913 |
0.00000000003201080894622027371326044756031368229004518966007708513643592596054077148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000171685879377257001820764692453038808422904892836413637269288301467895507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
288.3897800 |
39.7294996 |
721.0879059 |
71.7464891 |
| ENSG00000141068 |
8844 |
KSR1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVT5 |
FUNCTION: Part of a multiprotein signaling complex which promotes phosphorylation of Raf family members and activation of downstream MAP kinases (By similarity). Independently of its kinase activity, acts as MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2-dependent allosteric activator of BRAF; upon binding to MAP2K1/MEK1 or MAP2K2/MEK2, dimerizes with BRAF and promotes BRAF-mediated phosphorylation of MAP2K1/MEK1 and/or MAP2K2/MEK2 (PubMed:29433126). Promotes activation of MAPK1 and/or MAPK3, both in response to EGF and to cAMP (By similarity). Its kinase activity is unsure (By similarity). Some protein kinase activity has been detected in vitro, however the physiological relevance of this activity is unknown (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29433126}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Kinase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables 14-3-3 protein binding activity; ATP binding activity; and protein C-terminus binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of MAPK cascade. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and membrane. Part of protein-containing complex. Implicated in breast adenocarcinoma. Biomarker of breast cancer. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8844; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; MAP-kinase scaffold activity [GO:0005078]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043405]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15520853_KSR1 kinase activity is essential for anti-apoptotic protection of the intestinal epithelium [review] 15899786_KSR1-mediated regulation of ERK activity represents a novel determinant of CDDP sensitivity of cancer cells. 16732322_1,25D selectively increases the expression of the gene encoding kinase suppressor of Ras-1 (KSR-1) in HL60 cells 18332145_Human KSR1 proteins promote assembly of multivalent Raf.MEK complexes that are required for c-Raf kinase activation and functional coupling of active kinases to downstream substrates. 18426801_human 14-3-3gamma binds to the ERK1/2 molecular scaffold KSR1, which is mediated by the C-terminal stretch of 14-3-3gamma 18719367_Down-regulation of KSR1 in pancreatic cancer xenografts by antisense oligonucleotide correlates with tumor drug uptake. 19188442_KSR1 regulated the threshold required for MAPK activation in T cells without affecting the nature of the response. 19718030_DC-SIGN was constitutively associated with a signalosome complex consisting of the scaffold proteins LSP1, KSR1 and CNK and the kinase Raf-1. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20945381_Oncoprotein Cot1 represses kinase suppressors of Ras1/2 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced differentiation of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. 21435442_KSR1 is overexpressed in endometrial carcinoma and regulates proliferation and TRAIL-induced apoptosis by modulating FLIP levels 21555152_Genetic disruption of the scaffolding protein, Kinase Suppressor of Ras 1 (KSR1), differentially regulates GM-CSF-stimulated hyperproliferation in hematopoietic progenitors expressing activating PTPN11 mutants D61Y and E76K. 21829671_simulations constitute a multi-dimensional exploration of how EGF-dependent EGFR endocytosis and ERK activation are dynamically affected by scaffolds KSR and MP1, co-regulated by Cbl-CIN85 and Endophilin A1 22752157_VRK2A can form a high molecular size complex with both MEK1 and KSR1; the KSR1 complex assembled and retained by VRK2A in the endoplasmic reticulum can have a modulatory effect on the signal mediated by MAPK,locally affecting the magnitude of its responses 23250398_the atypical C1 domain, the CC-SAM domain is required to target KSR-1 to the plasma membrane. 23416464_Elevated levels of phosphorylated KSR were detected in the nuclear fractions. 24095280_Data indicate that phosphorylation of BRAF by AMPK disrupts its association with KSR1. 24129246_Our findings integrate KSR1 into a network involving DBC1 and SIRT1, which results in the regulation of p53 acetylation and its transcriptional activity. 24909178_KSR1 stabilizes BRCA1 by reducing BRCA1 ubiquitination, inhibits tumor growth through BRCA1, and regulates BRCA1 stability via elevated BARD1 abundance and increased BRCA1-BARD1 interaction 25002533_Data show that caveolin-1 is necessary for optimal KSR1-dependent ERK activation by growth factors and oncogenic Ras. 25287073_KSR1 rs2241906 variants may predict survival in patients with advanced ERalpha+ BC treated with adjuvant TAM. 25608512_KSR1 is coordinately regulated with Notch signaling and oxidative phosphorylation in papillary thyroid cancer. 25962735_the relative mRNA copy values of KSR1, ERK1 and ERK2 in the cancer tissues were 2.43 +/- 0.49, 2.10 +/- 0.44 and 3.65 +/- 0.94..EGb 761 enhanced the chemotherapy sensitivity through suppression of the KSR1-mediated ERK1/2 pathway in gastric cancer 26549023_Data show that neurofibromin 2 (Merlin) suppresses proliferation and adhesion, at least partly, through inhibiting kinase suppressor of Ras 1 (KSR1) and DCAF1 protein. 26673620_Upregulation of KSR1 is associated with Colorectal cancer. 27195677_praja2 regulates KSR1 stability and mitogenic signaling. 28003362_These results suggest that Rap1 activation of ERKs requires PKA phosphorylation and KSR binding. 29433126_findings demonstrate that KSR-MEK complexes allosterically activate BRAF through the action of N-terminal regulatory region and kinase domain contacts and challenge the accepted role of KSR as a scaffold for MEK recruitment to RAF 29596465_Homozygous KSR1 deletion attenuates morbidity but does not prevent tumor development in a mouse model of RAS-driven pancreatic cancer 29980571_Erbin interacted with kinase suppressor of Ras 1 (KSR1) and displaced it from the RAF/MEK/ERK complex to prevent signal propagation..These findings establish the scaffold protein Erbin as a negative regulator of EMT and tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer through direct suppression of Akt and RAS/RAF signaling 30917119_Findings demonstrate a role for kinase suppressor of Ras 1 as a positive regulator of neurotensin secretion from human endocrine cells and indicate that this effect is mediated by the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 signaling pathway. 33461174_Praja2 suppresses the growth of gastric cancer by ubiquitylation of KSR1 and inhibiting MEK-ERK signal pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000018334 |
Ksr1 |
59.982883 |
0.4216959382 |
-1.245725 |
0.365963926 |
11.285548 |
0.00078112768445641694945585919995778567681554704904556274414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001855696865053390459676663226673554163426160812377929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.5575431 |
9.1091674 |
82.6033234 |
15.6722131 |
| ENSG00000141258 |
9905 |
SGSM2 |
protein_coding |
O43147 |
FUNCTION: Possesses GTPase activator activity towards RAB32, RAB33B and RAB38 (PubMed:26620560, PubMed:21808068). Regulates the trafficking of melanogenic enzymes TYR, TYRP1 and DCT/TYRP2 to melanosomes in melanocytes by inactivating RAB32 and RAB38. Inhibits RAB32 and RAB38 activation both directly by promoting their GTPase activity and indirectly by disrupting the RAB9A-HPS4 interaction which is required for RAB32/38 activation (PubMed:26620560). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21808068, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26620560}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a GTPase activator with activity towards RAB32 and RAB33B, which are regulators of membrane trafficking. The encoded protein inactivates RAB32 and can bind RAB9A-GTP, a protein required for RAB32 activation. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:9905; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; late endosome to Golgi transport [GO:0034499]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547] |
17509819_Identification of novel protein SGSM2 which modulate small G protein (RAP and RAB)-mediated signaling pathway 21808068_RUTBC1 is a Tre2/Bub2/Cdc16 domain-containing protein that binds to Rab9A-GTP both in vitro and in cultured cells, but is not a GTPase-activating protein for Rab9A. 26620560_Data suggest RUTBC1/SGSM2 in melanocytes functions as physiological GTPase-activating protein for Rab32/Rab38 in regulation of transport of melanogenic enzymes (tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein 1, dopachrome isomerase) into melanosomes. 30489189_Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identifies specific modules and hub genes related to subsyndromal symptomatic depression. 30744493_Increased expression of SGSM2 is associated with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer metastasis. 35264562_SGSM2 inhibits thyroid cancer progression by activating RAP1 and enhancing competitive RAS inhibition. |
ENSMUSG00000038351 |
Sgsm2 |
92.221495 |
0.3478487034 |
-1.523468 |
0.274289524 |
30.121727 |
0.00000004057597550388984922750348514550178258275536791188642382621765136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000166176858611935121997821621607493991490400730981491506099700927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
45.0850695 |
9.6457049 |
129.6261480 |
19.2251007 |
| ENSG00000141295 |
90507 |
SCRN2 |
protein_coding |
Q96FV2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable cysteine-type exopeptidase activity and dipeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90507; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; cysteine-type exopeptidase activity [GO:0070004]; dipeptidase activity [GO:0016805]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
|
ENSMUSG00000020877 |
Scrn2 |
103.559285 |
0.4071014716 |
-1.296540 |
0.170063631 |
58.871802 |
0.00000000000001682867076303163548675654173049894188387014433427868453918563318438827991485595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000111436150947665738464619488044677202243462089958914162934888736344873905181884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
64.2454312 |
7.8883013 |
158.7836404 |
12.8953384 |
| ENSG00000141378 |
51651 |
PTRH2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3E5 |
FUNCTION: The natural substrate for this enzyme may be peptidyl-tRNAs which drop off the ribosome during protein synthesis. {ECO:0000250}.; FUNCTION: Promotes caspase-independent apoptosis by regulating the function of two transcriptional regulators, AES and TLE1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15006356}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a mitochondrial protein with two putative domains, an N-terminal mitochondrial localization sequence, and a UPF0099 domain. In vitro assays suggest that this protein possesses peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase activity, to release the peptidyl moiety from tRNA, thereby preventing the accumulation of dissociated peptidyl-tRNA that could reduce the efficiency of translation. This protein also plays a role regulating cell survival and death. It promotes survival as part of an integrin-signaling pathway for cells attached to the extracellular matrix (ECM), but also promotes apoptosis in cells that have lost their attachment to the ECM, a process called anoikos. After loss of cell attachment to the ECM, this protein is phosphorylated, is released from the mitochondria into the cytosol, and promotes caspase-independent apoptosis through interactions with transcriptional regulators. This gene has been implicated in the development and progression of tumors, and mutations in this gene have been associated with an infantile multisystem neurologic, endocrine, and pancreatic disease (INMEPD) characterized by intellectual disability, postnatal microcephaly, progressive cerebellar atrophy, hearing impairment, polyneuropathy, failure to thrive, and organ fibrosis with exocrine pancreas insufficiency (PMID: 25574476). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. |
hsa:51651; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; aminoacyl-tRNA hydrolase activity [GO:0004045]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of anoikis [GO:2000210] |
15006356_Results identify Bit1, a mitochondrial protein released into the cytoplasm during apoptosis that forms a complex with AES, a small Groucho/transducin-like enhancer of split (TLE) protein 17511679_Reduced expression of the proapoptotic proteins Bit1 or overexpression of Bcl-2 improved myoblast transplantation survival. 18703509_the PKD serine/threonine kinase is one of the signaling molecules through which integrin-mediated cell attachment controls Bit1 activity and anoikis 19578750_TAp63gamma could induce apoptosis in human esophageal squamous cancer EC9706 cells, through at least releasing AIF and Bit1 from mitochindria into cytosol and nucleus, where apoptotic cascade takes place. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21383007_Bit-1 mediates integrin-dependent cell survival through activation of the NFkappaB pathway 21886829_downregulation of Bit1 conferred cancer cells with enhanced anoikis resistance, adhesive and migratory properties in vitro 22952044_TLE1 inhibits the Bit1 anoikis pathway by reducing the formation of the proapoptotic Bit1-AES complex in part through sequestration of AES in the nucleus. 23248118_Data indicate that the cell death domain (CDD) to the N-terminal 62 amino acids of Bit1 was more potent in killing cells than the full-length Bit1 protein when equivalent amounts of cDNA were transfected. 23259782_Bit1 may be a useful pathological marker and a prognostic marker for serous papillary adenocarcinomas outcome. 23955799_Bit1 plays pivotal roles in the development and progression of ESCC, and its biological functions in ESCC may be closely associated with AIF and Bcl-2 levels. 25003198_these findings suggest a tumor suppressive role of the caspase-independent anoikis effector Bit1 in lung cancer. 25211327_Reduction of the Bit1 level in cytosol, regulated by E2 binding to ESR1, was mainly mediated through PI3K/AKT pathways. 26956728_Bit1 may be an important regulator in cell growth, apoptosis, migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting FAK-paxillin pathway. 27129381_This study reports on five infantile-onset multisystem neurologic, endocrine, and pancreatic disease (IMNEPD) patients with a different homozygous PTRH2 mutation, broaden the phenotypic spectrum of the disease and differentiate common symptoms and interindividual variability in IMNEPD associated with a unique mutation. 27655370_studies indicate Bit1 is an inhibitor of EMT and metastasis in lung cancer and hence can serve as a molecular target in curbing lung cancer aggressiveness 28175314_Our data establishes a PTRH2 mutation as a novel driver of congenital muscle degeneration and identifies a potential novel target to treat muscle myopathies. 28328138_Homozygous mutation in PTRH2 gene causes progressive sensorineural deafness and peripheral neuropathy in three sisters from a consanguineous family. 28488526_Bcl-2 expression patterns in various differentiated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma were higher than those in corresponding normal esophageal tissues with no statistical differences ( p > 0.05). Importantly, Bit1 expression was positively correlated with both matrix metalloproteinase 2 and Bcl-2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal adenocarcinoma tissues ( p A (p.W108*) mutation in PTRH2 that encodes peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase 2, causing infantile-onset multisystem neurologic, endocrine, and pancreatic disease 31368047_Bit1 may serve as a novel regulator of astrocyte biological behaviors interplaying with vascular endothelial cell during retinal development. 35737738_Bit1 is involved in regulation between integrin and TGFbeta signaling in lens epithelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000072582 |
Ptrh2 |
138.727635 |
2.0800222499 |
1.056599 |
0.132590440 |
63.867171 |
0.00000000000000133097207320690203619448648088506695925547671736227650640671527071390300989151000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000009472105979042369341749071936746865018333851535259348963791126152500510215759277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
177.6581942 |
14.7881844 |
86.0509732 |
5.5133603 |
| ENSG00000141384 |
6875 |
TAF4B |
protein_coding |
Q92750 |
FUNCTION: Cell type-specific subunit of the general transcription factor TFIID that may function as a gene-selective coactivator in certain cells. TFIID is a multimeric protein complex that plays a central role in mediating promoter responses to various activators and repressors. TAF4B is a transcriptional coactivator of the p65/RELA NF-kappa-B subunit. Involved in the activation of a subset of antiapoptotic genes including TNFAIP3. May be involved in regulating folliculogenesis. Through interaction with OCBA/POU2AF1, acts as a coactivator of B-cell-specific transcription. Plays a role in spermiogenesis and oogenesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:G5E8Z2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10828057, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10849440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16088961, ECO:0000303|PubMed:24431330}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Oogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
TATA binding protein (TBP) and TBP-associated factors (TAFs) participate in the formation of the TFIID protein complex, which is involved in initiation of transcription of genes by RNA polymerase II. This gene encodes a cell type-specific TAF that may be responsible for mediating transcription by a subset of activators in B cells. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014]. |
hsa:6875; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription factor TFIID complex [GO:0005669]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity [GO:0016251]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060261]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly [GO:0051123]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter [GO:0006367] |
15601843_histone fold domain mediated interaction enhances the DNA binding activity of each of the TAF6-TAF9 and TAF4b-TAF12 pairs and of a histone-like octamer complex composed of the four TAFs 16088961_work suggests that pre-mRNA processing and post-translational modification represent two important regulatory steps for the gonad-specific functions of human TAF(II)105 18206971_TAF4b incorporation into TFIID induces an open conformation at the lobe involved in TFIIA & putative activator interactions, correlating with differential activator-dependent transcription & promoter recognition by 4b/4-IID. 19020761_Expression of the TAF4b gene is induced by MYC through a non-canonical, but not canonical, E-box which contributes to its specific response to MYC. 19508998_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19635797_Findings suggest that DNA binding by TAF4/4b-TAF12 facilitates the association of TFIID with the core promoter of a subset of genes. 20353996_We show evidence for the first time of an interdependence of TAF4b and AP-1 family members in cell type-specific promoter recognition and initiation of transcription in the context of cancer progression and EMT. 24431330_Two candidate loci in each family and homozygous truncating mutations p.R611X in TAF4B in family 1 and p.K507Sfs*3 in ZMYND15 in family 2, were identified. 27341508_The existence of a highly conserved TAF4b-dependent gene regulatory network. 30336530_The methionine synthase reductase (MTRR), TAF4B protein, PIWI protein (PIWIL1) four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are not shown to be significantly related with non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA). 31377750_Nonobstructive Azoospermia variants included MTRR c.537T>C (rs161870), odds ratios (OR), 3.686, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.228-11.066; MTRR, c.1049A>G (rs162036), OR, 3.686, 95% CI, 1.228-11.066; PIWIL1, c.1580G>A (rs1106042), OR, 4.737, 95% CI, 1.314-17.072; TAF4B, c.1815T>C (rs1677016), OR, 3.599, 95% CI, 1.255-10.327; and SOX10 c.927T>C (rs139884), OR, 3.192, 95% CI, 1.220-8.353. 32502024_The c.11G>T mutation of the TAF4B gene may be associated with NOA in a Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000054321 |
Taf4b |
34.153443 |
3.0652824912 |
1.616020 |
0.313246003 |
26.901827 |
0.00000021405641599144302972208874294435254626023379387333989143371582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000814927185977224410852947592692752110110632202122360467910766601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.5906703 |
10.5291861 |
17.5971809 |
2.7645642 |
| ENSG00000141424 |
25800 |
SLC39A6 |
protein_coding |
Q13433 |
FUNCTION: May act as a zinc-influx transporter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12839489}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
Zinc is an essential cofactor for hundreds of enzymes. It is involved in protein, nucleic acid, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism, as well as in the control of gene transcription, growth, development, and differentiation. SLC39A6 belongs to a subfamily of proteins that show structural characteristics of zinc transporters (Taylor and Nicholson, 2003 [PubMed 12659941]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:25800; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; zinc ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0071578]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577] |
11911440_LIV-1 co-clusters with estrogen receptor alpha in microarray analysis of breast cancer biopsies. 12659941_Review of LIV-1 and other LZT proteins. 12839489_LIV-1, a member of the ZIP family of zinc transporters, is an integral plasma membrane protein that transports zinc into cells. 12839489_Structure-function analysis of LIV-1. 12960427_LIV-1 is coregulated with estrogen receptor in some breast cancers. 15986450_data suggest that LIV-1 protein is a promising candidate for a novel marker for breast cancer patients with better outcome 17786585_regulation of LIV-1 protein in human breast cancer xenografts 17825787_Hence, our data provide the first evidence that LIV-1 mRNA is overexpressed in cervical cancer in situ and is involved in invasion of cervical cancer cells through targeting MAPK-mediated Snail and Slug expression. 17959546_LIV-1 mRNA upregulation is associated with the progression of cervical cancer but not with the development of endometrial carcinoma. 18330719_LIV-1 may be a regulator of E-cadherin 19066393_Single nucleotide polymorphism in SLC39A6 gene is associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19724917_LIV-1 enhances the aggressive phenotype through the induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. 19852955_Zip6 over-expression is not an underlying mechanism initiating breast cancer, but in fact may play a 'tumor-constraining' role. 19887557_The present study identifies LIV1 as a critical mediator responsible for HDACi-induced apoptosis. The effect of LIV1 is, at least in part, mediated by affecting intracellular zinc homeostasis. 22110740_LIV-1 is involved in prostate cancer progression as an intracellular target of growth factor receptor signaling which promoted EMT and cancer metastasis 22349685_The results of this study showed evidence for a positive correlation between LIV1 and ZnT6 insuperior temporal, occipital, and frontal gyri in patient with alzheimer disease. 22852056_Some studies correlate LIV-1 expression with a more aggressive cancer phenotype and increased likelihood for metastasis to lymph nodes. In contrast, other evidence suggests this transporter is associated with a more favorable prognosis. [review] 23437163_Down-regulated LIV-1 cells showed significant inhibition of proliferation in vitro and reduction of tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, E-cadherin expression increased in LIV-1 siRNA expressing Hep-G2. 23644492_SLC39A6 has an important role in the prognosis of esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma and may be a potential therapeutic target. 23919497_a causative role for ZIP6 in cell motility and migration 24587242_Zinc and its transporters, ZIP6 and ZIP10, are required for the breast cancer cells motility stimulated with high glucose level, such as in diabetes. 25420545_drug resistance of ovarian cancer cells to trichostatin A may be related to expression of the LIV1 gene 25969539_Knock-down of ZIP6 but not ZIP7 in MIN6 beta cells impaired the protective effects of GLP-1 on fatty acid-induced cell apoptosis, possibly via reduced activation of the p-ERK pathway 26444413_SLC39A6 may have a tumor promoting role in esophageal carcinoma 26684241_Upregulation of SLC39A6 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 28209530_SLC39A6 promotes aggressiveness of esophageal carcinoma cells by increasing intracellular levels of zinc, activating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling, and up-regulating genes that regulate metastasis. 28833062_ZIP6 deficiency disturbs intracellular Zn2+ homeostasis, leading to increased cell survival in hypoxia and reduced E-cadherin expression, indicating that decreased ZIP6 expression is strongly associated with resistance to hypoxia. 30339739_ZIP10 is predominantly expressed in the interfollicular epidermis, epidermal appendages and hair follicles. ZIP10 depletion resulted in epidermal malformations in a reconstituted human skin model via downregulation of the epigenetic enzyme histone acetyltransferase (HAT). Decreased HAT activity, resulting from either ZIP10 depletion or treatment with the zinc chelator TPEN, was readily restored by zinc supplementation. 30552163_this work shows that zinc entry into activated lymphocytes depends on Zip6 and that this transporter is essential for the correct function of the cellular activation machinery 31636012_These data demonstrate that LIV-1-GRPEL1 axis dually regulates mitotic exit as well as apoptosis by interacting with PP2A B55alpha and AIF. 31703635_SLC39A6 is involved in gastric adenocarcinoma, and genotype at SLC39A6 rs1050631 can predict post-resection prognosis of gastric adenocarcinoma patients, at least in a population in an area with high gastric adenocarcinoma incidence. 32797246_The ZIP6/ZIP10 heteromer is essential for the zinc-mediated trigger of mitosis. 34394081_Zap70 Regulates TCR-Mediated Zip6 Activation at the Immunological Synapse. 34453638_Oestrogen-regulated protein SLC39A6: a biomarker of good prognosis in luminal breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024270 |
Slc39a6 |
391.622540 |
2.1049490114 |
1.073785 |
0.086889095 |
153.512910 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000002959228034004000953382389535958860728374360884877510744435505051007245440643617895881711289673976494896123767830431461334228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000440748796991917814650118607927971030344203038824077079001415006562217156679451020730826308474670227610658912453800439834594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
538.0956079 |
26.8293297 |
257.6199998 |
10.1087527 |
| ENSG00000141441 |
64762 |
GAREM1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H706 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Acts as an adapter protein that plays a role in intracellular signaling cascades triggered either by the cell surface activated epidermal growth factor receptor and/or cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases. Promotes activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Plays a role in the regulation of cell proliferation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19509291}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Mitogen;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes an adaptor protein which functions in the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-mediated signaling pathway. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:64762; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19509291_Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation is regulated by the expression of GAREM in COS-7 and HeLa cells. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24003223_Data indicate that a subtype of GAREM, GAREM2, is specifically expressed in the mouse, rat, and human brain. 26164232_suggest that the interplay between 14-3-3, SAM domain and CABIT domain might be responsible for the distribution of GAREM1 in mammalian cells. 29273731_We have provided evidence that GAREM1 is involved in the PR interval of ECGs. These findings increase our understanding of the regulatory signals of heart rhythm through intracardiac ganglia of the autonomic nervous system and can be used to guide the development of a therapeutic target for heart conditions, such as atrial fibrillation. 30177387_the miR-128-GAREM-MAPK signaling pathway forms a critical feedback loop and mediates gastric carcinoma development 36084556_GAREM1 is involved in controlling body mass in mice and humans. |
ENSMUSG00000042680 |
Garem1 |
112.838091 |
0.3702311107 |
-1.433502 |
0.190713323 |
56.378892 |
0.00000000000005976856767489139954751280360405978127227681617750221221285755746066570281982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000384897058848777092537251393812868512729532394223141977818158920854330062866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.2222282 |
6.8974494 |
155.6713170 |
12.4396845 |
| ENSG00000141458 |
4864 |
NPC1 |
protein_coding |
O15118 |
FUNCTION: Intracellular cholesterol transporter which acts in concert with NPC2 and plays an important role in the egress of cholesterol from the endosomal/lysosomal compartment (PubMed:9211849, PubMed:9927649, PubMed:10821832, PubMed:18772377, PubMed:27238017, PubMed:12554680). Unesterified cholesterol that has been released from LDLs in the lumen of the late endosomes/lysosomes is transferred by NPC2 to the cholesterol-binding pocket in the N-terminal domain of NPC1 (PubMed:9211849, PubMed:9927649, PubMed:18772377, PubMed:19563754, PubMed:27238017, PubMed:28784760). Cholesterol binds to NPC1 with the hydroxyl group buried in the binding pocket (PubMed:19563754). Binds oxysterol with higher affinity than cholesterol. May play a role in vesicular trafficking in glia, a process that may be crucial for maintaining the structural and functional integrity of nerve terminals (Probable). Inhibits cholesterol-mediated mTORC1 activation throught its interaction with SLC38A9 (PubMed:28336668). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10821832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12554680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18772377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19563754, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27238017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28336668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28784760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9211849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9927649, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as an endosomal entry receptor for ebolavirus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21866103, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25855742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32855215}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Niemann-Pick disease;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a large protein that resides in the limiting membrane of endosomes and lysosomes and mediates intracellular cholesterol trafficking via binding of cholesterol to its N-terminal domain. It is predicted to have a cytoplasmic C-terminus, 13 transmembrane domains, and 3 large loops in the lumen of the endosome - the last loop being at the N-terminus. This protein transports low-density lipoproteins to late endosomal/lysosomal compartments where they are hydrolized and released as free cholesterol. Defects in this gene cause Niemann-Pick type C disease, a rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by over accumulation of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids in late endosomal/lysosomal compartments.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:4864; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; sterol binding [GO:0032934]; sterol transporter activity [GO:0015248]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; adult walking behavior [GO:0007628]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; bile acid metabolic process [GO:0008206]; cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0071404]; cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus [GO:0071383]; cholesterol efflux [GO:0033344]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; cholesterol transport [GO:0030301]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; establishment of protein localization to membrane [GO:0090150]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; intestinal cholesterol absorption [GO:0030299]; intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032367]; lysosomal transport [GO:0007041]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; membrane raft organization [GO:0031579]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016242]; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904262]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sterol transport [GO:0015918]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] |
11754101_Mutational analysis of the complete genomic sequence of NPC1 and characterization of haplotypes suggest that the expression of missense mutations is influenced by haplotypic background. 11907140_Niemann-Pick C1 protein regulates cholesterol transport to the trans-Golgi network and plasma membrane caveolae. 12125814_Review of NPC1 and HE1/NPC2 roles regulating cholesterol transport through endosomal/lysosomal system and in Niemann-Pick type C disease 12398991_NPC2, NPC1 and MLN64 may act in an ordered sequence to sense cholesterol, effect sterol movement, and consequently, influence the process of vesicular trafficking. 12401890_15 mutations, eight of which were previously unreported, from Niemann-Pick type C disease patients 12408188_Our results will contribute to defining the association between the clinical phenotypes and the genetic abnormalities in Niemann-Pick C disease. 12719428_NPC1 and NPC2 have a role in the regulation of sterol homeostasis through generation of LDL cholesterol-derived oxysterols 15069562_findings suggest that sequestration of theta-toxin to raft-enriched cell surface vesicles may underlie reduced sensitivity of NPC1-deficient cells to theta-toxin. 15314240_Results demonstrate that there is direct binding between Niemann-Pick type C1 protein (NPC1) and azocholestanol, which does not require NPC2 but requires a functional sterol-sensing domain within NPC1. 15347664_Data show that multiple signals are responsible for the trafficking of NPC1 to the endosomal compartment, including the dileucine motif and a previously unidentified signal residing within the putative sterol-sensing domain transmembrane domain 3. 15459971_first example of a splicing defect due to a mutation in the lariat branch point sequence in an intron of NPC1, found in Niemann-Pick type C patients 15632139_fatty acid flux through NPC1-deficient lysosomes is normal 15681833_ATP7B resides in the late endosomes with Rab7 and the Niemann-Pick C1 protein and translocates copper from the cytosol to the late endosomal lumen, participating in biliary copper excretion via lysosomes 15774455_Six novel NPC1 mutations were identified of which three are missense mutations located in the cysteine-rich domain. These are the first NPC1 mutations reported from Chinese patients with NPC. 15908696_D787N and L657F are activating NPC1 mutations provide evidence for a conserved mechanism for the sterol-sensing domain among cholesterol homeostatic proteins. 16054367_proposes a new hypothesis for the potential action or function of the NPC1 protein in the endosome; in this context, the relationship of NPC2 and NPC1 is also discussed. 16174794_NPC1 has a role in a vesicle-mediated pathway responsible for the clearance of drugs from cells and provides an explanation for a drug sequestration phenotype exhibited by the MDR HL-60 cell line 16644737_cholesterol contributes directly to the sequestration of Rab9 on Niemann-Pick type C cell membranes, which in turn, disrupts mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking 16757520_Ubiquitylation of NPC1 and its association with the ESCRT complex are controlled by endosomal cholesterol levels utilizing a mechanism that involves NPC2. 16778374_We report a Japanese patient with NPC caused by a homozygous c.2974 G > T mutation of the NPC1 gene,presenting with cataplexy at the age of 9 years and moderately low CSF-hypocretin 1 level. 17008555_Modulation of human NPC1L1 expression and promoter activity by cholesterol in a =sterol regulatory element binding protein-2 dependent mechanism. 17020879_NPC1 protein function is non-essential for the trafficking and removal of cellular cholesterol by ApoAI if the down-stream defects in ABCA1 and ABCG1 regulation in NPC disease cells are corrected using an LXR agonist 17160616_mutations in the NPC1 gene impair verbal working memory more than visuospatial working memory 17183645_I1061T NPC1 NPC1 mutant cells displayed an inappropriate homeostatic response to accumulated intracellular cholesterol. In addition, a number of striking parallels were observed between NPC disease and Alzheimer's disease. 17662536_human NPC1 can functionally substitute for the Caenorhabditis elegans genes ncr-1 and/or ncr-2. 17989072_Sterol binding site on luminal loop-1 is not essential for NPC1 function in fibroblasts, but may function in other cells where NPC1 deficiency produces more complicated lipid abnormalities. 18216017_novel approaches to treat NPC disease caused by the NPC1(I1061T) mutation 18272927_Transport of LDL-derived cholesterol from late endosomes/lysosomes to the sterol-regulatory pool is regulated by the NPC1 protein and promotes feedback inhibition of the SREBP pathway. 18272928_NPC-1 is sterol-regulated, achieved by SREBP protein acting via the sterol regulated element and the E-box sequences. 18591242_Niemann-Pick C1 functions in regulating lysosomal amine content 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774957_NPC1 deficiency causes an imbalance in the intracellular redox state, which could be restored by ALLO treatment in vitro 18834923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18834923_This study show an association of genetic variation in NPC1 with SLAD and/or aging. 19007772_ATP7B localizes in the late endosomes. Copper in the late endosomes is transported to the secretory compartment via NPC1-dependent pathway and incorporated into apo-ceruloplasmin to form holo-ceruloplasmin. 19029290_The use of fluorescent cholesterol analogs provides novel information on the molecular properties of the sterol-binding site in the full-length NPC1 protein. 19074461_Tau plays a critical role in the regulation of autophagy in NPC1-deficient cells. 19151714_In addition to FTO and MC4R, we detected significant association of obesity with three new risk loci in NPC1 (endosomal/lysosomal Niemann-Pick C1 gene), near MAF (encoding the transcription factor c-MAF) and near PTER (phosphotriesterase-related gene). 19206179_NPC1 gene mutation analysis identified all of the mutant alleles including three novel mutations. 19252935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19252935_Results characterize mutations in the NPC1 and 2 genes in 34 unrelated patients including 32 patients with mutations in NPC1 gene and two patients in NPC2 gene, with 33 distinct genotypes encountered. 19474101_Cholesterol trafficking mediated by NPC1 is needed for efficient HIV-1 production and Gag accumulation in endosomal/lysosomal compartments. 19563754_High-resolution structures of the N-terminal domain (NTD) of NPC1 and complexes with cholesterol & 25-hydroxycholesterol are described; NPC1(NTD) binds cholesterol in an orientation opposite to NPC2: 3beta-hydroxyl buried and isooctyl side chain exposed. 19746448_physiological and coordinate downregulation of the NPC1 and NPC2 genes/proteins promotes the sequestration of LDL-derived cholesterol within endocytic compartments and serves a role in maintaining intracellular cholesterol homeostasis 19815536_Data show that the BCG phagosome is relatively depleted in LAMP-2, NPC1, flotillin-1, vATPase, and syntaxin 3. 19851340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965586_a transport pathway for endosomal cholesterol to mitochondria that requires MLN64, but not NPC1 20007703_The results suggest that NPC1 and NPC2 can function independently of one another in the egress of certain membrane-impermeable lysosomal cargo. 20489167_Common variations in NPC1 contributes to serum triglyceride levels in humans with Niemann-Pick disease type C1. 20489167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497909_Total cholesterol levels were reduced in hippocampus from AD (Alzheimer's disease) patients compared to control individuals, and it is therefore possible that the increased expression of NPC1 is linked to perturbed cholesterol homeostasis in AD. 20521171_Case Report: loss of NPC1 function, with attendant changes in membrane cholesterol composition, does not significantly modify the insulin resistance phenotype, even in the context of severely impaired INSR function. 20571217_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20571217_Testing for epistatic interaction between genes in the pathway of cholesterol metabolism NPC1 protein and ABCA1 protein might be useful for predicting Alzheimer's disease risk 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20607864_Increased level and processing of amyloid protein precursor may be associated with the development of pathology and/or degenerative events observed in Npc1-deficient mouse brains. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20843981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20955564_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20955564_results of the present study suggest that NPC1 variants seem to be contributors to coronary heart disease occurrence in Chinese population 21866101_NPC1 is essential for Ebola virus entry and a target for antiviral therapy 21866103_membrane fusion mediated by filovirus glycoproteins and viral escape from the vesicular compartment require the NPC1 protein, independent of its known function in cholesterol transport 22179027_overexpression of ABCA1 alone is able to correct the mobilization of cholesterol from late endosomes/lysosomes and the formation of HDL particles in NPC1- but not NPC2-deficient human fibroblasts 22212234_NPC1 traffic to Anaplasma phagocytophilum inclusions is crucial for infection. 22273177_Loss of Niemann Pick type C proteins 1 and 2 greatly enhances HIV infectivity and is associated with accumulation of HIV Gag and cholesterol in late endosomes/lysosomes. 22326530_NPC1 homozygous mutation of S865L correlated with a relatively severe juvenile neurological form of Niemann-Pick disease type C disease in chinese patients 22395071_Purified human NPC1 binds only to a cleaved form of Ebola virus spike glycoprotein that is generated within cells during entry, and only viruses containing cleaved glycoprotein can utilize a receptor retargeted to the cell surface. 22437840_Data show that that NPC1 (Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 protein) neurons have strong spontaneous activation of autophagy. 22495346_Neuron-only expression of NPC1 does not completely prevent neurodegeneration; the addition of astrocyte expression decreases the rate of decline. 22607065_NPC1 silencing does not result in accumulation of sphingosine. Thus, NPC1 does not play significant role in sphingosine export from endosomal/lysosomal compartment. 22962690_The NPC2 delivers cholesterol to the perimeter membrane of late endosomes, where it becomes available for transport to mitochondria without requiring NPC1. 23010472_this is the first report, showing a role of NPC1 in platelet function and formation but further studies are needed to define how cholesterol storage interferes with these processes 23142039_Characterization of novel chromosomal microdeletions at 18q11-q12 involving the NPC1 gene in two patients with Niemann-Pick type C disease. 23382922_lack of Npc1 protein can alter the expression profile of selected transcripts as well as proteins, and APP overexpression influences cerebral pathology by enhancing changes triggered by Npc1 deficiency in the bigenic line. 23521797_there is an additional sterol-binding site on NPC1 23567849_the NPC1 promoter methylation is a probable mechanism that can result in reduced/impaired NPC1 expression/activity and may thus contribute to progression of cardiovascular diseases. 23701245_A novel NPC1 mutation causing the Niemann-Pick type C disease and segregating to a Greek island has been identified. 23733943_Treatment of NPC1-null or NPC2-deficient cells with cyclodextrin was effective in reducing cholesterol storage as well as the endocytic accumulation of sialoglycoproteins, demonstrating a direct link between cholesterol storage and abnormal recycling. 24001314_an atomistic model is proposed of the transfer of cholesterol from NPC2 to NPC1(NTD) through the formation of an intermediate NPC1(NTD)-NPC2 complex 24064683_The minor G allele frequency of the rs1788799 polymorphisms in NPC1 might be a protective factor while the rs3764650 polymorphisms of ABCA7 might not be related to sporadic Alzheimer's disease in the Han Chinese population. 24296264_role of NPC1 in regulating intracellular cholesterol trafficking and atherosclerosis. 24790103_elevated mitochondrial cholesterol levels in NPC1-depleted cells and in NPC2-depleted cells expressing mutant NPC2 that allows endosomal cholesterol trafficking to mitochondria were associated with increased expression of antioxidant response factor Nrf2 24866237_These findings show that the AD-like phenotype of NPC model cells can be partly reverted by promoting a non-amyloidogenic processing of APP through the upregulation of GGA1 supporting its preventive role against AD 24915861_twelve individuals were subsequently confirmed to be NP-C by DNA analysis of NPC1 and NPC2 genes, with the early infantile form, the late infantile form, the juvenile form, and the adult form 25220527_heterozygous mutations in the NPC1/2 gene might be a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease 25238906_NPC1 gene sequencing revealed that he was a compound heterozygote for the p.S954L and p.N1156S mutations. 25251378_Data suggest that in order for the ligand cholesterol to slide from one binding pocket to the other (from NPC2 to NPC1), cholesterol undergoes conformational change/isomerization to accommodate the bent transfer pathway between the 2 binding pockets. 25310500_This study showed that Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1), is required for Lloviu virus (LLOV) entry, suggesting that receptor binding would not impose a barrier to LLOV infection. 25764212_Our data suggest an incidence rate for NPC1 and NPC2 of 1/92,104 and 1/2,858,998, respectively. Evaluation of common NPC1 variants, however, suggests that there may be a late-onset NPC1 phenotype with a markedly higher incidence. 25771912_Results identified six novel mutations (PKHD1: p.Thr777Met, p.Tyr2260Cys; ABCB11: p.Val1112Phe, c.611+1G > A, p.Gly628Trpfs*3 and NPC1: p.Glu391Lys) for the diagnostic of inherited infantile cholestatic disorders. 25873482_An isobaric labeling-based quantitative analysis of proteome of NPC1(I1061T) primary fibroblasts when compared with wild-type cells identified 281 differentially expressed proteins based on stringent data analysis criteria, is reported. 26019327_In a transgenic mouse model, human NPC1 disease was faithfully recapitulated in a NPC1 I1061T mutation knock-in model. 26283546_results uncover Akt as a key regulator of NPC1 degradation and link NPC1 to cancer cell proliferation and migration. 26338816_NPC1 mutations are substantially enriched in unexplained early onset ataxia, making it high risk group for Niemann-Pick disease type C. 26468524_Here, using live cell imaging, the authors obtained evidence that in contrast to the new model, ebolavirus enters cells through endolysosomes that contain both NPC1 and TPC2. 26507101_Fibroblasts from Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease patients with low levels of NPC1 protein have high amounts of procathepsin D but reduced quantities of the mature protein, thus showing a diminished cathepsin D activity. 26578804_These experiments support a model in which NPC1 protein functions to transfer cholesterol past a lysosomal glycocalyx. 26771495_Study determined the crystal structure of the primed GP (GPcl) of Ebola virus bound to domain C of NPC1 (NPC1-C); NPC1-C utilizes two protruding loops to engage a hydrophobic cavity on head of GPcl. Upon enzymatic cleavage and NPC1-C binding, conformational change in the GPcl further affects the state of the internal fusion loop, triggering membrane fusion. 26790753_Two mutations were identified in the NPC1 gene, one of which was novel and its pathogenetic nature was unknown 26818574_these results clearly demonstrated that the over-expression of NPC1 with a defective function in an imatinib-resistant Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line 26846330_Structure of glycosylated NPC1 luminal domain C reveals insights into NPC2 and Ebola virus interactions 26890452_We identified major events in NPC1 evolution and revealed and compared orthologs and paralogs of the human NPC1 gene through phylogenetic and protein sequence analyses. We predicted whether an amino acid substitution affects protein function by reducing the organism's fitness. 27095633_Furthermore saturation and intracellular distribution of alpha-Toc seem to be strongly dependent on the availability of this vitamin as well as on the presence of the lysosomal protein NPC1 27307437_Here we report a crystal structure of a large fragment of human NPC1 at 3.6 A resolution, which reveals internal twofold pseudosymmetry along TM 2-13 and two structurally homologous domains that protrude 60 A into the endosomal lumen, and we propose a model for NPC1 function in cholesterol sensing and transport. 27339554_identification of NPC1 and/or NPC2 mutations combined with descriptions of clinical phenotype, will improve our knowledge of pathogenic mutations and our understanding of genotype-phenotype correlations. 27378690_knockdown of TMEM97 also increases levels of residual NPC1 in NPC1-mutant patient fibroblasts and reduces cholesterol storage in an NPC1-dependent manner. Our findings propose TMEM97 inhibition as a novel strategy to increase residual NPC1 levels in cells and a potential therapeutic target for Niemann-Pick type C disease (NP-C). 27551080_Docking of the NPC1-NPC2 complex onto the full-length NPC1 structure reveals a direct cholesterol transfer tunnel between NPC2 and N-terminal domain cholesterol binding pockets, supporting the 'hydrophobic hand-off' cholesterol transfer model. 27792009_This study demonistrated that heterozygous mutations of NPC1 genes could contribute to dementia plus, at least in a subset of patients. 27900365_this case provides support for the V950M variant being sufficient for adult-onset Niemann-Pick type C disease. 28130309_Rare loss-of-function NPC1 mutations were identified as being associated with human adiposity with a high penetrance in a Chinese population. 28134274_pronounced alterations in several proteins linked to autophagy and lysosomal catabolism reflecting vesicular transport obstruction and defective lysosomal turnover resulting from NPC1 deficiency, were observed. 28167839_Mutation in the NPC1 gene is associated with Niemann-Pick type C. 28193631_The mutant NPC1 did not significantly reduce cholesterol accumulation, but approximately 85% of the mutants showed reduced cholesterol accumulation when treated with vorinostat or panobinostat. 28328115_Sequencing of genomic DNA from GM03123 Led to the identification of a mutation in NPC1 GENE, g.41940G>C (c.1947 + 5G>C; rs770321568) (Fig. 1A), with a minor allele frequency of 0.0000082 28472934_The splicing mutation IVS23 + 3insT was associated in homozygocity with a severe biochemical and clinical phenotype. A possible founder effect for this mutation was demonstrated in the Greek Island, as well as a different origin for each novel mutation 28784760_Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) protein structures suggest mapping of all of the disease-causing mutations for future molecular insights into the pathogenesis of Niemann-Pick type C disease (NPC) disease. 28865947_New variant associated with Niemann-Pick disease type C: Neurological manifestations and biochemical, molecular, and cellular characterisation.', trans 'Nueva variante asociada a enfermedad de Niemann-Pick tipo C: manifestaciones neurologicas y caracterizacion bioquimica, molecular y celular. 29031163_Taken together, these studies suggest that Ebola virus requires phosphatidylinositol (3,5) bisphosphate production in cells to promote efficient delivery to NPC1. 29325023_NPC1 gene variations may predispose to common metabolic diseases by modulating steroid hormone synthesis and/or lipid homeostasis. 29479887_Niemann-Pick C1 protein (NPC1) gene expression showed positive significant correlation with interleukin 10 (IL-10) serum concentration. 29617956_We identified CD22 as a marker of dysregulated microglia in Npc1 mutant mice and subsequently demonstrated that elevated cerebrospinal fluid levels of CD22 in NPC1 patients responds to HPbetaCD administration. Collectively, these data provide the first in-depth analysis of microglia function in NPC1 and suggest possible new therapeutic approaches. 29659804_these findings confirm the utility of high-content image-based compound screens of NPC1 patient cells and support extending the approach into larger compound collections. 29878115_Mutation in the NPC1 gene is associated with Niemann-Pick type C1 disease. 30010949_Human NPC1 SNPs may likely affect host susceptibility to filoviruses. 30047864_These data support the hypothesis that cholesterol is transported through interactions between two or more NPC1 molecules. 30133337_We also identified LNA ASOs targeting human host factor NPC1 and demonstrated reduced infection by chimeric vesicular stomatitis virus harboring the Ebola glycoprotein, which directly binds to NPC1 for viral infection. 30181526_Results propose that, depending on the location of the cholesterol ligand, a dynamical interface between the NPC2 and NPC1 N-terminal domain (NTD) proteins exists. Structural features of a particular interface can lower the energy barrier and stabilize the passage of the cholesterol substrate from NPC2 to NPC1(NTD). 30183109_In contrast to the benign Q92S mutation, Q92R significantly reduces electrostatic potential around S-opening, and thus likely affects NPC1 (NTD)-NPC2 interaction and/or cholesterol transfer from NPC2 to NPC1. 30202070_mutant NPC1 degradation is regulated by selective endoplasmic reticulum autophagy and MARCH6-dependent endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation 30820861_This study aims to identify the spectrum of sequence alterations associated to Niemann-Pick type C in individuals with clinical suspicion of this disease. 30923329_Different Niemann-Pick C1 Genotypes Generate Protein Phenotypes that Vary in their Intracellular Processing, Trafficking and Localization. 31506030_Molecular dynamics simulations reveal structural differences among wild-type NPC1 protein and its mutant forms. 31537798_The authors report a role for Niemann-Pick type C protein 1 (NPC1) in tethering endoplasmic reticulum-endocytic organelle Membrane contact sites where it interacts with the endoplasmic reticulum-localised sterol transport protein Gramd1b to regulate cholesterol egress. 31601621_NPC1 inhibition or disease mutations potentiate store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) due to a presenilin 1 (PSEN1)-dependent reduction in ER Ca(2+) levels alongside elevated expression of the molecular SOCE components ORAI1 and STIM1 31699992_Study determines the sequence-to-function-to-structure relationships of the NPC1 polypeptide fold required for membrane trafficking and generation of a tunnel that mediates cholesterol flux in late endosomal/lysosomal (LE/Ly) compartments. 32144825_High-content imaging and structure-based predictions reveal functional differences between Niemann-Pick C1 variants. 32204338_Different Trafficking Phenotypes of Niemann-Pick C1 Gene Mutations Correlate with Various Alterations in Lipid Storage, Membrane Composition and Miglustat Amenability. 32248828_Transcript, protein, metabolite and cellular studies in skin fibroblasts demonstrate variable pathogenic impacts of NPC1 mutations. 32371106_Variants in the Niemann-Pick type C gene NPC1 are not associated with Parkinson's disease. 32392809_Selective Degradation Permits a Feedback Loop Controlling Annexin A6 and Cholesterol Levels in Endolysosomes of NPC1 Mutant Cells. 32410728_Inter-domain dynamics drive cholesterol transport by NPC1 and NPC1L1 proteins. 32541946_Exosome mimicry by a HAVCR1-NPC1 pathway of endosomal fusion mediates hepatitis A virus infection. 32544384_Structural Basis of Low-pH-Dependent Lysosomal Cholesterol Egress by NPC1 and NPC2. 32609483_Examining the Role of Niemann-Pick C1 Protein in the Permissiveness of Aedes Mosquitoes to Filoviruses. 32611759_A Virion-Based Assay for Glycoprotein Thermostability Reveals Key Determinants of Filovirus Entry and Its Inhibition. 33021976_Cholesterol binding to the sterol-sensing region of Niemann Pick C1 protein confines dynamics of its N-terminal domain. 33129690_Toll-like receptor mediated lysozyme expression in Niemann-pick disease, type C1. 33139814_Signatures of natural selection and ethnic-specific prevalence of NPC1 pathogenic mutations contributing to obesity and Niemann-Pick disease type C1. 33144569_A trimeric Rab7 GEF controls NPC1-dependent lysosomal cholesterol export. 33257258_Application of a glycinated bile acid biomarker for diagnosis and assessment of response to treatment in Niemann-pick disease type C1. 33308480_NPC1-mTORC1 Signaling Couples Cholesterol Sensing to Organelle Homeostasis and Is a Targetable Pathway in Niemann-Pick Type C. 33990640_Identification and Classification of Rare Variants in NPC1 and NPC2 in Quebec. 34023384_Enrichment of NPC1-deficient cells with the lipid LBPA stimulates autophagy, improves lysosomal function, and reduces cholesterol storage. 34138521_Hepatocellular carcinoma as a complication of Niemann-Pick disease type C1. 34420959_Niemann-Pick Type C 1 (NPC1) and NPC2 Gene Variability in Demented Patients with Evidence of Brain Amyloid Deposition. 34481829_HSP90 inhibitors reduce cholesterol storage in Niemann-Pick type C1 mutant fibroblasts. 34544283_Anaplasma phagocytophilum Hijacks Flotillin and NPC1 Complex To Acquire Intracellular Cholesterol for Proliferation, Which Can Be Inhibited with Ezetimibe. 34676491_Ebola viral receptor Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) in human cancers: a potential biomarker and immunotherapeutic target. 34830064_Patient-Specific iPSC-Derived Neural Differentiated and Hepatocyte-like Cells, Carrying the Compound Heterozygous Mutation p.V1023Sfs*15/p.G992R, Present the ''Variant'' Biochemical Phenotype of Niemann-Pick Type C1 Disease. 35022465_Annexin A6 and NPC1 regulate LDL-inducible cell migration and distribution of focal adhesions. 35038048_Whole-exome sequencing analysis to identify novel potential pathogenetic NPC1 mutations in two Chinese families with Niemann-Pick disease type C. 35086560_Identification of novel mutations among Iranian NPC1 patients: a bioinformatics approach to predict pathogenic mutations. 35567899_Variants in the Niemann-pick type C genes are not associated with Alzheimer's disease: a large case-control study in the Chinese population. 35850050_The point mutation of the cholesterol trafficking membrane protein NPC1 may affect its proper function in more than a single step: Molecular dynamics simulation study. |
ENSMUSG00000024413 |
Npc1 |
469.099878 |
2.0286675151 |
1.020532 |
0.136534804 |
55.076609 |
0.00000000000011592228403760235390885089569255814100317940329443189284575055353343486785888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000730889753265702985548301346239138048333297548175835345318773761391639709472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
635.4321318 |
72.2249699 |
316.6904271 |
26.5318554 |
| ENSG00000141506 |
23533 |
PIK3R5 |
protein_coding |
Q8WYR1 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the PI3K gamma complex. Required for recruitment of the catalytic subunit to the plasma membrane via interaction with beta-gamma G protein dimers. Required for G protein-mediated activation of PIK3CG (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3Ks) phosphorylate the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositol at the 3-prime position, and play important roles in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking. The PI3Ks are divided into three classes: I, II and III, and only the class I PI3Ks are involved in oncogenesis. This gene encodes the 101 kD regulatory subunit of the class I PI3K gamma complex, which is a dimeric enzyme, consisting of a 110 kD catalytic subunit gamma and a regulatory subunit of either 55, 87 or 101 kD. This protein recruits the catalytic subunit from the cytosol to the plasma membrane through high-affinity interaction with G-beta-gamma proteins. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two distinct isoforms have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:23533; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IA [GO:0005943]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IB [GO:0005944]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding [GO:0031683]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897] |
12507995_p101 has a role in membrane recruitment and activation of PI3K gamma 15611065_analysis of functional domains in the p101 regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma 17486067_Overexpression of p101 activates PI3Kgamma signaling and is associated with T-cell lymphomas 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22065524_Our characterization of the PIK3R5 protein and findings suggest that it may play a role in the development of the cerebellum and vermis. 24014027_expression and activities of PI3Kgamma are modified differently by p87 and p101 in vitro and in living cells, arguing for specific regulatory roles of the non-catalytic subunits in the differentiation of PI3Kgamma signaling pathways. 25374236_PIK3R5 promoter hypermethylation is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 26173259_data argue for differential regulatory functions of the non-catalytic subunits and a specific Gbetagamma-dependent regulation of p101 in PI3Kgamma activation. 33493514_G protein betagamma translocation to the Golgi apparatus activates MAPK via p110gamma-p101 heterodimers. 34187569_HCP5, as the sponge of miR-1291, facilitates AML cell proliferation and restrains apoptosis via increasing PIK3R5 expression. 34775477_PIK3R5 genetic predictors of hypertension induced by VEGF-pathway inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000020901 |
Pik3r5 |
270.913029 |
2.5577042149 |
1.354849 |
0.132707691 |
103.947374 |
0.00000000000000000000000207761884284357764871389555072267182210165659916584622449740846791658988035322863652254454791545867919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000021810564808229877413748865958058625777404579796583620767904423921532131025458056683419272303581237792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
394.6601341 |
36.6178158 |
155.5890469 |
11.1438724 |
| ENSG00000141510 |
7157 |
TP53 |
protein_coding |
P04637 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a tumor suppressor in many tumor types; induces growth arrest or apoptosis depending on the physiological circumstances and cell type (PubMed:11025664, PubMed:12524540, PubMed:12810724, PubMed:15186775, PubMed:15340061, PubMed:17317671, PubMed:17349958, PubMed:19556538, PubMed:20673990, PubMed:20959462, PubMed:22726440, PubMed:24051492, PubMed:9840937, PubMed:24652652). Involved in cell cycle regulation as a trans-activator that acts to negatively regulate cell division by controlling a set of genes required for this process (PubMed:11025664, PubMed:12524540, PubMed:12810724, PubMed:15186775, PubMed:15340061, PubMed:17317671, PubMed:17349958, PubMed:19556538, PubMed:20673990, PubMed:20959462, PubMed:22726440, PubMed:24051492, PubMed:9840937, PubMed:24652652). One of the activated genes is an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Apoptosis induction seems to be mediated either by stimulation of BAX and FAS antigen expression, or by repression of Bcl-2 expression. Its pro-apoptotic activity is activated via its interaction with PPP1R13B/ASPP1 or TP53BP2/ASPP2 (PubMed:12524540). However, this activity is inhibited when the interaction with PPP1R13B/ASPP1 or TP53BP2/ASPP2 is displaced by PPP1R13L/iASPP (PubMed:12524540). In cooperation with mitochondrial PPIF is involved in activating oxidative stress-induced necrosis; the function is largely independent of transcription. Induces the transcription of long intergenic non-coding RNA p21 (lincRNA-p21) and lincRNA-Mkln1. LincRNA-p21 participates in TP53-dependent transcriptional repression leading to apoptosis and seems to have an effect on cell-cycle regulation. Implicated in Notch signaling cross-over. Prevents CDK7 kinase activity when associated to CAK complex in response to DNA damage, thus stopping cell cycle progression. Isoform 2 enhances the transactivation activity of isoform 1 from some but not all TP53-inducible promoters. Isoform 4 suppresses transactivation activity and impairs growth suppression mediated by isoform 1. Isoform 7 inhibits isoform 1-mediated apoptosis. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing CLOCK-BMAL1-mediated transcriptional activation of PER2 (PubMed:24051492). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11025664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12524540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12810724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15186775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15340061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17317671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17349958, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19556538, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20673990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20959462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22726440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24051492, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24652652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9840937}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Biological rhythms;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Li-Fraumeni syndrome;Metal-binding;Methylation;Mitochondrion;Necrosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a tumor suppressor protein containing transcriptional activation, DNA binding, and oligomerization domains. The encoded protein responds to diverse cellular stresses to regulate expression of target genes, thereby inducing cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence, DNA repair, or changes in metabolism. Mutations in this gene are associated with a variety of human cancers, including hereditary cancers such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene and the use of alternate promoters result in multiple transcript variants and isoforms. Additional isoforms have also been shown to result from the use of alternate translation initiation codons from identical transcript variants (PMIDs: 12032546, 20937277). [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:7157; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; germ cell nucleus [GO:0043073]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity [GO:0036310]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001046]; disordered domain specific binding [GO:0097718]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; general transcription initiation factor binding [GO:0140296]; histone acetyltransferase binding [GO:0035035]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; histone deacetylase regulator activity [GO:0035033]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding [GO:0097371]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; protein phosphatase 2A binding [GO:0051721]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding [GO:0001094]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; B cell lineage commitment [GO:0002326]; bone marrow development [GO:0048539]; cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010659]; cardiac septum morphogenesis [GO:0060411]; cellular response to actinomycin D [GO:0072717]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to gamma radiation [GO:0071480]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; cellular response to UV-C [GO:0071494]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; chromosome organization [GO:0051276]; circadian behavior [GO:0048512]; determination of adult lifespan [GO:0008340]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0030330]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest [GO:0006977]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in transcription of p21 class mediator [GO:0006978]; double-strand break repair [GO:0006302]; embryonic organ development [GO:0048568]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; ER overload response [GO:0006983]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; gastrulation [GO:0007369]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate [GO:0019661]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; hematopoietic stem cell differentiation [GO:0060218]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hypoxia [GO:1990144]; mitochondrial DNA repair [GO:0043504]; mitophagy [GO:0000423]; mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0031571]; mRNA transcription [GO:0009299]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA replication [GO:0008156]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of G1 to G0 transition [GO:1903451]; negative regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060253]; negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate [GO:1904024]; negative regulation of helicase activity [GO:0051097]; negative regulation of miRNA maturation [GO:1903799]; negative regulation of mitophagy [GO:1901525]; negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007406]; negative regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt [GO:1905856]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; negative regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000647]; negative regulation of telomerase activity [GO:0051974]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007405]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; nucleotide-excision repair [GO:0006289]; oligodendrocyte apoptotic process [GO:0097252]; oxidative stress-induced premature senescence [GO:0090403]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010666]; positive regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000774]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis [GO:1900119]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of histone deacetylation [GO:0031065]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability [GO:0035794]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of programmed necrotic cell death [GO:0062100]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly [GO:0045899]; positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070245]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1990440]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia [GO:0061419]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to stress [GO:0036003]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein tetramerization [GO:0051262]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition [GO:1902749]; regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0043516]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process [GO:2000269]; regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:1902253]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process [GO:1902108]; regulation of tissue remodeling [GO:0034103]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to DNA damage [GO:1990248]; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0001836]; replicative senescence [GO:0090399]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to salt stress [GO:0009651]; response to X-ray [GO:0010165]; rRNA transcription [GO:0009303]; signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:0072331]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; T cell lineage commitment [GO:0002360]; T cell proliferation involved in immune response [GO:0002309]; thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070242]; transcription initiation-coupled chromatin remodeling [GO:0045815]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209]; type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060333]; viral process [GO:0016032] |
10794522_There was a differential upregulation of p53-responsive genes by genotoxic stress in hematopoietic cells containing wild-type p53 (MOLT-4) or a mutant p53 with a codon 161 mutation (U266). 11002963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11024482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11045785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11097227_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11130248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11146230_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11165394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11174479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11240705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11251969_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11255264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11259085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11293726_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11328884_Binding to the p53 binding sites of the Mdm2 promoter alleviates the requirement for p53 C-terminal activation. 11403041_P72R polymorphism in human papillomavirus associated premalignant laryngeal neoplasm 11429426_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11447225_phosphorylation of p53 was rapidly induced in human fibroblasts upon exposure of cells to hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) 11458982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11501650_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11504770_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11507974_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11518545_A loss of wild-type p53 gene function and consequent p53 overexpression in gastric carcinomas may be involved in early stages of tumor progression. 11519852_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11535556_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11559355_protein stability measured by hydrogen exchange 11564578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11566488_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11597326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11602059_Restoration of wt-p53 activity in Hep3B leads to sensitiveness to chemotherapeutic agents because of the decrease of p-glycoprotein expression. 11668523_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11682637_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11692157_differentiation status of the tumor was found for the p53 aberration but not for CD95 expression. 11708408_No association was found between the p53 codon 72 polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis. 11708408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11710828_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11718557_interactions with DNA in solution using time lapse atomic force microscopy 11733360_Mutations of p53 gene were present in 24% (5 of 21) of the evaluable cases, all of them overexpressing p53 in the majority of tumor cells. 11737306_Tissue samples from 42 ulcerative colitis patients were evaluated for p53 alterations by immunohistochemistry, loss of heterozygosity analysis, polymerase chain reaction-single-strand conformation polymorphism and direct sequencing. 11744990_WOX1/p53 has a potential role as a signaling complex in mitochondrial apoptosis. 11746272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11751390_different genotype combinations of p53 and GSTM1 increase the risk of developing specific histological subtypes of NSCLC. 11751391_DNA-PK and p53 may form a sensor complex that detects the disruption of DNA replication caused by nucleoside analogue incorporation and may subsequently signal for apoptosis. 11751402_Expression of Id helix-loop-helix proteins in colorectal adenocarcinoma correlates with p53 expression and mitotic index. 11751853_We show a novel alternative pathway of apoptosis in human primary cells that is mediated by transcriptionally dependent decreases in p53 and c-Myc and decreases in p21. 11753428_pH-sensitive molecular defect of p53 (R337H)suggests that pH-dependent p53 dysfunction is the molecular basis for cases of adrenocortical carcinoma in Brazilian children 11755471_New mutations of p53 identified by SSCP in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. Loss of p53 is not the decisive event causing tumor cells to proliferate in vitro without externally added growth factors. 11756653_To determine whether genotoxic stress regulates DNA binding by p53 in vivo, we have performed quantitative chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays on tumor and normal cell lines containing wild-type p53 11763417_A lower invasiveness and shorter survival was seen in tumors with a TP53 mutation 11764099_higher expression in childhood leukemias with poor prognosis compared to long-term survivors 11776898_Mutation pattern included base substitution (point mutation, G-->T, T-->G) and frame-shift mutation (base insertion and base loss). 11779500_acetylation of p53 activates transcription through recruitment of coactivators/histone acetyltransferases 11779589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11779855_role in inducing CD95 gene expression in endothelial cells exposed to doxorubicin 11783017_P53 protein overexpression is an early event in esophageal carcinogenesis and useful biomarkers for early detection. 11783119_P53 protein expression and intratumoral microvessel density (IMVD) can be considered as a biological indicator of malignant potential in brain astrocytoma. 11786482_These results demonstrate that butyrate inhibited the growth of breast cancer cells in a P53-independent manner. 11788578_protein inhibitor of activated Stat1 (PIAS1) interacts with the tetramerization and C-terminal regulatory domains of p53 in yeast two-hybrid analyses 11788906_Telomerase activity in microdissected human breast cancer tissues: association with p53, p21 and outcome 11793443_TP53-mutated tumors need fewer additional genetic alterations to develop metastases in primary head and neck tumors compared with TP53 wild-type primary tumors. 11793474_systematic automated analysis of the effects of p53 mutations on the structure of the core domain of the protein 11799106_IkappaBalpha x p53 complex plays an important role in responses involving growth regulation, apoptosis, and hypoxic stress 11804609_These results suggest that p53 might modulate the repair of DNA adducts generated from the human bladder carcinogen ABP in its target human uroepithelial cells. 11804688_nuclear mutant p53 protein is expressed in early precancerous stages suggesting this is an early change in NSCLC tumorigenesis; may be a potential marker for development of NSCLC 11805092_biogenesis in vitro to determine how wild type and mutant forms form hetero-oligomers 11807792_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11807792_Polymorphism at p53 codon 72: A striking reduction in Pro/Pro allele frequency has been found in HPV positive cases, indicating Arg/Arg genotype to be more susceptible to HPV infection and oral carcinogenesis 11809417_p53, activated by NF-kappa B, is essential for H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis in glioma cells 11814547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11815410_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11818510_Repression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha tumor suppressor p53: involvement of the ligand-binding domain and histone deacetylase activity 11818669_p53 expression was an independent parameter related to a poor prognosis in diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. 11828992_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11836677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11838964_The temperature sensitive mutant p53-143ala extends in vitro life span, promotes errors in DNA replication and impairs DNA repair in normal human oral keratinocytes. 11838966_TSG101 expression in gynecological tumors: relationship to cyclin D1, cyclin E, p53 and p16 proteins. 11839095_inhibition by TP53 of G2 phase checkpoint abrogation and radiosensitization induced by PD0166285 11840332_MDMX post-translational processing may be regulated by p53 11844595_A link between the p53 germ line polymorphisms and white blood cells apoptosis in lung cancer patients 11844595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11844788_role in regulating growth-promoting gene IEX-1 11844800_Transactivation-deficient Delta TA-p73 inhibits p53 by direct competition for DNA binding: implications for tumorigenesis. 11844810_aberrent expresion correlates with VEGF and IL-8 mRNA expression and neoangiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer 11845987_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11852106_Curcumin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through p53-dependent Bax induction. 11854266_effect of phosphorylation on structure and fold of transactivation domain 11856771_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11857304_overexpression may be marker of radioresistance in head and neck cancer 11859067_p53 binds telomeric single strand overhangs and t-loop junctions in vitro 11859195_the presence or absence of wild-type p53, may be an important determinant of response to antiangiogenic therapy 11859970_Immunostaining of p53 accumulation in families with multiple glioma pts showed that p53 alterations are as common in familial as in sporadic gliomas.Germline p53 mutations in exons 4-10 were not found. 11861393_Targeted inactivation of p53 in human cells does not result in aneuploidy. 11861400_Human tumor suppressor ARF impedes S-phase progression independent of p53. 11865061_Under severe hypoxic conditions p53 protein accumulates only in S phase; this correlates with replication arrest. Inhibition of ATR kinase activity substantially reduces hypoxia-induced phosphorylation of p53 protein on ser 15 as well as p53 accumulation 11867628_NO induces the accumulation of transcriptionally active p53 in a variety of cell types and NO signaling to p53 does not require ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1, or the ARF tumor suppressor protein 11872638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872638_We investigated three common sequence variants in TP53 and p21 for possible associations with the risk of breast cancer and with various phenotypic features of this disease 11875057_phosphorylation at multiple sites by ATM in response to ionizing radiation 11875500_The low-molecular-weight compound PRIMA-1 restored sequence-specific DNA binding and the active conformation to mutant p53 proteins in vitro and in living cells. 11877395_role for IGF-I in the regulation of the MDM2/p53/p21 signaling pathway during DNA damage 11880381_p53 contributes to the reversible, growth factor-dependent arrest of quiescence 11881786_The first direct demonstration of p53 mutations in pleuropulmonary blastomas (PPB)suggests p53 inactivation can occur as a nonrandom genetic change involving the pathogenesis and outcome of PPB. 11883440_minor role of exon 5-9 among Sudanese breast cancer patients 11887018_Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck shows a high incidence of p53 tumor suppressor gene alterations; the latter therefore appears to play an important role in the pathogenesis and progression of such neoplasms. 11888672_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11890931_SN2 DNA-alkylating agent-induced phosphorylation of p53 increases its DNA-binding properties to cause an increased expression of p21 that may play a role in cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis of human colon cancer cells HCT-116. 11892796_SV40 large T antigen associates with a cellular phosphoprotein, p53, in virus-transformed cells.Monoclonal antibodies, PAb1101, PAb1102 and PAb1103 define at least two non-overlapping determinants on human p53. 11893247_Involvement of TP53 in apoptosis induced in human lymphoblastoid cells by fast neutrons 11893750_role in inhibiting p63 activity 11895857_Resveratrol enhances the expression of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1) by increasing the expression of p53 11900859_review on mutations in brain neoplasms 11904448_Wild-type and mutated presenilins 2 trigger p53-dependent apoptosis and down-regulate presenilin 1 expression in HEK293 human cells and in murine neurons 11911244_Interaction between bcl-2 and P53 in neoplastic progression of basal cell carcinoma of the head and neck 11914273_A senescence rescue screen identifies BCL6 as an inhibitor of anti-proliferative p19(ARF)-p53 signaling 11915341_role in the regulation of ceramide biosynthesis 11919562_binding and activation of PIG3 promotoer via a pentanucleotide microsatellite sequence 11920528_expression has an independent effect on prediction of survival, progression, and development of metastasis in transitional cell bladder carcinoma 11923280_Akt enhances Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53. 11923872_Deubiquitination of p53 by HAUSP is an important pathway for p53 stabilization 11925449_description of a novel MDM2 binding interface in p53 that plays a regulatory role in MDM2-dependent ubiquitination of p53 11925591_Results indicate that loss of RAR-beta expression and accumulation of p 53 and Ki67 proteins may serve as biomarkers for early identification of esophageal cancer in the high-risk populations. 11927843_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11934017_inverse relationship seen between HPV infection and p53 positivity suggests loss of p53 function in cervical cancer, either by binding to E6 oncoprotein of HPV or by mutation in p53 11935300_mutations in p53 gene can lead to enhanced chemoresistance; p53 gene may serve as a marker for NSCLC response to chemotherapy 11936585_not very likely that TP53 mutations are involved in the etiology of meningiomas 11940482_Apoptotic index (includes nick-end labeling) and bcl-2 do not correlate with key clinical data (prognosis and blood counts at diagnosis) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, while p53 protein levels do. 11943780_Peg3/Pw1 is a mediator between p53 and Bax in DNA damage-induced neuronal death 11948395_Characterization of the p53-rescue drug CP-31398 in vitro and in living cells 11948396_p53 and recombination intermediates: role of tetramerization at DNA junctions in complex formation and exonucleolytic degradation. 11948632_Evaluation of relationship between chromosome 22 and p53 gene alterations and the subtype of meningiomas by the interphase-FISH technique. 11949842_expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins p53, Bcl-2, and Bax in primary resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 11949843_Expression of p53 and bcl-2 proteins in acute leukemias: an immunocytochemical study 11953423_MDMX, when exceedingly overexpressed, inhibits MDM2-mediated p53 degradation by competing with MDM2 for p53 binding 11953436_Mutation of human thioredoxin reductase 1 promotes p53-dependent gene expression 11953857_p53 mutational pathway may favor selection for ErbB2 gene amplification during tumor progression in breast cancer 11953859_high level of p53 protein in cPNETs measured by immunostaining intensity associated with poor patient survival 11956602_expression in pelvic lymph nodes and primary tumors in early stage cervical carcinomas 11956638_p53 expression and vascular density in colon cancer 11957139_the lack of correlation between p73 or p63 and p53 expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma suggests an independent and/or compensatory functional role 11960374_P53 mediates ceramide-induced apoptosis in SKN-SH cells 11960383_C-terminus of p53 is required for G(2) arrest. 11960904_summarize the current understanding of post-translational modifications and their effect on conformation-based functional relationship between Mdm2 and p53 11960918_Genetic status of cell cycle regulators in squamous cell carcinoma of the oesophagus: the CDKN2A (p16(INK4a) and p14(ARF) ) and p53 genes are major targets for inactivation. 11961303_VEGF and p53 are highly expressed in esophageal carcinomas 11964141_These results suggest that p53 is vulnerable to free radical-mediated oxidation at cysteine residues. 11971958_These results demonstrate direct activation of the human DDB2 gene by p53. The corresponding region in the mouse DDB2 gene shared significant sequence identity with the human gene but was deficient for p53 binding and transcriptional activation. 11971968_Identification of a novel mouse gene, mRTVP-1, as a p53 target gene. The mRTVP-1 protein has 255 amino acids and differs from the human RTVP-1 protein by two short in-frame deletions of two and nine amino acids. (mRTVP-1) 11978184_P53 protein accumulation may be responsible for gastric carcinogenesis and tumor aggressiveness of gastric cancer in northern China. 11979459_pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in children may involve EBV infection leading to LMP-1 expression and p53 overexpression 11980658_Expression of mitotic spindle checkpoint protein hsMAD1 correlates with cellular proliferation and is activated by a gain-of-function p53 mutant. 11983757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11988847_cyclin K is targeted for transcription by p53 11992381_O-phospho-L-tyrosine protects TP53 wild-type cells against ionizing radiation 11992547_A HLA-A2 restricted human CTL line recognizes a novel tumor cell expressed p53 epitope 11992551_disrupted p53/BAX pathway is associated with a poor clinical outcome in UICC III tumors 11992552_Prognostic significance of p53 mutations in colon cancer at the population level 11996107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11997498_mtCLIC/CLIC4, an organellular chloride channel protein, is increased by DNA damage and participates in the apoptotic response to p53. 11999565_p53 protein overexpression was noted in 59% of T-cell ltymphoblastic lymphoma cases and was correlaed with higher rate of relapse 12007715_Mutations for basal cell carcinoma (BCC), were screened in 15 cases of sporadic BCCs that developed in sun-exposed skin region in a Korean population 12011055_placental transforming growth factor-beta as an important downstream mediator of DNA damage signaling and a transcriptional target of p53 (PTGF-beta) 12014634_Resistance to p53-mediated growth suppression in human ovarian cancer cells retain endogenous wild-type p53. 12019159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12032659_p53 protein transport in hepatoma cells with VP22 12032848_DN-p73 is activated after DNA damage in a p53-dependent manner to regulate p53-induced cell cycle arrest. 12034444_Refolding and structural characterization of the human p53 tumor suppressor protein. 12034820_Redox state of tumor suppressor p53 regulates its sequence-specific DNA binding in DNA-damaged cells by cysteine 277. 12034830_Interactions between p53, hMSH2-hMSH6 and HMG I(Y) on Holliday junctions and bulged bases 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12036943_Induction of gene amplification is a gain-of-function phenotype of mutant p53 proteins. 12039466_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12039466_were not able to confirm that the TP53 polymorphism at exon 4 increases the susceptibility to be infected by HPV or to develop high-grade intra-epithelial lesion of the cervix 12045262_p53 negatively regulates intestinal immunity by delaying mucosal T cell cycling 12046064_Changes of NF-kB, p53, Bcl-2 and caspase in apoptosis induced by JTE-522 in human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line AGS cells: role of reactive oxygen species. 12046074_The point mutation of p53 gene exon7 in hepatocellular carcinoma from Anhui Province, a non HCC prevalent area in China. 12048243_reacts with glycogen synthase kinase-3beta after DNA damage 12049739_Deregulated c-Myc partially disabled the p53-mediated DNA damage response 12051912_Recognition of DNA by p53 core domain and location of intermolecular contacts of cooperative binding. 12060398_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12060398_TP53 arginine/arginine genotype could represent a potential risk factor for the development of squamous cell carcinoma in renal transplant recipients 12062821_Perturbations of chromosome 17 in general and the p53 locus in particular occur frequently in severe/late stage endometriosis. 12065086_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12065086_polymorphism in codon 72 and risk of head and neck neoplasms 12071291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12071847_UVB-mediated activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances resistance of normal human keratinocytes to apoptosis by stabilizing cytoplasmic p53. 12073053_Coexpression of P-glycoprotein, Ets-1, and p53 in oral carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis 12077306_use of p53MH algorithm in detection of p53-responsive genes 12077343_A two-stage, p16(INK4A)- and p53-dependent keratinocyte senescence mechanism that limits replicative potential independent of telomere status. 12080066_recombinant p53 binds to BLM and WRN helicases and attenuates their ability to unwind synthetic Holliday junctions in vitro 12080348_Nucleophosmin (NPM) interacts directly with p53, regulates the increase in stability and transcriptional activation of p53 after different types of stress, and induces p53-dependent premature senescence on overexpression in diploid fibroblasts 12082526_RNA polymerase III transcription can be derepressed by mutations that compromise p53 function in tumours and Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Substitution R175H, the most common mutation in cancers, converts p53 from a pol III repressor to an activator. 12082529_UV-induced DNA damage in epidermal KCs triggers p53 activation and apoptosis. Lack of activation in aging KCs and psoriatic Regulation of apoptosis by p53 in UV-irradiated human epidermis, psoriatic plaques and senescent keratinocytes 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12082608_Anoxia induces macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) in glioblastoma cells independently of p53 and HIF-1.The macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) gene was identified as a most prominent p53 target gene upon gene expression profiling. 12082615_Sequential extension of proliferative lifespan in human fibroblasts is induced by over-expression of CDK4 or 6 and loss of p53 function. 12082636_Human p14(ARF)-mediated cell cycle arrest strictly depends on intact p53 signaling pathways. 12084347_A cytoplasmic accumulation of wild-type p53 in human primary glioblastomas correlates with GFAP and vimentin expression. Cytoplasmic p53 is inactive in growth suppression. 12084746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085209_A new germline p53 mutation was found associated with a choroid plexus papilloma. The 7-BP insertion in exon 5 causes a frameshift from 161-182 and affected transactivation but not apoptosis induction. 12089322_identified executioner caspase-6 as a transcriptional target of p53. The mechanism involves DNA binding by p53 to the third intron of the caspase-6 gene and transactivation. 12093899_Mutations in APC, Kirsten-ras, and p53--alternative genetic pathways to colorectal cancer. The most common combination of mutations was p53 and APC (27.1%), whereas mutations in both p53 and K-ras were extremely rare. 12096336_Novel gain of function activity of p53 mutants: activation of the dUTPase gene expression leading to resistance to 5-fluorouracil. 12096338_Adenovirus encoding HIV-1 Vpr activates caspase 9 and induces apoptotic cell death in both p53 positive and negative human tumor cell lines. 12101184_role in adriamycin-induced senescence in breast tumor cells 12105992_persistence of induced levels of ROS in normal diploid human cells for 1 month after X-ray exposure and the role of TP53 in this oxidant response 12107116_Genetic signature of oligoastrocytomas correlates with tumor location and denotes distinct molecular subsets. 12110584_role of tyrosine phosphorylation of Mdm2 by c-abl in p53 regulation 12110597_binding sites of 53BP1 12112314_mutations in epithelial ovarian cancer 12115545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12119414_mutations in rheumatoid arthritis synovium 12124396_two sequence motifs from HIF-1alpha bind to the DNA-binding site of p53 12127401_An identical single nucleotide deletion within the C/EBP-like site of the promoter in 2 OF 18 Li-Fraumeni families. This site is not utilized in the wild type TP53 promoter and mutation of this site in LFS/LFL does not have a functional effect. 12127695_Expression of this molecule and its correlation with prognostic markers in patients with head and neck tumors 12136132_p53 status is an important modulator of nitric oxide-induced mutagenesis and apoptosis, and suggest that level of the Apaf-1 ans XIAP proteins are regulated by p53 12138177_Data suggest a model in which p53 directly recruits a TRRAP/acetyltransferase complex to the mdm2 gene to activate transcription. In addition, this study defines a novel mechanism utilized by the p53 tumor suppressor to regulate gene expression. 12138209_These data indicate a novel p53-dependent mechanism in which cell stress mobilizes nucleolin for transient replication inhibition and DNA repair. 12144687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12144822_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12145207_Syncytia from cells expressing the HIV-1 Env gene fused with cells expressing CD4/CXCR4 undergo apoptosis after nuclear translocation of mTOR, mTOR-mediated p53 phosphorylation, p53-dependent Bax upregulation & mitochondrial death pathway activation. 12145320_enhanced microtubule-dependent trafficking and p53 nuclear accumulation by suppression of microtubule dynamics 12151395_Inactivation of p21WAF1 sensitizes cells to apoptosis via an increase of both p14ARF and this protein and an alteration of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio 12154087_CARF is co-regulated with ARF and cooperates with it in activating p53 12160929_GSH plays a vital role in the protection of tri- and perchloroethylene-induced oxidative stress & apoptosis, which may be mediated through a p53-dependent pathway. 12161031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12161427_These results demonstrate that overexpression of Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death of HUVECs, at least in part, through down-regulating the transcription of p53 gene. 12162806_MDMX-mediated regulation of p53 activity during development. 12163498_p53 represses TauT and is involved in renal development and apoptosis. 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12164929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12164929_Relationship between p53 codon 72 polymorphism and susceptibility to sunburn and skin cancer. 12165799_p53 is acetylated by tumor necrosis factor alpha, then p53 attenuates its trans-activation by depleting CREB binding protein in rheumatoid synoviocytes 12167711_Hypophosphorylation of Mdm2 augments p53 stability. 12167722_Human wild-type p53 inhibits homologous recombination between substrates for conservative HR & for gene deletions. Non-homologus end-joining was downregulated after p53 expression. p53 mutations at codon 281, 273, 248, 175, or 143 disrupted DSB repair. 12168882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12168898_Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression correlates with p53 and ki-67 expressions in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 12168936_Genetic alterations of INK4alpha/ARF locus and p53 are observed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 12169206_MYCL1, FHIT, SPARC, p16(INK4) and TP53 genes associated to lung cancer in idiopathic pulmoary fibrosis 12170762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12171773_Mutations in exons 4-10 of the p53 gene in acute myeloid leukemia patients screened in an epidemiologic study in Brazil were found to correlate with poor prognosis and to occur at frequencies similar to those reported for Northern America and Europe. 12171773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12172977_The lack of Bcl2 accompanied by p53 overexpression affects the distribution of cells among the cell cycle phases and modifies the sensitivity to cytotoxic drugs and the type of cell death. 12174591_In response to irradiation, the amount of p53 protein synthesized in patients with AT and NBS was significantly lower than that in normal cells. 12174820_Wild-type p53 protein conformation is stabilized upon CP-31398 exposure. 12175902_Efficient repair of bulky anti-BPDE DNA adducts from non-transcribed DNA strand requires functional p53 but not p21(waf1/cip1) and pRb. 12186903_E1B-55K-anchored proteome is linked to polyubiquitination of p53 in vitro 12190289_p53 was detected more frequently in CIN I compared with CIN II/III and invasive carcinoma 12194286_Affects relative biological effectiveness of light ions in human tumoural cell lines. 12198151_The suppression of STK15 oncogenic activity by p53 might be explained by the finding that p53 inhibited STK15 kinase activity via direct interaction with the latter's Aurora box. This revealed a novel mechanism for the tumor suppressor function of p53. 12203403_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12208736_The candidate tumor suppressor ING1b can stabilize p53 by disrupting the regulation of p53 by MDM2. 12209584_Cellular effects of CPT-11 on colon carcinoma cells: dependence on p53 and hMLH1 status. 12209590_TP53 mutations in breast cancer tumors of patients from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: association with risk factors and tumor characteristics. 12217802_bcl-2/Jh lymphomas show molecular heterogeneity and that bcl-6 and p53 mutations may be acquired during the evolution of such lymphomas 12221910_A case-control study showed that polymorphism in codon 72 of the p53 gene was not a cervico-uterine cancer risk factor in Mexico. 12221910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12232053_p53 proteasomal degradation is regulated by NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 and independent of MDM2 and ubiquitin 12234998_p53 controls global nucleotide excision repair of low levels of structurally diverse benzo(g)chrysene-DNA adducts in human fibroblasts. 12235242_studies define a novel p53-survivin signaling pathway activated by DNA damage that results in down-regulation of survivin, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis 12270344_Immunohistochemical expression of this protein in squamous cell carcinomas from immunosuppressed renal transplant recipients and immunocompetent individuals 12324477_CD27 and CD40 co-stimulatory signals regulated the p53-amplified apoptotic pathway in B cells through the inhibition of p53-independent apoptotic pathway primarily induced by BCR ligation 12351827_Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the BRCT domains of human 53BP1 bound to the p53 tumour suppressor 12365037_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12367518_Results indicate that full-length p53 is a modular protein consisting of defined structured and unstructured regions, which may allow the physiological inte |
ENSMUSG00000059552 |
Trp53 |
49.863174 |
0.4032146699 |
-1.310380 |
0.450008509 |
7.672141 |
0.00560798703269926000769540763712939224205911159515380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011348216150622576423034892911800852743908762931823730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1025403 |
6.7889994 |
56.6489845 |
11.7781906 |
| ENSG00000141526 |
9123 |
SLC16A3 |
protein_coding |
O15427 |
FUNCTION: Proton-dependent transporter of monocarboxylates such as L-lactate and pyruvate (PubMed:11101640, PubMed:23935841, PubMed:31719150). Plays a predominant role in L-lactate efflux from highly glycolytic cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11101640, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23935841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31719150}. |
Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Lactic acid and pyruvate transport across plasma membranes is catalyzed by members of the proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) family, which has been designated solute carrier family-16. Each MCT appears to have slightly different substrate and inhibitor specificities and transport kinetics, which are related to the metabolic requirements of the tissues in which it is found. The MCTs, which include MCT1 (SLC16A1; MIM 600682) and MCT2 (SLC16A7; MIM 603654), are characterized by 12 predicted transmembrane domains (Price et al., 1998 [PubMed 9425115]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:9123; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0098688]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; synapse [GO:0045202]; lactate:proton symporter activity [GO:0015650]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; pyruvate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0050833]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; lactate transmembrane transport [GO:0035873]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718]; plasma membrane lactate transport [GO:0035879]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; pyruvate transmembrane transport [GO:1901475] |
17502341_Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) is a substrate for both MCT2 and MCT4. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20035863_Ocular absorption of monocarboxylic acid drugs may be enhanced by MCT transporter SLC16A3, and the absorption route provided by the transporter may be utilized to improve the bioavailability of topically applied ophthalmic drugs. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26854723_MCT1 may be acting as an uptake transporter and MCT4 as an efflux system across the basolateral membrane for ferulic acid, and that this process is stimulated by butyric acid. 30051648_these data suggest that the key effect of MCT4 depletion on NK cells probably utilizes inductive autophagy as a compensatory metabolic mechanism to minimize the acidic extracellular microenvironment associated with lactate export in tumors. 34097251_The tissue expression of MCT3, MCT8, and MCT9 genes in women with breast cancer. 34791637_MCT4 as a potential therapeutic target to augment gemcitabine chemosensitivity in resected pancreatic cancer. 34975331_Identification and Validation of a Prognostic Model Based on Three MVI-Related Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000025161 |
Slc16a3 |
2550.832636 |
3.0863627902 |
1.625908 |
0.035372233 |
2142.702755 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3802.1266077 |
82.4599654 |
1240.7263666 |
21.5722457 |
| ENSG00000141564 |
57521 |
RPTOR |
protein_coding |
Q8N122 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the control of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activity which regulates cell growth and survival, and autophagy in response to nutrient and hormonal signals; functions as a scaffold for recruiting mTORC1 substrates. mTORC1 is activated in response to growth factors or amino acids. Growth factor-stimulated mTORC1 activation involves a AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of TSC1-TSC2, which leads to the activation of the RHEB GTPase that potently activates the protein kinase activity of mTORC1. Amino acid-signaling to mTORC1 requires its relocalization to the lysosomes mediated by the Ragulator complex and the Rag GTPases. Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. mTORC1 phosphorylates EIF4EBP1 and releases it from inhibiting the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). mTORC1 phosphorylates and activates S6K1 at 'Thr-389', which then promotes protein synthesis by phosphorylating PDCD4 and targeting it for degradation. Involved in ciliogenesis. mTORC1 complex in excitatory neuronal transmission is required for the prosocial behavior induced by the psychoactive substance lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K4Q0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12150925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12150926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23727834}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Lysosome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a component of a signaling pathway that regulates cell growth in response to nutrient and insulin levels. The encoded protein forms a stoichiometric complex with the mTOR kinase, and also associates with eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein-1 and ribosomal protein S6 kinase. The protein positively regulates the downstream effector ribosomal protein S6 kinase, and negatively regulates the mTOR kinase. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:57521; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; TORC1 complex [GO:0031931]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0030291]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001002]; RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001003]; RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001006]; TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding [GO:0001156]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to leucine [GO:0071233]; cellular response to nutrient levels [GO:0031669]; cellular response to osmotic stress [GO:0071470]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; negative regulation of autophagy [GO:0010507]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:1900087]; positive regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045821]; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0046889]; positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt [GO:1905857]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032008]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0045945]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; TOR signaling [GO:0031929]; TORC1 signaling [GO:0038202] |
12150925_Raptor is a missing component of the mTOR pathway that through its association with mTOR regulates cell size in response to nutrient levels 12150926_raptor is an essential scaffold for the mTOR-catalyzed phosphorylation of 4EBP1 and mediates TOR action in vivo. 12604610_raptor binds to p70S6k and 4E-BP1 through their respective TOS (conserved TOR signaling) motifs. 16183647_A redox-sensitive mechanism regulates the phosphorylation of the raptor-mTOR effector S6K1, the interaction between raptor and mTOR, and the kinase activity of the raptor-mTOR complex. 16354680_Raptor directly binds to and serves as a scaffold for mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of IRS-1 on Ser636/639. 16914728_These studies suggest that, through serine phosphorylation, Raptor-mTOR and S6K1 promote the depletion of IRS1 from specific intracellular pools in pathological states of insulin and IGF-I resistance and in lesions associated with tuberous sclerosis. 16959881_These data suggest that, during HCMV infection, the rictor- and raptor-containing complexes are modified such that their substrate specificities and rapamycin sensitivities are altered. 17329400_ASCT2 silencing inhibits mTORC1 (mTOR/raptor) signaling and leads to growth repression, followed by enhanced survival signaling via mTORC2 (mTOR/rictor) and apoptosis of hepatoma cells. 17656678_Proarteriosclerotic effects of interferon gamma are associated with mammalian target of rapamycin raptor complex (mTORC1) and PI-3 kinase activiation. 18439900_The phosphorylation of raptor by AMPK is required for the inhibition of mTORC1 and cell-cycle arrest induced by energy stress. 18497260_Rag GTPases bind raptor and are necessary and sufficient to mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1 18722121_RSK-mediated phosphorylation of Raptor regulates mTORC1 activity. 18776922_there are two parallel cell-survival pathways in prostate cancer cells: a strong Akt-independent, but rapamycin-sensitive pathway downstream of mTORC1, and an AR-dependent pathway downstream of mTORC2 and Akt, that is stimulated by mTORC1 inhibition 19139211_no evidence was found for association of SNPs mapping to the NAT9, SLC9A3R1 and RAPTOR loci with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis 19145465_S2448 phosphorylated mTOR binds to both raptor and rictor. 19561084_It has been shown that knockdown of Raptor suppresses insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-636/639 and stabilizes IRS-1 after long term insulin stimulation. 19724909_Report involvement of mTORC1 and mTORC2 in regulation of glioblastoma multiforme growth and motility. 19864431_Complex raptor phosphorylation functions as a biochemical rheostat that modulates mTORC1 signaling in accordance with environmental cues. 19921495_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20169205_Study demonstrates that Serine 696 and Threonine 706 represent two key sites in raptor phosphorylation during mitosis, and that the mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase cdc2/CDK1 is the kinase responsible for phosphorylating these sites. 20354165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20439490_These data suggest that the raptor/mTORC1 pathway may play a role in increased IRES-dependent mRNA translation during mitosis and in rapamycin insensitivity. 21060808_Data show that a SNP (rs11868112) 26 kb upstream to the transcription start site of RPTOR exhibiting the strongest association with temperature variables. 21071439_a novel regulatory mechanism by which mitogenic and oncogenic activation of the Ras/MAPK pathway promotes mTOR signaling 21283628_show that E2F1 is capable of inducing growth by regulating mTORC1 activity 21321085_results suggest that GRp58/ERp57 is involved in the assembly of mTORC1 and positively regulates mTORC1 signaling at the cytosol and the cytosolic side of the endoplasmic reticulum 21325048_The study identified raptor as a substrate for p44/42 MAPK. 21454807_Adiponectin induces vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation via repression of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 and FoxO4 21460630_ULK1 contributes to mTORC1 inhibition through hindrance of substrate docking to Raptor. 21613227_a previously unrecognized function of miR-21 that is the reciprocal regulation of PTEN levels and Akt/TORC1 activity that mediate critical pathologic features of diabetic kidney disease 21900751_Phosphorylated forms of Raptor are significantly increased in mitotic cells. Raptor resides at the nucleoplasm and nucleolus of interphase cells and remains targeted to nucleolar organizer regions during mitosis. 22258093_An essential role of mTORC1 in autophagy inhibition in cell-free system in which, membrane association of Barkor/Atg14(L), a specific autophagosome-binding protein, is suppressed by cytosol from nutrient-rich medium, is shown. 22356909_an important role for ICK in modulating the activity of mTORC1 through phosphorylation of Raptor Thr-908. 22493283_found that osmotic stress activates mTORC1 kinase activity in a JNK-dependent manner. Our findings suggest that the molecular link between JNK and Raptor is a potential mechanism by which stress regulates the mTORC1 signaling pathway 23423739_Raptor polymorphism is associated with gastric cancer. 23541542_There is a significant downregulation of mTOR, DEPTOR, and Raptor in preterm labouring myometria when compared to non-pregnant tissues taken from the same area. 23563607_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in RPTOR gene is associated with obesity. 23898069_Histolopathological and clinical information including tumour stage, invasion characteristic and endocrine status were analysed against the gene transcript expression of mTOR, RAPTOR and RICTOR. 24005976_suggest no connection of RPTOR variants with psoriasis or its subphenotypes. 24337580_Amino acids promote mTORC1 activation without altering Rag GTP charging. 24403073_peptides that encompass the Raptor cross-linking region of 4E-BP1 inhibit cross-linking and interaction of 4E-BP1 with Raptor. 24516643_phosphorylating the T-loop Akt residue Thr(308) by PDK1 requires Raptor of the mTORC1 complex as a platform or scaffold protein. 25053281_RPTOR was not associated with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. 25249372_Common genetic variation in RPTOR is associated with overweight/obesity but does not discernibly contribute to either essential hypertension or isolated systolic hypertension in the Hawaiian population studied. 25533680_Studied the impact of SNPs in/near UCP3 and RPTOR on obesity-related traits. 25849663_microRNA-210 and raptor are involved in mithramycin-mediated erythroid differentiation of K562 cells and participate to the fine-tuning and control of gamma-globin gene expression in erythroid precursor cells. 26361958_Our results demonstrate for the first time that the expression quantitative trait loci of RPTOR, rs7502563, is susceptible to glioma 26363527_the expressions of Beclin1, Raptor, and Rictor are related to the development and progression of colorectal carcinoma and multidrug resistance. 26522726_Data show that mTOR protein forms a complex with Raptor and estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha). 26582740_The positive regulation of mTORC1 activity by NPRL2 is mediated through NPRL2 interaction with Raptor. 26608079_Propose regulation of placental SNAT2/LAT1 ubiquitination by mTORC1 and Nedd4-2. 27006450_Up-regulation of mTORC1 via raptor by aldosterone is a critical pathobiologic mechanism that controls pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell survival to promote hypertrophic vascular remodeling and pulmonary arterial hypertension. 27211906_In this study we began by validating the expression of four main mTOR pathway components, mTOR, DEPTOR, rictor and raptor, at gene and protein level in in vitro models of endometrioid (MDAH2774) and clear cell (SKOV3) ovarian cancer 27284727_RPTOR (regulatory associated protein of mTOR, complex 1) is a novel target of miR-155 in CF lung epithelial cells. The suppression of RPTOR expression and subsequent activation of TGF-beta signaling resulted in the induction of fibrosis by elevating connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) abundance in CF lung epithelial cells. 27577081_Hypomethylation of CpG sites in RPTOR, MGRN1 and RAPSN in blood is associated with breast cancer. 27637333_revealed more than 170 NFAT-associated proteins, half of which are involved in transcriptional regulation. Among them are many hitherto unknown interaction partners of NFATc1 and NFATc2 in T cells, such as Raptor, CHEK1, CREB1, RUNX1, SATB1, Ikaros, and Helios. 27729429_Hgh mTOR activity and Rictor overexpression could be markers of a bad prognosis. Combined phosphoprotein and Rictor/Raptor expression evaluation revealed even stronger statistical correlation with prognosis. 28341829_Study shows that USP9X deubiquitylating enzyme maintains RAPTOR protein levels, mTORC1 signalling and proliferation in neural progenitors. USP9X is the first deubiquitylating enzyme shown to stabilize RAPTOR. 29128895_Study found that nuclear expression of raptor in luminal A-like breast tumors predicted a group of patients with good prognosis but with no clear benefit of tamoxifen treatment. Additionally, study found co-localization of raptor and estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) upon estrogen stimulation in ERalpha-positive, but not in ERalpha-negative breast cancer cells. 29344641_Results suggest that RPTOR mediates, at least partially, the resistance to EGFR inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer cells. 29389967_data reveal that RAPTOR up-regulation contributes to PI3K-mTOR inhibitor resistance, and suggest that RAPTOR expression should be included in the pharmacodynamic assessment of mTOR kinase inhibitor trials 30539788_Persistent mTORC1 deficiency in macrophages contributes to the progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. 30972602_Knocking down raptor in human keratinocytes affects ornithine decarboxylase in a post-transcriptional Manner following ultraviolet B exposure. 31112131_Here, the authors report that G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) paired to Galphas proteins increase cyclic adenosine 3'5' monophosphate (cAMP) to activate protein kinase A (PKA) and inhibit mTORC1. Mechanistically, PKA phosphorylates the mTORC1 component Raptor on Ser 791, leading to decreased mTORC1 activity. 31601708_The Raptor alpha-solenoid directly detects the nucleotide state of RagA while the Raptor 'claw' threads between the GTPase domains to detect that of RagC. Mutations that disrupted Rag-Raptor binding inhibited mTORC1 lysosomal localization and signaling. 31601764_ryo-electron microscopy structure of RagA/RagC in complex with mTORC1 shows the details of RagA/RagC binding to the RAPTOR subunit of mTORC1 and explains why only the RagAGTP/RagCGDP nucleotide state binds mTORC1 31886628_RAPTOR promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by inducing mTORC1 and upregulating ribosome assembly factor URB1. 32039630_Expression of Raptor and Rictor and their relationships with angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. 32576051_The Association between the Plasma Sugar and Lipid Profile with the Gene Expression of the Regulatory Protein of mTOR (Raptor) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. 32861747_Upregulation of Akt/Raptor signaling is associated with rapamycin resistance of breast cancer cells. 33155352_Different Role of Raptor and Rictor in Regulating Rasfonin-Induced Autophagy and Apoptosis in Renal Carcinoma Cells. 33482765_Raptor and rictor expression in patients with human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 33852892_The dynamic mechanism of 4E-BP1 recognition and phosphorylation by mTORC1. 34767153_RPTOR methylation in the peripheral blood and breast cancer in the Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000025583 |
Rptor |
396.764002 |
5.8197044998 |
2.540946 |
0.727670660 |
10.879755 |
0.00097221111279063095363117685820952829089947044849395751953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002265525106534529899832142163518255983944982290267944335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
585.7317626 |
352.2799308 |
100.7351039 |
42.9374706 |
| ENSG00000141570 |
57332 |
CBX8 |
protein_coding |
Q9HC52 |
FUNCTION: Component of a Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC1-like complex, a complex class required to maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of many genes, including Hox genes, throughout development. PcG PRC1 complex acts via chromatin remodeling and modification of histones; it mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119', rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21282530}. |
3D-structure;Chromatin regulator;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables methylated histone binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in chromatin and nucleoplasm. Part of PRC1 complex. Biomarker of esophagus squamous cell carcinoma and glioblastoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57332; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PcG protein complex [GO:0031519]; PRC1 complex [GO:0035102]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; single-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003727]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity [GO:0097027]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone ubiquitination [GO:0016574]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122] |
17332741_CBX8 is an essential component of one of the polycomb repressive complexes, which directly regulate the expression of numerous target genes, including the INK4A-ARF locus, involved in cell-fate decisions. 22094252_CBX8 plays an essential role in MLL-AF9 transcriptional regulation and leukemogenesis. 23474493_CBX8 cooperated with SIRT1 for suppressing p53 acetylation induced by Sirtinol and etoposide/TSA. Upon ectopic expression, CBX8 or SIRT1 repressed the expression of p21(WAF1) by inhibiting p53 binding to the promoter. 23891621_Interaction with CBX8 precludes AF9-DOT1L binding. 24460908_The presence of CBX8-GFP in the same focus had a minor impact on BMI1 and RING1 recovery kinetics. 25197352_CBX8 might emerge as an oncogene for promoting the proliferation of tumor cells and raising the resistance of neoplasms to chemotherapy. 25360999_Low CBX8 expression was associated with distant metastasis in colorectal cancer. 25398592_IGF1 can promote the colon cancer cell line, HCT116 cell, proliferation via promoting Cbx8 expression 26718407_These data suggest that CBX8 modulates SIPS through the RB-E2F1 pathway in CML cells and provide important insight into its application in CML treatment. 26837964_The difference in the SUZ12 and CBX8 genes expression were significantly divergent between tumors and their marginal tissues. 27505670_CBX8 binds to H3K27me3 at bivalent promoters during germinal center formation, and recruits a novel PRC1-BCOR complex at BCL6 binding sites to specifically silence genes in the germinal center and promote lymphomagenesis 27555324_CBX8 plates roles in epigenetic regulation in DNA damage response. 28837252_The data suggest that high expression of CBX8 plays a critical oncogenic role in aggressiveness of urothelial carcinoma cells of the bladder through promoting cancer cell proliferation by repressing the p53 pathway, and CBX8 could be used as a novel predictor for muscle invasive bladder cancer patients. 28912889_CBX8 binds with the Snai1 promoter, represses Snai1 transcription and suppresses esophageal carcinoma metastasis. 29066512_CBX8 functions as an oncogene to upregulate EGR1 and miR-365-3p to stimulate the AKT/beta-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.CBX8 expression is increased and associated with poor outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. 29763603_PIM1 can phosphorylate CBX8 to promote its degradation, thereby up-regulating p16, during PIM1-induced cell senescence. 30504704_Circular RNA circ_0005230 was proved to be a sponge of miR-618, and expression of miR-618 could regulate CBX8 expression via targeting the 3'UTR of CBX8. 30597065_function of the CBX8 chromodomain (CD) in vitro and in vivo; the CD is in fact a major driver of CBX8 chromatin association and this is driven by both histone and previously unrecognized DNA binding activity; characterization of the structural basis of histone and DNA binding and determine how they integrate on multiple levels 30718464_Results establish CBX8 as a critical driver of HCC stem cell-like and metastatic behaviors and characterize its role in modulating BMP4 expression. 31255735_Report shows that CBX8 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues and cells and serves as an indicator of poor prognosis for ESCC patients. CBX8 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation capability, DNA repair and promotes cell apoptosis. 31495785_Chromobox homolog 8 (CBX8) Interacts with Y-Box binding protein 1 (YBX1) to promote cellular proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 31755685_Optimization of Ligands Using Focused DNA-Encoded Libraries To Develop a Selective, Cell-Permeable CBX8 Chromodomain Inhibitor. 33417156_CBX8 acts as an independent RNA-binding protein to regulate the maturation of miR-378a-3p in colon cancer cells. 33731128_KPNA2 interaction with CBX8 contributes to the development and progression of bladder cancer by mediating the PRDM1/c-FOS pathway. 34592789_CBX8 interacts with chromatin PTEN and is involved in regulating mitotic progression. 34651663_hsamiR429 targets CBX8 to promote cell apoptosis in diffuse large Bcell lymphoma. 35681547_High Expression of a Cancer Stemness-Related Gene, Chromobox 8 (CBX8), in Normal Tissue Adjacent to the Tumor (NAT) Is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer Patients. 35894945_CBX8 Together with SET Facilitates Ovarian Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis by Suppressing the Transcription of SUSD2. |
ENSMUSG00000025578 |
Cbx8 |
44.700960 |
0.4214188644 |
-1.246673 |
0.429888637 |
8.056900 |
0.00453306682792600518921988239640086248982697725296020507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009347312989688157797152356920378224458545446395874023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.1454619 |
7.0718171 |
60.3986057 |
11.7577293 |
| ENSG00000141582 |
8535 |
CBX4 |
protein_coding |
O00257 |
FUNCTION: E3 SUMO-protein ligase which facilitates SUMO1 conjugation by UBE2I (PubMed:12679040). Involved in the sumoylation of HNRNPK, a p53/TP53 transcriptional coactivator, hence indirectly regulates p53/TP53 transcriptional activation resulting in p21/CDKN1A expression. Monosumoylates ZNF131 (PubMed:22825850). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12679040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22825850}.; FUNCTION: Component of a Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC1-like complex, a complex class required to maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of many genes, including Hox genes, throughout development (PubMed:12167701, PubMed:19636380, PubMed:21282530). PcG PRC1 complex acts via chromatin remodeling and modification of histones; it mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119', rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility (PubMed:12167701, PubMed:19636380, PubMed:21282530). Binds to histone H3 trimethylated at 'Lys-9' (H3K9me3) (By similarity). Plays a role in the lineage differentiation of the germ layers in embryonic development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O55187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12167701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19636380, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21282530}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein sumoylation. |
Enables SUMO binding activity; SUMO ligase activity; and enzyme binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nuclear body. Part of PRC1 complex. Implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8535; |
nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PcG protein complex [GO:0031519]; PRC1 complex [GO:0035102]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; single-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003727]; SUMO binding [GO:0032183]; SUMO ligase activity [GO:0061665]; SUMO transferase activity [GO:0019789]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925] |
12679040_Pc2 dramatically enhances CtBP sumoylation. Pc2 is a SUMO E3, and Polycomb Group bodies may be sumoylation centers. 15710417_polycomb group (PcG) protein HPC2, which functions as a transcriptional suppressor, is a candidate of KyoT2-binding proteins 16061479_SIP1 sumoylation by Pc2 attenuates transcriptional repression of E-cadherin 17018294_Pc2 binds to and colocalizes with homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) and serves as a SUMO E3 ligase for this kinase. 18178578_The Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) machinery may thus be important for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease pathogenesis because the regulation of PC2 expression by the ERAD pathway is altered by mutations in PC2. 18567530_Results show that DNA methyltransferase 3B enhances polycomb protein 2-mediated transcriptional repression of FGFR3, and suggest that DNMT3B is a co-repressor of hPc2 in inducing transcriptional repression independent of DNA methylation. 19336002_A phage display screen using the N-terminus of JARID1B as bait identified one of the JARID1B interacting proteins, namely PcG protein (Polycomb group) hPc2. 19933700_Huntingtin is a novel stimulator of polycomb repressive complex 2. 21256122_the hPc2-induced SUMOylation of alpha-synuclein could function as a cytoprotector by increasing alpha-synuclein aggregate formation within fibroblast cells. 21282530_14-3-3 protein binding to chromobox homolog 4 (CBX4) appears to modulate the interaction between CBX4 and the BMI1/PCGF components of polycomb recessive complex 1, but has no effect on CBX4-RING1/RNF2 interaction 21549310_Data show that PRC2 can integrate information provided by pre-existing histone modifications to accurately tune its enzymatic activity within a particular chromatin context. 21885019_plays role in regulation of epidermal stem cell proliferation and senescence 22028491_High Polycomb repressive complex protein is associated with mesothelioma. 22078878_Pc2, methylation controls the protein's interaction with two distinct ncRNAs, TUG1 and NEAT2, which results in the exclusive subnuclear localization of methylated and unmethylated Pc2 in Polycomb bodies and interchromatin granules, respectively. 22897849_ASXL1 associates with the PRC2 and loss of ASXL1 in vivo collaborates with NRASG12D to promote myeloid leukemogenesis. 23943028_High cytoplasmic expression of CBX4 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 24434214_our findings demonstrate that Cbx4 plays a critical role in tumor angiogenesis by governing HIF-1alpha protein 24460908_The presence of CBX4-GFP in the same focus had a minor impact on BMI1 and RING1 recovery kinetics. 24838576_Role of Cbx4 in migration and metastasis of a metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Results show that Cbx4 overexpression increases the in vitro vessel formation of vascular endothelial cells in its SUMO interaction motifs-dependent manner. 25766328_Cbx4 is an independent prognostic factor for HCC patients, and the patients with high Cbx4 expression should receive postoperative TACE treatment to improve their survival 27864346_provide evidence to show that CBX4 may serve as a tumor suppressor in colorectal carcinoma by recruiting HDAC3 to the Runx2 promoter to impede Runx2 expression 28740167_Data show that SUMO E3 ligase CBX4 sumoylates subpopulation of CtIP to regulate recruitment to breaks and resection. 28839133_Data show that USP26 interacts with PRC1 components chromobox (CBX)-containing proteins CBX4 and CBX6. 29229426_Data suggest that CBX4 expression is up-regulated in breast cancer and is correlated with unfavorable overall survival; CBX4 promotes cell growth and migration via transcriptionally suppressing expression of miR137 to trigger Notch1 signaling pathway. (CBX4 = chromobox homolog 4; miR137 = microRNA 137; Notch1 = neurogenic locus notch homolog protein-1) 29539416_Results identify a modifying enzyme for Prdm16, and they demonstrate a central role of Cbx4 in the control of Prdm16 stability and white fat browning. 29940764_CBX4 is up-regulated in breast cancer tissues and while its over-expression promotes cell proliferation, its knockdown suppresses cell proliferation in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, CBX4 mediates miR-129-5p-induced inhibition of cell proliferation and negatively correlates with the expression of miR-129-5p expression. 30917318_role of CBX4 in maintaining cellular homeostasis in mesenchymal stem cells 31211140_findings suggest that CBX4 rs2289728 and CBX7 rs139394 are protective SNPs against HCC. The two SNPs may reduce the risk of HCC while suppressing the expression of CBX4 and CBX7. 31581881_This is the evidence supporting the interaction between GRM4 and CBX4, which could inhibit the malignant behavior of osteosarcoma cells through the GRM4/CBX4/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway 31724308_CBX4 promotes the proliferation and metastasis via regulating BMI-1 in lung cancer. 32111827_Chromobox homolog 4 (CBX4) is overexpressed in osteosarcoma cell lines and tissues. CBX4 promotes metastasis by transcriptionally up-regulating Runx2 via the recruitment of GCN5 to the Runx2 promoter. The phosphorylation of CBX4 at T437 by casein kinase 1alpha (CK1alpha) facilitates its ubiquitination at both K178 and K280 and subsequent degradation by CHIP, and this phosphorylation of CBX4 could be reduced by TNFalpha. 32141558_Circular RNA hsa_circ_0008039 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through upregulating CBX4 via sponging miR-515-5p. 32926159_SUMO E3 ligase CBX4 regulates hTERT-mediated transcription of CDH1 and promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion. 33387960_Chromobox 4 facilitates tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 33464142_Long intergenic noncoding RNA00265 promotes proliferation of gastric cancer via the microRNA-144-3p/Chromobox 4 axis. 34856763_The predictive potential of genetic single nucleotide polymorphisms in CBX4 for hepatocellular carcinoma survival. 34980138_CBX4-dependent regulation of HDAC3 nuclear translocation reduces Bmp2-induced osteoblastic differentiation and calcification in adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma. 35251476_CBX4 Regulates Replicative Senescence of WI-38 Fibroblasts. 35358396_CBX4 Regulates Long-Form Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-mediated Airway Inflammation through SUMOylation in House Dust Mite-induced Asthma. 35819589_MiR-507 inhibits the progression of gastric carcinoma via targeting CBX4-mediated activation of Wnt/beta-catenin and HIF-1alpha pathways. 35880565_Chromobox homolog 4 overexpression inhibits TNF-alpha-induced matrix catabolism and senescence by suppressing activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in nucleus pulposus cells. 36215729_MicroRNA-6838-5p suppresses the self-renewal and metastasis of human liver cancer stem cells through downregulating CBX4 expression and inactivating ERK signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000039989 |
Cbx4 |
89.288925 |
0.4450083037 |
-1.168096 |
0.217943847 |
28.525918 |
0.00000009245259324452836002724973778546524449950538837583735585212707519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000365648519906012509422327727212631565123501786729320883750915527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.6274067 |
8.8484924 |
133.2868112 |
13.6447896 |
| ENSG00000141655 |
8792 |
TNFRSF11A |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6Q6 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFSF11/RANKL/TRANCE/OPGL; essential for RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis. Involved in the regulation of interactions between T-cells and dendritic cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9878548}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Osteopetrosis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Sodium;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptors can interact with various TRAF family proteins, through which this receptor induces the activation of NF-kappa B and MAPK8/JNK. This receptor and its ligand are important regulators of the interaction between T cells and dendritic cells. This receptor is also an essential mediator for osteoclast and lymph node development. Mutations at this locus have been associated with familial expansile osteolysis, autosomal recessive osteopetrosis, and Paget disease of bone. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this locus. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:8792; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; tumor necrosis factor receptor activity [GO:0005031]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to zinc ion starvation [GO:0034224]; circadian temperature homeostasis [GO:0060086]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; multinuclear osteoclast differentiation [GO:0072674]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade via TNFSF11-mediated signaling [GO:0071848]; positive regulation of fever generation by positive regulation of prostaglandin secretion [GO:0071812]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; TNFSF11-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0071847]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
11771666_Expansile skeletal hyperphosphatasia is caused by a 15-base pair tandem duplication (84dup15) in TNFRSF11A encoding RANK. 12043011_immunohistochemical localization of this protein and its ligand in deciduous teeth 12200385_MIP-1alpha and MIP-1beta induce expression of RANK ligand by stromal cells, thereby stimulating osteoclast differentiation of preosteoclastic cells. 12296995_TAK1-dependent activation of AP-1 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase by receptor activator of NF-kappaB. 12362049_Analysis of a large Spanish kindred confirms that exon 1 contains an insertional mutation in the RANK gene. 12393586_Long-lived immature dendritic cells mediated by TRANCE-RANK interaction 12568416_a tandem duplication in exon 1 of the TNFRSF11A gene may have a role in familial expansile osteolysis 12709501_associated with external apical root resorption 12929927_the 75dup27 mutation causes a Paget's disease of bone-like phenotype 12933809_transforming growth factor-beta promotes osteoclastogenesis in monocytes by stimulation of the p38 mitogen activated protein kinase but continuous exposure abrogates osteoclastogenesis by down-regulation of receptor activator of NF-KB(RANK) expression 15248232_These data suggest that RANK is expressed by monocytes whose activation by RANKL stimulates directed migration involving phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, phosphodiesterase, and Src kinases. 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15377473_RANK is expressed in bone marrow stroma cells & endothelial cells but not myeloma cells. It is involed in IL-6 & IL-11 secretion. 15564564_Review. The RANKL/RANK/OPG system may mediate links between the vascular, skeletal, & immune systems and play a central role in regulating the vascular calcification coincident with declines in skeletal mineralization with age, osteoporosis, or disease. 15615497_disruption of the RANKL-RANK axis with OPG inhibited tumor-induced osteoclastogenesis and decreased bone cancer pain. 16052586_Involvement of RANK/RANKL in dendritic cell-T cell interactions during inflammatory process. RANK expression appears to be limited to sites of immune reaction, both in synovium and in lymph nodes. 16083856_PU.1 regulates RANK gene transcription; this may represent one of the key roles of PU.1 in osteoclast differentiation 16151677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16215261_OPG dimer formation is required for the mechanism of inhibition of the RANK-L/RANK receptor interaction 16240334_We review the etiology of inflammatory bone loss, the RANK/RANK-ligand/OPG pathway, and the clinical development of anti-RANK-ligand therapy. 16249885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16270354_By upregulating IL-8, the RANKL/RANK system may contribute to the pathogenesis of B chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 16328004_a functional RANK expressed on osteosarcoma cells 16556708_Expression of RANK-Fc by genetically modified Mesenchymal stem cells may be a feasible option for the prevention of bone loss induced by ovariectomy. 16583245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16953816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16960694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17115234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17115234_results suggest that +34863G > A and +35928insdelC polymorphisms in RANK are possible genetic factors for low Bone mineral density in postmenopausal women 17288531_This review describes the most recent knowledge on the OPG-receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANK)-RANK ligand (RANKL) triad and its involvement in bone oncology. 17331078_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17447113_Although the mutation in the Iranian and four of the previously described FEO pedigrees was the same, haplotypes based on the intragenic SNPs suggest that the mutations do not share a common descent. 17546619_A major haplotype in block 5 of Tumor Necrosis Factor receptor superfamily member 11a (RANK) was significantly associated with higher stature in Caucasians. 17546619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17580719_The expression levels of RANKL and RANK were markedly increased in the perimatrix of cholesteatoma. 17634140_Review highlights the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin (OPG) system and its role in the regulation of bone resorption. 17876645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17876645_RANK contributes to osteoclastic bone resoption in RA patients. 17895323_RANK/RANKL/OPG system mediates the effects of calciotropic hormones and, consequently, alterations in their ratio are key in the development of several clinical conditions--REVIEW 17966895_The OPG/RANKL/RANK system constitutes the important element of controlling the number of active osteoclasts by the osteoblasts. 17982618_cDNA microarray and quantitative RT-PCR analyses demonstrate that RANK-positive osteosarcoma cells are the target of RANKL as well as osteoclasts/osteoclast precursors. 18008334_RANK is expressed on prostate cancer cells and promotes invasion in a RANKL-dependent manner 18061491_differences in the RANK, RANKL, and OPG expression in odontogenic epithelial tumors...could contribute to the differential bone/tooth resorption activity in these lesions 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18311801_The relative protection against bone erosions in spondylarthritis cannot be explained by qualitative or quantitative differences in the synovial expression of RANKL, OPG, and RANK. 18367263_Data reveals for the first time that OPG/RANK/RANKL are expressed in the pathological thyroid gland by follicular cells, by malignant parafollicular cells as well as in metastatic lymph node microenvironment. 18606301_Osteoclast-poor osteopetrosis with agammaglobulinemia due to TNFRSF11A (RANK) mutation is reported. 18632421_ligation of RANK on DC cell surfaces is not only a survival stimulus, but also induces a partial and specific mature DC phenotype 18802807_Ineffective modulation of the OPG/RANK/RANKL system in active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis may account for bone damage in this disease. 18928898_might locally modulate [odontogenic] tumor-associated bone resorption 19008470_Based on their role in atherogenesis, this enhanced expression of RANKL and RANK could contribute to the increased risk of cardiovascular disease in hyperhomocystinemia 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19079262_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19085839_RANKL/RANK have roles in bone-associated tumors (review) 19213753_no significant association was detected between the three RANK tag single nucleotide polymorphisms tested and rheumatoid arthrirtis in our white European family sample 19416721_The binding affinity of RANKL for RANK was measured with surface plasmon resonance technology and K(D) value is about 1.09 x 10(-10) M. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19507210_Mutations in TCIRG1, OSTM1, ClCN7, and TNFRSF11A genes were detected in nine, three, one, and one patientswith infantile malignant osteopetrosis, respectively. 19554506_The expression of RANK gene of NF-kappaB pathway in multiple myeloma using bone marrow aspirates obtained at diagnosis is reported. 19578385_A novel 27-bp duplication in exon 1 (78dup27) in TNFRSF11A was found in four affected individuals and one asymptomatic individual for early onset familial Paget's disease of bone. 19672874_High-throughput copy number and gene expression data of 36 microsatellite stable sporadic colon cancers resected from patients of a single institution characterized for mutations in APC, KRAS, TP53 and loss of 18q were analyzed. 19705167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19728335_IKKalpha, IKKbeta, RANK, Maspin, c-FLIP, Cip2 and cyclinD1 were found to show significant differences between hepatocellular tumor tissue and its corresponding adjacent tissue. 19890054_Our findings identify a new mechanism of homeostatic regulation of osteoclastogenesis that targets RANK expression and limits bone resorption during infection and inflammation. 19896533_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19896533_Results suggest that gene-gene interactions between RANK and OPG, and RANK and RANKL influence BMD in postmenopausal women. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940926_data identify an entirely novel and unexpected function for the key osteoclast differentiation factors RANKL/RANK in female thermoregulation and the central fever response in inflammation 20205168_Genetic variation in the RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling pathway influences bone turnover and bone mineral density in European men. 20205168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20231205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436471_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436471_These studies provide new insights into the pathogenesis of PDB and identify OPTN, CSF1 and TNFRSF11A as candidate genes for disease susceptibility. 20506523_Results suggest that the RANKL acts through MEK/ERK, which in turn activates IKKalpha/beta and NF-kappaB, resulting in the activation of beta1 integrin and contributing to the migration of human chondrosarcoma cells. 20531232_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20531232_The TNFRSF11A (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11a) and TNFSF11(RANKL) genes are associated with the age of onset of menarche and natural menopause in white women 20534768_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564239_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564239_The possible relationship between TNFRSF11A polymorphisms and sporadic Paget's disease of bone, was investigated. 20623281_Our study represents the first preliminary indication about a local increase of RANK concentration during fracture healing immediately after surgery. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20694489_Receptor activator for nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (0.54 +/- 0.26 vs. 0.16 +/- 0.15 pmol/l, P 300% increases in luciferase activity after RANK motif activation and Z '-factor values over 0.55 21159522_Increasing concentrations of FSH caused a biphasic dose-response, with a maximal (1.5-fold) increase in RANK(high) cells 21270824_RANK might be involved in the development and maintenance of melanoma-initiating cells and possibly in metastatic spreading for melanoma 21326202_RANKL and RANK are involved in mammary/breast cancer metastasis 21352301_no significant association of SNPs with susceptibility to disease in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients 21472776_Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB occurred in HEK293 cells overexpressing wild-type or mutant RANK but not in stably transfected cell lines expressing low levels of each RANK gene. 21479680_results suggested that mechanisms other than the RANKL/RANK signalling pathway might be involved in the osteoclastogenic response mediated by MG63 cells 21514280_hypoxia upregulates RANK and RANKL expression and increases RANKL-induced cell migration via the PI3K/Akt-HIF-1alpha pathway. 21541702_a common genetic variant near the 5'-end of TNFRSF11A, rs7226991, is associated with breast cancer risk in the general population and among carriers of mutations in the breast cancer 2, early onset (BRCA2) gene 21559440_RANK in primary breast tumors has a role in bone metastasis occurrence in breast cancer patients; OPG has a role in survival 21643971_The molecular system of RANK/RANKL/OPG is variably expressed in odontogenic keratocysts, radicular cysts, and ameloblastomas 21742767_Presented is a comprehensive reaction map of the RANKL/RANK-signaling pathway based on an extensive manual curation of the published literature. 21814016_The receptor of RANKL whick stimulates osteoclast differentiation and functionand ists mutation causes osteoclatst abnormalities. (review) 21814020_It is critical to the development and progression of bone metastases in breast neoplasms. (review) 21814022_It is involved in the development of osteoclasts, cooperating with another key molecule, M-CSF.(review) 21814026_the central RANKL/RANK pathway has an important role for thermoregulation.(review) 21964949_There were five RANK SNPs associated with geometric parameters, including rs8083511 associated with distal radius cross-sectional area. 21987421_Two nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (C421T, H141Y and T575C, V192A) in the TNFRSF11A gene, associated with Paget's disease of bone, were identified. 22001124_Results describe the relationship between bone metabolism and OPG/RANK/sRANKL concentrations in females with anorexia nervosa. 22001292_AF groups had higher atrial gene expression of OPG/RANK/RANKL axis and RANKL/OPG ratio, particularly in paroxysmal AF. 22023082_The results of the present study suggest that RANK is associated with Age at menarche in Chinese women. 22176920_Radiographic emphysema is correlated with low BMD in current and former smokers with COPD. IL-1beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and the osteoporosis-related protein system OPG/RANK/RANKL. 22178057_The atrial expression of RANK (and RANKL/osteoprotegerin ratio) was higher in normal controls compared to persistent atrial fibrillation patients. 22214279_RANK, RANKL and OPG proteins are differentially expressed in periodontal tissues and may play a major role in the bone loss occurring in periodontitis 22271396_Novel mutations in the TNFRSF11A gene in Autosomal recessive osteopetrosis, are reported. 22402034_serum OPG concentration was significantly lower in carotid population compared to femoral population while RANK and RANKL were equally expressed in both arterial beds 22496457_RANK expression in primary breast cancer associates with poor prognosis. 22531921_regulated RANK expression contributes to the fine tuning of PMN migration, for example, on and through inflamed endothelium that is known to express RANKL. 22546829_Genetic variations using representative single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of OPG (rs2073618), RANK (rs1805034) and RANKL (rs2073618), were analysed. 22705116_summary of recent advances in understanding osteoclastogenic signaling/osteoimmunology: RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling in osteocytes plays role in bone remodeling as seen in bone resorption or arthritis. [REVIEW] 22753650_In hemophilic arthropathy, the synovium highly expressed RANK and RANKL, whereas OPG immunopositivity decreased, suggesting an osteoclastic activation. 22787434_We conclude that RANK/TNFRSF11A is a novel and frequent target for de novo methylation in gliomas, which affects apoptotic activity and focus formation thereby contributing to the molecular pathogenesis of gliomas. 22824341_Novel RANK variants, providing evidence of a complex regulatory pathway for RANK receptor signaling, with possible implications in various systems, tissues and cells. 22848465_the increase in RANK-RANKL expression is a response to podocyte injury, and RANK-RANKL may be a novel receptor-ligand complex for the survival response during podocyte injury. 23116709_One mechanism of RANK inhibition by 1,25(OH)2D3 is down-regulation of the M-CSF receptor c-Fms, which is required for the expression of RANK. 23267146_Our data suggest that RANK, RANKL and OPG may potentially be used as novel prognostic markers for bone metastasis and provide new therapeutic targets in the treatment of breast cancer 23478294_EEIG1 is a novel RANK signaling component controlling RANK-mediated osteoclast formation. 23516466_Differential expression of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system is associated with bone metastasis in human non-small cell lung cancer. 23531404_OPG and RANK but not RANKL genetic polymorphisms influence bone mineral density mainly in the femoral neck in peri- and postmenopausal Chinese women. 23553199_The genotypes, combined genotypes and allele frequencies of C421T and C575T polymorphisms of the RANK gene have not been found to be associated with bone mineral density in Turkish women. 23572233_Data show that cystatin C inhibits osteoclast differentiation and formation by interfering intracellularly with signaling pathways downstream RANK. 23664977_RANK-e5a is produced through splicing out part of exon 5, resulting in a truncation of its extracellular domain. This isoform seems to have lower binding capacity towards RANK ligand and at the same time it is unable to activate NF-kB, neither after RANKL stimuli, nor by its overexpression. Furthermore, RANK-e5a is specifically expressed in human brain raising the possibility of a tissue specific function. 23664977_When TNFRSF11A-e5a is stimulated by RANK ligand, its capability to activate NF-kappaB is reduced compared to the wild type RANK receptor. 23697850_RANKL/RANK signal promotes Bcl-2 and Ki67 and decreases FasL expression, and further as a positive regulator for stimulating the proliferation and growth of DSCs through up-regulating CCL2/CCR2 signal 23702841_The study prospectively evaluated levels of RANK, RANK-L and OPG transcripts in the peripheral blood of 49 consecutive patients with advanced breast, lung or prostate cancer. 23744843_Genome-wide association associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) near candidate genes such as RANK and RANKL suggest that these single nucleotide polymorphisms and/or other variants nearby may be involved in bone phenotype determination. 23766243_RANK signaling interferes with mammary cell commitment, contributing to breast carcinogenesis. 23821519_silencing of miR-503 using a specific antagomir in ovariectomy (OVX) mice increased RANK protein expression, promoted bone resorption 24118270_we could not identify any association between external apical root resorption and two SNPs, rs1805034 from TNFRSF11A (encoding RANK) and rs3102735 from TNFRSF11B (encoding OPG). 24200492_High RANK expression is associated with Avascular Necrosis of Femur Head. 24340030_Mechanistic studies showed that IL-10 downregulated RANK expression in monocytes and thus, inhibited RANKL-induced OC formation 24478054_RANKL, either derived from the prostate tumor or from the host, plays a key role in cancer bone metastasis. 24549600_Changes in bone markers, OPG, sRANKL and/or the OPG/sRANKL ratio exhibited by girls with Anorexia nervosa have been found to be associated with changes in the levels of the selected adipose tissue hormones. 24651623_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of RANK and PTGS1 show genetic associations with osteoproliferative changes in ankylosing spondylitis. 24676805_RANKL and IL-6 mediate direct paracrine-autocrine signaling between cells of the osteoblast lineage and cancer cells. 24726460_These findings demonstrate that RANKL-RANK signal activation is essential to ABC tumor progression. RANKL-targeted therapy may be an effective alternative to surgery in select ABC presentations. 24729980_The effect of rs1054016(RANKL) adds to the evidence that the RANK pathway plays a role in BC pathogenesis and progression with respect to BMFS, emphasizing the connection between BC and bone health. 24737168_Higher RANK expression in the primary breast tumor is associated with a higher sensitivity to chemotherapy, but also a higher risk of relapse and death. 24842377_we identified RANK expression as a negative prognostic factor regarding disease-free survival in osteosarcoma 24891336_The involvement of TNFRSF11A in hereditary recurrent fever highlights the key role of this receptor in innate immunity. 25019155_Functional polymorphisms RANK rs1805034 T>C may be an indicator for individual susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 25047443_In the present study, we investigated the ability of triptolide, a diterpenoid isolated from Thunder of God Vine, to inhibit signaling by receptor activator of NF-kappaB (RANK) and its ligand (RANKL) and to modulate osteoclastogenesis 25111682_High RANK protein expression is associated with breast cancer. 25138264_Genetic polymorphism in TNFRSF11A influences bone mineral density in post-menopausal women. 25171769_The urinary mRNA of RANK might be used to differentiate histologic subtypes of glomerulonephritis, particularly between minimal change disease and membranous nephropathy. 25268581_RANKL could potentiate migration and invasion ability of RANK-positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells through NF-kappaB pathway mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 25270538_Data show that icariin decreases the expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL) and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (RANK) in interleukin 1 beta-stimulated chondrocytes. 25333856_High levels of RANK, RANKL and OPG expression can help to identify prostate cancer patients at high risk of developing bone metastasis. 25406312_PGRN and PIRO form a new regulatory axis in osteoclastogenesis that is included in RANK signaling in cell fusion and OC resorption of osteoclastogenesis 25464125_The data support an association between SNPs in the RANK/RANKL/OPG signalling pathway and the development of stress fracture injury. 25478860_he top hit rs17069906 (p = 5.6 e-10) is located within the genomic region of RANK, recently demonstrated to be an important player in the adaptive recovery response in podocytes and suggested as a promising therapeutic target in glomerular diseases. 25618600_This review study has focused on the association of RANKL-RANK-OPG pathway in the pathogenesis and progression of giant cell tumor of bone as well as discussed the possible therapeutic strategies by targeting this pathway 25722033_These findings indicate that epidermal leukocytes gradually acquire RANK during gestation - a phenomenon previously observed also for other markers on LCs in prenatal human skin. 25738879_Microcomputed tomography analysis demonstrated that the mice treated with rhRANK exhibited an increased bone volume and structure model index, and decreased trabecular spacing compared with those treated with rhOPG-Fc. 25810067_genetic variation associated with hypertension in Chinese women 25884698_Three single nucleotide polymorphisms of TNFRSF11A (rs4500848, rs6567270 and rs1805034) are associated with Age at menarche and Age at natural menopause in Chinese women. 25893522_Response to sRANKL in normal and tumor cells suggests a role for RANK/ERK-mediated signaling in normal osteoblasts chemotactic migration during bone remodeling that is altered or lost during osteosarcoma tumorigenesis. 25956608_Results demonstrated that the type of inflammatory infiltrate present in periradicular cysts appears to influence the expression of RANK, RANKL, and osteoprotegerin 25973136_this study is the first to identify RANK overexpression as a novel esophageal cancer marker in both Kazakh and Han ethnic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 26087197_Results suggest that Cbl-b improves the prognosis of RANK-expressing breast cancer patients by inhibiting RANKL-induced breast cancer cell migration and metastasis. 26200837_Src expression showed a significantly positive linear relationship with RANK, suggesting a potential mechanism of the RANKL-RANK axis in regulating breast cancer cell differentiation and antiapoptosis. 26276390_results indicate that the RANK IVVY motif cooperates with the TRAF-binding motifs to promote osteoclastogenesis, which provides novel insights into the molecular mechanism of RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis. 26398902_high level of mRANKL/RANK expression in cervical cancer lesions plays an important role in the rapid growth of cervical cancer cells possibly through strengthening the dialogue between cervical cancer cells and regulation of IL-8 secretion 26451891_Based on our findings, the functional SNP RANK rs1805034 T>C may be an indicator for individual susceptibility to GCA. 26528707_RANK/OPG ratio of expression in primary ccRCC is associated with BM. 26617755_expression of OPG, RANK and RANKL genes exert a crucial role in the progression of avascular necrosis 26734994_High RANK expression is associated with endometrial metastasis. 26749530_In this review, we will provide a summary of the biological functions of RANK signaling pathway (receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand RANKL and its receptor RANK ) and downstream pathways in bone remodeling, immunity and epithelial homeostasis, with a particular emphasis on cancer 26762414_The RANK/RANKL system induces chemoresistance. 26914636_Postmenopausal women with Rheumatoid Arthritis, carrying either the RANKL-290T allele or possessing the RANK 575CC genotype were more likely to develop osteoporosis. 26977008_Study showed that endogenous RANK expression changes might influence prostate cancer cell behavior since reduced RANK expression resulted in significantly increased PC-3 cell proliferation and adhesion. 27171030_Twenty-one single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of TNFSF11, TNFRSF11A, and TNFRSF11B were genotyped. This study suggests that TNFRSF11B but not TNFSF11 and TNFRSF11A genetic polymorphisms are associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Southern Han Chinese women. 27187610_In this study, whole exome sequencing (WES) was successfully used in six patients with malignant infantile osteopetrosis (MIOP) and identified mutations in four MIOP-related genes (CLCN7, TCIRG1, SNX10, and TNFRSF11A). 27191503_RANK SNP rs34945627 has a high allelic frequency in patients with breast cancer and Bone metastases, and is associated with decreased disease-free survival and Overall Survival. 27279652_RANK is frequently expressed by cancer cells in contrast with RANKL which is frequently detected in the tumor microenvironment, and together they participate in every step in cancer development. (Review) 27304650_RANK 575C>T polymorphisms did not show any statistically significant differences between the study groups (Osteoporosis and Osteopenia) and Postmenopausal women. 27322743_In histologically normal tissue of BRCA1-mutation carriers and showed that RANK(+) cells are highly proliferative, have grossly aberrant DNA repair and bear a molecular signature similar to that of basal-like breast cancer. 27507811_Vav3 is a novel TRAF6 interaction partner that functions in the activation of cooperative signaling between T6BSs and the IVVY motif in the RANK signaling complex. 27822475_RANK and CCR6 expressed on monocytes may be novel targets for the regulation of bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis. 27862210_Studies showed that the central hypothalamic-pituitary regulatory system, via it's relative hormones, seems to control OPG/RANKL/RANK system function, and the pulsatility and circadian rhythmicity of these hormones may induce an oscillatory fluctuation of the OPG/ RANKL ratio. Also, psycological characteristics may provoke a shift of the OPG/ RANKL ratio towards an unbalanced or a balanced status. [review] 27881737_Studies strongly implicates RANK and RANKL as key molecules involved in the initiation of BRCA1-associated breast cancer. [review] 28244588_OPG rs2073618, RANK rs75404003, and RANKL rs9594782 single nucleotide poymorphisms may predispose LVH in thalassemia patients. 28246602_the OPG/RANKL/RANK system might be directly influenced by genetic variants of NOTCH1 in aortic valve calcification. 28252575_Our results suggest that the polymorphism of the RANKL, RANK, and OPG genes does not make a significant genetic contribution to heel ultrasound measurements in a population of young Caucasian adults. Further studies replicating the results in independent populations are needed to support these initial findings. 28373003_RANK/RANKL signaling is involved in the androgen deprivation therapy-induced acceleration of bone metastasis in castration-insensitive prostate cancer and is inhibited by osteoprotegerin to prevent bone metastasis. 28417335_triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients that expressed both RANK and RANKL proteins had significantly worse RFS and OS than patients with RANK-positive, RANKL-negative tumors. RANKL was an independent, poor prognostic factor for RFS and OS in multivariate analysis in samples that expressed both RANK and RANKL. 28464982_For the RANK gene, the AGTGC haplotype was associated with the lowest risk of presenting chronic joint pain in individuals without TMD (P=0.03). This study supports the hypothesis that changes in the OPG and RANK genes influence the presence of chronic joint pain in individuals with and without TMD. 28483017_KLF5 and TNFRSF11a are related to cervical cancer. KLF5 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of cervical cancer cells partly by upregulating the transcription of TNFRSF11a. 28577080_RANK is increased in hormone receptor negative and basal breast cancer, and correlates with worse recurrence-free survival and risk of bone metastasis. 29025596_EGFR and RANK combinatorial in vitro analyses revealed a significant upregulation of AKT and ERK signaling after EGF stimulation in cell lines and also an increase of breast cancer cell invasiveness. 29074954_The role of the RANK pathway in the skeletal derangement in the chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients. 29118048_RANK rewires energy homeostasis in human lung cancer cells and promotes expansion of lung cancer stem-like cells. 29122885_findings indicate that C/EBPalpha is a stronger inducer of osteoclast differentiation than c-Fos, partly via C/EBPalpha regulation by the RANK (535)IVVY(538) motif 29146991_KLF5 and TNFRSF11a promote cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasiveness. 29204705_The mRNA expression of RANK was highest in prostate tumour tissue from patients with bone metastases as compared to BPH or locally confined tumours, also shown in clinical subgroups distinguished by Gleason Score or PSA level. 29241686_RANK/RANKL were identified as crucial regulators for BRCA1 mutation-driven breast cancer. Current prevention strategies for BRCA1 mutation carriers are associated with wide-ranging risks; therefore, the search for alternative, non-invasive strategies is of paramount importance 29334613_Reduced miR-144-3p expression in serum and bone mediates osteoporosis pathogenesis by targeting RANK. 29494398_study indicates that the expression of RANK and RANKL in parotid gland neoplasms is associated with the acquisition of a malignant phenotype and this pathway may represent an attractive therapeutic target in patients with parotid gland carcinomas. 29568001_study identified the second disease gene for DOS. TNFRSF11A isoforms may have the different roles in skeletal development and metabolism 29920311_that TNFR2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) tissues was positively correlated with progression and poor prognosis of ESCC patients 29920500_Changes in cerebrospinal fluid levels of the RANKL/RANK/OPG axis are associated with multiple sclerosis, particularly at disease onset. 29932437_RANK protein expression increased from normal to malignant endometrium, and the expression level was related with tumor grade but not with stage or the age of subjects in endometrial cancer. 30066839_gammadelta T cells suppressed iDCs osteoclastogenesis by downregulation of the RANK/cFos/ATP6V0D2 signaling pathway. 30093448_Results from current studies also point to a role of RANK/RANKL signaling in patients with multiple myeloma, who have increased se |
ENSMUSG00000026321 |
Tnfrsf11a |
23.347774 |
0.3407362005 |
-1.553273 |
0.456388729 |
11.315694 |
0.00076854743749012806742354486644330791023094207048416137695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001827280956403719378716710153298663499299436807632446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.0729522 |
3.4868843 |
29.9241018 |
7.1122242 |
| ENSG00000141858 |
90378 |
SAMD1 |
protein_coding |
F8WDT5 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable chromatin binding activity and histone binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and extracellular region. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
16159594_atherin is present only in atherosclerotic lesions, not in normal intima 27703004_The nuclear importin IPO5 was identified as a novel interacting protein of SMAD1. Overexpression of IPO5 in various cell lines specifically increases nuclear localization of BMP receptor-activated SMADs (R-SMADs) confirming a functional relationship between IPO5 and BMP but not TGF-beta R-SMADs. 34006929_The miR-378c-Samd1 circuit promotes phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth muscle cells and foam cells formation in atherosclerosis lesions. |
|
|
183.252458 |
0.3201125089 |
-1.643349 |
0.391316941 |
16.136452 |
0.00005893865429233162200666970576001801873644581064581871032714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000168038349885032804471168832449734509282279759645462036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.8104522 |
26.7833580 |
270.5379823 |
62.6792829 |
| ENSG00000142046 |
641649 |
TMEM91 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZNR0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to act upstream of or within hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in intracellular membrane-bounded organelle and membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:641649; |
intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000061702 |
Tmem91 |
22.456935 |
0.2810946913 |
-1.830872 |
0.396581879 |
21.520050 |
0.00000350148589912209688324745172904872703156797797419130802154541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011590610254050088200831331031182003243884537369012832641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3486262 |
2.6037530 |
37.5830641 |
5.4669389 |
| ENSG00000142082 |
23410 |
SIRT3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NTG7 |
FUNCTION: NAD-dependent protein deacetylase (PubMed:12186850, PubMed:12374852, PubMed:16788062, PubMed:18680753, PubMed:18794531, PubMed:23283301, PubMed:24121500, PubMed:24252090, PubMed:19535340). Activates or deactivates mitochondrial target proteins by deacetylating key lysine residues (PubMed:12186850, PubMed:12374852, PubMed:16788062, PubMed:18680753, PubMed:18794531, PubMed:23283301, PubMed:24121500, PubMed:24252090). Known targets include ACSS1, IDH, GDH, SOD2, PDHA1, LCAD, SDHA and the ATP synthase subunit ATP5PO (PubMed:16788062, PubMed:18680753, PubMed:24121500, PubMed:24252090, PubMed:19535340). Contributes to the regulation of the cellular energy metabolism (PubMed:24252090). Important for regulating tissue-specific ATP levels (PubMed:18794531). In response to metabolic stress, deacetylates transcription factor FOXO3 and recruits FOXO3 and mitochondrial RNA polymerase POLRMT to mtDNA to promote mtDNA transcription (PubMed:23283301). Acts as a regulator of ceramide metabolism by mediating deacetylation of ceramide synthases CERS1, CERS2 and CERS6, thereby increasing their activity and promoting mitochondrial ceramide accumulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12186850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12374852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16788062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18680753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18794531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19535340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23283301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24121500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24252090}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;NAD;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide;Zinc |
|
SIRT3 encodes a member of the sirtuin family of class III histone deacetylases, homologs to the yeast Sir2 protein. The encoded protein is found exclusively in mitochondria, where it can eliminate reactive oxygen species, inhibit apoptosis, and prevent the formation of cancer cells. SIRT3 has far-reaching effects on nuclear gene expression, cancer, cardiovascular disease, neuroprotection, aging, and metabolic control. [provided by RefSeq, May 2019]. |
hsa:23410; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; NAD+ binding [GO:0070403]; NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity [GO:0017136]; NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity [GO:0034979]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; peptidyl-lysine deacetylation [GO:0034983]; positive regulation of catalase activity [GO:1902553]; positive regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:2000304]; positive regulation of superoxide dismutase activity [GO:1901671]; protein deacetylation [GO:0006476] |
12186850_hSIRT3 is a mitochondrial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-dependent deacetylase. hSIRT3 is proteolytically processed in the mitochondrial matrix to a 28-kD product. 12374852_the role of SIRT3 in mitochondria involves protein deacetylation 15676284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15676284_the underexpression of a human sirtuin gene seems to be detrimental for longevity as it occurs in model organisms. 17059877_The SIRT3 5' flanking region encompasses the PSMD13 gene encoding the p40.5 regulator subunit of the 26S proteasome. 17437997_Using a highly specific antibody against the N terminus of SirT3, we found that SirT3 is transported from the nucleus to the mitochondria upon cellular stress. 17957139_Pro-apoptotic functioning of SIRT3 is selectively coupled with defined pathways regulating cell survival under basal conditions. 18215119_full-length mouse SIRT3 protein is a 37 kDa mitochondrial precursor protein contrary to the previously suggested 29 kDa protein 18680753_Results describe the substrates and regulation mechanisms for the human mitochondrial sirtuins Sirt3 and Sirt5. 18710944_These studies underscore an essential role of SIRT3 in the survival of cardiomyocytes in stress situations. 18781224_Data propose that SIRT3 and FOXO3a comprise a potential mitochondrial signaling cascade response pathway. 19209188_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343720_results show SIRT1 & SIRT3 are localized in different intracellular compartments, mainly nuclei & mitochondria; identified novel SIRT protein interacting partners which may be critically involved in anti-aging & metabolic regulatory activities of sirtuins 19367319_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19535340_the acetylated peptide is the first substrate to bind to SIRT3, before NAD(+). 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714312_Results established that GATA2 and AP-1 Activator elements c-Jun/c-Fos act additively in modulating the SIRT3-VNTR enhancer function. 20129246_These results identify SIRT3 as a genomically expressed, mitochondria-localized tumor suppressor. 20132432_SIRT3 (sirtuin3) reduces lipid accumulation via AMP-Activated Protein Kinase activation in human hepatic cells 20198340_Report the impact of SIRT3 SNPs on protein stability and cellular energy metabolism. 20463968_These studies identify a complex relationship between p53, SirT3, and chaperoning factor BAG-2 that may link the salvaging and quality assurance of the p53 protein for control of cellular fate independent of transcriptional activity. 20661474_Results indicate that Sirt3 functions as a downstream target gene of PGC-1alpha and mediates the PGC-1alpha effects on cellular ROS production and mitochondrial biogenesis. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20945913_SIRT3 substrates are involved in several metabolic pathways such as the urea cycle, ATP synthesis, and fatty acid oxidation. 21358671_SirT3 acts to suppress the growth of tumors, at least in part through its ability to suppress ROS and HIF-1alpha. 21397863_SIRT3 expression is reduced in human breast cancers, and its loss correlates with the upregulation of HIF1alpha target genes. 21449565_Human rSIRT3 was treated with 4-Hydroxynonenal, an endogenous product of lipid peroxidation to identify modified residues using nLC-MS/MS. 21566644_Mitochondrial deacetylase SIRT3 binds to, deacetylates and activates SOD2 21701047_Data show that Sirt1 and Sirt3 act on homologous substrates based on their evolutionary relationship. 22016654_Studies indicate that sirtuin 3 (Sirt3) as a genomically expressed, mitochondrial localized tumor suppressor. 22155639_Ethanol-induced eNOS activation in HAECs may be dependent on ALDH2 hyperacetylation by SIRT3 inactivation. 22326535_The expression of the SIRT3 gene was down-regulated in cybrids harboring mtDNA of the J haplogroup. 22416140_SIRT3 protein deacetylates isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) and regulates mitochondrial redox status 22585829_NAD(+)-dependent SIRT deacetylase has a role in regulating the expression of mitochondrial steroidogenic P450 22589271_SIRT3 is a mitochondrial tumor suppressor: a scientific tale that connects aberrant cellular ROS, the Warburg effect, and carcinogenesis.( 22595756_SIRT3 inhibits mitochondrial permeability transition and loss of membrane potential by preventing HKII binding to the mitochondria and increases carbonic anhydrase VB, thereby preventing intracellular acidification. 22609775_these data suggests that Sirt3 may play an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. Sirt3 overexpression upregulated p53 protein level through downregulating Mdm2 and thereby slowing p53 degradation. 22674009_Receptor-interacting protein (RIP) and Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3) are on opposite sides of anoikis and tumorigenesis. 22750084_The present study demonstrates a sex-specific effect of genetic variants in UCP1 and SIRT3 on cIMT 23045395_nuclear full-length (FL) SIRT3 is subjected to rapid degradation under conditions of cellular stress, including oxidative stress and UV irradiation, whereas the mitochondrial processed form is unaffected 23046812_Sirt3 physically interacted with the OSCP and led to its subsequent deacetylation. 23075334_Studies indicate that SIRT1, SIRT3 and SIRT6 are induced by calorie restriction conditions and are considered anti-aging molecules. 23139766_These data suggest a role for SIRT3 in mechanisms sensing and tackling reactive oxygen species- and Alzheimer's disease-mediated mitochondrial stress. 23272146_SIRT3 is decreased in HCC and is a novel unfavorable marker for prognosis of patients with this fatal disease. 23397292_Data suggest that SIRT3 expression is markedly decreased in islets isolated from type 2 diabetes patients (compared to islets from normal subjects); down-regulation of beta cell SIRT3 level seems key step in onset of beta cell dysfunction. 23494737_SIRT3 overexpression antagonizes high glucose-induced cellular senescence in human diploid fibroblasts via the SIRT3-FOXO1 signaling pathway. 23665396_our finding that SIRT3 deacetylates FOXO3 to protect mitochondria against oxidative stress provides a possible direction for aging-delaying therapies and disease intervention. 23790338_Abnormal expression of SIRT3 is closely related to the biological behavior of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. 23800187_a non-synonymous point mutation in SIRT3 contributes to reduced catalytic activity of the protein and affects redox balance in OSCCs. 23839864_We found an increased level of SIRT3 in subjects homozygous for the (T) allele. We suggest that SIRT3 genetic variability might be relevant for the modulation of human longevity in the Italian population. 23842789_Loss of SIRT3 expression is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 23856293_Sirt3 is a novel contributor to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. 23868064_Regulation of the acetylation and turnover of OGG1 by Sirt3 plays a critical role in repairing mitochondrial DNA. 23898059_Both NAMPT and SIRT3 to be highly expressed in well-differentiated thyroid carcinomas. 23928404_Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppressed SIRT1, SIRT3, and SIRT6 expression in human monocytes 23956348_reduced skeletal muscle SIRT3 activity may play a role in the increased oxidative stress associated with pregnancies complicated by obesity. 24042441_High expression of SIRT3 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 24121500_Sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) protein regulates long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by deacetylating conserved lysines near the active site. 24194516_SIRT3-induced down-regulation of mitochondrial oxidative stress attenuates keratinocyte differentiation. 24252090_Our data suggest that acetylome signaling contributes to mitochondrial energy homeostasis by SIRT3-mediated deacetylation of ATP synthase proteins. 24287180_these results provide the first evidence showing that an aberrantly decreased expression of SIRT3 occurred in gastric cancer (GC) patients, suggesting that SIRT3 might function as a mitochondrial tumor suppressor in GC. 24322174_Gastric cancer patients with SIRT3 expression have a better prognosis than those without. SIRT3 expression is an independent prognostic marker for overall survival and may act as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer. 24324009_Inhibition of SirT3 in cells undergoing proteotoxic stress severely impairs the mitochondrial network and results in cellular death 24339251_These findings suggest that SIRT3 is an endogenous negative regulator in response to ANE-induced oxidative stress and demonstrate an essential role for redox balance in human oral keratinocytes cells. 24464653_Expression of SIRT3 inversely correlates with the progression of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic change in the entorhinal cortex, hippocampus, and white matter. It is found in mitochondria and cytosol. 24486017_the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is regulated by Tyr phosphorylation of PDP1, which toggles recruitment between ACAT1 and SIRT3 24491532_Depletion of the Sirt3 proteins with siRNA causes defects of mitotic progression. Sirt3 is involved in spindle polymerization and chromosome alignment. 24503539_SIRT3 can function as either oncogene or tumor suppressor on influencing cell death by targeting a series of key modulators and their relevant pathways in cancer. [review] 24746213_results highlight the importance of the SIRT3 as a tumor suppressor protein in breast cancer and suggest that SIRT3 may be a potential molecular biomarker to identify high-risk patients across all molecular subtypes of breast cancer. 24771001_SIRT3 and glutamate dehydrogenase are altered in follicular cells of women with reduced ovarian reserve or advanced maternal age 24774224_Down-regulation of intratumoral and peritumoral Sirt3 were both associated with poor outcome in HCC, moreover, intratumoral Sirt3 was a favorable prognostic predictor in early stage patients. 24877629_Activation of SIRT3 could result in enhanced folliculogenesis and luteinization processes in luteinized granulosa cells, possibly by sensing and regulating oxidative stress 24889606_NAD(+) and SIRT3 regulate microtubule polymerization and the efficacy of antimicrotubule agents 24909164_SIRT3 overexpression decreases TfR1 expression by inhibiting IRP1 and represses proliferation in pancreatic cancer cells. 24924131_demonstrate that SIRT3 expression is responsive to rapamycin, a small inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin that has been extensively employed as a caloric restriction mimetic 25005846_Increased SIRT3 expression correlates with unfavorable prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 25103363_Pfn1 is a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer that acts via a novel mechanism of regulating the SIRT3-HIF1alpha axis. 25105144_This study provides evidence supporting that SIRT3 is closely associated with the clinical outcomes of colon cancer. SIRT3 may be considered as a marker for colon cancer. 25109285_The induction of Sirt1 and Sirt3 may be a determinant of thyroid cancer cell survival under genotoxic stress conditions. Further examination of the Sirt1-Foxp3 signal may improve our understanding of thyroid carcinogenesis 25128872_Silencing of SIRT3 increased the levels of Lon protein and of its acetylation, suggesting that Lon is a target of SIRT3, likely at K917. 25162939_In endothelial cells, SIRT3 stabilizes FOXO3 via deacetylation. 25165814_Results show that mitochondrial sirtuins SIRT3, SIRT4, and SIRT5 can promote increased mitochondrial respiration and cellular metabolism and respond to excess glucose by inducing a coordinated increase of glycolysis and respiration. 25194924_A human Sirt3-myc transgene was expressed as a 45kDa pro-form in the cytosol and a 30kDa processed form in mitochondria in differentiated PC12 cells. It protected them from apoptosis due to trophic withdrawal and from glucose and/or oxygen deprivation. 25210848_These results suggest that the active short isoform of SIRT3 protects hMSCs from oxidative injury by increasing the expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes. 25221980_We report a model for base exchange inhibition that relates such kinetic properties to physicochemical properties of SIRT3:NAD+, SIRT3:NAM, and analogous complexes for Sir2. 25227106_The proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of EC9706 cells mediated by SIRT3 downregulation may be closely associated with the expression levels of p21, Bcl-2 and Bax proteins. 25284742_A SIRT3 loss-of-function polymorphism is associated with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension in humans. 25329972_EGCG also differentially modulated the mRNA expressions of SIRT3-associated downstream targets including glutathione peroxidase 1 and superoxide dismutase 2 in normal and oral cancer cells. 25361925_This study demonstrated that SIRT3 downregulation in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. 25369635_Sirt1, Sirt2, and Sirt3 can catalyze the hydrolysis of lysine crotonylated histone peptides and proteins. 25562154_Our results suggest that SIRT 3 may serve as a marker for clinical feature and prognosis for breast cancer. 25607838_results indicate that SIRT3 is protective against AKI and suggest that enhancing SIRT3 to improve mitochondrial dynamics has potential as a strategy for improving outcomes of renal injury. 25755250_GOT2 K159 acetylation is increased in human pancreatic tumors, which correlates with reduced SIRT3 expression. 25755722_Our data suggested that SIRT3 protects endothelial cells from high glucose-induced cytotoxicity 25829495_Sirt1, Sirt2, and Sirt3 are expressed in enucleate platelets. Sirtuins act as a central player in the determination of platelet aging. 25915406_overexpression of SIRT3 inhibits induction of ER stress by palmitate. Collectively, we conclude that overexpression of SIRT3 alleviates palmitate-induced beta-cell dysfunction. 25915842_Study reveals a role of SIRT3/GSK-3beta/Bax signaling pathway in the suppression of HCC growth. 25961022_suggested that MIAM might be a promising candidate compound which could develop as a potent anticancer agent targeting NOX4 and SIRT3 activation 26042459_Suggest that SIRT3 may play a role in increasing antioxidant defense and conferring resistance to oxidative stress-induced damage under hyperglycemic conditions in the HepG2 cells. 26045440_Mitochondrial sirt3 participates in the development of Alzheimer's disease, in a transgenic mouse model, via mitochondrial dysfunction. 26109058_The results suggest that NRF-2 is a regulator of SIRT3 expression and may shed light on how SIRT3 is upregulated during nutrient stress. 26120888_These results suggest that melatonin exerts a hepatoprotective effect on mitochondrial-derived superoxide-stimulated autophagic cell death that is dependent on the SIRT3/SOD2 pathway. 26121130_SIRT3 and SIRT7 possess tumour suppressor properties in the context of pancreatic cancer. 26121691_SIRT3 may enhance glycolysis and cell proliferation in SIRT3-expressing cancer cells. 26138757_further studies on SIRT3 will help uncover important new pathways driving the aging process--{REVIEW} 26141949_CDK1-mediated SIRT3 phosphorylation is a potential effective target to sensitize tumor cells to radiotherapy. 26223796_SIRT3 plays a role in protection in Angiotensin II-induced HUVECs dysfunction via regulation of ROS generation. 26225774_Metabolic sensors via Sirt3 maximize the cellular reserve respiratory capacity through activating mitochondrial complex II, which enhances cell survival after hypoxia. 26317998_Up-regulation of SIRT3 in prostate cancer suppressed the phosphorylation of Akt, leading to the ubiquitination and degradation of oncoprotein c-MYC. 26456643_siRNA-mediated silencing of sirtuin 3 expression decreased complex I activity in NNMT-expressing SH-SY5Y cells to that observed in wild-type SH-SY5Y, and significantly reduced cellular ATP content also 26520405_Benzyl butyl phthalate selectively disrupts sirtuins 1/3 in HepG2 cells to alter epigenetic processes and mitochondrial biogenesis. 26577410_These results reveal a novel post-translational regulation of MPC1 by Sirt3, which is important for its activity and colon cancer cell growth. 26625292_microseed matrix seeding (MMS) was used to obtain crystals of human Sirt3 in its apo form and of human Sirt2 in complex with ADP ribose (ADPR). 26631723_Data suggest SIRT3-mediated inhibition of cell proliferation in B-cell malignancies is dependent on down-regulation of IDH2 and SOD2 activities via deacetylation; loss of SIRT3 stimulates cell proliferation via generation of reactive oxygen species. 26667041_Studies indicate that Many of the metabolic disorders have been associated with a reduction of sirtuins SIRT1 and SIRT3 at critical developmental windows throughout development. 26701732_Data indicate that compared to non-neoplastic endometria (NNE), endometrial cancer (EC) showed SIRT7 mRNA overexpression, whereas SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT4 and SIRT5 were underexpressed, and no significant differences were observed for SIRT3 and SIRT6. 26722027_Development of novel SIRT3 inhibitors, such as LC-0296, might enable the development of new targeted therapies to treat and improve the survival rate of patients with head and neck cancer. 26743598_SIRT3 has a pro-proliferative function in melanoma 26787646_Insufficient expression of Sirt3 leads to inefficient mitochondrial biogenesis with decreased developmental competence of human in vitro matured oocytes. 26893145_SIRT3 overexpression disrupts mitochondrial proteostasis that causes overproduction of reactive oxygen species and the cell cycle arrest to suppress cell proliferation. 26950437_physiological significance of SIRT3 on HBx-induced oxidative stress 27034011_Results show that curcumin at low doses can increase the level of sirtuins including sirtuin 1 and sirtuin 3) without delaying senescence of vascular smooth muscle (VSMC) cells. 27053302_SIRT3 overexpression dramatically increased cell viability in a cell model of Parkinson's disease. 27078640_Data suggest that DNA sequence variants (DSVs) identified in myocardial infarction (MI) patients may change sirtuin 3 (SIRT3) level by affecting the transcriptional activity of SIRT3 gene promoter, contributing to the MI development as a risk factor. 27114304_Our findings suggest that Sirt3 plays a tumor-progressive role in human RCC by regulating glutamine-derived mitochondrial respiration, particularly in cells where mitochondrial usage of cytosolic pyruvate is severely compromised. 27125970_Sirtuin 3 protects against urban particulate matter-induced autophagy in human bronchial epithelial cells. 27164052_The function of the three mitochondrial sirtuins (SIRT3, SIRT4, SIRT5) and their role in disease are reviewed. 27216459_SIRT3 is decreased in the metastatic tissues and highly metastatic cell line of ovarian carcinoma. SIRT3 suppresses ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro. 27232755_Contrary to what has been known in solid tumors, in K562 human leukemia cells, Sirt3 plays an opposite role in relieving oxidative stress. Basal but not enhanced autophagy activity maintains ubiquitination-proteasomal degradation of Sirt3 to limit reactive oxygen species level. 27270321_Current study reveal Sirt3 as a novel regulator coupling mitophagy and apoptosis, two important cellular processes that determine cellular survival and death. 27277143_This study underscores an essential role of SIRT3 in the antitumor effect of Bcl-2 inhibitors in human ovarian cancer through regulating both metabolism and apoptosis. The manipulation of Bcl-2 inhibitors combined with the use of classic glycolysis inhibitors may be rational strategies to improve ovarian cancer therapy. 27295248_Since mitochondrial ATP regeneration is inevitably linked to the maintenance of cardiac pump function, it is not surprising that recent studies revealed a role for mitochondrial sirtuins in the regulation of myocardial energetics and function. In addition, mitochondrial sirtuins modulate the extent of myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury and the development of cardiac hypertrophy and failure. [review] 27337034_SIRT3 whole muscle protein content was unaltered after fasting. 27367026_SIRT3 could enhance the drug sensitivity of hepatoma cells to an array of chemotherapeutic agents through glutathione S-transferase pi 1/JNK signaling pathway 27420645_survival curves showed that higher SIRT3 expression is correlated to a poorer prognosis for patients with grade 3 breast cancer. In conclusion, SIRT3 could be a therapeutic target for breast cancer, improving the effectiveness of CDDP and TAM treatments. 27483432_SIRT3 expression was significantly associated with overall survival in gastric cancer (HR = 0.62, 95% CI = 0.43-0.89, P = 0.009) and hepatocellular carcinoma patients (HR = 0.56, 95% CI = 0.42-0.74, P |
ENSMUSG00000025486 |
Sirt3 |
66.201418 |
0.4396439289 |
-1.185593 |
0.236985003 |
24.862045 |
0.00000061583039698732387428703298482002281843961100094020366668701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002233330874578108293104653295224615305869519943371415138244628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
44.8043866 |
6.4212435 |
102.8126617 |
9.7331650 |
| ENSG00000142102 |
80162 |
PGGHG |
protein_coding |
Q32M88 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of glucose from the disaccharide unit linked to hydroxylysine residues of collagen and collagen-like proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26682924}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Reference proteome |
|
Enables protein-glucosylgalactosylhydroxylysine glucosidase activity. Involved in carbohydrate metabolic process. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80162; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds [GO:0004553]; protein-glucosylgalactosylhydroxylysine glucosidase activity [GO:0047402]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975] |
19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000062031 |
Pgghg |
181.388585 |
0.2142582873 |
-2.222577 |
0.137759016 |
281.432326 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000365990824097271986908345770666583639392577081902920069768289020146156018721036889908410948079326167971356888280458884168943561890029138499316493634238683626061505727022904466139152646064758300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000098218628430467894755400569347119012560592631575863925164471502462418041508315051525355359604041211332676432623291870197702377172043042962901642445127216654587876121240697102621197700500488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.2612730 |
6.6941797 |
306.4985831 |
18.8671439 |
| ENSG00000142156 |
1291 |
COL6A1 |
protein_coding |
P12109 |
FUNCTION: Collagen VI acts as a cell-binding protein. |
Cell adhesion;Collagen;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The collagens are a superfamily of proteins that play a role in maintaining the integrity of various tissues. Collagens are extracellular matrix proteins and have a triple-helical domain as their common structural element. Collagen VI is a major structural component of microfibrils. The basic structural unit of collagen VI is a heterotrimer of the alpha1(VI), alpha2(VI), and alpha3(VI) chains. The alpha2(VI) and alpha3(VI) chains are encoded by the COL6A2 and COL6A3 genes, respectively. The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha 1 subunit of type VI collagen (alpha1(VI) chain). Mutations in the genes that code for the collagen VI subunits result in the autosomal dominant disorder, Bethlem myopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1291; |
collagen type VI trimer [GO:0005589]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; platelet-derived growth factor binding [GO:0048407]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649] |
11932968_COL6 genes encoding type VI collagen 11973338_keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), a key stimulator of epithelial cell proliferation during wound healing, preferentially binds to collagens I, III, and VI. 12011280_Haplotype analysis clearly suggested linkage of Ullrich muscular dystrophy to the COL6A1/2 locus in two cases and to the COL6A3 loci in the third case. In the remaining nine patients, primary collagen VI involvement was excluded 12374585_Bethlem myopathy is an autosomal dominantly inherited myopathy with contractures caused by mutations in the COL6A1 gene. 12736748_Collagen VI deficiency might have caused electron microscopic changes of capillaries, while function of capillaries is apparently retained. 12840783_a de novo heterozygous deletion of the COL6A1 gene results in a severe phenotype of classical Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy 12958705_linkage disequilibrium and association studies that SNPs in the collagen 6A1 gene (COL6A1) were strongly associated with Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament 14981181_The failure of collagen VI to anchor the basal lamina to the interstitium is the cause of Ullrich disease. 15563506_dominant mutations are common in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD). 16130093_we report a genotype-phenotype correlation demonstrating that heterozygous glycine substitutions in the triple-helix domain of COL6A1 are dominant and responsible for a milder Ullrich scleroatonic muscular dystrophy phenotype. 16227896_COL6A1 could be responsible for the hyperostotic state, leading to ectopic bone formation in the spinal ligament. 16227896_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16434404_beta ig-h3 can differentially modulate the aggregation of collagen VI with biglycan and decorin 17334655_Major promoter and enhancer sequences regulating COL6A1 expression are present in this bacterial artificial chromosome clone. 17537636_This study identified a novel homozygous COL6A1 premature termination mutation in a UCMD patient that causes nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. 17602442_This study demonstrates a homogeneous overexpression of the genes encoding for alpha1 and alpha2 chains for collagen type VI in nuchal skin of human trisomy 21 fetuses. 18246005_COL6A1 may be a common susceptibility gene for ossification of the ligamentum flavum and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in Chinese Han population. 18246005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18366090_Study reports 10 unrelated patients with a Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy clinical phenotype and de novo dominant negative heterozygous splice mutations in COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3. 18378883_Immunofluorescent labeling of collagen VI in fibroblast cultures is a useful addition to current diagnostic services for Bethlem myopathy (BM). It can be used to guide molecular genetic testing in a cost-effective and time-saving manner. 18551403_Results found COL6A1 to be differentially expressed in human astrocytomas. 18634150_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18634150_SNP of COL6A1 were not related to radiographic progression of ankylosing spondylitis. 18825676_These data indicate that collagen VI glycine mutations impair the assembly pathway in different ways and disease severity correlates with the assembly abnormality. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19309692_Four patients affected by Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and carrying unusual mutations of COL6 genes affecting RNA splicing, were identified. 20721706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20976770_This study revealed several genotype-phenotype correlations, providing new insights into the natural history and course of ColVI myopathies. 21037586_the accumulation of abnormal mitochondria and sarcoplasmic reticulum is caused by a defect of autophagy and that restoration of a proper autophagic flux in Col6a1-/- muscles ameliorates these alterations. 22012643_the COL6A1 rs35796750 TT genotype is associated with increased performance during the bicycling of the South African Ironman triathlon 22583932_TP-alpha, collagen alpha-1(VI) chain and S100A9 are potential biomarkers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and may play an important role in tumorigenesis and development of ESCC. 23013106_COL3A1 rs1800255, COL6A1 rs35796750 and COL12A1 rs970547 were not significantly associated with sit-and-reach, straight leg raise or total shoulder rotation range of motion 23221806_XPD mutations in trichothiodystrophy hamper COL6A1 expression. 24271325_The resulting proposed clinical classification system of collagen VI-related myopathy is unique in that it is based on the integration of both motor function and pulmonary function criteria. 24357721_Absence of ANXA2 leads to retention of COL6 in a late-Golgi, VAMP2-positive compartment. 24443028_Mutations in each of the three collagen VI genes, COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3, cause four types of muscle disorders: Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, Bethlem myopathy, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and autosomal recessive myosclerosis. (Review) 24737472_These results suggest that these SNPs of BMP-2 and COL6A1 may not directly influence the expression of OPLL. 24801232_In UCDM, 1 mutation was indentified in COL6A1 in Chinese patients. 25073002_The second main finding of this study was that COL6A1 rs35796750 did not associate with the risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury in the self-reported Caucasian South African cohort. 25176343_Data suggest the potential role of COL6 in promoting lung neoplasia in diseased lungs where COL6 is overexpressed. 25204870_Parental mosaicism was confirmed in the four families through quantitative analysis of the ratio of mutant versus wild-type allele (COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3) in genomic DNA from various tissues; consistent with somatic mosaicism, parental samples had lower ratios of mutant versus wild-type allele compared with the fully heterozygote offspring. 25325876_Data indicate that collagen-VI-alpha-1 (COL6A1) is expressed in all grades of glioma. 25535305_worsening of the functional disability appeared typically after the age of 40 in 47% of our patients with Bethlem myopathy, and was frequently associated with COL6A1 exon 14 skipping 25925694_upregulated in the airways of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients and exposed upon epithelial desquamation 25978941_is the first report of UCMD recurrence in 2 siblings due to a germline mosaic COL6 gene mutation 26317545_COL6A1 may have a role in progression and outcome of clear cell renal cell carcinoma 26447986_Type VI collagen and activated retinal Muller cells are present in iERM. 26753503_These data demonstrate, for the first time, a functional relationship between collagens VI and XII during osteogenesis. 27246988_Missense mutations in COL6A1, COL11A2, FGFR1, and BMP2 genetically predispose patients to ossification of posterior longitudinal ligaments. 27628582_Data suggest that, compared with obese white women, obese black women exhibit higher expression of HIF1A (hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha), COL5A1 (collagen Valpha1), and COL6A1 (collagen VIalpha1) in gluteal but not abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue depots; up-regulation of expression of these proteins correlates with reduced insulin sensitivity in black women only. 28984114_the donor splice site of COL6A1 intron 14, associated with the phenotype of Bethlem myopathy or intermediate form, is a hot spot for ColVI myopathies 29244830_We have used RNA-Seq to identify differentially expressed genes in cultured dermal fibroblasts from 13 COL6-RD individuals (8 dominant negative and 5 null) and 6 controls. To better assess the transcriptional changes induced by abnormal collagen VI in the extracellular matrix (ECM); we compared transcriptional profiles from subjects with DN mutations and subjects with null mutations to transcriptional profiles 29659864_The polypeptide is a novel non-triple helical polypeptide of type VI collagen alpha1 chain encoded by COL6A1, or NTH alpha1(VI). 29673351_FKBP10 interacts with collagen VI and deficiency of FKBP10 reduces lung fibroblast migration by down-regulation of collagen VI synthesis. 29764467_Five SNPs in the COL6A1 (and IL17RC) genes were found to be associated with susceptibility to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in Han Chinese patients. 30321347_determined the common epitope between COL4A1 and COL6A1 as PXXGXPGLRG, with surface plasmon resonance analyses revealing KD values for the COL4A1 epitope as 5.56+/-1.81x10-9 M and for the COL6A1 epitope as 7.15+/-0.44x10-10 M 30706156_The most frequent mutation in a series of 16 Bethlem myopathy patients was the COL6A3 variant c.7447A>G, p.Lys2486Glu, with either an homozygous or compound heterozygous presentation. Five new mutations were found in COL6A1 gene and other two in COL6A3 gene, all of them with a dominant heritability pattern. 30895940_A recurrent COL6A1 pseudoexon insertion causes muscular dystrophy and is effectively targeted by splice-correction therapies. 31268154_High COL6A1 expression is associated with metastasis in pancreatic cancer. 31273343_Results identified compound heterozygous pathogenic COL6A1 variants (c.[98-6G>A];[301C>T]) in patients presenting with a clinical phenotype overlapping with collagen VI-related myopathies and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. The COL6A1 variants abolished collagen VI and V deposition and increased tenascin-X levels. 31831033_The COL6A1 gene rs201153092A site polymorphism is a potential pathogenic mutation in thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. 31939624_The COL6A1 rs201153092 single nucleotide polymorphism, associates with thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. 32053901_Tendon Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Defective Cell Polarization in the Presence of Collagen VI Mutations. 32389683_Coexistence of digenic mutations in the collagen VI genes (COL6A1 and COL6A3) leads to Bethlem myopathy. 32894152_Non-canonical Fzd7 signaling contributes to breast cancer mesenchymal-like stemness involving Col6a1. 32999266_COL3A1, COL6A3, and SERPINH1 Are Related to Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Occurrence According to Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. 33000277_Involvement of nontriple helical type VI collagen alpha1 chain, NTH alpha1(VI), in the proliferation of cancer cells. 33261612_The impact of COL1A1 and COL6A1 expression on hypospadias and penile curvature severity. 33337382_Intrafamilial Phenotypic Variability of Collagen VI-Related Myopathy Due to a New Mutation in the COL6A1 Gene. 33391546_H3K27 acetylation activated-COL6A1 promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis by repressing STAT1 and activating pulmonary cancer-associated fibroblasts. 33970702_Identification of COL6A1 as the Key Gene Associated with Antivascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme. 33982770_Collagen type VIalpha1 and 2 repress the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells. 34287704_Association analysis and functional study of COL6A1 single nucleotide polymorphisms in thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum in the Chinese Han population. |
ENSMUSG00000001119 |
Col6a1 |
1719.730029 |
4.4118448136 |
2.141382 |
0.043024849 |
2646.782677 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2849.9135515 |
74.7368067 |
650.7003790 |
14.7142060 |
| ENSG00000142173 |
1292 |
COL6A2 |
protein_coding |
P12110 |
FUNCTION: Collagen VI acts as a cell-binding protein. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Collagen;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes one of the three alpha chains of type VI collagen, a beaded filament collagen found in most connective tissues. The product of this gene contains several domains similar to von Willebrand Factor type A domains. These domains have been shown to bind extracellular matrix proteins, an interaction that explains the importance of this collagen in organizing matrix components. Mutations in this gene are associated with Bethlem myopathy and Ullrich scleroatonic muscular dystrophy. Three transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1292; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; response to glucose [GO:0009749] |
12011280_Haplotype analysis clearly suggested linkage of Ullrich muscular dystrophy to the COL6A1/2 locus in two cases and to the COL6A3 loci in the third case. In the remaining nine patients, primary collagen VI involvement was excluded 12218063_the C-terminal globular domain of COL6A2 is not essential for triple-helix formation but is critical for microfibrillar assembly in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy 12297580_A case of Ullrich disease is associated with complete deficiency of collagen VI and compound heterozygous mutations in the collagen VI alpha 2 gene with absence of microfibrils on electron microscopy. 12374585_Bethlem myopathy is an autosomal dominantly inherited myopathy with contractures, caused by mutations in COL6A1 gene, COL6A2 gene or COL6A3 gene. 14981181_In Ullrich syndrome, a heterozygous G-to-A substitution at position +5 in intron 23 & the corresponding heterozygous 6-bp deletion in exon 26 which deleted 1 of the 2 tandem repeats of the sequence CATCGG in nt 2268-2273 & 2274-2279 in COL6A2 ORF. 15563506_dominant mutations are common in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD). 16075202_diminished COL6A2 mRNA expression found to be primary pathogenic mechanism in UCMD patient 17602442_This study demonstrates a homogenoeous overexpression of the genes encoding for alpha1 and alpha2 chains of collagen type VI in nuchal skin of human trisomy 21 fetuses. 18366090_Study reports 10 unrelated patients with a Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy clinical phenotype and de novo dominant negative heterozygous splice mutations in COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3. 18852439_Results describe the characteristic features of myosclerosis myopathy with a homozygous collagen type 6A2 mutation responsible for a peculiar pattern of collagen VI defects. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19309692_Four patients affected by Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and carrying unusual mutations of COL6 genes affecting RNA splicing, were identified. 19698785_The alpha2(VI) chain modulates matrix-metalloproteinase (MMP) availability by sequestering proMMPs in the extracellular matrix, blocking proteolytic activity. 20106987_the C2A splice variant has a role in recessive COL6A2 C-globular missense mutations in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy 20302629_A deletion within intron 1A of the COL6A2 gene, occurring in compound heterozygosity with a small deletion in exon 28, was identified in a BM patient. 23138527_Homozygous COL6A2 mutation, p.Asp215Asn, was identified in both affected siblings. We conclude that the COL6A2 p.Asp215Asn mutation is likely to be responsible for PME (Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy) in this family. 23452080_COL6A2 is overexpressed in Down syndrome-affected umbilical cords at early and term gestational ages. 24443028_Mutations in each of the three collagen VI genes, COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3, cause four types of muscle disorders: Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, Bethlem myopathy, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and autosomal recessive myosclerosis. (Review) 24801232_In UCMD, 8 mutations were identified in COL6A2 in Chinese patients. 25204870_Parental mosaicism was confirmed in the four families through quantitative analysis of the ratio of mutant versus wild-type allele (COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3) in genomic DNA from various tissues; consistent with somatic mosaicism, parental samples had lower ratios of mutant versus wild-type allele compared with the fully heterozygote offspring. 25533456_Mutations in COL6A2 gene are associated with aberrant mitochondria in Bethlem myopathy. 26944560_binding of collagen VI to NG2 is essential for the direction of tendon fibroblasts migration in vitro. 27563703_Genetic study showed a missense mutation in COL6A2 (c.820 G>A, p.Gly268Ser) that causes a glycine substitution in the Gly-X-Y collagenous motif, at the beginning of the collagenous triple helical domain. The c.820 G>A mutation segregated in all the affected patients. 32053901_Tendon Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Defective Cell Polarization in the Presence of Collagen VI Mutations. 32350230_Proteomics Profiling Reveals Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1, Collagen Type VI alpha-2 Chain, and Fermitin Family Homolog 3 as Potential Biomarkers of Plaque Erosion in ST-Segment Elevated Myocardial Infarction. 33537799_Use of RNAsequencing to detect abnormal transcription of the collagen alpha2 (VI) chain gene that can lead to Bethlem myopathy. 33982770_Collagen type VIalpha1 and 2 repress the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells. 36292982_The Presentation of Two Unrelated Clinical Cases from the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania with the Same Previously Undescribed Variant in the COL6A2 Gene. |
ENSMUSG00000020241 |
Col6a2 |
1043.184720 |
2.7206609419 |
1.443957 |
0.099982273 |
203.375820 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000038298551482716621524353680277375949415580080822164086247701471699738061237462845067489488092582843663787707167074116088034685390084632672369480133056640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007408736826800752006969716970152304094136033249347693195681182266805597827089439355106088063684935026616940955486358827419834938154963310807943344116210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1509.6543652 |
102.3895717 |
558.2117031 |
28.2630770 |
| ENSG00000142207 |
9875 |
URB1 |
protein_coding |
O60287 |
|
Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in maturation of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) and maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA). Located in fibrillar center. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9875; |
fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; maturation of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000466]; maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000463] |
31886628_RAPTOR promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by inducing mTORC1 and upregulating ribosome assembly factor URB1. 32888357_Ribosome assembly factor URB1 contributes to colorectal cancer proliferation through transcriptional activation of ATF4. |
ENSMUSG00000039929 |
Urb1 |
299.464703 |
2.1264609501 |
1.088454 |
0.246784126 |
19.025873 |
0.00001289580137323702867561351498304489382462634239345788955688476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000039929101797562102833544922519948272565670777112245559692382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
405.3767091 |
71.1946551 |
192.2218698 |
24.7301028 |
| ENSG00000142227 |
2014 |
EMP3 |
protein_coding |
P54852 |
FUNCTION: Probably involved in cell proliferation and cell-cell interactions. |
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the PMP-22/EMP/MP20 family of proteins. The protein contains four transmembrane domains and two N-linked glycosylation sites. It is thought to be involved in cell proliferation, cell-cell interactions and function as a tumor suppressor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:2014; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; bleb assembly [GO:0032060]; cell death [GO:0008219] |
15583422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16015083_The five genes, and three of the encoded proteins, were shown differentially expressed between a group of keratoconus patients and a reference group using different techniques 17187361_EMP3 overexpression is associated with oligodendroglial tumors 17610521_Oligodendroglial and astrocytic gliomas show EMP3 hypermethylation and aberrant expression. Primary and secondary glioblastomas have distinct genetic profiles and also differ in their epigenetic aberrations. 18823699_Loss of EMP3 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19270820_Epithelial membrane protein 3 overexpression in breast carcinomas was significantly related to histological grade III , lymph node metastasis , and strong Her-2 expression. 20388442_The promoter methylation and mRNA expressions of EMP3 and PCDH-gamma-A11 are closely related with the malignant development of glioma. 22992787_LOH 19q determines the complete loss of EMP3 function, as the conserved allele is frequently hypermethylated, and this may represent the molecular basis of the higher risk of relapse in this subgroup of grade II oligodendroglioma patients. 23920144_Decreased expression of EMP3 by promoter methylation is associated by lung cancer 24083241_The aim of this study was to investigate the EMP3 promoter hypermethylation status in a series of 229 astrocytic and oligodendroglial tumors and in 16 glioblastoma cell lines. 26398721_EMP3 functions as an oncogene and is regulated by microRNA-765 in primary breast carcinoma. 26472188_The study provided a new insight into EMP3, suggesting that EMP3 enhances malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells 27279240_The studies implicating GAS3 protein family (EMP1, EMP2, EMP3 and PMP22) in cancer pathogenesis as well as probe the structural similarities between the family members were highlighted. 27527869_High EMP3 expression is associated with high grade glioma. 27801851_Independent validation with glioma patients tissue (n = 70) and normal brain tissue (n = 19) found PPIC, EMP3 and CHI3L1 were up-regulated in glioma tissue. Survival value validation showed that the three genes correlated with patient survival by Kaplan-Meir analysis, including grades, age and therapy. 28718375_epithelial membrane protein 3 is a downstream effector of TWIST1/2 in inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Epithelial membrane protein 3 upregulation might be associated with gastric cancer metastasis and is a potential indicator of unfavorable overall survival and progression-free survival in gastric cancer patients 29794476_This study identified and validated a three-gene (EMP3, GSX2 and EMILIN3) prognostic signature in Lower-Grade Gliomas. 30614533_Results found that EMP3 interacts with proteins involved in trafficking and signaling regulation. Its knockdown downregulates mitogenic signaling pathways and reduces cell proliferation and migration of HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell line. 32678083_Disruption of the tumour-associated EMP3 enhances erythroid proliferation and causes the MAM-negative phenotype. 33964937_EMP3 mediates glioblastoma-associated macrophage infiltration to drive T cell exclusion. 34067658_The Multifunctional Role of EMP3 in the Regulation of Membrane Receptors Associated with IDH-Wild-Type Glioblastoma. 34268874_Establishment of a nomogram with EMP3 for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with glioma: A bi-center study. 34476496_Epithelial membrane protein 3 regulates lung cancer stem cells via the TGFbeta signaling pathway. 34511602_EMP3 negatively modulates breast cancer cell DNA replication, DNA damage repair, and stem-like properties. 34617578_Expression of epithelial membrane protein (EMP) 1, EMP 2, and EMP 3 in thyroid cancer. 34856762_Identification of candidate biomarker EMP3 and its prognostic potential in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000040212 |
Emp3 |
801.097345 |
8.7696768712 |
3.132524 |
0.078671200 |
1769.228676 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1457.7458077 |
70.1831897 |
167.4030032 |
7.1925681 |
| ENSG00000142303 |
81794 |
ADAMTS10 |
protein_coding |
Q9H324 |
FUNCTION: Metalloprotease that participate in microfibrils assembly. Microfibrils are extracellular matrix components occurring independently or along with elastin in the formation of elastic tissues. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21402694}. |
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene belongs to the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain with thrombospondin type-1 motifs) family of zinc-dependent proteases. ADAMTS proteases are complex secreted enzymes containing a prometalloprotease domain of the reprolysin type attached to an ancillary domain with a highly conserved structure that includes at least one thrombospondin type 1 repeat. They have been demonstrated to have important roles in connective tissue organization, coagulation, inflammation, arthritis, angiogenesis and cell migration. The product of this gene plays a major role in growth and in skin, lens, and heart development. It is also a candidate gene for autosomal recessive Weill-Marchesani syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:81794; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; microfibril [GO:0001527]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
15355968_ADAMTS10 is a functional metalloprotease as demonstrated by cleavage of alpha2-macroglobulin 15358598_Expression in human colonic cell lines. 15368195_ADAMTS10 plays a major role in growth and in skin, lens, and heart development in humans. 18567016_infer that folding of the complex C-terminal ancillary domain is the rate-limiting step in biosynthesis of ADAMTS10, and that it (but not catalytic domain) is sensitive to subtle changes in efficiency of signal peptide cleavage. 19696795_Mutations in ADAMTS10 gene is not responsible for microspherophakia. 19836009_Homozygous mutation in ADAMTS10 causes lenticular myopia, ectopia lentis, glaucoma, spherophakia, and short stature. 21402694_ADAMTS10 participates in microfibril biogenesis rather than in fibrillin-1 turnover 23422823_These findings support the Gly661Arg mutation of ADAMTS10 as the likely cause of POAG in beagles. 27779234_Using siRNA, over-expression and mutagenesis, it was found ADAMTS6 inhibits and ADAMTS10 is required for focal adhesions, epithelial cell-cell junction formation, and microfibril deposition. 35925524_ADAMTS10 inhibits aggressiveness via JAK/STAT/c-MYC pathway and reprograms macrophage to create an anti-malignant microenvironment in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000024299 |
Adamts10 |
22.288738 |
0.3007498603 |
-1.733364 |
0.673816387 |
5.537188 |
0.01861647111419295272383145345429511507973074913024902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.033632694448652140917221942117976141162216663360595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.7617978 |
5.3822460 |
36.9099927 |
11.6600628 |
| ENSG00000142327 |
57140 |
RNPEPL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HAU8 |
FUNCTION: Broad specificity aminopeptidase which preferentially hydrolyzes an N-terminal methionine, citrulline or glutamine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19508204}. |
Aminopeptidase;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Enables metalloaminopeptidase activity. Involved in proteolysis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57140; |
metalloaminopeptidase activity [GO:0070006]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
19508204_RT-PCR analysis of RNPEPL1 expression revealed a ubiquitous tissue distribution, consistent with a general housekeeping function, but also revealed alternative splicing of the mRNA in all tissues examined. 20414141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000026269 |
Rnpepl1 |
511.517086 |
0.4625498090 |
-1.112319 |
0.170652009 |
41.670224 |
0.00000000010804196954536289380854376736786266223477870340730078169144690036773681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000557392335019069031182368384458314380935917142778635025024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
349.7565565 |
38.1887341 |
762.1055035 |
59.4615615 |
| ENSG00000142549 |
402665 |
IGLON5 |
protein_coding |
A6NGN9 |
|
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:402665; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576] |
24703753_The target antigen of patients with rapid-eye-movement parasomnia who produce antibodies (mainly IgG4) against IgLON5 is a neuronal cell adhesion molecule that suggests a tauopathy 30956130_Findings report 89 unpublished cell-surface ligand-receptor pairs and describe structural models of trans interactions of cell adhesion molecules, neuronal (IgLON5), showing that their structures are compatible with a model of interaction across the synaptic cleft. 33531378_Anti-IgLON5 Disease: A New Bulbar-Onset Motor Neuron Mimic Syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000013367 |
Iglon5 |
17.474754 |
0.1829444404 |
-2.450523 |
0.449197960 |
32.763874 |
0.00000001040609120648388331744415782756721378099484809354180470108985900878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000045254539247997084832130052379356444092195488337893038988113403320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0645853 |
1.6981407 |
27.9760974 |
5.4850961 |
| ENSG00000142552 |
57333 |
RCN3 |
protein_coding |
Q96D15 |
FUNCTION: Probable molecular chaperone assisting protein biosynthesis and transport in the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:16433634, PubMed:28939891). Required for the proper biosynthesis and transport of pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A/SP-A, pulmonary surfactant-associated protein D/SP-D and the lipid transporter ABCA3 (By similarity). By regulating both the proper expression and the degradation through the endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation pathway of these proteins plays a crucial role in pulmonary surfactant homeostasis (By similarity). Has an anti-fibrotic activity by negatively regulating the secretion of type I and type III collagens (PubMed:28939891). This calcium-binding protein also transiently associates with immature PCSK6 and regulates its secretion (PubMed:16433634). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BH97, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16433634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28939891}. |
Calcium;Chaperone;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Metal-binding;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transport |
|
Enables calcium ion binding activity. Involved in several processes, including collagen biosynthetic process; positive regulation of peptidase activity; and regulation of protein kinase B signaling. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57333; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032964]; ERAD pathway [GO:0036503]; lung epithelium development [GO:0060428]; phospholipid homeostasis [GO:0055091]; positive regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010952]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051896]; surfactant homeostasis [GO:0043129] |
16433634_Autoactivation & secretion of rat PACE4 was increased upon co-expression with recombinant human RCN-3. Selective and transient association of RCN-3 with the precursor of PACE4 plays an important role in the biosynthesis of PACE4. 27468573_RCN3 expression in systemic sclerosis was not statistically significantly different to healthy controls. 28939891_Study identified reticulocalbin-3 (RCN-3) as a common molecule down-regulated by aldosterone (Aldo), galectin-3 and cardiotrophin-1 - key factors in the cardiac remodeling induced by Aldo associated with cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Moreover, RCN-3 emerges as a new potential negative regulator of collagen production. 29844224_genome-wide association study in US: Data suggest, among white subjects, an SNP in RCN3 (rs34459162) and a missense mutation in GCKR (rs1260236) are associated with serum levels of glycated albumin; among black subjects, an intergenic SNP in PRKCA (rs2438321) is associated with fructosamine levels and intronic variant in PRKCA (rs59443763) is associated with glycated albumin levels. (GCKR = glucokinase regulatory protein) 33531801_Rcn3 Suppression Was Responsible for Partial Relief of Emphysema as Shown by Specific Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell Rcn3 CKO Mouse Model. 34753797_An Expanded Genome-Wide Association Study of Fructosamine Levels Identifies RCN3 as a Replicating Locus and Implicates FCGRT as the Effector Transcript. |
ENSMUSG00000019539 |
Rcn3 |
339.640188 |
0.1446760283 |
-2.789102 |
0.159159316 |
295.996591 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000245470129575649876475403316094150455078632807831003127117467540942038920035529089542572793350174530362586934872721382667154822501718479943306918642446623496146146815172217614531291474122554063796997070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000070215874273964966946276782790742246137416795654244540354592828130562765864190789183241564284323510032286284746871615932406220759848165831599912039931529173609559349444886322544334689155220985412597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.2471917 |
9.1228219 |
614.6390661 |
40.9249121 |
| ENSG00000142632 |
128272 |
ARHGEF19 |
protein_coding |
Q8IW93 |
FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RhoA GTPase. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;GTPase activation;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) such as ARHGEF19 accelerate the GTPase activity of Rho GTPases (see RHOA, MIM 165390).[supplied by OMIM, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:128272; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:0060071]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
24405610_overcomes the suppressive influence of miR-503 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 29164615_These findings suggest that ARHGEF19 upregulation, due to the low expression of miR-29 in non-small cell lung cancer tissues, may play a crucial role in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis by activating MAPK signaling 32993957_ARHGEF19 regulates MAPK/ERK signaling and promotes the progression of small cell lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000028919 |
Arhgef19 |
52.209564 |
0.4422520729 |
-1.177059 |
0.290131368 |
16.090544 |
0.00006038480723889154552167651823779692676907870918512344360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000171928965055177329721708412435532409290317445993423461914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.2680260 |
6.7997093 |
73.6334536 |
10.6053531 |
| ENSG00000142684 |
51042 |
ZNF593 |
protein_coding |
O00488 |
FUNCTION: Involved in pre-60S ribosomal particles maturation by promoting the nuclear export of the 60S ribosome (PubMed:32669547). Negatively modulates the DNA binding activity of Oct-2 and therefore its transcriptional regulatory activity (PubMed:9115366). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9115366, ECO:0000305|PubMed:32669547}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables zinc ion binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity and positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleolus and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51042; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; preribosome binding [GO:1990275]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; negative regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:1903026]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; ribosome biogenesis [GO:0042254] |
18287285_The tertiary structure of the zinc finger domain of ZNF593 is composed of a beta-hairpin that positions the cysteine side chains for zinc coordination, followed by an atypical kinked alpha-helix containing the two histidine side chain ligands. 33550812_LncRNA ZNF593-AS Alleviates Contractile Dysfunction in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000028840 |
Zfp593 |
54.230710 |
2.4077552230 |
1.267689 |
0.209945934 |
37.259128 |
0.00000000103429714759155462108204909748134306402000959224096732214093208312988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000004945327469533963571298793010641223211187877950578695163130760192871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.9431801 |
10.0144624 |
32.2145528 |
3.3729526 |
| ENSG00000142700 |
63950 |
DMRTA2 |
protein_coding |
Q96SC8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in sexual development. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II and sex differentiation. Predicted to act upstream of or within nervous system development and skeletal muscle cell differentiation. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:63950; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cerebral cortex regionalization [GO:0021796]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007405]; neuron fate specification [GO:0048665]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sex differentiation [GO:0007548]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; stem cell fate specification [GO:0048866] |
25082981_This study reveals, for the first time, the requirement of DMRTA2 for normal human female embryonic germ cell development. 26757254_Data suggest that loss of function of doublesex and mab-3-related transcription factor a2 (DMRTA2) leads to disorder of cortical development. |
ENSMUSG00000047143 |
Dmrta2 |
269.994165 |
0.2871965773 |
-1.799890 |
0.104511416 |
308.791011 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000400494349138334111266815529871411767297452283327029314066267388316877684516095581150719543577582665047632040916160274770384641640714910226895743139128897817751636709586579229713798611101083224639296531677246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000118939569281324176127573325133592714534275528828070985938794367320810755567755608066363215382780656551459531831765883340328327453192584789124734135480750882445098758673912575645204015017952769994735717773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
124.2288287 |
8.5856687 |
435.4424287 |
18.3157261 |
| ENSG00000142765 |
84958 |
SYTL1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYJ3 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in vesicle trafficking (By similarity). Binds phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. Acts as a RAB27A effector protein and may play a role in cytotoxic granule exocytosis in lymphocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11278853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18266782}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Exocytosis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable neurexin family protein binding activity. Involved in exocytosis. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84958; |
exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of plasma membrane [GO:0019897]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; neurexin family protein binding [GO:0042043]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886] |
11773082_Jfc1/synaptotagmin-like protein 1 (Slp1) contains an N-terminal Slp homology domain (SHD) (PMID: 11327731). The SHD of Slp1/Jfc1 specifically and directly binds the GTP-bound form of Rab27A (J. Biol. Chem. 277, (2002) 9212-9218; PMID: 11773082). 12137562_transcriptional activation of JFC1 by the TNFalpha/NF-kappaB pathway is significant in prostate carcinoma cell lines 16004602_evidence that JFC1 differentially regulates the secretion of PSAP and PSA, and that Rab27a and PI3K play a central role in the exocytosis of prostate-specific markers 18266782_These results suggest that both Slp1 and Slp2-a may form part of a docking complex, capturing secretory lysosomes at the immunological synapse. 19528539_Slp1 inhibits dense granule secretion in platelets and that Rap1GAP2 modulates secretion by binding to Slp1. 22438581_during exocytosis, actin depolymerization commences near the secretory organelle, not the plasma membrane, and secretory granules use a JFC1- and GMIP-dependent molecular mechanism to traverse cortical actin. 23082202_Cdk2 also binds the N-terminal domain of Fbw7-gamma as well as SLP-1. 27018596_results reveal that MEIS1, through induction of SYTL1, promotes leukemogenesis and supports leukemic cell homing and engraftment, facilitating interactions between leukemic cells and bone marrow stroma. 36107384_ELK1 suppresses SYTL1 expression by recruiting HDAC2 in bladder cancer progression. |
ENSMUSG00000028860 |
Sytl1 |
27.397929 |
0.4234066766 |
-1.239884 |
0.285879845 |
19.378373 |
0.00001072143535424212742416128635314365169506345409899950027465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000033491721868489695158443292255512346855539362877607345581054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
15.5773512 |
2.9125162 |
37.1211422 |
4.3167428 |
| ENSG00000142875 |
5567 |
PRKACB |
protein_coding |
P22694 |
FUNCTION: Mediates cAMP-dependent signaling triggered by receptor binding to GPCRs. PKA activation regulates diverse cellular processes such as cell proliferation, the cell cycle, differentiation and regulation of microtubule dynamics, chromatin condensation and decondensation, nuclear envelope disassembly and reassembly, as well as regulation of intracellular transport mechanisms and ion flux. Regulates the abundance of compartmentalized pools of its regulatory subunits through phosphorylation of PJA2 which binds and ubiquitinates these subunits, leading to their subsequent proteolysis (PubMed:12420224, PubMed:21423175). Phosphorylates GPKOW which regulates its ability to bind RNA (PubMed:21880142). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12420224, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21423175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21880142}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;cAMP;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. The encoded protein is a catalytic subunit of cAMP (cyclic AMP)-dependent protein kinase, which mediates signalling though cAMP. cAMP signaling is important to a number of processes, including cell proliferaton and differentiation. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:5567; |
cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex [GO:0005952]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; AMP-activated protein kinase activity [GO:0004679]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0004691]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034380]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning [GO:1901621]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010737]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of protein processing [GO:0070613]; renal water homeostasis [GO:0003091]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12420224_c-MYC induces the activity of protein kinase A by inducing the transcription of the gene encoding the PKA catalytic subunit beta in multiple tissues, independent of cell proliferation by direct binding of c-MYC to promoter sequences. 12682012_Data describe the identification of a variant of the beta catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKACbeta) as a p75 neurotrophin receptor(NTR)-interacting protein, which phosphorylates p75(NTR) at Ser304. 14744463_there are abnormalities in [3H]cAMP binding and catalytic activity kinase A in brain of depressed suicide victims, which could be due to reduced expression of RIIbeta and Cbeta. 15723830_there is a PKA-Cbeta-mediated inhibitory mechanism of p73 function 16889664_Murine lymphoid tissues express a protein that is a homologue of human protein kinase c subunit beta2 16949795_In conclusion, it seems that the Cbeta isoforms of PKA play different roles in proliferation and differentiation and could therefore be potential markers for prostate cancer progression. 17549442_Data provide the first evidence that Protein kinase C -beta play pivotal role in the regulation of AA production and cellular proliferation of human monocytoid MonoMac-6 cells. 17594903_Nuclear PKA C subunit co-locates with HA95 in splicing factor compartments and regulates pre-mRNA splicing, possibly through a cAMP-independent mechanism. 18499756_Recruitment of coactivator glucocorticoid receptor interacting protein 1 to an estrogen receptor transcription complex is regulated by the 3',5'-cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. 19383776_In human primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease tissues, dexamethasone paradoxically stimulates cortisol release through a glucocorticoid receptor-mediated effect on PKA catalytic subunits. 19483721_Findings show that PKIB and PKA-C kinase can have critical functions of aggressive phenotype of PCs through Akt phosphorylation and that they should be a promising molecular target for PC treatment. 19573263_Report expression of protein kinase A and C subunits in post-mortem prefrontal cortex from persons with major depression and normal controls. 19711044_Results suggest that PKA can negatively regulate ERalpha, at least in part, through FoxH1. 19965870_Data show that Phosphorylation of The(197) in the activation loop on protein kinase A decreased the K(m) by approximately 15- and 7-fold for kemptide and ATP, respectively. 20033853_activated by podophyllotoxin 20086095_Data show that PI3K activation and PIP3 production lead to recruitment of the PKB/beta-arrestin/PDE4 complex to the membrane via the PKB PH domain, resulting in degradation of the TCR-induced cAMP pool and allowing full T-cell activation to proceed. 20093341_PGE(2)-induced CYP1B1 expression is mediated by ligand-independent activation of the ERalpha pathway as a result of the activation of ERK, Akt, and PKA in breast cancer cells. 20379146_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20564261_The previously unknown small molecule inhibitor-dependent interaction of Cbeta1 with the cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory protein-1 was verified. 24294386_The gene polymorphism loci rs12132032 in PRKACB maybe a potential risk factor for anencephaly in Chinese population from Shanxi, while gender susceptibility may influence the correlation. 25831493_analysis of the mechanism underlying synergistic up-regulation of PDE4B2 via a cross-talk between PKA-Cbeta and p65 27838142_Cbeta2 subunit of protein kinase A mRNA was up-regulated in prostate cancer and low expression of Cbeta2 mRNA in prostate cancer biopsies correlated with poor survival. 31678302_We identified fusions in PRKACA and PRKACB genes in pancreatic and biliary IOPNs, as well as in PDACs and pancreatic cyst fluid and bile duct cells from the same patients. These fusions might be used to identify patients at risk for IOPNs and their associated invasive carcinomas. 31998791_MicroRNA-384 Inhibits the Progression of Papillary Thyroid Cancer by Targeting PRKACB. 33055300_PRKACB variants in skeletal disease or adrenocortical hyperplasia: effects on protein kinase A. 33058759_Germline and Mosaic Variants in PRKACA and PRKACB Cause a Multiple Congenital Malformation Syndrome. 34244791_The conserved Tpk1 regulates non-homologous end joining double-strand break repair by phosphorylation of Nej1, a homolog of the human XLF. 34667254_Novel implications of a strictly monomorphic (GCC) repeat in the human PRKACB gene. 34787019_Expressing MLH1 in HCT116 cells increases cellular resistance to radiation by activating the PRKAC. |
ENSMUSG00000005034 |
Prkacb |
214.542924 |
0.3385707342 |
-1.562471 |
0.117051779 |
182.774578 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000001201274923373634901753444887696449595126289561335324199128749275437834703528913330891630170996666226491695478317822676217474509030580520629882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000209832164130116557764671914264568882521500519219703966083936650477821473506019021929169615698976236164898651059829148834978695958852767944335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
110.3161507 |
8.6886579 |
328.0307905 |
16.3853086 |
| ENSG00000142949 |
5792 |
PTPRF |
protein_coding |
P10586 |
FUNCTION: Possible cell adhesion receptor. It possesses an intrinsic protein tyrosine phosphatase activity (PTPase) and dephosphorylates EPHA2 regulating its activity.; FUNCTION: The first PTPase domain has enzymatic activity, while the second one seems to affect the substrate specificity of the first one. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Hydrolase;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The extracellular region contains three Ig-like domains, and nine non-Ig like domains similar to that of neural-cell adhesion molecule. This PTP was shown to function in the regulation of epithelial cell-cell contacts at adherents junctions, as well as in the control of beta-catenin signaling. An increased expression level of this protein was found in the insulin-responsive tissue of obese, insulin-resistant individuals, and may contribute to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode distinct proteins, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5792; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:0035373]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0005001]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; negative regulation of receptor binding [GO:1900121]; neuron projection regeneration [GO:0031102]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048679]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase signaling pathway [GO:0007185] |
12095414_regulation of expression by cell density through functional E-cadherin complexes 12376545_interactions between RPTP-domain1s and RPTP-domain 2s are a common but specific mechanism that is likely to be regulated- domain2s and the wedge structures are crucial determinants of binding specificity, thus regulating cross-talk between RPTPs 12496362_LAR PTPase domains play distinct functional roles in phosphorylation and dephosphorylation 15150650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15896785_LAR as a crucial regulator of the sensitivity of two key insulin signalling pathways to insulin 16478662_Results identify a protein tyrosine phosphatase as a potential substrate of TACE and describe proteolytic processing of PTP-LAR as a means of regulating phosphatase activity downstream and thus under the control of EGFR-mediated signaling pathways. 17259169_PS/gamma-secretase-mediated cleavage of LAR controls LAR-beta-catenin interaction, suggesting an essential role for PS/gamma-secretase in the regulation of LAR signaling 17419996_Regulated degradation of liprinalpha1 is important for proper LAR receptor distribution, and could provide a mechanism for localized control of dendrite and synapse morphogenesis by activity and CaMKII. 17803936_LAR and Src are identified as Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) regulators through their reciprocal modification of DAPK Y491/492 residues and establishes a functional link of this DAPK-regulatory circuit to tumor progression. 18925540_the PTPase activity in patients with insulin receptor gene mutation and severe insulin resistance may differ from that in ordinary type 2 diabetes 19910497_LAR functions as a negative regulator of adipogenesis. 20139422_Trans-synaptic adhesions between netrin-G ligand-3 (NGL-3) and receptor tyrosine phosphatases LAR, protein-tyrosine phosphatase delta (PTPdelta), and PTPsigma via specific domains regulate excitatory synapse formation. 23986473_Interaction between the tripartite NGL-1, netrin-G1 and LAR adhesion complex promotes development of excitatory synapses. 24470239_PTPRF is down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma-facilitated tumor development. 24781087_Homozygous truncating PTPRF mutation causes athelia. 26291013_PTPRF may have value as a predictive marker to identify which patients can obtain the greatest benefit from erlotinib in the post-first-line setting. 29570275_transferred nuclear Overhauser effects (trNOEs) have been employed in the docking program HADDOCK to generate models for the LAR-fondaparinux complex. These models are further analyzed by postprocessing energetic analysis to identify key binding interactions. 30217560_Data show that protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F (PTPRF) activity suppressed CD133/transmembrane 4L six family member 5 (TM4SF5)-mediated sphere growth. 31799666_PPARgamma inhibits breast cancer progression by upregulating PTPRF expression. 32355037_Crystal and solution structures of fragments of the human leucocyte common antigen-related protein. 32973331_Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F suppresses Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. 34969357_miR-647 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell progression by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F. 35735010_Cytoneme-like protrusion formation induced by LAR is promoted by receptor dimerization. |
ENSMUSG00000033295 |
Ptprf |
65.748080 |
0.2232359942 |
-2.163358 |
0.236166473 |
86.768456 |
0.00000000000000000001219999626826011536092829798247592678708264720078577344575081198296828688398818485438823699951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000110473585840195892757607005808276451598350681975789044746150135978268735925666987895965576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.9861525 |
6.8103715 |
92.8595317 |
20.9095796 |
| ENSG00000143013 |
8543 |
LMO4 |
protein_coding |
P61968 |
FUNCTION: Transcription cofactor. Plays a role in establishing motor neuron identity, in concert with MNX1, acting, at least in part, to disrupt LDB1-LHX3 complexes thereby negatively modulating interneuron genes in motor neurons. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P61969}. |
3D-structure;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a cysteine-rich protein that contains two LIM domains but lacks a DNA-binding homeodomain. The encoded protein may play a role as a transcriptional regulator or as an oncogene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:8543; |
cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cell activation [GO:0050865]; regulation of cell fate specification [GO:0042659]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; spinal cord association neuron differentiation [GO:0021527]; spinal cord motor neuron cell fate specification [GO:0021520]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; ventral spinal cord interneuron differentiation [GO:0021514]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281] |
11751867_These findings reveal a novel complex between BRCA1, LMO4, and CtIP and indicate a role for LMO4 as a repressor of BRCA1 activity in breast tissue. 12153047_1H, 15N and 13C assignments of FLIN4, an intramolecular LMO4:ldb1 complex 12877980_Lmo4 RNA overexpression interferes with neuritic outgrowth,anti-sense Lmo4 RNA expression favors neuritogenesis in SH-SY5Y cells. Changes in Lmo4 RNA expression levels might alter the rate of neuritic outgrowth in the developing and adult nervous system. 15677447_LMO4 interaction modulates the interleukin-6 receptor subunit glycoprotein 130 complex and its signaling 15894532_LMO4 is consistently more highly expressed in the embryonic right perisylvian cerebral cortex than in the left 15897450_LMO4 in breast epithelium contributes directly to breast neoplasia by altering the rate of cellular proliferation and promoting cell invasion. 17001033_Artificial intramolecular cyclic protein complex between two interacting proteins: the largely unstable LIM-only protein 4 (LMO4) and an unstructured domain of LIM domain binding protein 1 (ldb1). 18231110_In this study, patients whose tumours exhibited high LMO4 expression had a significant survival advantage following operative resection 18950845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020036_LMO4 protects neurons from ischemic brain injury, in part through its requirement as an essential cofactor of PPAR gamma 19099607_Results suggested that LMO4 is overexpressed at late stages in carcinogenesis of pancreatic cancer. 19111533_Lmo4 expression coincides with the timing of the development of the somatosensory barrel field. 19648968_LMO4 is a novel cell cycle regulator with a key role in mediating ErbB2-induced proliferation, a hallmark of ErbB2-positive disease. 19733838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20526802_data indicate that LMO4 has similar cellular effects in normal mammary epithelial cells and breast cancer cells, and also provide direct evidence for the idea that normal development and carcinogenesis share conserved molecular mechanisms 21271214_LMO4 is over-expressed in highly invasive rhabdomyosarcoma, alveolar cells 21362019_LMO4 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the anterior tongue 22906635_LMO4 is a direct target of p53 and inhibits p53-mediated proliferative inhibition of breast cancer cells through interacting p53 23291272_oncoprotein HBXIP is able to activate the transcriptional coregulatory protein LMO4 through transcription factor Sp1 in promotion of proliferation of breast cancer cells. 23353824_Data suggest that overexpression of LMO4 may disrupt some of the normal tumour suppressor activities of CtIP, thereby contributing to breast cancer progression. 23407556_Low LMO4 mRNA levels were associated with response to erlotinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. 23407937_the association of high levels of LMO4 with aggressive neuroblastomas is dependent on LMO4 regulation of cadherin expression and hence, tumor invasiveness 25057208_Existence of a region in the lateral portion of the mammalian cochlea that is competent to make an organ of Corti is demonstrated in the absence of LMO4 function. 25079073_Clim2, in a complex with LMO4, supports mammary stem cells by directly targeting the Fgfr2 promoter in basal cells to increase its expression 25310299_LMO4 appears to form a hub in protein-protein interaction networks, linking numerous pathways within cells. 26048572_Lmo4 participates in the regulation of lung epithelial cell proliferation but is not essential for tumor progression. 29258893_LMO4 appears to mediate IL-23-related responses in psoriatic keratinocytes and is a potential therapeutic target in psoriasis. 32323846_Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 promotes breast cancer progression by regulation of LMO4. 33906487_Research and Clinical Significance of the Differentially Expressed Genes TP63 and LMO4 in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Related Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 34725544_MicroRNA-139-5p Alleviates High Glucose-Triggered Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell Injury by Targeting LIM-Only Factor 4. 34925640_CircLDLR Promotes Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Tumorigenicity by Regulating miR-637/LMO4 Axis. |
ENSMUSG00000028266 |
Lmo4 |
703.510485 |
2.6589044045 |
1.410832 |
0.197713594 |
48.087106 |
0.00000000000407698716642153399296136757987326899952545966598904669808689504861831665039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000023279044710399166450385148434736525772242865528482980153057724237442016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1012.4588754 |
123.8404304 |
384.3406431 |
34.3999677 |
| ENSG00000143061 |
3321 |
IGSF3 |
protein_coding |
O75054 |
|
Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an immunoglobulin-like membrane protein containing several V-type Ig-like domains. A mutation in this gene has been associated with bilateral nasolacrimal duct obstruction (LCDD). [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:3321; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; membrane [GO:0016020]; lacrimal gland development [GO:0032808] |
24372406_Based on IGSF3 mutation in a family with congenital nasolacrimal duct obstruction we conclude that the disruption of IGSF3 is the very likely cause of autosomal recessive nasolacrimal duct obstruction. 31560140_the IGSF23 mutation led to decreased c-Fos and NFATC1 expression levels by inhibiting the mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways 32573489_IGSF3 mutation identified in patient with severe COPD alters cell function and motility. |
ENSMUSG00000042035 |
Igsf3 |
25.392350 |
2.7068710000 |
1.436626 |
0.353053116 |
16.637090 |
0.00004525729032259002851488333130092200917715672403573989868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000131211472237562125570456417200659871014067903161048889160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9994316 |
8.4779471 |
14.0946834 |
2.4905976 |
| ENSG00000143067 |
90874 |
ZNF697 |
protein_coding |
Q5TEC3 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90874; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000050064 |
Zfp697 |
339.784397 |
3.5883299398 |
1.843313 |
0.355763193 |
24.376800 |
0.00000079216972132573739824671623863117098096608970081433653831481933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002831781323993190862512055183675130365372751839458942413330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
588.9277306 |
131.0594031 |
166.1750748 |
27.2391793 |
| ENSG00000143106 |
5686 |
PSMA5 |
protein_coding |
P28066 |
FUNCTION: Component of the 20S core proteasome complex involved in the proteolytic degradation of most intracellular proteins. This complex plays numerous essential roles within the cell by associating with different regulatory particles. Associated with two 19S regulatory particles, forms the 26S proteasome and thus participates in the ATP-dependent degradation of ubiquitinated proteins. The 26S proteasome plays a key role in the maintenance of protein homeostasis by removing misfolded or damaged proteins that could impair cellular functions, and by removing proteins whose functions are no longer required. Associated with the PA200 or PA28, the 20S proteasome mediates ubiquitin-independent protein degradation. This type of proteolysis is required in several pathways including spermatogenesis (20S-PA200 complex) or generation of a subset of MHC class I-presented antigenic peptides (20S-PA28 complex). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15244466, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27176742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8610016}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proteasome;Reference proteome |
|
The proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex with a highly ordered ring-shaped 20S core structure. The core structure is composed of 4 rings of 28 non-identical subunits; 2 rings are composed of 7 alpha subunits and 2 rings are composed of 7 beta subunits. Proteasomes are distributed throughout eukaryotic cells at a high concentration and cleave peptides in an ATP/ubiquitin-dependent process in a non-lysosomal pathway. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. This gene encodes a member of the peptidase T1A family, that is a 20S core alpha subunit. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:5686; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; proteasome complex [GO:0000502]; proteasome core complex [GO:0005839]; proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex [GO:0019773]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0010498]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161] |
11771738_Selective upregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway proteins, proteasome zeta chain and isopeptidase T in fetal Down syndrome. 30738879_increased ubiquitin B mRNA expression followed by significant downregulation of proteasome subunits; 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 1, and proteasome subunit alpha-type 5 was found in pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PEXS) individuals. Decrease in chymotrypsin-like proteasome activity and increased apoptosis were also observed in PEX subjects. 30807553_PSMA5 promotes the tumorigenic process of prostate cancer and is related to bortezomib resistance. 34831298_Conserved Mitotic Phosphorylation of a Proteasome Subunit Regulates Cell Proliferation. 35605971_PSMA5 contributes to progression of lung adenocarcinoma in association with the JAK/STAT pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000068749 |
Psma5 |
663.578754 |
2.7203492064 |
1.443792 |
0.194347232 |
53.261743 |
0.00000000000029193711454262605726945734528178129498854689871656375999009469524025917053222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001801417981040618956313119793045949467097735507969957780005643144249916076660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1007.7508064 |
169.5691015 |
372.0945481 |
45.4810566 |
| ENSG00000143110 |
128346 |
C1orf162 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEQ5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:128346; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000074342 |
I830077J02Rik |
41.189569 |
2.1921326064 |
1.132335 |
0.279057398 |
16.541585 |
0.00004759473722409885776754578934344408480683341622352600097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000137529037084514337181684329181052817148156464099884033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.9616536 |
8.6609142 |
26.1824917 |
3.0933326 |
| ENSG00000143126 |
1952 |
CELSR2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCU4 |
FUNCTION: Receptor that may have an important role in cell/cell signaling during nervous system formation. |
Calcium;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Laminin EGF-like domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. The flamingo subfamily consists of nonclassic-type cadherins; a subpopulation that does not interact with catenins. The flamingo cadherins are located at the plasma membrane and have nine cadherin domains, seven epidermal growth factor-like repeats and two laminin A G-type repeats in their ectodomain. They also have seven transmembrane domains, a characteristic unique to this subfamily. It is postulated that these proteins are receptors involved in contact-mediated communication, with cadherin domains acting as homophilic binding regions and the EGF-like domains involved in cell adhesion and receptor-ligand interactions. The specific function of this particular member has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1952; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cerebrospinal fluid secretion [GO:0033326]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; motor neuron migration [GO:0097475]; neural plate anterior/posterior regionalization [GO:0021999]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022407]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055]; Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:0060071] |
18179892_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193044_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18649068_The novel CAD-associated locus in the vicinity of the PSRC1 and CELSR2 genes on chromosome 1 probably enhances CAD risk through an effect on plasma LDL cholesterol. 19198609_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19299407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19487539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031591_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20370913_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20442857_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20570916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20679960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20691829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20864672_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20971364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24674750_CELSR2 in the cholesterol gene cluster shows a significant association with coronary artery disease and its single nucleotide polymorphism regulates plasma cholesterol levels. 26464717_no association was found between the SNPs of rs599839, rs464218 and rs6698843 at the CELSR2-PSRC1-SORT1 and the risk of coronary artery disease or ischemic stroke 28052552_we report bi-allelic mutations in CELSR2 in a Joubert patient with cortical heterotopia, microophthalmia, and growth hormone deficiency. 29240829_findings suggest a rare variant in CELSR2 as causative for idiopathic scoliosis in a family with dominant segregation and further highlight common variation in CELSR2 in general susceptibility to idiopathic scoliosis in the Swedish-Danish population 29489009_Both CELSR2 and ING4 display increased cytoplasmic staining in breast cancer cells compared to benign epithelium, suggesting a possible role of both genes in the pathogenesis of human mammary neoplasia. 32293343_Identification of CELSR2 as a novel prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. 33810964_rs629301 CELSR2 polymorphism confers a ten-year equivalent risk of critical stenosis assessed by coronary angiography. 34478580_CELSR2 deficiency suppresses lipid accumulation in hepatocyte by impairing the UPR and elevating ROS level. 34983065_Inactivating Celsr2 promotes motor axon fasciculation and regeneration in mouse and human. |
ENSMUSG00000068740 |
Celsr2 |
56.914037 |
0.4928786485 |
-1.020696 |
0.239299471 |
18.160565 |
0.00002030398477446622551687190061375787308861617930233478546142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000061499449060357369036509955773084357133484445512294769287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.4070963 |
7.7329054 |
78.4769052 |
11.1374052 |
| ENSG00000143224 |
5498 |
PPOX |
protein_coding |
P50336 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the 6-electron oxidation of protoporphyrinogen-IX to form protoporphyrin-IX. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21048046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23467411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7713909}. |
3D-structure;Disease variant;FAD;Flavoprotein;Heme biosynthesis;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Oxidoreductase;Porphyrin biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Porphyrin-containing compound metabolism; protoporphyrin-IX biosynthesis; protoporphyrin-IX from protoporphyrinogen-IX: step 1/1. |
This gene encodes the penultimate enzyme of heme biosynthesis, which catalyzes the 6-electron oxidation of protoporphyrinogen IX to form protoporphyrin IX. Mutations in this gene cause variegate porphyria, an autosomal dominant disorder of heme metabolism resulting from a deficiency in protoporphyrinogen oxidase, an enzyme located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5498; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxygen-dependent protoporphyrinogen oxidase activity [GO:0004729]; heme biosynthetic process [GO:0006783]; porphyrin-containing compound biosynthetic process [GO:0006779]; protoporphyrinogen IX biosynthetic process [GO:0006782] |
12017191_Two previously undescribed mutations were identified: PPOX1423-1426-delATCT and PPOX2272insG. 12556518_This enzyme in its regular and mutagenized forms is targeted to mitochondria when transfected. 14535846_Information required for targeting to the mitochondria is contained within the first 250 amino acid residues of human PPOX. 14669009_Modulation of penetrance by the wild-type allele in dominantly inherited erythrohepatic and acute hepatic porphyrias was studied using PPOX. 16621625_Protoporphyrinogen oxidase targeting mechanism to the mitochondrion. 16947091_Mutation in protoporphyrinogen oxidase is associated with variegate porphyria 18191920_GATA-1 binding sites in exon 1 constitute key regulatory elements in differential expression of PPOX in erythroid and non-erythroid cells. 19229653_sequenced 27 members of a family with variegate porphyria with a T>A transversion at the intron 6 consensus splicing site in 8 patients and 4 SNPs: c.-414A>C; IVS2+121G>C; c.1188G>A and IVS12+34C>T 19656455_The c.851G>T and the c.1013C>G of PPOX gene were found in two and four unrelated families respectively. 1 experienced only photosensitivity, 1 only neurological symptoms and the 2 both clinical manifestations. 19656457_The mutation 1082-1083insC(1 base pair insertion at position 1082) in exon 10 of the PPOX gene was prevalent in the Swiss population. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048046_Forty-seven variegate porphyria-causing mutations were purified by chromatography and kinetically characterized in vitro. 21910705_data deliver further confirmation that the South African and Dutch variegate porphyria families carrying mutation p.R59W shared a common ancestor. 23324528_findings emphasize the usefulness of MLPA analysis as a complement to PPOX gene sequencing analysis for comprehensive genetic diagnostics in patients with variegate prophyria 23467411_VP-causing mutation affect the catalytic activity of hPPO by affecting the ability of hPPO to sample the privileged conformations 23601071_Variegate porphyria is the result of decreased protoporphyrinogen oxidase activity. Diet supplementation with vitamins E and C restores PPOX gene expression in lymphocytes of variegate porphyria patients. 25445397_in the hepatic cancer tissue of two acute porphyria patients, somatic second-hit mutations result in nearly complete inactivation of PPOX and HMBS 25944804_GAPDH and protoporphyrinogen oxidase were shown to have higher expression in faster growing cell lines and primary tumors. Pharmacologic inhibition of GAPDH or PPOX reduced the growth of colon cancer cells in vitro 27667166_the regulation of PPOX gene expression can also occur through a post-transcriptional modulation of the amount of gene product and this modulation can be mediated by 5' untranslated exon 1. 29550908_The genetic test showed a heterozygous mutation in the gene encoding Protoporphyrinogen Oxidase (PPOX); c.2T > A (p.Met1Lys) on chromosome 1q23, which supports the diagnosis of Variegate Porphyria 30385147_Mount Sinai Porphyrias Diagnostic Laboratory diagnosed 54 unrelated Variegate Porphyria individuals with 20 PPOX novel mutations. 32247286_Two new mutations in the PPOX gene in a patient with variegate porphyria. 33857841_The hydrogen bonding network involved Arg59 in human protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase is essential for enzyme activity. 34968794_Molecular characterization of a novel His333Arg variant of human protoporphyrinogen oxidase IX. |
ENSMUSG00000062729 |
Ppox |
161.789443 |
0.2477535269 |
-2.013022 |
0.190298710 |
108.891244 |
0.00000000000000000000000017143904897700418994087850251132993158319452211094136647596356506819802872909619395613844972103834152221679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000001868862897267785615921381609573613248872253693339875944289390781016119147395215804863255470991134643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
67.1101242 |
8.8619737 |
271.0948039 |
23.8424729 |
| ENSG00000143256 |
5202 |
PFDN2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHV9 |
FUNCTION: Binds specifically to cytosolic chaperonin (c-CPN) and transfers target proteins to it. Binds to nascent polypeptide chain and promotes folding in an environment in which there are many competing pathways for nonnative proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9630229}. |
3D-structure;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the prefoldin beta subunit family. The encoded protein is one of six subunits of prefoldin, a molecular chaperone complex that binds and stabilizes newly synthesized polypeptides, thereby allowing them to fold correctly. The complex, consisting of two alpha and four beta subunits, forms a double beta barrel assembly with six protruding coiled-coils. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5202; |
chaperone complex [GO:0101031]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; prefoldin complex [GO:0016272]; RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex [GO:1990062]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation [GO:1905907]; positive regulation of cytoskeleton organization [GO:0051495]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821] |
19450687_Is part of an RNA polymerase II-associated complex with possible chaperone activity. 23720755_knockdown of PFD2 and PFD5 disrupted prefoldin formation in HTT-expressing cells, resulting in accumulation of aggregates of a pathogenic form of HTT and in induction of cell death. 23914742_prefoldin is amplified at 1q23.3-q24.1 in bladder cancer |
ENSMUSG00000006412 |
Pfdn2 |
311.694464 |
2.1043566778 |
1.073379 |
0.093198523 |
133.701278 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000063506633028653254533116970118028854963813731965016542390043780532901236273781722056069876103379101550672203302383422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000008406797340833380972238525501174826800001619564570813315929238810054607861375940494608194342163187684491276741027832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
429.0875506 |
23.5384132 |
205.5067256 |
8.8947479 |
| ENSG00000143322 |
27 |
ABL2 |
protein_coding |
P42684 |
FUNCTION: Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that plays an ABL1-overlapping role in key processes linked to cell growth and survival such as cytoskeleton remodeling in response to extracellular stimuli, cell motility and adhesion and receptor endocytosis. Coordinates actin remodeling through tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins controlling cytoskeleton dynamics like MYH10 (involved in movement); CTTN (involved in signaling); or TUBA1 and TUBB (microtubule subunits). Binds directly F-actin and regulates actin cytoskeletal structure through its F-actin-bundling activity. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion and motility through phosphorylation of key regulators of these processes such as CRK, CRKL, DOK1 or ARHGAP35. Adhesion-dependent phosphorylation of ARHGAP35 promotes its association with RASA1, resulting in recruitment of ARHGAP35 to the cell periphery where it inhibits RHO. Phosphorylates multiple receptor tyrosine kinases like PDGFRB and other substrates which are involved in endocytosis regulation such as RIN1. In brain, may regulate neurotransmission by phosphorylating proteins at the synapse. ABL2 acts also as a regulator of multiple pathological signaling cascades during infection. Pathogens can highjack ABL2 kinase signaling to reorganize the host actin cytoskeleton for multiple purposes, like facilitating intracellular movement and host cell exit. Finally, functions as its own regulator through autocatalytic activity as well as through phosphorylation of its inhibitor, ABI1. Positively regulates chemokine-mediated T-cell migration, polarization, and homing to lymph nodes and immune-challenged tissues, potentially via activation of NEDD9/HEF1 and RAP1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4JIM5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15735735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15886098, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16678104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17306540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18945674}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Abelson family of nonreceptor tyrosine protein kinases. The protein is highly similar to the c-abl oncogene 1 protein, including the tyrosine kinase, SH2 and SH3 domains, and it plays a role in cytoskeletal rearrangements through its C-terminal F-actin- and microtubule-binding sequences. This gene is expressed in both normal and tumor cells, and is involved in translocation with the ets variant 6 gene in leukemia. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:27; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin monomer binding [GO:0003785]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; exploration behavior [GO:0035640]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of establishment of T cell polarity [GO:1903905]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of oxidoreductase activity [GO:0051353]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell motility [GO:2000145]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12220663_The highest Arg transcript and protein levels are in the mature B cells. 12374288_Review. ABL protein tyrosine kinases regulate cell proliferation, survival, adhesion, migration, stress responses, and cytoskeletal dynamics. 12777400_c-Abl and Arg regulate catalase and that this signaling pathway is of importance to apoptosis in the oxidative stress response 12950161_findings indicate that, in addition to stimulating catalase activity, c-Abl and Arg promote catalase degradation in the oxidative stress response 15679048_High Arg expression is correlated with thymoma stage 15729383_several critical domains within TEL/ARG necessary for function 16678104_The present study demonstrates that c-Abl and Arg (abl-related gene) tyrosine kinases associate with and phosphorylate the proteasome PSMA7 (alpha4) subunit at Tyr-153. 18660502_ABL2/ARG is a novel mediator of SEMA3F-induced RhoA inactivation and collapsing activity. 19275932_Abl kinases not only are activated by PDGFR and promote PDGFR-mediated proliferation and migration, but also act in an intricate negative feedback loop to turn-off PDGFR-mediated chemotaxis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20077570_Results describe the NMR structure of human Arg F-actin-binding domain. 20150913_The Arg tyrosine kinase regulated lysosomal degradation of antiapoptotic Gal3 may provide one of the important arms in Arg tyrosine kinase dependent antiapoptotic pathways. 20448119_A 35-bp insertion in the BCR-ABL2 gene is associated with resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors, but sensitivity to omacetaxine in chronic myelogenous leukemia. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21257711_Our findings suggest a novel mechanism by which an EGFR-Src-Arg-cortactin pathway mediates functional maturation of invadopodia and breast cancer cell invasion 21543883_Knockout mutation of p27-p55 operon in Mycobacterium bovis severely decreased the virulence of the bacteria when assessed in a progressive model of pulmonary tuberculosis in Balb/c mice. 21892207_c-Abl and Arg not only promote in vitro processes important for melanoma progression, but also promote metastasis in vivo 22777352_Arg acts as a switch in metastatic cancer cells that governs the decision to 'grow or go' (divide or invade). 23552693_Beta1 integrin regulates Arg to promote invadopodial maturation and matrix degradation. 23648710_data provide evidence that Aurora A, AMPK, ABL and CDKs are functionally integrated into human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) replication; inhibition of AMPK and ABL kinases exerted a negative effect, inhibition of Aurora A kinase a slightly positive effect on HCMV replication 24096484_Data shows that c-Abl and Arg induce NM23-H1 degradation by increasing expression and activation of cathepsin L and B, which directly cleave NM23-H1 in the lysosome. 24464651_Knockdown of ABL2 promoted cell invasion and migration and we identified miR-20a-induced cell invasion and migration can be rescued by ABL2. 25373509_the ETV6/ARG oncoprotein contributes to autonomous cell growth by compensating for the requirement of growth factor through activating STAT5 signaling, which leads to the up-regulation of c-Myc. 25694433_Two distinct interfaces mediate direct binding of integrin beta1 with Arg in vitro and in cells and promote Arg kinase activation. 27913209_Q112H mutation hinders the ability of the protein to interact with Abl kinase, leading to defective tyrosine phosphorylation and a resultant defect in respiration 28555614_c-Abl/Arg are oncogenic kinases that regulate differential gene expression 29767389_High expression of ABL2 suppresses apoptosis in gastric cancer cell lines 32035133_Arg kinase mediates CXCL12/CXCR4-induced invadopodia formation and invasion of glioma cells. 32188731_Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Abl2 Kinase Regulate Distinct Steps of Human Papillomavirus 16 Endocytosis. 32196963_miR-143 inhibits renal cell carcinoma cells metastatic potential by suppressing ABL2. 33122628_Combating acquired resistance to MAPK inhibitors in melanoma by targeting Abl1/2-mediated reactivation of MEK/ERK/MYC signaling. 33318173_The ABL2 kinase regulates an HSF1-dependent transcriptional program required for lung adenocarcinoma brain metastasis. 33550941_microRNA-1296 Inhibits Glioma Cell Growth by Targeting ABL2. 33722655_Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-19b-1-5p reduces proliferation and raises apoptosis of bladder cancer cells via targeting ABL2. 33770321_Depletion of Arg/Abl2 improves endothelial cell adhesion and prevents vascular leak during inflammation. 34144039_Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta activates Abl2 via direct binding and phosphorylation. 34787058_CircSLC7A6 promotes the progression of Wilms' tumor via microRNA-107/ ABL proto-oncogene 2 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000026596 |
Abl2 |
332.660983 |
3.3491999483 |
1.743817 |
0.120361693 |
207.685984 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004392699971773620452934637804504824053085869657299358080992501070268227117507070799779457641362072780789937527563628386594041241863806135370396077632904052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000871454994400250586685257461201259533141623198327669396803365417676614103350989643194937363061533691412478095793432697480085380448144860565662384033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
527.1862877 |
39.0428020 |
158.6420993 |
9.2128542 |
| ENSG00000143333 |
6004 |
RGS16 |
protein_coding |
O15492 |
FUNCTION: Regulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form (PubMed:11602604, PubMed:18434541). Plays an important role in the phototransduction cascade by regulating the lifetime and effective concentration of activated transducin alpha. May regulate extra and intracellular mitogenic signals (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11602604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18434541}. |
3D-structure;GTPase activation;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal transduction inhibitor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the 'regulator of G protein signaling' family. It inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits. It also may play a role in regulating the kinetics of signaling in the phototransduction cascade. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6004; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12588871_Src mediates RGS16 tyrosine phosphorylation, which may promote RGS16 stability. 12642592_results suggest that palmitoylation of a Cys residue in the regulator of G protein signaling(RGS) box is critical for RGS16 and RGS4 GAPase activating protein activity and their ability to regulate G protein signaling in mammalian cells 12642593_results suggest that the amino-terminal palmitoylation of regulator of G-protein signaling 16 protein(RGS16) promotes its lipid raft targeting that allows palmitoylation of a poorly accessible cysteine residue 14634662_RGS16 inhibits G alpha 13-mediated, RhoA-dependent reversal of stellation and Serum Response Element activation, thus regulating G alpha 13-mediated signal transduction independently of the RGS box. 15998835_RGS16 is a negative regulator of SDF-1-CXCR4 signaling in megakaryocytes 17347170_G alpha(i2) is specifically localized in human Fallopian tube epithelial cells, particularly in cilia, & is likely to have cilia-specific role in reproduction. 17613536_B4GALT3, DAP3, RGS16, TMEM183A and UCK2--were significantly overexpressed in dup(1q)-positive ALLs compared with high hyperdiploid ALLs without dup(1q). 17635928_Regulator of G Signaling 16 has a role in the distinct endoplasmic reticulum stress state associated with aggregated mutant alpha1-antitrypsin Z in the classical form of alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency 18262772_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18521847_The promoter region of RGS16 was found to be methylated in 10% human breast carcinomas 19509421_the loss of RGS16 in some breast tumors enhances PI3K signaling elicited by growth factors and thereby promotes proliferation and TKI evasion downstream of HER activation 19760045_Increased RGS16 levels are associated with colorectal cancer. 20571966_RGS16 and FosB are underexpressed in pancreatic cancer with lymph node metastasis and associated with reduced survival 20627871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21135262_Missense mutations in RGS16 gene is associated with breast cancer. 23248035_Data indicate that multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) probes (Fig. 2) corresponding to the RGSL2, RGSL1 and RGS16 genes showed 64.5 % tumour samples with copy number gains and 5 % tumour samples with copy number losses. 23354309_cotreatment with RGS16 siRNA reversed the downregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB expression induced by combined inhibition of LSD1 and HDACs, suggesting a crucial role of RGS16 in controlling key pathways of cell death in response to combination therapy. 25366993_these results indicate that RGS16 restricts the activation-induced pro-inflammatory profile in myeloid cells. 26013170_The data establish miR-181a as an oncomiR that promotes chondrosarcoma progression through a new mechanism involving enhancement of CXCR4 signaling by inhibition of RGS16. 26823172_suggest that deltaEF1 family proteins promote cell motility of breast cancer cells directly or indirectly through repressing expression of RGS16 28502923_Data suggest that RGS16 functions as a GAP (GTPase accelerating protein) in the SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus) and is required for circadian timing. [REVIEW] 30117167_Data show that bothregulator of G protein signaling (RGS16 and RGS18) inhibit protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2)/G-protein, Gi-Go subunits (Galphai/o) -mediated signaling. 32319728_RGS16 promotes glioma progression and serves as a prognostic factor. 35830366_Critical roles of RGS16 in the mucosal inflammation of ulcerative colitis. |
ENSMUSG00000026475 |
Rgs16 |
1841.387702 |
14.2503801341 |
3.832928 |
0.055656750 |
6312.290994 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3473.4985032 |
118.6923802 |
245.5095434 |
7.9751548 |
| ENSG00000143341 |
83872 |
HMCN1 |
protein_coding |
Q96RW7 |
FUNCTION: Involved in transforming growth factor beta-mediated rearrangement of the podocyte cytoskeleton which includes reduction of F-actin fibers and broadening, flattening and elongation of podocytes (PubMed:29488390). Plays a role in basement membrane organization (By similarity). May promote cleavage furrow maturation during cytokinesis in preimplantation embryos (By similarity). May play a role in the architecture of adhesive and flexible epithelial cell junctions (By similarity). May play a role during myocardial remodeling by imparting an effect on cardiac fibroblast migration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3YXG0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29488390}. |
Age-related macular degeneration;Alternative splicing;Basement membrane;Calcium;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Sensory transduction;Signal;Vision |
|
This gene encodes a large extracellular member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. A similar protein in C. elegans forms long, fine tracks at specific extracellular sites that are involved in many processes such as stabilization of the germline syncytium, anchorage of mechanosensory neurons to the epidermis, and organization of hemidesmosomes in the epidermis. Mutations in this gene may be associated with age-related macular degeneration. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:83872; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; basement membrane [GO:0005604]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; muscle tendon junction [GO:0005927]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; actin filament reorganization [GO:0090527]; basement membrane organization [GO:0071711]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
14570714_We mapped the ARMD1 gene. Identification of the genes involved in AMD will lead to a better understanding of this disease at the molecular level. 15370542_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15467524_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16885922_None of our subjects (258 macular degeneration,AMD, cases, 72 non-AMD controls) had the Gln5345Arg variant in the HMCN1 gene. 16885922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17057786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17057786_We were not able to demonstrate an association between the Hemicentin-1, hOgg1, and E-selectin SNPs and age-related macular degeneration development in the currently available cases and controls. 17157600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17157600_The CFH gene and Hemicentin-1 genes do not appear to be involved in a statistically significant fraction of dry AMD (age-related macular degeneration) cases in the Japanese population. 17216616_Data shows that low-frequency variants encoding possible functional amino acid polymorphisms in the HMCN1 gene may not contribute substantially to disease, but HMCN1 mutations may still confer disease susceptibility in a small subset of patients. 17216616_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17591627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17591627_hemicentin-1 gene appears to play a role in both age-related macular degeneration and renal pathophysiology 19190085_down-regulated in salivary gland epithelial cell from Sjogren's syndrome patients following in vitro treatment with anti-Ro/SSA auto-antibodies; associated with increase in anoikis cell death 19229767_Dysregulation of fibulin expression by anti-Ro/SSA antibodies may contribute to disorganization of the extracellular environment and thus cause injury to the salivary gland architecture and functionality observed in Sjogren syndrome 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20299368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22981695_Constructs show that EGF repeats 4 and 5 are required for hemicentin-dependent assembly and function of transgenic fibulin-1D in native locations. 24604465_this is the first association study based on a candidate gene approach to confirm that a HMCN1 polymorphism (rs2891230) is associated with postpartum depression diagnosis. heterozygosity (GA) for this SNP was associated with an increased risk of PPD. 24912920_HMCN1 mutation is associated with gastric and colorectal cancers. 24951538_Fibulin-6, a fibroblast-released extracellular matrix protein, may play an important role during myocardial remodelling by imparting an effect on cardiac fibroblasts migration in close and complementary interplay with TGF-beta1 signalling 25338956_The identified variants of HMCN1 are on conserved domains, particularly the two variants on calcium-binding epidermal growth factor domain. 25986072_A null-variant in HMCN1 (c.4162delC), has been identified in a Tunisian Jewish family with early-onset age-related macular degeneration. 29488390_Identify HMCN1 as a new molecule involved in the dynamic changes of podocyte foot processes in glomerular disease. 29500156_In the group that combined individuals affected by isolated cleft lip and palate, tooth agenesis, supernumerary teeth, molar incisor hypomineralization, or dental caries, we found an association with rs622260 but not with the rs10798049 marker. We determined that allele C of rs622260 was overrepresented in all individuals studied compared with a group of unrelated individuals who did not present any of these conditions. 31638245_the findings of the present study suggest that targeting the Cancerassociated fibroblasts genes, SRPX and HMCN1, can inhibit ovarian cancer migration and invasion. 35886066_Comprehensive Analysis of HMCN1 Somatic Mutation in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000066842 |
Hmcn1 |
115.172282 |
0.1987821047 |
-2.330740 |
0.172363842 |
194.117708 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000004013964965537369844956943598113691939537396809848330177177928640791487508216548871857456401395245666547069234800920733974294307699892669916152954101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000738729711861989828136665231661149320869622212965606808398059794632205900839353530231153597544607256592568886831295937867025713785551488399505615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.3996695 |
5.0828881 |
204.6622891 |
15.7984367 |
| ENSG00000143344 |
23179 |
RGL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZL6 |
FUNCTION: Probable guanine nucleotide exchange factor. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23179; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 35257782_Structures of RGL1 RAS-Association Domain in Complex with KRAS and the Oncogenic G12V Mutant. |
ENSMUSG00000026482 |
Rgl1 |
142.964489 |
5.2291046820 |
2.386564 |
0.155027013 |
255.138383 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000196911169382900410124250531749588450816790508745425165934892190167189208961405221628072144905069644750109296783344417405481588223307356671126821037742793407687713624909520149230957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000048199151908650252852389355863099542115476828388209365858841013052931866112748496577142380492883785805457678377904526977332365375568494085577533891928680986893596127629280090332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
243.7062008 |
23.7156230 |
46.8818114 |
3.9236933 |
| ENSG00000143368_ENSG00000014914 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
67.935765 |
0.3336452899 |
-1.583613 |
0.312221353 |
24.722322 |
0.00000066212840506216512267832112817456113873504364164546132087707519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002392414996014089901280518998816226883263880154117941856384277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.8715560 |
19.8515550 |
106.4668003 |
41.4819253 |
| ENSG00000143369 |
1893 |
ECM1 |
protein_coding |
Q16610 |
FUNCTION: Involved in endochondral bone formation as negative regulator of bone mineralization. Stimulates the proliferation of endothelial cells and promotes angiogenesis. Inhibits MMP9 proteolytic activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11165938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11292659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16512877}. |
Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Biomineralization;Disease variant;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Mineral balance;Osteogenesis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a soluble protein that is involved in endochondral bone formation, angiogenesis, and tumor biology. It also interacts with a variety of extracellular and structural proteins, contributing to the maintenance of skin integrity and homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with lipoid proteinosis disorder (also known as hyalinosis cutis et mucosae or Urbach-Wiethe disease) that is characterized by generalized thickening of skin, mucosae and certain viscera. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:1893; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; interleukin-2 receptor binding [GO:0005134]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; biomineral tissue development [GO:0031214]; chondrocyte development [GO:0002063]; endochondral bone growth [GO:0003416]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030502]; negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001960]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; ossification [GO:0001503]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000404]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of type 2 immune response [GO:0002828]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12603844_Extracellular matrix protein 1 gene (ECM1) mutations in lipoid proteinosis and genotype-phenotype correlation. Seven new homozygous nonsense or frameshift mutations. Exons 6 and 7 most common sites for ECM1 mutations. 14550953_These results indicate that ECM1 tends to be preferentially expressed by metastatic epithelial tumors. 16274456_Frther emphasizes the role of ECM-1 in lipoid proteinosis and highlights unresolved genotype-phenotype correlation in this disease. 16512877_it is reported here that ECM1 interacts with MMP9 and that such interactions diminish the proteolytic activity of MMP9 16646403_ECM1 played an important role in the growth, metastasis and angiogenesis of laryngeal carcinoma. 17721643_We report here mutation analysis of the ECM1 gene in a Chinese family with lipoid proteinosis. 17927570_This article provides an update on the molecular pathology of lipoid proteinosis, including the addition of 15 new mutations in ECM1 to the mutation database [review] 18200062_ECM1 is a basement membrane protein of the skin 18438406_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in ECM1 gene is associated with ulcerative colitis 18443958_A survey of ECM1 expression in different tumors indicated that ECM1, although not tumor specific, is significantly elevated in many malignant epithelial tumors that give rise to metastases, emphasizing its relevance in the cancer process. Review. 19068216_ECM1 variation was not associated with Crohn's disease. 19219685_ECM proteins such as EDBFN and collagen are upregulated in ERM and PDR, and are regulated by TGF-beta. 19230975_Functional and structural characterisation of human colostrum free secretory component. 19275936_ECM1 is a multifunctional binding core and/or a scaffolding protein interacting with a variety of extracellular and structural proteins, contributing to the maintenance of skin integrity and homeostasis. 19519837_A novel homozygous 62-bp insertion in exon 8 of ECM1 in this Pakistani family is a rare mutation affecting both alleles and it may help in further understanding the multifunctional role of ECM1 19521735_Overexpression of ECM1 is associated with invasive breast carcinomas. 19734986_Identify novel mutations in the human ECM-1 gene in lipoid proteinosis and report lack of genotype-phenotype correlation. (Case report) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014019_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20805453_The ECM/SULF1 and ECM/COLLAGEN metagenes showed inconsistent association with DMFS in the three prognostic data sets in both breast neoplasm subtypes, and the combined P values were not significant. 20870722_PLSCR1 interacts with the tandem repeat region of ECM1a in the dermal epidermal junction zone of human skin. 21128013_The expression of ECM1 was found to be an independent factor for predicting overall and disease-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. 21349189_neurologic and neuroradiologic characteristics and ECM1 gene mutations of seven individuals with lipoid proteinosis (LP) from three unrelated consanguineous families 21791056_Case Report: a novel mutation in Pakistani family extends the body of evidence that supports the importance of ECM1 gene for the development of lipoid proteinosis. 22489696_Overexpression of ECM1 contributes to migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma. 23534907_Lipoid proteinosis (LP) is a rare autosomal recessive genodermatosis caused by mutations in extracellular matrix protein 1 (ECM1) that involves deposition of basement membrane-like material in the skin and other organs. 23682690_splicing mutation in Chinese lipoid proteinosis family 23696932_Suggest that ECM1 plays promotive roles in the occurrence, development and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma. 24023917_role for TFAP2C in melanoma via its regulation of ECM1 24079542_Genetic testing of theECM1 gene showed a homozygous nonsense mutation c.1441C > T (p.Arg481X) in exon 10, confirming the diagnosis of lipoid proteinosis. 24259048_Clinical assays for ECM1 and TEX101 have the potential to replace most of the diagnostic testicular biopsies and facilitate the prediction of outcome of sperm retrieval procedures, increasing the reliability and success of assisted reproduction techniques 24413997_The data supports the conclusion that the c.742G>T mutation nonsense mutation in ECM1 is the pathological cause of lipoid proteinosis. 24708644_homozygous missense mutation p.C220G of ECM1 was identified by Sanger sequencing, which is a major allele in Chinese patients with LP 24779890_High extracellular matrix protein 1 expression is correlated to carcinogenesis and lymphatic metastasis of gastric cancer 25446258_ECM1 induced the expression of genes that promote the Warburg effect, such as glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha). 25517360_Report a global loss of 5hmC identified three new genes (ECM1, ATF5, and EOMES) with potential anti-cancer functions that may promote the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. 25518807_Lipoidproteinosis results from a large homozygous deletion of ECM1 gene in a Chinese family. 25529926_This large cohort revealed extensive phenotypic variability in individuals with the same mutation in ECM1. 25746001_association between beta-catenin and the MUC1 cytoplasmic tail was increased by ECM1 25812648_MMP-2 protein and ECM1 gene are useful preoperative markers for defining malignancy in suspicious thyroid nodules 25824756_High extracellular matrix protein-1 expression is associated with the growth, metastasis and angiogenesis of laryngeal carcinoma 26564090_Lipoid proteinosis is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in ECM1, encoding extracellular matrix protein 1, a glycoprotein expressed in many organs and which has important protein-protein interactions in tissue homeostasis 26738999_For 1q21 loci, we confirmed gene ECM1 as the most plausible gene from this region to be involved in pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease 26826312_In conclusion, the domain-specific anti-ECM1 MAbs produced in this study should provide a useful tool for investigating ECM1's biological functions, and cellular pathways in which it is involved. 27133046_Overexpression of miR-486-3p inhibited cell growth and metastasis by targeting ECM1. 27241643_Our results indicate that although mutation in ECM1gene is responsible for lipoid proteinosis, it is likely that this is not the only gene causing this disease and probably other genes may be involved in the pathogenesis of the LP disease. 27316685_our work has identified a novel function of ECM1 in inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model 27460906_ECM1, which displayed a high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimens, was closely associated with clinicopathologic data and may promote migration and invasion of HCC cells by inducing epithelia-mesenchymal transition. 27770373_Cell invasion (matrigel) was reduced only in the Hs578T cells (p |
ENSMUSG00000028108 |
Ecm1 |
1171.891345 |
0.4149781039 |
-1.268893 |
0.050131962 |
649.734457 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002551887180710347312357849620696208382355662996250062110158927647167394307225344956591750415752781198116038864568637901606026308574606419301825929017338101018208672891148046543015606635845 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001550035176431470282751839381588991238545461198915454819033412108165725303516578463776571190446459345655476328129355152429332688831018308909835612844455847022339333912721489327361226048707 |
Yes |
No |
694.8742968 |
22.4185222 |
1686.3878634 |
35.2070635 |
| ENSG00000143382 |
54507 |
ADAMTSL4 |
protein_coding |
Q6UY14 |
FUNCTION: Positive regulation of apoptosis. May facilitate FBN1 microfibril biogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16364318, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21989719}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is a member of ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs)-like gene family and encodes a protein with seven thrombospondin type 1 repeats. The thrombospondin type 1 repeat domain is found in many proteins with diverse biological functions including cellular adhesion, angiogenesis, and patterning of the developing nervous system. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:54507; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; interstitial matrix [GO:0005614]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; epithelial cell development [GO:0002064]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; pigment cell development [GO:0070285]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065] |
19200529_Mutations in ADAMTSL4 are responsible for autosomal-recessive simple ectopia lentis and this proteins affectsthe development of the zonular fibers. 20141359_Herein we show a consanguineous family that carries a novel homozygous splice mutation IVS4-1G>A/IVS4-1G>A in ADAMTSL4 responsible for isolated autosomal recessive ectopia lentis. 20564469_This study confirms that homozygous mutations in ADAMTSL4 are associated with autosomal-recessive ectopia lentis in British families. 20702823_Ectopia lentis et pupillae is associated with a number of malformations primarily in the anterior segment of the eye. 21051722_The results emphasize the association of ADAMTSL4 null mutations with isolated ectopia lentis and the presence of a founder mutation in the European population. 21989719_Enhanced fibrillin-1 deposition in the presence of ADAMTSL4 and colocalization of ADAMTSL4 with fibrillin-1 in the ECM of cultured fibroblasts suggest a potential role for ADAMTSL4 in the formation or maintenance of the zonule. 22736615_Mutations in ADAMTSL4 appear to cause earlier manifestation of ectopia lentis and are associated with increased axial length. 22871183_This is the first detailed report of a possible genetic determinant of craniosynostosis with ectopia lentis. 23426735_Patients from a family with ectopia lentis et pupillae (ELP) in four generations have autosomal recessive ELP caused by novel mutations in ADAMTSL4. 23846871_We have confirmed the gene and protein expression of ADAMTSL4 in human ocular tissue. The pattern of expression may suggest further functions of this gene beyond those suggested by its causative role in isolated ectopia lentis. 24802351_Compound heterozygous c.1783dupT and c. 2594G>A mutations of ADAMTSL4 gene were causative mutations for this family with isolated non-syndromic ectopia lentis 25975359_ADAMTSL4 mutations are the main cause for isolated ectopia lentis with an early onset of symptoms and possible severe ocular complications. 26653794_study reports a novel founder mutation in ADAMTSL4 gene in children of Bukharian Jewish origin presenting with early-onset bilateral ectopia lentis 28394649_A recurrent pathogenic ADAMTSL4 variant is a major cause of early onset autosomal recessive ectopia lentis in a Cook Island Maori population and associated with a common haplotype, suggesting a founder effect. |
ENSMUSG00000015850 |
Adamtsl4 |
120.461558 |
0.2282424868 |
-2.131361 |
0.200814680 |
112.141488 |
0.00000000000000000000000003326996037494302916195665626415019353621706908261052062072183518374687317964433219685815856792032718658447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000370614803874837021330478406120247290912259670211763325336817558194012212080536983194178901612758636474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
44.7037925 |
6.6256596 |
197.1272395 |
19.3420785 |
| ENSG00000143507 |
11221 |
DUSP10 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6W6 |
FUNCTION: Protein phosphatase involved in the inactivation of MAP kinases. Has a specificity for the MAPK11/MAPK12/MAPK13/MAPK14 subfamily. It preferably dephosphorylates p38. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10597297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22375048}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
Dual specificity protein phosphatases inactivate their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues. They negatively regulate members of the MAP kinase superfamily, which is associated with cellular proliferation and differentiation. Different members of this family of dual specificity phosphatases show distinct substrate specificities for MAP kinases, different tissue distribution and subcellular localization, and different modes of expression induction by extracellular stimuli. This gene product binds to and inactivates p38 and SAPK/JNK. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:11221; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; JUN kinase binding [GO:0008432]; MAP kinase phosphatase activity [GO:0033549]; MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0017017]; mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 binding [GO:0048273]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008330]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010633]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of epithelium regeneration [GO:1905042]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043508]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048715]; negative regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1903753]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity by regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0044387]; negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response [GO:0060266]; oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048709]; peptidyl-threonine dephosphorylation [GO:0035970]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation involved in inactivation of protein kinase activity [GO:1990264]; positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045591]; regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002819]; regulation of brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0090335]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0051403] |
16806267_Structural information provides an explanation of constitutive activity of MKP5 as well as the structural insight into substrate-induced activation occurred in other MKPs. 17151092_Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-5 (MKP5) mediates anti-inflammatory activities of phytochemicals curcumin, resveratrol and [6]-gingerol. 17400920_Catalytic domain of MKP5 is in an active conformation, and two loops in the active site have backbone shifts of up to 5 A. 17681939_The transcription factor ATF2, which is phosphorylated and activated by JNK, is a critical mediator for inducible expression of DUSP1 and DUSP10 in this signaling pathway. 18314537_p38 MAP kinase down-regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase via activation of MKP-3 in human monocytes exposed to asbestos to enhance TNF-alpha gene expression. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21487011_a function for ASC that is distinct from the inflammasome in modulating MAPK activity and chemokine expression and further identify DUSP10 as a novel ASC target. 22245064_DUSPs 10 and 16 are positive regulators of activation, apparently acting by modulating cross-talk between the p38 and ERK pathways. 22375048_A distinct interaction mode revealed by the crystal structure of the kinase p38alpha with the MAPK binding domain of the phosphatase MKP5. 22711061_MKP-5 interacts with ERK, retains it in the cytoplasm, suppresses its activation and downregulates ERK-dependent transcription. 23233447_Data indicate that the activities of phosphoprotein phosphatases MKP5 and MKP7 were determined in the system. 23872954_Certain mutations in DUSP10 correlate with the incidence of colorectal cancer(CRC). Thus, the function of the DUSP10 gene product may contribute toward CRC in the Han Chinese population. 23936387_Single nucleotide polymorphism in DUSP10 gene is associated with celiac disease. 23993976_Depletion of miR-181 family members by miRNA inhibitors enhanced the expression of MKP-5 and suppressed the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK after exposure to PAHs, which promotes cancer cell migration. 24975273_Data suggest that vitamin D receptor target genes (DUSP10; THBD, thrombomodulin; NRIP1, nuclear receptor interacting protein 1; TRAK1, trafficking protein kinesin binding 1) can be used as markers for individual's response to vitamin D3 supplements. 25772234_Increased Dusp10 expression is associated with better survival rate in colorectal cancer patients. 25973098_In females, three SNPs were associated with decreased colorectal cancer risk: rs11118838, rs12724393, and rs908858. However, in males, only one SNP, rs908858, was associated with decreased colorectal cancer risk. 26733232_This study demonstrates that AGR2, which is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers and provides a poor prognosis, up-regulates DUSP10 which subsequently inhibits p38 MAPK and prevents p53 activation by phosphorylation. 28674078_High DUSP10 expression is associated with Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 29986742_Our findings uncover novel associations of progressive supranuclear palsy with SLCO1A2 (rs11568563) and DUSP10 (rs6687758) variants 30333178_Data found DUSP10 downregulated by rhinovirus (RV) infection. siRNA-mediated knockdown of DUSP10 identified a role for the protein in negatively regulating inflammatory cytokine production in response to IL-1beta alone and in combination with RV, without any effect on RV replication. This study identifies DUSP10 as an important regulator of airway inflammation in respiratory viral infection. 31122150_Study of genome-wide epigenetic changes in bronchial epithelial cells of asthmatic patients, following cells treatment with vitamin D3 and Poly (I:C)(a viral analogue) allows the identification of biologically plausible candidate genes for viral infections and asthma, such as DUSP10 and SLC44A1. 31202710_Gene overexpression and knockdown demonstrated that MKP-5 could alleviate glucolipotoxicity-induced apoptosis via the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways owing to the altered regulation of caspase family members and ER stress-related molecules. MKP-5 is a main mediator for glucolipotoxicity-induced islet cell dysfunction and apoptosis, with JNK and P38 as critical downstream pathways. 31483681_High DUSP10 expression is associated with pulmonary fibrosis. 32843541_An allosteric site on MKP5 reveals a strategy for small-molecule inhibition. 33232789_SETD8 potentiates constitutive ERK1/2 activation via epigenetically silencing DUSP10 expression in pancreatic cancer. 34782469_De novo germline mutation in the dual specificity phosphatase 10 gene accelerates autoimmune diabetes. 35488020_MiRNA-363-3p/DUSP10/JNK axis mediates chemoresistance by enhancing DNA damage repair in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. |
ENSMUSG00000039384 |
Dusp10 |
452.307339 |
4.9019321497 |
2.293351 |
0.109644200 |
435.782875 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000089591150689500718494045510053516951764384437583223682658390853407584870461964623712839525337384480699542929569090235296613453177017702547048431830444347161489650438395492473893310263302922414819587885654699982377670710392284442120979 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000036428798462177150360000629911849171736449830046601102605273604542833352006297325840383309637178297076043917854837630852784472521670694361355738011647764396094715801849521312672534908259718856364422406703934335333557318496759740112864 |
Yes |
No |
764.3330010 |
48.8562342 |
156.9033795 |
8.2449608 |
| ENSG00000143554 |
11000 |
SLC27A3 |
protein_coding |
Q5K4L6 |
FUNCTION: Mainly functions as an acyl-CoA ligase catalyzing the ATP-dependent formation of fatty acyl-CoA using LCFA and very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) as substrates (PubMed:23936004). Can mediate the levels of long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) in the cell by facilitating their transport across membranes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88561, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23936004}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Fatty acid metabolism;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene belongs to a family of integral membrane proteins and encodes a protein that is involved in lipid metabolism. The increased expression of this gene in human neural stem cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells suggests that it plays an important role in early brain development. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with autism spectrum disorders. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:11000; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; long-chain fatty acid transporter activity [GO:0005324]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; very long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031957]; fatty acid transport [GO:0015908]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676] |
19920185_ACSVL3 maintains oncogenic properties of malignant glioma cells via a mechanism that involves, in part, the regulation of Akt function. 20965718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23936004_all of 69 different lung tumors tested, including adeno-, squamous cell, large cell, and small cell carcinomas, had robustly elevated ACSVL3 levels. 24893952_Our findings indicate that the lipid metabolism enzyme ACSVL3 is involved in GBM stem cell maintenance and the tumor-initiating capacity of GBM stem cell enriched-neurospheres in animals 26548558_we resequenced the SLC27A3 and SLC27A4 genes using 267 autism spectrum disorders(ASD) patient and 1140 control samples and detected 47 and 30 variants for the SLC27A3 and SLC27A4, revealing that they are highly polymorphic with multiple rare variants. |
ENSMUSG00000027932 |
Slc27a3 |
151.729877 |
0.2007709868 |
-2.316377 |
0.238340179 |
90.385933 |
0.00000000000000000000195954345029425312564181169385924600884306304868425062002627173862734366593940649181604385375976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000018352069369507091558993324656748411289417353746308871607385848623295032666646875441074371337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.9999816 |
10.2996855 |
238.6726485 |
35.4580159 |
| ENSG00000143771 |
29097 |
CNIH4 |
protein_coding |
Q9P003 |
FUNCTION: Involved in G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface; it promotes the exit of GPCRs from the early secretory pathway, likely through interaction with the COPII machinery (PubMed:24405750). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24405750}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables CCR5 chemokine receptor binding activity. Involved in endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:29097; |
COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle [GO:0030134]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; CCR5 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031730]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
28130019_hsa_circ_0000190 (gene symbol is CNIH4) may be a novel non-invasive biomarker for the diagnosis of gastric cancer 36220450_Screening and identification of CNIH4 gene associated with cell proliferation in gastric cancer based on a large-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screening database DepMap. |
ENSMUSG00000062169 |
Cnih4 |
688.981038 |
2.1988226186 |
1.136731 |
0.077626190 |
213.610964 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000223916917292227367088976143394375646317383839096257530656877866037700811554744744239292226800389540973076641686388586424422825205127196568355429917573928833007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000045902968044906611164814612988787687252494944892680680589872682565243383131581551688639696635981727166660128995765365825937331933914720139000564813613891601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
916.6535490 |
41.0829673 |
419.9069456 |
14.3399988 |
| ENSG00000143819 |
2052 |
EPHX1 |
protein_coding |
P07099 |
FUNCTION: Biotransformation enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of arene and aliphatic epoxides to less reactive and more water soluble dihydrodiols by the trans addition of water (By similarity). Plays a role in the metabolism of endogenous lipids such as epoxide-containing fatty acids (PubMed:22798687). Metabolizes the abundant endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) to free arachidonic acid (AA) and glycerol (PubMed:24958911). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22798687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24958911}. |
Aromatic hydrocarbons catabolism;Detoxification;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Methylation;Microsome;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Epoxide hydrolase is a critical biotransformation enzyme that converts epoxides from the degradation of aromatic compounds to trans-dihydrodiols which can be conjugated and excreted from the body. Epoxide hydrolase functions in both the activation and detoxification of epoxides. Mutations in this gene cause preeclampsia, epoxide hydrolase deficiency or increased epoxide hydrolase activity. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:2052; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; cis-stilbene-oxide hydrolase activity [GO:0033961]; epoxide hydrolase activity [GO:0004301]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; aromatic compound catabolic process [GO:0019439]; epoxide metabolic process [GO:0097176]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
11124296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11191882_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11255266_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11283205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11375900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11406608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11440964_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11471167_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11480169_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11489754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11520401_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11535253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11551408_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11597790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11692079_Common polymorphisms within EPHX1 do not appear to be important risk factors for Parkinson's disease. 11692079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11751440_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11809533_Polymorphisms in microsomal epoxide hydrolase is associated with ovarian cancer 11813302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11849215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11859435_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11940289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11967624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085365_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12085365_polymorphisms were significantly associated with hepatitis C virus-related liver disease severity and hepatocellular carcinoma risk 12121132_evidence that microsomal epoxide hydrolase is a target for tamoxifen and that target proteins are implicated in cell lipid metabolism 12141066_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12160895_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12173035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12173035_Two exonic single nucleotide polymorphisms in the gene are jointly associated with preeclampsia. 12234472_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12359356_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12359356_Polymorphisms in microsomal epoxide hydrolase is associated with laryngeal cancer 12376511_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12397416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12419832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12491039_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12496064_Microsomal epoxide hydrolase variants are not associated with risk of breast neoplasms. 12552594_A significant increase in risk for neoplasia was observed for the low-activity mEH 113 His allele after adjustment for smoking 12552594_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12579334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579334_Polymorphism in EPHX1 might be associated with development of emphysematous changes in the lung. 12605384_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12631667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12670526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12670526_polymorphisms in microsomal epoxide hydrolase is associated with esophageal tumorigenesis 12717779_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12747973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12760253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12798882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12854128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12915882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12915882_polymorphisms in microsomal epoxide hydrolase associated with lung cancer risk 12935919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14642084_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14669306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14669306_Tyr113His polymorphism is not associated with susceptibility to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a population of North China. 14681495_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14719475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14751678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14984931_GATA-4 plays a transactivator role in the regulation of the transcription of the EPHX1 gene 14988221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15036125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15061915_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15138035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15150264_EPHX1 expression is regulated by C/EBPalpha interacting with DNA-bound NF-Y 15199549_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15256148_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15280903_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15298956_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15352038_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15355699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15465926_Exon 1 sequence promoter functions as the primary driver of EPHX1 expression in human tissues. 15466980_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15488121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15531751_Results suggest that mEH 'slow' genotypes increase the annual decline rate of lung function for subjects occupationally exposed to airborne endotoxin 15535985_In liver microsomes, no major differences were evident in the reaction rates generated among preparations representing the different EPHX1 alleles. 15536330_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15582499_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15640066_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15640939_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15640939_The slow 113His EPHX1 allele tends to be more frequent among the patients with lung cancer than in normal controls 15654505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15668489_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15692831_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15702235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15702235_results suggest that codon 113 polymorphism may modify risk for development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 15714076_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15716486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15719050_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15734960_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15746160_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15774926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15817713_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15838728_Nuclear genetic polymorphisms related to oxidative stress or apoptosis may modify the age at onset of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON). 15838728_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15894702_Significant differences were not found for the risk of colon cancer and smoking for mEH genotype polymorphisms Y113H and H139R. 15900282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15901990_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15924351_individuals exposed to tobacco carcinogens were at increased risk of colorectal cancer and that overall risk is related to microsomal epoxide hydrolase and CYP2C9 genotype 15928955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15938845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16005144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16029924_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16029924_the mEH His113His genotype can differentiate the association between smoking, areca chewing, and esophageal squamous-cell-carcinoma 16039674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043197_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16125881_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16147638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16201204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16201204_Results suggest that polymorphisms at codon 113 and 139 in microsomal epoxide hydrolase do not play a significant role in susceptibility to the mutagenic effects of vinyl chloride occupational exposure. 16357600_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16369102_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16456143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16535827_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16538176_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16585076_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16598069_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16614101_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16614120_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16630050_The present study demonstrates a significant increase in mEH expression in the AD hippocampus, a region showing abundant neuropathology in AD. 16697254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16926176_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16985026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17022435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17035385_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17048007_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17078101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17082176_EPHX1 gene polymorphisms is associated with sporadic distal colorectal adenomas 17082176_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17159790_Low EPHX1 activity genotype may be protective for people occupationally exposed to asbestos. 17159790_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17164366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17167268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17203192_Genetic polymorphisms in HOX-1 and mEPH genes are associated with the development of COPD in Southwest China 17203192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17212663_Genetic variability in exon 3 and 4 of EPHX may be a risk factor for pre-eclampsia. 17212663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17273734_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17273734_the expression level of mEH is as important as genetic polymorphism in non-small cell lung cancer; could be involved in drug resistance and prognosis of patients 17363767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17363767_Polymorphic variants in EPHX1 are associated with both emphysema distribution and COPD susceptibility 17365145_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17380322_EPHX1 genotype was not associated with risk of myocardial infarction, regardless of smoking status, suggesting EPHX1 does not play a significant role in the development of coronary heart disease. 17380322_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17412371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17416769_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17416773_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17449559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17498780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17526865_EPHX1 genotypes modified the association between maternal passive smoking and infant birth weight, which is suggestive of possible gene-environment interaction. 17526865_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17532303_In conclusion, 105V/114V alleles of GSTP1 and 113H/139H alleles of mEPHX and the combination of genotypes with same alleles associated with imbalanced oxidative stress and lung function in patients. 17532303_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17548684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17548691_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17564249_Finds neither EPHX1 exon 3 nor EPHX1 exon 4 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of COPD. Finds also that none of the EPHX1 haplotypes are associated with an increased risk of any COPD phenotype. 17564249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17588204_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17590289_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17608547_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17608547_genetic variation of the detoxification enzymes EPHX1 and GSTP1 do not increase the risks of orofacial clefting, nor do they influence the risks associated with maternal smoking. 17611777_EPHX1 polymorphism is not associated with the risk of head and neck cancer 17611777_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17686149_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17690329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17695473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17711870_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17767854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17767854_The interaction between the polymorphisms of mEH gene and the indoor air pollution plays an important role in the carcinogenesis of lung. 17885617_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17896209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17908297_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17996038_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18093316_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18093316_The biotransformation enzymes GSTM1, GSTP1 and EPHX1 may modify the effect of dietary factors on the risk of developing colorectal carcinoma and adenoma. 18200441_our study demonstrated that exon 3 His genotype of the mEH are more prone to the risk of sporadic bladder cancer in North India 18258609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18298806_C-Allele of EPHX1(His113Tyr)plays a protective role in early onset lung cancer susceptibility 18298806_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18383527_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18394656_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18406439_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18406439_gene-environment interaction of EPHX1 genotypes with tobacco, alcohol and occupational exposures did not appear to modulate the cancer susceptibility 18423013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18423013_mEH (C/C) mutant and the NAT2 slow acetylator genotypes were significantly associated with breast carcinoma risk (p = 0.02; p = 0.01. 18461673_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18461673_The researchers found evidence that the homozygus exon 3 mutatnt variant of the EPHX1 gene when combined with the GSTM1 null genotype is associated with an increased risk of COPD in a Slovak population. 18495522_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18510611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18513744_These results provide a mechanistic basis for understanding the cell-specific and tissue-specific localization of hsEH in vivo. 18550614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18569587_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18571762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571762_analysis of lung cancer in subjects under age 45 supports the hypothesis that EPHX1 polymorphisms may have a role in cancer susceptibility in this age group. 18614560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18614560_analysis of microsomal epoxide hydrolase and glutamate-cysteine ligase variants in COPD 18619701_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18632753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18642288_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18680736_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18768509_EPHX1 polymorphisms were not associated with an earlier age of onset for colorectal neoplasms. 18768509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18784359_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18784359_genetic polymorphisms in EPHX1 may contribute to risk of chronic benzene poisoning in a Chinese occupational population. 18811882_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18811882_The polymorphisms of EPHX1 113 and EPHX1 139 are genetic contributors to COPD susceptibility in Asian populations. The phenotypes of EPHX1 were contributors to overall COPD susceptibility. 18816171_GST and mEPHX variants share a positive association with viral-related hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Indian population. 18816171_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18836923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18990750_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18992263_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19012698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19017876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19017876_in severe COPD, SNPs in EPHX1 and SERPINE2 were associated with hypoxemia in two separate study populations, and SNPs from SFTPB were associated with pulmonary artery pressure 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19111454_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19131562_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19162321_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19177501_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19181923_EPHX1 polymorphisms do not have an effect on the level or change of forced expiratory volume 19181923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19287329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287329_Results show that The EPHX1 Y113H variant is not associated with pancreatic diseases indicating that EPHX1 does not play a significant role in the initiation of pancreatic inflammation or cancer. 19307236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19330589_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19364907_Upstream EPHX1 promoter polymorphisms are associated with reduced transcriptional activities and may represent important contributors to interindividual differences in EPHX1 activity. 19415745_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19479063_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19528831_Characterize a series of polymorphisms of genes, such as CYP2E1, GSTM1, GSTT1, and particularly EPHX1, involved in butadine (BD) metabolism in very low BD exposure level. 19528831_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19575027_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19589345_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19593802_EPHX1, NQO1, and MPO variant genotypes were significantly associated with a reduced risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia 19593802_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19620853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19620853_This proof-of-principle study suggests that genetic variants in EPHX1 can be used to predict maintenance doses of carbamazepine. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657367_Single nucleotide polymorphism in EPHX1 gene is associated with bone disease in myeloma. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19736056_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19751749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19754350_In India, 113Tyr-139Arg and 113His-139His haplotypes of mEPHX significantly elevated the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma by 1.4- and 1.5-folds, respectively. 19754350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19794411_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933216_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19952982_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19952982_maternal polymorphisms may be associated with risk of fetal anomalies among pregnant women taking phenytoin 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19958090_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20091863_Modifying effect of EPHX1 polymorphisms on the risk of early-onset lung cancer.M 20091863_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20095411_Genetic peculiarities particularly xenobiotic detoxification enzymes CYP1A1, CYP2E1, EPHX1 and GSTM1, GSTT1 play important role in pulmonary diseases development. 20095411_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20233420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20375710_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20403997_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20437850_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20461808_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20516053_EPHX1 polymorphisms do not have major roles in COPD or asthma in the Danish population 20516053_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20525719_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20568895_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602612_Functional variants from the gene encoding EPHX1 were highly polymorphic in North Indian epilepsy patients, and might account for differential drug response to first-line anticonvulsants. 20602612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20637790_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20659238_EPHX1 exon 4 139His/Arg, and 139Arg/Arg genotypes were associated with a higher risk of esophageal cancer in a high-risk area of India. 20659238_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20716240_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20731606_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20731606_the association between glutathione S-transferase M1 (GSTM1), GSTT1, GSTP1, EPHX1, and p53 codon 72 polymorphisms as risk factors in 120 adult acute myeloid leukemia 20842355_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20847076_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20878130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20886582_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20886582_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of EPHX1 is associated with colorectal cancer. 20932192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20932192_these results showed that there is a weak relation between 113His EPHX1 genotype and COPD, and no apparent relation between 139Arg and COPD in the studied Tunisian population. 20935060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20951227_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21044285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21044285_The 'slow' activity-associated genotypes of EPHX1 were associated with increased risk of COPD. 21057703_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21183608_Children with high EPHX1 activity may have increase risk of asthma and wheezing outcomes, and can be mediated through airway oxidative stress generation. 21192345_Despite a sig |
ENSMUSG00000038776 |
Ephx1 |
281.977737 |
0.3521837028 |
-1.505600 |
0.139299145 |
115.942100 |
0.00000000000000000000000000489377561130528537825582976940084635254335378332640889625640374085960748913592954778550847549922764301300048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000056475471479957789700386761804457191846417958323499434672529786991587545663673353146805311553180217742919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
146.8580075 |
12.4537455 |
419.8104036 |
23.6948999 |
| ENSG00000143847 |
8497 |
PPFIA4 |
protein_coding |
O75335 |
FUNCTION: May regulate the disassembly of focal adhesions. May localize receptor-like tyrosine phosphatases type 2A at specific sites on the plasma membrane, possibly regulating their interaction with the extracellular environment and their association with substrates (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
PPFIA4, or liprin-alpha-4, belongs to the liprin-alpha gene family. See liprin-alpha-1 (LIP1, or PPFIA1; MIM 611054) for background on liprins.[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:8497; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0098688]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; synapse [GO:0045202]; synapse organization [GO:0050808] |
19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20599943_liprin-alpha4 is a hypoxia-induced gene potentially involved in cell-cell adhesion 21829649_presence of Liprin-alpha4 and nickel increased tyrosine phosphatase activity that reduced the global levels of tyrosine phosphorylation in the cell 28460022_The results identify PP1IFA4 loci associated with early onset atrial fibrillation in a Korean population. 29187440_Data show that liprin-alpha4 plays a pivotal role in inducing malignant phenotypes such as increased proliferation and invasion in pancreatic cancer, and that liprin-alpha4 could be a new effective therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer. 30842147_Hypoxia appears to up-regulate the expression of liprin-alpha4, which induces the expression of HIF1alpha. HIF1alpha contributes to increased proliferation and lower chemosensitivity. Therefore, inhibition of liprin-alpha4 or HIF1alpha led to reduced proliferation and increased chemosensitivity of SBC-5 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000026458 |
Ppfia4 |
127.806501 |
0.4338342660 |
-1.204784 |
0.337209920 |
12.157921 |
0.00048879833429329338275598493268603306205477565526962280273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001202043221287739296204710726101438922341912984848022460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.5708765 |
19.1554470 |
209.7241628 |
31.4318989 |
| ENSG00000143869 |
151449 |
GDF7 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z4P5 |
FUNCTION: May play an active role in the motor area of the primate neocortex. {ECO:0000250}. |
Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. This protein may play a role in the differentiation of tendon cells and spinal cord interneurons. A mutation in this gene may be associated with increased risk for Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:151449; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032924]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; forebrain morphogenesis [GO:0048853]; gland morphogenesis [GO:0022612]; midbrain development [GO:0030901]; morphogenesis of an epithelial fold [GO:0060571]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of tendon cell differentiation [GO:2001051]; reproductive structure development [GO:0048608]; roof plate formation [GO:0021509]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; spinal cord association neuron differentiation [GO:0021527] |
12741987_In mouse, the expression of Gdf7 in roof plate cells is required for the fidelity of commissural axon growth. 20102312_stimulates expression of both chondrogenic and osteoblstic markers in pluripotent mesenchymal C3H10T1/2 cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20334610_induces ligamentogenic differentiation in mesenchymal progenitors 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21702718_studies show that even though tenogenic (BMP 12 and BMP 13) and osteogenic (BMP2) BMPs bind the same receptors with high affinity they signal much differently and result in differential activation of osteogenic and tenogenic markers 24155967_BMP12 induces tenogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells via the Smad1/5/8 pathway. 25447851_closest protein-coding genes were respectively GDF7 (rs3072), which encodes a ligand in the bone morphogenetic protein pathway, and TBX5 (rs2701108), which encodes a transcription factor that regulates esophageal and cardiac development 26783083_The Barrett-associated variants at GDF7 and TBX5 also increase esophageal adenocarcinoma risk. 28214472_BMP-12 activates tenogenic pathway in human adipose stem cells. 33388417_TET-dependent GDF7 hypomethylation impairs aqueous humor outflow and serves as a potential therapeutic target in glaucoma. 34408239_Secretome screening reveals immunomodulating functions of IFNalpha-7, PAP and GDF-7 on regulatory T-cells. |
ENSMUSG00000037660 |
Gdf7 |
35.959843 |
0.2139596089 |
-2.224590 |
0.288823717 |
65.271860 |
0.00000000000000065246398394808605813413708133470323732704408735763590421186108869733288884162902832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004720768825036151725449981470541554898807544340261221904597732645925134420394897460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8537976 |
2.5301330 |
60.6567517 |
6.6689393 |
| ENSG00000143882 |
245973 |
ATP6V1C2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEY4 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of the V1 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons (By similarity). V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment (By similarity). Subunit C is necessary for the assembly of the catalytic sector of the enzyme and is likely to have a specific function in its catalytic activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21282, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21283, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31412}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of eukaryotic intracellular organelles. V-ATPase dependent organelle acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A,three B, and two G subunits, as well as a C, D, E, F, and H subunit. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. This gene encodes alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different V1 domain C subunit isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:245973; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain [GO:0000221]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31901859_Multi-cancer V-ATPase molecular signatures: A distinctive balance of subunit C isoforms in esophageal carcinoma. 31959358_Whole exome sequencing identified ATP6V1C2 as a novel candidate gene for recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. |
ENSMUSG00000020566 |
Atp6v1c2 |
1705.290526 |
0.0324176400 |
-4.947077 |
0.129434024 |
1338.519147 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004814642836617912950180643883672581247 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006641507314811251980415982917887098062 |
Yes |
Yes |
109.7607377 |
14.2093935 |
3386.2860741 |
292.9246303 |
| ENSG00000143891 |
130589 |
GALM |
protein_coding |
Q96C23 |
FUNCTION: Mutarotase that catalyzes the interconversion of beta-D-galactose and alpha-D-galactose during galactose metabolism (PubMed:12753898). Beta-D-galactose is metabolized in the liver into glucose 1-phosphate, the primary metabolic fuel, by the action of four enzymes that constitute the Leloir pathway: GALM, GALK1 (galactokinase), GALT (galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase) and GALE (UDP-galactose-4'-epimerase) (PubMed:30451973). Involved in the maintenance of the equilibrium between the beta- and alpha-anomers of galactose, therefore ensuring a sufficient supply of the alpha-anomer for GALK1 (PubMed:12753898). Also active on D-glucose although shows a preference for galactose over glucose (PubMed:12753898). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12753898, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30451973}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Isomerase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate metabolism; hexose metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12753898}.; PATHWAY: Carbohydrate metabolism; galactose metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12753898}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the epimerization of hexose sugars such as glucose and galactose. The encoded protein is expressed in the cytoplasm and has a preference for galactose. The encoded protein may be required for normal galactose metabolism by maintaining the equilibrium of alpha and beta anomers of galactose.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:130589; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; aldose 1-epimerase activity [GO:0004034]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; galactose catabolic process via UDP-galactose [GO:0033499]; galactose metabolic process [GO:0006012]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006] |
12753898_Gene encodes a functional aldose 1-epimerase (mutarotase). The enzyme exhibits (approx. four-fold) preference for galactose over glucose. Mutation E307A results in no detactable activity. 12753898_Identification and characterisation of human aldose 1-epimerase. 15026423_The enzyme is a monomer and has a similar structure to the Lactococcus lactis mutarotase. 21339755_This study demonistrated that polymorphism in galactose mutarotase (GALM) is associated with serotonin transporter binding potential in the human thalamus. |
ENSMUSG00000035473 |
Galm |
75.136479 |
0.4617274971 |
-1.114886 |
0.247178214 |
20.236815 |
0.00000684234028186897577666512534899645459063322050496935844421386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000021912115981858556909523880196211109705473063513636589050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.5641378 |
7.3111460 |
99.3575335 |
10.9464868 |
| ENSG00000143919 |
79823 |
CAMKMT |
protein_coding |
Q7Z624 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the trimethylation of 'Lys-116' in calmodulin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20975703}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a class I protein methyltransferase that acts in the formation of trimethyllysine in calmodulin. The protein contains a AdoMet-binding motif and may play a role in calcium-dependent signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2012]. |
hsa:79823; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; calmodulin-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018025]; heat shock protein binding [GO:0031072]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; peptidyl-lysine methylation [GO:0018022]; protein methylation [GO:0006479]; regulation of rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway [GO:0022400] |
18234729_a deletion of C2orf34 causes atypical hypotonia-cystinuria syndrome 19575798_Two key transcription factors, NRF-2 and YY-1, were further identified to coordinately participate in driving gene expressions of PREPL-C2ORF34 genes pairin an additive manner. 20200953_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20975703_Calmodulin methyltransferase is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that trimethylates Lys-115 in calmodulin. 23285036_The CaM KMT is the major, possibly the single, methyltransferase of calmodulin in human cells with a wide tissue distribution and is a novel Hsp90 client protein. 23794250_Deletion of CAMKMT is associated with Hypotonia-cystinuria syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000071037 |
Camkmt |
19.142303 |
2.3591024228 |
1.238238 |
0.381734510 |
10.555577 |
0.00115838052219994266239799785012110078241676092147827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002671932568787490757528102491846766497474163770675659179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.8944172 |
6.4121001 |
11.4847853 |
2.1214856 |
| ENSG00000143942 |
494143 |
CHAC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8WUX2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of glutathione into 5-oxo-L-proline and a Cys-Gly dipeptide. Acts specifically on glutathione, but not on other gamma-glutamyl peptides. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27913623}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Lyase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a gamma-glutamyl cyclotransferase that catalyzes the conversion of glutathione to 5-oxoproline and cysteinylglycine. It is thought that this gene is upregulated in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress and that the glutathione depletion enhances apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:494143; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase activity [GO:0003839]; glutathione specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase activity [GO:0061928]; glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:0006750]; glutathione catabolic process [GO:0006751] |
27913623_Human and mouse ChaC2 proteins purified in vitro show 10-20-fold lower catalytic efficiency than ChaC1, although they showed comparable Km values 28837156_Results showed for the first time that CHAC2 was degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and CHAC2 expression inhibited tumor cell growth, proliferation, migration in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistic study showed that CHAC2 induced mitochondrial apoptosis and autophagy through unfolded protein response. 29054545_The data revealed that CHAC2 prevented CHAC1-mediated GSH degradation, which suggests that CHAC2 competes with CHAC1 to maintain GSH homeostasis. 31878259_Structural and Functional Analyses of Human ChaC2 in Glutathione Metabolism. |
ENSMUSG00000020309 |
Chac2 |
15.062621 |
2.2741857673 |
1.185350 |
0.414070471 |
8.354080 |
0.00384822335607852951747109848668060294585302472114562988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008052137331403331002577239416950760642066597938537597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6298802 |
5.5152505 |
9.6147234 |
1.9355152 |
| ENSG00000144199 |
151313 |
FAHD2B |
protein_coding |
Q6P2I3 |
FUNCTION: May have hydrolase activity. {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable hydro-lyase activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:151313; |
hydro-lyase activity [GO:0016836]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
|
|
|
18.368039 |
0.3711882331 |
-1.429777 |
0.390006113 |
13.705492 |
0.00021382823129182743299506186396286011586198583245277404785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000556828633356981866735224695474926193128339946269989013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.4140097 |
2.3298548 |
25.5669518 |
4.0481741 |
| ENSG00000144218 |
3899 |
AFF3 |
protein_coding |
P51826 |
FUNCTION: Putative transcription activator that may function in lymphoid development and oncogenesis. Binds, in vitro, to double-stranded DNA. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Dwarfism;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a tissue-restricted nuclear transcriptional activator that is preferentially expressed in lymphoid tissue. Isolation of this protein initially defined a highly conserved LAF4/MLLT2 gene family of nuclear transcription factors that may function in lymphoid development and oncogenesis. In some ALL patients, this gene has been found fused to the gene for MLL. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different proteins have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3899; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; super elongation complex [GO:0032783]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612] |
12203795_The LAF4 gene mapped on chromosome region 2q11.2-q12 has been identified as a fusion partner of the MLL gene in a case of infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 12743608_This gene is fused to MLL in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(2;11)(q11;q23). 15704140_LAF-4 may be a proto-oncogene that is transcriptionally activated in some cases of breast cancer. 18616733_array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) analysis revealed a de novo interstitial microdeletion of 500 kb on chromosome 2q11.1 containing the LAF4/AFF3 (lymphoid-nuclear-protein-related AF4) gene 18622426_A novel fusion 5'AFF3/3'BCL2 originated from a t(2;18)(q11.2;q21.33) translocation in follicular lymphoma. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19359276_AFF3 is a novel rheumatoid arthritis susceptibile gene. 20072139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21330300_overexpression of AFF2/3/4 interferes with the organization and/or biogenesis of nuclear speckles. 22983539_Significant evidence for association of AFF3 rs10865035 with systgemic lupus erythmatgosus was detected. 24763282_FRA2A-expressing individuals have mosaic expansions of the AFF3 CGG repeat. 25819087_Both the AFF3 and NTM triglyceride associations were replicated among Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis study participants (P = 1.00 x 10(-7) and 8.00 x 10(-5), respectively). 28401970_Data identified AFF3 as an interactive protein with beclin1 and suggest that AFF3 is probably a key regulator of Beclin-1. 30326937_AFF3 was overexpressed in tamoxifen-resistant tumors. AFF3 overexpression in breast cancer cells resulted in tamoxifen resistance, whereas RNA interference-mediated gene knockdown reversed this phenotype. 33961779_Variants in the degron of AFF3 are associated with intellectual disability, mesomelic dysplasia, horseshoe kidney, and epileptic encephalopathy. 34104118_Association of AFF3 Gene Polymorphism rs10865035 with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Case-Control Study on a Pakistani Cohort. |
ENSMUSG00000037138 |
Aff3 |
11.441680 |
0.1438402417 |
-2.797461 |
0.708984127 |
14.642169 |
0.00012997354617852666515236126354437828922527842223644256591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000351485808280515503020796641564515994105022400617599487304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5605882 |
1.6890596 |
15.8236982 |
6.3870990 |
| ENSG00000144231 |
5433 |
POLR2D |
protein_coding |
O15514 |
FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB4 is part of a subcomplex with RPB7 that binds to a pocket formed by RPB1, RPB2 and RPB6 at the base of the clamp element. The RBP4-RPB7 subcomplex seems to lock the clamp via RPB7 in the closed conformation thus preventing double-stranded DNA to enter the active site cleft. The RPB4-RPB7 subcomplex binds single-stranded DNA and RNA (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9852112}. |
3D-structure;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription |
|
This gene encodes the fourth largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in eukaryotes. In yeast, this polymerase subunit is associated with the polymerase under suboptimal growth conditions and may have a stress protective role. A sequence for a ribosomal pseudogene is contained within the 3' untranslated region of the transcript from this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5433; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; RNA polymerase II, core complex [GO:0005665]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; translation initiation factor binding [GO:0031369]; mRNA export from nucleus in response to heat stress [GO:0031990]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, deadenylation-dependent decay [GO:0000288]; positive regulation of translational initiation [GO:0045948]; recruitment of 3'-end processing factors to RNA polymerase II holoenzyme complex [GO:0034402]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter [GO:0006367] |
16282592_Identification of the RNA binding region of Rpb4. 19237606_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000024258 |
Polr2d |
392.338769 |
2.1876474295 |
1.129380 |
0.105782993 |
113.044916 |
0.00000000000000000000000002109417408365641715178835077523096597598627952990784347963499564622869182628495110520816524513065814971923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000236768068041649217713302954031949488979579372268743141323694778528673524076175738173333229497075080871582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
516.0621127 |
35.6138964 |
237.3995907 |
12.2195447 |
| ENSG00000144320 |
80856 |
LNPK |
protein_coding |
Q9C0E8 |
FUNCTION: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-shaping membrane protein that plays a role in determining ER morphology (PubMed:30032983). Involved in the stabilization of nascent three-way ER tubular junctions within the ER network (PubMed:24223779, PubMed:25404289, PubMed:25548161, PubMed:27619977). May also play a role as a curvature-stabilizing protein within the three-way ER tubular junction network (PubMed:25404289). May be involved in limb development (By similarity). Is involved in central nervous system development (PubMed:30032983). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TQ95, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24223779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25404289, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25548161, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27619977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30032983}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Involved in endoplasmic reticulum tubular network maintenance and positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization. Located in endoplasmic reticulum tubular network membrane and nucleoplasm. Is integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80856; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network [GO:0071782]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network membrane [GO:0098826]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network maintenance [GO:0071788]; endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization [GO:0071786]; limb development [GO:0060173]; positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum tubular network organization [GO:1903373]; regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032330] |
22729086_Propose that Lnp1p and Sey1p act antagonistically to balance endoplasmic reticular polygonal network formation. 24223779_Protein N-myristoylation plays a critical role in the endoplasmic reticulum morphological change induced by overexpression of protein Lunapark. 25548161_used live cell imaging to show that mammalian Lnp1 affects endoplasmic reticulum junction mobility and hence network dynamics 27387505_Despite its interaction with gp78, Lnp does not seem to have a broad function in degradation of misfolded ER proteins. 30032983_LNPK was expressed during brain development. 30498943_The proposed mechanism ensures coordinated actions of ATL and Lnp in generating and maintaining three-way junctions. 31511573_CAND1 regulates lunapark for the proper tubular network of the endoplasmic reticulum. 32433973_Ubiquitylation of the ER-Shaping Protein Lunapark via the CRL3(KLHL12) Ubiquitin Ligase Complex. 34206552_Roles of the Endogenous Lunapark Protein during Flavivirus Replication. 34879280_Lunapark-dependent formation of a virus-induced ER exit site contains multi-tubular ER junctions that promote viral ER-to-cytosol escape. |
ENSMUSG00000009207 |
Lnpk |
274.032971 |
2.3024859603 |
1.203192 |
0.189826477 |
39.040571 |
0.00000000041508901889170607695408513354454280858130132969563419464975595474243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002047698502286625213926793382486143957343927013425854966044425964355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
347.5669877 |
60.8698899 |
153.3197707 |
19.6434121 |
| ENSG00000144381 |
3329 |
HSPD1 |
protein_coding |
P10809 |
FUNCTION: Chaperonin implicated in mitochondrial protein import and macromolecular assembly. Together with Hsp10, facilitates the correct folding of imported proteins. May also prevent misfolding and promote the refolding and proper assembly of unfolded polypeptides generated under stress conditions in the mitochondrial matrix (PubMed:1346131, PubMed:11422376). The functional units of these chaperonins consist of heptameric rings of the large subunit Hsp60, which function as a back-to-back double ring. In a cyclic reaction, Hsp60 ring complexes bind one unfolded substrate protein per ring, followed by the binding of ATP and association with 2 heptameric rings of the co-chaperonin Hsp10. This leads to sequestration of the substrate protein in the inner cavity of Hsp60 where, for a certain period of time, it can fold undisturbed by other cell components. Synchronous hydrolysis of ATP in all Hsp60 subunits results in the dissociation of the chaperonin rings and the release of ADP and the folded substrate protein (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11422376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1346131, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25918392}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chaperone;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Host-virus interaction;Isomerase;Isopeptide bond;Leukodystrophy;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the chaperonin family. The encoded mitochondrial protein may function as a signaling molecule in the innate immune system. This protein is essential for the folding and assembly of newly imported proteins in the mitochondria. This gene is adjacent to a related family member and the region between the 2 genes functions as a bidirectional promoter. Several pseudogenes have been associated with this gene. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. Mutations associated with this gene cause autosomal recessive spastic paraplegia 13. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:3329; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; coated vesicle [GO:0030135]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lipopolysaccharide receptor complex [GO:0046696]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; sperm plasma membrane [GO:0097524]; apolipoprotein A-I binding [GO:0034186]; apolipoprotein binding [GO:0034185]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; DNA replication origin binding [GO:0003688]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; high-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0008035]; isomerase activity [GO:0016853]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; 'de novo' protein folding [GO:0006458]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; biological process involved in interaction with symbiont [GO:0051702]; cellular response to interleukin-7 [GO:0098761]; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly [GO:0051131]; isotype switching to IgG isotypes [GO:0048291]; mitochondrial unfolded protein response [GO:0034514]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043032]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell [GO:0002842]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein import into mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0045041]; protein maturation [GO:0051604]; protein refolding [GO:0042026]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
11860186_H9724, a monoclonal antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi's flagellin, binds within live neuroblastoma cells, a potential role in peptide hormone signaling in an autoimmune pathogenesis of the neuropathy of Lyme disease. 11862386_promoter polymorphism of the IL-6 gene is associated with levels of antibodies to 60-kDa heat-shock proteins 11898127_Hereditary spastic paraplegia SPG13 is associated with a mutation in the gene encoding the mitochondrial chaperonin Hsp60 (HSPD1) 12215374_Gene expression of HSP1 was down-regulated during early apoptosis in human hepatoma cells exposed to Paeoniae Radix in vitro. 12218165_A regulatory role for human HSP60 autoreactivity is demonstrated by DNA vaccine therapy of rat adjuvant arthritis that results in increased T cell proliferation and variable changes in cytokine production. 12406306_HSP60 reactivity showed no apparent difference between normal and neoplastic odontogenic epithelium 12461076_HLA-E can present a peptide derived from the signal sequence of human hsp60. 12483302_The genome structure of this gene has been established. 12515899_Deficiency of chaperonin 60 in Down's syndrome. A quantitative analysis by Western blots showed a marked reduction of Cpn60 per equal amount of total protein in DS cells to an average of 35% of normal. 12594256_Maturation of murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells is strongly induced by human HSP60 and paralleled by release of Th1-promoting cytokines. 12686536_The recombinant protein does not induce the release of tumor necrosis factor alpha from murine macrophages 12869561_the host factor, Hsp60, is essential for in vivo hepatitis B virus replication, and the mechanism of Hsp60 is probably through an activation of HBV pol by Hsp60 12965262_Evidence of elevated anti-HSP60 reactivity in the serum of patients with tic disorder supports HSP60 as an autoantigen and implicates the involvement of autoimmunity in tic disorders. 14500649_A regulatory HSP60 peptide specifically recognized by the T cells of DNA-vaccinated rats is successfully used as an effective vaccine to inhibit the development of adjuvant arthritis in rats. 15249499_A novel association between anti-heat shock protein 65 autoantibodies and occurrence of postoperative atrial fibrillation. 15251360_The perioperative kinetics of HSP60 in serum may result from suppressed protein synthesis caused by a reduced energy charge of hepatocytes during early reperfusion in liver transplantation. 15529360_T cell immunity to Hsp70 and Hsp90, like Hsp60-specific immunity, can modulate arthritogenic response in adjuvant arthritis. Regulatory mechanisms induced by Hsp60, Hsp70, and Hsp90 are reinforced by an immune network that connects their reactivities. 15546885_Hsp10 exerts anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting Toll-like receptor signaling possibly by interacting with extracellular Hsp60 15590416_The HSP60 is a mitochondrial chaperonin, highly preserved during evolution, responsible of protein folding. Its function is strictly dependent on HSP10 in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic elements. 15661886_A defined region of HSP60 (amino acids 354-365) is involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding, thereby implicating a physiological role of human HSP60 as an LPS-binding protein. 15763499_a decrease of Hsp60 in the cytoplasmic fraction of dilated cardiomyopathy-affected left ventricles was observed; at the same time an increase in P450 2E1 expression in dilated hearts' cytoplasmic fractions was observed 15784682_Overall, we found clear evidence for the occurrence of HSP60 on the surface of stressed HUVECs in a very similar patchy distribution pattern in living and fixed cells 15879154_Atherosclerotic plaques harbor in vivo-activated CD4+ T cells that recognize the human 60-kDa HSP and become target for both autoreactive T cells and cross-reactive T cells to Chlamydia pneumoniae 60-kDa HSP via a mechanism of molecular mimicry. 15957980_Mortalin and HSP60 interact both in vivo and in vitro, and that the N-terminal region of mortalin is involved in these interactions. 16116071_Autoantibodies recognizing amino acid residues 288 to 366 of HSP60 induce atherosclerosis via the mechanisms of autoimmune reactions to HSP60 expressed on arterial endothelial cells, which can be prevented by F(ab)2 segments derived from these antibodies 16148103_human HSP60 induced naive mouse B cells to proliferate and to secrete IL-10 and IL-6 and up-regulate their expression of MHC class II and accessory molecules 16215457_The 14-3-3 protein forms molecular complex with Hsp60 and PrPC in human CNS under physiological conditions, and this complex might become disintegrated in pathologic process of prion diseases. 16253146_HSP60 and HSP10 are expressed in large bowel carcinomas with lymph node metastases 16254226_Our study provides the first prospective data confirming an association between high levels of sHSP60 and early carotid atherosclerosis. 16320351_Hsp60 is an important target for anti-endothelial antibodies; such an interaction contributes to pathogenic effects, especially in vasculitis-associated systemic autoimmune disease 16705742_With HSP60, results from cell-lines correlated with clinical results, indicating that this model can be used for dissection of mechanisms involved in transformation to androgen resistance and assignment of protein markers in prostate cancer. 16843693_HSP60 is a potent inducer of venous smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation; HSP60 uses TLR2 as well as TLR4 to cause its mitogenic effect on VSMCs 16887805_Mitochondrial heat shock protein 60 is able to neutralize the inhibition of electron transport complex IV by amyloid beta-protein. 16978514_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17072495_Investigation of single-nucleotide variations in the Hsp60 gene and their disease-causing potential. 17075864_Yersinia Hsp60-specific T cells of one patient cross-reacted directly with human Hsp60 17174952_dysregulated expression of DHX32 might lead to as of yet unknown changes in mitochondrial homeostasis manifested by cytoplasmic redistribution of the molecular chaperon Hsp60 17202307_A negative association between Hsp60 in plasma, and seropositivity for three microbial agents which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease, suggest a protective effect of circulating stress protein Hsp60. 17206383_Plasminogen bound to hsps 27, 60, and 70 and Angiostatin predominantly bound to hsp 27 and to hsp 70 in a concentration- and kringle-dependent manner. 17420921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17420924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17420924_found that the function of the p.Gln461Glu heat shock protein 60 was mildly compromised. The c.1381C > G mutation likely represents a novel low-penetrance HSP allele. 17553457_HSP60 and HSP70 released upon tissue damage might play a role in the regulation of bacteria-induced inflammation 17588138_Extracellular Hsp60 levels are significantly elevated in children with septic shock compared with both healthy controls and critically ill children without sepsis. Extracellular Hsp60 may play a role in the pathogenesis of sepsis in children. 17670764_HSP60 was present in the uterus and oviduct epithelial cells and was shown to bind to human spermatozoa. Hsp60 partially prevented the increase in p81 phosphotyrosine content induced by the phosphodiesterase inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine. 17675567_Abnormal trafficking of HSP60 to the cell surface may be an early trigger for myocyte loss and the progression of heart failure. 17823127_Cytosolic accumulation of HSP60 during apoptosis with or without apparent mitochondrial release: evidence that its pro-apoptotic or pro-survival functions involve differential interactions with caspase 3. 17915559_Hsp60 and Hsp72 activation and inflammatory markers were correlated with the extent of cardiac and microvascular dysfunction in patients with angiographycally normal coronary arteries. 17925998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925998_Three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were studied in 100 RA trio families. Genetic analyses were performed by comparing allelic frequencies, applying the transmission disequilibrium test, and assessing the genotype relative risk. 18229457_The extended range of plasma Hsp60 concentrations in the general population is genuine and is likely to be related to genetic, biological, and psychosocial risk factors for coronary artery disease. 18240224_human (self) Hsp60 is a disease-relevant autoantigen in juvenile dermatomyositis 18320357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18320357_The GCTC haplotype in the hsp60 gene is significantly associated with higher coronary heart disease risk in a Chinese population. 18322079_Intracellular chaperone heat-shock protein 60 (HSP60) induces extensive axonal loss and neuronal death in microglial cultures from wild-type (but not TLR4 loss-of-function mutant) mice. 18372523_a strong association between in vitro resistance to platinum compounds and increased HSP60 mRNA expression 18399535_Hsp60 is a key player in the resistance mechanism against oxidative stress and aging 18400758_Co-expression of Hsp60-(p.V98I) and wild-type Hsp60 exerted a dominant negative effect only when the chaperonin genes were expressed at relatively low levels. 18458233_HSP60 is a rare cause of hereditary spastic paraparesis, but may act as a genetic modifier. 18571143_Mitochondrial HSP60 chaperonopathy causes an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative disorder linked to brain hypomyelination and leukodystrophy. 18692161_HSP60 exerted a protective role in digoxin-induced apoptosis through inhibition of caspase-3 activity in HUVEC. 18790094_mitochondrial ribosomal protein S12 3'-UTR interacts specifically with TRAP1 (tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein1), hnRNPM4 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein M4), Hsp70 and Hsp60 (heat shock proteins 70 and 60), and alpha-tubulin 18815895_Data show that mtDNA variability is able to influence the cellular response to heat stress by modulating both the transcription of HSP60 and 75 and their intra-mitochondrial protein levels. 18987317_The GroEL-GroES chamber behaves as a passive 'Anfinsen cage' whose primary role is to prevent multimolecular association during folding. 19008717_HSP60 is a potent activator of vascular endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. It is possible that long-term stimulation of these cell populations by blood-borne HSP60 acts to drive blood vessel changes resulting in decreased arterial elasticity. 19022255_These results indicate that c-MYC may promote transformation through the induction of HSP60 expression. 19106391_A strong positive relationship is identified between circulating levels of heat shock protein 60 and the risk of coronary heart disease. 19109096_Although oxidative stress may induce early apoptosis in NCI-H292 cells, Hsp60 exerts an anti-apoptotic effect in these cells. 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19132982_HSP27 and HSP60 are predictors of biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. 19205928_There were no significant differences in serum anti-Hsp60, anti-Hsp65, and anti-Hsp70 antibody levels between the control and preeclamptic groups. 19207939_the aminoacid sequences of the human HSP60 was compared with the bacterial counterpart to better elucidate how CTHSP60 may simulate HSP60 from human origin during infection and may induce an autoimmune response. 19210880_Serum IgG anti-hHSP60, but not anti-Chlamydia pneumoniae, antibodies were significantly increased in giant cell arteritis patients 19261350_siRNA silencing of Hsp60 in Dengue virus infected monocytes resulted in decrease of viral RNA copy number and increased IFN-alpha expression 19264393_impairment of Hsp60 function through binding of HCV core protein contributes to HCV viral pathogenesis by ROS generation and amplification of the apoptotic effect of TNF-alpha. 19306954_Up-regulation of TLR-2 by HSP60 may play a critical role in promoting bone loss in the estrogen-deficient state. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19346294_Mitochondrial HSP70 (mtHSP70) was identified as an HSP60 receptor. Stress was required for endothelial cells to up-regulate mRNA and express mtHSP70 on their surface. 19369584_Coexpression of HSP60 and nuclear beta-catenin predicts a worse prognosis of metastatic head and neck cancer patients. 19386281_This novel data demonstrates that human endomyocardial HSP60 is increased following an acute rejection episode. 19423133_SPG4 cases & their hereditary spastic paraplegic relatives were genotyped for the modifying variant in HSPD1. A sporadic patient was homozygous for the potential modifying variation. This variation's effect was not supported by identification in 1 family. 19475432_A single hemodialysis session raised the median value of Hsp60 19565483_Pan-DR-binding Hsp60 self epitopes induce an interleukin-10-mediated immune response in rheumatoid arthritis. 19568603_The results suggest that HSP60 may be involved in the development of cervical cancer and have profound biological and prognostic significance. 19576649_An association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and HSP60, suggesting that HSP60 may play an important role in the type 2 diabetes mellitus pathology. 19635199_The mRNA and protein levels of HSP60, HSP70 and HSP90alpha, as well as their positive rates were significantly increased in colorectal cancer tissues compared with those in para-cancerous tissues. 19706612_These results suggest that the D3G mutation leads to entropic destabilization of the mHsp60 oligomer, which severely impairs its chaperone function, thereby causing MitCHAP disease. 19764566_HSP60, TLR4 and NF-kappaBp65 are overexpressed in the peripheral blood of patients with atopic dermatitis. 19875724_Report HSP60-induced apoptosis via toll-like receptors in myocardium. 19913588_this study suggests that HSP gene family, particularly HSP60, is involved in alveolar macrophage functions in a context of allergic asthma 20082317_the association of PKM2 and HSPD1, two differentially expressed proteins, with MDR were analyzed, and the results showed that they could contribute considerably to the cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cell 20169074_Data suggest that Hsp60 release is the result of an active secretion mechanism. 20351780_cytosolic Hsp60 is likely to be a regulatory component of IKK complex and a mitochondrial factor that regulates cell survival via NF-kappaB pathway 20362058_Results obtained demonstrated that recombinant human heat shock protein 60 was secreted efficiently from cells when fused to the leader peptide of interleukin-2 and the secreted protein was modified by N-linked glycosylation. 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20686813_cHSP60- and cHSP10-induced caspase expression, proinflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis of primary cervical epithelial cells might play a role in the pathogenesis of infertility in women with persistent chlamydial infection. 20694586_High gene expression of Hsp60 is associated with leukemia. 20708221_Hsp60 is overexpressed in poorly differentiated prostate cancers & is associated with prognostic clinical parameters, like Gleason score, initial serum PSA, lymphatic metastasis, hormone-refractory disease & reduced cancer-specific survival. 20806039_The aim of this study is to examine the expression of HSP60, HSP72, and HSP90, and heat-shock cognate 70 (HCS70) at the mRNA and protein level in differentiating corneal cells from limbal stem cells following air exposure. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20947377_The elevated titer of anti-Hsp60 autoantibody could be a risk factor for cerebral small-vessel disease. 20953657_Externalized Heat-shock protein 60 in apoptotic cells and senescent platelets influences events subsequent to apoptosis, such as the clearance of apoptotic cells by phagocytes. 20978188_Data show that show that the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) directly associates with cyclophilin D (CypD). 21361146_HSP60 expression was increased in HepG2 cells during cooling and rewarming. Cellular response to hypothermia could be associated with the synergistic induction of Hsp expression. 21497776_Hsp60 and HO-1 play distinct roles in the pathogenesis of AMI and subsequent AMI-related pathology 21642380_Loss of the tumor suppression function of Hsp60 or GANAB contribute to aggressive cancers. 21671464_High prognosis is associated with recurrence in lung adenocarcinoma. 21717087_The folding of mitochondrial-targeted green fluorescent protein, a well-known substrate protein of HSP60, was consistently impaired in cells expressing HSP60 variant with a mutation (Asp423Ala) in the ATPase domain. 21748374_The study reports the presence of elevated levels of HSP60 in both saliva and serum of type 2 diabetic patients compared to non-diabetic controls. 22140545_This is the first report clearly pointing to participation of heat shock proteins, particularly Hsp60, in chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases pathogenesis. 22258649_Hsp60 proteins from humans and two common pathogens, Chlamydia trachomatis and Chlamydia pneumoniae, share various sequence segments of potentially highly immunogenic epitopes with acetylcholine receptor alpha1 subunit (AChRalpha1). 22315307_Hsp60 might be a factor underlying adipose tissue inflammation and obesity-associated metabolic disorders. 22492505_pan-DR-binding HSP60 peptides induced low peptide-specific proliferative responses and peptide-specific production of some, mainly intracellular, cytokines in type 1 diabetes patients, without major differences between patients at various time points 22575645_both GroEL and its isolated apical domain form amyloid-like fibrils under physiological conditions, and that the fibrillation of the apical domain is accelerated under acidic conditions. 22753410_a novel interaction between APP and HSP60, which accounts for its translocation to the mitochondria. 22847064_results indicate that LOX-1 is essential in microglia for promoting an inflammatory response in the presence of soluble neuronal-injury signals such as extracellular HSP60, thereby linking neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity 22848686_a multistage process for the translocation of Hsp60 from the inside to the outside of the cell 22882677_In cardiovascular patients, a greater burden of subgingival infection with increased levels of P. gingivalis and T. forsythia is associated with modestly higher anti-hHSP60 levels. 22901435_HSP60-reactive T-cells initiate atherosclerosis by recognition of atherogenic HSP60 epitopes. 22931585_Immune reactivity to human hsp60 contributes to immunopathology in primary Sjogren's syndrome. 22933632_HSP65-induced effects on allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation are associated with modulation of dendritic cell function and CD4+ T helper cell type (Th)1 cytokine production. 23028910_Elevated circulating levels of Hsp60 may contribute to the immune dysfunction and non-AIDS clinical events seen in HIV-infected patients. 23192457_These data provide evidence for a role of C. pneumoniae as a potent primary endothelial stressor for arterial endothelial cells leading to enrichment of hHSP60 on the cellular membrane and, as such, a potential initiator of atherosclerosis. 23276948_Hsp60 is a key factor for protein homeostasis and cell survival, and this chaperonin is involved in various ways in the onset and progression of aging-related diseases.[review] 23357787_Inhibited the activation of NF-kappaB in HSP60-stimulated macrophages. 23388486_Suggest role for anti-HSP 60/65 antibodies in atherogenesis in patients with type 2 diabetes and lower limb ischemia. 23424650_association between elevated levels of antibodies against human HSP60 and disease may reflect a general activation of the immune system and an increased expression of human HSP60 in the synovium of patients with SpA 23429486_High HSP60 mRNA expression was associated with advanced serous ovarian cancer. 23466130_The expression of HSP-65 increased in myasthenia gravis patients and most individuals produced antibodies to it. 23807299_Hsp60 levels were significantly higher than those of Hsp70 in neuroepithelial tumors, while levels of both molecules were not significantly different from each other in meningeal neoplasms 23823174_The pathogenic variant of rs72466451 may play a role in a subgroup of sudden infant death syndrome cases with impaired Hsp60-mediated stress response. 24015183_Hyperacetylation of Hsp60 seems to be associated with anticancer activity of geldanamycin. 24057177_Regions in the Hsp60 molecule show structural similarity with the thyroglobulin (TG) and thyroid peroxidase (TPO) molecules supporting the notion that autoantibodies against TG and TPO are likely to recognize Hsp60 on the plasma membrane of oncocytes. 24084737_In type 2 diabetes, there is hypothalamic insulin resistance and mitochondrial dysfunction due to downregulation of the mitochondrial chaperone HSP60. HSP60 reduction was due to a lack of proper leptin signaling. 24099319_Citrullination of HSP60 is associated with neoplasms. 24113772_In acute cellular rejection and cyclophilin toxicity, distal tubules showed increased immunopositivity for Hsp27, 60 and 70i. In chronic allograft nephropathy there was also induction of Hsp27, 60 and 70i in the distal tubules but this was less pronounced 24123003_HSP60 protein expression may inhibit lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinomas harboring the BRAF mutation. 24327239_In postmenopausal women, serum HSP60 and anti-HSP70 concentrations increased with accumulating features of the metabolic syndrome. Results suggest an immune activation associated with cardiovascular risk in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. 24347824_Increased circulating level of HSP60 and HSP70 might play a role in initiation and/or progression of atherosclerosis in CKD subjects through perturbation of CD4(+)CD28(null) cells. 24582286_Lysine biotinylation and methionine oxidation in the heat shock protein HSP60 synergize in the elimination of reactive oxygen species. 24618330_The immunological response to Hsp60/65 is increased in early clinical stages of ovarian cancer and the level of anti-hsp60/65 antibodies may be then a helpful diagnostic marker. 24643797_Levels of circulating autoantibodies against Hsp60, Hsp70, and Hsp90 were elevated and positively correlated with both cutaneous disease activity in dermatitis herpetiformis. 24672802_Data suggest that up-regulation of HSP60/HSPD1 binding/reactivity leads to increased cytokine synthesis/secretion and other proinflammatory responses in adipocytes, especially in mature visceral adipocytes. 24680363_Antibodies to human HSP60 were found in 19 (15.8%) of 120 patients with a history of recurrent miscarriages. 24738046_These seven proteins, especially HSP 60, may serve as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of RHD. 24749912_Low level of HSP60 may lead to lack of anti-inflammatory response due to less Treg activation, hence, could be a counterpart in the pathogenesis of ITP. 24830947_Hsp60 mitochondrial import signal is stable in solution 24838263_Increased levels of anti-heat-shock protein 60 (anti-Hsp60) indicate endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases in patients with mixed connective tissue disease 25207654_HSP60 overexpression was associated with the disease progression and prognosis in gastric cancer, and its expression significantly correlated with the expression of MMP-9. 25395618_Modified forms of LDL activate human T cells through dendritic cells. HSP60 and 90 contribute to such T-cell activation. 25506707_The present study indicated that HSPD1 interacted with IRF3 and it contributed to the induction of IFN-beta. 25654359_no significant relationship between anti-hsp60 antibodies and serological markers of infection was observed, which may only indicate an indirect role of infection in the assessment of breaking the immunological tolerance against autologous HSPs 25687758_Data inticate that heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) interacted constitutively with NKG2D ligand ULBP2 and phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL-3) regulated HSP60 tyrosine phosphorylation. 25801186_Hsp60 is increased in both animals and patients with TLE in affected tissues, and in plasma in response to epileptic seizures, and point to it as biomarker of hippocampal stress potentially useful for diagnosis and patient management. 25918392_structural analysis of mutated human Hsp60-human Hsp10 complex 25957474_an HLD4-associated (Asp-29-to-Gly) mutant of mitochondrial heat shock 60-kDa protein 1 (HSPD1) causes short-length morphologies and increases the numbers of mitochondria due to their aberrant fission and fusion cycles 26060090_Hsp60 was found to be increased in cancerous tissue in patients with large bowel cancer 26078803_exposure of human promyelocytic HL-60 cells to a nontoxic concentration (10 muM) of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) yielded a HSP60 modified with HNE. 26275591_Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies promote apoptosis of mature human osteoblasts via cell-surface binding to citrullinated heat shock protein 60. 26335776_Biochemical and genetic data demonstrate that FUS interacts with a mitochondrial chaperonin, HSP60, and that FUS translocation to mitochondria is, at least in part, mediated by HSP60 26431161_Studies show that contrary to its role as a target for pathogenic autoimmune inflammatory processes, heat-shock protein 60 (HSP60) has been shown to activate immunoregulatory pathways that may lead to suppression of these diseases. 26442925_The data show that immunohistochemistry for CD1a and Hsp60 can be of help in differential diagnosis between Keratoacantomas and well-differentiated forms of squamous cell carcinomas. 26477505_Heat shock protein 60 stimulates the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via Toll-like receptor 4 and ERK MAPK activation 26577462_This review article presents accumulating proof that supports the idea that tolerization with antigenic HSP60 protein or its peptides may arrest or even prevent atherosclerosis by increased production of regulatory T cells and/or anti-inflammatory cytokines. [review] 26585937_Data indicate that on addition of the heat-shock proteins GroEL-GroES molecular chaperone system, the folding of the nascent chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) was significantly enhanced. 26672742_Data show that Eclipta extract upregulates heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) which is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 26810190_High HSP60 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 26902796_The cardioprotective effect of 40-60 g/d of alcohol consumption could be due in part, to increased intracellular HSPA1A, a potent anti-inflammatory protein. Excessive intake of alcohol increases antibodies anti-Hsp60, stimulating proinflammatory cytokines. This fact may explain the mortality from cardiovascular disease in heavy drinkers. 27056903_Low HSP60 expression is associated with beta-cell hypertrophy and dysfunction. 27106586_The mechanism involved in the interaction of HSP60-Ass conjugate with HLA-DR-DRB allele considering the fact that Ass (1-42) is highly immunogenic in human and interactions evoked highly robust T-cell response through MHC class II binding predictions. 27118120_HSP60 regulation of SOX9 ubiquitination mitigates the development of knee osteoarthritis. 27246978_high level of ROS is needed for tumorigenesis and progression in tumors with low HSP60 expression 27259322_Elevated expression of HSPD1 in osteosarcoma tissues correlated with poor prognosis of the osteosarcoma patients. 27325206_HSP60 silencing deactivates the mTOR pathway to suppress glioblastoma progression 27491302_Hsp10 and Hsp60 may be implicated in carcinogenesis from its very early steps in colorectal cancer. 27665089_Phosphorylation and subsequent transient degradation of mitochondrial Hsp60 during early hours of rotavirus-SA11 infection resulted in inhibition of premature import of nonstructural protein 4 into mitochondria, thereby delaying early apoptosis. 27677587_the effect of Hsp60 on differentiation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells might be associated with mitochondrial biogenesis 27742830_data indicate that HSP65 suppresses cholesterol efflux and increases cellular cholesterol content through an Lck-mediated pathway in T cells 27836734_Doxorubicin treatment of lung mucoepidermoid cells results in Hsp60 post-translational modifications leading to the Hsp60/p53 complex dissociation and instauration of replicative senescence. 28011268_NIP-SNAP-1 and -2 localized in the mitochondrial inner membrane space, whereas HSP60 localized in the matrix. Expression levels of NIP-SNAP-1 and -2 in cells were decreased by knockdown of HSP60, but not HSP10. The findings indicate that HSP60 promotes folding and maintains the stability of NIP-SNAP-1 and -2. 28178129_expression elevated in lung adenocarcinoma tissue 28212901_These findings shed some light on how a tumor cell may avert apoptosis using Hsp60 and point to the anti-cancer potential of drugs, such as CubipyOXA, which interfere with Hsp60/pC3 complex formation, and thus allow the apoptotic cascade to proceed. 28254432_Data show that the interaction between cell cycle and apoptosis regulator 2 (CCAR2) and heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) increases in the presence of rotenone. 28347227_In this instance, the ATP5B/CALR/HSP90B1/HSPB1/HSPD1-signaling network was revealed as the predominant target which was associated with the majority of the observed protein-protein interactions. As a result, the identified targets may be useful in explaining the anticancer mechanisms of ursolic acid and as potential targets for colorectal cancer therapy. 28434777_The results demonstrate that HSP60 participates in mitochondrial progesterone synthesis. These findings provide novel insights into progesterone synthesis in the human placenta and its role in maintaining pregnancy. 28549691_27-Hydroxycholesterol upregulates the production of HSP60 in monocytic cells. 28591216_The associations of diabetes, combined with the polymorphisms in the genes of fat mass and obesity-associated gene (FTO), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and heat shock protein 60 (HSPD1), with breast cancer risk and survival in a Chinese Han population, was evaluated. 28680529_Clinical data showed that upregulation of miR-382/3-NT and downregulation of HSPD1/Trx were also observed in IgA nephropathy patients with renal interstitial fibrosis. These data supported a novel mechanism in which miR-382 targets HSPD1 and contributes to the redox imbalance in the development of renal fibrosis. 28976240_HSP60 showed pro-inflammatory properties in bronchial epithelial cells mediated by activation of TLR-4-related molecules. 29134442_When conditioned media was immuno-depleted of Hsp60, there was a significant reduction in the release of TNF-alpha from the human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 29415987_both HSP60 knockdown and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) inhibition by metformin decreased Erk1/2 phosphorylation and induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. 29682763_WHO GS was found to be significantly and negatively associated with ANX2, and positively with SPINK1/TATI and Hsp60 expression. 29885667_HSP60 mediates microglial IL-1beta production by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and reduction of HSP60 leads to reduction of inflammation in JEV infection. 30337218_High HSP60 expression is associated with disease recurrence and progression in bladder cancer. 30365075_Data demonstrated that HSPD1 expression was indirectly regulated by EHMT2, and an unknown target regulated by EHMT2 modulates the downregulation of HSPD1 in breast neoplasm. 30614112_this study shows that the balance between circulating HSP60 and HSP70 interfere with the phenomenon of miscarriage 30746790_Helicobacter pylori (Hp)-positive patients with gastritis or coronary heart disease produce IgG autoantibodies to a specific epitope (P1 peptide) of human heat shock protein (Hsp)60 homologous to Hp Hsp60 (HspB) in the sera. Monocytes respond to P1 by production of proinflammatory cytokines. Upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines by P1 contributes to the pathogenesis of Hp infection. 31112866_our data show that HSP60 kn |
ENSMUSG00000025980 |
Hspd1 |
2080.790522 |
2.1704229681 |
1.117976 |
0.049955442 |
497.214459 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003837524907982818657343246076072580319098790043826673867059615048721719691177830579413507535014228233077930541965888999941078158115205918894508554851986201209469269367383643836029383280613445415649682475030904665835343132 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001809644333604677631119474399046373637242618611573871380260480373511292344471406606686404496810682791932306881525301614834480791875616279089097468046804593874980517859669235300127217160336424140911132267044803267099288231 |
Yes |
No |
2880.7520882 |
80.3811789 |
1336.4862058 |
28.5120295 |
| ENSG00000144596 |
80852 |
GRIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9C0E4 |
FUNCTION: May play a role as a localized scaffold for the assembly of a multiprotein signaling complex and as mediator of the trafficking of its binding partners at specific subcellular location in neurons. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable protein C-terminus binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane; positive regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor clustering; and positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential. Predicted to act upstream of or within Notch signaling pathway; artery smooth muscle contraction; and positive regulation of blood pressure. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm; dendritic shaft; and neuron spine. Predicted to be active in glutamatergic synapse and postsynaptic density. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80852; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuron spine [GO:0044309]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density, intracellular component [GO:0099092]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035254]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098887]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045777]; vesicle-mediated transport in synapse [GO:0099003] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000030098 |
Grip2 |
78.446705 |
0.1065824752 |
-3.229958 |
0.282275217 |
137.839907 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000007899535893565222274441089031124869836028431273352835913971024551055180885227525371203999293712172402592841535806655883789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000001074628108654586928021682869240223793303937185517929209611836144977308249599394799830842650578688335372135043144226074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.4631271 |
4.4318107 |
146.1677208 |
27.3479206 |
| ENSG00000144619 |
152330 |
CNTN4 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWV2 |
FUNCTION: Contactins mediate cell surface interactions during nervous system development. Has some neurite outgrowth-promoting activity. May be involved in synaptogenesis. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the contactin family of immunoglobulins. Contactins are axon-associated cell adhesion molecules that function in neuronal network formation and plasticity. The encoded protein is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored neuronal membrane protein that may play a role in the formation of axon connections in the developing nervous system. Deletion or mutation of this gene may play a role in 3p deletion syndrome and autism spectrum disorders. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:152330; |
axon [GO:0030424]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell-cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098632]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axonal fasciculation [GO:0007413]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; brain development [GO:0007420]; dendrite self-avoidance [GO:0070593]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007158]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167] |
15106122_Our results demonstrate the association of CNTN4 disruption with the 3p deletion syndrome phenotype and strongly suggest a causal relationship 17030759_The contactin 4 gene (CNTN4) is associated with cerebellar degeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 16. Additional studies are necessary to prove 4,256C-->T to be a causative mutation. 17915252_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17915252_pathological examinations and molecular biological examinations are needed to confirm that this mutation is a true cause of SCA16 18349135_This report suggests that mutations affecting CNTN4 function may be relevant to Autism spectrum disorder pathogenesis. 19509545_results do not support the candidacy of CHL1, CNTN6, and CNTN4 as tumor suppressor genes in the 3p26-pter region in ovarian cancer 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21079607_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21308999_Using array comparative genome hybridization (CGH), we identified a maternally inherited approximately 535 kb deletion at 3p26.3 encompassing the 5' end of the contactin 4 gene (CNTN4) in a patient with autism. 22750301_these results suggest that rare copy number variations in CNTN4 may also influence autism susceptibility in Asian populations. 24764060_We identified CNTN4 as a novel candidate gene for POAG. 25959733_data reveal critical and novel roles for CNTN4/amyloid precursor protein in promoting target-specific axon arborization 26146898_By combining methylation and SNP data, CNTN4 was identified as a risk factor for regular alcohol use. 27039371_SNPs in ITPR1 and CNTN4 are involved in the regulation of serum uric acid concentrations in Mexican Americans 27995817_Association between contactin 4 (CNTN4) and antisaccade and P300 in schizophrenia. 28595731_SNPs within the CNTN4 gene are associated with increased risk of oral cancer. 28938490_High CNTN4 expression is associated with Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. 29258006_PPARGC1B and CNTN4 genotypes are associated with elevated thromboxane A2 formation and with an excess of cardiovascular events. Aspirin appears to blunt these associations. |
ENSMUSG00000064293 |
Cntn4 |
10.208423 |
0.3787202072 |
-1.400796 |
0.544373683 |
6.562671 |
0.01041399508330710307890676347142289159819483757019042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019890083777123816061171979185928648803383111953735351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6711671 |
1.6621149 |
12.7679955 |
2.4805364 |
| ENSG00000144642 |
27303 |
RBMS3 |
protein_coding |
Q6XE24 |
FUNCTION: Binds poly(A) and poly(U) oligoribonucleotides. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10675610}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
This gene encodes an RNA-binding protein that belongs to the c-myc gene single-strand binding protein family. These proteins are characterized by the presence of two sets of ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence (RNP-CS) that contain conserved motifs, RNP1 and RNP2, originally described in RNA binding proteins, and required for DNA binding. These proteins have been implicated in such diverse functions as DNA replication, gene transcription, cell cycle progression and apoptosis. The encoded protein was isolated by virtue of its binding to an upstream element of the alpha2(I) collagen promoter. The observation that this protein localizes mostly in the cytoplasm suggests that it may be involved in a cytoplasmic function such as controlling RNA metabolism, rather than transcription. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:27303; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding [GO:0035925]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; poly(A) binding [GO:0008143]; poly(U) RNA binding [GO:0008266]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; defense response to tumor cell [GO:0002357]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628] |
17586524_These results suggest that RBMS3, by binding Prx1 mRNA in a sequence-specific manner, controls Prx1 expression and indirectly collagen synthesis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21844183_a tumor suppression function for the human RBMS3 gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, acting through c-Myc downregulation, with genetic loss of this gene contributing to poor outcomes in disease 22267851_genetic susceptibility plays a role in the pathophysiology of Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ), with RBMS3 having a significant effect in the risk. 22957092_RBMS3 at 3p24 inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma development via inhibiting cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and inducing apoptosis 23045156_one interacting gene pair (RBMS3 versus ZNF516) which, even after Bonferroni correction for multiple testing, showed consistently significant effects on hip bone mineral density. 25588924_RBMS3 is a novel tumor suppressor gene in lung squamous cell carcinoma 27503288_We identified rs117026326 on GTF2I with GWAS significance (P = 1.10 x 10(-15)) and rs13079920 on RBMS3 with suggestive significance (P = 2.90 x 10(-5)) associating with Primary Sjogren's syndrome in women. 27902480_These findings implicated that RBMS3 and nuclear HIF1A could act as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for GC. 28409548_RBMS3 inhibited the proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells, at least in part, through inactivation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway 30279231_Results indicate that genetic ablation of RNA binding motif single stranded interacting protein 3 (RBMS3) contributes to chemoresistance RBMS3-deleted epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). 30819235_our study revealed a novel mechanism of the RBMS3/Twsit1/MMP2 axis in the regulation of invasion and metastasis of breast cancer 32016951_RBMS3 delays disc degeneration by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 32627033_Increased expression of RBMS3 predicts a favorable prognosis in human gallbladder carcinoma. 33845141_LncRNA MEG3 regulates breast cancer proliferation and apoptosis through miR-141-3p/RBMS3 axis. 33910421_Tumor Suppressor Effect of RBMS3 in Breast Cancer. 34608266_RNA binding protein RBMS3 is a common EMT effector that modulates triple-negative breast cancer progression via stabilizing PRRX1 mRNA. |
ENSMUSG00000039607 |
Rbms3 |
8.751945 |
0.2180354433 |
-2.197365 |
0.667680852 |
11.358696 |
0.00075095545713631435286866677714101570018101483583450317382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001786893849320006369754687547413141146535053849220275878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8941034 |
1.9184674 |
17.8087131 |
5.1095922 |
| ENSG00000144655 |
64651 |
CSRNP1 |
protein_coding |
Q96S65 |
FUNCTION: Binds to the consensus sequence 5'-AGAGTG-3' and has transcriptional activator activity (By similarity). May have a tumor-suppressor function. May play a role in apoptosis. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11526492}. |
Activator;Apoptosis;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that localizes to the nucleus and expression of this gene is induced in response to elevated levels of axin. The Wnt signalling pathway, which is negatively regulated by axin, is important in axis formation in early development and impaired regulation of this signalling pathway is often involved in tumors. A decreased level of expression of this gene in tumors compared to the level of expression in their corresponding normal tissues suggests that this gene product has a tumor suppressor function. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:64651; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705] |
23292452_Three candidate tumor-suppressor genes, SEMA3B, AXUD1 and GNAT1 may be involved in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 30440036_cFos bound to the AP-1 cis element within the proximal MMP1 promoter only when the gene was transcriptionally silent as previously observed for MMP13. cFos contributes to MMP1 expression. Silencing of ATF3 (a prime MMP13 modulator) did not affect MMP1 expression whilst silencing CSRNP1 resulted in substantial repression of MMP1 but not MMP13. |
ENSMUSG00000032515 |
Csrnp1 |
257.505225 |
3.4030366354 |
1.766823 |
0.107353345 |
279.901863 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000788827339966220376532983857977118695660947427248455895524045504642810264365896877879864422921493258711221414128683201557978306366037979243800273810192035493782380939364884397946298122406005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000210544150775794080105091268143661690637207530863314563569947671878316727010665941392615555072645932018070832208851687195292221547191782141102433580928058459713625438780582044273614883422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
400.6914896 |
26.5650040 |
118.5349274 |
6.4940615 |
| ENSG00000144668 |
3680 |
ITGA9 |
protein_coding |
Q13797 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-9/beta-1 (ITGA9:ITGB1) is a receptor for VCAM1, cytotactin and osteopontin. It recognizes the sequence A-E-I-D-G-I-E-L in cytotactin. {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an alpha integrin. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane glycoproteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain that mediate cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion. The protein encoded by this gene, when bound to the beta 1 chain, forms an integrin that is a receptor for VCAM1, cytotactin and osteopontin. Expression of this gene has been found to be upregulated in small cell lung cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3680; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593] |
15247268_role in chemotaxis in conjuction with plasmin 15479742_spermidine acetyltransferase directly binds to the alpha9 cytoplasmic domain and mediates alpha9-dependent enhancement of cell migration 15590642_VEGF-C and VEGF-D are ligands for the integrin alpha9beta1 16005200_integrin alphavbeta6, alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, alpha5beta1 and alpha9beta1 binding to osteopontin is controlled by specific structural motifs that are recognized by extracellular proteases 16430945_The integrin receptors of tenascin (TN) and fibronectin (FN) may be involved in cell processes such as growth, adhesion, migration and apoptosis. 18230652_Data found that alpha9beta1 is a receptor for nerve growth factor and two other neurotrophins, and interaction of alpha9beta1 with NGF was confirmed in an ELISA assay by direct binding to purified integrin. 18794852_tumor-cell expressions of alpha9 and beta1 integrins in combination with extracellular tenascin are necessary for medulloblastoma adhesion to the leptomeninges. 18973153_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18973153_Possible link between ITGA9 missens mutation and human fetuses with severe chylothorax. 19140316_Down-regulation of RBSP3/CTDSPL, NPRL2/G21, RASSF1A, ITGA9, HYAL1 and HYAL2 genes in non-small cell lung cancer 19346516_Polymerization of OPN generates a novel alpha9beta1-binding site and that the interaction of this site with the alpha9beta1 integrin is critical to the neutrophil chemotaxis induced by polymeric OPN. 19403822_After forced expression of alpha9 integrin, extensive neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells and adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurons occurs. 19478819_A genetic variation(s) in ITGA9 may influence susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the Malaysian Chinese population. 19478819_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19494327_Inhibition of alpha(9) integrin function with an anti-alpha(9) integrin Ab significantly reduces the production of arthrogenic cytokines and chemokines and ameliorates ongoing arthritis 19608669_The integrin alpha9beta1 is expressed on hematopoietic stem cells, and contributes to adhesion and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells in the endosteal stem cell niche 19686679_Results reveal an important role for integrin-alpha9 signaling during lymphatic valve morphogenesis and implicate it as a candidate gene for primary lymphedema caused by valve defects. 19796635_although alpha9beta1 integrin can induce and localise to focal adhesions in a high activation state, its intermediate activity state normally supports cell adhesion consistent with migration. 20159768_Expression and activation of alpha9 integrin greatly enhances the ability of retinal pigment epithelial cells to adhere to wet age-related macular degeneration-affected Bruch's membranes. 20362630_Data show that alpha9beta1 integrin engagement leads to the activation of integrin signaling pathways and potently reduces neutrophil spontaneous apoptosis, and that these effects are dependent on the activation of PI3K and MAPK pathways. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20412120_dysregulation of hMLH1, ITGA9, and RBSP3 associated multiple cellular pathways are needed for the development of early dysplastic lesions of the head and neck. 20414254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20435742_up-regulation of alpha9beta1 expression among all beta1 integrins during neutrophil activation and transendothelial migration and a synergy between alpha9beta1 and beta2 integrins in stabilizing neutrophil adhesion to endothelium under flow conditions 20479155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21071450_the three-amino acid sequence, EYP, encoded by exon 3 of VEGF-A is essential for binding of VEGF to integrin alpha9beta1 and induces adhesion and migration of endothelial and cancer cells 21341269_expression of alpha9beta1 in breast cancer; alpha9beta1 acts as novel marker of basal-like breast cancer subtype; expression associated with reduced survival; its ability to promote cell migration and invasion suggests it contributes to aggressiveness of this subtype 21465533_endostatin reduces colorectal tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis, at least in part, by inhibiting EDA-integrin alpha9 pathway. 21764681_rs189897 and rs2212020 genotypes of the ITGA9 are closely related to cerebral infarction, and the A-C haplotype is a protective factor against cerebral infarction. 21975548_Integrin alpha9 (ITGA9) expression and epigenetic silencing in human breast tumors 22370635_integrin alpha9beta1 is expressed in primary small cell lung cancer and patients having a high expression of alpha9beta1 demonstrated significantly worse long-term survival compared with patients with low alpha9beta1 expression 22545097_Differential capacity for VEGF-D production and integrin alpha 9 beta 1 expression by human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468LN jointly contributed to their lymphatic metastatic phenotype. 22976797_Neuronal cadherin and alpha9-integrin are postulated as leading actors in the association between the Notch pathway and promotion of cell adhesion, motility and invasion in rhabdomyosarcoma cells 24241034_alpha9beta1 integrin acts as a critical intrinsic regulator of human rheumatoid arthritis. 25748048_p75(NTR) and alpha9 integrin subunit are not closely associated through their cytoplasmic domains, most probably because of the molecular interference with other cytoplasmic proteins such as paxillin. 26372814_ITGA9 gene promoter is hypermethylated and downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 26596831_our results demonstrate that upregulation of ITGA9 in response to the decrease in miR-125b in metastatic melanoma is responsible for melanoma tumor cell migration and invasion. 27287342_the expression levels of DLEC1 and ITGA9 were prominently decreased in lung tumor samples 28416479_findings identify a novel physiological context for combinatorial integrin signaling, laying the foundation for therapeutic strategies that manipulate alpha9beta1 and/or alpha3beta1 during wound healing 28844950_ITGA9 expression was found to be increased in the suprabasal psoriatic epidermis. 28916657_Metastatic prostate cancer cells cultured on osteo-mimetic surfaces coated with tenascin C exhibited enhanced adhesion and colony formation as mediated by integrin alpha9beta1. 29038247_this study demonstrates the central role of alpha9 in pathogenic behaviors of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes 29951557_Our data suggest ITGA9, as a suppressor of HCC, prevents tumor cell migration and invasiveness through FAK/Src-Rac1/RhoA signaling. 30819933_This review summarises the known shared and specific roles for alpha4 and alpha9 integrins and highlights the importance of these receptors in controlling cell migration within both homeostatic and disease settings. 30945681_rs2212020 and rs189897 polymorphisms of the ITGA9 gene is associated with epithelial ovarian cancer. 31008533_ITGA9 level is significantly higher in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) than other breast cancer subtypes. Hhigher ITGA9 level is associated with significantly worse metastasis- and recurrence-free survival. Experimentally, ITGA9 KO significantly reduced TNBC cell cancer stem cell-like property, tumor angiogenesis, tumor growth and metastasis by promoting beta-catenin degradation through ILK/PKA/GSK3 pathway. 31489579_miR-148a can suppress the malignant phenotype of glioblastoma by targeting ITGA9 and identify ITGA9 as a potential therapeutic target for glioblastoma. 32232710_Integrin-alpha9 and Its Corresponding Ligands Play Regulatory Roles in Chronic Periodontitis. 32981677_Integrin alpha9 is involved in the pathopoiesis of acute aortic dissection via mediating phenotype switch of vascular smooth muscle cell. 33491517_Association study of hypertension susceptibility genes ITGA9, MOV10, and CACNB2 with preeclampsia in Chinese Han population. 34058037_Tenascin-C regulates migration of SOX10 tendon stem cells via integrin-alpha9 for promoting patellar tendon remodeling. 35490433_ITGA9: Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets in Different Tumors. 36221013_Integrin alpha9 emerges as a key therapeutic target to reduce metastasis in rhabdomyosarcoma and neuroblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000039115 |
Itga9 |
15.377523 |
0.2507010937 |
-1.995960 |
0.681105678 |
8.184751 |
0.00422439809899517737523666482957196421921253204345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008766390410646945907657823227054905146360397338867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8632412 |
2.6949906 |
23.2899678 |
7.1922611 |
| ENSG00000144677 |
10217 |
CTDSPL |
protein_coding |
O15194 |
FUNCTION: Recruited by REST to neuronal genes that contain RE-1 elements, leading to neuronal gene silencing in non-neuronal cells (By similarity). Preferentially catalyzes the dephosphorylation of 'Ser-5' within the tandem 7 residue repeats in the C-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2A. Negatively regulates RNA polymerase II transcription, possibly by controlling the transition from initiation/capping to processive transcript elongation. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12721286}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat phosphatase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein dephosphorylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle and negative regulation of protein phosphorylation. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10217; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat phosphatase activity [GO:0008420]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933] |
15051889_analysis of RBSP3/HYA22located in the AP20 region, and evidence for tumor suppressor function 17085434_SCP3 acts as a phosphatase for regulatory phosphorylations in the linker regions of Smad1 and Smad2. 19016758_Frequent alterations of RBSP3 at chromosomal 3p22.3 region in early and late-onset breast carcinoma are reported with reference to clinical and prognostic significance. 19047128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19140316_Down-regulation of RBSP3/CTDSPL, NPRL2/G21, RASSF1A, ITGA9, HYAL1 and HYAL2 genes in non-small cell lung cancer 19478941_This is the first report of high frequencies of somatic mutations in RASSF1 and RBSP3 in different cancers suggesting it may underlay the mutator phenotype of cancer. 19885927_In cervical intraepithelial neoplasms and uterine cervical carinoma, RBSP3 is oftne deletd, compared with other genes. 20193080_tumor suppressor genes RBSP3/CTDSPL, NPRL2/G21 and RASSF1A are downregulated in primary non-small cell lung cancer 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20412120_dysregulation of hMLH1, ITGA9, and RBSP3 associated multiple cellular pathways are needed for the development of early dysplastic lesions of the head and neck. 21643017_identified RBSP3, a phosphatase-like tumor suppressor, as a bona fide target of miR-100 and validated that RBSP3 was involved in cell differentiation and survival in acute myeloid leukemia 27414789_CTDSPL and Rb directly interact and can be involved in the common mechanism of cell cycle regulation. 27458253_data suggest that overexpression of p-RB1 in basal-parabasal layers of normal cervical epithelium was due to methylation/low functional-linked non-synonimous SNPs of P16 and RBSP3. This pattern was maintained during cervical carcinogenesis by additional deletion/mutation 29382357_we have presented herein the novel finding that miR-181b contributes to cell cycle progression through depressing the expression of CTDSPL, which in turn activates the downstream effector E2F1 and promotes S-phase entry. 29672635_our data also suggests the importance ofLIMD1 and CDC25A in conjunction with HPV for use as diagnostic and prognostic markers of HNSCC, whereas RBSP3 as a prognostic marker only. 31774910_Tumor suppressor properties of the small C-terminal domain phosphatases in non-small cell lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000047409 |
Ctdspl |
142.223287 |
0.4328288341 |
-1.208131 |
0.269050151 |
19.739622 |
0.00000887422859626095778646463069216920871440379414707422256469726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027981972672679286434811729566973781402339227497577667236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.5154266 |
16.7324350 |
202.8138157 |
27.4422950 |
| ENSG00000144746 |
10550 |
ARL6IP5 |
protein_coding |
O75915 |
FUNCTION: Regulates intracellular concentrations of taurine and glutamate. Negatively modulates SLC1A1/EAAC1 glutamate transport activity by decreasing its affinity for glutamate in a PKC activity-dependent manner. Plays a role in the retention of SLC1A1/EAAC1 in the endoplasmic reticulum. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R5J9, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ES40}. |
Acetylation;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Expression of this gene is affected by vitamin A. The encoded protein of this gene may be associated with the cytoskeleton. A similar protein in rats may play a role in the regulation of cell differentiation. The rat protein binds and inhibits the cell membrane glutamate transporter EAAC1. The expression of the rat gene is upregulated by retinoic acid, which results in a specific reduction in EAAC1-mediated glutamate transport. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10550; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic cytosol [GO:0099523]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to oxidative stress [GO:0008631]; L-glutamate import across plasma membrane [GO:0098712]; L-glutamate transmembrane transport [GO:0015813]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; negative regulation of L-glutamate import across plasma membrane [GO:0002037]; negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010917]; negative regulation of transport [GO:0051051]; neuron death in response to oxidative stress [GO:0036475]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032874]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
12119102_highly conserved protein and genomic organization amongst vertebrates 12562531_protein expression is upregulated by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin and not by retinoic acid 15864752_Rsults suggest that JWA can be regulated by oxidative stress and is actively involved in the signal pathways of oxidative stress in the cells. 16331563_Data show that the JWA -76G-->C variant genotype may play an important role in transcription regulation of JWA gene and in the susceptibility to bladder cancer. 16331563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16430862_JWA may function as a lineage-restricted gene during differentiation along the monocyte/macrophage-like or granulocytic pathway 16468075_all-trans retinoic acid up-regulates JWA expression by stimulating the transcriptional activity of JWA gene promoter 16481131_This paper deals primarily with PRAF2, but comparisons with PRAF3 are also provided. 16638297_all-trans retinoic acid increased JWA gene expression in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 16640902_The JWA determined might function as a potential effective environmental responsive gene and actively participated in the process of B (a) P exposure associated with intracellular signal pathways of DNA damage and repair 16766476_JWA participates in the signal pathways of H2O2 induced oxidative stress in K562 cells 16922813_The effects of All Trans Retinoic Acid in regulating cellular proliferation and apoptosis may be mediated in part by JWA expression. 17336041_JWA regulated-tumor cellular migration might involve MAPK cascades activation and F-actin cytoskeleton rearrangement mechanisms. 17479401_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17479401_Three novel functional genetic poly- morphisms of JWA gene, -76C, 454A, and 723G, appear to contribute to the etiology of bladder cancer 17479402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17479402_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of JWA were associated with enhanced risk of gastric cancer and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. 17479403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17479403_The potentially functional genetic polymorphism 454CA of the JWA gene appears to contribute to the risk of multiple kinds of leukemia in a south Chinese population. 17646425_These results show GTRAP3-18 to negatively and dominantly regulate cellular GSH content via interaction with EAAC1 at the plasma membrane. 18167356_Expression of GTRAP3-18 delays the ER exit of EAAC1, as well as other members of the excitatory amino acid transporter family. 19080375_JWA night play an important role in neoplastic transformation of HBE cells through regulation of p53 expression. 20201924_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22357531_The gene polymorphisms at site 76 and GG/CT haploid type of JWA gene were associated with hypertension in workers exposed to high temperature. 22433565_PRAF3 plays an important role in the regulation of tumor progression and metastasis and serves as a tumor suppressor in human ESCC. We propose that PRAF3 might be used as a potential therapeutic agent for human ESCC. 22452940_JWA and XRCC1 protein levels were downregulated in gastric cancer lesions compared with adjacent noncancerous tissues;JWA and XRCC1 protein expressions in tumor are candidate prognostic markers and predictive factors for benefit from adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy in resectable gastric carcinoma 23109897_This review gives an overview of EAAC1-mediated GSH synthesis, and its regulatory mechanisms by GTRAP3-18 in the brain, and a potential approach against neurodegeneration. 23169062_data demonstrate that JWA plays a crucial role in HCC progression and suggest JWA may be a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC. 23285001_A combined effect of p53 with JWA as efficient prognostic indicators was found for the first time. 23461062_JWA plays an important role in the occurrence and progress of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and that high expression level of JWA may predict a favorable prognosis in ESCC patients. 24064223_A significant negative correlation between JWA and ILK in melanoma biopsies. 24072772_Loss of JWA expression was strongly correlated with increased gastric cancer angiogenesis. 24157826_JWA has an important role in ING4-regulated melanoma angiogenesis, and ING4/JWA/ILK are promising prognostic markers and may be used as anti-angiogenic therapeutic targets for melanoma. 25476899_JWA reverses cisplatin resistance via the CK2-XRCC1 pathway in human gastric cancer cells. 25586271_the JWA gene may regulate human breast cancer cells through the MAPK signaling pathway using different types of regulation. 26046674_JWA and topoisomerase II alpha regulate each other in tumor cells arrested in G2/M. 27167206_our results demonstrate that JWA is a novel negative regulator of HER2 expression...in HER2-positive gastric cancer cells 28428137_Protective effect of JWA against paraquat neurotoxicity involves regulation of the MEK/PI3K-Nrf2 axis. 29481911_increased RNF185 expression facilitated GC cell migration in vitro and promoted GC metastasis in vivo by downregulating JWA expression. 29658570_These data demonstrated that JWA suppressed the migration/invasion of breast carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression of CXCR4, and suggested that JWA may harbor prognostic and therapeutic potential in patients with breast cancer. 31726816_Correlation between JWA gene polymorphism and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 35293383_ARL6IP5 reduces cisplatin-resistance by suppressing DNA repair and promoting apoptosis pathways in ovarian carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000035199 |
Arl6ip5 |
864.749162 |
2.1178864121 |
1.082625 |
0.059236485 |
336.148412 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000440242245554461721629631182429605330117539363724262608764706437208287527462598754851276814703946861396171475156707243429450039453687791943235862919243527922487393052579572716106596260831479439090685445989947766065597534179687500000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000140042576387583082486103077992187882902780453037178883929434782202424967217970662197813599580118182831823535193005338717410446057544490745805002364875593752955227803429997702869041955459072923417807032819837331771850585937500000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1187.9658093 |
39.9927290 |
565.0183100 |
14.9796221 |
| ENSG00000144852 |
8856 |
NR1I2 |
protein_coding |
O75469 |
FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11297522, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11668216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12578355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18768384, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19297428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9727070}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene product belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily, members of which are transcription factors characterized by a ligand-binding domain and a DNA-binding domain. The encoded protein is a transcriptional regulator of the cytochrome P450 gene CYP3A4, binding to the response element of the CYP3A4 promoter as a heterodimer with the 9-cis retinoic acid receptor RXR. It is activated by a range of compounds that induce CYP3A4, including dexamethasone and rifampicin. Several alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms, some of which use non-AUG (CUG) translation initiation codon, have been described for this gene. Additional transcript variants exist, however, they have not been fully characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8856; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear receptor binding [GO:0016922]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; xenobiotic catabolic process [GO:0042178]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805]; xenobiotic transport [GO:0042908] |
9727070_In-vitro transcription/translation studies show that translation of pregnane X receptor mRNA initiates at a non-AUG (CUG) codon. 11865669_promiscuous nuclear receptor that responds to a wide variety of drugs, xenobiotics and endogenous compounds, and plays a critical role in mediating drug-drug interactions in humans 12072427_Role of SXR in xenobiotic inhibition of CYP3A4 promotor activity 12397176_mediates the proliferative action of mast-cell tryptase: possible relevance to human fibrotic disorders 12413960_alternative splicings for hPXR may largely contribute to the interindividual variability in CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein induction 12485946_Pregnane X receptor mRNA expression levels are compared in a panel of 12 individual human liver samples; a 27-fold variability in PXR mRNA expression is found. 12569201_human PXR requires a specific agonist different from that required in mice to induce cyp3A expression 12606758_results provide evidence that the nuclear import of SXR is mediated by bipartite type of nuclear localization signal, which is recognized by three groups of importin adaptors for targeting the nuclear rim 12644700_control of steroid, heme, and carcinogen metabolism by this protein in transgenic mice 12760308_The present data indicate that SXR is a key system to induce, maintain and reverse a cisplatin-resistant phenotype in endometrial cancer cells. 12909012_2.0A crystal structure of the human PXR ligand-binding domain (LBD) in complex with the cholesterol-lowering compound SR12813 and a 25 amino acid residue fragment of the human steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) containing one LXXLL motif 12920130_steroid and xenobiotic receptor(SXR) has a novel role as a mediator of bone homeostasis in addition to its role as a xenobiotic sensor 14977869_individual variation in pregnane X receptor expression may account for differential expression of some UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms between subjects 14977870_pregnane X receptor is a major determinant of CYP2B6-inducible expression 15252010_pregnane X receptor (PXR) and constitutively activated receptor (CAR) mediate induction of CYP3A5 in human liver and intestine 15316010_PXR-mediated gene regulation is affected by its DNA binding site 15322103_ligand-activated PXR interferes with HNF-4 signaling by targeting the common coactivator PGC-1, which underlies physiologically relevant inhibitory cross-talk between drug metabolism and cholesterol/glucose metabolism 15535420_expressed approximately 250-fold lower in peripheral blood mononuclear cells than in liver, and significantly correlated to MDR1 mRNA 15630458_xenobiotics and drugs can modulate 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3)-24-hydroxylase gene expression and alter vitamin D(3) hormonal activity and calcium homeostasis through the activation of PXR 15690482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15713537_findings demonstrated age-related differences in the body's capacity to metabolize steroids and xenobiotic compounds and suggest an important role for SXR and its target genes, CYP3A4 and MDR1 in this process 15772695_pxr polymorphism is associated with decreased expression of MDR1 mRNA in intestinal villi 15919766_there is cross talk between distal CAR/PXR sites and HNF4alpha binding sites in the CYP2C9 promoter and that the HNF4alpha sites are required for maximal induction of the CYP2C9 promoter. 15933212_role in transcriptional regulation of CYP2C8 15985196_May be involved in metabolic detoxification in drug-induced osteomalacia. 16085054_PXR expression is required for Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL up-regulation upon PXR activators treatment in human and rat hepatocytes. 16297466_PXR was observed to be a predominantly nuclear protein maintaining a dynamic equilibrium between the nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments of interphase cells. 16328955_The minimal essential region for promoter activity has been mapped to a 160 bp region upstream of the transcription initiation site, an area that also showed nuclear protein binding. 16452398_structural models of the pregnane X receptor (PXR)complexes PXR-LBD/SMRT-ID1 and PXR-LBD/SMRT-ID2 reveal key interactions that account for binding preferences. 16472590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16472590_genetic variation in the PXR encoding gene, which has been associated with altered activity of PXR, is strongly associated with susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease, crohn disease and ulcerative colitis. 16507781_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16556603_cross-regulation of CD36 by PXR and PPARgamma suggests that this fatty acid transporter may function as a common target of orphan nuclear receptors in their regulation of lipid homeostasis 16606623_SXR mediates vitamin K2-activated transcription of extracellular matrix-related genes and collagen accumulation in osteoblastic cells 16608838_NF-kappaB p65 directly interacted with the DNA-binding domain of RXRalpha and may prevent its binding to the consensus DNA sequences, thus inhibiting the transactivation by the PXR.RXRalpha complex. 16691293_Data show that activation of steroid and xenobiotic receptor does not induce cytochrome P450, family 24 (CYP24)-mediated expression, but inhibits vitamin D receptor-mediated CYP24 promoter activity. 16831602_The pregnane X receptor is transcriptionally functional in human hepatic stellate cells and activators inhibit transdifferentiation and proliferation. 16834332_These results suggest that the unique Trp-Zip-mediated PXR homodimer plays a role in the function of this nuclear xenobiotic receptor. 16837625_hPXR activation in vivo increased P-glycoprotein activity and tightened the blood-brain barrier to methadone, reducing the drug's CNS efficacy. This is the first demonstration of the ability of PXR to alter the efficacy of a CNS-acting drug. 16841097_clinical consequences for individuals undergoing therapeutic exposure to the wide variety of drugs that are also SXR agonists 16857725_CYP2A6 is induced via PXR and PGC-1alpha through the DR4-like element at the distal response region. 16952547_Functional SXR gene variants appear to modify disease course in PSC. 16952547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16973756_PXR is a potential endocrine disrupting factor that may have broad implications in steroid homeostasis and drug-hormone interactions 17028159_Dietary isothiocyanate sulforaphane is the first identified naturally occurring antagonist for SXR. 17048007_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17050801_Human pregnane X receptor gene polymorphisms and alternative mRNA splicing were investigated as possible contributors to individual variability in CYP3A metabolic activity. 17050801_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17088262_there may be an intestine-specific PXR/CYP27A1/LXRalpha pathway that regulates intestine cholesterol efflux and HDL assembly. 17262809_PXR protein levels were equal in uninflamed and inflamed tissue of CD and UC patients despite low PXR mRNA levels in inflamed tissue. 17279585_PXR plays a critical role in the regulation of P450 3A4 expression in osteosarcoma and that its expression and activation in these tumors may influence the effect of chemotherapeutic agents on the induction of target genes implicated in drug resistance 17327420_Study of molecular structure provides detailed insights into the manner in which human PXR responds to a wide range of endobiotic compou 17404718_In comparison with previously published data, we identified 13 novel polymorphisms. Genetic variation contributing to altered NR1I2 function may have an important clinical impact. 17404718_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17418145_T0901317 binds and activates PXR with the same nanomolar potency with which it stimulates LXR activity. 17429319_not only the Q158K variant found in Chinese, but also in native pregnane X receptor variants in other ethnic groups (D163G, A370T, R381W, and I403V) affect CYP3A4 induction by altering steroid receptor coactivator-1 recruitment 17436120_Comparative genomics of xenobiotic metabolism: a porcine-human PXR gene comparison. 17438109_Some azole anticancer agents repress the coordinated activation of genes involved in drug metabolism by blocking PXR activation. 17507630_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17507630_There were significant phytoestrogen interactions with polymorphisms in ESR1 and NR1I2 genes in affecting estrone levels; we conclude that phytoestrogens modulate sex hormone and SHBG levels in postmenopausal women. 17526937_Tamoxifen activated the SXR-mediated transcription through CYP3A4 and MDR1 promoters in a ligand- and receptor concentration-dependent manner. 17573484_Discovery of a highly active ligand of human pregnane X receptor is reported. 17576789_Human pregnane X receptor antagonists and agonists define molecular requirements for different binding sites. 17635106_Nuclear PXR represses the transcription of the glucose-6-phosphatase gene by inhibiting the DNA-binding ability of cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB). 17712488_Reduction of sperm motility by tryptase through the PAR-2 receptor involves epidermal growth factor receptor pathways. 17761971_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17764444_CYP3A4 enhancers co-ordinate the proximal promoter in responding similarly to the pregnane X receptor but differentially to hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha 17827782_we have utilized a target selective human pregnane X receptor-siRNA (hPXR-siRNA)-adenovirus expression system to examine the contribution of hPXR on the gene regulation of drug-metabolizing P450s in human hepatocytes 17828778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17828778_The data seem to support the association of the PXR locus with extensive ulcerative colitis and the interaction between PXR and MDR1 genes. 17876342_Inter-individual/inter-ethnic variations of docetaxel and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics exist, but genotypic variability of PAR cannot account for this variability. 17876342_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17924830_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17924830_Polymorphisms in the NR1I2 gene are not significantly associated with epilepsy treatment responses. 17925385_PXR promoter and intron 1 SNPs associated with PXR target gene expression (CYP3A4) 17962194_PAR2 up-regulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression via an ERK1/2-mediated activation. 18056193_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18095058_Besides functioning as a xenobiotic biosensor, our findings show that SXR is also a vitamin K2 target and an important transcriptional factor that regulates bone homeostasis in bone cells[review] 18192894_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18220558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18268015_miR-148a post-transcriptionally regulated human PXR, resulting in the modulation of the inducible and/or constitutive levels of CYP3A4 in human liver. 18276839_These results extend the 5'UTR sequence of PXR1 and PXR2 and define new proximal promoters for both; in addition, PXR2 has transcriptional activity comparable to that of PXR1. 18294295_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18305370_In this review, pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a nuclear receptor that plays a critical role in modulating hepatic energy metabolism. 18305375_The activities of the human pregnane X receptor promoter are significantly increased by co-expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha. 18381611_NR1I2 gene haplotype is not associated with Crohn's disease 18381611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18391510_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18391510_there are marked differences in the mutant frequencies of A11156C and T11193C of PXR between Han Chinese and other ethnic groups. The mutant frequency in the coding region (exons 2 and 4) of PXR was very low in Han Chinese 18502461_Influence of NR1I2 polymorphism on prednisolone pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients was evaluated. Those carrying the allele possessed higher intestinal metabolic activity for prednisolone, greatly reducing its maximal plasma concentration. 18502461_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18518855_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18765524_PXR activation, regardless of the type of ligand agonist present, promotes the 'malignant' phenotype of cancer cells. 18784074_Cdk2 negatively regulates the activity of hPXR, and suggest an important role for Cdk2 in regulating hPXR activity and CYP3A4 expression in hepatocytes passing through the cell cycle 18800312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18800312_The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of coding variation in hPXR (NR1I2) in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) and to functionally asses the response of PXR variants to ligands of interest in ICP. 18831695_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18831695_investigated pregnane X receptor polymorphisms in relation to unboosted atazanavir plasma concentrations in 2 cohorts of patients. The polymorphism 63396T-->C predicted concentrations below the minimum effective concentration with odds ratios of 18 18981011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18981011_This study showed that PXR*1B was associated with reduced hepatic mRNA expression of PXR and its downstream targets, CYP3A4 and ABCB1 19010908_the interplay between a xenobiotic nuclear receptor PXR and OATP1A2 that could contribute to the pathogenesis of breast cancer. 19011999_the expression of SXR in breast cancer cells may alter the ER signaling, which may play crucial role for growth and differentiation of breast cancer cells 19034627_Bioactive terpenoids and flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba extract induce the expression of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes through pregnane X receptor, constitutive androstane receptor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated pathways. 19115096_Hybrid scoring and classification approaches to predict human pregnane X receptor activators. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19129222_findings indicate that PXR is involved in the regulation of CYP4F12 and that PXR along with SRC1 binds to a broad range of promoters but that many of these are not inducible by rifampicin. 19141612_the species-specific impact of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase signaling on pregnane x receptor and provide a molecular explanation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-mediated repression of human pregnane x receptor activity. 19144646_demonstrated mutual interactions and functional interplays between PXR and PRMT1, and this interaction may be important for the epigenetics of PXR-regulated gene expression 19171678_a functionally significant phosphomimetic mutant (hPXR(T57D)) and show p70 S6K phosphorylation and regulation of hPXR transactivation to support the notion that phosphorylation plays important roles in regulating hPXR function 19173680_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19232333_The 6bp-deletion affects the PAR-2(SV1) expression greatly, contributing to the adjustment of expression and function of total PXR--which leads to the changed target gene expressions, partly explaining interindividual variations in CYP3A4 and MDR1. 19297428_results presented demonstrate that there is a species-specific difference in the activation of Pregnane X receptor (PXR) by isoflavones and equol 19401882_Comparing tumors treated with primary enucleation with tumors treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation showed no significant differences in the expression of multi-drug resistance proteins or pregnane xenobiotic receptor. 19460945_Rifampicin-activated human pregnane X receptor and CYP3A4 induction enhance acetaminophen-induced toxicity. 19470925_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19505191_expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes cytochromes is controlled by pregnane X receptor--REVIEW 19516190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19516190_We could not confirm an association of the -25385C/T polymorphism in pediatric patients with IBD. 19593667_The results suggested that pregnane X receptor, associated with multiple resistance related protein 3, may play an important role in human colon cancer resistance to chemotherapeutics. 19617467_18 potential phosphorylation sites are identified in the PXR protein by use of in silico consensus site prediction methods; seven are further characterized based on their ability to modulate PXR activation function in reporter gene analysis. 19702932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19739075_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19746521_Data suggest a potential role of hPXR in breast cancer resistance to drug treatments. 19833192_This study provides the first demonstration of pregnane x receptor involvement in oltipraz transcriptional activation of CYP2B6 gene and of the inhibitory effect of oltipraz on CYP2B6 activity. 19842932_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19902988_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940802_polymorphisms and related haplotypes may contribute to disease severity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by influencing susceptibility to progress to more severe stages of the disease 19958310_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20082578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20082578_PXR-3'UTR single nucleotide polymorphisms rs3732359 and rs3732360 associated with higher CYP3A activity in vivo in African-Americans 20107201_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20171174_these results demonstrate that nuclear receptor binding to PXR response elements interferes with PXR-mediated expression and induction of CYP3A4 and thereby contributes to the interindividual variability of induction. 20218903_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20218903_Six haplotypes were determined for three PXR single nucleotide polymorphisms. 20222094_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354687_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20361990_Data support the role of endosulfan-alpha as a strong activator of PXR and inducer of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4, which may impact metabolism of CYP2B6 or CYP3A4 substrates. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20518891_Our data suggest that SXR is a prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer and may represent a useful marker to identify patients at risk of recurrence or death. 20531417_PXR inhibits the proliferation and tumourigenicity of colon cancer cells by controlling cell cycle at G(0)/G(1) cell phase by regulating p21(WAF1/CIP1) and E2F/Rb pathways. 20538049_This study provided molecular evidence that cytokine secretion directly contributed to the decreased capacity of oxidative biotransformation in human liver. 20538721_results implicate a novel and important role for PP2Cbetal in regulating hPXR activity and CYP3A4 expression by inhibiting or desensitizing signaling pathways that negatively regulate the function of pregnane X receptor in liver cells 20624854_For the first time a synergistic interplay was found between pregnane X receptor-mediated induction and a CYP2B6 polymorphism. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20635135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635135_data suggest that among the many known transporters common variations of PXR, SLCO1A2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, and SLCO2B1 do not contribute to breast carcinogenesis 20818746_Stable PXR overexpression markedly increases the potential of HepG2 for bioartificial liver application. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20836841_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20836841_Polymorphism in PXR was not associated with colorectal cancer. 20840328_For patients with invasive bladder cancer, SXR expression has value as a predictor of survival independent of the standard pathological predictors. 20846001_Similar patterns of induction in PXR and ABCG2 genes suggest a probable relationship between these two factors 20861742_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20861742_distribution of SNPs in NR1I2, CYP3A4, CYP2B6 genes in white and sub-Saharan Africans with HIV; presence of NR1I2 polymorphisms can alter induction of CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 promoter, potentially adding to unpredictable nature of anti-HIV drug interactions 20876786_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20876786_it is suggested the NR1I2 TGT genotype decreases the bupropion hydroxylation induced by treatment with rifampin, particularly in CYP2B6*6 carriers 20970601_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21127053_PXR activates the GADD45beta gene, increasing p38 MAPK phosphorylation, and leading HepG2 cells to change morphology and migrate. 21245992_PXR and LXR polymorphisms, but not NF-kB or PPARgamma, may contribute to risk of IBD, especially among never smokers 21316268_There is no association between PXR and ABCB1 polymorphisms and their haplotypes, and interaction between them, with response to monotherapy treatment of epilepsy in Chinese, Indian, and Malay subgroups. 21323950_PXR nuclear expression was able to separate high-grade dysplasia from low-grade and no dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus patients 21329659_the acetylation status of PXR regulates its selective function independent of ligand activation. 21342487_PXR promoter methylation is involved in the regulation of intestinal PXR and CYP3A4 mRNA expression and might be associated with the inter-individual variability of the drug responses of colon cancer cells. 21359593_Both PXR mRNA and protein were significantly up-regulated in obstructive cholestasis compared with the controls 21391917_PAR1 receptor signalling desensitization is counteracted through PAR4 receptor signalling in platelets. 21402137_Repeated MDMA use in combination with other therapeutic drugs, may result in adverse drug-drug interactions via PXR and/or CYP3A inhibition. 21438836_association between ABCB1 or PXR expression in PBMCs and lipid or apolipoprotein plasma concentrations were not significant in this subset of healthy subjects 21461878_Data show that frog TFF2 activates protease-activated receptor (PAR) 1 to induce human platelet aggregation, and suggest that human TFF2 promotes cell migration via PAR4. 21517853_Down-regulation of pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor proteins with small-interfering RNA decreases P-glycoprotein expression. 21532337_novel transcription factor binding partners for PIAS3 including ETS, EGR1, NR1I2, and GATA1 were identified. 21596433_Expression of PXR was found to be very low in both normal and cholestatic placenta. 21733184_The SXR pathway is involved in colon cancer irinotecan resistance in colon cancer cell line via the upregulation of select detoxification genes. 21742782_These results suggest that acetyl tributyl citrate specifically induces CYP3A in the intestine by activating SXR. 21747170_Pregnane X receptor activation induces FGF19-dependent tumor aggressiveness in humans and mice 21805522_Presented is the 2.8 A resolution crystal structure of the human PXR ligand-binding domain in complex with PNU-142721. 21808872_Our results suggest that variants in the PXR gene should be considered in pharmacogenetic studies involving Brazilians from the southeast region, since the miscegenation varies from region to region. 21830270_NR1I2 single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 21913896_All atorvastatin metabolites induced the assembly of PXR and activated CYP3A4 promoter activity. 21918980_tested the hypothesis that common polymorphisms in the ABCB1, ABCC2, ABCG2, NR1I2 genes could be implicated in lymphoma risk. We selected 68 SNPs in the four genes, and we genotyped them in 1,481 lymphoma cases and 1,491 controls 21954916_A rare haplotype of the NR1I2 (PXR) locus was associated with the individual susceptibility for chronic periodontitis in a German cohort. 21977915_This study aimed to investigate the expression and genetic variation of PXR in reflux esophagitis (RE), Barrett's esophagus (BE) and esophageal adenocarcinoma. 22000295_Competitive binding of rifampicin-activated PXR with RXRalpha arrests G0/G1 cell-cycle phase through inhibiting combination of RXRalpha with other partners. 22023334_These results suggest that PROX1 could negatively regulate SXR signals in some tumor cells, such as HCC cells, where both SXR and PROX1 are expressed. 22050110_Combined data of present and previous studies showed that high immunoreactivity scores for both the SXR and CYP3A4 correlated with significantly better cancer-specific survival rates in multivariate regression analyses. 22076448_The CYP3A4 reporter activity enhanced by overexpression of human pregnane X receptor is further increased by treatment with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. 22093699_CAR transactivates ABCG2 through the DR5 motif located in its distal promoter in hepatocytes and the motif prefers CAR to pregnane X receptor. 22126990_All the four P450 isoforms, including CYP2C9, were elevated by RIF treatment. 22166712_Pregnane X receptor regulates drug metabolism and transport in the vasculature and protects from oxidative stress. 22185585_The mechanism of ligand-dependent activation in pregnane X receptor differs significantly from that seen in many other nuclear receptors. 22285937_Results provide a way to development of a dual PXR agonist/FXR antagonist with a robust immunomodulatory activity and endowed with the ability to modulate the expression of bile acid-regulated genes in the liver. 22292071_Pregnane X receptor and yin yang 1 contribute to the differential tissue expression and induction of CYP3A5 and CYP3A4. 22333269_Suggest that lower expression of HNF4alpha and PGC1alpha may impair rifampicin-mediated CYP3A4 induction under conditions of PXR overexpression in fetal liver cells. 22453080_Curation of the data resulted in 270 human PXR agonists and 248 non-agonists. 22453193_PXR may be associated with risk of Delayed graft function (DGF), independent of previously identified risk factors. 22750628_Similar patterns of induction and reduction in PXR and ABCG2 genes and NF-kappaB activity suggest a probable relationship between ABCG2, PXR and NF-kappaB. 22829544_Roscovitine stimulated the expression of UGT1A1 by inhibiting CDK2, which phosphorylated PXR at Ser350 to suppress binding with RXR and coactivator and maintain the acetylation of PXR protein. 22952895_The present study identified a promoter region of mouse PXR gene and the transregulatory factors responsible for PXR promoter activity. 22968811_In therapeutic doses ketoconazole does not inhibit pregnane X receptor-mediated induction of CYP3A in vivo. 23160820_Suggest that RBCK1 is important for the ubiquitination of PXR and may play a role in its proteasomal degradation. 23160821_Study reveals that alpha-tocopherol is a partial agonist of PXR and that PXR is necessary for Cyp3a induction by alpha-tocopherol Pxr-null and PXR-humanized mice. 23288240_Letter: report PXR/CYP2B6 polymorphisms interact to impact methadone metabolism in treated heroin addicts. 23303387_Common genetic variants in the xenobiotic transport and metabolism regulator genes PXR and CAR do not have a significant association with multiple myeloma risk. 23479137_This study suggests a malfunctioning of PXR and thus a minor relevance for iatrogenic chemotherapy resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinom 23503472_A total of 101 renal transplant recipients receiving cyclosporine were genotyped for CYP3A4(*)1G, CYP3A5(*)3, ABCB1 C1236T, G2677T/A, C3435T, NFKB1 -94 ins/del ATTG, and NR1I2 polymorphisms. 23525103_Antagonist binding sites mapped to the surface of the nuclear xenobiotic pregnane X receptor using a novel yeast-based strategy. 23527115_No correlation of hsa-miR-148a with expression of PXR or CYP3A4 in human livers from Chinese Han population. 23562850_SMRT may be recruited in the SXR-cofactor complex even in the presence of ligand; SMRTmay be involved not only in SXR-mediated suppression without ligand, but also in ligand-activated transcription to suppress 23574760_Deactivation of pregnane X receptor is associated with Crohn's disease. 23602807_These structures establish that PXR and RXRalpha form a heterotetramer unprecedented in the nuclear receptor family of ligand-regulated transcription factors. 23609392_NR1/2 polymorphisms had an influence on RLAI (risperidone long-acting injection) exposure and on drug-induced adverse effects 23614276_Report PXR expression in human parotid glands. 23840296_Genetic variations in PXR affect induction of Bupropion hydroxylation by sodium ferulate. 23878263_Results indicate that pregnane X receptor (PXR) represents a flow-activated detoxification system to protect endothelial cells (ECs) against damage by xeno- and endobiotics. 23977680_Developed a protocol using the nonradioactive electrophoretic mobility shift assay to study interactions between human pregnane X receptor with promoter CYP3A4 response element DNA sequences. 24052258_Neutrophil elastase and proteinase-3 trigger G protein-biased signaling through proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1). 24088131_In the promoter region of SXR. 24097976_PAR1 and PAR4 require allosteric changes induced via receptor cleavage by alpha-thrombin to mediate heterodimer formation 24166671_It could be speculated that, due to its dual role as a xenosensor and a regulator of energy metabolism, PXR, in concert with a mixture of PXR agonists in the environment, contributes to the present-day type 2 diabetes epidemic. 24184507_For the first time, direct evidence is provided that PXR is phosphorylated at specific residues, suggesting that further investigation is warranted to fully understand the regulation of PXR by phosphorylation. 24204015_Activation of PXR in hepatocytes is mediated through serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (SGK |
ENSMUSG00000022809 |
Nr1i2 |
8.324317 |
0.2038927817 |
-2.294117 |
0.582820594 |
17.224813 |
0.00003320707791874590719813017947181776889920001849532127380371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000097796670269660815745342563598541119063156656920909881591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0325319 |
1.2089432 |
14.7718762 |
3.2122270 |
| ENSG00000144867 |
58477 |
SRPRB |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5M8 |
FUNCTION: Component of the signal recognition particle (SRP) complex receptor (SR) (By similarity). Ensures, in conjunction with the SRP complex, the correct targeting of the nascent secretory proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane system (By similarity). May mediate the membrane association of SR (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P47758}. |
3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;GTP-binding;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has similarity to mouse protein which is a subunit of the signal recognition particle receptor (SR). This subunit is a transmembrane GTPase belonging to the GTPase superfamily. It anchors alpha subunit, a peripheral membrane GTPase, to the ER membrane. SR is required for the cotranslational targeting of both secretory and membrane proteins to the ER membrane. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:58477; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; signal recognition particle receptor complex [GO:0005785]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; protein targeting to ER [GO:0045047]; SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, signal sequence recognition [GO:0006617] |
12918107_APMCF1 may be the gene coding human signal recognition particle receptor beta and belongs to the small-G protein superfamily. Its strong expression pattern in colon cancer suggests it may play a role in colon cancer development. 17080297_APMCF1 participates at least partially in cell cycle regulation through regulating genes such as p21 and TIMP3. 28902358_Results show that SRPRB promotes cell apoptosis through NF-kappaB activation. Its expression is regulated by SERP1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 31002879_Variation in SRPRB was associated with lower blood alcohol content in Korean subjects, suggesting likely involvement in alcohol metabolism and possible association with the development of alcohol-related diseases in Korea. |
ENSMUSG00000032553 |
Srprb |
325.351853 |
3.1890965165 |
1.673148 |
0.179785367 |
82.783107 |
0.00000000000000000009156921318563346621456291899142724402129753508424600213534694237438316122279502451419830322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000802590015807571182819182165989525384384902722549641950963716929834390612086281180381774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
469.8651054 |
51.8869848 |
147.9766741 |
12.1571196 |
| ENSG00000145014 |
93109 |
TMEM44 |
protein_coding |
Q2T9K0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:93109; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000022537 |
Tmem44 |
132.486531 |
0.4620397360 |
-1.113911 |
0.191026630 |
33.789987 |
0.00000000613940464068339729330364852978932366234232631541090086102485656738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000027294461595327393363921949826118862336699066872824914753437042236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
83.7094988 |
10.0921517 |
182.4243603 |
15.1983885 |
| ENSG00000145020 |
275 |
AMT |
protein_coding |
P48728 |
FUNCTION: The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16051266}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aminotransferase;Disease variant;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide |
|
This gene encodes one of four critical components of the glycine cleavage system. Mutations in this gene have been associated with glycine encephalopathy. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:275; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; aminomethyltransferase activity [GO:0004047]; transaminase activity [GO:0008483]; glycine catabolic process [GO:0006546]; glycine decarboxylation via glycine cleavage system [GO:0019464] |
16051266_x-ray crystallographic structure of human T-protein of glycine cleavage system 16450403_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20307617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22171071_Two unique non-synonymous changes were identified in the AMT gene in patients with neural tube defects. 25231368_Data indicate no mutation was found in glycine cleavage system protein-H (GCSH) and suggest that mutations in both glycine decarboxylase (GLDC) and aminomethyltransferase (AMT) are the main cause of glycine encephalopathy in Malaysian population. 27362913_The position and frequency of the breakpoint for CNVs correlated with intron size and presence of Alu elements. Missense mutations, most often recurring, were the most common type of disease-causing mutation in AMT |
ENSMUSG00000032607 |
Amt |
17.789686 |
0.0343237330 |
-4.864650 |
0.741673057 |
61.142110 |
0.00000000000000531001334253387237216152924036420040437118331860810727107491402421146631240844726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000036218020765157092023127688505201381012935882980352531035350693855434656143188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2635036 |
0.7499991 |
35.2301634 |
10.1994280 |
| ENSG00000145050 |
7873 |
MANF |
protein_coding |
P55145 |
FUNCTION: Selectively promotes the survival of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral mid-brain (PubMed:12794311). Modulates GABAergic transmission to the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra (By similarity). Enhances spontaneous, as well as evoked, GABAergic inhibitory postsynaptic currents in dopaminergic neurons (By similarity). Inhibits cell proliferation and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced cell death (PubMed:18561914, PubMed:22637475, PubMed:29497057). Retained in the ER/sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) through association with the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone protein HSPA5 under normal conditions (PubMed:22637475). Up-regulated and secreted by the ER/SR in response to ER stress and hypoxia (PubMed:22637475). Following secretion by the ER/SR, directly binds to 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, a lipid sulfatide in the outer cell membrane of target cells (PubMed:29497057). Sulfatide binding promotes its cellular uptake by endocytosis, and is required for its role in alleviating ER stress and cell toxicity under hypoxic and ER stress conditions (PubMed:29497057). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P0C5H9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12794311, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18561914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22637475, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29497057}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Lipid-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Secreted;Sialic acid;Signal;Stress response;Unfolded protein response |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and golgi, and is also secreted. Reducing expression of this gene increases susceptibility to ER stress-induced death and results in cell proliferation. Activity of this protein is important in promoting the survival of dopaminergic neurons. The presence of polymorphisms in the N-terminal arginine-rich region, including a specific mutation that changes an ATG start codon to AGG, have been reported in a variety of solid tumors; however, these polymorphisms were later shown to exist in normal tissues and are thus no longer thought to be tumor-related. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:7873; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0033018]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; sulfatide binding [GO:0120146]; dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:0071542]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; regulation of response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1905897]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
18561914_Armet is a novel secreted mediator of the adaptive pathway of unfolded protein response. 18718866_The widespread expression of MANF together with its evolutionary conserved nature and regulation by brain insults suggest that it has important functions both under normal and pathological conditions in many tissue types. 19258449_structures of MANF and CDNF were solved; structure explains why MANF and CDNF are bifunctional; neurotrophic activity may reside in the N-terminal domain and ER stress response in the C-terminal domain 20685313_Pretreatment with adeno-associated-virus vector containing human MANF reduces the volume of cerebral infarction and facilitates behavioral recovery in experimental stroke rats. 21047780_MANF and C-MANF protect neurons intracellularly as efficiently as Ku70. 23255601_MANF binding to the plasma membrane also required the RTDL sequence and was inhibited with a peptide known to interact with KDELRs, suggesting MANF binds KDELRs at the surface. 23956175_We demonstrate that Armet and Creld2 are genotype-specific ER stress response proteins with substrate specificities, and that aggregation of mutant matrilin-3 is a key disease trigger in MED that could be exploited as a potential therapeutic target 25543119_MANF is a protein that interacts with RTN1-C 26429332_the selective expression of MANF in splenocytes may be involved in plasma cell differentiation and immune regulation. 26720341_the role of two short sequence motifs within the carboxy-(C) terminal domain of MANF in its neuroprotective activity, was studied. 27356471_Our data indicate that increased MANF concentrations in serum are associated with the clinical manifestation of type 1 diabetes in children, but the exact mechanism behind the increase remains elusive 28216543_Serum MANF level was higher in patients with newly diagnosed prediabetes and T2 Diabetes Mellitus than in normal glucose tolerance controls. MANF appears to be associated with Matsuda Index, QUICKI and HOMA-IR in prediabetes patients. 28740209_Single nucleotide polymorphism in MANF gene is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. 29349573_The results show that GDNF, CDNF, and MANF have divergent effects on dopaminergic neurotransmission, as well as on dopamine synthetizing and metabolizing enzymes. 29497057_Sulfatide binding promotes cellular MANF uptake and cytoprotection from hypoxia-induced cell death. 29649564_High MANF expression is associated with hepatitis B. 29959908_Our results showed MANF alleviated progressive neuronal degeneration and prevented locomotion defects 30032427_MANF has antiapoptotic and mitogenic properties that protect pancreatic beta cells against stress-induced cell death 30365109_the present study demonstrated that the AP-1 complex may be a novel regulator of MANF transcriptional enhancement, and that MANF is a novel downstream target of AP-1, which may indicate a novel role of AP-1 in regulating inflammatory pathways. 31469428_Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Inhibits Liver Cancer Through Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier (SUMO)ylation-Related Suppression of NF-kappaB/Snail Signaling Pathway and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. 31586115_Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is Upregulated with Therapeutic Fasting in Humans and Diet Fat Withdrawal in Obese Mice. 31785307_Effects of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor on cerebral angiogenesis in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. 31789884_Circulating Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Negatively Correlates With Atrial Apoptosis in Human Chronic Atrial Fibrillation. 32382531_Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of MANF Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 32472754_Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor: A treatment option for parkinson's disease. 33064897_Hepatocyte-derived MANF alleviates hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury via regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in mice. 33460650_The cytoprotective protein MANF promotes neuronal survival independently from its role as a GRP78 cofactor. 33559083_The relationship of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor with hyperlipidemia in patients with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus. 33766221_Decreased Plasma MANF Levels are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes. 34220710_Correlation of Significantly Decreased Serum Circulating Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Level With an Increased Risk of Future Cardiovascular Disease in Adult Patients With Growth Hormone Deficiency. 34475050_Analysis of Mesencephalic Astrocyte-derived Neurotrophic Factor in Multiple Myeloma. 35110525_Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor reprograms macrophages to ameliorate acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via p38 MAPK pathway. 35405395_Mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor attenuates acute lung injury via inhibiting macrophages' activation. 35847585_MANF Inhibits alpha-Synuclein Accumulation through Activation of Autophagic Pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000032575 |
Manf |
376.757838 |
2.0191755036 |
1.013766 |
0.086599043 |
137.769503 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000008184628842507966914853388257269845207634451888245401784500436074687131917565461355738853921337749852682463824748992919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000001111362665275230863718698055422099157214926876148199009050863871006148501789542433829116596655239845858886837959289550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
508.0445078 |
25.2720401 |
253.4443419 |
9.8908892 |
| ENSG00000145107 |
116211 |
TM4SF19 |
protein_coding |
Q96DZ7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the four-transmembrane L6 superfamily. Members of this family function in various cellular processes including cell proliferation, motility, and adhesion via their interactions with integrins. In human brain tissue, this gene is expressed at high levels in the parietal lobe, occipital lobe, hippocampus, pons, white matter, corpus callosum, and cerebellum. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:116211; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
33059922_TM4SF19 aggravates LPS-induced attenuation of vascular endothelial cell adherens junctions by suppressing VE-cadherin expression. 35987447_TM4SF19-AS1 facilitates the proliferation of lung squamous cell carcinoma by recruiting WDR5 to mediate TM4SF19. |
ENSMUSG00000079625 |
Tm4sf19 |
665.632301 |
9.4677030246 |
3.243014 |
0.084927535 |
1667.951115 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1205.8283740 |
61.0454421 |
128.1926273 |
5.9115818 |
| ENSG00000145147 |
9353 |
SLIT2 |
protein_coding |
O94813 |
FUNCTION: Thought to act as molecular guidance cue in cellular migration, and function appears to be mediated by interaction with roundabout homolog receptors. During neural development involved in axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube and projection of axons to different regions. SLIT1 and SLIT2 seem to be essential for midline guidance in the forebrain by acting as repulsive signal preventing inappropriate midline crossing by axons projecting from the olfactory bulb. In spinal cord development may play a role in guiding commissural axons once they reached the floor plate by modulating the response to netrin. In vitro, silences the attractive effect of NTN1 but not its growth-stimulatory effect and silencing requires the formation of a ROBO1-DCC complex. May be implicated in spinal cord midline post-crossing axon repulsion. In vitro, only commissural axons that crossed the midline responded to SLIT2. In the developing visual system appears to function as repellent for retinal ganglion axons by providing a repulsion that directs these axons along their appropriate paths prior to, and after passage through, the optic chiasm. In vitro, collapses and repels retinal ganglion cell growth cones. Seems to play a role in branching and arborization of CNS sensory axons, and in neuronal cell migration. In vitro, Slit homolog 2 protein N-product, but not Slit homolog 2 protein C-product, repels olfactory bulb (OB) but not dorsal root ganglia (DRG) axons, induces OB growth cones collapse and induces branching of DRG axons. Seems to be involved in regulating leukocyte migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10102268, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10864954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10975526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11239147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11309622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11404413}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Leucine-rich repeat;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the slit family of secreted glycoproteins, which are ligands for the Robo family of immunoglobulin receptors. Slit proteins play highly conserved roles in axon guidance and neuronal migration and may also have functions during other cell migration processes including leukocyte migration. Members of the slit family are characterized by an N-terminal signal peptide, four leucine-rich repeats, nine epidermal growth factor repeats, and a C-terminal cysteine knot. Proteolytic processing of this protein gives rise to an N-terminal fragment that contains the four leucine-rich repeats and five epidermal growth factor repeats and a C-terminal fragment that contains four epidermal growth factor repeats and the cysteine knot. Both full length and cleaved proteins are secreted extracellularly and can function in axon repulsion as well as other specific processes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:9353; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTPase inhibitor activity [GO:0005095]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; laminin-1 binding [GO:0043237]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; proteoglycan binding [GO:0043394]; Roundabout binding [GO:0048495]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; apoptotic process involved in luteolysis [GO:0061364]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to heparin [GO:0071504]; cellular response to hormone stimulus [GO:0032870]; chemorepulsion involved in postnatal olfactory bulb interneuron migration [GO:0021836]; corticospinal neuron axon guidance through spinal cord [GO:0021972]; induction of negative chemotaxis [GO:0050929]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030837]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0090288]; negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070100]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of lamellipodium assembly [GO:0010593]; negative regulation of leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002689]; negative regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090027]; negative regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071676]; negative regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090024]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090260]; negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051058]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell chemotaxis [GO:0071672]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014912]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; response to cortisol [GO:0051414]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; Roundabout signaling pathway [GO:0035385]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
12141424_Analysis of alternative splicing and conserved domains in human and mouse slit genes 12384551_SLIT2, a human homologue of the Drosophila Slit2 gene, has tumor suppressor activity and is frequently inactivated in lung and breast cancers. 12615722_SLIT2 is an excellent candidate tumor suppressor gene for colorectal cancer. 12881718_Our data indicate that SLIT2 is frequently inactivated by promoter region CpG island hypermethylation in gliomas and may be a good candidate for a glioma tumour suppressor gene (TSG) located at 4p15.2. 14645233_effect of Slit (=Slit-2) on the metastatic properties of breast cancer cells 16162649_evidence showing that Slit1 and Slit2 proteins are selective inhibitors and repellents for dorsally projecting, but not for ventrally projecting, cranial motor axons 16439689_Slit2 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration by suppressing small GTPase Rac1 activation. 16636676_Both medulloblastoma and glioma tumors express Robo1 and Slit2, but only medulloblastoma invasion is inhibited by recombinant Slit2 protein. 16840550_Slit-2 inhibited neurite outgrowth in stem cell cultures. 17268810_Slit2 induces targeted migration and may play a role in brain metastasis of breast cancer cells. 17448996_long-range Ca(2+) signaling coordinates the Slit-2-induced changes in motility at two distant parts of migrating neurons by regulating RhoA distribution 17496152_SLIT2 mRNA decreases with vascular function decline in pulmonary fibrosis. 17609981_Inactivation of SLIT2-ROBO1 signaling pathway may have an important role in uterine cervical carcinoma development. 17848514_the crystal structures of the second LRR domain of human Slit2 and the minimal complex between these proteins (Slit2 D2-Robo1 Ig1). 17903301_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17968499_a chemorepulsive effect mediated by interaction of Slit2 and Robo1 participates in glioma cell guidance in the brain. 18611862_Slit-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells exhibit tumor suppressor capabilities through the novel mechanism of beta-catenin modulation. 18829537_Slits are negative regulators of Sdf1 and Cxcr4 in breast cancer cells. 19033678_Slit2 plays a role in regulating in vitro osteoblast differentiation. 19048120_Slit2 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis of fibrosarcoma and squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on cell cycle and apoptosis signal pathways is an important mechanism for Slit2-mediated tumor suppression 19100240_These results suggest that epigenetic inactivation of SLIT2 in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) may be important in the development and progression of HCC. 19350278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19350278_gene variants in SLIT2 are rare causes of VUR in humans. Our results provide further evidence for the genetic heterogeneity of this disorder 19351956_HDAC5 represses angiogenic genes, such as FGF2 and Slit2, which causally contribute to capillary-like sprouting of endothelial cells. 19498462_Fourth Slit2 domain heparan sulphate binding contributes to a Slit-Robo signalling mechanism more intricate than previously thought. 19550140_The SLIT2 5' CpG island is methylated in chronic and acute lymphocytic leukemia. 19706539_Data uncover a previously unknown function of USP33 and reveal a new player in Slit-Robo signaling in cancer cell migration. 19759280_Slit2 potently inhibits chemotaxis but not random motion of circulating neutrophils 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19855388_data reveal that a Slit2-Robo4-paxillin-GIT1 network inhibits the cellular protrusive activity underlying neovascularization and vascular leak, and identify a new therapeutic target for ameliorating diseases involving the vascular system 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20008733_Downregulation of Slit2 expression is associated with gliomas. 20029409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20029409_This study suggested that the importance of axonal guidance genes(SLIT2) in shaping an individual's vulnerability to suicidality, likely in the direction of the aggression/impulsivity endophenotype. 20068157_Findings indicate that SLIT2 suppresses lung cancer progression, defining it as a novel 'theranostic' factor with potential as a therapeutic target and prognostic predictor in lung cancer. 20153733_These results suggest that Slit2 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of temporal lobe epilepsy 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20375003_Activating with the soluble ligand Slit an endothelium-specific, Robo4-dependent signaling pathway that strengthens the vascular barrier, diminishing deleterious aspects of the host's response to the pathogen-induced cytokine storm. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20438712_these findings reveal that through interacting with Robo1, Slit2 is a novel and potent lymphangiogenic factor and contributes to tumor lymphatic metastasis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20944010_the newly identified Slit2 gradient at the bronchus-alveoli axis induces attractive PI3K signaling in eosinophils and repulsive srGAP1 signaling in neutrophils through differential srGAP1 expression during lung inflammation. 21264840_Because slit2-DeltaE15 splice variant is present in low invasive cancer cells and nontumor lung tissues, loss of this splice variant is an important event in tumor progression and invasion 21283129_Colorectal carcinoma cells secrete Slit2 for signaling through Robo1 expressed on these same cells. 21349947_Findings establish the critical role of the neuronal differentiation factor NeuroD1 in neuroblastoma as well as its functional relationship with the neuronal repellent factor Slit2. 21385904_Data show that epigenetic silencing of SLIT2 promoter was discovered as an underlying mechanism by which miR-218 is suppressed in NPC. 21465248_three major members (Slit2/3 and Robo1) of Slit/Robo family are widely expressed in the human normal and malignant ovarian tissues; but Slit/Robo signaling may not play an important role in regulating human ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration 21627385_SLIT2 is epigenetically silenced in ovarian cancers. 21686327_SLIT-ROBO signaling potentially contributes to the development of diabetic retinopathy. 21857494_studies demonstrate a novel role for Slit2/Robo1 axis in HIV replication and may contribute to the understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis 21894562_Slit2 promoter hypermethylation appears to be responsible for functionally silencing Slit2 expression 21986575_Over-expression of human Slit2 in transgenic mouse significantly increased brain vessel density and the permeability of brain vessels to large molecules. 22011669_We confirmed that the expression of SLIT2 in squamous cell carcinoma is regulated by DNA methylation of its specific promoter region. 22198087_New insights into the role of Slit proteins during the angiogenic process that relies on the directional migration not only of endothelial cells but also of pericytes. 22241990_targeting Slit2/Robo4 signaling may protect the integrity of the lymphatic barrier and limit the dissemination of HIV in the host. 22315090_Promoter methylation status analysis of hereditary breast tumors revealed high methylation frequencies for the three genes (67% RASSF1A, 80% SLIT2, and 72% WIF1). 22532293_Methylation of SLIT2 gene is associated with colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's colitis. 22613430_aberrant methylation of the SLIT2 promoter was present in ovarian tissue from 29/36 (80.6%) ovarian cancer patients, but not in the 25 healthy controls; hypermethylation of the SLIT2 promoter may be a relatively early event in ovarian cancer 22719878_data suggests the importance of abrogation of SLIT2-ROBO1 and SLIT2-ROBO2 interactions in the initiation and progression of CACX and also for early diagnosis and prognosis of the disease 22826604_we report that the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells is determined by an interaction between the Robo1 receptor and its ligand Slit2 22865890_The cell motility modulator Slit2 is a potent inhibitor of platelet function. 22875847_Slit2 overexpression increases the lesion size in endometriosis and increases microvessel density. 22898079_Silencing of miRNA-218 promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer via Slit2-Robo1 pathway 23119100_Data indicate that slit2N alters the localization and binding of Robo1 to WASp and LSP1 in HIV-1-gp120-treated immature dendritic cells (iDCs). 23294842_N-terminal of Slit2 inhibits HIV-1 replication by regulating the actin cytoskeleton 23314850_SLIT2 suppresses colon tumor metastasis, and it exerts its suppressive activity against colorectal cancer metastasis by restraining AKT-GSK3beta signaling. 23381221_hypomethylation of LINE-1 and hypermethylation of SLIT2, MAL and IGFBP7 were frequently detected in NSCLCs and associated with various clinical features. 23671423_Loss of expression of SLIT2 by promoter hypermethylation and loss of heterozygosity events is significantly associated with serrated adenoma development 23694962_Hypermethylation of SLIT2 is associated with colorectal cancer. 23702092_Slit2 inhibits Andes virus and Hantaan virus induced permeability and adherens junctions disassembly of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by interactions with Robo4 23933755_Slit2 was highly expressed in gastric cancer patients with less advanced clinicopathological features. Slit2 levels were correlated with beta-catenin level and subcellular localization. 24272999_Slit2-Robo4 is a key regulator of endothelial inflammation, and its dysregulation during endotoxemia is a novel mechanism for LPS-induced vascular pathogenesis. 24287947_Slit2 is downregulated in renal cell carcinoma and may have a role as a tumor suppressor 24297051_Slit2 knockdown promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis through activation of the AKT/betacatenin-mediated signaling pathway. 24448236_An N-terminal SLIT2 cleavage fragment stimulated such migration. 24673457_Biological activity of Slit2 and its binding to Robo1 have no affect on the dimer formation of Robo1. 24777535_In this review, we summarize recent findings demonstrating that the neuronal guidance cues, Slit and Roundabout (Robo), prevent the migration of multiple leukocyte subsets towards diverse inflammatory chemoattractants. 24840330_Results suggest that Slit2 might be involved in skin tumorigenesis. 24981056_Data show that ubiquitin specific peptidase 33 (USP33) mediates nerve tissue proteins Slit-Robo signaling in lung cancer cell migration. 25114073_These findings of this study demonstrated that Slit2 overexpression may be responsible for AD-like alterations and the increased BBB permeability in these mice 25130654_Slit2 is decreased in human myometrium after labor and knock-down studies describe an anti-inflammatory effect of Slit2 in myometrial cells. 25329354_reduced expression in obese placenta and in primary trophoblast cells treated with pro-inflammatory mediators IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and LPS 25333347_PDGFD, CDH1 and SLIT2 are upregulated in low grade meningiomas and schwannomas compared with healthy tissue. 25465073_Inactivation of SLIT2 and/or ROBO1 is one of the early events in development of dysplastic lesions of head and neck and has prognostic importance. 25489114_data may explain why fibrocytes are rarely observed in healthy tissues, may suggest that the relative levels of Slit2 present in healthy tissue and at sites of fibrosis may have significant effect on decision of monocytes to differentiate into fibrocytes 25490006_Results provide novel evidence that low expression of SLIT2 correlates with poor prognosis and promotes metastasis in ESCC, which may be regulated by the Cdc42-mediated pathways. 25590802_SLIT2 expression and cancer-associated fibroblasts are correlated with neural remodeling. 25605242_Slit2/Robo1 signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through Src-mediated activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 25786906_Data indicate that SLIT2, miR-218-1, RET/PLAG1 and SLIT2/ROBO1 pathway involved in Hirschsprung's disease. 26002231_VEGFR2 activation was not affected by Slit2, but eNOS phosphorylation was diminished 26021305_Slit2-exon 15 splicing variants have different roles in angiogenesis and HUVEC permeability 26026792_Mutations of the SLIT2-ROBO2 pathway genes SLIT2 and SRGAP1 confer risk for congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract 26264936_Significantly increased serum Slit2 levels and hepatic expression of Slit2 and Robo1 were observed in patients with liver fibrosis. 26282852_temporary up-regulation in remodeling vessel and down-regulation in remodeled vessel of polygonal-shape extravillous trophoblast cells occurred in tubal pregnancies 26400100_our findings indicated that Slit2/Robo1 axis possibly be regarded as a significant clinical parameter for predicting brain metastasis in breast cancer patients. 26456684_expression of the evolutionarily conserved slit2 Gene Promoter Requires Sp1 26542734_Overexpression of Slit2 induces its tumor suppressive effects in Breast cancer. 26713366_These results suggest that Slit2/Robo1 binding exerts an effect on cell migration, which is negatively regulated by Robo4, and Robo1 may function by interacting with CdGAP in HUVECs. 26745454_human placental multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell express Slit2 and both Robo1 and Robo4 are present in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 26935705_Study shows that Slit2 mRNA and protein levels were significantly reduced in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) specimens and implicates Slit2 functions as a negative regulator in the development and progression of PTC. 27176045_We postulate that Robo1 promotes tumor invasion partly by the upregulation of MMP2 after activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Notably, Slit2 knockdown caused the upregulation of Robo1 expression both at the mRNA and protein levels. Thus, the stimulatory effects of Slit2 knockdown on tumor progression can be ascribed, at least in part, to the upregulation of Robo1 and its positive role in tumor progression. 27431199_Slit2-Robo1 signaling promoted the adhesion, invasion and migration of tongue carcinoma cells by upregulating the expression levels of MMP2 and MMP9 and, downregulating the expression of E-cadherin. 27659325_Results indicate the importance of SLIT2-ROBO1-CDC42 signaling pathway in predicting tumor progression. 27888432_findings suggest that AK3 and SLIT2 may be potential candidates involved in genetic susceptibility to colorectal cancer 27916173_Low Slit2 expression is associated with glioma. 28402926_Curcumin up-regulates Slit-2 and down-regulates the expression of CXCR4, SDF-1, MMP2 and MMP9 in Ishikawa, Hec- 1B and primary human endometrial carcinoma cells. 28406573_The findings indicate that the migration of human neural progenitor cells from the fetal subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb is partially regulated by the Slit2-Robo1 axis. 28485101_SLIT2/ROBO1 signalling may regulate trophoblast differentiation and invasion causing restricting beta human chorionic gonadotrophin (beta-hCG) production, shallow trophoblast invasion and inhibiting placental angiogenesis in missed and threatened miscarriage during the first trimester. 28973045_The alteration of Slit2 and Robo1 expression in the retinas of diabetic rats and patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy suggests a role for the Slit-Robo signal in the various stages diabetic retinopathy. 29107007_Elevated SLIT2 promoter methylation contributed to the risk of NPC. 29299781_findings indicate that in a diabetic-like environment, in addition to mesangial cells, autocrine activation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling of HRGECs may contribute to angiogenesis of HRGECs through PI3K/Akt/VEGF pathway. 29317497_an interaction between the BMP2-Gremlin and SLIT2 pathways in human kidney cells 29523788_SLIT2 and ROBO1promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and contributes to the Warburg effect in osteosarcoma. 29610848_The novel CAPN5 mutation (p.R289W) is responsible for the present autosomal dominant neovascular inflammatory vitreoretinopathy (ADNIV) family. The mutant CAPN5 stimulated secretion and cleavage of SLIT2 fragments that may act as a bystander to regulate abnormal RPE cell proliferation for ADNIV. 29752312_TSH induces Slit2 levels in GD-OF by enhancing both Slit2 gene transcription and mRNA stability. 30510066_this study shows that different isoforms of the neuronal guidance molecule Slit2 directly cause chemoattraction or chemorepulsion of human neutrophils 30648543_Study demonstrated a role for Slit2 as a tumor suppressor of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). Slit2 suppressed thyroid cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Loss of Slit2 expression was associated with poor prognostic factors, such as lymphovascular invasion, cervical LN metastasis, distant metastasis, advanced stage, and recurrence in PTC. 30739251_Low Expression and Promoter Hypermethylation of the Tumour Suppressor SLIT2 is Associated with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. 30842157_SLIT2 induced motility and a SLIT2 gradient induced chemotaxis of breast cancer cells, which was amplified by heparin. ROBO1 was abundantly expressed in BMs of breast and colon cancer as well as in PM of ovarian cancer. Together, this suggests that ROBO-expressing tumor cells are attracted to the brain and peritoneum by SLIT2-mediated chemotaxis. 30896071_Our study reveals the inhibitory function of Slit-Robo signalling in gastric cancer (GC) and uncovers a role of USP33 in suppressing cancer cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by enhancing Slit2-Robo1 signalling. USP33 represents a feasible choice as a prognostic biomarker for GC. 31194736_SLIT2-ROBO1 signaling was linked with regulation of genes involved in inflammation, pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein genes, decidualization and fetal growth. We propose that this receptor-ligand couple is a component of the signaling network that promotes Spontaneous preterm birth (SPTB). 31393085_The mRNA levels of SLIT2 and ROBO1 were higher in the basal plate of SPTB placentas when compared to those of infants born at term or from elective preterm deliveries 31571851_The gene SLIT2 was decreased in patients with COPD and this decreases was significantly negatively correlated with the disease stages of COPD 31791578_Engagement of Robo1 by Slit2 induces formation of a trimeric complex consisting of Src-Robo1-E-cadherin for E-cadherin phosphorylation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32086386_Slit2 May Underlie Divergent Induction by Thyrotropin of IL-23 and IL-12 in Human Fibrocytes. 32213157_A Study Based on the Correlation Between Slit2/Robo1 Signaling Pathway Proteins and Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis. 32738556_TUG1 Represses Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Inflammatory Response by Regulating miR-27a-3p/SLIT2 in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Vascular Endothelial Cells. 32999457_Tumoural activation of TLR3-SLIT2 axis in endothelium drives metastasis. 33028376_Overexpression of Slit2 decreases neuronal excitotoxicity, accelerates glymphatic clearance, and improves cognition in a multiple microinfarcts model. 33068960_Role of Slit2 upregulation in recurrent miscarriage through regulation of stromal decidualization. 33079290_Slit2 is a potential biomarker for renal impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus. 33236535_Crosstalk between the activated Slit2-Robo1 pathway and TGF-beta1 signalling promotes cardiac fibrosis. 33275139_Placental multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell-derived Slit2 may regulate macrophage motility during placental infection. 33318575_Structural insights and evaluation of the potential impact of missense variants on the interactions of SLIT2 with ROBO1/4 in cancer progression. 33481259_Exome sequencing identifies SLIT2 variants in primary CNS lymphoma. 33574432_The neurorepellent, Slit2, prevents macrophage lipid loading by inhibiting CD36-dependent binding and internalization of oxidized low-density lipoprotein. 34400395_Slit2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis by Activating M1-Like Phagocytic and Antifibrotic Macrophages. 34414975_Expression of the axon guidance factor Slit2 and its receptor Robo1 in patients with Hirschsprung disease: An observational study. 34490644_Ductular reaction promotes intrahepatic angiogenesis through Slit2-Roundabout 1 signaling. 34543483_Genomic evolution and the impact of SLIT2 mutation in relapsed intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 34777365_Slit2-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming in Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Enhances Antitumor Immunity. 35426130_Slit guidance ligand 2 promotes the inflammatory response of periodontitis through activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 35813663_The Role of Slit-2 in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Pregnancy Outcome. 36250924_RNA m6A reader IGF2BP3 promotes metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer via SLIT2 repression. 36411451_SLIT2 promoter hypermethylation predicts disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000031558 |
Slit2 |
82.080217 |
3.3942865496 |
1.763108 |
0.631712964 |
7.181098 |
0.00736756041793136615819515000680439698044210672378540039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014509031590215739487836899002104473765939474105834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
145.5293002 |
59.0592973 |
42.7606186 |
12.6677105 |
| ENSG00000145217 |
10861 |
SLC26A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H2B4 |
FUNCTION: Mediates sulfate transport with high affinity (PubMed:12713736). Mediates oxalate transport (PubMed:12713736). Mediates bicarbonate transport (By similarity). Does not accept succinate as cosubstrate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P45380, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P58735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12713736}. |
Alternative splicing;Anion exchange;Antiport;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene is a member of a family of sulfate/anion transporter genes. Family members are well conserved in their genomic (number and size of exons) and protein (aa length among species) structures, but have markedly different tissue expression patterns. This gene is primarily expressed in the liver, pancreas, and brain. Three splice variants that encode different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10861; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antiporter activity [GO:0015297]; bicarbonate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015106]; chloride transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015108]; oxalate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019531]; secondary active sulfate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008271]; sulfate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015116]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0050428]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; oxalate transport [GO:0019532]; sulfate transport [GO:0008272] |
12713736_Characterization of the SAT1 gene and protein function. 17119850_The expression of three messengers coding for SAT-1, SAT-2 and GalNAcT-1 in human samples of intestinal cancer and some cell lines (breast cancer and melanomas), was evaluated. 17881426_No mutation was found in the coding regions and intron-exon boundaries of the genes for CA II, CA IV, CA XIV, kNCB1, NHE3, NHE8, NHRF1, NHRF2 and SLC26A6 amplified from genomic DNA of family members with pRTA. 21093948_The oxalate precursor glyoxylate was identified as a substrate of sat-1. Upregulated expression of sat-1 mRNA and of sat-1 protein indicates that glyoxylate may be responsible for the elevated oxalate release from hepatocytes observed in hyperoxaluria. 23815884_SLC26A1 protein,point mutation is highly responsible for the hearing loss of newborns. 24250268_Screened the SLC26A1 gene in a cohort of 13 individuals with recurrent calcium oxalate urolithiasis, which is the commonest type. DNA sequence analyses showed missense mutations in seven patients. 27125215_Human SLC26A1 resembles SLC26 paralogs in its inhibition. 27210743_Mutations in SLC26A1 gene is associated with Nephrolithiasis. 27412988_SLC26A1 L348P was associated with lower whole-body bone mineral density (BMD) and higher serum calcium, consistent with the osteochondrodysplasia exhibited by dogs and sheep with naturally occurring, homozygous, loss-of-function mutations in Slc13a1 |
ENSMUSG00000046959 |
Slc26a1 |
35.867109 |
0.2333019017 |
-2.099730 |
0.333049076 |
40.521574 |
0.00000000019445707204536365377516908640185069878647539098892593756318092346191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000984626546617347328123188740880457336945852375720278359949588775634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.7842641 |
4.0549739 |
63.9966480 |
11.6933324 |
| ENSG00000145358 |
115265 |
DDIT4L |
protein_coding |
Q96D03 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits cell growth by regulating the TOR signaling pathway upstream of the TSC1-TSC2 complex and downstream of AKT1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15545625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632201}. |
Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of signal transduction. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:115265; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968] |
15632201_RTP801 and RTP801L work downstream of AKT and upstream of TSC2 to inhibit mTOR functions 19268525_mediates monocyte cell death through a reduction in thioredoxin-1 expression 19491193_Promoter methylation and differential gene expression of five markers: COL1A2, NPM2, HSPB6, DDIT4L and MT1G were validated by sequencing of bisulfite-modified DNA and real-time reverse transcriptase PCR, respectively. |
ENSMUSG00000046818 |
Ddit4l |
1127.371815 |
0.3016057363 |
-1.729264 |
0.049702769 |
1268.143621 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009465110871534260458443579047732750213583737203037966 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012043537626193593942913657893843313636384960235799541 |
Yes |
No |
523.8463900 |
16.7907811 |
1749.5448445 |
33.5346731 |
| ENSG00000145362 |
287 |
ANK2 |
protein_coding |
Q01484 |
FUNCTION: Plays an essential role in the localization and membrane stabilization of ion transporters and ion channels in several cell types, including cardiomyocytes, as well as in striated muscle cells. In skeletal muscle, required for proper localization of DMD and DCTN4 and for the formation and/or stability of a special subset of microtubules associated with costameres and neuromuscular junctions. In cardiomyocytes, required for coordinate assembly of Na/Ca exchanger, SLC8A1/NCX1, Na/K ATPases ATP1A1 and ATP1A2 and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptors at sarcoplasmic reticulum/sarcolemma sites. Required for expression and targeting of SPTBN1 in neonatal cardiomyocytes and for the regulation of neonatal cardiomyocyte contraction rate (PubMed:12571597). In the inner segment of rod photoreceptors, required for the coordinated expression of the Na/K ATPase, Na/Ca exchanger and beta-2-spectrin (SPTBN1) (By similarity). Plays a role in endocytosis and intracellular protein transport. Associates with phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P)-positive organelles and binds dynactin to promote long-range motility of cells. Recruits RABGAP1L to (PI3P)-positive early endosomes, where RABGAP1L inactivates RAB22A, and promotes polarized trafficking to the leading edge of the migrating cells. Part of the ANK2/RABGAP1L complex which is required for the polarized recycling of fibronectin receptor ITGA5 ITGB1 to the plasma membrane that enables continuous directional cell migration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C8R3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12571597}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Endocytosis;Endosome;Long QT syndrome;Lysosome;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ankyrin family of proteins that link the integral membrane proteins to the underlying spectrin-actin cytoskeleton. Ankyrins play key roles in activities such as cell motility, activation, proliferation, contact and the maintenance of specialized membrane domains. Most ankyrins are typically composed of three structural domains: an amino-terminal domain containing multiple ankyrin repeats; a central region with a highly conserved spectrin binding domain; and a carboxy-terminal regulatory domain which is the least conserved and subject to variation. The protein encoded by this gene is required for targeting and stability of Na/Ca exchanger 1 in cardiomyocytes. Mutations in this gene cause long QT syndrome 4 and cardiac arrhythmia syndrome. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:287; |
A band [GO:0031672]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; costamere [GO:0043034]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; M band [GO:0031430]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; cytoskeletal anchor activity [GO:0008093]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; phosphorylation-dependent protein binding [GO:0140031]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086014]; atrial cardiac muscle cell to AV node cell communication [GO:0086066]; atrial septum development [GO:0003283]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; membrane depolarization during SA node cell action potential [GO:0086046]; paranodal junction assembly [GO:0030913]; positive regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901021]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of cation channel activity [GO:2001259]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901018]; positive regulation of potassium ion transport [GO:0043268]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein localization to cell surface [GO:0034394]; protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0070972]; protein localization to M-band [GO:0036309]; protein localization to organelle [GO:0033365]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein localization to T-tubule [GO:0036371]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098910]; regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901019]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction [GO:0086004]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0055117]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by calcium ion signaling [GO:0010882]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; regulation of SA node cell action potential [GO:0098907]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization [GO:0060307]; response to methylmercury [GO:0051597]; SA node cell action potential [GO:0086015]; SA node cell to atrial cardiac muscle cell communication [GO:0086070]; sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ion transport [GO:0070296]; T-tubule organization [GO:0033292]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086005] |
11781319_The ankyrin-B C-terminal domain determines activity of ankyrin-B/G chimeras 12571597_Loss-of-function (E1425G) mutation in ankyrin-B (also known as ankyrin 2), a member of a family of versatile membrane adapters, causes dominantly inherited type 4 long-QT cardiac arrhythmia in humans 14657231_Data show that L1-cell adhesion molecule interactions with ankyrinB (but not with ankyrinG) are involved in the initial formation of neurites. 15075330_An amphipathic alpha-helix in the divergent regulatory domain of ankyrin-b interacts with the molecular co-chaperone Hdj1/Hsp40. 15262991_interaction between members of the ankyrin and beta-spectrin families previously established in erythrocytes and axon initial segments also occurs in neonatal cardiomyocytes with ankyrin-B and beta(2)-spectrin 15310273_Quantitative analysis of erythrocyte membrane proteins revealed increase in ankyrin from patients with homozygous and heterozygous forms of beta-thalassemia. 15851119_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16253912_Genotype-negative LQTS patients with a single ANK2 variant displayed nonexertional syncope, U waves, sinus bradycardia, and extracardiac findings. 16864073_study identified T to A transition mutation at position 4,603 in exon 40 resulting in substitution of arginine for tryptophan at amino acid residue 1,535 in regulatory domain of ankyrin-B; this novel mutation may be a cause of type 4 long QT syndrome 17161064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17161064_Six novel mutations--4 in ANK2, 1 in KCNQ1, and 1 in SCN5A--were found in the patients with torsades de pointes. 17242276_role of ankyrin-B-dependent protein interactions in regulating cardiac electrogenesis 17940615_Ankyrin-B has a role in cardiac function, cardiac death and premature senescence 18052691_ANK2 mutations were not found to directly cause long QT syndrome. 18275062_the ankyrin-binding site is located on the cytoplasmic face of the InsP(3) receptor, thus validating the feasibility of in vivo ankyrin-InsP(3) receptor interactions. 18303017_Ankyrin B modulates the function of Na,K-ATPase/inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor signaling microdomain 18782775_ANK2 is subject to alternative splicing that gives rise to unique polypeptides with diverse roles in cardiac function. 18790697_Exon organization and novel alternative splicing of the human ANK2 gene: implications for cardiac function and human cardiac disease 18832177_dysfunction in AnkB-based trafficking pathways causes abnormal sinoatrial node (SAN) electrical activity and sinus node dysfunction. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031550_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031550_The common genetic variation in the ANK2 gene is modified the physiological variability of the QT interval in the general population. 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20573981_Data show that DAnk2-binding is critical for beta spectrin function in vivo. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21859974_Reduced ankyrin-B expression or mutations in ankyrin 2 are associated with atrial fibrillation. 22778271_Ankyrin-B protein in heart failure: identification of a new component of metazoan cardioprotection. 22861190_Residues 63-73 of cdB3 is also essential for ankyrin binding. 23142288_Gankyrin plays an essential role in estrogen-driven and GPR30-mediated endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 23569209_ankyrin-B linker suppresses activity of the ANK repeat domain through an intramolecular interaction, likely with a groove on the surface of the ANK repeat solenoid, thereby regulating the affinities between ankyrin-B and its binding partners 25383926_the structures of ANK repeats in complex with an inhibitory segment from the C-terminal regulatory domain and with a sodium channel Nav1.2 peptide, are reported. 26109584_The identification and characterization of two functionally distinct ankyrin-B isoforms in heart provide compelling evidence that alternative splicing of the ANK2 gene regulates the fidelity of ankyrin-B interactions with proteins 27005929_Clinical manifestations of ANK2 variants may include QT prolongation and torsades de pointes, often precipitated by strenuous exercise or stress. 27298202_we support classification of Ankyrin-B p.L1622I as a 'mild' loss-of-function variant that may confer arrhythmia susceptibility in the context of secondary risk factors including environment, medication, and/or additional genetic variation. 27784853_VariousANK2mutations are associated with a wide range of phenotypes, including aLQTS, especially with ventricular fibrillation, representing 'ankyrin-B' syndrome. 27818464_Rare Variants in ANK2 Associated With Various Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes. 28196901_Report disease-causing ANK2 variant localized to the membrane-binding domain resulting in reduced ankyrin-B expression and abnormal localization in a First Nations population with a high rate of long QT syndrome. 28841137_The authors discovered that the entire 24 ankyrin repeats are inhibited by combinatorial and quasi-independent bindings of multiple disordered segments located in the ankyrin-B/G linkers and tails, suggesting a mechanistic basis for differential regulations of membrane target bindings by ankyrins. 28988699_Disruption of Ankyrin B and Caveolin-1 Interaction Sites Alters Na(+),K(+)-ATPase Membrane Diffusion 29133412_Cell-autonomous adiposity results from increased cell surface GLUT4 due to ankyrin-B deficiency in humans and mice. 30929919_ANK2 functionally interacts with KCNH2 leading to a stronger current suppression and marked aggravation of long QT syndrome in the patient carrying variants in both proteins. 31264976_findings introduce what we believe to be a new pathway for Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, a role of ankyrin-B in cardiac structure and signaling, a molecular link between ankyrin-B and beta-catenin, and evidence for targeted activation of the WNT/beta-catenin pathway as a potential treatment for this disease. 31285321_Gain of axon branching due to giant ankB deficiency/mutation is a candidate cellular mechanism to explain aberrant structural connectivity and penetrant behavioral consequences in mice as well as humans bearing autism spectrum disorder-related ANK2 mutations. 31477143_These novel findings have important implications for understanding the role of AnkB and Cav2.1 in the regulation of neuronal function in health and disease. 32023981_Mechanisms and Alterations of Cardiac Ion Channels Leading to Disease: Role of Ankyrin-B in Cardiac Function. 32164423_Established Loss-of-Function Variants in ANK2-Encoded Ankyrin-B Rarely Cause a Concerning Cardiac Phenotype in Humans. 32640013_Giant ankyrin-B suppresses stochastic collateral axon branching through direct interaction with microtubules. 32770099_Genetic heterogeneity and prognostic impact of recurrent ANK2 and TP53 mutations in mantle cell lymphoma: a multi-centre cohort study. 32853419_lncRNA ZNF667-AS1 (NR_036521.1) inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer via regulating ANK2/JAK2 expression. 33218035_ANK2 Hypermethylation in Canine Mammary Tumors and Human Breast Cancer. 33410423_Human ankyrins and their contribution to disease biology: An update. |
ENSMUSG00000032826 |
Ank2 |
34.630522 |
2.0479593580 |
1.034187 |
0.390748061 |
6.855755 |
0.00883562016765314026112143608315818710252642631530761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017101200324489949228246032930655928794294595718383789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.6727433 |
12.1685561 |
24.3086216 |
4.4608625 |
| ENSG00000145439 |
84869 |
CBR4 |
protein_coding |
Q8N4T8 |
FUNCTION: Component of the heterotetramer complex KAR (3-ketoacyl-[acyl carrier protein] reductase or 3-ketoacyl-[ACP] reductase) that forms part of the mitochondrial fatty acid synthase (mtFAS). Beta-subunit of the KAR heterotetramer complex, responsible for the 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase activity of the mtFAS, reduces 3-oxoacyl-[ACP] to (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] in a NADPH-dependent manner with no chain length preference, thereby participating in mitochondrial fatty acid biosynthesis (PubMed:25203508). The homotetramer has NADPH-dependent quinone reductase activity (in vitro), hence could play a role in protection against cytotoxicity of exogenous quinones (PubMed:19000905). As a heterotetramer, it can also reduce 9,10-phenanthrenequinone, 1,4-benzoquinone and various other o-quinones and p-quinones (in vitro) (PubMed:19000905, PubMed:19571038, PubMed:25203508). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19000905, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19571038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25203508}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;NAD;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19571038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25203508}. |
Enables several functions, including 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity; NADPH binding activity; and NADPH dehydrogenase (quinone) activity. Involved in fatty acid biosynthetic process; glycoside metabolic process; and protein tetramerization. Located in mitochondrial matrix. Part of oxidoreductase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84869; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; oxidoreductase complex [GO:1990204]; 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH) activity [GO:0004316]; NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) activity [GO:0003955]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; NADPH dehydrogenase (quinone) activity [GO:0008753]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016616]; quinone binding [GO:0048038]; daunorubicin metabolic process [GO:0044597]; doxorubicin metabolic process [GO:0044598]; fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006633]; protein heterotetramerization [GO:0051290]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289] |
19000905_CBR4 is a mitochondrial NADPH-dependent reductase for o- and p-quinones. 19571038_Hs17beta-HSD8 and HsCBR4 show a strong genetic interaction in vivo in yeast, where, only if they are expressed together, they rescue the respiratory deficiency and restore the lipoic acid content of oar1Delta cells. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000031641 |
Cbr4 |
204.582842 |
0.1852687665 |
-2.432308 |
0.870856164 |
5.759664 |
0.01639820833564193183762291994298720965161919593811035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029984830901149023968388362959558435250073671340942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.1052222 |
37.3009566 |
363.3512301 |
161.8747096 |
| ENSG00000145545 |
6715 |
SRD5A1 |
protein_coding |
P18405 |
FUNCTION: Converts testosterone into 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone and progesterone or corticosterone into their corresponding 5-alpha-3-oxosteroids. It plays a central role in sexual differentiation and androgen physiology. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2339109}. |
Differentiation;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Microsome;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Sexual differentiation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Steroid 5-alpha-reductase (EC 1.3.99.5) catalyzes the conversion of testosterone into the more potent androgen, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Also see SRD5A2 (MIM 607306).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:6715; |
cell body fiber [GO:0070852]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; myelin sheath [GO:0043209]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003865]; amide binding [GO:0033218]; cholestenone 5-alpha-reductase activity [GO:0047751]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; progesterone 5-alpha-reductase activity [GO:0050213]; androgen biosynthetic process [GO:0006702]; androgen catabolic process [GO:0006710]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to epinephrine stimulus [GO:0071872]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; cellular response to testosterone stimulus [GO:0071394]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; circadian sleep/wake cycle, REM sleep [GO:0042747]; diterpenoid metabolic process [GO:0016101]; female genitalia development [GO:0030540]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; hypothalamus development [GO:0021854]; liver development [GO:0001889]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; pituitary gland development [GO:0021983]; progesterone metabolic process [GO:0042448]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to follicle-stimulating hormone [GO:0032354]; response to fungicide [GO:0060992]; response to growth hormone [GO:0060416]; response to muscle activity [GO:0014850]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; serotonin metabolic process [GO:0042428]; sex determination [GO:0007530]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694]; thalamus development [GO:0021794]; urogenital system development [GO:0001655] |
11903314_role in blood pressure 11948017_examination of differential methylation of isoenzyme genes in lymphocytes 12670724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12670724_polymorphisms of SRD5A1 and SRD5A2 genes may not be directly associated with the development of baldness or generation of different clinical phenotypes. 12738739_Loss of 5alpha-reductase type I expression is associated with metastatic prostate cancer 14671189_Changes in 5alpha-reductase, 11beta-HSD1, and 20alpha/beta-HSD enzyme activities observed in polycystic ovary syndrome may contribute to increased production of cortisol and androgens. 14739525_Mutant SRD5A1 isoenzyme does not seem to play a crucial role in the development of hypospadias. 14997014_The direct challenge of beta-adrenergic agonists to glioma cells resulted in the rapid and transient elevation of 5alpha-R mRNA levels through the activation of the cyclic AMP (cAMP)/protein kinase A-mediated signaling pathway. 15004407_Glucocorticoids and androgens differentially regulate 5alphaR1 mRNA in the rat liver. Regulation of 5alphaR1 gene is primarily at the post-transcriptional level. 15136785_Candidate gene for benign prostatic hyperplasia. 15136785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15212687_Expression of SRD5A1 (5alphaR1) and SRD5A2 (5alphaR2) is elevated, and expression of AKR1C1 (20alpha-HSO), AKR1C2 (3alpha-HSO3) and AKR1C3 (3alpha-HSO2) is reduced in tumorous as compared to normal breast tissue. 15538746_5alpha-reductase type 1 (5alphaR1) immunostaining is increased and 5alpha-reductase type 2(5alphaR2) immunostaining is decreased during development of prostate cancer and there is increased expression of both in recurrent and metastatic cancers 15543614_Serenoa repens inhibits this enzyme in the prostate, but does not suppress prostate-specific antigen secretion in prostate cancer. 15792368_5alpha-reductase is expresed in human embryonic kidney cell line HEK293 15862960_The expression of 5alpha-reductase type I mRNA was not regulated by calcitriol in a prostate tumor cell line. 15941927_SRD5A1 is abundantly transcribed in normal human genital skin fibroblasts and may play an important role in masculinization of SRD5A2-deficient males. 16100771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16155734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16818707_The SRD5A1 mRNA expression is 2-fold lower than SRD5A2 in normal rat. 16849416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17066438_These results suggest that intratumoral 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone concentration is mainly determined by 5alphaRed1 and aromatase in breast carcinoma tissues. 17218734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18008328_Both 5-alpha-reductase I and II are expressed in normal human prostate stromal and epithelial cells. Only 5-alpha-reductase isoenzymes of prostate epithelium are modulated by oxytocin. 18215136_Hepatocyte growth factor stimulates 5alpha-R1 expression through up-regulation of the transcription factor early growth response 1 18258185_Our results demonstrate that the 5alphaR activities of either bDPCs or sDPCs are stronger than that of dermal fibroblasts, despite the fact that the major steroidogenic activity is attributed to 17beta-HSD rather than 5alphaR among the three cell types. 18422030_Testosterone 5-alpha-Reductase deficiency is associated with gender identity 18483391_the SRD5A2 V89L VV genotype interacts with VDR FokI TT/CT genotypes in non-Hispanic White men and VDR CDX2 GG genotypes in Hispanic White men to increase the risk for prostate cancer. 18633104_Enhanced 5alphaR activity in both sexes is associated with insulin resistance but not body composition 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19246976_A decreased local enzymatic conversion of testosterone may contribute to PAD genetic susceptibility. 19246976_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19383266_Report changes in human placental 5alpha-reductase isoenzyme expression with advancing gestation: effects of fetal sex and glucocorticoid exposure. 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19846565_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19886072_hyperandrogenemia is associated with high levels of expression of 5-alpha reductase type 1 and, to a less extent, of type 2 isoenzyme in pubian skin cultured fibroblasts 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056642_We investigated associations between single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes HSD3B1, SRD5A1/2, and AKR1C2 and prostate cancer risk 20086173_Data indicate that enzymes CYP17A1 and HSD3B1 showed low expression, while AKR1C3 and SRD5A1 were abundantly expressed. 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20214802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20519274_High nuclear SRD5A1 expression is associated with higher prostate cancer stage. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21323680_Evidence of association of two alleles for alcohol dependence (AD) is found in SRD5A1 and AKR1C3, mediating a protective effect of the minor allele at each AD marker based on the genotype of the second marker. 21447938_Pitfalls in the diagnosis of 5alpha-reductase type 2 deficiency during early infancy. 21530059_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the two isoforms of 5alpha-reductase, SRD5A1 and SRD5A2, are associated with lean patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. 21676395_A statistically significant reduction of SRD5A1, SRD5A2, and CYP19A gene expression was found in the dermal papillae cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in idiopathic hirsutism. 21715084_Show positive associations of several SRD5A1 and SRD5A2 variations as independent predictors of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. 21795608_the dominant route of Dihydrotestosterone synthesis in castration-resistant prostate cancer bypasses testosterone, and instead requires 5alpha-reduction of androstenedione by SRD5A1 to 5alpha-androstanedione, which is then converted to DHT 21947678_Postmenopausal breast cancer risk associated with combined therapy may be modified by genetic variation in SRD5A1 22194926_The different expression levels of 5alpha-reductase isoenzymes may confer response or resistance to 5alpha-reductase inhibitors. 22273344_Ten percent of cases and 44% of controls had the cytosine/cytosine (C/C) genotype for the SRD5A1 SNP, rs501999 indicating that this genotype may protect women against severe premenstrual symptoms. 22509838_Based on a limited selection of gene variants, no involvement of SRD5A1, SRD5A2, ESR1, ESR2 or PGR in female pattern hair loss is evident. 23183084_Different effects were seen for progesterone, which significantly decreased SRD5A1 protein levels. 23499746_SRD5A1 and SRD5A2 single nucleotide polymorphisms are significantly associated with the clinical characteristics of benign prostatic hyperplasia and the efficacy of benign prostatic hyperplasia treatment. 24244276_Significantly higher levels of SRD5A1, AKR1C2, AKR1C3, and HSD17B10 mRNA were however found in bone metastases than in non-malignant and/or malignant prostate tissue 24277450_SRD5A1 rs166050C risk variant was associated with greater prostatic exposure to androsterone 24986533_Increased 5alphaR activity and glucocorticoid secretion rate over time are linked with the development of metabolic disease, and may represent targets for therapeutic intervention. 25463305_In model cell lines of endometrial cancer, AKR1C2 and SRD5A1 have crucial roles in progesterone metabolism. 25475427_Results show that 5alpha-reductase type 1 was associated with intratumoral dihydrotestosterone concentrations and is an independent prognostic factor in endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma. 25850410_study found SRD5A enzyme is present in spermatozoa and that its cellular content is lowered in sperm samples from varicocele patients compared to healthy subjects 25960412_A total of 2 SNPs in SRD5A1-rs3822430 and rs1691053-were associated with prostate-specific antigen level at diagnosis. 26174685_the genotypic distribution of 22 single nucleotide polymorphisms in SRD5A1 and SRD5A2 in a set of Spanish prostate cancer patients, were evaluated. 26243543_SRD5A1 small-interfering RNA knockdown led to significant increase in progesterone receptor-B nuclear import, ectopic, whereas SRD5A1 overexpression resulted in remarkable inhibition of nuclear progesterone receptor-B in P4-treated cells. Repression of SRD5A1 activated progesterone receptor-B responsive gene, whereas overexpression of SRD5A1 possessed an inhibitory effect. 26855069_Although 4-dione is the main source of 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone in human preadipocytes, production of this steroid by 5 alpha-reductase isoenzymes (SRD5A1, 2 and 3) mediates the inhibitory effect of both 4-dione and testosterone on preadipocyte differentiation. 28347315_Studies indicate that enhanced 5alpha-reductase activity in subjects with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) was associated with insulin resistance (IR) rather than obesity. 28947209_we demonstrated that AR, 5alphaR1 and 5alphaR2 immunoreactivity in bladder urothelial carcinoma cells significantly decreased with advanced tumor grade. 29084161_The study described in this article shows that selected SRD5A1 and SRD5A2 polymorphisms can alter the levels of metabolic and hormonal parameters in patients with BPH. Special attention should be paid to the SDR5A2 rs12470143 polymorphism, which is associated with a change in lipid profile, as well as with the inheritance and incidence rate of MetS among these patients. 29187470_Findings suggest that 5alpha-reductases (5-AR) isoenzymes could be explored as a therapeutic target for urothelial bladder cancer (UBC) with 5alpha-reductase inhibitors (5-ARI). 31199473_Deficiency or inhibition of 5alphaR1 predisposes men and mice to insulin resistance and fatty liver. 31870594_Associations of SRD5A1 gene variants and testosterone with dysglycemia: Henan Rural Cohort study. 32716491_Expression in Escherichia Coli, Purification, and Functional Reconstitution of Human Steroid 5alpha-Reductases. 33627630_Suppression of steroid 5alpha-reductase type I promotes cellular apoptosis and autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in multiple myeloma. 34764940_Steroid Metabolism in Children and Adolescents With Obesity and Insulin Resistance: Altered SRD5A and 20alpha/20betaHSD Activity. 34885733_Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Natural Drugs. 34996447_Epigenetic regulation of 5alpha reductase-1 underlies adaptive plasticity of reproductive function and pubertal timing. |
ENSMUSG00000021594 |
Srd5a1 |
329.250305 |
3.6465770525 |
1.866543 |
0.208906011 |
75.580540 |
0.00000000000000000350801864122005612593491343559395005569913702668169430687328258500201627612113952636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000028638470765712404226259685767335780972711356166067117601237157487048534676432609558105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
470.2440648 |
59.9427262 |
129.5969852 |
12.2607200 |
| ENSG00000145555 |
4651 |
MYO10 |
protein_coding |
Q9HD67 |
FUNCTION: Myosins are actin-based motor molecules with ATPase activity. Unconventional myosins serve in intracellular movements. MYO10 binds to actin filaments and actin bundles and functions as a plus end-directed motor. Moves with higher velocity and takes larger steps on actin bundles than on single actin filaments (PubMed:27580874). The tail domain binds to membranous compartments containing phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate or integrins, and mediates cargo transport along actin filaments. Regulates cell shape, cell spreading and cell adhesion. Stimulates the formation and elongation of filopodia. In hippocampal neurons it induces the formation of dendritic filopodia by trafficking the actin-remodeling protein VASP to the tips of filopodia, where it promotes actin elongation. Plays a role in formation of the podosome belt in osteoclasts. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16894163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18570893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27580874}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform Headless]: Functions as a dominant-negative regulator of isoform 1, suppressing its filopodia-inducing and axon outgrowth-promoting activities. In hippocampal neurons, it increases VASP retention in spine heads to induce spine formation and spine head expansion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F8VQB6}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Motor protein;Myosin;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the myosin superfamily. The protein represents an unconventional myosin; it should not be confused with the conventional non-muscle myosin-10 (MYH10). Unconventional myosins contain the basic domains of conventional myosins and are further distinguished from class members by their tail domains. This gene functions as an actin-based molecular motor and plays a role in integration of F-actin and microtubule cytoskeletons during meiosis. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:4651; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; filopodium tip [GO:0032433]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; myosin complex [GO:0016459]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; microfilament motor activity [GO:0000146]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; plus-end directed microfilament motor activity [GO:0060002]; spectrin binding [GO:0030507]; cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport [GO:0030705]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022409]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051489]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15158464_M10 is a specific motor carrying Mena/VASP from the root to the tip of the filopodia where extension of actin filament takes place 16371656_Results report that, in addition to full-length myosin 10 (Myo10), brain expresses a shorter form of Myo10 that lacks a myosin head domain. 16894163_Data demonstrate that Myo10 is a molecular motor that functions in filopodia formation. 18295593_Our data suggest that CLP functions to increase translation of Myo10 possibly by acting as a chaperone for the emerging Myo10 heavy chain protein. 18599451_myosin X recognizes the local structural arrangement of filaments in long bundles, providing a mechanism for sorting cargo to distant target sites. 18818677_increased CLP expression and CLP-mediated Myo10 function are important for skin differentiation and wound reepithelialization 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20123970_Results suggest that VE-cadherin trafficking along filopodia using myosin-X motor protein is a prerequisite for cell-cell junction formation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20930142_Results indicate that PtdIns(3,4,5)P binding to the Myo10-PH2 domain is involved in Myo10 trafficking and regulation of filopodia dynamics. 21321230_The structure of the MyoX MyTH4-FERM tandem in complex with the cytoplasmic tail P3 domain of the netrin receptor DCC, is reported. 21642953_Molecular basis by which myosin-X facilitates alternative dual binding to cargos and microtubules. 23083060_Authors conclude thatMyo10 generates the force to enhance bacterial-induced cell membrane protrusions by binding its head region to actin filaments and its PH tail domain to the peripheral membrane. 23943878_Study demonstrates a novel biological function for Hdl-Myo10 and an important new role for both Myo10 isoforms in the development of dendritic spines and synapses. 24379415_Phosphorylation of ADD1 at Ser12 and Ser355 by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 enables ADD1 to bind to myosin-X (Myo10). 24487586_Myo10 upregulation in mutant p53-driven cancers is necessary for invasion and that plasma-membrane protrusions. 24921915_Elevated MYO10 expression and involvement in invadopodia formation increases the aggressiveness of breast cancer . 25605337_PCTK1 regulates spindle orientation through phosphorylation of Ser83 on KAP0, a regulatory subunit of protein kinase A. 25749519_Results suggest that NF-kappaB-regulated miR-124 targets MYO10, inhibits cell invasion and metastasis, and is down-regulated in node-positive NSCLC. 25819274_New research implicates Myo10 in a number of disease states including cancer metastasis and pathogen infection. 26235048_Myo10 plays a key role in integrating the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons to position centrosomes and mitotic spindles. 26573744_MYO10 (myosin X), a direct miR340 target gene, mediated the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells 29738550_In two cohorts with available data, we identified one intronic SNP (rs13361131) in myosin X gene (MYO10) associated with C17:0 level (P = 1.37x10-8), and two intronic SNP (rs12874278 and rs17363566) in deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 1 (DLEU1) region associated with C19:0 level (P = 7.07x10-9) 29864913_miR-129 inhibited neuroblastoma growth and potentiated chemosensitivity by targeting MYO10 29934580_MYO10 represents a new clinical biomarker for this aggressive disease and due to its role in cellular motility and invasion 31665067_We demonstrated that circMYO10 is upregulated in OS tissues and cell lines. CircMYO10 activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by regulating miR-370-3p/RUVBL1 axis to promote H4K16Ac at the promoter region of beta-catenin/LEF1 target genes. 32329857_LncRNA SNHG7 enhances chemoresistance in neuroblastoma through cisplatin-induced autophagy by regulating miR-329-3p/MYO10 axis. 32618228_Elevated MYO10 Predicts Poor Prognosis and its Deletion Hampers Proliferation and Migration Potentials of Cells Through Rewiring PI3K/Akt Signaling in Cervical Cancer. 34525374_Myosin-X and talin modulate integrin activity at filopodia tips. 35470858_MYO10 promotes transzonal projection-dependent germ line-somatic contact during mammalian folliculogenesisdagger. 35912545_MYO10 contributes to the malignant phenotypes of colorectal cancer via RACK1 by activating integrin/Src/FAK signaling. 36283390_MYO10-filopodia support basement membranes at pre-invasive tumor boundaries. |
ENSMUSG00000022272 |
Myo10 |
206.451073 |
3.4087611107 |
1.769247 |
0.129743704 |
189.686964 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000037210064512454223243833596970866669787877049349438493012004321356218052926959534741747174053350294679219704930758783056887750717578455805778503417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000006705989648398343634696950078207989524115010944363319988390090125249327301598368022875066632453778004370795705335606129438019706867635250091552734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
332.1584141 |
26.8414375 |
98.0889183 |
6.4553230 |
| ENSG00000145623 |
9180 |
OSMR |
protein_coding |
Q99650 |
FUNCTION: Associates with IL31RA to form the IL31 receptor. Binds IL31 to activate STAT3 and possibly STAT1 and STAT5. Capable of transducing OSM-specific signaling events. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15184896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8999038}. |
Alternative splicing;Amyloidosis;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the type I cytokine receptor family. The encoded protein heterodimerizes with interleukin 6 signal transducer to form the type II oncostatin M receptor and with interleukin 31 receptor A to form the interleukin 31 receptor, and thus transduces oncostatin M and interleukin 31 induced signaling events. Mutations in this gene have been associated with familial primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. |
hsa:9180; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; oncostatin-M receptor complex [GO:0005900]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor binding [GO:0005127]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; growth factor binding [GO:0019838]; leukemia inhibitory factor receptor activity [GO:0004923]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; oncostatin-M-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038165]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response [GO:0002675]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097] |
12061840_expression and evidence for STAT3 activation in human ovarian carcinomas 15831292_The expression of OSM and its receptor in ovarian tissue from fetuses and women suggests a possible role of OSM in growth initiation of human primordial follicles. 17028186_sOSMR is able to bind OSM and interleukin-31 when associated to soluble gp130 or soluble interleukin-31R, respectively, and to neutralize both cytokine properties 18179886_FPLCA has been mapped to 5p13.1-q11.2, and by candidate gene analysis, study identified missense mutations in the OSMR gene, encoding oncostatin M-specific receptor beta (OSMRbeta), in three families. 18430728_murine OSMR initiates STAT5 activation directly via the receptor bound Janus kinases. Intriguingly, the murine receptor preferentially recruits JAK2, whereas the human receptor seems to have a higher affinity for JAK1. 18641356_IL-6 and Oncostatin M individually affect the profile of leukocyte trafficking 19158344_The renal parenchyma is capable of generating a strong acute phase response, likely mediated via OSM/OSMR. 19223499_Epigenetic silencing and DNA methylation of OSMR is associated with colorectal cancers. 19375894_study reporta a Japanese family with familial primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis in whom a novel OSMR mutation was observed 19466957_study provides evidence for the existence of a novel pathogenic mutation in the OSMR gene in a caucasian family with familial primary cutaneous amyloidosis 19662090_provides a biologic rationale for silencing of OSMR in colon cancer progression and highlight a new therapeutic target. Moreover, detection and quantification of OSMR promoter methylation in fecal DNA is a highly specific diagnostic biomarker for CRC 19690585_The identification of OSMR and IL31RA gene pathology provides an explanation of the high prevalence of primary cutaneous amyloidosis in Taiwan as well as new insight into disease pathophysiology. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20205591_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20507362_Two new pathogenic heterozygous missense mutations in the OSMR gene (p.Val631Leu and p.Asp647Tyr) were identified in two Dutch familial primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis families. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21394648_An alternatively spliced variant of OSMR transcribing a soluble form of this receptor has been characterized in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 21508378_Aberrant methylation of the OSMR gene is associated with non-invasive colorectal cancer. 21952923_We conclude that OSMR overexpression in cervical SCC cells provides increased sensitivity to OSM, which induces pro-malignant changes. 22062952_This study identified a new heterozygous OSMR missense mutation in primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis. 22137028_enhanced production by beta-defensin-2 in T cells 22829597_A unique loop structure in oncostatin M determines binding affinity toward oncostatin M receptor and leukemia inhibitory factor receptor. 23765377_We conclude that an OSMR/TGM2/integrin-alpha5beta1/fibronectin pathway is of biological significance in cervical squamous cell carcinoma 24219225_The disease severity of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus can be partially affected by the OSMR promoter polymorphisms. 24418171_oncostatin M is a cytokine possessing vigorous antiviral and immunostimulatory properties which is released by APC upon interaction with CD40L present on activated CD4+ T cells. 25054142_primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis has a missense mutation in oncostatin M receptor beta 25283844_The interleukin IL-31/IL-31receptor axis contributes to tumor growth in human follicular lymphoma. 25792357_this study offers new findings on the molecular genetics and disease relevance of mutations in OSMR in Familial primary localized cutaneous amyloidosis. 26198770_Oncostatin M and interleukin-31: Cytokines, receptors, signal transduction and physiology. 26311783_OSMRBeta in neurons is critical for neuronal survival during cerebral ischemic/reperfusion. 26356818_the RET p.S891A mutation combined with OSMR p.G513D may underlie a novel phenotype manifesting as familial medullary thyroid carcinoma and cutaneous amyloidosis 27351213_OSM:OSMR interactions are able to induce EMT, increased cancer stem cell-like properties and enhanced lung colonisation in SCC cells 28258089_OSMR-beta deficiency in macrophages improved high-fat diet-induced atherogenesis and plaque vulnerability 28368383_OSM and OSMR are highly expressed in inflammatory bowel disease intestinal mucosa compared to control mucosa. Intestinal stromal cells express abundant OSMR. 28375929_The PLAC1 expression has been demonstrated for the first time in cervical cancers. This preliminary study has further revealed a complex relationship between PLAC1 expression, cervical cancer histologic type, p53, and HPV type that requires further investigation. 29419851_Missense mutatios were found in exon 10 of the oncostatin-M specific receptor beta subunit (OSMR) gene in all of the six patients from family 1, and in exon 14 of the OSMR gene in all of the four patients from family 2. 29511087_substitution of the AB loop and D-helix in LIF with their OSM counterparts was sufficient for OSMR activation 29652994_Polymorphisms of the OSMR rs2292016 locus are related to the development and outcome of DCM. 30134804_The current study suggested that the OSMR gene is highly expressed in human chronic autoimmune urticaria (CAU) skin tissues, and cause the up-regulation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway-related genes. OSMR gene silencing in mice inhibits the activation of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby suppressing the development of CAU. 30684280_Overexpression of LINC00520 contributes to the aggravation of Acute kidney injury by targeting miR-27b-3p/ OSMR. 30734345_The present data indicate OSMR mutations as not only the main cause of fPLCA, but also the potential source of the pathogenesis of sPLCA, although the exact molecular mechanism remains unknown. 30755233_OSMR genotype frequencies were found to be associated with higher recurrence in bladder cancer, and it may serve as a biomarker candidate gene to predict prognosis of this disease. 30778797_High OSMR expression is associated with metastasis in gastric cancer. 31861914_Oncostatin M, A Profibrogenic Mediator Overexpressed in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Stimulates Migration of Hepatic Myofibroblasts. 32043609_Whole-exome analysis of metaplastic breast carcinomas with extensive osseous differentiation. 32248843_Annexin A2-STAT3-Oncostatin M receptor axis drives phenotypic and mesenchymal changes in glioblastoma. 32459958_Feline Interleukin-31 Shares Overlapping Epitopes with the Oncostatin M Receptor and IL-31RA. 33502684_OSMRbeta mutants enhance basal keratinocyte differentiation via inactivation of the STAT5/KLF7 axis in PLCA patients. 33917126_The OSMR Gene Is Involved in Hirschsprung Associated Enterocolitis Susceptibility through an Altered Downstream Signaling. 34117193_Oncostatin-M Does Not Predict Treatment Response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Pediatric Cohort. 34380633_Oncostatin M Receptor-Targeted Antibodies Suppress STAT3 Signaling and Inhibit Ovarian Cancer Growth. 34921158_Heterocellular OSM-OSMR signalling reprograms fibroblasts to promote pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. 35163735_The Role of Oncostatin M and Its Receptor Complexes in Cardiomyocyte Protection, Regeneration, and Failure. 35321549_Association of oncostatin M receptor polymorphisms with clinical recurrence of ovarian cancer in the Chinese Han population. |
ENSMUSG00000022146 |
Osmr |
171.440609 |
0.2456446887 |
-2.025355 |
0.245715567 |
64.152713 |
0.00000000000000115139348994178277744939067178879301439342337353560763446580494928639382123947143554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000008217876166122202001901713225402204310263989082974145361504270113073289394378662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
72.7002961 |
11.3561345 |
298.1526038 |
31.6801206 |
| ENSG00000145632 |
10769 |
PLK2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NYY3 |
FUNCTION: Tumor suppressor serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in synaptic plasticity, centriole duplication and G1/S phase transition. Polo-like kinases act by binding and phosphorylating proteins are that already phosphorylated on a specific motif recognized by the POLO box domains. Phosphorylates CENPJ, NPM1, RAPGEF2, RASGRF1, SNCA, SIPA1L1 and SYNGAP1. Plays a key role in synaptic plasticity and memory by regulating the Ras and Rap protein signaling: required for overactivity-dependent spine remodeling by phosphorylating the Ras activator RASGRF1 and the Rap inhibitor SIPA1L1 leading to their degradation by the proteasome. Conversely, phosphorylates the Rap activator RAPGEF2 and the Ras inhibitor SYNGAP1, promoting their activity. Also regulates synaptic plasticity independently of kinase activity, via its interaction with NSF that disrupts the interaction between NSF and the GRIA2 subunit of AMPARs, leading to a rapid rundown of AMPAR-mediated current that occludes long term depression. Required for procentriole formation and centriole duplication by phosphorylating CENPJ and NPM1, respectively. Its induction by p53/TP53 suggests that it may participate in the mitotic checkpoint following stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15242618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19001868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20352051, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20531387}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Tumor suppressor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the polo family of serine/threonine protein kinases that have a role in normal cell division. This gene is most abundantly expressed in testis, spleen and fetal tissues, and its expression is inducible by serum, suggesting that it may also play an important role in cells undergoing rapid cell division. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:10769; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-dependent protein binding [GO:0043008]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest [GO:0006977]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; long-term synaptic depression [GO:0060292]; long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:0060291]; memory [GO:0007613]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; mitotic spindle organization [GO:0007052]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of apoptotic process in bone marrow cell [GO:0071866]; negative regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000773]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; Rap protein signal transduction [GO:0032486]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of centriole replication [GO:0046599]; regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167] |
12897130_there is a mitotic checkpoint wherein p53-dependent activation of Snk/Plk2 prevents mitotic catastrophe following spindle damage 16203730_hVPS18 may play an important role in regulation of SNK activity through its ubiquitin ligase 17671831_Calcipotriol affects proliferation of keratinocytes by decreasing the expression of EGR1 and PLK2 17912033_increased cell death observed after aphidicolin treatment and release in Plk2-deficient cells may result from both higher levels of replication stress-induced DNA damage and a dysfunctional S-phase checkpoint 19001868_Plk2 mediated centriole duplication is dependent on Plk4 function 19004816_PLK2 directly phosphorylates alpha-synuclein at Ser-129 in an in vitro biochemical assay 19506885_overexpression of PLK2 in bladder carcinomas, suggesting a possible role of PLK2 in the pathogenesis of bladder carcinomas 19706541_Data show that PLK2 as a kinase that phosphorylates Ser-137 of PLK1, which is sufficient to mediate this survival signal. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20054236_Our results point to a novel Plk2-TSC1 interaction with effects on mTOR signaling during hypoxia, and tumor growth that may enable targeting Plk2 signaling in cancer therapy. 20056645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20352051_NPM/B23 is a direct target of Plk2 in the regulation of centriole duplication and that phosphorylation on serine 4 can trigger this process 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20531387_Results identify centrosomal P4.1-associated protein (CPAP), a human homologue of SAS-4, as a substrate of PLK2 whose activity oscillates during the cell cycle. 21067440_Identification of Snk/Plk2 as a novel methylated gene in multiple myeloma. 21340720_Polo-like kinase 2 (SNK/PLK2) is a novel epigenetically regulated gene in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. 21402713_Results implicate Plk2 as a clinically important determinant of chemosensitivity. 22100274_phosphorylation sites could play an important role in the rapid activation, expansion, and prolongation of Plk2 signaling 22134238_Mutant p53 oncogenic functions are sustained by Plk2 kinase through an autoregulatory feedback loop. 22138223_Acetylation of GATA-1 responsive elements in Polo-like kinase 2 plays a crucial role in Plk2 transcription and protein expression in MG-63 cells. 22248692_PLK2 and to a lesser extent PLK3 are superior over CK2, as catalysts of Ser-129 phosphorylation both in full length alpha-synuclein and in a peptide reproducing the C-terminal segment of the protein. 22289679_The methylation status of the PLK2 CpG island predicts outcomes in patients treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy. 22399798_Phosphorylation of Fbxw7 by Plk2 induces destabilization of the F-box protein resulting in accumulation of cyclin E and increased potential for centriole reproduction 22828320_have identified and validated as in vitro PLK2 and PLK3 substrates HSP90, GRP-94, beta-tubulin, calumenin, and 14-3-3 epsilon 23466428_PLK2 inhibition is a tractable CNS pharmacological target that does not cause genotoxicity at doses and exposures that engage the target in the sensory retina. 23677647_This study supports a role for PLK2 in the generation of aSyn inclusions by a mechanism that does not depend directly on serine 129 phosphorylation. 23703673_Polo-like kinase 2 is a mediator of hedgehog survival signaling in cholangiocarcinoma. 24338472_Our findings suggest a new role for PLK2 in the regulation of inflammatory diseases by modulating ADAM17 activity. 24384746_PLK2 SNPs were associated with Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. PLK2-rs15009 CC and GG genotypes and CC genotype at PLK2-rs702723 were protective for AD. 24887096_the regulation of redox homeostasis by PLK2 promotes the survival of cells with dysfunctional mitochondria 24969300_Study indicates that miR-126 is a tumor suppressor that inhibits gastric cancer cells proliferation by targeting PI3KR2, Crk and PLK2. 25239093_Data shows that PLK2 mRNA is a direct target of miR-27a in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 25338102_Unique PLK2-dependent protein phosphorylation sites identified by mass spectrometry. 25347426_Decreased PLK2 protein expression due to promoter hypermethylation was negatively correlated with JAK2 overexpression, a common occurrence in hematological malignancies. 25501818_Silencing of polo-like kinase 2 increases cell proliferation and decreases apoptosis in SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells. 25511705_this study reports the first crystal structure of the C-terminal polo-box domain of PLK2. 25590559_PLK2 indirectly activates ROCK2 via phosphorylating nucleophosmin during centrosome amplification. 25846005_Structural analysis of the polo-box domain of human PLK2 has been presented. 26004360_these findings reveal a conserved PLK2-RAP1 pathway that is crucial to regulate endothelial tip cell behavior in order to ensure proper vascular development and patterning in vertebrates. 26625870_our study demonstrates a novel mechanism of PLK2 in promoting tumor progression, whereby it directly binds to enriched TAp73, catalyzes Ser48 phosphorylation of TAp73, and inhibits TAp73 transcriptional activity 26719332_Data suggest wild-type SNCA (alpha-synuclein) binding to synaptosome membrane is not affected by phosphorylation by PLK2; A30P SNCA, a Parkinson disease mutation, binding is greatly increased; endocytosis of SNCA fibrils follows similar pattern. 26910911_Findings indicate the interaction network of viral oncogene HPV16 E7, miR-27b and PLK2, and support the potential strategies using antisense nucleic acid of miR-27b for therapy of cervical cancer. 27423313_Plk2 represents an independent prognostic marker and regulates tumor growth and apoptosis by targeting Fbxw7/Cyclin E pathway in colorectal carcinoma. 27579920_PLK2, functional kinase and polo-box domains were required for interaction with PFV Gag. Fluorescently-tagged PFV Gag, through its chromatin tethering function, selectively relocalized ectopically expressed eGFP-tagged PLK proteins to mitotic chromosomes i 27863657_Develop a DDS for continuous intracellular delivery of PLK2. 28154193_PLK2 kinase has a role in mediating alpha-synuclein selective autophagic degradation 28648742_study demonstrates that PLK-2 activity can rapidly change cellular alpha-synuclein levels in cell models and in mice brains, but this process does not require phosphorylation of S129. Instead, it operates via regulation of alpha-synuclein mRNA transcription in an open reading frame-dependent manner 28652211_CHOP negatively regulates Polo-like kinase 2 expression via recruiting C/EBPalpha to the upstream-promoter in human osteosarcoma cell line during ER stress 28698103_we discovered that PLK2 might be inactivated in microsatellite-instability high colorectal cancers, suggesting that PLK2 could be a tumor-suppressing gene in these cancers. 29448085_The p53 dependence of Plk2 loss and tumor suppressor function in relationship to mTOR signaling may have therapeutic implications. 29864920_FOXD1 promoted the expression of Plk2 mRNA and protein in colorectal cancer cells. 30049443_The phosphorylation by Plk2, like CDK5, shifts the ratio of GAP activity of synGAP to produce a greater decrease in active Ras than in active Rap, which would produce a shift toward a decrease in the number of surface AMPA receptors in neuronal dendrites. 30517871_In late G1, SIRT1 is hypophosphorylated and its affinity to Plk2 is decreased, resulting in a rapid accumulation of centrosomal Plk2, which contributes to the timely initiation of centriole duplication. 30638284_There were aberrant expressions of miR-27b and PLK2 in oral lichen planus tissues. Decreased miR-27b may have induced cell proliferation by increasing the levels of PLK2 in oral keratinocytes. 32192190_Insulin Resistance Promotes Parkinson's Disease through Aberrant Expression of alpha-Synuclein, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Deregulation of the Polo-Like Kinase 2 Signaling. 33176854_Loss of PLK2 induces acquired resistance to temozolomide in GBM via activation of notch signaling. 33799608_Genetic Deletion of Polo-Like Kinase 2 Induces a Pro-Fibrotic Pulmonary Phenotype. 34060415_Circular RNA 0102049 suppresses the progression of osteosarcoma through modulating miR-520g-3p/PLK2 axis. 34080290_Identification and assessment of PLK1/2/3/4 in lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma: Evidence from methylation profile. 34433292_Diminished PLK2 Induces Cardiac Fibrosis and Promotes Atrial Fibrillation. 35256538_Polo-like kinases as potential targets and PLK2 as a novel biomarker for the prognosis of human glioblastoma. 35579380_Combination of FOXD1 and Plk2: A novel biomarker for predicting unfavourable prognosis of colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000021701 |
Plk2 |
449.760574 |
0.1346810662 |
-2.892381 |
0.114808029 |
627.446488 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000179551310873794950463572290607356043590385819901336234236631703658769969952291343896464167286252763213140878400899762766114728387835337767280291011435555255911700472713941065268619137256280125 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000103522552675672393733573149001098784595412455334231006252630557968106226853975430174581672250225339022093177593594709387739646358763776365752176061888731065029678916465977695013138460938331969 |
Yes |
Yes |
85.5844909 |
39.7493445 |
635.5692787 |
210.3175764 |
| ENSG00000145687 |
23635 |
SSBP2 |
protein_coding |
P81877 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of a protein complex that interacts with single-stranded DNA and is involved in the DNA damage response and maintenance of genome stability. The encoded protein may also play a role in telomere repair. A variant of this gene may be associated with survival in human glioblastoma patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:23635; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
12079286_Member of a closely related, evolutionarily conserved, and ubiquitously expressed gene family, potential tumor suppressor 15782145_Our findings are consistent with human SSBP2 being a novel regulator of hematopoietic growth and differentiation, whose loss confers a block in differentiation advantage to myeloid leukemic cells. 17311003_Results suggest that subverting SSBP2 function by oncoprotein E1B55K may contribute to cell transformation by viral oncoproteins. 18559593_SSBP2 inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation and seems to represent a novel prostate cancer-specific DNA marker, especially in high stages of human prostate cancer. 18618714_SSBP2-JAK2 fusion gene resulting from a t(5;9)(q14.1;p24.1) is associated with pre-B acute lymphocytic leukemia. 19658100_ZNF198-FGFR1 is associated with phosphorylation of several proteins including SSBP2, ABL, FLJ14235, CALM and TRIM4 proteins. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20658532_results indicate that cigarette smoking is a cause of SSBP2 promoter methylation and that SSBP2 harbors a tumor suppressive role in ESCC through inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway 22472174_The minor allele of SSBP2 SNP rs17296479 and the increased tumor expression of SSBP2 were statistically significantly associated with poorer overall survival among glioblastoma patients 30541499_SSBP-2-positive hepatocellular carcinomas were significantly associated with aggressive phenotypes and poor clinical outcome. 30676665_This study reports a crystal structure of the highly conserved N-terminal LUFS domain of human SSBP2 at 1.52 A resolution. 31443132_The structural details of the interaction of single-stranded DNA binding protein hSSB2 (NABP1/OBFC2A) with UV-damaged DNA. 31882468_CcRCC with low SSBP2 expression was associated with adverse clinicopathological characteristics and poor patient outcomes. 31892537_Single-stranded DNA binding proteins (SSBPs) interact specifically with the LDB/Chip conserved domain (LCCD) of LDB proteins and stabilize LDBs by preventing their proteasomal degradation, thus promoting their functions in gene regulation. 33197935_SSBP2-CSF1R is a recurrent fusion in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia with diverse genetic presentation and variable outcome. |
ENSMUSG00000003992 |
Ssbp2 |
147.025162 |
0.3734658841 |
-1.420952 |
0.203299131 |
48.199344 |
0.00000000000385017148622230321355096701431529467810760403168046650534961372613906860351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000022022001931713494755862370309274758575085462197762353753205388784408569335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.9021618 |
10.8050402 |
207.3750718 |
20.1651188 |
| ENSG00000145715 |
5921 |
RASA1 |
protein_coding |
P20936 |
FUNCTION: Inhibitory regulator of the Ras-cyclic AMP pathway. Stimulates the GTPase of normal but not oncogenic Ras p21; this stimulation may be further increased in the presence of NCK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11389730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8360177}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Tumor suppressor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is located in the cytoplasm and is part of the GAP1 family of GTPase-activating proteins. The gene product stimulates the GTPase activity of normal RAS p21 but not its oncogenic counterpart. Acting as a suppressor of RAS function, the protein enhances the weak intrinsic GTPase activity of RAS proteins resulting in the inactive GDP-bound form of RAS, thereby allowing control of cellular proliferation and differentiation. Mutations leading to changes in the binding sites of either protein are associated with basal cell carcinomas. Mutations also have been associated with hereditary capillary malformations (CM) with or without arteriovenous malformations (AVM) and Parkes Weber syndrome. Alternative splicing results in two isoforms where the shorter isoform, lacking the N-terminal hydrophobic region but retaining the same activity, appears to be abundantly expressed in placental but not adult tissues. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:5921; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; potassium channel inhibitor activity [GO:0019870]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048514]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001953]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of RNA metabolic process [GO:0051252]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
11751853_We show a novel alternative pathway of apoptosis in human primary cells that is mediated by transcriptionally dependent decreases in p53 and c-Myc and decreases in p21. 11847220_N-terminal fragment generated by caspase cleavage protects cells in a Ras/PI3K/Akt-dependent manner that does not rely on NFkappa B activation 12730209_mutual regulation of Ras and NF1-GAP is essential for normal neuronal differentiation 15010862_p21Ras, hSOS1, and p120GAP are not involved in polycystic ovary disease 15041706_The induction of p21 gene expression is mediated by PPARgamma ligands in lung carcinoma. 15187129_ligation of CD40 on EC increased association of Ras with its effector molecules Raf, Rho, and PI3K. But, it was determined that only PI3K was functional for Ras-induced VEGF transcription. 15542850_executioner caspases control the extent of their own activation by a feedback regulatory mechanism initiated by the partial cleavage of RasGAP that is crucial for cell survival under adverse conditions 15688026_p52Shc couples tyrosine kinase receptors to Ras by recruiting Grb2/Sos complexes. 16046410_an uncleavable N-terminal RasGAP fragment in insulin-secreting cells has a role in increasing resistance toward apoptotic stimuli without affecting glucose-induced insulin secretion 16971514_These results demonstrate that integrin signaling through Arg activates p190 by promoting its association with p120, resulting in recruitment of p190 to the cell periphery where it inhibits Rho. 18024870_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18327598_novel mutation is decribed, which causes capillary malformation and limb enlargement in a patient from a family with vascular malformations 18363760_the spectrum of clinical manifestations due to mutations in RASA1 is wider than previously thought and also includes typical CMs not associated with AVM/AVF. 18446851_42 novel RASA1 mutations and the associated phenotype in 44 families. 18761085_RasGAP and Capns1 interaction in oncogenic Ras cells is involved in regulating migration and cell survival. 18784923_found a mean Ras activation of 23.1% in cell lines with known constitutively activating ras mutations 19012001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19151751_p120Ras-GAP binds the DLC1 Rho-GAP tumor suppressor protein and inhibits its RhoA GTPase and growth-suppressing activities. 19435801_Data show that fibroblast, endothelial and carcinoma polarity during cell migration requires FAK and is associated with a complex between FAK, p120RasGAP and p190RhoGAP (p190A), leading to p190A tyrosine phosphorylation. 19578876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773259_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19786546_CD200R inhibits the activation of human myeloid cells through direct recruitment of Dok2 and subsequent activation of RAS p21 protein activator 1. 19843518_the monomeric intracellular plexin-B1 binds R-Ras but not H-Ras. These findings suggest that the monomeric form of the intracellular region is primed for GAP activity and extend a model for plexin activation. 20007727_In a collaborative study, 5 index patients (2 females, 3 males) with spinal AVMs or AVFs and cutaneous multifocal capillary lesions were investigated for the RASA1 gene mutation. 20592250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610402_Sema4D/Plexin-B1 promotes the dephosphorylation and activation of PTEN through the R-Ras GAP activity, inducing growth cone collapse. 20676106_miR-132 acts as an angiogenic switch by suppressing endothelial p120RasGAP expression. 20688547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20702649_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20821215_A novel synonymous mutation (c.1229 G > A [p.K420K]) of RASA1 was identified in a Chinese population with sporadic Sturge-Weber syndrome 21368895_Ras mutation cooperates with beta-catenin activation to drive bladder tumourigenesis. 21460216_Ca2+-dependent monomer and dimer formation switches CAPRI Protein between Ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and RapGAP activities 21646295_An important role is revealed for p120 RasGAP (RASA1) as a transgenic regulator of CD4+CD8+ double-positive cell survival and positive selection in the thymus as well as naive T cell survival in the periphery. 21664272_Cell adhesion to the substrate is necessary for RasGAP to bind Nck1. Cell detachment makes RasGAP incapable of associating with Nck1 and decreases RasGAP activity. 21664272_Nck1 activates RasGAP by direct binding in the substrate-attached but not in the suspended cells. 21768288_The results assign an unexpected role for p120RasGAP in the regulation of integrin traffic in cancer cells and reveal a new concept of competitive binding of Rab GTPases and GAP proteins to receptors as a regulatory mechanism in trafficking. 22200646_multifocal capillary malformations is the key clinical finding to suggest a RASA1 mutation 22205990_arguments against G3BP1 being a genuine RasGAP-binding partner 22342634_An update of the associated phenotype variability in a family with hereditary capillary malformations caused by a mutation in the RASA1 gene. 22949691_Ras and GTPase-activating protein (GAP) drive GTP into a precatalytic state as revealed by combining FTIR and biomolecular simulations 23158644_capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome; study reports a family with a novel mutation in the RASA1 gene - a truncating mutation in exon 11 of RASA1 (Q503X) 23322774_MicroRNA-31 activates the RAS pathway and functions as an oncogenic MicroRNA by repressing RAS p21 GTPase activating protein 1 (RASA1) 23386617_14-3-3 negatively regulates the RGC downstream of the PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway 23447049_The results of the present study indicate that P110, in combination with chemotherapeutics, is likely to represent a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer. 23650393_RASA1 mutation is responsible for the aberrant lymphatic architecture and functional abnormalities, as visualized in the PKWS subject and in the animal model. 23826368_results indicate that, mTOR, Bad, or Survivin are not required for p120 RasGAP fragment N to protect cells from cell death; conclude that downstream targets of Akt other than mTORC1, Bad, or survivin mediate fragment N-induced protection or that several Akt effectors can compensate for each other to induce the pro-survival fragment N-dependent responses 23829194_Multifocal, small, round-to-oval, pinkish-to-red cutaneous capillary malformations are seen in more than 90% of people with RASA1 mutations. 24038909_RASA1 mutations specifically cause capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. 24347041_These results indicate that stress-activated caspase-3 might contribute to the suppression of metastasis through the generation of fragment N2( RasGAP 24443565_The novel findings of this study shed light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the DLC1 inhibitory effects of p120 and suggest a functional cross-talk between Ras and Rho proteins at the level of regulatory proteins. 24465899_A ubiquitous binding partner of p190RhoGAP, p120RasGAP (RasGAP), is expressed in much lower levels in DKO4 cells compared to DLD1, and this expression is regulated by KRAS. 24600991_our study reveals mir-182 suppresses cell proliferation in vivo. RASA1 is related to cell apoptosis. We further show that mir-182 downregulates RASA1 25040287_Capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome (CM-AVM) is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by RASA1 mutations. 25202123_Antisense-mediated knockdown (anti-miR) revealed that miR-206/21 coordinately promote RAS-ERK signaling and the corresponding cell phenotypes by inhibiting translation of the pathway suppressors RASA1 and SPRED1. 25246356_The individual contribution of each Akt isoform in p120 RasGAP fragment N-mediated cell protection against Fas ligand induced cell death, was investigated. 25394563_RASA1 expression is associated with breast cancer progression and poor survival and diseasefree survival of patients. 25663768_miR-21 promotes malignant behaviors of colon cancer cells by regulating RASA1 expression via RAS pathways. 25733681_Results show that report that RasGAP associates to PDGFRbeta and prevents its direct activation. This underlying mechanism raises the possibility that PDGFRbeta-mediated diseases involve indirect activation of PDGFRbeta. 25867276_Low RASA1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 26096958_Maternal and fetal capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation due to a novel RASA1 mutation presenting with prenatal non-immune hydrops fetalis have been found. 26109071_p120RasGAP shields Akt from deactivating phosphatases in FGF1 signaling, but loses this ability once cleaved by caspase-3. 26126858_Data showed that hypoxia regulated the expression of miR-182 and RASA1 to promote HCC angiogenesis. 26192947_This is the second largest study on isolated, non-syndromic Port-wine stain; data suggest that GNAQ is the main genetic determinant in this condition. Moreover, isolated port-wine stains are distinct from capillary malformations seen in RASA1 disorders. 26710849_Data suggest that, in response to netrin-1/netrin receptor (DCC) signaling, p120RasGAP is recruited to growth cones and supports axon outgrowth; p120RasGAP Src homology 2 domains exhibit scaffolding properties sufficient to support axon outgrowth. 26747707_Results show that oncogenic KRAS can activate Rho through miR-31-mediated regulation of RASA1 indicating miR-31 acts as a KRAS effector to modulate invasion and migration in pancreatic cancer. 26840794_PTP1B dephosphorylates PITX1 to weaken its protein stability and the transcriptional activity for p120RasGAP gene expression 26969842_These results and the extreme variable expressivity support the hypothesis that somatic 'second hits' are required for the development of vascular anomalies associated with CM-AVM syndrome. In addition, the phenotypes of the affected individuals further clarify that lymphatic manifestations are also part of the phenotypic spectrum of RASA1-related disorders. 26993606_RASA1 mutations are associated melanoma tumorigenesis. 27101583_MicroRNA-21 reduces RASA1 expression in cervical cancer cell lines and promotes cervical cancer cell migration via RASA1. Furthermore, Ras-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition contributes to miR-21/RASA1 axis promoting cervical cancer cell migration. 27752061_we demonstrated a novel oncogenic mechanism of PTP1B on affecting PITX1/p120RasGAP in colorectal carcinoma(CRC). Regorafenib inhibited CRC survival through reserving PTP1B-dependant PITX1/p120RasGAP downregulation. PTP1B may be a potential biomarker predicting regorafenib effectiveness, and a potential solution for CRC 27767378_QKI-5 stabilized RASA1 mRNA via directly binding to the QKI response element region of RASA1, which in turn prevented the activation of the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway, suppressed cellular proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest. 28108518_Low RASA1 expression is associated with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 28179330_Data show that patients with low level of Ras GTPase-activating protein 1 (RASA1) expression correlated with a significantly poorer survival compared to those with high level of RASA1 expression. 28687708_The interaction between RASA1 and EPHB4 is an indication of the major cause of capillary malformation with arteriovenous malformation. 28798331_Study found that RASA1, a known target of miR-132, was downregulated in human dermal fibroblasts upon miR-132 overexpression which contributes to the pro-migratory function of miR-132 in fibroblasts. 29024832_A somatic RASA1 mutation in addition to the germline RASA1 mutation, was detected within endothelial cells in capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. 29110021_RASA1 variants are rarely found in children with sporadic capillary malformations of lower limbs without capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation syndrome. 29127119_Cancer genomic and functional data nominate concurrent RASA1/NF1 loss-of-function mutations as a strong mitogenic driver in NSCLC, which may sensitize to trametinib 29891884_Our data suggest that screening for large RASA1 deletions and duplications in this disorder is important and suggest that NGS multi-gene panel testing is beneficial for the molecular diagnosis of cases with complex vascular phenotypes. 30243714_Data suggest that the anti-oncogenic function of circular RNA circ-ITCH (circ-ITCH) is via the circ-ITCH-miR-145-RASA1 (RAS p21 protein activator (GTPase activating protein) 1) axis in vitro and in vivo. 30569149_miR21 regulated cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by directly targeting RASA1, which may have been achieved via regulation of Snail and vimentin. 30635911_we report for the first time the presence of RASA1 constitutional mosaicism in CM-AVM. Constitutional mosaicism has implications for accurate molecular diagnosis and recurrence risk and helps to explain the great phenotypic variability in CM-AVM. 30864691_The results suggested that miRNA4530 suppresses cell proliferation and enhances apoptosis by targeting RASA1 via the ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. 31300548_RASA1 mosaic mutations can cause capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation. Even low-level mosaicism can cause the classical phenotype and increased risk for offspring. 31857500_CircAHNAK1 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by modulating miR-421 and RASA1. 32540970_The GTPase-activating protein p120RasGAP has an evolutionarily conserved ''FLVR-unique'' SH2 domain. 32588875_RASA1 inhibits the progression of renal cell carcinoma by decreasing the expression of miR-223-3p and promoting the expression of FBXW7. 32605345_[Neonatal capillary malformation-arteriovenous malformation complicated with acute heart failure: a case report and literature review]. 32776686_Prenatal pleural effusions and chylothorax: An unusual presentation for CM-AVM syndrome due to RASA1. 32900839_RASA1 phenotype overlaps with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: two case reports. 33118152_Parkes-Weber syndrome related to RASA1 mosaic mutation. 34173139_Abnormal H3K27 histone methylation of RASA1 gene leads to unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion by regulating Ras-MAPK pathway in trophoblast cells. 34238206_CircMTO1 inhibits ox-LDL-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via regulating the miR-182-5p/RASA1 axis. 34238211_The long noncoding RNA MEG3 regulates Ras-MAPK pathway through RASA1 in trophoblast and is associated with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. 34464226_Down-regulated placental miR-21 contributes to preeclampsia through targeting RASA1. 34491620_Assessing the association of common genetic variants in EPHB4 and RASA1 with phenotype severity in familial cerebral cavernous malformation. 35997118_Regulation of IncRNA ZNF667-AS1 in Proliferation and Invasion of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells via Mediating ceRNA Network. |
ENSMUSG00000021549 |
Rasa1 |
2384.451421 |
0.3496833098 |
-1.515879 |
0.057226033 |
688.677878 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008665679576780654104996886164012495209248233337244821914327632074855755074039237052774941208330249489018721760974851770932034193725914317770493455477064358656712128571239113085302 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005894259472501495415657198726015442024424879683801618099232418142657588151124822471120137916730690140328610890890748171450850797467741935696260291780909554779720311194725176389723 |
Yes |
Yes |
1252.2338761 |
45.0623495 |
3607.2001746 |
89.1695271 |
| ENSG00000145730 |
5066 |
PAM |
protein_coding |
P19021 |
FUNCTION: Bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the post-translational modification of inactive peptidylglycine precursors to the corresponding bioactive alpha-amidated peptides, a terminal modification in biosynthesis of many neural and endocrine peptides (PubMed:12699694). Alpha-amidation involves two sequential reactions, both of which are catalyzed by separate catalytic domains of the enzyme. The first step, catalyzed by peptidyl alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) domain, is the copper-, ascorbate-, and O2- dependent stereospecific hydroxylation (with S stereochemistry) at the alpha-carbon (C-alpha) of the C-terminal glycine of the peptidylglycine substrate (PubMed:12699694). The second step, catalyzed by the peptidylglycine amidoglycolate lyase (PAL) domain, is the zinc-dependent cleavage of the N-C-alpha bond, producing the alpha-amidated peptide and glyoxylate (PubMed:12699694). Similarly, catalyzes the two-step conversion of an N-fatty acylglycine to a primary fatty acid amide and glyoxylate (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P14925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12699694}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Copper;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Monooxygenase;Multifunctional enzyme;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Sulfation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Vitamin C;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a multifunctional protein. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature enzyme. This enzyme includes two domains with distinct catalytic activities, a peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) domain and a peptidyl-alpha-hydroxyglycine alpha-amidating lyase (PAL) domain. These catalytic domains work sequentially to catalyze the conversion of neuroendocrine peptides to active alpha-amidated products. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:5066; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; L-ascorbic acid binding [GO:0031418]; peptidylamidoglycolate lyase activity [GO:0004598]; peptidylglycine monooxygenase activity [GO:0004504]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; fatty acid primary amide biosynthetic process [GO:0062112]; heart development [GO:0007507]; lactation [GO:0007595]; limb development [GO:0060173]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; maternal process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060135]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; ovulation cycle process [GO:0022602]; peptide amidation [GO:0001519]; protein amidation [GO:0018032]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050708]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to copper ion [GO:0046688]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to pH [GO:0009268]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043]; toxin metabolic process [GO:0009404] |
16107699_nuclear retention of PAM mRNA is lost upon expressing the La proteins that lack a conserved nuclear retention element, suggesting a direct association between PAM mRNA and La protein in vivo 20351714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22080626_Data indicate that catalytic inactivation of PHM caused by pH changes is accompanied by structural change between two states of the protein involving strong Cu-S interaction that does not involve M314. 22554821_Detail the production of the catalytic core of human peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (hPHMcc) in Escherichia coli possessing a N-terminal fusion to thioredoxin (Trx). 24464100_Two missense variants in PAM, encoding p.Asp563Gly (frequency of 4.98%) and p.Ser539Trp (frequency of 0.65%), confer moderately higher risk of type 2 diabetes (OR = 1.23, P = 3.9 x 10(-10) and OR = 1.47, P = 1.7 x 10(-5), respectively) 26296884_Oxygen Sensitivity of the Peptidylglycine alpha-Amidating Monooxygenase (PAM) in Neuroendocrine Cells 26879543_PAM expression is increased in the secretory pathway of differentiated neurons. 26982589_Data suggest that His108 and a substrate molecule are involved in the reductive pathway while His172 and Tyr79 are important in the catalytic pathway in the copper-centered electron transfer catalyzed by peptidylglycine monooxygenase. 28377049_The ancient ability of PAM to localize to ciliary membranes, which release bioactive ectosomes, may be related to its ability to accumulate in intralumenal vesicles and exosomes 29162152_PAM single nucleotide polymorphism rs13175330 is associated with hypertension and insulin resistance in a Korean population. 29997255_PAM polyubiquitinates NMNAT2 and regulates NMNAT2 protein stability and degradation by the proteasome. 30054598_A role for PAM in beta-cell function. 30054598_The T2D risk-associated rs35658696 (p.Asp563Gly) allele of PAM confers decreased PAM expression in human islets. 30054598_The T2D risk-associated rs35658696 (p.Asp563Gly) allele of PAM confers reduced amidating activity. 30054598_siRNA-mediated knockdown of PAM in EndoC-BetaH1 cells caused reductions in insulin secretion and content. These effects were also observed in primary islets from human donors heterozygous for the T2D risk-associated rs35658696 variant. 31984442_PAM haploinsufficiency does not accelerate the development of diet- and human IAPP-induced diabetes in mice. 33197464_Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Induces Rapid Intermembrane Space/Matrix Translocation of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1 Protein through TIM23 Complex. 35394266_PAM variants were associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus risk in the Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000026335 |
Pam |
303.383178 |
2.3290487426 |
1.219741 |
0.192495055 |
39.284373 |
0.00000000036636164016979720486756890632359853071653432721177523490041494369506835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001815815248121627488070145929122730515947736762427666690200567245483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
416.9086764 |
50.6885741 |
180.2387207 |
16.3389474 |
| ENSG00000145736_ENSG00000289810 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50.149996 |
0.4970678064 |
-1.008485 |
0.330988740 |
9.195738 |
0.00242579236698835156577080951478819770272821187973022460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005275481853064398901631548710611241403967142105102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.2496941 |
8.6200803 |
69.8702433 |
12.2900302 |
| ENSG00000145777 |
85480 |
TSLP |
protein_coding |
Q969D9 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Cytokine that induces the release of T-cell-attracting chemokines from monocytes and, in particular, enhances the maturation of CD11c(+) dendritic cells. Can induce allergic inflammation by directly activating mast cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11418668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11480573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17242164}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: May act as an antimicrobial peptide in the oral cavity and on the skin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24850429}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a hemopoietic cytokine proposed to signal through a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor and the IL-7R alpha chain. It mainly impacts myeloid cells and induces the release of T cell-attracting chemokines from monocytes and enhances the maturation of CD11c(+) dendritic cells. The protein promotes T helper type 2 (TH2) cell responses that are associated with immunity in various inflammatory diseases, including asthma, allergic inflammation and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The protein is therefore considered a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of such diseases. In addition, the shorter (predominant) isoform is an antimicrobial protein, displaying antibacterial and antifungal activity against B. cereus, E. coli, E. faecalis, S. mitis, S. epidermidis, and C. albicans. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:85480; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; interleukin-7 receptor binding [GO:0005139]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 production [GO:0071654]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001961]; positive regulation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0071657]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-13 production [GO:0032736]; positive regulation of interleukin-5 production [GO:0032754]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of mast cell activation [GO:0033005]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT [GO:1904894]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531] |
11418668_This protein is a hemopoietic cytokine that signals through a heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of the human TSLP receptor and the IL-7R alpha-chain. 12055625_Epithelial cell-derived TSLP not only potently activates dendritic cells, but also endows DCs with the ability to polarize naive T cells to produce proallergic Th2 cytokines. 12707303_Data suggest that CD40L-expressing cells may act in combination with thymic stromal lymphopoietin to amplify and sustain pro-allergic responses. 14999427_Reviewer points out that epithelial- and stromal-cell-derived TSLP may represent one of the factors initiating allergic responses, and that it could be a target for a curative therapeutic approach to allergy. 15741223_TSLP is a major regulatory cytokine for CD40 ligand-induced IL-12 production by DCs, and TSLP-activated DCs could promote the persistence of Th2 inflammation even in the presence of IL-12-inducing signals 15944327_Elevated bronchial mucosal expression of TSLP is implicated in asthma pathogenesis; its action is partly through selective development and retention, or recruitment of T helper type 2, not Th1, receptor-bearing cells. 16785889_Review. TSLP influences the outcome of interactions between dendritic cells and CD4+ thymocytes and T cells in many situations. 17213320_inflammatory mediators IL-1beta and TNF-alpha regulate human TSLP gene expression in an NFkappaB-dependent manner 17320941_TSLP, acting upstream of CD4-positive T cell responses, may provide a functional 'missing link' between epithelial cells, Langerhans cells, and T-cell-mediated immunity. 17416344_Collectively, these results suggest that TSLP, as a downstream molecule of TNF-alpha, may be involved in the pathophysiology of inflammatory arthritis. 17513456_human airway smooth muscle cells may play a role in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease airway inflammation via TSLP-dependent pathway 17513717_Human CD4-positive T cells are direct targets for thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). 17635955_IL-25 produced by innate effector eosinophils and basophils may augment the allergic inflammation by enhancing the maintenance and functions of TSLP-DC activated adaptive Th2 memory cells 17666213_Master switch of allergic inflammation at epithelial cell and dendritic cell interface. Link between TSLP and atopic dermatitis and asthma. Review. 17959543_RSV F protein stimulates TSLP expression in human bronchial epithelial cells mediated partially by p38 and JNK signal pathways. 18049884_Dendritic cells exposed to diesel exhaust particle-treated human bronchial epithelial cells induced Th2 polarization in a thymic stromal lymphopoietin-dependent manner. 18060034_OX40 ligand (OX40L) is a critical in vivo mediator of TSLP-mediated Th2 responses. 18244952_In a sex-stratified analysis, there was significant evidence of linkage to IgE to cockroach on chromosome 5q23; in female subjects,the T allele of single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2289276 in TSLP was associated with reductions in IgE to cockroach 18445339_REVIEW: effect of the functional versatility of hTSLP-activated DCs (hTSLP-DCs) on T cells 18684970_There is distinct airways expression of TSLP and chemokines which preferentially attract T helper (Th) type 1- and Th2-type T cells, and influx of T cells bearing their receptors in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 18720075_TSLP was detected in all samples and the mRNA and protein expression of TSLP is increased significantly in allergic rhinitis nasal mucosa. TSLP production is tightly correlated with IL-4 and severity of allergic rhinitis. 18757306_Data demonstrate that lysophosphatidic acid stimulates thymic stromal lymphopoietin and CCL20 expression in bronchial epithelial cells via CARMA3-mediated NF-kappaB activation. 18768889_A TSLP-driven mouse model of inflammation exhibits many characteristics of human atopic dermatitis, including infiltrate of CD4-positive cells, eosinophils, mast cells; production of Th2 cytokines; and class switching to produce immunoglobulin E. 18787178_Data suggest that functional genetic polymorphism of the TSLP gene appears to contribute to Th2-polarized immunity through higher TSLP production by bronchial epithelial cells in response to viral respiratory infections. 18802341_expression correlates with presence/ severity of lesions in atopic dermatitis patients 18802347_high expression in lungs of patients with asthma; undetectable expression in epithelial cells of patients with Crohn disease 18802348_expression level is increased in patients with asthma 18832669_Inhibition of NF-kappaB-mediated TSLP expression by retinoid X receptor 18832690_thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and human DCs plays an essential role in evoking inflammatory Th2 responses in allergy through OX40 ligand expression on DCs. 18941246_Study of pathways engaged in transgenic model of thymic stromal lymphopoietin-driven airway inflammation demonstrates that simultaneous blockade of interleukin (IL)-13 and IL-4 can reverse established asthma-like chronic airway disease. 19055649_Through DC activation, human TSLP and TLR3 ligands promote differentiation of Th17 cells with the central memory T cell phenotype under Th2-polarizing conditions. 19056108_Cytokine milieu modulates release of thymic stromal lymphopoietin from human keratinocytes stimulated with double-stranded RNA. 19155513_The pathogenic phenotype that develops in the transgenic mouse lung in response to TSLP is governed almost exclusively by a TSLP-facilitated adaptive response directed against foreign antigen. 19164348_mast cells are able to store TSLP intracellularly and to produce TSLP following aggregation of FcepsilonRI in the presence of IL-4 19187393_The data suggest that TSLP plays a role in augmenting, through DC recruitment and activation, the development of Th2-type T cells in allergic inflammation. 19348931_Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a mediator of crosstalk between bronchial smooth muscles and mast cells. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19539984_A genetic variant in the region of the thymic stromal lymphopoietin gene is associated with the phenotypes of asthma and airway hyperresponsiveness. 19539984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19555430_C allele at the TSLP -847C>T polymorphism may increase susceptibility to generalized vitiligo through decreasing TSLP mRNA expression levels. 19555430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19561109_TSLP expression is induced in airway epithelial cells by exposure to allergen-derived proteases and PAR-2 is involved in the process. 19741251_The TSLP protein produced in conjunctival epithelial cells plays a role in severe ocular allergy through the activation of dendritic cells and mast cells in synergy with other cytokines 19763625_high expression of TSLP in the epithelium from patients with allergic rhinitis with recruitment and infiltration of dendritic cell 19770269_IL-7 and TSLP use different mechanisms to regulate human CD4(+) T cell homeostasis. 19841072_These results, together with the finding that TSLP was expressed by the epithelial cells of human follicular gastritis, suggest that H. pylori can directly trigger epithelial cells to produce TSLP. 19857905_reulates maternal-fetal immune tolerance during early human pregnancy 19968632_IL-17A and IL-25 had opposing effects on thymic stromal lymphopoietin regulation in human nasal epithelial cells 20079130_Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in nasal epithelial cells of patients with mugwort pollen sensitive-seasonal allergic rhinitis. 20086239_TSLP potently transduced a unique T helper type 2 inducing compound signal in DCs. Whereas activation of nuclear factor kappaB (predominantly p50) drove DCs to produce OX40L to induce T(H)2 differentiation 20109311_produced by nasal polyp fibroblasts in response to stimulation by tumor necrosis factor alpha and a Th2 cytokine 20127673_TSLP induced the tyrosine-phosphorylation of STAT5 and the proliferation of multilineage-commited progenitor cells, pro-B cells and pre-B cells. It increased the proportion and the absolute numbers of more mature human B cells. 20146705_Roles of Thymic stromal lymphopoietin in immunity. 20173030_TSLP-activated human plasmacytoid dendritic cells secrete macrophage-derived chemokine CCL-22 and thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine CCL-17 but not T helper type (Th)1- or Th2-polarizing cytokines. 20208534_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20228393_trophoblast cells express TSLP and TSLPR, suggesting that TSLP plays an important role in extravillous trophoblast invasion and placentation 20236697_Our data indicate that epithelial cells express TSLPR and that TSLP induces bronchial epithelial cell proliferation and increases injury repair through IL-13 production. 20335125_RSV infection can enhance the expressions of TSLP in human airway epithelial cells. IFN-gamma, anti-TLR3 and dexamethasone can inhibit the elevation of TSLP expression induced by RSV infection, but IL-4 synergistically enhances its expression. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444169_TSLP is present in human breast milk with Levels significantly higher (p |
ENSMUSG00000024379 |
Tslp |
23.422875 |
0.2427305636 |
-2.042572 |
0.344580283 |
38.014174 |
0.00000000070232567131536248731939583767091075938715505344589473679661750793457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003401025888653133534327126241431776820789423254609573632478713989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1162333 |
2.0786926 |
37.8319337 |
4.8698470 |
| ENSG00000145779 |
25816 |
TNFAIP8 |
protein_coding |
O95379 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a negative mediator of apoptosis and may play a role in tumor progression. Suppresses the TNF-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-8 activity but not the processing of procaspase-8, subsequently resulting in inhibition of BID cleavage and caspase-3 activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10644768, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11346652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14724590}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
|
Enables cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process. Involved in positive regulation of apoptotic process. Located in cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25816; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043027]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065] |
14724590_SCC-S2 is a novel oncogenic factor in cancer cells 19112178_A chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor I (COUP-TFI) complex represses expression of the gene encoding tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8). 20398053_SCC-S2 plays an important role in NSCLC and might be a useful therapeutic target of NSCLC. 20699119_Findings demonstrate that TNFAIP8 is one of critical components of a signal transduction pathway that links mesangial cell proliferation to diabetic renal injury. 22631659_results showed stronger staining of TNFAIP8 protein in pancreatic cancer tissues compared with normal pancreas tissue; TNFAIP8 expression positively correlated with EGFR levels; results indicate TNFAIP8 may play important roles in the progression of pancreatic cancer 22666399_polymorphism of TNFAIP8 rs1045241C>T may contribute to NHL susceptibility in a Chinese population 22886548_SCC-S2 is overexpressed in colon cancers. 23280553_TNFAIP8 functions in oncogenesis are likely to involve activation of the integrin, MMP and VEGFR-2 signaling pathways. TNFAIP8 expression revealed correlation of both cytoplasmic and nuclear TNFAIP8 overexpression with high grade prostatic adenocarcinomas 23299407_the TNFAIP8-rs11064 Single nucleotide polymorphism may function by affecting the affinity of miR-22 binding to the 3'-untranslated region of TNFAIP8 and regulating TNFAIP8 expression, thus contributing to cervical cancer risk 24136748_These results provide evidence that TNFAIP8 plays critical roles in non-small cell lung cancer 24464924_SCC-S2 may play roles in affecting both immune cells and tumor cells in the thyroid and may indicate a novel pathway for understanding the pathogenesis of the disease. 24590269_TNFAIP8 may be used as a prognostic marker for the recurrence of endometrial cancer (EC), and its promotion of the proliferation and metastasis in EC may be due to its mediation of Ki-67 and MMP9. 24621012_Our data suggest that TNFAIP8 overexpression may contribute to lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma. 24767861_our findings indicate that TNFAIP8 overexpression is an independent predictor of platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer 25936980_Expression of TNFAIP8 is up-regulated in human gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation, invasion and migration. 26373887_expression associated with cell survival and death in cancer cell lines infected with canine distemper virus 26886285_these findings suggest that TNFAIP8 overexpression is a potential biomarker to identify pN0 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients at higher risk of lymphatic recurrence who may benefit from adjuvant therapy. 27000849_Of these, three CpG sites on TNFAIP8 and PON1 genes (corresponding to: cg23917399; cg07086380; and cg07404485, respectively) were significantly differentially methylated between black and non-black individuals. The three CpG sites showed lower methylation status among infants of black women. 27341992_induction of TNFAIP8 is critical for the evasion of apoptosis by tumor cells expressing the K120R variant of p53. 27807832_TNFAIP8 seems to regulate the cell survival and cancer progression processes in a multifaceted manner. (Review) 27834950_TNFAIP8 v2 may contribute to both carcinogenesis and chemotherapeutic resistance by broadly suppressing p53 activity, thus offsetting p53-dependent tumor suppression. 28087477_TNFAIP8 overexpression is correlated with axillary lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 28127811_that MicroRNA-9-TNFAIP8 might represent a promising diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer patients and could be a potential therapeutic target in the prevention and treatment of gastric cancer 28152516_TNFAIP8 regulates Hippo (MST1/2) signaling through its interaction with LATS1. 28926138_TNFAIP8 regulates Hippo pathway through interacting with LATS1 to promote cell proliferation. 29534260_The indel chr5:118704153:D, located within TNFAIP8, showed an association with plantar fascial disorders at genome-wide significance (p |
ENSMUSG00000062210 |
Tnfaip8 |
447.168981 |
3.4927571516 |
1.804366 |
0.082241873 |
497.889741 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002736037691673875671711789636463036642545006875897416553410319035897644443033430077227013609101074866506982400252841035976734832421922019294895804792698528111625545289419322356948825364904449415429884519973330164557176511 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001294356292599564169169711014436422724192973437474956289142377377195151756274144387335842256922180368068372457351654910937432635745907827723719159072820671351791514662370424859101536374773241044384857929790184299199019486 |
Yes |
No |
706.9306419 |
34.3497880 |
203.8229527 |
8.2765160 |
| ENSG00000145824 |
9547 |
CXCL14 |
protein_coding |
O95715 |
FUNCTION: Potent chemoattractant for neutrophils, and weaker for dendritic cells. Not chemotactic for T-cells, B-cells, monocytes, natural killer cells or granulocytes. Does not inhibit proliferation of myeloid progenitors in colony formation assays. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10049774, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10946286}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Ubl conjugation |
|
This antimicrobial gene belongs to the cytokine gene family which encode secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally related to the CXC (Cys-X-Cys) subfamily of cytokines. Members of this subfamily are characterized by two cysteines separated by a single amino acid. This cytokine displays chemotactic activity for monocytes but not for lymphocytes, dendritic cells, neutrophils or macrophages. It has been implicated that this cytokine is involved in the homeostasis of monocyte-derived macrophages rather than in inflammation. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:9547; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12949249_CXCL14 displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 15548693_loss of BRAK expression from tumors may facilitate neovascularization and possibly contributes to immunologic escape 15651028_The finding that CXCL14 expression inhibits prostate tumor growth suggests this gene has tumor suppressive functions. 15843547_CXCL14 is a potent chemoattractant and activator of dendritic cells (DC) and may be involved in DC homing in vivo. 16175604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16884687_results indicate that BRAK/CXCL14 is a chemokine, having suppressive activity toward tumor progression of oral carcinoma in vivo 16987528_This study elucidates a post-translational mechanism for the loss of CXCL14 in cancer and a novel mode of chemokine regulation. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18054154_CXCL14 might play a pivotal role in the pathobiology of pancreatic cancer, probably by regulating cancer invasion. 18676742_CST6, CXCL14, DHRS3, and SPP1 are regulated by BRAF signaling and may play a role in papillary thyroid carcinoma pathogenesis 18762809_CXCL14 is a gene target of RhoBTB2 and supports downregulation of CXCL14 as a functional outcome of RhoBTB2 loss in cancer. 18765527_CXCL14-positive epithelial cells were found in all tissue types. The expression of CXCL14 was not associated with any tumor or patient characteristics analyzed 18809336_Data suggest that despite the structural homology and similarity in tissue distribution of human and murine CXCL14, distinct differences point to diverse, species-specific needs for CXCL14 in epithelial immunity. 19109182_Cell supernatant-derived CXCL14 fights bacteria at the earliest stage of infection, well before the establishment of inflammation, and thus fulfills a unique role in antimicrobial immunity. 19172796_regulates energy metabolism and eating behaviior, induces insulin resistance, suppresses induction of neovascularization. (review) 19218429_identify CXCL14 as a novel autocrine stimulator of fibroblast growth and migration, with multi-modal tumor-stimulatory activities 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19276362_CXCL14 expression is upregulated by ROS through the AP-1 signaling pathway and promotes cell motility through elevation of cytosolic Ca(2+) by binding to the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum in breast cancer. 19339694_-A-induced migration depends on the selective and polarized release of 2 chemokines, namely CXC chemokine ligands 12 and 14 19833716_Results suggest that CXCL14 plays an important role in regulating trophoblast invasion through an autocrine/paracrine manner during early pregnancy. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19903701_Data conclude that CXCL14 is likely to be regulated by progesterone in human endometrium and that it may exert a chemoattractive effect on uNK cells and in part be responsible for their clustering around the epithelial glands. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20067447_Data indicate that the expression of BRAK stimulated the formation of elongated focal adhesions of the HSC-3 cells in an autocrine or paracrine fashion, in which stimulation may be responsible for the reduced migration of the cells. 20212097_Increased severity of collagen-induced arthritis in CXCL14-transgenic mice is associated with enhanced T helper (Th) type 1 cytokine production, elevated autoantibody levels and increased inflammatory cell infiltration into the joints. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460540_CXCL14 removal from conditioned media abolished its chemotactic properties. Findings offer direct evidence for epigenetic regulation of chemokine expression in tumor cells. 20478268_Taken together, the data indicate that the respective stress-dependent action of p38 isoforms is responsible for the up-regulation of the gene expression of the chemokine BRAK/CXCL14. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20562917_CXCL14 methylation in sputum from asymptomatic early-stage lung cancer cases was associated with a 2.9-fold elevated risk for this disease compared with controls, substantiating its potential as a biomarker for early detection of lung cancer 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20737948_CEACAM-1 and CXCL-14 are involved in the occurrence and development of infantile hemangioma. 20815772_The results indicate that oxidative stress induced by H(2)O(2) or HO(*) stimulates angiogenesis and tumuor progression by altering the gene expression of CXCL14 via the EGFR/MEK/ERK pathway in human HNSCC cells. 21556757_The rs2237062 polymorphism in the CXCL14 gene might influence Hepatits B Virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma progression in a Chinese population. 22382027_These results indicated that upregulation of BRAK was accompanied by differentiation of epithelial cells induced by calcium/calmodulin signaling, and that SP1 binding to the BRAK promoter region played an important role in this signaling. 22910931_CXCL14 is a negative regulator of growth and metastasis in breast cancer. 23161284_CXCL14 binding to glycoproteins harboring heparan sulfate proteoglycans and sialic acids leads proliferation and migration of some cancer cells. 23294544_CXCL14 might be a potential novel prognostic factor to predict the disease recurrence and overall survival and could be a potential target of postoperative adjuvant therapy in CRC patients 23597004_Smoking-induced CXCL14 expression in the human airway epithelium links chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to lung cancer. 23669361_CXCL14 represents, along with CXCR7, molecules that co-evolved with the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis to modulate important physiological processes in development, stem cell maintenance, and immune responses 23982764_Downregulation of CXCL14 expression is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. 24033560_CXCL14 plays a pivotal role as a potential tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. 24099668_CXCL14 inhibits colorectal cancer migration, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by suppressing NF-kappaB signaling. 24710408_Genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of NOS1 reduced the growth of CXCL14-expressing fibroblasts. 24938992_CXCL14 overexpression influences proliferation and changes in cell cycle distributions of HT29 colorectal carcinoma cells. 25102097_Data indicate that site-specific CpG methylation in the CXC chemokine CXCL14 promoter is associated with altered expression. 25411967_three of these five genes (CXCL14, ITGAX, and LPCAT2) harbored polymorphisms associated with aggressive disease development in a human GWAS cohort consisting of 1,172 prostate cancer patients. 25451233_essential CXCL12-operated functions of CXCR4 are insensitive to CXCL14 25760073_Elevated S100A6 enhances tumorigenesis and suppresses CXCL14-induced apoptosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 25822025_Prometastatic effects of IRX1 were mediated by upregulation of CXCL14/NF-kappaB signaling. 26428435_Data indicate that CXC chemokine CXCL14, CXC chemokine receptor CXCR7 and the ratio between CXC chemokine receptor CXCR4-2 and CXCR4-1 could predict diseae free survival in Ewing sarcoma patients. 27115465_Epithelial CXCL14 expression is significantly associated with ERalpha positivity and low proliferation, whereas stromal CXCL14 expression is not linked to any of the established clinicopathological parameters, subtypes of breast cancer or tumour stroma abundance. 27143385_These results suggest that CXCL14 downregulation by human papillomaviruses plays an important role in suppression of antitumor immune responses. 27259322_Elevated expression of CXCL14 in osteosarcoma tissues correlated with poor prognosis of the osteosarcoma patients. 28087599_High CXCL14 expression is associated with metastatic progression of Ovarian Cancer. 28277316_These findings suggest a possibility that cells at the sites of MELF pattern had acquired increased invasiveness through the function of the CXCL14-CXCR4 and CXCL12-CXCR4 axes. 28359053_Platelets are a relevant source of CXCL14. Platelet-derived CXCL14 at the site of vascular lesions might play an important role in vascular repair/regeneration. 28360196_These results suggest that that CXCL14 is a positive allosteric modulator of CXCR4 via CXCL12 that enhances the potency of CXCR4 ligands. 28382159_These findings indicate that CXCL14 is a critical immunomodulator involved in the stroke-induced inflammatory reaction. 29504253_Therefore, Porphyromonas gingivalis not only directly stimulates CXCL14 expression via PAR-3 but also promotes its expression by antagonising EGF signalling. 29507348_Application of STRING database analysis and confirmation via in-vitro and histological assay highlights the CXCL14/CXCR4 chemokine axis with a possible role in the progression and/or activation of fibroblasts within the Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis lung. 29959905_CXCL14 peptides could have roles as anti-inflammatory agents and anti-microbials; the analog of CXCL1459-75 (named CXCL14-C17) corresponds to the C-terminal alpha-helix of CXCL14 30122557_The chemokine CXCL14 is secreted by brown fat in response to thermogenic activation. Brown-fat-secreted CXCL14 promotes the recruitment of M2-type macrophages. Lack of CXCL14 impairs brown fat activity and alters glucose homeostasis. CXCL14 induces browning of white fat via type 2 immune cells activation. 31087594_Serum CXCL14 levels were significantly decreased in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients compared with healthy individuals and in diffuse cutaneous SSc patients relative to limited cutaneous SSc patients. SSc patients with digital ulcers had serum CXCL14 levels significantly lower than those without. Results indicate that decreased CXCL14 expression may contribute to the maintenance of Th2-skewed immune polarization. 31117166_CXCL14 is a protumorigenic chemokine in Glioblastoma (GBM). The expression of CXCL14 correlates with several aggressive aspects of GBM. 31264681_The CXCL14-glycosaminoglycans system represents a promising approach to investigate the specificity of glycosaminoglycans-protein interactions, which represents an important topic for developing the rational approaches to novel strategies in regenerative medicine 31640472_IRX1 hypermethylation promotes heart failure by inhibiting CXCL14 expression. 31881212_Reduction in Human Epidermal Langerhans Cells with Age Is Associated with Decline in CXCL14-Mediated Recruitment of CD14(+) Monocytes. 32077118_Upregulated CXCL14 is associated with poor survival outcomes and promotes ovarian cancer cells proliferation. 32239134_The chemokine CXCL14 mediates platelet function and migration via direct interaction with CXCR4. 32408131_Inhibitory effect of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14 on the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells through transforming growth factor-beta1. 32552011_Effect of chemokine CXCL14 on in vitro angiogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 32708730_CXCL14 Maintains hESC Self-Renewal through Binding to IGF-1R and Activation of the IGF-1R Pathway. 33108937_CXCL14 inhibits the growth and promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing Akt/mTOR pathway. 33414488_The chemokine CXCL14 is negatively associated with obesity and concomitant type-2 diabetes in humans. 33564857_Integrative analyses of scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq reveal CXCL14 as a key regulator of lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. 34082276_Role of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14 promoter region DNA methylation and single nucleotide polymorphism in influenza A severity. 34085699_CXCL2/10/12/14 are prognostic biomarkers and correlated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34677618_Posterior Cervical Brown Fat and CXCL14 Levels in the First Year of Life: Sex Differences and Association With Adiposity. 34696665_The roles of Y-box-binding protein (YB)-1 and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14 (CXCL14) in the progression of prostate cancer via extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling. 34704819_MiR-3188 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting CXCL14. 34789307_CXCL14 facilitates the growth and metastasis of ovarian carcinoma cells via activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 35421632_Dysregulation of CXCL14 promotes malignant phenotypes of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells via regulating SRC and EGFR signaling. 35452413_Integrated analysis of 14 lymphoma datasets revealed high expression of CXCL14 promotes cell migration in mantle cell lymphoma. 35463668_Reduced Incidence of Necrotizing Enterocolitis due to the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of CXCL14 in Intestinal Tissue. 35511927_CXCL14 Promotes a Robust Brain Tumor-Associated Immune Response in Glioma. 35588310_BRAK and APRIL as novel biomarkers for ovarian tumors. 35776020_The negative feedback loop FAM129A/CXCL14 aggravates the progression of esophageal cancer. 35926119_CXCL14 Protects against Polymicrobial Sepsis by Enhancing Antibacterial Functions of Macrophages. 36012586_CXCL14 Attenuates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Progression by Regulating Immune Profiles of the Tumor Microenvironment in a T Cell-Dependent Manner. 36063806_Elevated CXCL14 in Induced Sputum Was Associated with Eosinophilic Inflammation and Airway Obstruction in Patients with Asthma. |
ENSMUSG00000021508 |
Cxcl14 |
12.089549 |
18.8237001589 |
4.234478 |
0.776129554 |
40.845707 |
0.00000000016473471757139988669034745605356060554891328706617059651762247085571289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000839600977677438655156737438273704954294629487776546739041805267333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.6251130 |
11.7369685 |
1.2044415 |
0.5866714 |
| ENSG00000145868 |
81545 |
FBXO38 |
protein_coding |
Q6PIJ6 |
FUNCTION: Substrate recognition component of a SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of PDCD1/PD-1, thereby regulating T-cells-mediated immunity (PubMed:30487606). Required for anti-tumor activity of T-cells by promoting the degradation of PDCD1/PD-1; the PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway being exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and facilitate tumor survival (PubMed:30487606). May indirectly stimulate the activity of transcription factor KLF7, a regulator of neuronal differentiation, without promoting KLF7 ubiquitination (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BMI0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30487606}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Immunity;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30487606}. |
This gene encodes a large protein that contains an F-box domain and may participate in protein ubiquitination. The encoded protein is a transcriptional co-activator of Krueppel-like factor 7 (Klf7). A heterozygous mutation in this gene was found in individuals with autosomal dominant distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type IID. There is a pseudogene for this gene on chromosome 4. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:81545; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell [GO:0002842]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] |
14729953_This publication identifies the F-box protein 38 mouse ortholog and characterizes its interaction with KLF7 during regulation of cell cycle progression. 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26643602_Our findings provide direct evidence for the association of FBXO38 and AP3B2 with severe chronic periodontitis in the Han Chinese population. 30487606_data indicate that FBXO38 regulates PD-1 expression and highlight an alternative method to block the PD-1 pathway 30804394_USP7 Regulates Cytokinesis through FBXO38 and KIF20B. 31269066_Study found that a COPD associated alternative splicing variant of previously unknown function may contribute to the inclusion of a new exon in the FBXO38 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000042211 |
Fbxo38 |
497.334486 |
0.4447288237 |
-1.169002 |
0.090746164 |
165.336004 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000007725225937766121872163753189233005248286520976134777324900003241276094200625680575039369364940882931036547631720168283209204673767089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001226068116574494183695792351013145153660046703260223004886545756463263073496415969651811445366353797714609186186862643808126449584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
319.7585329 |
18.2542938 |
724.0078034 |
28.5117645 |
| ENSG00000145907 |
10146 |
G3BP1 |
protein_coding |
Q13283 |
FUNCTION: ATP- and magnesium-dependent helicase that plays an essential role in innate immunity (PubMed:30510222). Participates in the DNA-triggered cGAS/STING pathway by promoting the DNA binding and activation of CGAS. Enhances also RIGI-induced type I interferon production probably by helping RIGI at sensing pathogenic RNA (PubMed:30804210). In addition, plays an essential role in stress granule formation (PubMed:12642610, PubMed:20180778, PubMed:23279204). Unwinds preferentially partial DNA and RNA duplexes having a 17 bp annealed portion and either a hanging 3' tail or hanging tails at both 5'- and 3'-ends (PubMed:9889278). Unwinds DNA/DNA, RNA/DNA, and RNA/RNA substrates with comparable efficiency (PubMed:9889278). Acts unidirectionally by moving in the 5' to 3' direction along the bound single-stranded DNA (PubMed:9889278). Phosphorylation-dependent sequence-specific endoribonuclease in vitro (PubMed:11604510). Cleaves exclusively between cytosine and adenine and cleaves MYC mRNA preferentially at the 3'-UTR (PubMed:11604510). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11604510, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12642610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20180778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23279204, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30510222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30804210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9889278}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;DNA-binding;Endonuclease;Helicase;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nuclease;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes one of the DNA-unwinding enzymes which prefers partially unwound 3'-tailed substrates and can also unwind partial RNA/DNA and RNA/RNA duplexes in an ATP-dependent fashion. This enzyme is a member of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-binding proteins and is also an element of the Ras signal transduction pathway. It binds specifically to the Ras-GTPase-activating protein by associating with its SH3 domain. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10146; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA helicase activity [GO:0003678]; DNA/RNA helicase activity [GO:0033677]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; positive regulation of stress granule assembly [GO:0062029]; positive regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032481]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; stress granule assembly [GO:0034063] |
15471883_involvement of cellular protein G3BP in transcription of intermediate stage genes may regulate the transition between early and late phases of vaccinia virus replication 15602692_G3BPs are scaffolding proteins linking signal transduction to RNA metabolism (review) 16996479_Hepatitis C virus viral gene and proteins may regulate the presence of host cellular proteins in detergent resistant membrane 17210633_Caprin-1/G3BP-1 complex is likely to regulate the transport and translation of mRNAs of proteins involved with synaptic plasticity in neurons 17253181_The expressions of G3BP and OPN proteins have a close relationship with lymphoid metastasis and survival in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients. 17297477_Both G3BP1 and G3BP2 isoforms may act as negative regulators of tumor suppressor protein p53. 17696235_The expression of G3BP and RhoC protein is closely related to the lymph node metastasis and survival in esophageal squamous carcinoma (ESC) patients. G3BP and RhoC proteins can be considered as predictors of prognosis in ESC patients. 20180778_Results illustrated a role for MK-STYX in regulating the ability of G3BP1 to integrate changes in growth-factor stimulation and environmental stress with the regulation of protein synthesis. 20424128_these results strongly indicate that (-)-epigallocatechin gallate suppresses lung tumorigenesis through its binding with G3BP1 20643132_The kinetics of assembly of stress granules(SGs) in living cells demonstrated that Tudor-SN co-localizes with G3BP and is recruited to the same SGs in response to different stress stimuli. 20663914_Molecular and functional studies indicate that the interaction of G3BP1 with beta-F1 mRNA inhibits its translation at the initiation level, supporting a role for G3BP1 in the glycolytic switch that occurs in cancer. 21206022_The nuclear transport factor 2-like (NTF2-like) domain of human G3BP1 was subcloned, overexpressed in Escherichia coli and purified. 21257637_TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) regulates stress granule dynamics via differential regulation of G3BP and TIA-1. 21266361_CD24 may play a role in the inhibition of cell invasion and metastasis, and that intracellular CD24 inhibits invasiveness and metastasis through its influence on the posttranscriptional regulation of BART mRNA levels via G3BP RNase activity. 21304914_interaction between IncA and G3BP1 of Hep-2 cells infected with Chlamydophila psittaci reduces c-Myc concentration 21665939_overexpression of the amino (N)-terminal region of G3BP, including the binding region for BART mRNA, dominant-negatively inhibits formation of the complex between endogenous G3BP and BART mRNA, and increases the expression of BART. 22205990_arguments against G3BP1 being a genuine RasGAP-binding partner 22703643_In this report, we demonstrate that a novel peptide GAP161 blocked the functions of G3BP and markedly suppressed HCT116 cell growth through the induction of apoptosis 22767504_These findings establish a novel function for Poly(ADP-ribose) in the formation of G3BP-induced stress granules upon genotoxic stress. 22833567_Data indicate that assembly of large RasGAP SH3-binding protein (G3BP)-induced stress granules precedes phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha (eIF2alpha). 23087212_Data show that the nsP3/G3BP interaction also blocks stress granules (SGs) induced by other stresses than virus infection. 23163895_MK-STYX inhibits stress granule formation independently of G3BP-1 phosphorylation at Ser149. 23279204_both G3BP1 and G3BP2 play a role in the formation of SGs in various human cells and thereby recovery from these cellular stresses. 24157923_Data revealed that knockdown of G3BP inhibited the migration and invasion of human lung carcinoma cells through the inhibition of Src, FAK, ERK and NF-kappaB and decreased levels of MMP-2, MMP-9 and uPA. 24321297_G3BP1 regulation of cell proliferation in breast cancer cells, may occur via a regulatory effect on PMP22 expression. 24324649_Binding motifs specificity has been determined for human G3BP1 NTF2-like domain. 24992036_G3BP1, G3BP2 and CAPRIN1 are required for translation of interferon stimulated mRNAs and are targeted by a dengue virus non-coding RNA. 24998844_These findings disclose a novel mechanism of resveratrol-induced p53 activation and resveratrol-induced apoptosis by direct targeting of G3BP1. 25229650_G3BP1 has a role in modulating stress granule assembly during HIV-1 infection 25520508_Authors show that the PXXP domain within G3BP1 is essential for the recruitment of PKR to stress granules, for eIF2alpha phosphorylation driven by PKR, and for nucleating stress granules of normal composition. 25578447_eQTLs acting across multiple tissues are significant carriers of inherited risk for CAD. FLYWCH1, PSORSIC3, and G3BP1 are novel master regulatory genes in CAD that may be suitable targets. 25653451_Stress granule components G3BP1 and G3BP2 play a proviral role early in Chikungunya virus replication. 25658430_ICP8 binding to G3BP also inhibits SG formation, which is a novel function of HSV ICP8. 25784705_The G3BP1-Caprin1-PKR complex represents a new mode of PKR activation and is important for antiviral activity of G3BP1 and PKR during infection with mengovirus. 25800057_these findings demonstrate a critical role for YB-1 in stress granule formation through translational activation of G3BP1, and highlight novel functions for stress granules in tumor progression. 25809930_Our data define G3BP1 as a novel independent prognostic factor that is correlated with gastric cancer progression. 25847539_G3BP1 is essential for normal stress granule-processing body interactions and stress granule function. 25962958_Our findings identified a novel function of G3BP1 in the progression of breast cancer via activation of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition 26350772_G3BP1 granules were assembled independently of TIA-1 and had a negative impact on Dengue virus replication. 26432022_Host G3BP1 captures HIV-1 RNA transcripts and thereby restricts mRNA translation, viral protein production and virus particle formation. 27022092_G3BP mediates the condensation of stress granules by shifting between two different states that are controlled by the phosphorylation of S149 and by binding to Caprin1 or USP10. 27303792_Based on insights from the structures and existing biochemical data, the existence of an evolutionarily conserved ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex consisting of Caprin-1, FMRP and G3BP1 is proposed. 27383630_Results show the crystal structure of the NTF2-like domain of G3BP-1 in complex with nsP3 protein revealing a poly-complex of G3BP-1 dimers interconnected through the FGDF motifs in nsP3. Although in vitro and in vivo binding studies revealed a hierarchical interaction of the two FGDF motifs with G3BP-1, viral growth curves clearly demonstrated that two intact FGDF motifs are required for efficient viral replication. 27601476_G3BP1 is differentially methylated on specific arginine residues by protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) 1 and PRMT5 in its RGG domain. 27920254_These data support a role for casein kinase 2 in regulation of protein synthesis by downregulating stress granule formation through G3BP1. 28011284_The data suggested that JNK-enhanced Tudor-SN phosphorylation promotes the interaction between Tudor-SN and G3BP and facilitates the efficient recruitment of Tudor-SN into stress granules under conditions of sodium arsenite-induced oxidative stress. 28523344_Activated glucocorticoid receptor induced phosphorylation of v-AKT Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homologue (AKT) kinase, which in turn phosphorylated and promoted nuclear translocation of G3BP1. The nuclear G3BP1 bound to the G3BP1 consensus sequence located on primary miR-15b~16-2 and miR-23a~27a~24-2 to inhibit their maturation. 28755480_G3BP1 interacts directly with the foot-and-mouth disease virus internal ribosome entry site and negatively regulates translation. 28972166_JMJD6 is a novel Stress Granule component that interacts with G3BP1 complexes, and its expression reduces G3BP1 monomethylation and asymmetric dimethylation at three Arg residues. 29463567_Ras GTPase-activating protein SH3-domain-binding protein (G3BP1) shows alternating binding in nanocores and anomalous diffusion in the liquid phase of stress granules. 29588351_Study demonstrated that the cytosolic lncRNA P53RRA is downregulated in cancers and functions as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cancer progression. P53RRA bound G3BP1 and cytosolic P53RRA-G3BP1 interaction displaced p53 from a G3BP1 complex, resulting in greater p53 retention in the nucleus, which led to cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and ferroptosis. 29626090_High G3BP1expression is associated with arteriosclerosis. 29717134_G3BP1 promotes tumor progression and metastasis through IL-6/G3BP1/STAT3 signaling axis in renal cell carcinomas. 30006004_The disruption of stress granules (SGs) during the late stage of Enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection is caused by viral protease 3C-mediated cleavage of G3BP stress granule assembly factor 1 (G3BP1). Over-expression of G3BP1-SGs negatively impacts viral replication at the cytopathic effect (CPE), protein, RNA, and viral titer levels. 30510222_this paper shows that G3BP1 promotes DNA binding and activation of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase 30804210_data reveal G3BP1 as a critical component of RIG-I signaling and possibly acting as a co-sensor to promote RIG-I recognition of pathogenic RNA. 30989663_results here elucidate that G3BP1-depletion suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion capabilities of esophageal cancer cells via the inactivation of Wnt/beta-catenin and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways 31199850_These data confirm that G3BP is a ribosomal binding protein and reveal that alphaviral nsP3 uses G3BP to concentrate viral replication complexes and to recruit the translation initiation machinery, promoting the efficient translation of viral mRNAs. 31481087_YBX1 interacts with G3BP1 to promote metastasis of RCC by activating the YBX1/G3BP1-SPP1-NF-kappaB signaling axis. 31481451_Replacement of endogenous G3BP1 with the K376Q mutant or the RNA binding-deficient F380L/F382L mutant interfered with SG formation. Significant G3BP1 K376 acetylation was detected during SG resolution, and K376-acetylated G3BP1 was seen outside SGs. G3BP1 acetylation is regulated by histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and CBP/p300. 31501480_G3BP1 inhibits ubiquitinated protein aggregations induced by p62 and USP10. 31560169_Elevated expression of G3BP1 associates with YB1 and p-AKT and predicts poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung cancer patients after surgical resection. 31827077_G3BP1 inhibits RNA virus replication by positively regulating RIG-I-mediated cellular antiviral response. 31941779_Typical Stress Granule Proteins Interact with the 3' Untranslated Region of Enterovirus D68 To Inhibit Viral Replication. 31941782_Sensitivity of Alphaviruses to G3BP Deletion Correlates with Efficiency of Replicase Polyprotein Processing. 31956030_UBAP2L Forms Distinct Cores that Act in Nucleating Stress Granules Upstream of G3BP1. 32302571_G3BP1 Is a Tunable Switch that Triggers Phase Separation to Assemble Stress Granules. 32302572_RNA-Induced Conformational Switching and Clustering of G3BP Drive Stress Granule Assembly by Condensation. 32406909_G3BP1-linked mRNA partitioning supports selective protein synthesis in response to oxidative stress. 32663095_Depletion of lncRNA MALAT1 inhibited sunitinib resistance through regulating miR-362-3p-mediated G3BP1 in renal cell carcinoma. 32692974_Translational Repression of G3BP in Cancer and Germ Cells Suppresses Stress Granules and Enhances Stress Tolerance. 32989225_G3BP1 interacts with YWHAZ to regulate chemoresistance and predict adjuvant chemotherapy benefit in gastric cancer. 33000280_Overexpression of G3BP1 facilitates the progression of colon cancer by activating betacatenin signaling. 33020468_G3BP1 controls the senescence-associated secretome and its impact on cancer progression. 33131924_Role of Chikungunya nsP3 in Regulating G3BP1 Activity, Stress Granule Formation and Drug Efficacy. 33199441_RNA partitioning into stress granules is based on the summation of multiple interactions. 33497611_G3BPs tether the TSC complex to lysosomes and suppress mTORC1 signaling. 33536604_G3BP1 promotes human breast cancer cell proliferation through coordinating with GSK-3beta and stabilizing beta-catenin. 33547245_Stress granule formation, disassembly, and composition are regulated by alphavirus ADP-ribosylhydrolase activity. 33726799_LncRNA SPOCD1-AS from ovarian cancer extracellular vesicles remodels mesothelial cells to promote peritoneal metastasis via interacting with G3BP1. 33941659_G3BP1 Inhibition Alleviates Intracellular Nucleic Acid-Induced Autoimmune Responses. 33945510_Huntington's disease mice and human brain tissue exhibit increased G3BP1 granules and TDP43 mislocalization. 33987877_G3BP1 may serve as a potential biomarker of proliferation, apoptosis, and prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 34287041_Orf Virus ORF120 Protein Positively Regulates the NF-kappaB Pathway by Interacting with G3BP1. 34432484_Resveratrol and related stilbene derivatives induce stress granules with distinct clearance kinetics. 34517025_Genomics-guided targeting of stress granule proteins G3BP1/2 to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 propagation. 34614161_G3BP1 binds to guanine quadruplexes in mRNAs to modulate their stabilities. 34739333_Ubiquitination of G3BP1 mediates stress granule disassembly in a context-specific manner. 34795264_G3BP1 inhibits Cul3(SPOP) to amplify AR signaling and promote prostate cancer. 34967276_Loss of Ras GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 1 (G3BP1) inhibits the progression of ovarian cancer in coordination with ubiquitin-specific protease 10 (USP10). 35017014_G3bp1 - microRNA-1 axis regulates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. 35075101_SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and N protein counteract the RIG-I signaling pathway by suppressing the formation of stress granules. 35085371_TDRD3 is an antiviral restriction factor that promotes IFN signaling with G3BP1. 35100495_Small nucleolar RNA SNORA71A promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by maintaining ROCK2 mRNA stability in breast cancer. 35176431_The roles of G3BP1 in human diseases (review). 35240128_SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Targets a Conserved Surface Groove of the NTF2-like Domain of G3BP1. |
ENSMUSG00000018583 |
G3bp1 |
1373.356844 |
3.0708754338 |
1.618650 |
0.237412667 |
44.219757 |
0.00000000002935040293218031535274893869616745674389068909704292309470474720001220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000157818560028772831342928129646618201631369515780534129589796066284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2039.3065522 |
250.0639550 |
669.5579228 |
59.8157732 |
| ENSG00000145911 |
23138 |
N4BP3 |
protein_coding |
O15049 |
FUNCTION: Plays a positive role in the antiviral innate immune signaling pathway. Mechanistically, interacts with MAVS and functions as a positive regulator to promote 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of MAVS and thus strengthens the interaction between MAVS and TRAF2 (PubMed:34880843). Also plays a role in axon and dendrite arborization during cranial nerve development. May also be important for neural crest migration and early development of other anterior structures including eye, brain and cranial cartilage (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A1L8GXY6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34880843}. |
Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Developmental protein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in nervous system development. Predicted to be located in axon and dendrite. Predicted to be active in cytoplasmic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23138; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; nervous system development [GO:0007399] |
29343084_N4BP3 was associated with the survival time of cervical squamous cell carcinoma patients. mir-451 and mir-486 were related to tumor differentiation stage. 35848906_N4BP3 promotes angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by binding with KAT2B. 36162713_N4BP3 promotes breast cancer metastasis via NEDD4-mediated E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000001053 |
N4bp3 |
34.197386 |
3.2817519340 |
1.714466 |
0.292205144 |
35.602715 |
0.00000000241950043612403727125944529971219437713969568903848994523286819458007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011177410465474425797049900827180579643282953838934190571308135986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.3474317 |
9.5033662 |
16.3727555 |
2.4051961 |
| ENSG00000145949 |
340156 |
MYLK4 |
protein_coding |
Q86YV6 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable myosin light chain kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein phosphorylation. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:340156; |
ATP binding [GO:0005524]; myosin light chain kinase activity [GO:0004687]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
12471243_First identification, named SgK085 and classified as one of four myosin light chain kinases in a comprehensive analysis of protein kinases encoded by the human genome. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33980265_MYLK4 promotes tumor progression through the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in osteosarcoma. |
ENSMUSG00000044951 |
Mylk4 |
14.771900 |
0.4977831190 |
-1.006411 |
0.404376378 |
6.266252 |
0.01230591615651624622096438343987756525166332721710205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.023158913796871866824789165661968581844121217727661132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.5152589 |
2.5936558 |
19.2391288 |
3.4356527 |
| ENSG00000146067 |
54540 |
FAM193B |
protein_coding |
Q96PV7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Located in cytoplasm; nuclear speck; and nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues mmu:212483; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634] |
21177767_Expression of full length IRIZIO cDNA also cooperated with PAX3-FOXO1 in the transformation of Arf-/- myoblasts. Given that IRIZIO is expressed at increased levels in rhabdomyosarcoma, it might contribute to rhabdomyosarcomagenesis in humans. 26188516_Identification of FAM193b as KCTD5 interaction partner. Formation of trimeric complexes of KCTD5/cullin3 with MCM7, ZNF711 and FAM193B. 34518442_The ceRNA PVT1 inhibits proliferation of ccRCC cells by sponging miR-328-3p to elevate FAM193B expression. |
ENSMUSG00000021495 |
Fam193b |
249.220908 |
0.2377137774 |
-2.072703 |
0.189617031 |
114.345300 |
0.00000000000000000000000001094828571550608477739208919949547030753766391635256840937475124929341213295130863514259544899687170982360839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000124400844619607261297145431795829791460726235466728206373418126143314856035804183420623303391039371490478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.3049242 |
16.8482788 |
389.8215152 |
50.4419007 |
| ENSG00000146070 |
7941 |
PLA2G7 |
protein_coding |
Q13093 |
FUNCTION: Lipoprotein-associated calcium-independent phospholipase A2 involved in phospholipid catabolism during inflammatory and oxidative stress response (PubMed:7700381, PubMed:8624782, PubMed:2040620, PubMed:16371369, PubMed:17090529, PubMed:10066756). At the lipid-aqueous interface, hydrolyzes the ester bond of fatty acyl group attached at sn-2 position of phospholipids (phospholipase A2 activity) (PubMed:2040620, PubMed:10504265). Specifically targets phospholipids with a short-chain fatty acyl group at sn-2 position (PubMed:2040620). Can hydrolyze phospholipids with long fatty acyl chains, only if they carry oxidized functional groups (PubMed:2040620, PubMed:8624782). Hydrolyzes and inactivates platelet-activating factor (PAF, 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine), a potent pro-inflammatory signaling lipid that acts through PTAFR on various innate immune cells (PubMed:10504265, PubMed:10066756, PubMed:7592717, PubMed:11590221, PubMed:7700381, PubMed:18434304, PubMed:16371369, PubMed:8675689, PubMed:8624782). Hydrolyzes oxidatively truncated phospholipids carrying an aldehyde group at omega position, preventing their accumulation in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles and uncontrolled pro-inflammatory effects (PubMed:2040620, PubMed:7700381). As part of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles, can hydrolyze phospholipids having long-chain fatty acyl hydroperoxides at sn-2 position and protect against potential accumulation of these oxylipins in the vascular wall (PubMed:17090529). Catalyzes the release from membrane phospholipids of F2-isoprostanes, lipid biomarkers of cellular oxidative damage (PubMed:16371369). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10066756, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10504265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11590221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16371369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17090529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18434304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2040620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7592717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7700381, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8624782, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8675689}. |
3D-structure;Asthma;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;HDL;Hydrolase;LDL;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Phospholipid degradation;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a secreted enzyme that catalyzes the degradation of platelet-activating factor to biologically inactive products. Defects in this gene are a cause of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase deficiency. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. |
hsa:7941; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034364]; low-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034362]; 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase activity [GO:0003847]; calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047499]; hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds [GO:0016788]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; lipid oxidation [GO:0034440]; low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034374]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0034638]; plasma lipoprotein particle oxidation [GO:0034441]; platelet activating factor catabolic process [GO:0062234]; platelet activating factor metabolic process [GO:0046469]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026] |
11248283_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11369691_Overexpression of hPLA2G7 by adenoviral gene transfer in mice diminished the neointima formation (restenosis) induced by a wire-guided denudation of endothelium of the common left carotid and spontaneous atherosclerosis in aortic roots. 11501940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11807372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11807372_The genetic mutation of plasma PAF-AH gene appear to be an independent risk factor for AAA (abdominal aortic aneurysm) 11810302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11850055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11861667_the ratio of HDL-associated PAF-AH-total plasma enzyme activity may be useful as a potential marker of atherogenicity in subjects with primary hypercholesterolemia. 12068200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12428682_electrotransfer of the human plasma PAF-AH gene to skeletal muscle reduces the extent of atherosclerosis in apoE(-/-) mice 12466264_role as oxidized phospholipid hydrolase of high density lipoprotein particles 12548211_colony-stimulating factors may modulate the local concentration of platelet-activating factor in the decidua via their inhibitory or stimulatory effect on the secretion of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase 12590019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12649088_Human plasma PAF-AH exerts an antiatherogenic effect by binding to all the lipoproteins and thereby protecting them from oxidation, producing less proatherogenic lipoproteins and preserving HDL functions. 12801611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12801611_This genotype is not major determinant of population genetic risk of coronary heart disease(CHD), but association of this genotype with low levels of Lp-PLA(2) strongly support pro-inflammatory causative, and not consequential, role of Lp-PLA(2) in CHD. 14671207_Platelet-activating factor inhibits PAF-AH secretion by decidual macrophages.Inhibitory action is mediated by signal transduction involving intracellular calcium and protein kinase C. 15081260_The PAF-AH gene missense mutation has no relation to either susceptibility or severity of conventional multiple sclerosis, yet its activity is down-regulated, and it may confer the severity of female opticospinal-MS. 15115767_Ala379 substitution to Val in PLA2G7 was less frequent in CAD patients than in controls, was associated with a lower risk of future CAD and showed higher plasma activity, thus Val379 may be protective against development of CAD. 15115767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15148590_mutations InsA191 and I317N impair function of the Lp-PLA2 gene in lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 deficiency patients 15215249_the mechanism by which LPS modulates expression of PAF AH at the transcriptional level 15318030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15364890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956136_OxLDL accumulates in arteries in nonhyperlipidemic transgenic animals within 1 week after injury and local expression of human PAFAH reduces this accumulation and exerts antiinflammatory, antithrombotic, and antiproliferative effects 16086290_The findings show that the 994(G--> T) mutation of plasma PAF-AH gene may be an independent risk for atherosclerotic cerebral infarction, but not for lacunar infarction. 16223884_lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) activity, but not the enzyme mass, is a marker of small, dense LDL in human plasma 16308493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16371369_PAF acetylhydrolases play key roles in the hydrolysis of F2-isoprostanes esterified on phospholipids in vivo 16438975_Lp-PLA2 activity and PLA2G7 A379V genotype were related to mediators of atherosclerosis in a diabetic study. 16530769_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) (Lp-PLA(2))is strongly correlated with several cardiovascular risk factors. 16787988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17090529_PON1 is neither a PLOOH peroxidase nor hydrolase and that the phospholipase A(2)-like activity previously attributed to PON1 in natural enzyme preparations was actually due to novel PLOOH hydrolytic activity of contaminating PAF-AH 17092424_COX-2 and PAF-AH play a role in the occurrence of MODS 17160904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17174223_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 A379V variant is associated with body composition changes in response to exercise training. 17174223_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17251670_The distribution of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) was associated with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) and may be a marker of inflammation in patients with paroxysmal AF. 17502572_Early coronary atherosclerosis in humans is characterized by local production of Lp-PLA2. Local coronary production of lysophosphatidylcholine, the active product of Lp-PLA2, is associated with endothelial dysfunction. 17509958_The increased values of VEGF, PLA2-LDL and P-selectin in patients with long standing pulmonary hypertension are related to severe endothelial dysfunction and may have prognostic values. 17587752_LDL-C level showed a significant interaction with the G994T genotype in Japanese 17908960_inactivation of PAF, produced by TEC, by the overexpression of plasma PAF-AH affects survival, migration, and the angiogenic response of TEC both in vitro and in vivo 17981297_PAF-AcH could play an anti-inflammatory role by reducing the concentration of PAF. 18001304_We described two new highly polymorphic markers located 31 bp downstream of the last nucleotide of exon 12 in the 3' UTR region of the gene PLA2G7 18061193_Race and sex independently influence Lp-PLA2 activity and mass 18094516_Lp-PLA2 may have different mechanisms of action among American and Japanese men. Lp-PLA2 levels can not explain the observed CAC differences between the two populations. 18165686_Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry identifies substrates and products of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in oxidized human low density lipoprotein 18201705_Elevated levels of Lp-PLA(2)(lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2) activity and mass, respectively, were in this study, independently of established risk factors related to the incidence of ischemic stroke 18204052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204052_PLA2G7 represents an important, potentially functional candidate in the pathophysiology of coronary artery disease based on replicated associations using two independent datasets and multiple statistical approaches. 18259035_Lp-PLA(2) was associated with incident ischemic stroke independently of C-reactive protein and traditional cardiovascular risk factors among nonusers of hormone therapy with highest risk in those who had both high C-reactive protein and high Lp-PLA(2) 18356547_These findings strongly support a role for Lp-PLA2 in the pathophysiology and clinical presentation of cerebrovascular disease. 18383322_association of Lp-PLA(2) levels with arterial disease events implies a role for this enzyme in atherogenesis, our findings suggest that it is not prothrombotic. 18408575_Lp-PLA2 is independently associated with progression of cardiac allograft vasculopathy and predicts a higher incidence of cardiovascular events and cardiovascular death in transplant patients 18431085_The aim of the present study was to evaluate the contribution of the PAFAH gene Arg92His, Ile198Thr and Ala379Val polymorphisms to resistance toward developing cardiovascular events in healthy Sicilian octogenarians. 18434304_mouse and human PAF-AHs associate with human HDL particles of different density 18587071_In atherogenic aortas, an imbalance between PAF-AH and transacetylase activity, as well as lyso-PAF accumulation, may lead to unregulated PAF formation and to progression of atherosclerosis 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18779277_Association of elevated Lp-PLA(2) activity with coronary disease risk in relation to oxidant stress supports a proatherogenic role of Lp-PLA(2). 18784071_crystal structure is also presented of PAF acetylhydrolase reacted with the organophosphate compound paraoxon via its active site Ser273 18789441_Plasma lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 has a role in heart failure 18832472_If Lp-PLA(2) independently influences clinical events, it does so by promoting atherosclerotic plaque instability rather than by stimulating atherogenesis. 18930040_Results describe the correlations between the plasma levels of adiponectin and two markers of inflammation: lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). 18983494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19034521_An independent association of increased plasma Lp-PLA(2) activity with coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction existed in this Chinese Han Population. 19034521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19069165_plasma PAF-AH deficiency may be considered as a genetic risk factor for stroke. (review) 19135199_Cardiovascular risk factors and genetic variation contribute to variability in Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19272461_The potential role of Lp-PLA2 associated with different lipoprotein classes in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, is discussed. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19359705_the relationship between Lp-PLA(2) and oxLDL in the atherosclerotic plaque 19373214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19373214_The 994T allele increased the plasma oxLDL/LDL ratio in a recessive manner, whereas 994T had a codominant effect on the Lp-PLA(2) activity. 19500354_Lp-PLA2 may compensate for the adiposity-associated increases in inflammatory and oxidative burden, in men. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19583678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19596311_PAF acetylhydrolase activity and distribution in women with polycystic ovaries could contribute to the low-grade chronic inflammation and increased risk of atherosclerosis in these patients 19644070_Lp-PLA2 mass levels decrease modestly, whereas hsCRP and Lp-PLA2 activity appear stable over time. Acutely after stroke and MI, hsCRP increases whereas Lp-PLA2 mass and activity levels decrease. 19763134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19763134_data suggest an ethnic difference and the possible involvement of genetic polymorphisms of PLA2G7 in the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in the hypertensive Japanese, especially in men 19804884_Lp-PLA(2) mass and activity were associated with incident CVD events in older adults in CHS. Lp-PLA(2) and CRP were independent and additive in prediction of events. 19850020_The alterations in lipoprotein profile, CETP, PON 1 and LpPLA(2) activities described in the present study indicate that non-treated iron deficiency anaemia might represent a proatherogenic state. 19886071_Patients with ischemic stroke and severe inflammatory reaction presented Lp-PLA2 (lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 ) with high levels more frequently than the healthy controls 19892409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19892409_PLA2G7 may influence the clinical manifestation of schizophrenia. 19910444_oxLDL, and more specifically its unhydrolyzed oxidized phospholipids, can up-regulate lp-PLA2 expression in monocytes through the PI3K and p38 MAPK pathway 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20067121_Patients with polycystic ovary syndrome have similar total plasma PAF-AH activity as healthy women. 20080080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080080_recessive effects of Lp-PLA(2) V279F on LDL-cholesterol and significant correlations between Lp-PLA(2) activity and LDL-cholesterol, 8-epi-PGF(2alpha) and fibrinogen support a pro-oxidative or pro-atherogenic role for this enzyme 20185515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185811_Levels of Lp-PLA(2) activity were significantly associated with incident CHD among men and women with type 2 diabetes, independent of traditional and inflammatory risk factors. 20200624_of 33 studies that met inclusion criteria, 30 showed a significant association between Lp-PLA2 and cardiovascular events; available body of evidence suggests that Lp-PLA2 is a reliable marker of risk for cardiovascular events [systematic review] 20331434_Studies designed to evaluate the ability of precursor forms of PAF-AH to mature to fully active proteins indicated that the N-terminal end of human and mouse PAF-AH played important and opposite roles in this process. 20367923_The elevated L-PAF-AH activity may be associated with insulin resistance in polycystic ovary syndrome patients. 20442857_analyses demonstrate that genetic polymorphisms may contribute to inter-individual variation in Lp-PLA(2) activity and mass. 20444451_Lp-PLA(2) activity is associated with allele-specific apo(a) levels, but this association differs across African American-Caucasian ethnicity 20479152_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20479152_Unlike Lp-PLA2 activity, PLA2G7 variants associated with modest effects on Lp-PLA2 activity were not associated with cardiovascular risk markers, coronary atheroma, or coronary heart disease. 20507838_The oxidative modification of low density lipoproteins and the higher activity of PAF-AH are related with the low Mg status. 20625038_patients with beta-thalassemia exhibit high plasma Lp-PLA(2) levels 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634581_Genetic deficiency of Lp-PLA2 activity is not associated with a reduced risk of AD in the Japanese population. 20634581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926117_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926117_Variants of PLA2G7 gene have been reported to be associated with coronary heart disease (CHD) 21107710_The V279F polymorphism in LP-PLA2 gene may contribute to coronary heart disease development. 21155029_Taiwanese female vegetarians have lower serum Lp-PLA2 activity. 21176638_LPS significantly upregulated Lp-PLA(2) in macrophages, and simvastatin suppressed this upregulation by inhibiting the p38MAPK pathway. 21247435_lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity was significantly increased in Metabolic Syndrome subgroups when compared with controls, and was higher in patients with carotid plaques than those without plaques 21281786_The PLA2G7, HPGD, EPHX2, and CYP4F8 genes are highly expressed in prostate cancer. 21316774_Of the inflammation markers, Lp-PLA2 levels are significantly higher in patients with good coronary collateral (CC) development than with poor CC in patients with isolated left coronary artery disease. 21432021_Data show that the proinflammatory mediators, lipopolysaccharide and platelet-activating factor, increased levels of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase mRNA via distinct signaling pathways. 21476960_Multiple regression analysis showed that apo B was significantly associated with LP-PLA2 adjusted for age, Body mass index, triglycerides and LDL-C (R2=0.32). 21490708_Natural deficiency in Lp-PLA activity due to carriage of PLA2G7 279F allele protects from CAD in Korean men. 21553808_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) interacts with phospholipid vesicles via a surface-disposed hydrophobic alpha-helix 21606947_Lp-PLA2 activity was significantly lower in rare non-synonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms carriers compared with non-carriers and seven variants had enzyme activities consistent with a null allele. 21616491_analysis of genetic and environmental regulation of inflammatory CVD biomarkers Lp-PLA2 and IgM anti-PC 21620406_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 may have a role in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic disease 21708876_Lp-PLA(2) is not associated with endothelial dysfunction, suggesting its role in atherosclerosis development is primarily related to other factors. 21714927_Whites have the highest Lp-PLA mass and activity levels, followed by Hispanics and Asians, and then African-Americans; in age- and sex-adjusted analyses, these differences are significant for each non-White race when compared to Whites. 21834908_We conclude that there is significant association between the rs16874954 mutation and CAD in the Chinese Han population. 21880383_subjects carrying the Ala/Val genotype are less likely to have essential hypertension, while hypertensive patients carrying the Ala/Val genotype have elevated fibrinogen levels 21882811_both the myristoyl group and the hydrophobic patch are essential for proper trafficking of the enzyme to the membranes following oxidative stress 21933589_Plasma Lp-PLA(2) activity is associated with plaque rupture in patients with CAD, independently of traditional CAD risk factors, hs-CRP level and IVUS parameters. 21942556_Data indicate that LpPLA2 seems to be a biomarker constantly correlated with heart failure, regardless of etiology. 22024276_Circulating Lp-PLA2 levels are associated with coronary plaque regression determined by intravascular ultrasonography in patients with acute coronary syndrome. 22028154_Serum level of Lp-PLA is associated with both eccentricity index and fibrous cap thickness in both UA and SA groups. Elevated levels of circulating Lp-PLA might to be a strong risk factor and more serious for unstable angina than stable angina. 22139405_Serum platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase levels were increased in patients with systemic sclerosis and associated with a lower frequency of pitting scars/digital ulcers and arthritis/ arthralgias. 22153151_Lp-PLA2 mass may add relevant information regarding early arterial recanalization in intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator treated stroke patients. 22164942_Lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is an inflammatory biomarker which provides information on plaque inflammation and stability; it is expressed in macrophages and foam cells in rupture-prone atherosclerotic plaque. 22178747_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) activity is associated with large-artery atherosclerotic etiology and recurrent stroke in transient ischemic attack patients. 22197603_apoE-containing HDL has a relatively high PAF-AH activity in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. 22202492_PLA2G7 is a cancer-selective biomarker in 50 % of prostate cancers and associates with aggressive disease. 22246459_Lp-PLA2 mass is altered in multiple scelrosis patients compared to healthy controls 22300679_Lp-PLA(2) and PCSK9 levels were both correlated positively with LDL cholesterol and non-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and Lp-PLA(2) was inversely related to PCSK9. 22338104_In this population-based cohort enriched with dysmetabolic phenotypes, LpPLA(2) mass and activity showed divergent associations with cardiovascular diseases. 22340269_Common genetic variation in PLA2G7 is associated with subclinical coronary atherosclerosis. 22359537_The lack of relation between circulating Lp-PLA(2) activity and Lp-PLA(2) activity in PBMCs was found in postmenopausal women with high ox-LDL 22447189_Elevated Lp-PLA(2) mRNA expression is associated with acute ischemic stroke. 22499993_The associations among Lp-PLA2, lysophosphatidylcholine, and proinflammatory cytokines in human plaques suggest that lysoPCs play a key role in plaque inflammation and vulnerability. 22632920_The presence of the apo E4 isoform was associated with a higher level of Lp-PLA(2) index, a marker of vascular inflammation, synergistically increasing cardiovascular risk. 22665167_associations between Lp-PLA(2) and vascular disease 22755553_It was concluded that Lp-PLA2 may be a new useful biomarker to evaluate clinical or subclinical activity of the disease besides CRP and ESR 22784637_variability of Lp-PLA(2) across gender, ethnicity, and levels of circulating lipids and markers of systemic inflammation are more consistent and appear not to vary importantly across categories defined by CVD or its risk factors. 22797139_The neonates of women with severe preeclampsia had significantly higher plasma PAF-AH levels. 22859728_In the WHI-OS Lp-PLA2 mass, but not activity, was independently associated with CVD. However, model fit did not significantly improve with Lp-PLA2 mass, and assay calibration remains a clinical concern 22898284_Val279Phe SNPs in the 9th exon of PAF-AH may be associated with intracranial hemorrhage in preterm infants. 23083783_Total plasma Lp-PLA(2) is a predictor of cardiac death, while HDL-Lp-PLA(2) is associated with lower risk for cardiac death in patients with stable CAD 23089713_aortic valve stenosis (AVS) is characterized by increased plasma Lp-PLA2 levels associated with the severity of AVS 23089916_the interaction between recombinant human Lp-PLA(2) and human HDL 23103135_Lp-PLA2 levels are significantly associated with coronary heart disease. 23118945_High Lp-PLA2 activity implies a worse prognosis at long term follow up in high-risk Caucasian patients referred for coronary angiography. 23140470_Our results demonstrated dynamic alterations in Lp-PLA2 levels during the early stages of ACS and, therefore, indirectly support the hypothesis of an active role for Lp-PLA2 in the pathogenesis of ACS. 23361301_PLA2G7 expression is elevated in colon tumors compared with normal tissues. 23413990_Lp-PLA2 activity changes in obesity and it shows important associations with markers of cardiovascular risk. 23439604_Darapladib produced sustained inhibition of Lp-PLA2 activity in Japanese dyslipidemic patients with/without the V279F SNP of Lp-PLA2. 23546765_Prediabetes patients have significantly decreased high-density lipoprotein-LP-PLA2 activity compared with subjects with glucose levels Phe Polymorphism of Lp-PLA2 may lead to decrease the enzymatic activity via changes of folding kinetics and recognition to its substrate. 26642708_circulating CETP and Lp-PLA2 might partly play a role in the atherogenic disturbances in patients with iron deficiency anemia through increased susceptibility to lipid peroxidation 26775119_Lp-PLA2 activity in Japanese men aged 50-79 years was associated significantly and positively with IMT and plaque in the carotid artery but Mendelian randomization did not support that Lp-PLA2 is a causative factor for subclinical atherosclerosis. 26791069_A V279F loss-of-function variant in the PLA2G7 gene resulting in 50% lower activity for each copy of the variant, is common in East Asians and associated with risk of Vascular diseases. 26801405_Increased plasma Lp-PLA2 activity portends increased risk of resistant hypertension. 26828804_no relationship with either proinflammatory cytokines or neopterin identified in Alzheimer disease 26848158_Higher Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were associated with development of both incident clinical peripheral arterial disease and low ankle brachial index. 27097870_results do not support added value of Lp-PLA2 for predicting cardiovascular events or mortality among CHD patients beyond traditional risk factor 27206945_LpPLA2 is found in both LDL and HDL and is distributed differently in men with T1D without any relationship to CAC score progression 27301456_Lifelong lower Lp-PLA2 activity was not associated with major risks of vascular or non-vascular diseases in Chinese adults. 27392709_Taken together, these results revealed that Lp-PLA2 silencing protected against ox-LDL-induced oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human THP1 macrophages. 27450918_PLA2G7 gene expression was co-regulated by 17-beta-estradiol and promoter methylation. 27461004_Data show that all the six inflammation-related CpG-SNPs genotypes including IL1B rs16944, IL1R2 rs2071008, PLA2G7 rs9395208, FAM5C rs12732361, CD40 rs1800686, and CD36 rs2065666 were associated with coronary heart disease (CHD), suggesting an important role of inflammation in the risk of CHD. 27487154_phospholipase A2 Group 7 (PLA2G7), to be important in regulating tumor cell migration and a novel tumor-promoting factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 27614353_Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 as a new marker to determine cardiovascular risk in hypercholesterolemic dyslipidaemic children 27641736_A considerable portion of Chinese ischemic stroke patients are insensitive to aspirin treatment, which may be correlated with the MDR1 C3435T, TBXA2R (rs1131882), and PLA2G7 (rs1051931-rs7756935) polymorphisms. 27710915_High Lp-PLA2 expression is associated with type 1 diabetes. 27776715_Elevated mass and activity of Lp-PLA2 related to inflammation and atherosclerosis may take part in the development of kidney injury and atherosclerosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. 27905470_A PLA2G |
ENSMUSG00000023913 |
Pla2g7 |
12.186060 |
2.6059333493 |
1.381800 |
0.437670918 |
10.341879 |
0.00130045570099118269237481460010030787088908255100250244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002974543025977043064767002533699269406497478485107421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5674164 |
4.8280259 |
7.1913057 |
1.5426716 |
| ENSG00000146147 |
90523 |
MLIP |
protein_coding |
Q5VWP3 |
FUNCTION: Required for precocious cardiac adaptation to stress through integrated regulation of the AKT/mTOR pathways and FOXO1. Regulates cardiac homeostasis and plays an important role in protection against cardiac hypertrophy. Acts as a transcriptional cofactor, represses transactivator activity of ISL1 and MYOCD. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A096MK47, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5FW52}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable lamin binding activity and transcription corepressor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II; and positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nuclear lumen. Predicted to be active in PML body; nuclear envelope; and sarcolemma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90523; |
nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear lumen [GO:0031981]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; lamin binding [GO:0005521]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010614]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:1903243]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26436652_CIP expression is reduced in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. 32719146_Regulation of myonuclear positioning and muscle function by the skeletal muscle-specific CIP protein. 33452295_MLIP genotype as a predictor of pharmacological response in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. 34400329_Cardiac CIP protein regulates dystrophic cardiomyopathy. 34581780_MLIP causes recessive myopathy with rhabdomyolysis, myalgia and baseline elevated serum creatine kinase. 34878397_[MLIP: a novel gene causing rhabdomyolysis].', trans 'MLIP : un nouveau gene de rhabdomyolyse. |
ENSMUSG00000032355 |
Mlip |
24.455417 |
4.4539986539 |
2.155101 |
0.745012330 |
7.532156 |
0.00606073419470498121752743969636867404915392398834228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012165978065258467935572106455310859018936753273010253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.8129531 |
19.3972192 |
9.0130984 |
3.2134532 |
| ENSG00000146197 |
222663 |
SCUBE3 |
protein_coding |
Q8IX30 |
FUNCTION: Is a positive regulator of the BMP signaling pathway, required for proper chondrogenesis, osteogenesis and skeletal development. It acts as coreceptor for BMP ligands, particularly BMP2 and BMP4, facilitating their interactions with BMP type I receptors (PubMed:33308444). It is required for ligand-induced recruitment of BMP receptors to lipid rafts (By similarity). Binds to TGFBR2 and activates TGFB signaling. In lung cancer cells, could serve as an endogenous autocrine and paracrine ligand of TGFBR2, which could regulate TGFBR2 signaling and hence modulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer progression. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NZL8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21441952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33308444}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the signal peptide, complement subcomponents C1r/C1s, Uegf, bone morphogenetic protein-1 and epidermal growth factor-like domain containing protein family. Overexpression of this gene in human embryonic kidney cells results in secretion of a glycosylated form of the protein that forms oligomers and tethers to the cell surface. This gene is upregulated in lung cancer tumor tissue compared to healthy tissue and is associated with loss of the epithelial marker E-cadherin and with increased expression of vimentin, a mesenchymal marker. In addition, the protein encoded by this gene is a transforming growth factor beta receptor ligand, and when secreted by cancer cells, it can be cleaved in vitro to release the N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like repeat domain and the C-terminal complement subcomponents C1r/C1s domain. Both the full length protein and C-terminal fragment can bind to the transforming growth factor beta type II receptor to promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor angiogenesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. |
hsa:222663; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; BMP binding [GO:0036122]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15234972_may act locally and/or distantly through a proteolytic mechanism, and may play an important role in bone cell biology 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21441952_in lung cancer cells, SCUBE3 could serve as an endogenous autocrine and paracrine ligand of TGF-beta type II receptor, which could regulate TGF-beta receptor signaling and modulate EMT and cancer progression 23420440_results show that SCUBE3 knockdown was associated with lower vascular permeability in the tumor and effectively inhibited the metastatic potential of non-small-cell lung carcinoma 24084593_Scube3 facilitates both TGFbeta and Hh signalling within an overall role of facillating inflammatory angiogenesis. 24390364_Results indicated that SCUBE3 might be involved in regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and malignant progression in NSCLC. 27259322_Elevated expression of SCUBE3 in osteosarcoma tissues correlated with poor prognosis of the osteosarcoma patients. 28238185_The results of this pioneering study indicate that SCUBE protein family appears to have a probable role in the pathogenesis and angiogenesis development in psoriasis and SCUBE 1 and 3 may be novel markers of angiogenesis in psoriasis. 31742430_Activation of TGF-beta1 Pathway by SCUBE3 Regulates TWIST1 Expression and Promotes Breast Cancer Progression. 31991528_The relationship of serum SCUBE-1, -2 and -3 levels with clinical findings and ultrasonographic skin thickness in systemic sclerosis patients. 33274247_SCUBE3 Is Likely a Susceptibility Gene for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus for Chinese Populations. 33308444_SCUBE3 loss-of-function causes a recognizable recessive developmental disorder due to defective bone morphogenetic protein signaling. 35088579_DEPDC1B Promotes Melanoma Angiogenesis and Metastasis through Sequestration of Ubiquitin Ligase CDC16 to Stabilize Secreted SCUBE3. |
ENSMUSG00000038677 |
Scube3 |
7.700035 |
0.1707493738 |
-2.550048 |
0.682392054 |
15.634769 |
0.00007682889468119957223322946671117961159325204789638519287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000215260912204727738452833540883091245632385835051536560058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0265447 |
1.1649443 |
11.9349366 |
4.0369246 |
| ENSG00000146242 |
7162 |
TPBG |
protein_coding |
Q13641 |
FUNCTION: May function as an inhibitor of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by indirectly interacting with LRP6 and blocking Wnt3a-dependent LRP6 internalization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22100263}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a leucine-rich transmembrane glycoprotein that may be involved in cell adhesion. The encoded protein is an oncofetal antigen that is specific to trophoblast cells. In adults this protein is highly expressed in many tumor cells and is associated with poor clinical outcome in numerous cancers. Alternate splicing in the 5' UTR results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:7162; |
axon terminus [GO:0043679]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; dendrite arborization [GO:0140059]; mesenchymal cell migration [GO:0090497]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; olfactory learning [GO:0008355]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0051932] |
11903056_Glycosylation and epitope mapping of the 5T4 glycoprotein oncofoetal antigen 16616918_Results sugest that 5T4 is a transient marker of human embryonic stem cell differentiation & that 5T4 phenotype, colony seeding density and culture conditions influence the maintenance of pluripotent hES cells and their differentiation to neural lineages. 16646078_there is a repertoire of CD8 T cell recognition of 5T4 in normal human donors and some candidate HLA-A*0201 epitopes have been identified 17978129_the mRNA expression of trophoblast glycoprotein is up-regulated in cells circulating within blood from women with preeclampsia. 18567615_5T4-based cancer vaccine: cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes identified in Trovax-vaccinated colorectal cancer patients 18833005_colorectal cancer patients who had preexisting cell proliferative responses to 5T4 were longer-term survivors 22498111_5T4 is a potential new antigen for targeted therapies such as immunotherapy in MPM, as it is overexpressed on mesothelioma cells and recognised by 5T4-specific cytotoxic T-cells. 22956548_The surface expression of 5T4 marks the use of the CXCR4 rather than the CXCR7 receptor, with distinct consequences for CXCL12 exposure. 24582434_Tyrosine 325 plus the leucine-rich repeat 1 surface centered on a second exposed aromatic residue, phenylalanine 97, are essential for inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 25066861_5T4 expression is mechanistically associated with the directional movement of cells through epithelial mesenchymal transition, facilitation of CXCL12/CXCR4 chemotaxis, blocking of canonical Wnt/beta-catenin while favouring non-canonical pathway signalling 25738465_In conclusion, the present study provided evidence that TPBG is involved in PDAC metastasis, and that TPBG and its associated signaling pathways may be a suitable target for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma therapy. 27780858_Collectively, these findings demonstrate that an anti-5T4 antibody-drug conjugate reduces the fraction of cancer stem cells (CSC), and prevents local recurrence and suggest a novel therapeutic approach for patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 28183528_We obtained GWS evidence (P |
ENSMUSG00000035274 |
Tpbg |
309.485870 |
0.4618919431 |
-1.114373 |
0.087284999 |
166.468582 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000004370286404467294498316653585606285823537851766792692689694723491017808133344381084575934199708963090458269107330124825239181518554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000697355971134456961802974420253597202644373747442585628510719825002972055591754347985564157727002287945339276120648719370365142822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
198.2619164 |
10.8748730 |
432.1592165 |
15.0596598 |
| ENSG00000146243 |
134728 |
IRAK1BP1 |
protein_coding |
Q5VVH5 |
FUNCTION: Component of the IRAK1-dependent TNFRSF1A signaling pathway that leads to NF-kappa-B activation and is required for cell survival. Acts by enhancing RELA transcriptional activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Predicted to be involved in I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:134728; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; immune response [GO:0006955] |
17079333_Together, these studies reveal that phosphorylation of the SIMPL protein plays a critical role in SIMPL regulation by affecting both SIMPL subcellular localization and the p65 coactivator function of SIMPL. |
ENSMUSG00000032251 |
Irak1bp1 |
29.712704 |
0.3946776901 |
-1.341253 |
0.282082432 |
23.223776 |
0.00000144203450318605060697188004203983524575960473157465457916259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005011638631275277726642453784977604414052620995789766311645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.7744525 |
3.0427129 |
42.7662724 |
4.7904707 |
| ENSG00000146281 |
135293 |
PM20D2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYS1 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the peptide bond hydrolysis in dipeptides having basic amino acids lysine, ornithine or arginine at C-terminus. Postulated to function in a metabolite repair mechanism by eliminating alternate dipeptide by-products formed during carnosine synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24891507}. |
Carboxypeptidase;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome |
|
Enables dipeptidase activity and identical protein binding activity. Acts upstream of or within proteolysis and regulation of cellular protein metabolic process. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:135293; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; carboxypeptidase activity [GO:0004180]; dipeptidase activity [GO:0016805]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of cellular protein metabolic process [GO:0032268] |
24891507_PM20D2 hydrolyzed beta-alanyl-lysine, beta-alanyl-ornithine, gamma-aminobutyryl-lysine, and gamma-aminobutyryl-ornithine as its best substrates. |
ENSMUSG00000054659 |
Pm20d2 |
129.169780 |
0.3361039754 |
-1.573020 |
0.448510940 |
11.277593 |
0.00078448197285353737928659256795071996748447418212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001862766074536391890104081170420613489113748073577880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.7937474 |
19.7199436 |
140.3872197 |
40.6374160 |
| ENSG00000146373 |
154214 |
RNF217 |
protein_coding |
Q8TC41 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Mediates the degradation of the iron exporter ferroportin/SLC40A1 and thus regulates iron homeostasis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3YYI7}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RING1-IBR-RING24 (RBR) ubiquitin protein ligase family, and it belongs to a subfamily of these proteins that contain a transmembrane domain. This protein can interact with the HAX1 anti-apoptotic protein via its C-terminal RING finger motif, which suggests a role in apoptosis signaling. It is thought that deregulation of this gene can be a mechanism in leukemogenesis. Mutations in the region encoding the protein GXXXG motif, which appears to be necessary for protein self-association, have been found in human cancers. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:154214; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25298122_The high expression of RNF217 in certain human leukemias suggests that the deregulation of this gene could be a more common mechanism in leukemogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000063760 |
Rnf217 |
283.978312 |
0.2449055779 |
-2.029702 |
0.232366671 |
72.050018 |
0.00000000000000002098113150755175238709928532671042590243614101811354261117870123598549980670213699340820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000164200159624318065911284037711132299102013791785442675674744350544642657041549682617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.2527743 |
21.6994221 |
404.5425927 |
62.7822116 |
| ENSG00000146648 |
1956 |
EGFR |
protein_coding |
P00533 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase binding ligands of the EGF family and activating several signaling cascades to convert extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses (PubMed:2790960, PubMed:10805725, PubMed:27153536). Known ligands include EGF, TGFA/TGF-alpha, AREG, epigen/EPGN, BTC/betacellulin, epiregulin/EREG and HBEGF/heparin-binding EGF (PubMed:2790960, PubMed:7679104, PubMed:8144591, PubMed:9419975, PubMed:15611079, PubMed:12297049, PubMed:27153536, PubMed:20837704, PubMed:17909029). Ligand binding triggers receptor homo- and/or heterodimerization and autophosphorylation on key cytoplasmic residues. The phosphorylated receptor recruits adapter proteins like GRB2 which in turn activates complex downstream signaling cascades. Activates at least 4 major downstream signaling cascades including the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK, PI3 kinase-AKT, PLCgamma-PKC and STATs modules (PubMed:27153536). May also activate the NF-kappa-B signaling cascade (PubMed:11116146). Also directly phosphorylates other proteins like RGS16, activating its GTPase activity and probably coupling the EGF receptor signaling to the G protein-coupled receptor signaling (PubMed:11602604). Also phosphorylates MUC1 and increases its interaction with SRC and CTNNB1/beta-catenin (PubMed:11483589). Positively regulates cell migration via interaction with CCDC88A/GIV which retains EGFR at the cell membrane following ligand stimulation, promoting EGFR signaling which triggers cell migration (PubMed:20462955). Plays a role in enhancing learning and memory performance (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q01279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10805725, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11116146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11483589, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11602604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12297050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12620237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12873986, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15374980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15590694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15611079, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17115032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17909029, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19560417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20462955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20837704, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21258366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27153536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2790960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7679104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8144591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9419975}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 may act as an antagonist of EGF action.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in hepatocytes and facilitates its cell entry. Mediates HCV entry by promoting the formation of the CD81-CLDN1 receptor complexes that are essential for HCV entry and by enhancing membrane fusion of cells expressing HCV envelope glycoproteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21516087}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Hydroxylation;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a member of the protein kinase superfamily. This protein is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family. EGFR is a cell surface protein that binds to epidermal growth factor, thus inducing receptor dimerization and tyrosine autophosphorylation leading to cell proliferation. Mutations in this gene are associated with lung cancer. EGFR is a component of the cytokine storm which contributes to a severe form of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) resulting from infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2020]. |
hsa:1956; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular vesicle [GO:0097708]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; multivesicular body, internal vesicle lumen [GO:0097489]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; Shc-EGFR complex [GO:0070435]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; epidermal growth factor binding [GO:0048408]; epidermal growth factor receptor activity [GO:0005006]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; MAP kinase kinase kinase activity [GO:0004709]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030296]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030297]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to cadmium ion [GO:0071276]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cerebral cortex cell migration [GO:0021795]; digestive tract morphogenesis [GO:0048546]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; ERBB2-EGFR signaling pathway [GO:0038134]; eyelid development in camera-type eye [GO:0061029]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; morphogenesis of an epithelial fold [GO:0060571]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cardiocyte differentiation [GO:1905208]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042059]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; ossification [GO:0001503]; peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:0038083]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045737]; positive regulation of DNA repair [GO:0045739]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:1900087]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0010750]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein kinase C activity [GO:1900020]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein insertion into membrane [GO:0051205]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046328]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050730]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014066]; response to UV-A [GO:0070141]; salivary gland morphogenesis [GO:0007435]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11467954_A truncated form of the hEGFR ectodomain comprising residues 1-501, unlike the full-length hEGFR ectodomain (residues 1-621), binds hEGF and hTGF-alpha with high affinity and is a competitive inhibitor of EGF-stimulated mitogenesis. 11504770_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11531336_Chemical/biological model for EGFR activation. 11533659_EGFR has been detected in the nucleus and might function as a transcription factor to activate gene transcription. 11751923_The data presented here demonstrate that, in contrast to activation by the cytokine, growth hormone (GH), the activation of STAT5b by the growth factor, epidermal growth factor (EGF), requires overexpression of the EGF receptor (EGFR). 11788593_effects of receptor-selective retinoid ligands on EGFR-associated signal transduction 11796728_Interaction of the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor with gangliosides 11814623_this study, 11 analogs of a fragment of the B-loop of EGF-related peptides from several species were synthesized to study binding to A431 human epidermoid carcinoma using both 125I-EGF and [3'4'-3H-Tyr(22,29), Abu(20,31)]EGF(20-31)-NH(2). 11831486_CsA affects EGF-r metabolism in gingival keratinocytes resulting in an increased number of cell surface receptors 11853560_Calmodulin binds to the EGFR 11875501_data demonstrate that prostaglandin E2 transactivates EGFR and triggers mitogenic signaling in gastric epithelial and colon cancer cells as well as in rat gastric mucosa in vivo 11886870_sequestration in non-caveolar lipid rafts inhibits lipid binding 11894095_Cbl-CIN85-endophilin complex mediates ligand-induced downregulation of EGF receptors 11897506_estrogen transactivates the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to MAP K signaling axis via GPR30;implications for breast cancer biology 11912208_Identification of epidermal growth factor receptor as a target of Cdc25A protein phosphatase 11916499_contig map for the EGFR region and markers positioned on its associated physical map to the analysis of 7p11.2 amplifications in a series of glioblastomas. 11935304_EGFR is often strongly expressed and is a potential therapeutic target in patients with malignant thymic tumors 11953893_Antisense epidermal growth factor receptor RNA transfection in human glioblastoma cells down-regulates telomerase activity and telomere length. 11966576_epidermal growth factor receptor activity on fertilization capacity of testicular harvested spermatozoa 11968000_results suggest a potential mechanism by which maintenance of low levels of EGFR expression and subsequent EGFR upregulation may be attributed to the loss of transcriptional repression of EGFR gene expression in hormone-dependent breast cancer cells 11983694_Src-dependent phosphorylation of the EGFR at Tyr-845 is required for EGFR transactivation and zinc-induced Ras activation 11992543_Effects of pharmacologic antagonists of epidermal growth factor receptor, PI3K and MEK signal kinases on NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation and IL-8 and VEGF expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. 11994282_blocking of ubiquitination by inhibiting Src family kinases 12006662_novel mechanism of EGFR internalization that does not require ligand binding, receptor kinase activity, or ubiquitylation and does not direct the receptor into a degradative pathway 12018405_Dephosphorylation of the EGFR and the consequent suppression of EGFR signalling. Review. 12023273_second cysteine-rich region contains targeting information for caveolae/rafts 12099696_Helicobacter pylori-stimulated EGF receptor transactivation requires metalloprotease cleavage of HB-EGF 12105206_determination of decorin binding site 12127695_Expression of this molecule and its correlation with prognostic markers in patients with head and neck tumors 12133497_Detection of serum epidermal growth factor receptor in the diagnosis of proliferation of pituitary adenomas 12134064_These data demonstrate a distinct radiation response profile at the transcriptional level that is dependent on enhanced EGFR/Ras/MAPK signaling. 12134089_These results indicate that epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors can form a ligand-independent inactive dimer and that receptor dimerization and activation are mechanistically distinct and separable events. 12135609_ErbB1 and ErbB2 employ different mechanisms of plasma membrane targeting during keratinocyte differentiation; cytoskeletal association may facilitate the coupling of activated ErbB1 and ERK. 12147707_Rac activation upon cell-cell contact formation is dependent on signaling from here 12152785_Differential EGFR patterns by interphase cytogenetics in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor and morphologically similar spindle cell neoplasms. 12161422_Results show that the juxtamembrane region of the epidermal growth factor receptor is necessary for accurate polarized expression of the native molecule. 12167618_The results of this study indicate that dual inhibition of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathways can cooperatively enhance apoptosis in breast cancers. 12180964_Stimulation of cells with EGF rapidly leads to phosphorylation of Hrs, raising the question whether the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates Hrs directly. Several downstream kinases, rather than the active receptor kinase are responsible. 12181310_These results demonstrate that 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) alters EGFR membrane trafficking and down-regulates EGFR growth signaling. 12192610_EGF receptor expression was elevated in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenic 12218189_Cbl-directed monoubiquitination of CIN85 is involved in regulation of ligand-induced degradation of EGF receptors. 12223352_findings suggest an increase in functional TGF-alpha and activation of the EGFr in response to IFN-gamma 12234920_Data show that human sprouty2 potentiates epidermal growth factor receptor signalling by specifically intercepting c-Cbl-mediated effects on receptor down-regulation. 12243760_Data indicate that phospholipase A2 downregulates the EGF receptor-mediated intracellular signal transduction that may be mediated by arachidonic acid and/or ceramide. 12297049_Crystal structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor alpha. 12297050_Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains 12354760_caveolin-1/EGFR association and is critical for the EGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 that is associated with its inhibition of EGFR activation. 12381737_determination of whether G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 can phosphorylate and desensitize epidermal growth factor receptor 12388817_Human cytomegalovirus infection inhibits epidermal growth factor (EGF) signalling by targeting EGF receptors 12397069_ligand-independent activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor is triggered by cholesterol depletion from the plasma membrane 12399475_Endocytosis is regulated by Grb2-mediated recruitment of the Rab5 GTPase-activating protein RN-tre. 12419588_Cell proliferation, nuclear ploidy, and EGFr and HER2/neu tyrosine kinase oncoproteins in infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma. 12429632_epidermal growth factor receptor may have a role in disease relapse and progression to androgen-independence in human prostate cancer 12429742_mediation of synergism with c-src by STAT5b 12435727_mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo 12444032_hydrogen peroxide increases cPLA(2) activity through its phosphorylation utilizing an epithelial growth factor/Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 pathway. 12446727_EGF receptor is activated in a pathway that requires ARF4 to induce phospholipase D2 12456372_Mutual interaction of EGFR with c-Src is required for many EGFR-mediated cellular functions including proliferation, migration, survival and EGFR endocytosis, as discussed in this review. 12479108_EGFR, DI, and the diploid are valuable targets for judging metastasis and recurrence of gastric cancer before and after operation. 12487410_Expression of the invasive phenotype in breast epithelial cells requires increased EGF receptor signaling, involving both PI 3-kinase and Erk 1,2 activities, which leads to enhanced secretion of MMP-9 and transcription of invasion-related genes. 12508124_Levels of this receptor are lowered in cryptorchism. 12517767_targeting in cancer, involved in apoptosis (REVIEW) 12517803_activation regulates mutation and epidermal growth factor receptor activation regulates vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA expression in human glioblastoma cells by transactivating the proximal VEGF promoter. 12527890_TPA-induced AP-1 activation requires EGFR protein, but not EGFR tyrosine kinase and EGFR autophosphorylation at tyrosine(1173), whereas both EGFR tyrosine kinase and EGFR autophosphorylation at Y(1173) play a critical role in EGF-induced AP-1 activation. 12532415_SKMG-3 cells produced high levels of EGFR protein. Signals from overexpressed EGFRs contribute to the constitutive phosphorylation of Erk, but these signals may not be required for the constitutive activation of PI3K or AKT1. 12534349_role in mediating thromboxane A2-dependent -signal-regulated kinase activation 12556561_the mechanism of attenuated ERK signaling in EGFR-overexpressing cells is a sequestration of ERKs at the cell membrane in EGFR-containing complexes. 12568494_Review. Mucin transcription in response to both gram-positive bacteria and tobacco smoke is mediated through activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). 12579331_Expression of EGFR seems to play an important role in metastasis, especially liver metastasis and recurrence of pancreatic cancer. 12582944_in glioblastoma multiforme patients a complex relationship exists between epidermal growth factor receptor expression and age 12586780_results demonstrate that tamoxifen resistant MCF-7 cell growth is mediated by the autocrine release and action of an epidermal growth factor receptor-specific ligand inducing preferential epidermal growth factor receptor/c-erbB2 dimerization 12603863_Inhibition of erbB receptor family members protects HaCaT keratinocytes from ultraviolet-B-induced apoptosis. This inhibition was specific for the erbB receptor family and specific for ultraviolet-B-induced apoptosis. 12604776_EGFR binds to c-src and has a role in oncogenesis 12606946_Exogenous OPN increased EGFR mRNA expression, as well as EGFR kinase activity. Inhibition of EGFR significantly impaired the cell migration response to OPN. 12607604_Comparative study in the expression of p53, EGFR, TGF-alpha, and cyclin D1 in verrucous carcinoma, verrucous hyperplasia, and squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck region. 12615082_Five autophosphorylation sites in the extra-kinase C-terminal domain of EGFR are not required for the ability of EGFR to induce morphological differentiation of PC12 cells. 12631599_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12642595_data indicate that growth hormone, by activating extracellular signal related kinases, can modulate epidermal growth factor-induced epidermal growth factor receptor trafficking and signaling 12643788_Epidermal growth factor and ionizing radiation up-regulate the DNA repair genes XRCC1 & ERCC1 in DU145 & LNCaP prostate carcinoma through MAPK signaling indicating a capacity of the EGFR-ERK signaling to modulate DNA repair in cancer cells. 12653106_EGFR microsatellite polymorphism is associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. 12653106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12654182_Expression of EGF and EGFR is involved in the gallbladder carcinogenesis, and is related to high activity of cell proliferation. 12657642_propose a role of Ent-1 in the trafficking of EGFR to down-regulate intestinal mitogenic signals, highlighting the mechanisms of cell growth arrest associated with enterocytic differentiation 12664617_Human colon carcinoma cells that overexpress cyclooxygenase exhibit growth stimulation and induction of this protein. 12673202_Overexpression of an introduced EGFR, under an E1A-insensitive heterologous promoter, blocked E1A induction of apoptosis in SCC cells. E1A-mediated EGFR downregulation appears to be the cause not consequence of E1A-induced apoptosis in these cells. 12681285_Data show that by using RNA interference , the expression of endogenous erbB1 can be specifically and extensively suppressed in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. 12683217_The study found that over-expression of EGFR occurred more often in cases of cervical cancer (50%) compared to breast cancer cases (36%), while in breast cancer EGFR expression correlated significantly with metastasis of the lymph nodes. 12686539_EGFR/HER2 heterodimers traffic as single entities; levels of HER2 in normal cells are barely at the threshold necessary to drive efficient heterodimerization 12694196_Nitric oxide and nitric oxide donors induce EGF receptor phosphorylations, in A431 tumor cells. 12704666_deltaEGFR may contribute to glioblastoma development 12708474_EGFRvIII expressed in human tumors is phosphorylated and hence activated; sustained activation of EGFRvIII is implicated in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancers 12708492_ZO-1 bound to EGFR irrespective of the phosphorylation status of EGFR. EGFR associated ZO-1 was highly tyrosine-phosphorylated only in primary colorectal cancers but was dephosphorylated in the liver-metastasized cancers. 12719950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12722480_The expression of this protein was not different in the clone cell variants or the A431 parental line. 12733059_Results suggest that epidermal growth factor receptor and protein kinase C activation are involved in 12- O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced cell signaling for modulation of cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion and cell shape in Caco-2 cells. 12734385_signaling intensity determines intracellular protein interactions, ubiquitination, and internalization 12743604_Loss of PTEN/MMAC1/TEP in tumor cells expression this protein counteracts the antitumor action of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 12746449_carboxyl-terminal mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor alters tyrosine kinase activity and substrate specificity 12746839_androgens promote an increase in the activity of the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-network by increasing ErbB1 levels, and this activity of is essential for androgen-induced proliferation and survival of the prostate cancer LNCaP cell line. 12754251_findings establish Cbl protein as the major endogenous ubiquitin ligase responsible for epidermal growth factor receptor degradation 12754350_EGFR gene expression is identified in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme 12757445_Seasonal allergic rhinitis subject showed significant elevation in EGFR expression, consistent with the observation of mucus hypersecretion in allergic rhinitis. 12768436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12782602_Epidermal growth factor receptor-independent constitutive activation of STAT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by the autocrine/paracrine stimulation of the interleukin 6/gp130 cytokine system. 12794748_HEGFR was expressed in the subventricular zone embryologically 12795333_Epidermal growth factor receptor negatively regulates intracellular kinase activation in the absence of ligand 12814937_Characterization and expression of novel 60-kDa and 110-kDa EGFR isoforms in human placenta. 12819035_Data show that stimulation of epidermal growth factor receptors differentially regulates chemokine expression in keratinocytes. 12824187_PGE2 regulates cell migration via the EGFR, and affects cell division and neoplasm invasiveneess. 12825853_Data support that EGFR and HER-2/neu play an important role in cell cycle control in ductal carcinoma in situ. 12828935_The results suggest that activation and nuclear localization of EGFR may be needed for induction of NOS-2 in response to elevated intraocular pressure in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. 12829707_Ligand-induced EGFR degradation is preceded by proteasome-dependent EGFR de-ubiquitination. 12839682_Bcl-2 and Bax, being nuclear matrix associated proteins, are probably involved in the EGFR-cDNA induced malignant conversion of glioblastoma cells by introducing EGFR cDNA into the tumor cells. 12844146_Data show that detachment-induced expression of Bim requires a lack of beta(1)-integrin engagement, downregulation of EGF receptor (EGFR) expression and inhibition of Erk signalling. 12871937_PLSCR1, through its interaction with Shc, promotes Src kinase activation through the EGF receptor. 12879076_EGFR is a necessary component for HCMV-triggered signalling and viral entry 12897150_endosomal epidermal growth factor receptor stimulates cell growth 12900408_EGFR has a role in beta2 tyrosine phosphorylation of AP-2 by interacting at receptor 974YRAL and di-leucine motifs 12925580_Results demonstrate that mice humanised for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) display tissue-specific hypomorphic phenotypes and describe a novel function for EGFR in bone development. 12930839_EGF receptor down-regulation by UVA may play an important role in the execution of the cell suicide program by attenuating its anti-apoptotic function 12939263_EGFR is an aldosterone-induced protein and is involved in the manifold (patho)biological actions of aldosterone 12953099_EGFR overexpression is frequent in NSCLC, is most prominent in SCC, and correlates with increased gene copy number per cell. High gene copy numbers per cell showed a trend toward poor prognosis. 12954170_identification of ligand-induced site-specific phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor 12955084_depending on their localization, oxytocin receptors transactivate EGFR and activate ERK1/2 using different signalling intermediates. The final outcome is a different temporal pattern of EGFR and ERK1/2 phosphorylation 13679441_These results indicate that the EGFR signaling pathway is involved in urothelial regeneration. 13679857_Mitogenic effects of gastrin-releasing peptide in head and neck squamous cells are mediated by activation of EGFR. 14506149_ERBB1 is overexpressed and may play a role in high-grade diffusely infiltrative pediatric brain stem glioma 14506242_Infection of primary cells with adenoviruses carrying the relevant point mutations confirmed the crucial role of putative YXX Phi and dileucine (LL) transport motifs within Ad2 10.4-14.5 for down-regulation of Fas, TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2, and EGFR. 14507652_Epidermal growth factor receptor (a potential therapeutic target) and SALL2 stained most cases of synovial sarcoma; staining was significantly less common among other tested sarcomas. 14512423_ganglioside GM3 inhibits integrin-induced, ligand-independent epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation (cross-talk) through suppression of Src family kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling 14520461_Up-regulation of EGFR is associated with renal cell carcinoma 14530278_cholesterol depletion with cyclodextrin induced an increase in both basal and EGF-stimulated EGF receptor phosphorylation, at specific tyrosine sites, that was associated with an increase in the intrinsic kinase activity of the EGF receptor kinase. 14551192_the EGF receptor is abundantly expressed in epithelioid vascular smooth muscle cells and the activation of this receptor results in cell cycle arrest through activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway 14557654_lysosomal degradation by adenovirus E3 RIDalpha protein dependent on specific domains 14607699_findings suggest that the coexpression of c-erbB-2 oncogene protein, epidermal growth factor receptor, and TGF-beta1 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is related to the histopathological grades and clinical stages of tumors 14632199_heregulin/EGFR system as a possible important physiologic growth regulatory system in melanocytes in which multiple deregulations may occur during progression toward melanoma, all resulting in, or indicating, growth factor independence. 14647423_demonstration that metalloproteinase-mediated transactivation of the EGFR is a key mechanism of the cellular signalling network that promotes MAPK activation as well as tumour cell migration and invasion 14660604_transactivation of the EGFr is required for the full expression of cAMP-dependent Cl- secretory responses 14670955_data suggest that agonist-induced binding of Src kinase to the Src homology 3 binding sites in the P2Y(2) purinergic receptor facilitates Src activation and allows Src to efficiently phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor 14681060_E-cadherin and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) are associated in mammary epithelial cells and that E-cadherin engagement in these cells induces transient activation of EGFR, as previously seen in keratinocytes. 14688027_The Id-1-induced androgen-independent prostate cancer cell growth was correlated with up-regulation of EGF-R. 14690686_results support a structural model for oligomerization of EGF receptors in which dimers are positioned head-to-head with respect to the ligand-binding site 14701753_SHP-2/Gab1 association is critical for linking EGFR to NF-kappaB transcriptional activity via the PI3-kinase/Akt signaling axis in glioblastoma cells 14702346_sorting of endocytosed epidermal growth factor receptor into the degradation pathway requires both its kinase activity and actin-binding domain 14704150_involvement urokinase plasminogen activator secretion and cell motility in breast cancer cells 14711810_EGFR and ErbB-2 have roles in ligand-dependent apoptosis that could be a natural mechanism to protect tissues from unrestricted proliferation 14718570_the adhesion-dependent activation of EGF receptor signaling is promoted by L1-type CAMs in vitro and in vivo 14729599_the relationship between the egfr polymorphism and breast cancer risk 14734462_Overexpression of EGFR is associated with recurrent non-small cell lung cancer 14764825_PGF(2 alpha)-FP receptor may promote endometrial tumorigenesis via phospholipase C-mediated phosphorylation of EGF receptor and MAPK signaling pathways. 14960328_CaM co-immunoprecipitates with EGF-activated and non-activated receptors 14963038_EGFR and c-Src-mediated Stat-3 activation is facilitated by Pyk2 14977086_A significantly higher frequency of EGFR expression occurred in PC than in AC glottic cancer. 14977838_EGFR and COX-2 cooperate to promote cervical neoplasm progression 14978035_a novel and important role for metalloprotease activation and EGFR transmodulation in mediating the cellular response to TNF 14988406_Sustained hyaluronan depolymerization is expected to cause tissue kallikrein activation, EGF release, and EGFR signaling. 15010475_Trypsin exerts robust trophic action on colon cancer cells and underline the critical role of EGF-R transactivation. 15026342_Cell surface expression of EGFR is associated with osteosarcoma pathogenesis 15031710_whole gene amplifications of egfr are rare in invasive breast cancer and explain protein overexpression in only about 12.5% of invasive breast cancer cases 15039424_epidermal growth factor receptor and CD95 activation are triggered by Src family kinase Yes 15042583_The EGFR pathway may be a specific, signal transduction pathway that regulates reactive astrocytes to form cavernous spaces in the glial scars following CNS injury and in the compressed optic nerve in glaucomatous optic nerve neuropathy. 15054105_PPARgamma and EGFR signalling have roles in urothelial terminal differentiation 15057284_EGFR regulation by E-cadherin was associated with complex formation between EGFR and E-cadherin that depended on the extracellular domain of E-cadherin but was independent of beta-catenin binding or p120-catenin binding 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15082004_Intensive staining of EGF-R is associated with invasive tumours of bladder 15082764_Data show that epidermal growth factor receptor signaling results in phosphorylation of CUG-BP1, and leads to increased binding of CUG-BP1 to CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBP beta) mRNA and elevated expression of the C/EBPbeta LIP isoform. 15100232_misfolding of the LDLR epidermal growth factor-AB pair results from low density lipoprotein receptor familial hypercholesterolemia mutations 15118073_A subgroup of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer have specific mutations in the EGFR gene, which correlate with clinical responsiveness to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. 15118125_somatic mutations of EGFR were found in 15 of 58 non-small cell lung cancer tumors from Japan and 1 of 61 from the United States; EGFR mutations may predict sensitivity to gefitinib 15123705_Results provide an explanation for cell surface receptor cross-talk involving the Met receptor and link G protein-coupled receptors and the epidermal growth factor receptor to the oncogenic potential of Met signaling in human carcinoma cells. 15134305_P. 445:'The EGF receptor (EGFR), a glycoprotein of 170 kDA, has also been intensily studied and finally located on chromosome 17, region p13l13-q22.' 15143334_Overexpression of EGFR was observed in only a small fraction of colorectal carcinomas, but were frequently accompanied by gene amplification. 15166244_the epidermal growth factor receptor has a role in activating ERK with extracellular oxidation by taurine chloramine 15166495_Endothelial cell vessel assembly requires EGFR signaling transduction pathways. 15182358_Data demonstrate that at least four different sets of endogenously expressed gangliosides, including GD3, did not have a significant effect on epidermal growth factor receptor distribution in the plasma membrane. 15185528_Statistically significant relation existed between the ovarian cancer metastatic potential and EGFR expression level. 15192046_The overall time-dependent activation of EGFR autophosphorylation was identical in cells treated with 1 nm BTC or 1.5 nm EGF. 15205458_EGFR inhibition promotes desmosome assembly in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells, resulting in increased cell-cell adhesion 15211117_The cytoplasmic overexpression of EGFr plays a significant role in the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, especially in the invasion and acquisition of aggressive clinical behavior. 15213840_EGFR, PYK2, Yes, and SHP-2 are involved in transduction of the TF/FVIIa signal possibly via transactivation of the EGF receptor. 15215236_epidermal growth factor receptor is dephosphorylated at endomembranes after ligand-mediated endocytosis 15219825_transactivation through CCR3 is a critical pathway that elicits mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and cytokine production in bronchial epithelial cells 15219850_trans-activation by calcium-sensing receptor 15221011_The tumor-specific mutation of epidermal growth factor receptor promotes cells survival and dimerization with the wild-type EGFR. 15226397_EGF receptor traffic is disrupted by farnesyltransferase inhibitors through modulation of the RhoB GTPase 15233293_c-erbB-2 and EGF-R are overexpressed in breast neoplasms and have an inverse association with Estrogen Receptor expression 15245434_Human leukocyte elastase induces keratinocyte proliferation by proteolytic activation of an EGFR signaling cascade involving TGF-alpha. 15248827_betacellulin may play a role as a local growth factor in promoting the differentiated villous trophoblastic function via ErbB-1 in early placentas and in contributing to placental growth through EVT cell function via ErbB-4 in term placentas. 15253134_The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is one of signalling pathways activated during premalignant proliferative changes in the airway epithelium. 15253384_an interrelationship is now known to exist between the IGF and EGF receptors [review] 15254267_amphiregulin- and ErbB1-dependent mechanism by which autocrine ERK activation is maintained in normal keratinocytes 15254682_EGFR, c-erbB-2, VEGF and MMP-2 and MMP-9 play an important role in tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 15269346_In each of these gliomas, the founding molecule was generated by a simple event that circularizes a chromosome fragment overlapping the epidermal growth factor receptor gene. 15271882_novel mechanism by which IGF-I induces ERK activation in a manner that is dependent on the basal level of EGFR-TK activity, but is independent of receptor transactivation. 15282549_Upregulation of leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 is followed by enhanced ubiquitylation and degradation of EGFR 15284455_mutant EGFRs selectively transduce survival signals on which nonsmall cell lung cancers become dependent 15298855_Carbon black causes oxidative stress-mediated proliferation of airway epithelium, involving activation of EGF-R. 15300588_IL-1beta-dependent prolonged EGFR transactivation involves multiple pathways, including an IL-8-dependent pathway. 15302576_EGFR signaling involves reinforcing altered gene expression of uPAR,thus further inducing cell motility. 15335267_In patients with breast cancer, most CNS metastatic tumor deposits showed expression for either EGFR or HER-2/neu, and less often for both. 15337524_Syk acts a negative control element of EGFR signalling. 15337756_Data show that activation of ADAM-17 results in discrete cellular responses, while G protein-coupled receptor agonists promote activation of the Ras/MAPK pathway and cell proliferation via the epidermal growth factor receptor. 15342520_The timing of lethality caused by homozygosity for a null allele of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mice is strongly dependent on genetic background. 15358139_Data report that antagonism of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor in combination with inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor synergistically sensitizes human malignant glioma cells to CD95L-induced apoptosis. 15364923_Results describe the role of epidermal growth factor receptor regulation in antiapoptosis, cell migration, and cell proliferation. 15366372_Egfr Wa5 is a novel ENU-induced antimorphic allele caused by a kinase-dead receptor acting as a dominant negative 15383630_data explain how thrombin exerts robust trophic action on colon cancer cells and underline the critical role of EGFR transactivation 15389641_GqPCR-induced FAK activation is mediated by via a pathway involving transactivation of the EGFr and alterations in the actin cytoskeleton. 15447984_serum epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 have roles in response of advanced non-small cell lung cancer to chemotherapy 15469987_a novel regulatory role for Galphas in EGF receptor degradation and provide mechanistic insights into the function of Galphas in endocytic sorting 15469991_NHERF stabilizes EGFR at the cell surface and slows the rate of endocytosis without affecting recycling 15485674_EGF signalling amplification is induced by dynamic clustering of EGFR 15494003_analysis of conformations of the epidermal growth factor receptor and antibody binding [review] 15519654_cholangiocarcinoma cells exhibit sustained EGFR activation due to defective receptor internalization 15522239_Data demonstrate that the alpha-hemolysin elevates the activity of receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma (rPTPsigma). 15524283_regulation of LMP1 on the nuclear translocation of EGFR is critical for the process of nasopharyngeal carcinoma 15540509_For genotype of EGFR gene Bsr I polymorphism, there was statistically significant differences between systemic lupus erythematosus and controls. In addition, there was significant association between the two groups in allelic frequency of the T allele. 15540509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15541730_Our results suggest a novel role for the juxtamembrane domain (JM) of EGFR in mediating intracellular dimerization and thus receptor kinase activation and function. 15542601_role for EGFR activity in the lifespan and inflammatory potential of RSV-infected epithelial cells 15545271_protein kinase B/Akt phosphorylation is stimulated by mechanical stretch in epidermal cells via angiotensin II type 1 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor 15556605_S1P transactivates c-Met and EGFR in gastric cancer cells. 15556944_Gene 33 is a physiologi |
ENSMUSG00000020122 |
Egfr |
52.608093 |
3.7374517283 |
1.902055 |
0.244169733 |
63.101773 |
0.00000000000000196297329587818266289442175450304415052784311190858801410286105237901210784912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000013783770621865831389661883763177464982182130609489334460704412776976823806762695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.0287938 |
13.0127971 |
22.9727218 |
2.9151366 |
| ENSG00000146674 |
3486 |
IGFBP3 |
protein_coding |
P17936 |
FUNCTION: IGF-binding proteins prolong the half-life of the IGFs and have been shown to either inhibit or stimulate the growth promoting effects of the IGFs on cell culture. They alter the interaction of IGFs with their cell surface receptors. Also exhibits IGF-independent antiproliferative and apoptotic effects mediated by its receptor TMEM219/IGFBP-3R. Inhibits the positive effect of humanin on insulin sensitivity (PubMed:19623253). Promotes testicular germ cell apoptosis (PubMed:19952275). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19623253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19952275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20353938}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is a member of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP) family and encodes a protein with an IGFBP domain and a thyroglobulin type-I domain. The protein forms a ternary complex with insulin-like growth factor acid-labile subunit (IGFALS) and either insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I or II. In this form, it circulates in the plasma, prolonging the half-life of IGFs and altering their interaction with cell surface receptors. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3486; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex [GO:0016942]; insulin-like growth factor ternary complex [GO:0042567]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; insulin-like growth factor binding [GO:0005520]; insulin-like growth factor I binding [GO:0031994]; insulin-like growth factor II binding [GO:0031995]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activator activity [GO:0008160]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014912]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043568]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906]; regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043567]; type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0044342] |
7566179_p53 induces the growth inhibitor IGF-binding protein 3 in apoptosis. 11238520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11319179_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11751851_This study defines a signaling pathway for IGFBP-3 from a cell surface receptor to nuclear transcriptional activity, requiring TGF-betaRII but not dependent on the nuclear translocation of IGFBP-3 11762714_Hypothyroidism is associated with significant reductions of IGFBP-3 11784719_Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 mutants that do not bind IGF-I or IGF-II stimulate apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells 11804742_The upstream AP2-binding site of IGFBP3's promoter is specifically hypermethylated in hepatomas. 11886859_interaction with STAT-1 during chondrogenesis 11914023_Reduced serum insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and IGF-binding protein-3 levels in adults with inflammatory bowel disease. 11914026_Total and free insulin-like growth factor I, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 and acid-labile subunit reflect clinical activity in acromegaly. 11940579_Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 activates a phosphotyrosine phosphatase 11948969_induces early apoptosis and has potential tumor suppressive effects in prostate cancer 11953210_study the changes of plasma insulin-like growth factor -1 (IGF-1) and IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) in patients with acute cerebral infarct (ACI) and acute cerebral hemorrhage (ACH) 11959812_A possible role for insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 autocrine/paracrine loops in controlling hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation 11971816_IGFBP-3 is essential for TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in PC-3 cells 11997031_identification of the proteolytic cleavage sites in circulating IGFBP-3 12006706_determination of blood levels in adult patients with severe liver disease before and after orthotopic liver transplantation 12011225_Insulin-like growth factor I, IGF-binding protein 3, and lung cancer risk in a prospective study of men in China. 12051736_Enhanced expression in gastric cancer cells increases paclitaxel and etoposide-induced growth inhibition 12054563_The amino-terminal region induces apoptosis of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. 12068000_Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 inhibits the growth of non-small cell lung cancer. 12111701_is inversely associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia risk 12122101_Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF binding protein-3 as predictors of advanced-stage prostate cancer. 12135130_circulating level of IGFBP3 is related to the extent of myocardial injury in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 12150454_high levels of IGFBP-3 predicted distant recurrence but not death in postmenopausal breast cancer patients and those with estrogen receptor-positive tumors 12163384_expression increases during immortalization of cervical keratinocytes 12200149_IGFBP-3 promoter is activated by Trichostatin A-upregulated Sp1 12210764_Variable mid-region is responsible for the specific pro-apoptotic functions of IGFBP-3; phosphorylation may provide a mechanism for regulation of this action 12213898_improves insulin resistance by GH-dependent and independent mechanisms 12219010_HT29 tumor cell proliferation in vitro was due, at least in part, to surgery-related depletion of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in peripheral blood. 12220677_These results provide evidence that a specific intracellular signal is triggered by IGFBP-3 binding to a cell surface receptor. 12242693_role in breast cancer cell growth - review 12473575_Hypermethylation of IGFBP-3 promoter is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 12508918_IGFBP-3 concentration significantly lower in acute ischemic stroke than in controls. 12519841_data demonstrate for the first time that serum levels of IGFs (including free fractions) and IGFBPs are not increased in euthyroid Graves' patients with active thyroid eye disease 12571183_Follicular fluid IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels were not significantly different among the groups; however, follicular fluid IGFBP-1 levels were lower in those patients with moderate/severe endometriosis 12571851_quantities of IGFBP-3 produced in culture by human cartilage are small compared with the amount supplied in the form of 'small complexes' from the circulation 12590636_Augmented serum levels of the IGF-I/IGF-binding protein-3 ratio in pre-menopausal patients with type I breast cysts. 12599210_IGFBP-3 supports myoblast differentiation 12725526_IGFBP-3 mRNA and protein are differentially expressed in distinct human brain microvascular endothelial cells populations. 12810533_isolated amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal domains of IGFBP-3 cooperate in the presence of IGFs to form high-affinity complexes that retain the ability to block IGF activity. 12865482_Divergent influences of sex steroids, IGF-1, and IGFBP3 on age-related changes in lean body mass in healthy elderly men and women. 12870155_endurance training improves glucose disposal and increases insulin-like growth binding protein-1 and -3 in men 12907612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12907612_The IGFBP-3 -202 A/C polymorphism was not associated with susceptibility to prostate cancer. 12925957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12925957_Polymorphic variation in IGFBP3 is associated with breast cancer risk. 12926118_During Tamoxifen treatment, IGFBP-3 proteolysis was increased in breast cancer. 12937269_IGFBP-3 degrading by MMP might have widespread consequences for the behavior of epidermal keratinocytes. 12962157_IGFBP-3 can bind to LTBP-1 and provide a potential mechanism whereby IGFBP-3 can interact with the TGF-beta system 14561895_functional effects of Humanin-IGFBP-3 interaction on cell survival and apoptosis 14576163_The metal-binding domain of IGFBP3 mediate cellular uptake and modulates apoptosis. 14576164_Actions of IGFBP-3 are mediated by internalization via distinct endocytic pathways. 14597676_LRP1 is the type V TGF-beta receptor and mediates growth inhibition by IGFBP-3 14598881_Upregulated with exposure to bone microenvironment and linked to TGF-beta mediated cell proliferaton 14644829_IGFBP-3 mRna expression is increased in endometriosis, compared to normal endomatrium. 14674122_breast malignant explants showed the progesterone induced IGFBP-3/IGF-I index decrease; the decrease was most evident in malignant explants expressing progesterone receptor 14693733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14710345_an apparent altered regulation of local IGFBP-3 production during malignancy 14744783_IGFBP-3 plays a crucial role in regulating IGF-I bioavailability, promoting cell survival. 14751238_IGFBP-3 directly triggers a specific intracellular signal in MCF-7 cells 15014034_an important additional prognostic marker in serum in ovarian cancer 15047131_Following severe burn, a shift occurs toward a predominant Th2 phenotype. Exogenous IGF-I/IGFBP-3 treatment partially reverses this response. 15066922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15067329_Down-regulation of IGFBP-3 gene expression is associated with Prostatic Neoplasms 15069073_IGFBP-3 is phosphorylated by tissue transglutaminase 2 15070968_Interaction between IGFBP-3 and EGF receptor system is central to whether IGFBP-3 acts as growth stimulator or inhibitor in breast cancer cells. Therapies targeting EGFR may have increased efficacy in breast tumors expressing high levels of IGFBP-3. 15086466_Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) expresses IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and is responsive to exogenous IGF-I stimulation. In metastatic RCC, autocrine IGF-I and IGFBP-3 stimulated and inhibited growth. IGF-I and IGFBP-3 possible treatment in advanced RCC. 15126567_Pregnancy-proteolyzed IGFBP-3, despite forming normal ternary complexes, is less effective than intact IGFBP-3 in retarding IGF egress from the circulation. 15140235_Reduced expression of IGFBP-3 in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa squamous cell carcinoma may provide a partial explanation for the aggressive behavior and poor prognosis of these tumors in this genodermatosis. 15178549_endogenous IGFBP-3 directly inhibits proliferation of human intestinal smooth muscle cells by activation of TGF-betaRI and Smad2, an effect that is independent of its effect on IGF-I-stimulated growth. 15198293_Patients with typical Sotos syndrome show low plasma IGF-II, IGFBP-3, IGFBP-4, and increased proteolysis of IGFBP-3 in serum. 15221971_Association between high IGF-I and IGFBP-3 levels and increased risk of breast cancer in premenopausal women. 15247132_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15247132_the IGFBP3 variants was not associated independently with colon cancer, but there was an association when examined with IRS1. The risk increased 70%. 15247904_interference with Sp-1 transactivation by MeCP2 may contribute to the transcriptional defect of IGFBP-3 expression in NSCLC cells with methylated promoter 15282325_These findings identify the repression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 gene by EWS/FLI-1 as a key event in the development of Ewing's sarcoma. 15298948_IGFBP3 polymorphism maybe associated with the level of blood IGFBP3 protein and an increase risk of breast cancer. 15298948_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15302288_Long-term use of both conjugated equine etrogens and raloxifene decreases serum IGF-I and the IGF-I/IGFBP-3 ratio, but raloxifene increases ISGFBP-3. 15379965_Mutation analysis in patients with undescended testis revealed functionally deleterious mutations, which may be responsible for the abnormal phenotype in some of the patients. (review) 15448002_Met proto-oncogene and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 have roles in metastasis of well-differentiated pancreatic endocrine neoplasms 15485880_N- and C-terminal residues of IGFBP-3 have roles in regulating IGF complex formation and receptor activation 15517912_The serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels were significantly elevated in esophageal cancer patients and there was a positive correlation between IGF-1 and IGFBP-3. 15625284_Increased circulating IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 may be stimulators of atherosclerosis. 15641262_IGFBP-3 levels decreased significantly six months after the iodine supplementation. 15641264_Serum IGFBP-3 levels differed significantly between pubertal developmental stages. 15642160_Increased breast epithelial IGFBP-3 expression is a feature of tumorigenesis with cytoplasmic immunoreactivity in the absence of significant nuclear localisation in IDCs and DCIS; IGFBP-3 suggested to be a potential mitogen 15642732_plasminogen binds with high affinity to IGF-II and IGF-binding protein-3 15651061_1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-induced up-regulation of IGFBP-3 is not required for the growth inhibitory effects of 1,25D in prostate cancer cells grown in serum-containing media. 15661050_The expression of certain IGFBP is significantly altered in renal cell carcinoma 15668470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15681824_Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 5 are xpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and have a role in extracellular matrix deposition 15703779_dysregulation of IGFBP-3 in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes 15734965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15769996_DNA damage and hypoxia are two important physiologic activators of p53. 15781645_IGFBP-3 is a target of transcriptional repression by DeltaNp63alpha and that this repression represents a mechanism by which tumors that overexpress p63 may be protected from apoptosis. 15800934_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15802501_Although IGFBP-3 and IGFBP-5 share much structural and functional homology, they can modulate distinct apoptotic pathways in human breast cancer cells. 15809062_PTEN may inhibit antiapoptotic IGF actions not only by blocking the IGF-IGFR-induced Akt activity, but also by regulating expression of components of the IGF system, in particular, upregulation of IGFBP-3 15817480_IEE (IGFBP-3 enhancer element) is a positive transcription regulatory element that contributes to the up-regulation of IGFBP-3 during cellular senescence 15844718_The level of intact IGFBP-3 is decreased in inflammatory bowel disease with moderate to severe disease activity. This decrease may be linked to altered IGFBP-3 production or to increased cleavage by proteases other than MMP-9. 15894673_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15894694_Finds IGFBP3 2133C variant allele associated with lower circulating IGFBP-3 hormone levels and an increased risk of colorectal cancer. 15894694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15927849_Preincubation of erythroid cells with thrombospondin 1 eliminated the inhibitory activity of IGFBP-3 15941947_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15959422_Maternal diabetes is not associated with suppressed levels of IGFBP-1 in cord serum. 15986122_Increased breast cancer risk in women with promoter polymorphisms in IGF1 and IGFBP3 genes, with increased risk for individuals homozygous for both polymorphisms. 15986122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15987847_IGF BP3 was associated with birth weight as measured in seconsd semestser amniotic fluid. 16015705_Imbalance of IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 may play a role in hepatocarcinogenesis and tumor development of liver cirrhosis patients 16030120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16049980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16181731_Loss of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 expression is associated with head and neck carcinogenesis. 16189247_In diabetics, nonglycosylated IGFBP-3 is degraded more rapidly than glycosylated IGFBP-3. By acting as substrate for IGFBP-3 protease, nonglycosylated IGFBP-3 protects endogenous, glycosylated IGFBP-3 from degradation, allowing total IGFBP-3 to increase. 16189260_Impacts on insulin signaling pathway to Inhibited insulin-stimulated glucose uptake independent of IGFs and through nonnuclear mechanisms. inhibited insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in omental but not s.c. adipose tissue explants. 16210470_insulin-like growth factor signaling is subject to negative regulation through IGF binding protein-3 and positive regulation by EGF 16211216_IGFBP-3 mediates growth suppression signals via the TGF-beta and/or retinoblastoma protein pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma 16215864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16275148_Using the rat insulinoma RINm5F cell line, we report the first studies in insulin-secreting cells that IGFBP-3 selectively suppresses multiple, key intracellular phosphorelays. 16306136_IGF1 and IGFBP3 tagging polymorphisms are associated with circulating levels of IGF1, IGFBP3 and risk of breast cancer. 16306136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16322329_IGFBP-3 is differentially expressed between stromal and epithelial components of normal and malignant colon, which may reflect its pro-apoptotic, IGF-I-independent effect on colonic epithelial cells. 16394092_IGF-I and IGFBP-3 levels were positively associated with weight gain and height gain from birth to 3 months in small for gestational weight versus appropriate weight children. 16404426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16448675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16455777_Rpb3 is a potential nuclear target of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 16489075_IGFBP-3 expression was higher in less aggressive tumors, but was not associated with disease progression. 16489531_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16540651_an IGFBP-3 mutant with deleted leader sequence localizes within the nucleus, its abundance is regulated by the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway, nuclear IGFBP-3 can induce apoptosis 16541420_C4-2 cell survival in an androgen-depleted environment may be facilitated through differential resistance to the apoptotic effects elicited by IGFBP-3 16543235_there are several conserved residues in the IGFBP-5 N-terminal region that are critical for transactivation and IGFBP-2 and -3 also have strong transactivation activity in their N-domains 16552541_The IGFBP3, hRas, JunB, Egr-1, Id1 and MIDA1 genes were up-regulated in psoriatic involved skin compared with uninvolved skin. 16614079_IGFBP-3 has positive or negative effects on growth and survival dependent upon the status of cholesterol-stabilized integrin receptor complexes 16617154_IGFBP-3 is a growth inhibitor molecule (news) 16645643_Both addition of IGFBP-3 protein to cell cultures or enforced expression of IGFBP-3 in the HT29 colon carcinoma cell line inhibited nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation in response to the induction of apoptosis by TRAIL. 16723126_By Northern blot, we confirm hypoxia-induced expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (igfbp3), thioredoxin-interacting protein (txnip), neuritin (nrn1). 16763062_results indicate a previously unrecognized and potentially important role for insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3(IGFBP-3) in the extracellular matrix 16775172_High levels of IGFBP-3 is associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer 16776662_IGFBP-1, IGFBP-3 and IGF-I show acute changes following a glucose load and there are marked gender differences in these responses. 16793770_IGFBP-3 can induce apoptosis in an IGF-independent manner without being secreted or concentrated in the nucleus 16825320_a novel functional androgen response element is present in the IGFBP-3 promoter that directly mediates androgen induction of IGFBP-3 expression 16887362_A decrease in free insulin-like growth factor 1 and IGFBP-3 levels, along with increases in blood pressure, significantly influenced the presence of diabetic complications 16915540_Blood level is not a marker for metabolic syndrome x. 16935391_High plasma levels of IGF-1, IGF-2, and IGFBP-3 were associated with good prognosis in patients with advanced NSCLC. 16965600_Low expression of IGFBP-3 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 16969385_This study demonstrates a direct interaction of the IGF and TGF-beta systems in human renal carcinoma cells. The observations that IGF-I enhances the TGF-beta signaling and that TGF-beta promotes IGFBP-3 production 17018785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17035411_Common genetic variation in the IGFBP3 gene does not substantially influence prostate and breast cancer susceptibility. 17035411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17044098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17047053_Cleavage of IGFBP-3 in breast carcinoma tissues was correlated with ADAM28 expression levels and inhibited by treatment with ADAM inhibitor or anti-ADAM28 antibody. 17051426_Genetic variation in IGFBP3 is associated with breast cancer risk 17051426_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17056474_IGFBP-3, IGFBP-4, and IGFBP-10/CYR61 mRNA levels were up-regulated in Barrett's and tumour tissue of oesophageal adenocarcinoma patients 17063263_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17063263_polymorphisms in the IGF-1R and IGFBP3 genes, but not IGF-1 or IGFALS, may be associated with altered survival among subgroups of breast cancer patients defined by menopausal status 17070193_High IGF-II, IGFBP-3, IGFBP-4, and low PAPP-A levels in FF at the time of oocyte retrieval suggest better oocyte maturation and early embryo development. 17085968_These results suggest that caspase-10, DR-3 and IGFBP-3 are involved in apoptosis in the preeclamptic placenta. 17096329_Results showed that IGFBP-3 methylation played an important role in the silencing of its expression, suggesting that IGFBP-3 may act as a tumor suppressor gene in several human cancers examined. 17113753_circulating levels may be lowered in patients with head and neck cancer 17119061_plasma levels of IGF1 and IGFBP-3 vary by ethnic group and have roles in development of obesity 17172410_results strongly suggest that IGFBP-3 expression may be a vital cell motility, migration, and proliferation factor necessary for melanoma metastasis and is an important biomarker in human melanoma 17187018_exposure to hypoxia and acidosis at birth strongly correlated with a fall in IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels in cord blood 17210081_the expression level of IGFBP3 in breast tissues may be involved in breast tumorigenesis 17237715_IGFBP-3 has potent insulin-antagonizing capability and suggest a role for IGFBP-3 in cytokine-induced insulin resistance and other mechanisms involved in the development of type-2 diabetes. 17264182_Circulating low levels of total IGFBP-3 was associated with increased risk of incident coronary events in older adults. 17287408_protective role of IGFBP-3 in risk of breast cancer 17289909_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17293864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17297462_CDX2 can function as a transcriptional repressor, and one mechanism by which CDX2 promotes anchorage-independent growth is by transcriptional repression of IGFBP-3. 17300730_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17350302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17388800_IGFBP-3 induces angiogenesis through IGF-I- and SphK1-dependent mechanisms 17396438_children with sickle cell anemia with poor growth had significantly more proteolyzed IGFBP-3 in serum compared to children with normal growth 17434446_The role of GalNAc-T14 as an intracellular mediator of the effects of IGFBP-3 need to be verified in future studies. 17434920_IGFBP-3 and Nur77 associate in the cytoplasmic compartment in 22RV1 human prostate cancer cells. 17446556_normal breast epithelial cells can induce apoptosis of breast cancer cells through IGFBP-3 and maspin. 17447118_Serum testosterone concentration and serum IGF-1/IGFBP-3 molar ratio are the major determinants of bone mineral density in boys at different pubertal stages. 17453001_Methylation of IGFBP3 may be involved in the early stages of prostate cancer development. 17457048_IGFBP-3 contributes to esophageal tumor development and progression through IGF-dependent and independent mechanisms. 17546465_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17555512_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17560154_Severely deficient in a case of insulin-resistance syndrome (Rabson-Mendenhall type). 17566087_Common genetic variation in IGFBP3 influences circulating levels of IGFBP-3 among African-Americans, Native Hawaiians, Japanese-Americans, Latinos, and whites. 17566087_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17567756_IGFBP3 suppresses retinopathy through suppression of oxygen-induced vessel loss and promotion of vascular regrowth. 17577982_Studies show that the purify of recombinant IGFBP3 is over 95% and was identified by Western-blot. 17593323_A 30-kDa proteolytic IGFBP-3 fragment was isolated from third trimester pregnancy human serum and identified by amino acid sequence analysis and mass spectrometry to correspond to residues 1-212 of the parent protein. 17597108_large prospective study showed no overall association between the insulin-like growth factor axis and prostate cancer risk, however, IGF-1:IGFBP-3 molar ratio was related to risk for aggressive prostate cancer in obese men 17624927_Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-3 mRNA is more abundantly expressed in hypoxia-related inflammatory angiogenesis and recent in vivo data suggest that IGFBP-3 has direct, IGF-independent inhibitory effects on angiogenesis. 17627014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17635417_These results suggest that IGFBP3 might play an important role in the cellular senescence of human umbilical vein endothelial cells as well as in vivo aging. 17655506_[(125)I]-labeled IGFBP-2 and -3, but not IGFBP-1, were proteolyzed by Ca(2+)-activated m-calpain in vitro. 17668637_Men who carry the IGFBP3 C allele were found to have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to controls, and the association was grade specific in both ethnic groups 17689128_No significant differences in levels in fibromyalgia patients. 17719815_IGFBP-3 sensitizes prostate cancer cells to interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-induced apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation 17724372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17724372_Serum levvels amd a single nucleotide polymorphism are indiative of prostate carcinogenesis. 17761791_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17763192_Perturbations in the IGF/IGFBP-3 axis may be potential additional targets for pharmacological manipulation in coronary heart disease. 17803702_IGFBP-3 were unrelated to carotid intima-media thickness. 17823260_study reports a methylation-dependent upstream stimulatory factor (USF) binding site influencing the basal and insulin-stimulated transcriptional activity of the IGFBP3 promoter 17827406_E7-mediated destruction of nuclear IGFBP-3 correlates with the inhibition of IGFBP-3-induced apoptotic cell death. 17879951_In a group of older US men, a strong inverse association between IGFBP-3 and lower urinary tract symptoms was observed. 17912004_Osteopenia is common in children with cerebral palsy and may be associated with lower IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels 17952116_IGFBP-3 plays an important role as an invasion-metastasis suppressor in ovarian endometrioid carcinoma. 17957164_Serum IGFBP-3 was not altered in neonates with intrauterine growth retardation. 17959403_The N-terminal IGF-binding protein-3 fragment induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells in an IGF-independent manner 17972510_This study supports the role of IGFBP-1, -3 and -7 as potential tumour suppressor genes in human breast cancer. 17997337_study established age- and sex-specific reference ranges for serum IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels 18006928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18031946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18031946_no major role of the assessed genetic variation within the IGF1 and the IGFBP3 genes in CRC risk. 18059035_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18084616_microsatellite instability in CPG-island-metahylator-high colorectal cancers, & this relationship is limited to p53-negative tumors. 18162523_in PC-3 cells, RXR-alpha is not required for the nuclear translocation of IGFBP-3 and that IGFBP-3 can induce apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells without binding RXR-alpha. 18163429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18171112_The role of IGFBP-3 on senescence depends on the genetic background of the donor, and additional factors might be important to maintain the senescent phenotype. 18177247_These findings suggest that serum levels of IGFBP-3 (and possibly IGF-I) are associated with the rate of HIV disease progression in women. 18178497_A concurrence of elevated GH levels and decreased IGF-I, IGFBP-3, and total ghrelin levels during the early burn injury period. 18259111_Higher early levels of the human milk IGF system might contribute to maturation of the infant gut. 18287864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18287864_functional variants of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 might be important markers for gastric cancer susceptibility 18329388_IGFBP-3 regulates the appearance of several biomarkers of senescence after repeated exposures of WI-38 fibroblasts to tert-butylhydroperoxide and ethanol. 18335323_data suggest that low concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) could be a reliable marker to differentiate benign from malignant ovarian tumors 18375957_Levels of circulating insulin growth factor I (IGF-I) and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 and breast cancer risk were investigated. 18398029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18410545_This study is the first to demonstrate that the systemic levels of IGF axis components are associated with the presence & severity of PAD, and that the inflammatory status of the ischaemic limb affects the transfemoral concentrations of IGF-1 & IGFBP-3. 18450319_IGFBP-3 promoter polymorphisms of -1590 C>A and -202 A>C might be a genetic risk factor for lung cancer 18450319_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18459102_The stroma--particularly reactivated stroma--is the main source of IGFBP-3 in the prostate, suggesting that this peptide acts as a mediator of stromal-epithelial interactions 18471292_associations of some breast cancer risk factors with intact levels of IGFBP-3 are different from those with total (intact and fragmented) IGFBP-3 levels 18481170_IGF-I, IGF-II and IGFBP-3 mRNA expression and tissue levels of IGF peptides are regulated by different mechanisms 18498652_Low expression of IGFBP-3 mRNA in normal colonic mucosa predicts increased risk of adenomas 18534134_This study suggests that there is an interaction between leptin, IGF-1, IGFBP-3 and insulin resistance in patients with chronic kidney disease. 18562769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18596909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18596909_the association between common genetic variation in the IGFBP3 genes in relation to circulating IGFBP3 levels and breast cancer risk 18602100_A new approach for designing protein delivery systems using IGFBP-3/5 derived peptides based on the molecular mechanisms of IGF-independent activities of IGFBPs. 18615538_None of the components in the IGF-1 pathway including IGFBP3, PI3k, and PTEN influence the relation between IRS-1 genotype and prostate cancer risk. Ther is no association between carriage of the variant IRS-1 gene and prostate cancer risk. 18618736_A high IGFI:IGFBP3 ratio was associated with increased benign prostate hyperplasia risk, and high serum IGFBP3 was associated with decreased BPH risk among men with severe symptoms. 18624627_results did not support a relationship between GH T1663A and IGFBP3-202A/C with ischemic stroke in Chinese 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18812263_Non-hispanic blacks have the highest molar ratio of IGF-I:IGFBP-3 at all ages 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18929499_Genetic and epigenetic variability in the gene for IGFBP-3 is associated with increased serum IGFBP-3 levels and retarded growth in short children born small for gestational age 18929499_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18984657_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18984657_The -202 A allele of IGFBP3 promoter region is associated with increased IGFBP-3 levels and growth velocity during rhGH treatment in prepubertal GHD children. 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18992263_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19004037_IGFBP-3(insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3)levels were significantly elevated in patients with Systemic Sclero |
ENSMUSG00000020427 |
Igfbp3 |
2914.993503 |
4.3007879161 |
2.104601 |
0.035345751 |
3671.314913 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4780.7610523 |
98.7004571 |
1119.6202675 |
19.5647620 |
| ENSG00000146826 |
55262 |
TRAPPC14 |
protein_coding |
Q8WVR3 |
FUNCTION: Specific subunit of the TRAPP (transport protein particle) II complex, a highly conserved vesicle tethering complex that functions in late Golgi trafficking as a membrane tether (PubMed:31467083, PubMed:30715179). TRAPP II complex has also GEF activity toward RAB1A (By similarity). TRAPPC14 is dispensable for TRAPPII complex integrity but mediates RAB3IP preciliary vesicle trafficking to the mother centriole during ciliogenesis (PubMed:31467083). Modulates YAP1 activity as transcriptional regulator (PubMed:30447097). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TLI0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30447097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30715179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31467083}. |
Alternative splicing;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Primary microcephaly;Reference proteome |
|
Enables alpha-tubulin binding activity. Involved in cilium assembly and regulation of cell population proliferation. Located in several cellular components, including microtubule cytoskeleton; midbody; and plasma membrane. Part of TRAPPII protein complex. Implicated in primary autosomal recessive microcephaly. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55262; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; TRAPPII protein complex [GO:1990071]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127] |
31467083_C7orf43 directly binds to Rabin8 and that C7orf43 knockdown diminishes Rabin8 preciliary centrosome accumulation. |
ENSMUSG00000036948 |
Trappc14 |
197.259982 |
0.4022371316 |
-1.313882 |
0.161091627 |
65.899555 |
0.00000000000000047449869967782936067838021530178623971030031896550793746314411691855639219284057617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000003456861207919427983909271570933045931952774191403543468936732097063213586807250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
113.7035761 |
15.3624121 |
284.2270712 |
27.1711789 |
| ENSG00000146830 |
64599 |
GIGYF1 |
protein_coding |
O75420 |
FUNCTION: May act cooperatively with GRB10 to regulate tyrosine kinase receptor signaling. May increase IGF1 receptor phosphorylation under IGF1 stimulation as well as phosphorylation of IRS1 and SHC1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12771153}. |
3D-structure;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the gyf family of adaptor proteins. The encoded protein contains a gyf protein interaction domain. It binds growth factor receptor bound 10, another adaptor protein that binds activated insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin receptors and regulates receptor signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2017]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:57330; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009] |
17672918_the apparent occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 8 is discussed 33053355_4EHP and GIGYF1/2 Mediate Translation-Coupled Messenger RNA Decay. 34234147_GIGYF1 loss of function is associated with clonal mosaicism and adverse metabolic health. 34732801_Gene-level analysis of rare variants in 379,066 whole exome sequences identifies an association of GIGYF1 loss of function with type 2 diabetes. 36189799_GIGYF1-disturbed IGF-1R recycling: a potential contributor to autism spectrum disorder pathogenesis? |
ENSMUSG00000029714 |
Gigyf1 |
782.648955 |
0.4114093840 |
-1.281353 |
0.125384255 |
101.945816 |
0.00000000000000000000000570613826404651334415441399120723017752880811793245217093349110851902006302793779468629509210586547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000059020743361826581680383817506152634331250068397980741092601932040739853846389451064169406890869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
473.0709522 |
39.8470777 |
1159.2791994 |
69.4609347 |
| ENSG00000146904 |
2041 |
EPHA1 |
protein_coding |
P21709 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously membrane-bound ephrin-A family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Binds with a low affinity EFNA3 and EFNA4 and with a high affinity to EFNA1 which most probably constitutes its cognate/functional ligand. Upon activation by EFNA1 induces cell attachment to the extracellular matrix inhibiting cell spreading and motility through regulation of ILK and downstream RHOA and RAC. Also plays a role in angiogenesis and regulates cell proliferation. May play a role in apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17634955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19118217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20043122}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family. EPH and EPH-related receptors have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Receptors in the EPH subfamily typically have a single kinase domain and an extracellular region containing a Cys-rich domain and 2 fibronectin type III repeats. The ephrin receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. This gene is expressed in some human cancer cell lines and has been implicated in carcinogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2041; |
neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005005]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
16737551_increased levels of ephrins A1 and A5 in the presence of high expression of Ephs A1 and A2 lead to a more aggressive ovarian cancer phenotype 16862074_EphA1 seems to be a marker of the differentiated normal epidermis and its downregulation in nonmelanoma skin cancer may contribute to carcinogenesis of these very frequent human tumors. 17980912_Increasing ephrin-A expression enhances T-cell interactions not only with purified integrin ligands but also endothelial cells, while EphA activation down-regulates these interactions. 18308734_I 12 acquired a higher affinity toward EphA2 with K(d) 18 nm and inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenic invasion in a Matrigel plug assay 18566674_EphA2 and EphrinA-1 may play an important role in the development of a subset of early cervical cancers 18590698_Results suggest that EphA1-receptor transmembrane domains contribute to the dimerization-mediated receptor activation. 18728013_analysis of the spatial structure and pH-dependent conformational diversity of dimeric transmembrane domain of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA1 18802966_In EphA1 null transgenic mice a possible role for EphA1 in tissue patterning and hormone-induced apoptotic processes is indicated. 18990944_We report selective targeting of PC-3 cells with nanoshells conjugated to ephrinA I, a ligand for EphA2 receptor that is overexpressed on PC-3 cells. 19011600_EphA1 may play different roles during the different stages of colorectal carcinoma progression. 19118217_EphA1 regulates cell morphology and motility through the ILK-RhoA-ROCK pathway. 19277044_Epigenetic silencing of EphA1 expression in colorectal cancer is correlated with poor survival. 19525919_The crystal structures of an A-class complex between EphA2 and ephrin-A1 and of unbound EphA2, are presented. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19949912_Eph-A1 staining intensity was significantly associated with tumor size and tumor histopathological stage in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 20043122_Suppression of EphA1 expression in Huh-7 cells reduced their outgrowth when inoculated in the subcutaneous space in the flank of nude mice, presumably through angiogenesis inhibition since microvessel density was found to be inhibited. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21042754_The EphA1 expression level is a potential prognostic marker in gastric carcinoma, and may provide a novel target of therapy for gastric carcinoma. 21460840_found independent evidence for association for Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci at EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP 21460841_Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 21503576_The present study reveals a novel function for EphA1 and EphB2 in the induction of autophagy, suggesting a tumor suppressor role for these proteins in colorectal cancer. 22261062_Ephrin-A1 activates EphA2 on the surface of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. 22362770_analysis of structural and functional characterization of monomeric EphrinA1 binding site to EphA2 receptor 22688511_EphrinA1 is released in three forms from cancer cells by matrix metalloproteases 23030051_Results show that EphA1 appears to be a differentiation marker for esophageal squamous cells, and its increased expression is positively associated with lymph node metastasis and advanced disease stage. 23429488_High Eph A1 expression is associated with choriocarcinoma invasion. 24040450_Suggest EphA1 receptor may have roles in carcinogenesis and progression of prostate cancer. 25025847_Lack of ephrin receptor A1 is a favorable independent prognostic factor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 25182741_This study suggests EPHA1 (rs11771145) interferes with the pathological alteration of the hippocampus and the lateral occipitotemporal and inferior temporal gyri throughout the Alzheimer's disease process, leading to a lower risk of Alzheimer's disease. 25286141_two states of the EphA1 transmembrane helix dimer 25391265_High expression of EphA1 was associated with metastasis and recurrence in Gastric Cancer. 25451169_EphrinA1 plays an important role in the TNF-alpha-mediated adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells. 26261568_Data indicate that EphA1 protein may be a new marker for the prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 26977017_EPHA1 suppresses spreading and adhesion of HRT18 colorectal cancer cells through deactivation of ERK and JNK signaling pathways. 27533087_Data show that Ephrin B3 was concomitantly expressed with EphA2 and Ephrin A1 with higher Ephrin B3 levels found in non-squamous than in squamous tumors. 28739735_Results show that EPHA1 expression is up-regulated in ovarian cancer (OC) cells and provide evidence that it may promote the aggression of some OC cells. 29332039_The rs11767557 variant could significantly regulate EPHA1 gene expression specifically in human whole blood. These findings may further provide important supplementary information about the regulating mechanisms of rs11767557 variant in Alzheimer's disease risk. 29393455_EphA1 expression is decreased in ovarian serous carcinoma compared with normal fallopian tube and benign ovarian serous cystadenoma. Decreased EphA1 expression was more often detected in high-grade tumors. 29491103_High erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular carcinoma receptor A (EphA) 1, 2, and 4 expression levels were significantly related to recurrence. 30401746_EphB1 and EphA1 phosphorylate the Cx32CT domain residue Tyr(243) Unlike for Cx43, the tyrosine phosphorylation of the Cx32CT increased gap junction intercellular communication. 31659653_ABCA7 and EphA1 Genes Polymorphisms in Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease. 32218416_Association Between EphA1 and Tumor Microenvironment in Gastric Carcinoma and its Clinical Significance. 32224528_Expression of cancer stem cell markers CD24, EPHA1 and CD9 and their correlation with clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian tumours. 32266818_SOCS2 affects the proliferation, migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via regulating EphA1. 33199830_Silencing of long non-coding RNA XIST represses gastric cancer progression through blocking NFkappaB pathway via inhibiting HNF4A-mediated transcription of EPHA1. |
ENSMUSG00000029859 |
Epha1 |
12.637012 |
0.4372390532 |
-1.193506 |
0.443956921 |
7.270367 |
0.00701014660494251110045560437811218434944748878479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013892288384660507472023738273492199368774890899658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7258791 |
2.3454657 |
18.0509528 |
3.5128926 |
| ENSG00000146950 |
357 |
SHROOM2 |
protein_coding |
Q13796 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in endothelial cell morphology changes during cell spreading. In the retinal pigment epithelium, may regulate the biogenesis of melanosomes and promote their association with the apical cell surface by inducing gamma-tubulin redistribution (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Membrane;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction |
|
This gene represents the human homolog of Xenopus laevis apical protein (APX) gene, which is implicated in amiloride-sensitive sodium channel activity. It is expressed in endothelial cells and facilitates the formation of a contractile network within endothelial cells. Depletion of this gene results in an increase in endothelial sprouting, migration, and angiogenesis. This gene is highly expressed in the retina, and is a strong candidate for ocular albinism type 1 syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:357; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical junction complex [GO:0043296]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; ligand-gated sodium channel activity [GO:0015280]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; apical protein localization [GO:0045176]; brain development [GO:0007420]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular pigment accumulation [GO:0043482]; ear development [GO:0043583]; establishment of melanosome localization [GO:0032401]; eye pigment granule organization [GO:0008057]; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0002089]; melanosome organization [GO:0032438] |
21248203_Data suggest that Shroom2 facilitates the formation of a contractile network within endothelial cells, the loss of which leads to an increase in endothelial sprouting, migration, and angiogenesis. 22634755_We identified three new CRC risk loci at 6p21 (rs1321311, near CDKN1A; P = 1.14 x 10(-10)), 11q13.4 (rs3824999, intronic to POLD3; P = 3.65 x 10(-10)) and Xp22.2 (rs5934683, near SHROOM2; P = 7.30 x 10(-10)). 29423651_These findings provide genetic and molecular insights into the effects of rare damaging variants in SHROOM2, indicating that such variants of SHROOM2 might contribute to the risk of human Neural tube defects 30160833_SHROOM2 deletion is associated with Ocular albinism with infertility and late-onset sensorineural hearing loss. 30683844_SHROOM2 is downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and is implicated in the suppression of cancer cell invasion and metastasis by preventing EMT, which is largely independent of Rho-ROCK signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000045180 |
Shroom2 |
18.537377 |
0.4533246845 |
-1.141383 |
0.509778848 |
4.895996 |
0.02691903497575261205998486957469140179455280303955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.046815713001308892349250356801348971202969551086425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.9079335 |
3.5612128 |
24.5805832 |
5.2897604 |
| ENSG00000147050 |
7403 |
KDM6A |
protein_coding |
O15550 |
FUNCTION: Histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-27' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code (PubMed:17851529, PubMed:17713478, PubMed:17761849). Demethylates trimethylated and dimethylated but not monomethylated H3 'Lys-27' (PubMed:17851529, PubMed:17713478, PubMed:17761849). Plays a central role in regulation of posterior development, by regulating HOX gene expression (PubMed:17851529). Demethylation of 'Lys-27' of histone H3 is concomitant with methylation of 'Lys-4' of histone H3, and regulates the recruitment of the PRC1 complex and monoubiquitination of histone H2A (PubMed:17761849). Plays a demethylase-independent role in chromatin remodeling to regulate T-box family member-dependent gene expression (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17713478, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17761849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17851529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18003914}. |
3D-structure;Chromatin regulator;Dioxygenase;Intellectual disability;Iron;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Zinc |
|
This gene is located on the X chromosome and is the corresponding locus to a Y-linked gene which encodes a tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) protein. The encoded protein of this gene contains a JmjC-domain and catalyzes the demethylation of tri/dimethylated histone H3. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:7403; |
histone methyltransferase complex [GO:0035097]; MLL3/4 complex [GO:0044666]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; histone demethylase activity [GO:0032452]; histone H3K27me2/H3K27me3 demethylase activity [GO:0071558]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; heart development [GO:0007507]; histone H3-K27 demethylation [GO:0071557]; histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051568]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] |
17500065_UTX associates with MLL3- and MLL4-containing histone H3 K4 methyltransferase complex(es) that also include ASH2L, RBBP5, WDR5, hDPY-30, PTIP, PA1, NCOA6. 17713478_the human JmjC-domain-containing proteins UTX and JMJD3 demethylate tri-methylated Lys 27 on histone H3 17761849_study shows that UTX is a di- and trimethyl H3K27 demethylase; results suggest a concerted mechanism for transcriptional activation in which cycles of H3K4 methylation by MLL2/3 are linked with the demethylation of H3K27 through UTX 17851529_critical role for UTX in regulating H3K27 methylation at the HOX gene loci and in animal posterior development 18003914_The JmjC domain-containing protein UTX specifically demethylates mono-, di- and trimethylated K27 of histone H3 in vitro. 18003914_UTX and JMJD3 may function as H3K27 demethylases in vivo 19330029_Here, we describe inactivating somatic mutations in the histone lysine demethylase gene UTX, pointing to histone H3 lysine methylation deregulation in multiple tumor types 20054297_identification of inactivating mutations in two genes--SETD2, a histone H3 lysine 36 methyltransferase, and JARID1C, a histone H3 lysine 4 demethylase--as well as mutations in the histone H3 lysine 27 demethylase, UTX in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 20123895_UTX removes H3K27me3 and maintains expression of several RB-binding proteins, enabling cell cycle arrest 20442750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21209387_The role of the H3K27 demethylases Jmjd3 and UTX in gene expression, is discussed. 21245294_KDM6A- and KDM6B-responsive Homeobox genes are expressed at significantly higher levels, suggesting that HPV16 E7 results in reprogramming of host epithelial cells 21515470_UXT is a potential interactor of HBV Pol. 21575637_inhibition measurements showed significant selectivity between KDM4C and KDM6A 21828135_Novel UTX, DNMT3A, and EZH2 mutations were found in 8%, 10%, and 5.5% of patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. 21841772_H3K27 demethylation by JMJD3 at a poised enhancer of anti-apoptotic gene BCL2 determines ERalpha ligand dependency 21865393_Correlating with the loss of H3K27me3, human papillomavirus 16 E6/E7-expressing cells exhibited derepression of specific EZH2-, KMD6A-, and BMI1-targeted HOX genes. 22002947_clarified how UTX discriminates H3K27me3/2 from the other methyllysines with distinct roles 22197486_This study identifies KDM6A mutations as another cause of Kabuki syndrome and highlights the growing role of histone methylases and histone demethylases in multiple-congenital-anomaly and intellectual-disability syndromes. 22306297_demonstrate that UTX directly associates with the promoters of the Mll1, Runx1, and Scl genes and modulate their transcription by controlling H3K27me3 marks on respective promoter regions. 22589717_PAN RNA interacts with demethylases JMJD3 and UTX, and the histone methyltransferase MLL2 22801502_identification of Utx as a novel mediator with distinct functions during the re-establishment of pluripotency and germ cell development 22840376_Microdeletions and microduplications have not been identified in the MLL2 and KDM6A genes of a large cohort of patients with Kabuki syndrome. 22907667_KDM6A contributes to the activation of WNT3 and DKK1 at different differentiation stages when WNT3 and DKK1 are required for mesendoderm and definitive endoderm differentiation. 23184418_This study demonistrated that KDM6A mutations were most commonly identified in subgroups in medulloblastoma. 23266085_KDM6A is overexpressed in breast cancer patients with an unfavorable prognosis (mortality at 1 year, p=8.65E-7). 23365460_UTX regulates stem cell migration and hematopoiesis. 23527641_UTX histone demethylase plays important functional role in epigenetic alteration of HOX clusters during retinoic acid-induced neural differentiation. 23644518_PBRM1, KDM6A, SETD2 and BAP1 were unmethylated in all tumor and normal specimens. 23913813_The identification of novel KDM6A mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. 24123378_Both Ezh2 and Kdm6a were shown to affect expression of master regulatory genes involved in adipogenesis and osteogenesis. 24465480_results demonstrate that UTX is implicated in IL-4 mediated transcriptional activation of the ALOX15 gene 24491801_High levels of UTX or MLL4 are associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. 24527667_A report of novel KDM6A mutations in patients with Kabuki syndrome. 24739679_One girl had a novel splice-site mutation in KDM6A. 25071154_Results show that UTX interacts with the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARalpha) and this interaction is essential for proper differentiation of leukemic U937 cells in response to retinoic acid. 25225064_This study is the first to identify frequent BAP1 and BRCA pathway alterations in bladder cancer, show TERT promoter alterations are independent of other bladder cancer gene alterations, and show KDM6A loss is a driver of the bladder cancer phenotype. 25281733_Mutations in KMT2D gene were identified in 10/16 (62%) of the patients, whereas none of the patients had KDM6A mutations. 25320243_H3K27me3 demethylase UTX is a gender-specific tumor suppressor in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 25972376_Our results provide further support for the similar roles of KMT2D and KDM6A in the etiology of KS by using a vertebrate model organism to provide direct evidence of their roles in the development of organs and tissues affected in KS patients. 26049589_Kabuki syndrome may be caused by mutations in one of two histone methyltransferase genes: KMT2D and KDM6A. 26138514_The KDM6A gene is a histone demethylase specific for histone H3 Lysin 27 and regulates gene transcription [35]. In approximately 24% of urothelial carcinoma, KDM6A is altered. 26303947_UTX is a prominent tumour suppressor that functions as a negative regulator of EMT-induced Cancer Stem Cell-like properties by epigenetically repressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition -TFs. 26431949_Turner Syndrome subjects, who are predisposed to chronic ear infections, had reduced UTX expression in immune cells and decreased circulating CD4(+) CXCR5(+) T cell frequency. 26762983_The results define UTX as a bivalency-resolving histone modifier necessary for stem cell differentiation 26819089_UTX positively regulates E-cadherin expression in colon cancer cells. 26841933_Pathogenic variants in KMT2D resulting in protein truncation in 43% (6/14; of which 3 are novel) of all cases were detected, while analysis of KDM6A was negative. MLPA analysis was negative in all instances. 26898171_Mutations of the epigenetic genes KMT2D and KDM6A cause dysregulation of certain developmental genes and account for the multiple congenital anomalies of the syndrome 27028180_we identified a novel de novo deletion of KDM6A in a Chinese girl with KS. We consider her allergic skin manifestations to be part of the phenotypic spectrum of KS 27151432_Here, we discuss the roles of lysine 27 demethylases, JMJD3 and UTX, in cancer and potential therapeutic avenues targeting these enzymes. Despite a high degree of sequence similarity in the catalytic domain between JMJD3 and UTX, numerous studies revealed surprisingly contrasting roles in cellular reprogramming and cancer, particularly leukemia 27302555_Study presents a mutation screening of patients with Kabuki syndrome type 1 which identified 208 mutations in KMT2D. Two of the KDM6A mutations were maternally inherited and nine were shown to be de novo. 27533081_both UTX and UTY function as dose-dependent suppressors of urothelial bladder cancer development 27869828_Mutation in KDM6A gene is associated with cancer more frequently in males. 27983522_UTX gene expression in renal cell carcinoma and bladder cancer. 28197626_Kdm6a and Kdm6b were found to be significantly overexpressed in Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) at the mRNA level. However, tests examining if targeting therapeutically Kdm6a/b using a specific small molecule inhibitor was potentially useful for treating MPM, revealed that members of the Kdm6 family may not be suitable candidates for therapy 28228601_inactivating mutations of KDM6A, which are common in urothelial bladder carcinoma, are potentially targetable by inhibiting EZH2. 28442529_Two novel missense mutations: p.G325A in the KDM6A gene responsible for Kabuki syndrome and p.G1877V in the SCN1A gene responsible for generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus were identified using the TruSight One sequencing panel. 28534508_Study identified a feed-forward loop between UTX and ER in the regulation of hormonally responsive breast carcinogenesis. 28968467_KDM6A and p21CIP1 expression are essential to curb E7 induced replication stress to levels that do not markedly interfere with cell viability 29045832_Rebalance of Histone h3 lysine 27 methylation 3 levels at specific genes through EZH2 inhibitors may be a therapeutic strategy in multiple myeloma cases harboring UTX mutations. 29136510_Data show that more mutations in the histone lysine demethylase KDM6A were present in non-invasive tumors from females than males. 29171124_Depletion of KDM6A inhibits the expression of SOX9, Col2a1, ACAN and results in increased H3K27me3 and decreased H3K4me3 levels. 29351209_High UTX expression is independently associated with a better prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and downregulation of UTX increases ESCC cell growth and decreases E-cadherin expression. Our results suggest that UTX may be a novel therapeutic target for patients with ESCC. 29846646_Study in Finnish Caucasian obesity patients demonstrated a different genome-wide DNA methylation pattern in autosomes and X-chromosome between males and females in human liver. Sex-specific differences in liver expression and methylation of KDM6A may contribute to higher HDL-cholesterol levels in females. 29902804_data suggest that haploinsufficiency for KDM6A due to mosaic X chromosome monosomy may be responsible for hyperinsulinism in Turner syndrome. 29907798_we retrospectively evaluated 100 infants with HI lacking a genetic diagnosis, for causative variants in KS genes. Molecular diagnoses of KS were established by identification of pathogenic variants in KMT2D (n = 5) and KDM6A (n = 4). 29973620_ut of twenty-seven genes culminating into leading hubs in the network, we identified two key regulators (KRs) i.e. KDM6A and BDNF 30006524_Lymphomas with low UTX expression express high levels of Efnb1, and cause significantly poor survival. 30107592_The mutation pattern of KMT2D and KDM6A in a cohort of 505 patients clinically diagnosed as Kabuki syndrome was reported. 30166694_The histone demethylase UTX/KDM6A is mutated in up to 10% of cases of multiple myeloma, activating genes by removing the H3K27me3 repressive histone mark, counteracting EZH2 activity. 30556125_KDM6A exhibited essential roles in human PDAC as a tumor suppressor and KDM6A deficiency could be a promising biomarker for unfavorable outcome in PDAC patients and a potential surrogate marker for response to HDAC inhibitors. 30556359_Three of the 27 children had a KDM6A mutation and had thesame hypermobility as the KMT2D subjects. Only one of the Kabuki syndrome chil-dren had a patellar luxation in here previous history and was not con-sidered hypermobile using both scores. 30718900_Study shows that UTX and 53BP1 directly interact and co-occupy promoters in human embryonic stem cells and differentiating neural progenitor cells. Data suggests that the 53BP1-UTX interaction supports the activation of key genes required for human neurodevelopment. 30753822_In clear cell renal cell carcinoma, KDM6A(UTX) is one of the most frequently mutated genes; In 101 cases of patient samples, 12 samples contained KDM6A mutations. Other studies provided additional evidence that KDM6A was highly mutated in different human solid tumors and leukemias 30872525_the H3K27 histone demethylase KDM6A/UTX, but not its paralog KDM6B, is oxygen sensitive. 30948420_targeting the KDM6A-KLF10 feedback loop may be beneficial to attenuate diabetes-induced kidney injury. 31097364_UTY is co-regulated with KDM6A. UTY compensates for KDM6A in eutherian males and is responsible for the association between the loss of the Y chromosome and poor prognosis in a range of cancers. [review] 31201358_our findings highlight KDM6A as a novel mediator of drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia 31221981_This article reviewed the most recent findings regarding cancer-specific metabolic reprogramming and the tumor-suppressive roles of IDH1/2, JARID1C/KDM5C and UTX/KDM6A. [review] 31285428_EZH2 methyltransferase and JMJD3/UTX demethylases were deregulated during hepatic differentiation of human HepaRG cells. 31335488_Expression of UTX Indicates Poor Prognosis in Patients With Luminal Breast Cancer and is Associated With MMP-11 Expression. 31403472_the X escapee Kdm6a regulates multiple immune response genes, providing a mechanism for sex differences in autoimmune disease susceptibility 31654559_Prenatal and perinatal history in Kabuki Syndrome. 31685800_GATA3 recruits UTX for gene transcriptional activation to suppress metastasis of breast cancer. 31883305_The phenotypic spectrum of Kabuki syndrome in patients of Chinese descent: A case series. 31935506_This study expands the number of naturally occurring KMT2D and KDM6A variants. The discovery of novel pathogenic variants will add to the knowledge on disease-causing variants and the relevance of missense variants in Kabuki syndrome. 31959746_Knock-out of KDM6s (JMJD3 and/or UTX) in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) showed that KDM6s (JMJD3 and/or UTX)-deficient human ESCs exit pluripotency and commit to neural progenitor cells (NPC) differentiation normally, but the resulting NPCs fail to transit into neurons and glia due to a lack of accessibility at loci essential for neurogenesis. 32071397_Cancer-derived UTX TPR mutations G137V and D336G impair interaction with MLL3/4 complexes and affect UTX subcellular localization. 32125007_Coordinated demethylation of H3K9 and H3K27 is required for rapid inflammatory responses of endothelial cells. 32154941_HNF1A recruits KDM6A to activate differentiated acinar cell programs that suppress pancreatic cancer. 32269126_KDM6A-Mediated Expression of the Long Noncoding RNA DINO Causes TP53 Tumor Suppressor Stabilization in Human Papillomavirus 16 E7-Expressing Cells. 32346926_Histone demethylase KDM6A promotes somatic cell reprogramming by epigenetically regulating the PTEN and IL-6 signal pathways. 32427586_Chemotherapy-induced S100A10 recruits KDM6A to facilitate OCT4-mediated breast cancer stemness. 32679064_UTX Regulates Human Neural Differentiation and Dendritic Morphology by Resolving Bivalent Promoters. 32732223_X- and Y-Linked Chromatin-Modifying Genes as Regulators of Sex-Specific Cancer Incidence and Prognosis. 32803813_Update of the genotype and phenotype of KMT2D and KDM6A by genetic screening of 100 patients with clinically suspected Kabuki syndrome. 32867456_[KDM6A mutation and expression in gastric cancer are associated with prognosis]. 32879445_Histone 3 lysine-27 demethylase KDM6A coordinates with KMT2B to play an oncogenic role in NSCLC by regulating H3K4me3. 32929331_Targeted inhibition of KDM6 histone demethylases eradicates tumor-initiating cells via enhancer reprogramming in colorectal cancer. 32977832_UTX/KDM6A suppresses AP-1 and a gliogenesis program during neural differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. 32989154_Loss of UTX/KDM6A and the activation of FGFR3 converge to regulate differentiation gene-expression programs in bladder cancer. 33174323_Combination of lysine-specific demethylase 6A (KDM6A) and mismatch repair (MMR) status is a potential prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. 33253789_Histone demethylase UTX/KDM6A enhances tumor immune cell recruitment, promotes differentiation and suppresses medulloblastoma. 33314698_Clinical and molecular characterization study of Chinese Kabuki syndrome in Hong Kong. 33456567_KDM6A promotes imatinib resistance through YY1-mediated transcriptional upregulation of TRKA independently of its demethylase activity in chronic myelogenous leukemia. 33546721_Molecular mechanics and dynamic simulations of well-known Kabuki syndrome-associated KDM6A variants reveal putative mechanisms of dysfunction. 34051747_Significance of KDM6A mutation in bladder cancer immune escape. 34257820_hsa-miR-199b-3p Prevents the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Dysfunction of the Renal Tubule by Regulating E-cadherin through Targeting KDM6A in Diabetic Nephropathy. 34262032_SMARCA4 deficient tumours are vulnerable to KDM6A/UTX and KDM6B/JMJD3 blockade. 34465286_Overexpression of UTX promotes tumor progression in Oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma patients receiving surgical resection: a case control study. 34526716_UTX condensation underlies its tumour-suppressive activity. 34583087_KDM6A Regulates Cell Plasticity and Pancreatic Cancer Progression by Noncanonical Activin Pathway. 34661759_EGFR transcriptionally upregulates UTX via STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer. 34667079_PROSER1 mediates TET2 O-GlcNAcylation to regulate DNA demethylation on UTX-dependent enhancers and CpG islands. 35022315_KDM6A Depletion in Breast Epithelial Cells Leads to Reduced Sensitivity to Anticancer Agents and Increased TGFbeta Activity. 35073341_Mutually exclusive mutation profiles define functionally related genes in muscle invasive bladder cancer. 35136209_The KDM6A-SPARCL1 axis blocks metastasis and regulates the tumour microenvironment of gastrointestinal stromal tumours by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of p65. 35185915_Inhibiting KDM6A Demethylase Represses Long Non-Coding RNA Hotairm1 Transcription in MDSC During Sepsis. 35384910_CircLDLR Modulates the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Coronary Artery Disease Through miR-26-5p/KDM6A Axis. 35676242_Histone H3K27 demethylase UTX compromises articular chondrocyte anabolism and aggravates osteoarthritic degeneration. 35791460_CircNFIX regulates chondrogenesis and cartilage homeostasis by targeting the miR758-3p/KDM6A axis. 36306422_KDM6A Loss Recruits Tumor-Associated Neutrophils and Promotes Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Pancreatic Cancer. 36412518_UTX deficiency in neural stem/progenitor cells results in impaired neural development, fetal ventriculomegaly, and postnatal death. |
ENSMUSG00000037369 |
Kdm6a |
13.286199 |
0.3624153992 |
-1.464284 |
0.490838739 |
8.854812 |
0.00292317256878020428206843561724781466182321310043334960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006273048431985434221502817564442011644132435321807861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6572524 |
2.0453164 |
18.1177683 |
3.4677586 |
| ENSG00000147130 |
9203 |
ZMYM3 |
protein_coding |
Q14202 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene is located on the X chromosome and is subject to X inactivation. It is highly conserved in vertebrates and most abundantly expressed in the brain. The encoded protein is a component of histone deacetylase-containing multiprotein complexes that function through modifying chromatin structure to keep genes silent. A chromosomal translocation (X;13) involving this gene is associated with X-linked cognitive disability. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:9203; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604] |
29332164_Data found skewing of the genetic architecture at the ZMYM3 short tandem repeats (STR) in schizophrenia. Further, results found a bell-shaped distribution of alleles and selection against alleles at the extreme ends of this STR. 30889214_AGS mutations in this cluster impair the interaction of RNase H2 with several members of the CoREST chromatin-silencing complex that include the histone deacetylase HDAC2 and the demethylase KDM1A, the transcriptional regulators RCOR1 and GTFII-I as well as ZMYM3, an MYM-type zinc finger protein. 30909162_The ZMYM3 'exceptionally long' 5' UTR STR findings may alter our perspective of disease pathogenesis in psychiatric disorders, and set an example in which the low frequency alleles at the extreme short and long ends of the human STRs are, at least in part, a result of natural selection against these alleles and their unambiguous link to major human disorders. 33173136_Evolving evidence on a link between the ZMYM3 exceptionally long GA-STR and human cognition. |
ENSMUSG00000031310 |
Zmym3 |
221.901920 |
0.4622120476 |
-1.113373 |
0.133040325 |
69.950181 |
0.00000000000000006082133612778952189769387980669813515987780574729298921354825324669945985078811645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000464659897125348518574094490530556308711505485078280264232830631954129785299301147460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
131.8267383 |
10.5001922 |
286.9592195 |
15.5681854 |
| ENSG00000147155 |
10682 |
EBP |
protein_coding |
Q15125 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of Delta(8)-sterols to their corresponding Delta(7)-isomers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12760743, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8798407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9894009}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cataract;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Ichthyosis;Isomerase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; cholesterol biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12760743, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8798407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9894009}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum. It is a high affinity binding protein for the antiischemic phenylalkylamine Ca2+ antagonist [3H]emopamil and the photoaffinity label [3H]azidopamil. It is similar to sigma receptors and may be a member of a superfamily of high affinity drug-binding proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum of different tissues. This protein shares structural features with bacterial and eukaryontic drug transporting proteins. It has four putative transmembrane segments and contains two conserved glutamate residues which may be involved in the transport of cationic amphiphilics. Another prominent feature of this protein is its high content of aromatic amino acid residues (>23%) in its transmembrane segments. These aromatic amino acid residues have been suggested to be involved in the drug transport by the P-glycoprotein. Mutations in this gene cause Chondrodysplasia punctata 2 (CDPX2; also known as Conradi-Hunermann syndrome). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10682; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; C-8 sterol isomerase activity [GO:0000247]; cholestenol delta-isomerase activity [GO:0047750]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; steroid delta-isomerase activity [GO:0004769]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via desmosterol [GO:0033489]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via lathosterol [GO:0033490]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; ossification involved in bone maturation [GO:0043931]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126] |
17378690_Molecular analysis of EBP mutations were made. 17498944_Emopamil binding protein (EBP)-shRNA sequences were designed and tested for their effectiveness. 17949453_We found two novel (3G-->T and 419-422delTTCT) and one known mutation in the EBP gene. The strong phenotypic variability in our patients suggests that there is no clear genotype-phenotype correlation. 18573709_two unrelated Thai girls with chondrodysplasia punctata type 2. Mutation analysis by PCR-sequencing the entire coding region of emopamil binding protein(EBP) successfully revealed two potentially pathogenic, novel mutations, c.616G-->T and c.382delC. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21931045_postzygotic mosaicism on an ichthyosiform skin lesion in the mother of a girl with X-linked dominant chondrodysplasia punctata associated with a novel EBP mutation. 22121851_Results show a clear relationship between abnormal sterol profile and the EBP gene mutation 24106871_Elastin binding protein and FKBP65 modulate the kinetics of self-assembly of tropoelastin in an in vitro system. 24459067_With non-mosaic EBP mutations in males. 24493593_Report steroidomimetic aminomethyl spiroacetals as novel inhibitors of the enzyme Delta8,7-sterol isomerase in cholesterol biosynthesis. 24700572_This study expands the current phenotypic spectrum of males with hypomorphic EBP mutations and supports to the hypothesis that there exists an X-linked recessive entity independent of CDPX2. 24915996_Mutation analysis revealed a heterozygous novel missense mutation, c.204G>T (p.W68C), in exon 2. 31165728_EBP adopts an unreported fold involving five transmembrane-helices (TMs) that creates a membrane cavity presenting a pharmacological binding site that accommodates multiple different ligands. Mutagenesis studies on specific residues abolish the isomerase activity and decrease the multidrug binding capacity. 31381990_The human sterol delta(8)-Delta(7) isomerase was expressed in P. pastoris to 200mgL-1. The membrane protein enzyme could be solubilized readily in dodecyl maltoside. The solubilized protein displayed a symmetric peak on size exclusion chromatography. 32105736_Thermostabilization of Membrane Proteins by Consensus Mutation: A Case Study for a Fungal Delta8-7 Sterol Isomerase. |
ENSMUSG00000031168 |
Ebp |
239.109915 |
2.2396207728 |
1.163254 |
0.118328115 |
96.702063 |
0.00000000000000000000008058525627751314596767785609510843299433285709314440292020482927565216968446293321903795003890991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000790324506748235185122201873349116227739055953358344686497031876537544548000369104556739330291748046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
335.7050370 |
25.3265787 |
150.8921991 |
8.8115878 |
| ENSG00000147162 |
8473 |
OGT |
protein_coding |
O15294 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of a single N-acetylglucosamine from UDP-GlcNAc to a serine or threonine residue in cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins resulting in their modification with a beta-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) (PubMed:26678539, PubMed:23103939, PubMed:21240259, PubMed:21285374, PubMed:15361863). Glycosylates a large and diverse number of proteins including histone H2B, AKT1, ATG4B, EZH2, PFKL, KMT2E/MLL5, MAPT/TAU and HCFC1 (PubMed:19451179, PubMed:20200153, PubMed:21285374, PubMed:22923583, PubMed:23353889, PubMed:24474760, PubMed:26678539, PubMed:27527864). Can regulate their cellular processes via cross-talk between glycosylation and phosphorylation or by affecting proteolytic processing (PubMed:21285374). Probably by glycosylating KMT2E/MLL5, stabilizes KMT2E/MLL5 by preventing its ubiquitination (PubMed:26678539). Involved in insulin resistance in muscle and adipocyte cells via glycosylating insulin signaling components and inhibiting the 'Thr-308' phosphorylation of AKT1, enhancing IRS1 phosphorylation and attenuating insulin signaling (By similarity). Involved in glycolysis regulation by mediating glycosylation of 6-phosphofructokinase PFKL, inhibiting its activity (PubMed:22923583). Component of a THAP1/THAP3-HCFC1-OGT complex that is required for the regulation of the transcriptional activity of RRM1. Plays a key role in chromatin structure by mediating O-GlcNAcylation of 'Ser-112' of histone H2B: recruited to CpG-rich transcription start sites of active genes via its interaction with TET proteins (TET1, TET2 or TET3) (PubMed:22121020, PubMed:23353889). As part of the NSL complex indirectly involved in acetylation of nucleosomal histone H4 on several lysine residues (PubMed:20018852). O-GlcNAcylation of 'Ser-75' of EZH2 increases its stability, and facilitating the formation of H3K27me3 by the PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex (PubMed:24474760). Regulates circadian oscillation of the clock genes and glucose homeostasis in the liver. Stabilizes clock proteins BMAL1 and CLOCK through O-glycosylation, which prevents their ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. Promotes the CLOCK-BMAL1-mediated transcription of genes in the negative loop of the circadian clock such as PER1/2 and CRY1/2 (PubMed:12150998, PubMed:19451179, PubMed:20018868, PubMed:20200153, PubMed:21285374, PubMed:15361863). O-glycosylates HCFC1 and regulates its proteolytic processing and transcriptional activity (PubMed:21285374, PubMed:28584052, PubMed:28302723). Regulates mitochondrial motility in neurons by mediating glycosylation of TRAK1 (By similarity). Glycosylates HOXA1 (By similarity). O-glycosylates FNIP1 (PubMed:30699359). Promotes autophagy by mediating O-glycosylation of ATG4B (PubMed:27527864). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P56558, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CGY8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12150998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15361863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19451179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20018852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20018868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20200153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21240259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21285374, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22121020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22923583, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23103939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23353889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24474760, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26678539, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27527864, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28302723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28584052, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30699359}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: The mitochondrial isoform (mOGT) is cytotoxic and triggers apoptosis in several cell types including INS1, an insulinoma cell line. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20824293}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Biological rhythms;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Host-virus interaction;Intellectual disability;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15361863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21240259, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21285374, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23103939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26678539}. |
This gene encodes a glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the addition of a single N-acetylglucosamine in O-glycosidic linkage to serine or threonine residues. Since both phosphorylation and glycosylation compete for similar serine or threonine residues, the two processes may compete for sites, or they may alter the substrate specificity of nearby sites by steric or electrostatic effects. The protein contains multiple tetratricopeptide repeats that are required for optimal recognition of substrates. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:8473; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; histone acetyltransferase complex [GO:0000123]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; NSL complex [GO:0044545]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase complex [GO:0017122]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; Sin3 complex [GO:0016580]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; protein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0016262]; protein O-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0097363]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; histone H4-K16 acetylation [GO:0043984]; histone H4-K5 acetylation [GO:0043981]; histone H4-K8 acetylation [GO:0043982]; mitophagy [GO:0000423]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032435]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902455]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of histone H3-K27 methylation [GO:0061087]; positive regulation of histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051571]; positive regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045862]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of dosage compensation by inactivation of X chromosome [GO:1900095]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0006110]; regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046626]; regulation of necroptotic process [GO:0060544]; regulation of neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0098696]; regulation of Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0035020]; regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051963]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11773972_We have delineated the complete genomic structure of human OGT spanning approx 43 kb of genomic DNA in Xq13.1 11846551_homology between O-linked GlcNAc transferases and proteins of the glycogen phosphorylase superfamily 12136128_O-linked GlcNAc transferase participates in a hexosamine-dependent signaling pathway that is linked to insulin resistance and leptin production 14601650_a novel HLA-A0201-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-epitope (28-SLYKFSPFPL; FSP06) derived from a mutant OGT-protein 15336570_OGT can respond rapidly to heat stress through the enhancement of nucleocytoplasmic protein O-GlcNAcylation. 15561949_Staining of OGT in streptozotocin diabetic rat liver is clearly diminished, but it was substantially restored after 6 days of insulin treatment 15795231_By using a series of 4-methylumbelliferyl 2-deoxy-2-N-fluoroacetyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside substrates, Taft-like linear free energy analyses of these enzymes indicates that O-GlcNAcase uses a catalytic mechanism involving anchimeric assistance 15896326_Thus, stably transfected HeLa cells provide an abundant source of enzyme that can be used to study the structure, function, and regulation of OGT. 16105839_analysis of the catalytic domain of O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase 16966374_Overall, transcriptional inhibition is related to the integrated effect of O-GlcNAc by direct modification of critical elements of the transcriptome and indirectly through O-GlcNAc modification of the proteasome. 18174169_O-GlcNAc modification stimulated by glucose deprivation results from increased OGT and decreased O-GlcNAcase levels and that these changes affect cell metabolism, thus inactivating glycogen synthase. 18536723_The structure of an intact OGT homolog and kinetic analysis of human OGT variants reveal a contiguous superhelical groove that directs substrates to the active site. 18653473_the O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes associate with kinases and phosphatases at M phase to regulate the posttranslational status of vimentin 19073609_Up-regulation of O-GlcNAc transferase with glucose deprivation in HepG2 cells is mediated by decreased hexosamine pathway flux. 20068230_Data show that forced overexpression of OGT increased the inhibitory phosphorylation of CDK1 and reduced the phosphorylation of CDK1 target proteins. 20190804_OGT regulates breast cancer tumorignenesis and cancer growth through targeting FixM1. 20200153_THAP1 was found to bind HCF-1 in vitro and to associate with HCF-1 and OGT in vivo. 20206135_OGT could be a co-regulatory subunit shared by functionally distinct complexes supporting epigenetic regulation of MIP-1alpha gene promoter. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20805223_regulating the amount of OGT during mitosis is important in ensuring correct chromosomal segregation during mitosis. 20824293_Enhanced OGT expression efficiently triggered programmed cell death. 20845477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20876116_OGT deletion in infarcted mice significantly exacerbated cardiac dysfunction. 21240259_two crystal structures of human OGT, as a binary complex with UDP (2.8 A resolution) and as a ternary complex with UDP and a peptide substrate (1.95 A). 21327254_Data identify Tau as potential substrates for the O-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (OGT). 21567137_Decrease in MGEA5 and increase in O-GlcNAc transferease expression in higher grade tumors suggests that increased O-GlcNAc modification may be implicated in breast tumor progression and metastasis. 22275356_as prostate cancer cells alter glucose and glutamine levels, O-GlcNAc modifications and OGT levels become elevated and are required for regulation of malignant properties 22294689_a 154-amino acid region of MIBP1 was necessary for its O-GlcNAc transferase binding and O-GlcNAcylation. 22311971_Data show that the interplay between O-GlcNAc and phosphorylation on proteins and indicate that these effects can be mediated by changes in hOGT and hOGA kinetic activity. 22371499_These studies identify a molecular mechanism of GR transrepression, and highlight the function of O-GlcNAc in hormone signaling. 22384635_O-GlcNAcylation may be an important regulatory modification involved in endometrial cancer pathogenesis but the actual significance of this modification for endometrial cancer progression needs to be investigated further. 22496241_Hsp90 is involved in the regulation of OGT and O-GlcNAc modification and that Hsp90 inhibitors might be used to modulate O-GlcNAc modification and reverse its adverse effects in human diseases. 22574218_AMPK functions as a physiological suppressor of 26S proteasomes through OGT 22783592_Analysis of urinary content of MGEA5 and OGT may be useful for bladder cancer diagnostics. 22883232_O-GlcNAc transferase/host cell factor C1 complex regulates gluconeogenesis by modulating PGC-1alpha stability. 23103939_we describe structural snapshots of all species along the kinetic pathway for human O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase (O-GlcNAc transferase), an intracellular enzyme that catalyzes installation of a dynamic post-translational modification 23103942_we define how human OGT recognizes the sugar donor and acceptor peptide and uses a new catalytic mechanism of glycosyl transfer, involving the sugar donor alpha-phosphate as the catalytic base as well as an essential lysine 23152511_The human respiratory syncytial virus-induced sequestration of p38-P in IBs resulted in a substantial reduction in the accumulation of a downstream signaling substrate, MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2). 23222540_The double epigenetic modifications on both DNA and histones by TET2 and OGT coordinate together for the regulation of gene transcription. 23487789_These studies identified OGT as a promising placental biomarker of maternal stress exposure that may relate to sex-biased outcomes in neurodevelopment. 23642195_Data suggest that changes in OGT (O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase) and OGA (peptide O-linked N-acetylglucosamine-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase) expression are correlated with cancer prognosis. [REVIEW] 23700425_The backbone carbonyl oxygen of Leu653 and the hydroxyl group of Thr560 in OGT contribute to the recognition of sugar moieties via hydrogen bonds. 23720054_Expression of c-MYC and OGT was tightly correlated in human prostate cancer samples. 24256146_Data suggest that with multi-substrate enzymes, such as OGT, specific inhibition can rarely be achieved with ligands that compete solely with one of the substrates; OGT is inhibited by bisubstrate UDP-oligopeptide conjugates. 24311690_study reports the tetratricopeptide-repeat domain of O-GlcNAc transferase binds the carboxyl-terminal portion of an HCF-1 proteolytic repeat such that the cleavage region lies in the glycosyltransferase active site above uridine diphosphate-GlcNAc; protein glycosylation and HCF-1 cleavage occur in the same active site 24365779_Estrogen replacement therapy and plyometric training influence muscle OGT and OGA gene expression, which may be one of the mechanisms by which HRT and PT prevent aging-related loss of muscle mass. 24394411_OGT catalyzes the O-GlcNAcylation of TET3, promotes TET3 nuclear export, and, consequently, inhibits the formation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine catalyzed by TET3. 24580054_Endogenous OTX2 from a medulloblastoma cell line is O-GlcNAcylated at several sites. 24928395_Instead, an adipogenesis-dependent increase in O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) glycosylation of EWS was observed. 25173736_Amino acid composition of splice variants, post-translational modifications, and stable associations with regulatory proteins influence subcellular distribution/substrate specificity of OGT and OGA (O-GlcNAcase beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase). [REVIEW] 25419848_O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase mediates O-GlcNAcylation of the SNARE protein SNAP-29 and regulates autophagy in a nutrient-dependent manner. 25568311_Phosphorylation of TET proteins is regulated via O-GlcNAcylation by the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT). 25663381_Hexosamine biosynthetic pathway flux is increased in idiopathic pulmonary artery hypertension and drives OGT-facilitated pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation via specific proteolysis and direct activation of host cell factor-1. 25773598_Histone demethylase LSD2 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and inhibits cancer cell growth through promoting proteasomal degradation of OGT. 25776937_miR4235p was associated with congestive heart failure and the expression levels of proBNP; in addition, OGT was found to be a direct target of miR4235p. 26041297_Inhibition of O-Linked N-Acetylglucosamine Transferase Reduces Replication of Herpes Simplex Virus and Human Cytomegalovirus. 26237509_This work reveals that although the N-terminal TPR repeats of OGT may have roles in substrate recognition, the sequence restriction imposed by the peptide-binding site makes a substantial contribution to O-GlcNAc site specificity. 26240142_Use of OGT(C917A) enhances O-GlcNDAz production, yielding improved cross-linking of O-GlcNDAz-modified molecules 26252736_These results suggested roles of O-GlcNAcylation in modulating serine phosphorylation, as well as in regulating PKM2 activity and expression. 26305326_These results demonstrate that distinct OGT-binding sites in HCF-1 promote proteolysis, and provide novel insights into the mechanism of this unusual protease activity. 26397041_We concluded that OGT plays a key role in gastric cancer proliferation and survival, and could be a potential target for therapy. 26399441_OGT expression is increased under hypoxic conditions. 26408091_a new function of histone O-GlcNAcylation in DNA damage response 26527687_E2F1 negatively regulates both Ogt and Mgea5 expression in an Rb1 protein-dependent manner. 26707622_OGT inhibited the formation of the Ecadherin/catenin complex through reducing the interaction between p120 and Ecadherin. 26807597_Data suggest RNA polymerase II (POLR2A) is extensively modified on its unique C-terminal domain (CTD) by O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT); efficient O-GlcNAcylation requires a minimum of 20 heptad CTD repeats in POLR2A and more than half of NTD of OGT. 26854602_Together, these findings suggest that induction of SNO-OGT by Ab exposure is a pathogenic mechanism to cause cellular hypo-O-GlcNAcylation by which Ab neurotoxicity is executed 27060025_The findings suggest that OGT promotes the O-GlcNAc modification of HDAC1 in the development of progression hepatocellular carcinoma. 27129214_data indicate that O-GlcNAc-transferase activity is essential for RNA pol II promoter recruitment and that pol II goes through a cycling of O-GlcNAcylation at the promoter 27131860_O-GlcNAcylation expression and its nuclear expression were associated with the carcinogenesis and progression of gastric carcinoma. 27217568_These results support a model in which OGT modifies HIRA to regulate HIRA-H3.3 complex formation and H3.3 nucleosome assembly and reveal the mechanism by which OGT functions in cellular senescence. 27231347_the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) processing enzymes, O-GlcNAc-transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA), interact with the (A)gamma-globin promoter at the -566 GATA repressor site 27294441_Beyond its well-known role in adding beta-O-GlcNAc to serine and threonine residues of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, OGT also acts as a protease in the maturation of the cell cycle regulator, HCF-1, and serves as an integral member of several protein complexes, many of them linked to gene expression. (Review) 27331873_Findings indicate O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT) as a cellular factor involved in human papillomaviruses type 16/18 E6 and E7 expressions and cervical cancer tumorigenesis, suggesting that targeting OGT in cervical cancer may have potential therapeutic benefit. 27505673_This work uncovers that URI-regulated OGT confers c-MYC-dependent survival functions in response to glucose fluctuations. 27705803_We identified two human PRC2 complexes and two PR-DUB deubiquitination complexes, which contain the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase OGT1 and several transcription factors. 27845045_OGT functions in metastatic spread of HPV E6/E7-positive HeLa cells to xenografted lungs through E6/E7, HCF-1 and CXCR4 28100784_Reducing endogenous mitochondrial OGT expression leads to alterations in mitochondrial structure and function, including Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fragmentation, reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential, and a significant loss of mitochondrial content in the absence of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. 28115479_The results of this study showed that the OGT is essential for sensory neuron survival and target innervation. 28232487_Fatty acid synthase fine-tunes the cell's response to stress and injury by remodeling cellular O-GlcNAcylation 28302723_Thus, a single amino acid substitution in the regulatory domain (the tetratricopeptide repeat domain) of OGT, which catalyzes the O-GlcNAc post-translational modification of nuclear and cytosolic proteins, appears causal for X-linked intellectual disability. 28347804_OGT, a unique glycosyltransferase enzyme, was identified to be upregulated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma tissues by transcriptome sequencing. Here, we found that OGT plays a role in cancer by promoting tumor growth and metastasis in cell models. This effect is mediated by the induction of palmitic acid. 28450392_Data suggest that O-GlcNAc transferase 1 (OGT1) specifically binds to, O-GlcNAcylates, and stabilizes nonspecific lethal protein3 (NSL3); stabilization of NSL3 by OGT1 up-regulates global acetylation levels of histone 4 at Lys-5, Lys-8, and Lys-16. 28455227_conclusion, our results demonstrated that miR24 inhibits breast cancer cells invasion by targeting OGT and reducing FOXA1 stability. These results also indicated that OGT might be a potential target for the diagnosis and therapy of breast cancer metastasis. 28584052_Mutations in N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) transferase in patients with X-linked intellectual disability 28625484_Nrf1 is regulated by O-GlcNAc transferase. 28663241_The authors show that O-GlcNAcylation of KEAP1 by OGT at serine 104 is required for the efficient ubiquitination and degradation of NRF2. 28742148_Tax interacts with the host OGT/OGA complex and inhibits the activity of OGT-bound OGA. 28929346_These data predict that under conditions where O-GlcNAc levels are high (breast cancer) progesterone receptor (PR) through an interaction with the modifying enzyme OGT, will exhibit increased O-GlcNAcylation and potentiated transcriptional activity. Therapeutic strategies aimed at altering cellular O-GlcNAc levels may have profound effects on PR transcriptional activity in breast cancer 29059153_High OGT expression promotes cancer lipid metabolism via SREBP-1 regulation. 29208956_Findings demonstrate a novel role of Poleta O-GlcNAcylation by OGT in translesion DNA synthesis regulation and genome stability maintenance. 29465778_The O-GlcNAc transferase OGT interacts with and post-translationally modifies the transcription factor HOXA1. 29556021_a novel ASXL1-OGT axis and raise the possibility that this axis has a tumor-suppressor role in myeloid malignancies. 29577901_LXRalpha interacts with OGT in its N-terminal domain and ligand-binding domain (LBD) in a ligand-independent fashion. 29606577_The intellectual disability L254F mutation in OGT affects activity. The L254F mutation leads to shifts up to 12 A in the OGT structure. Thermal denaturing studies reveal reduction in tetratricopeptide repeat domain stability caused by L254F. L254F OGT mutation leads to conformational changes of the tetratricopeptide repeats and reduced activity, revealing the molecular mechanisms contributing to pathogenesis. 29769320_O-GlcNAc transferase missense mutations is associated with X-linked intellectual disability. 29788742_miR-483 inhibited the expression level of OGT mRNA by direct binding to its 3'-untranslated region. Expression of miR-483 was negatively correlated with OGT in gastric cancer tissues. 29967448_Study found that levels of placental Ogt determine sex differences in fetally derived placental trophoblast transcriptome profiles associated with key developmental processes and shape genome-wide patterning of the ubiquitous epigenetic transcriptional repressive mark, H3K27me3. 30069701_O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) is a partner of the MCM2-7 complex and O-GlcNAcylation might regulate MCM2-7 complex by regulating the chromatin loading of MCM6 and MCM7 and stabilizing MCM/MCM interactions. 30106436_High OGT expression is associated with breast cancer. 30453909_O-GlcNAcylation and the expression of O-linked-beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT) were upregulated in bladder cancer cell lines and tissue specimens. 30543776_these findings provide a mechanistic link between the OGT-mediated glucose metabolic pathway and antiviral innate immune signaling by targeting MAVS, and expand our current understanding of importance of glucose metabolic regulation in viral infection-associated diseases. 30550897_The ligand transport mechanism in the OGT enzymatic process is described here and is a great resource for designing inhibitors based on UDP or UDP-GlcNAc. 30555541_These findings suggest that down-regulation of OGT enhances cisplatin-induced autophagy via SNAP-29, resulting in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. 30587575_novel regulatory mechanism for O-GlcNAcylation during FA complex formation, which thereby affects integrin activation and integrin-mediated functions such as cell adhesion and migration 30677218_our findings indicate that OGT promotes the stem-like cell potential of hepatoma cell through O-GlcNAcylation of eIF4E 30953348_HNF1A regulates ogt transcription in a time-dependent manner and that O-GlcNAcylation of HNF1A represses ogt transcription. 14 O-GlcNAc sites on HNF1A were revealed, six of which are predominantly modified, including Ser(303/304) , Ser(471) , Ser(560) and Thr(563/564). Loss of O-GlcNAcylation at Ser(303/304) or Thr(563/564) significantly elevates ogt transcription. 31149037_OGT is essential for proliferation of prostate cancer cells. OGT activity is required for the interaction between MYC and HCF-1 and expression of MYC-regulated mitotic proteins. 31296563_Pathogenic N567K mutation leads to loss of O-GlcNAcase activity and delayed differentiation down the neuronal lineage in mouse and Drosophila model. 31373491_Aspartate Residues Far from the Active Site Drive O-GlcNAc Transferase Substrate Selection. 31373757_silencing of OGT in HT29 cells upregulates E-cadherin (a major actor of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition) and changes its glycosylation. On the other hand, OGT silencing perturbs biosynthesis of glycosphingolipids resulting in a decrease in gangliosides and an increase in globosides. 31527085_O-GlcNAcylation does not affect sOGT activity but does affect sOGT-interacting proteins. S56A bound to and hence glycosylated more proteins in contrast to T12A and WT sOGT. 31567281_Two cases of hand myoepithelioma showing unusual clinicopathologic features and novel OGT-FOXO3 gene fusions are described. 31627256_A missense mutation in the catalytic domain of O-GlcNAc transferase links perturbations in protein O-GlcNAcylation to X-linked intellectual disability. 31628985_Disease related single point mutations alter the global dynamics of a tetratricopeptide (TPR) alpha-solenoid domain. 31847126_findings in this report are the first to describe a role for the OGT/O-GlcNAc axis in modulating VEGF expression and vascularization in Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. 31974291_O-GlcNAc Transferase Regulates Cancer Stem-like Potential of Breast Cancer Cells. 32272438_Epigenetic activation of O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase overrides the differentiation blockage in acute leukemia. 32310828_SIRT1 regulates O-GlcNAcylation of tau through OGT. 32471715_O-GlcNAc transferase affects the signal transduction of beta1 adrenoceptor in adult rat cardiomyocytes by increasing the O-GlcNAcylation of beta1 adrenoceptor. 32663610_Glucosamine regulates hepatic lipid accumulation by sensing glucose levels or feeding states of normal and excess. 32994395_Mutual regulation between OGT and XIAP to control colon cancer cell growth and invasion. 33006972_The O-GlcNAc transferase OGT is a conserved and essential regulator of the cellular and organismal response to hypertonic stress. 33215629_Inhibition of mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling decreases levels of O-GlcNAc transferase and increases serotonin release in the human placenta. 33307156_Exosomal O-GlcNAc transferase from esophageal carcinoma stem cell promotes cancer immunosuppression through up-regulation of PD-1 in CD8(+) T cells. 33333092_Elucidating the protein substrate recognition of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) toward O-GlcNAcase (OGA) using a GlcNAc electrophilic probe. 33419956_Mammalian cell proliferation requires noncatalytic functions of O-GlcNAc transferase. 33801653_Feedback Regulation of O-GlcNAc Transferase through Translation Control to Maintain Intracellular O-GlcNAc Homeostasis. 33909326_The crosstalk network of XIST/miR-424-5p/OGT mediates RAF1 glycosylation and participates in the progression of liver cancer. 34046694_Dual regulation of fatty acid synthase (FASN) expression by O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and mTOR pathway in proliferating liver cancer cells. 34288245_Upregulation of OGT by Caveolin-1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion. 34502531_OGT Protein Interaction Network (OGT-PIN): A Curated Database of Experimentally Identified Interaction Proteins of OGT. 34510715_P53 suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-15a by decreasing OGT expression and EZH2 stabilization. 34608265_CEMIP, a novel adaptor protein of OGT, promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through glutamine metabolic reprogramming via reciprocal regulation of beta-catenin. 34638625_Regulation of O-Linked N-Acetyl Glucosamine Transferase (OGT) through E6 Stimulation of the Ubiquitin Ligase Activity of E6AP. 34943826_Inhibition of O-GlcNAc Transferase Alters the Differentiation and Maturation Process of Human Monocyte Derived Dendritic Cells. 34948036_TET3- and OGT-Dependent Expression of Genes Involved in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Endometrial Cancer. 35190642_O-GlcNAc transferase regulates glioblastoma acetate metabolism via regulation of CDK5-dependent ACSS2 phosphorylation. 35868563_O-GlcNAc transferase regulates p21 protein levels and cell proliferation through the FoxM1-Skp2 axis in a p53-independent manner. 35931120_EGF promotes PKM2 O-GlcNAcylation by stimulating O-GlcNAc transferase phosphorylation at Y976 and their subsequent association. |
ENSMUSG00000034160 |
Ogt |
2647.471322 |
0.2664565525 |
-1.908028 |
0.085885040 |
467.874891 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009294160228387308396075650197134827802686723365729138353673203404144324914543318486359271783844982726992493091615283933073753675246311242160650681603686139578674516525738500808966437307616544977577474555429148272634080865018958 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004157024393060505358588638527477762838868619859958398283066613406345394560144017579706280237543624234072731069941651153153306730672987127278240240765864052727609615082055333800176715047613237487854078892867311420847050431795985 |
Yes |
Yes |
1156.0899340 |
93.3419175 |
4369.0253188 |
254.0981570 |
| ENSG00000147202 |
1730 |
DIAPH2 |
protein_coding |
O60879 |
FUNCTION: Could be involved in oogenesis. Involved in the regulation of endosome dynamics. Implicated in a novel signal transduction pathway, in which isoform 3 and CSK are sequentially activated by RHOD to regulate the motility of early endosomes through interactions with the actin cytoskeleton. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12577064}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Endosome;Oogenesis;Premature ovarian failure;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the diaphanous subfamily of the formin homology family of proteins. This gene may play a role in the development and normal function of the ovaries. Defects in this gene have been linked to premature ovarian failure 2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1730; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; female gamete generation [GO:0007292]; oogenesis [GO:0048477] |
18044991_Dia2 plays an important role in formation of lamellipodia. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21386871_Our results indicated that DIAPH2 may be a polygenic pleiotropy for premature ovarian failure (POF) and AMD. 22685410_Long HIV filopodial formation in infected dendritic cells was dependent on the formin diaphanous 2 (Diaph2) 23024796_Dia2 and DIP co-tether to nascent blebs and this linkage is required for bleb formation. 23620398_In podocytes, INF2 appears to be an important modulator of actin-dependent behaviors that are under the control of Rho/mDia signaling. 24037343_DIAPH2 has been associated with premature ovarian insufficiency, an aging phenotype in humans. 24403606_Dia1, Dia2, and Dia3 are involved in ErbB2-dependent capture of microtubules at the cell leading edge and ErbB2-driven guided migration. 28760985_Data show that diaphanous related formin 1 protein (Dia1) and diaphanous related formin 2 protein (Dia2) facilitated HIV-1-induced microtubule (MT) stabilization and the intracellular motility of virus particles. 29596520_Low DIA2 expression is associated with breast cancer. 30593440_DIAPH2 gene expression was an independent prognostic factors of clinical pregnancy rate and live birth in ICSI pregnancies. 30793164_Low DIAPH2 expression is associated with metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 34299935_DIAPH2, PTPRD and HIC1 Gene Polymorphisms and Laryngeal Cancer Risk. |
ENSMUSG00000034480 |
Diaph2 |
259.731706 |
2.2383499114 |
1.162436 |
0.234469005 |
23.993677 |
0.00000096652578316020655653149039332472369778770371340215206146240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003422725662054858073211167576732627537694497732445597648620605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
364.4979144 |
56.6341428 |
164.3341184 |
18.7066439 |
| ENSG00000147231 |
55086 |
RADX |
protein_coding |
Q6NSI4 |
FUNCTION: Single-stranded DNA-binding protein recruited to replication forks to maintain genome stability (PubMed:28735897). Prevents fork collapse by antagonizing the accumulation of RAD51 at forks to ensure the proper balance of fork remodeling and protection without interfering with the capacity of cells to complete homologous recombination of double-strand breaks (PubMed:28735897). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28735897}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosome;DNA-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Enables single-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination. Located in nuclear speck and replication fork. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55086; |
nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:2000042]; regulation of DNA repair [GO:0006282] |
28735897_By antagonizing RAD51 at forks, RADX allows cells to maintain a high capacity for homology-directed repair while ensuring that replication functions of RAD51 are properly regulated. Thus, RADX is essential to achieve the proper balance of RAD51 activity to maintain genome stability. 29021206_RADX interacts with single-stranded DNA to promote replication fork stability. 30021152_RADX buffers RAD51 to ensure the right amount of reversal and protection to maintain genome stability. 33453169_RADX controls RAD51 filament dynamics to regulate replication fork stability. 35120927_Oligomerization of DNA replication regulatory protein RADX is essential to maintain replication fork stability. |
ENSMUSG00000042498 |
Radx |
42.177650 |
6.6032601833 |
2.723178 |
0.392911112 |
47.510641 |
0.00000000000547061849832750129594852172506401651302238020591062195308040827512741088867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000030925441989779365124468557196667044262294865575313451699912548065185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
77.8560190 |
20.0307929 |
11.6437115 |
2.5222596 |
| ENSG00000147257 |
2719 |
GPC3 |
protein_coding |
P51654 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate (PubMed:14610063). Negatively regulates the hedgehog signaling pathway when attached via the GPI-anchor to the cell surface by competing with the hedgehog receptor PTC1 for binding to hedgehog proteins (By similarity). Binding to the hedgehog protein SHH triggers internalization of the complex by endocytosis and its subsequent lysosomal degradation (By similarity). Positively regulates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway by binding to the Wnt receptor Frizzled and stimulating the binding of the Frizzled receptor to Wnt ligands (PubMed:16227623, PubMed:24496449). Positively regulates the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway (By similarity). Binds to CD81 which decreases the availability of free CD81 for binding to the transcriptional repressor HHEX, resulting in nuclear translocation of HHEX and transcriptional repression (By similarity). Inhibits the dipeptidyl peptidase activity of DPP4 (PubMed:17549790). Plays a role in limb patterning and skeletal development by controlling the cellular response to BMP4 (By similarity). Modulates the effects of growth factors BMP2, BMP7 and FGF7 on renal branching morphogenesis (By similarity). Required for coronary vascular development (By similarity). Plays a role in regulating cell movements during gastrulation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6V9Y8, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CFZ4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14610063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16227623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17549790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24496449}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Heparan sulfate;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Proteoglycan;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to and inhibit the dipeptidyl peptidase activity of CD26, and it can induce apoptosis in certain cell types. Deletion mutations in this gene are associated with Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome, also known as Simpson dysmorphia syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:2719; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; peptidyl-dipeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0060422]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; body morphogenesis [GO:0010171]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell migration involved in gastrulation [GO:0042074]; cell proliferation involved in kidney development [GO:0072111]; cell proliferation involved in metanephros development [GO:0072203]; coronary vasculature development [GO:0060976]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; lung development [GO:0030324]; mesenchymal cell proliferation involved in ureteric bud development [GO:0072138]; mesonephric duct morphogenesis [GO:0072180]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of growth [GO:0045926]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:2000096]; regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060828]; regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000050]; regulation of protein localization to membrane [GO:1905475]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:0060071] |
11893651_Candidate lung tumor suppressor gene which may be regulated by tobacco exposure. 12085187_Mutations in GPC3 is associated with Wilm's tumor 12478660_GPC3 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and has a role in liver carcinogenesis 12816733_These findings suggest that GPC3 is a candidate lung tumor suppressor gene whose expression may be regulated by exposure to cigarette smoke and functions to modulate cellular response to exogenous damage. 12824919_Overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma, hence a good molecular marker. 14661052_involvement in the cellular protection against mitoxantrone in the atypical multidrug-resistant gastric carcinoma cell line EPG85-257RNOV 15083193_Although promoter methylation is likely to affect expression status of the GPC3 gene, study results suggest that deregulation of GPC3 transcriptional expression seen in neuroblastoma and Wilm's tumor involves other regulatory levels. 15475451_GPC3 is apparently a novel tumor marker useful for the diagnosis of melanoma, especially in early stages of the disorder. 16227623_glypican-3-induced stimulation of hepatocellular carcinoma growth does not require convertase processing 16299239_GPC3 and SPARC in combination diagnosed 47 of 75 (66.2%) melanoma patients at an early stage (0-II). 16675560_GPC3 peptides may be applicable to cancer immunotherapy for a large number of hepatocellular carcinoma patients 16682817_Data show that forced expression of glypican-3 (GPC3) reduced the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, and that FGF2-mediated cell proliferation was inhibited by GPC3. 17087938_Molecular data based on gene transcriptional profiles of a 3-gene set (GPC3, LYVE1, and survivin) allow a reliable diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma. 17549790_Both the glycosylated and unglycosylated forms of GPC3 interact with CD26 peptidase, resulting in inhibition of the enzyme. 17581422_Data show that GPC3 is observed in a significant fraction of primary and corresponding recurrent ovarian carcinomas. 17603795_No hot spot for GPC3 mutations or deletions in the patients with Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome. 17949778_GPC is detected by immunostaining in necroinflammatory lesions, therefore its use as a cancer stain should be interpreted cautiously. 17949790_GPC3 may play a role in the tumorigenesis of hepatoblastoma. 18264086_staining for glypican-3 is a highly sensitive and specific method capable of distinguishing HCC from other benign and malignant hepatic lesions 18277882_GPC3 seems to be a promising diagnostic marker for differentiating yolk sac tumors from ovarian clear cell carcinomas. 18413366_GPC3 confers oncogenecity through the interaction between IGF-II and its receptor, and the subsequent activation of the IGF-signaling pathway. 18462363_Glypican-3 appears to be a reliable markers for ovarian germ-cell tumors. 18469798_Glypican-3 expression is a potential candidate marker for early detection of lung squamous cell carcinoma. 18511877_GPC3 is expressed at an early stage, suggesting that GPC3 expression in thyroid cancer is an early event in developing papillary carcinoma. 18785116_Report expression pattern of glypican-3 (GPC3) during human embryonic and fetal development. 18813128_GPC3 is frequently expressed in noncutaneous small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of various origins, in particular in Merkel cell carcinoma, which, in combination with CK20 18813403_The effector cells stimulated with DCs that were transfected with pEF-hGPC3 plasmid could effectively lyse GPC3 expressing HepG2 cells. 18976006_GPC3 expression in HCCs did not correlate with the size, differentiation, or stage of the tumors; the presence or absence of cirrhotic background; or the underlying etiologies 19141032_Report the expression profile of glypican-3 and its relation to macrophage population in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 19215053_A patient with the Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome displays a loss-of-function point mutation in GPC3 that inhibits the attachment of this proteoglycan to the cell surface. 19231003_A reliable marker for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in liver biopsies. 19329941_overexpression of glypican-3 may be related to the development and aggressive behavior of ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma. 19405109_Our data supports the potentially significant diagnostic utility of GPC-3 in fine-needle aspiration biopsies in differentiating primary malignant from benign and preneoplastic liver lesions, and metastatic carcinomas. 19496787_GPC3 expression is correlated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19513517_Detection of glypican-3-specific CTLs in chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. 19574883_SALL4 is a more sensitive marker than PLAP, AFP, or glypican-3 for extragonadal yolk sac tumors. 19793164_Serum GPC3 is highly specific for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The combined use of serum GPC3 and alpha-fetoprotein may better differentiate HCC from benign liver disorders, as well as from other liver cancers. 19816934_Data show that mutated GPC3 lacking the GPI anchoring domain (sGPC3) significantly inhibited the in vivo growth, blocked Wnt signaling and Erk1/2 and Akt phosphorylation in tumors. 19838081_glypican-3 is involved in the recruitment of M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma 20546340_YST can display a variety of growth patterns that can be confused with other germ cell tumour components. GPC3 detects all growth patterns tested and has a higher sensitivity for detecting YST 20653060_GPC3, in conjunction with MMPs and growth signaling molecules, might play an important role in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. 20701957_Data demonstrate for the first time the presence of elevated levels of GPC3 protein associated with cell growth inhibition in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. 20725905_Mechanism mediating the oncogenic function of SULF2 in human hepatoma that includes GPC3-mediated activation of Wnt signaling. 20803547_GPC3 plays a role in glucose transport by interacting with GLUT1. 20845507_Data show that glypican 3 is a sensitive and specific serum marker for diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma. 20868507_GPC3 may be a useful adjunct immunohistochemical marker in differentiating placental site trophoblastic tumor from non-trophoblastic tumors. 20950395_loss of the functional GPC3 protein by 43% is closed to the threshold to develop the Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome phenotype 20964802_Circumferential membranous GPC3 immunoreactivity in hepatocellular carcionoma indicates poorer prognosis particularly in patients with hepatitis c virus infection. 21187490_Expression of GPC3 was found to be markedly elevated in HCCs. In the human HCC cell lines, GPC3 expression was consistently observed, and was mainly located in the cell membrane and cytoplasm. 21303616_Study confirm the differential GPC3 expression in two human HCC cells, Hep G2 (high) and HLF (negligible). 21371925_The results confirm the high expression of GPC3 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suggest its potential diagnostic value as a clinical marker for this disease. 21410073_overview of Gpc-3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and its expression of relationship between clinicopathological features of hepatocellular carcinoma, analysis expression of Gpc-3 in liver cell adenoma, heterosexual hyperplasia and hepatitis C 21429352_GPC3 is highly expressed in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, moderately expressed in well-differentiated HCC, and not expressed at all in dysplastic or cirrhotic nodules, focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma. 21438004_The sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis can be improved by combined detection of AFP and GPC3 mRNA expressions. 21493758_This study highlights expression of glypican-3 in rhabdomyosarcomas but not other soft tissue sarcomas. 21556932_High GPC3 mRNA expression is associated with lung squamous cell carcinoma. 21586223_GPC-3 was highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, moderately expressed in surrounding tissues and not expressed in distal tissues. 21617840_Results suggest that GPC3 contributes to the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma and that it may be a potential molecular target for HCC treatment. 21655958_GPC3 might be a valuable marker closely related with prognosis and post-operative metastasis/recurrence in hepatocellular cancer patients. 21822558_In a cohort analysis of disease-free survival, aberrant tumor expression of osteopontin and GPC3 were prognostic factors for recurrence and poor outcome. 21847365_molecular targeting of GPC3 at the translational level offers an effective option for the clinical management of GPC3-positive HCC patients. 21919070_Results show there was no correlation between GPC3 levels and prognostic parameters in hepatocellular carcinoma. GPC3 is not a useful diagnostic and prognostic marker for HCC. 21937079_Our data demonstrate that GPC3 is expressed in a subset of undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma and mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver. 22026458_GPC3 is a helpful ancillary diagnostic marker for pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasm 22119409_results show that GPC3 is specifically overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and may be regarded as a potential marker for differential diagnostic hepatocellular carcinoma 22298472_Loss of glypican 3 is associated with metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 22382024_The results suggest that GPC3 regulates cell proliferation by enhancing the resistance to apoptosis through the dysfunction of the Bax/Bcl-2/cytochrome c/caspase-3 signaling pathway and therefore plays a critical role in the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 22448662_glypican 3 is strongly positive in yolk sac tumors but is not as specific a tumor marker as SALL4 for that tumor type. 22449976_These findings indicate that miR-219-5p exerts tumor-suppressive effects in hepatic carcinogenesis through negative regulation of glypican 3 expression [MiR-219-5p]. 22706665_Elevated levels of c-Myc correlate with the overexpression of GPC3 in human Hepatocellular Carcinoma samples. 22865282_In a subgroup of hepatocellular carcinoma, the up-regulation of glypican-3 was associated with a concomitant down-regulation of its repressor miR-1271. 23060277_study reveals that GPC3 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by increasing cell proliferation, enhancing metastasis as well as invasion; GPC3 may collaborate with YAP to regulate the HCC development 23079207_Glypican-3 can be expressed in 14% of carcinomas/neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. 23084579_Evaluation of GPC3 immunoexpression may be a useful diagnostic tool to distinguish epithelioid sarcomas from malignant rhabdoid tumors. 23114924_results suggest that expression and activation of mitogenic receptors MET and EGFR, combined with potential mitoinhibitory effects of FAS and GPC3, create stimuli in which cell proliferation is limited and transdifferentiation process is enhanced. 23192642_High glypican-3 expression is associated with hepatoma. 23327927_We present a novel role for TFPI and GPC3 in regulating hematopoietic stem cell homing as well as retention in the bone marrow. 23348905_Glypican 3 and arginase-1 are the most reliable markers for identifying scirrhous hepatocellular carcinoma. 23471984_Therapeutically targeting glypican-3 via a conformation-specific single-domain antibody in hepatocellular carcinoma. 23526389_Data suggest that the use of monoclonal antibody (7D11 mAb) might be good for Glypican-3 (GPC3) large-scale applications for clinical diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 23530909_GPC3 positivity was limited to a small subset of central nervous system neoplasms and may thus serve as a useful positive diagnostic biomarker 23558072_GPC-3 protein/mRNA overexpression and alpha-fetoprotein levels could be used as markers for the diagnosis of HCC and monitoring its metastasis. 23598528_miR-1291 is a biologically relevant regulator of GPC3 expression in hepatoma cells and acts through silencing of the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1alpha. 23606591_In order to better delineate the phenotypic spectrum of SGBS caused by GPC3 mutations, and to try to define specific clinical criteria for GPC3 molecular testing, we reviewed the clinical features of all male cases with a GPC3 mutation 23624389_We now report that human primary suture mesenchymal cells coexpress GPC1 and GPC3 on the cell surface and release them into the media 23643963_average level of sGPC3 in HCC patients was 99.94+/-267.2ng/ml, which was significantly higher than in patients with chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, non-HCC cancer and healthy controls 23743582_GPC3 is comparable to AFP as a serum marker for the diagnosis of HCC, combination of AFP and GPC3 can elevate the sensitivity of diagnosis 24115482_The unique disease-causing mutation likely arose de novo in the mother. It is a deletion-insertion that leads to a frameshift at the p.S349 residue of GPC3 and a premature stop codon after five more amino acids 24186850_The usefulness of serum Transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1), Glypican-3 (GPC3), and Golgi protein-73 (GP73) mRNAs as early biomarkers in HCC Egyptian patients, was investigated. 24207089_Immunocytochemical staining for GPC3 in cell block material is a highly sensitive and specific method capable of distinguishing HCC from the vast majority of metastatic carcinomas of the liver. 24225756_GPC3 expression is frequent in squamous cell carcinomas and invasive urothelial carcinomas 24236824_It is a tumor marker for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 24362268_GPC-3 has moderate diagnostic accuracy for HCC. 24439425_We show that GPC3, an hepatocellular carcinoma biomarker and Hh mediator, regulates human stellate cell viability by regulating Hh signaling. 24459012_Both the GPC3 and the CTNNB1 mutations contributed to tumorigenesis. 24460300_High Serum glypican-3 level is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 24492943_Glypican-3 (GPC3) is an HSPG that is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, where it can attract Wnt proteins to the cell surface and promote cell proliferation. 24496449_Data demonstrate that GPC3 plays a more direct role in the stimulation of Wnt signaling. 24498024_Data suggest that glypican-3 (GPC3)-positive dysplastic nodules (DN) was really a late premalignant lesion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 24521523_in the current study we evaluated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic (PK) characteristics of GC33 ( a humanized mAb against human glypican-3)in Japanese patients. 24548704_GPC3 overexpression indicates a poor prognosis for patients with HCC, and it may also have predictive potential for HCC invasion and metastasis. 24747240_high expression was found for GPC-3 membrane protein in hepatocellular carcinoma 24804215_Extracellular matrix proteins expression profiling in chemoresistant variants of the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line. 24841158_Glypican-3 is the only oncofetal antigen that showed comparable high diagnostic accuracy as PIVKA-II in diagnosing HCC among Egyptian patients. 24876756_GPC3 overexpression tends to be associated with a poor prognosis (poor OS or DFS) in hepatocellular carcinoma [meta-analysis] 25073799_study presents the first case of mosaicism for a GPC3 mutation in a male member of a previously reported Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome family carrying an intragenic deletion in the GPC3 gene 25115442_This study identified heparan sulfate, partly through glypican-3, as a novel binding partner of GEP on the surface of liver cancer cells. 25168166_Data shows that GPC3 gene expression is downregulated in primary clear cell renal cell carcinoma; its overexpression arrest cells in G1 phase suggesting its role as tumor suppressor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 25195714_Data indicate that zinc-fingers and homeoboxes 2 (ZHX2) suppresses glypican 3 (GPC3) transcription by binding with its core promoter. 25270552_GPC3 is associated with the HCC cell biological behavior. 25344940_Most cases of hepatoblastoma and yolk sac tumor, and some cases of other tumors were found to express GPC3. On the other hand, GPC3 was physiologically expressed during the fetal and neoinfantile period under 1 year of age. 25366870_the elevated GPC3 expression in the majority of primary and metastatic Wilms tumors, but not in other renal neoplasms, indicates a possible role of GPC3 in Wilms tumor development 25432695_GPC3 expression is an independent prognostic factor for postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma 25542894_This study demonstrated that highly expression of GPC3 could enrich hepatocellular carcinoma -related genes' mRNA expression and positive associate with dysplasia in cirrhotic livers. 25572615_GPC3 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through impacting epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells, and the effects of GPC3 are associated with ERK activation. 25619476_GPC3 and E-cadherin expressions are not independent prognostic factors in CRC. 25653284_propose that the structural changes generated by the lack of cleavage determine a change in the sulfation of the HS chains and that these hypersulfated chains mediate the interaction of the mutant GPC3 with Ptc 25735325_High expression of glypican-3 is associated hepatoblastoma. 25784484_In HCC patients, sGPC3N levels were significantly increased (mean/median, 405.16/236.19 pg mL(-1) ) compared to healthy controls (p |
ENSMUSG00000055653 |
Gpc3 |
83.954467 |
0.4112050854 |
-1.282070 |
0.177642226 |
52.761517 |
0.00000000000037660843510903252541075239513608162255199965362528757850668625906109809875488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002308447052412508442658461679307014429753108775145165054709650576114654541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.0590663 |
6.1267569 |
127.5900542 |
9.9406699 |
| ENSG00000147383 |
50814 |
NSDHL |
protein_coding |
Q15738 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the NAD(P)(+)-dependent oxidative decarboxylation of the C4 methyl groups of 4-alpha-carboxysterols in post-squalene cholesterol biosynthesis (By similarity). Also plays a role in the regulation of the endocytic trafficking of EGFR (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R1J0}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Ichthyosis;Intellectual disability;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; zymosterol biosynthesis; zymosterol from lanosterol: step 4/6. |
The protein encoded by this gene is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in cholesterol biosynthesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with CHILD syndrome, which is a X-linked dominant disorder of lipid metabolism with disturbed cholesterol biosynthesis, and typically lethal in males. Alternatively spliced transcript variants with differing 5' UTR have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:50814; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; 3-beta-hydroxy-delta5-steroid dehydrogenase activity [GO:0003854]; 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/C4-decarboxylase activity [GO:0102175]; 4alpha-carboxy-4beta-methyl-5alpha-cholesta-8-en-3beta-ol:NAD(P)+ 3-oxidoreductase (decarboxylating) activity [GO:0103066]; 4alpha-carboxy-5alpha-cholesta-8-en-3beta-ol:NAD(P)+ 3-dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) activity [GO:0103067]; C-3 sterol dehydrogenase (C-4 sterol decarboxylase) activity [GO:0000252]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016616]; sterol-4-alpha-carboxylate 3-dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) activity [GO:0047012]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; labyrinthine layer blood vessel development [GO:0060716]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
12837764_NAD(P)H steroid dehydrogenase-like protein is localized to lipid droplets 14506130_NSDHL, an enzyme involved in cholesterol synthesis, traffics through the Golgi and accumulates on ER membranes and on the surface of lipid droplets. 15805545_microarray analysis of gene expression related to NSDHL sterol dehydrogenase in embryonic fibroblasts 16230564_A novel missense mutation (R199H) in exon 6 of the NSDHL gene was identified in a small subset of sporadic verruciform xanthomas. 17498944_NAD(P) dependent steroid dehydrogenase-like (NSDHL)-shRNA sequences were designed and tested for their effectiveness. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19880419_Lethality of Nsdhl deficient mouse embryos is rescued by transgenic mice expressing human Nsdhl. 19906044_The missense mutation of the NSDHL gene is detected in CHILD syndrome. 20403997_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21129721_found that males with intellectual disability in another reported family with an NSDHL mutation (c.1098 dup [p.Arg367SerfsX33]) have CKS 22113624_human NSDHL protein and mouse Nsdhl mRNA were expressed in tissues synthesizing cholesterol and steroids and in all peripheral tissues affected by CHILD or CK syndromes. 25900314_A novel missense mutation in the NSDHL gene identified in a Lithuanian family by targeted next-generation sequencing causes CK syndrome. 26014843_Our findings expand the spectrum of mutations in NSDHL in CHILD syndrome, and indicate that large exon deletions may be not rare. 26459993_Here we present the case of a 9-year-old Chinese girl born with the typical clinical features of CHILD syndrome. Evaluation of the skin lesions confirmed the diagnosis and led to identification of a heterozygous point mutation in exon 8 of the NSDHL gene. 30376821_NSDHL-containing duplication at chromosome Xq28 inherited from his mother in a male patient with autism spectrum disorder has been reported. 31078502_NSDHL gene mutations associated with CHILD syndrome are common in sporadic oral verruciform xanthoma cases, suggesting that these mutations confer a greater risk for the development of epithelial barrier defects 32140747_Crystal structures of human NSDHL and development of its novel inhibitor with the potential to suppress EGFR activity. 32366230_NAD(P)-dependent steroid dehydrogenase-like is involved in breast cancer cell growth and metastasis. 33169834_CHILD syndrome in a Malaysian adult with identification of a novel heterozygous missense mutation NSDHL c.602A>G. 33219617_NAD(P)-dependent steroid dehydrogenase-like protein and neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 serve as novel markers for early detection of gastric cancer identified using quantitative proteomics. 33864166_NSDHL promotes triple-negative breast cancer metastasis through the TGFbeta signaling pathway and cholesterol biosynthesis. |
ENSMUSG00000031349 |
Nsdhl |
130.684700 |
2.7021005946 |
1.434081 |
0.152216533 |
89.894304 |
0.00000000000000000000251229234474988383105119054626783392632139194629498778101994033162824848659511189907789230346679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000023424785223315401402493927090926420314441038445549344724962853581118338297528680413961410522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
191.5501773 |
20.1327221 |
71.2744671 |
5.8651416 |
| ENSG00000147437 |
2796 |
GNRH1 |
protein_coding |
P01148 |
FUNCTION: Stimulates the secretion of gonadotropins; it stimulates the secretion of both luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones. |
3D-structure;Amidation;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Hormone;Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism;Kallmann syndrome;Pharmaceutical;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate a peptide that is a member of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) family of peptides. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which is secreted and then cleaved to generate gonadoliberin-1 and GnRH-associated peptide 1. Gonadoliberin-1 stimulates the release of luteinizing and follicle stimulating hormones, which are important for reproduction. Mutations in this gene are associated with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:2796; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; gonadotropin hormone-releasing hormone activity [GO:0005183]; gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor binding [GO:0031530]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; negative regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001223]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of ovarian follicle development [GO:2000354]; reproduction [GO:0000003]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11875100_data indicate that the promoter region between -992 and -795 contains elements both essential and sufficient for targeting gene expression to GnRH neurons 12040003_Coupling of GnRH concentration and the GnRH receptor-activated gene program 12054733_JunD activated by LHRH acts as a modulator of cell proliferation and cooperates with the anti-apoptotic and anti-mitogenic functions of LHRH. 12447356_GnRH-II and GnRH-I interact directly with T cells and trigger gene transcription, adhesion, chemotaxis and homing to specific organs, which may be of clinical relevance. 12633791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12770744_regulation of GnRH-I and GnRH-II gene expression in the ovary 12788881_Genetic analysis has excluded sequence variations in GNRH1 and GNRHR in four families with recessive IHH, suggesting the existence of a novel, as-yet-undiscovered gene for this condition. 12969578_gonadotropin releasing hormone-II is more effective than gonadotropin releasing hormone-I in stimulating leptin secretion 14565958_Neurons respond to GnRH with time- and dose-dependent increases in GnRH gene expression and protein release. 14594454_Review. The proliferation of human ovarian cancer cell lines is time- and dose-dependently reduced by GnRH and its superagonistic analogs. 14726258_Experimental evidence indicates that GnRH-I is expressed, together with its receptors, in tumors of the reproductive tract. Activation of type I GnRH receptors consistently decreases cell proliferation, mainly by interfering with growth factors. 15001648_GnRH I and GnRH II have both common and discrete cellular distributions in the placenta and decidua and suggest that these two hormones are capable of eliciting their biological actions in an autocrine and/or paracrine manner 15062568_In placental cytotrophoblasts, the upstream transcription start site of GnRH gene was the major one and gave rise to an mRNA level three times higher than the downstream start site. Estradiol downregulated GnRH gene expression in a dose-dependent fashion. 15138251_expression of the GnRH gene is regulated in neurons by TALE homeodomain proteins and Oct-1 15229199_It is suggested that during the early to midfollicular phase the ovaries produce a gonadotrophin surge attenuating factor that antagonizes the pituitary-sensitizing effect of E2 to GnRH. (Gonadotrophin surge attenuating factor) 15283968_These galanin-LHRH and LHRH-galanin contacts may be functional synapses, and they may be the morphological substrate of the galanin-controlled gonadal functions in humans. 15490304_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15546906_Genetic variation in GNRH1 is not likely to be a substantial modulator of pubertal timing in the general population. 15546906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15562029_Progesterone receptor isoform p4 is a potent regulator of GnRHRI at the transcriptional level as well as GnRH I mRNA. 15578334_GnRH-I induced greater proliferation in normal B-cells than IL-2 treatment alone. 15809743_GnRH may protect ovarian cancer cells from stimulated apoptotic cell death. 16061872_LHRH receptors are expressed in human RCC specimens 16157590_analysis of gonadotropin-releasing hormone ligand conformation and receptor selectivity 16359986_GnRH1 gene is not responsible for idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, at least as mutations are concerned 17202595_we observed that LHRH-(1-5), the specific processed peptide of LHRH-I, upregulates LHRH-II mRNA expression in Ishikawa cells, an endometrial cell line but does not exert any influence on LHRH-I mRNA levels 17220347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17456575_estrogens may exert direct actions upon GnRH neurons exclusively through ER-beta 17605472_Our data indicate a bridging interaction between Arg500 of the N-domain and Arg8 of GnRH that involves a chloride ion may account for its role in the specificity of the N-domain for endoproteolytic cleavage of the substrate at the NH2-terminus in vitro 17680884_Data show that GnRH neurones morphologically interact with astrocytes and tanycytes in the human brain and suggest that glial cells may contribute to the process by which the neuroendocrine brain controls the function of GnRH neurones in humans. 17692113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18463157_12% of Kallman syndrome males have KAL1 deletions, but intragenic deletions of the FGFR1, GNRH1, GNRHR, GPR54 and NELF genes are uncommon in Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism/Kallman syndrome. 18467526_analysis of how GNRH I and GNRH II inhibit cell growth 18477660_GnRH-I and -II induce apoptosis in human granulosa cells through GnRH-I receptors, which mediate the proteolytic caspase cascade involving caspase-8 (the initiator) and caspase-3 and -7 (the effectors). 18959738_REVIEW: role of GnRH in the control of tumor growth, progression, and dissemination 18959739_summarize the current understanding of the antiproliferative actions of GnRH analogs, as well as the recent observations of GnRH effects on ovarian cancer cell apoptosis and motogenesis,and the molecular mechanisms that mediate GnRH actions 18980792_Data show that over half of meningiomas may be regulated by GnRH-GnRH-R expression in an autocrine fashion. 19064572_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19190109_the antitumor effect of gonadotropin-releasing hormone type i is mediated by the activation of type I (but not of type II) GnRH-R 19403562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19489874_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19535795_identified a homozygous GNRH1 frameshift mutation in the sequence encoding the N-terminal region of the signal peptide-containing prepro-GnRH in a teenage brother & sister who had normosmic idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 19567835_GNRH1 mutations are a genetic cause of idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. 19640273_Common variants of the GNRH1 and GNRHR genes are not associated with risk of invasive breast cancer in Caucasians 19640273_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19849976_GNRH1 is mutated in people with familial hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. 20118984_cadherin switching and p120(ctn) signaling as important targets of GnRH function and as novel mediators of invasiveness and tumor progression in ovarian cancer. 20138117_Metabolic signals are integrated at the levels of first-order neurons equipped with the proper receptors, ant that these neurons send their signals towards hypothalamic GnRH neurons which constitute the integrative element of this network. 20188792_The major genes associated with GnRH-dependent pubertal disorders, are reviewed. 20389089_GNRH1 mutations might cause congenital idiopathic (or isolated) hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (Review) 20400076_The role of GnRH-GnRHR signaling at the maternal-fetal interface therefore appears to be limited to the regulation of trophoblast hCG production. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484732_Review: Using human GnRH deficiency as a paradigm and presenting original data from the screening of numerous candidate genes, we discuss the emerging model of patient-focused clinical genetic research. 20529119_Data describe the distribution and sex dimorphism of kisspeptin-immunoreactive elements in hypothalami, reveal contacts between kisspeptin-immunoreactive fibers and GnRH cells, and colocalize kisspeptins and neurokinin B in the infundibular nucleus. 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20727862_Lactation is an important physiological model of the integration of energy balance and reproduction, as it involves activation of potent appetitive neuropeptide systems coupled to a profound inhibition of pulsatile GnRH/LH secretion--REVIEW 20727865_A large literature dealing with various stressors that regulate gonadotrophin-releasing hormone secretion in a variety of species provides evidence that stress modulates GnRH secretion by activating the corticotrophin-releasing factor system--REVIEW 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20807514_The sources of glutamatergic inputs to the GnRH neurons are only just beginning to be examined and include the anteroventral periventricular nucleus as well as the possibility that GnRH neurons--REVIEW 20887715_homozygous inactivating mutations in the GNRH1 gene causing hypothalamic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in patients were reported, validating definitively the pivotal role of GnRH in human pubertal development and reproduction--REVIEW 20951683_We then discuss possible neurobiological mechanisms underlying GnRH pulse generation, and conclude by proposing that kisspeptin neurons in the arcuate nucleus are key players--REVIEW 21368045_Deletion of the cell-specific enhancer region of GnRH implicates the GnRH promoter in mediating pubertal development and periodic reproductive cycling. 21646369_Sleep is associated with a significant decline in GnRH pulse frequency in both older and younger postmenopausal women 21714833_Data show that higher levels of GnRH IgM antibodies were detected in patients with IBS and dysmotility, but not organic GI diseases, compared with healthy controls. 21722705_Mutations in GNRH1 have been associated with both mild and severe forms of GnRH deficiency, and may work in combination with other gene mutations to produce GnRH-deficient phenotypes. 21827674_Assessment of CGB and GNRH1 expression level in cancer patients' blood may be useful for indicating metastatic spread of tumor cells. 21855365_[review] Existing evidence suggests that neural pathways originating in hindbrain and hypothalamic feeding nuclei transmit information concerning glucose availability to GnRH neurons, which integrate numerous physiological signals and metabolic cues. 22024993_molecular mechanisms involved in GnRH/GnRHR signaling at the maternal-fetal interface. [Review] 22074952_data demonstrate that GnRH transcription is repressed by AR via multiple sequences in GnRH-P, including three Oct-1 binding sites, and that this repression requires the complex interaction of several transcription factors 22161498_The role of several class 1 cytokines in regulating GnRH neuronal development, GnRH secretion, and GnRH expression in this REVIEW. 23077052_Spontaneous GnRH release is detected in the median eminence of transgenic mice that produce diurnal variations in GnRH. 23287110_GnRHI, GnRHII and GnRH receptor expression correlated significantly with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients 23404564_Olfactory ensheathing cells form a microenvironment for migrating GnRH-1 neurons during development. 23550003_Kisspeptin resets the GnRH pulse generator in men, but does not appear to do so in women 23550012_Kisspeptin and GnRH pulse generation. 23648337_AXL and MET crosstalk to promote gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) neuronal cell migration and survival. 23735672_This review summarizes the mechanisms used by glial cells to control GnRH neuronal ativity and secretion. 23936060_R31C GNRH1 is the only missense mutation that was identified in a CpG islet in nine congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism subjects from four unrelated families, giving evidence for a putative ''hot spot''. 24002956_No abnormalities were found in the patient group for the PROKR2 and GNRH1genes. In addition, no genomic rearrangements were identified in the healthy control individuals for the described genes 24010162_TRH, LH-RH and substance P are not affected in Alzheimer disease and Down's syndrome 24056171_Current research efforts aim to discover the mechanisms responsible for the decoding of the GnRH pulse signal by the gonadotrope. 24095645_This review will summarize the current understanding of the mechanisms by which PACAP modulates gonadotrope function, with a focus on interactions with GnRH. 24264576_GPR101 is a critical requirement for GnRH-(1-5) transactivation of EGFR in Ishikawa cells. 24472523_GnRH, through heterotopic expression of its receptor, may be a potential regulator of CYP11B2 expression levels in some cases of aldosterone-producing adenoma. 24603682_Data indicate that the gene expression pattern is profoundly different between human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist. 24722580_GnRH agonists fail to increase Bax expression and do not potentiate the cytotoxic activity of docetaxel 25248098_Haploinsufficiency of Dmxl2, encoding a synaptic protein, causes infertility associated with a loss of GnRH neurons in humans and mice. 25916694_Melatonin affects the secretion of GnRH, LH and testosterone, improves sperm quality thereby regulating the testicular development and male reproduction. (Review) 25955300_our results showed that GnRH participates in the self-renewal capacity and stemness maintenance of LCSLCs by upregulating the JNK signaling pathway, and GnRH may be useful as an alternative lung cancer stem-like cells therapy. 26308290_Data suggest differences in regulation of expression of PEDF (up-regulation) vs. VEGF (down-regulation) in granulosa cells explain reduced risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome due to ovulation induction using GnRH/GNRHR agonists rather than hCG. 26595427_mutations in the region encoding the decapeptide associated with complete Idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 26644469_analysis of information transfer via gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptors to extracellular signal-regulated kinase or nuclear factor of activated T-cells 26660506_GnRH regulates trophoblast invasion via RUNX2-mediated MMP2/MMP9 expression. 26920257_GNRH (and GNRHR) are expressed in trophoblast cell populations and fallopian tube epithelium at tubal ectopic pregnancy sites. 27639272_High LHRH expression is associated with sarcomas of bone and soft tissue. 27793127_High expression of LHRH is associated with ovarian cancer. 28385888_Modeling and high-throughput experimental data uncover the mechanisms underlying Fshb gene sensitivity to gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse frequency 33652606_Expression of Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone (LHRH) and Type-I LHRH Receptor in Transitional Cell Carcinoma Type of Human Bladder Cancer. 33964320_The KiNG of reproduction: Kisspeptin/ nNOS interactions shaping hypothalamic GnRH release. 34104122_Investigation of Specific Targeting of Triptorelin-Conjugated Dextran-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles as a Targeted Probe in GnRH(+) Cancer Cells in MRI. 34923491_GNRH1 Variants in Congenital Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism: Single-Center Experience and Systematic Literature Review. |
ENSMUSG00000015812 |
Gnrh1 |
12.489070 |
0.4117906793 |
-1.280017 |
0.563177165 |
5.100839 |
0.02391427788744711346868854207059484906494617462158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.042146237805220226890767776239954400807619094848632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.2455154 |
2.4406667 |
17.5869525 |
3.9823712 |
| ENSG00000147465 |
6770 |
STAR |
protein_coding |
P49675 |
FUNCTION: Plays a key role in steroid hormone synthesis by enhancing the metabolism of cholesterol into pregnenolone. Mediates the transfer of cholesterol from the outer mitochondrial membrane to the inner mitochondrial membrane where it is cleaved to pregnenolone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7761400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7892608, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8948562}. |
3D-structure;Congenital adrenal hyperplasia;Disease variant;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroidogenesis;Transit peptide;Transport |
PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism; cholesterol metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:7761400}. |
The protein encoded by this gene plays a key role in the acute regulation of steroid hormone synthesis by enhancing the conversion of cholesterol into pregnenolone. This protein permits the cleavage of cholesterol into pregnenolone by mediating the transport of cholesterol from the outer mitochondrial membrane to the inner mitochondrial membrane. Mutations in this gene are a cause of congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia (CLAH), also called lipoid CAH. A pseudogene of this gene is located on chromosome 13. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6770; |
mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cholesterol transfer activity [GO:0120020]; cellular lipid metabolic process [GO:0044255]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; glucocorticoid metabolic process [GO:0008211]; intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032367]; positive regulation of bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0070859]; regulation of steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0050810]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694] |
12044915_StAR protein is an absolute requirement in the rate-limiting step in steroidogenesis, the transfer of cholesterol into the mitochondria [review] 12372832_StAR can transfer cholesterol between synthetic membranes without other protein components found in mitochondria 12530644_StAR requires structural alterations to allow cholesterol binding, most evidently by C-terminal alpha-helix above U-shaped beta-barrel. Unfolding of helix probable and leads to 2% subpopulation of partially unfolded StAR. 12727988_modulation of DAX-1 and steroidogenic factor-1 intracellular levels in granulosa cells suggests that these transcription factors could be involved in mitogen-activated protein kinase suppression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression 12834921_Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression in the normal human brain and intracranial tumors. 12843197_hCG-stimulated steroidogenic response in the mid- and late luteal phase is correlated with increased StAR mRNA and protein abundance 12909641_StAR binding protein binds StAR protein in cells and enhances the ability of StAR protein to promote syntheses of steroid hormones. 12933667_increased histone H3 acetylation involving the EP2 receptor, protein kinase A, CREB, and CREB binding protein is responsible for PGE(2)-induced StAR gene activation in endometriotic stromal cells. 14565954_angiotensin II-dependent activation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein transcription requires janus kinase 2 and calcium 14764819_This mutation gives rise to a truncated StAR protein, which lacks an important N-terminal region and the entire lipid transfer domain. 15181096_LRH-1 could be the major transcription factor responsible for the rapid and significant increase in ovarian StAR gene expression after ovulation. 15546900_Mutated in congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. 15666812_Jak2 is novel pathway in Ang II-dependent activation of StAR expression and steroidogenesis in adrenocortical cells and is requirement for ongoing protein synthesis in Ang II-mediated StAR transcription. 15777208_Studies summarized in this review describe the critical role of the StAR protein in the regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. 15985476_importance of StAR-dependent steroidogenesis during fetal development and early infancy. new, prevalent StAR mutation (L260P) for the Swiss population. 16162390_presence of mature StAR in the luteal cell cytoplasm is consonant with the notion that StAR acts on the outer mitochondrial membrane to effect sterol import, and that StAR may interact with other cytoplasmic proteins involved in cholesterol metabolism 16234239_StAR activity requires a pH-dependent molten globule transition on the OMM 16901925_Results describe a novel cytosine/thymidine polymorphism of the human steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) gene promoter located 3 bp downstream of the steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1)-binding site and 9 bp upstream of the TATA box (ATTTAAG). 16990645_three-dimensional atomic models of the StART domains of metastatic lymph node 64 (MLN64) and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) proteins in complex with cholesterol 17374711_PPAR-gamma, insulin receptor with its signaling pathways, and StAR protein constitute a novel human ovarian regulatory system with complex interactions among its components 17433772_StAR appears to act in concert with the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, but the precise itinerary of a cholesterol molecule entering the mitochondrion remains unclear. 17666473_In most Palestinian cases of congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia, a founder c.201_202delCT mutation in StAR is the cause 18000307_Cholesterol sulphate affects the production of steroid hormones by reducing StAR protein level in adrenocortical cells. 18084157_phenotypic variations of 46, XX girls with mutations in the gene for StAR; majority of StAR 46,XX females developed irregular menses and ovarian cysts [review] 18191841_No difference in StAR and P450scc protein levels in granulosa cells obtained from older low-responder in vitro fertilization patients with that of young good-responder patients. 18250166_phosphorylated StAR interacts with voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1) on the OMM, which then facilitates processing of the 37-kDa phospho-StAR to the 32-kDa intermediate. 18331352_provide evidence for differential cholesterol binding of the two most closely related START domain proteins STARD1 and STARD3 18341481_StAR can readily bind to cholesterol with an apparent affinity that commensurates with monomeric cholesterol solubility in water. The proper function of the C-terminal alpha-helix is essential for the binding process 18450961_Orexin effects on StAR gene expression were primarily, but not exclusively, acting through the orexin receptor type 1. 18490834_Cholesterol sulfate has an inhibitory effect on progesterone production by regulating the expression of StAR and P450scc gene expression. 18505908_Data show that StAR mRNA was found throughout the whole adrenal cortex attached to adrenocortical adenomas, but not in the medulla. 18583320_PGE(2)-induced StAR promoter activity appears to be regulated by CREB and C/EBPbeta in a cooperative manner in ectopic human endometriotic stromal cells, providing a molecular framework for the etiology of endometriosis. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18665078_Differential expression of steroidogenic factors 1 and 2, cytochrome p450scc, and steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in the pancreas. 18729825_The mechanism of specific binding of fere cholesterol by the STAR protein: evidence for a role of the C-terminal alpha-helix in the gating of the binding site. 18829024_Case Report: Conception and pregnancy outcome in a patient with 11-bp deletion of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene. 18945429_Overexpression of mitochondrial cholesterol delivery protein, StAR, decreases intracellular lipids and inflammatory factors secretion in macrophages. 19001523_Endometriotic cells contain the full complement of steroidogenic genes for de novo synthesis of estradiol from cholesterol, which is stimulated by PGE2 via enhanced binding of SF1 to promoters of StAR and aromatase genes in a synchronous fashion. 19022561_both SF1 and LRH1 can transcriptionally cooperate with the AP-1 family members c-JUN and c-FOS, known to be associated with enhanced proliferation of endometrial carcinoma cells, to further enhance activation of the STAR, HSD3B2, and CYP19A1 PII promoters 19095060_A structural in silico analysis of StAR, is presented. 19231010_StAR overexpression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease suggests that mitochondrial free cholesterol may be involved in disease progression. 19271249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19272380_Differential regulation of STARD1 and D3 reflects their distinct roles in macrophage cholesterol metabolism, and may inform anti-atherogenic strategies. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19744555_FOXL2 is sumoylated by Ubc9, and this Ubc9-mediated sumoylation is essential to the transcriptional activity of FOXL2 on the StAR promoter. 19849856_Leptin acts through the MAPK pathway to downregulate cAMP-induced StAR protein expression and progesterone production in immortalized human granulosa cells. 19899816_StAR picks up cholesterol from a source in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and not from cytoplasmic cholesterol; StAR is stabilized at the OMM by cholesterol on its way to the mitochondrial matrix. 19903795_No mutations in MC2R, MRAP or STAR were identified in any patient with Addison's disease 19903795_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19930843_Increased steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression is associated with endometriosis severity. 19946756_Overexpression of StAR decreased number of apoptotic macrophages by decreasing expression of pro-apoptotic genes Caspase-3 & Bax mRNA, & through increasing expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 mRNA levels in absence & presence of Ox-LDL. 20199803_No associations between StAR SNPs and endometrial cancer risk were observed. 20199803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20444910_study describes four patients with nonclassic or atypical congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia (lipoid CAH) identifes their StAR mutations and characterizes the activities of the mutants to explore genotype/phenotype correlations 20601698_novel SF-1 binding sites between 3,000 and 3,400 bp upstream of StAR 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20660033_GDF9 attenuates the suppressive effects of activin A on StAR expression and progesterone production by increasing the expression of inhibin B, which acts as an activin A competitor. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21145937_The role of protein tyrosine phosphatases in the regulation of steroid biosynthesis, relating them to steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, arachidonic acid metabolism and mitochondrial rearrangement, is described. 21147196_The considerable extra energy expenditure that is required for synthesis of the long mRNA is used to provide a refined control of StAR expression. 21164258_StAR, its expression pattern and the clinical consequences of the loss of its activity. 21217523_a biological marker for Leydig cells and sex-cord stromal tumors 21334384_The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of adiponectin on StAR protein expression, steroidogenic genes, and cortisol production and to dissect the signalling cascades involved in the activation of StAR expression. 21350237_report a novel transcriptional cooperation between GATA factors and cJUN on the mouse Star and human STAR promoters in MA-10 Leydig cells. This cooperation was observed with different GATA members, whereas only cJUN could cooperate with GATA factors 21647419_StAR mutations located in the cholesterol binding pocket (V187M, R188C, R192C, G221D/S) seem to cause non-classic lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia 21846663_The STAR mutation spectrum has been investigated and a novel STAR mutation functionally analyzed in Korean patients with congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia; p.Q258X is the most common STAR mutation in Korea. 22213075_Allelic losses of the loci containing StAR have significant prognostic value for intermediate-risk prostate cancer. 22253417_analysis of angiotensin II-dependent transcriptional activation of human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene by a 25-kDa cAMP-responsive element modulator protein isoform and Yin Yang 1 22634420_The status of ARO and StAR contribute to estrogen synthesis in situ, especially for the regulation of elastic fiber formation, and to testosterone synthesis, which may be associated with hair growth, respectively. 23029457_Mutant FOXL2 in granulosa cell tumors is able to differentially regulate the expression of many genes, including two well known FOXL2 targets, StAR and CYP19A. 23158025_deficiencies in the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and the cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme cause neonatal adrenal failure 23211570_biochemical, genetic, and long-term clinical data in 5 Greek patients from 4 families with mutations in STAR gene (46, XX and 46, XY disorders of sex development): All patients presented in early infancy with adrenal insufficiency. [CASE STUDIES] 23330251_Mutations in the CYP11A1 gene encoding cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme cause disordered pregnenolone synthesis, and STAR mutations do not necessarily results in typical congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. 23748066_Data suggest that mutation analysis of the STAR gene is essential for definitive diagnosis, genetic counseling, and prenatal diagnosis of Lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia (LCAH). 23825130_Expression of StAR and P45011beta (cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily B polypeptide 1) is down-regulated in adrenocortical cells and neurons under oxidative stress by ALADIN (triple A syndrome protein, human) knockdown. 23920000_The novel mutation p.Trp147Arg of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein causes classic lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia with adrenal insufficiency and 46,XY disorder of sex development. 24053410_Cholesterol-mediated conformational changes in StAR are essential for steroidogenesis. 24140593_BMP15 down-regulates StAR expression and decreases progesterone production in human granulosa cells, likely via ALK3-mediated SMAD1/5/8 signaling. 24422629_StAR proteolysis is executed by at least 2 mitochondrial proteases, the matrix LON protease and the inner membrane complexes of the metalloproteases AFG3L2 and AFG3L2:SPG7/paraplegin. 25001622_Hypoxia in pulmonary artery endothelial cells results in upregulation of STAR protein. 25002576_Mutagenesis confirmed that Arg(312) and Arg(313) are crucial for this mode of regulation, and novel interactions with the START domain 26001835_activins A, B and AB down-regulate StAR expression and decrease progesterone production in human granulosa cells, likely via an ALK4-mediated SMAD2/SMAD4-dependent pathway. 26014698_amino acid of mutant position of the novel p.E123K was highly conserved in ten different species and was predicted to have impacts on the structure and function of StAR protein by the PolyPhen-2 prediction software 26271515_Current level of understanding on tissue-specific and hormone-induced regulation of STAR expression and steroidogenesis, and insights into a number of cholesterol and/or steroid coupled physiological consequences.[review] 27386819_Reduced fractalkine levels were found in follicular fluid and granulosa cells, accompanied by decreased progesterone production and reduced steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) expression in the granulosa cells of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Administration of fractalkine reversed the inhibition of progesterone and StAR expression. 27606678_immunohistochemical staining for StAR is a reliable pathological approach for the diagnosis and classification of adrenocortical adenomas with cAMP/PKA signaling-activating mutations. 27614897_Immunostaining of CLOCK and PER2 protein was detected in the granulosa cells of dominant antral follicles but was absent in the primordial, primary, or preantral follicles of human ovaries.Oscillating expression of the circadian gene PER2 can be induced by testosterone in human granulosa cells in vitro. Expression of STAR also displayed an oscillating pattern after testosterone stimulation 27813675_target of the microRNA let-7, which itself is regulated by the long noncoding RNA H19 28153708_The present study revealed that StAR overexpression can reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, regulate glucose metabolism and attenuate insulin resistance through a mechanism involving the activation of FXR. 28232277_Data suggest that expression of STAR (steroidogenic acute regulatory protein) and AKR1B10 (aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10) is down-regulated in high-grade versus low-grade endometrial tumors; expression of AKR1B10 correlates with body mass index, with up-regulation of expression of AKR1B10 in obese patients with endometrial tumors. 28467518_This study aimed to investigate the phenotypic and mutation spectrum of STAR defects and identify a founder effect of the p.Q258* mutation in Korean patients with congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. 28576490_solution structure of human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein STARD1 studied by small-angle X-ray scattering 28974714_We further explored the dissociation of mRNA from STAR domain using umbrella sampling simulations, and the results suggest that mRNA binding to STAR domain occurs in multi-step: first conformational selection of mRNA backbone conformations, followed by induced fit mechanism as nucleobases interact with STAR domain 29408456_Remarkably, in terms of fluorescence response, 20NP slightly outperforms commonly used 22NC and can thus be used for screening of various potential ligands by a competition mechanism in the future. 30595381_The StAR protein is abundantly expressed in breast cancer but not in normal mammary epithelial cells. StAR is identified as a novel acetylated protein. 30922932_noncoding-RNA-mediated regulation of STAR may play an important role in the regulation of steroid hormone production. 31029706_Studies of mice with liver-specific deletion of Stard1 and mice with humanized livers found that upregulation of STARD1 following endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates acetaminophen hepatoxicity via SH3BP5 and phosphorylation of JNK1 and JNK2. 32068072_Lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid acute regulatory protein (STAR) variants in Three Chinese patients. 32633081_Molecular basis for the recognition of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by the 14-3-3 protein family. 32867102_Characterization of Two Novel Variants of the Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein Identified in a Girl with Classic Lipoid Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. 33227378_Clinical and molecular characterization of thirty Chinese patients with congenital lipoid adrenal hyperplasia. 33515644_STARD1 promotes NASH-driven HCC by sustaining the generation of bile acids through the alternative mitochondrial pathway. 33864885_Distinctive functioning of STARD1 in the fetal Leydig cells compared to adult Leydig and adrenal cells. Impact of Hedgehog signaling via the primary cilium. 35183204_Growth differentiation factor-11 downregulates steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression through ALK5-mediated SMAD3 signaling pathway in human granulosa-lutein cells. |
ENSMUSG00000031574 |
Star |
18.552555 |
0.0440099012 |
-4.506028 |
0.652867046 |
83.580269 |
0.00000000000000000006118067943777692223089939308496593383794168635906877604622999822225892785354517400264739990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000541382990708385729773058043277892725316865372537863693863657843508008227217942476272583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6955381 |
0.7780994 |
38.7381769 |
5.6244884 |
| ENSG00000147614 |
245972 |
ATP6V0D2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N8Y2 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of the V0 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons. V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment (By similarity). May play a role in coupling of proton transport and ATP hydrolysis (By similarity). Regulator of osteoclast fusion and bone formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P61421, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80SY3}. |
Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable proton transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in vacuolar acidification and vacuolar transport. Located in apical plasma membrane. Part of vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:245972; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0033181]; proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain [GO:0033179]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0016471]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; vacuolar acidification [GO:0007035]; vacuolar transport [GO:0007034] |
19818731_these data suggest that Adrm1, a new Atp6v0d2-interacting protein, plays an important role in osteoclast differentiation, and in particular the fusion of preosteoclasts. 24631925_The secondary structures of d1 and d2 subunits were highly similar, but the relative stability against thermal stress was higher for d1 than d2. 30066839_gammadelta T cells suppressed iDCs osteoclastogenesis by downregulation of the RANK/cFos/ATP6V0D2 signaling pathway. 30431439_Lactate inhibits ATP6V0d2 expression in tumor-associated macrophages to promote HIF-2alpha-mediated tumor progression. 32240421_ATP6V0D2, a subunit associated with proton transport, serves an oncogenic role in esophagus cancer and is correlated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition. |
ENSMUSG00000028238 |
Atp6v0d2 |
122.174942 |
28.5589766422 |
4.835872 |
0.302574484 |
350.447232 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000338648153154152853636533035261108273815025823426396367035052966206303813801847066309724867725918554754435739610322292561781366050937639869573437904111769264495064162722496100143100840313927684180339561237360612722113728523254394531250000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000111076594234562127938801369061560887638577606434499531631284422721258208165870567364495198086286208954606831593437977755509990965663057691553971162320605868835802037069210556994185922993507303901949967439577449113130569458007812500000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
237.0972064 |
44.9202628 |
8.2852470 |
1.5032986 |
| ENSG00000147649 |
92140 |
MTDH |
protein_coding |
Q86UE4 |
FUNCTION: Down-regulates SLC1A2/EAAT2 promoter activity when expressed ectopically. Activates the nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kappa-B) transcription factor. Promotes anchorage-independent growth of immortalized melanocytes and astrocytes which is a key component in tumor cell expansion. Promotes lung metastasis and also has an effect on bone and brain metastasis, possibly by enhancing the seeding of tumor cells to the target organ endothelium. Induces chemoresistance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15927426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16452207, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18316612, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19111877}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell junction;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables NF-kappaB binding activity; double-stranded RNA binding activity; and transcription coactivator activity. Involved in several processes, including lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway; positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction; and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in endoplasmic reticulum; nuclear lumen; and perinuclear region of cytoplasm. Implicated in hepatocellular carcinoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92140; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; intercellular canaliculus [GO:0046581]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
14980505_3D3/lyric is localized to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear envelope, and the nucleolus. 15093543_overexpression of metadherin is associated with metastatic breast cancer 15383321_a novel protein LYRIC is recruited during the maturation of the tight junction complex. 17397930_findings indicate that AEG-1 might play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis, progression and metastasis of diverse cancers 17704808_AEG-1 is an oncogene cooperating with Ha-ras as well as functioning as a downstream target gene of Ha-ras; may perform a central role in Ha-ras-mediated carcinogenesis. 18316612_AEG-1 might function as a coactivator for NF-kappaB, consequently augmenting expression of genes necessary for invasion of glioma cells 18440304_LYRIC/AEG-1 is a negative regulator of BCCIPalpha, promoting proteasomal degradation either through direct interaction, or potentially through an indirect mechanism involving downstream effects of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 18519759_AEG-1 protein is a valuable marker of breast cancer progression. 19111877_establish MTDH as an important therapeutic target for simultaneously enhancing chemotherapy efficacy and reducing metastasis risk 19221438_AEG1 plays a central role in regulating diverse aspects of hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis and inhibition may lead to an effective therapeutic strategy for this disease. 19304953_Upregulation of AEG-1 plays an important role in the development and pathogenesis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression and pathogenesis. 19383828_Increased cytoplasmic distribution of LYRIC is associated with prostate cancer. 19448665_AEG-1 may play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of neuroblastoma and could represent a potential target for therapeutic intervention. 19633686_Studies were further confirmed in clinical primary breast cancer specimens, in which high-level expression of AEG-1 was inversely correlated with the expression of FOXO1. 19648967_one mechanism for cells with altered LYRIC/AEG-1 expression to evade apoptosis and increase cell growth during tumourigenesis through the regulation of PLZF repression 19740331_AEG-1 was suggested to be a LPS-responsive gene and involved in LPS-induced inflammatory response. 19940250_findings demonstrate that aberrant AEG-1 expression plays a dominant positive role in regulating oncogenic transformation and angiogenesis 20053777_AEG-1 may play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of glioma. 20236756_AEG-1 gene is clinically significant in human oligodendroglioma. 20300973_AEG-1 may play a role in Wnt/beta-catenin-mediated cancer progression 20388776_Findings show that AEG-1 contributes to glioma progression by enhancing MMP-9 transcription and tumor cell invasiveness, and underscore the importance of AEG-1 in glioma development and progression. 20388796_although AEG-1 does not affect MDR1 gene transcription, it facilitates association of MDR1 mRNA to polysomes, resulting in increased translation 20565850_MTDH overexpression could be identified in proliferative breast lesions and may contribute to breast cancer progression. 20625905_AEG-1 expression in colorectal carcinoma may be associated with tumor progression, and high AEG-1 expression correlates with poor overall survival 20802479_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20845990_AEG-1 protein is overexpressed in RCC and plays an important role in tumor differentiation and progression. 20952513_miR-26a functionally antagonizes human breast carcinogenesis by targeting MTDH and EZH2. 21084864_Observations link AEG-1 overexpression in glioblastoma with hypoxia and glucose deprivation. 21127263_AEG-1-mediated chemoresistance is because of protective autophagy and inhibition of AEG-1 results in a decrease in protective autophagy and chemosensitization of cancer cells. 21150314_Overexpression of AEG-1 increases cell migration and invasion of glioma cells. 21256156_historical perspective of AEG-1; evaluation of AEG-1 as a novel diagnostic/prognostic biomarker for a variety of cancers; understanding of the molecular and biochemical bases of oncogenic properties of AEG-1 [review] 21259255_AEG-1 expression may be related with tumor angiogenesis and progression and is a valuable prognostic factor in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. 21293286_high AEG-1 expression was associated with progression and prognosis of ovarian carcinoma. 21371176_results suggest that MTDH could promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells in driving the progression of their aggressive behavior 21408129_All variants of the MTDH gene were investigated and the association of the variants with breast cancer development, was explored. 21412050_Astrocyte elevated gene-1 activates AMPK in response to cellular metabolic stress and promotes protective autophagy. 21448238_Study revealed a modest gene-based significant association between migraine and the metadherin (MTDH) gene, previously identified in the first clinic-based GWA study (GWAS) for migraine (Bonferroni-corrected gene-based P-value=0.026). 21478147_SND1 as a novel MTDH-interacting protein and shown that it is a functionally and clinically significant mediator of metastasis. 21495225_AEG-1 overexpression is associated with carcinogenesis and tumor progression in endometrial cancer. 21543927_AEG-1 is overexpressed in a great portion of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) patients with peritoneal dissemination and/or lymph node metastasis and may be clinically useful for predicting metastasis in EOC. 21609571_The expression of EphA7 and/or MTDH might be closely related to the carcinogenesis, progression, clinical biological behaviors and prognosis of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 21750404_AEG-1 plays a crucial role in osteosarcoma progression through MMP-2, and AEG-1 could be a useful biomarker for the prediction of osteosarcoma progression and prognosis 21750868_Our results suggest that the AEG-1 protein is a valuable marker of GBC progression and could be a potential therapeutic target. 21753766_Data show that AEG-1/MTDH was directly regulated by miR-375. 21852380_AEG-1 contributes to glioma-induced neurodegeneration (a hallmark of this fatal tumo) through regulation of EAAT2 expression. 21957284_Gag interacts with endogenous Lyric via its matrix (MA) and nucleocapsid (NC) domains. 21957284_HIV-1 Gag interacts with endogenous MTDH (Lyric/Aeg-1) via its matrix (MA) and nucleocapsid (NC) domains. Lyric is incorporated into HIV-1 virions and is cleaved by the HIV protease. Lyric influences HIV protein expression and infectivity. 21957284_Via Affinity purifications, MTDH (aka Lyric) interacts with HIV-1 Gag, is incorporated in virions and cleaved by HIV PR. Lyric interaction is conserved for retroviral Gag proteins. Cotransfections suggest a role for Lyric in regulating HIV infectivity. 21964981_MTDH and EphA7 are markers for metastasis and poor prognosis of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 21976539_MTDH may promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition process 22031094_Data show that MiR-375 expression was significantly reduced, and conversely, metadherin (MTDH) was significantly increased in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) samples. 22056881_miR-375 targets AEG-1 in HCC and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo 22133054_AEG-1 expression is associated with salivary gland carcinomas progression. 22195048_MTDH is involved in inflammation-induced tumor progression. 22199357_implicate cytoplasmic MTDH in cell survival and broad drug resistance via association with RNA and RNA-binding proteins. 22204714_astrocyte-elevated gene-1 plays a crucial role in the carcinogenesis and aggressiveness of non-small cell lung cancer, promoting its metastasis by modulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and leading to a poor clinical prognosis. 22246354_Overexpression of EphA7 and/or MTDH might indicate poor prognosis in squamous cell cancer of the tongue. 22340175_AEG-1 might facilitate the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells by upregulating HER2/neu expression. 22351252_AEG-1 was highly expressed in colorectal cancer and may be a potential biomarker for liver metastatic tumors. 22367022_MTDH affects the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells and that MTDH may be a novel target to improve cervical cancer radiation response. 22372608_Tumour AEG-1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and cisplatin resistance in advanced serous ovarian cancer. 22431469_AEG-1 interacted with beta-catenin in CRC cells and AEG-1 expression was closely associated with progression of CRC. AEG-1 might be a potential therapeutic target in CRC. 22470125_study detected MTDH expression in normal liver, chronic hepatitis B and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)tissues; data showed that MTDH expression levels were elevated in the hepatitis B tissues and especially in the HBV-related HCC tissues compared to normal liver tissues 22643064_AEG-1 is up-regulated, at the mRNA and the protein level, during colorectal cancer development and aggressiveness. 22684557_These results suggested that the expression of MTDH/AEG-1 gene in HCC cell lines of different metastatic potentials was closely positively related to the abilities of orientation chemotaxis and adhesion of HCC cells. 22689379_AEG-1 provides strong protection from senescence, AEG-1 induces marked up-regulation of FXII protein, and is associated with induction of steatosis. 22768080_MTDH contributes to the pathogenesis of diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma mediated by activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway 22898150_MTDH protein may be a valuable marker of bladder cancer progression. MTDH expression is associated with poor overall survival in patients with bladder cancer. 22903204_MTDH overexpression contributes to an aggressive phenotype, thus leading to a poor prognosis for primary invasive breast cancer. 22938468_results demonstrated that expression of MTDH at the transcriptional level may be increased in gastric cancer tissue samples but with considerable heterogeneity 22967897_miR-136 might play a tumor-suppressive role in human glioma 23011158_Evidence that elevated expression of AEG-1 protein is correlated with poor prognosis and reduced survival of patients with neuroblastoma (P= 0.031). 23023948_findings demonstrate that AEG-1 plays a crucial role in T-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma growth and metastasis 23065261_The increased expression of MTDH and/or SND1 is closely related to carcinogenesis, progression, and prognosis of colon cancer. 23142337_High AEG-1 expression was associated with tongue carcinoma. 23240043_These data suggest that MTDH (-470G>A) could be a useful molecular marker for assessing ovarian cancer risk and for predicting ovarian cancer patient prognosis. 23307243_our results indicated that AEG-1 played a crucial role in the carcinogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer 23364922_MTDH overexpression was tightly associated with more aggressive tumour behaviour and a poor prognosis, indicating that MTDH is a valuable molecular biomarker for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression. 23408429_oncogene metadherin modulates the apoptotic pathway based on the tumor necrosis factor superfamily member TRAIL (Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand) in breast cancer 23499911_AEG-1 could potentially serve as an alternative target to AURKA for drug design and therapeutic treatment, to achieve more specific killing of AML cells while sparing normal cells. 23595222_MTDH expression is high in cervical cancer, and it contributes to chemoresistance of cervical cancer. 23640911_AEG-1 plays an important role in TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of p38 MAPK in proximal tubular epithelial cells. 23710918_AEG-1 protein might play a critical role in the initiation and progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma 23835593_Overexpression of astrocyte-elevated gene-1 is associated with cervical carcinoma progression and angiogenesis. 23851509_High metadherin is associated with breast tumor growth and metastasis. 23889986_Initial cloning, structure, expression profile, and regulation of expression of AEG-1 protein. [Review] 23889987_A comprehensive analysis of the existing literature to emphasize the common and conflicting findings relative to the clinical significance of AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC in cancer. [Review] 23889988_AEG-1 function relative to signaling changes, interacting partners, and angiogenesis and new perspectives on its potential as a significant target for the clinical treatment of cancers and other diseases. [review] 23889989_Discovery of agents that can block AEG-1 and its regulated pathways will be beneficial to cancer patients with aberrant expression of AEG-1.[review] 23889990_The multiple functions of AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC in drug resistance highlight that it is a viable target as an anticancer agent for a wide variety of cancers. [review] 23889991_As an oncogene that promotes aberrant cellular processes within the CNS, AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC represents an important therapeutic target for the treatment of neurological disease. [review] 23889992_Combination of AEG-1 inhibition and chemotherapy has documented significant efficacy in abrogating human hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) xenografts.[review] 23910058_LY294002 treatment down-regulated AEG-1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma 24063540_AEG-1 increases phosphorylation of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB, and regulates the expression of MMP1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. 24119914_AEG-1 gene expression associated with poor prognosis in children with Wilms tumor. 24136747_These findings suggest that AEG-1 may be an epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated biomarker in human hepatocellular carcinoma and play important roles in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma 24256614_High expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 is associated with progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. 24462870_Targeted inhibition of AEG-1 can lead to modification of key elemental characteristics, such as miRNAs, which may become a potential effective therapeutic strategy for CRC 24495449_MTDH/AEG-1 overexpression contributes to the neoplastic phenotype of bladder cancer cells by promoting survival, clonogenicity, and migration 24529480_Specific sites of LYRIC/AEG-1 ubiquitination are essential for regulating LYRIC/AEG-1 localisation and functionally interacting proteins. 24656097_Expression of AEG-1 may be correlated with tumor angiogenesis and metastasis and is a valuable prognostic factor in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma 24659263_AEG-1 promoter variant -483 A>C may be associated with the susceptibility to HCC in Iranian population 24674449_An association between MTDH rs1835740 SNP and migraine in a Swedish case-control study. 24675891_Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) in cervical cancer cells decreases their invasiveness, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, and chemoresistance. 24705862_AEG-1 appears to be a novel therapeutic target for preventing the metastasis of CRC. 24817955_Metadherin contribute to BCR signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 24829140_AEG-1 was overexpressed in bladder cancer tissues, compared with normal tissues.AEG-1 is associated with tumor progression in nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer. 24829520_Astrocyte elevated gene-1 mediates glycolysis and tumorigenesis in colorectal carcinoma cells via AMPK signaling 24855648_IL-1beta- or TNF-alpha-induced AEG-1 interaction with NF-kappaB p65 subunit. 24941119_AEG-1 promotes anoikis resistance and orientation chemotaxis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 24946951_Determination of MTDH expression in primary CRC may be useful in the earlier detection of lung metastases in patients with high expression and increased risk 24963474_Strong p50, p65, and metadherin expression was associated with a high probability to distinguish ovarian carcinomas over borderline and benign ovarian tumours 24981741_MTDH supports the survival of mammary epithelial cells under oncogenic/stress conditions by interacting with and stabilizing SND1. 24989027_Study suggests that AEG-1 protein was highly expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and associated with poor prognosis of the patients. 25074613_Findings establish a pivotal role for MTDH in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. 25092897_results demonstrate that AEG-1 can promote gastric cancer progression by a positive feedback TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling-related mechanism 25125681_Study establishes AEG-1 as a novel homeostatic regulator of RXR and RXR/RAR that might contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis. 25174891_MTDH mediated metastasis of Osteosarcoma through regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 25182604_Results demonstrate an increased expression of AEG-1 in malignant meningiomas correlated with grade; elevation of AEG-1 promotes malignant tumor progression in meningioma by an increase in cell proliferation, tumorigenicity, and a decrease in apoptosis 25193383_our findings offer in vivo proofs that AEG-1 is essential for NF-kappaB activation and hepatocarcinogenesis, and they reveal new roles for AEG-1 in shaping the tumor microenvironment for HCC development 25197376_our data suggest that AEG-1 may represent a novel prognostic marker for astrocytomas. 25204501_Taken together, our findings suggest that AEG-1 plays a crucial role in the aggressiveness of osteosarcoma via the JNK/c-Jun/MMP-2 pathway. 25266957_MiR-136 plays a key role in temozolomide (TMZ) resistance by targeting AEG-1 in glioma cell line, suggesting that miR-136 can be used to predict a patient's response to TMZ therapy as well as serve as a novel potential maker for glioma therapy. 25304263_Our study uncovers a novel molecular mechanism by which AEG-1 augments glioma progression and offers a rationale to block AEG-1-Akt2 signaling function as a novel GBM treatment. 25323629_microRNA-22 acts as a metastasis suppressor by targeting metadherin in gastric cancer. 25333261_MTDH up-regulation was associated with high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. 25346496_Data provide evidence that MTDH has a functional role in the progression and metastatic spread of ovarian cancer. 25407490_AEG-1 may be a novel predictor for metastasis and prognosis of the patients with GC. 25417825_MTDH mediates trastuzumab resistance, at least in part, by PTEN inhibition through an NFkappaB-dependent pathway, which may be utilized as a promising therapeutic target for HER2 positive breast cancer. 25428378_we have reported the altered expression of miR-145 in NSCLC cell lines and that miR-145 could modulate cell proliferation and invasion by targeting AEG-1/MTDH 25431427_Data suggest that AEG-1 plays an important role in renal cancer formation and development. 25432696_data suggest that miR-542-3p might function as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer, potentially by targeting the oncogene AEG-1 25483832_AEG1 is a valuable biomarker for the prediction of ovarian cancer prognosis, and AEG1 inhibition may be a potential therapeutic strategy for ovarian cancer treatment. 25484183_A competitive endogenous RNAs regulatory network among AEG-1, Snail and Vimentin mediated via competitive binding to miR-30a was proved. 25575438_The results demonstrate that MTDH is specifically expressed in B cell of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and exert a preservative role through activation of Wnt signaling pathway 25652471_our results suggest that the evodiamine suppress the proliferation of lung cancer cells, at least, in part, via inhibition of MTDH expression and activation of apoptosis. 25684730_Repression of metadherin inhibits biological behavior of prostate cancer cells and enhances their sensitivity to cisplatin. 25695541_AEG-1 was associated with the progression of cervical squamous cell carcinoma by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Wnt signaling pathway. 25787750_Real-time quantitative RT-PCR revealed a dose-dependent decrease in RNA-binding factor 1 (AUF-1) and astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) messenger RNA (mRNA) levels in TP-1-treated SMMC-7721 cells 25794773_Results indicated that MTDH was a direct downstream target of miR-153 and was involved in the miR-153-induced suppression of the migration and invasion in breast cancer cell. 25824750_Overexpression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 is associated with angiogenesis in cervical cancer. 25880337_These results reveal the critical role of AEG-1 in EMT and suggest that AEG-1 may be a prognostic biomarker and its targeted inhibition may be utilized as a novel therapy for NSCLC. 25902416_Study provides evidence that the knockdown of MTDH signi fi cantly inhibited angiogenesis suggesting that MTDH is a potential therapeutic target for anti-angiogenesis in breast cancer. 25913216_In patients with non-small cell lung cancer, AEG-1 expression was an independent prognostic factor for both overall and disease-free survival. 25944909_AEG-1 thus might play a role in NTIS associated with HCC and other cancers. 25987128_EFEMP1 might indirectly enhance the expression of MMP-2, providing a potential explanation for the role of AEG-1 in metastasis. NF-kappaB pathways might be one of the effective ways which EFEMP1 was induced by AEG-1. 26016795_ectopic miR-217 expression decreased AEG-1 expression and repressed luciferase reporter activity associated with the AEG-1 3'-untranslated region (UTR). 26035424_Data established that AEG-1 is frequently upregulated and functions as an oncogene by regulating several major signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) suggesting potential role as a biomarker or target for HCC therapy. [review] 26051629_MTDH might be used as a potential therapeutic target in the lymph node metastasis of ESCC 26096243_The present work aims to investigate the relationship between the expression of AEG-1(astrocyte elevated gene-1), b-FGF(basic-fibroblast growth factor), beta-catenin, Ki-67, TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor-alfa) other prognostic parameters in DC (Ductal Carcinomas) and ductal intraepithelial neoplasm. We found a relationship between these factors. 26122237_mRNA and protein expression level of metadherin in breast cancer cells both improved after transfection. The inhibition effect of 1 mg/L doxorubicin and 8 mg/L taxol on breast cancer cells decreased after metadherin transfection. 26134542_AEG-1 mediates CCL3/CCR5-induced EMT development via both Erk1/2 and Akt signaling pathway in CM patients, which indicates CCL3/CCR5-AEG-1-EMT pathway could be suggested as a useful target to affect the progression of CM. 26141861_our work revealed that MTDH promotes CSC accumulation and breast tumorigenicity by regulating TWIST1, deepening the understanding of MTDH function in cancer. 26156805_AEG-1 mediates CCL20/CCR6-induced EMT development via both Erk1/2 and Akt signaling pathway in cervical cancer, which indicates that CCL20/CCR6-AEG-1-EMT pathway could be suggested as a useful target to affect the progression of cervical cancer. 26176806_miR-302c-3p play a pivotal role in the progression of glioma by targeting MTDH and is a potential inhibitor in glioma treatment. 26236947_Data suggest that activation of AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) in triple negative breast cancer cells down-regulates expression of MTDH (metadherin) via up-regulation of GSK3B (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta) and SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) activities. 26287185_Knockdown of MTDH inhibits phosphorylation of AKT and increased apoptosis related protein expression. 26318406_We identified two powerful genes in the liver cancer metastasis process, AEG-1 and AKR1C2. 26336827_Results indicate that microRNA miR-497 directly inhibited the 3'-untranslated regions (3' UTRs) of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1). 26351209_Identify two novel factors, AKR1C2 (positive factor) and NF1 (negative factor), as the AEG-1 downstream players in the process of metastasis in liver cancer. 26418251_Data showed that AEG1 and MMP7 levels were both significantly increased and strongly correlated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues. AEG-1 promotes NSCLC cell invasiveness through MAPK-p42/p44-dependent activation of MMP7. 26589417_Our results suggest that underexpression of miR-30a-5p might function as a tumor suppressing miRNA by directly targeting MTDH in HCC and is therefore a potential candidate biomarker for HCC targeting therapy. 26595523_Data indicate metadherin (MTDH) as a direct target gene of microRNA miR-630. 26683226_High MTDH expression is associated with multiple myeloma. 26689985_AEG-1 overexpression is closely associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promote metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. 26710214_High AEG-1 staining index might be associated with tumor progression and poor survival status in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. Meta-analysis. 26823698_Suggest that miR-377 plays an important role in the development of NSCLC by regulating AEG-1 expression. 26884832_MiR-30a-5p may play an essential role in the cell growth and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, partially via targeting AEG-1. 27059438_rs1835740 associated with the need for neonatal resuscitation and Apgar scores 27090750_In-depth review of the role of AEG-1 in a diverse spectrum of diseases, from cancer to HIV-1 and aging, highlighting mechanistic processes that synergize with known AEG-1 functions and promoting the notion that AEG-1 occupies a unique niche in inflammation, mitochondrial, ER and nucleolar stress, culminating in excitotoxicity and other neurodegenerative outcomes. 27229534_Findings clearly demonstrate that miR-320a suppresses breast cancer metastasis by directly inhibiting MTDH expression. The present study provides a new insight into anti-oncogenic roles of miR-320a. 27339400_Knocking down TSPAN8 in AEG-1-overexpressing human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells markedly inhibited invasion and migration without affecting proliferation. TSPAN8 knockdown profoundly abrogated AEG-1-induced primary tumor and intrahepatic metastasis in an orthopic xenograft model in athymic nude mice 27565732_IL-8 was displayed to be capable of directly interacting with metadherin (MTDH), which in turn can up-regulate IL-8 expression. 27571703_these findings suggested that miR-124 was able to suppress cell proliferation, invasion and migration, as well as the EMT process in cervical carcinomas through directly targeting AEG-1. miR-124 and AEG-1 may be potential 27667169_our findings suggest that AEG-1 promotes mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma through the regulation of the Rho signaling pathway, resulting in tumor invasion, a primary characteristic of malignant brain tumors 27746178_AEG-1 is involved in miR-1297-regulated prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion.MiR-1297 targets and inhibits AEG-1 in prostate cancer. 27765924_Gene expression data and in silico database analysis showed that the metadherin gene (MTDH) was a direct target of both miR-145-5p and miR-145-3p regulation and high expression of MTDH predicted poorer survival of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients. 27793010_Study shows that expression of AEG-1 was significantly higher in macrophages and associated with elevated expression levels of MMP-9 in hypopharyngeal cancer. These results demonstrate that macrophage AEG-1 promotes tumor invasion through up-regulation of MMP-9 in both macrophages and cancer cells. 27835571_AEG-1 knockdown inhibits migration and invasion, as well as radiation-enhanced invasion both in vitro and in vivo I colonic cancer cells. 27903708_Expression of AEG-1 was strongly associated with stem cell markers CD133 and SOX2. AEG-1 facilitated beta-catenin translocation into the nucleus by forming a complex with LEF1 and beta-catenin, subsequently activating Wnt signaling downstream genes. 27917902_The results indicated that high MTDH expression is significantly correlated with higher mortality in breast, ovarian and cervical cancer. (Meta-analysis) 27923917_High MTDH expression is associated with glioblastomas. 27956703_c-Jun and p300 are novel interacting partners of AEG-1 in gliomas. 28107197_MTDH induces Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-like change and invasion of glioma via the regulation of miR-130b-competing endogenous RNAs, providing the first direct link between MTDH and miRNAs in cancer cells. 28112756_Long noncoding RNA FTX regulated astrocyte-elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) expression through microRNA miR-342-3p. 28174206_miR-26a is capable of suppressing the proliferation and migration of ESCC cells via negative regulation of metadherin 28184926_High MTDH expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 28276315_Results show that miR-342-3p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells through targeting AEG-1. 28323000_Study showed that AEG-1's knock down inhibited cell growth, triggered apoptosis, arrested cell cycle, retarded cell migration and invasion in ovarian cancer cells. These results provide evidence that AEG-1 plays an oncogenic role in ovarian cancer cells. 28401704_Results demonstrated that AEG-1 significantly enhanced invasion capabilities of OVCAR3 ovarian cancer cells and suggested that HIF-1alpha binds to AEG-1 promoter to upregulate its expression, which was correlated with metastasis in ovarian cancer. 28429540_oncogenic role of AEG-1 in melanoma 28534938_High MTDH expression is associated with gastric cancer metastasis. 28627585_Through the analysis of the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) datasets for estrogen receptor (ER)-positive endometrial and breast cancers, this study found that over 25% of all gene expression correlated with MTDH. 28661037_The findings suggest that AEG-1 promotes gastric cancer metastasis through upregulation of eIF4E-mediated MMP-9 and Twist. 28685276_MTDH expression does not correlate with prognosis in the esophageal adenocarcinoma patients. 28731152_We found that overexpression of AEG-1 in PTC was positively correlated with lymph node metastasis and MMP2/9 expression. Knockdown of AEG-1 reduced the capacity of migration and invasion through downregulation of MMP2/9 in thyroid cancer cells. Furthermore, we firstly found that AEG-1 interacted with MMP9 in thyroid cancer cells. 28849015_miR448 was downregulated in osteosarcoma and overexpression of miR448 inhibited cell proliferation and invasion by targeting AEG1, providing novel insights into the understanding of osteosarcoma pathogenesis. 28877780_High AEG-1 expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 28901527_Study confirmed that hypoxia increased MTDH expression via HIF-1alpha expression. Knockdown of MTDH expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell lines interrupted hypoxiainduced metastasis and glycolysis. Furthermore, reduced MTDH expression decreased HIF-1alpha expression. These results indicated the presence of a positive feedback loop between MTDH and HIF-1alpha in HNSCC. 28923415_we have identified a novel mechanism for DIM- and ring-DIM-induced protective autophagy, via induction of AEG-1 and subsequent activation of AMPK. Our findings could facilitate the development of novel drug therapies for prostate cancer that include selective autophagy inhibitors as adjuvants. 28927747_Our findings provided evidence that AEG-1 contributed to the production of inflammatory cytokines, migration and invasion of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes, and underscored the importance of AEG-1 in the inflammation process of rheumatoid arthritis 28938524_miR-384 and AEG-1 may serve as potential targets for the diagnosis and treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. 28941723_AEG-1 may play important roles at the transcription level in malignant transformation and tumor angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. 28952213_AEG-1 and CXCR4 activate and regulate the EMT pathway to participate in brain metastases. 29089083_Knockdown of MTDH gene effectively inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of SGC7901 cells. 29117631_Astrocyte elevated gene-1 shows the ability to promote bladder cancer metastasis, which is causally linked to induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 29133850_Study found AEG-1 to be overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues compared to normal oral mucosa. Knockdown or overexpression of AEG-1 in OSCC cell lines showed that AEG-1 is important for tumour growth, apoptosis, drug tolerance, and maintaining epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediate |
ENSMUSG00000022255 |
Mtdh |
3599.253478 |
2.7811774877 |
1.475696 |
0.040563727 |
1304.791134 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000102811726411311948667606445994806047963775335 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000135491168020621820651997666180647434981937805 |
Yes |
No |
5212.7410218 |
186.0538451 |
1889.1584626 |
50.2447758 |
| ENSG00000147650 |
29967 |
LRP12 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y561 |
FUNCTION: Probable receptor, which may be involved in the internalization of lipophilic molecules and/or signal transduction. May act as a tumor suppressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12809483}. |
Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the low-density lipoprotein receptor related protein family. The product of this gene is a transmembrane protein that is differentially expressed in many cancer cells. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:29967; |
clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0005041]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; locomotion [GO:0040011]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; regulation of growth [GO:0040008]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12809483_ST7 is a novel low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) with a cytoplasmic tail that interacts with proteins related to signal transduction pathways. 20439316_As the preplate separates, Lrp12/Mig13a-positive neurons polarize in the radial plane and form a pseudocolumnar pattern, prior to moving to a deeper position within the emerging subplate layer. 26639854_Results indicate that low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 12 silencing during brain development results in cortical dyslamination and seizure sensitization. 27142828_Accumulation of functional promoter-associated allelic variants with impact on the transcriptional regulation of LRP12 provides a new pathomechanism for GGs, i.e. highly differentiated epileptogenic brain tumors 30029672_LRP12 DNA methylation as a powerful predictive marker for carboplatin resistance. 31332380_GGC repeat expansions in LRP12 gene is associated with oculopharyngodistal myopathy. 32493488_Oculopharyngodistal myopathy with coexisting histology of systemic neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease: Clinicopathologic features of an autopsied patient harboring CGG repeat expansions in LRP12. |
ENSMUSG00000022305 |
Lrp12 |
425.165644 |
4.3655028091 |
2.126148 |
0.086156721 |
645.575996 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020476222161436679032370587688958842972059120520917351287425850401474686056637943707739822594799855608834917386883644086176768489090089076102623424235270959886099034988748883395217366983556 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012335879147053280859636028580673148682390855335199422036318916543841812026880413251913817731234219891981907034655878831343831342369968416251226460637302344573168068904254264392182636252144 |
Yes |
No |
702.2344624 |
35.2880558 |
162.0129677 |
7.0389288 |
| ENSG00000147813 |
93100 |
NAPRT |
protein_coding |
Q6XQN6 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of NAD from nicotinic acid, the ATP-dependent synthesis of beta-nicotinate D-ribonucleotide from nicotinate and 5-phospho-D-ribose 1-phosphate (PubMed:17604275, PubMed:21742010, PubMed:26042198). Helps prevent cellular oxidative stress via its role in NAD biosynthesis (PubMed:17604275). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17604275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21742010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26042198}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Ligase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; nicotinate D-ribonucleotide from nicotinate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17604275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21742010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26042198}. |
Nicotinic acid (NA; niacin) is converted by nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase (NAPRT; EC 2.4.2.11) to NA mononucleotide (NaMN), which is then converted to NA adenine dinucleotide (NaAD), and finally to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), which serves as a coenzyme in cellular redox reactions and is an essential component of a variety of processes in cellular metabolism including response to stress (Hara et al., 2007).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:93100; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase activity [GO:0004516]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; NAD salvage [GO:0034355]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
17604275_NA elevates cellular NAD levels through NAPRT function and, thus, protects the cells against stress, partly due to lack of feedback inhibition of NAPRT but not NamPRT by NAD 21492230_NAPRT expression was varied in lymphomas with 30-50% low expression except for Hodgkin's lymphoma where 85% displayed low expression 22570471_Inhibition of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) activity by small molecule GMX1778 regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated cytotoxicity in a p53- and nicotinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase1 (NAPRT1)-dependent manner 24097869_Tumor-specific promoter hypermethylation of NAPRT1 inactivates one of two NAD salvage pathways, resulting in synthetic lethality with the coadministration of a NAMPT inhibitor. 26675378_High NAPRTase expression is associated with neoplasms. 28416276_Synthesis and Degradation of Adenosine 5'-Tetraphosphate by Nicotinamide and Nicotinate Phosphoribosyltransferases 28860121_No correlation between IDH1/2 mutation status and sensitivity for NAMPT inhibitors was observed. Strikingly, higher methylation of the NAPRT promoter was observed in high-grade versus low-grade chondrosarcomas. In conclusion, this study identified NAMPT as a potential target for treatment of chondrosarcoma 31268507_Association of Schizophrenia Risk With Disordered Niacin Metabolism in an Indian Genome-wide Association Study. 31439867_Study demonstrated that PPM1D mutant astrocytes and patient-derived PPM1D mutant diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma lines are particularly sensitive to treatment with NAMPT inhibitors. Mutant PPM1D-induced NAMPT inhibitor sensitivity is driven by hypermethylation of CpG islands throughout the genome and the epigenetic silencing of NAPRT, a key gene involved in NAD biosynthesis. 31511522_these data identify NAPRT as a endogenous ligand for TLR4 and a mediator of inflammation. 34946971_NAPRT Expression Regulation Mechanisms: Novel Functions Predicted by a Bioinformatics Approach. 36432602_NAPRT, but Not NAMPT, Provides Additional Support for NAD Synthesis in Esophageal Precancerous Lesions. |
ENSMUSG00000022574 |
Naprt |
819.068868 |
0.4620546637 |
-1.113865 |
0.076062701 |
212.873144 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000324374785067151205169048682183653924875923528942746341330699660413384541359505667867277956449823077827941063317272578098854340922230221622157841920852661132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000066125231471036447644798088484899940615853830718969146493701632365332895796837581749223581024219722176495302902279915021471756730875313223805278539657592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
511.2854688 |
26.3230997 |
1113.7947636 |
39.8061275 |
| ENSG00000148057 |
414328 |
IDNK |
protein_coding |
Q5T6J7 |
|
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate acid metabolism; D-gluconate degradation. |
Predicted to enable gluconokinase activity. Predicted to be involved in D-gluconate catabolic process. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:414328; |
ATP binding [GO:0005524]; gluconokinase activity [GO:0046316]; D-gluconate catabolic process [GO:0046177]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] |
23067238_Data show that C9orf103 encodes a functional gluconokinase. |
ENSMUSG00000050002 |
Idnk |
31.842661 |
0.4384803795 |
-1.189416 |
0.396667104 |
8.941118 |
0.00278821975290971611066703772507935354951769113540649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006010533599086813338896462255434016697108745574951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.8250023 |
5.4362674 |
47.8781347 |
8.4898441 |
| ENSG00000148143 |
58499 |
ZNF462 |
protein_coding |
Q96JM2 |
FUNCTION: Zinc finger nuclear factor involved in transcription by regulating chromatin structure and organization (PubMed:20219459, PubMed:21570965). Involved in the pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cells by regulating SOX2, POU5F1/OCT4, and NANOG (PubMed:21570965). By binding PBX1, prevents the heterodimerization of PBX1 and HOXA9 and their binding to DNA (By similarity). Regulates neuronal development and neural cell differentiation (PubMed:21570965). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B1AWL2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20219459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21570965}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to C2H2-type zinc finger family of proteins. It contains multiple C2H2-type zinc fingers and may be involved in transcriptional regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:58499; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; negative regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043392]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468] |
18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22826440_Zinc finger protein 462 (ZNF462) is the first human O-GlcNAc-6-phosphate modified protein. 28513610_Loss of function variants in ZNF462 were identified in patients with ptosis, metopic ridging, craniosynostosis, dysgenesis of the corpus callosum, and developmental delay. 29427787_In the current study we describe a patient with a syndromic form of autism spectrum disorder and intellectual disability characterized by metopic craniosynostosis, ptosis and corpus callosum dysgenesis most likely caused by ZNF462 haploinsufficiency. The possible contribution of the disruption of KLF12 by one of the translocation breakpoints remains unclear. 31361404_a multiple congenital anomaly syndrome associated with haploinsufficiency of ZNF462 that has distinct clinical characteristics and facial features, is reported. |
ENSMUSG00000060206 |
Zfp462 |
62.955268 |
0.4308412510 |
-1.214772 |
0.284770210 |
17.776849 |
0.00002483873530726563562073296032028935087510035373270511627197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000074274662304546344064951068908442266547353938221931457519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
33.6694083 |
11.4809529 |
78.3951094 |
19.2362805 |
| ENSG00000148154 |
7357 |
UGCG |
protein_coding |
Q16739 |
FUNCTION: Participates in the initial step of the glucosylceramide-based glycosphingolipid/GSL synthetic pathway at the cytosolic surface of the Golgi (PubMed:8643456, PubMed:1532799). Catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to ceramide to produce glucosylceramide/GlcCer (such as beta-D-glucosyl-(11')-N-acylsphing-4-enine) (PubMed:1532799, PubMed:8643456). GlcCer is the core component of glycosphingolipids/GSLs, amphipathic molecules consisting of a ceramide lipid moiety embedded in the outer leaflet of the membrane, linked to one of hundreds of different externally oriented oligosaccharide structures (PubMed:8643456). Glycosphingolipids are essential components of membrane microdomains that mediate membrane trafficking and signal transduction, implicated in many fundamental cellular processes, including growth, differentiation, migration, morphogenesis, cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions (By similarity). They are required for instance in the proper development and functioning of the nervous system (By similarity). As an example of their role in signal transduction, they regulate the leptin receptor/LEPR in the leptin-mediated signaling pathway (By similarity). They also play an important role in the establishment of the skin barrier regulating keratinocyte differentiation and the proper assembly of the cornified envelope (By similarity). The biosynthesis of GSLs is also required for the proper intestinal endocytic uptake of nutritional lipids (By similarity). Catalyzes the synthesis of xylosylceramide/XylCer (such as beta-D-xylosyl-(11')-N-acylsphing-4-enine) using UDP-Xyl as xylose donor (PubMed:33361282). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1532799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33361282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8643456, ECO:0000303|PubMed:8643456}. |
Acetylation;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:33361282, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8643456}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the first glycosylation step in the biosynthesis of glycosphingolipids, which are membrane components containing lipid and sugar moieties. The product of this reaction is glucosylceramide, which is the core structure of many glycosphingolipids. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. |
hsa:7357; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ceramide glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0008120]; dihydroceramide glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0102769]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cornified envelope assembly [GO:1903575]; epidermis development [GO:0008544]; establishment of skin barrier [GO:0061436]; glucosylceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0006679]; glycosphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006687]; intestinal lipid absorption [GO:0098856]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; leptin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033210]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; protein lipidation [GO:0006497]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966] |
11915344_serve as negative regulator for ceramide 12489486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12873973_Glucosylceramide synthase and its functional interaction with RTN-1C regulate chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis in neuroepithelioma cells. 14766899_inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase led to increased CER galactosylation and protected U937 and HL-60 cells from DNR-induced apoptosis 15263008_glucosylceramide synthase is not solely responsible for drug resistance in cancer cells 15661399_p-gp confers resistance to ceramide-induced apoptosis, with modulation of the ceramide-glucosylceramide pathway GCS making a marked contribution to this resistance 15747776_10 genes were down-regulated following treatment of the T-ALL cells with 0.15 and 1.5 microg/mL of metal ores at 72 h. Transferase activity, transferring glycol groups 16500619_the reticulon family member RTN-1C has been expressed and purified in Escherichia coli and its molecular structure has been analysed by fluorescence and Circular Dichroism spectroscopy 17709137_it is suggested that a high level of GCS in leukemia is possible contributed to multidrug resistance of leukemia cells. 18155680_Western analysis for glucosylceramide synthase showed a significant decrease in Alzheimer disease brain consistent with the hypothesis that enzyme dysfunction contributes to neuronal decay. 18560890_High glucosylceramide synthase is associated with breast cancer. 19693666_GCSshRNA could efficiently suppress GCS and MDR1 expression in vitro and in vivo and these findings may be used as one of the methods to reverse multidrug resistance in breast cancer 20533270_Positive correlation was detected between the expression of GCS and MDR1 mRNA in K562/A02 cells and MDR1 mRNA expression was down regulated after silencing the GCS gene expression. 20540746_study demonstrates, for the first time, that GCS upregulates MDR1 expression modulating drug resistance of cancer. GSLs, in particular globo series GSLs mediate gene expression of MDR1 through cSrc and beta-catenin signaling pathway 20843709_Data indicate that a high expression of glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) seemed to be an indicator of poor prognosis. 21278235_Data show that GCS silencing increased the levels of phosphorylated p53 and p53-responsive genes. 21380926_inhibition of the GCS gene affects the expression of MDR1 mRNA and P-gp function. 21558327_GlcT-1 is up-regulated at the mRNA and protein levels during the course of U937 differentiation, resulting in increased amounts of GlcCer. 21617856_GCS overexpression was highly associated with ER-positive and HER2-positive breast cancer with metastasis. 21756066_Data show that nilotinib induces apoptosis through upregulating ceramide synthase genes and downregulating SK-1 in CML cells in addition to inhibition of BCR/ABL. 22270805_The authors conclude that hepatitis C virus proteins, especially NS5A and NS5B, have positive effects on the expression of human GlcT-1. 22936806_Ceramide glycosylation catalyzed by glucosylceramide synthase is important for cancer stem cells in drug resistance and tumorigenesis. 23133636_DOX could modulate the expression of GCS through the Sp1 site of GCS promoter in ERalpha-positive breast cancer cells 23555901_The results thus show that ARF6 regulates neuronal differentiation through an effect on glucosylceramide synthase and glucosylceramide levels. 23913449_our work indicates that some UGCG polymorphisms are modifying factors in the severity of GD. 24342307_GCS was upregulated in PTCs and might be an independent factor affecting prognosis. 24456584_Our data demonstrates a correlation between the expression of the GCS protein and ER-positive/HER-2 negative breast cancer 24510559_Glucosylceramide synthase mRNA were reduced by 62%. 24960545_We found upregulation of specific sphingolipid enzymes, namely sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1), sphingomyelinase 3 (SMPD3), and glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) in the endometrium of endometriotic women. 25535133_GCS was upregulated in colorectal carcinoma tissues compared to control tissues. 26811497_Glucosylceramide synthase upregulation is associated with sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. 27191984_Results suggest that the changes of DNA methylation status of the glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) promoter correlates with multidrug resistance in breast cancer. 29409484_Studies show a connection between UDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase (UGCG) and multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) overexpression and multidrug resistance development [Review]. 29982630_the GCS inhibitor lucerastat provides a viable mechanism to reduce Gb3 accumulation and lysosome volume, suitable for all Fabry patients regardless of genotype 30242129_findings suggest that complex formation between SMS1 and GCS is part of a critical mechanism controlling the metabolic fate of Cer in the Golgi. 31666638_UGCG influences glutamine metabolism of breast cancer cells. 32424263_UGCG overexpression leads to increased glycolysis and increased oxidative phosphorylation of breast cancer cells. 32980536_Tyrosine-phosphorylation and activation of glucosylceramide synthase by v-Src: Its role in survival of HeLa cells against ceramide. 33684145_beta-Sitosterol 3-O-D-glucoside increases ceramide levels in the stratum corneum via the up-regulated expression of ceramide synthase-3 and glucosylceramide synthase in a reconstructed human epidermal keratinization model. 34686508_UDP-Glucose Ceramide Glycosyltransferase Contributes to the Proliferation and Glycolysis of Cervical Cancer Cells by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Pathway. 35168060_Glucosylceramide in T cells regulates the pathology of inflammatory bowel disease. |
ENSMUSG00000028381 |
Ugcg |
657.233288 |
2.1977204869 |
1.136008 |
0.063631993 |
322.540268 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000405118935419344395524973434709969698156740007574196935991938242446186308441526115116153150756059252639873884240256989955421977079400806048995911298828638811707933174892345203500082506664625725534278899431228637695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000123289803851330375538229650061212191093950110173175972528582756558204630366326368460197824958164133921046258674888160966072739638628027613100723875467048108410936811522680607057511625868073679157532751560211181640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
920.1128454 |
33.8724105 |
421.7520260 |
12.4294381 |
| ENSG00000148218 |
210 |
ALAD |
protein_coding |
P13716 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11032836, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19812033}. |
3D-structure;Allosteric enzyme;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Heme biosynthesis;Lyase;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Porphyrin biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Porphyrin-containing compound metabolism; protoporphyrin-IX biosynthesis; coproporphyrinogen-III from 5-aminolevulinate: step 1/4. |
The ALAD enzyme is composed of 8 identical subunits and catalyzes the condensation of 2 molecules of delta-aminolevulinate to form porphobilinogen (a precursor of heme, cytochromes and other hemoproteins). ALAD catalyzes the second step in the porphyrin and heme biosynthetic pathway; zinc is essential for enzymatic activity. ALAD enzymatic activity is inhibited by lead and a defect in the ALAD structural gene can cause increased sensitivity to lead poisoning and acute hepatic porphyria. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:210; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; porphobilinogen synthase activity [GO:0004655]; proteasome core complex binding [GO:1904854]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; cellular response to lead ion [GO:0071284]; heme biosynthetic process [GO:0006783]; negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:1901799]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; protoporphyrinogen IX biosynthetic process [GO:0006782]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to aluminum ion [GO:0010044]; response to amino acid [GO:0043200]; response to arsenic-containing substance [GO:0046685]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to cobalt ion [GO:0032025]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to fatty acid [GO:0070542]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to herbicide [GO:0009635]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212]; response to iron ion [GO:0010039]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mercury ion [GO:0046689]; response to methylmercury [GO:0051597]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to platinum ion [GO:0070541]; response to selenium ion [GO:0010269]; response to vitamin B1 [GO:0010266]; response to vitamin E [GO:0033197]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043] |
11335187_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11413692_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11427399_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 11444968_Mechanistic based studies of porphobilinogen synthase with a proposed reaction intermediate analogue inhibitor suggest that the enzyme can be used as a drug target for the treatment of human microbial and parasitic infections. 11459423_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11800328_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11860952_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11909869_Species-specific inhibition of porphobilinogen synthase by 4-oxosebacic acid 12469218_CYP2E1 overexpression up-regulates both this enzyme and heme oxygenase-1 in a human hepatoma cell line. 12611663_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12896855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12972060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14527840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14694653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14694653_The genetic susceptibility of ALAD polymorphism to lead toxicity may exhibit in a lead dose-dependent manner. 15064157_A cross-sectional evaluation of differences of hematologic parameters by ALAD genotype in male lead workers from Korea. 15213514_Finds no association of animolevulinic acid dehydratase polymorphisms with patella lead concentrations in lead workers. 15213514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15258767_ALAD polymorphisms not found to be associated with levels of blood lead and blood zinc protoporphyrin in lead workers 15258767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15381398_The Porphobilinogen synthase (PBGS) catalyzes the first common reaction in the biosynthesis of the tetrapyrroles, the asymmetric condensation of two molecules of delta-aminolevulinic acid to form porphobilinogen 15386154_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15587989_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15915653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15954127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16140629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16203232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16263504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16377642_Octameric and hexameric morpheeins of PBGS are very close in energy. Also, W19A assembles into a mixture of dimers, which appear to be stable. 16445899_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16445899_significant interethnic differences in the distribution of G177C ALAD variants found in the Brazilian population is consistent with differences previously reported in other countries 16487505_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16497859_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16730797_Homozygote Rsa and Rsa39488 ALAD 2-2 seems to offer some protection against the effect of lead on motor dexterity function. 16730797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16757504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17164378_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17291479_Results point out that there is a correlation among diabetes, hypothyroidism and delta-ALA-D activity. 17366816_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17383846_A negative correlation was found between the alteration in delta-ALA-D activity and oxidative stress 17649958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17649958_study found that ALAD polymorphism had a small or only modest effect on blood lead levels in Thai workers who were exposed to lead 17823382_ALAD 1-1 carriers exhibit a greater likelihood than ALAD 1-2/2-2 carriers of psychiatric symptoms at a higher lead burden. 17823382_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17966070_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17966070_certain ALAD genotypes may affect the susceptibility of humans to lead 18271513_The morpheein equilibria of wild type (WT) human PBGS are found to respond to changes in pH, PBGS concentration, and substrate turnover. 18282196_Pregnancy is associated with increased plasma lead/whole blood lead ratio in ALAD 1-1 genotype. 18432999_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18569569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18784554_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18795909_A significant difference was seen in the frequency distribution of ALAD genotype between Uygur and Han races. The genetic susceptibility of ALAD polymorphism to lead toxicity may exhibit in a lead dose-dependent manner. 18795909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19028776_ALAD G177C polymorphism along with BLL and assessment of hematological parameters may play an important role in evaluation and better understanding of the consequences of lead exposure. 19028776_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19327888_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19440429_genotype was significantly associated with the blood lead concentration 19515364_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19548578_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19548578_Polymorphisms of ALAD and VDR gene may play an important role in lead nephrotoxicity in high lead-exposed workers. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19686844_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19723536_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19766174_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19766174_The frequencies of ALAD2 in Asian populations were comparable to those in Caucasians, while Africans had no mutation allele 19789817_ALAD has a major and limiting role in regulating protoporphyrin IX synthesis and photodynamic therapy outcome. 19812033_Allosteric inhibition of human porphobilinogen synthase. 20021040_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20021192_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20069172_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20123609_blood lead levels may be an important risk factor for hypertension and increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure. These associations may be modified by ALAD genotype. 20406759_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20510440_Lead-exposed workers with the ALAD2 allele appear to be more susceptible to the effects of lead on renal injury, whereas neurobehavioral functions in ALAD1 homozygote tend to be more vulnerable. 20510440_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20798009_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21293208_Examined whether the ALAD G177C single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) affects the relationship between lead and mortality; observed no convincing interaction effect between ALAD genotype and blood lead level on mortality risk. 21327641_ALAD2 and hPEPT2*2 polymorphisms may exaggerate Pb blood burden in boys. 21396434_Study suggests that the lead-exposure-induced increases in ALAD methylation may be involved in the mechanism of lead toxicity. 21439310_ALAD genotype modifies the relationship between Pb and its toxic effects on the peripheral nervous system. This must be considered in the assessment of risks at Pb exposure. 21762684_association between oxidative stress, abnormalities on lipid profile, distribution of body fat and delta-ALA-D activity inhibition; the enzyme is more oxidized in the DM2 patient 21799727_A common genetic variation in ALAD may alter the risk of renal cell carcinoma 22101007_This study demonostrated that modification by the genes ALAD lead-induced cognitive effects in children. 22298357_distribution of a single nucleotide polymorphism in two populations from the Iberian Peninsula 22851944_Workers with the ALAD 1-1 genotype were associated with higher blood lead levels than those with the ALAD 1-2 genotype. 24156693_The results lend support to the notion that ALAD polymorphism exerts no marked impact on lead body burden. 24500903_Genetic variation in ALAD may modify associations between Pb and prostate cancer 24631795_Report the effect of ALAD polymorphism on hematopoietic, hepatic and renal toxicity from lead in occupational exposure workers. 24855033_This study investigated the delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase (delta-ALA-D) activity in whole blood as well as the parameters of oxidative stress, in lung cancer. 25460652_The results indicate that the ALAD1-2/2-2 genotype may have a protective effect in terms of urinary aminolevulinic acid for environmentally lead exposed boys. 25514583_This study showed that ALAD2 and hPEPT2*2 may be valuable markers of risk, and indicate novel mechanisms of lead-induced neurotoxicity 25528913_The ff carriers in VDR FokI polymorphism were more susceptible to the effect of lead on the balance system, while other VDR or ALAD genotypes did not significantly modify the effect. 25820613_Genetic variation of ALAD is associated with blood lead level. 25963508_Study reveals relationship between ALAD genetic polymorphisms and basic lead toxicological parameters in occupationally exposed workers. 26261627_Maternal ALAD gene polymorphism can affect early neonatal neurobehavioral development by influencing the blood lead level. 26275098_Blood lead level affected ALAD but not GPx activities, and these were not modulated by polymorphisms in ALAD and GPx genes. 26701682_Results show statistically significant association between the maternal ALAD G177C polymorphism and placental lead levels. 27657831_Delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase activity and oxidative stress markers were significantly lowered in preeclampsia. 28276576_The frequencies of genotype and allelic variants of ALAD rs1800435 did not differ significantly between patients with essential tremor (ET) and controls, and were not influenced by gender. Subjects carrying the ALAD rs1800435CC genotype (wild-type) and the HMOX2 rs1051308GG genotype or the HMOX2 rs1051308G allele had significantly decreased risk for ET. 28403546_Overexpression of delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase (ALAD)suppresses breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion and inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype. 28960093_ALAD SNP rs818708 is significantly associated with risk of lead poisoning. 29028685_The ALAD gene influences bone density among lead workers. 29148924_The delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase activity was significantly lower in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. 29175793_Automobile paints workers with ALAD 1-2 genotype showed the positive association of blood lead levels with diastolic blood pressure whereas, a genotypic combination of ALAD 1-2/VDR BB showed the negative association of serum uric acid with BLL. 30025905_ALAD genetic polymorphisms contribute to high blood lead levels in occupational exposed workers and may predict risk of lead poisoning. 30557693_aminolevulinate dehydratase genotype may be a susceptibility factor for the effects of lead on child growth 31041926_delta-Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase gene polymorphism may be an effect modifier and a marker of genetic susceptibility to lead toxicity. 31851550_Activity of the enzyme delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase and parameters of oxidative stress in different modes of delivery. 31859063_Pb blood variability was found associated with ALAD polymorphisms (SNPs rs1805313, rs1800435) 33199206_5-Aminolevulinate dehydratase porphyria: Update on hepatic 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase induction and long-term response to hemin. 33298951_Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase. 34244947_Genetic susceptibility of delta-ALAD associated with lead (Pb) intoxication: sources of exposure, preventive measures, and treatment interventions. 34444495_Genetic Polymorphism of Delta Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase (ALAD) Gene and Symptoms of Chronic Mercury Exposure in Munduruku Indigenous Children within the Brazilian Amazon. |
ENSMUSG00000028393 |
Alad |
280.870857 |
0.4380536616 |
-1.190820 |
0.111066730 |
115.464594 |
0.00000000000000000000000000622607778298619682957135073237443222849816292589335225534531080177915417228629024748443043790757656097412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000071459493061334576632081063298844216985107828285782012217989084191160833320344281105462869163602590560913085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
169.4454532 |
14.3016215 |
389.7430706 |
22.5951857 |
| ENSG00000148248 |
6836 |
SURF4 |
protein_coding |
O15260 |
FUNCTION: Endoplasmic reticulum cargo receptor that mediates the export of lipoproteins by recruiting cargos into COPII vesicles to facilitate their secretion (PubMed:30251625, PubMed:29643117, PubMed:33186557). Acts as a cargo receptor for lipoproteins bearing both APOB and APOA1, thereby regulating lipoprotein delivery and the maintenance of lipid homeostasis (PubMed:29643117, PubMed:33186557). Synergizes with the GTPase SAR1B to mediate transport of circulating lipoproteins (PubMed:33186557). Promotes the secretion of PCSK9 (PubMed:30251625). Also mediates the efficient secretion of erythropoietin (EPO) (PubMed:32989016). May also play a role in the maintenance of the architecture of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment and of the Golgi (PubMed:18287528). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18287528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29643117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30251625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32989016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33186557}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene is located in the surfeit gene cluster, which is comprised of very tightly linked housekeeping genes that do not share sequence similarity. The encoded protein is a conserved integral membrane protein that interacts with endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment proteins. Disruption of this gene results in reduced numbers of endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment clusters and redistribution of coat protein I to the cytosol. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:6836; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipoprotein transport [GO:0042953]; positive regulation of organelle organization [GO:0010638]; regulation of lipid transport [GO:0032368] |
18287528_Silencing Surf4 together with ERGIC-53 or silencing the p24 family member p25 induced an identical phenotype characterized by a reduced number of ERGIC clusters and fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus without effect on anterograde transport. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 29643117_SFT-4 and Surf4 regulate the export of soluble proteins, including lipoproteins, from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and participate in ER exit site organization in animals. 29777698_SURF4 demonstrated aberrant amplification and increased expression in the tumor tissues of several human cancer patients. 30086131_Surf4 (or its yeast ortholog, Erv29p) binds amino-terminal tripeptide motifs of soluble cargo proteins with different affinities, enabling prioritization of their exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. 30251625_These findings support a model in which SURF4 functions as an endoplasmic reticulum cargo receptor mediating the efficient cellular secretion of PCSK9. 31645450_These results indicate that the cellular protein Surf4 is involved in the replication of positive-strand RNA viruses that use DMVs as RNA replication sites, providing new insights into DMV formation during virus replication and potential targets for the diagnosis and treatment of positive-strand RNA viruses. 31676436_Study findings revealed that knockdown of Surf4 increased expression and secretion of PCSK9, indicating a negligible role of Surf4 in PCSK9 secretion in cultured human hepatocytes. 32026660_SURF4 maintains stem-like properties via BIRC3 in ovarian cancer cells. 32989016_The Endoplasmic Reticulum Cargo Receptor SURF4 Facilitates Efficient Erythropoietin Secretion. 33186557_Receptor-Mediated ER Export of Lipoproteins Controls Lipid Homeostasis in Mice and Humans. 34919127_Efficient progranulin exit from the ER requires its interaction with prosaposin, a Surf4 cargo. 35051356_SURF4-induced tubular ERGIC selectively expedites ER-to-Golgi transport. 35271396_A SURF4-to-proteoglycan relay mechanism that mediates the sorting and secretion of a tagged variant of sonic hedgehog. 35901214_Selective inhibition of protein secretion by abrogating receptor-coat interactions during ER export. |
ENSMUSG00000014867 |
Surf4 |
1502.397876 |
2.0797810450 |
1.056432 |
0.039024686 |
744.134240 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007565464551713129469108549823085892377221957043186944959567792771520272880763387027784155324087469507197959133514765802242690444570978513369452704605591169195335658778 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005500800826762847159763373158161879138535520090780244467662461876528056900184475077267698682697360914574881437160072596231623639957020484423079604647028497676532050036 |
Yes |
Yes |
2054.7368919 |
50.0128974 |
994.7336528 |
19.1712700 |
| ENSG00000148288 |
26301 |
GBGT1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N5D6 |
FUNCTION: Has lost the ability to synthesize Forssman glycolipid antigen (FORS1/FG) (PubMed:10506200). Might have acquired an alternative function in glycosphingolipid metabolism, but it remains to be established. It appears to have drifted more slowly than confirmed pseudogenes in the glycosyltransferase 6 family, suggesting that it has remained under evolutionary pressure. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10506200, ECO:0000305}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
This gene encodes a glycosyltransferase that plays a role in the synthesis of Forssman glycolipid (FG), a member of the globoseries glycolipid family. Glycolipids such as FG form attachment sites for the binding of pathogens to cells; expression of this protein may determine host tropism to microorganisms. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:26301; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; globoside alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0047277]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; glycolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0009247]; lipid glycosylation [GO:0030259]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23255552_The Fs synthase gene, GBGT1, in A(pae) individuals encoded an arginine to glutamine change at residue 296. 25294702_GBGT1 expression is epigenetically silenced through promoter hypermethylation in ovarian cancer. 29898878_an amino acid substitution at codon 69 from methionine to threonine or serine (Met69Thr/Ser) modified enzymatic specificity of Blood group A/B glycosyltransferases and permitted FORS1 biosynthesis 30277576_extended the knowledge of GBGT1 variants, allele frequencies, and the characteristics of naturally occurring antibodies in our newest carbohydrate blood group system, FORS. The finding of c.363C>A-homozygous donors indicates that GBGT1 is dispensable. |
ENSMUSG00000026829 |
Gbgt1 |
45.055048 |
0.3239651339 |
-1.626090 |
0.261643368 |
39.304982 |
0.00000000036251519004805581493028804881213669059070170419545320328325033187866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001797958402254470388696612041269911469454356733876920770853757858276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.5397274 |
3.8093318 |
70.2743551 |
7.5075834 |
| ENSG00000148358 |
57720 |
GPR107 |
protein_coding |
Q5VW38 |
FUNCTION: Has been proposed to act as a receptor for neuronostatin, a peptide derived from the somatostatin/SST precursor (PubMed:22933024). Involved in blood sugar regulation through the induction of glucagon in response to low glucose (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZWZ9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22933024}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Required for intoxication by Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and Campylobacter jejuni CDT. May contribute to the retrograde transport of bacterial toxins, including cholera toxin, from the trans-Golgi network to the endoplasmic reticulum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25031321}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable clathrin heavy chain binding activity. Predicted to be involved in clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Located in Golgi apparatus and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57720; |
clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; clathrin heavy chain binding [GO:0032050]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583] |
17454009_The 18-exon human GPR107 gene is located at 9q34.2-3 and spans 86.4 kb and the cDNA encodes a 552 residue protein; murine Gpr108 cDNA encodes a 562 residue protein that has 49% identity to human GPR107. 22933024_GPR107 is a promising candidate receptor for neuronostatin, and neuronostatin, interacting with GPR107, may play an important role in the central control of cardiovascular function. 25031321_The N-terminal region of GPR107 is critical for its biological function. GPR107 might be one of the long-sought receptors that associates with G-proteins to regulate intracellular vesicular transport 33121311_Changes in expression of orphan receptors GPR99 and GPR107 during the development and establishment of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. |
ENSMUSG00000000194 |
Gpr107 |
893.479454 |
2.4765384902 |
1.308325 |
0.509646934 |
6.383295 |
0.01151993813007534499248674109139756183139979839324951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021813250391265182753786078251323488075286149978637695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1382.9321558 |
589.1000553 |
560.0088917 |
171.0089583 |
| ENSG00000148400 |
4851 |
NOTCH1 |
protein_coding |
P46531 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged-1 (JAG1), Jagged-2 (JAG2) and Delta-1 (DLL1) to regulate cell-fate determination. Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBPJ/RBPSUH and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus. Affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs. Involved in angiogenesis; negatively regulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration and angiogenic sprouting. Involved in the maturation of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells in the thymus. Important for follicular differentiation and possibly cell fate selection within the follicle. During cerebellar development, functions as a receptor for neuronal DNER and is involved in the differentiation of Bergmann glia. Represses neuronal and myogenic differentiation. May play an essential role in postimplantation development, probably in some aspect of cell specification and/or differentiation. May be involved in mesoderm development, somite formation and neurogenesis. May enhance HIF1A function by sequestering HIF1AN away from HIF1A. Required for the THBS4 function in regulating protective astrogenesis from the subventricular zone (SVZ) niche after injury. Involved in determination of left/right symmetry by modulating the balance between motile and immotile (sensory) cilia at the left-right organiser (LRO). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20616313}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Angiogenesis;ANK repeat;Calcium;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Metal-binding;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the NOTCH family of proteins. Members of this Type I transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple different domain types. Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway that regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells through binding of Notch family receptors to their cognate ligands. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed in the trans-Golgi network to generate two polypeptide chains that heterodimerize to form the mature cell-surface receptor. This receptor plays a role in the development of numerous cell and tissue types. Mutations in this gene are associated with aortic valve disease, Adams-Oliver syndrome, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4851; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; MAML1-RBP-Jkappa- ICN1 complex [GO:0002193]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; enzyme inhibitor activity [GO:0004857]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription regulator activator activity [GO:0140537]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; apoptotic process involved in embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:1902263]; arterial endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060842]; astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048708]; atrioventricular node development [GO:0003162]; atrioventricular valve morphogenesis [GO:0003181]; auditory receptor cell fate commitment [GO:0009912]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube [GO:0048754]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; cardiac atrium morphogenesis [GO:0003209]; cardiac chamber formation [GO:0003207]; cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0060317]; cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003214]; cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation [GO:0060379]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0055008]; cardiac right atrium morphogenesis [GO:0003213]; cardiac right ventricle formation [GO:0003219]; cardiac septum morphogenesis [GO:0060411]; cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell development [GO:0060948]; cardiac ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003208]; cell differentiation in spinal cord [GO:0021515]; cell migration involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003273]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to tumor cell [GO:0071228]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; collecting duct development [GO:0072044]; compartment pattern specification [GO:0007386]; coronary artery morphogenesis [GO:0060982]; coronary sinus valve morphogenesis [GO:0003182]; coronary vein morphogenesis [GO:0003169]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; distal tubule development [GO:0072017]; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035116]; endocardial cell differentiation [GO:0060956]; endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:0003203]; endocardium development [GO:0003157]; endocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003160]; endoderm development [GO:0007492]; epidermal cell fate specification [GO:0009957]; epithelial cell fate commitment [GO:0072148]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003198]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; foregut morphogenesis [GO:0007440]; glomerular mesangial cell development [GO:0072144]; growth involved in heart morphogenesis [GO:0003241]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; heart trabecula morphogenesis [GO:0061384]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; immune response [GO:0006955]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002437]; inhibition of neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0002085]; interleukin-17-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0097400]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; left/right axis specification [GO:0070986]; liver development [GO:0001889]; lung development [GO:0030324]; mesenchymal cell development [GO:0014031]; mitral valve formation [GO:0003192]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; negative regulation of biomineral tissue development [GO:0070168]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0045955]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy [GO:0010614]; negative regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0043086]; negative regulation of cell adhesion molecule production [GO:0060354]; negative regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090051]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cell proliferation involved in heart valve morphogenesis [GO:0003252]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000048]; negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010812]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:2001027]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0003332]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060253]; negative regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045608]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010832]; negative regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050768]; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048715]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of photoreceptor cell differentiation [GO:0046533]; negative regulation of pro-B cell differentiation [GO:2000974]; negative regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000737]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neural tube development [GO:0021915]; neuroendocrine cell differentiation [GO:0061101]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; Notch signaling involved in heart development [GO:0061314]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; Notch signaling pathway involved in regulation of secondary heart field cardioblast proliferation [GO:0003270]; oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048709]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; pericardium morphogenesis [GO:0003344]; positive regulation of aorta morphogenesis [GO:1903849]; positive regulation of apoptotic process involved in morphogenesis [GO:1902339]; positive regulation of astrocyte differentiation [GO:0048711]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0062043]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045603]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0045618]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription of Notch receptor target [GO:0007221]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis [GO:0060740]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development [GO:0060768]; regulation of extracellular matrix assembly [GO:1901201]; regulation of somitogenesis [GO:0014807]; regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:0072091]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to corticosteroid [GO:0031960]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to muramyl dipeptide [GO:0032495]; retinal cone cell differentiation [GO:0042670]; secretory columnal luminar epithelial cell differentiation involved in prostate glandular acinus development [GO:0060528]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; somatic stem cell division [GO:0048103]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:0072538]; tissue regeneration [GO:0042246]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; tube formation [GO:0035148]; vasculogenesis involved in coronary vascular morphogenesis [GO:0060979]; venous endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0060843]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222] |
11836628_expressed in human osteoblastic cells and that the expression is differentially regulated upon stimulation with osteogenic factors 11848684_Notch dysregulation may contribute to the neuritic dystrophy characteristically seen in Alzheimer's disease brain. 11940670_Notch signaling induces rapid degradation of achaete-scute homolog 1 11964309_Activated Notch1 signaling promotes tumor cell proliferation and survival in Hodgkin and anaplastic large cell lymphoma 11978185_Notch signalling involved in differentiation of normal adult human epidermis is altered under experimental conditions and pathologies which modify this program. 12048239_presenilin-1 mutation of leu 166 affects generation independent of its effect on Abeta42 production 12065598_acid alpha-glucosidase gene is a novel target of the Notch-1/Hes-1 signaling pathway 12145413_Expression of constitutively active recombinant human Notch1 proteins decreased neurite length and number after NGF treatment. 12208848_exerts specific protective effects against HPV-induced transformation through suppression of E6/E7 expression, and down-modulation of Notch1 expression is likely to play an important role in late stages of HPV-induced carcinogenesis 12357247_These data are the first to implicate the Notch pathway in the limited remyelination in multiple sclerosis. 12370358_Activation of Notch-1 signaling promotes the maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. 12482957_We show here that vascular endothelial growth factor but not basic fibroblast growth factor can induce gene expression of Notch1 and Dll4, in human arterial endothelial cells. The VEGF-induced specific signaling is mediated through VEGF receptors 1 and 2 12509463_Notch1 is required for transcriptional coactivator recruitment and cell growth in tumor cell lines 12527910_requirement for growth of SV40-transformed mesothelial cells 12532332_Data show that Notch1 signalling is differentially regulated in T-acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) and B-lymphoma cells. 12768030_inhibits p53-induced apoptosis and transactivation of PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway for HPV16 E6 and E7 cell transformation 12781689_The NOTCH signalling pathway regulates the basal layer of interfollicular epidermis clusters by controlling stem cell differentiation on the periphery of the clusters. 12829602_regulation of Notch1 activity at defined developmental windows is essential to control alphabeta versus gammadelta T-cell development and to avoid deregulated expansion of alphabeta-lineage cells. 12913000_The ankyrin domain of Notch1 receptor (N1IC) and zinc finger domains of YY1 were essential for the association of N1IC and YY1, which were both present in a large complex of the nucleus to suppress activity transactivated by Notch signaling 12960155_Notch activation directly engages gamma-secretase and subsequently leads to diminished PS1 expression, suggesting a complex set of feedback interactions following Notch activation 14602722_notch and erks have roles in prostate cancer bone metastases 14645224_Notch-1-mediated repression of activator protein-1 requires C promoter-binding factor 1 14670925_activation of only Notch-1, but not Notch-2, resulted in protection of tumor cells from melphalan- and mitoxantrone-induced apoptosis. This protection was associated with up-regulation of p21(WAF/Cip) and growth inhibition of cells. 14678992_Notch1 signaling may participate in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, affecting multiple pathways that control both cell proliferation and apoptosis. 14726396_Notch receptors 1&2 and their ligand Jagged1 are highly expressed in cultured and primary MM cells, suggesting Notch signaling is involved in the tight interactions between neoplastic plasma cells and their bone marrow microenvironment 14762442_NOTCH1 intracellular domain was found in a human malignant peripheral nerve sheath Schwann cell, indicative of ongoing Notch signaling. 14996707_Notch1 gene expression was decreased 5-fold in osteopontin-treated CD34+ cells 15044485_transcriptional transactivation by APP and Notch may involve distinct mechanisms; whereas the Notch intracellular domain directly functions in the nucleus, the AICD acts indirectly by activating Fe65 15058751_Notch1 gene is involved in the differentiation and leukemogenesis in ATRA-modulated process in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 15213460_NMR assignment of human Notch-1 calcium binding EGF domains 11-13 15240571_monoubiquitination and endocytosis of Notch are a prerequisite for its presenilin-dependent cleavage 15280477_upregulated in Papillomavirus-mediated cervical neoplasia and its activation is Jagged1 dependent. 15448134_ligand-induced reversal of controlled TMD dimerization by the Notch extracellular domain is unlikely to underlie the regulatory mechanism of intramembranous cleavage 15472075_more than 50% of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias, including tumors from all major molecular oncogenic subtypes, have activating mutations involving the extracellular heterodimerization domain and/or the C-terminal PEST domain of NOTCH1 15485896_two contiguous regions of noncovalently associated extracellular impose crucial restraints that prevent premature Notch receptor activation 15492044_the Numb/Notch biological antagonism has a role in homeostasis of the normal mammary parenchyma and its subversion contributes to human mammary carcinogenesis 15492845_Notch-1 may possess tumour-promoting functions in breast cancer. 15563463_Notch1 inhibits the development of erythroid/megakaryocytic cells by suppressing GATA-1 activity through HES1 15563588_Active gamma-secretase is present in the plasma membrane. Notch is processed at the cell surface and the majority of APP is processed by intracellular gamma-secretase 15650752_Notch1 fragments generated by caspase cleavage cannot inhibit apoptosis in a T-cells, confirming the abrogation of Notch1 antiapoptotic activity by caspases. 15756589_From 9q34 known genes, NOTCH1 could thus be the primary target of genomic DNA amplification in enteropathy-type t-cell lymphoma. 15774577_Notch1 protein is used reiteratively and cell-autonomously by endothelial cells to regulate vessel diameter, to limit branching at the tip of sprouts 15781650_Down-regulation of Notch-1, Delta-like-1, or Jagged-1 by RNA interference induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in multiple glioma cell lines. 15817159_Notch1 signaling was found to cause growth suppression of HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. 15824732_Pak1-SHARP interaction plays an essential role in enhancing the corepressor functions of SHARP, thereby modulating Notch1 signaling in human cancer cells. 15904468_Notch oncoproteins promote cell growth and cancer development partly by suppressing the growth inhibitory effects of TGF-beta through sequestrating p300 from Smad3 15976178_density of Notch ligands in different organ systems may be an important determinant in regulating cell-fate outcomes 15987768_Notch promotes changes in hVSMC phenotype via activation of CBF-1/RBP-Jkappa-dependent pathways in vitro and contributes to the phenotypic response of VSMCs to cyclic strain-induced changes in VSMC differentiation. 16011479_The crystal structure of human Notch 1, including its homology to Drosophila and other species, is reported. 16025100_mutations in the signalling and transcriptional regulator NOTCH1 cause a spectrum of developmental aortic valve anomalies and severe valve calcification in non-syndromic autosomal-dominant human pedigrees 16079893_Mutations of the Notch1 gene is associated with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 16096376_Notch-1 can participate in cross-talk with other signaling pathways such as Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK through the regulation of the phosphatase and tensin homolog tumor suppressor 16136053_Decreased Notch 1 mRNA is associated with ovarian adenocarcinomas compared with adenomas 16160079_manipulation of the Notch1 signaling pathway may be useful for expanding the targets for therapeutic and palliative treatment of patients with carcinoid tumors 16179393_Notch1-IC negatively regulates the JNK pathway by disrupting the scaffold function of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting protein 1. 16239965_Data suggest a beta-catenin-dependent, stage-specific role for Notch1 signaling in promoting the progression of primary melanoma. 16287852_a corepressor complex containing CtIP/CtBP facilitates RBP-Jkappa/SHARP-mediated repression of Notch target genes 16298817_Acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemias and lymphomas (T-ALL) have gain-of-function mutations in NOTCH1. 16317090_DL1-induced activation of the Notch1 pathway controls the lineage commitment of early thymic precursors by altering the levels between Spi-B and GATA-3. 16322473_HES-1 alone is not able to substitute for Notch-1 signaling to induce T-cell differentiation of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. 16365048_Notch protein binding to Hes5-GFP is extinguished fast and recovered slowly, whereas Hes1-GFP is inhibited late and recovered quickly 16378632_dominant-negative forms of c-Myc block transformation by activated Notch1, E6 and E7, suggesting that c-Myc is required for HPV16-mediated transformation 16434391_release of Abeta- or Nbeta-like peptides is a common feature of the proteolysis during regulated intramembrane proteolysis signaling 16449526_Notch1 is an important 'second hit' for the transformation of E2A deficient T cell lymphomas. 16507111_Cellular responsiveness to Notch signals depends on the activity of the PI3K-Akt pathway in cells as diverse as CHO cells, primary T-cells and hippocampal neurons. 16530044_Results report the crystal structure of a Notch transcriptional activation complex containing the ankyrin domain of human Notch1, the transcription factor CSL on cognate DNA, and a polypeptide from the coactivator Mastermind-like-1 (MAML-1). 16536739_Results suggest that intracellular domains of Notch and amyloid precursor protein are generated by gamma-secretase at the plasma membrane and/or early endosomes. 16608439_Results demonstrate that constitutively over-expressed active Notch1 resulted in growth suppression of the tongue cancer cell line Tca8113 in vitro and in vivo, accompanied by G(0)-G(1) cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. 16618808_p63 expression is suppressed by Notch1 activation in both mouse and human keratinocytes through a mechanism independent of cell cycle withdrawal 16622004_Notch up-regulation and subsequent signaling following macrophage activation modulate gene expression patterns known to affect the function of mature macrophages 16651424_Notch overexpression inhibits p53 induced apoptosis by activating mTOR signaling. Notch, thus makes cancer cells resistant to p53 dependent chemotherapy. Combination chemotherapy of p53 inducers and rapamycin was proved successful at the cell line level. 16688224_the CUTLL1 cell line has a strong dependence on NOTCH1 signaling for proliferation and survival 16707600_NOTCH1 mutations participate in the pathogenesis of T-ALL, providing a promising rationale for targeted therapies that interfere with NOTCH signaling pathway 16707600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16729972_NOTCH1 gene mutations do not only play a role in familiar bicuspid aortic valve, but can also be observed in approximately 4% of sporadic cases. 16738328_effect of 16 putative tumor-associated mutations on Notch1 signaling and heterodimerization domain stability 16785210_Full-length expressed WWP1 could interact in vitro with the cytoplasmic domain of human Notch1, which also regulate the nuclear localization of WWP1. 16822655_Plays a regulatory role in mesodermal development, cardiomyogenesis, the balanced generation of endothelial versus mural cells of blood vessels and hematopoietic development. 16871543_The functional role of AAH in relation to cell motility has been linked to increased activation of the Notch signaling pathway. 16880534_These studies indicate that WSSSSP (S4) sequence of Notch1 is an important negative regulatory sequence and that the deletion of S4 likely contributes to the development of human T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. 16887975_Transgenic intracellular Notch1 and C-terminal-deleted Notch1 mutant molecules behave collaboratively as oncogenes for T cells; these mice may represent relevant models of human T-cell leukemias. 16951331_Notch1 and IL-7 receptor pathways cooperate to synchronize cell proliferation and suppression of non-T lineage choices in primitive intrathymic progenitors. 16990763_Notch signaling is essential to open the T-cell pathway, but does not initiate the T-cell program itself 17008890_The presence of NOTCH1 mutations in myeloid and T-lymphoid clones in lineage switch leukemias establishes the common clonal origin of the diagnostic and relapse blast populations and suggests a stem cell origin of NOTCH1 mutations 17028268_These observations provide further support for a role for Notch-1 signaling in regulating pulmonary neuroendocrine cell differentiation. 17046738_Constitutive expression of the activated Notch1 intracellular domain in male reproductive organs of transgenic mice leads to sterility. 17090547_Medullary thyroid cancer cell growth inhibition by NOTCH1 is mediated by cell cycle arrest associated with up-regulation of p21. 17107915_This is the first paper to present an acute myeloid leukemia case with NOTCH1 mutation 17114293_identify c-MYC as an essential mediator of NOTCH1 signaling and integrate NOTCH1 activation with oncogenic signaling pathways upstream of c-MYC 17186020_Notch signaling downregulated p53-dependent apoptosis induced by ultraviolet irradiation. 17252014_Notch1 transgenes causes T-cell leukemia in zebrafish. Leukemia onset was dramatically accelerated in fish overexpressing bcl-2, indicating synergy between the Notch pathway and the bcl2-mediated antiapoptotic pathway. 17284587_A number of Notch-regulated targets are characterized by paired CSL-binding sites in a head-to-head arrangement; cooperative formation of dimeric Notch transcription complexes on promoters with paired sites is required to activate transcription 17301032_with supervised resistance exercise training, expression of Notch1 and Hes6 genes were increased and Delta-like 1 and Numb expression were decreased. 17309564_RNA interference of PS1 or Notch1 can block Notch signaling and consequently induce growth inhibition of HeLa cells. 17316355_NF-kappaB inhibition may contribute partially to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by Notch1 activation in human cervical cancer cells. 17317671_MAML1 has a coactivator function for p53, independent of its function as a coactivator of Notch signaling pathway 17344417_findings report that the Notch1 gene is a p53 target in human keratinocytes with a role in tumor suppression of this cell type through negative regulation of the ROCK1/2 and MRCKalpha kinases 17353266_Data demonstrate a novel link between p53 and Notch1 in keratinocyte differentiation upon genotoxic stress and suggest a novel tumor suppressor mechanism of p53 in the development of HPV-induced tumors. 17368826_Notch1 intracellular domain plays the role of a negative regulator in AICD signaling via the disruption of the AICD-Fe65-Tip60 trimeric complex. 17392684_Notch-1 was found to be expressed in the limbal basal region where stem cells reside 17404512_Notch1 mediates T cell and epithelial cell transformation at least in part by sustaining c-Myc levels. 17425682_Notch1 signaling may participate in the development of human cervical carcinoma cells, but overexpressed active Notch1 inhibits their growth through induction of cell cycle arrest. 17434929_Transcription factor Ying Yang 1 (YY1) indirectly regulates the C promoter-binding factor 1 (CBF1)-dependent Notch1 signaling via direct interaction with the Notch1 receptor. 17497677_Pathways of signaling by S100A4, by its interaction with and sequestration of p53, and by Notch also seem differentially operational in the induction of apoptosis 17513037_an important relationship exists between zinc and the Notch1 signaling pathway, and that this relationship is intimately involved with the cytoplasmic retention of Notch and RBP-Jk 17560996_Data suggest that the aberrantly high Notch1 signaling in T-ALL maintains SKP2 at a high level and reduces p27Kip1, leading to more rapid cell cycle progression. 17573339_NOTCHES N1, N2, and N3 all bound to FIH; results suggest the possibility that Notch ICDs are FIH substrates. 17604336_These studies suggest that Notch inhibition can initiate aberrant mitosis by inducing NF-kappaB activity that inappropriately increases cyclin B1 resulting in cell death via mitotic catastrophe. 17636029_HTATIP acts as a negative regulator of Notch1 signaling by means of acetylation. 17646409_FBW7 mutations in leukemic cells mediate NOTCH pathway activation and resistance to gamma-secretase inhibitors 17652726_Notch family members and ligands are expressed in the human corneal epithelium and appear to play pivotal roles in corneal epithelial cell differentiation 17662764_targeted analysis involving NOTCH1 exons previously implicated in familial and sporadic bicuspid aortic valve demonstrates overrepresentation of NOTCH1 missense variants among patients with bicuspid aortic valves and thoracic aortic aneurysms 17664272_Notch1 ligand, Delta-like ligand-4, stimulates R-Ras-dependent alpha 5 beta 1 integrin-mediated adhesion, demonstrating the physiological relevance of this pathway. 17671232_Acute myeloid/T-lymphoid leukemia with silenced CEBPA and mutations in NOTCH1. 17716607_There is no evidence of linkage of bicuspid aortic valve in our pedigree to either the NOTCH1 gene or to the chromosome 15 locus. The disorder in this family appears to be caused by a gene at a novel locus. 17804701_Hypoxia dramatically elevates NOTCH signaling (especially NOTCH-1) in lung tumor cell lines. 17822320_Overexpression of notch1 is associated with breast cancer 17851046_Human umbilical cord epithelial cells express Notch1 as in epidermal keratinocytes. 17873882_Mutational loss of PTEN induces resistance to NOTCH1 inhibition in T-cell leukemia. 17874453_Persistent expression of NOTCH1 in such cancers as adult T-cell leukemia lymphoma suggests that Notch pathway inhibitors could have a role in the treatment of these unusual neoplasms. 17901244_NOTCH1 can be an early or initiating event in T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia arising prenatally 17920003_Expression of Notch 1 receptors was upregulated and Notch signaling might be involved in development of hepatocellular carcinoma. 17922104_The Notch/Ngn3 signalling network is intact and functional in adult islets. 17927876_The activated Notch1 signaling pathway gives rise to the apoptosis of EC9706 cells. 17948123_Data demonstrate that Notch1 and VEGFR-3 interact genetically, that Notch directly induces VEGFR-3 in blood endothelial cells to regulate vascular development, and that Notch and VEGF signaling may function in tumor lymphangiogenesis. 17967789_Notch is activated upon coculture of EPCs with neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Gamma-secretase-dependent Notch activation is required for cardiac gene expression 17980397_These results demonstrate that EBV LMP2A activates the Notch pathway in both B cells and epithelial cells. 17984306_Ligand-induced Notch activation, through the induction of Slug, promotes tumor growth and metastasis characterized by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 17991315_The positive rate of Notch1 was significantly higher in gastric cancer than in normal gastric tissue. 18055449_The results indicate that cell-cell signaling through the NOTCH system provides a critical cue for the proliferation of human embryonic stem and embryonal carcinoma cell in vitro. 18056171_These results suggest that Notch-1 mutations can sometimes be acquired as secondary events in leukemogenesis and must be used cautiously as solitary minimal residual disease markers. 18069660_we conclude that in the ectatic ducts of CP, PDH activates signalling pathways such as Notch, which have transforming potential. 18079963_Notch-1 and the Notch ligand Jagged-1 were expressed at significantly higher levels in CCRCC tumors than in normal human renal tissue, and the growth of primary CCRCC cells was attenuated upon inhibition of Notch signaling. 18084619_Recombinant Notch-1 mediated the stimulating effects of recombinant erythropoietin on cultured cancer-initiating breast cancer cells from 3 cell lines. 18155729_the RBP-Jkappa-associated domain of Notch increases the effective concentration of the ankyrin domain for its binding site on CSL, enabling docking of the ankyrin domain and subsequent recruitment of the Mastermind-like coactivator. 18184405_NOTCH1 is mutated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias, but not in other common human cancers 18192230_The results thus showed that Jag-1-mediated Notch signaling in human bone marrow stromal cells was necessary to initiate chondrogenesis, but it must be switched off for chondrogenesis to proceed. 18192969_in UV-related squamous cell photocarcinogenesis Notch 1 downregulation could mirror a tumor suppressor function of the receptor, in sun-protected squamous cell carcinomas Notch 1 was upregulated 18219106_Primary colorectal carcinomas display aberrant expression of vimentin, and have activated Notch and TGFbeta signaling pathways. 18239137_Present a novel mechanism by which a balance between Notch-1/-2/-4 signaling, via CBF-1, and HRT-1/-2 activity determines the expression of smooth muscle differentiation markers including actin. 18292500_Notch1 signaling affects regulatory T cell effector function via its effect on transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta signaling rather than via a TGF-beta-independent mechanism. 18292942_Notch1 signaling pathway may participate in carcinogenesis of the esophagus. 18296446_long range calcium-dependent structural perturbations can influence the affinity of Notch for its ligand, in the absence of any post-translational modifications 18296609_Over-expression of constitutively activated Notch1 intracellular domain (Notch-ICD) also inhibited odontoblastic differentiation of DPSCs. Taken together, our results demonstrate Notch signaling can inhibit the odontoblastic differentiation of DPSCs. 18311147_activation of the Notch pathway, which is critical in glomerular patterning, contributes to the development of glomerular disease 18320325_Report the antitumor effects of COX2 inhibitors may be associated with effects on the Delta1/Notch1 pathway in colon tumor cells. 18347015_Pofut1 and O-fucose have roles in mammalian Notch signaling 18354251_Data show that Notch1 are abundantly expressed in osteoarthritis. 18359760_Notch-1 upregulates EGFR expression and also demonstrate Notch-1 regulation of p53 in gliomas. 18411416_a novel class of activating mutations in NOTCH1, juxtamembrane expansion alleles consisting of internal duplication insertions in the vicinity of exon 28, lead to aberrant activation of NOTCH1 signaling in T-cell lymphoblasts. 18427106_These data demonstrate a complex integration of the hypoxia and Notch signaling pathways in regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 18449208_Notch activation interferes with dedifferentiation of neoplastic B cells in Hodgkin lymphoma 18456406_These results demonstrate that Notch signaling has little relevance with resveratrol-induced differentiation and apoptosis and may not be a universal critical factor of MB cells. 18469855_Notch-1 might play a novel role in resistance to trastuzumab, which could be prevented or reversed by inhibiting Notch-1. 18490439_These results indicate that the activated Notch1 receptor and alpha-enolase or MBP-1 cooperate in controlling c-myc expression through binding the YY1 response element of the c-myc promoter to regulate tumorigenesis. 18497996_Down-regulation of Notch-1 expression is associated with leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia 18549623_Notch1 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways participate in bortezomib-inducing RPMI8226 cell apoptosis. 18552977_The inverse correlation between Notch signaling and the proliferative status of the corneal epithelium is consistent with the idea that Notch plays a role in corneal epithelial differentiation. 18559519_Overexpression of notch1 is associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer and neuroblastoma 18560356_Notch-1 stimulates NF-kappaB activity in CaSki cervical cancer cells by associating with the IKK signalosome through IKKalpha. 18570928_The HDAC inhibitor VPA activates Notch1 signaling in SCLC cells 18593473_Both in vitro Reelin treatment and overexpression of Notch-1 intracellular domain induced BLBP expression and a radial glial phenotype in an immortalized human neural progenitor cell line, isolated from the cortex of 14 weeks old fetus 18593716_Two mutations in the NOTCH1 found in patients with left ventricular outflow tract defects reduce JAGGED1 induced signaling. 18593923_Combinations of antiestrogens and Notch inhibitors may be effective in ERalpha(+) breast cancers; Notch signaling is a potential therapeutic target in ERalpha(-) breast cancers. 18593928_ER- breast cancer cells become dependent on Notch-survivin signaling for their maintenance, in vivo. 18593982_activation of Notch signaling might play a crucial role in brain metastasis 18604200_EGFR is a key negative regulator of Notch1 gene expression in primary human keratinocytes, intact epidermis and skin squamous cell carcinomas 18625637_Data suggest that defects in Notch1 upregulation upon activation of T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus are related to lupus disease activity. 18628966_AIP4/Itch regulates Notch receptor degradation in the absence of ligand 18633435_arsenite, by decreasing generation of the tumor suppressor Notch1, contributes to skin carcinogenesis 18660822_the conserved face of the Jagged/Serrate DSL domain is involved in Notch trans-activation and cis-inhibition 18663143_Slug is up-regulated by Notch in endothelial cells; Slug is required for Notch-mediated repression of the vascular endothelial cadherin promoter and for promoting migration of transformed endothelial cells. 18663146_K-RasG12D-induced T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemias harbor Notch1 mutations 18664540_Notch signaling is involved in the determination of thyroid cell fate and is a direct regulator of thyroid-specific gene expression. 18703315_Wnt (Wnt2), Stat3, and Notch-1 and -2 signaling are correlated in human epidermal tumors. 18758479_There is a complex interplay between Notch1 signaling & papillomaviruses in the context of cervical carcinogenesis. Moderate Notch1 levels upregulate c-Myc, activate PKB/Akt & induce transformation. High levels can induce apoptosis. Review. 18758480_Notch 1 is a tumor suppressor gene under direct p53 control. Review. 18777195_Notch1 expression correlated closely with colorectal cancer differentiation 18844067_In active phase AA patients, the levels of FOXP3 and Notchl mRNA were lower than that in the control group. 18924608_NOTCH1 is an effector of Akt and hypoxia in melanoma development. 18984862_major role of the NOTCH pathway activation in human T-cell acute leukemia development and in the maintenance of leukemia-initiating cells 19008176_Notch1 intracellular domain positive products were observed in the cells at the peripheral layer of most proliferating epithelial tumor nests in mandibular ameloblastoma. 19023031_Report requirement for Notch activation during regeneration of the intestinal epithelia. 19025652_High expression of Notch-1 is associated with breast cancer. 19047145_Evidence shows Notch-1 is elevated in the malignant setting, Notch-2 is diminished. This differential expression of the two Notch isoforms benefits cancer cell survival because reexpression of Notch-2 was toxic to MM cells. 19057901_Downregulation of Notch1 signaling by gamma-secretase inhibitors caused neither cell cycle block nor cell death in T-ALL cells 19074836_Notch signaling suppresses KLF4 expression in intestinal tumors and colorectal cancer cells 19091404_results demonstrated that down-regulation of Notch-1 signaling could sensitize SupT1 cells to adriamycin 19109228_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19109228_demonstrate that NOTCH1 pathway activation by either NOTCH1 or FBXW7 mutation identifies a large group of patients with a favorable outcome that could justify individual therapeutic stratification for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 19118200_a combinatorial regulatory program in which MYC cobinds to virtually all NOTCH1-bound promoters 19122673_Results suggest that repression of HPV18 E6/E7 expression by Notch1 signaling results in the activation of p53-mediated pathways with concomitant growth suppression of HPV18-positive EC109 esophageal carcinoma cells. 19147749_the involvement of Notch1 in human PCa invasion and that silencing of Notch1 inhibits invasion of human PCa cells by inhibiting the expression of MMP9 and uPA 19151708_In human breast cancers, we observed a strong correlation between Pin1 overexpression and high levels of activated Notch1. Thus, the molecular circuitry established by Notch1 and Pin1 may have a key role in cancer. 19151773_A second NOTCH1 chromosome rearrangement: t(9;14)(q34.3;q11.2) is associated with T-cell neoplasia. 19160126_Notch-1 may be a potential mechanism of bone marrow stromal cells involvement in the protection of hematopoietic malignant cells from drug-induced apoptosis 19167678_sustained Notch signaling can replace stroma in differentiation of a common CD7(+) lymphoid precursor from UCB CD34(+) progenitors and induce NK cell commitment. However, the NK cells are immature in their cytokine production profile, are hyporesponsive. 19209236_Neural stem/progenitor cells undergo chromosomal changes with repeated in vitro passages under mitogen stimulation, and up-regulation of hTERT and NOTCH1 associates with in vivo tumorigenicity. 19228774_Study reports that human osteosarcoma cell lines and primary human osteosarcoma tumor samples show significant up-regulation of Notch, its target genes and Osterix. 19234458_Notch maintains ependymal cell quiescence and phenotype in transgenic mice, suppressing neuronal differentation; after stroke, ependymal cells do not fulfill defining criteria for stem cells, serving instead as a reservoir that is recruited by injury. 19239437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19245433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247952_Studies indicate that the mechanisms that lead to Notch activity in the receiving cell include the cleavage of Notch at the cell membrane and the assembly of a nuclear complex with the transcription factors CSL. 19339697_Notch signaling in B cells and B-cell lymphomas is only compatible with proliferation if pathways leading to antiapototic signals are active. 19340001_In T-ALL, NOTCH1 mutations resulted in 1.3- to 3.3-fold increased transactivation of an HES1 reporter construct and consequent upregulation of several chemotherapy relevant genes. 19340001_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19349467_Notch1 controls early T cell development, in part by regulating the stage- and lineage-specific expression of IL-7Ralpha. 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19396152_In contrast with neuroendocrine tumors in other tissues, evident Notch-1 expression was found in Merkel cell carcinoma. 19404845_expression levels of Notch1 and Notch4 were absent or significantly decreased in renal cell carcinoma tissues 19407245_Sonic Hedgehog induces Notch target gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells via VEGF-A 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19479935_Defects in Notch-1 signaling may play a role in human prostate tumor formation in part via a mechanism that involves regulation of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene. 19491270_results suggest that activation of Notch1 signal pathway promotes progression of gastric cancer, at least in part through COX-2 19549918_The use of a constitutively active, truncated Notch transgene construct was used to determine if Notch1 activation or a 'driving' event in melanocytes is associated with melanoma progression. 19550121_Data show that Notch1 expression is negatively correlated to DDP-sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and could be used to predict DDP-sensitivity. 19590514_Observational study |
ENSMUSG00000026923 |
Notch1 |
2483.913537 |
2.6670175770 |
1.415227 |
0.044769604 |
992.284501 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008537756298808065529341305917127843640588162095675958116090866441013945233749616128132392123186375784459010313711 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008874456547211763907522992820048249136248614360940378398922940460074029994610919135447645794343473795374997150964 |
Yes |
Yes |
3670.3171085 |
88.3935394 |
1386.0513784 |
26.3617453 |
| ENSG00000148426 |
254427 |
PROSER2 |
protein_coding |
Q86WR7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:254427; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000045319 |
Proser2 |
18.347322 |
0.4215779308 |
-1.246129 |
0.506682494 |
5.954536 |
0.01467946211647446104475722705728912842459976673126220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027117504485502257061124709025534684769809246063232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.4769419 |
3.7801905 |
27.3039411 |
5.9794124 |
| ENSG00000148444 |
23412 |
COMMD3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBI1 |
FUNCTION: May modulate activity of cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL) complexes (PubMed:21778237). May down-regulate activation of NF-kappa-B (PubMed:15799966). Modulates Na(+) transport in epithelial cells by regulation of apical cell surface expression of amiloride-sensitive sodium channel (ENaC) subunits (PubMed:23637203). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15799966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23637203, ECO:0000305|PubMed:21778237}. |
Cytoplasm;Ion transport;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transport;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
Predicted to be involved in sodium ion transport. Predicted to be located in extracellular region and ficolin-1-rich granule lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23412; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814] |
31088898_complex determines GRK6 specificity for chemoattractant receptors 31467179_Data show that COMMD3 level is elevated in prostate cancer cell models, PDX models, and metastases. A positive correlation between increased COMMD3 expression and disease recurrence and poor survival was found. COMMD3 drives proliferation of normal cells and promotes migration/invasiveness of neoplastic cells. COMMD3:BMI1 fusion protein and COMMD3 regulate C-MYC transcription and C-MYC downstream pathway. 34493238_Transcriptional analysis of the expression, prognostic value and immune infiltration activities of the COMMD protein family in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34905616_Syntaxin 12 and COMMD3 are new factors that function with VPS33B in the biogenesis of platelet alpha-granules. |
ENSMUSG00000051154 |
Commd3 |
117.087252 |
0.4249327411 |
-1.234694 |
0.166178777 |
55.712512 |
0.00000000000008388268618515975359142749212188511699248797542916022962344868574291467666625976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000534127889600068150824745621177490505411024346305026710979291237890720367431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
70.7230868 |
7.0668101 |
167.1291191 |
10.6669734 |
| ENSG00000148468 |
221061 |
FAM171A1 |
protein_coding |
Q5VUB5 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the regulation of the cytoskeletal dynamics, plays a role in actin stress fiber formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30312582}. |
Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in regulation of cell shape and stress fiber assembly. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:221061; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; stress fiber assembly [GO:0043149] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30312582_APCN regulates the dynamics of the actin cytoskeletal and, thereby, the cell shape and invasive growth potential of tumor cells. |
ENSMUSG00000050530 |
Fam171a1 |
20.860297 |
0.2976205380 |
-1.748454 |
0.362596928 |
24.532201 |
0.00000073078268888031143542309770247400457776620896765962243080139160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002625694373873757613870039140380185926915146410465240478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.8398223 |
2.2330156 |
29.9337532 |
4.5889408 |
| ENSG00000148655 |
83938 |
LRMDA |
protein_coding |
Q9H2I8 |
FUNCTION: Required for melanocyte differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23395477}. |
Albinism;Differentiation;Leucine-rich repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a leucine-rich repeat protein. The encoded protein is thought to play a role in melanocyte differentiation. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive oculocutaneous albinism 7 (OCA7). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. |
hsa:83938; |
melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19844253_This finding suggests that haploinsufficiency of C10orf11 contributes to the cognitive defects in 10q22 deletion patients. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000063458 |
Lrmda |
20.427865 |
0.1639642456 |
-2.608547 |
0.868118672 |
7.520828 |
0.00609896276684179956817377643574218382127583026885986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012234396634762837591248185731274134013801813125610351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1389610 |
2.8772449 |
25.2053358 |
12.0239208 |
| ENSG00000148660 |
818 |
CAMK2G |
protein_coding |
Q13555 |
FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that functions autonomously after Ca(2+)/calmodulin-binding and autophosphorylation, and is involved in sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) transport in skeletal muscle and may function in dendritic spine and synapse formation and neuronal plasticity (PubMed:16690701). In slow-twitch muscles, is involved in regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) transport and in fast-twitch muscle participates in the control of Ca(2+) release from the SR through phosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor-coupling factor triadin (PubMed:16690701). In the central nervous system, it is involved in the regulation of neurite formation and arborization (PubMed:30184290). It may participate in the promotion of dendritic spine and synapse formation and maintenance of synaptic plasticity which enables long-term potentiation (LTP) and hippocampus-dependent learning. In response to interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) stimulation, catalyzes phosphorylation of STAT1, stimulating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q923T9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16690701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30184290}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
The product of this gene is one of the four subunits of an enzyme which belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family, and to the Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase subfamily. Calcium signaling is crucial for several aspects of plasticity at glutamatergic synapses. In mammalian cells the enzyme is composed of four different chains: alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. The product of this gene is a gamma chain. Many alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been described but the full-length nature of all the variants has not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:818; |
calcium- and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase complex [GO:0005954]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium-dependent protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004723]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0004683]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051924]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975]; regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation [GO:0014733] |
11889801_role in cell communication 12032636_cloning, genomic structure and detection of variants in subjects with Type II diabetes 14722083_measured differences in CaMKII binding affinities for CaM play a minor role in the autophosphorylation of the enzyme, largely dictated by autophosphorylation rate for alpha, beta, gamma and delta isoforms 15775983_CaMKIIgamma is necessary to suppress MCAK depolymerase activity in vivo. 16002660_A transgenic, constitutively active, Ca2+-independent form of CaMKgamma reduces positive selection of T cells by maintaining association of SHP-2 with the T cell receptor (TCR) complex, and halting TCR signaling. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17032905_Amphetamine in a cell line induces a robust increase in cytosolic Ca2+ and concomitant activation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). 17373700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17431504_Significant cross-talk between calcium and retinoic acid signaling pathways regulates the differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. 17553505_insulin in the presence of Angiotensin II inhibits protein phosphatase-2A (PP-2A) and stimulates autonomous CaM kinase II activities and thus vascular smooth muscle migration 18434368_IGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor signaling induced cell hypertrophy and atrial natriuretic peptide/BNP expression via Galphaq interaction and protein kinase C-alpha/CaMKII activation in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. 18483256_CaMKIIgamma is a critical regulator of multiple signaling networks regulating the proliferation of myeloid leukemia cells 19001023_In Turner yndrome, loss of voltage-dependent inactivation is an upstream initiating event for arrhythmia phenotypes that are ultimately dependent on CaMKII activation. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19603549_increased RyR2-dependent Ca2+ leakage due to enhanced CaMKII activity is an important downstream effect of CaMKII in individuals susceptible to AF induction. 19671701_These data demonstrate that alphaKAP exhibits a novel interaction with SERCA2a and may serve to spatially position CaMKII isoforms at the SR and to uniquely modulate the phosphorylation of PLN. 19682070_P2X7 receptor-triggered signalling pathways that regulate neurite formation in neuroblastoma cells. 19840793_Study further supports self-aggregation of CaMKII holoenzymes as the underlying mechanism that involves inter-holoenzyme T286-region/T-site interaction. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20060891_The interaction between CaMKII and its binding proteins was altered by the phosphorylation state of both the CaMKII and the partner. 20139089_CaMKII is a molecular link translating intracellular calcium changes, which are intrinsically associated with glioma migration, to changes in ClC-3 conductance required for cell movement 20149311_Our results suggest a first observation that CaMKII regulates TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of fibroblast-like synovial cells through Akt, standing an upstream of caspase-8-dependent cascades. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20851109_These results indicated that PP6 and CaMKII regulated apoptosis by controlling the expression level of p27. 21063097_Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent kinase II participate in control of cell cycle progression and survival of irradiated CML cells. 21513986_study shows CaMKII is recruited to the immunological synapse where it interacts with and phosphorylates Bcl10; propose a mechanism whereby Ca(2+) signals can be integrated at the immunological synapse through CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of Bcl10 21983898_increases in Ca(2+) lead to CaMKII activation and subsequent Lck-dependent p66Shc phosphorylation on Serine 36. This event causes both mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired Ca(2+) homeostasis, which synergize in promoting Jurkat T-cell apoptosis. 22049206_study demonstrates that premitotic condensation involves the activation of ClC-3 by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in glioma cells 22371496_CaMKII binding to and phosphorylation of the NHE3 C terminus are parts of the physiologic regulation of NHE3 that occurs in fibroblasts as well as in the brush border of an intestinal Na(+)-absorptive cell. 22592532_CaMKII was also necessary for the phosphorylation of Raf-1 at S338 by serum, fibronectin and Ras. 22612808_we review the cellular colocalization of CaMKII isoforms with special regard to the cell-type specificity of isoform expression in brain--REVIEW 22615928_CaMKII T286A showed a mildly but significantly reduced rate of Ca(2+)/CaM-stimulated phosphorylation for two different peptide substrates (to ~75-84% of wild type). 22952977_These findings revealed a fundamental role of CaMKII in the enteric nervous system. 23008441_The CaMKII phosphorylation motif in the Nav1.5 DI-DII cytoplasmic loop is a critical point for proarrhythmic changes. 23074277_Data indicate that CaMKII gamma as a specific and critical target of berbamine for its antileukemia activity. 23463379_results show that CAMKII and calmodulin contribute to IKK complex activation and thus to the induction of NF-kappaB in response to H. pylori infection 23502535_Activated CaMK-II interacts with the C-terminal domain of diacylglycerol lipase-alpha (DGLalpha) and inhibits DGLalpha activity. 23516528_the chronic gain-of-function defect in RyR2 due to CaMKII hyperphosphorylation is a novel mechanism that contributes to pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes 23543616_CaMKII overexpression in mushroom body neurons increases activity dependent calcium responses. 23960096_Our data suggest that berbamine and its derivatives are promising agents to suppress liver cancer growth by targeting CAMKII 24100685_it can be concluded that CaMKII regulates the activity of ASIC1, which is associated with the ability of GBM cells to migrate. 24206096_CAMKIIgamma, HSP70 and HSP90 transcripts are differentially expressed in chronic myeloid leukemia cells from patients with resistant mutated disease. 24269630_When inhibiting CaMKII, B-cell activating factor (BAFF) is attenuated and mediates protein phosphatase (PP)2A-Erk1/2 signaling and B-cell proliferation. 24634301_CaMKII-dependent microtube polymerization may be responsible for the enhanced uptake of PEI/ON complexes in A549 cells under oxidative stress conditions. 25446257_Inhibition of CaMKII activity results in an upregulation of CaMKIV mRNA and protein in leukemia cell lines. 25577293_Dysfunction in CaMKII-based signaling has been linked with a host of cardiovascular phenotypes including heart failure and arrhythmia, and CaMKII levels are elevated in human and animal disease models of heart disease. 25965829_High CaMKIIgamma expression is associated with lung cancer. 26803057_Demonstrate that calcium/CaMKIIgamma/AKT signaling can regulate apoptosis and autophagy simultaneously in colorectal cancer cells. 27624155_These findings indicate that the CaMKII-mediated GluA1 phosphorylation of S567 and S831 is critical for P2X2-mediated AMPAR internalization and ATP-driven synaptic depression. 27819676_novel mechanism by which CAMK2gamma antagonizes mTORC1 activation during hepatocarcinogenesis 27875595_CKIalpha-mediated NS5A S235 phosphorylation is critical for HCV replication. CaMKII gamma and delta may have negative roles in the HCV life cycle. 27964993_Laminin is instructive and CaMKII is non-permissive for the formation of complex aggregates of acetylcholine receptors on myotubes in culture. 28007458_oxidative stress activated the TRPM2-CaMKII cascade to further induce intracellular ROS production, which led to mitochondria fragmentation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential 28319059_A new molecular mechanism mediated by CAMK2gamma in intestinal epithelial cells during colitis-associated cancer (CAC) development, thereby providing a potential new therapeutic target for CAC. 29210177_The data further showed that mitochondrial fission significantly promoted the reprogramming of focal-adhesion dynamics and lamellipodia formation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells mainly by activating typical Ca(2+) /CaMKII/ERK/FAK pathway. 29391954_The data suggest T287 autophosphorylation regulates substrate gating, an intrinsic property of the catalytic domain, which is amplified within the multivalent architecture of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II holoenzyme. 29535221_The authors identify active CaMKII as a novel connection between organelle beta-oxidation and acetyl-CoA transport with cell survival, migration, and prostate cancer metastasis 29934532_point mutation R292P sufficient to disrupt gene expression and spatial learning 30142967_The effect of Ca(2+), domain-specificity, and CaMKII on CaM binding to NaV1.1 has been reported. 30184290_Results reveal an indispensable function of CAMK2G in neurodevelopment and indicate that the CAMK2G p.Arg292Pro de novo mutation acts as a pathogenic gain-of-function mutation causing severe intellectual disability. CAMK2G p.Arg292Pro has constitutive activity toward cytosolic targets, rather than impaired targeting to the nucleus. 30244168_BAFF promotes B-cell proliferation and survival by inhibiting autophagy. BAFF inhibits autophagy by activating Ca2+-CaMKII-dependent Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in B cells. 30418153_Subunit exchange enhances information retention by CaMKII in dendritic spines. 31221819_CaMKII/proteasome/cytosolic calcium/cathepsin B axis was present in tryspin activation induced by nicardipine. 31461344_Ca2+-activated Cl- channels encoded by the Tmem16a gene are regulated by calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and protein phosphatases 1 (PP1) and 2A (PP2A). 31481791_mark the CaMKII-delta9-UBE2T-DNA damage pathway as an important therapeutic target for cardiomyopathy and heart failure 31857698_The TRPV4-AKT axis promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation via CaMKII activation. 32068116_CaMKII and GLUT1 in heart failure and the role of gliflozins. 32658867_CAMKIIgamma is a targetable driver of multiple myeloma through CaMKIIgamma/ Stat3 axis. 33369192_CaMKIIgamma regulates the viability and self-renewal of acute myeloid leukaemia stem-like cells by the Alox5/NF-kappaB pathway. 33454324_CaMK II/Ca2+ dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells stimulated by transforming growth factor beta 1. 33568460_CaMKII Phosphorylation Regulates Synaptic Enrichment of Shank3. 34088288_Matrine suppresses cell growth of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma via inhibiting CaMKIIgamma/c-Myc/CDK6 signaling pathway. 34301850_A physiologic rise in cytoplasmic calcium ion signal increases pannexin1 channel activity via a C-terminus phosphorylation by CaMKII. 34521112_CAMK2G is identified as a novel therapeutic target for myelofibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000021820 |
Camk2g |
139.212238 |
0.3506832193 |
-1.511760 |
0.172066621 |
77.125307 |
0.00000000000000000160448179594814353468013956132947435087335214155693577375849656618811422958970069885253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000013289647198762398939995073868667301868736141607155176735943769017467275261878967285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.6146330 |
8.1668039 |
205.9222221 |
15.5961608 |
| ENSG00000148773 |
4288 |
MKI67 |
protein_coding |
P46013 |
FUNCTION: Required to maintain individual mitotic chromosomes dispersed in the cytoplasm following nuclear envelope disassembly (PubMed:27362226). Associates with the surface of the mitotic chromosome, the perichromosomal layer, and covers a substantial fraction of the chromosome surface (PubMed:27362226). Prevents chromosomes from collapsing into a single chromatin mass by forming a steric and electrostatic charge barrier: the protein has a high net electrical charge and acts as a surfactant, dispersing chromosomes and enabling independent chromosome motility (PubMed:27362226). Binds DNA, with a preference for supercoiled DNA and AT-rich DNA (PubMed:10878551). Does not contribute to the internal structure of mitotic chromosomes (By similarity). May play a role in chromatin organization (PubMed:24867636). It is however unclear whether it plays a direct role in chromatin organization or whether it is an indirect consequence of its function in maintaining mitotic chromosomes dispersed (Probable). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9PVX6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10878551, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24867636, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27362226}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Chromosome;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear protein that is associated with and may be necessary for cellular proliferation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. A related pseudogene exists on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:4288; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; regulation of chromatin organization [GO:1902275]; regulation of chromosome segregation [GO:0051983]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088] |
11570981_There is no significant correlation between Ki-67 labelling index and tumor size of anterior pituitary adenomas, even if this index can be considered a useful marker in the determination of the infiltrative behavior of these tumors. 11744991_Not significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis of breast invasive ductal carcinoma. 11759064_Use of tissue microarray technique shows immunohistochemical tumor heterogeneity in expression levels of Ki-67 in malignant fibrous histiocytoma cells. 11783017_Ki-67 antigen overexpressioin is an early event in esophageal carcinogenesis and useful biomarkers for early detection. 11839580_patients that progressed to breast cancer showed significantly higher Ki-67 expression in their HUT (hyperplasia of usual type)foci compared with controls 11857304_overexpression may be marker of radioresistance in head and neck cancer 11925591_Results indicate that loss of RAR-beta expression and accumulation of p 53 and Ki67 proteins may serve as biomarkers for early identification of esophageal cancer in the high-risk populations. 12051866_The combined evaluation of p27Kip1 and Ki-67 expression provides independent information on overall survival of ovarian carcinoma patients. 12125971_presence in CNS tumors correlates with histological type and grade 12432453_This marker is masked to MIB-1 staining after expression of its tandem repeats. 12434121_p53 and Ki-67 expression in epithelial gastric dysplasia and in gastric cancer. 12479099_Increase of CD44s, MMP-9, and Ki-67 were involved in the growth and local invasion of osteosarcoma. 12485163_Data suggest that marsupial chmadrin and human Ki-67 induce chromatin compaction across species, possibly via the interaction of its LR domain with heterochromatin protein 1. 12532420_No relationship was observed between Ki-67 staining & the E-cadherin mutation status. The presence of E-cadherin mutations does not correlate with Ki-67 staining. 12607601_increased p53 and Ki-67 expression in varying grades of urothelial dysplasia of bladder 12647790_Ki-67 proved to be a better prognostic marker, as compared to metallothionein, in large intestine adenocarcinomas 12649825_Ki-67 antigen reactivity was significantly higher in the patient with laryngeal carcinoma remission, compared with the control group. 12716386_a biological marker in Langerhans cell histiocytosis 14582704_distribution of staining pattern for Ki-67 paralleled the staining pattern of 34-betaE12 14627346_Detected in nuclei of neoplastic cells and in nuclei of epithelial cells in adjacent colonic mucosa. 14659764_nmr analysis of the solution structure of the FHA domain of human Ki67 and mapping of the binding surface for NIFK binding 14674120_compared the expression of Ki-67 between primary breast tumors and metastasis to regional lymph nodes; estimated the relationships between Ki-67 and the anatomoclinical features of the breast cancer 14707453_The expression of Ki67 and p53 in various forms of leukoplakia point to the increasing instability of the genome in parallel with the severity of leukoplakia. 15104289_Mutations in the cDNA of the proliferation marker Ki-67 protein is associated with cervix, colonic and lung neoplasms 15214825_study expands the immunophenotype of granular cell tumor (S100, CD68, protein gene product 9.5, and inhibin-alpha) regardless of location and supports a neural origin 15217948_Ki-67 may have a role in distant metastasis of radiotherapy-treated prostate neoplasms 15452376_Ki-67 LI (labeling index) is a useful prognosticator for PENs (pancreatic endocrine neoplasms). 15545971_Ki-67 is a factor of poor prognosis for survival in NSCLC. 15591788_ER alpha and Ki67 might be involved in distinct pathological and molecular features during breast cancer development 15638357_Expression correlates with intensity of apoptosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. 15638377_Expression of Ki-67, PCNA proteins were closely connected with the high grade of stomach tumour malignancy. 15638382_Evaluation of expression of PCNA and Ki-67 may provide an additional information about the progression of uveal melanoma. 15679862_Ki-67 and hTERT have roles in meningioma cell proliferation, but only hTERT has a role in disease recurrence 15809747_a useful msarkser in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. 15871722_Ki-67 by itself is a less reliable marker of dysplasia. 15931389_Altered expression is associated with therapy failure and death in patients with multiple types of cancer. 15953875_Study suggests that the clinical characteristics such as visual field defect and recurrence are correlated with the high Ki-67 labeling index. 15964376_Proliferative activity of 13 biopsy specimens of Kaposi sarcoma was assessed immunohistochemically using the monoclonal antibody to KI-67. 16045773_Aberrant proliferative patterns with Ki67 staining are not useful in differentiating reactive epithelia from low-grade dysplasia, but may prove useful in the diagnosis of high-grade dysplasia. 16097446_p27(kip1) and Ki-67 have roles in post-surgical disease progression of prostate cancer 16171567_ability of the gef gene to down regulate Ki-67 expression and induce apoptosis in a breast cancer cell line 16206250_ChIP assays provided evidence for a physical association of pKi-67 with chromatin of the promoter and transcribed region of the rRNA gene cluster. These data strongly suggest a role for pKi-67 in the early steps of rRNA synthesis. 16255765_liver expression in HBV and HCV cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with dysplastic cell changes and tumour grade 16295759_Ki 67 usefulness in studying cellular proliferation, and underline that chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with polymorphic cytology are more proliferate than typical CLL. 16351648_To investigate the prognostic and predictive relevance of p53 protein, Ki-67 antigen, MMP-2 and MMP-9 in patients with transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the upper urinary tract 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16479062_The expression rate of Ki-67 was relatively high in small cell lung cancer without any prognostic significance. 16533178_Increased expression of Ki-67 protein suggests an increased cellular proliferation which is involved in the process of occurrence and progression of epithelial dysplasia in the flat mucosa of colon. 16573167_Expression of iNOS and Ki-67 protein in hemangioma is significantly higher than that in vascular malformation. 16574316_Ki-67/podoplanin-immunoreactivity was useful to identify proliferating lymphatic vessels. 16609045_The Ki-67 Antigen expression was associated with the highest levels of proliferation, suggesting a synergistic effect. 16623776_Ki67 stain alone is a powerful tool for distinguishing benign from malignant proliferations within the selected groups. 16629645_The combination of MCM2, geminin and Ki67 could represent a valuable tool in the understanding of hepatocellular carcinoma progression in cirrhosis. 16681683_Ki67 was an independent prognosticator if nodal status, tumour size, age and histological grade were included in the analysis but not if analysed with standardized mitotic index. 16723309_changes in COX-2 and Ki-67 expression peaked during the proliferative phase and fell during the late luteal phase in endometrial polyps and disease-free endometria 16739374_Overexpression of Ki67 and VEGF were related to poor prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. 16804724_In univariate analyses, low Ki-67 proliferation index (P = 0.045) and negative p21 immunoreactivity (P = 0.04) were associated to patient's overall survival. 16882345_Ki-67 did not display apparent prognostic value in NSCLC in the study sample 16948516_Height of Ki-67 staining within the epithelium increased significantly between mild and moderate and between mild and severe dysplasia. 16984615_Based on these results it is suggested that Ki-67 is a reliable microscopic marker to predict metastatic potential of rectal carcinoids. 17065089_analysis of Ki67 and thymidylate synthase expression in primary tumour compared with metastatic nodes in breast cancer patients 17143016_In an analysis of breast cancer-specific survival up to 5 years, high Ki-67, high p53, and negative ER as well as aneuploidy of the tumour were significant prognostic factors. 17188136_p53 and Ki-67 were expressed with increasing frequency, and bcl-2, p21, and mdm-2 with decreasing frequency in thyroid carcinoma progression. p27 and cyclin D1 were expressed in 40% of the tumour cells are both associated with an improved relapse-free survival in colon cancer stages II and III, but not so in rectal cancer. 19774459_Ki67 appears to be a time-varying biomarker of risk of breast cancer in women with atypical hyperplasia 19777788_the quantitative and qualitative (pattern of distribution) evaluation of the expressions of Ki67, P27 and P53 may be helpful in differentiating malignant and premalignant epidermal lesions, particularly in unsatisfactory or fragmented specimens 19788614_Endothelial proliferation assessed on Ki-67 combined with the lack of CD105 expression is often associated with invasive cervical carcinoma. 19818763_MCM3 may be a more reliable proliferation marker than Ki-67 in accessing the growth of tumor and evaluating tumor aggressiveness of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 19832838_Genes previously shown to be of relevance in high-grade gliomas include MIB-1/Ki-67, tp53, and O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase(MGMT); however, they are not significant biomarkers of outcome in pilocytic astrocytomas. 19854077_Data show that the CIS surrounding morphologically normal urothelium with a high frequency of abnormal DNA content, clear aneuploid cells, p53 mutated protein expression, and a proliferative status underlying a field carcinogenesis. 19901884_Report correlation of the standardized uptake value in FDG-PET with the expression level of Ki-67 antigen in resected non-small cell lung cancers. 19935641_Ki67 is a prognostic factor in node-negative breast cancer 19946260_This study evaluates the association of Forkhead-box protein A1 (FOXA1) and GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) expressions with Oncotype DX recurrences scores in 77 cases of patients with ER-positive node-negative breast carcinomas 19952937_An immunochemical study of the expressions of Ki-67, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and p53 in 9 cases of symplastic uterine leiomyomas was performed. 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20001343_Toker cells and mammary Paget cells differ substantially in their expression of ER, c-erbB-2 and Ki-67. 20010526_patients with Gleason scale > 8 prostate cancer were characterized by the highest nuclear expression of p53, p16INK4a and Ki-67, and also by overexpression of cytoplasmic Bcl-2. 20030864_Studies indicate that Ki67 at baseline is a highly prognostic factor in breast cancer. 20030866_Studies indicate that Ki67 at baseline is a highly prognostic factor in breast cancer. 20038236_Data show that a positive correlation was observed between the SUVmax on FDG-PET at the biopsy site and the Ki-67 proliferation index (MIB-1 labeling index). 20082479_The expression of p53, c-erbB-2 and Ki67 proteins in 20 simple intestinal metaplasia (SIM), 27 atypical intestinal metaplasia (AIM), and 37 gastric carcinomas showed significant differences between SIM and gastric carcinomas. 20095356_CyclinB1, FHIT and Ki-67 may play significant roles in the occurrence and evolution of gastric carcinoma. 20099418_The Ki-67 Labeling Index in the malignant GIST group was higher than that in the benign group, in the p53-positive cases was higher than that in the p53-negative cases, in the C-kit-positive group was higher than that in the C-kit-negative group. 20103652_Data show that SOX9 expression was associated with increasing Gleason grades and higher Ki67 staining in prostate cancer samples. 20103726_The clinical trial of Kim et al. shows an effect of the cyclooxygenase-2-selective inhibitor celecoxib at a high dose on Ki-67 expression in the normal bronchial epithelia of current and former smokers. 20105109_no significant correlation with disease-free survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma 20181625_There is no statistically significant association between the expression of Ki-67 and overall survival or relapse of patients with laryngeal cancer. Nuclear MSH2 staining was statistically significantly correlated to Ki-67 expression. 20189840_MIB1 overexpression is associated with urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract. 20198771_There is a significant statistical difference between immunohistochemical expression of p16(INK4a) and Ki-67 in HPV-associated dysplastic and non-dysplastic vulvar lesions. 20223108_MLH1, MSH2 and MSH6 expression in initial glioblastoma lesions is significantly associated with the Ki67 antigen proliferation index. 20338617_Increased expression of Ki-67 was associated with the presence of lymph node metastasis, advanced stages of disease, tumors occurring in the floor of mouth, and moderately/well-differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma. 20353905_High MIB-1 expression is associated with gallbladder carcinoma. 20369488_The expressions of P53, P21 and Ki67 proteins are closely related with the pathogenesis and progression of nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. 20369584_Prognostic value of of the expression Ki-67, CD31, and VEGF in somatotropinomas 20381119_expression of CD147 was positively correlated with matrix metalloproteinase-2, Ki-67 labeling index, or both in invasive pituitary adenomas (P |
ENSMUSG00000031004 |
Mki67 |
642.498133 |
2.0518148603 |
1.036901 |
0.095826188 |
115.773185 |
0.00000000000000000000000000532886791566969534260666060204357924726335293676244410079207616347371414405875711395310645457357168197631835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000061304824969044976448666745216498146434578117385795586078146936303385431538126582040604262147098779678344726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
851.3326842 |
47.6458369 |
418.2709979 |
17.5705970 |
| ENSG00000148798 |
9118 |
INA |
protein_coding |
Q16352 |
FUNCTION: Class-IV neuronal intermediate filament that is able to self-assemble. It is involved in the morphogenesis of neurons. It may form an independent structural network without the involvement of other neurofilaments or it may cooperate with NEFL to form the filamentous backbone to which NEFM and NEFH attach to form the cross-bridges. May also cooperate with the neuronal intermediate filament protein PRPH to form filamentous networks (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P46660}. |
Acetylation;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Intermediate filament;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Neurofilaments are type IV intermediate filament heteropolymers composed of light, medium, and heavy chains. Neurofilaments comprise the axoskeleton and they functionally maintain the neuronal caliber. They may also play a role in intracellular transport to axons and dendrites. This gene is a member of the intermediate filament family and is involved in the morphogenesis of neurons. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:9118; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; neurofilament [GO:0005883]; postsynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0099160]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural constituent of postsynaptic intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0099184]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; neurofilament cytoskeleton organization [GO:0060052]; postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099170]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] |
12209604_alpha-internexin expression in neuroblastoma 15161649_The discovery of alpha-internexin in the cytoplasmic inclusions implicates novel mechanisms of pathogenesis in inclusion diseeae and other neurological diseases with pathological accumulations of IFs. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16722980_Abnormal neuronal intermediate filament inclusions of alpha-internexin have been identified as the pathological hallmark of neuronal intermediate filament inclusion disease 18528283_Expression of the 2 markers, alpha-internexin and peripherin, in a small round cell tumor strongly favors the diagnosis of neuroblastoma. 19110265_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19139367_Alpha-Internexin (INA) expression appears to be a simple, reliable prognostic marker and a surrogate marker of 1p19q codeletion. 20213320_the importance of alpha-internexin and NF-L in regulating the conformations of NF-M and NF-H 21990041_INA may provide additional biologic information relevant to delineation of both pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (NEN) tumor phenotypes and clinical behavior. 22890969_High INA expression is associated with grade II gliomas. 24197863_It is a supportive diagnostic marker for oligodendroglial tumors with the 1p/19q co-deletion. 24483152_alpha-Internexin was expressed in 53% of 350 pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Reduced expression of alpha-internexin was significantly associated with advanced stage metastases, recurrence and shorter overall survival. 25236435_Gonadotropinomas, null cell pituitary adenomas, and thyrotropinomas exhibit high levels of intracellular INA protein indicating neuronal transdifferentiation. 26233522_It is a neuronal marker, and has been indicated as an immunohistochemical surrogate of chromosome 1p/19q co-deletion in oligodendroglial tumors. 28526880_The proteins UCH-L1 and alpha-internexin could be independent prognostic biomarkers of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 29339073_Data suggest GRINL1A (GCOM1)-NMDA receptor-internexin-alpha (INA) interaction pathway may be relevant to neuroprotection. 29940892_reduced/loss of expression of alpha-internexin was closely related to tumors with aggressiveness and patient's adverse prognosis 33051252_Epigenetic Inactivation of alpha-Internexin Accelerates Microtubule Polymerization in Colorectal Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000034336 |
Ina |
88.657542 |
4.3025806555 |
2.105202 |
0.192185009 |
126.050711 |
0.00000000000000000000000000002997255656398392938026706356207064571289367457903103316701499558648201088615920656410551714543544221669435501098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000376827031417719615917094556993576887294218610856811504620082806669911646281316552897777683028834871947765350341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
146.3577358 |
16.9361003 |
34.2570756 |
3.3669714 |
| ENSG00000148824 |
92170 |
MTG1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BT17 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of the mitochondrial ribosome assembly and of translational activity. Displays mitochondrial GTPase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23396448}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;GTP-binding;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Translation regulation |
|
Enables GTPase activity. Involved in regulation of mitochondrial translation and regulation of respiratory system process. Located in mitochondrial inner membrane and mitochondrial ribosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92170; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial ribosome [GO:0005761]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; mitochondrial translation [GO:0032543]; regulation of mitochondrial translation [GO:0070129]; regulation of respiratory system process [GO:0044065]; translation [GO:0006412] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23396448_The results suggested that Mtg1 functions with the large subunit of the mitochondrial ribosome, and are involved in both the translation and assembly of respiratory complexes. 30085276_MTG1 establishes a quality control checkpoint in mitoribosome assembly. In conclusion, MTG1 controls mitochondrial translation by coupling mtLSU assembly with intersubunit bridge formation using the intrinsic GEF activity acquired by the mtSSU through mS27, a unique occurrence in translational systems. 30707992_dampening oxidative stress with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) lowered hypertrophy in MTG1 KO to WT levels. Collectively, our data indicate that MTG1 protects against pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction by preserving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress and downstream TAK1 stress signaling. 34385605_Potential pathogenetic link between angiomyofibroblastoma and superficial myofibroblastoma in the female lower genital tract based on a novel MTG1-CYP2E1 fusion. 36177509_Vulvar angiomyofibroblastoma is molecularly defined by recurrent MTG1-CYP2E1 fusions. |
ENSMUSG00000039018 |
Mtg1 |
78.260561 |
0.3354554119 |
-1.575807 |
0.311706386 |
24.648813 |
0.00000068787108514236204151638546036573451658568956190720200538635253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002479965123766796250944421595163724703070329269394278526306152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
34.0822477 |
6.2893560 |
102.1910895 |
13.5500551 |
| ENSG00000148841 |
85450 |
ITPRIP |
protein_coding |
Q8IWB1 |
FUNCTION: Enhances Ca(2+)-mediated inhibition of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor (ITPR) Ca(2+) release. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16990268}. |
Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a membrane-associated protein that binds the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (ITPR). The encoded protein enhances the sensitivity of ITPR to intracellular calcium signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. |
hsa:85450; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear outer membrane [GO:0005640]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902042] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16990268_DANGER appears to allosterically modulate the sensitivity of IP(3) RtoCa(2+) inhibition, which likely alters IP(3)R-mediated Ca(2+) dynamics in cells where DANGER and IP(3)R are co-expressed 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26769850_High DANGER expression is involved in high glucose-induced radioresistance through inhibiting DAPK-mediated anoikis in non-small cell lung cancer. 29899107_The suggested model of how long noncoding RNAs (lncI) TPRIP-1 orchestrates signal transduction for IFN production illustrates the essential role of lncRNAs in virus elimination. 34111521_ITPRIP promotes glioma progression by linking MYL9 to DAPK1 inhibition. |
ENSMUSG00000117975 |
Itprip |
296.183563 |
2.4865550978 |
1.314148 |
0.096053767 |
190.191068 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000028881853811501741210376431885990440408238042793917824647230673189854106088022019849218262539604455962509487257361406875588727416470646858215332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000005224217674727520967778600213814928946809678733299637565751805725203980983771053280998483495739125141473088113214240379988950735423713922500610351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
426.1165189 |
23.8650796 |
172.5299829 |
7.7937900 |
| ENSG00000148843 |
22984 |
PDCD11 |
protein_coding |
Q14690 |
FUNCTION: Essential for the generation of mature 18S rRNA, specifically necessary for cleavages at sites A0, 1 and 2 of the 47S precursor. Directly interacts with U3 snoRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17654514}.; FUNCTION: Involved in the biogenesis of rRNA. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;rRNA processing;Ubl conjugation |
|
PDCD11 is a NF-kappa-B (NFKB1; 164011)-binding protein that colocalizes with U3 RNA (MIM 180710) in the nucleolus and is required for rRNA maturation and generation of 18S rRNA (Sweet et al., 2003 [PubMed 14624448]; Sweet et al., 2008 [PubMed 17654514]).[supplied by OMIM, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:22984; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; small-subunit processome [GO:0032040]; NF-kappaB binding [GO:0051059]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] |
17654514_Evidence is presented for involvement of PDCD11 in processing of ribosomal RNA. 19332556_The 50S U3 snoRNP is an small subunit assembly intermediate that is likely recruited to the pre-rRNA through the RNA-binding proteins nucleolin and RRP5.[RRP5, DBP4] 28657695_data provide no evidence for the contribution of rare PDCD11 variations to the risk of schizophrenia in the Japanese population. |
ENSMUSG00000025047 |
Pdcd11 |
280.143891 |
2.6785371229 |
1.421445 |
0.210500268 |
44.135102 |
0.00000000003064755526717440977193214798863325418198932936775236157700419425964355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000164553625224988843904454423654681264471699719820207974407821893692016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
411.1593995 |
57.9672921 |
154.1150574 |
16.1294041 |
| ENSG00000148926 |
133 |
ADM |
protein_coding |
P35318 |
FUNCTION: AM and PAMP are potent hypotensive and vasodilatator agents. Numerous actions have been reported most related to the physiologic control of fluid and electrolyte homeostasis. In the kidney, am is diuretic and natriuretic, and both am and pamp inhibit aldosterone secretion by direct adrenal actions. In pituitary gland, both peptides at physiologically relevant doses inhibit basal ACTH secretion. Both peptides appear to act in brain and pituitary gland to facilitate the loss of plasma volume, actions which complement their hypotensive effects in blood vessels. |
3D-structure;Amidation;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Hormone;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a preprohormone which is cleaved to form two biologically active peptides, adrenomedullin and proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide. Adrenomedullin is a 52 aa peptide with several functions, including vasodilation, regulation of hormone secretion, promotion of angiogenesis, and antimicrobial activity. The antimicrobial activity is antibacterial, as the peptide has been shown to kill E. coli and S. aureus at low concentration. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014]. |
hsa:133; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; adrenomedullin receptor binding [GO:0031700]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adrenomedullin receptor signaling pathway [GO:1990410]; aging [GO:0007568]; amylin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0097647]; androgen metabolic process [GO:0008209]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; antibacterial humoral response [GO:0019731]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; branching involved in labyrinthine layer morphogenesis [GO:0060670]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; developmental growth [GO:0048589]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; G protein-coupled receptor internalization [GO:0002031]; heart development [GO:0007507]; hormone secretion [GO:0046879]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; negative regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045906]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neuron projection regeneration [GO:0031102]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of heart rate [GO:0010460]; positive regulation of progesterone biosynthetic process [GO:2000184]; positive regulation of vasculogenesis [GO:2001214]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003073]; regulation of the force of heart contraction [GO:0002026]; regulation of urine volume [GO:0035809]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to starvation [GO:0042594]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spongiotrophoblast layer development [GO:0060712]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
10225288_Adrenomedullin has broad bacteriocidal activity against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. 11463752_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11712085_Endogenous ADM system plays a potentially important role in the paracrine or autocrine functional control of Conn's adenomas. 11744163_Adrenomedullin increases cycl AMP through amylin and CGRP1 receptors. 11774814_There were evident postburn changes in plasma adrenomedullin(ADM) contents, and the results implied that ADM played some roles in the development of postburn physiological disturbance. 11879669_role in microvasculature - review 11905404_data show a reduction of adrenomedullin and CGRP mRNAs in placenta specimens of women with preeclampsia or HELLP syndrome 11921362_role in carcinogenesis - review 11921363_role in the inflammatory response - review 11956648_The cardiovascular response in sepsis: proposed mechanisms of the beneficial effect of adrenomedullin and its binding protein (review). 11972292_the heart and the lungs release adrenomedullin peptides in moderate congestive heart failure and this secretion breaks down in severe CHF 12137974_Follicular fluid adrenomedullin concentrations in spontaneous and stimulated cycles are relationed to ovarian function and endothelin-1 and nitric oxide. 12189226_Cells that overexpressed adrenomedullin displayed a more pleiotropic morphology, an increased angiogenic potential both in vitro and in vivo, and less apoptosis after serum deprivation. 12193565_results indicate that adrenomedullin (AM) inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiac myocyte apoptosis through a cAMP-dependent mechanism and suggest that augmented production of AM by doxorubicin has an endogenous antiapoptotic effect 12220731_Release of this peptide into the blood is affected by exercise and altitude 12324915_The mature form of adrenomedullin is pathophysiologically significant as a useful marker of circulating blood volume in hemodialysis patients. 12375542_concentrations of mature adrenomedullin were elevated in pregnant women compared with non-pregnant women and its concentration in the third trimester was significantly higher than that in the first trimester 12376296_The changes of plasma ADM and PAMP concentrations at different stages of CHF indicate intramolecular regulation disturbances of vasodilator peptides of proadrenomedullin, and ADM may play a more important role in the development of CHF. 12383875_Immunoreactive-AM levels in the aqueous humor were significantly elevated in patients with uveitis and vitroretinal disorders and may be involved in the physiopathology of the uveitis and some vitreoretinal disorders. 12484513_plasma levels of AM, atrial natriuretic peptide(ANP)and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)increased with aging; ANP and BNP increased in association with pulse pressure; possible relation between levels and age-related changes in cardiovascular system 12529288_Responses to CGRP and ADM are mediated by CGRP(8-37)-sensitive receptors and that the endothelial ADM receptor induces vasodilation by a nitric oxide-guanylyl cyclase mechanism, whereas a smooth muscle CGRP receptor signals by a cAMP-dependent mechanism 12565880_ratio of mature AM/total AM was significantly decreased in the fetal membranes of the patients with chorioamnionitis compared with normal pregnancies, but not in the placenta; results suggested that mature AM may have some role in chorioamnionitis 12566732_Novel correlation of adrenomedullin and aquaporin 2(AQP2) which overlays an AVP-AQP2 system may play a key role in fluid homeostasis during general anesthesia. 12579522_Data show that mean values of plasma total nitrite and adrenomedullin levels in the autistic children are significantly higher than control values. 12601625_In patients with primary hyperparathyroidism, plasma adrenomedullin concentrations are increased and correlate with serum intact parathyroid hormone and blood pressure values. 12630817_adrenomedullin promotes proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells via a cAMP/PKA dependent pathway 12630823_existence of the 19-repeat allele is associated with genetic predispositions to develop essential hypertension and diabetic nephropathy. 12643861_decreased levels of AMBP-1 play a critical role in producing vascular AM (adrenomedullin) hyporesponsiveness during the late stage of sepsis (AMBP-1) 12646214_adrenomedullin has an autocrine/paracrine type of anti-proliferative effect via a cAMP-dependent pathway and may play a role in the local modulation of a process of de-differentiation by culturing chondrocyte phenotype cells 12660258_Increase in AM expression in endometrium may be responsible for frequent occurrence of irregular bleeding during initial 3 months of levonorgestrel-releasing intra-uterine system use. 12684703_Data show that an endogenous adrenomedullin system promotes the growth of keratinocytes and fibroblasts cultured in vitro, by enhancing their proliferative activity and lowering their apoptotic deletion. 12687457_AM levels were increased in bladder in children with detrusor instability 12716843_Increased oxidative stress is associated with elevated blood adrenomedullin levels in hypertensive NIDDM patients. 12720100_The expression of adrenomedullin in invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix may crucial role in promoting carcinoma progression. 12753312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12753312_The microsatellite DNA polymorphism of AM gene may be associated with the genetic predisposition to develop nephropathy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 12763641_Adrenomedullin is increased after liver transplant with increased creatinine and atrial natriuretic peptide, suggesting a potential role for ADM in volume regulation after liver transplantation. 12782295_AM plays significant roles in vascular regeneration, associated with PKA- and PI3K-dependent activation of Akt in endothelial cells, and possesses therapeutic potential for vascular injury and tissue ischemia 12805025_Adrenomedullin protects against myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, and apoptosis in ischemia and reperfusion injury via suppression of oxidative stress-induced Bax and p38 MAPK phosphorylation and activation of the Akt-Bad-Bcl-2 signaling pathway. 12835224_Transplantation of adrenomedullin gene-transduced endothelial progenitor cells [EPCs] caused greater improvement in pulmonary hypertension in MCT rats than transplantation of EPCs alone 12853384_Gastric epithelial cells exposed to inflammatory cytokines, Helicobacter pylori, E. coli, S. enterica, or Streptococcus bovis increased adrenomedullin expression & secretion. Epithelial infection, inflammation, & adrenomedullin expression are associated. 12903912_Human adrenomedullin produced a significant decrease in rat heart contractile force and perfusion pressure, but only amylin fragment 8-37 caused a decline in heart rate at the highest dose. 12920627_Adrenomedullin and nitrates may have a role in immunoinflammatory process of Henoch-Schonlein purpura, especially in active stage, although whether this perpetuates, or protects against, further vascular injury is not clear. 12969589_adrenomedullin may be involved in both normal and malignant tissue growth and because of the correlations with estrogen receptor alpha and beta status, there is evidence that ovarian cancer is endocrine-related 14517225_Adrenomedullin production is decreased in preeclampsia. 14534081_Role for adrenomedullin and ACTH in the regulation of the immune and inflammatory response. 14612905_Adrenomedullin peptide is widely expressed in breast cancer and that the degree of expression is associated with lymph node metastasis 14671210_In preeclampsia, regional increases in adrenomedullin mRNA may be induced by hypoxia and mediate local fetal/placental adaptive responses to reduced placental perfusion. 14714580_plasma adrenomedullin concentration could serve as a marker of advanced arterial sclerosis 14715486_AM was widely distributed in the human kidney with arterial stenosis. 14720432_Hybridization in situ showed that ADM mRNA expression was significantly higher in pulmonary artery walls in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) and ADM may play an important protective role in the development of COPD. 14759562_Plasma AM concentration was elevated in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) in proportion to the severity of the disease and associated with vascular inflammation 15016771_Both luteinized granulosa cells and macrophages actively secrete VEGF and adrenomedullin into follicular fluid in the human ovary. 15044509_Saliva from the submandibular and parotid glands contained higher concentrations of adrenomedullin than did the circulation, but lower concentrations than in whole saliva. Oral epithelium may contribute much of the adrenomedullin peptide found in saliva. 15192039_c-myc transactivates rat and human adrenomedullin genes and accelerates the degradation rate of adrenomedullin mRNA 15194870_ADM may be associated with the pathophysiology of schizophrenia 15242974_Recombinant human AM possesses novel angiogenic properties mediated by its ability to enhance VEGF expression and Akt activity in Am(+/-)knockout mice. 15300632_Data suggested that ADM may play a functional role in compensating the chronic heart failure in human. 15336545_AM (either overexpressed or exogenously added) causes an inhibition of prostate cancer cell growth. 15361766_Plasma mature-adrenomedullin showed significantly positive associations with carotid atherosclerosis and atherothrombotic ischemic stroke, independent of systolic blood pressure. 15527794_adrenomedullin has been identified as a host defense peptide and as such it plays a role in the inflammatory response 15531734_Adrenomedullin is highly expressed in blood monocytes associated with acute Kawasaki disease 15544858_the high AM plasma levels in patients with severe lung disease are not caused by a reduced pulmonary clearance 15665526_up regulation of ICAM-1 in oral keratinocytes by Adrenomedullin 15677761_adrenomedullin (ADM), a multifunctional neuropeptide, stimulates nitric oxide (NO) release by modulating intracellular free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) in neuron-like cells 15684700_ADM gene delivery protects against cerebral ischemic injury by promoting astrocyte migration and survival. 15702240_endothelin 1 and AM markedly stimulated the growth of SW-13 cells 15711093_Adrenoleukodystrophy/adrenomyeloneuropathy(ALD/AMN) shows less compromised glomerular function, indicating that AM is not completely correlated with mineralocorticoid insufficiency. Mechanism of increased AM levels in ALD/AMN is still unknown. 15758554_Ghrelin, as well as AM, may play an important role as vasodilator local hormones and regulation of blood pressure during hemodialysis, especially the occurrence of episodic hypotension. 15761041_CGRP and ADM are two differentially regulated novel adipose tissue secretion factors exerting autocrine/paracrine roles. 15788445_described for the first time that adrenomedullin down-regulates lipolysis in adipocytes through the chemical modification of a beta-agonist 15789277_Hyperinsulinemia may, at least in part, regulate levels of adrenomedullin in obesity, explaining the high levels of the peptide in these subjects. 15866060_Plasma levels correlate with inflammatory markers but not with endothelial dysfunction markers in Type 1 diabetic patients without atherosclerotic disease. 15902095_findings indicate that glomerular production of adrenomedullin was decreased in patients with IgA nephropathy 15908101_AM may contribute either in the penile erection and in the regulation of testicular function and sperm motility 15917349_ADM may be involved in the human implantation process via regulating trophoblast proliferation and differentiation 15974887_REVIEW: Cardiac adrenomedullin: its role in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure 16097366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16097366_possible mutation linked to the haplotype may indicate a genetic predisposition for proteinuria in essential hypertension 16115629_These results suggest that in addition to reducing blood pressure, proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide suppresses cardiac hypertrophy through negative regulation of the local cardiac renin-angiotensin system. 16154664_may play a role in the regulation of chemoreceptor discharge through paracrine releasing action and/or vasodilator effect. 16221100_Adrenomedullin, a smooth muscle relaxant peptide that is synthesized in urinary tract tissue might have a role in acute pyelonephritis 16256216_results suggest that AM plays a role in the regulation of HASMC contraction by antagonizing the Ang II effects and may be involved in conditions of altered regulation of the blood vessels. 16270874_high expression of AM in tissues of laryngeal carcinoma was related with the TNM stage of laryngeal carcinoma 16322067_Adrenomedullin regulates cellular glutathione content via modulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit expression 16356592_adrenomedullin has roles in neurotransmission and neuromodulation in the human medulla oblongata 16416151_We conclude that long-term water submersion has endocrine as well as plasma volume effects that are opposite to those seen after short-term immersion, and which increases plasma adrenomedullin. 16517613_Adrenomedullin protein content and mRNA expression in human fetal membranes was increased in pre-eclampsia. 16596251_Findings provide evidence that at least a subset of cardiac mast cells are able to synthesize and store adrenomedullin. 16609682_In Chinese, the ADM -1984G allele is associated with lower sodium excretion and in older subjects also with lower systolic pressure and narrower pulse pressure. 16609682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16622024_ADM may prevent or reduce rheumatoid arthritis-fibroblast-like synoviocyte apoptosis, via up-regulation of its functional receptor calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein-2 16797107_Our results suggest that AM plays a role in the regulation of HASMC growth antagonizing the AngII effect and may be involved in conditions of altered regulation of the blood vessels. 16815566_endothelin-1, but not adrenomedullin, has a role in pulmonary incremental resistance during low-dose dobutamine infusion 16821090_PC12 and U251 cells overexpressing PTEN had decreases in adrenomedullin mRNA levels. Cellular and secreted adrenomedullin peptide was similarly reduced. U251 cells overexpressing PTEN did not respond to exogenous adrenomedullin. 16854513_We conclude that in human seminal fluid adrenomedullin concentration is increased in infertile oligozoospermic patients and derives very likely from the prostate. Its role in the regulation of male fertility, however has to be understood. 16963041_Adrenomedullin may play a role in regulating the insulin metabolism in patients with PCOS. 17022943_The present study has shown that AM expression is up-regulated during adipocyte differentiation of hMSCs probably via the interaction between Sp1 or Sp1-related factor(s) and the AM promoter region (-70/-29). 17053041_We find that certain conditions, such as pregnancy, cardiovascular disease, and sepsis, are associated with robust and dynamic changes in the expression of AM and AM receptor proteins. 17290391_ADM increases invasiveness of some pancreatic cancer cells and might influence angiogenesis 17307261_Possible role of ADM in the regulation of Fontan circulation was studied. 17327422_The response of adrenomedullin to insulin via insulin responsive genetic elements is reported. 17384335_Adrenomedullin might play a role in the pathogenesis of diabetic angiopathy. 17584073_review describes the biochemistry, physiology, and circulating levels of AM--REVIEW 17719138_Data indicated that the synergistic activation of the human AM gene promoter by Sp1 and AP-2alpha may be mediated by the binding of Sp1 to the promoter region and the interaction with AP-2alpha, which binds to the promoter region. 17766467_In conclusion, ADM exerts Ca(2+)-dependent positive inotropic effects in human atrial and less-pronounced effects in ventricular myocardium. 17922433_Microsatellite DNA polymorphism of ADM gene may be associated with the genetic predisposition to ACI. 17922433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17941085_These data show that ADM acts as a survival factor in osteoblastic cells via a CGRP1 receptor-MEK-ERK pathway, which provides further understanding on the physiological function of ADM in osteoblasts. 17952853_Adrenomedullin (ADM) expression in the anterior pituitary is diminished in tumors as compared to the normal gland. 18000597_possesses several protective cardiovascular qualities, including protection of the microcirculation during inflammation, and was proven as an efficient counter-regulatory molecule in various models of sepsis and septic shock. 18080871_Depending on the clinical severity of the infection, both CT-proET-1 and MR-proADM levels exhibited a gradual increase from Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) to sepsis and septic shock. 18081029_Strong candidate gene for schizophrenia; upregulated in lymphoblastoid cells of monozygotic twins. 18371176_adrenomedullinexpression regulation constitutes a cortical response to hypobaria 18401334_Overexpression of exogenous adrenomedullin in the renal interstitium following ureteral obstruction significantly prevented fibrosis and proliferation of tubular and interstitial cells 18403050_ADM and AMBP-1 rescue experimental animals (rats) from shock. 18463805_An alteration in vascular equilibrium between AM and ET-1, favouring AM, may be a reason why the physiological adaptation of the maternal vascular system to pregnancy occurs during normotensive pregnancy. 18615773_Adaptive or maladaptive response to adenoviral adrenomedullin gene transfer is context-dependent in the heart. 18657357_adrenomedullin signaling is hypoxia-inducible and functionally active in hepatocellular carcinomas, and its expression may be a prognostic factor 18692535_in vascular endothelial cells the binding of adrenomedullin to its AM1 receptor could trigger a transactivation of the VEGFR-2 receptor, leading to a signaling cascade inducing proangiogenic events in the cells. 18705285_Adrenomedullin is a factor associated with progression of IM in human HCC. 18708640_AM promoted lymphatic epithelial cell proliferation at least in part through the cAMP/MEK/ERK pathway 18929609_AM plays role in controlling lymphatic endothelial permeability and lymphatic flow through reorganization of junctional proteins. 19009024_Data show that human adrenomedullin/adrenomedullin binding protein-1 in established sepsis markedly attenuated tissue injury, reduced proinflammatory cytokine levels, ameliorated intestinal-barrier dysfunction, and improved survival rate. 19010904_Human adrenomedullin up-regulates interleukin-13 receptor alpha2 chain in prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. 19126117_ADM is not a mediator of migraine headache and does not dilate intracranial arteries. 19166930_Adrenomedullin induced the phosphorylation of both c-Jun and JNK in glioblastoma cells. Adrenomedullin effects cell proliferation through up-regulation of cyclin D1. 19210874_findings provided no significant linkage or association of adrenomedullin and CRLR-RAMP-2 genes with rheumatoid arthritis in the studied trio families 19212702_Strong correlation between CT-proET-1 and MR-pro-ADM levels with inflammation in CHF is presented. 19247278_Plasma MR-proADM correlates to BMI and decreases in relation to leptin after gastric bypass surgery. 19253104_ADM is expressed in normal human ovaries and sex cord-stromal tumors, particularly in those of granulosa cell origin; its expression suggests a paracrine role in ovarian function 19306911_AM/AMBP-1 elevates cAMP levels, followed by activating PKA, to protect neural cells from the injury caused by hypoxia. 19323987_Significance of salivary ADM in the maintenance of oral health: stimulation of oral cell proliferation and anti-bacterial properties. 19346663_Intravenous infusion of adrenomedullin with atrial natriuretic peptide could be used therapeutically in acute decompensated heart failure. 19564455_MR-proADM, CT-proET-1, CT-proAVP, and MR-proANP were all elevated in patients with future cardiovascular events and independently correlated to serum creatinine. 19610056_High adrenomedullin mRNA expression is associated with clear-cell renal carcinoma. 19616043_AM is expressed in ovarian epithelial carcinoma tissue and bFGF can induce the expression of AM through the JNK-AP-1 pathway in ovarian epithelial carcinoma cell line CAOV(3). 19623513_Epicardial fat adrenomedullin gene and protein expression can be downregulated in coronary artery disease (CAD) subjects and intracoronary adrenomedullin levels are lower in CAD. 19627536_These parameters identify the role of ADM expression and Bcl-2 protein in relation to cell growth and vasodilating in the neoplastic changes 19636336_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19636336_Reporter gene assays showed that a SNP (rs11042725) in the upstream flanking region of ADM significantly altered expression. 19706311_results suggest active roles for the two molecular forms of AM in metabolic disorders associated with obesity in subjects without overt cardiovascular disease 19738161_Adrenomedullin promotes lung angiogenesis, alveolar development, and repair 19823891_increased expression in alveolar macrophages from patients with heart failure 19847298_ADMR mediates the stimulatory effects of adrenomedullin on cancer cells and on endothelial and stellate cells within the tumor microenvironment 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19932100_The results of the present study show that ADM regulates cellular ROS levels via the GSH and Trx system. 20016189_AM concentration in maternal plasma may mediate compensatory vascular responses in the uterine circulation 20151808_Periodontitis groups had a significantly higher total amount of gingival crevicular fluid adrenomedullin compared to the gingivitis and healthy control groups. Levels were positively correlated with clinical periodontal parameters. 20216319_In contrast with smoking cirrhotic patients, nonsmoking cirrhotic patients show an increased systemic vasodilation, which could depend on higher plasmatic levels of adrenomedullin 20467777_possible role for AM and proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide in the pathophysiology of early rheumatoid arthritis 20534761_ADM expression in human oviduct is hormone-dependent and is upregulated by sperm contact. ADM stimulates ciliary motility in the oviduct. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20691218_The mRNA levels of adrenomedullin appear to be increased in epicardial adipose tissue independent of their plasma levels in coronary artery disease. 20713499_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20798523_The expression of human ADM protein resulted in attenuation of myocardial oxidative stress and hypertrophic remodelling in the absence of blood pressure reduction in this model of chronic NO-deficiency. 20854881_In the context of brain ischemia, transgenic mice lacking complement factor H do not show alterations in expression or function of AM resulting from polymorphisms or other causes that may severely affect stroke outcome. 20942979_These results support a new role for adrenomedullin in rheumatoid synovial fibroblast pathobiology. 20954838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20954838_no difference in endometrial expression between fertile and infertile women 21050876_The total AM concentration in nasal discharge was higher in controls than in allergic rhinitis patients. AM-containing cells (mast cells) were observed in the nasal mucosa from subjects with and without nasal allergy, and also in nasal polyps. 21075100_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21075100_a potential role of genetic variants in the adrenomedullin gene in the development of dysglycemia 21094578_Hypoxia regulates adrenomedullin secretion and expression by human placenta, thereby promoting increased adrenomedullin concentration in the fetal circulation in clinical circumstances characterized by reduced oxygen levels. 21350119_results identify adrenomedullin as an endogenously generated vascular mediator that functions as a mucosal protective factor through fine tuning of HIF activity 21408188_Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin and mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide were shown to be associated with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality. 21458987_analysis of adrenomedullin expression and regulation in human glioblastoma, cultured human glioblastoma cell lines and pilocytic astrocytoma 21558311_Adrenomedullin (AM) is elevated in endometrium at the time of endometrial regeneration during the menstrual cycle. AM induces both angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. AM expression is up-regulated by 2 stimuli: cell hypoxia and PGF2alpha. 21558971_adrenomedullin was found to upregulate VEGF and bFGF 21695352_Data show that that plasma levels of adrenomedullin (AM) increased significantly, whereas plasma levels of AM binding protein (AMBP-1) decreased significantly after stroke. 21721459_Higher ADM plasma concentration in women with Preeclampsia suggests possible correlation between adrenomedullin level and pathological changes in cardiovascular system during pregnancy 21725669_A decreased midregional proadrenomedullin level is an independent correlate of the presence of coronary artery disease and of soft atherosclerotic plaques. 21791966_Increased adrenomedullin is associated with insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 21798961_ADM genotype should be included in future studies of cardiovascular risk prediction 21830197_Structure of micelle-bound adrenomedullin. 21839130_AM produced in colorectal tumors acts in concert with metalloproteinase-9 in the stroma to contribute to the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. 21889828_no difference in plasma levels between the controls and children with asthma attack 21957602_Reduced mRNA expression for ADM in the placenta connected with reverse correlation of systolic blood pressure in preeclamptic women suggests the significant role of disturbances in placental secretion of ADM in etiology of preeclampsia 21994414_study reveals a novel mechanism that tumor-associated macrophages enhance angiogenesis and melanoma growth via adrenomedullin 22070520_Midregional-proadrenomedullin is a powerful prognostic marker in AL amyloidosis, which may not only reflect cardiac dysfunction but also widespread systemic disease 22087514_Adrenomedullin also inhibited proliferation and collagen synthesis in fibroblasts induced by TGF-beta1. 22102369_Structural basis for extracellular interactions between calcitonin receptor-like receptor and receptor activity-modifying protein 2 for adrenomedullin-specific binding. 22178239_Increased adrenomedullin expression in endometrial cancer may result in amplifying both tumorigenic and angiogenic activities. A substantial impact on growth of tumours may result as a consequence of the synergism between adrenomedullin and VEGF. 22400488_AM contributed to the progression of EOC and had additional roles in EOC cell migration by activating the integrin alpha5beta1 signaling pathway. 22406979_ADM up-regulated the protein expressions of HIF-1alpha through down-regulation of proline hydroxylase (PHD) mRNA expression and PHD activity. 22456622_Lower ADM level in the oviducts of tubal pregnancy may lead to the decrease in ciliary beating and muscle contraction, with the result that the embryo is retained and implanted in the oviduct. 22608560_Adrenomedullin, a 52-amino acid regulatory peptide increases proliferation and regulates cell fate of stem cells of different origins. 22628306_role of adrenomedullin and its binding protein, AMBP-1, in neuroprotection 22801438_Proadrenomedullin is reliably expressed in patients with shock 22818355_In children admitted to hospital with community-acquired pneumonia, pro-ADM levels are related to the development of complications during hospitalization. 22859951_High expression of adrenomedullin in ovarian cancer was linked to positive outcome. 22880472_The observed tendency for overrepresentation of minor -1984G ADM allele in the GH and PE women and their newborns, despite lack of statistical significance, suggests participation of this genetic variant in the pathogenesis of the mentioned conditions. 22881718_AM can constitute, alone or combined with standard parameters, a promising predictor of low cardiac output syndrome in infants subjected to open-heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. 22885414_The use of pro-ADM in combination with other acute-phase reactants such as CRP and IL-6 for the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with neonatal sepsis has high sensitivity and specificity. 22932875_Genetic variations in the ADM gene were not associated with the risk of hypertension in a Chinese population, however, the genotype at common variation rs4399321 may influence the BP level in normotensive subjects, especially among non-drinkers. 22960655_Adrenomedullin is up-regulated in patients with pancreatic cancer and causes insulin resistance in beta cells and mice. 22971508_Adrenomedullin modulates the interaction between the heart and kidneys in early subclinical cardiorenal syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 23002189_Data demonstrate for the first time that plasma levels of both MR-proADM and CT-proET-1 levels are related to MetS and its components, thus suggesting that they possibly have a role as a surrogate biomarker. 23017815_The prognostic biomarker proadrenomedullin can potentially serve as an outcome monitoring marker in patients with lower respiratory tract infections. 23088295_Data indicate that plasma adrenomedullin (ADM) levels are related to the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs17147230 in interleukin-6 (IL6) gene. 23199555_Plasma levels of proadrenomedullin provide prognostic value for all-cause mortality in acute chest pain patients. 23258247_Daily walking activity independently predicts levels of circulating MRproANP and MRproADM in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. 23269582_we conclude that ADM expression is highly correlated with the degree of malignancy and metastasis of osteosarcoma. 23356193_Maternal circulating level of adrenomedullin is elevated in pregnant women with hypertension or pre-eclampsia. 23381795_The discovery of genetic variants in the kallikrein-kinin system and in the genes encoding pre-pro-endothelin-1 and pre-pro-adrenomedullin provides novel insights into the (co-)regulation of these vasoactive peptides in the vascular system. 23445133_ADM serum level is significantly increased in intrauterine growth restriction 23450059_Cancer protection elicited by a single nucleotide polymorphism close to the adrenomedullin gene. 23478664_MM cells, both in a hypoxia-dependent and -independent fashion, aberrantly express and secrete AM, which can mediate MM-induced angiogenesis. 23562132_Elevated MR-proADM plasma concentrations were strongly associated with classical cardiovascular risk factors and manifest cardiovascular diseases. 23564381_AM is expressed by peritoneal mesothelial cells and actively amidated in the abdominal cavity of patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis. 23583388_Data indicate that JMJD1A gene silencing abrogated the hypoxia-induced adrenomedullin (ADM) expression and inhibited HepG2 and Hep3B cell growth. 23634287_These findings highlight the potential importance of AM and its receptors in the progression of CRC and support the conclusion that alphaAM treatment inhibits tumor growth by suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth, suggesting that AM may be a useful therapeutic target. 23638647_Anxiety disorders are associated with elevated plasma adrenomedullin levels and increased left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with essential hypertension. The clinical significance of these changes requires further investi |
ENSMUSG00000030790 |
Adm |
163.637009 |
2.7807338954 |
1.475466 |
0.132622455 |
125.881249 |
0.00000000000000000000000000003264446180717675711287381608814777608457014619997206836515207119978266982836170168047473794104007538408041000366210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000409721306355381747780264866655279329450926426784935012651666675313970024602597264085090955632040277123451232910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
244.4642297 |
19.7833510 |
88.5305613 |
5.7655386 |
| ENSG00000149177 |
5795 |
PTPRJ |
protein_coding |
Q12913 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine phosphatase which dephosphorylates or contributes to the dephosphorylation of CTNND1, FLT3, PDGFRB, MET, KDR, LYN, SRC, MAPK1, MAPK3, EGFR, TJP1, OCLN, PIK3R1 and PIK3R2 (PubMed:10821867, PubMed:12062403, PubMed:12370829, PubMed:12475979, PubMed:18348712, PubMed:19494114, PubMed:19922411, PubMed:21262971). Plays a role in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation and differentiation (PubMed:12370829, PubMed:14709717, PubMed:16682945, PubMed:19836242). Involved in vascular development (By similarity). Regulator of macrophage adhesion and spreading (By similarity). Positively affects cell-matrix adhesion (By similarity). Positive regulator of platelet activation and thrombosis. Negative regulator of cell proliferation (PubMed:16682945). Negative regulator of PDGF-stimulated cell migration; through dephosphorylation of PDGFR (PubMed:21091576). Positive regulator of endothelial cell survival, as well as of VEGF-induced SRC and AKT activation; through KDR dephosphorylation (PubMed:18936167). Negative regulator of EGFR signaling pathway; through EGFR dephosphorylation (PubMed:19836242). Enhances the barrier function of epithelial junctions during reassembly (PubMed:19332538). Negatively regulates T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling (PubMed:9531590, PubMed:9780142, PubMed:11259588). Upon T-cell TCR activation, it is up-regulated and excluded from the immunological synapses, while upon T-cell-antigen presenting cells (APC) disengagement, it is no longer excluded and can dephosphorylate PLCG1 and LAT to down-regulate prolongation of signaling (PubMed:11259588, PubMed:12913111). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10821867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11259588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12062403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12370829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12475979, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12913111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14709717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16682945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18348712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18936167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19332538, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19494114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19836242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19922411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21091576, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21262971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9531590, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9780142}. |
3D-structure;Alternative initiation;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region containing five fibronectin type III repeats, a single transmembrane region, and a single intracytoplasmic catalytic domain, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. This protein is present in all hematopoietic lineages, and was shown to negatively regulate T cell receptor signaling possibly through interfering with the phosphorylation of Phospholipase C Gamma 1 and Linker for Activation of T Cells. This protein can also dephosphorylate the PDGF beta receptor, and may be involved in UV-induced signal transduction. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5795; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; delta-catenin binding [GO:0070097]; gamma-catenin binding [GO:0045295]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; contact inhibition [GO:0060242]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042059]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0010642]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050860]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive chemotaxis [GO:0050918]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:1905451]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
12089527_In this paper, frequent deletion of PTPRJ is shown in human colon, lung, and breast cancers. 12089527_This protein is frequently deleted in human breast cancers. 12685844_CD148 and CD27 are expressed in a wide range of B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and do not serve to distinguish between neoplastic cells of naive and memory B cell derivation 14709717_DEP-1 is a negative regulator of cell proliferation, cell-substratum contacts, motility and chemotaxis in fibroblasts 15123617_propose that the expression and activation of DEP-1/PTPeta is required for somatostatin inhibition of glioma proliferation 15231692_A candidate tumor suppressor gene because its expression was blocked in rat and human thyroid transformed cells, and its restoration reverted their neoplastic phenotype. 15378013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15378013_genotypic profile of PTPRJ affects susceptibility to thyroid carcinomas, loss involved in thyroid carcinogenesis 15384144_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16000320_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16000320_single nucleotide polymorphisms in protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type J is associated with breast cancer 16582570_Male, dizygotic twins were diagnosed with sensori-neural deafness at ages 5 and 21 months and later developed hypothyroidism at ages 24 and 28 months, respectively. Analysis for anti-DEP-1/CD148 autoantibodies described in Cogan syndrome proved positive. 16682945_Chemoprotective nutrients elevated transcription of endogenous DEP-1 mRNA & expression of DEP-1 protein. Upregulation of DEP-1 expression & inhibition of cell growth & migration may be a previously unrecognized mechanism of chemoprevention by nutrients. 18348712_These results demonstrate that CD148 may interact with and dephosphorylate p85 when it is phosphorylated and modulate the magnitude of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity. 18603590_The translation of the region between AUG(191) and AUG(356) inhibits the overall expression of PTPRJ mRNA. 18843023_No significant evidence for the A1176C allele of PTPRJ or previously described haplotypes of tagSNPs in PTPRJ on CRC risk. 18843023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936167_DEP-1 is a positive regulator of VEGF-mediated Src and Akt activation and endothelial cell survival. 19122201_The intact structure of the eighth fibronectin domain of PTPRJ is critical for its localization in plasma membrane and biological function. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332538_DEP-1 can modify the phosphorylation state of tight junction proteins and play a role in regulating permeability. 19413345_CD148 may have a role in mantle cell lymphoma 19494114_DEP-1 inhibits the RAS pathway by direct dephosphorylation of ERK1/2 kinases 19672627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19672627_PTPRJ SNPs were found to influence susceptibility to a wide spectrum of cancers. 19836242_DEP-1 is a tumor suppressor that dephosphorylates and thereby stabilizes EGFR by hampering its ability to associate with the CBL-GRB2 ubiquitin ligase complex. 19922411_Data reveal PTPN2, PTPRJ and PTEN as potent regulators of Akt signalling which contribute to ameliorating the consequences of oncogenic K-Ras activity. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20823296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20823296_Therefore, the results reported here show that the homozygous genotype for Asp872 of PTPRJ is associated with an increased risk to develop papillary thyroid carcinoma. 21036128_PTPRJ is a candidate colorectal cancer susceptibility gene 21091576_We propose that positive regulation of adhesion signaling by DEP-1 is involved in inhibition of meningioma cell motility, and possibly tumor invasiveness. 21262971_DEP-1 is negatively regulating FLT3 signaling activity and that its loss may contribute to but is not sufficient for leukemogenic cell transformation. 21304107_That DEP-1 plays a biologic role in angiogenic endothelial cell behavior was demonstrated in endothelial cell migration, proliferation, and capillary-like tube formation assays in vitro 21543337_differential effects of CD148 in T cells and other leukocyte subsets 21813734_Here the protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor CD148 is shown to be a key intermediary in cell adhesion to S2ED, with downstream beta1 integrin-mediated adhesion and cytoskeletal organization 22308318_These findings provide evidence that CD148 functions as a receptor for TSP1 and mediates its inhibition of cell growth. 22438257_DEP-1 oxidation is a novel event contributing to cell transformation by FLT3 ITD. 22564856_Data indicate that miR-328 regulated PTPRJ expression, and suggest that the interaction of miR-328 with PTPRJ is responsible for miR-328-dependent increase of epithelial cell proliferation. 22677127_CD148 polymorphisms affect platelet activation and probably exert a protective effect on the risk of Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with antibodies to PF4/Heparin complexes. 22815804_These data indicate that PTPRJ may regulate differentiation of normal mammary epithelia and that dysregulation of protein localisation may be associated with tumorigenesis. 23341091_haplotypes in PTPRJ gene may play a role in susceptibility to Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, by affecting activation of PTPRJ in these B-cell lymphomas. 23650535_FLT3 is a bona fide substrate of DEP-1 and that interaction occurs mainly via an enzyme-substrate complex formation triggered by FLT3 ligand stimulation. 24016860_Data indicate that CD148 is upregulated in macrophages and T cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) samples, and its activity is enhanced by treatment with tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha), and reduced by synovial fluid or oxidising conditions. 24027763_our data support the notion of DEP-1 as positive functional regulator in vascular cerebral arteriogenesis, involving differential PDGF-B gene expression. 24583284_Phosphorylation of T1318 is part of a regulatory mechanism that channels the activity of DEP-1 towards Src to allow its optimal activation and the promotion of endothelial cell permeability. 25386896_CD148 tyrosine phosphatase promotes e-cadherin cell adhesion. 25412306_The expression profiles of DEP1 and B2MG correlate with increased cell senescence and survival in breast cancer. 25634668_C33A cells lacking PTPRJ had increased cell viability, growth, migration, G1-S transition, and 5-FU resistance. PTPRJ negatively regulated the JAK1/STAT3 pathway by decreasing phosphorylation levels of JAK1 and STAT3 and expression of downstream factors. 25672645_The studies suggest induction of MMP-9 expression promoted by DEP-1 deficiency. 25772245_Moderate expression of DEP-1 was associated with the increased relapse. 25791119_the combination of CD200 and CD148 may have a potential differential diagnostic value in leukemic B-CLPDs, especially between CLL and MCL. 26063811_These results demonstrated Ptprj as a physiological enzyme that attenuates insulin signalling in vivo, and indicate that an inhibitor of Ptprj may be an insulin-sensitizing agent. 26248682_The strongest association with frailty was observed in the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, Receptor type, J (PTPRJ) (rs1566729, P = 0.001372, beta = 0.09397) gene. 26694178_Loss of PTPRJ expression may predict an aggressive clinical course in ESCC patients. 26871468_Authors demonstrate that mtp53 prevents the COP1/DET1 complex from ubiquitinating ETS2 and thereby marking it for destruction. Authors show that mtp53 destabilizes DET1 and also disrupts the DET1/ETS2 complex thereby preventing ETS2 degradation. 27309885_These data support that PTPN22 1858C/T, PTPRJ 2965C/G and 1176 A/C polymorphisms and ACP1 A, B and C alleles are not associated with a higher risk of immune thrombocytopenia P in adults. 28052032_Short variant of the receptor protein phosphatase PTPRJ generated by an alternative splicing promotes angiogenesis in HUVEC cells and tumor angiogenesis. 28316102_study reveals the crucial role of miR-155/PTPRJ/AKT axis in proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells and suggests a therapeutic potential of PTPRJ. 28823811_results support a scenario by which T cell-derived microvesicles act as intercellular carriers of functional miR-4443, which might exert heterotypic regulation of PTPRJ gene expression in mast cells 29762926_PTPRJ variant of uncertain significance in candidate gene was identified in Familial Mitral Valve Prolapse. 30591527_Loss-of-function mutations in PTPRJ gene is associated with a new form of inherited thrombocytopenia. 30661225_Arg326Gln polymorphism is associated with colorectal cancer. 31715329_Loss of PTPRJ/DEP-1 enhances NF2/Merlin-dependent meningioma development. 33455071_The relative expression levels of CD148 and CD180 on clonal B cells and CD148/CD180 median fluorescence intensity ratios are useful in the characterization of mature B cell lymphoid neoplasms infiltrating blood and bone marrow - Results from a single centre pilot study. 33784491_CD148 Deficiency in Fibroblasts Promotes the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis. 34791835_The effects of CD148 Q276P/R326Q polymorphisms in A431D epidermoid cancer cell proliferation and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. 35791609_PTPRJ is downregulated in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 35850306_Phagocytosis mediated by the human granulocyte receptor CEACAM3 is limited by the receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPRJ. |
ENSMUSG00000025314 |
Ptprj |
2621.828492 |
2.0770755852 |
1.054554 |
0.046187776 |
517.732742 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000131769816577846000762568345778441589033025208155457977305715364148832421876848300414296907033250391413702482568547305096178519407085125990695893905642332144552925705467225274040668310416921505495517533705278784429786 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000065265855459362649504767164210324240247438977556010545344418434701803808255763949429861440404092602542613102656711079510736121102496699538928919790119633314238211086945137431804657376429339222729036294838985262365762 |
Yes |
Yes |
3605.3653568 |
96.9368315 |
1748.4739395 |
35.8301154 |
| ENSG00000149260 |
726 |
CAPN5 |
protein_coding |
O15484 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-regulated non-lysosomal thiol-protease. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease |
|
Calpains are calcium-dependent cysteine proteases involved in signal transduction in a variety of cellular processes. A functional calpain protein consists of an invariant small subunit and 1 of a family of large subunits. CAPN5 is one of the large subunits. Unlike some of the calpains, CAPN5 and CAPN6 lack a calmodulin-like domain IV. Because of the significant similarity to Caenorhabditis elegans sex determination gene tra-3, CAPN5 is also called as HTRA3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:726; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; synapse [GO:0045202]; calcium-dependent cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15464980_Results describe the cloning and characterization of rat calpain-5, which is highly homologous to human and mouse sequences. 16396936_CAPN5 polymorphisms are associated with a risk of polycystic ovary syndrome. 16396936_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17227582_CAPN5 seems to influence traits related to increased risk for cardiovascular diseases and play a role as a candidate gene for metabolic syndrome 17227582_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18657264_We have found significant interaction between CAPN5 and PPARD genes that reduces risk for obesity in 55%. CAPN5 and PPARD gene products may also interact in vivo. 18787380_Data examine possible allelic imbalance in papillary thyroid cancer at EMSY, CAPN5, and PAK1, as candidate genes within 11q13.5-q14 region using a single nucleotide polymorphism-based analysis. 18829447_Calpain5 was expressed in endometrial stromal and glandular cells throughout the menstrual cycle and in decidua, and its expression was decreased in both stromal and glandular cells from women with endometriosis compared with that of fertile controls. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23055945_Calpain-5 mutations cause autoimmune uveitis, retinal neovascularization, and photoreceptor degeneration. 24381307_autosomal dominant neovascular inflammatory vitreoretinopathy is due to CAPN5 gain-of-function rather than haploinsufficiency. 25216694_CAPN5 expression can be suppressed by shRNA-based RNA interference 25856303_A novel CAPN5 (c.750G>T, p.Lys250Asn) missense mutation causes uveitis and neovascular retinal detachment. 25994508_CAPN5 mutation in hereditary uveitis: the R243L mutation increases calpain catalytic activity and triggers intraocular inflammation 27152965_CAPN5 localization at the photoreceptor synapse and with mitochondria explains the neural circuitry phenotype in human CAPN5 disease alleles. 27474374_The relative domain rotation of 60-100 degrees we found for mini-calpain-5 (a non-classical calpain) is significantly greater than the largest rotation previously observed for a classical calpain 29472286_We describe a pediatric patient with severe inflammatory vitreoretinopathy accompanied by hearing loss and developmental delay associated with a novel, de novo CAPN5 missense mutation (c.865C>T, p.Arg289Trp) that shows greater hyperactivation of the calpain protease, indicating a genotype-phenotype correlation. 29610848_The novel CAPN5 mutation (p.R289W) is responsible for the present autosomal dominant neovascular inflammatory vitreoretinopathy (ADNIV) family. The mutant CAPN5 stimulated secretion and cleavage of SLIT2 fragments that may act as a bystander to regulate abnormal RPE cell proliferation for ADNIV. 30024968_Our findings reveal a comprehensive CD81 network in human liver cells and show that hepatitis C virus and Plasmodium highjack selective CD81 interactions, including CAPN5 and CBLB for hepatitis C virus, to invade cells. 30029251_Capn5 may play a role in CNS development, photoreceptor maintenance, and photoreceptor regeneration. 31110225_Proteomic insight into the pathogenesis of CAPN5-vitreoretinopathy. 31403230_Study found 22 loss-of-function (LOF) CAPN5 variants located throughout the gene and in all major protein domains. Structural modeling of coding variants showed these LOF variants were nearby known vitreoretinopathy-causing variants within the proteolytic core and in regions of high homology between human CAPN5 and 150 homologs, yet the LOF of CAPN5 was tolerated as opposed to gain-of-function disease-causing variants. 31968260_Structural Insights into the Unique Activation Mechanisms of a Non-classical Calpain and Its Disease-Causing Variants. 32707200_Whole-Exome Sequencing of Patients With Posterior Segment Uveitis. 33607190_Characterization of mitochondrial calpain-5. 33811937_The C2 domain of calpain 5 contributes to enzyme activation and membrane localization. 35398613_Mitochondrial calpain-5 truncates caspase-4 during endoplasmic reticulum stress. |
ENSMUSG00000035547 |
Capn5 |
11.275582 |
0.3405269889 |
-1.554159 |
0.631205922 |
5.853972 |
0.01554193540075678170442330383593798615038394927978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028571299852431199933766592380379734095185995101928710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1886893 |
2.4982157 |
15.0430012 |
4.7709840 |
| ENSG00000149294 |
4684 |
NCAM1 |
protein_coding |
P13591 |
FUNCTION: This protein is a cell adhesion molecule involved in neuron-neuron adhesion, neurite fasciculation, outgrowth of neurites, etc.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for rabies virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9696812}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Zika virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32753727}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a cell adhesion protein which is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The encoded protein is involved in cell-to-cell interactions as well as cell-matrix interactions during development and differentiation. The encoded protein plays a role in the development of the nervous system by regulating neurogenesis, neurite outgrowth, and cell migration. This protein is also involved in the expansion of T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells which play an important role in immune surveillance. This protein plays a role in signal transduction by interacting with fibroblast growth factor receptors, N-cadherin and other components of the extracellular matrix and by triggering signalling cascades involving FYN-focal adhesion kinase (FAK), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). One prominent isoform of this gene, cell surface molecule CD56, plays a role in several myeloproliferative disorders such as acute myeloid leukemia and differential expression of this gene is associated with differential disease progression. For example, increased expression of CD56 is correlated with lower survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients whereas increased severity of COVID-19 is correlated with decreased abundance of CD56-expressing NK cells in peripheral blood. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:4684; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; commissural neuron axon guidance [GO:0071679]; regulation of semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:2001260] |
11681838_NCAM 105-115 kDa is a protease- and neuraminidase-susceptible fragment and was correlated with ventricular enlargement in chronic schizophrenia (p = 0.01). Release of NCAM fragments in schizophrenia may be part of the pathogenic mechanism. 11820619_Significance of cell adhesion molecules, CD56/NCAM in particular, in human tumor growth and spreading. 11915324_exists in lipid microdomains and transducts cell signalings via regulating the activation of signal transduction molecules 12003861_PSA-NCAM was found to be expressed in the somata, dendrites and axonal processes of some neurons, which were identified as chandelier cell axon terminals (chandelier terminals), in the adult human entorhinal cortex and neocortex. 12008081_CD56 expression predicts occurrence of CNS disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia but not CR or survival. CD56 may enable targeting of leukemic cells to tissues that express it. 12121226_CD56 molecules on NK cells interact with fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 on Jurkat T cells to trigger IL-2 production. 12594840_Preferential apoptosis of CD56dim natural killer cell subset in patients with cancer. 12727026_a useful immunohistochemical marker of Merkel cell carcinoma 12791681_which the polysialyltransferases bind to the first fibronectin type III repeat (FN1) of NCAM to polymerize polysialic acid chains on appropriately presented glycans in adjacent regions. 12937148_Strong overexpression of NCAM(CD56) and RUNX1(AML1) is a constant and characteristic feature of cardiomyocytes within or adjacent to scars in ICM. 14688313_Natural killer (NK) cells expressing high CD56 levels are terminally differentiated cells identical to mature NK cells recently activated in the presence of IL-12, and not a functionally distinct subset or progenitors to mature CD56+low NK cells. 14726964_there are two types of CD56+ epithelial cells in the pancreatic duct system: CD56+ endocrine cells are numerous during the early stage of gestation while CD56+ luminal cells may represent developmental and regenerative changes of pancreatic ducts. 14959847_CD56 is expressed in bone marrow of acute myelogenous leukemias but not acute lymphoblastic leukemia 15006709_Alzheimer patients presented values of low molecular weight-NCAM and high molecular weight-NCAM significantly higher than healthy controls of similar age (higher than 130 kDa) 15050861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15050861_genetic variations in neural cell adhesion molecule 1 or nearby genes could confer risks associated with bipolar affective disorder in Japanese individuals. 15061198_REVIEW: Prognostic significance of CD56 expressed in multiple myeloma 15223636_CD56 expression was associated with the leukemogenetic mutation at the primitive hematopoietic progenitor cell level 15231874_Unlike wild-type FGFR4, pituitary tumor derived-FGFR4 does not associate with neural cell-adhesion molecule (NCAM). 15246157_Cells expressing this antigen repond to a Wilms tumor cell line feeder cells and are precursors of NK cells. 15356097_Pre-activated, adherent-natural killer cells express low levels of CD56 and CD161 15459479_There is a close relationship between PSA-NCAM expression and neuronal migration. 15528382_CD56bright natural killer cells accumulate in inflammatory lesions and, in the appropriate cytokine environment, can engage with CD14+ monocytes in a reciprocal activatory fashion, thereby amplifying the inflammatory response. 15626024_first pediatric case describing coexpression of CD56 on B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia 15782066_CD56 seems to be the most sensitive marker for the diagnosis of SCC of the uterine cervix 15950781_A significant increase was observed in PSA-NCAM, NCAM-180, NCAM-140, and HSP70 expression as seen by Western blotting and immunocytofluorescent studies in NMDA-treated cultures. 16027151_polysialyltransferase ST8Sia IV/PST recognizes specific amino acids in the first fibronectin type III repeat of the neural cell adhesion molecule 16172115_analysis of polymerization of polysialic acid on neural cell adhesion molecules 16211277_NCAM is associated not only with a cell-to-cell adhesion mechanism, but also with tumorigenesis, including growth, development and perineural invasion in human salivary gland tumors 16316416_CD56(bright) and CD56(dim) human natural killer-cell subsets exert different functional and cytotoxic activities in response to a live bacterial pathogen. 16406048_The new role of Neural Cell Adhesion Molecules in tumor neo-angiogenesis relevant for endothelial cell organization into capillary-like structures. 16534119_NCAM is hyposialylated in hereditary inclusion body myopathy skeletal) muscle. 16572491_Tests whether activation and expansion of human NK cells with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) reveals differences between identical twins with regaard to C56 antigen. 16627685_The gene expression profile of hepatic stem cells throughout life consists of high levels of expression of neuronal cell adhesion molecule (NCAM). 16690409_identified co-induction of NKG2A and CD56 on activation of TH2 cells 16892559_Isolation of 3 novel isoforms of AML 1 (RUNX1) with different transactivating function, that might be a regulatory element of the NCAM (CD56) overexpression in chronic myocardial ischemia. 17003032_the FN1 alpha-helix is involved in an Ig5-FN1 interaction that is critical for the correct positioning of Ig5 N-glycans for polysialylation 17005551_Co-immunoprecipitation and co-clustering paradigms were used to show that both NCAM and N-cadherin can interact with the 3Ig IIIC isoform of the FGFR1 in a number of cell types. 17043020_NCAM1 along with RUNX1 is overexpressed during stress hematopoiesis in Down syndrome children and may contribute to the development of overt leukemia. 17085484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17161382_In the 'Europe only' stratum, there were nominally significant associations with five contiguous SNPs. 17181871_Neuroblastoma cells resistant to anticancer drugs have increased invasive capacity caused by down-regulation of NCAM adhesion receptor. 17208489_GPI-anchored NCAM-120 suppressed rabies virus replication via induction of IFN-ss even though NCAM-120 was able to promote virus penetration into the cells. 17216340_The pattern of serum NCAM bands could be useful to detect brain tumor pathology. NCAM immunostaining of tumors was inversely correlated with the histological grade of malignancy. Loss of NCAM staining was significantly associated with poor prognosis. 17337466_Renal NCAM-expressing interstitial cells can participate in the initial phase of interstitial fibrosis. 17413444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17413444_Single nucleotide polymorphisms within NCAM1 contribute differential risk for both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia possibly by alternative splicing of the gene. 17431094_HIV-1 Nef protein up-regulates the ability of dendritic cellss to stimulate the immunoregulatory naturak killer cells. 17467233_PSA-NCAM is expressed in the human PFC neuropil following a laminated pattern and in a subpopulation of mature neurons, which lack doublecortin expression. Most of these cells have been identified as interneurons expressing calbindin 17635242_Although CD56 expression level varies among the cases, this molecule might play some roles in the manner of growth and expansion of CD56-positive B-cell lymphomas 17683591_PSA-NCAM is not involved in masking Siglec-7 17761687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17761687_association studies of alcohol dependence and 43 SNPs mapped to the gene cluster of NCAM1, TTC12, ANKK1 and DRD2 17878347_may explain the preferential accumulation of CD56(bright) NK cells often seen in environments rich in reactive oxygen species, such as at sites of chronic inflammation and in tumors 17891186_lack of CD56 expression on MM cells is not a prognostic marker in patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy, but is associated with t(11;14). 17900814_fetal forebrain axonal PSA-NCAM expression is inversely related to primary myelination 17940597_that expansion of the CD56(bright) NK cell subtype in peripheral blood is not a hallmark of TAP deficiency, but can be found in other diseases as well 17971410_Ubiquitylation represents an endocytosis signal for NCAM. 17982624_NCAM expression may be used as a predictor of perineural invasion in adenoid cystic carcinoma 18209097_Monitoring of T cells driven to senescence showed de novo induction of CD56, the prototypic receptor of NK cells. 18213713_Ganglioneuromas and ganglioneuroblastomas express the adhesive 120 kDa NCAM isoform, while neuroblastomas preferentially express the 180 kDa isoform classically involved in cell motility 18231917_determined the clinical characteristics of 204 multiple myeloma (MM) patients and 26 plasma cell leukemia (PCL) patients with regard to CD56 expression. 18261743_NCAM-fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 interaction at the cell surface is likely to depend upon avidity effects due to receptor clustering 18289872_Neural cell adhesion molecule-extracellular domain overexpression disrupts aborization of basket cells during the major period of axon/dendrite growth in transgenic mice. 18323797_identified molecular characteristics of an aggressive subset of pediatric patients with AML through a prospective evaluation of CD56+ neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) and CD94 expression 18333845_relative frequency of CD19 and/or CD56 expression in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with t(8;21) was significantly higher than those without this translocation and co-expression of these two antigens may serve as the surrogate markers for AML with t(8;21) 18353777_direct receptor-receptor interactions are not required for high affinity GDNF binding to NCAM but play an important role in the regulation of NCAM-mediated cell adhesion by GFRalpha1 18368482_results provide evidence that the BCL motif is one of the multiple FGFR binding sites in NCAM 18384787_Enzymatic removal of PSA from NCAM or reduction of polysialyltransferase expression led to reduced association between NCAM and E-cadherin and subsequently increased E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell aggregation and reduced cell migration. 18425046_CD56 is often expressed by a wide variety of spindle cell sarcomas, thus, it has no value in differentiating GYN from non-GYN spindle cell tumors. 18432248_there was increased placental expression of NCAM (neural cell adhesion molecule) in small for gestational age cases 18462256_extramedullary relapse of MM is characterized by loss of CD56 expression 18594005_CD56-expressing gammadelta T lymphocytes are resistant to Fas ligand and chemically induced apoptosis 18601968_No genetic association between NCAM1 gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia in the Chinese population. 18601968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18628406_Immunological events associated with the luteinizing hormone surge induce alterations in all subsets of CD56(+) cells in the fertile menstrual cycle 18641363_CD56(bright) NK cells postallogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation exhibit peculiar phenotypic and functional properties 18755075_To identify the gene regulated by PKD2 and c-Myc, we performed gene expression profiling in PKD2 and c-Myc overexpressing cells. NCAM is an important molecule in the cystogenesis induced by PKD2 overexpression. 18828801_NCAM1 exon 12 markers are significant for specific haplotypes in a family sample of comorbid alcohol and drug dependence. 18828801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18972120_NCAM represents a marker for neuroblastomas irrespectively of their stages 18979395_N-CAM increased in cytotrophoblasts and decreased in extravillous trophoblasts and decidual cells of preeclamptic subjects. 18990213_The results obtained show that, in man, the expression of PSA-NCAM in selective populations of central and peripheral neurons occurs not only during prenatal life, but also in adulthood. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19153015_CD56 is extremely useful in the diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma 19222860_NCAM-positive neuroblastoma patients had more often metastases at diagnosis, and NCAM expression associated with advanced disease 19235015_propose four potential activators of the CD56 promoter and for CD56 to be involved in proliferation and anti-apoptosis, leading to disease progression in multiple myeloma 19328310_Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma with a phenotype showing a deficiency of cd56. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19393299_study implicates the major NCAM isoforms, PSA-NCAM and proteolytically cleaved NCAM in pre- and postnatal development of the human prefrontal cortex 19411161_This data suggests NCAM-180 mRNA expression is altered in a regionally-specific manner in schizophrenia and these changes are associated with the early period following diagnosis. 19507465_The role of NCAM in cell differentiation, survival and plasticity suggests an involvement in the development process of the carotid body and in cellular/molecular changes due to chronic hypoxia. 19587433_Structural change in NCAM1 caused by point mutation may be the reason for astrocytoma tumorigenesis. 19652998_Additional immunohistochemical detection of neuroendocrine differentiation (chromogranin-A, synaptophysin, and neural-cell adhesion molecule) in non-small cell lung cancer is presently not of prognostic importance. 19724850_Class III beta-tubulin and NCAM were expressed in 50 and 68% of basal cell carcinoma 19725832_polysialylated NCAM persistence, up-regulated polysialyltransferase-1 mRNA and previously uncovered defective myelin-associated glycoprotein may be early pathogenetic events in adult-onset autosomal-dominant leukodystrophy 19772585_Expression defines a committed T-lymphocyte lineage to the cytotoxic phenotype 19788570_results suggest a positive role of NCAM in neurogenesis in the periventricular region; expression of NCAM in stem cells might be one of many factors useful for therapeutic approaches in the future 19788615_Mucosal remodeling with alterations of NCAM+ or alpha-SMA+ subepithelial and interstitial cells may play a critical role in UC-associated tumorigenesis. 19864234_CD56 immunohistochemical analysis is useful for detecting residual plasma cell myeloma particularly in morphologically equivocal cases in which light chain restriction cannot be demonstrated, and may serve as a potential response criterion. 19897577_human CD56(bright) NK cells progress through a continuum of differentiation that ends with a CD94(low)CD56(dim) phenotype. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20015889_Neural cell adhesion molecules expressed on mesenchymal stem cells play a crucial role in the human hematopoiesis-supporting ability of the cell line. 20027291_The IL-23 induced cytokines allow for the subsequent production of IL-12 and amplify the IFN-gamma production in the type-1 cytokine pathway. 20029409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20049565_induction of SOX4 gene expression might be responsible for the CD56 expression in human myeloma cells 20059553_NCAM in the amygdala mediates consolidation of auditory fear conditioning; increased NCAM transgene expression in the amygdala is among the mechanisms whereby stress facilitates fear conditioning processes in floxed mice. 20083228_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20164549_This study suggested a potential involvement of NCAM expressing neurons in the cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease. 20187302_we suggest NCAM as a marker for the WT progenitor cell population. These findings provide novel insights into the cellular hierarchy of WT, having possible implications for future therapeutic options 20231901_SOCS-3 and PIAS-3 upregulation impairs IL-12-mediated interferon-gamma response in CD56 T cells in HCV-infected heroin users 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20414008_analysis of the effect of human colorectal carcinogenesis on the neural cell adhesion molecule expression and polysialylation 20483466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20483466_This study suggested that SNP variants in NCAM1 may impact on related traits, particularly by mediating inhibition of aggressiveness. 20524836_we confirmed the expression of NCAM in Wilms tumors, nephrogenic rests, and metanephric mesenchyme and its early derivatives in fetal renal cortex 20538416_CD56 cannot be used as a supplementary tool in the differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic biliary diseases in needle biopsies. 20557674_The predominance of extranodal involvement in our series may be associated with the adhesion-related function of CD56. A high frequency of bcl-6 expression may be associated with a more favorable clinical course and prognosis. 20610389_a decisive role for the neuronal K(+) channel in regulating NCAM-dependent neurite outgrowth and attribute a physiologically meaningful role to the functional interplay of Kir3.3, NCAM, and TrkB in ontogeny 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20664990_Assessment of natural killer-like T CD3+/CD16+ CD56+ cells may be helpful in determining a worsening of clinical course in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 20684989_Results confirm the favorable impact of NPM1 mutations and identify the adverse prognostic relevance of CD56 expression in this subgroup of AML. 20696944_CD56(dim) NK cells continue to differentiate. During this process, they lose expression of NKG2A, sequentially acquire inhibitory killer cell inhibitory immunoglobulin-like receptors and CD57. 20733159_assessed the transcriptional, phenotypic, and functional differences between CD57(+) and CD57(-) NK cells within the CD56(dim) mature NK subset 20805222_Sequences from the first fibronectin type III repeat of the neural cell adhesion molecule allow O-glycan polysialylation of an adhesion molecule chimera. 20875069_CD56 expression in odontogenic epithelium is highly suggestive of ameloblastoma and can help in differentiating this from odontogenic keratocyst 20932956_PSA-NCAM may modulate the functional interaction between BDNF and its high and low affinity receptors;possible clinical significance of neuronal trophism in cerebellar neurodegenerative disorders 21115007_Data suggest that the intra-cellular part of NCAM inhibits cis-dimerization, an effect mainly dependent on the palmitoylation sites. 21148082_CD56 expression is associated with coexpression of immaturity-associated and T-cell antigens and is an independent adverse prognostic factor for relapse in acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid and anthracycline-based regimens 21178331_CD6 expression on peripheral NK cells marks a novel CD56(dim) subpopulation associated with distinct patterns of cytokine and chemokine secretion. 21212386_Genetic variation in NCAM1 contributes to left ventricular wall thickness in hypertensive families. 21239711_CD56(bright)CD11c(positive) cells play a key role in the interleukin (IL)-18-mediated proliferation of gammadelta T cells. 21457956_Maturation of follicles is accompanied by a decrease in CD56+CD16+ natural killer cells that may have deleterious effects on follicular maturation. 21464126_STX(G421A) shows a dramatic decrease in polySia synthetic activity on NCAM, whereas STX(C621G) does not; polySia shows a dopamine (DA) binding activity 21467162_Excellent prognosis in a subset of patients with ewing sarcoma identified at diagnosis by CD56 using flow cytometry. 21515372_Abnormal synaptic innervation in transgenic mice expressing the NCAM extracellular proteolytic cleavage fragment impairs prefrontal cortex plasticity and alters working memory. 21577011_This study did not support the ncam1 is direct modulation of these genes on temperament 21666061_Natural killer (NK)-92 cell line retains the functional characteristics of the CD56(bright) NK cell subset; consequently, gene silencing of CD56 profoundly inhibits the ability of NK-92 cells to kill activated syngeneic T cells. 21669487_Soluble NCAM status was a significant independent factor predictive of long-term survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma 21691800_NCAM-140 interacts with APP, potentially playing a role in neurite outgrowth and neural development. 21717310_CD56 expression is associated with neuroectodermal differentiation in ameloblastomas. 21739604_These results point to NCAM-mediated stimulation of FGFR as a novel mechanism underlying epithelial ovarian carcinoma malignancy and indicate that this interplay may represent a valuable therapeutic target. 21940794_Together, these data indicate that polysialic acid regulates cell motility through NCAM-induced but FGF-receptor-independent signalling to focal adhesions 22001684_Multiple sclerosis is characterized by a dysregulation of CD8+CD56-perforin+ T cells that may play a role in the development of disability. 22081445_The CD56 antigen is an independent prognostic risk factor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia 22085395_Serum NCAM is hyposialylated in hereditary inclusion body myopathy. 22099865_This study demonistrated that the depressed patients showed decreases in PSA-NCAM expression in the basolateral and basomedial amygdala and in the lateral nucleus of bipolar patients 22211388_Prominent CD56 expression by damaged and regenerating muscle fibers in the skin. 22219127_Cerebrospinal fluid NCAM-1 is a potential biomarker for drug-effective epilepsy and drug-refractory epilepsy. 22228741_Dehydroepiandrosterone increased PSA-NCAM expression and inhibited monocyte binding in an estrogen- and androgen receptor-dependent manner. 22276608_CD56 expression in B cell lymphoma is a rare occurrence. 22281821_NCAM and polySia are expressed and developmentally regulated in chick corneas. Both membrane-associated and soluble NCAM isoforms are expressed in chick corneas. 22319021_results suggest that during differentiation CD56(bright) NK cells, similarly to mature activated NK cells, become highly cytotoxic and are relatively resistant to apoptosis induced by TNF family members. 22384114_Cytotoxicity of CD56(bright) NK cells towards autologous activated CD4+ T cells is mediated through NKG2D, LFA-1 and TRAIL and dampened via CD94/NKG2A 22384181_NCAM180 regulates Ric8A membrane localization and potentiates beta-adrenergic response 22423624_assessment of CD56 and CD117 expression by flow cytometry is a sensitive method for diagnostic evaluation of plasma cell neoplasms. 22449227_NCAM1, SYPT and CGA expressions are differently regulated by neuroendocrine phenotype-specific transcription factors in lung cancer cells. 22591692_CD56-positive T cells have a critical role in innate defense against HIV-1 infection. 22732936_TGF-beta1 contributes to HCC-induced vascular alterations by affecting the interaction between HCC-StCs and Ld-MECs through a down-modulation of NCAM expression 22792160_Intra-hepatic accumulation of the functionally impaired CXCR3(+)CD56Bright NK cell subset might be involved in HCV-induced liver fibrosis. 23015367_Bioinformatic analysis of NCAM-associated expression profiles predicted a highly interactive protein network, which further implies potential molecular mechanisms underlying the metastatic processes of thyroid cancer 23022470_In schizophrenia, abnormal PSA-NCAM and GAD67 expression may underlie the alterations observed in inhibitory neurotransmission. 23061666_Data indicate that UCHL1 is a novel interaction partner of both NCAM isoforms that regulates their ubiquitination and intracellular trafficking. 23258197_An unknown factor with a molecular weight >100 kDa plays a critical role in the impairment of CD56(dim) natural killer cells in malignant pleural effusion, which might lead to tumor progression. 23260340_Immunoblots revealed that depressed subjects displayed increased expression of PSA-NCAM. 23292839_the author showed that in cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, the expression of NCAM and c-KIT was high, PDGFRA was intermediate, and chromogranin A and synaptophysin was relatively low 23303482_SNPs in NCAM1 were not significantly associated with heroin dependence. 23365458_GATA2 is required for the maturation of human natural killer cells and the maintenance of the CD56(bright) pool in the periphery. 23418554_Data suggest that multi-antibody assay of TTF1, Vimentin, p63 CD56, chromogranin and synaptophysin may be of special value, especially in diagnosing small biopsies. 23462508_CD56(140kD) up-regulation plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of ischemic cardiomyopathy. 23470050_We recommend immunohistochemical analyses for CD123, CD56 and CD4 inblastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients, particularly in cases where the initial bone marrow study indicates normal morphology. 23480226_Women with age above 35 years and greater than 13% CD56 positive CD16 positive natural killer cells showed the highest risk of further pregnancy loss 23495921_Depletion of NCAM is one of the factors associated with or possibly responsible for disease progression in multiple sclerosis. 23557873_Results suggest that CD3+CD56+NKT cells do not play a role as a mediator in mental symptom such as depression in fibromyalgia syndrome patients. 23635388_CD56 and quantitative Ki-67 along with cytomorphology is a robust immunohistochemical panel to differentiate small cell lung carcinoma from other neuroendocrine neoplasms. 23671285_translational modification of the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM and the polysialyltransferase ST8SiaII in mammalian semen involves polysialic acid 23716295_NCAM polysialylation in small cell lung cancer progression regulates substrate adherence potential. 23810283_High CD56 expression is associated with relapse in acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21). 23960070_NCAM and dynein have roles in tethering dynamic microtubules and maintaining synaptic density in cortical neurons 24055371_Depletion of NCAM1(+) cells from human kidney epithelial cells abrogated stemness traits in vitro. 24206578_Positive CD56 expression was found in 23 APL patients. 24240977_Decreased proportion of NK cells expressing CD56dim/CD16 antigens in Franconi anemia patients correlates with the impairment in the differentiation process of the NK cells and of the immune surveillance. 24286519_Data indicate that the CD14bright/CD56+ monocyte subset is expanded in aging individuals as well as in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 24294395_Case Report: incidentally diagnosed CD56 positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 24349544_The described scFv has potential application in delivery of therapeutics to NCAM1-expressing cells in degenerated IVD. 24365773_Expression of NCAM was associated with worsening hemodynamic parameters and major metabolic genes. 24369228_CD56 can be expressed in normal immature granulocytes at a variety of expression levels in regenerative bone marrow. Attention should be paid when evaluating aberrant antigen expression of CD56 in granulocytes. 24526449_NCAM expression in myelinating Schwann cells is indicative of early Schwann cell abnormalities. 24715165_HBME-1, Galectin-3, Cytokeratin-19 and CD56 were used alone or in panels in a series of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and thyroid tumors of uncertain malignant potential. 24726913_NCAM140 interacts with ufc1 and its trafficking and endocytosis is upregulated in the presense of Ufm1. 24782118_CD56 positivity did not have any influence on the prognosis of these patients. 24807109_Women, w/ or w/o endometriosis, having larger populations of cytotoxic CD16(+) uterine NK cells and/or higher populations of NKp46(+)CD56(+) cells may be at greater risk of infertility resulting from inflammatory environment during implantation or later 24909369_Increased frequency of ILT2-expressing CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cells correlates with disease severity of pulmonary tuberculosis. 25137309_results showed that NCAM1 might play an important role in the pathogenesis of autism 25188863_Report differential diagnosis of Primary cutaneous NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type and CD56-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma. 25201755_Homophilic interaction between CD56 molecules may occur in tumor-cell recognition, leading to CIK-mediated cell death. 25326085_Report ontogenic development of nerve fibers in human fetal livers using immunohistochemical detection of NCAM1/neurone-specific enolase expression. 25363560_analysis of CD8+ T cell induction via Vgamma9gammadeltaT cell expansion by CD56(high+) Interferon-alpha-induced dendritic cells 25445624_Results provide direct evidence for NCAM1 as a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia, which offers support to a neurodevelopmental model and neuronal connectivity hypothesis in the onset of schizophrenia 25596273_CD56(low)CD16(low) natural killer cells are multifunctional cells, and that the presence of hematologic malignancies affects their frequency and functional ability at both tumor site and in the periphery. 25619885_improvement in behavioral performance (open-field and grip-strength tests), as well as increased life-span was observed in rodents treated with NCAM-VEGF or NCAM-GDNF co-transfected cells 25628040_Low NCAM1 in the sera is associated with active forms of inflammatory bowel disease. 25723856_CD56 is generally expressed in 70-80%11 of patients with MM, as observed in 69% of the t(14;16)-negative cases in this study. In contrast, none of the t(14;16)-positive cases showed CD56 positivity. 25769453_Determining the P-glycoprotein expression and function of the peripheral blood CD56+ cells may help predict the MDR of NHL, thus has profound guiding significance for NHL treatment 25779340_Human BDCA2+CD123+CD56+ dendritic cells (DCs) related to blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm represent a unique myeloid DC subset. 25889612_Aberrant NCAM expression plays a role in the pathogenesis of keratin producing odontogenic tumors. 25921109_Up-regulated level of serum sNCAM is associated with hepatic encephalopathy in hepatocelular carcinoma patients. 25924702_CD56 overexpression was associated with shorter OS. 25935537_Loss of CD56 expression is associated with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. 26013700_Case Report: chronic lymphocytic leukemia with aberrant CD56 and CD57 expression. 26039898_Results show significant increases in proportions of CD56+ T cells in relation to CMV infection in renal transplant patients and suggest that these cells have a cytotoxic function against CMV-infected cells. 26045862_CD56 could potentially become an adjunct diagnostic marker for ectomesenchymal chondromyxoid tumor instead of previously used CD57. 26087825_Renal graft CD56+ cell infiltrates were significantly associated with antibody mediated rejection. 26097548_for differential diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer it was found that the only marker with both sensitivity and specificity above 90% was CD56 negativity 26147745_this study shows that CD56 expression defines a poor prognosis subset in the cytogenetically intermediate prognosis pediatric AML. 26183877_CD56 expression remains to be a potentially unfavorable prognostic factor in acute promyelocytic leukemia patients. 26186733_CD56 was negative in 96% of the primary malignant thyroid tumors while being expressed in the cytoplasm of 68.5% of the benign thyroid nodules. 26255203_Our findings demonstrate a novel Wnt/beta-catenin-miR-30a-5p-NCAM regulatory axis which plays important roles in controlling glioma cell invasion and tumorigenesis. 26339384_CD56 marker is a useful alternative that is comparable to SSTR2A for the diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors. 26344352_the expression of CD56 in adenomyosis is positively associated with the severity of dysmenorrhea. 26391771_Letter/Case Report: CD56 positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma of the urinary bladder. 26437631_A FOXP3(+)CD3(+)CD56(+)-expressed T-cell population with immunosuppressive function and reduced patient survival has been identified in cancer tissues of human hepatocellular carcinoma. 26460482_The neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) is a glycoprotein implicated in cell-cell adhesion, neurite outgrowth and synaptic plasticity. 26463893_NCAM1 deletion is associated with neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroma. 26478212_L1 |
ENSMUSG00000039542 |
Ncam1 |
114.972905 |
6.1275436190 |
2.615309 |
0.213788014 |
168.892697 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000001291269879609430901255653682538648080320455809687867656118821352368775448905376436494518201097422100895317775837156659690663218498229980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000208752940011338433712266243280177587995743055159305108162329874644561538020387481059631301234780741127305958571014343760907649993896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
224.1976046 |
39.2779719 |
37.0777355 |
5.4276911 |
| ENSG00000149483 |
51524 |
TMEM138 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPI0 |
FUNCTION: Required for ciliogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22282472}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Joubert syndrome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Vacuole |
|
This gene encodes a multi-pass transmembrane protein. Reduced expression of this gene in mouse fibroblasts causes short cilia and failure of ciliogenesis. Expression of this gene is tightly coordinated with expression of the neighboring gene TMEM216. Mutations in this gene are associated with the autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder Joubert Syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:51524; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; vacuolar membrane [GO:0005774]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271] |
22282472_study reports that mutation of either TMEM138 or TMEM216 causes a phenotypically indistinguishable ciliopathy, Joubert syndrome; expression of the genes is mediated by a conserved regulatory element in the noncoding intergenic region 28102635_Here we present clinical and molecular characterization of the case of an Emirati boy with Joubert syndrome, probably resulting from a splice-site mutation in TMEM138 35394880_Tmem138 is localized to the connecting cilium essential for rhodopsin localization and outer segment biogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000024666 |
Tmem138 |
295.042615 |
2.2326889765 |
1.158782 |
0.117873431 |
96.161497 |
0.00000000000000000000010588422819775912096059186453396485999412927233763175300558794129923700921835916233249008655548095703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001032948584401139745939542580152826204256788823889030037883086932115617173622013069689273834228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
406.9210591 |
33.0696215 |
183.7282199 |
11.1592810 |
| ENSG00000149485 |
3992 |
FADS1 |
protein_coding |
O60427 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Acts as a front-end fatty acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) desaturase that introduces a cis double bond at carbon 5 located between a preexisting double bond and the carboxyl end of the fatty acyl chain. Involved in biosynthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) from the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) linoleic acid (LA) (18:2n-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) (18:3n-3) precursors. Specifically, desaturates dihomo-gamma-linoleoate (DGLA) (20:3n-6) and eicosatetraenoate (ETA) (20:4n-3) to generate arachidonate (AA) (20:4n-6) and eicosapentaenoate (EPA) (20:5n-3), respectively (PubMed:10601301, PubMed:10769175). As a rate limiting enzyme for DGLA (20:3n-6) and AA (20:4n-6)-derived eicosanoid biosynthesis, controls the metabolism of inflammatory lipids like prostaglandin E2, critical for efficient acute inflammatory response and maintenance of epithelium homeostasis. Contributes to membrane phospholipid biosynthesis by providing AA (20:4n-6) as a major acyl chain esterified into phospholipids. In particular, regulates phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate levels, modulating inflammatory cytokine production in T-cells (By similarity). Also desaturates (11E)-octadecenoate (trans-vaccenoate)(18:1n-9), a metabolite in the biohydrogenation pathway of LA (18:2n-6) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q920L1, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q920R3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10601301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10769175}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Does not exhibit any catalytic activity toward 20:3n-6, but it may enhance FADS2 activity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A4UVI1}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Electron transport;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fatty acid desaturase (FADS) gene family. Desaturase enzymes regulate unsaturation of fatty acids through the introduction of double bonds between defined carbons of the fatty acyl chain. FADS family members are considered fusion products composed of an N-terminal cytochrome b5-like domain and a C-terminal multiple membrane-spanning desaturase portion, both of which are characterized by conserved histidine motifs. This gene is clustered with family members FADS1 and FADS2 at 11q12-q13.1; this cluster is thought to have arisen evolutionarily from gene duplication based on its similar exon/intron organization. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3992; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; acyl-CoA delta5-desaturase activity [GO:0062076]; C-5 sterol desaturase activity [GO:0000248]; linoleoyl-CoA desaturase activity [GO:0016213]; omega-6 fatty acid desaturase activity [GO:0045485]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with oxidation of a pair of donors resulting in the reduction of molecular oxygen to two molecules of water [GO:0016717]; alpha-linolenic acid metabolic process [GO:0036109]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; icosanoid biosynthetic process [GO:0046456]; linoleic acid metabolic process [GO:0043651]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042759]; phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008654]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; unsaturated fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006636] |
16643857_This is the first report on characterization of human FADS, and the first cloning and over-expression of FADS from an organism higher than yeast. 16670158_FADS1 FADS2 genetic varients and their reconstructed haplotypes are associated with the fatty acid composition in phospholipids 16670158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16846730_support a significant role for reverse Delta5-desaturase as a natural antisense regulator of Delta5-desaturase 16893529_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17655842_SREBP-1 is involved in the early regulation of delta5 desaturase gene by simvastatin, in THP-1 cells. 17852835_The results indicate that when the supply of FA to HL60 cells is limited, the intracellular content of n-3 and n-6 FA decreases and this leads to upregulation of the desaturases, particularly D5D and D6D. 18320251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18320251_strong association of FADS1 gene polymorphisms with the levels of arachidonic acid, which is a precursor of molecules involved in inflammation and immunity processes, cardiovascular disease. 18479586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18626191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18842780_In populations following a Western diet, subjects carrying FADS haplotypes that are associated with higher desaturase activity may be prone to a proinflammatory response favoring atherosclerotic vascular damage. 18842780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936223_This study showed that genetic variants of FADS1 and FADS2 influence blood lipid and breast milk essential fatty acids in pregnancy and lactation. 19060906_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19060910_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148276_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19750004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19776639_Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the 2 desaturase encoding gene FADS1 is highly associated with the concentration of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. 19809313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19875987_Liver Delta-6D and Delta-5D activities in obese patients were 87% and 66% lower than controls (P |
ENSMUSG00000010663 |
Fads1 |
439.637963 |
3.0573023283 |
1.612259 |
0.087067540 |
349.376325 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000579367227769103166741917932492116478757213744840100255669191397140451501372667078985211664968491018366919562143845233821581636452604826295030193866160699691703263334231819133675370194932715325192296162981620000209659337997436523437500000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000189191599156459365322121015008785858357548208162854620326569596762878652633336958150070690981961589538805355109819208428593917733276105515223422283391246951979589365203444187541737213484240726080187755542283412069082260131835937500000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
681.1025431 |
35.2636373 |
224.3759538 |
9.5126214 |
| ENSG00000149499 |
256364 |
EML3 |
protein_coding |
Q32P44 |
FUNCTION: Regulates mitotic spindle assembly, microtubule (MT)-kinetochore attachment and chromosome separation via recruitment of HAUS augmin-like complex and TUBG1 to the existing MTs and promoting MT-based MT nucleation (PubMed:30723163). Required for proper alignnment of chromosomes during metaphase (PubMed:18445686). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18445686, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30723163}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Predicted to enable microtubule binding activity. Involved in mitotic metaphase plate congression and regulation of mitotic spindle assembly. Located in several cellular components, including midbody; mitotic spindle microtubule; and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:256364; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitotic spindle microtubule [GO:1990498]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle microtubule [GO:0005876]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; cell division [GO:0051301]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitotic metaphase plate congression [GO:0007080]; regulation of mitotic spindle assembly [GO:1901673] |
18445686_Functional analysis of EML3 demonstrates an important role for EML3 in correct metaphase chromosome alignment. 30723163_results indicate that EML3 regulates mitotic spindle assembly and the kinetochore-MT connection by regulating MT-based MT nucleation and recruiting Augmin/gamma-TuRC to MTs. |
ENSMUSG00000071647 |
Eml3 |
317.784164 |
0.4062607376 |
-1.299522 |
0.120654226 |
114.987176 |
0.00000000000000000000000000792080449533625624429209426807989080870934749181803064133563673539765613226815155201165907783433794975280761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000090699049147527648892293144823019195484740808852526623604394496010660739471198610317514976486563682556152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
191.5231546 |
16.5753438 |
474.5726066 |
28.9075459 |
| ENSG00000149534 |
2206 |
MS4A2 |
protein_coding |
Q01362 |
FUNCTION: High affinity receptor that binds to the Fc region of immunoglobulins epsilon. Aggregation of FCER1 by multivalent antigens is required for the full mast cell response, including the release of preformed mediators (such as histamine) by degranulation and de novo production of lipid mediators and cytokines. Also mediates the secretion of important lymphokines. Binding of allergen to receptor-bound IgE leads to cell activation and the release of mediators responsible for the manifestations of allergy. |
Disulfide bond;IgE-binding protein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The allergic response involves the binding of allergen to receptor-bound IgE followed by cell activation and the release of mediators responsible for the manifestations of allergy. The IgE-receptor, a tetramer composed of an alpha, beta, and 2 disulfide-linked gamma chains, is found on the surface of mast cells and basophils. This gene encodes the beta subunit of the high affinity IgE receptor which is a member of the membrane-spanning 4A gene family. Members of this nascent protein family are characterized by common structural features and similar intron/exon splice boundaries and display unique expression patterns among hematopoietic cells and nonlymphoid tissues. This family member is localized to 11q12, among a cluster of membrane-spanning 4A gene family members. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct proteins. Additional transcript variants have been described but require experimental validation. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:2206; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Fc-epsilon receptor I complex [GO:0032998]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; IgE binding [GO:0019863]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038095]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954] |
11142503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11245344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11447385_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11702205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11758232_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12047428_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12393595_Gene expression profiling after stimulation via high-affinity Fcepsilon receptor I (FcepsilonRI), showed the transcriptional levels of several CC chemokines were markedly increased. 12422339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12753743_Products of the beta gene may control the level of surface expression, influencing susceptibility to allergies. 12903039_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12903039_The data suggested that the Gly237Gly genotype of the Fc epsilon RI beta gene conferred genetic susceptibility to allergic asthma in Chinese, which affected the total plasma IgE levels in the allergic asthma patients. 12919239_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14687477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15087090_A statistically significant association was foundbetween atopy and FcERIint2 variant polymorphism FcERIint2 polymorphism is related to atopy and may influence its development. 15316148_The genomic region encompassing the beta-chain has been linked to atopy and a number of polymorphisms within the FcepsilonRIbeta gene are associated with various atopic diseases. 15453830_FcepsilonRI beta-chain gene expression is down-regulated by a transcription factor, MZF-1, adn its cofactor FHL-3. 15479187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528387_Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the Fc epsilon receptor I beta promoter are causally linked with atopy via regulation of Fc epsilon RI expression. 15953854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16750991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16839401_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16839402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16867043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17014622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17088130_The speed of allergic symptom generation depends on the degree of IgE Fc epsilon receptor type I receptor triggering. 17121586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17178032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17430357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17430357_in the Korean general population, airway hyper-responsiveness is significantly associated with the E237G polymorphism of FcepsilonRI-beta, which results in an intolerant amino acid substitution 17686114_In caucasian, allergic patients, FCER1A and FCER1B polymorphisms showed an additive association with total serum IgE levels. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18269668_FcepsilonRIbeta E237G allele may have a protective role in wheezing illness among Taiwanese schoolchildren, depending on airway oxidative stress levels. 18269668_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18379861_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18534082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18534082_The -237T>G polymorphism may be associated with the rate of atopy, which in turn could increase the release of histamine from basophils and may lead to the development of the aspirin-intolerant chronic urticaria 18579528_PLSCR1 is a novel amplifier of FcepsilonRI signaling that acts selectively on the Lyn-initiated LAT/phospholipase Cgamma1/calcium axis, resulting in potentiation of a selected set of mast cell responses 18691306_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18931892_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18949059_Fcgr4 is a mouse IgE receptor that resembles macrophage MS4A2 protein in humans and promotes IgE-induced lung inflammation. 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19218813_A promoter-dependent mechanism with altered transcriptional regulation of FcepsilonRIbeta may be involved for its association with asthma. 19218813_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19288130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19288130_Polymorphisms in the Fc epsilon R1beta gene confer susceptibility to atopy in Korean children and may have a disease-modifying effect on airways in asthmatic patients. 19479237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19514647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19559392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19796196_Methylation levels at the AluSp repeat analysed in MS4A2 were inconsistent with classical imprinting mechanisms and did not associate with atopy status 19824886_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19862939_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20028371_No associations with total and specific IgE levels as well as allergic sensitization were seen for FCER1B and FCER1G 20028371_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20085599_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085599_Significant associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms with wheeze in the past year were detected in only four genes (IL4R, TLR4, MS4A2, TLR9). Variants in IL4R and TLR4 were also related to allergen-specific IgE, but not for MS4A2 and TLR9. 20358027_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20395963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20703737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21061265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22150093_Demethylation of specific regulatory elements within the FCER1G locus contributes to FcepsilonRI overexpression on monocytes from patients with atopic dermatitis. 22845063_The interaction between Lyn and FcepsilonRIbeta is indispensable for FcepsilonRI-mediated human mast cell activation. 23643722_t-FcepsilonRIbeta mediates Ca2+ -dependent microtubule formation, which promotes degranulation and cytokine release. 24118172_Cytoplasmic FcepsilonRIbeta, which is not co-localized with FcepsilonRIalpha, may function as a negative regulator, as it can capture important signalling molecules such as Lyn. 24495860_Data indicated that the MS4A2 gene E237G variant may be a risk factor for developing atopic asthma and the promoter -109T allele is a potential risk factor of asthma in Asians. 24953255_no association between gene polymorphism and chronic spontaneous urticaria in Kashmiri population 24981302_study found a difference in the frequencies of genotypes of FcvarepsilonRIbeta subunit int 2 in allergic rhinitis patients and controls. The FcvarepsilonRIbeta subunit int 2 gene polymorphism was found to be associated with allergic rhinitis in the Polish cohort 25530133_FcepsilonRIbeta -109C/T and IFN-gamma 874T/A polymorphisms may be influencing factors for asthma in the Asian population 25658351_The results explain how initial membrane interactions of clustered IgE-Fcepsilon RI complexes lead to downstream cellular responses. 26792385_in patients with allergic rhinitis without asthma, the FCER1B rs569108 and rs512555 polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of developing allergic rhinitis and with lower IgE levels. 27157394_MS4A2 was differentially expressed between Fibromyalgia patients and healthy controls. 28775209_Using immunohistochemistry, we validated that MS4A2, the beta subunit of the IgE receptor expressed on mast cells, is a favorable prognostic indicator and show that MS4A2 gene expression is an independent prognostic marker for early-stage lung cancer patient survival. 34261469_Interaction between antibiotic use and MS4A2 gene polymorphism on childhood eczema: a prospective birth cohort study. |
ENSMUSG00000024680 |
Ms4a2 |
8.515385 |
17.1412764539 |
4.099403 |
0.840367585 |
35.182076 |
0.00000000300274571931227351567267215418696041373536331775540020316839218139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000013738539000945181328930200855432258721933180822816211730241775512695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.8022974 |
8.8816415 |
0.9376040 |
0.5023294 |
| ENSG00000149557 |
9638 |
FEZ1 |
protein_coding |
Q99689 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in axonal outgrowth as component of the network of molecules that regulate cellular morphology and axon guidance machinery. Able to restore partial locomotion and axonal fasciculation to C.elegans unc-76 mutants in germline transformation experiments. May participate in the transport of mitochondria and other cargos along microtubules. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20812761, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22354037}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is an ortholog of the C. elegans unc-76 gene, which is necessary for normal axonal bundling and elongation within axon bundles. Expression of this gene in C. elegans unc-76 mutants can restore to the mutants partial locomotion and axonal fasciculation, suggesting that it also functions in axonal outgrowth. The N-terminal half of the gene product is highly acidic. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms of this protein have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9638; |
axon [GO:0030424]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; establishment of mitochondrion localization [GO:0051654]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; mitochondrion morphogenesis [GO:0070584]; negative regulation of autophagosome assembly [GO:1902902]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of anterograde axonal transport of mitochondrion [GO:0061881]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976] |
11856312_interacts with NBR1 protein 12874605_FEZ1 is an interacting partner of DISC1. The interaction of DISC1 and FEZ1 is associated with direct FEZ1 binding to F-actin. 15466860_E4B serves as a ubiquitin ligase for FEZ1 and thereby regulates its function but not its degradation 15522253_A modest association between FEZ1 and Schizophrenia was found. 15522253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15843383_FEZ1 promotes neurite extension through its interaction with microtubules, and agnoprotein facilitates JCV propagation by inducing the dissociation of FEZ1 from microtubules 16484223_the C-terminal regions of FEZ1, and especially its coiled-coil region, are involved in its dimerization, its heterodimerization with FEZ2, and in the interaction with 10 of the identified interacting proteins 17200414_Binding of JIP1 and FEZ1 to Kinesin-1 is sufficient to activate the motor for microtubule binding and motility. 17374448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17374448_We concluded that the missense mutation Asp123Glu of the FEZ1 gene is unlikely to play a substantial role in the genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. 18439996_Data suggest that FEZ1 has an important centrosomal function and supply new mechanistic insights to the formation of flower-like nuclei, which are a phenotypical hallmark of human leukemia cells. 18470533_Data show that the expression of FEZ1,GAD1, and RGS4 are high correlated with one another in the prefrontal cortex of postmortem brain samples. 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18615714_Human FEZ1 has characteristics of a natively unfolded protein and dimerizes in solution. 19251251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19632097_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19632097_There was no strong evidence for association with FEZ1 in schizophrenia. 19667186_FEZ1 appears to represent a unique neuron-specific determinant of cellular susceptibility to infection in a cell type that is naturally resistant to HIV-1 19924516_Data report that NEK1 and CLASP2 colocalize with FEZ1 in a perinuclear region in mammalian cells, and observed that coiled-coil interactions occur between FEZ1/CLASP2 and FEZ1/NEK1 in vitro. 20084519_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20730382_Studies indicate that suppression of FEZ1 expression in cultured embryonic neurons causes deficiency of neuronal differentiation. 20812761_Demonstrated the formation of an intermolecular disulfide bond through FEZ1 Cys-133, which appears to be essential for dimerization. 21408165_FEZ2 interacted with 59 proteins and that of these only 40 interacted with FEZ1. 22017218_The data of this study suggested that FEZ1 may play important roles in human astrocytes, and that mood stabilizers might exert their cytoprotective and mood-stabilizing effects by inducing FEZ1 expression in astrocytes. 22099459_Genetic association analysis of two independent cohorts of schizophrenia patients and healthy controls reveals an epistatic interaction between FEZ1 and disrupted in schizophrenia (DISC)1. 22451907_FEZ1 operates as a kinesin adaptor for the transport of Stx, with cargo loading and unloading being regulated by protein kinases. 22832604_Short Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia (DISC)1 splice variants show reduced or no binding to NDEL1 and phosphodiesterase (PDE)4B proteins but fully interact with FEZ1 and GSK3beta. 24098481_SCOC forms a stable homogeneous complex with the coiled coil domain of FEZ1. SCOC dimerization and the SCOC surface residue R117 are important for this interaction. 24116125_Studies indicate that FEZ1 (fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 1), SCOCO (short coiled-coil protein) and kinesins (kinesin heavy chain) are involved in biological transport process. 25818806_FEZ1 promotes HIV-1 infection in non-neuronal cells via direct binding to the capsid and kinesin-1 to move the virus into the cell nucleus. 31422020_FEZ1 Is Recruited to a Conserved Cofactor Site on Capsid to Promote HIV-1 Trafficking. 32590821_Diagnosis of numerous cancers has been closely linked to the expression of certain long non-coding RNAs. This study aimed to evaluate levels of plasma FEZ family zinc finger 1 antisense RNA 1 (FEZF1-AS1) relative to non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) diagnosis. 33395696_Loss of FEZ1, a gene deleted in Jacobsen syndrome, causes locomotion defects and early mortality by impairing motor neuron development. 35172151_FEZ1 phosphorylation regulates HSPA8 localization and interferon-stimulated gene expression. |
ENSMUSG00000032118 |
Fez1 |
573.361565 |
3.8446093702 |
1.942837 |
0.093293214 |
432.337561 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000503641195016935213450785808836608185616438667647474596892169064583881751833063820116988020822510526965898498862517794891202521865375294361523289188046121657934834986015370147374488637510599589079168955040300034364409820890666460090849 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000202003914088314248676769557461368273288254789707757006995154167796353988792793706015787740982554405081075670016780585240016084478978648207309966292927425338114411400539806561029879817391827036120819005836442686716942861569630259053337 |
Yes |
No |
933.0349003 |
50.9469015 |
243.7512789 |
10.8076666 |
| ENSG00000149564_ENSG00000019102 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
603.470200 |
0.1352255805 |
-2.886560 |
0.082053137 |
1431.179495 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000035246138782696689 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000053085000860471724 |
Yes |
No |
145.8011073 |
8.0816915 |
1085.7130195 |
31.3290192 |
| ENSG00000149591 |
6876 |
TAGLN |
protein_coding |
Q01995 |
FUNCTION: Actin cross-linking/gelling protein (By similarity). Involved in calcium interactions and contractile properties of the cell that may contribute to replicative senescence. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Actin-binding;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Muscle protein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a shape change and transformation sensitive actin-binding protein which belongs to the calponin family. It is ubiquitously expressed in vascular and visceral smooth muscle, and is an early marker of smooth muscle differentiation. The encoded protein is thought to be involved in calcium-independent smooth muscle contraction. It acts as a tumor suppressor, and the loss of its expression is an early event in cell transformation and the development of some tumors, coinciding with cellular plasticity. The encoded protein has a domain architecture consisting of an N-terminal calponin homology (CH) domain and a C-terminal calponin-like (CLIK) domain. Mice with a knockout of the orthologous gene are viable and fertile but their vascular smooth muscle cells exhibit alterations in the distribution of the actin filament and changes in cytoskeletal organization. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:6876; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517] |
11773051_loss of transgelin gene expression may be an important early event in tumor progression and a diagnostic marker for breast and colon cancer development. 17082327_Transgelin functions as a suppressor to inhibit prostate cancer cell growth 17305610_crystallization and X-ray diffraction of transgelin. 17629319_SM22 expression in SMCs was dramatically higher than in GC cells, which indicates that SM22 is unlikely to be a proper biomarker for GC. 18245174_tagln is a novel target of TGF-beta/Smad3-dependent gene expression in alveolar epithelial type II cells 18291675_2.3 A resolution crystal structure of full length human transgelin, whose main structural feature is confirmed to be a CH domain. 18378184_acts as a tumour suppressor; expression is lost in prostate, breast and colon cancers 18446369_Identificaton of transgelin a novel biomarker for gastric adenocarcinoma. 19011151_Selective overexpression of airway smooth muscle genes in asthmatic airways leads to increased Vmax, thus contributing to the airway hyperresponsiveness observed in asthma. 19188659_Transgelin was expressed in pulmonary artery smooth myocytes under hypoxia compared with normoxia via and HIF-1alpha-independent pathway. Reducting transgelin expression by RNA interference impaired migration especially under hypoxia. 19329940_Loss of transgelin involves gene promoter hypermethylation and is closely associated with poor overall survival in colorectal cancer patients. 19724680_studies in colorectal cancer cell lines demonstrated roles for transgelin in promoting invasion, survival, and resistance to anoikis 19796641_Results demonstrate that SM22alpha can induce blockage of cell proliferation and cellular resistance to overcome the detrimental effects of damaging agents. 19848416_in pulmonary adenocarcinoma, overexpression of TAGLN was strictly localized to the tumor-induced reactive myofibroblastic stromal tissue compartment, whereas overexpression of TAGLN2 was exclusively localized to the neoplastic glandular compartment 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20012321_Expression of the actin-associated protein transgelin (SM22) is decreased in prostate cancer 20066125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20098441_results are indicative of p53-mediated mitochondria-associated apoptotic effects of transgelin on LNCaP cells in addition to its known suppressive effects on the AR pathway 20336793_Loss of SM22 is a molecular signature of colon cancer and is closely associated with progression, differentiation, and metastasis of colon cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20540360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20705054_these findings provide the first demonstration that SM22alpha modulates cellular senescence caused by damaging agents via regulation of the p16(INK4a)/pRB pathway in HepG2 cells and that these effects of SM22alpha are partially mediated by MT-1G. 20707403_Results indicate that the metastatic potential of CSCs arises from highly expressed Transgelin. 21051832_The expression of Transgelin in the uterine body smooth muscle tissue of pregnant women during labor was higher than in non-labor. 21092460_Down-regulation of SM22alpha in breast cancer is correlated with lymph node metastasis. 21677441_Strong transgelin expression is observed in renal tissue of patients with glomerulonephritis; its distribution is comparable to that of alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA), a marker of myofibroblast activation in the kidney. 21763649_We found an increased expression of the TAGLN gene in endometriotic lesions compared with the eutopic endometrium of the same patients by real-time polymerase chain reaction. 22245152_SM22alpha overexpression enhances tumor cell growth and activates the IGF1R/PI3K/Akt pathway via direct interaction with IGF1Rbeta. 22257561_Depletion of SM22 could contribute to tumourigenic properties of cells. Reduction in SM22 would tend to promote cell survival when cells are under hypoxic stress, and may also contribute to increases in actin dynamics that favour metastatic potential. 22365974_COX7A2, TAGLN2 and S100-A10 as novel prognostic markers in Barrett's adenocarcinoma. 23138394_the expressions of TAGLN were significantly reduced in colorectal carcinoma tissues and cells, and overexpression of TAGLN could decrease the proliferation and invasion and increase the apoptosis of LoVo cells 23174934_In leiomyosarcomas versus all other sarcomas transgelin emerged as the best diagnostic marker 23331552_Our results indicate that transgelin plays a promoting role in tumor progression, and appears to be a novel prognostic marker for advanced pancreatic cancer. 23538046_Expression of SM22 is inhibited in human CRC, and SM22 may act as a positive regulator of the processes of autophagy. 24464808_HIF-2alpha upregulates transgelin indirectly and accumulated TGF-beta1 is a mediator in the upregulation of transgelin by HIF-2alpha under hypoxia. 24476357_The expression and biological role of transgelin seem to differ among various types of tumor cells and stroma, and possibly change during tumor progression. 24657443_Downregulated proteins in gallbladder cancer included serine protease HTRA1 and transgelin, which have been reported to be downregulated in several other cancers. 24828686_They also antagonized the TGF-beta1 induced up-regulation of CTGF and transgelin. 24938684_our data suggest that TAGLN may be a viable therapeutic target and a potential biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. 25109740_TAGLN was highly expressed in NF1-deficient malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors compared to NF1-deficient plexiform neurofibromas. Upregulation was caused by increased transcriptional expression. The TAGLN gene was hypomethylated in the MPNST cells. 25318625_Results indicate that miR-144 may regulate osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion by downregulating its target gene, transgelin protein (TAGLN), suggesting that miR-144 may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of osteosarcoma. 25841305_Transgelin may be an excellent diagnostic marker of Triple negative tumors and could be useful in stratification of patients 25917318_EZH2 regulates the chromatin structure at the TAGLN promoter through tri-methylation of H3K27, acting as an epigenetic integrator of IL-1beta and TGFbeta2 signaling. 25937534_SM22alpha is a phosphorylation-regulated suppressor of IKK-IkappaBalpha-NF-kappaB signaling cascades. 26242444_Both tissue and salivary transgelin mRNA were closely correlated with various important clinicopathological parameters and were independent prognosis factors for oral squamous cell carcinoma. 26344167_Cofilin-1 and transgelin may play roles in the carcinogenesis and development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 26694173_activated AKT and JNK signaling pathways promote the overexpression of transgelin 26847345_Increases or decreases in transgelin levels have reciprocal effects on tumor cell behavior, with higher expression promoting metastasis 26934553_High expression level of TAGLN is associated with prostate cancer. 27270312_this study identified potential biochemical players involved in distant recurrence and indicates that R-Ras and Transgelin are potential post-surgical prognostic biomarkers for Stage III colorectal cancer 27320219_Smooth muscle 22 regulates the proliferation of aortic smooth muscle cells participates in the development of thoracic aortic dissection. 27490926_transgelin (TAGLN), a transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta)-inducible gene, was identified as an upregulated gene during in vitro osteoblastic and adipocytic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived stromal (skeletal) stem cells 27740519_Serum concentrations of CK-18 fragments and transgelin-2 correlate with the severity of NAFLD, but not with obesity. 28058861_regulates vasculogenic mimicry in breast cancer cells by enhancing interleukin-8 uptake 28117838_During transition from the pluripotent stage towards the neural developmental stage, TAGLN is differentially expressed in bipolar patient derived cells compared to control derived cells. 28525410_SM22 is released into the circulation upon severe ischemia of the intestinal muscle layers. Patients with transmural intestinal ischemia had significantly higher plasma SM22 levels than patients with only ischemic mucosal injury, other acute abdominal diseases, or healthy controls. 28898058_Data (including data from studies using cells cultured from transgenic/knockout mice) suggest that expression and degradation of transgelin in myofibroblasts and keratinocytes are regulated by mechanical tension in cytoskeleton produced by myosin II motor in response to stiffness of culture matrix/extracellular matrix. 29778753_SM22 plays a role in regulating the transitions and morphological appearance of bacterially generated actin-rich structures during infections. 30301526_transgelin-1 interacts with actin stress fibers and podosomes in smooth muscle cells via its type-3 CH-domain, while CLIK23 is dispensable for the binding to the actin structures 30580562_SM22alpha reduction in abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) because of the SM22alpha promoter hypermethylation accelerates AAA formation through the reactive oxygen species/NF-kappaB pathway. 31591355_Results indicate that TAGLN is a p53 and PTEN-upregulated gene, expressing higher levels in normal bladder epithelial cells than in carcinoma cells. Further, TAGLN inhibited cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and blocked tumorigenesis in vivo. Collectively, it can be concluded that TAGLN is an antitumor gene in the human bladder. 32061197_Transgelin Silencing Induces Different Processes in Different Breast Cancer Cell Lines. 32393769_Transgelin is a poor prognostic factor associated with advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) stage promoting tumor growth and migration in a TGFbeta-dependent manner. 32754278_Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by interacting with Transgelin in Colorectal Cancer. 32819569_Functional loss of TAGLN inhibits tumor growth and increases chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer. 33771884_TAGLN Is Downregulated by TRAF6-Mediated Proteasomal Degradation in Prostate Cancer Cells. 33961858_m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 suppresses proliferation and migration of enteric neural crest cells by regulating TAGLN in Hirschsprung's disease. 34001947_Identification of targets of JS-K against HBV-positive human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2.2.15 cells with iTRAQ proteomics. 34338296_The canonical smooth muscle cell marker TAGLN is present in endothelial cells and is involved in angiogenesis. 34538264_TAGLN mediated stiffness-regulated ovarian cancer progression via RhoA/ROCK pathway. 35776288_RNA-sequencing of human aortic valves identifies that miR-629-3p and TAGLN miRNA-mRNA pair involving in calcified aortic valve disease. |
ENSMUSG00000032085 |
Tagln |
37.126853 |
0.2601655644 |
-1.942498 |
0.575794869 |
10.007573 |
0.00155897843691071608281106808391314189066179096698760986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003522198335956247886024961246675957227125763893127441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.3143993 |
6.9575377 |
70.6255416 |
18.3834097 |
| ENSG00000149635 |
128506 |
OCSTAMP |
protein_coding |
Q9BR26 |
FUNCTION: Probable cell surface receptor that plays a role in cellular fusion and cell differentiation. Cooperates with DCSTAMP in modulating cell-cell fusion in both osteoclasts and foreign body giant cells (FBGCs). Involved in osteoclast bone resorption. Promotes osteoclast differentiation and may play a role in the multinucleated osteoclast maturation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Differentiation;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is orthologous to the mouse osteoclast stimulatory transmembrane protein (OCSTAMP), which is a membrane-anchored cell surface receptor that promotes nucleation of osteoclasts. The mouse protein is also involved in bone resorption and osteoclast differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:128506; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; multinuclear osteoclast differentiation [GO:0072674]; positive regulation of macrophage fusion [GO:0034241]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of osteoclast proliferation [GO:0090290] |
28981605_Results indicte that oc-stamp may play an important role in macrophage polarization and inhibit the M1 pro-inflammatory state. 32282962_Osteoclast stimulatory transmembrane protein (OC-STAMP) is a promising molecular prognostic indicator for multiple myeloma. |
ENSMUSG00000027670 |
Ocstamp |
47.768788 |
3.6987779300 |
1.887049 |
0.262460061 |
53.590098 |
0.00000000000024700125247126147534624123550526373678396310773486277412303024902939796447753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001531822893477235056586367327590592096091606788554884133191080763936042785644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
77.1365548 |
11.3479826 |
21.1118778 |
2.6726187 |
| ENSG00000149743 |
83707 |
TRPT1 |
protein_coding |
Q86TN4 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the last step of tRNA splicing, the transfer of the splice junction 2'-phosphate from ligated tRNA to NAD to produce ADP-ribose 1''-2'' cyclic phosphate. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:14504659}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;NAD;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;tRNA processing |
|
Predicted to enable tRNA 2'-phosphotransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in tRNA splicing, via endonucleolytic cleavage and ligation. Predicted to act upstream of or within regulation of protein kinase activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83707; |
tRNA 2'-phosphotransferase activity [GO:0000215]; regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045859]; tRNA processing [GO:0008033]; tRNA splicing, via endonucleolytic cleavage and ligation [GO:0006388] |
36018800_ADP-ribosylation of RNA in mammalian cells is mediated by TRPT1 and multiple PARPs. |
ENSMUSG00000047656 |
Trpt1 |
59.139968 |
0.3885856855 |
-1.363695 |
0.477036508 |
7.702014 |
0.00551592442780987710776452459526808524969965219497680664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011174175755486383254666549191824742592871189117431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
31.0723824 |
11.1168783 |
80.8401810 |
20.4030732 |
| ENSG00000149798 |
10435 |
CDC42EP2 |
protein_coding |
O14613 |
FUNCTION: Probably involved in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. May act downstream of CDC42 to induce actin filament assembly leading to cell shape changes. Induces pseudopodia formation in fibroblasts in a CDC42-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10490598, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11035016}. |
Acetylation;Cell shape;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
CDC42, a small Rho GTPase, regulates the formation of F-actin-containing structures through its interaction with the downstream effector proteins. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Borg family of CDC42 effector proteins. Borg family proteins contain a CRIB (Cdc42/Rac interactive-binding) domain. They bind to, and negatively regulate the function of CDC42. Coexpression of this protein with CDC42 suggested a role of this protein in actin filament assembly and cell shape control. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:10435; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; opioid peptide activity [GO:0001515]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly [GO:0031274]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
16395716_activations of Rac1 and Cdc42 are involved in the hypoxia-induced production of angiogenesis-promoting factors and tumor suppressors, and suggest that the Rho family GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42 may contribute to the hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis. 20934684_CDC42EP2 is upregulated in human PDLCs subjected to tensile stress related to mechano-induced cell cycle arrest. 27913681_Studies indicate some of the functional and mechanistic roles of the binder of Rho GTPases Borg1-5 proteins (Cdc42EP1-5), including cytoskeletal remodelling and signalling. |
ENSMUSG00000045664 |
Cdc42ep2 |
28.833903 |
0.2484764754 |
-2.008819 |
0.719786094 |
7.197629 |
0.00729999466279782679295484726367249095346778631210327148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014404802302526192869791543671453837305307388305664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9452906 |
7.2640566 |
41.8852642 |
21.0077853 |
| ENSG00000149927 |
8448 |
DOC2A |
protein_coding |
Q14183 |
FUNCTION: Calcium sensor which most probably regulates fusion of vesicles with membranes. Binds calcium and phospholipids. May be involved in calcium dependent neurotransmitter release through the interaction with UNC13A. May be involved in calcium-dependent spontaneous release of neurotransmitter in absence of action potentials in neuronal cells. Regulates Ca(2+)-dependent secretory lysosome exocytosis in mast cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18354201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9736751, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9804756}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium/phospholipid-binding;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Exocytosis;Lysosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Synaptosome |
|
There are at least two protein isoforms of the Double C2 protein, namely alpha (DOC2A) and beta (DOC2B), which contain two C2-like domains. DOC2A and DOC2B are encoded by different genes; these genes are at times confused with the unrelated DAB2 gene which was initially named DOC-2. DOC2A is mainly expressed in brain and is suggested to be involved in Ca(2+)-dependent neurotransmitter release. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:8448; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0098850]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; synapse [GO:0045202]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; calcium-dependent activation of synaptic vesicle fusion [GO:0099502]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0017158]; spontaneous neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0061669] |
19242545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20489179_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22036572_Study analyzed Doc2alpha and Doc2beta and found that Doc2 responds to changes in [Ca2+], with markedly slower kinetics as compared to the cytosolic domain of syt I (syt), and operates on a timescale consistent with asynchronous neurotransmitter release. 28539418_this study, members of the Doc2 family of presynaptic proteins were eliminated, which caused a reduction in spontaneous neurotransmission, whereas action potential-evoked neurotransmission remained relatively normal. 30844661_This study demonstrated that the DOCA2 increase expression in temporal lobe in temporal lobe epilepsy. |
ENSMUSG00000052301 |
Doc2a |
44.862216 |
0.0719086271 |
-3.797691 |
0.344285721 |
156.298753 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000728423437840601672881044115782128474644088109090445047331288461876145182973889678363160695047373582866612196085043251514434814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000109709489209462050274770465684259521899121934688830349330072889250369268585154193497503390467007200470561656402423977851867675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.0160575 |
1.5900718 |
83.3047060 |
11.6451885 |
| ENSG00000149968 |
4314 |
MMP3 |
protein_coding |
P08254 |
FUNCTION: Metalloproteinase with a rather broad substrate specificity that can degrade fibronectin, laminin, gelatins of type I, III, IV, and V; collagens III, IV, X, and IX, and cartilage proteoglycans. Activates different molecules including growth factors, plasminogen or other matrix metalloproteinases such as MMP9 (PubMed:11029580, PubMed:1371271). Once released into the extracellular matrix (ECM), the inactive pro-enzyme is activated by the plasmin cascade signaling pathway (PubMed:2383557). Acts also intracellularly (PubMed:22265821). For example, in dopaminergic neurons, gets activated by the serine protease HTRA2 upon stress and plays a pivotal role in DA neuronal degeneration by mediating microglial activation and alpha-synuclein/SNCA cleavage (PubMed:21330369). In addition, plays a role in immune response and possesses antiviral activity against various viruses such as vesicular stomatitis virus, influenza A virus (H1N1) and human herpes virus 1 (PubMed:35940311). Mechanistically, translocates from the cytoplasm into the cell nucleus upon virus infection to influence NF-kappa-B activities (PubMed:35940311). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11029580, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1371271, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21330369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22265821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2383557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35940311}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMP's are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. This gene encodes an enzyme which degrades fibronectin, laminin, collagens III, IV, IX, and X, and cartilage proteoglycans. The enzyme is thought to be involved in wound repair, progression of atherosclerosis, and tumor initiation. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4314; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to nitric oxide [GO:0071732]; cellular response to UV-A [GO:0071492]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolic process [GO:0010727]; positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death [GO:1903209]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150077]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645] |
11116068_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11380116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11438501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11546917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11836255_induction in fibroblasts by basic calcium phosphate crystals 11841844_can cleave all subclasses of igG at a specific conserved site 11977998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11977998_The 6A6A MMP3 genotype is a genetic susceptibility factor for restenosis after angioplasty without stenting. 11982752_Stromelysin-1 activation correlates with invasiveness in squamous cell carcinoma 11988625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12009331_involvement of MAPKs, AP-1 and NF-kappa B transcription factors in the IL-1 induction of MMP-3 and MMP-13 in chondrocytes 12034345_destruction of the surrounding matrix by endometriosis might be caused by various MMPs, which are mainly produced in stromal cells. 12034715_cooperative binding of promoter with ETS-1 transcription factor 12054564_lack of expresion in Ewing sarcoma may be due to loss of accessibility of regulatory element to the specific fusion protein in vivo 12071839_Activation of protein kinase CK2 is an early step in the ultraviolet B-mediated increase in interstitial collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1; MMP-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) protein levels in human dermal fibroblasts. 12103254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12124858_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12204805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12204805_The severe coronary atherosclerotic lesions were significantly associated with the MMP3 genotype as an independent factor of the coronary lesions. 12205736_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12229968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12230559_data provide evidence that MMP-3 can inhibit breast tumour cell invasion in vitro by a mechanism involving plasminogen degradation to fragments that limit plasminogen activation and the degradation of laminin 12364729_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12385578_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12432557_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12432557_With regard to the MMP-3 polymorphism, unexpectedly, the frequency of the 6A/6A genotype causing lower enzyme activity was significantly increased in patients (p = 0.0129; OR = 2.110; 95% CI = 1.165-3.822). 12473595_A single nucleotide polymorphism in MMP-3 promoter is associated with invasive behaviour in breast cancer 12473595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12477941_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12485468_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12485468_The presence of this protein has a higher risk for arteriosclerosis in men who are smokers. 12572877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12634064_N-TIMP-1 interaction with the catalytic domain of MMP-3 investigation by titration calorimetry and 15N NMR 12651627_expression and regulation by intestinal myofibroblasts in inflammatory bowel disease 12727228_Data demonstrate that blockade of the ERK pathway suppressed the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 3, 9, and 14, and CD44, and markedly inhibited the invasiveness of tumor cells. 12736398_stromelysin-1, which has the ability to degrade the mucosal extra-cellular matrix, may be responsible for the extensive tissue injury in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis 12750310_Matrix metalloproteinase-3 polymorphism contributes to age-related aortic stiffening through modulation of gene and protein expression. 12750310_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12761889_regulation of expression by ATP 12784383_The proliferative response to a MMP-3 epitope was similar in rheumatoid arthritis patients and controls; the MMP-3 epitope increased IL-4, and IL-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-a production of arthritis lymphocytes, but not cytokines in controls. 12821236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12832381_The increase in antigenic levels of uPA and MMP-3 in endometrium of women with endometriosis might contribute to the invasive potential of endometrial cells 12837283_MMP3 is a senescence-associated gene in normal human oral keratinocytes. 12866026_Increased matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression accounts for invasive properties of human astrocytoma cell lines 12867428_proteolysis of SPARC by MMP-3 produced peptides that regulate endothelial cell proliferation and influence angiogenesis 12876636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12952836_The present results indicate that MMP-2 can be helpful in diagnosing Takayasu arteritis [TA] and that MMP-3 and MMP-9 can be used as activity markers for TA 13129650_Cultured vascular smooth muscle cells infected with Chlamydia pneumoniae secreted increased quantities of MMP-3 protein 14712311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14715248_The observations are consistent with a downstream mediation role of MMP-3 in phosphoglucose isomerase/AMF-stimulated tumor cell metastasis. 14984923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14998290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14998290_The results suggest that the 5A/6A polymorphism of MMP-3 gene may not be linked with appearance and/or progression of ovarian cancer. 15009479_Polymorphism is not associated with myocardial infarct in Japan. 15033492_MMP3, MMP9, and TGFbeta1 are important for the modulation, composition, and maintenance of the ECM in oral squamous cell carcinoma 15070833_cleaves IGFBP-1 at (145)Lys/Lys(146), resulting in a small (9-kDa) C-terminal peptide of IGFBP-1 in first trimester decidua 15084374_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15094779_MMP-3 is specifically expressed in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck and its expression correlates with their invasion capacity. 15102660_MMP3 may have a role in response to chemotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, as demonstrated by an analysis of its polymorphism 15102660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15142265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15161710_MMP3 5A/6A promoter polymorphism does not appear to influence breast cancer susceptibility but may be linked to a higher risk for metastasizing among breast cancer patients 15161710_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15172469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15194213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15203551_Data suggest that proMMP-3 (prostromelysin 1) may play an essential role in degrading and remodeling the extracellular matrix in workers with pneumoconiosis, and that proMMP-3 may also reflect the stage of pneumoconiosis disease. 15234427_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15234427_Recent large Japanese case-control studies identified connexin-37 (GJA-4), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) polymorphisms as risk factors for myocardial infarction. 15274394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15274394_The presence of the MMP1-2G and MMP3-6A alleles seemed to be associated with decreased risk of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma but mainly when they were carried by the same haplotype. 15288468_No general associations of MMP-1 and MMP-3 genes to primary sclerosing cholangitis(PSC) or ulcerative colitis(UC) among Norwegians, but specific alleles were associated to subsets of PSC patients with UC and cholangiocarcinoma. 15288468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15290728_CD154 induced production of TNF-alpha, IL-6, and MMP-3 in rheumatoid arthritis chondrocytes. 15308783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15312099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15312099_polymorphisms do not influence susceptibility to periodontitis in Japanese patients 15319295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15319295_Polymorphisms in MMP-3 is associated with renal cell carcinoma 15319302_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15319302_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in matrix metalloproteinase-3 promoter is associated with lymphatic metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 15337261_In conclusion, our finding suggests that the MMP3 gene, especially together with APOE 4, may contribute to the development of AD. 15337261_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15342709_association of Crohn's disease susceptibility with the stromelysin-1 gene 5A/6A polymorphism in a cohort of German sporadic Crohn's disease trios 15355616_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15383690_Intra-articular hyaluronic acid may rescue inflamed joints from bone and cartilage destruction by reducing the production of MMP-3. 15389640_Results point to a functional link between matrix metalloproteinase-3 and E-cadherin. 15467919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15467919_the MMP3 -1612 5A/6A polymorphism is associated with myocardial infarction in a Chinese Han population 15474069_Progesterone inhibition of MMP-3 expression and its support of endometrial integrity were prevented by local expression of MMP-3 in response to embryonic signaling. 15528217_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15529384_Ox-LDL, mediated by LOX-1, enhanced MMP-3 production in articular chondrocytes. Increased ox-LDL with elevated of LOX-1 in rheumatoid arthritis(RA) cartilage indicates specific role of receptor-ligand interaction in cartilage pathology in RA. 15546966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15610507_heat shock-induced expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3 is mediated via an IL-6-dependent autocrine mechanism. 15640153_MMP-1 and MMP-3 secretion by gastric epithelial cells are differentially regulated by E prostaglandins and MAPKs 15665388_in an Irish population, the MMP-3 -1612 5A/6A polymorphism is not associated with ischaemic heart disease 15667946_Extracellular catalase induces STR1 in primary chondrocytes. 15701845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15701845_Polymorphism in the promoter region of the MMP-3 is associated with colorectal cancer 15716694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15716694_The stromelysin-1 5A-1171-6A genotype is an important determinant of blood pressure in this general population sample. 15748780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15757531_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15763339_Hepatitis B X protein exerts selective transcriptional control in hepatoma cells and induces cellular migration through the activation of MMP-3. 15823277_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15823277_the particular combination of MMP3 and MMP9 genotypes present at susceptibility loci may contribute to heterogeneity in the presentation of atherosclerosis. 15863497_extracellularly secreted alpha-synuclein is processed via the activation of MMP-3 15879464_MMP3 promoter SNP is unlikely to be associated with endometriosis in the population of North China. 15879464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15955221_MMP-3 gene polymorphisms account for some of the variability in the progression of HCV-related chronic liver diseases. 15955221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15993717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16080875_MMP-1 and MMP-3 promoter polymorphism is not associated with the susceptibility to ovarian cancer. 16080875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16082623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16088212_collagen III, and probably fibronectin, are degraded extracellularly in smooth muscle cells from varicose veins by a mechanism involving MMPs, and maybe MMP3 by a direct or an indirect pathway 16100452_Findings suggest that MMP-3 6A/6A genotype may be an independent risk factor for coronary artery lesions formation in Kawasaki disease. 16102106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16102106_The stromelysin-1 5A gene polymorphism was an independent survival predictor after index premature myocardial infarction. 16158251_The expression of MMP3 is consistently significantly higher in neoplastic brain tissue compared to normal brain tissue, and may be involved in the process of metastasis of breast cancer to the brain. 16202315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16238676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16278009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16302209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16311244_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16311244_matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 12 haplotypes may associated with development of lung cancer, particularly among never smokers and men 16323393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16405530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16430740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16516860_Finally, we found that induction of mmp-3 and mmp-10 gene expression by hypomethylation was cell-specific, suggesting that epigenetic changes may predispose cells to express stromelysin genes. 16532917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16615041_protein expression levels of MMP-3 were higher in colorectal tumor tissues than in the corresponding normal tissues. 16629857_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16677108_matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in human microvascular endothelial cells is sensitive to antiinflammatory Boswellia 16739355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16802342_CDK-4/6 modulated the production of MMP-3 and MCP-1. 16822591_We found that subjects APOE epsilon4 non-carriers and 6A/6A homozygous for the MMP-3 polymorphism were at increased risk of dementia. 16871440_myelin basic protein charge isomer, component-8, was more susceptible to stromelysin-1 cleavage than myelin basic protein component-1; increased susceptibility of component-8 to proteolytic digestion may play a role in pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis 16899023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16904077_The common 5A/6A promoter polymorphism of MMP3 appears to be functional only during specific environmental conditions involving inflammation. 16905683_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16919028_Loss of MMP-2, MMP-3 and FN in lichen planus may be associated with the destruction of the epidermal basal layer and these MMPs may be involved in the pathogenesis of interface dermatitis. 16935611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16935611_The two genes (MMP3 and TIMP1) may not play a crucial role for high myopia in young Taiwanese men. 16937230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16972019_sFas, sFas-L, and MMP-3, which were significantly elevated in sera of active untreated AOSD patients and paralleled disease activity, may be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease 16972255_Data show that UVB irradiation increases PTEN/Akt phosphorylation in dermal fibroblasts, and inhibition of PTEN and activation of Akt by phosphorylation are involved in UVB-induced MMP-1 and -3 secretions through upregulation of AP-1 activity. 16972994_MMPs play a key role in regulating the balance of structural proteins of the articular cartilage matrix according to local mechanical demands 16984617_TUNEL-positive cells and MMP-3- and -13-expressing cells were distributed in the degenerative articular cartilage and reparative fibrocartilage tissue in osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) of the elbow. 16998253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17000679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17000887_Smokers homo/heterozygous for stromelysin-1 5A/6A show an increased rish of Buerger disease. 17003494_Nuclear MMP-3 can induce apoptosis via its catalytic activity. 17024375_MMP3 sequence variation was significantly associated with variation in leukoaraiosis volume in Whites. 17024375_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17027562_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17033924_No convincing evidence was found to support the association of MMP3 SNPs with increased breast cancer risk or survival. 17033924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17058024_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17065356_MMP3 pathway is altered in human obesity, but this alteration may be the result of a combination of genetic variation within the MMP3 locus itself. 17077200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17125518_A MMP3 polymorphism is associated with increased risk of colorectal neoplasms and small adenomas. 17125518_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17137622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17145822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17151781_nicotine stimulates bone matrix turnover by increasing production of tPA and MMP-1, 2, 3, and 13, thereby tipping the balance between bone matrix formation and resorption toward the latter process 17178858_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17182940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17198194_Pancreatic myofibroblasts may play an important role in extracellular matrix turnover via MMP-3 secretion in the pancreas 17316652_enhanced cell cycle entry, increased MAPK signaling, and downregulated MMP-1 and MMP-3 seen in diabetic arterial vasculature could have a role in progressive atherosclerosis and postangioplasty restenosis in diabetic patients 17316907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17316907_These associations did not differ between strata of APOEepsilon4 genotype. Our observations do not suggest that variation in the MMP3 gene is causally involved in dementia or AD. 17319946_IL-4 suppression of IL-1-induced MMP-3 expression in HGF is independent of lipoxygenase activity and activation of PPARgamma. 17320799_MMP and TIMP plasma levels in premature coronary artery disease are linked to clinical presentation and markers of inflammation and metabolic disorders rather than to genetic polymorphisms. 17320799_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17381556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17381556_Taken together, our data suggest that numerous genes may influence ACE activity. 17383306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17434489_Accumulation of AGE may have a role in the development of osteoarthritis by increasing MMP-1, -3, and -13, and TNF-alpha. 17436000_Activin A suppresses interleukin-1-induced matrix metalloproteinase 3 secretion in human chondrosarcoma cells 17471097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17473191_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17502998_MMP-3 polymorphisms may not be independent factors to influence susceptibility to adult astrocytoma 17502998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17530713_MMP-3 is a significant independent predictor of radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, particularly in those with preexisting radiographic damage. 17537400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17537400_Significant differences between cases and controls were observed for MMP3, (but not for MMP1)[5A/6A allele frequencies (p=0.00001) and genotype frequencies (p=0.00001)]; and between cleft types and controls (p=0.00001 for CL/P; p=0.04 for CP). 17543900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17559909_describes the site-specific distribution and activities of MMPs and therefore might help in elucidating the molecular mechanisms in pathologies such as premature rupture of membranes 17564313_Expression of MMP3 was evaluated in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-tumor tissue. 17589947_Allelic composition at the examined SNPs in genes coding for TIMP-1 and MMP-3 affect Crohn's disease susceptibility and/or phenotype, i.e., fistulizing disease, stricture pathogenesis and first disease localisation. 17589947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17607721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17617834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17617837_MMP-3 transcript and protein levels were significantly higher in oral squamous cell carcinoma masses than in neighboring tissues. MMP-3 function may be required in most OSCCs; may support the anchorage-independent growth of OSCC and esophageal carcinoma. 17664256_Protein expression of pro-MMP3 was significantly increased with labour onset. Expression of these molecules was also observed in primary cultured human uterine SMCs. 17669621_Data suggest a role for MT1-MMP in early tumour progression, expression of MMP-1 during metastasis and focal expression pattern of MMP-3 and the expression profiles may provide markers for early breast cancer diagnoses and potential therapeutic targets. 17672933_MMP-3-1171 5A/6A polymorphism has no correlation to astrocytoma susceptibility. 17672933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703334_The median level of MMP-3 (matrix metallopeptidase 3) was elevated in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) patients as compared to controls; MMP3/TIMP-1 ratio correlated with measures of disease activity 17710450_The adducts of the catalytic domain of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3) with three different nonpeptidic inhibitors were structurally characterized. 17719307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17763214_Serum levels may be a potential marker of disease activity in spondyloarthropathy. 17763953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17763953_With MMP-3 promoter polymorphism (rs3025058), a lower peripheral blood platelet count, which was related to advanced liver cirrhosis, was observed in 5A carriers. 17765638_Finds the MMP-3 promoter haplotype -1612 5A/6A is a novel marker of an adverse disease course progession in patients with mitral valve prolpase. 17765638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17875574_It appears that an abnormality in the MMP3 gene is part of the genetic profile that predisposes to aneurysmal disease. 17875574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17893005_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17901377_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17911432_associate the 5A/6A polymorphism of the MMP-3 gene with radiographic progression of rheumatoid arthritis 17919326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17922906_High-expressing MMP-3 genotype is associated with breast tumor progression 17929133_matrix metalloproteinase-3 has a role in inflammation and progression of rheumatoid arthritis 17942123_In conclusion, our results indicate association of MMP-3 6A/6A genotype with significantly higher mean MS-SS values. 17942123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17958893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17958893_This study does not provide strong evidence for further investigation into the role of the MMP2 and MMP3 variants in melanoma progression 17975717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17975717_Polymorphisms of the stromelysin promoter may be relevant for systemic lupus erythematosus-related cardiovascular disease. 18006768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18007247_MMP-3 and IL-6 promoter polymorphisms constitute important factors for the genetic predisposition to scoliosis 18007247_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18028894_MMP-3 5A/6A polymorphism could be a risk factor for the susceptibility to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 18028894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18035073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18063811_FOXO3a (forkhead box O3) increased the expression of MMP-3 (stromelysin-1)in human umbilical vein endothelial cells 18076359_role of 5A/6A gene variation in myocardial ishemia 18077489_MMP-3 functional polymorphism is associated with serum MMP-3 titre, but is not a direct predictor for outcome measures in Japanese rheumatoid arthritis patients. 18077489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18091353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18172013_MMP3 interacts with transcription enhancer dominant in chondrocytes (TRENDIC) in the CCN2/CTGF promoter. MMP3 plays a role in the development, tissue remodeling, and pathology of arthritic diseases through CCN2/CTGF regulation. 18212480_Melittin may exert its anti-rheumatoid effects, at least in part, by inhibiting MMP3 production, most likely through inhibition of NF-kappaB activity. 18220784_Performed molecular docking simulations to study binding at the S1' pocket in the apo form of MMP3. 18225577_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18225577_The high expression 5A allele of the MMP-3 gene is associated with an increased risk for oral cancer in certain individuals. 18234553_MMP-3 is associated with left ventricular dysfunction, adverse left ventricular remodeling and prognosis after acute myocardial infarct. 18237197_The cleavage catalyzed by beta-hematin coincides with the first cleavage by matrix metalloproteinase-3, and preincubation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 with beta-hematin enhances the activation rate by matrix metalloproteinase-3 at least 6-fold. 18262287_significant elevation in MMP-3 levels was observed in 10% of seronegative and 17% of seropositive MG patients, indicating that MMP-3 may play a pathogenic role in a proportion of MG patients. 18275497_MMP-3 activity increases in hemodialysis patients with dialysis-related amyloidosis. 18303200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18303200_the T allele at the third position of codon 96 in the MMP-3 gene might be associated with persistent HBV infection. 18308831_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18342317_MMP3 haplotype may predict both cardiac events and stroke 18342317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18363112_our study demonstrates increased concentrations of VEGF and Bcl-2, but not MMP-3, in serum of melanoma patients 18426080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426080_Unlike MMP-1 and MMP-9 genotypes, MMP-3 5A allele, with higher transcriptional activity, may be a risk factor for the poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma 18445105_Matrix metalloproteinase-3 1171 promoter polymorphism plays no role in the genetic predisposition for liver cirrhosis in alcoholics 18445105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18469698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18485900_The increase in MMP3 was found in an AMF-high production tumor cell line, and c-Jun, c-Fos and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) were also highly phosphorylated compared with the parent line. 18496696_Epigallocatechin-3-gallate treatment resulted in dose-dependent inhibition of TNF-alpha-induced production of MMP-1 and MMP-3 at the protein and mRNA levels in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. 18513389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18541955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18566588_Study presents the structure of Ets-1 on the stromelysin-1 promoter element, revealing a ternary complex in which protein homo-dimerization is mediated by the specific arrangement of the two ETS-binding sites. 18571835_Autocrine motility factor transactivates the MMP-3 gene through the activation of Src-RhoA-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling to induce hepatoma cell migration. 18573993_To ascertain whether MMP-3 is up-regulated in vivo by orthodontic force, we examined human bone samples at the compressive site by realigning the angulated molars. MMP-3 distributed along the compressive site within 3 days of compression. 18606478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18606478_Our observations suggest that variation in the gene encoding MMP-3 is associated with changes in amyloid beta levels in humans. Factors modulating secretion or activity of MMP-3 influence the amount of Abeta concentration and deposition in the brain. 18609140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18619594_study demonstrates different patterns of association between inflammatory markers and MMPs in men and women, strengthening the hypothesis of gender specific differences in pathophysiological mechanisms of myocardial infarct 18634015_Hypoxia upregulates the expression of angiopoietin-like-4 in human articular chondrocytes: role of angiopoietin-like-4 in the expression of matrix metalloproteinases MMP1 and MMP3 and cartilage degradation 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_estrogen receptor 1, vitamin C receptors SLC23A1 and SLC23A2, and matrix metalloproteinase MMP3 and MMP9 are associated with susceptibility to lymphoma 18674944_MMP-3 may be a biomarker for disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis but supplies no additional information to the clinician. 18674955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18760468_The effect of MMP3 on non-collagenous extracellular matrix proteins of demineralized dentin and the adhesive properties of restorative resins are reported. 18801353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18801353_Subjects carrying genotypes with 6A allele of MMP3 had significantly higher susceptibility to carotid atherosclerosis. 18810583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18810583_while MMP-3 may play a role in the pathogenesis of KD, there is no apparent association between CAL and the MMP-3 (-439C/G) |
ENSMUSG00000043613 |
Mmp3 |
35.579027 |
3.0900243564 |
1.627618 |
0.296714075 |
30.701547 |
0.00000003009250524919000041130652772607134703974907097290270030498504638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000125081773437917309317609997586229209076691404334269464015960693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.4927744 |
14.3747680 |
16.4709659 |
3.5609354 |
| ENSG00000150093 |
3688 |
ITGB1 |
protein_coding |
P05556 |
FUNCTION: Integrins alpha-1/beta-1, alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-10/beta-1 and alpha-11/beta-1 are receptors for collagen. Integrins alpha-1/beta-1 and alpha-2/beta-2 recognize the proline-hydroxylated sequence G-F-P-G-E-R in collagen. Integrins alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-3/beta-1, alpha-4/beta-1, alpha-5/beta-1, alpha-8/beta-1, alpha-10/beta-1, alpha-11/beta-1 and alpha-V/beta-1 are receptors for fibronectin. Alpha-4/beta-1 recognizes one or more domains within the alternatively spliced CS-1 and CS-5 regions of fibronectin. Integrin alpha-5/beta-1 is a receptor for fibrinogen. Integrin alpha-1/beta-1, alpha-2/beta-1, alpha-6/beta-1 and alpha-7/beta-1 are receptors for lamimin. Integrin alpha-6/beta-1 (ITGA6:ITGB1) is present in oocytes and is involved in sperm-egg fusion (By similarity). Integrin alpha-4/beta-1 is a receptor for VCAM1. It recognizes the sequence Q-I-D-S in VCAM1. Integrin alpha-9/beta-1 is a receptor for VCAM1, cytotactin and osteopontin. It recognizes the sequence A-E-I-D-G-I-E-L in cytotactin. Integrin alpha-3/beta-1 is a receptor for epiligrin, thrombospondin and CSPG4. Alpha-3/beta-1 may mediate with LGALS3 the stimulation by CSPG4 of endothelial cells migration. Integrin alpha-V/beta-1 is a receptor for vitronectin. Beta-1 integrins recognize the sequence R-G-D in a wide array of ligands. When associated with alpha-7 integrin, regulates cell adhesion and laminin matrix deposition. Involved in promoting endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis. Involved in osteoblast compaction through the fibronectin fibrillogenesis cell-mediated matrix assembly process and the formation of mineralized bone nodules. May be involved in up-regulation of the activity of kinases such as PKC via binding to KRT1. Together with KRT1 and RACK1, serves as a platform for SRC activation or inactivation. Plays a mechanistic adhesive role during telophase, required for the successful completion of cytokinesis. Integrin alpha-3/beta-1 provides a docking site for FAP (seprase) at invadopodia plasma membranes in a collagen-dependent manner and hence may participate in the adhesion, formation of invadopodia and matrix degradation processes, promoting cell invasion. ITGA4:ITGB1 binds to fractalkine (CX3CL1) and may act as its coreceptor in CX3CR1-dependent fractalkine signaling (PubMed:23125415, PubMed:24789099). ITGA4:ITGB1 and ITGA5:ITGB1 bind to PLA2G2A via a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and this induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1 (PubMed:18635536, PubMed:25398877). ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and mediates R-G-D-dependent cell adhesion to FBN1 (PubMed:12807887, PubMed:17158881). ITGA5:ITGB1 is a receptor for IL1B and binding is essential for IL1B signaling (PubMed:29030430). ITGA5:ITGB3 is a receptor for soluble CD40LG and is required for CD40/CD40LG signaling (PubMed:31331973). Plays an important role in myoblast differentiation and fusion during skeletal myogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P07228, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10455171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12473654, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12807887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16256741, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17158881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18635536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18804435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19064666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21768292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23125415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24789099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25398877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29030430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31331973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7523423}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Interferes with isoform 1 resulting in a dominant negative effect on cell adhesion and migration (in vitro). {ECO:0000305|PubMed:2249781}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Isoform 5 displaces isoform 1 in striated muscles. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09055}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human echoviruses 1 and 8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8411387}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Cytomegalovirus/HHV-5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20660204}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Epstein-Barr virus/HHV-4. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17945327}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human parvovirus B19. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12907437}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human rotavirus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941907}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Mammalian reovirus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16501085}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, integrin ITGA5:ITGB1 binding to extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397733}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Interacts with CotH proteins expressed by fungi of the order mucorales, the causative agent of mucormycosis, which plays an important role in epithelial cell invasion by the fungi (PubMed:32487760). Integrin ITGA3:ITGB1 may act as a receptor for R.delemar CotH7 in alveolar epithelial cells, which may be an early step in pulmonary mucormycosis disease progression (PubMed:32487760). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32487760}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May serve as a receptor for adhesin A (nadA) of N.meningitidis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:21471204}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Integrin;Isopeptide bond;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Myogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
Integrins are heterodimeric proteins made up of alpha and beta subunits. At least 18 alpha and 8 beta subunits have been described in mammals. Integrin family members are membrane receptors involved in cell adhesion and recognition in a variety of processes including embryogenesis, hemostasis, tissue repair, immune response and metastatic diffusion of tumor cells. This gene encodes a beta subunit. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants which encode different protein isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3688; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cerebellar climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapse [GO:0150053]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glial cell projection [GO:0097386]; integrin alpha1-beta1 complex [GO:0034665]; integrin alpha10-beta1 complex [GO:0034680]; integrin alpha11-beta1 complex [GO:0034681]; integrin alpha2-beta1 complex [GO:0034666]; integrin alpha3-beta1 complex [GO:0034667]; integrin alpha4-beta1 complex [GO:0034668]; integrin alpha5-beta1 complex [GO:0034674]; integrin alpha7-beta1 complex [GO:0034677]; integrin alpha8-beta1 complex [GO:0034678]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; myelin sheath abaxonal region [GO:0035748]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; collagen binding involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098639]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; basement membrane organization [GO:0071711]; calcium-independent cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007161]; cardiac cell fate specification [GO:0060912]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation [GO:0060379]; CD40 signaling pathway [GO:0023035]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cell projection organization [GO:0030030]; cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033631]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0071404]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; establishment of mitotic spindle orientation [GO:0000132]; formation of radial glial scaffolds [GO:0021943]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; germ cell migration [GO:0008354]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159]; leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:0050901]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048333]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; myoblast differentiation [GO:0045445]; myoblast fate specification [GO:0048626]; myoblast fusion [GO:0007520]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007405]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of glutamate uptake involved in transmission of nerve impulse [GO:0051951]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:2000273]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; reactive gliosis [GO:0150103]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of collagen catabolic process [GO:0010710]; regulation of inward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:1901979]; regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission [GO:0150003]; regulation of synapse pruning [GO:1905806]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; visual learning [GO:0008542]; wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells [GO:0035313] |
11716783_the linkage between beta1 integrin and actin may be differentially regulated by its tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphorylation in normal and cancerous breast cells. 11728829_Mechanisms involved in alpha6beta1-integrin-mediated Ca(2+) signalling 11741908_Site-directed mutagenesis showed that Leu(135), Ile(138), and Ile(139) of Icap1 alpha, and Leu(82) and Tyr(144), are required for the Icap1 alpha-beta(1) integrin interaction 11751905_both VEGF-induced PI 3-kinase activation and beta(1) integrin-mediated binding to fibronectin are required for the recruitment and activation of PKC alpha. 11775028_Bromodeoxyuridine induces integrin expression at transcriptional (alpha2 subunit) and post-transcriptional (beta1 subunit) levels, and alters the adhesive properties of two human lung tumour cell lines. 11776052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11779688_Although cytoplasmic splice variants do not change the ligand-specificity of a beta 1 integrin, this review explains how clustering of different splice variants triggers signaling pathways that lead to a different cellular response. 11805102_beta 1-Integrin-mediated glioma cell adhesion and free radical-induced apoptosis are regulated by binding to a C-terminal domain of PG-M/versican 11861761_These results demonstrate that integrin-dependent cell to extracellular matrix adhesion reinforces E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion in Caco-2 cells. 11893752_Integrin activation involves a conformational change in the alpha 1 helix of the beta subunit A-domain 11907260_Data demonstrate that multiple tetraspanin (transmembrane 4 superfamily) proteins such as CD151 are palmitoylated, and that palmitoylation is not required for cd151-alpha3beta1 integrin association. 11909975_Activated Notch4 inhibits angiogenesis: role of beta 1-integrin activation. 11914080_role of the specificity-determining loop of the integrin beta subunit I-like domain in autonomous expression, association with the alpha subunit, and ligand binding 11918217_mechanical stress to the beta1-integrin subunit in osteoblasts revealed that cyclic forces of 1 Hz were more effective to stimulate the cellular calcium response than continuous load 11931654_beta1 and beta2 integrins activate different signalling pathways in monocytes. 11932920_Inv-induced cell death was mediated via beta1-integrins since Inv bound to the beta1-integrin subunit (CD29), anti-beta(1)-integrin antibodies blocked Inv-induced cell death and Inv-induced cell death was absent in two beta1-integrin- cell lines. 11941451_Beta1 integrin triggering affects leukemic cell line sensitivity to natural killer cells 11981820_Evidence for distinctive signaling of CD82- and beta1 integrin-mediated costimulation at the transcriptional level of IL-2 gene. 11989791_There is a desensitization of IL-8-mediated p42/p44 MAPK signaling in response to ligation of the alpha5beta1 integrin in PMNL. There may be an interplay between integrin and chemokine signaling during PMNL migration through the extracellular matrix. 11996105_Expression of beta1-integrins and N-cadherin in bladder cancer and melanoma cell lines 12020426_Ionizing radiation strongly induced the expression of functional beta1-integrin and ILK in the two lung cancer cell lines, A549 and SKMES1. 12054567_mediates adhesion of osteosarcoma to the core region of thrombospondin 1 (alpha 4 beta 1 integrin) 12091396_role in regulating beta 1 integrin-dependent leukocyte adhesion 12138201_results suggest that engagement of the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin promotes an NF-kappa B-dependent program of gene expression that coordinately regulates angiogenesis and inflammation 12163503_VLA4 integrin activation by chemokines requires cholesterol 12171996_role of Rap1 GTPase for Mn(2+)- and antibody-induced VLA-4-mediated cell adhesion [VLA-4] 12174366_Expression of focal adhesion kinase and alpha5 and beta1 integrins in carcinomas and its clinical significance. 12181350_Data show that, in vitro, under physiological conditions, CD98 is constitutively associated with beta1 integrins regardless of activation status. 12181354_Data report the identification of signaling pathways required for suppression of integrin alpha2beta1 function by c-erbB2. 12200131_ITGB1 activated by ERK1/2, p38 MAPK after hypoxia 12209735_data suggest that overexpression of beta 1-integrin confers resistance to apoptosis in hepatoma cells via a MAP kinase dependent pathway 12218055_regulation of alpha4beta1 integrin function in melanoma cells and T cells by ligands of CD47 12364323_role in mediating pro-angiogenic activity of CYR61 12372334_beta1 integrin engagement is required for bombesin-dependent pro-MMP-9 activation in prostatic cancer cells 12372334_beta1 integrin engagement is required for bombesin-dependent pro-MMP-9 activation in prostatic cancer cells 12372459_initial adhesion of endometrial cells to mesothelium is not mediated by beta1 integrins but attachment to collagen IV and collagen I, which are present in the submesothelial extracellular matrix, is mediated by beta1 integrins 12376466_molecular proximity of seprase and the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor on malignant melanoma cell membranes: dependence on the cytoskeleton and this protein 12392763_findings demonstrate that E-cadherin can interact with alpha2beta1 and suggest that heterotypic interactions between E-cadherin and integrins may be more common than originally thought 12393420_Temporal gene expression profile of precursor B leukemia cells induced by ITGB1 identifies pathways regulating B-cell survival. 12397575_results are consistent with an essential role for beta(1) integrins in maintenance of cardiomyocyte viability and interaction with extracellular matrix 12411441_Data show that the expression of the PAINS-13 epitope depends on CD9 association with alpha(6)beta(1) integrin. 12427871_Data show a novel mechanism by which ECM regulates membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) association with beta1 or alphavbeta3 integrins, thus modulating its internalization, activity, and function on human endothelial cells. 12456677_beta1 Integrin-dependent cell adhesion to EMILIN-1 is mediated by its gC1q domain 12486108_integrin alpha5beta1-mediated control of the levels of integrin alphaVbeta3 is important for the distribution of focal contacts 12496264_the GFOGER sequence in fibrillar collagens is a common recognition motif used by integrins, particularly alpha11beta1 12500944_integrin beta1 cytoplasmic peptides self-associate; role in beta1 integrin clustering and formation of focal adhesions 12509413_beta(1) integrin has a role in the syndecan-4 pathway for cell spreading, along with PKCalpha and RhoA 12517798_Overexpression of AKT2/protein kinase Bbeta leads to up-regulation, increased invasion, and metastasis of human breast and ovarian cancer cells. 12574205_that the expression of beta(1C) integrin, a very efficient inhibitor of cell proliferation, may be modulated by the maternal microenvironment and may play a fundamental role in mediating trophoblast outgrowth and migration during pregnancy. 12578911_Results establish, for the first time, mutation as a mechanism by which integrins can contribute to neoplasia. 12595495_Alterations in alpha5beta1 levels induced by TGF-beta are mediated at least in part through the induction of CTGF in glomerular mesangium 12637511_beta1 integrin has a role in selectively regulates Akt/protein kinase B signaling via local activation of protein phosphatase 2A 12639965_thymidine phosphorylase and 2-deoxyribose-induced focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation was blocked by the antibodies to integrins alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3, directly linking their migration and signaling components 12662928_determination of crystal structure in complex with an antibody Fab fragment 12681287_Data show that NADPH oxidase activation production of reactive oxygen species are involved in the increase of alpha2beta1-integrin plasma membrane expression in Caco-2 cells stimulated with type IV collagen. 12682293_endostatin competes with fibronectin/RGD cyclic peptide to bind alpha 5 beta 1 integrin 12694355_This study revealed detailed topography of integrins in malignant tumours derived from intercalated acinar segment of salivary gland which might be useful their diagnosis , especially of fine-needle aspiration products or from incisional biopsy. 12699087_expression of beta1 integrin subunit is responsible for differentiation-associated changes in cells behavior in terminally differentiated oral keratinocytes 12788934_capillary morphogenesis requires endothelial alpha2beta1 integrin engagement of a single type I collagen integrin-binding site, possibly signaling via p38 MAPK and focal adhesion disassembly/FAK inactivation. 12791669_adhesion to the alpha2beta1-specific peptide was disulfide-exchange dependent and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) mediated in platelets 12799374_identification of binding site in gamma C-domain of fibrinogen 12803239_Decidual beta1 integrin and FAK participate in this final step of implantation. 12807887_alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 are both important but cell-specific fibrillin-1 receptors 12826661_integrin alpha 6 beta 1 binds to CCN1 12844491_Alpha4beta1 integrin has a role in cell adhesion 12865438_VEGFR-1 secreted by endothelial cells interacts with the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin 12871973_visualized the head region of integrin alpha 5 beta 1 in an inactive (Ca2+-occupied) state, and in complex with a fragment of fibronectin containing the RGD and synergy recognition sequences 12883474_cells overexpressing beta 1-integrin exhibited increased proliferation in response to hepatocyte growth factor. 12893184_AlphaV- and beta1-integrin subunits are commonly expressed in malignant effusions from ovarian carcinoma patients. 12893831_identify intracellular signals involved in integrin BETA1-initiated internalization of S. aureus 12904899_in beta-thalassemic patients, significant reduction of CD49d, CD29 and CD71 antigen expression was found in peripheral blood nucleated red cells 12907437_upon treatment with phorbol esters, K562 cells become adherent and permissive for parvovirus B19 entry, which is mediated by alpha 5 beta 1 integrins, but only in their high-affinity conformation 12909644_alpha6beta1 integrins have roles as thrombospondin receptors in microvascular and large vessel endothelial cells 12915563_Monkey rotavirus binding to alpha2beta1 integrin requires the alpha2 I domain and is facilitated by the homologous beta1 subunit. 12918102_S-phase delay induced by overexpression of integrin beta1 subunit caused by decrease of protein kinase B phosphorylation and subsequent increases of p21(cip1) and p27(kip1) proteins. May be involved in unoccupied alpha5beta1 because of lack of ligands. 12919677_Data show that macrophage stimulating protein (MSP) and its receptor (Ron) induce phosphorylation of both Ron and alpha6beta4 integrin, and result in activation of alpha3beta1 integrin. 12931024_In pancreatic cancer, IL-1alpha enhanced alpha(6)beta(1)-integrin expression, probably via increased IL-1RI levels. 12947314_The beta1-integrin-ligand disengagement resulted in capillary disruption and stimulated p38 MAPK and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. 12954625_beta1 integrin/FAK-mediated signaling on osteoblasts could be involved in ICAM-1- and RANKL-dependent osteoclast maturation 12969374_results suggest that beta1 integrin is a common receptor for AfaD invasins and that additional AfaD-type-specific receptors exist 12970173_The structural conformation of this protein, complexed wigh integrin alpha5, complexed with fibronectin, is examined 14502569_Reduced beta1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion of HME cells to the substratum during mitosis may be induced by beta1 integrin phosphorylation at threonines 788-789 and its reduced ability to link with the actin cytoskeleton. 14512423_role in ganglioside GM3 blocking of epidermal growth factor receptor 14525968_following priming of human neutrophils with lipopolysaccharide or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), addition of formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLP) results in a 'stimulated', sepsis-like, four- to fivefold rise in CD49d expression 14532964_the failure of beta1 integrin dephosphorylation at threonines 788 and 789 may be due to a significant reduction in the PP2A-A expression in tumor cells 14550305_integrin beta1 interacts with galectin 1 14562042_Ras oncogene directs expression of a differentially sialylated, functionally altered beta1 integrin. 14563646_human platelet deposition on collagen depends on the concerted interplay of several receptors: GPIb in synergy with alpha(2)beta(1) mediating primary adhesion, reinforced by activation through GPVI, which further regulates the thrombus formation. 14602071_Data demonstrate that alpha6beta4 integrin mediates pancreatic epithelial cell adhesion to Netrin-1, whereas recruitment of alpha6beta4 and alpha3beta1 regulate the migration of putative pancreatic progenitors on Netrin-1. 14607975_ligand-binding specificities of integrin alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta1 14610084_Hox D3 coordinately regulates the expression of integrin alpha5beta1 and integrin alphavbeta3 during angiogenesis in vivo. 14612440_alpha3beta1 integrin binding to laminin-5 depends on its proteolytic processing 14612932_beta1C integrin splice variant is transcriptionally regulated in human prostate adenocarcinoma 14623330_integrin alpha4beta1 is induced by p53 and has a role in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia drug resistance 14633626_Key role of the regulation of beta 1C integrin expression in the pathogenesis of endometrial proliferative diseases: beta 1C integrin may act as growth modulator in cancer cells, playing a role in downstream intracellular signaling. 14645603_results suggest that a direct interaction occurs between the Adenovirus penton base protein and the integrin receptor alpha3beta1 in vitro and in vivo 14662754_results show how laterally associated EWI-2 might regulate alpha3beta1 function in disease and development, and demonstrate how tetraspanin proteins can assemble multiple nontetraspanin proteins into functional complexes 14666169_alpha3beta1, alpha4beta1 and alphaVbeta1 integrins may play an important role in the implantation process 14671618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14675422_Data show that stimulation-dependent recycling of integrin beta1 is regulated by ARF6 and Rab11, and also requires the actin cytoskeleton in an ARF6-dependent manner. 14679206_results suggest that matrix metalloproteinase-1 can stimulate dephosphorylation of Akt protein and neuronal death through a non-proteolytic mechanism that involves changes in integrin alpha2beta1 signaling 14699013_Alpha4beta1 is an important endothelial cell receptor for mediating motility and proliferative responses to thrombospondins and for modulation of angiogenesis. 14699139_beta1 integrin maturation and transport to the cell surface is regulated by low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 14766759_alpha(v)beta(1) supports fetal beta-cell migration and could play an important role in early motile processes required for islet neogenesis 14970227_Integrin alpha5beta1 and ADAM-17 interact in vitro and co-localize in migrating HeLa cells 14983010_beta I-like and alpha I domain activation involves structurally analogous alpha7-helix axial displacements. 14998999_beta1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase III inhibits the function of alpha5beta1 integrin 15024036_Data suggest that the early arrest of tumor cells in the pulmonary vasculature through interaction of alpha3beta1 integrin with laminin-5 in exposed basement membrane provides a basis for cell arrest during pulmonary metastasis. 15070678_EWI-2-dependent reorganization of alpha4beta1-CD81 complexes on the cell surface is responsible for EWI-2 effects on integrin-dependent morphology and motility functions 15090462_findings identify Glu-Pg as an adhesive ligand for integrins alphaMbeta2 and alpha5beta1 and suggest that alpha5beta1 may participate in the binding of soluble Glu-Pg and assist in its activation. 15100006_The marked decrease in integrin alpha5beta1 expressions was unique to aneurysmal aortic tissues and correlated to a decrease in density of smooth muscle cells 15117962_FHL2 and FHL3, respectively, are colocalized with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin receptor at the periphery of Z-discs, suggesting a role in mechanical stabilization of muscle cells 15158122_Overexpression of integrin beta(1)modifies the response of I(Ca)to beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation. 15166232_conformational activation of VLA-4 by inside-out signaling is independent of and additive to reduction-regulated integrin activation 15226304_very late antigen-4 affinity is modulated by shear 15240572_alpha2beta1 integrin has a role in endorepellin-induced endothelial cell disassembly of actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesions 15247268_role in chemotaxis in conjuction with plasmin 15256055_Increases in IGF-IR decrease beta1 integrin expression, and enhance cell migration in neuroblastoma cells. 15265786_alpha2beta1 integrin and GPVI regulate stress fiber formation in megakarocytes, the primary actin structures needed for cell contraction 15276495_Calu-1 lung cancer cells use primarily a beta1-integrin-mediated intracellular tyrosine phosphorylation phenomenon as the key regulatory mechanism for its binding advantage to Coll IV matrix. 15280429_alpha 3 beta 1 integrin is necessary and sufficient for maximal keratinocyte survival on laminin-5 15292185_alpha4beta1 integrin on sickle reticulocytes is a CD47-activated receptor for TSP, VCAM-1, and plasma fibronectin 15292257_alpha2beta1 integrin and CD44/CSPG receptor binding on human melanoma cell activation has been evaluated herein using triple-helical peptide ligands incorporating collagen peptides. 15302884_cAMP-Epac-Rap1 pathway regulates cell spreading and cell adhesion to laminin-5 through the alpha3beta1 integrin but not the alpha6beta4 integrin 15304053_ILK regulates alpha 2 beta 1 in HEL cells, is activated in platelets and associates with beta 1-integrins 15389531_integrin alpha5beta1 participates in the activation of both VEGFR-3 and its downstream PI3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway, which is essential for fibronectin-mediated lymphatic endothelial cell survival and proliferation. 15466867_16K expression inhibits beta(1) integrin surface expression and spreading on matrix by a novel mechanism that results in reduced levels of functional beta(1) integrin 15485856_alpha(1)beta(1) and Col-IV contribute to beta-cell functions known to be important for islet morphogenesis and glucose homeostasis 15500293_The integrin, beta 1 was expressed by prostate cancer cells in vitro and by prostate tumors in vivo, and their expression was elevated at sites of bone metastasis compared to original prostate tumor. 15507484_caspase-8 activation triggers anoikis induced by beta1-integrin blockade in human keratinocytes 15509657_Insulin-like growth factor I controls adhesion strength mediated by alpha5beta1 integrins in tumor cells 15514009_the interaction of platelet GP Ib with VWF mediates the activation of alpha2beta1, increasing its affinity for collagen 15522237_Data demonstrate that type I collagen synergistically enhances platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced smooth muscle cell proliferation through Src-dependent crosstalk between the alpha2beta1 integrin and the PDGF receptor beta. 15539082_Activation of PI3K following beta1-integrin engagement on human CD34+ cells results in subsequent phosphorylation of PYK2, and is required for the recruitment of the PI3K/PYK2 complex to beta1-integrins at the cell surface. 15567743_Integrin beta1 subunit was an important constituent receptor subunit for mediating chemotactic pseudopod protrusion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to laminin. 15572366_demonstrates a cooperative role between alpha5beta1 and alpha4beta1 integrins and suggests that interactions between the Hep II domain and alpha4beta1 integrin could modulate the strength of cytoskeleton-mediated processes in the trabecular meshwork 15583842_ICAM-1 molecules interacted only with group B Streptococcus(GBS)-III liquor 90356 strain while beta1 integrin interacted with GBS-III liquor 90356 and GBS-V blood 90186 invasive strains 15590642_VEGF-C and VEGF-D are ligands for the integrin alpha9beta1 15633218_The expressive fluorescent intensity of integrinbeta(1) in G(1) phase SMMC-7721 cells was depressed more significantly than the values of S phase. 15645131_analysis of transcriptional regulation of beta1 integrin expression in endometrium and endometrial neoplasms 15647274_Data show that the recombinant Scl protein p176 promotes adhesion and spreading of human lung fibroblast cells through an alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated interaction. 15647827_BMP-2 upregulates the expression of alphavbeta integrins, and these integrins, in turn, play a critical role in BMP-2 function in osteoblasts 15677332_Results indicate that CD151 association modulates the ligand-binding activity of integrin alpha3beta1 through stabilizing its activated conformation not only with purified proteins but also in a physiological context. 15677455_JAM1 regulates epithelial cell morphology and beta1 integrin expression by modulating activity of the small GTPase Rap1. 15684035_Direct binding and regulation of alpha5beta1 by uPAR implies a modified 'bent' integrin conformation can function in an alternative activation state with this and possibly other cis-acting membrane ligands. 15699160_Alpha5beta1 integrin is required for up-regulation of IL-1 beta-dependent airway smooth muscle secretory responses by fibronectin. 15713750_integrin beta1 function is modulated by CD98 in polarized epithelial cells 15731179_VEGF and alpha4beta1 integrin have roles in chemokine-induced motility on and through endothelium in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells but not in normal B lymphocytes 15737747_Alpha5beta1-mediated adhesion of Ntera2 neuronal cells to fibronectin decreased apoptosis in response to serum withdrawal. 15757908_integrin alpha5/beta1 exerts its tumor suppressor-like activity in colon cancer cells by inhibiting HER-2 signaling 15777792_Interacts with vimentin, but this association is lost after prolonged adhesion of endothelial cells to collagen. 15795318_Therefore, these data provide strong evidence that integrin-dependent STAT5A activation controls IL-3-mediated proliferation. 15805105_Beta ig-h3 induces keratinocyte differentiation via modulation of involucrin and transglutaminase expression through the integrin alpha3beta1 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway 15872091_activation of Vav1-Rac signaling pathway by CXCL12 represents an important inside-out event controlling efficient up-regulation of alpha4beta1-dependent T lymphocyte adhesion 15878864_KSHV gB can activate VEGFR-3 on the microvascular endothelium and modulate endothelial cell migration and proliferation via an interaction between the alpha3beta1 integrin and the VEGFR-3 receptor 15881415_findings suggest that only some P. aeruginosa strains can target Fn and their natural receptors alpha5beta1 integrins for adherence to A549 cells 15905178_matrix-derived mechanical forces sensed by beta1 integrin are capable of modulating ILK activity which regulates fibroblast viability via an Akt-dependent mechanism 15919367_alpha3beta1 integrin binding results in a suppression of the interleukin-1 signaling pathway leading to the activation of NF-(kappa)B 15947241_alpha2 gene may act in combination to modulate variations in platelets alpha2beta1 receptor density 15961545_FN has a role in controlling translation through beta1 integrin and eukaryotic initiation factors 4 and 2 coordinated pathways 15978109_analysis of platelet glycoprotein I(b)alpha and integrin alpha2beta1 polymorphisms in diverse populations 15978110_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15978110_platelet membrane integrins alpha IIb(beta)3 (HPA-1b/Pl) and alpha2(beta)1 (alpha807TT) polymorphisms may have a role in premature myocardial infarction 15983209_Expression pattern of integrin subunits in the human fetal pancreas (8-20 weeks fetal age) and the relevance of beta1 integrin function for insulin gene expression and islet cell survival. 15987639_PDGFR-dependent cell detachment is induced by S1P via inhibition of beta1 integrin in HEK293 cells 16002725_Three intracytoplasmic motifs of the tail of VLA-4 beta 1 subunit differentially regulate VLA-4-mediated adhesive functions under static adhesion and shear flow conditions. 16005200_integrin alphavbeta6, alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, alpha5beta1 and alpha9beta1 binding to osteopontin is controlled by specific structural motifs that are recognized by extracellular proteases 16043429_analysis of binding between collagen type III and integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 16055706_the signaling network involving Smad-dependent TGFbeta, PKCdelta, and integrin alpha2beta1/alpha3beta1, regulates cell spreading, motility, and invasion of the SNU16mAd gastric carcinoma cell variant 16103120_phenotypic conversion and reversion of bladder cancer cells is controlled by a glycosynapse 3 microdomain through GM3-mediated interaction of alpha3beta1 integrin with CD9 16105875_Results provide evidence for a novel species of beta1 integrin on the cell surface, which does not appear to be associated with any alpha chain. 16113793_alpha2beta1 and signaling via autocrine mediators facilitate and amplify the GPVI procoagulant activity of fibrillar and non-fibrillar collagens 16148152_IFN-gamma attenuates epithelial wound closure by microtubule-dependent redirection of beta(1) integrin transcytosis from the leading edge of migrating cells thereby inhibiting adequate turnover of focal adhesion complexes and cell migration. 16157583_mapping of the N-glycosylation sites on the beta1 integrin to better understand the potential effects of differential sialylation on integrin structure/function 16195423_The results show that occupancy of the alpha(v)beta(3)-integrin receptor modulates IGF-I-induced IGF-I receptor activation and function in human intestinal muscle cells. 16213489_Cells deficient in beta1 integrin can bind human ADAM12 via beta3 integrin. 16228294_the signals induced by integrin alpha6beta1 modulate at the level of PI3K and Cdc42 activity to allow platelets to actively form filopodia 16247454_suggests beta1-integrins as critical regulators of cell survival after radiation-induced genotoxic injury 16258728_beta 1 integrin has roles in cell adhesion and migration in development and metastasis [review] 16301336_beta1 integrin is critical for the alveolar morphogenesis of a glandular epithelium and for maintenance of its differentiated function 16357324_Outside-in signaling through integrin alpha2beta1 triggered inside-out activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 and promoted fibrinogen binding. (alpha2beta1 AND integrin alphaIIbbeta3 16363250_isolated beta1 cytoplasmic domain expression induces caspase-independent detachment of viable endothelial cells and that death is secondary to detachment (i.e. anoikis) 16365170_Alpha4beta1-dependent adhesion strengthening under mechanical strain is regulated by paxillin association with the alpha4-cytoplasmic domain 16373174_Our data show that alpha3beta1 integrin function may be altered by glycosylation, that both subunits contribute to these changes, and glycosylation may be considered a newly found mechanism in the regulation of integrin function. 16385340_Expression of integrins alphavbeta1, alphavbeta3, and alphavbeta5 in cerebral arteriovenous malformations and cavernous malformations. (Integrins alphavbeta1, alphavbeta3, and alphavbeta5) 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16390868_Results suggest that loss of E-cadherin function is linked to regulation of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion, based in part on cell surface expression of alpha2, alpha3 and beta1 integrins. 16415171_Platelets, by binding via P-selectin to PSGL-1 on monocytes, induce up-regulation and activation of beta1 and beta2integrins and increased adhesion of monocytes to activated endothelium. 16421008_The Integrin beta1 thrombogenic polymorphism and FcgammaRIIA expression could play a role in platelet sensitivity to collagen in type 2 diabetes. 16430945_The integrin receptors of tenascin (TN) and fibronectin (FN) may be involved in cell processes such as growth, adhesion, migration and apoptosis. 16448724_These results indicate that the alpha2beta1 and alphaVbeta1 integrin signaling pathway may be critical components of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. 16457822_CCN2/CTGF enhances chondrocyte adhesion to FN through direct interaction of its C-terminal CT domain with FN, and alpha5beta1 is involved in this adhesion. 16459165_decreased podocyte expression of alpha3beta1 integrins is closely related with podocyte depletion, glomerular sclerosis, and daily protein loss in patients with primary focal glomerulosclerosis 16501085_facilitates reovirus internalization and suggest that viral entry occurs by interactions of reovirus virions with independent attachment and entry receptors on the cell surface. 16504015_IL-1alpha can induce selective upregulation of alpha6beta1-integrin and uPA/uPAR in pancreatic cancer cells and these changes may modulate the aggressive functions of pancreatic cancer. 16510444_This study supports matrix-induced clustering of alpha3beta1 integrin promotes uPAR/alpha3beta1 interaction; potentiating cellular signal transduction pathways culminating in activation of uPA expression and enhanced uPA-dependent invasive behavior. 16537545_EWI proteins EWI-2 and EWI-F, alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrins, and protein palmitoylation have contrasting effects on cell surface CD9 organization 16547007_urokinase plasminogen receptor domain III controls a functional association with alpha5beta1 integrin and tumor growth 16547500_Beta1-integrin subunit is identified as a new gastrin-regulated gene in human pancreatic cancer cells. 16569430_Data indicate that integrin beta1 plays a major and complex role in osteoblastic differentiation modulated by either surface microarchitecture or 1alpha,25(OH)2D3. 16705158_RACK1 enhances IGF-I-mediated cell migration through its ability to exclusively associate with either beta1 integrin or PP2A in a complex at the IGF-IR. 16707493_Slug regulates integrin alpha3, beta1, and beta4 expression and cell proliferation in human epidermal keratinocytes 16731529_integrin alpha3beta1 is a receptor for the alpha3NC1 domain and transdominantly inhibits integrin alphavbeta3 activation 16732726_Data show that activation of beta1-integrin signaling markedly upregulated anoikis of the adenocarcinoma cells. 16762342_These results are consistent with the conclusion that the anti-tumor activity of angiocidin arises from its ability to ligate collagen and alpha2beta1 on endothelial cells and tumor cells. 16773720_Serum E-selectin, ICAM-1 and integrin beta1 expression levels are probably related to the metastasis and relapse of gastric cancer. 16807379_The formation of dendrites is shown to require the interaction between the beta1-integrin (CD29) on the surface of the DCs and fibronectin in the extracellular matrix. 16820945_Data show that the integrin beta1 repertoire in renal cell carcinoma is different from normal proximal tubule cells, and that valproic acid acts on all investigated integrin subtypes to restore the receptor pattern typical for non-malignant cells. 16882656_extracellular matrix fragments produced by apoptotic EC initiate a state of resistance to apoptosis in fibroblasts via an alpha2beta1 integrin/SFK (Src and Fyn)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent pathway 16908668_This is the first demonstration that the integrin beta1 tail can regulate centrosome function, the assembly of the mitotic spindle, and cytokinesis. 16908762_Cell attachment was significantly inhibited by function-blocking anti-alpha2 (56%) and -beta1 (98%) integrin antibodies. 16916750_Salivary progenitor epithelial cell survival is beta 1 integrin-dependent. 16920931_This is the first report of direct binding of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis molecule to a receptor on human T cells resulting in a change in CD4+ T cell function 16940508_the internalization of AAV2 in mammalian cells might follow a 'click-to-fit' mechanism that involves the cooperative binding of heparan sulfate and alpha5beta1 |
ENSMUSG00000025809 |
Itgb1 |
2179.829038 |
2.5172246644 |
1.331834 |
0.036235019 |
1369.765210 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000780844317885374614349907881392 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001152526213198812890462544004594 |
Yes |
No |
3155.9146798 |
65.2765801 |
1262.8534383 |
21.1211380 |
| ENSG00000150337 |
2209 |
FCGR1A |
protein_coding |
P12314 |
FUNCTION: High affinity receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulins gamma. Functions in both innate and adaptive immune responses. Mediates IgG effector functions on monocytes triggering antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of virus-infected cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10514529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11711607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21965667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8611682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9881690}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;IgG-binding protein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein that plays an important role in the immune response. This protein is a high-affinity Fc-gamma receptor. The gene is one of three related gene family members located on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2209; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; high-affinity IgG receptor activity [GO:0019771]; IgG binding [GO:0019864]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity [GO:0001788]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I [GO:0042590]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; phagocytosis, recognition [GO:0006910]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061098]; positive regulation of type IIa hypersensitivity [GO:0001798]; positive regulation of type III hypersensitivity [GO:0001805]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11714794_At least two alternate mechanisms of internalization of Fc gamma RI are influenced by the presence or absence of ligand and demonstrate the receptor's physiologic potential to transport a large antigenic load into antigen presenting cells for processing. 12130529_Distinct functions for STAT1 and PU.1 in transcriptional activation of Fc gamma receptor I promoter. 12200451_CY domain alters gamma-chain tyrosine-based signaling and phagocytosis 12217397_Activation of mast cells through the high affinity IgG receptor. 12377934_cross-linking FcgammaRI and -II but not FcgammaRIII activates transcription factor NF-kappaB 12581186_FcgammaRI plays a major role in anti-HPA-1a-mediated platelet phagocytosis by monocytes while FcgammaRIIa, is of little or minor importance only. 12756162_specific sequences in the FcgammaRIIIA and FcgammaRI transmembrane domains govern their different interactions with the gamma chain in cell surface expression and phagocytosis 12830330_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14728877_The levels of peripheral blood neutrophil CD(64) may help us distinguish infection from disease activation in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). 15087090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15229321_periplakin (PPL) as a selective interacting protein for the intracellular tail of FcgammaRI but no other activatory FcRs 15251320_FcgammaRIIa polymorphism is not an important genetic risk factor for chronic rejection of kidney allografts. 15528366_Fc fragments of IgG from healthy donors or purified monoclonal anti-human Fc gamma receptor (FcgammaR) antibody strengthen the participation of FcgammaRI (CD64) in HIV-1 inhibition on monocyte-derived macrophages. 15878871_analysis of C-reactive protein binding to FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIIa, and C1q 15883031_results imply a novel functional role of CD13 and Fc gamma receptors (CD32 and CD64)as members of a multimeric receptor complex 16140266_Thus, these results suggest that the lipid raft-associated 67LR plays an important role in mediating the FcepsilonRI-suppressive action of EGCG. 16603696_in human aortic endothelial cells, CRP upregulates monocyte-endothelial adhesion by activation of NF-kappaB through engaging the Fcgamma receptors CD32 and CD64 17005690_findings showed that that both Fcgamma RIA and FcgammaRIIA mediated enhanced dengue virus immune complex infectivity but that FcgammaRIIA appeared to do so far more effectively 17124586_Fcgamma receptor I Ab and Fcgamma receptor I play an important role in the regulation of alopecia areata (AA), are useful for a marker of the disease prognosis and are worth intense research for the reasonable and specific therapy of AA. 17511516_finding documents the capacity of FcgammaRI to mediate potent antimalaria immunity 17621550_kinetics of neutrophil membrane CD64 expression were examined during a standardized inflammatory response, using a human endotoxemia model 17764536_In platelets, GPVI-FcRgamma has evolved to transmit sustained signals in order to maintain spreading over several hours, as well as facilitating rapid activation through release of feedback agonists and integrin activation. 17827066_FcgammaRI is hyperexpressed in the intestinal mast cells of Crohn disease patients. 18023480_An alternatively spliced 4.1G product is shown to be associated with increased Fc gamma RI binding in yeast two-hybrid assays, and to be selectively enriched in most immune cells at the transcript level. 18063701_the response to vascular injury provoked by human C-Reactive Protein in ovariectomized C-reactive protein transgenic mice depends on Fc gamma RI and probably requires its expression by F4/80+ cells 18071883_Activation of mast cells through aggregation of Fc-gamma receptor I leads to degranulation, induction of prosurvival gene bfl-1, and promotion of cell survival. 18207250_FcgammaRI predominantly resides in thin detergent-insoluble buoyant membranes, together with FcRgamma-chain, but independent of cross-linking ligand 18279703_RAGE could also behave as a receptor for Mycobacterium tuberculosis 18320015_Data show that in cardiac surgical patients the expression of activation marker FcgammaR1 (CD64) on monocytes is increased earlier in comparison with granulocytes in both 'on-pump' and 'off-pump' patients. 18321309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18604302_Data show that CD64 indexes for neutrophils and monocytes, and CD163 index for neutrophils can all be used for discrimination of SIRS and sepsis in critically ill neonates and children. 18606652_These results provide a mechanism by which Fcgamma receptors can elevate circulating BLyS levels and promote autoantibody production in immune complex-mediated autoimmune diseases. 18798798_lower numbers of CD64-positive circulating DCs during gestation than in adults 18826388_Splenic macrophages that take up opsonized platelets via FcgammaRI are major APCs for cryptic GPIIb/IIIa peptides, and are central to the maintenance of anti-platelet autoantibody production in ITP patients 18941257_Aspartic acid at position 265 of IgG is a residue critically implicated in triggering the Fc-associated effector functions of IgG, probably by defining a crucial three-dimensional structure of the Fc region. 18974296_Data suggest that flagellin-specific IgG/Fc gamma receptor I complex immune responses activate mast cells in the intestine and play important roles in the pathogenesis of intestinal immune inflammation. 19011162_expression of CD49d and CD64 on blood neutrophils is upregulated in plasma from patients with sepsis 19144150_circulating monocytes activated by immune complexes and/or proinflammatory mediators upregulate surface expression of FcgammaRI/CD64 in systemic lupus erythematosus 19250681_Structural characterization of a human Fc fragment engineered for extended serum half-life. 19635920_Activation of monocytes via Fc gamma RI induces differentiation, imparting specific inflammatory functions of autoreactive T cells that may contribute to pathogenesis of immune complex-mediated tissue injury. 19833736_Data show that LILRB4 is a potent inhibitor of monocyte activation via FcgammaRI. 20071662_HRG has the unique property of complexing with IgG and facilitating a proinflammatory innate immune response to promote the clearance of necrotic cells via FcgammaRI 20080725_Aglycosylated immunoglobulin G can be engineered to display unique FcgammaR selectivity profiles that, in turn, mediate antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity. 20109752_Expression of TSLP receptor was upregulated on atopic DCs primed with H22-Fel d 1 through a pathway regulated by FcgammaRI-associated signaling components. 20306688_Data show that neutrophil expression of CD64 is a useful diagnostic tool for early detection of neonatal sepsis. 20418097_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20650300_elevated expression on CD1+ DC from allergic rhinitis patients 20840056_neutrophil expression has a good sensitivity and specificity in differentiating infection from disease flare in patients with inflammatory autoimmune diseases 21061041_Data show that IgG heavy chains and IgG receptors were detected in the intraocular epithelium and endothelium. 21239714_FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis of neutrophils requires intracellular depletion of divalent calcium stores for the internalization phase. 21243031_Expression of CD64 (FcgammaRI) in skin of patients with acute GVHD. 21325219_This review implicates high-affinity FcgammaRI as a potential immune mediator with a key role in antigen presentation and antibody-based immunotherapy. 21438869_increased expression on polymorphonuclear neutrophils in patients with familial Mediterranean fever in Japan 21965667_a molecular mechanism for the high affinity IgG recognition by FcgammaRI 22003208_A phosphoserine-dependent tethering role for protein 4.1G in lipid rafts provides insight into the unique phosphoserine-based regulation of FcgammaRI receptor signaling. 22237765_Simultaneous quantitative analysis of CD64 and CD35 expression on neutrophils might be useful to distinguish between bacterial and viral infections in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 22251373_Data indicate the simultaneous analysis of CD64 together with CD304 (Neuropilin-1) or the combination of CD11b and CD38 was suitable for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)patients with high current activity in synovitis. 22420242_Neutrophil CD64 appears to be a better diagnostic test than traditional hematological assays. 22493081_observations suggest that serum amyloid P, at least in part, uses FcgammaRI and FcRgamma to inhibit fibrocyte differentiation 22759273_Combinatorial immunophenotypic analyses showed that loss of PTEN expression with concomitant IGFR-1 expression correlated with poor disease-free survival 22967788_Screening identified 19 amino acid mutations contributing to the thermal stability and production rate of rhFcgammaRI 23023090_Data indicate a tool for measuring antibodies triggering activation of FcgammaRIIIA, FcgammaRIIA or FcgammaRI receptors. 23293080_FcgammaRI (CD64) promotes IgG-mediated inflammation, anaphylaxis, and antitumor immunotherapy. 23452299_Neutrophil CD64 (nCD64) expression was higher in patients with severe sepsis/septic shock (81.2%) and sepsis(78.8%) as compared to those with traumatic brain injury (5.5%) or controls (0.9%, p |
ENSMUSG00000015947 |
Fcgr1 |
267.500922 |
0.2970852026 |
-1.751051 |
0.180212639 |
91.480991 |
0.00000000000000000000112669347583160491358941878579834636041887274842784121993140115935982947803495335392653942108154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000010632989580098778842044838293283623414555253258584751149167305084297652228997321799397468566894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
120.4058301 |
16.3831530 |
407.5695773 |
38.6941954 |
| ENSG00000150403 |
55002 |
TMCO3 |
protein_coding |
Q6UWJ1 |
FUNCTION: Probable Na(+)/H(+) antiporter. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Antiport;Coiled coil;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the monovalent cation:proton antiporter 2 (CPA2) family of transporter proteins. Members of this family typically couple the export of monovalent cations, such as potassium or sodium, to the import of protons across cellular membranes. Mutations in this gene have been identified in patients with a rare inherited vision defect, cornea guttata with anterior polar cataract. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:55002; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; potassium:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015386] |
27484837_This study reveals, for the first time, that mutations in TMCO3 are associated with cornea guttata and anterior polar cataract, warranting further investigation into the pathogenesis of this disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000038497 |
Tmco3 |
379.526749 |
2.0362592663 |
1.025921 |
0.162712260 |
39.185980 |
0.00000000038529705701631882992263358923964652880123082923091715201735496520996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001907104145392644354664570132437510785461398654661024920642375946044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
534.3088392 |
52.2735477 |
264.5418692 |
19.1292175 |
| ENSG00000150456 |
221143 |
EEF1AKMT1 |
protein_coding |
Q8WVE0 |
FUNCTION: Protein N-lysine methyltransferase that selectively catalyzes the trimethylation of EEF1A at 'Lys-79'. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26545399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28663172}. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Methyltransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
Enables protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity. Involved in peptidyl-lysine methylation. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:221143; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; peptidyl-lysine methylation [GO:0018022]; protein methylation [GO:0006479] |
26545399_Data indicate that the methylation of lysine (Lys) in elongation factor 1A (eEF1A) by methyltransferase is conserved from yeast to human. |
ENSMUSG00000021951 |
Eef1akmt1 |
49.159258 |
2.5075985633 |
1.326306 |
0.500690959 |
6.713567 |
0.00956821355565099299078646311045304173603653907775878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018417688064868108915872468855923216324299573898315429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.1325993 |
28.1658289 |
20.6540907 |
7.5645737 |
| ENSG00000150471 |
23284 |
ADGRL3 |
protein_coding |
Q9HAR2 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and neuron guidance via its interactions with FLRT2 and FLRT3 that are expressed at the surface of adjacent cells (PubMed:26235030). Plays a role in the development of glutamatergic synapses in the cortex. Important in determining the connectivity rates between the principal neurons in the cortex. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80TS3, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26235030}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the latrophilin subfamily of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR). Latrophilins may function in both cell adhesion and signal transduction. In experiments with non-human species, endogenous proteolytic cleavage within a cysteine-rich GPS (G-protein-coupled-receptor proteolysis site) domain resulted in two subunits (a large extracellular N-terminal cell adhesion subunit and a subunit with substantial similarity to the secretin/calcitonin family of GPCRs) being non-covalently bound at the cell membrane. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23284; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] |
20157310_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21040458_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21040458_These results further support the LPHN3 contribution to combined type ADHD, and specifically to the persistent form of the disorder 21184580_The mutational analysis of the entire coding region of LPHN3 in a cohort of 139 attention deficit hyperactivity disorder subjects and 52 controls, is reported. 21432600_LPHN3, a new gene in which variants have recently been shown to be associated with adhd. 21606926_single-nucleotide polymorphisms harbored in the LPHN3 gene interact with SNPs spanning the 11q region that contains DRD2 and NCAM1 genes, to double the risk of developing ADHD. 22105624_This study identifying loci for aADHD and led to the identification of LPHN3 as novel genes associated with ADHD across the lifespan. 22405201_This study demonistrated that LPHN3 and its ligand FLRT3 play an important role in glutamatergic synapse development. 22486528_highly significant interaction between four SNPs and maternal stress during pregnancy and development of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder 22575564_The influence of LPHN3 genotype on attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and addiction is mediated through alterations in transgenic monoamine signaling. 22832519_A two-locus genetic interaction between LPHN3 and 11q predicts ADHD severity and long-term outcome. 23245769_genetic association studies in Germany: Data suggest that, within a sample of patients with attention deficit disorder hyperactivity, SNPs in LPHN3 gene impacts behavioral and neurophysiological measures of cognitive response control. 23317273_Increased LPHN3 mRNA expression levels correlated with axillary-node metastasis in breast cancer. 25871512_Study examined the association between the LPHN3 rs6551665 A/G polymorphism and Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in Korea; samples used in the study consisted of 150 ADHD children and 322 controls; ADHD children appeared to have a surplus of GG genotype, studies with larger sample sizes needed. 25989180_LPHN3 confers ADHD susceptibility, and moderates methylphenidate treatment response in children and adolescents with ADHD. 26235030_Results suggest that UNC5 and LPHN3 can simultaneously bind to FLRT3, forming a trimeric complex, and that FLRT3 may form transsynaptic complexes with both LPHN3 and UNC5. 27325752_Associations between LPHN1 and LPHN3 polymorphisms and severity of bronchial hyper-responsiveness in asthmatics were conducted; however, no associations were found. 27692237_An ultraconserved brain-specific enhancer within LPHN3 is associated with ADHD susceptibility. 30406846_LPHN3 gene has a significant effect on the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a Chinese population. 30652248_ADGRL3 rs6551665 as a Common Vulnerability Factor Underlying Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Autism Spectrum Disorder. 30696812_Study identified ADGRL3 as a risk gene for substance use disorder. 32691279_CDH13 and LPHN3 Gene Polymorphisms in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Their Relation to Clinical Characteristics. 32778842_G12/13 is activated by acute tethered agonist exposure in the adhesion GPCR ADGRL3. 32787626_Expression of the adult ADHD-associated gene ADGRL3 is dysregulated by risk variants and environmental risk factors. 33247693_Tissue Expression Of LPHN3 in Breast Cancer: An Immunohistochemistry Method. 33504901_Brain structural and functional substrates of ADGRL3 (latrophilin 3) haplotype in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 33914279_Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor L3 gene variants: Statistically significant association observed in the male Indo-caucasoid Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder probands. 34009035_Machine Learning Prediction of ADHD Severity: Association and Linkage to ADGRL3, DRD4, and SNAP25. 35013530_Driver mutations in ADGRL3 are involved in the evolution of ependymoma. 35393556_Convergent selective signaling impairment exposes the pathogenicity of latrophilin-3 missense variants linked to inheritable ADHD susceptibility. 35741042_Thwarting of Lphn3 Functions in Cell Motility and Signaling by Cancer-Related GAIN Domain Somatic Mutations. 36151371_ADGRL3 genomic variation implicated in neurogenesis and ADHD links functional effects to the incretin polypeptide GIP. |
ENSMUSG00000037605 |
Adgrl3 |
457.675802 |
0.1983021832 |
-2.334228 |
0.971356735 |
5.220183 |
0.02232619869082598518250648567118332721292972564697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.039578992634709528330994032785383751615881919860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
176.5290012 |
103.3205441 |
897.8754902 |
372.1623215 |
| ENSG00000150477 |
57536 |
KIAA1328 |
protein_coding |
Q86T90 |
FUNCTION: Competes with SMC1 for binding to SMC3. May affect the availability of SMC3 to engage in the formation of multimeric protein complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15656913}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:57536; |
|
15656913_Hinderin is a novel binding partner of SMC3. Based on its ability to modulate SMC1/SMC3 interaction we postulate that Hinderin affects the availability of SMC3 to engage in the formation of multimeric protein complexes. |
ENSMUSG00000033632 |
AW554918 |
82.224243 |
0.3376360442 |
-1.566459 |
0.269073375 |
33.449301 |
0.00000000731460457058183371421672370419481135073169753013644367456436157226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000032266456503821839930745376439150118308418768720002844929695129394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.6987824 |
7.2010067 |
124.4632774 |
14.4549712 |
| ENSG00000150540 |
3176 |
HNMT |
protein_coding |
P50135 |
FUNCTION: Inactivates histamine by N-methylation. Plays an important role in degrading histamine and in regulating the airway response to histamine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26206890}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
In mammals, histamine is metabolized by two major pathways: N(tau)-methylation via histamine N-methyltransferase and oxidative deamination via diamine oxidase. This gene encodes the first enzyme which is found in the cytosol and uses S-adenosyl-L-methionine as the methyl donor. In the mammalian brain, the neurotransmitter activity of histamine is controlled by N(tau)-methylation as diamine oxidase is not found in the central nervous system. A common genetic polymorphism affects the activity levels of this gene product in red blood cells. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different proteins have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3176; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; histamine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0046539]; histamine catabolic process [GO:0001695]; histamine metabolic process [GO:0001692]; histidine catabolic process [GO:0006548]; methylation [GO:0032259]; respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system [GO:0007585] |
12167489_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12167489_identification of several novel HNMT polymorphisms, identification of the HNMT core promoter 12417108_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12755416_for the histamine N-methyltransferase gene no differences in allele distribution were found in patients with food allergy and sprue compared to controls except for the 314t allele 12835614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12835614_Single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified in HNMT in Chinese and their relationship assessed with its activity. 12867290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12867290_the C314T polymorphism was functionally important and contributes in part to phenotypic variance of histamine N-methyltransferase activity in Chinese Han population 14667820_Studies showed a new brain HNMT mRNA species, named HNMT-Short (HNMT-S), which encodes a 126-amino-acid protein. 15551002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15551002_no evidence for the involvement of HNMT polymorphisms in the susceptibility to gastric ulcer 15693910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15770103_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15953854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16205835_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16205835_Polymorphisms and haplotypes in the the HNMT gene are not associated with asthma in the Indian population. 16489678_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16554448_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16669609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16950574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17651147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17985251_An association of the HNMT Thr105Ile polymorphism, but not of the ABP1 His645Asp polymorphism, with PD was observed. Patients with PD showed a higher frequency of homozygous HNMT genotypes 17985251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18086566_No association can be found in the involvement of HNMT C314T polymorphism in the susceptibility to duodenal ulcer 18086566_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18154359_Molecular dynamics simulations indicate that the histamine N-methyltransferase T105I polymorphism affects both active site structure and dynamics. 18254975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18266724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18266724_histamine N-methyltransferase is not related with the risk for migraine. 18543121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18543121_These results, combined with previous findings indicating alterations in the frequency for the HNMT Thr105Ile polymorphism in patients with PD, suggest that alterations of histamine homeostasis in the SNC are associated with risk of movement disorders. 19025430_Increased histamine levels in patients with atopic dermatitis may result, at least in part, from reduced enzymatic inactivation via HNMT. 19025430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19178400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19178400_The HNMT 939A>G polymorphism lowers HNMT enzymatic activity by decreasing HNMT mRNA stability, which leads to an increase in the histamine level and contributes to the development of aspirin intolerant chronic urticaria. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19538200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19538200_our results suggest that, despite the possible role of histamine in the inflammatory processes related with the pathogenesis of MS, HNMT polymorphism is not related with the risk for MS in Caucasian Spanish people 19773194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773194_This study do not support the HNMT Thr105Ile variant as a factor in disease development or a genetic link between the disorders. 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551163_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21040557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21138759_Lack of the association of HNMT Thr105Ile functional polymorphism with Alzheimer's disease is found. 21794955_The results of this study indicated that Histamine N-methyltransferase Thr105Ile polymorphism is associated Parkinson's disease. 23932992_The A939G HNMT polymorphism is associated with autoimmune MG, while no association with C314T SNP was found. 24835231_The polymorphisms of HNMT and HRH3 were irrelevant with breast cancer in the present study. 25768024_results suggest that the heterozygous Thr/Ile genotype at the HNMT-Thr105Ile locus and the minor Ile105 allele protect against Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia in Han Chinese. 25909280_HRH1-17 TT and HNMT-1639 TT genotypes were associated with the allergic asthma phenotype among African-American children and that the ABP 4107 GG genotype was associated with nonallergic asthma among white children. 26206890_HNMT is identified as a novel gene responsible for intellectual disability. The consequences of the identified missense mutations on the protein function are discussed. 26989676_The T allele of rs3787429 exhibited protective effect against CHF under the dominant and additive models , while, for SNPs in HRH2, DAO, and HNMT, no significant associations were observed in the present study 27130307_The C allele for the HNMT polymorphism was associated with a lower degree of disability due to migraine (OR, 10.0; 95% CI, 2.65-37.6). In contrast, presence of the T allele (in heterozygous individuals) was associated with higher degree of disability (OR, 37.1; 95% CI, 4.37-315.2) 27255477_this study shows that single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with the severity of allergic rhinitis in a group of Mexican children 27399132_The present meta-analysis confirms published evidence suggesting that the HNMT rs11558538 minor allele is related to a reduced risk of developing Parkinson disease 27769936_Histamine N-methyltransferase plays a central role in the degradation of the neurotransmitter histamine. Leucine 208 is a critical amino acid residue to maintain the structural integrity of the protein. Replacements by other amino acid residues have profound effects on stability and catalytic activity. 27837280_Genotype and allelic variant frequencies of HNMT rs11558538 SNP 205 restless legs syndrome (RLS) patients and 410 controls using a TaqMan assay: HNMT rs11558538 genotypes allelic variants frequencies were similar between RLS patients and controls and not influenced by gender, family history of RLS, or RLS severity. Some evidence that RLS patients carrying the genotype rs11558538TT had an earlier age at onset. 28400155_This study shown that eight linked SNPs (r(2) = 1) in the HNMT gene were associated with sedation according to the generalized linear model, adjusted for age, gender and BMI (false-discovery-rate-adjusted p = 0.013). 29506638_miR-223 participates in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis through upregulating HNMT indirectly to degrade the excessive histamine. 29564728_NHMT polymorphisms are not associated with Parkinson's disease, ALS and multiple system atrophy in Chinese population. 34680041_Inhibition of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase as a Possible Target for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. 35163585_HNMT Upregulation Induces Cancer Stem Cell Formation and Confers Protection against Oxidative Stress through Interaction with HER2 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000026986 |
Hnmt |
405.973878 |
2.1331169719 |
1.092963 |
0.154316222 |
49.159816 |
0.00000000000235934743067208506506045559144590126159080067935747138108126819133758544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000013726435978210476094919380182651384497347080149154407990863546729087829589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
534.6033746 |
63.9827665 |
252.3300959 |
22.2101065 |
| ENSG00000150630 |
7424 |
VEGFC |
protein_coding |
P49767 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor active in angiogenesis, and endothelial cell growth, stimulating their proliferation and migration and also has effects on the permeability of blood vessels. May function in angiogenesis of the venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis, and also in the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults. Binds and activates KDR/VEGFR2 and FLT4/VEGFR3 receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20145116}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Mitogen;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. The encoded protein promotes angiogenesis and endothelial cell growth, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. The proprotein is further cleaved into a fully processed form that can bind and activate VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:7424; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 binding [GO:0043185]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005172]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; morphogenesis of embryonic epithelium [GO:0016331]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043536]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of lymphangiogenesis [GO:1901492]; positive regulation of mast cell chemotaxis [GO:0060754]; positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation [GO:1902462]; positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation [GO:0002052]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030947]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; substrate-dependent cell migration [GO:0006929]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010]; vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038084] |
11877295_VEGF-C signaling through FLT-4 (VEGFR-3) mediates leukemic cell proliferation, survival, and resistance to chemotherapy. 11920583_VEGFC expression is closely related to invasion phenotype in cervical carcinomas 11999550_REVIEW:Association of expression of VEGFC and receptors in human leukemia and lymphoma, resulting in the generation of autocrine loops that may support cancer cell survival and proliferation 12168824_Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) and its ligand VEGF-C are expressed in human colorectal adenocarcinoma. 12213723_tumor-associated macrophages express VEGF-C-and play a role in peritumoral lymphangiogenesis and subsequent dissemination in human cancer 12388793_VEGF-C mediates cyclic pressure-induced vascular endothelium cell proliferation. 12452004_VEGF-C mainly promotes peri-tumor lymphangiogenesis and has a little effect on angiogenesis. 12469214_Expresssed in gallbladder cancer and is related to lymph node metastasis. 12471041_This factor is up-regulated in breast cancer cells by heregulin-beta; p38/NFKB play a critical role in signal transduction. 12594815_Malignant mesothelioma growth inhibition by agents that target the VEGF and VEGF-C autocrine loops. 12792749_Lymphagenesis correlates with increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C in colorectal cancer 12819011_Data demonstrate the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and vascular endothelial growth factor-C on corneal dendritic cells, which implicate a potential relationship between lymphangiogenesis and leukocyte trafficking in the eye. 12915657_VEGF-C expression is increased in papillary thyroid cancer, compared with paired normal thyroid tissues, but not in other thyroid cancers that are also prone to lymph node metastasis 12963694_Data show that the serine protease plasmin cleaved both propeptides from human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D, generating mature forms, and also activated VEGF-C. 14534690_VEGF-C expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma may play a role in lymphatic spread 14558949_VEGF-C/flt-4 system can promote vasculogenesis in stroma of breast cancer. The number of Flt-4 positive vessels is closely related to lymph node metastasis. 14568550_Ang2, PIGF and VEGF-C play a role in promote endothelial survival and vascular remodeling by human cytotrophoblast. 14676121_Increased vascular endothelial growth factor C mRNA expression correlates with stage of progression in patients with melanoma 14744769_COX-2 up-regulates VEGF-C and promotes lymphangiogenesis in human lung adenocarcinoma. 14760756_VEGF-C and its receptor FLT-4 play a role in the development of gastric cancer, and the tumors with expression of VEGF-C and FLT-4 are more likely to have lymph node metastasis. 14966375_Her-2/NEU oncogene is essential for the regulation of VEGF-C in ovarian carcinoma; p38 MAPK and NF-kappa B are critically involved in the transcriptional activation of the VEGF-C gene by Her-2/NEU. 15009103_VEGF family proteins regulate wound healing, chronic inflammation and tumour angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in fibroblasts. 15040017_The expression of VEGF-C and CCR7 is related to lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma and both of them may become new targets for the treatment of gastric carcinoma. 15151619_Expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas related to COX-2 expression. Also associated with depth of primary tumor, stage, and probably lymph node metastasis. May assist in management planning. 15173661_intratumoral VEGF-A expression is one of the significant prognostic factors in patients with adenocarcinomas, and that intratumoral VEGF-C expression is one of the significant prognostic factors in patients with squamous cell carcinomas 15240540_furin is responsible for VEGF-C processing in human oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression 15272284_VEGF-C expression occurred in 26 of the 68 tumor samples (38%). 15484296_VEGF-C expression may induce lymphangiogenesis in colorectal cancer, as a result, tumor cells can entry the lymphatic vessels easily. 15590642_VEGF-C and VEGF-D are ligands for the integrin alpha9beta1 15623620_High vascular endothelial growth factor C expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in human pancreatic cancer 15668894_VEGF-C as well as VEGF-A may be involved in the pathogenesis of ovarian endometrioma. 15756450_VEGF-C plays a pivotal role for lymphangiogenesis and tumor growth in gastric cancer 15870511_Increased VEGF-C expression is associated with papillary thyroid cancer 15880525_increased expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 play a role in prostate cancer progression and in metastasis to regional lymph nodes 15943035_VEGF-C expression was detected in 38 out of the 87 patients (43.7%) with primary human breast cancer 16044920_There was a close correlation between the expressions of VEGFR-3, CD31 and prostate tumor metastases. 16049374_Increased expression of VEGF-A and VEGF-C was found in tumor tissues compared to normal epithelium 16116610_Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor-C is associated with lung adenocarcinoma 16299237_VEGF-C expression may play a role in lymphangiogenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. 16322297_High vascular endothelial growth factor C expression is associated with cervical cancer 16375119_VEGF-C and its receptor FLT-4 play an important role in the lymphatic metastasis of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 16465426_The intratumoral VEGF-C level is a significant prognostic indicator of primary breast cancer. 16467091_The Lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis influence metastasis-free survival, and are regulated by VEGF-C expression. 16474989_in human colorectal carcinoma, vascular endothelial growth factor-C and cyclooxygenase-2 are coexpressed and significantly associated with lymph node metastasis and prognosis 16525158_results suggest for the first time that VEGF-C acts in an autocrine manner in cultured podocytes to promote survival, although the receptor or receptor complex activated has yet to be elucidated 16525637_VEGF-C was abundantly expressed in pancreatic cancer tissue and cancer cell lines. 16525666_Results suggest that expression of VEGF-C is a useful predictor for lymph node metastasis. 16584091_non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is not associated with increased expression of VEGF-C 16755294_This suggests that VEGF-C promotes lymph node metastasis while being influenced by the strength of the VEGF-C autocrine loop, and the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 ratio can be a useful predictor of lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. 16816121_VEGF-C reacts with neuropilin 2 in a heparin-independent way. 16874878_VEGF-C plays a role in lymphatic metastasis via lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). VEGF-C is one of the important predictors of the biological behavior in ESCC. 16879394_The absence of VEGF-C in blast cells predicts long-lasting remission in all leukaemic children. 16924525_results suggest the presence of lymphatic capillaries throughout the skeletal muscle, and present the localisation of VEGF-C and -D in the muscles. 16944571_Data show that there is close correlation between the VEGFR-3 expression and gastric cancer lymph metastasizing. 16964283_upregulation is controlled by RalA activation 17094484_Down-regulation of VEGF-C is associated with urothelial carcinomas of the bladder 17203176_VEGF-C expression in tumour tissues is indicative of lymphatic metastasis, whereas VEGF-A expression is more likely to be associated with haematogenous metastasis 17216674_Overexpression of VEGF-C in fibroblast-like synoviocytes by stimulation with TNF-alpha may play an important role in the progression of synovial inflammation and hyperplasia in RA by contributing to local lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis 17222375_In nasopharyngeal carcinoma, high expression of VEGF-C is closely correlated to regional lymph node metastasis. 17230534_Demethylation and Overexpression of Vascular endothelial growth factor-C gene is associated with lymphangiogenesis in gastric cancer 17353919_High levels of VEGF-C is associated with angio and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer 17393109_Effect of antisense oligonucleotide of VEGFC on lymphangiogenesis and angiogensis of pancreatic cancer is reported. 17409493_Results suggest that strong expression of VEGFA and VEGFC is essential to lymphatic metastasis of stomach neoplasms. 17465468_Serum VEGF-C level, VEGF-C and lymphatic vessel density are related to lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. 17536453_In papillary thyroid carcinoma, HIF-1 alpha, VEGF and VEGF-C expressions are significantly increased. 17640671_MMP-2, MMP-9, and vascular endothelial growth factor C were expressed to similar degrees at all time points in cells exposed to lymphatic flow. 17641542_VEGF-C contributed to lymphatic involvement and nodal metastasis in colorectal cancer. 17676294_Goal of study was to define role of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and Flt-4 with TMA technology for tumor biology of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. 17686546_In non-small-cell lung cancer cells, VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 coexpression suggests an autocrine/paracrine loop responsible for a high proliferation rate in tumour cells. 17926187_Expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and their receptor VEGFR-3 in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. 17931169_The balance between expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D at the invading colorectal tumour edge may enhance lymphatic metastasis, by promoting tumour lymphangiogenesis or by activation of pre-existing lymphatic vessels. 17935478_data suggest that VEGF-C alters lymphatic endothelial function through a mechanism involving VEGFR-3 17970036_the protein and mRNA levels of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 were not significantly different in patients with or without metastasis. 18006056_Increased expression of VEGF-C is associated with acute myeloid leukaemia 18035072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18057235_KSHV-infected endothelial cells are enriched, with VEGF-A and -C molecules playing key roles in KSHV biology. 18061373_expression of VEGF-C in the margine of tumor is associated with lymphatic metastasis and prognosis and may induced lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-C was important in the regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in PAC. 18190720_COX-2 may up-regulate VEGF-C expression and thus promote lymph node metastasis via lymphangiogenesis pathway in human breast cancer. 18192971_VEGF-C has an important role in lymphatic invasion via the preexisting lymphatic vessels in the tumor margin 18205092_The VEGF-C system may be involved in controlling tumour angiogenesis in the pituitary adenomas lacking lymphatic vessels, but may also play a role in starting the process of tumour lymphangiogenesis. 18245556_Higher endogenous VEGFC levels of acute myeloid leukemia cells are related to decreased in vitro and in vivo drug responsiveness. 18250037_The expressions of COX-2 and VEGF-C are closely correlated in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. 18261985_The expression of VEGF-C and VEGF receptors is regulated specifically in HL-60 cells during macrophage differentiation. 18292935_Under hypoxic conditions an autocrine loop between VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 and HIF-1 alpha is possible in breast carcinoma and lung carcinoma but not in colorectal carcinoma cell lines. 18295452_expression by malignant cells is not of predictive value for occult lymph-node metastasis in the early stages of oral squamous cell carcinoma 18307927_The high expressions of VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 and inactivation of nm23-H(1) may play an important role in lymphatic metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 18399170_Increased VEGF-C level was associated with bone marrow infiltration, skin involvement, and high-risk international prognostic index in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. 18440723_Report expression of VEGF-C/VEGFR3 in osteosarcomas. 18476628_IFN-gamma can inhibit the expression of VEGF-C in Hep-2 cells. 18509004_stimulation with insulin and sphinogsine-1-phosphate increased VEGF-C secretion in thyroid follicular cancer cells 18512120_VEGF-C and VEGF-D play an important role in lymphangiogenesis making the carcinoma more aggressive and leading to a poor prognosis. 18538739_Provide further evidence that VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 are expressed and function in cancer cells. 18561194_VEGF-C and VEGF-D expressions were associated with VEGFR-3 expression and were significantly correlated with both peritumoral lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis. 18564921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18609713_There was no significant difference in serum levels of VEGF-C and VEGFR-2 between gastic adenocarcinoma patients and controls. VEGF-C was associated with advanced tumor stage and presence of metastasis 18614759_Incubation of lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) with ESM-1 increased the stimulatory effects of both VEGF-A and VEGF-C on LEC proliferation and migration, whereas ESM-1 alone had no effect 18627789_Lysophosphatidic acid might regulate VEGF-C and lymphatic marker expression in endothelial cells, which contributes to endothelial cell tube formation in vitro and in vivo, thus facilitating endothelial cell participation lymphangiogenesis. 18630523_HIF-1alpha might play a crucial role in regional lymph node metastasis as a regulator of lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in OSCC with a possible novel pathway involving VEGF-C. 18652765_Results describe the relationship between protein expression of VEGF-C, MMP-2 and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer. 18679715_VEGF-C expression in melanoma cells was predictive of shorter overall & disease-free survival, without being independent predictor of survival. results confirm that VEGF-C expression in primary cutaneous melanoma plays role in lymphatic spread of tumor. 18717190_in breast cancer, VEGF-C and VEGF-D are involved in lymphatic vessel invasion prior to lymph node metastasis, and their expression decreases after lymph node metastasis occurs 18773737_cannot recommend VEGF-C serum level as a marker for tumor growth in prostate cancer 18798279_heparanase plays a unique dual role in tumor metastasis, facilitating tumor cell invasiveness and inducing VEGF C expression, thereby increasing the density of lymphatic vessels that mobilize metastatic cells 18826121_In nasopharyngeal carcinoma, the expression rate of VEGF-C was high and was positively correlated with microlymphatic vessel density, lymph node metastasis and tumor staging. 18924431_High expression of VEGFC allele is being associated with physical endurance of sportsmen. 18953835_The lymphatic microvessel density in the periphery of breast cancer is correlated with the lymph node metastasis and expression of VEGF-C. 18974119_regulation of VEGF-C expression by NKX3.1 provides a possible mechanism by which the loss of NKX3.1 protein level leads to lymphangiogenesis in the late stages of advanced prostate cancer 18983460_Expression of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors (VEGF-A, IL-8, VEGF-C,and VEGF-D) is up-regulated directly or indirectly by altitude-dependent hypoxia. Both factors could be involved in a mechanism of adaptation to high altitudes. 19002718_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19002718_VEGFC, which encodes the ligand for VEGFR3, was sequenced in all patients with typical Milroy disease and no mutations were identified. 19024518_VEGF-C expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma was significantly higher than in normal mucosa, and significantly higher in patients with lymph node metastasis than that in those without lymph node metastasis. 19041000_VEGF-C is elevated in patients with recurrent papillary thyroid cancer 19066962_The expression of VEGF-A, VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3 in was higher in peritumoral liver tissue, while VEGF-C expression was higher in tumor. 19084972_Low serum VEGF-C levels are associated with distant metastasis. 19099632_As2O3 can inhibit expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 of human gastric cancer xenografts in nude mice. 19107364_HIF-1alpha and VEGF-C were over-expressed in non-small cell lung cancer. 19117016_High expression of VEGF-C is associated with node micrometastasis in pN0 early gastric cancer 19141404_VEGF-C, CD34 and VEGFR-2 expressions were evaluated in cancer tissue of children diagnosed with stadium 4 neuroblastoma, by immunohistochemical assay. 19151999_VEGF-C was detected in 21 of 58 (36%) cavernous lymphangiomas, ten of 28 (36%) cystic hygromas, 0 of 12 (0%) lymphangioma circumscriptum, and four of ten (40%) intraabdominal lymphangiomas 19152186_PRL-3 induces microvascular and lymphatic vessel formation by facilitating VEGF and VEGF-C expression in lung cancer tissues 19276682_Overexpression of VEGFC is associated with lymphangiogenesis in colorectal carcinoma. 19280060_VEGFC might play an important role in tumor progression by stimualting lymphangiogenesis. 19291182_Endothelin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma growth by a decrease in the vascular endothelial growth factor expression. 19299706_VEGF C-producing uterine NK cells support endovascular processes 19302703_Nuclear HIF-1alpha expression (nHIF-1alpha) showed inverse correlation with diffuse cytoplasmic VEGF-A (p = 0.002) and VEGF-C (p = 0.053) 19304526_Celecoxib significantly down-regulated the expression of VEGF-C mRNA, but produced a weak effect on COX-2 mRNA expression in Tca8113 cell line. 19347719_role of VEGFC in lymphangiogenesis and/or autocrine VEGF signaling in the pathobiology of lymphoma [review] 19347725_Autocrine VEGF-A and VEGF-C crosstalks in lymphoma cells are important in the pathogenesis of lymphomas 19351758_Compared with breast cancers, soft-tissue sarcomas exhibited lower peritumoral lymphatic vessel density independent of VEGF-C expression 19420963_HuR expression in non-small cell lung cancer correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression and lymph node metastasis 19462898_The positive lymph node metastasis and advanced clinical stage were more common in esophageal squamous carcinoma cases with higher expression of VEGF-C and VEGF-D. Expression levels of VEGF-C and VEGF-D correlated significantly with each other. 19589137_Overexpression of VEGF-C is associated with lymphatic metastasis and lymphatic vessel invasion in cervical carcinoma. 19608016_COX-2 may play a pivotal role in lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis of prostate cancer via the regulation of VEGF-C expression. 19629892_VEGF-C and -D may play important roles in lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. 19648590_Expression of VEGF-C is related to histological grade, pT, pN and lymphatic invasion, and is a prognostic indicator for ESCC 19671876_Measuring HIF1a, HB-EGF, and VEGF-C expression may contribute to a better understanding of the prognosis of patients with soft tissue sarcoma and may even play a crucial role for the distribution of patients to multimodal therapeutic regimens. 19701853_The nuclear localization of VEGF-C and its receptor Flt-4 is a novel finding from this study. It was more common in follicular lymphoma than in peripheral T-cell or diffuse large-cell lymphomas. High VEGFC was associated with poor survival. 19717640_The lymphangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) C and D induce Lymphangioleiomyomatosis cell proliferation through activation of their cognate receptor VEGF-R3. 19771906_The expression of VEGF-C and -D in papillary thyroid carcinoma was significantly higher than those in follicular thyroid carcinoma and adenoma tissues. 19779139_The VEGF-C/FLT-4 autocrine loop in tumor cells was a potential enhancer system to promote cancer progression. 19781195_Down-regulation of VEGF-C by shRNA can inhibit the proliferation and invasion of MCF-7 cells. 19813623_There is a close relationship of laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas with the expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3. 19821158_Our study is the first analysis showing correlation between serum concentrations of three angiogenic factors: VEGF-A, VEGF-C, VEGF-D in breast cancer patients 19825968_VEGF-C has a pathogenic role in leukemia via regulation of angiogenesis through upregulation of COX-2 19828679_Our results underline the importance of autocrine VEGF for podocyte survival and indicate the delicate balance of VEGF-A and VEGF-C to influence progression of glomerular diseases. 19885590_overexpression of Pin-1 and VEGF-C may promote tumor progression and metastasis 19910455_studies of up-regulation of VEGF in endometrial stromal cells: possible role of retinoic acid as endogenous co-regulator 19911196_high VEGF-C expression is associated with aggressive tumor behavior in ovarian cancer 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923084_The high expressions of VEGF-C and C-erbB-2 are closely related to lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. 19934313_Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that LEDGF/p75 binds the VEGF-C promoter, and binding is augmented by FSH. A corresponding hormonally regulated increase in the LEDGF/p75 mRNA and protein levels was observed. 19956642_analysis of how an enediynyl peptide inhibitor of furin blocks processing of proPDGF-A, B and proVEGF-C 20021832_The expressions of PPARgamma and VEGF-C are significantly correlated with the clinicopathological characteristics and biological behavior of extrahepatic cholangioadenocarcinoma. 20107934_Increased VEGFC is associated with lymphatic metastasis in colorectal cancer. 20119692_VEGF-C overexpression was highly correlated with lymphatic vessel density and lymph node metastasis in human hilar cholangiocarcinoma. 20120873_COX-2 and VEGF-C were highly expressed in papillary thyroid carcinoma, with possible interaction of their expressions, and may play a critical role in the cervical lymph node metastasis. 20137690_In human pancreatic cancer and nude mouse model, the expression of VEGF-C on lymphatic metastasis was higher than in primary tumors. 20145116_Results provide significant insights into the structural features that determine the high affinity and specificity of VEGF/VEGFR interactions. 20179201_VEGF-C induced lung lymphangiogenesis and promoted intralymphatic spread of metastases in the lung and formation of tumor emboli in the pulmonary arteries. 20215856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20223440_Allelic variations in the vascular endothelial growth factor C gene are associated with pre-eclampsia in both blacks and whites. 20223440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20336393_VEGF-C was more markedly expressed in thyroid malignancies than in benign lesions 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20429385_LMP1 induce expression of VEGFC and COX2 which may contribute to lymphatic metastasis and development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 20429915_Results suggest that VEGF-C promoted cervical cancer metastasis by upregulation and activation of moesin protein through RhoA/ROCK-2 pathway. 20448355_The positive expression rate of VEGF-C and VEGF-D in gastric cancer tissue was significantly higher than that of normal gastric tissues, and was positively correlated with lymph node metastasis. 20450586_VEGF-C and VEGF-D are involved in the lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis in gallbladder carcinoma. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20522712_Data show that high VEGFC predicts adverse long-term prognosis and provides prognostic information in addition to well-known prognostic factors. 20584281_High VEGF-C is associated with lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer. 20608938_Data showed a positive correlation between HER-2 and COX-2 or VEGF-C mRNA levels in breast cancer. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20651394_VEGF-C and -D and CCR7 may play critical roles in lymphatic invasion in primary tumors. 20654122_MMP-2 and MMP-9 in conjunction with VEGF-C, promote lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis of breast cancer. 20672317_Circulating levels of VEGF-C and VEGF-D could play a role as biomarkers for serological detection and staging in gastric cancer. 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20723431_Increased protein expressions of nuclear CXCR4, VEGF-C, and CK-19 are independent risk factors for developing lymph node metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 20734221_gallbladder cancer cells express both VEGF-C and its receptors. VEGF-C may have a role in the progressive growth and invasion of human GBC through an autocrine mechanism. 20819530_ERalpha stable transfection inhibits proliferation and migration capacities of MDA-MB-231 cells and decreases expression of COX-2 and VEGF-C. 20825419_Data show that specific IL-17/VEGF-C staining by immunochemistry was observed mainly within the cytoplasm in NSCLC tissue sample. 20827282_VEGF-C is derived from tumor-associated macrophages in squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment 20864667_Investigate Bmx mediates VEGF-dependent lymphangiogenic signaling. 20878580_RECK expression is low in colorectal cancer, while MMP-9 and VEGF-C expressions are high. 21069476_Depressing COX-2 gene expression by shRNA reduced VEGF-C expression on both mRNA and protein levels in tongue cancer cells. 21159248_The overexpressions of VEGF-C and EGFR genes are closely related to lymph node metastasis. VEGF-C mRNA and EGFR mRNA are valuable biomarkers for early diagnosis, clinical prediction and prognosis for lung cancer. 21199729_Data show that positive VEGF-C was significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis of bladder carcinoma. 21264536_The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C in ovarian cancer was related to matrix metalloproteinase-2 and E-cadherin. 21269982_The expression level of VEGF-C was correlated to the Gleason score of prostate cancer. 21279519_expression of VEGF-C in melanoma fibroblasts was highly associated with the presence of metastasis in the sentinel node 21302621_Findings indicated that VEGF-C might be involved in lymph node metastasis of NSCLC. 21330458_Data show that VEGF-C and HIF1a mRNA were significantly upregulated in oxaliplatin-related SOS. 21374591_cytokines enhance secretion of VEGF-A and VEGF-C by human retinal and choroidal cells 21411409_The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the pretreatment serum levels of VEGF and VEGF-C and the outcome of endometrial cancer patients. 21448429_Data suggest that MTA1, as a regulator of tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis, promotes lymphangiogenesis in colorectal cancer by mediating the VEGF-C expression. 21482472_VEGF-C mediated biological function through transcription of CNTN-1, which is implicated in tumor invasion and metastasis. 21520987_our results suggest that high levels of both VEGF-C and VEGF-D proteins are associated with lymph node metastasis 21600223_COX-2 inhibition may diminish lymph node metastasis by suppressing VEGF-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis 21666710_new function of CEBP-delta in lymphangiogenesis through regulation of VEGFR3 signaling in lymphatic endothelial cells 21676077_Expression of VEGF-C is related to lymph node metastasis (pN1), and is a prognostic indicator for cervical cancer. 21680174_RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. 21698469_VEGF-C differentially regulates VEGF-A expression in ocular and cancer cells; promotes angiogenesis via RhoA mediated pathway. 21732038_in our ALL cases with TCF3/PBX1 fusion, VEGF-C autocrine stimulation plays an important role in the proliferation of ALL 21767323_The VEGF-C signaling pathway plays a role in the pathogenesis of cortical tubers. 21804602_Downregulation of VEGF-C expression in lung and colon cancer cells decelerates tumor growth and inhibits metastasis via multiple mechanisms 21821075_Patients with T2 stage, low level of VEGF-C and absence of bladder Tis were associated with high overall survival and disease-specific survival rate. VEGF-C level can evaluate disease progression and assist in choosing the appropriate treatment 21839498_the effects of vegfc/VEGFR3 on the progression of tumor cells to form lymph node metastases occur primarily under an hypoxic tumor microenvironment. 21910784_These results indicate that VEGF-C plays a critical role in lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer 21947598_VEGF-C may play an important role in cigarette smoking-associated cervical carcinogenesis. 21972089_Strong expression of VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors was not correlated with the clinical parameters of aggressiveness, nor with high lymphatic vessel density. 21986134_High VEGFC is associated with gastric carcinoma. 21999474_Maternally derived decidual natural killer cells are capable of influencing fetal-derived trophoblast secretion of VEGF-C. 22008106_Data shsow that VEGF-C expression is an independent prognostic factor of stage IIIa (N2) lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. 22023263_Study demonstrates that CYR61 protein enhances the expression of VEGFC by binding with alphaVbeta3 integrin receptor on the surface of Decidual natural killer cells through intracellular PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 22049531_miR-1826 plays an important role as tumor suppressor via CTNNB1/MEK1/VEGFC downregulation in bladder cancer. 22057733_VEGF-C is highly expressed in ESCC and correlated with lymph node metastasis, as high levels were observed in patients presenting with lymph node metastases relative to those who did not. 22082308_pSTAT3 may enhance the early lymphatic metastasis in pancreatic cancer through VEGF-C. 22179834_Studies indicate that Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) and VEGF receptor 3 signaling are essential for the development of lymphatic vessels and is a promising target for inhibition of tumor lymphangiogenesis. 22199311_the mTOR-HIF-1alpha-VEGF pathway affects the progression of oral squamous cell carcinomas 22206010_VEGF-C, rather than VEGF-A, is closely related to dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis 22292658_Lower expression of VEGF-C and lower invasive ability to recombinate basal membranes were apparent in the ASOND group. 22326635_A significant relationship was found in salivary gland tumors with myoepithelial differentiation regarding simultaneous positive staining for VEGF-C/VEGF-D and flt-4 22335030_Abnormal IGF-IR and VEGF-C expression may be important in lymph node metastasis of endometrial adenocarcinoma and might be used to evaluate the prognosis. 22336204_Syk might down-regulate the expression of VEGF-C by inhibiting the activity of NFkappaB, which thus suppresses lymph node metastasis of breast cancer. 22366442_VEGF-C is involved in the induction of lymphangiogenesis which results in lymphatic spread of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 22466647_A critical role for SIX1 in lymphatic dissemination of breast cancer cells, providing a direct mechanistic explanation for how VEGF-C expression is upregulated in breast cancer. 22496919_The data showed that extra domain A fibronection could play a role in tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis via upregulating autocrine secretion of VEGF-C in colorectal cancer via the PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway. [extra domain a fibronectin, human] 22502683_High VEGF-C gene expression is associated with lymphatic metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. 22537619_Data indicate that NGF (angiogenesis) and VEGF-C (lymphangiogenesis) might play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris and could be researched further as potential new targeted therapies for psoriasis vulgaris. 22552325_results demonstrated that ET-1 and hypoxia act, at list in part, through VEGF to induce lymphangiogenic events and that these two stimuli may cooperate to induce VEGF-A/-C/-D expression and lymphatic differentiation. 22574929_The extent of both lymphatic proliferation and drainage parallels the progression of lesion severity, as does the up-regulation of pro-lymphangiogenic factors VEGF-C, VEGFR-3, ANG-1, and ANG-2. IL-4-stimulated cells 22607367_Survivin regulates VEGF-C expression in lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer. 22626857_VEGF-C expression was |
ENSMUSG00000031520 |
Vegfc |
92.529423 |
7.4436381898 |
2.896008 |
0.205974219 |
226.965864 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000273561989221689860478496785782965056933655491422634355144448421923285710929443088478247128852880531930661915926840568886850308533142950295768969226628541946411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000060265297924061826405213668588596425115828087493790366337238152364888537196386865051133616623924628782028756334244889508193932133039982801392397959716618061065673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
165.2437375 |
21.6379211 |
22.3006443 |
2.6073934 |
| ENSG00000150637 |
10666 |
CD226 |
protein_coding |
Q15762 |
FUNCTION: Involved in intercellular adhesion, lymphocyte signaling, cytotoxicity and lymphokine secretion mediated by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) and NK cell (PubMed:8673704). Cell surface receptor for NECTIN2. Upon ligand binding, stimulates T-cell proliferation and cytokine production, including that of IL2, IL5, IL10, IL13, and IFNG. Competes with PVRIG for NECTIN2-binding (PubMed:26755705). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26755705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8673704}. |
3D-structure;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of NK cells, platelets, monocytes and a subset of T cells. It is a member of the Ig-superfamily containing 2 Ig-like domains of the V-set. The protein mediates cellular adhesion of platelets and megakaryocytic cells to vascular endothelial cells. The protein also plays a role in megakaryocytic cell maturation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:10666; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell recognition [GO:0008037]; positive regulation of Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway [GO:0060369]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin mediated immune response [GO:0002891]; positive regulation of mast cell activation [GO:0033005]; positive regulation of natural killer cell cytokine production [GO:0002729]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045954]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002860]; positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050862]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12847109_CD226 mediates platelet and megakaryocytic cell adhesion to vascular endothelial cells 12913096_Data show that both PVR and Nectin-2 represent specific ligands for the DNAM-1 triggering receptor. 14676297_CD226 is involved in LFA-1-mediated costimulatory signals for triggering naive T cell differentiation and proliferation. 15136589_DNAM-1 regulates monocyte extravasation via its interaction with cd155 protein expressed at endothelial junctions on normal cells. 15138281_PTA-1(CD226 antigen) is localized to membrane rafts and binds the carboxyl-terminal domain of isoforms of the actin-binding protein 4.1G and also can bind human discs large providing the structural basis for a regulated molecular adhesive complex 15693793_CD226 molecules play an important role in maturation of the megakaryocytes in combination with LFA-1 16015041_Loss of Dnam-1 gene copy number and retention of Cadh-7 might be indicators of worse prognosis, and Dnam-1 deletion might predict for a beneficial response to adjuvant 5-FU-based chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. 16388732_The cytotoxicity of NK cells enhanced by SEA or SEB may be correlation with the increased expression of CD226 molecule, and CD226 may be involved in synapse formation of NK cells at killing stage. 16831868_CD226/CD112 (DNAM-1/Nectin-2) mast cell stimulation has a role in the allergic process 16887814_CD226 promoters P1 and P2 are regulated by Ets-1 and AP-1 16987076_expression on CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells and on CD3- CD16+ NK cells of HIV-infected patients was significantly higher than that of normal controls. 17875681_NK cell-mediated killing of myeloma cell lines was dependent on either DNAM-1 or NKG2D but not both molecules. 18657862_EWS tumor cells are recognized and lysed by resting and with higher efficacy by activated NK cells through NKG2D and DNAM-1 dependent pathways. 18971939_CD226 Gly307Ser association with multiple autoimmune diseases is reported. 18971939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987646_CD226 is a multiple sclerosis susceptibility gene. 18987646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19380793_CD226-transgenic mice display enlarged thymus lobes resulting from increased thymus cellularity. 19536154_CD226 Gly307Ser polymorphism is associated with Wegener's granulomatosis and multiple sclerosis. 19536154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19580844_In the presence of DC-derived cytokines such as interleukin-12, in both patients & healthy individuals, DNAM-1 can cooperate with NKp30 to induce NK cells to kill DC, release tumor necrosis factor-alpha, & promote DC maturation. 19624611_CD226 gene as a susceptible candidate locus for type 1 diabetes outside the major histocompatibility complex region. 19624611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19690890_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19801517_evidence provided for the contribution of DNAM-1/CD155 interactions to the reduction of DNAM-1 expression, suggesting that chronic receptor-ligand interactions in the tumor environment may induce loss of DNAM-1 on tumor-associated NK cells. 19865102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19904767_Data show that pair-wise ligations of 2B4 with DNAM-1 and/or NKG2D lead to increased effector functions of primary CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells to suboptimal levels of anti-CD3 stimulation. 19951419_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20089178_The rs763361 SNP in the CD226 gene was associated with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes because disease-susceptible minor allele A maintains the wild type ESS sequence. 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20338887_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20399620_CD226 Gly307Ser gene polymorphism is associated with severity of psoriasis 20399620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20444755_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20498205_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508602_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20508602_rs763361 in CD226 confers susceptibility for multiple sclerosis. 20613786_speculate that reduced expression of DNAM-1 on bone marrow natural killer cells may facilitate disease progression in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome 20669283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20669283_This study identified an association of CD226 with systemic lupus erythematosus in individuals of European ancestry. 20887380_An association between the Gly307Ser single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and susceptibility to systemic lupus erythemtosus was identified 20887380_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21162102_CD226 as a new systemic sclerosis genetic susceptibility factor underlying the contribution of costimulation pathways in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. 21286723_Demonstrate a genetic association between the CD226 gene and rheumatoid arthritis in a Chinese Han population with a potentially greater genetic effect than in the European population. 21296979_The proportion of circulating CD226positive natural killer (NK) cells is reduced in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). 21383766_Data indicate that NK cells from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients younger than 65 years have a reduced expression of DNAM-1 compared with age-matched controls. 21406724_NK cells lysed allogeneic proliferating more efficiently than nonproliferating T lymphocytes, with a mechanism requiring the cooperation between DNAM-1 and NKG2D. 21521299_likely that the 307Ser variant of the CD226 receptor is associated with autoimmune polyendocrinopathy type 2 pathogenesis 21525383_Study provides evidence that (pre)malignant cells themselves can acquire the ability to lyse epithelial cells via DNAM-1. 22302395_CD226 gene polymorphisms may not be associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. 22427644_TIGIT can inhibit T cell functions by competing with CD226 and can also directly inhibit T cells in a T cell-intrinsic manner. 22512842_CD226 polymorphisms, rs727088, rs34794968 and rs763361 were not involved in giant cell arteritis susceptibility in the Spanish population. 22531499_A CD226 three-variant haplotype is related with genetic predisposition to systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary fibrosis. 22547693_A soluble nectin-2 immunoglobulin-like V-set domain (nectin-2v) has been successfully prepared and demonstrates binding to both soluble ectodomain and cell surface-expressed full-length DNAX accessory molecule (DNAM)-1. 22941566_This demonstrates the CD226 rs763361 polymorphism confers susceptibility to autoimmune disease in Europeans, South Americans and Asians 23073294_CD226 Gly307Ser (rs763361) is significantly associated with the risk of multiple autoimmune diseases. 23161903_Overexpression of DNAM-1 was detected in the skin of patients with SSc (systemic sclerosis) 23262348_The G allele and GG genotype of rs727088 polymorphism in CD226 gene contributes to increased Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma susceptibility in a Han Chinese population. 23922043_While prior studies have found CD226 polymorphisms to be significantly associated with inflammatory demyelinating diseases, our results indicate the CD226 polymorphisms to be not associated with the diseases in Korean population. 23980210_The CD226/CD155 interaction regulates the proinflammatory (Th1/Th17)/anti-inflammatory (Th2) balance in humans. 23999715_CD226 rs763361, but not rs727088, gene polymorphism increased the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in a sample of the Iranian population. 24451371_these results show that CD226 functions in immune synapse formation via its first extracellular domain. 24496997_XLP1 inhibitory effect by 2B4 does not affect DNAM-1 and NKG2D activating pathways in NK cells. 24673109_Balance between activating NKG2D, DNAM-1, NKp44 and NKp46 and inhibitory CD94/NKG2A receptors determine natural killer degranulation towards rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. 24769842_Downregulated NKG2D, NKp46, and DNAM-1 receptors associated with impaired NK cell effector function are important biomarkers of advanced disease with a poor prognosis in melanoma patients. 24882570_Up-regulation of DNAM-1 and NKp30, associated with improvement of NK cells activation after long-term culture of mononuclear cells from patients with ovarian neoplasms. 24891767_rs763361 variant of CD226 gene (TT genotype) is associated with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes, greater frequency of GAD65 autoantibody, and with the degree of aggressiveness of the disease in T1D patients from Brazil 25057181_The CD226 gene has been identified as novel association with JIA, and a SNP near CD28 as a suggestive association. 25209846_UPR decreases CD226 ligand CD155 expression and sensitivity to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in hepatoma cells. 25352670_CD112 downregulation resulted in a reduced ability of DNAM-1 to bind to the surface of both virus-infected and gD-transfected cells. 25465800_Findings suggest that TIGIT is a key checkpoint inhibitor of chronic antiviral and antitumor responses through impairing CD226 function when disrupting its homodimerization. 25510399_These findings indicated that functional polymorphism rs727088A>G in CD226 might modify the susceptibility for the development of Gastric cancer. 25597312_NKG2D and DNAM-1 ligand upregulation might sensitize B cells undergoing lytic Epstein-Barr virus replication to NK cell recognition. (Review) 25609078_The present study provides evidence that regulation of the PVR/CD155 DNAM-1 ligand expression by nitric oxide may represent an additional immune-mediated mechanism and supports the anti-myeloma activity of nitric oxide donors. 25645050_genetic polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis, meta-analysis 25684021_Data show that leucocyte function-associated antigen-1 (integrin alphaLbeta2), DNAX accessory molecule-1 (DNAM-1) or tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) enhance osteoclast survival when co-cultured with activated NK cells. 25818301_our data reveal the existence of a functional program of NK cell maturation marked by DNAM-1 expression. 25825444_the coordinated expression of LFA-1 and DNAM-1 is a central component of NK cell education and provides a potential mechanism for controlling cytotoxicity by functionally mature NK cells. 25854581_NKG2D and DNAM-1 receptor-ligand interactions were essential in cytolysis by resting NK cells, as simultaneous blocking of both pathways resulted in almost complete abrogation of the cytotoxicity. 25950680_DNAM-1 ligands CD112 and CD155 as well as the NKG2D ligands MICA and MICB were expressed on the hiPSC lines 25991472_Age and CMV serostatus influence the expression of NKp30, NKp46 and DNAM-1 activating receptors on resting and IL-2 activated natural killer cells. 25994968_Human regulatory T cells expressing the receptors TIGIT and CD226 display widely divergent phenotypes in regard to expansion and activation. 26109642_upregulated CD226 expression on CD8(+) T cells reflects disease severity and is involved in Systemic sclerosis pathogenesis via the production of various cytokines, including profibrotic IL-13 and endothelial cell injury 26359290_Effector and regulatory CD4+ memory T cells of healthy individuals carrying the predisposing CD226 variant showed, in comparison to carriers of the protective variant, reduced surface expression of CD226 and impaired induction of CD226 after stimulation. 26563374_our results support and explain the mechanism behind the recently reported finding that in EOC, NK-cell recognition and killing of tumor cells was mainly dependent on DNAM-1 signaling while the contribution of the NKG2D receptor-ligand pathway was complementary and uncertain. 26634488_CD226 rs763361 polymorphism was significantly associated with susceptibility to T1D. 26675069_we propose that expression of DNAM-1 on inflammatory monocytes are evolutionally conserved and act as an adhesion molecule on blood inflammatory monocytes. 26910838_Results indicate that low-grade inflammation coupled with elevated blood glucose increases CD226 expression, resulting in decreased endothelial cell glucose uptake in T2DM. 27221592_Sole engagement of NKG2D, 2B4 or DNAM-1 is insufficient for NF-kappaB activation. 27257974_cumulative incidences of acute graft-versus-host disease in patients with high maximal serum levels of sDNAM-1 (>/=30 pM) in the 7 days before allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation were significantly higher than those in patients with low maximal serum levels of sDNAM-1 in the same period. Our data suggest sDNAM-1 is potentially a unique candidate as a predictive biomarker for the development of acute GVHD. 27722794_Our results support an important association of rs4810485 in CD40 gene and rs763361 in CD226 gene polymorphism, combined effect of rs4810485 and rs763361 with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. 28035916_Natural killer cells and cytotoxic T cells express both TIGIT and DNAM-1 receptors, and in certain cases their effector functions are dictated by TIGIT or DNAM-1 signaling. Agonist and antagonist antibodies targeting either TIGIT or DNAM-1 present many therapeutic options for diseases spanning from cancer to auto-immunity. (Review) 28084312_These findings highlight the importance of the TIGIT/CD226/PVR axis as an immune checkpoint barrier that could hinder future 'cure' strategies requiring potent HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells 29319370_The Serum level of CD226 and not CD226 genotypes could be considered as an independent risk factor for the prediction of RA within healthy individuals and also for RA disease activity. 29338153_Our study did not show significant association of CD226 and CD247 genetic polymorphisms with the risk of SSc or the presence of clinical manifestations except than FVC. In other words, CD226 and CD247 genetic variants may not contribute to SSc pathogenesis in Iranian population. 30120122_this study shows that NK cells lyse Th2-polarizing dendritic cells via DNAM1 30128676_High-resolution melting curve analysis of polymorphisms within CD58, CD226, HLA-G genes and association with multiple sclerosis susceptibility in a subset of Iranian population: a case-control study. 30145014_T allele and TT genotype of the CD226 rs763361 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes and with a lower age of disease onset among Egyptian children 30242020_The importance of the CD226 and inhibitory killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors ratio of natural killer cells as critical determinants for solid cancer immune surveillance. 30255106_this paper shows that the decreased expression of activating receptor DNAM-1 on peripheral blood NK cells is positively associated with gastric cancer progression 30591568_The hybrid complex structure of CD226-ecto binding to the first domain of CD155 (hCD155-D1) reveals a conserved binding interface with the first domain of CD226 (D1), whereas the second domain of CD226 (D2) both provides structural supports for the unique architecture of CD226 and forms direct interactions with CD155. 30738249_CD226 is involved in megakaryocyte activation and early-stage differentiation. 30908480_study demonstrated that platelets robustly suppress surface expression of CD226 and CD96 on the NK cell surface and their associated ligands on the tumour cell to further enhance NK cell suppression 30999035_this study shows the indispensable role of DNAM-1 molecule in gammadelta T-cell cytolytic function 31253644_The DNAM-1/Necl-5 interaction was underpinned by conserved lock-and-key motifs located within their respective D1 domains, but also included a distinct interface derived from DNAM-1 D2. Mutation of the signature DNAM-1 'key' motif within the D1 domain attenuated Necl-5 binding and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. 31582819_DNAM-1 and TIGIT are involved in regulating mucosal T-cell activation and immune homeostasis, and an imbalance of this system in inflammatory bowel disease. 31782891_Expression and function of DNAM-1 on human B-lineage cells. 31854233_Role of CD226 Rs763361 Polymorphism in Susceptibility to Multiple Autoimmune Diseases. 32040157_Tumor-derived soluble CD155 inhibits DNAM-1-mediated antitumor activity of natural killer cells. 32082316_Boosting Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Targeting of Sarcoma Through DNAM-1 and NKG2D. 32265229_CD226(hi)CD8(+) T Cells Are a Prerequisite for Anti-TIGIT Immunotherapy. 32466852_Alteration of CD226/TIGIT immune checkpoint on T cells in the pathogenesis of primary Sjogren's syndrome. 32591463_IL15 Stimulation with TIGIT Blockade Reverses CD155-mediated NK-Cell Dysfunction in Melanoma. 32682212_Investigation of mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells expressing immune checkpoint receptors (TIGIT and CD226) in early-onset preeclampsia. 32793241_Imbalance of the CD226/TIGIT Immune Checkpoint Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Primary Biliary Cholangitis. 32802845_Characteristic of TIGIT and DNAM-1 Expression on Foxp3+ gammadelta T Cells in AML Patients. 33053330_CD155 on Tumor Cells Drives Resistance to Immunotherapy by Inducing the Degradation of the Activating Receptor CD226 in CD8(+) T Cells. 33053331_Eomes-Dependent Loss of the Co-activating Receptor CD226 Restrains CD8(+) T Cell Anti-tumor Functions and Limits the Efficacy of Cancer Immunotherapy. 33298247_Hitting the complexity of the TIGIT-CD96-CD112R-CD226 axis for next-generation cancer immunotherapy. 33303573_Nutlin-3a Enhances Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Killing of Neuroblastoma by Restoring p53-Dependent Expression of Ligands for NKG2D and DNAM-1 Receptors. 33469055_Impact of immune checkpoint gene CD155 Ala67Thr and CD226 Gly307Ser polymorphisms on small cell lung cancer clinical outcome. 33900821_Suppression of Th1 and Th17 Proinflammatory Cytokines and Upregulation of FOXP3 Expression by a Humanized Anti-DNAM-1 Monoclonal Antibody. 34367178_Increased Proportion of CD226(+) B Cells Is Associated With the Disease Activity and Prognosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 34373559_Association of elevated serum soluble CD226 levels with the disease activity and flares of systemic lupus erythematosus. 34504191_DNAM-1/CD226 is functionally expressed on acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and is associated with favorable prognosis. 34653731_Immune checkpoint molecule TIGIT manipulates T cell dysfunction in septic patients. 34669985_CD226 deficiency promotes glutaminolysis and alleviates mitochondria damage in vascular endothelial cells under hemorrhagic shock. 34694361_DNAM-1 versus TIGIT: competitive roles in tumor immunity and inflammatory responses. 34937746_Functional Competence of NK Cells via the KIR/MHC Class I Interaction Correlates with DNAM-1 Expression. 35273617_CD226 and TIGIT Cooperate in the Differentiation and Maturation of Human Tfh Cells. 35821240_The CD226/TIGIT axis is involved in T cell hypo-responsiveness appearance in long-term kidney transplant recipients. |
ENSMUSG00000034028 |
Cd226 |
14.337450 |
2.7897556768 |
1.480139 |
0.547177931 |
7.094116 |
0.00773374301633162827829259811096562771126627922058105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015171457591846735854512751018319249851629137992858886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.1115089 |
4.1527303 |
4.0520141 |
1.1464082 |
| ENSG00000150722 |
151242 |
PPP1R1C |
protein_coding |
Q8WVI7 |
FUNCTION: May increase cell susceptibility to TNF-induced apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19874272}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Protein phosphatase inhibitor;Reference proteome |
|
Protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) is a major serine/threonine phosphatase that regulates a variety of cellular functions. PP1 consists of a catalytic subunit (see PPP1CA; MIM 176875) and regulatory subunits that determine the subcellular localization of PP1 or regulate its function. PPP1R1C belongs to a group of PP1 inhibitory subunits that are themselves regulated by phosphorylation (Wang et al., 2008 [PubMed 18310074]).[supplied by OMIM, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:151242; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556] |
19874272_Overexpression of active mutant IPP5 inhibited anchorage-dependent growth and induced apoptosis in HeLa cells, which may be attributed to the up-regulation of p21, p53 and Bcl-2-antagonist/killer, and down-regulation of Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L). 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20468071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22939397_The effect of IPP5 on tumor growth and the underlying molecular mechanisms were investigated by overexpression of IPP5 in HeLa cells, a human cervical carcinoma cell line. 24935604_The data demonstrate a novel role for 8-60hIPP5(m) in the control of G2/M cell cycle progression, a process that involves the activation of ATM/p53/p21cip1/waf1/Cdc2/ cyclin B1 pathways. 25339026_IPP5 mutations are associated with response to paclitaxel in cervical cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000034683 |
Ppp1r1c |
6.181691 |
0.1244557617 |
-3.006295 |
0.900651158 |
13.423583 |
0.00024848069854475733631016254321366432122886180877685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000641520921903204082749339054458914688439108431339263916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3290170 |
0.9185860 |
10.7141298 |
3.5125089 |
| ENSG00000150753 |
22948 |
CCT5 |
protein_coding |
P48643 |
FUNCTION: Component of the chaperonin-containing T-complex (TRiC), a molecular chaperone complex that assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis (PubMed:25467444). The TRiC complex mediates the folding of WRAP53/TCAB1, thereby regulating telomere maintenance (PubMed:25467444). As part of the TRiC complex may play a role in the assembly of BBSome, a complex involved in ciliogenesis regulating transports vesicles to the cilia (PubMed:20080638). The TRiC complex plays a role in the folding of actin and tubulin (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080638, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25467444, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;Neuropathy;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a molecular chaperone that is a member of the chaperonin containing TCP1 complex (CCT), also known as the TCP1 ring complex (TRiC). This complex consists of two identical stacked rings, each containing eight different proteins. Unfolded polypeptides enter the central cavity of the complex and are folded in an ATP-dependent manner. The complex folds various proteins, including actin and tubulin. Mutations in this gene cause hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy with spastic paraplegia (HSNSP). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Related pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 5 and 13. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:22948; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; chaperonin-containing T-complex [GO:0005832]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; beta-tubulin binding [GO:0048487]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; mRNA 5'-UTR binding [GO:0048027]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; positive regulation of establishment of protein localization to telomere [GO:1904851]; positive regulation of protein localization to Cajal body [GO:1904871]; positive regulation of telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body [GO:1904874]; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase [GO:0032212]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
16399879_A missense mutation within the CCT5 gene is associated with autosomal recessive mutilating sensory neuropathy with spastic paraplegia. 16821082_mRNA expression of CCT5, RGS3, and YKT6 was significantly up-regulated in p53-mutated tumors and associated with a low response rate to docetaxel. 18421076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19651702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22232265_introduction of the truncated human CCT epsilon subunit into yeast cells 23612981_Both CCT4 and CCT5 homo-oligomers have the property of forming 8-fold double rings absent the other subunits, and these complexes carry out chaperonin reactions without other partner subunits. 25124038_H147R CCT5 was not as efficient in chaperoning these substrates as wild type CCT5. 25995452_CCT5 complex caps mutant mHTT fibrils at their tips and encapsulates mHTT oligomers, providing a structural description of the inhibition of mHTTQ46-Ex1 by CCT5 complex and a shared mechanism of mHTT inhibition between TRiC chaperonin and the CCT5 complex 33076433_A Novel CCT5 Missense Variant Associated with Early Onset Motor Neuropathy. 34217974_CCT5 interacts with cyclin D1 promoting lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and invasion. 35194191_CCT5 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote gastric cancer lymph node metastasis by activating the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000022234 |
Cct5 |
1164.772271 |
2.2999575362 |
1.201607 |
0.106725713 |
123.706909 |
0.00000000000000000000000000009765327463634458331481683972902173705586408507637126214209153480688235422226516069255097818313515745103359222412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001200135165389214116443611696579157765912869985429781888314616472058460826775883045769433010718785226345062255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1564.6804649 |
100.1808765 |
685.0367157 |
32.4011424 |
| ENSG00000150907 |
2308 |
FOXO1 |
protein_coding |
Q12778 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that is the main target of insulin signaling and regulates metabolic homeostasis in response to oxidative stress (PubMed:10358076, PubMed:12228231, PubMed:15220471, PubMed:15890677, PubMed:18356527, PubMed:19221179, PubMed:20543840, PubMed:21245099). Binds to the insulin response element (IRE) with consensus sequence 5'-TT[G/A]TTTTG-3' and the related Daf-16 family binding element (DBE) with consensus sequence 5'-TT[G/A]TTTAC-3' (PubMed:10358076). Activity suppressed by insulin (PubMed:10358076). Main regulator of redox balance and osteoblast numbers and controls bone mass (By similarity). Orchestrates the endocrine function of the skeleton in regulating glucose metabolism (By similarity). Also acts as a key regulator of chondrogenic commitment of skeletal progenitor cells in response to lipid availability: when lipids levels are low, translocates to the nucleus and promotes expression of SOX9, which induces chondrogenic commitment and suppresses fatty acid oxidation (By similarity). Acts synergistically with ATF4 to suppress osteocalcin/BGLAP activity, increasing glucose levels and triggering glucose intolerance and insulin insensitivity (By similarity). Also suppresses the transcriptional activity of RUNX2, an upstream activator of osteocalcin/BGLAP (By similarity). Acts as an inhibitor of glucose sensing in pancreatic beta cells by acting as a transcription repressor and suppressing expression of PDX1 (By similarity). In hepatocytes, promotes gluconeogenesis by acting together with PPARGC1A and CEBPA to activate the expression of genes such as IGFBP1, G6PC1 and PCK1 (By similarity). Also promotes gluconeogenesis by directly promoting expression of PPARGC1A and G6PC1 (PubMed:17024043). Important regulator of cell death acting downstream of CDK1, PKB/AKT1 and STK4/MST1 (PubMed:18356527, PubMed:19221179). Promotes neural cell death (PubMed:18356527). Mediates insulin action on adipose tissue (By similarity). Regulates the expression of adipogenic genes such as PPARG during preadipocyte differentiation and, adipocyte size and adipose tissue-specific gene expression in response to excessive calorie intake (By similarity). Regulates the transcriptional activity of GADD45A and repair of nitric oxide-damaged DNA in beta-cells (By similarity). Required for the autophagic cell death induction in response to starvation or oxidative stress in a transcription-independent manner (PubMed:20543840). Mediates the function of MLIP in cardiomyocytes hypertrophy and cardiac remodeling (By similarity). Regulates endothelial cell (EC) viability and apoptosis in a PPIA/CYPA-dependent manner via transcription of CCL2 and BCL2L11 which are involved in EC chemotaxis and apoptosis (PubMed:31063815). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A4L7N3, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:G3V7R4, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R1E0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10358076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12228231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15220471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15890677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17024043, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18356527, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19221179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20543840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21245099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31063815}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Apoptosis;Autophagy;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene belongs to the forkhead family of transcription factors which are characterized by a distinct forkhead domain. The specific function of this gene has not yet been determined; however, it may play a role in myogenic growth and differentiation. Translocation of this gene with PAX3 has been associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2308; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; protein phosphatase 2A binding [GO:0051721]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cellular glucose homeostasis [GO:0001678]; cellular response to cold [GO:0070417]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to hyperoxia [GO:0071455]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to nitric oxide [GO:0071732]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:1903243]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0046676]; negative regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0032873]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0045722]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein acetylation [GO:0006473]; regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000177]; regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000377]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to fatty acid [GO:0070542]; temperature homeostasis [GO:0001659] |
11735247_fuses with pax3 protein and affects the transcriptional regulation of IGF-I receptor 11893744_cooperation with C-EBP beta in differentiating human endometrial stromal cells 12039929_PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR gene fusions are prognostic indicators in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 12150827_Transcriptional repression of D-type cyclins (in Class III transcripts)is required for FKHR mediated inhibition of cell cycle progression and transformation. 12242297_Pax3-FKHR allele causes lethal developmental defects in knock-in mice but might be insufficient to cause muscle tumors 12482965_a new mechanism for androgen-mediated prostate cancer cell survival and establish FKHR as nuclear target for both AKT-dependent and -independent survival signals in prostate cancer cells. 12493691_FKHR and HOXA10 interact directly and can function cooperatively to stimulate IGFBP-1 promoter activity in endometrial cells 12519792_Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 is a novel downstream target of insulin via this protein, which acts a a signal-regulated transcriptional inhibitor. 12560069_results identify a novel signaling pathway linking estrogen action to Pak1 signaling, and Pak1 to FKHR, suggesting that Pak1 is an important mediator of estrogen's cell survival functions 12606503_results indicate that signaling via protein kinase B to forkhead transcription factor FKHR can account for the effect of insulin to regulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 promoter activity via the insulin response sequence 12921955_Constitutive phosphorylation of FKHR transcription factor is associated with acute myeloid leukemia 12960271_fMLP-stimulated neutrophils coordinate the regulation of FOXO transcription factors and the survival factor Mcl-1, a mechanism that may allow neutrophils to alter their survival. 14664696_Analysis of amino acids that contribute to the nuclear/cytoplasmic shuttling of FOXO1 protein. 14726521_androgens induce increased activity of an acidic cysteine protease, which in turn cleaves FKHR, a mechanism by which androgens protect prostate cancer cells from the killing effect of FKHR. 15047604_FOXO factors are important for glucocorticoid-stimulated hPDK4 expression 15109499_FOX01 induces atrophy-related uibiquiitin ligase and causes akeletal muscle atrophy. 15140004_A fusion of FOXO1A and PAX3 proteins was used in the diagnosis of a solid alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 15184910_in the RD embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cell line, PAX3-FKHR upregulates expression of the gene encoding the chemokine receptor CXCR4 15342912_data suggest that phosphorylation-dependent degradation of FoxO1 by means of proteasomes plays a role in oncogenic transformation by P3k and Akt 15582274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15613482_Chromatin immunoprecipitation results demonstrate in vivo the association of human FOXO1 with the cyclin D2 promoter in untreated rat granulossa cells and release of FOXO1 from the cyclin D2 promoter upon addition of FSH plus activin. 15632117_TNF induces activation of the FOXO1 transcription factor, which acts as a master switch to control apoptosis 15688035_Pax3/FKHR regulates a distinct but overlapping set of genes relative to Pax3 in tumor cells and the global set of Pax3 and Pax3/FKHR gene targets is cell-type specific. 15688409_PAX3, PAX7 and their fusions with FKHR are each expressed in rhabdomyosarcoma tumors as a consistent mixture of functionally distinct isoforms 15692560_FHL2 inhibits FOXO1 activity in prostate cancer cells by promoting the deacetylation of FOXO1 by SIRT1 15778376_persistent activation of PI3K results in Akt-dependent sequestration of FoxO1 outside the nucleus of T cells interacting with APCs; this compartmentalization process can affect T cell growth after Ag recognition 15890677_The carboxyl-terminal region lysines of Foxo1 is acetylated by p300 and stimulates Foxo1-induced transcription of IGF-binding protein-1. 15987820_FOXO1A regulation of the IGFBP1 expression is cell type-dependent 16076959_Acetylation, catalyzed by CREB-binding protein, regulates the function of Foxo1 through altering the affinity with the target DNA and the sensitivity for phosphorylation. 16100571_Data show that Foxo1 and Foxo3a are the most abundant Foxo isoforms in mature endothelial cells and that overexpression of constitutively active Foxo1 or Foxo3a, but not Foxo4, significantly inhibits endothelial cell migration and tube formation in vitro. 16123151_Differentiating HESCs become dependent on progesterone signaling for survival through induction and reversible inactivation of FOXO1 suggesting a novel mechanism that links decidualization of the endometrium to menstruation 16133873_These studies show IGF-I phosphorylation of FKHR and FKHRL1 via a PI3-K-dependent pathway in neuroblastoma cells. 16282329_Foxo1 is involved in the nucleocytoplasmic translocation of PDX-1 by oxidative stress and the JNK pathway 16485043_The mutant FoxO1 transgene prevents pancreatic beta cell replication in 2 mouse models of beta cell hyperplasia 16492665_FoxO proteins promote hepatic glucose production through multiple mechanisms and contribute to the regulation of other metabolic pathways important in the adaptation to fasting and feeding in the liver 16497530_FOXO1A variation is rare and is unlikely to contribute to type 2 diabetes in either Caucasian or African-American populations 16497530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16571842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16670089_C5b-9 regulation of the cell cycle activation in aortic endothelial cells through Akt pathway is dependent on inactivation of FOXO1 16690806_versatile nature of FOXO1A in the regulation of a number of decidualization-specific genes 16709600_Differential expression of FOXO1 and FOXO3a confers resistance to oxidative cell death upon endometrial decidualization. 16849544_Expression of FOXO1A inhibited, and its knockdown promoted, cell proliferation or survival in prostate cancer. FOXO1A inhibited androgen- and androgen receptor-mediated gene regulation and cell proliferation. 16885156_FOXO1 and SREBP-1c have roles in insulin regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase expression 16916907_We demonstrate, for the first time in human skeletal muscle, that the regulation of Akt and its downstream signalling pathways GSK-3beta, mTOR and Foxo1 are associated with both the skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy processes. 16943287_Expression of the EBV genes for latent membrane protein 1 and latent membrane protein 2A decreases FoxO1 expression.[FOXO1] 16950602_We show here that EGCG induces phosphorylation of insulin-sensitive residues on the transcription factor FOXO1a. 16952014_PAX3-FKHR fusion protein plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas by influencing the commitment and differentiation of the myogenic cell lineage. 16952980_these data implicate specific members of the FOX family of TFs (FOXC1, C2, P1, P4, and O1A) not previously suggested in heart failure pathogenesis. 16964289_PAX3-FKHR could induce myogenin expression in undifferentiated myoblasts by a MyoD independent pathway, and that PAX3-FKHR is directly involved in myogenin expression in aRMS cells 16973122_The PI3K/Akt pathway is activated in human hepatoma cells exposed to Cu2+ or Zn2+, resulting in the phosphorylation and subcellular relocalisation of transcription factor FoxO1a. 16979636_Potentially causal mutations in FOXO3A (2/90; 2.2%) and FOXO1A (1/90; 1.1%) were identified in POF patients. 17038621_functional interaction between CDK2 and FOXO1 provides a mechanism that regulates apoptotic cell death after DNA strand breakage 17077083_Knockdown of endogenous FOXO1 in human vascular endothelial cells decreases phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase. 17202144_Insulin-like growth factor 1/insulin signaling activates androgen signaling through direct interactions of Foxo1 with androgen receptor. 17218607_A mechanism involving FoxO1a decreases the activity and expression of hydroxy-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase via regulation by fluid shear stress in cultured vascular endothelial cells. 17258205_Foxo-1 and Ang-2/Tie2 are part of the molecular response to shear stress, which may regulate angiogenesis. 17285543_PAX3-FKHR fusion transcripts were positive in 3/7 and PAX 7-FKHR fusion transcripts were positive in 2/7 of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma patients, respectively, and were all negative in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma and Control tumors. 17404186_These results indicate that the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/FoxO1 pathway participates in Ang II suppression of hSR-BI/CLA-1 expression and suggests that the endothelial receptor for hSR-BI/CLA-1 is downregulated by the renin-angiotensin system. 17442120_Overexpression of FOXO1A may be the result of PER-453 neuroectodermal tumor line's specific epimutations or imbalances in regulatory factors acting at the promoter and/or 3'-untranslated region. 17478621_FoxO-1 mRNA expression and nuclear protein content were significantly increased in quadriceps of patients with COPD; transcriptional regulation of atrogin-1 and MuRF1 may occur via FoxO-1, but independently of AKT 17490646_In this work we show that PAX3-FKHR, which is a stronger transcriptional activator relative to PAX3, can lead to two apparently irreconcilable outcomes: transformation and terminal myogenic differentiation. 17491598_Expression of phosphorylated FOXO1A is a frequent and early event in gastric tumorigenesis and there is a significant correlation between pFOXO1A and better prognosis. 17525748_developed a pathophysiologically relevant transcriptional profile of PAX3/FKHR and identified a critical target gene for aRMS development 17555999_A protective effect of FOXO1A haplotype on type 2 diabetes development. 17555999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17556536_Exerts co-regulatory functions independent of DNA binding; DNA-binding defective form of FOXO1a is transcriptionally active as a co-regulator of progesterone receptor A. 17597184_the proapoptotic role of FKHR is probably regulated by several signaling pathways in prostate cancer 17599040_FOXO1 serves as a tumor suppressor in endometrial cancer cells and is involved in normal growth control and maintenance of genomic stability. 17609436_FOXO1 engages in transcriptional cross talk with progesterone receptor to coordinate cell cycle regulation and differentiation of endometrial stromal cells. 17613043_Significant differences in survival and clinical characteristics between PAX3-FKHR and PAX7-FKHR positive tumors were seen indicating their role in carcinogenesis. 17638879_PAX3-FKHR fusion gene of rhabdomyosarcoma cooperates with loss of p16INK4A to promote bypass of cellular senescence 17873969_FOXO1 transcript levels in RA patients and in SLE patients with active disease activity were significantly lower than those in normal controls, and the FOXO1 transcript levels were inversely correlated with lupus disease activity 17986608_isolated and characterized muscle cells from transgenic mice expressing PAX3-FOXO1 under control of PAX3 promoter. Demonstrate that myoblasts are unable to complete myogenic differentiation because of an inability to up-regulate p57Kip2 transcription 17993506_FOXC1 regulates the expression of FOXO1A and binds to a conserved element in the FOXO1A promoter 18006475_AMPK activated by fluid shear stress is a novel regulator of FoxO1a phosphorylation and protein levels. 18022385_These results suggest that PAX3-FKHR promotes malignant phenotypes such as proliferation, motility, and to suppress differentiation. 18096667_The regulation and function of the forkhead transcription factor, Forkhead box O1, is dependent on the progesterone receptor in endometrial carcinoma. 18280254_O-glycosylation of FoxO1 results in increased expression of a glucose-6-phosphatase reporter gene. 18301748_TXNIP is directly repressed by FOXO1a, modulating the cellular response to oxidative stress and affecting life span 18303411_The FOXO1 gene break-apart FISH probe is a simple and accurate tool to detect the translocations associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas. 18316359_FOXO1 expression and activity are increased in patients with steatohepatitis, and mRNA levels are correlated with hepatic insulin resistance. 18356527_findings define a conserved signaling link between Cdk1 and FOXO1 that may have a key role in diverse biological processes, including the degeneration of postmitotic neurons 18408765_Aberrant activation of CDK1 may contribute to tumorigenesis by promoting cell proliferation and survival via phosphorylation and inhibition of FOXO1. 18420577_GlcNAcylation of FoxO provides a new mechanism for direct nutrient control of transcription to regulate metabolism and stress response through control of FoxO1 activity 18483260_the transcriptional activity of PAX3/FKHR can be inhibited by the kinase inhibitor PKC412 18497882_MTP is a target of the transcription factor FoxO1 and excessive VLDL production associated with insulin resistance is caused by the inability of insulin to regulate FoxO1 transcriptional activation of MTP [commentary] 18497885_FoxO1 mediates insulin regulation of MTP production and augmented MTP levels may be a causative factor for VLDL overproduction and hypertriglyceridemia in diabetes 18612045_These findings present new insights into the role of the glucocorticoid receptor and FOXO family of transcription factors in the transcriptional regulation of the muscle specific ring finger protein 1 gene 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18692812_FOXO1, FOXO3, and FOXO4 are expressed in human luteinized mural granulosa cells, which may suggest that these transcription factors are also involved in human folliculogenesis and luteinization. 18713968_FOXO1 controls the expression of L-selectin and EDG1 and EDG6, receptors that regulate lymphocyte trafficking 18718910_Dehydroepiandrosterone stimulates phosphorylation of FoxO1 in vascular endothelial cells via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and protein kinase A-dependent signaling pathways to regulate ET-1 synthesis and secretion 18786403_The observation that FoxO-DNA affinity varies between response elements and with posttranslational modifications suggests that modulation of FoxO-DNA affinity is an important component of FoxO regulation in health and misregulation in disease. 18787186_Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits VEGF-FOXO1-dependent gene expression in endothelial cells. 18788887_there is ALK overexpression in rhabdomyosarcomas, most likely independent of PAX3/PAX7-FKHR fusion status 18805788_HNF-4 and Foxo1 are required for reciprocal transcriptional regulation of glucokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase genes in response to fasting and feeding 18815134_COP1 binds FoxO1, enhances its ubiquitination, and promotes its degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. 18844239_These data demonstrate that integrin/EGFR cross-talk is required for expression of Egr-1 through a novel regulatory cascade involving the activation of the PI3K/Akt/Forkhead pathway. 18951090_PRMT1 methylates FOXO1 at conserved Arg248 and Arg250 within a consensus motif for Akt phosphorylation which directly blocks Akt-mediated phosphorylation of FOXO1. 18988640_Detection of PAX3/7-FKHR fusion gene by one-step RT-PCR is useful in the diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcomas (RMS) and that AChR-gamma is overexpressed in Chinese RMS patients. 19049975_FoxO1 binds to STAT3 and prevents STAT3 from interacting with the SP1.POMC promoter complex, and consequently, inhibits STAT3-mediated leptin action. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19075016_inhibition of SIRT1 caused an increase in FOXO1 acetylation and transcriptional activation in PCa cells 19086408_regulates glucose, lipid and energy metabolism of skeletal muscle. (review) 19103600_novel post-translational modifications of PGC-1alpha, including O-GlcNAc, and describe a novel mechanism for how PGC-1alpha co-activates transcription by FoxO1. 19141580_Common genetic variations within the FOXO1 gene affects insulin secretion and glucose tolerance and associates with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. 19141580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19150739_mRNA expression 6-fold and 12-fold higher in the choriodecidua compared to placenta and amnion, respectively 19221179_MST1-FOXO1 signaling is an important link survival factor deprivation-induced neuronal cell death 19233123_FOXO1 binds HBV core promoter and activates its transcription. 19244250_Results suggest that the expression of FOXO1 and FOXO4 genes is stimulated by FOXO3 and possibly by other FOXO factors in a positive feedback loop, which is disrupted by growth factors. 19254690_upregulation of Txnip and subsequent impairment of thioredoxin antioxidative system through p38 MAPK and FOXO1 may represent a novel mechanism for glucose-induced increase in intracellular ROS. 19281796_These results suggest that PARP-1 acts as a corepressor for FOXO1, which could play an important role in proper cell proliferation by regulating p27(Kip1) gene expression. 19293131_Increased expression of acetylated-FOXO1 implicates its posttranslational modification and possible role in prelabor fetal membrane rupture. 19308286_an HDAC inhibitor induces apoptosis through the FoxO1 acetylation-Bim pathway. 19321440_MDM2 acts as an ubiquitin E3 ligase, downstream of p53, to regulate the degradation of mammalian FOXO factors. 19442434_Camptothecin sensitivity was increased by ectopic expression of PAX3-FKHR (PF) in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells & decreased by its knockdown. Sensitization required a transcriptionally active PF. Camptothecin downregulated PF. 19463968_Impaired regulation of FoxO1 may cause down-regulation of CYP7A1 gene expression and contribute to dyslipidemia in insulin resistance. 19483080_Data indicate that CHIP is a negative regulator of FoxO1 activity through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. 19503105_Resutls show that the IS formation induced antiapoptotic signaling events, including activation of the kinase Akt1 and localization of NF-kappaB and FOXO1 to the nucleus and cytoplasm. 19513505_Suggest that FOXO1 expression is a favorable prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer. 19535741_[Review] Regulation of fetal membrane rupture occurs via movement of FOX-O1, the most dominantly expressed of FOX-O proteins, to the nucleus, whereby FOX-O1 is acetylated (ac-FOX-O1) leading to cell death. 19549905_Targeting FOXO1 can effectively induce glioma cell death and inhibit tumor growth. 19563779_FoxO1 inhibits PAI-1 expression through the inhibition of TGF-beta/Smad-mediated signaling pathways. 19574223_Suppression of miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 resulted in an increase in FOXO1 expression. 19584310_Foxo1 activation in response to hyperglycemia brings about proatherogenic changes in vascular endothelial cell function. 19633686_Studies were further confirmed in clinical primary breast cancer specimens, in which high-level expression of AEG-1 was inversely correlated with the expression of FOXO1. 19675556_In UVA- or UVB-irradiated fibroblasts, the expression of FOXO1A mRNA decreased significantly. The expression of type I collagen (COLIAI) also decreased. 19727442_HoxA-11 is required for prolactin expression in decidualized embryonic stem cells and turns into an activator when combined with FOXO1A; HOXA-10 is unable to upregulate PRL expression when co-expressed with FOXO1A 19757185_The aim of this study was to ascertain the relationship between the phosphorylation of FOXO1 and the apoptosis and the proliferation of lymphoma cells so as to further clarify the cellular biology and pathogenesis of the disease. 19772960_Abundant level of the phosphorylated FOXO1, its impaired nucleocytoplasmic shuttling, and the lowered expression of 14-3-3 protein in leiomyoma induces a shift in the cellular machinery toward a prosurvival execution program. 19787258_the transcription factor FOXO1 may be a critical effector of medulloblastoma growth suppression. 19793722_FOXO1A is more closely associated with female than with male longevity, whereas FOXO3A is associated with longevity in both genders. 19887561_Epigallocatechin gallate decreases ET-1 expression and secretion from endothelial cells, in part, via Akt- and AMPK-stimulated FOXO1 regulation of the ET-1 promoter. 19893043_high PAX3-FKHR expression plays a crucial role in regulating myoblast proliferation, transformation, and differentiation 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19953635_The fusion oncoproteins PAX3-FOXO1 typify alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, but may lack specific translocations. 19956688_tolerance to increased levels of intracellular ROS provided by the Mst1-FoxOs signaling pathway is crucial for the maintenance of naive T cell homeostasis in the periphery 20018872_Findings provide evidence that FoxO1, hypoxia-stimulated expression of FoxO3a and its nuclear accumulation are required for the induction of CTGF by hypoxia in endothelial cells. 20033803_FOXO1 may negatively regulate beta cell differentiation in the human fetal pancreas by controlling critical transcription factors 20061393_findings provide the first evidence that TAK1-NLK pathway is a novel regulator of FOXO1 20095040_FOXO1 was identified as a down-regulated gene in the minimal overlapping region of the 13q hemizygous deletion in CRCC. Decreased FOXO1 expression was significantly correlated with metastasis and poor survival outcome. 20125105_Increased hepatic ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2 mRNA in insulin-resistant obese subjects may, at least, reflect a compensatory mechanism for reduced plasma adiponectin, FOXO1 may contribute to enhanced ADIPOR1, but not ADIPOR2 transcription in insulin resistance. 20151947_Various receptor-mediated growth factor signals are integrated at the level of PI3K/Akt activation which finally results in nuclear FoxO1 deficiency. 20351326_The clinical behavior and molecular characteristics of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma without a PAX/FOXO1 fusion gene are indistinguishable from embryonal cases and significantly different from fusion-positive alveolar cases. 20353756_Advanced glycation end-products impair the expression and distribution of transcription factors PDX1 and FOXO1 involved in regulating insulin gene transcription. 20357092_HCV infection of human hepatocytes impaired insulin-induced FoxO1 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and reduced accumulation of FoxA2 in the nucleus. 20406953_derepression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma transcription by the high levels of FOXO1 could partially account for the lower levels of SLC2A4 found in polycystic ovary syndrome 20412774_FoxOs inhibit mTORC1 and activate Akt by inducing the expression of Sestrin3 and Rictor 20543840_Endogenous FoxO1 was required for autophagy in human cancer cell lines in response to oxidative stress or serum starvation, but this process was independent of the transcriptional activity of FoxO1. 20682687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20868688_Data suggest the ability of FoxO1 to inhibit LXRalpha binding with the LXRE in the SREBP-1c promoter. 20884733_At very advanced ages 92-110, adjusted for various confounders, positive effects of FOXO3A on survival remain statistically significant, but no significant effects of FOXO1A alone. 20884733_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20933505_these results suggest that suppression of FOXO1 function by EWS-Fli1 fusion protein may contribute to cellular transformation in Ewing's family tumors. 21069157_Results indicate that beta-thujaplicin, diethyldithiocarbamate (DEDTC) and its clinically-used dimer disulfiram, induce insulin-like dose-dependent effects on signalling to FOXO1a in a manner that is strictly dependent on the presence of zinc ions. 21075101_These data suggest the involvement of FoxO1 transcription factor in TNF-alpha-induced expression of a cell cycle regulatory protein and apoptosis of SMCs. 21116854_These results suggest loss of FOXO1 expression and elevated AURKA/B and EZH2 expression in lesional psoriatic tissues have potential contribution to the development of psoriasis. 21177767_Expression of full length IRIZIO cDNA also cooperated with PAX3-FOXO1 in the transformation of Arf-/- myoblasts. Given that IRIZIO is expressed at increased levels in rhabdomyosarcoma, it might contribute to rhabdomyosarcomagenesis in humans. 21177856_Protein kinase A-alpha directly phosphorylates FoxO1 in vascular endothelial cells to regulate expression of vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1 mRNA. 21179458_FOXO transcription factors mediate anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of resveratrol, in part due to activation of extrinsic apoptosis pathway 21185807_These results allow us to identify FOXO1 as a regulator of ceruloplasmin expression to promote the anti-oxidant pathway in response to IL-6 signaling. 21238503_Studies indicate that SKP2 works in concert with Akt to induce FOXO1 ubiquitination and proteasome degradation. 21298325_analysis revealed that insulin regulates nuclear localization of FOXO1, which is an important co-activator for STAT3 mediated transcription 21320536_Studies indicate that CNK1-driven proliferation relies on Akt-dependent phosphorylation and inactivation of FoxO proteins. 21321994_MyoD can play an active role in Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma by augmenting Pax7-FKHR function. 21373837_Studies indicate that new targets have recently been investigated as potential modulators in myeloid leukemia pathogenesis, including miR-328, BMI1, FOXOs and IL1RAP. 21388494_gene study of FOXO1, reveals no association with human longevity in Germans 21396404_Studies indicate that Akt phosphorylates acetylated-FoxO and then phosphorylated FoxO interacts with 14-3-3 proteins in the nucleus, which in turn results in cytoplasmic retention of FoxO. 21423212_Data show reduced CCN3 levels in aRMS cells following small interfering RNA knockdown of PAX3-FKHR. 21440011_Studies indicate that FoxOs have emerged as an important effector arm of PI3K/Akt signaling by driving multiple apoptotic gene expression. 21440577_Studies indicate that the inhibition of mTORC1 by FOXO could lead to the activation of Akt via the inhibition of the negative feedback loop driven by mTORC1 and S6K1. 21442235_Results indicate the interaction between HNF4A and FOXO1 genes in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. 21505104_Data reveal FOXO1 as a critical negative regulator of Runx2 in prostate cancer cells. Inactivation of FOXO1 due to frequent loss of PTEN in prostate cancer cells may leave the oncogenic activities of Runx2 unchecked. 21510935_DEPP is regulated at the level of transcription by FoxO in human vascular endothelial cells 21539865_Studies indicate that in addition to the direct control of FOXO by PKB, a number of proteins are controlled separately by PKB and FOXO giving rise to antagonistic control. 21541992_This review focuses on FoxO1 and its emerging set of functions in and through bone cells. 21613825_Studies indicate that FoxO1, 3 and 4 genes were discovered at the chromosomal breakpoints found in cancers and were initially implicated in cancer. 21655267_The results indicate that in cancer cells E2A, FOXO1 and FOXP1 regulate RAG1 and RAG2 expression, which initiates Ig gene rearrangement much in the way similar to B lymphocytes. 21666686_Case Report: identify a novel fusion partner FGFR1 for the known anchor gene FOXO1 in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 21670150_Cdc25A enhances Foxo1 stability by dephosphorylating Cdk2, and Foxo1 was shown to directly regulate transcription of the metastatic factor MMP1. 21696576_pFOXO1 expression in cancer cells plays a role in gastric cancer angiogenesis via mechanisms involving various angiogenesis-related molecules. 21697492_Taken together, these observations suggest that hepatitis C virus promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis through an NS5A-mediated, FoxO1-dependent pathway. 21708191_Studies indictet that the mammalian FoxO family consists of FoxO1, 3, 4 and 6 and are regulated by by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins. 21747041_Data show that siRNA-mediated MR-silencing prevented DHEA-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation and its effects on FoxO1. 21775495_FoxO1 is a repressor for monoaminoxidase A (MAO A) transcription, and its phosphorylation is involved in valproic acid activation of MAO A. 21804543_Data show that FOXO1 activates the expression of OCT4 and SOX2 pluripotency genes in hESCs by binding directly to their regulatory regions. 21993163_Older muscle contained significantly more transcript for Forkhead Box O 1 (FoxO1, p=0.001), Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1, p=0.009), and Inhibitor of DNA Binding 3 (ID3, p=0.043) than young muscle. 22072736_In endometriotic stromal cells, overactivation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling pathway contributes to the reduced expression of the decidua-specific gene, IGFBP1, potentially through reduced levels of nuclear FOXO1. 22089931_The presence of PAX3/7-FOXO1 translocation was significantly associated with a higher frequency of metastatic disease. 22159921_Mirk/Dyrk1B plays an important role in ovarian cancer cell survival through modulating FoxO translocation. 22180177_findings seem to suggest a relationship between m/z 905, FOXO1A and the development and growth of colorectal cancer 22197543_Detection of PAX3/PAX7-FKHR fusion transcripts is a novel tool for Rhabdomyosarcoma diagnosis 22213032_Loss of FOXO1 is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 22315317_A high fat diet increased resting forkhead box class O transcription factor 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor transcription factor alpha, while decreasing pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activation. 22343918_FOXO1 repression contributes to classical Hodgkin lymphoma lymphomagenesis. 22374423_PAX7-FKHR fusion gene inhibits myogenic differentiation via NF-kappaB upregulation. 22389493_FoxO1 deacetylation can promote vascular endothelial changes conducive to atherosclerotic plaque formation 22400069_Finding sugget that Foxo1 regulates Na(V)1.5 expression by directly binding the SCN5a promoter and affecting its transcriptional activity. 22411791_Inhibition of endogenous FOXO proteins attenuated tetradecanoylphorbol Acetate/PDGF-BB mediated differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. 22417654_B55alpha-containing PP2A is a key regulator of FOXO1 activity in pancreatic islet beta-cells. 22454413_FOX01 fusion gene status is a specific molecular marker in patients diagnosed with rhabdomyosarcoma. 22489460_HCV core protein expression-mediated FOXO1 activation and the increased PGC-1alpha leaded to the elevation of PCK1 at the mRNA level 22515357_Helicobacter pylori infection resulted in activation of the PI3K p85 subunit and inactivation of FoxO1 and FoxO3a. 22538365_The pattern of FOXO1 expression suggests a potential role for FOXO1 in implantation and decidualization. 22552808_interacts with thrombin leading to expression of cell cycle regulating genes and smooth muscle cell proliferation 22569260_Data suggest that when miR-223 is over-expressed in neoplastic cell lines, FOXO1 is down-regulated in cytoplasm, while nuclear FOXO1 is high compared to cytoplasm; as unphosphorylated FOXO1 increases, cyclin D1/inhibitors are up-regulated. 22653055_A transcriptional network involving the tumor suppressors Kruppel-like factor 6 and forkhead box O1 negatively regulate activated EGFR signaling in both cell culture and in vivo cancer models 22675169_Data indicate that golgi phosphoprotein 3 (GOLPH3) overexpression decreased FOXO1 transcriptional activity. 22761423_STAT3 protein interacts with Class O Forkhead transcription factors in the cytoplasm and regulates nuclear/cytoplasmic localization of FoxO1 and FoxO3a proteins in CD4(+) T cells. 22761592_These results implicate FOXO1 as a Parkinson disease-relevant gene and warrant further functional analyses of its transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. 22821817_The activity of the androgen receptor variant AR-V7 is regulated by FOXO1 in a PTEN-PI3K-AKT-dependent way. 22865884_FOXO1 transcription factor inhibits luteinizing hormone beta gene expression in pituitary gonadotrope cells 22931788_FOXO1 play |
ENSMUSG00000044167 |
Foxo1 |
21.997664 |
0.4852389491 |
-1.043233 |
0.343337525 |
9.392170 |
0.00217914155619873366187544405647713574580848217010498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004777796994874228958538608935668889898806810379028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.0577019 |
3.4639958 |
31.3824092 |
4.6945932 |
| ENSG00000150961 |
9871 |
SEC24D |
protein_coding |
O94855 |
FUNCTION: Component of the coat protein complex II (COPII) which promotes the formation of transport vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The coat has two main functions, the physical deformation of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane into vesicles and the selection of cargo molecules for their transport to the Golgi complex (PubMed:17499046, PubMed:20427317, PubMed:18843296). Plays a central role in cargo selection within the COPII complex and together with SEC24C may have a different specificity compared to SEC24A and SEC24B (PubMed:17499046, PubMed:20427317, PubMed:18843296). May more specifically package GPI-anchored proteins through the cargo receptor TMED10 (PubMed:20427317). May also be specific for IxM motif-containing cargos like the SNAREs GOSR2 and STX5 (PubMed:18843296). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17499046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18843296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20427317}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Craniosynostosis;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the SEC24 subfamily of the SEC23/SEC24 family, which is involved in vesicle trafficking. The encoded protein has similarity to yeast Sec24p component of COPII. COPII is the coat protein complex responsible for vesicle budding from the ER. This gene product is implicated in the shaping of the vesicle, and also in cargo selection and concentration. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Cole-Carpenter syndrome, a disorder affecting bone formation, resulting in craniofacial malformations and bones that break easily. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:9871; |
COPII vesicle coat [GO:0030127]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070971]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; COPII-coated vesicle cargo loading [GO:0090110]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886] |
17210573_concentrative endoplasmic reticulum-export is contingent on a direct interaction of GAT1 with Sec24D. 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20889976_Mutations in the carboxyl-terminal SEC24 binding motif of the serotonin transporter impair folding of the transporter 22404651_A triple arg motif mediates alpha(2B)-adrenergic receptor interaction with Sec24C/D and export 25683121_three mutant SEC24D alleles in a rare autosomal-recessively inherited skeletal disorder characterized by pre- and postnatal bone fragility, skull ossification defects, craniofacial dysmorphism, and short stature 27942778_The study found missense mutations in the SEC24D gene in Chinese families with autosomal recessive osteogenesis imperfect. 31530870_Identification and characterization of SEC24D as a susceptibility gene for hepatitis B virus infection. 32433667_ERp29 as a regulator of Insulin biosynthesis. |
ENSMUSG00000039234 |
Sec24d |
387.791510 |
2.2370436070 |
1.161593 |
0.105765645 |
120.309012 |
0.00000000000000000000000000054135623129642969592121123106637191174742431843571293646901230609028664569198907585700908384751528501510620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000006459513317651821042549709179334970231227673487143686479180690579269549051952270524168397969333454966545104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
553.8100500 |
33.7485747 |
248.9204660 |
11.8027298 |
| ENSG00000150990 |
57647 |
DHX37 |
protein_coding |
Q8IY37 |
FUNCTION: ATP-binding RNA helicase that plays a role in maturation of the small ribosomal subunit in ribosome biogenesis (PubMed:30582406). Required for the release of the U3 snoRNP from pre-ribosomal particles (PubMed:30582406). Plays a role in early testis development (PubMed:31287541, PubMed:31337883). Probably also plays a role in brain development (PubMed:31256877). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30582406, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31256877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31287541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31337883}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Helicase;Hydrolase;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a DEAD box protein. DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57647; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; U3 snoRNA binding [GO:0034511]; brain development [GO:0007420]; maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000462]; positive regulation of male gonad development [GO:2000020]; ribosome assembly [GO:0042255]; ribosome biogenesis [GO:0042254] |
31287541_In 46,XY Gonadal dysgenesis, we identified four heterozygous missense rare variants, classified as pathogenic or likely pathogenic in the Asp-Glu-Ala-His-box (DHX) helicase 37 (DHX37) gene.Two variants were recurrent: p.Arg308Gln and p.Arg674Trp. The variants were specifically associated with embryonic testicular regression syndrome. DHX37 is a player in the complex cascade of male gonadal differentiation and maintenance. 31337883_Results identified heterozygous missense pathogenic variants involving DHX37 gene as a new cause of an autosomal dominant form of 46,XY DSD, including gonadal dysgenesis and testicular regression syndrome (TRS), showing that these conditions are part of a clinical spectrum. Some of the variants are clustered in two highly conserved functional domains. 33490273_Integrative Expression and Prognosis Analysis of DHX37 in Human Cancers by Data Mining. 33490290_DHX37 Impacts Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Lung Adenocarcinoma through Immune Infiltration. 34293745_Expanding DSD Phenotypes Associated with Variants in the DEAH-Box RNA Helicase DHX37. 35290436_RNA Helicase DHX37 Facilitates Liver Cancer Progression by Cooperating with PLRG1 to Drive Superenhancer-Mediated Transcription of Cyclin D1. 35835064_DHX37 and 46,XY DSD: A New Ribosomopathy? |
ENSMUSG00000029480 |
Dhx37 |
216.739348 |
2.2616470925 |
1.177374 |
0.109446426 |
117.644558 |
0.00000000000000000000000000207418094926950447768552981801725628920789688665678206073353341846493460686601251197203055198770016431808471679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000024316847348068218131296346931847375204761571832480558784445234875808529786955780593871168093755841255187988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
297.1807103 |
29.8488992 |
132.7515137 |
10.1553736 |
| ENSG00000151006 |
339105 |
PRSS53 |
protein_coding |
Q2L4Q9 |
FUNCTION: In vitro can degrade the fibrinogen alpha chain of as well as pro-urokinase-type plasminogen activator. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16566820}. |
Disulfide bond;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable serine-type endopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:339105; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
16566820_Comparative analysis of polyserase-3 with the two human polyserases described to date, revealed that this novel polyprotein is more closely related to polyserase-2 than to polyserase-1. |
ENSMUSG00000044139 |
Prss53 |
24.818255 |
0.1363092055 |
-2.875045 |
0.587470064 |
22.647520 |
0.00000194611219067890818729994750757583688027807511389255523681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006669286262925629312197511877613465003378223627805709838867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6182355 |
2.4651639 |
48.4130099 |
11.0111987 |
| ENSG00000151012 |
23657 |
SLC7A11 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPY5 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-independent, high-affinity exchange of anionic amino acids with high specificity for anionic form of cystine and glutamate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15151999}. |
3D-structure;Amino-acid transport;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of a heteromeric, sodium-independent, anionic amino acid transport system that is highly specific for cysteine and glutamate. In this system, designated Xc(-), the anionic form of cysteine is transported in exchange for glutamate. This protein has been identified as the predominant mediator of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus fusion and entry permissiveness into cells. Also, increased expression of this gene in primary gliomas (compared to normal brain tissue) was associated with increased glutamate secretion via the XCT channels, resulting in neuronal cell death. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:23657; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; astrocyte projection [GO:0097449]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; cystine:glutamate antiporter activity [GO:0015327]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; dipeptide import across plasma membrane [GO:0140206]; glutamate homeostasis [GO:0090461]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; glutathione transmembrane transport [GO:0034775]; L-glutamate import across plasma membrane [GO:0098712]; lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:0070306]; limb development [GO:0060173]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903204]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:1904717]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cysteine metabolic process [GO:1901494]; regulation of glutamate metabolic process [GO:2000211]; regulation of glutathione biosynthetic process [GO:1903786]; regulation of melanin biosynthetic process [GO:0048021]; regulation of neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0033029]; regulation of protein transport [GO:0051223]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to redox state [GO:0051775]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; striatum development [GO:0021756]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
14722095_Cys(327) is a functionally important residue accessible to the aqueous extracellular environment and is structurally linked to the permeation pathway and/or the substrate binding site 15151999_topological model for xCT of 12 transmembrane domains with the N and C termini located inside the cell 15326101_Expression of Tat led to decrease in glutathione and increase in gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. The transport function of xc-was upregulated and was accompanied by increases in mRNAs for xCT and 4F2hc and in corresponding protein levels. 16574866_xCT was identified as the receptor mediating KSHV cell fusion; KSHV target cell permissiveness correlated closely with endogenous expression of xCT messenger RNA and protein in diverse cell types 18054200_These results suggest that reduced calcium signaling impairs AP-1 activation and that xCT expression may directly affect cell proliferation. 18287333_Induction of xCT led to glutamate-inhibitable cystine uptake and an increased rate of cysteine release from cells; overexpression of xCT in smooth muscle cells or endothelial cells led to glutamate-inhibitable cysteine release. 18469825_Small interfering RNA-mediated xCT silencing in gliomas inhibits neurodegeneration and alleviates brain edema. 18648370_The results suggest that the x(c)(-) transporter by enhancing glutathione biosynthesis plays a major role in pancreatic cancer growth, therapy resistance and represents a potential therapeutic target for the disease. 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19015640_Caveolin-1 was upregulated and beta-catenin was recruited to the plasma membrane when xCT was deficient, which were followed by the inhibition of beta-catenin transcriptional activity. 19017641_long term activation of the phospho-eIF2alpha/ATF4/xCT signaling module by the specific eIF2alpha phosphatase inhibitor, salubrinal, induces resistance against oxidative glutamate toxicity in the hippocampal cell line HT22 and primary cortical neurons 19207949_Expression of xCT is significantly reduced in low-grade oligodendroglial tumours harbouring LOH1p 20007406_x(c)(-) transporter provides a useful target for glioma therapy. 20053169_Review discusses system xc- function in vitro and in vivo, its role as an ambivalent drug target, and the relevance of oxytosis mediated by inhibition of xCT for identification of neuroprotective proteins and signaling pathways. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20733204_The cystine/glutamate antiporter demonstrates its major role of cystine and glutamate transport while modulating intracellular glutathione content and efflux in dendritic cells during cell differentiation and cross-presentation in a transgenic system. 21369940_The pathways modify system activity beyond the level of xCT transcription, including regulation on the level of membrane trafficking and substrate availability, especially the regulation by glutamate transport through excitatory amino acid transporters. 21510944_Data show that SLC7A11 is the direct target of miR-26b and its expression is remarkably increased in both breast cancer cell lines and clinical samples. 21555518_SLC7A11 is a functional target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq and knockdown analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21639880_Results reveal that increased expression of the cystine/glutamate antiporter system xCT in multiple sclerosis provides a link between inflammation and excitotoxicity in demyelinating diseases. 21689549_Both IGF-1 and TGF-beta stimulated system xc-mediated cystine uptake in dental pulp cells. 23096413_These findings suggest that xCT is an independent predictive factor in glioblastomas 23771433_These observations suggest that the expression of xCT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells might affect the G1/S checkpoint and impact on the prognosis of ESCC patients 24094812_the xCT antiporter, which is expressed on one-third of triple-negative breast tumors in this study, may have a role in glutamine updake and dependence 24516043_Our findings indicate that miRNA-27a negatively regulates SLC7A11 in cisplatin-resistant bladder cancer, and shows promise as a marker for patients likely to benefit from cisplatin-based chemotherapy 24686172_IGF-I regulates cystine uptake and cellular redox status by activating the expression and function of xCT in estrogen receptor-positive (ER(+)) breast cancer cells by a mechanism that relies on the IGF receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). 25002527_Results show that Nrf2 and ATF4 were upregulated by proteasome inhibition and cooperatively enhance human xCT gene expression upon proteasome inhibition. 25399695_Data indicate that cystine-glutamate exchange transporter protein SLC7A11 mRNA is regulated by cellular stress and nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD). 25860939_We discovered that many genes involved in oxidative stress/antioxidant defense system, apoptosis/anti-apoptosis/cell death, and cellular response to unfolded proteins/topologically incorrect proteins are potentially regulated by xCT. 26019222_increased SLC7A11 expression predicted shorter malignant glioma patient survival. 26252954_the rate of cystine uptake was significantly faster than the rate of glutamate release in human glioma cells. 26254540_Sulfasalazine, a relatively non-toxic drug that targets cystine transporter, may, in combination with CDDP, be an effective therapy for colorectal cancer. 26540405_Study demonstrated that the mRNA expression levels of the two system xc- subunits, SLC7A11 and SLC3A2, in peripheral white blood cells are lowered in patients with schizophrenia than healthy individuals 26729415_Although LCN2 increased intracellular iron concentrations, LCN2-induced GSH may catalyze and override oxidative stress via CD44 and xCT, and subsequently enhance the survival of clear cell carcinoma tumor cells in oxidative stress-rich environment. 26865117_The most frequent SLC7A7 mutation in Japanese LPI patients is p.R410*, which is a founder effect mutation in northern Japan. 26930718_MUC1-C binds directly with CD44v and in turn promotes stability of xCT in the cell membrane 26980765_High SLC7A11 expression is associated with glioma. 27129162_Authors found that the xCT expression was increased in peripheral blood monocyte of active tuberculosis. xCT expression in macrophage was induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) through TLR2/Akt- and p38-dependent signaling pathway. 27279909_Mechanistically, CD44v interacts with and stabilizes xCT and thereby promotes the uptake of cysteine for glutathione synthesis and stimulates side-population cell enrichment. 27658422_Results suggest that expression of SLC7A11 in the context of glioma contributes to tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and resistance to standard chemotherapy. 27705786_simultaneous mutations at all four acetylation sites completely abolish its ability to regulate metabolic targets, such as TIGAR and SLC7A11. Moreover, p53(4KR) is still capable of inducing the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop, but p53-dependent ferroptotic responses are markedly abrogated 28057599_Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of xCT potentiated the cytotoxic effects of aspirin plus sorafenib; this effect was diminished by xCT overexpression. Low-dose aspirin plus sorafenib enhanced the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in resistant HNC cells through xCT inhibition and oxidant and DNA damage. 28081640_While the transsulfuration pathway plays a primary role in supplying Cys to the redox system in the liver, xCT is induced in cases of emergencies, by compensating for Cys supply systems. 28202313_As targets of oncogenes with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity, STAT3 and STAT5 become constitutively active in hematologic neoplasms and solid tumors, promoting cell proliferation and survival and modulating redox homeostasis via regulation xCT expression. (Review) 28348409_accumulated mutant-p53 protein suppresses the expression of SLC7A11, a component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter, system xC(-), through binding to the master antioxidant transcription factor NRF2. 28429737_In some breast cancer cells, xCT antiporter expression is upregulated through the antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 and contributes to their requirement for glucose as a carbon source. 28553953_ATF4 expression fosters the malignancy of primary brain tumors and increases proliferation and tumor angiogenesis; experiments revealed that ATF4-dependent tumor promoting effects are mediated by transcriptional targeting the glutamate antiporter xCT 28610554_overexpression of SLC7A11 in the context of glioblastoma multiforme may contribute to tumor progression. 28627030_miR-375 served as a tumor suppressor via regulating SLC7A11. 28630042_Data suggest that glucose starvation of various neoplasm cell lines induces SLC7A11 expression; SLC7A11 overexpression decreases intracellular glutamate, an alternative source of metabolic energy; provision of alpha-ketoglutarate, a key downstream metabolite of glutamate, restores survival in SLC7A11-overexpressing neoplasm cell lines under glucose starvation. 28630426_the over-expression of SLC7A11, or supplementation with sufficiently cystine, or treatment with N-acetylcysteine significantly decreased P-gp expression and activity. It was suggested that ROS and SLC7A11/cystine were the two relevant factors responsible for the expression and function of P-gp, and that SLC7A11 might be a potential target modulating ADR resistance. 28648777_Identify mTORC2 as a critical regulator of amino acid metabolism in cancer via phosphorylation of the cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT. mTORC2 phosphorylates serine 26 at the cytosolic N terminus of xCT, inhibiting its activity. 28974116_Aberrant neuronal or neuroendocrine system may be involved in the suppressed reproductive performance in xCT deficient male mice. 28985506_ARF inhibits tumor growth by suppressing the ability of NRF2 to transcriptionally activate its target genes, including SLC7A11, a component of the cystine/glutamate antiporter that regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced ferroptosis. 29048627_these observations suggest that SLC7A11 may be a vital biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) and targeting SLC7A11 appears to be a potentially significant method for LSCC treatment. 29259101_Oncogenic PIK3CA alters methionine and cysteine utilization, partly by inhibiting xCT to contribute to the methionine dependency phenotype in human breast cancer cells. 29385995_CD44v9 in tumor specimens has potential as a novel indicator for identifying a cisplatin-chemoresistant population among urothelial cancer patients. CD44v8-10 contributes to reactive oxygen species defenses, which are involved in chemoresistance, by promoting the function of xCT, which adjusts the synthesis of glutathione. 29404978_In a multivariate analysis, high xCT expression and WHO tumor grade but not IDH1 R132H mutation, were significantly associated with epileptic seizures at diagnosis. 29441937_the level of antisense SLC7A11 was markedly reduced in epithelial ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines compared with those of normal control; reduction of antisense SLC7A11 level prompted ovarian cancer cell migration mainly by suppressing the expression of SLC7A11 29528250_High expression of cystine-glutamate antiporter SLC7A11 is associated with advanced pathological stages of liver carcinoma. SLC7A11 overexpression is a novel biomarker and a potential unfavorable prognostic factor as well as a potential therapeutic target for liver carcinoma. 29761734_System xC(-)-mediated TrkA activation therefore presents a promising target for therapeutic intervention in cancer pain treatment. 29764521_Studies indicate that SLC7A11 plays critical roles in glutamine metabolism and regulates the glucose and glutamine dependency of cancer cells. 29789716_Smoking could induce the expression of xCT (SLC7A11) in oral cancer cells. 30298963_Results showed that xCT-mediated glutamate release promotes glioma cell migration via N-methyl-d- aspartate- sensitive glutamate receptor signaling. 30448176_CD44v overexpression is not involved in cancer stem cell properties but increases xCT expression, which leads to the acquisition of Cisplatin-resistance. 30760873_mTOR-dependent upregulation of xCT blocks melanin synthesis and promotes tumorigenesis. 30799686_This study demonstrated that xCT knockdown in human breast cancer cells delays onset of cancer-induced bone pain. 31071489_Study have shown that a response to reactive oxygen species and up-regulation of xCT activity is crucial for reprogramming of zymogenic chief cells into pasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia. 31152846_The cystine/glutamate antiporter xCT is a key regulator of EphA2 S897 phosphorylation under glucose-limited conditions. 31419780_The expression of SLC7A11, but not of the other genes, was significantly higher in melanoma patients than in healthy individuals. 31692172_Identification of drugs for combination with xCT inhibitors that are able to overcome resistance to xCT-targeted therapy . 31705320_Cystine and glutamate bind xCT with favorable binding energies. 31874110_Suppression of the SLC7A11/glutathione axis causes synthetic lethality in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. 31931281_xCT (SLC7A11) expression confers intrinsic resistance to physical plasma treatment in tumor cells. 32109492_MiR-139-5p/SLC7A11 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 32144264_Study identified two previously unreported epigenome-wide significant associations with Parkinson's disease (PD), including cg06690548 on chromosome 4 and demonstrated that cg06690548 hypermethylation in PD is associated with down-regulation of the SLC7A11 gene and show this is consistent with an environmental exposure, as opposed to medications or genetic factors with effects on DNA methylation or gene expression. 32231310_The results identify a coupling between SLC7A11-associated cystine metabolism and the pentose phosphate pathway, and uncover an accompanying metabolic vulnerability for therapeutic targeting in SLC7A11-high cancers. 32265299_High cell density increases glioblastoma cell viability under glucose deprivation via degradation of the cystine/glutamate transporter xCT (SLC7A11). 32321821_Allelic-Specific Regulation of xCT Expression Increases Susceptibility to Tuberculosis by Modulating microRNA-mRNA Interactions. 32471991_TGF-beta1-mediated repression of SLC7A11 drives vulnerability to GPX4 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 32532810_Immunotargeting of the xCT Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter Potentiates the Efficacy of HER2-Targeted Immunotherapies in Breast Cancer. 32818320_Loss of the cystine/glutamate antiporter in melanoma abrogates tumor metastasis and markedly increases survival rates of mice. 33000412_Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. 33016372_Consensus mutagenesis approach improves the thermal stability of system xc (-) transporter, xCT, and enables cryo-EM analyses. 33019976_SLC7A11 as a biomarker and therapeutic target in HPV-positive head and neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 33285240_Epidermal growth factor promotes glioblastoma cell death under glucose deprivation via upregulation of xCT (SLC7A11). 33358859_RNA binding protein DAZAP1 promotes HCC progression and regulates ferroptosis by interacting with SLC7A11 mRNA. 33531365_Autophagy is required for proper cysteine homeostasis in pancreatic cancer through regulation of SLC7A11. 33629335_Insights into the novel function of system Xc- in regulated cell death. 33689883_KDM4A-mediated histone demethylation of SLC7A11 inhibits cell ferroptosis in osteosarcoma. 33722571_PARP inhibition promotes ferroptosis via repressing SLC7A11 and synergizes with ferroptosis inducers in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer. 33744468_Inhibition of xCT suppresses the efficacy of anti-PD-1/L1 melanoma treatment through exosomal PD-L1-induced macrophage M2 polarization. 33878705_Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates xCT stability through persulfidation of OTUB1 at cysteine 91 in colon cancer cells. 33980655_Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Determine Response to SLC7A11 Inhibition. 34004141_Signals of pseudo-starvation unveil the amino acid transporter SLC7A11 as key determinant in the control of Treg cell proliferative potential. 34074015_Mutant p53 Mediates Sensitivity to Cancer Treatment Agents in Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma Associated with MicroRNA and SLC7A11 Expression. 34091991_Amino acid transporters as emerging therapeutic targets in cancer. 34283663_The Knockdown of ETV4 Inhibits the Papillary Thyroid Cancer Development by Promoting Ferroptosis Upon SLC7A11 Downregulation. 34288020_IL-1beta-Induced Elevation of Solute Carrier Family 7 Member 11 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis Through Up-regulating Programmed Death Ligand 1 and Colony-Stimulating Factor 1. 34427100_SLC7A11 negatively associates with mismatch repair gene expression and endows glioblastoma cells sensitive to radiation under low glucose conditions. 34445395_Glutathione and Related Molecules in Parkinsonism. 34446045_SLC7A11 regulated by NRF2 modulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma radiosensitivity by inhibiting ferroptosis. 34571083_SLC7A11/ xCT is a target of miR-5096 and its restoration partially rescues miR-5096-mediated ferroptosis and anti-tumor effects in human breast cancer cells. 34609072_Hypoxia blocks ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via suppression of METTL14 triggered YTHDF2-dependent silencing of SLC7A11. 34609966_RBMS1 regulates lung cancer ferroptosis through translational control of SLC7A11. 34857913_Epigenome-wide association study of alcohol consumption in N = 8161 individuals and relevance to alcohol use disorder pathophysiology: identification of the cystine/glutamate transporter SLC7A11 as a top target. 34927544_The ubiquitin hydrolase OTUB1 promotes glioma cell stemness via suppressing ferroptosis through stabilizing SLC7A11 protein. 35064112_RNA binding protein NKAP protects glioblastoma cells from ferroptosis by promoting SLC7A11 mRNA splicing in an m(6)A-dependent manner. 35245456_Kynurenine importation by SLC7A11 propagates anti-ferroptotic signaling. 35311457_Long non-coding RNA ADAMTS9-AS1 attenuates ferroptosis by Targeting microRNA-587/solute carrier family 7 member 11 axis in epithelial ovarian cancer. 35325354_Novel insights into the SLC7A11-mediated ferroptosis signaling pathways in preeclampsia patients: identifying pannexin 1 and toll-like receptor 4 as innovative prospective diagnostic biomarkers. 35367340_Functional role of the SLC7A11-AS1/xCT axis in the development of gastric cancer cisplatin-resistance by a GSH-dependent mechanism. 35440604_xCT contributes to colorectal cancer tumorigenesis through upregulation of the MELK oncogene and activation of the AKT/mTOR cascade. 35509981_A Comprehensive Prognostic and Immune Analysis of Ferroptosis-Related Genes Identifies SLC7A11 as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 35522946_The N6-methyladenosine modification enhances ferroptosis resistance through inhibiting SLC7A11 mRNA deadenylation in hepatoblastoma. 35707044_lncRNA AGAP2-AS1 Facilitates Tumorigenesis and Ferroptosis Resistance through SLC7A11 by IGF2BP2 Pathway in Melanoma. 35757509_SLC7A11/GPX4 Inactivation-Mediated Ferroptosis Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Triptolide-Induced Cardiotoxicity. 35867762_Hypersensitivity to ferroptosis in chromophobe RCC is mediated by a glutathione metabolic dependency and cystine import via solute carrier family 7 member 11. 36046690_MITD1 Deficiency Suppresses Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Growth and Migration by Inducing Ferroptosis through the TAZ/SLC7A11 Pathway. 36084707_The amino acid transporter SLC7A11-mediated crosstalk implicated in cancer therapy and the tumor microenvironment. 36147463_PHGDH Inhibits Ferroptosis and Promotes Malignant Progression by Upregulating SLC7A11 in Bladder Cancer. 36164726_Circular RNA hsa_circ_0018189 drives non-small cell lung cancer growth by sequestering miR-656-3p and enhancing xCT expression. 36216119_lncRNA BBOX1-AS1 silencing inhibits esophageal squamous cell cancer progression by promoting ferroptosis via miR-513a-3p/SLC7A11 axis. 36439690_Hypoxia Enhances Glioma Resistance to Sulfasalazine-Induced Ferroptosis by Upregulating SLC7A11 via PI3K/AKT/HIF-1alpha Axis. |
ENSMUSG00000027737 |
Slc7a11 |
347.895845 |
23.4397744456 |
4.550887 |
0.226610693 |
392.797899 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000203599499780331955199057202960467325584740774720803387511406273997614489848368908567345207886355629288807965249135283399922837002393584385374968389376773391672450971692819110110258199604964991390614469686029395145351883478213039779802784323692 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000075316506685656631842564003658534383794546501021240257463431170366365196745584049606222141380628858602627622677975671232028846331387531064694998614181662981151766092454884590721987178398889381557173905641541485425638491335575963603332638740540 |
Yes |
No |
700.3481455 |
87.9478280 |
29.7135831 |
3.3626307 |
| ENSG00000151151 |
253430 |
IPMK |
protein_coding |
Q8NFU5 |
FUNCTION: Inositol phosphate kinase with a broad substrate specificity (PubMed:12027805, PubMed:12223481, PubMed:28882892, PubMed:30420721, PubMed:30624931). Phosphorylates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) first to inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and then to inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5) (PubMed:12027805, PubMed:12223481, PubMed:28882892, PubMed:30624931). Phosphorylates inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,6)P4) (PubMed:12223481). Phosphorylates glycero-3-phospho-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate to glycero-3-phospho-1D-myo-inositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PubMed:30420721, PubMed:28882892). Plays an important role in MLKL-mediated necroptosis via its role in the biosynthesis of inositol pentakisphosphate (InsP5) and inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6). Binding of these highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates to MLKL mediates the release of an N-terminal auto-inhibitory region, leading to activation of the kinase. Essential for activated phospho-MLKL to oligomerize and localize to the cell membrane during necroptosis (PubMed:29883610). Required for normal embryonic development, probably via its role in the biosynthesis of inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5) and inositol hexakisphosphate (InsP6) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TT16, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12027805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12223481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28882892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29883610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30420721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30624931}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phospholipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; phosphatidylinositol metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12027805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12223481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28882892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30624931}. |
This gene encodes a member of the inositol phosphokinase family. The encoded protein has 3-kinase, 5-kinase and 6-kinase activities on phosphorylated inositol substrates. The encoded protein plays an important role in the biosynthesis of inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate, and has a preferred 5-kinase activity. This gene may play a role in nuclear mRNA export. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on the long arm of chromosome 13 and the short arm of chromosome 19. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:253430; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; flavonoid binding [GO:0097243]; inositol tetrakisphosphate 3-kinase activity [GO:0000824]; inositol tetrakisphosphate 5-kinase activity [GO:0047326]; inositol tetrakisphosphate 6-kinase activity [GO:0000825]; inositol tetrakisphosphate kinase activity [GO:0051765]; inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase activity [GO:0008440]; inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 6-kinase activity [GO:0000823]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myo-inositol-1,2,3,4,6-heptakisphosphate 5-kinase activity [GO:0102732]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate 5-kinase activity [GO:0052812]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase activity [GO:0046934]; inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032958]; inositol phosphate metabolic process [GO:0043647]; inositol trisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0032957]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310] |
12027805_cloning of a full-length 1248-bp cDNA encoding a human inositol phosphate multikinase (IPMK); localized predominantly in the nucleus when transiently expressed in mammalian cells 12223481_the major activity of human InsP(4) 5-kinase is phosphorylation at the D-5 position [InsP(4) 5-kinase] 22715467_Data show that inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) interacts with the nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) and phosphorylates its bound ligand Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP). 22718630_Phosphorylation of S284 by protein kinase CK2 significantly decreases nuclear targeting of IPMK in HEK-293 cells. 23050966_overview of possible roles of IPMK in regulation of metabolism: IPMK appears to mediate activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in response to essential amino acids. IPMK appears to mediate hypothalamic control of food intake. [REVIEW] 23322705_Knockdown of expression and/or inhibition of function of phospholipase Cgamma1, inositol polyphosphate multikinase, which generates inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP) and InsP, and inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1/2 23550211_Results suggest that inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) acts as a transcriptional coactivator for p53 and that it is an integral part of the p53 transcriptional complex facilitating cell death. 24074953_Our findings implicate IPMK in a transcript-selective mRNA export pathway controlled by phosphoinositide turnover that preserves genome integrity in humans. 24632208_Future research should focus on the hitherto unknown non-conventional import of IPMK and the potential impact of its dysregulation on IPMK signaling pathways regulating cellular growth and proliferation. 25865046_A hereditary form of small intestinal carcinoid associated with a germline mutation in IPMK. 26195796_a severe loss of IPMK in the striatum of Huntington disease patients and in several cellular and animal models of the disease, is reported. 26682649_IPMK is a versatile regulator of nuclear signaling events. (Review) 27088644_This study demonstrated that identified genetic overlap between Alzheimer Disease disease and immune-mediated diseases, implicating the HLA locus and IPMK in the pathobiology of Alzheimer Disease. 27825921_No IPMK mutation was found in constitutional or tumor DNA in patients with familial small-intestine neuroendocrine carcinoids. CGH array revealed recurrent chromosome-18 deletions but no alteration in the IPMK region. 28882892_Data suggest that IPMK exhibits constrained, horseshoe-shaped substrate pocket, formed from an alpha-helix, a 3(10) helix, and a recently evolved tri-proline loop; headgroups of substrates (inositol 4,5-bisphosphate and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate) bind in precisely the same orientation, indicative of evolutionary optimization of 3-kinase activities against both substrates. 30744060_rs2790234 and rs6481383 are associated with longevity in women. 30840891_Deletion of IPMK in cell lines and intact mice virtually abolishes lipophagy, promotes liver damage as well as inflammation, and impairs hepatocyte regeneration. 33290695_Inositol Polyphosphate Multikinase Inhibits Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of TFEB to Negatively Regulate Autophagy Activity. 33497757_IP6K3 and IPMK variations in LOAD and longevity: Evidence for a multifaceted signaling network at the crossroad between neurodegeneration and survival. |
ENSMUSG00000060733 |
Ipmk |
62.919854 |
2.3390575146 |
1.225927 |
0.223026746 |
30.315543 |
0.00000003671719117875999891128957377910146941957236776943318545818328857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000151339218597737412515792329061048437921499498770572245121002197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.3258443 |
11.8253045 |
37.6925226 |
4.0216390 |
| ENSG00000151208 |
9231 |
DLG5 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDM6 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of the Hippo signaling pathway (PubMed:28087714, PubMed:28169360). Negatively regulates the Hippo signaling pathway by mediating the interaction of MARK3 with STK3/4, bringing them together to promote MARK3-dependent hyperphosphorylation and inactivation of STK3 kinase activity toward LATS1 (PubMed:28087714). Positively regulates the Hippo signaling pathway by mediating the interaction of SCRIB with STK4/MST1 and LATS1 which is important for the activation of the Hippo signaling pathway. Involved in regulating cell proliferation, maintenance of epithelial polarity, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell migration and invasion (PubMed:28169360). Plays an important role in dendritic spine formation and synaptogenesis in cortical neurons; regulates synaptogenesis by enhancing the cell surface localization of N-cadherin. Acts as a positive regulator of hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway. Plays a critical role in the early point of the SMO activity cycle by interacting with SMO at the ciliary base to induce the accumulation of KIF7 and GLI2 at the ciliary tip for GLI2 activation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q9R9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28087714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28169360}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the family of discs large (DLG) homologs, a subset of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) superfamily. The MAGUK proteins are composed of a catalytically inactive guanylate kinase domain, in addition to PDZ and SH3 domains, and are thought to function as scaffolding molecules at sites of cell-cell contact. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to the plasma membrane and cytoplasm, and interacts with components of adherens junctions and the cytoskeleton. It is proposed to function in the transmission of extracellular signals to the cytoskeleton and in the maintenance of epithelial cell structure. Alternative splice variants have been described but their biological nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9231; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; apical protein localization [GO:0045176]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060441]; establishment or maintenance of epithelial cell apical/basal polarity [GO:0045197]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0030011]; metanephric collecting duct development [GO:0072205]; midbrain development [GO:0030901]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035331]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060563]; polarized epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030859]; positive regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060999]; positive regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035332]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; postsynapse organization [GO:0099173]; protein localization to adherens junction [GO:0071896]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; zonula adherens assembly [GO:0045186] |
12657639_findings suggest that lp-dlg/KIAA0583 is a novel scaffolding protein that can link the vinexin-vinculin complex and beta-catenin at sites of cell-cell contact 15107852_Genetic variation in DLG5 is associated with inflammatory bowel disease 15665285_Collaboration of RAB6KIFL and DLG5 is likely to be involved in pancreatic cancer. 15841097_DLG5 constitutes a true inflammatory bowel diseases risk factor of modest effect 15841097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15843420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15930978_Genetic variation in DLG5 is associated with inflammatory bowel disease 15955786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16344053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16391570_there are significant population allele frequency differences at the DLG5 gene [letter] 16437728_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16437728_The G113A polymorphism of the DLG5 gene was completely absent in Greek Crohn disease cases as well as the Greek healthy population 16446977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16446977_R30Q variant constitutes a susceptibility factor for Crohn disease (CD) in men. 16450402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16450402_The results indicate a role for DLG5 variants in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) susceptibility. 16493449_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16494592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16534418_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16670523_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16670524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16773680_The initial report of DLG5 as a novel inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) susceptibility gene sparked a multitude of studies concerning its role in the aetiology of Crohn disease and IBD. 16944184_The R30Q variant in the DLG5 gene does not appear to be associated with an overall increase in the risk of disease in a British IBD cohort 17100974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17156146_DLG5 has a gender-specific role in the susceptibility of pediatric CD. Significant negative association found between DLG5 R30Q and CD in female children suggests DLG5 may have a protective effect in CD susceptibility for female children. 17156146_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17307543_DLG5 gene missense mutation is associated with increased susceptibility to inflammatory bowel diseases in children. 17307543_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17451203_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17451203_polymorphism exerts a weak influence on Crohn's disease phenotype 17455201_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17455201_the DLG5 haplotype A is associated with reduced risk of inflammatory bowel disease in the New Zealand Caucasian population 17476680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17476680_polymorphisms 3020insC in CARD15 and SNP rs2165047 in DLG5 may have a role in pediatric-onset Crohn's disease 17544013_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17693570_DLG5 30Q is associated with a small reduction in risk of Crohn disease in women in a Caucasian cohort. 17693570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18335190_Results provide evidence that the scaffolding protein DLG5 belongs to the CARD protein family. 18338763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18397186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18433468_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18466472_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18559397_findings show that the inflammatory bowel disease-susceptibility gene DLG5 is also associated with gluten-sensitive enteropathy 18715515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18804983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18824555_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037206_In the studied population, DLG5 R30Q was associated with all forms of IBD. An elevated presence of the R30Q variant was observed in all members of a familial IBD registry 20037206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20796250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20886065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21674725_Increased expression of discs large homolog 5 gene is associated with ulcerative colitis. 22065243_Examined the genetic association of DLG5 SNP P1371Q with inflammatory bowel disease and its interaction with R30Q in disease susceptibility. P1371Q is complementary to R30Q, with R30Q exhibiting a dominant effect in IBD susceptibility. 22118696_Polymorphisms in the DLG5 gene were found to be associated with Crohn's disease patients in Malaysia. 23624079_Overexpression of Dlg5 enhances the degradation of TGFBRI. 24662825_Findings demonstrate that Dlg5 interacts with and inhibits the activity of Girdin, thereby suppressing the migration of prostate cancer cells. 24910533_DLG5 plays a role in cell migration, cell adhesion, precursor cell division, cell proliferation, epithelial cell polarity maintenance, and transmission of extracellular signals to the membrane and cytoskeleton. 25478998_These data suggest that inhibition of Dlg5 by DNA hypermethylation contributes to provoke invasive phenotypes in bladder tumor. 26898345_study has identified several new proteins like RHOC, DLG5, UGDH, TMOD3 in addition to known chemoresistance associated proteins in non-small cell lung carcinoma. 27309475_Pooled data indicated no significant association between DLG5113G/A gene polymorphism and the development of Crohn's disease 27338058_G113A variant may be significantly associated with Crohn's disease risk in children and colonic involvement (Meta-Analysis) 27633114_both polymorphisms of DLG5 are correlated with inflammatory bowel disease susceptibility in an ethnic-specific manner. 27760079_Low expression of DLG5 is associated with Crohn's disease. 28087714_DLG5 inhibits the association between MST1/2 and large tumor suppressor homologs 1/2 (LATS1/2), uses its scaffolding function to link MST1/2 with MARK3, and inhibits MST1/2 kinase activity 28169360_Loss of DLG5 expression promoted breast cancer progression by inactivating the Hippo signaling pathway and increasing nuclear YAP. 28390157_Data found that Dlg5 expression was significantly lower in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and indicate that Dlg5 acts as a novel regulator of invadopodium-associated invasion via Girdin and by interfering with the interaction between Girdin and Tks5, which might be important for Tks5 phosphorylation in HCC cells. 30450766_Down-regulated DLG5 expression increases the stemness of breast cancer cells by enhancing TAZ expression, contributing to TAM resistance in breast cancer. 32631816_DLG5 variants are associated with multiple congenital anomalies including ciliopathy phenotypes. 34984467_The scaffolding protein DLG5 promotes glioblastoma growth by controlling Sonic Hedgehog signaling in tumor stem cells. 35638431_Recent Hints on the Dual Role of Discs Large MAGUK Scaffold Protein 5 in Cancers and in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000021782 |
Dlg5 |
304.031476 |
0.3514054269 |
-1.508792 |
0.103862753 |
215.200841 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100752106921890866873390955820387298239919591265176626986644135447052420815382577692143695092232143617287044414430994561772750306438695133692817762494087219238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000020798616757581947327903440483091639044358230813982986265901307604276759624014345303100121010943957303367998882415546653325971737658051097241695970296859741210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
161.8433024 |
10.6287173 |
463.7340152 |
19.1644169 |
| ENSG00000151376 |
10873 |
ME3 |
protein_coding |
Q16798 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of (S)-malate to pyruvate using NADP(+) as a cofactor (PubMed:7818469). Can also reverse the decarboxylation reaction, but only with significantly lower efficiency (PubMed:7818469). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7818469}. |
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Malic enzyme catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of malate to pyruvate using either NAD+ or NADP+ as a cofactor. Mammalian tissues contain 3 distinct isoforms of malic enzyme: a cytosolic NADP(+)-dependent isoform, a mitochondrial NADP(+)-dependent isoform, and a mitochondrial NAD(+)-dependent isoform. This gene encodes a mitochondrial NADP(+)-dependent isoform. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene, but the biological validity of some variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10873; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NAD+) activity [GO:0004471]; malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NADP+) activity [GO:0004473]; malic enzyme activity [GO:0004470]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; NAD binding [GO:0051287]; NADP+ binding [GO:0070401]; oxaloacetate decarboxylase activity [GO:0008948]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; malate metabolic process [GO:0006108]; oxygen metabolic process [GO:0072592]; pyruvate metabolic process [GO:0006090] |
18959763_ATP inhibition is proposed to be determined by the electrostatic potential involving the positive charge on the side chain of Lys346 19236308_Studies demonstrate that the Lys57 residue plays dual functional roles in the structural integrity of the allosteric site and in the subunit-subunit interaction at the dimer interface of m-NAD(P)-ME. 19416979_human c-NADP-ME exists mainly as a tetramer, whereas human m-NAD(P)-ME exists as a mixture of dimers and tetramers 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 31607129_ME3 is extensively involved in carcinogenesis of pancreatic cancer 33619771_Adaptive and Constitutive Activations of Malic Enzymes Confer Liver Cancer Multilayered Protection Against Reactive Oxygen Species. |
ENSMUSG00000030621 |
Me3 |
82.995073 |
0.4310009741 |
-1.214237 |
0.170817317 |
51.771696 |
0.00000000000062344097787381585963146281846065385008268111555196355766383931040763854980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003760518526120768914925131933899767077734976883363060551346279680728912353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.2269953 |
16.9457250 |
82.2169857 |
28.0521311 |
| ENSG00000151490 |
5800 |
PTPRO |
protein_coding |
Q16827 |
FUNCTION: Possesses tyrosine phosphatase activity. Plays a role in regulating the glomerular pressure/filtration rate relationship through an effect on podocyte structure and function (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19167335}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the R3 subtype family of receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatases. These proteins are localized to the apical surface of polarized cells and may have tissue-specific functions through activation of Src family kinases. This gene contains two distinct promoters, and alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed. The encoded proteins may have multiple isoform-specific and tissue-specific functions, including the regulation of osteoclast production and activity, inhibition of cell proliferation and facilitation of apoptosis. This gene is a candidate tumor suppressor, and decreased expression of this gene has been observed in several types of cancer. [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:5800; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; axon [GO:0030424]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0005001]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; glomerulus development [GO:0032835]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010812]; negative regulation of glomerular filtration [GO:0003105]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090260]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation involved in inactivation of protein kinase activity [GO:1990264]; podocyte differentiation [GO:0072112]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of glomerular filtration [GO:0003093]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807]; slit diaphragm assembly [GO:0036060] |
12949066_conclude that an intronic promoter within the protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type(GLEPP1) gene drives the expression of the protein tyrosine phosphatase-osteoclast(PTP) in a cell type-specific manner 16888096_overexpression of PTPROt inhibited BCR-triggered SYK tyrosyl phosphorylation, activation of the associated adaptor proteins SHC and BLNK, and downstream signaling events, and inhibition lymphoma cell proliferation and inducion of lymphoma cell apoptosis 17545520_PTPRO methylation and silencing has a role in chronic lymphocytic leukemia tumorigenesis 17593862_GLEPP1 expression may be a useful marker of podocyte injury in immunoglobulin A nephropathy, and may be predictive of clinical and pathological severity 18644370_PTPRO gene is co-regulated by both E2F1 and miR-17-92. 19095770_These data suggest that estrogen-mediated suppression of PTPRO is probably one of the early events in estrogen-induced tumorigenesis and that expression of PTPRO could facilitate endocrine therapy of breast cancer. 19573017_Dimerization of neuronal type III receptor-protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPRO in living cells is regulated by disulfide linkages in the PTPRO intracellular domain. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19855081_BCL6 repressed PTPROt transcription via a direct interaction with functional BCL6 binding sites in the PTPROt promoter 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21722858_The present study introduces mutations in PTPRO as another cause of autosomal-recessive nephrotic syndrome. 22001392_These findings further substantiate the role of TCL1 in PTPROt suppression and its importance in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 22099875_hypermethylated PTPRO occurs frequently in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 22126837_Three intronic SNPs in PTPRO were associated with learning and memory. 22851698_ErbB2 is a direct substrate of PTPRO and decreased expression of PTPRO predicts poor prognosis for ErbB2-positive breast cancer patients. 23533167_methylation and downregulation of PTPRO in a subset of primary human HCC and establish VCP as a novel functionally important substrate of this tyrosine phosphatase that could be a potential molecular target for HCC therapy. 24090193_PTPRO methylation is associated with poor survival only in HER2-positive patients. 24128416_PTPRO level was decreased in the early phase but reversed in the late phase of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. 25034527_Our study suggests an interesting PTPRO/TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling feedback loop in Hhepatocellular carcinomcarcinogenesis and progression 25301722_Results highlight the PTPRO contribution in negative regulation of SRC/EGFR signaling in colon cancer. 25339662_PTPRO was drastically decreased in fulminant hepatitis, and this was associated with enhanced beta-catenin accumulation but reduced IFN-gamma secretion. 25462809_The optimal pH value of PTP-oc is approximately 7.0. 25482129_Loss of PTPRO expression is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 25633279_These observations confirm that PTPRO plays a critical role in liver fibrogenesis by affecting PDGF signaling in HSC activation and might be developed into a feasible therapeutic approach for the treatment of chronic fibrotic liver diseases. 26117839_PTPRO truncated serves as an important tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma microenvironment. 27272414_Single nucleotide polymorphism in PTPRO gene is associated with Acute Renal Graft Rejection. 27345410_Results provide evidence that PTPRO inhibits ERBB2-driven breast cancer through dephosphorylation leading to dual effects of ERBB2 signaling suppression and endosomal internalization of ERBB2. 28199135_PTPRO is a novel candidate gene in emphysema with severe airflow obstruction. 28586036_the present study demonstrated that PTPRO inhibits tumor growth in vitro and in vivo, indicating the tumor suppressive function of PTPRO in LSCC. This study highlights PTPRO as an epigenetically silenced gene, and a candidate tumor-suppressor of LSCC. 30443949_PTPRO was significantly upregulated and negatively associated with miR-548c-5p in placental mononuclear cells in patients with preeclampsia. 31448453_LncRNA HULC promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma by regulating PTPRO via NF-kappaB. 31452237_PTPRO exaggerates inflammation in ulcerative colitis through TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. 32581055_IL-6 promotes PD-L1 expression in monocytes and macrophages by decreasing protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type O expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 34007244_MiR-6869-5p Induces M2 Polarization by Regulating PTPRO in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. 34719307_Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type O (PTPRO) knockdown enhances the proliferative, invasive and angiogenic activities of trophoblast cells by suppressing ER resident protein 44 (ERp44) expression in preeclampsia. 35527665_PTPRO activates TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling to intensify lipopolysaccharide-induced pneumonia cell injury. 36003382_PTPRO-related CD8(+) T-cell signatures predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in patients with breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000030223 |
Ptpro |
166.953221 |
4.0335020367 |
2.012033 |
0.306166130 |
40.297041 |
0.00000000021813910021562223629978100895632003516921848529364069690927863121032714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001101516633315971259556562662578448053007917906143120490014553070068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
264.1026869 |
53.7100583 |
65.9781147 |
9.9117347 |
| ENSG00000151491 |
2059 |
EPS8 |
protein_coding |
Q12929 |
FUNCTION: Signaling adapter that controls various cellular protrusions by regulating actin cytoskeleton dynamics and architecture. Depending on its association with other signal transducers, can regulate different processes. Together with SOS1 and ABI1, forms a trimeric complex that participates in transduction of signals from Ras to Rac by activating the Rac-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity. Acts as a direct regulator of actin dynamics by binding actin filaments and has both barbed-end actin filament capping and actin bundling activities depending on the context. Displays barbed-end actin capping activity when associated with ABI1, thereby regulating actin-based motility process: capping activity is auto-inhibited and inhibition is relieved upon ABI1 interaction. Also shows actin bundling activity when associated with BAIAP2, enhancing BAIAP2-dependent membrane extensions and promoting filopodial protrusions. Involved in the regulation of processes such as axonal filopodia growth, stereocilia length, dendritic cell migration and cancer cell migration and invasion. Acts as a regulator of axonal filopodia formation in neurons: in the absence of neurotrophic factors, negatively regulates axonal filopodia formation via actin-capping activity. In contrast, it is phosphorylated in the presence of BDNF leading to inhibition of its actin-capping activity and stimulation of filopodia formation. Component of a complex with WHRN and MYO15A that localizes at stereocilia tips and is required for elongation of the stereocilia actin core. Indirectly involved in cell cycle progression; its degradation following ubiquitination being required during G2 phase to promote cell shape changes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15558031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17115031}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Membrane;Non-syndromic deafness;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Synapse;Synaptosome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the EPS8 family. This protein contains one PH domain and one SH3 domain. It functions as part of the EGFR pathway, though its exact role has not been determined. Highly similar proteins in other organisms are involved in the transduction of signals from Ras to Rac and growth factor-mediated actin remodeling. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been observed but have not been thoroughly characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2059; |
brush border [GO:0005903]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex [GO:0017146]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium tip [GO:0032426]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; signaling adaptor activity [GO:0035591]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; actin polymerization-dependent cell motility [GO:0070358]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; barbed-end actin filament capping [GO:0051016]; behavioral response to ethanol [GO:0048149]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; dendritic cell migration [GO:0036336]; exit from mitosis [GO:0010458]; positive regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900029]; Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0016601]; regulation of actin filament length [GO:0030832]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels [GO:0099072]; regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035023]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
15273867_Involved in the growth factor-controlled regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation in the seminiferous epithelium. 17115031_These results support a model whereby the synergic bundling activity of the IRSp53-Eps8 complex, regulated by Cdc42, contributes to the generation of actin bundles, thus promoting filopodial protrusions. 17537571_Eps8 is essential for actin dynamics and cell interactions, independent of Eps8-like gene products. 18566210_These findings implicate the involvement of Eps8 in chemoresistance and show its importance in prognosis of cervical cancer patients. 19008210_overexpression of EPS8 in HN4 cells was sufficient to induce growth of non-tumorigenic cells in orthotopic transplantation assays. EPS8 expression in samples of squamous cell carcinoma showed variable expression levels and paralleled expression of MMP-9 19116338_A role of Eps8 in amplifying growth factor receptor signaling in human pituitary tumors to promote proliferation and cell survival. 19448673_Results show that alphavbeta6- and alpha5beta1-integrin-dependent activation of Rac1 was mediated through Eps8. 19528316_the crystal structures of human LanCL1, both free of and complexed with glutathione, revealing glutathione binding to a zinc ion at the putative active site formed by conserved GxxG motifs 20184880_Eps8 is recruited to lysosomes and subjected to chaperone-mediated autophagy in cancer cells 20351091_Overexpression of EPS8 induced expression of the chemokine ligands CXCL5 and CXCL12 in a FOXM1-dependent manner, which was blocked by LY294002 or a dominant-negative form of AKT 20418908_IRSp53, through its interaction with Eps8, not only affects cell migration but also dictates cellular growth in cancer cells. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21118970_Study implicates that the integrity of SOS1/EPS8/ABI1 tri-complex is a determinant of ovarian cancer metastasis. 21357683_critical role for JNK2 and EPS8 in receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and trafficking to convey distinctly different effects on cell migration. 21814501_Studied generation of filopodia with regards to the dynamic interaction established by Eps8, IRSp53 and VASP with actin filaments. 22449706_The ITSN2 interacts with Eps8 and stimulates the degradation of Eps8 proteins. 22493489_Eps8 is a key regulator of the LPS-stimulated TLR4-MyD88 interaction and contributes to macrophage phagocytosis 22683923_silencing of the protein by siRNA abrogated the migratory and invasive capacity of three different glioblastoma cell lines both in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional in vitro assays. 22876043_The loss of EPS8 expression in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas suggests that down regulation of this gene contributes to the development of a subset of colorectal cancers. 22897151_Eps8 is frequently expressed in OSCC. The aberrant expression of Eps8 closely correlated with poor survival in patients with OSCC. 23203811_Eps8 functions as a key coordinator in the interplay between FGFR signalling and trafficking. 23229386_We found that Eps8 mediates cell proliferation and survival of glioma cells, at least in part, by affecting phosphorylated ERK and Akt/beta-catenin activities. 23314863_Identify Fbxw5-driven fluctuation of Eps8 levels as an important mechanism that contributes to cell-shape changes during entry into-and exit from-mitosis. 23626693_Novel binding partners and differentially regulated phosphorylation sites clarify Eps8 as a multi-functional adaptor. 24409660_results suggest that Eps8 may serve as a prognostic factor of responsiveness to chemotherapy in AML patients 24741995_EPS8 is an F-actin capping and bundling protein. Mutant mice lacking EPS8 (Eps8-/- mice), which is present in the hair bundle, the sensory antenna of the auditory sensory cells that operate the mechano-electrical transduction 25031323_determined the alpha-synuclein-binding domain of beta-III tubulin and demonstrated that a short fragment containing this domain can suppress alpha-synuclein accumulation in the primary cultured cells 25333707_Eps8 is overexpressed in human breast cancers, possibly by regulating ERK signaling, MMP9, p53 and EMT-like transition to affect breast cancer cell growth, migration and invasion. 25359883_Eps8 is a crucial mediator of Src- and FAK-regulated processes. 25376540_These results indicate that employing the native and modified epitopes identified here in Eps8-based immunotherapy for HLA-A2.1 positive cancer patients may result in efficient anticancer immune responses for diverse tumor types. 25843487_EPS8, as MDR1 and WT1, may be a clinically valuable biomarker for assessing the outcome of ALL patients. 26163656_Erk activity promotes actin bundling by Eps8 to enhance cortex tension and drive the bleb-based migration of cancer cells under non-adhesive confinement. 26976596_Eps8 is required for continuous membrane blebbing. 27573546_Immunohistochemistry revealed that Eps8 was significantly increased in cervical cancer specimens compared with squamous intraepithelial lesion and normal cervical tissues. Additionally, it was revealed that Eps8 expression not only correlated with cervical cancer progression, but also exhibited a close correlation with the epithelialmesenchymal transition (EMT) markers, Ecadherin and vimentin. 28214294_These results indicate that plasma-membrane-associated PTK6 phosphorylates Eps8, which promotes cell proliferation, adhesion, and migration 28608476_Eps8/Abi1/Sos1 tricomplex acts as a key molecular switch altering the balance between Rac1 and Rho activation; its presence or absence in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells modulates alphavbeta6-dependent functions, resulting in a pro-migratory (Rac1-dependent) or a pro-TGF-beta1 activation (Rho-dependent) functional phenotype 29107665_Eps8 is involved in tumor invasion but not necessarily the development of regional lymph node metastasis 29192326_Data showed that chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients expressed a higher level of EPS8 mRNA in bone marrow mononuclear cells. Functional results revealed that EPS8 regulated multiple biological functions such as proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, drug sensitivity of CML cells possibly by mediating the regulation of the BCR-ABL/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. 30203615_LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 acts as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-137 and regulates EPS8 to promote cell reproduction and suppresses cell apoptosis in Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer 30431134_Comparative analyses revealed that Eps8 protein was abundant in exosomes derived from metastatic pancreatic tumors and ascites and that the amount of exosomal Eps8 was quantitatively correlated with the in vitro cell migratory activity. 30858505_we focused on EPS8 because its expression had the greatest impact on patient prognosis (overall survival, p |
ENSMUSG00000015766 |
Eps8 |
267.802780 |
0.3965696173 |
-1.334354 |
0.124673749 |
113.758628 |
0.00000000000000000000000001471765178714548574578427340752362471894450864971653792164026205057031967265990246573892363812774419784545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000166461716764955823737883963007223930949671533699630773630261534282593488542900672655378002673387527465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
148.5306685 |
20.7395687 |
376.9976382 |
37.4774379 |
| ENSG00000151575 |
374618 |
TEX9 |
protein_coding |
Q8N6V9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:374618; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451] |
31481019_Testis-expressed protein 9 (TEX9) expression is positively associated with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit b (eIF3b) expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). TEX9 expression is positively correlated with tumor-node-metastasis stage in ESCC. eIF3b binding to TEX9 mRNA functionally synergizes to promote the proliferation and migration, and inhibit the apoptosis of ESCC cells. |
ENSMUSG00000090626 |
Tex9 |
266.936899 |
2.1904814198 |
1.131248 |
0.164788567 |
46.276138 |
0.00000000001027072198186956334272146928202358432714869085344844279461540281772613525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000056883998668816040146296505760194293227494100051444547716528177261352539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
353.4998454 |
35.0802770 |
162.3688700 |
12.0141466 |
| ENSG00000151576 |
79691 |
QTRT2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H974 |
FUNCTION: Non-catalytic subunit of the queuine tRNA-ribosyltransferase (TGT) that catalyzes the base-exchange of a guanine (G) residue with queuine (Q) at position 34 (anticodon wobble position) in tRNAs with GU(N) anticodons (tRNA-Asp, -Asn, -His and -Tyr), resulting in the hypermodified nucleoside queuosine (7-(((4,5-cis-dihydroxy-2-cyclopenten-1-yl)amino)methyl)-7-deazaguanosine). {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03043}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;tRNA processing;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of tRNA-guanine transglycosylase. tRNA-guanine transglycosylase is a heterodimeric enzyme complex that plays a critical role in tRNA modification by synthesizing the 7-deazaguanosine queuosine, which is found in tRNAs that code for asparagine, aspartic acid, histidine, and tyrosine. The encoded protein may play a role in the queuosine 5'-monophosphate salvage pathway. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:79691; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transferase complex [GO:1990234]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; queuine tRNA-ribosyltransferase activity [GO:0008479]; tRNA-guanine transglycosylation [GO:0101030] |
20354154_TGT is composed of a catalytic subunit, QTRT1, and QTRTD1, not USP14. QTRTD1 has been implicated as the salvage enzyme that generates free queuine from QMP. 21044367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000022704 |
Qtrt2 |
185.130163 |
2.4082903932 |
1.268009 |
0.212461246 |
34.941022 |
0.00000000339844892130087317145780162355814951746779684071952942758798599243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015467501103423030261244041044625674441448381912778131663799285888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
277.7476578 |
38.9901394 |
116.1161090 |
12.2832020 |
| ENSG00000151615 |
5458 |
POU4F2 |
protein_coding |
Q12837 |
FUNCTION: Tissue-specific DNA-binding transcription factor involved in the development and differentiation of target cells (PubMed:19266028, PubMed:23805044). Functions either as activator or repressor modulating the rate of target gene transcription through RNA polymerase II enzyme in a promoter-dependent manner (PubMed:19266028, PubMed:23805044). Binds to the consensus octamer motif 5'-AT[A/T]A[T/A]T[A/T]A-3' of promoter of target genes. Plays a fundamental role in the gene regulatory network essential for retinal ganglion cell (RGC) differentiation. Binds to an octamer site to form a ternary complex with ISL1; cooperates positively with ISL1 and ISL2 to potentiate transcriptional activation of RGC target genes being involved in RGC fate commitment in the developing retina and RGC axon formation and pathfinding. Inhibits DLX1 and DLX2 transcriptional activities preventing DLX1- and DLX2-mediated ability to promote amacrine cell fate specification. In cooperation with TP53 potentiates transcriptional activation of BAX promoter activity increasing neuronal cell apoptosis. Negatively regulates BAX promoter activity in the absence of TP53. Acts as a transcriptional coactivator via its interaction with the transcription factor ESR1 by enhancing its effect on estrogen response element (ERE)-containing promoter. Antagonizes the transcriptional stimulatory activity of POU4F1 by preventing its binding to an octamer motif. Involved in TNFSF11-mediated terminal osteoclast differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19266028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23805044}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the POU-domain transcription factor family and may be involved in maintaining visual system neurons in the retina. The level of the encoded protein is also elevated in a majority of breast cancers, resulting in accelerated tumor growth. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:5458; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; euchromatin [GO:0000791]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to oxygen levels [GO:0071453]; dorsal root ganglion development [GO:1990791]; heart development [GO:0007507]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator [GO:0072332]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of adipose tissue development [GO:1904178]; negative regulation of amacrine cell differentiation [GO:1902870]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuromuscular process controlling balance [GO:0050885]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010666]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043068]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding [GO:2000679]; regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051090]; regulation of retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0090259]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
14726699_Levels of CDK4 mRNA and protein correlate with levels of Brn-3b in breast cancer cell lines manipulated to express different levels of Brn-3b and in human breast cancer biopsies; Brn-3b can activate the CDK4 promoter 14970234_Brn-3b transcription factor contributes to proliferation of neuroblastoma cells in vivo and in vitro but may also influence progression and/or invasion during tumorigenesis. 15833836_Brn-3b can, directly and indirectly (via interaction with the ER), activate HSP-27 expression, and this may represent one mechanism by which Brn-3b mediates its effects in breast cancer cells. 15968082_Brn-3b expression has been shown to be a prerequisite for developmental survival of most retinal ganglion cells. 16152597_first time that a Brn-3b POU family transcription factor has been shown to regulate a member of the catenin family, which provides insight into the molecular mechanisms by which Brn-3b expression may favour breast cancer progression and tumor invasion 17490655_Two different microRNAs that potentially regulate the stability of Brn-3b have been identified in neuroblastoma cells. 17637757_May act to alter growth properties of breast cancer and neuroblastoma cells by enhancing cyclin D1 expression in these tumor cells. 18367606_Brn3b specifies the RGC fate from multipotential precursors not only by promoting RGC differentiation but also by suppressing non-RGC differentiation programs as a safeguard mechanism. 23056278_Methylation levels of EOMES, HOXA9, POU4F2, TWIST1, VIM, and ZNF154 in urine specimens are promising diagnostic biomarkers for bladder cancer recurrence surveillance 25482012_The genes BCL6, NFE2, POU4F2 and ELF4 are primary 1,25(OH)2D3 targets in THP-1 cells 26700620_DNA methylation in a combination of POU4F2/PCDH17 has yielded the highest sensitivity and specificity of 90.00% and 93.96% in all the 312 individuals, showing the capability of detecting bladder cancer effectively among pathologically varied sample groups. 32597291_No association between POU4F1, POU4F2, ISL1 polymorphisms and normal-tension glaucoma. |
ENSMUSG00000031688 |
Pou4f2 |
50.138327 |
0.4005674322 |
-1.319883 |
0.223766135 |
35.620498 |
0.00000000239751423643519834819039986215788440304663708957377821207046508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011086250040659000340965874016174036453818985137331765145063400268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.7103050 |
4.4364017 |
74.8854138 |
7.0377662 |
| ENSG00000151617 |
1909 |
EDNRA |
protein_coding |
P25101 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for endothelin-1. Mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. The rank order of binding affinities for ET-A is: ET1 > ET2 >> ET3. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hypotrichosis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes the receptor for endothelin-1, a peptide that plays a role in potent and long-lasting vasoconstriction. This receptor associates with guanine-nucleotide-binding (G) proteins, and this coupling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Polymorphisms in this gene have been linked to migraine headache resistance. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:1909; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endothelin receptor activity [GO:0004962]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; artery smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014824]; atrial cardiac muscle tissue development [GO:0003228]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cardiac chamber formation [GO:0003207]; cardiac neural crest cell migration involved in outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003253]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus [GO:0071372]; cellular response to human chorionic gonadotropin stimulus [GO:0044751]; cellular response to luteinizing hormone stimulus [GO:0071373]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cranial skeletal system development [GO:1904888]; developmental pigmentation [GO:0048066]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0086100]; endothelin receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process [GO:0086101]; enteric nervous system development [GO:0048484]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; face development [GO:0060324]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; glomerular endothelium development [GO:0072011]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; heparin metabolic process [GO:0030202]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; left ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0003220]; meiotic cell cycle process involved in oocyte maturation [GO:1903537]; mesenchymal cell apoptotic process [GO:0097152]; middle ear morphogenesis [GO:0042474]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; multicellular organism aging [GO:0010259]; neural crest cell fate commitment [GO:0014034]; neuromuscular process [GO:0050905]; neuron remodeling [GO:0016322]; noradrenergic neuron differentiation [GO:0003357]; norepinephrine metabolic process [GO:0042415]; pharyngeal arch artery morphogenesis [GO:0061626]; podocyte apoptotic process [GO:1903210]; podocyte differentiation [GO:0072112]; positive regulation of cation channel activity [GO:2001259]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010737]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; protein transmembrane transport [GO:0071806]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010827]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of protein localization to cell leading edge [GO:1905871]; renal albumin absorption [GO:0097018]; renal sodium ion absorption [GO:0070294]; respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system [GO:0007585]; response to acetylcholine [GO:1905144]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway involved in axon guidance [GO:1902287]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939]; sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0055078]; sympathetic nervous system development [GO:0048485]; sympathetic neuron axon guidance [GO:0097492]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084]; vasoconstriction [GO:0042310] |
11376172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11601839_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11601839_The endothelin system plays a role in the complex pathophysiology of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. 11930911_The vasoconstrictor effect of endothelin-1 in small resistance arteries of normotensive subjects and, in part, also in hypertensive patients is mediated by ET(A) receptors, while ET(B) receptors play a minor role, if any 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12595285_endothelin-1 increased diastolic distensibility of acutely loaded myocardium and this effect was mediated by endothelin (A) receptors and Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activation 12629276_In autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease, neo-expression of ETA receptors has been found overlying glomeruli and cysts and markedly increased in medium-sized renal arteries. 12768436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12875994_Data show that in a human Kaposi sarcoma cell line, blockade of endothelin receptors A and B blocked the endothelin-1-induced increase in secretion and activation of matrix-metalloproteinases. 14519635_ET(A)R expression in breast cancer corrrelated with favorable prognosis. 14616768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14636059_It is clear from the present data for lung fibroblasts that for both stimulated and unstimulated states of ETA receptors, there exist multiple covalent forms differing in the number and location of sites of posttranslational modifications. 14729387_Endothelin ETA receptor mRNA levels are significantly higher in arteries from patients with ischemic heart disease as compared to congestive heart failure and controls. 15041798_there is an increased microvessel density (MVD) in metastatic bone lesions from different primary tumors, and ETA and ET1 are upregulated in metastatic bone lesions 15047866_ET-1 induces collagen matrix contraction through the ETA, but not the ETB, receptor 15073116_increased ET-1, ET(A)R, and ET(B)R expression are associated with increased VEGF expression and higher vascularity of breast carcinomas and could be involved in the regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer 15139053_Endothelin receptor type A was significantly down-regulated in papillary renal tumor specimens 15187089_endothelin A receptor regulates cell migration through the Cdc42-dependent c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway and is mediated by Nck1 15213100_ET-1/ETA/ETB autocrine/paracrine loops on DCs appear to be essential for the normal maturation and function of human dendritic cells 15713850_Recycling of ET(A) receptor is mediated by a motif with the structural characteristics of an internal PDZ ligand. This structural motif may represent a more general principle of endocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors. 15838262_Examine therapeutic targeting of the endothelin-A receptor in human ovarian carcinoma. Report that efficacy of cytotoxic agents is markedly enhanced by co-administration with atrasentan. 15838285_Compared kidney endothelin-A and endothelin-B receptor distribution visualized by radioligand binding versus immunocytochemical localization using subtype selective antisera. 15838315_Results suggest that [F]-SB209670 binds rapidly and primarily to endothelin-A receptors in the heart. 15838329_Report pharmacological characterization of YM598, a selective endothelin-A receptor antagonist. 15838364_Targeting the endothelin-A receptor, but not the endothelin-B receptor, may be a valid tool in the therapy of cervical carcinoma. 15838366_Report the effects of the selective ET(A) receptor antagonist, sitaxsentan sodium, in a patient population with pulmonary arterial hypertension that meets traditional inclusion criteria of previous pulmonary arterial hypertension trials 15838367_Endothelin-A receptor antagonism promotes decreased vasodilation but has no differential effect on coronary artery compliance in hypertensive patients. 15988412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15988412_The polymorphism of EDNRA/C+70G may be related to NTG (normal tension glaucoma) risk factors. 16002759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16002759_Polymorphisms in the ET-1 gene (K198N), the ET receptor type A (ETA), (-231G>A and +1222C>T), and the ET type B (ETB) receptor (G57S and L277L) do not play a role in cerebral small-vessel disease 16149067_in human lung fibroblasts ET-1 exerts a profibrogenic action via an ET(A) receptor-dependent, MAPK-mediated induction of IL-11 release and cell proliferation 16208144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16531800_Observations strongly suggest that the expression of ETA receptor is enhanced in neointimal smooth muscle cells at early stages after percutaneous coronary intervention injury in human coronary arteries. 16567585_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16582543_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16618267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16648553_Integrin-linked kinase functions as a downstream mediator of the ET-1/ET(A)R axis to potentiate aggressive cellular behavior in ovarian cancer cells. 16816835_Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed mRNA the ETA receptor subtype in the human trigeminal ganglion. Immunocytochemistry revealed numerous cell bodies containing ETA proteins. 16879994_endothelin receptor type A(ETR-A) is selectively up-regulated in placental tissue of delayed miscarriages as compared to normal pregnancies 16947775_Associations between endothelin receptors A and B in aystemic ssclerosis subsets supports the role of endothelin and its receptors in the pathogenesis of this disease. 16947775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16962346_ET receptors in pigment cells of vertebrate species were identified by RT-PCR assays, and the differential expression of the various subtypes in each species was compared by quantitative PCR. 16971893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16971893_Polymorphism of EDNRA:c.*1222C > T was significantly associated with normal tension glaucoma. AA genotype of EDNRA:c.-231G > A polymorphism was associated with lower baseline intraocular pressure than in GG+GA genotype group. 16984730_Endothelin receptor A has a role in progression of prostate cancer 17016617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17122448_ET-1 mediates the increased vascular tone of extremely inactive legs of SCI individuals by increased activation of ET(A)-receptors 17198909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17198909_association of genetic variation with aortic pressure in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy 17203161_analysis of Endothelin-1, ETAR and ETBR expression in different histologic subtypes of renal cell carcinoma 17353514_Endogenous endothelin, predominantly via ET(A) receptor stimulation, contributes to basal constrictor tone and endothelial dysfunction, whereas ET(B) activation mediates vasodilation in human coronaries. 17437213_No association between the -231 G > A polymorphism in the EDNRA gene and preeclampsia as well as any correlation with the main clinical features of the disorder were found. 17437213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17468950_Hypoxia-induced breast carcinoma invasiveness was reduced by ETRA antagonist atrasentan. 17470272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17525706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17575543_neutrophils taken from healthy donors damage the endothelium by a mechanism dependent on ETs acting via ET(A) receptor, whereas neutrophils from acute pancreatitis patients cause more severe damage that is not dependent on ETs 17616673_Endothelin receptor type B counteracts tenascin-C-induced endothelin receptor type A-dependent focal adhesion and actin stress fiber disorganization 17616694_endothelin A receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor are targeted by the combination of ZD4054 and gefitinib in ovarian carcinoma 17706018_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17706018_The CC genotype could be protective in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease females. This genotype was described to be associated with lower pulse pressure. 18172451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18212505_endogenous ET-1 is involved in the regulation of microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes and microangiopathy 18326801_Activation of ET(A) localized in T tubules was associated with a strong positive iontropic effect, whereas the activation of ET(A) in surface sarcolemma was not. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18678984_These results suggest that possible coupling of NHE with NCX via Na+ transport is involved in ET(A)R-mediated sustained [Ca2+]i increase. 18756291_review of heterodimerization involving the ETA receptor and renal endothelin ETB-dopamine D(3) receptor interactions at the cellular level that appear to have functional consequences in vivo 18945538_Lack of ET(A)R expression may be an independent negative marker for recurrence-free survival in bladder cancer. 19217622_Endothelin-1 activates ETA receptors on human vascular smooth muscle cells to yield proteoglycans with increased binding to LDL 19225824_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19367425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19460784_NF-kappaB, endothelin-1, and ET-1 receptor A (ETAR) have roles in pulmonary vascular dysfunction in end-stage cystic fibrosis 19479828_ET-1-dependent vasoconstrictor tone is increased predominantly in the subgroup of SSc patients with dcSSc, in whom acute blockade of ETA receptors was able to improve impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilator function. 19558538_No significant association was detected between migraine with aura end-diagnosis and three migraine trait components and 32 single nucleotide polymorphisms in endothelin-1 and its receptors EDNRA and EDNRB 19558538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19575782_Endothelin-1 acts primarily via the ETA receptors to induce phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in human aortic smooth muscle cells. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19593212_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19626996_Expression levels of ET-1, ET(A)R and ET(B)R were not associated with r-AFS staging of endometriosis. 19653178_Systemic hypertension is associated with increased ET-1 and ET(A) receptor mRNA expression;insulin-dependent diabetes down-regulates ET(A) receptors in the internal mammary artery in patients with coronary artery disease undergoing bypass grafting 19898645_Selective endothelin A-receptor blockade attenuates coronary microvascular dysfunction after coronary stenting in patients with type 2 diabetes. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20028935_A significant association between EDNRA 3'-untranslated region (UTR) variant rs5335 and pulmonary function, was demonstrated. 20034471_these results suggest that the amount of Jab1 bound to ETR regulates the degradation rate of ET(A)R and ET(B)R by modulating ubiquitination of these receptors, leading to changes in ET(A)R and ET(B)R levels. 20043107_Both ET(A)R and ET(B)R are present in lung carcinomas but at different levels, according to the histological type of tumor. 20083432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083432_SNPs as susceptibility factors for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome 20100616_Endothelin receptor type A polymorphism rs 5335 may be associated with congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens penetrance. 20100616_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20150570_Our data demonstrate that the level of circulating ET-1 is regulated by ETA receptor-mediated negative feedback. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20371740_Expression of ETA receptor in normal endometrium and decidua is regulated by homeobox protein A10 (HOXA10). 20401344_The results suggested that during the luteal phase, ET(A) and ET(B) receptors participate in contractile effects of endothelins on isthmic segment of fallopian tubes, probably regulating the length of time the oocyte remains in the ampulla 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20725140_Similar to ETB receptors, ETA receptors are also present in human aortic vascular endothelial cells (hVECs). ETA, but not ETB receptors mediate the effect of ET-1 on total intracellular Ca2+ of hVECs. 20963824_Study of a novel enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) reporter (Ednra) transgenic mouse line enables visualization of placode-derived inner ear sensory cell lineage. 20964792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20964792_Our results show additional findings for a role of endothelin receptor type A as a susceptibility factor for migraine without aura 21057729_Studies indicate that understanding the mechanisms of how cigarette smoke causes up-regulation of endothelin receptors in the vasculature and airways may provide new strategies for treatment of cigarette smoke-associated cardiovascular and lung diseases. 21220476_Data show that blockade of ET(A)R-driven EMT can overcome chemoresistance and inhibit tumor progression, improving the outcome of EOC patients' treatment. 21356562_The mRNA expressions of endothelin A and B receptors and endothelin-1 are significantly increased in failed Fontan patients. 21418087_Renal medullary endothelin-1/endothelin receptor second messenger signaling regulates sodium/water balance via control of natriuresis and renin-angiotensin system; both endothelin 1 receptor and endothelin 2 receptor are involved. [REVIEW] 21424380_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in EDNRA gene is associated with breast cancer. 21453125_the role of EDNRA -231 G>A and APOE HhaI polymorphism for a possible association with migraine 21487064_Data show that EDNRA/H323H polymorphism is a novel and independent prognostic marker, which may help identify patient subgroups at high risk for poor disease outcome. 21498912_Increased expression of ET-1, ETRA/B, and activation of signaling pathways were observed in the pulmonary arteries and arterioles of irreversible pulmonary arterial hypertension patients associated with congenital heart defects. 21515378_ET1 induced calcium responses are only mediated by endothelin A receptors, possibly due to sub-threshold endothelin B receptor expression. 21601190_Immunohistochemical evaluation of spermatic and control vein samples from 55 patients with varicocele showed overexpression of ET-1 and its receptors ETA and ETB in varicose veins. 21773759_Findings suggest a potential link between specific genotypes in the ednra gene and susceptibility to pulmonary arterial hypertension. 22106312_Results demonstrated significant association of IA with rs6841581 on chromosome 4q31.23, immediately 5' of the endothelin receptor type A with P = 2.2 x 10(-8) [odds ratio (OR) = 1.22, PPA = 0.986]. 22129540_four TRPC isoforms, TRPC3, TRPC5, TRPC6, and TRPC7, can function as endothelin type A receptor-operated Ca2+ channels. 22286173_SNP, rs6842241, near EDNRA at chromosome 4q31.22 (combined P-value = 9.58 x 10(-9); odds ratio = 1.25), was found to be significantly associated with intracranial aneurysm 22365955_ETB receptors predominated in normal human liver and displayed the highest ratio (ETB:ETA 63:47) compared with other peripheral tissues; liver ETB expression was upregulated in cirrhosis (ETB:ETA 83:17) 22480520_endothelin A receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling converge on beta-catenin to promote ovarian cancer metastasis 22510270_Data show that optical imaging with a fluorescent ET(A)R tracer allows the noninvasive imaging of tumor-associated ET(A)R expression in vivo. 22561246_Expressed recombinant ET(A) as a fusion protein with phi6 p9 envelope protein. The purified protein showed specific binding to ET-1 and the alpha subunit of G(q) protein. 22580289_Early onset preeclampsia (PE)(=GW34) with or without fetal growth restriction is associated with increased mRNA expression of the ET/ETR system, while in late onset PE and gestational diabetes, the opposite effect was observed 22688668_Both endothelin A and B receptors were reduced in pulmonary arterial hypertension, particularly type B, and type B signaling through protein kinases was markedly reduced in vascular smooth cells with a mutation in bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2. 22997346_We used this sample of 250 surgical patients to describe the distribution of ET-1, ETA and ETB polymorphisms in the aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage population. 23058564_A significant difference existed between migraineurs & controls with AA genotype vs. AG+GG. Pooled relative risk with fixed effect was 4.04. This meta-analysis suggests a significant association between EDNRA -231G>A polymorphism and migraine. 23217151_Genetic deletion of a nephron-specific endothelin A receptor causes very modest fluid retention that does not alter arterial pressure, nor doea it play a major role in regulating sodium excretion or systemic hemodynamics. 23233754_Right ventricular hypertrophy myocardial endothelin type A receptor level is increased compared to nonhypertrophied right ventricular endothelin receptor level. 23384184_EDNRA mRNA expression was increased in reflux esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus compared to controls. 23436727_C-terminus of ETA/ETB receptors regulate endothelin-1 signal transmission. 23515723_The presence ETr-A and ETr-B in rheumatic mitral valves suggests its interaction with the system of c endothelins, particularly ETr-B detected in a greater proportion, which could explain the lack of expression of endothelin in rheumatic mitral valve. 23683481_the positive correlation between ET-1 and ETAR in lesional compared with perilesional normal epidermis suggest an important role of this receptor in vitiligo. 23754170_Mutation of EDNRA is involved in ACTH-independent macronodular adrenal hyperplasia. 23818293_ETAR overexpression promoted colon cancer liver metastases. 23987636_ETAR and CXCR4 expression levels are potential prognostic biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. 24064210_Desensitization and internalization of endothelin receptor A: impact of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2)-mediated phosphorylation. 24291390_no association between Graves' disease and genetic polymorphism 24332749_In thyroid cancer, endothelin 1 and endothelin receptor A are associated with growth in advanced stages and lymph node metastases, likely through known angiogenic linkages. 24570333_Polymorphisms of EDNRA have been associated with the development of group I pulmonary hypertension, dilated cardiomyopathy and essential hypertension 24582810_The aim was to quantify the density of ETA and ETB receptors in cardiopulmonary tissue from pulmonary arterial hypertension patients and the monocrotaline (MCT) rat. 24612997_findings suggest a role for agonistic autoantibodies-induced activation of immune cells mediated by the AT1R and the ETAR in the pathogenesis or even the onset of systemic sclerosis 24627317_Report serum levels ETAR autoantibodies in peripheral arterial disease. 24633486_effect of SNP polymorphisms of EDN1, EDNRA, and EDNRB gene on ischemic stroke 24815860_no significant association between EDNRA (C+70G, G-231A) allele and Hashimoto's thyroiditis in Turkish population; this polymorphism relates to decreased risk for early disease onset 24856242_Data suggest that subjects with metabolic syndrome in association with overweight/obesity exhibit higher vasoconstrictor tone than normal weight subjects; enhanced vasoconstrictor activity is mediated via endothelin-1/endothelin A receptor signaling. 24958810_genetic association study in population in India: Data suggest that (in addition to mutations in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) an SNP in EDNRA (rs5335) is associated with congenital absence of vas deferens in population studied. 25048859_role of ET-1/ETR-A signalling in Gd-induced fibrosis and calcification in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis 25056169_Suggest a functional link between endothelin receptor autoantibody formation and down-regulated midkine serum levels, that may be relevant in the pathogenesis of clinically relevant peripheral artery occlusive disease. 25194819_These results indicate a novel function for Galphas signaling in ET-1/ETAR-mediated ovarian cancer oncogenesis. 25225183_significant single nucleotide polymorphism associations with birth weight near coding regions for two genes involved in oxygen sensing and vascular control, PRKAA1 and EDNRA, respectively, were identified. 25377471_our findings reveal the existence of a novel mechanism by which ETAR/beta-arr1 signaling is integrated with the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to sustain chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer, and they offer a solid rationale for clinical evaluation 25381251_Data show that upon endothelin-1 (ET-1) stimulation, ET type A receptor (ETAR) is recycled back to plasma membrane, whereas ET type B receptor (ETAR) is targeted to lysosome for degradation. 25424718_Genebased analyses revealed associations of the EDNRA gene with longitudinal Blood Pressure phenotypes, associations with essential hypertension, Blood Pressure salt sensitivity, preeclampsia, or preclinical stages of atherosclerosis. 25772936_Mutations in the endothelin receptor type A cause mandibulofacial dysostosis with alopecia. 25801761_Plasma proET-1 levels increase in CKD and may be useful biomarkers of renal injury. Increases in response to endothelin A antagonism may reflect EDN1 upregulation, which may partly explain fluid retention with these agents. 25946671_Endothelin receptor A was detected in all patients with squamous cell carcinoma and psoriasis, with a higher frequency and grade of expression than controls and basal cell carcinoma. 26176954_Ednra, encoding Endothelin receptor A (ETA)-the target of Endothelin 1 (ET-1)-was significantly increased in Systemic Capillary Leak Syndrome blood-outgrowth endothelial cells compared to healthy controls. 26357964_Data show that macitentan interferes with the profibrotic action of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), blocking the endothelin receptor type A (ET-1 receptor) portion of the ET-1/TGF-beta receptor complex. 26522724_Data show that endothelin A receptor drives invadopodia function by direct interaction of beta-arrestin-1 (beta-arr1) with Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) 11 protein (PDZ-RhoGEF). 26675258_High ETAR expression is associated with ovarian carcinoma. 26773103_Patients with lung fibrosis and patients with high modified Rodnan skin score showed a reduced endothelin 1 Type A receptor (ETAR)/ETBR ratio. 26874031_presence of ET-1 receptors in the chronic thrombus in proximal CTEPH suggests ET-1 could act not only on the distal vasculopathy in the unobstructed vessels but may also stimulate smooth muscle cell proliferation within chronic clot 27072656_Data show that auriculo-condylar syndrome (ACS)-associated mutations in G protein subunit alpha i3 (GNAI3) produce dominant-negative Galpha(i3) mutant proteins that couple to endothelin type A receptor (ET(A)R). 27367030_endothelin-A receptor-activated ABCB1 expression has a role in nintedanib resistance in FGFR1-driven small cell lung cancer 27422754_Data suggest that TNFalpha (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) induces proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells via ET1 (endothelin-1), GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), and IL6 (interleukin 6) signaling; ET1 induces cell proliferation via ETAR (endothelin receptor type A); ETBR (endothelin receptor type B) is up-regulated by TNFalpha and appears to mediate ET1 effects on cell proliferation. 27777505_Polymorphic variants of endothelin EDN (K198N) and endothelin receptor type A genes EDN RA (C1222T, C70G, G231A) affected ET plasma concentrations. There was no association between the plasma endothelin levels and the risk factors for normal tension glaucoma. 27876299_The interaction between stages of essential hypertension and risk factors with the polymorphism H323H of the receptor gene A ET-1 (ETRA) was analyzed. For the H323H polymorphism, images showed a higher frequency of dilations of left auricular and auricular fibrillation (P=.03) in the T/T carrier. A higher frequency of cardiomegaly was detected in C/C patients. The T/T genotype may indicate worse outcome. 27899487_Increased circulating Edn1 and expression of Ednra in endothelial cells are characteristic of diabetic kidney disease. 28095606_ETA and ETB receptors are present in human haemorrhoids with ETB receptors predominating 28249901_ETAR stimulation acted via downstream G-protein Galphaq/11 and Rho GTPase to suppress the Hippo pathway, thus leading to YAP/TAZ activation, which was required for ETAR-induced tumorigenesis. Overall, these results indicate a critical role of the YAP/TAZ axis in ETAR signaling 28548598_Common endothelin SNPs were found to be associated with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) and its sequelae. The T allele of the END1 T/G SNP (rs1800541) was associated with aSAH. The G allele of the EDNRA G/C SNP (rs5335) was associated with clinical vasospasm. 28606962_In control arteries, ETAR was expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells in the media whereas ETBR was hardly detected. In giant cell arteritis, both ETAR and ETBR receptors were expressed by alphaSMA-positive cells at the intima-media border. Endothelial cells and inflammatory cells also expressed both ET receptors. 28732172_Endothelin-1 possesses an anti-apoptotic effect in vascular endothelial cells and this effect is mediated, to a great extent, via the activation of EDNRB, with a minor contribution via activation of EDNRA. 29064794_There is no association between the C+70G polymorphism of the EDNRA gene and the development of ischemic atherothrombotic stroke. 29097630_Subjects with either TC or CC genotypes at rs5333 exhibited significantly greater increases in brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity with age 29272493_High ETAR expression is associated with Colitis-Associated colon Cancer. 29286062_miR200c regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells through the downregulation of EDNRA expression. 29696364_Presence of SST5, CXCR4 and ETA on tumor cells and of SST3, CXCR4 and ETA on microvessels gradually increased from grade II to grade IV tumors. 29849817_No link between EDNRA rs5335 and large artery stroke risk in a Ukrainian population was found. 29999581_fluctuations in ovarian hormones modulate ETBR and ETAR responses in young women. 30384975_our results suggest a role for Ednra in Hoxa9/Meis1-driven leukemogenesis. 30411193_The GG genotype of EDNRA + 70 SNP was associated with threefold increased papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) risk (p = 0.01), and the combined CG + GG genotype was 2.48 fold higher among PTC patients compared to controls. The variant EDNRA - 231 allele was overrepresented in PTC patients according to controls (p = 0.05). 30672385_The ENDRA rs5333 gene polymorphism may be associated with genetic predisposition to steroid resistance in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome Egyptian children 30937921_The findings suggest that ETAR expression, as detected by Immunohistochemical staining, could be useful as a molecular marker to predict prognosis for gastric cancer patients. 31106465_Endothelins and their receptors in embryo implantation. 31150867_These findings support the important role of EDNRA and EDNRB polymorphisms in intracerebral hemorrhage, and suggest that they do not interact with blood pressure levels on altering intracerebral hemorrhage risk. 31295611_In this systematic review, the genetic variant of EDNRA, rs6841581, was significantly associated with increased risk of intracranial aneurysm. 31661578_Effects of genotype on TENS effectiveness in controlling knee pain in persons with mild to moderate osteoarthritis. 31705661_The role of endothelin A receptors in peripheral vascular control at rest and during exercise in patients with hypertension. 32133772_Loss-of-function of Endothelin receptor type A results in Oro-Oto-Cardiac syndrome. 32431219_Homology modeling, molecular dynamics and virtual screening of endothelin-A receptor for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. 32496159_Diabetes-related sex differences in the brain endothelin system following ischemia in vivo and in human brain endothelial cells in vitro. 32744876_Endothelin receptor heteromerization inhibits beta-arrestin function in HEK293 cells. 34165174_Endothelin-1 induces changes in the expression levels of steroidogenic enzymes and increases androgen receptor and testosterone production in the PC3 prostate cancer cell line. 34757123_Non-HLA antibodies targeting angiotensin II Type 1 receptor and endothelin-1 Type A receptors induce endothelial injury via beta2-arrestin link to mTOR pathway. 35043642_Association of polymorphisms in endothelin-1 and endothelin receptor a genes with vasovagal syncope. 36179900_Gender differences in genotypic distribution of endothelin-1 gene and endothelin receptor A gene in pulmonary hypertension associated with rheumatic mitral valve disease. 36384316_Endothelin A receptors contribute to senescence of brain microvascular endothelial cells. 36430296_High Glucose-Induced Cardiomyocyte Damage Involves Interplay between Endothelin ET-1/ETA/ETB Receptor and mTOR Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000031616 |
Ednra |
127.840214 |
0.3102779077 |
-1.688367 |
0.183319056 |
84.566070 |
0.00000000000000000003715876435952129644750633356688073664455576199975226877377648682099220422969665378332138061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000331397801780383258582473392072245573420018771857901247399058597409293724922463297843933105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.8412644 |
7.4274588 |
200.5258374 |
15.7502164 |
| ENSG00000151702 |
2313 |
FLI1 |
protein_coding |
Q01543 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcriptional activator (PubMed:24100448, PubMed:26316623, PubMed:28255014). Recognizes the DNA sequence 5'-C[CA]GGAAGT-3'. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24100448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26316623, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28255014}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor containing an ETS DNA-binding domain. The gene can undergo a t(11;22)(q24;q12) translocation with the Ewing sarcoma gene on chromosome 22, which results in a fusion gene that is present in the majority of Ewing sarcoma cases. An acute lymphoblastic leukemia-associated t(4;11)(q21;q23) translocation involving this gene has also been identified. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:2313; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; blood circulation [GO:0008015]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; hemostasis [GO:0007599]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12359731_role in regulating megakaryocyte-specific glycoprotein VI promoter 12724402_Fli-1 and GATA-1 work together to activate the expression of genes associated with the terminal differentiation of megakaryocytes 12739001_overexpression of this protein affects cell growth and differentiation of K562 cells 12875977_This study supports the role of Fli1 as a suppressor of collagen transcription in human skin in vivo. 14534527_FLI1 interacts with EWS and their oncogenic fusion protein. 15021903_oncogenic rearrangement of EWS to produce EWS/Fli-1 may enhance the antiapoptotic effect of Brn-3a and inhibit its ability to promote neuronal differentiation. 15232614_Overoverexpression of FLI1 in patient CD34(+) cells restores the megakaryopoiesis in vitro, indicating that FLI1 hemizygous deletion contributes to Paris-Troudeau syndrome hematopoietic defects. 15273724_Ability of Ewing Sarcoma-Fli-1/Fli-1 to target transcriptional cofactor(s) and modulate apoptotic pathways may be responsible for its antiapoptotic and tumorigenic activities. 15282325_These findings identify the repression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 gene by EWS/FLI-1 as a key event in the development of Ewing's sarcoma. 15798196_Two functional NLSs were shown to exist in Fli-1; each NLS is sufficient to target Fli-1 to the nucleus for activation of megakaryocyte-specific promoters. 15809330_Protein phosphatase 2A controls FLI-1 phosphorylation. Newly synthesized FLI-1 decreased during human T cell activation. Although the FLI-1 & ERG genes are highly homologous, their distinct properties may contribute to different roles in gene regulation. 15919668_EWS-Fli1 may play a role in the regulation of PDGF-induced tumor proliferation-signaling enzymes via PLD2 expression in Ewing sarcoma cells 16148010_the repressive properties of PIASxalpha/ARIP3 require its physical interaction with FLI-1, identifying PIASxalpha as a novel corepressor of FLI-1 16802366_The signal transduction leading to the systemic sclerosis (SSc) fibrotic phenotype appears to converge on DNA methylation and histone deacetylation at the FLI1 gene. 16829517_Fli1 and Ets1 have roles in the pathological extracellular matrix regulation during fibrosis and cancer 16930139_Fli-1 is rather constitutively expressed by bone marrow cells in Ph(-) CMPD independent of the underlying JAK2 status 16964281_EWS/Fli-1 and Fli-1 increase PLD2 gene expression by binding to an erythroblast transformation-specific domain of PLD2 promoter 17114343_The gene that was most reproducibly up-regulated by EWS/FLI was NR0B1. 17163154_variation in overall gene expression patterns downstream of EWS-FLIl was observed, but also differential regulation of directly EWS-FLI1-bound genes 17727680_results suggest that Fli-1 contributes to the malignancy of human breast cancer by inhibiting apoptosis through upregulated expression of the bcl-2 gene. 17884818_PCAF-dependent acetylation of lysine 380 abrogates repressor function of Fli1 with respect to collagen expression; TGFb-dependent acetylation of Fli1 may represent the principal mechanism for TGFb-induced dissociation of Fli1 from the collagen promoter 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18414662_EWS/FLI mediates transcriptional repression via NKX2.2 during oncogenic transformation in Ewing's sarcoma 18648544_IGF1 is a common target gene of Ewing's sarcoma fusion proteins EWS-FLI-1, EWS-ERG and FUS-ERG in mesenchymal progenitor cells 18785112_Expression of Fli-1 in malignant melanoma appears to be associated with biologically more aggressive tumors. 19158279_The phosphorylation-acetylation cascade triggered by PKC delta represents the primary mechanism whereby TGF-beta regulates the transcriptional activity of Fli1 in the context of the collagen promoter. 19349856_report FLI-1 expression in an expanded series of 75 cases of T-cell lymphoma and found high expression in anaplastic large cell lymphoma and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma 19417137_Interaction between EWSR1/FLI1 and EWSR1 in Ewing sarcoma may induce mitotic defects leading to genomic instability and subsequent malignant transformation. 19829305_The mouse (Fli1) and human Fli1 genes are similarly regulated by Ets factors in T cells. 19859563_GLI1 is a central mediator of EWS/FLI1 signaling in Ewing tumors 20019092_EWS/FLI1 inhibits both DKK-1 expression as well as beta-catenin/TCF-dependent transcription, which could contribute to progression of tumours of the Ewing family. 20103643_Findings suggest that EWS/FLI1 induces apoptosis, at least partially, through the activation of CASP3. 20228226_persistently reduced levels of Fli1 in endothelial cells may play a critical role in the development of SSc vasculopathy 20308669_Intensive treatment protocols for localized Ewing family sarcoma have erased the clinical differences observed in patients with EWS-FLI1/ERG fusions. 20308673_Propsectively evaluated the impact of EWS-FLI1/ERG fusions on disease progression in Ewing's sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20382729_EWS-FLI-1 and miRNA-145 function in a mutually repressive feedback loop and identify their common target gene, SOX2, in addition to miRNA145 itself, as key players in Ewing sarcoma family tumors cell differentiation and tumorigenicity 20665663_These results demonstrate that EWS-FLI blocks the ability of Runx2 to induce osteoblast specification of a mesenchymal progenitor cell. 20676125_a self-sustaining triad of LMO2/ERG/FLI1 stabilizes the expression of important mediators of the leukaemic phenotype such as 20879862_The rapid downregulation of FLI-1 expression after LPS stimulation attenuates the induction of various MMPs and IL-10 under inflammatory conditions. 20933505_these results suggest that suppression of FOXO1 function by EWS-Fli1 fusion protein may contribute to cellular transformation in Ewing's family tumors. 21087477_study demonstrates that a GA(n) microsatellite in the human Fli1 promoter is highly polymorphic 21321929_these results demonstrate that in SSc fibroblasts, c-Abl is an upstream regulator of the profibrotic PKCdelta/phospho-Fli-1 pathway, via induction of PKCdelta nuclear localization. 21451544_a role of Fli1 as a negative regulator of the estrogen receptor alpha gene in dermal fibroblasts. 21571218_The genome-wide binding sites for the FLI1 in primary human megakaryocytes to identify the essential regulator of complex mammalian differentiation processes. 21633373_we have demonstrated association between FLI1 and susceptibility to CL caused by L. braziliensis. 21643012_a novel oncogenic mechanism in Ewing sarcoma, involving post-transcriptional derepression of IGF signaling by the EWS/Fli1 fusion oncoprotein via miRs 21917756_FLI1 expression is frequently abnormal and prognostically adverse in acute myeloid leukemia. 21931859_Expression of FLI-1, ELF-1, and GABP activated the PF4 promoter in HepG2 cells. 22081504_FLI1 is a novel ETS transcription factor involved in gene fusions in prostate cancer and that intratumor genetic heterogeneity of ETS rearrangements can occasionally be found in index primary tumors. 22086061_EWS-FLI chimera acquired chromatin-altering activity, leading to mistargeting, chromatin disruption, and ultimately, transcriptional dysregulation. 22372906_Data show there are no differences in the distribution of immunohistochemical reactivity for CD31, CD34, D2-40, or FLI1 between AIDS-related and non-AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma (KS) or between nodular- and patch/plaque-stage KS. 22887642_Our findings of SNP array adn phenotype correclation do not support the traditional view that FLI1 deletion is the cause of thrombocytopenia in Jacobsen syndrome. 22930730_We found that transcriptional activation of PRKCB was directly regulated by the chimeric fusion oncogene EWSR1-FLI1 that drivesewing sarcoma growth. 22965552_In 5q- syndrome, but not Diamond-Blackfan anemia, blood & bone marrow mononuclear cells had high Fli1 mRNA levels. This protects megakaryocytic cells from ribosomal stress & permits effective though dysplastic megakaryopoiesis. 23041765_Ciprofloxacin has antifibrotic actions in Systemic sclerosis dermal and lung fibroblasts via the downregulation of Dnmt1, the upregulation of Fli1. 23145994_Data suggest that the junction region can be exploited further as target for drug development in future to specifically target EWS-FLI1 in Ewing's Sarcoma. 23165331_these results fill a gap in the literature: the confirmation that MCC is devoid of the EWS/FLI-1 rearrangement. 23178492_The results demonstrate that a previously less-well characterized transcriptional repressive function of the EWS/FLI fusion is also required for the transformed phenotype of Ewing sarcoma. 23327922_Transcriptional regulators cooperate to establish or maintain primitive stem cell-like signatures in leukemic cells. 23441188_Genomic EWS-FLI1 fusion sequences in Ewing sarcoma resemble breakpoint characteristics of immature lymphoid malignancies. 23518636_Podoplanin and Fli-1 immunohistochemistry may be useful in distinguishing atypical fibroxanthoma from angiosarcoma. 23663495_Fli1 and CTGF are important mediators of the fibrogenic actions of adenosine 23667468_a novel function for Fli-1 in T cell development and leukaemogenesis 23774214_Overexpression of the ETS-related transcription factor ETV1 can initiate neoplastic transformation of the prostate. 23926301_these data identify the 11q24.3 gain as a recurrent lesion in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma leading to ETS1 and FLI1 deregulated expression, which can contribute to the pathogenesis of this disease 23940108_Results show that EWSR1/FLI1 binding independent of E2F3 is predominantly associated with repressed differentiation genes. Thus, EWSR1/FLI1 appears to promote oncogenesis by simultaneously promoting cell proliferation and perturbing differentiation. 24058639_these results indicate that under quiescent conditions Fli1 recruits HDAC1/p300 to the COL1A2 promoter and suppresses the expression of the COL1A2 gene by chromatin remodeling through histone deacetylation. 24072183_Report FLI1 expression in epithelioid sarcomas. 24100448_alterations in FLI1 and RUNX1 may be common in patients with platelet dense granule secretion defects and mild thrombocytopenia. 24124617_we detected the Ewing sarcoma-specific EWS/Fli-1 mRNA in MVs from the culture medium of Ewing sarcoma cell lines. Also, we detected this fusion gene in approximately 40% of the blood samples from mice inoculated with xenografts of TC135 or A673 cells. 24292093_Fli1 bound to the CXCL5 promoter and its gene silencing significantly suppressed the CXCL5 mRNA expression in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells 24708674_bosentan...increased DNA binding of Fli1 and the suppression of type I collagen expression in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts 24735198_Case Report: primary subcutaneous Ewing sarcoma in a 16-year-old female composed entirely of spindle cells exhibiting strong, diffuse immunohistochemical reactivity for S100 and EWSR1-FLI1 fusion. 24923303_Results show that overexpression is intimately related to malignant phenotypes and poor clinical outcome of epithelial ovarian cancer. 25057021_EWS/FLI-induced repression of alpha5 integrin and zyxin expression promotes tumor progression by supporting anchorage-independent cell growth. 25062258_p16 and possibly Fli-1 may have utility in the assignment of growth phase for cutaneous melanomas. 25379017_FLI1 levels are reduced in human breast cancer samples and cell lines.FLI1 expression is correlated with breast cancer cellular growth, migration, and invasion and altered gene expression. 25421497_endothelial CCN1 downregulation at least partially due to Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the development of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis patients 25453903_EWS-FLI1 establishes an oncogenic regulatory program governing both tumor survival and differentiation. 25472652_FLI1 promoter hypermethylation is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 25483190_The similarity among the phenotypes of EWS/FLI1- and EWS siRNA-transfected HeLa cells points to the inhibition of EWS as the key mechanism for the induction of midzone defects. 25504335_Simultaneous downregulation of KLF5 and Fli1 is a key feature underlying systemic sclerosis. 25712098_Data suggest that aberrant cell cycle activation in Ewing sarcoma is due to the de-repression of transcription factor E2F targets of transcriptional induction and physical recruitment of E2F3 by fusion protein EWS-FLI1 replacing E2F4 on their promoters. 25779942_SLFN11 has a role as a transcriptional target of EWS-FLI1 and is a determinant of drug response in Ewing sarcoma 26055516_Fli1 is epigenetically suppressed and is a potential predisposing factor in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. (Review) 26063314_Overexpression of FLI1 and ERG genes is sufficient to transdifferentiate erythroblasts to megakaryocytes that can produce functional platelets. 26122367_ERG (or FLI1 if available) is useful marker for the diagnosis of Phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors. 26156017_This study for the first time identifies FLI1 as a clinically and functionally important target gene of metastasis, providing a rationale for developing FLI1 inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer. 26159733_erythrocyte lineage enforces exclusivity through upregulation of EKLF and its lineage-specific cytokine receptor (EpoR) while inhibiting both FLI-1 and the receptor TpoR (also known as MPL) for the opposing megakaryocyte lineage 26261664_Case Report: SMARCB1-deficient vulvar sarcoma expressing ERG and FLI1. 26305602_Fli-1 expression gradually increases in parallel with disease progression. 26316623_Mutation in FLI1 is associated with Paris-Trousseau thrombocytopenia. 26317314_study shows that FLI-1 is expressed variably in different subtypes of NSCLC, and its expression is related to clinicopathologic parameters and poorer prognosis 26336820_Identify SP1 and PI3K/AKT signaling as modulators of EWS/FLI1 gene expression in tumor cell lines. 26564800_FLI1 and MMP9 position differently in prostate cancer than in normal tissue and prostate hyperplasia, whereas MMP2 is repositioned in both prostate cancer and hyperplasia. 27052461_Concurrent exogenous expression of three transcription factors, GATA1, FLI1 and TAL1, enables large-scale production of megakaryocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. 27304058_miR-145 acts as a tumor suppressor by directly reducing expression of FLI-1, and the miR-145/FLI-1 pathway is important for tumor progression in osteosarcoma 28119029_In American cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania braziliensis infection, MMP1 is regulated by factors other than FLI1, and the influence of IL-6 on MMP1 was independent of its effect on FLI1. 28134926_Study found consistent DNA hypomethylation at enhancers regulated by the disease-defining EWS-FLI1 fusion protein, thus establishing epigenomic enhancer reprogramming as a ubiquitous and characteristic feature of Ewing sarcoma. 28232470_epithelial Fli1 deficiency might be involved in the systemic autoimmunity and selective organ fibrosis in systemic sclerosis (SSc). 28248553_loss of ERG and FLI1 might contribute to the pathogenesis of vascular lung complications through the induction of inflammation. 28255014_identification of two novel FLI1 variants (c.1010G>A and c.1033A>G) responsible for macrothrombocytopenia; study provides new insights into the phenotype, pathophysiology and diagnosis of FLI1 variant-associated thrombocytopenia 28370536_These results indicate that Fli1 deficiency promotes migration, proliferation and cell survival, while abating tube formation of endothelial cells, suggesting that Fli1 deficiency is potentially attributable to the development of both proliferative obliterative vasculopathy (occlusion of arterioles and small arteries) and destructive vasculopathy (loss of small vessels) characteristic of SSc vasculopathy. 28410216_This study uncovers FLI1 as an important driving factor that promotes tumor growth in SCLC through the miR-17-92 pathway. FLI1 may serve as an attractive target for therapeutic intervention of SCLC. 28507181_CXCL6 expression is upregulated by Fli1 deficiency in fibroblasts and endothelial cells, potentially contributing to the development of fibrosis and vasculopathy in the skin, lung, and heart of systemic sclerosis. 28561686_Recent advances in biologic and genomic understanding of these two cancers has expanded the potential for therapeutic advancement and prevention. In Ewing sarcoma, directed focus on inhibition of EWSR1-FLI1 and its effectors has produced promising results. 28586009_In contrast, expression of Spi1/PU.1 in a Fli1 producing erythroleukemia cell line in which fli1 is activated, resulted in increased proliferation through activation of growth promoting proteins MAPK, AKT, cMYC and JAK2 28720588_Studies demonstrate that the translocation-derived fusion protein EF (EWS-FLI1) misregulates numerous genes involved in metabolism suggesting that EF is a master regulator of metabolic reprogramming in Ewing sarcoma, diverting metabolites toward biosynthesis. 28844694_Fusion of short fragments of EWSR1 to FLI1 is sufficient to recapitulate BAF complex retargeting and EWS-FLI1 activities; studies thus demonstrate that the physical properties of prion-like domains can retarget critical chromatin regulatory complexes to establish and maintain oncogenic gene expression programs. 29038846_Decreased serum LIF levels may be associated with vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis (SSc) and that Fli1 deficiency may contribute to the inhibition of LIF-dependent biological effects on SSc endothelial cells by suppressing the expression of LIF, LIF receptor, and gp130. 29048432_This is the first report presenting CD13 and FLI1 as important mediators of resistance to BRAF inhibition with potential as drug targets in BRAF inhibitors refractory melanoma. 29138848_Fli1 functioned as an oncogene in HCC carcinogenesis and it exerted its promoting metastatic effect primarily by modulating the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2 signaling pathway. 29141862_this paper provides a mechanistic insight into the regulation of angiogenesis by TLRs and confirm a central role of Fli1 in regulating vascular homeostasis. 29358086_TAL1 mediates the function of MEIS1 in hemogenic endothelial progenitors specification. In addition, MEIS1 is vital for megakaryopoiesis and thrombopoiesis from hPSCs. Mechanistically, FLI1 acts as a downstream gene necessary for the function of MEIS1 during megakaryopoiesis 29374149_co-activation of FLI1 and PKC could induce differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into induced endothelial cells in a fast, efficient and economic manner. 29869379_FLI-1 is a novel and an extremely useful predictor for the poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer. The modulation of FLI-1 affected the mesenchymal characteristics, which was consistent with the changes in CSC-like phenotype. FLI-1 can induce EMT by binding to the promoters of EMT-related key genes (CDH1 and VIM), sustain CSC-like properties, and influence tumorigenesis in vivo. 29898995_e describe the dependency of EWS/ETS-driven transcription upon chromatin reader BET bromdomain proteins and investigate the potential of BET inhibitors in treating EWS. EWS/FLI1 and EWS/ERG were found in a transcriptional complex with BRD4, and knockdown of BRD2/3/4 significantly impaired the oncogenic phenotype of EWS cells. RNA-seq analysis following BRD4 knockdown or inhibition with JQ1 revealed an attenuated EWS/ETS 30279318_Comparative structure analysis of the ETSi domain of ERGB and its complex with the E74 promoter DNA sequence has been presented. 30429198_This study identifies FLI1 exonic circular RNAs as a new oncogenic driver that promotes tumor metastasis through the miR584-ROCK1 pathway. Importantly, serum exosomal FECR1 may serve as a promising biomarker to track disease progression of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). 30500808_Combined knockdown of two ETS family transcription factors, ERG and FLI1, induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition coupled with dynamic epigenetic changes in endothelial cells. 30503262_the forward programming of human pluripotent stem cells through overexpression of GATA1, FLI1, and TAL1 leads to the production of a population of progenitors that can differentiate into megakaryocyte or erythroblasts. 30537986_FECR1, a circular RNA in the FLI1 promoter chromatin complex, consisting of FLI1 exons 4-2-3, acts as an upstream regulator to control breast cancer tumor growth by coordinating the regulation of DNA methylating and demethylating enzymes. 31626853_The authors demonstrate that Fli-1 is a novel upstream transcriptional activator of NANOGP8 (Nanog homeobox retrogene P8) and provide the molecular details of Fli-1-mediated NANOGP8 gene expression. 31654502_Circular RNA USP1 regulates the permeability of blood-tumour barrier via miR-194-5p/FLI1 axis. 31675985_FLI1 hypermethylation was associated with more advanced gastric cancer (GC) and liver and distant lymphatic metastasis. Also, patients with FLI1 hypermethylation in plasma samples had a significantly worse 5-year disease free survival rate than those without suggesting that FLI1 hypermethylation was an independent prognostic factor for GC. 31782787_Fli1 deficiency induces endothelial adipsin expression, contributing to the onset of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis. 31810195_Inhibition of CXCR4 did not change spheroid count, or structure. Under simulated microgravity, the tumor marker EWS/FLI1 is intensified, while targeting CXCR4, which influences adhesion proteins, did not affect spheroid formation. 31894299_FLI1 promotes protein translation via the transcriptional regulation of MKNK1 expression. 32026343_Precision medicine in Ewing sarcoma: a translational point of view. 32196848_FLI-1 mediates tumor suppressor function via Klotho signaling in regulating CRC. 32239672_MicroRNA-33b regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, and mobility via targeting Fli-1-mediated Notch1 pathway. 32249526_Characterization of the relationship between FLI1 and immune infiltrate level in tumour immune microenvironment for breast cancer. 32323788_Epigenetic control of the EWSFLI1 promoter in Ewing's sarcoma. 32673994_TRIM28/TIF1beta and Fli-1 negatively regulate peroxynitrite generation via DUOX2 to decrease the shedding of membrane-bound fractalkine in human macrophages after exposure to substance P. 32696043_Association of functional (GA)n microsatellite polymorphism in the FLI1 gene with susceptibility to human systemic sclerosis. 32979864_FLI1 and ERG protein degradation is regulated via Cathepsin B lysosomal pathway in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. 33268481_Expression of GM-CSF Is Regulated by Fli-1 Transcription Factor, a Potential Drug Target. 33275876_Allosteric interference in oncogenic FLI1 and ERG transactions by mithramycins. 33293370_Chromosomal localization of Ewing sarcoma EWSR1/FLI1 protein promotes the induction of aneuploidy. 33547282_The genome-wide impact of trisomy 21 on DNA methylation and its implications for hematopoiesis. 33717090_FLI1 Induces Megakaryopoiesis Gene Expression Through WAS/WIP-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms; Implications for Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. 33930311_STAG2 mutations alter CTCF-anchored loop extrusion, reduce cis-regulatory interactions and EWSR1-FLI1 activity in Ewing sarcoma. 34009296_ERG transcription factors have a splicing regulatory function involving RBFOX2 that is altered in the EWS-FLI1 oncogenic fusion. 34314292_Expression of Friend Leukemia Integration-1 (Fli-1) and the Apoptosis Regulator B Cell Lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) in Gastric Carcinoma; an Immunohistochemical Study. 34329586_TRIM8 modulates the EWS/FLI oncoprotein to promote survival in Ewing sarcoma. 35550257_Oncogenic chimeric transcription factors drive tumor-specific transcription, processing, and translation of silent genomic regions. 35569064_Silencing of Fli1 Gene Mimics Effects of Preeclampsia and Induces Collagen Synthesis in Human Umbilical Arteries. 35653119_EWS::FLI1 and HOXD13 Control Tumor Cell Plasticity in Ewing Sarcoma. |
ENSMUSG00000016087 |
Fli1 |
695.793419 |
0.3648431842 |
-1.454652 |
0.079643206 |
333.054018 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002077912651122497764722023507379256287786517311138979149840384446636949177302645253727931348685957040004203090015748652962884757955443827454291480960514147301881530122865369963344002110505748248669988242909312248229980468750000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000653944365257314931500148331391189691347547653646935306225246722046771669124087464493827584253014766798316413795653888086463842310892683168094216582485479664725810010450701085637364995406528578314464539289474487304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
365.3680963 |
17.8141265 |
1008.6837056 |
32.4419269 |
| ENSG00000151704 |
3758 |
KCNJ1 |
protein_coding |
P48048 |
FUNCTION: In the kidney, probably plays a major role in potassium homeostasis. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. This channel is activated by internal ATP and can be blocked by external barium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7929082}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Bartter syndrome;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Potassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. It is activated by internal ATP and probably plays an important role in potassium homeostasis. The encoded protein has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell. Mutations in this gene have been associated with antenatal Bartter syndrome, which is characterized by salt wasting, hypokalemic alkalosis, hypercalciuria, and low blood pressure. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3758; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0015272]; inward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005242]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1990573]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] |
12221079_ROMK1 is a substrate of PKC and that serine residues 4 and 201 are the two main PKC phosphorylation sites that are essential for the expression of ROMK1 in the cell surface 12381810_One disease-causing mutation in the ROMK channel truncates the extreme COOH-terminus and induces a closed gating conformation. 12589089_In a heterozgous Bartter syndrome patient, AA exchanges Arg338Stop & Met357Thr in ROMK exon 5 alter the C-terminus of the ROMK protein & can affect channel function. 15895241_Findings support the proposed role of ROMK channels in potassium recycling and in the regulation of K+ secretion and present a rationale for the phenotype observed in patients with ROMK deficiency. 15987778_NH(2)-terminal phosphorylation modifying a COOH-terminal ER retention signal in ROMK1 could serve as a checkpoint for proper subunit folding critical to channel gating. 16428287_ROMK is antagonistically regulated by long and kidney-specific WNK1 isoforms 17380208_molecular mechanism for stimulation of endocytosis of ROMK1 by WNK kinases 17401586_A novel mutation in KCNJ1 in a Bartter syndrome case diagnosed as pseudohypoaldosteronism. 18211905_CD63 plays a role in the regulation of ROMK channels through its association with RPTPalpha, which in turn interacts with and activates Src family PTK, thus reducing ROMK activity. 18391953_Members of the Framingham Heart Study were screened for variation in three genes-SLC12A3, SLC12A1 and KCNJ1 causing rare recessive diseases featuring large reductions in blood pressure. 18391953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18443236_Five polymorphisms in the KCNJ1 gene coding for the potassium channel, ROMK, showed associations with mean 24-hour systolic or diastolic blood pressure. 18443236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18550644_Multiple intra- and/or intermolecular interactions of WNK1 domains are at play for regulation of ROMK1 by WNK1 in the kidney. 18755144_These results confirm the important role of the acidic motif of WNK4 in its protein-protein interaction with the ROMK channel. 19096086_In a large cohort of ante/neonatal Bartter syndrome, deafness, transient hyperkalaemia and severe hypokalaemic hypochloraemic alkalosis orientate molecular investigations to BSND, KCNJ1 and CLCNKB genes, respectively. 19170254_hydrophobic leucines at the cytoplasmic end of the inner transmembrane helices comprise the principal pH gate of Kir1.1, a gate that can be relocated from 160-Kir1.1b to 157-Kir1.1b. 19244242_KS-WNK1 is an important physiological regulator of renal K(+) excretion, likely through its effects on the ROMK1 channel. 19272129_These results suggest that the conformation of the cytoplasmic pore in the Kir1.1 channel changes in response to pHi gating such that the N- and C-termini move apart from each other at pHi 7.4, when the channel is open. 19349416_Regulation of renal outer medullary potassium channel and renal K(+) excretion by Klotho. 19706464_c-Src inhibits SGK1-mediated phosphorylation hereby restoring the WNK4-mediated inhibition of ROMK channels thus suppressing K secretion. 19710010_POSH inhibits ROMK channels by enhancing dynamin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis and by stimulating ubiquitination of ROMK channels. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20219833_KCNJ1 mutations are associated with Bartter syndrome. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21081491_THGP modulation of ROMK function confers a new role of THGP on renal ion transport and may contribute to salt wasting observed in FJHN/MCKD-2/GCKD patients. 21355052_PI3K-activating hormones inhibit ROMK by enhancing its endocytosis via a mechanism that involves phosphorylation of WNK1 by Akt1 and SGK1. 21631963_no mutation in the KCNJ1 gene, among patients suffering from bartter and Gitelman syndromes 22907731_A KCNJ1 SNP was associated with increased FG during HCTZ treatment. 23211697_Findings suggest that 11q24 is a susceptible locus for openness, with KCNJ1 as the possible candidate gene. 23782368_Molecular analysis revealed a compound heterozygous mutation in the KCNJ1 gene, consisting of a novel K76E and an already described V315G mutation, both affecting functional domains of the channel protein. 25165391_The association between polymorphisms in KCNJ1, SLC12A1, and 7 other genes and calcium intake and colorectal neoplasia risk was studied. 25344677_knockdown of KCNJ1 in HK-2 cells promoted cell proliferation. Collectively, these data highlight that KCNJ1, low-expressed in ccRCC and associated with poor prognosis, plays an important role in ccRCC cell growth and metastasis 25805816_WNK4 is a substrate of SFKs and the association of c-Src and PTP-1D with WNK4 at Tyr(1092) and Tyr(1143) plays an important role in modulating the inhibitory effect of WNK4 on ROMK 28630040_Data suggest underlying pathology for some patients with type II Bartter syndrome is linked to stability of ROMK1 in ERAD pathway; using a yeast expression system, cells can be rescued by wild-type (rat) ROMK1 but not by ROMK1 containing any one of four mutations found in (human) type II Bartter syndrome; mutant ROMKs are significantly less stable than wild-type ROMK. (ERAD = endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) 29311259_endosomal trafficking factors CORVET and ESCRT suppress plasma membrane residence of the renal outer medullary potassium channel 29458000_The presence of ROMK protein was observed in the inner mitochondrial membrane fraction. Moreover, colocalization of the ROMK protein and a mitochondrial marker in the mitochondria of fibroblast cells was shown by immunofluorescence. 30113482_We replicated the methods in a previous study to detect rare and potentially loss-of-function variants in SLC12A3, SLC12A1, and KCNJ1 reducing blood pressure in variant carriers as compared with noncarriers using whole exome sequencing data. Our study confirmed that SLC12A3, SLC12A1, and KCNJ1 are indeed genes protective of hypertension in the general population. 31731540_Single-Channel Properties of the ROMK-Pore-Forming Subunit of the Mitochondrial ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channel. 33058840_Eight novel KCNJ1 variants and parathyroid hormone overaction or resistance in 5 probands with Bartter syndrome type 2. 33444624_Solubilization, purification, and functional reconstitution of human ROMK potassium channel in copolymer styrene-maleic acid (SMA) nanodiscs. |
ENSMUSG00000041248 |
Kcnj1 |
8.526618 |
0.0536875177 |
-4.219269 |
0.893880017 |
29.961090 |
0.00000004408034305845166759997764385943519460653305941377766430377960205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000179681265822354762593952891627790968698263895930722355842590332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7765197 |
0.4836187 |
14.6463008 |
3.5256736 |
| ENSG00000151718 |
80014 |
WWC2 |
protein_coding |
Q6AWC2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WW-and-C2-domain-containing family of proteins. Members of this family have two N-terminal WW domains that mediate binding to target proteins harboring L/PPxY motifs, an internal C2 domain for membrane association, and C-terminal alpha protein kinase C binding sites and class III PDZ domain-interaction motifs. Proteins of this family are able to form homo- and heterodimers and to modulate hippo pathway signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:80014; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; negative regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035331]; negative regulation of organ growth [GO:0046621]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035330] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28815883_WWC2 functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating the Hippo signaling pathway and may serve as a prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32623387_miR-21-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting WWC2. |
ENSMUSG00000031563 |
Wwc2 |
433.549678 |
2.2215447159 |
1.151563 |
0.129162603 |
78.505892 |
0.00000000000000000079759996651171933078147856963224806195845543400273040812731295545745524577796459197998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000006696573097675186061345427888414701407920248098915158227462107731753349071368575096130371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
611.2853820 |
47.5309242 |
277.2660275 |
16.1266181 |
| ENSG00000151743 |
196394 |
AMN1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IY45 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be part of SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:196394; |
microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] |
Mouse_homologues 17971504_C730024G19Rik is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. |
ENSMUSG00000068250 |
Amn1 |
87.193064 |
2.4785266582 |
1.309483 |
0.195149187 |
44.854897 |
0.00000000002121894979658552450615074336573022710170088878101068985415622591972351074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000115271144275893395801708076884217659546782996926594933029264211654663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
114.7118507 |
13.8994919 |
46.5823273 |
4.3434747 |
| ENSG00000151790 |
6999 |
TDO2 |
protein_coding |
P48775 |
FUNCTION: Heme-dependent dioxygenase that catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of the L-tryptophan (L-Trp) pyrrole ring and converts L-tryptophan to N-formyl-L-kynurenine. Catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of the indole moiety. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25066423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27762317, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28285122}. |
3D-structure;Dioxygenase;Disease variant;Heme;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Tryptophan catabolism |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-tryptophan degradation via kynurenine pathway; L-kynurenine from L-tryptophan: step 1/2. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03020, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25066423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27762317}. |
This gene encodes a heme enzyme that plays a critical role in tryptophan metabolism by catalyzing the first and rate-limiting step of the kynurenine pathway. Increased activity of the encoded protein and subsequent kynurenine production may also play a role in cancer through the suppression of antitumor immune responses, and single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with autism. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:6999; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; amino acid binding [GO:0016597]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxygen binding [GO:0019825]; tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0004833]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; response to nitroglycerin [GO:1904842]; tryptophan catabolic process to acetyl-CoA [GO:0019442]; tryptophan catabolic process to kynurenine [GO:0019441] |
11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12634647_The activity and mRNA expression level of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in term placentas were significantly lower in preeclampsia. Could cause dysregulation of inflammatory response intrinsic to normal pregnancy. 14755447_Polymorphism of tryptophan 2,3 dioxygenase gene is associated with autism. 15390107_We found that astrocytes, neurons, and microglia expressed IDO but only microglia were able to produce detectable amounts of quinolinic acid. However, astrocytes and neurons had the ability to catabolize quinolinic acid. 18370401_significant mechanistic differences exist across the heme dioxygenase family, and the data are discussed within this broader framework 19218188_The tyrosine 42 of recombinant human TDO is responsible for the cooperative binding of l-Trp by participating in the active site of the adjacent subunit. 19502010_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19637229_TDO mediates antimicrobial and immunoregulatory effects. TDO-dependent inhibition of T-cell growth might be involved in the immunotolerance observed in vivo during allogeneic liver transplantation. 20361220_subtle differences between the TDO and IDO reactions 21361337_Studies indicate that the heme dioxygenases are differentiated by their ability to catalyze the oxidation of l-tryptophan to N-formylkynurenine. 21892828_The data suggest that TDO uses a ring-opening mechanism during N-formylkynurenine formation, rather than Criegee or dioxetane mechanisms as previously proposed. 22082147_Data suggest that T342 in hTDO has critical role in controlling substrate binding, substrate stereoselectivity, H-bonding interaction between enzyme and intermediates, and regulating the dynamics of protein structure. 23558111_Identification of 12 polymorphisms in the human TDO2 promoter region, 2 of them corresponding to previously unknown single-nucleotide polymorphisms and 3 of them located in putative glucocorticoid-responsive elements. 23630570_TDO is highly expressed in the brains of Alzheimer disease patients. 24974860_IL-1beta is suggested to stimulate tryptophan catabolism and production of IL-6 and IL-8 by increasing TDO expression in endometriosis. 25066423_Crystal tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase structure revealed eight residues playing critical roles in L-tryptophan oxidation. 27563172_the potent antimicrobial as well as immunoregulatory effects of TDO were substantially impaired under hypoxic conditions that pathophysiologically occur in vivo. This might be detrimental for the appropriate host immune response towards relevant pathogens. 27578919_High TDO2 expression is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 28223212_Study demonstrated that n-butylidenephthalide (n-BP)functions by regulating the early part of the kynurenine pathway through the downregulation of tryptophan 2, 3-dioxygenase (TDO2), which decreases the downstream neurotoxic product, quinolinic acid (QA). Findings indicate a correlation between n-BP, TDO2, QA, calpain, and toxic fragment formation. 29676849_HOXC10 directly binds to the PD-L2 and TDO2 promoter regions thus stimulating proliferation, invasion and induction of immunosuppressive gene expression in glioma. 30134247_TDO2 overexpression was related to poor prognosis and associated with cancer cell proliferation and tumor stem cells in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 31806639_Tryptophan 2,3-Dioxygenase Expression Identified in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and in Intratumoral Pericytes of Most Cancers. 31866995_Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1alpha Inhibits the Expression of Immunosuppressive Tryptophan-2,3-Dioxygenase in Glioblastoma. 32165090_Gene expression of indoleamine and tryptophan dioxygenases and three long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. 32296044_Both IDO1 and TDO contribute to the malignancy of gliomas via the Kyn-AhR-AQP4 signaling pathway. 32776284_Different effects of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase inhibition on SK-Mel-28 and HCT-8 cancer cell lines. 33846800_Tryptophan 2, 3dioxygenase promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. 34051337_TDO2 knockdown inhibits colorectal cancer progression via TDO2-KYNU-AhR pathway. 34101386_TDO2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis, cancer stemness, and resistance to cetuximab in bladder cancer. 34423034_TDO2 Was Downregulated in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Inhibited Cell Proliferation by Upregulating the Expression of p21 and p27. 34520819_IDO1/TDO dual inhibitor RY103 targets Kyn-AhR pathway and exhibits preclinical efficacy on pancreatic cancer. 34714577_Stemness and immune evasion conferred by the TDO2-AHR pathway are associated with liver metastasis of colon cancer. 34943977_Immuno-Metabolic Modulation of Liver Oncogenesis by the Tryptophan Metabolism. 34969166_Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase 2 plays a key role in regulating the activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in autoimmune arthritis. 35056756_MiR-126-5p Promotes Tumor Cell Proliferation, Metastasis and Invasion by Targeting TDO2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 35733134_High levels of TDO2 in relation to pro-inflammatory cytokines in synovium and synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis. 35970080_Tryptophan degradation enzymes and Angiotensin (1-7) expression in human placenta. |
ENSMUSG00000028011 |
Tdo2 |
763.443471 |
11.6299792769 |
3.539777 |
0.092482369 |
1608.705251 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1408.1933883 |
73.9749948 |
121.8786906 |
5.8547090 |
| ENSG00000151835 |
26278 |
SACS |
protein_coding |
Q9NZJ4 |
FUNCTION: Co-chaperone which acts as a regulator of the Hsp70 chaperone machinery and may be involved in the processing of other ataxia-linked proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19208651}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Neurodegeneration;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes the sacsin protein, which includes a UbL domain at the N-terminus, a DnaJ domain, and a HEPN domain at the C-terminus. The gene is highly expressed in the central nervous system, also found in skin, skeletal muscles and at low levels in the pancreas. This gene includes a very large exon spanning more than 12.8 kb. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS), a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by early-onset cerebellar ataxia with spasticity and peripheral neuropathy. The authors of a publication on the effects of siRNA-mediated sacsin knockdown concluded that sacsin protects against mutant ataxin-1 and suggest that 'the large multi-domain sacsin protein is able to recruit Hsp70 chaperone action and has the potential to regulate the effects of other ataxia proteins' (Parfitt et al., PubMed: 19208651). A pseudogene associated with this gene is located on chromosome 11. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:26278; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell body fiber [GO:0070852]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; Hsp70 protein binding [GO:0030544]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; proteasome binding [GO:0070628]; negative regulation of inclusion body assembly [GO:0090084]; protein folding [GO:0006457] |
11788093_Report of a reliable and inexpensive method to detect more than 95% of the ARSACS disease alleles. 14718706_The authors report a new mutation (1859insC), leading to a frameshift with a premature termination of the gene product sacsin, in two sisters from consanguineous parents. The phenotype is similar to previously described patients with ARSACS 14718707_The authors identified three new SACS mutations in two Italian patients whose phenotype closely matches that of Quebec cases, but without retinal striation. 14718708_A homozygous missense mutation (T7492C) in the SACS gene, which resulted in the substitution of arginine for tryptophan at amino acid residue 2498 (W2498R) was identified in two sibling Japanese early onset spastic ataxia patients 15156359_analysis of SACS mutations in autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay families 15985586_The authors describe two Japanese siblings with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay without spasticity, usually a core feature of this disorder. They had a novel homozygous missense mutation (T987C) of the SACS gene. 16198375_The authors report here identical twin sisters with novel compound heterozygous mutations (c.[2951_2952delAG]+[3922delT]) in the SACS gene. 16606928_Japanese autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS) patient with a compound heterozygous mutation in a new exon of the SACS gene. 17290461_report of Japanese siblings with a new missense mutation (C922T, L308F) in exon 7 of SACS 17716690_We describe four patients in a Belgian family with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (ARSACS). A novel homozygous missense mutation of the SACS gene was identified in the present family. 17853117_As more SACS mutations are identified worldwide, the clinical spectrum of 'sacsinopathies' will expand 18398442_Both point mutation and deletion associated with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. 18465152_In a Dutch cohort of 43 index patients with ataxia onset before age 25, we identified 16 index patients (total 23 patients) with mutations in the SACS gene. Nine of them had homozygous mutations, and seven of them had compound heterozygous mutations. 18484239_The authors report a clinical and genetic analysis of a Japanese family with ARSACS with novel compound heterozygous mutations in the SACS gene (N161fsX175, L802P). The phenotype is similar to that of previously reported ARSACS patients. 19031088_Results report the identification of an unconventional SACS mutation, a large-scale deletion sized approximately 1.5 Mb encompassing the whole gene, in two unrelated patients. 19880797_Compares the GHKL-type-ATPase domain of this human protein to that of related plant, protozoan, yeast and bacterial proteins. 19892370_Our results expand the genotype phenotype correlation of mutations in the sacsin gene in ataxia patients 20488193_These data indicate that sacsin repeating regions necessitate nucleotide hydrolysis for their function, provided by the common Hsp90 ATPase domain, which may give rise to a novel activity related to protein quality control. 20852969_Data show that uniparental isodisomy of the paternal chromosome 13 carrying the mutated SACS gene played an etiologic role in a case of the disease. 20876471_This study, author enlargeg the ARSACS phenotype and the underlying genetic spectrum of SACS mutations. Patients with ARSACS are more common than previously known and risk underdiagnosis due to late onset age and unusual presentation. 21507954_novel insights into the oligomerization state of sacsin and functions that are lost in mutations that cause ARSACS. 21745802_This study demonistrated that Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay with compound heterozygotes for nonsense mutations of the SACS gene. 22751902_Novel compound heterozygous frameshift mutations were detected in the SACS gene in two siblings with a sensorimotor neuropathy, ataxia, and spasticity 22805644_we describe two unrelated Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix Saguenay patients from central Italy carrying two novel mutations in SACS 22816526_This study demonistrated that 16 novel SACS gene mutations in recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay showed Supratentorial and pontine abnormalitie. 23043354_We identified a new mutation in the SACS gene in Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia 23280630_the relative position of mutations in subrepeats will variably influence sacsin dysfunction 23338241_A novel missense mutation in sacsin, p.Arg272His, was identified in a patient with sacsin-related spastic ataxia. 23598833_Widespread tissue damage may be associated with extensive loss of sacsin protein in the brain and may explain a wide range of progressive neurologic abnormalities in patients with spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. 23800155_study reports an Italian family affected by an autosomal recessive form of hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) and peripheral neuropathy caused by a novel mutation in the SACS 24164681_To clarify the segregation pattern of the mutations found in this family, having excluded somatic mosaicism for the specific mutations, we fully reanalyzed the SACS gene 24180463_Whole-exome sequencing identified a hemizygous novel spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay (SACS) stop-codon mutation in 2 brothers 24457356_Abnormal retinal thickening is a common feature in patients with SACS mutation phenotype. 26288984_Various SACS mutations have functional consequences on the mitochondrial compartment in ARSACS patients. 26366743_The results are consistent with the HEPN domain contributing to the functional activity of sacsin by binding to nucleotides or other multiply charged anionic compounds in neurons. 27133561_the twins described by Fitzsimmons had heterozygous mutations in the SACS gene, the gene responsible for autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix Saguenay as well as a heterozygous mutation in the TRPS1, the gene responsible in Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1A TBL1XR1 mutation was identified in the patient described in 2009 as contributing to his cognitive impairment and autistic features.. 27601211_We established a genetic diagnosis in six families with autosomal recessive HSP (SPG11 in three families and TFG/SPG57, SACS and ALS2 in one family each). A heterozygous mutation in a gene involved in an autosomal dominant HSP (ATL1/SPG3A) was also identified in one additional family 28658676_This study provides a potential genetic diagnosis for the patient and expands the spectrum of SACS mutations. 28843771_we present the first Polish family with a comprehensive clinical and neuropsychological assessment, harboring two novel mutations in the SACS gene 29449188_Novel homozygous variants in ATCAY, MCOLN1, and SACS in a complex movement disorder in five consanguineous Pakistani families. 29945973_The Sr1 structure reveals that ARSACS-causing missense mutations (R272H, R272C, and T201K) disrupt protein folding, most likely leading to sacsin degradation. This work lends structural support to the view of sacsin as a molecular chaperone and provides a framework for future studies of this protein. 30098244_The c.5236dupA (p.T1746fs) and c.13085T to G (p.I4362R) mutations of the SACS gene probably underlie spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay 30332300_Loss of SACSIN expression is associated with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of the Charlevoix-Saguenay. 30460542_Our findings confirm the broad clinical spectrum associated with SACS mutations, including pure polyneuropathy without characteristic clinical and brain imaging manifestations of autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. 30835349_novel pathogenic mutation of the SACS gene was discovered 31701440_A novel homozygous SACS mutation identified by whole exome sequencing-genotype phenotype correlations of all published cases. 33559790_A novel SACS p.Pro4154GlnfsTer20 mutation in a family with autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay. 33746006_Autosomal recessive spastic ataxia of Charlevoix-Saguenay caused by novel mutations in SACS gene: A report of two Chinese families. 34429451_Integrative genetic, genomic and transcriptomic analysis of heat shock protein and nuclear hormone receptor gene associations with spontaneous preterm birth. 35933016_The ARSACS disease protein sacsin controls lysosomal positioning and reformation by regulating microtubule dynamics. |
ENSMUSG00000048279 |
Sacs |
255.906572 |
2.0015016188 |
1.001083 |
0.179901318 |
30.647941 |
0.00000003093547806525132759002938149898997988174187412369064986705780029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000128440972220284003418896263092052745236060218303464353084564208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
361.1967714 |
43.4992070 |
181.8861067 |
16.3378230 |
| ENSG00000151882 |
56477 |
CCL28 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRJ3 |
FUNCTION: Chemotactic activity for resting CD4, CD8 T-cells and eosinophils. Binds to CCR3 and CCR10 and induces calcium mobilization in a dose-dependent manner. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This antimicrobial gene belongs to the subfamily of small cytokine CC genes. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. The cytokine encoded by this gene displays chemotactic activity for resting CD4 or CD8 T cells and eosinophils. The product of this gene binds to chemokine receptors CCR3 and CCR10. This chemokine may play a role in the physiology of extracutaneous epithelial tissues, including diverse mucosal organs. Multiple transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:56477; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cytolysis in another organism [GO:0051715]; immune response [GO:0006955]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; negative regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903237]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584] |
12538707_CCL28 may play dual roles in mucosal immunity as a chemoattractant for cells expressing CCR10 and/or CCR3 such as plasma cells and also as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial protein secreted into low-salt body fluids. 12671049_CCR10 and its mucosal epithelial ligand CCL28 have roles in the migration of circulating IgA plasmablasts 16433680_CCL28 produced by keratinocytes is mediated by different signal pathways from CCL27, and both CCL27 and CCL28 are involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory skin diseases. 16581045_CCL28 is one link between microbial insult and the exacerbation of pathologies such as asthma, through an NFkappaB-dependent mechanism 16785557_Expression of CCL28 by epithelial cells from chronically inflamed liver in response to microbial products or interleukin-1 provides a signal to localize CCR10-expressing regulatory T cells at mucosal surfaces. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17912348_CCL28 mediates mucosal immunity in HIV exposure and infection 18426876_These studies are the first to show increased CCL28 production during gastrointestinal infection in humans and provide an explanation for the large influx of IgA-secreting cells to the gastric mucosa in H. pylori-infected individuals. 19003934_There was a robust migration of specific IgA- and IgM-antibody-secreting cells induced by Salmonella vaccination toward the mucosal chemokines CCL25 and CCL28 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19659860_data reinforce concept that CCL28 may contribute to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis probably through selective migration & infiltration of effector/memory T-helper-2 cells in the skin; CCL28 may represent a prognostic marker for disease severity 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21447959_These results indicate a role for IL-17A in the human lung by enhancing the expression of CCL28 and hence driving the recruitment of IgE-secreting B cells. 21753853_tumour hypoxia promotes the recruitment of regulatory T (T(reg)) cells through induction of expression of the chemokine CC-chemokine ligand 28 (CCL28), which, in turn, promotes tumour tolerance and angiogenesis 23509159_CCL28 is a potent growth-promoting factor with the ability to support the in vitro and in vivo functional properties of cultured human hematopoietic cells. 24917456_CCL28-CCR3 interactions are involved in the homeostatic trafficking of CD4(+) T cells to the upper airways. 25567740_CCL28 was absent in saliva of primary Sjogren's syndrome patients. This finding did not correlate with salivary IgA levels. 25740824_High CCL28 gene methylation is associated with gastric tumor aggressiveness. 26642722_disease severity of atopic dermatitis in children is not correlated to the level of CCL28, but rather related to that of total IgE 27250766_Results show that CCL28 expression was up-regulated under hypoxic condition in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Besides other effects on tumor biology such as immunosuppression, CCL28 could promote angiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma by directly activating its receptor, CCR3, on microvascular endothelial cells. 27716621_HCC recruits Tregs to promote angiogenesis under hypoxic condition by upregulating CCL28 expression. These findings establish a link between Tregs and hypoxia in HCC growth and may provide a new potential therapeutic target for treating HCC. 28713975_our results show for the first time that CCL28 contributes to breast cancer progression through the ERK/MAPKmediated anti-apoptotic and metastatic signaling pathway. Antagonists of CCL28 and the MAPK signaling pathway may be used synergistically to treat breast cancer patients. 28843907_this review discusses the role of CCL28 in innate and adaptive immunity 32102131_Expression of Chemokine CCL28 in Ulcerative Colitis Patients. 33639074_Hypoxia Induces Overexpression of CCL28 to Recruit Treg Cells to Enhance Angiogenesis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 34913072_Knockdown of CCL28 inhibits endometriosis stromal cell proliferation and invasion via ERK signaling pathway inactivation. 34939465_CCL28 Downregulation Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer Progression Through Tumor Cell-Intrinsic and -Extrinsic Mechanisms. 35494513_Expression of CX3CL1 and CCL28 in Spinal Metastases of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Their Correlation with Clinical Features and Prognosis. 35899992_Inhibition of CCL28/CCR10-Mediated eNOS Downregulation Improves Skin Wound Healing in the Obesity-Induced Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. |
ENSMUSG00000074715 |
Ccl28 |
84.065849 |
0.2439455445 |
-2.035369 |
0.218324664 |
89.486314 |
0.00000000000000000000308767064182230137496809952556015510616669489728460660556011788124841643821127945557236671447753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000028662904825973063438648543444711186672321351796208888746894660748409933148650452494621276855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.4809281 |
4.5298330 |
126.1440346 |
11.6284448 |
| ENSG00000152056 |
130340 |
AP1S3 |
protein_coding |
Q96PC3 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1 that plays a role in protein sorting in the late-Golgi/trans-Golgi network (TGN) and/or endosomes. The AP complexes mediate both the recruitment of clathrin to membranes and the recognition of sorting signals within the cytosolic tails of transmembrane cargo molecules. Involved in TLR3 trafficking (PubMed:24791904). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24791904}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma subunit genes. The encoded protein is a component of adaptor protein complex 1 (AP-1), one of the AP complexes involved in claathrin-mediated vesicular transport from the Golgi or endosomes. Disruption of the pathway for display of HIV-1 antigens, which prevents recognition of the virus by cytotoxic T cells, has been shown to involve the AP-1 complex (PMID: 15569716). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014] |
hsa:130340; |
AP-1 adaptor complex [GO:0030121]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; melanosome assembly [GO:1903232]; platelet dense granule organization [GO:0060155]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24791904_AP1S3 silencing disrupted the endosomal translocation of the innate pattern-recognition receptor TLR-3 (Toll-like receptor 3) and resulted in a marked inhibition of downstream signaling. 27079945_study demonstrated that AP1S3 interacts with hepatitis C virus E2 and protects it from proteasome-dependent degradation 34367317_Adaptor Protein Complex 1 Sigma 3 Is Highly Expressed in Glioma and Could Enhance Its Progression. |
ENSMUSG00000054702 |
Ap1s3 |
93.453953 |
2.4696609356 |
1.304313 |
0.159730223 |
68.360375 |
0.00000000000000013618685432565393965461562937430096688227436493249383753223469284421298652887344360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001019846762986632305199248737632694887635524433507072661342363062431104481220245361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
135.7895895 |
12.9661691 |
55.3222398 |
4.3015195 |
| ENSG00000152076 |
91409 |
CCDC74B |
protein_coding |
Q96LY2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:91409; |
|
31521166_The authors characterized CCDC74A and CCDC74B as microtubule-associated proteins that localize to spindles and are important K-fiber crosslinkers required for bipolar spindle formation and chromosome alignment. |
ENSMUSG00000041617 |
Ccdc74a |
17.661756 |
0.4966758390 |
-1.009624 |
0.448283612 |
5.056226 |
0.02453761573475543578126689681084826588630676269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043110963962027168405732879818970104679465293884277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.7240401 |
2.7655672 |
17.6473991 |
3.6908524 |
| ENSG00000152117 |
150776 |
SMPD4BP |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
86.103587 |
0.4750466626 |
-1.073859 |
0.160271769 |
45.729307 |
0.00000000001357761272045997952358117818052890839360113961475917676580138504505157470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000074638943670014632863224626812479996565419249066053453134372830390930175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.1603888 |
6.5303479 |
121.4419965 |
9.1677433 |
| ENSG00000152223 |
57724 |
EPG5 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCE0 |
FUNCTION: Involved in autophagy. May play a role in a late step of autophagy, such as clearance of autophagosomal cargo. Plays a key role in innate and adaptive immune response triggered by unmethylated cytidine-phosphate-guanosine (CpG) dinucleotides from pathogens, and mediated by the nucleotide-sensing receptor TLR9. It is necessary for the translocation of CpG dinucleotides from early endosomes to late endosomes and lysosomes, where TLR9 is located (PubMed:29130391). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20550938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23222957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29130391}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Autophagy;Cataract;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Lysosome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a large coiled coil domain-containing protein that functions in autophagy during starvation conditions. Mutations in this gene cause Vici syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:57724; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; autophagosome maturation [GO:0097352]; cellular response to dsDNA [GO:1990786]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; nucleotide transport [GO:0006862]; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034162] |
17549423_We characterized the KIAA1632 gene by computational methods: detailed investigation of the genomic structure, protein prediction, identification of orthologs in other species and phylogenetic analysis. 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23222957_Recessive mutations in EPG5 cause Vici syndrome, a multisystem disorder with defective autophagy. 25331754_A mutation affecting the penultimate exon of EPG5 and presenting with typical clinical manifestations of Vici syndrome. 26854214_We report two sisters with a nonsense mutation within exon 14 of the EPG5 gene and a phenotype consistent with Vici syndrome 27343256_This article confirms in silico predictions of aberrant splicing in the EPG5 gene due to the mutation NM_020964.2; c.1007A>G p.Gln336Arg 27586004_Seven SNPs were significantly associated with the risk of Alzheimer disease, and eight SNPs were associated with the age at onset of AD. 27588602_The Vici syndrome protein EPG5 is a Rab7 effector that determines the fusion specificity of autophagosomes with late endosomes/lysosomes. 28168853_Our report further reinforces that EPG5-related Vici syndrome is both a neurodevelopmental disorder, which can be diagnosed as early as the second trimester of pregnancy, as well as a neurodegenerative disorder. 28615637_To investigate the function of EPG5, siRNA based EPG5 knock-down, and CRISPR/Cas9 mediated EPG5 knock-out HeLa cells were generated. EPG5-depleted cells exhibited a complete block of autophagic flux caused by defective autophagosome-lysosome fusion. 28748650_Our findings expand the phenotypical spectrum of EPG5-related Vici syndrome and suggest that this severe condition may already present in utero 29130391_these findings indicate that EPG5, by controlling nucleic acids intracellular trafficking, links macroautophagy/autophagy to innate and adaptive immunity. 29227033_this is a report of a novel EPG5 mutation in a 21 week fetus and its sibling affected with Vici syndrome. This is the second report of brain histology in Vici syndrome in the prenatal period, at earliest reported gestation till date; with previously unreported finding of focal cortical microdysgenesis, thereby expanding the spectrum of disordered cortical development in this syndrome 30152144_we successfully identified novel compound heterozygous mutations in EPG5 in a patient who was clinically considered to have Vici syndrome. 31184778_EPG5 c.1007A > G mutation in a sibling pair with rapidly progressing Vici syndrome. 31410206_C-myc/miR-150/EPG5 axis mediated dysfunction of autophagy promotes development of non-small cell lung cancer. 33674710_Insights on autophagosome-lysosome tethering from structural and biochemical characterization of human autophagy factor EPG5. 34264147_Ophthalmic findings as clues for early diagnosis of Vici syndrome in a neonate. 34689707_Human platelets display dysregulated sepsis-associated autophagy, induced by altered LC3 protein-protein interaction of the Vici-protein EPG5. |
ENSMUSG00000039840 |
Epg5 |
393.698416 |
0.1640663878 |
-2.607648 |
0.875427250 |
6.858539 |
0.00882186536480849929631187222867083619348704814910888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017081297754764981911002053038828307762742042541503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
117.3185016 |
63.7086286 |
752.0426205 |
290.3818649 |
| ENSG00000152229 |
9050 |
PSTPIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H939 |
FUNCTION: Binds to F-actin. May be involved in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable actin filament binding activity. Predicted to be involved in actin filament polymerization. Predicted to be located in cytoskeleton and membrane. Predicted to be active in actin filament; cytoplasm; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9050; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; cell migration [GO:0016477] |
20032092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24407241_PSTPIP2 dysregulation contributes to aberrant terminal differentiation in GATA-1-deficient megakaryocytes by activating LYN. 31247120_Methylation on PSTPIP2 is associated with the development of anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury. 33311489_PSTPIP2 inhibits cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000025429 |
Pstpip2 |
40.654973 |
0.3857017098 |
-1.374443 |
0.305772881 |
20.166233 |
0.00000709951789195012634043095364755338039230991853401064872741699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000022701231387604824774962067324146630653558531776070594787597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.4509382 |
4.4840633 |
58.5140242 |
7.7815141 |
| ENSG00000152284 |
83439 |
TCF7L1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCS4 |
FUNCTION: Participates in the Wnt signaling pathway. Binds to DNA and acts as a repressor in the absence of CTNNB1, and as an activator in its presence. Necessary for the terminal differentiation of epidermal cells, the formation of keratohyalin granules and the development of the barrier function of the epidermis (By similarity). Down-regulates NQO1, leading to increased mitomycin c resistance. {ECO:0000250}. |
Activator;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor family of transcription factors. These transcription factors are activated by beta catenin, mediate the Wnt signaling pathway and are antagonized by the transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway. The encoded protein contains a high mobility group-box DNA binding domain and participates in the regulation of cell cycle genes and cellular senescence. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:83439; |
beta-catenin-TCF complex [GO:1990907]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030111] |
19308021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20532534_No difference in nuclear beta-catenin signal intensity was found, which may be caused by an alteration in Wnt pathway in microsatellite stable sporadic tumors by unknown mechanisms leading to lower TCF-3, 4 protein expression. 21285352_HIPK2 up-regulates transcription by phosphorylating TCF3, a transcriptional repressor, but inhibits transcription by phosphorylating LEF1, a transcriptional activator. 22930747_Data indicate that median methylation levels of BCAN, HOXD1, KCTD8, KLF11, NXPH1, POU4F1, SIM1, and TCF7L1 were >/=30% higher than in normal samples, representing potential biomarkers for tumor diagnosis. 23063976_Tcf3is partially responsible for the butyrate-resistant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells, as this DNA-binding protein suppresses the hyperinduction of Wnt activity by butyrate. 23090119_Our results identify TCF3 as a central regulator of tumor growth and initiation. 23492770_TCF3, a novel positive regulator of osteogenesis, plays a crucial role in miR-17 modulating the diverse effect of canonical Wnt signaling in different microenvironments. 24596249_TCF/TLE tetramer complex promotes structural transitions of chromatin to mediate repression. 25659031_These results indicate that a dynamic interplay of TCF transcription factors governs MYC gene expression in colorectal cancers. 26764381_report the identification of two independent missense variants in human TCF7L1, p.R92P and p.R400Q, in a cohort of patients with forebrain and/or pituitary defects 27333864_TCF7L1, a Wnt pathway repressor, buffers CTNNB1/TCF target gene expression to promote CRC growth 28467300_Through transcriptome profiling and combined gain- and loss-of-function studies, the authors identified LCN2 as a major downstream effector of TCF7L1 that drives tumor growth. 29361574_TCF7L1 plays a major role in maintaining hESC pluripotency, which has implications for human development during gastrulation 30811526_Data indicate that transcription factor transcription factor 7-like 1 (TCF7L1) could regulate antioxidant response in gastric cancer cells by regulating Keap1/NRF2 [Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1/nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2] pathway. 31322782_Results provide some new insights into how extracellular signals modulate the self-renewal of liver CSCs and highlight the inhibitory roles of Tcf7l1 in cancer. 31381875_High TCF7L1 expression is associated with non-seminomatous testicular germ cell tumors. 32403323_Diverse LEF/TCF Expression in Human Colorectal Cancer Correlates with Altered Wnt-Regulated Transcriptome in a Meta-Analysis of Patient Biopsies. 33824876_TCF7L1 Genetic Variants Are Associated with the Susceptibility to Cervical Cancer in a Chinese Population. 35078577_[T cell factor 3 (TCF3) is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes their invasion and metastasis]. |
ENSMUSG00000055799 |
Tcf7l1 |
15.596215 |
0.3653216002 |
-1.452761 |
0.518271509 |
7.906782 |
0.00492498137903325718806035737884485570248216390609741210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010082208759296931374627170896474126493558287620544433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6542904 |
3.1940792 |
27.1024022 |
5.3063764 |
| ENSG00000152315 |
56659 |
KCNK13 |
protein_coding |
Q9HB14 |
FUNCTION: Potassium channel displaying weak inward rectification in symmetrical K(+) solution. {ECO:0000250}. |
Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Potassium channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a potassium channel containing two pore-forming domains. This protein is an open channel that can be stimulated by arachidonic acid and inhibited by the anesthetic halothane. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:56659; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; outward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0015271]; potassium ion leak channel activity [GO:0022841]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; stabilization of membrane potential [GO:0030322] |
16683720_expression in cell hypoxia 18209473_THIK-1 and THIK-2 are abundantly expressed in the proximal and distal nephron of the mammalian kidney. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25148687_In cell and tissues co-expressing THIK1 and THIK2, heterodimeric channels may contribute to cell excitability. 27566292_Dysregulation of a potassium channel, THIK-1, targeted by caspase-8, accelerates cell shrinkage. |
ENSMUSG00000045404 |
Kcnk13 |
33.446677 |
2.4055689444 |
1.266378 |
0.281084344 |
20.611515 |
0.00000562567236659194739570224313984780906139349099248647689819335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000018185484916972654407217591110423882128088735044002532958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.1323530 |
7.6182098 |
20.1419110 |
2.5828567 |
| ENSG00000152377 |
6695 |
SPOCK1 |
protein_coding |
Q08629 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. May contribute to various neuronal mechanisms in the central nervous system. |
Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Heparan sulfate;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes the protein core of a seminal plasma proteoglycan containing chondroitin- and heparan-sulfate chains. The protein's function is unknown, although similarity to thyropin-type cysteine protease-inhibitors suggests its function may be related to protease inhibition. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6695; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; node of Ranvier [GO:0033268]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; sarcoplasm [GO:0016528]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004869]; metalloendopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0008191]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; central nervous system neuron differentiation [GO:0021953]; negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010812]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558] |
16596217_Significant overexpression of osteonectin mRNA is associated with pancreatic cancer 19282985_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19282985_SPOCK gene underlies variation of age at menarche 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23022495_In the present study, we showed that SPOCK1 could inhibit apoptosis and promote cancer invasion. 23873022_Testican-1-induced EMT signaling. 24134845_this study showed that SPOCK1 is a novel metastasis related biomarker in lung cancer and may be new diagnostic and therapeutic target for lung cancer. 25623055_SPOCK1 activates PI3K/Akt signaling. 26077618_These results suggest that up-regulation of SPOCK1 in ESCC induces EMT, thus promotes migration and invasion in ESCC cells. 26138584_Collectively, altered expression of PKP1 and SPOCK1 appears to be a frequent and critical event in prostate cancer 26638890_SPOCK1 is highly expressed in ovarian cancer.SPOCK1 contributes to ovarian cancer development and metastasis. 27108836_This study suggests that SPOCK1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in glioma cells by activating PI3K/AKT and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways, which provides a potential theoretical basis for clinical treatment of glioma. 27486308_findings suggest that SPOCK1 is a critical mediator of tumor growth and metastasis in prostate cancer 27626636_a novel TGF-beta-induced myoepithelial marker and enhanced invasion in breast cancer cells and correlated with poor prognosis 27889608_SPOCK1 expression is significantly up-regulated in colorectal cancer tissues and associated with tumor size and stage. SPOCK1 stimulates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to inhibit cell apoptosis and promote tumor growth. 28103946_Transcriptomic analysis of EPCR-silenced tumors unveiled an effect mediated by matricellular SPOCK1/testican 1. SPOCK1 silencing suppressed in vitro 3D growth. SPOCK1 ablation decreased orthotopic tumor growth and reduced metastatic osteolytic tumors. High SPOCK1 levels were also associated with poor clinical outcome in a subset of breast cancer patients. 28281964_Knockdown of SPOCK1 inhibits the proliferation. 28486750_Functional assessment in cocultures demonstrated that SPOCK1 strongly affects the composition of the extracellular collagen matrix and by doing so, enables invasive tumor cell growth in Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 28534948_High SPOCK1 expression is associated with castration-resistant prostate cancer. 28653880_Our results suggested that microRNA-129-5p could directly specifically suppress SPOCK1, which might be one of the potential mechanisms in inhibiting cell processes including viability, proliferation, cell mitosis, migration, and invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. 28659612_downregulation of both strands of pre-miR-150 and overexpression of SPOCK1 are involved in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). pathogenesis. The involvement of passenger strand miRNAs in the regulation of cancer cell aggressiveness is a novel concept in RNA research 28869894_is significantly upregulated in osteosarcoma tissue. 28940639_The elevated SPOCK1 expression is closely correlated with cancer metastasis and patient survival, and SPOCK1 promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer through Slug-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 29233721_Overexpression of SPOCK1was confirmed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma clinical specimens. Overexpression of SPOCK1 contributes to the aggressive nature of HNSCC. 29315764_Testican-1 blood level is related to the severity of sepsis and Testican-1 could be used as a biomarker to determine the severity of sepsis. 29461591_expression of SPOCK1 served as a tumor promoter, possibly through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in NSCLC; targeting SPOCK1 could be a potential therapeutic strategy in NSCLC 30710422_SPOCK1 overexpression promoted proliferation and invasion, and restrained apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. MiR-139-5p, miR-940 and miR-193a-5p inhibited HCC development through targeting SPOCK1. 30825234_SPOCK1 contributes to the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors resistance in lung cancer. 31478239_A potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target: SPOCK1 promotes the proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. 32555336_SPOCK1 is a novel inducer of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in drug-induced gingival overgrowth. 33012508_SPOCK1 induces adipose tissue maturation: New insights into the function of SPOCK1 in metabolism. 33293473_SPOCK1/SIX1axis promotes breast cancer progression by activating AKT/mTOR signaling. 33321927_The Central Region of Testican-2 Forms a Compact Core and Promotes Cell Migration. 33517826_Long non-coding RNA TTN antisense RNA 1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulating miR-139-5p/SPOCK1 axis. 33884883_SPOCK1 promotes the proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells by regulating the NF-kappaB pathway and inducing EMT. 34156309_Multiomic analysis of the function of SPOCK1 across cancers: an integrated bioinformatics approach. 34855159_SPOCK1 promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer via NF-kappaB-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition by interacting with IkappaB-alpha. 35221802_Expression and Potential Prognostic Value of SOX9, MCL-1 and SPOCK1 in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. 35462225_SPOCK1 silencing decreases 5-FU resistance through PRRX1 in colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000056222 |
Spock1 |
83.387994 |
4.1316752127 |
2.046727 |
0.193717700 |
117.933165 |
0.00000000000000000000000000179330030014814939732663019964783024638119365581419489292038627921890684736860865911012297146953642368316650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000021124590925927123235822714509195780887294990032094434318115210561281986853532366410490794805809855461120605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
136.1046158 |
16.2805235 |
33.1766872 |
3.3609175 |
| ENSG00000152402 |
2977 |
GUCY1A2 |
protein_coding |
P33402 |
FUNCTION: Has guanylyl cyclase on binding to the beta-1 subunit.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 acts as a negative regulator of guanylyl cyclase activity as it forms non-functional heterodimers with the beta subunits. |
Alternative splicing;cGMP biosynthesis;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Lyase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Soluble guanylate cyclases are heterodimeric proteins that catalyze the conversion of GTP to 3',5'-cyclic GMP and pyrophosphate. The protein encoded by this gene is an alpha subunit of this complex and it interacts with a beta subunit to form the guanylate cyclase enzyme, which is activated by nitric oxide. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:2977; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanylate cyclase complex, soluble [GO:0008074]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; guanylate cyclase activity [GO:0004383]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0007263]; positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0010750]; response to oxygen levels [GO:0070482]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11752394_Soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) is the major cellular receptor for the intercellular messenger nitric oxide (NO) and mediates a wide range of physiological effects through elevation of intracellular cGMP levels 15094474_No significant changes were found in sGC subunit mRNAs in people with schizophrenia or in controls. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948239_The sGC alpha 1observed in OVCAR-3 and MDA-MB-468 cancer cells which correlated well with the sGC activity and a marked increase in cGMP levels upon exposure to the combination of a NO donor and a sGC activator. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20978832_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22426988_The CO binding affinity of soluble guanylate cyclase alpha 2 subunit is threefold greater than that of human soluble guanylate cyclase alpha 1 subunit. 24669844_The data support a novel regulatory mechanism whereby sGC activity is tuned by distinct domain interactions that either promote or inhibit catalytic activity. |
ENSMUSG00000041624 |
Gucy1a2 |
39.190527 |
3.6006490039 |
1.848257 |
0.356189330 |
25.819303 |
0.00000037492015793936749128609470065043307585028742323629558086395263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001391106468372313827980128221606381799801965826191008090972900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.8796642 |
19.8599539 |
17.5581287 |
4.2058712 |
| ENSG00000152413 |
9456 |
HOMER1 |
protein_coding |
Q86YM7 |
FUNCTION: Postsynaptic density scaffolding protein. Binds and cross-links cytoplasmic regions of GRM1, GRM5, ITPR1, DNM3, RYR1, RYR2, SHANK1 and SHANK3. By physically linking GRM1 and GRM5 with ER-associated ITPR1 receptors, it aids the coupling of surface receptors to intracellular calcium release. May also couple GRM1 to PI3 kinase through its interaction with AGAP2. Isoform 1 regulates the trafficking and surface expression of GRM5. Isoform 3 acts as a natural dominant negative, in dynamic competition with constitutively expressed isoform 1 to regulate synaptic metabotropic glutamate function. Isoform 3, may be involved in the structural changes that occur at synapses during long-lasting neuronal plasticity and development. Forms a high-order complex with SHANK1, which in turn is necessary for the structural and functional integrity of dendritic spines (By similarity). Negatively regulates T cell activation by inhibiting the calcineurin-NFAT pathway. Acts by competing with calcineurin/PPP3CA for NFAT protein binding, hence preventing NFAT activation by PPP3CA (PubMed:18218901). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18218901}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the homer family of dendritic proteins. Members of this family regulate group 1 metabotrophic glutamate receptor function. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9456; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; axon [GO:0030424]; costamere [GO:0043034]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuron spine [GO:0044309]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic cytosol [GO:0099524]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; G protein-coupled glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035256]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling adaptor activity [GO:0035591]; structural constituent of postsynapse [GO:0099186]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031802]; behavioral response to cocaine [GO:0048148]; chemical homeostasis within a tissue [GO:0048875]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007216]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007206]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009967]; protein localization to synapse [GO:0035418]; protein tetramerization [GO:0051262]; regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090279]; regulation of cation channel activity [GO:2001257]; regulation of dendritic spine maintenance [GO:1902950]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0098962]; regulation of store-operated calcium entry [GO:2001256]; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051966]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; skeletal muscle contraction [GO:0003009]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741] |
12815733_HOMER1 was screened for an association with schizophrenia. 12815733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16314758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16314758_Polymorphism in the Homer1 gene is a potential risk factor for the development of cocaine dependence in an African American population. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19376111_Data indicate that Homer1 plays a critical role in determining the apoptotic susceptibility to TRAIL. 19648775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19648775_study implicates the effects of allele A of the rs4704559 marker in susceptibility to psychotic symptoms in Parkinson disease 20333726_Haplotypes of the HOMER 1 and 2 genes are unlikely to play a major role in the pathophysiology of alcohol dependence. 20333726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20598711_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20598711_This study reported significant associations between different polymorphisms of the HOMER 1 gene and psychopathology of schizophrenic patients at baseline and between HOMER 1 polymorphisms and therapy response after treatment with atypical antipsychotics. 20673876_HOMER1 plays a role in the etiology of major depression and genetic variation affects depression via the dysregulation of cognitive and motivational processes. 20673876_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926133_Homer dissociation from its targets evoked by the PPKKFR peptide led to Imin calcium channel activation but not to Imax calcium channel activation in A431 cells. 21172614_Homer1a transgene expression is transiently upregulated during increases in network activity and evokes agonist-independent signaling of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors that scales down expression of synaptic AMPA receptors. 21885651_monitored Homer1 and Homer2 expression and subcellular localization in skeletal muscle biopsies following 60 days of bedrest 22558107_HOMER1 encodes a postsynaptic density-localized scaffolding protein that interacts with Shank3 to regulate mGluR activity, and is a novel autism-risk gene. 22749857_This review discusses the association of Homer 1 variants with the etiology of many neurological diseases, such as pain, mental retardation syndromes, Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, addiction and traumatic brain injury. 23044706_Polymorphisms of DRD1, DLG4 and HOMER1 are associated with opiate abuse. 23685007_Overexpression of HOMER1A reduces neuropathic pain hypersensitivity. 23821062_The uncoupling of synaptic protein homer 1c from target proteins activates store-operated calcium entry in a neurotransmitter-like manner in human neuroblastoma cells. 24126708_data suggest that HOMER1 rs4704559 G allele has a protective role for the development of levodopa adverse effects 24815486_Homer1 promotes lymphatic invasion and associates with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 25551602_The mRNA levels of Homer1, IL-1beta, and TNF-alpha in coronary artery disease patients were significantly higher than those in the control group, but not Homer2 and Homer3. 25712868_these findings provide evidence for a new role of Homer1 supporting the regulation of Cav1.2 channels by STIM1. 26641965_The main focus of the present review is to offer an overview of the current knowledge about the potential role of Homer1a in depression and the signaling pathways responsible for Homer1a regulation. [review] 26718835_The present study was undertaken to determine the expression and functional significance of Homer1b/c in multiple myeloma 27075036_Study shows that Homer1b/c is constitutively expressed in astrocytes, where it clusters with mGlu5 and endoplasmic reticulum tubules to form sub-plasmalemmal microdomains; propose that Homer1a may represent one of the cellular mechanisms by which inflammatory astrocytic reactions are beneficial for limiting brain injury 27832625_Homer1 and Homer2 might be considered as novel diagnostic biomarkers for large-artery atherosclerosis stroke. 27964944_Resequencing three candidate genes (HOMER1, SLC6A4, and TEF) discovers seven potentially deleterious variants susceptibility to major depressive disorder and suicide attempts in Chinese. 28815330_This study demonstrate that altered Homer1a levels in specific brain regions and cell types of patients suffering from schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depression. 29079138_Homer 1 rs7713917 gene variant associated with brain structure and function, severity of depression, and antidepressant response in patients affected by a major depressive episode in course of bipolar disorder. 29923011_Monomeric Homer 1a proteins increase activity of Imin channels, but did not modulate their electrophysiological properties. Recombinant Homer 1c protein did not block the induced calcium currents. 30219717_Study found the common variant rs7713917 in the HOMER1 gene to be significantly associated with suicide attempt in Chinese patient. 31078268_Homer1 regulates RyR1 by direct interaction. 32142100_Self-reported Sleep Problems Related to Amyloid Deposition in Cortical Regions with High HOMER1 Gene Expression. 32645048_A single nucleotide polymorphism in the HOMER1 gene is associated with sleep latency and theta power in sleep electroencephalogram. 33431662_Multiple signaling pathways are essential for synapse formation induced by synaptic adhesion molecules. 34204449_The mTORC2 Regulator Homer1 Modulates Protein Levels and Sub-Cellular Localization of the CaSR in Osteoblast-Lineage Cells. 34225586_The Role of Stress-Induced Changes of Homer1 Expression in Stress Susceptibility. 34788607_Homer1a regulates Shank3 expression and underlies behavioral vulnerability to stress in a model of Phelan-McDermid syndrome. 36181383_CircHOMER1 aggravates oxidative stress, inflammation and extracellular matrix deposition in high glucose-induced human mesangial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000007617 |
Homer1 |
117.556748 |
4.4376389237 |
2.149792 |
0.189878851 |
130.464488 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000324282060701985058804698881334299994099926493670094882077942120642916062431423095124838340552742010913789272308349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000041729757767753260566972297578178283974637507074728720175104858314465808321377243705896376013697590678930282592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
180.3407627 |
21.0532532 |
40.9176415 |
3.9325515 |
| ENSG00000152457 |
64421 |
DCLRE1C |
protein_coding |
Q96SD1 |
FUNCTION: Nuclease involved in DNA non-homologous end joining (NHEJ); required for double-strand break repair and V(D)J recombination (PubMed:11336668, PubMed:11955432, PubMed:12055248, PubMed:14744996, PubMed:15071507, PubMed:15574326, PubMed:15936993). Required for V(D)J recombination, the process by which exons encoding the antigen-binding domains of immunoglobulins and T-cell receptor proteins are assembled from individual V, (D), and J gene segments (PubMed:11336668, PubMed:11955432, PubMed:14744996). V(D)J recombination is initiated by the lymphoid specific RAG endonuclease complex, which generates site specific DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:11336668, PubMed:11955432, PubMed:14744996). These DSBs present two types of DNA end structures: hairpin sealed coding ends and phosphorylated blunt signal ends (PubMed:11336668, PubMed:11955432, PubMed:14744996). These ends are independently repaired by the non homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway to form coding and signal joints respectively (PubMed:11336668, PubMed:11955432, PubMed:14744996). This protein exhibits single-strand specific 5'-3' exonuclease activity in isolation and acquires endonucleolytic activity on 5' and 3' hairpins and overhangs when in a complex with PRKDC (PubMed:15071507, PubMed:15574326, PubMed:11955432, PubMed:15936993). The latter activity is required specifically for the resolution of closed hairpins prior to the formation of the coding joint (PubMed:11955432). Also required for the repair of complex DSBs induced by ionizing radiation, which require substantial end-processing prior to religation by NHEJ (PubMed:15456891, PubMed:15468306, PubMed:15574327, PubMed:15811628). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11336668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11955432, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12055248, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14744996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15071507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15456891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15468306, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15574326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15574327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15811628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15936993}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;Endonuclease;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Immunity;Magnesium;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SCID |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear protein that is involved in V(D)J recombination and DNA repair. The encoded protein has single-strand-specific 5'-3' exonuclease activity; it also exhibits endonuclease activity on 5' and 3' overhangs and hairpins. The protein also functions in the regulation of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. Mutations in this gene can cause Athabascan-type severe combined immunodeficiency (SCIDA) and Omenn syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:64421; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nonhomologous end joining complex [GO:0070419]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 5'-3' exodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0035312]; 5'-3' exonuclease activity [GO:0008409]; damaged DNA binding [GO:0003684]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; single-stranded DNA endodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0000014]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:0006303]; interstrand cross-link repair [GO:0036297]; protection from non-homologous end joining at telomere [GO:0031848]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212]; V(D)J recombination [GO:0033151] |
11955432_DNA-PKcs regulates Artemis by both phosphorylation and complex formation to permit enzymatic activities that are critical for the hairpin-opening step of V(D)J recombination and for the 5' and 3' overhang processing in nonhomologous DNA end joining. 12055248_A nonsense founder mutation discovered in exon 8 of Artemis results in the truncation of the deduced protein product and indicates that the SNM1-like gene (Artemis) is the gene responsible for SCID in Athabascan-speaking Native Americans. 12406895_deletions and missense mutations in the Artemis gene can cause radiosensitive-SCID with defective coding joint formation and lead to an early and complete B-cell differentiation block 12569164_Artemis has a role in T and B lymphocyte immunodeficiency and in predisposition to lymphoma through the NHEJ pathway of DNA repair 12592555_the genomic exon 3 deletion is unique to Japan and may be considered as a founder haplotype. 14628082_Properties of the Artemis proteins are integrated into the processes of V(D)J recombination and non-homologous end-joining factors. 14726805_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 14744996_Artemis uses one or two Zn(II) ions to exert its catalytic activity, like bacterial class B beta-Lact enzymes hydrolyzing beta-lactam compounds. 15071507_The hairpin-opening activity of ARTEMIS and/or its overhang endonucleolytic activity are necessary but its exonuclease activity is not sufficient for the process of V(D)J recombination. 15456891_Data show that Artemis interacts with cell cycle checkpoint proteins and is a phosphorylation target of the checkpoint kinases ATM or ATR after exposure of cells to IR or UV irradiation, respectively. 15468306_Atemis is an effector of dna repair that can be phosphorylated by ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated kinase (ATM) and possibly by DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit and ATM-and Rad3-related kinase depending on the type of DNA damage. 15574327_ATM, Artemis, and proteins locating to gamma-H2AX foci have roles in double-strand break rejoining 15723659_our finding places Artemis at the signaling crossroads downstream of DNA-PKcs and ATM in IR-induced DSB repair. 15731174_report on a first patient with clinical and immunologic features of OS caused by hypomorphic ARTEMIS mutations. Sequencing of the ARTEMIS gene revealed a compound heterozygosity in this nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) factor 15936993_Artemis:DNA-PKcs nuclease may be important in removing secondary structures that hinder processing of DNA ends during nonhomologous DNA end joining . 16093244_The uncharacterized C-terminal domain of Artemis has important regulatory roles; results lead to a model for how DNA-PKcs activates Artemis by phosphorylation 16600297_characterization of six DNA-PK phosphorylation sites on Artemis whose phosphorylation shows dependence on its association with DNA-PK catalytic subunit and is induced by double-stranded DNA damage 16857680_Ku-mediated assembly of DNA-PK on DNA ends is responsible for a dissociation of the DNA-PKcs.Artemis complex. 16874298_DNA-PK autophosphorylation regulates Artemis access to DNA ends, providing insight into the mechanism of Artemis mediated DNA end processing. 17121861_Artemis efficiently trims long 3'-phosphoglycate-terminated overhangs induced in DNA by radiation and other radical-based toxins. 17169382_analyzed the phenotype of cells derived from SCID patients with different mutations in the Artemis gene 17242184_ATM regulates G(2)/M checkpoint recovery through inhibitory phosphorylations of Artemis that occur soon after DNA damage, thus setting a molecular switch that, hours later upon completion of DNA repair, allows activation of the Cdk1-cyclin B complex. 17932067_There is some sequence-dependent variation in the efficiency and position of hairpin opening by Artemis:DNA-PKcs; providing more clarity on the extent to which the hairpin opening position contributes to junctional diversity in V(D)J recombination. 18034425_The Artemis C terminus is essential for V(D)J recombination at the normal Artemis expression level. 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19022407_H254 plays a key role in the Artemis function, as it is critical for its full activity in vitro. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19075292_Results link Artemis to the predominant nonhomologous end-joining pathway during immunoglobulin class switch recombination. 19075392_Results identify the first human RS-SCID patient with a DNA-PKcs missense mutation, which also affects Artemis activation and function. 19398950_Artemis and DNA-PKcs participate in a new, signaling pathway to modulate p53 function in response to oxidative stress produced by mitochondrial respiration. 19423708_recovery from the S phase checkpoint in that in response to replication stress phosphorylation of Artemis by ATR enhances its interaction with Fbw7, which in turn promotes ubiquitylation and the ultimate degradation of cyclin E 19692705_Mutations in Artemis leads to reduced immunoglobulin class switch recombination. 19779458_ATM and DNA cross-link repair 1C (PSO2 homolog S. cerevisiae) are required for efficient formation of single-stranded DNA and Rad51 foci at radiation-induced double-strand breaks in G2 phase. 19859091_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19953608_Functional analyses on patients' fibroblasts demonstrated that the corresponding alleles carry null mutations of the DCLRE1C gene. 20003485_Plays role in the 3'-processing reaction and protection of the ends of viral DNA (HIV-1) after reverse transcription. Involved in multiple steps including integration and pre-integration steps during retroviral replication. 20496165_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20522537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20610542_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20975951_Studies indicate that codon-based models of gene evolution yielded statistical support for the recurrent positive selection of five NHEJ genes during primate evolution: XRCC4, NBS1, Artemis, POLlambda, and CtIP. 21390052_antisense oligonucleotide (AON) covering the intronic mutation restored WT Artemis transcript levels and non-homologous end-joining pathway activity in the patient fibroblasts 21531702_Restoration of chemo/radioresistance by wild-type, but not D165N Artemis suggests that the lack of endonucleolytic trimming of DNA ends is the principal cause of sensitivity to double-strand cleaving agents in Artemis-deficient cells. 21596788_Artemis is required for the repair of DNA double strand breaks that arise endogenously or following oxidative stress. 21641068_The dominant negative mutant Artemis fragment (D37N-413aa) enhanced tumor cell radiosensitivity through blocking activity of endogenous Artemis and DNA repair. 21785230_analysis of differences in sensitivity to DNA-damaging Agents between XRCC4- and Artemis-deficient human cells 22134138_Regulation of p27 by Artemis and DDB2 is important for cell cycle progression in normally proliferating cells. 22527898_study identified a new SCID mutation in a consanguineous Israeli Arab family; sequencing identified an 8 bp insertion in exon 14 (1306ins8) of DCLRE1C in all affected patients; this causes an alteration in amino acid 330 of the protein from cysteine to a stop codon (p.C330X) 22529269_Point mutations in Artemis that disrupt its interaction with Ligase IV or DNA-PKcs reduce V(D)J recombination. 22713703_Artemis levels significantly influence radiation toxicity in human cells 22730303_Results show that during S-phase Artemis but not ATM is dispensable for homologous recombination of radiation-induced double-strand breaks. 23044421_these results suggest that Artemis functions as a positive regulator of AMPK signaling by stabilizing the LKB1-AMPK complex. 23219551_Structural basis of DNA ligase IV-Artemis interaction in nonhomologous end-joining. 23465063_Our findings indicate a novel function of Artemis as a molecular switch that converts stalled replication forks harboring single-stranded gap DNA lesions into double-strand breaks, thereby activating the ATM signaling pathway 23967291_DNA ligase IV and Artemis act cooperatively to promote nonhomologous end-joining 24230999_2 siblings are described with combined immunodeficiency (CID) and immunodysregulation caused by compound heterozygous Artemis mutations. 24500713_the 5'-exonuclease is intrinsic to ARTEMIS, making it relevant to the role of ARTEMIS in nonhomologous DNA end joining 25512557_uncovered a nuclease, Artemis, as a PTIP-binding protein 25917813_the nature and location of mutations correlate with the clinical phenotype of severe combined immunodeficiency 25981738_DCLRE1C and NCF1 mutations have been found by whole-genome sequencing to cause primary immunodeficiency in unrelated patients. 26476407_Data demonstrate that DCLRE1C mutations can cause a phenotype presenting as only antibody deficiency. 28082683_An N-terminal fragment comprising the catalytic domain can interact both with itself and with a C-terminal fragment. Amino acid exchanges N456A+S457A+E458Q in the C terminus of full-length SCIDA resulted in unmasking of the N terminus and in increased SCIDA activity in cellular V(D)J recombination assays. 28696258_Data suggest that stimulation of Artemis nuclease/DCLRE1C activity by XRCC4-DNA ligase IV hetero-complex and efficiency of blunt-end ligation are determined by structural configurations at the DNA ends. (XRCC4 = X-ray repair cross complementing 4) 30059501_Study provides evidence that Replication forks can break quickly in S-phase upon DNA replication stress induction by an endonucleolytic mechanism independent of MUS81. Two nucleases ARTEMIS and XPF-ERCC1 are responsible for this Rapid-Replication Fork Breakage (RRFB) which takes place during S and G2 phases of the cell cycle. 30113698_The results suggest that TDP1 and Artemis perform different functions in the repair of terminally blocked double-stranded breaks (DSBs) by the classical nonhomologous end joining pathway, and that whereas an Artemis deficiency prevents end joining of some DSBs, a TDP1 deficiency tends to promote DSB misjoining. 30947362_study presents one of three affected siblings who was diagnosed with DCLRE1C-deficient combined immunodeficiencies 32092471_Unusual phenotype in patients with a hypomorphic mutation in the DCLRE1C gene: IgG hypergammaglobulinemia with IgA and IgE deficiency. 32576658_Structural analysis of the catalytic domain of Artemis endonuclease/SNM1C reveals distinct structural features. 34210101_Staring at the Naked Goddess: Unraveling the Structure and Reactivity of Artemis Endonuclease Interacting with a DNA Double Strand. 35801871_Structural analysis of the basal state of the Artemis:DNA-PKcs complex. 36270581_Dynamics of the Artemis and DNA-PKcs Complex in the Repair of Double-Strand Breaks. |
ENSMUSG00000026648 |
Dclre1c |
103.738220 |
0.4609324835 |
-1.117373 |
0.180179303 |
38.502108 |
0.00000000054694588290690913631648201472077071294553007874128525145351886749267578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002669616809426580394376047450887001755148730808286927640438079833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
66.7546441 |
7.8314461 |
145.8317298 |
11.6866161 |
| ENSG00000152465 |
9397 |
NMT2 |
protein_coding |
O60551 |
FUNCTION: Adds a myristoyl group to the N-terminal glycine residue of certain cellular and viral proteins (PubMed:25255805, PubMed:9506952). Also able to mediate N-terminal lysine myristoylation of proteins: catalyzes myristoylation of ARF6 on both 'Gly-2' and 'Lys-3' (PubMed:32103017). Lysine myristoylation is required to maintain ARF6 on membranes during the GTPase cycle (PubMed:32103017). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255805, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32103017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9506952}. |
3D-structure;Acyltransferase;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes one of two N-myristoyltransferase proteins. N-terminal myristoylation is a lipid modification that is involved in regulating the function and localization of signaling proteins. The encoded protein catalyzes the addition of a myristoyl group to the N-terminal glycine residue of many signaling proteins, including the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) proteins, Gag and Nef. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:9397; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; host cell [GO:0043657]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase activity [GO:0004379]; peptidyl-lysine N6-myristoyltransferase activity [GO:0018030]; intracellular transport of virus [GO:0075733]; N-terminal peptidyl-glycine N-myristoylation [GO:0018008]; regulation of rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway [GO:0022400] |
11731439_induction of NMT2 may play a central role in dioxin carcinogenicity. 16123142_NMT1 and NMT2 have only partially overlapping functions; NMT1 is critical for tumor cell proliferation 16364039_Involved in progression and regulation of telomerase 16530191_Protein-protein interaction of NMTs revealed that m-calpain interacts with NMT1 while caspase-3 interacts with NMT2. 17568424_Disruption of the gene for NMT2 by a t(8;10) translocation in a male with hypogonadism. 18089753_Nef is preferentially myristoylated by NMT2, suggesting that selective inhibition of NMT2 may provide a novel means of blocking HIV virulence. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 26621918_ligand binding properties of the NMT/ACBD6 complex can explain how the NMT reaction can proceed in the presence of the very abundant competitive substrate, C(16)-CoA. 35930829_N-mytistoyltransferase 1 and 2 are potential tumor suppressors and novel targets of miR-182 in human non-small cell lung carcinomas. |
ENSMUSG00000026643 |
Nmt2 |
56.060590 |
0.4410701333 |
-1.180920 |
0.235616703 |
25.213886 |
0.00000051311411906138265748397904453259599222292308695614337921142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001880696398645643779262812307628838226492007379420101642608642578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.5204735 |
4.8737925 |
72.0200324 |
7.4592796 |
| ENSG00000152484 |
219333 |
USP12 |
protein_coding |
O75317 |
FUNCTION: Deubiquitinating enzyme. Has almost no deubiquitinating activity by itself and requires the interaction with WDR20 and WDR48 to have a high activity (PubMed:19075014, PubMed:27373336). Not involved in deubiquitination of monoubiquitinated FANCD2 (PubMed:19075014). In complex with WDR48, acts as a potential tumor suppressor by positively regulating PHLPP1 stability (PubMed:24145035). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075014, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24145035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27373336}. |
3D-structure;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc |
|
Enables cysteine-type endopeptidase activity and thiol-dependent deubiquitinase. Involved in protein deubiquitination. Predicted to be located in nucleoplasm. Predicted to be active in cytosol and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:219333; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
19075014_two novel multisubunit deubiquitinating enzyme complexes containing USP12 and USP46, respectively. Both complexes contain the UAF1 protein as a bona fide subunit. Interestingly, UAF1 20147737_WDR20 serves as a stimulatory subunit for preserving and regulating the activity of the subset of the UAF1 x USP12 complexes 22778262_The ubiquitin-specific protease 12 (USP12) is a negative regulator of notch signaling acting on notch receptor trafficking toward degradation. 24056413_Usp12 acts in a pro-proliferative manner by stabilizing AR and enhancing its cellular function. 24145035_our results reveal WDR48 and USP12 as novel PHLPP1 regulators and potential suppressors of tumor cell survival 24850727_Coimmunoprecipitation experiments indicated that human papillomavirus type 31 E1 assembles into a ternary complex with UAF1 and any one of these three USPs: USP1, USP12 and USP46. 25216524_Usp12 directly deubiquitinates and stabilises the Akt phosphatases PHLPP and PHLPPL resulting in decreased levels of active pAkt. 25855980_Results suggest role for USP46/USP12 in Epstein-Barr virus induced growth transformation. 26811477_Usp12 deubiquitylates and prevents lysosomal degradation of LAT and Trat1 to maintain the proximal TCR complex for the duration of signaling. 27373336_UAF1 and WDR20 interact with USP12 at two distinct sites far from its catalytic center, allosterically activating the enzyme. 27650958_Our results highlight the interfaces essential for regulation of USP12 activity and show a conserved second binding of UAF1 which could be important for regulatory functions independent of USP12 activity. 29755129_USP12 deubiquitinates MDM2 and AR, which in turn controls the levels of the TP53 tumour suppressor and AR oncogene in prostate cancer. 30266909_Findings indicate that deubiquitinase Usp12 (Usp12) overexpression accelerates autophagic flux and induces an approximately sixfold increase in autophagic structures as determined by ultrastructural analyses. 30466959_WDR20 plays a crucial role in as a 'targeting subunit' that modulates CRM1-dependent shuttling of the USP12/UAF1/WDR20 complex between the plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus. 33174033_Downregulation of USP12 inhibits tumor growth via the p38/MAPK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34381028_USP12 downregulation orchestrates a protumourigenic microenvironment and enhances lung tumour resistance to PD-1 blockade. 35898171_USP12 positively regulates M-MDSC function to inhibit antitumour immunity through deubiquitinating and stabilizing p65. |
ENSMUSG00000029640 |
Usp12 |
453.747178 |
2.7889896246 |
1.479743 |
0.086259814 |
297.234796 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000131894076661646302109719630147755131750645177629517952779128946100092031336633598160905787383701821394124893790929238657275069646628340433593385115743219080354183860015471196902581141330301761627197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000037801098476231060530733651916790337133839125935690142290625577339132045126032170502681205670192606176394959161282381300367766921844148639343509373147784034699218913555540666493470780551433563232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
678.5070771 |
39.4845531 |
245.1643016 |
11.2135621 |
| ENSG00000152503 |
55521 |
TRIM36 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ86 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Involved in chromosome segregation and cell cycle regulation (PubMed:28087737). May play a role in the acrosome reaction and fertilization. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80WG7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28087737}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55521; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; acrosome reaction [GO:0007340]; mitotic cytokinesis [GO:0000281]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507]; spindle organization [GO:0007051] |
15145053_The overexpression of the TRIM36 in the vast majority of prostate cancer suggest that this gene might be involved in the prostate tumorigenesis. 15955891_molecular cloning and characterization of a human haprin ortholog. 19232519_TRIM36 has a ubiquitin ligase activity and interacts with centromere protein-H, potentially associated with chromosome segregation and its excess may cause chromosomal instability. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 28087737_TRIM36 is the causative gene for autosomal recessive anencephaly 28087737_The siRNA knock down of TRIM36 in HeLa and LN229 cells also led to reduced cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. We suggest that microtubule disruption and disorganized spindles mediated by mutant TRIM36 affect neural cell proliferation during neural tube formation, leading to Anencephaly . 28359976_aberrant hypermethylation of TRIM36 might be involved in the acquisition of malignant phenotype and could be served as a biomarker for risk assessment of PAHs exposure 29449534_TRIM36 is a novel androgen-responsive gene, and it dramatically enhanced the efficacy of anti-androgen drugs against prostate cancer. 30238687_Results suggest that high expression of TRIM36 is associated with favorable prognosis and that TRIM36 plays a tumor-suppressive role by inhibiting cell proliferation and migration as well as promoting apoptosis in prostate cancer. 35768649_TRIM36 suppresses cell growth and promotes apoptosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 36058131_TRIM36 enhances lung adenocarcinoma radiosensitivity and inhibits tumorigenesis through promoting RAD51 ubiquitination and antagonizing hsa-miR-376a-5p. |
ENSMUSG00000033949 |
Trim36 |
92.935359 |
2.8758284547 |
1.523978 |
0.171903154 |
80.269378 |
0.00000000000000000032669285662391539328932141747604425352438429008463261892653006768227896827738732099533081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000002792117292280828703340377019023517659307182827815559458817240567896078573539853096008300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
139.4348116 |
14.1913802 |
48.9426193 |
4.0685995 |
| ENSG00000152520 |
255967 |
PAN3 |
protein_coding |
Q58A45 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the poly(A)-nuclease (PAN) deadenylation complex, one of two cytoplasmic mRNA deadenylases involved in general and miRNA-mediated mRNA turnover. PAN specifically shortens poly(A) tails of RNA and the activity is stimulated by poly(A)-binding protein (PABP). PAN deadenylation is followed by rapid degradation of the shortened mRNA tails by the CCR4-NOT complex. Deadenylated mRNAs are then degraded by two alternative mechanisms, namely exosome-mediated 3'-5' exonucleolytic degradation, or deadenlyation-dependent mRNA decaping and subsequent 5'-3' exonucleolytic degradation by XRN1. PAN3 acts as a positive regulator for PAN activity, recruiting the catalytic subunit PAN2 to mRNA via its interaction with RNA and PABP, and to miRNA targets via its interaction with GW182 family proteins. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03181, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14583602, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23932717}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Contributes to poly(A)-specific ribonuclease activity. Predicted to be involved in nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening. Predicted to act upstream of or within deadenylation-dependent decapping of nuclear-transcribed mRNA; positive regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA processing body assembly; and protein targeting. Part of PAN complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:255967; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; P-body [GO:0000932]; PAN complex [GO:0031251]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; poly(A) binding [GO:0008143]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening [GO:0000289]; positive regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA processing body assembly [GO:0010606]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis, exonucleolytic [GO:0090503] |
14583602_hPan2 and hPan3 have roles in mRNA decay and exhibit cytoplasmic co-localization 25446091_arsenite-induced oxidative stress inhibits deadenylation of mRNA primarily through downregulation of Tob and Pan3, both of which mediate the recruitment of deadenylases to mRNA 28559491_These results reveal a new fundamental step governing mammalian mRNA metabolism. We propose that the first phase of deadenylation, coordinated through the interplay among the two Pan3 isoforms, Pan2, and PABP, represents a cytoplasmic mRNA maturation step important for proper mRNA turnover. 31401408_the present study revealed that circPAN3 is most likely a key modulator for acquired drug resistance of AML, which may facilitate drug resistance in AML cells by regulating autophagy as an autophagy inducer via the AMPK/mTOR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000029647 |
Pan3 |
710.622820 |
0.3452768895 |
-1.534174 |
0.097437620 |
243.553826 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000066044400893353519412417285627173339819535911923625843756314279229405854750614747295203094605092546635271663842231717385017525828516871859788506249344663956435397267341613769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000015522537534807292081244590652240050823256338718498633848453783174077363771327661474019775786585162609404962945908144066775623739966685245283972705010455683805048465728759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
378.0927347 |
23.3315300 |
1102.3926750 |
46.9507278 |
| ENSG00000152527 |
130271 |
PLEKHH2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVE3 |
FUNCTION: In the kidney glomerulus may play a role in linking podocyte foot processes to the glomerular basement membrane. May be involved in stabilization of F-actin by attenuating its depolymerization. Can recruit TGFB1I1 from focal adhesions to podocyte lamellipodia. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable actin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of actin filament depolymerization. Located in several cellular components, including cytosol; lamellipodium; and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:130271; |
cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; negative regulation of actin filament depolymerization [GO:0030835] |
18752002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18752002_PLEKHH2, which has mRNA and protein expression exclusively in the glomerulus, may be a genetic risk factor for susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in the diabetic population 22832517_Suggest a structural and functional role for Plekhh2 in the podocyte foot processes. |
ENSMUSG00000040852 |
Plekhh2 |
18.190349 |
0.2240863628 |
-2.157873 |
0.765798229 |
6.860192 |
0.00881370594755075120740883676262455992400646209716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017068486322047691366998733997206727508455514907836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5287033 |
2.4850929 |
20.5173030 |
7.4904072 |
| ENSG00000152582 |
79925 |
SPEF2 |
protein_coding |
Q9C093 |
FUNCTION: Required for correct axoneme development in spermatozoa. Important for normal development of the manchette and sperm head morphology. Essential for male fertility. Plays a role in localization of the intraflagellar transport protein IFT20 to the manchette, suggesting function as an adapter for dynein-mediated protein transport during spermatogenesis (PubMed:31278745, PubMed:31151990, PubMed:31048344). Also plays a role in bone growth where it seems to be required for normal osteoblast differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C9J3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31048344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31151990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31278745}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Disease variant;Flagellum;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis |
|
Involved in sperm axoneme assembly. Located in sperm flagellum. Implicated in spermatogenic failure 43. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79925; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; manchette [GO:0002177]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; brain morphogenesis [GO:0048854]; epithelial cilium movement involved in extracellular fluid movement [GO:0003351]; respiratory system development [GO:0060541]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31048344_SPEF2 is a novel gene for human MMAF (multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella) across the populations. Functional analyses suggested that the deficiency of SPEF2 in the mutated subjects could alter the localisation of other axonemal proteins. 31151990_Loss-of-function mutations in the SPEF2 gene can cause the Multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella (MMAF) phenotype in human. 31278745_Biallelic mutations in Sperm flagellum 2 cause human multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella (MMAF) phenotype. 31545650_In individuals with primary ciliary dyskinesia and central pair defects, the CP-associated protein SPEF2 is absent in HYDIN-mutant cells. 41 of 189 individuals had undetectable SPEF2 and were subjected to a genetic analysis, which revealed one novel loss-of-function mutation in SPEF2 and 3 reported and 13 novel HYDIN mutations in 15 individuals. A mutation of SPEF2 is causative for PCD with a CP defect. 31942643_Mutations in SPEF2 are associated with multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella and primary ciliary dyskinesia. 34755699_Sperm flagellar 2 (SPEF2) is essential for sperm flagellar assembly in humans. |
ENSMUSG00000072663 |
Spef2 |
58.258654 |
0.2065401266 |
-2.275506 |
0.405504397 |
29.940966 |
0.00000004454023509725048569002220908742695204551864662789739668369293212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000181405593276881103585021818257183578992908223881386220455169677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.0004324 |
6.0275127 |
97.3567733 |
19.9988176 |
| ENSG00000152601 |
4154 |
MBNL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR56 |
FUNCTION: Mediates pre-mRNA alternative splicing regulation. Acts either as activator or repressor of splicing on specific pre-mRNA targets. Inhibits cardiac troponin-T (TNNT2) pre-mRNA exon inclusion but induces insulin receptor (IR) pre-mRNA exon inclusion in muscle. Antagonizes the alternative splicing activity pattern of CELF proteins. Regulates the TNNT2 exon 5 skipping through competition with U2AF2. Inhibits the formation of the spliceosome A complex on intron 4 of TNNT2 pre-mRNA. Binds to the stem-loop structure within the polypyrimidine tract of TNNT2 intron 4 during spliceosome assembly. Binds to the 5'-YGCU(U/G)Y-3'consensus sequence. Binds to the IR RNA. Binds to expanded CUG repeat RNA, which folds into a hairpin structure containing GC base pairs and bulged, unpaired U residues. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10970838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15257297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16946708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18335541, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19470458}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Corneal dystrophy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the muscleblind protein family which was initially described in Drosophila melanogaster. The encoded protein is a C3H-type zinc finger protein that modulates alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs. Muscleblind proteins bind specifically to expanded dsCUG RNA but not to normal size CUG repeats and may thereby play a role in the pathophysiology of myotonic dystrophy. Mice lacking this gene exhibited muscle abnormalities and cataracts. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described but the full-length natures of only some have been determined. The different isoforms are thought to have different binding specificities and/or splicing activities. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:4154; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; regulatory region RNA binding [GO:0001069]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; mRNA processing [GO:0006397]; myoblast differentiation [GO:0045445]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; regulation of alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000381]; regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0043484]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
15257297_MBNL proteins promote opposite splicing patterns for cardiac troponin T and insulin receptor alternative exons 15546872_small interfering RNA-mediated down-regulation of MBNL1 in normal myoblasts results in abnormal insulin receptor splicing 15961406_The GFP-MBNL1 in CUG and CAG foci have similar half-times of recovery and fractions of immobile molecules, suggesting GFP-MBNL1 is bound by both CUG and CAG repeats and formation of RNA foci and disruption of MBNL1-regulated splicing are separable events. 16273094_localized expression of the integrin alpha3 protein is regulated at the level of RNA localization by MBNL1; integrin alpha3 transcripts are physically associated with MLP1 in cells and MLP1 binds to a specific ACACCC motif in the integrin alpha3 3' UTR 16394256_The fact that a human protein works in a Drosophila cellular context illustrates the use of an in vivo test to prove functional conservation. 16920640_findings show that MBNL1 nuclear sequestration in protein foci is a molecular pathology marker of DM1 and DM2 patients where ribonuclear inclusions of transcripts with expanded CUG/CCUG repeats are also present 16946708_Elevated levels of MBNL1 show RNA-independent interaction with hnRNP H and dampen the inhibitory activity of increased hnRNP H levels on IR splicing in normal myoblasts. 17846170_MBNL1 (muscleblind-like protein 1) is an alternative splicing factor that becomes highly concentrated with mutant RNA foci. 17942744_MBNL may bind all of its RNA substrates, both normal and pathogenic, as structured stem-loops containing pyrimidine mismatches. 18335541_Examination of dynamics of MBNL1 in response to stress, and suggestion of a role for MBNL1 in mRNA metabolism in the cytoplasm. 19043415_Both the ZnF3 and the ZnF4 zinc-finger domains target GC steps, with site-specific recognition mediated by a network of hydrogen bonds formed primarily with main chain groups of the protein. 19095965_MBNL1 and MBNL2 always co-distributed. Functional differences between MBNL1 and MBNL2 have not yet been found 19345584_Our data seem indicate that the presence of ribonuclear inclusions and MBNL1 nuclear foci are involved in alteration of alternative splicing but do not impair DM2 myogenic differentiation. 19805260_Data show that ligand 1 selectively destabilizes the MBNL1N-poly(CUG) complex. 20519504_Findings demonstrate a role for Mbnl1 in controlling insulin receptor exon 11 inclusion via binding to a downstream intronic enhancer element. 21439371_results indicate the occurrence of a mis-splicing event in myotonic dystrophy type 1 that is induced neither by a loss of muscleblind-like 1 (MBNL1) function nor by a gain of CUGBP1 21454535_the abnormally high inclusion of the exon 5 and 7 regions in DM1 is expected to enhance the potential of MBNL1 of being sequestered with nuclear CUG expansions, which provides new insight into DM1 pathophysiology. 21548961_Although MBNL1 contains four Zn fingers, it appears that only two Zn fingers binding GC motifs are necessary for high affinity RNA binding. 21685920_MBNL1 regulates pre-miR-1 biogenesis. 21832083_Deletion of the MBNL1 response element eliminated MBNL1 splicing regulation and led to complete inclusion of exon 5, which is consistent with the suppressive effect of MBNL1 on splicing. 21900255_Expanded CUG repeats Dysregulate RNA splicing by altering the stoichiometry of the muscleblind 1 complex 22106026_The removal of one pair of zinc fingers greatly impairs the binding affinity of MBNL1, which indicates that the two pairs of zinc fingers might possibly interact with RNA targets cooperatively. 22113158_congenital myotonic dystrophy muscle has nuclear foci that contain muscleblind-like 1 (MBNL1) protein. 22306654_Common variants near MBNL1 and NKX2-5 are associated with infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. 22355723_study suggests that regulation of CUGBP1 and MBNL1 is essential for accurate control of destabilization of a broad spectrum of mRNAs as well as of alternative splicing events 22520280_The present results show that the MBNL1 protein is expressed and more or less sequestered into the CCUGexp nuclear foci also in analyzed non-muscle tissues of DM2 patients. 22890842_It was demonstrated that functionally distinct classes of MBNL1-mediated splicing events exist as defined by requirements for zinc finger-RNA interactions. 23161457_This report demonistrated that the association of several genetic variants of the MBNL1 gene with DM1 or with the severity of the disease. 23166594_MBNL1 loss shows a graded effect on the number and severity of the ensuing RNA splice defects. 23739326_consistent with a central and negative regulatory role for MBNL proteins in pluripotency, their knockdown significantly enhances the expression of key pluripotency genes and the formation of induced pluripotent stem cells during somatic cell reprogramming 23807294_in both dystrophic and sarcopenic muscles MBNL1 undergoes intranuclear relocation, accumulating in its usual functional sites but also ectopically moving to domains which are usually devoid of this protein in healthy adults 23949219_MBNL142-43 bind the Src-homology 3 domain of Src family kinases (SFKs) via their proline-rich motifs. 24048253_MBNL1 and RBFOX2 cooperate to establish a splicing programme involved in pluripotent stem cell differentiation. 24354850_MBNL1 is highly mobile and changes localization in response to altered transcription and splicing activity, providing an insight into the sensitivity of the lens to changes in MBNL1 distribution. 24373687_Results highlight the importance of RNA binding by MBNL Zinc Finger domains 1 and 2 for splicing regulatory activity, even when the protein is artificially recruited to its regulatory location on target RNAs. 24440524_both MBNL1 and MBNL2 are involved in the regulation of Tau exon 2 splicing and the mis-splicing of Tau in DM1 is due to the combined inactivation of both. 25211016_Reduced RBFOX1 activity in myotonic dystrophy type 1 tissues may amplify several of the splicing alterations caused by the deficiency in MBNL1. 25274774_Results show that nuclear localization is a major determinant of MBNL1 function. It promotes the nuclear retention of repeat-containing transcripts, which results in repression of aberrant protein expression from the expanded repeats. 25403273_The result is consistent with the hypothesis that MBNL proteins are trapped by expanded CUG repeats and inactivated in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) and that CELF1 is activated in DM1. 25977444_MBNL1 binds with C allelic pre-miR-1307 leading to low expression of miR-1307-3p in colorectal cancer. 26018658_abnormal splicing of DMD exon 78 found in dystrophic muscles of DM1 patients is due to the functional loss of MBNL1 and leads to the re-expression of an embryonic dystrophin in place of the adult isoform. 26218986_Nuclear retention of full-length HTT RNA is mediated by splicing factors MBNL1 and U2AF65 26339785_Sense DMPK RNA foci clearly co-localize with MBNL1 and MBNL2 proteins and accumulate in myotonic dystrophy 1 tissues during development. 26883358_muscleblind-like 1 (MBNL1) is a robust suppressor of multiorgan breast cancer metastasis. It binds the 3' untranslated regions of DBNL and TACC1 -two genes that are implicated as metastasis suppressors. 27222292_Heterozygous missense mutations and one in-frame deletion in MBNL1 were identified in 3 myotonic dystrophy patients. 28718627_Binding of the MBNL zinc fingers to cardiac troponin T pre-mRNA is specific and relatively simple, unlike the complex multiple dimer-trimer stoichiometries postulated in some previous studies. 28886202_Our work suggests that DM1 patients are at risk for Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD). DMPK mutations contribute to the genetic burden of FECD but are uncommon. We establish a connection between two repeat expansion disorders converging upon RNA-MBNL1 foci and FECD. 28910618_RAN Translation Regulated by Muscleblind Proteins in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 2 28949831_For exogenous activation of MBNL transcription, MBNL1 transcription start site T2 seems to be the most suitable target, as the ensuing pre-mRNA is susceptible to both major loops, e1 and e5, and hence, theoretically, following induction each cell in the body could reach the optimal MBNL content. 29331264_MBNL1 overexpression altered cerebral cortical responsiveness by decreasing the response in the contralateral hemisphere evoked by electrical stimulation. 29771377_MBNL1 is an important alternative splicing regulator during differentiation of monocytes. 29789616_RBFOX1/MBNL1 competition for CCUG RNA repeats binding contributes to myotonic dystrophy type 1/type 2 differences. 29946070_Functional depletion of the alternative splicing factors Muscleblind-like (MBNL 1 and 2) is at the basis of the neuromuscular disease myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). Here, we screen for miRNAs that regulate MBNL1 and MBNL2 in HeLa cells. We thus identify miR-23b and miR-218, and confirm that they downregulate MBNL proteins in this cell line. 29955876_The structure of targeted RNAs is a prevalent component of the mechanism of alternative splicing regulation by MBNLs. 30664186_The knockdown of muscleblindlike 1 (MBNL1) induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like morphological changes in the colorectal cancer (CRC) HCT-116 cells, accompanied by an enhanced cell motility, and by the downregulation of E-cadherin and the upregulation of Snail expression. Overexpression of MBNL1 suppresses EMT, characterized by the upregulation of Ecadherin and the downregulation of Snail expression. 31371437_MBNL1 promotes cell differentiation through regulation of alternative splicing, and we demonstrate that TRIM71 promotes embryonic splicing patterns through MBNL1 repression 31469403_Identification of novel splicing patterns and differential gene expression in RE+/FECD- samples provides new insights and more relevant gene targets that may be protective against FECD disease in vulnerable patients with TCF4 CTG TNR expansions. 31861407_Our data showed that overexpression of hsa-miR-30b-5p led to downregulation of MBNL1 in VSMCs. This process influences VSMC proliferation and might be involved in VSMC differentiation. 32398749_MBNL1 regulates essential alternative RNA splicing patterns in MLL-rearranged leukemia. 32601196_A tumor-associated splice-isoform of MAP2K7 drives dedifferentiation in MBNL1-low cancers via JNK activation. 32683410_MBNL1 reverses the proliferation defect of skeletal muscle satellite cells in myotonic dystrophy type 1 by inhibiting autophagy via the mTOR pathway. 32928918_The Alternative Splicing Factor, MBNL1, Inhibits Glioblastoma Tumor Initiation and Progression by Reducing Hypoxia-Induced Stemness. 33142236_The SRSF3-MBNL1-Acin1 circuit constitutes an emerging axis to lessen DNA fragmentation in colorectal cancer via an alternative splicing mechanism. 33789374_[Effect of long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1 expression on prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia patients]. 33893082_Altered Expression of MBNL Family of Alternative Splicing Factors in Colorectal Cancer. 33896245_MBNL1 Suppressed Cancer Metastatic of Skin Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via by TIAL1/MYOD1/Caspase-9/3 Signaling Pathways. 34459372_The Regulatory Role of Both MBNL1 and MBNL1-AS1 in Several Common Cancers. 36064939_The MBNL1/circNTRK2/PAX5 pathway regulates aerobic glycolysis in glioblastoma cells by encoding a novel protein NTRK2-243aa. 36204878_MBNL1 and MRTF-A form a positive feedback loop in regulating the migration of esophageal cancer cells. 36217202_STAT3/miR-130b-3p/MBNL1 feedback loop regulated by mTORC1 signaling promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth. |
ENSMUSG00000027763 |
Mbnl1 |
2011.832693 |
0.3281275603 |
-1.607671 |
0.137338045 |
129.069192 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000654949601454865521168242559921201956529863173611590234315072388215841601587143688822933995652419980615377426147460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000083842637619027017154117572900770540683208957296547650417829525191240745994386215911298165792686631903052330017089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1009.8776177 |
92.2058950 |
3104.8991535 |
204.1101790 |
| ENSG00000152661 |
2697 |
GJA1 |
protein_coding |
P17302 |
FUNCTION: Gap junction protein that acts as a regulator of bladder capacity. A gap junction consists of a cluster of closely packed pairs of transmembrane channels, the connexons, through which materials of low MW diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell. May play a critical role in the physiology of hearing by participating in the recycling of potassium to the cochlear endolymph. Negative regulator of bladder functional capacity: acts by enhancing intercellular electrical and chemical transmission, thus sensitizing bladder muscles to cholinergic neural stimuli and causing them to contract (By similarity). May play a role in cell growth inhibition through the regulation of NOV expression and localization. Plays an essential role in gap junction communication in the ventricles (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08050, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23242}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cataract;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Gap junction;Hypotrichosis;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Palmoplantar keratoderma;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the connexin gene family. The encoded protein is a component of gap junctions, which are composed of arrays of intercellular channels that provide a route for the diffusion of low molecular weight materials from cell to cell. The encoded protein is the major protein of gap junctions in the heart that are thought to have a crucial role in the synchronized contraction of the heart and in embryonic development. A related intronless pseudogene has been mapped to chromosome 5. Mutations in this gene have been associated with oculodentodigital dysplasia, autosomal recessive craniometaphyseal dysplasia and heart malformations. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:2697; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell-cell contact zone [GO:0044291]; connexin complex [GO:0005922]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; gap junction [GO:0005921]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi-associated vesicle membrane [GO:0030660]; intercalated disc [GO:0014704]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tight junction [GO:0070160]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; efflux transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015562]; gap junction channel activity [GO:0005243]; gap junction channel activity involved in cardiac conduction electrical coupling [GO:0086075]; gap junction channel activity involved in cell communication by electrical coupling [GO:1903763]; gap junction hemi-channel activity [GO:0055077]; glutathione transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034634]; ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015075]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086014]; bone development [GO:0060348]; bone remodeling [GO:0046849]; cardiac conduction system development [GO:0003161]; cell communication by electrical coupling [GO:0010644]; cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction [GO:0086064]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; establishment of mitotic spindle orientation [GO:0000132]; export across plasma membrane [GO:0140115]; gap junction assembly [GO:0016264]; glutamate secretion [GO:0014047]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; microtubule-based transport [GO:0099111]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion [GO:0032277]; negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration [GO:1901164]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:1905772]; positive regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium [GO:1905332]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; xenobiotic transport [GO:0042908] |
11470490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11741942_This evidence adds Cx-43 to the list of transmembrane proteins capable of transducing survival signals in response to extracellular cues and raises the possibility that it may serve in this capacity for endogenously produced molecules or even other drugs. 11746825_results demonstrate a new role of Cx43 in the mediation of apoptosis under low serum conditions 11815667_The fast transjunctional voltage-sensitive gating mechanism of Cx43 cell-cell channel can serve as a selectivity filter, which allows electrical coupling but limits metabolic communication. 12003820_homocysteine (Hcy)-induced upregulation of Cx43 transcript and protein expression are associated with unaltered intercellular communication and redistribution of Cx43 in HUVEC 12019157_Connexin 43 suppresses human glioblastoma cell growth by down-regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein 1, as discovered using protein array technology. 12042301_overexpression of Cx43 or Cx26 in breast cancer cells down-regulated fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 12064615_Data suggest that the dynamic changes of connexins 43, 40 and 45 during mouse cardiac development appear to be mirrored in the human. 12064622_Results establish a role for connexin43 hemichannels in bisphosphonate action, and a novel function of connexin43 in the regulation of survival signaling pathways. 12064631_Results provide evidence for Cx43 being targeted to lysosomes as a result of misfolding and aggregation, while in other cases, the delivery of wild-type Cx43 to lysosomes appears to be due to defects innate to the breast tumor cell type. 12203365_and expression of the transcription factor E2F1 correlated inversely with tumor grade 12205082_alpha-catenin facilitates trafficking of connexins 32 and 43 to the cell surface and induces gap junction assembly 12397213_Our data show that the presence of Cx43 allows an inter-trophoblastic GJIC and is associated with the fusion process leading to the villous syncytiotrophoblast 12452056_abnormal expression of connexin43 and connexin45 in nasopharynx tissues may be associated with cancerization and squamatization of human nasopharynx tissue 12457340_We found mutations in the GJA1 gene in all 17 families with oculodentodigital dysplasia that we screened. 12484567_These findings suggest that expression of Cx26 and Cx43 might be related to the differentiation of the arachnoid villi and meningiomas, and exhibit the different origin of various subtypes of meningiomas. 12489165_Connexin 43 in human teeth. Tooth development, Cx43 in epithelial and mesenchymal dental cells. Adult teeth, Cx43 in odontoblasts. Cx43 downregulated in mature teeth, upregulated in odontoblasts facing caries. In dental pulp Cx43 in mineralized nodules. 12619863_plasma membrane localization and formation of channels are not required for growth inhibition by Cx43, and nuclear localization of CT-Cx43 may exert effects on gene expression and growth 12619876_Focal disorganization of gap junction distribution and downregulation of Cx43 are typical of myocardial remodeling that may play an important role in the development of an arrhythmogenic substrate in human cardiomyopathies 12637502_connexin 43 gap junction communication induced by EGF is regulated by ERK5 12644583_the transcriptional up-regulation of Cx43 by Ras-Raf-MAPK is mediated via the interaction of a novel Cx43 promoter element with a protein complex that contains both HSP90 and c-Myc. 12717835_gap junctional intercellular communication in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, and signal transduction mechanism of gap junction genes connexin32, connexin43 in hepatocarcinogenesis 12730291_the tyrosine-based motif of human connexin43 is a prime determinant controlling connexin43 stability, and consequently GJC, by targeting connexin43 for degradation in the endocytic/lysosomal compartment. 12767974_proteasomal degradation regulates the stability of phosphorylated Cx43 and appears to promote the internalization of Cx43 from the cell surface 12840075_Cx43 is directly involved in human trophoblast cell-cell communication, fusion and differentiation. 12861055_the point mutations in the second extracellular region of Cx43 do not affect the ability of the mutant proteins in vitro to suppress cell growth 12881039_mouse connexin43 promoter is regulated by GDF5 in osteoblasts ans embryos 12907686_connexin 43 is phosphorylated in ovarian tumor cells and has a role in gap junctional intercellular communication 13130072_examination of gating and regulation of hemichannels 14519646_Cx43 mRNA in adjacent normal tissue surrounding lung tumor simply detected by RT-PCR may act as a molecular marker of nodal micrometastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. 14639017_Heterogeneous expression of Cx 43 protein may contribute to impaired ventricular conduction. 14667880_mRNA levels of connexins in different sizes of luteinized normal and hyperstimulated follicles. 14681024_Opening of non-junctional connexin 43 (Cx43) hemichannels plays a role in cell physiology 14713573_Low doses of ionizing radiation induce the transcriptional upregulation of connexin 43 expression employing NFAT and AP1 sites. 14729836_A missense mutation in the cytoplasmic loop of GJA1 results in an atypical ophthalmological phenotype, displaying type III syndactyly but not the characteristic dental or skeletal features. 14766937_Staining for Cx43 and Cx40 along regions of intimate cell-to-cell contact between human mesenchymal stem cells. 14974090_Homozygous GJA1 point mutations in a conserver codon, one base change results in a Oculodentodigital dysplasia phenotype in one patient, another base change in the same codon resultes in a Hallermann-Streiff syndrome phenotype in another patient. 15140236_the downregulation of Cx43 is an important event in human wound healing. 15181016_Cx43 is able to regulate cell growth via an up-regulation of NOV transcription 15334670_mRNA level correlates with cell differentiation, nd is predictive of postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. 15338868_Laryngeal cancer presented inactivation of Cx43 gene and E-cad gene and down regulation of Cx43 and E-cad proteins. 15534005_PKC-dependent phosphorylation of Cx43 at S368 creates dynamic communication compartments that can temporally and spatially regulate wound healing. 15576650_In nonischemic heart failure in humans, there is a decrease in both Cx43 expression and phosphorylation that contributes to uncoupling. 15704645_The connexin 43 expression was seen in the circular layer of muscularis externa. 15817491_charged residues present in Cx43 and related connexins help prevent endoplasmic reticulum oligomerization by stabilizing the third transmembrane domain in the membrane bilayer 15870276_existence of internal ribosome entry sites in connexin mRNAs permits connexin expression in density-inhibited or differentiated cells, where cap-dependent translation is generally reduced 15944608_Connexin43 is increased in vitro during process of intimal hyperplasia, supporting a critical role for Cx43-mediated gap-junctional communication in the human vein during the development of intimal hyperplasia. 15948121_Phosphorylated Cx43, is up-regulated in hyperplasias and dysplasias and fibroadenoma and is strongly up-regulated in invasive carcinomas. 15978203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15979566_These data suggest that Cx43del(130-136) produces connexin-specific inhibition of intercellular communication through formation of heteromeric connexons that are non-functional and/or retained in the cytoplasm. 15987459_study demonstrated for the first time that Cx43 protein can be localized at the cell-cell interface between endothelial cells and tumor cells during the process of diapedesis 16010294_Disturbances in both the expression and distribution of Cx43 were found in children with tetralogy of Fallot 16103109_aquaporin-4 has species-specific roles in astrocytes and a functional relationship with Connexin43 16112082_These results suggest that the newly identified domain is essential for the proper phosphorylation and localization of Cx43, and CIP150 is a novel partner protein targeting this domain. 16219735_Our results demonstrate a new mutation (P59H) in the GJ1A gene, identified in a family with ODDD (oculodentodigital dysplasia) syndrome. 16319124_These results suggest that gap junctional intercellular communication and expression of Cx43 contribute to alkaline phosphatase activity, as well as osteocalcin, osteopontin, and Cbfa1 expression in osteoblastic cells. 16361362_This is the first study to demonstrate that flow simultaneously and differentially regulates expression of the Cx37, Cx40, and Cx43 proteins. 16378922_GJA1 mutations is associated with oculo-dento-digital dysplasia 16407179_Cx26 and Cx43 have roles in closed gap junction channel formation 16424398_This study evaluated whether the gap junction protein connexin (Cx) 43 could serve as a negative cell surface marker for human corneal epithelial stem cells. Cx43 expression was evaluated in corneo-limbal tissue and primary limbal epithelial cultures. 16442184_Results demonstrate that TGF-beta1 significantly up-regulates connexin 43 expression and intercellular communication, in concert with increased expression of alpha-actin, calponin and SM1. 16480955_revealed a significant influence of cardiopulmonary bypass and the underlying heart defect on Cx43 expression 16580773_Results showed that Cx43 was phosphorylated during lung tumorigenesis. 16638984_The frequency of mutations in the FOXC1, GJA1, PITX2, and CYP1B1 genes in this study were 25%, 12.5%, 0% and 0%, respectively. 16647893_Detected with RT-PCR profiling in ovarian cancer cells. 16674815_High expression of connexin 43 & syndecan 3 & their co-localization to smooth muscle bundles during normal labour, with significant reduction in prolonged labour, may indicate a role for these proteins in co-ordination of myometrial contractility. 16675599_downregulation of Cx43 expression by high glucose promotes the senescence of glomerular mesangial cells, which may be involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy 16677845_The present review highlights the emerging role of connexin43 in the physiology and physiopathology of human erectile function and its possible medical application. 16684925_Cx43 expression and cell-to-cell communication increased in response to high glucose and may protect the collecting duct from renal damage associated with more established diabetic nephropathy. 16741927_Conditional expression of AML1-ETO by the ecdysone-inducible system dramatically increases the expression of connexin 43 together with growth arrest at G1 phase in leukemic U937 cells. 16816024_Oculodentodigital syndrome is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, results from missense mutations in the gap junction protein connexin 43. 16820096_connexin 43 is downregulated in Sertoli cells and germ cells during the transition from preinvasive carcinoma in situ to seminoma 16820904_Cx43 plays a role as a tumor suppressor, however, no definite correlation was found between Cx43 and cell migration and invasion. 16823880_Based on these data, we propose a working hypothesis in which Cx43 could be an intermediate target for T3 inhibition of neonatal Sertoli cell proliferation. 16886200_These findings suggested that the brain may generate neuronal protection by increasing the levels of Cx43 and amplifying the astrocytic gap junctional intercellular communication under hypoxic condition. 16891658_the 46 aberrant amino acid residues of GJA1 associated with the frameshift mutant are, at least in part, responsible for the manifestation of palmoplantar keratoderma symptoms 16958087_We conclude that activation of the innate immune response in astrocytes is associated with functional loss of CX43 through a pathway involving NF-kappaB and PI3 kinase. 17072341_Inhibition of Cx43 function in high expressing cells led to an increase in drug resistance. 17143533_A rational strategy for treating patients with advanced hormone refractory prostate cancer using CX43 gene therapy and docetaxel. 17183550_Cx43 was colocalized with actin in tenocytes; colocalization increased significantly after cyclic strain 17189315_Cx40/Cx45 junctions demonstrate electrical signal transfer asymmetry that can be modulated between unidirectional and bidirectional by small changes in the difference between holding potentials of the coupled cells. 17275998_Cx43 expression may be in part responsible for the malignancy of hepatoma cells through a decrease in GJIC composed of Cx32 17420259_The potency difference in the dominant negative properties of Cx43 mutants may have clinical implications for the various symptoms and disease severity observed in oculodentodigital dysplasia patients. 17486593_Cx43 expression level could influence the action of Endothelin-1 on human osteoblastic cell differentiation 17541973_the interaction between Cx43 and ZO-1 is regulated by the proteasome 17551925_Activation of the EGFR pathway in response to HP leads to decrease of GJIC via tyrosine phosphorylation of Cx43 in ONH astrocytes. In glaucoma, astrocytes may lose GJIC altering the homeostasis of RGC axons. 17572641_as in primary cultured limbal epithelial cells, Cx43 expression and extent of GJIC may serve as markers for the differentiation status of nasal epithelial cells. 17624368_Connexin43 expression can be influenced by Ang II and IGF-1 through ERK and p38 pathways and may contribute to the pathogenesis of vein graft disease following coronary artery bypass grafting. 17687502_the increased hemichannel activity may be directly caused by an altered conformation of the mutated channel forming protein in patiets with oculodentodigital dysplasia 17708781_Cx43 expression level and gap junction function in acute leukemia bone marrow stromal cells was lower than in normal cells. 17760848_It is concluded that in patients with heart failure, down-regulation of ZO-1 matches the diminished expression levels of connexin 43, suggesting that ZO-1 plays an important role in gap junction formation and gap junction plaque stability. 17878326_levels of connexin-43 are below those detectable by immunofluorescence 17885214_The connexin 43 density was significantly increased in the mid-myocardium of transgenic hearts compared with wild type in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 17895291_In myometrial smooth muscle cells, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)enhances Cx43 mRNA and protein expression through upregulation of c-Fos expression. Blockade of AP-1 sites to the Cx43 promoter can neutralize the CRH-induced upregulation of Cx43. 17898133_Physiological concentrations of intracellular Ca(2+) regulate the permeability of Cx43 in a calmodulin-dependent manner that does not require the major portion of the COOH terminus of Cx43. 17901047_CaM binds to a specific region of the ubiquitous gap junction protein Cx43 in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner, providing a molecular basis for the well characterized Ca(2+)-dependent inhibition of Cx43-containing gap junctions 17922338_This study investigates the responses of endothelial connexin 37, connexin 40, and connexin 43 (Cx37, Cx40, and Cx43) to shear stress and substrate. 18047584_Cx43 hyperphosphorylation induced by UVA is, at least in part, mediated through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation as Ser279 and Ser282 sites, two downstream direct targets of p38 MAPK found to be phosphorylated after UVA treatment. 18056766_Findings suggest that ZO-1, by interacting with Cx43, plays a role in the down-regulation and decreased size of Cx43 gap junctions in congestive heart failure. 18068673_These findings indicate that Cx43 contributes to RPE differentiation via cAMP signaling. 18079109_A novel connexin43-interacting protein, CIP75, which belongs to the UbL-UBA protein family, regulates the turnover of connexin43 18085635_found in the myocytes, but not fibroblasts, of the atrioventricular junction 18089569_review of autosomal dominant mutations of the genes encoding Cx26 and Cx43 [review] 18161618_Oculodentodigital dysplasia is caused by heterozygous mutations in the 6q22-q23 located GJA1 gene, that encodes connexin 43 18162455_Connexin 43 was absent or decreased in testis of humans with impaired spermatogesis. 18162583_The Cx43/Cavs association occurs during exocytic transport, and they clearly indicate that caveolin regulates gap junctional intercellular communication. 18193170_Overexpression of Cx43 is associated with breast cancer cell metastatic potential 18267319_Polarized Caco-2/TC7 cells express significant amounts of Cx26, Cx32 and Cx43. 18269311_germ line reduction of Cx43-based gap junctional intercellular communication leads to impaired osteoblast differentiation, which may account for the bone phenotypes observed in oculodentodigital dysplasia patients 18297686_These results identify JNK, and not NFkappaB, as a critical mediator of TNF-alpha repressory effect on connexin 43 gene expression. 18396685_The decreasing expression of connexin Cx32 and Cx43 is obviously correlated with the occurrence, development and metastatic potential of stomach cancers. 18405916_These data demonstrate the role of Cx43 in the proliferation and migration of human saphenous vein smooth muscle cells and angiotensin II-induced Cx43 expression via mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK)-AP-1 signaling pathway. 18412120_We report here the first case of oculodentodigital dysplasia (ODDD) in a black African person, and the first case with taurodontism in ODDD, associated with a novel GJA1 mutation. 18425059_L113P represents a pathogenic mutation in GJA1 (Cx43) and results in oculo dentodigital dysplasia (ODDD) with marked intrafamilial variation in glaucoma type and severity. 18435417_These data suggest that changes are apparent in markers for abnormal glial-neuronal communication (connexin 43 and aquaporin 4) in brains of subjects with autism. 18445604_Report activation of endothelial cells to pathological status by down-regulation of connexin43. 18600256_the level of expression, the localization and the functionality of connexin43 (Cx43) in three glioblastoma cell lines. Cx43 was responsible for the gap-junctional intercellular communication and thebystander effect 18636092_domain-swapped dimerization of zonula occludens-1 PDZ2 generates a distinct interface that functions together with the well-separated canonical carboxyl tail-binding pocket in each PDZ unit in binding to connexin43 (Cx43) 18647409_Upregulation in tumor cell-endothelial cell contact areas in vitro and in vivo, and in areas of intratumor blood vessels and in micrometastatic foci 18660473_Our evaluation not only expands the phenotypes associated with GJA1 gene mutations but also demonstrates that a great degree of variability in neurological defects. 18662195_Reduced connexin43 expression and localization to the intercalated disk occurs in heterozygous human PKP-2 mutations, potentially explaining the delayed conduction and propensity to develop arrhythmias seen in this disease. 18675253_Clathrin associates with both connexin 43 gap junction plaques and pentilaminar gap junction vesicles. 18687515_Cx43 is present in human bladder tissue both of overactive bladders and those of controls. However, it is expressed in very small amounts and is not always detectable. The role of Cx43 for the origin of detrusor overactivity remains unclear. 18823947_Cx43 mediates the expression of an array of genes involved in human cardiogenesis, in addition to intercellular communication. 18839320_Reduced expression of connexin 43 is associated with lung metastasis in breast cancer 18946008_mutations underlie oculodentodigital syndrome 18951659_Calcium levels in a microenvironment functionally connecting plasma membrane connexin hemichannels to downstream inositol triphosphate-dependent calcium release channels in the endoplasmic reticulum were disrupted by the connexin mimetic peptide. 18988928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19001515_Melatonin increased expression of the gap junction protein, connexin 43 in myometrial smooth muscle. 19027966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19056535_Over-expression of connexin 43 significantly induced E-cadherin expression 19084810_Their expression did not disrupt localization of endogenous PKP2, connexin-43 (Cx43), or desmoplakin (DP). However, we observed reduced abundance of Cx43 after R79x expression. 19174466_Cx43 establishes residency at all cell-surface membrane domains, and progressively acquires assembly states that probably reflect differences in either channel packing and/or its interactions with Cx43-binding proteins. 19297036_Cx43 mutations are not responsible for criss-cross heart in humans or are not a major cause for this defect 19297523_Cx43 and Cx32 undergo a multistep conformational maturation process in which folding of connexin monomers within the endoplasmic reticulum is a prerequisite for multisubunit assembly in the trans-Golgi network. 19321193_The changes of Cx43 expression in human autoimmune thyroid disease were associated with variations in thyroid function and hormone secretion. 19321666_This supports a new role for ERp29 as a chaperone that helps stabilize monomeric Cx43 to enable oligomerization to occur in the Golgi apparatus. 19396169_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423654_p54nrb is a transcriptional corepressor of the progesterone receptor that modulates transcription of the labor-associated gene, connexin 43 (Gja1) 19460861_Cx43 is a potential mediator of the neuroprotective actions of CRH 19490996_High-frequence electromagnetic field exposure significantly and selectively increased trophoblast Cx40 and Cx43, without altering protein expression. 19544087_Caveolin-3 (Cav3) is a new Cx43-interacting protein. 19556520_Report novel pharmacophores of connexin43 based on the 'RXP' series of Cx43-binding peptides. 19563063_Phosphorylation of Cx43 leads to decrease in the expression, which makes ovarian cancer cells less chemosensitive. 19604543_The reduced levels of Cx43 protein should not to be ascribed to a reduced genetic transcription, but to an alteration of the post-transcriptional mechanisms such as the regulation of its synthesis and/or the intracellular transport to membrane sites. 19615768_Chinese congenital heart defect patients have three novel non-synonymous genetic variants close to the hydrophobic c-terminus in connexin 43 19615768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19679555_Overexpression of protease-activated receptor-1 contributes to melanoma metastasis via regulation of connexin 43. 19706598_CCN3 increases the activity of the small GTPase Rac1, thereby revealing a pathway that links Cx43 directly to actin reorganization. 19710532_TGF-beta1 mediates glucose-evoked up-regulation of CX43 cell-to-cell communication in collecting tubules of the kidney. 19716642_obtained 3-dimensional structural information on the complex between the cytoplasmic loop of cx43 and calmodulin; data indicates that calmodulin binds to the peptide from cx43 in the classical 'collapsed' conformation 19726320_nNOS, Pax3 and Cx43 proteins are closely related to the growth and development of the spinal cord in human embryos and fetuses. 19808103_lack of genotype-phenotype correlation for GJA1 mutations in oculo-dento-digital dysplasia 19808665_analysis of intermolecular interactions between the connexin40 and connexin43 carboxyl-terminal and cytoplasmic loop domains 19820388_Loss of functional gap junctions may occur because of the aberrant expression and localization of Cx26 and Cx43 in endometrial cancer. 19847613_A novel GJA1 mutation was detected in a Japanese oculodentodigital dysplasia syndrome (ODDD) patient. 19854014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19860828_the expression of these Cx43-eYFP mutant constructs and found that the L90V mutation disrupted basolateral expression. 19864031_Expression of connexin 43 appears to be involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in the radial artery. 19883623_Studies indicate that 21 different Cxs have been detected and they are generally named according to their approximate molecular mass in Kda, e.g. Cx32, Cx43 and Cx45. 19908168_Low connexin-43 is associated with pancreatic cancer. 19910046_Our findings suggest Cx43 and gap junction intercellular communication might be involved in the courses of occurrence, development and termination of acute leukemia 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19935872_Results suggest that asymmetric dimethylarginine inhibits endothelial gap junction function via downregulating Cx43 expression. 20038810_Limited forward trafficking of connexin 43 reduces cell-cell coupling in stressed human and mouse myocardium. 20086016_although Panx1 and Panx3 share a common endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi secretory pathway to Cx43, their ultimate cell surface residency appears to be independent of cell contacts and the need for intact microtubules 20117462_In atrial fibrillation, angiotensin II activates CTGF via activation of Rac1 and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase, leading to up-regulation of Cx43, N-cadherin, and interstitial fibrosis. 20130915_Data suggest that the three mutations in GJA1 or rhoGJA1 result in at least partial loss of normal functions carried out by CX43. 20137634_Over-expression of Cx32 and Cx43 was found in samples of hippocampus from epileptic patients. 20167932_Connexin 43 gap junctions with highly variable morphology are formed between cardiomyocyte lateral membranes with increased frequency in heart failure and GJ turnover likely occurs via an autophagic pathway. 20233983_Cx43Hcs were found to be involved in sustaining proliferation of T cells, as assessed by cell cycle staining, thymidine incorporation assays. 20346202_concomitant electrical pacing increased gap junction expression by paracrine action. 20347265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20373058_increased expression of Cx43 and E-cadherin may contribute to the efficient metastasis of gastric cancer to the lymph nodes. 20375327_In the human retina and optic nerve, connexin43 is present on glia, blood vessels, and epithelial cells. 20406988_The tumor-suppressive function of Connexin43 in keratinocytes is mediated in part via interaction with caveolin-1. 20413811_these findings demonstrate the distribution of c-kit- and connexin 43-positive interstitial cells in the connective tissue and smooth musculature of the corpus cavernosum. 20512920_Our study shows for the first time that a free C-tail is sufficient to induce Cx43-dependent changes in cell morphology and that Cx43 signaling is linked to the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. 20512937_enhanced Cx43 expression and not gap junction-mediated communication, is involved in regulating cell cycle traverse 20530971_Results show that Cx40, Cx37, Cx43 and Cx45 were expressed within the glomeruli. 20593197_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20606116_findings implicate somatic genetic defects of Cx43 as a potential cause of atrial fibrillation and support the paradigm that sporadic, nonfamilial cases of lone AF may arise from genetic mosaicism 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639392_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20651379_Both aberrant localization and epigenetic changes are associated with aberrant expression of connexin 43 in human NSCLC. 20668687_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20684953_Androgens excess downregulates connexin 43 in granulosa cells. 20803237_studies indicate cell surface sialic acid on cancer cells may suppress Cx43 gap junction functions via inhibiting Cx43 traffic 20876208_Data show that Cx43 plaques on the plasma membranes of cells within KGN and NHF spheroids 24 h postseeding. 20878577_Cx43 gene may be involved in the mechanism of peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. 20881238_hemichannels formed by Cx43 are activated by extracellular alkalinization. 20934339_In glaucomatous eyes, increased connexin43 immunoreactivity was observed at the level of the lamina cribrosa and in the peripapillary and mid-peripheral retina in association with glial activation. 20940304_although CIP75 can interact with ubiquitinated cellular proteins, its interaction with Cx43 and stimulation of Cx43 proteasomal degradation does not require the ubiquitination of Cx43. 21176558_Down-regulation of Cx43 expression and ultrastructure changes in the junction zone might play an important role in pathogenesis of adenomyosis. 21205823_connexin43 transcriptional suppression by TBX18 undermines cardiomyocyte cell-cell electrical coupling 21328609_Cx-43 participation is critical for heterocellular gap junction intercellular communication between mast cells and fibroblasts. 21378309_Autophagy is involoved in the degradation of CX43 and CX50. 21383325_This study pointed out that a rearrangement of Cx43-positive elements is part of abnormal tissue organization in FCD type IIB, and that cryptogenic epilepsies include forms with increased Cx43 mRNA expression. 21385904_Data show direct interaction between miR-218 and the 3'UTR of mRNAs encoding ROBO1, survivin (BIRC5), and connexin43 (GJA1). 21411628_ZO-1 regulates the rate of undocked connexon aggregation into gap junctions, enabling dynamic partitioning of Cx43 channel function between junctional and proximal nonjunctional domains of plasma membrane 21424225_Study shows that fusion of a V5/6-His tag (hexa moiety M r = 0.93 kDa) to the CT segment of Cx40, Cx43 and Cx45 does not prevent the cells from forming channels. 21442291_we propose that the increase in Cx43 expression induced by mechanical strain in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament cells plays an important role in the progression of Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. 21532342_Enhanced PKCepsilon mediated phosphorylation of connexin43 at serine 368 by a carboxyl-terminal mimetic peptide is dependent on injury. 21538160_The Tbx3, SOX4, and SOX2 ChIP data, identify a region in intron 1 of Connexin 43 bound by all tree proteins and subsequent ChIP experiments verify that this sequence is bound, in vivo, in the developing heart. 21606502_Cx43 and Cx46 have novel functions in regulating each other's expression and turnover in a reciprocal manner in addition to their conventional roles as gap junction proteins in lens cells. 21642545_A possible mechanism of Cx43 transgene activity is proposed in a newly discovered signaling pathway that regulates Foxp3 expression in regulatory T (Treg) lineage cells. 21665377_Alendronate may enhance the proliferation of osteoblastic cell line through connexin 43 activation. 21669459_Cx43 reduced expression in both maternal uterine decidua and fetal chorionic villi samples of REPL patients could contribute to recurrent early pregnancy loss. 21670345_Optic nerve and retinal dysplasia was observed in both patients, and ciliary body cysts were observed in 1 patient. Both patients carried isolated in-frame deletion and missense mutations of the GJA1 gene on chromosome 6. 21716323_Cx43 has an important role in hair regeneration, growth, and cuticle formation. 21718795_These data suggest that Cx43 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of pulmonary giant cell carcinoma cells by modulating the secretion of FSTL1, which is regulated by histone acetylation. 21726529_this study provides novel insights into the regulation of gap junction function by CYPOR and suggests that Cx43 may play an important role(s) in CYPOR-mediated bone defects seen in patients. 21727092_increased activation of associated PAK1 can contribute to enhanced Cx43 dephosphorylation and impaired intercellular coupling that may underlie slow conduction in heart failure 21763271_Connexin43 phosphorylation and cytoprotection in the heart [review] 21819962_review of connexin43 phosphorylation in brain, cardiac, endothelial and epithelial tissues [review] 21839722_review of functional consequences of abnormal Cx43 expression in the heart [review] 21856279_connexin |
ENSMUSG00000055691 |
Gja6 |
53.731437 |
0.2752526104 |
-1.861172 |
0.231880535 |
68.073993 |
0.00000000000000015747397304204321216848436209267303298348353779358838044899471242388244718313217163085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001175083843326874588099482344732787899456354714818051565572432082262821495532989501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1169901 |
3.4960754 |
84.5491172 |
7.5094717 |
| ENSG00000152700 |
51128 |
SAR1B |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6B6 |
FUNCTION: GTP-binding protein involved in transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus (By similarity). Activated by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor PREB (By similarity). Involved in the selection of the protein cargo and the assembly of the COPII coat complex (By similarity). Synergizes with the cargo receptor SURF4 to mediate the export of lipoproteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby regulating lipoprotein delivery and the maintenance of lipid homeostasis (PubMed:33186557). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QVY3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33186557}. |
Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a small GTPase that acts as a homodimer. The encoded protein is activated by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor PREB and is involved in protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. This protein is part of the COPII coat complex. Defects in this gene are a cause of chylomicron retention disease (CMRD), also known as Anderson disease (ANDD). Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:51128; |
COPII vesicle coat [GO:0030127]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070971]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class I [GO:0002474]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipoprotein transport [GO:0042953]; membrane organization [GO:0061024]; positive regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0070863]; regulation of COPII vesicle coating [GO:0003400]; regulation of lipid transport [GO:0032368]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050] |
12692552_identify eight mutations in SARA2 that are associated with three severe disorders of fat malabsorption 15943909_Sara2 is an important gene in processes involving erythroid cell proliferation and differentiation. 17945526_Five mutations in the SAR1B gene causing Anderson disease. 18786134_muscular as well as cardiac abnormalities that could be related to the reported expression of SARA2 in these tissues 19846172_Variable phenotypic expression of chylomicron retention disease in a kindred carrying a mutation of the Sara2 gene. 21836065_Sar1b expression may promote intestinal lipid transport with the involvement of the coat protein complex II network and the processing of SREBP-1c. 22974979_the behavior of the human of Sar1A and Sar1B, a key component of the COPII family of vesicle coat proteins, was examined. 24338480_although Sar1A antagonizes the lipoprotein secretion-promoting activity of Sar1B, both isoforms modulate the expression of genes encoding cholesterol biosynthetic enzymes and the synthesis of cholesterol de novo. 25703997_SAR1B polymorphisms were associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) risk; results were not significant after correction for multiple tests. Simultaneous screening using SAR1B rs11948613 and ApoE epsilon4 status offered a better sensitivity for AD screening. 25826777_Our data also suggest that Sar1B overexpression contributes to regulation of CHOL transport and metabolism by facilitating rapid uptake and transport of CHOL. 28982670_Report compensatory Sar1a elevation after Sar1b gene deletion in Caco-2/15 cells prevents chylomicron collapse. 29540175_Targeted next generation DNA sequencing revealed several rare heterozygous missense variants in both MTTP and APOB genes known or predicted to be deleterious, in addition to a novel heterozygous missense variant in SAR1B, which encodes the gene causing chylomicron retention disease 30251687_Study data suggest that SAR1A and SAR1B are the critical regulators of trafficking of Nav1.5. Moreover, SAR1A and SAR1B interact with MOG1, and are required for MOG1-mediated cell surface expression and function of Nav1.5. 30640893_Chylomicron retention disease is an autosomal recessive disorder, in which intestinal fat malabsorption is the main cause of diverse severe manifestations due to mutations in the SAR1B. (Review) 30782561_Twenty-three patients were genetically confirmed as affected by primary hypobetalipoproteinemia. In this group of patients, the most prevalent mutated genes were APOB (in 17 patients, with eight novel mutations identified), SAR1B (in 3 patients, with one novel mutation identified), ANGPTL3 (in 2 patients), and MTTP (in 1 patient). The other 21 patients could not be genetically diagnosed with hypobetalipoproteinemia despit 31409740_SAR1B GTPase is necessary to protect intestinal cells from disorders of lipid homeostasis, oxidative stress, and inflammation 32358066_Small sequence variations between two mammalian paralogs of the small GTPase SAR1 underlie functional differences in coat protein complex II assembly. 33186557_Receptor-Mediated ER Export of Lipoproteins Controls Lipid Homeostasis in Mice and Humans. 34290409_SAR1B senses leucine levels to regulate mTORC1 signalling. |
ENSMUSG00000020386 |
Sar1b |
372.607342 |
2.2515777224 |
1.170936 |
0.099959323 |
136.491057 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000015581382015465417656207579725183446166509134992769497729936822836459796611314256595606786426344569918001070618629455566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000002100284918249037258856115765078477732540950235352654923896950894732927998549004700024056546681094914674758911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
495.8885321 |
31.4087710 |
221.7762329 |
10.5693336 |
| ENSG00000152749 |
160897 |
GPR180 |
protein_coding |
Q86V85 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. This protein is produced predominantly in vascular smooth muscle cells and may play an important role in the regulation of vascular remodeling. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:160897; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; response to pheromone [GO:0019236] |
12730718_22 SNPs were isolated from the ITR locus by systematically screening genomic DNA from 48 healthy Japanese individuals 25772937_A null GPR180 mutation segregates over two generations with iridocorneal angle dysgenesis, consistent with the view that deletions of this gene are the cause of MCOR. 32200002_Microcoria due to first duplication of 13q32.1 including the GPR180 gene and maternal mosaicism. 34880217_GPR180 is a component of TGFbeta signalling that promotes thermogenic adipocyte function and mediates the metabolic effects of the adipocyte-secreted factor CTHRC1. |
ENSMUSG00000022131 |
Gpr180 |
138.904769 |
5.2897985236 |
2.403213 |
0.298732570 |
59.048783 |
0.00000000000001538110278652712673087650488208282137947706565139771583972105872817337512969970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000102033742529950738799729697878180473741066211501582472465088358148932456970214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
215.2323410 |
87.1820837 |
41.3499558 |
12.1063729 |
| ENSG00000152760 |
200132 |
DYNLT5 |
protein_coding |
Q8N7M0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable dynein intermediate chain binding activity. Predicted to be involved in microtubule-based movement. Predicted to be part of cytoplasmic dynein complex. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:200132; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic dynein complex [GO:0005868]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
31896777_TCTEX1D1 is a genetic modifier of disease progression in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. |
ENSMUSG00000028523 |
Dynlt5 |
1675.679100 |
0.2543419763 |
-1.975159 |
0.082533048 |
546.037374 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000091627925144614548578336742961822782113978358053672977358221812226452227386473867667172874437775752488288291407157217463929599736034281362889373956719151634049113890794984196294893994102256066671317362556787346 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000047958445926755703406927810562332204340822083450236961262445798985457809518329396911881594593738572250361025358575731234285366976225931881974369215578965699188855553623312602080529437549431583767531974183822600 |
Yes |
Yes |
625.9752318 |
219.8392405 |
2485.7974165 |
627.3808652 |
| ENSG00000152766 |
118932 |
ANKRD22 |
protein_coding |
Q5VYY1 |
|
ANK repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:118932; |
|
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 28667340_ANKRD22 exhibits oncogene activity that promotes tumor progression in NSCLC through the transcriptional regulation of E2F1. 31903135_ANKRD22, a novel tumor microenvironment-induced mitochondrial protein promotes metabolic reprogramming of colorectal cancer cells. 34584137_ANKRD22 is an N-myristoylated hairpin-like monotopic membrane protein specifically localized to lipid droplets. |
ENSMUSG00000024774 |
Ankrd22 |
10.026200 |
10.8229284962 |
3.436019 |
0.678348830 |
32.754134 |
0.00000001045836199459146930378017554316011361592586581537034362554550170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000045468460394748179096020677556963529575284610473318025469779968261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.7489025 |
8.2664499 |
1.7469560 |
0.7117812 |
| ENSG00000152767 |
10160 |
FARP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y4F1 |
FUNCTION: Functions as guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RAC1. May play a role in semaphorin signaling. Plays a role in the assembly and disassembly of dendritic filopodia, the formation of dendritic spines, regulation of dendrite length and ultimately the formation of synapses (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Synaptosome |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing a FERM (4.2, exrin, radixin, moesin) domain, a Dbl homology domain, and two pleckstrin homology domains. These domains are found in guanine nucleotide exchange factors and proteins that link the cytoskeleton to the cell membrane. The encoded protein functions in neurons to promote dendritic growth. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2013]. |
hsa:10160; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; extrinsic component of postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098890]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0098974]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; retrograde trans-synaptic signaling by trans-synaptic protein complex [GO:0098942]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416] |
19475631_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26911374_We have reported here for the first time a reduced activity of both Rac1 and Cdc42 in human pheochromocytoma resection as well as tumor-associated expression changes of FARP1, ARHGEF1, and ARHGAP36 31021836_FARP1 facilitates malignant melanoma cell proliferation and migration by modulating the MAPK signaling pathway. 34731623_FARP1, ARHGEF39, and TIAM2 are essential receptor tyrosine kinase effectors for Rac1-dependent cell motility in human lung adenocarcinoma. 35045883_circFARP1 enables cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via the LIF/STAT3 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000025555 |
Farp1 |
21.250559 |
0.3609741764 |
-1.470032 |
0.574667209 |
5.880214 |
0.01531195995771480848623991022350310231558978557586669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028194177766450917443918910976208280771970748901367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7155617 |
3.8364090 |
30.1837986 |
7.5092744 |
| ENSG00000152784 |
56978 |
PRDM8 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQV8 |
FUNCTION: Probable histone methyltransferase, preferentially acting on 'Lys-9' of histone H3 (By similarity). Involved in the control of steroidogenesis through transcriptional repression of steroidogenesis marker genes such as CYP17A1 and LHCGR (By similarity). Forms with BHLHE22 a transcriptional repressor complex controlling genes involved in neural development and neuronal differentiation (By similarity). In the retina, it is required for rod bipolar and type 2 OFF-cone bipolar cell survival (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BZ97}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Epilepsy;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Neurodegeneration;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to a conserved family of histone methyltransferases that predominantly act as negative regulators of transcription. The encoded protein contains an N-terminal Su(var)3-9, Enhancer-of-zeste, and Trithorax (SET) domain and a double zinc-finger domain. Knockout of this gene in mouse results in mistargeting by neurons of the dorsal telencephalon, abnormal itch-like behavior, and impaired differentiation of rod bipolar cells. In humans, the protein has been shown to interact with the phosphatase laforin and the ubiquitin ligase malin, which regulate glycogen construction in the cytoplasm. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:56978; |
nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; methylation [GO:0032259]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
26909595_Aberrant hypermethylation is particularly observed in PRDM8 and this may support identification and classification of bone marrow failure syndromes 27278638_alteration of hydroxymethylation and methylation of PRDM8 correlates with changes in its expression in the peripheral blood of children with DS. Given the proposed function of PRDM8 in cognitive disability in DS 29572888_Through regulating NAP1L1, PRDM8 inhibits PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32819411_PRDM8 reveals aberrant DNA methylation in aging syndromes and is relevant for hematopoietic and neuronal differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000035456 |
Prdm8 |
20.097215 |
0.3812998472 |
-1.391002 |
0.370122507 |
14.300240 |
0.00015584500161557846248210068562656260837684385478496551513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000415887221812680891400854088502114791481290012598037719726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.5765993 |
3.1006818 |
30.4454733 |
5.2432883 |
| ENSG00000152804 |
3087 |
HHEX |
protein_coding |
Q03014 |
FUNCTION: Recognizes the DNA sequence 5'-ATTAA-3' (By similarity). Transcriptional repressor (By similarity). Activator of WNT-mediated transcription in conjunction with CTNNB1 (PubMed:20028982). Establishes anterior identity at two levels; acts early to enhance canonical WNT-signaling by repressing expression of TLE4, and acts later to inhibit NODAL-signaling by directly targeting NODAL (By similarity). May play a role in hematopoietic differentiation (PubMed:8096636). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P43120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20028982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8096636}. |
3D-structure;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the homeobox family of transcription factors, many of which are involved in developmental processes. Expression in specific hematopoietic lineages suggests that this protein may play a role in hematopoietic differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3087; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-DNA complex [GO:0032993]; DNA binding, bending [GO:0008301]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; eukaryotic initiation factor 4E binding [GO:0008190]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; TBP-class protein binding [GO:0017025]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; DNA conformation change [GO:0071103]; mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0006406]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045736]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by competitive promoter binding [GO:0010944]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transcription by transcription factor localization [GO:0010621]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030948]; poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0016973]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504]; regulation of leukocyte proliferation [GO:0070663]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11701950_genomic organization and chromosome 10 mapping 12554669_PRH is a negative regulator of eIF4E in myeloid cells, interacting with eIF4E through a conserved binding site typically found in translational regulators 12588764_HEX may not affect the differentiation of endothelial cells but acts as a negative regulator of angiogenesis. 12826010_PRH interacts with the HC8 subunit of the proteasome in the context of both 20 and 26 S proteasomes and is associated with the proteasome in K562 hematopoietic cells; the proline-rich PRH N-terminal domain is responsible for this interaction. 14517947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14555989_Hex can act as a T lineage oncogene when misexpressed in hematopoietic precursor cells 15016828_Tgf-beta mediated repression of flk-1/KDR and mediated repression of flk-1/KDR and VEGF signaling involves the inducible formation of inhibitory Hex-GATA signaling Hex-GATA involves the formation of Hex-GATA complexes. 15024728_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15062550_Pax8 regulates the transcriptional activity of Hex promoter; several Pax8 binding sites in the Hex promoter are present 15242862_Hex, a hematopoietically expressed homeobox protein, induces transcription of the SM22alpha gene by facilitating the interaction between SRF and its cognate binding site in embryonic fibroblasts. 16540119_region of PRH contains a novel proline-rich dimerisation domain that mediates oligomerisation 16854221_HEX may play a role in differentiation of the epithelial breast cell 17293876_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463246_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463248_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17463249_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17618412_Variations are not linked to diabetes mellitus. 17632701_Genetic variation predisposes to type 2 diabetes. 17786204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17804762_CDKAL1 and HHEX/IDE diabetes-associated alleles are associated with decreased pancreatic beta-cell function, including decreased beta-cell glucose sensitivity that relates insulin secretion to plasma glucose concentration. 17804762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17827400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17827400_Variations confer impaired glucose- and tolbutamide-induced insulin release in middle-aged and young healthy subjects. 17928989_HHEX is a common type 2 diabetes-susceptibility gene across different ethnic groups. 17928989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17971426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17971426_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the HHEX gene are associated with susceptibility to type 2 diaabetes across the boundary of race. 18039816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18039816_Single nucleotid polymorphismallele represents a risk allele for beta-cell dysfunction and, mayconfer increased susceptibility of beta-cells toward adverse environmental factors and type 2 diabetes. 18162508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162508_The association of 6 loci with type 2 diabetes risk in Japanese patients is reported. 18210030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18231124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18231124_variants near the HHEX gene contribute to the risk of type 2 diabetes in a Dutch population 18388181_translocation involving nucleoporin 98 (NUP98) fused to the DNA-binding domain of the hematopoietically expressed homeobox gene found in acute myeloid leukemia 18426861_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18437351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18461161_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18469204_Data confirmed the associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms in HHEX with risk for type 2 diabetes in Asians. 18469204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18477659_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18516622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18544707_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18591388_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18597214_Gene variants of CDKAL1, PPARG, IGF2BP2, HHEX, TCF7L2, and FTO predispose to type 2 diabetes in the German KORA 500 K study population. 18597214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18598350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18618095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18633108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18713067_Results demonstrate that transcriptional repression by PRH is dependent on TLE availability and suggest that subnuclear localization of TLE plays an important role in transcriptional repression by PRH. 18719881_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18755198_PRH octamers wrap DNA in order to bring about transcriptional repression 18984664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18991055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18991055_Single nucleotide polymorphism in HHEX is associated with type 2 diabetes. 19002430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19008344_Data show that SNPs in HHEX did not confer a significant risk for type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 19008344_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19020323_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19020324_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19033397_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19033397_Type 2 diabetes susceptibility of HHEX was confirmed in Japanese. 19053027_Located on chromosome 10 and suscptibility of polymorphisms are related to type 2 diabetes. 19072826_HEX/Hex is a novel bile acid-induced FXR/Fxr target gene during adaptation of hepatocytes to chronic bile acid exposure. 19082521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19117022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19117022_Variations within the HHEX gene conferred the impaired insulin secretion and changes of insulin degradation but no alteration in insulin sensitivity in carriers of risk for gluccose intolerance. 19139842_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19172244_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225753_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19228808_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19247372_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258404_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258437_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19279076_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19324937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19368707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19380854_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19401414_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19502414_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19592620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19602701_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19622614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19622614_The association of low birth weight and type 2 diabetes risk alleles of the HHEX-IDE locus is confirmed in children of mothers with type 1 diabetes. 19720844_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741166_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19741467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19794065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19808892_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19862325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19862325_there is an association between PPARG, KCNJ11, CDKAL1, CDKN2A-CDKN2B, IDE-KIF11-HHEX, IGF2BP2 and SLC30A8 and type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population 19892838_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19933996_the same genetic HHEX-IDE variant, which is associated with type 2 diabetes from previous studies, also influences pediatric body mass index 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20028982_the interaction between Hhex and SOX13 may contribute to control Wnt/TCF1 signaling in the early embryo. 20041287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20041287_There was no association of the genetic polymorhism rs1111875 of HHEX with the occurrence of polycystic ovary syndrome in the Chinese population. 20043145_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20075150_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20080751_HHEX has been implicated in pancreas development and the regulation of insulin secretion and risk of type 2 diabetes. 20161779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20176809_PRH is a key regulator of the VEGF signaling pathway and describe a mechanism whereby PRH plays an important role in tumorigenesis and leukemogenesis. 20203524_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20215779_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20384434_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460429_Type 2 diabetes susceptibility alleles at HHEX are associated with low body mass index at 8 years in children who were born large for gestational age. 20490451_Data report a novel association between the fetal ADCY5 type 2 diabetes risk allele and decreased birthweight, and confirm in meta-analyses associations between decreased birthweight and the type 2 diabetes risk alleles of HHEX-IDE and CDKAL1. 20490451_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20509872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20550665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20580033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20597906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20616309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647405_Our data indicate that common genetic variants in two genes previously related to obesity (FTO) and diabetes (HHEX) by genome-wide association scans were not associated with endometrial cancer risk. 20703447_HHEX, IDE and SLC30A8 showed strongest tissue-specific mRNA expression bias and are associated with increased risk of type 2 diabete. 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20724036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20879858_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20927120_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20929593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21056935_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21059810_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21368910_Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis revealed that the sequence variant (rs5015480) near HHEX and two SNPs (rs7756992 and rs9465871) in CDKAL1 were associated with the susceptibility of type 2 diabetes mellitus in females, but not in males. 21510814_HHEX, is more likely to represent the genuine signals of T2DM in the Tunisian population. 21656028_Loss of HHEX is associated with colorectal cancer. 22443257_None of the 12 SNPs in the six genes (KCNJ11, TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HHEX, FTO and CDKAL1) uncovered in the genome-wide association studies were associated with polycystic ovary syndrome. 22487833_The associations between SNPs of TCF7L2, CDKAL1, SLC30A8 and HHEX and the development of DR and DN. 22506066_Genetic variants of the IDE-KIF11-HHEX region at 10q23.33 contribute to type 2 diabetes susceptibility. 22540015_The proline rich homeodomain protein PRH/Hhex forms predominantly octameric and/or hexadecameric species in solution as well as larger assemblies. 22874537_re-establishment of gene control by PRH is in part responsible for the therapeutic effects of dasatinib. 22923468_Association to type 2 diabetes was found for rs13266634 (SLC30A8), rs7923837 (HHEX), rs10811661 (CDKN2A/2B), rs4402960 (IGF2BP2), rs12779790 (CDC123/CAMK1D), and rs2237892 (KCNQ1). 23036584_In conclusion, this epistatic interaction showed a high degree of consistency when stratifying by sex, the epsilon4 allele of apolipoprotein E genotype, and geographic region. 23166797_A significant association of rs1111875, rs5015480 and rs7923837 in HHEX gene with type 2 diabetes. 23349771_Data indicate associations of SNPs in eight loci CXCR4, HHEX, FOXA2, NGN3, TCF7L2, FLJ39370 (C4orf32), LOC646279 (RPL21P7) and THADA with body mass index (BMI) and weight. 23445342_Tissue-specific knockdown of the HHEX ortholog dHHEX (CG7056) directed metabolic defects and enhanced lethality; for example, fat-body-specific loss of dHHEX led to increased hemolymph glucose and reduced insulin sensitivity 23929257_In all the CHD patients, we did not find any causative mutations in the coding region of the HHEX gene. 24112421_Data indicate the potential importance of CDKAL1 protein and homeobox protein HHEX in glucose homeostasis in this Alaska Native population with a low prevalence of type 2 diabetes (T2D). 24240683_PRH controls the migration of multiple epithelial cell lineages in part at least through the direct transcriptional regulation of Endoglin 24651531_HHEX promotes hepatic specification by repressing EOMES expression. 25220416_Data suggest that Hhex is a novel regulator of c-Myc function that limits c-Myc activity in transformed cells. 26563606_The SNPs in TCF7L2 and HHEX were genotyped by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism. There were no significant differences in the distribution of genotypes and alleles between polycystic ovary syndrome cases and controls 26728554_Hhex binds to the Cdkn2a locus and directly interacts with the Polycomb-repressive complex 2 (PRC2) to enable H3K27me3-mediated epigenetic repression 26757609_Low HHEX mutation is associated with Thyroid Dysgenesis. 27052408_Data suggest that hematopoietically expressed homeobox protein (HHEX) downmodulation by promyelocytic leukemia-retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion oncoprotein (PML-RARalpha) is a key event during acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) pathogenesis. 27105501_This finding highlights the potentially functional alteration with HHEX rs1111875 and rs7923837 polymorphisms may increase colorectal cancer susceptibility. 27151212_These studies identify uPA-dependent de-repression of vegfr1 and vegfr2 gene transcription through binding to HHEX/PRH as a novel mechanism by which uPA mediates the pro-angiogenic effects of VEGF and identifies a potential new target for control of pathologic angiogenesis. 27335261_Two differentiation-related genes, HHEX and HLX, are promoters of early phase reprogramming toward pluripotency. 27377502_The multivariate logistic regression analysis with reference to both alleles and genotypes of CDKAL1 SNPs showed significant association, suggesting an important role for this gene in the T2DM pathophysiology. INTERPRETATION & CONCLUSIONS: A significant association was seen of all the three SNPs of CDKAL1 and CDKN2A/B genes with T2DM but none of the two SNPs of HHEX. 27684496_The aim of this study was to examine the association between HHEX (rs5015480) and PROX1 (rs340874) gene polymorphisms and Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) .The HHEX gene rs5015480 C allele may be a risk allele of GDM that is associated with increased BMI during pregnancy 27965937_HHEX over expression induced by human cytomegalovirus infection closely associated with vascular proliferative diseases. 28927755_Vascular smooth muscle protein kinase CK2 inhibition suppresses neointima formation via a proline-rich homeodomain-dependent mechanism. 29263042_HHEX is expressed in multiple types of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), with the highest levels seen in t(8;21) AML. 29720110_Study clearly demonstrates that rs5015480 genetic variant in HHEX influences fasting glucose levels in Korean women and male heavy smokers. 30207601_Genetic risk scores were calculated by summing the risk alleles of 4 selected single nucleotide polymorphisms, CDKAL1 rs7754840 and rs9460546, HHEX rs5015480, and OAS3 31237015_HHEX gene polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control report from Iran. 31843982_A Runaway PRH/HHEX-Notch3-Positive Feedback Loop Drives Cholangiocarcinoma and Determines Response to CDK4/6 Inhibition. 32195947_This study concluded that HHEX rs5015480 represents a risk factor for the development of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, and pregnant women carrying the CC genotype have an increased risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. 34321041_Hhex inhibits cell migration via regulating RHOA/CDC42-CFL1 axis in human lung cancer cells. 34623901_Integrated single-cell transcriptomics and epigenomics reveals strong germinal center-associated etiology of autoimmune risk loci. 35887298_Unraveling the Influence of HHEX Risk Polymorphism rs7923837 on Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. 36008411_CK2-induced cooperation of HHEX with the YAP-TEAD4 complex promotes colorectal tumorigenesis. |
|
|
87.050872 |
0.3357072893 |
-1.574724 |
0.174549998 |
84.615237 |
0.00000000000000000003624611941553820008100055453510296944392959506008320194874600117529439557984005659818649291992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000323453883055226005105001834441144807928801990165801815910184835445306816836819052696228027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.6417839 |
4.9781893 |
130.8821543 |
9.1553163 |
| ENSG00000152894 |
5796 |
PTPRK |
protein_coding |
Q15262 |
FUNCTION: Regulation of processes involving cell contact and adhesion such as growth control, tumor invasion, and metastasis. Negative regulator of EGFR signaling pathway. Forms complexes with beta-catenin and gamma-catenin/plakoglobin. Beta-catenin may be a substrate for the catalytic activity of PTPRK/PTP-kappa. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19836242}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem catalytic domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The extracellular region contains a meprin-A5 antigen-PTP mu (MAM) domain, an Ig-like domain and four fibronectin type III-like repeats. This PTP was shown to mediate homophilic intercellular interaction, possibly through the interaction with beta- and gamma-catenin at adherens junctions. Expression of this gene was found to be stimulated by TGF-beta 1, which may be important for the inhibition of keratinocyte proliferation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5796; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; leading edge membrane [GO:0031256]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; gamma-catenin binding [GO:0045295]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0005001]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; focal adhesion assembly [GO:0048041]; negative regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045786]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010839]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; protein localization to cell surface [GO:0034394]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
16263724_RPTP-kappa is a key regulator of EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation and function in human keratinocytes 16672235_the crystal structure of catalytically active, monomeric D1 domain of RPTPkappa at 1.9 A. RPTPkappa is monomeric in solution and crystal structure. 16849327_EGF receptor is activated in human keratinocytes by oxidative inhibition of receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase kappa by ultraviolet irradiation 17720884_EBNA1 apparently disables TGF-beta signaling, which subsequently decreases transcription of the PTPRK tumor suppressor 18276111_PTPRK influences transactivating activity of beta-catenin in non-tumoral and neoplastic cells by regulating the balance between signaling and adhesive beta-catenin, thus providing biochemical basis for the hypothesis of PTPRK as a tumor suppressor gene. 19236842_overexpression of GnT-V in a hepatoma cell line not only induced the addition of beta1,6 GlcNAc branch to N-glycan of RPTPkappa but also decreased the protein level of RPTPkappa 19800317_These data indicate that PPTRK positively regulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation, which impacts CD4(+) T cell development. 19864455_These data describe a novel mechanism of cross-talk between EGFR and TGF-beta pathways, in which RPTP-kappa functions to integrate growth-promoting and growth-inhibiting signaling pathways. 19911372_Our results suggest that GnT-V could decrease human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cell adhesion and promote cell proliferation partially through RPTPkappa. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21094132_PTPkappa was scissored by the processed form of proprotein convertase 5, and galectin-3 binding protein which is over-produced in colon cancer cells and tissues. 23552869_PTPRK is a negative regulator of adhesion, invasion, migration, and proliferation of breast cancer cells. 23696788_Tumor derived mutations of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type k affect its function and alter sensitivity to chemotherapeutics in glioma. 23820479_PTPRK showed lower mRNA expression in duodenal mucose of celiac disease patients. 24002526_High expression of PTPRK is associated with prostate cancer. 24882578_Findings strongly indicate that the tyrosine phosphorylation of CD133, which is dephosphorylated by PTPRK, regulates AKT signaling and has a critical role in colon cancer progression. 25378349_By regulating phosphorylation of SRC, RPTPkappa promotes the pathogenic action of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes, mediating cross-activation of growth factor and inflammatory cytokine signalling by TGFbeta in RA FLS. 25609089_Notch and TGF-beta act in concert to stimulate induction of PTPRK, which suppresses EGFR activation in human keratinocytes. 25612622_PTPRK underexpression leads to STAT3 activation and contributes to nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma pathogenesis 26924569_PTPRK-RSPO3 fusions and RNF43 mutations were found to be characteristic genetic features of traditional serrated adenomas (TSAs). 28259897_PTPRK plays dual roles in coordinating angiogenesis. It plays a positive role in cell proliferation, adhesion and tubule formation, but suppresses cell migration, in particular, the FGF-promoted migration. 28543708_The present study identified RSPO fusion transcripts, including three novel transcripts, in one-third of colorectal Traditional serrated adenoma (TSA) and showed that PTPRK-RSPO3 fusions were the predominant cause of RSPO overexpression in colorectal TSA. 28987514_Study found a significant association between PTPRK genetic variants and the risk and age at onset of Alzheimer's disease in two independent samples, and provided initial evidence of several genetic variants in PTPRK influencing the risk of cancer and cholesterol levels. 29628123_PTPRK was identified as a direct target of miR-1260b, and PTPRK expression was inversely correlated with miR-1260b in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines and clinical tissues 30185827_Study show that RAS at the Golgi is selectively activated by apoptogenic stimuli and antagonizes cell survival by suppressing ERK activity through the induction of PTPRkappa, which targets CRAF for dephosphorylation. RAS oncogenic potential is strictly dependent on its sublocalization, with Golgi complex-located RAS antagonizing tumor development. 30838170_These results suggested that PTPRK functions as a novel tumor suppressor in NSCLC, and its suppressive ability may be involved in STAT3 activation. 30924770_The authors report here that the homophilic receptor PTPRK is stabilized at cell-cell contacts in epithelial cells. PTPRK directly and selectively dephosphorylates at least five substrates, including Afadin, PARD3 and delta-catenin family members, which are all important cell-cell adhesion regulators. 30947381_Knockdown of PTPRK potentiates the pro-oncogenic CD133-AKT pathway in colon cancer cells. 31027318_the lower PTPRK expression was observed in Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1 Family Member A1 (ALDH1A1) positive cancer stem cells (CSCs) population, suggesting the role of PTPRK downregulation in primary as well as acquired resistance to cytotoxic drugs. 31934854_The tumor suppressor PTPRK promotes ZNRF3 internalization and is required for Wnt inhibition in the Spemann organizer. 33068671_Simulation of multiple microenvironments shows a pivot role of RPTPs on the control of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. 34590584_A MET-PTPRK kinase-phosphatase rheostat controls ZNRF3 and Wnt signaling. 36129915_Investigation of cell signalings and therapeutic targets in PTPRK-RSPO3 fusion-positive colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000019889 |
Ptprk |
501.091865 |
4.6325584745 |
2.211809 |
0.112595348 |
377.791850 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000376455587132342440261880264718120512638557077915057920466501984667793510253176425357438849164087984013339060439357851091058849860564135688512173468613447287129002932576039278908352177955701776057114304357194972672218113984854426234960556030273438 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000133891191953575283000753475477919553487855497050950098057716869412800860400909779943991247128620069912500848417801768082607334029616249432889575742881417633418449510517977613926003554348462615453439024035264814926904364256188273429870605468750000 |
Yes |
No |
846.8116402 |
50.8511339 |
184.0935772 |
9.0452260 |
| ENSG00000152954 |
140767 |
NRSN1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZ57 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in neural organelle transport, and in transduction of nerve signals or in nerve growth. May play a role in neurite extension. May play a role in memory consolidation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12463420}. |
Cell projection;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in nervous system development. Predicted to be located in cytoplasmic vesicle and growth cone. Predicted to be active in neuron projection; neuronal cell body; and transport vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:140767; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; nervous system development [GO:0007399] |
12463420_Cloning, expression and characterization of VMP gene. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20807314_dilysine retrieval signal-containing p24 proteins, p24alpha(2) and p24delta(1), bind with gamma-secretase complexes and collaborate in attenuating gamma-cleavage of beta-amyloid precursor protein 29654647_GAL, GAP43 and NRSN1 single nucleotide polymorphisms and related gene-gene interaction networks might be involved in the altered susceptibility to Hirschsprung disease in the Han Chinese population. 32037595_Neuregulin-1 promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction, and prevents hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in neonatal cardiomyocytes. |
ENSMUSG00000048978 |
Nrsn1 |
37.625474 |
7.0905551329 |
2.825899 |
0.382003022 |
55.928354 |
0.00000000000007516072488301906593495888420855524086482309098489196230730158276855945587158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000481080788930338820074606496822398532856555897208039596080197952687740325927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.5933673 |
14.6314226 |
9.5495526 |
1.8028289 |
| ENSG00000153071 |
1601 |
DAB2 |
protein_coding |
P98082 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein that functions as clathrin-associated sorting protein (CLASP) required for clathrin-mediated endocytosis of selected cargo proteins. Can bind and assemble clathrin, and binds simultaneously to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2) and cargos containing non-phosphorylated NPXY internalization motifs, such as the LDL receptor, to recruit them to clathrin-coated pits. Can function in clathrin-mediated endocytosis independently of the AP-2 complex. Involved in endocytosis of integrin beta-1; this function seems to redundant with the AP-2 complex and seems to require DAB2 binding to endocytosis accessory EH domain-containing proteins such as EPS15, EPS15L1 and ITSN1. Involved in endocytosis of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator/CFTR. Involved in endocytosis of megalin/LRP2 lipoprotein receptor during embryonal development. Required for recycling of the TGF-beta receptor. Involved in CFTR trafficking to the late endosome. Involved in several receptor-mediated signaling pathways. Involved in TGF-beta receptor signaling and facilitates phosphorylation of the signal transducer SMAD2. Mediates TFG-beta-stimulated JNK activation. May inhibit the canoniocal Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway by stabilizing the beta-catenin destruction complex through a competing association with axin preventing its dephosphorylation through protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Sequesters LRP6 towards clathrin-mediated endocytosis, leading to inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. May activate non-canonical Wnt signaling. In cell surface growth factor/Ras signaling pathways proposed to inhibit ERK activation by interrupting the binding of GRB2 to SOS1 and to inhibit SRC by preventing its activating phosphorylation at 'Tyr-419'. Proposed to be involved in modulation of androgen receptor (AR) signaling mediated by SRC activation; seems to compete with AR for interaction with SRC. Plays a role in the CSF-1 signal transduction pathway. Plays a role in cellular differentiation. Involved in cell positioning and formation of visceral endoderm (VE) during embryogenesis and proposed to be required in the VE to respond to Nodal signaling coming from the epiblast. Required for the epithelial to mesenchymal transition, a process necessary for proper embryonic development. May be involved in myeloid cell differentiation and can induce macrophage adhesion and spreading. May act as a tumor suppressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11387212, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12805222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16267015, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16984970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19306879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21995445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22323290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22491013}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Coated pit;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Endocytosis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport;Tumor suppressor;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a mitogen-responsive phosphoprotein. It is expressed in normal ovarian epithelial cells, but is down-regulated or absent from ovarian carcinoma cell lines, suggesting its role as a tumor suppressor. This protein binds to the SH3 domains of GRB2, an adaptor protein that couples tyrosine kinase receptors to SOS (a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras), via its C-terminal proline-rich sequences, and may thus modulate growth factor/Ras pathways by competing with SOS for binding to GRB2. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:1601; |
clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:0050750]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; clathrin coat assembly [GO:0048268]; leading edge cell differentiation [GO:0035026]; negative regulation of androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060766]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903077]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of aldosterone biosynthetic process [GO:0032349]; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion [GO:2000860]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:2000370]; positive regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:2000643]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:2000096]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of Rho-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:2000298]; response to salt [GO:1902074]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11812785_mechanism of growth inhibitory effect in prostate cancer 12473651_DOC2 has a role in regulating c-Src in prostatic epithelium and cancer 12805222_Results suggest that disabled-2 functions as a negative regulator of canonical Wnt signaling by stabilizing the beta-catenin degradation complex. 14596919_CIN85 association with Dab2 is essential for its recruitment to clathrin coat and appears to be modulated by growth factor stimulation 14669280_Loss in dab-2 expression is correlated with the loss of epithelial basement membrane in morphologically normal areas 15134832_a binding affinity of Dab phosphotyrosine interaction domain for megalin CT of K(D) = 2.6 x 10(-7) +/- 5.3 x 10(-8) 15280374_findings indicate Ser(24) phosphorylation as a molecular basis for DAB2 acting as a negative regulator in alpha(IIb)beta(3) inside-out signaling 15894542_signaling pathway proceeding from the TGFbeta receptors to Dab2 and TAK1, leading to TGFbeta-stimulated JNK activation, FN expression, and cell migration 16061224_DAB2 expression during megakaryocytic differentiation expression is regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. 16267015_DOC-2/DAB2 can modulate androgen receptor-mediated cell growth in both normal and malignant prostatic epithelial cells. 16870701_Dab2 expression is exceptionally low in hepatocytes, likely accounting for the pathological hypercholesterolemia that accompanies ARH loss. 16984970_Results suggest that Dab2 is a cargo-specific endocytic adaptor protein, stably associating with phospholipids and clathrin to sort LDLR to nascent-coated pits. 17009406_Loss of Disabled-2 (DAB2) protein expression occurs in early pre-neoplastic stages of development of esophageal cancer and is sustained down the tumorigenic pathway. 17115114_analysis of Dab2 protein loss and infrequent promoter hypermethylation in breast cancer 17671122_Decreased DOC-2/DAB2 expression is associated with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder 18070591_These results suggest that Dab2 is a ligand dependent bi-directional regulator of ERK1,2 activity. 18354201_Doc2alpha-Muunc13-4 system regulates Ca(2+)-dependent secretory lysosome exocytosis in mast cells 18582465_These results suggest that DAB2, via Src and focal adhesion signaling, plays a role in human endothelial cell function. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19581412_Dab2 internalizes integrins freely diffusing on the cell surface and Dab2 regulates migration. 19767570_Conditional Dab2 knockout mice maintain normal numbers of circulating regulatory T cells (Tregs), suggesting that DAB2 may be required for amplification, rather than maintenance, of transforming growth factor (TGF)beta signaling. 19855435_Data show that downregulation of myosin VI expression results in a significant reduction in PSA and VEGF secretion in LNCaP cells, and the intracellular targeting seems to involve myosin VI-interacting proteins, GIPC and LMTK2 and Dab2. 19956625_two pools of Dab2 co-exist at the platelet surface, in both sulfatide- and integrin receptor-bound states, and their balance controls the extent of the clotting response 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20383146_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20525238_Demonstrate frequent DAB2 promoter hypermethylation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and support the putative tumour suppressor effect of DAB2. 20592473_DAB2 acts as a tumor suppressor by dictating tumor cell TGF-beta responses, identify a biomarker for squamous cell carcinomas progression. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21063401_Loss of Dab2 expression, commonly observed in breast cancer, may facilitate TGFbeta-stimulated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and therefore increase the propensity for metastasis. 21097498_Dab2 is part of an accommodation of the cell to the altered physicochemical conditions prevalent in mitosis, aimed at allowing endocytic activity throughout the cell cycle. 21496867_Expressions of Disabled-2 and Axin were concurrently reduced and correlated with the malignant phenotype of lung cancers. 21725366_Results indicate that miR-187 directly targeted Disabled homolog-2 (Dab2). 21995445_Dab2 depletion increased the CFTR half-life ~3-fold, in addition to inhibiting CFTR endocytosis. 22218591_It was concluded that PKB/Akt is part of an endocytic machinery and it mediates albumin uptake through its interaction with Dab2. 22265793_Dab2 is required for the TGFbeta-induced gene expression of angiogenic factors such as VEGF and FGF2 22323290_FCHO2 regulates the size of clathrin structures, and its interaction with Dab2 is needed for LDLR endocytosis under conditions of low AP2. 22399289_Dab2 mediates AP-2 independent recruitment of CFTR to CCVs in polarized human airway epithelial cells. 22648170_These data suggest that Dab2-mediated recruitment of EH domain proteins selectively drives the internalization of the Dab2 cargo, integrin b1. 22705885_These findings thereby define an adaptor-specific mechanism in the control of fibrinogen uptake and implicate that DAB2 is the key adaptor in the clathrin-associated endocytic complexes to mediate fibrinogen internalization. 22898784_inhibition of Dab2 decreases phosphorylation of SMAD-1, 5, and 8 22977233_Data indicate that disabled-2 (Dab2) sulfatide-binding motif contains two helices when embedded in micelles, reversibly binds to sulfatides with moderate affinity, lies parallel to the micelle surface. 23005040_The Dab2 gene is inactivated in part by DNA methylation, and the suppression of Dab2 expression by DNA methylation may play a role in the development of myelodysplastic syndrome. 23909735_Megalin and Dab2 were expressed in prostate and colon epithelial cells, which was markedly enhanced following treatment with retinoic acid 24002585_Aberrant hypermethylation and reduced expression of disabled-2 promote the development of lung cancers. 24186266_Exposure to follicular fluid transiently increased the transcript levels of IL8 and PTGS2, and decreased the expression of SOD2, GPX3, DAB2, and NR3C1. TNF and IL6 levels were also decreased while those of NAMPT were unaffected. 24252604_Results suggest that endogenous Dab2 exacerbates central nervous system inflammation, potentially acting to up-regulate reactive oxygen species expression in macrophages and microglia, and that it is of potential pathogenic relevance in multiple sclerosis 24608456_Reduced Dab2 or loss of Dab2 expression significantly correlates with lower classification of meningiomas and negatively correlates with the invasive ability of adjacent tissues. 24638085_breast cancer cell was deficient in Dab2 expression and related receptor endocytosis-mediated TGF-beta depletion, which may contribute to the accumulation of TGF-beta in tumor microenvironment and the induction of immune tolerance. 24648493_The data support a model in which Dab2 regulates the domain localization of TbetaRI in the membrane, balancing TGF-beta signaling via the Smad and JNK pathways. 24846918_miR-145 regulates the migration and invasion of highly invasive prostate cancer cells through targeting DAB2 gene 24889971_Attenuating Dab2 expression in K562 cells diminished TfR internalization and increased surface levels of TfR concomitantly with a decrease in Tf uptake and erythroid differentiation. 25253241_Akt1 and Akt2 are involved in albumin endocytosis, and phosphorylation of Dab2 by Akt induces albumin endocytosis in proximal tubule epithelial cells. 25331956_Numb specifically regulates NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol absorption both in human intestine and liver, distinct from ARH and Dab2, which selectively participate in LDLR-mediated LDL uptake. 25719979_DAB2 expression is decreased in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer , and the frequent methylation event at sites -86 to 226 of the DAB2 gene could contribute to the downregulation of DAB2. 25879443_Dab2 depletion also increases the rescued protein half-life of DeltaF508 CFTR by ~18% and ~91%, respectively 25892549_These results indicated that miR-93 plays an important role in the initiation and progression of NPC by targeting Dab2 and the miR-93/Dab2 pathway may contribute to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for NPC in the future. 26143155_DAB2 regulated the cell migration associated genes in PC3 cells, and the differential DAB2 expression between LNCaP and PC3 cells was partly regulated by histone 4 acetylation. 26755607_inhibition of WNT/beta-catenin signaling by DAB2 is essential for establishing the correct number of cardiomyocytes in the developing heart. 26769181_Data show that miR106b was frequently up-regulated in human cervical carcinoma tumors and cell lines and inversely correlated with DAB2 expression. Its regulation in under TGF-beta1 which contributes to cell migration by targeting DAB2 in cervical carcinoma. 26927671_these findings reveal that DAB2 is critical for controlling inflammatory signaling during phenotypic polarization of macrophages 27036032_DAB2 can suppress the ERK signaling, but correlate to have TGF-beta-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas (ESCCs). 27072056_abundances of megalin and Dab2 (p = 0.046) were reduced in infected placentas from women with LBW deliveries 27398911_cathepsin B (CTSB) inhibition or expression of a CTSB-resistant Dab2 mutant maintains Dab2 expression and shifts long-term TGF-beta-treated cells from autophagy to apoptosis 27417122_The various novel mechanisms are described by which Dab2 mediates an array of signaling events with vast physiological consequences. 28394802_In conclusion, DAB2 and Intelectin-1 are newly identified positive markers of mesothelioma and have potential to be included in future immunohistochemical marker panels for differentiation of epithelioid mesothelioma from pulmonary adenocarcinoma 28498390_the results indicated that substrate stiffness could regulate EMT of cervical cancer cell lines HeLa and SiHa at least partially through miR-106b and its downstream target DAB2. 28514805_DAB2 might be involved in excessive aldosterone biosynthesis and correlate with specific clinical characteristics of aldosterone-producing adenoma patients. 28876503_Dab2 Ser723 phosphorylation is a key molecular event in thrombin-stimulated inside-out signaling and platelet activation, contributing to a new function of Dab2 in thrombin signaling. 29247596_Estrogen-induced miR-191 was identified as a direct upstream regulator of DAB2 in ER-positive breast cancer cells. 29254794_DAB2 is a frequent target of epigenetic silencing in oral carcinomas and may be potentially used for tumor detection 30275566_Putative causal genes were enriched for proximal tubule expression and endolysosomal function, where DAB2, an adaptor protein in the TGF-b pathway, formed a central node. Functional experiments confirmed that reducing Dab2 expression in renal tubules protected mice from Chronic kidney disease. 30543885_MiR-93 promoted PC progression and metastasis by repressing DAB2. 31101868_Loss of Disabled-2 Expression in Pancreatic Cancer Progression. 32571632_Involvement of Disabled-2 on skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. 32617970_Proper E-cadherin membrane location in colon requires Dab2 and it modifies by inflammation and cancer. 32629690_Our data indicates that the AA genotype of rs2855512 and rs2255280 in the Dab2 gene may be a genetic marker of coronary artery disease risk in Chinese Han population. 33372034_Dynamic multimerization of Dab2-Myosin VI complexes regulates cargo processivity while minimizing cortical actin reorganization. 34237899_A dynamic Dab2 keeps myosin VI stably on track. 34476495_MicroRNA93 knockdown inhibits acute myeloid leukemia cell growth via inactivating the PI3K/AKT pathway by upregulating DAB2. |
ENSMUSG00000022150 |
Dab2 |
1926.602854 |
0.4302418873 |
-1.216780 |
0.045169920 |
725.206599 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000098741649353071503290246904389604052606019862298768386298148096735228320250086138514743191171064357428623400522728431102241226189053797373392609616067077629147229097782915 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000070407089103929245296979365049257467080301180060261888554767696556214118638858924050664903168904795182406186741061824936836713575000396235703182898117506123014291224558777 |
Yes |
Yes |
1156.3424445 |
53.3774060 |
2706.8231072 |
88.1039088 |
| ENSG00000153093 |
55289 |
ACOXL |
protein_coding |
Q9NUZ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;FAD;Flavoprotein;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable acyl-CoA oxidase activity; fatty acid binding activity; and flavin adenine dinucleotide binding activity. Predicted to be involved in fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA oxidase and lipid homeostasis. Predicted to be located in peroxisomal matrix. Predicted to be active in peroxisome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55289; |
peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; acyl-CoA oxidase activity [GO:0003997]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; fatty acid binding [GO:0005504]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA oxidase [GO:0033540]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20731705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26237329_The study identified two proteins, TMEM79 and ACOXL, with potential to differentiate between benign and cancerous prostatic glands in tissue biopsies. |
ENSMUSG00000027380 |
Acoxl |
25.375460 |
0.2088873263 |
-2.259203 |
0.447710455 |
25.694521 |
0.00000039996088854291030172805184936257738570475339656695723533630371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001481782809963191813027632084964757552825176389887928962707519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9362702 |
2.9905908 |
47.9972923 |
8.6182709 |
| ENSG00000153094 |
10018 |
BCL2L11 |
protein_coding |
O43521 |
FUNCTION: Induces apoptosis and anoikis. Isoform BimL is more potent than isoform BimEL. Isoform Bim-alpha1, isoform Bim-alpha2 and isoform Bim-alpha3 induce apoptosis, although less potent than isoform BimEL, isoform BimL and isoform BimS. Isoform Bim-gamma induces apoptosis. Isoform Bim-alpha3 induces apoptosis possibly through a caspase-mediated pathway. Isoform BimAC and isoform BimABC lack the ability to induce apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11997495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15486195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15661735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9430630}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the BCL-2 protein family. BCL-2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. The protein encoded by this gene contains a Bcl-2 homology domain 3 (BH3). It has been shown to interact with other members of the BCL-2 protein family and to act as an apoptotic activator. The expression of this gene can be induced by nerve growth factor (NGF), as well as by the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1, which suggests a role of this gene in neuronal and lymphocyte apoptosis. Transgenic studies of the mouse counterpart suggested that this gene functions as an essential initiator of apoptosis in thymocyte-negative selection. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:10018; |
Bcl-2 family protein complex [GO:0097136]; BIM-BCL-2 complex [GO:0097141]; BIM-BCL-xl complex [GO:0097140]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; apoptotic process involved in embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:1902263]; B cell homeostasis [GO:0001782]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus [GO:0071385]; developmental pigmentation [GO:0048066]; ear development [GO:0043583]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:0097192]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; meiosis I [GO:0007127]; myeloid cell homeostasis [GO:0002262]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of autophagy in response to ER overload [GO:0034263]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902237]; positive regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process [GO:2000271]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response [GO:1903896]; positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process [GO:1902110]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070234]; post-embryonic animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0048563]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of developmental pigmentation [GO:0048070]; regulation of organ growth [GO:0046620]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; spleen development [GO:0048536]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070242]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; tube formation [GO:0035148] |
11859372_Functional study of the mouse homolog 11997495_Identification of novel isoforms of the BH3 domain protein Bim which directly activate Bax to trigger apoptosis. 12095614_direct addition of BimL to mitochondria does not lead to cytochrome c release 12118373_Bim has an ability to activate directly the voltage-dependent anion channel, which plays an important role in apoptosis of mammalian cells. 12198137_BimEL activate Bax by damaging the mitochondrial membrane structure directly, in addition to its binding and antagonizing Bcl-2/Bcl-XL function. 12486001_BIM has a role in facilitating HIV-1 tat-induced apoptosis 12844146_Data show that detachment-induced expression of Bim requires a lack of beta(1)-integrin engagement, downregulation of EGF receptor (EGFR) expression and inhibition of Erk signalling. 14527951_Bim mRNA and protein levels increase after up-regulation of FoxO3a by paclitaxel, causing apoptosis in breast cancer cells 14555991_phosphorylation of Bim-EL by Erk1/2 on serine 69 selectively leads to its proteasomal degradation and therefore represents a new and important mechanism of Bim regulation 14676826_The proapoptotic effect of BIM (through transcriptional induction of two of its isoforms)is inhibited by the activation of Raf/ERK signalling which prevents BIM up-regulation and leads to phosphorylation of the BimEL isoform. 14681225_new insights into the post-translational regulation of Bim(EL) 14732682_Bim(EL) can be activated downstream of the caspase cascade, leading to a positive feedback amplification of apoptotic signals. 14764673_A new pathway for Bim regulation is based on extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent phosphorylation of the BimEL isoform and proteasome-ddependent degradation of BimEL, followed by increased expression of shorter apoptotic isoforms BimL and BimS. 14970329_Immunosuppressive agents block Bim up-regulation and rescue T cells from death receptor-independent cell death. 14996839_Bim appears to be a key event in cAMP-promoted apoptosis in both murine and human T-cell lymphoma and leukemia cells and thus appears to be a convergence point for the killing of such cells by glucocorticoids and agents that elevate cAMP. 15014070_Mcl-1L degradation by either GrB or caspase-3 interferes with Bim sequestration by Mcl-1L 15030401_Lovastatin-induced cell death occurs in correlation with significantly increased levels of the BH3-only protein, Bim in susceptible glioblastoma cell lines; up-regulation of Bim was directly associated with increased incidence of apoptosis 15147734_expression pattern of Bim isoforms shows tissue specificity; the BH3 domain is sufficiency for proapoptotic activity; the functional state of Bims might be regulated both in the transcript and post transcript process 15378010_Cleavage of Mcl-1 by caspases modifies its subcellular localization, increases its association with Bim and inhibits its antiapoptotic function. 15459900_In myeloma cells, Mcl-1 neutralizes Bim through complex formation and therefore prevents apoptosis. 15486195_BimEL is an important determinant for induction of anoikis sensitivity by mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitors 15509554_the induction of Bim by GC is a required event for the complete apoptotic response in pre-B ALL cells 15653751_T cell blasts surviving activation-induced cell deathare memory CD44 high cells with increased BIM expression. 15688014_activation of transcription is activated by FoxO3A 15711598_Bim is a critical molecular link between the microtubule poison, paclitaxel, and apoptosis. 15728578_The region unique to BimEL (amino acids 41-97, exon 3) accounts for ERK1/2 binding, ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation, and turnover of BimEL. 15731037_degraded during Chlamydia trachomatis infection 15731089_degraded in Chlamydia trachomatis-infected cells 15767553_Bik and Bim have roles in bortezomib sensitization of cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL 15824087_results show that Forkhead transcription factor 4-dependent expression of Bim protein plays a pivotal role for endothelial progenitor cell apoptosis 15843898_expression of Bim is increased by zinc pyrithione, which induces apoptosis 15899862_Bim is a critical regulator of luminal apoptosis during mammary acinar morphogenesis in vitro and may be an important target of oncogenes that disrupt glandular epithelial architecture. 16022280_identified the transcriptional initiation site and three candidate remote enhancer/silencer regions of the Bim gene. However, none of these transcriptional regulatory elements was IL-3-dependent 16051596_Repression of BIM is favored in human glioblastoma. 16091744_Melphalan-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells is associated with a cleavage of MCL1 and BIM and a decrease in the MCL1/BIM complex. 16148027_Bax, Bad, and Bim are upregulated, while Bcl-2 is downregulated in human neuroblastoma cells treated with propargylamine 16183168_The muscarinic receptor-protein kinase C signaling pathway is a regulator of Bim in neuroblastoma cells; activation of muscarinic receptors and protein kinase C o induces Bim phosphorylation, followed by down-regulation of this proapoptotic protein. 16260615_TGF-beta is involved in the physiological loss of gastric epithelial cells by activating apoptosis mediated by Smad7, Bim, and caspase-9 16282323_Ser(87) of Bim(EL) is an important regulatory site that is targeted by Akt to attenuate the pro-apoptotic function of Bim(EL), thereby promoting cell survival 16373335_RUNX3 cooperates with FoxO3a/FKHRL1 to participate in the induction of apoptosis by activating Bim 16476732_concomitant induction of E2F1 targets ASK1 and Bim by HDACIs warrants an effective activation of E2F1-dependent apoptosis in response to suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid 16478725_Mcl-1 may serve as a direct substrate for TRAIL-activated caspases implying the existence of a novel TRAIL/caspase-8/Mcl-1/Bim communication mechanism between the extrinsic and the intrinsic apoptotic pathways 16773715_Ceramide induces apoptosis of human colon carcinoma HT-29 cells by affecting the expression of Bcl-2 family gene members and impacting the mitochondrial function. 16810067_Radiation therapy for squamous cell carcinoma of cervix results in increased apoptosis with the up-regulation of Bax, a proapoptotic protein, the down-regulation of Bcl-XL, an antiapoptotic protein, and no significant change in the levels of Bcl-2. 16888645_We conclude that Noxa and Bim establish a connection between FKHRL1 and mitochondria, and that both BH3-only proteins are critically involved in FKHRL1-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma. 16951744_These results suggest that the high expression of cell adhesion-related proteins might be responsible for the different apoptosis status after the transfection of Bim L. 17051334_Bim plays an essential role in synergistic induction of apoptosis by SBHA and TRAIL in melanoma. 17062728_The main pathway by which Fas signaling regulates the levels of Bim expression in human T-cell blasts is the death-domain- and caspase-independent generation of discrete levels of H2O2, which results in the net increase of Foxo3a levels. 17067554_Inhibition of endogenously produced IGFBP-5 is associated with Bim-dependent apoptosis in NB cells. 17074758_in addition to interacting with the pro-apoptotic protein Bak, vaccinia F1L also functions to indirectly inhibit the activation of Bax, likely by interfering with the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins such as BimL 17105963_TLR stimulation of macrophages can regulate Bim levels in opposing ways, namely by transcriptional induction and by phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the protein. 17151701_results implicate BIM in glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells through proteasome degradation. 17158029_results indicate that IFN-alpha causes apoptosis in myeloma cells through a moderate triggering of the mitochondrial route initiated by Bim 17188240_Our results confirm that ultrasound induces apoptosis via a pathway that involves Bak, Bcl-2, and caspases, but not ROS. 17203211_Bax and Bim are upregulated in human B cells during arsenic trioxide induction of apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway 17218274_A cytokine-mediated posttranscriptional regulation of Bim mRNA by heat-shock cognate protein 70 (Hsc70), which binds to AU-rich elements (AREs) in the 3'-untranslated region of specific mRNAs and enhances their stability, is presented. 17251431_Bim is an essential mediator of amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity. 17276340_These data provide important mechanistic information on the processes involved in sculpting the mammary gland and demonstrate that BIM is a critical regulator of apoptosis in vivo. 17289999_results indicate that BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis at least primarily by engaging the multiple pro-survival relatives guarding Bax and Bak 17486061_Loss of expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim is associated with renal cell carcinoma 17499214_These results demonstrate that BimL is involved in UV irradiation-induced apoptosis by indirectly activating Bax. 17525735_preformed Bim(EL)/Mcl-1 and Bim(EL)/Bcl-x(L) complexes can be rapidly dissociated following activation of ERK1/2 by survival factors 17531220_FXa plays a key role in cellular processes in which Bim is the central player in determining cell survival. 17538248_a Bim-dependant pathway modulated by cytokines is involved in apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells induced by imatinib and nilotinib 17637819_Bim loss may play an important role in melanoma progression 17653091_In the absence of Bim, EBNA3A and EBNA3C appear to provide no survival advantage in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. 17686764_TRAIL can trigger an apoptotic pathway that involves JNK-dependent activation of Bim, which in turn induces Bax-mediated permeabilization of lysosomes. 17698840_Mcl-1 confers TRAIL resistance by serving as a buffer for Bak, Bim, and Puma, and sorafenib is a potential modulator of TRAIL sensitivity 17716672_Bim mediates particulate matter-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial pathway. 17717606_The open reading frame of BimSs3 may initiate at the second ATG and encodes a 36 amino-acid peptide with BH3 domain. 18006817_Mcl-1 degradation primes the cell for Bim and Bax activation and anoikis, which can be blocked by oncogenic signaling in metastatic cells 18063582_PINCH-1 contributes to apoptosis resistance through suppression of Bim. Mechanistically, PINCH-1 suppresses Bim not only transcriptionally but also post-transcriptionally. 18064628_Bim is a novel regulator of osteoblast apoptosis and may be a therapeutic target. 18089817_BIM is induced by lung cancer cell lines that are sensitive to erlotinib but not by those resistant. 18165867_In the absence of serum, the suppression of either Bad, Bim or Bid expression delayed cell death under several stress conditions 18182577_In addition to its proapoptotic effect, IL-21 promoted STAT1 and STAT5 phosphorylation in natural killer cells with concurrent enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against rituximab-coated CLL cells 18195012_BIM and tBID follow different strategies to trigger BAX-driven mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization with strong potency 18246127_Bad and Bim are major B-RAF responsive proteins regulating apoptosis in melanoma cells. 18251703_data indicate that Bim, Bak, and Bax actively mediate osteoblast apoptosis induced by trophic factor withdrawal 18345036_Bim-mediated apoptosis following actin damage due to deregulation of Cdk2 and the cell cycle by the absence of functional p53. 18348176_variations in c-myc and p21(WAF1) expression delay apoptosis making PBL resistant to sodium butyrate for several hours 18354037_arsenic trioxide upregulated expression of Bmf, Noxa, and Bim. Silencing of Bmf, Noxa, and Bim significantly protected MM cells from ATO-induced apoptosis 18391004_Activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase in epithelial cells infected with N. gonorrheae targeted Bad and Bim for downregulation at the protein level. 18398508_Data suggest that Bim-mediated attrition of HBV-specific CD8(+) T cells contributes to the inability of these cell populations to persist and control viral replication. 18413764_ABT-737 augments TRAIL-induced cell killing by unsequestering Bim and Bak and enhancing a Bax conformational change induced by TRAIL. 18420585_RACK1 has a role in protecting cancer cells from apoptosis by regulating the degradation of BimEL, which together with CIS could play an important role of drug resistance in chemotherapy 18508762_B-Raf-initiated inactivation of Bad and Bim only partly contributes to the anti-apoptotic activities of this oncogene and that other points within the cell death machinery are also targeted by deregulated ERK signaling 18549468_The identification of a novel putative human BCL2L11 promoter provides new insights into the structure and regulation of the BCL2L11 locus. 18651223_These findings suggest JNK to have an important pro-apoptotic function following ultraviolet rays B irradiation in human melanocytes, by acting upstream of lysosomal membrane permeabilization and Bim phosphorylation. 18668139_N-RAS(Q61K) and B-RAF(V600E) contribute to melanoma's resistance to apoptosis in part by downregulating Bim expression 18677096_Endogenous MIF may regulate the pro-apoptotic activity of Bim and inhibit the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria. 18715233_These data suggest that regulation of BIM expression by BRAF-->MEK-->ERK signaling is one mechanism by which oncogenic BRAF(V600E) can influence the aberrant physiology of melanoma cells. 18715501_BIM plays a significant role in T cell receptor (TCR)-induced death of activated human T cells, working in tandem with FAS signaling as a separate signal to kill T cells. 18806830_study concludes a single endogenous BRAF(V600E) allele is sufficient to repress BIM & prevent death from growth factor withdrawal; colorectal cancer cells with V600E mutations are addicted to the ERK1/2 pathway for repression of BIM 18812174_The crystal structure of Bfl-1, the last anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member to be structurally characterized, in complex with a peptide corresponding to the BH3 region of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim is presented. 18925930_In early severe sepsis a gene expression pattern with induction of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members Bim and Bid is observed in peripheral blood. 18949058_Treatment of B-RAF mutant tumor cells with a MEK inhibitor requires BIM and is enhanced by a BH3 mimetic. 18981303_Scleroderma serum-induced EPC apoptosis is mediated chiefly by the Akt-FOXO3a-Bim pathway, which may account, at least in part, for the decreased circulating EPC levels in scleroderma patients. 19052714_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19064725_loss of Bim preserved clonal survival upon FLT3-ITD inhibition in hematopoietic progenitor cells, human leukemic cell lines, and primary AML cells 19100522_A proapoptotic signaling pathway involving RasGRP, Erk, and Bim in B cells 19101511_Bim is not absolutely required for paclitaxel cytotoxicity in breast cancer cell lines. 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19150432_betaTrCP promotes cell survival in cooperation with the ERK-RSK pathway by targeting BimEL for degradation. 19285955_This study demonstrated the physical association of the MCL-1 and IEX-1 proteins, the modulatory role of MCL-1 in IEX-1-induced apoptosis, and the role of BIM as an essential downstream molecule for IEX-1-induced cell death. 19300516_Our data indicate a synergistic role for both bim and Bmf in an apoptotic pathway leading to the clearance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae -infected cells. 19305426_destabilization of BIM(EL) in the absence of pVHL contributes to the increased resistance of VHL-null renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells to certain apoptotic stimuli. 19308286_an HDAC inhibitor induces apoptosis through the FoxO1 acetylation-Bim pathway. 19330811_The Bax activator BimEL increased rapidly, driving cells towards apoptosis likely controlled by c-Myc and p21(WAF1) activities. 19332026_These data showed that BimL expression induced by BCR activation may result from the splicing of BimEL mRNA independently of Bim promoter regulation. 19336552_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336552_Variants in BCL2L11 were strongly related to follicular lymphoma. 19403302_down-regulation of BIM is epigenetically controlled by methylation in a percentage of CML patients, has a bad prognosis, the combination of imatinib with a demethylating agent may result in improved responses in patients with decreased expression of BIM. 19407828_The survival cytokines (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor ) induce Bcl-2-like protein 11 gene expression in neutrophils. 19494111_TGFbeta stimulates Bim transcription by up-regulating the expression of the transcription factor Runx1 through an internal ribosome entry site -dependent mechanism. 19541822_Forodesine activates p53-independent mitochondrial apoptosis by induction of p73 and BIM. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19574221_The rate of TGF-beta1-induced osteoclast apoptosis was lower when Bim expression was suppressed. 19587239_MAP4K3 orchestrates activation of BAX via the concerted posttranscriptional modulation of PUMA, BAD, and BIM. 19641506_Bim is involved in the regulation of cell death induction in many cells & tissues by various stimuli: growth factor or cytokine deprivation, calcium flux, ligation of antigen receptors on T & B cells, glucocorticoids or loss of adhesion. Review. 19737817_Toxoplasma gondii infection confers resistance against Bim-induced apoptosis by preventing the activation of mitochondrial Bax. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773546_Bim, and Mcl-1, but not Bad, integrate death signaling triggered by concomitant disruption of the PI3K/Akt and MEK1/2/ERK1/2 pathways in human leukemia cells. 19850739_KIT D816V suppresses expression of proapoptotic Bim in neoplastic mast cells 19881544_provide evidence that Notch3 regulates Bim, a BH-3-only protein, via MAPK signaling. 19893569_Data show that E2F1 induces EZH2 expression, which in turn antagonizes the induction of E2F1 pro-apoptotic target Bim expression. 19914305_Data indicate that Bim is the key mediator of dexamethasone-induced apoptosis and is responsible for the potentiating effect of rapamycin, providing molecular criteria for the use of glucocorticoids combined with mTOR inhibitors in myeloma therapy. 20010785_Data show an important role for the p73-Bim axis in regulating cell death during mitosis that is independent of p53. 20066663_the crystal structure of human Mcl-1 bound to a BH3 peptide derived from human Bim and the structures for three complexes that accommodate large physicochemical changes at conserved Bim sites was reported. 20074640_These results refine the minimal sequence for ERK1/2-driven degradation and further define the functional importance of key regions within BIM(EL), highlighting the complexity of this pro-apoptotic protein. 20082325_increase of the function of SIAH1 to upregulate the expression of Bim may play an important role in the progression of breast cancer 20086250_IGF-1 induces significant down-regulation of the proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bim in multiple myeloma cells 20160166_Bim is a key effector molecule in JAK2 inhibition-induced apoptosis and that targeting this apoptotic pathway could be a novel therapeutic strategy for patients with activating JAK2 mutations. 20206402_palmitoleate inhibits lipoapoptosis by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated increases of the BH3-only proteins Bim and PUMA 20231287_Up-regulation of BIM is associated with increased sensitivity to Imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. 20237869_the induction of BIM was a common apoptotic mechanism of epithelial tumor cells that depended upon survival signaling in targeted treatment, but not for chemotherapy 20332261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20348947_the COX-2/PGE(2) pathway as an important negative regulator of Bim expression in colorectal tumours. 20404322_Mitochondrial p53 functions as a Bim derepressor by releasing Bim from sequestrating complexes with Mcl-1, Bcl-2, and Bcl-XL, and allowing its engagement in Bak/Bax activation. 20431602_The displacement of Bim protein from antiapoptotic proteins is the important step committing the cell to death. 20697841_the absence of BIM up-regulation is one of the important mechanisms of glucocorticoids resistance in acute lymphoblast leukemia 20700448_The data suggest that inhibitory targeting of vIRF-1:Bim interaction may provide an effective antiviral strategy. 20705940_Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor causes a paradoxical increase in the BH3-only pro-apoptotic protein Bim in human neutrophils 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20841506_Follicular dendritic cells protect B-cell lymphoma cells against apoptosis, in part through activation of a miR-181a-dependent mechanism involving down-regulation of Bim expression 20855536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20855536_We replicated the association of BCL2L11 and CASP9 with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma risk at the gene and SNP level, and identified novel associations with BCLAF1 and BAG5. 20861305_Data show that hypoxic conditions inhibit anoikis and block expression of proapoptotic BH3-only family members Bim and Bmf in epithelial cells. 20877573_CXCL12 chemokine regulates colorectal carcinoma cell anoikis through bim-mediated apoptosis. 20878914_In rheumatoid arthritis, the DNA-PKcs-JNK-Bim/Bmf axis transmits genotoxic stress into shortened survival of naive resting T cells, imposing chronic proliferative turnover of the immune system and premature immunosenescence. 20885957_Apoptosis induction by MEK1/2 inhibition in human lung cancer cells is mediated by Bim. 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041309_BH3 peptides other than Bim and Bid exhibited various degrees of direct activation of the effector Bax or Bak 21130142_Upregulation of BIM by PRED in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells regardless of molecular subtype is significantly prognostic of outcomes, confirming BIM's essential regulatory role in the PRED-induced apoptosis. 21148306_The BH3 alpha-helical mimic BH3-M6 disrupts Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2, and MCL-1 protein-protein interactions with Bax, Bak, Bad, or Bim and induces apoptosis in a Bax- and Bim-dependent manner. 21148799_Bim regulates the balance of survival versus apoptosis in peripheral T cells undergoing recombination-activating gene (RAG)-dependent T cell receptor rearrangements during TCR revision, thereby ensuring the utility of transgenic postrevision repertoire. 21247487_that Bim and Mcl-1 have key opposing roles in regulating JAK2V617F cell survival and propose that inactivation of aberrant JAK2 signaling leads to changes in Bim complexes that trigger cell death. 21333317_These results are consistent with the Epstein-Barr Virus miRNAs downregulating Bim post-transcriptionally in part through the 3'UTR and suggest that there are miRNA recognition sites within other areas of the Bim mRNA. 21339291_TDP-43-induced death is associated with altered regulation of BIM and Bcl-xL and attenuated by caspase-mediated TDP-43 cleavage. 21367852_BH3-only activator proteins Bid and Bim are dispensable for Bax activation and mitochondrial apoptosis induced by Bcl-xL deficiency 21375523_belinostat and bortezomib interact synergistically in both cultured and primary AML and ALL cells, and raise the possibilities that up-regulation of Bim and interference with NF-kappaB pathways contribute to this phenomenon. 21415216_Data show that ALK inhibitor-induced apoptosis is mediated both by BIM upregulation resulting from inhibition of ERK signaling as well as by survivin downregulation resulting from inhibition of STAT3 signaling in EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer cells. 21481848_During chronic HCV infection non-reactive HCV-specific CD8(+) cells targeting the virus are PD-1(+)/CD127(-)/Bim(+) and, blocking apoptosis and PD-1/PD-L1 pathway on them enhances in vitro reactivity. 21555518_BCL2L11 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21625639_Loss of Bim expression is associated with glioma. 21655183_Findings suggest that BIM plays an important role in regulating p-AKT by activating caspase-3 and that BIM mediates the level of AKT phosphorylation to determine the threshold for overcoming cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. 21659544_Distribution of Bim determines Mcl-1 dependence or codependence with Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 in Mcl-1-expressing myeloma cells. 21671007_Bim is required for the combretastatin-A4 induced cell death in the H460 lung cancer cell line via activation of the mitochondrial signalling pathway. 21673341_A pathway through c-Raf to Bim that contributes to tipifarnib cytotoxicity in human lymphoid cells but also identify potential determinants of sensitivity to this agent. 21729544_Anti-CD44 mAb A3D8 can inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of HL-60 cells by enhancing expression of Bim. 21732363_These results suggest that 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid induces apoptosis in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells via caspase activation and modulation of Akt/FOXO3a/Bim pathway. 21808067_Up-regulation of Bim appears to be an important determinant of cAMP/PKA-mediated apoptosis in immature T cells 21899728_breast cancer cells overexpressing HER2 undergo apoptosis upon depletion of Mcl-1, and this Mcl-1 dependence is due to their constitutive expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bim 21924351_CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of BIM(EL) drives its polyubiquitylation and proteasome-dependent degradation to protect cells during mitotic arrest 21937453_Cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis through STAT1-mediated Bim protein activation. 21958719_The mRNA and protein expression of an isoform of Bim (Bcl-2 interacting mediator of cell death) denoted as BimEL, which is proapoptotic was increased following efavirenz administration. 21984578_Findings suggest that local IFN production may interact with a genetic factor (PTPN2) to induce aberrant proapoptotic activity of the BH3-only protein Bim, resulting in increased beta-cell apoptosis via JNK activation and the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. 22071694_Cdk1/cyclin B1-dependent hyper-phosphorylation of Bim during prolonged mitotic arrest is an important cell death signal. 22076535_miR-25 directly regulates apoptosis by targeting Bim in ovarian cancer. 22081075_for optimal tumor suppressive activity, Bim must be able to interact with all and not just select pro-survival Bcl-2 family members 22093624_The lack of Bim up-regulation contributes to the resistance of melanoma cells to ER stress-induced apoptosis and may be a mechanism by which melanoma cells adapt to ER stress conditions. 22131152_Bim overexpression was not correlated with Bcl-2 inhibition (P > 0.05) and was accompanied by increase in Bax expression (P |
ENSMUSG00000027381 |
Bcl2l11 |
378.209426 |
0.2525370612 |
-1.985433 |
0.163973760 |
140.615804 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000001952331586667909959152757599626228169902282892134309839978325740902344469168558510076792733567430104812956415116786956787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000270322835077095222587079301670331585080707469037257568083065159299490895688239801113172955382424333947710692882537841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
163.8546875 |
27.0590280 |
649.5138796 |
75.8005147 |
| ENSG00000153162 |
654 |
BMP6 |
protein_coding |
P22004 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor of the TGF-beta superfamily that plays essential roles in many developmental processes including cartilage and bone formation (PubMed:31019025). Also plays an important role in the regulation of iron metabolism by acting as a ligand for hemojuvelin/HJV (By similarity). Initiates the canonical BMP signaling cascade by associating with type I receptor ACVR1 and type II receptor ACVR2B (PubMed:18070108). In turn, ACVR1 propagates signal by phosphorylating SMAD1/5/8 that travel to the nucleus and act as activators and repressors of transcription of target. Can also signal through non-canonical pathway such as TAZ-Hippo signaling cascade to modulate VEGF signaling by regulating VEGFR2 expression (PubMed:33021694). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P20722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18070108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31019025, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33021694}. |
3D-structure;Chondrogenesis;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytokine;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Osteogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. This protein regulates a wide range of biological processes including iron homeostasis, fat and bone development, and ovulation. Differential expression of this gene may be associated with progression of breast and prostate cancer. Mutations in this gene may be associated with iron overload in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:654; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to BMP stimulus [GO:0071773]; cellular response to iron ion [GO:0071281]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; eye development [GO:0001654]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; multicellular organismal iron ion homeostasis [GO:0060586]; negative regulation of adherens junction organization [GO:1903392]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000048]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of aldosterone biosynthetic process [GO:0032349]; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion [GO:2000860]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; positive regulation of endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045603]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031666]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043117]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to magnesium ion [GO:0032026]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; type B pancreatic cell development [GO:0003323] |
13130469_the presence of BMP-6 in adult human articular cartilage indicates a functional role for this growth factor in the maintenance of joint integrity. 14558086_BMP-2 and BMP-6 are expressed in arthritic synovium and are strongly up-regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. 15186723_results revealed a novel potent effect of PTH and vitamin D(3) plus BMPs in inducing bone development by human mesenchymal stem cells 15516325_BMP-6 increases the levels of osteopontin, BMP-2, alkaline phosphatase and core binding factor alpha 1 mRNAs in human periodontal (HPL) ligament cells. 15548695_Recombinant noggin inhibited the function of BMP-6, suggesting a negative feedback regulation of BMP activity and indicating a strategy for the development of a novel therapeutic target in treatment of osteosclerotic bone metastases of prostate cancer 15784727_several single nucleotide polymorphisms in bone morphogenic protein 6, annexin A2, and klotho were associated with sickle cell osteonecrosis 15861517_To analyze the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in prostate and breast cancers with established metastasis in bone 15877825_In mature human B cells, BMP-6 inhibited cell growth, and rapidly induced phosphorylation of Smad1/5/8 followed by an upregulation of Id1. 16527843_endogenous BMP-6 system plays critical roles in aldosterone production between Ang II and K through ERK signaling pathway. 16547600_Excess numbers of BMP6-deficient myofibroblast progenitor cells may favour adverse tissue remodelling in patients with diabetes. 16604289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16886151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17238135_a distinct BMP and TGFbeta-receptor repertoire may explain the reduced chondrogenic capacity of adipose tissue stromal cells in vitro 17262821_strong BMP staining is seen in maturing chondrocytes, and thus may play a role in chondrocyte differentiation and/or apoptosis; BMP release by osteoclasts may promote osteoblastic differentiation at sites of bone remodeling 17574840_BMP-6 promoter methylation status is correlated with estrogen receptor status in breast cancer 17575215_BMP-6 promoter methylation may be a potential new biomarker of risk prediction in DLBCL. 17577985_Data show that pcDNA-BMP2/6 produced more rhBMP6 than pcDNA-BMP6. 17879955_BMP6 induced cell cycle arrest in estrogen-insensitive breast cancer cells. BMP6 inhibits stress-induced apoptosis via both Smad and p38 signal pathways. 17899540_A functional bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) signalling pathway is present in adult pre-T-leukemia lymphoma cell line Jurkat TAg. 17924656_presents the crystal structure of BMP-6 18070108_The crystal structure of human BMP-6 was determined to a resolution of 2.1 A. 18187665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18308844_Affects aldosterone breakthrough induced by long-term treatment with agtr1 stimulated aldosterone production by adrenocortical cells. 18326817_BMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-6 are endogenous ligands for Hemojuvelin in hepatoma-derived cell lines, and all 3 of these ligands are expressed in human liver 18349123_Expression of BMP1, BMP6, BMP7, and BMP-receptor 2 was significantly increased in advanced stages of myelofibrosis compared and enhanced levels of BMP6 expression were already evident in prefibrotic stages of primary myelofibrosis. 18436533_BMP-2/4 and BMP-6/7 differentially utilize cell surface receptors to induce osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells 18632632_Wnt3a and Wnt5a have roles in inducing BMP-4 and 6 expression in prostate cancer osteoblast differentiation 18683889_BMP signaling plays a role in the induction of an osteoblastic phenotype in human dermal fibroblasts in response to vitamin D(3) stimulation 18688853_BMP-6 promoter methylation is likely to be a common epigenetic event at later stages of ATL and that the methylation profiles may be useful for the staging of ATL as well as for evaluation of the individual risk of developing the disease. 18805502_significant role of BMP-6 in inhibiting MDA-MB-231 migration through decreasing deltaEF1 expression which subsequently relieves deltaEF1-mediated invasion. 18931653_the potential use of bone-morphogenetic protein-6, noggin and sclerostin expression together as a prognostic predictor for metastatic progression of prostate cancer. 18949431_BMP3b and BMP6 genes were suppressed by DNA methylation and methylation of BMP3b is significantly frequent in Japanese malignant pleural mesotheliomas (MPMs), suggesting its pathogenic role and the ethnic difference in MPMs. 19075223_S1P induces osteoblast precursor recruitment and promotes mature cell survival. Wnt10b and BMP6 also were significantly increased in mature osteoclasts, whereas sclerostin levels decreased during differentiation. 19093115_study confirmed association of a single SNP, BMP6-3 (rs3812163), suggesting a potential role for BMP6 in the development of sickle avascular necrosis in sickle cell disease patients. 19245827_attenuates oxidant injury in kidney cells via Smad-dependent HO-1 induction 19252488_Mtations in BMP6 mayause iron overload in humans with severe juvenile hemochromatosia. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19308091_Bone morphogenetic protein-6 may function as an anti-metastasis factor by a mechanism involving transcriptional repression of microRNA-21 in breast cancer. 19539911_BMP-6 is an important mediator to support healthy follicle growth in the human ovary. 19543302_Data show that bone morphogenetic protein 6 ameliorates TGF-beta1-induced changes in HK-2 cells. 19694819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19718049_A high BMP6 expression in primary myeloma cell samples delineates significantly superior overall survival for patients undergoing high-dose chemotherapy 19765379_regulates hepcidin an iron metabolism in humans 20016212_Malignant human clear cell renal carcinoma tissue had significantly higher BMP-6 mRNA expression than healthy tissue 20048150_Using BMP-6/7 chimeras, we identified lysine 60 as a key residue conferring noggin resistance within the BMP-6 protein. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20401668_Results suggest that PTHrP (ParaThyroid Hormone-related Protein) acts upstream of BMP-6, and exerts its antimitogenic effect by reducing BMP-6 mRNA expression through PKA signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. 20460105_BMP6, Smad1, Smad2 mRNA and protein expression were significantly higher in during sickle-cell pathology with orthopedic complications. 20530805_c/hemojuvelin is a broad spectrum bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonist and inhibits both BMP2- and BMP6-mediated signaling and gene expression 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20567515_conclude that BMP-2/6 is more potent than BMP-2 or BMP-6 for inducing differentiation of human embryonic stem cells, and it can be used as a more powerful substitute of these BMPs in in vitro differentiation guidance 20573596_the cBMP6 mRNA and H3K27me3 levels revealed significant differences between patients with local local advanced, or metastatic disease 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20605837_AGTR1 gene deletion is associated with congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20844121_Ass-associated increases in BMP6 expression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease may have deleterious effects on neurogenesis in the hippocampus. 21136273_a novel role of BMP-6/HO-1 cascade to relieve breast cancer metastasis by regulating the secretion of growth factors in tumor microenvironment. 21374653_BMP-6 secreted by prostate cancer cells induces IL-6 expression in macrophages; IL-6, in turn, stimulates the neuroendocrine differentiation of prostate cancer cells. 21622652_BMP6 and iron not only induce hepcidin expression but also induce TMPRSS6, a negative regulator of hepcidin expression 21898381_BMP-6 mainly inhibited plasmablast differentiation, and BMP-7 mainly induced apoptosis in human memory B cells 22086350_The methylation of BMP6 was correlated with decreased levels of mRNA transcripts. 22305102_Growth differentiation factor 3 is induced by bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP-6) and BMP-7 and increases luteinizing hormone receptor messenger RNA expression in human granulosa cells. 22364398_investigated role of BMP6 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) development and progression;high BMP6 activity, defined by strong BMP6 expression with weak noggin or SOST expression, was associated with shorter survival in esophageal SCC patients; results suggest BMP6, noggin and SOST could be used in combination as a prognostic indicator in cancer progression 22641693_BMP4 and BMP6, from two different BMP subclasses, and their antagonists noggin and sclerostin were variably expressed in melanocytes and keratinocytes in human skin 22792339_Estrogen is involved in hepcidin expression via a GPR30-BMP6-dependent mechanism 23674072_BMP6 plays a critical role in breast cancer cell aberrant proliferation and chemoresistance and may serve as a novel diagnostic biomarker or therapeutic target for breast cancer. 23799295_Marker gene screening for human mesenchymal stem cells in early osteogenic response to bone morphogenetic protein 6 with DNA microarray. 23853066_determined whether BMP-2, -6, and -7 differentially regulate the proliferation, mineralization, and mRNA expression of bone/mineralized tissue associated genes of human periodontal ligament stem cells obtained from periodontal ligament tissue 24012720_High BMP6 expression is associated with breast cancer. 24185914_Prostate cancer-derived BMP-6 stimulates tumor-associated macrophages to produce IL-1a through a crosstalk between Smad1 and NF-kB1; IL-1a, in turn, promotes angiogenesis and prostate cancer growth. 24263212_the patients carried genotype TA of rs 267196 and genotype AG of rs267201 present a high risk factor for developing osteonecrosis RR=1.317 and RR=1.3 respectively 24406789_BMP-6 attracted neutrophils and controlled the regulation of the neutrophils in the ovary. 24498236_The BMP-6 staining intensity was downregulated. 24518599_WNT5A derived from bone stromal cells induced the expression of BMP-6 by CaP cells; BMP-6 in turn stimulated cellular proliferation of CaP cells. 24658703_these data highlight a therapeutically innovative role for BMP6 by providing a means to enhance the amount of myogenic lineage derived brown fat. 24875397_There were no correlations between iron parameters and the expression of the BMP-6 in granulosa cells from polycycstic ovary syndrome patients. 24890613_Data indicated that hypermethylation modifications contributed to the regulation of BMP6 and induced an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype of breast cancer during the acquisition of drug resistance. 25011936_In vitro analysis revealed that recombinant BMP6 inhibited the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and reduced proinflammatory and profibrogenic gene expression in already activated HSCs 25121767_demonstrate that BMP6 is associated with radiographic severity in AS, supporting the role wingless-type like/BMP pathway on radiographic progression in AS 25227796_CpG island methylation of BMP6 is found in high frequency in CRC and this epigenetic event is associated with suppressed protein expression in the tumor tissue. 25753222_These observations imply that crosstalk between the VEGF and BMP-6 signaling pathways enhances osteogenic differentiation of MSCs. 26410368_BMP6 and oxidized low-density lipoprotein independently and synergistically induced osteogenic differentiation and mineralization in vascular endothelial cells. 26475719_the combined delivery of VEGF and BMP-6 to the bone defect significantly enhanced bone repair through the enhancement of angiogenesis and the differentiation of endogenously recruited MSCs into the bone repair site. 26582087_Identify 3 heterozygous missense mutations in BMP6 in patients with unexplained iron overload. These mutations lead to loss of signaling to SMAD proteins and reduced hepcidin production. 26598555_BMP-dependent physical interaction of VE-cadherin with the BMP receptor ALK2 (BMPRI) and BMPRII, resulting in stabilization of the BMP receptor complex and, thereby, the support of BMP6-Smad signaling. 26751737_These observations suggest a novel role of BMP-6 in the inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by regulating secretion of MMPs(MMP-1) in the tumor microenvironment. 26779985_BMP-6 upregulates somatostatin receptor actions, leading to reduction of GnRH-induced secretion of luteinizing hormone. 26855134_These results demonstrated that Hcy up-regulated hepcidin expression through the BMP6/SMAD pathway, suggesting a novel mechanism underlying the hyperhomocysteinemia-associated perturbation of iron homeostasis. 27051019_study shows that patients with CRA had high expression of BMP6 and hepcidin and low expression of s-HJV. BMP6 was found to be negatively correlated with s-HJV; both regulate hepcidin expression and play important roles in the development of anemia. 27592865_Plasma BMP6 was significantly increased in chronic heart failure patients. 27959431_Further investigation on clinical ESCC samples and non-tumorous adjacent tissue found that tumors with triple-positive BMP6, ALK2 and BMPRII had deeper growth than tumors with only BMP6 expression 28335084_Our results independently add further evidence to the role of BMP6 mutations as likely contributing factors to late-onset moderate IO unrelated to mutations in the established five HH genes. 28434979_Synergistic effects of BMP-2, BMP-6 or BMP-7 with human plasma fibronectin onto hydroxyapatite coatings. 28523310_Study demonstrated that the mesenchymal epithelial/myoepithelial potential of transdifferentiation of the luminal cells that make up the proliferative units is certified by the immunohistochemical expression of some BMP6 purely mesenchymal protein cells. 28733457_both bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) and BMP6 are proangiogenic in vitro and ex vivo and that the BMP type I receptors, activin receptor-like kinase 3 (ALK3) and ALK2, play crucial and distinct roles in this process. 29767257_The present study demonstrated that BMP6 may protect retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative stress injury to a certain extent, which may be associated with alterations in the MAPK signaling pathway. 30171260_This study elucidates a novel role of BMP6-induced modulation of the tumor microenvironment. 30230035_All these data suggest that BMP6 decrease KC proliferation and promote KC differentiation. Together, these findings raise the possibility that BMP6 acts as the HIF-1alpha target, mediating the effects of HIF-1alpha on hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation. 30510168_Hepatitis C virus (HCV) blunted induction of hepcidin expression by hepatic bone morphogenetic protein BMP6. In HCV patients, disruption of the BMP6/hepcidin axis and genetic variation associated with the BMP/SMAD pathway predicts the outcome of infection. BMP6 enhances the transcriptional and antiviral response to type I interferon (IFN), but BMP6 also potently blocks HCV replication independently of IFN. 30542109_BMP-6 is downregulated in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 30633987_The results demonstrate that BMP6 increases the production of TGF-beta1 by up-regulating the expression of furin in human granulosa cells via an ALK2/ALK3-mediated SMAD1/5/8-SMAD4 signaling pathway. 30878675_Study detected that BMP6 is significantly increased in skin-derived fibroblasts of patients with localized scleroderma. Moreover, it was shown that BMP6 significantly impacts proliferation, migration, cytoskeletal organization, and collagen expression, as well as activity of the major pro-fibrogenic transcription factor AP-1 in dermal fibroblasts. 30982140_Identification of Pathogenic Genes and Transcription Factors in Osteosarcoma. 31276102_Nrf2 controls iron homeostasis in haemochromatosis and thalassaemia via Bmp6 and hepcidin. 31434001_demonstrate that ALK2 and ALK3 BMP type I receptors are involved in BMP6-induced suppressive effects on Cx43 expression 31495245_Bone morphogenetic protein 6 expression in cumulus cells is negatively associated with oocyte maturation. 32059748_miR-765 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting BMP6 via regulating the BMP6/Smad1/5/9 signaling pathway. 32076051_Inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein 6 receptors ameliorates Sjogren's syndrome in mice. 32464486_Novel mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein 6 gene in patients with iron overload and non-homozygous genotype for the HFE p.Cys282Tyr mutation. 32524577_BMP-6 and SMAD4 gene expression is altered in cumulus cells from women with endometriosis-associated infertility. 32641001_Association analysis of polymorphisms rs12997 in ACVR1 and rs1043784 in BMP6 genes involved in bone morphogenic protein signaling pathway in primary angle-closure and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma patients of Saudi origin. 32845956_BMP6 Regulates Corneal Epithelial Cell Stratification by Coordinating Their Proliferation and Differentiation and Is Upregulated in Pterygium. 32854680_Synergistic interaction of hTGF-beta3 with hBMP-6 promotes articular cartilage formation in chitosan scaffolds with hADSCs: implications for regenerative medicine. 33232799_BMP6 binding to heparin and heparan sulfate is mediated by N-terminal and C-terminal clustered basic residues. 33332786_Genome-wide Association Analysis Across 16,956 Patients Identifies a Novel Genetic Association Between BMP6, NIPAL1, CNGA1 and Spondylosis. 34037557_Novel BMP6 gene mutation in patient with iron overload. 34314740_BMP6 increases CD68 expression by up-regulating CTGF expression in human granulosa-lutein cells. 34611951_Runx3 regulates iron metabolism via modulation of BMP signalling. 34740612_Bone morphogenetic protein 6-mediated crosstalk between endothelial cells and hepatocytes recapitulates the iron-sensing pathway in vitro. 34933731_The effect of cellular and physiological indicators on gender determination. 35033126_Immunohistochemical analysis revealed the expression of bone morphogenetic proteins-4, 6, 7, and 9 in human induced membrane samples treated with the Masquelet technique. 35694925_Blood BMP6 Associated with Cognitive Performance and Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis: A Longitudinal Study of Elders. 36153321_RNF4~RGMb~BMP6 axis required for osteogenic differentiation and cancer cell survival. |
ENSMUSG00000039004 |
Bmp6 |
15.717988 |
2.5312939332 |
1.339875 |
0.380409764 |
12.751464 |
0.00035573058892021973062536055465443496359512209892272949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000897842594470322076342927442027530560153536498546600341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.2500168 |
4.9523883 |
8.8675026 |
1.6286580 |
| ENSG00000153531 |
113622 |
ADPRHL1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NDY3 |
FUNCTION: Required for myofibril assembly and outgrowth of the cardiac chambers in the developing heart (By similarity). Appears to be catalytically inactive, showing no activity against O-acetyl-ADP-ribose (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6AZR2, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BGK2}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
ADP-ribosylation is a reversible posttranslational modification used to regulate protein function. ADP-ribosyltransferases (see ART1; MIM 601625) transfer ADP-ribose from NAD+ to the target protein, and ADP-ribosylhydrolases, such as ADPRHL1, reverse the reaction (Glowacki et al., 2002 [PubMed 12070318]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:113622; |
sarcomere [GO:0030017]; ADP-ribosylarginine hydrolase activity [GO:0003875]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; cardiac chamber ballooning [GO:0003242]; cardiac myofibril assembly [GO:0055003]; protein de-ADP-ribosylation [GO:0051725] |
27217161_Hybrid human-Xenopus Adprhl1 protein constructs were produced by utilizing restriction sites from one species and engineering the same site into the second species by PCR. Hearts containing human ADPRHL1 developed normally. Engineered human-Xenopus hybrid proteins cause extensive branching of myofibrils with sarcomere division occurring at the actin-Z-disc boundary. 34528284_Non-genetic and genetic rewiring underlie adaptation to hypomorphic alleles of an essential gene. |
ENSMUSG00000031448 |
Adprhl1 |
99.089235 |
12.5164486285 |
3.645753 |
0.232068303 |
306.466137 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001285484645783380745680918577872197018287651857942861684986549964490451603736463413876144088600512924229643366863736620951562413947034124708715623807028936891527423624914661104412516579031944274902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000380235538512278507809174357010643983065777963931514064383963532397794436962548087987191667119143455466910449864751019572423312471566158828301626456194877356356358853728405478022978059016168117523193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
184.3788893 |
26.5586659 |
14.7441065 |
1.9762020 |
| ENSG00000153823 |
55022 |
PID1 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z2X4 |
FUNCTION: Increases proliferation of preadipocytes without affecting adipocytic differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16815647}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in several processes, including mitochondrion morphogenesis; negative regulation of phosphate metabolic process; and positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55022; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to interleukin-6 [GO:0071354]; cellular response to leptin stimulus [GO:0044320]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; energy reserve metabolic process [GO:0006112]; mitochondrion morphogenesis [GO:0070584]; negative regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001170]; negative regulation of glucose import [GO:0046325]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903077]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001171]; positive regulation of fat cell proliferation [GO:0070346]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of mitochondrial fusion [GO:0010635]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881]; regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000377] |
16815647_A novel gene named NYGGF4, which was expressed at a higher level in obese subjects, was isolated and characterized and could play a role in cell growth and adipogenesis process 17124247_Q7Z2X4 protein (PID1) identified as a cytosolic ligand of LRP1 in a trimeric complex with Cubilin. Q7Z2X4 named PCLI1 (PTB-containing, Cubilin and LRP1 Interacting protein 1) 19079291_Data show that NYGGF4 regulates the functions of IRS-1 and Akt, decreases GLUT4 translocation and reduces glucose uptake in response to insulin. 19849947_NYGGF4 over-expression impairs the insulin sensitivity of 3T3-L1 adipocytes through decreasing GLUT4 translocation and had no effects on the secretory function of adipocytes. 20010835_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140872_TNFA up-regulated the expression of NYGGF4 during preadipocyte differentiation. 20165904_Overexpression of NYGGF4 caused mitochondrial dysfunction in adipocytes, which might be responsible for the development of NYGGF4-induced insulin resistance. 22284633_NYGGF4 acts directly on the IRS1/PI3K/AKT insulin pathway to reduce glucose uptake and transport, impairs mitochondrial function and causes insulin resistance, and thus may be a useful therapeutic target for obesity-associated insulin resistance. 22968630_NYGGF4 plays a role in IR and its effects on IR could be reversed by metformin through activating IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK-PGC1-alpha pathways. 23274913_overexpression of TFAM can restore mitochondrial function to normal levels in NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes 24300787_Overall survival and radiation-free progression-free survival were longer in medulloblastoma patients whose tumors had higher PID1 mRNA levels. 30100244_By acting as an insulin-dependent retention adaptor, PID1 serves as a regulator of LRP1 function controlling the disposal of postprandial lipoproteins. 31339628_PID1 reduces serum HDL-Cholesterol levels. |
ENSMUSG00000045658 |
Pid1 |
16.854695 |
2.0192029515 |
1.013786 |
0.408777225 |
6.193720 |
0.01282044135812609661484451351043389877304434776306152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024056663417994048059789236049255123361945152282714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.3514009 |
5.9381816 |
11.6553656 |
2.3066166 |
| ENSG00000153898 |
255231 |
MCOLN2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZK6 |
FUNCTION: Nonselective cation channel probably playing a role in the regulation of membrane trafficking events. Acts as Ca(2+)-permeable cation channel with inwardly rectifying activity (PubMed:19940139, PubMed:19885840). May activate ARF6 and be involved in the trafficking of GPI-anchored cargo proteins to the cell surface via the ARF6-regulated recycling pathway (PubMed:17662026). May play a role in immune processes. In adaptive immunity, TRPML2 and TRPML1 may play redundant roles in the function of the specialized lysosomes of B cells (By similarity). In the innate immune response, may play a role in the regulation of chemokine secretion and macrophage migration (By similarity). Through a possible and probably tissue-specific heteromerization with MCOLN1 may be at least in part involved in many lysosome-dependent cellular events (PubMed:19885840). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17662026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19885840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19940139, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Immunity;Innate immunity;Ion channel;Ion transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Mucolipins constitute a family of cation channel proteins with homology to the transient receptor potential superfamily. In mammals, the mucolipin family includes 3 members, MCOLN1 (MIM 605248), MCOLN2, and MCOLN3 (MIM 607400), that exhibit a common 6-membrane-spanning topology. Homologs of mammalian mucolipins exist in Drosophila and C. elegans. Mutations in the human MCOLN1 gene cause mucolipodosis IV (MIM 262650) (Karacsonyi et al., 2007 [PubMed 17662026]).[supplied by OMIM, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:255231; |
late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; NAADP-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0072345]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; macrophage migration [GO:1905517]; neutrophil migration [GO:1990266]; positive regulation of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 production [GO:0071651]; positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production [GO:2000343]; positive regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha production [GO:0071642]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production [GO:0071639]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
16606612_there is a hierarchy controlling the subcellular distributions of the TRPMLs such that TRPML1 and TRPML2 dictate the localization of TRPML3 and not vice versa 17662026_MCOLN2 traffics through the ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (Arf6)-associated pathway, colocalizing with major histocompatibility protein class I and CD59 in long recycling endosomes. 19763610_TRPML1 appears to play a novel role in the tissue-specific transcriptional regulation of TRPML2. 19885840_Data show that TRPMLs form distinct functional channel complexes. 19940139_constitutively active h-TRPML2 leads to cell death by causing Ca(2+) overload 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20736310_TRPML 1, 2 and 3 assemblies regulated cell viability and starvation-induced autophagy. 22753890_TRPML2 is activated by lowering the extracellular sodium concentration as well as by a subset of small chemical compounds that were previously identified as activators of TRPML3. 25445271_MCOLN2 is transcriptionally activated by PAX5 and has roles in B cell development and function 27248469_High TRPML-2 expression in glioma cells resulted in increased survival and proliferation signaling, suggesting a pro-tumorigenic role played by TRPML-2 in glioma progression. 29382735_The authors show that MCOLN2 specifically promotes viral vesicular trafficking and subsequent escape from endosomal compartments. This mechanism requires channel activity, occurs independently of antiviral signaling, and broadly applies to enveloped RNA viruses that require transport to late endosomes for infection, including influenza A virus, yellow fever virus, and Zika virus. 31178222_The acidic TRPML2 extracytosolic/lumenal domain (ELD) pre-pore loop exhibits a pH-dependent Ca2+ interaction, suggesting a mechanism for channel activity regulation in the endolysosomal system. 34548638_Endolysosomal ion channel MCOLN2 (Mucolipin-2) promotes prostate cancer progression via IL-1beta/NF-kappaB pathway. 35054871_Functional In Vitro Assessment of VEGFA/NOTCH2 Signaling Pathway and pRB Proteasomal Degradation and the Clinical Relevance of Mucolipin TRPML2 Overexpression in Glioblastoma Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000011008 |
Mcoln2 |
95.882764 |
2.9013284367 |
1.536714 |
0.211870219 |
52.425397 |
0.00000000000044690679648638907386081186621983455303569118810536053842952242121100425720214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002728016673341233493969318505511283882818129864489264946314506232738494873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
141.6936699 |
17.4700774 |
49.1784151 |
4.8673196 |
| ENSG00000153902 |
163175 |
LGI4 |
protein_coding |
Q8N135 |
FUNCTION: Component of Schwann cell signaling pathway(s) that controls axon segregation and myelin formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K1S1}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Involved in regulation of myelination. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. Implicated in arthrogryposis multiplex congenita-1 and childhood absence epilepsy. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:163175; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; myelination in peripheral nervous system [GO:0022011]; neuron maturation [GO:0042551]; regulation of myelination [GO:0031641] |
12217514_has seven copies of the EPTP repeat, a unifying protein sequence motif of a heterogenous group of proteins linked to epileptic diseases. The EPTP repeat probably forms a beta-propeller structure. 14505228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14505228_Screening of the LGI4 coding region in BFIC and childhood absence epilepsy (CAE) revealed several frequent exonic polymorphisms. 19815358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19815358_The positive genotypic association between benign familial infantile convulsions (BFIC)and c.1722G/A polymorphism suggests that LGI4 might contribute to the susceptibility to BFIC. 20220021_Schwann cells are the principal cellular source of Lgi4 in the developing nerve; transgenic Lgi4 binds directly to Adam22 without a requirement for additional membrane associated factors. 24662834_Intratumoral heterogeneity of ADAM23 promotes tumor growth and metastasis through LGI4 and nitric oxide signals. 28318499_in four unrelated multiplex families presenting with severe arthrogryposis multiplex congenital, identified biallelic loss-of-function mutations in LGI4; functional tests showed these germline mutations caused aberrant splicing of the endogenous LGI4 transcript and in a cell-based assay impaired the secretion of truncated LGI4 protein 34288120_Characterizing the molecular etiology of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita in patients with LGI4 mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000036560 |
Lgi4 |
5.938032 |
0.0841783567 |
-3.570407 |
0.865025307 |
23.671031 |
0.00000114290016768393502659146437894222003706090617924928665161132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004017434264114046691405198602486947834222519304603338241577148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7777164 |
0.4887613 |
9.2945499 |
2.5554738 |
| ENSG00000153904 |
23576 |
DDAH1 |
protein_coding |
O94760 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes N(G),N(G)-dimethyl-L-arginine (ADMA) and N(G)-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMA) which act as inhibitors of NOS. Has therefore a role in the regulation of nitric oxide generation. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Zinc |
|
This gene belongs to the dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH) gene family. The encoded enzyme plays a role in nitric oxide generation by regulating cellular concentrations of methylarginines, which in turn inhibit nitric oxide synthase activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23576; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; amino acid binding [GO:0016597]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; dimethylargininase activity [GO:0016403]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; arginine catabolic process [GO:0006527]; arginine metabolic process [GO:0006525]; citrulline metabolic process [GO:0000052]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of cellular response to hypoxia [GO:1900038]; negative regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043116]; nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0007263]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003073] |
11811522_hydrolyzes methylated inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase is present in circulating human red blood cells 15501905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15501905_The first evidence of the importance of DDAH1 polymorphisms in pre-eclampsia susceptibility was provided. 15781754_By increasing the synthesis of the proangiogenic factor nitric oxide, DDAH promotes postnatal angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. 16920729_DDAH-1 and DDAH-2 messenger RNA and protein were demonstrated in first trimester placental tissue, primary extravillous trophoblasts and extravillous trophoblast-derived cell lines. 17075694_it is concluded that L-arginine regulates asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) metabolism dose-dependently by competing for DDAH thus maintaining the metabolic balance of L-arginine and ADMA, and endothelial NO homeostasis 17273169_DDAH-1 activity leads to accumulation of asymmetric dimethylarginine and reduction in nitric oxide signaling. 17881609_Demonstrate a critical role for DDAH-1 and endogenous methylarginines in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction. 17895252_human dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 is inhibited by S-nitroso-L-homocysteine and hydrogen peroxide 18251679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18292189_maintenance of normoglycemia and not glycemia-independent actions of insulin maintained dimethylarginine tissue levels by preserving physiological DDAH activity. 19666120_Expression of hDDAH1 messenger RNA is found in all organs of DDAH1 transgenic mice investigated, whereas human DDAH1 is absent in wild-type littermates. 19682581_Recent studies in this review suggest that DDAH may regulate endothelial nitric oxide activity and endothelial function through both asymmetric dimethylarginine-dependent and -independent mechanisms. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010544_Circulating methylarginine levels and the decline in renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease are modulated by DDAH1 polymorphisms. 20010544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20019334_Recombinant human DDAH1 overexpression protects transgenic mice from adverse structural and functional changes in cerebral arterioles in hyperhomocysteinemia but not from accelerated carotid artery thrombosis induced by the HM/LF diet. 20167924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167924_Results suggest that the DDAH1 loss-of-function polymorphism is associated with both increased risk of thrombosis stroke and coronary artery disease in the Chinese Han population. 20209122_DDAH1 and DDAH2 polymorphisms are strongly and additively associated with serum ADMA concentrations in individuals with type 2 diabetes 20209122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex from patients with schizophrenia 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21174581_did not find evidence for association with pre-eclampsia 21212404_DDAH1 exerts a unique role in activating Akt that affects endothelial function independently of degrading endogenous nitirc oxide synthase inhibitors. 21264497_HDL significantly increased the attenuated endothelial cell NO production induced by ox-LDL, which was attributed to its effect on DDAH/ADMA pathway 21303562_Results provide evidence that SNP rs1241321 in DDAH1 is associated with type 2 diabetes and its long-term outcome. 21420186_A significant decrease in asymmetric dimethylarginine levels was found in ex-extremely low birth weight young adults compared to term birth weight young adults. 21493890_Indicate that DDAH1 is required for metabolizing asymmetrical dimethylarginine and N(omega)-monomethyl-L-arginine. 21677199_Data show that DDAH inhibition reduces fibroblast-induced collagen deposition in an ADMA-independent manner and reduces abnormal epithelial proliferation in an ADMA-dependent manner. 21722652_In acute congestive heart failure acute renal impairment function and the modulation of metabolism and extracellular transport by the DDAH-1/CAT-1 system determine high ADMA and SDMA levels after therapy for acute congestive heart failure. 21975354_Non-diabetic hypertensive subjects with a hypertensive response to exercise compared to those with normal response were characterized by augmented asymmetric dimethylarginine and osteoprotegerin levels. 22492959_High DDAH1 is associated with pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. 22521321_Genetic polymorphisms in DDAH genes influence serum ADMA levels in individuals with T1 diabetes mellitus. 22700861_DDAH1 gene DNA methylation is impoetant in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 22982060_Data suggest that estradiol alone has no effect on DDAH/asymmetric dimethylarginine/nitric oxide pathway in arterial endothelium, but rather counters oxidized LDL; estradiol restores DDAH activity and prevents loss of eNOS (nitric oxide synthase 3). 23022711_Elevated asymmetric dimethylaginine is not a part of the proatherogenic risk profile in the young adult offspring of patients with premature Coronary artery disease. 23766377_the advanced glycation end products-receptor for advanced glycation end products-mediated reactive oxygen species generation could be involved in endothelial dysfunction in diabetic end-stage renal disease patients 23864585_Only the DDAH1-V1 transcript is responsible for ADMA metabolism, and transcript specific primers are recommended to determine DDAH1 mRNA expression. 23892448_DDAH1 genotypes were closely related to asymmetric dimethylarginine levels, but not to measures of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in an elderly population. 24260221_DDAH1 deficiency attenuates endothelial cell cycle progression and angiogenesis. 25194333_increased ADMA levels in rheumatoid arthritis do not appear to relate to DDAH genetic polymorphisms 25424718_Genebased analyses revealed associations of the DDAH1 gene with longitudinal Blood Pressure phenotypes, associations with essential hypertension, Blood Pressure salt sensitivity, preeclampsia, or preclinical stages of atherosclerosis. 26082478_Inhibiting the expression of DDAH1, but not DDAH2, resulted in a significant increase in the sensitivity of the EVT cell line SGHPL-4 to tumour necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) induced apoptosis 26226438_FoxO1 regulates asymmetric dimethylarginine via downregulation of dimethylaminohydrolase 1 in HUVECs and subjects with carotid atherosclerosis. 26455824_results suggest that miR-21 may regulate renal fibrosis by the Wnt pathway via directly targeting DDAH1 26662939_The most significant associations were detected for PECAM1*V/V + DDAH1*C (OR = 4.17 CI 1.56-11.15 Pperm = 0.005) 26663142_wild-type rs480414 was 92% sensitive and 53% specific for pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia 26786611_rs3087894 in DDAH1 was significantly associated with hypertension and showed conflicting results in different ethnic groups. This is therefore a candidate for further studies with the aim of helping to ascertain the mechanisms of hypertension in different populations. 26996393_DDAH1 plays dual roles in a particular matter-induced cell death in alveolar epithelial cells. 27663503_Results confirmed DDAH1 3'-UTR as a target for miR-21, and endogenous miR-21 showed increased inhibitory effect on DDAH1-V3 transcript. 28145161_Inflammatory factors expressed in response to myocardial ischemia contributed to up-regulation of DDAH1. 28580735_These findings suggest that DDAH1 functions as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer (GC) and may be exploited as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for GC. 28594240_Data demonstrate that DDAH1 deficiency promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells and causes fibrosis, and oxidative stress in aging and diabetic kidneys. The study provides the first direct evidence that the DDAH1 has a marked effect on kidney fibrosis and oxidative stress induced by aging or diabetes. 28741166_DDAH-1 expression is associated with promotion of angiogenesis stimulating factor VEGF. 29070803_High DDAH1 expression is associated with breast cancer cell migration and vasculogenic mimicry. 29150732_DDAH1 is an important mediator of PCa progression and NO/DDAH pathway needs to be considered in developing therapeutic strategies targeted at PCa. 29682517_MiR-21-mediated DDAH1/ADMA/NO signal pathway. 30284143_DDAH1 rs997251 TC + CC genotypes were associated with 2.3-fold higher risk of coronary artery disease than TT genotype (p = 0.0063). DDAH1 rs997251 CC genotype was associated with the highest ADMA. 30538005_In a parallel experiment, the genotype of eight polymorphisms of the DDAH1 gene was also determined (Additional file 1: Table S5). Genotyping was undertaken using a proprietary competitive allele-specific PCR technique known as Kompetitive Allele Specific (KASP) PCR genotyping system which has been extensively used for uniplex SNP analysis 31503013_Long non-coding RNA H19 confers resistance to gefitinib via miR-148b-3p/DDAH1 axis in lung adenocarcinoma. 31639806_Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase 1 Polymorphisms and Venous Intimal Hyperplasia in Hemodialysis Patients. 31669648_The oncogenic function of circ-EZH2 was partly dependent on its modulation of DDAH1 and CBX3. 31733101_DDAH1 promoter -396 4N insertion variant is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes in a gender-dependent manner. 33221779_Serum asymmetric-dimethylarginine, apelin and NT-pro BNP levels in dialysis patients. 33849119_Abnormalities of the PRMT1-ADMA-DDAH1 metabolism axis and probucol treatment in diabetic patients and diabetic rats. 35598478_On the kinetic mechanism of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase. 36233204_Assessment of DDAH1 and DDAH2 Contributions to Psychiatric Disorders via In Silico Methods. |
ENSMUSG00000028194 |
Ddah1 |
9.843947 |
0.3805138493 |
-1.393979 |
0.484600030 |
8.621616 |
0.00332196979464714596541607960489272954873740673065185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007039809643789213082498701368194815586321055889129638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5529930 |
1.7283611 |
14.7113697 |
2.7311462 |
| ENSG00000153976 |
9955 |
HS3ST3A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y663 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) to catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group to an N-unsubstituted glucosamine linked to a 2-O-sulfo iduronic acid unit on heparan sulfate (PubMed:10520990, PubMed:9988768, PubMed:10608887, PubMed:15304505). Catalyzes the O-sulfation of glucosamine in IdoUA2S-GlcNS and also in IdoUA2S-GlcNH2 (PubMed:10520990, PubMed:9988768, PubMed:15304505). The substrate-specific O-sulfation generates an enzyme-modified heparan sulfate which acts as a binding receptor to Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) and permits its entry (PubMed:10520990). Unlike HS3ST1/3-OST-1, does not convert non-anticoagulant heparan sulfate to anticoagulant heparan sulfate (PubMed:10520990). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10520990, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10608887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15304505, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9988768}. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzymes are key components in generating a myriad of distinct heparan sulfate fine structures that carry out multiple biologic activities. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the heparan sulfate biosynthetic enzyme family. It is a type II integral membrane protein and possesses heparan sulfate glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase activity. The sulfotransferase domain of this enzyme is highly similar to the same domain of heparan sulfate D-glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase 3B1, and these two enzymes sulfate an identical disaccharide. This gene is widely expressed, with the most abundant expression in liver and placenta. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]. |
hsa:9955; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 1 activity [GO:0008467]; [heparan sulfate]-glucosamine 3-sulfotransferase 3 activity [GO:0033872]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; glycosaminoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0006024]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012] |
20487506_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22475533_Genetic variants of HS3ST3A1 and HS3ST3B1 are associated with Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia. 26410339_decreased in pre-eclamptic placental tissue 27041583_Our findings define 3-OST3A as a novel regulator of breast cancer pathogenicity, displaying tumor-suppressive or oncogenic activities in a cell- and tumor-dependent context, and demonstrate the clinical value of the HS-O-sulfotransferase 3-OST3A as a prognostic marker in HER2+ patients. 28618938_Detection of MUC1 and HS3ST2 promoter methylation status appears to be useful molecular markers for assessing the progressive state of the disease and could be helpful in discriminating breast cancer molecular subtypes. These results validate the methylation-based microarray analysis, thus trust their output in the future. |
ENSMUSG00000047759 |
Hs3st3a1 |
138.642271 |
12.9231525896 |
3.691886 |
0.231392062 |
278.611219 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001507433462036949915768503150799886736440301921217707970540143406018066580607291565593819960420818930848427218369687349503838023736977827477044399521576966555214127652106981258839368820190429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000401619456672660310449728096148770632664983244269924687478551179277333387057350923841095359886778931181660106875771524884055427444055153605186361065275662401985456995134882163256406784057617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
251.3279862 |
37.8110067 |
19.5094062 |
2.5871763 |
| ENSG00000153982 |
284161 |
GDPD1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N9F7 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes lysoglycerophospholipids to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and the corresponding amines (PubMed:27637550, PubMed:25596343). Shows a preference for 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lyso-PAF), lysophosphatidylethanolamine (lyso-PE) and lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC) (PubMed:27637550, PubMed:25596343). May be involved in bioactive N-acylethanolamine biosynthesis from both N-acyl-lysoplasmenylethanolamin (N-acyl-lysoPlsEt) and N-acyl-lysophosphatidylethanolamin (N-acyl-lysoPE) (PubMed:27637550, PubMed:25596343). In addition, hydrolyzes glycerophospho-N-acylethanolamine to N-acylethanolamine (PubMed:27637550). Does not display glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity, since it cannot hydrolyze either glycerophosphoinositol or glycerophosphocholine (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CRY7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25596343, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27637550}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of deacylated glycerophospholipids to glycerol phosphate and alcohol. The encoded protein is localized to the cytoplasm and concentrates near the perinuclear region. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:284161; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphoric diester hydrolase activity [GO:0008081]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; N-acylethanolamine metabolic process [GO:0070291] |
14612981_A novel splice variant of the gene is mainly expressed in human ovary and small intestine. 18991142_3-D model provides the structural information; subcellular localization is in the cytoplasm; over-expression of GDE4 did not induce neurite formation or change cell morphology 33022222_Structural Variants Create New Topological-Associated Domains and Ectopic Retinal Enhancer-Gene Contact in Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa. 34673020_Development of a selective fluorescence-based enzyme assay for glycerophosphodiesterase family members GDE4 and GDE7. |
ENSMUSG00000061666 |
Gdpd1 |
73.007029 |
0.4956590258 |
-1.012580 |
0.182426393 |
31.262501 |
0.00000002253913960965154572741620680759871975240571373433340340852737426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000094834008163756207963188322486447479064963772543705999851226806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.9422037 |
5.7450211 |
101.5900684 |
7.5391384 |
| ENSG00000154016 |
10750 |
GRAP |
protein_coding |
Q13588 |
FUNCTION: Couples signals from receptor and cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases to the Ras signaling pathway. Plays a role in the inner ear and in hearing (PubMed:30610177). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30610177}. |
Deafness;Disease variant;Membrane;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the GRB2/Sem5/Drk family and functions as a cytoplasmic signaling protein which contains an SH2 domain flanked by two SH3 domains. The SH2 domain interacts with ligand-activated receptors for stem cell factor and erythropoietin, and facilitates the formation of a stable complex with the BCR-ABL oncoprotein. This protein also associates with the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor SOS1 (son of sevenless homolog 1) through its N-terminal SH3 domain. In general, it couples signals from receptor and cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases to the Ras signaling pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:10750; |
COP9 signalosome [GO:0008180]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12491092_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15174222_Results suggest that the GRAP gene might have a role in the pathogenesis of Sjogren's syndrome. 18295596_Our findings define a pathway involving CD28 binding to Grb-2 and its co-operativity with Vav1 in the regulation of T-cell co-stimulation. 19836472_Grb2-related adaptor protein (GRAP) was up-regulated in kidney tubules from fibrotic kidneys from diabetic patients, and subsequently confirmed as a novel component of TGF-beta signaling in cultured human renal tubule cells. 29364705_Findings suggest that the miR-654-5p/GRAP/Ras/Erk signaling pathway in OSCC cells might contribute to the underlying mechanism through which miR-654-5p participates in the regulation of OSCC progression. 30610177_The function of the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2)-related adaptor protein (GRAP) in the auditory system is not known. 35972996_m(6)A Modification-mediated GRAP Regulates Vascular Remodeling in Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension. |
ENSMUSG00000004837 |
Grap |
34.968115 |
0.4047859592 |
-1.304769 |
0.303582678 |
18.624169 |
0.00001591895827589149869972853790223155101557495072484016418457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000048707260396384440567871948468692266942525748163461685180664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.0107761 |
3.6986085 |
47.2453299 |
6.0153032 |
| ENSG00000154102 |
404550 |
C16orf74 |
protein_coding |
Q96GX8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:404550; |
|
21203532_C16orf74 expression level represents a potentially useful marker for predicting progression in primary non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients 31597713_Role of Dimerized C16orf74 in Aggressive Pancreatic Cancer: A Novel Therapeutic Target. 32314545_LncRNA HAND2-AS1 represses cervical cancer progression by interaction with transcription factor E2F4 at the promoter of C16orf74. |
ENSMUSG00000043687 |
1190005I06Rik |
14.095412 |
0.3335096722 |
-1.584199 |
0.424298617 |
14.763275 |
0.00012188635315055546177488710046787900864728726446628570556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000331437467299594437728643692153696065361145883798599243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.1256768 |
2.0507309 |
21.4640513 |
3.6305738 |
| ENSG00000154122 |
56172 |
ANKH |
protein_coding |
Q9HCJ1 |
FUNCTION: Regulates intra- and extracellular levels of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi), probably functioning as PPi transporter. |
Alternative splicing;Deafness;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphate transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a multipass transmembrane protein that is expressed in joints and other tissues and controls pyrophosphate levels in cultured cells. Progressive ankylosis-mediated control of pyrophosphate levels has been suggested as a possible mechanism regulating tissue calcification and susceptibility to arthritis in higher animals. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal dominant craniometaphyseal dysplasia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56172; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; outer membrane [GO:0019867]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; inorganic diphosphate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0030504]; inorganic phosphate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005315]; phosphate ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015114]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; cementum mineralization [GO:0071529]; diphosphate metabolic process [GO:0071344]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0055062]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; response to sodium phosphate [GO:1904383]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
12185249_ANKH is upregulated by androgen in the LNCaP prostate cell line. 12297987_Mutations in ANKH cause chondrocalcinosis 12297989_Autosomal dominant familial calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease is caused by mutation in the transmembrane protein ANKH. 12632434_ANKH-OR and ANKH-TR are novel genetic markers that are significantly associated with ankylosing spondylitis. 12707589_ANKH gene is found in patients with familial calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease. 13130483_haplotypes among the 3 families with P5 mutations suggest the mutations arose independently and the evolutionarily conserved P5 position of ANKH may be a hot spot for mutation in families with autosomal-dominant calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease. 14558096_ANKH is not significantly involved in susceptibility to or clinical manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis. 15461680_ANKH is associated with infantile epilepsy in a large family showing complete co-segregation of seizures and chondrocalcinosis. 15474385_Numerous ANKH gene mutations cause familial calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease; they enhance ANKH protein activity, elevating extracellular pyrophosphate levels and promoting formation of pyrophosphate crystals. Review. 15780964_ANKH may be a candidate gene affecting bone size and geometry variation, and thus may be relevant for osteoporosis fracture risk. 15818664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15818664_Some cases of apparently sporadic chondrocalcinosis are caused by polymorphisms of the ankh gene. 16724232_Data showed significant associations of ANKH gene polymorphisms with body weight and height, limb length. 16724232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17147692_ANKH genetic polymorphisms in the area between SNP rs2291943 and rs2288474 are strongly associated with OPG plasma levels. 17147692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17186460_mutations in ANKH cause human skeletal disease 17403715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17403715_examined whether nine single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in ANKH-one of the key genetic factors involved in bone mineralization-can be associated with PTH and BGP levels 17563703_Cuff tear arthropathy is associated with variants in ANKH and TNAP that alter extracellular inorganic pyrophosphate concentrations causing calcium crystal deposition. 17563703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17950726_These results revealed a novel function of ANKH in the promotion of early erythroid differentiation and that ank/ank mice have lower serum levels of Epo than the normal littermates, and this is the likely cause of microcytosis in these mutant mice. 18299954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18821330_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18821330_The present study examines the possible phenotype-haplotype specificity of the associations in osteoprotegerin and parathyroid hormone gene regions. 19369455_Our results suggested that there is a coordinated interrelationship between 2 key participants of Pi and PPi metabolism, ANKH and PiT-1. 19419319_ANK expression and function in vitro and in vivo are repressed in hypoxic environments and that the effect is regulated by HIF-1. 19449425_Craniometaphyseal dysplasia and chondrocalcinosis cosegregating in a family with an ANKH mutation are reported. 19888898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888898_in a cohort study of candidate genes and BMD, a few modest associations were observed between SNPs in or near ALPL and several bone traits, but no association was observed with ANKH 20231843_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20231843_The ANKH gene was associated with all four studied obesity-related traits, body mass index (BMI), the waist-hip ratio (WHR), the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and leptin (P |
ENSMUSG00000022265 |
Ank |
681.198839 |
2.3147613158 |
1.210863 |
0.096117116 |
156.569859 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000635539143187624781513703808628153974516279545314927145466156044480735609372707923472381328277788781200285939121386036276817321777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000096013897169389374323048083712083888689044001088041681723925802459748318536038062110815757225351640968824540323112159967422485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
896.9845158 |
57.7554993 |
390.4680081 |
18.6692038 |
| ENSG00000154124 |
90268 |
OTULIN |
protein_coding |
Q96BN8 |
FUNCTION: Deubiquitinase that specifically removes linear ('Met-1'-linked) polyubiquitin chains to substrates and acts as a regulator of angiogenesis and innate immune response (PubMed:26997266, PubMed:23708998, PubMed:23746843, PubMed:23806334, PubMed:23827681, PubMed:27523608, PubMed:27559085, PubMed:24726323, PubMed:24726327, PubMed:28919039). Required during angiogenesis, craniofacial and neuronal development by regulating the canonical Wnt signaling together with the LUBAC complex (PubMed:23708998). Acts as a negative regulator of NF-kappa-B by regulating the activity of the LUBAC complex (PubMed:23746843, PubMed:23806334). OTULIN function is mainly restricted to homeostasis of the LUBAC complex: acts by removing 'Met-1'-linked autoubiquitination of the LUBAC complex, thereby preventing inactivation of the LUBAC complex (PubMed:26670046). Acts as a key negative regulator of inflammation by restricting spontaneous inflammation and maintaining immune homeostasis (PubMed:27523608). In myeloid cell, required to prevent unwarranted secretion of cytokines leading to inflammation and autoimmunity by restricting linear polyubiquitin formation (PubMed:27523608). Plays a role in innate immune response by restricting linear polyubiquitin formation on LUBAC complex in response to NOD2 stimulation, probably to limit NOD2-dependent pro-inflammatory signaling (PubMed:23806334). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23708998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23746843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23806334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23827681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24726323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24726327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26670046, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26997266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27523608, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27559085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28919039}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Angiogenesis;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase C65 family of ubiquitin isopeptidases. Members of this family remove ubiquitin from proteins. The encoded enzyme specifically recognizes and removes M1(Met1)-linked, or linear, ubiquitin chains from protein substrates. Linear ubiquitin chains are known to regulate the NF-kappa B signaling pathway in the context of immunity and inflammation. Mutations in this gene cause a potentially fatal autoinflammatory syndrome in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:90268; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; LUBAC complex [GO:0071797]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway [GO:0070431]; protein linear deubiquitination [GO:1990108]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060828]; regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010803]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23708998_2.4 A and 2.8 A crystal structures of gumby (Fam105b) in the presence of free ubiquitin and linear diubiquitin substrate, respectively 23746843_reveal a previously unannotated human DUB, OTULIN (also known as FAM105B), which is exquisitely specific for Met1 linkages; data suggest that OTULIN regulates Met1-polyUb signaling. 23806334_OTULIN restricts Met1-ubiquitin formation after immune receptor stimulation to prevent unwarranted proinflammatory signaling. 24461064_cylindromatosis (CYLD) and OTULIN/Gumby/Fam105B, directly interact with the N-terminal PUB domain-containing region of HOIP. 24726323_Phosphorylation of OTULIN prevents HOIP binding, whereas unphosphorylated OTULIN is part of the endogenous LUBAC complex. 24726327_HOIP binding to OTULIN is required for the recruitment of OTULIN to the TNF receptor complex. 27523608_OTULIN is critical for restraining life-threatening spontaneous inflammation and maintaining immune homeostasis. 27559085_Biallelic hypomorphic mutations in OTULIN define otulipenia, an early-onset autoinflammatory disease. 28481361_results establish a role for the linear Ubiquitin coat around cytosolic S. Typhimurium as the local NF-kappaB signalling platform and provide insights into the function of OTULIN in NF-kappaB activation during bacterial pathogenesis 31541095_Authors define an additional, non-catalytic function of OTULIN in the regulation of SNX27-retromer assembly and recycling to the cell surface. 31825842_Post-translational Modification of OTULIN Regulates Ubiquitin Dynamics and Cell Death. 32231246_OTULIN protects the liver against cell death, inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer. 32543267_LUBAC and OTULIN regulate autophagy initiation and maturation by mediating the linear ubiquitination and the stabilization of ATG13. 32770022_ABL1-dependent OTULIN phosphorylation promotes genotoxic Wnt/beta-catenin activation to enhance drug resistance in breast cancers. 35587511_Human OTULIN haploinsufficiency impairs cell-intrinsic immunity to staphylococcal alpha-toxin. 35939695_Reciprocal interplay between OTULIN-LUBAC determines genotoxic and inflammatory NF-kappaB signal responses. |
ENSMUSG00000046034 |
Otulin |
320.132338 |
2.0803477749 |
1.056825 |
0.125565993 |
70.443171 |
0.00000000000000004737182159729323877497566384708984834279917866192710640405039157485589385032653808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000364550618757063721238188599859093300747256102302407132498274222598411142826080322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
402.4381411 |
31.1744428 |
194.7200151 |
11.3998058 |
| ENSG00000154134 |
64221 |
ROBO3 |
protein_coding |
Q96MS0 |
FUNCTION: Thought to be involved during neural development in axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube (By similarity). In spinal cord development plays a role in guiding commissural axons probably by preventing premature sensitivity to Slit proteins thus inhibiting Slit signaling through ROBO1 (By similarity). Required for hindbrain axon midline crossing (PubMed:15105459). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z2I4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15105459}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the Roundabout (ROBO) gene family that controls neurite outgrowth, growth cone guidance, and axon fasciculation. ROBO proteins are a subfamily of the immunoglobulin transmembrane receptor superfamily. SLIT proteins 1-3, a family of secreted chemorepellants, are ligands for ROBO proteins and SLIT/ROBO interactions regulate myogenesis, leukocyte migration, kidney morphogenesis, angiogenesis, and vasculogenesis in addition to neurogenesis. This gene, ROBO3, has a putative extracellular domain with five immunoglobulin (Ig)-like loops and three fibronectin (Fn) type III motifs, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic tail with three conserved signaling motifs: CC0, CC2, and CC3 (CC for conserved cytoplasmic). Unlike other ROBO family members, ROBO3 lacks motif CC1. The ROBO3 gene regulates axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube. In mouse, loss of Robo3 results in a complete failure of commissural axons to cross the midline throughout the spinal cord and the hindbrain. Mutations ROBO3 result in horizontal gaze palsy with progressive scoliosis (HGPPS); an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by congenital absence of horizontal gaze, progressive scoliosis, and failure of the corticospinal and somatosensory axon tracts to cross the midline in the medulla. [provided by RefSeq, May 2019]. |
hsa:64221; |
axon [GO:0030424]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell-cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098632]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axon midline choice point recognition [GO:0016199]; dendrite self-avoidance [GO:0070593]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156] |
15105459_identified mutations in the ROBO3 gene in patients affected with horizontal gaze palsy with progressive scoliosis (HGPPS);ROBO3 is required for hindbrain axon midline crossing 15105459_mutations in the ROBO3 gene, which shares homology with roundabout genes important in axon guidance in developing Drosophila, zebrafish, and mouse. 15824346_The major clinical characteristics of patients with mutated ROBO3 were horizontal gaze palsy, progressive scoliosis, and brainstem malformations. 16226035_Here we describe and compare two human Robo3 isoforms, Robo3A and Robo3B, which differ by the insertion of 26 amino acids at the N-terminus, and these forms appear to be evolutionary conserved 16525029_Incidence of scoliosis in individuals harbouring heterozygous ROBO3 mutations may be greater than in the general population. 17671968_No evidence for association between Gilles de la Tourette Syndrome and either the ROBO3 gene. Thus, this gene is unlikely to be the susceptibility genes contributing to GTS on 11q24. 17671968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18270976_Four SNPs of ROBO3 showed associations with autism 18270976_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18829051_This study found five novel homozygous ROBO3 mutations (four missense mutations and one base deletion) distributed throughout the extracellular domain of the gene in consanguineous families with horizontal gaze palsy and progressive scoliosis. 19041479_This is the second reported patient with synergistic convergence and the first associated with a documented pathologic genotype. 20298552_Slit3 inhibits Robo3-induced invasion of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. 21187438_RIG-I or melanoma differentiation-associated gene (MDA)5 signaling through mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein MAVS is required for activation of interferon (IFN)-beta production by rotavirus-infected intestinal epithelial cells. 21510772_This patient had clinical and neuroimaging characteristics considered pathognomonic of horizontal gaze palsy and progressive scoliosis and yet did not have ROBO3 mutations 21592015_The novel ROBO3 mutation in this family may be among the most deleterious 21850172_Three novel ROBO3 mutations have been identified in consanguineous patients with horizontal gaze palsy and progressive scoliosis. 24936616_Robo3.1A may prevent the Slit responsiveness by recruiting Robo1/2 into a late endosome- and lysosome-dependent degradation pathway. 24969490_We report the case of a 10-month-old girl with cross-fixation and inability to abduct who was genetically proven to have horizontal gaze palsy with progressive scoliosis (recessive ROBO3 mutations). 25882844_human AKAP79-anchored PKC selectively phosphorylates the Robo3.1 receptor subtype on serine 1330 26070964_confirmed that ROBO3 increases with clinical grade and miR-383 expression is inversely correlated to that of ROBO3 27267957_In our case, we found a novel homozygous mutation p.R842* (c.2524C>T) causing a premature stop codon which is a disease-making mutation. 30985235_Two novel mutations in the ROBO3 gene were identified in two Jordanian families with six affected individuals. To our knowledge, this is the first molecular study of Horizontal gaze palsy and progressive scoliosis (HGPPS) in Jordan. 32077773_Horizontal gaze palsy and progressive scoliosis-a tale of two siblings with ROBO3 mutation. 32421468_HistoryA 13-year-old girl was born to consanguineous parents 32580277_Mutation in ROBO3 Gene in Patients with Horizontal Gaze Palsy with Progressive Scoliosis Syndrome: A Systematic Review. 32705527_Introducing and Reviewing a Novel Mutation of ROBO3 in Horizontal Gaze Palsy with Progressive Scoliosis from a Chinese Family. 33541130_High ROBO3 expression predicts poor survival in non-M3 acute myeloid leukemia. 35993361_Axon guidance receptor ROBO3 modulates subtype identity and prognosis via AXL-associated inflammatory network in pancreatic cancer. 36057630_ROBO3s: a novel ROBO3 short isoform promoting breast cancer aggressiveness. 36208230_[Expression of ROBO3 and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Pediatric Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia]. |
ENSMUSG00000032128 |
Robo3 |
81.258496 |
0.3154178912 |
-1.664664 |
0.207206085 |
65.852538 |
0.00000000000000048595411596367306019399303928643366292938483418789585854824508714955300092697143554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000003538570671743371662060683965079239861813999688811005484012639499269425868988037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
37.2796991 |
4.9310672 |
118.8546102 |
9.8208463 |
| ENSG00000154146 |
4900 |
NRGN |
protein_coding |
Q92686 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a 'third messenger' substrate of protein kinase C-mediated molecular cascades during synaptic development and remodeling. Binds to calmodulin in the absence of calcium (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Calmodulin-binding;Citrullination;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Neurogranin (NRGN) is the human homolog of the neuron-specific rat RC3/neurogranin gene. This gene encodes a postsynaptic protein kinase substrate that binds calmodulin in the absence of calcium. The NRGN gene contains four exons and three introns. The exons 1 and 2 encode the protein and exons 3 and 4 contain untranslated sequences. It is suggested that the NRGN is a direct target for thyroid hormone in human brain, and that control of expression of this gene could underlay many of the consequences of hypothyroidism on mental states during development as well as in adult subjects. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4900; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic spine head [GO:0044327]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; trans-Golgi network transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012510]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099170]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537] |
12808095_IL-2 deprivation raises the level of RC3 and other apoptotic factors, which induce apoptosis by increasing the intracellular Ca(2+) concentration 16677608_Nevertheless, by gel shift assays, Sp1 and Sp3 were not found to be responsible for the protein-DNA complexes formed by the GC-rich sequence. 17140601_Genotype distribution showed association of the rs7113041 SNP with schizophrenia in males of Portuguese origin, which was confirmed by the analysis of the proband-parent triads. 17140601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18855024_Data suggest that BSX is essential for global cognitive function and that haplo-insufficiency may cause severe mental retardation, and that deletion of Neurogranin contributes to the auditory attention deficit observed in most 11q- patients. 19571808_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20875798_Elevated cerebrospinal fluid neurogranin levels together with Alzheimer disease biomarkers may reflect synaptic degeneration. 21037240_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21112188_No association between the schizophrenia associated NRGN variant rs12807809 and cognition could be detected in these samples. 21538840_our study provides strong evidence that common exonic variation does not account for the genome-wide signi fi cant association between schizophrenia and variation at NRGN 21647148_Hippocampal activation diminished during the acquisition of contextual fear in healthy carriers of the genome-wide-supported risk variant for schizophrenia, rs12807809 in neurogranin. 21799211_The influence of NRGN genotype on the neural correlates of memory encoding and retrieval is manifest in the cingulate cortex and is involved in hippocampal formation. 22253779_The genome-wide associated genetic risk variant in the NRGN gene may be related to a small gray matter volume in the anterior cingulate cortex in the left hemisphere in patients with schizophrenia. 22306195_This study demonistrated that multiple rare mutations in schizophrenia, and provides genetic clues that indicate the involvement of NRGN in this disorder. 22461181_This study provides further evidence of the association of the NRGN gene with schizophrenia. 22856365_single nucleotide polymorphism located upstream of the neurogranin (NRGN) gene has been identified as a risk variant for schizophrenia. 23903071_Our results support an association between the NRGN gene and schizophrenia and a hypothesis that the NRGN gene may mediate the risk associated with schizophrenia via intellectual dysfunction. 24098564_NRGN risk variants contribute to subtle changes in neural functioning and anatomy. 24386483_These findings help to clarify underlying NRGN mediated pathophysiological mechanisms involving cortical-subcortical brain networks in schizophrenia. 24713697_Data indicate that neurogranin makes contacts with both the N- and C-domains of calmodulin that functionally leads to altered calcium binding kinetics. 25446004_neurogranin binds to alpha-synuclein in the human cortex, and this interaction decreases in Parkinson's disease along with the phosphorylation of neurogranin, a molecular process thought to be involved in learning and memory 26025774_This report provides evidence to support larger and controlled traumatic brain injury clinical studies for NRGN validation and prediction of outcomes. 26366630_Within-person levels of NGRN increased in cognitively normal participants but not in patients with later stage mild cognitive impairment or Alzhiemer's disease; NGRN may reflect presymptomatic synaptic dysfunction or loss. 26373605_Cerebrospinal fluid neurogranin was increased in patients with Alzheimer's dementia, progressive mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and stable MCI compared with controls, and in Alzheimer's dementia and progressive MCI compared with stable MCI. 26698298_Neurogranin and YKL-40 are promising AD biomarkers, independent of and complementary to the established core Alzheimer's disease (AD) biomarkers, reflecting additional pathological changes in the course of AD 26826204_These results confirm an increase in CSF Ng concentration in patients with AD as previously reported and show that this is specific to AD and not seen in a range of other neurodegenerative diseases. 26828755_Polymorphisms in NRGN are associated with schizophrenia, major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder in the Han Chinese population. 27018940_The results of this results showed that increased CSF neurogranin levels in Alzheimer Disease. 27604409_associations of neuromodulin and neurogranin to Alzheimer's disease 28389239_Study observed an association of rs12807809 with schizophrenia in a South Indian population. This study contributes toward the establishment of neurogranin as a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia South Indian Population. 28449373_The dynamics of calmodulin interactions with neurogranin and Ca(2+) /CAMKII alpha proteins has been reported. 28854881_Plasma neurogranin did not correlate with stroke severity. 29429972_This study, cross-sectional analysis showed that high CSF Ng was significantly associated with lower memory scores in pooled participants with NC and MCI. 29523639_Although the 3 assays target different epitopes on neurogranin and have different calibrators, the high correlations and the similar group differences suggest that the different forms of neurogranin in CSF carry similar diagnostic information 29700597_These data support that CSF Ng is increased specifically in Alzheimer disease, that high CSF Ng concentrations likely reflect synaptic dysfunction and that CSF Ng is associated with beta-amyloid plaque pathology. 30733168_In first episode psychosis patients, levels of the synaptic marker CSF neurogranin appear unaltered. 30953482_These findings are the first to suggest an association between rs12807809 and abnormal Papez circuit function in patients with SZ. This study also implicates NRGN variation and abnormal Papez circuit function in SZ pathophysiology. 31234132_NRGN, S100B and GFAP levels are significantly increased in patients with structural lesions resulting from mild traumatic brain injuries. 31837067_Cerebrospinal fluid levels of neurogranin in Parkinsonian disorders. 31861040_significant association between SNP rs12807809 and schizophrenia susceptibility in Caucasians but not Asians [meta-analysis] 32894885_Interrelations of Alzheimer s disease candidate biomarkers neurogranin, fatty acid-binding protein 3 and ferritin to neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. 32926148_Neurogranin as a Novel Biomarker in Alzheimer's Disease. 33028119_The role of synaptic biomarkers in the spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases. 33032807_Neurogranin, Encoded by the Schizophrenia Risk Gene NRGN, Bidirectionally Modulates Synaptic Plasticity via Calmodulin-Dependent Regulation of the Neuronal Phosphoproteome. 33249594_Molecular forms of neurogranin in cerebrospinal fluid. 33924468_Brain CHID1 Expression Correlates with NRGN and CALB1 in Healthy Subjects and AD Patients. 35461266_Increased levels of the synaptic proteins PSD-95, SNAP-25, and neurogranin in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. |
ENSMUSG00000053310 |
Nrgn |
3421.989941 |
0.1384903441 |
-2.852143 |
0.036078247 |
6928.145699 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
839.5314229 |
20.6406623 |
6106.0840680 |
83.0387505 |
| ENSG00000154217 |
26207 |
PITPNC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKF7 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Catalyzes the transfer of phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidic acid (PA) between membranes (PubMed:10531358, PubMed:22822086). Binds PA derived from the phospholipase D signaling pathway and among the cellular PA species, preferably binds to the C16:0/16:1 and C16:1/18:1 PA species (PubMed:22822086). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10531358, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22822086}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Catalyzes the transfer of phosphatidylinositol between membranes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22822086}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipid transport;Lipid-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein family. The encoded cytoplasmic protein plays a role in multiple processes including cell signaling and lipid metabolism by facilitating the transfer of phosphatidylinositol between membrane compartments. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene, and a pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:26207; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; phosphatidic acid transfer activity [GO:1990050]; phosphatidylglycerol binding [GO:1901611]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol transfer activity [GO:0008526]; phospholipid transport [GO:0015914]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
21728994_The phosphatidylinositol transfer protein RdgBbeta binds 14-3-3 via its unstructured C-terminus, whereas its lipid-binding domain interacts with the integral membrane protein ATRAP (angiotensin II type I receptor-associated protein). 22822086_Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 (PITPNC1) binds and transfers phosphatidic acid 22865700_The most significantly associated SNPs to type 2 diabetes mellitus in this study are expression SNPs to the lymphocyte antigen 75 gene, the ubiquitin-specific peptidase 36 gene, and the phosphatidylinositol transfer protein, cytoplasmic 1 gene. 26977884_PITPNC1-mediated vesicular release. 30089250_We propose that Pitpnc1a-expressing neurons alter behavior via modification of neuro-modulatory IGF that acts on downstream wake-promoting circuits 30555557_Elevated expression of PITPNC1 in gastric cancer is correlated with an advanced clinical stage and a poor prognosis. PITPNC1 promotes anoikis resistance through enhanced fatty acid oxidation, which is regulated by omental adipocytes and consequently facilitates gastric cancer omental metastasis. 35292404_Aberrant overexpression of HOTAIR inhibits abdominal adipogenesis through remodelling of genome-wide DNA methylation and transcription. |
ENSMUSG00000040430 |
Pitpnc1 |
102.112892 |
0.1518530599 |
-2.719252 |
0.513610443 |
24.656113 |
0.00000068527043109498470930212145682536295510089985327795147895812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002471192661363785516111983911469174302055762382224202156066894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.3094384 |
11.4037953 |
159.8924778 |
52.5005665 |
| ENSG00000154310 |
23043 |
TNIK |
protein_coding |
Q9UKE5 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase that acts as an essential activator of the Wnt signaling pathway. Recruited to promoters of Wnt target genes and required to activate their expression. May act by phosphorylating TCF4/TCF7L2. Appears to act upstream of the JUN N-terminal pathway. May play a role in the response to environmental stress. Part of a signaling complex composed of NEDD4, RAP2A and TNIK which regulates neuronal dendrite extension and arborization during development. More generally, it may play a role in cytoskeletal rearrangements and regulate cell spreading. Phosphorylates SMAD1 on Thr-322. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10521462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15342639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19061864, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19816403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20159449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21690388}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;Intellectual disability;Kinase;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
Wnt signaling plays important roles in carcinogenesis and embryonic development. The protein encoded by this gene is a serine/threonine kinase that functions as an activator of the Wnt signaling pathway. Mutations in this gene are associated with an autosomal recessive form of cognitive disability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:23043; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic density, intracellular component [GO:0099092]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; microvillus assembly [GO:0030033]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; response to organonitrogen compound [GO:0010243]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
15342639_TNIK is a specific effector of Rap2 to regulate actin cytoskeleton 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19023125_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21710359_TNIK is essential for the activation of both the canonical Wnt pathway and the JNK pathway, and serves as a pro-survival factor. 22904686_TNIK mediates proliferation and survival of EBV-transformed B-cells. 23355318_Dynamic change of TNIK offers a way to protect cells from outside stimulus. 25160513_nuclear p-TNIK expression was studied in hepatocellular carcinoma, and p-TNIK nuclear expression was associated with poor prognosis and is a candidate prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma 26269113_Our results demonstrated that TNIK might play a crucial role in pancreatic carcinogenesis and serve as a novel therapeutic target of pancreatic cancer. 26499327_High expression of TNIK in colorectal cancer was associated with recurrence in stage II and III colorectal cancer patients. 26645429_Endogenous substrates of TNIK were identified in neurons, along with consensus sequences for TNIK. 26995282_results provide new evidence that TNIK may be involved in the proliferation of multiple myeloma IM-9 cells and in the anti-cancer activity of dovitinib via inhibition of the endogenous Wnt signaling pathway. 27106596_Exome sequencing of the index in each family revealed the same homozygous truncating mutation in TNIK that results in complete loss of the protein. TNIK is a kinase with a well-established role in dendrite development and synaptic transmission. The phenotype we observe in human patients who lack TNIK is consistent with the previously published Tnik (-/-) phenotype in the murine model 27562646_TNIK is required for the tumour-initiating function of colorectal cancer stem cells. Its inhibition is a promising therapeutic approach. 28334814_Here we present the result of a 4-stage genome-wide association study composed of 5,953 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients and 8,137 controls. Overall, we identified three novel susceptible loci including rs7593846 at 2p14 near MEIS1 , rs7633294 at 3p14.1 near MAGI1 and rs9810566 at 3q26.2 near TNIK 28467797_Results indicate that Traf2- and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK) is involved in the interleukin-6-dependent proliferation of multiple myeloma cells. 30107698_Genome-wide association study on the etiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using samples from more than 5 000 patients and 6 000 normal controls showed two genes: LBX1-AS1 on 10q24.32 and TNIK on 3q26.2 highly related to AIS initiation and progression [review] 31382054_We also show that the TNIK protein isoforms including/excluding exon 15 differently regulate cell spreading in non-neuronal cells and neuritogenesis in primary cortical neurons. Our data suggest a complex regulation between the ubiquitous TDP-43 and the neuron-specific NOVA-1 splicing factors in the brain that may help better understand the pathobiology of both neurodegenerative diseases and schizophrenia. 32828291_Effect of TNIK upregulation on JQ1-resistant human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells. 32853717_Methylome-wide association study of first-episode schizophrenia reveals a hypermethylated CpG site in the promoter region of the TNIK susceptibility gene. 34350475_TNIK influence the effects of antipsychotics on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 35698907_The influence of TNIK gene polymorphisms on risperidone response in a Chinese Han population. |
ENSMUSG00000027692 |
Tnik |
106.515512 |
2.1698445742 |
1.117592 |
0.240841380 |
21.232705 |
0.00000406764145798513209823172101509136666663835057988762855529785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013380518814321494639211704291703597391460789367556571960449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
132.9103896 |
21.4312086 |
61.5466522 |
7.4149529 |
| ENSG00000154358 |
84033 |
OBSCN |
protein_coding |
Q5VST9 |
FUNCTION: Structural component of striated muscles which plays a role in myofibrillogenesis. Probably involved in the assembly of myosin into sarcomeric A bands in striated muscle (PubMed:11448995, PubMed:16205939). Has serine/threonine protein kinase activity and phosphorylates N-cadherin CDH2 and sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit ATP1B1 (By similarity). Binds (via the PH domain) strongly to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4)P2) and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2), and to a lesser extent to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P), phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P), phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate (PtdIns(5)P) and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) (PubMed:28826662). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2AAJ9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16205939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28826662}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Lipid-binding;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Muscle protein;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;SH3 domain;Transferase |
|
The obscurin gene spans more than 150 kb, contains over 80 exons and encodes a protein of approximately 720 kDa. The encoded protein contains 68 Ig domains, 2 fibronectin domains, 1 calcium/calmodulin-binding domain, 1 RhoGEF domain with an associated PH domain, and 2 serine-threonine kinase domains. This protein belongs to the family of giant sacromeric signaling proteins that includes titin and nebulin, and may have a role in the organization of myofibrils during assembly and may mediate interactions between the sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:84033; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; M band [GO:0031430]; myofibril [GO:0030016]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding [GO:0005547]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; titin binding [GO:0031432]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; protein localization to M-band [GO:0036309]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214] |
12631729_Results suggest that obscurin binds small ankyrin 1, and document a specific and direct interaction between proteins of the sarcomere and the sarcoplasmic reticulum. 16625316_The complete gene giant muscle protein obscurin was analysed. The fusion of the conventional obscurin A, containing only the GEF domain, and obscurin B, fusing into the 3' kinase exons, was experimentally confirmed and analysed. 17360660_OBSCN and C9orf65 comprise a highly accurate two-gene classifier for differentiating gastrointestinal stromal tumors and leiomyosarcomas. 17716621_Studies suggest that the obscurin abnormality may be involved in the pathogenesis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 17720975_Structural and mutational studies of the binding region on small Ank1 for obscurin suggest that it consists of two ankyrin repeats with very similar structures. 18350308_Obscurin was never lacking in myofibrillar alterations, but was either preserved at the M-band level or diffusely spread over the sarcomeres. 19258391_These findings reveal a novel signaling pathway in human skeletal muscle that involves obscurin and the Rho GTPase TC10 and implicate this pathway in new sarcomere formation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20489725_Results describe the molecular basis for the head-to-tail interaction of the carboxyl terminus of titin and the amino-terminus of obscurin-like-1 by X-ray crystallography. 22251166_OBSCN polymorphisms, in particular, highly conserved nonsynonymous Leu2116Phe variant, might contribute to aspirin hypersensitivity in asthmatics 22441987_Nontumorigenic MCF10A breast epithelial cells stably transduced with shRNAs targeting giant obscurins exhibited increased viability ( approximately 30%) and reduced apoptosis ( approximately 20%) following exposure to the DNA-damaging agent etoposide. 22573887_Obscurin and KCTD6 regulate cullin-dependent small ankyrin-1 (sAnk1.5) protein turnover 25261370_Loss of the obscurin-RhoGEF downregulates RhoA signaling and increases microtentacle formation and attachment of breast epithelial cells. 25381817_Findings indicate that loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelium results in disruption of the cell-cell contacts and acquisition of a mesenchymal phenotype that leads to enhanced tumorigenesis, migration and invasiveness in vitro and in vivo. 25490259_this study presents here the X-ray structure of the human titin:obscurin M10:O1 complex extending our previous work on the M10:OL1 interaction. 26147384_Gene-based association analyses shows nominal significant association with multifocal fibromuscular dysplasia for obscurin. 26406308_OBSCN mutations may result in the development of a familial dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) phenotype via haploinsufficiency. These mutations should be considered as a significant causal factor of DCM, alone or in concert with other mutations. 27323778_demonstrate that loss of giant obscurins from breast epithelial cells is associated with significantly increased phosphorylation and subsequent activation of the PI3K signaling cascade 27855815_association of frameshift and splicing variants, all clustering to the C terminus of the same isoform group, with occurrence of rare left ventricular noncompaction phenotype 27989621_Crystal structure of the obscurin(-like-1):myomesin complex reveals a trans-complementation mechanism whereby an incomplete immunoglobulin-like domain assimilates an isoform-specific myomesin interdomain sequence. 29073160_suggest that the combination of the OBSCN p.Arg4444Trp variant and of the FLNC c.5161delG mutation, can cooperatively affect myofibril stability and increase the penetrance of muscular dystrophy in the French family 30666746_This study finds in all cases tested that tandem obscurin Ig domains interact at the poles of each domain and tend to stay relatively extended in solution. NMR, SAXS, and MD simulations reveal that while tandem domains are elongated, they also bend and flex significantly. 33042279_Intracellular calcium current disorder and disease phenotype in OBSCN mutant iPSC-based cardiomyocytes in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. 33438037_When is an obscurin variant pathogenic? The impact of Arg4344Gln and Arg4444Trp variants on protein-protein interactions and protein stability. 34601892_Truncating Variants in OBSCN Gene Associated With Disease-Onset and Outcomes of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. 34826548_Giant obscurin regulates migration and metastasis via RhoA-dependent cytoskeletal remodeling in pancreatic cancer. 34957489_Bi-allelic loss-of-function OBSCN variants predispose individuals to severe recurrent rhabdomyolysis. |
ENSMUSG00000061462 |
Obscn |
168.754445 |
0.1208397676 |
-3.048833 |
0.395678731 |
51.966149 |
0.00000000000056465749231186795358203047858139970928848666575916581678029615432024002075195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003414315684769836539141127562289780171447123313654969933850225061178207397460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.1733351 |
10.6205499 |
243.4559791 |
62.7133259 |
| ENSG00000154359 |
91694 |
LONRF1 |
protein_coding |
Q17RB8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:91694; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630] |
|
ENSMUSG00000039633 |
Lonrf1 |
202.344176 |
2.4015218400 |
1.263949 |
0.162523663 |
60.078604 |
0.00000000000000911437550043216130258618033921195455440927932905248454176216910127550363540649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000061316400358422374938539865371919617125645585176130225590895861387252807617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
298.2997572 |
27.1355654 |
125.0799174 |
8.9021923 |
| ENSG00000154380 |
55740 |
ENAH |
protein_coding |
Q8N8S7 |
FUNCTION: Ena/VASP proteins are actin-associated proteins involved in a range of processes dependent on cytoskeleton remodeling and cell polarity such as axon guidance and lamellipodial and filopodial dynamics in migrating cells. ENAH induces the formation of F-actin rich outgrowths in fibroblasts. Acts synergistically with BAIAP2-alpha and downstream of NTN1 to promote filipodia formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11696321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18158903}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3-binding;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the enabled/ vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein. Members of this gene family are involved in actin-based motility. This protein is involved in regulating the assembly of actin filaments and modulates cell adhesion and motility. Alternate splice variants of this gene have been correlated with tumor invasiveness in certain tissues and these variants may serve as prognostic markers. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 3. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:55740; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; profilin binding [GO:0005522]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; WW domain binding [GO:0050699]; actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008154]; actin polymerization-dependent cell motility [GO:0070358]; axon guidance [GO:0007411] |
12672821_mena phosphorylation is regulated by Abi-1 and c-Abl 16533770_overexpression of ENAH is associated with breast cancer 18158903_Oservations identify Tes as an atypical binding partner of EVH1 domain of Mena and a regulator specific to a single Ena/VASP family member. 18676769_the hMena(+11a) isoform is associated with an epithelial phenotype and identifies EGFR-dependent cell lines that are sensitive to the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib 18985426_two isoforms of Mena, ++ and +++, are upregulated in the invasive tumor cells and one isoform, 11a, is downregulated 19081071_the Mena invasion isoform potentiates EGF-induced carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis 19082477_Increased hMena expression is associated with colorectal carcinomas. 19277120_hMena possesses properties which help to regulate the formation of lamellipodia through the modulation of the activity of Rac1. 19434313_Mena was not expressed in the normal cervical squamous epithelium but its expression was increased in parallel with the increasing grade of CIN, with up-regulation upon transition to CIN3 and further to invasive carcinoma. 19641378_ENAH polymorphisms are associated with increased susceptibility, development of proteinuria and gross hematuria, and pathological progression of childhood IgAN. 19641378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20083228_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21209853_hMena and HER2 signalling has a role in breast cancer 21335464_Mammalian enabled (Mena) is a critical regulator of cardiac function. 21398369_ENA/VASP-family proteins are functionally redundant in homologous recombination, and MENA, VASP and EVL may be involved in the DSB repair pathway in humans 21423205_Data show that VASP and Mena interact with RSK1. 21769917_results indicate that by mediating intensive F-actin accumulation at the sites of cell infiltration, WAVE2, N-WASP, and Mena are crucial for PI3K-dependent cell invasion induced by PDGF 22472896_Mena protein seems to play a role in malignant transformation and its intensity is correlated with the type and grade of tumor and also with vascular invasion. Its positivity in endothelial cells may suggest its potential role in tumor angiogenesis. 22615875_Overexpression of Wnt1 and Wnt3a ligands increased MENA mRNA levels. 22971274_High Menacalc levels identify a subgroup of breast cancer patients with poor disease-specific survival, suggesting that Menacalc may serve as a biomarker for metastasis. 23062752_This study demonistrated that dysregulation of ENAH eeox in brain of patient with schizophrenia. 23129656_These data suggest that polarized and growth-arrested cellular architecture correlates with absence of alternative hMENA isoform expression. 23956979_we consider that it is necessary to analyze the expression of Mena splice variants in a higher number of cases, in different epithelial lesions, and also in experimental studies to define its exact role in carcinogenesis 24076656_this study suggests a novel mechanism in which Lpd mediates EGFR endocytosis via Mena downstream of endophilin. 24683008_High expression of Mena is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 25031323_determined the alpha-synuclein-binding domain of beta-III tubulin and demonstrated that a short fragment containing this domain can suppress alpha-synuclein accumulation in the primary cultured cells 25109497_the higher relative expression of hMena(11a) compared with hMena(INV) may predict malignant transformation in breast epithelial cells, and, furthermore, a reversal of expression of hMena(11a) and hMena(INV) may dictate the state of cancer progression 25429076_Invasive breast ductal-carcinoma cells that migrated thru a layer of human endothelial cells were enriched for the transcript encoding Mena(INV), an invasive isoform of Mena. 25449779_High ENAH expression is associated with trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer. 25961924_our results indicate that hMENA11a is an anti-apoptotic regulator involved in the HER3-mediated mechanisms of resistance to PI3K inhibition in breast cancer 26112005_we evaluate the prognostic value of Menacalc in a cohort of ANN patients. Our primary objective was to determine if there was an association between Menacalc and overall patient mortality. 26680363_these data provide the first description of endogenous Mena(INV) protein expression in mouse and human breast tumors. 26956036_PPARgamma might inhibit the proliferation and migration of GC cell lines through suppressing the expression of TERT and ENAH 27597754_SHIP2 recruits Mena to invadopodia and disruption of SHIP2-Mena interaction in cancer cells leads to attenuated capacity for ECM degradation and invasion in vitro, as well as reduced metastasis in vivo. 27748415_the difference between mRNAs encoding constitutive Mena sequences and those containing the 11a exon correlates with metastasis in colorectal cancer, suggesting that 11a exon exclusion contributes to invasive phenotypes and leads to poor clinical outcome 27824079_Mena(INV) promotes invadopodium maturation by inhibiting normal dephosphorylation of cortactin at tyrosine 421 by the phosphatase PTP1B. 29439204_Endothelin-1 is a regulator of Mena expression in the serous ovarian cancer.Mena expression is associated with a poor prognosis in serous ovarian cancer patients.Mena is recruited to mature invadopodia in endothelin-1 and beta-arrestin-1 signaling. 29907768_hMENA regulates beta1 integrin expression and hMENA(11a) reduces and hMENADeltav6 increases beta1 integrin activation and signaling 30250066_Enah is upregulated in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines and is correlated with clinicopathological parameters and survival of gastric cancer patients. 31075540_Findings show that Mena is a splicing target of PTBP1 which regulates exon11a skipping to promote lung cancer cells metastasis. 31323325_Scaffold stiffness influences breast cancer cell invasion via EGFR-linked Mena upregulation and matrix remodeling. 32535200_IRSp53 is a novel interactor of SHIP2: A role of the actin binding protein Mena in their cellular localization in breast cancer cells. 32698859_Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes deliver microRNA-375 to downregulate ENAH and thus retard esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. 35030977_Enabled homolog (ENAH) regulated by RNA binding protein splicing factor 3b subunit 4 (SF3B4) exacerbates the proliferation, invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Notch signaling pathway. 35254597_MiR-139-5p/ENAH Affects Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. 35790431_[Screening and identification of key genes ATP1B3 and ENAH in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma: based on data mining and clinical validation]. |
ENSMUSG00000022995 |
Enah |
1204.998882 |
0.2214031540 |
-2.175252 |
0.096228080 |
482.714848 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005482796617604727311983913731800942468946306931599975091120069510753005787501717389461195592255732325837047984143604672635379429421414312888008561793293769176631524433299421280832132313905490801159607791712424595456029681138 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002536867651280432129536726991764277014210346993984378881395370841450696936403918420789393369877251258435661020454516352280687359832030228892904374687057780787064318618028513451449893675575683453297647278549857422066010083331 |
Yes |
Yes |
412.6685422 |
29.9481780 |
1876.1703012 |
95.1791193 |
| ENSG00000154451 |
115362 |
GBP5 |
protein_coding |
Q96PP8 |
FUNCTION: As an activator of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, plays a role in innate immunity and inflammation. Promotes selective NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in response to microbial and soluble, but not crystalline, agents (PubMed:22461501). Hydrolyzes GTP, but in contrast to other family members, does not produce GMP (PubMed:20180847). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20180847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22461501}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antimicrobial;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene belongs to the TRAFAC class dynamin-like GTPase superfamily. The encoded protein acts as an activator of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and has a role in innate immunity and inflammation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:115362; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900017]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-18 production [GO:0032741]; positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:1900227]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; protein localization to Golgi apparatus [GO:0034067]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
15175044_Eight of nine melanoma cell lines expressed GBP-5a/b and four of nine additionally low levels of GBP-5ta. 17266443_GBP5 is constitutively localized in the Golgi apparatus of endothelial cells. 18260761_3 genes were upregulated in patients with chronic EBV infection: guanylate binding protein 1, tumor necrosis factor-induced protein 6, and guanylate binding protein 5; they may be associated with the inflammatory reaction or with cell proliferation. 20180847_analysis of guanylate binding protein 5 and a tumor-specific truncated splice variant 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21151871_The in vivo localization of GBP-5 at the Golgi apparatus is regulated by isoprenylation and dimerization. 22461501_guanylate binding protein 5 (GBP5) stimulates inflammasome assembly; GBP5 promoted selective NLRP3 inflammasome responses to pathogenic bacteria and soluble but not crystalline inflammasome priming agents; GBP5 serves as a unique rheostat for NLRP3 inflammasome activation 26025597_GZMA, GBP5 and CD64 genes show promise as a rapid diagnostic markers separating tuberculosis from other pulmonary diseases. 26996307_Antiviral activity requires Golgi localization of GBP5, but not its GTPase activity. 28376501_these results reveal that GBP5 inhibited influenza virus replication through the activation of IFN signaling and proinflammatory factors 28580591_Previously reported tetrameric and dimeric species of hGBP-1 and hGBP-5 were unmasked as dimers and monomers, respectively, with their shapes depending on both the bound nucleotide and the ionic strength of the solution. 28941629_GBP5 and KLF2 may be useful as a diagnostic tool for active tuberculosis, also the two-gene set may serve as surrogate biomarkers for monitoring tuberculosis therapy. 29618166_we identified that the LG domains of hGBP-1 and hGBP-5 build an interaction site within the hetero dimer. Our in vitro study provides mechanistic insights into the homomeric and heteromeric interactions of hGBP-1 and hGBP-5 and present useful strategies to characterise the hGBP network further. 30408130_the two top differentially expressed genes in our sample, IRF1 and GBP5, both have primary inflammation and immune functions, and were significantly negatively correlated with total scores on our self-report of anhedonia across all 48 subjects with cocaine-use disorder 31091448_Guanylate-Binding Proteins 2 and 5 Exert Broad Antiviral Activity by Inhibiting Furin-Mediated Processing of Viral Envelope Proteins. 32796072_GBP5 Is an Interferon-Induced Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. 33608513_GBP5 drives malignancy of glioblastoma via the Src/ERK1/2/MMP3 pathway. 33615742_Regulation of Synovial Inflammation and Tissue Destruction by Guanylate Binding Protein 5 in Synovial Fibroblasts From Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Rats With Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis. 33876762_Structural basis for GTP-induced dimerization and antiviral function of guanylate-binding proteins. 34958688_GBP5 promotes liver injury and inflammation by inducing hepatocyte apoptosis. 35369870_Whole blood GBP5 protein levels in patients with and without active tuberculosis. |
ENSMUSG00000105504 |
Gbp5 |
82.680925 |
2.8420558189 |
1.506935 |
0.207805719 |
52.436232 |
0.00000000000044444808853341808125808817716341728317440418205563901210553012788295745849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002714130652359640779271593097920975683635252950764993329357821494340896606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
116.5157970 |
15.3794662 |
41.3484022 |
4.2380782 |
| ENSG00000154608 |
|
CEP170P1 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.791102 |
5.8756645609 |
2.554752 |
0.999837597 |
6.095801 |
0.01355034606707189448471240211802069097757339477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025240170109790658475867886068044754210859537124633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5580615 |
9.9965803 |
1.7074882 |
1.2263863 |
| ENSG00000154640 |
10950 |
BTG3 |
protein_coding |
Q14201 |
FUNCTION: Overexpression impairs serum-induced cell cycle progression from the G0/G1 to S phase. |
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the BTG/Tob family. This family has structurally related proteins that appear to have antiproliferative properties. This encoded protein might play a role in neurogenesis in the central nervous system. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:10950; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045930] |
17690688_by disrupting the DNA binding activity of E2F1, BTG3 participates in the regulation of E2F1 target gene expression. Therefore, our studies have revealed a previously unidentified pathway through which the activity of E2F1 may be guarded by activated p53. 18590053_These data support the hypothesis that BTG3 may act to suppress tumorigenesis and that hypermethylation is an important mechanism for inactivation of BTG3 and perhaps other tumor suppressor genes. 19221000_BTG3 is epigenetically silenced in renal cancer 22020331_loss of BTG3 in normal cells induced cellular senescence, which was correlated with enhanced ERK-AP1 signaling and elevated expression of the histone H3K27me3 demethylase JMJD3/KDM6B 23533280_BTG3-dependent CHK1 ubiquitination contributes to its chromatin localization and activation and a defect in this regulation may increase genome instability and promote tumorigenesis 23657964_BTG3 protein expression may be considered as a good marker to indicate the favorable prognosis of epithelial ovarian carcinoma. 23810394_These results disclosed an important role of BTG3 in lung tumorigenesis. 25238703_Down-regulation of BTG3 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer. 25569101_BTG3 binds and suppresses AKT, a kinase frequently deregulated in cancers. 25701359_The suppressed migration and invasion abilities found in BTG3-overexpressing esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Our findings suggested that BTG3 is suppressor in the progression of esophageal adenocarcinoma 25904053_BTG3 overexpression might reverse the aggressive phenotypes and be employed as a potential target for gene therapy of gastric cancer. 27468874_BTG3 overexpression inhibited cell growth, induced cell cycle arrest and suppressed the metastasis of SW480 cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. BTG3 may be considered as a therapeutic target in CRC treatment. 28183228_Taken together, the results of our study suggest that BTG3 overexpression could inhibit cell proliferation and invasion and promotes cell apoptosis in EOC cell, possibly by regulating the AKT/GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway 28337446_ANA and ASMA evaluation in patients with liver transplantation and no history of autoimmune disease has no clinical relevance, since it varies in time and is not related to any risk factors or liver injury. Routine autoimmunity evaluation should be avoided. 28407690_BTG3 overexpression inhibited tumor growth of SW620 cells by suppressing proliferation and inducing apoptosis. It was suggested that down-regulated BTG3 expression might be considered as a marker for colorectal carcinogenesis. 29197876_BTG3 is a direct downstream target of miR-106b-5p. 29268856_Data show that miR-139 can repress the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells via directly inhibiting the expression of ANA protein, human Add B-cell translocation gene 3 protein (BTG3). 29270670_BTG3 expression might contribute to CRC carcinogenesis. BTG3 knockdown might strengthen the aggressive colorectal cancer behavior. 30689165_Inhibition of miR-93-5p may have blocked HPV-positive cervical cancer development by targeting of BTG3. 31261026_HOTAIRM1 might act as a tumor-suppressor in 5-fluorouracil resistant colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through downregulating miR-17-5p/BTG3 pathway and inhibiting multi-drug resistance. 31387005_miR-519c-3p functions as a tumor promotor in regulating the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting BTG3. 32620986_Hypoxia-induced downregulation of B-cell translocation gene 3 confers resistance to radiation therapy of colorectal cancer. 33051589_Long noncoding RNA CA3-AS1 suppresses gastric cancer migration and invasion by sponging miR-93-5p and targeting BTG3. 33311481_Loss of the tumor suppressor BTG3 drives a pro-angiogenic tumor microenvironment through HIF-1 activation. 35045800_Long non-coding RNA cancer susceptibility candidate 2 regulates the function of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes via the microRNA-18a-5p/B-cell translocation gene 3 signaling axis in rheumatoid arthritis. 35362324_Correlation between BTG3, CASP9 and LRP4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms and susceptibility to papillary thyroid carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000022863 |
Btg3 |
138.112528 |
3.0721643239 |
1.619255 |
0.242518566 |
43.492709 |
0.00000000004255419790712408753680612730836869961326129896406200714409351348876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000225691685630309566804774404275349668907990619004522159229964017868041992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
216.0170920 |
30.2355986 |
70.7315136 |
7.5835193 |
| ENSG00000154678 |
5137 |
PDE1C |
protein_coding |
Q14123 |
FUNCTION: Calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase with a dual specificity for the second messengers cAMP and cGMP, which are key regulators of many important physiological processes (PubMed:8557689, PubMed:29860631). Has a high affinity for both cAMP and cGMP (PubMed:8557689). Modulates the amplitude and duration of the cAMP signal in sensory cilia in response to odorant stimulation, hence contributing to the generation of action potentials. Regulates smooth muscle cell proliferation. Regulates the stability of growth factor receptors, including PDGFRB (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29860631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8557689, ECO:0000305|PubMed:29860631}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Calmodulin-binding;cAMP;cGMP;Deafness;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme that belongs to the 3'5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family. Members of this family catalyze hydrolysis of the cyclic nucleotides, cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine monophosphate, to the corresponding nucleoside 5'-monophosphates. The enzyme encoded by this gene regulates proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells, and neointimal hyperplasia. This enzyme also plays a role in pathological vascular remodeling by regulating the stability of growth factor receptors, such as PDGF-receptor-beta. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:5137; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0047555]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-activated 3',5'-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0048101]; calmodulin-activated dual specificity 3',5'-cyclic-GMP, 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004117]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
16455054_PDE1C levels decreased in all conditions that inhibited proliferation 17726023_PDE1C1 is expressed at high levels in human cardiac myocytes with an intracellular distribution distinct from that of PDE3A 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20110084_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25608528_PDE1C is an important regulator of SMC proliferation, migration, and neointimal hyperplasia, in part through modulating endosome/lysosome-dependent PDGFRbeta protein degradation via low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1. 25620587_PDE1C is a proliferation-associated gene in glioblastoma multiforme cells in vitro. 29860631_By combining population-specific mutation arrays, targeted deafness genes panel, whole exome sequencing (WES), we identified PDE1C (Phosphodiesterase 1C) c.958G>T (p.A320S) as the disease-associated variant. Structural modeling insights into p.A320S strongly suggest that the sequence alteration will likely affect the substrate-binding pocket of PDE1C. 33789162_Phosphodiesterase 1C integrates store-operated calcium entry and cAMP signaling in leading-edge protrusions of migrating human arterial myocytes. 34312235_Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1C contributes to abdominal aortic aneurysm. |
ENSMUSG00000004347 |
Pde1c |
17.453136 |
5.3272353588 |
2.413387 |
0.467841443 |
27.194596 |
0.00000018397219086575187468909193221067166490456656902097165584564208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000705672956647218743074468846887548068025353131815791130065917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.7196964 |
10.7521683 |
5.4677764 |
1.6029273 |
| ENSG00000154734 |
9510 |
ADAMTS1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHI8 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves aggrecan, a cartilage proteoglycan, at the '1938-Glu-|-Leu-1939' site (within the chondroitin sulfate attachment domain), and may be involved in its turnover (By similarity). Has angiogenic inhibitor activity. Active metalloprotease, which may be associated with various inflammatory processes as well as development of cancer cachexia. May play a critical role in follicular rupture. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10438512}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif) protein family. Members of the family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The protein encoded by this gene contains two disintegrin loops and three C-terminal TS motifs and has anti-angiogenic activity. The expression of this gene may be associated with various inflammatory processes as well as development of cancer cachexia. This gene is likely to be necessary for normal growth, fertility, and organ morphology and function. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9510; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; heart trabecula formation [GO:0060347]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; ovulation from ovarian follicle [GO:0001542]; positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:1900087]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration [GO:1904754]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
11831030_extracellular matrix degrading enzyme 12054626_properties investigated through protein engineering 12054629_cleaves aggrecan at multiple sites and is differentially inhibited by metalloproteinase inhibitors 12716911_ADAMTS1 significantly blocks VEGFR2 phosphorylation due to direct binding and sequestration of VEGF165, with consequent suppression of endothelial cell proliferation. 14760803_ADAMTS-1 is the first matrix-degrading enzyme downregulated by the catabolic factor IL-1beta in vitro. 14996435_ADAMTS-1 expression was significantly reduced in the presence of HDL subfraction 3. 15184385_results suggest that conserved residues other than the furin cleavage site in the prodomain of a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I motif(ADAMTS-1) are involved in its biosynthesis 15599946_negative effect of TGFbeta1 on ADAMTS-1, -5, -9, and -15 coupled with increases in their inhibitor, TIMP-3 may aid the accumulation of versican in the stromal compartment of the prostate in BPH and prostate cancer 15661359_ADAMTS-1-immunoreactivity was manifold increased in brain with Down syndrome and neurodegeneration. 15878613_specific distribution pattern of ADAMTS-1 in a variety of organs during embryogenesis suggests a role of the molecule in tissue remodelling, vasculogenesis and angiogenesis 15967414_Expression of ADAMTS1 was downregulated by cAMP in normal, but not in SV40-transformed cells, suggesting that in normal cells epiregulin and amphiregulin activity is downregulated by a feedback mechanism that may be lost in SV40-transformed cells 16061471_fibulin-1 is a new regulator of ADAMTS-1-mediated proteoglycan proteolysis and may play an important role in proteoglycan turnover in tissues where there is overlapping expression 16314835_Overexpression of ADAMTS-1 promotes pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinoma and Lewis lung carcinoma cells and that a proteinase-dead mutant of ADAMTS-1 inhibits their metastasis 16328961_Has a previously unreported gelatinolytic activity. 16495931_results provide evidence for an overexpression of ADAM-12 and a lower expression of ADAMTS-1 in non-small-cell lung cancer suggest that these proteases play different functions in cancer progression 16641089_role of TFPI-2 as a maintenance factor of extracellular remodeling suggests the indirect function of ADAMTS1 as an additional homeostatic player by its ability to alter the extracellular location of TFPI-2 16675485_ADAMTS-1 expression is associated with decidualization of the endometrial stroma in vivo. IL-1beta increased whereas TGF-beta1 decreased ADAMTS-1 mRNA and protein levels in decidual stromal cell cultures in a concentration- and time-dependent manner. 17167179_Hypermethylation was subsequently identified for three of four analyzed genes, ADAMTS1 (85%), CRABP1 (90%), and NR3C1 (35%). 17560840_These results show that ADAMTS-1 has both the opportunity in bone and capability in vitro to induce collagen type I processing, together with a positive influence on osteoblastic three-dimensional growth. 17897672_Results show that crystal structures contain catalytic and disintegrin-like domains, both in the inhibitor-free form and in complex with the inhibitor marimastat. 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18076023_Expression of several genes associated with angiogenesis was altered during transition into androgen-independency. Among these, a significant decrease was found for ADAMTS1, whose expression inversely correlated with microvessel density. 18174457_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18192475_ADAMTS-1 was significantly upregulated in thrombosed hemodialysis grafts. 18775505_ADAMTS1 proteolytic action mimics the outcome of genetic deletion of this proteoglycan with regards to focal adhesion. Findings suggest that the shedding of syndecan-4 by ADAMTS1 disrupts cell adhesion and promotes cell migration. 19007777_These data suggest the involvement of HDAC6 and SP1 in the HDACi-induced expression of angiostatic ADAMTS1. 19010931_catalytically active ADAMTS-1 contribution to tumor development, which consists of the recruitment of fibroblasts involved in tumor growth and tumor-associated stroma remodeling. 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19027488_results suggest that aberrant methylation of ADAMTS1 frequently occurs in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and that it may play a role in the pathogenesis of NSCLC 19349275_ADAMTS1 is transiently induced by hypoxia in endothelial cells, and its transcription is mediated by HIF-1 binding 19404339_These results demonstrate that the ADAMTS1 3'-untranslated region may regulate the stability and expression of ADAMTS1 mRNA. 19608765_disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS1) and matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP1), orchestrate a paracrine signaling cascade to modulate the bone microenvironment in favor of osteoclastogenesis and bone metastasis 19915008_cleavage of semaphorin 3C induced by ADAMTS1 promotes the migration of breast cancer cells, indicating that the co-expression of these molecules in tumors may contribute to the metastatic program 20103648_results indicate that the antiangiogenic activity of TSP1 is differentially regulated by ADAMTS1 in the liver and lung, emphasizing the concept that regulation of angiogenesis is varied in different tissue environments. 20484033_Study documents the expression of ADAMTS1 in aggressive and highly plastic melanoma and Ewing sarcoma cells. Inhibiting ADAMTS1 compromised the endothelial mimetic attributes observed. 20546609_ADAMTS1 is an important regulatory factor of angiogenesis and tumor growth in prostate tumors, where modified ADAMTS1 expression resulted in markedly changed blood vessel morphology, possibly related to altered thrombospondin 1 levels. 20655981_The correlation between its expression in cumulus granulosa cells and oocyte fertilization capacity suggests a role for ADAMTS-1 in human cumulus function 20795945_AHR, a novel acute hypoxia-response sequence, drives reporter gene expression under hypoxia in vitro and in vivo. 20840749_ADAMTS1 expression is elevated in endometrial adenocarcinoma 21037509_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21345877_ADAMTS-1 was present in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques; ADAMDTS-1 was differentially expressed between acute myocardial infarction and stable angina; and ADAMTS-1 immunopositive cells were mainly macrophages. 21937160_variable effects that chemical modifications/mutations in vWF have on proteolysis by ADAMTS13 22383695_Pericyte-derived TIMP3 stabilized and ADAMTS1 destabilized the capillary tubular networks 22562232_Data show that the expression of ADAMTS4, 9, 16 and was up-regulated during chondrogenesis, ADAMTS1 and 5 were down-regulated. 22735305_study showed that ADAMTS-1, -4, -5 and TIMP3 were expressed at differential levels in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines 22776012_our results demonstrated that ADAMTS1 gene transfer inhibited angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo 23001403_These findings suggest that ADAMTS1 expression is altered in primary gastric cancer and paired lymph node metastasis and has angioinhibitory effects. 23289900_ADAMTS-1 expression was decreased in human breast tumors, and ADAMTS-1 knockdown stimulated migration, invasion and invadopodia formation in breast cancer cells in vitro. 23681936_ADAMTS1 expression is decreased in breast tumor specimens. 23859810_We have demonstrated that the expression of ADAMTS-1, -4 and -5 is induced during the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. 24631293_ADAMTS1 formed a complex with VEGFC, attenuated VEGFR3 phosphorylation and inhibited lymphangiogenesis in vitro. 24646063_Dysregulated expression of ADAMTS-1 in polycystic ovary syndrome may influence oocyte quality-via Granulosa cells-oocyte paracrine and endocrine mechanism. 24998958_Data show that ADAMTS1 was expressed at a significantly higher level in extravillous trophoblast cells (EVTs) than in villous trophoblast cells (VTs), while both ADAM10 and ADAM12 were expressed at significantly higher levels in VTs than in EVTs. 25689086_All ADAMTS tested in our study were expressed in both stable and unstable carotid plaques, especially in smooth muscle cells and macrophages. Analysis of the expression pattern on mRNA level showed significant higher expression of ADAMTS1 in unstable plaques compared with stable plaques. 25936341_The aberrant methylation of ADAMTS1 may be involved in the development and progression of gastric cancer. 25998153_Results show that ADAMTS1 expression is negatively regulated in breast neoplasm cells due to mir-365 targeting its 3'UTR. 26124221_single-nucleotide missense mutation in the ADAMTS1 gene (c. 742I>T) was found to segregate in the family, given that the affected individuals must be heterozygous for the mutation 26299656_Ectopic expression of SP1 and USF transcription factors resulted in the decrease in ADAMTS1 transcriptional activity of all promoter constructs 26563155_increased expression of ADAMTS1 protein in macrophages and neutrophils that infiltrated aortic tissues may promote the progression of acute aortic dissection 26663063_Data suggest that the rs416905 and rs402007 single nucleotide polymorphisms of the a disintegrin and metallo-proteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motifs (ADAMTS-1) gene may be associated with ischemic stroke caused by large artery atherosclerosis (LAA). 26675551_High ADAMTS1 expression was significantly associated with tumorigenicity of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infected endothelial cells. 26888488_ADAMTS1 protein levels in semen were significantly lower in males with infertility. Sperm count and motility showed a negative correlation with levels of ADAMTS1 protein expression. 26916548_progesterone acts via the progesterone receptor to modulate ADAMTS 1 and 4 levels in ovarian cancer cell lines. 27053287_implicated in knee destruction in Kashin-Beck disease 27447109_Adamts1 acts as an extracellular matrix 'modifier', with miR-181d-induced downregulation, that regulates adipocyte lineage commitment and obesity. 27764205_Findings indicate that ADAMTS-1 has proteolytic functions in the nucleus through its interaction with aggrecan substrate in normal and tumoral breast cells. 27908842_Data indicate that serum versican levels were significantly decreased in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) patients, and that serum ADAMTS-1 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif-1) and versican levels were significantly and positively correlated with each other. 28067899_Patients with Marfan syndrome showed elevated NOS2 and decreased ADAMTS1 protein levels in the aorta. 28417352_Our study demonstrated that altered levels of ADAMTS-1 and aggrecan may have a partial role in the etiopathogenesis of Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and ADAMTS-1 could be a predictive marker for implantation success in PCOS patients. 28674292_ADAMTS1 has diverse roles in angiogenesis, tumor microenvironment and lymphangiogenesis. 28700319_we identified Adamts1 as the modulator of a potent pathway that converts changes in diet into a cellular signal in adipose tissue that controls APC activity in vivo 28814085_This study showed that ADAMTS1, 8, and 18 are highly expressed in GC and its nodal metastases, suggesting important roles of these proteases in carcinogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. The findings from the present study indicate that these proteases may be promising candidates for novel and alternative treatments in GC (gastric cancer) 28890348_Taken together, our findings suggested that miR-362-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of VSMCs by directly targeting ADAMTS1, which might provide novel insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying the action of miR-362-3p in atherosclerosis. 28949770_ADAMTS 1 may be necessary during the decidualization and implantation stages of early normal pregnancy. 29038419_Significant differences in gene expression profiles were observed between patients with post-kidney transplant bladder tumors and those with conventional bladder tumors. ADAMTS1 expression was significantly lower in first group than in the second. 29086015_Increased levels of ADAMTS-1 could be a potential marker for the etiopathogenesis of PCOS in adolescents and younger-aged females and predict the development of CVD [cardiovascular disease ] risk and IR among all patients with the same age. 29135310_ADAMTS 1, 4, 12, and 13 levels in the maternal and cord blood were lower in the preeclampsia group than in the control group. ADAMTS 1, 4, and 12 levels in placental tissues were higher in the preeclampsia group. 29737873_expressed 2.56-fold less in Sertoli cells in nonobstructive azoospermia than in obstructive azoospermia; insufficient expression in Sertoli cells may have an important role in the etiology of male infertility 30446843_The results of the present study indicated that ADAMTS-1 and ADAMTS-9 as well as PRs are downregulated in the human CCs (cumulus cells) in PCOS polycystic ovary syndrome) patients, which could be associated with impaired oocyte maturation and may result in a lower oocyte recovery and oocyte maturity rates, as well as lower fertilization rate. 30655094_The expression level of ADAMTS1 in Hip Degenerative Arthritis group were decreased 2.5, 2 and 2.5 fold when compared with Femoral neck fractures group. 30989556_JNK1 siRNA knockdown assay confirmed that ADAMTS-1 was regulated through JNK pathway, and lauric acid interfered with this pathway to down-regulate ADAMTS-1 expression. 31974739_ADAMTS1 and HSPG2 mRNA levels in cumulus cells are related to human oocyte quality and controlled ovarian hyperstimulation outcomes. 32269093_ADAMTS-1 and syndecan-4 intersect in the regulation of cell migration and angiogenesis. 32408377_Melatonin-triggered post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications of ADAMTS1 coordinately retard tumorigenesis and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. 32502021_A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type motifs 1 rs402007 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 rs9619311 polymorphisms are associated with essential hypertension in a Chinese Han population, and there was a positive interaction among rs402007, rs9619311, and smoking. 33161094_Metalloprotease ADAMTS-1 decreases cell migration and invasion modulating the spatiotemporal dynamics of Cdc42 activity. 33396280_ADAMTS1 Supports Endothelial Plasticity of Glioblastoma Cells with Relevance for Glioma Progression. 34135477_ADAMTS1, MPDZ, MVD, and SEZ6: candidate genes for autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. 34169995_Role of Adamts-1 in Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma Tumor Cells Progression. 35725415_The role of serum ADAMTS-1 levels in Hyperemesis Gravidarum. |
ENSMUSG00000022893 |
Adamts1 |
21.186683 |
2.3217380134 |
1.215205 |
0.458390506 |
6.720402 |
0.00953161403942699020364059947496571112424135208129882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018356814094721080748984221031605557072907686233520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.9326019 |
8.1545777 |
12.9226205 |
2.6615111 |
| ENSG00000154864 |
63895 |
PIEZO2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H5I5 |
FUNCTION: Component of a mechanosensitive channel required for rapidly adapting mechanically activated (MA) currents. Required for Merkel-cell mechanotransduction. Plays a major role in light-touch mechanosensation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CD54}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains more than thirty transmembrane domains and likely functions as part of mechanically-activated (MA) cation channels. These channels serve to connect mechanical forces to biological signals. The encoded protein quickly adapts MA currents in somatosensory neurons. Defects in this gene are a cause of type 5 distal arthrogryposis. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:63895; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cation channel activity [GO:0005261]; mechanosensitive ion channel activity [GO:0008381]; cation transport [GO:0006812]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; detection of mechanical stimulus [GO:0050982]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception [GO:0050974]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612] |
22921401_piezo2 sensitization may contribute to PKA- and PKC-mediated mechanical hyperalgesia. 23487782_Gain-of-function mutations in the mechanically activated ion channel PIEZO2 cause a subtype of Distal Arthrogryposis. 24726473_this study used exome sequencing to discover that mutations in PIEZO2 cause Gordon syndrome, Marden-Walker syndrome, and distal arthrogryposis type 5. 25037583_family of mechanically activated channels that counts only two members in human, piezo1 and 2, has emerged recently. [review] 25469543_we demonstrate that the mechanosensitivity of human embryonic stem cell-derived touch receptors depends on PIEZO2 25712306_Whole-exome sequencing revealed a novel heterozygous mutation c.4456G>C (p.A1486P) of PIEZO2. 26551544_Transgenic mouse lines lacking Piezo2 in proprioceptive neurons showed severely uncoordinated body movements. 27392819_Enterochromaffin cells in the human and mouse small bowel GI epithelium selectively express the mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo2, and also that activation of Piezo2 by force leads to inward currents, 5-HT release and an increase in mucosal secretion 27607563_we report a consanguineous family with three siblings who showed short stature, scoliosis, gross motor impairment, and a progressive form of contractures involving the distal joints that is distinct from that found in patients with domina Recessive mutations in PIEZO2 thus appear to cause a progressive phenotype that overlaps with, while being mostly distinct from that associated with dominant mutations in the same gene 27653382_Our results show that PIEZO2 is a determinant of mechanosensation in humans. 27714920_we report the developmental phenotypic spectrum of familial Gordon syndrome in one family due to the previously characterized PIEZO2 mutation c.8057G>A. 27743844_The Piezo2 convert a variety of mechanical stimuli into channel activation and subsequent inactivation, and what molecules and mechanisms modulate Piezo function. 27843126_We identified homozygous loss of function variants in PIEZO2 as the underlying cause for an autosomal-recessive distal muscular atrophy with arthrogryposis, kyphoscoliosis, and neonatal respiratory insufficiency distinct from previously described dominant PIEZO2 diseases. 27974811_Sensory ataxia and proprioception defect with dorsal column involvement together with arthrogryposis, myopathy, scoliosis and progressive respiratory failure may represent a distinct clinical phenotype, and indicate recessive mutations in PIEZO2 28905996_The present results demonstrate the occurrence of Piezo2 in cutaneous sensory nerve formations that functionally work as slowly adapting (Merkel cells) and rapidly adapting (Meissner's corpuscles) low-threshold mechanoreceptors and are related to fine and discriminative touch but not to vibration or hard touch 29212024_Study demonstrate the splicing of Piezo2 to be cell type specific. Biophysical characterization revealed substantial differences in ion permeability, sensitivity to calcium modulation, and inactivation kinetics among Piezo2 splice variants. 29432180_This study identified Piezo2 mechanosensitive cationic channel as a transducer of environmental physical cues into mechanobiological responses. 30181649_The molecular defects identified through clinical exome sequencing in this study expands the phenotypic spectra of CHD7-associated disorders and implicate PIEZO2 as a candidate gene for major eye developmental defects. 30285720_Novel mutations in TPM2 and PIEZO2 are responsible for distal arthrogryposis (DA) 2B and mild DA in two Chinese families. 30305456_individuals with loss-of-function mutations in PIEZO2 completely failed to develop sensitization and painful reactions to touch after skin inflammation. 30324494_the presence of both Piezo1 and 2 in enteric neurons throughout the gastrointestinal tract from guinea pigs, mice and humans, were studied. 30628892_identify a functionally conserved inactivation gate in the pore-lining inner helix of mouse Piezo1 and Piezo2 that is distinct from the two constrictions 30745454_Results indicate the critical prognostic values of the piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel components PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 30938034_we present a 3-generation family affected with DA5, who all carry a variant of unknown clinical significance c.8068A>C (p.Ser2690Arg) in the PIEZO2 gene. DA5 is a very rare condition with less than 20 cases previously reported. Our report expands the phenotype and contributes to evidence of this variant's pathogenicity. 31015490_The Piezo2 ion channel is mechanically activated by low-threshold positive pressure. 31513102_Studied role of piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 2 (PIEZO2) expression in development of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. 31609726_A neuromuscular disorder with homozygosity for PIEZO2 gene variants: an important differential diagnosis for kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. 32561714_A dietary fatty acid counteracts neuronal mechanical sensitization. 32996126_Glans clitoris innervation: PIEZO2 and sexual mechanosensitivity. 33057202_PIEZO2 in sensory neurons and urothelial cells coordinates urination. 33369052_Confirming the involvement of PIEZO2 in the etiology of Marden-Walker syndrome. 34153212_The Form and Function of PIEZO2. 34220183_Piezo2 downregulation via the Cre-lox system affects aqueous humor dynamics in mice. 34825354_Molecular Sensors of Temperature, Pressure, and Pain with Special Focus on TRPV1, TRPM8, and PIEZO2 Ion Channels. 35507012_Is the Sex Difference a Clue to the Pathomechanism of Dry Eye Disease? Watch out for the NGF-TrkA-Piezo2 Signaling Axis and the Piezo2 Channelopathy. 35581325_Piezo2 is not an indispensable mechanosensor in murine cardiomyocytes. 35689908_PIEZO2 ion channels in proprioception. 35906671_Distal Arthrogryposis type 5 in an Italian family due to an autosomal dominant gain-of-function mutation of the PIEZO2 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000041482 |
Piezo2 |
52.671799 |
0.2569625394 |
-1.960370 |
0.777640122 |
5.886090 |
0.01526094684597220293986730155211262172088027000427246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028121295311679117556735718608251772820949554443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.5386078 |
14.9052155 |
103.2184714 |
41.0610379 |
| ENSG00000154914 |
124739 |
USP43 |
protein_coding |
Q70EL4 |
FUNCTION: May recognize and hydrolyze the peptide bond at the C-terminal Gly of ubiquitin. Involved in the processing of poly-ubiquitin precursors as well as that of ubiquitinated proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
Predicted to enable ISG15-specific protease activity. Predicted to be involved in translesion synthesis. Predicted to be located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:124739; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; ISG15-specific peptidase activity [GO:0019785]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; translesion synthesis [GO:0019985]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30135474_study identifies USP43 to be an H2BK120 deubiquitinase and a potential tumor suppressor and reveals a reciprocally inhibitory loop between USP43 and EGFR/PI3K/AKT, whose imbalance drives breast carcinogenesis 35321978_Prognostic Value and Oncogenic Effects of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 43 in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 36137995_Cav2.2-NFAT2-USP43 axis promotes invadopodia formation and breast cancer metastasis through cortactin stabilization. |
ENSMUSG00000020905 |
Usp43 |
9.201626 |
0.3873912199 |
-1.368137 |
0.522141029 |
7.049716 |
0.00792778057164762219033438128690249868668615818023681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015521162121968285971251866328657342819496989250183105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5552293 |
1.7863285 |
11.7575126 |
2.8816851 |
| ENSG00000154928 |
2047 |
EPHB1 |
protein_coding |
P54762 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Cognate/functional ephrin ligands for this receptor include EFNB1, EFNB2 and EFNB3. During nervous system development, regulates retinal axon guidance redirecting ipsilaterally ventrotemporal retinal ganglion cells axons at the optic chiasm midline. This probably requires repulsive interaction with EFNB2. In the adult nervous system together with EFNB3, regulates chemotaxis, proliferation and polarity of the hippocampus neural progenitors. In addition to its role in axon guidance also plays an important redundant role with other ephrin-B receptors in development and maturation of dendritic spines and synapse formation. May also regulate angiogenesis. More generally, may play a role in targeted cell migration and adhesion. Upon activation by EFNB1 and probably other ephrin-B ligands activates the MAPK/ERK and the JNK signaling cascades to regulate cell migration and adhesion respectively. Involved in the maintenance of the pool of satellite cells (muscle stem cells) by promoting their self-renewal and reducing their activation and differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CBF3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12223469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18034775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9430661, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9499402}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for ephrin-B family members. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2047; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; filopodium tip [GO:0032433]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; axon guidance receptor activity [GO:0008046]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005005]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis [GO:0021952]; dendritic spine development [GO:0060996]; dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0060997]; detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050965]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; hindbrain tangential cell migration [GO:0021934]; immunological synapse formation [GO:0001771]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of satellite cell differentiation [GO:1902725]; negative regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation [GO:1902723]; neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:0061351]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; optic nerve morphogenesis [GO:0021631]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046328]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; skeletal muscle satellite cell activation [GO:0014719]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12084815_Human platelets express EphA4 and EphB1, and the ligand, ephrinB1. Forced clustering of EphA4 or ephrinB1 led to cytoskeletal reorganization, adhesion to fibrinogen, and alpha-granule secretion. 14576067_Eph/ephrin signaling enhances the ability of platelet agonists to cause aggregation provided that those agonists can increase cytosolic Ca(++) and this is accomplished in part by activating Rap1 15722342_analysis of EphB1, EphB2, and EphB4-binding peptides interaction with antagonists with ephrin-like affinity 18034775_The ubiquitin ligase Cbl induces the ubiquitination and lysosomal degradation of activated EphB1, a process requiring EphB1 and Src kinase activity. 18057206_Transgenic EphB1 and ephrin-B3 cooperatively regulate the proliferation and migration of neural progenitors in the hippocampus. 18424888_Loss of expression of EphB1 protein in gastric carcinoma is associated with invasion and metastasis 18628988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18931529_EphB1 may have roles in the pathogenesis and development of colorectal cancer. 19736353_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21041834_No association is found for EPH receptor B1 and susceptibility to schizophrenia. 21041834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21085126_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21124932_Data shew that the identification of three novel candidates as EPH receptor genes might indicate a link between perturbed compartmentalization of early neoplastic lesions and breast cancer risk and progression. 21763378_EPHB1 polymorphisms may be associated with susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma in the Korean population. 21804545_Data show that EphB receptors interact with E-cadherin and with the metalloproteinase ADAM10 at sites of adhesion. 23118026_EphB1 stimulation triggered approximately 50% serine-threonine PTEN dephosphorylation and PTEN-Cbl complex disruption, a process requiring PTEN protein phosphatase activity. 24121831_Low EphB1 expression is associated with glioma. 24427352_Our data indicate that loss of EphB1 protein is associated with metastasis and poorer survival in patients with serous ovarian cancer 24606480_EphB1 and Ephrin-B could be regarded as independent good prognostic factors and important biological markers for Squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of gallbladder. 24677421_The study presents the first structure of the EphB1 tyrosine kinase domain determined by X-ray crystallography to 2.5A. 24716914_The genes CD248, Ephb1 and P2RY2 were detected as the top overexpressed in GC biopsies. 25120806_Our results indicate that EphB1 may be involved in carcinogenesis of renal cell carcinoma 25879388_In medulloblastoma cell lines, EphB1 downregulation or knockdown reduced cell growth, viability, cell-cycle regulator expression, and migration, but increased radiosensitivity and the percentage of cells in G1 phase of the cell cycle. 25944917_The tumor-suppressor function of EphB1 is clinically relevant across many malignancies, suggesting that EphB1 is an important regulator of common cancer cell transforming pathways. 27028544_Association of EPHB1 rs11918092 with symptoms of schizophrenia in Chinese Zhuang and Han populations. 27541794_investigate NET could modulate one's attention orientation to facial expressions, we categorized individuals according to the genotypes of the -182 T/C (rs2242446) polymorphism. Our results indicated that the -182 T/C polymorphism significantly modulated attention orientation to facial expressions, of which the CC genotype facilitated attention reorientation to the locations where cued faces were previously presented. 28108514_some of the mutations found in EPHB1 may contribute to an increased invasive capacity of cancers. 29550816_SUMOylation of EphB1 repressed activation of its downstream signaling molecule PKC-gamma, and consequently inhibited neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. 30401746_EphB1 and EphA1 phosphorylate the Cx32CT domain residue Tyr(243) Unlike for Cx43, the tyrosine phosphorylation of the Cx32CT increased gap junction intercellular communication. 33356837_Peripheral EphrinB1/EphB1 signalling attenuates muscle hyperalgesia in MPS patients and a rat model of taut band-associated persistent muscle pain. 33627480_Identification of tetracycline combinations as EphB1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treatment of neuropathic pain. |
ENSMUSG00000032537 |
Ephb1 |
64.180918 |
0.4852123737 |
-1.043312 |
0.209440097 |
25.156424 |
0.00000052863277110073136437473888954441392229455232154577970504760742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001933255624739047412859139704610633714310097275301814079284667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.4272666 |
5.7381671 |
79.8189168 |
7.9220484 |
| ENSG00000154930 |
84532 |
ACSS1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NUB1 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from short-chain fatty acids (PubMed:16788062). Acetate is the preferred substrate (PubMed:16788062). Can also utilize propionate with a much lower affinity (By similarity). Provides acetyl-CoA that is utilized mainly for oxidation under ketogenic conditions (By similarity). Involved in thermogenesis under ketogenic conditions, using acetate as a vital fuel when carbohydrate availability is insufficient (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99NB1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16788062}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
This gene encodes a mitochondrial acetyl-CoA synthetase enzyme. A similar protein in mice plays an important role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle by catalyzing the conversion of acetate to acetyl CoA. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:84532; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; acetate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0003987]; AMP binding [GO:0016208]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; propionate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0050218]; acetate biosynthetic process [GO:0019413]; acetyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0006085]; acetyl-CoA biosynthetic process from acetate [GO:0019427]; ethanol oxidation [GO:0006069]; propionate biosynthetic process [GO:0019542] |
19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27363021_citrate synthase and ACSS1 have tumorigenic functions in hepatocellular carcinoma 27539851_ACSS1 is essential for glucose-independent acetate-mediated cell survival and tumor growth. |
ENSMUSG00000027452 |
Acss1 |
179.476215 |
0.1611289336 |
-2.633713 |
0.141510718 |
397.792728 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016650732220131013238648887495715431716778028193546348700200002827226073637771725700529246243439037856653836622119312201798229232768283276077013683920005502218870587778642022980836926067186565066091531135633200532710461450047745302072144113481 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006269510397171779431840807219084560680089081991041895682214751537019078329187912612865667871151764539355958297723078483217381982148204706290941666798499926139177075507025284659738063899513362406126422592399870096536995678349057925515808165073 |
Yes |
No |
49.8507981 |
4.6460611 |
311.6305878 |
14.8151533 |
| ENSG00000155008 |
139322 |
APOOL |
protein_coding |
Q6UXV4 |
FUNCTION: Component of the MICOS complex, a large protein complex of the mitochondrial inner membrane that plays crucial roles in the maintenance of crista junctions, inner membrane architecture, and formation of contact sites to the outer membrane. Specifically binds to cardiolipin (in vitro) but not to the precursor lipid phosphatidylglycerol. Plays a crucial role in crista junction formation and mitochondrial function (PubMed:23704930), (PubMed:25764979). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23704930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25764979}. |
Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein which contains an apolipoprotein O superfamily domain. This domain is found on proteins in circulating lipoprotein complexes. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:139322; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; MIB complex [GO:0140275]; MICOS complex [GO:0061617]; mitochondrial crista junction [GO:0044284]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; SAM complex [GO:0001401]; cristae formation [GO:0042407]; inner mitochondrial membrane organization [GO:0007007] |
23704930_APOOL is a cardiolipin-binding component of the Mitofilin/MINOS protein complex. 32788226_MIC26 and MIC27 cooperate to regulate cardiolipin levels and the landscape of OXPHOS complexes. |
ENSMUSG00000025525 |
Apool |
384.726284 |
4.2746324041 |
2.095800 |
0.878611439 |
4.986940 |
0.02553932979581954518244479857003170764073729515075683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044674153565571993185212562593733309768140316009521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
271.6613785 |
178.1244622 |
63.5285276 |
29.4063065 |
| ENSG00000155011 |
27123 |
DKK2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBU2 |
FUNCTION: Antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling by inhibiting LRP5/6 interaction with Wnt and by forming a ternary complex with the transmembrane protein KREMEN that promotes internalization of LRP5/6. DKKs play an important role in vertebrate development, where they locally inhibit Wnt regulated processes such as antero-posterior axial patterning, limb development, somitogenesis and eye formation. In the adult, Dkks are implicated in bone formation and bone disease, cancer and Alzheimer disease (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is a member of the dickkopf family. The secreted protein contains two cysteine rich regions and is involved in embryonic development through its interactions with the Wnt signaling pathway. It can act as either an agonist or antagonist of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, depending on the cellular context and the presence of the co-factor kremen 2. Activity of this protein is also modulated by binding to the Wnt co-receptor LDL-receptor related protein 6 (LRP6). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27123; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; co-receptor binding [GO:0039706]; receptor antagonist activity [GO:0048019]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12167704_Analysis of individual Dkk domains and chimeric Dkks shows that the carboxy-terminal domains of both Dkk1 & 2 associate with LRP6 and are necessary and sufficient for Wnt8 inhibition. 16568085_loss of DKK expression plays a role in development or progression of malignant melanoma 18461655_Down-regulation of the Dkks associated to promoter hypermethylation appears to be frequently involved in gastrointestinal tumorigenesis. 18524778_analysis of the structural basis of the interaction between Dkk and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 19247449_Given the mutually exclusive expression of DKK1 and DKK2, EWS/ETS regulates the transcription of the DKK family, and the EWS/ETS-mediated DKK2 up-regulation could affect the tumorigenicity of EFT in an indirect manner 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19562778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19659606_Dickkopf-4 and -2 are significantly upregulated in most colorectal tumors 19755393_DKK2 is epigenetically silenced by methylation in higher grades and stages of renal cell carcinoma; results suggest that DKK2 inhibits renal cancer progression through apoptotic and cell cycle pathways 20004015_Data indicate major roles for Dkk1 and the canonical Wnt pathway in early-stage differentiation, and for Dkk2 and Wnt/Ca2+-dependent signaling in late-stage differentiation on microstructured and hydrophilic surfaces, during osseointegration. 20332099_In the study of the genetics of alcoholism, three SNPs in DKK2 (rs427983; rs419558; rs399087) demonstrated empirical significance. 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21312269_Elevated TGF-beta1 levels in osteoarthritic osteoblasts can stimulate DKK2 expression. 21540552_there are distinct functions of DKK1 and DKK2 in controlling angiogenesis 22964660_DKK2 may contribute to tumorigenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer(EOC) through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mechanisms. 23204234_Our results provide strong evidence that DKK2 is a key player in Ewing sarcoma invasion and osteolysis and also in the differential phenotype of Ewing sarcoma cells. 23999978_MiR-21 overexpression was significantly correlated with the DKK2-/beta-catenin- immunohistochemical phenotype. 24117450_We found 1 DKK2 SNP to be significantly associated with alcohol-related harm in alcoholic subjects 25312721_Data indicate that inhibiting dickkopf-related protein 2 (DKK2)with siDKK2 reduced the expression of DKK2, but had no effect on leptin expression. 26715268_Genetic variant in DKK2 gene is associated with gallbladder cancer. 27203079_the genotyping and functional findings are consistent with the hypothesis that DKK2 is a tumor suppressor; by selectively retaining a transcriptionally inactive DKK2 allele, the reduction of DKK2 function results in unchecked Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma oncogenesis. 27296949_these findings reveal that the miR-187-5p-DKK2 pathway regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, cell growth, and apoptosis. Our findings provide the first evidence of a role for miR-187-5p in promotion of B-cell ALL. 27363011_Knock down of the dickkopf WNT signaling pathway inhibitor 2 (DKK2) resulted in a significant suppression of HOXD10, HOXD11 and HOXD13 while over-expression of DKK2 and stimulation with factors of the WNT signaling pathway. 27431620_The present report suggested that DKK2 downregulation suppressed the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by inhibiting the Wnt/betacatenin signaling pathway. 27542661_targeting of DKK2 by miR-154 leads to upregulation of beta-catenin expression and activation of the classical Wnt signaling pathway and cardiac fibroblasts. 28152305_epigenetic silencing of Wnt antagonists was associated with gastric carcinogenesis, and concurrent hypermethylation of SFRP2 and DKK2 could be a potential marker for a prognosis of poor overall survival. 28467796_our findings demonstrate that DKK2 functions as a tumor suppressor through inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis via regulating Wnt signaling during breast tumorigenesis. 29749862_Both DKK2 and sFRP4 polymorphisms are found to play a crucial role; especially for smokers towards modulating risk for lung cancer. 30320375_Study confirmed the low DKK1 expression in patients with grade 1 breast cancer and a high DKK1 expression in ER-negative breast cancer. DKK2 may be a potential prognostic biomarker for the Normal-like subtype of breast cancer. 30867812_Here, the authors found that Dickkopf associated protein 2 (DKK2), a secretory protein highly expressed in metastatic colorectal cancer tissues, could stimulate angiogenesis via a classic VEGF/VEGFR independent pathway. 30990378_the critical role of MEG3-miR-4261-DKK2-Wnt/beta-catenin signalling axis in ESCC 31489578_AWPPH inhibits GC cell proliferation and invasion via miR-203a/DKK2 axis. 31583260_We then confirmed these results and demonstrated that a higher expression of DKK2 imparts the recruitment of CD8(+) T cells. Our work suggested that DKK2 imparts tumor immune evasion and is associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 31800554_Dickkopf 2-Expressing Adenovirus Increases the Survival of Random-Pattern Flaps and Promotes Vasculogenesis in a Rat Model. 32945363_miR4833p promotes the osteogenesis of human osteoblasts by targeting Dikkopf 2 (DKK2) and the Wnt signaling pathway. 33679613_G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor Correlates With Dkk2 Expression and Has Prognostic Impact in Ovarian Cancer Patients. 33909798_RNAM EXPRESSION AND DNA METHYLATION OF DKK2 GENE IN COLORECTAL CANCER. |
ENSMUSG00000028031 |
Dkk2 |
110.920177 |
0.4800957905 |
-1.058606 |
0.164077121 |
41.988885 |
0.00000000009179369765719369977384095798952716969976162175726130953989923000335693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000476062887357757916687410928421658393161486344524746527895331382751464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.3386452 |
7.2171639 |
149.6017900 |
9.9792500 |
| ENSG00000155085 |
221264 |
AK9 |
protein_coding |
Q5TCS8 |
FUNCTION: Involved in maintaining the homeostasis of cellular nucleotides by catalyzing the interconversion of nucleoside phosphates. Has both nucleoside monophosphate and diphosphate kinase activities. Catalyzes the phosphorylation of AMP, dAMP, CMP and dCMP with ATP as phosphate donor and of CMP with GTP as phosphate donor. Also catalyzes the production of ATP, CTP, GTP, UTP, dATP, dCTP, dGTP and TTP from the corresponding diphosphate substrates with either ATP or GTP as phosphate donor. Shows substrate preference of CDP > UDP > ADP > GDP > TDP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23416111}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide metabolism;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the interconversion of nucleosides, possessing both nucleoside monophosphate and diphosphate kinase activities. The encoded protein uses these interconversions to maintain nucleoside homeostasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:221264; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; adenylate kinase activity [GO:0004017]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity [GO:0004550]; nucleoside monophosphate kinase activity [GO:0050145]; AMP phosphorylation [GO:0006756]; ATP generation from ADP [GO:0006757]; CDP phosphorylation [GO:0061508]; CMP phosphorylation [GO:0061566]; dADP phosphorylation [GO:0006174]; dAMP phosphorylation [GO:0061565]; dCDP phosphorylation [GO:0061570]; dCMP phosphorylation [GO:0061567]; dGDP phosphorylation [GO:0006186]; GDP phosphorylation [GO:0061568]; TDP phosphorylation [GO:0061571]; UDP phosphorylation [GO:0061569] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27966543_AK2 identified as a novel disease modifier in RASPN-associated limb girdle myasthenia. |
ENSMUSG00000091415 |
Ak9 |
51.201071 |
0.4537835049 |
-1.139924 |
0.293243721 |
14.954560 |
0.00011013154879997289327473591891148885224538389593362808227539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000301416959074281461117283953399237361736595630645751953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.5683890 |
10.8206678 |
68.9006139 |
16.7068457 |
| ENSG00000155093 |
5799 |
PTPRN2 |
protein_coding |
Q92932 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in vesicle-mediated secretory processes. Required for normal accumulation of secretory vesicles in hippocampus, pituitary and pancreatic islets. Required for the accumulation of normal levels of insulin-containing vesicles and preventing their degradation. Plays a role in insulin secretion in response to glucose stimuli. Required for normal accumulation of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin in the brain. In females, but not in males, required for normal accumulation and secretion of pituitary hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (By similarity). Required to maintain normal levels of renin expression and renin release (By similarity). May regulate catalytic active protein-tyrosine phosphatases such as PTPRA through dimerization (By similarity). Has phosphatidylinositol phosphatase activity; the PIPase activity is involved in its ability to regulate insulin secretion. Can dephosphorylate phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate (PI(4,5)P2), phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (By similarity). Regulates PI(4,5)P2 level in the plasma membrane and localization of cofilin at the plasma membrane and thus is indirectly involved in regulation of actin dynamics related to cell migration and metastasis; upon hydrolyzation of PI(4,5)P2 cofilin is released from the plasma membrane and acts in the cytoplasm in severing F-actin filaments (PubMed:26620550). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P80560, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63475, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26620550}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Diabetes mellitus;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phospholipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein with sequence similarity to receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. However, tyrosine phosphatase activity has not been experimentally validated for this protein. Studies of the rat ortholog suggest that the encoded protein may instead function as a phosphatidylinositol phosphatase with the ability to dephosphorylate phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate, and this function may be involved in the regulation of insulin secretion. This protein has been identified as an autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2015]. |
hsa:5799; |
ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; synapse [GO:0045202]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0005001]; insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0035773]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0007269]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of secretion [GO:0051046] |
15220191_IA-2beta is involved in insulin secretion, but despite its importance as a major autoantigen in human type 1 diabetes, it is not required for the development of diabetes in NOD mice. 18398821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19361477_In mice IA-2beta expressed exclusively in dense core secretory vesicles (DCV) and with fractions rich in synaptic vesicles (SV) of neuroendocrine cells of brain and impairment of conditioned learning. 19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20097759_While PTPRN2 shares sequence similarity with protein tyrosine phosphatases, this study in rat suggests that this protein instead functions as a membrane bound phosphatidylinositol phosphatase. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22950449_The findings in this patient raise the possibility that PTPRN2 may be active during early development of the human brainstem and that its overexpression may cause bilateral Duane retraction syndrome as occurs in patients with homozygous HOXA1 mutations. 25421040_Data indicate the X-ray structure of the mature ectodomain of mature ectodomain of phogrin/IA-2beta (PTPRN2) (ME phogrin) at pH 7.4 and 4.6. 25877877_ProPTPRN2 elicited these effects through direct interaction with TRAF2. 26620550_Reduction in plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 abundance by PTPRN2 and PLCbeta1 releases the PI(4,5)P2-binding protein cofilin from its inactive membrane-associated state into the cytoplasm where it mediates actin turnover dynamics. 27153397_Haplotype-dependent allele-specific methylation of PTPRN2 gene is associated with neurological disorders. 27489308_Copy-number variations are enriched for PTPRN2 and other neurodevelopmental genes in children with developmental coordination disorder. 30890718_The association of genetically controlled CpG methylation (cg158269415) of protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type N2 (PTPRN2) with childhood obesity. 34272834_HOXD13 promotes the malignant progression of colon cancer by upregulating PTPRN2. 34448213_Rab35 regulates insulin secretion via phogrin in pancreatic beta cells. |
ENSMUSG00000056553 |
Ptprn2 |
64.932523 |
0.4069169862 |
-1.297194 |
0.254854555 |
25.908239 |
0.00000035803766048679865296289854745270808678014873294159770011901855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001331477921084693485419075086040319177982382825575768947601318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.2405052 |
5.6586966 |
89.5839503 |
9.2185118 |
| ENSG00000155097 |
528 |
ATP6V1C1 |
protein_coding |
P21283 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of the V1 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons (PubMed:33065002). V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment (By similarity). Subunit C is necessary for the assembly of the catalytic sector of the enzyme and is likely to have a specific function in its catalytic activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21282, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P31412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33065002}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of intracellular compartments of eukaryotic cells. V-ATPase dependent acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c'', and d. Additional isoforms of many of the V1 and V0 subunit proteins are encoded by multiple genes or alternatively spliced transcript variants. This gene is one of two genes that encode the V1 domain C subunit proteins and is found ubiquitously. This C subunit is analogous but not homologous to gamma subunit of F-ATPases. Previously, this gene was designated ATP6D. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:528; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; ATPase complex [GO:1904949]; clathrin-coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030665]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0098850]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex [GO:0016469]; transmembrane transporter complex [GO:1902495]; vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain [GO:0000221]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961]; proton transmembrane transport [GO:1902600]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; synaptic vesicle lumen acidification [GO:0097401] |
12890556_proximal promoter region contains cis-acting elements required for expression in cancer cells 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21526910_Immunohistochemical localization of C1 subunit of V-ATPase (ATPase C1) in oral squamous cell cancer and normal oral mucosa. 24454753_results of our study suggest that high expression of Atp6v1c1 affects the actin structure of cancer cells such that it facilitates breast cancer metastasis 25901422_We assessed ATPaseC1 expression in a sample of oral squamous cell carcinoma using tissue microarrays to analyze the relation between ATPaseC1 expression and clinical, histopathological and prognostic parameters. 28504970_knockdown of C1 reduces breast cancer growth, metastasis, and osteolytic lesion formation. 30781750_MIR29a plays an important role during the trans-differentiation of Activated hepatic stellate cells in the resolution of liver fibrosis, in part, through regulation of ATP6V1C1. 31901859_Multi-cancer V-ATPase molecular signatures: A distinctive balance of subunit C isoforms in esophageal carcinoma. 33183740_The ATPase subunit of ATP6V1C1 inhibits autophagy and enhances radiotherapy resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000022295 |
Atp6v1c1 |
600.325492 |
2.1914492877 |
1.131885 |
0.133288124 |
70.912593 |
0.00000000000000003734068384511450031029993869049226801176104764278147751799252773707848973572254180908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000289013368407912954802936894583144993561691607660002478752403476391918957233428955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
749.4787021 |
75.0951733 |
344.5161114 |
25.1509759 |
| ENSG00000155158 |
158219 |
TTC39B |
protein_coding |
Q5VTQ0 |
FUNCTION: Regulates high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol metabolism by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of the oxysterols receptors LXR (NR1H2 and NR1H3). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BYY4}. |
Alternative splicing;Lipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
Predicted to be involved in several processes, including cholesterol homeostasis; negative regulation of cholesterol storage; and regulation of cholesterol efflux. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:158219; |
cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010874]; regulation of cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0090181] |
19060906_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20686565_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20972250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25920552_Two new polymorphisms associated with gall bladder disease and obesity in women have been identified, GCKR rs1260326, and TTC39B rs686030. 27453397_association of rs519664[T] in TTC39B on 9p22 with endometriosis, is reported. |
ENSMUSG00000038172 |
Ttc39b |
76.904248 |
7.6755020450 |
2.940261 |
0.279148270 |
106.274069 |
0.00000000000000000000000064211205836146281923786115278447854022720272344769935808055150893358317687464875689329346641898155212402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000006872787513716600076207204025675743693587517163078722575270966999201605052149943730910308659076690673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
124.2089746 |
20.5151413 |
16.3630361 |
2.1463149 |
| ENSG00000155189 |
55326 |
AGPAT5 |
protein_coding |
Q9NUQ2 |
FUNCTION: Converts 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate (lysophosphatidic acid or LPA) into 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate (phosphatidic acid or PA) by incorporating an acyl moiety at the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone (PubMed:21173190). Acts on LPA containing saturated or unsaturated fatty acids C15:0-C20:4 at the sn-1 position using C18:1-CoA as the acyl donor (PubMed:21173190). Also acts on lysophosphatidylethanolamine using oleoyl-CoA, but not arachidonoyl-CoA, and lysophosphatidylinositol using arachidonoyl-CoA, but not oleoyl-CoA (PubMed:21173190). Activity toward lysophosphatidylglycerol not detectable (PubMed:21173190). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21173190}. |
Acyltransferase;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phospholipid biosynthesis;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthesis; CDP-diacylglycerol from sn-glycerol 3-phosphate: step 2/3. |
This gene encodes a member of the 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase family. This integral membrane protein converts lysophosphatidic acid to phosphatidic acid, the second step in de novo phospholipid biosynthesis. A pseudogene of this gene is present on the Y chromosome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014]. |
hsa:55326; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0003841]; acyltransferase activity [GO:0016746]; acylglycerol metabolic process [GO:0006639]; CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthetic process [GO:0016024]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; phosphatidic acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006654]; phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008654] |
15367102_This publication describes the molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and enzyme characterization of the mouse homolog, mAGPAT5. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21173190_enzymatic properties, tissue distribution, and subcellular localization of human AGPAT3 and AGPAT5 |
ENSMUSG00000031467 |
Agpat5 |
472.023559 |
2.2945619575 |
1.198219 |
0.078662103 |
234.003116 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007986597882660315335959415629363365183672835533382226227149897644117027520165801025157342756188790668458299393446195623250441752847455026409484446503483923152089118957519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001805240195223066425054473385534217346803220791147238339321041982455958423972133020439186959389671577467393021609978948844735322908777730432916541758459061384201049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
662.8009503 |
31.4112113 |
291.1207166 |
10.9176703 |
| ENSG00000155363 |
4343 |
MOV10 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCE1 |
FUNCTION: 5' to 3' RNA helicase that is involved in a number of cellular roles ranging from mRNA metabolism and translation, modulation of viral infectivity, inhibition of retrotransposition, or regulation of synaptic transmission (PubMed:23093941). Plays an important role in innate antiviral immunity by promoting type I interferon production (PubMed:27016603, PubMed:35157734, PubMed:27974568). Mechanistically, specifically uses IKKepsilon/IKBKE as the mediator kinase for IRF3 activation (PubMed:27016603, PubMed:35157734). Blocks HIV-1 virus replication at a post-entry step (PubMed:20215113). Counteracts HIV-1 Vif-mediated degradation of APOBEC3G through its helicase activity by interfering with the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (PubMed:29258557). Inhibits also hepatitis B virus/HBV replication by interacting with HBV RNA and thereby inhibiting the early step of viral reverse transcription (PubMed:31722967). Contributes to UPF1 mRNA target degradation by translocation along 3' UTRs (PubMed:24726324). Required for microRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene silencing by the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Required for both miRNA-mediated translational repression and miRNA-mediated cleavage of complementary mRNAs by RISC (PubMed:16289642, PubMed:17507929, PubMed:22791714). In cooperation with FMR1, regulates miRNA-mediated translational repression by AGO2 (PubMed:25464849). Restricts retrotransposition of long interspersed element-1 (LINE-1) in cooperation with TUT4 and TUT7 counteracting the RNA chaperonne activity of L1RE1 (PubMed:30122351, PubMed:23093941). Facilitates LINE-1 uridylation by TUT4 and TUT7 (PubMed:30122351). Required for embryonic viability and for normal central nervous system development and function. Plays two critical roles in early brain development: suppresses retroelements in the nucleus by directly inhibiting cDNA synthesis, while regulates cytoskeletal mRNAs to influence neurite outgrowth in the cytosol (By similarity). May function as a messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) clearance factor (PubMed:24726324). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16289642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17507929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20215113, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22791714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23093941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24726324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25464849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27016603, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27974568, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29258557, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30122351, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31722967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35157734}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Required for RNA-directed transcription and replication of the human hepatitis delta virus (HDV). Interacts with small capped HDV RNAs derived from genomic hairpin structures that mark the initiation sites of RNA-dependent HDV RNA transcription. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18552826}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Helicase;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;RNA-mediated gene silencing;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables 5'-3' RNA helicase activity and RNA binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus; negative regulation of transposition, RNA-mediated; and posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression. Located in P-body and cytosol. Implicated in hypertension. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4343; |
cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P granule [GO:0043186]; P-body [GO:0000932]; 5'-3' RNA helicase activity [GO:0032574]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization [GO:0061158]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; miRNA-mediated gene silencing [GO:0035195]; miRNA-mediated gene silencing by mRNA destabilization [GO:0035279]; negative regulation of transposition, RNA-mediated [GO:0010526]; positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process [GO:0061014]; regulation of neuron projection arborization [GO:0150011]; RNA-mediated post-transcriptional gene silencing [GO:0035194] |
16289642_Mov10 coimmunoprecipitates with human Ago1 and Ago2 and also colocalizes with them in cytoplasmic P-bodies. 18552826_The identification of capped small RNAs and the involvement of MOV10 in hepatitis delta virus replication further suggest a conserved mechanism related to RNA-directed transcription in lower eukaryotes. 19665004_These data suggest that MOV10 is involved in the progression of telomerase-catalyzing reaction via the interaction of telomerase protein and telomere DNA. 20140200_Results suggest that Mov10 could be required during the lentiviral lifecycle and that its perturbation disrupts generation of infectious viral particles. 20543829_MOV10, co-purifies and interacts with components of Polycomb-repressive complex 1 from human cells. Knockdown of MOV10 in human fibroblasts leads to the upregulation of the INK4a. 22105071_identified two critical MOV10 packaging determinants and eight other critical residues for anti-HIV-1 activity 22727223_Depletion of endogenous MOV10 significantly enhances the retrotransposition of endogenous retroelements. 22791714_APOBEC3G inhibits microRNA-mediated repression of translation by interfering with the interaction between Argonaute-2 and MOV10 23754279_MOV10 contributes to the cellular control of long interspersed element 1 replication. 23926332_Authors conclude that HIV-1 virion incorporation and the antiviral activities of Mov10 and APOBEC3G do not require their localization to P bodies. 24338417_Association of the SNP rs2932538 in MOV10 and SNP rs4373814 in CACNB2 with an increased risk of hypertension in a Chinese Han population. 24726324_Results show that MOV10 predominantly binds to 3' UTRs upstream of regions predicted to form local secondary structures and provide evidence that MOV10 helicase mutants are impaired in their ability to translocate 5' to 3' on their mRNA targets. 25464849_A dual function for MOV10 in regulating translation: it facilitates microRNA-mediated translation of some RNAs, but it also increases expression of other RNAs by preventing AGO2 function. 25533532_The endogenous Mov10 could promote hepatitis B virus replication in vitro. 26379090_The DEAG-box of huamn MOV10 was required for the enhancement of Rev/RRE-dependent nuclear export. 26842467_MOV10 acts as an anti-influenza virus factor through specifically inhibiting the nuclear transportation of nucleoprotein and subsequently inhibiting the function of the viral ribonucleoprotein complex 27016603_these results establish MOV10, an evolutionary conserved protein involved in RNA silencing, as an antiviral gene against RNA viruses that uses an retinoic acid-inducible gene I-like receptor-independent pathway to enhance IFN response 27666477_MOV10 is a highly conserved cellular protein belonging to SF1 helicase family that plays critical roles in EV71 infection 27974568_IRAV is an RNA binding protein and localizes to cytoplasmic processing bodies (P bodies) in uninfected cells, where it interacts with the MOV10 RISC complex RNA helicase, suggesting a role for IRAV in the processing of viral RNA. 29258557_Through interference with the ubiquitin-proteasome system, MOV10 enhances the level of apolipoprotein-B-mRNA-editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like 3G in HIV-1-infected cells and virions, and synergistically inhibits the replication and infectivity of HIV-1. 29315404_MOV10 interacts with RNASEH2, and their interplay is crucial for restricting L1 retrotransposition. 30617221_the antiviral activity of MOV10 is partially countered by viral NS1 protein that interferes with the interaction of MOV10 with viral NP and causes MOV10 degradation through the lysosomal pathway. 30621721_MOV10 / circ-DICER1 / miR-103a-3p (miR-382-5p) / ZIC4 pathway plays a vital role in regulating the angiogenesis of glioma. 31722967_MOV10 restricts hepatitis B virus replication by inhibiting viral reverse transcription 33269545_The association of MOV10 polymorphism and expression levels with preeclampsia in the Chinese Han population. 33491517_Association study of hypertension susceptibility genes ITGA9, MOV10, and CACNB2 with preeclampsia in Chinese Han population. 34065512_CRL4-DCAF12 Ubiquitin Ligase Controls MOV10 RNA Helicase during Spermatogenesis and T Cell Activation. |
ENSMUSG00000002227 |
Mov10 |
623.200924 |
0.4086006128 |
-1.291237 |
0.099900375 |
164.834206 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000009943230496428229929500388509266486289803465648807197115240782812906904986027541596292157634865869694773543585597508354112505912780761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001571328502433412104365407598108964025243510035028263176969050936598962009284650820061843794336539636979921397141879424452781677246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
372.3931261 |
23.7595419 |
917.6697016 |
40.3334977 |
| ENSG00000155367 |
333926 |
PPM1J |
protein_coding |
Q5JR12 |
|
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes the serine/threonine protein phosphatase. The mouse homolog of this gene apparently belongs to the protein phosphatase 2C family of genes. The exact function of this gene is not yet known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:333926; |
myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000002228 |
Ppm1j |
14.776203 |
0.0858759175 |
-3.541603 |
0.558756456 |
50.673961 |
0.00000000000109056868318452999757641970552939650546467320602062045509228482842445373535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006472373849539068161255779400096971960484881769559706299332901835441589355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3019693 |
0.9238829 |
26.6540897 |
5.2911984 |
| ENSG00000155380 |
6566 |
SLC16A1 |
protein_coding |
P53985 |
FUNCTION: Bidirectional proton-coupled monocarboxylate transporter (PubMed:12946269, PubMed:33333023, PubMed:32946811). Catalyzes the rapid transport across the plasma membrane of many monocarboxylates such as lactate, pyruvate, acetate and the ketone bodies acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate, and thus contributes to the maintenance of intracellular pH (PubMed:12946269, PubMed:33333023). The transport direction is determined by the proton motive force and the concentration gradient of the substrate monocarboxylate. MCT1 is a major lactate exporter (By similarity). Plays a role in cellular responses to a high-fat diet by modulating the cellular levels of lactate and pyruvate that contribute to the regulation of central metabolic pathways and insulin secretion, with concomitant effects on plasma insulin levels and blood glucose homeostasis (By similarity). Facilitates the protonated monocarboxylate form of succinate export, that its transient protonation upon muscle cell acidification in exercising muscle and ischemic heart (PubMed:32946811). Functions via alternate outward- and inward-open conformation states. Protonation and deprotonation of 309-Asp is essential for the conformational transition (PubMed:33333023). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P53986, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P53987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12946269, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32946811, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33333023}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter that catalyzes the movement of many monocarboxylates, such as lactate and pyruvate, across the plasma membrane. Mutations in this gene are associated with erythrocyte lactate transporter defect. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:6566; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0046943]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lactate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015129]; lactate:proton symporter activity [GO:0015650]; mevalonate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015130]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; organic cyclic compound binding [GO:0097159]; succinate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015141]; behavioral response to nutrient [GO:0051780]; carboxylic acid transmembrane transport [GO:1905039]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; mevalonate transport [GO:0015728]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718]; plasma membrane lactate transport [GO:0035879]; pyruvate transmembrane transport [GO:1901475]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; response to food [GO:0032094]; succinate transmembrane transport [GO:0071422]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11882670_substrate-induced regulation of human colonic MCT1. The basis of this regulation is a butyrate-induced increase in mRNA abundance, resulting from the dual control of gene transcription and stability of the transcript 11944921_the structural organization of the human MCT1 gene and 5'-flanking region which contains potential binding sites for a variety of transcription factors with known association with butyrate's action in the colon 11953883_Carcinoma samples displaying reduced levels of MCT1 were found to express the high affinity glucose transporter, GLUT1, suggesting that there is a switch from butyrate to glucose as an energy source in colonic epithelia during transition to malignancy 12479094_MCT1 and NHE1 genes play important regulation roles in proliferation and growth of tumor cells, probably by affecting pHi. 12759536_MCT1 is involved in cellular transportation of butyrate, which induces cellular differentiation. Down-regulation is suggested to be involved in human breast cancers. 12949353_MCT mediates biotin uptake in human lymphoid cells. 14724187_MCT1 content in skeletal muscle in Type 2 diabetes is lower compared with healthy men. Strength training increases MCT1 content in healthy men and in Type 2, thus normalizing the content in Type 2. 15135232_studies demonstrate that the opposing plasma membranes of human syncytiotrophoblast are polarized with respect to both monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 and MCT4 activity and expression 15765403_These results show the importance of MCT1 to the ability of butyrate to induce cell-cycle arrest and differentiation, and suggest fundamental differences in the mechanisms by which butyrate modulates specific aspects of cell function. 15804185_MCT1 is functionally active and is the only MCT isoform involved in the apical uptake of monocarboxylates by retinal pigmented epithelial ARPE-19 cells 15901598_Distinct MCT isoforms may be involved in short-chain fatty acid transport across the apical or basolateral membranes in polarized colonic epithelial cells. 16136905_MCT1 gene plays an important role in pHi regulation, lactate transport and cell growth in tumor cells. 16150873_studies demonstrate inhibition of MCT1-mediated butyrate uptake in Caco-2 cells in response to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection 16370372_The inhibition of MCT1 during T lymphocyte activation results in selective and profound inhibition of the extremely rapid phase of T cell division essential for an effective immune response. 16403470_Monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 is strongly expressed by glial cells often associated with blood vessels that were identified as astrocytes. (Monocarboxylate transporter MCT1) 16408234_this study shows conflicting adaptations in MCT1 and MCT4 protein and mRNA levels following training, which may indicate post-transcriptional regulation of MCT expression in human muscle. 16441976_demonstrated greater activity of the RBC monocarboxylate cotransporter MCT-1, lower RBC deformability and impaired hematological indices in sickle cell trait (SCT) carriers compared to control subjects 17016429_Targeting the Map kinase signal transduction cascademay provide a potential therapeutic approach in lymphomas and related malignancies that exhibit high levels of the MCT-1 protein. 17082373_A single bout of high-intensity exercise decreased both MCT relative abundance (MCT1 and MCT4) in membrane preparations. 17182800_DL-2-Hydroxy-(4-methylthio)butanoic acid is transported into the colonic cancer cell line cell membrane by a transport mechanissm involving MCT1. 17701893_These studies show that promoter-activating mutations in exercise-induced hyperinsulinism induce SLC16A1 expression in beta cells, permitting pyruvate uptake and pyruvate-stimulated insulin release despite ensuing hypoglycemia. 18079261_In obesity, MCT1 expression appears linked both to changes in oxidative parameters and to changes in visceral adipose tissue content. 18188595_Expression of MCT1 and MCT4 showed a significant gain in plasma membranes of colorectal neoplasms. 18539591_the effective movement of H(+) into the bulk cytosol is increased by CAII, thus slowing the dissipation of the H(+) gradient across the cell membrane, which drives MCT1 activity 18832090_Report effects of high-intensity training on muscle MCT1/4 and postexercise recovery of muscle lactate and hydrogen ions in women. 19033536_PKC-zeta dependent stimulation of the human MCT1 promoter involves transcription factor AP2. 19033663_MCT1 was found to be expressed by an array of primary human tumors, we suggest that MCT1 inhibition has clinical antitumor potential. 19427019_miR-124 is frequently down-regulated in medulloblastoma and is a negative regulator of SLC16A1. 19850519_carriers of the A1470T polymorphism in the MTC1 (monocarboxylate transporter 1) gene exhibit a worse lactate transport capability 19876643_Data suggest that hypoxia increases lactate release from adipocytes and modulates MCT expression in a type-specific manner, with MCT1 and MCT4, but not MCT2 expression, being hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 (HIF-1) dependent. 19881260_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19881260_the -363-855T>C is a novel mutation. The 1282G>A (Val(428)Ile) is a novel SNP and was found as heterozygotic in 4 subjects. The 1470T>A (Asp(490)Glu) was found to be a common polymorphism in this study. 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19905008_close correlation between the [Ca2+](in) level and pH(in), and NHEs were involved with the MCT mediated uptake process 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20035863_Monocarboxylic acid transporter 1 was expressed in the human corneal epithelium at mRNA and protein levels. 20454640_MCT1, MCT2, and MCT4 protein expression in breast, colon, lung, and ovary neoplasms, as well as CD147 and CD44, were analysed. 20501436_Increased MCT1 association with CD147 at the apical membrane in response to somatostatin (SST) is p38 MAP kinase dependent and underlies the stimulatory effects of SST on butyrate uptake in human intestinal epithelial cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20636790_results provide evidence for a prognostic value of MCT1 in breast carcinoma 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21081165_Loss of MCT1 on brain microvessels is mechanistically involved in the pathophysiology of drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy; re-expression of MCT1 may represent a novel therapeutic approach for this disease. 21306479_We found that the expression of the monocarboxylate transporters MCT1 and MCT4, but not MCT5, in human lung cancer cell lines was significantly correlated with invasiveness 21646425_miR-29a, miR-29b selectively target MCT1 3'UTR ; the miR-29 isoforms are highly expressed in islets and contribute to silencing Mct1 in beta cells; miR-29 isoforms contribute to beta-cell-specific silencing of the MCT1 transporter and may affect insulin release 21787388_Data show that a significant increase of MCT2 and MCT4 expression in the cytoplasm of tumour cells and a significant decrease in both MCT1 and CD147 expression in prostate tumour cells was observed when compared to normal tissue. 21870331_both MCT1 and CD147, but not MCT4, were associated with GLUT1 and CAIX expression in a large series of invasive breast carcinoma samples 21930917_CD147 subunit of lactate/H+ symporters MCT1 and hypoxia-inducible MCT4 is critical for energetics and growth of glycolytic tumors. 21987487_Reduced SLC16A1 is associated with impaired butyrate oxidation in ulcerative colitis. 22184616_our findings identify MCT1 as a target for p53 repression and they suggest that MCT1 elevation in p53-deficient tumors allows them to adapt to metabolic needs by facilitating lactate export or import depending on the glucose availability. 22281667_Co-expression of monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) and its chaperone (CD147) is associated with low survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 22428047_The lactate transporter monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) is the main regulator of HIF-1 activation by lactate in endothelial cells. 22516692_The data suggested that MCT1 polymorphism influenced lactate transport across sarcolemma in males but not in females. 23073708_Data suggest that MCT1 is expressed in insulin-secreting cells; overexpression of MCT1 insulin-secreting cells (1 patient versus 3 organ donors) can possibly lead to exercise-induced hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycemia. [CASE REPORT] 23187830_Combined application of GLUT-1, MCT-1, and MCT-4 immunohistochemistry might be useful in differentiating malignant pleural mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial hyperplasia. 23574725_MCT1 and MCT4 biomarkers were employed to determine the metabolic state of proliferative cancer cells. 23628675_MCT1 gene A1470T polymorphism is associated with endurance athlete status and blood lactate level after intensive exercise. 24012639_MCT1 inhibition and or gene knockdown has antitumor potential associated with the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. 24013424_MCT1 is an efficient lactate exporter in MM cells and plays a role in tumor growth within an acidic microenvironment. 24166504_Study identifies the mitochondrion as a glucose sensor promoting tumor cell migration, MCT1 is also revealed as a transducer of this response, providing a new rationale for the use of MCT1 inhibitors in cancer. 24277449_Small cell lung cancer patients with tumors expressing MCT1 and lacking in MCT4 are most likely to respond to the antineoplastic agent AZD3965. 24338019_Coexpression of CAIV with MCT1 and MCT4 resulted in a significant increase in MCT transport activity. 24485392_The findings indicated that theMCT1 TT genotype was overrepresented in sprint/power athletes compared to both endurance athletes and non-athlete controls. 24486553_Both L- and D-CysNO also inhibited cellular pyruvate uptake and caused S-nitrosation of thiol groups on monocarboxylate transporter 1, a proton-linked pyruvate transporter 24708341_T-allele frequency was significantly higher among swimmers compared with runners. 24797797_These results indicate there are no additional benefits of IHT when compared to similar normoxic training. Hence, the addition of the hypoxic stimulus on anaerobic performance or MCT expression after a three-week training period is ineffective. 24858043_Study demonstrated that PTEN loss and MCT-1 induction synergistically promoted the neoplastic multinucleation via the Src/p190B signaling activation. 25068893_Data indicate that pteridine showed substantial anticancer activity in monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1)-expressing Raji lymphoma cells. 25225794_We provide novel information of MCT1 as a candidate marker for prognostic stratification in NSCLC. 25241983_We demonstrate, for the first time, that 3 different pHi regulators responsible for acid extruding, i.e. NHE and NBC, and MCT, are functionally co-existed in cultured radial artery smooth muscle cells. 25263481_The possible cooperative role of CD147 and MCT1 in determining cisplatin resistance. 25371203_H(+)-coupled 5-oxoproline transport is mediated solely by SLC16A1 in astrocytes 25390740_exome sequencing in a patient with ketoacidosis and identified a homozygous frameshift mutation in the gene SLC16A1. Genetic analysis in 96 patients suspected of having ketolytic defects yielded seven additional inactivating mutations in MCT1 25447800_MCT1 was up-regulated by exposure to DL-2-hydroxy-(4-methylthio)butanoic acid(HMTBA). Moreover, total monolayer MCT1 immunoreactivity increased 1.8-fold in HMTBA-supplemented cultures, this effect mainly being localised at the apical membrane. 25456395_Overexpression of MCT1, MCT4, and CD147 predicts tumor progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 25492048_SNPs in MCT1 and MCT2 genes may affect clinical outcomes and can be used to predict the response to adjuvant chemotherapy in CRC patients who received surgical treatment 25578492_Our findings suggest that SNPs in MCT1 and MCT2 genes may affect clinical outcomes and can be used to predict the response to adjuvant chemotherapy in NSCLC patients who received surgical treatment once validated in future study. 25656974_Data suggest that expression of MCT1 in intestinal mucosa can be altered by diet; here, expression of MCT1 is down-regulated in Caco-2 Cells by products of fermentation of dietary proteins by intestinal microbes. 25755717_CD147 interacts with MCT1 to regulate tumor cell glycolysis, resulting in the progression of thyroid carcinoma. 25957999_The first IF method has been developed and optimised for detection of MCT 1 and MCT4 in cancer patient circulating tumour cells 26024713_interaction of rmEMMPRINex with U937 cells leads to inhibition of MCT1 membrane expression, intracellular activation of procaspase-9, followed by DNA fragmentation and apoptosis. 26045776_Down regulation of MCT1 promote the sensitivity to cisplatin in ovarian cancer cells. This effect appeared to be mediated by antagonizing Fas. 26340466_The aim of this study was to investigate the association between the MCT1 A1470T polymorphism and fat-free mass in young Italian elite soccer players. The MCT1 T allele is associated with the percentage of fat-free mass in young elite male soccer players. 26539827_MCT1 and GLUT1 may be potential prognostic markers in adenocarcinoma. 26563366_MCT1 expression associates with the SCC type and metastatic behavior of AC, whereas MCT4 expression concomitantly increases from in situ SCC to invasive SCC and is significantly associated with the AC type. Consistently, FOXM1 expression is statistically associated with MCT1 positivity in SCC, whereas the expression of FOXO3a, a FOXM1 functional antagonist, is linked to MCT1 negativity 26595136_The most important finding from the present study was that wild-type allele carriers, 2917(1414)T and IVS3-17C, have been associated with higher blood lactate levels at submaximal intensities of exercise for the first time. 26615136_MCT1 is highly expressed in anaplastic thyroid cancer compared to non-cancerous thyroid tissue and papillary thyroid cancer. 26765963_Data suggest that inhibition of mnocarboxylate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 may have clinical relevance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). 26779534_MCT1 expression was not clearly associated with overall or disease-free survival. MCT4 and CD147 expression correlate with worse prognosis across many cancer types. These results warrant further investigation of these associations. 26854723_MCT1 may be acting as an uptake transporter and MCT4 as an efflux system across the basolateral membrane for ferulic acid, and that this process is stimulated by butyric acid. 26876179_MCT1 inhibition impairs proliferation of glycolytic breast cancer cells co-expressing MCT1 and MCT4 via disruption of pyruvate rather than lactate export. 26944480_The reversible H(+)/lactate(-) symporter MCT1 cotransports lactate and proton, leading to the net extrusion of lactic acid in glycolytic tumors. A model of its role in pH control in tumor cells is described. Review. 27026015_MCT1 affects the plasma lactate decrease . 27105345_MCT1 and MCT4 expression levels were associated with worse prognosis and shorter overall survival. 27127175_MCT1 expression, independent of transporter activity, is required for growth factor-induced tumor cell motility. 27144334_our finding that the expression of MCT1 and MCT4 is reduced in mutant IDH1 gliomas highlights the unusual metabolic reprogramming that occurs in mutant IDH1 tumors and has important implications for our understanding of these tumors and their treatment 27240355_Results found that MCT contributes to endothelial cell growth and tube formation via up-regulation of angiopoietin-1 expression suggesting that MCT plays an important role in pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and tumor growth via activating the angiopoietin-1 pathway. 27331625_Hypoxia-induced MCT1 supports glioblastoma glycolytic phenotype, being responsible for lactate efflux and an important mediator of cell survival and aggressiveness 27373212_The targeting of MCT1 and PFKFB3 regulated cell proliferation. 27634412_This study investigated MCT1 protein abundance in various human intestinal tissues. 27813046_AA genotype of the MCT1 T1470A polymorphism is over-represented in wrestlers compared with controls and is associated with lower blood lactate concentrations after 30-s Wingate Anaerobic test and during intermittent sprint tests in Japanese wrestlers 27957817_Monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) are expressed in normal and cancer cells and are involved in cell metabolism and survival. 28099149_Increased miR-210 and concomitant decreased ISCU RNA levels were found in ~40% of tumors and this was significantly associated with HIF-1alpha and CAIX, but not MCT1 or MCT4, over-expression. 28235486_Data show that metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 (MACC1) and monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) are highly expressed in gastric cancer indicating poor prognosis. 28260082_After indirect co-culture, OP was increased in the BxPc-3 and Panc-1 cells; correspondingly, succinate dehydrogenase, FH and MCT expression were increased. After the MCT1-specific inhibitor removed 'tumor-stromal' metabolic coupling, the migration and invasion abilities of the pancreatic cancer cells were decreased. 28559188_The structures and functions of hMCT1 and hMCT4 transporters. 28762551_Data suggest that targeting monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) in both tumor cells and brain endothelial cells (EC) may be a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of Glioblastoma (GBM). 28827372_Silencing or genetic deletion of MCT1 in vivo inhibited migration, invasion, and spontaneous metastasis. 28846107_Metabolism-dependent clonal growth of HCT15 colorectal cancer cells was induced by Nrf2-dependent activation of MCT1-driven lactate exchange. 28923861_MCT1 inhibitor AZD3965 increased MCT4-dependent accumulation of intracellular lactate, inhibiting monocarboxylate influx and efflux. 29066459_Using in vitro models, we demonstrate that tumor-excreted branched-chain amino acid (BCKA)s can be taken up and re-aminated to BCAAs by tumor-associated macrophages. Our data further suggest that the anti-proliferative effects of MCT1 knockdown observed by others might be related to the blocked excretion of BCKAs. 29248132_TOMM20 and MCT1 were highly expressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma lymphocytes, indicating an OXPHOS phenotype, whereas non-neoplastic lymphocytes in the control samples did not express these markers. 29248133_TOMM20, MCT1, and MCT4 expression was significantly different in Hodgkin and Reed Sternberg (HRS) cells. HRS have high expression of MCT1, while tumor associated macrophages have absent MCT1 expression. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes have absent MCT1 expression. Reactive lymph nodes in contrast to cHL tumors had low TOMM20, MCT1, and MCT4 expression in lymphocytes and macrophages. 29351758_Activation of autophagy can promote metastasis and glycolysis in HCC cells, and autophagy induces MCT1 expression by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 29481555_Study demonstrated that the high mRNA level of both MCT1 and GLUT1 correlated with poor prognosis, high- Fuhrman grade clear-cell renal cell carcinoma and metabolic reprogramming. 29572438_7ACC2 is an inhibitor of mitochondrial pyruvate transport; the blockade of pyruvate import into mitochondria prevents extracellular lactate uptake as efficiently as a MCT1 inhibitor 29657088_High MCT-1 expression is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 29775610_These results demonstrate that Monocarboxylate transporters tend to play a role in the aggressive breast cancer subtypes through the dynamic interaction between breast cancer cells and adipocytes. 29809145_Study shows that proton-driven lactate flux is enhanced by the intracellular carbonic anhydrase CAII, which is colocalized with the monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells; the results suggest that CAII features a moiety that exclusively mediates proton exchange with the MCT to facilitate transport activity. 29882205_MCT1 might act as a new regulator to improve invasion and migration of NPC cells and be correlated with activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. 29985759_Sub-Saharan African groups show extremely high values of the T allele of 1470T > A polymorphism. The TT genotype preeminence in African groups could explain the better predisposition to sprint/power performances of African athletes. Caucasian and Asian populations show variable proportions of TT and AA genotypes allowing inter-individual differences in lactate transport. 30115973_Loss of function of miR-342-3p results in MCT1 over-expression and contributes to oncogenic metabolic reprogramming in triple negative breast cancer 30290372_the MCT1 A allele is associated with forward soccer player status 30655616_MCT1 expression was significantly increased in HPV-negative tumours, and inhibition suppressed tumour cell invasion, colony formation and promoted radiosensitivity. HPV-positive and negative head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) have different metabolic profiles which may have potential therapeutic applications. 30720131_MCT1 mRNA expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) was analyzed in The Cancer Genome Atlas database and in ESCC cells. MCT1 expression was found to correlate with neoplasm stage. Survival analysis showed that patients in a highMCT1 group had a lower overall and progressionfree survival. Downregulation of MCT1 suppressed proliferation and survival of ESCC cells in vitro. 31101938_we were interested in the molecular mechanism responsible for the difference in substrate specificity between hMCT1 and hMCT4. Therefore, we generated 3D structure models of hMCT1 and hMCT4 to identify amino acid residues involved in the substrate specificity of these transporters. We found that the substrate specificity of hMCT1 was regulated by residues involved in turnover number (M69) and substrate affinity 31209810_Lactate promoted Wnt activity and increased the expression of CD133 cancer stem cell organoids. Silencing MCT1, the prominent path for lactate uptake in human tumor with siRNA significantly impaired organoid forming capacity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 31395464_Monocarboxylate transporters in cancer. 31404019_Monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) expression is associated with better prognosis and reduced nodal metastasis in pancreatic cancer. 31564440_Hyperpolarized MRI of Human Prostate Cancer Reveals Increased Lactate with Tumor Grade Driven by Monocarboxylate Transporter 1. 31593685_K38 plays an essential role in hMCT1 transport activity 31605138_Neural crest-derived tumor neuroblastoma and melanoma share 1p13.2 as susceptibility locus that shows a long-range interaction with the SLC16A1 gene. 31678436_The concentration gradients (Api - BL) of glucose and lactate correlated with the gene expression of respective SLC2A1 and SLC16A1 transporters. 31723238_CAIX forms a transport metabolon with monocarboxylate transporters in human breast cancer cells. 31727576_Relationships between plasma lactate, plasma alanine, genetic variations in lactate transporters and type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. 31729681_CD147 augmented monocarboxylate transporter-1/4 expression through modulation of the Akt-FoxO3-NF-kappaB pathway promotes cholangiocarcinoma migration and invasion. 31853067_MCT1 inhibition had little effect on the growth of primary subcutaneous tumours 32111097_Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 (MCT1) in Liver Pathology. 32123312_Targeting metabolic activity in high-risk neuroblastoma through Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 (MCT1) inhibition. 32703414_Identification of the HT-29 cell line as a model for investigating MCT1 transporters in sigmoid colon adenocarcinoma. 32748357_SLC16A1-AS1 enhances radiosensitivity and represses cell proliferation and invasion by regulating the miR-301b-3p/CHD5 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32761447_Delayed Myelination Pattern and an Abnormal Thyroid Profile Caused by a Novel Mutation in the SLC16A2 Gene. 32819565_Identification of the essential extracellular aspartic acids conserved in human monocarboxylate transporters 1, 2, and 4. 32839325_Hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]pyruvate-to-[1-(13)C]lactate conversion is rate-limited by monocarboxylate transporter-1 in the plasma membrane. 32863950_LncRNA-SLC16A1-AS1 induces metabolic reprogramming during Bladder Cancer progression as target and co-activator of E2F1. 32872409_Intratumoral Distribution of Lactate and the Monocarboxylate Transporters 1 and 4 in Human Glioblastoma Multiforme and Their Relationships to Tumor Progression-Associated Markers. 32887638_Tissue expression of lactate transporters (MCT1 and MCT4) and prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma (brief report). 33212210_Immunoreactivity of receptor and transporters for lactate located in astrocytes and epithelial cells of choroid plexus of human brain. 33559958_Monocarboxylate transporter 1 promotes proliferation and invasion of renal cancer cells by mediating acetate transport. 33633176_Monocarboxylate transporter-1 (MCT1) protein expression in head and neck cancer affects clinical outcome. 33641091_Overexpression of Cell-Surface Marker SLC16A1 Shortened Survival in Human High-Grade Gliomas. 34022218_Excess exogenous pyruvate inhibits lactate dehydrogenase activity in live cells in an MCT1-dependent manner. 34077729_Therapy-induced DNA methylation inactivates MCT1 and renders tumor cells vulnerable to MCT4 inhibition. 34480633_Influence of the MCT1-T1470A polymorphism (rs1049434) on repeated sprint ability and blood lactate accumulation in elite football players: a pilot study. 34619707_Coexpression of MCT1 and MCT4 in ALK-positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. 34769160_miR-31-NUMB Cascade Modulates Monocarboxylate Transporters to Increase Oncogenicity and Lactate Production of Oral Carcinoma Cells. 35023320_A Novel Metabolic Reprogramming Strategy for the Treatment of Diabetes-Associated Breast Cancer. 35627255_Transmission Distortion of MCT1 rs1049434 among Polish Elite Athletes. 35926947_Functional coupling of organic anion transporter OAT10 (SLC22A13) and monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 (SLC16A1) influencing the transport function of OAT10. |
ENSMUSG00000032902 |
Slc16a1 |
891.580335 |
3.3933466938 |
1.762709 |
0.062180385 |
819.109010 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000377988967833668277559036991376486690093190975641585323868575490668486034314233355611512955024481210742107432310550801827585576470347986429542926149994 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000306544899188183719745775733838335780467501288711481866924436331992407176217815060166612517051182539848773984970249360766563509575453298665464087704188 |
Yes |
No |
1386.1387188 |
51.6507173 |
411.2496029 |
12.5357414 |
| ENSG00000155629 |
118788 |
PIK3AP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZUJ8 |
FUNCTION: Signaling adapter that contributes to B-cell development by linking B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling to the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt signaling pathway. Has a complementary role to the BCR coreceptor CD19, coupling BCR and PI3K activation by providing a docking site for the PI3K subunit PIK3R1. Alternatively, links Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling to PI3K activation, a process preventing excessive inflammatory cytokine production. Also involved in the activation of PI3K in natural killer cells. May be involved in the survival of mature B-cells via activation of REL. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15893754}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding activity and signaling receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of inflammatory response; regulation of signal transduction; and toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and membrane. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:118788; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding [GO:0036312]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway [GO:0034134]; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034142]; toll-like receptor 7 signaling pathway [GO:0034154]; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034162] |
15893754_Abi-1 promotes Abl-mediated BCAP phosphorylation and suggest that Abi-1 in general coordinates kinase-substrate interactions 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197460_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27909057_Dimeric BCAP associates with the TIR domains of TLR2/4 and MAL/TIRAP, suggesting that it is recruited to the TLR signalosome by multitypic TIR-TIR interactions. 30093532_induction of BCAP serves as a positive feedback circuit to enhance PI3K signaling in activated CD8(+) T cells, thereby acting as a molecular checkpoint regulating effector and memory T cell development. 32793186_PIK3AP1 and SPON2 Genes Are Differentially Methylated in Patients With Periodic Fever, Aphthous Stomatitis, Pharyngitis, and Adenitis (PFAPA) Syndrome. 34839795_Overexpression of long non-coding RNA WT1-AS or silencing of PIK3AP1 are inhibitory to cervical cancer progression. 34870753_MiR-1246 regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by targeting PIK3AP1 and inhibits thyroid cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. |
ENSMUSG00000025017 |
Pik3ap1 |
512.104638 |
3.1523054280 |
1.656407 |
0.072338258 |
543.433052 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000337740858998813160180363798673193904492921391456675922186506757805548026930736766733721955669475442478610544480834947263419920766384795179351184817214523365823611545299418747002341739603644400695447867278138852 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000176150356142137177809016744844861352607260633369357063419554999454372796643561908481359298447374047685047342923532487105898658881132164400626717149122989034199797175973033412681336748615282594358031288585169536 |
Yes |
No |
781.9930293 |
33.6387266 |
249.8183419 |
8.9595169 |
| ENSG00000155792 |
64798 |
DEPTOR |
protein_coding |
Q8TB45 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of the mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways. Inhibits the kinase activity of both complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19446321}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of TOR signaling; negative regulation of cell size; and negative regulation of protein kinase activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64798; |
intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of cell size [GO:0045792]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; negative regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032007]; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904262]; negative regulation of TORC2 signaling [GO:1903940]; regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001236] |
19446321_DEPTOR is highly overexpressed in a subset of multiple myelomas harboring cyclin D1/D3 or c-MAF/MAFB translocations. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20858096_High expression levels of DEPTOR are predictive of response to thalidomide in myeloma. 21643629_DEPTOR is a novel prognostic marker for differentiated thyroid carcinoma. 21992080_These novel findings are indicative of a higher order of complexity of DEPTOR signalling in the human placenta that is affected by maternal stress. 22017875_misregulation of the DEPTOR destruction pathway might contribute to aberrant activation of mTOR in disease. 22017876_DEPTOR, an mTOR inhibitor, is a physiological substrate of SCF(betaTrCP) E3 ubiquitin ligase and regulates survival and autophagy 22017877_mTOR generates an auto-amplification loop by triggering the betaTrCP- and CK1alpha-dependent degradation of DEPTOR. 22160218_GNMT regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth in part through interacting with DEPDC6/DEPTOR and modulating mTOR/raptor signaling pathway 22282237_Raf-1/JNK /p53/p21 pathway may be involved in apoptosis, and NFkappaB1 may play a possible role in inhibiting apoptosis. 22454292_this review discusses beta-TrCP's new downstream substrate, DEPTOR, as well as summarize the novel functional aspects of beta-TrCP in controlling cell growth and regulating autophagy, in part through governing the stability of DEPTOR.[Review] 23503641_the downregulation of DEPTOR induces apoptosis, increases chemosensitivity to doxorubicin, and suppresses autophagy and the activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in RPMI8226 human multiple myeloma cells. 23541542_There is a significant downregulation of mTOR, DEPTOR, and Raptor in preterm labouring myometria when compared to non-pregnant tissues taken from the same area. 23563706_Deptor is induced by the Baf60c-Six4 transcriptional complex and mediates activation of Akt and glycolytic metabolism by Baf60c in a cell-autonomous manner 23613505_Downregulation of DEPTOR inhibited proliferation and increased chemosensitivity to melphalan in human multiple myeloma RPMI-8226 cells via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway. 23881914_these findings define DEPTOR as a critical upstream regulator of endothelial cell activation responses. 24969890_Downregulation of DEPTOR (p=0.331) in CRC. 25119265_In Alzheimer's disease patients the mTOR pathway can be overactive, leading to a dysfunction of autophagy and a lack of amyloid beta clearance so the excess of amyloid beta will cause a further decrease in DEPTOR and an increase in mTOR expression. 25258312_DEPTOR plays a key role in maintaining stem cell pluripotency by limiting mTOR activity in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells 25333702_our data provide evidence for the requirement of TGFbeta-activated mTORC1 only by deptor downregulation, which dominates upon the bystander mTORC2 activity for enhanced expression of collagen I (alpha2). 25544749_Data suggest that DEPTOR has a tumor suppressive activity against pancreatic cancer cells, and its loss of expression may contribute to pancreatic tumorigenesis. 25605718_Receptor CXCR4 signaling promotes lysosomal and ESCRT-dependent degradation of DEPTOR, an antagonist of mTORC2, that regulates Akt activation and signaling. 25810016_Deptor enhances triple-negative breast cancer metastasis and chemoresistance through coupling to survivin expression 25843797_conclude that DEPTOR-related mTOR suppression is involved in metformin's anti-cancer action in liver, and could be a novel target for anti-cancer therapy 25936805_Data indicate that phosphatidic acid (PA) specifically disrupts DEPTOR-mTORC1 interaction. 26608079_Propose regulation of placental SNAT2/LAT1 ubiquitination by mTORC1 and Nedd4-2. 26717892_Cul1 promoted mTORC1 activity and cap-dependent translation by enhancing the ubiquitination and degradation of DEPTOR. 26871578_Association between insulin sensitivity and genetic variants in DEPTOR gene suggest DEPTOR and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway to be potential target for future research and pharmacological interventions. 26893358_Low DEPTOR expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 26896556_Results provide evidence that DEPTOR acts as a tumor suppressor by limiting EGFR-driven lung adenocarcinoma progression. 26992219_DEPTOR overexpression is associated with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 27211906_In this study we began by validating the expression of four main mTOR pathway components, mTOR, DEPTOR, rictor and raptor, at gene and protein level in in vitro models of endometrioid (MDAH2774) and clear cell (SKOV3) ovarian cancer 27593934_High DEPTOR expression is associated with T-cell leukemia. 27655709_Deptor depletion induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and synergizes the effect of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (Bz) in multiple myeloma (MM) cells. 28086984_Studies provide evidence that Deptor appears to play an important role in the pathogenesis of many types of cancers, mainly through its role in controlling the activity of mTOR and many other possible functions. [review] 28267437_High expression of DEPTOR benefits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients in early stage but not advanced stage. 28349073_the present findings supported the fact that DEPTOR-mTOR signaling is a central regulator of lipid metabolism-mediated inflammation in lymphocytes of PBMC culture. 28358054_In ASS1-knockout cells, DEPTOR, an inhibitor of mTORC1 signal, was downregulated and mTORC1 signaling was more activated in response to arginine. 28420429_that DEPTOR expression is required to maintain myeloma cell differentiation and high level of its expression are associated with better outcome. 29330362_Using computational modeling, systems analysis and dynamic simulations, study shows that DEPTOR confers remarkably rich and complex dynamic behaviours to mTOR signalling, including abrupt, bistable switches, oscillations and co-existing bistable/oscillatory responses. Transitions between these distinct modes of behavior are enabled by modulating DEPTOR expression alone. 29382726_findings reveal a mechanism that stabilizes the mTORC1 inhibitor DEPTOR via OTUB1's deubiquitinase activity. 29457836_The dysregulation of SIRT1-DEPTOR-mTORC1 signaling is a critical determinant of alcoholic liver disease pathology; targeting SIRT1 and DEPTOR and selectively inhibiting mTORC1-S6K1 signaling may have therapeutic potential for treating alcoholic liver disease in humans 29666061_Study shows that DEPTOR, a suppressor of mTOR, is a direct target of Wnt/beta-catenin/c-Myc signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin or knockdown of c-Myc decreased, while activation of Wnt/beta-catenin or overexpression of c-Myc increased the expression of DEPTOR. c-Myc bound the promoter of DEPTOR and transcriptionally regulated DEPTOR expression. 29897294_key modulator that plays important roles in fine tuning the activity of mTOR and the activation state of the PI3K-AKT axis, with a deep impact on cancer, metabolism, and immunity [review] 29940800_TNFAIP3-DEPTOR complex-induced early-onset autophagy is vital for immune inhibition in autoimmune disease. 31176743_Mechanistically, DEPTOR inhibited both mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1) and 2 (mTORC2) activities in PA cells. In addition, DEPTOR expression level was increased to suppress mTOR kinase activity via decreasing E3 ubiquitin ligase, betaTrCP1, in response to CAB. 31228948_Data found that DEPTOR was frequently overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, and its high expression was associated with high serum AFP levels, increased tumor size, vascular invasion and more advanced TMN and BCLC stage, as well as an overall poor prognosis. DEPTOR promotes the EMT and metastasis of HCC cells by activating the TGF-beta1-smad3/smad4-snail pathway via mTOR inhibition. 31453770_The role of DEPTOR polymorphism in T2D vascular complication. 31525175_These findings may provide valuable molecular information for improving venous permeability through manipulation of DEPTOR and related mTOR pathways. 31685947_DEPTOR is an in vivo tumor suppressor that inhibits prostate tumorigenesis via the inactivation of mTORC1/2 signals. 31710517_We identified and replicated three new genome-wide significant signals of association with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosissusceptibility (associated with altered gene expression of KIF15, MAD1L1, and DEPTOR). The observation that decreased DEPTOR expression associates with increased susceptibility to IPF supports recent studies demonstrating the importance of mTOR signaling in lung fibrosis. 32702393_DEPTOR is a microRNA-155 target regulating migration and cytokine production in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. 32798656_Insights into DEPTOR regulation from in silico analysis of DEPTOR complexes. 33110214_Deubiquitinase OTUD5 is a positive regulator of mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways. 33184290_DEPTOR is a direct p53 target that suppresses cell growth and chemosensitivity. 33412518_Function of Deptor and its roles in hematological malignancies. 33416146_Regulatory role of DEPTORmediated cellular autophagy and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. 33854045_Nuclear ErbB2 represses DEPTOR transcription to inhibit autophagy in breast cancer cells. 33865870_Structural Basis of DEPTOR to Recognize Phosphatidic Acid Using its Tandem DEP Domains. 33995662_DEPTOR stabilizes ErbB2 to promote the proliferation and survival of ErbB2-positive breast cancer cells. 34153521_Neddylation inhibition ameliorates steatosis in NAFLD by boosting hepatic fatty acid oxidation via the DEPTOR-mTOR axis. 34320372_DEPTOR inhibits lung tumorigenesis by inactivating the EGFR-mTOR signals. 34519268_Regulation of human mTOR complexes by DEPTOR. 34634301_Tyrosine phosphorylation of DEPTOR functions as a molecular switch to activate mTOR signaling. 35216969_Turnover of the mTOR inhibitor, DEPTOR, and downstream AKT phosphorylation in multiple myeloma cells, is dependent on ERK1-mediated phosphorylation. 35923131_DFNA5 inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation by suppressing the mTORC1/2 signaling pathways via upregulation of DEPTOR. |
ENSMUSG00000022419 |
Deptor |
39.139018 |
0.2566379215 |
-1.962194 |
0.712517689 |
5.894197 |
0.01519085110635808900936272181070307851769030094146728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028002618000480254678574709714666823856532573699951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4548206 |
6.1795333 |
52.6290951 |
16.8859322 |
| ENSG00000155849 |
9844 |
ELMO1 |
protein_coding |
Q92556 |
FUNCTION: Involved in cytoskeletal rearrangements required for phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cell motility. Acts in association with DOCK1 and CRK. Was initially proposed to be required in complex with DOCK1 to activate Rac Rho small GTPases. May enhance the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity of DOCK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11595183, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12134158}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phagocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3-binding |
|
This gene encodes a member of the engulfment and cell motility protein family. These proteins interact with dedicator of cytokinesis proteins to promote phagocytosis and cell migration. Increased expression of this gene and dedicator of cytokinesis 1 may promote glioma cell invasion, and single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with diabetic nephropathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:9844; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor complex [GO:0032045]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0016601]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790] |
12134158_Dock180 ELMO complex functions as an unconventional two-part exchange factor for Rac. 12829596_the association of DOCK2 with ELMO1 is critical for DOCK2-mediated Rac activation, thereby suggesting that their association might be a therapeutic target for immunologic disorders caused by lymphocyte infiltration 14638695_Rac activation by the ELMO.Dock180 complex at discrete intracellular locations mediated by the N-terminal 330 amino acids of ELMO1 plays a role in cell migration 14737186_Nef binds the DOCK2-ELMO1 complex to activate rac and inhibit lymphocyte chemotaxis 15700267_while N-terminal SH3 of CrkII promotes assembly between CrkII and DOCK180, the C-terminal SH3 of CrkII regulates the stability and turnover of the DOCK180/ELMO complex 15723800_ELMO binding to the SH3 domain of Dock180 disrupted the SH3:Docker interaction, facilitated Rac access to the Docker domain, and contributed to the GEF activity of the Dock180/ELMO complex. 15793258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793258_These results indicate that ELMO1 is a novel candidate gene that both confers susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy and plays an important role in the development and progression of this disease. 15952790_Src family kinase mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of ELMO1 might represent an important regulatory mechanism that controls signaling through the ELMO1/Crk/Dock180 pathway. 16213822_ARNO and ARF6 coordinate with the Dock180/Elmo complex to promote Rac activation at the leading edge of migrating cells. 17173036_Using pulldown assays, we identified engulfment and cell motility (ELMO) protein as the IpgB1 binding partner. IpgB1 colocalized with ELMO and Dock180 in membrane ruffles induced by Shigella. 17671188_Overexpression of ELMO1 and Dock180, a bipartite Rac1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor is associated with glioma cell invasion 18095154_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18768751_The DOCK180-ELMO1 interaction is mapped to the N-terminal 200 amino acids of DOCK180, and to the C-terminal 200 amino acids of ELMO1, comprising the ELMO1 PH domain. 19183347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19183347_Variants in intron 13 of the ELMO1 gene appear to confer risk for diabetic nephropathy in African Americans. 19651817_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19651817_Report of genetic associations in ELMO1 with diabetic nephropathy, further establishing its role in the susceptibility of this disease. 19929986_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20299368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20732417_The protein-protein interaction between ELMO1 and COX-2 increased the cyclooxygenase activity of COX-2 and, correspondingly, fibronectin expression.(ELMO1 protein, human) 20826100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20826100_We sequenced 17.4 kb of ELMO1 and identified 19 variants. 20958313_findings demonstrate an in vivo role for ELMO1-dependent clearance in the testes, with implications for spermatogenesis 22331897_The C-terminal Pro-rich tail of ELMO1 winds around the Src-homology 3 domain of DOCK2 to form an intermolecular 5-helix bundle. The entire regions of both DOCK2 a& ELMO1 assemble to create a rigid structure required for the DOCK2 & ELMO1 binding. 22415709_Over-expression of NELL1 is associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 22503503_findings suggest that clearance of apoptotic cells in living vertebrates is accomplished by the combined actions of apoptotic cell migration and elmo1-dependent macrophage engulfment 22842811_genetic association study in population in China: Data suggest that 2 SNPs in ELMO1 (rs741301; rs10951509) are associated with diabetic nephropathy in Chinese subjects with type 2 diabetes. 23156397_Analysis of SNP databases of Japanese patuients with diabetic nephropathy revealed ELMO1 as a gene related to the above-cited diabetic complication. 23525077_ELMO1 mutations are associated with esophageal adenocarcinoma. 23591873_findings indicate that a chemokine-controlled pathway, consisting of Galphai2, ELMO1/Dock180, Rac1 and Rac2, regulates the actin cytoskeleton during breast cancer metastasis 24433479_For ELMO1 (+9170 G>A), the GG genotype frequency was higher in the diabetic versus control group, but there were no differences between diabetic patients with and without nephropathies. 24819662_High ELMO1 expression is associated with serous ovarian cancer. 24821968_findings reveal a previously unknown, nonredundant role for Elmo1 in controlling Dock2 levels and Dock2-dependent T cell migration in primary lymphocytes. 25167351_There is a low frequency rate of the ancestral genotype for the ELMO1 polymorphism rs1345365 in mestizos from the western and southeastern regions of Mexico. 25360637_high ELMO1 expression is an independent negative prognostic factor in normal karyotype (NK) acute myeloid leukemia. 25586182_Thus, Elmo1 and Dock180 facilitate blood vessel formation by stabilization of the endothelium during angiogenesis. 25901943_ELMO1 is expressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovium, promotes cell migration and invasion, and regulates Rac1 activity, thereby mediating rheumatoid arthritis pathogenicity. 26205662_Src-mediated Y724 phosphorylation in ELMO1 plays a critical role for cell spreading via activation of Rac1, leading to promotion of cell migration. 26882976_Cdc27 is a novel binding partner of Elmo1.Cdc27-Elmo1 has a cellular role independent from the Elmo-Dock1-Rac signal module. 27699784_A significant association of the SLC12A3 rs11643718 and ELMO1 rs741301 (Single nucleotide Polymorphism) SNPs with diabetic nephropathy in south Indians. 28752301_ELMO1 genetic variation is associated with with type 2 diabetes. 29615491_FE65 is found to activate ELMO1 by diminishing ELMO1 intramolecular autoinhibitory interaction and to promote the targeting of ELMO1 to the plasma membrane, where Rac1 is activated. We also show that FE65, ELMO1, and DOCK180 form a tripartite complex 29938964_This study revealed the association of the SNP rs1345365 of the ELMO1 gene in a Mexican population 30643265_Study data identify 'noncanonical' roles for ELMO1 as an important cytoplasmic regulator of specific neutrophil receptors and promoter of arthritis. 31909452_Association of single nucleotide polymorphism (rs741301) of the ELMO1 gene with diabetic kidney disease in Polish patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot study. 32043290_Association of ELMO1 gene polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy among Egyptian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 32634861_The single nucleotide polymorphism rs11643718 in SLC12A3 is associated with the development of diabetic kidney disease in Chinese people with type 2 diabetes. 32651375_Structure of the DOCK2-ELMO1 complex provides insights into regulation of the auto-inhibited state. 33047393_ARF6-Rac1 signaling-mediated neurite outgrowth is potentiated by the neuronal adaptor FE65 through orchestrating ARF6 and ELMO1. 33216373_Engulfment and cell motility 1 (ELMO1) and apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) as candidate genes for sickle cell nephropathy. 34508078_TNF-alpha-mediated m(6)A modification of ELMO1 triggers directional migration of mesenchymal stem cell in ankylosing spondylitis. 35668246_Role of ELMO1 in inflammation and cancer-clinical implications. 36288887_Engulfment and Cell Motility 1 (ELMO1) Regulates Tumor Cell Behavior and Predicts Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000041112 |
Elmo1 |
253.250803 |
0.3839017522 |
-1.381191 |
0.124185448 |
123.909132 |
0.00000000000000000000000000008819122862493458965043964646344330338357645579174621229247422688708060945156699816926959556440124288201332092285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001086563050504202460538100390350448902251688776305430478742702673504307399939688982826169194595422595739364624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
137.2477915 |
11.2755522 |
359.9845714 |
19.8981179 |
| ENSG00000155926 |
6503 |
SLA |
protein_coding |
Q13239 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein, which negatively regulates T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Inhibits T-cell antigen-receptor induced activation of nuclear factor of activated T-cells. Involved in the negative regulation of positive selection and mitosis of T-cells. May act by linking signaling proteins such as ZAP70 with CBL, leading to a CBL dependent degradation of signaling proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11696592}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Lipoprotein;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation; innate immune response; and transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in dendritic spine and focal adhesion. Predicted to be extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:6503; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
16521218_The SLA molecule and its functionally relevant residues have been highly conserved throughout the evolution. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19631983_Although SLA is a prominent glucocorticoids response gene, it does not seem to contribute to the anti-leukemic effects of glucocorticoids. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22798681_These data provide evidence for src-like adaptor protein-dependent regulation of CD3 zeta-chain in the fine control of TCR signaling. 23300935_upon ligand stimulation SLAP stably associates with Flt3 through multiple phosphotyrosine residues in Flt3. SLAP mRNA is differentially expressed in different cancers and its expression significantly increased in patients carrying the Flt3-ITD mutation 24284075_Taken together the data demonstrate that SLAP negatively regulates wild-type c-Kit signaling, but not its oncogenic counterpart, indicating a possible mechanism by which the oncogenic c-Kit bypasses the normal cellular negative feedback control 25800872_results suggest that cytoplasm-specific transduction of the SH3 and SH2 domains of SLAP has a therapeutic potential of being an immunosuppressive reagent for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases 31156621_SLAP Is a Negative Regulator of FcepsilonRI Receptor-Mediated Signaling and Allergic Response. |
ENSMUSG00000022372 |
Sla |
363.833971 |
7.9887979698 |
2.997978 |
0.123372511 |
620.326748 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006348786407430033311490873196038682186249379887687462322301789856806301598172007131552659491535548773085434176733766335401753243645960314417136484752980553612040162675737191004278334522226442356 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003604157206679511260962296928543755627418591430084744617339727374766516432709764129853287258087533300294779083663304282832581566447727637869217553174347919628565329038142833623626377691982882620 |
Yes |
No |
655.5703360 |
46.2279580 |
82.5955326 |
5.1307374 |
| ENSG00000155962 |
1193 |
CLIC2 |
protein_coding |
O15247 |
FUNCTION: Can insert into membranes and form chloride ion channels. Channel activity depends on the pH. Membrane insertion seems to be redox-regulated and may occur only under oxydizing conditions. Modulates the activity of RYR2 and inhibits calcium influx. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15147738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15916532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17945253}. |
3D-structure;Chloride;Chloride channel;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Intellectual disability;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a chloride intracellular channel protein. Chloride channels are a diverse group of proteins that regulate fundamental cellular processes including stabilization of cell membrane potential, transepithelial transport, maintenance of intracellular pH, and regulation of cell volume. This protein plays a role in inhibiting the function of ryanodine receptor 2. A mutation in this gene is the cause of an X-linked form of cognitive disability. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:1193; |
chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; voltage-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005244]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060315]; positive regulation of binding [GO:0051099]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0010880]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15147738_CLIC2 inhibited cardiac ryanodine receptor Ca2+ release channels in lipid bilayers when added to the cytoplasmic side of the channels and inhibited Ca2+ release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles 17945253_CLIC2 forms pH-dependent chloride channels in vitro with higher channel activity at low pH levels and that the channels are subject to redox regulation 18007051_Human CLIC2 was crystallized in 2 different forms, in presence of GSSH. Form A displayed P2(1)2(1)2(1) symmetry, with unit-cell parameters a=44.0, b=74.7, c=79.8 A. Form B displayed P2(1) symmetry, with unit-cell parameters a=36.0, b=66.9, c=44.1 A. 18186468_crystal structure of soluble human CICL2 and implications for function 22814392_a vital role for the CLIC2 protein in maintaining normal cognitive function via its interaction with RyRs in the brain. 29198705_We have determined the crystal structure of soluble Clic2 from the euryhaline teleost fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Structural comparison of tilapia and human CLIC2 with other CLICs shows that these proteins are highly conserved. 34229297_Chloride intracellular channel protein 2 is secreted and inhibits MMP14 activity, while preventing tumor cell invasion and metastasis. |
|
|
15.297051 |
0.2857043619 |
-1.807405 |
0.431736474 |
17.782795 |
0.00002476122387662967326863935890735035627585602924227714538574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000074057885393931916872926890516026787736336700618267059326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6938082 |
1.8280635 |
23.3567362 |
3.9314372 |
| ENSG00000155974 |
23426 |
GRIP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3R0 |
FUNCTION: May play a role as a localized scaffold for the assembly of a multiprotein signaling complex and as mediator of the trafficking of its binding partners at specific subcellular location in neurons (PubMed:10197531). Through complex formation with NSG1, GRIA2 and STX12 controls the intracellular fate of AMPAR and the endosomal sorting of the GRIA2 subunit toward recycling and membrane targeting (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10197531}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the glutamate receptor interacting protein family. The encoded scaffold protein binds to and mediates the trafficking and membrane organization of a number of transmembrane proteins. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:23426; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; neurotransmitter receptor transport, endosome to postsynaptic membrane [GO:0098887]; positive regulation of neuron projection arborization [GO:0150012] |
12011465_after regulated endocytosis, binding to GRIP/ABP stabilizes the internalized receptors in an intracellular pool and prevents them from being recycled back to the plasma membrane or entering a degradative pathway. 15226318_GRIP1c 4-7 plays a role not only in glutamatergic synapses but also in GABAergic synapses 17303296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17303296_study showed neither single marker nor haplotype analysis revealed an association between variants at GRIP1 locus & schizophrenia; suggests it is unlikely that the GRIP1 polymorphisms investigated play a substantial role in schizophrenia susceptibility 18155042_Supramodular nature of GRIP1 revealed by the structure of its PDZ12 tandem in complex with the carboxyl tail of Fras1. 18315564_GRIP1 splice forms interact with gephyrin and play a role in synaptic function at GABAergic and glycinergic synapses in cultured hippocampal neurons. 18950845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877300_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21383172_Gain-of-function glutamate receptor interacting protein 1 variants alter GluA2 recycling and surface distribution in patients with autism 22510445_In three unrelated families with parental consanguinity, GRIP1 mutations were found to segregate with Fraser syndrome in an autosomal recessive manner. 24700879_In 15 of 590 families, we identified recessive mutations in the genes FRAS1, FREM2, GRIP1, FREM1, ITGA8, and GREM1, all of which function in the interaction of the ureteric bud and the metanephric mesenchyme. 25673849_the Trip6-GRIP1-myosin VI interaction and its regulation on F-actin network play a significant role in dendritic morphogenesis 27425598_GRIP1 was identified as one of the most important differentially expressed, topologically significant proteins in the protein-protein interaction network in Alzheimer's disease. 27941904_Data suggest that molecules in the erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular receptor B family (EPHB) / ephrinB (EFNB) signalling pathways, specifically ephrin B3 and GRIP1, are involved blood pressure regulation. 29170386_GRIP1 is phosphorylated at an N-terminal serine cluster by cyclin-dependent kinase-9 (CDK9), which is recruited into GC-induced GR:GRIP1:CDK9 hetero-complexes, producing distinct GRE-specific GRIP1 phospho-isoforms. 31757889_The adaptor proteins HAP1a and GRIP1 collaborate to activate the kinesin-1 isoform KIF5C. |
ENSMUSG00000034813 |
Grip1 |
73.653310 |
0.1249261822 |
-3.000852 |
1.197994821 |
5.287520 |
0.02147878722946283333583572527913929661735892295837402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.038228252683814231693837371039990102872252464294433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3720932 |
12.2093529 |
108.8075279 |
68.4705766 |
| ENSG00000156017 |
138199 |
CARNMT1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N4J0 |
FUNCTION: N-methyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of anserine (beta-alanyl-N(Pi)-methyl-L-histidine) from carnosine. Anserine, a methylated derivative of carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine), is an abundant constituent of vertebrate skeletal muscles. Also methylates other L-histidine-containing di- and tripeptides such as Gly-Gly-His, Gly-His and homocarnosine (GABA-His). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26001783}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a methyltransferase that converts carnosine to anserine, a dipeptide found abundantly in skeletal muscle. The encoded protein can methylate other dipeptides as well. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:138199; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; carnosine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0030735]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase activity [GO:0008757]; carnosine metabolic process [GO:0035498]; histidine catabolic process [GO:0006548]; methylation [GO:0032259] |
29463897_This study solved the cofactor-bound binary, substrate- and product-bound ternary crystal structures of human CARNMT1. These structural studies revealed the substrate binding mode of carnosine, in which N1 position specificity is achieved by precise anchoring of the histidine imidazole ring in a recognition pocket such that N1 but not N3 is exposed and deprotonated for methylation. |
ENSMUSG00000024726 |
Carnmt1 |
111.077354 |
2.0617750942 |
1.043887 |
0.145495584 |
52.168916 |
0.00000000000050925912986837835408543028909787929957558166860209780679724644869565963745117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003086113051896283087164986276076634010619853532020329112128820270299911499023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
145.2799220 |
12.7501949 |
70.9665451 |
4.9609503 |
| ENSG00000156052 |
2776 |
GNAQ |
protein_coding |
P50148 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. Required for platelet activation. Regulates B-cell selection and survival and is required to prevent B-cell-dependent autoimmunity. Regulates chemotaxis of BM-derived neutrophils and dendritic cells (in vitro) (By similarity). Transduces FFAR4 signaling in response to long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) (PubMed:27852822). Together with GNA11, required for heart development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27852822}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
This locus encodes a guanine nucleotide-binding protein. The encoded protein, an alpha subunit in the Gq class, couples a seven-transmembrane domain receptor to activation of phospolipase C-beta. Mutations at this locus have been associated with problems in platelet activation and aggregation. A related pseudogene exists on chromosome 2.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:2776; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding [GO:0031683]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; action potential [GO:0001508]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; entrainment of circadian clock [GO:0009649]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007215]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; phototransduction, visible light [GO:0007603]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060828]; regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010543] |
11686331_The increase in Gqalpha and Gialpha1/2 expression was accompanied by an increase in Ca2+ signaling triggered by thrombin and other agonists known to signal to Ca2+ via these G-proteins in platelets. 11848441_A hemorrhagic diathesis patient has a defect in Galphaq gene expression in platelets but not neutrophils, possibly due to defects in transcriptional regulation or mRNA stability, and suggest a hematopoietic-lineage specific defect. 12016230_existence of a novel molecular mechanism by which Galpha(q) and the large family of G(q)-coupled receptors can regulate the activity of Rho and its downstream signaling pathways 12193606_regulation of signaling by ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50 12626493_Galpha protein signaling can lead to internalization of GPCRs, with specificity in both the Galpha proteins and GPCRs that are involved 12670961_Gq/11 proteins mediate KDR tyrosine phosphorylation and KDR-mediated HUVEC proliferation through interaction with KDR. 12704201_agonist binding to Gq-coupled receptors blocks Akt activation via the release of active Galphaq subunits that inhibit phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase 12714438_The rapid, shear-induced activation of Ras is mediated by Galpha(q) through the activity of Gbetagamma subunits in human vascular endothelial cells. 12807915_G protein-coupled receptors might evoke G alpha and G beta gamma to orchestrate regulation of phospholipase signaling by tubulin dimers and control of cell shape by microtubules 14561750_Gq-coupled receptors activate glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and C-terminal Src kinase 14617636_G alpha q and platelet activating factor receptor lead to stimulation of Src and focal adhesion kinase in vascular endothelium 15115661_the co-operative effect between Gbetagamma-mediated signaling and the increased intracellular Ca(2+) level represents a robust mechanism for the stimulation of JNK by G(q)-coupled receptors 15383626_(HEK) 293 cells expressing recombinant Galpha(q/11)-coupled muscarinic M3 receptors showed transient coexpression of RGS proteins 15466861_PC1 signaling elevates intracellular Ca(2+), activates Galpha(q) and PLC, which then activates calcineurin and NFAT 15471870_analysis of the GRK2 binding site of Galphaq 15611106_beta-Arrestin 1 and Galphaq/11 have roles in activating RhoA and stress fiber formation following receptor stimulation 15694379_These data indicate that the preserved integrity of plasma membrane domains/caveolae is required for complete agonist-induced phosphorylation of G(q)/G(11)alpha. 15698833_PKC epsilon and delta are the main PKC isozymes involved in G alpha(q)-mediated signaling in human atria 15794946_Galphaq potentiation of AC9 activity involves Ca2+/calmodulin and CaMKII. 16038796_Alpha-betagamma binding is necessary at a point downstream from receptor activation of the heterotrimeric G protein for signal transduction by alpha q. 16218966_Results suggest that the G(q) class proteins are degraded through the proteasome pathway and that cellular localization and/or other protein interactions determine their stability. 16481068_Quantitative analysis indicated that Galpha(q/11) subunits are abundant polypeptides in human brain, with values ranging from about 1200 ng/mg in cerebral cortex to close to 900 ng/mg of membrane protein in caudate 16650966_Our results support a novel model where activated Galpha(q) forms molecular complexes with ARNO and ARF6, possibly through a direct interaction with ARNO, leading to ARF6 activation. 16860758_alternative pathway operates in the absence of Lck-dependent tyrosine-phosphorylation events and was initiated by the T cell receptor-dependent activation of raft-enriched heterotrimeric Galpha11 proteins 16893886_Contractile dysfunction and pathological structural changes in the myocardium of Galpha(q) transgenic mice improve significantly after termination of the Galpha(q) signal, even in animals with overt heart failure. 16995904_GTP-Binding Protein alpha Subunits, Gq-G11, gene is regulated during megakaryocytic differentiation by early growth response 1 transcription factor. 17197445_Galphaq activation of TRPC6 signals the activation of PKCalpha, and thereby induces RhoA activity and endothelial cell contraction 17307333_These lines of evidence suggested that a Gq-coupled receptor activates specifically p38 MAPK through lipid rafts and Src kinase activation, in which flotillins positively modulate the Gq signaling. 17535809_two distinct regions of the Cav3.3 channel are necessary and sufficient for complete M1 receptor-mediated channel inhibition 17552882_Solubilization of this class of Galpha proteins was observed after prolonged agonist stimulation, induced by ultra high concentration of hormone and in cells expressing a large number of GPCRs, revealing tight binding of G(q)alpha protein to the membrane. 17606614_Galphaq directly activates p63RhoGEF and Trio via a conserved extension of the Dbl homology-associated pleckstrin homology domain 17720980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17720980_Polymorphism of the Galphaq gene is associated with accelerated mortality in heart failure 18096806_the crystal structure of the Galphaq-p63RhoGEF-RhoA complex, detailing the interactions of Galphaq with the Dbl and pleckstrin homology (DH and PH) domains of p63RhoGEF was determined 18322150_The M(1) receptor is the predominant mAChR subtype coupling to the Galpha(q/11) G protein in the cerebral cortex. 18326504_A novel polymorphism in the Gq promoter region is associated with enhanced promoter activity, Gq expression, intracellular signal transduction, and increased prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy, particularly in women. 18424071_These novel data demonstrate an IKK2-dependent, predominantly G-protein-independent pathway involved in PAR-2 regulation of NFkappaB phosphorylation in keratinocytes. 18434368_IGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor signaling induced cell hypertrophy and atrial natriuretic peptide/BNP expression via Galphaq interaction and protein kinase C-alpha/CaMKII activation in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. 18514160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18632858_We show that Env-mediated Rac-1 activation is dependent on the activation of Galpha(q) and its downstream targets. 18719078_GNAQ mutations occur in about half of uveal melanomas, representing the most common known oncogenic mutation in this cancer. 18851832_MLK3 functions in a regulated way to limit levels of the activated GTPase Rho by binding to the Rho activator, p63RhoGEF/GEFT, which, in turn, prevents its activation by Galphaq. 18989526_Report phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate responsive sequence in Galphaq promoter during megakaryocytic differentiation. Regulation by EGR-1 and MAP kinase pathway. 18991294_a role of Galphaq in the fine-tuning of proximal TCR signals at the level of Lck and a negative regulatory role of Galphaq in transcriptional activation of cytokine responses. 19074439_AT2 oligomers inducing Galphaq/11 arrest are causally involved in inducing symptoms of neurodegeneration 19074441_Abeta induces the formation of cross-linked AT2 oligomers that contribute to the dysfunction of Galphaq/11 in an animal model of Alzheimer disease. 19078957_frequent somatic mutations in the heterotrimeric G protein alpha-subunit, GNAQ, in blue naevi (83%) and ocular melanoma of the uvea (46%) 19332487_In the vascular endothelium, G alpha(q/11)-PECAM-1 forms a mechanosensitive complex which localization suggests the G alpha(q/11)-PECAM-1 complex is a critical mediator of vascular diseases. 19426503_knockdown of Galphaq significantly enhanced basal migration in T cells and reduced CXCL12-induced SHP-1 phosphorylation 19445628_GNAQ hotspot mutations may not have a role in papillary thyroid carcinomas 19551532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19654573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19654573_The GNAQ mutation status is not suitable to predict DFS. However, the high frequency of GNAQ mutations may render it a promising target for therapeutic intervention. 19718445_data indicate that the occurrence of GNAQ mutations display a unique pattern being present in a subset of melanocytic tumors but not in malignancies of glial, epithelial and stromal origin analyzed in this study 19903011_The [Ca2+] response is induced by glucagon mainly via the coupling of GCGR to the Galphaq/11 and Galphai/o proteins. 19936769_GNAQ-dependent mitogen-activated kinase signaling is a promising therapeutic target in melanocytic neoplasms 20007712_Data show that activation of PLCbeta(2) by alpha(q) and beta1gamma2 differ from activation by Rac2 and from each other. 20237586_Increased activation of the Galphaq protein alters eNOS protein expression and phosphorylation only in transgenic males. 20379146_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20399743_activation of Galphaq weakened the kinase activity of GSK-3beta and enhanced cellular accumulation of beta-Catenin. 20562673_GNAQ promoter diplotypes are associated with insulin resistance and obesity in polycystic ovary syndrome. 20562673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20590159_possibility of ligand-free constitutive TBXA2R signaling through Galphaq binding 20631239_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20631239_The lack of GNAQ mutations in conjunctival melanocytic lesions suggests the involvement of a different tumorigenic pathway from that of uveal melanoma. 20664004_Basic amino acids in the amino-terminus of alpha(q) can affect its lateral segregation on plasma membranes; changes in such lateral segregation may be responsible for the observed signaling defects of alphaq4Q. 20714830_GNAq mutations seem not to play an important role in the development of thyroid follicular neoplasms 20805136_The cases harbouring the GNAQ mutation did not differ significantly in the expression of ERK1/2 and pERK1/2 or in the expression of proliferation markers from cases without the mutation. 20865267_A detailed analysis of morphology combined with GNAQ mutational analysis aids in the differential diagnosis of melanotic schwannoma with leptomeningeal melanocytic lesions. 21056896_presence of GNAQ mutations in the amelanotic/hypomelanotic blue nevus indicates mechanisms underlying pigment homeostasis in this variant appear to be similar to those of its melanotic counterpart 21072599_results exclude GNAQ as a candidate gene in uveal melanoma patients with a high risk for hereditary cancer predisposition 21083380_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21083380_Of the uveal melanomas we analyzed, 83% had somatic mutations in GNAQ or GNA11. 21304157_Studies indicate that the complex between the effector protein phospholipase C-beta3 (PLC-beta3) and its activator, Galpha(q), suggests that several effectors independently evolved a structurally similar helix-turn-helix segment for G protein recognition. 21366456_Benign and malignant blue nevi harbor frequent mutations in the Galphaq class of G-protein alpha subunits, Gnaq and Gna11 proteins. 21464134_Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel by the RH domain of G protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK2, and Galphaq/11. 21487925_We did not find any mutation in the GNAQ, AKT3, and PIK3R1 genes in various types of thyroid cancer. 21515378_ET1 stimulated calcium response depends on phospholipase C and is likely mediated through the G-ALPHA-q signaling pathway. 21592972_Negative regulation of Gq-mediated pathways in platelets by G(12/13) pathways through Fyn kinase 21923740_Gaq controls the apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis peripheral blood lymphocytes through regulating the activity of Mcl-1 and caspase-3. 21940795_WDR36 acts as a scaffold protein tethering a G-protein-coupled receptor, Galphaq and phospholipase C beta 2 in a signalling complex 21945171_The DNA obtained is of sufficient quality to carry out genotyping for markers on chromosome 3, 6 and 8, as well as screening for somatic mutations in GNAQ and GNA11 genes. 22056876_a novel paradigm in which a fraction of the cellular RARalpha pool is present in membrane lipid rafts, where it forms complexes with G protein alpha Q (Galphaq) in response to RA 22307269_THe results expand the spectrum of GNAQ mutations that may occur in melanocytomas. 22701657_Vesicle-associated Galphaq/11 is required for the turnover of LFA-1 adhesion that is necessary for immune cell migration. 22710260_analysis of molecular complexes of Gq/11alpha protein in HEK293 cells 22758774_In primary melanocytic tumours of the CNS, GNA11 and N-RAS mutations represent a mechanism of MAPK pathway activation alternative to the common GNAQ mutations 22905097_gamma-synuclein has a role in promoting a more robust G protein Galphaq activation of PLCbeta2 22977135_The vast majority of primary large uveal melanomas harbor mutually-exclusive mutations in GNAQ or GNA11, but very rarely have the oncogenic mutations that are reported commonly in other cancers. 23066026_Src family kinases, PI3 kinase and protein kinase C synergize to mediate Gq-dependent platelet activation 23159116_V600E point mutation was identified in the BRAF gene in 3 intramucosal nevi and in 2 melanomas. Only 1 blue nevus harbored the GNAQ209 mutation 23315865_the GNAQ promoter polymorphism is not a genetic risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis in the Han Chinese population. 23572068_Letter/Case Report: role of GNAQ/GNA11 mutational analysis in management of choroidal melanoma metastatic to the contralateral orbit. 23572156_Letter/Case Report: oncogenic GNAQ mutation in congenital choroidal melanoma. 23599145_This study identifies HRAS mutations in deep penetrating nevi. The presence of HRAS mutations and absence of GNAQ or GNA11 mutations in deep penetrating nevi suggests classification of these nevi within the Spitz rather than the blue nevus category. 23634288_Mutant alleles of the GNA11 or GNAQ genes, which are highly specific for uveal melanoma, were identified in cell-free DNA of 9 of 22 (41%) patients. 23656586_The Sturge-Weber syndrome and port-wine stains are caused by a somatic activating mutation in GNAQ. This finding confirms a long-standing hypothesis. 23665327_The ubiquitination of Galphai2 and Galphaq is suppressed by expression of Ric-8A. The suppression likely requires Ric-8A interaction with these Galpha proteins; the C-terminal truncation of Galphaq and Galphai2 completely abrogates their interaction with Ric-8A. 23685997_GNAQ mutations are present in uveal melanocytomas and in a case of transformation to melanoma, implicating GNAQ-dependent mitogen activation signals, in the pathogenesis of uveal melanocytoma. 23778528_GNAQ and GNA11 mutations are, in equal matter, not associated with uveal melanoma patient outcome. 23884432_Signaling efficiency of Galphaq through its effectors p63RhoGEF and GEFT depends on their subcellular location. 23993961_These results showed that Fhit was up-regulated specifically by activating Galpha subunits of the Gq subfamily but not by those of the other G protein subfamilies. 24141786_Metastatic uveal melanoma with GNAQ or GNA11 mutations is responsive to PKC inhibitors. 24299002_observations support the concept of a functional activation-dependent p63RhoGEF-Galphaq-RGS2 complex 24470488_Melanocytes use an ultraviolet radiation phototransduction mechanism involving the GNAQ cascade. 24595385_PKC inhibitors combined with IR significantly decreased the viability, proliferation, and clonogenic potential of GNAQ(mt), but not GNAQ(wt)/BRAF(mt) cells, compared with IR alone. 24882515_GNAQ oncogenic signaling induced YPA nuclear translocation and YAP-dependent transcription activation throuch Rho-GTPases and actin remodeling. 24927141_Our finding of the frameshift deletion (p.H387fs) in exon 4 of SOX10 in uveal melanoma (UM) provides an important insight and complements earlier findings of mutations in GNAQ and SF3B1 on the genomic basis of UM. 24970262_There was no association of GNAQ mutation status with metastatic status in uveal melanoma. 25280020_Oncogenic GNAQ mutation is associated with uveal melanoma. 25304237_review discusses the multiple activated signaling targets downstream of mutant GNAQ and GNA11 in uveal melanoma, including MEK, PI3-kinase/Akt, protein kinase C, and YAP 25316767_Results uncovered that Gaq binding to GRK2 enhances the recruitment of GRK2 to M3-ACh receptors. 25363280_no GNAQ mutations were observed in African acral melanomas 25374402_These findings suggest that the recurrent somatic GNAQ mutation c.548G>A is the major determinant genetic factor for Sturge-Weber syndrome and imply that other mutated candidate gene(s) may exist in Sturge-Weber syndrome 25420509_Diacylglycerol mediates regulation of TASK1 and TASK3 potassium channels by GNAQ. 25433904_This study demonstrated that the GNAQ protein was reduced in auditory cortex patient with schizophreia. 25653058_Knockdown of GNAQ with siRNA-AuNPs effectively reduced downstream signals and decreased cell viability in GNAQ mutant uveal melanoma cells. 25695059_Involved in the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and GNAQ/11 pathways. 25732870_Galphaq expression was negatively associated with interleukin-17A expression in RA patients, indicating that Galphaq negatively controlled the differentiation of Th17 cells. 25955651_The results suggested that GNAQ mutation induced viability and migration of uveal melanoma cells via Notch signaling activation, which is mediated by YAP dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation. 26192947_This is the second largest study on isolated, non-syndromic Port-wine stain; data suggest that GNAQ is the main genetic determinant in this condition. Moreover, isolated port-wine stains are distinct from capillary malformations seen in RASA1 disorders. 26368812_Distribution of GNAQ and GNA11 Mutation Signatures in Uveal Melanoma Points to a Light Dependent Mutation Mechanism. 26399561_Driver mutations are rare in mutational hotspots of BRAF, NRAS, KIT, and GNAQ/GNA11 in oral mucosal melanoma. 26746047_Phospholipase C beta connects G protein signaling with RNA interference. (Review) 26775782_We conclude that enrichment of GNAQ (R183Q) in port-wine stain (PWS) blood vessels may induce consecutive activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases and extracellular signal regulated kinases, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of PWS. 26778290_extensive dermal melanocytosis and phakomatosis pigmentovascularis are associated with activating mutations in GNA11 and GNAQ, genes that encode Galpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins 26823487_The findings of the work indicate a role for Galphaq and/or Galpha14 and in CCR2a/CCR2b-stimulated Rho A GTPase-mediated serum response factor activation. 26859074_we report a previously unknown role for Gaq in maintenance of MLL-AF9-induced acute myeloid leukemia leukemia 26865629_findings demonstrate that hNPS-(1-10) is a biased agonist favoring Galphaq-dependent signaling. It may represent a valuable chemical probe for further investigation of the therapeutic potential of human NPS receptor-directed signalingin vivo. 26887939_data suggest that the interaction between this novel region in Galphaq and the effector PKCzeta is a key event in Galphaq signaling. 27058448_The Glu209 GNAQ and GNA11 missense variants we identified are common in uveal melanoma and have been shown to constitutively activate MAPK and/or YAP signaling. Our data indicate that chorangioma is probably not the placental counterpart of congenital hemangiomas associated with mutations altering Gln209 in GNAQ or GNA11. 27089234_GNAQ/GNA11Q209 mutations characterized a distinct, albeit uncommon subtype of non-uveal melanoma (0.5-1%). These mutations were essentially melanoma-specific, occurred in all subtypes of this disease (including cutaneous, mucosal, uveal, and unknown primary), and were mutually exclusive with other common melanoma mutations. 27265506_Data show that GNAQ promotes ARF6 activation to control the proliferation of Uveal Melanoma Cells. 27330078_The Galphas and Galphaq peptides adopt different orientations in beta2-AR and V1AR, respectively. The beta2-AR/Galphas peptide interface is dominated by electrostatic interactions, whereas the V1AR/Galphaq peptide interactions are predominantly hydrophobic. 27498141_GNAQ and GNA11 mutations occur frequently in mucosal melanoma and may be a prognostic factor for MM. Our data implicate that GNAQ/11 may be potential targets for targeted therapy of mucosal melanoma. 27566546_CGRP family of receptors displays both ligand- and RAMP-dependent signaling bias among the Galphas, Galphai, and Galphaq/11 pathways. 27919468_Study demonstrated that the GNAQ p.R183Q mutation resides within endothelial cells in Sturge-Weber syndrome (SWS) brain lesions, and that the SWS brain endothelial cells can be isolated and expanded in culture and further confirm that the GNAQ p.R183Q mutation is present in brain endothelial cells. 28083870_The results show that postzygotic mosaicism for GNAQ mutations causes an overlapping phenotypic spectrum of vascular and melanocytic birthmarks. 28084343_Nine of 13 cases (69%) of anastomosing hemangiomas harbored a somatic mutation at GNAQ codon 209 28148497_These findings suggest that Galphaq/11 participates in the sensing/transducing of shear stress independently of GPCR activation in ECs. 28197018_Galphaq regulates the development of rheumatoid arthritis by modulating Th1 differentiation 28248732_The Role of Mutation Rates of GNAQ or GNA11 in Cases of Uveal Melanoma in Japan. 28350126_Results found that GNAQ was highly expressed in gastric cancer (GC) patient samples and suggest that GNAQ plays a critical role in regulating GC cell growth and survival via canonical oncogenic signaling pathways including MAPK and p53. 28363951_Parathyroid hormone controls bone and kidney homeostasis via GNAS and Gq-G11 heterotrimeric G proteins. (Review) 28369206_It is therefore concluded that Gnaq plays a pivotal role in antioxidation in neural cells. A possible mechanism for this would be that the overexpressed Gnaq inhibits the cellular damaging effect mediated by NF-kappaB and Erk1/2 signal pathways. 28422819_The GC/GC genotype of the TT(-695/-694)GC polymorphism is associated with increased Gq protein expression, augmented angiotensin II receptor type 1-related vasoconstriction, and increased myocardial injury after coronary artery bypass grafting. 28444874_There were no significant differences in the prevalence of GNAQ and GNA11 mutations between patients with or without metastatic disease 28486107_RasGRP3 mediates ERK MAPK pathway activation in GNAQ mutant uveal melanoma. 28571101_Results demonstrate that the somatic GNAQ mutation in Sturge-Weber syndrome is not confined to the venous vascular malformation but can directly (although less severely) affect underlying brain parenchyma, not directly affected by leptomeningeal angiomatosis, and possibly contribute to Sturge-Weber syndrome brain pathology. 28584054_Data suggest that allosteric communication between heterodimeric AT1R and PTGFR is mediated through GNAQ and may also involve proximal phospholipase C but not distal protein kinase C signaling partners; PTGFR activation has negligible effects on AT1R-based conformational biosensors. (AT1R = angiotensin II receptor, type 1; PTGFR = prostaglandin F2alpha receptor; GNAQ = GTP-binding protein G[q] subunit alpha) 28700778_we find iris melanomas to be related genetically to choroidal and ciliary body melanomas, frequently harboring GNAQ, GNA11, and EIF1AX mutations. 28705934_Data (including data from studies using cells from knockout mice) suggest that CLEC2/CLEC2R signaling is dependent on thromboxane A2 generation and is potentiated by co-stimulation with different GNAQ agonists. (CLEC2 = C-type lectin CLEC2; CLEC2R = CLEC2 receptor; GNAQ = guanine nucleotide-binding protein G[q] subunit alpha) 28809862_GNAQ/11 mutant clones make up a fraction of the cells in choroidal nevi. Nevus cells are furthermore characterised by heterogeneous YAP expression. Combined GNAQ/11 and YAP may constitute a putative precursor tumour pathway with an activated oncogene (GNAQ/11) and downstream effector (YAP). 28842497_These results indicate that the mechanism by which Galphaq and PLC-beta3 mutually regulate each other is far more complex than a simple, two-state allosteric model and instead is probably kinetically determined. 28854843_We conclude that the crosstalk between angiotensin AT1 receptor and insulin receptor signaling shows a high degree of specificity, and involves Galphaq protein, and activation of distinct kinases. Thus, the BRET(2) technique can be used as a platform for studying molecular mechanisms of crosstalk between insulin receptor and 7TM receptors. 28982892_Mutations in GNAQ and GNA11 genes in Greek uveal melanoma population present frequencies that qualify them as potential targets for customized therapy. 29059311_Adenocarcinomas or adenomas derived from pigmented ciliary epithelium is distinguished from uveal melanoma by the absence of SOX10 expression and presence of the BRAF V600E mutation. 29107092_the induction of luteal Akr1c18 by Galphaq/11 is mediated by the activation of phospholipase C. 29209985_GNAQ Mutation is associated with Uveal Melanomas. 29332123_common conjunctival melanocytic nevi have mutually exclusive mutations in BRAF and NRAS. The two conjunctival blue nevi harbored GNAQ mutations. This suggests the driver mutations of conjunctival nevi are similar to those of nevi of the skin. At the molecular level, conjunctival nevi appear more like cutaneous nevi than choroidal nevi 29570931_Mutation in GNAQ is associated with numerous protumorigenic changes within melanocytes. 29574926_14 of 15 (93%) anastomosing haemangiomas in the case series showed recurrent mutations in GNAQ or GNA14. 29853161_We conclude that the C825T polymorphism of the beta 3 subunit of G protein is significantly and independently associated with the occurrence of hypertension in the study population 29878304_In patients with port-wine macrocheilia (PWM), GNAQ was mutated in all tissues except for glands. Given the advantages of mucosal biopsy, including practicality, lack of scarring and rapid healing, GNAQ mutation in the lip mucosa may be a useful predictor for early-stage PWM in patients with port-wine stains affecting the lips. 29925530_Interplay between negative and positive design elements in Galpha helical domains of G proteins determines interaction specificity toward RGS2. 29975248_All hepatic small vessel neoplasms in our series demonstrated recurrent mutations in GNAQ or GNA14 in a mutually exclusive manner 29977933_data suggest that Galphaq is involved in Primary Sjogren's syndrome pathogenesis regulation, possibly due to its regulation of Th17 30112971_GNAQ expression is low in Sturge-Weber syndrome leptomeningeal blood vessel endothelial cells. 30204251_In the current sample, the genes GNAS, GNAQ, and GNA11 were widely altered across cancer types, and these alterations often were accompanied by specific genomic abnormalities in AURKA, CBL, and LYN. 30278445_Gq protein-coupled receptors-induced apoptosis is general, and includes a two-branched pathway downstream of PKC. One branch consists on c-Src activation that transmit the signal to the JNK cascade and the second branch that consists on PKC-dependent inactivation of AKT and a phosphatase activity. 30315589_GNAQ/GNA11 activating mutations arising earlier during development may trigger agminated blue nevi, explaining the broader field of involvement in these cutaneous lesions. 30321592_Galphaq/14-regulated CCR2 non canonical receptor signaling was analyzed. the 8th helix of both CCR2a and CCR2b is critically involved in selectively activating Galphaq/14-regulated signaling. 30327411_CCR5 signals through both Gi/o and Gq/11 IP1 accumulation and Ca(2+) flux arise from Gq/11 activation, rather than from Gbetagamma subunit release after Gi/o activation as had been previously proposed 30352874_the molecular properties of Galphaq Q209P are fundamentally different from those in other active Galphaq proteins 30422215_The results suggest that a more accurate description for choroidal hemangioma in patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome is choroidal capillary malformation. 30446620_GTPase-deficient G-ALPHA-qQL and Galpha13QL variants formed stable complexes with G protein beta gamma, impairing its interaction with P-REX1. 30537484_GNAQ mutations occur in both diffuse and solitary hemangiomas, although at distinct codons. An R183 codon is mutant in diffuse choroidal hemangiomas, consistent with other Sturge-Weber vascular malformations. By contrast, solitary choroidal hemangiomas have mutations in the Q209 codon, similar to other intraocular melanocytic neoplasms. 30552676_CXCL2-CXCR2 axis mediates through Galphai-2 and Galphaq/11 to promote tumorigenesis and contributes to cancer stem cell properties of CPT-11-resistant LoVo cells. 30558566_Sequencing of melanoma driver genes revealed GNAQ (p.Q209L) mutations in two samples with primary orbital melanoma; although it is possible that these samples represent extraocular spread of an occult uveal melanoma. 30654308_In this study, we first reported that Galphaq expression in PBMCs of psoriasis patients were decreased, and it was negatively related to disease activity and some test parameters, such as CRP, cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein. Galphaq gene expression might be involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. 30773340_GNAQ activates FAK via the non-canonical Hippo pathway to drive uveal melanoma (UM) cell proliferation and survival. 30783010_The mutations increase mitogenic signaling through the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (RhoA) axis that may represent cancer drivers operating in a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit, G11 (Galphaq/11)-independent manner. 30870248_Several studies confirm the GNAQ R183Q mutation in 90% of nonsyndromic and Sturge-Weber syndrome (SWS) capillary malformations. The mutation is enriched in endothelial cells and blood vessels isolated from skin, brain, and choroidal capillary malformations. 30890659_FR900359 enabled suppression of malignant traits in cancer cells that are driven by activating mutations at codon 209 in Galphaq/11 proteins, we envision that similar approaches could be taken to blunt the signaling of non-Galphaq/11 G proteins. 31173078_Our results indicate that there is marked variation in MAPK activation in uveal melanoma (UM) with GNAQ/11 mutations. Thus, GNAQ/11 mutational status is not a sufficient biomarker to adequately predict UM patient responses to single-agent selective MEK inhibitor therapy. 31189994_our study demonstrated recurrent GNA14/GNAQ/GNA11 mutations were present in the majority of cherry hemangiomas and established its neoplastic nature 31533929_Heterogeneity of GNAQ/11 mutation inversely correlates with the metastatic rate in uveal melanoma. 31580399_Intraocular Metastasis in Unilateral Multifocal Uveal Melanoma Without Melanocytosis or Germline BAP1 Mutations. 31614358_Mutations of GNAQ, GNA11, SF3B1, EIF1AX, PLCB4 and CYSLTR in Uveal Melanoma in Chinese Patients. 31692010_Port-wine stains associated with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome caused by mutations in GNAQ and SLC26A4 genes: A case report. 31726051_Reverse Phenotyping in Patients with Skin Capillary Malformations and Mosaic GNAQ or GNA11 Mutations Defines a Clinical Spectrum with Genotype-Phenotype Correlation. 31906951_Melatonin restores Muc2 depletion induced by V. vulnificus VvpM via melatonin receptor 2 coupling with Galphaq. 32064597_GNAQ and GNA11 mutant nonuveal melanoma: a subtype distinct from both cutaneous and uveal melanoma. 32126208_Structures of Galpha Proteins in Complex with Their Chaperone Reveal Quality Control Mechanisms. 32420639_The P2Y6 receptor signals through Galphaq /Ca(2+) /PKCalpha and Galpha13 /ROCK pathways to drive the formation of membrane protrusions and dictate cell migration. 33003441_Dissecting Gq/11-Mediated Plasma Membrane Translocation of Sphingosine Kinase-1. 33361125_CRISPR/Cas9-Based Knockout of GNAQ Reveals Differences in Host Cell Signaling Necessary for Egress of Apicomplexan Parasites. 33550208_Targeted Gq-GPCR activation drives ER-dependent calcium oscillations in chondrocytes. 33568347_Synthetic Lethal Screens Reveal Cotargeting FAK and MEK as a Multimodal Precision Therapy for GNAQ-Driven Uveal Melanoma. 33639168_An experimental strategy to probe Gq contribution to signal transduct |
|
|
1141.237148 |
0.4300120799 |
-1.217551 |
0.137981639 |
75.055645 |
0.00000000000000000457632712433993307258425011036576625285163575797124126121051546078888350166380405426025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000037195257904877426486726157940029638042196293538791188049152935946040088310837745666503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
721.4576156 |
92.5022396 |
1693.0831871 |
156.4545003 |
| ENSG00000156113 |
3778 |
KCNMA1 |
protein_coding |
Q12791 |
FUNCTION: Potassium channel activated by both membrane depolarization or increase in cytosolic Ca(2+) that mediates export of K(+) (PubMed:29330545, PubMed:31152168). It is also activated by the concentration of cytosolic Mg(2+). Its activation dampens the excitatory events that elevate the cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration and/or depolarize the cell membrane. It therefore contributes to repolarization of the membrane potential. Plays a key role in controlling excitability in a number of systems, such as regulation of the contraction of smooth muscle, the tuning of hair cells in the cochlea, regulation of transmitter release, and innate immunity. In smooth muscles, its activation by high level of Ca(2+), caused by ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, regulates the membrane potential. In cochlea cells, its number and kinetic properties partly determine the characteristic frequency of each hair cell and thereby helps to establish a tonotopic map. Kinetics of KCNMA1 channels are determined by alternative splicing, phosphorylation status and its combination with modulating beta subunits. Highly sensitive to both iberiotoxin (IbTx) and charybdotoxin (CTX). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29330545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31152168}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Ion channel;Ion transport;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes the alpha subunit of calcium-activated BK channel. The encoded protein is involved in several physiological processes including smooth muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release and neuronal excitability. Mutations in this gene are associated with a spectrum of neurological disorders including Paroxysmal Nonkinesigenic Dyskinesia 3, Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy 16 and Liang-Wang syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2022]. |
hsa:3778; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; caveola [GO:0005901]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; calcium-activated potassium channel activity [GO:0015269]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity [GO:0060072]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; cellular potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0030007]; micturition [GO:0060073]; negative regulation of cell volume [GO:0045794]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; relaxation of vascular associated smooth muscle [GO:0060087]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to carbon monoxide [GO:0034465]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to osmotic stress [GO:0006970]; smooth muscle contraction involved in micturition [GO:0060083] |
11832330_The targets of H2O2 action are located in the intracellular aspect of the channel and the H2O2 effect on channel activity is mediated by hydroxyl radical 11986367_Inhibited by hypoxia by a mechanism which is membrane delimited and Ca(2+) sensitive. 12009018_besides its conductance function, hSlo channel can behave in bone cells, as a true transduction protein intervening in the bone remodeling induced by PGE2 12016222_N-terminal variation and strex exon splicing in rSlo interact to produce BK(Ca) channels with a physiologically relevant phenotype. 12161564_Stepwise contribution of each subunit to the cooperative activation of channels by calcium 12223479_pore-forming alpha subunit of the hSlo channel promotes N-linked glycosylation of its auxiliary beta4 subunit, and this in turn influences the modulation of the channel by the beta4 subunit 12391293_propose that MaxiK channels via direct c-Src-dependent phosphorylation play a significant role supporting vasoconstriction after activation of G protein-coupled receptors by vasoactive substances and neurotransmitters 12438308_the cytoplasmic tail of rbslo1 is important for the cell surface expression of MaxiK channels 14522958_Chronic hypoxia caused no change in alpha-subunit but evoked a 3-fold increase in beta-subunit expression, and augmented alpha/beta-subunit co-localization at the plasma membrane; maxiK channel function is modulated via post-transcriptional mechanisms. 14523450_electrophysiological and structural evidence showing that haem directly regulates cloned human Slo1 channels and wild-type BK channels in rat brain 14584897_pp125FAK interacts with the large conductance calcium-activated hSlo potassium channel in human osteoblasts: potential role in mechanotransduction 15280542_cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylation of the conserved C-terminal PKA consensus site (S899) in all four BKCa alpha-subunits is required for channel activation 15528406_Hemoxygenase-2 is part of the BK channel complex and enhances channel activity in normoxia 15703204_Actin cytoskeleton is involved as part of a caveolar complex in the regulation of myometrial maxi-K channel function. 15849354_Present findings suggest that hslo gating structures targeted by ethanol are accessible to sense changes in bilayer stress. 15937479_mutated in generalized epilepsy and paroxysmal dyskinesia and have implications for the pathogenesis of human epilepsy, the neurophysiology of paroxysmal movement disorders and the role of BK channels in neurological disease 16042390_The Maxi-K channel domain ranging from the N-terminus through the S6 linker region contains the determinants necessary for formation and surface expression of tetramers, while the C-terminus is needed for normal channel gating and surface expression. 16100257_analysis of C-terminal residues that contribute to the Ca2+ sensitivity of a BKCa channel 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16396928_Oxidation of M536, M712 or M739 may enhance the Slo1 BK activity during conditions of oxidative stress, such as those associated with ischaemia-reperfusion and neurodegenerative disease, or in response to metabolic cues. 16790810_Evidence is provided for functional association of the MaxiK channel and toll-like receptor signaling complexes in human macrophages. 16895996_Results describe the conformational changes that the large conductance voltage- and Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel undergoes during activation. 16951373_Appears to be a central molecule in the NF-kappa B-dependent inflammatory response of macrophages to bacterial lipopolysaccharides. 17146446_Amplification of chromosomal region 10q22 drives KCNMA1 expression and cell proliferation in prostate cancer. 17150299_Alternative splicing of this protein may represent a mechanism with which relaxation of corporal tissue may be triggered as a result of a diabetes-related decline in erectile capacity. 17166942_RACK1 binds to the BK(Ca) channel and it may form part of a BK(Ca)-channel regulatory complex in vascular smooth muscle. 17468961_both the inner and outer domains of the KCNMA1 channel where these two channel functions are localized respond to deformation and that a fixed amount of distortion results in reciprocal changes in protein function. 17483867_The activity of BK(Ca) channels present in human cardiac fibroblasts may contribute to the functional activities of heart cells through transfer of electrical signals between these two cell types. 17521822_reports that coexpression of beta2 subunit (KCNMB2) with hSlo can also modulate hSlo surface expression levels in HEK293T cells 17586600_Interactions with filamin A stimulate surface expression of KCNMA1 in the absence of direct actin binding. 17591987_A study evaluating the mechanism of gating of MaxiK is reported. 17591990_the beta(2) subunit of BK(Ca) channels facilitates channel activation by changing the voltage sensor equilibrium and that the beta(2)-induced inactivation process does not follow a typical N-type mechanism 17901123_data suggest sensory nerves and BKCa channels play major roles in the EDHF component of reactive hyperaemia and appear to work partly independent of each other 17989352_Slo1-actin interactions are necessary for normal trafficking of calcium channels to the plasma membrane. 18084004_Acute alcohol tolerance is intrinsic to the BKCa protein, but is modulated by the lipid environment 18162557_analysis of how the RCK2 domain of the human BKCa channel is a calcium sensor 18180950_Show that a motif in the S9-S10 part of the C-terminal of KCNMA1 is essential for carbon monoxide activation. CO may activate KCNMA1 by redox-independent changes in gating. 18227273_The influence of the intrinsic electrostatic potential on the channel conductance of KCNMA1 was studied experimentally and theoretically by amino acid substitution. 18316727_Carbon monoxide acts as a partial agonist for the high-affinity divalent cation sensor in the RCK1 domain of the Slo1 BK channel. 18345016_common motif in the RCK1 domain of SLO1 mediates the stimulatory effects of both H+ and Ca2+, and provides a basis for the bidirectional coupling of cell metabolism and membrane electrical excitability 18367663_insulin activates BK in the plasma membrane of mesangial cells and stimulates, via MAPK, an increase in cellular and plasma membrane BK-alpha 18385281_NO-induced regulation of human trabecular meshwork cell volume and aqueous humor outflow facility involve the BKCa ion channel. 18404672_BK channels play a functional role in carcinogenesis. BK channels exhibit antitumoral properties in OS in vivo and affect the tumor microenvironment through the modulation of both chemokine expression and leukocyte infiltration. 18414909_Nonsense mutation (R419X) CRBN disturbs the development of adult brain BK(Ca) isoforms. These changes are predicted to result in BK(Ca) channels with a higher intracellular Ca(2+) sensitivity, faster activation, and slower deactivation kinetics. 18480178_Reduction of endogenous nephrin expression by application of siRNA to differentiated cells of an immortalized podocyte cell line markedly reduced steady-state surface expression of Slo1. 18559348_Structural basis for toxin resistance of beta4-associated calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels. 18719396_the evolutionarily preserved splicing of the Slo1 S6-RCK1 linker segment possess great potential to fine-tune neuronal excitability 18854754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18854754_The present findings are compatible with an association of KCNMA1 genetic variations with increased risk of systolic severe hypertension and myocardial infarction. 19052171_Cytosolic domains of the pore-forming subunits of BKCa channels associate with TRPC6 and TRPC3 channels, both of which are expressed in podocytes. 19096717_BK channels coupled directly to these Ca2+ channels may provide a good tool for negative feedback control of the L-type Ca2+ channels. 19118164_Nardilysin convertase regulates the function of the maxi-K channel isoform mK44 in human myometrium. 19168436_TRPC1 associates with BK(Ca) channel to form a signal complex in vascular smooth muscle cells. 19204046_Report beta subunit (KNMB1-4)-specific modulations of BK channel function by a Slo1 mutation associated with epilepsy and dyskinesia. 19344525_Expression of BKCa alpha- and beta-subunit in pregnant myometrium is reduced during labour. 19430934_The expressed hSloalpha + beta1 subunit complex demonstrated to be fully functional for its typical single-channel traces, Ca(2+)-sensitivity, voltage-dependency, high conductance (151 +/- 7 pS), and its pharmacological activation and inhibition. 19456106_The solution structure of KCNMA1 alpha subunit reveals a helix-turn-helix motif, which is in agreement with crystal structures of other voltage-gated potassium channels, thus indicating that it is feasible to study the isolated fragment. 19552602_BKCa channel activation increases outflow facility and decreases cell volume suggesting that K+ efflux regulates trabecular meshwork cell function 19617704_comparative mechanisms of the channel activation by Ca(2+) and H(+). 19640305_KCNMA1 has a role in breast cancer invasion and metastasis to brain 19718020_the first single-particle cryo-EM study of a membrane protein, the human large-conductance calcium- and voltage-activated potassium channel (BK), in a lipid environment 19738431_Data showed that KCa channel activity appears to increase with the increased glioma malignancy. 20012488_These results indicated that activation of cloned BK(Ca) channel was involved in nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of HEK293 cells. 20037152_Slo1 BK channels represent a positive and direct effector of Zn(2+) signaling and may participate in sculpting cellular response to an increase in intracellular Zn(2+) concentration 20051533_Dominant-negative regulation of cell surface expression by a pentapeptide motif at the extreme COOH terminus of an Slo1 calcium-activated potassium channel splice variant. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20427280_Data suggest that the thiol/disulfide switch in the HBD is a mechanism by which activity of the BK channel can respond quickly and reversibly to changes in the redox state of the cell. 20457834_In transfected HEK293 cells, activation of cloned BK(Ca) channel induced apoptosis, whereas inhibition of cloned BK(Ca) channel decreased apoptosis. 20479001_Alternative splicing of the intracellular RCK1-RCK2 linker plays a critical role in determining cell surface expression of BK channels by controlling the inclusion/exclusion of multiple trafficking motifs. 20508092_study determined the x-ray structure of the BK Ca2+ gating apparatus at a resolution of 3.0 angstroms and deduced its tetrameric assembly by solving a 6 angstrom resolution structure of a Na+-activated homolog 20574420_crystal structure of the entire cytoplasmic region of the human BK channel in a Ca(2+)-free state 20624858_RCK1 domain is a high-affinity Ca(2+) sensor that transduces Ca(2+) binding into structural rearrangements, likely representing elementary steps in the Ca(2+)-dependent activation of human BK(Ca) channels. 20630939_Podocyte BK(Ca) channels are regulated by synaptopodin, Rho, and actin microfilaments. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20808839_Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels do not play a critical role in proliferation of glioma cells 20959415_vasoconstrictor TP receptor and MaxiK-channel direct interaction facilitates G-protein-independent TP to MaxiK trans-inhibition, which would promote vasoconstriction. 21072171_Findings show that miR-211 is a direct posttranscriptional regulator of KCNMA1 expression. 21078868_Relative motion of transmembrane segments S0 and S4 during voltage sensor activation in the human BK(Ca) channel 21301863_a specific cysteine residue in the C-terminal domain, which is close to the Ca(2+) bowl but which is not involved in Ca(2+) activation, confers significant CO sensitivity to BK(Ca) channels 21413024_Cloned BK(Ca) channel directly regulated apoptosis and proliferation of HEK293 cell under hyperglycemia condition. 21613417_WNK4 WT inhibits Maxi K activity by reducing Maxi K protein at the membrane, but the inhibition is not due to an increase in clathrin-mediated endocytosis of Maxi K, but likely due to enhancing its lysosomal degradation. 21670298_Myristoylation occurs mainly at hSlo1 intracellular loop 1 or 3, and is an additional mechanism for channel surface expression regulation 21708048_Genome wide association study identifies KCNMA1 contributing to human obesity 21724437_The BK(Ca) K(+) channel was impaired in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome cells as reflected by reduced single channel conductance and a 50 mV rightward shift in the channel activation voltage. 21757754_the nongenomic PI3K signaling pathway plays a role in estrogen/hERalpha-stimulated hSlo1 gene expression; whereas c-Src activity leads to hSlo1 gene tonic repression independently of estrogen, likely through ERK activation. 22074915_identified the calcium- and voltage-gated KCa1.1 channel (BK, Maxi-K, Slo1, KCNMA1) as the major potassium channel expressed at the plasma membrane of FLS isolated from patients with RA (RA-FLS). 22140451_Membrane cholesterol influences ethanol's modulation of BK. 22194818_These studies identify for the first time a central role for beta-catenin in mediating Slo surface expression. 22331907_Cym04 reversibly left-shifts the Slo1 half-activation voltage. It interacts with the S6/RCK linker & mimics site-specific shortening of this passive spring, transmiting force from the cytosolic gating ring structure opening the channel's gate. 22446331_BK(Ca) channels are involved in the response of podocytes to chronic hypoxia via the upregulation of the beta4-subunit. 22474334_Multiple cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motifs in cytosolic C tail of Slo1 subunit determine cholesterol sensitivity of Ca2+- and voltage-gated K+ (BK) channels. 22538239_The effects of protein kinase C on Slo surface expression might be indirect; when clustered on hair cell membranes, Slo contributes to increasing amounts of channel clusters on high-frequency responsiveness of hair-cell membranes. 22710124_TM1 of the beta2-subunit physically binds to the transmembrane S1 domain of the alpha-subunit of BK potassium channels 22896041_Phosphodiesterase blockade causes relaxation of human urinary bladder smooth muscle by increasing transient K(Ca)1.1 channel current activity, hyperpolarizing cell membrane potential, and decreasing the global intracellular Ca(2+). 22899999_enhanced expression of KCNMA1 correlates with and contributes to high proliferation rate and malignancy of breast cancer. 23232643_whole-cell current, spontaneous transient outward current, and Ca(2+) sensitivity of BK(Ca) channels are reduced in human vascular smooth muscle cells. This may account for the dysfunction of artery relaxation in primary hypertension. 23237801_These results strongly suggest that cav3 possesses direct interaction with KCa1.1, presumably at the same domain for cav1 binding. 23267835_BK(Ca) as a crucial part of the signaling cascade of LH/hCG in Leydig cells. 23508624_HIV and methamphetamine -induced elevated miR-9 lead to suppression of miR-response element-containing splice variants of KCNMA1 23626738_A novel Cav3-KCa1.1 signaling complex has been identified where Cav3-mediated calcium entry enables KCa1.1 activation over a wide range of membrane potentials. 23831469_BK-IS1 (44-113) alpha subunit has been over-expressed using a bacterial system and purified in the presence of detergent micelles for multidimensional heteronuclear nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) structural studies. 23992640_A molecular and functional link between BKCa channel and IP3R3 in cancer cells as an important mechanism for tumor cell proliferation. 24067659_The SLO1 gating ring is not required for voltage activation but is required for Ca2+ and Mg2+ activation. 24127525_Here we examined the action of docosahexaenoic acid on the Slo1 channel without any auxiliary subunit and sought to elucidate the biophysical mechanism and the molecular determinants of the DHA sensitivity. 24137539_show that Slo1 is localized to the sperm flagellum and is inhibited by progesterone. Inhibition of hKSper by progesterone may depolarize the spermatozoon to open the calcium channel CatSper 24260325_The reduced KCa1.1 channel protein expression was also observed. 24375290_We conclude that arachidonic acid itself selectively activates the beta1-associated BKCa channel, destabilizing its closed state probably by interacting with the beta1-subunit, without modifying the channel voltage sensitivity 24414257_Overexpression of KCNMA1, the pore-forming subunit of BK, overcame the reduction of airway surface liquid volume induced by IFN-gamma. 24476761_Bisphenol A activates BK alpha via an extracellular site and that Bisphenol A-sensitivity is increased by the beta1 subun 24569989_N-terminal isoforms of the large-conductance Ca(2)-activated K channel are differentially modulated by the auxiliary beta1-subunit. 24602615_Activation of GalR2 leads to elevation of intracellular Ca(2+) due to Ca(2+) efflux from endoplasmic reticulum through IP3R sequentially opening BK alpha channels. 24696148_Overexpression of JAK2 in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells significantly enhanced BK channel mRNA and protein abundance. 24705869_hSlo1c associates with Cav-1 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells.A 57-amino acid (966-1022) fragment in hSlo1c was identified to be critical for hSlo1c/Cav-1 interaction. 24759175_Recombinant martentoxin selectively blocks KCNMA1/KCNMB4 channels. 25070892_our results strongly suggest that AT1R regulates BK channels through a close protein-protein interaction involving multiple BK regions and independent of G-protein activation. 25345746_DS-201 selectively targets the pore-forming alpha subunit of human BKCa channels, thus enhancing the channel activities and increasing the subunit expression and trafficking. 25511389_The present study revealed that 11,12-EET targets the TRPV4-TRPC1-KCa1.1 complex to induce smooth muscle cell hyperpolarization and vascular relaxation in human LIMAs. 25796627_Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid enhanced the expression of malignant genes such as KCNMA1 in lung cancer cells remaining after treatment, creating a more drug-resistant state. 26009545_Suggest that BK channel modulation by auxiliary gamma subunits depends on intra- and/or juxta-membrane mechanisms. 26386726_MiR-31 represses KCNMA1 expression. 26390131_Results indicate that silencing BKCa (KCa1.1) inhibits cell mobility, while silencing IKir (Kir2.1) increases cell mobility in human cardiac c-kit+ progenitor cells. 26893360_High BK channel is associated with glioblastoma. 26993604_High BKCA expression is associated with breast cancer. 27217576_By introducing lanthanide binding tags in the extracellular region of the alpha- or beta1-subunit, we determined (i) a basic extracellular map of the BK channel, (ii) beta1-subunit-induced rearrangements of the voltage sensor in alpha-subunits, and (iii) the relative position of the beta1-subunit within the alpha/beta1-subunit complex. 27233075_BKCa has a role in promoting growth and metastasis of prostate cancer through facilitating the coupling between alphavbeta3 integrin and FAK 27245839_Results show that reduced miR-17 expression is correlated with increased expression of KCNMA1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Computational analysis identified KCNMA1 gene is a direct target of miR-17. 27537208_GSK3b may up-regulate BK channels, an effect disrupted by lithium or additional expression of AKT and possibly participating in the regulation of cell volume and excitability. 27567911_Our report defines a novel autosomal recessive KCNMA1-related epileptic phenotype that encompasses cerebellar atrophy without paroxysmal dyskinesia, and highlights the sensitivity of the developing brain to both increased and decreased activity of the KCNMA1-encoded channels 27592226_A directed proteomic approach discovered the novel interaction of BKCa with Tom22, a component of the mitochondrion outer membrane import system, and the adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT). 27729549_Oxidant signaling underlies PKGIalpha modulation of Ca2+ sparks and BKCa in myogenically active arterioles 27758860_These findings provide significant new evidence that BKalphaDeltae2 can modulate cellular responses to physiological stimuli in human chondrocyte and contribute under pathophysiological conditions, such as osteoarthritis. 27763639_These results identify KCa1.1 channels as crucial regulators of skeletal myogenesis. 28028617_Implicating both KCa1.1 and KCa3.1 channels. 28075010_Thiourea derivative, compound 326, stimulates the activity of large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels. 28231797_Study identified a novel tumor suppressive gene, KCNMA1, which is frequently inactivated in gastric cancer because of promoter methylation. KCNMA1 exerts a tumor suppressive function by regulating the PTK2 expression to activate the PI3K-AKT pathway. 28428266_These data outline a new signaling mechanism by which KCa1.1 regulates beta1-integrin function and therefore invasiveness of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs). 28474046_Heme-independent activation of the CFTR channel and the Slo1 BKCa channel by carbon monoxide (CO) may represent two different modes of gating regulation of ion channels by CO. In the case of CFTR, Fe3+ is bound to the R-ICL3 interface.15,16 This interfacial Fe3+ site is formed by traditional coordination ligands such as H950 and H954 from ICL3 and C832 and D836 from the R domain.[Review] 28750098_These results provide further insights into the mechanism of modulation of the different N-terminal regions of the BKCa channel by beta-subunits. 28966112_Data suggest that large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels, alpha subunit (BK channel) mutations affect the Ca2 +-sensing more than the voltage- sensing mechanism. 29211342_Data suggest that BKCa channels play important role in cell cycle progression and cell self-renewal in cardiac stem cells. 29330545_KCNMA1 mutation causes epilepsy and changes voltage gating but not calcium sensitivity. 29477869_An important role of BKCa in proliferation and migration of endometrial cancer HEC-1-B cells. 30445932_BKCa and the key downstream effectors p-ERK1/2 could be involved in important signaling pathways. 31136842_Side-chain oxidized oxysterols inhibited the activity of Slo1 BK channels. 31152168_LoF KCNMA1 variants are associated with a new syndrome characterized by a broad spectrum of neurological phenotypes and developmental disorders. LoF variants of KCNMA1 cause a new syndrome distinctly different from gain-of-function variants in the same gene. 31509109_These results indicate that Ca(2+) sensor occupancy has a strong impact on voltage-sensing domain activation through a coordinated interaction mechanism in which Ca(2+) binding to a single alpha-subunit affects all voltage-sensing domains equally. 31815672_This study presents cryo-EM structures of Slo1 in complex with the auxiliary protein, beta4. Four beta4, each containing two transmembrane helices, encircle Slo1, contacting it through helical interactions inside the membrane. 31851553_Comparative gain-of-function effects of the KCNMA1-N999S mutation on human BK channel properties. 32132200_Study identified single loss-of-function mutation (BKG354S) in KCNMA1, in a child with congenital and progressive cerebellar ataxia with cognitive impairment. Study in mouse model and multiple human and rat cell lines using recombinant mutant protein and gene knockdown revealed that loss-of-function KCNMA1 mutation causes ataxia and acts by reducing mitochondrial and subsequently cellular viability. 32513714_Coupling of Ca(2+) and voltage activation in BK channels through the alphaB helix/voltage sensor interface. 32586284_Opening large-conductance potassium channels selectively induced cell death of triple-negative breast cancer. 32597752_Aromatic interactions with membrane modulate human BK channel activation. 32933717_Functional coupling between BKCa and SOC channels. 32958651_Melatonin promotes sleep by activating the BK channel in C. elegans. 33076484_Differences in Gating Dynamics of BK Channels in Cellular and Mitochondrial Membranes from Human Glioblastoma Cells Unraveled by Short- and Long-Range Correlations Analysis. 33248202_Dynamical diversity of mitochondrial BK channels located in different cell types. 33660797_Upregulation of KCNMA1 facilitates the reversal effect of verapamil on the chemoresistance to cisplatin of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. 33974928_Piezo1 and BKCa channels in human atrial fibroblasts: Interplay and remodelling in atrial fibrillation. 34035423_Single channel properties of mitochondrial large conductance potassium channel formed by BK-VEDEC splice variant. 34181803_Ca(2+) -activated K(+) channel KCa 1.1 as a therapeutic target to overcome chemoresistance in three-dimensional sarcoma spheroid models. 34445066_TRPM2 Oxidation Activates Two Distinct Potassium Channels in Melanoma Cells through Intracellular Calcium Increase. 34499417_Two novel presentations of KCNMA1-related pathology--Expanding the clinical phenotype of a rare channelopathy. 34623245_The Changes of Gene Expression and Protein Level of Stretch-Activated Chloride Channel in Atrial Myocardium of Dogs with Atrial Fibrillation. 34948357_KCa1.1 K(+) Channel Inhibition Overcomes Resistance to Antiandrogens and Doxorubicin in a Human Prostate Cancer LNCaP Spheroid Model. 35156297_Identification and functional analysis of two new de novo KCNMA1 variants associated with Liang-Wang syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000063142 |
Kcnma1 |
140.770551 |
0.3843676399 |
-1.379441 |
0.157682841 |
76.772807 |
0.00000000000000000191800428943033293617062588402691026553738649653411702661331972308289550710469484329223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000015815499056978612016279641593267666421892804362744032464771493096122867427766323089599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.3747361 |
7.6901323 |
200.0709387 |
13.4112228 |
| ENSG00000156218 |
57188 |
ADAMTSL3 |
protein_coding |
P82987 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to be involved in extracellular matrix organization. Located in intracellular membrane-bounded organelle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57188; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198] |
14667842_Highest expression of ADAMTSL3 was found in liver, kidney, heart and skeletal muscle. 17597111_ADAMTSL3 is expressed in numerous tissues, suggesting a broader regulatory role than in colorectal epithelium alone, and that colorectal cancer has both structural mutations as well as decreased expression of ADAMTSL3. 18391952_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20397748_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21239144_The results of this study suggested that the ADAMTSL3 as a candidate gene for schizophrenia. 24793337_Compared with the George-Abraham' study [2012], ADAMTSL3 might be more related to the cardiac disorders in tetrasomy 15q patients 29162515_A137T in ADAMTSL3 may be a susceptibility mutation for diabetes. 32266537_knocking out either the ADAMTSL3 or PTEN genes promoted either the proliferation or metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, respectively |
ENSMUSG00000070469 |
Adamtsl3 |
11.117540 |
0.3899871816 |
-1.358501 |
0.604199538 |
4.993555 |
0.02544188271944017309955654582154238596558570861816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044514247147811401850159285231711692176759243011474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8265521 |
2.1108239 |
14.6005284 |
3.4576193 |
| ENSG00000156234 |
10563 |
CXCL13 |
protein_coding |
O43927 |
FUNCTION: Chemotactic for B-lymphocytes but not for T-lymphocytes, monocytes and neutrophils. Does not induce calcium release in B-lymphocytes. Binds to BLR1/CXCR5. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
B lymphocyte chemoattractant, independently cloned and named Angie, is an antimicrobial peptide and CXC chemokine strongly expressed in the follicles of the spleen, lymph nodes, and Peyer's patches. It preferentially promotes the migration of B lymphocytes (compared to T cells and macrophages), apparently by stimulating calcium influx into, and chemotaxis of, cells expressing Burkitt's lymphoma receptor 1 (BLR-1). It may therefore function in the homing of B lymphocytes to follicles. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:10563; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR10 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031735]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; CXCR3 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048248]; CXCR5 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031724]; fibroblast growth factor binding [GO:0017134]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; B cell chemotaxis [GO:0035754]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chronic inflammatory response [GO:0002544]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; endothelial cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor [GO:0035768]; germinal center formation [GO:0002467]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; lymphocyte chemotaxis across high endothelial venule [GO:0002518]; negative regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis to fibroblast growth factor [GO:2000545]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033634]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of integrin activation [GO:0033625]; positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010820]; regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045765]; regulation of humoral immune response [GO:0002920] |
11877260_The effect of surrogate antigen on B-cell chemotaxis response to BCA-1 is biphasic: After an initial phase of suppression, chemotaxis toward BCA-1 is strongly up-regulated. 12393412_expression by malignant B-lymphocytes and vascular endothelium in primary central nervous system lymphoma 12732660_overlapping role with interleukin 7 recedptor alpha and CCR7 ligands in lymph node development 12949249_CXCL13 displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14763921_CXCR5 and CXCL13 play an essential role in maintaining B- and T-cells in lymphocytic infiltrates and ectopic follicles in thyroid tissue from patients affected by autoimmunity. 15284119_most CXCL13-expressing cells in rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis are of monocyte/macrophage lineage. 15780119_Potenetial role of CXCL13 and its specific receptor CXCR5 in recruitment of B cells in renal allograft rejection. 15929033_persistent production of CXCL13 and IgG within infected tissue, two characteristics of ectopic germinal centers, are definitive features of Lyme neuroborreliosis 15934082_The data support expression of CXCL13 and CCL21 in regulating the progressive lymphoid organization and maintenance of periductal foci in Sjogrens syndrome. 15965952_Data suggest that CXCL12 and CXCL13 may directly modulate cellular proliferation and collagen type I in osteoarthritis patients. 16318584_elevated levels of CXCL13 could cause impaired or altered trafficking of B cells during HIV infection and could contribute to the previously reported loss of CXCR5 16543475_a high CXCL13 production by epithelial cells could be responsible for germinal center formation in myasthenia gravis thymus 17082584_CXCL13 and CCL19 cooperatively induce significant resistance to TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis in acute and chronic B cell leukemia CD23+CD5+ B cells, but not in the cells from cord blood. 17082648_CXCL13 promotes recruitment of B and T lymphocytes within the islets of Langerhans of transgenic mice. 17474076_prostate-associated lymphoid aggregates, frequently below the epithelia, arranged in B cell follicles expressed CXCL13, and parafollicular T cell areas showed CCL21 expression. 17495955_CXCL13 and CCL21 are expressed in ectopic lymphoid follicles in cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders. 17592274_Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma T cells localize in the skin allowing accurate diagnosis in skin specimens using CXCL13 immunostaining on paraffin-embedded tissues. 17652619_CXCR5 plays a role in Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cell positioning and cognate interactions between CLL and CXCL13-secreting CD68+ accessory cells in lymphoid tissues. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17709502_CCL19 plus CXCL13 regulate interaction between B-ALL CD23+CD5+ B cells and CD8+ T cells by inducing activation of PEG10, in turn, resulting in IL-10 overexpression and impairment of tumor-specific cytotoxicity in syngeneic CD8+ T cells. 17949547_knee synovial fluid levels of CXCL 13 were higher in Rheumatoid arthritis and Behcets disease patients compared to Osteoarthritis patients 18172003_These findings indicate a previously unreported role for the BAFF/BAFF-R pair in mature B-cell chemotaxis. 18292286_AITL is a morphologically heterogeneous T-cell lymphoma commonly expressing CXCL13 and CD10; high level of CD10 and CXCL13 did not affect survival. 18354239_in salivary gland MALT lymphoma the lymphoid chemokines CXCL13 and CCL21 are directly implicated in the organization of ectopic reactive lymphoid tissue 18528326_Expression of CXCL13 was found in cells of a dendritic-like morphology. 18550853_up-regulation of CXCL13 gene expression is a feature of HCV-infected patients. Higher levels of this chemokine in liver as well as skin of patients with active mixed cryoglobulinemia vasculitis suggest a possible interrelation. 18566383_report an effective method to establish human allo-reactive Th17 cell clones and demonstrate that human Th17, but not Th1 or Th2, cells express B cell chemoattractant CXCL13, by using DNA chips 18668547_CCL23, M-CSF, TNFRSF9, TNF-alpha, and CXCL13 are predictive of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity and may be useful in the definition of disease subphenotypes and in the measurement of response to therapy in clinical studies. 18757429_experiments performed to investigate the survival, adhesion, and metalloproteases secretion indicate that CXCL13 combined with CCL19 and CCL21 mainly affects the chemotaxis of Sezary syndrome cells 18773213_Survival after UVA irradiation was greater in human keratinocytes compared to mouse skin with no S100A2 expression, showing a protective role for S100A2. A S100A2-dependent difference was observed in the induction of Cxcl13 transcripts in transgenic mice. 18780835_Altered expression of the chemokine receptor-ligand pair, CXCR5/CXCL13, may participate in the establishment of B-cell dysfunctions during HIV-1 infection. 18781150_CXCL13 is overexpressed in the tumour tissue and in the peripheral blood of breast cancer patients 18792075_study demonstrates that CXCL13 is produced by dysplastic and neoplastic follicular dendritic cells and can be instrumental in recruiting intratumoural CXCR5+ lymphocytes 19031272_CXCL13 dramatically increased in intra-amniotic infection/inflammation but did not change with spontaneous parturition. 19095563_The similar pattern of expression of CXCL13 and PD-1 in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma provides further evidence that AITL is a neoplasm derived from germinal-center T-helper cells. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19375853_the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis is significantly associated with prostate cancer progression 19575892_Expressions of CXCL13, CD10 and bcl-6 were significantly higher in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma patients than in peripheral T-cell lymphoma patients. 19671684_NFATc3 is a downstream target of the CXCL13/CXCR5 axis to stimulate RANKL expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas cells. 19773382_Production of CXCL13 within the CNS of CNS lymphoma patients, which decreases with response to therapy; CXCL13 may represent a marker for further diagnostic and prognostic studies. 19774453_elevated production is correlated with systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity 19805441_We conclude that the serum levels of the B cell chemokine CXCL13 are associated with active multiple sclerosis 19807029_New putative control elements in the promoter OF CXCL13 chemokine gene, a target of alternative NF-kappaB pathway 19816883_data implicate a functional role for CXCL13 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tumor invasion into bone and may be a potential therapeutic target to prevent osteolysis associated with OSCC tumors in vivo 19955043_Results suggest that BLC/CXCL13 as well as its corresponding receptor, CXCR5, may play important roles in the pathogenesis of SLE and in lupus nephritis. 19965843_The study confirms the relevance of CXCL13 as a diagnostic biomarker of neuroborreliosis and suggests that CSF CXCL13 in NB is linked to duration of disease 19996075_Chemokine CXCL13 may play a major role in recruitment of B cells and T-cell subsets expressing the chemokine receptor CXCR5 to the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. 20011704_the fallopian tissue infected with C. trachomatis expressed CXCL13 and other characteristics of tertiary lymphoid tissue. 20042073_our study suggests a key role of CXCL13 in B cell migration to sites of infection as shown here for the cerebrospinal fluid of acute Lyme neuroborreliosis patients 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20109310_expression up-regulated in polyp tissue of chronic rhinosinusitis 20223524_Both protein and mRNA of CXCL13 and CXC chemokine receptor 5 (CXCR5) in the thymic tissues were significantly higher in MG patients with lymphoid hyperplasia than those with thymoma. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400187_Human neural precursor cells express the CXCL13 receptor and migrate across brain endothelial cells in response to CXCL13 expression. 20412587_CXCL13 caused CXCR5-dependent activation of the PI3Kp85alpha in prostate cancer cells 20495539_Aberrant expression of selectin E, CXCL1, and CXCL13 occurs in chronic endometritis. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21078761_stable serum marker for disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus patients, but concomitant infections can also lead to increased CXCL13 levels 21084753_found enhanced plasma levels of CXCL13 in patients suffering from type IV lupus nephritis 21135023_CXCL13 was associated with disease exacerbations and unfavourable prognosis in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. 21191639_CXCL10 and CXCL13 Expression were highly up-regulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in acute rejection and poor response to anti-rejection therapy. 21211990_Data show negative correlations for BAFF concentration vs blood B cell percentage and serum CXCL13 concentration. 21305530_Our findings indicate that CXCL13 is a novel serologic marker predictive of rheumatoid arthritis severity. 21320077_CXCL13 serum levels show great variance even in the healthy population and are not indicative of active neuroborreliosis. 21372118_BAFF/CXCL12 may work in concert to affect B-cell homeostasis in multiple sclerosis and contribute to the pathophysiology of the disease. 21576203_Data indicate that an increased level of CXCL13 is a feature of systemic lupus erythematosus that correlates with disease activity and severity. 21642390_these results add new information about the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis in neuroblastic tumors and in the crosstalk between neuroblastic and stromal cells. 21645150_Our results show CXCL13-mediated PCa cell invasion requires Akt and ERK12 activation and suggests a new role for DOCK2 in proliferation of hormone-refractory CXCR5-positive PCa cells. 22000402_Expression of CXCL13 is significantly increased in types B1 and B2 thymoma patients with generalized myasthenia gravis, compared to those with ocular myasthenia gravis. 22008312_CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL12 and CXCL13 chemokines are biomarkers in serum and cerebrospinal fluid in patients with tick borne encephalitis 22036953_Neuromyelitis optica patients with higher relapse rates exhibit higher CXCL13 concentrations in their cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) as well as a trend of increased disease disability with increased CSF CXCL13 levels. 22044682_Data show that the mean CXCL13 concentration in sera from Sjogren's patients was 170 pg/ml, compared to 92.0 pg/ml for sera from healthy controls. 22330139_c-Myc activation through CXCL13-CXCR5 signaling axis stimulates RANKL expression in stromal/preosteoblast cells. Thus, our results implicate CXCL13 as a potential therapeutic target to prevent OSCC invasion of bone/osteolysis 22335599_Elevated sCXCL13 levels were detected up to 2 years prior to PTLD diagnosis and correlated well with response to cytoreductive treatment in individual patients. sCXCL13, thus, may be a readily available surrogate marker for the diagnosis of PTLD 22591862_Elevated CSF CXCL13 levels reflect a strong humoral immune response and cell recruitment to the central nervous system compartment during neuroinflammation. 22607768_The CXCL13-CXCR5 axis is associated with classic determinants of poor prognosis, such as high grade, hormone receptor negativity, and axillary node involvement. 22718279_findings show decidual stromal cells and follicular dendritic cells shared some of each other's distinctive features such as expression of B cell-activating factor, C-X-C motif chemokine 13 secretion and the capacity to rescue B cells from apoptosis 22840692_Levels of CXCL13 are increased in carotid atherosclerosis both systemically and within the atherosclerotic lesion. Based on our in vitro findings, we hypothesize a potential plaque stabilizing effects of CXCL13-CXCR5 interaction 22913878_Data indicate that EBI2 expression modulates CXCL13 binding affinity to CXCR5. 22975753_CXCL13, MMP-3 and TIMP-1 distinguish active ANCA-associated vasculitis from remission better than the other markers studied, including ESR and CRP. 23109547_The Blc appeared to be not fully compatible with our approach, owing to problems with refolding of the hybrid constructs, loop-grafted versions of OmpA delivered encouraging results 23175382_we found correlations between high mean levels of CXCL13 in the CSF and some of the genotypes that are associated with an increased risk of multiple sclerosis 23189125_Interruption of CXCL13-CXCR5 axis increases upper genital tract pathology and activation of NKT cells following chlamydial genital infection. 23250934_Increased serum CXCL13 levels are associated with HIV-associated non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma. 23322500_CXCL13 correlated with CSF WBC in neuromyelitis optica, the IgG index in multiple sclerosis and serum CXCL13 was elevated in neuromyelitis optica. 23570798_Elevated CXCL13 expression is associated with central nervous system lymphomas. 23904442_CXCL13 may be pathogenically involved in SS and may serve as a new marker and a potential therapeutic target. 23925290_CXCL13 is expressed in an age-dependent manner in both adult mouse and human hepatic macrophages during hepatitis B infection. 24138885_The CXCL13 and IL21 expression is pivotal for the T-helper/B cell axis correlating with survival. 24337540_CXCL13 stimulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via RANKL-Src axis in breast cancer cell lines. 24393484_overexpressed in myasthenia gravis thymus 24628285_CXCL13 is increased and is a prognostic biomarker in patients with Idiopathic Pulm Fibrosis (IPF), and more so than in patients with COPD. This contrast indicates CXCL13 overexpressions are intrinsic to IPF, rather than an epiphenomenon of lung injury. 24732574_Suggest that platelet-mediated signaling through CXCR5 may be active in vivo during plaque destabilization, enhancing the anti-inflammatory effects of CXCL13. 24764267_Synovial CXCL13 appears to be a marker of a more severe pattern of rheumatoid arthritis disease, characterized by increased lymphocyte activation and bone remodelling beyond the level of conventional markers of inflammation. 24766912_marked elevations of serum CXCL13 levels resided nearly completely within the seropositive population of rheumatoid arthritis patients 24907903_the CXCL13 concentration was significantly This study demonistrated that elevated in the CSF of the group with aseptic meningoencephalitis compared with the group with aseptic meningitis. 25010623_Expression features of CXCR5 and its ligand, CXCL13 associated with poor prognosis of advanced colorectal cancer 25031316_In the presence of endometriosis, proliferative-phase endometrial expression of CXCL13 markedly increased. 25077417_three SNPs (rs497916, rs3922, rs676925) in CXCR5 and one SNP (rs355687) in CXCL13 were associated with hepatitis B vaccine efficacy 25217476_MMP3 and CXCL13 are systemic biomarkers that reflect the aggregate burden of these pathological features across total lung tissue. 25249397_Data indicate that patients with high baseline plasma C-X-C motif chemokine 13 (CXCL13) levels had an improved chance of remission after 2 years. 25267627_Myofibroblast activation and CXCL13 expression also occur in the normal prostate after androgen deprivation, and CXCL13 is expressed by myofibroblasts in human prostate cancer. 25271023_After validation in larger patient groups, CXCR5 and CXCL13 may prove useful as biomarkers for nonsmall cell lung carcinoma Correspondingly, blockade of this axis could serve as an effective therapy for nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. 25433721_CXCL13 up-regulation may be differently linked to the development of primary central nervous system lymphomas and to the accumulation of tumor-infiltrated lymphocytes. 25476740_our findings suggest that CXCL13-CXCR5 axis promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells, probably via PI3K/AKT pathway 25533286_a direct target of IRF5 resulting in the enhanced recruitment of B and T cells to IRF5-positive tumor-conditioned media 25627620_In primary biliary cirrhosis, CXCL13 promotes aggregation of CD19(+) B cells and CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells. 25667414_Data show that chemokine CXCL13 production by monocytes required toll-like receptor 7 activation and secretion of interferon-alpha. 25769888_Therefore, CSF CXCL13 concentrations could improve the diagnosis of ANS in HIV-infected patients 25812350_highly significant stepwise progressive increase in CXCL 13 level was recorded through controls, inactive SLE and active disease (P |
ENSMUSG00000023078 |
Cxcl13 |
130.638550 |
13.1650210566 |
3.718638 |
0.210111905 |
388.655719 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001623790983011551736084101441750366430966532277399721016920163494126318574120585943229296582351321208145235556399329044256808439828411175895673382969656464426292175918027248520513263117842812509543758358523805104128845400168756896164268255233765 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000593246408644814437807427149801096256619056179810502454738320908430169730088062494304772028787567656137784909992657127394096325188663629398888104721741915429452723762230693608488839814193434669390381204441596921239643336321023525670170783996582 |
Yes |
No |
243.3730867 |
31.5738921 |
18.6283297 |
2.2486573 |
| ENSG00000156265 |
56911 |
MAP3K7CL |
protein_coding |
P57077 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Located in cytosol and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56911; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634] |
32401115_Genome-wide identification of lncRNAs and mRNAs differentially expressed in human vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by high phosphorus. |
|
|
442.801655 |
0.1772282087 |
-2.496320 |
0.091421397 |
815.987861 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001803245929005616415442881343127428427487448448429443298883760133344461867620190480905778780115874036805849919428209330042624502369092162514086009537482 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001446516843050157585551380314917207708969576455237732075029750109278569661986288446015158930114028406175564860608561084745994852761932899557842651164751 |
Yes |
Yes |
134.7115338 |
8.4054531 |
765.5662213 |
27.0787933 |
| ENSG00000156298 |
7102 |
TSPAN7 |
protein_coding |
P41732 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in cell proliferation and cell motility. |
Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. This encoded protein is a cell surface glycoprotein and may have a role in the control of neurite outgrowth. It is known to complex with integrins. This gene is associated with X-linked cognitive disability and neuropsychiatric diseases such as Huntington's chorea, fragile X syndrome and myotonic dystrophy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7102; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
14735593_The role of TMSF2 in mental retardation 19339915_coding mutations in TSPAN7 are not associated with our cohort of autism patients 19535787_associated with spermatozoa 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20479760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20630051_The interaction of VP26 with tetraspanin-7 plays an essential role in normal HSV-1 replication. 20850477_Studies indicate that The thymus leukemia (TL) antigen and CD8alphaalpha are interacting surface molecules that are expressed at the frontline of the mucosal immune system. 20951001_TM4SF2 was identified as a putative antigenic target in Wegener's granulomatosis 22213152_Loss of TSPAN7 is associated with metastasis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. 22445342_This study identified that TSPAN7 as a key molecule for the functional maturation of dendritic spines via PICK1 and ampa receptor trafficking. 25637218_Elevated TSPAN7 may be associated with better outcomes for multiple myeloma patients. 28223337_These results disclosed a previously uncharacterized role of TSPAN7 in the regulation of the expression and functional activity of DRD2 by postendocytic trafficking. 28620031_The role of TSPAN7 in immune system response to HIV-1 is reviewed. TSPAN7 appears to be a positive regulator of actin nucleation and stabilization, through the ARP2/3 complex. By doing so, TSPAN7 limits HIV-1 endocytosis and maintains viral particles on actin-rich dendrites for an efficient transfer toward T lymphocytes. 32181159_Dendritic Cell Maturation Regulates TSPAN7 Function in HIV-1 Transfer to CD4(+) T Lymphocytes. 32314012_Autoimmunity to tetraspanin-7 in type 1 diabetes. 32468130_Tetraspanin 7 and its closest paralog tetraspanin 6: membrane organizers with key functions in brain development, viral infection, innate immunity, diabetes and cancer. 36264270_Loss of tetraspanin-7 expression reduces pancreatic beta-cell exocytosis Ca[2+] sensitivity but has limited effect on systemic metabolism. |
ENSMUSG00000058254 |
Tspan7 |
59.155168 |
0.3542135839 |
-1.497309 |
0.223019237 |
46.256959 |
0.00000000001037175351886366131954532357590010476812436568394559799344278872013092041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000057400480666827013459218957818698167959448053210280704661272466182708740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.7397910 |
4.5333967 |
87.4094217 |
8.1405771 |
| ENSG00000156398 |
118980 |
SFXN2 |
protein_coding |
Q96NB2 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial amino-acid transporter that mediates transport of serine into mitochondria (PubMed:30442778). Involved in mitochondrial iron homeostasis by regulating heme biosynthesis (PubMed:30570704). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30442778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30570704}. |
Acetylation;Amino-acid transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable serine transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in mitochondrial transmembrane transport. Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:118980; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022889]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; mitochondrial transmembrane transport [GO:1990542]; serine import into mitochondrion [GO:0140300] |
12670026_molecular cloning of SFXN2 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30570704_SFXN2 functions in mitochondrial iron metabolism by regulating heme biosynthesis. 36163342_Elevated SFXN2 limits mitochondrial autophagy and increases iron-mediated energy production to promote multiple myeloma cell proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000025036 |
Sfxn2 |
36.280978 |
2.4419013448 |
1.288005 |
0.313857272 |
16.484062 |
0.00004906075549088814594187596407337537129933480173349380493164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000141379500298552710727678638491511264874134212732315063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
47.5011843 |
9.2510776 |
19.6224184 |
2.6761497 |
| ENSG00000156471 |
9791 |
PTDSS1 |
protein_coding |
P48651 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes a base-exchange reaction in which the polar head group of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) or phosphatidylcholine (PC) is replaced by L-serine (PubMed:19014349, PubMed:24241535). Catalyzes mainly the conversion of phosphatidylcholine (PubMed:19014349, PubMed:24241535). Also converts, in vitro and to a lesser extent, phosphatidylethanolamine (PubMed:19014349, PubMed:24241535). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19014349, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24241535}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Endoplasmic reticulum;Intellectual disability;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phospholipid biosynthesis;Phospholipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Phospholipid metabolism; phosphatidylserine biosynthesis. |
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the formation of phosphatidylserine from either phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine. Phosphatidylserine localizes to the mitochondria-associated membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, where it serves a structural role as well as a signaling role. Defects in this gene are a cause of Lenz-Majewski hyperostotic dwarfism. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:9791; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; L-serine-phosphatidylcholine phosphatidyltransferase activity [GO:0106258]; L-serine-phosphatidylethanolamine phosphatidyltransferase activity [GO:0106245]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; phosphatidylserine biosynthetic process [GO:0006659] |
19014349_Purification and characterization of human phosphatidylserine synthases 1 and 2. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24241535_Gain-of-function missense mutations in the phosphatidylserine synthase 1 (PTDSS1) gene cause Lenz-Majewski syndrome. 26742492_RYR2, PTDSS1 and AREG are autism susceptibility genes that are implicated in a Lebanese population-based study of copy number variations in this disease. 27044099_PSS1 mutations not only affect cellular PS levels and distribution but also lead to a more complex imbalance in lipid homeostasis by disturbing PI4P metabolism. 29341480_we report here three patients with LMS and heterozygous mutations in PTDSS1. We describe an adult phenotype and two novel PTDSS1 mutations. We suggest that LMS should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a newborn with CL. 31231513_used transpose-mediated transgenesis to attempt to stably express wild-type and mutant forms of human PTDSS1 ubiquitously or specifically in chondrocytes, osteoblasts or osteoclasts in zebrafish 34516042_Topology of phosphatidylserine synthase 1 in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. |
ENSMUSG00000021518 |
Ptdss1 |
2717.928578 |
4.1280752734 |
2.045469 |
0.039610906 |
2656.701066 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4279.1527921 |
134.6490530 |
1043.8251885 |
25.1376338 |
| ENSG00000156500 |
159091 |
PABIR3 |
protein_coding |
Q6P4D5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable protein serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of catalytic activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:159091; |
protein serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004865] |
|
ENSMUSG00000036013 |
Fam122c |
61.479613 |
0.3153348087 |
-1.665044 |
0.478801979 |
10.986790 |
0.00091763615826419178515827024256168442661873996257781982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002151598045429622095559007988185840076766908168792724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.3606524 |
5.6893968 |
39.3609745 |
12.8028558 |
| ENSG00000156509 |
286151 |
FBXO43 |
protein_coding |
Q4G163 |
FUNCTION: Required to establish and maintain the arrest of oocytes at the second meiotic metaphase until fertilization. Acts by inhibiting the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin ligase. Probably recognizes and binds to some phosphorylated proteins and promotes their ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:34052850, PubMed:34595750). Plays a vital role in modulating the ubiquitilation of CCNB1 and CDK1 during gametogenesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CDI2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34052850, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34595750}. |
Disease variant;Meiosis;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Members of the F-box protein family, such as FBXO43, are characterized by an approximately 40-amino acid F-box motif. SCF complexes, formed by SKP1 (MIM 601434), cullin (see CUL1; MIM 603134), and F-box proteins, act as protein-ubiquitin ligases. F-box proteins interact with SKP1 through the F box, and they interact with ubiquitination targets through other protein interaction domains (Jin et al., 2004 [PubMed 15520277]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:286151; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; negative regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010948]; negative regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045835]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088] |
18550795_Cdc2 and Mos regulate Emi2 stability to promote the meiosis I-meiosis II transition 30878252_The mutation in FBXO43 is a causative factor of male infertility and teratozoospermia. 32253818_EMI2 expression as a poor prognostic factor in patients with breast cancer. 34052850_FBXO43 variants in patients with female infertility characterized by early embryonic arrest. 34595750_A homozygous loss-of-function mutation in FBXO43 causes human non-obstructive azoospermia. 34645483_Downregulation of the FBXO43 gene inhibits tumor growth in human breast cancer by limiting its interaction with PCNA. |
ENSMUSG00000048230 |
Fbxo43 |
76.005763 |
0.0461325921 |
-4.438070 |
1.310178219 |
8.730008 |
0.00313015057361650276754327926198584464145824313163757324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006673555173563424335048122060243258601985871791839599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.2943585 |
4.8428053 |
92.8720654 |
70.0754208 |
| ENSG00000156521 |
219743 |
TYSND1 |
protein_coding |
Q2T9J0 |
FUNCTION: Peroxisomal protease that mediates both the removal of the leader peptide from proteins containing a PTS2 target sequence and processes several PTS1-containing proteins. Catalyzes the processing of PTS1-proteins involved in the peroxisomal beta-oxidation of fatty acids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22002062}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Peroxisome;Protease;Reference proteome;Serine protease |
|
This gene encodes a protease that removes the N-terminal peroxisomal targeting signal (PTS2) from proteins produced in the cytosol, thereby facilitating their import into the peroxisome. The encoded protein is also capable of removing the C-terminal peroxisomal targeting signal (PTS1) from proteins in the peroxisomal matrix. The full-length protein undergoes self-cleavage to produce shorter, potentially inactive, peptides. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:219743; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0031998] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17255948_characterization of protease function and self-cleavage of mouse Tysnd1 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22002062_The proteolytic activity of oligomeric Tysnd1 is in turn controlled by self-cleavage of Tysnd1 and degradation of Tysnd1 cleavage products by PsLon. |
ENSMUSG00000020087 |
Tysnd1 |
58.428169 |
0.1369282111 |
-2.868508 |
0.729935331 |
13.382904 |
0.00025392821881361490399600655543110860890010371804237365722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000654669084661826461771227947394891089061275124549865722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7645073 |
7.5962897 |
115.9381663 |
39.2401978 |
| ENSG00000156642 |
27020 |
NPTN |
protein_coding |
Q9Y639 |
FUNCTION: Probable homophilic and heterophilic cell adhesion molecule involved in long term potentiation at hippocampal excitatory synapses through activation of p38MAPK. May also regulate neurite outgrowth by activating the FGFR1 signaling pathway. May play a role in synaptic plasticity (By similarity). Also acts as a chaperone for ATP2B1; stabilizes ATP2B1 and increases its ATPase activity (PubMed:30190470). Promotes localization of XKR8 at the cell membrane (PubMed:27503893). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27503893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30190470}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the Ig superfamily. The protein is believed to be involved in cell-cell interactions or cell-substrate interactions. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2009]. |
hsa:27020; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; inhibitory synapse [GO:0060077]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; cell-cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098632]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; type 1 fibroblast growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005105]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; dendrite self-avoidance [GO:0070593]; excitatory synapse assembly [GO:1904861]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:0060291]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045743]; positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048170]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of protein localization [GO:1903829]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; regulation of receptor localization to synapse [GO:1902683]; trans-synaptic signaling by trans-synaptic complex, modulating synaptic transmission [GO:0099557]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
17123723_NPTN may be involved in genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. 17196182_In human brain np65 is prominently present in cerebellum while np55 is the predominant isoform in mouse and rat cerebellum. 24514566_This study showed that Single nucleotide polymorphism in the neuroplastin locus associates with cortical thickness and intellectual ability in adolescents. 25040546_correct synaptic membrane protein localization, neuronal energy supply, expression of LTP and LTD, animal and human behaviour, and pathophysiology and disease--{review} 27503893_Xkr8-BSG/NPTN complex is required for phosphatidylserine scrambling in apoptotic cell membranes. 28779130_these results indicate that epilation induces McSCs activation through EDN3/EDNRB signaling and in turn leads to skin and hair hyperpigmentation. The findings suggest that EDN/EDNRB signaling may serve as a potential therapeutic target to promote repigmentation in hypopigmentation disorders. 30190470_Cryoelectron microscopy structure offers important insight into how the NPTN binds to the PMCA1. 30488668_Hippocampal expression of neuroplastin is altered in Alzheimer's disease. 30720226_Expression profiling of NPTNbeta showed significantly high expression levels in lung cancer cell lines. NPTNbeta has strong ability to induce cancer-related cellular events, including anchorage-independent growth, motility and invasiveness, in lung cancer cells in response to extracellular S100A8/A9, eventually leading to the expression of a cancer disseminative phenotype in lung tissue in vivo. |
ENSMUSG00000032336 |
Nptn |
1592.171285 |
2.5323627335 |
1.340484 |
0.045987633 |
855.989538 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003626047286485460472258831402658394726254485775833880661676045326547423599744761799430498142598748066048876605759291598843736843820580519963844 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003093668089510138317406381555818997415645621066460179684431890109095350480194383879975746479953498700447023921161389009311018368508255458061437 |
Yes |
No |
2338.1653373 |
67.3860677 |
930.1775705 |
21.1624038 |
| ENSG00000156650 |
23522 |
KAT6B |
protein_coding |
Q8WYB5 |
FUNCTION: Histone acetyltransferase which may be involved in both positive and negative regulation of transcription. Required for RUNX2-dependent transcriptional activation. May be involved in cerebral cortex development. Component of the MOZ/MORF complex which has a histone H3 acetyltransferase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10497217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11965546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16387653}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Chromosomal rearrangement;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a histone acetyltransferase and component of the MOZ/MORF protein complex. In addition to its acetyltransferase activity, the encoded protein has transcriptional activation activity in its N-terminal end and transcriptional repression activity in its C-terminal end. This protein is necessary for RUNX2-dependent transcriptional activation and could be involved in brain development. Mutations have been found in patients with genitopatellar syndrome. A translocation of this gene and the CREBBP gene results in acute myeloid leukemias. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:23522; |
MOZ/MORF histone acetyltransferase complex [GO:0070776]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleosome [GO:0000786]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; histone acetyltransferase activity [GO:0004402]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; histone H3K14 acetyltransferase activity [GO:0036408]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; peptide-lysine-N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0061733]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; histone H3 acetylation [GO:0043966]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; nucleosome assembly [GO:0006334]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of developmental process [GO:0050793]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of hemopoiesis [GO:1903706] |
15271374_role in regulating interleukin-5 expression 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17460191_MORF4 has a role in cellular aging, and MRG15 associates with both histone deacetylases and histone acetyl transferase complexes [review] 18794358_These findings indicate that BRPF proteins play a key role in assembling and activating MOZ/MORF acetyltransferase complexes. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21804188_Data show that H3 acetylation by Myst4 is important for neural, craniofacial, and skeletal morphogenesis, mainly through its ability to specifically regulating the MAPK signaling pathway. 21880731_Recognition of unmodified histone H3 by the first PHD finger of bromodomain-PHD finger protein 2 provides insights into the regulation of histone acetyltransferases monocytic leukemic zinc-finger protein (MOZ) and MOZ-related factor (MORF). 22077973_Whole-exome-sequencing identifies mutations in histone acetyltransferase gene KAT6B in individuals with the Say-Barber-Biesecker variant of Ohdo syndrome 22265014_By exome sequencing, we found de novo heterozygous truncating mutations in KAT6B. 22265017_we identified de novo mutations of KAT6B in five individuals with Genitopatellar syndrome. 22715153_Propose that haploinsufficiency or loss of a function mediated by the C-terminal domain causes the common features, whereas gain-of-function activities would explain the features unique to genitopatellar syndrome. Review. 23063713_These data suggest that the tandem of plant homeodomain 1/2 fingers play a role in MOZ and MORF histone acetyltransferase association with histon H3 regions enriched in acetylated marks. 23436491_Our results confirm the implication of KAT6B mutations in typical SBBYS syndrome and emphasize the importance of genotype-phenotype correlations at the KAT6B locus. 24150941_MORF double PHD finger binds to Histone H3 in a manner that is enhanced by acetylation of the lysine residues K9 and K14 24294372_KAT5 and KAT6B regulate prostate cancer cell growth through PI3K-AKT signaling. 24444492_The study showed that markers rs11001178 (MYST4) showed weak associations. 24458743_Similar to those observed in other genetic disorders resulting from KAT6B mutations. 24698832_The relationship between MYO1C and KAT6B suggests that the two are interacting in chromatin remodelling for gene expression in human masseter muscle. This is the nuclear myosin1 (NM1) function of MYO1C. 25424711_KAT6B sequence variants are being reported in the Say-Barber-Biesecker type of blepharophimosis mental retardation syndromes (SBBS) and in the more severe genitopatellar syndrome. 25840828_This study shown MYST4 to be the risk factor for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 26208904_Homozygous deletions of KAT6B and the loss of its mRNA occur in SCLC cell lines and primary tumors. KAT6B loss enhances cancer growth. Restoration induces tumor suppressor-like features involving a new type of histone H3 Lys23 acetyltransferase activity. 26334766_Kat6 c.3147G>A splice site mutation causes Say-Barber-Biesecker/Young-Simpson syndrome by inducing aberrant splicing. 27185879_Studies show that misregulation of MOZ/MORF results in tumorigenesis and developmental disorders. Results also provide evidence that these 2 proteins play important role in regulating cell proliferation and stem cell maintenance. [review] 27447113_chronic inflammation compromises unfolded protein response function through MORF-mediated-PERK transcription. 27452416_Our findings support that phenotypes associated with typical KAT6B disease-causing variants should be referred to as 'KAT6B spectrum disorders' or 'KAT6B related disorders', rather than their current SBBYSS and GTPTS classification 27880066_With ptosis, hypotonia, and developmental delay as the main diagnostic features of our patient, the effect of histone acetyltransferase-encoding KAT6B gene haploinsufficiency was suspected to have a significant role in determining the phenotype. 28286003_Study identified the double plant homeodomain finger (DPF) of the lysine acetyltransferase MORF as a reader of global histone H3K14 acylation. 28696035_KAT6B mutation is associated with Craniosynostosis. 29226580_The present report highlights the pivotal role of clinical genetics in avoiding clear-cut genotype-phenotype categories in syndromic forms of intellectual disability. In addition, it further supports the evidence that a continuum exists within the clinical spectrum of KAT6B-associated disorders 30569622_The clinical and genetic characterization of these patients could contribute to the understanding of the KAT6B-related disorders. 30921092_A novel pathogenic frameshift variant of KAT6B identified by clinical exome sequencing in a newborn with the Say-Barber-Biesecker-Young-Simpson syndrome. 31624313_Data indicate that the acetyltransferase function of the catalytic histone acetyltransferase KAT6B (MORF) subunit is positively regulated by the DPF domain of MORF (MORFDPF). 32424177_Further delineation of the clinical spectrum of KAT6B disorders and allelic series of pathogenic variants. 32448279_High methylation of lysine acetyltransferase 6B is associated with the Cobb angle in patients with congenital scoliosis. 32722658_CircKIAA0907 Retards Cell Growth, Cell Cycle, and Autophagy of Gastric Cancer In Vitro and Inhibits Tumorigenesis In Vivo via the miR-452-5p/KAT6B Axis. 33136874_Novel Approach of Mandibular Distraction to Avoid Tracheostomy in KAT6B-related Gene Disorders. 34464167_Low Expression of KAT6B May Affect Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 34519438_Novel variants in KAT6B spectrum of disorders expand our knowledge of clinical manifestations and molecular mechanisms. 35575789_Recurrent KAT6B/A::KANSL1 Fusions Characterize a Potentially Aggressive Uterine Sarcoma Morphologically Overlapping With Low-grade Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma. |
ENSMUSG00000021767 |
Kat6b |
68.309593 |
0.4823911571 |
-1.051725 |
0.184328459 |
33.078545 |
0.00000000885100213295929273531102113737462078191242653701920062303543090820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000038765813496284618637932362387663043357122205634368583559989929199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.5808195 |
6.2375486 |
91.0304004 |
8.7278772 |
| ENSG00000156671 |
142891 |
SAMD8 |
protein_coding |
Q96LT4 |
FUNCTION: Sphingomyelin synthases synthesize sphingolipids through transfer of a phosphatidyl head group on to the primary hydroxyl of ceramide. SAMD8 is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transferase that has no sphingomyelin synthase activity but can convert phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and ceramide to ceramide phosphoethanolamine (CPE) albeit with low product yield. Appears to operate as a ceramide sensor to control ceramide homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum rather than a converter of ceramides. Seems to be critical for the integrity of the early secretory pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19506037}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable ceramide cholinephosphotransferase activity and sphingomyelin synthase activity. Involved in ceramide biosynthetic process and regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process. Located in cytosol and endoplasmic reticulum. Is integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:142891; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ceramide cholinephosphotransferase activity [GO:0047493]; ceramide phosphoethanolamine synthase activity [GO:0002950]; sphingomyelin synthase activity [GO:0033188]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; ceramide phosphoethanolamine biosynthetic process [GO:1905373]; regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:2000303]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingomyelin biosynthetic process [GO:0006686] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24259670_These results indicate a primary role of SMSr in monitoring endoplasmic reticulum ceramide levels. 28659495_findings underscore a role of SMSr as negative regulator of ceramide-induced cell death 33621517_Sphingomyelin synthase-related protein generates diacylglycerol via the hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids in the absence of ceramide. |
ENSMUSG00000021770 |
Samd8 |
127.555753 |
2.3295508877 |
1.220052 |
0.166300245 |
53.746485 |
0.00000000000022810194016445075221518500326175182531338730962389149681257549673318862915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001418788300390768405230345147464523142049816484266955285420408472418785095214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
180.1400190 |
16.9588038 |
78.0230962 |
5.7861874 |
| ENSG00000156711 |
5603 |
MAPK13 |
protein_coding |
O15264 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK13 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as pro-inflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors such as ELK1 and ATF2. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. MAPK13 is one of the less studied p38 MAPK isoforms. Some of the targets are downstream kinases such as MAPKAPK2, which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. Plays a role in the regulation of protein translation by phosphorylating and inactivating EEF2K. Involved in cytoskeletal remodeling through phosphorylation of MAPT and STMN1. Mediates UV irradiation induced up-regulation of the gene expression of CXCL14. Plays an important role in the regulation of epidermal keratinocyte differentiation, apoptosis and skin tumor development. Phosphorylates the transcriptional activator MYB in response to stress which leads to rapid MYB degradation via a proteasome-dependent pathway. MAPK13 also phosphorylates and down-regulates PRKD1 during regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11500363, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11943212, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17256148, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18006338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18367666, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20478268, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9731215}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. The encoded protein is a p38 MAP kinase and is activated by proinflammatory cytokines and cellular stress. Substrates of the encoded protein include the transcription factor ATF2 and the microtubule dynamics regulator stathmin. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:5603; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; MAP kinase activity [GO:0004707]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to anisomycin [GO:0072740]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to sodium arsenite [GO:1903936]; cellular response to sorbitol [GO:0072709]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; response to osmotic stress [GO:0006970]; stress-activated MAPK cascade [GO:0051403] |
12080077_Novel protein kinase C isoforms regulate human keratinocyte differentiation by activating a p38 delta mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade that targets CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha 12482858_p38 has a role in mediating induction of VEGF mRNA expression by sodium arsenite 12810719_observations suggest that p38 delta is the major p38 isoform driving suprabasal hINV gene expression and that p38 delta directly regulates ERK1/2 activity via formation of a p38 delta-ERK1/2 complex 15340077_p38delta mitogen-activated protein kinase as a downstream carrier of the PKCdelta-dependent death signal in keratinocytes 16644870_sapk4 activation mediates apoptosis and neurodegeneration in infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis 18367666_activation of p38 isoforms by hypertonicity does not contribute to activation of TonEBP/OREBP because of opposing effects of p38alpha and p38delta. 18559936_These results suggest that, in SupT1-based cell lines, p38alpha, p38gamma and p38delta, but not p38beta, are implicated in both HIV-1 induced replication and apoptosis in infected and uninfected bystander cells. 19816939_results indicate that p38delta is important for motility and invasion of CC cells, suggesting that p38delta may play an important role in CC metastasis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20090411_Function of p38delta in regulating of epidermal keratinocyte differentiation, apoptosis and skin tumor development, is discussed. 20478268_Taken together, the data indicate that the respective stress-dependent action of p38 isoforms is responsible for the up-regulation of the gene expression of the chemokine BRAK/CXCL14. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20804750_Isoforms of p38MAPK gamma and delta contribute to differentiation of human AML cells induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. 20805296_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22199349_PRMT5 inhibits the PKCdelta- or 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-dependent increase in human involucrin expression, and PRMT5 dimethylates proteins in the p38delta complex. 22730327_SEPW1 silencing increases MKK4, which activates p38gamma, p38delta, and JNK2 to phosphorylate p53 on Ser-33 and cause a transient G(1) arrest. 23187130_MAPK13 is responsible for IL-13-driven mucus production in human airway epithelial cells. 23590314_DNA methylation alterations are widespread in melanoma; epigenetic silencing of MAPK13 contributes to melanoma progression 23722928_esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines which are p38delta-negative grew more quickly than cell lines which express endogenous p38delta. 23798682_GSK3alpha, GSK3beta, and MAPK13 were found to be the most active tau kinases, phosphorylating tau at all four epitopes. 23878395_Data indicate that p38delta mediates oncogene-induced senescence through a p53- and p16(INK4A)-independent mechanism. 24599959_PKCdelta activates a MEKK1/MEK3/p38delta MAPK cascade to increase p53 levels and p53 drives p21(Cip1) gene expression. 25849390_MAPK13 undergoes a larger interlobe configurational rearrangement upon activation compared with MAPK14. 26666822_p38delta expression was significantly higher in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues compared with paired normal controls. No significant association was found for p38delta between its expression and other clinicopathological parameters. In Eca109 cells, p38delta can promote the cell growth and motility. p38delta overexpression promotes tumorigenesis in nude mice when p38delta was stably over-expressed and p38ga... 26843485_p38gamma and p38delta reprogram liver metabolism by modulating neutrophil infiltration and provide a potential target for NAFLD therapy 26969274_MAPK13 gene knockdown using siRNA reduced the aldehyde dehydrogenase high cell population and abrogated the tumor-initiating ability. 27417584_The p38delta mitogen-activated protein kinase was identified as a novel regulator of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in primary human macrophages, and thus, represents a potential target for modulation of atherosclerotic inflammation. 27992079_expression of claudin-11 in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells depended on the activity of p38delta MAPK 28783172_Study proposes MAPK p38delta protein as a key factor in breast cancer. 29287762_Study identified p38alpha and p38delta as critical regulators of ASC oligomerization, inflammasome activation, and IL-1beta secretion in keratinocytes. Furthermore, data suggest that the nature of the mitogen-activated protein kinase regulating inflammasome activity exhibits a certain cell specificity, with p38 playing a predominant role in keratinocytes and Jun N-terminal kinase 1 in cells of myeloid origin. 29344643_The knockdown of MAPK13 also blocked the effect of miR23a5p in osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 29661910_Mitogen-activated protein kinases p38gamma/p38delta deficiency protects against Candida albicans infection by increasing reactive oxygen species and iNOS enzyme production and thus the antifungal capacity of neutrophils and macrophages. 29930081_p38delta promotes micro-aggregate transport by phosphorylating SQSTM1, a major scaffold protein that assembles soluble ubiquitylated proteins into micro-aggregates. 29979672_These observations indicate that p38alpha probably blocks brown adipose tissue thermogenesis through p38delta inhibition. 31695024_MKK3 sustains cell proliferation and survival through p38DELTA MAPK activation in colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000004864 |
Mapk13 |
35.967484 |
0.2997499788 |
-1.738168 |
0.459053775 |
13.338497 |
0.00026001262652226132072660891303428343235282227396965026855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000669420262945853348189595433126442003413103520870208740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.3463629 |
5.4050350 |
59.1114593 |
12.5152680 |
| ENSG00000156787 |
93594 |
TBC1D31 |
protein_coding |
Q96DN5 |
FUNCTION: Molecular adapter which is involved in cilium biogenesis. Part of a functional complex including OFD1 a centriolar protein involved in cilium assembly. Could regulate the cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of OFD1, and its subsequent ubiquitination by PJA2 which ultimately leads to its proteasomal degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33934390}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Located in centrosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:93594; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000022364 |
Tbc1d31 |
105.339451 |
2.0039491566 |
1.002846 |
0.181830551 |
30.229205 |
0.00000003838850723186866396297430232067982025512264954159036278724670410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000157787348020713317652249430868283130990903373458422720432281494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
135.7294776 |
15.8967702 |
68.0121415 |
5.9964256 |
| ENSG00000156869 |
391059 |
FRRS1 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZNA5 |
FUNCTION: Ferric-chelate reductases reduce Fe(3+) to Fe(2+) before its transport from the endosome to the cytoplasm. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K385}. |
Alternative splicing;Electron transport;Glycoprotein;Heme;Iron;Membrane;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Members of the cytochrome b561 (CYB561; MIM 600019) family, including FRRS1, reduce ferric to ferrous iron before its transport from the endosome to the cytoplasm (Vargas et al., 2003 [PubMed 14499595]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:391059; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on metal ions [GO:0016722]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000033386 |
Frrs1 |
171.790204 |
5.8103205018 |
2.538618 |
0.627731856 |
14.051902 |
0.00017783384006348485601410602807703753569512628018856048583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000470471102276928329621874524946179008111357688903808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
253.1655410 |
119.4624782 |
44.9369654 |
15.2106240 |
| ENSG00000156966 |
93010 |
B3GNT7 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFL0 |
FUNCTION: N-acetyl glucosamine (GlcNAc) transferase that catalyzes the transfer of GlcNAc via a beta1->3 linkage from UDP-GlcNAc to the non-reducing terminal galactose (Gal) in the linearly growing chain of N- and O-linked keratan sulfate proteoglycans. Cooperates with B4GALT4 galactosyltransferase and CHST6 and CHST1 sulfotransferases to construct and elongate mono- and disulfated disaccharide units [->3Galbeta1->4(6-sulfoGlcNAcbeta)1->] and [->3(6-sulfoGalbeta)1->4(6-sulfoGlcNAcbeta)1->] within keratan sulfate polymer (PubMed:14706853, PubMed:17690104). Involved in biosynthesis of N-linked keratan sulfate proteoglycans in cornea, with an impact on proteoglycan fibril organization and corneal transparency (PubMed:17690104) (By similarity). May play a role in the maintenance of tissue architecture by suppressing cellular motility and invasion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0J2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14706853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17690104}. |
Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:14706853, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17690104}. |
Predicted to enable UDP-glycosyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:93010; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008532]; UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0008499]; UDP-glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0008194]; keratan sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0018146]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0030311] |
17690104_sulfated keratan sulfate is produced by beta3GNT7, beta4GalT4, CGn6ST, and KSG6ST 24418929_The nude mice xenograft model demonstrated that ectopic expression of the B3GNT7 gene in colon cancer cells diminished the migration capability and the liver-metastasis potential, respectively, of colon cancer cells. 34864058_Interleukin-22 regulates B3GNT7 expression to induce fucosylation of glycoproteins in intestinal epithelial cells. |
ENSMUSG00000079445 |
B3gnt7 |
43.348702 |
0.3827904665 |
-1.385373 |
0.253009943 |
30.684581 |
0.00000003035677311145880456686767180814190414395170591888017952442169189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000126138256388771251461619659142709970467421953799203038215637207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.2679961 |
4.7760268 |
63.6701064 |
8.2746252 |
| ENSG00000157168 |
3084 |
NRG1 |
protein_coding |
Q02297 |
FUNCTION: Direct ligand for ERBB3 and ERBB4 tyrosine kinase receptors. Concomitantly recruits ERBB1 and ERBB2 coreceptors, resulting in ligand-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of the ERBB receptors. The multiple isoforms perform diverse functions such as inducing growth and differentiation of epithelial, glial, neuronal, and skeletal muscle cells; inducing expression of acetylcholine receptor in synaptic vesicles during the formation of the neuromuscular junction; stimulating lobuloalveolar budding and milk production in the mammary gland and inducing differentiation of mammary tumor cells; stimulating Schwann cell proliferation; implication in the development of the myocardium such as trabeculation of the developing heart. Isoform 10 may play a role in motor and sensory neuron development. Binds to ERBB4 (PubMed:10867024, PubMed:7902537). Binds to ERBB3 (PubMed:20682778). Acts as a ligand for integrins and binds (via EGF domain) to integrins ITGAV:ITGB3 or ITGA6:ITGB4. Its binding to integrins and subsequent ternary complex formation with integrins and ERRB3 are essential for NRG1-ERBB signaling. Induces the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK3/ERK1, MAPK1/ERK2 and AKT1 (PubMed:20682778). Ligand-dependent ERBB4 endocytosis is essential for the NRG1-mediated activation of these kinases in neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P43322, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10867024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1348215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7902537}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Secreted;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane glycoprotein that mediates cell-cell signaling and plays a critical role in the growth and development of multiple organ systems. An extraordinary variety of different isoforms are produced from this gene through alternative promoter usage and splicing. These isoforms are expressed in a tissue-specific manner and differ significantly in their structure, and are classified as types I, II, III, IV, V and VI. Dysregulation of this gene has been linked to diseases such as cancer, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder (BPD). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:3084; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; ErbB-3 class receptor binding [GO:0043125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030296]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030297]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; activation of transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0007171]; animal organ development [GO:0048513]; cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055007]; cardiac muscle cell myoblast differentiation [GO:0060379]; cell communication [GO:0007154]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; endocardial cell differentiation [GO:0060956]; ERBB signaling pathway [GO:0038127]; ERBB2-ERBB3 signaling pathway [GO:0038133]; ERBB2-ERBB4 signaling pathway [GO:0038135]; ERBB3 signaling pathway [GO:0038129]; ERBB4 signaling pathway [GO:0038130]; ERBB4-ERBB4 signaling pathway [GO:0038138]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; negative regulation of secretion [GO:0051048]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neural crest cell development [GO:0014032]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060045]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:1900086]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051155]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization [GO:0099149]; sequestering of metal ion [GO:0051238]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:0055012]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11896060_Molecular determinants of the sensory and motor neuron-derived factor insertion into plasma membrane 12082616_HRG stimulation of mammary epithelial cells induces the expression of GADD153 mRNA and protein and transcription of GADD153 promoter. 12145742_the behavioral phenotypes of the NRG1 hypomorphs are partially reversible with clozapine, an atypical antipsychotic drug used to treat schizophrenia. 12204892_NRG-1 activates the JAK-STAT signal transduction pathway through its high-affinity receptor, the HER2/HER3 heterodimer. This pathway plays an important role in NRG-1-stimulated proliferation of pulmonary epithelial cells. 12471041_HRG-beta 1 could stimulate NF-kappa B nuclear translocation and DNA-binding activity via the I kappa B alpha phosphorylation-degradation mechanism 12478479_Association of neuregulin 1 with schizophrenia confirmed in a Scottish population 12478479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12509456_heregulin downregulates BRCA1 in the extracellular matrix of breast cancer cells 12528817_Synaptic loss, gliosis, inflammation, and neuronal death occurring in Alzheimer disease is associated with altered expression of NRG-1 and its receptors (the erbB membrane tyrosine kinases). 12556556_HRG up-regulation was sufficient for the development of mammary tumors in the absence of E2 stimulation 12600989_neuregulin-1 plays an important modulatory role in glioma cell invasion. 12646923_Segregation of receptor and ligand regulates activation of epithelial growth factor receptor; following a mechanical injury, heregulin-alpha activates erbB2 in cells at the edge of the wound, and this process hastens restoration of epithelial integrity 12768307_Betacellulin and heregulin/NDF-alpha are involved in epidermal morphogenesis and/or in maintenance of the differentiated phenotype. 12800145_A total of seven breakpoints are described that target the NRG1 gene on chromosome 8 in breast cancer and pancreatic cancer cell lines. 12808428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12808428_risk haplotype was more common in cases than controls (9.5 : 7.5%; P=0.04), and especially in our subset of 141 cases with a family history of schizophrenia (11.6%; P=0.019). 12874607_Linkage disequilibrium studies of 3 polymorphisms in schizophrenic Han Chinese families show the NRG1 gene may play a role in conferring susceptibility to schizphrenia. 14569272_No effect on the NRG-1 mRNA levels of this genotype at two SNPs previously associated with schizophrenia. 14632199_heregulin/HER system as a possible important physiologic growth regulatory system in melanocytes in which multiple deregulations may occur during progression toward melanoma, all resulting in, or indicating, growth factor independence. 14647391_Schizophrenia associated with 5' polymorphisms in nrg1 in Chinese 14699424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14699424_no linkage of neuregulin 1 to schizophrenia in Japan 14729827_Mutations in the promoter region of NRG1 are associated with schizophrenia in the Chinese population. 14966480_'at-risk' haplotype is positioned close to an EST cluster of unknown function (Hs.97362) within intron 1 of NRG1. 14966480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15007393_different haplotypes within the boundaries of the NRG1 gene may be associated with schizophrenia in the Han Chinese. 15073182_Heregulin regulates the ability of the ErbB3-binding protein Ebp1 to bind E2F promoter elements and repress E2F-mediated transcription 15159416_Stimulation of cells with neuregulin-1beta induced Ser-978 dephosphorylation, translocation of SSH1L onto F-actin-rich lamellipodia, and cofilin dephosphorylation. 15162166_This review summarizes recent findings that suggest involvement of altered NRG1-erbB signaling in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. 15197397_If NRG1 does contain susceptibility alleles for schizophrenia, they impact quite weakly on risk in the Irish study of high-density schizophrenia families. 15219675_The data show a widespread expression of NRG-1 in the adult human brain, including, but not limited to, brain areas and cell populations implicated in schizophrenia. 15248869_NRG1 gene analysis was dominated by the presence of over-transmitted haplotypes. Data provides no evidence for a contribution of G72 to schizophrenia. 15276238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15303101_The association of neuregulin 1 polymorphisms in schizophrenia with and without deficit syndrome was investigated. Evidence supports NRG1 as a schizophrenia susceptibility gene. 15326116_Eight forms of Nrg-1 were expressed in cornea that differ by alternate use of four exons. This altered the predicted coding sequence in three domains of Nrg-1 which direct ligand/receptor interaction and trafficking, processing, and release of Nrg-1. 15466169_Breaks in NRG1 were detected in 6% (19 of 323) of breast cancers and in some lung and ovarian cancers. 15498868_before extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and aquaporin synthesis, the membrane-bound prohormone neuregulin 1-beta is cleaved and binds to human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 15527969_NRG1, with nine potential promoter, plays a central role in neural development and is most likely involved in regulation of synaptic plasticity, or how the brain responds or adapts to the environment. 15538186_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15545978_Comparison of NRG1 transcript expression in peripheral leukocytes from schizophrenia patients and unaffected siblings identified 3.8-fold higher levels of the type III isoform SMDF variant in patients. 15584912_These results indicate that GGF2 is neurotrophic and neuroprotective for developing dopaminergic neurons and suggest a role for NRGs in repair of the damaged nigrostriatal system that occurs in Parkinson's disease. 15609326_heregulin stimulates aggregation and inhibits invasion of MCF-7/6 cells via activation of the E-cadherin/catenin complex 15645137_Prolactin and heregulin override DNA damage-induced growth arrest and promote PI-3 kinase-dependent proliferation in breast cancer cells 15703820_One mechanism of HRG-regulated breast cancer cell proliferation, survival, and/or sensitivity to genotoxic damage is to stabilize and promote a nuclear accumulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 15897877_autocrine and/or paracrine NRG-1/erbB signaling promotes neoplastic Schwann cell proliferation 15939841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16082692_NRG1 plays a role in increasing the genetic risk to positive symptoms of psychosis in a proportion of late onset Alzheimer's disease families. 16082692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16155362_May play important role in development of coronary artery disease and expansion of the atherosclerotic plaque and may locally regulate expression of angiogenetic factor CYR61. 16158055_MUC1 is delivered to mitochondria by a mechanism involving activation of the ErbB receptor-->c-Src pathway and transport by the molecular chaperone HSP70/HSP90 complex 16189508_NRG1 presents extreme population differences in allele and haplotype frequencies 16189508_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16219117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16219118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16249994_Data suggest that NRG1 may mediate its effects on schizophrenia susceptibility through functional interaction with erbB4, and that genetic interaction between variants at the two loci increases susceptibility to schizophrenia. 16249994_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16287046_Findings support a role for NRG1 in schizophrenia in African Americans and suggest that polymorphic differences in regions of the gene that recognize AT-binding proteins may be a factor in disease pathogenesis. 16287046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16326006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16326006_Our data support the hypothesis that NRG1 gene is a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia. 16428439_Activation of Rac by heregulin beta1 is mediated not only by ErbB3 and ErbB2 but also by transactivation of EGFR, and it is independent of ErbB4. 16442083_type IV and type I NRG1 may be particularly relevant to schizophrenia, with initial data showing altered expression of these isoforms in the disorder or in association -with NRG1 risk alleles--{REVIEW} 16446404_These observations strongly support the notion that HRG1 splice variants have multifunctional properties, including previously unknown regulatory functions within the nucleus that are different from the activation of ErbB receptor signaling. 16470843_In neuregulin-stimulated SCs the activation of cAMP-mediated pathways accelerates G1-S progression by prolonging ERK activation and concurrently enhancing Akt activation. 16483744_No significant association of the 5' end of neuregulin 1 and schizophrenia in a large Danish sample 16520822_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16520822_Our meta-analysis provides support for the association of NRG1 with schizophrenia, but indicates that firmly establishing the role of NRG1 gene in schizophrenia by genetic association requires much larger sample sizes than have hitherto been reported. 16526041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16526041_Study provides additional suggestive evidence for both the linkage and association of schizophrenia with NRG1, which might either play a role in the predisposition to schizophrenia or be in linkage disequilibrium with a causal locus of this illness. 16618933_data implicate variation in isoform expression as a molecular mechanism for the genetic association of NRG1 with schizophrenia 16638076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16687441_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16687441_This meta-analysis supports the involvement of NRG1 in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia, but with association between two different but adjacent haplotypes blocks in the Caucasian and Asian populations. 16690615_Muc4 potentiates neuregulin signaling by increasing the cell-surface populations of ErbB2 and ErbB3 16730337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16730337_This study report the finding of a missense mutation in the neuregulin 1 gene associated with schizophrenia. 16767099_enhanced NRG1 signaling may contribute to NMDA hypofunction in schizophrenia. 16825199_neuregulin 1 N-terminal domains confer signal attenuation 16867224_the neuregulin/ERBB3 signaling pathway is constitutively activated in clear cell sarcoma of soft tissue 16868568_no evidence of association of NRG1 with bipolar disorder in family-based association analysis 16891421_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16940976_new 136kb region of NRG1 involved in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in the Scottish population 17033632_role of NRG1 in the abnormal brain development in schizophrenia 17072305_In subjects at high risk of schizophrenia, a variant in the human NRG1 promoter region is associated with decreased activation of frontal and temporal lobe regions, increased development of psychotic symptoms and decreased premorbid IQ. 17214955_In summary, results indicate that Heregulin beta-induced store-operated calcium channels were regulated by c-erbB2 level and dependent on activation of phospholipase C in human breast cancer cells. 17275115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17300918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17336946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17336946_might exert gene-specific modulating effects on schizophrenia endophenotypes at the population level 17366345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17405926_neuregulin-1 signaling is impaired in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and in unipolar depression 17408693_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17447867_NRG-1 single nucleotide polymorphism SNP8NRG221533 (T to C) was found to moderate the association between job strain and IMT in men (p = .04). 17447867_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17499242_NRG-1 is expressed by vascular endothelial cells and regulates angiogenesis by mechanisms involving paracrine up-regulation of VEGF-A. 17503451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17503451_These results do not seem to suggest that the investigated NRG1 markers play a role in schizophrenia in the Spanish popula 17519028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17562386_Results describe the regulation of ErbB-4 endocytosis by neuregulin in GABAergic hippocampal interneurons. 17565985_type IV is a unique brain-specific NRG1 that is differentially expressed and processed during early development, is translated, and its expression regulated by a schizophrenia risk-associated functional promoter or single nucleotide polymorphism 17598910_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17602072_Neuregulin has a role in modulating response to trastuzumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer 17631867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17631867_missense mutation on rs3924999 of the neuregulin 1 gene may have a functional effect on prepulse inhibition in both schizophrenia and healthy control populations. 17652086_In Schwann cells neuregulin-1 increases the transcription of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutarylcoenzyme A reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol biosynthesis. 17884806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17884806_the molecular mechanism of the association between NRG1 risk alleles and schizophrenia may include down-regulation of nAChR alpha7 expression 17901998_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17901998_Our results suggest that there is an interaction between the Interleukin-1 beta and neuregulin-1 genes in schizophrenia 17925794_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925794_This study provides the first imaging evidence that genetic variation in NRG1 is associated with reduced white matter density and integrity in human subjects. 17941827_HRG activates NF-kappaB in a Rac1- and MEK-dependent fashion, and inhibition of NF-kappaB abrogates cyclin D1/p21(Cip1) induction and proliferation by HRG 17962208_NRG1 was expressed in 80% of breast cancers studied. 18032396_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18159252_findings suggest that a mechanism of the NRG1 genetic association with schizophrenia may involve the molecular biology of cell adhesion 18180429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18198266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18234478_RNA expression was lower in SZ than in controls before (-28%; p=0.02) and after (-30%; p=0.01) olanzapine stimulation. 18255317_the first demonstration that SNP8NRG221533 of the NRG1 gene affects medial frontal white matter microstructure in humans 18282690_Failure to replicate the association between NRG1 and schizophrenia using Japanese large sample. 18282690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18286587_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18286587_unable to replicate previous associations of rs6994992 with schizophrenia and, moreover, did not find significant associations with age of onset, an estimate of pre-morbid IQ, or neurocognition 18291420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18291420_Patients and relatives carrying haplotype HAP(ICE) both had smaller relative hippocampal volumes as compared to patients or relatives who did not carry this haplotype. 18395550_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18455303_These results demonstrated that Nrg-1 gene has association with schizophrenia. It is possible to select Nrg-1 mRNA expression of PBLs in schizophrenia patients as a potential therapeutic marker. 18455369_NRG1 protein is associated with schizophrenia risk. 18455369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18466879_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18466881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18466881_Our data provide significant levels of support for NRG1 as a susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. 18470533_Data show that NRG1 expression changes during the years of greatest risk for the development of schizophrenia. 18494263_The genetic advances and their neurodevelopmental implications are summarised, with a particular focus on neuregulin 1. 18497096_Linkage of deficits in Nrg1 signals to perturbations of synaptic transmission, myelination, and the survival of particular sets of neurons and glia.[REVIEW] 18516516_Data show that the specific alleles in the genes for neuregulin (NRG1) reveal associations for each of both affective and schizophrenic disorders in the same direction in some. 18543275_A polymorphism of the NRG1 gene affects reactivity to expressed emotion in schizophrenia. 18543275_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18571900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571900_We hypothesise that variation in NRG1 may convey risk for schizophrenia by disrupting neural connectivity. 18583979_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18584117_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18585932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18606232_A linear effect of NRG1 SNP8NRG221533 carrier status on neuronal activation emerged in the fMRI experiment. 18606232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18668031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18704261_Interaction between variants in NRG1 and ERBB4 might contribute to susceptibility for schizophrenia 18714568_in breast DCIS patients, strong cytoplasmic and/or nuclear immunoexpression was revealed in 17 cases for NRGalpha, 13 cases for p-AKT, and nuclear immunoexpression with p-MAPK was found in 17 cases. 18728681_NRG1 signaling is functional and cytoprotective in brain microvascular endothelial cells 18798975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18799465_Protein kinase A-mediated gating of neuregulin-dependent ErbB2-ErbB3 activation has a role in the synergistic action of cAMP on Schwann cell proliferation 18806920_Data show Neuregulin 1 ICE-single nucleotide polymorphism in first episode schizophrenia correlates with cerebral activation in fronto-temporal areas. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19058791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19058791_genetic variations of the NRG1 gene can contribute to the enlargement of the lateral ventricles described in early phases of schizophrenia. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19127563_NRG1 may be specifically associated with the psychotic subset of bipolar disorder. 19127563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148499_The biological function and clinical implications of heregulin, HER-3 and HER-4 in breast cancers negative/low expression of HER-2 remain unclear 19150438_These results suggest that human neuregulin is selectively targeted from cortical neurons to white matter extracellular matrix where it exists in steady-state equilibrium with cerebral spinal fluid. 19156152_NRG1 is one of the most important candidate genes playing a crucial role in many aspects of the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and schizophreniform disorder in people at high risk for psychosis. 19184335_Association of the NRG1 core haplotype was tested for with age-at-onset and with three phenotypes: major psychosis, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder; neither age of onset nor the major psychosis phenotype was associated with the core haplotype. 19184335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19196962_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19196962_highly significant association findings are backed-up by the important role of NRG1 as regulator of the development of the enteric ganglia precursors 19199244_NRG1 gene polymorphism is significantly associated with schizophrenia in Chinese Han, especially in the positive subtype of schizophrenia. 19199244_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19229203_In the first tractography investigation of NRG1 and white matter integrity, authors show that both risk-associated variants of NRG1 are associated with reduced white matter integrity in the left anterior thalamic radiation. 19269083_Snail upregulation by HRG-beta1 is mediated via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and Snail plays a key role in HRG-beta1 induced breast cancer cell metastasis through induction of EMT 19306381_These findings suggest that NRG-1 beta enhances malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors migration and that NRG-1 beta and NRG-1 alpha differentially modulate this process. 19328558_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339916_supports the hypothesis that NRG1 may play a role in the development of bipolar disorder, especially in psychotic subtypes, albeit with different alleles to previous association reports in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder 19350564_NRG1 might be one of several genes that influence semantic language capacities. 19350564_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19367584_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19367584_findings do not provide evidence that NRG1 plays a role in major depressive disorder or that this gene explains part of the genetic overlap with bipolar disorder 19394386_NRG1 is an appropriate candidate gene for methamphetamine (METH)-induced psychosis; however, no significant association has been found between NRG1 and METH-induced psychosis in allele/genotype-wise or haplotype-wise analyses of Japanese patients. 19394386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19439994_present Scandinavian results do not verify previous associations between the analyzed DTNBP1, NRG1, DAO, DAOA, and GRM3 gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia 19448847_Our results suggest that NRG1 variation may play a role in the pathophysiology of anterior cingulum abnormalities in patients with schizophrenia. 19449332_genetic variation in NRG1 is associated with different levels of prefrontal engagement in children as young as 10-12 years of age 19497323_Data demonstrate a more stable binding of heregulin to cells co-expressing HER3 and HER2 than those expressing HER3 alone. 19521112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19521112_The findings suggest that homozygosity for rs725588 could be a risk genotype for schizophrenia. 19545856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19545856_The NRG-1 Arg38Gln genotype did not have a significant impact on PPI. Startle reactivity was not affected by any of the investigated polymorphisms. 19556605_NRG1beta1 is a novel mediator of MUC5AC and MUC5B expression in HBECs, and may represent a novel therapeutic target for mucus hypersecretion in respiratory diseases. 19569180_Data suggest that five novel genes, LUM, PDE3B, PDGF-C, NRG1 and PKD2, have great potential for predicting the efficacy of cisplatin-based chemotherapy against OSCC. 19573260_The results showed no evidence of association between variation in COMT genotype and lateral ventricular, and left or right hippocampal volumes. Neither was there any effect of the BDNF, 5-HTTLPR, NRG1 and DTNBP1 genotypes on these regional brain volumes. 19575259_The results do not suggest that NRG-1 genotype significantly affects antisaccade and smooth pursuit eye movements task.performance. 19594860_Here, I show that a biologically relevant polymorphism of the promoter region of the neuregulin 1 gene (SNP8NRG243177/rs6994992) is associated with creativity in people with high intellectual and academic performance. 19597049_Circulating NRG-1beta is independently associated with heart failure severity and risk of death or cardiac transplantation. 19626024_Results provide additional evidence for transcriptional dysregulation as a biological mechanism implicating NRG1 in schizophrenia risk. 19644050_Report preventive effects of heregulin-beta1 on macrophage foam cell formation and atherosclerosis. 19652122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19659570_Results show that NRG1/ERBB3 signaling inhibits melanocyte (MC) maturation and promotes undifferentiated, migratory and proliferative cellular characteristics. 19733651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19733651_Our results support the hypothesis that NRG1 may qualify as an endogenous protector during fetal development. 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19782967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19797898_might affect colon cancer growth by regulating VEGF secretion via the erbB3 signaling pathway through autocrine and paracrine mechanisms 19801490_Neuregulin-1 attenuated doxorubicin-induced decrease in cardiac troponins. 19802002_NRG1 may be the major tumour suppressor gene postulated to be on 8p: it is in the correct location, is antiproliferative and is silenced in many breast cancers. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913623_NRG1 and DISC1 genes may be associated with brain abnormalities in schizophrenia 19913623_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19937977_A homogeneous sample of 280 schizophrenia patients and 230 healthy controls of Hungarian, Caucasian descent were genotyped for polymorphisms in schizophrenia candidate genes NRG1, DTNBP1, RGS4, G72/G30, and PIP5K2A. 19937977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965935_NRG1 genotype variations were related to smooth eye pursuit variations both at the SNP level and at the haplotype level adding to the validation of this gene as a candidate gene for the disorder. 19965935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19967439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19967439_genetic variation in NRG1 significantly affects cortical function during perceptual and monitoring processes in healthy children as young as 10-12 years of age 20036336_NRG1 genotype does modulate brain activation during episodic memory processing in key areas for memory encoding and retrieval. 20036336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20061032_No association was found for any of the polymorphisms tested, either in single locus or in haplotype analysis in schizophrenia. 20061032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20102668_The evidence from our large study suggests that any such association between P50 indices and NRG1, COMT Val158Met or BDNF Val66Met genotypes, if present, must be very subtle. 20182055_No association between neuregulin 1 and psychotic symptoms in Alzheimer's disease patients. 20182055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20215529_Cytokine-activated metalloproteinase cleavage of neuregulin may play an important role in autocrine activation of endothelial cell signaling pathways 20218976_NRG1 type IV expression levels can selectively modify signaling of NRG1 released from somato-dendritic compartments, in contrast to the type III NRG1 that is also associated with axons 20227043_NRG1 has a role in cell proliferation in ovarian cancer. 20371257_If NRG1-induced AKT phosphorylation is similar in patients and in their unaffected co-twins, then this alteration reflects the shared genetic background rather than the developed schizophrenia. 20374152_Several risk-associated genes have now been identified that encode for proteins which have effects on white matter integrity. These genes include neuregulin-1 (NRG1) polymorphisms. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20427670_our studies suggest that there may be two distinct steps in Schwann cell myelination: an initial phase dependent on juxtacrine Nrg1 signaling and a later phase that can be promoted by paracrine stimulation 20435087_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20435087_This study supports the involvement of NRG1 variants in the less well studied 3' region in conferring susceptibility to SCZ and BPD in the Scottish population. 20472376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20472376_The NRG221533 CC genotype might be protective in newborns. The protective effect might not be directly related to increased systemic NRG levels. 20497232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497232_These findings indicate that NRG1 rs3924999 affects spatial accuracy on the AS task, suggesting an influence of the gene on the neural mechanisms underlying visuospatial sensorimotor transformations. 20520724_Genetic and functional interactions between COMT and AKT1 may provide novel insights into pathogenesis of schizophrenia and other ErbB-associated human diseases such as cancer. 20526724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20526724_These findings suggest that serum NRG1 levels are decreased in patients with chronic schizophrenia and influenced by their SNP8NRG243177 alleles. 20580130_No significant change in age-related loss of spiral ganglion neurons in either NRG1 -/+ mice or mice overexpressing NRG1 is observed, while a negative association between NRG1 expression level and survival of inner hair cells during aging is observed. 20582876_analysis showed that NRG1 (rs783406) was significantly associated with the auditory mismatch negativity amplitude; data indicate that variations within NRG1 may alter the sensitivity to the cognitive effects of cannabinoids 20625696_This is the first report of association of a neuregulin 1 mutation with immune dysregulation. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20638435_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20671236_Signaling by neuregulin-1beta/ErbB regulates the ratio of sinoatrial node- to working-type cells in differentiating embryonic stem cell cardiomyocyte cultures and presumably functions similarly during early human heart development. 20682778_direct NRG1-integrin interaction mediates integrin-ErbB3 cross-talk and that alpha6beta4 plays a major role in NRG-ErbB3 signaling in these cancer cells. 20736300_Neuregulin-1 regulates the constitutive color and melanocyte function in human skin. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20921115_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20921115_We observed epistasis between NRG1 (rs10503929; Thr286/289/294Met) and its receptor ERBB4 (rs1026882; likelihood ratio test P = .035); a 3-way interaction with these 2 SNPs and AKT1 (rs2494734) was also observed. 20926259_The l |
ENSMUSG00000062991 |
Nrg1 |
796.144566 |
5.6459966814 |
2.497228 |
0.170722809 |
195.863896 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000001669047209175883948020459571142591804871194065471167990972535555771356316194270714551511825707611254181486311939236477641657074855174869298934936523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000309875934684730171396812536153529876013298267042433333309202089509289756592026953437599289593409421776495167501902505691191436199005693197250366210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1334.5472115 |
135.1980571 |
237.4919598 |
18.1992300 |
| ENSG00000157193 |
7804 |
LRP8 |
protein_coding |
Q14114 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor for Reelin (RELN) and apolipoprotein E (apoE)-containing ligands (PubMed:20223215). LRP8 participates in transmitting the extracellular Reelin signal to intracellular signaling processes, by binding to DAB1 on its cytoplasmic tail. Reelin acts via both the VLDL receptor (VLDLR) and LRP8 to regulate DAB1 tyrosine phosphorylation and microtubule function in neurons. LRP8 has higher affinity for Reelin than VLDLR. LRP8 is thus a key component of the Reelin pathway which governs neuronal layering of the forebrain during embryonic brain development. Binds the endoplasmic reticulum resident receptor-associated protein (RAP). Binds dimers of beta 2-glycoprotein I and may be involved in the suppression of platelet aggregation in the vasculature. Highly expressed in the initial segment of the epididymis, where it affects the functional expression of clusterin and phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (PHGPx), two proteins required for sperm maturation. May also function as an endocytic receptor. Not required for endocytic uptake of SEPP1 in the kidney which is mediated by LRP2 (By similarity). Together with its ligand, apolipoprotein E (apoE), may indirectly play a role in the suppression of the innate immune response by controlling the survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q924X6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12807892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12899622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12950167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20223215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30873003}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Semliki Forest virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34929721}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family. Low density lipoprotein receptors are cell surface proteins that play roles in both signal transduction and receptor-mediated endocytosis of specific ligands for lysosomal degradation. The encoded protein plays a critical role in the migration of neurons during development by mediating Reelin signaling, and also functions as a receptor for the cholesterol transport protein apolipoprotein E. Expression of this gene may be a marker for major depressive disorder. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:7804; |
axon [GO:0030424]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; apolipoprotein binding [GO:0034185]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; high-density lipoprotein particle binding [GO:0008035]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0005041]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; reelin receptor activity [GO:0038025]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity [GO:0030229]; ammon gyrus development [GO:0021541]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; layer formation in cerebral cortex [GO:0021819]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793]; positive regulation of dendrite development [GO:1900006]; positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061003]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061098]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; reelin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038026]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045088]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; retinoid metabolic process [GO:0001523]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; ventral spinal cord development [GO:0021517] |
12399018_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12621059_transmembrane domain and PXXP motif excludes it from carrying out clathrin-mediated endocytosis 12871934_Sequential proteolytic processing of murine ApoER2 results in the release of its intracellular domain by the protease gamma-secretase. The prior cleavage of its extracellular domain is determined by the glycosylation state of the receptor. 12950167_Data show that the apolipoprotein E receptor 2 binding domain of apolipoprotein E is in the 1-165 amino terminal region, whereas the carboxy terminal 230-299 region of apoE is required for efficient initial association with phospholipids. 15950758_The effects of apoE on receptor proteolysis were mediated by the ligand binding domain of the receptor. We suggest that signaling promoted by these receptors depends in part on these regulated proteolytic events. 16034672_Complete molecular structure examined by nuclear magnetic resonance. 16332682_ApoEr2 can form a multiprotein complex with NMDA receptor subunits and PSD95 16481437_Reelin signals by binding to two transmembrane receptors, apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (Apoer2) and very-low-density lipoprotein receptor. 16642433_In conclusion, results from the two independent samples of black women provide consistent evidence that SNP rs2297660 in LRP8 is associated with fetal growth. 16642433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16951405_The effect of Dab1 on APP and apoEr2 processing in transfected cells and primary neurons is reported. 17470198_The presence of three splice variants of ApoER2 on platelets was confirmed by immuno-blotting, with ApoER2Delta4-5 being the most abundantly expressed splice variant. 17614163_However, this polymorphism increased the risk of AD conferred by the MAPK8IP1 G allele. 17614163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17847002_A nonconservative substitution, R952Q, in LRP8 was significantly associated with susceptibility to premature CAD and/or MI by use of both population-based and family-based designs. 17847002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18039658_the activity of PCSK9 and its binding affinity on VLDLR and ApoER2 does not depend on the presence of LDLR. 18089558_Fyn, due in part to its effects on Dab1, regulates the phosphorylation, trafficking, and processing of APP and apoEr2. 18489431_protein C and APC may directly promote cell signaling in other cells by binding to ApoER2 and/or GPIbalpha 18592168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18592168_Study showed no evidence for association of genetic variants in the LRP8 gene with familial and sporadic myocardial infarction. 19116273_ligation of ApoER2 by APC signals via Dab1 phosphorylation and subsequent activation of PI3K and Akt and inactivation of GSK3beta, thereby contributing to APC's beneficial effects on cells. 19439088_Our data suggest that LRP8 R952Q variant may have an additive effect to APOE epsilon2/epsilon3/epsilon4 genotype in determining ApoE concentrations and risk of MI in an Italian population 19661487_apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (ApoER2, LRP8), a member of the LDL receptor family, is a platelet receptor for FXI. 19720620_ApoEr2 regulates cell movement, and both X11alpha and Reelin enhance this effect. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948739_Differential functions of ApoER2 and very low density lipoprotein receptor in Reelin signaling depend on differential sorting of the receptors. 20208369_There were seven polymorphisms in apoE receptor 2 in Japanese sporadic Alzheimer disease patients, but no association of these polymorphisms with Alzheimers. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20493228_the expression of ApoER2 may serve as a trait marker for major depressive disorder. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21157031_Deficient sLRP-amyloid-beta binding might precede and correlate later in disease with an increase in the tau/Abeta42 CSF ratio and global cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment individuals converting into Alzheimer's disease. 21316997_LRP8 gene polymorphisms influence plasma cholesterol levels as well as size and composition of LDL particles 21347244_ApoEr2 plays important roles in structure and function of CNS synapses and dendritic spines 21601501_In later stages of cerebral cortical development, ApoER2 is expressed earlier than VLDLR in migrating neurons. 22170052_activation of VLDLR and apoER2 by reelin and apoE induces ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux via a Dab1-PI3K-PKCzeta-Sp1 signaling cascade. 22404453_genetic variant R952Q of LRP8 is associated with increased plasma TG levels in patients who are overweight and have premature CAD/MI and history of smoking. 22419519_Variation in genes encoding proteins at the gateway of Reelin signaling: ligands RELN and APOE, their common receptors APOER2 and VLDLR, and adaptor DAB1, was examined. 22589174_results identify LRP8 as a novel positive factor of canonical Wnt signaling pathway 22889673_In a Chinese unrelated Han population, variants within the LRP8 gene do not convey the risk of developing Parkinson's disease. 23524007_TCCGC haplotype at the 3'-terminal block of the LRP8 gene confers a protective role in the development of familial and early-onset coronary artery disease and/or myocardial infarction. 23739027_By incorporating the information from bioinformatics and RNA expression analyses, we identified at least two of the most promising risk genes for alcohol dependence: APOER2 and UBAP2 24076391_ectopic expression of HIC1 in U2OS and MDA-MB-231 cell lines decreases expression of the ApoER2 and VLDLR genes, encoding two canonical tyrosine kinase receptors for Reelin. 24344333_Data suggest that PS1/gamma-secretase-dependent processing of the reelin receptor ApoER2 inhibits reelin expression and may regulate its signaling. 24844606_results of this study demonstrated the presence of reelin, its receptors VLDLR and ApoER2 as well as Dab1 in the ENS and might indicate a novel role of the reelin system in regulating neuronal plasticity and pre-synaptic functions in the ENS. 24867879_A novel TACGC risk haplotype in the LRP8 gene that is present in patients with CAD and MI but not in normal controls. 26637325_LRP8 is a risk gene for psychosis. 26800564_ApoER2 contributes cooperatively with endothelial cell protein C receptor and protease activated receptor 1 to APC-initiated endothelial antiapoptotic and barrier protective signaling. 26817215_two SNPs (rs3737984 and rs2297660) in ApoER2 gene had significant association with dyslipidemia in Thai ethnic 26902204_These results reveal an association between ApoER2 isoform expression and Alzheimer's disease. 27853278_ABGL4, LRP8 and PCSK9 polymorphisms and gene interactions increase cardiometabolic risk. 28255385_The presence of reelin was elevated in junctional areas as in dysplastic nevi. VLDLR presented positive values in 16 cases (16/ 32) and ApoER2 was weak positive in 7 cases. 28446613_This study elucidates that the contracted-open conformation of ligand-bound ApoER2 at neutral pH resembles the contracted-closed conformation of ligand-unbound low-density lipoprotein receptor at acidic pH in a manner suggestive of being primed for ligand release even prior to internalization. 28495490_Further evidence for the association between LRP8 and schizophrenia. 29032149_Results show that none of the SNPs were significantly associated with myocardial infarction (MI). Interestingly, haplotype based association analysis showed TG and CG of rs10788952 and rs7546246 significantly associated with MI and in particular, haplotype TG was positively correlated with the risk of MI, as this increased the LDL and total cholesterol level in MI patients in south Indians. 29442527_ApoER2-CTF levels are decreased in AD brain at advanced Braak stages and after Abeta treatment. 30227220_Data indicate low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 8 (LRP8) as a therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) as inhibition of LRP8 can attenuate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling to suppress breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs). 30552869_CSF-ApoER2 fragments as a read-out of reelin signaling: Distinct patterns in sporadic and autosomal-dominant Alzheimer disease 30575334_Our findings suggest that new approaches targeting LRP8 may constitute promising treatments for hormone-negative breast cancers, those overexpressing HER2 and TNBCs. 31994910_LRP8, modulated by miR-1262, promotes tumour progression and forecasts the prognosis of patients in breast cancer. 32312520_Genome-scale CRISPR activation screening identifies a role of LRP8 in Sorafenib resistance in Hepatocellular carcinoma. 33054597_LRP8 activates STAT3 to induce PD-L1 expression in osteosarcoma. 33079740_LRP8 (rs5177) and CEP85L (rs11756438) are contributed to schizophrenia susceptibility in Iranian population. 33779882_miR-30b-5p inhibits cancer progression and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in lung cancer through targeting LRP8. 35414534_Human APOER2 Isoforms Have Differential Cleavage Events and Synaptic Properties. |
ENSMUSG00000028613 |
Lrp8 |
661.356533 |
2.3568770634 |
1.236877 |
0.079344254 |
241.523325 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000183044587116199992832942315917121453823266702198421220198428915414690755639126988063260215490077297602219923715453398672414828861221432719508239728156695491634309291839599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000042480158896778486256430809677593825170659261505103054891125140807957056869919293167114268455886143838140413843938825647695981418169430127163010979529644828289747238159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
896.6194364 |
43.2268474 |
383.3445711 |
14.0695775 |
| ENSG00000157240 |
8321 |
FZD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UP38 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for Wnt proteins (PubMed:10557084). Activated by WNT3A, WNT3, WNT1 and to a lesser extent WNT2, but apparently not by WNT4, WNT5A, WNT5B, WNT6, WNT7A or WNT7B (PubMed:10557084). Contradictory results showing activation by WNT7B have been described for mouse (By similarity). Functions in the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway (PubMed:10557084). The canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway leads to the activation of disheveled proteins, inhibition of GSK-3 kinase, nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin and activation of Wnt target genes (PubMed:10557084). A second signaling pathway involving PKC and calcium fluxes has been seen for some family members, but it is not yet clear if it represents a distinct pathway or if it can be integrated in the canonical pathway, as PKC seems to be required for Wnt-mediated inactivation of GSK-3 kinase. Both pathways seem to involve interactions with G-proteins. May be involved in transduction and intercellular transmission of polarity information during tissue morphogenesis and/or in differentiated tissues (Probable). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10557084, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for C.difficile toxin TcdB in the colonic epithelium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27680706}. |
Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
Members of the 'frizzled' gene family encode 7-transmembrane domain proteins that are receptors for Wnt signaling proteins. The FZD1 protein contains a signal peptide, a cysteine-rich domain in the N-terminal extracellular region, 7 transmembrane domains, and a C-terminal PDZ domain-binding motif. The FZD1 transcript is expressed in various tissues. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8321; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; Wnt receptor activity [GO:0042813]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; astrocyte-dopaminergic neuron signaling [GO:0036520]; autocrine signaling [GO:0035425]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [GO:0044338]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in osteoblast differentiation [GO:0044339]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; hard palate development [GO:0060022]; membranous septum morphogenesis [GO:0003149]; muscular septum morphogenesis [GO:0003150]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903204]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; planar cell polarity pathway involved in neural tube closure [GO:0090179]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; presynapse assembly [GO:0099054]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; Wnt signaling pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation [GO:1904953] |
14739301_Fz1 and LRP1 bind, which disrupts the receptor/coreceptor complex formation and leads to the repression of the canonical Wnt signaling 15252441_subcellular Fz localization, through the association with other membrane proteins, is a critical aspect in regulating the signaling specificity within the Wnt/Fz signaling pathways 16442268_Bone morphogenetic protein-2 modulates Wnt and frizzled expression and enhances the canonical pathway of Wnt signaling in normal keratinocytes 17496152_FZD1 links epithelial/mesenchymal disruption to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 17895994_Data demonstrate that Frizzled receptors can functionally replace mating factor receptors in yeast and offer an experimental system to study modulators of Frizzled receptors. 18382662_a frizzled module in cell surface collagen 18 inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling 18715140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18715140_a cis-regulatory polymorphism in the FZD1 promoter region may have a functional role in determining bone structural geometry 19148501_The proportion of frizzled-1 positive ovaries was lower in normal patients than in those with ovarian cancer or bening neoplasia 19421142_RNA samples from 21 neuroblastoma showed a highly significant FZD1 and/or MDR1 overexpression after treatment, underlining a role for FZD1-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in clinical chemoresistance. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19543507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20051274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20051274_These results suggest that FZD1 expression is regulated in a haplotype-dependent manner in osteoblasts and that these same haplotypes may be associated with biomechanical indices of bone strength. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22303445_Soluble FZC18 and Wnt3a physically interact in a cell-free system and soluble FZC18 binds the frizzled 1 and 8 receptors. 22484497_FZD1 appears to mediate multidrug resistance by regulating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway 23442549_Fz1 is a Wnt responsive gene in colon-derived tissues. Fz1 expression exhibited increased expression in normal mucosa only in close proximity to colon cancer 23806799_Experiments demonstrate a role of E2F1 in osteoblast differentiation and mineralization and suggest that FZD1 is required, in part, for E2F1 regulation of osteoblast mineralization. 23921915_ACE2 and FZD1 are prognosis markers in squamous cell/adenosquamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of gallbladder. 24386373_Polymorphisms in several genes involved in the Wnt signaling pathway were associated with hepatic fibrosis or inflammation risk in HCV-infected males. 24814288_our data demonstrate that FZD1 regulates PKCdelta, and the PKCdelta/AP-1 signalling transduction pathway plays an important role in drug resistance in MES-SA/Dx5 cells. 25197350_Our study suggests that Sox9 siRNA inhibits the proliferation capability of human osteosarcoma cells by down-regulating the expression of Wnt1 and its receptor Fzd1 25369469_FZD1 expression was down-regulated by AP2 expression and mediated osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. 27643554_The amplification of miR-135b suppressed non-small cell lung cancer chemoresistance by directly mediating FZD1 down-regulation. 27695039_aken together, our results suggest that Sp1 plays a role in human osteoblast differentiation and mineralization, which is at least partially mediated by Sp1-dependent transactivation of FZD1. 28921449_FZD1 and CAIX might be important biological markers for the carcinogenesis, metastasis, invasion, and prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 29482174_activated FZD1 observed in leukemic cells likely confers acquired drug resistance, whereas FZD1 silencing may be more effective in reversing multidrug resistance 30719180_FZD1 expression levels were remarkably reduced in the articular cartilage of patients with Kashin-Beck disease. 30808872_study has demonstrated that aberrant CpG island hypermethylation of the FZD1 gene is present in patients with ONFH, resulting in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inactivation and subsequent cell dysfunction. 31735061_Wnt receptor gene FZD1 was associated with schizophrenia in genome-wide SNP analysis of the Australian Schizophrenia Research Bank cohort. 31900623_Frizzled 1 and Wnt1 as new potential therapeutic targets in the traumatically injured spinal cord. 33402389_Hypoxia-Induced Suppression of Alternative Splicing of MBD2 Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis via Activation of FZD1. 34253104_LINC00942 Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis in Lung Adenocarcinoma via FZD1 Upregulation. 34781823_Protein disulfide isomerase family 6 promotes the imatinib-resistance of renal cell carcinoma by regulation of Wnt3a-Frizzled1 axis. 34893109_[RBM38 Mediates the Proliferation of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells HL-60 by Regulating FZD1 mRNA Stability]. 35296808_Epigenetic repression of Wnt receptors in AD: a role for Sirtuin2-induced H4K16ac deacetylation of Frizzled1 and Frizzled7 promoters. |
ENSMUSG00000044674 |
Fzd1 |
293.280256 |
2.4229192551 |
1.276746 |
0.114999523 |
123.339220 |
0.00000000000000000000000000011753457278034487301854489724165781986107089475194655883179425377192748973509406340554050984792411327362060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001442070070023183996074536238832967273930085457915081450392441074727291772800130686960073944646865129470825195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
421.2132574 |
26.3065059 |
175.0582212 |
8.6387056 |
| ENSG00000157303 |
203328 |
SUSD3 |
protein_coding |
Q96L08 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in breast tumorigenesis by promoting estrogen-dependent cell proliferation, cell-cell interactions and migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24413080}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sushi;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:203328; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
24413080_Data indicate that sushi domain containing 3 (SUSD3) is a promoter of estrogen-dependent cell proliferation and regulator of cell-cell and cell-substrate interactions and migration in breast cancer. 26745129_High expression of SUSD3 is associated with breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000021384 |
Susd3 |
80.880223 |
0.3355535289 |
-1.575385 |
0.629672511 |
5.836801 |
0.01569433332618226303867281501425168244168162345886230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028804819683468069202447736643080133944749832153320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.7953454 |
18.2303278 |
133.0419776 |
38.8428449 |
| ENSG00000157350 |
6483 |
ST3GAL2 |
protein_coding |
Q16842 |
FUNCTION: A beta-galactoside alpha2-3 sialyltransferase primarily involved in terminal sialylation of ganglio and globo series glycolipids (PubMed:8920913, PubMed:9266697). Catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid (N-acetyl-neuraminic acid; Neu5Ac) from the nucleotide sugar donor CMP-Neu5Ac onto acceptor Galbeta-(1->3)-GalNAc-terminated glycoconjugates through an alpha2-3 linkage (PubMed:8920913, PubMed:9266697, PubMed:25916169). Sialylates GM1/GM1a, GA1/asialo-GM1 and GD1b gangliosides to form GD1a, GM1b and GT1b, respectively (PubMed:8920913, PubMed:9266697). Together with ST3GAL3, primarily responsible for biosynthesis of brain GD1a and GT1b that function as ligands for myelin-associated glycoprotein MAG on axons, regulating MAG expression and axonal myelin stability and regeneration (By similarity). Via GT1b regulates TLR2 signaling in spinal cord microglia in response to nerve injury (By similarity). Responsible for the sialylation of the pluripotent stem cell- and cancer stem cell-associated antigen SSEA3, forming SSEA4 (PubMed:12716912). Sialylates with low efficiency asialofetuin, presumably onto O-glycosidically linked Galbeta-(1->3)-GalNAc-O-Ser (PubMed:9266697, PubMed:25916169). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q11204, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12716912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25916169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8920913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9266697}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9266697}.; PATHWAY: Glycolipid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9266697}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that catalyzes the transfer of sialic acid from CMP-sialic acid to galactose-containing substrates. The encoded protein is normally found in the Golgi but can be proteolytically processed to a soluble form. This protein, which is a member of glycosyltransferase family 29, can use the same acceptor substrates as does sialyltransferase 4A. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6483; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; beta-galactoside (CMP) alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase activity [GO:0003836]; monosialoganglioside sialyltransferase activity [GO:0047288]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; sialyltransferase activity [GO:0008373]; ganglioside biosynthetic process via lactosylceramide [GO:0010706]; globoside biosynthetic process via lactosylceramide [GO:0010707]; glycolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0009247]; glycoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0009101]; keratan sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0018146]; lipid glycosylation [GO:0030259]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0009312]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486]; protein sialylation [GO:1990743]; sialylation [GO:0097503]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
12504121_Genomic structure, expression, and transcriptional regulation of ST3GALII. 12716912_ST3Gal II is a MSGb5 (stage-specific embryonic antigen-4) synthase and its increased expression level is closely related to renal carcinogenesis 25916169_This suggests that the C-terminal domain of ST3Gal-II depends on N-glycosylation to attain an optimum conformation for proper exit from the endoplasmic reticulum 28698248_Data suggest that ganglioside glycosyltransferases ST3GAL5, ST8SIA1, and B4GALNT1 are S-acylated at conserved cysteine residues located close to cytoplasmic border of their transmembrane domains; ST3Gal-II is acylated at conserved cysteine residue in N-terminal cytoplasmic tail; for B4GALNT1 and ST3Gal-II, dimer formation controls their S-acylation status. 35507766_Overlapping and unique substrate specificities of ST3GAL1 and 2 during hematopoietic and megakaryocytic differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000031749 |
St3gal2 |
244.817276 |
2.1517206894 |
1.105491 |
0.247515068 |
19.449070 |
0.00001033181104141905223251125811589901104525779373943805694580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000032315645469664172834481363771885753521928563714027404785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
327.0793646 |
58.1575139 |
151.9741651 |
19.7425648 |
| ENSG00000157404 |
3815 |
KIT |
protein_coding |
P10721 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for the cytokine KITLG/SCF and plays an essential role in the regulation of cell survival and proliferation, hematopoiesis, stem cell maintenance, gametogenesis, mast cell development, migration and function, and in melanogenesis. In response to KITLG/SCF binding, KIT can activate several signaling pathways. Phosphorylates PIK3R1, PLCG1, SH2B2/APS and CBL. Activates the AKT1 signaling pathway by phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Activated KIT also transmits signals via GRB2 and activation of RAS, RAF1 and the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1. Promotes activation of STAT family members STAT1, STAT3, STAT5A and STAT5B. Activation of PLCG1 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. KIT signaling is modulated by protein phosphatases, and by rapid internalization and degradation of the receptor. Activated KIT promotes phosphorylation of the protein phosphatases PTPN6/SHP-1 and PTPRU, and of the transcription factors STAT1, STAT3, STAT5A and STAT5B. Promotes phosphorylation of PIK3R1, CBL, CRK (isoform Crk-II), LYN, MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1, PLCG1, SRC and SHC1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12444928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12511554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12878163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17904548, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19265199, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21135090, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21640708, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7520444, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9528781}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase. This gene was initially identified as a homolog of the feline sarcoma viral oncogene v-kit and is often referred to as proto-oncogene c-Kit. The canonical form of this glycosylated transmembrane protein has an N-terminal extracellular region with five immunoglobulin-like domains, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain at the C-terminus. Upon activation by its cytokine ligand, stem cell factor (SCF), this protein phosphorylates multiple intracellular proteins that play a role in in the proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis of many cell types and thereby plays an important role in hematopoiesis, stem cell maintenance, gametogenesis, melanogenesis, and in mast cell development, migration and function. This protein can be a membrane-bound or soluble protein. Mutations in this gene are associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumors, mast cell disease, acute myelogenous leukemia, and piebaldism. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. |
hsa:3815; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; stem cell factor receptor activity [GO:0005020]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0097067]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound [GO:0050910]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; embryonic hemopoiesis [GO:0035162]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; erythropoietin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038162]; Fc receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038093]; germ cell migration [GO:0008354]; glycosphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006687]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; hematopoietic stem cell migration [GO:0035701]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; immature B cell differentiation [GO:0002327]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; Kit signaling pathway [GO:0038109]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002320]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; mast cell chemotaxis [GO:0002551]; mast cell degranulation [GO:0043303]; mast cell differentiation [GO:0060374]; mast cell proliferation [GO:0070662]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; melanocyte adhesion [GO:0097326]; melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318]; melanocyte migration [GO:0097324]; myeloid progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002318]; negative regulation of developmental process [GO:0051093]; negative regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043069]; negative regulation of reproductive process [GO:2000242]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; pigmentation [GO:0043473]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of colon smooth muscle contraction [GO:1904343]; positive regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production [GO:0002732]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048170]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mast cell cytokine production [GO:0032765]; positive regulation of mast cell proliferation [GO:0070668]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; positive regulation of pseudopodium assembly [GO:0031274]; positive regulation of pyloric antrum smooth muscle contraction [GO:0120072]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of small intestine smooth muscle contraction [GO:1904349]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation [GO:1905065]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of bile acid metabolic process [GO:1904251]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; somatic stem cell division [GO:0048103]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; spermatid development [GO:0007286]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863]; stem cell population maintenance [GO:0019827]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; tongue development [GO:0043586]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
11642722_a tumor marker for cardiac myxoma 11786393_The complexity of KIT gene mutations and chromosome rearrangements and their clinical correlation in gastrointestinal stromal (pacemaker cell) tumors. 11825908_Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Src family kinases are required for phosphorylation and membrane recruitment of Dok-1 in c-Kit signaling. 11861291_Mutations of c-KIT causing spontaneous activation of the KIT receptor kinase are associated with sporadic adult human mastocytosis (SAHM) and with human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 11919394_role of c-KIT mutations in the biology of mast cell malignancies 12008077_We have shown for the 1st time that CD117 is expressed at a much higher level in AML myeloblasts than in normal myeloid precursors. 12041664_REVIEW: Signal transduction though the KIT pathway in mast cells and involvement in MC activation and mediator release. 12072198_all classes of interstitial cells of Cajal express CD117, thus it serves as a marker for gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) derived from these cells; mutations in CD117 or aberrations of chromosome 4 are often found in GIST - review 12091362_Evidence for the involvement of a hematopoietic progenitor cell in systemic mastocytosis from single-cell analysis of mutations in the c-kit gene. 12111653_Asn(822)-Lys mutation affecting a highly conserved codon within the tyrosine kinase activation loop leading to constitutive ligand-independent activation of the KIT receptor was identified in the Kasumi-1 cell 12134042_essential role for c-Kit in KS tumorigenesis 12172985_c-Kit-expressing Ewing tumor cells are resistant to imatinib mesylate. 12204004_Mutations were not detected in over 100 normal individuals and are likely to be the cause of piebaldism in our subjects. 12379771_findings demonstrate a unique KIT sequence and expression pattern among mediastinal seminomas; KIT sequencing may assist in differentiating primary from metastatic MS 12393703_stem cell factor has 'late' effects on fetal hemoglobin modulation during erythropoiesis, related to the expression pattern of CD117. 12429808_the SCF-c-kit system, possibly with the contribution of mast cells, may have a growth-regulating role in the normal pancreas, which is altered during malignant transformation. 12444928_Data show that the adapter protein APS preferentially associates with phosphorylated Tyr-568 and Tyr-936 of the receptor for stem-cell factor (c-Kit). 12457234_Fibroblat-like cells lacking this protein express SK3 in smooth gut muscle in health and dissease. 12485499_c-kit gene mutation may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of GIST and also may be a prognostic marker. 12511554_KIT isoforms have remarkable differences in their signaling capabilities 12522257_KIT and PDGFRA mutations appear to be alternative and mutually exclusive oncogenic mechanisms in gastrointestinal stromal tumors 12584564_KIT could be a useful marker for chromophobe renal cell carcinomas 12592353_Point mutations in c-Kit in core binding factor leukemias correlate with white blood cell count and the white blood cell index 12598308_Point mutation may be associated with urticaria pigmentosa in children. 12666065_c-kit+ cells were found in glomeruli and interstitium. Colocalization of CD34+ and c-kit+ was seen in some rounded interstitial and spindle-shaped cells. This shows potential involvement of SCF/c-kit in crescentic glomerulonephritis. 12711118_overexpression of the c-kit protein is associated with large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung 12759497_gain-of-function mutation in exon 11 of the c-kit gene is an important prognostic factor for gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors, including myogenic and neurogenic tumors as well as GISTs 12796027_overexpression of c-KIT is associated with extensive-stage small-cell lung carcinoma 12824871_Mutations of the c-kit gene is associated with testicular germ cell tumors 12824925_types of mutations in sinonasal NK/T cell lymphoma in northeast district of China 12878163_c-Src phosphorylates the receptor KIT, thereby creating docking sites for SH2 domain containing proteins, leading to recruitment of Crk to the receptor. 12918066_Mutations and deletions in c-kit protooncogene is associated with metastatic behavior of gastrointestinal stromal tumors 14625290_surface expression of c-Kit is regulated by TACE, which controls mast cell survival 14634801_the presence of c-Kit and VEGF overexpression is associated with the presence of second primary tumors in patients with melanoma; overexpression of c-Kit is more likely to be seen in the superficial spreading type 14647465_tr-kit promotes the formation of a multimolecular complex composed of Fyn, PLCgamma1 and Sam68, which allows phosphorylation of PLCgamma1 by Fyn, and may modulate RNA metabolism. 14654075_findings of co-expression of KIT and/or FMS with their respective ligands implies these receptors might contribute to leukemogenesis in some patients with AML through autocrine, paracrine, or intracrine interactive stimulation. 14657715_c-kit overexpression observed in a subset of colorectal neuroendocrine carcinomas may not be mediated via activating mutations, and does not appear to be an initiating event during tumorigenesis 14669790_This result suggests that the loss of expression of this protein might correlate with malignant breast cancer progression, but it is most likely involved at an early stage of human breast cancer development. 14677065_KIT expression is a rare event in multiple myeloma and not detectable in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma 14695343_activating KIT mutations may contribute to tumorigenesis in a subset of seminomas, but are not involved in non-seminomatous germ cell tumors. 14724587_kit expression likely identifies a subset of neuroblastomas with conserved capacity for differentiation, which may represent the embryonal variety of the disease 14745431_results confirm the high frequency of BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations in patients with secondary resistance to imatinib and exclude mutations of the activation loops of KIT, PDGFRA and PDGFRB as causes of resistance in patients without ABL mutations 14871970_ligand-activated KIT and platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta tyrosine kinase receptors are expressed in synovial sarcoma 14994370_involvement of c-Kit receptor in the regulation of leukemic myeloblasts egress to the peripheral blood 15018431_c-kit expression was demonstrated in all 11 sarcomas of the uterus regardless of histologic type 15033665_c-KIT is expressed in ovarian carcinoma and it is statistically correlated with chemotherapy resistance. 15044924_In mammary phyllodes tumors, there was increasing c-kit expression with increasing degree of malignancy. 15062876_High eexpression level of both mutated and wild-type allele transcripts of c-kit suggests that interactions between spontaneously activated and normal c-kit receptors are important in GIST tumorigenesis. 15073597_Study demonstrates that the expression pattern and one mutation of c-kit may distinguish papillary renal cell carcinomas. 15073598_CD117 immunoreactivity identifies a peculiar subset of stage I adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung with highly proliferative tumors and may have prognostic relevance in adenocarcinoma patients. 15112348_Data show that c-kit gene mutations occur preferentially in malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors and might be a clinically useful adjunct marker in their evaluation. 15145934_acquisition of autonomous growth during uveal melanoma progression may involve the SCF/c-Kit axis 15154005_KIT mutations were found in 14 (50%) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), the majority being within exon 11, and the other comprised exon 9 AY 502-503 duplications and exon 17 Lys --> Aln822 missense mutations. 15161681_gastrointestinal stromal tumors have distinct kit expression depending on genotype and tumor location 15167915_c-kit mutation may account for the transient bone marrow mastocytosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia. 15194144_These six new mutations are associated with phenotypes that are well in accordance with our knowledge of genotype-phenotype correlations in KIT. 15217946_neither c-kit nor its mutational status have a role in progression of small cell lung cancer 15224284_Kit mutatation is associated with gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumors. 15234225_Human vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) express stem cell factor (SCF) and its receptor, c-kit. SCF/c-kit signaling may affect SMC function via an autocrine pathway. 15308671_c-Kit makes both kinase-independent and -dependent contributions to the proliferative synergy induced by SCF in combination with GM-CSF 15315962_The activated KIT in turn induces phosphorylation and activation of Cbl proteins 15326474_gene expression profiling of 26 gastrointesstinsal stromsal tumors with known KIT and PDGFRA mutational status 15337769_induction of Slug by autocrine production of SCF and c-Kit activation plays a key role in chemoresistance of malignant mesothelioma 15339674_KIT gene is activated in Acute myeloid leukemiea characterized by distinct cytogenetic and molecular genetic patterns. 15363457_mutations of specific residues located in the activation loop (D835X and 836-deletion in Flt-3; D816V in c-Kit) as well as a 6-base pair (6-bp) insertion at residue 840 in Flt-3 operate in a similar way 15370139_c-kit expression could also be added to the immunoprofile in the diagnosis of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast. 15471556_c-kit gene mutations is associated with intracranial germinomas 15502806_A significant proportion (27%) of small cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder expressed c-kit, suggesting that it may prove useful as a therapeutic target in small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. 15507672_mast cells and lymphocytes within focal aggregates of bone marrow from mastocytosis are frequently positive for the codon 816 activating mutation of kit 15507676_gastrointestinal stromal tumors show KIT gene deletions at the intron 10-exon 11 boundary 15512818_CD117 is expressed on plasma cells in monoclonal gammopathies 15583854_Kit is an human oncogenic tyrosine kinase [review] 15617841_c-kit expression may be a good prognostic indicator for HCC. 15618474_KIT exon 8 mutations represent gain-of-function mutations 15618926_c-kit expression may be an early event in the transformation of Merkel cell carcinoma, but not a marker for tumor progression. 15621809_review of the 'two hits' model of leukemogenesis exemplified by c-kit gene mutations in the Kasumi-1 cell line and the effect of tyrosine kinase kit mutant on the main KIT-regulated signal transduction pathways 15623596_Overexpression and phosphorylatiom of kit receptor is associated with small cell lung cancer 15671569_c-kit may have a role in development of neuroblastic tumors 15685537_High sensitivity of the imatinib-resistant KIT -T670I and KIT -V654A and of PDGFRA -D842V mutants to PKC412 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 15688149_expression of c-kit mRNA and c-kit protein significantly decreased in the colon of slow-transit constipation (STC), suggesting that the c-kit signal pathway may play an important role in interstitial cells of Cajal reduction in STC 15725473_Capability of Imatinib to induce an anti-leukemic effect in Core Binding Factor (CBF)-leukemia patients with KIT mutation. 15780567_KIT gene was expressed in 6/7 chromophobe RCCs and 7/8 oncocytomas while 0/15 clear cell RCCs and 1/15 papillary RCCs expressed kit gene. 15791568_study demonstrates that platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and beta, and c-kit protein are expressed in a high percentage of epithelial ovarian cancers 15791570_found a significant elevation of c-kit protein messenger RNA and protein overexpression not only in chromophobe renal cell carcinomas but also in oncocytomas 15795882_Homozygous point mutation in c-KIT exon 9, codon 456 in pediatric gastrointestinal stromal tumor. 15869870_KIT overexpression in GISTs is rarely related to a gene amplification. 15897742_The point mutations of c-kit and platelet- derived growth factor receptor alpha genes may play a limited role in the tumorigenesis of type 1 neurofibromatosis-associated gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 15991300_C-kit mutation is undoubtedly pivotal event in gastrointestinal stromal tumors and may be associated with poor prognosis. Evaluation of C-kit gene mutation may have both prognosis and therapeutic significances. 16015387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16029447_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16076867_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16082245_REVIEW of KIT-positive neoplasms and disruption of KIT-dependent functions caused by KIT deficiency due to hereditary nonsense/missense mutations 16135486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16143141_Familial gastrointestinal stromal tumors and mastocytosis caused by a germline mutation in KIT. 16188233_The KIT-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt protein pathway is constitutively activated in testicular germ cell tumors, due to overexpression of KIT protein and/or gain-of-function mutations in the c-kit gene. 16220461_The mutation of V604I of KIT gene is the cause of clinical phenotype of the family with piebaldism. 16235251_The expression levels for c-Kit are high for Schwann cells derived from MPNST of neurofibromatosis type 1 tumors patients. 16242000_The absence of mutations in exon 17 of CD117+ SCLC suggests this tumour may respond to therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors 16271084_CD117 expression can be detected sporadically in DLBCL (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma) of follicle center-cell origin and a subset of plasmablastic lymphomas. 16320053_CD117 is expressed in Thai adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia 16352739_A disease with striking similarities to human mastocytosis develops spontaneously in transgenic mice expressing the human Asp816Val mutant Kit protooncogene specifically in Mast Cells. 16357008_describes frequence mutation of PDGFRA in malignant periphaerl nerve sheath tumors often associated with coamplification of KIT 16365291_KIT is a target of microRNA genes (miR-146a, miR-146b, miR-221, miR-222) but their regulatory impact is impaired by SNP within KIT sequence 16373964_activating mutations of PDGFR-alpha, c-kit and B-RAF are absent in gliosarcomas 16426921_findings suggest that the expression of c-KIT protein might define a subset of poorly differentiated, HER-2-positive ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast with decreased expression of steroid hormone receptors, comedonecrosis, and a solid growth pattern 16445822_KIT protein was diffusely and weakly expressed, but DNA analysis revealed no mutational change in exon 9 or 11 of the c-kit gene. 16460801_7 out of 20 patients carried missense mutations in the c-Kit gene in polycythemia vera whereas no sequence variation was detected in 15 healthy controls. 16479070_Only one case (1/13, 7.7%) of serous cystadenocarcinoma had positive staining, and no mutation was identified at exon 11. 16533529_Genetic abnormality in the KIT gene, particularly at codon 816, might contribute to the progression of myelodysplastic syndromes to acute myelocytic leukemia. 16551858_Results show that the identification of newly acquired KIT mutations in addition to the primary mutation is dependent on the number of tissue samples analyzed and has high implications for further therapeutic strategies. 16597595_rapamycin induction of apoptosis appears specific to the C-Kit D816V mutation in systemic mastocytosis 16623778_Approximately one-third of plasma cell myeloma express high levels of c-kit. 16685437_KIT mutations, especially deletions in exon 11, are markers of poor prognosis for gastric intestinal stromal tumors. 16697720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16741248_a KIT mutation in mast cells and other bone marrow hematopoietic cell lineages may have a role in systemic mast cell disorders 16760463_receptors alphaGMR and c-Kit could interact to coordinate their signal initiation; alphaGMR inhibited c-Kit auto-phosphorylation induced by the ligand stem cell factor 16773696_Activated mutations of kit exon 11 are detectable in the vast majority of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GISTs). There is no difference in the PR rate for patients whose GISTs have kit exon 9 and exon 11 mutations. 16780420_A study evaluating the mechanisms by which Cbl negatively regulates c-Kit-mediated signalling is presented. 16784237_putative quadruplex forming 21-nucleotide sequence upstream of the c-kit transcription initiation site (c-kit21), on the G-rich strand, which occupies a site required for core promoter activity. c-kit21 forms quadruplexes under physiological conditions. 16785193_Gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) with platelet-derived growth factor receptor mutations often have reduced expression of the KIT protein in immunohistochemistry (IHC), suggesting that IHC may be potentially useful in identification of such GISTs. 16786129_a KIT exon 13 mutation may have a role in resistance to imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal neoplasms 16830365_Positivity of CD117 and CD34 is the most valuable factor in diagnosing gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). 16840725_identified a tandem repeat involving exons 11 and 12 in childhood AML that induces cell proliferation, and identified constituitively activated pathways and proteins phosphorylated 16842246_KIT mutations involving exons 11 or 9 were identified in 22 (88%) of gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GISTs) and none of the non-GISTs 16905672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16905672_Our data indicate that the KIT/KITLG system may be involved in a low sperm count trait in humans. 16928224_C-kit gene mutations were frequently found in patients with large GIST, more commonly in men than in women. However, the presence of a mutation was not predictive of prognosis in patients with large GIST. 17018686_study showed that c-kit is expressed in some osteosarcomas but protein expression is not of predictive value for the outcome of osteosarcoma patients; mutations in exon 9 & exon 11 of c-kit gene were not detected in the group showing protein expression 17024483_Acquired resistance of GIST to imatinib mesylate appears to be linked to a novel mutation in Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-kit. 17060458_intracellular, non-plasma membrane receptor signaling is sufficient to drive neoplasia caused by mutant c-KIT 17072721_Patients with an exon 11 mutation of the c-kit gene are reported to have a high response to STI571 (imatinib mesylate, Glivec). 17119051_fragile histidine triad and c-kit have roles in progression of fragile histidine triad and c-kit 17124503_a kit mutation may have a role in survival or proliferation of melanocytes from patients with piebaldism 17193822_KIT mutations in GIST are clustered in four exons. Most common are exon 11 mutations .Secondary mutations usually occur in KIT kinase domains in patients after imatinib treatment resulting in resistance to this drug. 17289809_A potential role of the c-Kit/mbKitL interaction in pathological settings is sustained by the expression of the membrane-bound KitL on endothelial cells lining intraplaque neovessels. 17298867_c-kit activating mutations are not coincident with KIT protein expression in Ewing sarcoma in most samples 17337216_The expression of KIT protein in normal human skin suggests its possible role in regulation of cutaneous development and function. 17367465_KIT may have a significant role in the oncogenesis of mesenchymal tumours of the uterus and ovary. 17372901_Results suggest that a subset of anal melanomas show activating KIT mutations, which are susceptible for therapy with specific kinase inhibitors. 17438095_Genomic alterations were present at disease onset in 1/3 of the examined cases. They therefore represent an early event possibly related to primary imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 17448763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17487504_Overexpression of c-KIT is observed in a subset of primary and CRC metastases in the absence of c-kit mutations. 17487541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17487541_These findings indicate that KIT-ht3 may be a useful genetic marker for osteoporosis and that KIT may have a role on bone metabolism in humans. 17495964_the MAGE-A3 and MAGE-C2 gene promoter regions are de-methylated in the presence of activated KIT but become methylated on inhibition of KIT, consistent with the downregulation of mRNA and protein 17519280_Phosphorylation of c-Kit receptor may be involved in mediating early beta-cell differentiation and survival. 17525721_N822 mutation of KIT gene is frequent in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients with t(8;21) in Japan 17526803_A sensitive, specific and cost-effective assay to detect the D816V mutation in archived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues from cases of SM has been developed. 17532173_GISTs were commonly associated with KIT mutation, but rarely associated with PDGFRA mutation in Taiwan. 17545544_KIT and PDGFRbeta gatekeeper mutations are involved in tumor progression and are resistant to imatinib, but are inhibited by sorafenib 17546049_Gastrointestinal stromal tumor secondary KIT mutations can be associated with KIT hyperactivation and imatinib resistance. 17551405_Point mutations of the C-KIT gene, in mastocytosis, were discovered in the bone marrow and the peripheral blood of the patient, abd in the tissue of the previously diagnosed germ cell tumor as well. 17573850_Further understanding of KIT signaling in testicular germ cell tumors may lead to novel therapeutic approaches for these tumours. 17595334_shows a major function of FES downstream of activated KIT receptor and thereby points to FES as a novel target in KIT-related pathologi 17623951_Finds that fifty-seven percent of GIST had mutations at exon 11 of c-KIT gene. Finds no mutations at exons 9, 13, and 17 of KIT gene. 17632543_Presence of homozygous KIT exon 11 mutations is associated with malignant course of disease and should be considered an adverse prognostic marker in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 17645464_The size of the mucosal mast cell (MC) population in patients with inactive inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is not altered by disease or by stress, yet MC in IBD are different (fewer c-kit receptors) and respond differently (greater activation). 17658483_This study evaluated ISCK03 as a skin-whitening agent that regulates c-kit activity. 17673922_Gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors have a lower expression of KIT compared to intestinal GISTs. 17681176_Adult intestine contained c-Kit positive immune precursor cells committed to the natural killer cell lineage. 17691909_Dysregulated kit function is an important component of oncogenesis in a large number of neoplastic disorders, including systemic mastocytosis. 17706113_The occurrence of c-kit mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors also correlates with patient's age. 17710669_Systemic mast cell activation disorder was pathogenetically characterized by two or more alterations in the Kit tyrosine kinase providing not only a means of confirming the diagnosis, but also of assessing prognosis. 17720713_The 22-nt c-kit87 promoter sequence possesses distinctive three-dimensional structural features that are only present in at most a handful of other genes. 17726262_The frequency of KIT overexpression in gliomas was assessed and the genetic mechanisms underlying KIT overexpression were investigated. 17767956_CD117 (c-kit) is aberrantly expressed on a subset of MGUS and MM with a more indolent presentation and is functionally antinomic to CD221 (IGF-1R). 17827398_The incidence of both KIT and PDGFRA mutations in a Portuguese series was 63%. The great majority of mutations were located in KIT exon 11, statistically associated with worse prognosis and indicative of favourable response to imatinib-based therapy. 17850794_VEGF receptor Flk-1 is involved in c-kit up regulation via ERK-mediated pathway 17855052_Early myeloid cells expressing GNNK+ or GNNK-c-KIT show different responses to stem cell factor. 17875504_Our study suggests that KIT activating mutations in AML with t(8; 21) are associated with diminished CD 19 and positive CD56 expression on leukemic blasts and, thus, can be phenotypically distinguished from AML1-ETO leukemias 17894554_Loss of heterozygosity of the c-kit gene in resected liver Gastrointestinal Stromal Neoplasms may be a helpful factor in the prediction of the prognosis of patients with liver metastasis. 17904548_Grb2 mediates c-Kit degradation through recruitment of Cbl to c-Kit, leading to ubiquitination of c-Kit followed by internalization and degradation. 17909012_study shows that pediatric KIT-wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) exhibit KIT activation at levels comparable with KIT-mutant pediatric and adult GISTs although they do not have KIT (or PDGFRA) mutations 17928050_Increased C-kit intensity is associated with acute myeloid leukemia 17943970_Frequently mutated in seminoma germ cell tumors, but not associated with bilateral disease as opposed to unilateral. 17949810_Endogenous KIT and beta-catenin were found to associate in mast cell leukemia cells, and in vitro kinase assay demonstrated that active KIT phosphorylates tyrosine residues of beta-catenin directly. 17960171_c-KIT but not CSF1R mutations play a role in the leukemogenesis of childhood CBF-AML 17965221_KIT overexpression is rare in Wilms' tumours, although it appears to confer a worse prognosis; clear cell sarcomas of the kidney are associated with an increased expression of KIT, however, in the absence of gene amplification and/or activating mutation 17989000_study found low frequency of KIT gene mutation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13q22) 17993265_Whereas FcvarepsilonRI required Lyn and Syk for NTAL phosphorylation, Kit appeared to directly phosphorylate NTAL 18006222_Presence of c-kit gene mutations in testicular germ cell tumours may not be associated with bilateral diseases, at least in Japan. 18042065_Four mixed cell-type GISTs showed somatic KIT mutations... mixed cell-type GISTs 18066592_C-kit protein expression correlated with activating mutations indicating the pertinent role of the proto-oncogene KIT in the tumorigenesis of oral musosal melanoma. 18084259_Silent mutations of KIT and PDGFRA were found in Merkel cell carcinoma that have the potential to lead to alternate protein function. 18165278_These data suggest that KIT(D816V+) systemic mastocytosis (SM) can co-exist with JAK2(V617F+) chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis (CIMF) and in some of these SM-CIMF cases, the two mutations are present in the neoplastic cells of both disease components. 18183595_study shows a novel germline mutation in the juxtamembrane domain of KIT, identified in 2 brothers, both presenting with recurrent, high risk/malignant rectal gastrointestinal stromal tumors 18187489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18192885_Pancreatic adenocarcinoma does not express CD117 antigen/KIT as assessed using a primary immunohistochemical antibody for CD117/KIT detection 18212542_CD117 proved to be a very sensitive marker of Atypical fibroxanthoma 18214972_The computational results presented here indicate that the dissociation of juxtamembrane region from the kinase domain is prerequisite to c-Kit activation, which is consistent with previous experiments. 18239612_Production of the soluble form of KIT, s-KIT, abolishes stem cell factor-induced melanogenesis in human melanocytes. 18245707_c-Kit positive cardiosphere-forming cells were isolated from biopsy samples from patients with ischemic heart disease. 18246046_evaluate the clinicopathologic profile of GISTs that have KIT exon 13 or exon 17 mutations. 18259950_Exon 11 mutation of CD-117 is associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumor 18265633_c-kit protein expression may play an important role in neoplasia of pancreatic neoplasms. 18265649_C-kit oncogenic mutations are more likely seen in CD-117-positive GISTs arising in the gastrointestinal tract and have no obvious relationship with biological behavior of GISTs. 18270328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18294292_Additional cis-positioned mutations in the kinase domains of the KIT gene are a major cause of secondary resistance to imatinib in Japanese gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients. 18312355_KIT genotyping is important for gastrointestinal stromal tumours diagnosis and assessment of sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.(Review) 18314611_may be mutated in gastrointtestinal stromal tumors. 18314612_KIT mutation D816V is associated with relative resistance against imatinib therapy in mastocytosis. 18337018_Immunohistochemical CD117 positivity was detected in a wide range of neoplastic and inflammatory thyroid diseases. 18350628_Data show that KIT exon 11 codon 557/558 deletion/insertion mutations define a subset of gastrointestinal stromal tumors with malignant potential. 18360281_When critically applied, CD117/PDGFRA immunophenotyping is a useful diagnostic tool correctly predicting the presence of PDGFRA mutations in most cases. 18372228_modifiers of SCF/c-Kit signalling, or the unidentified regulators of the c-Kit-negative melanocyte stem cells, could offer future routes to alter hair pigmentation for clinical effect in androgen-modulated hair disorders. 18385756_a second c-kit mutant model for t(8;21) AML. 18390729_study found the KIT D816V variant induces cluster formation & expression of several mast cell differentiation & adhesion antigens; it is hypothesized that KIT D816V as a single hit may be sufficient to cause indolent systemic mastocytosis 18404201_c-kit activating mutations have a role in determining the pathogenesis of mastocytosis, which significantly differs according to the age at disease's onset 18413817_GIST-type KIT mutations induce an activation-dependent alteration of normal maturation and trafficking, resulting in the intracellular retention of the activated kinase within the cell. 18416137_Significant correlation between c-Kit mutations, on the one hand, and tumor site and histological pattern of GastroIntestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST), on the other. 18424727_CD300a as a novel regulator of Kit in human MC and suggest roles for this receptor as a suppressor of Kit signaling in MC-related disorders. 18436868_Subepicardial localization of CD117-positive cells and expression of laminin-1 and alpha(6) integrin subunits may all correspond to the activation of regeneration involving an epithelial-mesenchymal transition in adult heart 18443272_c-Kit expression in multiple myeloma cells is functional, and coupled to survival pathways that may modulate cell death in response to therapeutic compounds used in the treatment of this disease 18486988_overexpression of KIT does not indicate gene mutation in thymic carcinoma. 18488000_The mechanism of the second hit resulting in homozygous KIT-activating mutation and loss of heterozygosity is achieved by mitotic nondisjunction. 18492696_Only 2 of 21 cases of ovarian granulosa cell tumors show positive immunoreaction for c-kit. Both epithelial and stromal components of the normal ovarian tissue demonstrate complete absence of staining for c-kit. 18500266_C-kit has neither a diagnostic nor a prognostic role in phyllodes tumors. 18521081_Protein kinase C-theta regulates KIT expression and proliferation in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 18521824_Elevated p21 expression is associated with poor prognosis of rectal stromal tumors after resection. 18542042_Mutations in the c-kit gene result in the constitutive ligand-independent activation of the c-KIT receptor and, consequently, aberrant cell division and tumor growth 18568298_in normal conditions, c-kit may be involved in the pituitary-adrenal axis regulation 18588518_Data show that Lnk bound directly to c-Kit through Tyr(568) on juxtamembrane domain of c-Kit. 18592792_Using a semi-quantitative immunohistochemical score we found that KIT expression was very weak in the majority of tumors, while none of the uterine sarcomas tested showed strong expression 18618605_KIT gene mutations in exon 11 are associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumor 18622894_The low or lacking c-kit expression in undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma together with the lack of mutation |
ENSMUSG00000005672 |
Kit |
65.471359 |
0.1861590633 |
-2.425392 |
0.270606916 |
81.801660 |
0.00000000000000000015045211559432433587742517516393797308716994861173483002958484178179787704721093177795410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001304743376129393138466013969778279595981843421658677873581355655119295988697558641433715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.8141315 |
3.6471507 |
107.2112183 |
12.2885038 |
| ENSG00000157510 |
134265 |
AFAP1L1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TED9 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in podosome and invadosome formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21333378}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable SH3 domain binding activity. Predicted to be located in cell junction; cell projection; and podosome. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:134265; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; podosome [GO:0002102]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124] |
21333378_Data suggest that AFAP1L1 may forge unique protein interactions in which AFAP1 is less efficient, and these interactions may allow AFAP1L1 to affect invadosome formation. 21516130_AFAP1L1 has a role in the progression of spindle cell sarcomas and is a prognostic biomarker. 23326307_Findings indicate a role for transcription factor Sp3 in sarcomas as a driver for expression of the metastasis-related gene AFAP1L1 (actin filament-associated protein 1-like 1). 24723436_AFAP1L1 plays a role in the progression of colorectal cancer by modulating cell shape and motility and by inhibiting anoikis, presumably through interactions with vinculin-including protein complexes. 26212012_data define a novel pathway that directs Lyn/Src family tyrosine kinase signals to sarcoma cell invadopodia through specific recruitment of Vav2 and Nck2 to phosphorylated AFAP1L1, to control cell migration and invasion 29323101_AFAP1L1 promotes cell proliferation, accelerates cell cycle progression, and prevents cell apoptosis in lung cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000033032 |
Afap1l1 |
120.513377 |
0.1094849497 |
-3.191196 |
0.502104266 |
35.007231 |
0.00000000328483208851094267545803389652444431723310458437481429427862167358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014978103684405781140645934628070901073471077324938960373401641845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.6096271 |
8.5465203 |
234.6043931 |
54.5588282 |
| ENSG00000157613 |
90993 |
CREB3L1 |
protein_coding |
Q96BA8 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in unfolded protein response (UPR). Binds the DNA consensus sequence 5'-GTGXGCXGC-3' (PubMed:21767813). In the absence of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, inserted into ER membranes, with N-terminal DNA-binding and transcription activation domains oriented toward the cytosolic face of the membrane. In response to ER stress, transported to the Golgi, where it is cleaved in a site-specific manner by resident proteases S1P/MBTPS1 and S2P/MBTPS2. The released N-terminal cytosolic domain is translocated to the nucleus to effect transcription of specific target genes. Plays a critical role in bone formation through the transcription of COL1A1, and possibly COL1A2, and the secretion of bone matrix proteins. Directly binds to the UPR element (UPRE)-like sequence in an osteoblast-specific COL1A1 promoter region and induces its transcription. Does not regulate COL1A1 in other tissues, such as skin (By similarity). Required to protect astrocytes from ER stress-induced cell death. In astrocytes, binds to the cAMP response element (CRE) of the BiP/HSPA5 promoter and participate in its transcriptional activation (By similarity). Required for TGFB1 to activate genes involved in the assembly of collagen extracellular matrix (PubMed:25310401). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12054625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21767813, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25310401}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May play a role in limiting virus spread by inhibiting proliferation of virus-infected cells. Upon infection with diverse DNA and RNA viruses, inhibits cell-cycle progression by binding to promoters and activating transcription of genes encoding cell-cycle inhibitors, such as p21/CDKN1A (PubMed:21767813). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21767813}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Nucleus;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Unfolded protein response |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is normally found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). However, upon stress to the ER, the encoded protein is cleaved and the released cytoplasmic transcription factor domain translocates to the nucleus. There it activates the transcription of target genes by binding to box-B elements. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:90993; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cAMP response element binding [GO:0035497]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; extracellular matrix constituent secretion [GO:0070278]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902236]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040037]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903671]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1990440]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12054625_a transcriptional activator of CREB/ATF family with a transmembrane domain 17721195_Presence of FUS/CREB3L2 and FUS/CREB3L1 in low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma suggests these neoplasms may be related. 21041443_The human Creb3L1 can activate SPCG transcription in a heterologous system(Drosophila embryos), which suggests a general and direct role for this family of bZip transcription factors in mediating high-level secretory capacity. 21536545_FUS-CREB3L2/L1-positive sarcomas show a specific gene expression profile with upregulation of CD24 and FOXL1. 21767813_CREB3L1 may play an important role in limiting virus spread by inhibiting proliferation of virus-infected cells. 21767813_Upon infection with diverse DNA and RNA viruses, CREB3L1 was proteolytically cleaved, allowing its NH(2) terminus to enter the nucleus and induce multiple genes encoding inhibitors of the cell cycle to block cell proliferation of infected cells. 21987447_Rapid amplification of cDNA ends revealed exon 6 of the cAMP-responsive element binding protein 3-like 1 gene (CREB3L1) fused in-frame to the EWSR1 exon 11. 22705851_OASIS is notably unstable proteins that are easily degraded via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway under normal conditions. 23256041_CREB3L1 expression may be a useful biomarker in identifying cancer cells sensitive to doxorubicin. 23335989_OASIS is important for the ER stress response and maintenance of some extracellular matrix proteins in human glioma cells. 23383089_a novel regulatory mechanism for VEGFA transcription by OASIS in human retinal pigment epithelial cells 23588368_We report 2 cases of Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma serendipitously found to harbor a novel alternative EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusion. 23955342_Fbxw7 controls osteogenesis and chondrogenesis by targeting OASIS and BBF2H7, respectively, for degradation. 24126059_CREB3L1 plays an important role in suppressing tumorigenesis and that loss of expression is required for the development of a metastatic phenotype. 24242870_Temporally regulates the differentiation from neural precursor cells into astrocytes [review] 24441665_EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusions are predominant over FUS and CREB3L2 rearrangements in pure sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma. 24896634_Case Report: low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the kidney found to harbor the EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusion. 25310401_Cleavage of CREB3L1 releases its NH2-terminal domain from membranes, allowing it to enter the nucleus where it binds to Smad4 to activate transcription of genes encoding proteins required for assembly of collagen-containing extracellular matrix. 25353281_Case Reports: genetically confirmed primary renal sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma with EWSR1-CREB3L1 gene fusion. 25625847_CREB3L1 mRNA expression is downregulated in human bladder cancer.CREB3L1 is epigenetically silenced in human bladder cancer facilitating tumor cell spreading and migration in vitro. 26110425_CREB3L1 was expressed in 19% of RCC, which is generally resistant to doxorubicin, but in 70% of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma that is sensitive to doxorubicin. 26810754_Our data further strengthens the role for CREB3L1 as a metastasis suppressor in breast cancer and demonstrates that epigenetic silencing is a major regulator of the loss of CREB3L1 expression 26917262_The results suggest that CREB3L1 is required for decidualization in mice and humans and may be linked to the pathogenesis of endometriosis in a progesterone-dependent manner. 27121396_These findings indicate that the miR-146a-CREB3L1-FGFBP1 signaling axis plays an important role in the regulation of angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 27499293_Ceramide inverts the membrane orientation of TMS4SF20, creating a form of TM4SF20 that stimulates the cleavage of CREB3L1. 28750683_Identification of novel prostate cancer drivers, ERF, CREB3L1, and POU2F2, using RegNetDriver, a framework for integration of genetic and epigenetic alterations with tissue-specific regulatory network. 28817112_ConclusionThis report confirms that CREB3L1 is an OI-related gene and suggests the pathogenic mechanism of CREB3L1-associated OI involves the altered regulation of proteins involved in cellular secretion. 29093023_Our findings support a model in which CREB3L1 acts as a downstream effector of TSH to regulate the expression of cargo proteins, and simultaneously increases the synthesis of transport factors and the expansion of the Golgi to synchronize the rise in cargo load with the amplified capacity of the secretory pathway 29531016_There was a relationship between the expression levels of both proteins and survival time. CREB3L1 and PTN expression levels serve as biomarkers with utility in grading gliomas. Absence of CREB3L1 and presence of PTN in brain glioma cells correlate with survival time of the glioma patients. 30103710_These results suggest that CREB3L1 expression level may be used as a biomarker to identify TNBC patients who are more likely to benefit from doxorubicin-based chemotherapy. 30657919_Here, we presenta Turkish family, in which molecular analysis of the proband revealeda previously unreported homozygous missense variant(c.911C>T,p.(Ala304Val))of the CREB3L1 31207160_Study reports a novel homozygous CREB3L1 mutation in a large Indonesian family with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI); the homozygous affected members have survived to adulthood and they present a more severe phenotype than previously reported, expanding the clinical spectrum of OI for this gene. 32234057_Mutations in COL1A1/A2 and CREB3L1 are associated with oligodontia in osteogenesis imperfecta. 33150680_Transcription factor old astrocyte specifically induced substance is a novel regulator of kidney fibrosis. 34990868_A group of sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcomas with low-level amplified EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusion gene in children. 35689957_Clinical and biological relevance of CREB3L1 in Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. 35802566_Reduced CREB3L1 expression in triple negative and luminal a breast cancer cells contributes to enhanced cell migration, anchorage-independent growth and metastasis. 36192735_CREB3L1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by remodeling the tumor microenvironment. |
ENSMUSG00000027230 |
Creb3l1 |
34.762353 |
2.7789673220 |
1.474549 |
0.308296958 |
23.126520 |
0.00000151684140001567123958348300150067444747037370689213275909423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005256768974931042215847573628728639505425235256552696228027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.8419943 |
8.5119561 |
17.5728046 |
2.5153381 |
| ENSG00000157654 |
445815 |
PALM2AKAP2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IXS6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene belongs to the paralemmin downstream gene (PDG) family defined in PMID:22855693. Paralemmin downstream genes may have evolved contiguously with the paralemmin genes and are associated with other paralemmin paralogs in humans and several other taxa. The gene encodes three distinct protein isoforms, the PALM2 isoform, the AKAP2 isoform and the PALM2-AKAP2 isoform. The biological significance of the PALM2-AKAP2 isoforms is yet unknown. Earlier, PALM2 and AKAP2 were annotated as separate genes and PALM2-AKAP2 was annotated as a readthrough gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2019]. |
hsa:445815; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
12646697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17273791_The complex phenotype with Kallmann syndrome and bone anomalies observed in the patient could be the result of the interruption of the AKAP2 gene. 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19893584_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20306291_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26432469_AKAP2 is expressed in human prostates, its expression is elevated in metastatic prostate cancer. 26989089_AKAP2 was therefore implicated as a novel gene mutated in a Chinese family with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. 28838314_study of the variants in AKAP2 gene did not support its association with the susceptibility of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in the Chinese population. 28849175_expression of AKAP2 was elevated in ovarian cancer. Furthermore, overexpression of AKAP2 promoted the growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells, whereas knockdown of AKAP2 expression reduced the growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000038729 |
Pakap |
178.813866 |
0.2948092881 |
-1.762146 |
0.145363885 |
148.377396 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000039231489945169608449548973780885595956345725189071948530738715835325137948493469182458448160644159941057296236976981163024902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000005721905055244105018772078989463372461871787821085822634080559876005631781042011700199982626724448664390365593135356903076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
78.3991649 |
10.8089040 |
268.8533811 |
25.3697856 |
| ENSG00000157741 |
254048 |
UBN2 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZU65 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to be involved in DNA replication-independent chromatin assembly. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:254048; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325] |
Mouse_homologues 30285846_This study demonstrates that the UBN1 or UBN2 subunit is mainly responsible for specific recognition and direct binding of H3.3 by the HIRA complex. |
ENSMUSG00000038538 |
Ubn2 |
161.386127 |
0.3926749880 |
-1.348592 |
0.161616629 |
68.719041 |
0.00000000000000011353937730100074568834995263615418292351419773944520841268968069925904273986816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000853714319390102380605848022656400120724403334741131610385878047964069992303848266601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
98.5612482 |
11.1444422 |
253.0618346 |
20.3081264 |
| ENSG00000157800 |
84255 |
SLC37A3 |
protein_coding |
Q8NCC5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in carbohydrate transport and transmembrane transport. Is integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84255; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; carbohydrate transport [GO:0008643] |
21752829_SLC37A3 protein localizes in lysosomes in HeLa cells |
|
|
82.493830 |
2.7136238024 |
1.440221 |
0.479249266 |
8.491603 |
0.00356789401152039385364811430179088347358629107475280761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007525309461280510307801261404847537050954997539520263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
87.2202331 |
46.7838124 |
32.1579483 |
12.2628923 |
| ENSG00000157827 |
114793 |
FMNL2 |
protein_coding |
Q96PY5 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. Required in the cortical actin filament dynamics. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a formin-related protein. Formin-related proteins have been implicated in morphogenesis, cytokinesis, and cell polarity. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described but their full-length nature has yet to be determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:114793; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
18665374_FMNL2 may play an important role in the metastasis of CRC and may be a useful marker for metastasis of CRC. 19401682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20101212_a novel regulatory and functional interaction between RhoC and FMNL2 for modulating cell shape and invasiveness and provide mechanistic insight into RhoC-specific signalling events. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21071512_Findings identify a novel EMT and tumor promoting function for FMNL2, which is involved in TGF-beta-induced EMT and colorectal carcinoma cell invasion via Smad3 effectors, or in collaboration with MAPK/MEK pathway. 21496865_formin-like 2 expression correlated positively with tumor differentiation (P = .046) and vascular invasion (P = .008). Patients whose tumors had lower formin-like 2 expression had shorter overall survival times 22608513_FMNL2 is a novel elongation factor of actin filaments that constitutes the first Cdc42 effector promoting cell migration and actin polymerization at the tips of lamellipodia. 22790947_Protein N-myristoylation plays critical roles in the cellular morphological changes induced by FMNL2 and FMNL3. 23201162_miR-137, induced by its upstream transcription factor HMGA1, can suppress colorectal cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting FMNL2. 25963737_The two interacting FMNL-Cdc42 heterodimers expose six membrane interaction motifs on a convex protein surface, the assembly of which may facilitate actin filament elongation at the leading edge of lamellipodia and filopodia. 25963818_Rac1-induced actin assembly and subsequent AJ formation critically depends on FMNL2. 26103003_MiR-34a was down-regulated in colorectal cancer cells and inversely correlated with FMNL2 and E2F5 expressions. Our study suggests that miR-34a is an important tumor suppressor of CRC progression by targeting FMNL2 and E2F5. 26256210_These data establish a role for FMNL2 in the regulation of beta1-integrin and provide a mechanistic understanding of the function of FMNL2 in cancer invasiveness. 26515696_miR-206 functioned as a tumor suppressor in the progression of colorectal cancer(CRC) by targeting FMNL2 and c-MET. Restoration of miR-206 expression may represent a promising therapeutic approach for targeting malignant CRC. 26564775_Capping protein and FMNL2 functionally coregulate filament barbed-end assembly. 27578625_FMNL2 is likely to be generally required in melanoma cells for invasion. 27906963_Our data proved that RMRP acted as an oncogene LncRNA to promote the expression of KRAS, FMNL2 and SOX9 by inhibiting miR-206 expression in lung cancer. These data suggested that RMRP might serve as a therapeutic target in lung adenocarcinoma 28817833_Data demonstrate that the FMNL2/COMMD10/p65 NF kappaB axis acts as a critical regulator in the maintenance of metastatic phenotypes in colorectal cancer. 29374558_Data indicate that the interaction of cortactin and formin-like 2 (FMNL2) could promote the invadopodia formation and matrix degradation. 29579104_FMNL2 knockout cells were characterized by impaired filopodia formation similar to depletion of the Rho GTPase Cdc42. 30594388_The outcome of this study illustrated that LINC00483 promoted colorectal cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via modulating FMNL2 by acting as a competitive RNA of miR-204-3p. 31175924_Findings reveal that the aberrant activation of FMNL2 promotes the pathogenesis of adenomyosis through inducing the EMT process. 31298385_MicroRNA-22 targets FMNL2 to inhibit melanoma progression via the regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 31751425_Results demonstrated that N-myristoylation-dependent phosphorylation in FMNL2 occurs at a single Ser residue at position 171, which is a Ser residue conserved between FMNL2 and FMNL3, corresponding to Ser-174 in FMNL3 32046858_CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via modulating of miR-1207-5p/FMNL2 signal. 32294157_FMNL2 regulates dynamics of fascin in filopodia. 34043722_Characterization of a L136P mutation in Formin-like 2 (FMNL2) from a patient with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. 35608697_FMNL2 regulates gliovascular interactions and is associated with vascular risk factors and cerebrovascular pathology in Alzheimer's disease. 35772391_Formin-Like 2 Is a Potential Biomarker of Poor Prognosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. 36335129_LINC00839 promotes malignancy of liver cancer via binding FMNL2 under hypoxia. |
ENSMUSG00000036053 |
Fmnl2 |
1947.678063 |
0.3061146380 |
-1.707856 |
0.042366831 |
1656.706596 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
922.1616721 |
28.4845377 |
3033.0970263 |
61.1349567 |
| ENSG00000157870 |
127281 |
PRXL2B |
protein_coding |
Q8TBF2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reduction of prostaglandin-ethanolamide H(2) (prostamide H(2)) to prostamide F(2alpha) with NADPH as proton donor. Also able to reduce prostaglandin H(2) to prostaglandin F(2alpha) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DB60}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Prostaglandin biosynthesis;Prostaglandin metabolism;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable antioxidant activity and prostaglandin-F synthase activity. Predicted to be involved in prostaglandin biosynthetic process. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:127281; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; myelin sheath [GO:0043209]; antioxidant activity [GO:0016209]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016616]; prostaglandin-F synthase activity [GO:0047017]; prostaglandin biosynthetic process [GO:0001516] |
Mouse_homologues 33418484_Deletion of the gene encoding prostamide/prostaglandin F synthase reveals an important role in regulating intraocular pressure. |
ENSMUSG00000029059 |
Prxl2b |
92.709337 |
3.3440984666 |
1.741617 |
0.167907253 |
113.252574 |
0.00000000000000000000000001899671504306626908015261646148841989323764347970603860172400338939685537908985679678153246641159057617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000213876059523766711277601254907702867231898279273977594805145634784251593152326620383973931893706321716308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
142.7017399 |
14.4111049 |
42.9616716 |
3.6819750 |
| ENSG00000157873 |
8764 |
TNFRSF14 |
protein_coding |
Q92956 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for four distinct ligands: The TNF superfamily members TNFSF14/LIGHT and homotrimeric LTA/lymphotoxin-alpha and the immunoglobulin superfamily members BTLA and CD160, altogether defining a complex stimulatory and inhibitory signaling network (PubMed:9462508, PubMed:10754304, PubMed:18193050, PubMed:23761635). Signals via the TRAF2-TRAF3 E3 ligase pathway to promote immune cell survival and differentiation (PubMed:19915044, PubMed:9153189, PubMed:9162022). Participates in bidirectional cell-cell contact signaling between antigen presenting cells and lymphocytes. In response to ligation of TNFSF14/LIGHT, delivers costimulatory signals to T cells, promoting cell proliferation and effector functions (PubMed:10754304). Interacts with CD160 on NK cells, enhancing IFNG production and anti-tumor immune response (PubMed:23761635). In the context of bacterial infection, acts as a signaling receptor on epithelial cells for CD160 from intraepithelial lymphocytes, triggering the production of antimicrobial proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines (By similarity). Upon binding to CD160 on activated CD4+ T cells, down-regulates CD28 costimulatory signaling, restricting memory and alloantigen-specific immune response (PubMed:18193050). May interact in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on other cells) with BTLA (PubMed:19915044) (By similarity). In cis interactions, appears to play an immune regulatory role inhibiting in trans interactions in naive T cells to maintain a resting state. In trans interactions, can predominate during adaptive immune response to provide survival signals to effector T cells (PubMed:19915044) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80WM9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10754304, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18193050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19915044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23761635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9153189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9162022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9462508}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpes simplex virus 1/HHV-1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11511370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9696799}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpes simplex virus 2/HHV-2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11511370, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9696799}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the TNF (tumor necrosis factor) receptor superfamily. The encoded protein functions in signal transduction pathways that activate inflammatory and inhibitory T-cell immune response. It binds herpes simplex virus (HSV) viral envelope glycoprotein D (gD), mediating its entry into cells. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:8764; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; tumor necrosis factor receptor activity [GO:0005031]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of adaptive immune memory response [GO:1905675]; negative regulation of alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:0046642]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] |
11742858_Data suggest involvement of TNF superfamily receptor members and ligands in human atherosclerosis. TNFRSF14 (HVEM, TR2, LIGHTR)analysis, found this receptor in regions rich in CD68-positive macrophage-derived foam cells and HLA-DR-positive cells. 11976496_Crystallization and preliminary diffraction studies of the ectodomain of the envelope glycoprotein D from herpes simplex virus 1 alone and in complex with the ectodomain of the human receptor HveA 12466117_Data show that mRNA encoding LIGHT and its receptors [HVEM, LTbetaR, and TR6 (DcR3)] are present in placentas and cytotrophoblast cells at term. 12915568_association of HVEM and nectin-1 with lipid rafts during herpes simplex virus entry 14749527_sHVEM levels were elevated in sera of patients with allergic asthma, atopic dermatitis and rheumatoid arthritis 15110526_both nectin 1 and HVEM receptors play a role during HSV infection in vivo and both are highly efficient even at low levels of expression 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15568026_HVEM binds to B T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), an Ig family member, which inhibits T cell proliferation. 15647361_Binding of HVEM to BTLA attenuates T cell activation, identifying HVEM/BTLA as a coinhibitory receptor pair. 15767456_in cells a complex forms through physical associations of HVEM, HSV-1 gD, and at least gH 15917993_both LTbetaR and HVEM can discriminatively mediate the expression of different genes in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells, including LIGHT, a proinflammatory cytokine 16131544_distinct herpesviruses target the HVEM-BTLA cosignaling pathway, suggesting the importance of this pathway in regulating T cell activation during host defenses. 16169851_2.8-A crystal structure of the BTLA-HVEM complex shows that BTLA binds the N-terminal cysteine-rich domain of HVEM and employs a unique binding surface 16797773_Real-time RT-PCR confirmed up-regulation of IL-8, osteopontin, and TNFRSF14 and down-regulation of SAMeS and CD209 in AH. 17010447_HVEM, a membrane-bound receptor that protects against apoptosis, was expressed only on syncytiotrophoblast 17405920_HSV-1-gD-HveA interaction initiates a signal transduction pathway leading to NF-kappaB activation 17947707_Ca(2+)is a downstream mediator of the LIGHT/HVEM interaction in monocytes 18193050_CD160 serves as a negative regulator of CD4+ T cell activation through its interaction with HVEM. 18502984_Expression of entry receptors nectin-1 and HVEM prevent entry of HSV-1 into human conjunctival epithelium. 18671825_These results establish that HVEM is involved in NF-kappaB activation by herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein D. 18794853_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987746_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19023130_LIGHT-mediated upregulation of PAR-2 in endothelial cells is mediated through the HVEM receptor, involving Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways. 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332782_HVEM-B and T lymphocyte attenuator bidirectional signaling may serve as a critical cell-survival system for lymphoid and epithelial cells 19473566_tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 14 (TNFRSF14) and signal regulatory protein, gamma (SIRPG) appear to contribute to gender difference in incidence of systemic lupus erythematosus. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19680232_Results provide evidence of an existing relationship between HVEM and obesity, which suggest that this TNF superfamily receptor could be involved in the pathogenesis of obesity and inflammation-related activity. 19701890_unknown killing effect of LIGHT through HVEM on a lymphoid malignancy is described. 19762537_results suggest that down-regulation of the BTLA-HVEM pathway may be involved in germinal center B-cell activation. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915044_the HVEM-BTLA cis-complex competitively inhibits HVEM activation by ligands expressed in the surrounding microenvironment, thus helping maintain T cells in the naive state. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20187130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20187130_We have identified and replicated a novel gene-gene interaction between 2 polymorphisms of TNFRSF members in Spanish patients with RA, based on the hypothesis of shared pathogenic pathways in complex diseases. 20233754_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20439292_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20884631_Findings identify TNFRSF14 as a candidate gene associated with a subset of FL, based on frequent occurrence of acquired mutations and their correlation with inferior clinical outcomes. 20884631_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20962851_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20962851_Polymorphisms were associated with MS predisposition, with stronger effect in patients with HHV6 active replication-TNFRSF6B-rs4809330(*)A: P=0.028, OR=1.13; TNFRSF14-rs6684865(*)A: overall P=0.0008, OR=1.2. 21533159_data show that HVEM stimulatory signals promote experimental colitis driven by innate or adaptive immune cells 21920726_HVEM-BTLA cis complex provides intrinsic regulation in T cells serving as an interference mechanism silencing signals coming from the microenvironment. 21941365_TNFRSF14 appears to be a serious candidate gene that might contribute to follicular lymphoma development. 21959263_The results of a mutagenesis study of HVEM suggest that the CD160 binding region on HVEM was slightly different from, but overlapped with, the BTLA binding site. 22113134_Results indicate that mHVEM on leukocytes and sHVEM in sera may contribute to the development and/or progression of gastric cancer. 22179929_study described the expression and spatial distribution of HVEM and BTLA in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues, and results indicated that HVEM/BTLA may be involved in regulating the progress of joint inflammation 22239829_These results suggest that the C-terminal portion of the soluble HVEM ectodomain inhibits herpes simplex virus type 1 gD activation and that this effect is neutralized in the full-length form of HVEM in normal infection. 22459947_These findings support role for BTLA and/or HVEM as potential, novel diagnostic markers of innate immune response/status and as therapeutic targets of sepsis. 22634623_HVEM-B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) interactions impair minor histocompatibility antigen (MiHA)-specific T cell functionality, providing a rationale for interfering with BTLA signaling in post-stem cell transplantation. 23375291_BTLA and HVEM may have roles in graft rejection after kidney transplantation 23445872_Sequencing of TNFRSF14 located in the minimal region of loss in 1p36.32 showed nine mutations in pediatric follicular lymphoma. 23470321_Studies indicate co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory receptors B7-1, B7-2, CD28 and TNFRSF14 have a pivotal role in T cell biology, as they determine the functional outcome of T cell receptor (TCR) signalling. 23761635_HVEM functions as a regulator of immune function that activates NK cells via CD160 and limits lymphocyte-induced inflammation via association with B and T lymphocyte attenuator 23976978_HVEM gene polymorphisms are associated with sporadic breast cancer in Chinese women. 24249528_HVEM plays a critical role in both tumor progression and the evasion of host antitumor immune responses, possibly through direct and indirect mechanisms. 24314649_The conformation of the N-terminus of herpes simplex virus gD is induced by direct binding to HVEM and nectin-1. 24980868_Relative expression of HVEM and LTbetaR modulates canonical NF-kappaB and pro-apoptotic signals stimulated by LIGHT. 25468715_Data indicate that tumour-expressing herpes virus entry mediator (HVEMplays a critical role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting targeting HVEM may be a promising therapeutic strategy for HCC. 25750286_HVEM may play a critical role in tumor progression and immune evasion 26202493_Study report the crystal structure of unbound HVEM, which further contributes to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms controlling recognition between HVEM and its ligands. 26650888_In eight cases (42%) we observed recurrent copy number loss of chr1:2,352,236-4,574,271, a region containing the candidate tumor suppressor TNFRSF14. 26965583_Report a variant of t(14;18) negative nodal diffuse follicular lymphoma with CD23 expression, 1p36/TNFRSF14 abnormalities, and STAT6 mutations. 27103745_The increased immune-stimulatory capacity of lymphoma B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations had clinical relevance, associating with higher incidence of acute GVHD in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 27257180_genetic landscape of Pediatric-type follicular lymphoma suggests that TNFRSF14 mutations accompanied by copy-number neutral loss of heterozygosity of the 1p36 locus in over 70% of mutated cases, as additional selection mechanism, might play a key role in the pathogenesis of this disease. 27297871_These results suggest that TNFRSF14 mutations point towards a diagnosis of follicular lymphomas , and can be used in the sometimes difficult distinction between marginal zone lymphomas and follicular lymphomas 27458100_the overexpression of HVEM in ovarian cancer cells may suppress the proliferation and immune function of T cells, thus leading to the development of ovarian cancer. The current study partially explains the immune escape mechanism of ovarian cancer cells. 27987232_Roles of HVEM are likely to be immunosuppressive rather than activating tumor immunity and it in peripheral blood is a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. 28365939_HVEM is highly expressed in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma tissues and correlated with the patient clinicopathological features. 28470686_Low HVEM expression is associated with pancreatic and ampullary cancer. 28533310_TNFRSF14 and MAP2K1 mutations are the most frequent genetic alterations found in pediatric-type follicular lymphoma (PTFL) and occur independently in most cases, suggesting that both mutations might play an important role in PTFL lymphomagenesis. 28612127_High HVEM Expression is Associated with Cancer Progression in Breast Cancer. 28671524_Transgenic mice expressing HVEMIg showed a complete resistance to the lethal infection even with 300 MLD50 (survival rate of 100 %). 28809154_HIV-1 produced from CD4+ T cells bears HSV-2 receptor HVEM and can bind to and enter HSV-2-infected epithelial cells depending on HVEM-gD interaction and the presence of gB/gH/gL. 29061848_Data suggest that both HVEM and UL144 bind a common epitope of BTLA, whether engaged in trans or in cis; these studies were conducted in cell lines representing B-lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and natural killer cells. (HVEM = human herpes virus entry mediator; UL144 = membrane glycoprotein UL144 of Human herpesvirus 5; BTLA = human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator) 29339444_LIGHT signaling through HVEM in epidermal keratinocytes directly induced proliferation and periostin expression, and both keratinocyte-specific deletion of HVEM or antibody blocking of LIGHT-HVEM interactions after disease onset prevented expression of periostin and limited atopic dermatitis symptoms. 29858685_Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphomas with concomitant 1p36 deletion and TNFRSF14 mutations frequently express high levels of EZH2 protein. 30066919_TNFRSF14 may serve a tumor suppressive role in bladder cancer by inducing apoptosis and suppressing proliferation, and act as a novel prognostic biomarker for bladder cancer. 30116751_our data suggested that the BTLA/HVEM pathway contributes to peripheral T cell suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients 30429008_HVEM was found to have a significant negative correlation with PD-L1 expression. 30508197_These data provide the first evidence of overexpression of LIGHT and its receptors HVEM and LT beta receptor in systemic sclerosis and suggest that the LIGHT axis might contribute to the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. 30770415_we have shown that soluble Fc-disabled HVEM-(Fc*) augments NK cell activation, IFN-gamma production, and cytotoxicity of NK cells without inducing NK cell fratricide by promoting cross-talk between NK cells and monocytes without Fc receptor-induced effects 30918139_the BTLA-TNFRSF14 immune modulation pathway seems to play a role in the pathobiology and prognosis of FL. 30984188_BTLA/HVEM Signaling: Milestones in Research and Role in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. 30987862_Our data highlights the importance of HVEM in the development of GBM and as a potential molecular target in combination with current immune checkpoint blockades for treatment of GBM. 31313042_High TNFRSF14 expression is associated with Colorectal Liver Metastasis. 31522034_HVEM expression on CD3+ cells increases after trauma. Patients developing secondary infections have less circulating HVEM+CD3+. This implies HVEM signaling in lymphocytes plays a role in maintaining host defense to infection in after trauma. 32027253_expression of BTLA and its ligand HVEM, the proportion of T lymphocytes and the expression of BTLA on the surface of gammadelta T cells in patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia are reduced 32312328_HVEM/HIF-1alpha promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells under hypoxic microenvironment conditions. 32454905_The Analysis of PTPN6 for Bladder Cancer: An Exploratory Study Based on TCGA. 32795404_Redesigning HVEM Interface for Selective Binding to LIGHT, BTLA, and CD160. 33238640_Fragments of gD Protein as Inhibitors of BTLA/HVEM Complex Formation-Design, Synthesis, and Cellular Studies. 34478526_Frequent mutated B2M, EZH2, IRF8, and TNFRSF14 in primary bone diffuse large B-cell lymphoma reflect a GCB phenotype. 34709351_HVEM structures and mutants reveal distinct functions of binding to LIGHT and BTLA/CD160. 35196150_Clinical Significance of BTLA and HVEM Expression on Circulating CD4(+) T and CD8(+) T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. 35537322_The role of the BTLA-HVEM complex in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. 36081508_BTLA inhibition has a dominant role in the cis-complex of BTLA and HVEM. |
ENSMUSG00000022074+ENSMUSG00000042333 |
Tnfrsf10b+Tnfrsf14 |
214.199254 |
2.1968749776 |
1.135453 |
0.111057653 |
105.320074 |
0.00000000000000000000000103918048611183423727294961153598898410627056000034046807486008321373682772303936872049234807491302490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000011066597384567585288532194660002779768344655864431736330580851148178145315625897637801244854927062988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
296.9343032 |
20.3567350 |
136.1188006 |
7.2650660 |
| ENSG00000157933 |
6497 |
SKI |
protein_coding |
P12755 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in terminal differentiation of skeletal muscle cells but not in the determination of cells to the myogenic lineage. Functions as a repressor of TGF-beta signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19049980}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Craniosynostosis;Disease variant;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes the nuclear protooncogene protein homolog of avian sarcoma viral (v-ski) oncogene. It functions as a repressor of TGF-beta signaling, and may play a role in neural tube development and muscle differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:6497; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone deacetylase inhibitor activity [GO:0046811]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cell motility [GO:0048870]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0002089]; myelination in peripheral nervous system [GO:0022011]; myotube differentiation [GO:0014902]; negative regulation of activin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0032926]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of Schwann cell proliferation [GO:0010626]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; nose morphogenesis [GO:0043585]; olfactory bulb development [GO:0021772]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
12034730_c-Jun associates with the oncoprotein Ski and suppresses Smad2 transcriptional activity 12419246_determined the crystal structure of a complex between a conserved Smad4 binding fragment of Ski and the MH2 domain of Smad4 at 2.85 A resolution 12764135_the ability of Ski and SnoN to repress the growth inhibitory function of the Smad proteins is required for their transforming activity. 12793438_I discuss the basis for repression of intracellular TGF-beta signaling by SKI, some additional activities of this protein, and propose that by disrupting multiple tumor suppressor pathways, SKI functions as a melanoma oncogene. 12874272_c-ski and HIPK2 play an important role in the negative regulation of BMP-induced transcriptional activation 14583455_SKI regulates crucial events required for melanoma growth, survival, and invasion. 14712482_c-Ski protein has a role as a transcriptional co-repressor in TGF-beta signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 15107821_These results suggest that stabilization of inactive Smad complexes on DNA is a critical event in c-Ski-mediated inhibition of TGF-beta signaling. 15122324_Our data suggest that regulated proteolysis of Ski is one of the key mechanisms that control the threshold levels of this proto-oncoprotein, and thus prevents epithelial cells from becoming TGF-beta resistant. 15128733_ski is repressed by Smad7 15312649_Functional Ski overexpression inhibits TGF-beta-mediated proliferation and prevents growth-arrested Schwann cells from reentering the cell cycle. 15542823_Ski cooperates in the process of transformation in erythroid cells by interfering with GATA1 function 15806149_Ski's increased level and specific relocalization during mitosis 16054854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16054854_a novel polymorphism of the SKI gene was found to be associated with a decreased risk for orofacial defects 16327884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424870_Ski seems to be involved in the blocking of differentiation in AML via inhibition of RARalpha signaling 17054724_subcellular localization of c-Ski may be regulated by proteasome-sensitive processes through amino acid residues 94-210 and 491-548 17469184_These results indicate that impaired competition with p300 is the possible cause of dysfunction of c-Ski/SnoN in scleroderma fibroblasts and that this might contribute to maintenance of the autocrine TGFbeta loop in this disease. 17592292_Inhibition of Ski through RNA interference restored TGF-beta signaling and growth inhibition in vitro, and decreased tumor growth in vivo. 17621263_Ski-mediated repression of PU.1 is due to Ski's ability to recruit histone deacetylase 3 to PU.1 bound to DNA. 18261624_Ski and SnoN proteins are overexpressed in Barrett's esophagus 18451154_The ability of TGF-beta to induce degradation of Ski could be an additional mechanism contributing to its protumorigenic activity. 18508800_Ski is expressed in patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid 18782659_c-Ski and SnoN, mediators in TGF-beta resistance, might be implicated in melanoma growth and progression. 19032343_These results indicate that Ski complexes serve to maintain a TGF-beta-responsive promoter at a repressed basal level via the activities of histone deacetylase and histone arginine methyltransferase. 19049980_SKI and MEL1 knockdown synergistically restored TGF-beta responsiveness in MKN28 cells and reduced tumor growth in vivo 19096149_SnoN and Ski were overexpressed both in adenomas with severe dysplasia and colorectal carcinomas. 19112531_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19112531_This study explores the association of STRA6 and SKI genes in a cohort of subjects with anophthalmia and microphthalmia. 19341714_Ski can stabilize RARalpha and HDAC3 thus Ski represses retinoic acid signaling by stabilizing corepressor complex. 19546161_Ski may act as a tumor proliferation-promoting factor or as a metastatic suppressor in human pancreatic cancer. 19594546_c-Ski overexpression promotes the growth of diffuse-type gastric carcinoma through induction of angiogenesis 19845874_Results indicate that SKI exploits multiple regulatory levels of the TGF-beta pathway and its deficiency restores TGF-beta tumor suppressor and apoptotic activities in spite of the likely presence of oncogenic mutations in melanoma tumors. 19875456_Akt modulates TGF-beta signaling by temporarily adjusting the levels of two TGF-beta pathway negative regulators, Ski and Smad7 19959502_findings show that Arkadia regulates the levels of expression of c-Ski protein in cell-type-dependent fashion, and exhibits a tumour suppressor function by inhibiting tumour cell growth 20404506_SKI promotes the switch of Smad3 from repressor of proliferation to activator of oncogenesis by facilitating phosphorylations in the linker domain. 20572854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20624875_Results identified serine 515 as a phosphorylation site of c-Ski which affects its electrophoretic motility. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20691163_the results suggest that association with Ski leads to inhibition of Siah2 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity and in this way, the Ski protein inhibits Siah2-mediated proteasomal degradation of HDAC3. 20853076_These results suggest that c-Ski is likely involved in the carcinogenesis of CCA induced by O. viverrini infection 20959473_c-Ski overexpression is associated with tumor progression. 21107877_Ski correlated with poor survival in the patients with TGF-beta-positive advanced gastric cancer. 21149449_Suppression of p53 activity through the cooperative action of Ski and histone deacetylase SIRT1. 21466664_impairment of SKI expression is not the leading mechanism involved in the growth-suppressive effect of miR-155 found in this malignancy. 21600873_These data identify Ski as a novel target of Aurora A and contribute to an understanding of the role of these proteins in the mitotic process. 21685371_Forced expression of miR-29a down-regulated SKI and its target gene, Nr-CAM, whereas miR-29a inhibition induced SKI expression. 22194822_Two genes were consistently retained in the models with clinical variables: SKI (v-SKI avian sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) and SLAMF1 (signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 1; CD150). 22229264_Ski expression in breast neoplasms is associated with longer overall and disease-free survival. 22411991_A mutant SKI defective in transformation fails to increase p53 ubiquitination and is unable to increase MDM2 levels and to increase mono-sumoylation of Ubc9 22853316_Transgenic K562 cells have distinct gene expression profiles both in steady state and during terminal erythroid differentiation, with GATA1s expression characterised by lack of repression of MYB, CCND2 and SKI. 22984993_The study data provide limited support for the hypothesis that common SKI variants are susceptibility factors for non-syndromic cleft lip/palate. 23023332_We identified causative variation in ten individuals with SGS in the proto-oncogene SKI, a known repressor of TGF-beta activity. 23103230_our findings show that in-frame mutations in exon 1 of SKI cause Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome (SGS). 23441061_Ski expression is a novel negative feedback mechanism acting on retinoic acid signaling 23809940_Overall, these studies demonstrate altered Ski protein levels, degradation and localization in human papillomavirus16-transformed human keratinocytes and in cervical cancer. 23892090_The 1p36.33-1p36.32 deletion encompassing SKI may represents a previous undescribed microdeletion disorder. 24011664_c-Ski is an important regulator in the activation of CAFs and may serve as a potential therapeutic target to block breast cancer progression. 24641900_acetaldehyde up-regulates COL1A2 by modulating the role of Ski and the expression of SMADs 3, 4, and 7. 24736733_Eight recurrent and three novel SKI mutations from eleven SGS patients were located in the R-SMAD binding domain, except for one in the DHD domain. 25670202_Ski regulates Hippo and TAZ signaling to suppress breast cancer progression. 25955797_our findings suggest that Ski represses TGF-b-induced EMT and invasion by inhibiting SMAD-dependent signaling in non-small cell lung cancer 26138431_Overexpression of Ski wild type, but not S326D and S383D mutants inhibited centrosome amplification and cellular transformation induced by AURKA. 27256397_miR-1908 had a positive role in scar formation by suppressing Ski-mediated inflammation and fibroblast proliferation in vitro and in vivo. 27473823_Transforming Growth Factor beta inhibitor peptide P144 downregulates SKI and an upregulates SMAD7 at both transcriptional and translational levels in glioblastoma cell lines. 28398634_Study identified Ski as a functional tumor suppressor with frequent epigenetic inactivation in lung cancer. 28607031_A microRNA miR-155 regulates transforming growth factor-beta TGF-beta-induced human coronary artery endothelial cells fibrogenic endothelial-mesenchymal transition via the regulator of TGF-beta signaling c-Ski to affect cardiac fibrosis, and miR-155/c-Ski may represent novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cardiac fibrosis. 29471413_Our work demonstrates for the first time the predominant co-repressive function of SKI in acute myeloid leukemia cells on a genome-wide scale and uncovers the transcription factor RUNX1 as an important mediator of SKI-dependent transcriptional repression. 29534839_The correlation between serum concentrations of IgG4 and SKI methylation levels suggest SKI might be involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). 29570207_c-Ski expression in cardiac muscle cells could be down-regulated by TGF-b1. Silencing of c-Ski gene was accompanied by down-regulation of E-cadherin, up-regulation of a-SMA and/or FN and Smad3 phosphorylation induced by TGF-b1, promoting EMT process. 29734252_Ski, SnoN, and Smad4 seem to play a role in oral squamous cell carcinoma oncogenesis, and it is likely that Ski and SnoN functions may take place independent of Smad4. 30249787_Ski is required for the fitness of hematopoietic stem cells , in which it suppresses TGF-beta signaling and abnormal RNA splicing. Active TGF-beta signaling and abnormal RNA splicing occur in a subset of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome who exhibit loss of SKI because of miR-21. 30642396_Data demonstrates gene expression changes in differentially methylated SKI gene in patients with age-related macular degeneration. 30896889_Over-expressed c-Ski could enhance cell viability, promote cell invasion, and migration of gastric cancer associated fibroblasts. 30972853_Findings suggest that c-Ski suppresses transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) signaling in clear cell renal carcinoma (ccRCC) cells, which, in turn, attenuates the tumor-suppressive effect of TGF-beta. 31746363_Knockdown of Ski decreases osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration by suppressing the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 31980905_new mutational hotspot in the SKI gene in the context of MFS/TAA molecular diagnosis. 33416497_Mutations in SKI in Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome lead to attenuated TGF-beta responses through SKI stabilization. |
ENSMUSG00000029050 |
Ski |
191.966971 |
0.4618985122 |
-1.114352 |
0.112425425 |
100.086027 |
0.00000000000000000000001459193382200227762318419772820318659575311699745224507814735765386104926477628396241925656795501708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000147822198498801373823573044774078020110072003038105132704518526742809569896053289994597434997558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
123.7561932 |
11.6505379 |
270.5121665 |
17.2467468 |
| ENSG00000158050 |
1844 |
DUSP2 |
protein_coding |
Q05923 |
FUNCTION: Dephosphorylates both phosphorylated Thr and Tyr residues in MAPK1, and dephosphorylation of phosphotyrosine is slightly faster than that of phosphothreonine (PubMed:8107850). Can dephosphorylate MAPK1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q05922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8107850}. |
3D-structure;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual specificity protein phosphatase subfamily. These phosphatases inactivate their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues. They negatively regulate members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase superfamily (MAPK/ERK, SAPK/JNK, p38), which are associated with cellular proliferation and differentiation. Different members of the family of dual specificity phosphatases show distinct substrate specificities for various MAP kinases, different tissue distribution and subcellular localization, and different modes of inducibility of their expression by extracellular stimuli. This gene product inactivates ERK1 and ERK2, is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic tissues, and is localized in the nucleus. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1844; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0017017]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008330]; endoderm formation [GO:0001706]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
12673251_During apoptosis, p53 activates transcription of PAC1 by binding to a palindromic site in the PAC1 promoter 12826159_relationships between the expression levels of CD61, CD63, and PAC-1 on the platelet surface and the incidences of acute rejection and tubular necrosis as well as the recovery of graft function after renal transplantation 14680939_variation in large granular lymphocyte leukemia 17471234_These results reveal a crucial role of PAC1 in E2F-1-directed apoptosis. 17827388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18178562_a novel, stimulus-specific, and phosphatase-specific mechanism of ERK2 regulation in the nucleus by DUSP1, -2, and -4. 18600034_Induction of hypercortisolism in healthy volunteers was not associated with changes in the platelet activation marker PAC-1 or the number of circulating platelet-leucocyte aggregates. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20723301_Dipyridamole reduced expression of PAC-1 and CD62p in patients with malignant lymphoma. 21490398_DUSP2 is a key downstream regulator of HIF-1-mediated tumor progression and chemoresistance 21984126_DUSP2 is an important molecule in endometrial physiology and that hypoxia-inhibited DUSP2 expression is a critical factor for the development of endometriosis. 25596742_Data show that hypoxia promotes lapatinib resistance in ERBB2-positive breast cancer cells through activation of the MEK-ERK pathway a HIF-1-dependent manner via regulation of dual-specificity phosphatase 2 (DUSP2). 26207425_identified among the key genes in circulating monocytes that were altered by exercise 26658840_Highly recurrent mutation of DUSP2 is associated with nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. 26833217_Our data show that aberrant epigenetic inactivation of DUSP2 occurs in carcinogenesis and that CTCF is involved in the epigenetic regulation of DUSP2 expression. 28026024_Hypoxia inhibits DUSP2 expression in colon cancer, leading to up-regulation of IL-8, which facilitates angiogenesis and tumour metastasis. 28252035_Regulation of atypical MAP kinases ERK3 and ERK4 by the phosphatase DUSP2 has been reported. 28440564_hypoxia-induced IL-6 production in endometriotic lesions is mediated via downregulation of DUSP2, which causes aberrant activation of STAT3 signaling pathway and helps the endometriotic cells survive under the ectopic environment 28652251_Authors report that hypoxia-mediated downregulation of the dual specificity phosphatase 2 (DUSP2) is critical for the accumulation of CSC in colorectal cancer. 30458195_Taken together, our findings for the first time suggested DUSP2 as a progression and prognosis biomarker for bladder cancer. 31889045_Down-regulation of DUSP2 expression in serous ovarian carcinoma was an independent risk factor for patient survival. 31932812_PAC1 is selectively upregulated in exhausted tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and is associated with poor prognosis of patients with cancer. PAC1(hi) effector T cells lose their proliferative and effector capacities and convert into exhausted T cells. |
ENSMUSG00000027368 |
Dusp2 |
78.464072 |
8.3966266353 |
3.069810 |
0.226015508 |
215.655247 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000080191271817637363105815683841737641469052973562421316994405476692283545729948003426467460526152500506359758134361800666826784744767309121016296558082103729248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016600605498293511690662015645535597161310709130732411597882842764145258506609795893328748870097251755492220397157362521498719099000140886346343904733657836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
141.8388647 |
19.7284357 |
17.0140117 |
2.1471761 |
| ENSG00000158106 |
114822 |
RHPN1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TCX5 |
FUNCTION: Has no enzymatic activity. May serve as a target for Rho, and interact with some cytoskeletal component upon Rho binding or relay a Rho signal to other molecules. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61085}. |
Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in signal transduction. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including focal adhesion assembly; glomerular filtration; and negative regulation of stress fiber assembly. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114822; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; negative regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051497]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
31982726_The positive feedback loop of RHPN1-AS1/miR-1299/ETS1 accelerates the deterioration of gastric cancer. 32435875_LncRNA RHPN1-AS1 accelerates proliferation, migration, and invasion via regulating miR-485-5p/BSG axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000022580 |
Rhpn1 |
120.904330 |
0.1908079999 |
-2.389806 |
0.188730945 |
168.014754 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000002008069057409917797460346451284169954132172167777798749598002660591399759619918780575087088365585823515613306256000214489176869392395019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000323570952918890700966829094499247755642725794474274376663595767112373778630558801329308963399948063932587416502428823150694370269775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.1788316 |
4.8252988 |
206.7823025 |
14.9383946 |
| ENSG00000158186 |
22808 |
MRAS |
protein_coding |
O14807 |
FUNCTION: Serves as an important signal transducer for a novel upstream stimuli in controlling cell proliferation. Activates the MAP kinase pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16630891, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28289718}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Ras family of small GTPases. These membrane-associated proteins function as signal transducers in multiple processes including cell growth and differentiation, and dysregulation of Ras signaling has been associated with many types of cancer. The encoded protein may play a role in the tumor necrosis factor-alpha and MAP kinase signaling pathways. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:22808; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein activity [GO:0003925]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTP-dependent protein binding [GO:0030742]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265] |
12138204_implicated in a novel pathway of neuronal differentiation by coupling specific trophic factors to the MAPK cascade through the activation of B-Raf 17538012_These findings proved a crucial role of the cross-talk between two Ras-family GTPases M-Ras and Rap1, mediated by RA-GEF-2, in adhesion signaling. 18628988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19198612_Identification of one new CAD risk locus on 3q22.3 in MRAS, and suggestive association with a locus on 12q24.31 near HNF1A-C12orf43. 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20971364_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24211266_Both MRAS and SHOC2 play a key role in polarized migration. 25800439_The MRAS gene loci might have a minor effect in conferring susceptibility to coronary artery disease in the Chinese population. 25973078_The association of the MARS rs6782181 polymorphism and serum lipid levels is different between the Mulao and Han populations, or between males and females in the both ethnic groups. 27891760_Results discovered for the first time that MRAS is recurrently mutated, indicating that MRAS mutations could drive tumorigenesis of Type IV gastric neoplasm. 29264877_acute coronary syndrome in Czechs (30.4% vs 29.4% carriers of the minor T allele of MRAS[recessive model], p = 0.54; OR 1.05; 95% CI 0.89-1.24 for males and 32.1% vs 29.7% carriers of the minor T allele, p = 0.28; OR 1.12; 95% CI 0.91-1.37 for females) 30431558_In human dorsal root ganglia and blood indicated this variant is an expression quantitative trait locus, with the minor allele associated with decreased expression of the nearby muscle RAS oncogene homolog (MRAS) gene. 31108500_Activating MRAS mutations cause Noonan syndrome associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. 31173466_We confirmed that the MRAS gene represents a causative gene for RASopathy. 31770223_In Chinese Han population, no association of MRAS single nucleotide polymorphisms with Ischemic Stroke risk was observed, while G allele of rs40593 was associated with increased risk of cerebral infarction. rs40593, rs751357, rs6782181 were associated with increased total cholesterol levels. 32495899_Correlation between MRAS gene polymorphism and atherosclerosis. 34080768_Atypical, severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a newborn presenting Noonan syndrome harboring a recurrent heterozygous MRAS variant. 35768504_Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. 35830882_Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. 35831509_Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. 36175670_Structure of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C complex provides insights into RAF activation and Noonan syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000032470 |
Mras |
125.114961 |
2.1997527094 |
1.137341 |
0.169767536 |
44.998153 |
0.00000000001972203339814917214036929634109304894373781991134819691069424152374267578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000107455597252374234029171637002216194503589896669382142135873436927795410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
173.9964458 |
16.1358297 |
79.5740743 |
5.8171705 |
| ENSG00000158234 |
55179 |
FAIM |
protein_coding |
Q9NVQ4 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role as an inducible effector molecule that mediates Fas resistance produced by surface Ig engagement in B cells. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene protects against death receptor-triggered apoptosis and regulates B-cell signaling and differentiation. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:55179; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902042]; positive regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050769] |
17912957_Human keratinocytes were transfected with either Flip, Faim, or Lifeguard (LFG). Our results suggest that heterotopic expression of antiapoptotic proteins can induce the resistance of keratinocytes to a major mechanism of rejection. 17942717_Expression of the long form of Fas apoptotic inhibitory molecule (FAIML) results in the protection of neurons from the cytotoxic actions of death ligands. 19592656_FAIM acts to specifically enhance CD40 signaling for NF-kappaB activation, IRF-4 expression, and BCL-6 down-regulation in vitro, but has no effect on its own 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20693673_FAIM (1-90) was crystallized and diffracted to a resolution of 2.5 A; the crystal belonged to space group P3(1), with unit-cell parameters a=b=58.02, c=71.11 A, alpha=beta=90, gamma=120 degrees. 23138182_FAIM modulates IGF-1-induced Akt activation and IRF4 expression and has a role in multiple myeloma cell survival 26866272_Data indicate that FAIM is a novel regulator of insulin signalling and plays an essential role in energy homoeostasis. 28383554_the anti-apoptotic effect of SRT1720 was mitigated by FAIM knockdown with a small interfering RNA-targeted FAIM. These results indicated that pretreatment with SRT1720 improves survival of aged hMSCs, and enhances their therapeutic efficacy for rat myocardial infarction (MI). 28981531_subcellular fractionation experiments revealed that, in contrast to FAIM-S and FAIM-L, FAIM-S_2a and FAIM-L_2a are able to localize to the nucleus, where they may have additional functions. In summary, here we report on two novel FAIM isoforms that may have relevant roles in the physiology and pathology of the nervous system 31270932_PACAP ameliorates hepatic metabolism and inflammation through up-regulating FAIM in obesity. 33249986_FAIM-S functions as a negative regulator of NF-kappaB pathway and blocks cell cycle progression in NSCLC cells. 34720024_FAIM regulates autophagy through glutaminolysis in lung adenocarcinoma. 36233145_Small Heat Shock Proteins Collaborate with FAIM to Prevent Accumulation of Misfolded Protein Aggregates. |
ENSMUSG00000032463+ENSMUSG00000096316 |
Faim+Faiml |
28.781072 |
2.4889804824 |
1.315555 |
0.305800977 |
18.730290 |
0.00001505715757229234522281396263521102696358866523951292037963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000046185296294063807082293238170933591391076333820819854736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.1013888 |
7.6065324 |
17.0537073 |
2.4498516 |
| ENSG00000158258 |
64084 |
CLSTN2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H4D0 |
FUNCTION: May modulate calcium-mediated postsynaptic signals. {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of synapse assembly and positive regulation of synaptic transmission. Predicted to be located in postsynaptic density. Predicted to be active in cell surface; glutamatergic synapse; and postsynaptic membrane. Predicted to be integral component of postsynaptic density membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64084; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; X11-like protein binding [GO:0042988]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050806] |
15037614_Alcadein and amyloid beta-protein precursor regulates FE65-dependent gene transactivation [alcalpha1, alcbeta, alcgamma] 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19058786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19058786_calsyntenins play an essential role in learning and this role is modulated both by CLSTN2 genotype and, during adolescent development, by exposure to tobacco smoke. 19174780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19606085_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19804789_This study showed that the KIBRA and CLSTN2 genes interactively modulate episodic memory performance. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20691427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21643791_No increased risk of any type of late development, and cognitive impairment was associated with CLSTN2 (rs6439886) 25080189_The results of this study supports the view that effects of KIBRA and CLSTN2 polymorphisms genetic polymorphisms on cognitive functioning may be most easily disclosed at suboptimal levels of cognitive ability, such as in old-age depression. 26415670_Study did not find support for an association of KIBRA either alone or in combination with CLSTN2 with memory performance or hippocampal volume, nor did variation in these genes influence longitudinal memory decline or hippocampal atrophy in older adults 34673103_Calsyntenin-3 interacts with the sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter-2 to regulate vitamin C uptake. |
ENSMUSG00000032452 |
Clstn2 |
1584.486463 |
0.1335334760 |
-2.904727 |
0.050827238 |
3780.236493 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
377.7355874 |
13.7553748 |
2850.9553824 |
56.8499343 |
| ENSG00000158301 |
114928 |
GPRASP2 |
protein_coding |
Q96D09 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in regulation of a variety of G-protein coupled receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15086532}. |
Deafness;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family that regulates the activity of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The encoded protein has been shown to be capable of interacting with several GPCRs, including the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor and the calcitonin receptor. Several transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:100528062;hsa:114928; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis [GO:0061484] |
16835690_that huntingtin protein and GASP2 form a complex in cotransfected mammalian cells 20479760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28096187_A missense variation of GPRASP2 was first identified to be implicated in X-linked SHL. 28849214_Dynamic expression analysis of armc10, the homologous gene of human GPRASP2, in zebrafish embryos, has been reported. |
ENSMUSG00000072966 |
Gprasp2 |
12.510128 |
0.0376511758 |
-4.731161 |
1.220447779 |
13.751090 |
0.00020869968493017281539747553864572182646952569484710693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000544819127974770201459919771735940230428241193294525146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9862194 |
0.8975759 |
30.2235992 |
14.9166368 |
| ENSG00000158470 |
9334 |
B4GALT5 |
protein_coding |
O43286 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the synthesis of lactosylceramide (LacCer) via the transfer of galactose from UDP-galactose to glucosylceramide (GlcCer) (PubMed:24498430). LacCer is the starting point in the biosynthesis of all gangliosides (membrane-bound glycosphingolipids) which play pivotal roles in the CNS including neuronal maturation and axonal and myelin formation (By similarity). Plays a role in the glycosylation of BMPR1A and regulation of its protein stability (By similarity). Essential for extraembryonic development during early embryogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JMK0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24498430}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation.; PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. |
This gene is one of seven beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase (beta4GalT) genes. They encode type II membrane-bound glycoproteins that appear to have exclusive specificity for the donor substrate UDP-galactose; all transfer galactose in a beta1,4 linkage to similar acceptor sugars: GlcNAc, Glc, and Xyl. Each beta4GalT has a distinct function in the biosynthesis of different glycoconjugates and saccharide structures. As type II membrane proteins, they have an N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence that directs the protein to the Golgi apparatus and which then remains uncleaved to function as a transmembrane anchor. By sequence similarity, the beta4GalTs form four groups: beta4GalT1 and beta4GalT2, beta4GalT3 and beta4GalT4, beta4GalT5 and beta4GalT6, and beta4GalT7. The function of the enzyme encoded by this gene is not clear. This gene was previously designated as B4GALT4 but was renamed to B4GALT5. In the literature it is also referred to as beta4GalT2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9334; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0008378]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; N-acetyllactosamine synthase activity [GO:0003945]; UDP-galactose:glucosylceramide beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0008489]; central nervous system myelination [GO:0022010]; central nervous system neuron axonogenesis [GO:0021955]; ganglioside biosynthetic process via lactosylceramide [GO:0010706]; glycoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0009101]; glycosylation [GO:0070085]; neuron maturation [GO:0042551]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0030311]; positive regulation of embryonic development [GO:0040019]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647] |
12385586_Over-expression of beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase V increases the growth of astrocytoma cell line 15263012_2.3-kb 5'-flanking region of the human beta-1,4-GalT V gene was cloned and the region -116/-18 relative to the transcription start site as that having promoter activity. 16461357_results suggest that GalT V functioned as a novel glioma growth activator and might represent a novel target in glioma therapy 17656364_Ets-1 enhances expression of the beta-1,4-GalT V gene through activation of the Sp1 gene in cancer cells 17690104_sulfated keratan sulfate is produced by beta3GNT7, beta4GalT4, CGn6ST, and KSG6ST 20417617_These data reveal a critical role of beta1,4GalT V in the self-renewal and tumorigenicity of glioma-initiating cells. 22687727_The expression of the beta-1,4-GalT V gene has been shown to be regulated by transcription factors Sp1 and Ets-1 in cancer cells.(review) 23744354_B4GALT1 and B4GALT5, two members of B4GALT gene family, are involved in the development of multidrug resistance of human leukemia cells. 29415997_Results demonstrated B4GalT5 downregulation improved insulin resistance by promoting adipogenic commitment and decreasing M1 macrophage infiltration. 30502090_beta-1,4-GalT-V gene/protein expression is specifically increased in colorectal cancer, compared to visibly normal tissue. Furthermore, we observed a marked increase in its enzymatic activity, and its product lactosylceramide. beta-1,4-GalT-V may serve as a diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for the progression of colorectal cancer. 30607818_Hsc70 Interacts with beta4GalT5 to Regulate the Growth of Gliomas. 34709725_Circ_0009910 sponges miR-491-5p to promote acute myeloid leukemia progression through modulating B4GALT5 expression and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000017929 |
B4galt5 |
297.383257 |
2.3351938500 |
1.223542 |
0.092708344 |
176.922508 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000022771572128497552206011966657178644207166910155139616373405333198244241862060335007187015512973374140254581576847670021379599347710609436035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000003823758869358633042399229050351149704471623280061294392358360232535540228790347446528313473931224826876662525876326981233432888984680175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
419.5131534 |
22.9205197 |
180.9440067 |
7.9477043 |
| ENSG00000158473 |
912 |
CD1D |
protein_coding |
P15813 |
FUNCTION: Antigen-presenting protein that binds self and non-self glycolipids and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17475845}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a divergent member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:912; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; beta-2-microglobulin binding [GO:0030881]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; endogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030883]; exogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030884]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; lipid antigen binding [GO:0030882]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; antigen processing and presentation, endogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048006]; antigen processing and presentation, exogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048007]; detection of bacterium [GO:0016045]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; T cell selection [GO:0045058] |
9374463_CD1d presents lipid and glycolipid antigens to T cells 11580851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12239218_Data show that CD1d associates in the ER with both calnexin and calreticulin and with the thiol oxidoreductase ERp57 in a manner dependent on glucose trimming of its N-linked glycans. 12368486_CD1d ligand at the human maternal-fetal interface 12454749_B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells significantly down-regulated transcripts from CD1c and CD1d genes, permitting cells to evade the immune response 12618910_the CD1d alpha1-alpha2 domains of both rhesus monkeys and humans are highly homologous (95.6%) 12730881_CD1d is expressed functionally on IECs with a polarity of presentation (basal > apical) predicting a role in presentation of mucosal glycolipid antigens to local CD1d-restricted T cells. 12952923_a novel autocrine pathway of CD1d regulation by Hsp110. 14551186_CD1d proteins sre strong binders of small hydrophobic probes such as 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonic acid and 4,4'-dianilino-1,1'-naphthyl-5,5'-disulfonic acid. 14716312_saposins mobilize monomeric lipids from lysosomal membranes and facilitate their association with CD1d 15100293_Investigation of the 5' upstream region of human CD1D reveals multiple transcription initiation sites and TATA boxless dual promoters located within 700 base pairs 5' upstream of the coding region. 15128771_Transgenic overexpression of CD1d within pancreatic islets of nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice protects them from autoimmune diabetes through activation of NKT cells and improvement of IL-4 secretion at the site of autoimmunity (i.e., peripheral lymph nodes). 15187105_CD1d can inhibit NK cell-mediated cytolysis; the putative inhibitory receptor does not recognize CD1d molecules loaded with alpha-GalCer 15243159_Data show that phosphatidylinositol mannoside represents a mycobacterial antigen recognized by T cells in the context of CD1d. 15265953_Hepatic inflammatory cells & biliary cells near portal tract fibrotic areas of HCV-infected donors specifically up-regulate CD1d. CD1d presentation of liver Ag may be beneficial in acute viral clearance, but in chronic infection could add to liver injury. 15345586_The ability of CD1d-unrestricted natural killer T cells to recruit innate immune system cells might play a role in cancer cell eradication and contribute to inflammatory diseases. 15654963_TGFbeta produced by keratinocytes contribute to selectively downregulate CD1d expression on intraepidermal-resident Langerhans cells 15665086_CD1d-dimer staining revealed human natural killer T cells reactivity toward Sphingomonas glycosphingolipids. 15916790_ability of Nef to alter the cell surface expression of human CD1d. In cells co-expressing CD1d and Nef, a reduction in the cell surface level of CD1d was observed. 16007090_analysis of the crystal structure of human CD1d in complex with synthetic alpha-galactosylceramide at a resolution of 3.0 A 16091469_CD1d ligation alone, in the absence of iNKT, could rapidly (within 24 h) stimulate production of bioactive IL-12p70 by CD1d+ human peripheral blood monocytes as well as immature dendritic cells 16148122_CD1d continues to play a role in late-stage NKT cell development and, in particular, during the functionally significant acquisition of NK1.1 that is indicative of NKT cell maturity 16178273_CD1d has a role in intrahepatic T-cell recognition in hepatocytes 16456021_Time-course studies of CD1d gene expression indicated that keratinocytes slowly increased gene expression with CaCl(2)-induced terminal differentiation 16517731_These results highlight the variation in Ag recognition among CD1d-restricted Receptors, Antigen, T-Cell (TCRs) and suggest that TCR alpha-chain elements contribute to alpha-linked glycosphingolipid specificity [CD1d] 16675349_CD1d-restricted gamma delta T cells specific for phospholipids can represent a key mucosal regulatory subset for the control of early host reactivity against tree pollens. 16818729_This review highlights the role of the CD1d antigen processing pathway and the immunopotentiating effects of the ligands that can be presented by CD1d to natural killer (NK)T cells or other CD1d-restricted T cells during cancer and infections. 16820217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17015708_Schwann cells activated iNKT cells in a CD1d-dependent manner in the presence of alpha-galactosylceramide 17071498_CD1d has a role in cytolysis of lymphoblastic lymphoma cells 17071611_One of the N-linked glycans (at position asparagine-42) exists mainly in a form that is sensitive to endoglycosidase H. Deletion of Asn-42 affects stability of the CD1d heavy chain beta 2-microglobulin heterodimer. 17363727_CD4 potentiates human iNKT cell activation by engaging CD1d molecules. These results indicate that the CD4 coreceptors may contribute to the fine tuning of iNKT cells reactivity. 17372201_saposin B may facilitate lipid binding to CD1d molecules throughout the endocytic pathway 17475845_Cotrafficking with major histocompatibility class II molecules and the invariant chain (Ii) selectively enhances CD1d-mediated presentation of exogenous antigens. 17476670_CD1d-restricted NKT cells have roles in the intestine and in inflammatory bowel diseases [review] 17581592_The structure provides a basis for the interaction between the highly conserved NKT TCR alpha-chain and the CD1d-antigen complex 17726154_These results indicate that CD4 can contribute to natural killer cell activation independently of the presence of a CD4-ligand on antigen presenting cells and suggest that it preferentially modulates cytokine and proliferative responses. 18068183_Used a lentiviral system to generate stable cell lines producing beta2m-CD1d single chain protein which was used to form CD1d tetramer. 18253929_Data indicate that viral danger signals trigger NKT cell activation by enhancing CD1d de novo synthesis through increasing the abundance of CD1D mRNA in human myeloid dendritic cells. 18337560_monocyte-derived DCs cultured in an immunoglobulin-rich milieu expressed CD1d but not CD1a, CD1b, and CD1c, whereas DCs cultured in the presence of low levels of immunoglobulins had an opposite CD1 profile 18378792_An alanine scanning mutagenesis approach was undertook to define the energetic basis of this interaction between the natural killer cell T cell receptors and CD1d. 18385757_PKCzeta is an important transduction molecule downstream of TNF-alpha signaling and is associated with increased expression of CD1d that may enhance CD1d-natural killer T cell interactions in psoriasis lesions. 18433720_Trophoblast differentiation is characterized by TGF-beta1-mediated decreases in trophoblast cell CD1d expression. 18458073_CD1D expression and ligand induced cytokine production in mucosal epithelial cells from lower reproductive tract is tissue specific and CD1d-mediated cytokine production in penile urethral cells was abrogated by C. trachomatis infection. 18535199_a distinct population of human CD1d-restricted T cells specific for inflammation-associated lysolipids suggest a novel mechanism for inflammation mediated immune regulation in human cancer 18684921_Protection from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis afforded by the enrichment of natural killer T cells is independent of extrathymic CD1d transgene expression. 18713998_Although the allogeneic activation of iNKT cells is invariant TCR-CD1d interaction-dependent, glycosphingolipid (GSL) profiling suggests it does not involve the recognition of disparate CD1d/GSL complexes 19056691_A novel function of CD1d in the regulation of cell death with tumor survival and progression in humans. 19124746_CD1d overlaps with Ig-like transcript 4 (ILT4) both at the cell surface and in the cytoplasm; its interaction with ILT4 provides insights into the regulation of natural killer T cell-mediated immunity. 19415116_CD1d molecules bind a surprising diversity of lipid structures within the secretory pathway 19446558_Report ex vivo induction and expansion of natural killer T cells by CD1d1-Ig coated artificial antigen presenting cells. 19454494_infiltrating NKT cells are mainly observed in CD1d nodules 19592659_C/EBP-beta binds to the CCAAT box in the CD1d promoter, required for its expression in keratinocytes 19637196_Data suggest that IL-18-mediated activation and subsequent dysregulation of the CD1d-restricted iNKT-cells plays a role in the pathogenesis of AE. 19651460_Uncoupling between CD1d upregulation induced by retinoic acid and conduritol-B-epoxide and iNKT cell responsiveness. 19724888_The amount of sCD1d proteins in plasma was significantly decreased in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared with healthy donors. Plasma sCD1d protein levels correlated with the number of NKT cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 19734232_Preferential stimulatory activities of two alpha-galactosylceramide C-glycoside analogues against human vs mouse invariant natural killer (NK)T cells are due to the differences between human vs mouse CD1d molecules. 19757161_A novel, high-level amplicon at 1q22-23.1 occurs in both hepatocellular carcinoma cell line and tissues. 19830742_Studies indicate that during bacterial infections, NKT cells can be activated either indirectly by DC or directly by bacterial lipid antigens presented by CD1d. 20080535_show that the mouse and human CD1d present glycolipids having different fatty acids, based in part upon a difference at a single amino acid position that is involved in positioning the sugar epitope. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368272_A heretofore unknown tyrosine-based signal is demonstrated in the cytoplasmic tail of CD1d that may have relevance to other type I integral membrane proteins that traverse through the endocytic pathway. 20520738_These data indicate that bone marrow-dendritic cells express an endogenous CD1d ligand and B7-H1 to ihibit type II but not type I natural killer T cells. 20530791_Data show that the Vpu protein interacts with CD1d and suppresses its recycling from endosomal compartments to the cell surface by retaining CD1d in early endosomes. 20810727_CD1d is downregulated by the HPV16 E5 and HPV6 E5 protein. 20861015_Calreticulin controls the rate of assembly of CD1d molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum. 21095162_Studies indicate that NKTs can suppress tumor growth indirectly by targeting CD1d-positive elements of tumor-supportive stroma such as tumor-associated macrophages. 21185200_Studies indicate that iNKT cells, CD1d dependent natural killer T cells are a unique population of T cells. 21198755_Myeloid dendritic cells did not change their numbers or CD1d-expression during treatment 21258883_CD1d gene polymorphisms are associated with breast, colorectal and lung cancers. 21451111_both CD1d and CD1c are upregulated by retinoic acid receptor alpha signaling in human B cells 21454514_Binding strength and dynamics of invariant natural killer cell T cell receptor/CD1d-glycosphingolipid interaction on living cells by single molecule force spectroscopy. 21557213_Data show that CD1d knock-out mice, which are deficient in NKT cells and resistant to ConA-induced hepatitis, no longer expressed IL-33 in hepatocytes following ConA administration. 21632718_Although zinc finger protein PLZF is known to direct the effector program of natural killer (NK)T cells, this study shows that CD1d naive-like cells express it at a significantly lower amount than NKT cells. 21646050_Studies indicate that CD1d-restricted T-cells can rapidly produce large amounts of Th1 and/or Th2//Treg/Th17-type cytokines, thereby regulating immunity. 21653669_identified gB and US3 as two viral factors that together downregulate CD1d surface expression; results suggest that HSV-1 uses gB and US3 to rapidly inhibit NKT cell function in the initial antiviral response 21695190_Breast cancer cells, through downregulation of CD1d and subsequent evasion of natural killer T-mediated antitumor immunity, gain increased potential for metastatic tumor progression. 21846915_CD1d can differentiate chronic lymphocytic leukemia from other B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorders with high accuracy. 21853044_These findings provide the basis for investigations into a role for CD1d in lung mucosal immunity. 21900247_Identification of self-lipids presented by CD1c and CD1d proteins. 21925141_these results suggest that antigen presentation by CD1d is largely unaffected by the multiple immune-modulating functions of human cytomegalovirus. 21956730_The serine-containing variant showed the strongest CD1d binding, offering an explanation for its predominance in vivo. 21980475_CD1d appears to modulate some metabolic functions through an iNKT-independent mechanism 21987790_phenyl glycolipids showed greater binding avidity and stability for iNKT T-cell receptor when complexed with CD1d 22395072_These findings provide insight into how lysophospholipids are presented by human CD1d molecules and how this complex is recognized by some, but not all, human Invariant Natural Killer T cells. 22406267_Defective B cell-mediated stimulation of iNKT cells in SLE patients was associated with altered CD1d recycling. 22407918_Enhancing immunostimulatory function of human embryonic stem cell-derived dendritic cells by CD1d overexpression. 22419072_The binding of Sp1 to CD1d promoter and histone H3 acetylation on Sp1 sites were increased by histone deacetylase inhibitors. 22829134_Recombinant Vdelta1 TCRs from different individuals were shown to bind recombinant CD1d-sulfatide complexes in a sulfatide-specific manner. 22888216_Data suggest that when CD1c is up-regulated, ILT4 is recruited to CD1c, thus reducing the inhibitory effect of immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4) on CD1d recognition. 22995911_Human and mouse type I natural killer T cell antigen receptors exhibit different fine specificities for CD1d-antigen complex 23049754_A correlation between CD1d expression (a negative prognostic marker) and the soluble CTLA-4 in B-ALL patients was observed. 23109910_crystallographic and biophysical analyses of alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer) recognition by a human CD1d-restricted TCR 23171451_Antigen presentation of keratinocyte to invariant killer cells show that these cells do not activate the cytotoxicity effector genes in resting iNKT-cells, but had the capacity to serve as targets for activated iNKT-cells dependent on CD1d expression. 23265858_Total CD1d levels are upregulated in pollen lipid-treated dendritic cells, which are then able to activate invariant natural killer (NK)T cells through a CD1d-dependent pathway. 23280365_CD1d protein structure determines species-selective antigenicity of isoglobotrihexosylceramide (iGb3) to invariant NKT cells. 23347583_Downregulation of both CD1c and CD1d expression through a Vpu-dependent and Nef-independent mechanism, and the concomitant HIV-1-induced production of host cholesterol decreased the extent of CD1c and CD1d modulation. 23372165_A novel, autoreactive, CD1d-restricted, GPI-specific T-cell population, enriched in an invariant TCRalpha chain, is expanded in paroxysmal noctural hemoglobinuria and may be responsible for bone marrow failure. 23468111_Type II NKT cells are absolutely dependent on CD1d expression in the thymus for their selection. CD1d trafficks between the cell surface & endosomes. It plays a role in presentating lipid antigens & mycobacterial antigens. Review. 23668820_Data indictate variable expression of CD1d on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)lymphocytes and an association between high expression of CD1d with shorter time to treatment and overall survival of patients. 23677998_for isoforms CD1b through CD1e, our simulations show the near-complete collapse of the hydrophobic cavities in the absence of the antigen. This event results from the spontaneous closure of the binding domain entrance, flanked by two alpha-helices. 23710894_our findings strongly suggest that T322 and S323 form a dual residue motif that can regulate the functional expression of CD1d during a viral infection. 23808994_CD1d was found selectively expressed on the surface of hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis C, but not those subjects with history of alcohol usage or resolved chronic hepatitis C. 24009709_MHC class I physically associates with CD1d and regulates its functional expression on the cell surface. 24076636_The gamma-delta TCR docked orthogonally, over the A' pocket of CD1d, in which the Vdelta1-chain, and the germ line-encoded CDR1d loop, dominated interactions with CD1d. 24104458_We suggest that unique set of interactions between CEACAM5, CD1d, and CD8 render CD1d more class I-like molecule, facilitating antigen presentation and activation of CD8(+)-suppressor regulatory T cells. 24213674_results showed the interaction between endoplasmic reticulum (ER)- lumenal domain of HCMV US2 and alpha3 domain of hCD1d was observed within ER; these results show the function of HCMV US2 in immune evasive mechanisms against anti-viral immunity of invariant NKT cells 24307737_these results provide new insight into the control of CD1d gene expression, and they have implications for the evolution of CD1d and type I NKT cells. 24418751_Relationship between high CD1d expression and shorter time to treatment and overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. CD1d expression in individual patients significantly changed over time. 24513807_CXCL16, iNKT cell-associated cell marker Valpha24, and CD1d were significantly upregulated in esophageal biopsies from EoE patients and correlated with the expression of inflammatory mediators associated with allergy. 24556395_[review] Humans express both Group 1 (CD1a, CD1b and CD1c) and Group 2 (CD1d) CD1 molecules with nonredundant functions in response to the presentation of endogenous lipids. 25115738_High CD1d expression is associated with medulloblastomas. 25381357_Expression of CD1d on B cells is suggestive of the ability of these cells to present antigens to, and form cognate interactions with, invariant natural killer T-Cells. (Review) 25390653_simplexide, apart from activating iNKT cells, induces the production of cytokines and chemokines from human monocytes by direct interaction with CD1d 25452463_These findings highlight how components from alphabeta and gammadeltaTCR gene loci can recombine to confer antigenic specificity. 25477528_CD1d expression in renal cell carcinoma correlated with aggressive disease and poorer clinical outcomes. 25618030_CD1d acts as a cell surface receptor that recognizes and binds oxysterols and initializes a pathway connecting oxysterol binding to PPARgamma activation 25649790_Using diffraction-based dotReadytrade mark immunoassays, the present study showed that staphylococcal enterotoxin B directly and specifically conjugated to CD1d. 25878107_Ablation of this phosphorylation abolished herpes simplex virus 1 US3-mediated downregulation of CD1d expression, suggesting that phosphorylation of KIF3A is the primary mechanism of viral suppression of CD1d expression. 25929465_our results demonstrate that both Ets1 and miR-155 can directly regulate the expression of CD1d on B-cells 26041373_This suggests that CD1D is more polymorphic than previously assumed 26119195_both membrane-bound (V4) and soluble (V5) isoforms of CD1d were over-expressed in gastric tumor tissues, suggesting that they are involved in anti-tumor immune responses. 26260288_by controlling a fundamental step in CD1d-mediated lipid antigen presentation, STAT3 signalling promotes innate immune responses driven by CD1d 26798067_the spatiotemporal distribution of CD1d molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) modulates activation of Invariant natural killer T cells. 26969612_Data suggest that CD1d antigen-restricted B lymphocytes (Bc) presentation of NGcGM3 drives effective invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT) activation. 27069116_CD1d-restricted peripheral T cell lymphoma in mice and humans 27327902_These findings suggest that VP22 is required (but not sufficient) for the inhibition of CD1d-mediated antigen presentation in herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. 27368347_Importantly, among the analyzed molecules, only CD1d expression showed an association with the activation of double-negative T cells, as well as with worse ventricular function in patients with Chagas disease. 27385215_CD1D has a role in disease progression and survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and may interact with CD161 27513300_BCR-ABL-dependent ROCK, but not TK, is involved in CD1d downregulation. We propose that ROCK, which is most likely activated by the DH/PH domain of BCR-ABL, mediates iNKT-cell immune subversion in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) patients by downregulating CD1d expression on CML mDCs. 28338767_The expression of CD1d showed a significantly negative correlation with CD86 level in B cells from imiquimod (IMQ)-treated mice, B6.MRLlpr mice, and lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. 28505514_FasL expression in splenic CD5(+)CD1d(hi) B cells was decreased compared to the control group after TLR4 ligation. 28633979_We have studied the relation of CD1d expression in various breast cancer cell lines to their viability and progression. We observed a novel phenomenon that CD1d expression level increases with the progressive stage of the cancer. 29108995_CD1d-expressing cells isolated from peripheral blood of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients showed the suppressive activity of T cell proliferation and higher expression of MyD88 and IDO compared with CD1d(-) cells. 29509047_It provides the additional data of adipocyte CD1d-dependent regulation of adipose iNKT cell responses as well as systemic insulin sensitivity. In addition, we discuss how the interaction between adipocytes and iNKT cells would be regulated with the progression of obesity. 29643189_The increased CD1d expression in HBV-infected liver. 30210497_Role of CD1d- and MR1-Restricted T Cells in Asthma. 30864713_In samples from lung cancer patients, the antitumor activities of all the T cells were enhanced with the increase of CD1D+DCs. Analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data revealed that high levels of CD1D indicated better outcomes for patients. Collectively, CD1D enhanced DCbased antitumor immunity, not only by targeting NKT, but also by activating CD4+T and CD8+T cells. 31050367_Expression of CD1d by astrocytes corresponds with relative activity in multiple sclerosis lesions. 31354710_Invariant NKT Cells From Donor Lymphocyte Infusions (DLI-iNKTs) Promote ex vivo Lysis of Leukemic Blasts in a CD1d-Dependent Manner. 31560833_Increased cytoplasmatic expression of cancer immune surveillance receptor CD1d in anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. 32244759_Structural Dynamics of the Lipid Antigen-Binding Site of CD1d Protein. 32512511_Low oxygen saturation during sleep reduces CD1D and RAB20 expressions that are reversed by CPAP therapy. 33128583_CD1d expression in glioblastoma is a promising target for NKT cell-based cancer immunotherapy. |
ENSMUSG00000028076+ENSMUSG00000041750 |
Cd1d1+Cd1d2 |
387.394976 |
0.3027762664 |
-1.723676 |
0.115039379 |
222.777804 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002241251506376652163177748576484991775551546385460152386924811990152330946927376036065025376953257739766597908252470896415885865879391580790525040356442332267761230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000482932441374005676410909477246961975678145388837237057264609781932139627127894123883157564104267137271377784640277840285619431748287411210185382515192031860351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
176.5394359 |
12.9297741 |
587.6587579 |
28.4861642 |
| ENSG00000158477 |
909 |
CD1A |
protein_coding |
P06126 |
FUNCTION: Antigen-presenting protein that binds self and non-self lipid and glycolipid antigens and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11231314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16272286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18178838}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to the plasma membrane and to recycling vesicles of the early endocytic system. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:909; |
endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030883]; exogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030884]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation, endogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048006]; antigen processing and presentation, exogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048007]; immune response [GO:0006955]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916] |
11580851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12925210_outstanding ability of Langerhans cells to mediate CD1a-dependent lipid antigen presentation and thus, Langerhans-cell-mediated skin immunity may involve T cell recognition of both peptide and lipid antigens. 14991068_CD1a and langerin have roles in antigen presentation to T cells 15099564_Review. CD1a on tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells may present immunogenic tumor-specific glycolipid antigens to T-cells. 15556687_CD1a expression was detected on monocytes in the majority of sickle cell anemia patients, and was predominant in SDPunjab patients. 15723809_structural study illustrates how a single chain lipid can be presented by CD1 and that the peptide moiety of the lipopeptide is recognized by the T cell receptor 15749918_hypothesis that CD1-restricted T cells might be activated and home to target tissues involved in Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease 15756258_CD1a may be a novel biomarker for Barrett metaplasia and that its expression may help to predict the prognosis of this pathology. 16272286_identified CD1a-, CD1b-, and CD1c-restricted T cells from normal human donors that induce cytolysis and secrete copious IFN-gamma in response to self-CD1 expressed on monocyte-derived dendritic cells 16598657_In this study, we show that PTX can selectively block the expression of CD1a isoform during the differentiation of human monocytes into dendritic cells. 16670277_In humans, CD1a-expressing antigen- presenting cells located close to the lymphatic vessels in the upper layers of the dermis may fulfill some of the roles previously ascribed to Langerhans cells. 16820217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17082618_A 1000-base pair region upstream of CD1A translation start site is identified as necessary for CD1A proximal promoter activity. 17197902_The mature dentritic cells express CD83 and high CD40/80/86, whereas the immature cells express CD1a and low CD40/80/86 17428545_Associated with chronic dysimmune neuropathies 17428545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17652534_In cystic teratomas of the ovary, CD1-positive Langerhans cells appeared to cross the basal membrane and penetrate the subepidermal tissue, and they were associated there with T-cell line lymphocytes (CD3 positive). 18178838_These findings identify Ii and lipid rafts as key regulators of CD1a organization on the surface of immature DCs and of its immunological function as Ag-presenting molecule. 18184269_The positive and significant correlations between the number of CD1a+ cells and positivity of the primary tumour for estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor suggest a possible role for CD1a as a prognostic marker for breast cancer. 18251780_CD1a expression can be an additional new marker for PEComas and also supports the distinct and integrated disease entity of PEComas. 18287231_HCMV encodes multiple blocking strategies targeting group 1 CD1 molecules CD1a, CD1b, and CD1c 18337560_monocyte-derived DCs cultured in an immunoglobulin-rich milieu expressed CD1d but not CD1a, CD1b, and CD1c, whereas DCs cultured in the presence of low levels of immunoglobulins had an opposite CD1 profile 18337829_Dermal dendritic cells comprise two distinct populations: CD1+ dendritic cells and CD209+ macrophages. 18624350_Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein regulates endogenous and exogenous antigen presentation by group 1 CD1 molecules. 18838176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18838176_SNPs in CD1A and CD1E were not associated with GBS susceptibility, specific clinical subgroups, anti-ganglioside antibodies, antecedent infections and prognosis. 19257981_Data show high expression of CD86 and CD11C, moderate expression of CD1a and CD123, low levels of CD83 on dendritic cells after induction by GM-CSF and IL-4. 19317050_The quantity of CD1a-positive Langerhans cells in the lesions of epidermodysplasia verruciformis patients was significantly lower than in normal skin. 19321495_CD1a and CD83 may be involved in pain generation and the pathogenesis of endometriosis 19426597_Data show that the expression of CD1a and CD207 is markedly down-regulated in CA epidermis. 19605355_dideoxymycobactin antigens presented by CD1a show T cell fine specificity for natural lipopeptide structures 19952356_The effect of transient stimulation of the canonical Wnt pathway in the differentiation potential of Lin(-)CD34(+) CD1a(-) human thymic progenitors, was analyzed. 20026739_The intracellular trafficking route of CD1a is essential for efficient presentation of lipid antigens that traffic through the early endocytic and recycling pathways. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20592474_microsomal triglyceride transfer protein deficiency was associated with increased proteasomal degradation of group 1 CD1 molecules in human abetalipoproteinemia. 20890667_Accumulation of CD1a-positive Langerhans cells and mast cells in actinic cheilitis. 20954848_CD1E and CD1A genes may be involved in networks which determine susceptibility to multiple sclerosis types RR-MS and PP-MS, respectively. 20954848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21194729_We do not believe that there is a role for CD1a immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms. 21496400_CD1A and CD1E polymorphisms contribute to the polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis 21696499_In Guillain-Barre syndrome, an initially positive association study with polymorphism of CD1A and CD1E genes was not confirmed 21900947_GM-CSF independent signaling directed toward the CD1a genome is important in Langerhans cell biology. 22003931_allelic variation in CD1A does not play a major role in determining multifocal motor neuropathy susceptibility. 22007938_In the intratumoral and peritumoral areas, the expression of CD1a, tryptase, and CD68 was significantly higher in papillary thyroid carcinoma than in thyroid adenomas. 22331868_Saposins utilize two strategies for lipid transfer and CD1 antigen presentation 22670773_these results reveal that CD1 expression is modified in MS and provide novel information on the regulation of lipid antigen presentation in myeloid cells. 23334517_Case Report: cutaneous-limited self-regressing S100 negative/CD1a positive histiocytosis. 23468110_Molecular mechanisms by which CD1a captures distinct classes of self- and mycobacterial antigens are reviewed. Review. 23677998_binding cavity of CD1a is largely preserved in the unliganded state because of persistent electrostatic interactions that keep the portal alpha-helices at a constant separation. 23766460_Dysregulated CD1 profile in myeloid dendritic cells in CVID is normalized by IVIg treatment. 23858036_CD1a deficiency on in vitro-derived DCs was detected in 15% of study subjects. A common SNP in the 5' UTR of CD1a is associated with both low surface expression & mRNA levels. It directly regulates gene expression in a promoter-luciferase assay. 24500401_A polymorphism in human CD1A is associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis. 24556395_[review] Humans express both Group 1 (CD1a, CD1b and CD1c) and Group 2 (CD1d) CD1 molecules with nonredundant functions in response to the presentation of endogenous lipids. 25343480_The presence of CD1a(+) T-cells in all of the LCH lesions that we have studied to date warrants further investigation into their biological function to determine whether these cells are important in the pathogenesis of LCH 25901368_the expression of WNT4, a Wnt ligand, and three targets of Wnt-ss-catenin transcription activation, namely, MMP7, cyclinD1 (CD1) and c-MYC in 141 penile tissue cores from 101 unique samples, were investigated. 26073685_High CD1a-positive dendritic cell density is associated with improved disease-free survival in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 26284469_Studies indicate that many CD1 antigen-restricted T cells do not require foreign antigens for activation but instead can be activated by self-lipids presented by CD1. 26388332_Studies indicate that the antigen-presenting molecules CD1 and MHC class I-related protein (MR1) display lipids and small molecules to T cells. 26419626_Findings suggest that dermal survivin+CD1a+ (CD1a antigen) cell infiltration may be a potential biomarker of systemic sclerosis skin lesions. 26442925_The data show that immunohistochemistry for CD1a and Hsp60 can be of help in differential diagnosis between Keratoacantomas and well-differentiated forms of squamous cell carcinomas. 26460687_plasma-derived lipids drive functional levels of CD1d expression. 26518708_NDN and CD1A are novel prognostic methylation markers in patients with head and neck squamous carcinomas 27094031_these observations suggest that CD99 is involved in the regulation of CD1a transcription and expression by increasing ATF-2. 27548435_this study shows that CD1a drove the pathogenesis of poison-ivy dermatitis and psoriasis, and that CD1a-mediated skin inflammation was abrogated by CD1a-blocking antibodies, which highlights CD1a as a target for treatment of inflammatory skin diseases 27670592_The findings suggest that PLA2 inhibition or CD1a blockade may have therapeutic potential for psoriasis. 27809916_CD1a+ CD11b+ macrophages and NK T-cells were found to be significantly increased in inflamed colons of ulcerative colitis patients. 28386696_In this review, authors summarize the current knowledge about CD1 proteins, their structures, lipid-binding profiles, and roles in immunity, and evaluate the role of CD1 proteins in eliciting humoral immune response 28847997_CD207(+)CD1a(+) cells are circulating in patients with active Langerhans cell histiocytosis, and TSLP and TGF-beta are potential drivers of Langerhans-like cells in vivo. 29273672_CD1a expression is up-regulated by TSLP (thymic stromal lymphopoietin) at levels observed in the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis, and the response is dependent on PLA2G4A. 29301656_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in exon 2 of CD1A (*01/*02) and CD1E (*01/*02) cannot be recognized as a susceptibility or disease-causative factor for Guillain-Barre syndrome in the Bangladeshi population 30308433_CD1 antigen presenting molecules are nonpolymorphic and specialized for lipid antigen presentation to T cells [Review]. 31295725_rs16840041, rs2269714, and rs2269715 in high linkage disequilibrium and significantly associated with increase in plasma NFL levels 31464097_No statistically significant differences were found between groups of patients studied according to Guillain-Barre Syndrome diagnosis and other covariates ana-lyzed: sex, age, genotypes CD1A. 33348245_CD1a function in human skin disease. 33384157_Animal models for human group 1 CD1 protein function. 33393500_Human skin is colonized by T cells that recognize CD1a independently of lipid. |
|
|
54.764731 |
22.3301889903 |
4.480924 |
0.386038431 |
202.936431 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000047759482634344167305550238455396821362803192219450209559038730031334326639378123174892841115061428463695859155795650843878696889532875502482056617736816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009226831985378532889926044105322952947287561599481049515839631235234619281044817670783451639233164167061270754285721984455648225775803439319133758544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.9636114 |
26.3876389 |
4.8956617 |
1.1562172 |
| ENSG00000158481 |
911 |
CD1C |
protein_coding |
P29017 |
FUNCTION: Antigen-presenting protein that binds self and non-self lipid and glycolipid antigens and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10786796, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10890914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10899914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21167756}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipid-binding;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene is broadly distributed throughout the endocytic system via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail. Alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been observed, but their full-length nature is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:911; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030883]; exogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030884]; glycolipid binding [GO:0051861]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation, endogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048006]; antigen processing and presentation, exogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048007]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; T cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002286] |
11580851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12454749_B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells significantly down-regulated transcripts from CD1c and CD1d genes, permitting cells to evade the immune response 14551186_CD1b and CD1c show strong binding of nitrobenzoxadiazole (NBD)-labeled dialkyl-based ligands. 15556687_CD1c expression was detected on monocytes in the majority of sickle cell anemia patients, and was highly expressed in Sbeta thalassemia patients. 15749918_hypothesis that CD1-restricted T cells might be activated and home to target tissues involved in Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease 16272286_identified CD1a-, CD1b-, and CD1c-restricted T cells from normal human donors that induce cytolysis and secrete copious IFN-gamma in response to self-CD1 expressed on monocyte-derived dendritic cells 18287231_HCMV encodes multiple blocking strategies targeting group 1 CD1 molecules CD1a, CD1b, and CD1c 18337560_monocyte-derived DCs cultured in an immunoglobulin-rich milieu expressed CD1d but not CD1a, CD1b, and CD1c, whereas DCs cultured in the presence of low levels of immunoglobulins had an opposite CD1 profile 18624350_Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein regulates endogenous and exogenous antigen presentation by group 1 CD1 molecules. 19468063_Data show that CD1c represents the second member of the CD1 family to present lipopeptides. 19556741_CD1c+ myeloid dendritic cells were increased in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients versus controls. 19828201_A model of CD1c with bound mannosyl-beta(1)-phosphomycoketide was constructed and analyzed through molecular dynamics simulations. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20888334_Expression of dendritic cell markers CD11c/BDCA-1 and CD123/BDCA-2 in coronary artery disease upon activation in whole blood. 21436634_Accumulation of BDCA-1 and BDCA-2 around neovessels showed that mDCs and pDCs are recruited to advanced arteriosclerotic plaques. 21451111_both CD1d and CD1c are upregulated by retinoic acid receptor alpha signaling in human B cells 21900247_Identification of self-lipids presented by CD1c and CD1d proteins. 22678905_Escherichia coli-activated CD1c(+) dendritic cells suppressed T-cell proliferation in an IL-10-dependent manner 22888216_Data suggest that when CD1c is up-regulated, ILT4 is recruited to CD1c, thus reducing the inhibitory effect of immunoglobulin-like transcript 4 (ILT4) on CD1d recognition. 23347583_Downregulation of both CD1c and CD1d expression through a Vpu-dependent and Nef-independent mechanism, and the concomitant HIV-1-induced production of host cholesterol decreased the extent of CD1c and CD1d modulation. 23468110_Molecular mechanisms by which CD1c captures distinct classes of self- and mycobacterial antigens are reviewed. Review. 23530121_CD1c-PM complexes stain T cell receptors (TCRs), providing direct evidence for a ternary interaction among CD1c-lipid-TCR. 23677998_for isoforms CD1b through CD1e, our simulations show the near-complete collapse of the hydrophobic cavities in the absence of the antigen. This event results from the spontaneous closure of the binding domain entrance, flanked by two alpha-helices. 23766460_Dysregulated CD1 profile in myeloid dendritic cells in CVID is normalized by IVIg treatment. 23829893_RSV infection induces a distinct pattern of costimulatory molecule expression and cytokine production by BDCA-1(+) and BDCA-3(+) mDCs, and impairs their ability to stimulate T cell proliferation. 24049150_Activated dendritic cell subsets expressing CD141/CLEA9A/CD1c, likely recruited into the tubulointerstitium, are positioned to play a role in the development of fibrosis and, thus, progression to chronic kidney disease. 24556395_[review] Humans express both Group 1 (CD1a, CD1b and CD1c) and Group 2 (CD1d) CD1 molecules with nonredundant functions in response to the presentation of endogenous lipids. 24573986_decidual CD1c(+) dendritic cells with Toxoplasma gondii infection have enhanced cytotoxicity of decidual natural killer cells 24918929_hMPV-infected BDCA-1(+) and BDCA-3(+) mDCs induced expansion of Th17 cells, in response to RSV, BDCA-1(+) mDCs induced expansion of Th1 cells and BDCA-3(+) mDCs induced expansion of Th2 cells and Tregs 24935257_mLPA-specific T cells efficiently kill CD1c(+) acute leukemia cells, poorly recognize nontransformed CD1c-expressing cells, and protect immunodeficient mice against CD1c(+) human leukemia cells. 25784146_There was a significant increase of blood CD1c(+) myeloid dendritic cells in autoimmune uveitis patients. The mature phenotype and function of CD1c(+) mDC1 were regulated by TNFalpha via a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. 26884207_human CD1c adopts different conformations dependent on ligand occupancy of its groove, with CE and ASG stabilizing CD1c conformations that provide a footprint for binding of CD1c self-reactive T-cell receptors 26888163_Stressed beta-cells have little effect on human BDCA1-expressed dendritic cells activation and function, while enterovirus-infected beta-cells impact these cells significantly. 27296666_these results demonstrated the mechanism that suppression of CD1c by BCG infection is mediated by miR-381-3p 27701668_Circulating atopic dermatitis pre-dendritic CD1c+ cells are premature and bear atopic characteristics even without tissue-specific stimulation, suggesting that their development is not only influenced by the skin microenvironment, but also by the local milieu in the blood. 28331853_We found a significant difference in the density of intraepidermal CD1c+ cells between the examined lesions; the mean CD1c cell count was 7.00/mm(2) for invasive melanomas, 2.94 for in situ melanomas, and 13.35 for dysplastic nevi 29718193_The expression of histones, small nucleolar RNA H/ACA box (SNORA) and small nucleolar RNA C/D/box (SNORD), and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is also substantially upregulated in the DCs from aged. In contrast, the antigen-presenting and energy generating pathways are downregulated 33384157_Animal models for human group 1 CD1 protein function. 34536421_Rational design of a hydrolysis-resistant mycobacterial phosphoglycolipid antigen presented by CD1c to T cells. |
|
|
71.134901 |
8.4173322809 |
3.073363 |
0.282244547 |
124.157199 |
0.00000000000000000000000000007782708955388363319590341986490428216248268448198839838853884683566080598536747470195251707991701550781726837158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000960474784126523781857029184876714949573507398904752131258156652836858102259554037516409152885898947715759277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
129.2178868 |
19.6295358 |
15.4131047 |
2.1073028 |
| ENSG00000158488 |
913 |
CD1E |
protein_coding |
P15812 |
FUNCTION: T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1e, soluble binds diacetylated lipids, including phosphatidyl inositides and diacylated sulfoglycolipids, and is required for the presentation of glycolipid antigens on the cell surface. The membrane-associated form is not active. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10948205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16311334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21788486}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipid-binding;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes within Golgi compartments, endosomes, and lysosomes, and is cleaved into a stable soluble form. The soluble form is required for the intracellular processing of some glycolipids into a form that can be presented by other CD1 family members. Many alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. Additional transcript variants have been found; however, their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:913; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; endogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030883]; exogenous lipid antigen binding [GO:0030884]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation, endogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048006]; antigen processing and presentation, exogenous lipid antigen via MHC class Ib [GO:0048007]; immune response [GO:0006955]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916] |
11580851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12144626_substitutions lead to amino acid changes at position 73 and 77 of the alpha1 domain in the former and at position 30 of the alpha2 domain in the latter suggesting that the CD1E gene is much more polymorphic than previously assumed. 12671734_cellular and biochemical properties of the human and simian CD1e molecules are similar, suggesting that the particular intracellular distribution of CD1e is important for its physiological and/or immunological function 16311334_required for processing of the mycobcterial antigens hexamannosylated phosphatidyl-myo-inositols(PIM6); propose that, through this form of glycolipid editing, CD1e helps expand the repertoire of glycolipidic T cell antigens to optimize immune response 16820217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17428545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18208508_Data show that ubiquitination of CD1e appears to trigger its exit from Golgi compartments and its transport to endosomes. 18325888_A polymorphism related to the capacity of the CD1E molecule to participate in the immune response to complex glycolipids is discovered in individuals who might display a CD1e-altered immune response to complex glycolipid antigens. 18838176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18838176_SNPs in CD1A and CD1E were not associated with GBS susceptibility, specific clinical subgroups, anti-ganglioside antibodies, antecedent infections and prognosis. 19196239_CD1e propeptide is conserved during evolution, suggesting that it may also optimize the generation of CD1e molecules in other species. 20954848_CD1E and CD1A genes may be involved in networks which determine susceptibility to multiple sclerosis types RR-MS and PP-MS, respectively. 20954848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21481186_in the late endosomes/lysosomes of dendritic cells, the acid pH promotes the binding of lipid antigens to CD1e through increased hydrophobic and ionic interactions 21496400_CD1A and CD1E polymorphisms contribute to the polygenic susceptibility to multiple sclerosis 21696499_In Guillain-Barre syndrome, an initially positive association study with polymorphism of CD1A and CD1E genes was not confirmed 21788486_These data support that CD1e could have evolved to mediate lipid-exchange/editing processes. 21844346_CD1e may positively or negatively affect lipid presentation by CD1b, CD1c, and CD1d. 22003931_allelic variation in CD1E does not play a major role in determining multifocal motor neuropathy susceptibility. 22782895_Deciphering the role of CD1e protein in mycobacterial phosphatidyl-myo-inositol mannosides (PIM) processing for presentation by CD1b to T lymphocytes 22880058_The interaction of LAPTM5 with CD1e and their colocalization in antigen processing compartments both suggest that LAPTM5 might influence the role of CD1e in the presentation of lipid antigens. 23677998_for isoforms CD1b through CD1e, our simulations show the near-complete collapse of the hydrophobic cavities in the absence of the antigen. This event results from the spontaneous closure of the binding domain entrance, flanked by two alpha-helices. 27653862_There was no association between polymorphisms of CD1E genes and the susceptibilities to Guillain-Barre syndrome. 29301656_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in exon 2 of CD1A (*01/*02) and CD1E (*01/*02) cannot be recognized as a susceptibility or disease-causative factor for Guillain-Barre syndrome in the Bangladeshi population 32467040_CD1 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to celiac disease: Association of CD1E*02/02 in Moroccans. |
|
|
36.822929 |
21.3882373855 |
4.418746 |
0.510319506 |
100.919555 |
0.00000000000000000000000957961132052839308721696347732523372141503245076165276701000603990637793927476195676717907190322875976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000098122875149895278819258293744721061855771164450754708782965790754559964881309497286565601825714111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.6711457 |
23.6120761 |
3.4952304 |
1.0697149 |
| ENSG00000158517 |
653361 |
NCF1 |
protein_coding |
P14598 |
FUNCTION: NCF2, NCF1, and a membrane bound cytochrome b558 are required for activation of the latent NADPH oxidase (necessary for superoxide production). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19801500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2547247, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2550933}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chronic granulomatous disease;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a 47 kDa cytosolic subunit of neutrophil NADPH oxidase. This oxidase is a multicomponent enzyme that is activated to produce superoxide anion. Mutations in this gene have been associated with chronic granulomatous disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:653361; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; NADPH oxidase complex [GO:0043020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; phagolysosome [GO:0032010]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding [GO:0043325]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; superoxide-generating NAD(P)H oxidase activity [GO:0016175]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to cadmium ion [GO:0071276]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular response to testosterone stimulus [GO:0071394]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0045741]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612]; reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903409]; regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response [GO:0060264]; respiratory burst [GO:0045730]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] |
16326715_the C-terminal alpha-helical region of the p22phox peptide increases the binding affinity for the tandem SH3 domains of p47phox more than 10-fold 16608528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16778989_Data show that GM-CSF and TNF-alpha induce phosphorylation of Ser345 on p47phox, a cytosolic component of NADPH oxidase, in human neutrophils. 17150107_The phox homology (PX) domain of p47phox localizes to the plasma membrane in human neutrophils, but is not translocated to the membrane of mature phagosomes. 17217339_Thr133, Ser288 and Thr356, targets for IRAK-4 phosphorylation in vitro, are also phosphorylated in endogenous p47phox after LPS stimulation and regulates NADPH oxidase activation. 17438039_These results indicate that a functional NADPH oxidase and the generation of oxidants in the neutrophil phagosome prevent the activation of the cytoplasmic caspase cascade. 17478731_Increased expression of NAD(P)H oxidase-p47phox and nuclear factor-kappaB p65 may contribute to endothelial oxidative stress with aging in humans. 17586618_Homocysteine increased intracellular reactive oxygen species by NAD(P)H oxidase activation, as shown by the membrane translocation of its p47(phox) subunit. 17651608_There is an increased expression of NADPH oxidase p47(-PHOX) and p67(-PHOX) factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. 17922419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17925180_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18004884_the cytosolic regulatory subunit p47phox modulates the conformation of Cyt b (in addition to serving as an adapter protein) during oxidase activation. 18028450_these results indicate that activation of the ASK1/p38 MAPK/p47phox cascade plays a central role in PPD/TLR2-induced ROS generation and suggests the existence of a 'ROS/ASK1' inflammatory amplification feedback loop in monocytes/macrophages. 18045865_CD95L-induced endosomal acidification, ceramide formation, and downstream events, such as p47(phox) phosphorylation, ROS formation, CD95 activation, and apoptosis. 18070887_Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent membrane recruitment of Rac-1 and p47phox is critical for alpha-platelet-derived growth factor receptor-induced production of reactive oxygen species. 18287880_nox1, nox2, and p47 have distinct roles in NADPH oxidase activity in human veins. 18390927_The kinetics of p47phox activation was investigated by comparing neutrophils from diabetic and healthy subjects, and the mechanism of hyperglycemia-induced changes was studied by using neutrophil-like HL-60 cells as a model. 18424721_As(2)O(3) induced phosphorylation and membrane translocation of the NADPH oxidase subunit p47(phox) and it also increased translocation of Rac1 and p67(phox). 18523147_NF-kappaB is necessary for CYBB and NCF1 gene expression and activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase normal and anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia leukocytes. 18546332_mutations in CYBB, NCF1, CYBA or NCF2 may play a role in chronic granulomatous disease 18765662_Ile67 of the cPLA2-C2 domain is identified as a critical, centrally positioned residue in a hydrophobic interaction in the p47phox-PX domain 18983267_The direct interaction of PI3Kgamma with PKCalpha forms a discrete regulatory module of N-formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-dependent reactive oxygen species production in neutrophils. 19077231_NCF1DeltaGT/GTGT ratios were correlated with clinical parameters and ROI (reactive oxygen intermediates) production during Plasmodium falciparum malaria and with susceptibility to the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS) 19077231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19130504_Nef regulates the NADPH oxidase p47(phox)activity through the activation of the Src kinases and PI3K 19192478_Conformational changes in p47(phox) upon activation highlighted by mass spectrometry coupled to hydrogen/deuterium exchange and limited proteolysis are reported. 19329991_Mutation in NCF1 in Chronic granulomatous disease patient is associated with liver abscess. 19366706_These results demonstrate a role of PLD in hyperoxia-mediated IQGAP1 activation through Rac1 in tyrosine phosphorylation of Src and cortactin, as well as in p47(phox) translocation and reactive oxygen species formation in human lung endothelial cells. 19410294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632255_NADPH oxidase and lipid raft-associated redox signaling are required for PCB153-induced upregulation of cell adhesion molecules in human brain endothelial cells. 19717732_Conclude that acute exercise increases intracellular NO in endothelial progenitor cells through an NADPH oxidase-inhibition mechanism in sedentary men. 19833721_These results suggest that hyperoxia induces caveolin-1-dependent, c-Abl-mediated dynamin 2 phosphorylation required for recruitment of p47(phox) to caveolin-enriched microdomains and subsequent ROS production in lung endothelium. 19929442_Expression of the p47phox subunit and NOX activity was evaluated in affected (superior and middle temporal gyri) and unaffected (cerebellum) brain regions from a longitudinally followed group of patients with varying degrees of cognitive impairment. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20167518_All mutations and some polymorphisms identified in the NCF1 gene in the autosomal forms of chronic granulomatous disease are listed. Review. 20407811_granulomatous disease in Iran is predominantly due to mutations in p47-phox, while the number of mutations in p22-phox is roughly equal to that in gp91-phox, indicating that the genetics of CGD are ethnically variable 20495074_Loss of p47phox is associated with inflammasome activation resulting in chronic granulomatous disease. 20592030_p47phox molecular activation for assembly of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase complex. 20817944_a differential and agonist-dependent role of the p47(phox) PX domain for neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation. 21506107_Direct contact of solid tumor cells and ECs activates endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase-mediated superoxide production. The oxidative stress contributes to EC apoptosis which in turn facilitates tumor cell extravasation. 21518975_Results demonstrate that PBEF can prime for PMN respiratory burst activity by promoting p40 and p47 translocation to the membrane. 21566280_There is no correlation between C923T(Ala308Val)polymorphism and cerebral hemorrhage in Han people in Hunan province. 21728841_an increased copy number of NCF1 can be protective against developing RA and add support to previous findings of a role of NCF1 and the phagocyte NADPH oxidase complex in RA pathogenesis. 21789723_autosomal recessive mutational defects are the predominant subtype in Iranian patients with chronic granulomatous disease 21791598_tein disulfide isomerase redox-dependent association with p47(phox): evidence for an organizer role in leukocyte NADPH oxidase activation. 21813271_Resveratrol decreases hyperglycemic induced superoxide production via up-regulation of SIRT1, induction of FOXO3a and inhibition of p47phox in monocytes. 21911753_Data implicate p47phox as one of the sources of oxidative stress in diabetic islets or beta cells during hyperglycemia; evidence supports accelerated Rac1-Nox-ROS-JNK1/2 signaling pathway leading to mitochondrial dysregulation. 21956105_cooperation of p40(phox) with p47(phox) for Nox2-based NADPH oxidase activation during Fcgamma receptor (FcgammaR)-mediated phagocytosis 22219181_MLCK is essential for the translocation and association of cortactin and p47phox. 22460559_Phosphorylation of p47(phox) at different serine sites plays distinct roles in endothelial cell response to TNFalpha stimulation. 22493288_The low affinity and selectivity of the atypical phosphoinositide-binding site on the p47(phox) PX domain suggest that different types of phosphoinositides sequentially bind to the p47(phox) PX domain 22690528_A diffuse cytosolic distribution of p47-phox was observed in neutrophils from HIV-infected patients. 23216310_Patients with p47(phox) hereditary deficiency have intermediate flow mediated dilation and oxidative stress compared to healthy subjects and patients with NOX2 deficiency. 23386289_this study identified a 10 % incidence of diabetes in p47 (phox) deficient chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), but none in X-linked CGD. 23393912_Defining p47-phox deficient Chronic Granulomatous Disease in a Malay family. 23671702_Data show that curcumin-loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles (CURN) decreased the expression of ICAM-1, inhibited NADPH oxidase (NOX)-derived ROS generation, and reduced MAPKs and AP-1 transcription factor binding activities. 23688784_three different cross-over points exist within the NCF1 gene cluster, indicating that autosomal p47(phox)-deficient CGD is genetically heterogeneous but can be dissected in detail by MLPA 23870057_p47(phox) and Rac2 accumulate only transiently at the phagosome at the onset of NADPH activity and detach from the phagosome before the end of reactive oxygen species production. 23975181_There was an increase in p47-phox phosphorylation in neutrophils from myeloproliferative disorder patients with the JAK2 (V617F) mutation. 24081483_Two novel mutations are identified in Greek patients with chronic granulomatous disease: one in NCF1 and one in cytochrome CYBB. 24126171_Williams syndrome patients are at risk for increased aortic stiffness. This vascular stiffness is caused by elastin insufficiency and is modified by NCF1 copy number. 24596025_Four novel mutations in the NCF1, NCF2, and CYBB genees have been identified in chronic granulomatous disease patients in Morocco. 24967690_Suggest eupafolin attenuated COX-2 expression leading to reduced production of prostaglandin E2 by blocking Nox2/p47(phox) pathway. 25239440_Reduced carotid but not coronary artery atherosclerosis in patients with chronic granulomatous disease despite the high prevalence of traditional risk factors raises questions about the role of NADPH oxidase in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 25761062_Results identifies p47phox-dependent NADPH oxidase activity as a critical component of Angpt-1-mediated endothelial barrier defense against classic inflammatory permeability factors. 25877926_TLR8, but not TLR7, is involved in priming of human neutrophil reactive oxygen species production by inducing the phosphorylation of p47phox and p38 MAPK. 25981738_DCLRE1C and NCF1 mutations have been found by whole-genome sequencing to cause primary immunodeficiency in unrelated patients. 26317224_increased levels of gp91phox, p47phox and p22phox likely account for the interferon-gamma mediated enhancement of dimethyl sulfoxide-induced Nox2 activity. 26460255_A rare mutation in NCF1 encoding p47phox of the leukocyte NADPH oxidase causes lack of superoxide generation, leads to chronic granulomatous disease and was recently (1200-2300 years ago) introduced into the Kavkazi Jewish population 26728380_Data show that diphenylene iodonium (DPI) and apocynin can reduce hyperoxia-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by decreasing the translocation and level of NADPH Oxidase p47phox. 26760964_Overexpression of p47phox is associated with increased migration/metastasis rate in melanoma. 27040869_Study provides evidence for a novel PKC-zeta to p47phox interaction that is required for cell transformation from blebbishields and ROS production in cancer cells. 27343196_A novel role for Spns2 and S1P1&2 in the activation of p47(phox) and production of reactive oxygen species involved in hyperoxia-mediated lung injury. 27531930_Lysophosphatidylcholines prime polymorphonuclear neutrophil through Hck-dependent activation of PKCdelta, which stimulates PKCgamma, resulting in translocation of phosphorylated p47(phox). 27723093_patients with hereditary p47phox deficiency show reduced platelet activation suggesting a role for this Nox cytosolic subunit in platelet activation. 27765769_Skeletal muscle protein expression of the NADPH oxidase subunits p22(phox), p47(phox), and p67(phox) was increased in obese relative to lean subjects, where p22(phox) and p67(phox) expression was attenuated by exercise training in obese subjects. 28135245_Decreased and increased copy numbers of NCF1 predispose to and protect against SLE. 28240310_IL-27 enhances the potential of reactive oxygen species generation from monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells by induction of p47(phox). 28606963_There was an increased frequency of the NCF1-339 T allele in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. The NCF1-339 T allele reduced extracellular ROS production in neutrophils and led to an increase expression of type 1 interferon-regulated genes. 28939422_p47phox, but not p67phox or p40phox, binds to and activates Nrf2, enhancing the function of Nrf2 in suppressing inflammation. 29195919_p47phox S-glutathionylation plays an essential key role in the sustained ROS generation by human neutrophils. 29311151_Tyrosine kinase substrate (Tks) proteins, analogous to the related proteins p47(phox), p40(phox) and NoxO1, also facilitate local generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which aid in signaling at invadopodia and/or podosomes to promote their activity. As their name suggests, Tks adaptor proteins are substrates for tyrosine kinases, especially Src. [review] 29331982_In six additional Ashkenazi carriers of the NCF1 c.579G>A mutation, we found five individuals with three complete NCF1 genes of which one was mutated (like the parents), and one individual with in addition a fusion gene of NCF1 with a pseudogene 29360265_Our findings in experiments on activated human retinal endothelial cells provide translational corroboration of studies in experimental models of retinal vasculopathy and support the therapeutic application of Nox4 inhibition by GKT136901 and GKT137831 in patients with retinal vascular diseases. 29411231_Correlation between genotype and phenotype is unpredictable, although clinically, the Kavkazi patients were more severely affected than other patients with p47phox deficiency. 30078213_we discovered the existence of p47(phox) /Hyal2 complex. LSS induced the dissociation of p47(phox) /Hyal2 complex, which was inhibited by LKB1 overexpression and AICAR. Furthermore, knockdown of Hyal2 performed a positive feedback on LKB1 activity 30323221_Activation of PAD4 by membranolytic insults that result in high levels of intracellular calcium (higher than physiological neutrophil activation) leads to rapid citrullination of p47(phox)/NCF1 and p67(phox)/NCF2, as well as their dissociation from PAD4 30465301_NCF1, a critical gene in the ROS system, was upregulated in THP-1 cell and monocytes under lipopolysaccharides stimulation. Moreover, we identified the upregulation of NCF1 in a sepsis model. 30470980_of the total molecularly characterized Indian patients with chronic granulomatous disease (n = 90), 56% of the patients had a mutation in the NCF1 gene 30580571_we identify specific cysteine residues of protein disulfide isomerase and p47phox necessary for the direct interaction of these proteins, the assembly of the Nox1 complex and subsequent activation of Nox1 in vascular disease. 30651282_flow cytometry for p47(phox) expression quickly identifies patients and carriers of p47(phox) CGD, and genomic ddPCR identifies patients and carriers of DeltaGT NCF1, the most common mutation in p47(phox) CGD. 30963593_this study shows genetic and molecular findings of 38 Iranian patients with chronic granulomatous disease caused by p47-phox defect 31492810_Data showed that proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) associated with neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 (p47phox), a key subunit of NADPH oxidase in neutrophils and that this association regulated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. 31704719_Polymorphism NCF1-339, rs201802880 mediated decreased NADPH oxidase function, is associated with high interferon activity and impaired formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic lupus erythematosus, allowing dependence on mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Also a striking connection between the ROS deficient NCF1-339 genotypes and the presence of phospholipid antibodies and antiphospholipid syndrome 31705128_Association of NCF1 polymorphism with systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis but not with ANCA-associated vasculitis in a Japanese population. 31973815_P-Tyr42 RhoA GTPase amplifies superoxide formation through p47phox, phosphorylated by ROCK. 33596590_Neutrophil Cytosolic Factor-1 Genotyping in Acne Vulgaris. 33903979_Whole genome sequencing identifies variants associated with sarcoidosis in a family with a high prevalence of sarcoidosis. 34556485_Human SLE variant NCF1-R90H promotes kidney damage and murine lupus through enhanced Tfh2 responses induced by defective efferocytosis of macrophages. 34708124_NCF1/2/4 Are Prognostic Biomarkers Related to the Immune Infiltration of Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. 35108370_Impaired p47phox phosphorylation in neutrophils from patients with p67phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease. |
ENSMUSG00000015950 |
Ncf1 |
365.527275 |
2.4416175000 |
1.287837 |
0.088560498 |
214.231601 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000163943095656260487102144834046275935125020849999928797799288176650203445626927995613064878357005242420492395984460700736557239864943369411776075139641761779785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000033748955256435213661468639726241103186737140926020080093841990296506074857395096936837081188337221139329883641457002605920645343928754300577566027641296386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
521.8215069 |
27.3410490 |
215.3090504 |
9.0239910 |
| ENSG00000158710 |
8407 |
TAGLN2 |
protein_coding |
P37802 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is similar to the protein transgelin, which is one of the earliest markers of differentiated smooth muscle. The specific function of this protein has not yet been determined, although it is thought to be a tumor suppressor. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2013]. |
hsa:8407; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855] |
19848416_in pulmonary adenocarcinoma, overexpression of TAGLN was strictly localized to the tumor-induced reactive myofibroblastic stromal tissue compartment, whereas overexpression of TAGLN2 was exclusively localized to the neoplastic glandular compartment 21378409_Data indicate that TAGLN2 may have an oncogenic function and may be regulated by miR-1, a tumor suppressive miRNA in HNSCC. 21577206_our data propose a novel, oncogene-tumor suppressor interplay, where oncogenic PFTK1 confers HCC cell motility through inactivating the actin-binding motile suppressing function of TAGLN2 via phosphorylation. 23527717_PTTG1 and TAGLN2 are highly expressed in human pancreatic cancer, and the positive expression of PTTG1 is associated with the gender of cancer patients, suggesting that it may represent a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer 24476357_Transgelin-2, a sequence homolog of transgelin, whose role in the tumor development might be contradictory to the role of transgelin. 25421410_TAGLN2 modulates hypoxia-induced apoptosis via caspase-8 apoptotic pathway. Taken together, our data demonstrated the roles of miR-133a in hypoxia-induced apoptotic and implicate its potential in cardiac dysfunctions therapy. 26081836_Proteomics result showed TAGLN2 as the most significant overexpression in individual bladder cancer tissues and urine specimens, and thus represents a potential biomarker for noninvasive screening for bladder cancer. 26176734_Salvianolic acid A can reverse the paclitaxel resistance and inhibit the migration and invasion abilities of human breast cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of transgelin 2. 26414725_It is a target gene of miR-1. 26891454_Transgelin-2 plays functional roles in the progression of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Suppression of Transgelin-2 may be a new strategy for the treatment of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 27402267_Our data demonstrated that TAGLN2 might be an HBx induced positive host factor involved in HBV transcription and replication and HBx related liver fibrosis and tumorigenesis 28521289_Our data support a novel mechanism in diabetes-associated PDAC by which transgelin-2 mediates proliferation of PDAC cells upon insulin stimulation. 28639888_we reviewed the basic characteristics and function of Transgelin-2 and its biological role in various types of diseases in order to provide the theoretical basis for further research and new perspectives on cancer development. 28910360_Results suggest that TAGLN2 might regulate activation and migration of B-cells, in particular, the entry of activated B-cells into the follicle. 29110682_Results show that Increased expression of TAGLN2 is associated with increasing tumor grade in glioma and poor patient survival. Knockdown experiments highlighted the function of TAGLN2 in promoting glioma cell invasion, the EMT phenotype, and tumor growth. 29615809_dual functional nature of TAGLN2-G-actin polymerization and Arp2/3 complex inhibition-may account for the mechanisms of filopodia development at the edge of Arp2/3-rich lamellipodia in various cell types 30041673_Authors found transgelin-2 expression was induced by KRAS mutation. In the case of KRAS mutation, ERK2 interacted with 29-31 amino acids of transgelin-2 and subsequently phosphorylated the S145 residue of transgelin-2. 30191639_Study provides important evidence that hypoxia-inducible TAGLN2 is involved in the selection of cancer cells with enhanced EMT properties to overcome the detrimental environment of cancer cells as gamma radiation. 30942422_TAGLN 2 overexpression in HeLa cells could inhibit cell viability, migration and invasion, and it was suggested that this may occur via upregulation of the expression levels of E cadherin and inhibitor of nuclear factor kappalightchainenhancer of activated B cells (NFkappaB) (IkappaB), and downregulation of C XC chemokine receptor type 4, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2, MMP9, p50 and transcription factor p65. 31144206_Transgelin-2 was highly overexpressed in breast cancer and relevant to progression. High transgelin-2 expression might predict poor outcome in patients with ER-negative tumors. 31256982_REVIEW: Biochemical and Clinical Implications in Cancer and Asthma 31485630_The present study proposed TAGLN2 to function as a tumor suppressor and that loss of TAGLN2 may promote the metastasis of breast cancer by activating the ROS/NFkappaB signaling pathway. 31941608_Transgelin-2 contributes to proliferation and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating Annexin A2. 32467330_Transgelin-2 and phosphoregulation of the LIC2 subunit of dynein govern mitotic spindle orientation. 34498538_Quercetin Antagonizes Esophagus Cancer by Modulating miR-1-3p/TAGLN2 Pathway-Dependent Growth and Metastasis. 34553339_Transgelin-2 interacts with CD44 to regulate Notch1 signaling pathway and participates in colorectal cancer proliferation and migration. 35011306_Transgelin-2 in Multiple Myeloma: A New Marker of Renal Impairment? 35219353_Mechanisms of Transgelin-2 in Tumorigenesis. 35683019_Variations in Blood Platelet Proteome and Transcriptome Revealed Altered Expression of Transgelin-2 in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients. |
ENSMUSG00000026547 |
Tagln2 |
4048.699618 |
2.5495985319 |
1.350270 |
0.029206257 |
2149.176618 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5875.9404102 |
108.5266595 |
2321.4891045 |
33.6161316 |
| ENSG00000158714 |
56833 |
SLAMF8 |
protein_coding |
Q9P0V8 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in B-lineage commitment and/or modulation of signaling through the B-cell receptor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11313408}. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the CD2 family of cell surface proteins involved in lymphocyte activation. These proteins are characterized by Ig domains. This protein is expressed in lymphoid tissues, and studies of a similar protein in mouse suggest that it may function during B cell lineage commitment. The gene is found in a region of chromosome 1 containing many CD2 genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56833; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; membrane [GO:0016020]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; B-1 B cell lineage commitment [GO:0002336]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; leukocyte chemotaxis involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002232]; negative regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000509]; negative regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010760]; negative regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090027]; negative regulation of neutrophil migration [GO:1902623]; negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response [GO:0060266]; phagosome acidification [GO:0090383]; regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045577]; regulation of kinase activity [GO:0043549]; regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity [GO:0033860] |
20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29498772_Thus, SLAMF8 is involved in oncogenic KIT-mediated RAS-RAF- ERK signalling and the subsequent growth of human neoplastic mast cells mediated by SHP-2. 32054954_SLAM family member 8 is expressed in and enhances the growth of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 35259711_Knockout of SLAMF8 attenuates collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis in mice through inhibiting TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 35432371_SLAMF8 Participates in Acute Renal Transplant Rejection via TLR4 Pathway on Pro-Inflammatory Macrophages. 35506438_SLAMF8 promotes the proliferation and migration of synovial fibroblasts by regulating the ERK/MMPs signalling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000053318 |
Slamf8 |
1699.830602 |
3.8913454708 |
1.960269 |
0.051051973 |
1479.098245 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001482197 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002277643 |
Yes |
No |
2709.7157809 |
81.3668328 |
701.3114644 |
17.0850629 |
| ENSG00000158715 |
85414 |
SLC45A3 |
protein_coding |
Q96JT2 |
FUNCTION: Proton-associated sucrose transporter. May be able to transport also glucose and fructose. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0H7}. |
Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable sucrose:proton symporter activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of small molecule metabolic process; regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation; and sucrose transport. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:85414; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sucrose:proton symporter activity [GO:0008506]; sugar transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0051119]; hexose transmembrane transport [GO:0008645]; positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045723]; positive regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010907]; regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048713]; sucrose transport [GO:0015770] |
15048720_T cells that recognize naturally processed epitopes from prostein were expanded from healthy donors and characterized. T cells isolated from males were of low avidity and recognized subdominant epitopes while those from females were of higher avidity 15176054_Prostein is expressed in the vast majority of prostatic tissues, regardless of grade and metastatic status. No expression was detected in 4,700 normal and malignant tissue samples representing the great majority of essential tissues and tumors. 17721190_P501S is a sensitive and highly specific marker for identifying prostate tissue. Combined use of prostein/prostate specific antigen used to detect prostatic origin of metastatic carcinomas. 18172298_A SLC45A3:ETV5 gene fusion was identified in prostate cancer. 18193184_Intronic miRNAs from tissue-specific transcripts, or their natural absence, make cardinal contributions to cellular gene expression and phenotype. 19136943_SLC45A3-ELK4 may represent the first description of a recurrent RNA chimaeric transcript specific to prostate cancer that does not have a detectable DNA aberration 19649210_This study demonstrates that most ERG-overexpressing prostate cancers harbor hormonally regulated TMPRSS2-ERG, SLC45A3-ERG, or NDRG1-ERG fusions 20118910_This is the first study to report concurrent TMPRSS2 and SLC45A3 rearrangements in the same tumor focus in prostate cancer 21777423_Double sequential immunohistochemical staining with p63 and P501S is highly specific and can be a useful tool in distinguishing urothelial carcinoma from prostate carcinoma. 22719019_Data suggest that chimeric SLC45A3-ELK4 controls prostate cancer cell proliferation, and the chimera level correlates with prostate cancer disease progression. 22821757_This study provides first evidence that the expression of SLC45A3 protein is down regulated through SLC45A3-ERG fusion in prostate cancer. 23269536_Genome-wide association study identified novel genetic variant on SLC45A3 gene associated with serum levels prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in a Chinese population. 25434496_genome-wide association studies show that the top SNP associated with log PSA 9Prostate-specific antigen) levels was rs2153904 in SLC45A3. 26938874_CTCF has a role in regulating SLC45A3-ELK4 Chimeric RNA 27700103_Identification of a novel autoimmune peptide epitope of prostein in prostate cancer has been reported. 33045005_Novel loci for childhood body mass index and shared heritability with adult cardiometabolic traits. 34099864_Mapping genetic variability in mature miRNAs and miRNA binding sites in prostate cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000026435 |
Slc45a3 |
238.778903 |
0.4739521622 |
-1.077187 |
0.106955956 |
102.551053 |
0.00000000000000000000000420393076601028881950373297924523517540233504991445177776860134787051404003932475461624562740325927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000043666444832028055757329098346474630567040626376683083704035095995443782612710492685437202453613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
154.1911315 |
12.5789438 |
327.4158882 |
18.1907306 |
| ENSG00000158806 |
10361 |
NPM2 |
protein_coding |
Q86SE8 |
FUNCTION: Core histones chaperone involved in chromatin reprogramming, specially during fertilization and early embryonic development. Probably involved in sperm DNA decondensation during fertilization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21863821}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Chromatin regulator;Developmental protein;Fertilization;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity; chromatin binding activity; and histone binding activity. Involved in several processes, including blastocyst development; oocyte differentiation; and regulation of cell cycle process. Located in chromatin and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10361; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; blastocyst development [GO:0001824]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; oocyte differentiation [GO:0009994]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0045836]; regulation of exit from mitosis [GO:0007096]; single fertilization [GO:0007338] |
12209603_Expression of NPM2 in HeLa cells 19491193_Promoter methylation and differential gene expression of five markers: COL1A2, NPM2, HSPB6, DDIT4L and MT1G were validated by sequencing of bisulfite-modified DNA and real-time reverse transcriptase PCR, respectively. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21863821_The crystal structure of a truncated Npm2-core shows that the N-terminal domains of Npm2 and Np form similar pentamers, providing insights into the mechanism of histone binding by nucleoplasmins. 22362753_Characterization of the sperm chromatin decondensation and nucleosome assembly activities of homo- and hetero-oligomers of NPM1,NPM2 and NPM3. 22968912_Studies indicate that histone chalerones nucleoplasmin (NPM2/NPM3) preferentially associated with histones H2A-H2B in the egg and the nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP) families. 36280841_Loss of NPM2 expression is a potential immunohistochemical marker for malignant peritoneal mesothelioma: a single-center study of 92 cases. |
ENSMUSG00000047911 |
Npm2 |
10.917373 |
0.1298499834 |
-2.945082 |
0.570127518 |
31.212725 |
0.00000002312453176263992433373769305304107346543673884298186749219894409179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000097186243968270283982568296960585785271291570097673684358596801757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.7032015 |
0.6915177 |
13.2205604 |
2.7244548 |
| ENSG00000158828 |
65018 |
PINK1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXM7 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase which protects against mitochondrial dysfunction during cellular stress by phosphorylating mitochondrial proteins such as PRKN and DNM1L, to coordinate mitochondrial quality control mechanisms that remove and replace dysfunctional mitochondrial components (PubMed:14607334, PubMed:18957282, PubMed:18443288, PubMed:15087508, PubMed:19229105, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:20404107, PubMed:22396657, PubMed:20798600, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:23754282, PubMed:23933751, PubMed:24660806, PubMed:24898855, PubMed:24751536, PubMed:24784582, PubMed:24896179, PubMed:25527291, PubMed:32484300, PubMed:20547144). Depending on the severity of mitochondrial damage and/or dysfunction, activity ranges from preventing apoptosis and stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis to regulating mitochondrial dynamics and eliminating severely damaged mitochondria via mitophagy (PubMed:18443288, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24898855, PubMed:20798600, PubMed:20404107, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:32484300, PubMed:22396657, PubMed:32047033, PubMed:15087508). Mediates the translocation and activation of PRKN at the outer membrane (OMM) of dysfunctional/depolarized mitochondria (PubMed:19966284, PubMed:20404107, PubMed:20798600, PubMed:23754282, PubMed:24660806, PubMed:24751536, PubMed:24784582, PubMed:25474007, PubMed:25527291). At the OMM of damaged mitochondria, phosphorylates pre-existing polyubiquitin chains at 'Ser-65', the PINK1-phosphorylated polyubiquitin then recruits PRKN from the cytosol to the OMM where PRKN is fully activated by phosphorylation at 'Ser-65' by PINK1 (PubMed:19966284, PubMed:20404107, PubMed:20798600, PubMed:23754282, PubMed:24660806, PubMed:24751536, PubMed:24784582, PubMed:25474007, PubMed:25527291). In damaged mitochondria, mediates the decision between mitophagy or preventing apoptosis by promoting PRKN-dependent poly- or monoubiquitination of VDAC1; polyubiquitination of VDAC1 by PRKN promotes mitophagy, while monoubiquitination of VDAC1 by PRKN decreases mitochondrial calcium influx which ultimately inhibits apoptosis (PubMed:32047033). When cellular stress results in irreversible mitochondrial damage, functions with PRKN to promote clearance of damaged mitochondria via selective autophagy (mitophagy) (PubMed:14607334, PubMed:20798600, PubMed:20404107, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:23933751, PubMed:15087508). The PINK1-PRKN pathway also promotes fission of damaged mitochondria by phosphorylating and thus promoting the PRKN-dependent degradation of mitochondrial proteins involved in fission such as MFN2 (PubMed:18443288, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24898855). This prevents the refusion of unhealthy mitochondria with the mitochondrial network or initiates mitochondrial fragmentation facilitating their later engulfment by autophagosomes (PubMed:18443288, PubMed:23620051). Also promotes mitochondrial fission independently of PRKN and ATG7-mediated mitophagy, via the phosphorylation and activation of DNM1L (PubMed:18443288, PubMed:32484300). Regulates motility of damaged mitochondria by promoting the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of MIRO1 and MIRO2; in motor neurons, this likely inhibits mitochondrial intracellular anterograde transport along the axons which probably increases the chance of the mitochondria undergoing mitophagy in the soma (PubMed:22396657). Required for ubiquinone reduction by mitochondrial complex I by mediating phosphorylation of complex I subunit NDUFA10 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99MQ3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14607334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15087508, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18443288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18957282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19229105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19966284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20404107, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20547144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20798600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22396657, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23620051, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23754282, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23933751, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24660806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24751536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24784582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24896179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24898855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25474007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25527291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32047033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32484300}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Parkinson disease;Parkinsonism;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a serine/threonine protein kinase that localizes to mitochondria. It is thought to protect cells from stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Mutations in this gene cause one form of autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinson disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:65018; |
astrocyte projection [GO:0097449]; axon [GO:0030424]; cell body [GO:0044297]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; Lewy body [GO:0097413]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; C3HC4-type RING finger domain binding [GO:0055131]; calcium-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0010857]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; peptidase activator activity [GO:0016504]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase B binding [GO:0043422]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; TORC2 complex binding [GO:1904841]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:0000422]; cellular response to hydrogen sulfide [GO:1904881]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cellular response to toxic substance [GO:0097237]; dopamine secretion [GO:0014046]; establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion [GO:0072655]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; maintenance of protein location in mitochondrion [GO:0072656]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; mitochondrion to lysosome transport [GO:0099074]; mitophagy [GO:0000423]; negative regulation of autophagosome assembly [GO:1902902]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced neuron intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1903384]; negative regulation of hypoxia-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1903298]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:1903751]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016242]; negative regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090258]; negative regulation of mitophagy [GO:1901525]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death [GO:1903202]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903204]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; peptidyl-serine autophosphorylation [GO:0036289]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001171]; positive regulation of cristae formation [GO:1903852]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0033603]; positive regulation of free ubiquitin chain polymerization [GO:1904544]; positive regulation of histone deacetylase activity [GO:1901727]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; positive regulation of mitochondrial electron transport, NADH to ubiquinone [GO:1902958]; positive regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090141]; positive regulation of mitophagy in response to mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0098779]; positive regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor activity [GO:1904783]; positive regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010952]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein dephosphorylation [GO:0035307]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:1903955]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, dopaminergic [GO:0032226]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0051443]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:1903146]; regulation of cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:1900407]; regulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolic process [GO:0010310]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881]; regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010821]; regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0002082]; regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0061136]; regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:1903214]; regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031396]; regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0043254]; regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000377]; regulation of synaptic vesicle transport [GO:1902803]; respiratory electron transport chain [GO:0022904]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; TORC2 signaling [GO:0038203]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
12447943_The subclinical loss of striatal dopamine storage capacity found in PARK6 carriers implies that the unidentified gene on the short arm of chromosome 1 exhibits either haploinsufficency or a dominant negative effect. 12548343_Autosomal recessive early onset parkinsonism is linked to three loci: PARK2, PARK6, and PARK7. 12548371_PARK6 appears to be an important locus for autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism in Europe. 15087508_mutations in PINK1 are associated with PARK6 a locus linked to a rare familial form of Parkinson disease; cell culture studies suggest that PINK1 is mitochondrially located and may exert a protective effect on the cell that is abrogated by the mutations 15349859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15349859_Strong evidence indicates that, although important in mendelian forms of Parkinson's disease (PD), PINK1 does not influence the cause of sporadic nonmendelian forms of PD. 15349860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15349870_Six novel pathogenic PINK1 mutations suggest that PINK1 may be the second most common causative gene next to parkin in parkinsonism with the recessive mode of inheritance. 15505170_The results indicate worldwide distribution of PARK6-linked parkinsonism. 15505171_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15505171_Overall, these data indicate that PINK1 mutations are a rare cause of PD in Ireland. 15542245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15596610_Autosomal recessive mutations in PINK1 are a rare cause of young-onset Parkinson disease. 15596610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824318_These results show that PINK1 is processed at the N terminus in a manner consistent with mitochondrial import, but the mature protein also exists in the cytosol. 15876334_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15876334_The G309D and W437OPA mutations in PINK1 gene probably do not represent common causes of familial or sporadic PD in a Caucasian population. 15955953_Thus, early-onset PD with dementia may be considered PINK1-linked parkinsonism. Furthermore, patients with PINK1 mutations form 8.9% of parkin- and DJ-1-negative ARPD families. 15955954_A patient homozygous for A PINK1 mutation was characterized clinically. All clinical and laboratory features, including SPECT and assessment of autonomic function, were indistinguishable from typical idiopathic Parkinson disease. 15970950_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16009891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16009891_PINK1 homozygous mutations are a relevant cause of disease among Italian sporadic patients with early-onset parkinsonism. 16046032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16079129_PINK1 reduces the basal neuronal pro-apoptotic activity and protects neurons from staurosporine-induced apoptosis; loss of this protective function may underlie degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons in patients with PINK1 mutations 16157901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16207731_Both wild-type and mutant PINK1 proteins localize to mitochondria and prove that a short N-terminal part of PINK1 is sufficient for its mitochondrial targeting. 16226715_PINK1 participates in the protection of dopaminergic neurons 16257123_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16354302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16482571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16482571_The phenotypic spectrum associated with PINK1-positive Parkinson disease patients may be wider than previously reported. 16547921_PINK1 mutations (homozygous nonsense and heterozygous missense) that highlight issues in Parkinson disease diagnosis. 16632486_PINK1 and DJ-1 may have a role in early-onset Parkinson's disease and physically associate and collaborate to protect cells against stress via complex formation 16672981_Expression of human PINK1 in the Drosophila testes restores male fertility and normal mitochondrial morphology in a portion of pink1 mutants, demonstrating functional conservation between human and Drosophila Pink1 16700027_A patient, heterozygote for W437X mutation, was affected by Parkinson's disease and 3 further relatives were reported affected, according to an autosomal dominant transmission. 16769864_Heterozygous PINK1 mutations may predispose to PD, as was previously suggested by the presence of dopamine hypometabolism in asymptomatic mutation carriers. 16966503_This study extends the phenotypic and molecular spectrum of the PINK1 gene and the geographic origin of patients with PINK1 gene mutations. 16969854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16969854_PINK1 mutations mutations are a significant risk factor in the development of later onset Parkinson's disease 17000703_Thus, in addition to the activation segment, the C-terminal tail of PINK1 also contains regulatory motifs capable of governing PINK1 kinase activity. 17013904_This finding suggests a role not only of homozygous but also of heterozygous PINK1 mutations in the development of parkinsonian signs and underlines the necessity to carefully investigate family members of affected mutation carriers. 17017532_PINK-1 encodes the PTEN induced kinase 1 and is located to provide a link between mitochondria and the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease--REVIEW 17055324_We genotyped eight known mutations in three clinic-based cohorts with Parkinsonism and found one homozygous p.L347P mutation in PINK1. 17084972_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17084972_PINK1 A340T variant may contribute to the risk for late-onset PD in Chinese. 17141510_These data indicate that PINK1 function is critical to prevent oxidative damage and that peripheral cells may be useful for studies of progression and therapy of PARK6. 17154281_Deletion of the entire PINK1 gene and a splice site mutation (g.15445_15467del23) which produces several aberrant mRNAs in Parkinson disease. 17172567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17172567_PINK1 mutations are rare in Norwegian patients with EOP and familial Parkinson's disease;however, the data suggest that some heterozygous mutations might increase the risk of developing Parkinson's disease 17202228_affective and psychotic symptoms may be part of the phenotypic spectrum or even the sole manifestation of PINK1 mutations 17219214_Absence of correlation between PINK1 mRNA levels and clinical status in heterozygous mutation carriers suggests that other genetic or environmental factors play a role in determining the phenotypic variability in Parkinson disease. 17362513_a mammalian non-coding antisense molecule can positively influence the abundance of a cis-transcribed mRNA; dsRNA-mediated mechanism for stabilizing the expression of svPINK1 17557243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17557243_possible association of IVS5-5G>A polymorphism, positioned in the upstream region of exon 5 of PINK1 gene with the risk for sporadic late onset Parkinson disease (LOPD) in Chinese 17567565_regulation of the PINK1 locus, linked to neurodegenerative disease, is altered in obesity, NIDDM and inactivity, while the combination of RNAi experiments and clinical data suggests a role for PINK1 in cell energetics 17579517_PINK1 protects against oxidative-stress-induced cell death by suppressing cytochrome c release from mitochondria, and this protective action of PINK1 depends on its kinase activity to phosphorylate TRAP1. 17707122_PINK1 exerts anti-apoptotic effect by inhibiting the opening of mPTP and that PARK6 mutant PINK1 loses its ability to prevent mPTP opening and cytochrome c release. 17724286_Relative to controls without a mutation, Parkin and PINK1 mutation carriers displayed a bilateral increase in gray matter volume in the putamen and the internal globus pallidus 17766179_sleep disturbances were not found in PARK6 parkinsonism patients 17950257_humans PINK1 message is expressed in neurons with very little to no signal in glia and no difference in parkinson disease. 17960343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17960343_The incidence of carrying PINK1 mutations in the present cohort of Taiwanese EOPD patients was low, accounting for 2/39 (5.1 %) in familial cases, and 2/99 (2 %) in sporadic cases. 17989306_PINK1 deficiency in humans results in mitochondrial abnormalities associated with cellular stress, a pathological phenotype, which can be ameliorated by enhanced expression of parkin. 18003639_document the influence of Parkin on Pink1 subcellular distribution, providing further evidence for a common pathogenic pathway in recessive Parkinson's disease 18031932_DeltaN 54 kDa PINK1 undergoes constitutive degradation by proteasome, and underscore the significance of its localization in cytoplasm, especially in the N-terminally processed form. 18068301_no PINK1 gene mutation was found in any of the probands from six Caucasian early-onset Parkinson disease families 18211709_No mutations were found in PINK1 in Parkinson disease patients from Portugal. 18211709_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18261714_Limbic and frontal cortical degeneration is associated with psychiatric symptoms in PINK1 mutation carriers. 18272063_May be involved in apoptosi, oxidative stress, and development of Parkinson disease. 18286320_Homozygous mutations in the PINK1 gene have been shown to cause early-onset parkinsonism. Here, we describe a novel homozygous mutation (Q126P), identified in two affected German sisters with a clinical phenotype typical for PINK1-associated parkinsonism. 18307263_Homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations in the PINK1 gene represent the second most frequent cause of autosomal recessive parkinsonism after Parkin protein. 18330912_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18330912_retrospectively analyzed the occurrence of PINK1 heterozygous rare variants in over 1100 sporadic and familial Parkinson disease patients of all onset ages and in 400 controls 18359116_Hsp90 and Cdc37 are binding partners of PINK1 which regulate its stability 18378882_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18378882_Patients with Parkin or PINK1 mutations benefit from subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation, but clinical response is not superior to non-mutation carriers and may be limited by more advanced axial motor symptoms at a relatively early disease stage. 18397367_Our findings support a dual subcellular localization, implying that PINK1 can reside in the mitochondria and the cytosol. This raises intriguing functional roles that bridge these two cellular compartments. 18469032_PINK1 gene mutations are linked to Parkinson disease 18486522_In this study found one patient carried a p.G411S heterozygous amino acid change in the PINK1 gene. 18486522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18495756_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18495756_PINK1 polymorphisms are associated with PINK1 transcript levels and measures of fatty acid metabolism in a concordant manner, whereas our RNAi data imply that PINK1 may indirectly influence lipid metabolism. 18524835_Results show a co-segregation of a Parkinson's disease related nuclear gene (PINK1) mutation with mtDNA mutation. 18541801_Data emphasize the importance of heterozygous PINK1 mutations as a possible risk factor for developing the common classic form of sporadic Parkinson disease. 18546294_A new heterozygous mutation (p.R58-V59insGR) was found in exon 1 of PINK1. PINK1 mutation may modify parkin-mutation-positive Parkinsonism. PINK1 mutations may be associated with schizophrenia. 18560593_phenotypic effects of PINK1 loss-of-function described here in mammalian neurons provides mechanistic insight into the age-related degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons seen in Parkinson disease 18584234_Data show that higher tactile and visuo-tactile temporal discrimination threshold and temporal order judgement are detected in in PINK1 mutation carriers. 18584234_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18685134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18685134_Only four PINK1 mutations were pathogenic. Several PINK1 sequence variants are potentially benign and there was no evidence that PINK1 heterozygosity increases susceptibility to idiopathic Parkinson disease. 18704525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18785233_Mutations of PINK1 gene are found in Chinese families with autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinsonism. 18957282_These results demonstrate the biochemical relationship between PINK1, Parkin, and the mitochondria and thereby suggest the possible mechanism of PINK-Parkin-associated PD pathogenesis. 18973254_A novel missense mutation was found in exon 3 (c.709A>G;p. M237V). The high conservation of residue 237 among PINK1 homologs and its critical location in the protein kinase domain suggests that the novel M237V variant may affect PINK1 function. 18973254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19006224_3 patients with heterozygous PINK1 mutations (2 new:M341I & P209A)were found in a Taiwanese PD cohort, but it is dubious whether any of the novel PINK1 mutations were sufficient in the heterozygous state to cause disease. 19006224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19038850_Mutations in pink1 protein,linked to recessively inherited Parkinson disease, are associated with an additional recruitment of supplementary motor area and premotor cortex during a motor sequence task. 19048950_Its missense mutation causes autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. 19076428_Mutations in PINK1 are associated with the PARK6 autosomal recessive, early-onset, Parkinson disease-susceptibility locus 19087301_The PINK1 gene in Jordanian families with incidences of young-onset and juvenile parkinsonism is identified two novel putative pathogenic substitutions, P416R and S419P, located in a conserved motif of the serine/threonine kinase domain. 19139432_Combined expression of BUB1B and PINK1 was the best predictor of overall survival in malignant adrenal cortex neoplasms. Combined expression of DLG7 and PINK1 was the best predictor of disease free survival. 19152501_Findings suggest that Pink1 functions in the trafficking of mitochondria in cells. 19167501_Data show that parkin and PINK1 affect each other's stability, solubility and tendency to form aggresomes, and have important implications regarding the formation of Lewy bodies. 19205068_In this study identified one novel mutation in PINK1 (homozygous deletion of exon 7). 19205068_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19214605_Data report a third large rearrangement of PINK1, which enlarges the mutation spectrum involved in recessive early onset Parkinson's disease. 19224617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19224617_This study found that no associations were seen for PINK1 in Australia patient with Parkinson's disease 19229105_Functional ubiquitin E3 ligase complex consisting of parkinson disease (PD)-associated Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 to promote degradation of un-/misfolded proteins. 19242547_mutant PINK1 or PINK1 knock-down caused deficits in mitochondrial respiration and ATP synthesis 19270741_Silencing of PINK1 expression affects mitochondrial DNA and oxidative phosphorylation. 19276113_FOXO3a controls Pink1 transcription in both mouse and human cells subjected to growth factor deprivation, and this regulation is exerted through evolutionarily conserved FOXO binding elements 19279012_PINK1 and Parkin may cooperate through different mechanisms to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis. 19285945_PINK1-associated Parkinson's disease is caused by neuronal vulnerability to calcium-induced cell death. 19330279_PINK1 mutation carriers showed saccade abnormalities indicating of an impaired saccadic basal ganglia path and posterior parietal cortex 19351622_Studied the frequency of parkin and PINK1 gene mutations in early-onset Parkinson's disease; data support a trend towards a higher frequency of heterozygosity in patients compared with normal controls, but effect small and not significant in this study. 19358826_These results indicate that Parkin regulates PINK1 stabilization via direct interaction with PINK1, and operates through a common pathway with PINK1 in the pathogenesis of early-onset Parkinson disease. 19405094_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19492085_Drp1 is dephosphorylated in PINK1 deficient cells due to activation of the calcium-dependent phosphatase calcineurin. 19500570_Mutations of PINK1 cause abnormal mitochondrial morphology, bioenergetic function and oxidative metabolism in human tissues; the biochemical consequences may vary between mutations. 19562775_No pathogenic mutation of PINK1 was seen in a Brazilian cohort of early-onset Parkinson disease patients, supporting the hypothesis that mutations in PINK1 may not be a relevant cause of EOPD. 19562775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692353_LRRK2 with other Parkinson's disease causing genes, Parkin, DJ-1 and PINK-1. 19726410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19822161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19822161_The responsiveness to distracting stimuli is decreased in asymptomatic PINK1 mutation carrier. 19847793_study experimental evidence that clinically reported PINK1 heterozygous mutations exert a gene dosage effect, suggesting that haploinsufficiency of PINK1 is the most likely mechanism that increased the susceptibility to dopaminergic cellular loss 19880420_Phosphorylation of parkin by PINK1 activates parkin E3 ligase function and NF-kappaB signaling. 19889566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19889566_This study suggested that three SNPs (rs3738133 or rs7550319 and rs3738136 & rs1043424) could be preferably used for the Indian population groups for genetic studies utilizing PINK1 markers. 19890973_The data of this study indicated that olfactory dysfunction is common in PINK1 Parkinsonism and consists typically in defective odor identification and discrimination. 19904588_coexistence of mutations in PINK1 and complex I genes appear to have an impact on the development of the parkinsonism [REVIEW] 19944740_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19944740_The interaction of PINK1 SNP IVS1-7 A-->G and environmental risk factors is associated with a significant effect in anticipating the disease clinical onset. 20012177_PINK1, Omi/HtrA2 and parkin participate at different levels in mitochondrial quality control, converging through some overlapping and some distinct steps to maintain a common phenotype of healthy mitochondrial networks [REVIEW] 20034704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20034704_The results of this study indicated that genetic variants at the parkin and PINK1 loci do not play a critical role in the pathogenesis of multiple system atrophy. 20045449_Our data indicate that PINK1 plays an important and specific physiological role in protecting cells from proteasomal stress, and suggest that PINK1 might exert its cytoprotective effects upstream of mitochondria engagement. 20098416_PINK1 kinase activity and its mitochondrial localization sequence are prerequisites to induce translocation of the E3 ligase Parkin to depolarized mitochondria. 20146068_Mutations of DJ-1 and PINK1 gene are also found in Chinese patients with sporadic early onset parkinsonism. 20146068_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153330_study shows PINK1 in combination with parkin results in the perinuclear mitochondrial aggregation followed by their elimination; results suggest mitophagy controlled by the PINK1/parkin pathway might be associated with Parkinson's disease pathogenesis 20164189_mutant PINK1 mitochondrial perturbations can be rescued by the mitochondrial division inhibitor mdivi-1 20171192_These findings suggest that both PINK1 and parkin play important roles in regulating the formation of Lewy bodies during the pathogenesis of sporadic and familial Parkinson's disease. 20179104_There is a Drp1- and Fis1-induced, and PINK1-mediated protection mechanism in senescent cells. 20356854_Two mutations were identified in PINK1 that are associated with an early-onset, slowly progressive form of Parkinson's disease in a large Spanish family. 20376796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20376796_The exon CNV in the PINK1 gene was rare in Chinese patients with autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinsonism. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20399249_Mutations in parkin gene are common in Chinese EOPD patients, and mainly are exon rearrangements, while mutation in PINK1 might be not common in Chinese EOPD patients. 20399249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20404107_Data show that PINK1 is degraded in a mitochondrial membrane potential-dependent manner, and that PINK1 recruits Parkin from the cytoplasm to mitochondria with low membrane potential to initiate the autophagic degradation of damaged mitochondria. 20461815_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20483373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506312_Studies indicate that molecular genetic analyses have identified five disease genes associated with familial Parkinson disease; SNCA, PARK2, PINK1, PARK7 and LRRK2. 20508036_Data show that mitochondrial accumulation of full-length PINK1 is sufficient but not necessary for the stress-induced loss of Parkin signal and its mitochondrial translocation. 20513816_This study findings strengthen the hypothesis that heterozygous PINK1 mutations act as a susceptibility factor to develop at least subtle Parkinson disease motor. 20547144_A mutation in PINK1 (Arginine492X) results in mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. 20558144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20558144_Results from the present study showed that point mutations and homozygous exonic deletions in PINK1 are not a common cause of PD in the South African population. 20637729_The phosphorylation of p66(Shc) at Ser36 is significantly increased in PINK1 deficient cell lines under normal tissue culture conditions, further still in the presence of compounds which elicit oxidative stress. 20798600_Data suggest that reduced binding of PINK1 to Parkin leads to failure in Parkin mitochondrial translocation, resulting in the accumulation of damaged mitochondria, which may contribute to disease pathogenesis. 20842103_Data show that mitochondrial fragmentation induced by expression of alpha-synuclein is rescued by coexpression of PINK1, parkin or DJ-1 but not the PD-associated mutations PINK1 G309D and parkin Delta1-79 or by DJ-1 C106A. 20871098_Ubiquitination of several mitochondrial proteins, including mitofusin 1 and mitofusin 2 were reduced following the silencing of parkin or PINK1. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20971498_our findings indicate that the physiologic functions of PINK1 go beyond its regulatory role of mitochondria-mediated cell survival in neurons. 21138942_Mitochondrial protease PARL cleaves PINK1 at position A103. 21145388_observed PINK1 immunostaining in both AD and MS lesions, predominantly in reactive astrocytes associated with these lesions, suggesting that the increase in astrocytic PINK1 protein might be an intrinsic protective mechanism to limit cellular injury. 21177249_PINK1 exerts its cytoprotective function not only in mitochondria but also in the cytoplasm through activation of mTORC2 21187721_PINK1 and Parkin physically associate and functionally cooperate to identify and label damaged mitochondria for selective degradation via autophagy. 21242281_We show that silencing PINK1 is synthetically lethal with MMR deficiency in cells with MSH2, MLH1, or MSH6 dysfunction 21322020_Mutations in PINK1 were not observed among Iranian parkinson disease patients 21366594_These results indicate a novel pathway by which the defect of PINK1 inhibits the oxidative stress-induced HO-1 production 21408142_The impact of mutations in endogenous PINK1 and Parkin on the ubiquitination of mitochondrial fusion and fission factors and the mitochondrial network structure, was investigated. 21412950_Phylogenetic and in silico structural analysis of the Parkinson disease-related kinase PINK1 21426348_the PARL-catalyzed removal of the Pink1 signal sequence in the canonical import pathway acts as a cellular checkpoint for mitochondrial integrity 21606348_Data demonstrate that PINK1 activity is crucial for postnatal myocardial development, through its role in maintaining mitochondrial function, and redox homeostasis in cardiomyocytes. 21677397_association study revealed a significant association between Asn521Thr variation in PINK1 gene and type 2 diabetes suggesting that PINK1 gene Thr521 allele carriers have significantly increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes 21743139_Two SNPs c.189C>T and c.960-5G>A may contribute to the risk of early-onset Parkinsonism in Chinese Han people. 21784538_molecular genetics and functions of PINK1 in Parkinson's disease (Review) 21925922_This study showed that the role played by PINK1 in early onset parkinsonism in southern Italy and illustrate the existence of mutations in this gene also in the late-onset form of the disease 22043288_results provide insight into the molecular pathology of PINK1 mutations in Parkinson disease and also confirm the critical role of substrate availability in determining the biochemical phenotype 22048964_DLGAP5-PINK1 and BUB1B-PINK1 were strong predictors of disease-free survival and overall survival, respectively, among adult patients with ACT. 22057787_PINK1 and parkin are associated with autosomal recessive parkinsonism and can functionally interact to maintain mitochondrial integrity and to promote clearance of damaged and dysfunctional mitochondria. 22076283_PINK1-specific siRNA remarkably downregulated Bcl-xL and TRAP1 proteins and upregulated BAX protein expression. 22078885_Study shows that both PINK1 and Parkin halt mitochondrial movement; PINK1 phosphorylates Miro (1 and 2) and thereby initiates the rapid degradation of Miro through a Parkin- and proteasome-dependent pathway. 22212487_By preventing mitochondrial dysfunction and reinforcing anti-apoptotic and neuronal survival pathways such as PI3K/AKT, PINK1 confers a neuroprotective effect against the neurotoxin C2-ceramide. 22233331_This study identified that In two families, two new PINK1 point mutations (L31X and P416L) were identified. 22238344_The results identify MARK2 as an upstream regulator of PINK1 and DeltaN-PINK1 and provide insights into the regulation of mitochondrial trafficking in neurons and neurodegeneration in PD. 22354088_These results highlight a new role for MPP in PINK1 import and mitochondrial quality control via the PINK1-Parkin pathway. 22434215_Parkin mutation carriers showed a slightly reduced ability to recognize facial emotions that was least severe in individuals who showed the strongest increase of ventrolateral premotor activity 22445250_Pathogenic mutations were not detected in SNCA, PINK1, or DJ-1 in this study. 22486164_Mutations in PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) cause PARK6 type Parkinson disease. 22547060_Multiple targeting signals featured by the Pink1 sequence result in the final localization of both the full-length protein and its major Deltapsi-dependent cleavage product to the cytosolic face of the outer mitochondrial membrane. 22643835_PINK1 positively regulates two key molecules, TRAF6 and TAK1, in the IL-1beta-mediated signaling pathway, consequently up-regulating their downstream inflammatory events 22724072_PINK1 is specifically activated by mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization, enabling it to phosphorylate Parkin at Ser(65). Activated PINK1 autophosphorylates at several residues, including Thr(257). 22910362_Autophosphorylation of Ser228 and Ser402 in PINK1 is essential for mitochondrial localization of Parkin. 22956510_from >5800 unique cases.The weighted mean proportion of cases with PARK2 (parkin), PINK1, and PARK7 (DJ-1) mutations was 8.6%, 3.7%, and 0.4%, respectively. PINK1 mutations were more common in Asian subjects. 23212910_Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)-dependent ubiquitination of endogenous Parkin attenuates mitophagy 23251494_results corroborate the hypothesis that PINK1 mutations result in reduced neuronal survival, most likely due to impaired cellular stress resistance 23256036_the molecular mechanism underlying the PINK1-dependent mitochondrial translocation and activation of Parkin as an initial step of mitophagy. 23261939_These results indicate a novel pathway by which the P209A defect in the PINK1 kinase domain inhibits oxidative stress-induced HO-1 and SOD2 induction, which may accelerate the neurodegeneration in PD with PINK1 defect. 23303188_analysis of PINK1 (PTEN-induced putative kinase 1) mutations associated with Parkinson disease in mammalian cells and Drosophila 23319602_PINK1 activates the formation of a Parkin-ubiquitin thioester intermediate, a hallmark of HECT E3 ligases, both in vitro and in vivo. 23393160_AF-6 is a positive modulator of the PINK1/parkin pathway and is deficient in Parkinson's disease. 23459931_PINK1 kinase function could be restored for a subset of patients with PINK1 mutations, and perhaps alter the course of their disease. 23472196_PINK1 is imported into mitochondria by a unique pathway that is independent of the TOM core complex but crucially depends on the import receptor Tom70 23519076_PINK1 protects against cell death induced by mitochondrial depolarization, by phosphorylating Bcl-xL and impairing its pro-apoptotic cleavage. 23525905_Overexpression of TRAP1 is able to mitigate Pink1 but not parkin loss-of-function phenotypes. 23533695_PINK1 is posttranslationally processed, whose level is definitely regulated in healthy steady state of mitochondria. 23751051_study found dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential triggers phosphorylation of PINK1 and Parkin and, in response, Parkin translocates to depolarized mitochondria; Parkin's E3 activity is re-established concomitant with ubiquitin-ester formation at Cys431 of Parkin; as a result mitochondrial substrates in neurons become ubiquitylated 23885119_These results indicate that association of PINK1 with SARM1 and TRAF6 is an important step for mitophagy. 23986421_The frequency of the PARK2, PINK1, PARK7 mutations among Polish EO-PD patients seems to be low. 24121706_PINK1 steady-state elimination by the N-end rule identifies a novel organelle to cytoplasm turnover pathway that yields a mechanism to flag damaged mitochondria for autophagic elimination. 24128678_PINK1 mRNA and protein are reduced in human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis muscle. 24149440_Blockade of mitochondrial protein import triggers the recruitment of PARK2, by PINK1, to the TOMM machinery. 24149988_The expression of unfolded proteins in the matrix causes the accumulation of PINK1 on energetically healthy mitochondria, resulting in mitochondrial translocation of PARK2, mitophagy and subsequent reduction of unfolded protein load. 24151868_Our data support a novel role for PINK1 in regulating dendritic morphogenesis. 24184327_PINK1 expression is significantly increased upon CCCP-induced mitophagy in a calcium-dependent manner. PINK1 may play a role in mitophagy that is downstream of ubiquitination of mitochondrial substrates 24189060_Formation of phosphorylated PINK1 dimer stimulates Parkin recruitment in HeLa mitochondria. 24357652_Two distinct cellular pools of PINK1 have different effects on Parkin translocation and mitophagy. 24374372_Our findings highlight a potential novel function of extramitochondrial PINK1 in dopaminergic neurons 24383081_this data correlate BA |
ENSMUSG00000028756 |
Pink1 |
298.245780 |
0.4092076902 |
-1.289095 |
0.101061785 |
164.287571 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000013090023657553165576767378599637940521716452259476512452231520978232327935639463431375849387076513649641462677664094371721148490905761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000002057601162784714922041166812500670021779748194014533352755631175977745558190160139064870523290841364261183343842276372015476226806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
179.9685870 |
11.3848307 |
442.5725829 |
18.2146510 |
| ENSG00000158859 |
9507 |
ADAMTS4 |
protein_coding |
O75173 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves aggrecan, a cartilage proteoglycan, and may be involved in its turnover. May play an important role in the destruction of aggrecan in arthritic diseases. Could also be a critical factor in the exacerbation of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer disease. Cleaves aggrecan at the '392-Glu-|-Ala-393' site. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. Members of this family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The enzyme encoded by this gene lacks a C-terminal TS motif. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This protease is responsible for the degradation of aggrecan, a major proteoglycan of cartilage, and brevican, a brain-specific extracellular matrix protein. The expression of this gene is upregulated in arthritic disease and this may contribute to disease progression through the degradation of aggrecan. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:9507; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] |
11796708_activation of proteolytic activity by C-terminal truncation 11801682_Aggrecanase-1 is expressed by fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients and is induced by cytokines, especially TGF-beta. 11831030_extracellular matrix degrading enzyme 11854269_has a specific cleavage site at the matrix metalloproteinase site in its interglobular domain 11956193_Inhibition of ADAM-TS4 and ADAM-TS5 prevents aggrecan degradation in osteoarthritic cartilage. 12202483_Autocatalytic cleavage reveals multiple glycosaminoglycan-binding sites 12646579_ADAMTS-2 metalloproteinase is shown to cleave procollagen III N-propeptides as effectively as those of procollagens I and II 14561220_Multiple forms of ADAMTS4 protein characterized by Western analysis in human brain tissue lead to the conclusion that the 'aggrecanase' group of the ADAMTS family (ADAMTS 1, 4, 5 and 9) is responsible for turnover of versican V2 in the adult brain. 14662755_ADAMTS-4 lacking the spacer domain has promiscuous substrate specificity considerably different from that previously reported for aggrecan core protein 14701864_ADAMTS-4 activation involves the coordinated activity of both glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-anchored MT4-MMP and the proteoglycan form of syndecan-1 on the cell surface 14715656_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 are inhibited by alpha2-macroglobulin 14744861_pro-ADAMTS4 is cleaved by proprotein convertase furin in the trans-Golgi network 15161923_the aggrecanase activity of ADAMTS4 is inhibited by fibronectin through interaction with their C-terminal domains 16003758_ADAMTS4 and 5 are upregulated on proliferating glioblastoma cells, and these proteases may contribute to their invasive potential 16099106_Taken together, these data suggest that aggrecanase-1 and alpha1-antitrypsin bind in vivo, although the physiological significance of the interaction between aggrecanase-1 and alpha1-antitrypsin remains unclear. 16677612_The ADAMTS-4 promoter would serve as a valuable mechanistic tool to better understand the regulation of ADAMTS-4 expression by signaling pathways that modulate cartilage matrix breakdown. 16723216_analysis of osteoarthritic synovium using primers designed to amplify across the exon 8/9 junction resulted in amplification of the expected product and a smaller product missing 161 bp from the 5' end of exon 9, the result of alternative splicing 16741450_Macrophages infiltrating granulation and adjacent disc tissues express ADAMTS-4, suggesting its involvement in herniated disc regression. 16771712_The inhibition of ADAMTS-2 by TIMP-3 alone out of 4 TIMP proteins is reported. 17009305_The induction of ADAMTS-4 by B burgdorferi results in the cleavage of aggrecan, which may be an important first step that leads to permanent degradation of cartilage. 17095512_analysis of aggrecanase (ADAMTS-4) conformation, affinity and sequence specificity 17208315_oncostatin M-stimulated ADAMTS-4 and matrix metallopeptidase 13 expression is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinases, Janus kinase 3/STAT1/3 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and by cross talk between these pathways 17265492_Our data suggest that both ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 contribute to the structural damage that characterizes human osteoarthritis. 17295438_Inhibition of NF0kappaB results in the decreased expression of several destructive metalloproteinases and also the ADAMTS4 aggrecanase 17311924_recombinant ADAMTS-4 effectively cleaved intact matrilin-3 at the predicted motif at Glu435/Ala436 generating two species of 45 and 5 kDa 17430884_ADAMTS-5 is a major aggrecanase in cartilage metabolism and pathology, with aggrecanase activity at least 1,000-fold greater than that of ADAMTS-4 under physiological conditions 17470431_TIMP-3 inhibition of ADAMTS-4 is modulated by interactions between aggrecan and the C-terminal domain of ADAMTS-4 17606262_ADAMTS-4 and -8 are inflammatory regulated enzymes expressed in macrophage-rich areas of atherosclerotic plaques. 17978660_In both nucleus pulposis and anulus fibrosus, ADAMTS4 was higher in discs with a higher level of degeneration. Aggrecan fragmentation profile analysis showed the involvement of aggrecanases and other proteases during disc degeneration. 18039650_after stimulation, the protease activity of PC5A is enhanced, as evidenced by the cleavage of the PC5A substrates Lefty, ADAMTS-4, endothelial lipase, and PCSK9. 18042673_Crystal structures of the two most active human aggrecanase isoforms, ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5, each in complex with bound inhiitor. 18050214_PKCzeta is involved in regulation of IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB signaling in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes, which regulates downstream expression of ADAMTS-4 and NOS2 via NF-kappaB. 18156631_the catalytic domain of ADAMTS-5 has higher intrinsic catalytic ability than that of ADAMTS-4 18221525_Human ADAMTS-4 was expressed in rodent pyramidal neurons and neuropil of stratum oriens and the lacunosum moleculare. 18387286_Both ADAMTS-4 mRNA and protein processing may be differentially regulated in normal and damaged tendons. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18671934_PACE4 is a proprotein convertase responsible for activation of aggrecanases in osteoarthritic and cytokine-stimulated cartilage; posttranslational activation of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 in the extracellular milieu of cartilage results in aggrecan degradation 18941754_Expression of ADAMTS4 by chondrocytes in the surface zone of human osteoarthritic cartilage is regulated by epigenetic DNA de-de-methylation. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19342688_findings suggest that Ras, ROS along with MyD88, IRAK1, or TRAF6 synergistically mediate ADAMTS-4 regulation by IL1-beta 19643179_The C-terminal domains of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 affect the structure around the active site, favouring interaction with TIMP-3. 19944557_Plasma ADAMTS4 was measured in stable-effort angina pectoris, acute coronary syndrome & controls. The pattern of its release was clearly different in various forms of ACS. It showed a weak correlation with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. 20625753_Patients with acute coronary syndrome showed increased ADAMTS4 expression, which may aggravate the development of atherosclerosis and instability of atherosclerotic plaques. 20664926_ADAMTS4 expression was found to be regulated by EWS-FLI1 fusion gene-dependent manner. ADAMTS4 protein was highly expressed in tumor samples of the patients with EWS by using immunohistochemistry. 20857147_Multiple matrix metalloproteinases and ADAMTS-4 are involved in the natural history of interverteral lumbar disc herniation. 21334453_effect of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) on ADAMTS-4 expression in macrophages along with the regulatory mechanisms underlying its actions 21345877_ADAMTS-4 is present in human coronary atherosclerotic plaques. 21664283_results suggest that during the acute phase after knee injury there is an increased aggrecanase activity against both the interglobular domain (IGD) and the CS2 cleavage sites of joint cartilage aggrecan 21946608_Serum ADAMTS4 levels are associated with the presence and the severity of coronary artery disease. 22065068_Sp1 transcription factor partly mediates IL-1 induction of ADAMTS-4. 22324945_Suggest IL-6 may participate in cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis as an inducer of ADAMTS-4 expression from synoviocytes. 22562232_Data show that the expression of ADAMTS4, 9, 16 and was up-regulated during chondrogenesis, ADAMTS1 and 5 were down-regulated. 22670872_Data suggest that cleavage of aggrecan by matrix metalloproteinases in knee cartilage from injured or osteoarthritic subjects is low compared with cleavage by aggrecanase-1 (at least early in osteoarthritis, as suggested by other evidence). 22735305_study showed that ADAMTS-1, -4, -5 and TIMP3 were expressed at differential levels in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines 23082219_The serine protease tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and two matrix metalloproteinases, ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5, were identified as Reelin cleaving enzymes. 23137648_Citrullinated fibronectin is less effective in inhibiting the proteolytic activity of ADAMTS4 and may contribute to the destruction of joint cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis. 23295731_Cartilage affected by varying degrees of osteoarthritis stained strongly for active ADAMTS-4 where surface fibrillation and clustered chondrocytes were observed. 23319426_AMTS4 has roles in melanoma growth and angiogenesis 23406982_Our results indicate that miR-125b plays an important role in regulating the expression of ADAMTS-4 in human chondrocytes 23438438_The purpose of the present study was to investigate the precise molecular mechanisms of high molecular weight hyaluronic acid on ADAMTS4 expression induced by IL- 1b in vitro. 23859810_We have demonstrated that the expression of ADAMTS-1, -4 and -5 is induced during the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. 23897278_ADAMTS-4_v1 is expressed as a protein in vivo in human osteoarthritis synovium, functions as an aggrecanase, and cleaves other proteoglycan substrates. 24051360_ADAMTS-4 and its substrate biglycan are involved in tubulogenesis by endothelial cells 24126638_This is the first evidence of crosstalk between TNF-alpha and ADAMTS-4 in relation to osteoarthritis cartilage degradation. 24474687_This study highlights that the affinity between a ligand and LRP1 dictates the rate of internalization and suggests that LRP1 is a major traffic controller of the two aggrecanases, especially under inflammatory conditions, where the protein levels of ADAMTS-4 increase, but those of ADAMTS-5 do not. 24732836_We conclude that the upregulation of TNF-alpha and ADAMTS-5, but not ADAMTS-4, may play an important role in degenerative cartilage endplate-induced low back pain. 24786121_The restricted expression of ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 and their increased expression in gestational trophoblastic diseases suggest that these 2 ADAMTS subtypes are associated with human placentation and the development of gestational trophoblastic diseases. 25225099_ADAMTS4 is largely associated with synapses, and is the main brevican-processing protease. 25433723_in degenerative intervertebral discs, IL1b upregulates NFkB, MMP13 and ADAMTS4 25477257_Evaluate ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 immunohistochemical expression in human TMJ discs from patients affected by internal derangement. 25501175_ADAMTS-4 is a potential biomarker and an early diagnostic indicator of knee osteoarthritis. 25592103_ADAMTS4 may be responsible for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. ADAMTS4 serum levels were also higher in diabetic cases. There is an association between ADAMTS4 and TGFb1 serum levels in the progression of atherosclerosis in coronary artery disease. 25707877_A positive feedback loop involving sSema4D/IL-6 and TNFalpha/ADAMTS-4 may contribute to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 25709087_CCN1 suppresses ADAMTS-4 activity and that CCN1 overexpression is directly correlated with chondrocyte cloning in osteoarthritis cartilage. The TGFbeta/CCN1 axis plays a role in chondrocyte cluster formation through inhibition of ADAMTS-4. 26152337_Results show that ADAMTS4 mRNA is the target of mir-1268a and its expression might be modified by MIR-1268a rs28599926 polymorphism in hepatocellular carcinoma. 26495885_The SNP rs4233367 in the exon of ADAMTS-4 gene may be associated with lumbar disc degeneration. 26612259_These data demonstrate that the antibody is specific to ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 and inhibits their aggrecanase activity at molecular and cellular levels. 26916548_progesterone acts via the progesterone receptor to modulate ADAMTS 1 and 4 levels in ovarian cancer cell lines. 27182768_ADAMTS4 may have a role in the pathogenesis by causing increased oxidative and inflammatory environment in preterm premature rupture of membranes . 27401455_HipHop-based pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening of the Maybridge database to identify novel ADAMTS-4 inhibitors. These novel lead compounds act as potent and specific inhibitors for the ADAMTS-4 enzyme and could have therapeutic potential in the treatment of OA. 27706574_we investigated whether important polymorphisms in the ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 genes affect osteoarthritis (OA) susceptibility. ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 genotypes were determined using the ABI Prism StepOnePlus Real-Time system. Our findings suggest that the ADAMTS4 (rs4233367 and rs11807350) and ADAMTS5 (rs226794 and rs2830585) variants examined may not contribute to susceptibility to knee OA in the Turkish population. 28005267_ADAMTS4 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28081267_Single Nucleotide Variants of Candidate Genes in Aggrecan Metabolic Pathway Are Associated with Lumbar Disc Degeneration and Modic Changes 28099917_Using in vitro approaches and cultured breast cancer cell lines authors demonstrate that Fibulin-2 is a better substrate for ADAMTS-5 than it is for ADAMTS-4. Fibulin-2 degradation is associated to an enhancement of the invasive potential of T47D, MCF-7 and SK-BR-3 cells. 28323982_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS15 were upregulated in symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. 28829887_ADAMTS-4 protein expression increased in cartilage tissue from spinal tuberculosis patients. 28888475_methylation status of the ADAMTS4 gene is altered in patellar tendinopathy 28955046_Study showed significant ADAMTS-4 expression in aortic tissues from patients with sporadic ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection, particularly in smooth muscle cells. 29135310_ADAMTS 1, 4, 12, and 13 levels in the maternal and cord blood were lower in the preeclampsia group than in the control group. ADAMTS 1, 4, and 12 levels in placental tissues were higher in the preeclampsia group. 29153440_ADAMTS4 expression was upregulated during carotid atherosclerotic plaque development. Serum levels of ADAMTS4 were associated with increased plaque vulnerability in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with carotid artery stenosis. 29694979_ADAMTS4 was associated macrophages infiltration and polarization in the tumor microenvironment of CRC and ADAMTS4 knockdown had no inhibitory implications on cell proliferation and invasion in vitro, but significantly attenuated tumor growth in vivo. 30016600_High ADAMTS4 expression is associated with osteoarthritic cartilage deterioration. 30187439_The lower levels of ADAMTS4 in the primary ovarian insufficiency group, when compared with the idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism patients pointed out that even limited hormone secretion and ovulation in the POI group, may have protective effect on cardiovascular system. The higher levels of ADAMTS4 and lipid accumulation in the IHH group demonstrated the increased risk of these patients for cardiovascular disease. 30369484_Since only two of the collected studies referred to ADAMTS4, we did not perform meta-analysis for these comparisons. Taken together, rs226794 and rs2830585 in ADAMTS5 gene were not associated with musculoskeletal degenerative diseases in overall population, but there seemed to be an ethnicity-dependent effect of rs2830585 in the risk of musculoskeletal degenerative diseases 30426203_ADAMTS4 was exclusively expressed in oligodendrocytes 30730845_significantly higher second-trimester amniotic fluid levels in pregnant women with spontaneous preterm birth 31663692_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the coding region of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 and hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective case-control study. 31734379_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS5 may be considered as new molecular therapeutic targets for cartilage damages with Kashin-Beck Disease. 32067610_Expression Levels of A Disintegrin-like Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs-4 and -5 (ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5) in Inflamed and Healthy Gingival Tissues. 32490633_The utility of synovial fluid levels of ADAMTS9 and ADAMTS4 in predicting treatment responses to intraarticular steroid injections in patients with knee osteoarthritis 33116313_Exuberant fibroblast activity compromises lung function via ADAMTS4. 33350314_Interrelationship of Osteopontin, MMP-9 and ADAMTS4 in Patients With Osteoarthritis Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty. 33358865_Requirement for C-mannosylation to be secreted and activated a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 4 (ADAMTS4). 33444494_ADAMTS proteoglycanases downregulation with impaired oocyte quality in PCOS. 34718343_Synergistic upregulation of ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) by cytokines and its suppression in knee osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts. 35051931_The Role of ADAMTS-4 in Atherosclerosis and Vessel Wall Abnormalities. 35701493_Identification of Adamts4 as a novel adult cardiac injury biomarker with therapeutic implications in patients with cardiac injuries. |
ENSMUSG00000006403 |
Adamts4 |
96.170017 |
2.3510777098 |
1.233322 |
0.366265394 |
11.025453 |
0.00089869310727892261214666547175511368550360202789306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002113224512256953787486812856855067366268485784530639648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
142.9752125 |
34.8648670 |
61.1265468 |
10.9547640 |
| ENSG00000158863 |
64760 |
FHIP2B |
protein_coding |
Q86V87 |
FUNCTION: Able to activate MAPK/ERK and TGFB signaling pathways (PubMed:22971576). May regulate the activity of genes involved in intestinal barrier function and immunoprotective inflammation (By similarity). May play a role in cell proliferation (PubMed:22971576). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80YR2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22971576}. |
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:64760; |
|
22971576_Retinoic acid induced 16 enhances tumorigenesis and serves as a novel tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. 25900241_RAI16 interacted with the type II regulatory subunit of protein kinase A(PKA-RIIalpha), acting as a novel protein kinase A anchoring protein (AKAP). In addition, RAI16 also interacted with heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and 14-3-3theta;. 31353455_FAM160B1 deficit associated with microcephaly, severe intellectual disability, ataxia, behavioral abnormalities and speech problems. 31862898_Retinoid acid induced 16 deficiency aggravates colitis and colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. 32014455_Identification of retinoid acid induced 16 as a novel androgen receptor target in prostate cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000022095 |
Fhip2b |
403.793544 |
0.3879081485 |
-1.366213 |
0.136974283 |
97.656903 |
0.00000000000000000000004975341652435619609511629190116245509515466241498784678396486097842754681153110141167417168617248535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000492528791347751507301817376631039992528665378658224296911120540509720910904434276744723320007324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
217.7268264 |
18.1216799 |
565.6745120 |
32.8407415 |
| ENSG00000158882 |
84134 |
TOMM40L |
protein_coding |
Q969M1 |
FUNCTION: Potential channel-forming protein implicated in import of protein precursors into mitochondria. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Ion transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Porin;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane beta strand;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable protein transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in protein import into mitochondrial matrix. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84134; |
mitochondrial outer membrane translocase complex [GO:0005742]; pore complex [GO:0046930]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; mitochondrion targeting sequence binding [GO:0030943]; porin activity [GO:0015288]; preprotein binding [GO:0070678]; protein transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008320]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; protein import into mitochondrial matrix [GO:0030150] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33016906_APOEvarepsilon4-TOMM40L Haplotype Increases the Risk of Mild Cognitive Impairment Conversion to Alzheimer's Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000005674 |
Tomm40l |
394.905647 |
0.2759695847 |
-1.857419 |
0.496463916 |
12.636620 |
0.00037826326912955126604773403720116675685858353972434997558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000949679512221836383441264661797731605474837124347686767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
186.0989826 |
46.3072559 |
681.5720628 |
122.2665577 |
| ENSG00000158887 |
4359 |
MPZ |
protein_coding |
P25189 |
FUNCTION: Is an adhesion molecule necessary for normal myelination in the peripheral nervous system. It mediates adhesion between adjacent myelin wraps and ultimately drives myelin compaction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10545037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337304}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Deafness;Dejerine-Sottas syndrome;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is specifically expressed in Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous system and encodes a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is a major structural protein of the peripheral myelin sheath. The encoded protein contains a large hydrophobic extracellular domain and a smaller basic intracellular domain, which are essential for the formation and stabilization of the multilamellar structure of the compact myelin. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal dominant form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1 (CMT1B) and other polyneuropathies, such as Dejerine-Sottas syndrome (DSS) and congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy (CHN). A recent study showed that two isoforms are produced from the same mRNA by use of alternative in-frame translation termination codons via a stop codon readthrough mechanism. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. |
hsa:4359; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; myelin sheath [GO:0043209]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; synapse [GO:0045202]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cell aggregation [GO:0098743]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; myelination [GO:0042552]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066] |
11545686_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11835375_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12211648_SSCP analysis for this gene in Croatian patients 12911457_We suggest that axonal and demyelinating forms of CMT are not two distinct classes, but rather parts of a spectrum of genotypically related conditions, particularly with some MPZ mutations 12940837_DNA sequencing analysis shows the Asn131Lys mutation in the myelin protein zero gene in three members of an affected family. 15036333_A novel mutation, Thr65Ala, in the MPZ gene in a patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1B disease with focally folded myelin. 15050444_Four missense mutations and one 4-base pair (bp) deletion, respectively, were identified in five patients, of which one mutation, c.173 T>A, has never been previously reported 15050444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15094849_MPZ gene screening should be performed for wide phenotype spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. 15159512_Chronic cough was associated with a Thr124 Met mutation. MPZ must be critical for maintenance of axonal function in addition to its role in myelin. All MPZ mutations associated with tonic pupils affect the same region of the extracellular domain. 15184631_A novel Thr124Lys mutation in the MPZ gene is associated with congenital neuropathy with hypomyelination. 15261887_Within 94 MPZ gene mutations reported up to now, only a few were identified in the exon 4 of the MPZ gene. In this study we have identified a novel Leu190fs mutation in the MPZ gene. 15326256_A novel mutation, 290 A-->T (Glu97Val), in the myelin protein zero gene (P0) is reported in a family with late-onset Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2. 15555916_PMP22 and P0 are involved in both trans-homophilic and trans-heterophilic interactions. Disease-related point mutations of P0 resulted in a decreased adhesion capability correlating with the severity of the respective disease phenotype. 15596778_4 patients had a Val102/fs null mutation (306delA at codon 102), age-dependent variability of clinical & electrophysiologic phenotype, segmental conduction abnormalities mainly in ulnar nerves at the elbow, & excessive myelin foldings & thickenings. 15729519_There was concordance between median MNCV and specific MPZ mutations. 16162811_P0, the major myelin protein, is also expressed during nephrogenesis and in mature kidney, mostly in podocytes. 16198109_family in which five members of three consecutive generations had a heterozygous mutation in nucleotide position 143 with a T-C transition in exon 2 of the MPZ gene. The resulting substitution of Leu48 with proline has not been previously described. 16279991_Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease due to the Thr124Met mutation in the myelin protein zero gene associated with multiple sclerosis. 16398147_Polymorphic short tandem repeats for PCR-based diagnosis of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A duplication in Ukraine was performed. 16414078_Peripheral neuropathies caused by mutations in the myelin protein zero. 16488608_Two patients of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1B from subsequent generations were homozygous for an Asp195Tyr mutation in the intracellular domain of P0 (P0ic). 16543539_MPZ gene showed a novel point mutation in the extracellular domain in two families with axonal CMT. 16856127_Data confirm that a mutation in myelin protein zero can cause axonal neuropathy, in the absence of segmental demyelination, thus uncoupling the two pathological processes. 17030746_Intronic mutations cause CMT1B by disrupting splicing and certain MPZ mutations may cause neuropathy by interacting with the wild type MPZ in the extracellular space of compact myelin. 17142269_the cytoplasmic apposition (major dense line) in compact myelin may be stabilized via the hydrogen-bonding of beta-strands formed as a result of local P0-P0 aggregation. 17143884_a new myelin protein zero gene mutation (c.89T>C,Ile30Thr) was detected in a family with the Dejerine-Sottas disease phenotype 17602703_A patient with Charcot Marie Tooth Disease, Type Ib had a MPZ mutation with A-C transversion (nucleotide: 116, codon: 10, histidine-to-proline). 17663472_a novel Pro105Thr mutation in the MPZ gene 17825553_Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy is a rare condition characterized by prenatal, neonatal or early infantile onset of hypotonia, paresis and areflexia.Here we describe a family with a heterozygous mutation in MPZ, confirmed in two generations. 17940173_In all patients, molecular analysis demonstrated a novel heterozygous missense mutation (208C>T) in MPZ exon 2, causing the Pro70Ser substitution in the extracellular domain. The diagnosis of CMT2 associated with MPZ 18209201_The novel mutation causes a late-onset demyelinating polyneuropathy, putatively resulting from aberrant intracellular trafficking of the mutant P(0) protein, which compromises the adhesiveness of the cells. 18337304_Results suggest that at least some late-onset MPZ mutations cause a partial loss of function in the transfected cells, whereas multiple abnormal gain of function pathways can result in early-onset neuropathy. 18422810_Our study provides further evidence that phenotypic features of MPZ mutations can vary within and among different families with CMT Ib 18663734_A heterozygous nonsense mutation (Tyr145Stop) corresponding to a T-to-A transition at nucleotide position 435 in exon 3 of the MPZ gene was identified in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1B patients. 19259128_Data show that the CMT1Adup, GJB1, MPZ and PMP22 mutation frequencies were in the range of those described in other CMT patient collectives with different ethnical backgrounds. 19259128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19293842_Findings suggest that the clinical features associated with MPZ mutations depend partly on the nature of amino acid change. 19293842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19475438_mutations in MPZ may have a role in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1B [case report] 19882637_The index patient of this family with unusual Charcot-Marie-Tooth phenotype is found to have a missense mutation within the intracellular domain of myelin protein zero. 19906531_Here we describe an unusual presentation of the Val102fs mutation characterized by symptoms of spinal root hypertrophy with no overt peroneal muscular atrophy. This report adds new data concerning the clinical presentations of MPZ mutations. 19928689_A genetic test disclosed a heterozygous mutation of myelin protein zero (MPZ); p.Thr124Met. 19950375_novel mutation in vocal cord paralysis 20215982_The results of this study concluded that ARG98HIS MPZ mutation may cause hereditary and relatively mild and asymmetric demyelinating sensorimotor polyneuropathy 20456450_Phenotypes associated with each of the new mutations include severe hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type III, and mild phenotype CMT1B presented with only decreased or absent reflexes, foot deformities and mild or absent lower limb atrophies 20461396_Cells expressing mutant P(0), as compared with those expressing wild-type P(0), demonstrated variable degrees of reduction in the cell adhesiveness 20516806_A novel frameshift mutation affecting the transmembrane domain (Leu144fs)in a patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease presenting as with late-onset, remitting neurologic symptoms. 20544920_Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with intermediate conduction velocities caused by a novel mutation in the MPZ gene. 20556410_five patients with four novel MPZ mutations were identified by molecular genetic testing 20621479_two new MPZ mutations causing congenital hypomyelinating neuropathies; c.368_382delGCACGTTCACTTGTG (in-frame deletion of five amino acids) and c.392A>G, Asn131Ser 21107784_we present here, for the first time, morphological data obtained in two sural nerve biopsies pointing to a hypomyelination-dysmyelination process in a family harboring the Pro132Leu mutation in the myelin protein zero gene 21179557_a rare myelin protein zero (MPZ) variant alters enhancer activity in vitro and in vivo 21503568_The identified mutation in MPZ may be the underlying cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in this family. 21787890_Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease has been described in a large Norwegian family caused by a copy number variation in myelin protein zero. 21971831_The crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human MPZ fused with maltose binding protein 22018721_This study expanded the spectrum of the MPZ mutations and revealed two disparate mechanisms of MPZ mutations associated with a typical Charcot Marie Tooth 1b phenotype 22222859_The p.Arg106Cys allele in MPZ causes late-onset predominantly axonal sensory and motor neuropathy. 22243284_The overall frequency of MPZ mutation was 0.58% in a Greek population of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1. 22275255_MPZ plays an important role in a family with 6 affected members in 3 consecutive generations, presenting with motor and sensory demyelinating polyneuropathy. 22433810_The new allelic variants of hereditary motor-sensor neuropathy caused by mutations in the MPZ (P0) gene are described. 22457349_L-MPZ, a novel isoform of myelin P0, is produced by stop codon readthrough. 22490868_Myelin protein P0 is a major Aire-regulated peripheral nervous system antigen demonstrating defective tolerance to P0 in both Aire-deficient mice and humans. 22622165_Thiss study demonistrated that two affected member of the same family with the same genotype had an 8-base pair deletion, c.160_167delTCCCGGGT in MPZ exon 2. 22633464_this mutation is especially important because it implicates the significance of the immunoglobulin-like structure of MPZ protein 22704856_Myelin protein zero is a key structural component of compact myelin, and over 100 mutations in this protein have been reported, which can give rise to neuropathies with either axonal, demyelinating, or other features encompassing a range of severity. 22734905_Patients with CMT1B caused by Ser63del MPZ have a classical CMT1 phenotype that is much less severe than that of patients with Arg98Cys MPZ 23197742_report of 2 siblings who presented with early onset severe Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; a novel heterozygous C to T base substitution at neucleotide position 199 (c.199C>T) was identified in exon 2 of MPZ resulting in substitution of arginine for cysteine at codon 67 (p.Arg67Cys) 23279346_MPZ-related neuropathy should be considered in the diagnostic work up of patients with painful axonal neuropathy 23743332_This study showed that mutation of MPZ in patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. 24028194_This study demonistrated that The mutation c.419C>G of MPZ exhibited relatively late onset and slowly progressive CMT1 phenotype. 24762602_P0 protein in serum may be an early effective biomarker for peripheral nerve neuropathy 24819634_2 heterozygous missense mutations were identified among 38 Italian CMT2 patients. 25720167_As a result of the haplotype analysis, based on ten markers (seven SNPs, two microsatellites and an intronic polyA stretch), the founder effect hypothesis for this allele migration is suggestive. 26135405_The obtained results depict that the protein with I30T mutation had variable structural conformation and dynamic behavior than native and mutant I30M of MPZ protein. 26310628_Genotype of MPZ mutations and phenotype of Charcot Marie Tooth Disease are correlated. 26406915_interaction with neurofascins impaired by mutations D6Y, D32G, and H52Y responsible for late onset forms of the human disease 27639257_The authors report a large Italian family affected Palmoplantar Keratoderma and Charcot Marie Tooth disease. Two different mutated genes, KRT1 and MPZ were responsible for the two main clinical signs. Exome analysis detected two missense mutations, one in KRT1 and one in MPZ. 27862672_In this Chinese Han population six novel Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease-associated gene mutations of MPZ (c.440T>C) was discovered. 29465609_The novel MPZ base-pair substitution in the family is associated with inherited distal demyelinating neuropathy and should be reclassified as pathogenic for Charcot-Marie-Tooth. 29627640_Studied the structural and functional changes of genetic variants of Mannose-Binding Lectin 2 (MBL2) and myelin protein zero (MPZ) in Colombian families with leprosy. 30677751_Pathology was consistent with a myelinopathy of the auditory, vestibular, and facial nerves bilaterally. The pathophysiology of cranial nerve dysfunction in CMT is unknown. Findings in the current case suggested, at least in cranial nerves 7 and 8, that a myelinopathy may be causative. 30679613_structure and function of myelin protein P0 in membrane stacking 30755303_Myelin basic protein and the cytoplasmic domain of myelin protein zero bound and aggregated negatively charged lipid vesicles, while simultaneously folding, and both ionic strength and calcium had systematic effects on these interactions. 31173589_membrane binding properties of the human myelin protein P0 cytoplasmic tail 32506583_Diagnostic yield of targeted sequential and massive panel approaches for inherited neuropathies. 32829291_Myelin protein zero gene dose dependent axonal ion-channel dysfunction in a family with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. 33179255_Genetic spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease associated with myelin protein zero gene variants in Japan. 33960567_Loss of function MPZ mutation causes milder CMT1B neuropathy. 34205075_Emerging Therapies for Charcot-Marie-Tooth Inherited Neuropathies. 35174662_MPZ gene variant site in Chinese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. |
ENSMUSG00000056569 |
Mpz |
32.933829 |
0.3805735722 |
-1.393753 |
0.309024938 |
20.167580 |
0.00000709452173385391293540264828765273819044523406773805618286132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000022690171352477520207288272380274918305076425895094871520996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
19.3047732 |
3.5541396 |
51.2635941 |
6.3154576 |
| ENSG00000159128 |
3460 |
IFNGR2 |
protein_coding |
P38484 |
FUNCTION: Associates with IFNGR1 to form a receptor for the cytokine interferon gamma (IFNG) (PubMed:8124716, PubMed:7673114,PubMed:7615558). Ligand binding stimulates activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway (PubMed:8124716, PubMed:7673114, PubMed:15356148). Required for signal transduction in contrast to other receptor subunit responsible for ligand binding (PubMed:7673114). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15356148, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7615558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7673114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8124716}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene (IFNGR2) encodes the non-ligand-binding beta chain of the gamma interferon receptor. Human interferon-gamma receptor is a heterodimer of IFNGR1 and IFNGR2. Defects in IFNGR2 are a cause of mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD), also known as familial disseminated atypical mycobacterial infection. MSMD is a genetically heterogeneous disease with autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant or X-linked inheritance. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3460; |
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; type II interferon receptor activity [GO:0004906]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; positive regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor activity [GO:1904783]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060333] |
11240951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12020266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12420205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14651967_Phages displaying fusion proteins with full-length PNRC2 (proline-rich nuclear receptor co-regulatory protein 2), already shown to be a cofactor for other nuclear receptors, and with a polypeptide of the bHLH corepressor TLE1 bound to AF-1. 15004750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15182327_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15585559_In pre eclampsia IFN-gamma R2 protein expression mimicked that in early placental development. 15952126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15952126_The IFN-GammaR2 Arg64/Arg64 genotype does not determine susceptibility to SLE in Chinese people, and the combination of IFN-Gamma R2 Arg64/Arg64 genotype and IFN-Gamma R1 Val14/Val14 genotype does not, either. 15979955_Higher frequency of +874T interferon gamma, both in hetero and in homozygosis and mostly whether simultaneous, plays a role in predisposing to gluten intolerance and an increased risk for coeliac disease. 16115485_IFNG T874A, IFNGR1 C-56T and IFNGR2 A839G genotypes were not associated with the incidence of angiographic and clinical restenosis (P>0.23). 16115485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16467876_Two IFN-gammaR2 chains interact through species-specific determinants in their extracellular domains. Finally, these determinants also participate in the interaction of IFN-gammaR2 with IFN-gammaR1. 16467883_interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) receptor 16690980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16867043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16885196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16885196_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in IFNGR2 is associated with gastric cancer 16944293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16944293_no statistically significant association with susceptibility to persistent HBV infection was observed with the IFN-gamma, IFNGR-1 and 2, and IRF-1 gene polymorphisms under the codominant, dominant, and recessive models 17220333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17546485_Variation in transcriptional activity of genes encoding INF-gamma receptor subunits may affect function of microvasculature and thereby participate in the pathology of cardiac syndrome X 17618444_IFNGR polymorphisms (Val14Met and Gln64Arg) are protective in systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese patients 17618444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17697357_expressed IFNgamma and IFNgamma-Ralpha together with the nuclear localization of IFNgamma-Rbeta, could be a tumoral cell response 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18249187_Therefore, our results suggest that the interaction between Sirt2 and 14-3-3 beta/gamma is a novel mechanism for the negative regulation of p53 beside the well-characterized Mdm2-mediated repression. 18620489_with progression of HIV-1 infection, interferon-gamma production declines whereas expression of interferon-gamma receptors (R1 and R2) increases 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19172849_the transcriptional of IFNgRb/IFNgRa in the heart bioptates appeared to be an early and sensitive marker of inflammatory status of patients with myocarditis 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19269302_No significant change was demonstrated in the expression of IFN-gamma receptor beta-chain on surfaces of alveolar macrophages acquired from smokers. 19505916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657228_Results show that the discovery of the anti-Bax activity of the cytoplasmic domain of IFNgammaR2 may shed new light on the mechanism of how cell death is controlled by IFNgamma and Bax. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20039824_The existence of abnormalities in the intracellular processing and protein expression of the IFN-gamma R2 in response to specific stimuli such as IFN-gamma and M. leprae membrane proteins in adherent cells of LL patients. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554027_These results suggesedt that the microglial and oligodendrocytic expression levels of IFN-gamma-R2 are much lower than the astrocytic expression levels in the human CNS. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_between the two IFNg receptors, IFNgR2 expression appears to be the deciding factor that controls the way in which target cells physiologically respond to IFNgamma. 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20709103_Data indicate that perturbation of IFN-gammaR2 internalization by mutating the LI(255-256) motif induces a timely coordinated activation of IFN-gamma/STAT1 signaling pathways that leads to the apoptosis of T cells. 20952689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20980339_HBV viraemia appears to have substantial heritability and polymorphisms in the IFNGR2 gene appear to be associated with the variability of viraemia. 20980339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22057826_We conclude that the polymorphisms of IFNGR2 may confer resistance to the TB development of newly infected individuals 22219326_JAK2 is a critical factor that stabilizes IFN-gammaR2 surface expression in Th17 cells from AMS patients, making them sensitive to IFN-gamma. 23161749_IFNGR2 haploinsufficiency may underlie clinical tuberculosis in children living in areas of endemic disease. 23459074_IFN-gammaR2-deficient monocytes induce a higher percentage of IL-17(+) cells from both healthy and IFN-gammaR2-deficient CD4(+) T cells. 23963039_We report a molecular study of the two known patients with autosomal recessive, partial interferon-gamma receptor (IFN-gammaR)2 deficiency 23980639_It related to persistence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and viral load in chronic HBV. 25301852_This is the first study that shows an association between SNPs and liver fibrosis in the general population 25592983_Fatal hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis has been described in two unrelated pediatric patients with underlying IFNGR2 deficiency. 25708927_The expression of IFNGR2 was significantly higher in patients with RA compared with control subjects and was significantly higher in patients in whom radiographic damage was more severe. 25815589_Statistical analyses revealed that four genetic variants in IFNGR1 were marginally associated with the risk of Tuberculosis (P = 0.02-0.04), while other single nucleotide polymorphisms in IFNGR1 and IFNGR2 did not exhibit any associations 26601495_The variability of potentially important functional polymorphic variants of the IFNG, IFNGR2 and NEIL2 genes was characterized in representatives of four ethnic groups living in the Siberian region. 27499022_IFN-gammaR2 T168N mutant diffusion is confined by distinct actin nanodomains where conformational changes required for JAK/STAT activation by IFN-gamma could not occur. Removing IFN-gammaR2 T168N-bound galectins restored lateral diffusion in lipid nanodomains and JAK/STAT signaling in patient cells, whereas adding galectins impaired these processes in control cells. 27522156_Successful unrelated cord blood transplant for complete IFN-gamma receptor 2 deficiency. 27563937_The IFNGR2Q64R polymorphism is correlated with male sex and paranoid schizophrenia in Tunisians. 27599734_A crystal structure of the extracellular part of human interferon-gamma receptor 2 (IFNGR2) was solved by molecular replacement at 1.8 A resolution. 28652404_Data suggest IFNG plays various roles in dynamics of inflammation in subjects with underlying autoimmunity modeled as 'canonical' and 'non-canonical' pathways; in canonical pathway, IFNG dimerizes and binds to IFNGR1 in IFNGR1/IFNGR2 hetero-multimer; STAT transcription factors are involved in non-canonical pathway. (IFNG = interferon gamma; IFNGR = IFNG receptor; STAT = signal transducers and activators of transcription) 29106381_A digenic human immunodeficiency characterized by IFNAR1 and IFNGR2 mutations 29434065_The study identified an SNP rs9978223 on IFNGR2 gene, associated with increased risk in acute myocardial infarctionpatient from India. 31222290_A purely quantitative form of partial recessive IFN-gammaR2 deficiency caused by mutations of the initiation or second codon. 33260695_Susceptibility to Heart Defects in Down Syndrome Is Associated with Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in HAS 21 Interferon Receptor Cluster and VEGFA Genes. |
ENSMUSG00000022965 |
Ifngr2 |
1877.518971 |
3.9059004981 |
1.965655 |
0.039355204 |
2631.348181 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3033.4805595 |
71.1031940 |
782.1631152 |
15.6469925 |
| ENSG00000159164 |
9900 |
SV2A |
protein_coding |
Q7L0J3 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the control of regulated secretion in neural and endocrine cells, enhancing selectively low-frequency neurotransmission. Positively regulates vesicle fusion by maintaining the readily releasable pool of secretory vesicles (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Receptor for the C.botulinum neurotoxin type A2 (BoNT/A, botA); glycosylation is not essential but enhances the interaction (PubMed:29649119). Probably also serves as a receptor for the closely related C.botulinum neurotoxin type A1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29649119, ECO:0000305|PubMed:29649119}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Neurotransmitter transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is one of three related synaptic vesicle proteins. The encoded protein may interact with synaptotagmin to enhance low frequency neurotransmission in quiescent neurons. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:9900; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion [GO:0014052]; synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0016082] |
18524768_Synaptic vesicle protein 2 binds adenine nucleotides 18977120_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18977120_We found no association between genetic variation in SV2A and response to levetiracetam or epilepsy predisposition 19220410_The pattern of SV2A immunoreactivity with reduced neuropil expression and altered cellular and subcellular distribution suggests a possible contribution of SV2A to the epileptogenicity of these malformations of cortical development. 19399787_Botulinum toxin type A (BTA) inhibits the growth of LNCaP human PCa cells in vitro and in vivo. BTA acts on the cells by virtue of the BTA receptor, the SV2 protein. 20167814_the role of SV2A in epileptogenesis in patients with glial tumors is questionable 21795655_expression of SV2A in tumor and peritumoral tissue is correlated to the clinical response to levetiracetam and predicts levetiracetam efficacy 21936812_Data report a combined modelling and mutagenesis study that successfully identifies another 11 residues in synaptic vesicle protein 2A that appear to be involved in ligand binding. 23017826_This study in the German population provides evidence, at a genetic level, for the involvement of the SV2A gene region in schizophrenia. 23244111_High SV2A expression is associated with breast cancer. 23530581_agents that act on the conformation of SV2A might hold great potential in the search for new SV2A-based anticonvulsant therapies 23617838_In classical mesial temporal sclerosis 1A, the expression of SV2 isoforms is altered with a marked decrease of SV2A paralleling synaptic loss. 24284412_The SV2A/FE65 interaction might play a role in synaptic signal transduction. 25326386_The newly identified galactose transport capability of SV2A may have an important role in regulating/modulating synaptic function. 25692762_the way LEV analogues may interact with SV2A 26241848_SV2A expression in the bladder urothelium increases after BoNT-A injection. 26339411_Botulinum neurotoxin type A inhibits synaptic vesicle 2 expression in breast cancer cell lines. 31168673_Expression of SV2A in brain tissue predicts adverse events following levetiracetam in patients with brain tumor-related epilepsy. 31317476_SV2 was highly expressed in neuroblastoma (NB) and can thus be useful marker in NB diagnostics. VMAT1 and VMAT2 were also expressed in NB but similar to syn less reliable as tumor markers. 32400950_In vivo measurement of widespread synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease with SV2A PET. 32944949_Reduced synaptic vesicle protein 2A binding in temporal lobe epilepsy: A [(11) C]UCB-J positron emission tomography study. 33588752_Differentiation of two human neuroblastoma cell lines alters SV2 expression patterns. 34884893_Validation of SV2A-Targeted PET Imaging for Noninvasive Assessment of Neuroendocrine Differentiation in Prostate Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000038486 |
Sv2a |
95.803439 |
0.2220438045 |
-2.171084 |
0.183280630 |
151.482378 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000008221622659807838754066373311141622218738587817655575392946627582796286814816405161774075151942531292093008232768625020980834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000001212299205382254837120653603569513892151621243704387751368240366304740844578190941504929056815598187313298694789409637451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.8786287 |
4.6043169 |
162.3466463 |
12.1939364 |
| ENSG00000159167 |
6781 |
STC1 |
protein_coding |
P52823 |
FUNCTION: Stimulates renal phosphate reabsorption, and could therefore prevent hypercalcemia. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hormone;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted, homodimeric glycoprotein that is expressed in a wide variety of tissues and may have autocrine or paracrine functions. The gene contains a 5' UTR rich in CAG trinucleotide repeats. The encoded protein contains 11 conserved cysteine residues and is phosphorylated by protein kinase C exclusively on its serine residues. The protein may play a role in the regulation of renal and intestinal calcium and phosphate transport, cell metabolism, or cellular calcium/phosphate homeostasis. Overexpression of human stanniocalcin 1 in mice produces high serum phosphate levels, dwarfism, and increased metabolic rate. This gene has altered expression in hepatocellular, ovarian, and breast cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6781; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus [GO:0071385]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; chondrocyte proliferation [GO:0035988]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; endothelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0001886]; growth plate cartilage axis specification [GO:0003421]; negative regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051926]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of renal phosphate excretion [GO:1903403]; ossification [GO:0001503]; positive regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090280]; regulation of anion transport [GO:0044070]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction [GO:0086004]; response to vitamin D [GO:0033280] |
11861508_Transgenic overexpression of hSTC1 results in severe post-natal dwarfism (30-50%) indepedent of GH or IGF-I and a reduction female reproductive competence. 12223480_Data characterize the STC receptor and the functional targeting of ligand and receptor to mitochondria. 12663264_Stanniocalcin 1 may regulate calcium currents in cardiomyocytes and may contribute to the alterations in calcium homeostasis of the failing heart 14500721_STC1 may play a selective modulatory role in angiogenesis, possibly serving as a 'stop signal' or stabilizing factor contributing to the maturation of newly formed blood vessels 15062564_STC1 plays a role in breast cancer 15131261_The observed STC1 suppression of progesterone, but not estradiol, production further suggests the potential role of this paracrine hormone as a luteinization inhibitor 15149855_Neoplastic adipocytes in well-differentiated liposarcomas stained for STC1, but the frequency of STC-1-positive cells was lower in high-grade liposarcomas; STC1 may function as a 'survival factor', contributing to the maintenance of mature adipose tissue. 15383693_STC-1 is a novel marker for minimal residual disease of acute leukemia, and for an early diagnosis of relapse. 16109785_Evidence of HIF-1 regulation of stanniocalcin-1(STC1) expression in human cancer cells. Implications as to role of STC1 in hypoxia induced adaptive responses in tumor cells. 16377640_Stanniocalcin 1 acts as a paracrine regulator of growth plate chondrogenesis 17032941_STC1 plays a critical role in transendothelial migration of inflammatory cells and is involved in the regulation of numerous aspects of endothelial function. 17272771_Induced brain injury elicits a stronger STC-1 response in brains of transgenic mice, with targeted astroglial IL-6 expression, than in brains of wild-type mice. 17395153_Collectively, the present findings provide the first evidence of p53 regulation of STC1 expression in human cancer cells. 17457011_STC1 prevented increase in diastolic Ca(2+) overload and ouabain-induced cell hypercontracture. STC1 could effectively prevent cytosolic Ca(2+) overload and protect cardiomyocytes from pathophysiological conditions such as heart failure. 18164591_Support a role for NP-1 in mediating synergistic effects between VEGF-A(165) and FGF-2, which may occur in part through a contribution of NP-1 to KDR stability. 18309109_results suggest an important role for STC1 in regulating endothelial functions during cardiovascular inflammation. 18355956_elevated expression of STC-1 or STC-2 act as survival factors also for breast cancer cells and thereby contribute to tumor dormancy. 18590575_Increased mRNA expression during progression of colorectal cancer with liver metastases 18652825_Results show that histone hyper-acetylation and the recruitment of activated NFkappaB stimulated stanniocalcin-1 gene expression. 18786506_These data indicate a key role of STC1 in the response of human brain microvascular endothelial cells to beta-amyloid exposure. 19267325_The data demonstrate that STC-1 mediates the antiapoptotic effects of multipotent stromal cells in two distinct models of apoptosis in vitro. 19444628_Wnt2 acts as an angiogenic growth factor for non-sinusoidal endothelial cells and inhibits expression of stanniocalcin-1. 19628018_Data show that stanniocalcin-1 is a 'factor inhibiting HIF-1'-inhibited gene with a functional hypoxia-responsive element motif located at the upstream region between -2322/-2335. 19712479_STC1 is a dimer of slightly elongated shape in solution. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20174869_Human stanniocalcin-1 or -2 expressed in mice reduces bone size and severely inhibits cranial intramembranous bone growth. 20422040_STC1 plays an important role in the early response to mechanical injury by epithelial cells by modulating signaling of extracellular ATP 20484106_STC1 protein may be involved in ovarian tumorigenesis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20827662_STC1 induction by thyroid hormone depends on both TRbeta and PI3K activation. 21273618_High STC1 gene expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 21465530_STC1 is a downstream target of Sp1. 21474827_Vascular endothelial growth factor-D stimulates endothelial cell VEGF-A, stanniocalcin-1, and neuropilin-2 and has potent angiogenic effects. 21656524_Level of circulating STC1 mRNA in NSCLC was significantly higher than in benign pulmonary disease or healthy volunteers. Higher levels of circulating STC1 mRNA were associated with more advanced tumor stages and histological subtypes. 21672207_STC-1 could promote angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo, and the angiogenesis was consistent with VEGF expression in vitro. Inhibition of VEGF expression in supernatants with neutralizing antibody markedly abolished angiogenesis induced by STC-1 in vitro. 21720730_The results demonstrate that PKCalpha suppresses the expression of STC1 in breast cancer cells. 22200953_Overexpression of STC1 was an independent prognostic factor in patients with esophageal cancer who had undergone curative surgery. 22537917_STC-1 mRNA expression is a reliable marker for detection of DTCs in PB and BM of ESCC patients, and STC-1-positive DTCs may be a promising tool for diagnosis and prognosis assessment in ESCC. 22588538_Stanniocalcin (STC1) plays an important role in functional adaption in pediatric kidney transplantation. 22693564_STC1 activates a novel anti-oxidant pathway in cardiac myocytes through induction of UCP3 22889960_STC1 is a potentially useful blood marker for predicting biological tumor aggressiveness in patients with gastric cancer 23243022_Data indicate that the secreted glycoprotein stanniocalcin-1 (STC1) as a mediator of metastasis by PDGF receptor function in the setting of colorectal cancer. 23382863_Thus, these results provided evidence that STC1 inhibited cell proliferation and invasion through NF-kappaB p65 activation in cervical cancer. 23566487_Data of this experiment showed that higher STC-1 expression during 96 h of preconditioning correlated with more effective MMP protection through the regulation of intracellular level of ROS and cytosolic free Ca2 + and preservation of cell viability. 23664860_Stanniocalcin-1 and -2 promote angiogenic sprouting in HUVECs via VEGF/VEGFR2 and angiopoietin signaling pathways. 23667669_An anti-apoptotic protein stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) can prevent loss of retinal ganglion cells in the rat retina with optic nerve transection 23757035_STC1 is differentially expressed in the culprit coronary plaques of patients with acute myocardial infarction versus those with stable angina. STC1 may play a role in plaque instability. 24729417_High STC1 expression is associated with glioma. 24743310_Circulating STC1 and STC2 mRNA are potentially useful blood markers for LSCC 25056605_was indicated that secreted STC-1 promotes metastatic potential of breast cancer cells via activation of PI3K/AKT 25370841_Stanniocalcin 1 downregulation is responsible for sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity through activated ROS generation. 25373521_Mesenchymal stem cells correct inappropriate epithelial-mesenchyme relation in pulmonary fibrosis using Stc1. 25391215_This is the first study to show definitively that STC1 plays an oncogenic role in breast cancer, and indicates that STC1 could be a potential therapeutic target for treatment of breast cancer patients. 25591908_STC1 interferes with CALCRL signaling during osteoblastogenesis via adenylate cyclase inhibition. 25647164_Stanniocalcin 1 is expressed in thyroid side population cells and thyroid cancer cells. 25740019_These findings demonstrate a role for STC1 in metastasis of early stage clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 25783529_These results suggested that STC1 may be a valuable biomarker in diagnosing malignant degree of glioma and evaluating prognostic following surgery 26187698_Results show that STC1 have an important role in the carbohydrate metabolism regulation, in particular gluconeogenesis from glutamine in the kidney, across the vertebrates. 26195635_Data show that co-transfection with cDNA encoding stanniocalcin-1 abrogates the proteolytic activity of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) toward IGF-binding protein 4 (IGFBP-4). 26469082_High expression levels of stanniocalcin-1 is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 26531219_Data revealed the existence of a moderating effect between Klotho and STC1, where Klotho may inhibit thyroid tumor progression by inhibiting the tumor marker level of STC1. 26547904_STC1 gene expression at diagnosis might be a useful prognostic marker for clinical outcome and monitoring therapeutic response in patients with acute leukemia. 26577859_our findings strongly suggest that elevated expression of STC1 protein at the III-IV stage of lung adenocarcinoma promotes tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and positively associates with the cancer progression, which may be of potential value as tumor marker in clinical tracking lung adenocarcinoma progression. 26640170_STC1 blunts bleomycin-induced rise in thrombin protein and activity, diminishes thrombin-induced signaling through PAR1 to ERK, and inhibits bleomycin-induced pneumonitis. 26874357_Data suggest that stanniocalcin 1 and 2 (STC1, STC2) participate in inhibition of proteolytic activity of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) during folliculogenesis. 27322879_STC1 protein is significantly up-regulated in midsecretory endometrial fluid and is dysregulated in eutopic endometrial tissue from women with endometriosis. It is likely regulated by cAMP and may be involved in the pathogenesis of decidualization defects. 27346255_Our results demonstrated the contrasting effects of STC1 and STC2-derived peptides on human macrophage foam cell formation associated with ACAT1 expression and on HASMC migration. 27459971_we demonstrated that aberrant STC1 expression is associated with poor prognosis and stimulates the invasiveness of triplenegative breast cancer cells 27461417_elevated STC-1 expression is associated with poor clinical outcome in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients, and STC-1 is directly involved in the invasiveness of TNBC cells 27603899_Increased STC1 plasma level represents a hallmark of late-onset preeclampsia; STC1 gene variants modulate placental gene expression and maternal hormone levels. 27730346_In the fed state, STC1 increases the incorporation of (14)C from glucose into lipids in the white retroperitoneal adipose tissue (WRAT). STC1 is one of the hormonal factors that control glucose metabolism in WRAT in the fed state. 28005267_STC1 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28350121_Study demonstrates that STC1 is overexpressed in the prostate carcinoma cell lines and suggests that it promotes prostate carcinoma cell proliferation via cyclin E1/CDK2. 28435144_Glycolysis from glucose is regulated by hSTC-1, decreasing the adequate supply of glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) needed for fatty acid esterification and triacylglycerol (TG) storage in brown adipose tissue (BAT). The decrease of TG capacity synthesis from glucose by hSTC-1 compromises the BAT thermogenic capacity. 28538979_Latanoprost-induced reduction of intraocular pressure is mediated through the downstream signaling molecule STC-1. When used by itself, STC-1 exhibits ocular hypotensive properties. 28545028_these data demonstrated that STC1 can promote cell apoptosis via NF-kappaB phospho-P65 (Ser536) by PI3K/AKT, IkappaBalpha and IKK signaling in cervical cancer cells 28688970_Ssecretory STC1 enhances metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinomas via JNK signaling. 29196129_Data indicate that stanniocalcin 1 (STC1) is a non-canonical NOTCH1 ligand and acts as a crucial regulator of stemness in glioblastoma (GBM). 29721098_CAPG competes with the transcriptional repressor arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) for binding to the STC-1 promoter. 29857240_these results suggest that mesenchymal stem cells protect vascular cells from inflammatory injury partially by secreting STC1 29940774_High serum levels of osteopontin, stanniocalcin-1 and FGF 23 at the time of surgery are important prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma 30582210_Taken together, the results revealed that upregulation of STC1 could repress proliferation of OA-FLS cells and inflammatory reaction, and enhance apoptosis of OA-FLS cells, which was negatively regulated by miR-454. 30683904_In the clinic, diabetic kidney disease (DKD) patients with high levels of stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) have a better prognosis than patients with low STC-1 levels. 30747219_STC1 may serve an oncogenic role in hypoxic GC via dysregulating Bcl2. 31100207_Study shows for the first time an opposite effect of hSTC-1 and hSTC-2 on glyceride-glycerol generation from glucose in epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) of fed rats and provides evidence for a direct role of hSTC-1 and hSTC-2 in the regulation of lipid and glucose metabolism in eWAT of rats. 31348577_In a coculture system of HaCaT cells and fibroblasts, used as a model of dermal-epidermal interaction, knockdown of STC1 in HaCaT cells with siRNA reduced the negative effects (i.e., induction of MMP1 and decrease of collagen1A1 and elastin) of STC1 on fibroblasts. 31432189_STC1 expression levels were increased in the present study, and it was revealed that STC1 regulated glioblastoma malignancy. This phenotype was observed in the SMAD2/3 and SMAD4 pathways. 31494675_Women with polycystic ovary syndrome present with altered endometrial expression of stanniocalcin-1dagger. 31676369_MLL2 promotes cancer cell lymph node metastasis by interacting with RelA and facilitating STC1 transcription. 31816356_Stanniocalcin-1 protein expression profile and mechanisms in proliferation and cell death pathways in prostate cancer. 32037949_The stress-activated protein kinase pathway and the expression of stanniocalcin-1 are regulated by miR-146b-5p in papillary thyroid carcinogenesis. 32140959_Multifactor dimensionality reduction reveals a strong gene-gene interaction between STC1 and COL11A1 genes as a possible risk factor of knee osteoarthritis. 32162740_Regulation of stanniocalcin-1 secretion by BeWo cells and first trimester human placental tissue from normal pregnancies and those at increased risk of developing preeclampsia. 32273636_Editors' Choice Stanniocalcin-1 mRNA expression in soft-tissue tumors. 32364536_Mesenchymal niche remodeling impairs hematopoiesis via stanniocalcin 1 in acute myeloid leukemia. 32579928_Fibroblast-Derived STC-1 Modulates Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Lung Adenocarcinoma Development. 33156861_Effects of stanniocalcin-1 overexpressing hepatocellular carcinoma cells on macrophage migration. 33826244_Targeting stanniocalcin-1-expressing tumor cells elicits efficient antitumor effects in a mouse model of human lung cancer. 34384344_Stanniocalcin 1 is overexpressed in multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells from acute myeloid leukemia patients. 34432025_Stanniocalcin-1 in the female reproductive system and pregnancy. 34650342_Low Expression of Stanniocalcin 1 (STC-1) Protein Is Associated With Poor Clinicopathologic Features of Endometrial Cancer. 34941085_Early-stage serum Stanniocalcin 1 as a predictor of outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. 35122667_Stanniocalcin 1 is a serum biomarker and potential therapeutic target for HBV-associated liver fibrosis. 35392966_Stanniocalcin 1 promotes metastasis, lipid metabolism and cisplatin chemoresistance via the FOXC2/ITGB6 signaling axis in ovarian cancer. 35607443_Comprehensive Analyses of Stromal-Immune Score-Related Competing Endogenous RNA Networks In Colon Adenocarcinoma. 35798563_Identification and characterization of a membrane receptor that binds to human STC1. |
ENSMUSG00000014813 |
Stc1 |
45.197835 |
4.9342977931 |
2.302845 |
0.303885720 |
59.212037 |
0.00000000000001415652278254707983261699751684978274914354038488406573037536873016506433486938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000094079367974063428955968936898627784156811000582099069333708030171692371368408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.4632556 |
13.0740515 |
15.1861650 |
2.2674976 |
| ENSG00000159214 |
149473 |
CCDC24 |
protein_coding |
Q8N4L8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to act upstream of or within blastocyst hatching. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:149473; |
blastocyst hatching [GO:0001835] |
|
ENSMUSG00000078588 |
Ccdc24 |
22.307022 |
0.4114425949 |
-1.281237 |
0.346128004 |
14.121895 |
0.00017133783566368812611990790628624381497502326965332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000454519492163198558613845801090747045236639678478240966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.4404701 |
2.9422431 |
30.5689105 |
4.4316190 |
| ENSG00000159231 |
874 |
CBR3 |
protein_coding |
O75828 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of carbonyl compounds to their corresponding alcohols (PubMed:18493841). Has low NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase activity. Acts on several orthoquinones, acts as well on non-quinone compounds, such as isatin or on the anticancer drug oracin (PubMed:18493841, PubMed:15537833, PubMed:19841672). Best substrates for CBR3 is 1,2- naphthoquinone, hence could play a role in protection against cytotoxicity of exogenous quinones (PubMed:19841672). Exerts activity toward ortho-quinones but not paraquinones. No endogenous substrate for CBR3 except isatin has been identified (PubMed:19841672). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15537833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18493841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19841672}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Carbonyl reductase 3 catalyzes the reduction of a large number of biologically and pharmacologically active carbonyl compounds to their corresponding alcohols. The enzyme is classified as a monomeric NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase. CBR3 contains three exons spanning 11.2 kilobases and is closely linked to another carbonyl reductase gene - CBR1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:874; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; carbonyl reductase (NADPH) activity [GO:0004090]; NADPH binding [GO:0070402]; NADPH dehydrogenase (quinone) activity [GO:0008753]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; cognition [GO:0050890]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
10728668_carbonyl reductase has an important function in modifying the metastatic behavior of malignant tumors. 11592776_Decreased Carbonyl Reductase expression in epithelial ovarian cancer is associated with RLN metastasis and poor survival 15537833_The common carbonyl reductase 3 (CBR3)valine244methionine polymorphism encodes for CBR3 isoforms with distinctive enzymatic properties, as revealed in DNA variation panels from 10 ethnic groups. 18457324_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18457324_There was a trend toward an association between the CBR3 V244M polymorphism and the risk of CHf 18493841_These results suggested that hCBR3 and hCBR1 play distinct physiological roles. 18551042_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18551042_Polymorphisms in CBR3 may explain interindividual and interethnic variability of doxorubicin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19016765_CBR3 polymorphisms have no significant influence on the pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin in Asian breast cancer patients. 19016765_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19590938_identified the promoter of human CBR3. Liver samples from black donors showed higher relative CBR3 mRNA levels than samples from whites 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19671875_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19841672_analysis of the structural basis for substrate specificity in human monomeric carbonyl reductases CBR3 20494980_The CBR3 distal promoter contains an activating cis-regulatory element that is responsive to Trichostatin A (TSA) treatment according to promoter reporter assays in HEK 293 cells. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20806931_CBR3 is regulated via NRF2-dependent signaling pathways, a finding and plays an important role in the cellular response to oxidative stress. 21256830_a physiological role of CBR1, but not for CBR3, in S-nitrosoglutathione reduction and thus ultimately in regulation of NO signaling 22001310_Computational searches identify a conserved antioxidant response element(ARE) in the distal carbonyl reductase 3 (CBR3) promoter region. 22124095_CBR3 polymorphisms contribute to increased cardiomyopathy risk associated with anthracycline treatment of childhood cancer. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22425771_CBR3 is a novel target gene of inflammatory stimuli; elucidation of its detailed role in inflammation deserves further investigation. 22527884_genetic polymorphism in the CBR3 gene conferred risk of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance in Chinese. The association was probably mediated through modulation of adipogenesis. 23182048_Variants of CBR3 and GSTP1 enzymes may be associated with changes in short-term functional cardiac parameters. 26563179_No significant correlation between cardiotoxicity and SNPs within the CBR pathway. Further investigation into CBR SNPs in a larger adult sample is needed. 26799497_association of SNPs in ABCB1 and CBR3 with chronic cardiotoxicity in a cohort of breast cancer patients treated with anthracyclines. 30096220_patients with advanced stage retinoblastoma had higher levels of PlncRNA-1 expression than patients with early stage retinoblastoma. There was an inverse correlation between PlncRNA-1 expression and CBR3 expression in retinoblastoma tissues, and PlncRNA-1 negatively regulated mRNA and protein expressions of CBR3. 30125887_CBR3 730G>A is significantly associated with recurrence- free survival in patients who received intravesical chemotherapy with pirarubicin after complete transurethral resection. 32945466_Long noncoding RNA CBR3 antisense RNA 1 promotes the aggressive phenotypes of nonsmallcell lung cancer by sponging microRNA5093p and competitively upregulating HDAC9 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000022947 |
Cbr3 |
7.247464 |
0.1401957597 |
-2.834485 |
0.936392234 |
9.189245 |
0.00243441327727577641257261653606747131561860442161560058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005293450202208375802992446068628851207904517650604248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.4097121 |
1.3360906 |
14.1257257 |
4.1433997 |
| ENSG00000159307 |
80274 |
SCUBE1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWY4 |
FUNCTION: Could function as an adhesive molecule and its matrix bound and soluble fragments may play a critical role in vascular biology. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16753137}. |
Calcium;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein that is a member of the SCUBE (signal peptide, CUB domain, EGF (epidermal growth factor)-like protein) family. Family members have an amino-terminal signal peptide, nine copies of EGF-like repeats and a CUB domain at the carboxyl terminus. This protein is expressed in platelets and endothelial cells and may play an important role in vascular biology. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:80274; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; adult heart development [GO:0007512]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; endothelial cell differentiation [GO:0045446]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12270931_identification as secreted protein that is expressed in vascular endothelium and may play important roles in development, inflammation, and thrombosis 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22874483_SCUBE1 level, a potential acute ischemia marker, is elevated in hemodialysis patients with no clinical ischemic event. 23136397_Primary prostatic cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) were isolated and the expression of CAF markers, Dlk1 and SCUBE1 transcripts were characterised. 23220851_SCUBE 1 levels in patients with gastric cancer were found higher compared to healthy subjects. 23632301_SCUBE1 levels are a new biomarker that can be used in the differential diagnosis and monitoring of patients hospitalized with suspected CCHF. 26438214_SCUBE1 may indicate hypercoagulability in patients with BC and thus help identify patients at greater risk of thrombosisSCUBE1 may indicate hypercoagulability in patients with breast cancer and thus help identify patients at greater risk of thrombosis 26699903_describe novel mechanisms in targeting S1 to the plasma membrane and demonstrate that N-glycans are required for S1 functions during primitive haematopoiesis in zebrafish. 26940951_SCUBE1 might be a novel prognostic biomarker after traumatic brain injury 27265525_enhanced SCUBE1 concentrations are correlated with increasing severity and poor outcomes of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients, indicating SCUBE1 might have the potential to identify aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients at risk of poor prognosis 27496080_Increased serum SCUBE1 concentrations have close relation to increasing severity and poor prognosis of intracerebral hemorrhage 28238185_The results of this pioneering study indicate that SCUBE protein family appears to have a probable role in the pathogenesis and angiogenesis development in psoriasis and SCUBE 1 and 3 may be novel markers of angiogenesis in psoriasis. 30777551_Hemodialysis may contribute to cardiovascular events because of increased SCUBE1 levels after hemodialysis; however, no association was shown between SCUBE1 and electrocardiography/echocardiography findings. 31668102_Evaluation of SCUBE-1 levels as a placental dysfunction marker at gestational diabetes mellitus. 31771860_De Novo Damaging DNA Coding Mutations Are Associated With Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Overlap With Tourette's Disorder and Autism. 31991528_The relationship of serum SCUBE-1, -2 and -3 levels with clinical findings and ultrasonographic skin thickness in systemic sclerosis patients. 34292290_Pericardial SCUBE1 levels may help predict postoperative results in patients operated on for coronary artery bypass graft surgery. 36334396_SCUBE1 is associated with thrombotic complications, disease severity, and in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients. |
ENSMUSG00000016763 |
Scube1 |
167.766427 |
0.2842259457 |
-1.814890 |
0.221481017 |
64.088445 |
0.00000000000000118957190229550967490710857156604535364203298168639388876499651814810931682586669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000008482164868541895210443888113951246071487290005552761584795007365755736827850341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.2760807 |
12.8519280 |
264.6233687 |
31.7723442 |
| ENSG00000159363 |
23400 |
ATP13A2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ11 |
FUNCTION: ATPase which acts as a lysosomal polyamine exporter with high affinity for spermine (PubMed:31996848). Also stimulates cellular uptake of polyamines and protects against polyamine toxicity (PubMed:31996848). Plays a role in intracellular cation homeostasis and the maintenance of neuronal integrity (PubMed:22186024). Contributes to cellular zinc homeostasis (PubMed:24603074). Confers cellular protection against Mn(2+) and Zn(2+) toxicity and mitochondrial stress (PubMed:26134396). Required for proper lysosomal and mitochondrial maintenance (PubMed:22296644, PubMed:28137957). Regulates the autophagy-lysosome pathway through the control of SYT11 expression at both transcriptional and post-translational levels (PubMed:27278822). Facilitates recruitment of deacetylase HDAC6 to lysosomes to deacetylate CTTN, leading to actin polymerization, promotion of autophagosome-lysosome fusion and completion of autophagy (PubMed:30538141). Promotes secretion of exosomes as well as secretion of SCNA via exosomes (PubMed:25392495, PubMed:24603074). Plays a role in lipid homeostasis (PubMed:31132336). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22186024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22296644, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24603074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25392495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26134396, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27278822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28137957, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30538141, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31132336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31996848}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Lipid-binding;Lysosome;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Nucleotide-binding;Parkinsonism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the P5 subfamily of ATPases which transports inorganic cations as well as other substrates. Mutations in this gene are associated with Kufor-Rakeb syndrome (KRS), also referred to as Parkinson disease 9. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:23400; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; multivesicular body membrane [GO:0032585]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; ABC-type polyamine transporter activity [GO:0015417]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0019829]; cupric ion binding [GO:1903135]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; P-type transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0140358]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0080025]; polyamine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015203]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; autophagosome organization [GO:1905037]; autophagosome-lysosome fusion [GO:0061909]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular cation homeostasis [GO:0030003]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; cellular response to manganese ion [GO:0071287]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cellular response to zinc ion [GO:0071294]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; extracellular exosome biogenesis [GO:0097734]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lysosomal transport [GO:0007041]; negative regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process [GO:1905166]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; peptidyl-aspartic acid autophosphorylation [GO:1990938]; polyamine transmembrane transport [GO:1902047]; positive regulation of exosomal secretion [GO:1903543]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein localization to lysosome [GO:0061462]; regulation of autophagosome size [GO:0016243]; regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:1903146]; regulation of chaperone-mediated autophagy [GO:1904714]; regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0052548]; regulation of glucosylceramidase activity [GO:1905123]; regulation of intracellular protein transport [GO:0033157]; regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process [GO:1905165]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010821]; regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900180]; regulation of ubiquitin-specific protease activity [GO:2000152]; spermine transmembrane transport [GO:1903710]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0055069] |
17485642_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17485642_Our data also suggest that ATP13A2 single heterozygous mutations might be etiologically relevant for patients with YOPD and further studies of this gene in Parkinson disease are warranted. 18413573_Findings expand the phenotypic spectrum associated with PARK9-linked parkinsonism into multiple-system disorders. 18785233_Mutations in ATP13A2 gene may be rare in Chinese families with autosomal recessive early-onset Parkinsonism. 19015489_A rare variant(AL746Thr) of the ATP13A2 was associated with an increased risk of Parkinson disease among ethnic Chinese in Asia. Further studies are needed to clarify the functional role of this genetic risk factor. 19015489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19085912_Neither ATP13A2 genetic variability nor quantitative gene expression in brain appears to contribute to familial parkinsonism or nonfamilial PD. 19085912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19097176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19224617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19224617_This study found that no associations were seen for ATP13A2 in Australia patient with Parkinson's disease 19705361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19705361_Our data suggest that two mutated ATP13A2 alleles are not a common cause of Parkinson's disease 19806583_ATP13A2 gene mutations are rare in Chinese patients with familial autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. 20036179_ATP13A2 G2236A variant is rare in early-onset Parkinson's disease and familial Parkinson's disease patients from mainland China, which differs from the study in ethnic Chinese patients from Taiwan and Singapore 20036179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20137506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20137506_Research studied the prevalence of mutations in ATP13A2 genes in 30 unrelated Chinese families with AREP and found no pathogenic mutations. 20227461_Ala746Thr variant was not a major susceptible factor for PD in Han Chinese people. 20227461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20310007_KRD should be considered in patients with dystonia-parkinsonism with iron on brain imaging and we suggest classifying as NBIA type 3 20483373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20669327_We identified genetic deficits in ATP13A2 that were associated with Levodopa responsive parkinsonism with pyramidal signs. 20816920_No clearly pathogenic mutations are identified in ATP13A2 and GIGYF2 in Brazilian patients with early-onset Parkinson's disease. 20816920_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20842691_We found no evidence for a correlation between a single heterozygous mutation in the ATP13a2 gene and the development of distinct oculomotor disturbances. 20853184_report clinical, instrumental, and genetic findings in an Italian family with novel PARK9 and PARK15 mutations 20976737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20976737_These results suggested that ATP13A2 p.A746T variant is unlikely to play a role as a common risk factor or a pathogenic mutation for PD at least in Japanese. Our data on Japanese differ from those reported recently on Han-Chinese. 21060012_Single ATP13A2 heterozygous mutations may be associated with clinical signs of parkinsonism and contribute to structural and functional brain changes. 21094623_A novel frameshift mutation in ATP13A2 causes juvenile dystonia-parkinsonism and dementia. 21362476_To see if ATP13A2 mutations could be responsible for some cases of human adult-onset NCL (Kufs disease), we resequenced ATP13A2 from 28 Kufs disease patients. None of these patients had ATP13A2 sequence variants likely to be causal for their disease 21542062_premature degradation of mutant ATP13A2 mRNA contribute to the aetiology of Kufor-Rakeb syndrome (KRS). 21665991_Mutant Atp13a2 proteins are degraded by endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and sensitize cells to cell death. 21696388_a novel frame-shift mutation in exon 22 of ATP13A2 (c.2473C>AA, p.Leu825AsnfsX32). 21714071_rare variants of ATP13A2 may contribute to Parkinson's disease susceptibility in Taiwan 21724849_Regulation of intracellular manganese homeostasis by Kufor-Rakeb syndrome-associated ATP13A2 protein. 22104014_This study demonistrated that contralateral silent period duration was increased in the symptomatic ATP13A2 mutation carriers suggested that compound heterozygous mutation in the ATP13A2 gene is associated with increased intracortical inhibition. 22117566_The altered apoptotic pattern of subjects with mutated ATP13A2 suggests a correlation between apoptosis alteration and the mutated ATP13A2 protein 22186024_study reveals a number of intriguing neuronal phenotypes due to the loss- or gain-of-function of ATP13A2 that support a role for this protein in regulating intracellular cation homeostasis and neuronal integrity 22285144_ATP13A2 variation may be a risk marker for neurotoxic effects of manganese in humans. 22288903_hypoxia signaling plays a very important role in the regulation of human ATP13A2 gene expression 22296644_These findings collectively suggest that ATP13A2 contributes to the maintenance of a healthy mitochondrial pool, supporting the hypothesis that impaired mitochondrial clearance represents an important pathogenic mechanism underlying KRS. 22388936_Data show that a family with typical neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs) pathology carried a single homozygous mutation in ATP13A2 that fully segregates with disease. 22442086_This study demonistrated that restoration of ATP13A2 function may lead to improved lysosomal function and decreased accumulation of alpha-syn. 22457822_results confirm a role for Ypk9 in manganese homeostasis and illuminates cellular pathways and biological processes in which Ypk9 likely functions 22490479_The SNPs investigated in the BST1, PARK15 and PARK9 genes associated with PD susceptibility are not associated with PD in the northern Han Chinese population. 22645275_ATP13A2 and alpha-syn are functionally linked in neurodegeneration. 22647602_results unravel an instrumental role of ATP13A2 deficiency on lysosomal function and cell viability and demonstrate the feasibility and therapeutic potential of modulating ATP13A2 levels in the context of PD 22743658_Our results indicate that ATP13A2 mutations are a rare cause of both NBIA and dystonia-parkinsonism. 22768177_This study provides support for common loss-of-function effects of homozygous and heterozygous missense mutations in ATP13A2 associated with early-onset forms of parkinsonism. 22847264_ATP13A2 protects against manganese & nickel toxicity, & proteasomal, mitochondrial, & oxidative stress. ATP13A2 may import a cofactor required for the function of a lysosome enzyme(s). 23121889_ATP13A2 knockout exacerbates apoptosis and autophagy in infarct penumbra of cerebral cortex, with no influence on the infarct size in mice with ischemic stroke. 23196729_Mutations in ATP13A2 is often associated with rapidly progressive parkinsonism and with additional features including pyramidal signs, cognitive decline and loss of sustained Levodopa responsiveness. 23205587_the human P5B-ATPase ATP13A2 is involved in polyamine uptake. 23499937_Cathepsin D activity was decreased in ATP13A2-knockdown cells that displayed lysosome-like bodies characterized by fingerprint-like structures 23522931_No association is found between ATP13A2 Ala746Thr and early onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD) or late onset Parkinson's in a Chinese cohort; this variant is not a strong risk factor in the Chinese population. 24252509_Data show that patients with Lewy body diseases have an overall deficit in ATP13A2 protein levels, with the remaining protein being more insoluble and partially redistributing towards Lewy bodies 24334770_PARK9 loss of function leads to dyshomeostasis of intracellular Zn(2+) that in turn contributes to lysosomal dysfunction and accumulation of alpha-Syn. 24399444_human ATP13A2 deficiency results in zinc dyshomeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction. 24603074_Reduced ATP13A2 expression significantly decreased vesicular zinc levels, indicating ATP13A2 facilitates transport of zinc. 24949580_Present results of homozygosity mapping in two siblings affected with early onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD) and mutation screening of ATP13A2. The variation identified represents the 13th known disease causing mutation in ATP13A2. 25197640_A review of recent advances in the emerging association of ATP13A2 mutations with Parkinsonism and neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. 25374329_The mutation rates of Thr12Met and Ala1144Thr of ATP13A2 in the Uygur and Han Parkinson's disease patients in the Xinjiang region are low. 25392495_these data suggest the involvement of PARK9 in the biogenesis of exosomes and alpha-synuclein secretion. 25855184_This study demonistrated that loss of ATP13A2 causes a specific protein trafficking defect, and that Atp13a2 null mice develop age-related motor dysfunction that is preceded by neuropathological changes. 25912790_ATP13A2 overexpression improves the lysosome membrane integrity and protects against iron-induced cell damage. 26000924_The ATP13A2 A746T variant is rare in Han Chinese patients and controls and is not associated with PD susceptibility in this ethnic group. 26134396_that ATP13A2 contains a unique N-terminal hydrophobic extension that lies on the cytosolic membrane surface of the lysosome, where it interacts with the lysosomal signaling lipids phosphatidic acid and phosphatidylinositol(3,5)bisphosphate. 26818499_tre results of this study suggests that the expression of ATP13A2 regulated by the PHD2-HIF1alpha signaling pathway,and this is instrumental in maintaining cellular iron homeostasis and cell viability in mitochondrially compromised DAergic neurons. 26965689_Hereditary Parkinsonism-associated genetic variations in PARK9 locus lead to functional impairment in the ion transport function of this protein. (Review) 27278822_ATP13A2 and SYT11 form a functional network in the regulation of the autophagy-lysosome pathway, which may contribute to forms of Parkinson's Disease-associated neurodegeneration. 27282395_we describe, for the first time, the deleterious effect arising from the interaction between the ATP13A2 familial mutant Dup22 with a-Syn. We show that this ATP13A2 mutant can enhance a-Syn oligomerization and aggregation in cell culture 27399248_This study showed that LRRK2, PARK2 and ATP13A2 are under copy number variations influence in patient with Parkinson disease. 28137957_This study demonstrated that loss of ATP13A2 function causes a combination of lysosomal and mitochondrial dysfunction that affects multiple neuronal populations. 28302480_ATP13A2 inhibition by hsa-miR-4306 efficiently restored manganese-induced cytotoxicity in cultured neurons. 28334751_Study unravels a novel activity-independent scaffolding role of ATP13A2 in trafficking/export of intracellular cargo in response to proteotoxic stress. 28894968_This study showed that Lysosomal defects in ATP13A2 associated familial Parkinson's disease. 29442384_This study showed that the Single Heterozygous ATP13A2 Mutations Cause Cellular Dysfunction Associated with Parkinson's disease. 30232368_Results find that two missense variants, p.G360E and p.T733M, with 'uncertain significance' classification were identified in the ATP13A2 gene and five synonymous variants were significantly over-represented in early-onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD) suggesting they might be associated with higher risk for sporadic EOPD in Chinese population. 30538141_The results suggest that ATP13A2 recruits HDAC6 to lysosomes to deacetylate CTTN and promotes autophagosome-lysosome fusion and autophagy which are impaired in Parkinson disease patients. 30992063_We here expand the phenotypic spectrum associated with genetic variants in ATP13A2 that previously comprised Kufor-Rakeb syndrome, spastic paraplegia 78, and neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 12 (CLN12), to also include juvenile-onset ALS, as supported by both genetic and functional data 31132336_Result suggests that ATP13A2 may be modifying the lipid digestion capacity and/or the redistribution of lipids in these subcellular organelles. In addition, ATP13A2-overexpression decreased the total content of triglycerides (TGs), cholesterol and lipid droplets. 31393918_results suggest Atp13a2 Isoform-1 protein confers cytoprotection against toxic insults, including those that cause Parkinson's disease syndromes. 31944623_Clinical and genetic analysis of ATP13A2 in hereditary spastic paraplegia expands the phenotype. 31996848_ATP13A2 deficiency disrupts lysosomal polyamine export 32019516_We used bcftools to filter variants and annovar software for the annotation. Rare variants were prioritised using MetaLR and MetaSVM prediction scores. The effect of a variant on ATP13A2's protein structure was investigated by molecular modelling... Protein modelling showed that the S1004R variant in ATP13A2 possibly alters the conformation of the protein 32032734_Dysregulated iron metabolism in C. elegans catp-6/ATP13A2 mutant impairs mitochondrial function. 33091395_Novel mutations in ATP13A2 associated with mixed neurological presentations and iron toxicity due to nonsense-mediated decay. 33229544_ATP13A2-mediated endo-lysosomal polyamine export counters mitochondrial oxidative stress. 33335927_ATP13A2 Gene Variants in Patients with Parkinson's Disease in Xinjiang. 33799982_ATP13A2 Regulates Cellular alpha-Synuclein Multimerization, Membrane Association, and Externalization. 34695705_Mutation analysis of the ATP13A2 gene in patients with PD and MSA from Italy. 34715013_Structural basis of polyamine transport by human ATP13A2 (PARK9). 34715014_Structural mechanisms for gating and ion selectivity of the human polyamine transporter ATP13A2. 34798056_Cryo-EM reveals mechanistic insights into lipid-facilitated polyamine export by human ATP13A2. |
ENSMUSG00000036622 |
Atp13a2 |
145.197063 |
0.4606492346 |
-1.118259 |
0.164422449 |
46.296330 |
0.00000000001016541720203332921233630306615908179754259599292254279134795069694519042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000056385403195043941975529238459595828339421252906049630837514996528625488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.0154655 |
9.9706700 |
205.5290921 |
14.9021971 |
| ENSG00000159388 |
7832 |
BTG2 |
protein_coding |
P78543 |
FUNCTION: Anti-proliferative protein; the function is mediated by association with deadenylase subunits of the CCR4-NOT complex. Activates mRNA deadenylation in a CNOT6 and CNOT7-dependent manner. In vitro can inhibit deadenylase activity of CNOT7 and CNOT8. Involved in cell cycle regulation. Could be involved in the growth arrest and differentiation of the neuronal precursors (By similarity). Modulates transcription regulation mediated by ESR1. Involved in mitochondrial depolarization and neurite outgrowth. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12771185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15788397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18773938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23236473}. |
3D-structure;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the BTG/Tob family. This family has structurally related proteins that appear to have antiproliferative properties. This encoded protein is involved in the regulation of the G1/S transition of the cell cycle. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7832; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; central nervous system neuron development [GO:0021954]; dentate gyrus development [GO:0021542]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045930]; negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000178]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:0061351]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening [GO:0060213]; protein methylation [GO:0006479]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914] |
8891336_PC3 / BTG2 inhibits the proliferation of different types of cells, including neural cells. 8944033_First evidence that BTG2 is a target of p53 and is activated p53-dependently by DNA damage. 10669755_First evidence showing that PC3 / BTG2 acts as cell cycle checkpoint at G1 phase by inhibiting the expression of cyclin D1 11267995_This review describes BTG2 / PC3 as link between p53 and pRb. p53 via BTG2 / PC3 may activate pRb, since the BTG2 / PC3 product promotes accumulation of hypophosphorylated pRb by reducing cyclin D1 protein levels and thereby inhibiting CDK4 activity. 11814693_Transient expression assays with BTG2/TIS21/PC3 promoter deletions and electrophoretic mobility shift analysis identified a major wild-type p53 response element located -74 to -122 relative to the start codon. 12135500_Antiproliferative proteins of the BTG/Tob family are degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. the C-terminal regions are necessary and sufficient to control the stabilities of BTG1, BTG2, Tob, and Tob2 proteins. 12771185_BTG2 interacts with the CCR4 complex and has a role in cell-cycle regulation 15056715_PC3 / BTG2 induces neural precursors to shift from proliferation to differentiation. This differentiative action occurs in cerebellar progenitors by a dual mechanism: inhibition of cell cycle (of cyclin D1) and induction of the proneural gene Math1. 15378000_deregulation of BTG2 may be an important step in the development of mammary tumors 15741235_DeltaNp73alpha not only acts as an inhibitor of p53/TAp73 functions in neuroblastoma tumors, but also cooperates with wt-p53 in playing a physiological role through the activation of BTG2TIS21/PC3 gene expression 15788397_binding of tis21/BTG2/pc3 to Pin-1 or cyclin B1-Cdc2 complex and induction of mitochondrial depolarization are responsible for the antiproliferative effects of EGF in human tumor cells 16418486_BTG2 expression was found to be significantly reduced in a large proportion of human kidney and breast carcinomas, suggesting that BTG2 is a tumor suppressor that links p53 and Rb pathways in human tumorigenesis. 16782888_BTG2 contributes to retinoic acid activity by favoring differentiation through a gene-specific modification of histone H4 arginine methylation and acetylation levels. 16997058_Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction confirmed increased expression of GADD45A, BTG2, PDE4B, and CEBPD and downregulation of TOB1 in skeletal muscle intradialysis. 17371797_PC3 / BTG2 acts as a tumor suppressor of medulloblastoma by its antiproliferative and prodifferentiative effect on cerebellar progenitors. This antagonizes Shh and appears physiologic since endogenous PC3 / BTG2 decreases in human medulloblastomas. 18196550_T3 upregulates proliferation of LNCaP cells by downregulating BTG2 gene expression through the consensus TRE pathway. 18288394_BTG2 expression may play a role at a very early point during the differentiation processes of hematopoietic cells. 18337750_BTG2 is a general activator of mRNA decay, thereby contributing to gene expression control. 18393292_TIS21 negatively regulated hepatocarcinogenesis in part by disruption of the FoxM1-cyclin B1 regulatory loop, thereby inhibiting proliferation of transformed cells developed in mouse and human livers. 18840609_BTG2/TIS21/PC3 enhances cancer cell death by accumulating H2O2 via imbalance of the antioxidant enzymes in response to chemotherapy. 18974182_Crystal structure of human BTG2 reveal the putative CAF1 binding site. 19117054_Estradiol downregulation of the tumor suppressor gene BTG2 requires estrogen receptor-alpha and the REA corepressor 19203451_miR-18 may negatively regulate the expression of BTG2 in HepG2 cells. 19468252_BTG2 may be a modulator of neuron survival and differentiation 19546886_Deregulation of BTG2, which was identified to be a miR-21 target gene, may be responsible for the miR-21-mediated abnormal cellular phenotype. 19615363_These data indicate that TIS21 is a novel target of SCF-Skp2 ubiquitin ligase, which is regulated by expression of FoxM1. 19728149_The influence of BTG2 on the growth, proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and cell cycle of the gastric cancer cell lines, was investigated. 20020054_Study of murine BTG2 suggests that BTG2 is essential for terminal differentiation of neural progenitors. Genetic ablation of BTG2 in rodents impairs terminal differentiation and shortens G1 phase of cell cycle duration of neural progenitor cells. 20553615_High-level BTG2 protein expression correlates with prolonged survival in patients with breast carcinoma. 20569234_The neutralization of Pin1 by BTG2 provides a critical mechanism to maintain senescent arrest in the presence of mitogenic signals in normal primary fibroblasts. 21120602_Estrogen receptor beta causes a G2 cell cycle arrest by inactivating CDK1 through the repression of cyclin B1 and stimulation of GADD45A and BTG2 expression. 21172304_These findings, for the first time, demonstrate that BTG2 complexes with AR via an LxxLL-dependent mechanism and may play a role in prostate cancer via modulating the AR signaling pathway. 22266859_MIR32 is upregulated in prostate cancer and regulates expression of BTG2. 22392501_Results suggest that the overexpression of B cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2) may inhibit the growth, proliferation, and invasiveness of the A549 lung cancer cell line. 22493435_a novel role for BTG2 as a co-activator for NFE2L2 in up-regulating cellular antioxidant defenses. 22562501_study reveals that BTG2 negatively regulated cancer cell migration by inhibiting Src activity through downregulation of reactive oxygen species generation in mitochondria 22614007_Downregulation of the basal protein B-cell translocation gene 2 is associated with prostate cancer transformation and progression. 23089312_TIS21 regulates DNA double strand break repair and apoptosis via increasing Mre11 methylation. 23299537_These results indicate that endogenous BTG2 expression contributes to the migratory potential of bladder cancer cells. Moreover, high levels of BTG2 in bladder cancers are linked to decreased cancer-specific survival. 23857284_Data indicate that the pattern of B cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2) protein expression was exactly the opposite of miRNA-21 expression in lung cancer cells. 23876794_Reactive oxygen spieces regulate Btg2/TIS21/PC3 expression via Protein kinase C-NFkappaappaB pathway. 23907596_TIS21 suppresses invadopodia formation as well as invasion activity along with F-actin remodeling. 23917204_TIS21 decreased interleukin-6 (IL-6) expression in human dermal fibroblast. 24047462_BTG2 mediates crosstalk between PI3K-Akt1 and NF-kappaB pathways, which regulates p53-independent induction of G2/M phase arrest both in normal and cancer cells. 24308156_BTG2 can improve the radiosensitivity of breast cancer cells by affecting cell cycle distribution, enhancing radiation-induced apoptosis, and inhibiting DNA repair-related protein expression. 24440351_pro-apoptotic pathway of CRP-CD32-Nox2-p53-BTG2 may contribute to the retardation of the atherogenic process 24698107_BTG2 is a significant factor in tamoxifen response, acting through modification of AKT activation in ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. 24780075_An association with Graves disease was shown for several SNPs in BTG2. 24821435_miR-21 is involved in MNNG-induced gastric carcinogenesis in vivo and in vitro via FASLG/BTG2 pathway. 24981574_Our results indicated that cisplatin attenuates prostate cancer cell proliferation partly mediated by upregulation of BTG2 through the p53-dependent pathway or p53-independent NFkappaB pathway. 25284287_BTG2 expression was inversely correlated with increased expression of the DNA methyltransferases DNMT1 and DNMT3a in MIBC, but not NMIBC, suggesting a potential role for BTG2 expression in muscle invasion of bladder cancer 25405282_In this review, we summarize the latest findings in BTG2 studies, highlighting the mechanisms for the regulatory effects of microRNAs (miRNAs) on BTG2 gene expression in the most common human cancers. 25576360_By applying loss-and-gain function analysis in NSCLC cell lines, we demonstrated that miR-25-BTG2 axis could directly regulated BTG2 expression and affect radiotherapy sensitivity of NSCLC cells. 25626081_Results indicate that miR27a and BTG2 promote the migration and the growth of glioblastoma (GBM) cells and miR27a directly targets BTG2 in GBM cells. 26151427_miR-21 was found to be overexpressed and BTG2 was found to to be downregulated in HepG2 liver cancer cells. 26394836_SETD1A suppresses BTG2 expression through its induction of several BTG2-targeting miRNAs. 26722427_Overexpression of BTG2 inhibited the proliferation and migration/invasion of human osteosarcoma cells in vitro 26818199_clinical data support conclusions generated from patient-derived xenograft models and indicate that BTG2 expression is a candidate prognostic biomarker for TNBC. 26912148_BTG2 stimulates mRNA deadenylation via CAF1 activation through interaction with PABPC1. Interaction of BTG2 with the first RRM domain of PABPC1 is required for BTG2 to control cell proliferation. 26925784_Authors have provided data for attenuated BTG2 expression in the ccRCC cells. Overexpressed BTG2 could inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion of human ccRCC, and the suppressive effects might be due to down-regulation of MMP-9, Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E expression. 27208501_Effect of TIS21 on the regulation of p53 activity was confirmed by knockdown of TIS21 expression by RNA interference. 27409164_we found that miR-27-3p was overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines and that BTG2 was a direct and functional target of miR-27a-3p in gastric cancer 27510158_The results indicated that BTG2 expression was downregulated in skin cancer cell lines. Overexpression of BTG2 significantly inhibited cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and the invasion and migration of skin cancer cells. 27613090_Data indicate that BTG2, MAP3K11, RPS6KA1 and PRDM1 as putative targets of microRNA miR-125b. 27932314_TIS21 attenuated Doxorubicin-induced cancer cell senescence by inhibiting linear actin nucleation via Nox4-ROS-ABI2-DRF signal cascade 29098552_decreases tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell line side population cells 29239139_BTG2 expression was lower in human bladder cancer tissues than normal bladder tissues. Highly differentiated bladder cancer cells expressed higher BTG2 than the less-differentiated. Reporter assays with site-mutation of p53 response element within BTG2 promoter area showed that p53-induced BTG2 gene expression was dependent on the p53 response element. 29310680_oncogenic miR-25-3p directly targets BTG2 in TNBC. Further studies revealed that the biological effects of miR-25-3p on TNBC cell proliferation and apoptosis were mediated through regulation of BTG2 and subsequent activation of AKT and ERK-MAPK signaling pathway. 29352138_Authors found that miR-663 regulates apoptosis by controlling mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) through the expression of two novel direct targets PUMA/BBC3 and BTG2. 29441724_Authors found that PRMT5-induced ERK phosphorylation regulated BTG2 expression in HCC cells, whereas pretreatment with a selective ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD184352) significantly reversed the effect of PRMT5 on BTG2 expression. 29472702_We suggest that BTG2(/TIS21) is a potential inhibitor of nucleolin in the cytoplasm, leading to inhibition of carcinogenesis after H. pylori infection. 29656435_The methylation and integrated prognostic signatures based on BTG2 are stable and reliable biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. 29808317_Open data and immunohistochemical analysis were performed to confirm the role of TIS21(/BTG2) expression in various human breast cancer tissues. It was observed that TIS21(/BTG2) inhibited mTORc1 activity by reducing Raptor-mTOR interaction along with upregulation of tsc1 expression. 30912184_The effect of decitabine on the expression and methylation of the PPP1CA, BTG2, and PTEN in association with changes in miR-125b, miR-17, and miR-181b in NALM6 cell line. 31138781_C-terminal domain of Twist1 and Box B of BTG2 interact with each other, which abrogate Twist1 activity. BTG2 inhibits translational initiation by depleting eIF4E availability via inhibiting 4EBP1 phosphorylation. Expression of BTG2 maintains p-eIF2alpha that downregulates initiation of protein translation. 31603257_NUSAP1 knockdown inhibits cell growth and metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer through regulating BTG2/PI3K/Akt signaling. 31721211_CircZNF609 served as a competing RNA to bind miR-134-5p, promoting BTG-2 expression leading to reduced proliferation and migration of glioma cells. 31819167_A fail-safe system to prevent oncogenesis by senescence is targeted by SV40 small T antigen. 31924214_TEAD4 modulated LncRNA MNX1-AS1 contributes to gastric cancer progression partly through suppressing BTG2 and activating BCL2. 31959200_Up-regulated LINC01234 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell metastasis by activating VAV3 and repressing BTG2 expression. 32409840_miR-487a performs oncogenic functions in osteosarcoma by targeting BTG2 mRNA. 32746503_SRXN1 stimulates hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis through modulating ROS/p65/BTG2 signalling. 33025678_LINC01089 inhibits the progression of cervical cancer via inhibiting miR-27a-3p and increasing BTG2. 33334784_Akt Downregulates B-Cell Translocation Gene-2 Expression Via Erk1/2 Inhibition for Proliferation of Cancer Cells. 33844600_The miR-146b-5p promotes Ewing's sarcoma cells progression via suppressing the expression of BTG2. 34082648_MicroRNA miR-92a-3p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via regulating B-cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2). 34337864_Exosomal microRNA-15a from ACHN cells aggravates clear cell renal cell carcinoma via the BTG2/PI3K/AKT axis. 34557203_Integrated Analysis of Prognostic Genes Associated With Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Renal Transplantation. 34699325_MicroRNA-934 facilitates cell proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting B-cell translocation gene 2. 34852712_Circular RNA circFLNA inhibits the development of bladder carcinoma through microRNA miR-216a-3p/BTG2 axis. 35388633_Elevated BTG2 improves the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) through apoptosis. 35640718_Structural Model of the Human BTG2-PABPC1 Complex by Combining Mutagenesis, NMR Chemical Shift Perturbation Data and Molecular Docking. 35730068_Gene amplification-driven RNA methyltransferase KIAA1429 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating BTG2 via m6A-YTHDF2-dependent in lung adenocarcinoma. 35880434_Emerging role of anti-proliferative protein BTG1 and BTG2. |
ENSMUSG00000020423 |
Btg2 |
2889.646448 |
3.0970812619 |
1.630909 |
0.033162107 |
2466.112187 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4416.9536185 |
82.7428382 |
1436.1950241 |
22.2014919 |
| ENSG00000159399 |
3099 |
HK2 |
protein_coding |
P52789 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of hexose, such as D-glucose and D-fructose, to hexose 6-phosphate (D-glucose 6-phosphate and D-fructose 6-phosphate, respectively) (PubMed:23185017, PubMed:26985301, PubMed:29298880). Mediates the initial step of glycolysis by catalyzing phosphorylation of D-glucose to D-glucose 6-phosphate (PubMed:29298880). Plays a key role in maintaining the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane by preventing the release of apoptogenic molecules from the intermembrane space and subsequent apoptosis (PubMed:18350175). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18350175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23185017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26985301, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29298880}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Allosteric enzyme;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Glycolysis;Kinase;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate metabolism; hexose metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:29298880}.; PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and glycerone phosphate from D-glucose: step 1/4. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:29298880}. |
Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate, the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. This gene encodes hexokinase 2, the predominant form found in skeletal muscle. It localizes to the outer membrane of mitochondria. Expression of this gene is insulin-responsive, and studies in rat suggest that it is involved in the increased rate of glycolysis seen in rapidly growing cancer cells. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:3099; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; fructokinase activity [GO:0008865]; glucokinase activity [GO:0004340]; glucose binding [GO:0005536]; hexokinase activity [GO:0004396]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; canonical glycolysis [GO:0061621]; carbohydrate phosphorylation [GO:0046835]; cellular glucose homeostasis [GO:0001678]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; establishment of protein localization to mitochondrion [GO:0072655]; fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0006002]; glucose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0051156]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096]; lactation [GO:0007595]; maintenance of protein location in mitochondrion [GO:0072656]; negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability [GO:0035795]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000378]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of autophagy of mitochondrion in response to mitochondrial depolarization [GO:1904925]; regulation of glucose import [GO:0046324]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931] |
11688991_hypoxia-induced gene in pancreatic cancer cell lines 14672622_Both HIF-1 alpha and HK II protein expressions were co-localized in the cancer cells near necrosis, and the intensity of HIF-1 alpha protein expression was significantly correlated with HK II mRNA expression in both tumors. 14747281_SRE binding protein-1c is involved in the effect of insulin on HKII gene transcription. 15710218_Hexokinase II induction may participate in hepatocellular carcinoma progrssion and the blockage of this enzyme may therapeutically be efficacious. 15967114_Glut-1, HK-II, and PCNA expression are related to uptake of 18F-FDG uptake in lung cancer 16551620_cyclophilin D suppresses apoptotic cell death via a mitochondrial hexokinase II-dependent mechanism in cancer cells 17785433_HIF-1 cooperates with dysregulated c-Myc to promote glycolysis by induction of hexokinase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. 18271924_hexokinase 2 contributes to the increased metabolism of glucose, especially in moderately and poorly differentiated Cholangiocellular carcinoma. 18535403_hexokinase II gene inhibits human colon cancer LoVo cell growth 18579725_The NR5A1 gene expression was activated in mesenchymal stem cells by siRNA directed against hexokinase 2. 18772588_targeting HK II may be beneficial for patients with colon cancer treated with 5-FU 19003546_PIM-1 and hK2 were expressed higher in prostate cancer than those in benign prostatic glandular hyperplasia and normal prostate tissues, the differences among which had statistic significance (P |
ENSMUSG00000000628 |
Hk2 |
159.075699 |
3.4034528081 |
1.766999 |
0.151767081 |
137.626174 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000008797218403548713615426876973531224648632096068214253834912162907318828661395524576814552997205964857130311429500579833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000001193446173128483595802338950855591936381651571891839598278730751727091847430795501158740101743660488864406943321228027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
247.0325819 |
20.0608744 |
73.0461365 |
4.9517485 |
| ENSG00000159433 |
57519 |
STARD9 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2P6 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-dependent motor protein required for spindle pole assembly during mitosis. Required to stabilize the pericentriolar material (PCM). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22153075}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables microtubule binding activity and microtubule motor activity. Involved in spindle assembly. Located in centriole; cytoplasm; and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57519; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22153075_Analysis of 592 mitotic microtubule copurifying proteins by functional RNAi screens for mitotic arrest, checkpoint bypass, and induction of apoptosis resulted in identification of a kinesin, STARD9, with a critical role in cancer cell division. 25501367_STARD9 could be regulated by Plk1 and SCFbeta-TrCP to promote proper mitotic spindle assembly. 28777490_STARD9 frame shift mutation is associated with abnormal spindle morphology in Intellectual disability. 30160609_STARD9 regulates the assembly and stability of both interphase and spindle microtubules. |
|
|
64.332629 |
0.4500403158 |
-1.151874 |
0.357294390 |
10.145342 |
0.00144666341675785646569973863506675115786492824554443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003285038774053224835958175731320807244628667831420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.8839315 |
24.0259111 |
65.2551948 |
36.5341066 |
| ENSG00000159450 |
7062 |
TCHH |
protein_coding |
Q07283 |
FUNCTION: Intermediate filament-associated protein that associates in regular arrays with keratin intermediate filaments (KIF) of the inner root sheath cells of the hair follicle and the granular layer of the epidermis. It later becomes cross-linked to KIF by isodipeptide bonds. It may serve as scaffold protein, together with involucrin, in the organization of the cell envelope or even anchor the cell envelope to the KIF network. It may be involved in its own calcium-dependent postsynthetic processing during terminal differentiation. |
Calcium;Citrullination;Keratinization;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene forms crosslinked complexes with itself and keratin intermediate filaments to provide mechanical strength to the hair follicle inner root sheath. The encoded protein also is important for structural integrity of the filiform papillae of the tongue. Defects in this gene are a cause of uncombable hair syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:7062; |
cornified envelope [GO:0001533]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; transition metal ion binding [GO:0046914]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; keratinization [GO:0031424] |
18643848_BMP-4 signalling activates AHF transcription in hair follicles. 18643848_In human keratinocytes, we found BMP-4 facilitates trichohyalin (THH) transcription, and lamin C plays a key role in the posttranslational stabilization of THH. 19896111_Common variants in the TCHH gene are associated with straight hair in Europeans. 19896111_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20585627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20722389_Data suggest that an immune response to trichohyalin and K16 may have a role in the pathogenesis of the enigmatic disorder. 27460132_The difference between the twoinduced pluripotent stem cell(IPSC) clones in TCHH methylation did not have an obvious effect on its expression in 3D human epidermal equivalent, suggesting that differentiation and tissue formation may mitigate variations in the iPSC methylome. 27487801_To evaluate the relative contribution of these variants, we performed a second genome-wide scan in 709 samples from the Uyghur, an admixed population with both eastern and western Eurasian ancestries. In Uyghurs, both EDAR (rs3827760: P = 1.92 x 10(-12)) and TCHH (rs11803731: P = 1.46 x 10(-3)) are associated with hair straightness, but EDAR (OR 0.415) has a greater effect than TCHH (OR 0.575). 27866708_The two enzymes PADI3 and TGM3, responsible for posttranslational protein modifications, and their target structural protein TCHH are all involved in hair shaft formation. 34110642_Methylome profiling identifies TCHH methylation in CfDNA as a noninvasive marker of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000052415 |
Tchh |
31.498806 |
0.0989724988 |
-3.336828 |
0.376060036 |
101.916466 |
0.00000000000000000000000579131208429018166535531461405225431720773632397391149777207957228403190086396534752566367387771606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000059859780367032977093880827125556698808428009051390754704808500052948261327401269227266311645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7133361 |
1.4791467 |
57.8460909 |
6.8143308 |
| ENSG00000159674 |
10417 |
SPON2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BUD6 |
FUNCTION: Cell adhesion protein that promotes adhesion and outgrowth of hippocampal embryonic neurons. Binds directly to bacteria and their components and functions as an opsonin for macrophage phagocytosis of bacteria. Essential in the initiation of the innate immune response and represents a unique pattern-recognition molecule in the ECM for microbial pathogens (By similarity). Binds bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable antigen binding activity; lipopolysaccharide binding activity; and metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell adhesion. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including defense response to other organism; opsonization; and positive regulation of cytokine production. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10417; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; induction of bacterial agglutination [GO:0043152]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; mast cell mediated immunity [GO:0002448]; opsonization [GO:0008228]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0060907]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760] |
19153605_The structure of the F-spondin domain of mindin was determined at 1.8-A resolution. 19903741_Spondin 2, which is regulated by T(3), has an important role in cell invasion, cell migration, and hepatoma tumor progression. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21098016_High Mindin is associated with diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes. 21632881_mindin serves as a novel mediator that protects against cardiac hypertrophy and the transition to heart failure by blocking AKT/GSK3beta and TGF-beta1-Smad signalling. 22615945_Using tissue microarray by immunohistostaining, we found SPON2 to be over-expressed in prostate cancer (PCa). SPON2 staining was more intense in Gleason score sum 7-8 and in PCa patients with metastasis. 25751394_Mindin protects against vascular hyperplasia by suppression of abnormal VSMC proliferation, migration and phenotypic switching in an AKT-dependent manner. 25945835_Data suggest that spondin-2 could be an independent diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of colon cancer. 26686083_SPON2 is a transcriptional target of the metastasis gene MACC1. SPON2 induces cell motility in vitro and CRC metastasis in mice. In patients, SPON2 serves as prognostic indicator for CRC metastasis and survival, and might represent a promising target for therapeutic approaches. 28060752_Spondin-2 overexpression contributes to tumor aggressiveness and prognosis in gastric cancer. 28991232_Egr-1 regulates mindin expression by directly binding to the mindin promoter; mindin suppresses colon cancer progression by blocking angiogenesis. 29440144_Matricellular protein SPON2 acts as an HCC suppressor and utilizes distinct signaling events to perform dual functions in HCC microenvironment 30318967_High SPON2 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 30527359_spondin-2 might be a novel therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker for squamous cell carcinoma patients 31168562_Study identified the extracelular matrix protein mindin in the secretome of prostate adenocarcinoma cells and show that mindin overexpression in human and mouse TRAMP-C1-induced prostate tumors correlates with upregulated levels of bone-related genes in the tumorigenic prostate tissues. Mindin silencing decreased osteomimicry in adenocarcinoma cells and in the prostate tumor mice model. 31691494_Spondin 2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. 32793186_PIK3AP1 and SPON2 Genes Are Differentially Methylated in Patients With Periodic Fever, Aphthous Stomatitis, Pharyngitis, and Adenitis (PFAPA) Syndrome. 32952742_Overexpression of Spondin-2 Is Associated with Recurrence-Free Survival in Patients with Localized Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 33998076_The clinical significance of spondin 2 eccentric expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in bronchial asthma. 34183385_Cancer-associated Fibroblast-derived Spondin-2 Promotes Motility of Gastric Cancer Cells. 34583750_Tumor cell-derived SPON2 promotes M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and cancer progression by activating PYK2 in CRC. |
ENSMUSG00000037379 |
Spon2 |
22.669590 |
0.3389217485 |
-1.560976 |
0.341485319 |
21.747817 |
0.00000310943550720689032153373938804907794519749586470425128936767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010371246979946125812738384752709208669330109842121601104736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.3683454 |
2.8094279 |
33.8109406 |
5.2946444 |
| ENSG00000159733 |
57732 |
ZFYVE28 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCC9 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling. Acts by promoting EGFR degradation in endosomes when not monoubiquitinated. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19460345}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity. Located in cytosol and early endosome membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57732; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042059]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor-activated receptor activity [GO:0007175] |
19460345_Study concludes that endosomal localization of Lst2 (ZFYVE28), along with an ability to divert incoming EGFR molecules to degradation in lysosomes, is regulated by ubiquitinylation/deubiquitinylation cycles. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000037224 |
Zfyve28 |
46.552096 |
9.1500064563 |
3.193773 |
0.374963747 |
72.004815 |
0.00000000000000002146728762681153109593071004196032324335398786744992516428709450337919406592845916748046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000167915826906061582602813071895241148281324939295008902284678242722293362021446228027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.9018876 |
18.1663525 |
8.9463935 |
1.6759281 |
| ENSG00000159761 |
388284 |
C16orf86 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZW13 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:388284; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000013158 |
4933405L10Rik |
17.363092 |
0.2815742052 |
-1.828413 |
0.595278559 |
8.769664 |
0.00306281895263239931775922642032128351274877786636352539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006547973311247712834004541804233667789958417415618896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6273194 |
3.1905337 |
32.4131152 |
7.3917522 |
| ENSG00000159788 |
6002 |
RGS12 |
protein_coding |
O14924 |
FUNCTION: Regulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08774}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Behaves as a cell cycle-dependent transcriptional repressor, promoting inhibition of S-phase DNA synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12024043}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Signal transduction inhibitor;Synapse;Transcription;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the 'regulator of G protein signaling' (RGS) gene family. The encoded protein may function as a guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase)-activating protein as well as a transcriptional repressor. This protein may play a role in tumorigenesis. Multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Other alternative splice variants have been described but their biological nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6002; |
condensed nuclear chromosome [GO:0000794]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; GTPase regulator activity [GO:0030695]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277] |
9168931_shows chromosomal mapping information for human locus. 17042716_RGS12 is essential for the terminal differentiation of osteoclasts induced by RANKL. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20627871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26987813_Data support the notion that the Galpha, but not Gbetagamma, arm of the Gi/o signalling is involved in TRPC4 activation and unveil new roles for RGS and RGS12 in fine-tuning TRPC4 activities. 28611045_Findings identify RGS12 as a candidate tumor-suppressor gene in AA prostate cancer, which acts by decreasing expression of AKT and MNX1, establishing a novel oncogenic axis in this disparate disease setting. 33198557_RGS12 Represses Oral Cancer via the Phosphorylation and SUMOylation of PTEN. 33686240_RGS12 is a novel tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma that inhibits YAP-TEAD1-Ezrin signaling. 34796776_RGS12 Drives Macrophage Activation and Osteoclastogenesis in Periodontitis. 34931491_RGS12 inhibits the progression and metastasis of multiple myeloma by driving M1 macrophage polarization and activation in the bone marrow microenvironment. |
ENSMUSG00000029101 |
Rgs12 |
130.492882 |
0.2131602311 |
-2.229990 |
0.871495402 |
5.801854 |
0.01600928608871260427903848722053226083517074584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029320891260627625352075398268425487913191318511962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.2507070 |
31.3634651 |
322.9162116 |
104.0160930 |
| ENSG00000159899 |
4882 |
NPR2 |
protein_coding |
P20594 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the C-type natriuretic peptide NPPC/CNP hormone. Has guanylate cyclase activity upon binding of its ligand. May play a role in the regulation of skeletal growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15146390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1672777, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24001744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24471569, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26980729}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;cGMP biosynthesis;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Glycoprotein;GTP-binding;Lyase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Osteogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes natriuretic peptide receptor B, one of two integral membrane receptors for natriuretic peptides. Both NPR1 and NPR2 contain five functional domains: an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a single membrane-spanning region, and intracellularly a protein kinase homology domain, a helical hinge region involved in oligomerization, and a carboxyl-terminal guanylyl cyclase catalytic domain. The protein is the primary receptor for C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), which upon ligand binding exhibits greatly increased guanylyl cyclase activity. Mutations in this gene are the cause of acromesomelic dysplasia Maroteaux type. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4882; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; guanylate cyclase activity [GO:0004383]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; natriuretic peptide receptor activity [GO:0016941]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; peptide receptor activity [GO:0001653]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; cGMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006182]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; negative regulation of meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051447]; negative regulation of oocyte maturation [GO:1900194]; ossification [GO:0001503]; positive regulation of cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0010753]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; receptor guanylyl cyclase signaling pathway [GO:0007168]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11208455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11464256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11556325_protein structure: ligand binding domains 12709393_NPR-B is highly expressed in glomeruli and proximal tubules, whereas NPR-Bi(the splice form) shows strong signals in the distal nephron 14988324_a marker for left ventricular dysfunction in diabetic patients. 15146390_Mutations in the transmembrane natriuretic peptide receptor NPR-B impair skeletal growth and cause acromesomelic dysplasia, type Maroteaux 15262909_The 5' terminus of the hNPR-B gene transcript is ~732 base pairs upstream from the presumed translation start site. Its activity is dominated by a single cluster of Sp1-binding elements in the proximal 5' flanking sequence of the gene. 15371450_hyperosmotic and lysophosphatidic acid-dependent inhibition of NPRB is mediated by calcium-dependent phosphorylation 15459247_NPR-A and NPR-B are desensitized in cells in which they are not internalized. 15911070_discussion of C-type natriuretic peptide and guanylyl cyclase B receptor [review] 15911610_ATP does not activate NPRA and NPRB as has been repeatedly reported. Instead, ATP increases activity primarily by maintaining proper receptor phosphorylation status but also serves a previously unappreciated enzyme stabilizing function. 17429599_Study focus on the role of NPR-B and its ligand C-type natriuretic peptide in cardiovascular physiology and disease. 17652215_intact kinase homology domain of NPR-B is essential for skeletal development 18945719_Defective cellular trafficking of NPR-B resulted from missense mutation is associated with acromesomelic dysplasia-type Maroteaux. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19108585_The extracellular domain of human GC-B folds independently of the remainder of the protein. 19167912_BNP level on arrival in the intensive care unit may support early diagnosis and allow optimal management of heart failure after aortic valve replacement 19326473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19413180_It appears that subjects homozygous for C allele at position 381 of the BNP precursor gene promoter are more prone to develop atherosclerotic lesions in renal arteries. 19458086_Data indicate that the familial ANP mutation associated with atrial fibrillation has only minor effects on natriuretic peptide receptor interactions but markedly modifies peptide proteolysis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20079378_Results show that VILIP-1 regulates the cell surface localization of natriuretic peptide receptor B. 20123316_A polymorphism in natriuretic peptide receptor 2 influences the susceptibility to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy in a Chinese cohort. 20600420_Data show that serum B-type natriuretic peptide strongly correlates with new-onset heart failure development at the optimal cut-off value of 175 pg/mL. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20664698_These studies showed the presence of NPR-A and NPR-B (mRNAs and protein) in human corneal epithelial tissue. 20700369_The data indicates that ANP, BNP, and CNP and natriuretic peptide receptor transcripts are expressed and are functional in human lens epithelial cells. 20977274_we identified and characterized new phosphorylation sites in GC-A and GC-B and provide the first evidence of phosphorylation sites within human guanylyl cyclases. 21366551_Cellular exposure to Go6976 reduced basal and natriuretic peptide-dependent, but not detergent-dependent, GC-A and GC-B activity. 21828054_Go6976 reduces GTP binding to the catalytic site of GC-A and GC-B and that ATP increases the magnitude of the inhibition. 22039354_results provide evidence for a potential causal role of the B-type natriuretic peptide system in the aetiology of type 2 diabetes 22133375_GC-B activity is increased in non-myocytes from failing human ventricles, possibly as a result of increased fibrosis. 22421372_Report the presence of CNP and its receptors, NPR2/3 in atherosclerotic plaques of human carotid artery. 22633662_Patients with BNP on admission greater than 150/pg/ml have higher probability of death in follow up. 22645228_NPR2 expression in normal human fetal and adult pituitaries and adenomatous pituitary tissue suggests a role for these receptors in both pituitary development and oncogenesis. 22691581_Two novel missense mutations in the gene NPR2 were identified six consanguineous families of Pakistani origin. The presence of the same mutation (p. T907M) and haplotype in five families (A, B, C, D, E) is suggestive of a founder effect. 22870295_An overgrowth disorder associated with excessive production of cGMP due to a gain-of-function mutation of the natriuretic peptide receptor 2 gene. 22884919_Gene expression of C-type natriuretic peptide and of its specific receptor NPR-B in human leukocytes of healthy and heart failure subjects 22949736_Guanylyl cyclases A and B are asymmetric dimers that are allosterically activated by ATP binding to the catalytic domain. 23186809_ACNP stimulated both human natriuretic peptide receptors (NPRs), NPRA and NPRB, as potent as their native ligands in receptor transfected cells. 23586811_Although no novel phosphorylation sites that influenced the suppression of guanylate cyclase-B were identified, experiments revealed that mutations in Tyr808 markedly enhanced GC-B activity. 23827346_study concludes V883M mutation increases maximal velocity in absence of C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), eliminates requirement for ATP in the CNP-dependent Km reduction and disrupts normal inactivation process; established a molecular mechanism for how an amino acid substitution in GC-B activates the enzyme, which results in abnormally long and fragile bones 23835779_KIdney NPR2 protein quantity is significantly impacted by genetic variation. 24001744_We identified heterozygous NPR2 mutations in 6% of patients initially classified as idiopathic short stature. Affected patients have mild and variable degrees of short stature without a distinct phenotype. 24259409_Overgrowth syndrome associated with a gain-of-function mutation of the natriuretic peptide receptor 2 (NPR2) gene. 24431432_In transgenic mice, complete absence of Npr2 activity prohibits the bifurcation of cranial sensory axons. 24471569_Identification of heterozygous dominant negative NPR2 mutations in 2% of Japanese patients with short stature. 24699414_Molecular dynamics analysis indicated decreases in the values of Van der Waals, electrostatic energy and potential energy of NPRB/Vasonatrin peptide compared to NPRA/Vasonatrin peptide. 25117468_Cardiac fibrosis and the endogenous natriuretic peptide system were evaluated in end-stage heart failure to assess the anti-fibrotic actions of the dual GC-A/-B activator. 25703509_Heterozygous mutations in natriuretic peptide receptor-B (NPR2) gene as a cause of short stature 25959430_3 consanguineous families segregating Acromesomelic dysplasia Maroteaux type in an autosomal recessive manner studied. Linkage in the families was established to the NPR2 gene on chromosome 9p12-21. Sequence analysis revealed 2 novel missense variants (p.Arg601Ser; p.Arg749Trp) in 2 families and a previously reported splice site variant (c.2986+2T>G) in the third family. 26075495_NPR2 mutations account for approximately 3% of patients with disproportionate short stature and/or clinical or radiographic indicators of SHOX deficiency and in whom no SHOX defect has been identified. 26567084_Loss-of-function mutations of the NPR2 gene is associated with acromesomelic dysplasia, type maroteaux. 26888452_IL1R2 hypomethylation and androgen receptor hypermethylation may constitute an important determinant of disease severity, whereas NPR2 hypomethylation and SP140 hypermethylation may provide a biomarker for vulnerability to excessive daytime sleepiness in Obstructive Sleep Apnea 26926249_Mutations in three genes (GDF5, NPR2, BMPR1B) have been reported to cause different forms of acromesomelic dysplasia 27283501_Atenolol treatment normalized the altered expression of Npr1 and Npr2 genes. 27941173_Heterozygous mutation in NPR2 gene is associated with short stature. 27994189_in 4 Indian families with acromesomelic dysplasia, type Maroteaux, 4 homozygous mutations in four different families were identified; these include 3 novel mutations including a deletion frameshift mutation (p.Cys586Ter), one nonsense mutation (p.Arg479Ter), one missense mutation (p.Val187Asp) and one reported missense mutation (p.Tyr338Cys) 28450398_Data suggest mutations in NPR2 in patients with skeletal overgrowth alter conformation: A488P/R655C missense mutations yield conformation mimicking allosterically activated NPR2; A488P mutation sets phosphorylation as requirement for CNP-dependent activation; R655C mutation abrogates need for phosphorylation; ATP analog inhibits mutants. (NPR2 = atrial natriuretic factor receptor B; CNP = C-type natriuretic peptide) 28765884_These results of the distinct presence of NPRA and NPRBpositive cells in unstable plaques underlying acute myocardial infarction suggested that natriuretic peptides serve a role in regulating plaque instability in humans. 29409758_It was the aim to investigate the expression of natriuretic peptide receptors NPR-A, NPR-B and NPR-C during adipocyte differentiation (AD), upon stimulation with fatty acids (FA), and in murine and human adipose tissue depots. 30016695_homozygous mutations in the NPR2 gene underlying variable phenotypes of Acromesomelic dysplasia, type Maroteaux 30359775_Five novel variants in NPR2 were identified in unrelated patients with acromesomelic dysplasia type Maroteaux. 30696704_Data show that all the residues of the ATP-binding site of the are conserved in the phosphorylated pseudokinase domain (PKD) of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor type A (GC-A) and atrial natriuretic factor receptor B (GC-B). 31075302_NPR2 mRNA was down-regulated in cumulus cells surrounding mature oocytes. Further results showed that CNP signaling is downregulated in human ovarian follicles containing mature oocytes. 31077548_Maroteaux-type acromesomelic dysplasia caused by NPR2 mutation has been found in a pedigree from Vietnam. 31883339_Low and elevated B-type natriuretic peptide levels are associated with increased mortality in patients with preserved ejection fraction undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement: an analysis of the PARTNER II trial and registry. 31927522_Familial hypophosphatemic rickets caused by a PHEX gene mutation accompanied by a NPR2 missense mutation. 31960617_Role of NPR2 mutation in idiopathic short stature: Identification of two novel mutations. 31990356_NPR2 Variants Are Frequent among Children with Familiar Short Stature and Respond Well to Growth Hormone Therapy. 32268070_C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP)/guanylate cyclase B (GC-B) system and endothelin-1(ET-1)/ET receptor A and B system in human vasculature. 32506268_A novel nonsense mutation in NPR2 gene causing Acromesomelic dysplasia, type Maroteaux in a consanguineous family in Southern Punjab (Pakistan). 32720985_Short Stature is Progressive in Patients with Heterozygous NPR2 Mutations. 33073519_A new family with epiphyseal chondrodysplasia type Miura. 33205215_Clinical Characteristics of Short-Stature Patients With an NPR2 Mutation and the Therapeutic Response to rhGH. 33288834_Further defining the clinical and molecular spectrum of acromesomelic dysplasia type maroteaux: a Turkish tertiary center experience. 34162036_Acromesomelic dysplasia-Maroteaux type, nine patients with two novel NPR2 variants. 34565054_NPR2 gene variants in familial short stature: a single-center study. 35455946_Novel NPR2 Gene Mutations Affect Chondrocytes Function via ER Stress in Short Stature. 35741827_Heterozygous NPR2 Variants in Idiopathic Short Stature. 36322898_Identification of Diagnostic Variants in FGFR2 and NPR2 Genes in a Chinese Family Affected by Crouzon Syndrome and Acromesomelic Dysplasia, Type Maroteaux. |
ENSMUSG00000028469 |
Npr2 |
9.003853 |
0.0804607285 |
-3.635571 |
0.808158976 |
26.167300 |
0.00000031307955232956433130352461545464759495871476246975362300872802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001169591038315456761186462292245735739015799481421709060668945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1494957 |
0.6880723 |
13.7916969 |
3.6914035 |
| ENSG00000159958 |
115650 |
TNFRSF13C |
protein_coding |
Q96RJ3 |
FUNCTION: B-cell receptor specific for TNFSF13B/TALL1/BAFF/BLyS. Promotes the survival of mature B-cells and the B-cell response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11591325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12387744}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Immunity;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
B cell-activating factor (BAFF) enhances B-cell survival in vitro and is a regulator of the peripheral B-cell population. Overexpression of Baff in mice results in mature B-cell hyperplasia and symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Also, some SLE patients have increased levels of BAFF in serum. Therefore, it has been proposed that abnormally high levels of BAFF may contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases by enhancing the survival of autoreactive B cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for BAFF and is a type III transmembrane protein containing a single extracellular cysteine-rich domain. It is thought that this receptor is the principal receptor required for BAFF-mediated mature B-cell survival. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:115650; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell costimulation [GO:0031296]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
12456020_BAFF-R is a receptor for the TNF family member ligand, BAFF [review] 12471121_BAFFR-mediated NF-kappa B activation and IL-10 production in B cells is downregulated by TNFR-associated factor-3. 12715002_crystal structure and interaction with BAFF protein 12755599_BAFF/BLyS receptor 3 comprises a minimal TNF receptor-like module that encodes a highly focused ligand-binding site. 14512299_Expression of BCMA, TACI, and BAFF-R by multiple myeloma cells support cell growth and survival. 15585864_This study reports the crystal structure of a 24-residue fragment of the cytoplasmic portion of BAFF-R bound in complex with TRAF3. 15644327_the PVPAT sequence of BAFFR not only functions as a key signaling motif of BAFFR but also determines its signaling specificity in the induction of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway 16160919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16160919_amino acid sequence of genomic DNA from blood of common variable immunodeficiency patients;mutations may result in humoral immunodeficiency 16226112_BAFF-R is expressed on most mature B cells and B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. 16320342_BAFF-R is consistently occupied on blood B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus 16769579_Detection in lymphoma tissue biopsies may be of clinical relevance in predicting response to treatment. 16840730_BR3, which is expressed on all mature B cells, is a specific receptor for the B-cell survival and maturation factor BAFF. 16914324_Review. The splice variants, binding specificities, structural determinants for ligand selectivity, and signaling pathways are reviewed. 16919470_Review. BLyS signaling via BR3 is the dominant homeostatic regulator of primary B cell pools. 16931038_Review. BAFF and its receptor have roles in B cell biology outside of a survival mechanism. These include germinal center maintenance, isotype switching, and regulation of specific B cell surface markers. 16931039_Review. Direct BAFF/APRIL signalling in T cells and/or T cell modulation in response to a BAFF-modified B cell compartment may play an important role in inflammation and immunomodulation. 17119117_recombinant gelonin/B lymphocyte stimulator fusion toxin may have potential therapeutic efficacy for B-CLL patients 17154264_BAFF-R and CD40 enhance B cell responsiveness to transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI)-mediated suppression. 17963166_Widely expressed in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 18025170_The BAFF-binding receptor profile may serve as a footprint of the activation history and stage of differentiation of normal human B cells. 18051214_Of 9 CVID patients...No mutations of SAP, ICOS, TACI, BAFFR, and CD19 were identified 18775026_We propose that an aberrant BAFF/BAFF-R-dependent autocrine mechanism may play a role in the development of certain types of nonhematopoietic cancer cells. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19207947_the assessment of expression of BAFF-binding receptors aids subclassification and prognostication of DLBCL 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19666484_deletion of the BAFF-R gene in humans causes a characteristic immunological phenotype but it does not necessarily lead to a clinically manifest immunodeficiency 19726767_molecular mechanisms underlying this crosstalk between B cell receptor and BAFF receptor signaling that maintain B cell survival and metabolic fitness 19731825_BLyS and its receptors might have a potential role in the growth and survival of malignant plasma cells. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20025535_the mechanism of transcriptional regulation of BAFF-R 20230666_IFN-gamma and the NF-kappaB pathway could be involved in regulating the transcription and mRNA expression of BAFF-R gene. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20460528_This report is the first showing universal expression of BAFF-R by pre-B ALL cells. 20554963_Data from BAFF-R-expressing cells suggested potential regulatory sites in TNFRSF13C promoter region. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20945608_inverse correlation between BAFF and APRIL in Kawasaki disease is reversed by IVIG treatment 20974656_Elevated plasma BAFF and reduced BAFF receptor 3 (BR3) protein expression on peripheral B cells could act as biomarkers for active disease in systemic lupus erythematosus patients 21041452_a novel lymphoma-associated mutation in human BAFF-R that results in NF-kappaB activation and reveals TRAF6 as a necessary component of normal BAFF-R signaling. 21099364_Results describe the mechanisms underlying aberrant BAFF-R expression in precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia (precursor B-ALL) and mature B chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). 21123970_BAFF-R was rather specifically related to low growth activity of germinal center B-cell-like -type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of nodal origin. 21483105_This is the first study, presenting together the TNFSF members APRIL, BAFF, TWEAK and their receptors in different areas of normal renal tissue and renal cell carcinoma. 21515993_reduced expression via inhibition of the NF-KappaB pathway in B cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients 21607696_It was also found that NF-kappaB was an important transcription factor involved in regulating BAFF-R expression through one NF-kappaB binding site in the BAFF-R promoter 21687682_primary leukemia B-cell precursors aberrantly express receptors of the BAFF-system, BAFF-R, BCMA, and TACI 21744373_The human BAFF-R gene might be regulated via a transcriptional event through one putative NF-kappaB site on the BAFF-R gene promoter. 21871426_The activation profile of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas/posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders was not associated with BAFF/BAFF-R expression, whereas nuclear p52 activation might be linked to Epstein-Barr virus. 22028296_BAFF-R expression is tightly regulated during B-cell development in mouse and human and this exprssion is correlated with posirive selection. 22124120_Soluble BAFF levels inversely correlate with peripheral B cell numbers and the expression of BAFF receptors. 22699762_P21R/H159Y TNFRSF13C compound heterozygous mutation and P21R heterozygous mutations were detected in Turkish patients with common variable immunodeficiency. 23272079_BAFF-R, but not BAFF, may have a role in progression-free survival and overall survival in follicular lymphoma 23276925_BLyS and its receptors are expressed by B lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and the bone marrow of patients with multiple myeloma. 24602383_Our study demonstrates that BR3 is involved in the survival of cultured epithelial cells due to an autocrine effect of BAFF. 24809296_Availability of BAFF determines BAFF-R and TACI expression on B cells in common variable immunodeficiency. 24825858_In view of the restricted expression of the BAFF-R on normal cells and the multiple anti-pre-B ALL activities stimulated by this antibody, a further examination of its use for treatment of pre-B ALL is warranted. 25301447_Data show significant differences in expression of tumour necrosis factor family (BAFF) receptors BAFF-R, BCMA and TACI in patients with and without anti-Jo-1 or anti-Ro52/anti-Ro60 autoantibodies. 25454804_the common TLR4-D299G, TLR4-T399I and BAFFR-P21R polymorphisms provide the carriers with a protective advantage against ICU-acquired sepsis; this finding was more profound for medical patients compared to trauma or surgical ones 25569260_Expression of mutant caspase-9 correlated with a downregulation of BAFFR (B-cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family (BAFF) receptor) in B cells and ICOS (inducible T-cell costimulator) in T cells. 26097183_There is an increased prevalence of the BAFF-R His159Tyr mutation in patients with Sjogren's syndrome (SS), particularly in those with SS complicated by MALT lymphoma whose disease onset occurred at a younger age. 26122175_Variants of TNFRSF13C were associated with common variable immunodeficiency. 26214745_BAFF and BAFF-R are expressed in the thyrocytes derived from patients with either autoimmune thyroid disorders or multinodular goiter, as well in the infiltrating immune cells of Graves' disease and Hashimoto's thyroiditis 26327569_Negative expression of BAFF-R, but not of BAFF, could be an independent risk factor for progression-free survival and Overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with standard R-CHOP. 26613719_genetic polymorphism contributes to the pathogenesis of primary antibody deficiency 26749059_BAFF-R, as the principal receptor of BAFF, not only decreased the apoptosis of B cells and CD8+ T cells by upregulating the expression of Bcl-2 and BclxL, but also promoted B-cell proliferation in immune thrombocytopenia. 27436754_the B-cell receptor BR3 modulates cellular branching via Rac1 during neuronal migration 27468724_Variants in BAFF-R gene is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 28028945_The expression levels of serum BAFF and the three receptors (TACI, BCMA and BAFF-R) in non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients were significantly higher than in healthy controls. 28249164_Inhibition of ADAM10 augments BAFF-dependent survival of primary human B cells, whereas inhibition of ADAM17 increases BAFFR expression levels. 28441631_up-regulated expression in intractable temporal lobe epilepsy 28573703_This study assessed TNFRSF13C expression on leukaemic cells ofchildhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia patients. Of note, during the early drug treatment, its expression is maintained or even increased on residual tumour cells, suggesting a positive selection and survival of TNFRSF13C positive blast cells. 28800164_Relationships between serum BAFF and BBR expression [(BAFFR, calcium signal modulating cyclophilic ligand interactor (TACI) and B cell maturation antigen (BCMA)] were determined on B cell subsets, defined using immunoglobulin (Ig)D/CD38. Twenty pre-RTX and 18 rheumatoid arthritis patients relapsing after B cell depletion were included. 28834574_Among the BAFF receptors in a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, the AA have shown, by fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis of median fluorescence intensity (MFI), that transmembrane activator and calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI) and B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) do not change 29087261_Expression patterns of BAFF and its receptor BAFF-R differ according to lupus nephritis class. 29309290_these data indicate that BR3 neutralization increases the activation and cytolytic function of CD4 and CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes 30467093_To evaluate the expression of the cytokines BAFF and APRIL and their association with the receptors BAFF-R and TACI on CD3+ T cells. 32172995_TNFRSF13C/BAFFR P21R and H159Y polymorphisms in multiple sclerosis. 32506205_Expression of BAFF and BAFF receptors in primary Sjogren's syndrome patients with ectopic germinal center-like structures. 32523317_Decreased of BAFF-R expression and B cells maturation in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 32576236_Elevated expression of BAFF receptor, BR3, on monocytes correlates with B cell activation and clinical features of patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. 34075170_BAFF, APRIL and BAFFR on the pathogenesis of Immunoglobulin-A vasculitis. 34201032_The TNFRSF13C H159Y Variant Is Associated with Severe COVID-19: A Retrospective Study of 500 Patients from Southern Italy. 34311146_BAFF receptor polymorphisms and deficiency in humans. 34352467_BAFF signaling in health and disease. 34503766_Editorial overview: BAFF family ligands and receptors - a license to live. 35017485_A BAFF ligand-based CAR-T cell targeting three receptors and multiple B cell cancers. 35250986_Circulating Memory B Cells in Early Multiple Sclerosis Exhibit Increased IgA(+) Cells, Globally Decreased BAFF-R Expression and an EBV-Related IgM(+) Cell Signature. 35460540_B-cell activating factor (BAFF), BAFF promoter and BAFF receptor allelic variants in hepatitis C virus related Cryoglobulinemic Vasculitis and Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. 35563492_Decreased BAFF Receptor Expression and Unaltered B Cell Receptor Signaling in Circulating B Cells from Primary Sjogren's Syndrome Patients at Diagnosis. 35767961_BAFFR activates PI3K/AKT signaling in human naive but not in switched memory B cells through direct interactions with B cell antigen receptors. |
ENSMUSG00000068105 |
Tnfrsf13c |
8.826895 |
0.3061365890 |
-1.707753 |
0.636448449 |
7.184571 |
0.00735331456326368277515159732615757093299180269241333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014488709511917228014987735207341756904497742652893066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.2975212 |
1.7022903 |
14.2613563 |
3.4716558 |
| ENSG00000160013 |
5739 |
PTGIR |
protein_coding |
P43119 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for prostacyclin (prostaglandin I2 or PGI2). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G(s) proteins which activate adenylate cyclase. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Prenylation;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor family 1 and has been shown to be a receptor for prostacyclin. Prostacyclin, the major product of cyclooxygenase in macrovascular endothelium, elicits a potent vasodilation and inhibition of platelet aggregation through binding to this receptor. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5739; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; prostacyclin receptor activity [GO:0016501]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0010642]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496] |
11854299_Impaired receptor binding and activation associated with polymorphism 11895442_role in protein isoprenylation 12119468_Data show that prostacyclin receptor mediated increases in cAMP play a role in enhancing LPS/IFN-gamma-induced iNOS expression in human monocytes/macrophages and may contribute to the increased production of NO during peritonitis. 12446735_identification of a unique ligand-binding pocket by site-directed mutagenesis and molecular modeling 12481546_current state of knowledge of the prostacyclin receptor, its signaling and regulation, and its biological role in vivo [review] 12664600_activation-dependent internalization of this receptor 12850828_the presence of a free heavy chain IgG in the circulation from spinal cord-injured subjects blocked insulin receptor binding sites and also blocked the prostacyclin receptor interaction in platelets; insulin-induced NO synthesis was markedly impaired. 15053924_Iloprost stimulation (1 microM, 2 h) of IP prostanoid receptor expressed in HEK293 cells resulted in specific decrease of endogenous G(s)alpha protein in detergent-insensitive, caveolin-enriched, membrane domains 15248755_elucidated the molecular requirements for receptor activation within the region of the ligand-binding pocket, identifying transmembrane residues affecting potency 15469414_The -CSLC motif of the IP is a direct target for inhibition by the FTI SCH66336, and in the presence of strong farnesyltransferase inhibition, the IP does not undergo compensatory geranylgeranylation. 15471868_prostacyclin and thromboxane receptor dimerization facilitates thromboxane receptor-mediated cAMP generation 15979846_results demonstrate for the first time that prostacyclin receptor activation by cicaprost can lead to STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylations via signaling pathways involving pertussis toxin-insensitive G proteins, ERK and JNK 16114876_The first intracellular loop of human prostacyclin receptor (IP) was proposed to be involved in signaling via its interaction with the Galphas protein. 16373414_PGI-IP interaction within glandular epithelial cells can promote the expression of proangiogenic genes in human endometrium via cross talk with the EGFR. 16399867_These data suggest that iloprost modulates VSMC phenotype via G(s) activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway. 16885208_AC6 overexpression in endothelial cells may have use as a means to enhance prostacyclin function and reduce endothelial barrier permeability. 16942748_results indicate that the three residues (E392-L394) of the Galphas protein predicted from NMR peptide studies, and the IP iLP1 and iLP3 play important roles in the Galphas-mediated IP receptor signaling in the cells. 17015447_analysis of roles of cysteine residues in human prostacyclin receptor structure and function 17481829_Three Arg-targeted changes at the same 212 position within the third cytoplasmic loop of the human prostacyclin (hIP) receptor were detected. 17496729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17704830_The charged residues and the presence of naturally occurring mutations in prostacyclin receptor have important implications in the rational design of prostacyclin agonists for treating cardiovascular disease. 18005048_Prostaglandin I(2) receptor (IP) was more specifically expressed in hair cuticle layer and outer root sheath (ORS) basal layer. 18042246_A profile of the residues in the second extracellular loop that are critical for ligand recognition of human prostacyclin receptor 18162607_IP-receptor agonists may limit the mitogenic actions of thrombin in human SMC by downregulating PAR-1 via modulation of cAMP-/PKA- and Rac1-dependent signaling pathways. 18323528_diminished prostacyclin receptor signaling may contribute, in part, to the underlying adverse cardiovascular outcomes observed with cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition. 18551041_A propensity of enhanced platelet activation in deep vein thrombosis patients with PTGIR polymorphisms V53V/S328S; A dysfunctional PTGIR polymorphism (R212C) associated with intimal hyperplasia. 18551041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18573679_Data suggest that expression of prostanoid receptors (prostaglandin E2 EP3-I, prostacyclin, and thromboxane A2 receptors) in vascular inflammation could influence cell responses dependent on the constitutive activation of ghrelin receptors. 18755267_Co-stimulation of G(s) and G(q) can result in the fine-tuning of STAT3 activation status, and this may provide the basis for cell type-specific responses following activation of hIP. 18832025_The prostacyclin receptor plays a central role in regulating its recycling following agonist activation by rab11 protein binding domain within its C-tail domain. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19118563_These data provide critical insights into the transcriptional regulation of the IP gene in human megakaryocytic and endothelial cells, identifying Sp1, PU.1 and Oct-1 as the critical factors involved in its basal regulation in humans. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20070947_The human IP gene is directly regulated by estrogen that largely occurs through an ERalpha-dependent transcriptional mechanism. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20357748_Observed induction of the PG receptors EP2 and IP in atherosclerotic femoral arteries in the arterial intima, medial layer, as well as the associated atherosclerotic plaque. 20482519_decreased maternal plasma levels in severe preeclamptic pregnant women 20522800_IP(R212C) exerts a dominant action on the wild-type IP and thromboxane receptor through dimerization. This likely contributes to accelerated cardiovascular disease in individuals carrying 1 copy of the variant allele. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21052031_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21189259_of 18 non-synonymous mutations, all with frequencies less than 2% in our study cohort, eight of the 18 had defects in binding, activation, and/or protein stability/folding 21223948_study identified a novel 8 residue ER export motif within the functionally important alpha-H8 of the hIP. 21653824_Human prostacyclin receptor interacts with the PDZ adapter protein PDZK1; this interaction plays important role in endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. 22159995_VDAC is the ATP conduit in the IP receptor-mediated signaling pathway in human erythrocytes. 22336225_Prostacyclin receptor-dependent inhibition of human erythroleukemia cell differentiation is STAT3-dependent 22380928_the IP receptor was expressed in blood vessels of renal cell carcinoma specimens, but not in glomerular vessels of normal renal tissue; findings suggest the IP receptor might maintain an angiogenic switch in the 'on' state in tumor endothelial cells (TEC); suggest that the IP receptor is a TEC-specific marker and might be a useful therapeutic target 22381139_these data provide critical insights into the transcriptional regulation of the human prostacyclin receptor gene within the vasculature, including during megakaryocytic differentiation 22884631_IKEPP was also found to be expressed in vascular endothelial cells where it co-localizes and complexes with the hIP 23162015_IP receptor heteridimerization with thromboxane receptor facilitates receptor trafficking to membrane lipid rafts. 23628440_The present report is the first to show an association between the A984C polymorphism of the IP gene and platelet activation in Japanese subjects. 24035274_Prostaglandin I2- Prostaglandin I2 receptor signaling regulates human Th17 and Treg cell differentiation. 24886841_A total of 38 non-synonymous mutations were identified within the coding region of the hIP receptor, mapping to 36 distinct residues, including several mutations previously reported to affect the signaling of the hIP receptor. 25617843_these findings suggest that reduced IPR expression in DM2 platelets may contribute to platelet hyperactivity in humans with type 2 diabetes. 26661245_role of IP-PPARdelta signal transduction pathway in the production of sAPPalpha in cerebral microvasculature. 26775637_cPGI2 generates via its cognate cell-surface receptor IP-R, converting white adipocytes to brite adipocytes. 26868296_Data (including data from studies using transgenic mice, an murine experimental model of diabetes, and mouse/human cell lines) suggest prostaglandin I2 receptor (PTGIR) is involved in insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells and in permselectivity in glomerular podocytes; the mechanism appears to involve regulation of post-translational phosphorylation of nephrin. 27365208_The human prostacyclin receptor gene is under the transcriptional regulation of dihydrotestosterone, where this regulation is further influenced by serum-cholesterol levels. 28739266_these studies are not only the first to identify alpha4 helix of Rab11a as a protein binding domain on the GTPase but also reveal novel mechanistic insights into the intracellular trafficking of the human prostacyclin receptor (hIP), and potentially of other members of the GPCR superfamily, involving Rab11-dependent mechanisms. 32531060_Rare loss-of-function mutations of PTGIR are enriched in fibromuscular dysplasia. |
ENSMUSG00000043017 |
Ptgir |
71.952997 |
5.7203089162 |
2.516093 |
0.208593664 |
159.918488 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000117884775570099003266121750829456374660786017549703460803563726662612058574384645941861230470293006589166395770007511600852012634277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000018049577670276570340448695507648913161439732425648030937833739638797628308496384620951085808564229306938386798719875514507293701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
121.3509971 |
15.2502159 |
21.3852073 |
2.3543731 |
| ENSG00000160050 |
79140 |
CCDC28B |
protein_coding |
Q9BUN5 |
FUNCTION: Involved in ciliogenesis. Regulates cilia length through its interaction with MAPKAP1/SIN1 but independently of mTORC2 complex. Modulates mTORC2 complex assembly and function, possibly enhances AKT1 phosphorylation. Does not seem to modulate assembly and function of mTORC1 complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23015189, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23727834}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Ciliopathy;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Obesity;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The product of this gene localizes to centrosomes and basal bodies. The protein colocalizes with several proteins associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) and participates in the regulation of cilia development. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:79140; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271] |
16327777_identification of a novel locus, MGC1203, that contributes epistatic alleles to Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a pleiotropic, oligogenic disorder; MGC1203 encodes a pericentriolar protein that interacts and colocalizes with the BBS proteins 19402160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23015189_reports CCDC28B as a novel protein involved in the process of ciliogenesis whilst providing functional insight into the cellular basis of its modifier effect in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 23727834_Findings implicate CCDC28B in the regulation of mTORC2, and uncover a novel function of SIN1 regulating cilia length that is likely independent of mTOR signaling. 29445114_these studies demonstrate that kinesin 1 regulates ciliogenesis through CCDC28B 34294890_A CVID-associated variant in the ciliogenesis protein CCDC28B disrupts immune synapse assembly. |
ENSMUSG00000028795 |
Ccdc28b |
14.288245 |
0.4896712124 |
-1.030115 |
0.421530659 |
5.999364 |
0.01431103373966015855633937547963796532712876796722412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026523211702333491374128371376173163298517465591430664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5511263 |
2.8776461 |
21.9449170 |
3.6467362 |
| ENSG00000160051 |
55721 |
IQCC |
protein_coding |
Q4KMZ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:55721; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000040795 |
Iqcc |
14.527461 |
0.4220179263 |
-1.244624 |
0.454399792 |
7.624638 |
0.00575762321792456024938111625033343443647027015686035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011612806599694793646682100529687886592000722885131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.8197729 |
3.0014650 |
21.0303006 |
4.7105599 |
| ENSG00000160055_ENSG00000224066 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.833443 |
0.1724906247 |
-2.535410 |
0.961135808 |
6.667597 |
0.00981814561191864110245575147928320802748203277587890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018849613583756391621548686998721677809953689575195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0864911 |
3.6241088 |
23.6462276 |
13.6853510 |
| ENSG00000160094 |
149076 |
ZNF362 |
protein_coding |
Q5T0B9 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:149076; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000028799 |
Zfp362 |
134.107101 |
0.3113233755 |
-1.683514 |
0.387447963 |
17.956042 |
0.00002260657161113302328413025843456551911003771238029003143310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000068027114572950754187163902031443285522982478141784667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.0851658 |
16.2890763 |
216.1339395 |
37.3158788 |
| ENSG00000160145 |
8997 |
KALRN |
protein_coding |
O60229 |
FUNCTION: Promotes the exchange of GDP by GTP. Activates specific Rho GTPase family members, thereby inducing various signaling mechanisms that regulate neuronal shape, growth, and plasticity, through their effects on the actin cytoskeleton. Induces lamellipodia independent of its GEF activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10023074}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disulfide bond;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;SH3 domain;Transferase |
|
Huntington's disease (HD), a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of striatal neurons, is caused by an expansion of a polyglutamine tract in the HD protein huntingtin. This gene encodes a protein that interacts with the huntingtin-associated protein 1, which is a huntingtin binding protein that may function in vesicle trafficking. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:8997; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
14742910_we have identified multiple transcriptional start sites in rats and humans. These multiple transcriptional start sites result in full-length Kalirin transcripts possessing different 5' ends encoding proteins with differing amino termini 15950621_Kalirin GEF1 domain induces lamellipodia through activation of Pak, where Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) activity is not required. 17357071_Three SNPs from the kalirin (KALRN) gene are associated with early-onset coronary artery disease. 17640372_ARF6 recruits KALRN to the cell membrane facilitating Rac activation. 17851188_Our observation is the first to relate kalirin to Alzheimer's disease. Kalirin was consistently under-expressed in Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. 18199770_Kalirin-7 is an essential component of both shaft and spine excitatory synapses in hippocampal interneurons. 18839057_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18953434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19706030_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20107840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20107840_Two SNPs in the KALRN gene region (rs17286604 and rs11712619)constitute risk factors for ischemic stroke. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20604901_SNX1 and SNX2 interact with Kalirin-7. Overexpression of SNX1 or SNX2 and Kalirin-7 partially redistributes both SNXs to the plasma membrane, and results in RhoG-dependent lamellipodia formation. 20730383_Studies indicate that Kalirin-7 plays a key role in excitatory synapse formation and function. 21041834_Missense mutations in KALRN may be genetic risk factors for schizophrenia. 21041834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21664346_KALRN gene variation is not associated with overall ischemic stroke 22120753_We found Kalirin-9 expression to be paradoxically increased in schizophrenia 22194219_Neuronal guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) kalirin is emerging as a key regulator of structural and functional plasticity at dendritic spines. 22429885_The kalirin expression were reduced in Alzheimer disease with psychosis. 22458949_In both anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), study found a reduction of Duo expression and PAK1 phosphorylation in schizophrenia. Cdc42 protein expression was decreased in ACC but not in DLPFC 22720673_The age-at-onset of Huntington disease (HD) is not associated with eleven SNPs, including SNP rs10934657 in the kalirin gene in 680 European HD patients. 25224588_A sequence variant in human KALRN impairs protein ability to activate Rac1 and coincides with reduced cortical thickness. 25316661_consider the GG genotype and the G allele of rs9289231 polymorphism of KALRN to be genetic risk factors for CAD in an Iranian population, especially in early-stage atherosclerotic vascular disease 25917671_4 KALRN gene SNPs were studied in Han ischemic stroke patients. rs11712619 seemed associated with lacunar stroke until risk factors were considered. re6438833 was significantly associated with ischemic and lacunar stroke. 27218147_GG genotype and the G allele of the rs9289231 polymorphism of KALRN and the rs224766 polymorphism of ADIPOQ genes may be considered genetic risk factors for Iranian type 2 diabetic patients with coronary artery disease. 27421267_DNA sequencing provided evidence linking KALRN to monogenic intellectual disability in two patients. 28152519_Data suggest protein levels of kalirin and CHD7 in circulating extracellular vesicles (EVs) as endothelial dysfunction markers to monitor vascular condition in hypertensive patients with albuminuria. 28706949_The GG genotype and G allele of SNP rs7620580 were associated with a risk for ischemic stroke with an adjusted OR of 3.195 and an OR of 1.446, respectively. Haplotype analysis revealed that A-T-G,G-T-A, and A-T-A haplotypes were associated with ischemic stroke. Our results provide evidence that kalirin gene variations were associated with ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han population. 29241584_The data of this study reveal a novel mechanism for disease-associated single nucleotide variants of KALARN and provide a platform for modeling morphological changes in mental disorders. 29554915_Combination of polymorphisms in the NOD2, IL17RA, EPHA2 and KALRN genes could play a significant role in the development of sarcoidosis by maintaining a chronic pro-inflammatory status in macrophages 29789657_The interaction of kalirin with the C-terminal region of Htt influences the function of kalirin and modulates the cytotoxicity induced by C-terminal Htt. 30232674_SNPs of the KALRN gene are associated with intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in the northern Chinese population. 31801062_Synaptic Kalirin-7 and Trio Interactomes Reveal a GEF Protein-Dependent Neuroligin-1 Mechanism of Action. 33037113_KALRN mutations promote antitumor immunity and immunotherapy response in cancer. 33658318_Kalirin-RAC controls nucleokinetic migration in ADRN-type neuroblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000061751 |
Kalrn |
92.094769 |
0.2245230620 |
-2.155064 |
0.201010524 |
128.060120 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001088939611444934479827260365710457085965825805352758903638494060912050823857789849657962122364551760256290435791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000138677727911365237435086532002198770026413485297537952429649270871465451297147725151504005225433502346277236938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.2261554 |
7.1915040 |
148.2692321 |
21.0285553 |
| ENSG00000160209 |
8566 |
PDXK |
protein_coding |
O00764 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of the dietary vitamin B6 vitamers pyridoxal (PL), pyridoxine (PN) and pyridoxamine (PM) to form pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP), pyridoxine 5'-phosphate (PNP) and pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate (PMP), respectively (PubMed:9099727, PubMed:10987144, PubMed:17766369, PubMed:19351586, PubMed:31187503) (Probable). PLP is the active form of vitamin B6, and acts as a cofactor for over 140 different enzymatic reactions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10987144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17766369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19351586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31187503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9099727, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Cobalt;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sodium;Transferase;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; pyridoxal 5'-phosphate salvage; pyridoxal 5'-phosphate from pyridoxal: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31187503, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17766369}.; PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; pyridoxal 5'-phosphate salvage; pyridoxine 5'-phosphate from pyridoxine: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:17766369}.; PATHWAY: Cofactor metabolism; pyridoxal 5'-phosphate salvage; pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate from pyridoxamine: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:17766369}. |
The protein encoded by this gene phosphorylates vitamin B6, a step required for the conversion of vitamin B6 to pyridoxal-5-phosphate, an important cofactor in intermediary metabolism. The encoded protein is cytoplasmic and probably acts as a homodimer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8566; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; lithium ion binding [GO:0031403]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; potassium ion binding [GO:0030955]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; pyridoxal kinase activity [GO:0008478]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; sodium ion binding [GO:0031402]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; pyridoxal 5'-phosphate salvage [GO:0009443] |
15082224_Pyridoxal kinase expression was compared in fetal Down syndrome (DS) brain and controls; PDXK levels were found to be similar. 16704963_A promoter mutation with potential erythroid-specific properties that could be the basis of a novel mechanism of controlling cell-specific decreased activity of an essential enzyme in erythrocytes. 17766369_The crystal structure of the MgATP complex also reveals Mg(2+) and Na(+) acting in tandem to anchor the ATP at the active site of pyridoxal kinase. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19351586_These results document the role of Asp235 in PL kinase activity. 20035503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20035503_This study identified a DNA variant (rs2010795) in PDXK associated with an increased risk of PD in the German cohort This association was confirmed in the British and Italian cohorts individually and reached a combined value. 20373357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639122_The pyridoxal kinase showed decreased levels and was highly carbonylated in the gene-on mice 22647618_The affected pyridoxine metabolism is discussed as an inborn genetic trait in epilepsy in general, rather than a specific sign of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy solely. 31578392_The expression of four pyridoxal kinase (PDXK) human variants in Drosophila impacts on genome integrity. 32696745_[Pyridoxal kinase (PDXK) promotes the proliferation of serous ovarian cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis]. |
ENSMUSG00000032788 |
Pdxk |
799.483196 |
2.1215043444 |
1.085088 |
0.115508875 |
86.319493 |
0.00000000000000000001530920182426126865214677551539973654982633330473993835650625694455584380193613469600677490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000138119693720107768297849559483982494192924307827676823085677471070198407687712460756301879882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
993.9096928 |
69.9566978 |
471.6233780 |
24.3828855 |
| ENSG00000160213 |
1476 |
CSTB |
protein_coding |
P04080 |
FUNCTION: This is an intracellular thiol proteinase inhibitor. Tightly binding reversible inhibitor of cathepsins L, H and B. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Thiol protease inhibitor |
|
The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and kininogens. This gene encodes a stefin that functions as an intracellular thiol protease inhibitor. The protein is able to form a dimer stabilized by noncovalent forces, inhibiting papain and cathepsins l, h and b. The protein is thought to play a role in protecting against the proteases leaking from lysosomes. Evidence indicates that mutations in this gene are responsible for the primary defects in patients with progressive myoclonic epilepsy (EPM1). One type of mutation responsible for EPM1 is the expansion in the promoter region of this gene of a CCCCGCCCCGCG repeat from 2-3 copies to 30-78 copies. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:1476; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004869]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861] |
11697734_Oligonucleotides containing EPM1 repeat adopt secondary structures that may facilitate strand slippage thereby causing the expansion. 11697735_Intramolecular i-motif structure at acidic pH for progressive myoclonus epilepsy (EPM1) repeat d(CCCCGCCCCGCG)n. 12215838_analysed eight markers flanking CSTB(GT10-D21S1890-D21S1885-D21S2040-D21S1259- CSTB-D21S1912-PFKL-D21S171) and one intragenic variant in the CSTB 3' UTR (A2575G) 12452481_first demonstration of cysteine protease activity being regulated by CSTB activity in a biological context; effects of decreased CSTB activity in EPM1 pathogenesis may be mediated by cathepsins through increased activity of cathepsins S and L 15048832_By using ThT fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, and atomic force microscopy (AFM), it has been shown that human stefins A and B (subfamily A of cystatins) form amyloid fibrils 15832773_Protein and mRNA levels of stefin B (p= 0.007), but not cystatin C, were significantly lower in atypical compared with benign meningiomas 15955063_Prefibrillar oligomers/aggregates of stefin B also increase the surface pressure at an air-water interface, i.e. they have amphipathic character and are surface seeking. 16205844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16321512_These data show that cystatin B inhibits bone resorption by down-regulating intracellular cathepsin K activity despite increased osteoclast survival. 16342276_Chimeras of stefinA and B have been prepared and guanidine denaturation curves and folding rates have been examined. 16939620_Study shows that copper binding by stefin B inhibits the amyloid fibril formation and, to a lesser degree, the initial aggregation. 16969475_only stefins A and B, i.e. type I cystatins, are up-regulated in lung tumours and thus able to counteract harmful tumour-associated proteolytic activity 17003839_Several alternatively spliced CSTB isoforms were identified in patients with progressive myoclonus epilepsy of Unverricht-Lundborg type . 17701471_Results describe the influence of pH and trifluoroethanol on amyloid fibril growth and morphology from human stefin B. 17920138_cystatin B in vivo has a polymeric structure sensitive to the redox environment and that overexpression of the protein generates aggregates. 18281540_CSTB is specifically overexpressed in most HCCs and is also elevated in the serum of a large proportion of HCC patients 18397316_Data show that wild-type stefin B and its Y31 isoform are able to form pores in planar lipid bilayers, whereas the G4R isoform destroys the bilayer by a non pore-forming process. 18636508_The mechanism of amyloid-fibril formation by stefin B: temperature and protein concentration dependence of the rates;the observed kinetics follow the nucleation and growth behavior observed for many other amyloidogenic proteins. 18951626_potential role for CSTB in HIV replication in placental macrophages 19342095_cystatin B interacts with STAT-1 and the levels of STAT-1 tyrosine phosphorylation (but not serine phosphorylation) between uninfected and HIV-infected PM and MDM are differentially regulated. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955183_oligomers of stefin B and amyloid-beta interact in vitro and in cells 20075068_Stefin B interacts with histones and cathepsin L in the nucleus 20078424_Intracellular stefin b aggregation shows a negative correlation with cell survival 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21757863_patients compound heterozygous for the dodecamer repeat expansion and the c.202C>T mutations seem to have a severer form of Unverricht-Lundborg disease (EPM1) than patients homozygous for the expansion mutation 22033403_At pH 7.0 the mutant H75W folded in three kinetic phases to a native-like intermediate, analogous to folding of stefin B at pH 4.8. 22057043_S-glutathionylation and S-cysteinylation were described as extensive PTM of a salivary protein and the first time that these PTMs were detected in naturally occurring cystatin B. 22287159_Elevated StefA mRNA level is associated with invasive glioblastoma. 23010349_Skull thickening and an increased prevalence of abnormal findings in skeletal radiographs of patients with EPM1 suggest that this condition is connected to defective cystatin B function. 23205931_This study suggested that CSTB mutations other than the common dodecamer expansion predict particular phenotypes, including marked seizure severity and polymorphous seizure types. 23362198_The co-localization of stefin B wild type and EPM1 mutants with cathepsins showed that cathepsins accumulate around the aggregates formed by the EPM1 mutants. 23656633_High levels of bioactive recombinant stefins A and B can be produced by fermentation in P. pastoris. 23883076_detected a homozygous expansion of dodecamer repeats in the CSTB gene in four patients with clinical diagnosis of ULD. 24234043_A reciprocal influence of CSTB and SOD1 at the gene expression level and for a direct interaction of the two proteins, is reported. 24452274_The increased CSTB expression in ovarian tissue represents tumor progression and is dysregulated by the TGF-beta signaling pathway. 24909779_The present study was performed on two more missense mutants of human stefin B, G50E and Q71P, and they similarly showed numerous aggregates upon overexpression. 25047918_The study shows detection of stefin B dimers in HEK293 cells and the importance of their residual activity. 25263734_glutamate dehydrogenase is a euchromatin-associated enzyme, and its H3 clipping activity is regulated by chromatin structure, histone modifications and an in vivo inhibitor. 25633807_Data shows that CYTB and ANXA4 overexpression may be involved in carcinogenesis and histopathological differentiation of ovarian clear cell carcinoma and suggest they may serve as a potential diagnostic biomarkers. 25752200_A role for disease-causing mutations in cystatin B gene in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy was not supported. 25770194_Even though the majority of EPM1 patients have a uniform genetic mutation, the actual size of the longer CSTB expansion mutation allele is likely to have a modulating effect on the age at disease onset, myoclonus severity, and cortical neurophysiology. 26753874_High expression of stefin B may be an important factor contributing to the development and metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 26843564_CSTB null mutation associated with microcephaly, early developmental delay, and severe dyskinesia. 26908626_It was shown that decreased expression of cystatin B enhances cathepsin activity in Niemann-Pick C cerebellar degeneration patient fibroblasts. 27137788_The results demonstrate that cystatin B interferes with the STAT-1 signaling and IFN-beta-antiviral responses perpetuating HIV in macrophage reservoirs. 28281969_CSTB downregulation may promote the development of gastric cancer. 28378817_Homozygous for a c.218dupT (p.His75Serfs*2) mutation in exon 3 of CSTB causes neurodegeneration, progressive cerebral volume loss and diffuse hypomyelination. 28543404_apoptosis is accompanied by degradation of the cysteine cathepsin inhibitor stefin B (StfB). CatD did not exhibit a crucial role in this step. However, this degradation was partially prevented through pre-incubation with the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine 28766361_While novel diagnostic tumour markers are urgently needed, the examined potential tumour markers, with the exception of PIVKAII seem to be inadequate for diagnosing HCC in ALC 29037838_cystatin B expression was significantly and inversely correlated with lung tumor stage and tumor grade 30652348_The findings suggest that the cleaved Bid protein acts as an amplifier of apoptotic signaling through mitochondria, thus enhancing the activity of cysteine cathepsins following stefin B degradation. 31180557_CSTB was overexpressed and miR1433p was downregulated in ovarian malignant tumors. Mature miR1433p directly bound CSTB 3'UTR, leading to a decrease in CSTB expression in OC cells, which was regulated by TGFbeta1. 32378798_Cystatin B is essential for proliferation and interneuron migration in individuals with EPM1 epilepsy. 32920378_Genetic testing and the phenotype of Polish patients with Unverricht-Lundborg disease (EPM1) - A cohort study. 35488257_Evaluation of CSTB and DMBT1 expression in saliva of gastric cancer patients and controls. 35647202_The Role of NMP22 and CSTB Levels in Predicting Postoperative Recurrence of Bladder Cancer. 36083516_Brief Report: Intracellular Cystatin B Levels Are Altered in HIV-Infected Participants With Respect to Neurocognitive Status and Antiretroviral Therapy. 36429055_Decreased CSTB, RAGE, and Axl Receptor Are Associated with Zika Infection in the Human Placenta. |
ENSMUSG00000005054 |
Cstb |
1286.464630 |
2.8843018904 |
1.528222 |
0.050265254 |
937.034325 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008733368480733113380610618408991892736095935297541282853339877978267085478569956963448292553484706942723730832131333253328400 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008316420566169080331100701776503584294096991267197608880053424880424952956071693515344220289939636616619063863218375839435992 |
Yes |
No |
1932.5349106 |
55.5047903 |
674.8652022 |
15.7487643 |
| ENSG00000160223 |
23308 |
ICOSLG |
protein_coding |
O75144 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for the T-cell-specific cell surface receptor ICOS. Acts as a costimulatory signal for T-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion; induces also B-cell proliferation and differentiation into plasma cells. Could play an important role in mediating local tissue responses to inflammatory conditions, as well as in modulating the secondary immune response by co-stimulating memory T-cell function (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;B-cell activation;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in T cell receptor signaling pathway and positive regulation of interleukin-4 production. Located in cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23308; |
cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; defense response [GO:0006952]; hyperosmotic response [GO:0006972]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
12456022_ICOS-L is a ligand for ICOS and plays an important functional role in the activation of memory T cells by endothelial cells [review] 12707012_These results demonstrate that airway epithelial cells express the costimulatory molecule B7-H2, and suggest the possibility that B7-H2 may participate in antigen presentation by epithelial cells. 12800259_ICOS-B7H costimulatory pathway may be involved in the negative regulation of cell-mediated immune responses. 12960306_A critical role of the B7-like protein-ICOS costimulatory pathway is demonstrated in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. 14603470_ICOSL protein and mRNA was expressed in 7 of 12 glioma cell lines and expression is upregulated by the inflammatory cytokine, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), whereas interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) has no such effect 15047568_Expression of B7-H3 by nasal epithelial. Expands range of potential costimulatory signals through which these cells may interact with activated mucosal T lymphocytes. Extent of mucociliary differentiation of cultured cells may influence this capability. 15131796_B7h-ICOS protein costimulatory pathway may be important in intestinal epithelial cell(iec):T-cell interactions. IEC expressed B7h and B7-H1. 16115907_Results indicate the expression of functional B7-H2 molecule may facilitate progression of acute myeloid leukemia. 16221208_Interaction of tubular epithelial cells and kidney infiltrating T cells via ICOS-L and B7-H1 may change the balance of positive and negative signals to the T cells 16951355_ICOSL receptor binding site is mediated solely by the immunoglobulin (Ig) variable domain but requires the Ig constant domain for maintaining structural integrity of the protein. 17242332_ICOS-L may be relevant in inducing an acute immune response and may be critically involved in perpetuating inflammation in chronically immune-mediated disorders of the peripheral nervous system. 18294651_The generated a 3T3 cellular library retrovirally expressing mutants of the murine B7h gene. Screening of this unbiased cellular library identified residues of murine B7h. These residues are located on the same of human B7h by mutagenesis. 18587394_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19202444_Genetic variation in this protein affects the outcome and failure of kidney tranplantation. 19347721_role of stimulus by B7 in myeloblastic leukemic 19395451_ICOSL:ICOS+ pathway costimulates effector T cells, shaping the Th2 response and regulating humoral immunity. 19726311_B7RP-1 is expressed on the membrane of HCAECs. 19737469_Oxidized low density lipoprotein up-regulates the expression of ICOSL in coronary artery endothelial cells. 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20176734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20217071_Suppressed ICOSLG gene expression is associated with cigarette smoking. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21098714_Data show that ICOS-L expression by melanoma tumor cells may directly drive Treg activation and expansion in the tumor microenvironment as another mechanism of immune evasion. 21530327_Similar to B7-1 and B7-2, B7-H2 costimulation via CD28 induced survival factor Bcl-xL, downregulated cell cycle inhibitor p27(kip1), and triggered signaling cascade of ERK and AKT kinase-dependent pathways 22577174_A model of positive feedback conferred by ICOS-LICOS interaction between TGN1412-treated T cells and endothelial cells. 22706735_ICOS-ICOSL signaling plays a direct role in proliferation and differentiation of thyroid gland cells and may have important effects on the initiation, maintenance and exaggeration of autoimmune responses in local tissue. 23024058_ICOSL-expressing macrophages and mRNA levels of ICOSL were increased in the lesional skin of patients with early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. 23026134_Results highlight an important relationship between Treg and pDC in breast tumors, and show that ICOS/ICOS-L interaction is a central event in immunosuppression of tumor-associated memory CD4(+) T cells. 23196741_These data suggest that rs2294020 SNP of FOXP3 gene and rs378299 SNP of ICOSLG gene are associated with alopecia areata and with a reduced expression of the FOXP3 and ICOSLG genes in alopecia patients. 23688438_Findings suggest that the single nucleotide polymorphism (snp) rs4819388 in B7-H2 3'-UTR, through disrupting the regulatory role of miR-24 on B7-H2 expression, contributes to the occurrence of gastric cancer. 24661627_Our data show that mDCs from patients with AR display impaired expression of ICOSL, and this defect licenses mDCs to promote aberrant IL-13- and IL-5-producing Th2 cell responses. 24729612_the B7h-ICOS interaction may modulate the spread of cancer metastases 24837102_a critical role is described for the rs7282490 ICOSLG region polymorphism associated with immune-mediated diseases in amplifying pattern-recognition receptor initiated inflammatory signaling and cytokine secretion 25406581_Loss-of-function mutations in NIK cause impaired ICOSL expression. 25769613_ICOS-ICOS-L interaction promoted cytokine production and survival in type 2 innate lymphoid cells through STAT5 signaling in asthma. 26560438_The ICOS and ICOSL SNPs examined do not have an apparent effect on the disease susceptibility and prognosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases. 27798154_results showed that monocyte-derived osteoclast (OC)-like cells (MDOCs) express B7h during their differentiation, and that B7h triggering reversibly inhibits OC differentiation and function both in vitro and in vivo 28290526_ICOSL-ICOS signaling promoted Treg differentiation from CD4(+) T cells through activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt pathway. MSCs primed with Interleukin-1beta significantly induced Tregs through ICOSL upregulation. We demonstrated that the Treg-inducing activity of MSCs is proportionate to their basal ICOSL expression. 28814605_study confirms the importance of ICOSL shedding in ICOS/ICOSL function and expression and it identifies ADAM10 as the most important sheddase for controlling ICOSL levels 29414642_this study found that B7-H2 expression on CD8(+) T cells in colorectal cancer patients' tumor tissues was significantly higher than in non-tumor tissues 30319662_The expression of ICOSL of patient acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and ICOS+ Tregs were found to be predictors for survival in patients with AML, with ICOS+ Treg cell subset being a stronger predictor than total Tregs. Results suggested that AML cells expressed ICOSL promote the expansion of ICOS+ Tregs in tumor environment, and ICOS+ Tregs further promote the proliferation of AML cells through secreting IL-10. 30498080_study identifies human ICOSLG deficiency as a novel cause of a combined immunodeficiency. 30575933_High glucose and advanced glycation end products cause T cell inflammatory response and vascular endothelial dysfunction by upregulating ICOS/ICOSL activity. 31998801_The ICOSL Expression Predicts Better Prognosis for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma via Enhancing Oncoimmunity. 33033255_Structural characterization of the ICOS/ICOS-L immune complex reveals high molecular mimicry by therapeutic antibodies. 33051240_Dysregulated NF-kappaB-Dependent ICOSL Expression in Human Dendritic Cell Vaccines Impairs T-cell Responses in Patients with Melanoma. 33325362_[High expression of ICOS on CD4(+) T cells and ICOSL on CD19(+) B cells in peripheral blood and its positive correlation with TRAb in Graves' disease]. 33662168_Mesenchymal stem cells regulate type 2 innate lymphoid cells via regulatory T cells through ICOS-ICOSL interaction. 34185422_Activated neutrophils polarize protumorigenic interleukin-17A-producing T helper subsets through TNF-alpha-B7-H2-dependent pathway in human gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000000732 |
Icosl |
644.646939 |
2.3135631765 |
1.210116 |
0.086393572 |
195.115871 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000002430651287985266564003428845855497096458688202036590282735473246177109556185924533308979891127269207160372852232627094437589221342932432889938354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000449016433174750111429437574486633992843415427745247353346963985835648061731363074163843355954596555112131402078684550005505116132553666830062866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
904.1144953 |
45.1460283 |
393.6420124 |
15.1170313 |
| ENSG00000160255_ENSG00000183250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
339.988045 |
2.1556537603 |
1.108125 |
0.129206796 |
73.050149 |
0.00000000000000001263970464048762150759949783123973305546529029475986624642125377704360289499163627624511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000100410140201074963044003294865511443031700351108913282782708620288758538663387298583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
473.6487174 |
35.3641201 |
221.3671323 |
12.5343787 |
| ENSG00000160307 |
6285 |
S100B |
protein_coding |
P04271 |
FUNCTION: Weakly binds calcium but binds zinc very tightly-distinct binding sites with different affinities exist for both ions on each monomer. Physiological concentrations of potassium ion antagonize the binding of both divalent cations, especially affecting high-affinity calcium-binding sites. Binds to and initiates the activation of STK38 by releasing autoinhibitory intramolecular interactions within the kinase. Interaction with AGER after myocardial infarction may play a role in myocyte apoptosis by activating ERK1/2 and p53/TP53 signaling. Could assist ATAD3A cytoplasmic processing, preventing aggregation and favoring mitochondrial localization. May mediate calcium-dependent regulation on many physiological processes by interacting with other proteins, such as TPR-containing proteins, and modulating their activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20351179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22399290}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21; however, this gene is located at 21q22.3. This protein may function in Neurite extension, proliferation of melanoma cells, stimulation of Ca2+ fluxes, inhibition of PKC-mediated phosphorylation, astrocytosis and axonal proliferation, and inhibition of microtubule assembly. Chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in several neurological, neoplastic, and other types of diseases, including Alzheimer's disease, Down's syndrome, epilepsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, melanoma, and type I diabetes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6285; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ion binding [GO:0043167]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RAGE receptor binding [GO:0050786]; S100 protein binding [GO:0044548]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; memory [GO:0007613]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048168] |
11809917_This study provides evidence that circulating S100beta protein is increased in IUGR fetuses and correlates with cerebral hemodynamics, suggesting that it may represent an index of cerebral cell damage in the perinatal period. 11888280_role of N-terminal helix I for dimerization and stability 11969402_A study of S100B identifying key regions required for the interaction with S100B-binding epitope TRTK-12 shows that the S100B linker region contributes about 50% to binding while the C-terminus contributes the remaining 50% of the binding energy. 12351263_preoperative S100B concentrations correlate inversely with the size of the ascending aorta in hypoplastic left heart syndrome and may serve as a marker for preexisting brain injury and mortality 12377780_the major cytoplasmic S100B target protein in different glial cell lines in the presence of Zn(2+) and Ca(2+) is IQGAP1 12480931_A new target is revealed by the solution structure of a peptide fragment. 12490005_Serum S100B is increased in almost half of children after mild, moderate, and severe inflicted and noninflicted closed head injury; the increase is transient, lasting less than 12 h after injury, except in children with severe injury. 12505619_Cerebrospinal fluid S100B correlates with brain atrophy in Alzheimer's disease, suggesting that S100B is of pathological relevance for degeneration of the central nervous system in Alzheimer's disease. 12527118_presence in human milk - may contribute to biochemical communication between mother and child 12569284_Elevated serum S100B level was associated with metastatic malignant melanoma 12630517_S 100 B may be a reliable marker of brain damage in TBI without multiple trauma 24 h after trauma and thereafter 12645009_increased levels have been detected in brain trauma and ischemia, and in neurodegenerative, inflammatory and psychiatric diseases, probably due to release from damaged astrocytes 12927678_Results in high-risk pregnancies demonstrated that S100B concentration increased in amniotic fluid and in cord blood of fetuses with brain damage [review] 14530578_Review summarizes current knowledge about S-100B serum measurements in severe head injury and concludes that S-100B belongs to a new generation of molecular serum markers of brain damage. 14642437_S100 beta showed a significant decrease in CSF over the disease course (P=0.024). 14675567_positively correlated with Phe blood level in phenylketonuria patients; blood estimation could be a useful peripheral marker of CNS lesions in patients with demyelinated disease such as PKU 14699277_Protein S-100b might be a promising serum marker with prognostic significance in the event of spinal cord compression resulting from epidural empyema. 14967825_results indicate that human S100B expressed in E Coli interacts with the tubulin homologue FtsZ in vivo, modulating its activity in bacterial cell division. 14997170_S100B in schizophrenic patients either promotes apoptotic mechanisms by itself or is released from astrocytes as part of an attempt to repair a degenerative or destructive process 15178678_when p53 protein levels increase, it contributes to its own demise by up-regulating the transcription of S100B protein as part of a negative feedback loop 15236402_results support the idea that elevated levels of S100B in the brain are associated with increased vulnerability to neurological injury 15257081_S100B and IL-1beta in the cerebrospinal fluid may have a role in the progression of traumatic brain injury 15306236_S100B overexpression in young (70 days) and aged (200 days) adult transgenic mice leads to alterations in cytoskeletal markers with aging. 15670788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15670788_Our results suggest that S100B could be a susceptible gene for schizophrenia and provide indirect evidence for the GGF/SD hypothesis. 15708543_The present study offers data consistent with the putative neurotrophic role of S100B and suggests the usefulness of saliva in the clinical monitoring of S100B levels. 15781852_S100B regulates the oligomerization of p53 tumor suppressor by binding to its tetramerization domain. 15820773_The higher levels of S100B in Down Syndrome patients may reflect a general and persistent increase in the extracellular space and may be associated with neurodegenerative lesions observed in these patients. 16143320_Study indicates that the serum concentration of S100B in patients with neural tube defects is similar to that of normal individuals. 16340181_determination of urinary S-100B concentrations might be helpful in term infants with severe asphyxia, while high urinary S-100B concentrations in preterm infants are to be attributed to immaturity 16511125_X-ray diffraction studies on human Ca2+-binding protein S100B 16931519_IP-10 mRNA is stabilized by RNA-binding proteins in monocytes treated with S100b 17008613_Increased plasma S100B level is found following acute spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage, in association with a worse early and late evolution, and closely related to initial hematoma volume. 17010455_Phosphorylation of specific serine and/or threonine residues reduces the affinity of the S100B-p53 interaction. 17020600_Serum S100beta levels may serve as a potentially useful early marker of postcraniotomy brain damage in patients undergoing elective meningioma resection. 17023485_Amniotic fluid S100B protein concentration of the pre-eclampsia & normotensive IUGR cases was significantly higher than that of the control. Amnion could be a source responsible for the increased concentration of S100B in amniotic fluid. 17043297_finding of increased levels of S100B in patients with schizophrenia without an indication for significant glial (GFAP, MBP) or neuronal (NSE) damage may be interpreted as indirect evidence for increased active secretion of S100B during acute psychosis 17091777_S100B protein levels are affected differently in alcohol-dependent individuals with either mild or high alcohol consumption during the period of up to one year before assessment. 17199889_S100B is localized in many neural cell-types and is less astrocyte-specific than GFAP. 17264538_S-100B and MIA concentrations were significantly higher in patients with uveal melanoma metastases 17348038_Review examines S100B's potential role as a neurologic screening tool, or biomarker of CNS injury, analogous to the role of CRP as a marker of systemic inflammation. 17396138_Report concludes that S100A1 and S100B are transcriptional targets of the SOX trio and mediate its inhibition of terminal differentiation of chondrocytes. 17408991_No significant release of S100beta protein in CSF during stenting of the thoracic aorta in this subgroup of patients at high risk for spinal cord ischemia. 17525977_Genetic variants within S100B are associated with bipolar affective disorder with psychosis 17525977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17536784_Amide exchange shows calcium-induced conformational changes are transmitted to the dimer interface of S100B. 17579612_Genetic variant in S100beta increases the risk of low cognitive performance and dementia, possibly by favouring a splicing event increasing S100beta2 isoform expression in the brain. 17579612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17624933_An elevated concentration of amniotic fluid S100B may reflect intra-amniotic infection/inflammation and not necessarily fetal neurologic damage. 17660747_Structural and the binding data suggest that tetrameric S100B triggers RAGE activation by receptor dimerisation. 17661202_An antigen in melanoma, elevated amd present in Stage III melanoma patients undergoing adjuvant vaccine immunotherapy. . 17678654_Enteric glial-derived S100B is increased in the duodenum of patients with celiac disease and plays a role in nitric oxide production. 17705023_Serum S100B levels cannot serve as peripheral marker in the evaluation of brain disease in X-ALD and GD. 17719207_serum level increased in psoriasis 17726019_S100B modulates cell survival by interacting with distinct RAGE immunoglobulin domains. 17955279_serum and CSF S100B levels were raised in neruopsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus, especially in patients with organic brain syndrome, seizures, cerebral vascular accident, and psychosis. 17984171_upregulated expression of chromosome 21 genes such as S100B and amyloid precursor protein activated the stress response kinase pathways, and furthermore, could be linked to upregulation of the water channel aquaporin 4 in Down syndrome neural progenitors 17984926_A significant increase of S-100B protein blood plasma concentrations was seen in patients with severe stroke; S-100 protein blood plasma concentration assessed on the 1st day after the stroke has highest diagnostic utility. 17984939_The difference between the evening and morning S100B levels correlated negatively with apnea/hyponea index and oxygen desaturation index and positively with basal saturation and average minimal oxygen saturation. 18039581_The approach allows the use of small animal PET and provides novel probes to delineate functional expression of RAGE under normal and pathophysiological conditions in rodent models of disease. 18173564_Serum S100b (astrocyte-specific protein) is a useful marker of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with fulminant hepatitis. 18181515_The low levels of S100b detected using the present assay, despite its high sensitivity and despite the routine use of cardiotomy suction, suggest that the assay may have higher specificity for cerebral S100b than previously used assays. 18193148_Both S100A1B and S100BB were related to outcome after severe traumatic brain injury. Even though this study is small, it seems unlikely that separate analyses of the dimers are of any advantage compared with measuring S100B alone. 18337650_evaluation of S100B in bone marrow (BM) plasma from malignant melanoma patients; median S100B level in BM plasma was 9.0 microg/l, an unexpectedly high value compared with the median S100B level in blood; S100B levels in BM seems to be sex dependent 18384084_The structure of human apo-S100B at 10 degrees C was determined to examine whether temperature might be responsible for structural differences. 18385926_We investigated the influence of chronic fasting and subsequent weight gain on serum levels of S100B in patients with anorexia nervosa. We found that nutritional status was an important factor influencing serum levels of S100B. 18445708_A novel interaction is identified between S100B and the dopamine D2 receptor; binding of S100B to the dopamine D2 receptor may enhance receptor signaling. 18451356_S100B has a role in exacerbating brain damage and periinfarct reactive gliosis (astrocytosis and microgliosis) during the subacute phase of middle cerebral artery occlusion 18454941_Ooor dualistic views that consider S100B elevation as 'bad' or 'good' simplify clinical practice and delay our comprehension of the role of this protein, both in physiological conditions and in brain disorders. [REVIEW] 18494933_S100B inducs tau protein hyperphosphorylation via Dickopff-1 up-regulation and disrupts the Wnt pathway in neural stem cells. 18552513_Findings demonstrate that greater S100beta levels are associated with poorer cognitive function in healthy older adults. 18587628_Only the first IQ motif of IQGAP1 interacts with MYL6B. The first and second IQ motifs of IQGAP1 interact with S100B in the presence of calcium ions. 18596106_HIV-1 NEF expression prevents AP-2-mediated internalization of the MHC Class II-associated invariant chain. 18614943_S-100beta concentrations do not necessarily increase in response to exercise-heat strain, and no effect of heat acclimation on S-100beta could be observed despite other quantifiable physiological adaptations. 18706914_Results identify of a dimeric intermediate in the unfolding pathway for the calcium-binding protein S100B. 18783450_During migraine attacks elevated s100b levels could be observed 18805362_Data show that total serum bilirubin and mean serum S100B levels of infants who manifest auditory neuropathy, neurologic abnormalities, or EEG abnormalities are significantly higher than in infants without these abnormalities. 18854308_HNRNP K and microRNA-16 have roles in cyclooxygenase-2 RNA stability induced by S100b, a ligand of the receptor for advanced glycation end products 18939940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18939940_investigated the association of the rs9722 C > T polymorphism of the S100B gene and susceptibility to major depressive disorder by comparing 152 major depressive patients with 150 healthy individuals in a Chinese population 18948614_A diagnostic tool incorporating the values of matrix metalloproteinase 9, brain natriuretic factor, d-dimer, and S-100beta into a composite score was sensitive for acute cerebral ischemia. 18982242_These findings confirmed an increase in serum S100B levels in major depressive patients and presence of a sexual dimorphism. Moreover, numbers of depressive episodes in depression seemed to have an additional increasing effect on S100B levels. 19011512_Circulating S100A1B and S100BB are potential biomarkers in patients with malignant melanoma. S100BB should be considered as the preferred biomarker, showing potential in predicting both relapse and survival, in contrast to both S100 and S100A1B. 19042077_A strong positive correlation exists between amniotic fluid S100B and erythropoietin concentrations in pregnancies at high risk for chronic fetal hypoxia. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19103440_Our results provide support for a reduction of S100B levels during reconvalescence from acute paranoid schizophrenia that is regulated by its scavenger advanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor 19147496_S100B interacts with Src kinase, thereby stimulating the PI3K/Akt and PI3K/RhoA pathways. 19183802_Increased S100B protein urine levels in term newborns suffering perinatal asphyxia seem to suggest a higher risk of neonatal death for these infants. 19202335_Criteria for a clinically informative serum biomarker in acute ischaemic stroke: a review of S100B. 19205880_These results confirm previous S100beta evaluations in human serum and cerebrospinal fluid reporting the protein's function as a biomarker for brain damage 19216510_Studies show that monomeric S100B and S100A11 proteins are alpha-helical and retain a significant amount of tertiary structure. 19220958_Levels of plasma S-100 beta and NSE cannot predict encephalopathy after orthotopic liver transplantation. 19221847_There are no differences in S100B and NSE levels between patients with ischemic stroke or intracerebral hemorrhage. 19229202_Results of this meta-analysis indicate S100B is involved in the pathogenesis of both schizophrenia and mood disorders; further, it dissociates major depressive and bipolar I disorder [review]. 19297317_S100B bound the tetramer and also disrupted the dimer by binding monomeric p53 19307814_The timing, intensity, and duration of serum NSE and S-100B biomarker concentration patterns are associated with neurologic and survival outcomes following pediatric cardiac arrest. 19330775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19330775_results suggest an important role of S100B SNPs on S100B serum concentrations and S100B mRNA expression. It hereby links recent evidence for both, the impact of S100B gene variation on various neurological or psychiatric disorders 19468240_findings provide evidence of an association between S100B levels and memory processes in patients with recurrent depression and further suggest a neuroprotective role of moderately increased S100B serum levels in the course of affective disorders 19482672_S100A1B and S100BB are increased in urine collected from asphyxiated newborns who will develop hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) since first urination, and their measurement may be useful to early predict HIE. 19487970_Increased S100B level is found after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage and may contribute to the inflammatory process of ICH, in association with a poor clinical outcome. 19497163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19497163_Our findings did not suggest association of S100B gene polymorphisms in patients with MDD in China. We found there were differences in depressive episodes among different genotypes of S100B gene. 19505208_Serum S100b and BNP levels in the first 24 h after injury accurately predict neurological function at discharge after supratentorial intracerebral haemorrhage 19539717_serum S100B levels in chronic schizophrenia under antipsychotic medication may be increased 19558426_Results describe the association of S100B and nitric oxide production in ulcerative colitis. 19636631_Elevated S-100B level is associated with recurrence in melanoma patients. 19654082_Adding the measurement of S-100B serum concentration to clinical decision rules for a CT scan in patients with minor head injuries could allow a 30% reduction in scans. 19671853_Only sULBP2 is an independent predictor of prognosis, the significance of which is superior to the well-established and widely used melanoma serum marker S100B. 19674846_Physiological S100B levels in humans appear to closely reflect adipose tissue mass, which should therefore be considered as an important confounding factor in clinical studies examining the role of S100B. 19705461_These results provide evidence that (over)-expression of S100B acts to accelerate AD-like pathology, and suggest that inhibiting astrocytic activation by blocking S100B biosynthesis may be a promising therapeutic strategy to delay AD progression. 19812958_Following brain injury, the S100B passage from the CSF to the blood was significantly impaired and higher ratios of S100B serum/CSF were correlated with better neurological function 19910580_interaction of RAGE and its ligand S100B after myocardial infarction may play a role in myocyte apoptosis by activating ERK1/2 and p53 signaling. 19939849_Findings show that oxidative stress affects sEng and S100B protein expression from villous and amniotic tissues, and S100B protein up-regulate sEng release from endothelial cells leading to endothelial dysfunction. 20036852_Neural tube defects are associated with increased serum concentration of S100B in fetuses and mothers. 20036866_Near Infrared Spectroscopy parameters and S100B protein correlation may be of help in brain function monitoring. 20042890_a higher percentage of S100B antigen-positive cells were observed in benign melanocytic lesions than in melanomas 20093730_S100B plays a role in schizophrenia [review] 20105309_serum levels of S100B may be a marker for brain functional condition and serum NSE levels may be a marker for morphological status in Alzheimer's disease 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20351179_Data show that ATAD3A is a calcium-dependent S100B target protein in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and suggest that S100B could assist the newly synthesized ATAD3A protein in proper folding and subcellular localization. 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20437790_Most patients had increased serum levels of S100beta (mean .25 microg/L, median .15 microg/L) following surgery. 20473040_The genetic variant (rs2300403) of S100B was tested for association with cognitive abilities and lifetime cognitive ageing in approximately 1000 elderly Scots. 20509936_there were no clear signs (S100B) that the glial functions were compromised in attention deficit and hyperactivity 20559426_data support the use of S100B as an adjunctive biomarker to assess suicidal risk in patients with mood disorders or schizophrenia 20581773_Body mass index, creatinine clearance, and age are determinants of steady-state serum S100B concentrations in renal transplant recipients. 20587415_marker for malignant melanoma, S100B, likely contributes to cancer progression by down-regulating the tumor suppressor protein, p53. 20591429_S100A1, S100A2, S100A4, S100A6 and S100B interacted with MDM2 (2-125). 20592382_S100B and LDH are not expressed in sentinel node progression of melanoma 20604725_behavior of S100B in biological fluid during mental and physical stress 20614004_hs-CRP, PAI-1, and S100B levels did not differ at all time points between appropriate-for-gestational-age and intrauterine growth-restricted groups. 20628824_S100B overexpression is associated with relapse in colon cancer. 20686797_Study of development of secondary injuries following traumatic brain injury includes measurement of release of S100B and neuron-specific enolase (NSE) into the cerebrospinal fluid and blood. 20708613_S100B is a potential alternative calcium sensor for hEAG1 potassium channels. 20716661_Serum levels of S100B protein do not differentiate systemic lupus erythematosus patients with and those without central neurological manifestations. 20947022_Results enhance understanding of the functional outcomes of S100 protein binding to RAGE and provide insight into mechanistic models for how the receptor is activated. 20950652_Zn(2+)-Ca(2+)-loaded S100B the C-termini of helix IV adopt a distinct conformation. 21034449_Data show that the degree of systemic inflammation is associated with S100B concentration in acute ischaemic stroke, independent of the size of the ischaemic lesion. 21070816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21070816_The results of this study implicated a role for S100B gene polymorphisms in the cognitive functions of schizophrenia patients and encourage further investigation into spatial disability as an endophenotype of schizophrenia. 21079180_Outcome prediction after traumatic brain injury can be improved with determination of serum levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and S100B at the time of hospital admission. 21112154_Men homozygous for the 2757C>G or 5748C>T SNPs scored higher in self-directedness on the Temperament and Character Inventory. 21144594_This meta-analysis indicates a modifying effect of S100B in mood disorders in the interaction with age, with an increasing role across the lifespan. 21273622_Increase S-100beta level was associated with metastatic uveal melanoma. 21293918_The findings of increased ictal serum S100B and NSE levels together with increased interictal levels of S100B suggested that migraine might be associated with glial and/or neuronal damage in the brain. 21303299_REVIEW: S100B protein in neurodegenerative disorders 21311479_There was no correlation between the S100beta level and the type of brain lesion, its localization or volume and the fracture of cranial bones. 21368691_The relationship of clinical outcome with cerebrospinal fluid neuron-specific enolase (NSE), S100B and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) levels in patients with severe traumatic brain injury was investigated 21376255_Results suggest that S100B may be a potential cause of pathogenesis in Parkinson's disease. 21423669_Upon binding to nucleic acids, S100B activated intracellular TLRs eventually resolve danger-induced inflammation via transcriptional inhibition of S100B. 21447379_In various physiological and pathological conditions S100B might function as an interface to immunological processes, distinct from known cytokine- and chemokine-mediated pathways. 21455324_S100B protein in the gut has a role in enteroglial-sustained intestinal inflammation [review] 21458434_S-100B can be used as a reliable and early predictor of poor physiological and cognitive neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest. 21473859_S100B is pregnancy-dependent with the presence of a protein's gradient between fetal and maternal bloodstreams 21487066_Data suggest that plasma markers: CEACAM, ICAM-1, osteopontin, MIA, TIMP-1 and S100B particularly when assessed in combination, can be used to monitor patients for disease recurrenc. 21504113_A drastic rise in the level of S100beta is observed one week after coronary artery bypass grafting, a mark of a severe generalized cerebral injury that correlates with the development of cognitive dysfunction. 21553520_The increased level of serum S100beta and NSE may be one of the mechanisms of brain damage and memory impairment in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. 21587126_Serum s-100beta protein was significantly higher in off-pump coronary artery bypass graft patients with intracranial and cervical artery stenosis. 21601568_This study provides useful serum S100B values from the largest cohort of healthy children aged 0-3 years old. 21620650_After treatment of carotid stenosis patients with an increased S-100B coefficient of variation showed diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging positive for ischemic brain lesions. 21628886_nvestigation into whether S100B is involved in Parkinson's disease: creation of transgenic mice with brain-specific overexpression of human S100B creates mouse model with symptoms of Parkinson's disease (i.e., motor incoordination by Rota-rod test) 21640093_Increased serum S100B levels were associated with the severity of cardiac dysfunction, renal insufficiency and an adverse prognosis in chronic heart failure patients. 21663912_Serum levels of S100B, S100A6 and S100P are associated with acute coronary syndrome, and serum levels and myocardial expression of these proteins are related to infarct size. 21674567_Some neurofibromas include a subpopulation of S100B(+) /Nfn(-) cells consistent with clonal expansion of a Schwann cell progenitor that has lost function of both NF1 alleles. 21688665_concentration of IL-1beta, INF-gamma, TNF-alpha, S100beta, AMA-M2 increase, IL-10 decrease were detected in peripheral blood of 25 patients with stroke 21714070_These studies have identified S100B as a potential biomarker for illness severity and therapeutic response in psychiatric patients. 21725169_Treadmill exercise training decreased the expression of S100 beta in the striatum of chronic Parkinsonian mice, which can partially explain the beneficial neuroprotective role of exercise in patients with parkinson disease. 21738758_S100B protein, BDNF, and GDNF are present in all samples of human milk, and they may be responsible for the long term effects of breast feeding. 21779383_S100B and APP levels are simultaneously increased within Down syndrome neural progenitors, their secretions are synergistically enhanced in a paracrine fashion, and their overexpressions disrupt mitochondrial membrane potentials and redox states. 21810220_Data indicate that measurements of serum S100B during regular follow-up of patients with CM are a useful tool for discovering disease progression in asymptomatic patients. 21858537_Results show that S-100B, MIA and LDH levels were significantly higher in patients with advanced melanoma than in disease-free patients or healthy controls. 21861214_High S-100B is associated with treatment response in stage III melanoma. 21861268_S100B depletion induces apoptosis of PC14/B cells. 21906477_The level of S100beta protein in CSF from CH patients increases. It may be a biomarker as reflecting degree of pathogenetic and predicting outcome in the CH patients. 21932834_Peptide array experiments identify the carboxy-terminal 58 residues of the third intracellular loop of the dopamine D2 receptor as the major interacting site for S100B. 21976236_S100B levels in patients with worst outcome after traumatic brain injury in patients with worst outcome are already significantly higher at day zero. 22011044_Results suggest that S100B, TM4SF3, and OLFM4 overexpression may affect metastatic behavior of tumor cells in Taiwanese colorectal cancer patients. 22019077_for both schizophrenia patients and healthy controls two SNPs in S100B were significantly associated with prefrontal functions in the spatial domain,with the AA genotype of rs9722 and the GG genotype of rs2839357 linked to poorer performance. 22025532_The expression of eosinophil RAGE, soluble RAGE and RAGE ligands may be pivotal to the functions of eosinophils in various human diseases involving RAGE and S100 ligands. 22114731_S100B polymorphism is associated with aspergillosis in stem cell transplant recipients. 22177239_The IL-1alpha-positive microglias and S100beta-positive astrocytes may be of certain significance in transformation of diffuse non-neuritic plaques to diffuse neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease. 22224444_The serum levels of pro-inflammatory marker S-100beta protein increased after total hip-replacement in elderly patients and may serve as predicting parameters for the occurrence of post-operative cognitive dysfunction 22285378_Significantly higher values of serum S100B were found in CT positive than in CT negative patients with mild head injury. 22286962_S100B could be involved in the development of brain metastasis in -small cell lung cancer. 22306257_The significant elevations of HMGB1 and S100B in CSF, and S100B in serum are associated with the neurologically poor outcome in OHCA patients. 22322856_Patients with the apolipoprotein (APO)epsilon4 allele may be more predisposed to brain cellular damage measured as S100B and neuron-specific enolase (NSE). 22326439_despite the observation of an increase in S100B+ NK cells in schizophrenia patients, the lack of a correlation with serum S100B concentrations suggests that these cells are probably not a major source of S100B in the blood of schizophrenia patients 22348227_This review summarizes the available data regarding the use of S100B as a biomarker of brain damage following birth asphyxia. 22359053_an increase in glutamate uptake and S100B secretion, and a decrease in glutamine synthetase, which might be linked to the altered glutamatergic communication in diabetes mellitus 22565174_Determination of S100B concentration in jugular samples appears to be better than in arterial to predict clinical outcome after brain injury. 22766253_plasma S100B was correlated with initial stroke score, and was significantly higher in patients with poor clinical outcome 22782342_Visceral metastases other than lung (hazard ratio (HR) 1.8), elevated S100B (HR 1.7) and elevated LDH (HR 1.6) had the highest negative impact on survival. 22916238_Study is the first in vivo study validating the specificity of the glial marker S100B for the human brain, and supporting the assumption that radial diffusivity represents a myelin marker. 22935566_The results showed a close association between S100B and depressive symptoms in patients undergoing hemodialysis. 22982200_decreased level of S100B in CSF is related to increased symptoms of depression in the neurological patients with non-inflammatory disorders. 23030834_Cord blood S100B levels of infants born through meconium-stained amniotic fluid were not different from those with clear amniotic fluid. 23031665_the determination of S100B levels both in urine and serum acts as a sensitive and an effective biomarker for the early prediction of mortality after severe traumatic brain injury 23053124_this study concludes that neither increased blood lactate nor serum prolactin play an exclusive role in the regulation of S100B. 23130680_S100B mRNA was detected not only in S100B lymphocytes, but also in every S100B lymphocytes, although the expression levels of S100B mRNA in S100B lymphocytes were much lower than those of S100B lymphocytes. 23141161_S100B might be a factor in the pathogenesis of early-onset preeclampsia. 23146618_Increased S-100B protein serum levels appear to reflect neuronal damage in the brains of children with temporal lobe epilepsy. 23161189_Serum S100B protein level is increased in patients with OSAS and may be a useful biochemical marker in those patients. 23163123_Elevated levels of serum S100B is associated with the presence and outcome of haemorrhagic shock. 23169921_results demonstrate a role of S100B in the pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. 23190274_This study evaluated S100b as a prognostic biomarker in adult subjects with severe traumatic brain injury 23208248_s100b concentration is not a useful predictor of individuals at risk of more severe long-term cognitive decline 23261835_there was no correlation between whole-body tumor volume and S100beta concentration for the overall group of neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1), NF2, and schwannomatosis patients. 23262371_S100B in LP infants is gestational age and gender dependent 23292665_Pathogens, but not probiotics, significantly induced S100B protein overexpression |
ENSMUSG00000033208 |
S100b |
18.022292 |
22.0728715270 |
4.464202 |
0.708147635 |
55.320547 |
0.00000000000010239264046173108974172535968579562185032123117212066176762164104729890823364257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000648076918188315222536914295600761332896873334608045524873887188732624053955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.8243921 |
14.9053758 |
1.4998254 |
0.6507079 |
| ENSG00000160323 |
11093 |
ADAMTS13 |
protein_coding |
Q76LX8 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves the vWF multimers in plasma into smaller forms thereby controlling vWF-mediated platelet thrombus formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19880749}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood coagulation;Calcium;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins containing several distinct regions, including a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. The enzyme encoded by this gene specifically cleaves von Willebrand Factor (vWF). Defects in this gene are associated with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:11093; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; glycoprotein metabolic process [GO:0009100]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; peptide catabolic process [GO:0043171]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to amine [GO:0014075]; response to potassium ion [GO:0035864]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636] |
11586344_incodes a zinc proteinase involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 11586351_mutation of gene causes thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 11843286_VWF-CPis composed of a single polypeptide with a molecular mass of approx. 190 kD,and cDNA cloning indicated it is uniquely produced in the liver. Its gene is on chromosome 9q34. 11920264_role of the vWF protease and vWF proteolysis in the pathogenesis of bone marrow transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy of the fulminant type 12038781_Complete defect in vWF-cleaving protease activity is associated with increased shear-induced platelet aggregation in thrombotic microangiopathy. 12084165_An acquired deficiency of vWF-CP due to an autoantibody is associated with responsiveness to plasma exchange therapy in TTP. Patients whose TTP is not caused by autoimmunity to vWF-CP may not respond to PE. 12091044_Deficiency of vWF-cp activity in patients with colon cancer was shown to be associated with the progression of the disease and metastasis. 12091372_A severely deficient activity is specific for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 12130486_ADAMTS13 is deficient in recurrent and familial thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome; its activity level cannot be used to distingush between TTP and HUS. 12172456_REVIEW: role of ADAMTS13 mutations and deficiencies in thrombotic microangiopathies 12181489_mutations and common polymorphisms in ADAMTS13 gene responsible for von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease activity 12195022_role of variation in modulating risk of thrombosis in cardiovascular disorders 12223999_a sensitive blood indicator for diagnosing thrombocytopenic thrombotic purpura 12393397_ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge VWF multimers on the vascular endothelial surface under flowing conditions 12393399_Cloning, expression, and functional characterization of the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13). 12393505_Mutation analysis of the ADAMTS13 gene in the childhood TTP patients deficient in VWF-CP by direct sequencing of all 29 exons identified 8 different mutations. 12395148_vWF proteolysis by ADAMTS13 is critical in regulating vWF-platelet interaction and set the stage for improving the diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 12615692_This article reviews the role of this cleavage in regulating vWF-platelet interaction and proposes a scheme for understanding how a deficiency of ADAMTS13 results in the development of microthrombi in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 12753286_deficiency of ADAMTS13 is a molecular mechanism responsible for familial thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 12855569_high titers of IgM and IgG antibodies that bound to ADAMTS-13, but did not neutralize protease activity, in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura probably influenced the half-life of ADAMTS-13 or its binding to the endothelial cell surface. 12869506_truncation of the cysteine-rich/spacer domains caused a remarkable reduction in VWF-CP activity 12871390_REVIEW: mechanisms by which defects in ADAMTS13 cause TTP 12871391_REVIEW: defects in ADAMTS13 cause TTP and HUS 12923577_Acquired deficiency of this enzyme causes Schistocytic anaemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and renal dysfunction 12975358_The ADAMTS13 propeptide is not required for folding or secretion, and does not perform the common function of maintaining enzyme latency. 14512308_VWF73 is a specific substrate for ADAMTS-13 14512317_Severe deficiency of the von Willebrand Factor (VWF)-cleaving proteinase, ADAMTS13, is associated with the development of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 14525793_an amino acid polymorphism in VWF may influence susceptibility to ADAMTS13 proteolysis 14563640_Molecular models of the metalloprotease, fifth domain of thrombospondin 1 (Tsp1-5), and Tsp1-8 domains of ADAMTS13 suggest that the missense mutations could cause structural defects in the mutants. 14644076_No significant difference in ADAMTS-13 activity between the age- and sex-matched patients with benign and malignant brain tumors nor between the age matched patients with prostatic cancer. 14727254_REVIEW: role in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 14727255_REVIEW: processing of von Willebrand factor by ADAMTS-13 on endothelial cells 14727256_REVIEW: recent advances in cell culture expression and functional characterization of human rADAMTS-13 14727257_REVIEW: mutations in hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 14727259_the substitution of ADAMTS-13 by means of recombinant drug instead of plasma 14727263_REVIEW: ADAMTS-13 deficiency in childhood 14962303_thrombotic microangiopathy with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency is a distinct pathologic process. 14976043_ADAMTS13 auto-antibodies from 25 patients with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency (acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura) was evaluated in vitro 15009458_Role of ADAMTS13 mutations in the pathogenesis of congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 15009467_The metalloprotease ADAMTS-13 cleaves von Willebrand factor (VWF) at the Y842/M843 peptide bond located in the A2 domain. 15126318_ADAMTS13 may have a role in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 15175818_in a Chinese population, the heterozygous 1423T polymorphism was not associated with ischemic stroke nor myocardial infarction 15182579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15249683_Results suggest that von Willebrand factor domain A1 inhibits the cleavage of domain A2 by ADAMTS13, and that inhibition can be relieved by interaction of domain A1 with platelet platelet glycoprotein Ibalpha or certain glycosaminoglycans. 15388580_This study demonstrates the susceptibility of ADAMTS13 to proteolytic inactivation and suggests possible roles for thrombin and plasmin at sites of vascular injury. 15583740_analysis of the changing levels of ADAMTS13 activity during pregnancy and puerperium 15692254_The acquired or sporadic form of TTP is caused by circulating autoantibodies inhibiting ADAMTS-13 activity 15710227_Inhibited in the blood of a paatient with hepatitis C virus-related liver cirrhosis causes thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 15711742_the 130-amino-acid cysteine-rich spacer domain harbors a major binding site for anti-ADAMTS-13 antibodies found in blood of patients 15774619_mutant lacking the TSP-1 and CUB domains was hyperactive under flow, suggesting that the C-terminal region may negatively regulate ADAMTS-13 activity 15774620_More than 50 ADAMTS13 mutations resulting in familial TTP have been reported 15809291_the interaction between von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS-13 is modulated by chloride ions 15824096_analysis of ADAMTS13 binding to von Willebrand factor 15842379_the ADAMTS-13 Pro475Ser polymorphism is not found in caucasians [letter] 15855280_ADAMTS13 was detected immunohistochemically in perisinusoidal cells which also expressed alpha-smooth muscle actin, confirming that these cells were activated HSCs. These results suggest that HSCs may be major cells producing ADAMTS13 in human liver. 15865866_Review. ADAMTS13 deficiency is a risk factor for the development of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and related syndromes. 15886321_reduction in the number of terminal sugars on N-linked glycan increases susceptibility of globular VWF to ADAMTS13 proteolysis and is associated with reduced plasma VWF:Ag and VWF:CB levels. 15890682_IgG antibodies directed against ADAMTS13 were found in 97% of untreated patients with acute acquired thrombotic microangiopathies who had plasma levels of ADAMTS13 activity below 10%. The corresponding prevalence of IgM antibodies was 11%. 15975930_the proximal carboxyl-terminal domains of ADAMTS13 determine substrate specificity and are all required for recognition and cleavage of von Willebrand factor between amino acid residues Asp(1595) and Arg(1668). 16102037_ultra-large von Willebrand factor is cleaved by ADAMTS-13 under flow conditions (review) 16113782_analysis of transcriptional regulation of ADAMTS13 16141351_CUB-1 domain may serve as the docking site for ADAMTS13 to bind unusually large forms of von Willebrand factor (ULVWF) under flow, a critical step to initiate ULVWF proteolysis 16160007_Analysis of the individual effect and combinations of any amino acid substitutions showed that several sequence variations can interact with each other, thereby altering the phenotype of ADAMTS13 deficiency 16189276_Severe secondary ADAMTS13 deficiency is associated with sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation and may contribute to the development of renal failure 16203734_truncation of the ADAMTS13 protein at its cysteine-rich region eliminates its recognition by the antibodies without abolishing its von Willebrand factor-cleaving activity 16221672_ADAMTS13 controls the multimeric size of circulating von Willebrand factor by reacting at several binding sites. 16286459_substrate recognition of ADAMTS13 for VWF depends on structural features or exosites on multimeric VWF that are missing from FRETS-VWF73 16322474_results imply that increased VWF susceptibility for ADAMTS13 is a constitutive property of classical VWD type 2A in an investigation of the impact of mutations commonly found in patients with VWD type 2A on ADAMTS13-dependent proteolysis of VWF 16391894_Decreased activity of ADAMTS13 was associated with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 16453338_A homogeneous distribution of ADAMTS13(WT) in the Cis-Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) compartments, a reduction of ADAMTS13(Val88Met) in both compartments, while ADAMTS13(Gly1239Val) failed to reach the Cis-Golgi compartment and remained in the ER. 16597588_CUB domains have a critical role in a novel cargo-selective mechanism for apical sorting of a soluble ADAMTS protease (ADAMTS13) in polarized cells 16634765_ADAMTS-13 activity, von Willebrand factor level and platelet activation are modified by physical stress (letter) 16755777_Mutation analysis of the ADAMTS 13 gene one single base frameshift insertion, 4143insA in 8 of 9 unrelated patients. 16794526_present the cases of two lung transplant recipients who experienced a thrombotic microangiopathy associated with an acquired severe ( type 2B > type 2M > rVWF-WT 17121983_Ionic interactions of the Pro-1645-Lys-1668 region of the von Willebrand factor A2 domain with exosite on ADAMTS-13 play a significant role in mediating substrate recognition. 17229645_ADAMTS-13 deficiency may play a role in the development of sepsis-associated thrombocytopenia and organ failure 17294528_Renal thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) may be responsible for acquired ADAMTS13 deficiency and thereby triggered the generalization of TMA lesions. 17296575_the L1565 variant of von Willebrand factor has a role in susceptibility to proteolysis by ADAMTS13 17395589_overexpression of protein O-fucosyltransferase 2 did not affect the secretion of wild-type ADAMTS13, it did increase the secretion of the ADAMTS13 TSR1,2 double mutant but not that of ADAMTS13 TSR1-8 mutant 17725738_heterogeneity with regard to ADAMTS13 activity and the absence of inhibitors in the majority of patients indicate that other factors are important in the pathogenesis of HIV-related thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 17764538_VWF parameters are reciprocally correlated with ADAMTS-13 activity in severe sepsis and septic shock but have no prognostic value regarding outcome 17768109_ADAMTS13/factor XI complexes are insignificant in plasma 17849048_Four mutations in ADAMTS13 which led to a secretion defect, a loss of enzymatic activity and a decreased binding to the substrate, are responsible for the hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 17901248_ADAMTS13 preferentially acts on platelet-VWF complexes under fluid shear stress 17922807_Specific to the type 2B VWD group was an increase in the percentage of high molecular weight VWF multimers, a decrease in the mean platelet count, and an increase in the ADAMTS-13 level 17928530_provided visual evidence for a shear rate-dependent action of ADAMTS13 that limits thrombus growth directly at the site of the ongoing thrombus generation process 17988227_ADAMTS13 MUTATIONS IN THE FAMILY OF A Upshaw-Schulman syndrome PATIENTS 18031293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18031293_The high prevalence of R1060W ADAMTS-13 in adult onset TTP, together with its absence in childhood congenital TTP cases reported elsewhere, suggests it may be a factor in the development of late-onset thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 18166799_systemic inflammation results in an ADAMTS13 deficiency which activates hemostasis 18175284_ADAMTS-13 levels in multisystem thrombotic microangiopathy and other pathologic conditions [review] 18194418_It appears unlikely that ADAMTS-13 appreciably affects VWF antigen levels. It correlated positively with serum cholesterol, triglycerides & BMI, & negatively with HDL-cholesterol. Only multivariate analysis showed association with myocardial infarction. 18223285_Survivors of an acute episode of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with severely reduced levels of ADAMTS13 and/or with anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies during remission have 18240172_ADAMTS13 deficiency is associated with severe thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia in conjunction with severe bilateral otitis media 18263586_a new mechanism of anthrax coagulopathy affecting the levels and functional activities of both VWF and its natural regulator ADAMTS13. This mechanism may contribute to hemorrhage and thrombosis typical in anthrax. 18327408_MgSO(4) significantly enhanced the cleavage of the newly released ultra-large von Willebrand factor strings by ADAMTS-13. 18332284_ADAMTS13 is decreased in malignant hypertension and associated with the severity of thrombotic microangiopathy, likely because of the release of VWF after endothelium stimulation 18433458_certain inflammatory cytokines selectively inhibit ADAMTS13 synthesis without triggering release of its known substrate, vWF. 18449422_There was no association between VWF clearance and ADAMTS-13-mediated proteolysis in type 1 von Willebrand disease. 18492805_FVIII plays a role in regulating proteolytic processing of von Willebrand factor (VWF) by ADAMTS13 under shear stress, which depends on the high-affinity interaction between FVIII and its carrier protein, VWF. 18492952_By kinetic analysis of recombinant ADAMTS13 constructs, we show that the first thrombospondin-1, Cys-rich, and spacer domains of ADAMTS13 interact with segments of VWF domain A2 between Gln(1624) and Arg(1668). 18502798_A molecular model of the FRETS-VWF73 showed that the substrate can fit into the active site only if ADAMTS13 assumes a C-like shape and, interacting with the acidic 1653-1668 region of VWF 18521503_An imbalance between the decreased ADAMTS13:AC and its increased substrate may reflect the predisposing state for platelet thrombi formation in patients with advanced liver cirrhosis. 18581589_Data show that the Pro475Ser polymorphism seems to be popular in the Korean population, and attenuates ADAMTS-13 plasma activity. 18581589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18609162_The imbalance between decreased ADAMTS13 activity and increased unusually large von Willebrand factor could contribute to severe acute pancreatitis pathogenesis through enhanced thrombogenesis. 18665921_P475S polymorphism of ADAMTS13 resulted in moderately lowered activity without urea, and the P475S mutant was more labile to urea than the wild-type 18725999_in type 2B vWD, prolonged lifetimes of vWF bonds with GPIbalpha on circulating platelets may allow ADAMTS-13 to deplete large vWF multimers, causing bleeding 18756543_The short-term prognostic usefulness of ADAMTS13 testing during acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura warrants further investigation because of limited prospective studies. 18801485_the disintegrin-like domain of ADAMTS-13 functions in attenuating thrombus growth on diseased arteries exposed to a high shear rate 18833927_It cleaves Tyr842-Met843 peptide bonding in A2 domain on von Willebrand factor and Its deficiency leads to thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 18835837_Work reports how two different ADAMTS13 gene defects acting at two different levels lead to a severe deficiency of ADAMTS13. 18981290_After its secretion, ADAMTS13 does not require N-glycans for its von Willebrand factor cleaving activity 18983500_The rapid expulsion and unfolding of long VWF strings that remain anchored to endothelial cells after secretion from Weibel-Palade bodies can alter the structure or exposure of some VWF monomeric A2 domains to create an ADAMTS-13-cleavable form. 18988930_decreased ADAMTS13 is associated with consumptive coagulopathy. 18996572_Findings suggest that the imbalance between plasma VWF and ADAMTS13 levels caused by left atrial remodeling might be closely associated with intra-atrial thrombus formation in atrial fibrillation patients. 19027144_The CUB-1 domain is critical for ADAMTS-13 secretion and stability upon secretion. 19041237_ADAMTS13 is a specific von Willebrand factor -cleaving metalloprotease found in plasma. This protease limits admission and persistence of large VWF multimers in the circulation, where they form abnormally large thrombi in the microvasculature. 19047683_major influence of Ca(2+) upon ADAMTS13 function is mediated through binding to a high-affinity site adjacent to its active site cleft. 19054323_VH1-69 derived antibodies directed towards ADAMTS13 develop in the majority of patients with acquired TTP. 19069166_Functional deficiency of ADAMTS13 caused by genetic mutation and inhibitory autoantibodies leads to the accumulation of VWF multimers in the plasma and results in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). 19116307_In a family with a history of chronic recurrent TTP, genetic analysis revealed a homozygous deletion of nucleotides 2930-2935 in ADAMTS13, leading to the replacement of Cys977 by a Trp and the deletion of Ala978 and Arg979 in the TSP1-6 repeat domain 19162307_Correlation between plasma activity of ADAMTS13 and coagulopathy, and prognosis in disseminated intravascular coagulation is reported. 19190804_Rituximab as pre-emptive treatment in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and evidence of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies. 19190805_Variations in the ratio between von Willebrand factor and its cleaving protease, ADAMTS13, during systemic inflammation and association with severity and prognosis of organ failure. 19190814_Increased plasma von Willebrand factor antigen levels but normal von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) activity in preeclampsia. 19234142_Essential role of the disintegrin-like domain in ADAMTS13 function. 19253359_Postmortem ADAMTS13 activity levels may not be valid in establishing a diagnosis of TTP, and high inhibitor levels in this setting may be related to elevated PFH. 19260037_thrombocytopenia and schistocytosis can be seen in quinine-associated TTP/HUS, the pathophysiology seems to be distinct from that seen in most cases of idiopathic TTP (i.e., severely decreased ADAMTS13 with an inhibitor). 19270304_The effects of mutations in ADAMTS13 on the von Willebrand factor release and proteolysis in malaria patients is reported. 19389207_ADAMTS13 binds to CD36: a potential mechanism for platelet and endothelial localization of ADAMTS13 is reported. 19422343_Development of a hyperreactive primary hemostatic system, as evidenced by high levels of fully functional VWF and a temporary ADAMTS13 deficiency during liver transplantation. 19422532_In brains from aged individuals and patients with vascular dementia, ADAM-TS13 was localized to neurons, but was most prominently localized to corpora amylacea. 19427680_An association is reported bewteen ADAMTS13 polymorphisms and risk of cardiovascular events in chronic coronary disease. 19427680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19439298_Lower levels of ADAMTS13 are associated with cardiovascular disease in young patients. 19492149_low activity in sickle cell disease patients inversely correlates with extracellular haemoglobin levels 19506365_Assessing ADAMTS13 antigen & activity shows whether or not it is fully active in various conditions: liver cirrhosis, inflammatory bowel disease, cardiac surgery, pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, in the neonatal state & in normal individuals. Review. 19541819_Leukocyte proteases cleave von Willebrand factor at or near the ADAMTS13 cleavage site. 19574655_preliminary Xray structure 19584892_microthrombosis has a role in the pathogenesis of delayed cerebral ischemia, as a result of decreased ADAMTS13 activity and endothelium dysfunction 19587373_This novel VWF C-terminal binding site may participate as the initial step of a multistep interaction ultimately leading to proteolysis of VWF by ADAMTS13. 19644711_Human renal tubular epithelial cells synthesize biologically active ADAMTS13 which may, after release from tubuli, regulate hemostasis in the local microenvironment. 19654870_We have used flow cytometry to estimate the binding of these antibodies to ADAMTS13 and demonstrate that antibodies raised against the TSP and disintegrin domains detect conformation changes in the ADAMTS13 19682236_The Cys-rich and spacer domains are required for recognition of the cell-bound ultralarge VWF, but that the TSP1 2-8 repeats and the CUB domains appear to be dispensable. 19718479_von Willebrand factor antigen and von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) activity may have roles in chronic heart failure 19729451_ADAMTS13 bound to endothelial cells and enhanced cleavage of VWF. 19765208_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19765208_genetic association study of six ADAMTS13 snps in ischemic stroke patients 19765212_ADAMTS-13 binds to circulating VWF and may therefore be incorporated into a platelet-rich thrombus, where it can immediately cleave VWF that is unfolded by fluid shear stress. 19809308_possible link between ADAMTS13 and microangiopathy in diabetes mellitus patients 19812385_Reactive oxygen species released by activated neutrophils have a prothrombotic effect, mediated in part by inhibition of VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13. 19822897_Constitutive ADAMTS-13 released from endothelial cells may contribute to the maintenance of cell surfaces free of hyperadhesive VWF multimeric strings. 19847791_review of ADAMTS13 gene variants associated with inherited ADAMTS13 deficiency and congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [review] 19880749_2 crystal structures of ADAMTS13-DTCS (residues 287-685), an exosite-containing human ADAMTS13 fragment, at 2.6-A and 2.8-A resolution, were determined. 19897584_Force-induced cleavage of single VWFA1A2A3 tridomains by ADAMTS-13. 19944670_two epitope sites for VWF binding in the spacer domain of ADAMTS13 using the lambda-phage surface display system were explored. 19996632_quantify ADAMTS13 production in proliferating and nonproliferating human umbilical vein endothelial cells 20032502_An autoantibody epitope comprising residues R660, Y661, and Y665 in the ADAMTS13 spacer domain identifies a binding site for the A2 domain of VWF. 20054668_decreased ADAMTS13 activity may be involved in not only sinusoidal microcirculatory disturbances, but also subsequent progression of liver injuries, eventually leading to multiorgan failure 20058209_Deficiency of ADAMTS13, due to autoimmune inhibitors in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and mutations of the ADAMTS13 gene in hereditary cases, leads to VWF-platelet aggregation and microvascular thrombosis 20062916_Results suggest that decreased ADAMTS13 activity in combination with increased VWF concentrations may contribute to the complications in severe malaria. 20075158_Site-directed mutagenesis, kinetic analyses, and peptide inhibition assays have identified a role for amino acid residues Arg(659), Arg(660), and Tyr(661) of ADAMTS13 in proteolytic cleavage of various substrates. 20141578_Letter: Report HLA-DRB1*11 as a strong risk factor for acquired severe ADAMTS13 deficiency-related idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in Caucasians. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20307901_reduced ADAMTS13 might be associated with diabetic nephropathy 20390223_genetic polymorphism is associated with meningococcal sepsis 20553378_ADAMTS13 inactivation by plasmin as a potential cause of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 20605782_FVIII and platelets are cofactors that regulate proteolysis of multimeric VWF by ADAMTS13 under physiological conditions. 20624874_Results describe the amino acid residues involved in ADAMTS13 cleavage and the carbohydrate moieties of this enzyme. 20647566_Two subsites, D187-R193 and D252-P256, in the ADAMTS13 metalloprotease domain play an important role in cleavage efficiency and site specificity in the proteolysis of von Willebrand factor. 20664912_Report a spliced ADAMTS13 transcript in hepatic stellate cells and a hepatoma cell line that retains the 25th intron, retaining VWF-cleaving capability. 20682599_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682599_change ADAMTS13 activity might modulate the risk of DVT by altering vWF and FVIII levels, the polymorphisms analyzed in this study did not correlate with DVT risk among patients investigated. 20695979_ADAMTS13 CUB and T2-8 domains influence proteolysis of platelet-decorated VWF strings in vivo 20704649_von Willebrand factor clearance does not involve proteolysis by ADAMTS-13 20705333_ADAMTS13 interacted with the rVWF A1, A2, A3 domains and full-length VWF, while TSP1 also bound to three A domains, especially to A2 and A3 domains. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20923926_Loss of ADAMTS13 is associated with benign nephrosclerosis. 20946172_novel disulfide-bond-reducing activity of ADAMTS-13 may prevent covalent lateral association and increased platelet adherence of plasma-type VWF multimers induced by high fluid shear stress 20958794_E2 may play a role in the regulation of VWF and ADAMTS13 gene expression and in its production in human endothelial cells 21077328_Determined protein structure of ADAMTS13 from D domain to S domain. (review) 21103662_Evaluation of collagen binding and fluorescence resonance energy transfer based assays to measure plasma ADAMTS13. 21136020_von Willebrand factor and ADAMTS13 have a role in clinical outcome after cardioversion for atrial fibrillation 21196718_ADAMTS-13 levels in Kuwait. ADAMTS-13 was found to be severely deficient in TTP patients; significantly lower levels of ADAMTS-13 were not specific for TTP and can be found in other thrombocytopenic disorders 21238935_The current knowledge of structure-function aspects of ADAMTS13 and its involvement in the pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathies, are discussed. 21275971_ADAMTS13 activity and the risk of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura relapse in pregnancy 21350095_An evaluation for systemic lupus erythematosus/antiphospholipid syndrome is warranted in children and adolescents with reduced ADAMTS13 activity and thrombotic microangiopathy. 21385852_Cleavage assays consistently demonstrated that Ca((2)+) binding stabilized the A2 domain and impeded its unfolding, and consequently protected it from cleavage by ADAMTS13 21479334_a region in the ADAMTS13 CUB-2 domain, with conserved polar residues, might be involved in protein-protein interactions within the nucleus 21488199_Mutations within the ADAMTS13 gene were investigated in children with hemolytic uremic syndrome. 21512165_Preeclampsia is associated with decreased levels of ADAMTS13, independently of von Willebrand factor. 21535387_a model is presented for the development of anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies in previously healthy individuals that incorporates the recent identification of HLA DRB1*11 as a risk factor for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.[review] 21573942_Sustained deficiency of ADAMTS13 appears characteristic of idiopathic noncirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension, irrespective of severity of liver disease. 21605335_Oxidized von Willebrand factor multimers are cleaved by leukocyte serine proteases, under conditions where high concentrations of oxidant species would severely reduce the proteolytic efficiency of ADAMTS-13. 21606162_evaluation of ADAMTS13 antigen levels during the course of therapy and follow-up may offer additional useful information for the management of patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 21676167_Letter: Report SNPs/mutations of ADAMTS13 in the Japanese population and estimation of the number of patients with Upshaw-Schulman syndrome. 21705658_The recognition of VWF Leu1603 by ADAMTS13, in conjunction with previously reported remote exosites C terminal of the cleavage site, suggests a mechanism whereby the VWF P1-P1' scissile bond is brought into position over the active site for cleavage. 21712537_Residues Arg568 and Phe592 contribute to an antigenic surface for anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies in the spacer domain. 21715306_Protease activity of ADAMTS13 is controlled by conformational changes in its substrate, von Willebrand factor (VWF), which are induced when VWF is subject to elevated rheologic shear forces. (Review) 21720563_Glomerular endothelial cells express and secrete ADAMTS13. 21732076_Human neuroblastoma, astroglioma, foetal microglia & adult human brain endothelial cell lines expressed ADAMTS-13 mRNA constitutively. (IL)-1beta down-regulated ADAMTS-13 mRNA expression in astroglioma cells and microglial cells. 21779388_Data show that an anti-VWF mAb against the VWF-A2 domain (A1555-G1595) reduces the proteolytic cleavage of VWF by ADAMTS13 under shear stress, suggesting the role of this region in interaction with ADAMTS13. 21781265_Analysing the natural history of these USS patients based on ADAMTS13 gene mutations may help characterise their clinical phenotypes 21799176_Results suggest that the amino terminus of ADAMTS13, specifically the variable region of the spacer domain, is crucial for modulation of arterial thromboses under (patho)physiological conditions. 21843064_This article considers the effect of polymorphisms on the expression and function of ADAMTS13 and speculates on their relevance in future therapies based on pharmacogenomics--{REVIEW} 21896483_Local elongation of endothelial cell-anchored von Willebrand factor strings precedes ADAMTS13 protein-mediated proteolysis. 21901237_Suggest that the novel cell-based assay may be applicable for rapid identification and mapping of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies in patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 22070827_Findings suggest that ADAMTS13/VWF profiles may have important roles in the pathogenesis of DIC. 22075512_A novel homozygous missense ADAMTS13 mutation Y658C was found in a patient with recurrent thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. 22110247_Data suggest that high VWF and low ADAMTS13 plasma levels both increase the risk of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction, and the risks associated with high VWF or low ADAMTS13 levels are further increased by the use of oral contraceptives. 22163125_ADAMTS13 levels do not appear to be related t |
ENSMUSG00000014852 |
Adamts13 |
59.775205 |
0.2507068438 |
-1.995927 |
0.323360209 |
36.442709 |
0.00000000157220137287882480712869201283036352245758848766854498535394668579101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007385643623071755203598208109174241831063056906714336946606636047363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.5108636 |
4.6941005 |
95.5178005 |
12.7757857 |
| ENSG00000160325 |
11094 |
CACFD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UGQ2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in vesicle-mediated transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:11094; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
34864683_Biomarkers for C9orf7-ALS in Symptomatic and Pre-symptomatic Patients: State-of-the-art in the New Era of Clinical Trials. |
ENSMUSG00000015488 |
Cacfd1 |
47.965350 |
0.3435018925 |
-1.541610 |
0.268597344 |
33.267469 |
0.00000000803150080117975153520887618549192743522269211098318919539451599121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000035291739156121799635852778536868057379649599170079454779624938964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.3942626 |
4.6991108 |
71.6425197 |
9.1108972 |
| ENSG00000160326 |
11182 |
SLC2A6 |
protein_coding |
Q9UGQ3 |
FUNCTION: Probable sugar transporter that acts as a regulator of glycolysis in macrophages (Probable). Does not transport glucose (PubMed:30431159). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30431159, ECO:0000305|PubMed:30431159}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Hexose transport into mammalian cells is catalyzed by a family of membrane proteins, including SLC2A6, that contain 12 transmembrane domains and a number of critical conserved residues.[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2002]. |
hsa:11182; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0055056]; dehydroascorbic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0033300]; fructose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005353]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; dehydroascorbic acid transport [GO:0070837]; fructose transmembrane transport [GO:0015755]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659]; hexose transmembrane transport [GO:0008645]; regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0006110]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
19554504_The expression pattern of GLUT9 is reported in newly diagnosed esophageal adenocarcinoma by means of immunohistochemistry. 20413573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 32512041_The NF-kappaB signalling pathway regulates GLUT6 expression in endometrial cancer. 36327817_SREBP2/Rab11s/GLUT1/6 network regulates proliferation and migration of glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000036067 |
Slc2a6 |
412.514556 |
3.6976310725 |
1.886601 |
0.087895718 |
475.347370 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000219864768647525273710873081941154683271208752379249109703641091258088152754289820821013168778764172227248640778715845803554481797573505433844211061563008460403873845528656881460526544494121487233329403800309732635978049083082 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000099241712086772876891776846890317718278506214333349274178877337381120612238062772919161209244098181958862635421215153045994346446460813821197357262743794363223222087149991680102110215790077880118691697273589096942918140341493 |
Yes |
Yes |
657.9634485 |
35.0677812 |
179.1903302 |
7.9145793 |
| ENSG00000160447 |
29941 |
PKN3 |
protein_coding |
Q6P5Z2 |
FUNCTION: Contributes to invasiveness in malignant prostate cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15282551}. |
ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in epithelial cell migration. Predicted to be located in Golgi apparatus and cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:29941; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity [GO:0004698]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; epithelial cell migration [GO:0010631]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15282551_PKN3 might represent a preferred target for therapeutic intervention in cancers that lack tumor suppressor PTEN function or depend on chronic activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase 21754995_PKN isoforms are not simply redundant in supporting migration, but appear to be linked through isoform specific regulatory domain properties to selective upstream signals. It 22609186_PKN3 can be considered a novel protein implicated in remodeling the actin-adherens junction, possibly by linking ICAM-1-signaling with actin/AJ dynamics. 26742562_PKN3 is the major regulator of angiogenesis in humans and mice and tumor metastasis in mice. 27919031_Steady-state kinetic analysis revealed that PKN1-3 follows a sequential ordered Bi-Bi kinetic mechanism, where peptide substrate binding is preceded by ATP binding. This kinetic mechanism was confirmed by additional kinetic studies for product inhibition and affinity of small molecule inhibitors. 30422386_a novel interaction of p130Cas with Ser/Thr kinase PKN3, is reported. 33092266_A Screen for PKN3 Substrates Reveals an Activating Phosphorylation of ARHGAP18. |
ENSMUSG00000026785 |
Pkn3 |
55.576450 |
0.3690757376 |
-1.438011 |
0.434061685 |
10.295179 |
0.00133378239010885639610759501039183305692858994007110595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003044167013763216227822949733194946020375937223434448242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.4865860 |
11.5652163 |
91.4865088 |
21.9639417 |
| ENSG00000160469 |
84446 |
BRSK1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDC3 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays a key role in polarization of neurons and centrosome duplication. Phosphorylates CDC25B, CDC25C, MAPT/TAU, RIMS1, TUBG1, TUBG2 and WEE1. Following phosphorylation and activation by STK11/LKB1, acts as a key regulator of polarization of cortical neurons, probably by mediating phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins such as MAPT/TAU at 'Thr-529' and 'Ser-579'. Also regulates neuron polarization by mediating phosphorylation of WEE1 at 'Ser-642' in postmitotic neurons, leading to down-regulate WEE1 activity in polarized neurons. In neurons, localizes to synaptic vesicles and plays a role in neurotransmitter release, possibly by phosphorylating RIMS1. Also acts as a positive regulator of centrosome duplication by mediating phosphorylation of gamma-tubulin (TUBG1 and TUBG2) at 'Ser-131', leading to translocation of gamma-tubulin and its associated proteins to the centrosome. Involved in the UV-induced DNA damage checkpoint response, probably by inhibiting CDK1 activity through phosphorylation and activation of WEE1, and inhibition of CDC25B and CDC25C. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15150265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20026642, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21985311}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;DNA damage;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Synapse;Transferase |
|
Enables magnesium ion binding activity; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; and tau-protein kinase activity. Involved in mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling and protein phosphorylation. Acts upstream of or within G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; and response to UV. Located in cell junction; cytoplasm; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84446; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; distal axon [GO:0150034]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; tau protein binding [GO:0048156]; tau-protein kinase activity [GO:0050321]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; centrosome duplication [GO:0051298]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in establishment of planar polarity [GO:0090176]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0007269]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050770]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; regulation of synaptic vesicle clustering [GO:2000807]; response to UV [GO:0009411]; synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0099504] |
15150265_acts as checkpoint kinase upon DNA damage induced by UV 18339622_protein phosphatase 2C is a likely candidate for catalyzing the dephosphorylation and inactivation of BRSK1/2. 18854318_STRADalpha.MO25alpha complexes containing LKB1 variants were equally effective at phosphorylating and activating AMPK, BRSK1, and BRSK2 19448619_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19448621_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19648910_SADB kinase activity controls centrosome homeostasis by regulating phosphorylation of gamma-tubulin. 22131368_Single nucleotide polymorphism in BRSK1 is associated with the length of reproductive lifespan. 25036402_BRSK1 is a novel tumor suppressor in breast cancer which inversely correlated with Jab1 expression. 27677186_These results suggest that frameshift mutations of EGR1 and BRSK1 might play a role in tumorigenesis through tumor suppressor gene inactivation in colorectal cancer and gastric cancer. 31895179_Relationship between BRSK1 rs12611091 variant and age at natural menopause based on physical activity. |
ENSMUSG00000035390 |
Brsk1 |
9.523291 |
0.3962850440 |
-1.335390 |
0.539180690 |
6.320612 |
0.01193424144896739098886673247079670545645058155059814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022534144017750886573869806284164951648563146591186523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9856557 |
2.2944867 |
15.1011262 |
3.7661173 |
| ENSG00000160602 |
284086 |
NEK8 |
protein_coding |
Q86SG6 |
FUNCTION: Required for renal tubular integrity. May regulate local cytoskeletal structure in kidney tubule epithelial cells. May regulate ciliary biogenesis through targeting of proteins to the cilia (By similarity). Plays a role in organogenesis and is involved in the regulation of the Hippo signaling pathway. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23418306}. |
ATP-binding;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nephronophthisis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serine/threionine protein kinase family related to NIMA (never in mitosis, gene A) of Aspergillus nidulans. The encoded protein may play a role in cell cycle progression from G2 to M phase. Mutations in the related mouse gene are associated with a disease phenotype that closely parallels the juvenile autosomal recessive form of polycystic kidney disease in humans. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:284086; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary base [GO:0097546]; ciliary inversin compartment [GO:0097543]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; chromosome segregation [GO:0007059]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; heart development [GO:0007507]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035330] |
15019993_Data demonstrate for the first time that Nek8 is a novel tumor associated gene, and shares considerable sequence homology with the Nek family of protein kinases and may be involved in G(2)/M progression. 15872312_characterization of the proteome in mice that have a double point mutation in the related gene. 18199800_mutations cause nephronophthisis; mutant forms show defects in ciliary localization 21068128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22106379_study finds that induction of ciliogenesis upon cell cycle exit is accompanied by both activation and proteasomal degradation of Nek8, and that activation is dependent upon phosphorylation within the catalytic domain 23026745_NPHP9 promotes signalling through the transcriptional co-activator TAZ. 23418306_NEK8 is essential for organ development and that the complete loss of NEK8 perturbs multiple signalling pathways resulting in a severe early embryonic phenotype. 23793029_ANKS6 as a new NPHP family member that assembles a distinct module of nephronophthisis-associated proteins, encompassing NEK8, INVS and NPHP3. 23973373_Mutation in NEK8 is associated with renal ciliopathies 25451921_NEK8 may be a new target gene of HIFs; pVHL can down-regulate NEK8 via HIFs to maintain the primary cilia structure in human renal cancer cells 26697755_The mutations: c.2069_2070insC variant (p.Ter693LeufsTer86), and a c.1043C>T variant (p.Thr348Met) in RCC1 domain of NEK8 in two brothers with cardiac, renal, and hepatic anomalies 26967905_our study demonstrates that NEK8 human mutations cause major organ developmental defects due to altered ciliogenesis and cell differentiation/proliferation through deregulation of the Hippo pathway 27892797_NEK8 plays a critical role in replication fork stability through its regulation of the DNA repair and replication fork protection protein RAD51. 31633649_Homozygous NEK8 Mutations in Siblings With Neonatal Cholestasis Progressing to End-stage Liver, Renal, and Cardiac Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000017405 |
Nek8 |
58.738765 |
0.4636580810 |
-1.108867 |
0.198083642 |
31.864289 |
0.00000001653289368653832448088198368851831077108727185986936092376708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000070385206464755024509112428521273585602102684788405895233154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.4599921 |
4.6172424 |
81.4590987 |
6.4283940 |
| ENSG00000160678 |
6271 |
S100A1 |
protein_coding |
P23297 |
FUNCTION: Small calcium binding protein that plays important roles in several biological processes such as Ca(2+) homeostasis, chondrocyte biology and cardiomyocyte regulation (PubMed:12804600). In response to an increase in intracellular Ca(2+) levels, binds calcium which triggers conformational changes (PubMed:23351007). These changes allow interactions with specific target proteins and modulate their activity (PubMed:22399290). Regulates a network in cardiomyocytes controlling sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) cycling and mitochondrial function through interaction with the ryanodine receptors RYR1 and RYR2, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase/ATP2A2 and mitochondrial F1-ATPase (PubMed:12804600). Facilitates diastolic Ca(2+) dissociation and myofilament mechanics in order to improve relaxation during diastole (PubMed:11717446). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11717446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12804600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22399290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23351007}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Glutathionylation;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-nitrosylation;Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in stimulation of Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release, inhibition of microtubule assembly, and inhibition of protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation. Reduced expression of this protein has been implicated in cardiomyopathies. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6271; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; S100 protein binding [GO:0044548]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] |
11829317_The presence of the S100A1 in myocardial sarcoplasmic reticulum and myofibrils may be related to the known target proteins for S100A1 at these sites. 11909974_Impaired cardiac contractility response to hemodynamic stress in S100A1-deficient mice. 12721284_identification of the S100A1 C terminus (amino acids 75-94) and hinge region (amino acids 42-54) to differentially enhance sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release with a nearly 3-fold higher activity of the C terminus 12804600_S100A1 has a reglatory role in the contraction-relaxation cycle in the human heart 12960148_S100A1 protein serves as a cardioprotective factor in vitro 14638689_identified S100A1, but not calmodulin or other S100 proteins, as a potent molecular chaperone and a new member of the Hsp70/Hsp90 multichaperone complex 15147519_Synapsins and S100A1 interact in nerve terminals where coexpresssed; S100A1 cannot bind SV-associated synapsin I and may function as a cytoplasmic store of monomeric synapsin I; synapsin dimerization and interaction with S100A1 are mutually exclusive 15578088_Results demonstrate that restoration of S100A1 protein levels in failing myocardium by gene transfer may be a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of heart failure. 15654019_This study provides the first evidence that intracellular S100A1, depending on its subcellular location, modulates cardiac Ca2+-turnover via different Ca2+-regulatory proteins. 15780567_S100A1 was expressed in 2/15 clear cell RCCs, 11/15 papillary RCCs, 7/8 oncocytomas and in 0/7 chromophobe RCCs. 16169012_the three-dimensional structure of calcium-bound S100A1 was determined by multidimensional NMR spectroscopy and compared to the previously determined structure of apo-S100A1 16760135_S-100 protein expression in tumour cells was associated with significantly decreased survival 16969478_analysis of the different reactivity pattern of S100A1 in the external auditory canal cholesteatoma 17210106_There may be a reverse relationship between the expression of VEGF and S100(+) DC in esophageal tumor tissue, VEGF could decrease the number of S100(+) DC and impair the immunological function of the body. 17396138_Report concludes that S100A1 and S100B are transcriptional targets of the SOX trio and mediate its inhibition of terminal differentiation of chondrocytes. 17483815_S100A1 immunodetection is potentially useful for the differential diagnosis between chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma. 17512776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18193148_Both S100A1B and S100BB were related to outcome after severe traumatic brain injury. Even though this study is small, it seems unlikely that separate analyses of the dimers are of any advantage compared with measuring S100B alone. 18360353_S100A4 immunohistochemistry may be valuable for predicting metastatic potential in papillary microcarcinomas 18845991_Elevated serum S-100 is associated with malignant melanoma. 19011512_Circulating S100A1B and S100BB are potential biomarkers in patients with malignant melanoma. S100BB should be considered as the preferred biomarker, showing potential in predicting both relapse and survival, in contrast to both S100 and S100A1B. 19037854_The cytologic differential diagnosis of spindle cell neoplasm with expression of S-100 protein should be broadened to include sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma 19297317_S100A2 bound monomeric p53 as well as tetrameric, whereas S100A1 only bound monomeric p53. 19302533_the combination of CK7, S100A1 and claudin 8 immunohistochemistry can be useful for classifying tumours of overlapping histology as chromophobe renal cell carcinoma or renal oncocytomas. 19384190_S100A1 is a specific and sensitive immunohistochemical marker to differentiate nephrogenic adenoma from prostatic adenocarcinoma 19482672_S100A1B and S100BB are increased in urine collected from asphyxiated newborns who will develop hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) since first urination, and their measurement may be useful to early predict HIE. 19538970_S100A1 has been proven to play a critical role both in cardiac performance, blood pressure regulation and skeletal muscle function. 19601998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19680475_Data have identified S100A1 as valuable markers for chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. 19926575_These data suggest that S100A1 is a marker for poor prognosis of endometrioid subtypes of cancer. 20042890_The expression of S100A1 was low in benign melanocytic tumours and increased in malignant melanomas 20347987_A single phenyl-Sepharose column was sufficient for the purification of human S100A11 whereas HiTrap Q anion exchange followed by phenyl-Sepharose columns were required for the purification of S100A1. 20429377_COX-2 and S-100 positive dendritic cells are highly expressed in laryngeal carcinoma tissue. 20591429_S100A1, S100A2, S100A4, S100A6 and S100B interacted with MDM2 (2-125). 20864512_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21090249_Thermodynamics of zinc binding to human S100A2 21296671_The three-dimensional structure of human apo(calcium free)S100A1 protein was determined by NMR spectroscopy 22399290_S100A1 and permanently active S100P inhibited the apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and PP5 interaction, resulting the inhibition of dephosphorylation of phospho-ASK1 by PP5 22451665_Calmodulin and S100A1 protein interact with N terminus of TRPM3 channel. 22647434_Uremia clearance using NHD is accompanied by improvement in LV strain, rotation, reduction in mass and volume index. Dialysis downregulates genes for cardiomyocyte apoptosis and fibrosis and upregulates S100A1, which may improve LV contractility. 22989881_S-Nitrosylation of S100A1 increases Ca(2+) binding and tunes the overall protein conformation. 23048072_Report downregulation of S100A1 expression in critical limb ischemia impairs postischemic angiogenesis via compromised proangiogenic endothelial cell function and nitric oxide synthase regulation. 23351007_the increased calcium binding affinity of S100A1 upon thionylation arises, most probably, from rearrangement of the hydrophobic core in its apo form 23595519_This study showed that overexpression of S100A10, may play a role in irritable bowel syndrome, and that the IL10-819 CC is a candidate genotype for irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis. 23662436_In this review we will focus on the roles of S100A proteins in intracellular and extracellular calcium signalling and homeostasis. 23671622_The triple mutation Arg852/Lys859/Arg860 exhibited significant disruption of the binding of S100A1 to TRPC6 implicating their involvement in the binding site. 23683996_For autopsy material, all human cases of definite myocardial infarction and suspected early infarction showed well-defined areas without S100A1 staining. 24244340_hypoxia-induced MiR-138 is an essential mediator of EC dysfunction via its ability to target the 3'UTR of S100A1. 24402969_It was suggested that S100A1 and S100B be used as markers to develop potency assays for cartilage regeneration cell therapies, and as a redifferentiation readout in monolayer cultures aiming to investigate stimuli for chondrogenic induction. 24501865_Twenty-seven out of thirty-two (84.38%) cases of serous ovarian carcinoma were found to express S100A1. S100A1 expression was observed in one out of the two mucinous and three out of the six endometroid ovarian carcinomas. 24833748_Patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI) showed significantly increased S100A1 serum levels. S100A1 signaling in cardiac fibroblasts occurs through endosomal TLR4/MyD88. 25157660_In this review, we aim to describe the molecular basis and regulatory function of S100A1--{REVIEW} 25269953_Data indicate that Cu-oxidized S100 calcium binding protein A4 (S100A4) interacted with S100 calcium binding protein A1 (S100A1) and prevented protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) activation. 25611268_The relationship between the degree of infiltration by S100-positive (S100+) dendritic cells and prognostic factors, including histological subtype, histological grade, peritumor inflammatory infiltration, and stromal desmoplasia, were examined. 26943607_High Serum protein S100 levels are associated with postoperative delirium after off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery. 26958883_molecular dynamics simulations of S100A1 in the apo/holo (Ca(2+)-free/bound) states, is reported. 27226555_CaM and S100A1 can concurrently bind to and functionally modulate RyR1 and RyR2, but this does not involve direct competition at the RyR CaM binding site. 27356898_In line with these observations, rhesus monkey rhadinovirus infection resulted in rapid degradation of SP100, followed by degradation of PML and the loss of ND10 structures, whereas the protein levels of ATRX and DAXX remained constant. 27435061_a molecular mechanism for the potential regulation of TRPM1 by S100A1 27644758_Results identified amino acids motif in S100A1 for protein binding to 2-oxohistidine which appears to be an evolutionarily conserved capacity from bacteria to human. 27861869_a correlation between S100B + A1-positive Human Articular Chondrocytes in monolayer culture and their neochondrogenesis capacity in pellet culture, is reported. 28368280_X-ray crystal structure of human calcium-bound S100A1 has been reported. 28408431_Data suggest that three dimers of S100A1 (S100 calcium binding protein A1) associate with one molecule of STIP1 (stress-inducible phosphoprotein 1) in a calcium-dependent manner; individual STIP1 TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat) domains, TPR1, TPR2A and TPR2B, bind a single S100A1 dimer with significantly different affinities; TPR2B domain possesses highest affinity for S100A1. 28595036_The results indicated that S100A1 enhanced the ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration. 28819010_Data suggest that calcium signaling plays important role in prevention of protein misfolding; complexes of S100A1 and STIP1 are key players in this pathway; the stoichiometry of S100A1/STIP1 interaction appears to be three S100A1 dimers plus one STIP1 monomer; each S100A1-STIP1-binding interaction is entropically driven. (S100A1 = S100 calcium binding protein A1; STIP1 = stress-induced-phosphoprotein 1) [REVIEW] 28825380_The results indicate that changes in the circulating level of S100A1 protein occur in metabolic syndrome patients. The strong correlation between serum zinc-alpha2-glycoprotein and S100A1 might suggest that production or release of these two proteins could be related mechanistically. 29240297_Data suggest that TRPM4 exhibits binding sites for calmodulin (CaM) and S100 calcium-binding protein A1 (S100A1) located in very distal part of TRPM4 N-terminus. (TRPM4 = transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4) 29248577_Study provides evidence that mir-363 and its target S100A1 are under the regulatory function of FOXD2-AS1 aggravating nasopharyngeal carcinoma carcinogenesis. 29444082_found that S100B plays a crucial role in blocking the interaction site between RAGE V domain and S100A1. A cell proliferation assay WST-1 also supported our results. This report could potentially be useful for new protein development for cancer treatment 29901195_Data found that S100A1 was upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues, and its upregulation was associated with large tumor size, low differentiation, and shorter survival rates. Further results supports the hypothesis that S100A1 functions as an oncogene and may be a biomarker for the prognosis of patients with HCC. S100A1 exerted its oncogenic function by interacting with LATS1 and activating Hippo pathway. 31523180_The elevated plasma S100A1 level is an important predictor of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. 32497081_S100A1 blocks the interaction between p53 and mdm2 and decreases cell proliferation activity. 32945354_Long noncoding RNA FOXD2AS1 regulates the tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer via the S100 calcium binding protein A1/Hippo signaling pathway. 33217795_Comprehensive analysis of the expression and prognosis for S100 in human ovarian cancer: A STROBE study. 33257194_Elevated serum levels of S100A1 and zinc alpha2-glycoprotein in patients with heart failure. 33605572_The Role of CK7, S100A1, and CD82 (KAI1) Expression in the Differential Diagnosis of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma and Renal Oncocytoma. |
ENSMUSG00000044080 |
S100a1 |
33.403719 |
0.3737639546 |
-1.419801 |
0.349209326 |
16.653406 |
0.00004486966355892544466984692141942048237979179248213768005371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000130138776602424749255504377032366392086260020732879638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.3324299 |
5.1026846 |
57.4292480 |
9.0245420 |
| ENSG00000160683 |
643 |
CXCR5 |
protein_coding |
P32302 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine receptor that binds to B-lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC). Involved in B-cell migration into B-cell follicles of spleen and Peyer patches but not into those of mesenteric or peripheral lymph nodes. May have a regulatory function in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) lymphomagenesis and/or B-cell differentiation. |
Alternative splicing;B-cell activation;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a multi-pass membrane protein that belongs to the CXC chemokine receptor family. It is expressed in mature B-cells and Burkitt's lymphoma. This cytokine receptor binds to B-lymphocyte chemoattractant (BLC), and is involved in B-cell migration into B-cell follicles of spleen and Peyer patches. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:643; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; C-X-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016494]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0030595]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; positive regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032467]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204] |
11688722_structural requirements for the activation of signal transduction pathways by CXCR5 11714765_CXCR5 is a common and early marker for newly generated memory CD4+ T cell subsets during ongoing immune responses. 12070001_Most Natural killer t-cells express receptors for extralymphoid tissue or inflammation-related chemokines (CCR2, CCR5, and CXCR3), while few NKT cells express lymphoid tissue-homing chemokine receptors (CCR7 and CXCR5). 12324654_Data show that blr1 was induced early during cell differentiation and because its overexpression accelerated monocytic differentiation, it may be important for signals controlling cell differentiation. 14618028_Data demonstrate a significant age-dependent difference in the response of osteoblasts to CXCR3 and CXCR5 activation. 14763921_CXCR5 and CXCL13 play an essential role in maintaining B- and T-cells in lymphocytic infiltrates and ectopic follicles in thyroid tissue from patients affected by autoimmunity. 15713799_studies suggest that IRBP and S-Ag can initiate innate and, in sensitive individuals, adaptive immune response by attracting iDCs and T and B cells expressing CXCR3 and CXCR5 15780119_Potenetial role of CXCL13 and its specific receptor CXCR5 in recruitment of B cells in renal allograft rejection. 16225771_Data show that CXCL13 and CCL19 together by means of activation of CXCR5 and CCR7 up-regulated PEG10 expression and function in leukemic B cells. 16318584_elevated levels of CXCL13 could cause impaired or altered trafficking of B cells during HIV infection and could contribute to the previously reported loss of CXCR5 16888899_CCR7 and CXCR5 are differentially expressed on the cell surface of lymphocytes and dendritic cells depending of the stage of cellular differentiation and activation. (review) 17015714_expression of CXCR5 identifies a unique subset of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells which express the costimulatory molecules ICOS and CD40L, secrete IL-2, IL-4, and IL-10 and help B cells for Ab production 17018614_Expression of CXCR5 on tumor cells promotes the growth of colon carcinoma cells in the liver. 17652619_CXCR5 plays a role in Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cell positioning and cognate interactions between CLL and CXCL13-secreting CD68+ accessory cells in lymphoid tissues. 17786442_CXCR5 is the first chemokine receptor so far identified able to attract in vitro primary metastatic neuroblastoma cells 18528326_Most B cells expressed CXCR5. 18780835_Altered expression of the chemokine receptor-ligand pair, CXCR5/CXCL13, may participate in the establishment of B-cell dysfunctions during HIV-1 infection. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19228923_High levels of CXCR5 is associated with mantle cell lymphoma. 19375853_the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis is significantly associated with prostate cancer progression 19536742_Low-expression frequency for the chemokine receptor CXCR5 is associated with mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 19610059_Overexpression of CXCR5 is associated with prostate cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955043_Results suggest that BLC/CXCL13 as well as its corresponding receptor, CXCR5, may play important roles in the pathogenesis of SLE and in lupus nephritis. 20412587_CXCL13 caused CXCR5-dependent activation of the PI3Kp85alpha in prostate cancer cells 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20809769_Sections of the mouse CXCR5 intron significantly align plus/plus with sections of the human intron; the aligned segments are in the same order in mouse as in man and overall cover 13% of the mouse sequence and 17% of the human sequence. 21471443_Central memory CD4 T cells expressing CXCR5 efficiently induced PC differentiation and Ig secretion, and displayed a different profile in terms of cytokine and costimulatory molecule expression. 21642390_these results add new information about the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis in neuroblastic tumors and in the crosstalk between neuroblastic and stromal cells. 21750724_Data indicate that the percentages of CD4(+)CXCR5(+) TFH in IA patients were positively correlated with AST. 21785430_A Bcl-6-CXCR5 axis in T(reg) cells drive the development of follicular regulatory T cells that function to inhibit germinal center reactions. 22607768_The CXCL13-CXCR5 axis is associated with classic determinants of poor prognosis, such as high grade, hormone receptor negativity, and axillary node involvement. 22707196_C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5 gene polymorphisms are associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 22840692_Levels of CXCL13 are increased in carotid atherosclerosis both systemically and within the atherosclerotic lesion. Based on our in vitro findings, we hypothesize a potential plaque stabilizing effects of CXCL13-CXCR5 interaction 22913878_Data indicate that EBI2 expression modulates CXCL13 binding affinity to CXCR5. 23189125_Interruption of CXCL13-CXCR5 axis increases upper genital tract pathology and activation of NKT cells following chlamydial genital infection. 23250934_Polymorphisms in CXCR5 are associated with HIV-associated non-hodgkin B-cell lymphoma. 23739915_A single nucleotide polymorphism in CXCR5, rs630923, is associated with genetic risk for multiple sclerosis. 23773523_specific G protein isoforms coupled to CXCR5 in its resting and active states, were identified. 23807677_Data suggest the involvement of CD4+ CXCR5+ T cells (circulating follicular helper T cells Tfh) in the pathogenesis and progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). 23812490_Results provide additional evidence for a role of host genetic variation in CXCR5 in lymphomagenesis, particularly for FL. 24001599_study discovered multiple susceptibility variants for systemic lupus erythematosus in the 11q23.3 region, including variants in/near PHLDB1 (rs11603023), DDX6 (rs638893) and CXCR5 (rs10892301) 24035365_Human circulating memory T-helper cells expressing PD-1 and CXCR5 are highly functional and correlate with broadly neutralizing HIV antibody responses. 24138884_Circulating precursor cd4+ T cells expressing CCR7(low)PD-1(high) CXCR5+ indicate T-helper cell activity and promote antibody responses upon antigen re-exposure. 24337540_expression of CXCR5 was significantly associated with both stage and lymph node metastasis, but not with tumor size, tumor differentiation grade, or menopausal status of the patient. 24732574_Suggest that platelet-mediated signaling through CXCR5 may be active in vivo during plaque destabilization, enhancing the anti-inflammatory effects of CXCL13. 24833093_healthy controls with rs6421571CT and TT genotypes had higher mRNA and protein levels of CXCR5 than those with wild-type CC genotype specifically in CD4+ T cells 24966908_CD4+CXCR5+ helper T cells may contribute to the pathogenesis of primary Sjogren's syndrome by promoting the maturation of B cells. 25010623_Expression features of CXCR5 and its ligand, CXCL13 associated with poor prognosis of advanced colorectal cancer 25015289_FANCA-modulated neddylation pathway involved in CXCR5 membrane targeting and cell mobility. 25077417_three SNPs (rs497916, rs3922, rs676925) in CXCR5 and one SNP (rs355687) in CXCL13 were associated with hepatitis B vaccine efficacy 25271023_After validation in larger patient groups, CXCR5 and CXCL13 may prove useful as biomarkers for nonsmall cell lung carcinoma Correspondingly, blockade of this axis could serve as an effective therapy for nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. 25279986_11q23.3 with rs4938573 near CXCR5 gene is associated with follicular lymphoma. 25476740_our findings suggest that CXCL13-CXCR5 axis promotes the growth, migration, and invasion of colon cancer cells, probably via PI3K/AKT pathway 25654980_Circulating CXCR5+CD4+helper T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients share phenotypic properties with germinal center follicular helper T cells and promote antibody production. 25666935_A negative correlation between levels of miR-346 and percentages of CD4(+)CXCR5(+) T cells was confirmed in Graves' disease 25714983_IL-33 enhances humoral immunity against chronic hbv infection through activating CD4(+)CXCR5(+) helper-Inducer T-Lymphocytes. 25726157_CXCR5 expression positively related to the lymph node and distal metastasis, tumor stage and relapse of colorectal cancer. 25786345_elevated CXCR5 expression may contribute to abnormal cell survival and migration in breast tumors that lack functional p53. 26333070_study showed that induction of circulating CXCR5+CD4+ Tfh-like subsets can be detected following immunization with HPV vaccines, and potentially be useful as a marker of immunogenicity of vaccines 26462153_Authors demonstrate that CD40 expression upregulates the chemokine receptor CXCR5 and promotes MDSC migration toward and accumulation within cancer. 26517519_In patients with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma the phenotype and function of CXCR5+CD45RA-CD4+ T cells were altered. 26640404_down-regulation of CXCR5 inhibited the growth and proliferation of LNCaP cells. 26752644_findings reveal a neuronal/astrocytic interaction in the spinal cord by which neuronally produced CXCL13 activates astrocytes via CXCR5 to facilitate neuropathic pain. 26818544_HCV infection increased the frequency of CD4+CXCR5+ T cells and decreased the frequency of CD27+IgG+ B cells. CD4+CXCR5+ T cells activated CD27+IgG+ B cells via the secretion of IL-21. 26928629_Neoplastic cells of PCSM-TCL are medium- to-large-sized T cells with cerebriform nuclei, which lack the expression of TFH-cell defining chemokine receptor CXCR5. These features are highly distinctive and can be invaluable in separating this rather indolent cutaneous T-cell lymphoid neoplasm from more aggressive lymphomas of TFH-cell phenotype, including primary cutaneous TFH-cell lymphoma and skin involvement of AITL 27873133_Levels of CXCR5 mRNA and protein levels were up-regulated in brain from temporal lobe epilepsy patients. 28004828_basal CXCR5(+)Th17 cell frequency may indicate underlying differences in disease phenotype between patients and predict ultimate success of TNF inhibitor therapy 28402859_we demonstrate that PKCepsilon cooperates with the loss of the tumor suppressor Pten for the development of prostate cancer in a mouse model. Mechanistic analysis revealed that PKCe overexpression and Pten loss individually and synergistically upregulate the production of the chemokine CXCL13, which involves the transcriptional activation of the CXCL13 gene 28412245_the data demonstrate that CXCR5(+)CD8(+) T cells represent a significant CD8(+) T cell subset in colorectal tumors and have the potential to contribute to antitumor immunity, but their specific roles require further studies in vivo. 28454789_these findings demonstrate that CXCR5 overexpression increases the ability of MSCs to respond to migratory stimuli and highly intensifies their immunomodulatory effects in vivo. This strategy for enhancing targeted stem/progenitor cell homing may improve the efficacy of MSC-based therapies. 28551095_The A allele of rs613791 and G allele of rs523604 located in CXCR5 were observed to be significantly associated with vitiligo in the Chinese Han population. 28733085_These results provide clear evidence that CXCR4- or CCR5-beta-arrestin complexes induce receptor endocytosis and signaling in the absence of G protein coupling and ligand-induced conformational changes of the receptor. 28783539_identified the miR-19a/CXCR5 pathway as a candidate p53-induced migration mechanism 28931218_CXCL13/CXCR5 mediated the aggregation of B cells, that directed the aberrant humoral immune responses via the formation of ectopic germinal centers, which suggests a molecular mechanism of neurological damage in neurosyphilis. 29107083_all three p53 family members mediate the effects of genotoxic stress on the CXCR5 promoter using the same mechanism associated with attenuation of NFkB activity. 29377743_The leptin upregulated RA CD4(+)CXCR5(+)ICOS(+) T cells via increased IL-6 by activation of STAT1 and STAT3. 29453859_The authors link a genetic susceptibility allele for Sjogren's syndrome to a functional phenotype in terms of decreased CXCR5 expression. The decrease of CXCR5(+) cells in circulation was also related to homing of B and T cells to the autoimmune target organ. 29490514_miR-192 suppresses T follicular helper cell differentiation by targeting CXCR5 in childhood asthma. 30087107_CXCR5 and ICOS expression identifies a CD8 T-cell subset with TFH features in Hodgkin lymphomas. 30209639_overexpressed miR-155 and detected decreased protein levels of CXCR5 30276608_CXCR5 drove migration toward its ligand, CXCL13, and probed for interactions with several candidates using flow cytometry-based Forster resonance energy transfer. 30553016_in RelA high conditions, low Nrf2 and lack of cxcr5 promoter DNA-methylation govern CXCL13-CXCR5 co-expression within breast tumors, and thus drive disease progression and metastasis. 30866951_Circulating CXCR5-expressing CD8+ T-cell has diagnostic value for current bacterial pneumonia severity. 31126860_Altered proportions of circulating CXCR5+ helper T cells do not dampen influenza vaccine responses in children with rheumatic disease. 31229843_An upregulation of Th17-like CD4(+)CXCR5(+) T cells was present in lean T2D patients and was associated with autoantibody positivity. 31562329_C-X-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CXCR5) programmed cell death 1 (PD1) T follicular helper (Tfh) subset of CD8(+) T cells whose development and function contribute to the breakdown of B-cell tolerance. 31628349_Transcriptome Network Analysis Identifies CXCL13-CXCR5 Signaling Modules in the Prostate Tumor Immune Microenvironment. 32584200_CXCL13-producing PD-1(hi)CXCR5(-) helper T cells in chronic inflammation. 32847038_CXCL13/CXCR5 Interaction Facilitates VCAM-1-Dependent Migration in Human Osteosarcoma. 32896997_Correlation between CXCR4, CXCR5 and CCR7 expression and survival outcomes in patients with clinical T1N0M0 non-small cell lung cancer. 33000253_Long noncoding RNA PLK1S1 was associated with renal cell carcinoma progression by interacting with microRNA653 and altering CXC chemokine receptor 5 expression. 33098668_Human CXCR5(+) PD-1(+) CD8 T cells in healthy individuals and patients with hematologic malignancies. 33161233_CXCL13/CXCR5 signalling is pivotal to preserve motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 33264451_Possible roles of CXCL13/CXCR5 axis in the development of bullous pemphigoid. 33378752_CXC Chemokine Receptor Type 5 Gene Polymorphisms in a Cohort of Egyptian Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. 33452206_CXCL13 shapes immunoactive tumor microenvironment and enhances the efficacy of PD-1 checkpoint blockade in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. 33707428_Targeting Erbin in B cells for therapy of lung metastasis of colorectal cancer. 33717056_Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cells Expressing CXCR5 Are Detectable in HIV-1 Elite Controllers After Prolonged In Vitro Peptide Stimulation. 34035252_Intratumoral CXCR5(+)CD8(+)T associates with favorable clinical outcomes and immunogenic contexture in gastric cancer. 34114971_CXCR5 induces perineural invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma by inhibiting microRNA-187. 34382069_CXCR5/CXCL13 pathway, a key driver for migration of regulatory B10 cells, is defective in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 34427969_CXC chemokine ligand-13 promotes metastasis via CXCR5-dependent signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. 34446066_The CXCL13/CXCR5-chemokine axis in neuroinflammation: evidence of CXCR5+CD4 T cell recruitment to CSF. 34518512_CXCL13/CXCR5 axis facilitates endothelial progenitor cell homing and angiogenesis during rheumatoid arthritis progression. 34557191_Simulating CXCR5 Dynamics in Complex Tissue Microenvironments. 34582976_ETV4 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis through activation of the CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling axis. 34991160_Hypermethylation at the CXCR5 gene locus limits trafficking potential of CD8+ T cells into B-cell follicles during HIV-1 infection. 36341562_Association of Gene Polymorphisms in CXC Chemokine Receptor 5 with Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility. |
ENSMUSG00000047880 |
Cxcr5 |
45.746182 |
14.2923982045 |
3.837176 |
0.493886849 |
59.025777 |
0.00000000000001556199373305390261654880432815133459479597054231359010145752108655869960784912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000103141009205152938198697645016384034463599421449497839375908370129764080047607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
87.9102391 |
22.5909150 |
6.3760303 |
1.4627122 |
| ENSG00000160741 |
200186 |
CRTC2 |
protein_coding |
Q53ET0 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional coactivator for CREB1 which activates transcription through both consensus and variant cAMP response element (CRE) sites. Acts as a coactivator, in the SIK/TORC signaling pathway, being active when dephosphorylated and acts independently of CREB1 'Ser-133' phosphorylation. Enhances the interaction of CREB1 with TAF4. Regulates gluconeogenesis as a component of the LKB1/AMPK/TORC2 signaling pathway. Regulates the expression of specific genes such as the steroidogenic gene, StAR. Potent coactivator of PPARGC1A and inducer of mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells. Also coactivator for TAX activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) long terminal repeats (LTR). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14506290, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14536081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16809310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16817901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16980408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17210223}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the transducers of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein activity family of transcription coactivators. These proteins promote the transcription of genes targeted by the cAMP response element-binding protein, and therefore play an important role in many cellular processes. Under basal conditions the encoded protein is phosphorylated by AMP-activated protein kinase or the salt-inducible kinases and is sequestered in the cytoplasm. Upon activation by elevated cAMP or calcium, the encoded protein translocates to the nucleus and increases target gene expression. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:200186; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cAMP response element binding protein binding [GO:0008140]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; histone H3-K9 acetylation [GO:0043970]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
16809310_Thus, both TORC1/2 and p300 families of coactivators are essential for optimal activation of HTLV-1 transcription by Tax. 16980408_These results strongly suggest that TORCs play a key role in linking these external signals to the transcriptional program of adaptive mitochondrial biogenesis by activating PGC-1alpha gene transcription. 17476304_latent cytoplasmic coactivator TORC2 mediates target gene activation in response to cAMP signaling by associating with CBP/p300 and increasing its recruitment to a subset of CREB target genes 17548807_TORC2 regulates germinal center repression of the TCL1 oncoprotein to promote B cell development and inhibit transformation. 17950019_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17950019_genetic variants of LKB1-AMPK-TORC2 pathway components may exert a weak influence on the occurrence of type 2 diabetes in Japanese 18626018_identify Ser-275 of TORC2 as a 14-3-3 binding site that is phosphorylated under low glucose conditions and which becomes dephosphorylated by calcineurin in response to glucose influx 19164291_TORC2, a coactivator of cAMP-response element-binding protein, promotes Epstein-Barr virus reactivation from latency through interaction with viral BZLF1 protein. 19509226_The regulation of aromatase by CRTC2, in response to the altered hormonal milieu associated with menopause and obesity, provides a critical link between obesity and breast cancer. 20101207_Tax binds the cyclin D1 promoter-proximal cyclic AMP response element (CRE) in the presence of phosphorylated CREB (pCREB) in vitro, and together the Tax-pCREB complex recruits the cellular co-activator p300 to the promoter. 20675384_the association of Pin1 with CRTC2 to decrease the nuclear CBP.CRTC.CREB complex. 20693566_The lipogenic effects of GIP in the presence of insulin are therefore at least partially mediated by upregulation of adipocyte LPL gene transcription through a pathway involving PI3-K/PKB/AMPK-dependent CREB/TORC2 activation. 23213254_Mechanism of CREB recognition and coactivation by the CREB-regulated transcriptional coactivator CRTC2 23584792_Phosphorylation of CRTC2 at its AMPK target site, Ser 171, dictated its subcellular localization, and the activation of aromatase PII in preadipocytes. 23671120_CRTC2 enhances CREB phosphorylation through an association with the protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5). 24484648_The data from the current study demonstrated novel PROM1 and CRTC2 mutations, which could promote lung cancer development. 24529027_These results clearly indicate that non-phosphorylated CRTC2 strongly enhances hepatitis b virus biosynthesis through inducing PGC1alpha expression. 25256670_the high expression of CRTC2 and PROM1 may play an important role in the occurrence and hereditary, and also advance the potential pathways that integrate genetic variants in the development of NSCLC. 26004186_Our results establish a role for CRTC2 as a lymphoma tumor suppressor gene 26644205_CRTC2 polymorphism as a risk factor for the incidence of metabolic syndrome in transplant recipients after solid organ transplantation. 26652733_CRTC2 strongly enhances GR-induced transcriptional activity of glucocorticoid-responsive genes. 28212844_Thyroid stimulating hormone activates CRTC2 via the TSHR/cAMP/PKA pathway. 29192248_Study suggests that Creb/Crtc2 negatively regulates the Sirt1/Pparalpha/Fgf21 axis via the induction of miR-34a under diet-induced obesity and insulin-resistant conditions. 29733854_Data report crystal structures of a complex containing the CRTC2 CREB binding domain, the CREB basic leucine zipper domain and a CRE-containing DNA. The structures revealed that CRTC and CREB form a 2:2 complex on CRE-containing DNA, and CRTC interacts with both CREB and DNA through highly conserved residues. 30782776_Results identified CRTC2 as a downstream substrate of constitutively activated p38. Constitutive, rather than transient, activation of p38 led to hyperphosphorylation of CRTC2, resulting in CRTC2 cytosolic relocation and subsequent inactivation of cyclic AMP response element (CRE)-mediated transcription. 31355336_CRTC2 is unphosphorylated and therefore constitutively activated in LKB1-mutant non-small cell lung cance, where it promotes tumor growth, in part via the induction of the inhibitor of DNA binding 1. 33000695_Phosphorylation of CREB-Specific Coactivator CRTC2 at Ser238 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer Cells. 33013689_SIK1 Regulates CRTC2-Mediated Gluconeogenesis Signaling Pathway in Human and Mouse Liver Cells. 33723808_The CREB Regulated Transcription Coactivator 2 Suppresses HIV-1 Transcription by Preventing RNA Pol II from Binding to HIV-1 LTR. 33780908_TORC2/3-mediated DUSP1 upregulation is essential for human decidualization. 34099657_Sam68 promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis via CRTC2. 35037420_cAMP-Induced Nuclear Condensation of CRTC2 Promotes Transcription Elongation and Cystogenesis in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. 35504112_Activation of the CREB Coactivator CRTC2 by Aberrant Mitogen Signaling promotes oncogenic functions in HPV16 positive head and neck cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000027936 |
Crtc2 |
630.439011 |
0.4600699898 |
-1.120075 |
0.218701897 |
25.540880 |
0.00000043310841911580277184944261746613047847631605691276490688323974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001598569708964553527389611080333775561257425579242408275604248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
416.8215026 |
82.5447698 |
909.1355580 |
130.1795856 |
| ENSG00000160752 |
2224 |
FDPS |
protein_coding |
P14324 |
FUNCTION: Key enzyme in isoprenoid biosynthesis which catalyzes the formation of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP), a precursor for several classes of essential metabolites including sterols, dolichols, carotenoids, and ubiquinones. FPP also serves as substrate for protein farnesylation and geranylgeranylation. Catalyzes the sequential condensation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate with the allylic pyrophosphates, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate, and then with the resultant geranylpyrophosphate to the ultimate product farnesyl pyrophosphate. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Host-virus interaction;Hydroxylation;Isoprene biosynthesis;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Isoprenoid biosynthesis; farnesyl diphosphate biosynthesis; farnesyl diphosphate from geranyl diphosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate: step 1/1.; PATHWAY: Isoprenoid biosynthesis; geranyl diphosphate biosynthesis; geranyl diphosphate from dimethylallyl diphosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate: step 1/1. |
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the production of geranyl pyrophosphate and farnesyl pyrophosphate from isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. The resulting product, farnesyl pyrophosphate, is a key intermediate in cholesterol and sterol biosynthesis, a substrate for protein farnesylation and geranylgeranylation, and a ligand or agonist for certain hormone receptors and growth receptors. Drugs that inhibit this enzyme prevent the post-translational modifications of small GTPases and have been used to treat diseases related to bone resorption. Multiple pseudogenes have been found on chromosomes 1, 7, 14, 15, 21 and X. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:2224; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; dimethylallyltranstransferase activity [GO:0004161]; geranyltranstransferase activity [GO:0004337]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; farnesyl diphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0045337]; geranyl diphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0033384] |
15713990_This study provides the first evidence of the presence of FPPs activity in human CRC. Moreover, FPPs enzyme was found to play a significant role in colon cancer proliferation. 17198737_mitochondrial targeting of FPS may be widespread among eukaryotes 17368768_findings suggest that a single nucleotide polymorphism in the FDPS gene (rs2297480) may be a genetic marker for lower bone mineral density in postmenopausal Caucasian women 17387528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18494934_FDPS is involved in the resistance to zoledronic acid of osteosarcoma cells. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18687167_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19056481_characterized functionally the minimal basal promoter of the human FDPS gene by means of deletion mutants and we have identified two cis-acting elements which modulate the FDPS gene expression and are recognized by Pax5 and OCT-1 transcription factors 19494338_FPPS knockdown cells activated Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells, as measured by increased levels of CD69 and CD107a, killing of FPPS knockdown cells, and induction of IFN-gamma secretion 20191015_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20450493_characterized the sterol-response-element-binding protein 2 and nuclear factor Y-binding site in the farnesyl diphosphate synthase promoter 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21151198_Common polymorphisms of the FDPS gene influence the response to bisphosphonates in osteoporotic women. 21196316_The A/C rs2297480 polymorphism of FDPS was highly differently distributed among osteonecrosis-of-the-jaw patients and controls, with a correlation between AA carrier status and occurrence of ONJ after 18-24 months of treatment with bisphosphonates. 22278941_findings reveal a FDPS-dependent mechanism in the internalization and down-regulation of beta2AR, identify FDPS as a potential target for improving the therapeutic efficacy of beta-agonists 22338925_first study on the gene FDPS rs2297480 SNP in postmenopausal Thai women.The effect did not contribute to the baseline of bone mineral density nor bone turnover markers. 22407328_FPPS was more highly expressed in prostate cancer vs. normal prostate tissue. The association of FPPS with established histopathological risk parameters and biochemical recurrence implicates a contribution of the mevalonate pathway to PC progression. 23234314_The crystal structure of human FPPS in complex with a novel bisphosphonate YS0470 and in the absence of a second substrate showed partial ordering of the tail in the closed conformation. 23238007_LRP5 and FDPS loci age-specifically affect skeletal traits in healthy fertile women. 23277274_FPPS might play an important role in Ang II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in vivo, at least in part through RhoA, p-38 MAPK and TGF-beta1. 23847096_The iPA-driven modulation of FDPS can cause an enhancement of post-translational prenylation essential for the biological activity of key proteins in NK signaling and effector functions, such as Ras. 23998921_Data indicate compounds represent a new structural class of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (hFPPS) inhibitors and suggest a development of therapeutics. 24311107_Results suggest that polymorphisms of the FDPS gene may influence the bone response to drugs targeting the mevalonate pathway, like statins. 24369118_These observations suggest that an increase in the expression of endogenous FPPS could confer at least partial resistance to the pharmacological effect of N-BP drugs such as ZOL in vivo 24534219_our study indicated that DR patients have higher VEGF levels than diabetic patients without retinopathy, and -2578A/C (rs699947) and +405C/G (rs2010963) may be important factors in determining serum VEGF levels. 24598914_A co-crystal structure of human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase in complex with a bisphosphonate and two molecules of inorganic phosphate. 24927548_The results identify new classes of FPPS inhibitors, diterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids, that bind to the IPP site and may be of interest as anticancer and antiinfective drug leads. 25630225_These results are consistent with the previously proposed hypothesis that the allosteric pocket of human FPPS, located near the active site, plays a feed-back regulatory role for this enzyme. 28098152_Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) allosterically regulated the activity of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. 29036218_Crystallographic and thermodynamic characterization of phenylaminopyridine bisphosphonates binding to human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase 29075041_Deregulated expression and activity of Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase (FDPS) in Glioblastoma 29337059_FPPS mediates TGF-beta1-induced lung cancer cell invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the RhoA/Rock1 pathway. 30561051_A novel premature termination mutation in FDPS in a Chinese family with disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis. 30914801_FDPS plays an oncogenic role in PTEN-deficient Prostate cancer through GTPase/AKT axis. Identifying mevalonate pathway proteins could serve as a therapeutic target in PTEN dysregulated tumors. 31774873_FDPS rs2297480 is associated with postmenopausal osteoporosis. 34751146_Novel missense mutations of MVK and FDPS gene in Chinese patients with disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis. 34885721_Towards an Improvement of Anticancer Activity of Benzyl Adenosine Analogs. |
ENSMUSG00000059743 |
Fdps |
874.946302 |
2.0461904807 |
1.032940 |
0.078999443 |
169.416114 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000992417117401306156622225054319032456321851090538754171979462446328998043783079002687479036159861668121850986068466227152384817600250244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000161144957677043774343917775377998365016011694113628895745208206106272642332280368369905659348606183356444887522229691967368125915527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1215.6036214 |
54.3909652 |
597.7346856 |
20.4264779 |
| ENSG00000160781 |
79957 |
PAQR6 |
protein_coding |
Q6TCH4 |
FUNCTION: Plasma membrane progesterone (P4) receptor coupled to G proteins (PubMed:23763432, PubMed:23161870). Seems to act through a G(s) mediated pathway (PubMed:23161870). Involved in neurosteroid inhibition of apoptosis (PubMed:23161870). May be involved in regulating rapid P4 signaling in the nervous system (PubMed:23763432). Also binds dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), pregnanolone, pregnenolone and allopregnanolone (PubMed:23763432, PubMed:23161870). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23161870, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23763432}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Steroid-binding;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor activity. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79957; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; steroid binding [GO:0005496] |
18603275_PAQR6 is a previously uncharacterized PAQR which is also capable of responding to progesterone. 23161870_The results suggest that PAQR6 and PAQR9 (mPRdelta and mPRepsilon) function as mPRs coupled to G proteins and are potential intermediaries of nonclassical antiapoptotic actions of neurosteroids in the central nervous system. 34572596_PAQR6 Upregulation Is Associated with AR Signaling and Unfavorite Prognosis in Prostate Cancers. |
ENSMUSG00000041423 |
Paqr6 |
31.348121 |
0.2509878051 |
-1.994311 |
0.364336360 |
30.667326 |
0.00000003062793666307154663045814657271193048870827624341472983360290527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000127199872016583012228409005524298880374090003897435963153839111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8454639 |
3.2687347 |
55.6154959 |
8.0171783 |
| ENSG00000160789 |
4000 |
LMNA |
protein_coding |
P02545 |
FUNCTION: Lamins are components of the nuclear lamina, a fibrous layer on the nucleoplasmic side of the inner nuclear membrane, which is thought to provide a framework for the nuclear envelope and may also interact with chromatin. Lamin A and C are present in equal amounts in the lamina of mammals. Recruited by DNA repair proteins XRCC4 and IFFO1 to the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) to prevent chromosome translocation by immobilizing broken DNA ends (PubMed:31548606). Plays an important role in nuclear assembly, chromatin organization, nuclear membrane and telomere dynamics. Required for normal development of peripheral nervous system and skeletal muscle and for muscle satellite cell proliferation (PubMed:10080180, PubMed:22431096, PubMed:10814726, PubMed:11799477, PubMed:18551513). Required for osteoblastogenesis and bone formation (PubMed:12075506, PubMed:15317753, PubMed:18611980). Also prevents fat infiltration of muscle and bone marrow, helping to maintain the volume and strength of skeletal muscle and bone (PubMed:10587585). Required for cardiac homeostasis (PubMed:10580070, PubMed:12927431, PubMed:18611980, PubMed:23666920). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10080180, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10580070, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10587585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10814726, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11799477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12075506, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12927431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15317753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18551513, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18611980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22431096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23666920, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31548606}.; FUNCTION: Prelamin-A/C can accelerate smooth muscle cell senescence. It acts to disrupt mitosis and induce DNA damage in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), leading to mitotic failure, genomic instability, and premature senescence. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Coiled coil;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy;Intermediate filament;Isopeptide bond;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Lipoprotein;Methylation;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is part of the nuclear lamina, a two-dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane. The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. During mitosis, the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability, chromatin structure and gene expression. Vertebrate lamins consist of two types, A and B. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Mutations in this gene lead to several diseases: Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, familial partial lipodystrophy, limb girdle muscular dystrophy, dilated cardiomyopathy, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. |
hsa:4000; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; lamin filament [GO:0005638]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear lamina [GO:0005652]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; site of double-strand break [GO:0035861]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; DNA double-strand break attachment to nuclear envelope [GO:1990683]; establishment or maintenance of microtubule cytoskeleton polarity [GO:0030951]; heterochromatin formation [GO:0031507]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:1903243]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0072201]; negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090201]; nuclear envelope organization [GO:0006998]; nuclear migration [GO:0007097]; nuclear pore localization [GO:0051664]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of histone H3-K9 trimethylation [GO:1900114]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein localization to nuclear envelope [GO:0090435]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900180]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of telomere maintenance [GO:0032204]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055015] |
11243729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11440372_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11792809_Some lamin A mutants causing disease can be aberrantly localized, partially disrupt the endogenous lamina and alter emerin localization, whereas others localize normally in transfected cells. 11792810_Certain dilated cardiomyopathy- and Emery-Dreyfuss muscular dystrophy-associated LMNA mutations result in misassembly of A-type lamins and give rise to a variety of nuclear structure abnormalities which may contribute to disease progression. 11792811_A population of cultured skin fibroblasts from lipodystrophic patients with heterozygous R482Q/W mutations in the lamin A/C gene present dysmorphic nuclei or a disorganization of the nuclear lamina, or both. 11792821_Lamin A-binding is mediated by the central region of emerin, residues 70-178, outside the LEM-domain. 11799477_homozygous defects in LMNA, encoding lamin A/C nuclear-envelope proteins, cause autosomal recessive axonal neuropathy in human (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disorder type 2) and mouse 11897440_LMNA gene mutations account for 33% of the dilated cardiomyopathies with atrioventricular block, all familial autosomal dominant. 11973618_genes known to be responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy 12015247_Novel missense mutations in two families with the Dunnigan variety of familial partial lipodystrophy, cardiac conduction system defects, and cardiomyopathy suggest a multisystem dystrophy syndrome due to LMNA mutations. 12018485_1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the C-terminal domain 12032588_LMNA mutation is associated with autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss mucular dystrophy amd limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 12057196_solution structure of the human lamin A/C C-terminal globular domain which contains specific mutations causing four different heritable diseases 12075506_mutation causes mandibuloacral dysplasia 12112001_regions of PKC-alpha that are crucial for binding to lamin A, and vice versa 12138353_Absence of mutations in exon 8 of the gene in combination antiretroviral therapy-associated partial lipodystrophy. 12145775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12196663_Mutations in the lamin A/C gene found associated with lipodystrophy, cardiac abnormalities, and muscular dystrophy. 12409453_In this study, we identify a novel interaction between lamin A/C and hsMOK2 by using the yeast two-hybrid system 12467734_The autosomal recessive axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2 due to mutation (c.892C>T-p.R298C) in a gene encoding Lamin A/C nuclear envelope proteins and the first gene in which a mutation leads to autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2. 12524233_LMNA missense mutations in nondiabetic carriers with Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD) are associated with elevated levels of serum C-reactive protein and free fatty acid, particularly in women. 12628721_Mutations in LMNA cause a severe and progressive dilated cardiomyopathy in a relevant proportion of patients. 12673789_French family affected with a new phenotype composed of autosomal dominant severe dilated cardiomyopathy & a specific quadriceps muscle myopathy;identified missense mutation in the lamin A/C gene that cosegregated with the disease 12702809_Hutchinson-Gilford progeria appears to represent a novel laminopathy, caused by a single heterozygous splicing mutation in the LMNA gene, leading to a major loss of Lamin A expression, intimately associated to nuclear alterations 12714972_point mutations in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome 12718522_The carboxyl-terminal region common to lamins A and C contains a DNA binding domain. 12729796_Results suggest that nuclear aggregate formation is in part due to overexpression of lamin A, but that there are also mutant-specific effects. 12768443_LMNA mutation was studied in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria. It does not occur in Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch progeroid syndrome. 12783988_the lamin a-emerin complex might have a role in muscular dystrophy and cardiomyopathy 12844477_In this study, we excluded mutations within the complete coding region and the promoter of LMNA and the CRABP II gene in HIV-1 infected patients 12920062_A specific phenotype characterized by early atrial fibrillation is associated with LMNA mutation. 13129702_REVIEW: The recent explosion in the number of identified mutations within the LMNA gene, which encodes two protein products lamins A and C, has allowed the identification of an allelic series of disorders, all caused by mutations within this one gene 14597414_Nuclear lamin A/C aggregates and a reduced incorporation of bromouridine were noted in fibroblasts from a familial partial lipodystrophy patient carrying an R482L lamin A/C mutation, demonstrating RNA transcription interference 14644157_data demonstrate that lamin C and lamin A interact in vivo directly with nesprin-1alpha and with emerin and that lamin A or C is sufficient for the correct anchorage of emerin and nesprin-1alpha at the nuclear envelope in human cells 14675861_A new LMNA mutation (1621C>T, R541C) was found in two members of a French family with a history of ventricular rhythm disturbances and an uncommon form of systolic left ventricle dysfunction. 14985400_LMNA represents the first gene implicated in both recessive and dominant forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 15026149_identified the epitope recognized by a new panel of mAbs against lamin A/C as a sequence of 9 amino acids that contain a complete beta-strand of the Ig-like globular domain; the major site of lipodystrophy missense mutation, R482 is present in the epitope 15080529_Review. Naturally occurring mutations in LMNA have been shown to be responsible for distinct diseases called laminopathies, including dilated cardiomyopathy with or without conduction defect and with or without variable skeletal muscle involvement. 15205219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15205219_The H566H polymorphism was associated with metabolic syndrome and also higher mean fasting triglyceride and lower mean HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the Old Order Amish. 15205220_Review. Laminopathies are genetic diseases that encompass a wide spectrum of phenotypes with diverse tissue pathologies and result mainly from mutations in the LMNA gene encoding nuclear lamin A/C. 15219508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15284226_the distinctive ensemble of heterotypic lamin interactions in a particular cell type affects the stability of the lamin polymer 15298354_a novel mutation associated with familial partial lipodystrophy 15317753_Heterozygous splicing mutation in the LMNA gene, leading to the complete or partial loss of exon 11 in mRNAs encoding Lamin A in restrictive dermopathy was found. 15342704_partial splice site selection in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome 15372542_mutations in lamins A and C may lead to a weakening of a structural support network in the nuclear envelope in fibroblasts and that nuclear architecture changes depend upon the location of the mutation 15551023_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15622532_this is the first report of a patient combining features of these two phenotypes because of a single mutation(S143F) mutation in LMNA. 15636422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15639119_This study identified a novel mutation in the 5' region of the LMNA gene -3del15, resulting in the loss of 15 nucleotides from -3 to +12, including the translation ATG initiator codon. 15748902_Our findings suggest a loss of function of A-type lamin mutant proteins in the organization of intranuclear chromatin and predict the loss of gene regulatory function in laminopathies. 15798706_Mutations in LMNA cause a severe and progressive dilated cardiomyopathy in a relevant proportion of patients. 15919811_This study further extends the vast range of diseases linked to LMNA mutations and identifies another genetic cause for the type A insulin resistance syndrome. 15961312_Two patients with 'Dropped head syndrome' due to mutations in LMNA genes. 15982412_results suggest that a mutant truncated lamin A, even when expressed at low levels, causes defective cell stability, which may be responsible for phenotypic abnormalities in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome 15998779_Two homozygous missense LMNA mutations involving the arginine 527 and alanine 529 residues cause MAD with subtle variations in phenotype. 16084085_Missense mutation in peripheral nerve disease in an individual. 16117820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16126733_These results implicate the abnormal farnesylation of progerin in the cellular phenotype in HGPS cells and suggest that FTIs may represent a therapeutic option for patients with HGPS 16129833_blocking farnesylation of authentic progerin in transiently transfected HeLa, HEK 293, and NIH 3T3 cells with farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) restored normal nuclear architecture 16179429_Our results identify the absence of A-type lamin expression as a novel marker for undifferentiated ES cells and further support a role for nuclear lamins in cell maintenance and differentiation. 16218190_These data identify specific functional roles for the emerin-lamin C- and emerin-lamin A- containing protein complexes and is the first report to suggest that the A-type lamin mutations may be differentially dysfunctional for the same LMNA mutation. 16239243_The presence of the expanded CGG-repeat FMR1 mRNA results in reduced cell viability as well as the disruption of the normal architecture of lamin A/C within the nucleus. 16246140_Data show that chromosome positioning is largely unaffected in lymphoblastoid cell lines containing emerin or A-type lamin mutations. 16248985_Thus, we did not find evidence for uniquely interacting partner proteins using this approach, but did identify four new lamin A/C interactive partners 16262891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16266469_The missense mutation E82K in LMNA gene was associated with a malignant phenotype of severe clinical symptoms of familial dilated cardiomyopathy. 16288872_This study reports a case of early onset myopathy due to a heterozygous LMNA mutation in exon 9, characterized by the presence of a marked number of cytoplasmic bodies with extensive myofibrillar abnormalities and Z-disk disruption in skeletal muscle. 16289535_The redistribution into lamin A-/pre-lamin A-containing aggregates of proteins such as pRb and SREBP1a could represent a key aspect underlying the molecular pathogenesis of certain laminopathies. 16344005_lamin A has a role in sensitivity to DNA damaging agents, the DNA damage response, and a senescent phenotype 16357800_Description of the clinical, morphological and biological features that should lead clinicians to consider the diagnosis of laminopathy in a diabetic patient. (review) 16371512_Ser-4 phosphorylation inhibits BAF binding to emerin and lamin A, and thereby weakens emerin-lamin interactions during both mitosis and interphase. 16410549_Results suggest that the C-terminus of nuclear titin binds lamins A and B in vivo and might contribute to nuclear organization during interphase. 16415973_The Charcot-Marie-Tooth diseases resulted from the mutations of LMNA gene are rare. 16461887_The mutant lamin A (progerin) accumulates in the nucleus in a cellular age-dependent manner. 16481476_Lamin A/C and emerin are critical for skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation, with deficient cells displaying delayed differentiation kinetics that may underlie dystrophic phenotypes. 16518869_caspase-6 and its cleavage of lamin A are critical in apoptotic signaling triggered by resveratrol in the colon carcinoma cells, which can be activated in the absence of Bax or p53 16645051_observations implicate lamin A in physiological aging 16697197_Lamin A/C mutations form 'nuclear aggregates' when overexpressed by transfection and in cultured skin fibroblasts from EDMD patients. However, inappropriate lamin A/C assembly may be preventable by manipulation of cell growth conditions. 16738054_The epigenetic changes described most likely represent molecular mechanisms responsible for the rapid progression of premature aging in Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS) patients. 16772334_A subset of lamin A mutants might hinder the response of components of the DNA repair machinery to DNA damage by altering interactions with chromatin. 16823856_We found that in inclusion-body myositis (IBM) muscle vacuoles were immunoreactive for the inner nuclear membrane proteins emerin and lamin A/C. 16825283_Expression of a lamin A mutant that induces alterations in nuclear morphology can cause tissue and organ damage in mice with a normal complement of wild-type lamins. 16981056_The most frequently encountered mutations associated with Dilated Cardiomiopathy are found in LMNA, coding for lamins A and C, intermediate filament proteins. 17090536_This review summarizes the abnormalities caused by an LMNA gene mutation which targets the nuclear envelope, where it interferes with the integrity of the nuclear envelope and causes misshapen cell nuclei, leading to progeroid syndromes. 17097067_Mislocalization of emerin to the endoplasmic reticulum in human cells lacking A-type lamin leads to its degradation and provides the first evidence that its degradation is mediated by the proteasome. 17117676_Neither emerin nor LMNA mutations in a subset of families with EDMD-like phenotypes that may imply an existence of other genes causing similar disorders. 17136397_If neurogenic atrophy is combined with a cardiac disease in a family, this should prompt LMNA mutation analysis. 17150192_Since it has been reported that progeroid features are associated with increased extracellular matrix in dermal tissues, we compared a subset of these components in fibroblast cultures from LMNA mutants with those of control fibroblasts. 17227891_Results suggest that LAP2alpha and lamin A/C are involved in controlling retinoblastoma protein localization and phosphorylation, and a lack or mislocalization of either protein leads to cell cycle arrest in fibroblasts. 17291448_data suggest that the unprenylated prelamin A is not toxic to the cells 17301031_The major causal mutation associated with HGPS triggers abnormal messenger RNA splicing of the lamin A gene leading to changes in the nuclear architecture. 17327437_Eight tag single nucleotide polymorphisms in the LMNA locus were genotyped in 7,495 Danish whites and related to metabolic and anthropometric traits. 17327437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17327460_A meta-analysis and a case-control study evaluating the role of LMNA mutations in the development of type 2 diabetes are reported. 17327460_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17327461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17327461_The results of 2 case-control studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus and a separate study of metabolic syndrome and LMNA polymorphisms is reported. 17334235_found three LMNA mutations including a case having a previously described (Glu161Lys) mutation and two having novel mutations (Glu53Val and Glu186Lys) 17352743_a change in the amount of lamin A, rather than appearance of its truncated form, is responsible for growth retardation in affected cells 17360326_These results provide insights into the mechanisms responsible for premature aging and also shed light on the role of lamins in the normal process of human aging. 17360355_Progerin/LADelta50 mislocalizes into insoluble cytoplasmic aggregates and membranes during mitosis and causes abnormal chromosome segregation and binucleation. 17428859_US3 kinase activity regulates HSV-1 capsid nuclear egress at least in part by phosphorylation of lamin A/C 17454124_a lamin A/C mutation has a role in amyotrophic quadricipital syndrome with cardiac involvement 17459035_LMNA p.G608G mutation results in a uniform phenotype through early to mid-childhood, in keeping with that described in classical Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome 17469202_Unusual LMNA mutations associated with severe progeria. 17536044_findings highlight the crucial role of lamin A/C-emerin interactions, with evidence for synergistic effects of these mutations that lead to Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy as the worsened result of digenic mechanism in this family 17605093_Malignant mutation in lamin A/C gene causing progressive conduction system disease and early death in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. 17612587_LMNA mutations and protease inhibitor treatment result in accumulation of farnesylated prelamin A and oxidative stress that trigger premature cellular senescence. 17701980_The findings from these cases further expand the clinical spectrum associated with mutations in the LMNA gene. 17711925_Mutations in the LMNA gene are responsible for several laminopathies, including lipodystrophies, with complex genotype/phenotype relationships 17718387_Mutations in LMNA gene are the cause of many different diseases, called laminopathies. Among laminopathies are muscle tissue diseases, adipose tissue diseases and also progerias, the premature aging syndromes. 17760566_Results indicate that pathogenic mutations in lamin A/C lead to sequestration of hsMOK2 into nuclear aggregates, which may deregulate MOK2 target genes. 17848622_RNA interference (RNAi) knockdown of XPA in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome cells partially restored double-strand breaks repair as evidenced by Western blot analysis, immunofluorescence and comet assays 17870066_Our findings raise a hypothesis that changes in lamina organization may cause accelerated telomere attrition, with different kinetics for overexpession of wild-type and mutant lamin A, which leads to rapid replicative senescence and progroid phenotypes. 17881656_The S143F lamin A/C point mutation causes a phenotype combining features of myopathy and progeria. Dermal fibroblast cells have dysmorphic nuclei containing numerous blebs and lobulations, which progressively accumulate as cells age in culture. 17893350_both patients had markedly increased neck fat content, specifically surrounding the trachea.The association with sleep apnea might be related to the repartitioning of adipose tissue in patients with this type of lipodystrophy. 17935239_Homozygous missense mutation in LMNA gene is associated with Mandibuloacral dysplasia and severe progressive skeletal changes 17987279_Nonsense mediated decay is not sufficient to completely prevent the expression of truncated lamin A and that even trace amounts of it may negatively interfere with structural and/or regulatory functions of lamin A/C. 17994215_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18031308_A novel clinical form of familial partial lipodystrophy 2, due to a mutation affecting lamin A only, with cardiac involvement. 18035086_study highlights the role of LMNA mutations in dilated cardiomyopathy and related disorders. A severe phenotype in p.N195K mutation carriers and preferential cardiac conduction disease in p.R225X carriers was encountered. 18041775_present case illustrates that mutations of the LMNA codon cause familial partial lipodystrophy that is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern with variable expressivity 18077842_Correlation between LMNA adipose expression and cytokine and adipogenic gene markers in HIV-positive patients, regardless of presence or absence of lipodystrophy. 18093584_These results may be used to evaluate downstream effects of FTIs or other prelamin A inhibitors potentially useful for the therapy of laminopathies. 18308323_Systematic comparison of the mechanical behavior of the wild-type protein and a missense mutated protein with the point mutation p.Glu358Lys show that the nanomechanical tensile behavior of the dimer segment does not vary with the mutation. 18311132_Data suggest that Lamin A-dependent misregulation of adult stem cells is associated with accelerated aging. 18337098_patients bearing a LMNA gene mutation associated to an apparently selective cardiac phenotype may present subclinical skeletal muscle involvement 18339564_We present a 6-year-old girl with premature aging associated with mild myopathy, displaying muscle weakness, joint contractures and hyporeflexia. Genetic analysis revealed rare heterozygous point mutation in lamin A/C gene. 18348272_Association of homozygous LMNA mutation R471C with new phenotype: mandibuloacral dysplasia, progeria, and rigid spine muscular dystrophy. 18364375_In these LMNA-linked lipodystrophic patients, the prevalence of PCOS, infertility, and gestational diabetes was higher than in the general population. 18396274_The influence of expression of the Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy R453W mutation and of the Dunnigan-type partial lipodystrophy R482W mutation of lamin A on transcription and epigenetic regulation of the myogenin gene and on chromatin organization. 18442054_bone resorption activity of osteoclasts obtained in the presence of high prelamin A levels is lower with respect to control osteoclasts 18442998_Expression of progerin leads to alterations in nuclear morphology, which may underlie pathology in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. 18478590_This report provides further evidence of the extreme phenotypic diversity and low penetrance associated with the R644C mutation. 18497734_Lamin A/C may be involved in the adipocyte gene profile observed in obesity and type 2 diabetes. 18502446_D192G mutation in LMNA gene may lead to the disruption of the nuclear wall in cardiomyocytes, thus supporting the mechanical hypothesis of dilated cardiomyopathy development in humans, which might be mutation-specific. 18524819_lamin A/C, lamin B1, and viral US3 kinase have roles in viral infectivity, virion egress, and the targeting of herpes simplex virus U(L)34-encoded protein to the inner nuclear membrane 18538321_The inability of lamin C mutants to join the nuclear rim in the absence of lamin A is a potential pathophysiological mechanism for laminopathies. 18549403_Founder effect and estimation of the age of the c.892C>T (p.Arg298Cys) mutation in LMNA associated to Charcot-Marie-Tooth subtype CMT2B1 in families from North Western Africa. 18551513_study describes a new entity of congenital muscular dystrophies caused by de novo LMNA mutations 18564364_the first cases of laminopathies from Russia are reported: In 10 unrelated families, 9 different mutations were identified and three phenotypes were observed 18585512_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18604166_results indicate that accumulation of the lamin A precursor protein determines a defect in DNA damage response after X-ray exposure, supporting a crucial role of lamin A in regulating DNA repair process and cell cycle control 18606848_These results suggest that SUMO modification is important for normal lamin A function and implicate an involvement for altered sumoylation in the E203G/E203K lamin A cardiomyopathies. 18611980_A mutation within the LMNA gene is associated with heart-hand syndrome of Slovenian type. 18612243_The silencing of lamin A/C expression resulted in a decrease in the volume and surface area of chromosome territories, especially in chromosomes with high heterochromatin content. 18643848_In human keratinocytes, we found BMP-4 facilitates trichohyalin (THH) transcription, and lamin C plays a key role in the posttranslational stabilization of THH. 18646565_Mutations in the genes for nuclear envelope proteins of emerin (EMD) and lamin A/C (LMNA) are known to cause Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) and limb girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD). 18667561_Binding of T. foetus to LMN-1 rendered the parasite toxic to HeLa cell monolayers. 18691775_we present a family with sudden cardiac death in the absence of left ventricular dysfunction, related to a Lamin A/C mutation 18714339_Report links A-type lamin expression to colorectal tumour progression and raises the profile from one implicated in multiple but rare genetic conditions to a gene involved in one of the commonest diseases in the Western World. 18714801_Studiy identified a large French Canadian family with the LGMD 1B phenotype and a cardiac conduction disease phenotype that carried a new new (IVS9-3C > G) LMNA gene mutation. 18767923_lamin A/C is essential for proper RANKL-dependent osteoblastogenesis 18795223_Testing LMNA in families of people with familial dilated cardiomyopathy is recommended because genotype information in an individual could definitely be useful for the clinician. 18805829_prelamin A accumulation in peripheral scAT is associated with a reduced expression of several genes involved in adipogenesis. 18816602_We report the clinical characteristics, genetic analysis, and muscle biopsy findings of a family with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and a novel mutation (Leu162Pro) in the LMNA gene. 18830724_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18843043_Data show that hTERT activity or inactivation of p53 can suppress the cell proliferation defects associated with lamin A mutants that are incorrectly processed. 18848371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18848371_The mechanisms underlying the associations with cognitive impairment and LOAD require further elucidation, but both genes are interesting candidates for involvement in age-related cognitive impairment. 18923140_Results suggest that prelamin A is imported directly into the nucleus where it is processed by Zmpste24 and Icmt, which exhibit a dual localization to the inner nuclear membrane as well as the ER membrane. 18926329_Dilated cardiomyopathies caused by LMNA gene defects are highly penetrant, adult onset, malignant diseases characterized by a high rate of heart failure and life-threatening arrhythmias. 18946024_plasma-membrane-anchored growth factor pro-amphiregulin binds A-type lamin and regulates global transcription 18950579_The intranuclear accumulation of lamin A precursors which cannot be fully processed & exert a toxic effect on nuclear homeostasis leads to various genetic syndromes. Review. 18959190_During detailed studies of the cells from this patient the nuclear lamina aberrations were detected. 18982914_Progeria is caused by mutation in the gene of LMNA, encoding a nuclear protein, lamin A, which has been shown to affect RNA polymerase II transcription. 19015316_Fast regulation of AP-1 activity through interaction of lamin A/C, ERK1/2, and c-Fos at the nuclear envelope. 19022376_Knockdown of A-type lamins and emerin in HeLa and C2C12 stimulated phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of ERK as well as activation of genes encoding downstream transcription factors. 19084400_We present a consanguineous family in which two children have early onset LMNA-related myopathy likely due to paternal germinal mosaicism. 19124654_Lamin A/C-mediated neuromuscular junction defects contribute to the autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy disease phenotype 19126678_process of adipogenesis is affected by a dynamic link between complexes of emerin and lamins A/C at the nuclear envelope and nucleocytoplasmic distribution of beta-catenin, to influence cellular plasticity and differentiation. 19141474_Silencing lamin B1 expression dramatically increases the lamina meshwork size and the mobility of nucleoplasmic lamin A 19144202_lamin A/C is involved in the pathogenesis of gastric carcinoma 19172989_lamin A Delta 150 transcript is present in unaffected controls but its expression is >160-fold lower than in HGPS patients. Lamin A Delta 150 transcript increases in late passage cells from HGPS patients and parental controls. 19201734_Transgenic mice express the LMNA mutation that causes familial partial lipodystrophy of the Dunnigan type (FPLD2). The phenotype in FPLD-transgenic mice resembles human FPLD2, including lack of fat accumulation, insulin resistance, and fatty liver. 19204888_Male subjects with familial partial lipodystrophy due to a lamin A/C R482W mutation may develop metabolic abnormalities. including hypoleptinemia 19220582_The R439C mutation causes oligomerization of the C-terminal globular domain of lamins A and C, which increases its binding affinity for DNA. 19247430_Regulation of the D4Z4 array depends on both the number of repeats and the presence of CTCF and A-type Lamins in facio-scapulo-humeral dystrophy. 19270485_Atypical Werner's syndrome with the severe metabolic complications, the extent of the lipodystrophy is associated with A133L mutation in the LMNA gene and these patients present with phenotypically heterogeneous disorders. 19283854_Two unrelated young women experienced premature ovarian failure, and both were found to have the same heterozygous novel missense mutation c.176T>G in exon 1 of the LMNA gene. 19318026_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19323649_Non-farnesylated and farnesylated carboxymethylated lamin A precursors in human fibroblasts modifies emerin localization. 19328042_mutations in LMNA were identified in individuals with isolated cardiac involvement, specifically DCM, AVB, and infrequently atrial arrhythmias, including AF 19351612_inhibition of the prelamin A endoprotease ZMPSTE24 mostly elicits accumulation of full-length prelamin A in its farnesylated form, while loss of the prelamin A cleavage site causes accumulation of carboxymethylated prelamin A in progeria cells 19384091_Lamin A/C deficiency is an important cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. 19401371_Common variation in the lamin a/c gene does not contribute to the etiology of PCOS in women of European ancestry. 19401371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19424285_Mutations in the LMNA gene do not cause axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth. 19424285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19427440_LMNA mutations rarely cause lone AF and routine genetic testing of LMNA in these patients does not appear warranted. 19427440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19442658_This is the first study of a direct link between LaA mutant expression and reduced nuclear protein import. 19446900_We describe 7 transplanted heart recipients from a single family with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1B linked to a mutation of the LMNA gene in the splice donor site of the exon 9 (IVS 9+1:g>a). 19490114_Data demonstrated that the phosphorylation of hsMOK2 interfered with its ability to bind lamin A/C. 19524666_Results suggest that a functional emerin-lamin A/C complex is required for cell spreading and proliferation, possibly acting through ERK1/2 signalling. 19574635_The crystal structure of the lamin A/C mutant R482W, a variant that causes FPLD, has been determined at 1.5 A resolution. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19589617_Impaired nuclear functions lead to increased senescence and inefficient cell differentiation in human myoblasts with a dominant p.R545C mutation in the LMNA gene. 19638735_Lamin A/C gene mutations may have a role in familial cardiomyopathy with advanced atrioventricular block and arrhythmia 19644448_These findings reveal the existence of an 80 bp D4Z4 human subtelomeric repeat sequence that is sufficient to position an adjacent telomere to the nuclear periphery in a CTCF and A-type lamins-dependent manner. 19645629_results suggest that LMNA, ZMPSTE24, and LBR sequence variations are not major genetic determinants involved in scleroderma pathogenesis 19672032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19768759_the exon 1 c.178 C/G, p.Arg 60 Gly LMNA gene mutation is associated with a novel phenotype featuring cardiac involvement followed by late lipodystrophy, diabetes, and peripheral axonal neuropathy. 19775189_Results show that decline in Hela lamin A/C expression correlates with modified cell signaling and minor alterations in metabolism coupled with changes in expression in structural proteins of the cytoskeleton. 19841875_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19855837_analysis of Drosophila and human A-type lamins 19859838_A clinical picture related to the LMNA |
ENSMUSG00000028063 |
Lmna |
4064.298025 |
3.3093836720 |
1.726563 |
0.087139654 |
373.918029 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002625002673502741428347404800239859907244758071201162725053652339778037720088345457489219684992647385280654164379221394576754387956965055089073839577110648220118057794109069055631983549167161888337358179815878012064445101714227348566055297851562500 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000920309725912124974335963208201673261945047058181705420498450115889235462884675940506163925558441326643559753277881916225827037274949122555893036140335786358590532111510865219994498304640109985838439601857352556635305518284440040588378906250000000 |
Yes |
No |
5966.5081799 |
352.6535895 |
1815.3234115 |
78.6981944 |
| ENSG00000160796 |
23218 |
NBEAL2 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZNJ1 |
FUNCTION: Probably involved in thrombopoiesis. Plays a role in the development or secretion of alpha-granules, that contain several growth factors important for platelet biogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21765411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21765412}. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains a beige and Chediak-Higashi (BEACH) domain and multiple WD40 domains, and may play a role in megakaryocyte alpha-granule biogenesis. Mutations in this gene are a cause of gray platelet syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:23218; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; platelet formation [GO:0030220]; protein localization [GO:0008104] |
19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21765411_NBEAL2 mutation is associated with gray platelet syndrome. 21765412_NBEAL2 mutation is associated with gray platelet syndrome. 21765413_Mutations in NBEAL2, encoding a BEACH protein is associated with gray platelet syndrome. 28082341_we herein show a long-distance regulatory region with GATA1 binding sites as being a strong enhancer for NBEAL2 expression. 28783043_NBEAL2 has an essential role in neutrophil and NK cell function and pathogen defense 29187380_Nbeal2 interacts with Dock7, Sec16a, and Vac14. 29869935_Author observed absence of NBEAL2 in platelets from GPS patients with 3 different genotypes, and reduced/truncated platelet NBEAL2 has been reported for others. 30354215_NBEAL2 is required for the retention of both endocytosed and megakaryocyte-synthesized proteins by maturing alpha-granules, and possibly by platelet-borne granules. This function may involve interaction of NBEAL2 with P-selectin. 31171812_Defective Zn(2+) homeostasis in mouse and human platelets with alpha- and delta-storage pool diseases. 32384141_The endoplasmic reticulum protein SEC22B interacts with NBEAL2 and is required for megakaryocyte alpha-granule biogenesis. 33300270_Gray platelet syndrome: NBEAL2 mutations are associated with pathology beyond megakaryocyte and platelet function defects. |
ENSMUSG00000056724 |
Nbeal2 |
709.134490 |
0.2548607067 |
-1.972219 |
0.135699371 |
199.685337 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000244623778905779997885889883260399974025611387597659543604253873533222427250753906419760815083894172399620468989192480918637428999318217393010854721069335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000046588993247087910628690106995089642150673067305387647129305076654032936105494732689689193527381504550086380070199332248392920519108884036540985107421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
304.3278302 |
35.3123963 |
1200.1467342 |
98.9744828 |
| ENSG00000160818 |
54865 |
GPATCH4 |
protein_coding |
E9PPY4 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues mmu:66614; |
nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 33933995_G-patch domain-containing protein 4 localizes to both the nucleoli and Cajal bodies and regulates cell growth and nucleolar structure. |
ENSMUSG00000028069 |
Gpatch4 |
181.130500 |
2.5354878256 |
1.342263 |
0.217407954 |
36.923784 |
0.00000000122838299583801280618110627072857646280290566664916696026921272277832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005827482788204114005502648612018143370328004948532907292246818542480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
241.8837368 |
31.7934350 |
95.9778991 |
9.4815248 |
| ENSG00000160883 |
3101 |
HK3 |
protein_coding |
P52790 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of hexose, such as D-glucose and D-fructose, to hexose 6-phosphate (D-glucose 6-phosphate and D-fructose 6-phosphate, respectively) (PubMed:8717435). Mediates the initial step of glycolysis by catalyzing phosphorylation of D-glucose to D-glucose 6-phosphate (PubMed:8717435). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8717435}. |
3D-structure;Allosteric enzyme;ATP-binding;Glycolysis;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate metabolism; hexose metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:8717435}.; PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation; glycolysis; D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and glycerone phosphate from D-glucose: step 1/4. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:8717435}. |
Hexokinases phosphorylate glucose to produce glucose-6-phosphate, the first step in most glucose metabolism pathways. This gene encodes hexokinase 3. Similar to hexokinases 1 and 2, this allosteric enzyme is inhibited by its product glucose-6-phosphate. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:3101; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; fructokinase activity [GO:0008865]; glucokinase activity [GO:0004340]; glucose binding [GO:0005536]; hexokinase activity [GO:0004396]; canonical glycolysis [GO:0061621]; carbohydrate phosphorylation [GO:0046835]; cellular glucose homeostasis [GO:0001678]; fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0006002]; glucose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0051156]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; glycolytic process [GO:0006096] |
17868400_Data demonstrated that in addition to galectin-3, HK III and cyclin A profiles could be important biomarkers in predicting malignancy in follicular thyroid nodules. 19448621_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19554504_The expression pattern of HK3 is reported in newly diagnosed esophageal adenocarcinoma by means of immunohistochemistry. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072205_Data show that HKIII exerts protective effects against oxidative stress, perhaps by increasing ATP levels, reducing oxidant-induced ROS production, preserving mitochondrial membrane potential, and increasing mitochondrial biogenesis. 22498738_HK3 is: (1) directly activated by PU.1, (2) repressed by PML-RARA, and (3) functionally involved in neutrophil differentiation and cell viability of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. 24584857_Altogether, our data provide an explanation for low HK3 and KLF5 expression in particular AML subtype and establish these genes as novel CEBPA targets during neutrophil differentiation. 25172542_Through glycolysis and arachidonic acid metabolism, HK3 and PTGS2 might play important roles in pediatric ALL and its prognosis, and thus, might be potential targets for therapeutic intervention to suppress pediatric ALL. 25766729_The transport of glucose across the cell membrane by glucose transporters (GLUTs) and intracellular phosphorylation by hexokinases (HKs) are the initial steps of the glycolytic pathway. 26855992_HK1 and HK2 expression alterations were detected, that could be explained by common deregulation mechanisms of these genes in colorectal tumors. The HK3 expression level was significantly increased in 60% of samples. 28005267_HK3 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 29504907_Upregulation of HK3 is associated with EMT in CRC and may be a crucial metabolic adaptation for rapid proliferation, survival, and metastases of CRC cells 34239350_Hexokinase 3 dysfunction promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape by upregulating monocyte/macrophage infiltration into the clear cell renal cell carcinoma microenvironment. 35538058_Hexokinase 3 enhances myeloid cell survival via non-glycolytic functions. |
ENSMUSG00000025877 |
Hk3 |
53.579924 |
0.1807953804 |
-2.467570 |
0.318456585 |
59.690303 |
0.00000000000001110222324344496522453881892890566962768061996108537314853492716792970895767211914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000074418172149522110516759067234783522670543351451577507305046310648322105407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.5653675 |
4.2640513 |
74.7789377 |
15.7241336 |
| ENSG00000160991 |
80228 |
ORAI2 |
protein_coding |
Q96SN7 |
FUNCTION: Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+)-like (CRAC-like) channel subunit which mediates Ca(2+) influx and increase in Ca(2+)-selective current by synergy with the Ca(2+) sensor, STIM1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16807233, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17452328}. |
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable store-operated calcium channel activity. Predicted to be involved in store-operated calcium entry. Predicted to be located in growth cone. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80228; |
growth cone [GO:0030426]; membrane [GO:0016020]; store-operated calcium channel activity [GO:0015279]; store-operated calcium entry [GO:0002115] |
17452328_Results suggest that Orai1, -2, and -3 channels are similarly inhibited by extracellular calcium, indicating similar affinities for Ca(2+) within the selectivity filter. 18403424_The effects of 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate on orai1, orai2, orai3 metabolism in HEK293 cells with and without STIM1 are reported. 19506081_analysis of activation of Orai1-3 channels by a STIM1 coiled-coil mutant 19706554_Data show that the fast Ca(2+)-dependent inactivation is mediated by three conserved glutamates in the C termini (CT) of Orai2 and Orai3, which show prominent fast Ca(2+)-dependent inactivation compared with Orai1. 20607548_With these data we show a new Ca(2)(+) entry pathway linked to the Ca(2)(+)/inositolphosphate second-messenger system in RPE cells which help to further understand regulatory pathways of agonists. 22640869_Orai1 and Orai2 operate in a STIM-dependent manner, Orai3 does not interact with STIM isoforms upon calcium store depletion in platelets. 24040356_Orai1 but not Orai2 plays a major role in the influx of extracellular Ca2+ into and mediator release from HLMCs following their activation 24603752_The higher amplitude of store-operated Ca2+ entry was associated to the over-expression for Stim2, Orai2-3, and TRPC1 while Stim2 levels remained constant and Stim1, Orai1, Orai3, TRPC1 and TRPC4 proteins were over-expressed in primary myelofibrosis. 25769459_Orai1, Orai2 and STIM1 form functional Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) channels in OUMS-27 cells (chondrocytes) and that these complexes are responsible for sustained Ca(2+) entry in response to agonist stimulation. 26956485_results identified the ORAI-NOX2 feedback loop as a determinant of monocyte immune responses. 27865925_findings provide evidence for a role for Orai1 and Orai2, in SOCE and migration in the human HL60 promyeloblastic cell line 29203863_ORAI1-3, are preferentially expressed in proximal tubular epithelial cells and downregulated in patients with diabetic nephropathy. 31772693_Higher expression of Orai2 was independently associated with a worse prognosis of patients with the classical and mesenchymal subtypes of glioblastoma.A strong association between Orai2 expression and apoptosis, stemness, and an epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the glioblastoma. 32722509_ORAI2 Down-Regulation Potentiates SOCE and Decreases Abeta42 Accumulation in Human Neuroglioma Cells. 32882268_Orai-1 and Orai-2 regulate oral cancer cell migration and colonisation by suppressing Akt/mTOR/NF-kappaB signalling. 32896813_Distinct pharmacological profiles of ORAI1, ORAI2, and ORAI3 channels. 33310726_ORAI2 Promotes Gastric Cancer Tumorigenicity and Metastasis through PI3K/Akt Signaling and MAPK-Dependent Focal Adhesion Disassembly. 34857756_Atlas of RNA editing events affecting protein expression in aged and Alzheimer's disease human brain tissue. |
ENSMUSG00000039747 |
Orai2 |
299.993781 |
2.5044794902 |
1.324511 |
0.182331574 |
51.527271 |
0.00000000000070609419478674364097135671787840192155285418129651020535675343126058578491210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004241738019964320451075187619678115305901777709607358701759949326515197753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
429.0133030 |
65.7403185 |
172.7021807 |
19.4112584 |
| ENSG00000161010 |
51149 |
MRNIP |
protein_coding |
Q6NTE8 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the cellular response to DNA damage and the maintenance of genome stability through its association with the MRN damage-sensing complex (PubMed:27568553). Promotes chromatin loading and activity of the MRN complex to facilitate subsequent ATM-mediated DNA damage response signaling and DNA repair (PubMed:27568553). |
Alternative splicing;DNA damage;DNA repair;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables chromatin binding activity. Involved in several processes, including mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling; regulation of double-strand break repair; and response to ionizing radiation. Located in nucleoplasm. Colocalizes with Mre11 complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51149; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:1905168]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; protein localization to chromatin [GO:0071168]; regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining [GO:2001032]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212] |
27568553_these data reveal that MRNIP is an important component of the human DNA damage response. |
ENSMUSG00000020381 |
Mrnip |
199.050949 |
0.4842104837 |
-1.046294 |
0.130833143 |
64.270245 |
0.00000000000000108471618805801269182985785086333965535135010881812034355675677943509072065353393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000007756982042507882401521169648138568536002213950342198955922867753542959690093994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
133.1662887 |
10.2495078 |
277.1080360 |
14.0678908 |
| ENSG00000161513 |
2232 |
FDXR |
protein_coding |
P22570 |
FUNCTION: Serves as the first electron transfer protein in all the mitochondrial P450 systems including cholesterol side chain cleavage in all steroidogenic tissues, steroid 11-beta hydroxylation in the adrenal cortex, 25-OH-vitamin D3-24 hydroxylation in the kidney, and sterol C-27 hydroxylation in the liver. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08165}. |
Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Deafness;Disease variant;Electron transport;FAD;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;NADP;Neuropathy;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transit peptide;Transport |
PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism; cholesterol metabolism. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P08165}. |
This gene encodes a mitochondrial flavoprotein that initiates electron transport for cytochromes P450 receiving electrons from NADPH. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:2232; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase activity [GO:0004324]; NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase activity [GO:0015039]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; generation of precursor metabolites and energy [GO:0006091]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694]; ubiquinone biosynthetic process [GO:0006744] |
12137805_comparison of catalytic properties between conditions of limiting and saturating adrenodoxin reductase [cytochrome P450scc] 12370809_The ferredoxin reductase gene is regulated by the p53 family and sensitizes cells to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis 12782149_ADXR rate of hydroxylation was linear with incubation time. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22101253_results suggest that both FDX1 and FDX2 and their likely reductase partner, FDXR, contribute to iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis 24321386_These results indicated that abundant FDXR expression in these steroidogenic cells was maintained through SF-1 binding to the intronic enhancer of the FDXR gene 25712867_NOS-3 overexpression resulted in an increased sensitivity to anti-Fas induced cell death, independently of AR expression and CatD activity. 28905435_Using surface plasmon resonance, physiologically relevant concentrations of isatin (25-100 muM) were found to increase affinity of interactions between human recombinant ferrochelatase (FECH) and NADPH-dependent adrenodoxin reductase (ADR). 28965846_Mutation in FDXR gene is associated with Sensorial Neuropathies. 29040572_we identified a novel disease-causing gene FDXR associated with mitochondrial diseases. The biallelic FDXR mutations cause optic atrophy and neuropathy. we found that FDXR levels are significantly lower in the patient fibroblast cells with the homozygous mutations R392W. Fourteen missense or nonsense FDXR mutations were identified in this study and eight of them (I143F, V158M, T211A, I213F, K280*, R315*, C359Y, D374N) clu 30250212_These data provide further insight into the pathogenic mechanism of FDXR-mediated central neuropathy, and suggest an avenue for mechanistic studies that will ultimately inform treatment. 32304229_FDXR regulates TP73 tumor suppressor via IRP2 to modulate aging and tumor suppression. 33113898_In Vivo Validation of Alternative FDXR Transcripts in Human Blood in Response to Ionizing Radiation. 33271253_Substrate-induced modulation of protein-protein interactions within human mitochondrial cytochrome P450-dependent system. 33348459_Expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum of FDXR deficiency by functional validation of variants of uncertain significance. 33938912_Expanding the FDXR-Associated Disease Phenotype: Retinal Dystrophy Is a Recurrent Ocular Feature. 34979083_Characterization of a Cleavable Fusion of Human CYP24A1 with Adrenodoxin Reveals the Variable Role of Hydrophobics in Redox Partner Binding. |
|
|
21.812635 |
0.4355121215 |
-1.199215 |
0.353705829 |
11.682862 |
0.00063078415970688054333764815950758020335342735052108764648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001522049075898897771766393738346323516452684998512268066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4649501 |
2.9328590 |
31.2018139 |
4.3374136 |
| ENSG00000161533 |
51 |
ACOX1 |
protein_coding |
Q15067 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the initial and rate-limiting step of peroxisomal beta-oxidation of straight-chain saturated and unsaturated very-long-chain fatty acids (PubMed:7876265, PubMed:15060085, PubMed:17458872, PubMed:17603022, PubMed:32169171, PubMed:33234382). Catalyzes the desaturation of fatty acyl-CoAs such as palmitoyl-CoA (hexadecanoyl-CoA) to 2-trans-enoyl-CoAs ((2E)-enoyl-CoAs) such as (2E)-hexadecenoyl-CoA, and donates electrons directly to molecular oxygen (O(2)), thereby producing hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) (PubMed:7876265, PubMed:17458872, PubMed:17603022). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15060085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17458872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17603022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32169171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33234382, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7876265}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Shows highest activity against medium-chain fatty acyl-CoAs. Shows optimum activity with a chain length of 10 carbons (decanoyl-CoA) in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17603022}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Is active against a much broader range of substrates and shows activity towards long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17603022}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Deafness;Disease variant;FAD;Fatty acid metabolism;Flavoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Neuropathy;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; peroxisomal fatty acid beta-oxidation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:17603022}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is the first enzyme of the fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway, which catalyzes the desaturation of acyl-CoAs to 2-trans-enoyl-CoAs. It donates electrons directly to molecular oxygen, thereby producing hydrogen peroxide. Defects in this gene result in pseudoneonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, a disease that is characterized by accumulation of very long chain fatty acids. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; acyl-CoA oxidase activity [GO:0003997]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; fatty acid binding [GO:0005504]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; palmitoyl-CoA oxidase activity [GO:0016401]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; fatty acid beta-oxidation using acyl-CoA oxidase [GO:0033540]; fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0009062]; fatty acid oxidation [GO:0019395]; generation of precursor metabolites and energy [GO:0006091]; hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process [GO:0050665]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; peroxisome fission [GO:0016559]; prostaglandin metabolic process [GO:0006693]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; very long-chain fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0140493]; very long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0000038] |
17458872_Mutational spectrum of peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase deficiency. 18536048_report on two new patients with ACOX1 deficiency and mutational analyses 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20195242_Data show that human ACOX1b isoform is more effective than the ACOX1a isoform in reversing the Acox1 null phenotype in the mouse. 23933200_ACOX1 and GNPAT silencing up-regulated ceramide galactosyltransferase (UGT8) mRNA expression, and down-regulated UDP-glucoseceramide glucosyltransferase (UGCG). 24418004_Because patients with AOx deficiency suffer from more severe symptoms than those with X-ALD, accumulation of VLC-PUFA and/or reduction of DHA may be associated with the severity of peroxisomal diseases. 31126802_In non-alcoholic fatty liver disease miR-222 promotes the accumulation of triglycerides by inhibiting ACOX1. 32169171_Loss- or Gain-of-Function Mutations in ACOX1 Cause Axonal Loss via Different Mechanisms. 32434419_Enterovirus 71 induces neural cell apoptosis and autophagy through promoting ACOX1 downregulation and ROS generation. 33234382_Novel ACOX1 mutations in two siblings with peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase deficiency. 34763625_Association Between ACOX1 and NRF1 Gene Expression and Hepatitis B and C Virus Infections and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Liver Transplant Patients (Shiraz, Iran). 35149097_Crystal structures of apo- and FAD-bound human peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase provide mechanistic basis explaining clinical observations. 35606603_MiR-103-3p promotes hepatic steatosis to aggravate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by targeting of ACOX1. |
ENSMUSG00000020777 |
Acox1 |
517.184772 |
2.4782473720 |
1.309320 |
0.171202999 |
56.798023 |
0.00000000000004829517886661066088092193528696336702016149444727233230878482572734355926513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000312100192675645071140763686795463207571555558361708904158149380236864089965820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
690.6832835 |
76.4270194 |
280.4218583 |
22.7418935 |
| ENSG00000161609 |
147872 |
KASH5 |
protein_coding |
Q8N6L0 |
FUNCTION: As a component of the LINC (LInker of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton) complex, involved in the connection between the nuclear lamina and the cytoskeleton. The nucleocytoplasmic interactions established by the LINC complex play an important role in the transmission of mechanical forces across the nuclear envelope and in nuclear movement and positioning. Required for telomere attachment to nuclear envelope in the prophase of meiosis and for rapid telomere prophase movements implicating a SUN1/2:KASH5 LINC complex in which SUN1 and SUN2 seem to act at least partial redundantly. Required for homolog pairing during meiotic prophase in spermatocytes and probably oocytes. Essential for male and female gametogenesis. Recruits cytoplasmic dynein to telomere attachment sites at the nuclear envelope in spermatocytes. In oocytes is involved in meiotic resumption and spindle formation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80VJ8}. |
3D-structure;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Meiosis;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Telomere;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable dynein complex binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including cytoskeleton organization; homologous chromosome segregation; and spindle localization. Predicted to act upstream of or within double-strand break repair via homologous recombination; oogenesis; and spermatogenesis. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be part of meiotic nuclear membrane microtubule tethering complex. Predicted to be active in chromosome; meiotic spindle pole; and nuclear outer membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:147872; |
chromosome, telomeric region [GO:0000781]; lateral element [GO:0000800]; meiotic nuclear membrane microtubule tethering complex [GO:0034993]; meiotic spindle pole [GO:0090619]; nuclear outer membrane [GO:0005640]; dynein complex binding [GO:0070840]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; chromosome localization to nuclear envelope involved in homologous chromosome segregation [GO:0090220]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis [GO:0007129]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization involved in homologous chromosome segregation [GO:0090172]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225]; spindle localization [GO:0051653]; telomere localization [GO:0034397] |
33058875_Structural Analysis of Different LINC Complexes Reveals Distinct Binding Modes. 33980926_A human infertility-associated KASH5 variant promotes mitochondrial localization. 35587281_Homozygous missense mutation in CCDC155 disrupts the transmembrane distribution of CCDC155 and SUN1, resulting in non-obstructive azoospermia and premature ovarian insufficiency in humans. 35708642_Homozygous Variant in KASH5 Causes Premature Ovarian Insufficiency by Disordered Meiotic Homologous Pairing. |
ENSMUSG00000038292 |
Kash5 |
12.135652 |
0.2145478791 |
-2.220628 |
0.645850047 |
11.176190 |
0.00082853723689997648207961056243675557198002934455871582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001960123355769138354942615620757351280190050601959228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.2863390 |
1.6817272 |
21.0968388 |
4.9152936 |
| ENSG00000161640 |
114132 |
SIGLEC11 |
protein_coding |
Q96RL6 |
FUNCTION: Putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,8-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin family. These cell surface lectins are characterized by structural motifs in the immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains and sialic acid recognition sites in the first Ig V set domain. This family member mediates anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive signaling. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:114132; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; sialic acid binding [GO:0033691]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155] |
11986327_cloning and characterization; a recently evolved signaling that can interact with SHP-1 and SHP-2 and is expressed by tissue macrophages including brain microglia 16151003_expressed in human but not in chimpanzee brain microglia; findings indicate that human SIGLEC11 emerged through human-specific gene conversion by an adjacent pseudogene 18629938_SIGLEC16 encodes a DAP12-associated receptor expressed in macrophages that evolved from its inhibitory counterpart SIGLEC11 and has functional and non-functional alleles in humans. 20203208_Siglec-11 ectopically expressed on murine microglia interacts with PSA on neurons, reduces LPS-induced gene transcription of proinflammatory mediators, impairs phagocytosis and alleviates microglial neurotoxicity. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21467073_The results indicate potential roles for Siglec-11 in ovarian physiology and human evolution. 28100677_The authors demonstrated that the human-specific pathogen Escherichia coli K1 uses its polysialic acid capsule as a molecular mimic to engage Siglec-11 and escape killing. In contrast, engagement of the activating counterpart Siglec-16 increases elimination of bacteria. 32845322_Human-specific microglial Siglec-11 transcript variant has the potential to affect polysialic acid-mediated brain functions at a distance. |
ENSMUSG00000030468 |
Siglecg |
79.427628 |
0.2909822720 |
-1.780997 |
0.231050385 |
60.223242 |
0.00000000000000846863010764941823798624955325446684011730935637274342298042029142379760742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000057050196434918034837351322192739813031958293065848408787132939323782920837402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.1300221 |
5.3005485 |
125.3876764 |
11.4686757 |
| ENSG00000161643 |
400709 |
SIGLEC16 |
protein_coding |
|
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3- or alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid (PubMed:20038598). The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, seems to act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules (By similarity). Involved in negative regulation of B-cell antigen receptor signaling and specifically acts on B1 cells to inhibit Ca(2+) signaling, cellular expansion and antibody secretion (PubMed:17572677). The inhibition of B cell activation is dependent on PTPN6/SHP-1 (PubMed:23836061). In association with CD24 may be involved in the selective suppression of the immune response to danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) such as HMGB1, HSP70 and HSP90 (PubMed:19264983). In association with CD24 may regulate the immune repsonse of natural killer (NK) cells (By similarity). Plays a role in the control of autoimmunity (PubMed:20200274). During initiation of adaptive immune responses by CD8-alpha(+) dendritic cells inhibits cross-presentation by impairing the formation of MHC class I-peptide complexes. The function seems to implicate recruitment of PTPN6/SHP-1, which dephosphorylates NCF1 of the NADPH oxidase complex consequently promoting phagosomal acidification (PubMed:27548433). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q96LC7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17572677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19264983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20038598, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20200274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27548433}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) During infection by RNA viruses inhibits RIG-I signaling in macrophages by promoting its CBL-dependent ubiquitination and degradation via PTPN11/SHP-2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23374343}. |
Mouse_homologues Adaptive immunity;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable sialic acid binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of defense response to bacterium and positive regulation of interleukin-6 production. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues mmu:243958; |
Mouse_homologues plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; sialic acid binding [GO:0033691]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050849]; negative regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002638]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to wounding [GO:0106015]; regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030888]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776] |
18629938_SIGLEC16 encodes a DAP12-associated receptor expressed in macrophages that evolved from its inhibitory counterpart SIGLEC11 and has functional and non-functional alleles in humans. 28100677_The authors demonstrated that the human-specific pathogen Escherichia coli K1 uses its polysialic acid capsule as a molecular mimic to engage Siglec-11 and escape killing. In contrast, engagement of the activating counterpart Siglec-16 increases elimination of bacteria. |
ENSMUSG00000030468 |
Siglecg |
99.784002 |
0.2422664818 |
-2.045333 |
0.179074047 |
138.500481 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000005664167027952514158735369644934962999063247721874800742913880528781721691421874309568806893366854637861251831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000772671953166165445686171994090254377319971986201122754167822305578670296308883944265410992358056319062598049640655517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.8127312 |
4.8297187 |
165.4383266 |
11.8974980 |
| ENSG00000161647 |
4356 |
MPP3 |
protein_coding |
Q13368 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene product is a member of a family of membrane-associated proteins termed MAGUKs (membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs). MAGUKs interact with the cytoskeleton and regulate cell proliferation, signaling pathways, and intracellular junctions. This protein contains a conserved sequence, called the SH3 (src homology 3) motif, found in several other proteins that associate with the cytoskeleton and are suspected to play important roles in signal transduction. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified. One transcript variant is experimentally supported, but it doesn't encode a protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4356; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165] |
13679854_MPP3, a human homologue of a Drosophila tumor suppressor gene (Discs large), associates with TSCL1, a tumor suppressor gene. 16519681_These data implicate a role for MPP3 in photoreceptor polarity and, by association with MPP5, pinpoint MPP3 as a functional candidate gene for inherited retinopathies. 17669239_TSLC1 strongly inhibits the growth of HepG2 cells in vitro and induces apoptosis. 23011156_Data suggested that epigenetic inactivation of MPP3 frequently occurred during the development of colorectal cancer and might also be a potential biomarker for molecular classification of colorectal cancer patients. 24503895_MPP3 and Dlg, membrane-associated guanylate kinase homologs (MAGuK) proteins, connect CADM1 with p85 of PI3K by forming a multi-protein complex at the periphery of cells. 24513266_MPP3 plays an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by promoting cell migration and invasion via up-regulating MMP1 25780926_a central role of CADM1 in stabilizing the complex with 4.1B and MPP3 |
ENSMUSG00000052373 |
Mpp3 |
36.837569 |
0.3432540185 |
-1.542651 |
0.471336036 |
10.335144 |
0.00130520935882191477239722132708266144618391990661621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002983104697462289189163753277966861787717789411544799804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8868476 |
5.6767622 |
41.1076241 |
11.8140930 |
| ENSG00000161664 |
92591 |
ASB16 |
protein_coding |
Q96NS5 |
FUNCTION: May be a substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin-Cullin-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. {ECO:0000250}. |
ANK repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing (ASB) family of proteins. They contain ankyrin repeat sequence and a SOCS box domain. The SOCS box serves to couple suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS) proteins and their binding partners with the elongin B and C complex, possibly targeting them for degradation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:92591; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32572790_ASB16-AS1 up-regulated and phosphorylated TRIM37 to activate NF-kappaB pathway and promote proliferation, stemness, and cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000034768 |
Asb16 |
10.600318 |
0.3151958175 |
-1.665680 |
0.512837129 |
10.976735 |
0.00092262860007492420236219210494255094090476632118225097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002161587005889822454135495988225557084660977125167846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5207999 |
1.5559474 |
14.5103037 |
3.0717116 |
| ENSG00000161905 |
246 |
ALOX15 |
protein_coding |
P16050 |
FUNCTION: Non-heme iron-containing dioxygenase that catalyzes the stereo-specific peroxidation of free and esterified polyunsaturated fatty acids generating a spectrum of bioactive lipid mediators (PubMed:1944593, PubMed:8334154, PubMed:17052953, PubMed:24282679, PubMed:25293588, PubMed:32404334). It inserts peroxyl groups at C12 or C15 of arachidonate ((5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoate) producing both 12-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoate/12-HPETE and 15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoate/15-HPETE (PubMed:1944593, PubMed:8334154, PubMed:17052953, PubMed:24282679). It may then act on 12-HPETE to produce hepoxilins, which may show pro-inflammatory properties (By similarity). Can also peroxidize linoleate ((9Z,12Z)-octadecadienoate) to 13-hydroperoxyoctadecadienoate/13-HPODE (PubMed:8334154). May participate in the sequential oxidations of DHA ((4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoate) to generate specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs)like resolvin D5 ((7S,17S)-diHPDHA) and (7S,14S)-diHPDHA, that actively down-regulate the immune response and have anti-aggregation properties with platelets (PubMed:32404334). Can convert epoxy fatty acids to hydroperoxy-epoxides derivatives followed by an intramolecular nucleophilic substitution leading to the formation of monocyclic endoperoxides (PubMed:25293588). Plays an important role during the maintenance of self-tolerance by peroxidizing membrane-bound phosphatidylethanolamine which can then signal the sorting process for clearance of apoptotic cells during inflammation and prevent an autoimmune response. In addition to its role in the immune and inflammatory responses, this enzyme may play a role in epithelial wound healing in the cornea through production of lipoxin A4 (LXA(4)) and docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1; 10R,17S-HDHA), both lipid autacoids exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Furthermore, it may regulate actin polymerization which is crucial for several biological processes such as the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. It is also implicated in the generation of endogenous ligands for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR-gamma), hence modulating macrophage development and function. It may also exert a negative effect on skeletal development by regulating bone mass through this pathway. As well as participates in ER stress and downstream inflammation in adipocytes, pancreatic islets, and liver (By similarity). Finally, it is also involved in the cellular response to IL13/interleukin-13 (PubMed:21831839). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P39654, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17052953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1944593, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21831839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24282679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25293588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32404334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8334154}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Direct protein sequencing;Fatty acid metabolism;Iron;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; hydroperoxy eicosatetraenoic acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1944593}. |
This gene encodes a member of the lipoxygenase family of proteins. The encoded enzyme acts on various polyunsaturated fatty acid substrates to generate various bioactive lipid mediators such as eicosanoids, hepoxilins, lipoxins, and other molecules. The encoded enzyme and its reaction products have been shown to regulate inflammation and immunity. Multiple pseudogenes of this gene have been identified in the human genome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:246; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arachidonate 12(S)-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0004052]; arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0050473]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; linoleate 13S-lipoxygenase activity [GO:0016165]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on single donors with incorporation of molecular oxygen, incorporation of two atoms of oxygen [GO:0016702]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to interleukin-13 [GO:0035963]; fatty acid oxidation [GO:0019395]; hepoxilin biosynthetic process [GO:0051122]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; linoleic acid metabolic process [GO:0043651]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipid oxidation [GO:0034440]; lipoxin A4 biosynthetic process [GO:2001303]; lipoxygenase pathway [GO:0019372]; long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042759]; negative regulation of adaptive immune response [GO:0002820]; ossification [GO:0001503]; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006646]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010811]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; regulation of engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:1901074]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035358]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
9700053_Characterizes the 15-lipoxygenase-1 promoter region and maps the gene to human chromosome 17p13.3. 10200270_Kelavkar and Badr (1999) stated that the ALOX15 gene maps to 17p13.3 in close proximity to the tumor-suppressor gene TP53 and stated that the ALOX15 gene product is implicated in antiinflammation, membrane remodeling, and cancer development/metastasis. 11023533_15-LO-1 expression was significantly high in prostate adenocarcinoma and seen in secretory cells of peripheral zone glands, prostatic ducts and seminal vesicles, but not in the basal cell layer or stroma. 11956198_metabolizes 2-arachidonylglycerol, an endo cannabinoid, to a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonist 12084190_This article emphasizes the key role of 15-Lipoxygenase-1 in prostate, colorectal, and breast cancers. 12664577_This enzyme is overexpressed in prostatic adenocarcinoma. 12664628_This enzyme is induced when Ku antigen is the transcripion factor in human cells. 12748293_Results provide evidence that interleukin-13 induces p38 MAP kinase phosphorylation and activation, which regulates Stat1 and Stat3 serine 727 phosphorylation. 12907138_human breast tumours aber;antly express decreased level of ALOX15. Lobular carcinomas had a lower level of ALOX15 than ductal carcinomas; the lowest level of ALOX15 was seen in TNM3 and TNM4 tumours and from patients who died of breast cancer. 14643174_In athymic nude mice, transplantable tumors derived from 15-LO-1 HCT-116 cells were smaller than tumors derived from vector HCT-116 cells 14757756_PKCdelta plays an important role in regulating 15-lipoxygenase expression in human monocytes and subsequently modulates the inflammatory responses mediated by 15-LO products 15111312_12/15-lipoxygenase is increased in Alzheimer's disease and has a possible role in brain oxidative stress 15194425_Demethylation of the 15-LO promoter is a prerequisite for the gene transactivation, which contributes to tissue- and cell-type-specific regulation of 15-LO expression. 15459485_Studies using transgenic mice overexpressing human 15-lipoxygenase suggest a role for 15-LO in the natural selection of thymocytes. 15838625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15838625_These findings suggest that the ALOX15 gene is one of the genetic determinants of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Accordingly, this polymorphism could be useful as a genetic marker for predicting the risk of osteoporosis. 15879104_The suppressive activity of antiproliferative myeloid suppressor cells (MSC) in the peritoneal cavity of mice infected with Taenia crassiceps depends on a switch from nitric oxide- to 12-15-lipoxygenase-dependent alternative activation MSC phenotype. 15912043_15-LOX-1 gene expression is significantly reduced in both human colorectal adenomas and carcinomas and is associated with decreased survival. Down regulation of 15-LOX-1 is an early event in the adenoma to carcinoma sequence. 15967444_Strong overexpression of 15-lipoxygenase1 was paralleled by downregulation of CD4 and CXCR4. 15996861_15-LO-1 is related to the differentiation of human nasal epithelium, and that it may mediate the mucociliary differentiation of human nasal epithelium. 16000313_ALOX15 generation of 15S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid activates specific growth factor receptor-related signaling pathways, thereby initiating signal transduction events leading to increased cell adhesion to extracellular matrix in breast carcinoma cells 16179498_Overexpression of 15-lipoxygenase-1 induces growth arrest through phosphorylation of p53 in human colorectal cancer cells 16320347_The c.-292 T allele in the ALOX15 promoter generates a novel binding site for the transcription factor SPI1 that results in higher transcription of the gene in macrophages. 16357157_Down-regulation of 15-Lipoxygenase-1 is associated with colorectal adenomas 16556493_Reduction of isoforms of 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX)-1 and 15-LOX-2 in human breast cancer 16598376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847316_Results describe the shared stabilization functions of pyrimidine-rich determinants in the erythroid 15-lipoxygenase and alpha-globin mRNAs. 16997127_Results suggest that aberrant 15-lipoxygenase-1 overexpression in normal prostate can trigger events leading to prostate epithelial and stromal cell proliferation. 17043146_12/15-lipoxygenase expression suppresses the growth of human Bcr-Abl+ leukemia K562 cells. 17227895_proposed a possible reaction pathway in 15-lipoxygenase reactions at lower oxygen content 17344094_The data presented link the stimulation of ERK-cPLA(2)-15-LO pathway by oxidized LDL to the prooxidant mechanism of the lipoprotein complex. 17439326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17439326_the c.-292C>T polymorphism was associated with higher enzyme activity in heterozygous carriers; this polymorphism also showed a tendency to be protective against atherosclerosis 17520163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17520163_there is no association between polymorphism in ALOX15 and bone mineral density phenotypes, but genetic variation in ALOX12 seems to play a role in determining bone structure in Caucasian women 17652958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17652958_variant alleles of rs2619112 and rs916055 and their haplotypes of ALOX15 are associated with high bone mineral density(BMD) in pre-menopausal women but low BMD in post-menopausal women 17662651_Results report that interleukin-4 (IL-4) induced the expression of 15-LO-1 in human cord blood derived mast cells (CBMC). 17711445_The switching of linoleic acid metabolism by reversal of the expression of 15LOX-1 and COX-2 is associated with acquisition of malignant potential in colonic neoplasia. 17959182_A coding single nucleotide polymorphism in ALOX15 (T560M) results in a near null variant of human 12/15-LOX and this variant does not protect against coronary artery disease 17959182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17991885_expression of endogenous rabbit peroxisome proliferator-activating receptor and VEGFR2 were significantly increased in the growth factor-transduced muscles, but these inductions were efficiently prevented by 15-LO-1. 18067895_increased expression of 15-LOX-2 induced by hypoxia may participate in T cell recruitment in diseases such as atherosclerosis 18090132_15-lipoxygenase-2 mRNA is strongly augmented during ovarian carcinogenesis and that the enzyme may constitute a suitable candidate as a tumor marker. 18180398_Increased expression of 15-lipoxygenase-1 increases acetylcholine relaxation in arteries and hypotensive responses in rabbits because of increased hydroxy-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid and trihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid synthesis. 18187376_These results demonstrate a novel mechanism of parathyroid hormone-induced human bone cell proliferation operating through 12- and 15-lipoxygenase enzymes. 18198215_DNMT-1 has a direct suppressive role in 15-LOX-1 transcriptional silencing that is independent of 15-LOX-1 promoter DNA methylation 18227726_study demonstrated increased 15-LO-1 protein, mRNA, and enzyme activity, respectively, in normal human bladder tissues in comparison with stage T3/T4 human bladder tumors 18239141_REVIEW: inhibitory effect of 15-LO-1 on VEGF- or PlGF-induced angiogenesis 18392641_ALOX15 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)have a possible role in focal atherosclerosis plaque formation. 18392641_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18547056_Kinetic isotope effects (KIEs) in the reactions of three human LOs (platelet 12-hLO, reticulocyte 15-hLO-1, and epithelial 15-hLO-2) with arachidonic acid (AA). 18647347_The Hodgkin lymphoma-derived cell line L1236 has high expression of 15-lipoxygenase-1 and that these cells readily convert arachidonic acid to eoxin C(4), eoxin D(4) and eoxin E(4). 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18684974_Modification with 15-lipoxygenase significantly impairs the ability of high density lipoprotein (HDL)3 to contrast the effect of a proinflammatory stimulus on endothelial cells. 18692814_ALOX15 -292 C/T functional polymorphism was not correlated either with the risk of developing an endometriosis or with the risk of infertility. 18692814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18755188_The effects of UV on 12/15-LOX gene expression in the human keratinocyte cell line, HaCaT, were studied. 18774388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774388_association study found the 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) associations with airway hyperresponsiveness and allergic asthma significant in 2 Canadian samples 18785202_The 15-LOX-1 protein binds to DNA-PK, increasing its kinase activity and results in downstream activation of the tumor suppressor p53, thus revealing a new mechanism by which lipoxygenases (LOX) may influence the phenotype of tumor cells. 18799463_histone modification in the 15-LOX-1 promoter is important to 15-LOX-1 transcriptional silencing in colon cancer cells 19046748_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19089921_15-LOX-2 suppresses VEGF gene expression and sustains tumor dormancy in prostate cancer 19130894_putative role in airway inflammatory disease (i.e., asthma, COPD) and Hodgkin lymphoma--REVIEW 19131063_ALOX15 may play a less prominent role during later stages of atherosclerosis involving atherothrombotic mechanisms than eventually during early plaque development 19131063_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131661_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19198625_NuRD contributes to 15-LOX-1 transcription suppression in colon cancer cells 19296842_15-lipoxygenases may have chondroprotective properties by reducing MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression. 19325142_Overexpression of human 15(S)-lipoxygenase-1 in RAW macrophages leads to increased cholesterol mobilization and reverse cholesterol transport. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19429775_An increased expression and activity of 15-LOX-1 in lung epithelial cells is a proinflammatory event in the pathogenesis of asthma and other inflammatory lung disorders. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19469483_The mechanism and kinetics of the oxydation of arachidonic acid by both 15-lipoxygenase and 12-lipoxygenase was studied using recombinant enzymes. 19481615_The reaction specificities of wild-type vertebrate lipoxygenase isoforms are largely resistant towards pH alterations. 19497113_A detailed study of 15-LO-1 enzyme expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovium (RA) shows that it is highly expressed in the synovial lining, and that its expression overall is significantly lower in osteoarthritis synovium compared with RA. 19528634_The 15-LO-1 is present and functional on cytoplasmic neutral lipid droplets in macrophage foam cells, and these droplets may act to accumulate the anti-inflammatory lipid mediator 15(S)-HETE. 19568414_omega-3 fatty acids slow prostate cancer growth by altering omega-6/omega-3 ratios through diet and by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation in tumors by directly competing with omega-6 fatty acids for 15-LO-1 and COX-2 activities. 19576981_The 15-lipoxygenase-mediated formation of 15(S)-HpETE was in the forms of free fatty acid and esterified lipids, which was subsequently converted to 4-oxo-2(E)-nonenal. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19663136_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19663136_The genetic effects of ALOX12 and ALOX15 polymorphisms for developing aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease may be minimal compared with those of ALOX5. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19752603_Up-regulation of 15-LOX-1 alone may possibly be sufficient to treat colorectal cancer; further studies are awaited. 19775287_expression of 15-LO-1 significantly decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19942621_Genetic variations in LEP, CAPNS1 and ALOX15 show significant association with IL-6 expression. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20308035_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20382140_The mRNA levels of ALOX15 implicated pathways differed significantly in gliomas according to the histological type. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20570249_Genetic absence of this enzyme results in a significant reduction in amyloid-beta (Abeta) production and deposition and an improvement of cognitive deficits. 20592751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20649594_Induction of 15-LOX-1-mediated down-regulation of a PPAR-gamma and COX-2 pathway by honokiol may be a promising therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer. 20668019_White tea extract induces apoptosis via PPAR gamma and 15-lipoxygenases. 20676957_ALOX15 SNPs are associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese Han population. 20676957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20861348_These studies characterize an important regulatory role for ERK1/2 in mediating IL-13-induced monocyte 15-LO expression via the transcription factors Egr-1 and CREB 21094135_the 12 and 15 ALOX expression, localization and downstream cytokine expression in subcutaneous and omental adipose tissue in human obesity were shown. 21544861_15-lipoxygenase-1 exerts its tumor suppressive role by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B via activation of PPAR gamma 21558275_Molecular basis for the reduced catalytic activity of the naturally occurring T560M mutant of human 12/15-lipoxygenase that has been implicated in coronary artery disease. 21771656_cPLA(2)alpha gene activation by IL-1beta is dependent on an upstream kinase pathway, enzymatic activation and downstream 15-lipoxygenase activity: a positive feedback loop 21831839_Colocalization of Raf-1 to PEBP1 is low in asthmatic tissue and cells compared with normals, whereas there is striking colocalization of 15LO1 with PEBP1 in asthma. 21881028_15-lipoxygenase-1 expression loss is associated with cancer cells to terminal cell differentiation evasion. 22037943_15-LOX-1 promotes various anti-tumorigenic events, including cell differentiation and apoptosis, and inhibits chronic inflammation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. [review] 22078795_Data indicate that expressions of 15-LO-1 and 15-LO-2 in placentas and umbilical artery (HUA) rings in preeclampsia (PE) increased more than that in normal groups. 22089472_The results suggest that the genetic polymorphisms in both human ALOX12 and ALOX15 may contribute to variations in the peak BMD of Chinese women. 22094113_STAT6 activation and chromatin remodeling by DNA demethylation and histone acetylation are crucial for transcriptional activation of 15-LOX-1 in cultured Hodgkin lymphoma cells. 22210710_Results support the pro-apoptotic role of 15-lipoxygenase-1 and suggest that 15-lipoxygenase-1 could be a potential new target gene for the therapy of malignant glioma. 22275252_12/15-lipoxygenase-overexpressing transgenic mice have elevated levels of BACE1, whereas 12/15-LO-deficient mice have reduced levels. 22301860_rs916055 in ALOX15 gene was significantly associated with the percentage of fat mass in Chinese nuclear families with male offspring in the family-based association study using quantitative transmission disequilibrium test approach. 22351111_The rs7217186 and rs2619112 polymorphisms of the ALOX15 gene are associated with ischemic stroke in males and in patients with atherosclerosis in northern Chinese Han population. 22472308_Mice with human 15-LOX-1 expression in colonic epithelial cells were less susceptible than wild-type mice to AOM-induced colonic tumorigenesis. 15-LOX-1 appears to act as a tumor suppressor and an inhibitor of TNF-alpha-iNOS signaling and NF-kappaB activation. 22516296_phosphorylation of 5-LOX at S663 not only down-regulates leukotriene synthesis but also stimulates lipoxin production in inflammatory cells that do not express 15-LOX, redirecting lipid mediator biosynthesis to the production of mediators of inflammation. 22652554_promoter polymorphisms of the ALOX15 gene affect ALOX15 activity leading to increased eosinophil infiltration in aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease 22750246_increased ALOX15 in human ischemic heart biopsies was demonstrated. 22825379_increased 15-LOX-1 and decreased 5- and 12-LOX levels at the onset of kidney cancer reversing with the progressing stage of the disease or the grade of tumor 22879973_This study suggests that vimentin binds the ALOX15 promoter and regulates its promoter activity and protein expression 22960430_COX-2 promotes while 15-LOX-1 inhibits colonic tumorigenesis (Review). 23066085_findings demonstrate that 15-LOX-1-mediated metabolism of DHA is required for it to upregulate SDC-1 and trigger the signaling pathway that elicits apoptosis in prostate cancer cells 23079635_In transgenic knock-out 12/15-LOX mice, there is a reduction in dopamine striatal levels following neurotoxicant challenge compared to wild-type. 23181793_Genetic variant may play a role in NSAID induced acute urticaria. 23249676_Evidence suggests that up-regulation of 15-LO in vascular endothelium results in increased synthesis of arachidonic acid metabolites, increased membrane hyperpolarization, and enhanced contribution to relaxation by endothelial agonists. [REVIEW] 23285160_histone methylation/demethylation at the 15-LOX-1 promoter is important in the transcriptional regulation of the gene in cultured cells. 23404351_Genetic variability in FLAP and ALOX15 may modify the protective effect of NSAID use against colorectal neoplasia. 23474367_15-LO-1/15-HETE pathway prevents hepatocellular carcinoma cells from apoptosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via a specific intracellular signaling pathway centered by the interaction of Akt with heat shock protein 90 23528921_Findings suggest 12/15-LOX expressed in non-epithelial cells such as macrophages and fibroblasts leads to bronchial epithelial injury. 23828562_The results of our study failed to confirm whether the selected variants in ALOX15 gene within the LT metabolism pathway contribute to platelet reactivity in a diabetic population treated with ASA. 23838566_Our data support a role for 12/15-LOX activation as an inflammatory mediator of injury in periventricular leukomalacia 23844124_Data indicate a strong negative correlation between ALOX15, FADS2, and IL5RA expression with 2-arachidonoylglycerophosphocholine levels in dual asthmatic responses. 23872364_h15-LO-1-derived metabolites are highly vasoactive and may play a critical role in regulating coronary blood flow 23958500_The conserved glycine is of functional importance for ALOX15 enzyme variants; most mutants at this position lose catalytic activity. 24465480_results demonstrate that UTX is implicated in IL-4 mediated transcriptional activation of the ALOX15 gene 24634093_These findings demonstrate that 15-LOX-1 expression loss in cancer cells promotes metastasis and that therapeutically targeting ubiquitous 15-LOX-1 loss in cancer cells has the potential to suppress metastasis. 24668884_enzymatic activity and the intracellular membrane-binding function of 15-LO1 appear to contribute to HIF-1alpha suppression 24742828_Positive ALOX15 expression is more prevalent in eosinophilic esophagitis than in gastroesophageal reflux disease 24955608_ALOX 12 may have a critical role in regulation of inflammation in visceral adipose tissue in obesity and type 2 diabetes. 25105362_Loss of Alox15 altered expression of PTEN, PI3K/AKT, and the transcription factor ICSBP 25549319_IGF-1 reduces lipid oxidation and foam cell formation via downregulation of 12/15-LOX to prevent atherosclerosis. 25576922_Effect of 12/15-LOX on colorectal tumorigenesis in mouse models could be affected by tumor cell type (human or mouse), relative 12/15 LOX activity in tumor cells and stroma as well as the relative tumor 13-HODE and 12-HETE levels. 25708815_The 12/15-lipoxygenase as an emerging therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease 26036173_variation in inflammation related genes ALOX15 and IL6 was associated with bone microarchitecture and density in young adult women, but appears to be less important in the elderly 26067486_Significant associations with NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease were identified for: ALOX15 homozygous genotype and PTGS-1 rs5789 A/A homozygous genotype 26194111_The role of 15-LOX-1 in colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer 26276392_limiting ALOX15 expression by AMPK may promote an anti-inflammatory phenotype of IL-4-stimulated human macrophages 26646740_The molecular origin of substrate specificity of 15-LOX-1 for linoleic acid in comparison with arachidonic acid has been analyzed. 26826164_Compound heterozygous mutations in DYNC2H1 and ALOX15 were identified in miscarriages from two families with RPL. DYNC2H1 is involved in cilia biogenesis and has been associated with fetal lethality in humans. ALOX15 is expressed in placenta and its dysregulation has been associated with inflammation, placental, dysfunction, abnormal oxidative stress response and angiogenesis. 26871724_Hypoxia increase the production of ROS through the 15-Lipoxygenase/15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoiccid pathway. 27320813_15-LOX-1 re-expression downregulates the expression of MTA1 in colorectal cancer cell lines. 27412860_Results suggest an evolution of ALOX15 (12/15-lipoxygenase)specificity. 27552229_we propose that increased ALOX15 expression in heart tissue under ischemic conditions may lead to increased production of 15-HETE, potentially contributing to thrombosis. 27665716_the results of the present study indicated that the natural products, CA, quercetin and morin hydrate, offer potential as adjuvant therapeutic agents for SMinduced toxicity, not only by reducing inflammation mediated by the p38 and LOX signaling pathways, but also by decreasing the generation of ROS and nitrate/nitrite. 27825104_These results indicated that 15-LOX-1 is a potential target for inhibiting the trafficking of DCs to lymphoid organs and inflamed tissues and decreasing the inflammatory response attenuating symptoms of certain immunologic and inflammatory disorders such as dermatitis. 28258529_Studied human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (hucMSCs) transplantation in DSS-induced inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); hucMSC transplantation significantly relieved IBD symptoms thru the regulation of 15-LOX-1 expression and modulation of inflammatory responses in macrophages. 28339608_present in late-stage germ cells of the testis 28492741_Polymorphisms in the ALOX15 gene may influence periodontal disease pathogenesis. Hence, investigation of such polymorphisms could benefit the evaluation of lipoxins role in periodontal disease 28566277_Findings suggest that 12/15-lipoxygenase (12/15-LO)-mediated enzymatic lipid oxidation serves as a key mechanism controlling eosinophil-directed coagulation and physiological hemostasis. 28757355_15-LOX-1 expression in colon and prostate cancer cells leads to reduced angiogenesis. These changes could be mediated by an increase in the expression of both ICAM-1 and the anti-angiogenic protein TSP-1. 28812459_ALOX15 expression was positive in pauci-eosinophilic biopsies from children with eosinophilic esophagitis and negative in healthy controls. 28837253_Immunofluorescence analyses revealed that the ALOX15 protein consistently localizes to cell membrane during the course of ferroptosis. Importantly, treatments of cells with ALOX15-activating compounds accelerated cell death at low, but not high doses of erastin and RSL3 28887380_Results identify ALOX15, which was upregulated under low oxygen conditions and is associated with an increase in the rate of phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. 29022900_the results indicate that 15-LO-1 has an important role in the disease progression of osteoarthritis. Thus 15-LO-1 may be a good target for developing drugs in the treatment of osteoarthritis. 29068244_The present study shows that rs7217186:C > T and rs2619112:G > A of ALOX15 are associated with increased risk of CAD in the North Indian population. 29235036_indicate regulation of Alox15 mRNA expression in neuroblastoma cells by histone modifications, and increasing Alox15 expression in differentiating neurons 29555013_Pinosylvin enhances the apoptosis of LPS preconditioned leukocytes by up-regulating ALOX 15 expression through ERK and JNK. 29702245_Study in the dextran sulfate sodium colitis model utilizing transgenic mice overexpressing human ALOX15 suggests a pro-inflammatory activity of human 15-LOX1. 30021838_MAO-A expression is co-induced with 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) in interleukin 13 (IL-13)-activated primary human monocytes and A549 non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. 30138423_Results demonstrate the expression of ALOX15 and ALOX15B in failing as well as in donor hearts. ALOX15/B signaling may play an important role in heart disease, including heart failure. Isolated fibroblasts from all four chambers of the heart expressed ALOX15 as well as ALOX15B, and gene expression levels were further increased under hypoxia. 30237084_ALOX15 orthologs, commonly known as 12/15-lipoxygenases, were suggested to exhibit mainly arachidonic acid 12-lipoxygenating specificity in mammals ranked in evolution lower than gibbons and 15-lipoxygenating specificity in the higher ranking primates [Review]. 30368068_The activity of 15-Lipoxygenase expression levels were increased in patients with multiple sclerosis compared to healthy controls. 30407793_5-LOX does not react with 5,15-diHpETE, although it can produce lipoxin A4 when 15-HpETE is the substrate. In contrast, both 12-LOX and 15-LOX-1 react with 5,15-diHpETE, forming specifically lipoxin B4. 30472260_This review summarizes our current knowledge on the role of 12/15-LOX in inflammation and various human diseases. [Review] 30743046_High ALOX15 expression is associated with Rett syndrome OxInflammation. 31288808_ALOX15 expression and up-regulation in the functional and non-functional pituitary adenomas. 31420013_Low 15-LOX-1 expression is associated with lung carcinogenesis. 31565963_Association between ALOX15 gene polymorphism and brick-tea type skeletal fluorosis in Tibetans, Kazaks and Han, China. 31918007_Stereochemical analysis revealed that Trihydroxyoctadecenoic acids produced by eosinophils predominantly evidenced the 13(S) configuration, suggesting 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX)-mediated synthesis. 32151768_A role of Gln596 in fine-tuning mammalian ALOX15 specificity, protein stability and allosteric properties. 32324389_Biosynthesis of the Maresin Intermediate, 13S,14S-Epoxy-DHA, by Human 15-Lipoxygenase and 12-Lipoxygenase and Its Regulation through Negative Allosteric Modulators. 32768245_12/15-Lipoxygenase choreographs the resolution of IgG-mediated skin inflammation. 32867639_The Emerging Role of COX-2, 15-LOX and PPARgamma in Metabolic Diseases and Cancer: An Introduction to Novel Multi-target Directed Ligands (MTDLs). 33218117_Enhanced 15-Lipoxygenase 1 Production is Related to Periostin Expression and Eosinophil Recruitment in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. 33816635_Characterization of Mice Ubiquitously Overexpressing Human 15-Lipoxygenase-1: Effect of Diabetes on Peripheral Neuropathy and Treatment with Menhaden Oil. 34762602_15LO1 dictates glutathione redox changes in asthmatic airway epithelium to worsen type 2 inflammation. 35290903_Poly(rC)-binding protein 1 represses ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis in head and neck cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000018924 |
Alox15 |
20.820698 |
0.0633600789 |
-3.980282 |
0.564506160 |
73.537363 |
0.00000000000000000987491439936394309869532728545941070782453753267591048392581853931915247812867164611816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000078913771810834752269091953076731000921756132356500029745305369033303577452898025512695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2.5408138 |
1.0620084 |
39.8759423 |
7.2428505 |
| ENSG00000161911 |
340205 |
TREML1 |
protein_coding |
Q86YW5 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor that may play a role in the innate and adaptive immune response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15128762}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-like (TREM) family. The encoded protein is a type 1 single Ig domain orphan receptor localized to the alpha-granule membranes of platelets. The encoded protein is involved in platelet aggregation, inflammation, and cellular activation and has been linked to Gray platelet syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:340205; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet alpha granule [GO:0031091]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; platelet activation [GO:0030168] |
12393607_initial characterization of TREM-like transcript (TLT)-1 results indicate it is likely that TLT-1 regulates the signaling of the TREM family receptors(TLT-1) 15128762_In contrast to previously characterized immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif (ITIM) receptors, TLT1 enhances rather than inhibits calcium signaling in rat RBL-2H3 cells, a property dependent on the SHP-2 recruiting classical Tyr281 ITIM. 16505478_A soluble fragment of the TLT-1 extracellular domain is found in serum of humans and mice and that an isoform of similar mass is released from platelets following activation with thrombin. 17549298_Define a platelet specific function for TLT1 in regulation of aggregation. 18612537_Phenotypic heterogeneity in the Gray platelet syndrome extends to the expression of TREM family member, TLT-1. 19230638_antibody against the extracellular domain inhibits platelet aggregation in vitro 19436112_TLT-1 plays a protective role during inflammation by dampening the inflammatory response and facilitating platelet aggregation at sites of vascular injury 20093931_These results suggest that during inflammation, sTLT-1 may mediate hemostasis by enhancing actin polymerization, resulting in increased platelet aggregation and adherence to the endothelium. 22283904_Serum sTREM-1 level measurements may be helpful in diagnosing and predicting outcome for non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. 22551551_Platelet-derived soluble TLT-1 is a potent endogenous regulator of sepsis-associated inflammation. 25147325_Levels of sTLT-1 in plasma from patients with potential acute coronary syndrome were compared with an age-matched control group with similar risk factors for cardiovascular disease. 27939925_Study characterized the expression of TREM genes in cerebellum and temporal cortex and determined TREML1 and TREM2 to be the only reliably expressed TREM genes in these brain regions; identified rs9357347 as a putative regulatory variant that is associated with protection from Alzheimer's disease and with increased TREML1 and TREM2 brain levels. 30120105_TREM-like transcript 1: a more sensitive marker of platelet activation than P-selectin in humans and mice. 30545930_we show that gene expression profiling of RUNX1 knock-down or mutated MK provides a suitable approach to identify novel RUNX1 targets, among which downregulation of TREML1 and ITGA2 clearly contribute to the platelet phenotype of familial platelet disorder with predisposition to AML. 31713591_binding with macrophage membrane receptor, FcR1, initiates inflammatory signals in macrophages 31923473_Defining the TLT-1 interactome from resting and activated human platelets. 32831023_P-selectin (CD62P) and soluble TREM-like transcript-1 (sTLT-1) are associated with coronary artery disease: a case control study. 33958244_Low-soluble TREM-like transcript-1 levels early after severe burn reflect increased coagulation disorders and predict 30-day mortality. 35277419_TLT-1 Promotes Platelet-Monocyte Aggregate Formation to Induce IL-10-Producing B Cells in Tuberculosis. 35348422_Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM) like transcript-1 (TLT-1) reveals platelet activation in preeclampsia. |
ENSMUSG00000023993 |
Treml1 |
121.093464 |
0.2209093309 |
-2.178474 |
0.185977231 |
142.098135 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000925600597176025921415632092215055209616454673755908262220471493560524392308098183079854287536036849814991001039743423461914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000129742305928947212225145203123280355098190465159469502154284626050341046257757110764935459812363660603296011686325073242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.5768677 |
5.5387829 |
208.0858776 |
14.9190366 |
| ENSG00000161996 |
197335 |
WDR90 |
protein_coding |
Q96KV7 |
FUNCTION: Required for efficient primary cilium formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28781053}. |
Alternative splicing;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Involved in cilium assembly. Located in centriole. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:197335; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271] |
28781053_This study identified POB15 and POC16 as two proteins of the central core region, the distribution of which correlates with that of tubulin glutamylation; POB15 is an inner barrel protein within this region. Two poc16 mutants exhibit flagellar defects, indicating that POC16 is important for flagellum biogenesis. Human WDR90 is required for ciliogenesis, echoing the findings in Chlamydomonas. 31276698_Study describes WD repeat containing protein 90 (WDR90) as a new inflammasome component. Reconstitution experiments of the human inflammasome in HEK293cells demonstrated that WDR90 was able to physically interact with and to alter the cellular distribution of NLRC4, but not of NLRP3 and AIM2. 32946374_WDR90 is a centriolar microtubule wall protein important for centriole architecture integrity. |
ENSMUSG00000073434 |
Wdr90 |
191.009659 |
0.3886607907 |
-1.363417 |
0.231408642 |
33.867277 |
0.00000000590027960907727375895936297654602309403770732387783937156200408935546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000026318563623445321553406096122193491559926314948825165629386901855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
110.9916773 |
17.2090963 |
287.9273801 |
31.4785495 |
| ENSG00000162032 |
90864 |
SPSB3 |
protein_coding |
Q6PJ21 |
FUNCTION: May be a substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. {ECO:0000250}. |
Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Predicted to be involved in proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be part of SCF ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90864; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
20532202_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29059170_Low SPSB3 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in Ovarian and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000024160 |
Spsb3 |
225.577170 |
0.3915383669 |
-1.352774 |
0.134536460 |
101.142892 |
0.00000000000000000000000855815014850232307409493964435752862906533215040045428230272995650390610578028827148955315351486206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000087781998743498453744202112308674100158207415400876193544313992773997501473104421165771782398223876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
139.5581473 |
12.3756544 |
359.1658038 |
21.2776788 |
| ENSG00000162104 |
115 |
ADCY9 |
protein_coding |
O60503 |
FUNCTION: Adenylyl cyclase that catalyzes the formation of the signaling molecule cAMP in response to activation of G protein-coupled receptors (PubMed:9628827, PubMed:12972952, PubMed:15879435, PubMed:10987815). Contributes to signaling cascades activated by CRH (corticotropin-releasing factor), corticosteroids and beta-adrenergic receptors (PubMed:9628827). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10987815, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12972952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15879435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9628827}. |
ATP-binding;cAMP biosynthesis;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Lyase;Magnesium;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Adenylate cyclase is a membrane bound enzyme that catalyses the formation of cyclic AMP from ATP. It is regulated by a family of G protein-coupled receptors, protein kinases, and calcium. The type 9 adenylyl cyclase is a widely distributed adenylyl cyclase, and it is stimulated by beta-adrenergic receptor activation but is insensitive to forskolin, calcium, and somatostatin. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:115; |
axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0004016]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway [GO:0071880]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cAMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006171]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11299302_The HIV-1 regulatory protein Tat was shown to inhibit the activity of adenylyl cyclase in rat microglial cells. 11840511_A case-control study using Ile772Met and a repeat (TTTA)n showed no significant association with mood disorders in Japan. 11840511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082561_associated with bipolar disorder using pedigree linkage disequilibrium 14996950_blocking glycosylation of AC9 significantly attenuates Galpha(s) stimulation. 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20175803_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20459687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20522523_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22778270_in heart, Yotiao brings together PKA, PP1, PDE4D3, AC9, and the I(Ks) channel to achieve localized temporal regulation of beta-adrenergic stimulation. 24269684_Data indicate that adenylyl cyclase 9 (AC9) transcript is a direct target of miR-181b. 24722286_The importance of miR-181a-mediated AC9 downregulation in acute promyelocytic leukemia, is reported. 25583994_The effects of dalcetrapib on atherosclerotic outcomes are determined by correlated polymorphisms in the ADCY9 gene. 25959651_The stronger TNF-alpha responses in young males compared to females may be partly associated with male-specific down-regulation of ADCY7 and ADCY9. 28076799_polymorphisms in the ADCY9 gene are significantly associated with asthma and/or allergy markers 29292367_ADCY9 immunoreactivity score was significantly higher (P=0.002) in tumor tissues (6.40+/-1.26, n=200) than in adjacent normal samples (4.13+/-0.83, n=8). The IRS and mRNA expression of ADCY9 were correlated to colon cancer TNM staging. 30121334_deductive reasoning leads to the suggestion that proteolytic cleavage of the C2b auto-inhibitory domain may govern the activation of AC9 by Gs-coupled receptors . 32515353_G protein-regulated endocytic trafficking of adenylyl cyclase type 9. 33232543_Assessment of ADCY9 polymorphisms and colorectal cancer risk in the Chinese Han population. 33326832_The ADCY9 genetic variants are associated with glioma susceptibility and patient prognosis. 33416140_miR1423p targets AC9 to regulate sciatic nerve injuryinduced neuropathic pain by regulating the cAMP/AMPK signalling pathway. 34609279_A sex-specific evolutionary interaction between ADCY9 and CETP. 36111722_[Association of the ADCY9 gene and gene-environmental interaction with the susceptibility to childhood bronchial asthma].', trans 'ADCY9. |
ENSMUSG00000005580 |
Adcy9 |
493.037026 |
0.2750484522 |
-1.862242 |
0.107922065 |
292.812991 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001212386137226761237111613736229955340059375975358567401085193032451370875374649430627900882367380961322746713122173076330807317606013344958148648128634228418538986218888631185564008774235844612121582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000344131142028211460625745397061206638337381558605165809766636717765867318484887311865759361236085142325520091262297995969203752731767530019290766073972356035208866598118504498415859416127204895019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
220.2508695 |
16.1019984 |
805.1261468 |
39.5949956 |
| ENSG00000162129 |
81570 |
CLPB |
protein_coding |
Q9H078 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a regulatory ATPase and participates in secretion/protein trafficking process. Involved in mitochondrial-mediated antiviral innate immunity, activates RIG-I-mediated signal transduction and production of IFNB1 and pro-inflammatory cytokine IL6 (PubMed:31522117). Has ATP-dependent protein disaggregase activity and is required to maintain the solubility of key mitochondrial proteins (PubMed:32573439, PubMed:34115842). Plays a role in granulocyte differentiation (PubMed:34115842). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31522117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32573439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34115842}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;ATP-binding;Cataract;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Hydrolase;Intellectual disability;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transit peptide |
|
This gene belongs to the ATP-ases associated with diverse cellular activities (AAA+) superfamily. Members of this superfamily form ring-shaped homo-hexamers and have highly conserved ATPase domains that are involved in various processes including DNA replication, protein degradation and reactivation of misfolded proteins. All members of this family hydrolyze ATP through their AAA+ domains and use the energy generated through ATP hydrolysis to exert mechanical force on their substrates. In addition to an AAA+ domain, the protein encoded by this gene contains a C-terminal D2 domain, which is characteristic of the AAA+ subfamily of Caseinolytic peptidases to which this protein belongs. It cooperates with Hsp70 in the disaggregation of protein aggregates. Allelic variants of this gene are associated with 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, which causes cataracts and neutropenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:81570; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein disaggregase activity [GO:0140545]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030851]; RIG-I signaling pathway [GO:0039529] |
18488042_ClpB-DnaK reactivated all aggregated fusion proteins with similar efficiency, without unfolding native domains, demonstrating that partial threading of the misfolded moiety is sufficient to solubilize aggregates. 19698713_formation of the DnaK-ClpB bichaperone network is a three step process 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25288401_ClpB can passively thread soluble denatured proteins. 25595726_Case Reports: bi-allelic CLPB mutations cause cataract, renal cysts, nephrocalcinosis and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, a novel disorder of mitochondrial protein disaggregation. 25597510_Mutations in CLPB define a syndrome with intellectual disability, congenital neutropenia, progressive brain atrophy, movement disorder, cataracts, and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria. 25597511_CLPB is proposed to function as a mitochondrial chaperone involved in disaggregation of misfolded proteins, resulting from stress such as heat denaturation. 25650066_Disruption of CLPB is associated with congenital microcephaly, severe encephalopathy and 3-methylglutaconic aciduria 28687938_The neonatal presentation of CLPB deficiency predicts the course of disease in later life, which is extremely important for counselling. 31917998_It present for the first time the biochemical characteristics of the human CLPB protein with the aim of shedding light on its physiological function and the pathogenesis of MEGCANN syndrome. 32573439_Skd3 (human ClpB) is a potent mitochondrial protein disaggregase that is inactivated by 3-methylglutaconic aciduria-linked mutations. 32866687_Human CLPB forms ATP-dependent complexes in the mitochondrial intermembrane space. 34115842_Heterozygous variants of CLPB are a cause of severe congenital neutropenia. 34140661_Neutropenia and intellectual disability are hallmarks of biallelic and de novo CLPB deficiency. 36074910_Premature Ovarian Insufficiency in CLPB Deficiency: Transcriptomic, Proteomic and Phenotypic Insights. |
ENSMUSG00000001829 |
Clpb |
263.108066 |
2.1790725328 |
1.123714 |
0.136799409 |
66.984779 |
0.00000000000000027361158341416207634408132957871589157271039025216829987385835920576937496662139892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002018244363414808699545240187976892649541549914354865435939245799090713262557983398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
344.9952099 |
26.6497590 |
159.6273089 |
9.3036483 |
| ENSG00000162337 |
4041 |
LRP5 |
protein_coding |
O75197 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a coreceptor with members of the frizzled family of seven-transmembrane spanning receptors to transduce signal by Wnt proteins (PubMed:11336703, PubMed:11448771, PubMed:15778503, PubMed:11719191, PubMed:15908424, PubMed:16252235). Activates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway that controls cell fate determination and self-renewal during embryonic development and adult tissue regeneration (PubMed:11336703, PubMed:11719191). In particular, may play an important role in the development of the posterior patterning of the epiblast during gastrulation (By similarity). During bone development, regulates osteoblast proliferation and differentiation thus determining bone mass (PubMed:11719191). Mechanistically, the formation of the signaling complex between Wnt ligand, frizzled receptor and LRP5 coreceptor promotes the recruitment of AXIN1 to LRP5, stabilizing beta-catenin/CTNNB1 and activating TCF/LEF-mediated transcriptional programs (PubMed:11336703, PubMed:25920554, PubMed:24706814, PubMed:14731402). Acts as a coreceptor for non-Wnt proteins, such as norrin/NDP. Binding of norrin/NDP to frizzled 4/FZD4-LRP5 receptor complex triggers beta-catenin/CTNNB1-dependent signaling known to be required for retinal vascular development (PubMed:27228167, PubMed:16252235). Plays a role in controlling postnatal vascular regression in retina via macrophage-induced endothelial cell apoptosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91VN0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11336703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11448771, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11719191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14731402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15778503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15908424, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16252235, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24706814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25920554, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27228167}. |
Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Endocytosis;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Osteopetrosis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane low-density lipoprotein receptor that binds and internalizes ligands in the process of receptor-mediated endocytosis. This protein also acts as a co-receptor with Frizzled protein family members for transducing signals by Wnt proteins and was originally cloned on the basis of its association with type 1 diabetes mellitus in humans. This protein plays a key role in skeletal homeostasis and many bone density related diseases are caused by mutations in this gene. Mutations in this gene also cause familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:4041; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; Wnt signalosome [GO:1990909]; Wnt-Frizzled-LRP5/6 complex [GO:1990851]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; coreceptor activity involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:1904928]; coreceptor activity involved in Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0071936]; Wnt receptor activity [GO:0042813]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; adipose tissue development [GO:0060612]; anatomical structure regression [GO:0060033]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; apoptotic process involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:1902262]; bone marrow development [GO:0048539]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; bone remodeling [GO:0046849]; branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060444]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell migration involved in gastrulation [GO:0042074]; cell-cell signaling involved in mammary gland development [GO:0060764]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; extracellular matrix-cell signaling [GO:0035426]; gastrulation with mouth forming second [GO:0001702]; glucose catabolic process [GO:0006007]; mesodermal cell migration [GO:0008078]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071901]; Norrin signaling pathway [GO:0110135]; osteoblast development [GO:0002076]; osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033687]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0002053]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033690]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0061178]; retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0060042]; retinal blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0061304]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019] |
11741193_mutation results in an autosomal dominant high-bone-mass trait 11793484_seven novel sequence variants/polymorphisms 12015390_The LRP5V171 mutation causes high bone density by impairing the action of a normal antagonist of the Wnt pathway and thus increasing Wnt signaling. These findings demonstrate the role of altered LRP5 function in high bone mass. 12054167_localization to chromosome 11q12-13 in autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type I 12579474_Six novel missense mutations in this gene shown in various conditions with an increased bone density and bone diseases. 12700977_disease association data, largely focused in the LRP5 region with 1,106 type 1 diabetes families, provided no further evidence for disease association at LRP5 or at D11S987 12817748_G171V transgenic mice showed an increase in actively mineralizing bone surface and enhanced alkaline phosphatase staining in osteoblasts 14727154_LRP5 is a bone mineral density determinant and also contributes to a risk of osteoporosis 14727154_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14735475_LRP5 has a role in neoplasm metastasis 15024691_Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy has mutations in a second gene at the EVR1 locus, low-density-lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5), a Wnt coreceptor 15077203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15201508_no association was found between a LRP5 polymorphism and peak bone mass in young men 15221492_LRP5 gene is a candidate for the genetic determinants of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women 15221492_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15346351_Mutations in LRP5 can cause autosomal recessive or dominant Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 15355556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15619672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15777745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15777745_genetic variation in LRP5 seems to be of importance for regulation of bone mass and osteoporotic fractures 15781005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824851_heterozygous mutations in the LRP5 gene can cause osteoporosis in both children and adults 15824861_a novel LRP5 mutation may be responsible for oropharyngeal skeletal disease 15908424_SOST antagonizes Wnt signaling by binding to the extracellular domain of the Wnt coreceptors LRP5 and LRP6 and disrupting Wnt-induced Frizzled-LRP complex formation. 15923613_These data suggest that HBM mutant proteins can transit to the cell surface in sufficient quantity to transduce Wnt signal and that the likely mechanism for the HBM mutations' physiologic effects is via reduced affinity to and inhibition by DKK1. 15979013_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15981244_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15981244_mutations in the LRP5 and/or FZD4 genes may have roles in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy 16115379_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16168727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16168727_These data indicate an association between LRP5 variants and idiopathic osteoporosis in males, pointing to a role of LRP5 in this disease. 16234968_Carrying an LRP5 mutation is a risk factor for idiopathic osteoporosis, but idiopathic osteoporosis in men is infrequently underlied by such a mutation. 16355283_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16513652_active CKIepsilon generation may induce a negative feedback loop by phosphorylation of sites on LRP5/6 that modulate axin binding and hence beta-catenin degradation 16613987_Lrp5 locus was discovered to confer vitamin D response to a heterologous promoter when introduced into osteoblastic cells 16622736_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16631011_LRP5 was increased in the calcified aortic valves by protein and gene expression. 16679074_observed mutations may affect the molecular interactions of LRP5 and so lead to the observed osteoporosis pseudoglioma syndrome phenotypes 16723389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16754270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16754270_The Q89R polymorphism is an independent factor for hypertension in Japanese females. 16772034_Splice forms of crucial genes of the Wnt-pathway, beta-Catenin, LRP5, GSK3beta, Axin-1 and CtBP1 are expressed in human colorectal tissue. 16956801_This study examined human LRP5 signaling and the effects of an intracellular domain single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP: p.V1525A) on osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. 16958596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17002572_functional interactions between Sost or Wise and LRP5 have the potential to regulate bone deposition by modulating Wnt signaling 17052975_SOST-LRP5 antagonistic interaction plays a central role in bone mass regulation and may represent a nodal point for therapeutic intervention for osteoporosis and other bone diseases 17086708_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17087607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17087607_we found a relationship between the LRP5 genotype and serum follicle stimulating hormone but not luteinizing hormone levels 17137849_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17137849_Wnt-LRP5 signalling may play a role in the adaptation of bone to mechanical load in humans, and may explain some gender-related differences in bone mass 17202888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17223614_In comparison with subjects with the AlaAla genotype (n=215), those with AlaVal genotype (n=20) had lower femoral neck BMC (P=0.029) and BMD (P=0.012), trochanter BMC (P=0.0067) and BMD (P=0.015), and total hip BMC (P=0.0044) and BMD (P=0.0089). 17229572_1,25(OH)(2)D(3) can enhance the expression of a critical component of the Wnt signaling pathway which is known to impact osteogenesis 17241106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17276019_Results indicate the importance of LRP5 beta-propeller 1 for Dkk1 function and Wnt signaling. 17306638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17306638_genetic variations in LRP5 are important factors affecting BMD in adult women, and 1330 V may contribute to osteoporosis susceptibility, at least in Japanese 17307038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17307038_Premenopausal women drove the association as expected from the proposed role of LRP5 in peak bone mass 17505772_LRP5 polymorphism effect on bone mineral density is apparent in childhood 17505772_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17680723_LRP5 mutations and the level of Wnt signaling determine differentiation fate of hMSCs into osteoblasts or adipocytes. 17700537_concludes that bone-derived prostate cell line that produces osteoblastic lesions induces new bone formation through Wnt canonical signaling, that LRP5 mediates this effect, and that DKK1 is involved in the balance between bone formation and resorption 17953969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17972053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18026682_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18044981_an internally truncated LRP5 receptor is strongly implicated in deregulated activation of the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hyperparathyroid tumors 18058054_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18058054_The Ala1330Val and Val667Met polymorphisms in the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 gene are significantly associated with peak bone mass in physically active men. 18073493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18073493_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the LRP5 promoter are associated with bone mineral density variation in young Chinese females 18285546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18349089_LRP5 may be the first gene to reach a genome-wide significance level for a phenotype related to osteoporosis. 18349089_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18406176_No association was seen between FRZB, LRP5 and LRP6 variants with radiographic osteoarthritic outcomes in two population-based cohorts 18406176_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18418639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18418639_The association between LRP5 V667M and LS BMD is confirmed but not that between ESRRA repeats and LS BMD. 18455228_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18455228_Two gene variants of key biological proteins increase the risk of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture. 18493104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18493104_We found no evidence for a substantial effect of LRP5 or LRP6 SNPs on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes or clinical characteristics of diabetic subjects in Japanese population. 18502762_Kremen may not be essential for Dkk1-mediated Wnt antagonism and Kremen may only play a role when cells express a high level of LRP5/6 18521528_DKK1 and sclerostin are independent, and not synergistic, regulators of LRP5 signaling and that the function of each is impaired by HBM-LRP5 mutations 18524778_analysis of the structural basis of the interaction between Dkk and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5/6 18588671_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18588671_there is a modest effect of the A1330V polymorphism on BMD in the general population, and that the modest association may limit its clinical use 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18684085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18684085_analysis of LRP5 haplotypes in relation to osteoporosis phenotypes in Spanish postmenopausal women 18721193_Genetic variation in LRP5 did not predispose to premature adrenarche but was associated with metabolic characteristics, especially lipid profile, in healthy prepubertal children. 18721193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18825883_Follow-up of pamidronate therapy in two brothers with osteoporosis-pseudoglioma syndrome (OPPG) carrying an LRP5 mutation. 18932002_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18932002_This meta-analysis shows that LRP5 A1330V polymorphism is associated with bone density, and that individuals with the AA genotype have a higher bone density than those with the AV/VV or VV genotype. 19023643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023643_results suggest that the LPR5 polymorphism does not appear to be a clinically useful marker for the prediction of fracture risk in Japanese female rheumatoid arthritis patients, although it is associated with increased serum total cholesterol levels. 19107203_Phosphorylated LRP6/5 both recruits and directly inhibits GSK3beta using two distinct portions of its cytoplasmic sequence. 19147944_This review finds that LRP5 and LRP6 play overlapping roles in both early and late stages of osteoblast differentiation. 19148563_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19148563_the LRP5 A1330V polymorphism is associated with hip bone mineral density in osteoporotic men, but allelic variations in LRP5 do not appear to be associated with response to bisphosphonate treatment. 19158955_the LRP5Delta receptor is strongly implicated in mammary gland tumorigenesis 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19177549_identifying two novel types of mutation in related individuals whose presenting features were profound muscle hypotonia, mild mental retardation, blindness, and growth retardation 19225709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225709_The geometric dimensions of the proximal femur in perimenopausal women are not associated with LRP5 polymorphism. 19233690_Gene Ontology analysis indicated a significant alteration of oxygen transport (increased hemoglobin gene expression) and lipid metabolism [including monoglyceride lipase and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) gene]. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506792_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19571442_association between the A1330V SNP and total body BMD were replicated in 739 postmenopausal Japanese women (AA vs. VV; P = 0.0026). These data suggest that the V1330 variant in the LRP5 gene decreases Wnt activity, which in turn decreases the BMD. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19629617_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19673927_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19673927_We found high prevalence of osteoporosis and abnormal glucose metabolism in subjects with LRP5 mutation(s). 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19746449_a high bone mass mutant LRP5(G171V), has subtly reduced Dkk1 binding, and, in contrast to LRP5, no enhancement of binding with MesD 19789208_Increased LRP5 polymorphisms may contribute to bone mass accrual in prepubertal premeture adrenarche children. 19810105_Catabolic role of LRP5 may be mediated by Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in human osteoarthritis. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19898734_results suggest that A1330V in LRP5, is not associated with bone mineral density in the Slovenian population 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20034086_found various types of LRP5 mutations, including an exon-level deletion that is undetectable by standard PCR-based mutation screening. Oligonucleotide tiling microarray seems to be a powerful tool in identifying cryptic structural mutations 20045498_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20045498_Our study shows that in children LRP5 mutations are not a common cause of increased fractures. 20101398_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20141633_Both Kruppel-like factor 15 and specificity protein 1 binding motifs are essential for human LRP5 promoter activity. 20146170_Evidence of an allele of LRP5 in Chinese increases the total cholesterol level in a general Han population. 20146170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200960_circulating serotonin levels mediate the increased bone mass resulting from gain-of-function mutations in Lrp5 in humans 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20534768_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20613673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20630166_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20630166_These findings demonstrate that both LRP5 polymorphism and its interaction with calcium intake are associated with BMD, whereas higher calcium intake was shown to decrease the negative effect of this polymorphism on BMD 20846389_The mRNA expression levels of DKK-1 binding receptor LRP5/6 and Krm1/2 in SCs from patients with MM were significantly higher than those in myeloma cells and in SCs from healthy donors. 20926594_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20926594_We found common polymorphisms of LRP5 associated with osteoporotic fractures, and polymorphisms of the LRP6 gene associated with BMD, thus suggesting them as likely candidates to contribute to the explaination of the hereditary influence on osteoporosis. 20953208_Common polymorphic variations of the LRP5 gene do not influence peak bone mass acquisition and obesity phenotypes in young Chinese men. 20953208_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20960157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20961463_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21116122_association of Ala1330Val and Val667Met polymorphisms in LRP5 with volumetric BMD and macro-architectural bone parameters in a population-based sample of men and women 21147715_LRP5 gene was stronly associated with the BMD in Europeans and North Americans. 21351148_Increased bone mass in Lrp5-high bone mass patients seems to be caused primarily by changes in trabecular and cortical bone mass and structure. 21397183_Two structural and functional domains of MESD required for proper folding and trafficking of LRP5/LRP6. 21407258_Study present clinical and genetic data for four Osteoporosis-pseudoglioma sydrome patients with novel LRP5 mutations, three of which affect splicing 21432225_Analysis of variance and post hoc Tukey test indicated that mean bone mass density was significantly lower in subjects with VV genotype than in those with AA genotype (0.540 +/- 0.048 versus 0.562 +/- 0.062 g/cm(2)). 21471826_The LRP5 c.266A > G and c.3893C > T polymorphisms may be associated with risk of nonresponse to hormone therapy in postmenopausal Korean women. 21528003_The LRP5.Q89R polymorphism did not change protein expression, interaction with the molecular chaperone MESD, protein trafficking, Wnt signaling transduction, or its efficacy in DKK1-mediated inhibition. 21542013_This is the first time that the direct action of RUNX2 on LRP5 has been described. 21774378_SNP (IVS17-1677C>A) located in intron 17 of LRP5 has effects on bone density of postmenopausal Japanese women.[review] 21821287_LRP5 gene rearrangement in 11q13.2 is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 21840657_These findings demonstrate that the A1330V and V667M polymorphisms are associated with low bone mineral density in peri- and postmenopausal Greek women. 21885484_Data suggest that LRP5 may be involved in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. 21887268_These studies uncover a new and important molecular tuning mechanism for differential regulation of LRP5 and LRP6 phosphorylation and signaling activity. 22000856_The LRP5 is a coreceptor for Wnt growth factors, and also bind Dkk proteins, secreted inhibitors of Wnt signaling. 22167346_These results suggest that LRP5 alleles influence the type of hip fractures 22207519_osteosarcoma patients whose primary tumors expressed LRP-5 sustained a higher risk of developing metastasis 22303459_LRP5 oligomerization results in its localization to disheveled-containing punctate structures and sequestration of scaffold protein Axin, leading to robust beta-catenin-mediated signaling. 22487062_Two novel LRP5 mutations (c.3446 T > A; p.L1149Q and c.3553 G > A; p.G1185R) were identified in two patients and their affected family members. 22513174_Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activation through LRP-5 may contribute to chondrocyte hypertrophy and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis. 22589387_Crystal structures of the LRP6 ectodomain in complex with DKK1, along with mutagenesis studies, provide considerable insights into the molecular basis for DKK-mediated inhibition and Wnt signaling through LRP5/6 22696217_peptide derived from the loop 2 region of sclerostin blocked the interaction of sclerostin with LRP5/6 and also inhibited Wnt1 but not Wnt3A or Wnt9B signaling. This suggests that these Wnts interact with LRP6 in different ways 22848540_LRP5-Tie2-Ang signaling axis plays a central role in control of both angiogenesis and alveolarization during postnatal lung development 23041840_Six Dkk-1, three Sost, one Kremen-1 and 10 LRP-5 polymorhpisms were significantly associated with radiological progression of rheumatoid arthritis joint destruction. 23054017_Demonstration of the additive effect of four polymorphisms on the LRP5, LEPR, near MC4R and SH2B1 genes on metabolic syndrome risk. 23077402_Six mutations have been found in the LRP5 gene in five Chinese families with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 23238007_LRP5 and FDPS loci age-specifically affect skeletal traits in healthy fertile women. 23242660_Our results supported the association of LRP5 with osteoporosis and showed the potential value of LRP5 haplotypes to identify risk of osteoporosis in Mexican population. 23318847_In this osteosclerotic Chinese family, the A242T mutation in the LRP5 gene results in a high bone mass phenotype with an elongated mandible and torus palatinus in the center of the hard palate. 23441120_Six different nonsynonymous DNA variants in are identified in the coding region of either the FZD4 gene (p.H69Y, p.R127H, and p.Y211H) or the LRP5 gene (p.R1219H, p.H1383P, and p.T1540M) in seven patients with advanced retinopathy of prematurity 23490293_Identify rs4988300 and rs3781590 LPR5 polymorphisms as independent genetic markers of abdominal aortic aneurysms. 23800666_Studies indicate that splice site mutation that leads to aberrant splicing often causes genetic skeletal system disease, like COL1A1, SEDL and LRP. 24130145_The Val genotype of the rs3736228 (p.A1330V) of LRP5 was significantly associated with bone mineral density (BMD) variations at the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck. None of the three polymorphisms of TNFRSF11B was associated with BMD variations. 24266894_LRP5 negatively regulates differentiation of monocytes through abrogation of Wnt signaling. 24337955_These results underscore the significance of the LRP5 gene in bone metabolism and emphasize the significance of the replication of previous results in independent cohorts. 24376863_LRP5 polymorphisms may be modestly associated with bone mineral density of the lumbar spine and the femur neck. 24403228_LRP5 plays a role in prostate cancer invasion growth and skeletal metastasis in vitro and in vivo. 24412065_GSK3 is sequestered into multivesicular bodies through and interaction between p120-catenin/cadherin and LRP5/6. 24479426_Our findings indicate that LRP5 plays an essential role in osteoarthritis cartilage destruction 24606091_Circulating plasma sclerostin concentrations are increased in both LRP5 and non-LRP5 High bone mass patients compared with controls. 24706814_Functional activity analyses indicated that mutant LRP5 led to reduced wingless signal activation 24715757_Two new novel LRP5 mutations in Chinese patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy and mild reduced bone mineral density, were identified. 24736728_evidence of lack of LRP5 mutations and of a putative HBM-causing mutation in DKK1 24743782_The results suggested that the lack of affinity between human DKK3 and human LRP5/6 results from: i) insertion of the 7 amino acids, and ii) P258 in human DKK3. 24885293_The Ala1330Val polymorphism in LRP5 is weakly associated with lower lumbar spine bone density in Tunisian post-menopausal women. 24897288_The A1330V polymorphism of LRP5 is possibly correlated with response to alendronate treatment in Chinese women. 24921217_The Wnt coreceptor, Lrp5, is a genetic driver of lung fibrosis in mice and a marker of disease progression and severity in humans with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 24927689_Serum levels of Wnt inhibitors are not changed in individuals with high bone mass causing mutations in LRP5. 25329009_Independently or combined with APOE, LRP5 polymorphisms may lead to dyslipidemia and are associated with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Dyslipidemia may be a risk indicator for generalized aggressive periodontitis in the Chinese population. Furthermore, two LRP5 polymorphisms (rs682429 and rs312016) might be useful for identifying subjects at higher risk of generalized aggressive periodontitis. 25384351_Although AFFs have been reported in other rare bone diseases, this is the first in a genetic condition of primary osteoblast dysfunction. The relatively low bone turnover observed, and knowledge of LRP5 function 25392953_This is the first study to suggest the genetic influence of LRP5 A1330V polymorphism on bone mineral density in COPD patients, independent of the development of emphysema. 25515155_This study show LRP5 polymorphism may associate with body composition and bone mineral density in Iranian children. 25580429_These results suggest that there is a modest effect of the LRP5 rs3736228 C>T on the increased susceptibility of bone fracture and osteoporosis. 25651180_Reciprocally, a low bone mineral density-associated common LRP5 allele correlated with increased abdominal adiposity. 25762437_finding corroborates the relationship between LRP5 genotype and bone phenotype in postmenopausal women, however, the complete mechanism of this relationship requires further investigations. 25783012_No mutations in LRP5 and LRP6 could be identified 25863010_no association of single nucleotide polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility in Chinese population 25902418_Lrp5 binds to Frizzled, preventing Frz-regulated non-canonical Wnt pathway activation and further non-canonical pathway-mediated tumour metastasis. 25920554_we identified a total of four different LRP5 variants that were predicted to be pathogenic by in silico tools. One ADPKD patient has a positive family history for ADPKD and variant LRP5 segregated with the disease. 25945592_Molecular testing identified biallelic lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) mutations (NM_002335.3:c. [889dupA]; [2827 + 1G > A]) confirming a diagnosis of osteoporosis-pseudoglioma (OPPG) syndrome. 25959626_findings suggest that rescuing LRP5/6-mediated Wnt signaling improves neuronal cell survival and reduces tau phosphorylation, which support the hypothesis that Wnt signaling might be an attractive therapeutic strategy for managing AD 26117992_mechanism of LRP protein action in the process of bone tissue metabolism and etiology of osteoporosis. 26244290_Among the patients with pathogenic mutations detected, FZD4 mutations accounted for the largest proportion of autosomal inheritance FEVR cases (13/18 patients, 72.2%), followed by LRP5 (4/18 patients, 22.2%) and TSPAN12 (1/18 patients, 5.6%). 26248735_No LRP5 variant was found to be associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Han Chinese, but haplotype TT was found to be associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus . 26666179_LRP5 is a signature of the anti-inflammatory defensive phenotype of macrophages. 26681532_Data show that LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) gain-of-function mutations do not activate beta-catenin signaling in osteoblasts. 26711269_Lrp5 controls glucose uptake and growth of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. 26739212_LRP5 is a novel anti-inflammatory macrophage marker that positively regulates migration, phagocytosis, lipid uptake and metabolism. 26774446_miR-23a plays an inhibitory role in osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs, which may act by targeting LRP5 27007396_The authors report a case of familial exudative vitreoretinopathy in the spectrum of osteoporosis pseudoglioma syndrome associated with novel mutations of the LRP5 and TSPAN12 genes that resulted in a phenotype similar to bilateral persistent fetal vasculature. 27051030_Meta-analysis indicates that the LRP5 Ala1330Val polymorphism may not be correlated with fracture susceptibility. 27228167_We identified four novel LRP5 missense mutations in these FEVR families: c.C1042T (p.R348W), c.G1141A (p.D381N), c.C1870T (p.R624W), and c.A4550G (p.Y1517C). All four of these LRP5 mutations led to significant reduction of enzymatic activity with response to NORRIN. Our findings expand the mutational spectrum of FEVR in the Indian population and provide some guidelines in clinical diagnosis. 27486893_A genetic evaluation of the known genes associated with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR) revealed a novel variant in the LRP5 gene that co-segregated with the phenotype in the family. 27582019_This study did not identify LRP5 polymorphisms as a risk factor for osteoporosis in Thai menopausal women. 27821587_findings revealed an unrecognized role of Caprin-2 in facilitating LRP5/6 constitutive phosphorylation at G2/M through forming a quaternary complex with CDK14, Cyclin Y, and LRP5/6. 28028632_LRP5 might be an important genetic marker contributing to bone mass accrual early in life. 28067456_Data suggest that the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) may be associated with interactions between the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) gene and overweight and obesity. 28111184_In this study, the splice site mutation c.2827thorn1G > A found in LRP5 (603506) gene is thought to cause microphthalmia in this family. 28139941_LRP5 (rs556442) had a significant influence on trigylceride (TG) levels in unadjusted analysis and when adjusted for interacting factors. Higher TG levels were observed in AA/AG genotype of rs566442 in comparison to GG genotype (OR = 2.028, 95% CI = 0.997-4.127, p = 0.049). 28145787_To our knowledge, these are the first two cases of the syndrome described in Italy. Genetic testing proved to be fundamental for definition of the syndrome and confirms the importance of early detection of LRP5 variants for management of systemic features of the disease in patients and carrier relatives. 28283687_The data do not support the hypothesis that HBM-causing LRP5 mutations, associated with increased Wnt signaling, improve glucose metabolism in humans. However, it does appear that LRP5 variants may affect LDL metabolism, a major risk factor for coronary artery disease. 28420620_wild-type and all five mutant LRP5 proteins were assayed for the ability to activate the Norrin/beta-catenin pathway by established luciferase reporter assays, and all mutants failed to activate the pathway. 28425175_VAP1 cleaved the extracellular region of LRP5. This cleavage removes four inhibitory beta-propeller structures, resulting in activation of LRP5/6. 28494495_Among the detected mutations, LRP5 accounted for the largest proportion with a mean mutation rate of 16.1% (5/31, 16.1%), followed by NDP (3/31, 9.7%), FZD4 (2/31, 6.5%), TSPAN12 (1/31, 3.2%), and KIF11 (1/31, 3.2%). All the novel changes were predicted to be pathogenic by a series of bioinformatics analyses. 28677207_In conclusion, the LRP5 mutation influences cell proliferation through the Wnt signaling pathway, thereby reducing the number of supporting cells and hair cells and leading to nonsyndromic hearing loss in this Chinese family. 28867931_We identified two novel heterozygous deletion mutations [LRP5, c.4053 DelC (p.Ile1351IlefsX88); TSPAN12, EX8Del] using targeted NGS as a causative mutation for Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR). 28893644_A novel heterozygous mutation (p.N198Y) in LRP5 was identified in a patient with significantly increased bone mineral density. 28973524_The presence of GIIA in the LRP5 complex pinpoints a potential functional connection with PRKCSH. Interestingly, all three PLD-associated protein complexes included filamin A (FLNA), a multifunctional protein described to play a role in ciliogenesis as well as canonical Wnt signalling. 29038835_An interaction was found between LRP5 SNP rs648438 and periostin SNP rs9547970 on serum periostin levels and on radial cortical porosity. 29131652_Phenotypic variability was observed in |
ENSMUSG00000024913 |
Lrp5 |
111.019305 |
0.1187426985 |
-3.074089 |
0.514032348 |
30.041455 |
0.00000004229080886428265707351008121685220775276548010879196226596832275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000172577367662928382655685528510036697014129458693787455558776855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.7587559 |
15.4142130 |
159.1962137 |
78.6373813 |
| ENSG00000162390 |
26027 |
ACOT11 |
protein_coding |
Q8WXI4 |
FUNCTION: Has an acyl-CoA thioesterase activity with a preference for the long chain fatty acyl-CoA thioesters hexadecanoyl-CoA/palmitoyl-CoA and tetradecanoyl-CoA/myristoyl-CoA which are the main substrates in the mitochondrial beta-oxidation pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22897136}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Fatty acid metabolism;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine esterase;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid metabolism. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:22897136}. |
This gene encodes a member of the acyl-CoA thioesterase family which catalyse the conversion of activated fatty acids to the corresponding non-esterified fatty acid and coenzyme A. Expression of a mouse homolog in brown adipose tissue is induced by low temperatures and repressed by warm temperatures. Higher levels of expression of the mouse homolog has been found in obesity-resistant mice compared with obesity-prone mice, suggesting a role of acyl-CoA thioesterase 11 in obesity. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:26027; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; acyl-CoA hydrolase activity [GO:0047617]; carboxylic ester hydrolase activity [GO:0052689]; long-chain acyl-CoA hydrolase activity [GO:0052816]; long-chain fatty acyl-CoA binding [GO:0036042]; myristoyl-CoA hydrolase activity [GO:0102991]; palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase activity [GO:0016290]; acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0006637]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to temperature stimulus [GO:0009266] |
11696000_BFIT supports the transition of thermogenic brown adipose tissue towards increased metabolic activity, probably through alteration of intracellular fatty acyl-CoA concentration. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22897136_The N-terminal region of human fat inducible thioesterase variant 2 constitutes a mitochondrial location signal sequence, which undergoes mitochondrion-dependent posttranslational cleavage. 32820071_Allosteric regulation of thioesterase superfamily member 1 by lipid sensor domain binding fatty acids and lysophosphatidylcholine. |
ENSMUSG00000034853 |
Acot11 |
176.683766 |
0.3310245901 |
-1.594990 |
0.146259436 |
120.055125 |
0.00000000000000000000000000061526967730828075761125569676337364212537562116866366681911198483945668775974002784323602099902927875518798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000007335525393433136900635398808683507350531227547593927712654434074838636845039552270009153289720416069030761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.3822237 |
7.8652600 |
259.9792586 |
15.2561086 |
| ENSG00000162426 |
50651 |
SLC45A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2W3 |
FUNCTION: Proton-associated glucose transporter in the brain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28434495}. |
Disease variant;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene was isolated initially from a region on chromosome 1p that is frequently deleted in human neuroblastoma, although no causal relationship has since been demonstrated. The encoded protein belongs to the glycoside-pentoside-hexuronide cation symporter transporter family and may play a role in glucose uptake. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:50651; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; galactose:proton symporter activity [GO:0015517]; glucose:proton symporter activity [GO:0005356]; sucrose:proton symporter activity [GO:0008506]; galactose transmembrane transport [GO:0015757]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659] |
28434495_Our data strongly suggest that recessive mutations in SLC45A1 cause intellectual disability and epilepsy. SLC45A1 thus represents the second cerebral glucose transporter, in addition to GLUT1, to be involved in neurodevelopmental disability. |
ENSMUSG00000039838 |
Slc45a1 |
8.063140 |
0.3287874492 |
-1.604773 |
0.562770971 |
8.526727 |
0.00349968594689475595571614974232943495735526084899902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007389894789151158632778404466989741194993257522583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5105578 |
1.4095092 |
10.7745593 |
2.6042857 |
| ENSG00000162430 |
57190 |
SELENON |
protein_coding |
Q9NZV5 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Plays an important role in cell protection against oxidative stress and in the regulation of redox-related calcium homeostasis. Regulates the calcium level of the ER by protecting the calcium pump ATP2A2 against the oxidoreductase ERO1A-mediated oxidative damage. Within the ER, ERO1A activity increases the concentration of H(2)O(2), which attacks the luminal thiols in ATP2A2 and thus leads to cysteinyl sulfenic acid formation (-SOH) and SEPN1 reduces the SOH back to free thiol (-SH), thus restoring ATP2A2 activity (PubMed:25452428). Acts as a modulator of ryanodine receptor (RyR) activity: protects RyR from oxidation due to increased oxidative stress, or directly controls the RyR redox state, regulating the RyR-mediated calcium mobilization required for normal muscle development and differentiation (PubMed:19557870, PubMed:18713863). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18713863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19557870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25452428}.; FUNCTION: Essential for muscle regeneration and satellite cell maintenance in skeletal muscle (PubMed:21131290). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21131290}. |
Alternative splicing;Desmin-related myopathy;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Myofibrillar myopathy;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Selenocysteine;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a glycoprotein that is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It plays an important role in cell protection against oxidative stress, and in the regulation of redox-related calcium homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are associated with early onset muscle disorders, referred to as SEPN1-related myopathy. SEPN1-related myopathy consists of 4 autosomal recessive disorders, originally thought to be separate entities: rigid spine muscular dystrophy (RSMD1), the classical form of multiminicore disease, desmin related myopathy with Mallory-body like inclusions, and congenital fiber-type disproportion (CFTD). This protein is a selenoprotein, containing the rare amino acid selenocysteine (Sec). Sec is encoded by the UGA codon, which normally signals translation termination. The 3' UTRs of selenoprotein mRNAs contain a conserved stem-loop structure, designated the Sec insertion sequence (SECIS) element, that is necessary for the recognition of UGA as a Sec codon, rather than as a stop signal. A second stop-codon redefinition element (SRE) adjacent to the UGA codon has been identified in this gene (PMID:15791204). SRE is a phylogenetically conserved stem-loop structure that stimulates readthrough at the UGA codon, and augments the Sec insertion efficiency by SECIS. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:57190; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; cellular response to caffeine [GO:0071313]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; multicellular organismal response to stress [GO:0033555]; positive regulation of response to oxidative stress [GO:1902884]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle cell proliferation [GO:0014858]; regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060314]; respiratory system process [GO:0003016]; response to muscle activity involved in regulation of muscle adaptation [GO:0014873]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741]; skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation [GO:0014816]; skeletal muscle satellite cell maintenance involved in skeletal muscle regeneration [GO:0014834] |
12192640_Mutations of the selenoprotein N gene, which is implicated in rigid spine muscular dystrophy, cause the classical phenotype of multiminicore disease 15668457_A new SEPN1 point mutation, 943g->A causing G315S was found in a rigid spine muscular dystrophy patient with cor pulmonale. 15792869_SEPN1 mutation analysis revealed that the patient was a compound heterozygote: a previously described insertion (713-714 insA), and a novel nonsense mutation (R439stop). 15961312_Two patients with 'Dropped head syndrome' due to mutations in SEPN1 genes. 16365872_SEPN1 is the second genetic cause of CFTD and the first cause of autosomal recessive CFTD to be identified to our knowledge. CFTD is the fourth clinicopathological presentation that can be associated with mutations in SEPN1. 16498447_identification of this mutation affecting a conserved base in the selenocysteine insertion sequence functional motif thereby reveals the structural basis for a novel pathological mechanism leading to SEPN1-related myopathy 16779558_We report on the possible molecular mechanism behind these mutations in SEPN1. Our study clarifies molecular mechanisms of this muscular disorder. 18713863_SEPN1 and RYR1 are required for the same cellular differentiation events and are needed for normal calcium fluxes 18841251_The Alu-derived exon 3 of human SEPN1 acquired its muscle-specific splicing activity after the divergence of humans and chimpanzees, suggesting its potential role in human evolution. 19067361_Data highlights the importance of the SRE element during SelN expression and illustrates a novel molecular mechanism by which point mutations may lead to SEPN1-related myopathy. 19557870_SelN plays a key role in redox homeostasis and human cell protection against oxidative stress. 20937510_this series of patients illustrates the clinical, histopathological and MRI findings of SEPN1-related myopathy. It also adds new mutations to the limited number of fully described pathogenic SEPN1 variants. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21241449_Data show that Argonaute 2 expression is critical for stem cells to escape senescence by downregulating miR10b and miR23b, and that selenoprotein N1 is also involved in ATSC survival and self-renewal through ROS-mediated p38 MAPK inactivation. 21670436_Data show that the spectrum of severity of SEPN1-related myopathiesis wider than previously reported. 22527882_The physiological function of SelN in muscle tissue and the pathogenesis leading to SEPN1-related myopathies. [Review] 26780752_We report two previously undescribed mutations in SEPN1. Our study adds two novel homozygous mutations to the number of reported pathogenic SEPN1 variants. 27863379_Case Report: rigid spine muscular dystrophy 1 in a compound heterozygote with two novel mutations in SEPN1 gene; a novel missense mutation (c.1384T>C; p.Sec462Arg) and a novel nonsense mutation (c.1525C>T; p.Gln509Ter), inherited from his father and mother respectively. 31880214_significantly down-regulated in mesangial cells exposed to high glucose or TGF-beta1 32661288_Defective endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts and bioenergetics in SEPN1-related myopathy. 32796131_The clinical, histologic, and genotypic spectrum of SEPN1-related myopathy: A case series. 32817544_Selenoprotein N is an endoplasmic reticulum calcium sensor that links luminal calcium levels to a redox activity. 32864802_The first report of two homozygous sequence variants in FKRP and SELENON genes associated with syndromic congenital muscular dystrophy in Iran: Further expansion of the clinical phenotypes. 33037864_Selenoprotein N-related myopathy: a retrospective natural history study to guide clinical trials. 33762497_[Selenoprotein-related myopathy in a patient with old-age-onset type 2 respiratory failure: a case report]. |
ENSMUSG00000050989 |
Selenon |
716.680741 |
0.4759727969 |
-1.071049 |
0.067532582 |
252.478758 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000748270152020682554883646061762762537441013486680714672719683036255022147778395388853199530530720149854335963077844630865717786252531812352887380379584669753967318683862686157226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000181652425062915688157275724316474668699910058186032184191368634092564159080519968490890254848073863834287358057863279473445954228921219667652886542441592609975486993789672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
466.5011248 |
18.9718438 |
987.0197749 |
26.5119679 |
| ENSG00000162433 |
205 |
AK4 |
protein_coding |
P27144 |
FUNCTION: Involved in maintaining the homeostasis of cellular nucleotides by catalyzing the interconversion of nucleoside phosphates (PubMed:19073142, PubMed:19766732, PubMed:23416111, PubMed:24767988). Efficiently phosphorylates AMP and dAMP using ATP as phosphate donor, but phosphorylates only AMP when using GTP as phosphate donor (PubMed:19073142, PubMed:19766732, PubMed:23416111). Also displays broad nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity (PubMed:19073142, PubMed:19766732, PubMed:23416111). Plays a role in controlling cellular ATP levels by regulating phosphorylation and activation of the energy sensor protein kinase AMPK (PubMed:24767988, PubMed:26980435). Plays a protective role in the cellular response to oxidative stress (PubMed:19130895, PubMed:23474458, PubMed:26980435). {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19073142, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19130895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19766732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23416111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23474458, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24767988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26980435}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;GTP-binding;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the adenylate kinase family of enzymes. The encoded protein is localized to the mitochondrial matrix. Adenylate kinases regulate the adenine and guanine nucleotide compositions within a cell by catalyzing the reversible transfer of phosphate group among these nucleotides. Five isozymes of adenylate kinase have been identified in vertebrates. Expression of these isozymes is tissue-specific and developmentally regulated. A pseudogene for this gene has been located on chromosome 17. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. Sequence alignment suggests that the gene defined by NM_013410, NM_203464, and NM_001005353 is located on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:205; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; adenylate kinase activity [GO:0004017]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity [GO:0004550]; nucleoside monophosphate kinase activity [GO:0050145]; nucleoside triphosphate adenylate kinase activity [GO:0046899]; ADP biosynthetic process [GO:0006172]; AMP metabolic process [GO:0046033]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; GTP metabolic process [GO:0046039]; nucleobase-containing small molecule interconversion [GO:0015949]; nucleoside diphosphate phosphorylation [GO:0006165]; nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0009142]; regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001169]; regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0002082] |
19073142_To investigate the role of hinge IV, crystal structure of human adenylate kinase 4 (AK4) L171P mutant was determined. 19766732_The AK4 cDNA was expressed in Escherichia coli and the substrate specificity and kinetic properties of the recombinant protein were characterized. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23002211_Data indicate that patients with high adenylate kinase-4 (AK4) and low transcription factor ATF3 expression showed unfavorable outcomes compared with patients with low AK4 and high ATF3 expression. 23474458_a stress-protective function of AK4 26980435_Results found that AK4 was involved in hypoxia tolerance, resistance to anti-tumor drug, and the regulation of mitochondrial activity. 29866054_Our data revealed that both miR-199a-3p and its target gene AK4 are reversely correlated with the osteosarcoma drug resistance. 30696468_The overexpression of AK4 stabilizes HIF-1alpha protein by increasing intracellular ROS levels and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer. 31444368_A co-expressed gene status of adenylate kinase 1/4 reveals prognostic gene signature associated with prognosis and sensitivity to EGFR targeted therapy in lung adenocarcinoma. 31463832_Study found that AK4 was positively correlated with poor prognosis of bladder cancer (BC) patients. Its knockdown in bladder cancer cell lines inhibited proliferation and invasion and suppressed tumor formation and metastasis in mice. AK4 may therefore represent a potential biomarker for the prognosis of bladder cancer. 31827645_High AK4 expression is associated with Breast Cancer by Facilitating Cell Proliferation and Invasion. 31931771_Knockdown of circ-ABCB10 promotes sensitivity of lung cancer cells to cisplatin via miR-556-3p/AK4 axis. 32956623_Adenylate Kinase 4 Modulates the Resistance of Breast Cancer Cells to Tamoxifen through an m(6)A-Based Epitranscriptomic Mechanism. 33361582_MiR-3666 serves as a tumor suppressor in ovarian carcinoma by down-regulating AK4 via targeting STAT3. 34638712_Adenylate Kinase 4-A Key Regulator of Proliferation and Metabolic Shift in Human Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells via Akt and HIF-1alpha Signaling Pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000028527 |
Ak4 |
26.039556 |
2.2135066806 |
1.146334 |
0.343411979 |
11.132823 |
0.00084813415962794362970567085824313835473731160163879394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002002633210063741765749600887147607863880693912506103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.3156056 |
7.7068947 |
16.1273479 |
2.6866126 |
| ENSG00000162461 |
284723 |
SLC25A34 |
protein_coding |
Q6PIV7 |
|
Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
SLC25A34 belongs to the SLC25 family of mitochondrial carrier proteins (Haitina et al., 2006 [PubMed 16949250]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:284723; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; blastocyst hatching [GO:0001835] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23266187_Compares and contrasts all the known human SLC25A* genes and includes functional information. 27864352_The SLC25A34 transcript, based on single cell transcriptomics, is specific to the beta cells in the human islet. |
ENSMUSG00000040740 |
Slc25a34 |
9.897492 |
0.2928857902 |
-1.771590 |
0.531683822 |
11.501011 |
0.00069558328199212946050394856811749377811793237924575805664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001667501907130717817007159453623899025842547416687011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8301022 |
1.6547877 |
16.4316712 |
3.2575126 |
| ENSG00000162493 |
10630 |
PDPN |
protein_coding |
Q86YL7 |
FUNCTION: Mediates effects on cell migration and adhesion through its different partners. During development plays a role in blood and lymphatic vessels separation by binding CLEC1B, triggering CLEC1B activation in platelets and leading to platelet activation and/or aggregation (PubMed:14522983, PubMed:15231832, PubMed:17616532, PubMed:18215137, PubMed:17222411). Interaction with CD9, on the contrary, attenuates platelet aggregation induced by PDPN (PubMed:18541721). Through MSN or EZR interaction promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) leading to ERZ phosphorylation and triggering RHOA activation leading to cell migration increase and invasiveness (PubMed:17046996, PubMed:21376833). Interaction with CD44 promotes directional cell migration in epithelial and tumor cells (PubMed:20962267). In lymph nodes (LNs), controls fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and contraction of the actomyosin by maintaining ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation through association with unknown transmembrane proteins. Engagement of CLEC1B by PDPN promotes FRCs relaxation by blocking lateral membrane interactions leading to reduction of ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation (By similarity). Through binding with LGALS8 may participate in connection of the lymphatic endothelium to the surrounding extracellular matrix (PubMed:19268462). In keratinocytes, induces changes in cell morphology showing an elongated shape, numerous membrane protrusions, major reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, increased motility and decreased cell adhesion (PubMed:15515019). Controls invadopodia stability and maturation leading to efficient degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in tumor cells through modulation of RHOC activity in order to activate ROCK1/ROCK2 and LIMK1/LIMK2 and inactivation of CFL1 (PubMed:25486435). Required for normal lung cell proliferation and alveolus formation at birth (By similarity). Does not function as a water channel or as a regulator of aquaporin-type water channels (PubMed:9651190). Does not have any effect on folic acid or amino acid transport (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14522983, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15231832, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15515019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17046996, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17222411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17616532, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18215137, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18541721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19268462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20962267, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21376833, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25486435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9651190}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cell shape;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sialic acid;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a type-I integral membrane glycoprotein with diverse distribution in human tissues. The physiological function of this protein may be related to its mucin-type character. The homologous protein in other species has been described as a differentiation antigen and influenza-virus receptor. The specific function of this protein has not been determined but it has been proposed as a marker of lung injury. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10630; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; leading edge of lamellipodium [GO:0061851]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; tetraspanin-enriched microdomain [GO:0097197]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; chemokine binding [GO:0019956]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; actin-mediated cell contraction [GO:0070252]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; lung development [GO:0030324]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; lymphangiogenesis [GO:0001946]; lymphatic endothelial cell fate commitment [GO:0060838]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0090091]; positive regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:1901731]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis [GO:2000392]; regulation of myofibroblast contraction [GO:1904328]; regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900024]; response to hyperoxia [GO:0055093]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266]; wound healing, spreading of cells [GO:0044319] |
14522983_Aggrus is a platelet aggregation-inducing factor expressed in colorectal tumors 15515019_a novel biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinomas that might be involved in migration/invasion 15743802_podoplanin may have a role in tumor progression 16408168_Interstitial cells in the endolymphatic duct express poloplanin protein. 16528371_Podoplanin expression in pretreatment biopsy material may be a useful marker to predict lymphatic metastasis and patient outcome. 16574316_Ki-67/podoplanin-immunoreactivity was useful to identify proliferating lymphatic vessels. 16596424_These data suggest that podoplanin expression might be associated with malignancy of astrocytic tumors. 16616332_podoplanin induces an alternative pathway of tumor cell invasion in the absence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition 16718353_podoplanin expression may be a sensitive immunohistochemical marker for germinoma 17179989_Podoplanin is a small mucin-like transmembrane protein, widely expressed in various specialised cell types throughout the body and podoplanin-mediated tumour invasion. 17222411_Total glycosylation profile of podoplanin weas surveyed by lectin microarray. 17284957_Strong immunostaining with D2-40 antibody was observed at the periphery of sebaceous glands and in skin lymphatic endothelium of all specimens, demonstrating that podoplanin is expressed in sebaceous glands of normal skin. 17343736_in human osteoblast-like MG63 cells, Sp1 and Sp3 stimulate basal PDPN transcription in a concerted, yet independent manner, whereas Saos-2 cells lack sufficient nuclear Sp protein amounts for transcriptional activation. 17348451_Evaluation of lymphangiogenesis using podoplanin immunohistochemistry may be useful in predicting lymph node metastasis and the prognosis in patients with esophageal carcinoma. 17377811_Data showed podoplanin (D2-40 monoclonal antibody) was positive in thin-wall branching vessels and confirmed the current concept of lymphangiogenic origin of the tumor vessels in lymphangioleiomyoma/lymphangioleiomyomatosis. 17543889_conformational comparison of MGP40 and HUMGP39 17616532_CLEC-2 is a physiological target protein of podoplanin and imply that it is involved in podoplanin-induced platelet aggregation, tumor metastasis 17951198_Diffuse membranous immunoreactivity for podoplanin as detected by monoclonal antibody D2-40 is highly sensitive and specific for primary and metastatic seminoma. 17951199_Podoplanin is a highly sensitive marker for follicular dendritic cell tumors that is useful in the differential diagnosis of dendritic cell and histiocytic lesions. 18162779_cytoplasmic podoplanin expression may be useful in the diagnosis of sarcomatoid mesothelioma 18165897_podoplanin may have a role in axillary lymph node metastases of breast neoplasms 18202409_Overexpression of PDPN protein is associated with oral premalignancy 18212541_Three of the 4 Retiform hemangioendothelioma (RH) biopsies failed to demonstrate D2-40, none expressed VEGFR-3...RH is a vascular entity which usually does not have lymphatic differentiation, but may rarely express D2-40. 18215137_a direct interaction between CLEC-2 and podoplanin was confirmed; podoplanin is a ligand for CLEC-2 on renal cells. 18539139_Podoplanin is a novel marker to enrich tumor-initiating cells with stem-cell-like properties from squamous cell carcinoma cell line A431. 18541721_Because HT1080 cells express the metastasis-promoting, platelet aggregation-inducing factor Aggrus/podoplanin on their surface, we examined the relationship between CD9 and Aggrus. 18546264_Podoplanin-positive CAFs (Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts) were found only in invasive adenocarcinoma and none were found in noninvasive adenocarcinoma. Conventional prognostic factors were significantly correlated with podoplanin expression by CAFs. 18564921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18650031_This study adds Microvenular hemangioma to the list of vascular lesions that fail to express the allegedly lymphatic marker podoplanin 18657337_Patient age and a novel biological prognostic marker, podoplanin, are useful for predicting a poor outcome of patients after complete resection of stage IB SqCC of the lung. 18658274_Podoplanin silencing in human lung lymphatic microvascular endothelial cells has no effect on cell viability or cell morphology in tissue culture. 18707544_NZ-1 neutralizes the interaction between podoplanin and CLEC-2, which may lead to the development of therapeutic antibodies against podoplanin-dependent cancer metastasis. 18772332_CCR10+ T cells accumulate preferentially both around and within CCL27+ lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) podo-low precollector vessels in skin biopsies of human inflammatory disease. 18820665_Podoplanin still remains the only positive marker for chondrosarcoma, though its accuracy is less than previously reported 19146981_PDPN) is transcribed in cells derived from sarcomas, embryonal carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas and endometrial tumours, while cell lines derived from colon, pancreatic, ovarian and ductal breast carcinomas do not express PDPN transcripts. 19268462_These data suggest a role for galectin-8 and podoplanin in supporting the connection of the lymphatic endothelium to the surrounding extracellular matrix, most likely in cooperation with other glycoproteins on the surface of lymphatic endothelial cells. 19356249_Lymph vessel invasion was detected in higher ratios by immunostaining with podoplanin monoclonal antibody D2-40. 19363443_one should always interpret results of podoplanin staining in the context of the histologic appearance and/or consider evaluation of additional endothelial or ME immunostains 19483399_Internal ligand for CLEC-2. (review) 19483629_This study evaluates the use of the markers, podoplanin, SOX2, NANOG, and OCT3/4 in ovarian tumors 19550098_increased expression in gingival epithelium is related to the progression of chronic periodontitis 19554509_Tumor cell expression of PDPN correlates with nodal metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19556810_Negative podoplanin expression in stromal fibroblasts was significantly associated lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. 19630798_CLEC-2 is the receptor for podoplanin, a sialoglycoprotein implicated in tumor-induced platelet aggregation and tumor metastasis[review] 19691459_Expression of podoplanin in AMs is considered to be associated with neoplastic odontogenic tissues; this molecule might play a role in the collective cell migration of tumor nests in AMs. 19773378_Together, DeltaNp63, podoplanin, and intraepithelial inflammatory cells may be used as biomarkers to identify oral preneoplastic lesion patients with substantially high oral cancer risk. 19925582_Podoplanin is strongly expressed in KCOTs in comparison with OOCs. The pattern of staining for podoplanin in KCOT could be related to its neoplastic nature, and suggests a role of the protein in tumor invasiveness. 20042851_podoplanin is excellent for assessing lymphatic invasion in breast, prostate, and cervix 20066519_High podoplanin expression is associated with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. 20146302_Membranous podoplanin immunoreactivity, in conjunction with calretinin, would be more specific than CK5/6 and WT-1 in differentiating epithelioid malignant mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma of the lung, breast, and ovary. 20191305_The results of this study showed that immunohistochemical staining with both the antibodies anti-podoplanin and anti-LYVE-1 detected lymph vessels in 18 of the 25 human neuroblastoma specimens. 20196862_Podoplanin expression increases in the early stages of laryngeal tumourigenesis and it seems to be associated with a higher laryngeal cancer risk. 20200437_The expressions of podoplanin and ABCG2 in Oral lichen planus were significantly associated with malignant transformation risk 20376776_Podoplanin expression is an early event in tumorigenesis, predicting the evolution of preneoplastic lesions in oral cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20393745_We concluded that podoplanin is expressed frequently in OSCC and that podoplanin expression correlates with cervical lymph node metastases and clinical outcome. 20403045_Podoplanin mRNA was expressed at a high level in bone marrow tissue and cartilage, and was upregulated with differentiation to osteoblasts in bone marrow cells. Podoplanin mRNA was highly expressed in several osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma cell lines 20414092_D2-40 expression for PDPN, noted in the peripheral layer of the outer root sheath, was similar in 73% and increased in 27% in the infundibular region of cases of scarring alopecia in comparison to its 90% no expression noted in nonscarring alopecia 20482880_Virion incorporation of podoplanin mediates CLEC-2 interactions of HIV-1 derived from 293T cells, while incorporation of a different cellular factor seems to be responsible for CLEC-2-dependent capture of PBMC-derived viruses. 20559122_podoplanin expression could be a useful potential marker to distinguish basal cell carcinomas from trichoepitheliomas 20616339_Data show that podoplanin expression promoted tumor cell motility in vitro and, unexpectedly, increased tumor lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to regional lymph nodes in vivo, without promoting primary tumor growth. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20665731_demonstrated that these microRNAs directly target the 3' untranslated region of PDPN and inhibit invasion, apoptosis, and proliferation of glioblastomas 20709739_High Podoplanin is associated with encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis. 20716773_These findings reveal an important role of podoplanin in lymphatic vessel formation and indicate the potential of podoplanin-Fc as an inhibitor of lymphangiogenesis. 20736762_Podoplanin might have utility as a marker for ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma in pathologic diagnosis. 20821344_Podoplanin expression in atypical neurofibroma was not associated with tumour progression towards malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours. 20850695_podoplanin is a sensitive marker for the recognition of intratubular germ cell neoplasia and seminomas, and is relatively specific for these lesions in the context of testicular germ cell tumors. 20923309_podoplanin expression in stromal myofibroblasts may function as a proangiogenic biomarker and may serve as a predictive marker of cancer cell spread. 20962267_Podoplanin promotes directional persistence of motility in epithelial cells, a feature that requires CD44, and that both molecules cooperate to promote directional migration in SCC cells. 21034514_Findings suggested that lung squamoid cancer cells -associated podoplanin was functional and could attenuate the potential for lymph node metastasis, possibly based on the suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis 21036919_Expression of constitutively active Cdc42 construct, like podoplanin knockdown, decreasea RhoA-GTP level in human lung microvascular lymphatic endothelial cells. 21095001_D2-40/podoplanin expression in the human placenta. 21185581_The aim of this study was to determine if podoplanin was expressed by rudiment chondrocytes in human foetal cartilages. 21194851_Suggest that immunohistochemical analysis for podoplanin may serve as a marker of risk of nodal metastasis and prognosis in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma. 21226415_podoplanin plays a crucial role in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell functions. 21234520_Podoplanin is considered to have little value in the differential diagnosis of soft tissue tumors. 21237498_podoplanin expression was significantly associated with an increased risk of death for the whole group of thymomas 21326813_D2-40 immunohistochemistry reliably identifies the myoepithelial cells of breast in a variety of lesions in a pattern similar to that of calponin and p63. 21385358_podoplanin might be involved in the synovial tissue transformation and increased migratory potential of activated fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rhematoid arthritis. 21801875_Podoplanin is regulated by AP-1 and promotes platelet aggregation and cell migration in osteosarcoma 22081310_The present findings suggest that podoplanin is associated with tumor development via the oral dysplasia-carcinoma sequence and could be involved in a signaling pathway governing tumor growth and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinomas. 22175904_podoplanin expression by cancer-associated fibroblasts could be an unfavourable prognostic marker for invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast 22189341_TGF-beta1, IFN-gamma, IL-6, and IL-22 induce PDPN-expression of keratinocytes, which might be significantly involved in the wound healing process as well as in the pathomechanism of hyperproliferative psoriatic epidermis. 22213642_High podoplanin is associated with response to therapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22257901_Report immunohistochemical staining for podoplanin in differential diagnosis of epithelioid and spindle cell tumors of the skin. 22283975_These results suggest that podoplanin contributes to thrombotic property of advanced stages of atherosclerosis and that it might be a novel molecular target for an anti-thrombus drug. 22326634_have demonstrated for the first time differential localizations of podoplanin among the four odontogenic tumors 22350732_Podoplanin-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to the prognosis of invasive breast cancer, indicating a highly aggressive subgroup. 22394497_PDPN expression in human glioblastoma multiforme is caused by loss of PTEN function and activation of the PI3K-AKT-AP-1 signaling pathway, accompanied by epigenetic regulation of PDPN promoter activity 22495364_expression of podoplanin by more undifferentiated tumor cells suggests that this protein could be an indicator of tumor aggressiveness 22556408_platelets regulate blood/lymphatic vessel separation by inhibiting the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of LECs, mainly because of the release of BMP-9 upon activation by CLEC-2/podoplanin in 22575513_human fibroblasts expressing PDPN may promote tumor formation via a higher RhoA activity level. 22580922_A close correlation is found between podoplanin expression and distant metastasis and disease-free survival. 22588067_Podoplanin has the potential to provide valuable prognostic information to clinic-ians for risk assessment of neuroblastomas. 22593499_Podoplanin expression in Keratocystic odontogenic tumour (KCOT) is possibly associated with slow invasion of the adjacent structures and the well-known frequent local tumour recurrences of this odontogenic tumour. 22669451_High podoplanin positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in metastatic lymph nodes is associated with lung adenocarcinoma 22682130_Here, the bidirectional relationship between CLEC-2 and podoplanin is described and considered in the context of tumour growth and metastasis. 22830405_Overexpression of podoplanin is a rare event in sporadic gastrointestinal stromal tumors and is not associated with amplification of 1p36 22840788_regulation of podoplanin expression is positively and negatively regulated by TGF-beta receptor/Smad signaling pathway and epigenetic mechanism leading to squamous differentiation, respectively. 22844530_a lectin from the seeds of Maackia amurensis (MASL) with affinity for O-linked carbohydrate chains containing sialic acid targets PDPN to inhibit transformed cell growth and motility 22859271_Low PDPN expression is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 23161183_Overexpression of podoplanin expressing cancer associated fibroblasts are associated with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. 23246488_These data reveal a key role of miR-363-PDPN in HNSCC metastasis and support biological and clinical links between miR-363-PDPN and HNSCC. 23262786_The results indicate that podoplanin can be regarded as a novel myoepithelial marker in salivary gland tumors 23266472_The cell density dependent podoplanin induction required activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and its effector, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). 23291918_Expression of podoplanin contributes to the invasive growth properties of mesothelioma cells and their resistance to apoptosis. 23300922_we confirm the increased expression of podoplanin in encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis (EPS), and distinguish EPS biopsies according to different podoplanin expression patterns which are associated with clinical parameters. 23306662_The presence of podoplanin/D2-40-positive pericryptal stromal cells is associated with epithelial tumorigenesis in the colorectum. 23349470_In oral squamous cell carcinoma the probability to have or develop metastases was very low when high E-cadherin expression was found in a preoperative sample or when a low podoplanin expression was found 23455186_Breast carcinomas of different grades, subtypes, and basal marker expression are characterized by different composition of the stroma, that is different LVD, podoplanin expression in stromal fibroblasts, and pattern/intensity of lymphocytic infiltration 23473850_Podoplanin could be a valuable biomarker for risk assessment of malignant transformation in patients with OPL along with histological assessment 23518636_Podoplanin and Fli-1 immunohistochemistry may be useful in distinguishing atypical fibroxanthoma from angiosarcoma. 23541579_HSPA9 secreted by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells interacts with podoplanin (PDPN) on their cell surface in an autocrine manner and regulates their growth and invasiveness. 23564785_High podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts is associated with invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 23790170_Podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts may have impact on angio- and lymphangiogenesis processes in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast 23812230_We suggest that podoplanin is involved in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis, particularly in the intraepithelial migration of inflammatory infiltrates. 23816822_Podoplanin and clusterin are reliable markers of human synovium 23817087_We have demonstrated the primary function of PDPN in cell adhesion to extracellular matrix , which is to secondarily promote oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation. 23975429_Ebp1 has a key role in the upregulation of podoplanin and may contribute to oral tumorigenesis. 23991201_Because Aggrus knockdown suppressed platelet-induced proliferation in vitro and tumor growth of the lung squamous cell carcinoma in vivo, Aggrus may be involved in not only tumor metastasis but also tumor growth by promoting platelet-tumor interaction 24023336_results suggest that the strong podoplanin and VEGF-C expression by malignant cells is associated with perineural invasion in patients with OSCC 24103048_These data suggest that podoplanin is significantly associated with and likely contributes to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion in the absence of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 24222607_High aggrus expression is associated with pulmonary metastasis in bladder cancer. 24275092_HEK293T and MDCK cells transfected with an eGFP-tagged podoplanin construct (PDPNeGFP, 50-63kDa) constitutively express two C-terminal fragments (CTFs): a approximately 33kDa membrane-bound PCTF33, and a approximately 29kDa cytosolic podoplanin ICD (PICD). 24281769_High podoplanin expression is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24293622_Identification of cells expressing podoplanin within lymphocytic aggregates can reveal the pathogenesis of primary Sjogren syndrome. 24354864_PDPN-expressing cancer associated fibroblasts enhance the progression of pancreatic invasive ductal carcinoma. 24588302_The presence of podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts correlates with aggressive behavior in melanoma and might therefore serve as a useful prognostic factor for patients with melanoma 24797369_PDPN mediates the invasive properties of cells derived from papillary thyroid carcinomas, suggesting that podoplanin might promote PTC progression. 24804195_Expressions of ABCG2, CD133, and podoplanin in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. 24815836_Dual expression of podoplanin in tumor cells and lymphatics with particular patterns correlated with histopathology and lymph node status in oral cancer. 24844673_PDPN-positive/EpCAM-positive CTC ratio is a prognostic factor and defining the ratio in patients with HNSCC might be valuable to clinical management 24885398_GAS5 levels modify cell proliferation in vitro; GAS5 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma tissue is associated with cell quiescence and podoplanin expression. 24932813_In rheumatoid arthritis, synovial expression of gp38 is strongly associated to lymphoid neogenesis and it is reduced after anti-TNF-alpha therapy. 24938315_Podoplanin positive cancer cells have functions which are associated with invasion so podoplanin downregulation inhibits tumor invasion. 24944097_Prox1 regulates PDPN expression at the transcriptional level in the lymphatic vascular system 24964963_Studies indicate podoplanin as a biomarker for predictive assessment of malignant transformation as well as biologic behavior in both precancer and cancer. 24966946_Lymphatic vessel invasion and podoplanin positivity in cancer cells are associated with lymphatic metastasis, recurrence and overall survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 25098985_podoplanin may be considered as a predictor marker in assessing malignant transformation of premalignancies and prognosis of oral malignancy 25119595_High Podoplanin expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts are associated with oral cancer. 25142945_The current experimental and human clinical data on the involvement of podoplanin in tumor progression is discussed. 25197355_Our data suggest that interaction between podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells is important in tumor biology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . 25304618_High PDPN expression is asasociated with lung adenocarcinoma. 25486435_Podoplanin mediates extracellular matrix degradation by squamous carcinoma cells through control of invadopodia stability. 25648219_Our results indicated that PDPN(+)CAFs were tumor-promoting CAFs that lead and enhance the local invasion of cancer cells, suggesting that the invasion activity of CAFs themselves could be rate-determining for cancer cell invasion. 25726183_in our case series, podoplanin expression is not correlated with invasive potential and has no independent prognostic value in oral squamous cell carcinoma 26026095_Positive reaction of LAM cells with podoplain demonstrates the existence of an additional lymphatic endothelial lineage in LAM cells 26081937_high podoplanin expression is associated with aggressive tumor behavior, poor prognosis and metastatic regulation through interaction with VEGF-C. 26090592_Podoplanin overexpression is associated with osteosarcoma. 26090595_Podoplanin overexpression is associated with osteosarcoma. 26339454_Podoplanin increased migration of tumor cells and enhanced tube formation activity in endothelial cells independent from VEGF. 26492618_Almost all anti-PDPN MAbs recognize a platelet aggregation-inducing (PLAG) domain. 26684030_High podoplanin expression is associated with lung metastasis. 26700593_podoplanin membrane expression, not only its localization, is a useful prognostic indicator of lung squamous cell carcinoma 26722465_In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, high p-mTOR expression was significantly associated with high podoplanin expression and high tumor grade 26728373_Data show that the CHO cell line with the stable and high expression of recombinant podoplanin (PDPN)-enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) was constructed successfully, and it could induce platelet aggregation. 26867059_These data support a role of podoplanin as an antiapoptotic prosurvival factor in angiotensin II-induced injury of human podocytes. 26881521_High podoplanin expression is associated with lymphatic spread of the breast cancer. 26937552_interest, LpMab-17 did not bind to monkey PDPN, whereas the homology is 94% between human PDPN and monkey PDPN, indicating that the epitope of LpMab-17 is unique compared with the other anti-PDPN mAbs. The combination of different epitope-possessing mAbs could be advantageous for the PDPN-targeting diagnosis or therapy 26977704_the epitope of PMab-21 was identified as Leu44-Glu48, which is corresponding to platelet aggregation-stimulating (PLAG) domain, indicating that Ser61-Ala68 of rabbit PDPN is a more appropriate epitope for immunohistochemistry compared with PLAG domain. PMab-32 could be useful for uncovering the function of rabbit PDPN 27031228_LpMab-12 could serve as a new diagnostic tool for determining whether hPDPN possesses the sialylation on Thr52, a site-specific post-translational modification critical for the hPDPN association with CLEC-2. 27035421_the present results also suggest that podoplanin+ cells can function as stromal cells for blast cell retention in the AML tumor microenvironment. 27066737_this study uncovers a unique molecular mechanism of lymphangiogenesis in which galectin-8-dependent crosstalk among VEGF-C, podoplanin and integrin pathways plays a key role. 27069135_Expression of Podoplanin in Non-melanoma Skin Cancers and Actinic Keratosis 27153448_this study suggests that podoplanin can be used as a prognostic marker to determine the malignant potential in oral leukoplakias 27240861_podoplanin expression is significantly associated with malignant transformation of chronic lip discoid lupus erythematosus into lip squamous cell carcinoma 27313335_Low PDPN expression is associated with Uterine Cervical Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions. 27328060_NZ-1 inhibits the hPDPN-CLEC-2 interaction and is also useful for anti-PA tag MAb.The minimum epitope of LpMab-13 was identified as Ala42-Asp49 of hPDPN using Western blot and flow cytometry. The combination of different epitope-possessing MAbs could be advantageous for the hPDPN-targeting diagnosis and therapy 27389969_high tumoral podoplanin expression could independently predict an adverse clinical outcome for ccRCC patients, and it might be useful in future for clinical decision-making and therapeutic developments. 27606906_The prevalence of Oct-3/4 and D2-40-(podoplanin) positive staining of germ cells in testicular biopsies of boys with cryptorchidism were in age groups less than 6 months, 100% and 50%; 6-12 months, 60% and 17%; and 1-2 years, 12% and 4%. In all cases, the Oct-3/4 and D2-40 positive germ cells turned negative and the histological pattern normalized completely with age. 27775879_PDPN acts as an oncogene to promote hypopharyngeal cancer cell viability, migration and invasion. miR-203 directly targets PDPN to suppress its expression, thus exerting inhibitory effects on cancer metastasis. 27859466_This article provides evidence supporting the implication of podoplanin expression as a marker of bad prognosis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma 27960039_Review of C-type lectin-like receptor 2 and podoplanin interactions [review] 28011493_We revealed that podoplanin expression in Cancer-associated Fibroblasts was an independent indicator of worse prognosis, irrespective of the expression status of the tumor cells in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. 28059107_Study provided evidence that high clonal expansion capacity of podoplanin-positive tumor initiating cells populations was the result of reduced cell death by podoplanin-mediated signaling. 28073783_high podoplanin expression in primary brain tumors induces platelet aggregation, correlates with hypercoagulability, and is associated with increased risk of VTE 28122639_Data show that podoplanin (PDPN), CD106 (VCAM-1) and CD248 protein were increased in diseased compared to healthy tendon cells. 28176852_TGF-beta release from platelets is necessary for podoplanin-mediated tumor invasion and metastasis in lung cancer. 28182302_Data suggest that podoplanin (PDPN) might be a pathogenetic determinant of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) dissemination and aggressive growth and may thus be an ideal therapeutic target. 28348421_A possible crosstalk between epithelial and stromal tumor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma tumor microenvironment may be mediated by podoplanin 28381343_The presence of podoplanin expression in peritumoral keratinocytes correlates with aggressive behavior in extramammary Paget's disease (EMPD). 28416768_PDPN was induced by hypoxia and its overexpression undergoes a reduction of adhesion, making it an anti-adhesion molecule in the absence of CCL21, in the tumor. 28702871_podoplanin expression in cancer-related fibrotic tissues is associated with a poor prognosis, especially in patients with large tumors or lymph node metastases. 28871005_PDPN contributes to the malignant potential of hepatocellular carcinoma. 28878118_data support the hypothesis that PDPN may serve as a marker of a nonpathogenic Th17 cell subset and may also functionally regulate pathogenic Th17 inflammation 28881047_Podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts could be an independent predictor of increased risk of recurrence in patients with p-stage IA lung adenocarcinoma. 28938000_Study showed that podoplanin increases the motility of fibroblasts and facilitates their interaction with endothelial cells. This, respectively, favors movement of fibroblasts into the breast tumor stroma and affects tumor angiogenesis, what creates a favorable microenvironment for breast cancer progression. 28982860_Increased expression of twist/podoplanin in ductal breast carcinoma was associated with shorter patient survival. 29377768_High PDPN expression is associated with Inflammatory Rheumatoid Synovial Tissues. 29511884_In lung adenocarcinoma, the presence of podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) was associated with higher numbers of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in cancer cells. 29550835_PDPN gene and protein expression is specific to Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) and that, by leading to platelet binding, activation and aggregation, it may contribute to the hemostatic anomalies associated with this disease. 29575529_Studies found that PDPN is expressed by many types of tumor cells and cancer associated fibroblasts. Moreover, high levels of PDPN expression is associated with reduced survival and cancer aggression. [review] 29577431_It participates in tumorigenesis of odontogenic t umors. 29588189_expression as a predictive marker of dysplasia in oral leukoplakia 29676036_Although brain tumor patients with IDH1 mutation are at very low risk of venous thromboembolism, the risk of VTE in patients with IDH1 wild-type tumors is strongly linked to podoplanin expression levels. 29678517_Lymphatic vessels were identified by the expression of podoplanin 29715091_Gastric tumor cells revealed no expression of PDPN. However, PDPN was expressed in some cases in spindle-shaped stromal cells within the tumor microenvironment, except for lymphatic vessels. PDPN expression was detected in neither tumor cells nor stromal cells of metastatic regions, such as lymph node and peritoneal metastases. 29719198_Podoplanin regulates the interaction between oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts via the mutual paracrine effects of TGF-beta1. 30173230_Our results suggest that podoplanin expression by cancer associated fibroblasts could predict poor patient outcome in breast carcinoma 30384554_Studied expression of podoplanin in placentas of normotensive and preeclamtic women with and without HIV infections using immunohistochemistry. 30396932_The mRNA high expression levels of both podoplanin and LYVE-1 genes had a statistically significantly higher rate of LN metastasis (p |
ENSMUSG00000028583 |
Pdpn |
149.368335 |
2.3607310439 |
1.239234 |
0.159121936 |
60.610014 |
0.00000000000000695791485660655093494348314545987168182767388172060840645372081780806183815002441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000047087951986938414181569865719265944337145780862474708783338428474962711334228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
199.6667187 |
21.1838079 |
85.2722275 |
6.9566231 |
| ENSG00000162512 |
9672 |
SDC3 |
protein_coding |
O75056 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that may bear heparan sulfate (By similarity). May have a role in the organization of cell shape by affecting the actin cytoskeleton, possibly by transferring signals from the cell surface in a sugar-dependent mechanism. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11527150}. |
Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Heparan sulfate;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the syndecan proteoglycan family. It may play a role in the organization of cell shape by affecting the actin cytoskeleton, possibly by transferring signals from the cell surface in a sugar-dependent mechanism. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with obesity. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:9672; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microspike [GO:0044393]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cell migration [GO:0016477] |
11968010_Augmented synthesis and differential localization of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 16052590_Selective induction of CXCL8 binding site on endothelial syndecan-3 in rheumatoid arthritis(RA) synovium. This site may be involved in leukocyte trafficking into RA synovial tissue. 16674815_The high expression of syndecan 3 and its localization to the smooth muscle bundles during normal labour, together with the significant reduction in prolonged labour, may indicate a role for this protein in the co-ordination of myometrial contractility. 17018662_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17018662_There are ethnic differences in the SDC3 polymorphisms, and the polymorphisms are strongly associated with obesity. 17368428_Midkine, pleiotrophin (PTN), and their receptors syndecan-3 and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta, were highly expressed in the striatum during developmen 18040049_Syndecan-3 was identified as a major HIV-1 attachment receptor on DCs. 18093920_syndecan TMD homodimerization and heterodimerization can be mediated by GxxxG motifs and modulated by sequence context 18599487_pleiotrophin (PTN) and syndecan-2 and -3 as direct binding partners of Y-P30. 18716876_found in 57.9% of pancreatic ductal carcinoma specimens 19820907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19820907_These findings indicate that SDC3 polymorphisms could contribute to the link between female hyperandrogenism and obesity and suggest a novel potential role for SDC3 as a modulator of gonadal steroid function. 19822079_Data report that the bFGF, FGFR1/2 and syndecan 1-4 expressions are altered in bladder tumours. 21050724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21200028_Syndecan-3 may directly transduce Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family ligands (GFL) signals or serve as a coreceptor, presenting GFLs to the signaling receptor RET. 21555518_SDC3 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 23351331_Syndecan-3 expression was not associated with disease progression and outcome in specific subtypes of mammary carcinoma. 24659893_frequently expressed in pancreatic cancer and associated with perineural invasion 24956062_Data indicate that the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of syndecans 1/2/3/4 are intrinsically disordered regions. 25617766_Syndecan-3 and TFPI colocalize on the surface of endothelial-, smooth muscle-, and cancer cells 28638231_High PTN and N-syndecan expression was closely associated with metastasis and poor prognosis, suggesting that they may promote tumor progression and perineural invasion in the orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. 31300004_Data show that soluble syndecan-3 occurred naturally in the sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. 31719623_Contribution of syndecans to cellular uptake and fibrillation of alpha-synuclein and tau. 33117401_Hypoxia Promotes Syndecan-3 Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment. 33621194_LncRNA TRPM2-AS promotes ovarian cancer progression and cisplatin resistance by sponging miR-138-5p to release SDC3 mRNA. 34209175_The Interplay of Apoes with Syndecans in Influencing Key Cellular Events of Amyloid Pathology. 34445387_Syndecan Family Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values for Prostate Cancer. 35628603_The Cell Surface Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Syndecan-3 Promotes Ovarian Cancer Pathogenesis. 36447229_A genome-wide association study identifies a novel association between SDC3 and apparent treatment-resistant hypertension. |
ENSMUSG00000025743 |
Sdc3 |
227.606113 |
0.4813409006 |
-1.054869 |
0.109662266 |
93.451374 |
0.00000000000000000000041630364069893807192028043625471666006346135206377387284764788819013681120395631296560168266296386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000003997815053166119562382626038574821549699859597666481937291993453698069060919806361198425292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
152.1841481 |
10.0998854 |
318.2655617 |
13.7095715 |
| ENSG00000162542 |
255104 |
TMCO4 |
protein_coding |
Q5TGY1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:255104; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000041143 |
Tmco4 |
66.223406 |
0.4200189626 |
-1.251474 |
0.266497942 |
21.774016 |
0.00000306726173947729720251531744523720846018477459438145160675048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010242711148118756970875828371525528837082674726843833923339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.0953959 |
6.5904270 |
91.0997491 |
10.7596975 |
| ENSG00000162572 |
6339 |
SCNN1D |
protein_coding |
P51172 |
FUNCTION: Sodium permeable non-voltage-sensitive ion channel inhibited by the diuretic amiloride. Mediates the electrodiffusion of the luminal sodium (and water, which follows osmotically) through the apical membrane of epithelial cells. Controls the reabsorption of sodium in kidney, colon, lung and sweat glands. Also plays a role in taste perception. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16423824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7499195}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Sodium;Sodium channel;Sodium transport;Taste;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable ligand-gated sodium channel activity. Predicted to be involved in sodium ion transmembrane transport. Located in actin cytoskeleton and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:6339; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sodium channel complex [GO:0034706]; ligand-gated sodium channel activity [GO:0015280]; cellular response to acidic pH [GO:0071468]; cellular response to aldosterone [GO:1904045]; cellular response to amiloride [GO:0036254]; cellular response to vasopressin [GO:1904117]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; sensory perception of salty taste [GO:0050914]; sensory perception of sour taste [GO:0050915]; sodium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098719]; sodium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0035725]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814] |
14645214_delta ENaC is regulated by Murr1 14726523_ENaCdelta activity is regulated by protons, and may contribute to the pH sensation and/or pH regulation in the human brain 15084585_delta ENaC is a proton sensor 15308635_ENaCdelta is chemically activated by capsazepine by a proton-dependent mechanism 16423824_the interactions of delta-ENaC with alpha beta gamma-human epithelial sodium channel subunits could account for heterogeneity of native epithelial channels 16930535_analysis of anovel spliced variant of the ENaC delta-subunit in the human brain 17472699_ENaC delta isoforms are widely expressed in pyramidal cells of the human and monkey cerebral cortex and in different neuronal populations of telencephalic subcortical nuclei. 18073141_Expression analyses at the level of mRNA clearly revealed that ENaC delta transcript was strongly expressed in human melanoma cells using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and cell-based in situ hybridization techniques. 18298571_EIPA [5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride hydrochloride] inhibition of ENaCs, possibly ENaC-alpha and ENaC-delta, significantly improved the sperm motility in healthy donors and in asthenospermia patients. 18951889_ENaCdelta is a candidate molecule for pH sensing in the gastrointestinal system in humans, providing a novel therapeutic target for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease 19359370_Regulation of epithelial sodium channels by cGMP/PKGII. 19717556_the delta-subunit of ENaC alters proteolytic channel activation and enhances base-line channel activity 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631247_Data support a physiological role for SGK1.1 in the regulation of delta-ENaC through a pathway that differs from the classical one and suggest that the kinase could serve as an integrator of different signaling pathways converging on the channel. 21307123_Identify the specific domains of epithelial sodium channels that are responsible for the differences in the response to flow of alphabetagamma and deltabetagamma channels. 21419751_Cpt-cAMP activates human epithelial sodium channels via relieving self-inhibition. 21562313_CPT-cGMP Stimulates Human Alveolar Fluid Clearance by Releasing External Na+ Self-Inhibition of ENaC. 21741370_These results suggest that COMMD1 downregulates deltaENaC activity by reducing deltaENaC surface expression through promoting internalization of surface deltaENaC to an intracellular recycling pool, possibly via enhanced ubiquitination. 22159085_delta-ENaC undergoes dynamin-independent endocytosis as opposed to alphabetagamma-channels. 22505667_study characterized a new variant, delta2 ENaC, in lung epithelial cells; heterologous delta2betagamma ENaC exhibited a number of divergent features from the delta1betagamma counterpart in biophysics and pharmacology, regulation, and the lifespan of proteins 25677639_delta-ENaC expression is low in NCI-H441, Calu-3, and ATI cells and does not contribute to transepithelial sodium absorption 27941075_deltabetagamma-ENaC is inhibited by CFTR but activated by cyclic AMP. 28708422_The Epithelial Sodium Channel Is a Modifier of the Long-Term Nonprogressive Phenotype Associated with F508del CFTR Mutations 31754387_Proliferative regulation of alveolar epithelial type 2 progenitor cells by human Scnn1d gene. 33673381_CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated Knock Down of delta-ENaC Blunted the TNF-Induced Activation of ENaC in A549 Cells. |
|
|
8.414486 |
0.2090058304 |
-2.258385 |
0.603021611 |
15.783822 |
0.00007100709957840459695885271251825088256737217307090759277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000199936052990700482544922378380647387530189007520675659179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3170783 |
1.5291079 |
11.1782763 |
4.7016790 |
| ENSG00000162591 |
1953 |
MEGF6 |
protein_coding |
O75095 |
|
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1953; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] |
29719292_MEGF6 accelerated Colorectal Cancer cell growth and inhibited apoptosis, and promoted Colorectal Cancer metastasis by inducing the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. 33026655_A role for the MEGF6 gene in predisposition to osteoporosis. |
ENSMUSG00000057751 |
Megf6 |
235.942462 |
0.2689058157 |
-1.894827 |
0.219002953 |
70.900339 |
0.00000000000000003757333572131154407893655165787418798160795914095090586304337421097443439066410064697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000290661653693164762624312246105245579544746134395896697277805742487544193863868713378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
75.9922179 |
22.0694126 |
276.1221486 |
57.3746532 |
| ENSG00000162592 |
148870 |
CCDC27 |
protein_coding |
Q2M243 |
|
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:148870; |
|
18597038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000039492 |
Ccdc27 |
23.619798 |
0.2167981109 |
-2.205576 |
0.407521955 |
32.108094 |
0.00000001458284855866670990961897214901674124654107345122611150145530700683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000062407319433435960689828360999781287077325941936578601598739624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4365948 |
2.2405807 |
40.1290823 |
5.6548173 |
| ENSG00000162592_ENSG00000078900 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.774409 |
0.0728281900 |
-3.779359 |
0.817525682 |
20.666588 |
0.00000546615731092636839049195285333837546204449608922004699707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017689208925514844471119438318318373148940736427903175354003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1531100 |
1.5389985 |
29.1245368 |
12.7255353 |
| ENSG00000162631 |
22854 |
NTNG1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2I2 |
FUNCTION: Involved in controlling patterning and neuronal circuit formation at the laminar, cellular, subcellular and synaptic levels. Promotes neurite outgrowth of both axons and dendrites. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21946559}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Laminin EGF-like domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a preproprotein that is processed into a secreted protein containing eukaroytic growth factor (EGF)-like domains. This protein acts to guide axon growth during neuronal development. Polymorphisms in this gene may be associated with schizophrenia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:22854; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; laminin complex [GO:0043256]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone membrane [GO:0048787]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; cell-cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098632]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; basement membrane assembly [GO:0070831]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001222]; regulation of neuron projection arborization [GO:0150011]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
14595443_Netrin-G1 is an important part of the NGL-1 receptor and functions to promote the outgrowth of dorsal thalamic axons. 15508520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15508520_findings suggest that netrin G1 or a nearby gene may contribute to overall genetic risk for schizophrenia 15705354_Specific haplotypes encompassing alternatively spliced exons of NTNG1 were associated with schizophrenia, and concordantly, messenger ribonucleic acid isoform expression was significantly different between schizophrenic and control brains. 15870826_Sequence analysis of the cloned junction fragment indicated that on chromosome 1 the predominantly brain-expressed Netrin G1 (NTNG1) gene is disrupted, whereas on chromosome 7 there was no indication for a truncated gene 15901489_NTNG1 may use alternative splicing to diversify its function in a developmentally and tissue-specific manner. 16502428_Mutations in the NTNG1 gene appear to be a rare cause of Rett syndrome but NTNG1 function demands further investigation in relation to the central nervous system pathophysiology of the disorder. 17507910_The data of this stusty implicate NTNG1 in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, but do not support the hypothesis that altered mRNA expression is the mechanism by which genetic variation of NTNG1 may confer disease susceptibility. 17903671_Netrin G1 is not involved in atypical Rett syndrome or in unexplained encephalopathy with epilepsy, but in specific forms to be delineated better in the future. 18384956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18628988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20029409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21079607_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22227940_Genotype and allele frequencies of single nucleotide polymorphisms on NTNG1 are significantly associated with schizophrenia. 23769687_Our finding nominates the minor G allele of the NTNG1 rs628117 single nucleotide polymorphism as a risk factor for ischemic stroke at least in Armenian population. 23986473_Interaction between the tripartite NGL-1, netrin-G1 and LAR adhesion complex promotes development of excitatory synapses. 25325217_examined the hypothesis that NTNG1 allelic variation contributes to the risk for schizophrenia 28074533_Significant genetic family-based associations were detected between NTNG1 polymorphisms and cocaine dependence. NTNG1 expression in BA10, BA46 and the cerebellum, however, were not significantly associated with any allele or haplotype of this gene. 32503821_A 117-base pair SARS-CoV-2 orf1b sequence matched a sequence in the human genome with 94.6% identity. The sequence was in chromosome 1p within an intronic region of the netrin G1 (NTNG1) gene, implicated in schizophrenia. 34073619_A Genetic Study of Cerebral Atherosclerosis Reveals Novel Associations with NTNG1 and CNOT3. |
ENSMUSG00000059857 |
Ntng1 |
48.145041 |
0.2299443428 |
-2.120643 |
0.418795196 |
24.618809 |
0.00000069866458174063949967497145696060378838865290163084864616394042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002515806105511548745943921356893469010174158029258251190185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.4939845 |
4.8821987 |
72.1044180 |
14.3629205 |
| ENSG00000162676 |
2672 |
GFI1 |
protein_coding |
Q99684 |
FUNCTION: Transcription repressor essential for hematopoiesis. Functions in a cell-context and development-specific manner. Binds to 5'-TAAATCAC[AT]GCA-3' in the promoter region of a large number of genes. Component of several complexes, including the EHMT2-GFI1-HDAC1, AJUBA-GFI1-HDAC1 and RCOR-GFI-KDM1A-HDAC complexes, that suppress, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development. Regulates neutrophil differentiation, promotes proliferation of lymphoid cells, and is required for granulocyte development. Inhibits SPI1 transcriptional activity at macrophage-specific genes, repressing macrophage differentiation of myeloid progenitor cells and promoting granulocyte commitment (By similarity). Mediates, together with U2AF1L4, the alternative splicing of CD45 and controls T-cell receptor signaling. Regulates the endotoxin-mediated Toll-like receptor (TLR) inflammatory response by antagonizing RELA. Cooperates with CBFA2T2 to regulate ITGB1-dependent neurite growth. Controls cell-cycle progression by repressing CDKNIA/p21 transcription in response to TGFB1 via recruitment of GFI1 by ZBTB17 to the CDKNIA/p21 and CDKNIB promoters. Required for the maintenance of inner ear hair cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11060035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12778173, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16287849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17197705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17646546, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18805794, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19026687, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19164764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20190815, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20547752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8754800}. |
Disease variant;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear zinc finger protein that functions as a transcriptional repressor. This protein plays a role in diverse developmental contexts, including hematopoiesis and oncogenesis. It functions as part of a complex along with other cofactors to control histone modifications that lead to silencing of the target gene promoters. Mutations in this gene cause autosomal dominant severe congenital neutropenia, and also dominant nonimmune chronic idiopathic neutropenia of adults, which are heterogeneous hematopoietic disorders that cause predispositions to leukemias and infections. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2672; |
nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; negative regulation of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0010956]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of vitamin D biosynthetic process [GO:0010957]; positive regulation of interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070105]; regulation of histone H3-K4 methylation [GO:0051569]; regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034121]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transcription involved in G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000083]; viral process [GO:0016032] |
12778173_Mutations in proto-oncogene GFI1 cause human neutropenia and target ELA2 15131254_role for auto- and trans-regulation of Gfi1 by GFI1 and GFI1B in maintaining the normal expression patterns of Gfi1 15947108_GFI1 in prostate cancer cells acts as a repressor of 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha hydroxylase gene. 16287849_findings highlight the role of epigenetics in the regulation of development and oncogenesis by Gfi1 16888099_Gfi1 levels are regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. It binds the promoters of several granulocyte-specific genes in primary monocytes. This correlated with low expression of these genes in monocytes compared with granulocytes. 17207994_GFI1 may play a significant role in the down regulation of endogenous production of 1,25D in prostate cancer cells and could provide a novel insight to future diagnosis and treatment 17213822_the interaction between ETS1 and GFI1 facilitates their binding to specific sites on the Bax promoter and represses Bax expression 17244686_Decreased Gfi-1 levels in our SGD patient, together with the mutant C/EBPepsilon, block secondary granules proteins expression, thereby contributing to the underlying etiology of the disease in our patient. 17636019_Results identify PRDM5, which acts as a sequence-specific, DNA binding transcription factor that targets hematopoiesis-associated protein-coding and microRNA genes, some of which are targets of Gfi1. 17646546_The fine-tuning of Gfi1 protein levels regulated by Triad1 defines an unexpected role for this protein in hematopoiesis. 18371060_The measurement of CD34 and GFI1 mRNA expressions could be useful as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for myelodysplastic syndrome. 18701459_the T cell receptor-mediated induction of Gfi1 controls Th2 cell differentiation through the regulation of GATA3 protein stability 18805794_Ajuba is utilized as a corepressor selectively on Gfi1 target genes 19026687_These results reveal novel contributions of MTGR1 and GFI1 to the regulation of neurite outgrowth and identify novel repressors of integrin-dependent neurite outgrowth. 19164764_data reveal a mechanism of transcriptional repression by Gfi-1 and may have important implications for understanding the roles of Gfi-1 in normal development and tumorigenesis 19506020_Data suggest that expression of PFAAP5 allows neutrophil elastase to potentiate the repression of Gfi1 target genes. 19887785_Gfi1 mRNA level in both the mononuclear cells and purified CD34(+) cells from CML were significantly higher as measured by quantitative real-time PCR. 20075157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075157_a variant allele of GFI1 (GFI1(36N)) is associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in white subjects 20087403_An analysis and fine mapping of GFI-EVI5-RPL5-FAM69A locus, genotyping eight Tag-single nucleotide polymorphisms in 732 multiple sclerosis patients and 974 controls from Spain, was performed. 20087403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20571393_Studies indicate that Gfi1 is central to several transcriptional circuits whose dysregulation leads to abnormal or malignant hematopoiesis. 20723283_GFI1 may play an important role in leukemia, especially in CML incidence and progression. 20723286_GFI-1 expression is upregulated in leukemia patients and may contribute to leukemogenesis. 22042697_Data suggest that Gfi1 may have an important role in prolonged multiple myeloma (MM)-induced osteoblast (OB) suppression and provide a new therapeutic target for MM bone disease. 22932805_Our data suggest that the presence of a GFI136N variant allele induces a preleukemic state in myeloid precursors by deregulating the expression of Hoxa9 and other AML-related genes. 23466061_The competition for this binding site inhibits the expression of HOXA9 and induces different transcriptional outcomes, which suggests a new direction for investigation of the mechanism underlying targeted therapy of malignant gliomas. 23528269_Studies indicate that Gfi1 recruits LSD1 to p53 and dampens its activity by de-methylating p53 at C-terminal lysines to prevent immediate apoptosis. 24018353_the expression of Gfi-1 contributes to SOCS1 silencing in AML cells through epigenetic modification, and suppression of histone methyltransferase can provide new insight in AML therapy. 24023884_GFI1 is repressed by p53 24121275_Data shows that MYB regulates the expression of endogenous human GFI1. 24198842_Lymphoid progenitor cells from childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia are functionally deficient and express high levels of the transcriptional repressor Gfi-1. 24830456_During infection, the incoming HCMV rapidly downregulates the GFI1 mRNA and protein in both wild-type cells and in cells in which EZH2, NDY1/KDM2B or JARID2 were knocked down. 25043047_results, supported by evidence from mouse models, identify GFI1 and GFI1B as prominent medulloblastoma oncogenes and implicate 'enhancer hijacking' as an efficient mechanism driving oncogene activation in a childhood cancer 26160036_miR-495 directly interacts with the Gfi1 3'UTR to regulate Gfi1 at a post-transcriptional level and the expression level of miR-495 is inversely correlated with the Gfi1 protein level in medulloblastoma specimens. 26447191_Gfi1 acts as a transcriptional repressor by recruiting histone-modifying enzymes to promoters and enhancers of target genes. Mutations of the C-terminal zinc finger domain causes congenital neutropenia. It may be involved in leukemia and lymphoma. Review. 27080012_GFI1(36S) homozygous patients exhibited a sustained response to treatment with hypomethylating agents, whereas GFI1(36N) patients had a poor sustained response to this therapy. Because allele status of GFI1(36N) is readily determined using basic molecular techniques, we propose inclusion of GFI1(36N) status in future prospective studies for MDS patients to better predict prognosis and guide therapeutic decisions. 27143377_Gfi1 gene expression is regulated by cytokines in activated T cells. 27403598_Maternal-smoking sensitive CpG sites in newborns were significantly associated with cg18146737 SNP located proximal to GFI1. 27480105_combination of the sequence-specific and nonspecific DNA-binding modes of SATB1 should be advantageous in a search for target loci during transcriptional regulation 27677632_In this study, the influence of prenatal smoking exposure on the childrens' DNA methylation state of a CpG island located upstream of the promoter of the growth factor independent 1 (GFI1) gene was analyzed. Significant hypomethylation was observed in this CpG island in SIDS cases with cigarette smoke exposure compared to non-exposed cases. 27840243_Simvastatin attenuates the tumor-associated macrophage mediated gemcitabine resistance of PDAC by blocking the TGF-beta1/Gfi-1 axis. 28387757_GFI1 downregulation promotes inflammation-linked metastasis of colorectal cancer. 28574132_High GFI1 expression is associated with Acute myeloid leukemia. 28820654_Differential methylation was observed in the CYP1A1 promoter and AHRR gene body regions between women who smoked throughout pregnancy and non-smokers on the fetal-side of the placenta and in the GFI1 promoter between women who quit smoking while pregnant and non-smokers on the maternal-side of the placenta 28894287_our results call for a more elaborate stratification of AML patients to ensure proper diagnosis and effective treatment and demonstrate that high GFI1 expression is a reliable and powerful prognostic indicator for CN-AML. 29147018_These results suggest that increasing GFI1 level in leukemic cells with low GFI1 expression level could be a therapeutic approach. 29651020_GFI1 facilitates efficient DNA repair by regulating PRMT1 dependent methylation of MRE11 and 53BP1. 29674496_expression of GFI1 is higher in RUNX1/ETO+ AML samples compared to other AML types and that absence of Gfi1 delays the growth of RUNX1/ETO9a+ cells both in vitro and in vivo. 30286780_Gfi1 plays a key role in MM tumor growth, survival, and bone destruction and contributes to bortezomib resistance. 30296465_the results of western blot analysis showed that miR-650 suppression inhibits the expression of Gfi1. Interestingly, suppression of Gfi1 exhibited similar effects on cell proliferation, migration and invasion of the oral cancer cells as that of miR-650 suppression. 30442561_Epigenetic changes at the GFI1 were linked to smoking exposure in-utero/in-adulthood and robustly associated with cardio-metabolic risk factors. 30606770_Results demonstrate that GFI1 acts as a tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer, where deficiency of Gfi1 promotes malignancy in the colon. 31289136_The oncogenic role of the transcription factor GFI1 in gastric cancer.GSK3B controls GFI1 expression via phosphorylation of Serine 94 and Serine 98 sites, which leads to SCFFBXW7-mediated polyubiquitination and proteasome degradation. 31676828_LSD1-mediated repression of GFI1 super-enhancer plays an essential role in erythroleukemia. 32066420_We identified and classified a pathogenic GFI1 variant and a likely pathogenic variant in MYO6 which together explain the complex phenotypes seen in this family. 32362605_Evaluation of growth factor independence 1 expression in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. 32630147_Epigenetic Regulation of Gfi1 in Endocrine-Related Cancers: a Role Regulating Tumor Growth. 33028609_Human yolk sac-like haematopoiesis generates RUNX1-, GFI1- and/or GFI 1B-dependent blood and SOX17-positive endothelium. 33051558_Gfi1 upregulates c-Myc expression and promotes c-Myc-driven cell proliferation. 33827680_DNA methylation of GFI1 as a mediator of the association between prenatal smoking exposure and ADHD symptoms at 6 years: the Hokkaido Study on Environment and Children's Health. 33993920_The transcription factors GFI1 and GFI1B as modulators of the innate and acquired immune response. 34368875_GFI1 promotes the proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through the inhibition of SOCS1 expression. 34980595_GFI1 Cooperates with IKZF1/IKAROS to Activate Gene Expression in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. 35504619_GFI1 regulates chromatin state essential in human endothelial-to-haematopoietic transition. 35819844_Hematopoietic transcription factor GFI1 promotes anchorage independence by sustaining ERK activity in cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000029275 |
Gfi1 |
367.298820 |
0.1053854302 |
-3.246253 |
0.127537624 |
689.696354 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005203832625127255455767154657691413736822291084696270822319657723579652021194558993708532864049062561725561024615984040090436775765689736040418110989848226161857962582764732712221 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003555952293836957643226054543214305619533371749672852544911640111182960756709661337691836755482854506944475422022518026808930926567207372415227708248326703877457466399646306692306 |
Yes |
No |
71.0267441 |
6.6216977 |
678.6803225 |
37.7670114 |
| ENSG00000162734 |
8682 |
PEA15 |
protein_coding |
Q15121 |
FUNCTION: Blocks Ras-mediated inhibition of integrin activation and modulates the ERK MAP kinase cascade. Inhibits RPS6KA3 activities by retaining it in the cytoplasm (By similarity). Inhibits both TNFRSF6- and TNFRSF1A-mediated CASP8 activity and apoptosis. Regulates glucose transport by controlling both the content of SLC2A1 glucose transporters on the plasma membrane and the insulin-dependent trafficking of SLC2A4 from the cell interior to the surface. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10442631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9670003}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a death effector domain-containing protein that functions as a negative regulator of apoptosis. The encoded protein is an endogenous substrate for protein kinase C. This protein is also overexpressed in type 2 diabetes mellitus, where it may contribute to insulin resistance in glucose uptake. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:8682; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; carbohydrate transport [GO:0008643]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902042]; negative regulation of glucose import [GO:0046325]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902043]; response to morphine [GO:0043278] |
11790785_role of mitogen-activated protein kinase family members in anti-apoptotic function 11976344_role in modulating tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced death-inducing signaling complex 12796492_interaction with p90 ribosomal S6 kinase isoenzyme regulates its activity 12808093_phosphorylation by Akt regulates the antiapoptotic function of PED/PEA-15 at least in part by controlling the stability of PED/PEA-15 15328349_apoptosis following Omi/HtrA2 mitochondrial release is mediated by reduction in ped/pea-15 cellular levels 15331596_PEA-15 is inhibited by adenovirus E1A and has a role in ERK nuclear export and Ras-induced senescence 15916534_The mechanism controlling PEA-15 binding to ERK/MAPK or FADD, and its subsequent role in cell proliferation and apoptosis is reported. 16044159_Raised expression of the antiapoptotic protein pea-15 increases susceptibility to chemically induced skin tumor development 16061647_Human breast cancer cells express high levels of PED and that AKT activity regulates PED protein levels. AKT-dependent increase of PED expression levels represents a key molecular mechanism for chemoresistance in breast cancer. 16170361_cytoplasmic sequestration of the activated form of ERK by PEA15 enables the action of E1A in ovarian neoplasms 16822839_Akt overactivation prevents the nuclear translocation of ERK1/2 and the AngII-induced proliferation through interaction with and stabilization of endogenous PEA-15. 16987961_These data reveal a new function for PEA-15 in the inhibitory control of astrocyte motility through a PKC delta-dependent pathway involving the constitutive expression of a catalytic fragment of PKC delta. 17021921_PEA15 overexpression represents a common defect in first degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes and is correlated with reduced insulin sensitivity in these individuals. 17227770_TPA increases PED/PEA-15 expression at the post-translational level by inducing phosphorylation at serine 116 and preventing ubiquitinylation and proteosomal degradation 17658892_In addition to sequestering protein kinases ERK1/2 in the cytoplasm, PEA-15 has the potential to modulate the activity of ERK2 in cells by competing directly with proteins that contain D-recruitment sites. 17700518_Elevated PEA-15 levels provide a survival advantage for glioblastoma cells confronted with a poor microenvironment and low glucose levels. 18077417_PEA-15 functions as a scaffold to enhance extracellular signal-regulated MAP kinase (ERK) activation of ribosomal S6 kinase polypeptide RSK2, an activity that is regulated by phosphorylation. 18284607_transfection with PED siRNA, but not with cFLIP siRNA, sensitized NSCLC cells to TRAIL-induced cell death 18765665_COUP-TFII antagonizes the repression of the PED/PEA-15 gene by HNF-4alpha. 19010903_PEA-15 expression is an important prognostic marker in ovarian cancer. 19103758_PTEN influences Fas signaling, at least in part, by regulating PEA-15 phosphorylation and activity that, in turn, regulate the ability of Bcl-2 to suppress Fas-induced apoptosis. 19382910_Vitamin D3 signalling in the brain enhances the function of phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes--15 kD (PEA-15) 19531639_Strategies are being devised to target key signaling events in PED/PEA-15 action aimed at improving glucose tolerance and at facilitating cancer cell death. 19771552_Results suggest that PEA-15 expression is likely to be associated with the tumorigenesis of alignant pleural mesothelioma. 20032303_Data show that PEA-15 prevents ERK1/2 localization to the plasma membrane, thereby inhibiting ERK1/2-dependent threonine phosphorylation of FRS2alpha to promote activation of the ERK1/2 MAP kinase pathway. 20396999_The results show that HNF-4alpha serves as a scaffold protein for histone deacetylase activities, thereby inhibiting liver expression of genes including PED. 20406097_PED/PEA-15 modulates Coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor expression and adenoviral entry, by sequestering ERK1/2. 20452983_PEA-15 promotes autophagy in glioma cells in a JNK-dependent manner 20537721_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20537721_There was no significant difference in the frequency of three marker haplotype in the PEA15 gene in patient with schizophrenia. 20648624_Data show that PED and Rac1 interact and that this interaction modulates cell migration/invasion processes in cancer cells through ERK1/2 pathway. 20825483_provide molecular basis of the PED/PEA-15 functional interactions and detailed surface for the design and development of PED/PEA-15 binders 20979872_The expressions of PED/PEA-15 and XIAP are elevated in hepatocellular carcinoma as compared with adjacent tissues and normal tissues. 21198825_The protective effect of melatonin is likely mediated, in part, by inhibition of peroxynitrate-mediated nitrosative stress, which in turn relieves imbalance of mitochondrial HtrA2-PED signaling and endothelial cell death. 21895963_The 67 kD laminin receptor is a novel PED/PEA-15 interacting protein. PED/PEA-15 overexpression increases 67LR-mediated cell adhesion and migration to laminin and extracellular matrix invasion. 22144664_Data show that knockdown of PEA-15 expression resulted in reversal of selumetinib-sensitive cells to resistant cells, implying that PEA-15 contributes to selumetinib sensitivity. 22213050_PEA15 impairs cell migration and correlates with clinical features predicting good prognosis in neuroblastoma 22694972_The article hypothesizes that only unphosphorylated PEA-15 can act as a tumor-suppressor and that phosphorylation alters the interaction with binding partners to promote tumor development. 22732408_the solution death effector domain (DED) structure of the PED/PEA-15 protein, a representative member of DED subfamily, using traditional NMR restraints with the addition of residual dipolar coupling restraints was refined. 22820249_NMR chemical shift perturbation and backbone dynamic studies at the fast ps-ns timescale of PED/PEA-15, in its free form and in the complex with ERK2. 23481023_study demonstrates that the PEA-15 protein decreases proliferation, clonogenicity, and invasiveness, but increases resistance to apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells 23543364_Our findings highlight the importance of pPEA-15 as a promising target for improving the efficacy of paclitaxel-based therapy in ovarian cancer. 23575685_PEA-15 binding protects ERK2 from dephosphorylation, thus setting the stage for immediate ERK activity upon its release from the PEA-15 inhibitory complex 24477641_Up-regulated chaperone-mediated autophagy activity characteristic of most types of cancer cell enhances oncogenesis by shifting the balance of PED function toward tumor promotion. 24657708_New therapeutic targets based around PEA-15 and its associated interactions are now being uncovered and could provide novel avenues for treatment strategies in multiple diseases. 24710276_Tumor suppressor PEA15 is a regulator of genome integrity and is an integral component of the DNA damage response pathway. 25075716_Results suggest that neurochemical adaptations of brain FADD, as well as its interaction with PEA-15, could play a major role to counteract the known activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in major depression 25484138_Omi/HtrA2 overexpression promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis and the ped/pea-15 expression level causes this difference of the Omi/HtrA2 pro-apoptotic marker in the various hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines 25489735_PED/PEA-15 overexpression is sufficient to block hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in Ins-1E cells through a PLD-1 mediated mechanism 25725291_The nuclear translocation of SApErk1/ 2 apart from PEA-15 as an important mechanism to reverse senescence phenotype. 25775393_High PED expression is associated with esophageal carcinoma. 25796184_Data show that phosphoprotein enriched in astrocytes of 15 kDa (PEA-15) influences dephosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) via extracellular signal-regulated kinases ERK1/2 sequestration in the cytoplasm. 25957098_Latent HCMV infection of CD34 + cells protects cells from FAS-mediated apoptosis through the cellular IL-10/PEA-15 pathway. 26470725_Integrin alpha5beta1 and p53 convergent pathways in the control of anti-apoptotic proteins PEA-15 and survivin in high-grade glioma. 27053111_Data suggest the role of the phospholipase C epsilon-Protein kinase D-PEA15 protein-ribosomal S6 kinase-IkappaB-NF-kappa B pathway in facilitating inflammation and inflammation-associated carcinogenesis in the colon. 27317964_PP4 regulates breast cancer cell survival and identifies a novel PP4c-PEA15 signalling axis in the control of breast cancer cell survival. 27669502_PEA15 expression was not significantly correlated with ovarian cancer antineoplastic drug resistance. 29072691_Data suggest that PED has a prominent role in HCC biology. It acts particularly on promoting cell migration and confers resistance to sorafenib treatment. 30317603_This study identified EA15, MIR22, and LINC00472 may serve as the potential diagnostic markers of diabetic nephropathy. 30365128_Study showed that PEA15 was highly expressed in colorectal cancer and liver metastatic cancer tissues and positively correlated with TNM staging, liver metastasis and poor prognosis. PEA15 may be a potential biomarker for liver metastasis of colorectal cancer therapy. Collectively, PEA15 promoted the development of liver metastasis of colorectal cancer through the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. 30569123_Study results indicated that PEA15 expression was associated with clinicopathology and prognosis in gastric cancer and was regulated by AKT to participate in cisplatin resistance, indicating that it may be a potential target for overcoming cisplatin resistance in the treatment of gastric cancer. 32102425_Non-Phosphorylatable PEA-15 Sensitises SKOV-3 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin. 33246486_ZNF703 promotes tumor progression in ovarian cancer by interacting with HE4 and epigenetically regulating PEA15. 34241740_Nonphosphorylatable PEA15 mutant inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer partly through the regulation of IL-8 expression. 34615962_Proteomics analysis identifies PEA-15 as an endosomal phosphoprotein that regulates alpha5beta1 integrin endocytosis. 34907034_Transcription Factor FOSL1 Enhances Drug Resistance of Breast Cancer through DUSP7-Mediated Dephosphorylation of PEA15. 34997083_PEA-15 engages in allosteric interactions using a common scaffold in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. |
ENSMUSG00000013698 |
Pea15a |
1302.014656 |
2.2753642419 |
1.186098 |
0.044607180 |
717.236135 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005341433243490800446011512125488313812053574106709803141084247743817749096658199107523175627231450347850649838215791862909130996161452440758531926487641650778662724530624234 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003790363205477126015546594772407595809210026880010857937007897728135614015773264368729253820251350202815977025891228297367859647801834989717566246509171454593869086912811105 |
Yes |
No |
1825.5499861 |
49.6583023 |
808.0057139 |
17.4840333 |
| ENSG00000162745 |
25903 |
OLFML2B |
protein_coding |
Q68BL8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an olfactomedin domain-containing protein. Most olfactomedin domain-containing proteins are secreted glycoproteins. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:25903; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30866865_The high expression of OLFML2B was associate with a short overall survival in gastric cancer patients. |
ENSMUSG00000038463 |
Olfml2b |
11.040173 |
5.2298528040 |
2.386770 |
0.646928711 |
13.404746 |
0.00025098838332898796687348008660478626552503556013107299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000647542132133519052900050283483324164990335702896118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.3775479 |
6.0189841 |
2.9616928 |
0.9613772 |
| ENSG00000162769 |
28982 |
FLVCR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5Y0 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Heme transporter that exports cytoplasmic heme. It can also export coproporphyrin and protoporphyrin IX, which are both intermediate products in the heme biosynthetic pathway. Does not export bilirubin. Heme export depends on the presence of HPX and is required to maintain intracellular free heme balance, protecting cells from heme toxicity. Heme export provides protection from heme or ferrous iron toxicities in liver, brain, sensory neurons and during erythtopoiesis, a process in which heme synthesis intensifies. Causes susceptibility to FeLV-C in vitro. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10400745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15369674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20610401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27923065}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Heme transporter that promotes heme efflux from the mitochondrion to the cytoplasm. Essential for erythroid differentiation. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Erythrocyte maturation;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the major facilitator superfamily of transporter proteins. The encoded protein is a heme transporter that may play a critical role in erythropoiesis by protecting developing erythroid cells from heme toxicity. This gene may play a role in posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa and the hematological disorder Diamond-Blackfan syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:28982; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; heme transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015232]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; erythrocyte maturation [GO:0043249]; head morphogenesis [GO:0060323]; heme biosynthetic process [GO:0006783]; heme export [GO:0097037]; heme transport [GO:0015886]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; mitochondrial transport [GO:0006839]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; regulation of organ growth [GO:0046620]; spleen development [GO:0048536] |
15996880_the FLVCR gene on 1q31 is not involved in Diamond-Blackfan anemia in families studied 16439531_results suggest that multiple FLVCR1 regions are critical for mediating efficient feline leukemia virus subgroup C (FeLV-C) infection and that these regions are distinct from the FeLV-C envelope binding site 18815190_Alternative splicing of FLVCR1 transcripts and subsequent FLVCR1 insufficiency is an additional contributing factor to the erythropoietic defect observed in Diamond-Blackfan anemia. 20610401_hemopexin directly interacts with FLVCR 21070897_These results suggest that aberrant FLVCR1 causes a selective degeneration of a subpopulation of neurons in the retina and the posterior columns of the spinal cord via dysregulation of heme or iron homeostasis. 21267618_Posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa is caused by mutations in FLVCR1. 21593354_relative protein expression of 2 heme transporters, Feline Leukemia Virus, Subgroup C, Receptor 1 (FLVCR1) and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein, was assessed in placental tissue in relation to maternal/neonatal iron status and placental iron concentration 22279524_Study identified sequence variants in the known disease-causing genes SLC6A3 and FLVCR1, and present evidence to strongly support the pathogenicity of variants identified in TUBGCP6, BRAT1, SNIP1, CRADD, and HARS. 22483575_FLVCR1 mutants failed to fold properly in the ER, were rapidly degraded in the lysosomes, and therefore, could not export heme out of cells. Thus, accumulation of heme in FLVCR1-mutant cells could cause cellular toxicity. 23187127_FLVCR1b regulates erythropoiesis by controlling mitochondrial heme efflux, whereas FLVCR1a expression is required to prevent hemorrhages and edema. 24576667_both HIF2alpha and ETS1 are involved in the transcriptional regulation of Flvcr1a and that HIF2alpha is absolutely required for Flvcr1a induction upon hypoxia 25795718_Flvcr1 regulates differentiation of erythroid progenitors by controlling intracellular heme accumulation. 26058344_RPS19-downregulated erythroleukemia cells show reduced FLVCR1a and FLVCR1b mRNA levels associated with heme overload. 26067085_Data shows that FLVCR1a participates in the control of intestinal mucosa homeostasis by exporting the excess of de novo synthesized heme from intestinal cells. 27923065_Using fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with sensory neurodegeneration, we here show that the FLVCR1-mutations reduce heme export activity, enhance oxidative stress and increase sensitivity to programmed cell death. Our data link heme metabolism to sensory neuron maintenance and suggest that intracellular heme overload causes early-onset degeneration of pain-sensing neurons in humans 28706239_Altogether, these findings showed a direct association between FLVCR1 mRNA levels and hyperglycemia, suggesting that increased adipose tissue heme exportation might disrupt, or is the consequence of, impaired systemic glucose metabolism during the progression to type 2 diabetes. 28766925_Mutation in FLVCR1 gene is associated with Posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa coexisting with sensory-autonomic neuropathy and leukemia. 29192808_Here, we describe a patient with non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa homozygous for a splice-site variant in FLVCR1 (c.1092 + 5G>A) without evidence of posterior column ataxia or cerebellar degeneration. 30309647_findings suggested that FLVCR1-AS1/miR-573/E2F3 axis was an important signaling pathway in mediating tumorigenesis and progression of NSCLC 30444160_We describe clinical and retinal imaging features in the one of the largest cohorts of affected patients in the literature. Given the availability of genetic testing for this phenotype, testing for FLVCR1 mutations should be considered in pediatric and adult patients with sensory ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa. 30656474_Mutations in FLVCR1 can present with the clinical picture of a non-syndromic autosomal recessive RP (in this case RP without PCA), RP with mild cerebellar signs, but also PCARP. 31884612_FLVCR1 p.Tyr341Cys mutation was observed homozygously in seven Retinitis Pigmentosa affected Irish patients across four pedigrees. 34433355_Isolated juvenile macular dystrophy without posterior column ataxia associated with FLVCR1 mutation. 34931442_Extending the phenotype of posterior column ataxia with retinitis pigmentosa caused by variants in FLVCR1. |
ENSMUSG00000066595 |
Flvcr1 |
149.349085 |
2.0893389861 |
1.063047 |
0.323839244 |
10.541697 |
0.00116711216162121520639738392333129013422876596450805664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002688711644377889467549813673485914478078484535217285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
195.8138985 |
42.8221851 |
94.2401411 |
15.1119009 |
| ENSG00000162825 |
100288142 |
NBPF20 |
protein_coding |
P0DPF2 |
|
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene is a member of the neuroblastoma breakpoint family (NBPF) which consists of dozens of recently duplicated genes primarily located in segmental duplications on human chromosome 1. This gene family has experienced its greatest expansion within the human lineage and has expanded, to a lesser extent, among primates in general. Members of this gene family are characterized by tandemly repeated copies of DUF1220 protein domains. Gene copy number variations in the human chromosomal region 1q21.1, where most DUF1220 domains are located, have been implicated in a number of developmental and neurogenetic diseases such as microcephaly, macrocephaly, autism, schizophrenia, cognitive disability, congenital heart disease, neuroblastoma, and congenital kidney and urinary tract anomalies. Altered expression of some gene family members is associated with several types of cancer. This gene family contains numerous pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:100288142; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737] |
|
|
|
36.069971 |
2.1516745388 |
1.105460 |
0.269299193 |
17.046246 |
0.00003648041578912925145044762742507771235977998003363609313964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000106771948651110002923014796749612287385389208793640136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.3825013 |
7.9040384 |
22.6826170 |
2.9338039 |
| ENSG00000162849 |
55083 |
KIF26B |
protein_coding |
Q2KJY2 |
FUNCTION: Essential for embryonic kidney development. Plays an important role in the compact adhesion between mesenchymal cells adjacent to the ureteric buds, possibly by interacting with MYH10. This could lead to the establishment of the basolateral integrity of the mesenchyme and the polarized expression of ITGA8, which maintains the GDNF expression required for further ureteric bud attraction. Although it seems to lack ATPase activity it is constitutively associated with microtubules (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an intracellular motor protein thought to transport organelles along microtubules. The encoded protein is required for kidney development. Elevated levels of this protein have been found in some breast and colorectal cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:55083; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; establishment of cell polarity [GO:0030010]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022409]; ureteric bud invasion [GO:0072092] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23585914_High expression of KIF26B in breast cancer associates with poor prognosis. 25652119_KIF26B plays an important role in colorectal carcinogenesis and functions as a novel prognostic indicator and a potential therapeutic target for CRC. 28581513_KIF26B, a novel oncogene regulated by miR-372, promotes proliferation and metastasis through the VEGF pathway in gastric cancer 29880787_Upregulation of KIF26B enhanced proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells in vitro 30151950_KIF26B may play a critical role in the brain development and, when mutated, cause pontocerebellar hypoplasia with arthrogryposis. 30248545_KIF26B promoted the development and progression of breast cancer and might act as a potential therapeutic target for treating breast cancer. 31077021_Our results did prove a statistical association of both rs2228557 and rs12407427 genotypes (TT and CT + CC) and allele (T) with KTCN susceptibility in Iranian population. 34817735_ELK1-induced up-regulation of KIF26B promotes cell cycle progression in breast cancer. 35866054_KIF26B Is Overexpressed in Medulloblastoma and Promotes Malignant Progression by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway. 36012474_The Kinesin Gene KIF26B Modulates the Severity of Post-Traumatic Heterotopic Ossification. 36417404_Whole exome sequencing identifies KIF26B, LIFR and LAMC1 mutations in familial vesicoureteral reflux. |
ENSMUSG00000026494 |
Kif26b |
37.923206 |
0.0875094754 |
-3.514417 |
0.368788719 |
118.506553 |
0.00000000000000000000000000134309706006089822230357106369666014349594888203406568001198721483604580240883707986654371779877692461013793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000015910202733947718469548628577169068795270266342273592452920889254435886546457101786700150114484131336212158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8098686 |
1.4422712 |
66.7525366 |
7.2009797 |
| ENSG00000162878 |
91461 |
PKDCC |
protein_coding |
Q504Y2 |
FUNCTION: Secreted tyrosine-protein kinase that mediates phosphorylation of extracellular proteins and endogenous proteins in the secretory pathway, which is essential for patterning at organogenesis stages. Mediates phosphorylation of MMP1, MMP13, MMP14, MMP19 and ERP29 (PubMed:25171405). Probably plays a role in platelets: rapidly and quantitatively secreted from platelets in response to stimulation of platelet degranulation (PubMed:25171405). May also have serine/threonine protein kinase activity. Required for longitudinal bone growth through regulation of chondrocyte differentiation. May be indirectly involved in protein transport from the Golgi apparatus to the plasma membrane (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5RJI4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25171405}. |
ATP-binding;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Osteogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transferase;Transport;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
Enables non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity. Involved in peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation and skeletal system development. Located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:91461; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; embryonic digestive tract development [GO:0048566]; limb morphogenesis [GO:0035108]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0042997]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032332]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501] |
19961619_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24407380_our results suggest that genes CA10 and also SGK493 may be an important risk factor for asthma development, especially for a nonatopic phenotype. 25171405_VLK is rapidly and quantitatively secreted from platelets in response to stimuli and can tyrosine phosphorylate coreleased proteins utilizing endogenous as well as exogenous ATP sources. 25862977_The Fam20C-and VLK-family of kinases mediate the phosphorylation of proteins in the secretory pathway and extracellular space.Mutation in several secretory pathway kinases cause human disease 27591737_VLK secretion can be regulated by external cues, intracellular signal proteins, and mechanical stretch, and VLK can in turn regulate TyrP of ECM proteins secreted by trabecular meshwork cells and control cell shape, actin stress fibers, and focal adhesions. 30478137_Each patient had a homozygous gene disrupting variant in PKDCC considered to explain the skeletal phenotypes shared by both. 31845979_Taken together, these results suggest that Vlk may function as a signaling regulator in extracellular space to modulate the Hedgehog pathway 34329392_The secreted tyrosine kinase VLK is essential for normal platelet activation and thrombus formation. |
ENSMUSG00000024247 |
Pkdcc |
772.804778 |
0.4803654222 |
-1.057796 |
0.096717600 |
117.930685 |
0.00000000000000000000000000179554395234213154150234500832755154775122767125514407903322006846521705861891016198228498979005962610244750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000021134153697424131834223295592503514021860021782239489171220283250825482807000454954504675697535276412963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
512.6091869 |
29.9079458 |
1075.0664693 |
43.8718466 |
| ENSG00000162882 |
23498 |
HAAO |
protein_coding |
P46952 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxidative ring opening of 3-hydroxyanthranilate to 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate semialdehyde, which spontaneously cyclizes to quinolinate. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7514594}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Dioxygenase;Disease variant;Iron;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; quinolinate from L-kynurenine: step 3/3. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03019, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28792876}. |
3-Hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase is a monomeric cytosolic protein belonging to the family of intramolecular dioxygenases containing nonheme ferrous iron. It is widely distributed in peripheral organs, such as liver and kidney, and is also present in low amounts in the central nervous system. HAAO catalyzes the synthesis of quinolinic acid (QUIN) from 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid. QUIN is an excitotoxin whose toxicity is mediated by its ability to activate glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Increased cerebral levels of QUIN may participate in the pathogenesis of neurologic and inflammatory disorders. HAAO has been suggested to play a role in disorders associated with altered tissue levels of QUIN. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23498; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase activity [GO:0000334]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; ferrous iron binding [GO:0008198]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process from tryptophan [GO:0034354]; anthranilate metabolic process [GO:0043420]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435]; neuron cellular homeostasis [GO:0070050]; quinolinate biosynthetic process [GO:0019805]; quinolinate metabolic process [GO:0046874]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043]; tryptophan catabolic process [GO:0006569] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724865_GTF2A1 alone, or GTF2A1 plus HAAO are excellent candidate biomarkers for detecting Ovarian cancer 20211485_Methylation status of CIDEA, HAAO and RXFP3 had significant association with microsatellite instability in endometrial tumors. 20468071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28375145_Here, the first crystal structure of human 3-HAO with the native iron bound in its active site is presented, together with an additional structure with zinc (a known inhibitor of human 3-HAO) bound in the active site. 30063927_Genetic variations of HAAO and IRX6 influence susceptibility to hypospadias in the Japanese population. 32390008_Dysregulation at multiple points of the kynurenine pathway is a ubiquitous feature of renal cancer: implications for tumour immune evasion. 33767242_Expression analysis of selected genes involved in tryptophan metabolic pathways in Egyptian children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and learning disabilities. 35362267_Re-sequencing of candidate genes FOXF1, HSPA6, HAAO, and KYNU in 522 individuals with VATER/VACTERL, VACTER/VACTERL-like association, and isolated anorectal malformation. |
ENSMUSG00000000673 |
Haao |
31.098899 |
0.3976307363 |
-1.330499 |
0.341143618 |
15.253984 |
0.00009397829733702242204114452039931393301230855286121368408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000259517243909158240328799438501050644845236092805862426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5969848 |
4.6950613 |
46.7601836 |
7.9437136 |
| ENSG00000162888 |
574431 |
C1orf147 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.673987 |
0.4818456262 |
-1.053357 |
0.359670964 |
8.792799 |
0.00302421910296969600334682226616678235586732625961303710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006472650730771093742499378009824795299209654331207275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.0547213 |
2.6713870 |
23.1002454 |
3.5687674 |
| ENSG00000162896 |
5284 |
PIGR |
protein_coding |
P01833 |
FUNCTION: [Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor]: Mediates selective transcytosis of polymeric IgA and IgM across mucosal epithelial cells. Binds polymeric IgA and IgM at the basolateral surface of epithelial cells. The complex is then transported across the cell to be secreted at the apical surface. During this process, a cleavage occurs that separates the extracellular (known as the secretory component) from the transmembrane segment. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10229845, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15530357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9379029}.; FUNCTION: [Secretory component]: Through its N-linked glycans ensures anchoring of secretory IgA (sIgA) molecules to mucus lining the epithelial surface to neutralize extracellular pathogens (PubMed:12150896). On its own (free form) may act as a non-specific microbial scavenger to prevent pathogen interaction with epithelial cells (PubMed:16543244). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12150896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16543244}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The encoded poly-Ig receptor binds polymeric immunoglobulin molecules at the basolateral surface of epithelial cells; the complex is then transported across the cell to be secreted at the apical surface. A significant association was found between immunoglobulin A nephropathy and several SNPs in this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:5284; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; secretory IgA immunoglobulin complex [GO:0071751]; polymeric immunoglobulin receptor activity [GO:0001792]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of bitter taste [GO:0001580]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; Fc receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038093]; immunoglobulin transcytosis in epithelial cells mediated by polymeric immunoglobulin receptor [GO:0002415]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; retina homeostasis [GO:0001895] |
11034397_IL-4 responsiveness mediated by an enhancer located in intron 1; both direct and indirect involvement of STAT6 11579946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11714807_A novel NF-kappa B/Rel site in intron 1 cooperates with proximal promoter elements to mediate TNF-alpha-induced transcription of the human polymeric Ig receptor 12121890_characterization of the human pIgR promoter and the essential role that eight different nuclear complexes have in controlling basal expression of this gene in Caco-2 cells 12165516_cooperative binding of multiple transcription factors regulates basal activity of the human PIGR promoter 12183558_facilitates invasion of epithelial cells by Streptococcus pneumoniae in a strain-specific and cell type-specific manner 12213814_The carboxyl-terminal domains of IgA and IgM direct isotype-specific polymerization and interaction with this receptor 12546713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12654638_This protein is cleaved by neutrophil serine proteinases but its epithelial production is increased by neutrophils through NF-kappa B- and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanisms. 12740691_It seems that a gene associated with susceptibility to immunoglobulin A nephropathy lies within or close to the PIGR gene locus on chromosome 1q in the Japanese population. 12740691_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13679368_there is a conformational CbpA-binding motif in the D3/D4 region of human polymeric immunoglobulin receptor, which is functionally separated from the IgA-binding site 14644095_transcription factors upstream stimulatory factor (USF) and c-Myc may exert opposing effects on PIGR promoter activity 14660617_Ectodomains 3 and 4 of human polymeric Immunoglobulin receptor have a role in mediating adherence and internalization of Streptococcus pneumoniae into epithelial cells 15265917_TNF-induced up-regulation of the human pIgR critically depends on an NF-kappa B site and flanking sequences within a 204-bp region of the first intron in the pIgR gene, a region largely overlapping with a recently characterized IL-4-responsive enhancer. 15864740_USF1 and USF2 mRNA levels were reduced in non-small cell lung carcinoma; AP2-alpha levels were elevated; regression analysis demonstrated that reduced USF2 mRNA & increased AP2-alpha mRNA levels were predictive of downregulated PIGR mRNA expression 15972671_TLR3 and TLR4 signal primarily through NF-kappaB to enhance transcription of pIgR mRNA. 16048543_This review expands our view of the immunobiology of pIgR, a key component of the mucosal immune system that bridges innate and adaptive immune defense. 16086865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16272325_interaction of dimeric IgA (dIgA) (the predominant form of IgA polymer) with the pIgR 16288892_Secretory component (SC) is derived from the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR). The purified free form of SC binds IgM with a physiological equilibrium dissociation constant of 4.6x10(-8) M and shares structural similarity to native SC. 17428798_This work represents the first analysis of the three-dimensional structure of full-length free secretory component (SC) and paves the way to a better understanding of the association between SC and its potential ligands. 17460948_In cultured Caco-2 cells, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) dose-dependently increased polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIg) mRNA. 19338768_Fcalpha/muR had different tissue distribution patterns to pIgR in the intestine. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20829350_Data illustrate the importance of a coordinated signaling between Src PTKs, ERK1/2, and JNK during pIgR-mediated uptake of pneumococci by host epithelial cells. 21454571_Streptococcus pneumoniae infection of host epithelial cells via polymeric immunoglobulin receptor transiently induces calcium release from intracellular stores. 21965228_Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (PIGR)expression was lost in most lung cancers and pre-invasive bronchial lesions, suggesting that PIGR downregulation is an early event in lung tumourigenesis. PIGR overexpression inhibited cell proliferation. 22022593_Both native and phage-bound variable domain of camelid derived heavy chain only antibodies, were only able to get across polarized MDCK cells that express the human pIgR gene in a basolateral to apical fashion. 22025622_Results identify pIgR as a potential link between hepatitis B virus-derived hepatitis and HCC metastasis and provide evidence in support of pIgR as a prognostic biomarker for HCC and a potential therapeutic target. 22053820_The comparison of nonsmokers, smokers, and smokers with moderate COPD revealed 15 changed proteins with the majority, including polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (PIGR), being elevated in smokers and subjects with COPD. 23809084_Results indicated that the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) can be divided into several functionally distinct regions. 24568264_Report PIGR expression in human fallopian tubes, primary epithelial ovarian tumours and metastases. 24694107_High PIGR expression independently predicts a decreased risk of recurrence and an improved survival in patients with adenocarcinoma of the upper gastrointestinal tract 24699841_Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor expression is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. 25078120_pIgR down-regulation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease correlates with severity. Bronchial epithelium in vitro retains aberrant imprinting for pIgR expression. pIgR down-regulation is linked to TGF-beta-driven reprogramming of bronchial epithelium. 25397670_Reduced expression of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in pancreatic and periampullary adenocarcinoma signifies tumour progression and poor prognosis. 25455218_In conclusion these data suggest that Streptococcus pneumoniae PspC-promoted uptake via the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor of epithelial cells is mediated by both clathrin and caveolin dependent pathway. 25922073_the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) is highly expressed by renal cyst-lining cells. pIgR expression is, in part, driven by aberrant STAT6 pathway activation. 25956706_Crohn disease patients were characterized as having decreased median expression of PIGR, in non-inflamed colonic mucosa. By contrast, Ulcerative colitis patients exhibited decreased expression of PIGR in colon mucosa. 26176052_Positive expression of pIgR was statistically significantly associated with poor prognosis of patients with colon carcinoma hepatic metastasis. 26239418_These results demonstrate that SLPI down-regulates pIgR expression through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway by inhibiting degradation of IkappaBbeta protein. 26943617_The polymeric immunoglobulin receptor secretory component structure comprises five immunoglobulin-like domains (D1-D5) arranged as a triangle, with an interface between ligand-binding domains D1 and D5. 27663566_We identified two SLN genes (PIGR and TFAP2A) that provided high prognostic accuracy in SLN-positive melanoma patients (AUC = 0.864). These two SLN genes, along with clinicopathological features, can differentiate the high- and low-risk groups in node-positive melanoma patients. 28173980_pIgR may be involved in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression and may be linked stromal activity. Further work on its precise role is mandated in in vivo models, to understand its influence on cancer progression. 28355232_A genome-wide trans-ethnic interaction study links the PIGR-FCAMR locus to coronary atherosclerosis via interactions between genetic variants and residential exposure to traffic pollution. 28515075_RrgA, binds both polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) and PECAM-1, whereas the choline binding protein PspC binds, but to a lower extent, only pIgR 31188867_Data provide evidence that pIgR protein is targeted directly by Slp protein contributing to E. coli adherence. 31404540_High PIGR expression is associated with kidney diseases. 32427855_Associations of urinary polymeric immunoglobulin receptor peptides in the context of cardio-renal syndrome. 32627041_High expression levels of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor are correlated with chemoresistance and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. 33390805_Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (PIGR) exerts oncogenic functions via activating ribosome pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33937393_A Bioinformatic Analysis of Correlations between Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor (PIGR) and Liver Fibrosis Progression. 34922977_Patient pIgR-enriched extracellular vesicles drive cancer stemness, tumorigenesis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 36207349_M1 macrophages evoke an increase in polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (PIGR) expression in MDA-MB468 breast cancer cells through secretion of interleukin-1beta. |
ENSMUSG00000026417 |
Pigr |
241.482998 |
4.9921561150 |
2.319663 |
0.245152516 |
83.639110 |
0.00000000000000000005938650013459644702122841936626740278133017729104558158487181529494591814000159502029418945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000526137300112030928008940211895553243891476332476614223565558603468161891214549541473388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
399.3585240 |
69.8690873 |
80.5247028 |
10.4680892 |
| ENSG00000162897 |
83953 |
FCAMR |
protein_coding |
Q8WWV6 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a receptor for the Fc fragment of IgA and IgM. Binds IgA and IgM with high affinity and mediates their endocytosis. May function in the immune response to microbes mediated by IgA and IgM. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11779189}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable IgA binding activity; IgM binding activity; and transmembrane signaling receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in adaptive immune response. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83953; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250] |
18379868_Comprehensive survey of naturally occurring polymorphisms in rhesus macaques and in humans. 19338768_These results indicate for the first time that Fcalpha/muR protein is expressed by human intestinal tissues 19393604_the cytoplasmic portion of human Fcalpha/microR is required in the internalization. 19682689_LPS, through the TLR4 receptor, activates the p38MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways and up-regulate the expression of Fcamr in human macrophages 19945166_These results suggest that the cytoplasmic portion is required for the dimer formation and thus for efficient cell surface expression of Fcalpha/microR. 20059578_ADAM10 and ADAM17 are involved in the shedding of FcalphaR 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25845491_A significantly worse survival was found in patients with IgA serum levels>2.85 g/l compared to patients with lower IgA serum levels. 26138065_rs3125923 FCAMR gene represents a validated SNP to predict grade 3-4 Taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy . Genetically determined AA race represents the most significant predictor of TIPN. 28355232_A genome-wide trans-ethnic interaction study links the PIGR-FCAMR locus to coronary atherosclerosis via interactions between genetic variants and residential exposure to traffic pollution. |
ENSMUSG00000026415 |
Fcamr |
28.999738 |
3.6811796208 |
1.880168 |
0.334564502 |
32.819381 |
0.00000001011315235792405349609902008838763221021395111165475100278854370117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000044045479139262029035296240825694824572167362930485978722572326660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.6655756 |
10.1109153 |
12.7283376 |
2.3001567 |
| ENSG00000162913 |
574407 |
OBSCN-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.901863 |
0.0624008639 |
-4.002290 |
0.650016656 |
53.479172 |
0.00000000000026134896941971019548096246210059993944933506848649074072454823181033134460449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001618083384494514413975788820569617307851620346959009566489839926362037658691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.2668615 |
1.0155095 |
36.5044890 |
6.1909284 |
| ENSG00000162931 |
51127 |
TRIM17 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y577 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays important roles in the regulation of neuronal apoptosis, selective autophagy or cell proliferation (PubMed:22023800, PubMed:19358823, PubMed:27562068). Stimulates the degradation of kinetochore ZW10 interacting protein ZWINT in a proteasome-dependent manner, leading to negative regulation of cell proliferation (PubMed:22023800). Inhibits autophagic degradation of diverse known targets while contributing to autophagy of midbodies. Autophagy-inhibitory activity involves MCL1, which TRIM17 assembles into complexes with the key autophagy regulator BECN1 (PubMed:27562068). Controls neuronal apoptosis by mediating ubiquitination and degradation of MCL1 to initiate neuronal death. In addition, regulates NFAT transcription factors NFATC3 and NFATC4 activities by preventing their nuclear localization, thus inhibiting their transcriptional activities. Decreases TRIM41-mediated degradation of ZSCAN2 thereby stimulating alpha-synuclein/SNCA transcription in neuronal cells (By similarity). Prevents the E3 ubiquitin-ligase activity of TRIM28 and its interaction with anti-apoptotic BCL2A1, blocking TRIM28 from ubiquitinating BCL2A1 (PubMed:19358823). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TPM3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19358823, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22023800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27562068}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Lysosome;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. The protein localizes to cytoplasmic bodies. The protein is expressed almost exclusively in the testis, but its function is unknown. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51127; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880] |
19358823_terf interacts with TRIM44;TRIM44 inhibited ubiquitination of terf, and thus stabilized the protein. 19472918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22023800_the E3 ubiquitin ligase terf causes protein degradation of ZWINT and negatively regulates cell proliferation 25215946_NFATc3 interacted in a SUMO-dependent manner with Trim17, an E3 ubiquitin ligase necessary for neuronal apoptosis 27562068_TRIM17 promoted the removal of midbodies, remnants of the cell division machinery that are known autophagy targets. 30042493_overexpression of TRIM28 or knock-out of TRIM17 reduced BCLA1 protein levels and restored sensitivity of melanoma cells to BRAF-targeted therapy. Therefore, our data describe a molecular rheostat in which two proteins of the TRIM family antagonistically regulate BCL2A1 stability and modulate cell death. 30485814_deregulation of the TRIM17/TRIM41/ZSCAN21 pathway may be involved in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. 31409898_data suggest LSD1 largely plays a tumor suppressor role in luminal breast cancer and the oncogenic program associated with LSD1-inhibition may be suppressed via TRIM37-inhibition 35894553_MiR-1246 is responsible for lung cancer cells-derived exosomes-mediated promoting effects on lung cancer stemness via targeting TRIM17. |
ENSMUSG00000036964 |
Trim17 |
8.078550 |
0.3062895133 |
-1.707032 |
0.682807856 |
5.983621 |
0.01443932792674947063193968688210588879883289337158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026737483402185693859287596296780975535511970520019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9466748 |
1.9197943 |
12.8353568 |
3.6638685 |
| ENSG00000162994 |
130162 |
CLHC1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NHS4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:130162; |
|
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000020461 |
Clhc1 |
66.768815 |
0.4462084379 |
-1.164210 |
0.258049973 |
20.306971 |
0.00000659598207141144869788875609861733551042561884969472885131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000021173704953030227955820471996695175675995415076613426208496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.3766787 |
6.6607047 |
89.0147720 |
10.2043239 |
| ENSG00000163040 |
90557 |
CCDC74A |
protein_coding |
Q96AQ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:90557; |
|
31521166_The authors characterized CCDC74A and CCDC74B as microtubule-associated proteins that localize to spindles and are important K-fiber crosslinkers required for bipolar spindle formation and chromosome alignment. |
ENSMUSG00000041617 |
Ccdc74a |
37.511177 |
0.4554222101 |
-1.134723 |
0.267123616 |
18.280340 |
0.00001906647777945154762706085616041917774055036716163158416748046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000057857979445868598959105272294678457001282367855310440063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.3143281 |
3.9989291 |
53.7040262 |
5.6630824 |
| ENSG00000163050 |
56997 |
COQ8A |
protein_coding |
Q8NI60 |
FUNCTION: Atypical kinase involved in the biosynthesis of coenzyme Q, also named ubiquinone, an essential lipid-soluble electron transporter for aerobic cellular respiration (PubMed:25498144, PubMed:21296186, PubMed:25540914, PubMed:27499294). Its substrate specificity is unclear: does not show any protein kinase activity (PubMed:25498144, PubMed:27499294). Probably acts as a small molecule kinase, possibly a lipid kinase that phosphorylates a prenyl lipid in the ubiquinone biosynthesis pathway, as suggested by its ability to bind coenzyme Q lipid intermediates (PubMed:25498144, PubMed:27499294). Shows an unusual selectivity for binding ADP over ATP (PubMed:25498144). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25498144, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27499294, ECO:0000305|PubMed:21296186, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25540914}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Kinase;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubiquinone biosynthesis |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; ubiquinone biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25498144}. |
This gene encodes a mitochondrial protein similar to yeast ABC1, which functions in an electron-transferring membrane protein complex in the respiratory chain. It is not related to the family of ABC transporter proteins. Expression of this gene is induced by the tumor suppressor p53 and in response to DNA damage, and inhibiting its expression partially suppresses p53-induced apoptosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found; however, their full-length nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56997; |
extrinsic component of mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0031314]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; ubiquinone biosynthetic process [GO:0006744] |
11888884_play an important role in mediating p53-inducible apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. 18319072_CABC1 gene mutations in four ubiquinone-deficient patients in three distinct families were reported. 18319074_Five additional mutations in ADCK3 were found in three patients with sporadic ataxia, including one known to have CoQ10 deficiency in muscle. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22036850_These observations highlight the importance of screening for a potentially treatable cause, CABC1/ADCK3 mutations 25216398_a structural foundation for investigating the role of transmembrane association in regulating the biological activity of ADCK3 25498144_Mitochondrial ADCK3 employs an atypical protein kinase-like fold to enable coenzyme Q biosynthesis. 25540914_work reveals Mg(2+)-dependent ATPase activity of ADCK3, providing strong support for the theoretical prediction of this protein being a functional atypical kinase. 26866375_ADCK3/COQ8 localises to mitochondrial cristae and is targeted to this organelle via the presence of an N-terminal localisation signal 27499294_Loss of COQ8a results in cerebellar ataxia and coenzyme Q deficiency. 30968303_expand the clinical, molecular and biochemical spectrum of ADCK3 related CoQ10 deficiencies 32337771_Clinico-Genetic, Imaging and Molecular Delineation of COQ8A-Ataxia: A Multicenter Study of 59 Patients. 33622667_Photoparoxysmal response in ADCK3 autosomal recessive ataxia: a case report and literature review. |
ENSMUSG00000026489 |
Coq8a |
394.962751 |
0.4182759582 |
-1.257473 |
0.103833929 |
146.592461 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000096343409915923453398859999548285868233385995903146764110098919520174426430055011800763619528309433803769934456795454025268554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000013832964303103405791597947794686053754189284489258358727624092837020426068213658956761874518903709940786939114332199096679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
229.2636830 |
22.6044504 |
551.4204447 |
38.1710203 |
| ENSG00000163053 |
151473 |
SLC16A14 |
protein_coding |
Q7RTX9 |
FUNCTION: Proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter. May catalyze the transport of monocarboxylates across the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in monocarboxylic acid transport. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:151473; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718] |
27364523_Study presented a phylogenetic analysis revealing that Slc16a14 is closely related to Slc16a2, Slc16a9 and Slc16a10; provided a detailed expression analysis of Slc16a14 expression, finding widespread expression in the mouse brain and establishing its expression in neurons and epithelial cells. QRT-PCR on a panel of mouse tissues revealed high Slc16a14 expression in the kidney and moderate levels in the CNS. |
ENSMUSG00000026220 |
Slc16a14 |
9.199372 |
0.3554391424 |
-1.492326 |
0.494088716 |
9.509050 |
0.00204461041975423406594214448261936922790482640266418457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004504918614057694566110701117622738820500671863555908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5541697 |
1.5375215 |
12.8814377 |
2.7384142 |
| ENSG00000163069 |
6443 |
SGCB |
protein_coding |
Q16585 |
FUNCTION: Component of the sarcoglycan complex, a subcomplex of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex which forms a link between the F-actin cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sarcoglycan family. Sarcoglycans are transmembrane components in the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex which help stabilize the muscle fiber membranes and link the muscle cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. Mutations in this gene have been associated with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:6443; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex [GO:0016010]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoglycan complex [GO:0016012]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; vascular associated smooth muscle cell development [GO:0097084] |
12060343_Defective assembly of sarcoglycan complex in patients with beta-sarcoglycan gene mutations 16088906_beta-sarcoglycan and SPATA18 may have a role in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2E 16934466_While the quantity of beta-sarcoglycan was nearly normal in the limb girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD)2E carrier, the levels of dysferlin protein were reduced to 50% of controls in the carriers of LGMD2B. 17036316_These data suggest that formation of the beta-delta-core may promote the export and deposition of sarcoglycan subcomplexes at the plasma membrane, and therefore identifies a mechanism for sarcoglycan transport. 18996010_The limb-girdle muscular dystrophy patients with beta-sarcoglycan deficient LGMD2E do not enable an accurate prediction of the genotype. 25862795_Clinical severity of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2Emay be predicted by SGCB gene mutation and sarcoglycan protein expression. 28687063_This study demonstrated that LGMD2E is the most common type of sarcoglycanopathies in the Iranian population. 35416532_Clinical, genetic profile and disease progression of sarcoglycanopathies in a large cohort from India: high prevalence of SGCB c.544A > C. |
ENSMUSG00000029156 |
Sgcb |
142.096140 |
2.1284826938 |
1.089825 |
0.133240357 |
67.736810 |
0.00000000000000018684253332456946570703763880670825763726165097931841696521360063343308866024017333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001389317779279922113196029387375679565454992397954825378292298410087823867797851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
194.9713969 |
17.0127673 |
92.2774716 |
6.2822931 |
| ENSG00000163126 |
200539 |
ANKRD23 |
protein_coding |
Q86SG2 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the energy metabolism. Could be a molecular link between myofibrillar stretch-induced signaling pathways and muscle gene expression. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene is a member of the muscle ankyrin repeat protein (MARP) family and encodes a protein with four tandem ankyrin-like repeats. The protein is localized to the nucleus, functioning as a transcriptional regulator. Expression of this protein is induced during recovery following starvation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:200539; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; I band [GO:0031674]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; titin binding [GO:0031432]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; regulation of sarcomere organization [GO:0060297]; response to muscle stretch [GO:0035994] |
25125175_Report structure activity relationships for ANKRD23. 31103742_The promise of DARPin-siRNA bioconjugates for tumor targeting. |
ENSMUSG00000067653 |
Ankrd23 |
12.547718 |
0.3336836684 |
-1.583447 |
0.517017485 |
9.302849 |
0.00228797771772168423431992323457961902022361755371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004997122094343305412356137651386234210804104804992675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5698456 |
2.0453604 |
17.0416787 |
4.1768316 |
| ENSG00000163191 |
6282 |
S100A11 |
protein_coding |
P31949 |
FUNCTION: Facilitates the differentiation and the cornification of keratinocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18618420}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in motility, invasion, and tubulin polymerization. Chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in tumor metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6282; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; S100 protein binding [GO:0044548]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA replication [GO:0008156]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11873942_S100C is a new tumor marker protein, the expression of which significantly decreases after malignant transformation of human tissues. 14623863_S100Cis a key mediator of the Ca(2+)-induced growth inhibition of human keratinocytes in culture, and may be mediate growth regulation in vivo as well. 14962086_that redistribution along microtubules is a mechanism whereby S100A11 is positioned at the cell periphery in preparation for transglutaminase-dependent crosslinking. 15051732_PKCalpha-S100C/A11-mediated pathway is involved in and essential for the growth inhibition of normal human keratinocytes cells by TGFbeta1. 15138568_Up-regulation of S100A11 was associated with the development of lymph node metastases in gastric cancer 15241500_Of several tested, only an N-terminal peptide with 19 amino acid residues induces apoptosis in human keratinocyte and squamous-cell carcinoma cell lines 15322223_findings suggest that S100A11 has an anti-apoptotic function and is related to the process of growth of human uterine leiomyoma 15701847_Down-regulation of S100C expression is associated with increasing tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis in bladder cancer patients. 15701847_Down-regulation of S100C is associated with bladder cancer progression 17000675_Expression of S100A11, a putative tumor suppressor gene, is increased in the early stage of pancreatic carcinogenesis and decreased during subsequent progression to cancer. 17476473_S100C/A11-mediated pathway is at least partly involved in conferring upon human squamous cell cancers resistant to TGFbeta-induced growth suppression 17537172_The results indicated that the upregulation of S100A11 expression in non-small cell lung cancer tissues was significantly associated with higher tumor-node-metastasis stage (P = 0.001) and positive lymph node status 17624315_Proteomic mapping using a selective subcellular extraction kit revealed S100A11 as a new member of the S100 protein family modulated by glucocorticoids in keratinocytes. 17932043_Ca(2+)-dependent binding of S100A11 to ANXA1 facilitated the binding of the latter to cPLA(2), resulting in inhibition of cPLA(2) activity 17978094_These findings indicate that S100A11 plays a dual role in growth regulation of epithelial cells. 18340452_These findings suggest S100A11 could be helpful in the pathological study of colorectal cancer, especially for the classification of different stages in colorectal cancer. 18385759_S100/A11 and p21 gene expression was also found to be significantly lower in acute and chronic atopic dermatitis skin. 18463164_S100A11 targets Rad54B to sites of DNA DSB repair sites and has a role in p21-based regulation of cell cycle 18523305_Following transformation by transglutaminase 2, S100A11 acquires the capacity to signal through the p38 MAP kinase pathway, accelerate chondrocyte hypertrophy, and couple inflammation with chondrocyte activation to promote progression of osteoarthritis. 18589612_The expression level of S100C in lung cancer tissue was lower than that in ambient tissue. 18618420_Phosphorylation of S100A11 induces a structural perturbation in the N-terminal edge of helix 1 and enables the phosphoryl group to be exposed to the solvent, allowing it to be recognized by the binding partner, nucleolin. 18694925_These results identify two categories of S100 proteins: those exemplified by S100A4 that exclusively bind to the p53 TET domain; and those exemplified by S100B that additionally bind to the NRD. 19048101_S100A11 differentially expressed in primary hepatocellular carcinoma , primary colorectal, and liver 19577285_Inhibition of S100A11 gene expression impairs the ability of keratinocytes to control vaccinia virus replication via downregulation of IFN-lambda receptor IL-10R2. 20347987_A single phenyl-Sepharose column was sufficient for the purification of human S100A11 whereas HiTrap Q anion exchange followed by phenyl-Sepharose columns were required for the purification of S100A1. 20372844_Data support that S100A11 is a novel diagnostic marker in breast carcinoma. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21139050_S100A11 mediates HIMF-induced smooth muscle cell migration, vesicular exocytosis, and nuclear activation. 21861103_investigated S100A11 expression in various subtypes of lung cancer and explored its role in cell proliferation. 22319637_Using transcriptional signatures of blood samples,identified S100A11 as a potential diagnostic marker of infective endocarditis, and AQP9 as a potential prognostic factor. 22430872_All three markers correlated significantly with regional lymph node metastasis: FXYD3 (p = 0.0110), S100A11 (p = 0.0071), and GSTM3 (p = 0.0173) in colon cancer lymphatic metastasis. 22869607_Endometrial S100A11 is a crucial intermediator in EGF-stimulated embryo adhesion, endometrium receptivity, and immunotolerance via affecting Ca2+ uptake and release from intracellular Ca2+ stores. 22903637_the structure of human calcium-bound S100A11. 23745637_Data suggest that S100A11 is involved in maintenance of p21-CIP1 (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A) protein stability (up-regulation; down-regulation) and appears to function as inhibitor of apoptosis in keratinocytes. 23928665_Our data indicate that S100A11 overexpression exerts a protumoral functional role in papillary thyroid carcinoma pathogenesis. 24376686_The EGFRvIII-STAT3 pathway promotes cell migration and invasion by upregulating S100A11 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 24631019_Proteomic data suggest a limited protein set is involved in SET- (template activating factor-I-) mediated cytotoxicity of TCE (trichloroethylene) in hepatocytes; this set includes CFL1 (cofilin 1), PRDX2 (peroxiredoxin 2), and S100-A11 (calgizzarin). 24806074_metastatic cancer cells have elevated rate of cell injury and they rely on the S100A11-ANXA2 complex to enable cell membrane repair. S100A11 in a complex with Annexin A2 helps reseal the plasma membrane. 26472670_higher S100A11 expression was associated with statistically significant decrease in disease-free survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 26544866_the up-regulation of S100A11 plays a role in tumor progression, particularly in KRAS-mutated lung adenocarcinomas 26574635_S100A11 overexpression correlates with an aggressive malignant phenotype and may constitute a novel prognostic factor for HGSC 27181092_Furthermore, we identify flotillin-1 (FLOT1) and histone H1 as downstream factors for cytoplasmic and nuclear pathway of S100A11, which are required for LASP1-S100A11 axis-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and colorectal cancer progression. 27590262_S100A11 is involved in homologous recombination by regulating the appearance of RAD51 in double strand break repair sites. 28277927_Results show that S100A11 expression is up-regulated by BC200 through stabilizing its mRNA and that S100A11 critically mediates the ability of BC200 RNA to induce cancer cell migration and invasion. 28446208_In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, S100A11 is up-regulated and is associated with inflammation and disease activity. 28513300_we studied S100A11 and noted knockdown of S100A11 using short hairpin RNA, which inhibited proliferation, invasion, and migration of renal carcinoma cells as well as increased expression of E-cadherin and decreased expression of epidermal growth factor receptor/Akt in renal carcinoma cells. Therefore, S100A11 may be a key molecular target for treating renal carcinoma. 28739510_identified as a new regulator of Aldo-induced collagen production in human cardiac fibroblasts. 29569474_Our present study indicated that S100A11 promotes EMT through accumulation of TGF-beta1 expression, and TGF-beta1-induced upregulation of p-SMAD2 and 3. 29922945_findings revealed that S100A11 and TGF-beta1/SMAD4 signaling pathway were related but mutually independent in regulating PANC-1 cells proliferation and apoptosis. 30182496_High S100A11 expression is associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 30455460_this study shows that alarmin S100A11 initiates a chemokine response to the human pathogen Toxoplasma gondii 30684913_The authors report an accumulation of S100A11 protein in the muscle tissue of patients with myositis, particularly in the regenerating and necrotizing muscle fibres. 30850029_our results support the notion that S100A11 secretion induced by PDAC cells initiates a paracrine activation loop through the RAGE-mTOR-p70 S6 kinase-mediated proliferation pathway in adjacent fibroblasts 30963564_Because of the formation of the annexin A1/S100A11 complex. 31046874_our data reveal a novel role of the secretory S100A11 in PDAC disseminative progression through activation of surrounding fibroblasts triggered by the S100A11-RAGE-TPL2-COX2 pathway. The findings of this study will contribute to the establishment of a novel therapeutic antidote to PDACs that are difficult to treat by regulating cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) through targeting the identified pathway 31430050_S100A11 functions as novel oncogene in glioblastoma via S100A11/ANXA2/NF-kappaB positive feedback loop. 31442606_The LINC00997-STAT3-S100A11 axis may promote the development of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. 31856598_Serum S100A6, S100A8, S100A9 and S100A11 proteins in colorectal neoplasia: results of a single centre prospective study. 33075563_S100A11 Promotes Liver Steatosis via FOXO1-Mediated Autophagy and Lipogenesis. 33571540_The S100 calcium-binding protein A11 promotes hepatic steatosis through RAGE-mediated AKT-mTOR signaling. 33727634_S100A11 (calgizzarin) is released via NETosis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and stimulates IL-6 and TNF secretion by neutrophils. 33763485_Serum Levels of S100A11 and MMP-9 in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer and Their Clinical Significance. 33902363_S100A11 Promotes Glioma Cell Proliferation and Predicts Grade-Correlated Unfavorable Prognosis. 34653793_S100A11 regulates nasal epithelial cell remodeling and inflammation in CRSwNPs via the RAGE-mediated AMPK-STAT3 pathway. 34654357_Circular RNA FOXP1 relieves trophoblastic cell dysfunction in recurrent pregnancy loss via the miR-143-3p/S100A11 cascade. 34663163_Tranilast inhibits angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis through S100A11/ transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1)/Smad axis. 35419674_Inhibitory Effect of S100A11 on Airway Smooth Muscle Contraction and Airway Hyperresponsiveness. |
ENSMUSG00000027907 |
S100a11 |
1494.226900 |
3.4142816501 |
1.771582 |
0.044973471 |
1601.307156 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2336.4357855 |
60.6180720 |
689.4066517 |
14.9878845 |
| ENSG00000163220 |
6280 |
S100A9 |
protein_coding |
P06702 |
FUNCTION: S100A9 is a calcium- and zinc-binding protein which plays a prominent role in the regulation of inflammatory processes and immune response (PubMed:12626582, PubMed:15331440, PubMed:20103766, PubMed:8423249, PubMed:16258195, PubMed:19122197, PubMed:21325622). It can induce neutrophil chemotaxis, adhesion, can increase the bactericidal activity of neutrophils by promoting phagocytosis via activation of SYK, PI3K/AKT, and ERK1/2 and can induce degranulation of neutrophils by a MAPK-dependent mechanism (PubMed:12626582, PubMed:15331440, PubMed:20103766). Predominantly found as calprotectin (S100A8/A9) which has a wide plethora of intra- and extracellular functions (PubMed:8423249, PubMed:16258195, PubMed:19122197). The intracellular functions include: facilitating leukocyte arachidonic acid trafficking and metabolism, modulation of the tubulin-dependent cytoskeleton during migration of phagocytes and activation of the neutrophilic NADPH-oxidase (PubMed:15331440, PubMed:21325622). Activates NADPH-oxidase by facilitating the enzyme complex assembly at the cell membrane, transferring arachidonic acid, an essential cofactor, to the enzyme complex and S100A8 contributes to the enzyme assembly by directly binding to NCF2/P67PHOX (PubMed:15642721, PubMed:22808130). The extracellular functions involve pro-inflammatory, antimicrobial, oxidant-scavenging and apoptosis-inducing activities (PubMed:8423249, PubMed:19534726). Its pro-inflammatory activity includes recruitment of leukocytes, promotion of cytokine and chemokine production, and regulation of leukocyte adhesion and migration (PubMed:15598812, PubMed:21487906). Acts as an alarmin or a danger associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule and stimulates innate immune cells via binding to pattern recognition receptors such as Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (AGER) (PubMed:19402754). Binding to TLR4 and AGER activates the MAP-kinase and NF-kappa-B signaling pathways resulting in the amplification of the pro-inflammatory cascade (PubMed:19402754, PubMed:22804476). Has antimicrobial activity towards bacteria and fungi and exerts its antimicrobial activity probably via chelation of Zn(2+) which is essential for microbial growth (PubMed:19087201). Can induce cell death via autophagy and apoptosis and this occurs through the cross-talk of mitochondria and lysosomes via reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the process involves BNIP3 (PubMed:19935772). Can regulate neutrophil number and apoptosis by an anti-apoptotic effect; regulates cell survival via ITGAM/ITGB and TLR4 and a signaling mechanism involving MEK-ERK (PubMed:22363402). Its role as an oxidant scavenger has a protective role in preventing exaggerated tissue damage by scavenging oxidants (PubMed:22489132, PubMed:21912088). Can act as a potent amplifier of inflammation in autoimmunity as well as in cancer development and tumor spread (PubMed:16258195). Has transnitrosylase activity; in oxidatively-modified low-densitity lipoprotein (LDL(ox))-induced S-nitrosylation of GAPDH on 'Cys-247' proposed to transfer the NO moiety from NOS2/iNOS to GAPDH via its own S-nitrosylated Cys-3 (PubMed:25417112). The iNOS-S100A8/A9 transnitrosylase complex is proposed to also direct selective inflammatory stimulus-dependent S-nitrosylation of multiple targets such as ANXA5, EZR, MSN and VIM by recognizing a [IL]-x-C-x-x-[DE] motif (PubMed:25417112). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12626582, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15331440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15598812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15642721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16258195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19087201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19122197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19402754, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19534726, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19935772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20103766, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21325622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21487906, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22363402, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22804476, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22808130, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25417112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8423249, ECO:0000303|PubMed:21912088, ECO:0000303|PubMed:22489132}. |
3D-structure;Antimicrobial;Antioxidant;Apoptosis;Autophagy;Calcium;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;S-nitrosylation;Secreted;Zinc |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in the inhibition of casein kinase and altered expression of this protein is associated with the disease cystic fibrosis. This antimicrobial protein exhibits antifungal and antibacterial activity. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:6280; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; antioxidant activity [GO:0016209]; arachidonic acid binding [GO:0050544]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; RAGE receptor binding [GO:0050786]; Toll-like receptor 4 binding [GO:0035662]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; astrocyte development [GO:0014002]; autocrine signaling [GO:0035425]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; chronic inflammatory response [GO:0002544]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002523]; modulation of process of another organism [GO:0035821]; neutrophil aggregation [GO:0070488]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation [GO:0018119]; peptidyl-cysteine S-trans-nitrosylation [GO:0035606]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; regulation of cytoskeleton organization [GO:0051493]; regulation of integrin biosynthetic process [GO:0045113]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; sequestering of zinc ion [GO:0032119] |
10551823_S100A8/A9 accounts for the entire arachidonic acid-binding capacity of the neutrophil cytosol, indicating that S100A8/A9 plays an essential role in arachidonic acid-dependent enzymes and arachidonic acid-consuming pathways. 11851337_crystal structure of the calcium-bound form, analyzed at 2.1 A resolution 12137245_These data indicate that calprotectin (MRP8 and MRP14) has higher specific activity to induce apoptosis than the individual subunits, and that the mechanism is exclusion of zinc from target cells. 12167632_identifies regulatory elements within the promoter that drive the cell type-specific and differentiation-dependent protein expression 12218151_Proinflammatory myeloid-related protein S100A9 induces a dose- and time-dependent activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat promoter region that can be blocked by specific polyclonal antibody and by physical denaturation of the protein. 12489193_S100A8 and S100A9 calcium-binding proteins: localization within normal and cyclosporin A-induced overgrowth gingiva, in spino-cellular layer and extracellularly in desmosomes, in cytoplasm and nuclei. 12553726_the localization of the arachidonic acid-binding site within the unique C-tail of S100A9 correlates with the fact that fatty acid binding has not yet been reported for other S100 proteins 12626582_S100A9 stimulates shedding of L-selectin, up-regulates and activates Mac-1/CD11b, induces neutrophil adhesion to fibrinogen in vitro, and is involved in neutrophil migration to in vivo inflammatory sites. 12645005_plays a prominent role in leukocyte trafficking and arachidonic acid metabolism; elevated levels of S100A9 and S100A8 in body fluids of inflamed tissues strengthen the view that these molecules are important players in fighting inflammation [review] 12710851_increased levels in fetal disease, premature rupture of membranes, and preterm labor 12719414_MRP8/MRP14 dimer behaves as a positive mediator of phagocyte NADPH oxidase regulation 12748056_Abrogation of MRP-14 activity with a specific antibody reduced the IL-8-stimulating potential of bronchial secretions, suggesting it was a stimulus to IL-8 production in the lung and may amplify neutrophilic inflammation in bronchial disease 12874352_Calprotectin, an antimicrobial peptide with antibacterial activity inhibits the growth of Borrelia burgdorferi. 12937135_MRP8/MRP14 complex inhibited proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts and induced apoptosis via activation of caspase-3 in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Activated macrophages can destroy and regenerate myocytes via MRP8/MRP14. 13130482_Since MRP-8/MRP-14 exhibit direct effects on leukocyte adhesion to the vascular endothelium, their extensive expression in the epidermis indicates an active role for these S-100 proteins in the initial phase of this systemic autoimmune disease. 14654085_protein expression profiles in HL-60 cells with ATRA treatment revealed a protein remarkably expressed in the differentiated cells, which was identified as S100A9 15040889_Results of this study suggest that reduction of MRP14 expression is a frequent event in Chinese human esophageal cancer. 15069705_decreased expression of MRP8 and MRP14 might play an important role in the pathogenesis of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, being particularly associated with poor differentiation of tumor cells. 15075348_S100A8/A9 might induce apoptosis in tumor cells through a dual mechanism: one is zinc exclusion from the target cells, and the other represents an as yet undefined mechanism, possibly in a ligand-receptor dependent fashion. 15277376_Fibronectin adhesive capacity and integrin expression of monocytes of type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients is related to the subjects' serum levels of MRP14. 15598812_expression of MRP8/MRP14 closely correlated with the inflammatory activity in systemic vasculitis 15642721_S100A8/A9 promotes phagocyte NADPH oxidase activation by supplying the enzyme with its cofactor arachidonic acid 15740587_Correlated with degree of differentiation. Absent in undifferentiated basalioma and strongly expressed in carcinoma in situ, keratoacanthoma, and differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Expressed in superficial, differentiated region of normal epithelium. 15905572_MRP-14 is a potential mediator of p38 MAP kinase-dependent functional responses in human neutrophils. 16033829_data suggest that enhanced expression of S100A8, S100A9, and RAGE is an early event in prostate tumorigenesis and may contribute to development and progression or extension of prostate carcinomas 16216873_S100A8 and S100A9 in atherosclerotic plaque and calcifying matrix vesicles may significantly influence redox- and Ca2+-dependent processes during atherogenesis 16253391_This study indicates a potential role for pro-inflammatory S100A9 and S100A12 in pathogenesis caused by inflammation and protein complex formation in Alzheimer's disease 16573830_heterodimeric S100 calcium binding protein A8/S100 calcium binding protein A9 might play a hitherto unknown role in triggering atherosclerosis in diabetes and renal failure 16613612_S100A8/A9 heterodimer, secreted extracellularly from activated tissue macrophages, may amplify proinflammatory cytokine responses in rheumatoid arthritis. 16682612_MRP-14 expression increases before ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), and increasing plasma concentrations of MRP-8/14 among healthy individuals predict the risk of future cardiovascular events. 16690079_calcium-dependent formation of (S100A8/S100A9)2 tetramers is an essential prerequisite for biological function. 16806487_MRP-8/14 was mainly detected in human cervical mucus and showed a positive correlation with proinflammatory cytokines 16979015_MRP-8/MRP-14 are exclusively secreted by granulocytes in patients with acute Kawasaki disease, and intravenous immune globulin treatment suppresses their gene expression. 17050004_Zinc-binding, like calcium, induces (S100A8/S100A9)(2)-tetramers. 17090475_S100A8 and S100A9 are involved in the innate defense of the bronchial epithelium 17095618_Excessive release of cytotoxic MRP8/MRP14 by activated phagocytes might therefore present an important molecular pathomechanism contributing to endothelial damage during vasculitis and other inflammatory diseases 17126494_Authors hypothesize that L1AG might become internalized nonspecifically into target cells, perhaps by pinocytosis. This predicts cell survival of cultured stomach tumor cells as a function of L1AG concentration. 17187679_poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 and Ku70/Ku80 are transcriptional regulators of S100A9 gene expression 17222807_In contrast, neutrophil adhesion to fibronectin was completely inhibited by anti-beta2 integrins, suggesting that S100A9-induced specific activation of beta2 integrin is essential to neutrophil adhesion. 17237603_data suggest unidentified natural ligands for CD69 and/or CD69 autoantibodies possibly affect joint-composing cell types through increased production of S100A9 in neutrophils, providing insight into functions of CD69 on neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis 17328050_The pattern of S100A4 expression differed significantly from that of the proinflammatory proteins S100A9 and S100A12, which were restricted to phagocytes and granulocytes. 17429438_HaCaT keratinocytes overexpressing the S100 proteins S100A8 and S100A9 show increased NADPH oxidase and NF-kappaB activities. 17636430_Report showed S100A9 was expressed human bone and cartilage cells and may contribute to calcification of the cartilage matrix and its replacement with trabecular bone, and to regulation of redox in bone resorption. 17787039_Data suggest that S100 proteins calprotectin and S100A12 are related to radiographic changes rather than disease activity in psoriatic arthritis with low disease activity. 17852869_Serum calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9)and S100A12 are increased in children with inflammatory bowel disease and indicate disease activity. 17895549_MRP8/14 may be involved in the pathogenesis of sarcoid granulomas. The measurement of serum MRP8/14 levels is useful for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. 17936757_The homo-oligomeric forms of S100A8 and S100A9 are readily degraded by proteases, and the preferred hetero-oligomeric S100A8/A9 complex displays a high resistance even against proteinase K degradation. 18044712_presence of a positive feedback loop for growth stimulation involving S100A8/A9 and cytokines in human epidermal keratinocytes 18060880_These data indicate that S100A8/A9-induced cell death involves Bak, selective release of Smac/DIABLO and Omi/HtrA2 from mitochondria, and modulation of the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins. 18339893_S100A8/A9-promoted cell growth occurs through RAGE signaling and activation of NF-kappaB. 18537548_It is suggested that S100A8 is S100A9-dependently expressed and acquires the protein stability by S100A8/A9 heterocomplex formation; S100A8 and S100A9 overexpression should be considered marker of poor prognosis in invasive ductal carcinoma 18588753_S100A9 expression was significantly decreased in CRS without nasal polyps 18689872_RAGE, carboxylated glycans and S100A8/A9 play essential roles in tumor-stromal interactions, leading to inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis. 18784990_analysis of calgranulin B (S100A9) levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with interstitial lung diseases 18786929_annexin A6 contributes to the calcium-dependent cell surface exposition of the membrane associated-S100A8/A9 complex 18803290_S100A9 is gene with moderate CpG-density that show a less stringent relationship between DNA methylation and gene expression 18922970_This study revealed S100A8/A9 genes as candidate markers for metastatic potential of breast epithelial cells. 18927283_Overexpression of S100A9 is associated with barrett's esophagus-associated high-grade dysplasia. 19059406_These data suggested that upregulation of S100A9 mediated by P. gingivalis is an important event in the development of aortic intimal hyperplasia. 19079333_Calprotectin mobilization was listeriolysin O-dependent and required calcium 19087201_Data indicate that both S100A8 and S100A9 are required for their fully active antifungal effect and that oxidation regulates S100A8/A9 antifungal activity through mechanisms that remain to be elucidated and evaluated. 19122197_invasion. Mutations in S100A9 E36Q, E78Q were predicted to cause loss of the calcium-induced positive face in calprotectin, reducing interactions with microtubules and appearing to be crucial for keratinocyte resistance to bacterial invasion. 19142861_L-plastin and S100A9 were differentially expressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and normal nasopharyngeal epithelial tissue 19165585_the rapidly evolving role of Calgranulin B as a biomarker of systemic malignancies 19186948_S100A8 and S100A9 as candidates for serological biomarkers in combination with other serum markers that aid CRC diagnosis. 19201880_S100A9 was induced in human monocytes and macrophages, by polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid, a dsRNA mimetic 19203362_transcript levels of CXCL8, CXCL10, calgranulin B and CXCL2 are correlated to ulcerative colitis severity 19232095_MRP8/14 may be a potentially selective novel biomarker for microcirculatory defects in diabetic nephropathy. 19248102_MRP-8/MRP-14 and IL-1beta represent a novel positive feedback mechanism activating phagocytes via 2 major signaling pathways of innate immunity during the pathogenesis of systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 19284577_Serum S100A9, S100A8 and S100A12 and RAGE levels were associated not just with RA inflammation and autoantibody production but also with classical vascular risk factors for end-organ damage. 19440546_Data suggest a link between bacterial infection, inflammation and amyloid deposition of S100A8/A9 in the prostate gland, such that a self-perpetuating cycle can be triggered and may increase the risk of malignancy in the ageing prostate. 19534726_Down-regulation of the gene S100A9 induces cellular apoptosis that is partly dependent on p53 and the p53 apoptosis pathway. 19601998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19608587_Plasma MRP8/14 levels are associated with paediatric obstructive sleep apnea and may reflect increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity 19670424_S100A8 and S100A9 are novel nuclear factor kappa B target genes during malignant progression of murine and human liver carcinogenesis. 19752232_S100A8/A9 kills Finegolidia magna bacteria of strain 505 via a bactericidal effect, which most likely is a consequence of an interaction of S100A8/9 with the cell membrane, causing lysis of the bacteria. 19755614_Serum levels of S100A8/A9 are significantly raised in SLE versus pSS patients and healthy controls and can be correlated to a disease activity index. 19762566_contributes to bacterial dissemination 19823685_Plasma calprotectin has a role in obesity in individuals without type 2 diabetes 19935772_S100A9-induced cell death involves BNIP3 and increase of ROS production by mitochondria, subsequently followed by mitochondrial damage and lysosomal activation. 19957061_S100A8 and S100A9 have inhibitory effects on the proliferation of CaSki carcinoma cells by inducing cell apoptosis and on the invasiveness of CaSki cells. 20098622_results suggest that S100a9 induced by Abeta or CT contributes to cause inflammation, which then affects the neuropathology including amyloid plaques burden and impairs cognitive function 20103766_S100A9 induces the degranulation of secretory and specific/gelatinase granules but not of azurophilic granules 20130364_S100A9 and NMP238 expression is associated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy sensitivity in cervical carcinoma. 20219570_Results characterize a pathway leading to NOX2 activation in which iPLA(2)-regulated p38 MAPK activity is a key regulator of S100A8/A9 translocation via S100A9 phosphorylation. 20226301_Levels of calprotectin were dramatically increased in polyp tissue of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps 20231196_Serum calprotectin increased in patients with adult-onset Still's disease, in close correlation with disease activity and severity. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20422274_Calgranulin B concentrations were significantly higher in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) than controls; it may be a trigger molecule involved in the evolution and progression of IPF 20550547_Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid MRP14 levels are elevated in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary arcoidosis and are associated with disease severity in sarcoidosis. 20555353_bacterial flagellin induces the upregulation of S100A8/S100A9 via a TLR5-dependent mechanism in epidermal keratinocytes 20594128_Studies indicate that both calprotectin and lactoferrin are markers of inflammatory bowel disease. 20812987_LASP-1, S100A9 and RhoGDI were detected by proteomic analysis to be differentially expressed between normal mucosa, non-metastatic colorectal carcinoma and metastatic CRC tissue 20819668_S100A8, S100A9 was up-regulated in the lung adenocarcinoma and end stage lung cancer tissue, the correlation of their higher expression in inflammatory lung tissues indicate the collaborative effect of inflammation on the progression of cancer. 21067798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21192933_S100A8/A9 is induced in epithelial cells in response to stress 21228116_These results thus reveal a novel role for myeloid-derived S100A8/A9 in activating specific downstream genes associated with tumorigenesis and in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. 21239714_FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis of neutrophils requires the complex formed by S100 calcium-binding protein-A8 and -A9 as the site of interplay between extracellular calcium entry and intraphagosomal reactive oxygen species production. 21325622_S100A9 stimulates neutrophil microbicidal activity mainly by promoting phagocytosis. 21334078_S100A8/A9 complex is a useful biomarker as a predictor for one year mortality and its combination with IL-6 is able to provide additive prognostic information in this vulnerable heart failure population in the elderly. 21369941_Our results suggest that overexpression of S100A9 is associated with a poor prognosis among non-small cell lung cancer patients 21376380_These results demonstrate the critical role of calprotectin in human innate immune defense against Aspergillus infection. 21380506_Increased calprotectin expression is an early step in the neoplastic transformation during colorectal carcinogenesis. 21472666_The cytokine-induced potentiated S100A8 and S100A9 expression under conditions with a high AGE burden is able to aggravate proinflammatory conditions via activation of the RAGE pathway. 21492422_Patients with Systemic lupus erythematosus had increased cell surface S100A8/A9, which could be important in amplification and persistence of inflammation 21592353_Increased serum myeloid-related protein 8/14 level is associated with atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients. 21738950_The increased levels of calprotectin in obesity and obesity-associated type 2 diabetes and its positive association with inflammation suggests a potential role as a chemotactic factor in the recruitment of macrophages to visceral adipose tissue. 21766173_Serum MRP8/14 complex levels might be associated with the severity of renal injury and endothelial cell dysfunction in Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis patients. 21782178_In acute coronary syndromes, MRP8 and MRP8/14 complex are specific ligands of TLR4, which induce the release of TNFalpha and probably other pro-inflammatory agents from monocytes 21791097_S100A8/9 might potentially be a predictive marker for improvement in the total number of swollen joints in patients in the early phase of rheumatoid arthritis 21799753_Cell proteins associated with M1 and M2 macrophages are also expressed by other cell types in the tumour islets and stroma of patients with non-small cell lung cancer 21839816_Data show six differentially expressed proteins were identified as HSP70, PPIA and alpha-Enolase (up-regulated) S100-A9, PIMT and beta-5 tubulin (down-regulated), most of which had been shown to play a potential role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 21912088_current understanding of the pro- and anti-tumorigenic functions of S100A8 and S100A9. 22029973_Of inflammatory markers, calprotectin has the highest correlation coefficients with total synovitis and Doppler ultrasonography scores, as well as for evaluation of calprotectin responsiveness compared to other inflammatory markers. 22074005_Aimed to discover markers of drug resistance in breast cancer before neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Found FKBP4 and S100A9 might be putative prediction markers in discriminating the drug resistant group from the drug sensitive group of breast cancer patients. 22093455_Fecal calprotectin concentrations serve as a screening tool for hepatic encephalopathy and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis. 22127564_Alarmins S100A8 and S100A9 elicit a catabolic effect in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes that is dependent on Toll-like receptor 4. 22209981_Involvement of the danger molecule S100A8/A9 in the resistance against viruses. 22230807_the expansion and activation of low density granulocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus seems to underlie this prominent S100A9 signature. 22253789_Biliary S100A9 levels may be a useful marker for primary sclerosing cholangitis activity. 22282267_Elevated S100A9 expression causes glucocorticoid resistance in MLL-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 22304731_S100A9 staining in combination with anti-CD14 could be used to identify myeloid-derived suppressor cells in whole blood from colon cancer patients, who had an increase in the population of these cells. 22318783_sustained activation of S100A8/A9 critically contributes to the development of post-ischemic heart failure (HF) driving the progressive course of HF through activation of RAGE. 22363402_S100 A8/9 complex regulates cell survival via a signaling mechanism involving MEK-ERK via TLR4. 22446997_Patients presenting with MI had elevated levels of serum MRP-8/14 compared to patients with non-cardiac chest pain. However, overall diagnostic performance of MRP-8/14 was poor. 22457725_demonstrate that the pro-inflammatory protein S100A9 interacts with the Abeta1-40 peptide and promotes the formation of fibrillar beta-amyloid structures 22505354_identified hypoxia and HIF-1 as novel regulators of S100A8/A9 expression in prostate cancer. S100A9 might be useful as prognostic marker for prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy 22555971_Fecal calprotectin and alpha(1)-AT levels at the time of diagnosis are predictive for responses to treatment but are not diagnostic markers for initial stage 1 to 3 gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. 22583932_TP-alpha, collagen alpha-1(VI) chain and S100A9 are potential biomarkers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and may play an important role in tumorigenesis and development of ESCC. 22622474_Elevated levels of S100A9 is associated with increased aggressiveness in breast cancer. 22634002_The upregulation of S100A8/A9 in tumor-infiltrated myeloid cells could be triggered by IL-6 and IL-8 released from myofibroblasts. 22660800_The data suggest that serum S100A8/A9 may be a useful biomarker for evaluating disease activity in patients with adult-onset Still's disease. 22683330_the upregulated production of S100A8 and S100A9 by psoriatic epidermal keratinocytes activated adjacent keratinocytes to produce several cytokines. 22691358_The expression of S100A9 significantly increases in the serum and tissues of patients with breast cancer, which indicates that S100A9 may function as a marker of diagnosis and treatment effect in breast cancer. 22699162_The 3-year survival rate is significantly lower in Chinese peritoneal dialysis patients with higher MRP8/14 levels. 22804476_S100A9 induced stronger NF-kappaB activation albeit weaker cytokine secretion than LPS, suggesting that S100A9 and LPS activated NF-kappaB in a qualitatively distinct manner 22822112_Circulating and urinary concentrations of calprotectin are linked to chronic low-grade inflammation and insulin resistance beyond obesity. 22838504_Our results suggested S100A9-positive inflammatory cells in gastric cancer tissues are associated with early stage of gastric cancer and good prognosis. 22864818_Knocking down galectin-7 or S100A9 enhanced tumor cell invasion. 22962574_Elevated S100A9 expression in colonic epithelial cells mediated by an IL-6/STAT3 signaling cascade may play an important role in the development of colitis. 23018243_these findings suggest that S100A8 and S100A9 are negative regulators of lymph node metastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma and can be used as biomarkers for prediction of lymph node metastasis in gastric adenocarcinoma. 23029420_Plasma levels of FLT and S100A9 proteins are up-regulated and CNDP1 levels are down-regulated in patients with glioblastoma. 23135911_our results establish EMMPRIN as a receptor for S100A9 23165982_As(III) enhanced S100A8 and S100A9 expression in human-derived cells, and As(III)-induced S100A9 expression is dependent on Nrf2 activation. 23194008_Data indicate that the fecal calprotectin (fCAL) levels of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients are higher than the fCAL levels of controls. 23207880_This study identified for the first time genotype-related alterations in gene expression and circulating levels of S100A9, which were associated with insulin sensitivity and the risk of type 2 diabetes. 23223301_Mrp14 promotes APP processing and Amyloid beta accumulation under neuroinflammatory conditions. 23248262_S100A8/A9, produced by myeloid-derived suppressor cells, plays a role in myeloid-derived suppressor cells activation in gastric cancer patients, identifying S100A8/A9 as a potential target for gastric cancer treatment. 23299480_Our study demonstrated a dual role for MRP8/14 in bacterial keratitis. 23320892_Levels of S100A8/A9 and sIL-2R, but not ACE or lysozyme, are elevated in the serum of patients with Hidradenitis suppurativa. 23340902_expression of RAGE and its ligand (S100A9) in cervical lesions 23354417_S100A9 increased the phosphorylation of p38 and ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinases in HepG2 cells. 23378728_In inflamed limbal tissues, expression of S100 A4,8,9 and B proteins is dramatically decreased. 23423260_Serum calprotectin (s100A8/S100A9)is a potential disease biomarker in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis and glomerulonephritis, and may have a role in disease pathogenesis. 23426492_The influence of immunosuppressive drugs on S100A8/A9-RAGE mRNA expression may suggest a role of these proteins in early-stage SCC development in immunosuppressed patients 23431180_The S100A8/S100A9 heterodimer calprotectin (CP) functions in the host response to pathogens through a mechanism termed 'nutritional immunity.' CP binds Mn(2+) and Zn(2+) with high affinity and starves bacteria of these essential nutrients. 23456298_S100A8/A9 promotes cell migration and invasion through p38 MAPKdependent NF-kappaB activation leading to an increase of MMP2 and MMP12 in gastric cancer. 23563247_IL-1alpha is strongly suggested to increase S100A9 expression in a human epidermal keratinocyte cell line by signaling through the IL-1 receptor and p38 MAPK, increasing C/EBPbeta-dependent transcriptional activity 23626736_S100A9 protein is extremely unstable but can be rescued upon co-expression with S100A8 protein or inflammatory stimuli, via proteolytically resistant homodimer formation. 23637971_S100A8 and S100A9 are linked to the colorectal cancer progression. 23664529_Activation of BANF1 possibly suppresses S100A9 expression and inactivates c-Jun, resulting in suppression of cutaneous inflammation 23667563_S100A9 and S100A4 appears to be expressed in distinct CD11b+ cell populations in vivo; thus their interaction would likely be in the extracellular space. 23806524_MAC387 and desmoglein-3 are reliable diagnostic markers for supporting the morphologic impression of squamous differentiation in urinary bladder carcinoma. 23836528_Taken together, these results indicate that the tumorigenesis potential of CSCs arises from highly expressed S100A9. 23850136_Data suggest that expression of S100A8 and S100A9 mRNA and protein is up-regulated in endometrial decidua of patients with recurrent early pregnancy loss as compared to controls suggesting roles of these proteins in pregnancy maintenance/failure. 23868055_Expression of S100A9 and CCTgamma was significantly elevated in liver tissue of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with controls. 23874958_S100A8/A9 (calprotectin) negatively regulates G2/M cell cycle progression and growth of squamous cell carcinoma. 23883959_High fecal calprotectin levels are associated with relapse in patients with ulcerative colitis receiving infliximab maintenance therapy. 23907944_A study of expression of S100 proteins in gallbladder mucosa of the patients with calculous cholecystitis indicated close relationship between S100A8 and S100A9 proteins in their proinflammatory functions. 23915068_calgranulin A and B distinguish borderline and malignant ovarian tumors from benign tumors 23942785_associated with cardiovascular disease in patients with inactive systemic lupus erythematosus 23954397_Studies indicate that RAGE and Toll-like receptor (TLR) share several common ligands including HMGB1, the S100A8/A9 heterodimeric protein complex and LPS. 23977231_S100A8 and S100A9 regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome and enhance the inflammatory response by inducing cytokine secretion of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 24041228_S100A8 and S100A9 appear to suppress breast cancer malignancy through an increase in mesenchymal to epithelial transitioning. 24054362_S100A9 in sputum may be a biomarker of neutrophilic inflammation in severe uncontrolled asthma. 24064546_Overexpression of S100A9 is associated with glioma 24077667_The aim was to study fecal MMP-9 and HBD-2 in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease to compare their performance to calprotectin and to study whether they would provide additional value in categorizing patients according to their disease subtype. 24122301_These data demonstrate for the first time that S100A8/A9 expression in epithelial cancer cells causes enhanced infiltration of immune cells, especially neutrophils, and stimulates settlement of the cancer cells in the lung. 24128654_Data suggest that calprotectin content of neither maternal nor infant feces (a marker for intestinal inflammation) is affected by diet (here, maternal consumption of salmon or methods of infant feeding, breastfeeding versus infant formula). 24144106_Milk beta2-microglobulin and S100A9 are host factors that are found to be associated with mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1. 24156302_These data show that S100A9 protein, through ligation with CD85j, can stimulate the anti-HIV-1 activity of NK cells. 24175291_activity. The aim of the current review is to summarize the latest findings concerning the role of Calprotectin in a diverse range of inflammatory and noninflammatory conditions among children 24177755_S100A8/A9 at low concentrations promoted metastasis and invasion of breast cancer cells and RAGE was required for cell metastasis and invasion mediated by S100A8/A9. 24202303_Study supports the value of S100A8/A9 as a potentially important link between neutrophils, traditional cardiovascular risk factors, and CV disease. 24231443_MRP8/14 can activate cells by binding to TLR4, leading to the release of proinflammatory cytokines. These mediators can lead to increased disease activity in enthesitis-related arthritis. 24245608_The results from analytical size-exclusion chromatography, Mn(II) competition titrations, and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy establish that the C-terminal tail is essential for high-affinity Mn(II) coordination by calprotectin in solution. 24262203_It si one of the amyloid-associated proteins, is known to play an important role in the biological responses to vascular injuries by promoting leukocyte recruitment and in the damaged vessels with deposition of Ab amyloid fibrils 24286299_Data suggest that tissue infiltrating macrophages secreting MRP8/14 may contribute to myositis, by driving the local production of cytokines directly from muscle. 24326364_Data indicate that moderate or high expression of S100A8 or S100A9 proteins was associated with a median disease recurrence-free survival. 24439044_We focus on the S100A8 and S100A9 which are involved in the regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis and inflammation related to ocular surface diseases such as dry eye, meibomian gland dysfunction, pterygium, and corneal neovascularization. 24461178_Serum levels of MRP-8/MRP-14 complex were positively correlated with the number of endothelial cells in the circulation (r=0.69, P |
ENSMUSG00000096621+ENSMUSG00000056071 |
Gm5849+S100a9 |
119.526566 |
2.4909114148 |
1.316674 |
0.156662648 |
71.583035 |
0.00000000000000002658324495338382714306209710342130050085178469916526861061001341113296803086996078491210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000206727447582689829607039681412584987495894387767546296341691913767135702073574066162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
172.7169725 |
15.7689495 |
69.8199194 |
5.1124202 |
| ENSG00000163221 |
6283 |
S100A12 |
protein_coding |
P80511 |
FUNCTION: S100A12 is a calcium-, zinc- and copper-binding protein which plays a prominent role in the regulation of inflammatory processes and immune response. Its pro-inflammatory activity involves recruitment of leukocytes, promotion of cytokine and chemokine production, and regulation of leukocyte adhesion and migration. Acts as an alarmin or a danger associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule and stimulates innate immune cells via binding to receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (AGER). Binding to AGER activates the MAP-kinase and NF-kappa-B signaling pathways leading to production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and up-regulation of cell adhesion molecules ICAM1 and VCAM1. Acts as a monocyte and mast cell chemoattractant. Can stimulate mast cell degranulation and activation which generates chemokines, histamine and cytokines inducing further leukocyte recruitment to the sites of inflammation. Can inhibit the activity of matrix metalloproteinases; MMP2, MMP3 and MMP9 by chelating Zn(2+) from their active sites. Possesses filariacidal and filariastatic activity. Calcitermin possesses antifungal activity against C.albicans and is also active against E.coli and P.aeruginosa but not L.monocytogenes and S.aureus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11522286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17208591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18292089, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19386136}. |
3D-structure;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Calcium;Cell membrane;Copper;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Fungicide;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein is proposed to be involved in specific calcium-dependent signal transduction pathways and its regulatory effect on cytoskeletal components may modulate various neutrophil activities. The protein includes an antimicrobial peptide which has antibacterial activity. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:6283; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RAGE receptor binding [GO:0050786]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; mast cell activation [GO:0045576]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
11522286_The antimicrobial peptide calcitermin was isolated from human airway secretions and targets Gram-negative bacteria. 11884208_Circulating CGRP in fulminant hepatic failure seems to reflect hemodynamic changes in the systemic rather than in the cerebral circulation. 11884210_Deficiency of CGRP in Familial Dysautonomia patients may explain some of their symptoms. 12218151_Proinflammatory myeloid-related protein S100A12 induces a dose- and time-dependent activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat promoter region that can be blocked by specific polyclonal antibody and by physical denaturation of the protein. 12697438_S100A12 induces inflammatory activation of endothelial cells [review]. 12699958_S100A12 is highly expressed and shows a close correlation with disease activity in a systemic human vasculitis (Kawasaki disease). 12740341_S100A12 is highly expressed in inflammatory bowel disease and down-regulated by anti-TNF therapy. Secretion of S100A12 is induced by TNF. 15077313_Serum concentrations of S100A12 are useful markers for monitoring disease activity in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. 16253391_This study indicates a potential role for pro-inflammatory S100A9 and S100A12 in pathogenesis caused by inflammation and protein complex formation in Alzheimer's disease 16804393_Fecal S100A12 is expressed in feces of children with Crohn's disease 16864903_the function of S100A12 is suppressed by olopatadine in THP-1 monocytes 17158877_Ca2+ binding creates two symmetric hydrophobic surfaces on Ca2+-calgranulin C that allow calgranulin C to bind to the C-type immunoglobulin domain of the receptor for advanced glycation products (RAGE). 17328050_The pattern of S100A4 expression differed significantly from that of the proinflammatory proteins S100A9 and S100A12, which were restricted to phagocytes and granulocytes. 17787039_Data suggest that S100 proteins calprotectin and S100A12 are related to radiographic changes rather than disease activity in psoriatic arthritis with low disease activity. 17852869_Serum calprotectin and S100A12 are increased in children with inflammatory bowel disease and indicate disease activity. 18050248_Calculating the S100A12:sRAGE ratio might help to detect patients with KD who are at risk of being unresponsive to IVIG therapy. 18257809_These results suggest that S100A12 may be a sensitive marker of subclinical inflammation and that an increased S100A12 level may be related to the high peritoneal solute transport rate 18292089_Mast cell and monocyte recruitment by S100A12 18346834_thermodynamic study of the recombinant S100A12 using circular dichroism, fluorescence and isothermal titration calorimetry 18443896_Human S100A12 is markedly overexpressed in inflammatory compartments, and elevated serum levels of S100A12 are found in patients suffering from various inflammatory, neurodegenerative, metabolic, and neoplastic disorders. 18663285_S100A12 protein is involved in the acceleration of atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients 19201044_treatment of THP-1 cells with 100 microg of CRP/ml/10(6) cells for 24 h, augmented the expression of RAGE and EN-RAGE genes 19284577_Serum S100A9, S100A8 and S100A12 and RAGE levels were associated not just with RA inflammation and autoantibody production but also with classical vascular risk factors for end-organ damage. 19386136_Oligomerization and target recognition by S100A12 is regulated by zinc and calcium. A potential role of calcium-binding S100 proteins in zinc metabolism and, in particular, the role of S100A12 in the cross talk between zinc and calcium in cell signaling. 19501594_The zinc complex structure shows significant differences from those of both calcium-loaded and apo-S100A12 structures, and comparisons suggest an explanation for the zinc-induced 1500-fold increase in calcium affinity. 19530996_increased expression in sera, synovial tissues and in PBMC of rheumatoid arthritis patients 19542470_S100A12 may represent a new marker of atheroma and may protect advanced atherosclerotic lesions from rupture by inhibiting excessive matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 colocalized in dimeric zinc-dependent S100A12 complexes. 19576587_Report increased expression of RAGE and EN-RAGE in non-diabetic pre-mature coronary artery disease. 19875725_S100A12 expression is sufficient to activate pathogenic pathways through the modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation and vascular remodeling in vivo. 20025991_study demonstrates that besides RAGE also scavenger receptors contribute to distribution, tissue association and elimination of circulating proinflammatory S100A12 20437698_Data suggest that increased S100A12 levels may point to synovial inflammation of the temporomandibular joint in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 20461025_Data suggest that the S100A12 expression on circulating endothelial cells may be involved in the development of coronary artery lesions in children with Kawasaki disease. 20512925_carboxylated N-glycans on RAGE enhance binding potential and promote receptor clustering and subsequent signaling events following oligomeric S100A12 binding. 20537326_expression increased in endometriotic cells 20847094_Circulating S100A12 and soluble RAGE are both elevated in hemodialysis patients. However, only S100A12 associates with mortality, partly explained by its links with inflammation. 20966394_Vascular smooth muscle S100A12 accelerates atherosclerosis and augments atherosclerosis-triggered osteogenesis, reminiscent of features associated with plaque instability. 21067798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21258041_plasma S100A12 protein level is strongly associated with the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients. 21418345_Transgenic expression of S100A12 in the lung of mice does not exacerbate lung inflammation in a model of OVA-induced allergic inflammation. 21724696_Levels of serum RAGE are reduced in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and correlate negatively with disease activity and S100A12 levels. 21822023_Although S100A12 levels are not elevated in patients with decreased kidney function, a relation to markers of inflammatory disease is found. 21906738_Suggest that elevated plasma EN-RAGE and decreased sRAGE level could play a crucial role in systemic inflammation and carotid atherosclerosis in peritoneal dialysis patients. 22549347_Significant relationship was found between MMP9 and HMGB1 and EN-RAGE in diabetic patients. 22609404_these data indicate the possible involvement of S100A12 in the development of osteoarthritis by up-regulating MMP-13 and VEGF via p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. 22786469_S100A12 could be a novel biomarker for predicting cardiovascular events for predicting MACE in patients with stable CAD. 22796048_Fecal S100A12 levels were significantly higher in patients with severe necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) at onset of disease and also, in contrast to fecal calprotectin, at 4-10 days before onset of NEC compared with unaffected reference infants. 22818064_Data indicate that S100A12 is up-regulated in Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Dissection (TAAD) and may contribute to the pathogenesis of TAAD by initiating apoptosis of SMC, at least in part via increased oxidative stress. 23171632_Data indicate that resistin, S100A12 and soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products (sRAGE) are involved in the pathophysiology of Kawasaki disease (KD). 23324110_The results indicate that plasma S100A12 level is an independent predictor for two-year all-cause mortality. A simple integer scoring system was therefore established for predicting mortality on the basis of plasma S100A12 levels. 23377171_High S100A12 expression is associated with intestinal inflammation and relapse in inflammatory bowel disease. 23398829_EN-RAGE inflammatory ligand has an increased expression in Takayasu's arteritis patients. 23609464_High S100A12 levels are associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 23921255_Excessive expression of the S100A12 gene in uremic leukocytes is relevant to its increased serum concentration, particularly in those affected with cardiovascular disease. 23942785_associated with cardiovascular disease in patients with inactive systemic lupus erythematosus 24307989_S100A12 and hBD2 correlate with the fecal microbiota thus linking the intestinal innate immune response to the bacterial colonization. 24341566_Serum S100A12 concentrations are correlated with angiographic coronary lesion complexity in patients with coronary artery disease. 24378957_Correlation of human S100A12 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein as gingival crevicular fluid and serum markers of inflammation in chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. 24622086_Data indicate that the plasma levels of S100A9, S100A8, and S100A12 were elevated in acute pancreatitis but a definitive difference between the severe and mild forms of the disease. 24691129_Suggest that an elevated S100A12 level could play a crucial role in systemic inflammation and may be a promising biomarker for predicting perioperative complications in patients with thoracic aortic dissection. 24887223_S100A12 is associated with duration of cardiopulmonary bypass, pulmonary inflammation, hypoxia and prolonged mechanical ventilation and may contribute to acute lung injury in cardiac surgery patients. 24944024_Using a computational approach, the study investigated the modulation of protein structure by different ions in the solution, at different ionic strengths. 24975020_these data reveal the capacity of these three S100 proteins to induce MUC5AC production in airway epithelial cells, suggesting that they all serve as key mediators linking neutrophil-dominant airway inflammation to mucin hyperproduction. 25282581_The S100A12 protein was significantly associated with synovitis score in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 25302747_Worse overall survival of OPSCC patients with simultaneous reduction of S100A8 and S100A12 expression. 25313445_S100A12 might participate in the damage of biliary epithelial cells and hepatocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis. 25341801_highlight EN-RAGE as an inflammatory marker for future coronary heart disease (CHD) in a general population, beyond traditional CHD risk factors and inflammatory markers 25438075_S100A12 is a biomarker of chronic heart failure that may also predict major cardiovascular events in patients with chronic heart failure. 25625487_High serum S100A12 expression is associated with poor response to therapy in Crohn's disease. 25650963_These findings suggested that S100A12 is an effective marker for inflammatory diseases. 25825217_serum level elevated in acute liver failure 25854354_High mRNA expression of S100A12 is associated with bladder transitional cell carcinoma. 25964473_These assays showed that S100A12 is induced in response to Helicobacter pylori infection and inhibits bacterial growth and viability in vitro by binding nutrient zinc. 26274928_This is the first kinetics study of levels of RAGE main isoforms and ligands during ARDS. Elevated sRAGE, HMGB1 and S100A12, with decreased esRAGE and AGEs, were found to distinguish patients with ARDS from those without. 26333514_Among the investigated S100-proteins, S100A12 showed the closest association with disease activity and therapeutic response and might therefore provide a valuable biomarker for psoriasis 26339162_Our findings indicate that chitotriosidase and S10012A are useful in diagnosis and detection of subclinical inflammation and/or assessment of disease activity in FMF patients. 26638166_the expression of S100A12 protein and mRNA was downregulated in a large number of clinical samples of GC. Low expression of S100A12 exhibited a marked propensity toward the clinicopathologic features such as tumor size, depth of invasion, TNM stage, Lauren classification, tumor cell differentiation, and poor survival in GC patients. 26767827_Serum S100A12 was significantly higher in rheumatoid arthritis patients than controls, and was correlated with disease activity. 26914918_an elevated serum level of S100A12 was an independent determinant of the progression of abdominal aortic calcification determined by lateral lumbar X-ray in Hemodialysis patients. 27057553_Findings suggest that S100 proteins S100A12 and S100A8/A9 are secreted independently either via distinct mechanisms of secretion or following the activation of different signal transduction pathways. 27355424_These data suggest that S100A12 is part of an innate and adaptive inducible antimicrobial network that contributes to host defense against mycobacteria in infected macrophages 27539060_S100A12 was a significant predictor of lung alveolar infiltration (OR 2.60, 95%CI 1.35-5.00, p = 0.004). These results suggest that S100A12 has the potential to assess the extent of alveolar infiltration in Pulmonary tuberculosis. 27598566_The binding interface between S100A12 and the V domain of RAGE has been identified and mapped. 27689623_serum levels had significant, positive correlations with intensive care unit length of stay, 28-day mortality, and in-hospital mortality after major abdominal surgery 27734162_S100A12 binds to CD36 in the low nanomolar range at the CD36 thrombospondin-1 binding site. 27840235_S100A12 functions as a proinflammatory cytokine and activates dermal fibroblasts, causing dermal fibrosis 28110121_data on the antimicrobial activity of S100A12 have been reported. Proinflammatory role of S100A12 is supported by another newly found receptor, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). 28125622_Expression of S100A8, S100A9 and S100A12 is modulated by eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid during Inflammation in adipose tissue and mononuclear cells. 28381820_S100A9 and S100A12 may have a role in the pathogenesis of pneumonia: S100A9 and CXCL1 may contribute solely in mild pneumonia, and CCL5 and CXCL11 may contribute in severe pneumonia. 28735301_Report role of fecal S100A12 assay in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease. 28756107_S100A12-CD36 axis: A novel player in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis? 28816402_Results indicated that S100A12 could increase the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in HASMCs via activation of ERK1/2 signal pathway, which leads to injury of HASMCs. 28834384_The results suggest that S100A12 does not participate in the induction of inflammation in dental pulp. However, RAGE can participate in the inflammation in the pulp of males. 28964306_Elevated S100A8 and S100A9 gene expression in SP-infected HMEECs and in the middle ear mucosa of OM, minor co-localized with neutrophil markers suggests that middle ear epithelial cell secretion of S100A8 and S100A9 may play a role in the pathogenesis of recurrent and chronic OM 29080693_The aim of this mini-review was to outline the pleiotropic actions of S100A12 and to highlight the potential clinical importance of this protein in kidney and cardiovascular diseases. [review] 29902210_Used fluorescence and NMR spectroscopy to analyze the interaction of S100A9 with S100A12. Binary complex models of S100A9-S100A12 were developed using data obtained from 1H-15N HSQC NMR titrations and the HADDOCK program; overlaid the complex models of S100A9-S100A12 with the same orientation of S100A9 and the RAGE V-domain. Complex showed that S100A12 protein blocks the interaction between S100A9 and the RAGE V-domain. 29906464_S100A12 activates NLPR3 inflammasomes to induce MUC5AC production in airway epithelial cells. ATP induces MUC5AC production in a mechanistically similar mode to S100A12. 29943619_S100A12 is differentially expressed in chronic rhinosinusitis subtypes and is significantly elevated in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and associated with chronic rhinosinusitis-specific disease severity 29944393_High S100A12 expression due to DNA hypermethylation is associated with inflammation in cystic fibrosis. 30235276_the direct effects of S100A12 on human osteoclasts in vitro, were examined. 30406853_In the active phase, S100A12 levels were significantly higher in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and familial Mediterranean fever compared with those with Blau syndrome. 30426025_serum S100A12 levels were higher in juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients 30447136_In its role as a highly expressed mediator of sterile inflammation in Kawasaki disease, S100A12 appears to activate human coronary artery endothelial cells in an IL-1beta-dependent manner. These data provide new mechanistic insights into the contributions of S100A12 and IL-1beta to disease pathogenesis. 30563403_Evaluation of the S100 protein A12 as a biomarker of neonatal sepsis. 30594066_mRNA expression of TLR4 and its ligand S100A8, S100A9, and S100A12 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of Takayasu arteritis patients was higher as compared to healthy controls. 30957488_Ca(2+) binding to S100A12's EF-hand motifs and Zn(2+) binding to its dimeric interface cooperate to induce reversible self-assembly of S100 calcium binding protein A12 (S100A12). 31035738_Investigated association of serum S100 calcium binding protein A12 (S100A12) and S100 calcium binding protein B (S100B) levels with the presence and severity of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and the possibility that these proteins might be useful biomarkers in diagnosing and classifying severity of OSA. 31199706_MiR-30a Regulates S100A12-induced Retinal Microglial Activation and Inflammation by Targeting NLRP3. 31666644_High plasma level of S100A8/S100A9 and S100A12 at admission indicates a higher risk of death in septic shock patients. 31818258_Serum S100A12 is elevated and reflects disease severity in the tuberculosis patients with diabetes. 31865833_Serum S100A12 levels are correlated with clinical severity in patients with dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. 32015423_S100A12 is a promising biomarker in papillary thyroid cancer. 32082330_S100A12 Expression Is Modulated During Monocyte Differentiation and Reflects Periodontitis Severity. 32228516_Downregulation of S100 calcium binding protein A12 inhibits the growth of glioma cells. 32514673_Impact of chorioamnionitis on maternal and fetal levels of proinflammatory S100A12. 32582175_Epigenetic Regulation of S100A9 and S100A12 Expression in Monocyte-Macrophage System in Hyperglycemic Conditions. 32723832_Urine and serum S100A8/A9 and S100A12 associate with active lupus nephritis and may predict response to rituximab treatment. 33068321_Serum S100A12 levels: Possible association with skin sclerosis and interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. 33259383_Higher salivary expression of S100A12 in patients with ulcerative colitis and chronic periodontitis. 33469045_Tumour inflammation signature and expression of S100A12 and HLA class I improve survival in HPV-negative hypopharyngeal cancer. 33576586_Evaluation of S100A12 protein levels in children with familial Mediterranean fever 34108608_A single transcript for the prognosis of disease severity in COVID-19 patients. 34514516_Fecal S100A12 in Takayasu arteritis predicts disease activity and intestinal involvement. 34745092_Associations of Serum S100A12 With Severity and Prognosis in Patients With Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Prospective Cohort Study. 35016442_Study on the relationship between the expression of S100A12, CaSR, and IL-7R in the synovium of knee osteoarthritis and angiogenesis. 35140322_Evaluation of S100A12 and Apo-A1 plasma level potency in untreated new relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients and their family members. 35938962_S100 calcium-binding protein A12 knockdown ameliorates hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced inflammation and apoptosis in human cardiomyocytes by regulating caspase-4-mediated non-classical pyroptosis. 36062187_Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Role of S100A12 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Biomarker in Acute Myocardial Infarction. |
|
|
7.694353 |
7.8535983357 |
2.973354 |
0.697028160 |
21.872491 |
0.00000291381161390951480083619934413619034785369876772165298461914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009756773915903911047393416711148717013202258385717868804931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.0863978 |
6.4028802 |
1.7915776 |
0.7365261 |
| ENSG00000163346 |
57326 |
PBXIP1 |
protein_coding |
Q96AQ6 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factors (BPXs) function. Inhibits the binding of PBX1-HOX complex to DNA and blocks the transcriptional activity of E2A-PBX1. Tethers estrogen receptor-alpha (ESR1) to microtubules and allows them to influence estrogen receptors-alpha signaling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10825160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12360403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17043237}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene interacts with the PBX1 homeodomain protein, inhibiting its transcriptional activation potential by preventing its binding to DNA. The encoded protein, which is primarily cytosolic but can shuttle to the nucleus, also can interact with estrogen receptors alpha and beta and promote the proliferation of breast cancer, brain tumors, and lung cancer. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. More variants exist, but their full-length natures have yet to be determined. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:57326; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; articular cartilage development [GO:0061975]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; gene expression involved in extracellular matrix organization [GO:1901148]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; histone H3-K56 acetylation [GO:0097043]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of chondrocyte proliferation [GO:1902732]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; production of molecular mediator involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002532]; regulation of Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:2001106] |
22187427_HPIP is a target of GATA1 and CTCF in erythroid cells and plays an important role in erythroid differentiation by modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway 24038948_These data highlight the important role of HPIP in liver cancer cell growth and suggest that HPIP may be a good target for liver cancer therapy. 24470547_PBXIP1 is a novel protein overexpressed in astrocytoma and ependymoma, involved in tumor cell proliferation and migration 25060351_HPIP may play critical role in oral carcinogenesis and is potential target for anticancer therapy, with particular emphasis on its involvement in differentiation and migration/metastasis. 26497366_Copy number variations in PBXIP1 gene is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 26590606_our findings identified HPIP plays an important role in the progression and EMT of spinal glioblastoma, by which cell growth is improved. Thus, HPIP gene or protein could act as a useful target in the clinical practice. 27178820_Knockdown of HPIP suppressed TGF-beta1-induced EMT. 27748944_HPIP promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation through positive regulation of cap-dependent translation. 32131934_HPIP is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tissue. Knockdown of HPIP promotes the apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation and G0/G1 to S transition of PDAC cells. |
ENSMUSG00000042613 |
Pbxip1 |
603.979857 |
0.4490912081 |
-1.154920 |
0.082474851 |
196.116668 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000001469949714442795853318929704364108394966436693445061288957567521575187764275672985405825671966837542005613610307090260986839780343871098011732101440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000273255135833446667143092025967065709258724812221116856145642322607641452735182012603361381497919279308769286611704996126093192287953570485115051269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
382.1897974 |
19.2663404 |
857.0630784 |
29.1204878 |
| ENSG00000163347 |
9076 |
CLDN1 |
protein_coding |
O95832 |
FUNCTION: Claudins function as major constituents of the tight junction complexes that regulate the permeability of epithelia. While some claudin family members play essential roles in the formation of impermeable barriers, others mediate the permeability to ions and small molecules. Often, several claudin family members are coexpressed and interact with each other, and this determines the overall permeability. CLDN1 is required to prevent the paracellular diffusion of small molecules through tight junctions in the epidermis and is required for the normal barrier function of the skin. Required for normal water homeostasis and to prevent excessive water loss through the skin, probably via an indirect effect on the expression levels of other proteins, since CLDN1 itself seems to be dispensable for water barrier formation in keratinocyte tight junctions (PubMed:23407391). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23407391}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a co-receptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in hepatocytes (PubMed:17325668, PubMed:20375010, PubMed:24038151). Associates with CD81 and the CLDN1-CD81 receptor complex is essential for HCV entry into host cell (PubMed:20375010). Acts as a receptor for dengue virus (PubMed:24074594). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17325668, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20375010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24038151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24074594}. |
Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Ichthyosis;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Tight junctions represent one mode of cell-to-cell adhesion in epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, forming continuous seals around cells and serving as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space. These junctions are comprised of sets of continuous networking strands in the outwardly facing cytoplasmic leaflet, with complementary grooves in the inwardly facing extracytoplasmic leaflet. The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the claudin family, is an integral membrane protein and a component of tight junction strands. Loss of function mutations result in neonatal ichthyosis-sclerosing cholangitis syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9076; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; tight junction [GO:0070160]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; aging [GO:0007568]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; calcium-independent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell-adhesion molecules [GO:0016338]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell junction maintenance [GO:0034331]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; cellular response to butyrate [GO:1903545]; cellular response to lead ion [GO:0071284]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; establishment of blood-nerve barrier [GO:0008065]; establishment of endothelial intestinal barrier [GO:0090557]; establishment of skin barrier [GO:0061436]; hyperosmotic salinity response [GO:0042538]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; positive regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:1903348]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in wound healing [GO:0060054]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; response to dexamethasone [GO:0071548]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to interleukin-18 [GO:0070673]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; xenobiotic transport across blood-nerve barrier [GO:0061772] |
11889141_Claudin-based tight junctions occur in the epidermis and they are crucial for the barrier function of the mammalian skin. 11939410_Involvement in the beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in human colorectal cancers 12736707_CLDN1, clustered with CLDN16 at human chromosome 3q28, is a four-transmembrane protein with WWCC motif, defined by W-X(17-22)-W-X(2)-C-X(8-10)-C. 12909588_Airway tight junctions are regulated by claudin interactions that confer the selectivity of the junction. 15260435_Showed that residues located C-terminal to the last transmembrane domain of claudin 1 are required for the proper targeting to apical TJ.s. 15521008_Lack of claudin-1 in neonatal sclerosing cholangitis syndrome may lead to increased paracellular permeability between epithelial cells and bile duct disease. 15547692_Arrangement of expression and distribution of claudin-1 is closely related to cell dissociation status in pancreatic cancer cells through MEK2 activation 15743508_significant loss of CLDN1 protein in breast cancer cells suggests that CLDN1 may play a role in invasion and metastasis 15820559_This review summarizes the role of claudins in cancer and points out that claudin 1 (CLDN1) may support tumor suppressive functions in tissues such as the brain, where dramatic loss of CLDN1 expression has been demonstrated in glioblastoma multiforme. 15965503_Genetic manipulations of claudin-1 expression in colon cancer cell lines induced changes in cellular phenotype, with structural and functional changes in markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 16232121_Claudin-1 was downregulated by Snail and Slug in MDCK and human breast neoplasm cells. 16253248_The expression of claudin-1, -3 and -4 was upregulated 5.7-, 1.5- and 2.4-fold, respectively, in colorectal tumor tissues in comparison to the normal ones. 17047970_Differential expression of genes encoding claudins in colorectal cancer suggests that these tight junction proteins may be associated to and involved in tumorigenesis. 17091452_Claudin1 gene shows increased expression in papillary thyroid cancer. 17283368_Expression of cytoplasmic claudin-1 was decreased in acute acalculous cholecystitis. 17325668_CLDN1 is required for HCV infection of human hepatoma cell lines and is the first factor to confer susceptibility to HCV when ectopically expressed in non-hepatic cells 17359339_Tight junction proteins contribute to the permeability barrier in epidermal keratinocytes 17418912_Squamous cell carcinomas and carcinoids showed different CLDN1 expression. 17440968_Claudin-1 immunohistochemistry should be considered for use as a new diagnostic tool for distinguishing malignant from benign lesions of the prostate. 17585317_Squamous cell carcinomas were positive for CLDN-1 and negative for CLDN-5, whereas adenocarcinomas were positive for CLDN-5 and negative for CLDN-1. 17611630_CLDN1 expression correlated with the recurrence status and malignant potential of breast cancer. 17644758_Nine potential tetraspanin CD9 partners, including claudin-1, were identified. 17941058_Cell-cell transmission of hepatitis C virus is dependent on CLDN1 expression. 17970035_The expression of claudin-1 and claudin-2 in cancer tissues was upregulated 40- and 49.2-fold, respectively, at the mRNA level, as compared with that in normal tissues 18095941_CLDN1 is unlikely to play a critical role in migration of Langerhans cells (or their precursors) to the epidermis or their positioning within the epidermis. 18204077_Inhibition of claudin-1 expression may represent a novel mechanism that contributes to RON-mediated invasive activities, leading to increased tumor malignancy 18211898_specific localization pattern of CLDN1 may be crucial in the regulation of hepatitis C virus cellular tropism 18227718_in 5 cases of follicular dendritic cell sarcoma, study found diffuse intense positivity of the tumor cells for Glut-1 in all 5 cases and focal and weak immunoreaction for Claudin-1 in 3 cases 18234789_Here, we confirm the role of claudin-1 in HCV entry. 18337570_fluorescent protein-tagged forms of CD81 and CLDN1 colocalized. 18480547_Claudin-1 expression is correlated with recurrence status and poor prognosis in esophageal cancer. 18550469_claudins 1 and 3 had a significant effect on overall survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. 18711353_Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression was elevated in active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), adenomas, and IBD-associated dysplasia, but not acute self limiting colitis 18756604_Suggest that claudin-1 participates in the transformation of biological behaviors in gastric adenocarcinomas. 18802961_Hepatocyte tight junctions-associated proteins occludin, claudin-1, and Zonula Occludens protein-1 (ZO-1) disappeared from the borders of adjacent cells in hepatoma cells harboring genomic hepatitis c virus replicons. 18817843_For the first time this study proves the presence of Claudin-1, Claudin-3 and Claudin-5 in ECV304 (obtained from ECACC) cell layers and the inducibility of their expression by glioma-conditioned media. 18949385_claudin-1 expression is responsible for TNF-alpha-dependent growth signals and the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. 19052094_Mutational study of CLDN1 revealed that its tight junctional distribution plays an important role in mediating hepatitis C virus entry. 19073886_VHL loss-of-function also has striking effects on the expression of the tight junction (TJ) components occludin and claudin 1 in vitro in VHL-defective clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) cells and in vivo in VHL-defective sporadic CCRCCs. 19077439_We investigated common genetic variation in CLDN1 in four self-described ethnically distinct U.S. populations to look for genetic variation and signatures of selection and compared CLDN1 with CLDN7, the most similar of the claudin genes. 19184060_Tight junction proteins claudin-1, claudin-3, claudin-4, and the adherens junction protein beta-catenin are overexpressed in colorectal carcinoma. 19297469_cell-cell contacts formed by claudin-1 may generate specialized membrane domains that are amenable to hepatitis C virus entry 19414319_Increased Claudin-1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 19540561_claudin-1 is significantly expressed in low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas. 19578981_claudin-1 may be a useful tumor marker for papillary thyroid carcinoma 19661441_is altered in early-stage psoriasis 19674288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19674288_These results indicate that genetic variants in regulatory regions of CLDN1 may alter susceptibility to hepatitis C infection. 19706291_The tight junction protein claudin-1 has gastric tumor suppressive activity and is a direct transcriptional target of RUNX3 19739116_Data demonstrate the regulation and novel biological function of claudin-1 and indicate the important role of claudin-1 in NPC tumorigenesis. 19776133_CLDN1 overexpression in subconfluent cells was unable to recapitulate this effect, whereas increased SR-BI expression enhanced hepatitis C virus internalization, demonstrating a rate-limiting role for SR-BI. 19881542_Data indicate that inhibition of claudin-1 expression by HDAC-2-specific small interfering RNA supported the role of HDAC-2 in this regulation. 19897486_Activation of c-Abl-PKCdelta signaling pathway is critically required for the claudin-1-induced acquisition of the malignant phenotype. 19903817_An electrostatic attraction between the basic claudin region and the acidic Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin cleft is involved in their interaction. 19962368_this study identified claudin-1 as a novel interacting partner of DENV prM protein. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20478039_Claudin-1, -3, -4, -5, and -7 are expressed in developing human lung from week 12 to week 40 with distinct locations and in divergent quantities. 20490282_Recent advances in the understanding of the potential role of claudin 1 in breast cancer are discussed. 20546350_Claudins 1,expression in meningiomas. 20685314_Monoclonal antibodies against the HCV entry factor CLDN1 might be used to prevent HCV infection, such as after liver transplantation, and might also restrain virus spread in chronically infected patients. 20871038_speculate that increased CL-1 expression may be involved in the early stages of transformation in ulcerative colitis (UC)-associated neoplasia. CL-1 protein may therefore be a good candidate for surveillance of patients with UC 20937153_claudin-1 has anti-apoptotic effects, and is involved in the regulation of the expression and subcellular localization of beta-catenin and E-cadherin in MCF-7, but not T47 D cells 21233676_Alterations in claudin expression occur in prostate cancer cells, although we have not found an association with the main clinicopathological parameters. 21356207_Results suggest that lactate dehydrogenase B suppression plays an important role in triggering or maintaining the mitochondrial defects and then contributes to cancer cell invasiveness by inducing claudin-1 protein. 21428935_Structural characterization of CD81-Claudin-1 hepatitis C virus receptor complexes. 21480761_claudin-1 was strongly expressed, whereas claudin-7 and tricellulin were weakly expressed or were absent in primary SCC and metastatic lymph nodes. 21489616_these findings implicate CLDN1 mutations in susceptibility to widespread herpes simplex virus 1 skin infections in subjects with atopic dermatitis 21493012_Claudin-1 and 4 expressions were found to be significantly lower in cases of colon carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. 21536752_occludin S408 dephosphorylation regulates paracellular permeability by remodeling tight junction protein dynamic behavior and intermolecular interactions between occludin, ZO-1, and select claudins 21551950_Expression of human factors CD81, claudin-1, scavenger receptor, and occludin in mouse hepatocytes does not confer susceptibility to hepatitis B virus entry into the liver. 21620107_Report claudin-1 expression in patients with recurrent hepatitis c after liver transplantation for virally induced liver cirrhosis. 21624620_claudin-1 might play a role in airway remodeling in asthmatic patients by means of regulation of airway smooth muscle cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and inflammation 21720707_Patients with high CLDN1 expression were statistically shown to have a relatively better prognosis. 21757541_ESCRT function is required for claudin-1 trafficking and for epithelial cell polarity 21873169_Reduced CL-1 expression of CL-1 correlated significantly with tumor differentiation, perineural invasion and poor prognosis in stage II & III rectal cancer. 21909685_Claudin-1 expression is associated with distinguish schwannoma from fibroblastic meningioma. 21997594_Claudin-1 expression in squamous cell carcinoma varies in organ-specific manner reflecting influence of local factors and different mechanisms of claudin-1 expression. 22030598_Claudin-1 involved in neonatal ichthyosis sclerosing cholangitis syndrome regulates hepatic paracellular permeability. 22408413_dystopic subcellular localizations of Snail-1 and claudin-1 may participate in changes of cellular morphology and behavior which might be associated with altered effectory pathways of proteins and thus substantially contribute to the cancer development. 22531683_suggest an important role of claudin-1 in the development of metastasis in LLSCCs 22588068_Claudin expression may help in the diagnosis of papillary tumors of the pineal region and can be used in combination with other markers. 22641667_These observations suggest that CL-1 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of cellular morphology and in the behavior of metastatic processes in colorectal cancer 22671588_suggests that primarily S53 and potentially D68 in Cld-1 are involved in sealing of the paracellular cleft and that charge-unselective pores may be induced by substituting S53E. 22719836_conclude that homeodomain transcription factors Cdx1, Cdx2 and GATA4 regulate claudin-1 gene expression in human colon cancer cells 22776839_Claudin-1 decreased expression in colonic carcinoma contributes to tumor dedifferentiation, invasion and metastasis. 22897233_Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer studies confirm a role for these CD81 residues in claudin-1 association and Hepatitis C virus infection. 22941059_Claudin-1 expression confers resistance to anoikis in colon cancer cells in a Src-dependent manner. 23136956_Data show that CLDN1 snps are associated with contact sensitization to nickel, organic compounds and fragences.No associations were found for GST gene polymorphisms 23137868_Results suggest a possible participation of erbB1-4 and claudin-1 in tissue remodelling in chronic hypertrophic rhinitis. 23160379_CLDN1 is necessary for the induction of EMT in human liver cells 23422483_M14K and M38K malignant pleural mesothelioma cell lines preserve the same claudin-based phenotype in vivo. 23426649_Studied DEC1 & claudin-1 in invasive breast ductal carcinomas;found DEC1 elevated in invasive breast ductal carcinoma. DEC1 knockdown led to the enhanced expression of claudin-1 at both the mRNA and protein levels in breast cancer cell lines. 23449973_Keratin 8 and 18 loss in epithelial cancer cells increases collective cell migration and cisplatin sensitivity through claudin1 up-regulation. 23498955_HRas signal transduction promotes hepatitis C virus cell entry by triggering the host CD81-CLDN1 complex formation. 23523916_miR-155 may prevent tumorigenesis in human ovarian cancer through downregulation of CLDN1 23588589_Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of claudin-1 expression. 23591077_Expression of CLDN1 and CLDN10 was lower in invasive lepidic predominant adenocarcinoma than in lung adenocarcioma in situ. Overexpression of CLDN1 and CLDN10 indicates a favorable prognosis in some patients with lung adenocarcinoma. 23721519_our studies strongly suggest that claudin 1 directly participates in promoting breast cancer progression 23775920_All tested strains of hepatitis C virus efficiently utilize CLDN1 for cell entry; some are able to use CLDN6 as well. 23792687_Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), an inflammatory atopic disease of the esophagus, causes massive eosinophil infiltration, basal cell hyperplasia, and sub-epithelial fibrosis. We examined pinch biopsies from EoE and normal pediatric patients. Western analysis indicated reduced expression of intercellular junction proteins, E-cadherin and claudin-1 and increased expression of occludin and vimentin. 23813140_The increased therapeutic efficacy of the PEG-IFNalpha2b plus RBV treatment could be secondary to the inhibition of claudin-1 and E-cadherin cell membrane expression. 23844228_DNA promoter methylation is causally associated with downregulation of claudin 1 in a subgroup of breast cancer that includes mostly ER+ tumors. 23898096_The significance of low expression of claudin-1 as a predictor of poor prognosis of colorectal cancer, is reported. 23900598_This describes the intermediate claudin pattern of RCs, demonstrating that it differs from that of cervical glandular and squamous basal cells, but showing an expression similar to the strong claudin 1 expression detected in cervical neoplastic cells. 23914916_the CLDN1 receptor distortion is prominent due to the double mutation with large surface accessibility. 24074594_These results suggest that the interaction between viral protein prM and host protein claudin-1 was essential for dengue entry. 24112161_the expression of CLDN1 and IGF2 indicate a poor prognosis in stage N2 non-small cell lung cancer 24141423_In subjects with diabetes, the levels of SIRT1 and Claudin-1 were correlated with proteinuria levels. 24265314_PKD3 negatively regulates human airway epithelial barrier formation and integrity through down-regulation of claudin-1, which is a key component of tight junctions. 24294371_Report altered claudin 1 expression when comparing normal skin to actinic keratosis and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. 24304426_Claudin 1 did not show any specific placental disease associations. 24305709_Low CLDN1 expression is associated with adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma. 24321518_CLDN1 is highly up-regulated in gastric cancer, and is independently associated with a poor post-operative prognosis. 24479816_there was a significant association between the CLDN1 genotype (c.369C>T) in tumor samples and a higher risk of colon cancer development 24529330_In diabetic glomerulosclerosis, inflammatory crescents were almost exclusively composed of claudin 1-positive cells 24535143_CLDN1 is a biomarker for intestinal-type gastric cancer with shorter survival. The expression of CLDN1 was strongly associated with beta-catenin in gastric cancer patients and a gastric cancer cell model. 24576965_The inverse correlation was revealed between the level of cell proliferation and the intensity of claudin-1 expression in oral hyperplasia, squamous intraepithelial neoplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. 24641442_Results from this Turkish family confirm the causal relationship betwen mutation in CLDN1 and NISCH syndrome. 24696415_Increased expression of claudin-1 is associated with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. 24815833_The present study demonstrates that high expression of claudins 1, 4, 5 and down-regulation of claudin-7 are positive prognostic markers and are associated with good outcome and increased survival rates. 24899196_The forced expression of CLDN1 restored HCV entry. 25001509_CLDN1 is a novel target of miR-375, and high miR-375 expression shortens survival in NSCLC. 25038829_Claudin 1, 4, and 7 are important building blocks of paracellular adhesion molecules; their decreased expression in colorectal cancer seems to have critical effects on cell proliferation, motility, invasion, and immune response against the tumor. 25046141_Claudin-1 suppresses the malignant phenotype of melanoma brain metastasis. 25277410_MIR29 targets and reduces expression of CLDN1 and NKRF to increase intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel disease. 25319490_The expressions of MARVELD2, CLDN1 and CLDN3 mRNA were significantly lower in cholesteatoma tissue and may be involved in epithelium permeability. 25323998_Claudin-5 overexpression promoted the interactions of claudin-1 and claudin-2 and enhanced the barrier function of retinal cells. 25342221_Data show that C-terminal domain of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin (cCPE)-binding to claudin 1 and claudin 5 is prevented by two residues in extracellular loop 2 of Cld1 (Asn(150) and Thr(153)) and Cld5 (Asp(149) and Thr(151)). 25345514_The findings suggest that down regulated CLDN1 and CLDN5 genes have potential relevance in relation to the progression of glioblastoma multiforme. 25393310_CLDN1-negative phenotype predicts a high risk of recurrence and death in triple-negative breast cancer. 25512082_Mold exposure in early life is a risk factor for atopic dermatitis (AD), and CLDN1 polymorphism may influence the development of AD and IgE production in children. 25517868_The highest expression of claudin-1 was observed in well-differentiated oral squamous cell carcinomas, whereas poorly differentiated tumors exhibited mostly no expression of claudin-1. 25544763_Findings suggest that CLDN1 is oncogenic in gastric cancer and its malignant potential may be attributed in part to regulation of anoikis, by mediating membrane beta-catenin-regulated cell-cell adhesion and cell survival. 25548484_Suggest that claudin 1 is an important messenger that regulates TNF-alpha-induced gene expression and migration in gastric cancer cells. 25755790_reduction of claudin-1 expression may contribute to the progression of gastric tumors 25778318_Report claudin 1 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma has no prognostic value. 25798937_Using a human liver-chimeric mouse model, we show that a monoclonal antibody specific for the TJ protein claudin-1 (ref. 7) eliminates chronic HCV infection without detectable toxicity 25849148_Data from live-cell imaging suggest at least two different cis-interaction interfaces within CLDN3 homopolymers as well as within CLDN1/CLDN3 heteropolymers. 25934191_findings suggest that homozygous CD81 rs708564 TT may be a genetic modifier for avoiding HCV infection whether as a sole single nucleotide polymorphism or combined with the CLDN1 rs893051 GG genotype 25956626_Report genetic polymorphism of TJ component claudin-1 and their haplotypes are associated with leukoaraiosis. 25964581_Our results indicate that CLDN4 expression is correlated with poor prognosis, and CLDN1 expression may be an indicator of recurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 25972430_Glutamine increased claudin-1 expression in the colonic mucosa of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. 26023235_Phosphorylation state of the tyrosine of claudin-1 and claudin-2 regulates interaction with ZO1. 26122225_Positive expressions of Claudin-1 in retinoblastoma were fewer than those in retina; higher positive expressions were found in differentiated tissues than in undifferentiated tissues; Claudin-1 expressed more positively in optic nerves without invasion. 26157141_CLD1-mediated hepatoma cell invasiveness occurs via heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) activation. 26219679_High CLAUDIN-1 expression is associated with metastasis in follicular thyroid carcinoma. 26361141_delocalization of claudin-1 induced by PKC phosphorylation contributes to metastatic capacity of osteosarcoma cells 26436506_Claudin-1 expression was correlated with lymphatic microvessel generation in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and with patient survival. 26463354_High CLDN1 expression is associated with Cervical cancer. 26554238_There was no difference in the frequency of fractures or renal lithiasis between the rs219780 genotype groups in PHPT patients. Nor was there any relationship between the T or C alleles and BMD or biochemical parameters. 26662145_autotypic tight junctions molecular composition, like claudin-1 and occludin expression could influence the demyelinating process by altering the permeability of the blood-nerve barrier. 26820697_The loss of claudin-1 appears to be involved in the pathogenesis of pterygium 26918943_Data show that miR-30a could bind to the 3'-untranslted region of Slug mRNA and increased expression of claudins, a family of tight junction transmembrane proteins. 27259233_Rab25 is amplified and enhances aggressiveness in luminal B cancers while in claudin-low tumors, Rab25 is lost indicating possible anti-tumor functions 27277258_These findings indicate a previously unrecognized mechanism that miR-142-5p, targeting CLDN1, plays an important role in Hashimoto's thyroiditis pathogenesis. 27436828_Aberrant expression of the tight junction molecules claudin-1 and zonula occludens-1 mediates cell growth and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 27581203_CLDN1 rather than variants in FLG may be involved in the susceptibility of AD in the Ethiopian population 27687058_CLDN1 overexpression is a good prognostic factor in NSCLC. 27733684_hypotonic stress induces dephosphorylation, clathrin-dependent endocytosis, and degradation of claudin-1 and -2 in lysosomes, resulting in disruption of the TJ barrier in renal tubular epithelial cells. 27742576_TNF-alpha mediated regulation of claudin-1 and tumorigenic abilities of colon cancer cells. 27766775_Studies showthat CLDN1 is downregulated in lung adenocarcinoma and that low CLDN1 messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression leads to shorter overall survival. 27914788_suggest that claudin-6 induces MMP-2 activation through claudin-1 membrane expression 27974683_CLDN1 promotes invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer cells via the expression of EMT/invasion-related genes. 28045912_Claudin-low tumors were associated with young age of onset, higher tumor grade, larger tumor size, extensive lymphocytic infiltrate and a circumscribed tumor margin. Patients with claudin-low tumors had a worse overall survival when compared to patients with luminal A type breast cancer. 28055967_Cycling hypoxia could induce significant changes in CLDN1 and CLDN7 expression in nasopharyngeal cancer cells, indirectly regulation P18 expression and affecting cell invasion/proliferation. 28126724_In human lung tissue, Claudin-1 is higher in RBFOX3-positive cells than in RBFOX3-negative cells. Immunostaining and mRNA quantification revealed that protein levels, but not mRNA levels, of Claudin-1 are increased by RBFOX3. 28273404_association of genetic polymorphisms of claudin-1 with small vessel vascular dementia 28316062_CLDN-1 promoted the migration and EMT through the Notch signaling pathway. 28342862_The data suggested that miR-29a may regulate tumor growth and migration by targeting CLDN1. 28381183_CLDN1 is significantly hypomethylated in tumor samples and that the membrane staining intensity for claudin 1, 4, and 7 is significantly lower in colorectal cancer tissues than in adjacent nonneoplastic tissue. 28415141_Studies indicate claudin 1 (CLDN-1) as a target for improving epidermal drug absorption and preventing HCV infection and of claudin 4 (CLDN-4) as a target for anticancer therapeutics. 28415153_Data show that the charge of Lys65 in claudin 1 (Cldn1) and Glu158 in claudin 3 (Cldn3), and of Gln57 in claudin 5 (Cldn5) are necessary for tight junction (TJ) strand formation. 28415156_Studies indicate that claudin-1 accumulate in early endosomes in both epithelial and endothelial cells. 28432260_Data suggest that epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is regulated by ZMYND8 (receptor for activated protein kinase C) which selectively activates gene promoters of CLDN1 (claudin 1) and CDH1 (E-cadherin) in breast cancer cells; thus, the presence of ZMYND8 could be implicated in maintaining epithelial phenotype of cells; ZMYND8 regulates invasion/migration of breast cancer cells. 28493289_Increased expression of intestinal epithelial claudin-1 with downregulation of claudin-3 has been observed in intestinal inflammatory disorders. 28614291_CLDN1 activates autophagy through up-regulation of ULK1 phosphorylation and promotes drug resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin. 28617312_Human Growth Hormone Inhibits CLAUDIN-1 Expression Through Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). 28651932_These results revealed that CLDN1 contributed to cancer stem cell features of hepatocellular carcinoma, which was altered by TMPRSS4 expression via ERK1/2 signaling pathway, providing promising targets for novel specific therapies. 28659146_Our data indicate that CLDN1 targeting with an anti-CLDN1 mAb results in decreased growth and survival of CRC cells. This suggests that CLDN1 could be a new potential therapeutic target. 28679754_Here, the authors identified an interaction between claudin-1 and Sec24C, a cargo-sorting component of the coat protein complex II (COPII) vesicular transport system. 29307823_This study is the first to show a cytoplasmic function of claudin 1 as an autophagy regulator and provides the evidence that claudin 1-mediated autophagy regulation is an integral part of the mechanism by which claudin 1 regulates cancer progression. 29524521_the accumulation and toxicity of doxorubicin were rescued by CLDN1 siRNA in A549R cells. We suggest that CLDN1 is upregulated by CDDP resistance through activation of a PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway, resulting in the inhibition of penetration of anticancer drugs into the inner area of spheroids 29704436_BHLHE40 suppressed CLDN1 transcription by preventing the interaction between SP1 and a specific motif within the promoter region of CLDN1. 29955965_CLDN1 is associated with tumorigenesis of human salivary gland tumors. 30098333_TUSC3 accelerates cancer growth and induces the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small-cell lung cancer cells by upregulating claudin-1. 30143655_Knock-down of the TJ protein claudin-1 results in impaired barrier function, decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis of hair keratinocytes. 30227306_CLaudin-1 contributes to malignant potentials of cervical adenocarcinoma cells.Claudin-1 expression is regulated by GPR30 signaling in the cervical adenocarcinoma cells. 30315595_Claudin-1 expression gradually decreased from healthy control skin to severe actinic keratosis, and particularly decreased in areas with epidermal atypia. 30504279_claudin-1 is incorporated in blood-brain barrier tight junction complex, impeding blood-brain barrier recovery and causing blood-brain barrier leakiness during poststroke recovery 30683478_our results suggest that the loss of claudin-1 expression significantly correlates with aggressive tumor behaviors in colorectal cancer 30844730_BMP4 increases E-cadherin and claudin expression in glioblastoma through activation of SMAD signaling, thereby suppressing tumor cell invasion 30856486_CLDN1 restricted the human parainfluenza virus type 2spread via cell-to-cell contact. 30910845_Genetic polymorphisms in CLDN1 gene were associated with age and differentiation of triple-negative breast cancer patients. There was no association between polymorphisms in CLDN1 and survival of triple-negative breast cancer patients. 30971761_Cld-1 is potential prognostic biomarker for Inflammatory bowel disease severity and Colitis-associated cancer, and a novel therapeutic target. 31044387_All Benign and Malignant Apocrine Breast Lesions Over-Express Claudin 1 and 3 and Are Negative for Claudin 4. 31115553_the findings of the present study demonstrated that the expression levels of CLDN1, 3, 7 and 8 varied between laryngeal squamous carcinoma tissues and nonneoplastic tissues 31161679_Joint detection of claudin-1 and junctional adhesion molecule-A as a therapeutic target in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. 31264974_eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) patient biopsy analysis identified a repressed HIF-1alpha/claudin-1 axis, which was restored via pharmacologic HIF-1alpha stabilization ex vivo. Collectively, these studies reveal HIF-1alpha's critical role in maintaining barrier and highlight the HIF-1alpha/claudin-1 axis as a potential therapeutic target for EoE. 31467400_ADAM15 mediates upregulation of Claudin-1 expression in breast cancer cells. 31498437_CLDN1 induces autophagy to promote proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous carcinoma through AMPK/STAT1/ULK1 signaling. 31545907_Extracellular pyruvate kinase M2 facilitates cell migration by upregulating claudin-1 expression in colon cancer cells. 31551535_Chrysin enhances anticancer drug-induced toxicity mediated by the reduction of claudin-1 and 11 expression in a spheroid culture model of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells. 31769164_Although the expression level of CLDN1 was not associated with tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) progression, within the high CLDN1 expression group, the incidence of intracellular localization of CLDN1 was correlated with cervical lymph node metastasis. Motility of TSCC-derived cells was increased by deficiency of CLDN1, suggesting that the decrease in cell-surface CLDN1 promoted the cell migration. 31810510_Human miR-155 (Hsa-miR-155) may positively regulate intestinal mucosal function by inhibiting the expression of claudin1, leading to intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction 31952355_Claudin-1, A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. 32029783_Claudin-1 decrease impacts epidermal barrier function in atopic dermatitis lesions dose-dependently. 32424433_Novel CLDN1 Deletion Associated with Ichthyosis, Sclerosing Cholangitis and Acquired Alopecia. 32692865_Tight junction protein claudin-1 is downregulated by TGF-beta1 via MEK signaling in benign prostatic epithelial cells. 32754286_DNA methylation maintains the CLDN1-EPHB6-SLUG axis to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy and inhibit lung cancer progression. 32907715_Upregulation of hsa-miR-31-3p induced by ultraviolet affects keratinocytes permeability barrier by targeting CLDN1. 32979166_Claudin 1 inhibits cell migration and increases intercellular adhesion in triple-negative breast cancer cell line. 33057875_LncRNA XIST Promotes Migration and Invasion of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cell by Modulating MiR-101-3p/CLDN1 Axis. 33186612_Single nucleotide variants c.-13G --> C (rs17429833) and c.108C --> T (rs72466472) in the CLDN1 gene and increased risk for familial colorectal cancer. 33416138_p53p72Delta225331V31I identified in a cholangiocarcinoma cell |
ENSMUSG00000022512 |
Cldn1 |
369.895636 |
53.6411333950 |
5.745268 |
0.214381807 |
1319.840487 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000055160815568089807356584056681326794253687 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000074694829154587655855082314456222802733717 |
Yes |
No |
728.2828252 |
100.8640539 |
13.6796890 |
1.8580224 |
| ENSG00000163359 |
1293 |
COL6A3 |
protein_coding |
P12111 |
FUNCTION: Collagen VI acts as a cell-binding protein. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Collagen;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dystonia;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
|
This gene encodes the alpha-3 chain, one of the three alpha chains of type VI collagen, a beaded filament collagen found in most connective tissues. The alpha-3 chain of type VI collagen is much larger than the alpha-1 and -2 chains. This difference in size is largely due to an increase in the number of subdomains, similar to von Willebrand Factor type A domains, that are found in the amino terminal globular domain of all the alpha chains. These domains have been shown to bind extracellular matrix proteins, an interaction that explains the importance of this collagen in organizing matrix components. Mutations in the type VI collagen genes are associated with Bethlem myopathy, a rare autosomal dominant proximal myopathy with early childhood onset. Mutations in this gene are also a cause of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, also referred to as Ullrich scleroatonic muscular dystrophy, an autosomal recessive congenital myopathy that is more severe than Bethlem myopathy. Multiple transcript variants have been identified, but the full-length nature of only some of these variants has been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:1293; |
collagen type VI trimer [GO:0005589]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517] |
11785962_Postranslational processing of type VI collagen in articular cartilage was investigated: alpha3(VI) collagen C5 domain is initially incorporated into the newly formed type VI fibrils, but after secretion is cut and not in the mature pericellular matrix 11992252_Mutations in COL6A3 cause severe and mild phenotypes of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy. 12011280_Haplotype analysis clearly suggested linkage of Ullrich muscular dystrophy to the COL6A1/2 locus in two cases and to the COL6A3 loci in the third case. In the remaining nine patients, primary collagen VI involvement was excluded 12077460_The C-terminal Kunitz-type domain from the alpha3 chain of human type VI collagen (C5), a single amino-acid residue chain with three disulfide bridges, was refined at 0.9 A resolution in a monoclinic form 15563506_dominant mutations are common in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD). 15965965_These results suggest that different alpha3(VI) chain isoforms, containing also domains of the N10-N7 region, are required for assembling a proper collagen VI network in the extracellular matrix. 16613849_the alpha3(VI) C5 domain is present in the extracellular matrix of SaOS-2 N6-C5 expressing cells and fibroblasts, which demonstrates that processing of the C-terminal region of the alpha3(VI) chain is not essential for microfibril formation 17918257_Col6A3 fusion with colony-stimulating factor-1 gene is associated with tenosynovial giant cell tumors. 18366090_Study reports 10 unrelated patients with a Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy clinical phenotype and de novo dominant negative heterozygous splice mutations in COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19837927_in humans increased COL6A3 mRNA is associated with adipose tissue macrophage chemotaxis and inflammation and that weight gain 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23818951_Data indicate that the aberrantly methylated and expressed genes in cancer process including IRS1 and collagen-related genes COL4A1, COL4A2 and COL6A3. 24443028_Mutations in each of the three collagen VI genes, COL6A1, COL6A2 and COL6A3, cause four types of muscle disorders: Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy, Bethlem myopathy, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and autosomal recessive myosclerosis. (Review) 24647224_Data indicate that endotrophin (COL6alpha3) levels are higher in diabetic patients. 24719315_Increased adipocyte COL6A3 expression associates with insulin resistance; COL6A3 mRNA associates with small adipocyte size 24801232_In UCMD, 1 mutation was indentified in Chinese patients. 25204870_Parental mosaicism was confirmed in the four families through quantitative analysis of the ratio of mutant versus wild-type allele (COL6A1, COL6A2, and COL6A3) in genomic DNA from various tissues; consistent with somatic mosaicism, parental samples had lower ratios of mutant versus wild-type allele compared with the fully heterozygote offspring. 25337653_This study showed that COL6A3 expression appeared to be lowered in obesity, whereas diet- and surgery-induced weight loss increased COL6A3 expression. 25449070_The heterozygous c.3353A>C mutation in exon 8 of the COL6A3 gene is associated with the Bethlem myopathy with autosomal dominant inheritance. 25635128_COL6A mutations were identified in eight cases having clinical phenotypes of Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy (UCMD) or Bethlem myopathy (BM). 26004199_Recessive mutations in the alpha3 (VI) collagen gene COL6A3 cause early-onset isolated dystonia. 26338966_Data indicate that circulating plasma COL6A3 in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients was upregulated significantly comparing with healthy peoples. 26687111_COL6A3-associated dystonia represents a newly identified autosomal-recessive entity characterized clinically by an early symptom onset with variable distribution. 26872670_In conjunction with the relatively high frequency of homozygous carriers of reported mutations in publically available databases, our data call a causal role for variants in COL6A3 in isolated dystonia into question. 27729337_Overexpression of endotrophin led to a fibrotic program in white adipose tissue (WAT) adipocytes, a proinflammatory program in (WAT) macrophages, and upregulation of both profibrotic and proinflammatory genes in the stromal vascular fraction isolated from WAT. 28403201_Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are at increased risk of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and early mortality. Serum endotrophin, a COL6A3 cleavage product was significantly associated with progression to ESRD. 29066004_Altered white matter structure especially in various parts of the cerebello-thalamo-cortical network in dystonia patients with COL6A3 mutations. 29465610_COL6A mutation Congenital Muscular Dystrophy showed the muscle weakness and poor respiratory function. 29620224_Study found COL6A3 expression to be downregulated and associated with poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer (CRC). In silico analysis of cell typespecific gene expression and COL6A3 knockout experiments indicated the clinical relevance of COL6A3 in the development of CRC. 29894794_two compound heterozygous mutations in COL6A3 gene lead to myopathy from Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy spectrum. 30014607_The morphology and immunophenotype of all 6 cases was analogous to those with the canonical COL1A1-PDGFB fusion; none of the cases showed fibrosarcomatous transformation. This study illustrates that the COL6A3-PDGFD fusion product is rare in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and associated with an apparent predilection for breast 30066698_COL6A3 could influence the viability and angiogenesis of bladder cancer cells. COL6A3 may have a certain relationship with the TGF-beta/Smad-induced EMT process. 30695889_two patients were diagnosed as spontaneous collagen type -related myopathy and carried different variants of COL6A3 gene 30706156_The most frequent mutation in a series of 16 Bethlem myopathy patients was the COL6A3 variant c.7447A>G, p.Lys2486Glu, with either an homozygous or compound heterozygous presentation. Five new mutations were found in COL6A1 gene and other two in COL6A3 gene, all of them with a dominant heritability pattern. 30896449_Human endotrophin as a driver of malignant tumor growth. 31122696_overexpressed circCOL6A3 promoted cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis of gastric cancer through rescission of miR-3064-5p-induced inhibitory effect on COL6A3; study will furnish theoretical grounds for future clinical diagnosis and treatment of GC patients 31286980_An association was determined between COL6A3 polymorphisms and lung cancer risk in a Chinese population. 31425922_study found that COL6A3 variants were associated with risk of esophageal cancer in the Chinese population 32037012_COL6A3 mutation associated early-onset isolated dystonia (DYT)-27: Report of a new case and review of published literature. 32245981_A Fragment of Collagen Type VI alpha-3 chain is Elevated in Serum from Patients with Gastrointestinal Disorders. 32389683_Coexistence of digenic mutations in the collagen VI genes (COL6A1 and COL6A3) leads to Bethlem myopathy. 32448721_Collagen VI-related limb-girdle syndrome caused by frequent mutation in COL6A3 gene with conflicting reports of pathogenicity. 32640306_Single cell sequencing revealed the underlying pathogenesis of the development of osteoarthritis. 32719005_Structure of a collagen VI alpha3 chain VWA domain array: adaptability and functional implications of myopathy causing mutations. 32934754_Identification of Key Prognostic Biomarker and Its Correlation with Immune Infiltrates in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. 33214660_COL6A3 expression in adipose tissue cells is associated with levels of the homeobox transcription factor PRRX1. 33749658_Clinical and Molecular Spectrum Associated with COL6A3 c.7447A>G p.(Lys2483Glu) Variant: Elucidating its Role in Collagen VI-related Myopathies. 33964895_Study of the collagen type VI alpha 3 (COL6A3) gene in Parkinson's disease. |
ENSMUSG00000048126 |
Col6a3 |
282.120287 |
38.4028101501 |
5.263140 |
0.951349323 |
21.552924 |
0.00000344197417502219295843009748414598192312041646800935268402099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011408834229357189037957522048660763402949669398367404937744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
529.0403945 |
304.2333281 |
13.9635945 |
5.7566136 |
| ENSG00000163376 |
84541 |
KBTBD8 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFY9 |
FUNCTION: Substrate-specific adapter of a BCR (BTB-CUL3-RBX1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that acts as a regulator of neural crest specification (PubMed:26399832). The BCR(KBTBD8) complex acts by mediating monoubiquitination of NOLC1 and TCOF1: monoubiquitination promotes the formation of a NOLC1-TCOF1 complex that acts as a platform to connect RNA polymerase I with enzymes responsible for ribosomal processing and modification, leading to remodel the translational program of differentiating cells in favor of neural crest specification (PubMed:26399832). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26399832}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
Involved in neural crest cell development; neural crest formation; and protein monoubiquitination. Part of Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84541; |
Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031463]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; spindle [GO:0005819]; neural crest cell development [GO:0014032]; neural crest formation [GO:0014029]; protein monoubiquitination [GO:0006513]; regulation of translation [GO:0006417] |
19893584_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29999490_The authors found that CUL3 complexed with KBTBD8 monoubiquitylates its essential targets only after these have been phosphorylated in multiple motifs by CK2, a kinase whose levels gradually increase during embryogenesis. 33109073_Downregulation of the ubiquitin ligase KBTBD8 prevented epithelial ovarian cancer progression. |
ENSMUSG00000030031 |
Kbtbd8 |
70.670770 |
5.7039554133 |
2.511963 |
0.217460633 |
144.038862 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000348412996088038403513864189094185608509482503095804716841939587204483215059892754674603088105300230381544679403305053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000049258389102101976845135664520806113071898224620324031701410981623109217687808850463532933661170432060316670686006546020507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
119.5904967 |
17.3073906 |
21.1341473 |
2.5832667 |
| ENSG00000163428 |
116064 |
LRRC58 |
protein_coding |
Q96CX6 |
|
Leucine-rich repeat;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:116064; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000034158 |
Lrrc58 |
767.267535 |
2.4887670296 |
1.315431 |
0.399635027 |
10.177550 |
0.00142160959759221410501905946688339099637232720851898193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003232623272294111744368239058644576289225369691848754882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1138.3041429 |
268.3441062 |
455.3343969 |
77.7261128 |
| ENSG00000163449 |
92691 |
TMEM169 |
protein_coding |
Q96HH4 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92691; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
20463177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000026188 |
Tmem169 |
22.693717 |
3.3321887609 |
1.736470 |
0.329632598 |
29.192581 |
0.00000006552962877127735688595439956030674899523091880837455391883850097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000262830793658710308515776389939877510926180548267439007759094238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.7847995 |
7.4271148 |
10.8032085 |
1.8740004 |
| ENSG00000163453 |
3490 |
IGFBP7 |
protein_coding |
Q16270 |
FUNCTION: Binds IGF-I and IGF-II with a relatively low affinity. Stimulates prostacyclin (PGI2) production. Stimulates cell adhesion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8117260, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8939990}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor binding;Immunoglobulin domain;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA editing;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein (IGFBP) family. IGFBPs bind IGFs with high affinity, and regulate IGF availability in body fluids and tissues and modulate IGF binding to its receptors. This protein binds IGF-I and IGF-II with relatively low affinity, and belongs to a subfamily of low-affinity IGFBPs. It also stimulates prostacyclin production and cell adhesion. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene, and one variant has been associated with retinal arterial macroaneurysm (PMID:21835307). [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:3490; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; insulin-like growth factor binding [GO:0005520]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular response to hormone stimulus [GO:0032870]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; regulation of steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0050810]; response to cortisol [GO:0051414]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526] |
12065244_that IGFBP-rP1 is an inhibitor of MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation and may act via a cellular senescence-like mechanism. 12592389_In prostate cancer cells, one of the downstream mediators of the senescence-associated tumor suppression effect of mac25/IGFBP-rP1 is superoxide dismutase 2 12679483_discovered the implication of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-related protein 1 in endometrial physiology, which seems related to endometrial receptivity 14633696_tumor-suppressive activity is through induction of apoptosis in an IGF-I independent manner in prostate cancer 15077158_SOX9 contributes to growth regulation by mac25 via inhibition of cell growth and promotion of differentiation 15708897_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16302002_data suggest that mac25/IGFBP-rP1 and 25.1 may play a functional role in the NE differentiation of NSCLC cell lines and may provide a novel therapeutic target for treating lung cancers, in particular NSCLC with NE differentiation 16873698_findings show for the first time that circulating IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) is increased with insulin resistance 17048309_IGFBP7 plays a potential tumor suppressor role against colorectal carcinogenesis and its expression is associated with DNA hypomethylation of exon 1. 17136345_mRNA expression was lost in six out of eight CRC cell lines as compared to normal colon cells. DNA methylation was found in the region of exon 1 and intron 1 of IGFBP-7. 17312390_IGFBP7 plays a potential tumor suppressor role in colorectal carcinogenesis. 17465992_Expression in tumor cells may reduce the anchorage-independent growth ability, leading to the marked loss of tumorigenicity. 17972510_This study supports the role of IGFBP-1, -3 and -7 as potential tumour suppressor genes in human breast cancer. 18267069_A genome-wide RNA-interference screening to identify genes required for an activated BRAF oncogene to block proliferation of fibroblasts and melanocytes revealed that a IGFBP7, has a central role in BRAF-mediated senescence and apoptosis. 18711401_Cultured human brain endothelial cells. exposed to either hypoxia or media conditioned by the human glioblastoma cell line are induced to express IGFBP-7 mRNA. 18981723_5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine(5-aza-dC) may have anticancer function for colon cancer and restoration of IGFBP7 may involve the biological effects induced by 5-aza-dC in colon cancer cell lines. 19019211_Patients with endometriosis and those with type II diabetes mellitus undergoing hemodialysis had significantly higher serum concentrations of IGFBP7 than the relevant control subjects. 19374835_IGFBP7 blocks VEGF-induced angiogenesis in human vascular endothelial cells. 19542015_Results demonstrate that the vascular-specific marker angiomodulin (AGM) modulates vascular remodeling in part by temporizing the proangiogenic effects of VEGF-A. 19638426_Epigenetic inactivation of IGFBP7 appears to play a key role in tumorigenesis of colorectal cancers with the CpG island methylator phenotype by enabling escape from p53-induced senescence. 19710688_IGFBP7 is a regulator of KC proliferation and differentiation 19829302_data argues against obligatory downregulation in IGFBP7 expression in BRAF mutated melanoma cells 19919630_Similar to oncogenic BRAF-positive common naevi without atypia, enhanced expression of the tumour suppressor IGFBP7 in oncogenic BRAF-positive atypical genital nevi supports that they are biologically inert. 20029996_Results suggest that IGFBP7 regulates morphological changes of glandular cells by interfering with the normal PKA and MAPK signaling pathways that are associated with the transformation and/or differentiation of endometrial glands. 20407444_IGFBP7 could be a useful predictor of the response to interferon-based therapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma 20433702_HSP60 is an important downstream molecule of IGFBP7 in colorectal carcinoma 20440262_data suggest that loss of IGFBP7 expression has a functional role in thyroid carcinogenesis, and it may represent a possible basis for therapeutic strategies 20464481_Expression of Insulin like growth factor binding protein-7 reduces growth of human breast cancer cells 20478260_Study concludes that the secreted protein IGFBP7 is dispensable for B-RAF(V600E)-induced senescence in human melanocytes. 20535151_In contrast to BAALC, which likely represents only a surrogate marker of treatment failure in acute leukemia, IGFBP7 regulates the proliferation of leukemic cells and might be involved in chemotherapy resistance 20599521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20977730_IGFBP-rP1 was a potential key molecule associated with colon cancer differentiation. 21040219_aberrant IGFBP7 expression is regulated by DNA methylation in acute leukemia. 21095038_IGFBP7 is inactivated in lung cancer by DNA hypermethylation in both lung cancer cell lines and primary lung tumors 21328580_Results indicated that IGFBP7 expression correlated significantly with the malignant potential in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 21413833_IGFBP7 plays a positive contributing role in the interaction between leukemia cells and microenvironment, which may promote the leukemic cells' adhesion, invasion, and migration 21525788_IGFBP7 is involved in early metastatic dissemination in colorectal cancer 21562573_IGFBP7 is involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis 21835307_The BRAF/MEK/ERK pathway is upregulated in progressive retinal arterial macroaneurysm patients, caused by mutation in IGFBP7. 21908579_Findings provide evidence that IGFBP7 functions as a novel putative tumor suppressor for HCC and establish the corollary that IGFBP7 downregulation can effectively modify AEG-1 function. 22005787_higher IGFBP7 mRNA levels were associated with lower leukemia-free survival (Cox regression model, P=0.003) in precursor B-cell Ph(-) ALL patients (n=147) treated with a contemporary polychemotherapy protocol 22173745_The externalization of saw-tooth architecture in serrated polyps was endoscopically observed more frequently in those with high levels of IGFBP7 methylation (P = 0.03). 22277373_These findings suggest a novel molecular mechanism responsible for the tumor suppressive function of IGFBP7 in cisplatin-resistant human lung cancer. 22383111_IGFBP7 could also inhibit the phosphorylation of ERK and the expression of PCNA, MMP2 and MMP9 in HTR-8 and JEG-3 cells. 22392074_Transfection of IGFBP-rP1 or addition of condition medium (CM) from IGFBP-rP1-transfected cells in MCF-7 cells caused induction of a variety of senescent phenotypes. 22544761_Hyperinsulinemia and high IGFBP-rP1 levels confer altered risks for endometrial carcinoma. 22622471_Low expression of IGFBP7 is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 22750143_editing of IGFBP7 transcripts impacts the protein's susceptibility to proteolytic cleavage, thus providing a means for a cell to modulate its functionality through A-to-I RNA editing 22906661_Results demonstrate that CpG methylation of IGFBP7 may represent a novel biomarker of prostate cancer and pre-invasive neoplasms 23250396_a model whereby IGFBP7 binds to unoccupied IGF1R and suppresses downstream signaling, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis, cell growth, and survival. 23381221_hypomethylation of LINE-1 and hypermethylation of SLIT2, MAL and IGFBP7 were frequently detected in NSCLCs and associated with various clinical features. 23388612_IGFBP7 in urine was identified as a reliable marker of cell cycle arrest induction in acute kidney injury. 23543219_Report A-to-I editing in the coding sequence of IGFBP7 in cancerous human keratinocytes. 23546957_Data indicate that desmoplakin (DSP) and cystatin A (CSTA) interaction and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), IGF-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) and syndecan 1 (SDC1) interaction were observed in protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. 23600329_Results indicate that restoration of IGFBP-rP1 to PC-3 cells increases both their radiosensitivity and chemosensitivity. 23713052_Perfomed proteomic analysis on a transgenic mouse model of severe cardiac hypertrophy; compared data to dataset of heart failure found MYH7, IGFBP7, ANXA2, and DESM to be biomarker candidates for heart failure. 24067438_as urinary marker, discriminated between early and late/non-recovery patients and patients with and without acute kidney injury 24075854_These data suggest that IGFBP7 is a critical regulator of memory consolidation and might be used as a biomarker for AD. 24357797_Methylation of the IGFBP7 promoter was associated with silencing of gene expression and was frequent in Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma 24373620_IGFBP-rP1 contributes to the development of liver fibrosis and may be a novel molecule involved in the progression of hepatic fibrogenesis. 24427302_High expression of IGFBP7 in fibroblasts induced by colorectal cancer cells is co-regulated by TGF-beta and Wnt signaling in a Smad2/3-Dvl2/3-dependent manner. 24632618_in contrast to its tumor-suppressor function in epithelial cells, IGFPB7 can promote anchorage-independent growth in malignant mesenchymal cells and in epithelial cells with an EMT phenotype when IGFBP7 is expressed by the tumor cells 24675717_The decline in urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 values was the strongest predictor for renal recovery following cardiac surgery. 24737780_These results suggest that AGM cooperates with VEGF to induce the aberrant functions of cancer vasculature as a ligand of integrin alpha5beta3. 24743871_IGFBP7 down-regulation is associated with poor prognosis in glioma, and this molecule may represent both a prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target. 24894674_Data indicate that insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) was downregulated in gastric cancer, and its low expression was potentially correlated with increased cell proliferation and could be used to predicate poor prognosis in patients. 24967962_AML patients with high IGFBP7 expression have a better outcome than patients with low IGFBP7 expression, indicating a positive role for IGFBP7 in treatment and outcome of AML. 25789970_we demonstrated that IGFBP-rP1 suppresses EMT and tumor metastasis by repressing TGF-b-mediated EMT through the Smad signaling cascade. 25880247_IGFBP-7 can alter EMT relative marker genes and suppress cell invasion in A253 cell through AKT/GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling. 25886299_The low levels of IGFBP7 in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma are associated with survival rate. 25887188_Our data indicate that IGFBP7 expression is a marker for a specific methylation pattern in myeloma 25984973_serum IGFBP7 levels are associated with IR and MetS, providing new insight into the mechanism of IR and Mets. IGFBP7 may be a potential interventional target for IR and Mets. 26043748_Overexpression of IGFBP7 was associated with tumour progression and poor survival in gastric cancer. IGFBP7 may play a role in tumour progression in gastric cancer. 26387651_low expression in breast cancer tissue 26450156_Inhibition of IGF1-R overcomes IGFBP7-induced chemotherapy resistance in T-ALL 26474694_This process not only provides a remarkable high expression at ~50mg/L and pure glycosylated mammalian rhIGFBP7, also highlights that transient gene expression technology is practical to be used for production 26606754_This study shows that urinary [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] has a good diagnostic performance in predicting adverse outcomes in neonatal and pediatric AKI of heterogeneous etiology. 26706909_Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) was proven to be associated with metastatic clinicopathological features and high lymphatic vascular density 26797672_quantitative urine test is available to assess the risk of developing AKI by measuring the concentrations of two protein biomarkers, TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7 26974954_data suggest that TGF-beta1 enhances IGFBP7 via Smad2/4 pathways, and that IGFBP7 might be involved in the TGF-beta1-induced tubular injury in DN. 27174659_biomarker for acute kidney injury 27342580_High IGFBP7 expression is associated with acute kidney injury. 27342582_High IGFBP7 expression is associated with acute kidney injury. 27744089_In patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, IGFBP7 may be a novel biomarker of diastolic function and exercise capacity. 27989801_loss of IGFBP7 and upregulation of IGF1 activates the FGF4-FGFR1-ETS2 pathway in Tumor-associated endothelial cells (TECs) and converts naive tumor cells to chemoresistant tumor stem-like cells (TSCs), thereby facilitating their invasiveness and progression. 28003188_TIMP-2 is both expressed and secreted preferentially by cells of distal tubule origin, while IGFBP7 is equally expressed across tubule cell types yet preferentially secreted by cells of proximal tubule origin. In human kidney tissue, strong staining of IGFBP7 was seen in the luminal brush-border region of a subset of proximal tubule cells, and TIMP-2 stained intracellularly in distal tubules. 28035363_Data report that IGFBP7 is a novel target gene of ADAR2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma where its RNA is edited and protein stabilized by ADAR2. 28107490_Urine [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] is a promising candidate for early detection of AKI, especially in ruling-out AKI 28288210_NEAT1-associated paraspeckle proteins P54nrb and PSF have been reported as positive regulators of c-Myc translation through interaction with c-Myc IRES 28382566_Study results demonstrate that urinary TIMP-2*IGFBP-7 concentration can be used in infants to predict subsequent serum creatinine-defined acute kidney injury following cardiopulmonary bypass. 28682920_Meta-analysis indicated that urinary [TIMP-2].[IGFBP7] may be a reliable biomarker for the early detection of acute kidney injury in adults. 28684903_Serum IGFBP7 levels were raised during acute exacerbation in COPD patients. 28803769_Urine levels of IGFBP7 (and TIMP2) are predictive for acute kidney injury following cardiac surgical procedures. 29067463_IGFBPrP1 transfection inhibited cell growth, and induced G1 phase arrest and cellular senescence in HEC1A cells while gene silencing presented the adverse functional changes. 29145491_epithelial cells and leukocytes from the urinary sediment. CONCLUSION: The gene expression pattern of IGFBP7 and TIMP-2 from urinary sediment, which contains desquamated renal tubular epithelial cells, did not correlate with [IGFBP7]x[TIMP-2] protein, indicating that IGFBP7 and TIMP-2 measured in the NephroCheck(R) test originated predominantly from intact but stressed cells of the kidney itself 29242275_IGFBP7 upregulation promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 29563502_Placenta and appetite genes GDF15 and IGFBP7 are associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. 29580038_Low IGFBP7 expression is associated with Gastric Cancer. 29592874_Reduced RNA editing of IGFBP7 gene is associated with psoriasis. 29622288_IGFBP-7 was lower in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction than heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction. 29991293_IGFBP7 is associated to prognosis and could suppress cell survival in cholangiocarcinoma 30300282_Study in cohort of donation after circulatory death kidney transplant recipients showed that urinary TIMP-2 is a promising biomarker predicting the occurrence and duration of prolonged functionally defined delayed graft function, whereas IGFBP7 was not sensitive enough in the setting of kidney transplantation. 30540936_Enhancing IGFBP7 by overexpression or addition of recombinant human IGFBP7 (rhIGFBP7) resulted in differentiation, inhibition of cell survival, and increased chemotherapy sensitivity of primary acute myeloid leukemia cells. 30769262_IGFBP-7 was not confirmed as a predictor of mortality in the myocardial infarction patients. 30834595_IGFBP7 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HPAEpiC cells in response to radiation. 30982674_Tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) * IGF-binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) levels are associated with adverse outcomes in patients in the intensive care unit with acute kidney injury. 31267558_Results identified IGFBP7 protein as highly upregulated in the mesenchymal-resistant melanoma cells to MAPK inhibitors (MAPKi). In addition, IGFBP7 levels in patient sera were shown to be higher after relapse. 31287495_IGFBP7 has a role in regulating sepsis-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through ERK1/2 signaling 31397492_Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 accelerates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 31545454_Study indicated that IGFBP7 overexpression leads to the direct targeting of EMTassociated genes, which in turn regulates the metastatic behavior of colon cancer cells (CC). These data suggest the biological and clinical importance of IGFBP7 in colon cancer. In addition, downregulation of IGFBP7 in CC associated with the development of liver metastasis may facilitate the proliferation and expansion of CC cells. 31730227_Phenotypic delineation of the retinal arterial macroaneurysms with supravalvular pulmonic stenosis syndrome. 31791043_The effectiveness of urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7 in predicting acute kidney injury in critically ill neonates. 31822054_Serum Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 as a Potential Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma. 31856559_Urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 as biomarkers of patients with established acute kidney injury. 32066522_Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes induce secretion of IGFBP7 to form type II rosettes and escape phagocytosis. 32406612_Echocardiographic assessment of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7 and early identification of acute heart failure. 32475626_Clinical study of serum IGFBP7 in predicting lymphatic metastasis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. 32479185_Will urinary biomarkers provide a breakthrough in diagnosing cardiac surgery-associated AKI? - A systematic review. 32529639_IGFBP6 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and morphology via cyclin E-CDK2. 32548968_Elevated plasma sRAGE and IGFBP7 in heart failure decrease after heart transplantation in association with haemodynamics. 33009198_Urinary cell cycle arrest proteins urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 predict acute kidney injury after severe trauma: A prospective observational study. 33158949_Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 Predicts Renal and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study. 33189655_Plasma Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 Contributes Causally to ARDS 28-Day Mortality: Evidence From Multistage Mendelian Randomization. 33253093_Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 as a candidate biomarker for systemic sclerosis. 33411755_(TIMP2) x (IGFBP7) as early renal biomarker for the prediction of acute kidney injury in aortic surgery (TIGER). A single center observational study. 33441876_The predictive value of TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 for kidney failure and 30-day mortality after elective cardiac surgery. 34040195_SNORD116 and growth hormone therapy impact IGFBP7 in Prader-Willi syndrome. 34217226_IGFBP7 and GDF-15, but not P1NP, are associated with cardiac alterations and 10-year outcome in an elderly community-based study. 34303194_IGFBP7 overexpression promotes acquired resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer. 34438446_Physiologic IGFBP7 levels prolong IGF1R activation in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 34606580_Prognostic impact of tumor-specific insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) levels in breast cancer: a prospective cohort study. 34946293_Renal Impairment Detectors: IGFBP-7 and NGAL as Tubular Injury Markers in Multiple Myeloma Patients. 35076852_Association of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7 promoter methylation with esophageal cancer in peripheral blood. 35170890_Evaluating TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7 as a predictive tool for kidney injury in ureteropelvic junction obstruction. 35204773_IGFBP7 Concentration May Reflect Subclinical Myocardial Damage and Kidney Function in Patients with Stable Ischemic Heart Disease. 35307071_[Advances in the clinical value of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 in sepsis associated-acute kidney injury]. 35469565_Elevated Urinary Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2 and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-7 Predict Drug-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. 35604859_Perioperative Urinary TIMP-2*IGFBP7 and Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review. 35625639_Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 7 (IGFBP-7)-New Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Symptomatic Peripheral Arterial Disease?-Pilot Study. 35900339_IGFBP7 enhances trophoblast invasion via IGF-1R/c-Jun signaling in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. |
ENSMUSG00000036256 |
Igfbp7 |
289.150301 |
0.1186522478 |
-3.075189 |
0.120976223 |
776.577781 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000667678809074407135641601750169677258024324678907328395815469727237508074742360790793050503289638128751247887766091026669861846294336337454189721740926658991004 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000505381498560935862104528418910996268950911620954197390507295144528099323950292869376205057019125930385116355468374672304264966017848627446784393576393637784825 |
Yes |
No |
61.5389802 |
5.3412892 |
522.2529082 |
23.8982840 |
| ENSG00000163462 |
80128 |
TRIM46 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z4K8 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated protein that is involved in the formation of parallel microtubule bundles linked by cross-bridges in the proximal axon. Required for the uniform orientation and maintenance of the parallel microtubule fascicles, which are important for efficient cargo delivery and trafficking in axons. Thereby also required for proper axon specification, the establishment of neuronal polarity and proper neuronal migration. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TNM2}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes zinc-binding domains, a RING finger region, a B-box motif and a coiled-coil domain. TRIM46 is reported to be involved in the proliferation of multiple types of cancer cells including lung and breast cancer. It has also been shown to control neuronal polarity and axon specification by forming uniform microtubule bundles in the axon. [provided by RefSeq, May 2022]. |
hsa:80128; |
axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; axon initial segment [GO:0043194]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; main axon [GO:0044304]; proximal neuron projection [GO:1990769]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anterograde synaptic vesicle transport [GO:0048490]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; negative regulation of axon extension [GO:0030517]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; positive regulation of anterograde dense core granule transport [GO:1901953]; protein localization to axon [GO:0099612]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880] |
31918570_Clostridium difficile toxin B induces colonic inflammation through the TRIM46/DUSP1/MAPKs and NF-kappaB signalling pathway. 33556457_Axonal TAU Sorting Requires the C-terminus of TAU but is Independent of ANKG and TRIM46 Enrichment at the AIS. 34459501_SNP rs4971059 predisposes to breast carcinogenesis and chemoresistance via TRIM46-mediated HDAC1 degradation. 35354796_TRIM46 activates AKT/HK2 signaling by modifying PHLPP2 ubiquitylation to promote glycolysis and chemoresistance of lung cancer cells. 35670901_TRIM46 upregulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by inhibiting Axin1 to mediate hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HK2 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000042766 |
Trim46 |
81.648125 |
0.4977345292 |
-1.006552 |
0.183378279 |
30.425857 |
0.00000003468736137320657861344853347893013584268828708445653319358825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000143292878216772743539487913050356482358438370283693075180053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.1339668 |
6.4105395 |
107.4905703 |
8.6695298 |
| ENSG00000163468 |
7203 |
CCT3 |
protein_coding |
P49368 |
FUNCTION: Component of the chaperonin-containing T-complex (TRiC), a molecular chaperone complex that assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis (PubMed:25467444). The TRiC complex mediates the folding of WRAP53/TCAB1, thereby regulating telomere maintenance (PubMed:25467444). As part of the TRiC complex may play a role in the assembly of BBSome, a complex involved in ciliogenesis regulating transports vesicles to the cilia (PubMed:20080638). The TRiC complex plays a role in the folding of actin and tubulin (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080638, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25467444, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Isopeptide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a molecular chaperone that is a member of the chaperonin containing TCP1 complex (CCT), also known as the TCP1 ring complex (TRiC). This complex consists of two identical stacked rings, each containing eight different proteins. Unfolded polypeptides enter the central cavity of the complex and are folded in an ATP-dependent manner. The complex folds various proteins, including actin and tubulin. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized for this gene. In addition, a pseudogene of this gene has been found on chromosome 8. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:7203; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; chaperonin-containing T-complex [GO:0005832]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; zona pellucida receptor complex [GO:0002199]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; pore complex assembly [GO:0046931]; positive regulation of establishment of protein localization to telomere [GO:1904851]; positive regulation of protein localization to Cajal body [GO:1904871]; positive regulation of telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body [GO:1904874]; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase [GO:0032212]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
12586295_Among ten hepatocellular carcinoma cases with amplicon 1q21-q22, significant gene expression level of JTB, SHC1, CCT3 and COPA in the tumors than the paired adjacent non-malignant liver tissues. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22399500_Our results implicate a novel cell signaling loop in HCt116 cells involving p53 and TCP1-gamma phosphorylation, which may be related to regulation and action of centrosomes. 23868055_Expression of S100A9 and CCTgamma was significantly elevated in liver tissue of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with controls. 26229401_Overexpression of CCT3 in the nuclei of cancerous cells is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression. CCT3 may be a target that affects the activation of STAT3 in HCC. 26739059_Suggest that CCT3 is indispensible for hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, and provides a potential drug target for treatment of HCC. 31501420_CCT3 acts upstream of YAP and TFCP2 as a potential target and tumour biomarker in liver cancer. 31859543_Data suggest that circCCT3 circular RNA plays an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer (CRC) metastasis through miR-613/vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and Wnt signaling. 31902948_High expression of chaperonin-containing TCP1 subunit 3 may induce dismal prognosis in multiple myeloma. 33508424_CCT3 suppression prompts apoptotic machinery through oxidative stress and energy deprivation in breast and prostate cancers. 34505628_Identification of CCT3 as a prognostic factor and correlates with cell survival and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 34612768_Chaperonin containing TCP1 subunit 3 (CCT3) promotes cisplatin resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells through targeting the Janus kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT3) pathway. 34651664_Upregulation of CCT3 promotes cervical cancer progression through FN1. 35773623_Upregulation of CCT3 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation via inhibition of ferroptosis and activation of AKT signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000001416 |
Cct3 |
1945.959296 |
2.1327086097 |
1.092687 |
0.042436657 |
664.339402 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001700691310578785371546572395450156238928197214266443193652292639869710802002933979246004238675117720414397024209386453402249766796536270684757576624326133760621383587788437802809481064 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001068178882729483901443865261682142939016671332505186557193762480884831004702851089332315444729716884209107938728449745219319197493754641991958202933456529246070966858137830641610810934 |
Yes |
No |
2683.6608920 |
63.1590669 |
1267.3058632 |
23.3812376 |
| ENSG00000163491 |
152110 |
NEK10 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZWH5 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the cellular response to UV irradiation. Mediates G2/M cell cycle arrest, MEK autoactivation and ERK1/2-signaling pathway activation in response to UV irradiation. In ciliated cells of airways, it is involved in the regulation of mucociliary transport (PubMed:31959991). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20956560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31959991}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Ciliopathy;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Primary ciliary dyskinesia;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Enables protein kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including mucociliary clearance; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation; and regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. Part of protein kinase complex. Implicated in primary ciliary dyskinesia 44. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:152110; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; protein kinase complex [GO:1902911]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; mucociliary clearance [GO:0120197]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition [GO:1902749]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372] |
19330027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20095854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20145138_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20956560_Nek10 physically associated with Raf-1 and MEK1 in a Raf-1-dependent manner, and the formation of this complex was necessary for Nek10-mediated MEK1 activation. 31959991_analysis of a bronchiectasis syndrome caused by mutations that inactivate NIMA-related kinase 10 (NEK10), a protein kinase with previously unknown in vivo functions in mammals 32414360_Homozygous truncating NEK10 mutation, associated with primary ciliary dyskinesia: a case report. 32561851_NEK10 tyrosine phosphorylates p53 and controls its transcriptional activity. |
ENSMUSG00000042567 |
Nek10 |
55.427855 |
6.3595943086 |
2.668935 |
0.553394782 |
20.963463 |
0.00000468126453327267976839637722563658428498456487432122230529785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000015293374172444612558909721178324048196373041719198226928710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.6797724 |
36.9277186 |
15.9757981 |
4.3390491 |
| ENSG00000163507 |
57650 |
CIP2A |
protein_coding |
Q8TCG1 |
FUNCTION: Oncoprotein that inhibits PP2A and stabilizes MYC in human malignancies. Promotes anchorage-independent cell growth and tumor formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17632056}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables protein homodimerization activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation and spermatogenesis. Located in cytosol and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57650; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803] |
17632056_Data show that CIP2A/KIAA1524 is a human oncoprotein that inhibits protein phosphatase 2A and stabilizes c-Myc in human malignancies. 18559589_CIP2A in tumor cells is required for sustained proliferation by preventing cell growth arrest, senescence, or differentiation. 19470954_CIP2A and MYC appear to be regulated in a positive feedback loop, wherein they promote each other's expression and gastric cancer cell proliferation. 19671842_CIP2A is associated with clinical aggressivity in human breast cancer and promotes the malignant growth of breast cancer cells. 19959630_CagA upregulated CIP2A expression and this upregulation effect was dependent on Src and Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. 20842459_Overexpression of CIP2A is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 20964854_Expression of the CIP2A protein is increased in prostate cancer specimens and its expression is associated with poorly differentiated and high-risk tumors. 21068540_Data suggest that CIP2A may play a significant role in oral malignant transformation and therefore, it may be a potential target for chemotherapy of OSCC. 21140243_CIP2A is significantly overexpressed in human esophageal tumors 21219591_The high expression of CIP2A in HL60 cells may be related to active cell proliferation and arrest of cell differentiation. 21445343_results also suggest that in addition to its established role in invasion and angiogenesis, ETS1 may support malignant cellular growth via regulation of CIP2A expression and protein phosphatase 2A inhibition 21479604_The data demonstrated that CIP2A expression is closely associated with the histopathological score of synovitis and invasive function of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. 21490338_CIP2A is biologically and clinically important in chronic myeloid leukemia and may be a novel therapeutic target. 21575984_CIP2A plays an important role in carcinogenisis of cervical cancer and shows promise for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer. 21655278_Silencing CIP2A by siRNA inhibited the proliferation and clonogenic activity of lung cancer cells. 21874565_CIP2A expression in Chinese non-small-cell lung cancer patients may be a useful biomarker of biological malignancy 21897396_High Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A is associated with serous ovarian cancer. 22072119_CIP2A expression is elevated in cervical cancer. 22075943_Higher-CIP2A expression positively correlates with the aggressive phenotype of RCCs, and predicts poor prognosis for patients 22085493_Bortezomib sensitized solid tumor cells to radiation-induced apoptosis through the inhibition of CIP2A. 22249265_The results both validated CIP2A's role in regulating MYC-mediated gene expression and provided a plausible novel explanation for the high MYC activity in basal-like and HER2thorn breast cancers. 22310977_Overexpression of CIP2A in colorectal cancer patients may be an important step in colorectal carcinogenesis. Based on findings, CIP2A shows no association with patient prognosis in colorectal cancer, but is associated with nuclear c-Myc. 22537152_Data suggest that nontumoral cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A)mRNA expression might serve as a novel biomarker for HCC patients undergoing resection. 22537901_CIP2A is a major determinant mediating bortezomib-induced apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. 22847158_CIP2A overexpression may be useful as an independent prognostic biomarker for overall survival and disease-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. 22923389_CIP2A overexpression is associated with ovarian cancer. 23117818_The binding of Ets1 and Elk1 together to the proximal CIP2A promoter is absolutely required for CIP2A expression in cervical, endometrial and liver carcinoma cell lines 23178652_CIP2A may be useful as a therapeutic biomarker for predicting clinical response to erlotinib in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. 23275123_Our findings suggest that CIP2A is an independent predictor of poor prognosis of bladder urothelial cell carcinoma patients 23306062_Data show that E2F1 overexpression, due to p53 or p21 inactivation, promotes expression of human oncoprotein CIP2A. 23342256_CIP2A is an oncogene involved in bladder cancer as it is specifically expressed in bladder tumor tissue and not normal tissue. 23383345_Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A mediates bortezomib-induced autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma independent of proteasome. 23455633_show that CIP2A expression in rheumatoid arthritis FLS is an important mediator of dysfunctional apoptosis independent of c-Myc stabilization 23467938_These results validate the role of CIP2A as a clinically relevant oncoprotein and establish CIP2A as a promising therapeutic target of astrocytoma. 23471718_CIP2A expression may be a potential biomarker for chemotherapeutic sensitivity and prognosis of breast cancer. 23552692_Tumor suppressor miR-375 regulates MYC expression via repression of CIP2A coding sequence through multiple miRNA-mRNA interactions. 23568706_results indicate that CIP2A expressioncorrelates with altered expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers, increased lymph node metastasis, and poorer survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 23743567_Cox-regression analysis showed that IL-10 and CIP2A mRNA levels may independently predict survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma, especially in patients with E6-positive tumors 23802697_CIP2A immunoreactivity was usually weak or absent in indolent B-cell lymphomas, but moderately positive or strongly positive in almost all aggressive lymphomas, such as DLBCL, BL, and BCLU. 23983103_A novel function for CIP2A in facilitating the stability and activity of the pivotal mitotic kinase Plk1 in cell-cycle progression and tumor development. 24014087_our data identified CIP2A as a critical oncoprotein involved in cell proliferation and invasion, which could serve as a therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. 24019920_599 peptide-mediated siRNA delivery promoted significant CIP2A mRNA and protein silencing which resulted in decreased oral cancer cell invasiveness and anchorage-independent growth 24098375_Expression of CIP2A was found to be dependent on MAPK activity, linking elevated c-Myc expression to deregulated signal transduction in colon cancer 24163288_The expression levels of mRNA for CIP2A and PP2A exhibited positive correlation in MDS/control bone marrow. 24204027_CIP2A is a novel anticancer target based on PP2A reactivation and inhibition of the oncogenic activity of its downstream effectors.[review] 24214971_CIP2A strongly interacts with NEK2 during G2/M phase, thereby enhancing NEK2 kinase activity to facilitate centrosome separation in a PP1- and PP2A-independent manner. 24280132_Estradiol enhances CIP2A expression by the activation of p70 S6 kinase. 24369732_Downregulation of CIP2A attenuates migration and metastatic potential of cutaneous malignant melanoma cells. 24398514_These findings suggest that H. pylori-induced upregulation of CIP2A contributes to the development and progression of gastric cancer. 24399648_p90/CIP2A can induce autoantibody response in sera from patients with breast cancer 24493623_High CIP2A expression is associated with drug resistance in colon cancer. 24590173_CIP2A is a distinct regulator of mTORC1 and mTORC1-dependent control of CIP2A degradation is a mechanism that links mTORC1 activity with c-Myc stability to coordinate cellular metabolism, growth, and proliferation. 24839010_miR-218 is downregulated in melanoma. By targeting CIP2A and BMI1, miR-218 regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of the melanoma cell lines A375 and SK-MEL-2. 24874844_overexpression of CIP2A diminished NSCLC cell chemosensitivity to cisplatin by inducing activation of Akt pathway, suggesting critical roles of CIP2A in NSCLC cell chemoresistance to cisplatin 24884612_Downregulation of CIP2A suppresses cell proliferation and growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 24927563_SET is overexpressed in about 50-60% and CIP2A in about 90% of breast cancers. 24954871_The CIP2A-dependent pathway mediates the tumoricidal effects of erlotinib on NSCLC cells without EGFR mutations in vitro and in vivo. 25012485_findings indicate tumor suppressor protein PP2A and its inhibitor CIP2A are widely distributed in meningiomas with a tendency for higher CIP2A expression in at least some higher-grade meningiomas; findings raise the possibility that CIP2A may participate in biology of meningiomas 25015035_Studies indicate that oncoprotein CIP2A (KIAA1524) controls oncogenic cellular signals by suppressing protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A). 25023053_CIP2A is overexpressed in chronic myelocytic leukemia patients.Cip2a plays an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic myelocytic leukemia. 25086622_CIP2A as a crucial oncoprotein has been involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis, which may serve as a therapeutic target in breast cancer treatment. 25109354_study addressed a novel role of CIP2A in mediating lung cancer progression through interacting with the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. 25187431_Which increased PP2A activity. 25228280_Inhibition of CIP2A determines the effects of tamoxifen-induced apoptosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. 25325377_CIP2A regulates cancer metabolism and CREB phosphorylation in non-small cell lung cancer 25458953_High CIP2A expression is associated with cervical-cancer progression. 25474139_CIP2A is an Oct4 target gene involved in head and neck squamous cell cancer oncogenicity and radioresistance 25537503_Data show that afatinib reduced Elk-1 transcription factor binding to the CIP2A protein promoter and suppressed CIP2A transcription. 25736928_our findings strongly suggest that CIP2A promotes cell cycle progression, premature chromosome segregation, and aneuploidy, possibly through a novel interaction with Sgol1. 25765543_High cancerous inhibitor of PP2A (CIP2A) protein levels at diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukaemia are associated with disease progression in imatinib-treated patients 25833693_we provide a novel therapeutic mechanism for inhibiting CIP2A function in cancerous cells via targeting the CIP2A-LRRC59 interaction. 25896895_CIP2A is an independent prognostic marker in patients with wild-type KRAS metastatic colorectal cancer after colorectal liver metastasectomy. 25965834_Identify CIP2A as a common denominator for androgen receptor-signaling and prostate cancer stem cell functionality, and suggest as possible therapeutic target. 26234767_Alterations affecting PP2A subunits together with the deregulation of endogenous PP2A inhibitors such as CIP2A and SET have been described as contributing mechanisms to inactivate PP2A in prostate cancer. 26243398_These results suggest that CIP2A is involved in tumor progression in bladder cancer 26327467_CIP2A is a critical oncoprotein involved in cell invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition in clear cell renal carcinoma. 26404133_CIP2A is involved in regulating multidrug resistance of cervical adenocarcinoma. 26436875_CIP2A copy number increase is associated with poor patient survival in human HNSCC. 26522733_CIP2A was detected in tongue cancer and tongue hyperplasia, whereas local inflammation was stronger in cancer, CIP2A expression was increased in metastasized cancer compared to non-metastasized 26560124_CIP2A is a tumor-associated autoantigen in lung cancer, which promote lung cancer proliferation partially through MKK4/7-JNK signaling pathway. 26813457_CIP2A levels were significantly associated with the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) stage, histological grade and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients. 26823836_patients with a stronger expression of CIP2A in tgastric umor tissues had no significant relationship with these genes that are related to gastric cancer chemotherapy drug resistance 26894380_High CIP2A expression is associated with gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. 26987906_poor prognosis of chronic myeloid leukemia patients with high CIP2A levels is due to an antiapoptotic phenotype 27029072_These results are the first evidence that the inhibition of HDAC1 by (S)-2 downregulates CIP2A transcription 27144172_These results indicate that CIP2A modulates myeloma cell proliferation and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and suggest that it can potentially serve as a drug target for the treatment of multiple myeloma. 27348236_low expression associates with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps with aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease 27350399_Silencing CIP2A enhanced CuB-induced growth inhibition. 27484817_CIP2A is upregulated in MM, and CIP2A expression promotes cell proliferation and clonogenic formation ability by regulating the expression of AKT phosphorylation and c-Myc. 27694903_Cip2a effectively promotes triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell cycle progression and tumor growth via regulation of PP2A/c-myc/p27Kip1 signaling, which could serve as a potential therapeutic target for TNBC patients. 27779687_Gambogenic acid is a CIP2A inhibitor that interferes with the ubiquitination and destabilization of CIP2A. 28174209_Oncoprotein CIP2A is stabilized via interaction with tumor suppressor PP2A/B56 28521777_These data reveal that CIP2A is a crucial mediator of FN-induced bladder cancer cell proliferation via enhancing the stabilization of beta-catenin. 28534965_High expression of CIP2A is associated with cisplatin resistant gastric cancer. 28656258_High CIP2A expression is associated with laryngeal carcinoma. 29034804_Membranous CIP2A expression as a potential novel prognostic and predictive indicator for tamoxifen resistance. 29103022_CIP2A has higher expression in DDP-resistant GC patients. DDP-resistant GC patients with high CIP2A expression presented with poorer overall survival rates than those with low CIP2A expression. 29175329_confirmed the high mRNA and protein expression levels of CIP2A in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and found high CIP2A mRNA expression level was associated with unfavorable overall and recurrence-free survival in patients with HCC 29274810_that CIP2A plays an important role in the carcinogenesis of endometrioid adenocarcinoma 29491003_These data suggest that CIP2A promotes primary cilia disassembly and that CIP2A depletion induces metabolic reprogramming independent of primary cilia. 29703716_CIP2A- and SETBP1-mediated PP2A inhibition reveals AKT S473 phosphorylation to be a new biomarker in AML. 29846820_This study is the first to describe a pathogenic CIP2A mutation in humans, which might disrupt neuronal development via enhancing mTOR and c-Myc protein expressions, shedding light in mechanisms of Dandy-Walker variant pathogenesis. 29893470_CIP2A facilitates the G1/S cell cycle transition via B-Myb in human papillomavirus 16 oncoprotein E6-expressing cells. 30011381_High CIP2A expression is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 30021167_CIP2A-mediated PP2A inhibition drives tau/APP hyperphosphorylation and increases APP beta-cleavage and Abeta production. 30021854_MycN/CIP2A-mediated cell-fate bias may reflect a possible mechanism underlying early priming of some aggressive forms of neuroblastoma. 30063110_Endoplasmic reticulum stress-related ATF6 upregulates CIP2A and contributes to the prognosis of colon cancer. 30106121_Study revealed that the mechanism underlying the involvement of CIP2A in cisplatin sensitivity enhancement is that CIP2A mediates cisplatininduced cell apoptosis and DNA damage. 30119963_Aberrant expression of cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A) indicates poor prognosis and promotes EMT and metastasis. 30144452_CIP2A overexpression is associated with lung metastasis in colorectal cancer . 30181389_imultaneous presence of HOXB13 T and CIP2A T alleles confers for high prostate cancer risk and aggressiveness of disease, earlier biochemical relapse, and lower disease-specific life expectancy. HOXB13 protein binds to CIP2A gene and functionally promotes CIP2A transcription. 30671469_MiR-548b-3p regulates proliferation, apoptosis and mitochondrial function by targeting CIP2A in HCC. 31350330_The data demonstrate that AMPK mediates this novel CIP2A effect on energy generation in malignant cells. 31431792_Downregulation of CIP2A inhibits cancer cell proliferation and vascularization in renal clear cell carcinoma. 31490389_biomarker for metastasis and prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 32071079_Phosphoproteome and drug-response effects mediated by the three protein phosphatase 2A inhibitor proteins CIP2A, SET, and PME-1. 32321509_Effect of CIP2A and its mechanism of action in the malignant biological behavior of colorectal cancer. 32810922_Upregulation of CIP2A in estrogen depletion-resistant breast cancer cells treated with low-dose everolimus. 33078202_CIP2A regulates MYC translation (via its 5'UTR) in colorectal cancer. 33674272_Discovery of a Novel CIP2A Variant (NOCIVA) with Clinical Relevance in Predicting TKI Resistance in Myeloid Leukemias. 33804833_Constitutive Cell Proliferation Regulating Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A (CIP2A) Mediates Drug Resistance to Erlotinib in an EGFR Activating Mutated NSCLC Cell Line. 33892085_Depletion of CIP2A inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells. 34077593_Cip2A modulates osteogenic differentiation via the ERK-Runx2 pathway in MG63 cells. 34145035_CIP2A Interacts with TopBP1 and Drives Basal-Like Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis. 34739970_Integrative assessment of CIP2A overexpression and mutational effects in human malignancies identifies possible deleterious variants. 34984583_Cancerous Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A (CIP2A): Could It Be a Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Parkinson's Disease? 35286657_Chk1 Inhibition Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Cognitive Dysfunction Through CIP2A/PP2A Signaling. 35842428_The CIP2A-TOPBP1 complex safeguards chromosomal stability during mitosis. |
ENSMUSG00000033031 |
Cip2a |
100.951518 |
2.1203922907 |
1.084331 |
0.172077844 |
39.876969 |
0.00000000027047365364193445105194972575364444761225612978705612476915121078491210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001354662751189328971748352488033151352908589615253731608390808105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
134.0993180 |
13.7557028 |
63.6611782 |
5.0818588 |
| ENSG00000163513 |
7048 |
TGFBR2 |
protein_coding |
P37173 |
FUNCTION: Transmembrane serine/threonine kinase forming with the TGF-beta type I serine/threonine kinase receptor, TGFBR1, the non-promiscuous receptor for the TGF-beta cytokines TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3. Transduces the TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 signal from the cell surface to the cytoplasm and thus regulates a plethora of physiological and pathological processes including cell cycle arrest in epithelial and hematopoietic cells, control of mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation, wound healing, extracellular matrix production, immunosuppression and carcinogenesis. The formation of the receptor complex composed of 2 TGFBR1 and 2 TGFBR2 molecules symmetrically bound to the cytokine dimer results in the phosphorylation and activation of TGFBR1 by the constitutively active TGFBR2. Activated TGFBR1 phosphorylates SMAD2 which dissociates from the receptor and interacts with SMAD4. The SMAD2-SMAD4 complex is subsequently translocated to the nucleus where it modulates the transcription of the TGF-beta-regulated genes. This constitutes the canonical SMAD-dependent TGF-beta signaling cascade. Also involved in non-canonical, SMAD-independent TGF-beta signaling pathways. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7774578}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Has transforming growth factor beta-activated receptor activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8635485}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Has transforming growth factor beta-activated receptor activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8635485}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Binds TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 in the picomolar affinity range without the participation of additional receptors. Blocks activation of SMAD2 and SMAD3 by TGFB1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34568316}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aortic aneurysm;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Craniosynostosis;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth regulation;Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer;Kinase;Magnesium;Manganese;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane protein that has a protein kinase domain, forms a heterodimeric complex with TGF-beta receptor type-1, and binds TGF-beta. This receptor/ligand complex phosphorylates proteins, which then enter the nucleus and regulate the transcription of genes related to cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, wound healing, immunosuppression, and tumorigenesis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Marfan Syndrome, Loeys-Deitz Aortic Aneurysm Syndrome, and the development of various types of tumors. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:7048; |
caveola [GO:0005901]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; transforming growth factor beta ligand-receptor complex [GO:0070021]; activin binding [GO:0048185]; activin receptor activity [GO:0017002]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glycosaminoglycan binding [GO:0005539]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding [GO:0031435]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; transforming growth factor beta binding [GO:0050431]; transforming growth factor beta receptor activity [GO:0005024]; transforming growth factor beta receptor activity, type II [GO:0005026]; transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004675]; type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034713]; type III transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034714]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; aging [GO:0007568]; animal organ regeneration [GO:0031100]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; atrioventricular valve morphogenesis [GO:0003181]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; brain development [GO:0007420]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; bronchus morphogenesis [GO:0060434]; cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis [GO:0003214]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; common-partner SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0007182]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; embryonic cranial skeleton morphogenesis [GO:0048701]; embryonic hemopoiesis [GO:0035162]; endocardial cushion fusion [GO:0003274]; gastrulation [GO:0007369]; growth plate cartilage chondrocyte growth [GO:0003430]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; inferior endocardial cushion morphogenesis [GO:1905317]; Langerhans cell differentiation [GO:0061520]; lens development in camera-type eye [GO:0002088]; lens fiber cell apoptotic process [GO:1990086]; lung lobe morphogenesis [GO:0060463]; mammary gland morphogenesis [GO:0060443]; membranous septum morphogenesis [GO:0003149]; miRNA transport [GO:1990428]; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0043011]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060044]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0060389]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of B cell tolerance induction [GO:0002663]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:2000563]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:1905007]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0002053]; positive regulation of NK T cell differentiation [GO:0051138]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue regeneration [GO:0043415]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of T cell tolerance induction [GO:0002666]; positive regulation of tolerance induction to self antigen [GO:0002651]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:0072091]; response to cholesterol [GO:0070723]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; secondary palate development [GO:0062009]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; trachea formation [GO:0060440]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; tricuspid valve morphogenesis [GO:0003186]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11158177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11251969_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11741970_Altogether, these results identify a mechanism by which RhoB antagonizes TGF-beta action through transcriptional down-regulation of AP1 in T beta R-II promoter. 11744689_treatment with the HDAC inhibitor induces TbetaRII promoter activity by the recruitment of the PCAF protein to the NF-Y complex, interacting with the inverted CCAAT box in the TbetaRII promoter 11777969_Overexpression of a dominant negatively acting mutant of TGFBR2 in primitive hemopoietic progenitor cells renders them transiently unresponsive to both autocrine and paracrine TGF-beta signaling and leads to their enhanced survival and proliferation. 11820800_TGF beta type II receptor mRNA concentration on the surface of human osteoblasts is increased by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 due to changes in receptor mRNA stability not associated with an increase in the rate of gene transcription. 11850637_crystal structure of the human TbetaR2 ectodomain--TGF-beta3 complex 12060054_present in diabetic foot ulcer 12077447_TGFBII receptors were purified and refolded; they have an apparent molecular weight of 14 kDa as by size-exclusion chromatography 12174910_data suggest the existence of a further definite subgroup of diffuse-type gastric carcinomas with altered TGFbeta-IIR expression, independent from a mutator phenotype with TGFbeta-IIR gene mutations 12202987_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12215842_Differential rates of frameshift alterations in four repeat sequences of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer tumors.These repeats consisted of (A)10 in the TGF beta RII, (G)8 in the BAX, (A)8 in the CASP1, and (CCA)7 in the APP genes. 12479849_Coding region microsatellite mutations characteristic of defective mismatch repair Identification of TGFbetaRII coding region microsatellite mutations in vivo implicates this gene in the pathogenesis of human T-LBL/ALL. 12515396_This protein was expressed locally in the media and adeventitia at injected arterial segments without any significant dissemination to remote areas. 12607775_TGF-beta2 receptor expression in peritoneal fibroblasts was increased by hypoxia or hypoxia plus TGF-beta1, but decreased by TGF-beta1 alone. 12736050_The loss of TbetaR-II expression in the primary tumor is associated with clinical stage (P A (D446N)in a patient with Loeys-Dietz syndrome; DNA from leukocytes, buccal cells, hair root cells, & nails in the father indicated 52%, 25%, 0%, & 35% of cells harbored the mutation 19020727_sTbetaRII attenuates the biological activities of TGF-beta in colorectal cancer 19088080_the TGFbeta pathway activation leads to recruitment of a KLF14-mSin3A-HDAC2 repressor complex to the TGFbetaRII promoter, as well as the remodeling of chromatin to increase histone marks that associate with transcriptional silencing. 19147499_TGF-beta1 elevates TbetaRII homodimerization to some degree and strongly enhances TbetaRI.TbetaRII heteromeric complex formation. 19161338_High-affinity binding of TGF-beta1/3 to TGF-betaRII is primarily due to hydrogen bonding between Arg25 and 94 of TGF-beta1/3, and Glu119 and Asp32 of TbetaR-II. Arg25 and 94 are substituted by Lys in TGF-beta2, which binds with low affinity to TbetaR-II. 19193655_hENT1 is down-regulated by activation of TbetaRII by TGF-beta1 in endothelium from umbilical veins. 19229971_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19293232_The TGFBR2 presence reduced binding of probes specific for a core substitution and increased branch length in N-glycosylation, even reaching a P-value of 0.0016. 19299629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19335617_Data show that co-expressing constitutively active type I and type II receptors resulted in the phosphorylation of both R-Smad subclasses in a ligand-independent manner. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19356148_These results indicate that the extracellular domain of TbetaRII mediates receptor partitioning into membrane rafts and efficient entrance into caveolin-positive endosomes. 19366699_Critical role of type II receptors in balancing BMP9 signaling via ALK1 and emphasize the essential role for BMPR-II in a subset of BMP9 responses in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. 19424605_1167Cright curved arrow T (Asn389Asn) polymorphism of TGFBR2 were most significantly associated with chronic kidney disease in low-risk individuals. 19426152_loss of TGFbetaRII in hepatocellular carcinoma triggers activation of the TNF pathway known to be regulated by TGF-beta(1) network 19434696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19503063_The four most frequently mutated genes in colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability were ACVR2 (92%), TAF1B (84%), ASTE1/HT001 (80%) and TGFBR2 (77%). 19533785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19533785_Out of 41 probands with Marfan syndrome, six were identified to have novel TGFBR2 mutations (one frameshift and five missense mutations). 19538865_Low expression of Smad4 and TbetaRII may promote metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 19542084_Individuals with TGFBR2 mutations are more likely to dissect at aortic diameters C transition in exon 4 of TGFBR2; the other was heterozygous for a c.1561 T > C transition in exon 7 of TGFBR2 20374083_upregulation of the TGFbeta2 level is a common pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains and suggests that it may be closely linked to the development of neuronal death related to AD. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20410122_Disruption of TGF-beta due to ttranscriptional dysregulation of TGF-beta receptor type II is associated with polyglutamine-induced motor neuron damage in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. 20428796_The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of TGF-beta1 targeting by antisense oligonucleotides on the RNA synthesis and protein expression of TGF-beta isoforms and their receptors in keloid-derived fibroblasts. 20457266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20518838_All 3 SNPs tested were significantly different between nonsegmental vitiligo patients & controls (rs2005061, rs3773645, & rs3773649). Haplotype 1 (CG) and haplotype 2 (GA) of the linkage disequilibrium block were associated with a risk of NSV. 20518838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20565851_TGFbetaRII mutations are relatively late events in the genesis of colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability. 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20599261_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20621662_Downregulation of TGF beta R-II expression by cigarette smoke-induced Egr-1 may contribute to smoking-induced premature skin aging. 20628007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628007_TGFBR2 mutations alter smooth muscle cell phenotype and predispose to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20662850_the connective tissue weakness does not relate to mutations in the genes FBN1, TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 20701609_miR-21 expression in cord and increased TGFBR2 expression is associated with antenatal IgE production and development of allergic rhinitis 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20805453_The TGFBR2 metagene(s) showed significant association with a better outcome in ER-positive breast tumors (without stratification by proliferative status) in two of the three data sets. 20840324_TGFBRII protein expression in benign prostatic hyperplasia is associated with prostate gland volume and with CD4 T-lymphocyte prostatitis. 20864512_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20878063_The simultaneous expression of Endoglin (CD105), transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 and TGF-beta receptor (R) II were quantified in normal human colon, pre-malignant dysplastic tissue, and invasive colon cancer specimens 21098638_The balance between defects in Smad and ERK signaling might be an important determinant of phenotypic severity in disorders related to mutations in TGFBR2. 21131601_Data suggest a novel mechanism for MEK1 in regulating the sensitivity to TGF-beta signaling by stabilizing TbetaRII. 21170488_Studies indicate that endoglin (CD105) interacts with type I and type II TGF-beta receptors and modulates TGF-beta signaling. 21172820_TbetaRII alone is able to mediate TGFbeta signaling to ERK1/2 without participation of TbetaRI. 21249319_Expression of TssRII mRNA was significantly higher in clear cell adenocarcinoma and mucinous adenocarcinoma, while it was lower in serous adenocarcinoma and endometrioid adenocarcinoma. 21270064_findings indicate that TGFBR2 gene mutations are responsible for sCAD in 3.6% (95% CI 0.0 to 8.4) of cases. 21295082_CD109 regulates TGF-beta receptor endocytosis and degradation to inhibit TGF-beta signaling. 21324918_Case Report: Loeys-Dietz syndrome can result from TGF-bR2 mutations in the absence of obvious physical features and can exhibit a fulminant course. 21352603_The restoration of the expression of TbetaRII and TbetaRIII in oral cancerous tissues may represent a novel strategy for the treatment of oral carcinoma. 21423151_These results provide evidence that the two TbetaRI:TbetaRII heterodimers bind and mediate TGF-beta3 signalling. 21609163_The synonymous SNP (rs2228048, Asn389Asn) of the TGFBR2 gene was found to be associated with the development of intracerebral hemorrhage in the South Korean population. 21666718_study concludes that miR-370 is a miRNA that is associated with GC progression by downregulating TGFbeta-RII 21701930_Global comparison of gene expression profiles identified 2 striking differences in treated tumors relative to untreated tumors: a marked increase in IGBFP3 and concomitant decrease in TGFb-R2 gene and protein expression. 21725601_RNA interference (RNAi) technology was used to silence the expression of TGF-beta receptor, type II (TGFbetaRII) in the LAC cell line, A549, and its effects on cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis were examined. 21737283_This study provided that TGFR-beta2-875 G/G genotype is a risk factor for brain arteriovenous malformation. 21757750_Histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat represses survivin expression through reactivation of transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) receptor II leading to cancer cell death 21785915_TGFBR1 Int7G24A and TGFBR2 G-875A polymorphisms may play important roles in the risk of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma in North China. 21789464_in 4 families linkage with the FBN1 and TGFBR2 genes was excluded, and no mutations were identified in the coding region of TGFBR1, indicating the existence of other genes involved in Marfan syndrome. 21815248_TGFBR1, TGFBR2, and ACTA2 mutations were found in 4 families with thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections and predominantly fusiform intracranial aneurysms. 21855067_This study suggests that two common genetic polymorphisms in TGFBR2 are associated with the risk of developing abdominal aortic aneurysm 21924348_atypical protein kinase C isoforms regulate transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) signaling by altering cell surface TGFB receptor trafficking and degradation 21949851_TGFBR2 mutations are not associated with the microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer. 21978186_The evidence suggests that TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 are not susceptibility genes for intracranial aneurysm in this populati |
ENSMUSG00000032440 |
Tgfbr2 |
1127.476796 |
0.4386699176 |
-1.188792 |
0.046170450 |
676.901081 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003153813512987653066527308868291301212784028319340587391443911610711496785021355140175791928823176474195112797851592279501518920127998725261533948461884138385584218270958473808433809 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002068901664519900356072945880472156509518487220723422905974091980004047053884244397738429281461282826182762951333425779858106770379850320924899039352270259083151038770537880777830651 |
Yes |
Yes |
706.2035653 |
21.0399273 |
1621.3541835 |
31.0488729 |
| ENSG00000163516 |
55139 |
ANKZF1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H8Y5 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the cellular response to hydrogen peroxide and in the maintenance of mitochondrial integrity under conditions of cellular stress (PubMed:28302725). Involved in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28302725}. |
ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. Involved in cellular response to hydrogen peroxide. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55139; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
28302725_loss-of-function mutations in ANKZF1 result in deregulation of mitochondrial integrity, and this may play a pathogenic role in the development of infantile-onset inflammatory bowel disease 29632312_ANKZF1 peptidyl-tRNA hydrolases release nascent chains from stalled ribosomes 30244831_Rendering 60S RNCs resistant to Ptrh1 but susceptible to ANKZF1. 31257922_High ANKZF1 is an independent factor of poor survival (overall survival and recurrence-free survival) in colon cancer by taking part in angiogenesis and some cancer signaling pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000026199 |
Ankzf1 |
198.525638 |
0.4179395062 |
-1.258634 |
0.172365070 |
52.667931 |
0.00000000000039498818949383776406018741608303738717215825015927066488075070083141326904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002419097791256865315205506126796835338500085699209307676937896758317947387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
119.0396024 |
12.8432681 |
287.4180965 |
21.2900631 |
| ENSG00000163517 |
79885 |
HDAC11 |
protein_coding |
Q96DB2 |
FUNCTION: Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11948178}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a class IV histone deacetylase. The encoded protein is localized to the nucleus and may be involved in regulating the expression of interleukin 10. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:79885; |
histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; histone deacetylase activity [GO:0004407]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003] |
11948178_cloning and functional characterization 16142391_Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis localized HDAC11 gene to chromosome 3p25, a region characterized by frequent gains and losses of chromosomal material in a number of various types of cancer. 17201809_the absence of tumour-specific somatic events in WNT7A and HDAC11 suggests that these genes are unlikely to have a classical tumour suppressor gene role in sporadic malignant pancreatic endocrine tumours 19011628_HDAC11 negatively regulated expression of the gene encoding interleukin 10 in antigen-presenting cells. 19276081_Cdt1 undergoes acetylation and is reversibly deacetylated by HDAC11 20467334_We found a reduction of HDAC 11 mRNA and increased HDAC 2 levels in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis brain and spinal cord compared with controls. 20980834_HDAC11 associates with replication origins inhibits Cdt1-induced re-replication and suppresses MCM loading. 21239696_These results demonstrate for the first time that HDAC11 plays an essential role in regulating OX40L expression. 21806350_Data indicate a pronounced deregulation of HDAC genes HDAC9 and HDAC11 in patients with Philadelphia-negative chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms: essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV) and primary myelofibrosis (PMF). 23024001_High HDAC11 expression is associated with neoplasms. 28252645_Our study identified a group of cell cycle-promoting genes regulated by HDAC11. 28782861_Results showed that the high levels of HDAC11 and lower levels of p53 were detected in pituitary tumor cells. A negative correlation was detected between the data of HDAC11 and p53. 29222071_HDAC11 was initially identified as a negative regulator of the well-known anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Hence, antagonizing HDAC11 activity may have anti-tumor potential, whereas activating HDAC11 may be useful to treat chronic inflammation or autoimmunity. 29336543_report in vitro profiling of HDAC11 deacylase activities 29523311_Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection disturbs the HDAC6/HDAC11 levels to induce IL-10 expression in macrophages. 29655790_The results indicated that HDAC11 was significantly expressed in human and mouse diabetic heart failure (DHF) hearts. 30007011_IL-10 expression was compromised in the peripheral B cells of allergic rhinitis (AR) patients. Inhibition of HDAC11 restored the IL-10 expression ability in the AR-B cells. We also found a negative correlation between HDAC11 and the expression of IL-10 in B cells; this fact indicates that HDAC11 interferes with the expression of IL-10 in B cells. 30063898_HDAC11 is a regulatory molecule in Th2 response and plays a critical role in the restriction of the biased IL-13 expression in CD4(+) T cells of the heart. 30819897_regulates type I interferon signaling through defatty-acylation of SHMT2 32170113_Novel HDAC11 inhibitors suppress lung adenocarcinoma stem cell self-renewal and overcome drug resistance by suppressing Sox2. 32705287_Long noncoding RNA BCYRN1 promotes prostate cancer progression via elevation of HDAC11. 33602787_HDAC11 Regulates Glycolysis through the LKB1/AMPK Signaling Pathway to Maintain Hepatocellular Carcinoma Stemness. 33891374_HDAC11: a multifaceted histone deacetylase with proficient fatty deacylase activity and its roles in physiological processes. 35657209_A pan-cancer analysis identifies HDAC11 as an immunological and prognostic biomarker. 36087429_HDAC11 negatively regulates antifungal immunity by inhibiting Nos2 expression via binding with transcriptional repressor STAT3. |
ENSMUSG00000034245 |
Hdac11 |
45.578213 |
0.1380581094 |
-2.856652 |
0.783066801 |
11.706100 |
0.00062295537408909641176324445410728003480471670627593994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001505200682636874702155505012513003748608753085136413574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.4229874 |
7.2622549 |
76.9479025 |
37.1580260 |
| ENSG00000163536 |
5274 |
SERPINI1 |
protein_coding |
Q99574 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease inhibitor that inhibits plasminogen activators and plasmin but not thrombin (PubMed:9442076, PubMed:26329378, PubMed:19265707, PubMed:19285087, PubMed:11880376). May be involved in the formation or reorganization of synaptic connections as well as for synaptic plasticity in the adult nervous system. May protect neurons from cell damage by tissue-type plasminogen activator (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11880376, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19265707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19285087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26329378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9442076, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Neurodegeneration;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serpin superfamily of serine proteinase inhibitors. The protein is primarily secreted by axons in the brain, and preferentially reacts with and inhibits tissue-type plasminogen activator. It is thought to play a role in the regulation of axonal growth and the development of synaptic plasticity. Mutations in this gene result in familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies (FENIB), which is a dominantly inherited form of familial encephalopathy and epilepsy characterized by the accumulation of mutant neuroserpin polymers. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5274; |
cytoplasmic vesicle lumen [GO:0060205]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155] |
11880376_Mutant Neuroserpin (S49P) that causes familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies is a poor proteinase inhibitor and readily forms polymers in vitro 12228252_The interactions between NSP and t-PA were distinct from those between plasmin and NSP, suggesting that the physiologic effect of t-PA-NSP interactions may be more complex than previously thought. 14983220_Neuroserpin has a role as a selective inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator in the central nervous system [review] 15090543_neuroserpin mutants that cause dementia accumulate as polymers within the endoplasmic reticulum 15269833_tissue plasminogen activator and neuroserpin are widely expressed in the human central nervous system 15291813_reactive centre loop of neuroserpin Portland being partially inserted into beta-sheet A to adopt a conformation similar to an intermediate on the polymerization pathway 15664988_Data show that the S49P mutant of neuroserpin that causes the dementia familial encephalopathy with neuroserpin inclusion bodies (FENIB) forms a latent species in vitro and in vivo in addition to the formation of polymers. 16849336_neuroserpin interacts with Abeta(1-42) to form off-pathway non-toxic oligomers and so protects neurons in Alzheimer disease 17212813_intergenic region of the head-to-head PDCD10-SERPINI1 gene pair provides an interesting and informative example of a complex regulatory system 17606885_in a French family with the S52R mutation of the neuroserpin gene, progressive myoclonic epilepsy was associated with a frontal syndrome 17961231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17961231_This study provides the first evidence that neuroserpin is associated with early-onset ischemic stroke among Caucasian women. 18051703_conformational modification in the protein under oxidative stress 18591508_We report a neuroserpin mutation that causes electrical status epilepticus of slow-wave sleep. 19222708_Neuroserpin and tissue plasminogen activator are associated with amyloid-beta plaques in Alzheimer brain tissue. 19265707_Human neuroserpin: structure and time-dependent inhibition 19423540_Analyses restricted to glioblastoma (n = 254) yielded significant associations for the SELP, DEFB126/127, SERPINI1, and LY96 genetic regions. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423713_intracellular neuroserpin polymers activate NF-kappaB by a pathway that is independent of the IRE1, ATF6, and PERK limbs of the canonical unfolded protein response but is dependent on intracellular calcium 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20691191_investigated the refolding and polymerization pathways of wild-type neuroserpin and of the pathogenic mutants S49P and H338R 21081089_The latent and polymer hNS forms obtained at 45 degrees C and 85 degrees C differ in their chemical and thermal stabilities; furthermore, the human neuroserpin polymers also differ in size and morphology 21174006_high serum neuroserpin levels before intravenous tPA and neuroserpin levels decrease at 24 h after ischaemic stroke, independently of tPA treatment, may have a role in good functional outcome 21487809_our study did not provide any evidence for an association between genetic variation at the SERPINI1 locus and ischemic stroke 21507957_Hrd1 and gp78 mediate mutant neuroserpin turnover through the ERAD pathway. 21569344_Neuroprotective properties of neuroserpin may be related to the inhibition of excitotoxicity, inflammation, as well as blood brain barrier disruption that occur after acute ischemic stroke. 21961602_the origins of conformational lability 24036060_Alzheimer's disease brain tissues with elevated neuroserpin protein also showed increased expression of THRbeta1 and HuD 25450507_Molecular Dynamics simulations suggest that Neuroserpin conformational stability and flexibility arise from a spatial distribution of intramolecular salt-bridges and hydrogen bonds. 25670787_Neuroserpin is expressed in naive effector memory and central memory CD4 and CD8 T cell subsets, and monocytes, B cells, and NK cells. T-cell activation caused its translocation to the immunologic synapse, secretion, and delayed downregulation. 26176694_the protective effect of neuroserpin maybe independent from its canonical interaction with a tissue-type plasminogen activator 26329378_The thermal and chemical stability along with the polymerisation propensity of both Wild Type and Glu289Ala NS were characterized. 26367528_This C-terminal lability is not required for neuroserpin polymerisation in the endoplasmic reticulum, but the additional glycan facilitates degradation of the mutant protein during proteasomal impairment. 26892864_SERPINI1 is an important regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in an orthotopic implantation model of colorectal cancer 27737651_Data indicated that rs9853967 and rs11714980 polymorphisms in CCM3 and SERPINI1respectively could be associated with a protective role in cerebral cavernous malformations disease. 28631894_We present two pediatric cases of progressive myoclonic epilepsy with SERPINI1 pathogenic variants that lead to a severe presentation. 30644551_Neuroserpin expression during human brain development and in adult brain revealed by immunohistochemistry and single cell RNA sequencing. 31805346_Deficits in developmental neurogenesis and dendritic spine maturation in mice lacking the serine protease inhibitor neuroserpin. 32003693_Neuroserpin in Bipolar Disorder. 33516851_Contrasting conformational dynamics of beta-sheet A and helix F with implications in neuroserpin inhibition and aggregation. 33893722_Detection of truncated isoforms of human neuroserpin lacking the reactive center loop: Implications in noninhibitory role. |
ENSMUSG00000027834 |
Serpini1 |
913.315115 |
0.4317729845 |
-1.211655 |
0.070869201 |
290.070014 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004800659676463470336061455938491643024500178056450957682853216057400426207752943832524695391822123857056657543211653558886173006446478986607469646367727318905425058781499814131166203878819942474365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001344549085855803058224992545597894233299976876086010382420499092106282742222343559125052923887278286361308358366383406263701333700605396842672601246915063547340829508414117299253121018409729003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
585.6174031 |
25.8396097 |
1366.5971233 |
41.2915093 |
| ENSG00000163545 |
81788 |
NUAK2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H093 |
FUNCTION: Stress-activated kinase involved in tolerance to glucose starvation. Induces cell-cell detachment by increasing F-actin conversion to G-actin. Expression is induced by CD95 or TNF-alpha, via NF-kappa-B. Protects cells from CD95-mediated apoptosis and is required for the increased motility and invasiveness of CD95-activated tumor cells. Phosphorylates LATS1 and LATS2. Plays a key role in neural tube closure during embryonic development through LATS2 phosphorylation and regulation of the nuclear localization of YAP1 a critical downstream regulatory target in the Hippo signaling pathway (PubMed:32845958). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14575707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15345718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19927127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32845958}. |
Acetylation;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Enables ATP binding activity; magnesium ion binding activity; and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to glucose starvation; negative regulation of apoptotic process; and protein phosphorylation. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. Implicated in anencephaly. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:81788; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035330] |
11284715_This study describes the cloning and characterization of the rat SNARK homolog, mapping of the human SNARK gene to 1q32, and a potential functional role as mediator of the cellular response to metabolic stress. 15345718_SNARK is an NF-kappaB-regulated anti-apoptotic gene that contributes to the tumor-promoting activity of CD95 in apoptosis-resistant tumor cells 18023418_These data suggests different phosphorylation and regulation of MYPT1 activity by NUAK2. 18452098_EBV LMP1 upregulated the expression of SNARK; SNARK expression increased drug resistance in response to doxorubicin increased of cancer cell survival 18992219_The nuclear localizing SNARK altered transcriptome profiles and a considerable part of these alterations were canceled by the mutation of NLS, suggesting the ability of SNARK to modulate gene expression dependent on its nuclear localization. 19652946_Skeletal muscle SNARK expression is increased in human obesity, and in response to metabolic stressors, but not type 2 diabetes. Partial SNARK depletion failed to modify either glucose or lipid metabolism. 20713714_Data show that SNARK is activated by muscle contraction and is a unique mediator of contraction-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle. 21242312_MLCP (myosin light chain phosphatase) activation is counteracted by a previously unrecognized association between MRIP (myosin phosphatase Rho-interacting protein) and the inducible kinase NUAK2 21460252_This study further supports the importance of NUAK2 in cancer development and tumor progression, while AMPK has antioncogenic properties. 21911917_Considers possible roles of NUAK2 in tumorigenesis in general and suggest that NUAK2 has pivotal roles in acral melanomagenesis. 22796592_Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase protects the integrity of the blood-brain barrier by suppressing the induction of NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide anions. 23831117_The AMPK-related kinase SNARK regulates hepatitis C virus replication and pathogenesis through enhancement of TGF-beta signaling. 25732129_Sucrose non-fermenting AMPK related kinase/Pentraxin 3 combined role in immunometabolic signaling and DNA damage response is proposed to accelerate cardiovascular complications in systemic lupus erythematosus patients 25832654_NUAK2 silencing and inactivation of the PI3K pathway efficiently controlled CDK2 expression, whereas CDK2 inactivation specifically abrogated the growth of NUAK2-amplified and PTEN-deficient melanoma cells. 27081712_miR143 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of the glioblastoma cells by degrading NUAK2 in glioblastoma. 29298809_Data (including data from studies in knockout and transgenic mice) suggest that NUAK2/SNARK is involved in both adipose inflammation and energy metabolism in adipocytes; additionally, genome-wide association studies suggest that 2 SNPs in NUAK2/SNARK (rs4682880, rs4682676) are associated with obesity in women. 32001115_NUAK2 localization in normal skin and its expression in a variety of skin tumors with YAP. 32845958_A loss-of-function NUAK2 mutation in humans causes anencephaly due to impaired Hippo-YAP signaling. 33880593_lncRNA FGD5AS1 promotes breast cancer progression by regulating the hsamiR1955p/NUAK2 axis. 34558636_NUAK2 silencing inhibits the proliferation, migration and epithelialtomesenchymal transition of cervical cancer cells via upregulating CYFIP2. 35343079_GPR65 promotes intestinal mucosal Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation and gut inflammation through downregulating NUAK2. |
ENSMUSG00000009772 |
Nuak2 |
27.456010 |
0.2618889339 |
-1.932973 |
0.363284811 |
29.131256 |
0.00000006763696381985328476781592355049355091978213749825954437255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000270841450347540504382814769562815016001877665985375642776489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.6339429 |
2.6321974 |
44.7367904 |
6.0189478 |
| ENSG00000163568 |
9447 |
AIM2 |
protein_coding |
O14862 |
FUNCTION: Involved in innate immune response by recognizing cytosolic double-stranded DNA and inducing caspase-1-activating inflammasome formation in macrophages (PubMed:17726700, PubMed:19158675, PubMed:19158676, PubMed:19158679, PubMed:20566831). Upon binding to DNA is thought to undergo oligomerization and to associate with PYCARD initiating the recruitment of caspase-1 precursor and processing of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-18 (PubMed:17726700, PubMed:19158675, PubMed:19158676, PubMed:19158679, PubMed:20566831). Detects cytosolic dsDNA of viral and bacterial origin in a non-sequence-specific manner (PubMed:17726700, PubMed:19158675, PubMed:19158676, PubMed:19158679, PubMed:20566831). Also acts as a mediator of pyroptosis, necroptosis and apoptosis (PANoptosis), an integral part of host defense against pathogens, in response to bacterial infection (By similarity). Can also trigger PYCARD-dependent, caspase-1-independent cell death that involves caspase-8 (By similarity). Tumor suppressor which may act by repressing NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity (PubMed:16432157). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91VJ1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16432157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17726700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19158675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19158676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19158679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20566831}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor |
|
AIM2 is a member of the IFI20X /IFI16 family. It plays a putative role in tumorigenic reversion and may control cell proliferation. Interferon-gamma induces expression of AIM2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9447; |
AIM2 inflammasome complex [GO:0097169]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; activation of innate immune response [GO:0002218]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to interferon-beta [GO:0035458]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:0044546]; pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002221]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:2001056]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; pyroptosome complex assembly [GO:1904270]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209] |
15076139_AIM-2 antigen is expressed in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) in primary cultured cells and established GBM cell lines 15582594_AIM2 could homodimerise via the amino-terminal (PAAD/DAPIN) region and heterodimerise with the related IFI 16 protein 16432157_AIM2 associates with tumor suppression activity 17726700_inactivation of AIM2 by genetic and epigenetic mechanisms is frequent in Mismatch repair -deficient colorectal cancers, thus suggesting that AIM2 is a mutational target relevant for the progression of MSI-H colorectal cancers. 19158675_observations identify AIM2 as a new receptor for cytoplasmic DNA, which forms an inflammasome with the ligand and ASC to activate caspase-1 19158676_identification of AIM2 as an important inflammasome component that senses potentially dangerous cytoplasmic DNA, leading to activation of the ASC pyroptosome and caspase-1 19293232_The AIM2 influenced core 1 mucin-type O-glycosylation differentially, downregulation by AIM2. 19795419_AIM2 mediates reduction of cell proliferation by cell cycle arrest, thereby conferring an invasive phenotype in colon cancer cells. 20401524_[REVIEW] role of AIM2 in innate immunity against F. tularensis in particular, and how infection of macrophages with this pathogen is thought to activate AIM2 20595294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21471287_Differential roles for the interferon-inducible IFI16 and AIM2 innate immune sensors for cytosolic DNA in cellular senescence of human fibroblasts 21550598_supragingival and subgingival biofilms differentially regulate the gene expressions of AIM2 in gingival fibroblasts 21804607_data indicate that AIM2 mediates both IFN-gamma dependent and independent induction of several interferon-stimulated genes 21883803_The author show that Francisella mutant strains deficient for membrane-associated proteins or deficient for genes involved in O-antigen or LPS biosynthesis lyse more intracellularly, thus activating AIM2-dependent pyroptosis. 22092578_Human keratinocytes express a functional AIM2 inflammasome which triggers a strong IL-1beta release in response to cytosolic dsDNA. 22140256_a pathway activating DNA damage signaling plays an important independent role in detecting intracellular foreign DNA, thereby complementing the induction of IFN and activation of the AIM2 inflammasome 22320325_expression of AIM2 and IFI16 may have oncogenic activities in the OSCC cells that have inactivated the p53 system. 22483801_crystal structures of their HIN domains in complex with double-stranded (ds) DNA. 22869553_End binding protein 1 directly interacted with AIM2 and ASC in vitro and in vivo. 23171461_Our data highlight the dynamics of epidermal AIM2 expression, showing Langerhans cell and melanocyte-restricted expression in normal epidermis but a pronounced induction in subpopulations of epidermal keratinocytes under inflammatory conditions. 23376086_Data suggest that AIM2 (absent in melanoma 2) expression is correlated with the immune clearance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in the host. 23479181_AIM2 might act as an important DNA sensor and a potential biomarker for apopDNA-induced macrophage functional maturation and SLE disease 23530044_Novel structural features of the AIM2 pyrin domain and insights into the potential mechanisms of domain interactions important for AIM2 autoinhibition and inflammasome assembly. 23764897_Binding of Human papillomavirus 16 DNA leads to AIM2 inflammasome activation. 23790454_Vascular endothelial/smooth muscle cells are able to respond to inflammatory signals by upregulation of AIM2 expression, indicating a role of AIM2 in vascular pathogenesis. 23811549_this study was to investigate the mRNA levels of AIM2 and ASC in a lymphocyte cell line (Jurkat) before and after MiR-143 introducing. 23864729_AIM2 mRNA levels were higher in benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH)than normal prostate; levels of AIM2 mRNA were lower in clinical tumor specimens; constitutive levels of AIM2 mRNA and protein were lower in a subset of prostate cancer cells compared with BPH cells; Implication that AIM2 inflammasome has a fundamental role in the generation of prostatic diseases 24164899_Studies indicate that the HIN (hematopoietic expression, interferon-inducible nature, and nuclear localization) domains exhibit either absent in melanoma2 (Aim2) HIN-like or p202 HINa-like modes of DNA binding. 24244322_Ethanol inhibits activation of NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes in human macrophages--a novel anti-inflammatory action of alcohol. 24419611_These results, together with the reported data on p202 HINb, lead to an interaction model for full-length p202 and dsDNA which provides a conceivable mechanism for the negative regulation of Aim2 inflammasome activation by p202. 24618883_Increased expression and activation of absent in melanoma 2 inflammasome components in lymphocytic infiltrates of abdominal aortic aneurysms 24701032_caspase-1, IL-1beta, and IL-18 are regulated by AIM2, which mediates inflammation-associated renal damage in hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis 24729378_Lack of Absent in Melanoma 2 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 24971542_Thus, autophagy may function as a negative counter-regulatory mechanism for HMGB1-DNA complex-induced inflammasome activation, and provide a checkpoint to limit the development of inflammation. 24986444_These results suggest that AIM2 expressed in human dental pulp plays an important role in the immune defense by activating the inflammasome signaling pathway. 25164813_EB1 has a role in linking AIM2 inflammasomes with autophagy-dependent secretion 25173967_activation of the AIM2 inflammasome did not require a priming signal in ascitic fluid-derived macrophages, demonstrating the preactivated state of the inflammasome in these cells. 25888795_The comparison shows mouse AIM2 PYD domain adopts a unique alpha2-alpha3 helix conformation distinct from its human homologues, but similar to the pyrin domain of human NLRP10/PYNOD, which belongs to another family. 26197926_pyrin domain drives both filament formation and dsDNA binding 26258904_analysis of a subset of inflammasome receptors including NLRP3, NLRC4 and AIM2 that triggers formation of the micrometer-sized spherical supramolecular complex called the ASC speck 26313692_A significant upregulation of the PYHIN inflammasomes AIM2 and IFI16 in active inflammatory bowel disease versus controls was found. 26378020_The extent of NLRC3 and AIM2 gene reduction was correlated with cancer progression. 26506473_Lung tumor-associated plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are responsive to the activation of AIM2 that promotes calcium efflux and reactive oxygen species from mitochondria, leading to calpain activation and high levels of IL-1alpha. 26838050_AIM2 contributes to the maintenance of intestinal integrity via Akt and protects against Salmonella mucosal infection. 26944367_The findings reveal an age-dependent reduction of AIM2 expression and activation which may explain reduced cytokine responses to the cytosolic DNA mimic poly(dA:dT) in healthy elderly individuals. Reduced AIM2-mediated sensing with age may contribute to increased vulnerability to bacterial or viral infections in the elderly. 27037024_Molecular docking analysis reveals that the conformation switching may be important for the autoinhibition of the AIM2 protein. 27167192_Overexpression of AIM2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells suppressed mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-S6K1 pathway and further inhibited proliferation of HCC cells. 27498865_TRIM11 suppresses AIM2 inflammasome by degrading AIM2 via p62-dependent selective autophagy. 28219398_These data indicate that human cytomegalovirus pUL83 interacts with human AIM2 in the cytoplasm during the early stages of virus infection. The pUL83/AIM2 interaction deregulates the activation of AIM2 inflammasome. 28342645_AIM2 inflammasome expression and activation is increased early during the course of acute pancreatitis, and suggests that AIM2 activation may affect systemic inflammation and organ failure in these patients 28369146_knockdown of AIM2 by small interfering RNA attenuated caspase-1 activation. the results suggest that EBV infection of human monocytes induces caspase-1-dependent IL-1beta production, and that AIM2, acting as an inflammasome, is involved in this response. 28387608_This study found IFI16 and AIM2 SNPs associated with higher levels of periodontal microorganisms and an increased percentage of periodontal disease clinical parameters. 28397969_AIM2 is an important component of the inflammasome in tegumentary leishmaniasis (TL) patients and is directly associated with the severity of lesions. 28424239_results suggest that the function of AIM2 is focused on the innate immune response, and AIM2 is a detrimental host factor for influenza-induced lung injury and mortality. 28480966_Human cytomegalovirus infection induces an AIM2 inflammasome response, which negatively influences viral life cycle. 28526809_These results provide evidence for the role of AIM2 in the progression of cSCC and identify AIM2 inflammasome function as a potential therapeutic target in these invasive and metastatic tumors. 28580773_HBx-induced loss of AIM2 is associated with poor outcomes and facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by triggering the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process. 28724943_AIM2 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis is an important mechanism of neuronal cell death and it could play an important role in limiting EV-A71 replication. 28802238_Clinicopathological analysis of colorectal cancer tissue revealed that low AIM2 expression was significantly associated with some clinicopathological features such as depth of invasion, TNM clinical stage and lymph node metastasis 28809949_Study conclude that functional AIM2 is preferentially expressed in adult human CD27+ B-cells, but is absent in cord blood mononuclear cells. 28867284_C-reactive protein polymorphisms and DNA methylation of the AIM2 gene influence associations between trauma exposure, posttraumatic stress disorder, and C-reactive protein. 28947539_study identifies the AIM2 inflammasome and cGAS/IFI16-STING-type I IFN pathway as a novel mechanism for host innate immunity to the ALVAC vaccine vector. 29178062_Caspase-1-dependent IL-1beta processing and secretion require the AIM2 inflammasome pathway in human dental pulp cells and the AIM2 inflammasome pathway is critical for regulation of the dental pulp immune response. 29216786_rs855867 in AIM2 is not significantly associated with childhood autism spectrum disorder or the severity of the disease in a Chinese Han population. 29263272_RSAD2 and AIM2 Modulate Coxsackievirus A16 and Enterovirus A71 Replication in Neuronal Cells in Different Ways That May Be Associated with Their 5' Nontranslated Regions. 29439156_In kidneys from patients with diabetic or nondiabetic CKD, immunofluorescence showed AIM2 expression in glomeruli, tubules, and infiltrating leukocytes. In vitro, macrophages that engulfed necrotic debris showed AIM2-dependent activation of caspase-1 and IL-1beta, and the formation of AIM2(+) ASC specks indicating inflammasome activation. 29675024_In conclusion, our findings identify a novel molecular mechanism whereby the activation of AIM2 could lead to the activation of the non-canonical inflammasome (caspase-4 dependent) that induces the release of IL-1alpha responsible for the release of TGF-beta from PBMCs of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. 29844574_SIRT1 enabled HPV-infected cervical cancer cells to continue growing by nullifying AIM2 inflammasome-mediated immunity 29947343_expression and activation of AIM2, and the increase in circulating mtDNA levels may contribute to the inflammatory process in patients with T2D. 30031129_that AIM2 might serve as a novel prognostic indicator as well as a potential therapeutic target for renal carcinoma treatment 30104205_Enforced expression of IFI16-b inhibits the activation of AIM2 inflammasome, whereas knockdown of IFI16-b augments interleukin-1b secretion triggered by dsDNA but not dsRNA Thus, cytoplasm-localized IFI16-b is functionally equivalent to mouse p202 that exerts an inhibitory effect on AIM2 inflammasome. 30160343_these results indicated the therapeutic effect of PEI600-CyD (H1) nanoparticle-mediated AIM2 gene (H1/pAIM2) nanoparticles was mainly attributable to its capability to enhance the inflammasome activation 30222506_In humans with acute and chronic Hepatitis B exists activation of the AIM2 and IFI16 (in acute Hepatitis B), and the activation of the AIM2 and IFI16 can be inhibited by hepatitis B e antigen in chronic Hepatitis B. 30587341_In in vitro assays using oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines, the high migration and invasion capacity of OSCC cells were dependent on the increased expression of AIM2, resulting in enhanced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), with EMT-related gene expression. 30755509_Here, the authors used clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) genome editing to demonstrate that the dsDNA receptor absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) is required for secretion of IL-1beta following human cytomegalovirus infection. 30758522_We demonstrated that patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) show increased protein levels of the dsDNA sensor AIM2 in peripheral monocytes, granulocytes, T cells, and B cells, compared with controls. Moreover, our data present evidence that PBMC of AAA patients respond to foreign DNA with higher inflammasome activation and IL-1beta release than PBMC from patients without AAA. 30816544_In the hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC) samples, low AIM2 expression was closely related to lymph node metastasis and intravascular tumor thrombus and were strongly associated with poor survival. AIM2 expression was negatively correlated with pSTAT3 expression in the HSCC tissue samples, and combined analysis revealed that patients with low AIM2 and high pSTAT3 levels had the worst survival rate. 30904426_Interferon (IFN)-inducible Absent in Melanoma 2 proteins in the negative regulation of the type I IFN response: Implications for lupus nephritis. 30953357_AIM2 functioned as an oncogene in NSCLC in an inflammasome-dependent way. 30980272_The aim of the present study is to determine the expression levels of PYHIN (IFI16 and AIM2) and APOBEC3 (A3A, A3B, A3C, A3D, A3F, A3G, and A3H) gene family members in a cohort of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and assess their potential correlation with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection status, clinical characteristics, and survival. 31078283_AIM2, NLRP1, and P2RX7 promoted susceptibility to Leishmania braziliensis infection. 31186453_Differential Expression Profile of NLRs and AIM2 in Glioma and Implications for NLRP12 in Glioblastoma. 31210372_Absent in melanoma 2 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Akt and inflammasome pathways in human colorectal cancer cells. 31280432_High AIM2 expression is associated with glioblastoma multiforme. 31372985_Role of AIM2 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases, cancer and infection has been summarized. (Review) 31694740_Expression of inflammasomes NLRP1, NLRP3 and AIM2 in different pathologic classification of lupus nephritis. 31794744_Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. 31836304_Expression and activity of AIM2-inflammasome in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 31837587_EFLA 945 restricts AIM2 inflammasome activation by preventing DNA entry for psoriasis treatment. 32005973_AIM2 promotes the development of non-small cell lung cancer by modulating mitochondrial dynamics. 32295112_The DNA Sensor AIM2 Protects against Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes by Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis via the IL-18 Pathway. 32383175_Elevated cell-free fetal DNA contributes to placental inflammation and antiangiogenesis via AIM2 and IFI16 during pre-eclampsia. 32564199_CCL19 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through the CCL19/CCR7/AIM2 pathway. 33162829_Expression of AIM2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Role on Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. 33291082_AIM2 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration through suppression of Gli1. 33391539_Molecular stratification by BCL2A1 and AIM2 provides additional prognostic value in penile squamous cell carcinoma. 33429941_Genetics and Pathogenetic Role of Inflammasomes in Philadelphia Negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Narrative Review. 33505023_AIM2 in regulatory T cells restrains autoimmune diseases. 33643304_The Trinity of cGAS, TLR9, and ALRs Guardians of the Cellular Galaxy Against Host-Derived Self-DNA. 33667383_Post-injury immunosuppression and secondary infections are caused by an AIM2 inflammasome-driven signaling cascade. 33678651_Significance of expression of AIM2, IL-1beta, and IL-18 in plasma of patients with acute cerebral infarction.', trans 'AIM2IL-1betaIL-18. 33689708_Dihydroartemisinin induces pyroptosis by promoting the AIM2/caspase-3/DFNA5 axis in breast cancer cells. 33760111_Cytokine secretion and pyroptosis of cholesteatoma keratinocytes mediated by AIM2 inflammasomes in response to cytoplasmic DNA. 33859277_Absent in melanoma 2 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via inactivation of AKT signaling pathway. 33868225_Single-Nucleotide Variants in the AIM2 - Absent in Melanoma 2 Gene (rs1103577) Associated With Protection for Tuberculosis. 34006824_Perfluoroalkyl substance pollutants activate the innate immune system through the AIM2 inflammasome. 34047695_Inflammation drives alternative first exon usage to regulate immune genes including a novel iron-regulated isoform of Aim2. 34099337_Up-regulation of AIM2 and TLR4 and down-regulation of NLRC4 are associated with septicemia. 34117866_AIM2-driven inflammasome activation in heart failure. 34216617_Antimycin A-induced mitochondrial dysfunction regulates inflammasome signaling in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. 34220810_Enhanced IL-1beta Release Following NLRP3 and AIM2 Inflammasome Stimulation Is Linked to mtROS in Airway Macrophages in Pulmonary Fibrosis. 34325468_AIM2 regulates anti-tumor immunity and is a viable therapeutic target for melanoma. 34384029_The regulation of long non-coding RNA 00958 (LINC00958) for oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells death through absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) depending on microRNA-4306 and Sirtuin1 (SIRT1) in vitro. 34391864_Investigation of C-reactive protein and AIM2 methylation as a marker for PTSD in Australian Vietnam veterans. 34471287_AIM2 forms a complex with pyrin and ZBP1 to drive PANoptosis and host defence. 34521812_AIM2 deficiency in B cells ameliorates systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating Blimp-1-Bcl-6 axis-mediated B-cell differentiation. 34595244_The Role of Inflammasome Activation in Early HIV Infection. 34696702_Silencing of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 improves Treg/Th17 imbalance in preeclampsia via the miR-485-5p/AIM2 axis. 34710506_AURKA facilitates the psoriasis-related inflammation by impeding autophagy-mediated AIM2 inflammasome suppression. 34740957_AIM2 Suppresses Inflammation and Epithelial Cell Proliferation during Glomerulonephritis. 34913077_AIM2 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by inactivating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. 34963084_AIM2 Inflammasome Activation Contributes to Aortic Dissection in a Sporadic Aortic Disease Mouse Model. 35199647_Tumor Treating Fields dually activate STING and AIM2 inflammasomes to induce adjuvant immunity in glioblastoma. 35216346_Absent in Melanoma 2 (AIM2) Regulates the Stability of Regulatory T Cells. 35312143_Methylation of the AIM2 gene: An epigenetic mediator of PTSD-related inflammation and neuropathology plasma biomarkers. 35343082_The IL-21-TET2-AIM2-c-MAF pathway drives the T follicular helper cell response in lupus-like disease. 35608258_The DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16 are SLE autoantigens that bind neutrophil extracellular traps. 35646157_The Association of Serum AIM2 Level with the Prediction and Short-Term Prognosis of Coronary Artery Disease. 35806450_The P2X7R-NLRP3 and AIM2 Inflammasome Platforms Mark the Complexity/Severity of Viral or Metabolic Liver Damage. 35844548_Activation of the AIM2 Receptor in Circulating Cells of Post-COVID-19 Patients With Signs of Lung Fibrosis Is Associated With the Release of IL-1alpha, IFN-alpha and TGF-beta. 35880661_AIM2-inflammasome role in systemic lupus erythematous and rheumatoid arthritis. 36037355_Cross-talk between IL-6 trans-signaling and AIM2 inflammasome/IL-1beta axes bridge innate immunity and epithelial apoptosis to promote emphysema. 36068262_Expression of NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome in Peripheral blood in Chinese patients with acute and chronic brucellosis. 36248785_Pan-cancer analysis of AIM2 inflammasomes with potential implications for immunotherapy in human cancer: A bulk omics research and single cell sequencing validation. |
ENSMUSG00000037860 |
Aim2 |
12.235107 |
0.3766626094 |
-1.408655 |
0.453398360 |
10.043017 |
0.00152926501711576315507834511464579918538220226764678955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003458242937433532102065036895055527566000819206237792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5769245 |
1.9181583 |
17.6268628 |
3.0181501 |
| ENSG00000163577 |
56648 |
EIF5A2 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZV4 |
FUNCTION: mRNA-binding protein involved in translation elongation. Has an important function at the level of mRNA turnover, probably acting downstream of decapping. Critical for the efficient synthesis of peptide bonds between consecutive proline residues. Can resolve ribosomal stalling caused by consecutive prolines during translation (By similarity). Involved in actin dynamics and cell cycle progression, mRNA decay and probably in a pathway involved in stress response and maintenance of cell wall integrity. Functions as a regulator of apoptosis. Mediates effects of polyamines on neuronal process extension and survival. May play an important role in brain development and function, and in skeletal muscle stem cell differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14622290}. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Elongation factor;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hypusine;Membrane;mRNA transport;Nuclear pore complex;Nucleus;Protein biosynthesis;Protein transport;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Translocation;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable translation elongation factor activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of translational elongation. Located in intracellular membrane-bounded organelle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56648; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; translation elongation factor activity [GO:0003746]; mRNA transport [GO:0051028]; polyamine homeostasis [GO:0010509]; positive regulation of translational elongation [GO:0045901]; positive regulation of translational termination [GO:0045905]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
11161802_Eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) (eIF-4D, eIF-5A) stimulates ribosomal peptidyltransferase activity, transport of HIV-1-mRNAs and binds exportins 1 and 4. Contains hypusine at lys 50. Human EIF5A1 and EIF5A2 encode two isoforms: eIF5AI and eIF5AII. 14622290_role in eukaryotic cell survival similar to that of the ubiquitous eIF5A-1 15205331_eIF-5A2 overexpression was significantly associated with the advanced stage of ovarian cancer. 16169419_Mutations in the human EIF5A2 gene are not common causes of infertility in man 16169419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17876542_In clinical samples, the expression of PTMA was significantly higher in the minor effect group than in the major effect group (P = 0.004), but there were no significant differences in EIF5a2 expression between the two groups. 17949776_These findings suggest that overexpression of EIF-5A2 in colorectal carcinomas may be important in the acquisition of a metastatic phenotype and plays an important role in colorectal carcinoma development and progression. 19054548_Increased expression of EIF-5A2 in ovarian carcinoma may represent an acquired malignant phenotypic feature of tumor cells. Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is an independent molecular marker for shortened survival time of patients with ovarian carcinoma. 19155439_Overexpression of EIF-5A2 is an independent predictor of outcome in patients of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder treated with radical cystectomy. 19298601_protein expression of eIF-5A2 might be regulated not only by gene amplification, but also by other molecular mechanisms 20112425_EIF5A2 plays an important role in hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition, as well as stimulating cytoskeleton rearrangement through activation of RhoA and Rac1. 21813470_EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce epithelial-mesenchymaltransition. 22927971_eIF-5A as well as the hypusine-forming enzymes deoxyhypusine synthase (DHS) and deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH) are highly overexpressed in glioblastoma patient sample 24178756_None of the latter died within 5 years in EIF5A2-negative staining group. 24250246_focus on updating current knowledge of the EIF5A2 gene in human cancers 24262005_It significantly inhibited activity of eIF5A2. 24504366_EIF5A2 elevated TGF-beta1 expression through STAT3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes aggressiveness in bladder cancer. 24561231_Increased expression of eIF5A2 increases metastasis and angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the HIF1alpha-mediated signaling pathway. 24638963_eIF-5A2 plays an important role in doxorubicin chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. 25793713_Our findings indicate that EIF5A2 upregulation plays an important oncogenic role in gastric cancer. EIF5A2 may represent a new predictor for poor survival and is a potential therapeutic target for gastric cancer. 26309359_MiR-30b suppresses tumor migration and invasion by targeting EIF5A2 expression in gastric cancer cells. 26317793_Data suggest that eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) inhibitors might be considered as combination therapy to enhance chemosensitivity in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 26465952_Data indicate that regulation of sonic hedgehog (SHh)-GLI family zinc finger 1 (Gli1) signals to migration of pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 Cells through mediating eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A (EIF5A2) gene expression. 26799253_EIF5A2 overexpression may contribute to cancer progression and poor prognosis. Therefore, EIF5A2 could be a novel potential prognostic marker for Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage I-II cervical cancer. 27028999_Data suggest that inhibition of eIF5A2 alters progression of the EMT to decrease the invasion and metastasis of HCC cells via ROS-related pathways. 27203388_The model had 92% sensitivity and 92% specificity. We obtained similar results in the independent validation cohort. AIB1 and EIF5A2 show promise for the noninvasive detection of bladder cancer. The model based on AIB1, EIF5A2, and NMP22 outperformed each of the three individual biomarkers for detecting Bladder cancer. 27376958_EIF5A2 as a direct and functional target of miR-203. 27879277_High EIF5A2 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 30551723_the tumor suppressive role of miR-221-3p in MB cell proliferation at least in part via targeting EIF5A2 30801960_MicroRNA-383 inhibits doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2. 30931608_In cohort of patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma EIF5A2 low expression group had significantly longer overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) than the EIF5A2 high expression group. The high expression of EIF5A2 significantly predict poor OS and PFS in the subset patients. EIF5A2 was an independent prognostic factor for OS and PFS. 31222822_MicroRNA-33b regulates sensitivity to daunorubicin in acute myelocytic leukemia by regulating eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-2. 31558321_DHPS-dependent hypusination of eIF5A1/2 is necessary for TGFbeta/fibronectin-induced breast cancer metastasis and associates with prognostically unfavorable genomic alterations in TP53 31841179_MicroRNA-588 regulates migration capacity and invasiveness of renal cancer cells by targeting EIF5A2. 31863776_High EIF5A2 expression is associated with renal interstitial fibrosis. 32466797_Long non-coding RNA LINC00520 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of malignant melanoma by inducing the miR-125b-5p/EIF5A2 axis. 33174013_Knockdown of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 enhances the therapeutic efficiency of doxorubicin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by triggering lethal autophagy. 33308276_Circ_0003998 enhances doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-218-5p/EIF5A2 pathway. 33726845_EIF5A2 enhances stemness of epithelial ovarian cancer cells via a E2F1/KLF4 axis. 34428509_The deubiquitinating enzyme ATXN3 promotes the progression of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by stabilizing EIF5A2. 35064108_HERC3 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by directly ubiquitination degradation EIF5A2 and inhibits metastasis of colorectal cancer. 35358571_Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 5A2 Regulates Expression of Antiviral Genes. 35792239_EIF5A2 promotes proliferation and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells. |
ENSMUSG00000050192 |
Eif5a2 |
107.121867 |
2.1218076785 |
1.085294 |
0.291639791 |
13.586530 |
0.00022781430531721008343574996768410301228868775069713592529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000590955913265732999187229701476553600514307618141174316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
153.9213739 |
33.7837533 |
72.7413521 |
11.7484799 |
| ENSG00000163584 |
200916 |
RPL22L1 |
protein_coding |
Q6P5R6 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ribonucleoprotein;Ribosomal protein |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Predicted to be a structural constituent of ribosome. Predicted to be involved in cytoplasmic translation. Predicted to be located in ribosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:200916; |
ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; ribosome [GO:0005840]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; structural constituent of ribosome [GO:0003735]; cytoplasmic translation [GO:0002181] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31581233_RPL22L1 might be a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer and predict 5-Fluorouracil responsiveness. |
ENSMUSG00000039221 |
Rpl22l1 |
53.554732 |
2.4047156588 |
1.265866 |
0.219819905 |
33.748108 |
0.00000000627300357070244521960223013927644697407259855026495642960071563720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000027846476001073110869662961277225254885792082859552465379238128662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.7334564 |
10.7357892 |
32.1726872 |
3.5703898 |
| ENSG00000163596 |
130026 |
ICA1L |
protein_coding |
Q8NDH6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable protein domain specific binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transport. Predicted to act upstream of or within spermatid development. Predicted to be located in acrosomal vesicle. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:130026; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; regulation of transport [GO:0051049] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 35328582_ICA1L Is Associated with Small Vessel Disease: A Proteome-Wide Association Study in Small Vessel Stroke and Intracerebral Haemorrhage. |
ENSMUSG00000026018 |
Ica1l |
41.616311 |
0.2822542546 |
-1.824933 |
0.260136652 |
50.220613 |
0.00000000000137396929360926907970122716596201290872696076927894637265126220881938934326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000008079596324172434800724396763870518425529332340317978378152474761009216308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.7181260 |
5.3383079 |
63.3962642 |
13.3451221 |
| ENSG00000163597 |
100507246 |
SNHG16 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27396952_SNHG16 may play an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer. 27683121_A three-lncRNA signature (LOC285194, RP11-462C24.1 and Nbla12061) identified via stepwise regression analysis showed potential as a diagnostic marker for colorectal cancer. 28232182_Taken together, these findings indicated that SNHG16 induces breast cancer cell migration by competitively binding miR-98 with E2F5. 29081409_The expression of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) SNHG16 in gastric cancer (GC) tissue, significantly associated with invasion depth, lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and histological differentiation, was upregulated compared with adjacent tissues. 29126969_SNHG16 could serve as an oncogene that promotes tumor progression by acting as an endogenous 'sponge' to regulate miR-216A-5p/ZEB1 in cervical cancer. 29234154_mechanism experiments revealed that SNHG16 could epigenetically silence the expression of p21. The facts above pointed out that lncRNA-SNHG16 might be quite vital for the diagnosis and development of bladder cancer, and could even become an important therapeutic target for bladder cancer. 29461589_SNHG16 was highly expressed in ovarian cancer, and was correlated with staging, distant metastasis and poor prognosis of ovarian cancer; SNHG16 may activate phosphorylation of AKT and upregulate the expression of MMP9 to promote cell proliferation, invasion and migration of ovarian cancer 29529599_SNHG16 acts as an oncogenic lncRNA that promoted glioma tumorigenesis via acting as a competing endogenous RNA that regulated the expression of PRMT5 through directly sponging miR-4518. 29685003_SNHG16 promotes glioma tumorigenesis by sponging miR-20a-5p, leading to the enhancement of its endogenous targets E2F1 29949155_Knockdown of SNHG16 suppressed proliferation and invasion and induced apoptosis of ESCC cells. Mechanistically, Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways were actively modulated by SNHG16 in ESCC cells. 30119242_SNHG16 can act as a ceRNA to modulate miR-15a/16 cluster, thereby affecting LSP-induced inflammatory pathway which was downregulated by miR-15a/16 cluster. 30287374_expression of long non-coding RNA SNHG16 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer 30380185_Hsa-miR-124-3p was demonstrated to interact with SNHG16, and upregulated in SNHG16-downregulated Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells. In addition, inhibiting hsa-miR-124-3p reversed SNHG16-downregulation-mediated tumor suppressive functions in ALL. SNHG16 is upregulated in ALL, and its inhibition has tumor suppressive effect in ALL, likely through epigenetic interaction on hsa-miR-124-3p 30453308_SNHG16 could upregulate zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) expression by acting as an endogenous sponge of miR-205 and the effects of SNHG16 on the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells were dependent on miR-205. 30607006_we conclude that c-Myc-induced upregulation of SNHG16 enhances progression and carcinogenesis in OSCC. 30657551_LncSNHG16 was highly expressed in osteosarcoma (OS) tissues and cell lines and negatively correlated with survival and positively with the tumor stage of OS patients. MicroRNA-146a-5p was predicted to be the target gene of lncSNHG16 and NOVA1 was predicted to be the target gene of microRNA-146a-5p. LncSNHG16 participates in the development of OS by downregulating microRNA-146a-5p to upregulate NOVA1 expression. 30726150_SNHG16 involves in the migration and invasion of OS cells. 30784284_SNHG16 promoted liver cancer cells proliferation via the SNHG16/miR-302a-3p/FGF19 axis 30893293_Authors found that SNHG16 was upregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines and that it was negatively correlated with survival time in HCC patients. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that SNHG16 was a significant and independent predictor for the overall survival of HCC patients. 30909141_SNHG16 promotes BCL9 expression by sponging miR-1301 to facilitate the proliferation, migration and invasion of OS cells. 30923843_LncRNA SNHG16 regulated cellular processes in osteosarcoma by sponging miR-98-5p 30962265_MiR-200a-3p was inversely correlated with SNHG16 expression in CRC tissues. 30972632_lncRNA SNHG16 Exerts Oncogenic Functions in Promoting Proliferation of Glioma Through Suppressing p21. 30981105_SNHG16 could serve as a likely therapeutic intervention in PC. 31026378_the present study demonstrated the regulatory contribution of SNHG16/miR-17-5p/TIMP3 axis to viability, apoptosis, proliferation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells, which directly affected tumor progression. 31180520_Bioinformatics analysis revealed that SNHG16 regulated cell proliferation in NB through transcriptional and translational pathways. Results suggested that SNHG16 may serve important roles in the development and progression of NB. 31226483_lncRNA SNHG16 promotes glioma tumorigenicity through miR-373/EGFR axis by activating PI3K/AKT pathway. 31306653_High SNHG16 expression is associated with proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31355606_lncRNA SNHG16 in myocardial cell injury induced by acute myocardial infarction and the underlying functional regulation mechanism. 31427084_the importance of the regulatory axis of SNHG16/miR-16/ATG4B underlying osteosarcoma progression and chemoresistance to cisplatin. 31441592_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 regulates human aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via sponging miR-205 and modulating Smad2. 31483572_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by targeting miR-497-5p/PIM1 axis. 31502038_Long-Non Coding RNA SNHG16 Supports Colon Cancer Cell Growth by Modulating miR-302a-3p/AKT Axis. 31561329_SNHG16 was found to be upregulated whereas DKK3 was downregulated in tumor tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues. It showed that the expressions of SNHG16 and DKK3 were negatively correlated in clinical GC tissues.All these results suggested that SNHG16 promotes GC progression via regulation of DKK3 directly or indirectly. 31580045_SNHG 16 was upregulated in LAD tissues and cell lines. Furthermore, SNHG 16 promoted LAD cell proliferation and invasion via sponging let-7a-5p. 31646601_LncRNA SNHG16 promoted proliferation and inflammatory response of macrophages through miR-17-5p/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in patients with atherosclerosis. 31664866_Both the knock down of lncRNA SNHG16 and SREBP2 and overexpression of miR-195 suppressed the proliferation, migration, invasion and lipogenesis in pancreatic cancer cells. LncRNA SNHG16 directly sponged miR-195 to modulate the lipogenesis via regulating the expression of SREBP2. LncRNA SNHG16 accelerated the development of pancreatic cancer and promoted lipogenesis via directly regulating miR-195/SREBP2 axis. 31696971_SNHG16 as the miRNA let-7b-5p sponge facilitates the G2/M and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating CDC25B and HMGA2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31773673_SNHG16 promotes the progression of osteoarthritis through activating microRNA-93-5p/CCND1 axis. 31774223_Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 promotes the tumorigenicity of cervical cancer cells by recruiting transcriptional factor SPI1 to upregulate PARP9. 31841752_SNHG16 and IGF2 were upregulated while miR-370-3p was downregulated in serum of acute pneumonia patients and lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced A549 cells. SNHG16 regulated proliferation, apoptosis and inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting miR-370-3p. MiR-370-3p targeted IGF2 and inhibited LPS-induced inflammatory injury via IGF2. SNHG16 was verified to promote IGF2 expression by sponging miR-370-3p in A549 cells. 31919621_SNHG16 Silencing Inhibits Neuroblastoma Progression by Downregulating HOXA7 via Sponging miR-128-3p. 31953899_LncRNA SNHG16 promotes non-small cell lung cancer development through regulating EphA2 expression by sponging miR-520a-3p. 31956270_The USP21/YY1/SNHG16 axis contributes to tumor proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer. 32122142_The SNHG16/miR-30a axis promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating RRM2. 32324343_SNGH16 regulates cell autophagy to promote Sorafenib Resistance through suppressing miR-23b-3p via sponging EGR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32335807_Bupivacaine-Induced Neurotoxicity Is Modulated by Epigenetic Axis of Long Noncoding RNA SNHG16 and Hsa-miR-132-3p. 32345959_Breast cancer-derived exosomes transmit lncRNA SNHG16 to induce CD73+gammadelta1 Treg cells. 32412051_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 regulates cell behaviors through miR-542-3p/HNF4alpha axis via RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in pediatric neuroblastoma cells. 32436333_SNHG16/miR-605-3p/TRAF6/NF-kappaB feedback loop regulates hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. 32612026_Long Noncoding RNA SNHG16 Facilitates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Progression through the miR-106b-5p/STAT3 Feedback Loop. 32677912_Clinicopathological significance and prognosis of long noncoding RNA SNHG16 expression in human cancers: a meta-analysis. 32705162_Knockdown of SNHG16 suppresses the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of leukemia cells via miR193a5p/CDK8. 32859986_LncRNA SNHG16 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through miR-124-3p/MCP-1. 32864914_SNHG16 promotes cell proliferation and migration through sponging miR-132 in melanoma. 32945414_Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 inhibits the oxygenglucose deprivation and reoxygenationinduced apoptosis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells by regulating miR15a5p/bcl2. 33015794_LncRNA SNHG16 drives proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cell through modulation of miR-520/VEGF axis. 33105440_SNHG16 knockdown inhibits tumorigenicity of neuroblastoma in children via miR-15b-5p/PRPS1 axis. 33179372_SNHG16/miR-485-5p/BMP7 axis modulates osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 33222428_SNHG16 regulated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via sponging miR-183. 33235108_Correlation between lncRNA SNHG16 gene polymorphism and its interaction with environmental factors and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. 33300061_lncRNA SNHG16 promotes the occurrence of osteoarthritis by sponging miR3733p. 33530902_Decreased lncRNA SNHG16 Accelerates Oxidative Stress Induced Pathological Angiogenesis in Human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells by Regulating miR-195/mfn2 Axis. 33576342_LncRNA-SNHG16 promotes proliferation and migration of acute myeloid leukemia cells via PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis through suppressing CELF2 protein. 33661764_SUMOylation promotes extracellular vesicle-mediated transmission of lncRNA ELNAT1 and lymph node metastasis in bladder cancer. 33797690_lncRNA SNHG16 Mediates Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Cholangiocarcinoma by Directly Targeting miR-146a-5p/GATA6 Axis. 33836533_LncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 (SNHG16) silencing protects lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cell injury in human lung fibroblasts WI-38 through acting as miR-141-3p sponge. 34110517_LncRNA SNHG16 regulates trophoblast functions by the miR-218-5p/LASP1 axis. 34147082_Evaluation of expression of VDR-associated lncRNAs in COVID-19 patients. 34197720_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 regulates E2F1 expression by sponging miR-20a-5p and aggravating proliferative diabetic retinopathy. 34600815_SNHG16 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma development via activating ECM receptor interaction pathway. 34643247_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 functions as a tumor activator by sponging miR3733p to regulate the TGFbetaR2/SMAD pathway in prostate cancer. 34881626_SNHG16 lncRNAs are overexpressed and may be oncogenic in human gastric cancer by regulating cell cycle progression. 35170375_Mechanism of lncRNA SNHG16 in oxidative stress and inflammation in oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced SK-N-SH cells. 35199943_LncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 reduces sepsis-induced myocardial damage by regulating miR-421/suppressor of cytokine signaling 5 axis. 35320391_Downregulation of lncRNA SNHG16 inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in cerebral atherosclerosis by targeting the miR-30c-5p/SDC2 axis. 35441431_The correlation of lncRNA SNHG16 with inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, disease severity, and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke patients. 35622463_Correlation of small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 with acute respiratory distress syndrome occurrence and prognosis in sepsis patients. 35752286_Genome-wide association study for circulating FGF21 in patients with alcohol use disorder: Molecular links between the SNHG16 locus and catecholamine metabolism. 35779785_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 silencing inhibits proliferation and inflammation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages by targeting miR-140-5p expression. 36053032_Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 decreased SMAD4 to induce gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer via EZH2-mediated epigenetic modification. 36147462_SNHG16 upregulation-induced positive feedback loop with YAP1/TEAD1 complex in Colorectal Cancer cell lines facilitates liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by modulating CTCs epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 36221055_LncRNA SNHG16 promotes development of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by interacting with EIF4A3 and modulating RhoU mRNA stability. |
|
|
252.058623 |
2.4982712997 |
1.320930 |
0.148814430 |
77.466383 |
0.00000000000000000135000774211220139000540971556212030570754055465958328938191890244979731505736708641052246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000011219658937824376685005478408908557763333922293789123025842258130069239996373653411865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
356.7919579 |
31.7728321 |
143.6663423 |
9.8129989 |
| ENSG00000163623 |
4825 |
NKX6-1 |
protein_coding |
P78426 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor which binds to specific A/T-rich DNA sequences in the promoter regions of a number of genes. Involved in the development of insulin-producing beta cells in the islets of Langerhans at the secondary transition (By similarity). Together with NKX2-2 and IRX3 acts to restrict the generation of motor neurons to the appropriate region of the neural tube. Belongs to the class II proteins of neuronal progenitor factors, which are induced by SHH signals (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99MA9}. |
Activator;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Methylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In the pancreas, NKX6.1 is required for the development of beta cells and is a potent bifunctional transcription regulator that binds to AT-rich sequences within the promoter region of target genes Iype et al. (2004) [PubMed 15056733].[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:4825; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus [GO:0071375]; central nervous system neuron differentiation [GO:0021953]; detection of glucose [GO:0051594]; negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048715]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048709]; pancreas development [GO:0031016]; pancreatic A cell differentiation [GO:0003310]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type B pancreatic cell development [GO:2000078]; regulation of axon extension [GO:0030516]; regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001222]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; type B pancreatic cell maturation [GO:0072560]; type B pancreatic cell proliferation [GO:0044342] |
15056733_Nkx6.1 is a bifunctional transcription factor that serves to maintain the specific expression of its own gene during beta-cell differentiation while simultaneously effecting broader gene repression events 16873704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18347054_overexpression of Nkx6.1 in islets caused an increase in the level of [(3)H]thymidine incorporation that was twice the control level, along with complete retention of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion 18754095_Alterations of gastric NKX6.1 expression in Helicobacter pylori infection, incisural antralisation, and intestinal metaplasia. 20106981_identified an NKX6.1 recognition sequence in the distal region of the HNF1alpha promoter and demonstrated specific binding of NKX6.1 in beta cells 21108535_Data suggest that NKX6.1 activates immature pancreatic markers but not pancreatic hormone gene expression in human liver cells, and suggest a potential role for NKX6.1 in promoting PDX-1 reprogrammed maturation along a beta-cell-like lineage. 21985235_Smooth muscle cells expressing nestin and Nkx6.1 are the main cell population derived from culturing human spinal cord cells in adherent conditions with serum. 23863625_MAFA, MAFB, NKX6.1, and PDX1 activity provides a gauge of islet beta cell function, with loss of MAFA (and/or MAFB) representing an early indicator of beta cell inactivity 23897760_Mice transplanted with NKX6.1-low cells remained hyperglycemic throughout the 5-month post-transplant period whereas diabetes was reversed in NKX6.1-high recipients within 3 months. 24407576_NKX6-1 reveals wide variations in methylation levels in normal control samples of cervical adenocarcinomas. 25596704_a significant relationship was observed between NKX6.1 and EMT marker expression levels, and NKX6.1 knockdown inhibited cell invasion, and overexpression of NKX6.1 promotes cell proliferation in vitro. 25871618_study evaluated the potential use of NKX6-1 as a diagnostic marker for well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors 26257059_NKX6.1 directly enhances the mRNA level of E-cadherin by recruiting BAF155 coactivator and represses that of vimentin and N-cadherin by recruiting RBBP7 (retinoblastoma binding protein 7) corepressor. 27032575_NKX6.1 is a factor for IL-6-regulated growth and tumor formation in basal-like breast cancer. 27998294_Efficiency of differentiation of Induced pluripotent stem cells to insulin producing cells can be increased by concurrent expression of PDX1 and NKX6.1 during progenitor cells maturation. 28835709_Data indicate the secretory granule membrane glycoprotein 2 as a marker for PDX1+/NKX6-1+ pancreatic progenitors (PPs). 29363224_Data demonstrated that patients with NKX6.1 methylation presented poorer 5-year overall survival (P = 0.0167) and disease-free survival (P = 0.0083) than patients without NKX6.1 methylation after receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. 30284410_Intermediate and high-grade tumors expressed NKX6.1. 32707737_NKX6.1 Represses Tumorigenesis, Metastasis, and Chemoresistance in Colorectal Cancer. 32862769_MiR-190b impedes pancreatic beta cell proliferation and insulin secretion by targeting NKX6-1 and may associate to gestational diabetes mellitus. 33121533_NKX6.1 transcription factor: a crucial regulator of pancreatic beta cell development, identity, and proliferation. 33906647_NKX6-1 mediates cancer stem-like properties and regulates sonic hedgehog signaling in leiomyosarcoma. 34493754_Increased NKX6.1 expression and decreased ARX expression in alpha cells accompany reduced beta-cell volume in human subjects. 35256556_NKX6-1 Is a Less Sensitive But Specific Biomarker of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000035187 |
Nkx6-1 |
23.991892 |
2.1709367809 |
1.118318 |
0.376863676 |
8.669566 |
0.00323568305301614751040562012462942220736294984817504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006874720291135501953894149096413457300513982772827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.6437040 |
7.6073246 |
15.5994554 |
2.7389075 |
| ENSG00000163629 |
5783 |
PTPN13 |
protein_coding |
Q12923 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine phosphatase which regulates negatively FAS-induced apoptosis and NGFR-mediated pro-apoptotic signaling (PubMed:15611135). May regulate phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling through dephosphorylation of PIK3R2 (PubMed:23604317). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15611135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23604317}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP is a large intracellular protein. It has a catalytic PTP domain at its C-terminus and two major structural domains: a region with five PDZ domains and a FERM domain that binds to plasma membrane and cytoskeletal elements. This PTP was found to interact with, and dephosphorylate, Fas receptor and IkappaBalpha through the PDZ domains. This suggests it has a role in Fas mediated programmed cell death. This PTP was also shown to interact with GTPase-activating protein, and thus may function as a regulator of Rho signaling pathways. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants, which encode distinct proteins, have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:5783; |
cell body [GO:0044297]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding [GO:0036312]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; cellular response to toxic substance [GO:0097237]; negative regulation of excitatory synapse assembly [GO:1904890]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation [GO:0035335]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014066] |
11884147_Structure, dynamics and binding characteristics of the second PDZ domain of PTP-BL 11959286_expression and apoptosis induction in peripheral blood cells from liver graft 12095257_PDZ2 domain from cytosolic human phosphatase hPTP1E complexed with peptide, RA-GEF-2, reveals contribution of the beta2-beta3 loop to PDZ domain-ligand interactions 12354757_PTPL1/FAP-1 has a key role in the apoptotic process in human breast cancer cells independent of Fas but associated with an early inhibition of the insulin receptor substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway 12436199_Shares a promoter region with the tightly linked gene encoding stress-activated protein kinase JNK3. 12724420_FAP-1 has a role in binding to, and consequently inhibition of, Fas export to the cell surface 12870871_specificity of interaction between the second PDZ domain of human protein tyrosine phosphatase1E (PDZ2) and a C-terminal peptide, ENEQVSAV, from the guanine nucleotide exchange factor RA-GEF-2 was investigated using FTIR spectroscopy and ESI-MS 14516276_PTPL1 binds to tandem-PH-domain-containing protein (TAPP)-1. 14596806_Data report the solution structure of the PDZ2 domain splicing variant of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-Bas. 15611135_X-ray crystallographic analysis of the PTPL1 catalytic domain 15782144_We therefore report a novel transcriptional activation of a phosphatase involved in the oncogenesis of ESFT. 16306044_FAP-1 expression is often up-regulated in metastatic tumors, with a causal connection withNF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional regulation of FAP-1 gene expression. 16489062_FAP-1 could be inactivated during hepatocarcinogenesis, mainly attributed by allelic loss and promoter methylation. 16572203_The PTPN13 protein has proapoptotic functions and can fuction as TSGs to suppress tumorigenesis. 16888780_FAP-1 phosphatase activity could be responsible for NF-kappaB activation and resistance of SCCHN cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis. 17240990_use the second PDZ domain (PDZ2) of protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP1E) as a model to study the energetics of peptide binding to a class I PDZ domain. 17638892_PTPN13/PTPL1 induces apoptosis through insulin receptor substrate-1 dephosphorylation 17982484_cellular PTPN13 inhibits Her2 activity by dephosphorylating the signal domain of Her2 and plays a role in attenuating invasiveness and metastasis of Her2 overactive tumors. 18038312_Frameshift mutation in the polyadenine tracts in both FLASH and PTPN13 genes is rare in colorectal carcinomas. Both FLASH and PTPN13 mutations in the polyadenine tracts may not have a crucial role in the pathogenesis of colorectal carcinomas. 18038312_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18195016_The interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP/IRF8) represses PTPN13 gene transcription in differentiating myeloid cells 18684861_erythrocyte CR1 ligation induces its clustering in complex with scaffolding protein FAP-1 19004008_PTPL1 expression level is an independent prognostic indicator of favorable outcome for patients with breast cancer 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19672627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19672627_PTPN13 SNPs were found to influence susceptibility to a wide spectrum of cancers. 19734941_PTPN13 phosphatase activity has a physiologically significant role in regulating MAP kinase signaling 19892796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19892796_polymorphisms in the PTPN13 coding region may have a role in susceptibility to squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck 20039457_Transfection of FAP-1 siRNA into SW480 cells silenced the expression of FAP-1 and consequently abolished the inhibitory function of Fas/FasL-mediated apoptosis pathway, thus increasing the efficacy of chemotherapy for colon carcinoma with oxaliplatin. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20501847_PTPL1 regulates breast cancer cell aggressiveness through direct inactivation of Src kinase. 20620960_FAP-1 was demonstrated to be responsible for the reduced sensitivity to CD95-mediated apoptosis in cells with inhibited miR-200. 20839809_X-ray crystal structures of PDZ2 in the absence and presence of RA-GEF2 ligand; very minor structural changes in PDZ2 accompany peptide binding 21235435_REVIEW: the alterations in expression and the genetic and epigenetic arguments supporting an oncogenic or an anti-oncogenic impact of PTPL1 21741956_The Ret oncoprotein exerts opposing controls on Fap-1 and CD95, increasing Fap-1 expression and decreasing CD95 cell surface expression. 22262849_interaction between Tel and Tel-PdgfRbeta decreases Tel/Icsbp/Hdac3 binding to the PTPN13 cis element, resulting in increased transcription. 22274591_The PTPL1 is an important mediator of central cellular processes such as proliferation and invasion. 22279592_Data show that EphrinB1, a PTPN13 substrate, interacts with ErbB2, and Src kinase mediates EphrinB1 phosphorylation and subsequent MAP Kinase signaling. 22364882_CD95 signal transduction was not affected by FAP-1 expression in A818-6 monolayer cells; we found a polarisation-induced co-localisation of CD95 and FAP-1. 23209399_Studied the peptide binding induced dynamical changes at the side-chain level throughout the second PDZ domain of PTP1e, identifying as such the collection of residues involved in long-range communication. 23519466_Fap1-dependent inactivation of Gsk3beta and consequent stabilization of betacatenin in these cells. Consistent with this, Bcr-abl(+) cells exhibited a Fap1-dependent increase in betacatenin activity. 23559010_The loss of PTPL1 and PKC-delta expression in poorly differentiated, more aggressive human prostate cancers indicate that their absence could be related to apoptosis resistance and tumor progression. 23604317_PTPL1 dephosphorylates p85beta, promoting its binding to FBXL2 and degradation. 23906871_Low PTPN13 expression is associated with invasion and metastasis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. 23950995_HCV induced increased expression of miR200c can down modulate the expression of FAP1, a critical regulator of Src and MAP kinase pathway that play an important role in the production of fibrogenic growth factors and development of fibrosis. 24191246_Thus, our results suggest a previously unknown Stat3-PTPN13 molecular network controlling squamous cell lung carcinoma development 24316673_selective autophagic degradation of the phosphatase Fap-1 promotes Fas apoptosis. 24338422_Association of rs7014346 in POU5F1P1, rs989902 in PTPN13, and rs7003146 in TCF7L2 with variations in the risk of breast cancer in a Chinese Han population. 25365469_A comprehensive molecular dynamics simulation study of the PDZ2 domain of human tyrosine phosphatase 1E in the ligand-bound and -free state, as well as the photoswitchable protein in the cis and trans states of the photoswitch 25448478_A PDZ-mediated interaction of PTPN13 and PTEN is described with possible relevance for tumor suppression. 25494785_The effect of the viscogens sucrose, and glycerol on the kinetic response of a photoperturbed PTPN13 is investigated. 25893857_Necl-4 serves as a novel regulator for contact inhibition of cell movement and proliferation cooperatively with the VEGF receptor and PTPN13 25933631_This work studied heat diffusion in the well-known PDZ-2 protein, and confirmed that this protein has two cognate allosteric pathways and that heat flows preferentially through these. 26801674_PTPN13 overexpression significantly inhibited the progression of HCC cells. 26811494_Mutation in PTPN13 gene is associated with gastric cancer peritoneal carcinomatosis. 26984787_Fap1 inhibition increased Fas sensitivity and decreased beta-catenin activity in human CD34+ CML cells 27285768_we found that miR-26a confers epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting and silencing PTPN13 27544031_the crystal structure of the PTP-Bas PDZ1 domain at 1.6 A resolution, is reported. 28504867_The single nucleotide polymorphism genotype of PTPN13 exon 39 was determined in DNA extracted from blood samples from 174 sporadic colorectal cancer patients and 176 healthy individuals. The risk of colorectal cancer was 2.087 times greater for patients with the GG genotype than for those with the TT genotype. PTPN13 rs989902 is significantly associated with the risk of colorectal cancer in the Polish population. 28653805_MicroRNA-30e-5p promotes cell growth by targeting PTPN13 and indicates poor survival and recurrence in lung adenocarcinoma. 29415055_suggest that CAFs, irrespective of identity, have low influence on the degree of tumor infiltration by inflammatory- and/or immune-cells. However, CAFFAP may exert immuno-adjuvant roles in NSCLC, and targeting CAFs should be cautiously considered 29581186_This work demonstrates a novel function for PTEN during cell polarization in controlling apical membrane size and identifies PTPL1 as a critical apical membrane anchor for PTEN in this process. 31938048_PTPN13 induces cell junction stabilization and inhibits mammary tumor invasiveness. 32919955_PTPN13 acts as a tumor suppressor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by inactivating Akt signaling. 33051595_Anti-oncogene PTPN13 inactivation by hepatitis B virus X protein counteracts IGF2BP1 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 33536603_PTPL1 suppresses lung cancer cell migration via inhibiting TGF-beta1-induced activation of p38 MAPK and Smad 2/3 pathways and EMT. 35643866_Germline PTPN13 mutations in patients with bone marrow failure and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 36193770_Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1 suppresses lung cancer through Src/ERK/YAP1 signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000034573 |
Ptpn13 |
42.161010 |
19.2076022990 |
4.263606 |
0.451583274 |
109.307331 |
0.00000000000000000000000013897731040515836519045771310698456362345644556879498586812595715977731308798936993298411834985017776489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000001524000818410206247585510422479781917540368261451828061591808703288848658718990236593526788055896759033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.4021084 |
22.5364741 |
4.3227492 |
1.1128936 |
| ENSG00000163661 |
5806 |
PTX3 |
protein_coding |
P26022 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of innate resistance to pathogens, inflammatory reactions, possibly clearance of self-components and female fertility. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12763682}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the pentraxin protein family. The expression of this protein is induced by inflammatory cytokines in response to inflammatory stimuli in several mesenchymal and epithelial cell types, particularly endothelial cells and mononuclear phagocytes. The protein promotes fibrocyte differentiation and is involved in regulating inflammation and complement activation. It also plays a role in angiogenesis and tissue remodeling. The protein serves as a biomarker for several inflammatory conditions. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2016]. |
hsa:5806; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; (1->3)-beta-D-glucan binding [GO:0001872]; complement component C1q complex binding [GO:0001849]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; virion binding [GO:0046790]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation by host of viral exo-alpha-sialidase activity [GO:0044869]; negative regulation by host of viral glycoprotein metabolic process [GO:0044871]; negative regulation by host of viral process [GO:0044793]; negative regulation of exo-alpha-sialidase activity [GO:1903016]; negative regulation of glycoprotein metabolic process [GO:1903019]; negative regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046597]; opsonization [GO:0008228]; ovarian cumulus expansion [GO:0001550]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; response to yeast [GO:0001878] |
12004288_Expression of PTX3 by vIL-6-stimulated Kaposi's sarcoma cell cultures 12006390_By increasing tissue factor expression, PTX3 plays a potential role in thrombogenesis and ischemic vascular disease. 12006411_PTX3 is produced in advanced atherosclerotic plaques principally by macrophages and endothelial cells and may contribute to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 12538709_Detection of the long pentraxin PTX3 in mesangial cells of patients with IgA glomerulonephritis suggests its potential role in the modulation of glomerular and tubular injury. 12645945_Experiments with recombinant globular head domains of human C1q A, B, and C chains indicated that C1q interacts with PTX3 via its globular head region. Binding of C1q to immobilized PTX3 induced activation of the classical complement pathway. 14603263_The mRNA level of PTX3 was 3.5-fold higher in the melancholic group as compared to that in normal controls and in nonmelancholic depressives (n=8, all groups). 15262177_We provide evidence for expression of PTX3 by vascular smooth muscle cells induced by degraded lipoproteins, which may lead to a vascular acute-phase reaction, contributing to the inflammatory pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 15308113_serum PTX3 levels appear elevated selectively in response to infection 16020751_Local PTX3 upregulation may modulate vascular smooth muscle cell activation after arterial injury 16166594_PTX3 acts as a third-party agent between microbial stimuli and dying cells, contributing to limit tissue damage under inflammatory conditions and the activation of autoreactive T cells 16339571_TNF-alpha induced PTX3 expression in human lung cell lines and primary epithelial cells; knockdown of either JNK1 or JNK2 with small interfering RNA also significantly reduced the regulated PTX3 expression 16380821_Review discusses clinical significance of different levels of PTX3, its role in induction or protection from autoimmunity, and the presence of specific PTX3 autoantibodies in different autoimmune diseases. 16617159_The coordinated induction by primary, proinflammatory signals of C1q and PTX3 and their reciprocal regulation during inflammation influences the clearance of apoptotic cells by antigen-presenting cells and possibly plays a role in immune homeostasis. 16647920_Significantly higher levels of pentraxin 3 were found in preeclampsia. Intrauterine growth restriction pregnancies showed intermediate levels between normal and preeclamptic patients. 16769728_there is an FGF2-binding domain in the N-terminal extension of PTX3 spanning the PTX3-(97-110) region 16865225_PTX3 could be used as a further marker of disease activity of psoriasis. 16981714_These results provided evidence of an involvement of the PTX3 sugar moiety in C1q recognition and complement activation. 17095712_The levels of plasma PTX3 were increased in patients with arterial inflammation, especially unstable angina pectoris. 17277044_Sources of PTX3 in the lung and the regulatory mechanisms of its expression ni acute injury and infection. 17380301_PTX3 and p66((ShcA)) mRNA levels are significantly more elevated in WBCs and in adipose tissue samples of patients with high levels of LDL compared to those with low levels. 17424885_Innate factors PTX3 and C1q are involved in the homeostasis of nasal mucosa and the pathogenesis of nasal polyposis. 17441979_This study demonstrated a significant association between CSF levels of IL-1beta, Il-6, and IFN-gamma and the severity ot EV71 brain stem encephalitis. 17487767_Cardiac surgical procedures performed with cardiopulmonary bypass are associated with a more pronounced release of PTX3 immediately after operation. 17496115_PTX3 may have a role in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients 17611589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17611589_findings support previous data showing that VDR SNPs modulate the risk for pulmonary tuberculosis in West Africans and suggest that variation within DC-SIGN and PTX3 also affect the disease outcome 17675295_PTX3 directly interacts with inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor and has a role in hyaluronan organization and cumulus oophorus expansion 17786277_These data suggest that PTX3 protein may represent an additional and stable marker of inflammation in chronic renal failure. 17947708_PTX3 activates a complement-dependent humoral amplification loop of the innate response to a microbial ligand 18045580_Expression of pentraxin-3 (PTX3) not only in macrophages but also in neutrophils may reflect the role of PTX3 in inflammation. 18048494_Estradiol and progesterone are involved in PTX3 induction and regulation during implantation. Also, of the factors secreted by trophoblast, IL-1beta induces PTX3 in human endometrial stromal cells. 18292565_Human PTX3 binds to influenza A virus and mediates a range of antiviral activities, including inhibition of hemagglutination, neutralization of virus infectivity and inhibition of viral neuraminidase. 18417746_In stage 5 chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes with normal renal function, pentraxin 3 was independently associated with proteinuria. Pentraxin 3 and proteinuria were associated with endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. 18571180_visceral adipose tissue production of PTX3 seems to contribute to the mechanisms underlying the development of atherosclerosis 18650775_PTX3 was an early indicator of shock in patients with severe meningococcal disease that followed a pattern of induction distinct from CRP. 18676013_Emphasis on two new players involved in regulating inflammation at the maternal-fetal interface: the long pentraxin PTX3 and the decoy receptor for inflammatory chemokines D6. 18685085_Human chorionic gonadotropin-induced hormones progesterone and estrogen increase the PTX3 production by human monocytes. 18703503_Cell-specific regulation of PTX3 by glucocorticoid hormones in hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic cells 19014569_Plasma PTX3 levels may not only have laboratory values that differentiate NASH from non-NASH, but be a marker of the severity of hepatic fibrosis in NASH. 19050261_A role is proposed for PTX3 in the localization of complement factor H regulatory activity to surfaces that bind PTX3, thus modulating alternative pathway activation and preventing excessive inflammatory response to tissue injury. 19079137_study shows that intracellular PTX3 translocates at the surface of late apoptotic neutrophils and acts as an 'eat-me' molecule for their recognition and capture by macrophages 19131771_High serum PTX3 is associated with pulmonary fungal infections. 19164811_In these older adults, PTX3 was associated with CVD and all-cause death independent of CRP and CVD risk factors. 19211665_Report effect of renin angiotensin system blockade on pentraxin 3 levels in type-2 diabetic patients with proteinuria. 19273457_These results suggest that elevated serum PTX3 levels are associated with the disease severity of systemic sclerosis. 19327124_showed the relationship between plasma PTX3 levels and established coronary risk factors 19389798_myelomonocytic cells and MoDC are a major source of TSG-6 and that PTX3 and TSG-6 are coregulated 19396030_Determining the production and regulation of PTX3 during mechanical ventilation may be critical in preventing or reducing ventilator-induced lung injury 19565609_Increase in maternal plasma PTX3 in pregnancies that subsequently develop early preeclampsia is evident from 11-13 weeks but the underlying mechanism for such an increase remains uncertain. 19632990_These results demonstrate that PTX3 and Ficolin-2 may recruit each other on pathogens. 19718477_PTX3 may have a role in inflammation in acute chest pain 19772962_The study demonstrates a close association between PTX3 deposition and complement activation in failed arteriovenous fistula (AVF) and suggests a role for PTX3 in modulating innate immunity in the pathogenesis of AVF stenosis. 19792835_PTX3 is a physiologic constituent of the amniotic fluid, and its median concentration is elevated in the presence of intra-amniotic infection/inflammation. 19794969_PTX3-overexpressing clones showed a powerful anti-fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) activity in FGF2-dependent capillary morphogenesis. 19811281_PTX3 may represent a valuable marker for early detection and prediction of preeclampsia in patients with type 1 diabetes. 19846603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19846603_results reported here provide the first evidence that the long pentraxin PTX3 plays a role in female fertility in humans 19900712_role as a multifunctional soluble pattern recognition receptor acting as a non-redundant component of the humoral arm of innate immunity [Review] 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917159_Serum PTX3 (pentraxin-3) levels were similar in febrile systemic lupus erythematosus patients with infection and flare 20022320_Amniotic fluid pentraxin 3 appears to be a marker of intra-amniotic inflammation. 20121391_maternal plasma PTX3 (pentraxin 3) concentration increases with advancing gestational age and is significantly elevated during labor at term and in the presence of spontaneous preterm labor or preterm rupture of membranes 20134101_pentraxin 3 may have a role in obesity-induced decrease in arterial distensibility 20356766_in acute myocardial infarction and infectious myocarditis, pentraxin 3 is produced by macrophages, the endothelium, and, to a lesser extent, myocardiocytes, and localized in the interstitium 20363749_long pentraxin PTX3 forms an asymmetric octamer with two binding sites for FGF2 20378410_Expression of target genes was detected in cumulus cells, with relatively low concentrations of ObR-Long. Strong mutual correlations were found between mRNA levels of leptin receptor isoforms and between the short isoforms of the leptin receptor and PTX3 20391484_Coronary artery disease patients with inflammatory rheumatic disease (IRD) had higher mean serum Pentraxin3 levels than patients without IRD and healthy controls 20399512_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20430947_Antihypertensive drugs improve flow-mediated dilation and normalize proteinuria, PTX3, and sTWEAK in diabetic CKD stage I patients with hypertension. 20508541_Endurance-trained individuals had higher levels of circulating PTX3 than sedentary controls. PTX3 may play a partial role in endurance exercise training-induced cardioprotection. 20515753_PTX-3 in our patients with hypoxic respiratory failure is affected by the severity of the hypoxic insult and correlate with the cardio-vascular impairment 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20640440_Circulating pentraxin3 and C-reactive protein significantly increased immediately after peak ergometer exercise, while they did not increase after 70% anaerobic threshold exercise. 20683616_PTX3 provides a paradigm for the mode of action of humoral innate immunity. 20927127_In 172 Caucasian Cystic fibrosis patients homozygous for the F508del mutation Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization was significantly associated only with rs2305619 SNP. 20927127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072498_Acute increased concentrations of PTX3 found in CSF but not in plasma are related to vasopasm occurrence in subarachnoid hemorrhage. 21072499_data suggest that endogenously expressed PTX3 plays a protective role in pathogenesis of acute lung injury and a lack of PTX3 may enhance neutrophil recruitment, cell death, activation of coagulation cascades, and inflammatory responses in the lung. 21106539_Interaction between MBL and PTX3 led to communication between the lectin and classical complement pathways via recruitment of C1q, whereas SAP-enhanced complement activation occurs via a hitherto unknown mechanism 21112127_This study provides the first demonstration of a role for astrocytic CEBPD and the CEBPD-regulated molecule PTX3 in the accumulation of damaged neurons, which is a hallmark of AD pathogenesis. 21173097_High PTX3 is associated with Inflammation and thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. 21257721_Data suggest that more studies are needed to establish if PTX3 has clinical utility for lung cancer diagnosis and management. 21330486_Both PTX3 and soluble TWEAK levels associated with the endothelial dysfunction observed with progressive kidney failure. 21388349_The long pentraxin PTX3 at the crossroads between innate immunity and tissue remodelling. 21389698_Uric acid and pentraxin-3 may have a role in coronary artery disease risk in patients with stage 2 and 3 kidney disease 21391986_In individuals at high risk of cardiovascular disease, the PTX3 concentration is associated with hypertension, insulin resistance, & hypercholesterolemia risk factors but not with subclinical atherosclerosis. 21423699_PTX3 proved to be a specific independent prognostic biomarker in bacteremia. 21465531_SAA up-regulates PTX3 production via FPRL1 significantly, and thus, contributes to the inflammatory pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. 21490156_data indicate interaction of M-ficolin with PTX3 arises from its ability to bind sialylated ligands; M-ficolin-PTX3 interaction described represents a novel case of cross-talk between soluble pattern-recognition molecules 21501295_PTX3 protein may contribute to cell-mediated immune defense in inflamed colon tissue, and in particular in crypt abscess lesions, of patients with ulcerative colitis. 21529268_might be a more sensitive marker for cardiovascular disease than hsCRP and TNFalpha in patients with chronic kidney disease 21677138_Neutrophils in patients with acute myocardial infarction release PTX3, which modulates the activatory cross-talk between activated platelets and leukocytes and possibly contributes to its cardioprotective effects. 21716666_this is a review of the studies on PTX3, with emphasis on pathogen recognition and cross-talk with other components of the innate immune system. [Review] 21764903_These results identify PTX3 as a novel FGF8b antagonist endowed with antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activity with possible implications for the therapy of hormonal tumors. 21796992_Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM could induce the expression of PTX3 in Caco-2 cells. 21880642_pentraxin 3 is an early predictor of complications in hematologic patients with neutropenic fever. 21883907_Elevated PTX3 levels were associated with the development of primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients 21900125_PTX3 gene expression is upregulated in visceral adipose depots in obesity, despite lower plasma PTX3 protein, and by some proinflammatory cytokines in cultured adipocytes. 21914683_Serum levels of inflammatory marker pentraxin 3 decreased during cardiac rehabilation as exercise capacity increased. 21915248_Human pentraxin 3 binds to the complement regulator c4b-binding protein. 21920889_In COPD, airflow limitation and reduced transfer coefficient for carbon monoxide are associated with lower pulmonary interstitial expression of PTX3. 21933102_cord blood level not associated with histological chorioamnionitis 21948359_The long pentraxin PTX3 is a prototypic soluble pattern recognition molecule that is produced at sites of infection and inflammation by both somatic and immune cells. 21953577_Plasma pentraxin 3 levels could be a new biochemical marker for Parkinson's (PD)disease and may be associated with the severity of motor dysfunction and other clinical symptoms in PD patients. 21989653_Local expression of PTX3 is a feature of vascular inflammation in giant cell arteritis. 22053612_Levels of sPTX 3 and sIL-6 were significantly higher in RA patients than controls. 22072855_Data show that PTX3 expression is down-regulated in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma due to gene promoter hypermethylation. 22123215_high PTX3 is associated with peripheral artery disease. 22178425_Higher levels of PTX3 are independently associated with increased mortality after ischemic stroke. 22267482_TSG-6 reverts the inhibitory effects exerted by PTX3 on FGF2-mediated angiogenesis through competition of FGF2/PTX3 interaction. 22278372_AZU1 exhibited high affinity binding to PTX3 in a calcium ion-dependent manner 22304663_PTX3 level is increased in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome in concordance with insulin resistance. 22309253_PTX3 has been identified as a non-redundant protective factor against infections caused by A. fumigatus. [Review] 22319633_Level of PTX3 is independently associated with atherosclerosis and manifest cardiovascular disease but not early vessel pathology 22447522_Serum amyloid A (SAA) induces pentraxin 3 (PTX3) production in rheumatoid synoviocytes. 22529962_PTX3 expression is increased in asthmatic airways. HASMC can both produce and respond to PTX3. PTX3 is a potent inhibitor of HASMC migration induced by FGF-2 and can upregulate CCL11/eotaxin-1 release. 22546644_Data show in the renal transplant (RT) recipients serum Pentraxin3 (PTX3) was significantly higher than the hemodialysis (HD) patients. 22577258_Pentraxin 3(PTX 3) is an endogenous modulator of the inflammatory response [review] 22617341_The plasma level of PTX3 may be a useful biomarker for predicting the tissue characteristics of coronary plaque using integrated backscatter intravascular ultrasound. Statin therapy may have a beneficial effect with regard to the reduction of PTX3 levels. 22687644_PTX3 is negatively associated with insulin resistance and associated with changes in insulin resistance induced by physical activity in overweight and obese children. 22714118_PTX3 and TNF-alpha are increased in preeclampsia and are likely involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia 22747472_High PTX3 is associated with acute renal allograft rejection. 22785134_High PTX3 expression is associated with coronary atherosclerotic plaques. 22822025_Genetic variants of PTX3 protein are associated with primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. 22834944_selective pressure on PTX3 variants that affect the innate immune response to infectious agents, could also produce the observed high incidence of DZ twinning in Gambians. 22847671_In multiple myeloma PTX3 behaves as an anti-angiogenic molecule and an inhibitor of cross-talk between plasma cells and endothelial cells/fibroblasts. 22883522_The high expression of PTX3 in placentas from the preeclamptic patients suggests that PTX3 may be involved in the pathologic process of preeclampsia. 22889492_Data suggest that plasma PTX3 is up-regulated in first trimester in pregnant women with history of recurrent miscarriage or embryo loss; in patient group, pentraxin-3 showed significant positive correlation with number of previous miscarriages. 23012252_Plasma PTX3 level is associated with inflammatory responses in Multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica 23062219_Data suggest that elevated maternal PTX3 plasma level is biological marker of altered endothelial function, typical of preeclampsia or intrauterine growth retardation; elevation in maternal PTX3 increases with disease severity. 23100088_PTX3 and MMP-9, which are not affected by prednisolone, could be sensitive biomarkers for assessing Takayasu arteritis activity. 23169308_Increased PTX3 levels are associated with adverse outcomes following paracetamol-induced acute liver injury. 23182717_Data show that a photodynamic therapy (PDT) dose-dependent upregulation of CRP gene, as well as of PTX3 and ficolin 1 genes in lung tumor A549 cells, and indicate critical role played by PI3K/Akt/AP-1 pathway. 23235124_PTX-3 stands out as a rapid and sensitive marker of hemodialysis-induced inflammation. Membrane flux and hemodiafiltration did not alter the inflammatory response. 23237880_Serum pentraxin 3 levels are associated with the complexity and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with stable angina pectoris. 23245734_Increased levels of plasma PTX3 are associated with accelerated atherosclerotic change and increased albuminuria in young patients with type 1 diabetes. 23285251_PTX3 concentration itself is unlikely to be even a modest causal factor for acute myocardial infection but is a prognostic marker after. 23341967_A high PTX3 level on hospital admission predicts severe sepsis and case fatality in patients with suspected infection 23401658_importance of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cell pathways for regulated PTX3 expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells 23424081_Long pentraxin-3 is an epithelial-stromal fibroblast growth factor-targeting inhibitor in prostate cancer. 23434196_pentraxin 3 might modulate the inflammatory process involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease 23443958_PTX3 is significantly associated with kidney dysfunction. 23475792_increased levels in serums from cystic fibrosis patients, but low in their respiratory secretions 23527487_This review of the general properties of PTX3 and C-reactive protein (CRP) as prototypes of long and short pentraxins, respectively, emphasizing in particular the functional role of PTX3 as a prototypic pattern recognition molecule. 23579776_higher synovial fluid levels are associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis disease severity 23609129_Plasma pentraxin 3 may be a better marker of peripheral artery disease in hemodialysis patients than C-reactive protein. 23625866_PTX3 is an anti-inflammatory mediator which essentially protects against the perils of atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. [review] 23643952_Plasma PTX3 levels are elevated in heart failure (HF) and might be used as diagnostic value in classification of patients with HF. 23658833_Elevated circulating levels and tissue expression of PTX3 in uremia reflect endothelial dysfunction. 23664694_PTX3 expression differed across low and high-grade tumors based on histopathological diagnosis and clinical severity, positively correlating with tumor grade and severity. 23690668_The observations point to a cardiovascular protective effect of PTX3 associated with the ability of tuning inflammation and favor the hypothesis that the increased levels of PTX3 may reflect a protective physiological mechanism. 23735470_PTX3 levels were higher in SCD patients in VOC, being associated with longer hospital stay. Higher initial PTX3 concentrations were related to the development of ACS with a further increase in PTX3 levels observed upon progression to ACS. 23771016_Arterial stiffness is increased in overweight and obese individuals. The increase in arterial stiffness may, at least in part, be associated with an obesity-related reduction in plasma PTX3 concentrations 23817411_These results demonstrate that ficolin-1 and PTX3 heterocomplex formation acts as a noninflammatory 'find me and eat me' signal to sequester altered-host cells. 23863905_Human colostrum contains high levels of PTX3. Breast epithelial cell and CD11b(+) milk cells constitutively produce PTX3. PTX3 ingested during lactation was detected in neonates and may protect against infection. 23954061_Systemic PTX3 levels comprise a useful inflammatory marker that reflects coronary plaque vulnerability. 23979265_Local PTX3 production in the left atrium might reflect the local inflammation of atrial fibrillation. 23991979_High PTX3 expression is associated with lung cancer. 24012697_PTX3 levels are elevated in non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome. 24039869_Pentraxin-3 serum levels are associated with disease severity and mortality in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. 24060373_Gene expression in irradiated arteries compared to non-irradiated showed a consistent up-regulation of PTX3 in all patients and in a majority of veins. 24132243_Systemic pre-PCI PTX3 was associated with high-risk plaque components and impaired post-PCI myocardial perfusion. Thus, PTX3 may be a reliable predictor of outcome in STEMI patients. 24215445_Obesity is associated with low circulating PTX3 in acute coronary syndrome. This association is also observed in the presence of abdominal fat accumulation as reflected by elevated waist circumference. 24261762_Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have increased concentrations of PTX3 compared with control subjects. PTX3 was significantly associated with disease activity but not with carotid atherosclerosis. 24273922_findings suggest that PTX3 may be useful in early evaluation and prediction of the severity of acute pancreatitis 24279306_PTX3 plays a role in the fertilization process. 24333560_Plasma PTX3 level may be a useful marker for predicting post-percutaneous coronary intervention cardiac cTnT elevation, which is associated with inflammatory status of culprit lesions. 24347428_Plasma PTX3 levels were reduced in polycystic ovary syndrome women and independently associated with hyperandrogenism and other endocrine and ovarian features of PCOS. 24350299_The current study provided the first evidence that decreased plasma PTX3 levels are associated with T2DM and diabetic nephropathy (DN) in Malay men and also suggested that PTX3 may have different effects in DN and chronic kidney diseases. 24457902_PTX3 silencing using PTX3-specific siRNA prevented breast cancer cell migration, macrophage chemotaxis, and subsequent OC formation. 24462365_PTX3 plasma levels do not predict carotid intima media thickness progression and incidence of cardiovascular events in the general population 24474442_Peak level of PTX3 in acute aortic dissection was associated with the amount of transient pleural fluid accumulation, which may be associated with inflammatory vascular permeability. 24476432_Genetic deficiency of PTX3 affects the antifungal capacity of neutrophils and may contribute to the risk of invasive aspergillosis in patients treated with hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. 24503185_Interleukin-1-induced changes in the glioblastoma secretome suggest its role in tumor progression. 24568622_After a kidney transplant, pentraxin 3 may not be useful in determining inflammatory status. 24613562_PTX3 is a physiological constituent of the amniotic fluid and is elevated in the presence of spontaneous preterm labor reinforcing the theory that PTX3 plays a role in innate immune response during gestational complications associated with infectious/inflammatory conditions 24628740_PTX3 was associated with cardiovascular disease risk factors, subclinical CVD, coronary artery calcium and incident coronary heart disease events. 24652286_These results indicate that PTX3 is constitutively expressed and secreted by AM cells as an integral component of the AM HC-HA-PTX3 complex and contributes to the biological function of AM HC-HA-PTX3. 24664887_The PTX3-driven increase in the osteoclastogenic potential of precursor osteoblasts (pOB) appears to be mediated by the effect of PTX3 on pOB RANKL production. 24675235_PTX3 overexpression inhibited cholesterol efflux via activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2, down-regulated the expression of the key cholesterol transporter, ABCA1, and nuclear transcription factors, PPARgamma and LXRalpha. 24705587_the results do not indicate that PTX3 can predict recurrent coronary events among MI survivors. 24709882_Serum PTX3, MMP-9 and C-reactive protein expression was significantly higher in the acute coronary syndrome patients compared with controls. 24724970_There is no correlation between fetal and maternal serum levels of PTX3 in either healthy pregnancies or those complicated by preeclampsia. 24745336_genetic polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to acute pyelonephritis and cystitis 24936646_PTX3 may be a potential novel indicator of carotid plaque vulnerability. 24950910_There was an increase in PTX3 tissue expression between the first and second prostate biopsy. PTX3 serum levels were also higher in patients with prostate cancer than in patients with inflammation/BPH. 24958171_Results indicate that the oligomerization state of PTX3 is an indicator of sepsis outcome as its conversion from octamer to monomer correlates with greater survival. 24979323_Serum PTX3 was higher in patients with coronary artery disease compared to controls. Increased PTX3 correlated with disease severity. 25048680_PTX-3 might have an atheroprotective role as well as serving as a simple biomarker in coronary atherosclerosis. 25049357_Mechanistically, engagement of MD-2 by PTX3-opsonized Aspergillus conidia activated the TLR4/Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta-dependent signaling pathway converging on IL-10. 25131923_A positive correlation was found between the expression of PTX3 in coronary plaque and macrophage cells type 2. 25148605_Suggest pentraxin 3 could be a new diagnostic marker for excessive inflammatory response in cardiac surgery. 25159210_Plasma PTX3 is positively associated with diabetic retinopathy development and progression, and may be a more accurate predictor of its development than hsCRP. 25178940_The aim of this study was to determine the incidence and role of pentraxin-3 (PTX-3) overexpression as a predictive/prognostic marker in small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC). 25190808_Weak, transient cross-linking by products of the quaternary hyaluronan/inter-alpha-inhibitor/TSG-6/PTX3 interactions can simultaneously support two processes, matrix stabilization and matrix expansion. 25237185_Morning PTX3 levels reflect obstructive sleep apnea-related acute inflammation and are a useful marker for improvement in OSA following CPAP therapy. 25303877_Circulating levels of PTX3 were elevated in COPD patients. 25323314_Elevated PTX3 was an independent predictor of 30-day cardiac events and mortality. 25344970_In the early phase of acute pancreatitis (AP), the concentrations of PTX3 achieved maximum earlier than CRP or SAA, enabling to differentiate between mild, moderate or severe AP in the first day of the disease. 25373851_PTX3 is also associated with other cardiovascular risk factors. 25385504_In systemic sclerosis patients, exposure to high concentrations of PTX3 may suppress endothelial progenitor cell-mediated vasculogenesis and promote vascular manifestations such as digital ulcers and pulmonary arterial hypertension. 25394473_Arterial inflammation and progression of vascular involvement influence plasma PTX3 levels in Takayasu arteritis. 25401491_PTX3 concentrations in SLE patients might serve as a indicator of the activation/dysfunction of vascular endothelium. 25412085_Results showed elevated plasma PTX3 levels in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and can be used for disease detection. 25435748_It is possible that PTX3 can be used as a diagnostic biomarker of retinal vein occlusion. 25447599_This study demonistrated that POEMS activity does not influence PTX3 circulating levels. 25467846_Data suggest that up-regulation of plasma PTX3 by exercise is blunted in obesity; here, at baseline and after 30 min of continuous submaximal aerobic exercise, obese subjects exhibited 40% lower plasma PTX3 compared to normal-weight subjects. 25491620_Elevated levels of serum PTX3 were associated with severity of illness in psoriasis patients. 25496843_may differentiate normal and abnormal fetal growth among women presenting at third trimester of pregnancy with a small for gestational age fetus 25530683_review of the role of Pentraxin 3 as a prognostic biomarker in patients with systemic inflammation or infection 25538378_plasma pentraxin-3 levels has a prognostic role in patients with stable coronary artery disease after drug-eluting stent implantation 25543194_A high PTX3 level and IgM staining in skin biopsies from Henoch-Schonlein purpura patients may be harbingers of subsequent renal involvement. 25550806_PTX3 could exacerbate endothelial dysfunction, at least partially, through IKK/IkappaB/NF-kappaB activation and overexpression of iNOS and NO, and advance the development of atherosclerosis. 25553422_PTX3 is able to modulate the innate response to gliadin in celiac disease and it could regulate the adaptive immune response. 25604633_Data showed the association between the PTX3 rs3816527 gene polymorphism with susceptibility to migraine only in the male patients. 25620175_Increased expression of PTX3 is correlated with tumor invasion of lung adenocarcinoma. 25641196_Results indicate that GDF8 down-regulates PTX3 expression via SMAD-dependent si |
ENSMUSG00000027832 |
Ptx3 |
51.835533 |
6.0177892850 |
2.589234 |
0.274670919 |
95.593272 |
0.00000000000000000000014108506348227902711537302854431751025239124285302759073624980640238035789479908999055624008178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001370912137589491976393049003105779844010376332307306243676924342733691730700229527428746223449707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.1255828 |
13.7698460 |
15.0803735 |
2.0644405 |
| ENSG00000163694 |
54502 |
RBM47 |
protein_coding |
A0AV96 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Methylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within cytidine to uridine editing and hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54502; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cytidine to uridine editing [GO:0016554]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24898756_RBM47 is an RNA-binding protein that can suppress breast cancer progression 26923328_Our findings, together with the enhanced tumor formation and metastasis of xenografted mice by knockdown of the RBM47 expression, suggested tumor-suppressive roles for RBM47 through the inhibition of Nrf2 activity 28680090_Results show that down-regulation of RBM47 is associated with and functionally important for colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Therefore, detection of RBM47 down-regulation may serve as a new prognostic marker for CRC and might represent an important diagnostic option to identify patients with poor prognosis. 30403177_miR-25 could directly target the RNA-binding motif protein 47 (RBM47). RBM47 is a promising target for the treatment of melanoma. 30620390_Results identified and confirmed to have downregulated gene expression of SFRP5 in sporadic nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NFPanNETs) and CDCA7L and RBM47 in MEN1-related NFPanNETs. 31358901_The first RNA recognition motif (RRM) domain of RBM47 is critical in the regulation of alternative splicing and its recognition to pre-mRNA of TJP1. Furthermore, the TJP1-alpha- isoform enhances the assembly of actin stress fibers, thereby promoting cellular migration in a wound healing assay, providing a basis for studies related to the modulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via alternative splicing. 31511650_The RNA-binding protein RBM47 is a novel regulator of cell fate decisions by transcriptionally controlling the p53-p21-axis. 32891348_The RNA-binding protein RBM47 inhibits non-small cell lung carcinoma metastasis through modulation of AXIN1 mRNA stability and Wnt/beta-catentin signaling. 34105460_[RNA Binding Protein RBM47 Inhibits the K562 Cell Proliferation by Regulating HMGA2 mRNA Expression]. 34499322_RNA binding motif 47 (RBM47): emerging roles in vertebrate development, RNA editing and cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000070780 |
Rbm47 |
422.380625 |
2.1189146843 |
1.083326 |
0.087840013 |
152.590176 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000004708039114022387141467773270924682364409556697282617400265190060918848032388882163796245037233612062976817469461821019649505615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000697697362680425982763392806392334685459031736793420831321609520266816848402921880414309565437980253932437335606664419174194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
588.2688365 |
31.7821911 |
279.8645675 |
11.8003435 |
| ENSG00000163701 |
132014 |
IL17RE |
protein_coding |
Q8NFR9 |
FUNCTION: Specific functional receptor for IL17C. May be signaling through the NF-kappa-B and MAPK pathways. May require TRAF3IP2 /ACT1 for signaling. May be a crucial regulator in innate immunity to bacterial pathogens. Isoform 2 and isoform 4 may be either cytoplasmic inactive or dominant active forms. Isoform 3 and isoform 5 may act as soluble decoy receptors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21993848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21993849}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that functions as the receptor for interleukin-17C. The encoded protein signals to downstream components of the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Activity of this protein is important in the immune response to bacterial pathogens. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2013]. |
hsa:132014; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-17 receptor activity [GO:0030368]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954] |
20459687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21993849_IL-17RE as a receptor of IL-17C that regulates early innate immunity to intestinal pathogens. 27685606_Our findings suggest that the IL-25/IL-25R axis may play an important role in promoting the recruitment and proinflammatory function of eosinophils in allergic asthma. 31905037_Evaluation of Interleukin 25 and Interleukin 25 Receptor Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Breast Cancer Patients and Normal Subjects. 32174926_IL-17C/IL-17RE: Emergence of a Unique Axis in TH17 Biology. 35553626_Interleukin 17 receptor E identifies heterogeneous T helper 17 cells in peritoneal fluid of moderate and severe endometriosis patients. |
ENSMUSG00000043088 |
Il17re |
12.025915 |
0.1506284433 |
-2.730934 |
0.593921669 |
20.689970 |
0.00000539981202104322900389449940705688391062722075730562210083007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017505210944563597528795401148116184231184888631105422973632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8375282 |
1.7350352 |
25.6334861 |
7.4996507 |
| ENSG00000163702 |
84818 |
IL17RC |
protein_coding |
Q8NAC3 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for IL17A and IL17F, major effector cytokines of innate and adaptive immune system involved in antimicrobial host defense and maintenance of tissue integrity (By similarity). Receptor for IL17A and IL17F, major effector cytokines of innate and adaptive immune system involved in antimicrobial host defense and maintenance of tissue integrity. Receptor for IL17A and IL17F homodimers as part of a heterodimeric complex with IL17RA (PubMed:16785495). Receptor for the heterodimer formed by IL17A and IL17B as part of a heterodimeric complex with IL17RA (PubMed:18684971). Has also been shown to be the cognate receptor for IL17F and to bind IL17A with high affinity without the need for IL17RA (PubMed:17911633). Upon binding of IL17F homodimer triggers downstream activation of TRAF6 and NF-kappa-B signaling pathway (PubMed:16785495, PubMed:32187518). Induces transcriptional activation of IL33, a potent cytokine that stimulates group 2 innate lymphoid cells and adaptive T-helper 2 cells involved in pulmonary allergic response to fungi (By similarity). Promotes sympathetic innervation of peripheral organs by coordinating the communication between gamma-delta T cells and parenchymal cells. Stimulates sympathetic innervation of thermogenic adipose tissue by driving TGFB1 expression (By similarity). Binding of IL17A-IL17F to IL17RA-IL17RC heterodimeric receptor complex triggers homotypic interaction of IL17RA and IL17RC chains with TRAF3IP2 adapter through SEFIR domains. This leads to downstream TRAF6-mediated activation of NF-kappa-B and MAPkinase pathways ultimately resulting in transcriptional activation of cytokines, chemokines, antimicrobial peptides and matrix metalloproteinases, with potential strong immune inflammation (PubMed:18684971, PubMed:17911633). Primarily induces neutrophil activation and recruitment at infection and inflammatory sites (By similarity). Stimulates the production of antimicrobial beta-defensins DEFB1, DEFB103A, and DEFB104A by mucosal epithelial cells, limiting the entry of microbes through the epithelial barriers (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K4C2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16785495, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17911633, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18684971, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32187518}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Receptor for both IL17A and IL17F. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16785495}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 6]: Does not bind IL17A or IL17F. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16785495}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 7]: Does not bind IL17A or IL17F. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16785495}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 8]: Receptor for both IL17A and IL17F. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16785495}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a single-pass type I membrane protein that shares similarity with the interleukin-17 receptor (IL-17RA). Unlike IL-17RA, which is predominantly expressed in hemopoietic cells, and binds with high affinity to only IL-17A, this protein is expressed in nonhemopoietic tissues, and binds both IL-17A and IL-17F with similar affinities. The proinflammatory cytokines, IL-17A and IL-17F, have been implicated in the progression of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been detected for this gene, and it has been proposed that soluble, secreted proteins lacking transmembrane and intracellular domains may function as extracellular antagonists to cytokine signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:84818; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-17 receptor activity [GO:0030368]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; defense response to fungus [GO:0050832]; granulocyte chemotaxis [GO:0071621]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900017]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755] |
16688746_IL-17RL exists as multiple isoforms due to extensive alternative splicing. Changes in RNA IL-17RL splicing occur in advanced cancers. 16785495_The biologic activity of IL-17 is dependent on a complex composed of receptors IL-17RA and IL-17RC. 17911633_IL-17RC functions as a receptor for both IL-17A and IL-17F; a soluble version of this protein should be an effective antagonist of IL-17A and IL-17F mediated inflammatory diseases. 18097068_IL-17A-induced IL-6, IL-8, and CCL20 secretion was dependent on both IL-17RA and IL-17RC, which are overexpressed in RA patients. 18684971_Interleukin-17F is inhibited by the IL-17RC receptor, a combination of soluble IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptors is required for inhibition of the IL-17F/IL-17A activity. 20173024_IL-17 and its receptor IL-17RC are involved in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid-mediated chemotaxis in human lung microvascular endothelial cell culture. 22744455_Overall, our study found a significant association of IL-17RC gene polymorphisms with AIS in a Chinese Han population, indicating IL-17RC gene may be as a susceptibility gene for AIS. 22898922_Data show that IL-17RA, IL-17RC, IL-22R1, ERK1/2 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways are involved in Th17 cytokine-induced proliferation. 22999050_IL-17RC predisposes to the development of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in a Chinese Han population. 24885153_results suggested a potential involvement of IL-17RC+CD8+ T cells in pathogenesis of ocular sarcoidosis 25918342_human IL-17RC is essential for mucocutaneous immunity to C. albicans but is otherwise largely redundant. 26731132_methylation of IL17RC could play as a marker in CNV and degeneration of RPE cells in vitro. 27155366_Interleukin 17A (IL17a) and interleukin-23 (IL-23) - dependent interleukin-17 receptor C (IL-17RC) are expressed by sputum and neutrophils in deltaF508-CFTR protein (F508del) cystic fibrosis patients. 29584788_IL-17RC rs708567 polymorphism in A/A genotype, G/G genotype, and G/a genotype did not seem to influence RA susceptibility in Tunisian population. 29695654_Genetic Variants on IL-17 are associated with development of atherosclerotic diseases. 29764467_Five SNPs in the IL17RC (and COL6A1) genes were found to be associated with susceptibility to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament in Han Chinese patients. 30024651_Genetic study revealed no association between IL-17RC, and SNPs and acute kidney transplant graft rejection. Nevertheless, a significant improvement of graft survival was found in kidney transplant recipients carrying the IL-17RC*G/G, and *G/A genotypes. 31291973_An increase in IL17RC gene expression levels in peripheral blood samples was found in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament patients. 31481525_Interleukin-17 receptor C gene polymorphism reduces treatment effect and promotes poor prognosis of ischemic stroke. 32187518_The crystal structure of the interleukin 17 receptor C (IL-17RC):interleukin 17F (IL-17F) complex provides a structural basis for IL-17F signaling through IL-17RC. 35167487_IL-17 Receptor C Signaling Controls CD4(+) TH17 Immune Responses and Tissue Injury in Immune-Mediated Kidney Diseases. |
ENSMUSG00000030281 |
Il17rc |
15.109469 |
0.4274370806 |
-1.226216 |
0.399170218 |
9.694329 |
0.00184837538859900624675647318184701362042687833309173583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004110595259261915629389605442156607750803232192993164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.0058609 |
2.6090016 |
23.5027250 |
3.8442526 |
| ENSG00000163710 |
26577 |
PCOLCE2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKZ9 |
FUNCTION: Binds to the C-terminal propeptide of types I and II procollagens and may enhance the cleavage of that propeptide by BMP1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12393877}. |
Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Enables collagen binding activity; heparin binding activity; and peptidase activator activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of peptidase activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26577; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; peptidase activator activity [GO:0016504]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830] |
12063410_Assignment of Pcolce2 gene, which encodes procollagen C-proteinase enhancer protein 2, to human chromosome 3q23. 12393877_PCPE2 is shown to be a glycoprotein that differs markedly in the nature of its glycosylation from that of PCPE1 19237735_Data indicate that PCPE2 accelerates the proteolytic processing of pro-apolipoprotein (apo) AI by enhancing the cleavage of the hexapeptide extension present at the N terminus of apoAI. 26218419_Procollagen C-endopeptidase protein 2, atherosclerosis and HDL cholesteryl ester catabolism. [Review] |
ENSMUSG00000015354 |
Pcolce2 |
25.926550 |
3.8476656559 |
1.943983 |
0.419709744 |
20.768718 |
0.00000518225738046772683173882279028532593656564131379127502441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000016851755658890426486148234053175087865383829921483993530273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.2517625 |
12.7272087 |
11.5804810 |
2.6029286 |
| ENSG00000163734 |
2921 |
CXCL3 |
protein_coding |
P19876 |
FUNCTION: Ligand for CXCR2 (By similarity). Has chemotactic activity for neutrophils. May play a role in inflammation and exert its effects on endothelial cells in an autocrine fashion. In vitro, the processed form GRO-gamma(5-73) shows a fivefold higher chemotactic activity for neutrophilic granulocytes. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10095777}. |
Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This antimicrobial gene encodes a member of the CXC subfamily of chemokines. The encoded protein is a secreted growth factor that signals through the G-protein coupled receptor, CXC receptor 2. This protein plays a role in inflammation and as a chemoattractant for neutrophils. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:2921; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593] |
12949249_CXCL3 displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 16356540_demonstrates, for the first time, that BIRC3 (anti-apoptotic protein), COL3A1 (matrix protein synthesis), and CXCL3 (chemokine) were up-regulated in the thrombin-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells 17389786_GRO-gamma is a promising candidate for Th2-associated glomerular permeability factor in minimal change disease. 17466952_Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation decreased expression of GRO3. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19369450_Report gonadotropin-releasing hormone-regulated CXCL3 expression in human placentation. 19448742_propose that chemokines belonging to the CXC family could play an important role in the etiology of tendon xanthoma (TX), with CXCL3 being a possible biological marker of onset and development of TX 19741597_overexpression of CXCL13 in the intestine during inflammatory conditions favors mobilization of B cells and of LTi and NK cells with immunomodulatory and reparative functions. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20162422_A significantly increased expression of GRO-2, GRO-3, and IL-8 in colon carcinoma as compared to normal tissue, is reported. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23023221_Data show that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) directly regulate T cell proliferation by induction of CXCL3 chemokine and its receptor, CXCR2 on the surface in T cells. 23225384_This study demonistrated that CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL8, and CXCL11, absent from normal muscle fibers, were induced in DMD myofibers. 23589610_secreted growth-regulated oncogene chemokines, specifically GRO-gamma, in human Mesenchymal stromal cell-conditioned media have an effect on the differentiation and the function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. 23904157_our results demonstrate the diverse mechanisms by which CXCL2 and CXCL3 mediate normal and asthmatic airway smooth muscle cell migration 24605943_results support a functional role of CXCL3 in breast cancer metastasis and as a viable target for cancer therapy 26837773_Our findings suggest that CXCL3 and its receptor CXCR2 are overexpressed in prostate cancer cells, prostate epithelial cells and prostate cancer tissues, which may play multiple roles in prostate cancer progression and metastasis. 27255419_Exogenous CXCL3 induced Erk1/2 and ETS1 phosphorylation and promoted CD133 expression. 28018222_This report demonstrates that Cxcl3 induces the migration of normal and neoplastic cerebellar precursor cells (GCPs) from the surface to the internal part of the cerebellum, a region where the GCPs differentiate, thus exiting the neoplastic program. In this way Cxcl3 counteracts the growth of medulloblastoma, tumor of the cerebellum originating from the GCPs. 28928065_The studies revealed that, although overall structural and oligomerization features of CXCL3 and CXCL2 are similar, prominent differences were observed in their surface characteristics, thus implicating a functional divergence. 29524043_CXCL3 exerts its carcinogenic potential by directly and/or indirectly regulating the downstream signaling pathways and the expression of transcription factors in PCa. 29884302_Migration, invasion, proliferation and tube-formation capability of HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells transfected with siRNA-CXCL3 were suppressed by down-regulation of CXCL3, while those behaviors of HTR-8/SVneo cells transfected with pEZ-CXCL3 were enhanced by upregulation of CXCL3. Nevertheless, the apoptosis of HTR-8/SVneo cells was not affected by either siRNA or overexpression plasmid. 30528777_hydrophobic pocket is in the vicinity of GAG binding region of CXCL3, a molecular determinant in leukocyte trafficking 31545503_Study demonstrated that CXCL3 is not only considerably upregulated in colon cancer (CC) tumor tissue but also has potential diagnostic value in patients with CC. Survival analysis suggested that CXCL3 may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker in CC. 31667838_CXCL3 overexpression promotes the tumorigenic potential of uterine cervical cancer cells via the MAPK/ERK pathway. 31709538_Gene expression and methylation profiles identified CXCL3 and CXCL8 as key genes for diagnosis and prognosis of colon adenocarcinoma. 31931644_Relationship between polymorphisms of CXCL3 gene and preeclampsia. 33191645_CX3 CL1 promotes tumour cell by inducing tyrosine phosphorylation of cortactin in lung cancer. 33568427_Inflammatory cell-derived CXCL3 promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis through a novel myofibroblast-hijacked cancer escape mechanism. 34269159_Expression levels of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligands CXCL1 and CXCL3 as prognostic biomarkers in rectal adenocarcinoma: evidence from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) analyses. 34392586_CXCL3 overexpression affects the malignant behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via the MAPK signaling pathway. 34870709_Clinical significance and biological functions of chemokine CXCL3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 35188401_Tumor suppressive lncRNA MEG3 binds to EZH2 and enhances CXCL3 methylation in gallbladder cancer. 35664357_Plasma CXCL3 Levels Are Associated with Tumor Progression and an Unfavorable Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. 35789398_Knockdown of CXCL3-inhibited apoptosis and inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-treated BEAS-2B and HPAEC through inactivating MAPKs pathway. 36343679_Chronic restraint stress promotes the tumorigenic potential of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by reprogramming fatty acid metabolism via CXCL3 mediated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. |
|
|
41.095802 |
12.2511625539 |
3.614847 |
0.375521534 |
112.196537 |
0.00000000000000000000000003235890199662769716588476958929515765740437807199233267657793810696538298887769968814609455876052379608154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000361010879418159332535259072099215466647772166736464818477931105648393375617821732248557964339852333068847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
78.7418063 |
17.9022291 |
6.4593974 |
1.3674805 |
| ENSG00000163738 |
441024 |
MTHFD2L |
protein_coding |
Q9H903 |
FUNCTION: Bifunctional mitochondrial folate-interconverting enzyme that has both NAD/NADP-dependent methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase and methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activities. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZUA0}. |
Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Histidine biosynthesis;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Membrane;Methionine biosynthesis;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Multifunctional enzyme;NAD;One-carbon metabolism;Oxidoreductase;Purine biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: One-carbon metabolism; tetrahydrofolate interconversion. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZUA0}. |
Predicted to enable methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activity; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity; and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity. Predicted to be involved in tetrahydrofolate interconversion. Predicted to be located in mitochondrial matrix. Predicted to be active in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:441024; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase activity [GO:0004477]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004487]; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0004488]; 10-formyltetrahydrofolate metabolic process [GO:0009256]; folic acid metabolic process [GO:0046655]; histidine biosynthetic process [GO:0000105]; methionine biosynthetic process [GO:0009086]; purine nucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0006164]; tetrahydrofolate interconversion [GO:0035999] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 35712863_The First Structure of Human MTHFD2L and Its Implications for the Development of Isoform-Selective Inhibitors. |
ENSMUSG00000029376 |
Mthfd2l |
72.338337 |
2.4177494725 |
1.273665 |
0.378738278 |
10.885837 |
0.00096902355909829701943736246505523013183847069740295410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002259167229867456092029520675623643910512328147888183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
101.1321423 |
23.2563610 |
41.6167884 |
7.0946814 |
| ENSG00000163739 |
2919 |
CXCL1 |
protein_coding |
P09341 |
FUNCTION: Has chemotactic activity for neutrophils. May play a role in inflammation and exerts its effects on endothelial cells in an autocrine fashion. In vitro, the processed forms GRO-alpha(4-73), GRO-alpha(5-73) and GRO-alpha(6-73) show a 30-fold higher chemotactic activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10095777}. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Growth factor;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This antimicrobial gene encodes a member of the CXC subfamily of chemokines. The encoded protein is a secreted growth factor that signals through the G-protein coupled receptor, CXC receptor 2. This protein plays a role in inflammation and as a chemoattractant for neutrophils. Aberrant expression of this protein is associated with the growth and progression of certain tumors. A naturally occurring processed form of this protein has increased chemotactic activity. Alternate splicing results in coding and non-coding variants of this gene. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 4. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:2919; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11816717_GRO-alpha levels in blood, quantities released from platelets ex vivo, and quantities released from SFFLRN stimulated platelets ex vivo were compared for preeclamptic and normal pregnancies. 12012624_may play a role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, possibly by chemoattraction and activation of neutrophils present in higher numbers in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis 12388718_mediates angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma 12734381_Eosinophils produce large amounts of the CXC chemokine GRO-alpha, which may be important during resolution of inflammation and may explain the interaction between eosinophils and certain tumors. 12744776_The role of GROa in cultured nasal epithelial cells was studied for its ability to synthesize and deliver neutrophil chemotactic factors following TNF-alpha induction. 12949249_This protein displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. 14530367_Recombinant GROalpha induces articular chondrocyte hypertrophy and calcification through p38 MAP kinase and transglutaminase 2. 15218300_expression of GRO-1 in 9 oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell lines and 94 OSCC specimens; findings suggest a possible relationship between the expression level of GRO-1 and tumor progression 15492419_This suggests that GRO-alpha plays a role in the infiltration of neutrophils into the lesional skin and in bulla formation in linear IgA bullous dermatosis. 15843053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15994316_KC (CXCL1) mRNA is regulated by functionally independent AU-rich sequence motifs 16086366_We propose that the concurrence of CXCR2 on oligodendrocytes and induced CXCL1 on hypertrophic astrocytes in MS provides a novel mechanism for recruitment of oligodendrocytes to areas of damage, an essential prerequisite for lesion repair. 16098041_endothelin-1 (ET-1) induces CXCL1 and CXCL8 secretion in three human melanoma cell lines 16567391_CXCL1 released from prostaglandin E2-treated carcinoma cells induces microvascular endothelial cell migration and tube formation in vitro. 16617094_IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-stimulated expression of GRO-alpha from airway smooth muscle is regulated by independent pathways involving NF-kappaB activation and ERK and JNK pathways 16941962_GRO-1 can promote tumor growth and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 17022986_LDL lipoprotein subunit L5 induces human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) to express GRO-alpha. 17060621_Gro-1 may be a therapeutic target as well as a diagnostic marker in ovarian cancer 17062666_Coexpression of fibulin-1 with GROalpha abrogates key aspects of the transformed phenotype, including colonic tumor formation in a murine xenograft model. 17096385_GROalpha led to p38 MAPK activation in chondrocytes cultured in micromass but not as a high-density monolayer. This caused the downstream triggering of chondrocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis/anoikis following concurrence of matrix degrading activity. 17456471_CX3CR1 and CX3CL1 mediate heterotypic anchorage of foam cells to coronary artery smooth muscle cells in the context of atherosclerosis 17466952_Inhibition of ERK decreased expression of Groa. 17581194_PAR-2 plays a role in serine protease-mediated regulation of IL-8 and GRO-alpha in nasal epithelial cells and may be involved in the pathophysiology of rhinosinusitis. 17703315_During treatment of ulceretive colitis with corticosteroids CXCL1/CXCL9 were decreased. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17999991_rease of CXCL1 and -2 mediated by Curcumin is involved in the inhibition of metastasis in breast cancer cells. 18056965_GRO-alpha may be a novel diagnostic marker for age-related pathology, including cancer. 18065201_The production of GRO-alpha, IL-6 and IL-8 was shown to account for the ability of the HeLa cell culture medium to stimulate the migration of monocytes/macrophages, suggesting a key role for p38 MAPK and ERK1/ERK2. 18211687_In addition to transcriptional up regulation of CXCL1, these primary cells exhibited the greatest IL-8 secretion and cell damage in response to stimulation with an acapsular strain of C. neoformans. 18276907_GROalpha could be involved in atherogenesis and plaque destabilization, potentially contributing to inflammation, matrix degradation, and lipid accumulation within the atherosclerotic lesion. 18283335_CXCL1 secreted by endothelial cells induces tumor cell invasion 18451219_results suggest that CXCL1 modulates the invasive abilities of bladder cancer cells and this chemokine may be a potential candidate of urinary biomarker for invasive bladder cancer and a possible therapeutic target for preventing tumor invasion 19103522_observed that CCL4, CXCL1 and CXCL8 secretion, following PROK1 induction 19176759_Vascular endothelial growth factor induces protein kinase D-dependent production of proinflammatory cytokine GRO-alpha in endothelial cells. 19258312_a novel mechanism by which mutant p53 acquires its gain of function via transactivating the GRO1 gene in cancer cells. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19430878_Data show that oral fibroblasts respond to LPS stimulation by increasing GROalpha production via the transcription factor NF-kappaB, suggesting that this mechanism may be involved in development of periodontal inflammation. 19435811_Results indicate that EGR-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB mediate GRO/CXCR2 proliferative signaling in esophageal cancer and may represent potential target molecules for therapeutic intervention. 19549892_Data show that expression of CXCL1 and its receptor, CXCR2, are elevated in cancer tissue compared with normal endometrium. 19780053_The expression levels of four of the up-regulated genes, CXCL1, SPARC, SPP1 and SULF, were significantly higher in the cancerous tissue compared with the normal tissue (fold change 3.4-8.9). 19838218_Data show that the knockdown of Ron in PC-3 or DU145 cells results in a significant decrease in angiogenic chemokine production and is associated with a decreased activation of NF-kappaB. 19906815_Lysophosphatidic acid mediates trophoblast cells to produce GRO-alpha, IL-8, and MCP-1 via LPA1 receptors and nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent signal pathways. 20042592_CXCL1 transgene mRNA stabilization is dependent on AUUUA-containing sequence motifs that are recognized by the RNA binding protein tristetraprolin. 20195728_PGI(2) analogues enhanced LPS-induced GRO-alpha expression via the IP receptor-cAMP and p38-MAPK pathways in human dendritic cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20495539_Aberrant expression of selectin E, CXCL1, and CXCL13 occurs in chronic endometritis. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20621720_We conclude that primary human thymic epithelial cells produce GRO-alpha and that its expression is regulated primarily by autocrine IL-6 and IL-6-activated Jak2 signaling. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20685145_Our findings suggest up-regulation of GRO-alpha and down-regulation of RANTES at the onset of a septic episode in premature and term neonates. 20702723_CXCL1 functions through CXCR2 to transactivate theefgr by proteolytic cleavage of HB-EGF, leading to activation of MAPK signaling and increased proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. 20731665_Within gastric cancer patients, CXCL1 serum levels increased according to tumor stage and lymph node metastasis. 21042742_GRO-alpha may play a pivotal role in the invasion of human colorectal cancer. 21075844_Serglycin is a major proteoglycan in polarized human endothelial cells and is implicated in the secretion of the chemokine GROalpha/CXCL1. 21220697_Chemokines CCL2, CCL8, CXCL1, and CXCL2 rank highest among signaling and inflammatory genes significantly enriched in human antigen R (HuR) ribonucleoprotein from stimulated airway epithelial cells compared to controls. 21257927_Fas induces KC release by a mechanism requiring MyD88, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and likely activator protein-1 21343381_Cancer cells expressing CXCL1 stably exhibited an increase in their migration and invasion ability, whereas CXCL1 or CXCR2 depletion significantly reduced the migration and invasion ability of each cell line. 21396766_GROalpha regulates human embryonic stem cell self-renewal or adoption of a neuronal fate 21531038_GRO-alpha and IP-10 are the predominant CXC chemokines involved in neutrophil and activated T lymphocyte chemoattraction in endogenous uveitis, particularly in Behcet's disease 21820916_IL-8 and GRO-alpha were measured by enzyme immunoassay in the first 48 h. After multiple regression analysis only absence of preeclampsia was associated with high IL-8 levels 21928244_Serum CCL18 and CXCL1 are potentially useful as novel circulating tumor markers for the differential diagnosis between ovarian cancer and benign ovarian masses. 21994122_CD133(+) liver tumor-initiating cells promote tumor angiogenesis, growth, and self-renewal through neurotensin/interleukin-8/CXCL1 signaling. 22030312_The induction of IL-6, CXCL1 and CXCL8 upon the interaction of bronchial epithelial cells with mast cells was mediated by MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 22069268_elevated serum CXCL1, indicating a predisposition to autoimmunity, is a good marker of T1DM risk 22125641_Data show that tumour conditioned media obtained from cultured colorectal tumour explant tissue contained high levels of the chemokines CCL2, CXCL1, CXCL5 in addition to VEGF. 22129625_Down-regulation of CXCL1 resulted in a nearly complete prevention of tumor growth. 22173151_CXCL1 rs4074 A allele as a genetic risk factor for cirrhosis progression in hepatitis C. 22183310_CCL2-CCR2 and CX3CL1-CX3CR1 signaling are involved in age related macular degeneration. 22251138_Vitamin D3 oppositely regulated the expression of Growth-related oncogene-alpha in THP-1 cells in vitro and human primary monocytes ex vivo via different intracellular signal pathways. 22615136_Suppression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 by siRNA or by progesterone and calcitriol inhibits endometrial and ovarian tumor cell invasiveness. 22732298_Seminal plasma rapidly enhanced the expression of the angiogenic chemokines, interleukin (IL)-8 and growth regulated oncogene alpha (GRO) in HeLa cells. 22770218_Study uncovered a paracrine network, with the chemokines CXCL1 and 2 at its core, that mediates lung metastasis and chemoresistance in breast cancer. 22902060_IL-17A produced by neutrophils stimulates Gro-alpha secretion from endometrial stromal cells, thereby recruiting more neutrophils and inducing perpetuating inflammation in endometriosis. 22975476_CXCL1 was elevated in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and decreased after bone marrow transplantation. 23027620_CXCL1/GROalpha increases cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer by decreasing fibulin-1 expression through NF-kappaB/HDAC1 epigenetic regulation. 23043537_Upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CXCL-1 production in dermal fibroblasts by normal/malignant epithelial cells in vitro: Immunohistochemical and transcriptomic analyses. 23052840_The silencing of the pro-angiogenic chemokine GRO-alpha is proportionally correlated with decreased expression of CXCR2 in pro-inflammatory cytokine-stimulated SGEC indicating the GRO-alpha/CXCR2 complex as a novel therapeutic target for Sjogren's syndrome. 23198952_The CXCL1 gene and particularly T allele of rs3117604 was associated with ischemic stroke. 23207068_Cowpox virus but not Vaccinia virus induces secretion of CXCL1, IL-8 and IL-6 and chemotaxis of monocytes in vitro. 23225384_This study demonistrated that CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL8, and CXCL11, absent from normal muscle fibers, were induced in DMD myofibers. 23269549_Data indicate that in NIH3T3 cells expressing unsulfated vGPCR mutant (yydd-vGN) but not vGPCR (wt-vGN) could significantly inhibit the tumor growth triggered by hGRO-alpha. 23334998_When expressed, CXCL1 is limited to small areas with faint staining and PCa progression does not rely on CXCL1 expression. 23389772_findings of the current study suggest a broad involvement of the chemokine GRO-alpha/CXCR2 system in Sjogren's syndrome pathogenesis that is mediated by the involvement of ADAM17 23444042_A novel miRNA, miR-7641, significantly suppressed CXCL1 expression in embryonic stem cells. 23479735_Chemokine CXCL1 dimer is a potent agonist for the CXCR2 receptor. 23502337_decreased serum levels in patients with alopecia areata 23505918_Elevated levels of CXCL1 and CXCL10 could possibly be used as a marker of inflammation and angiogenesis/angiostasis in type 2 diabetes 23519936_sequence-linked, post-transcriptional activities provide substantial mechanistic diversity in the control of GRO family chemokine gene expression. 23554905_Neutrophil priming led to the rapid expression of a common set of transcripts for cytokines, chemokines and cell surface receptors (CXCL1, CXCL2, IL1A, IL1B, IL1RA, ICAM1). 23567329_CXCL1 mRNA expression was significantly higher in the lymphocytes of Thromboangiitis obliterans patients than control subjects. 23665907_VEGF markedly induces CXCL1 release in A549 lung epithelial cells. 23732813_expressed and secreted from endothelial cells 23815949_this is the largest study describing increased CXCL1 protein expression in more aggressive phenotypes in human bladder cancer 23890481_Normal keratinocytes and cancer cells can stimulate the CXCL-1 secretion from normal dermal fibroblasts and stromal fibroblasts from squamous cell carcinoma. 23953856_CXCL1 is a target for the embryos' secretion product IL-1beta in decidualised endometrial stromal cells during the peri-implantation period. 23967336_CXCL1 expressed by monocytes and CXCR2 on HBMEC is involved in monocytes migrating from blood to brain in AD patients 24023680_IgA1 complexes from IgA nephropathy patients could up-regulate the secretion of CXCL1 and TGF-beta1 in mesangial cells. 24250750_Expression of the CXCL8, CXCL6 and CXCL1 genes are under the primary control of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its receptor. 24260493_The rs4074 single nucleotide polymorphism within the CXCL1 gene is associated with increased CXCL1 blood levels and increased risk for development of cirrhosis in alcoholics. 24273934_IL-1alpha regulated its sub-network genes including CXCL1, CXCL10, and ICAM1 mRNA levels in time dependent but not in concentration dependent manner 24487964_TNF-alpha stimulates CXCL1 release from human endothelial cells through JNK-mediated CXCL1 mRNA expression and p38 MAPK- and PI-3K-mediated CXCL1 secretory processes. 24581860_Four genes showed increased expression in the epithelium of OLP patients: CD14, CXCL1, IL8, and TLR1, and at least two of these proteins, TLR1 and CXCL1, were expressed at substantial levels in oral keratinocytes. 24588865_CXCL1 is a negative regulator of mast cell chemotaxis to airway smooth muscle cell products in vitro. 24600982_findings of this study demonstrated that serum concentrations of CXCL1 and CXCL12 were elevated in SCD patients when compared with controls 24619879_Increased CXCL1/CXCL8 instigated polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion to cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, possibly contributing to Diabetic ketoacidosis-associated intracranial vascular complications. 24981451_CXCL1 inhibits airway smooth muscle cell migration via activation of the ERK-1/2 MAP kinase pathway. 24999605_High CXCL1 stromal protein expression is highly specific for the tumorous transition in cases of sporadic colorectal neoplasias. 25135733_The present study showed that nasal fibroblasts can produce GRO-alpha and IL-8, and their production is remarkably enhanced by IL-17 stimulation, thereby clarifying the mechanism of the IL-17 mediated neutrophil infiltration in nasal polyps. 25175281_CXCL1 expression was a negative prognostic factor. 25301363_The released CXCL1 enhanced monocyte migration. 25344051_Elevated CXCL1 expression in breast cancer stroma predicts poor prognosis and is inversely associated with expression of TGF-beta signaling proteins. 25349304_miR141-CXCL1-CXCR2 signaling-induced Treg recruitment regulates metastases and survival of non-small cell lung cancer. 25383568_In CSF, CXCL1 is up-regulated in opioid-tolerant patients (and rodents). 25393692_SF of BC OA displayed significantly higher concentrations for a number of proinflammatory cytokines [CXCL1, eotaxin, interferon (IFN)-gamma, interleukin (IL)-7, IL-8, IL-9, IL-12]. 25471749_Intense glomerular CXCL1 expression was observed in biopsy specimens from patients with lupus nephritis 25641338_CXCL1 increases local tumor growth through activation of VEGF signaling. 25766782_There was a significant positive correlation between CXCL-1 levels in the vitreous and the extent of the retinal detachment. 25802102_CXCL1 and CXCL2 chemokines stimulate osteoclast differentiation in vitro 25816025_urinary CXCL1 as a new non-invasive predictor of IgAN progression 25930080_CXCL1 expression was highly upregulated in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. 26104296_High CXCL1 expression is a poor prognostic biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer. 26252654_TGF-beta negatively regulates CXCL1 expression in CAFs through Smad2/3 binding to the promoter, and through suppression of HGF/c-Met autocrine signaling 26341115_increased amounts released by neutrophils from fibromyalgia patients 26345899_Polymorphisms in the promoter regions of the CXCL1 and CXCL2 genes contribute to increased risk of alopecia areata in the Korean population 26349659_The novel findings reveal the critical role of NLRP12-IL-17A-CXCL1 axis in host defense by modulating neutrophil recruitment against Klebsiella pneumoniae. 26397389_BBP also stimulated the production of CXCL1/GROalpha by TADCs, which increased the angiogenesis of breast cancer in a mouse model 26406865_Urine CXCL1 is a promising, non-invasive molecular marker for tumor detection and outcome prediction in patients with bladder cancer . 26499374_these findings suggest that CXCL1 plays critical roles in the growth and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma 26503598_CXCR2-CXCL1 axis is correlated with neutrophil infiltration and predicts a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma 26721883_hCXCL1-GAG interactions provide stringent control over regulating chemokine levels and receptor accessibility and activation, and that chemotactic gradients mediate cellular trafficking to the target site. 27049944_work shows parallel networks of necroptosis-induced CXCL1 and Mincle signalling that promote macrophage-induced adaptive immune suppression and thereby enable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression 27092462_Results suggest that CXCL1 is a key molecular link between senescence of stromal fibroblasts and tumor growth. 27190986_the serum levels of the soluble factors sCD40L and CXCL1 are not associated with endometriosis and are not suitable as biomarkers for disease diagnosis. 27241286_Adipose stromal cells recruitment to tumours, driven by CXCL1 and CXCL8, promotes prostate cancer progression. 27297392_Increased IL-8 and CXCL1 transcription in T84 and THP-1 cells compared to that in wild-type EPEC. 27446967_These results demonstrate that tumor-derived CXCL1 contributes to TANs infiltration in lung cancer which promotes tumor growth. 27472713_Elevated expression of GRO-alpha in cytoplasm of cancer cells (hazard ratio [HR] = 5.730, P = 0.007) and stroma (HR = 3.120, P = 0.022) were independent prognostic factors of pancreatic cancer. T classification (HR = 2.130, P = 0.023), lymphatic metastasis (HR = 4.211, P = 0.009) and TNM classification (HR = 0.481, P = 0.031) were also prognostic predictors in PC patients. 27542259_we identified the microRNA miR-200a as a putative post-transcriptional regulator of CXCL1 in hepatocellular carcinoma 27577959_IL-8, but not the CXCL1 circuit, is critical for the regulation of thyroid cancer stem cells. 27665197_this study shows that CXCL1 is expressed in epithelium of the endometrium with adenomyosis and demonstrate that VEGF is capable of inducing CXCL1 expression 27690238_CXCL1 signaling in the tumor microenvironment is highly responsible for repeated intravesical recurrence, disease progression, and drug resistance through enhanced invasion ability. In conclusion, disrupting CXCL1 signaling to dysregulate this chemokine is a promising therapeutic approach for human UCB. 27748927_Silencing of the CXCL1 gene inhibits HGC803 cell migration and invasion. The positive expression of CXCL1 is correlated with poor survival of gastric cancer patients and CXCL1 is an independent prognostic factor for gastric cancer. 27799352_These findings support a role for CXCL1 and IL-8 in cystic fibrosis lung disease severity and identify STAT3 as a modulating pathway. 27832972_CXCL1 secreted by tumor-associated lymphatic endothelial cells promotes lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer through integrin beta1/FAK/AKT signaling pathway. 27958346_the plasma concentrations of CXCL1 indicated the disease activity and prognosis in interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF). Thus, the CXCL1/CXCR2 axis appears to be involved in the progression of IPAF. 28176455_The results of the transwell chemotaxis assay also supported the above results. Our data suggest that APN can promote h-JBMMSC chemotaxis by up-regulating CXCL1 and CXCL8 28375674_GROalpha high in the tumor microenvironment can be used as potential indicators for the progression of non-small cell lung cancer 28381820_S100A9 and S100A12 may have a role in the pathogenesis of pneumonia: S100A9 and CXCL1 may contribute solely in mild pneumonia, and CCL5 and CXCL11 may contribute in severe pneumonia. 28455419_Study provides the first evidence that primary malignant cell-secreted VEGFA stimulates tumor-associated macrophages to produce CXCL1, which recruits CXCR2-positive MDSCs to form a premetastatic niche to promote liver metastases. 28514506_CXCL1/8 secreted by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells could promote breast cancer angiogenesis. 28518141_This study highlighted CAF-secreted CXCL1 as an attractive target to reverse tumor radioresistance. 28560447_GROA overexpression is associated with invasion in triple negative breast cancer. 28575019_The expressions of CXCL1 in cancer cells and CXCR2 in stromal cells are useful prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients 28637660_Taken together, the present study indicates that IL-33 localized in the human atherosclerotic plaque increases GRO-alpha mRNA expression and protein secretion via activation of ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB in HUVECs, suggesting that IL-33 plays an important role in the pathophysiology and development of atherosclerosis. 28831670_Thrombocytosis was more prevalent in patients with inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)than in those with non-IBC and it was associated with poor prognosis. GRO and TGF-beta were associated with thrombocytosis in IBC 28859336_This study describe elevated levels of CXCL1 and it receptor in the Solid Component and Cyst Fluid of Human Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma, relative to other pediatric brain tumors and normal cerebral tissue. 28870907_the presence of elevated circulating levels of VEGF and CXCL1 are predictive of liver and lung metastasis, respectively of colorectal cancer. 28960786_These results suggest that secretion of the myokine CXCL1 is stimulated by saturated fatty acids and that CXCL1 promotes myogenesis from satellite cells to maintain skeletal muscle homeostasis. 29283424_miR-204 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer by targeting CKS1B, CXCL1 and GPRC5A. 29360827_study demonstrates that CXCL1 can transform NOFs into senescent CAFs via an autocrine mechanism 29369549_Association of polymorphic markers of chemokine genes, their receptors, and CD14 gene with coronary atherosclerosis 29438938_CXCL1, which is produced by breast cancer cells, can promote cancer growth and development 29507619_Both GRO-alpha and IL-8 can activate TAK1/NFkappaB signaling via the CXCR2 receptor. 29520695_These results show that AKIP1 is crucial in cervical cancer angiogenesis and growth by elevating the levels of the NF-kappaB-dependent chemokines CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL8. 29784873_By inducing glycolysis, CXCL1 plays a crucial role in both cancer progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer patients. 30015110_CXCL1 gene expression was associated with the negative syndrome in non-deficit schizophrenia patients, while no association in deficit schizophrenia was observed. 30035347_GRO-alpha from OSF-associated fibroblasts paracrinally promotes oral malignant transformation and significantly contributes to OSCC development. 30115896_CXCL1 displays a specific microRNA (miR) upregulated by the prototypical colon cancer onco-miR miR-105. 30158589_TAMs/CXCL1 promotes breast cancer metastasis via NF-kappaB/SOX4 activation, and CXCL1-based therapy might become a novel strategy for breast cancer metastasis prevention. 30201019_The chemokine Gro1 induced in response to inflammation triggers senescence and arrests development of new neurons in the hippocampus and that the magnitude of this response is sex-dependent. 30230320_Distinct Differences in Structural States of Conserved Histidines in Two Related Proteins: NMR Studies of the Chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL8 in the Free Form and Macromolecular Complexes. 30259595_Results show that the expression of CXCL1 and CXCL2 in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrated CD11b+ myeloid cells is critically involved in the promotion of the generation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (mo-MDSC) from bone marrow cells. CXCL1 and CXCL2 were found to specifically promote the expansion of mo-MDSC rather than granulocytic MDSC (G-MDSC). 30489503_The rs1429638 polymorphism in the CXCL1 gene and the rs2297630 polymorphism in the CXCL12 gene were associated with altered susceptibility to sepsis and might be used as important genetic markers to assess the risks of sepsis in trauma patients. 30514120_Among 29 immune and inflammatory proteins, CXCL1, CD84 and TNFRSF10A were associated with early post-acute coronary syndrome (ACS) after initial ACS-admission 30669188_CXCL1 and CSF3 levels are controlled by MAFF in myometrial cells. 30676127_Sputum CXCL1 levels in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease andasthma-COPD overlap patients were higher than in interstitial pneumonia 30705034_High CXCL1 expression is associated with Colorectal Cancer Progression. 30802327_CXCL1-dependent neutrophil transendothelial migration was not associated with neutrophil microtubule polymerization. 30809313_Taken together, these results argue that CXCL1 plays an important role in sustaining the growth of bladder and prostate tumors via up-regulation of IL6 and down-regulation of TIMP4. 30967059_Adiponectin treatment of ovarian cancer cells induces angiogenesis via CXC chemokine ligand 1 independently of vascular endothelial growth factor. These findings suggest that adiponectin may serve as a novel therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. 31147602_MicroRNAs (miRNAs) profiling of the EVs and the transfection experiment suggested that several miRNAs played a role in the induction of chemokines such as CXCL1 and CXCL8 in fibroblasts 31239384_vCXCL-1 increases mouse cytomegalovirus dissemination kinetics for both primary and secondary dissemination. We confirm the hypothesis that vCXCL-1 is a Human cytomegalovirus virulence factor 31322183_Findings revealed that the expression levels of CXCL1 were upregulated in ERnegative breast cancer. It was demonstrated that CXCL1 can stimulate tumor cell invasion via the ERK1/2/MMP2/9 pathway axis. 31387444_Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of CXCL1 in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 31500632_CXCL1-LCN2 axis is a key contributor to prostate cancer cells migration 31617252_A-kinase interacting protein 1 might serve as a novel biomarker for worse prognosis through the interaction of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1/chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 in acute myeloid leukemia. 31722447_CXCL1 is upregulated during the development of ileus resulting in decreased intestinal contractile activity. 32132577_Oxidative stress enhanced the transforming growth factor-beta2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through chemokine ligand 1 on ARPE-19 cell. 32187449_Elevation of CXCL1 indicates poor prognosis and radioresistance by inducing mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma. 32326946_Associations of CXCL1 gene 5'UTR variations with ovarian cancer. 32694172_Fusobacterium nucleatum host-cell binding and invasion induces IL-8 and CXCL1 secretion that drives colorectal cancer cell migration. 32782028_Tumor-suppressor miRNA-27b-5p regulates the growth and metastatic behaviors of ovarian carcinoma cells by targeting CXCL1. 32910411_Epithelial-stromal communication via CXCL1-CXCR2 interaction stimulates growth of ovarian cancer cells through p38 activation. 32968020_14-3-3zeta-TRAF5 axis governs interleukin-17A signaling. 33223508_Histone methyltransferase SETD2 inhibits tumor growth via suppressing CXCL1-mediated activation of cell cycle in lung adenocarcinoma. 33571109_Regulation of tumor immune suppression and cancer cell survival by CXCL1/2 elevation in glioblastoma multiforme. 33579221_A 4-gene signature predicts prognosis of uterine serous carcinoma. 33867350_MicroRNA-532-5p protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by directly targeting CXCL1. 33959656_CXCL1 Clone Evolution Induced by the HDAC Inhibitor Belinostat Might Be a Favorable Prognostic Indicator in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 34049975_Apolipoprotein E Promotes Immune Suppression in Pancreatic Cancer through NF-kappaB-Mediated Production of CXCL1. 34269159_Expression levels of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligands CXCL1 and CXCL3 as prognostic biomarkers in rectal adenocarcinoma: evidence from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) analyses. 34403447_CXCL1: A new diagnostic biomarker for human tuberculosis discovered using Diversity Outbred mice. 34461944_Aiduqing formula inhibits breast cancer metastasis by suppressing TAM/CXCL1-induced Treg differentiation and infiltration. 34465514_Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote myeloid-derived suppressor cell enrichment by secreting CXCL1 to prevent graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 34860147_MicroRNA miR-145-5p regulates cell proliferation and cell migration in colon cancer by inhibiting chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 and integrin alpha2. 34961474_Chemokine CXCL1 as a potential marker of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. 35173310_EMT-mediated regulation of CXCL1/5 for resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. 35421427_Mechanotransduction-induced glycolysis epigenetically regulates a CXCL1-dominant angiocrine signaling program in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. 35481427_Adipose tissue from subjects with type 2 diabetes exhibits impaired capillary formation in response to GROalpha: involvement of MMPs-2 and -9. 35764974_High expression level of CXCL1/GROalpha is linked to advanced stage and worse survival in uterine cervical cancer and facilitates tumor cell malignant processes. 35864308_ROS-activated CXCR2(+) neutrophils recruited by CXCL1 delay denervated skeletal muscle atrophy and undergo P53-mediated apoptosis. 35958781_Expression and Prognostic Role of CXCL1 Gene in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. 36434686_CXCL1 promotes colon cancer progression through activation of NF-kappaB/P300 signaling pathway. |
|
|
65.758932 |
16.0792930789 |
4.007132 |
0.312038624 |
219.885027 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009582131405799381809754750895975813114087330843338992730103764132725950990765489440457901404548198388204120032291031594030069479250855124519148375838994979858398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002029157238875163099527535061154798099755992663536741189291065342516705296531647279204639104268810097833882189184488383567467328916222868429031223058700561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
122.5708633 |
23.8206322 |
7.7006239 |
1.4183834 |
| ENSG00000163754 |
2992 |
GYG1 |
protein_coding |
P46976 |
FUNCTION: Self-glucosylates, via an inter-subunit mechanism, to form an oligosaccharide primer that serves as substrate for glycogen synthase. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22160680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30356213}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Glycogen biosynthesis;Glycogen storage disease;Glycoprotein;Manganese;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Glycan biosynthesis; glycogen biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22160680, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30356213}. |
This gene encodes a member of the glycogenin family. Glycogenin is a glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of a short glucose polymer from uridine diphosphate glucose in an autoglucosylation reaction. This reaction is followed by elongation and branching of the polymer, catalyzed by glycogen synthase and branching enzyme, to form glycogen. This gene is expressed in muscle and other tissues. Mutations in this gene result in glycogen storage disease XV. This gene has pseudogenes on chromosomes 1, 8 and 13 respectively. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:2992; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; membrane [GO:0016020]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; glycogenin glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0008466]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; UDP-alpha-D-glucose:glucosyl-glycogenin alpha-D-glucosyltransferase activity [GO:0102751]; glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005978] |
15860684_Results show that glycogenin becomes inactivated with glycogen catabolism and that this event coincides with an increase in glycogenin gene expression as exercise and glycogenolysis progress. 15870102_during recovery from prolonged exhaustive exercise, glycogenin mRNA and protein content and activity increase in muscle 17311895_GN-1 is conserved, possibly as very small, or nascent, granules when glycogen concentration is low. This would provide the ability to rapidly restore glycogen during early recovery. 22198226_results explain the glycogen depletion in the patient expressing only Thr83Met glycogenin-1 and why heterozygous carriers without clinical symptoms show a small proportion of unglucosylated glycogenin-1 24239874_The glucosylation of glycogenin-2 was enhanced to 2-4 glucose units by the co-presence of enzymatically active glycogenin-1. 25272951_Depletion of glycogenin-1 and impaired interaction with glycogen synthase underlies a new form of glycogen storage disease. 26652229_This study found a single homozygous intronic mutation of GYG1 harbored by five patients, who, except for two siblings, appear to be unrelated but all five live in central or south Sardinian villages. 29143313_We present functional evidence for the pathogenicity of a novel GYG1 missense mutation located in the substrate binding domain. 29321365_we screened the susceptibility loci for Myocardial infarction (MI) using exome sequencing and validated candidate variants in replication sets. We identified that three genes (GYG1, DIS3L and DDRGK1) were associated with MI at the discovery and replication stages. 30356213_palladium-mediated enzyme activation suggests multiphase initiation of glycogenesis 31689353_Glycogenin is at the core of glycogen's structure and initiates its glucopolymerization.[review] 33989636_Crystal structure and mutational analysis of the human TRIM7 B30.2 domain provide insights into the molecular basis of its binding to glycogenin-1. 35793618_The structural mechanism of human glycogen synthesis by the GYS1-GYG1 complex. |
ENSMUSG00000019528 |
Gyg |
297.491377 |
0.4577898362 |
-1.127243 |
0.313389117 |
12.650306 |
0.00037550413889492819394591571757757719751680269837379455566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000943340220832476631165897096309436165029183030128479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
175.0350208 |
40.3634318 |
385.2274702 |
64.0227435 |
| ENSG00000163762 |
116441 |
TM4SF18 |
protein_coding |
Q96CE8 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:116441; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
30897168_TM4SF18 is highly expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tumor epithelium, expressed in normal acinar tissue and weakly expressed in normal ducts. Although there is minimal expression in normal ducts, study observed increased TM4SF18 levels in preneoplastic ducts and tumor epithelium. Knockdown of the TM4SF18 protein led to a significant decrease in Capan-1 cell growth. |
|
|
32.802361 |
0.0089383589 |
-6.805774 |
0.990542011 |
87.771509 |
0.00000000000000000000734696427774055053718921064365084357820675815315083259085179867575732259865617379546165466308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000067146249374272779336231157835060592756771708520043836316767982275166559702483937144279479980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5357553 |
0.4003296 |
60.5450747 |
13.6330416 |
| ENSG00000163788 |
54861 |
SNRK |
protein_coding |
Q9NRH2 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in hematopoietic cell proliferation or differentiation. Potential mediator of neuronal apoptosis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12234663, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15733851}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
SNRK is a member of the sucrose nonfermenting (SNF)-related kinase family of serine/threonine kinases (Kertesz et al., 2002 [PubMed 12234663]).[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:54861; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
15733851_SNRK could mediate some of the physiological effects of LKB1 22874833_SNRK inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation through calcyclin-binding protein up-regulation and beta-catenin degradation, which results in reduced proliferation signaling. 22874833_These findings reveal a novel function for SNRK in the regulation of colon cancer cell proliferation and beta-catenin signaling. 27780848_SNRK in cardiomyocytes is responsible for maintaining cardiac metabolic homeostasis, which is mediated in part by ROCK, and alteration of this homeostasis influences cardiac function in the adult heart. 28117339_Study shows that TRIB3 binds to SNRK, and downregulates UCP3 through PPARalpha. SNRK is increased in cardiomyopathy patients, and SNRK reduces infarct size after ischaemia/reperfusion. SNRK also decreases cardiac cell death in a UCP3-dependent manner. 28722495_Differential expression of SNRK in early versus late stage disease suggests specific roles for SNRK in ovarian cancer metastasis. 29061304_Report the crystal structure of an N-terminal SNRK fragment containing kinase and adjacent ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domains. This structure shows that the UBA domain binds between the N- and C-lobes of the kinase domain. The mode of UBA binding in SNRK largely resembles that in AMPK and brain specific kinase (BRSK), however, unique interactions play vital roles in stabilizing the KD-UBA interface of SNRK. |
ENSMUSG00000038145 |
Snrk |
271.854709 |
0.4734438302 |
-1.078735 |
0.099976018 |
117.893646 |
0.00000000000000000000000000182938926175201563427313040257954671461633560828251698641537873506532482434372433033331617480143904685974121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000021498236865811903171218139403153154317276873367824190647858358129326772877065732103574191569350659847259521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
180.3226908 |
12.2614200 |
383.6072781 |
17.3965305 |
| ENSG00000163794 |
7349 |
UCN |
protein_coding |
P55089 |
FUNCTION: Acts in vitro to stimulate the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (PubMed:8612563). Binds with high affinity to CRF receptor types 1, 2-alpha, and 2-beta (PubMed:8612563). Plays a role in the establishment of normal hearing thresholds (By similarity). Reduces food intake and regulates ghrelin levels in gastric body and plasma (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P55090, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P81615, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8612563}. |
3D-structure;Amidation;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Hearing;Hormone;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sauvagine/corticotropin-releasing factor/urotensin I family. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature peptide, an endogenous ligand for both corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 and corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 2. In the brain this peptide may be responsible for the effects of stress on appetite. This peptide may also play a role in mood disorders, neurodegeneration, and skeletal system disorders. In spite of the gene family name similarity, the product of this gene has no sequence similarity to urotensin-2. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:7349; |
axon terminus [GO:0043679]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; varicosity [GO:0043196]; corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 binding [GO:0051430]; corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 2 binding [GO:0051431]; histone deacetylase inhibitor activity [GO:0046811]; neuropeptide hormone activity [GO:0005184]; activation of protein kinase A activity [GO:0034199]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; drinking behavior [GO:0042756]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; gastric emptying [GO:0035483]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of appetite [GO:0032099]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; negative regulation of cell size [GO:0045792]; negative regulation of feeding behavior [GO:2000252]; negative regulation of gastric acid secretion [GO:0060455]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of hormone secretion [GO:0046888]; negative regulation of necrotic cell death [GO:0060547]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; pancreatic juice secretion [GO:0030157]; positive regulation of behavioral fear response [GO:2000987]; positive regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090280]; positive regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043950]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060452]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of corticotropin secretion [GO:0051461]; positive regulation of DNA replication [GO:0045740]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043117]; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051966]; response to auditory stimulus [GO:0010996]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to pain [GO:0048265]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; startle response [GO:0001964]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11836334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12519893_a highly significant, but negative, correlation has been found between Ucn levels and gastric inflammation, suggesting that Ucn may exert an antiinflammatory effect in gastric mucosa 14519439_SCP and UCN are potent activators of the p42/44 MAPK pathway, with SRP able to induce phosphorylation of p42/44 MAPK as well, albeit not as pronounced 14576187_human cord blood-derived cultured mast cells (hCBMC) at 10 wk, but not at 2 wk, are immunocytochemically positive for CRH and UCN 14764822_Adipose tissue expressed urocortin and stresscopin, the predominant ligands of peripheral CRH-R2. 15072543_mRNA expression of urocortin was low during the last weeks of pregnancy in the placenta, myometrium and choriodecidua 15784504_urocortin may regulate uterine artery tone at mid gestation. 15924674_Urocortin peptide and mRNA was significantly increased in women with preeclampsia. 16340217_Urocortin potently suppressed the generation of angiotensin II-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) in HUVECs. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma & pitavastatin increased the urocortin mRNA levels and its release from HUVECs. 16675846_CRH peptides can differentially influence hair follicle melanocyte behavior not only via CRH-R1 signaling but also by complex cross-talk between CRH-R1 and CRH-R2. 16698078_expression of UCN in extravillous trophoblast cells and the activation of the UCN gene promoter by the diacylglycerol/PKC pathway 16920724_The evidence that (i) UCN is highly expressed in the secretory phase of the endometrial cycle; (ii) cAMP & E(2) + MPA modulate secretion of UCN & (iii) UCN induces HESCs decidualization together suggest a possible role for UCN in endometrial physiology. 17154253_NPY, via NPY Y5 and to a lesser extent via the Y1 receptors, exerts a stimulatory action on Ucn1 cells in the nonpreganglionic Edinger-Westphal nucleus. 17597629_In allergic nasal mucosa, increased expression levels of urocortin and its receptors may contribute to increased mucosal swelling and vascular permeability, playing an important role in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. 18234674_CRF-BP has distinct and separable binding surfaces for CRF and Ucn 1 18329817_The Ucn1-mRNA level in non-preganglionic Edinger-Westphal nucleus neurons is about 9.12 times higher in male but unchanged in female suicide victims. 18443956_UCN inhibited the proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of endothelial cells and down-regulated VEGF expression in vivo via CRFR2. 18670748_Ucn showed a significant role in the regulation of local inflammation, proliferation, and relaxation of smooth muscle tone in different organs through activation of corticotropin releasing factor receptor 2 (CRFR2). 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19437022_nuclear translocation of Ucn along with the loss of CRFR2 in epithelial cells and microvasculature of tumoral specimens may be involved in the pathobiology of renal cell carcinoma 19619932_The low amniotic fluid concentrations of urocortin at mid-trimester may be a signal of predisposition to preterm delivery. 19703147_reverses LPS-induced TNF-alpha release from trophoblast 19808377_Plasma urocortin 1 is elevated in heart failure (in proportion to the degree of cardiac dysfunction) in concert with the generalized neurohormonal activation seen in this condition. 19893766_Results suggest that urocortin concentrations in the amniotic fluid of genetic amniocentesis are not predictive of preterm labor and birth. 19949969_UCN is produced during the development of mesenchymal progenitor cells to osteoblasts and differentially regulated during culture as well as by differentiation factors. 19961889_Results demonstrate that plasma concentrations of UCN are significantly increased in patients with heart failure (HF). UCN may participate in the neurohumoral response of HF. 20363214_This article provides a review of the role of urocortins in normal cardiovascular physiology and in the pathophysiology of heart failure. 20368512_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20480172_not found to be efficient in distinguishing endometrioma from other benign ovarian cysts or to be superior to CA125 in the diagnosis of endometrioma 20670842_Higher plasma levels of urocortin-1, but not urocortin-II, are associated with worse left ventricular diastolic performance in patients with chronic systolic heart failure. 21289256_Women with endometriosis show an impaired endometrial expression of CRH and Ucn mRNA. 21360527_Confirm the anti-inflammatory function of VIP, through the modulation of the expression of CRF system that impacts in a reduction of mediators with inflammatory/destructive functions. 22639902_Serum urocortin could not predict women who delivered preterm among women with signs of preterm labor. 23416839_in human melanoma HMV-II cells both CRF and Ucn1 regulate TRP1 gene expression via Nurr-1/Nur77 production, independent of pro-opiomelanocortin or alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone stimulation. 23531852_Urocortin expression inversely correlates with higher tumor grade and advanced tumor stage in gastric adenocarcinomas. 23801677_Dihydrotestosterone decrease the expression of urocortin in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 23803006_Data suggest that low urocortin-1 concentration in midtrimester amniotic fluid is an early indicative marker of preterm birth. 23846219_Ucn is both an essential chondrocyte survival signal peptide and a chondroprotective agent in the presence of pro-apoptotic stimuli. 23987517_during the midluteal phase of the cycle, metformin may decrease the production of corticotropin-releasing hormone and UCN in the endometrium. 24012814_all neonates expressed UCN1 in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus independent of the degree of neuropathological injury. 24290358_A detailed conformational model for the CRF1R-Ucn1 complex based on the many ligand-receptor interactions determined was here and eventually revealed unique features of peptide ligand binding to class B GPCRs. 24954177_Cardioplegic arrest failed to induce cardiac myocyte overexpression of urocortin in diabetic hearts. 25172671_down-regulated expression in the placenta and maternal serum during intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy may impair the blood flow regulation of the utero-placental-fetal unit and contribute to fetal distress 25239507_UCN I is secreted from human glioblastoma cells by exocytosis through constitutive secretory granules. 25240771_These data suggest that UVB-stimulated Ucn1 contributes to TRP1 production via the transcription of both Nurr-1 and Nur77. Ucn1, produced in melanoma cells, acts on melanoma cells themselves in an autocrine manner. 25339828_Production of CRF and UCN1 in human dendritic cells is strongly augmented by commensal intestinal bacteria. 25462164_Ucn1 prevents the development of atherosclerosis by suppressing EC inflammatory response and proliferation, macrophage foam cell formation, and VSMC migration and proliferation 25951715_In women with adnexal endometrioma versus teratoma, the medians were 105.31 pg/mL versus 120.84 pg/mL for urocortin, 7.16 pg/mL versus 9.13 pg/mL for leptin and 584.33 pg/mL versus 657.82 pg/mL for ghrelin (p > 0.05), respectively. 26138318_Findings identify Ucn as a potential mediator that inhibits TGFbeta1 oncogenic signaling in breast neoplasm. 27045550_Study found reduced miR-326 levels concomitant with elevated Ucn1 levels in Edinger-Westphal nucleus (EWcp) of depressed suicide completers and in the EWcp of depressed rats. In fully recovered rats, both serum and EWcp miR-326 levels rebounded to nonstressed levels. While downregulation of miR-326 levels in primary midbrain neurons enhanced Ucn1 expression levels, miR-326 overexpression selectively reduced its levels. 27567427_In deep infiltrating endometriotic lesions, CRH, Ucn and CRH-R2 mRNA levels were significantly higher than in ovarian endometrioma. 28228090_REVIEW: Cardioprotective Utility of Urocortin in Myocardial Ischemia- Reperfusion Injury: Where do We Stand? 28698554_Data report that Ucn1 is expressed in human articular chondrocytes (AC) and confirm that Ucn1 is essential for the survival of AC cells in the absence of pro-apoptotic stimuli. 28925754_In women with chronic pelvic pain, infertility, or both symptoms, the probability of endometriosis (positive predictive value) increased consistently with the increase of plasma Ucn1 levels. 32452055_Identification of a four immune-related genes signature based on an immunogenomic landscape analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35276788_Urocortin Neuropeptide Levels Are Impaired in the PBMCs of Overweight Children. |
ENSMUSG00000038676 |
Ucn |
11.939019 |
0.3648352763 |
-1.454683 |
0.486383288 |
9.210792 |
0.00240592584443454415507601673596127511700615286827087402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005234591017667138829194684035428508650511503219604492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6748233 |
2.0667055 |
18.4187935 |
3.4772228 |
| ENSG00000163814 |
64866 |
CDCP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H5V8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in cell adhesion and cell matrix association. May play a role in the regulation of anchorage versus migration or proliferation versus differentiation via its phosphorylation. May be a novel marker for leukemia diagnosis and for immature hematopoietic stem cell subsets. Belongs to the tetraspanin web involved in tumor progression and metastasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11466621, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12799299, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15153610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16007225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16404722, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8647901}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane protein which contains three extracellular CUB domains and acts as a substrate for Src family kinases. The protein plays a role in the tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cellular events that are involved in tumor invasion and metastasis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:64866; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
12660814_antibodies generated by subtractive immunization used to purify, identify and partially characterize SIMA135/CDCP1; properties indicate it is a multidomain cell surface antigen, highly expressed by certain cancer cells and normal and cancerous colon 14739293_tyrosine phosphorylation of CDCP1 is regulated by adhesion or plasmin in epithelial cells 15153610_CDCP1 is not only a novel marker for immature hematopoietic progenitor cell subsets but also unique in its property to recognize cells with phenotypes reminiscent of MSC and NPC. 16926850_When CDCP1 promoter was transfected exogenously, Jurkat showed comparable promoter activity with K562, suggesting that the factor to enhance transcription was present but interfered to function in Jurkat 17335815_quantitated CDCP1 gene expression in matched normal colon and tumour tissue and compared the level of expression to other genes upregulated in colorectal tumourigenesis 17785447_CUB-domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), is identified as an Src family kinases-binding phosphoprotein associated with the anchorage independence of human lung adenocarcinoma. 18269919_The clustering of Gp140 and signaling components in membrane microdomains in cell-cell contacts contributes to changes in cell behavior. 18467693_CDCP1 promotes invasion and peritoneal dissemination of cancer cells through the regulation of cell migration and anchorage independence. 18483259_CDCP1 may have a role in neoplasm metastasis; targeting it with a monoclonal antibody inhibits metastasis in a prostate cancer model 18483744_Overexpression of CUB-domain containing protein 1 is associated with metastasis and recurrence in renal cell carcinoma. 19077003_CDCP1 expression level is a useful marker for prediction of patients with lung adenocarcinoma 19318475_abberant Trask phosphorylation is seen in many epithelial tumors from all stages including preinvasive, invasive, and metastatic tumors. 19671673_These findings confirm that CDCP1 functions as an antiapoptotic molecule and indicate that during metastasis CDCP1 facilitates tumor cell survival likely during or soon after extravasation. 19916495_findings indicate a functional role for CDCP1 in cancer and underscore the therapeutic potential of function-blocking anti-CDCP1 antibodies targeting both primary and metastatic carcinoma cells 20372833_In endometrioid adenocarcinoma low CDCP1 and advanced stage were independent poor prognostic factors for both overall and disease-free survival. 20501830_Overexpression of CDCP1 is associated with pancreatic cancers. 20551327_biological role of this protein and, potentially, its function in cancer, may be mediated by both 70-kDa cell retained and 65-kDa shed fragments, as well as the full-length 135-kDa protein. 21189288_Trask signaling and focal adhesion signaling inactivate each other and signal in exclusion with each other, constituting a switch that underlies cell anchorage state. 21220330_Data provide molecular mechanisms for the metastasis-enhancing functions of CDCP1. 21233420_Signal transduction from CDCP1 to PKCdelta leads to its activation, increasing migration of CC-RCC. Furthermore, patient survival can be stratified by CDCP1 expression at the cell surface of the tumor 21490433_Src-Trask signaling and Src-focal adhesion signaling inactivate each other, constituting two opposing modes of phosphotyrosine signaling that define a switch underlining cell anchorage state. 21559459_analysis of structural features of Trask that mediate its anti-adhesive functions 21617380_CDCP1 is selectively expressed in ovarian tumor vasculature 21706059_Trask as one of several potential candidates for functionally relevant tumor suppressors on the 3p21.3 region of the genome frequently lost in human cancers. 21725358_Data show that the signaling events that accompany the CDCP1 tyrosine phosphorylation observed in cell lines and lung tumors may explain how the CDCP1/SFK complex regulates motility and adhesion. 21812858_CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) is a substrate of Src family kinases and has been shown to regulate anoikis resistance, migration and matrix degradation during tumor invasion and metastasis in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner. Review. 21994943_analysis of cellular settings mediating Src Substrate switching between focal adhesion kinase tyrosine 861 and CUB-domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) tyrosine 734 22315226_a novel role for CDCP1 in EGF/EGFR-induced cell migration and indicate that targeting of CDCP1 may be a rational approach to inhibit progression of cancers driven by EGFR signaling 22457534_Secreted CDCP1 can be a useful genetic marker for the diagnosis of metastatic prostate cancer. 23208492_Complexing of beta1 integrin the 70-kDa with CDCP1 fragment induced intracellular phosphorylation signaling, involving focal adhesion kinase-1 (FAK) and PI3 kinase (PI3K)-dependent Akt activation 23300860_strongly expressed in tumors derived from lung, colon, ovary, or kidney. for a full transformation capacity, the intact amino- and carboxy-termini of CDCP1 are essential. 23378636_These data support a critical role for CDCP1 as a unique HIF-2alpha target gene involved in the regulation of cancer metastasis. 23439492_CDCP1 is an essential regulator of the trafficking and function of MT1-MMP- and invadopodia-mediated invasion of cancer cells. 23510015_Expression and phosphorylation of exogenous CDCP1 by Fyn kinase reduced the formation of autophagosomes. 23747337_In migrating cancer stem cells isolated from primary human colorectal cancers, CD110(+) and CDCP1(+) subpopulations mediate organ-specific lung and liver metastasis. 24384474_CDCP1 represses the epithelial phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells. 24681947_EGF increases the lifespan of CDCP1 promoting its availability on the cell surface where the data indicate it is available to mediate procancer phenotypes such as cell migration. 24849519_decreased CDCP1 expression promoted the invasive and migratory abilities of esophageal cancer cell lines. 24939643_CDCP1 protein induced by oncogenic Ras/Erk signaling is essential for Ras-mediated metastatic potential of cancer cells. 25275584_These data suggest CDCP1 expression can be used to identify a subset of marrow fibroblasts functionally distinct from CD146+ fibroblasts. 25301083_CDCP1 modulates cell-substratum adhesion and motility in colon cancer cell lines. 25728678_Multiple tyrosine phosphorylation sites of CDCP1 are important for the functional regulation of SFKs in several tumor types. 25775948_The aim of this study was to examine whether activation of Trask may be potentially important in brain metastasis of lung cancers, the commonest site of organ spread and producing the deadliest consequences. 25820997_High CDCP1 expression is associated with Colorectal Cancer. 25892239_CDCP1 overexpression enhances HER2 activity. CDCP1 binds to HER2, promoting SRC-HER2 crosstalk. 25893298_CDCP1 protein plays an important role in the progression of ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Elevated CDCP1 levels correlates with poor patient outcome in ovarian clear cell carcinoma patients. 26307391_these data demonstrated that HIF-2alpha could promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration by regulating CDCP1 26497208_Our results establish that differential glycosylation, cell surface presentation and extracellular expression of CDCP1 are hallmarks of prostate cancer progression. 26553452_ADAM9 enhances CDCP1 protein expression by suppressing miR-218 for lung tumor metastasis 26876198_These studies have important implications for the development of a therapeutic to block CDCP1 activity and Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)metastasis. 26882065_Elevated CDCP1 was observed in 77% of HGSC cases. Silencing of CDCP1 reduced migration and non-adherent cell growth in vitro and tumour burden in vivo. 26956052_High expression level of CDCP1 is associated with recurrence in glioblastoma. 27495374_CDCP1 may facilitate loss of adhesion by promoting activation of EGFR and Src at sites of cell-cell and cell-substratum contact. 27626701_CDCP1 is a novel marker of the most aggressive N-positive triple-negative breast cancers; CDCP1 expression and gains in CDCP1 copy number synergized with nodal (N) status in determining disease-free and distant disease-free survival 27685922_Stromal expression patterns for both ADAM12 and CDCP1. 28537886_These results revealed that ADAM9 down-regulates miR-1 via activating EGFR signaling pathways, which in turn enhances CDCP1 expression to promote lung cancer progression. 28739932_CDCP1 knockdown reduced 3D invasion, which can be rescued by ACSL3 co-knockdown. In vivo, inhibiting CDCP1 activity with an engineered blocking fragment (extracellular portion of cleaved CDCP1) lead to increased LD abundance in primary tumors, decreased metastasis, and increased ACSL activity in two animal models of TNBC. 29351434_Low CDCP1 expression is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 29433983_Co-expression of CDCP1 and AXL is often observed in EGFR-mutation-positive tumors, limiting the efficacy of EGFR TKIs. Co-treatment with EGFR TKI and TPX-0005 warrants testing. 29447112_The CDCP1 is cleaved by serine proteases at adjacent sites, arginine 368 (R368) and lysine 369 (K369), which induces cell migration in vitro and metastasis in vivo. 29511352_Study discovered a new mechanism of regulation of CDK5 through loss of CDCP1, which dynamically regulates beta1-integrin in non-adherent cells and which may promote vascular dissemination in patients with advanced prostate cancer. 29574172_CDCP1 was the most significant (FDR adjusted p-value 0.006). Correlation with CDCP1 concentration was most significant for CD34+ concentration and nucleated cell count. Multivariate analysis showed that CD34 and gender seemed to influence the level of CDCP1. 29792166_Study identified PDGF-BB/PDGFRbeta-mediated pathway as a novel player in the regulation of CDCP1 in triple-negative breast cancer through ERK1/2 activation. 30396925_Expression of CDCP1 was reduced by AHCC treatment of KLM1-R cells, whereas expression of actin was not affected. The ratio of intensities of CDCP1/actin in AHCC-treated KLM1-R cells was significantly suppressed (p |
ENSMUSG00000035498 |
Cdcp1 |
64.536347 |
7.8303226435 |
2.969072 |
0.300140339 |
98.177435 |
0.00000000000000000000003825241454133248306067442679860100783398101453258304064559573503742639921654244972160086035728454589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000380205817259304700066001468194610152486007079125600512430548875292268817815966031048446893692016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
108.2759895 |
21.2558344 |
13.9225368 |
2.2344467 |
| ENSG00000163864 |
349565 |
NMNAT3 |
protein_coding |
Q96T66 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the formation of NAD(+) from nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and ATP. Can also use the deamidated form; nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) as substrate with the same efficiency. Can use triazofurin monophosphate (TrMP) as substrate. Can also use GTP and ITP as nucleotide donors. Also catalyzes the reverse reaction, i.e. the pyrophosphorolytic cleavage of NAD(+). For the pyrophosphorolytic activity, can use NAD(+), NADH, NaAD, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NHD), nicotinamide guanine dinucleotide (NGD) as substrates. Fails to cleave phosphorylated dinucleotides NADP(+), NADPH and NaADP(+). Protects against axonal degeneration following injury. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16118205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17402747}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Magnesium;Mitochondrion;NAD;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; NAD(+) from nicotinamide D-ribonucleotide: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:16118205, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17402747}.; PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; deamido-NAD(+) from nicotinate D-ribonucleotide: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:16118205, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17402747}. |
This gene encodes a member of the nicotinamide/nicotinic acid mononucleotide adenylyltransferase family. These enzymes use ATP to catalyze the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide or nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide from nicotinamide mononucleotide or nicotinic acid mononucleotide, respectively. The encoded protein is localized to mitochondria and may also play a neuroprotective role as a molecular chaperone. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:349565; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; nicotinamide-nucleotide adenylyltransferase activity [GO:0000309]; nicotinate-nucleotide adenylyltransferase activity [GO:0004515]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435]; nucleotide biosynthetic process [GO:0009165] |
16118205_NMNAT1 is a nuclear protein, whereas NMNAT2 and -3 are localized to the Golgi complex and the mitochondria 17402747_NMN binds before ATP with the mitochondrial isozyme NMNAT3. Only NMNAT3 utilizes ITP efficiently in place of ATP, and NMNH conversion to NADH by NMNAT1 and NMNAT3 occurs at similar rates. 20388704_analysis of isoform-specific targeting and interaction domains in human nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferases 20457531_Red blood cells represent the first human cell type with a remarkable predominance of NMNAT3 over NMNAT1; NMNAT2 is absent. 24155910_NMNAT3 is absent in mitochondria in human cells, and, akin to plants and yeast, cytosolic NAD maintains the mitochondrial NAD pool. |
ENSMUSG00000032456 |
Nmnat3 |
207.612604 |
0.2715018355 |
-1.880966 |
0.163536787 |
130.526408 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000314322692018173142527618279476294470454531498550165889771702823737509486921897676817150291128655226202681660652160644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000040483446197105021584341941615527788911899997137984647595128665330466844387972448482404530523126595653593540191650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
98.1815750 |
10.0768956 |
364.4188162 |
24.8794696 |
| ENSG00000163870 |
131601 |
TPRA1 |
protein_coding |
Q86W33 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable G protein-coupled receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within embryonic cleavage and negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:131601; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; aging [GO:0007568]; embryonic cleavage [GO:0040016]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition [GO:1901991] |
26451044_Gpr175 is a novel positive regulator of the Hh signaling pathway |
ENSMUSG00000002871 |
Tpra1 |
548.046281 |
2.2015212041 |
1.138501 |
0.085888272 |
175.422086 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000048421094406851798305128740380063966728974372128259581374218558456707511221612560534470566656199345793604865706427631266706157475709915161132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000008057444796450198037063347132858683626525299392374220311099802352233094117968605999859235088868985360383012661600332648959010839462280273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
769.1128376 |
40.1446475 |
351.8080616 |
14.1977291 |
| ENSG00000163874 |
80149 |
ZC3H12A |
protein_coding |
Q5D1E8 |
FUNCTION: Endoribonuclease involved in various biological functions such as cellular inflammatory response and immune homeostasis, glial differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells, cell death of cardiomyocytes, adipogenesis and angiogenesis. Functions as an endoribonuclease involved in mRNA decay (PubMed:19909337). Modulates the inflammatory response by promoting the degradation of a set of translationally active cytokine-induced inflammation-related mRNAs, such as IL6 and IL12B, during the early phase of inflammation (PubMed:26320658). Prevents aberrant T-cell-mediated immune reaction by degradation of multiple mRNAs controlling T-cell activation, such as those encoding cytokines (IL6 and IL2), cell surface receptors (ICOS, TNFRSF4 and TNFR2) and transcription factor (REL) (By similarity). Inhibits cooperatively with ZC3H12A the differentiation of helper T cells Th17 in lungs. They repress target mRNA encoding the Th17 cell-promoting factors IL6, ICOS, REL, IRF4, NFKBID and NFKBIZ. The cooperation requires RNA-binding by RC3H1 and the nuclease activity of ZC3H12A (By similarity). Together with RC3H1, destabilizes TNFRSF4/OX40 mRNA by binding to the conserved stem loop structure in its 3'UTR (By similarity). Self regulates by destabilizing its own mRNA (By similarity). Cleaves mRNA harboring a stem-loop (SL), often located in their 3'-UTRs, during the early phase of inflammation in a helicase UPF1-dependent manner (PubMed:19909337, PubMed:26320658, PubMed:26134560, PubMed:22561375). Plays a role in the inhibition of microRNAs (miRNAs) biogenesis (PubMed:22055188). Cleaves the terminal loop of a set of precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) important for the regulation of the inflammatory response leading to their degradation, and thus preventing the biosynthesis of mature miRNAs (PubMed:22055188). Also plays a role in promoting angiogenesis in response to inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the production of antiangiogenic microRNAs via its anti-dicer RNase activity (PubMed:24048733). Affects the overall ubiquitination of cellular proteins (By similarity). Positively regulates deubiquitinase activity promoting the cleavage at 'Lys-48'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains on TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), preventing JNK and NF-kappa-B signaling pathway activation, and hence negatively regulating macrophage-mediated inflammatory response and immune homeostasis (By similarity). Induces also deubiquitination of the transcription factor HIF1A, probably leading to its stabilization and nuclear import, thereby positively regulating the expression of proangiogenic HIF1A-targeted genes (PubMed:24048733). Involved in a TANK-dependent negative feedback response to attenuate NF-kappaB activation through the deubiquitination of IKBKG or TRAF6 in response to interleukin-1-beta (IL1B) stimulation or upon DNA damage (PubMed:25861989). Prevents stress granule (SGs) formation and promotes macrophage apoptosis under stress conditions, including arsenite-induced oxidative stress, heat shock and energy deprivation (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of macrophage polarization; promotes IL4-induced polarization of macrophages M1 into anti-inflammatory M2 state (By similarity). May also act as a transcription factor that regulates the expression of multiple genes involved in inflammatory response, angiogenesis, adipogenesis and apoptosis (PubMed:16574901, PubMed:18364357). Functions as a positive regulator of glial differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells through an amyloid precursor protein (APP)-dependent signaling pathway (PubMed:19185603). Attenuates septic myocardial contractile dysfunction in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) by reducing I-kappa-B-kinase (IKK)-mediated NF-kappa-B activation, and hence myocardial pro-inflammatory cytokine production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5D1E7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16574901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18364357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19185603, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19909337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22055188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22561375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24048733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25861989, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26134560, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26320658}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Binds to Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) and Dengue virus (DEN) RNAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23355615}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Exhibits antiviral activity against HIV-1 in lymphocytes by decreasing the abundance of HIV-1 viral RNA species. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24191027}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Antiviral defense;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA damage;DNA-binding;Endonuclease;Endoplasmic reticulum;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;RNA-binding;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
ZC3H12A is an MCP1 (CCL2; MIM 158105)-induced protein that acts as a transcriptional activator and causes cell death of cardiomyocytes, possibly via induction of genes associated with apoptosis.[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:80149; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extrinsic component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0042406]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0030867]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; endoribonuclease activity [GO:0004521]; exoribonuclease activity [GO:0004532]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; miRNA binding [GO:0035198]; mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding [GO:0035925]; mRNA 3'-UTR binding [GO:0003730]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA stem-loop binding [GO:0035613]; 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization [GO:0061158]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to chemokine [GO:1990869]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to ionomycin [GO:1904637]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cellular response to sodium arsenite [GO:1903936]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response-activating signaling pathway [GO:0002757]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; miRNA catabolic process [GO:0010587]; negative regulation by host of viral genome replication [GO:0044828]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0055118]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032691]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043031]; negative regulation of muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010656]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045019]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation [GO:2000320]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, endonucleolytic cleavage-dependent decay [GO:0000294]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis [GO:1900119]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010884]; positive regulation of miRNA catabolic process [GO:2000627]; positive regulation of mRNA catabolic process [GO:0061014]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of protein deubiquitination [GO:1903003]; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042307]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090501]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis, endonucleolytic [GO:0090502]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
16574901_May cause cell death and plays important role in development of ischemic heart disease. Could be a potential target for therapeutic intervention. 18178554_MCPIP1, 2, 3, and 4, encoded by four genes, Zc3h12a, Zc3h12b, Zc3h12c, and Zc3h12d, respectively, regulates macrophage activation. 18364357_MCP-1-induced angiogenesis is mediated via MCPIP, at least in part through transcriptional activation of cdh12 and cdh19 19185603_data demonstrate the role amyloid precursor protein (APP) has in glial differentiation of NT2 cells through MCP-1(MCP-1)/MCP-1-induced protein (MCPIP) signaling 19747262_Observations provide evidence for a novel negative feedback loop in the activation of NF-kappaB and point to potential significance of MCPIP in the treatment of pathological states that involve disturbances in the functioning of the NF-kappaB system. 20807520_REVIEW: Understanding ZC3H12A gives a comprehensive panorama that promises to improve our understanding of processes in which this gene is involved including autoimmune, infectious and cardiovascular diseases. 21971051_MCPIP1 coordinates SG formation and apoptosis during cellular stress and may play a critical role in immune homeostasis and resolution of macrophage inflammation. 22055188_MCPIP1 ribonuclease antagonizes dicer and terminates microRNA biogenesis through precursor microRNA degradation. 22132693_Our data suggest that Zc3h12a is a novel IL-6 regulator in fibroblast-like synovial cells, which may be involved in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. 22196138_Data indicate that absence of MCPIP1 exacerbates ischemic brain damage by upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and that MCPIP1 participates in LPS-induced ischemic stroke tolerance. 22820500_MCPIP-induces differentiation via induction of oxidative stress that leads to ER stress that causes autophagy involved in tube formation. 23185455_Taken together, these data demonstrate that MCPIP1 down-regulates via an ARE-independent pathway 23355615_MCPIP1 can act as a host innate defense via RNase activity for targeting and degrading viral RNA. 23658019_MCPIP1 is regulated by IL-17 and IL-1 24008336_These results demonstrate that MCPIP may be an important regulator of inflammatory angiogenesis and provide novel mechanistic insights into the link between MCP-1 and cardiovascular diseases. 24048733_The present results show for the first time that the antidicer RNase activity of MCPIP1 is critical in mediating the angiogenic function of MCPIP. 24191027_MCPIP1 acts as an RNase to limit HIV-1 production in resting CD4+ T cells. 24270572_MCPIP1-associated USP10 is essential for negative regulation of NF-kappaB activation. 25187114_Data show that regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2) was stabilized by deubiquitinase monocyte chemotactic protein-induced protein 1 (MCPIP1). 25225661_MCPIP1 may suppress hepatitis C virus replication and hepatitis C virus-mediated proinflammatory responses with infection, which might contribute to the regulation of host defense against the infection and virus-induced inflammation. 25955820_In this review we summarize current progress regarding the specific characteristics of sequences and structures in the 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs that are recognized by tristetraproline, Roquins, and Regnase-1. 26134560_MCPIP1 and MCPIP4 form a complex but they act independently in regulation of IL-6 mRNA degradation. 26308737_expression of miR-3613-3p might be regulated by MCPIP1 by cleavage of its precursor form. 26315540_In white blood cells from patients with SLE, MCPIP1 expression was elevated, and its expression correlated positively with the IFN score and negatively with the miR-146a transcript level. 26329288_Findings show increased MCP1P expression in a model of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury (I/R) and suggest a vital role for MCPIP1 in cell migration and apoptosis, resulting in increased angiogenesis and apoptosis during the late stages of I/R. 26399696_demonstrated induction of MCPIP1 in human fibroblasts embedded in the stress-released 3-D collagen matrix, which occurred through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and NF-kappaB 26450708_miR-139-mediated downregulation of MCPIP1 promotes IL-6 expression in osteoarthritis. 26617772_Suggest that MCPIP1 may play an important role in cholesterol induced damage in endothelial cells. 27044405_Regnase-1 can be induced by HMGB1 in microglia and negatively regulates HMGB1-mediated neuroinflammation and neuronal toxicity 27075251_both human and cynomolgus monkey MCPIP1 restrict simian immunodeficiency virus replication. Unlike SAMHD1, MCPIP1-mediated HIV-1 restriction cannot be overcome by SIV Vpx. 27180111_IL-17A-mediated induction of MCPIP1 is involved in the regulation of local altered gene expression in suprabasal epidermal layers in psoriasis 27322373_These data revealed that influenza A virus-induced expression of miR-9 negatively regulated MCPIP1 expression and partially acts as a brake on host MCPIP1-mediated antiviral effect. 27404795_SAHA-mediated suppression of the IL-6 expression is achieved through increased recruitment of CEBPalpha to the MCPIP1 promoter and by relieving the miR-9-mediated inhibition of MCPIP1 expression in OA chondrocytes. 27494113_The human conserved stem-loop structure is not sufficient for ZC3H12A-dependent degradation. 27513529_this study uncovered a novel IL-8-dependent mechanism via which MCPIP-1 maintains epithelial homeostasis 27782836_findings provide novel insight into the potential targeting of MCPIP1 or autophagy in the development of potential therapeutic strategies for silicosis 27866190_These findings reveal a new potential function of MCPIP1, suggesting a possible mechanism of fibrosis in pulmonary silicosis. 27893764_propose that KSHV infection inhibits a negative regulator of miRNA biogenesis (MCPIP1) and up-regulates critical miRNA processing components to evade host mechanisms that inhibit expression of viral miRNAs 27920272_MCPIP1 is a potent negative regulator of psoriatic skin inflammation through IL-17A and IL-17C 27935099_data extend knowledge on roles of MCPIP1 in our model and link the protein to regulation of expression and stability of MYCN through decrease of signaling via Akt/mTOR pathway. 28194024_A comprehensive update on the function, regulation and molecular mechanisms of Regnase-1 is provided. Authors propose that Regnase-1 may function as a master rapid response gene for cellular adaption triggered by microenvironmental changes. [Review] 28197812_MCPIP1 contributes to the clear cell renal cell carcinoma development. 28328949_MCPIP1 recognizes regions of the 3'UTR of C/EBPbeta mRNA. 28377026_MCPIP1 contributes to the UVB response of keratinocytes by altering metabolic and apoptotic processes and the release of inflammatory mediators. 28475459_Regnase-1 controls the magnitude of innate and adaptive immune responses, and thereby dysfunction of this protein in mice leads to the development of spontaneous systemic inflammation. 28716897_Loss of MCPIP1 expression is associated with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma metastasis. 28892164_Conclusively, these data demonstrate the MCPIP1 contributes to attenuate influenza A virus-induced host antiviral response by suppressing RIG-I expression. 28939056_MCPIP1 overexpression results in modulated levels of 58 miRNAs in adipocytes on day 2 of differentiation. Among them, 30 miRNAs showed significantly reduced levels and 28 showed increased levels in comparison to control. Approximately one third of the modulated miRNAs were not previously reported to be involved in adipocytes differentiation. 29054363_Zc3h12a may be a key factor for the aberrant increase in IL-6 after neonate infection. 29103983_The activation of p38 in response to low doses of ultraviolet radiation was postulated to be protective for p53-inactive cells. Therefore, MCPIP1 may favor the survival of p53-defective HaCaT cells by sustaining the activation of p38. 29379093_Based on these findings, ischemia/reperfusion-induced MCPIP1 expression regulates the migration and apoptosis of human vascular endothelial cells via HMGB1 and CaSR, respectively. 29471506_Evidence that MCPIP1 takes part not only in the destabilizing effect but also in translational silencing exerted by the NFKBIZ translational silencing element. 29545178_MCPIP1 is an important positive regulator of IFNs antiviral activity. 29551769_Low MCPIP1 expression is associated with breast neoplasms. 29742804_protective factor in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury 29743536_Substrate specificity of human MCPIP1 endoribonuclease was studied using RNA cleavage assays and affinity determination assays. 29913212_MALT1 paracaspase also targets MCPIP1 and degrade MCPIP1 protein in endothelial cells. 29920243_Data indicate a mechanism used by monocyte chemotactic protein-inducing protein 1 (MCPIP1) to negatively regulated type I IFN interferon-beta antiviral defense. 30096769_Although interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA level was higher in 3D-culured cells, its secretion levels were higher in 2D-cultured cells. In addition, the levels of mRNA and protein expression of regnase-1, regulatory RNase of inflammatory cytokine, significantly increased in 3D culture, suggesting post-translational modification of IL-6 mRNA via regnase-1. 30631045_MCPIP1 is a novel, powerful cytokine-induced protein in beta-cells that regulates beta-cell cytokine susceptibility by affecting a number of cytokine-sensitive pathways. 30842549_Study reveals that Regnase-1-mediated post-transcriptional regulation is required for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell maintenance and suggest that it represents a leukemia tumor suppressor. 31185306_MCPIP1 overexpression in HepG2 cells treated with oleate induces the level and activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). 31530713_The authors show that n transient transfection, MCPIP1 expression potently degraded the mRNA from exogenously transfected vectors and expression of MCPIP1 suppressed replication of Zika virus in infected cells. 31611552_CCL2 promotes macrophages-associated chemoresistance via MCPIP1 dual catalytic activities in multiple myeloma. 31651935_Up-regulated MCPIP1 in abdominal aortic aneurysm is associated with vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis and MMPs production. 31816951_MCP-1 and MCPIP potentially reduce the IL-1beta-mediated oncogenic effect in Renal Cell Carcinoma. 31893310_Integrative genomics reveal a role for MCPIP1 in adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism. 31919874_MCPIP1 overexpression in human neuroblastoma cell lines causes cell-cycle arrest by G1/S checkpoint block. 31926181_MCPIP1 inhibits Hepatitis B virus replication by destabilizing viral RNA and negatively regulates the virus-induced innate inflammatory responses. 32548715_How are MCPIP1 and cytokines mutually regulated in cancer-related immunity? 32615986_Increased expression of CDKN1A/p21 in HIV-1 controllers is correlated with upregulation of ZC3H12A/MCPIP1. 32757706_MCPIP1 ribonuclease can bind and cleave AURKA mRNA in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells. 32971087_The anti-inflammatory protein MCPIP1 inhibits the development of ccRCC by maintaining high levels of tumour suppressors. 33003343_MCPIP1 RNase and Its Multifaceted Role. 33007332_Loss of keratinocyte Mcpip1 abruptly activates the IL-23/Th17 and Stat3 pathways in skin inflammation. 33191882_Multifunctional RNase MCPIP1 and its Role in Cardiovascular Diseases. 33544962_MCPIP1 expression positively correlates with melanoma-specific survival of patients, and its overexpression affects vital intracellular pathways of human melanoma cells. 33756228_Elevated linc00936 or silenced microRNA-425-3p inhibits immune escape of gastric cancer cells via elevation of ZC3H12A. 33823555_Monocyte chemoattractant protein-induced protein 1 directly degrades viral miRNAs with a specific motif and inhibits KSHV infection. 33824311_MCPIP1-mediated NFIC alternative splicing inhibits proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer via cyclin D1-Rb-E2F1 axis. 34144091_MCPIP1 is a novel link between diabetogenic conditions and impaired insulin secretory capacity. 34298861_MCPIP1/Regnase-1 Expression in Keratinocytes of Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Preliminary Results. 34657130_MCPIP1 inhibits Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway activity and modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by targeting miRNAs. 34659213_Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-Induced Protein 1 (MCPIP-1): A Key Player of Host Defense and Immune Regulation. 35082795_Dynamic Regulation of the Nexus Between Stress Granules, Roquin, and Regnase-1 Underlies the Molecular Pathogenesis of Warfare Vesicants. 35257717_MCPIP1 regulates focal adhesion kinase and Rho GTPase-dependent migration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 35752346_MCPIP1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of glioma via VEGFA-mediated ERK pathway. 36138026_Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors promotes renal cancer progression through MCPIP1 tumor-suppressor downregulation and c-Met activation. 36165203_MCP-Induced Protein 1 Participates in Macrophage-Dependent Endotoxin Tolerance. 36272359_MCPIP1 alleviates inflammatory response through inducing autophagy in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis. |
ENSMUSG00000042677 |
Zc3h12a |
610.405696 |
4.2542233466 |
2.088896 |
0.081054899 |
675.991985 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004972040988941745471322785512320532886226470890077586279715851951055827911270357731944427390670904462005404593058183121691857341349358211646989004818530910735470575038809282254785781 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003247226769769033757239383891014190957927253568659409862336221278201757967171803544747825378627130342602185220167630567295649211414204248515725158239030581804323220166206965250152309 |
Yes |
No |
969.8681893 |
47.9168677 |
229.3363793 |
9.3161874 |
| ENSG00000163913 |
55764 |
IFT122 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBG6 |
FUNCTION: As a component of the IFT complex A (IFT-A), a complex required for retrograde ciliary transport and entry into cilia of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), it is required in ciliogenesis and ciliary protein trafficking (PubMed:27932497, PubMed:29220510). Involved in cilia formation during neuronal patterning. Acts as a negative regulator of Shh signaling. Required to recruit TULP3 to primary cilia (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6NWV3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27932497, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29220510}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Ectodermal dysplasia;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. This cytoplasmic protein contains seven WD repeats and an AF-2 domain which function by recruiting coregulatory molecules and in transcriptional activation. Mutations in this gene cause cranioectodermal dysplasia-1. A related pseudogene is located on chromosome 3. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:55764; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary tip [GO:0097542]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intraciliary transport particle A [GO:0030991]; membrane [GO:0016020]; non-motile cilium [GO:0097730]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; embryonic body morphogenesis [GO:0010172]; embryonic heart tube development [GO:0035050]; intraciliary retrograde transport [GO:0035721]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; limb development [GO:0060173]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512] |
20493458_we found a homozygous missense mutation in the IFT122 (WDR10) gene that cosegregated with Sensenbrenner syndrome 23826986_this study was able to find causative IFT122 mutations in a non-consanguineous family with recurrent abortions. 26792575_The three patients had different, novel, compound heterozygous mutations in IFT122. Consequently, we compared these three patients to those previously described with IFT122 mutations. Thus, our report serves to add 6 novel mutations to the IFT122 mutation spectrum and to contribute to the IFT122-related clinical characterization. 28370949_Using a panel of skeletal dysplasias genes, including 11 related to SRP, we identified biallelic mutations in IFT122 in a fetus with a typical phenotype of SRP-IV, finally confirmed that this phenotype is a ciliopathy and adding to the list of ciliopathies with major skeletal involvement. 29037998_All the nine probands with syndromic craniosynostosis were found to carry the possibly causative variants, among which three variants including two missense mutations in IFT122 gene, in SMC1A gene and a frameshift mutation in TWIST1 gene have never been reported in patients before. 29057857_This study demonstrated that the mutation in SPG 7 gene caused autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraparesis. 29220510_IFT122 mutations associated with cranioectodermal dysplasia 1 cause defects in ciliary protein trafficking, but not ciliogenesis when expressed in cells lacking endogenous IFT122 (IFT122 KO). 30476139_The C11ORF74, interacts with the IFT-A complex via the IFT122 subunit and is accumulated at the distal tip in the absence of an IFT-A subunit IFT139, suggesting that at least a fraction of C11ORF74 molecules can be transported towards the ciliary tip by associating with the IFT-A complex, although its majority might be out of cilia at steady state. |
ENSMUSG00000030323 |
Ift122 |
87.756897 |
0.4664279041 |
-1.100274 |
0.215767931 |
25.816749 |
0.00000037541648560193048146272775007770139410467891138978302478790283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001392597971220028627953009883744250885229121195152401924133300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.3467907 |
7.1544059 |
126.3949705 |
10.6415287 |
| ENSG00000163933 |
91869 |
RFT1 |
protein_coding |
Q96AA3 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in N-linked oligosaccharide assembly. May participate in the translocation of oligosaccharide from the cytoplasmic side to the lumenal side of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18313027}. |
Congenital disorder of glycosylation;Disease variant;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes an enzyme which catalyzes the translocation of the Man(5)GlcNAc (2)-PP-Dol intermediate from the cytoplasmic to the luminal side of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane in the pathway for the N-glycosylation of proteins. Mutations in this gene are associated with congenital disorder of glycosylation type In.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:91869; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; glycolipid floppase activity [GO:0034202]; carbohydrate transport [GO:0008643]; dolichol-linked oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0006488]; glycolipid translocation [GO:0034203] |
18313027_RFT1 deficiency in both yeast and human cells leads to the accumulation of incomplete DolPP-GlcNAc(2)Man(5) and to a profound glycosylation disorder in humans. 19856127_Six patients with RFT1-CDG show sensorineural deafness as part of a severe neurological syndrome 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23111317_Identification of novel missense mutations in exon 12 of the RFT1 gene in adult siblings with congenital disorder of glycosylation (CDG) syndrome caused by RFT1 deficiency. 26892341_showed that this patient was compound heterozygous for two mutations in the RFT1 gene: c.1325G>A (p.R442Q) and c.110G>T (p.R37L) 30071302_A novel RFT1 missense mutation was identified in a family with history of neonatal deaths due to severe respiratory insufficiency. |
ENSMUSG00000052395 |
Rft1 |
292.694304 |
2.0798086523 |
1.056451 |
0.095112189 |
124.031976 |
0.00000000000000000000000000008289691310231128759547733473553326007699971744631562126437152624962931082050303366326460263735498301684856414794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001022187499908199240686206668414475928650705090253792858650267214704614627141660010423152016301173716783523559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
383.9697305 |
22.9354048 |
185.9184069 |
8.5685226 |
| ENSG00000163947 |
50650 |
ARHGEF3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR81 |
FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RhoA and RhoB GTPases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12221096}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Rho-like GTPases are involved in a variety of cellular processes, and they are activated by binding GTP and inactivated by conversion of GTP to GDP by their intrinsic GTPase activity. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) accelerate the GTPase activity of Rho GTPases by catalyzing their release of bound GDP. This gene encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor, which specifically activates two members of the Rho GTPase family: RHOA and RHOB, both of which have a role in bone cell biology. It has been identified that genetic variation in this gene plays a role in the determination of bone mineral density (BMD), indicating the implication of this gene in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:50650; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
12221096_a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RhoA and RhoB, but not RhoC 18499081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18499081_genetic variation in ARHGEF3 plays a role in the determination of bone density in Caucasian women. This data implicates the RhoGTPase-RhoGEF pathway in osteoporosis. 19110211_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19427924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727905_the association between rs7646054 in ARHGEF3 and bone mineral density observed in Caucasians was not replicated in the chinese samples. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24043828_XPLN is an endogenous inhibitor of mTORC2. 24840563_ARHGEF3 and RHOA are potential regulators of a number of genes in bone cells, with influences on ACTA2 evident in both osteoblast-like and osteoclast-like cells. 25494542_ARHGEF3 has a crucial role in myeloid differentiation. 27028992_Our findings suggest that increased expression of ARHGEF3 plays a critical oncogenic role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma pathogenesis 28315487_This is the first study describing the involvement of XPLN in the regulation of the mTORC2-SPARC axis, and these findings may help uncover regulatory mechanisms mediated by XPLN in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis 28542600_Data suggest that modulation of ARHGEF3 gene expression in humans with a promoter-localized SNP plays a role in human megakaryocytes and human platelet function-a finding resulting from the biological follow-up of human genetic studies. Arhgef3 KO mice partially recapitulate the human phenotype. 29998287_The predicted expression of the ARHGEF3 gene in fibroblasts (effect, -0.48; P = 9.8 x 10-04) was associated with Major Depression. 32139661_Genetic variants in RET, ARHGEF3 and CTNNAL1, and relevant interaction networks, contribute to the risk of Hirschsprung disease. 34267198_Redefining the specificity of phosphoinositide-binding by human PH domain-containing proteins. 34350290_ARHGEF3 Associated with Invasion, Metastasis, and Proliferation in Human Osteosarcoma. 36241648_ARHGEF3 regulates the stability of ACLY to promote the proliferation of lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000021895 |
Arhgef3 |
1510.721455 |
0.3028774678 |
-1.723194 |
0.044396520 |
1562.491434 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
710.0351325 |
20.1407451 |
2360.9816956 |
40.5674873 |
| ENSG00000163975 |
4241 |
MELTF |
protein_coding |
P08582 |
FUNCTION: Involved in iron cellular uptake. Seems to be internalized and then recycled back to the cell membrane. Binds a single atom of iron per subunit. Could also bind zinc. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7556058}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Ion transport;Iron;Iron transport;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transport;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein found on melanoma cells. The protein shares sequence similarity and iron-binding properties with members of the transferrin superfamily. The importance of the iron binding function has not yet been identified. This gene resides in the same region of chromosome 3 as members of the transferrin superfamily. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4241; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900025]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0090091]; positive regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010756] |
11852110_The human genome contains a second melanotransferrin gene (MTf2). There are two isoforms of melanotransferrin. 12230555_its ability to donate 59Fe to SK-Mel-28 melanoma cells and other cell types 12710945_This melanoma-associated marker was detected in melanoma cell lines. 12750156_membrane-bound and soluble p97 affect the migration capacity of endothelial and melanoma cells and suggest that p97 could be involved in the regulation of plasminogen activation by interacting with pro-uPA and plasminogen. 12809550_Serum melanotransferrin exists in various conformations depending on the binding of bivalent cations or following post-translational modification; serum melanotransferrin levels are unchanged in subjects with Alzheimer's disease. 15716025_The distribution of MTf and its splice variants may provide clues to their possible biological roles in melanoma and other tumors. 16704991_melanotransferrin has a role in cell proliferation and tumorigenesis 16713448_Anti-angiogenic properties of soluble melanotransferrin may result from local overstimulation of plasminogen activation by tissue plasminogen activator, thus leading to subsequent degradation of the fibronectin matrix and endothelial cell detachment. 17196552_Altogether, these findings strongly suggest that MTf overexpression in melanoma cells contributes to tumor progression by stimulating plasmin generation as well as cell migration and invasion. 17227112_HMB-45 (melanoma-associated antigen p97) and Melan-A combined were positive in 100% of the renal angiomyolipomas 17449903_Novel molecular targets directly or indirectly regulated by MTf and the potential pathways involved in its function, including modulation of proliferation. 17452986_this review discusses the studies that have demonstrated that melanotransferrin is not involved in iron metabolism, but plays a vital role in melanoma cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. 17570828_results suggest a Plg-mediated internalization mechanism for the clearance of sMTf via annexin II and LRP 18691669_Biochemical and spectroscopic studies of MTF1 are reported. 21190562_PC3 tumors are sustained by a small number of tumor-initiating cells with stem-like characteristics, including strong self-renewal and pro-angiogenic capability and marked by the expression pattern FAM65Bhigh/MFI2low/LEF1low. 25216327_Melanotransferrin is a serological marker of colorectal cancer by secretome analysis and quantitative proteomics. 31704840_High MELTF mRNA expression was associated with Gastric Cancer. 33746574_The Role of Melanotransferrin (CD228) in the regulation of the differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hBM-MSC). 33931586_The hypoxia sensitive metal transcription factor MTF-1 activates NCX1 brain promoter and participates in remote postconditioning neuroprotection in stroke. |
ENSMUSG00000022780 |
Meltf |
424.932737 |
0.4804191371 |
-1.057634 |
0.130223330 |
65.195658 |
0.00000000000000067818790100280389269079718336850629216305293275532384278392328269546851515769958496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004894891647335641074076228118783491236851211983460707699578051688149571418762207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
277.3628470 |
25.8649735 |
580.2150082 |
38.3756257 |
| ENSG00000164023 |
166929 |
SGMS2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NHU3 |
FUNCTION: Sphingomyelin synthase that primarily contributes to sphingomyelin synthesis and homeostasis at the plasma membrane. Catalyzes the reversible transfer of phosphocholine moiety in sphingomyelin biosynthesis: in the forward reaction transfers phosphocholine head group of phosphatidylcholine (PC) on to ceramide (CER) to form ceramide phosphocholine (sphingomyelin, SM) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as by-product, and in the reverse reaction transfers phosphocholine from SM to DAG to form PC and CER. The direction of the reaction appears to depend on the levels of CER and DAG in the plasma membrane (PubMed:14685263, PubMed:17449912, PubMed:17982138, PubMed:18370930). Does not use free phosphorylcholine or CDP-choline as donors (PubMed:14685263). Can also transfer phosphoethanolamine head group of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) on to ceramide (CER) to form ceramide phosphoethanolamine (CPE) (PubMed:19454763). Regulates receptor-mediated signal transduction via mitogenic DAG and proapoptotic CER, as well as via SM, a structural component of membrane rafts that serve as platforms for signal transduction and protein sorting (PubMed:17449912, PubMed:17982138). To a lesser extent, plays a role in secretory transport via regulation of DAG pool at the Golgi apparatus and its downstream effects on PRKD1 (PubMed:18370930, PubMed:21980337). Required for normal bone matrix mineralization (PubMed:30779713). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14685263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17449912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17982138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18370930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19454763, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21980337, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30779713}. |
Cell membrane;Disease variant;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17982138}. |
Sphingomyelin, a major component of cell and Golgi membranes, is made by the transfer of phosphocholine from phosphatidylcholine onto ceramide, with diacylglycerol as a side product. The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme that catalyzes this reaction primarily at the cell membrane. The synthesis is reversible, and this enzyme can catalyze the reaction in either direction. The encoded protein is required for cell growth. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. There is evidence for more variants, but the full-length nature of their transcripts has not been determined.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:166929; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ceramide cholinephosphotransferase activity [GO:0047493]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; sphingomyelin synthase activity [GO:0033188]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingomyelin biosynthetic process [GO:0006686] |
17449912_Data show that sphingomyelin synthases SMS1 and SMS2 are co-expressed in a variety of cell types and function as the key Golgi- and plasma membrane-associated SM synthases in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, respectively. 17616479_Results indicate that both synthase (SMS)1 and 2 contribute to sphingomyelin (SM) de novo synthesis and control SM levels in the cells and on the cell membrane including plasma membrane. 17982138_SMS2 is a key factor in control of sphingomyelin and diacylglycerol metabolism within the cell, and thus it influences apoptosis. 18370930_SMS2 regulates subcellular pools of diacylglycerol-binding proteins in the Golgi apparatus. 18566297_SMS2 (Sphingomyelin synthase 2) physiologically contributes to de novo Sphingomyelin biosynthesis and plasma membrane Sphingomyelin levels 18694848_Both SMS1 and SMS2 contain two histidines and one aspartic acid which are conserved within the lipid phosphate phosphatase superfamily. Site-directed mutagenesis of these amino acids abolished SMS activity without altering cellular distribution. 19233134_These results suggested that posttranslational palmitoylation is important for determination of the subcellular localization of SMS2. 19286635_Sphingomyelin synthase 2 is one of the determinants for plasma and liver sphingomyelin levels in mice. 19454763_Data show that SMS2 acting as a bifunctional enzyme with both SM and CPE synthase activity. 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21235823_direct morphological evidence for the pro-atherogenic capabilities of sphingomyelin synthase 2 21980337_SMS1 and SMS2 are capable of regulating TGN-mediated protein trafficking and secretion 22106271_Data indicate that the increased sphingomyelin mass was due to a rapid and highly specific activation of sphingomyelin synthases SMS1 and SMS2. 25231990_F-actin polymerization in the region of HIV-1 membrane fusion was more prominent in Sms2-expressing cells than Sms-deficient cells. 27278004_PPARdelta activation may be a potential risk of atherosclerosis through enhancing activity of SMS2 27394416_SMS regulates the expression and function of drug transporters P-gp and MRP2. 27927984_findings suggest that the C-terminal tails of SMSs are involved in homodimer formation, which is required for efficient transport from the ER. 30770781_SGMS2 increased the expression of TGF-beta1 by upregulating ceramide, which subsequently activated the TGF-beta/Smad signalling pathway and promoted epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells, thus increasing the migration and invasiveness of breast cancer cells. 30779713_Study in 6 families with rare skeletal phenotypes and osteoporosis identified a heterozygous variant in SGMS2, a gene prominently expressed in cortical bone and encoding the plasma membrane-resident sphingomyelin synthase SMS2. Four unrelated families shared the same nonsense variant, c.148C>T (p.Arg50*), whereas the other families had a missense variant, c.185T>G (p.Ile62Ser) or c.191T>G (p.Met64Arg). 31212751_our results demonstrate that SMS2 can activate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and promote intracellular cholesterol accumulation, both of which can contribute to the induction of ER stress and finally lead to ED. 31517509_SGMS2-dependent signaling was investigated in human monocyte-derived macrophages of nonsmokers and human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells isolated from healthy nonsmokers and subjects with COPD. Reduced SGMS2 expression was seen in HBE cells isolated from subjects with COPD. SGMS2 overexpression reduced the production of several matrix metalloproteinases in HBE cells and monocyte-derived macrophages. 31596951_Chlamydia trachomatis-infected human cells convert ceramide to sphingomyelin without sphingomyelin synthases 1 and 2. 32451413_Sphingomyelin synthase 2 facilitates M2-like macrophage polarization and tumor progression in a mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer. 33727749_Genome-wide association study of serum prostate-specific antigen levels based on 1000 Genomes imputed data in Japanese: the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study. 34273804_LncRNA THAP9-AS1 accelerates cell growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through sponging miR-335-5p to regulate SGMS2. |
ENSMUSG00000050931 |
Sgms2 |
39.729743 |
2.7036912048 |
1.434930 |
0.541920895 |
6.476171 |
0.01093302861987959645473367231716110836714506149291992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020808704375167356298570453532192914281040430068969726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.7592576 |
20.2899079 |
22.6900222 |
5.6410145 |
| ENSG00000164040 |
10424 |
PGRMC2 |
protein_coding |
O15173 |
FUNCTION: Required for the maintenance of uterine histoarchitecture and normal female reproductive lifespan (By similarity). May serve as a universal non-classical progesterone receptor in the uterus (Probable). Intracellular heme chaperone required for delivery of labile, or signaling heme, to the nucleus (By similarity). Plays a role in adipocyte function and systemic glucose homeostasis (PubMed:28111073). In brown fat, which has a high demand for heme, delivery of labile heme in the nucleus regulates the activity of heme-responsive transcriptional repressors such as NR1D1 and BACH1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80UU9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28111073, ECO:0000305|PubMed:28396637}. |
Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Steroid-binding;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables heme binding activity. Involved in adipose tissue development. Located in endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear envelope. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10424; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; heme transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015232]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; steroid binding [GO:0005496]; adipose tissue development [GO:0060612] |
15702432_The expression of a novel progesterone-binding protein (hmPR1/PGMRC1) was investigated. Transcripts of this protein have been detected in human sperm. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23064006_PGRMC2 inhibits migration of SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells in vitro. 23276631_It deserves further examination as data point to a role of PGRMC2 as tumor suppressor, migration inhibitor and regulator of cytochrome P450 proteins. 23793472_In secretory phase endometrium from women with advanced stage endometriosis, PGRMC-2 expression is downregulated. 23970345_Reversely, in the HO-8910 cells treated with CDDP alone, levels of both PGRMC1 and PGR were increased while the level of PGRMC2 was decreased 25266650_Demonstrate a change in myometriumPGRMC1 expression and changes in PGRMC1 and PGRMC2 cell localisation in association with parturition. 31748741_show that progesterone receptor membrane component 2 (PGRMC2) is required for delivery of labile, or signalling haem, to the nucleus 31810911_Results found PGRMC2 to be targeted by miR-3687. Further data indicate that PGRMC2 mRNA expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) may be related to cell proliferation and local progression. 35526781_The role of progesterone receptor membrane component (PGRMC) in the endometrium. |
ENSMUSG00000049940 |
Pgrmc2 |
333.625710 |
2.0164882454 |
1.011845 |
0.124118163 |
66.082653 |
0.00000000000000043240465347425355790718811962583646074242084617923753686596910483785904943943023681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000003153306662687738409652636843172550218305849123803796807408161839703097939491271972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
429.5626908 |
31.3068113 |
214.5682852 |
11.7796440 |
| ENSG00000164061 |
8927 |
BSN |
protein_coding |
Q9UPA5 |
FUNCTION: Scaffold protein of the presynaptic cytomatrix at the active zone (CAZ) which is the place in the synapse where neurotransmitter is released (PubMed:12812759). After synthesis, participates in the formation of Golgi-derived membranous organelles termed Piccolo-Bassoon transport vesicles (PTVs) that are transported along axons to sites of nascent synaptic contacts (PubMed:19380881). At the presynaptic active zone, regulates the spatial organization of synaptic vesicle cluster, the protein complexes that execute membrane fusion and compensatory endocytosis (By similarity). Functions also in processes other than assembly such as the regulation of specific presynaptic protein ubiquitination by interacting with SIAH1 or the regulation of presynaptic autophagy by associating with ATG5 (By similarity). Mediates also synapse to nucleus communication leading to reconfiguration of gene expression by associating with the transcriptional corepressor CTBP1 and by subsequently reducing the size of its pool available for nuclear import (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12812759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19380881}. |
Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Neurotransmitters are released from a specific site in the axon terminal called the active zone, which is composed of synaptic vesicles and a meshwork of cytoskeleton underlying the plasma membrane. The protein encoded by this gene is thought to be a scaffolding protein involved in organizing the presynaptic cytoskeleton. The gene is expressed primarily in neurons in the brain. A similar gene product in rodents is concentrated in the active zone of axon terminals and tightly associated with cytoskeletal structures, and is essential for regulating neurotransmitter release from a subset of synapses. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8927; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cochlear hair cell ribbon synapse [GO:0098683]; cytoskeleton of presynaptic active zone [GO:0048788]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuron projection terminus [GO:0044306]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; structural constituent of presynaptic active zone [GO:0098882]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; presynapse to nucleus signaling pathway [GO:0099526]; presynaptic active zone assembly [GO:1904071]; protein localization to synapse [GO:0035418]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693]; synaptic vesicle clustering [GO:0097091] |
9679147_This paper describes the structure of the mouse and rat Bsn genes, and characterizes the subcellular distribution of the Bassoon protein. 12628169_Loss of Bassoon in Bsn mutant mice causes a reduction in normal synaptic transmission, which can be attributed to the inactivation of a significant fraction of glutamatergic synapses. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19567891_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657358_The effect of BSN-MST1 locus on Crohn's disease predisposition was replicated, but no influence on ulcerative colitis or multiple sclerosis predisposition could be detected 20024904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20307617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20846217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21092860_Short-term synaptic depression is enhanced in Bassoon knockout mice, but synaptic transmission is unaffected. 21092861_Bassoon protein and the synaptic ribbon create a large number of release sites by organizing calcium channels and synaptic vesicles. 21700703_D-amino acid oxidase activity is inhibited by an interaction with bassoon protein at the presynaptic active zone. 29339765_Three missense mutations in BSN that are very rarely listed in databases of healthy subjects were found in four sporadic progressive supranuclear palsy cases. Western blot analysis of tau following the overexpression of wild-type or mutated BSN revealed the possibility that wild-type BSN reduced tau accumulation, while mutated BSN lost this function. 32493491_No symphony without bassoon and piccolo: changes in synaptic active zone proteins in Huntington's disease. 32651614_Bassoon inhibits proteasome activity via interaction with PSMB4. |
ENSMUSG00000032589 |
Bsn |
61.736662 |
0.2122021171 |
-2.236489 |
0.253029742 |
81.067204 |
0.00000000000000000021817073414769614731474012618142040618608367917801262644145188218658404366578906774520874023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001878763148203030875488530009016677658163969356908129526573247858323156833648681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.0665253 |
3.6852001 |
104.8268609 |
10.5129502 |
| ENSG00000164161 |
64399 |
HHIP |
protein_coding |
Q96QV1 |
FUNCTION: Modulates hedgehog signaling in several cell types including brain and lung through direct interaction with members of the hedgehog family. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11472839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19561609}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the hedgehog-interacting protein (HHIP) family. The hedgehog (HH) proteins are evolutionarily conserved protein, which are important morphogens for a wide range of developmental processes, including anteroposterior patterns of limbs and regulation of left-right asymmetry in embryonic development. Multiple cell-surface receptors are responsible for transducing and/or regulating HH signals. The HHIP encoded by this gene is a highly conserved, vertebrate-specific inhibitor of HH signaling. It interacts with all three HH family members, SHH, IHH and DHH. Two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) near this gene are significantly associated with risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A single nucleotide polymorphism in this gene is also strongly associated with human height.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:64399; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; hedgehog family protein binding [GO:0097108]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; dorsal/ventral pattern formation [GO:0009953]; epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0060441]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009968]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; neuroblast proliferation [GO:0007405]; regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040036]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705] |
15294024_These results suggest that reduced expression of HIP, a naturally occurring Hh pathway antagonist, in tumor neo-vasculature may contribute to increased Hh signaling within the tumor and possibly promote angiogenesis. 15754313_The different pattern of expression and abnormal localization in the diseased pancreas suggest that the enhanced activation of hedgehog signaling in in pancreatic cancer and pancreatic duct carcinoma. 15970691_Aberrant methylation of the Human Hedgehog interacting protein is associated with pancreatic neoplasms 18391952_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18559595_The down-regulation of HHIP transcription is due to DNA hypermethylation and/or loss of heterozygoty in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19300482_Genome-wide significant association of the HHIP locus with lung function. The CHRNA 3/5 and the HHIP loci make a significant contribution to the risk of COPD. 19300482_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19561609_Results propose a role for Hedgehog-interacting protein as a structural decoy receptor for vertebrate Hedgehog. 19561611_Results describe a series of crystal structures for the human Hedgehog-interacting protein ectodomain and Desert hedgehog (DHH) in isolation, as well as HHIP in complex with DHH (HHIP-DHH) and Sonic hedgehog (Shh) (HHIP-Shh), with and without Ca2+. 19893584_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915594_show in mice and in human cartilage explants that pharmacological or genetic inhibition of Hh signaling reduces the severity of osteoarthritis and that RUNX2 potentially mediates this process by regulating ADAMTS5 expression 19996190_Genetic variation near the Hip gene was significantly associated with risk of COPD, depending on the number of pack-years of smoking. 19996190_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20010835_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20397748_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20656943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20656943_The HHIP locus was associated with the systemic components of COPD and with the frequency of COPD exacerbations. 20800318_Mutation of the hedgehog signaling patwhway play a key role in the development of basal cell carrcinomas. 20846217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20853133_results suggest the possibility of epigenetic regulation of HHIP in medulloblastoma 21119205_the GG genotype of the rs 1489759 HHIP single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and the CC genotype of the rs 2202507 GYPA SNP confers a ''protective'' effect on COPD (OR 0.59, p50.006 for HHIP and OR50.65, p50.006 for GYPA) and lung cancer. 21210262_We found that HIP, PDGFRalpha, SMO and Su(Fu) gene highly expressed in the primary esophageal squamous cell carcinomas 21397937_A subset of normal lung function genes, including HHIP, FAM13A, and PTCH1, together predict lung function abnormalities, a measure of severity in white and African American subjects with asthma. 22140090_Low HHIP expression is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 22301921_Resveratrol inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through the hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells.( 22406999_no correlation between hedgehog activity and SHH, Gli1 and Patched1 mRNA levels was observed. other mechanisms aside from transcriptional regulation of these factors are responsible for hedgehog activity in tumor cells derived from GBM. 22457212_GDC-0449 treatment is pharmacodynamically effective as evidenced by paracrine Hedgehog signaling inhibition and results in prostate cancer cell proliferation reduction. 22897141_Results suggest involvement of the Hedgehog pathway in CPHD and that both SHH and HHIP are investigated as a second screening in CPHD, after mutations in the classical CPHD genes have been ruled out. 23440386_The data demonstrated that loss of expression of HHIP and PTCH is associated with the methylation of gene promoters 23456936_HHIP, HDAC4, NCR3 and RARB polymorphisms may have a role in impaired lung function that begins in early life 23459001_Identification of potential HHIP targets of gene expression regulation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 23731023_Genetic variants in HHIP are associated with FEV1 in subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 23780909_These data suggest that activated Hedgehog signalling contributes to the biology of human fetal rhabdomyomas. 23935859_Data indicate that the Shh signaling transduction is facilitated by binding of Shh to its receptor protein, Ptch, and show the complex structure of Shh-Hhip. 23994291_our study suggests that the HHIP gene may be involved in COPD susceptibility in Chinese Han population. 24439425_We show that GPC3, an hepatocellular carcinoma biomarker and Hh mediator, regulates human stellate cell viability by regulating Hh signaling. 25006744_HHIP is located within genes previously associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease susceptibility. 25215859_Shh-mediated degradation of Hhip allows cell autonomous and non-cell autonomous Shh signaling. 25416442_HHIP might be a diagnostic or prognostic marker in glioma and help to the detection of these tumors in early stages of disease. 26482617_HHIP expression and Gli1 expression were independent prognostic factors in glioblastoma. 26527870_HHIP - candidate gene for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease identified by Genome-wide association studies. 27009877_This work supports a feasible vicious cycle in which EMPs generated during endothelial injury, in turn, aggravate endothelial damage by carrying HHIP into target ECs, contributing to the continuously deteriorating endothelial damage in the development of aGVHD. EMPs harboring HHIP would represent a potential therapeutic target for aGVHD. 27015549_HHIP underexpression is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 27553089_The rate of methylation of ZIC1, ZIC4, HHIP, and DACT2 in tumors was very high, while methylation of CXXC4 was low to moderate in OSCC and LSCC. 27612410_this study shows that HHIP confers a risk for airway obstruction in general that is not driven exclusively by cigarette smoking, which is the main risk factor for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 27845578_HHIP plays a role in lung branching development, and reduced levels of HHIP ultimately result in lung hypoplasia. 28640141_Results showed that smoking and HHIP variant rs7654947 were associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)development and lung function decline. Moreover, we found that cigarette smoking and gene susceptibility have cooperative effects on COPD risk and lung function decline 28722118_loss of AT2 R is associated with podocyte loss/dysfunction and is mediated, at least in part, via augmented ectopic hedgehog interacting protein expression in podocytes 28929109_Genetic variants in HHIP were related with FEV1/FVC in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Significant relationships between risk alleles and risk genotypes and FEV1/FVC in COPD were also identified. 28939338_Single nucleotide polymorphism in HHIP gene is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 28963460_HHIP regulates apoptosis evasion and angiogenic function of late endothelial progenitor cells. 29915314_HHIP SNPs were associated with the occurrence of lung cancer in COPD patients in the Chinese Han population. 30241415_HHIP G516R, a missense mutation increased cell proliferation and promoted cell migration in thyroid cancer. 31604528_HHIP-AS1 interacted with and positively regulated the stability of HHIP mRNA in a HuR-dependent manner in the hepatocellular carcinoma. 31631996_presence of the A allele in the rs13118928 polymorphism of the HHIP gene may be related to the emphysema-hyperinflation phenotype 32525231_Transfer of miR-25-3p by CHB-PNALT-Exo promoted the development of liver cancer by inhibiting the co-expression of TCF21 and HHIP. 32710611_Downregulation of hedgehog-interacting protein (HHIP) contributes to hexavalent chromium-induced malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. 33907231_Hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) represses airway remodeling and metabolic reprogramming in COPD-derived airway smooth muscle cells. 34643245_Long noncoding RNA HHIPAS1 inhibits lung cancer epithelialmesenchymal transition and stemness by regulating PCDHGA9. 34887403_Hedgehog-Interacting Protein is a multimodal antagonist of Hedgehog signalling. 35037818_Association of human Hedgehog interacting protein gene polymorphisms with the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a meta-analysis. 35276608_Differential promoter usages of PTCH1 and down regulation of HHIP are associated with HNSCC progression. 36374812_Natural Antisense Long Noncoding RNA HHIP-AS1 Suppresses Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Increasing HHIP Stability via Interaction with CELF2. |
ENSMUSG00000064325 |
Hhip |
11.737801 |
10.8055979911 |
3.433707 |
0.802788746 |
17.931883 |
0.00002289533475765045668305283643739755916612921282649040222167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000068853940713716531925488173460081497978535480797290802001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.2716828 |
11.2226669 |
1.8288598 |
0.8596938 |
| ENSG00000164163 |
6059 |
ABCE1 |
protein_coding |
P61221 |
FUNCTION: Cotranslational quality control factor involved in the No-Go Decay (NGD) pathway (PubMed:21448132). Together with PELO and HBS1L, is required for 48S complex formation from 80S ribosomes and dissociation of vacant 80S ribosomes (PubMed:21448132). Together with PELO and HBS1L, recognizes stalled ribosomes and promotes dissociation of elongation complexes assembled on non-stop mRNAs; this triggers endonucleolytic cleavage of the mRNA, a mechanism to release non-functional ribosomes and to degrade damaged mRNAs as part of the No-Go Decay (NGD) pathway (PubMed:21448132). Plays a role in the regulation of mRNA turnover (By similarity). Plays a role in quality control of translation of mitochondrial outer membrane-localized mRNA (PubMed:29861391). As part of the PINK1-regulated signaling, ubiquitinated by CNOT4 upon mitochondria damage; this modification generates polyubiquitin signals that recruit autophagy receptors to the mitochondrial outer membrane and initiate mitophagy (PubMed:29861391). RNASEL-specific protein inhibitor which antagonizes the binding of 2-5A (5'-phosphorylated 2',5'-linked oligoadenylates) to RNASEL (PubMed:9660177). Negative regulator of the anti-viral effect of the interferon-regulated 2-5A/RNASEL pathway (PubMed:9660177, PubMed:9847332, PubMed:11585831). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P61222, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11585831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21448132, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29861391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9660177, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9847332}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May act as a chaperone for post-translational events during HIV-1 capsid assembly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9847332}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays a role in the down-regulation of the 2-5A/RNASEL pathway during encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) and HIV-1 infections. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9660177}. |
3D-structure;4Fe-4S;ATP-binding;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the OABP subfamily. Alternatively referred to as the RNase L inhibitor, this protein functions to block the activity of ribonuclease L. Activation of ribonuclease L leads to inhibition of protein synthesis in the 2-5A/RNase L system, the central pathway for viral interferon action. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6059; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051539]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; endoribonuclease inhibitor activity [GO:0060698]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; ribosomal small subunit binding [GO:0043024]; negative regulation of endoribonuclease activity [GO:0060702]; regulation of translation [GO:0006417]; ribosomal subunit export from nucleus [GO:0000054]; translational initiation [GO:0006413]; translational termination [GO:0006415] |
11780123_During assembly of an immature HIV-1 capsid, HIV-1 Gag progresses through a pathway of sequential assembly intermediates that contain ABCE1, a cellular ATPase that was found to facilitate capsid formation. 11780123_host protein essential for assembly of immature HIV-1 capsids 14747530_HIV-1, HIV-2, SIV mac239, and SIVagm Gag proteins form ABCE1-containing assembly intermediates during immature capsid formation, indicating that Gag proteins of these diverse retroviruses bind to ABCE1 despite the limited homology between these Gags. 14747530_HIV-2 Gag associates with human HP68 in a cell-free system and that Gag proteins of HIV-2, simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239, and SIVagm associate with endogenous HP68 in primate cells, as is seen for HIV-1. 15107989_overexpression in a permissive cell line had no significant effect on varicella zoster virus replication 15809757_ABCE1 and its peptides could be target molecules in specific immunotherapy for HLA-A2(+) colon cancer patients. 16275648_For binding of WT HIV-1 Gag to the cellular ATPase ABCE1, which facilitates HIV-1 capsid assembly, the basic residues in the nucleocapsid domain of Gag are required but the cysteine and histidine residues in the nucleocapsid domain are dispensable. 17233757_Pulse chase experiments and immunoelectron microscopy shows that HIV-1 Gag associates transiently with ABCE1 during HIV-1 capsid assembly, including at the plasma membrane where assembly is completed. 18006034_The primary role of ABCE-1 in the effect of TULA appears to be the recruitment of TULA to the sites of HIV-1 assembly where TULA interferes with the late steps of the HIV-1 life cycle. 18189233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18189233_common variation in the putative prostate cancer susceptibility gene, RNASEL, or its inhibitor does not contribute significantly to prostate cancer risk in Tobago Afro-Caribbean population 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657357_were able to confirm the excess of rare genetic variation among HIV-1-positive African-American individuals (n=53; Tajima's D=-2.34). These results highlight the potential importance of ABCE1's role in infectious diseases such as HIV-1. 20122402_NTP hydrolysis by ABCE1 is stimulated by posttermination complexes and is required for its ribosomal recycling activity. 20372810_Results suggest that ABCE1 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of human small cell lung cancer cell. 21448132_Pelota/Hbs1 induced dissociation of elongation complexes from ribosomes and release of peptidyl-tRNA, but only in the presence of ABCE1. 22267055_Report high expression level of ABCE1 mRNA and protein in human lung adenocarcinoma tissues and metastatic lymph nodes, which was also correlated with clinical stages. 22851315_To form HIV-1 capsid assembly intermediates, HIV-1 Gag co-opts a complex found in infected and uninfected cells that contains the cellular ATPase ABCE1 and the RNA helicase DDX6, both of which facilitate HIV-1 capsid assembly. 23008114_ABCE1 protein regulates a broad range of biological functions including viral infection, tumor cell proliferation, and antiapoptosis. (Review) 23266104_Studies indicate a strong sequence conservation of ABC-type ATPase ABCE1 in eukaryotes and archaea. 24551278_ABCE1 is closely connected with the pathogenesis and development of esophageal carcinoma, which act through the cellular pathways of 2-5A/RNase L. 25337191_ABCE1 is closely connected with the pathogenesis and development of oral cancer, which acts through the cellular pathways of 2-5A/RNase L. 25659154_ABCE1 is able to suppress RNA silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana plants, in mammalian HEK293 cells and in the worm Caenorhabditis elegans. 25744244_Downregulation of ABCE1 via siRNA affects the sensitivity of lung cancer cells against chemotherapeutic agents. 25815591_ABCE1 is closely associated with cell proliferation, invasion and migration in esophageal cancer and silencing the ABCE1 gene by electroporation can significantly reduce the proliferation, invasion and migration capacity 26600528_Expression of the ABCE1-silencing gene, transfected by electrotransfer, could inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and migration of thyroid cancer cells. 26617714_miR-299-3p promotes the sensibility of lung cancer to doxorubicin through suppression of ABCE1, at least partly. Therefore, the disordered decreased of miR-299-3p and resulting ABCE1 up-expression may contribute to chemoresistance of lung cancer 26733164_ABCE1 plays an essential role in the progression and metastasis of lung cancers and may represent a valuable therapeutic target for the management of lung tumor 26985706_ABCE1 is involved in histone biosynthesis and DNA replication and therefore is essential for normal S phase progression. 27314749_The present study reported on the effects of ABCE1 overexpression on lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro, demonstrating its enhancing effect on cell proliferation and invasiveness with simultaneous downregulation of p27 protein expression. 27681415_Induction of ribosome rescue factors PELO and HBS1L is required to support protein synthesis when ABCE1 levels fall in platelets, including for hemoglobin production during blood cell development. 29861391_Damage-induced ubiquitination of ABCE1 protein by NOT4 generates poly-ubiquitin signals that attract autophagy receptors to mitochondrial outer membrane to initiate mitophagy. 30455394_This study demonstrated that ABCE1 was up-regulated in glioma tissues and cell lines. Down-regulation of ABCE1 inhibited temozolomide resistance of glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. The PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway was involved in ABCE1-mediated chemoresistance of glioma cells. 31088929_This study highlights the role of ABCE1 as a host factor required for efficient paramyxovirus and pneumovirus translation. 31665102_Ribosome recycling in mRNA translation, quality control, and homeostasis. 31841188_Long noncoding RNA FAM201A mediates the metastasis of lung squamous cell cancer via regulating ABCE1 expression. 32033097_ABCE1 Acts as a Positive Regulator of Exogenous RNA Decay. 32651259_Suppression of ABCE1-Mediated mRNA Translation Limits N-MYC-Driven Cancer Progression. 32668236_Ribosome Recycling by ABCE1 Links Lysosomal Function and Iron Homeostasis to 3' UTR-Directed Regulation and Nonsense-Mediated Decay. 32914432_FOXO3a-dependent Parkin regulates the development of gastric cancer by targeting ATP-binding cassette transporter E1. 32941650_Readthrough of stop codons under limiting ABCE1 concentration involves frameshifting and inhibits nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. 32945355_MicroRNA145 promotes the apoptosis of leukemic stem cells and enhances drugresistant K562/ADM cell sensitivity to adriamycin via the regulation of ABCE1. 33289941_A structural inventory of native ribosomal ABCE1-43S pre-initiation complexes. 33670646_ABCE1 Regulates RNase L-Induced Autophagy during Viral Infections. 35737213_The Expression and Effect of ABCE1 in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. 35792803_Human ABCE1 exhibits temperature-dependent heterologous co-functionality in S. cerevisiae. 36401432_A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of ATP binding cassette subfamily E member 1 (ABCE1) in human tumors: An observational study. |
ENSMUSG00000058355 |
Abce1 |
766.009175 |
2.7031526795 |
1.434643 |
0.091265431 |
243.227291 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000077809253875816536935137897283340613707269275705658532785370328087088445202903566714958678115566589749627443081271795399605070622355153893076606941292538976995274424552917480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018200706611839177615432408244621516497841882814971802835343757756709230344528501882875634650357011666514097603865651172570759879951966114797201612418575678020715713500976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1137.6451045 |
60.4926277 |
423.8117851 |
17.2487067 |
| ENSG00000164171 |
3673 |
ITGA2 |
protein_coding |
P17301 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-2/beta-1 is a receptor for laminin, collagen, collagen C-propeptides, fibronectin and E-cadherin. It recognizes the proline-hydroxylated sequence G-F-P-G-E-R in collagen. It is responsible for adhesion of platelets and other cells to collagens, modulation of collagen and collagenase gene expression, force generation and organization of newly synthesized extracellular matrix.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human rotavirus A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12941907}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA2:ITGB1 acts as a receptor for Human echoviruses 1 and 8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8411387}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Integrin;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes the alpha subunit of a transmembrane receptor for collagens and related proteins. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with a beta subunit and mediates the adhesion of platelets and other cell types to the extracellular matrix. Loss of the encoded protein is associated with bleeding disorder platelet-type 9. Antibodies against this protein are found in several immune disorders, including neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. This gene is located adjacent to a related alpha subunit gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:3673; |
axon terminus [GO:0043679]; basal part of cell [GO:0045178]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; integrin alpha2-beta1 complex [GO:0034666]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; collagen binding involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098639]; collagen receptor activity [GO:0038064]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:0043395]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; collagen-activated signaling pathway [GO:0038065]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050966]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; focal adhesion assembly [GO:0048041]; hepatocyte differentiation [GO:0070365]; hypotonic response [GO:0006971]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; mammary gland development [GO:0030879]; mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048333]; positive regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity [GO:0010694]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell projection organization [GO:0031346]; positive regulation of collagen binding [GO:0033343]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of leukocyte migration [GO:0002687]; positive regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0060100]; positive regulation of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050927]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045987]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of transmission of nerve impulse [GO:0051971]; response to amine [GO:0014075]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to L-ascorbic acid [GO:0033591]; response to muscle activity [GO:0014850]; response to parathyroid hormone [GO:0071107]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; skin morphogenesis [GO:0043589]; substrate-dependent cell migration [GO:0006929] |
11238113_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11246537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11323022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11395045_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11472360_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11568114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11698306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11728949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11775028_Bromodeoxyuridine induces integrin expression at transcriptional (alpha2 subunit) and post-transcriptional (beta1 subunit) levels, and alters the adhesive properties of two human lung tumour cell lines. 11776052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11809527_Reduction in integrin alpha 2 is related to changes seen during immortalization and malignant progression 11812069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11835340_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11877061_The C807T polymorphism of integrin alpha2 gene in Suzhou Han population was different from that observed in other populations. 11958806_Trimucytin, a collagen-like snake venom protein, activates platelets independent of I-domain within alpha2 subunit of alpha2beta1 integrin. 11978651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12038776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12070018_the rGPIa/IIa-collagen interaction dominates the adhesion of rGPIa/IIa-Ib alpha-liposomes to the collagen surface at low shear rates; the rGPIa/IIa-collagen and rGPIb alpha-VWF interactions synergistically support liposome adhesion at high shear rates. 12071877_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12073410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12181354_Data report the identification of signaling pathways required for suppression of integrin alpha2beta1 function by c-erbB2. 12208476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372459_initial adhesion of endometrial cells to mesothelium is not mediated by alpha(2)beta(1)integrin 12392763_findings demonstrate that E-cadherin can interact with alpha2beta1 and suggest that heterotypic interactions between E-cadherin and integrins may be more common than originally thought 12412731_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12412731_role of the GP Ia C807T/G873A polymorphism as a risk factor for thrombosis in Behcet disease 12486862_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12499711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12529399_R-Ras promotes focal adhesion formation by signaling to FAK and p130(Cas) through a novel mechanism that differs from but synergizes with the alpha2beta1 integrin. 12540964_genetic variation of platelet glycoprotein Ia may play a particularly important role during the advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy 12544734_twins developed ischaemic strokes and were shown to be homozygous for the alpha2 807T allele 12615788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12657625_linkage with extracellular signal-regulated kinase is functionally linked in highly malignant autocrine transforming growth factor-alpha-driven colon cancer cells 12681287_Data show that NADPH oxidase activation production of reactive oxygen species are involved in the increase of alpha2beta1-integrin plasma membrane expression in Caco-2 cells stimulated with type IV collagen. 12690916_role of polymorphisms in cardiovascular thrombotic disease [review] 12717361_signaling through both constitutively expressed alpha2 integrin and Matrigel-induced alpha3 integrin expression is required to acquire a differentiated phenotype in Caco-2 cells. 12724616_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12788934_capillary morphogenesis requires endothelial alpha2beta1 integrin engagement of a single type I collagen integrin-binding site, possibly signaling via p38 MAPK and focal adhesion disassembly/FAK inactivation. 12791669_adhesion to the alpha2beta1-specific peptide was disulfide-exchange dependent and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) mediated in platelets 12871362_results of a case-control study involving 180 stroke patients and 172 controls do not support a role for the integrin alpha2 C807T and GPVI Q317L polymorphisms in the development of first-ever ischemic stroke 12871600_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12915563_Monkey rotavirus binding to alpha2beta1 integrin requires the alpha2 I domain and is facilitated by the homologous beta1 subunit. 12928694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13679375_role in inhibiting Fas-mediated apoptosis in T-lymphocytes 14556196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14556196_There were significant differences in the distribution of T and C alleles between myocardial infarction and control groups. 14563646_human platelet deposition on collagen depends on the concerted interplay of several receptors: GPIb in synergy with alpha(2)beta(1) mediating primary adhesion, reinforced by activation through GPVI, which further regulates the thrombus formation. 14671618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14679206_results suggest that matrix metalloproteinase-1 can stimulate dephosphorylation of Akt protein and neuronal death through a non-proteolytic mechanism that involves changes in integrin alpha2beta1 signaling 14687991_Since the platelet alpha2 C807T gene polymorphism is associated with alpha2beta1 receptor density on the platelet surface, the level of alpha2beta1 on platelets may be an additional factor affecting Glanzmann's thromboasthenia clinical expression. 14701832_virus attachment to alpha(2) integrin on the cell surface was found to result in integrin clustering, which can give rise to signaling and facilitate the initiation of the viral entry 14746139_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15104219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15132990_VEGF-A induced alpha1 & alpha2 integrins, promoting lymphatic endothelial tube formation & haptotactic migration. Lineage-specific integrin receptor expression contribute to the distinct dynamics of wound-associated angiogenesis & lymphangiogenesis. 15205592_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15227729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15240572_alpha2beta1 integrin has a role in endorepellin-induced endothelial cell disassembly of actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesions 15265786_alpha2beta1 integrin and GPVI regulate stress fiber formation in megakarocytes, the primary actin structures needed for cell contraction 15292257_alpha2beta1 integrin and CD44/CSPG receptor binding on human melanoma cell activation has been evaluated herein using triple-helical peptide ligands incorporating collagen peptides. 15304053_ILK regulates alpha 2 beta 1 in HEL cells, is activated in platelets and associates with beta 1-integrins 15350465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15355503_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15355504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15514009_the interaction of platelet GP Ib with VWF mediates the activation of alpha2beta1, increasing its affinity for collagen 15522237_Data demonstrate that type I collagen synergistically enhances platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced smooth muscle cell proliferation through Src-dependent crosstalk between the alpha2beta1 integrin and the PDGF receptor beta. 15546585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15630502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15630502_alpha2807TT genotype of the platelet membrane integrin alpha2beta1 is associated with premature onset of early fetal loss. It appears that this risk factor does not induce the pathomechanism, but modulates the course of fetal loss 15647274_Data show that the recombinant Scl protein p176 promotes adhesion and spreading of human lung fibroblast cells through an alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated interaction. 15699160_Alpha2beta1 integrin is required for up-regulation of IL-1 beta-dependent airway smooth muscle secretory responses by fibronectin; while alpha2beta1 is also an important transducer for type I collagen. 15730528_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15777792_Binds to vimentin, but this association is lost after prolonged adhesion of endothelial cells to collagen. 15847651_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15892865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15947241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15947241_individual effect of each polymorphism located either in the coding or promoter sequence of the alpha2 gene may act in combination to modulate variations in platelets alpha2beta1 receptor density 15978109_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15978109_analysis of platelet glycoprotein I(b)alpha and integrin alpha2beta1 polymorphisms in diverse populations 15978110_platelet membrane integrins alpha IIb(beta)3 (HPA-1b/Pl) and alpha2(beta)1 (alpha807TT) polymorphisms may have a role in premature myocardial infarction 16043429_analysis of binding between collagen type III and integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 16055706_the signaling network involving Smad-dependent TGFbeta, PKCdelta, and integrin alpha2beta1/alpha3beta1, regulates cell spreading, motility, and invasion of the SNU16mAd gastric carcinoma cell variant 16113793_alpha2beta1 and signaling via autocrine mediators facilitate and amplify the GPVI procoagulant activity of fibrillar and non-fibrillar collagens 16140647_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16157382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16214444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16304451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16317580_Integrin alpha-2 gene polymorphisms is associated with breast cancer 16317580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16357324_Outside-in signaling through integrin alpha2beta1 triggered inside-out activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 and promoted fibrinogen binding. (alpha2beta1 AND integrin alphaIIbbeta3 16380674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16380674_Our results did not show the causative relationship between the existence of platelets GP Ia mutations and venous system thrombosis in the women in labor. 16390868_Results suggest that loss of E-cadherin function is linked to regulation of cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion, based in part on cell surface expression of alpha2, alpha3 and beta1 integrins. 16421008_The Platelet surface integrin, alpha 2-collagen interaction is an early step associated with platelet adhesion and activation and plays an important role in arterial thrombosis. 16513317_Common polymorphism (C807/T807), affecting the GPIa gene expression, in the development of oral cancer. 16513317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573563_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16622460_malignant phenotype of pancreatic cancer on type I collagen is mediated specifically by the alpha2beta1 integrin 16697311_Genetic polymorphism C807T of platelet glycoprotein Ia increases the risk for premature myocardial infarction. It is also an independent predictor for the release of sCD40L during acute MI and persists 1 year after event. 16697311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16732726_Acquisition of multiple antitumor drugs was accompanied by a drastically reduced expression of alpha2beta1 in the adenocarcinoma cells. 16820192_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16820192_This meta-analysis does not support an association between the C807T polymorphism of ITAG2 gene and stroke. 16828471_The ectopic expression of TM4SF5 in Cos7 cells reduced integrin signaling under serum-containing conditions, but increased integrin signaling upon serum-free replating on substrates. 16875034_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16882656_extracellular matrix fragments produced by apoptotic EC initiate a state of resistance to apoptosis in fibroblasts via an alpha2beta1 integrin/SFK (Src and Fyn)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent pathway 16905953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16908762_Cell attachment was significantly inhibited by function-blocking anti-alpha2 (56%) and -beta1 (98%) integrin antibodies. 16972245_Results show that alpha2beta1 integrin signalling enhances cyclooxygenase-2 expression in intestinal epithelial cells. 17003923_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17023078_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17023078_Our findings support the view that C807T polymorphism of the GPla gene is not a significant risk factor for CAD, either alone or in combination with other major cardiovascular risk factors. 17036337_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17070428_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17127487_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17157856_C807T/G873A polymorphisms, but not T837C, are associated with higher platelet reactivity and residual platelet activity after treatment with anti-platelet agents 17157856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17160992_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17164499_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17164499_glycoprotein Ia 807C/T and 873G/A dimorphisms were not shown as risk factors for VTE 17179151_activated EGF receptor transiently modulates integrin alpha2 cell surface expression and stimulates integrin alpha2 trafficking via caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis 17184645_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17196570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17264949_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17312461_pancretic cancer cells attach to 3D type I collagen scaffolds in an alpha2beta1-specific manner 17331499_Adhesion of breast cancer cells through the VLA integrins alpha2beta1 and alpha5beta1 was significantly reduced by an apoptosis-inducing natural triterpenoid, dehydrothyrsiferol (DT), when studied on low amounts of extracellular matrix. 17346829_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17408410_both the gpIb-VWF interaction and the integrin alpha(2)beta(1)-collagen interaction contribute to platelet adhesion under high shear stress; integrin alpha(II)beta(1) makes a greater contribution to adhesion to type I collagen because less VWF is bound 17495265_study indicates that the GPIa 807 C/T polymorphism does not represent a risk factor for Buerger's disease itself, but could be associated with premature onset of this disorder in predisposed individuals 17498594_findings suggest an important role of integrin alpha2beta1, alpha3beta1, and alpha5beta1 in the architectural characteristics of ameloblastomas and adenomatoid odentogenic tumor 17534386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17534386_genetic variability within ITGA2 may confer risk for ischemic stroke independent of conventional risk factors. 17538005_LOX-1 is important for ADP-stimulated inside-out activation of platelet alpha(IIb)beta(3) and alpha(2)beta(1) integrins 17598123_There is no indication that the presence of 807C/T polymorphism is present in platelet glycoprotein Ia gene and a risk factor for retinal vein occlusion. 17630485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17638891_CD44+alpha2beta1+ cell population is enriched in tumor-initiatin prostate cancer cells 17669516_thrombopoietin-induced in vitro differentiation of primary human cord blood mononuclear cells into megakaryocytes, we observed rapid, progressive CpG methylation of ITGA1, but not PELO or ITGA2. 17728329_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17890945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17890945_Our results do not support an independent association between the 807C/T polymorphism and stroke of undetermined etiology. 18026855_The result suggested that cytoskeleton was a possible mechanical sensor to centrifugal stimuli, and the cytoskeleton regulation to centrifugal loading was in an extracellular matrix-dependent and integrin-mediated manner. 18057877_Polymorphisms in human platelet alloantigen (HPA)-1 and HPA-3 (GPIIb/IIIa), HPA-2 (GPIb/IX), HPA-4 (GPIIIa) and HPA-5 (GPIa/IIa) were found to be associated with the symptoms and recurrence of ischemic stroke. 18231737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18231737_Platelet membrane glycoprotein Ia variations may have an important impact on aspirin resistance. 18362184_Initiation of the signal requires two collagen receptors, alpha2beta1 integrin and discoidin domain receptor (DDR). Each receptor propagates signals through separate pathways that converge to up-regulate N-cadherin. 18413316_induction of decorin expression in angiogenic, as opposed to quiescent, endothelial cells promotes a motile phenotype in an interstitial collagen I-rich environment by both signaling through IGF-IR and influencing alpha2beta1 integrin activity 18417478_collagen and a jararhagin-derived disintegrin peptide competitively bind to the integrin alpha2-I domain 18448666_alpha2beta1 integrin clustering defines its own entry pathway that is Pak1 dependent but clathrin and caveolin independent and that is able to sort cargo to caveosomes 18491034_The data suggest that phosphoenolpyruvate -dependent decrease of collagen biosynthesis in cultured human skin fibroblasts may undergo through depression of alpha(2)beta(1) integrin and IGF-IR signaling. 18502778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18513389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18554474_Integrin alpha2beta1 may promote migration and invasion of neuroblastoma cells. 18587047_These results indicate that NSP4 interaction with integrin alpha1 and alpha2 is an important component of enterotoxin function and rotavirus pathogenesis, further distinguishing this viral virulence factor from other microbial enterotoxins. 18608122_807C/T polymorphism of glycoprotein Ia (GPIa) gene were associated with higher risk of ischaemic stroke in atrial fibrillation 18608122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18613064_Generated high throughput platform to examine interactions of type I collagen receptor alpha(2)beta(1) and fibronectin receptor alpha(5)beta(1) with peptide ligands to evaluate the effects of integrin cross-talk on adhesive responses. 18638089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18787945_SEMA3A suppression of tumor cell migration is dependent on alpha2beta1, the expression of which is stimulated in breast tumor cells by an autocrine SEMA3A pathway. 18806884_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18820259_analysis of distinct roles of beta1 metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS), adjacent to MIDAS (ADMIDAS), and ligand-associated metal-binding site (LIMBS) cation-binding sites in ligand recognition by integrin alpha2beta1 18826391_high-affinity binding for alpha2beta1 can control the overall platelet-adhesive activity of native collagens. 18830231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18836731_ITGA2 807C>T polymorphism may be associated with reduced colorectal cancer risk. 18836731_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18974842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18983487_NO targets activation-dependent adhesion mediated by alpha(2)beta(1), possibly by reducing bioavailability of platelet-derived ADP, but has no effect on activation-independent adhesion mediated by GPVI 18990704_analysis of a prokaryotic Scl1 collagen sequence motif that mediates binding to human collagen receptors, integrins alpha2beta1 and alpha11beta1 19008959_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19082798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19110485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19132198_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19202951_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19235843_The increase in human platelet antigen, HPA-5b allelic frequency in Hepatitis C infection may indicate a possible association between HCV infection and HPAs. 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19350519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19388931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19395705_alpha2beta1 integrin acquired core3 O-glycans in cells expressing core3 synthase with decreased maturation of beta1 integrin, leading to decreased levels of the alpha2beta1 integrin complex 19411307_alpha(2)-, alpha(3)-, and beta(1)-integrins and E-cadherin expression in normal human lung and bronchopulmonary sequestration and congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation were evaluated using Western blot and immunohistochemistry. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19422573_Increased expression of integrin alpha2 and the increased response to TGF-beta1 of hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) fibroblasts may be related to the excessive collagen deposition in HGF patients. 19451223_Nox1 knockdown led to a loss of directional migration which takes place through a RhoA-dependent alpha2/alpha3 integrin switch. 19479237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19500323_nucleotide substitution at position 2235 induces a Q716H amino acid change in the GPIa mature protein that causes Fetal/neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. 19530321_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19549780_alpha2-integrin expression and Rho kinase activity are regulated by protein kinase signaling cascades upon activation of alpha7 nicotinic receptor 19559392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19570064_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19587357_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19622836_A GPVI-independent signaling role of alpha2beta1 in response to collagen stimulation. 19635510_Altogether these data suggest that integrins alpha2 and alpha v beta 3 do not play a major role in the rotavirus entry process. 19700757_a central role for alpha2beta1 integrin in experimental and developmental angiogenesis 19702628_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724904_AsialoGM1 and integrin alpha2beta1 mediate prostate cancer progression. 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19740098_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19740098_genetic polymorphisms in ITGA2 and P2RY1 combine with plasma VWF:Ag levels to modulate baseline platelet reactivity in response to collagen plus EPI, while genetic differences in P2RY1 and GP1BA significantly effect platelet responses to collagen plus ADP 19778317_In a Croatian population, the HPA-5 allele frequencies are 5a-0.895 and 5b-0.105. 19789264_TM4SF5 in hepatocytes negatively regulates integrin alpha2 function via an interaction between the extracellular loop 2 of TM4SF5 and integrin alpha2 during cell spreading on and migration through collagen I environment 19789387_SHP-1 coprecipitates with integrin alpha2. A novel functional interaction between the integrin alpha2 subunit and SHP-1 is described. 19827952_TGF-beta-mediated up-regulation of the expression of the integrin subunits alpha(2) and alpha(6) is mainly mediated in MSC by Smad2. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19927126_in its entry strategy human echovirus 1 seems to rely on the activation of signalling pathways that are dependent on alpha2beta1 clustering, but do not require the conformational regulation of the receptor 19948007_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19995941_Collagen type I inhibits the secretion of IL-8 by human neutrophils in a selective manner and this effect is mediated by the interaction of collagen with integrin alpha2beta1. 20063990_Data suggest that integrin alpha(2)beta(1), glycoprotein Ib and vWf interactions with collagen I and III contribute to platelet adhesion under high shear flow. 20076847_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20076847_the 807T allele of GP Ia and the PlA2 allele of GP IIIa, and specially its combination confer an additional risk for development of carotid atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis in type 2 diabetes 20149160_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20178602_Prostaglandin E2 enhances the migration of chondrosarcoma cells by increasing alpha2beta1 integrin expression through the EP1/PLC/PKCalpha/c-Src/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20204402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20336352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20336352_Polymorphisms in the alpha2 gene of integrin alpha2beta1 in patients with von Willebrand disease could significantly impact platelet function. 20351310_Measurement of thrombus height after specific receptor blockade or use of altered proportions of peptides indicates a signaling rather than adhesive role for glycoprotein VI, and primarily adhesive roles for both alpha(2)beta(1) and the VWF axis 20436081_Androgens increased INT alpha1 and alpha2 subunits in tubuloepithelial cells and in healthy labial salivary glands. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Single-nucleotide polymorphism in ITGA2 is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. 20532885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20536507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20598296_The syndecan- and alpha2beta1 integrin-binding peptides synergistically affect cells and accelerate cell adhesion. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20667040_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20691446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20806289_alpha2beta1 integrin may be a major regulatory molecule in Th17 cell functions. 20939067_The extracellular matrix rigidity affects the osteogenic outcome of mesenchymal stem cells through mechanotransduction events that are mediated by alpha(2)-integrin. 21034162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21126803_Domain V of perlecan, a known alpha2 integrin ligand, inhibits brain amyloid-beta neurotoxicity in an alpha2 integrin-dependent manner. 21134100_Results suggest a novel mechanism for pathogen entry into host cells as well as a new function for C1q- alpha2beta1 integrin interactions. 21135504_alpha2beta1 integrin functionally inhibits breast tumor metastasis, and alpha2 expression may serve as an important biomarker of metastatic potential and patient survival 21193198_Polymorphisms in IL5RA, LPL, ITGA2 and NOS3 genes were independently associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese diabetic population. 21262375_molecular forces of the alpha2beta1 integrin-collagen interaction 21370991_Expression of laminin beta1 and integrin alpha2 is elevated in the anterior temporal neocortex tissue from patients with intractable epilepsy. 21474814_in endothelial cells, ligation of alpha2beta1 and alpha6beta1 integrins induces the Notch pathway, and we disclose a novel role of basement membrane proteins in the processes controlling tip vs stalk cell selection 21508388_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of integrin alpha-2 gene is not associated with colorectal cancer. 21558389_PHLDA1 expression marks the putative epithelial stem cells, downregulates ITGA2 and ITGA6, and contributes to intestinal tumorigenesis 21596751_endorepellin requires both the alpha2beta1 integrin and VEGFR2 for its angiostatic activity 21632096_Findings do not support the influence of the IRGA2807T allele in the development of retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. 21647271_Integrin alpha2beta1 might play a more crucial role in maintaining the mechanical creep properties of the collagen matrix than does integrin alpha1beta1. 21652699_data suggest that extracellular membrane-bound CAIV, but not cytosolic CAII, augments transport activity of MCT2 in a non-catalytic manner, possibly by facilitating a proton pathway other than His-88 21658756_Blocking the alpha(2)beta(1) receptor on human mesenchymal stem cells also resulted in a reduction of cell adhesion on both types of collagen-like peptide surfaces. 21672359_Rapid initiation of collagen-induced platelet aggregation may be associated with the platelet membrane GPIa T807 allele, which may be important in unstable angina pectoris pathogenesis. 21734795_Data suggest that the ITGA2 gene C807T polymorphism may be associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer, differentiation and invasion of gastric cancer. 21743959_CDKN2A, GATA3, CREBBP, ITGA2, NBL1 and TGM4 were down-regulated in the prostate carcinoma glands compared to the corresponding normal glands 21765051_Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in ITAG2 is associated with chronic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes. 21787362_Under convertase inhibition, alpha2beta1 engagement led to enhanced phosphorylation of both FAK (focal adhesion kinase) and MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase). 21796158_The disturbance of alpha2beta1 mediated interactions to collagen I results in a tremendous reduction of hMSC numbers owing to mitochondrial leakage accompanied by Bcl-2-associated X protein upregulation. 21850018_Analysis of the data led to the elucidation of a new molecular mechanism by which SPARC promotes cathepsin B-mediated melanoma invasiveness using collagen I and alpha2beta1 integrins as mediators. 22015659_Platelet alphaIIbeta3 and alpha2beta1 levels were measured by flow cytometry in 320 acute coronary syndrome patients and 128 normal subjects and compared with MPV, platelet count, ITGA2 rs1126643, and ITGB3 rs5918 alleles. 22049795_Inflammation can up-regulate the expressions of |
ENSMUSG00000015533 |
Itga2 |
107.357956 |
2.9829102357 |
1.576721 |
0.165942937 |
92.372008 |
0.00000000000000000000071822819075854264392515781274554804886662121530419297572324626582895845672283030580729246139526367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000006817394273695233918642444578685121920115194069945460919037957814303752002160763368010520935058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
163.0278549 |
16.0290372 |
55.0202244 |
4.4298894 |
| ENSG00000164182 |
91942 |
NDUFAF2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N183 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a molecular chaperone for mitochondrial complex I assembly (PubMed:16200211, PubMed:19384974). Complex I functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone (PubMed:16200211, PubMed:27626371). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16200211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19384974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27626371}. |
Chaperone;Disease variant;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to ubiquinone (coenzyme Q) in the first step of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, resulting in the translocation of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This gene encodes a complex I assembly factor. Mutations in this gene cause progressive encephalopathy resulting from mitochondrial complex I deficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:91942; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly [GO:0032981]; negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0061179] |
15774466_the novel gene mimitin is a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc, and is involved in Myc-dependent cell proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells 17383918_B17.2L occurred in a 830 kDa subcomplex specifically in patients with mutations in subunits NDUFV1 and NDUFS4 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19384974_the homozygous substitution in NDUFAF2 is the disease-causing mutation, which results in a complex I deficiency in the fibroblasts 20308990_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20571988_Within the clinical spectrum of Leigh disease, patients with mutations in NDUFAF2 present with a distinct clinical pattern with predominantly brainstem involvement on MRI 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26033570_Mimitin and 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta are potential markers of paclitaxel resistance and prognostic factors in ovarian cancer. 27344355_One patient presented with Leigh syndrome and had a homozygous deletion in the NDUFAF2 gene, while the second patient had a homozygous mutation in the POLG gene, [c.1399G>A; p.Ala467Thr]. 32335026_NDUFS4 deletion triggers loss of NDUFA12 in Ndufs4(-/-) mice and Leigh syndrome patients: A stabilizing role for NDUFAF2. |
ENSMUSG00000068184 |
Ndufaf2 |
50.526318 |
2.4605193850 |
1.298963 |
0.238770411 |
29.895699 |
0.00000004559229782993006919296501730336224067485773048247210681438446044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000185485754126176335738988430919260697038453145069070160388946533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.1365091 |
10.6266430 |
29.9435646 |
3.4401747 |
| ENSG00000164219 |
5229 |
PGGT1B |
protein_coding |
P53609 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of a geranyl-geranyl moiety from geranyl-geranyl pyrophosphate to a cysteine at the fourth position from the C-terminus of proteins having the C-terminal sequence Cys-aliphatic-aliphatic-X. Known substrates include RAC1, RAC2, RAP1A and RAP1B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8106351}. |
Alternative splicing;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Prenyltransferase;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Zinc |
|
Protein geranylgeranyltransferase type I (GGTase-I) transfers a geranylgeranyl group to the cysteine residue of candidate proteins containing a C-terminal CAAX motif in which 'A' is an aliphatic amino acid and 'X' is leucine (summarized by Zhang et al., 1994 [PubMed 8106351]). The enzyme is composed of a 48-kD alpha subunit (FNTA; MIM 134635) and a 43-kD beta subunit, encoded by the PGGT1B gene. The FNTA gene encodes the alpha subunit for both GGTase-I and the related enzyme farnesyltransferase.[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:5229; |
CAAX-protein geranylgeranyltransferase complex [GO:0005953]; CAAX-protein geranylgeranyltransferase activity [GO:0004662]; protein geranylgeranyltransferase activity [GO:0004661]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; protein geranylgeranylation [GO:0018344]; protein prenylation [GO:0018342] |
14598891_results suggest that geranylgeranylation of RhoA is critical for cancer cell invasion 15451670_Results suggest that all peptide substrates adopt a common binding mode in the protein farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase active site. 19667218_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20403997_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20446922_RNAi knockdown of GGTase-Ibeta inhibited invasion, disrupted F-actin organization and decreased the level of cofilin in PC-3 cells. 22160308_our findings identify Geranylgeranyl transferase 1 as a key regulator of human airway smooth muscle cell viability 23475391_our study showed, for the first time, that HIF-1alpha was regulated by protein prenylation transferase GGTI and mediated the effect of GGTI on glioma cell migration and invasion 33548109_The diagnostic significance of PGGT1B in psoriasis. |
ENSMUSG00000024477 |
Pggt1b |
261.066076 |
2.0738207624 |
1.052291 |
0.196352949 |
27.957783 |
0.00000012399121373865711327734667832750625748872153053525835275650024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000484284285467737230368304775923737892640019708778709173202514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
323.2196543 |
46.5090269 |
157.5632099 |
16.4371521 |
| ENSG00000164306 |
201973 |
PRIMPOL |
protein_coding |
Q96LW4 |
FUNCTION: DNA primase and DNA polymerase required to tolerate replication-stalling lesions by bypassing them (PubMed:24126761, PubMed:24207056, PubMed:24240614, PubMed:24267451, PubMed:25255211, PubMed:24682820, PubMed:25262353, PubMed:25746449, PubMed:25550423, PubMed:27989484, PubMed:29608762, PubMed:30889508, PubMed:28534480). Required to facilitate mitochondrial and nuclear replication fork progression by initiating de novo DNA synthesis using dNTPs and acting as an error-prone DNA polymerase able to bypass certain DNA lesions (PubMed:24126761, PubMed:24207056, PubMed:24240614, PubMed:24267451, PubMed:25255211, PubMed:24682820, PubMed:25262353, PubMed:25746449, PubMed:25550423, PubMed:27989484, PubMed:29608762, PubMed:30889508, PubMed:30633872, PubMed:28534480). Shows a high capacity to tolerate DNA damage lesions such as 8oxoG and abasic sites in DNA (PubMed:24126761, PubMed:24207056, PubMed:24240614, PubMed:24267451, PubMed:25746449). Provides different translesion synthesis alternatives when DNA replication is stalled: able to synthesize DNA primers downstream of lesions, such as ultraviolet (UV) lesions, R-loops and G-quadruplexes, to allow DNA replication to continue (PubMed:24240614, PubMed:26626482, PubMed:28534480, PubMed:30478192). Can also realign primers ahead of 'unreadable lesions' such as abasic sites and 6-4 photoproduct (6-4 pyrimidine-pyrimidinone), thereby skipping the lesion (PubMed:25746449). Also able to incorporate nucleotides opposite DNA lesions such as 8oxoG, like a regular translesion synthesis DNA polymerase (PubMed:24207056, PubMed:25255211, PubMed:25746449). Also required for reinitiating stalled forks after UV damage during nuclear DNA replication (PubMed:24240614). Required for mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) synthesis and replication, by reinitiating synthesis after UV damage or in the presence of chain-terminating nucleotides (PubMed:24207056). Prevents APOBEC family-mediated DNA mutagenesis by repriming downstream of abasic site to prohibit error-prone translesion synthesis (By similarity). Has non-overlapping function with POLH (PubMed:24240614). In addition to its role in DNA damage response, also required to maintain efficient nuclear and mitochondrial DNA replication in unperturbed cells (PubMed:30715459). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P1E7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24126761, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24207056, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24240614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24267451, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24682820, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25255211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25262353, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25550423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25746449, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26626482, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27989484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28534480, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29608762, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30478192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30633872, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30715459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30889508}.; FUNCTION: Involved in adaptive response to cisplatin, a chemotherapeutic that causes reversal of replication forks, in cancer cells: reinitiates DNA synthesis past DNA lesions in BRCA1-deficient cancer cells treated with cisplatin via its de novo priming activity (PubMed:31676232). Repriming rescues fork degradation while leading to accumulation of internal ssDNA gaps behind the forks (PubMed:31676232). ATR regulates adaptive response to cisplatin (PubMed:31676232). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31676232}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA-directed DNA polymerase;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Manganese;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleotidyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transferase;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a DNA primase-polymerase that belongs to a superfamily of archaeao-eukaryotic primases. Members of this family have primase activity, catalyzing the synthesis of short RNA primers that serve as starting points for DNA synthesis, as well as DNA polymerase activity. The encoded protein facilitates DNA damage tolerance by mediating uninterrupted fork progression after UV irradiation and reinitiating DNA synthesis. An allelic variant in this gene is associated with myopia 22. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:201973; |
DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex [GO:0000428]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA primase activity [GO:0003896]; DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity [GO:0003887]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; error-prone translesion synthesis [GO:0042276]; mitochondrial DNA repair [GO:0043504]; mitochondrial DNA replication [GO:0006264]; R-loop disassembly [GO:0062176]; replication fork processing [GO:0031297]; response to UV [GO:0009411]; translesion synthesis [GO:0019985] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23579484_Identification of a novel missense variant of the CCDC111 gene in a high myopia family. 24126761_PRIMPOL depletion results in increased spontaneous DNA damage and defects in the restart of stalled replication forks. 24207056_Primpol is proposed to facilitate replication fork progression by acting as a translesion DNA polymerase or as a specific DNA primase reinitiating downstream of lesions that block synthesis during DNA replication. 24267451_PrimPol is an important player in replication fork progression in eukaryotic cells. 24682820_Although PrimPol's primase activity is required to restore wild-type replication fork rates in irradiated PrimPol-/- cells, the polymerase activity is sufficient to maintain regular replisome progression in unperturbed cells. 25255211_Data suggest that PrimPol exhibits fidelity that is 1.7-fold more accurate with magnesium as cofactor compared to manganese; activity of PrimPol is increased 400-1000-fold by manganese compared to magnesium based on steady-state kinetic parameters. 25262353_The data establishes that a point mutation identified in PrimPol from patients with high myopia results in a major disruption of the catalytic and replication activities associated with human PrimPol thus establishing a link between replication stress and high myopia. 25550423_The authors propose a mechanism whereby single-stranded DNA binding proteins greatly restrict the contribution of PrimPol to DNA replication at stalled forks, thus reducing the mutagenic potential of PrimPol during genome replication. 25746449_PrimPol tolerates DNA lesions, involving template and primer dislocations that can be operating during both mitochondrial and nuclear DNA replication. PrimPol could also operate as a translesion synthesis partner during DNA-directed RNA synthesis. 26552983_The molecular mechanism of polymerization and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor incorporation by human PrimPol have been described. 26626482_Implicate PrimPol in promoting restart of DNA synthesis downstream of, but closely coupled to, G4 replication impediments. 26627254_Rad51 recombinase prevents Mre11 nuclease-dependent degradation and excessive PrimPol-mediated elongation of nascent DNA after UV irradiation 26710848_Data suggest that, during genetic transcription, Prim-Pol-alpha-cat binds the DNA/RNA junction at 5prime-terminus of RNA primer (or initiating NTP, nucleoside-triphosphate). 26984527_findings establish that PolDIP2 can regulate the translesion synthesis polymerase and primer extension activities of PrimPol 27819052_PrimPol shows the ability to synthesize DNA opposite ultraviolet (UV) lesions; however, unexpectedly, the active-site cleft of the enzyme is constrained, which precludes the bypass of UV-induced DNA lesions by conventional translesion synthesis. 27989484_The ability of human PrimPol to discriminate against ribonucleotides (rNTPs) and to incorporate the triphosphates of four nucleoside analog drugs in the presence of Mn2+or Mg2+ was studied. 28396594_These new findings supports the existence of a functional PrimPol/RPA association that allows repriming at the exposed ssDNA regions formed in the leading strand upon replicase stalling. 28408491_Data propose that it is highly likely that PrimPol plays the same roles in mitochondria as in cell nucleus by repriming DNA replication to allow replication to be completed in an efficient and timely manner. Also, a range of PrimPol mutations have been found in cancer cells and other conditions suggesting possible connections to human diseases. [review] 28534480_RPA serves to stimulate the primase activity of PrimPol. 28754021_Growing evidence suggests that the main biological function of human PrimPol during replication of chromosomal DNA is a repriming of stalled replication downstream of DNA damage or naturally occurring obstacles. However, the mechanisms that regulate the repriming by PrimPol in cells are yet to be understood. PrimPol in cells are yet to be understood. [review] 28902865_Active PrimPol can be purified from E. coli and human suspension cell line in high quantities and the activity of the purified enzyme is similar in both expression systems. 29608762_Description of the sequential substrate interactions of human PrimPol during primer synthesis, and the relevance of the Zn finger-containing domain at each individual step. 30098578_the properties of PrimPol as a TLS polymerase in the presence of different metal ions in vitro 30715459_PrimPol is required for the maintenance of efficient nuclear and mitochondrial DNA replication in human cells. 30718533_A cancer-associated point mutation disables the steric gate of human PrimPol. 30889508_PrimPol active site requires a specific motif A (DxE) to favor the use of Mn(2+) ions in order to achieve optimal incoming nucleotide stabilization 31061318_The WRNIP1-mediated reduction in the amount of PrimPol was suppressed by treatment of the cells with proteasome inhibitors, suggesting that WRNIP1 is involved in the degradation of PrimPol via the proteasome. 31627881_REVIEW: Mechanism of DNA primer synthesis by human PrimPol 32191790_Mitochondrial genetic variation is enriched in G-quadruplex regions that stall DNA synthesis in vitro. 33203852_PrimPol-dependent single-stranded gap formation mediates homologous recombination at bulky DNA adducts. 33237263_The deubiquitinase USP36 Regulates DNA replication stress and confers therapeutic resistance through PrimPol stabilization. 33261049_Strand Displacement Activity of PrimPol. 33571927_The DNA ligands Arg47 and Arg76 are crucial for catalysis by human PrimPol. 34128550_PrimPol-mediated repriming facilitates replication traverse of DNA interstrand crosslinks. 34188055_Structural basis of DNA synthesis opposite 8-oxoguanine by human PrimPol primase-polymerase. 34302490_Motif WFYY of human PrimPol is crucial to stabilize the incoming 3'-nucleotide during replication fork restart. 34624216_Temporally distinct post-replicative repair mechanisms fill PRIMPOL-dependent ssDNA gaps in human cells. 34645815_BRCA2 associates with MCM10 to suppress PRIMPOL-mediated repriming and single-stranded gap formation after DNA damage. 34680882_Human PrimPol Discrimination against Dideoxynucleotides during Primer Synthesis. |
ENSMUSG00000038225 |
Primpol |
80.050261 |
0.4876056794 |
-1.036213 |
0.256611089 |
16.087365 |
0.00006048625921538794078264472675598995010659564286470413208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000172184606753929790590174064845996326766908168792724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.5842118 |
9.1454413 |
104.5713813 |
13.4172822 |
| ENSG00000164309 |
202333 |
CMYA5 |
protein_coding |
Q8N3K9 |
FUNCTION: May serve as an anchoring protein that mediates the subcellular compartmentation of protein kinase A (PKA) via binding to PRKAR2A (By similarity). May function as a repressor of calcineurin-mediated transcriptional activity. May attenuate calcineurin ability to induce slow-fiber gene program in muscle and may negatively modulate skeletal muscle regeneration (By similarity). Plays a role in the assembly of ryanodine receptor (RYR2) clusters in striated muscle (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q70KF4}. |
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sarcoplasmic reticulum |
|
Predicted to enable identical protein binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade; negative regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity; and regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Located in cytosol; nuclear speck; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:202333; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; M band [GO:0031430]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529] |
16407236_Functions directly downstream of MEF2A at the costamere in striated muscle potentially playing a role in myofibrillogenesis. 17872945_perinuclear localization of the TRIM-like protein myospryn requires its binding partner desmin 18344630_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18344630_Polymorphism of myospryn is associated with left ventricular hypertrophy, and an association between a Z-disc protein and cardiac adaptation in response to pressure overload. 19140017_Review discusses interactions that suggest myospryn is involved in two seemingly distinct processes, protein kinase A signalling and vesicular trafficking. 20634290_Interactions with M-band titin and calpain 3 link myospryn (CMYA5) to tibial and limb-girdle muscular dystrophies. 20838396_2 SNPS in CYMA5, rs4704591 & rs10043986, are significantly associated with schizophrenia. Haplotype conditioned analyses indicated that the association signals observed at these two markers are independent. 21295948_This study demonstrated that the association between CMYA5 and schizophrenia in Han Chinese. 23335746_CMYA5 is a new potential substrate of Kcna3 in human heart 23528614_Association of cardiomyopathy-associated 5 (CMYA5) gene of Schizophrenia, is reported. 23778016_In a Han Chinese sample of schizophrenic patients, SNPs within CMYA5 were associated with the disorder. 24524722_meta-analysis confirming association of CMYA5 polymorphisms and schizophrenia in East Asian population. 24988482_Specific alleles and haplotype in the CMYA5 confer genetic risk for both schizophrenia and major depressive disorder in the Han Chinese population. 26403435_association between CMYA5 gene polymorphisms and schizophrenia was confirmed in Asian population. 27350668_The results showed that MYBPC3 25-bp deletion polymorphism was significantly associated with elevated risk of left ventricular dysfunction (LVD), while TTN 18 bp I/D, TNNT2 5 bp I/D and myospryn K2906N polymorphisms did not show any significant association with LVD. 28776924_meta-analysis did not provide evidence supporting a contribution of CMYA5 rs3828611 and rs4704591 to schizophrenia susceptibility in Asian populations. |
ENSMUSG00000047419 |
Cmya5 |
39.373856 |
0.2100765951 |
-2.251013 |
0.460333994 |
22.389126 |
0.00000222630998353451852630178510461522733976380550302565097808837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007571382895247163729993741115853467249507957603782415390014648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.3854126 |
5.0716477 |
68.1657101 |
15.5883786 |
| ENSG00000164330 |
1879 |
EBF1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UH73 |
FUNCTION: Key pioneer transcription factor of B-cell specification and commitment (PubMed:27807034). Recognizes variations of the palindromic sequence 5'-ATTCCCNNGGGAATT-3'. Operates in a transcription factor network to activate B-cell-specific genes and repress genes associated with alternative cell fates. For instance, positively regulates many B-cell specific genes including BCR or CD40 while repressing genes that direct cells into alternative lineages, including GATA3 and TCF7 for the T-cell lineage. In addition to its role during lymphopoiesis, controls the thermogenic gene program in adipocytes during development and in response to environmental cold (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27807034}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a chromatin anchor for Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 to mediate the assembly of EBNA2 chromatin complexes in B-cells (PubMed:28968461). In addition, binds to the viral LMP1 proximal promoter and promotes its expression during latency (PubMed:26819314). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26819314, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28968461}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. Predicted to be part of chromatin. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:1879; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; C2H2 zinc finger domain binding [GO:0070742]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11994467_Three independent binding sites for EBF in the surrogate light chain VpreB promoter are important for the full function of the promoter and its collaborative activation by EBF and E47 in a preB cell line. 15920012_data suggest that Notch signaling may affect B-versus T-lineage commitment by the targeting of both EBF and E2A 16106032_EBF-1 and PPARgamma2 induce adipocyte differentiation with comparable kinetics and efficiency. 16255771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16255771_Two genetic markers within the EBF1 gene have been found associated with multiple sclerosis, indicative either of their causative role or that of some other polymorphism in linkage disequilibrium with them. 17101802_The regulation of Ebf1 via distinct promoters allows for the generation of several feedback loops and the coordination of multiple determinants of B lymphopoiesis in a regulatory network. 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20423929_our studies not only provided molecular basis of ATF5 transcriptional regulation, but also identified ATF5 as a target gene of EBF1 transcription factor. 20435627_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20592035_unique structural features of EBF domains and dimeerization motif 20861858_EBF1, BLK and TNFSF4 are all involved in B-cell differentiation and activation, and we conclude that polymorphisms in several susceptibility genes in the immune system contribute to the pathogenesis of primary SS. 20861858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21593590_Data show that ZNF521 can antagonize B-cell development and support the notion that it may contribute to conserve the multipotency of primitive lympho-myeloid progenitors by preventing or delaying their EBF1-driven commitment toward the B-cell lineage. 21606506_Ebf1 or Pax5 haploinsufficiency synergizes with STAT5 activation to initiate acute lymphoblastic leukemia 21735360_EBF1 functions as a tissue-specific regulator of chromatin structure at B cell-specific genes. [Review] 22473956_ectopic expression of EBF1 efficiently induced the development of B-1 cells at the expense of conventional B cells. 23174882_Loss of EBF1 expression is associated with Hodgkin lymphoma. 23775715_Using a capture sequencing strategy, we discovered the B-cell relevant genes IRF8, EBF1, and TNFSF13 as novel targets for IGH deregulation. 23863747_The transcription factor EBF1 is an interaction partner for TET2, suggesting a sequence-specific mechanism for regulating DNA methylation. 23951143_A novel cross talk between ERbeta and Early B-cell Factor 1 (EBF1) was also identified and characterized. 25271088_EBF1 plays a role in connecting chronic psychosocial stress and central obesity as a risk factor for CVD. 25791133_Studied whether EBF1 expression and biological activity in white adipose tissue is related to different metabolic parameters. 26468528_Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA1 bound to host genes of high significance for B-cell growth and function, including MEF2B, IL6R, and EBF1. 26788497_two multi-zinc finger transcription cofactors named ZNF423 and ZNF521 have been characterised as potent inhibitors of EBF1 and are emerging as potentially relevant contributors to the development of B-cell leukaemias 26819314_role in the expression of Latent membrane protein 1 26872634_Among 15 childhood ALL patients with EBF1-PDGFRB fusion proteins, the fusion arose from interstitial deletion of 5q33 (n = 11), balanced rearrangement (n = 2), or complex rearrangement (n = 2). 26900922_early B cell factor-1 (EBF1) was identified as a co-regulator of gene expression with MEF2C. 27424222_EBF1 is critical for transcriptional control of SLAMF1 gene in human B cells. 27744667_The four single-nucleotide polymorphisms that had strong linkage disequilibrium relationships (rs10061900, rs10070743, rs4704967, and rs10056564) demonstrated significant interactions with the waist-hip ratio in the dominant model. 27816938_A genome-wide significant association was observed for rs35715456 (log10BF = 6.3) on chromosome 18 for the dichotomous trait of having at least one long-lived parent versus not having any long-lived parent. The most significant association among single nucleotide polymorphisms in longevity candidate genes (APOE, MINIPP1, FOXO3, EBF1, CAMKIV, and OTOL1) was observed in the EBF1 gene region (rs17056207, p = .0002). 27918534_EBF1 polymorphism is associated with metabolic diseases. 28137879_Data show that GS Homeobox 2 (Gsx2) and Early B-cell factor 1 (Ebf1) combined overexpression in human embryonic stem (hES) cells achieves high yields of medium spiny neurons (MSNs). 28183271_In a Chinese population the TT genotype and T alleles in rs36071027 in the EBF1 gene are associated with an increased risk of coronary artery disease and its severity. 28555080_EBF1-PDGFRB is sufficient to drive leukemogenesis. 28877031_In this genomewide association study, we found that variants at the EBF1, EEFSEC, AGTR2, WNT4, ADCY5, and RAP2C loci were associated with gestational duration and variants at the EBF1, EEFSEC, and AGTR2 loci with preterm birth. 28978690_this study demonstrates a role for the AHR in regulating human B cell development, and it suggests that transcriptional alterations of EBF1 by the AHR are involved in the underlying mechanism 29099283_EBF1 modifies the breast cancer subtype-specific methylation and gene expression program. 29169115_EBF1 was down-regulated in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) tissues and cell lines. 29336845_EBF1 acts as a pioneer transcription factor that operates in a transcription factor network to activate B cell-specific genes and repress genes associated with alternative cell fates. (Review) 29789399_The results show that the mutation (CT+TT) at the rs987401919 and rs36071027 loci of EBF1 and its interaction with smoking and drinking are risk factors for coronary artery disease in Chinese patients. 30878028_Alleles rs115662534(T) and rs548231435(C), Disrupt the Binding of Transcription Factors STAT1 and EBF1 to the Regulatory Elements of Human CD40 Gene 32046385_EBF1 Gene mRNA Levels in Maternal Blood and Spontaneous Preterm Birth. 32237936_Maternal blood EBF1-based microRNA transcripts as biomarkers for detecting risk of spontaneous preterm birth: a nested case-control study. 32329523_Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00844 promotes apoptosis and represses proliferation of prostate cancer cells through upregulating GSTP1 by recruiting EBF1. 32364535_Genomic and epigenomic EBF1 alterations modulate TERT expression in gastric cancer. 32959224_EBF1-Correlated Long Non-coding RNA Transcript Levels in 3rd Trimester Maternal Blood and Risk of Spontaneous Preterm Birth. 33077726_Evaluating the precision of EBF1 SNP x stress interaction association: sex, race, and age differences in a big harmonized data set of 28,026 participants. 33159853_A Prion-like Domain in Transcription Factor EBF1 Promotes Phase Separation and Enables B Cell Programming of Progenitor Chromatin. 33188849_Inactivated STAT5 pathway underlies a novel inhibitory role of EBF1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 33452395_EBF1 drives hallmark B cell gene expression by enabling the interaction of PAX5 with the MLL H3K4 methyltransferase complex. 33626861_The EBF1-PDGFRB T681I mutation is highly resistant to imatinib and dasatinib in vitro and detectable in clinical samples prior to treatment. 34272166_Plasma EBF1 as a Novel Biomarker for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. 34272603_EBF1 is expressed in pericytes and contributes to pericyte cell commitment. 35761386_EBF1-mediated up-regulation of lncRNA FGD5-AS1 facilitates osteosarcoma progression by regulating miR-124-3p/G3BP2 axis as a ceRNA. 35857872_EBNA2-EBF1 complexes promote MYC expression and metabolic processes driving S-phase progression of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells. 35867755_EBF1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression by surveillance of the HIF1alpha pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000057098 |
Ebf1 |
46.422346 |
9.6187686826 |
3.265852 |
0.529283990 |
33.638498 |
0.00000000663661442522440258427570471686310349390680585202062502503395080566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000029407513934647905787002624290044083821271669876296073198318481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.5471945 |
28.4216611 |
8.8739721 |
2.3355605 |
| ENSG00000164400 |
1437 |
CSF2 |
protein_coding |
P04141 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that stimulates the growth and differentiation of hematopoietic precursor cells from various lineages, including granulocytes, macrophages, eosinophils and erythrocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:3925454}. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Pharmaceutical;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that controls the production, differentiation, and function of granulocytes and macrophages. The active form of the protein is found extracellularly as a homodimer. This gene has been localized to a cluster of related genes at chromosome region 5q31, which is known to be associated with interstitial deletions in the 5q- syndrome and acute myelogenous leukemia. Other genes in the cluster include those encoding interleukins 4, 5, and 13. This gene plays a role in promoting tissue inflammation. Elevated levels of cytokines, including the one produced by this gene, have been detected in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients that develop acute respiratory distress syndrome. Mice deficient in this gene or its receptor develop pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:1437; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor complex [GO:0030526]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor binding [GO:0005129]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097028]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; epithelial fluid transport [GO:0042045]; granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:0038157]; histamine secretion [GO:0001821]; immune response [GO:0006955]; macrophage activation [GO:0042116]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0043011]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; neutrophil differentiation [GO:0030223]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of interleukin-23 production [GO:0032747]; positive regulation of leukocyte proliferation [GO:0070665]; positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010744]; positive regulation of podosome assembly [GO:0071803]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259]; regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, sleep [GO:0045187]; response to fluid shear stress [GO:0034405]; response to silicon dioxide [GO:0034021] |
11763346_inhibition of signaling by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeting the common beta chain of receptors 11855781_GM-CSF-driven apoptosis, but not TNF-driven apoptosis was reversibly associated with bcl-2-expression (bcl-2-dependent mechanism)in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in children. 11880043_Protection of peritoneal macrophages by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) against dexamethasone suppression of killing of Aspergillus, and the effect of human GM-CSF. 11963838_Adenomyotic glandular epithelium had greater expression of the GM-CSF ligand compared with autologous endometrium from premenopausal women 12022701_Activated eosinophils release small amounts of anti-apoptotic GM-CSF by stabilizing its coding mRNA. Review. 12031914_secretion from acute myelogenous leukemia blasts was up-regulated by leptin 12144536_B-CLL patients with progressive disease had a significantly increased number of T cells spontaneously producing IL-2, IL-4 and GM-CSF, suggesting a role for T cells in the pathogenesis of B-CLL. 12171249_GM-CSF induced human myelopoiesis is regulated by transforming growth factor-beta isoforms 12356579_GMCSF is induced in bronchial epithelial cells by the MAP kinase signaling system in response to air pollutants 12356582_GM-CSF plays a critical role in lung homeostasis by regulating levels of MCSF, MCP-1 and IL-8. 12397015_Enhanced PMN survival was attributed to effects of epithelial G-CSF and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor expression, which inhibit PMN apoptosis.Both CF and normal cells responded to bacteria with increased cytokine production 12444058_data indicate that granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor regulates cell viability in human embryos 12496443_GM-CSF inhibits prolonged glucocorticoid-induced activation of eosinophil c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and preserves the expression of eosinophil antiapoptotic protein X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis. 12538575_signals for increased glucose transport via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and hydrogen peroxide-dependent mechanisms 12548211_Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor inhibited the platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase secretion by decidual macrophages 12568301_GM-CSF-mediated antiapoptosis is mediated through protein synthesis-independent mechanisms and involves the Janus kinase-STAT pathway. 12615367_IL-6 and GM-CSF may be involved in the autoimmune mechanism of non-segmental vitiligo. 12629028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12637324_functional studies demonstrated GMCSF-dependent activation of IkappaB kinase activity in endothelial cells, degradation of IkappaB, and activation of NF-kappaB 12646185_GM-CSF is up-regulated by ETS2, a target of protein kinase C 12663443_GM-CSF exerts a dual effect: it stimulates cell division but contemporaneously up-regulates Jak-Stat-dependent proapoptotic proteins. 12743567_ICAM-3 is highly expressed on the surface of human eosinophils and has a role in the downregulation of GM-CSF production. 12744771_GMCSF is induced in lung fibroblasts by IL-beta, TNF-alpha, and macrophage contact. 12759409_Incubation of eosinophils with GMCSF leads to reduced expression of IL-5R alpha that is sustained for up to 5 days; in contrast, eosinophil IL-3R alpha expression is increased by GMCSF, whereas eosinophil GMCSF receptor alpha is down-regulated by GMCSF. 12855588_induces cell cycle progression via internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation of c-myc though the PI3K pathway in human factor-dependent leukemic cells 12926133_IL-10 is one of the cytokines up-regulating the GM-CSF expression in non-small cell lung cancer. 12928384_GM-CSF induces expression of surface and total class II major histocompatibility antigens crucial for antigen presentation in human monocytes. 12935848_immunolocalization studies confirmed the presence of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor(GM-CSF) in the germ cell line in bovine and human testes and addition of GM-CSF enhances several parameters of sperm motility 12954601_TNF, GM-CSF, and G-CSF induce actin depolymerization and morphological changes through activation of ERK and/or p38 MAPK, and cytokine-induced actin reorganization may affect inhibitory effect of these cytokines on neutrophil chemotaxis. 13679820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13679820_The GM-CSF genotype is an important genetic marker predicting an individual's predisposition to atopic dermatitis. 14503968_GMCSF was highly expressed in dendritic cells with a bicistronic retroviral vector. 14512323_neutralizing anti-GM-CSF autoantibodies develop specifically in patients with idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis 14530365_GMCSF displays additive effects with TNF-alpha on the common p47phox phosphorylated site and on fMLP-induced NADPH oxidase activation in human neutrophils, which is evidence for a common priming pathway. 14564341_Hematopoietin receptor superfamily. Comprised of cytokine-specific alpha chain and common beta chain for signaling. Contributes to differentiation and function of leukocytes. Protective immunity and pathophysiology of immunologic diseases. Review. 14567558_results suggest that in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, GM-CSF synthesis is deficient and associated with negative regulation by IL-10 14628073_long-term exposure of primitive human hematopoietic cells to elevated levels of human IL-3, GM-CSF and SF in vivo may deleteriously affect the stem cell compartment, while expanding terminal myelopoiesis. 14630612_Results identify several transcriptional targets of interleukin-5 and granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor in human eosinophils and suggest that a number of protein products are critical to the responsiveness of airway eosinophils. 14662891_GM-CSF elicits chemotaxis and chemokinesis of neutrophils by a process correlated with activity of the ribosomal p70 S6 kinase signaling pathway. 14726527_the GM-CSF ARE controls translation and mRNA decay by interfering with poly(A)-binding protein-mediated mRNA circularization. 14730225_Local injection of recombinant human GM-CSF may improve the healing of ischemic and even normal colon anastomoses. 15009203_Data characterize recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) for glycosylation sites and the definition of the glycosidic moiety, including the degree of site occupancy. 15078892_Profound changes in the rate of neutrophil apoptosis following Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling occur via dynamic changes in the rate of Mcl-1 turnover via the proteasome. 15123671_Data suggest that glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-phosphorylated Ets1 is a target of Runx1-recruited calcineurin phosphatase at the granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter. 15129224_benzene metabolite hydroquinone stimulates proliferation via activation of ERK/AP-1 and is at least partially mediated via the production of GM-CSF 15136573_release of the eosinophil survival factor granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor from monocytes is stimulated by 5-oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid 15201279_mappin of an epitope on the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor at its C terminus 15218949_GM-CSF is associated with the expression of proliferation vascularization in memingioma. 15245433_E2 may enhance GM-CSF production via guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled membrane receptors and signaling cascade of PI-specific PLC/protein kinase Calpha/MEK/ERK. 15269821_TGF-beta and ET-1 have roles in mechanical force generation in keratinocyte-fibroblast co-cultures, and GM-CSF induces myofibroblasts acting indirectly 15308671_c-Kit makes both kinase-independent and -dependent contributions to the proliferative synergy induced by SCF in combination with GM-CSF 15340054_GM-CSF enhancer core elements are divided between two adjacent nucleosomes that become destabilized and highly accessible after activation. 15358207_In vitro human osteoclastogenesis is dependent on M-CSF and the stimulatory effects of GM-CSF are mediated by M-CSF. 15388258_IL-17 and IL-17F play a differential regulatory role in GM-CSF production by LMVECs stimulated with IL-1beta and/or TNF-alpha, which is sensitive to Th1 and Th2 cytokine modulation 15388264_a role for GM-CSF as a major mediator in increasing granuloma reaction in human schistosomiasis 15475489_roles for p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB in the potentiation of GM-CSF release 15479432_GM-CSF producing cells were present in both the divided and undivided airway smooth muscle cells populations 15528381_GM-CSF induces the protein expression of cyclin D3 and the kinase Pim-1, both of which are regulated by STAT-dependent processes in airway and blood eosinophils. 15541716_majority of neutrophil chemoattractant activity produced by female reproductive tract epithelial cells results from the synergistic effects of IL-8 and GM-CSF 15576295_The GM-CFS mRNA expression in these cell lines and recent studies have demonstrated that HCs can stimulate tumor progression. 15621725_GM-CSF governs the properties of the more mature myeloid cells of the granulocyte and macrophage lineages during host defence and inflammatory reactions [review] 15927668_Neither upregulation of CD20 antigen nor a change of the proportion of CD20 positive cells was observed after a dose of 5 microg/kg GM-CSFin B cell chronic leukemia. 16027123_Helix C of human GM-CSF plays a prominent role in the regulation of high affinity heparin binding 16167889_This review summarizes the evidence supporting a major role for GM-CSF in inflammation and autoimmunity and its functions as major regulator governing granulocyte and macrophage lineage populations at all stages of maturation. 16211258_Protein kinase C plays a role in activation of granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor in lung cancer. 16305336_Data describe coculture of human peripheral blood cells and mouse stromal cells transfected with c-kit ligand, thrombopoietin, flt-3/flk2 ligand, and granulocyte-macrophage-CSF or with weekly addition of these cytokines. 16380083_RNA containing the AU-rich element of GM-CSF is destabilized by dicer and positive charge of proteins 16487109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16491014_Histamine stimulated the activation of MAPK signals, which may regulate the expression or IL-8 and GM-CSF 16716376_The cytokines TNFalpha and GM-CSF activate CAEV transcription, and this effect occurs independently of AP-1. 16783532_IL2 and GMCSF do not cause a cumulative gain in peripheral dendritic cell counts or an increase in myeloid BDCA-1+ BDCA-2- dendritic cell subset in the peripheral blood. 16896315_We suggested that G-CSF has potentially neuroprotective effects on motor neurons in ALS and that downregulation of its receptor might contribute to ALS pathogenesis 16912178_A progression-promoting effect of G-CSF and GM-CSF in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. 16949316_Csf-2 regulates invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell effector differentiation during development by a mechanism that renders them competent for cytokine secretion. 17142110_increased activity of inhibitory molecules, such as Src homology domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) and suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS), is responsible for age-related failure of GM-CSF to stimulate neutrophil functions 17205286_Results indicate that elevated GM-CSF levels may contribute, at least in part, to high leukocyte numbers in sickle cell disease. 17273755_IL-3 can not replace GM-CSF to induce the differentiation of human monocytes into Langerhans cells in culture 17311927_recombinant GM-CSF-Bcl-XL binds the GM-CSF receptor on human monocyte/macrophage cells and bone marrow progenitors inducing differentiation and allowing Bcl-XL entry into cells 17342342_G-CSF and GM-CSF might accelerate tumor progression by directly regulating COX-2 expression, independently of an autocrine mechanism. 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17362254_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17512774_GM-CSF has a role in regulation of embryo development and pregnancy [review] 17533050_GM-CSF-stimulated CD34(+) cell proliferation is regulated by the JAK/STAT3/survivin signaling pathway. 17619839_Vascular smooth muscle cells-like endothelial cells appear to contribute to the maintenance of an inflammatory response in the atherosclerotic vessel wall upon CD40-CD154 co-stimulation. 17681858_Carriers of the CSF2 117Ile allele had a 2.4-fold higher risk of COPD than the wild type (Thr/Thr) carriers. 17681858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17713553_dysregulated production of GM-CSF by polycythemia vera (PV) T cells, contributes to the in vitro formation of erythroid colonies in the absence of exogenous cytokines by PV CD34+ cells and likely plays a role in sustaining hematopoiesis in PV 17894541_Higher concentrations of interleukin-8, G-CSF, and GM-CSF in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid are associated with the development of fibrosis in sulfur mustard victims. 17914409_gene expression profiling study of contribution of GM-CSF and IL-8 to the CD44-induced differentiation of acute monoblastic leukemia 17934321_GM-CSF is a prerequisite for the maintenance of structural integrity of the vessel wall. 17938902_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18027871_GM-CSF induced sprout formation in spheroids was found to be potently inhibited by siRNA specific for MT1-MMP 18089573_GM-CSF regulates MCP-1 expression via Janus kinase-2-Stat5 pathway and by a novel regulatory mechanism of statins to reduce inflammatory reactions by down-regulating the expression of monocytic MCP-1 18219369_Differential constitutive and cytokine-modulated expression of Toll-like receptors in primary neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages is reported. 18254319_IgE and GM-CSF may contribute to the recruitment of eosinophils in nasal polyps. 18353856_No association was found for CSF2(colony stimulating factor 2) single nucleotide polymorphisms and lung function, nor was there evidence of epistasis 18353856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18434187_GM-CSF operates downstream of CD40/CD40L interaction and that GM-CSF modulates Abeta production by influencing APP trafficking 18439101_These findings suggest that JNK1 and JNK2 are involved in TNF-alpha-induced neutrophil apoptosis and GM-CSF-mediated antiapoptotic effect on neutrophils, respectively. 18441098_activation of the TRPM8 variant in human lung epithelial cells leads to increased expression of IL-1alpha, -1beta, -4, -6, -8, and -13, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and TNF-alpha. 18523302_Within a three-dimensional collagen matrix, growth factor GM-CSF-induced eosinophil migration is only partially dependent on Rho kinase/Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) and is independent of RhoA GTP-binding protein activation. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18701168_GM-CSF modulates the CpG-independent, MyD88-dependent neutrophil response to bacterial DNA, by increasing the activation of the MAPKs p38 and ERK1/2. 18755511_GM-CSF can both synergize with TNFalpha in the case of expression of IL1-RA and antagonize in the case of CD83. 18804273_These results demonstrated that somatic cells derived from a cloned fetus can be used to produce recloned and transgenic pigs with the hGM-CSF gene. 18830265_STAT5 is recruited to phosphorylated tyrosine residues on the activated GM-CSF receptor, indicating that STAT5 signaling profile reflects juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia hypersensitivity to GM-CSF. 18926300_This review summarizes the role of different cytokine cocktails in the in vitro generation of human DCs from blood monocyte precursors, focusing on GM-CSF as a direct player in the generation of functionally distinct DCs. 18928604_The levels of EPO, SCF and GM-CSF in chronic aplastic anemia patients were obviously lower than those in the healthy individuals. 18971287_CCL11 induces SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression in murine macrophages, human monocytes, and dendritic cells and inhibits GM-CSF-mediated STAT5 activation and IL-4-induced STAT6 activation in a range of hematopoietic cells. 18974369_GM-CSF derived from cultured skeletal muscle cells after mechanical strain promote neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro. 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19050289_Recombinant GM-CSF stimulation of either eosinophilic leukemia (EoL-1) cells or blood eosinophils in vitro results in reorganization of actin and translocation of alpha-fodrin to the plasma membrane. 19131452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19131662_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19158269_These data argue that the regulation of the IL-3 and the GM-CSF promoters depends on the positions of their enhancers relative to the conserved CTCF/cohesin-binding sites. 19164476_Expression of CFS2 by decidua cells contributes to host defense in patients with chorioamnionitis. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19222422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19230854_GM-CSF regulates ileal homeostasis in Crohn's disease (CD) and in mouse models. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19263529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19282464_A novel potential mechanism of innate immune regulation, help define the therapeutic window for potential clinical use of GM-CSF autoantibodies to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, such as pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. 19324950_PKC(alpha) and PKC(epsilon) differentially regulate Legionella pneumophila-induced GM-CSF 19379606_stimulation of HNEC with SEB resulted in increased IL-5 and GM-CSF expression, which could be suppressed by dexamethasone (p |
ENSMUSG00000018916 |
Csf2 |
14.394876 |
15.8819530402 |
3.989316 |
0.661947517 |
48.664560 |
0.00000000000303705271714579187360608646539828094470039876462408301449613645672798156738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000017531051273004258785783891228355301211000449868038231215905398130416870117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.9018089 |
11.7788822 |
1.6995055 |
0.6950666 |
| ENSG00000164418 |
2898 |
GRIK2 |
protein_coding |
Q13002 |
FUNCTION: Ionotropic glutamate receptor. L-glutamate acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter at many synapses in the central nervous system. Binding of the excitatory neurotransmitter L-glutamate induces a conformation change, leading to the opening of the cation channel, and thereby converts the chemical signal to an electrical impulse. The receptor then desensitizes rapidly and enters a transient inactive state, characterized by the presence of bound agonist (PubMed:28180184). Modulates cell surface expression of NETO2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P39087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28180184}.; FUNCTION: Independent of its ionotropic glutamate receptor activity, acts as a thermoreceptor conferring sensitivity to cold temperatures (PubMed:31474366). Functions in dorsal root ganglion neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P39087, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31474366}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Ion channel;Ion transport;Isopeptide bond;Ligand-gated ion channel;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;RNA editing;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
Glutamate receptors are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain and are activated in a variety of normal neurophysiologic processes. This gene product belongs to the kainate family of glutamate receptors, which are composed of four subunits and function as ligand-activated ion channels. The subunit encoded by this gene is subject to RNA editing at multiple sites within the first and second transmembrane domains, which is thought to alter the structure and function of the receptor complex. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have also been described for this gene. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive cognitive disability. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2898; |
dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse [GO:0098686]; kainate selective glutamate receptor complex [GO:0032983]; mossy fiber rosette [GO:0097471]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005234]; glutamate receptor activity [GO:0008066]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kainate selective glutamate receptor activity [GO:0015277]; ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0015276]; ligand-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential [GO:0099507]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; transmitter-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:1904315]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; behavioral fear response [GO:0001662]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; detection of cold stimulus involved in thermoception [GO:0120169]; glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007215]; inhibitory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060080]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0098815]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051967]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; neuronal action potential [GO:0019228]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050806]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046328]; regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048169]; regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048172]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249] |
11920157_Linkage and association of the glutamate receptor 6 gene with autism 12467946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12821179_Specific alleles in GluR6 and CA150 locus were only observed in HD patients. 14567698_describes the time course of the open-channel form of the receptor as a function of glutamate concentration 15094479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15094479_Using three single nucleotide polymorphisms in GRIK2 and one in GRIK3, we found no evidence for association with Obssessive-Compulsive disorder in case-control or family-based analyses. 15305151_In this study, the maternal transmission disequilibrium of the glutamate receptor GRIK2 in schizophrenia. 16847693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16959037_The modifier effect is actually due to the TAA repeat itself, possibly via a functional consequence on the GRIK2 mRNA. 17167233_Our data on altered functional properties of GluR6(M836I) provide a functional basis for the postulated linkage of GluR6 to autism. 17379418_phosphorylation of the C-terminal tail of GluR6 by PKA leads to potentiation of whole cell response 17428563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17428563_These results suggest a potential association between GRIK2 and autism in the Korean population. 17712621_Mutations of GluR6 are unlikely to be associated with autism in the Indian population. 17712621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17847003_report a complex mutation in the ionotropic glutamate receptor 6 gene (GRIK2, also called 'GLUR6') that cosegregates with moderate-to-severe nonsyndromic autosomal recessive mental retardation in a large, consanguineous Iranian family 18289788_Overall, our data indicate that hGluR6c might have unique properties in non-nervous cells and in the first stages of CNS development. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18593792_results support the involvement of genes GRIA3 and GRIK2 in antidepressant treatment-emergent suicidal ideation 18658129_the apo state of GluR6 undergoes a cleft closure of 29-30 degrees upon binding full agonists, one of the largest observed in the glutamate receptor family. 18664604_Mutations to GLUR6 binding pocket that selectively affect domoate binding are freported. 18690046_nonconserved residues in GluR6 define the size of the agonist-binding pocket, exerting a steric influence on the bound agonist and the extent of binding-domain closure 18692513_GluR6 C-terminal domain KRIP6 regulates kainate receptors by inhibiting PICK1 modulation via competition or a mutual blocking effect 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19225180_in silico ligand-docking predicted that most partial agonists select for the closed and not, as expected, the open or intermediate conformations of the GluK2 agonist binding domain. 19260141_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19268276_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19295509_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19617541_Results indicate that ions can contribute substantial free energy to active state stabilization in GluR6, and provide quantitative measurements of the energetic consequences of allosteric ion binding to a ligand-gated ion channel. 19920140_phosphorylation of PKC sites on GluR6 regulates surface expression of GluR6 at distinct intracellular trafficking pathways 20230879_Spliced variants of ionotropic glutamate receptor GluR6 is associated with astrocytoma. 20370803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20370803_This study supports previously reported findings of association between proximal GRIK2 single nucleotide polymorphism and obsessive-compulsive disorder in a comprehensive evaluation of the gene 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20442744_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20859245_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20863077_human GluK2 is a slowly activating channel but more sensitive to glutamate, as compared to the rat ortholog; the M867I mutation does not affect the rate the equilibrium constants of the channel opening but does slow down the channel desensitization rate 21557188_Genotyping and linkage analysis excluded linkage of the GRIK2 gene and TUSC3 gene with mental retardation. 21912186_Convergent functional genomics allowed the identification of novel candidate genes, GRIK2 and NPAS2, involved in glutamatergic neurotransmission and the circadian rhythm, respectively, that are potentially associated with CFS. 22429480_The ACAG haplotype in the 13th haplotype block of the GRIK2 gene was associated with somatic anxiety. 22771793_Comprehensive analytical methods applied to a much larger sample than in previous studies do not support a role for GRIK2 as a genetic modifier of age at onset of clinical symptoms in Huntington's disease. 23037145_Eight chromosome 6 SNPs, having the most significant differences, were delineated: rs10499298, rs10499299, rs17827966, rs1224329, rs1150790, rs713050, rs2518344 and rs487083; all were associated with genes GRIK2. 23400781_Kainate receptor GluK2a post-translational modifications differentially regulate association with 4.1N to control activity-dependent receptor endocytosis 23660601_we found no association between rs1556995 in GRIK2 and clozapine-induced obsessive-compulsive (OC) symptoms, implying that that GRIK2 may not play a role in the development of OC symptoms in schizophrenia patients 23713029_Crosslinking the ligand-binding domain dimer interface locks kainate receptors out of the main open state. 23861400_14-3-3 proteins are an important regulator of GluK2a-containing KARs and may contribute to the slow decay kinetics of native KAR-EPSCs. 24662927_This study found in GRIK2 (glutamate receptor, ionotropic kainate 2) was most significant and also showed significant correlations with gene expression. 24821223_This study showed that Gluk2 association with obsessive-compulsive disorder. 25201974_The present study reveals an additional mechanism for the regulation of GluK2-containing kainate receptors by Src family kinases, which may be of pathological significance in ischemic stroke. 25316086_Parkin interacts with the kainate receptor GluK2 subunit and regulates KAR function. 25842862_High risk genetic markers of paranoid schizophrenia were GRIK2*ATG and GRIK2*TGG in Tatars. 26277340_Study demonstrates that co-assembly of recombinant kainate receptors (GluK1 and GluK2) with the Neto1 and Neto2 auxiliary subunits alters their onset and recovery from desensitization in a subunit-dependent manner 27324535_In the Han population in Central China, the polymorphisms of SNP rs9390754 in the GRIK2 gene may be associated with epilepsy susceptibility. 27607061_TTBK2 down-regulates GluK2 activity by decreasing the receptor protein abundance in the cell membrane via RAB5-dependent endocytosis. 28418868_these findings indicate that GRIK2 has a role in the maintenance of urothelial cancer stem cells and that GRIK2 and ALDH1 can be prognosis prediction markers for urinary tract carcinomas 28837400_results suggest that PKC SUMOylation is an important regulator of the 14-3-3 and GluK2a protein complex and may contribute to regulate the decay kinetics of kainate receptor-excitatory postsynaptic currents 29527240_Study identifies differentially variable CpG sites in GRIK2 gene displaying increased expression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 30587499_These results indicate involvement of GRIK2 in senescence and suggests GRIK2 as a potential target for therapeutic intervention of cancer cells. 30908586_Both the GRIK2 rs4840200-T and rs3213607-A, and the interactions between rs4840200 and rs9390754 are related to the increased risk of epilepsy risk. 31631587_This study suggests that the rs2227283 polymorphism of the GRIK2 gene is related to aggressive behaviors in bipolar manic patients and that the A/A genotype and A allele may increase the risk of the aggressive behavior in bipolar manic patients. 34375587_Clustered mutations in the GRIK2 kainate receptor subunit gene underlie diverse neurodevelopmental disorders. 34552241_Kainate receptor modulation by NETO2. 34730179_The Deletion of GluK2 Alters Cholinergic Control of Neuronal Excitability. |
ENSMUSG00000056073 |
Grik2 |
71.673584 |
2.0240166202 |
1.017221 |
0.367330069 |
7.503901 |
0.00615654930390557072333868049440752656664699316024780273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012338176201717069441210483660142926964908838272094726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.1768848 |
22.4577426 |
49.6526367 |
8.2765199 |
| ENSG00000164442 |
10370 |
CITED2 |
protein_coding |
Q99967 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional coactivator of the p300/CBP-mediated transcription complex. Acts as a bridge, linking TFAP2 transcription factors and the p300/CBP transcriptional coactivator complex in order to stimulate TFAP2-mediated transcriptional activation. Positively regulates TGF-beta signaling through its association with the SMAD/p300/CBP-mediated transcriptional coactivator complex. Stimulates the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors PPARA transcriptional activity. Enhances estrogen-dependent transactivation mediated by estrogen receptors. Acts also as a transcriptional corepressor; interferes with the binding of the transcription factors HIF1A or STAT2 and the p300/CBP transcriptional coactivator complex. Participates in sex determination and early gonad development by stimulating transcription activation of SRY. Plays a role in controlling left-right patterning during embryogenesis; potentiates transcriptional activation of NODAL-mediated gene transcription in the left lateral plate mesoderm (LPM). Plays an essential role in differentiation of the adrenal cortex from the adrenogonadal primordium (AGP); stimulates WT1-mediated transcription activation thereby up-regulating the nuclear hormone receptor NR5A1 promoter activity. Associates with chromatin to the PITX2 P1 promoter region. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11581164, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12586840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15051727}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Atrial septal defect;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene inhibits transactivation of HIF1A-induced genes by competing with binding of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha to p300-CH1. Mutations in this gene are a cause of cardiac septal defects. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:10370; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone acetyltransferase binding [GO:0035035]; LBD domain binding [GO:0050693]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; adrenal cortex formation [GO:0035802]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; cardiac neural crest cell development involved in heart development [GO:0061308]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular senescence [GO:0090398]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; cranial nerve morphogenesis [GO:0021602]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048596]; embryonic heart tube left/right pattern formation [GO:0060971]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; embryonic process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060136]; endocardial cushion development [GO:0003197]; erythrocyte development [GO:0048821]; granulocyte differentiation [GO:0030851]; heart development [GO:0007507]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; left/right axis specification [GO:0070986]; left/right pattern formation [GO:0060972]; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0002089]; liver development [GO:0001889]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060044]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia [GO:0061428]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; nodal signaling pathway involved in determination of lateral mesoderm left/right asymmetry [GO:1900164]; outflow tract morphogenesis [GO:0003151]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022409]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of male gonad development [GO:2000020]; positive regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035360]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; pulmonary artery morphogenesis [GO:0061156]; regulation of animal organ formation [GO:0003156]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to fluid shear stress [GO:0034405]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; sex determination [GO:0007530]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; spleen development [GO:0048536]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; trophectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0001829]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
12960175_Both TGFbeta and flow shear stimulated expression of CITED2 and also association of CIT-ED2 with p300 by dissociating Ets-1 from p300. Thus, CITED2 plays a major role in shear-induced down-regulation of MMP-1 and MMP-13 via a TGFbeta-dependent pathway. 15051727_CIT-ED2 is a coactivator of PPARalpha and both proteins may participate in signaling cascades of hypoxic response and angiogenesis 16287139_CITED2 mutations have a causative impact in the development of CHD in humans. 16287139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16675452_TGF-beta-mediated down-regulation of Cited2 is post-transcriptional, through the Smad pathway, and requires the presence of its coding sequence 17932483_Cited2, a coactivator of HNF4alpha, is essential for liver development 18054336_CITED2 regulates colon cancer invasion and might be a target for histone deacetylase inhibitor-based intervention of colon cancer. 18984668_CITED2 and PBX1 are likely to be important mediators of adrenal development and function in humans, but mutations in these genes are not common causes of adrenal failure. 19319572_The effects of endothelial-cell-conditioned medium (ECCM), as produced during the incubation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells for 24 h, on the promoter activity and mRNA and protein expression of CITED2 in adrenocortical cells, was examined. 19642106_Reducing CITED2 expression in a mammary tumor cell line inhibits the establishment of bone metastasis and osteolysis in vivo. 19904269_Both NCOR2 and CITED2 mRNA levels were associated with MFS, that is, tumour aggressiveness, independently of traditional prognostic factors 20392269_CITED2 may act as a mechanosensitive molecular switch regulating cartilage matrix breakdown. 20654020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20932315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21098220_CITED2 is a novel regulator of NF-kappaB in the nucleus, which reveals a negative feedback mechanism for NF-kappaB signaling. 21165656_CITED2 activation may induce mucosal apoptosis and erosion by activating p53 and thus play a critical role in linking enteric bacteria with mucosal inflammation in ulcerative colitis. 21660965_A combination of cisplatin and CITED2 shRNA may represent an effective treatment against p53-sensitive cancer cells. 22709740_We conclude that mutations in CITED2 may be involved in premature ovarian failure pathogenesis. 22735262_CITED2 variants decreased its ability to mediate the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and the expression of the paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2-gamma (PITX2C), both of which are closely related to cardiac development. 22814619_CITED2 functions as a molecular switch of TGF-alpha and TGF-beta-induced growth control, and MYC-CITED2 signaling axis provides a new index for predicting clinical outcome. 23082118_CITED2 is phosphorylated by MAPK1 in vitro at T166, and that MAPK1 activation enhances the coactivation function of CITED2 but not of CITED2-T166N. 23212831_CITED2 is a direct effector of PPARgamma for tumor suppression. 23811274_data indicate that CITED2 functions as a transcriptional co-activator of ER in breast cancer cells and that its increased expression in tumors may result in estrogen-independent ER activation 24456003_Our study suggests that CITED2 gene mutations and methylation may play an important role in the development of pediatric congenital heart disease. 24848765_CITED2 has a potential causative impact on congenital heart disease 25184385_The increased CITED2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia results in better hematopoietic stem cell survival, lower PU.1 levels, and perturbed myeloid differentiation program that contributes to leukemia persistence. 25956243_FBXL5-mediated degradation of CITED2 leads to the activation of HIF-1 alpha. 26812245_High Cited2 level in cumulus cells was associated with low embryo quality and pregnancy outcome in in vitro fertilization patients. 26851278_Intrinsic protein disorder plays a prominent role in the function and interactions of the transcriptional co-activators CBP and p300. (Review) 27627783_CITED2 plays important roles in the progression and chemoresistance of breast carcinoma and that CITED2 status is a potent prognostic factor in breast cancer patients. 27680315_down-regulation of Cited2 was associated with high glucose-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes in vitro 28008154_CITED2 regulates primary breast tumor growth, likely by influencing tumor vasculature via TGF-beta-dependent regulation of VEGFA. 28084522_the downregulation of CITED2 contributes to TGFbeta-mediated senescence. 28273070_Through allosteric enhancement of HIF-1alpha release, CITED2 activates a highly responsive negative feedback circuit that rapidly and efficiently attenuates the hypoxic response, even at modest CITED2 concentrations. 28436679_The results suggest that CITED2 mutations in conserved regions lead to disease-causing biological and functional changes and may contribute to the occurrence of conotruncal heart defects in Chinese children. 28501104_CITED2 supports gastric cancer cell colony formation and proliferation while inhibiting apoptosis making it a potential gene therapy target for gastric cancer. 28687891_CITED2 gene mutation may play a significant role in the development of pediatric congenital heart disease. 29072699_Knockdown of CITED2 led to a decreased interaction of p53 with its inhibitor MDM2, which results in increased amounts of total p53 protein. Data indicate that CITED2 functions in pathways regulating p53 activity. 29203644_Observations identify CITED2 as a novel negative regulator of macrophage proinflammatory activation that protects the host from inflammatory insults. 30177819_GINS2 plays an important role in cell proliferation and apoptosis of thyroid cancer by regulating the expressions of CITED2 and LOXL2, which may be a potential biomarker for diagnosis or prognosis and a drug target for therapy. 30291252_CITED2 acts as a molecular chaperone to guide PRMT5 and p300 to nucleolin, thereby activating nucleolin. Informatics and experimental data suggest that the CITED2-nucleolin axis is involved in prostate cancer metastasis. 30628655_The results showed that the core promoter area of MUC5AC was located within the 935/+48 region and that P300 reduced the expression of MUC5AC in A549 cells. 30891766_tested the hypothesis that CITED2 mediates cross-talk between IL-4 signaling and mechanical loading-induced pathways that result in chondroprotection, at least in part, by downregulating MMP13 30986495_These findings illustrate that combined PU.1/CITED2 deregulation induces a transcriptional program that promotes HSPC maintenance, which might be a prerequisite for malignant transformation. 31515672_Bioinformatics assay results showed that these novel cited2 mutations alter the RNA folding, protein structure, and, therefore, probable effect on the protein function and may play a significant role in the development of congenital heart diseases 33439552_Genetic analysis of the CITED2 gene promoter in isolated and sporadic congenital ventricular septal defects. 33691475_Downregulation of SUV39H1 and CITED2 Exerts Additive Effect on Promoting Adipogenic Commitment of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. 33706167_A gain-of-function mutation in CITED2 is associated with congenital heart disease. 35789404_CITED2 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and pyroptosis in - human lung fibroblast by inhibition of NF-kappaB pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000039910 |
Cited2 |
2643.862708 |
0.4802896185 |
-1.058023 |
0.040600499 |
678.647552 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001315336555980802294905621568520428267630990280973825349863959887306119723105739824125687077989993367879567627549781944069653533451438033808352427112645473023596038746608085872857538 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000866712837780207190958754879519296169012835848370039173548185414619464609696136800697138390282415564438629413596689198948548132309064869007515941196579691502394042364162038193245242 |
Yes |
No |
1708.5578598 |
43.3924573 |
3583.9209485 |
61.7422199 |
| ENSG00000164463 |
153222 |
CREBRF |
protein_coding |
Q8IUR6 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a negative regulator of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response or unfolded protein response (UPR). Represses the transcriptional activity of CREB3 during the UPR. Recruits CREB3 into nuclear foci. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18391022}. |
Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transport;Unfolded protein response |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response; positive regulation of transport; and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in cytoplasm and nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:153222; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:1900102]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of intracellular transport [GO:0032388]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of protein transport [GO:0051222]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
27278737_Findings provide new insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying hypoxia-induced glioblastoma cell autophagy and indicate that the hypoxia/CREBRF/CREB3/ATG5 pathway plays a central role in malignant glioma progression. 27455349_Missense Mutation in CREBRF gene is associated with obesity. 28405013_The rs373863828-A allele was not found in both AN-speaking and non-AN-speaking Melanesians living in Papua New Guinea. Our results suggest that rs373863828-A of CREBRF, a promising thrifty variant, arose in recent ancestors of AN-speaking Polynesians. 28928463_Studied CREBRF genetic variants in association to height and weight in young children; found that the rs373863828 variant was significantly associated with growth at 4 years of age; also found the variants to be prevalent in other Pacific populations, including Maori. 29721634_The presence of each additional CREBRF rs373863828 A allele is associated with increased BMI yet reduced odds of type 2 diabetes in adults of Maori and Pacific (Polynesian) ancestry living in Aotearoa/New Zealand. 29729692_CREBRF promotes the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells via the AKT signaling pathway. 29877158_The rs373863828-A allele (a missense variant of the CREBRF gene) may not directly affect the level of serum HDL-cholesterol independent of BMI. 29958463_We found that CREBRF and TRIM2 mRNA were significantly upregulated by rHDL, particularly in response to its phospholipid component 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-phosphatidylcholine, however, protein expression was not significantly altered. 31280340_CREBRF G allele (rs12513649) and A allele (rs373863828)are associated with higher BMI and lower risk of diabetes in Pacific Islander (Guam and Saipan) populations. 31543511_The Maori and Pacific specific CREBRF variant and adult height. 32190945_A missense variant in CREBRF is associated with taller stature in Samoans. 32491157_Population-specific reference panels are crucial for genetic analyses: an example of the CREBRF locus in Native Hawaiians. 32654027_The Pacific-specific CREBRF rs373863828 allele protects against gestational diabetes mellitus in Maori and Pacific women with obesity. 32884101_A missense variant in CREBRF, rs373863828, is associated with fat-free mass, not fat mass in Samoan infants. 35144939_CREBRF missense variant rs373863828 has both direct and indirect effects on type 2 diabetes and fasting glucose in Polynesian peoples living in Samoa and Aotearoa New Zealand. 35218947_The minor allele of the CREBRF rs373863828 p.R457Q coding variant is associated with reduced levels of myostatin in males: Implications for body composition. 35606300_The missense variant, rs373863828, in CREBRF plays a role in longitudinal changes in body mass index in Samoans. 36284436_The protective effect of rs373863828 on type 2 diabetes does not operate through a body composition pathway in adult Samoans. |
ENSMUSG00000048249 |
Crebrf |
216.801290 |
0.4819169514 |
-1.053144 |
0.132486285 |
63.260022 |
0.00000000000000181143666989601424318376967337665633994678890221485811906632079626433551311492919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000012768292859438954363730525003527490069871511667309871285169720067642629146575927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
135.7584591 |
14.8271385 |
283.6970048 |
21.5824189 |
| ENSG00000164466 |
94081 |
SFXN1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H9B4 |
FUNCTION: Amino acid transporter importing serine, an essential substrate of the mitochondrial branch of the one-carbon pathway, into mitochondria. Mitochondrial serine is then converted to glycine and formate, which exits to the cytosol where it is used to generate the charged folates that serve as one-carbon donors (PubMed:30442778). May also transport other amino acids including alanine and cysteine (PubMed:30442778). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30442778}. |
Acetylation;Amino-acid transport;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;One-carbon metabolism;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables D-serine transmembrane transporter activity and L-serine transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in D-serine transport; L-serine transport; and serine import into mitochondrion. Located in mitochondrion. Is integral component of mitochondrial inner membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:94081; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015194]; serine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022889]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; L-alanine transport [GO:0015808]; L-serine transport [GO:0015825]; mitochondrial transmembrane transport [GO:1990542]; one-carbon metabolic process [GO:0006730]; serine import into mitochondrion [GO:0140300] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30442778_SFXN1 functions as a mitochondrial serine transporter in one-carbon metabolism. 32950919_CircSFXN1 regulates the behaviour of trophoblasts and likely mediates preeclampsia. 33730581_The mitochondrial carrier SFXN1 is critical for complex III integrity and cellular metabolism. 35878532_Overexpression of SFXN1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression in lung adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000021474 |
Sfxn1 |
210.007201 |
3.8356878911 |
1.939485 |
0.164527884 |
135.467521 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000026090075443073275394307859835827433223870383762948253015973942037621566983908021628360551780190235149348154664039611816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000003503999213282634709044366484314568976625607175830622599013551701275396252048956007019153702231051283888518810272216796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
328.6636110 |
38.3358582 |
85.9310238 |
7.6130293 |
| ENSG00000164484 |
114801 |
TMEM200A |
protein_coding |
Q86VY9 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114801; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000049420 |
Tmem200a |
96.576763 |
5.9890205249 |
2.582320 |
0.190510861 |
202.311606 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000065373524765169994511573926265355528136123735245532370587126037302844539469248361919581397304484784983781024935624455983462777197701143450103700160980224609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012613244778221032807541346734818439672037414227227155130811173196516368844987048789200090024747922007612761858739124087858129996675415895879268646240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
166.4444412 |
20.2491574 |
27.9828073 |
2.9546415 |
| ENSG00000164604 |
54329 |
GPR85 |
protein_coding |
P60893 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Members of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, such as GPR85, have a similar structure characterized by 7 transmembrane domains. Activation of GPCRs by extracellular stimuli, such as neurotransmitters, hormones, or light, induces an intracellular signaling cascade mediated by heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins, or G proteins (Matsumoto et al., 2000 [PubMed 10833454]).[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2008]. |
hsa:54329; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15893849_The areas expressing high levels of SREB2 mRNA overlap with brain structures known to possess high levels of plasticity, namely, the hippocampal formation, olfactory system, and supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. 18413613_Theses data implicate SREB2 as a potential risk factor for psychiatric disorders. 22968816_Risk-associated variants in GPR85 are associated with phenotypes similar to those found in patients with schizophrenia. |
ENSMUSG00000048216 |
Gpr85 |
69.654376 |
2.4379475829 |
1.285667 |
0.221830816 |
33.543351 |
0.00000000696931967509059197273671163916884674360829876604839228093624114990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000030826238658776490548143870730479765285281246178783476352691650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.7105507 |
10.9734043 |
37.4169559 |
3.5673389 |
| ENSG00000164626 |
8645 |
KCNK5 |
protein_coding |
O95279 |
FUNCTION: pH-dependent, outwardly rectifying potassium channel (PubMed:9812978). Outward rectification is lost at high external K(+) concentrations (PubMed:9812978). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9812978}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. The message for this gene is mainly expressed in the cortical distal tubules and collecting ducts of the kidney. The protein is highly sensitive to external pH and this, in combination with its expression pattern, suggests it may play an important role in renal potassium transport. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8645; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; outward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0015271]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; potassium ion leak channel activity [GO:0022841]; potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0097623]; potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1990573]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; regulation of resting membrane potential [GO:0060075]; stabilization of membrane potential [GO:0030322] |
12634929_TASK-2 does not possess a histidine residue at homologous position. Inclusion of such a residue failed to produce expected increase in pH sensitivity; instead, a slight decrease was observed 15197476_TASK-2 is not highly expressed in cerebellum 18157847_KCNK5 is involved K(+)-channel in regulatory volume decrease in human spermatozoa, and channel activity is regulated beyond the extent of protein expression. 20582984_We here identify and characterize K2P5.1 as a critical player of T-cell effector function; selective targeting of K(2P)5.1 may hold therapeutic promise for multiple sclerosis and putatively other T-cell-mediated disorders. 20631251_Data suggest that the cytokine receptor-coupled JAK/STAT pathway is upstream of the swelling-induced phosphorylation and activation of TASK-2 in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. 21314928_Disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients correlates strongly with K(2P)5.1 expression levels in CD4+ T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood 21680658_17beta-estradiol induces the expression of KCNK5 via ERalpha(+) in breast cancer cells, and this channel plays a role in regulating proliferation in these cell lines. 21964404_Potassium channels, in particular K2P channels, are expressed and functional in the apical membrane of airway epithelial cells 24285684_The TASK-2 channel lower expression represents a hallmark of aldosterone-producing adenoma causing aldosteronism and is associated with a higher expression of hsa-miR-23 and hsa-miR-34. 24949484_Mutant genes (CELA1, HSPG2, and KCNK5) in Balkan endemic nephropathy patients encode proteins involved in basement membrane/extracellular matrix and vascular tone, tightly connected to process of angiogenesis. 26140335_Potassium channel TASK2 drives human NK-cell proliferation and cytolytic function. 26909737_Results show that up-regulated KCNK5 in activated human T cells does not play a volume regulatory role, due to decreased Cl- permeability suggesting that the KCNK5 upregulation might play a role in hyperpolarization of the cell membrane leading to increased Ca2+ influx and proliferation of T cells. 27228168_These results therefore provide further structural and functional insights into the possible pathophysiological effects of this missense variant in TASK-2. 28045995_HLA-DQB1*06:02 does not seem to be associated with hypoxic ventilatory response or hypercapnic ventilatory response; however there are point wise, uncorrected significant associations between two TASK2/KCNK5 variants (rs2815118 and rs150380866) and hypercapnic ventilatory response 28604387_In human aldosterone-producing adrenocortical cancer cell lines, roxithromycin inhibited KCNJ5MUT-induced induction of CYP11B2 (encoding aldosterone synthase) expression and aldosterone production. 28865245_As a novel finding, our study suggests a role for KCNK5 in the regulation of platelet size and maturity. Furthermore, our findings confirm an association between the SH2B3-locus and platelet count. 29293917_mutations in the promoter region of the TWIK-related acid-sensitive K(+) channel 2 (TASK-2) gene did not result in hypertension or primary aldosteronism (PA) during long-term follow-up in healthy participants thus they do not seem to be a factor in causing PA by themselves. 33762637_Common variants in KCNK5 and FHL5 genes contributed to the susceptibility of migraine without aura in Han Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000023243 |
Kcnk5 |
22.381638 |
5.6335847814 |
2.494053 |
0.374986999 |
49.573263 |
0.00000000000191100420893669761457667967848644618522949145678069271525600925087928771972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000011162019043888268595556675561816269278900271011423228628700599074363708496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.8394239 |
9.3322691 |
6.7609838 |
1.4519198 |
| ENSG00000164647 |
26872 |
STEAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHE8 |
FUNCTION: Metalloreductase that has the ability to reduce both Fe(3+) to Fe(2+) and Cu(2+) to Cu(1+). Uses NAD(+) as acceptor. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CWR7}. |
3D-structure;Copper;Electron transport;Endosome;FAD;Flavoprotein;Heme;Ion transport;Iron;Iron transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene is predominantly expressed in prostate tissue, and is found to be upregulated in multiple cancer cell lines. The gene product is predicted to be a six-transmembrane protein, and was shown to be a cell surface antigen significantly expressed at cell-cell junctions. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:26872; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072] |
15958640_Peptide STEAP-292.2L (MLAVFLPIV) may have potential as an antitumor peptide vaccine. 18793824_STEAP mRNA is used here as a marker to evaluate biological samples from individuals suspected of having cancers, and may provide prognostic information useful in defining appropriate therapeutic options. 18958632_STEAP1 is over-expressed in breast cancer and down-regulated by 17beta-estradiol. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19196137_STEAPs may represent novel markers of mesenchymal stem cells in man as well as mice. 19915386_Data suggest that zoledronic acid may affect cancer cells also by targeting the gene expression of STEAP. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21928126_Studies suggest that activated human gammadelta T cells can efficiently present PRAME and STEAP1-derived epitopes and allow breaking tolerance against these tumor-associated self-antigens. 22080479_EWS-FLI1 mediated overexpression of STEAP1 increases the invasiveness and oxidative stress levels of Ewing tumor cells. 22080479_STEAP1 is associated with the invasive behavior and oxidative stress phenotype of Ewing tumors, an unanticipated oncogenic function of STEAP1. 22317770_A total of 62.3% of the Ewing's Sarcoma samples displayed detectable STEAP1 expression with predominant localization of the protein at the plasma membrane. 22317770_STEAP1 overexpression predicts improved outcome of Ewing's sarcoma patients, possibly due to enhanced sensitivity towards ROS-generating chemotherapeutics. 23060075_STEAP1 is down-regulated by dihydrotestosterone and estradiols in LNCaP cells and in rat prostate. 24025158_The findings provide evidence that STEAP1 is a biomarker of worse prognosis in prostate carcinomas patients. 24239460_Data indicate that six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1 (STEAP1) is consistently overexpressed in malignant prostate tissue, namely adenocarcinoma and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) lesions. 25453051_These findings highlight the ability of immuno-PET with (89)Zr-2109A to detect acute changes in STEAP1 expression 27792302_Data suggest a solid basis for further research into understanding how six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate member 1 (STEAP1) activities may affect cancer progression. 29464393_High STEAP1 expression is associated with prostate cancer. 30027616_The expression of STEAP-1 is significantly associated with high-grade Gleason scores and seminal vesicle invasion of PCa. 30253922_Low STEAP1 expression was associated with Breast Cancer Metastasis. 30401882_we identified high STEAP1 transcript levels leading to reduced ROS production that prevented apoptosis via the NRF2 pathway in CRC cells as a pathological mechanism in CRC. 32382787_Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1 expression promotes ovarian cancer metastasis by aiding progression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 32409586_Cryo-electron microscopy structure and potential enzymatic function of human six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1 (STEAP1). 32515474_STEAP1 facilitates metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. 32802887_The Tumor Suppressive Roles and Prognostic Values of STEAP Family Members in Breast Cancer. 33128353_A research of STEAP1 regulated gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and in vivos. 33589770_Clinical significance of STEAP1 extracellular vesicles in prostate cancer. 34073779_Identification of a New Transcriptional Co-Regulator of STEAP1 in Ewing's Sarcoma. 34649092_Predictive potential of STEAP family for survival, immune microenvironment and therapy response in glioma. 35313641_The Prognostic Value and Immunological Role of STEAP1 in Pan-Cancer: A Result of Data-Based Analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000015652 |
Steap1 |
27.301680 |
2.3979423329 |
1.261797 |
0.295719827 |
18.620300 |
0.00001595129338422071623880202362322222597867948934435844421386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000048796080901781921845480893829005708539625629782676696777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.3312224 |
6.7620016 |
16.0746275 |
2.3036743 |
| ENSG00000164674 |
94120 |
SYTL3 |
protein_coding |
Q4VX76 |
FUNCTION: May act as Rab effector protein and play a role in vesicle trafficking. Binds phospholipids in the presence of calcium ions (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of peripheral membrane proteins that play a role in vesicular trafficking. This protein binds phospholipids in the presence of calcium ions. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:94120; |
exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; extrinsic component of plasma membrane [GO:0019897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; neurexin family protein binding [GO:0042043]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886] |
11773082_Synaptotagmin-like protein 3-a (Slp3-a) contains an N-terminal Slp homology domain (SHD) (PMID: 11327731). The SHD of Slp3-a specifically and directly binds the GTP-bound form of Rab27A. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 33657377_Transcriptional networks identify synaptotagmin-like 3 as a regulator of cortical neuronal migration during early neurodevelopment. |
ENSMUSG00000041831 |
Sytl3 |
117.188612 |
5.4011875995 |
2.433277 |
0.183178996 |
183.678625 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000762554802277618131768042985944285007218045630528831908487781946438826454209100489901707630111548101991701589102978786627318186219781637191772460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000133832448057284704620004942159988570718053596997141882322993932640965365350853655820035256841881549875333812238409336714539676904678344726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
204.1618378 |
20.9290961 |
38.0567344 |
3.3715625 |
| ENSG00000164684 |
619279 |
ZNF704 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZNC4 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor which binds to RE2 sequence elements in the MYOD1 enhancer. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ERQ3}. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:619279; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
31376183_tumor marker zinc finger protein 704 as part of a four gene transcript score has prognostic value for metastatic-lethal progression in men treated for localized prostate cancer 32651256_Circadian Rhythm Is Disrupted by ZNF704 in Breast Carcinogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000040209 |
Zfp704 |
238.558635 |
0.2469951541 |
-2.017445 |
0.232247307 |
71.160479 |
0.00000000000000003293190428422453262757475818004874888335614392361264113340268977481173351407051086425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000255157431619503441716546148772129612354388114017419986190304825868224725127220153808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
91.8755245 |
13.7762326 |
374.8418067 |
38.7028427 |
| ENSG00000164707 |
26266 |
SLC13A4 |
protein_coding |
Q9UKG4 |
FUNCTION: Sodium:sulfate symporter that mediates sulfate reabsorption in the high endothelial venules (HEV). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10535998, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15607730}. |
Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable sodium:sulfate symporter activity. Predicted to be involved in anion transmembrane transport. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26266; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sodium:sulfate symporter activity [GO:0015382]; anion transmembrane transport [GO:0098656]; sulfate transport [GO:0008272] |
15607730_Here, we characterized the functional properties of the human Na(+)-sulfate cotransporter (hNaS2), determined its tissue distribution, and identified its gene (SLC13A4) structure. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23453247_SLC13A4 and SLC26A2 were the most abundant sulfate transporter mRNAs, which localized to syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast cells, respectively. 23485456_To investigate the regulation of SLC13A4 gene expression, we analysed the transcriptional activity of the SLC13A4 5'-flanking region in the JEG-3 placental cell line using luciferase reporter assays. 28385533_Study found that despite differential expression of the two SLC13A4 transcripts, no detectable functional difference in the cellular sorting or sulfate transporting was found. However, some variants can influence both mechanism in specific cell membranes. This is like to have clinical implications based on the consequences of impaired sulfate transport during pregnancy in rodent models. 34840533_SLC13A4 Might Serve as a Prognostic Biomarker and be Correlated with Immune Infiltration into Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000029843 |
Slc13a4 |
13.151076 |
0.4600418141 |
-1.120163 |
0.474542030 |
5.521697 |
0.01878203056440004917182484689419652568176388740539550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.033890314319137498921818973940389696508646011352539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6343773 |
2.6008115 |
19.0053498 |
3.8174138 |
| ENSG00000164764 |
157869 |
SBSPON |
protein_coding |
Q8IVN8 |
|
Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to be an extracellular matrix structural constituent. Colocalizes with collagen-containing extracellular matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:157869; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576] |
|
ENSMUSG00000032719 |
Sbspon |
16.724633 |
0.3327856248 |
-1.587335 |
0.396284821 |
16.788050 |
0.00004179568643379426165843093521345963381463661789894104003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000121533556296848555444874151465484146683593280613422393798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.1048650 |
2.0740719 |
24.4892337 |
3.7530067 |
| ENSG00000164823 |
734 |
OSGIN2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y236 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in meiosis or the maturation of germ cells. |
Alternative splicing;Meiosis;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable growth factor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of cell growth. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:734; |
growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308] |
|
ENSMUSG00000041153 |
Osgin2 |
364.333291 |
2.0346442751 |
1.024777 |
0.096879004 |
112.043007 |
0.00000000000000000000000003496428474738976735542318014450007482548348436345161577286918094575928275813403445226867916062474250793457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000388901916255819837444657039102357673728633828682775867760051733800896051063133995739917736500501632690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
486.4602934 |
27.0485152 |
240.7695108 |
10.3709995 |
| ENSG00000164877 |
79778 |
MICALL2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IY33 |
FUNCTION: Effector of small Rab GTPases which is involved in junctional complexes assembly through the regulation of cell adhesion molecules transport to the plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton reorganization. Regulates the endocytic recycling of occludins, claudins and E-cadherin to the plasma membrane and may thereby regulate the establishment of tight junctions and adherens junctions. In parallel, may regulate actin cytoskeleton reorganization directly through interaction with F-actin or indirectly through actinins and filamins. Most probably involved in the processes of epithelial cell differentiation, cell spreading and neurite outgrowth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endosome;LIM domain;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Zinc |
|
Enables filamin binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion. Predicted to be located in several cellular components, including bicellular tight junction; neuron projection; and recycling endosome. Predicted to colocalize with stress fiber. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79778; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actinin binding [GO:0042805]; filamin binding [GO:0031005]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion [GO:1903955]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446] |
17891173_Involved in epithelial cell scattering. 25864591_Data indicate that MICAL-L2 may be an important regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in ovarian cancer cells. 28416812_We identified one new significant locus at 7p22.3 for the Stroop word interference time (rs11514810, P=3.42E-09 for discovery, P=0.01176 for replication and combined P=5.249E-09). Regulatory feature analysis and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) data showed that this locus contributes to MICALL2 expression in the human brain. 31034158_Up-regulation of MICAL-L2 is associated with gastric cancer cell migration. 33976349_JRAB/MICAL-L2 undergoes liquid-liquid phase separation to form tubular recycling endosomes. 36307841_MICALL2 as a substrate of ubiquitinase TRIM21 regulates tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000036718 |
Micall2 |
103.304341 |
0.4874919085 |
-1.036550 |
0.218759595 |
22.100842 |
0.00000258696210443962040383234120277666789888826315291225910186767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008719698712383831405887957277656141741317696869373321533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
70.6857493 |
12.3386480 |
146.0357778 |
18.1468121 |
| ENSG00000164904 |
501 |
ALDH7A1 |
protein_coding |
P49419 |
FUNCTION: Multifunctional enzyme mediating important protective effects. Metabolizes betaine aldehyde to betaine, an important cellular osmolyte and methyl donor. Protects cells from oxidative stress by metabolizing a number of lipid peroxidation-derived aldehydes. Involved in lysine catabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16491085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20207735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21338592}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Mitochondrion;NAD;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Amine and polyamine biosynthesis; betaine biosynthesis via choline pathway; betaine from betaine aldehyde: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:20207735}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of subfamily 7 in the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene family. These enzymes are thought to play a major role in the detoxification of aldehydes generated by alcohol metabolism and lipid peroxidation. This particular member has homology to a previously described protein from the green garden pea, the 26g pea turgor protein. It is also involved in lysine catabolism that is known to occur in the mitochondrial matrix. Recent reports show that this protein is found both in the cytosol and the mitochondria, and the two forms likely arise from the use of alternative translation initiation sites. An additional variant encoding a different isoform has also been found for this gene. Mutations in this gene are associated with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy. Several related pseudogenes have also been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:501; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004029]; betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase activity [GO:0008802]; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) (non-phosphorylating) activity [GO:0043878]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004043]; cellular aldehyde metabolic process [GO:0006081]; choline catabolic process [GO:0042426]; glycine betaine biosynthetic process from choline [GO:0019285]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
16491085_Children with pyridoxine-dependent seizures (PDS) have mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene, which encodes antiquitin; these mutations abolish the activity of antiquitin as a delta1-piperideine-6-carboxylate (P6C)-alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase. 17433748_allelic and non-allelic heterogeneities of pyridoxine dependent seizures, and cerebrospinal fluid glutamate elevation does not directly correlate with the presence of ALDH7A1 mutations. 18717709_report of 2 unrelated patients affected with pyridoxine-dependent seizures as a result of alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency caused by pathogenic ALDH7A1 mutations; 2 of the 3 mutations are novel & result in erroneous splicing 18854520_The diagnosis of pyridoxine-dependent seizures was confirmed with biochemical and molecular testing revealing elevated alpha-AASA excretion and the presence of 2 different mutations in the antiquitin ( ALDH7A1) gene. 19128417_From this study suggested that defects of ALDH7A1 are almost always the cause of neonatal-onset pyridoxine-dependent seizure and that defects in this gene are also responsible for some but not all later-onset cases. 19142996_In this study both patients in epilepsy reported here had increased CSF alpha-AASA, CSF pipecolic acid, and known or likely pathogenic mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene, consistent with alpha-AASA dehydrogenase deficiency. 19294602_Molecular analysis of the antiquitin gene revealed a novel missense mutation c.57insA, while the mutation of the other allele remained unidentified so far. 19885858_antiquitin was present not only in the cytosol but also in the mitochondria. 20072603_A SNP, rs13182402, within the ALDH7A1 gene was strongly associated with osteoporosis. 20072603_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20207735_ALDH7A1 is a novel aldehyde dehydrogenase expressed in multiple subcellular compartments that protects against hyperosmotic stress by generating osmolytes and metabolizing toxic aldehydes 20512086_KCNQ and AP3S1, but not MAN2A1 or ALDH7A1 have a role in risk of type 2 diabetes in the Chinese Northern Han population 20512086_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639122_The antiquitin 1 oxidation could result in decreased pyridoxal 5-phosphate availability necessary as a cofactor in transaminations, synthesis of glutathione, and synthesis of GABA and dopamine, two neurotransmitters that play a key role in HD pathology. 20814824_Report the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy due to mutations in ALDH7A1. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21185811_the structural basis for the substrate specificity 21338592_ALDH7A1 mechanistically appears to provide cells protection through multiple pathways 21647815_The aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme 7A1 is functionally involved in prostate cancer bone metastasis. 22249334_Ongoing diagnostic screening and monitoring revealed that in some individuals with milder ALDH7A1 variants. 22305855_Atypical pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy is due to a pseudoexon in ALDH7A1. 22784480_The effects of a series of twelve disease-associated ALDH7A1 missense mutations on antiquitin activity, were characterized. 23054014_A novel missense mutation c.1364T>C (p.Leu455Pro)was detected in in two unrelated Tunisian families with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy. 23376216_molecular analysis of seven Pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy Tunisian patients revealed a common missense c.1364T>C mutation in the ALDH7A1 gene; the conservation of a single genotype within the c.1364T > C mutation suggested that this variation has a single origin 23647301_For patients with NSCLC, low ALDH7A1 expression was associated with a decreased incidence of cancer recurrence. 23683770_Pyridoxine dependent epilepsy (PDE) is caused by mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene (PDE-ALDH7A1) encoding alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (alpha-AASAD) enzyme in the lysine catabolic pathway 24122892_Antiquitin is expressed within glial cells in the brain and its dysfunction in pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy is associated with neuronal migration abnormalities. 24664145_Clinical diagnosis, treatment, and ALDH7A1 mutations in pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy in three Chinese infants 25213698_our study indicated that the ALDH7A1 rs13182402 polymorphism was associated with risk of ESCC in Chinese populations. 26224730_Using a custom array, study identified heterozygous intragenic deletions in the ALDH7A1 gene in 5 of 6 patients with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy and positive biomarkers who had only a single mutation identified by conventional sequence analysis 26232297_Direct sequencing of the ALDH7A1 gene revealed one novel (c.297delG, p.Trp99*) and two already reported (c.328C>T, p.Arg110*; c.584A>G, p.Asn195Ser) mutations 26260980_Binding to ALDH7A1 is associated with movement of the C-terminus into the active site which stabilizes the substrate anchor loop. 26555630_This study found five novel mutations of ALDH7A1 gene in pyridoxin dependent epilepsy. 27186704_We present the clinical and molecular genetic findings of two patients with c.1597_1597delG mutations in ALDH7A1 gene. 28087462_Wild-type ALDH7A1 is shown to exist in a dimer-tetramer equilibrium with a dissociation constant of 16 muM. In contrast to the wild-type enzyme, the variants reside in monomer-dimer equilibria and are apparently incapable of forming a tetrameric species, even at high enzyme concentration. 28131559_Mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene encoding alpha-amino-adipic semialdehyde (alpha-AASA) dehydrogenase (antiquitin) have been identified as the cause of PDE. We report on a novel ALDH7A1 mutation in a Tunisian child with PDE. 29045138_results suggest that the C-terminus of ALDH7A1 is crucial for the maintenance of both the oligomeric state and the catalytic activity. 29061647_By using mass spectrometry techniques, we further explored the metabolic effect of aldh7a1 knockout. Impaired lysine degradation with accumulation of PDE biomarkers, B6 deficiency, and low gamma-aminobutyric acid levels were observed in the aldh7a1(-/-) larvae, which may play a significant role in the seizure phenotype and PDE pathogenesis. 30005813_We describe the case of two siblings, children of consanguineous parents, who carried a novel homozygous missense mutation of the ALDH7A1gene 30043187_This report provides a comprehensive overview of known ALDH7A1 mutations that cause pyridoxine dependent epilepsy (PDE), and suggests that PDE may be more common than initially estimated. [review] 30184263_Results suggest the NAD+ cofactor of aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family member A1 protein (ALDH7A1) dramatically enhances tetramerization of the enzyme. 30486822_Low ALDH7A1 protein levels correlated with poor clinical outcome. 30767241_The study provides first evidence that the saccharopine pathway is the major route of lysine degradation in cultured human brain cells. These results support inhibition of the saccharopine pathway as a new treatment option for antiquitin deficiency. 31492851_Data show that NADH generated by aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family, member A1 protein (ALDH7A1) targets brefeldin-A ADP-ribosylated substrate (BARS; CTBP1) to inhibit Coat Protein I (COPI) vesicle fission. 31652343_Structural analysis of pathogenic mutations targeting Glu427 of ALDH7A1, the hot spot residue of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy. 31930735_Condensation of delta-1-piperideine-6-carboxylate with ortho-aminobenzaldehyde allows its simple, fast, and inexpensive quantification in the urine of patients with antiquitin deficiency. 32956737_Impact of missense mutations in the ALDH7A1 gene on enzyme structure and catalytic function. 34391775_EPS8 supports pancreatic cancer growth by inhibiting BMI1 mediated proteasomal degradation of ALDH7A1. 35613852_The impact of ALDH7A1 variants in oral cancer development and prognosis. |
ENSMUSG00000053644 |
Aldh7a1 |
41.248572 |
0.4372461350 |
-1.193482 |
0.298844749 |
15.821236 |
0.00006961678267519912533412701494128782542247790843248367309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000196283421640102990601145505067393060016911476850509643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.3170324 |
4.9961484 |
62.8745001 |
7.8352399 |
| ENSG00000164929 |
79870 |
BAALC |
protein_coding |
Q8WXS3 |
FUNCTION: May play a synaptic role at the postsynaptic lipid rafts possibly through interaction with CAMK2A. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q920K5}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Synapse;Synaptosome |
|
This gene was identified by gene expression studies in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The gene is conserved among mammals and is not found in lower organisms. Tissues that express this gene develop from the neuroectoderm. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different proteins have been described for this gene; however, some of the transcript variants are found only in AML cell lines. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:79870; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; sarcoplasm [GO:0016528] |
15604894_The BAALC gene, located on chromosome 8q22.3, encodes a protein with no homology to any known proteins or functional domains. 15749074_High transcript levels occur in leukemic blasts from some patients with acute myeloid leukemia. 17646667_Low expression of both ERG and BAALC identifies T-ALL patients with a distinctly favorable long-term outcome. 18378853_high BAALC expression is an independent adverse prognostic factor and is associated with a specific gene-expression profile 18671757_Up-regulation of BAALC gene may be an important alteration in AML-M2 patients with t(8;21) translocation. 18752846_Presence of both EVI1 and/or BAALC in chronic myeloid patients was found to modulate the disease pattern 19555438_Overexpression of BAALC and ERG either separate or concomitant predict adverse clinical outcome and may define important risk factor in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia 19943049_BAALC is a relevant prognostic marker in intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia patients, with high versus low BAALC expressors showing lower complete remission rate after salvage therapy. 20065290_High BAALC expression is associated with chemoresistance in adult B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 20306678_CEBPA mutation status and BAALC expression are important prognostic factors in acute myeloid leukemia patients with normal cytogenetics. 20495894_1-5-6-8 BAALC isoform expression may be associated with an adverse prognosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. 20535151_In contrast to BAALC, which likely represents only a surrogate marker of treatment failure in acute leukemia, IGFBP7 regulates the proliferation of leukemic cells and might be involved in chemotherapy resistance 20841507_High BAALC expression levels are associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 21835957_Low ERG and BAALC expression (E/B(low)) and NOTCH1/FBXW7 (N/F) mutations have been proposed as powerful prognostic markers in large cohorts of adult T-ALL. 21967978_Presence of FLT3-ITD and high BAALC expression are independent prognostic markers in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. 22197554_These findings indicate that BAALC gene is 'paused' and that in leukemia cells its transcription can be activated or repressed by mechanisms acting on epigenetic marks. 22488406_A high MEBE (MN1,ERG, BAALC, EVI1) expression score is an unfavorable prognostic marker in Myelodysplastic syndrome and is associated with an increased risk for progression to Acute myeloid leukemia. 22493267_identify a heritable genomic feature predisposing to overexpression of an oncogene (BAALC), thereby possibly leading to enhanced AML leukemogenesis 22529287_high expression of miR-3151 is an independent prognosticator for poor outcome in cytogenetically normal-AML and affects different outcome end points than its host gene, BAALC 23287429_data show that higher levels of VEGF-A(CSF) are closely related to CNS leukemia (CNSL), and VEGF-A(CSF) may be a better predictor than the other risk factors elucidating the pathogenesis and development of CNSL 23647058_Higher BAALC expression and FLT3-ITD mutation, both individually and in combination, were associated with worse survival outcomes in CN-AML, and this was also applicable in NPM1-mutated CN-AML, known as a favorable-risk group. 23672350_higher post-HSCT BAALC and WT1 expressions in patients with CBF-AML may be good markers of minimal residual disease for the prediction of survival and relapse after HSCT. 23760853_BAALC overexpression retains its negative prognostic role across all cytogenetic risk groups in acute myeloid leukemia patients. 23865362_Investigated the prognostic impact of brain and acute leukemia, cytoplasmic (BAALC) expression in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. 24736457_miR-3151 introns within BAALC have roles in driving leukemogenesis by deregulating the TP53 pathway 24855032_Thus low MDR1/low BAALC expression identifies a subgroup of intermediate cytogenetic risk AML patients with a remarkably good long-term outcome achieved by chemotherapy alone. 25428390_study indicates that overexpression of BAALC serves as an independent prognostic biomarker in acute myeloid leukemia 26012361_Evaluating WT1 and BAALC gene expression at diagnosis may improve standard risk stratification and possibly refine the therapeutic approach for Myelodysplastic Syndromes patients. 26050649_demonstrated that BAALC blocks ERK-mediated monocytic differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells by trapping Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) in the cytoplasm and inhibiting its function in the nucleus 26430723_combined determination of both miR-3151 and BAALC improved this prognostic stratification, with patients with low levels of both parameters showing a better outcome compared with those patients harboring increased levels of one or both markers 26625814_BAALC and ERG genes are specific significant molecular markers in acute myeloid leukemia disease progression, response to treatment and survival. 27372260_Study provide evidence for an association of rs62527607 [GT] SNP of BAALC gene with multidrug resistance in childhood ALL. 27662611_BAALC expression-based minimal residual disease detection during therapy may be considered a strategy to identify patients at high risk of relapse. 29696374_despite of their well-known adverse role in prognosis of AML, neither BAALC nor ERG expression levels at diagnosis had effect on survival of AML patients who underwent allo-HSCT. 32129446_Downregulation of miR-326 and overexpression of BALLC in drug-resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line and patients compared with the parental cell line and drug-sensitive patients was found. The expression profiles of miR-326 and BAALC were inversely correlated. Bioinformatics data showed a possible regulatory role for miR-326 on BAALC mRNA. 32811810_Long non-coding RNA LRRC75A-AS1 facilitates triple negative breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion via functioning as a ceRNA to modulate BAALC. 32862286_Allogeneic stem cell transplantation mitigates the adverse prognostic impact of high diagnostic BAALC and MN1 expression in AML. 33242229_Prognostic significance of combined BAALC and MN1 gene expression level in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. 33453340_Physical interaction between BAALC and DBN1 induces chemoresistance in leukemia. 33894142_iPSC modeling of stage-specific leukemogenesis reveals BAALC as a key oncogene in severe congenital neutropenia. 35429905_BAALC gene expression tells a serious patient outcome tale in NPM1-wild type/FLT3-ITD negative cytogenetically normal-acute myeloid leukemia in adults. |
ENSMUSG00000022296 |
Baalc |
62.062683 |
4.3568584700 |
2.123288 |
0.619213183 |
10.822919 |
0.00100251307510492685022562842078741596196778118610382080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002330985032852665294472727097740971657913178205490112304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.6862800 |
26.0777012 |
12.4287608 |
4.3606245 |
| ENSG00000164933 |
81034 |
SLC25A32 |
protein_coding |
Q9H2D1 |
FUNCTION: Transports folate across the inner membranes of mitochondria (PubMed:15140890, PubMed:29666258). Can also transport FAD across the mitochondrial inner membrane (PubMed:16165386). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15140890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16165386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29666258}. |
Disease variant;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the P(I/L)W subfamily of mitochondrial carrier family transport proteins. The encoded protein transports folate across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2013]. |
hsa:81034; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; FAD transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015230]; folic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008517]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; folate import into mitochondrion [GO:1904947]; folic acid metabolic process [GO:0046655]; folic acid transport [GO:0015884]; mitochondrial FAD transmembrane transport [GO:1990548]; mitochondrial transport [GO:0006839]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
19362304_Patient with SLC25A32 deficiency was able to have a successful pregnancy after fertilization in vitro. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21768094_identified residues in the walls and at the base of the transport cavity that are involved in substrate recognition by the MFT 23266187_Compares and contrasts all the known human SLC25A* genes and includes functional information. 24354357_SLC25A32 gene polymorphism could be a risk factor for lower folate concentration and future fracture. 28443623_A novel SLC25A32 homozygous variant is associated with severe neuromuscular phenotype. 29666258_These data demonstrate that the loss of functional Slc25a32 results in cranial neural tube defects (NTDs) in mice and has also been observed in a human NTD patient. 34764427_Hypoketotic hypoglycemia without neuromuscular complications in patients with SLC25A32 deficiency. |
ENSMUSG00000022299 |
Slc25a32 |
354.558247 |
2.2006496319 |
1.137929 |
0.103517222 |
120.805292 |
0.00000000000000000000000000042153890700162349350058995076395544561420553286947610354248033996808176187935657264205246974597685039043426513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000005074970854277293869563415403772463872677346623185215883459581884869243504840308212067157001001760363578796386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
496.8441085 |
28.7894288 |
227.3405803 |
10.2896324 |
| ENSG00000164934 |
25879 |
DCAF13 |
protein_coding |
Q9NV06 |
FUNCTION: Possible role in ribosomal RNA processing (By similarity). May function as a substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16949367}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ribonucleoprotein;Ribosome biogenesis;rRNA processing;Ubl conjugation pathway;WD repeat |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Enables estrogen receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA). Located in several cellular components, including centrosome; cytosol; and nuclear lumen. Part of Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25879; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0080008]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; small-subunit processome [GO:0032040]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000462]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
20601284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20601284_This study suggests that non-synonymous WDSOF1 polymorphisms play a role in the genetic susceptibility to osteoporosis. 28631558_our findings revealed that the overexpression of DCAF13 in hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly associated with poor survival and may participate in the regulation of cell cycle progression 30003937_Two novel variants in the DCAF13 and NOV genes were identified that are associated with familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy in a Chinese pedigree. 30283081_The DCAF13 deficiency resulted in pre-rRNA accumulation in oocytes, whereas the total mRNA level was not altered. Further exploration showed that DCAF13 participated in the 18S rRNA processing in growing oocytes. 33300431_DCAF13 promotes triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by mediating DTX3 mRNA degradation. 34775691_Doxorubicin promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via DCAF13. 35178836_DCAF13 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by ubiquitin inhibiting PERP expression. 35932979_DCAF13 is essential for the pathogenesis of preeclampsia through its involvement in endometrial decidualization. |
ENSMUSG00000022300 |
Dcaf13 |
344.209586 |
2.5040491905 |
1.324263 |
0.099324059 |
178.078547 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000012733961835250099210139645876579916017443413791865011818575610364358650376485764159945682708054207055419632110826455573260318487882614135742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000002160382490670016809012296928031749452923868445873141468181916454680962244015390142067601188409588827254309562064804595138411968946456909179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
489.9401481 |
42.5340346 |
197.1234575 |
12.8245898 |
| ENSG00000164935 |
81501 |
DCSTAMP |
protein_coding |
Q9H295 |
FUNCTION: Probable cell surface receptor that plays several roles in cellular fusion, cell differentiation, bone and immune homeostasis. Plays a role in TNFSF11-mediated osteoclastogenesis. Cooperates with OCSTAMP in modulating cell-cell fusion in both osteoclasts and foreign body giant cells (FBGCs). Participates in osteoclast bone resorption. Involved in inducing the expression of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in osteoclast precursors. Plays a role in haematopoietic stem cell differentiation of bone marrow cells toward the myeloid lineage. Inhibits the development of neutrophilic granulocytes. Plays also a role in the regulation of dendritic cell (DC) antigen presentation activity by controlling phagocytic activity. Involved in the maintenance of immune self-tolerance and avoidance of autoimmune reactions. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Differentiation;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Immunity;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a seven-pass transmembrane protein that is primarily expressed in dendritic cells. The encoded protein is involved in a range of immunological functions carried out by dendritic cells. This protein plays a role in osteoclastogenesis and myeloid differentiation. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:81501; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0036006]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; membrane fusion [GO:0061025]; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0043011]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; osteoclast fusion [GO:0072675]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of macrophage fusion [GO:0034241]; positive regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045657] |
15601667_The dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein is a multimembrane-spanning protein preferentially expressed by human DC (hDC). 18952287_An interaction between OS9 and DC-STAMP was confirmed by yeast-2-hybrid analysis and cellular colocalization.ER-to-Golgi translocation of DC-STAMP following TLR stimulation in CHO cells was demonstrated, involving the DC-STAMP/OS9 interaction. The data indicate that OS9 is critically involved in ER-to-Golgi transport of DC-STAMP, and may be important in both myeloid differentiation and cell fusion. 19259350_2 differentially expressed genes over-expressed in papillary thyroid cancers were identified as DC-STAMP and type I collagen A1 20546900_DC-STAMP interacts with ER-resident transcription factor LUMAN which becomes activated during DC maturation. 20797317_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20839008_genetic risk for Paget's disease of bone is associated with variants close to CSF1, OPTN, TM7SF4, and TNFRSF11A genes 21987375_DC-STAMP is a potential osteoclast precursors biomarker in inflammatory arthritis. 21987375_DC-STAMP is an ITIM-bearing molecule. Based on the 4 distinct patterns of DCSTAMP on human PBMC, it has potential to serve as a susceptible biomarker of psoriasis (Ps) as well as severity marker of Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA). 22058328_Results show that T cells played a pivotal role in a new in vitro Langhans giant cells (LGCs) formation system, in which DC-STAMP was involved, and occurred via a molecular mechanism that involved CD40-CD40L interaction and IFN-gamma secretion. 23525827_DC-STAMP inhibition by RNA interference consequently suppressed fusion and bone resorption of human osteoclasts. 24370779_Rs62620995 in the TM7SF4 gene was found to have a marginal association with Paget's disease of bone in the French-Canadian population. 25151085_The EP in TKA differed from EP in aseptically failed THA by lower CCL3 and DC-STAMP mRNA and protein expression. EP of all studied inflammatory and osteoclastogenic molecules were similar in knee and hip OA. 25891874_Our findings also suggest that next generation sequencing may help explore the pathogenesis and aid the diagnosis of Juvenile Paget's disease. 26636523_TM7SF4 plays an essential role in regulating cell cycle progression in breast cancer. 28849122_TM7SF4 may be involved in the progression of lung cancer. 29145829_Our results suggest that the rare genetic variant of TM7SF4 gene, found in our French-Canadian cohort of patients with Paget's disease of bone and which encodes the DC-STAMP protein, increase the number of nuclei per multinucleated cells and affect DC-STAMP expression during osteoclastogenesis in Paget's disease of bone. 30705363_Genetic regulatory mechanisms in human osteoclasts suggest a role for the STMP1 and DCSTAMP genes in Paget's disease of bone. |
ENSMUSG00000022303 |
Dcstamp |
26.151700 |
7.4143201992 |
2.890314 |
0.479140628 |
35.781955 |
0.00000000220682501292909888922013482849115301176468051380652468651533126831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000010249445308632315585245377666853000553359720470325555652379989624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.6997890 |
13.0238516 |
5.8499780 |
1.4477804 |
| ENSG00000164938 |
94241 |
TP53INP1 |
protein_coding |
Q96A56 |
FUNCTION: Antiproliferative and proapoptotic protein involved in cell stress response which acts as a dual regulator of transcription and autophagy. Acts as a positive regulator of autophagy. In response to cellular stress or activation of autophagy, relocates to autophagosomes where it interacts with autophagosome-associated proteins GABARAP, GABARAPL1/L2, MAP1LC3A/B/C and regulates autophagy. Acts as an antioxidant and plays a major role in p53/TP53-driven oxidative stress response. Possesses both a p53/TP53-independent intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulatory function and a p53/TP53-dependent transcription regulatory function. Positively regulates p53/TP53 and p73/TP73 and stimulates their capacity to induce apoptosis and regulate cell cycle. In response to double-strand DNA breaks, promotes p53/TP53 phosphorylation on 'Ser-46' and subsequent apoptosis. Acts as a tumor suppressor by inducing cell death by an autophagy and caspase-dependent mechanism. Can reduce cell migration by regulating the expression of SPARC. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11511362, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22421968, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22470510}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Antioxidant;Apoptosis;Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor |
|
Predicted to enable antioxidant activity. Involved in autophagic cell death; positive regulation of autophagy; and positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in autophagosome; cytosol; and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:94241; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; antioxidant activity [GO:0016209]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; autophagic cell death [GO:0048102]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; cellular response to ethanol [GO:0071361]; cellular response to hydroperoxide [GO:0071447]; cellular response to methyl methanesulfonate [GO:0072703]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of myofibroblast differentiation [GO:1904761]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; response to heat [GO:0009408] |
12067065_Data show that induction of the stress-induced proteins (SIPs) SIP18 and SIP27, in human- and mouse-derived cell lines, is absent from cells with deleted, mutated or inactive p53, suggesting that regulation of SIP gene expression is dependent on p53. 12438758_Assignment of tumor protein p53 induced nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1) gene to human chromosome band 8q22 by in situ hybridization. 12851404_TP53INP1s and HIPK2 could be partners in regulating p53 activity. 16044147_TP53INP1s are functionally associated with p73 to regulate cell cycle progression and apoptosis. 16521180_TP53INP1 protein negativity is significantly associated with aggressive pathological phenotypes of gastric cancer. 17393983_TP531NP1 plays a significant role in the progression of anaplastic carcinoma or contributes to anaplastic transformation from papillary or follicular carcinoma, which is in sharp contrast to findings in previous in vitro and in vivo studies. 17537403_PLZF upregulates apoptosis-inducer TP53INP1, ID1, and ID3 genes, and downregulates the apoptosis-inhibitor TERT gene 18277906_The p53DINP1 mRna expression in the antral mucosa was significantly lower in the gastric cancer patients than in the chronic gastritis patients. 18277909_P53DINP1 mRNA expression promotes Ser46 phophlrylation of p53, without finding a significant correlation between mRNA expression of p53AIP1. 18974142_findings implicate a miR-93/miR-130b-TP53INP1 axis that affects the proliferation and survival of HTLV-1-infected/transformed cells 20889853_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21219856_TP53INP1 is a tumor suppressor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC0; c-Myc-mediated DNA methylation-associated silencing of TP53INP1 contributed to the pathogenesis of human ESCC. 21339733_This novel TP53INP1 activity on the regulation of SPARC expression could explain in part its tumor suppressor function in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by modulating cellular spreading during the metastatic process 21538421_In normal prostate tissues, TP53INP1 is only expressed in prostate basal cells. There is a de novo TP53INP1 expression in prostate luminal cells in inflammatory prostate tissues, high grade PIN lesions and in prostate cancer. 22213058_TP53INP1 antisense oligonucleotide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in castration-sensitive LNCaP tumor cells. 22421968_cell death observed after TP53INP1-LC3 interaction depends on both autophagy and caspase activity. 22470510_TP53INP1 identified two conserved regions in the DOR family that concentrate multiple functions crucial for autophagy and transcription. 22730212_miR-17-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in cervical cancer cells by targeting tumor protein p53-induced nuclear protein 1. 23333058_Fndings indicate that miR-17-5p/20a promote gastric cancer cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis via post-transcriptional modulation of p21 and TP53INP1. 23568502_Upregulation of miR-155, mediated by estradiol, and consequent downregulation of TP53INP1 potentially promotes breast cancer development and progression. 24152184_Expression of miR-155 is significantly higher in MCF-7 cells compared with MDA-MB-231 cells. Ectopic expression of TP53INP1 inhibits growth of MCF-7 cells by inducing cell apoptosis and inhibiting cell cycle progression. 24447717_miR-182/TP53INP1 signaling represents a novel pathway regulating chemoresistance in cisplatin-treated hepatocellular carcinoma 24551280_Study reveals that miR-155 acts as an oncogene by targeting TP53INP1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 24608790_TP53INP1 SUMOylation is essential for the regulation of p53 activity induced by oxidative stress. 24922517_GWAS identifies TP53INP1 as new susceptibility gene for Alzheimer's disease. 25490449_Results demonstrate that miR-569 is overexpressed in a subset of ovarian and breast cancers and alters cell survival and proliferation through downregulation of TP53INP1 expression. 25601564_miR-155 may play an important role in promoting the generation of stem cell-like cells and their self-renewal by targeting the gene TP53INP1. 25633840_TGFB1 induced miR-155 regulates TP53INP1 expression, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and acquisition of a stem cell phenotype. 26252115_MicroRNA205 promotes the tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through targeting TP53INP1 protein. 26367773_FOXP1, TP53INP1, TNFAIP3, and TUSC2 were identified as miR-19a targets. 26512655_silencing of TP53inp1 leads radiation induced autophagy impairment and induces accumulation of damaged mitochondria in primary human fibroblasts. 26813458_miR-205/TP53INP1 mediated autophagy pathway might be an important molecular mechanism regulating radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells 27341836_Results showed that TP53INP1 and E-cadherin mRNA and protein were significantly down-regulated in glioma tumors and positively correlated with higher grade and poor survival. Also, the study provides evidence that TP53INP1 3'-UTR could inhibit the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, thus hindering the migration and invasion of glioma via acting as a competitive endogenous RNA for E-cadherin. 28437838_Negative TP53INP1 protein levels correlated with a poor outcome in pediatric ependymoma. Direct binding of miR-124-3p to its target TP53INP1 is demonstrated. 28674078_Low TP53INP1 expression is associated with Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 29048685_these results revealed that TP53INP1 is a target gene of miR-504 and that miR-504 enhances osteosarcoma growth and promotes distant metastases by targeting TP53INP1. Thus, miR-504/TP53INP1 may be associated with osteosarcoma size and clinical stage. 29146309_Study elucidated StarD13 messenger RNA as a Competitive endogenous messenger RNA (ceRNA) in regulating migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. MicroRNA-125b was identified to induce metastasis of MCF-7 cells and bind with both StarD13 3'UTR and TP53INP1 3'UTR. Therefore, a ceRNA interaction between StarD13 and TP53INP1 mediated by competitively binding to miR-125b was indicated. 29329575_Upregulated miR-200a enhances treatment resistance via antagonizing TP53INP1 and YAP1 in breast cancer. 29655255_TP53INP1 inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and vasculogenic mimicry formation via the ROS/GSK-3beta/Snail pathway in breast cancer.TP53INP1 expression in the breast cancer tissues is negatively correlated with poor prognosis. 30365045_GATA3 and TP53INP1 were identified as targets of miR155. Exosomal miR155 inhibited these targets by directly targeting their 3' untranslated regions. Knockdown of miR1555p was observed to reverse the EMT and chemoresistant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells, potentially via GATA3 and TP53INP1 upregulation. 30855679_We show that low expression of TP53INP1 is an independent factor of poor prognosis in breast cancer patients, especially ERalpha-positive patients 31646552_MicroRNA-15a-5p down-regulation inhibits cervical cancer by targeting TP53INP1 in vitro. 31669646_TNF-alpha/miR-155 axis promoted the cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in a TP53INP1 independent manner. 32268073_miR-142-5p and miR-212-5p cooperatively inhibit the proliferation and collagen formation of cardiac fibroblasts by regulating c-Myc/TP53INP1. 32432745_Long non-coding RNA MIR155HG knockdown suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in NSCLC by upregulating TP53INP1 directly targeted by miR-155-3p and miR-155-5p. 32527448_Exosomal miR-155-5p promotes proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting TP53INP1 expression. 32741666_circCDYL Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer by Sponging miR-190a-3p and Upregulating TP53INP1. 32841649_Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cataractogenesis by upregulating TP53INP1 expression in age-related cataract. 33966044_TP53INP1 exerts neuroprotection under ageing and Parkinson's disease-related stress condition. 34152408_FOXO1 mediates hypoxia-induced G0/G1 arrest in ovarian somatic granulosa cells by activating the TP53INP1-p53-CDKN1A pathway. 34718338_MicroRNA-106a regulates autophagy-related cell death and EMT by targeting TP53INP1 in lung cancer with bone metastasis. 35164998_MiR-155 inhibits TP53INP1 expression leading to enhanced glycolysis of psoriatic mesenchymal stem cells. 35802258_LncRNA n339260 functions in hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of miRNA30e-5p/TP53INP1 expression. 35876212_miR-8485 alleviates the injury of cardiomyocytes through TP53INP1. |
ENSMUSG00000028211 |
Trp53inp1 |
199.494949 |
0.4735393633 |
-1.078444 |
0.125537822 |
74.431321 |
0.00000000000000000627849352118290617953756078709775831763437457165534169578613443718495545908808708190917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000050639652662655565495177604476384134830243688164515616922933816113072680309414863586425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
131.0247141 |
10.2055434 |
278.6849840 |
14.3227912 |
| ENSG00000164953 |
91147 |
TMEM67 |
protein_coding |
Q5HYA8 |
FUNCTION: Required for ciliary structure and function. Part of the tectonic-like complex which is required for tissue-specific ciliogenesis and may regulate ciliary membrane composition (By similarity). Involved in centrosome migration to the apical cell surface during early ciliogenesis. Involved in the regulation of cilia length and appropriate number through the control of centrosome duplication. Is a key regulator of stereociliary bundle orientation (By similarity). Required for epithelial cell branching morphology. Essential for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) of surfactant protein C (SFTPC). Involved in the negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling, and activation of the non-canonical cascade mediated by WNT5A and ROR2 (PubMed:26035863). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BR76, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17185389, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19515853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19596800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19815549, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26035863}. |
3D-structure;Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Joubert syndrome;Meckel syndrome;Membrane;Nephronophthisis;Obesity;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene localizes to the primary cilium and to the plasma membrane. The gene functions in centriole migration to the apical membrane and formation of the primary cilium. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Defects in this gene are a cause of Meckel syndrome type 3 (MKS3) and Joubert syndrome type 6 (JBTS6). [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
|
centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; MKS complex [GO:0036038]; filamin binding [GO:0031005]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; negative regulation of centrosome duplication [GO:0010826]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
12384791_mapping to chromosome 8 and possible role in Meckel-Gruber syndrome 16415887_Positional cloning of the Wpk gene suggested a MKS3 candidate gene, TMEM67, for which we identified pathogenic mutations for five MKS3-linked consanguineous families. 17160906_identified MKS3 mutations in four patients with JS, thus defining MKS3 as the sixth JS locus (JBTS6) 17185389_The Meckel-Gruber Syndrome proteins MKS1 and meckelin interact and are required for primary cilium formation. 17377820_Study concluded that MKS1 and MKS3 account for the majority of Meckel-Gruber syndrome; polydactyly is usually found in MKS1 but rare in MKS3; cases with no, or milder, CNS phenotypes were only found in MKS3. 17397051_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17397051_genotyping of MKS1 & MKS3 genes in a large, multiethnic cohort of 120 independent cases of Meckel syndrome; first results indicate that the MKS1 & MKS3 genes are each responsible for about 7% of MKS cases with various mutations in different populations 18327255_Mutations in MKS3 is associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome 19058225_Analysis of MKS3 in 14 COACH families identified mutations in 8 (57%). 19508969_Missense mutations within the MKS3 gene are associated with nephronophthisis with liver fibrosis. 19515853_Kidney tissue and cells from MKS1 and MKS3 patients showed defects in centrosome and cilia number, including multi-ciliated respiratory-like epithelia, and longer cilia. 19574260_Mutations in MKS3 are responsible for the majority of COACH syndrome, with minor contributions from CC2D2A and RPGRIP1L. 19815549_Data show that knockdown of MKS3 inhibited degradation of mutant SP-C. 20232449_mutation analysis of TMEM67 in Joubert syndrome and related disorders cases and Meckel syndrome fetuses; identification of 20 novel mutations; review of published mutations and discussion of genotype-phenotype correlates 21068128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23393159_The Meckel syndrome protein meckelin (TMEM67) is a key regulator of cilia function but is not required for tissue planar polarity. 27434533_Importantly, one Japanese and one Omani families carried compound biallelic mutations in two distinct genes (TMEM67/RPGRIP1L and TMEM138/BBS1, respectively). 28161324_Low expression of TMEM67 is associated with lymph node metastasis in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. 28719906_The authors results suggest that Asn242Ser in TMEM67 is a founder mutation in the Iranian population, which might explain a significant proportion of JS cases from eastern Iran. 28860541_Study identified two novel heterozygous mutations (p.Gly132Ala and p.Tyr920ThrfsX40) in the TMEM67 gene in a patient with COACH syndrome. Co-injection into zebrafish embryos of tmem67 morpholinos and RNAs encoding the two mutations show no rescue of the hydrocephalus phenotype. These findings indicate that the two mutations may cause COACH syndrome via altered Wnt signaling, at least in part. 29146704_Kidney disease occurs in up to one third of patients with Joubert syndrome, most commonly in those with mutations in CEP290, TMEM67, and AHI1. 29891882_Compound heterozygous mutations in TMEM67 cause RHYNS syndrome ranging from early lethality to adults with liver fibrosis. 32000717_This study confirms the diagnosis of Joubert syndrome in a Vietnamese family and expands the mutational spectrum of TMEM67 sequence variations. 32156598_TACC3 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation and restrains primary cilium formation. 35621037_Association of novel TMEM67 variants with mild phenotypes of high gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase cholestasis and congenital hepatic fibrosis. 36334440_TMEM67 is required for the gating function of the transition zone that controls entry of membrane-associated proteins ARL13B and INPP5E into primary cilia. |
ENSMUSG00000049488 |
Tmem67 |
22.258252 |
2.9021577446 |
1.537126 |
0.501845069 |
9.015807 |
0.00267654621451643079388382773231569444760680198669433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005786703109163984087848220383420994039624929428100585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.5580978 |
10.3479029 |
11.9183159 |
2.6673854 |
| ENSG00000164970 |
203259 |
FAM219A |
protein_coding |
Q8IW50 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has homologs that have been identified in mouse, macaque, etc organisms. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:203259; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000028439 |
Fam219a |
137.147073 |
0.4213440106 |
-1.246929 |
0.144069187 |
76.203372 |
0.00000000000000000255904360363985659815276303127441453809577776810088925452113528535846853628754615783691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000020984157549846821331513536938830570811777140376131953192206935909780440852046012878417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
81.8483033 |
7.5398433 |
195.6685448 |
11.5897454 |
| ENSG00000165023 |
54769 |
DIRAS2 |
protein_coding |
Q96HU8 |
FUNCTION: Displays low GTPase activity and exists predominantly in the GTP-bound form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12194967}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
DIRAS2 belongs to a distinct branch of the functionally diverse Ras (see HRAS; MIM 190020) superfamily of monomeric GTPases.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. |
hsa:54769; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21750579_Four single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and two haplotype blocks in DIRAS2 show evidence of association with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. 27364329_The results from the present study imply that rs1412005 in the DIRAS2 gene is in itself a causal variant, and that it is not only functional on the molecular, but also the inhibition-related brain activation level, the latter specifically in patients suffering from ADHD. 29488099_Our findings support the idea of DIRAS2 as a candidate gene for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder 32161311_Di-Ras2 promotes renal cell carcinoma formation by activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the absence of von Hippel-Lindau protein. 34990989_ADHD patients with DIRAS2 risk allele need more thalamic activation during emotional face-voice recognition. 35173535_Diverse Ras-related GTPase DIRAS2, downregulated by PSMD2 in a proteasome-mediated way, inhibits colorectal cancer proliferation by blocking NF-kappaB signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000047842 |
Diras2 |
144.762363 |
0.2463594417 |
-2.021163 |
0.188221180 |
116.673687 |
0.00000000000000000000000000338406538658515229197714012477894745684342319249400770900907016320368161411968888074852657155133783817291259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000039360760524820208368943887609388128680750733386009967212723281904427448038563674970191641477867960929870605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.1902804 |
6.8999149 |
226.1303517 |
17.7267777 |
| ENSG00000165028 |
55335 |
NIPSNAP3B |
protein_coding |
Q9BS92 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
NIPSNAP3B belongs to a family of proteins with putative roles in vesicular trafficking (Buechler et al., 2004 [PubMed 15177564]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:55335; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
23.853296 |
0.1066687830 |
-3.228790 |
0.440455283 |
57.460222 |
0.00000000000003448841551369236410154373603328898916105769989481899528982467018067836761474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000225442432675863270619228137193962039556797971595614171747001819312572479248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2232640 |
1.7789594 |
48.8353134 |
9.9270753 |
| ENSG00000165029 |
19 |
ABCA1 |
protein_coding |
O95477 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the translocation of specific phospholipids from the cytoplasmic to the extracellular/lumenal leaflet of membrane coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP (PubMed:24097981). Thereby, participates in phospholipid transfer to apolipoproteins to form nascent high density lipoproteins/HDLs (PubMed:14754908). Transports preferentially phosphatidylcholine over phosphatidylserine (PubMed:24097981). May play a similar role in the efflux of intracellular cholesterol to apolipoproteins and the formation of nascent high density lipoproteins/HDLs (PubMed:10533863, PubMed:14754908, PubMed:24097981). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10533863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14754908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24097981}. |
3D-structure;Atherosclerosis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intracellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the ABC1 subfamily. Members of the ABC1 subfamily comprise the only major ABC subfamily found exclusively in multicellular eukaryotes. With cholesterol as its substrate, this protein functions as a cholesteral efflux pump in the cellular lipid removal pathway. Mutations in both alleles of this gene cause Tangier disease and familial high-density lipoprotein (HDL) deficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2019]. |
hsa:19; |
endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; intracellular vesicle [GO:0097708]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; apolipoprotein A-I binding [GO:0034186]; apolipoprotein A-I receptor activity [GO:0034188]; apolipoprotein binding [GO:0034185]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cholesterol transfer activity [GO:0120020]; floppase activity [GO:0140328]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; phosphatidylcholine binding [GO:0031210]; phosphatidylcholine floppase activity [GO:0090554]; phosphatidylserine floppase activity [GO:0090556]; phospholipid transporter activity [GO:0005548]; protein transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008320]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; sphingolipid floppase activity [GO:0046623]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0071404]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cholesterol efflux [GO:0033344]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; export across plasma membrane [GO:0140115]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034380]; intracellular cholesterol transport [GO:0032367]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; peptide secretion [GO:0002790]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; phospholipid efflux [GO:0033700]; phospholipid homeostasis [GO:0055091]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; platelet dense granule organization [GO:0060155]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0090108]; protein lipidation [GO:0006497]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; protein transmembrane transport [GO:0071806]; regulation of Cdc42 protein signal transduction [GO:0032489]; regulation of high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0090107]; response to laminar fluid shear stress [GO:0034616]; reverse cholesterol transport [GO:0043691]; signal release [GO:0023061] |
11238261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11257261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11349008_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11700048_function as a regulator rather than an active transporter 11752403_in the presence of apoE, overexpression of ABCA1 modulates HDL as well as apoB-containing lipoprotein metabolism and reduces atherosclerosis in vivo 11809185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11855831_contributes to the secretion of interleukin 1beta from macrophages 11861672_a novel site in the human ABCA1 promoter involved in the regulation of ABCA1 gene expression. 11893753_Role as a phosphatidylserine translocase 11929608_Apo AI/ABCA1-dependent and HDL3-mediated lipid efflux 11940086_ABCA1 regulatory variants influence coronary artery disease independent of effects on plasma lipid levels 11940086_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11950847_Helical apolipoproteins stabilize ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 by protecting it from thiol protease-mediated degradation. 12084722_ABCA1 mutations can disrupt its direct interaction with apolipoprotein A-I. 12093886_Increased ABCA1 activity protects against atherosclerosis. ABCA1(human transgenic)(+)ApoE(-/-) mice developed dramatically smaller, less-complex lesions as compared with their ApoE(-/-) counterparts. 12111371_R1680W mutation associated with Tangier disease, phenotypes variable. 12151852_REVIEW: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and cholesterol trafficking 12176027_Dominant expression of ABCA1 on basolateral surface of Caco-2 cells stimulated by LXR/RXR ligands 12196520_A novel serine (Ser-2054) on the ABCA1 protein crucial for PKA phosphorylation and for regulation of ABCA1 transporter activity. 12204794_Recent data confirms that a single defective allele in ABCA1 may be assosiated with reduced HDL cholesterol and FHA. 12235128_The association of FADD with ABCA1 provides an unexpected link between high density lipoprotein metabolism and an adaptor molecule mainly described in death receptor signal transduction. 12359250_findings suggest an important role for hepatocyte basolateral membrane ABCA1 in the regulation of the levels of intracellular hepatic cholesterol, as well as plasma HDL 12426219_ABCA1 plays an important role in artery wall cell-mediated modification/oxidation of LDL by modulating the release of reactive oxygen species from artery wall cells that are necessary for LDL oxidation. 12511593_ABCA1 is regulated by PEST sequence-mediated calpain proteolysis that appears to be reversed by apolipoprotein-mediated phospholipid efflux 12535741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12551894_Golgi is involved in ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux. 12562845_examine the necessary structural features for a protein to promote lipid efflux by the ABCA1 transporter and find the amphipathic helix is a key structural motif for peptide-mediated lipid efflux from ABCA1, but there is no stereoselective requirement 12576507_Results describe two new point mutations of the ABCA1 gene found in one patient with Tangier disease and the sibling of another Tangier disease patient. 12600718_Genetic variability of ABCA1 influences development of Alzheimer's disease,possibly by interfering with CNS cholesterol homeostasis. 12600975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12615681_Review. Transgenic mice with human ABCA1 genes are used to study its function in cholesterol transport, apo B lipoproteins, and atherosclerosis. 12624133_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12624133_The K allele was significantly more frequent in FH subjects without premature CHD than in FH subjects with premature CHD suggesting that the genetic variant R219K in ABCA1 could influence the development and progression of atherosclerosis in FH subjects. 12700893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12706378_ABCA1 expression varies among tissues, and cholesterol conversion to hydroxycholesterol is an important mechanism for the maintenance of cholesterol homeostasis in fibroblasts 12709788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12709788_While genotype-phenotype associations were not reproduced across populations and loci, V825I and M883I were clearly associated with coronary artery disease status in Malays with no effects on HDL-C or apoA1. 12730295_hepatic overexpression of ABCA1 showed a selective increase in HDL cholesterol 12763760_In this study we review how genetic variation at the ABCA1 locus affects its role in the maintenance of lipid homeostasis and the natural progression of atherosclerosis. 12804586_regulation of ABCA1 mRNA levels exploits the use of alternative transcription start sites 12813037_ABCA1 has a role in the low levels of HDL-cholesterol and overaccumulation of cellular lipids in Niemann-Pick Disease type C 12860256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12869555_Phosphorylation of a pest sequence in ABCA1 promotes calpain degradation and is reversed by ApoA-I. 12870173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12870173_results indicate that the K219 allele frequency of adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter 1 differs markedly between blacks and whites 12928428_ABCA1-mediated vesicle release involves lipid raft plasma membrane domains 12952980_ABCA1 is phosphorylated and stabilized in a pathway in which apoA-I activates PKC alpha by PC-PLC-mediated generation of diacylglycerol 14560020_These studies indicate a direct role of retinoic acid receptor gamma/retinoid x receptor in induction of macrophage ABCA1. 14570867_ABCA7 compensates the function of ABCA1 for release of cell cholesterol in a certain condition(s). 14576201_ABCA1 gene sequence in a proband with very low HDL cholesterol and premature coronary heart disease family history revealed 2 mutations: G5947A (R1851Q) and single thymidine deletion in a polypyrimidine tract 33 to 46 bps upstream from start of exon 47 14644402_Of special interest was our finding that the effects of compromised ABCA1 function on HDL were more pronounced in women than in men. 14660648_association of apolipoprotein A-I with lipids reduces its ability to interact with ATP-binding cassette transporter A1(ABCA1) and the lipid translocase activity of ABCA1 generates alpha-LpA-I-like particles 14668333_results suggest that the interaction of apolipoproteins with ATP binding cassette transporter A1(ABCA1)-expressing cells activates JAK2 which enhances apolipoprotein interactions with ABCA1 and lipid removal from cells 14681836_first demonstration of an association between ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A member 1 gene expression and fasting glucose concentration in vivo 14701812_HDL(3) promotes ABCA1-mediated lipid efflux entirely through its lipid-poor fraction with pre-beta mobility 14701824_the ABCA1 transporter has a role in cellular cAMP signaling with Apolipoprotein A-I 14701850_an amphiphilic helical motif is the minimum structural requirement for a protein to stabilize ABCA1 against proteolytic degradation 14734645_ApoA-1 removes excess cholesterol & phospholipids from macrophages by an active pathway involving ABCA1. The slow component of this efflux is the ABCA1-dependent process. 14747463_ABCA1 converts pools of late endocytic lipids that retain NPC1 to pools that can associate with endocytosed apoA-I, and be released from the cell as nascent high density lipoprotein 14754908_ABCA1 is essential for the biogenesis of high density-sized lipoprotein containing only apoE particles in vivo 14767869_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14767869_the K219 allele of the ABCA1 gene is an anti-atherogenic allele with increased cholesterol efflux activity 14962947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14962947_Two polymorphisms were associated with plasma levels of ApoA1, 1 in the promoter (C-564T) and 1 in the coding (R1587K) regions, whereas only 1 polymorphism (R219K) was associated with the risk of myocardial infarction. 14967052_A two step model of cholesterol efflux is suggested that can explain the functional interactions of ABCA1 with apoA-I and other cholesterol acceptors, based on formation of a tight complex between ABCA1 and its ligands. 14967823_increased palmitate and stearate desaturation by stearoyl-CoA desaturase was associated with the destabilization of ABCA1 by saturated fatty acids palmitate and stearate 14986172_ABCA1 G(-273)C polymorphism has a significant effect on the HDL-C level in the general Japanese population, but not on the incidence of myocardia infarction 14986172_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14993242_ABCA1 does not differentiate between cholesterol and beta-sitosterol and thus is not responsible for the selectivity of sterol absorption by the intestine 15024730_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15024730_Several single nucleotide polymorphisms spanning the ABCA1 gene modify Alzheimer disease risk. 15033469_ATP-binding-cassette transporter A1 gene expression in macrophages is downregulated by statins 15066991_ABCA1 is not requied for a positive feedback pathway for stimulation of potentially anti-atherogenic apoE secretion by alpha-helix-containing molecules including apoA-I and apoE 15102890_The reciprocal inhibition of SR-BI and ABCA1 by BLT-4 and glyburide raises the possibility that these proteins may share similar or common steps in their mechanisms of lipid transport. 15135251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15140889_probucol inactivates ABCA1 in the plasma membrane with respect to its function in mediating binding of and lipid release by apolipoprotein and with respect to proteolytic degradation by calpain 15158913_Both mutations prevent normal trafficking of ABCA1, thereby explaining their inability to mediate apoA1-dependent lipid efflux 15163665_conclude that intact ATP binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) function is necessary for proper maturation of dense bodies in platelets 15201080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15262183_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15280376_the majority of ABCA1 exists as a tetramer that binds apoA; the homotetrameric ABCA1 complex constitutes the minimum functional unit required for the biogenesis of high density lipoprotein particles. 15288432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15292375_apoA-I mobilizes intracellular cholesterol for the ABCA1-mediated release from the compartment that is under the control of ACAT. The cholesterol mobilization process is presumably related to PKC activation by apoA-I. 15297675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15297675_tested whether rare sequence variants of ABCA1, APOA1, and LCAT collectively contribute to variation in plasma levels of high density lipoprotein cholesterol; nonsynonymous sequence variants were significantly more common in individuals with low HDL-C 15340333_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15358117_Serum amyloid A promotes ABCA1-dependent and ABCA1-independent lipid efflux from cells. 15358760_SREBP2 down-regulates ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in vascular endothelial cells 15469992_ABCA1 forms a complex with syntaxin 13 and flotillin-1, residing at the plasma membrane and in phagosomes 15492319_ABCA1 is not required for apolipoprotein A-1-mediated endothelial cholesterol efflux from vascular endothelial cells. 15500734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15520867_ABC transporter A1 has a role in regulating levels of HDL cholesterol 15520867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528463_We propose that the decreased level of ABCA1 protein is a key factor in the development of atherosclerotic lesions. 15528481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15528481_The ABCA1 gene -565C>T polymorphism was associated with coronary atherosclerosis severity. This variant had an effect on ABCA1 promoter activity. Common ABCA1 variants contribute to interindividual variability in atherosclerosis susceptibility & severity. 15574409_apolipoprotein A-I chlorination markedly impairs ABCA1-dependent cholesterol transport 15649702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15657615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15696473_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15696473_The allelic frequencies of A and G of ABCA1 gene are 53.4% and 46.6% and the genetic polymorphisms of ABCA1 in Chinese Han ethnic population are significantly different from Caucasians residing in USA or Europe. 15721294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15721294_type 2 diabetes is associated with ABCA1 gene polymorphisms in a Japanese population 15774904_Catalytic subunits of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, BRG-1 and brahma, play significant roles in enhancing LXR/RXR-mediated transcription of ABCA1 via the promoter DR-4 element 15817453_RhoA has a role in ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux 15829498_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15851589_Deficiency of macrophage ACAT1 accelerates atherosclerosis in apoE-/- mice but has no effect when hypercholesterolemia is corrected by apoE expression. ACAT1 deletion impairs ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux in macrophages regardless of apoE expression 15890646_cholesterol efflux via the ABCA1/apoA-I pathway is enhanced by the GSL synthesis inhibitor PDMP 15905177_analysis of headgroup-specific exposure of phospholipids in ABCA1-expressing cells 15930518_The ABCA1-mediated reaction produced two distinct HDLs, large cholesterol-rich and small cholesterol-poor particles, and the former is more prominently dependent on the increase of ABCA1 expression 15935359_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15935359_The role of high levels of HDL cholesterol in protection against development of atherosclerosis is generally attributed to its role in reverse cholesterol transport, and the ATP binding cassette transporter A1 is a key element of this process. 15951431_the internalization and trafficking of ABCA1 is functionally important in mediating cholesterol efflux from intracellular cholesterol pools 15952113_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15952113_Result exhibited an interaction of PON1 gene polymorphism A/B192 and ABCA1 genetic variation R219K on serum lipid level. 15958302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15961705_dramatic decrease of ABCA1 protein, the key molecule of cholesterol efflux, in atheroma 15983222_Glycolaldehyde and glyoxal strongly inhibited ABCA1-dependent transport of cholesterol from cells to apoA-I, while methylglyoxal had little effect. 16009332_In this report, a relationship between ApoA-I, DM and ABCA1 has been emphasized. 16030523_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16055210_An amino acid substitution in ABCA1 is associated with low levels of HDL and diabetes mellitus, type 2. 16080812_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16080812_The ABCA1 R219K polymorphism may be involved in the variability of serum HDL-C and the susceptibility to coronary artery disease. 16086925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16118212_intracellular unsaturated acyl-CoA derivatives destabilize ABCA1 by activating a PLD2 signaling pathway 16120575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16126721_the ABCA1 pathway is impaired by acrolein-induced apoA-I modification 16157450_Based on the results of genome-wide screens, along with biological studies, we selected three genes as candidates for AD risk factors: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), cholesterol 25-hydroxylase (CH25H) and cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CH24H). 16157450_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16166555_mABC1 protein plays a major role in cellular protection against oxidant stress. 16192269_beta1-syntrophin acts through a class-I PDZ interaction with the C terminus of ABCA1 to regulate the cellular distribution and activity of the transporter 16207713_ABCA1 plays a role in the pathogenesis of parenchymal and cerebrovascular amyloid pathology 16226177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16235041_A review of functions and mutations of ABCA1 in Tangier disease. 16254209_Glucocorticoid receptor ligands affected ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux from macrophages 16313984_ABCA! polymorphisms and prognosis after myocardial infarction were analyzed in a young male cohort. 16313984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16343503_Approximately 20% of French-Canadian patients with severe HDL deficiency are associated with a defective ABCA1. 16410457_ABCA1-mediated efflux to serum responds to the pool of lipid-free/poor apolipoproteins 16418537_Results show that the products of the apoA-I/ABCA1 interaction include discoidal HDL particles containing different numbers of apoA-I molecules. 16429166_Impact of genetic variation on ABCA1 function. 16443932_Results suggest that ABCA1 transduces signals from apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) by complexing and activating Cdc42 and downstream kinases and, therefore, acts as a full apoA-I receptor. 16446539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16456089_ABCA1 upregulation in macrophages inhibits the progression of atherosclerotic lesions 16497665_oxidation by myeloperoxidase impairs the ability of apoA-I to promote cholesterol efflux by the ABCA1 pathway, suggesting that this oxidative process might contribute to foam cell formation and atherogenesis 16500904_analysis of the biochemical basis of the mechanism for HDL formation mediated by ABCA1 16505586_ABCA1 is a rate-limiting factor of HDL assembly and is regulated by transcriptional and post-transcriptional factors. Post-transcriptional regulation of ABCA1 involves modulation of its calpain-mediated degradation. 16542392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16596262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16596262_data support the observation that ABCA1 polymorphisms influence cholesterol metabolism of the brain, but might not act as a major risk factor in Alzheimer's disease. 16709568_Fluorescence resonance energy transfer and native plyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analytical techniques were employed to assess the quaternary structure of ABCA1 16725228_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16725228_This study suggest a gender-specific and APOE and UBQLN1 independent association between the ABCA1/R219K polymorphism and late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 16730733_Suppression of both the ABCA1 and ABCG1 genes may indicate that unsaturated fatty acids suppress not only cholesterol efflux to apoA-I and thereby nascent HDL formation but also HDL-dependent cholesterol efflux from vascular cells. 16763159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16770077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16806540_ABCA1 polymorphisms are associated with varying plasma levels of HDL-C in Pakistani individuals. 16806540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16825673_ABCA1 is expressed in keratinocytes, where it is negatively regulated by a decrease in cellular cholesterol levels or altered permeability barrier requirements and regulated by activators of LXR, PPARs, and RXR or increases in cellular cholesterol levels 16855366_REVIEW: the presence of ABCA1 and ABCG1 in the AP-3 pathway will have major impact for membrane phospholipid processing and HDL metabolism and their relation to disorders of lysosome-related organelles 16873719_generation in vitro of 15 missense mutations that have been described in patients with Tangier disease and familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia. (ABCA1) 16879828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16901265_The role of SREBP-2 in the regulation of ABCA1 transcription via generation of oxysterol ligands for liver X receptor is reported. 16902247_ABCG1 and ABCG4 act in concert with ABCA1 to maximize the removal of excess cholesterol from cells and to generate cholesterol-rich lipoprotein particles 16928680_hepatic overexpression of ABCA1 in low density lipoprotein receptor-KO mice leads to: 1) expansion of the pro-atherogenic apoB-lipoprotein cholesterol pool size via enhanced transfer of HDL-cholesterol to apoB-lipoproteins 17001213_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17020879_NPC1 protein function is non-essential for the trafficking and removal of cellular cholesterol by ApoAI if the down-stream defects in ABCA1 and ABCG1 regulation in NPC disease cells are corrected using an LXR agonist 17070530_ABCA1 polymorphism is associated with the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease in Germany. 17082211_Two genes of the cholesterol efflux system (ABCA1 and ABCG1) were down-regulated in HCAECs exposed to uraemic plasma. 17113061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17121837_ABCA1 plays a significant role in the regulation of neuronal cholesterol efflux to apolipoprotein E discs. 17135302_ROS and NF-kappaB, but not LXR, mediate the IL-1beta-induced downregulation of ABCA1 via a novel transcriptional mechanism, which might play an important role of proinflammation in the alteration of lipid metabolism. 17135600_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17196163_The results suggest the promoting effects of AngII on the forming of foam cells are in a dose-dependent manner via down-regulating the expression of ABCA1. 17205124_in a system of forced expression by transfection, MEGF10 function can be modulated by the ATP binding cassette transporter ABCA1, ortholog to CED-7 17241464_Results show that ABCA1 mRNA expression increased in response to dexamethasone in primary rat hepatocytes however, the effect was absent or inhibitory in human HepG2 cells and THP-1 macrophages due to low glucocorticoid receptor levels. 17268197_ABCA1 gene I823M polymorphism altered plasma HDL-C level and also modified the effect of low-HDL-C on the risk of CAD. 17268197_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17287470_This is the first study reporting the association of the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 R230C variant with obesity and obesity-related comorbidities in the Mexican population. 17324514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17335784_An obvious association between polymorphisms of ABCA1 gene and AD was found; the risk for AD was significantly decreased in K allele (RK+KK genotypes) or KK homozygote carriers compared with RR genotypes carriers. 17335784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17368464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17368464_analysis of genetic variation in the ATP-binding cassette transporter A1, plasma lipids, and risk of coronary heart disease 17372331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17372331_Results suggest that defective ABCA1 function in cholesterol-loaded macrophages is one potential contributor to the impaired reverse cholesterol transport process and the increased coronary heart disease risk in subjects with familial low HDL. 17383594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17383594_Rare mutations in ABCA1 are associated with low HDL-C. However, at least 1 ABCA1 polymorphism (eg, E1172D) may contribute to the high HDL-C phenotype. 17407076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17407076_Results suggest that R219K polymorphism in ABCA1 gene is not only associated with serum HDL-C and TG levels in healthy Chinese subjects in Chengdu area, but also with HDL-C level and TC/HDL-C ratio in subjects with endogenous HTG. 17412755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17412755_an influence of common ABCA1 functional polymorphisms on age of symptom onset in coronary artery disease patients 17430597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17481640_ABCA1 expression in human leukocytes and muscle is associated with physical activity and alcohol consumption, respectively 17510466_Interaction of apoA-I with ABCA1 results in the simultaneous generation of pre-beta HDLs of discrete size and chemical composition. 17510946_the relationship between ABCA1 genetic variants and Alzheimer's disease (AD), independently or in concert with the APOE epsilon4 allele 17510949_Intronic polymorphism of ABCA1 gene is associated with sporadic Alzheimer's disease 17521614_Taken together, the current study demonstrates that APN might protect against atherosclerosis by increasing HDL assembly through enhancing ABCA1 pathway and apoA-1 synthesis in the liver. 17550732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17553166_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17553166_Our study does not support a major role for the ABCA1 gene as a risk factor for ischaemic stroke 17556657_Doxazosin inhibits AP2alpha activity independent of alpha(1)-adrenoceptor blockade and increases the ABCA1 expression and HDL biogenesis 17608096_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17656736_Our results provide a biochemical basis for the HDL biogenesis pathway that involves both ABCA1 and the 'high-capacity binding site', supporting a two binding site model for ABCA1-mediated nascent HDL genesis. 17689273_Results revealed that TNF-alpha could increase cholesterol content by down-regulating ABCA1 expression, IL-10 time-dependently decreased cholesterol accumulation by up-regulating ABCA1 expression. 17690481_results indicate that ABCG5/G8, unlike ABCA1, together with bile acids should participate in sterol efflux on the apical surface of Caco-2 cells. 17700364_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17710129_These results show that mutations in ABCA1 do not measurably reduce the rate of transbilayer movements of phospholipids in either the engulfing macrophage or the apoptotic target. 17855807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17923263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17923263_R219K polymorphism of ABCA1 related with low HDL in overweight/obese Thai males. 17951323_3 of 6 nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in ATP-binding cassette sub-family A (ABC1) member 1 (ABCA1) predict risk of ischemic heart disease in the general population. 17951323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17991739_Experiments employing an ABCA1 promoter-luciferase reporter confirmed that ORP8 silencing enhances ABCA1 transcription and the silencing effect was partially attenuated by mutation of the DR4 element in the ABCA1 promoter. 17992631_The interaction of ABCA1 with AOX1 modulates ABCA1-linked cellular functions such as lipid efflux and phagocytosis in hepatocytes (HC), and reduced expression of AOX1 in malignant transformed HC supports the differentiation dependent upregulation of AOX1. 18003760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18057374_plasma from men displayed an enhanced free cholesterol efflux capacity via the ABCA1 transporter pathway compared with that from women, which resulted from a 2.4-fold increase in the plasma level of prebeta particles 18097620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18097620_These results suggest that polymorphisms of ABCA1 and ROS1 are determinants of blood pressure and the development of hypertension in Japanese individuals. 18164264_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18199144_Mutations were identified in 5 low-HDL subjects. 4 SNPs in ABCA1 gene promoter identified the C-14T SNP & the TCCT haplotype to be over-represented in low-HDL individuals. Sequence variation in ABCA1 contributes significantly to variation in HDL levels. 18199144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18215356_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18218626_apoA-I specifically mediates the continuous endocytic recycling of ABCA1 18219093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18220685_ABC-A1 may be more than a determinant of HDL-cholesterol which may provide a link between components of the metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis. 18239666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18252847_Study of HDL particles formed when lipid-free apoA-I was incubated with fibroblasts in which expression of the ABCA1 was upregulated. 18287097_ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux requires an amphipathic helical region of the N-terminal barrel of phospholipid transfer protein 18343215_ABCA1 Q597R mutant trafficking to the plasma membrane was rapidly induced by thapsigargin or DTT, indicating that ER stress-induced QR trafficking. 18354102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18385134_ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1 is required for the lipidation of apolipoprotein A-I to generate high density lipoprotein (HDL). 18468402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18468402_Study results suggest that polymorphisms of ABCA1 C69T may be associated with plasma triacylglycerol and VLDL-cholesterol levels in coronary artery patients. 18484747_Physical interaction of ABCA1 and SPTLC1 results in reduction of ABCA1 activity and that inhibition of this interaction produces enhanced cholesterol efflux. 18523221_Lower plasma levels of HDL cholesterol due to heterozygosity for loss-of-function mutations in ABCA1 were not associated with an increased risk of IHD. 18523221_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18566305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18583707_Interaction of apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) with ATP binding cassette transporter 1 imparts a unique conformation that partially determines the in vivo metabolic fate of apoA-I in transgenic mice. 18617649_ApoA-I facilitates ABCA1 recycle/accumulation to cell surface by inhibiting its intracellular degradation and increases high density lipoprotein generation. 18621447_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18621447_The K allele of R219K polymorphism is an independent protective factor against ACI. Though there is no association of V825I with ACI, this polymorphism has synergistic effects with hypertension in susceptibility to ACI. 18640393_No associations between fasting glucose, hemoglobin A(1c), plasma lipids, or oxLDL and the expression of ABCG1, ABCA1, or SR-BI were found in diabetic patients. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18706283_Various studies have identified debatable and sometimes inconsistent results with respect to the risk on MI attributed by common genetic variation in ABCA1. 18711208_ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux is independent of cholesterol synthesis 18762171_Stimulation of hydrolysis of cholesteryl ester in macrophages induces the expression of ABCA1 gene primarily via the LXR-dependent pathway and can be useful for the prevention of atherosclerosis. 18767813_Ability of the lipid transporter ABCA1 and apolipoprotein CIII to pro |
ENSMUSG00000015243 |
Abca1 |
2288.469604 |
2.6440386015 |
1.402743 |
0.036152616 |
1534.839773 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3444.0036779 |
75.9988255 |
1311.4994971 |
23.5222874 |
| ENSG00000165046 |
137994 |
LETM2 |
protein_coding |
Q2VYF4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable ribosome binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cellular metal ion homeostasis. Predicted to be located in mitochondrial inner membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:137994; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; ribosome binding [GO:0043022]; cellular metal ion homeostasis [GO:0006875] |
|
ENSMUSG00000037363 |
Letm2 |
41.603018 |
0.4709819005 |
-1.086256 |
0.331403839 |
10.458924 |
0.00122058366975990131332585608703311663703061640262603759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002803145319068950456348199296030543337110430002212524414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.3707430 |
5.9227849 |
58.6955457 |
8.7075035 |
| ENSG00000165072 |
256691 |
MAMDC2 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z304 |
|
Alternative splicing;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable glycosaminoglycan binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within peptide cross-linking via chondroitin 4-sulfate glycosaminoglycan. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:256691; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32707597_MAM domain containing 2 is a potential breast cancer biomarker that exhibits tumour-suppressive activity. |
ENSMUSG00000033207 |
Mamdc2 |
40.241218 |
0.0815603786 |
-3.615988 |
0.385567973 |
106.623643 |
0.00000000000000000000000053827188574307523878048724087096833244513242482778645517099894412518454323013372686546063050627708435058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000005782309340296790962353759015207288680881901341767302510766885685709187692182808859797660261392593383789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7390849 |
1.5610181 |
70.9352720 |
9.6340741 |
| ENSG00000165113 |
80318 |
GKAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q5VSY0 |
FUNCTION: Regulates insulin-dependent IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation in adipocytes by modulating the availability of IRS1 to IR tyrosine kinase. Its association with IRS1 is required for insulin-induced translocation of SLC2A4 to the cell membrane. Involved in TNF-induced impairment of insulin-dependent IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JMB0}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is highly similar to the mouse cGMP-dependent protein kinase anchoring protein 42kDa. The mouse protein has been found to localize with the Golgi and recruit cGMP-dependent protein kinase I alpha to the Golgi in mouse testes. It is thought to play a role in germ cell development. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:80318; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046628]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
10671526_This paper describes the protein interaction, expression, localization and function of a highly similar gene in mouse. |
ENSMUSG00000021552 |
Gkap1 |
9.008468 |
0.4070701038 |
-1.296651 |
0.551338510 |
5.583480 |
0.01813066563454224233709055624785833060741424560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032823331873646936773791793484633672051131725311279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8592698 |
1.8705806 |
11.9212608 |
3.0016117 |
| ENSG00000165138 |
203286 |
ANKS6 |
protein_coding |
Q68DC2 |
FUNCTION: Required for renal function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23793029}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Hydroxylation;Joubert syndrome;Nephronophthisis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing multiple ankyrin repeats and a SAM domain. It is thought that this protein may localize to the proximal region of the primary cilium, and may play a role in renal and cardiovascular development. Mutations in this gene have been shown to cause a form of nephronophthisis (NPHP16), a chronic tubulo-interstitial nephritis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:203286; |
ciliary inversin compartment [GO:0097543]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; heart development [GO:0007507]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; kidney development [GO:0001822] |
18434273_Location, sequence and structure of the gene encoding human SamCystin have been determined. 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23793029_ANKS6 as a new NPHP family member that assembles a distinct module of nephronophthisis-associated proteins, encompassing NEK8, INVS and NPHP3. 24610927_Data indicate the importance of ANKS6 in human kidney development and suggest a mechanism by which mutations in ANKS6 may contribute to an nephronophthisis-like phenotype in chronic kidney disease. 24998259_Study finds that ANKS3-SAM polymerizes and ANKS6-SAM can bind to one end of the polymer; study presents crystal structures of both the ANKS3-SAM polymer and the ANKS3-SAM/ANKS6-SAM complex, revealing the molecular details of their association. 34740236_Biallelic ANKS6 mutations cause late-onset ciliopathy with chronic kidney disease through YAP dysregulation. |
ENSMUSG00000066191 |
Anks6 |
65.655847 |
0.4870071498 |
-1.037985 |
0.369423138 |
7.629180 |
0.00574314052209764103890110575889593746978789567947387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011593100944496880291834095544345473172143101692199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.7357341 |
9.3802337 |
84.6776508 |
13.6032269 |
| ENSG00000165140 |
2203 |
FBP1 |
protein_coding |
P09467 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate in the presence of divalent cations, acting as a rate-limiting enzyme in gluconeogenesis. Plays a role in regulating glucose sensing and insulin secretion of pancreatic beta-cells. Appears to modulate glycerol gluconeogenesis in liver. Important regulator of appetite and adiposity; increased expression of the protein in liver after nutrient excess increases circulating satiety hormones and reduces appetite-stimulating neuropeptides and thus seems to provide a feedback mechanism to limit weight gain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16497803, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18375435, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22517657}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Allosteric enzyme;Carbohydrate metabolism;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Gluconeogenesis;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate biosynthesis; gluconeogenesis. |
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1, a gluconeogenesis regulatory enzyme, catalyzes the hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate and inorganic phosphate. Fructose-1,6-diphosphatase deficiency is associated with hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2203; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; AMP binding [GO:0016208]; fructose 1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphatase activity [GO:0042132]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; monosaccharide binding [GO:0048029]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; cellular hyperosmotic salinity response [GO:0071475]; cellular hypotonic salinity response [GO:0071477]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to magnesium ion [GO:0071286]; cellular response to phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate [GO:1904628]; cellular response to raffinose [GO:0097403]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; fructose 1,6-bisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0030388]; fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0006002]; fructose metabolic process [GO:0006000]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0006111]; response to metformin [GO:1901558]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; sucrose biosynthetic process [GO:0005986] |
15965961_liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase coupled with phosphofructokinase (PFK) plays a crucial role in the metabolism of pancreatic islet cells 18375435_Upregulation of FBPase in pancreatic islet beta-cells in states of lipid oversupply and type 2 diabetes, contributes to insulin secretory dysfunction. 18460190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18780768_Human FBP1 was found to regulate mouse endogenous glucose production and whole body glucose homeostasis in a liver-specific transgenic model. 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19259699_first report on mutations in patients with FBP deficiency of Arab ethnicity,two novel mutations in the FBP1 gene encode for a duplication of two amino acids and a truncation in the FBP1 protein in these families. 19505453_Data show that EDTA and mercaptoethanol stabilized FBP-1 activity in stored urine. 19626708_this is the first experimental evidence confirming that the KKKGK motif can act as a functional NLS fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase . 19881551_Data show that NF-kappaB functions downstream of Ras to promote epigenetic downregulation of FBP1. 20096900_Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase gene cause hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis. 20151204_Case Reports: present reliable diagnostic system to verify an FBPase deficiency and find the genetic aberration. 22039417_epigenetic inactivation of FBP1 is also common in human liver and colon cancer. FBP1 appears to be a functional tumor suppressor involved in the liver and colon carcinogenesis 22057438_The Identification of FBPase interacting partners with mass spectrometry reveals a set of nuclear proteins involved in cell cycle regulation, mRNA processing and in stabilization of genomic DNA structure. 22120740_AMP binding pattern of the muscle isozyme of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase is quite similar to that of the liver isozyme and the T conformations of the two isozymes are nearly the same 22517657_This is the first study to identify liver FBPase as a previously unknown regulator of appetite and adiposity and describes a novel process by which the liver participates in body weight regulation. 23453623_study indicates that the loss of FBP1 is a critical oncogenic event in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and basal-like breast cancer 23755305_LSD1 regulates transcription activation of two gluconeogenic genes, FBP1 and G6Pase. 23881342_A novel missense mutation (c.841G>A) in the FBP1 gene seems to be prevalent in Pakistani-Indian patients with fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency. 24007283_A homozygous c.658delT mutation was detected at exon 5 of the FBP1 gene in the two siblings with FBPase deficiency. 24146906_Ca(2+) affects conformation of the catalytic loop 52-72 of muscle FBPase and inhibits its activity by competing with activatory divalent cations, e.g. Mg(2+) and Zn(2+). 25043030_the gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) is uniformly depleted in over six hundred clear cell renal cell carcinoma tumours examined. 25601412_Twelve different mutations were identified in 22 alleles: one missense mutation c.472C > T, one point deletion c.48del, one point duplication c.865dupA, one deletion-insertion, and two splice mutations (c.427-1del and c.825 + 1G > A). 25844935_There was a negative correlation with the level of FBP1 and recurrence of the lung cancer 26068981_NPM1 promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumor progression in patients with pancreatic cancer by inhibiting FBP1 26469968_FBP1 expression, which is closely correlated with c-Myc expression, is an independent prognostic factor and promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. 26546081_identified Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) bond to FBP1 promoter to enhance DNA methylation in lung cancer cells. Our findings indicate that the down-regulation of FBP1 is a critical oncogenic event in lung cancer progression 27079415_Cox multivariate regression analysis demonstrated that DUOX1, GLS2, FBP1 and age were independent risk factors for the prognosis of HCC patients after surgery 27197151_FBP1 underexpression is associated with Tumor Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 27742690_These findings indicate that FBP1 appears to be a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Strategies to restore the levels and activities of FBP1 might be developed to treat patients with HCC. 27780144_Elevated FBP1 is a critical modulator in breast cancer progression by altering glucose metabolism and the activity of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 27780225_we show that EV71 viral proteinase 2A is capable of cleaving far upstream element-binding protein 1 (FBP1), a positive internal ribosome entry sitet rans-acting factor that directly binds to the EV71 5' UTR linker region to promote viral IRES-driven translation 27841754_Here, the first crystal structure of human liver FBPase in the R-state conformation is presented, determined at a resolution of 2.2 A in a tetragonal setting that exhibits an unusual arrangement of noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) elements. 27978536_Downregulation of FBP1 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by facilitating EMT and acts as a potential prognostic factor and therapeutic target in gastric cancer. 28336726_Results identified FBP1 as a promising acute liver failure (ALF) biomarker among energy metabolism-related proteins. It may serve as a short-term prognosis indicator for ALF, with higher serum level of FBP1 correlated with higher ALF-related mortality in human studies. 28362515_FBP1 is highly expressed in human hypertrophic scars and increases fibroblast proliferation, apoptosis and collagen expression. 28387640_Studied association of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) expression with fluorine 18 ((18)F) fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) accumulation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Found that in patients with HCC, both 18F FDG accumulation and tumor grade (from differentiated to undifferentiated) were inversely correlated with the expression of FBP1. 28485159_overexpressed FBP1 may repress tumor growth, migration and glycolysis via targeting HIF-1alpha in breast cancer 28599390_Homozygous Alu element insertion in the FBP1 gene is associated with Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency. 28653874_fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 facilitated co-action between Bcl-2 and Beclin 1, which may be important in the mechanism of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1-mediated mitophagy inhibition. In summary, loss of mitophagy by fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1-mediated repression promotes apoptosis in breast cancer 28990097_decreased levels of FBP1 may be used as a predictor for poor prognosis of cervical cancer patients 29016355_FBP1 mutation was associated with fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency 29377004_The expansion of CB HSPCs by PPAR-gamma antagonism was completely suppressed by removal of glucose or inhibition of glycolysis. Moreover, knockdown of FBP1 expression promoted glycolysis and ex vivo expansion of long-term repopulating CB HSPCs, whereas overexpression of FBP1 suppressed the expansion of CB HSPCs that was induced by PPARG antagonism 29566023_Study identified for the first time that HNF4alpha and C/EBPalpha are important transcriptional regulators for FBP1 expression in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. 29678579_CBX3 serves as a positive regulator of aerobic glycolysis via suppressing of the FBP1 in pancreatic cancer cells. 29774539_Identification of a frequent variant (E281K) in Indian patients with fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency 29984231_findings implied the important roles of FBP1 expression in lung cancer development and progression 30171256_FOXC1 bound directly to the promoter regions of the FBP1 gene and negatively regulated its transcriptional activity. Aberrant FBP1 expression contributed to colorectal cancer tumorigenicity. Decreased FBP1 expression coupled with increased FOXC1 expression provided better prognostic information than did FOXC1 expression alone. The FOXC1/FBP1 axis induces CRC cell proliferation and reprograms metabolism in CRCs. 30193944_Low FBP1 expression is associated with metastasis in cholangiocarcinoma. 30201002_FBP1 modulates the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to BET inhibitors by decreasing the expression of c-Myc. These findings highlight FBP1 could be used as a therapeutic niche for patient-tailored therapies 30429463_Restoration of FBP1 suppressed Snail-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. 31278438_Exon 2 deletion (previously termed exon 1) was found to be the most common mutation in Turkish fructose-1,6-biphosphatase deficiency patients. 31444412_We propose that the reduced FBP1 level reprogrammed the metabolic state of glioblastoma (GBM) cells, and thus, FBP1 is a potential therapeutic target regulating GBM metabolism following radiotherapy. 31584309_Genetic Analysis of Tyrosinemia Type 1 and Fructose-1, 6 Bisphosphatase Deficiency Affected in Pakistani Cohorts. 31594093_FBP1 inhibited the autophagy and proliferation in liver cancer cells 31938049_Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase loss modulates STAT3-dependent expression of PD-L1 and cancer immunity. 32041737_A Noncanonical Role of Fructose-1, 6-Bisphosphatase 1 Is Essential for Inhibition of Notch1 in Breast Cancer. 32073734_SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex and glucose metabolism are deregulated in advanced bladder cancer. 32453596_Knockdown of FBP1 enhances radiosensitivity in prostate cancer cells by activating autophagy. 32472219_UCP1 regulates ALDH-positive breast cancer stem cells through releasing the suppression of Snail on FBP1. 32601971_CELF6 modulates triple-negative breast cancer progression by regulating the stability of FBP1 mRNA. 32754266_Fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase 1 interacts with NF-kappaB p65 to regulate breast tumorigenesis via PIM2 induced phosphorylation. 33232284_Loss of FBP1 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating fatty acid metabolism in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33529753_TRIM47 accelerates aerobic glycolysis and tumor progression through regulating ubiquitination of FBP1 in pancreatic cancer. 34221105_miR-18a-5p Targets FBP1 to Promote Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Liver Cancer Cells and Inhibit Cell Apoptosis. 34298040_FBP1 enhances the radiosensitivity by suppressing glycolysis via the FBXW7/mTOR axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 34363022_FBP1 regulates proliferation, metastasis, and chemoresistance by participating in C-MYC/STAT3 signaling axis in ovarian cancer. 35179010_Fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase deficiency: outcomes of patients in a single center in Turkey and identification of novel splice site and indel mutations in FBP1. 35404841_The role of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate-mediated glycolysis/gluconeogenesis genes in cancer prognosis. 35477823_Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1) is an independent biomarker associated with a favorable prognosis in esophageal adenocarcinoma. 35653238_Epigenetic regulation of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 by host transcription factor Speckled 110 kDa during hepatitis B virus infection. 36000567_FBP1 knockdown decreases ovarian cancer formation and cisplatin resistance through EZH2-mediated H3K27me3. 36050791_The role of LINC01419 in regulating the cell stemness in lung adenocarcinoma through recruiting EZH2 and regulating FBP1 expression. 36232688_FBP1-Altered Carbohydrate Metabolism Reduces Leukemic Viability through Activating P53 and Modulating the Mitochondrial Quality Control System In Vitro. 36266488_Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 functions as a protein phosphatase to dephosphorylate histone H3 and suppresses PPARalpha-regulated gene transcription and tumour growth. |
ENSMUSG00000069805 |
Fbp1 |
10.085225 |
0.0834523642 |
-3.582903 |
0.865403939 |
19.776512 |
0.00000870458073999635825431300806265255687321769073605537414550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027505804265113730953332821238532801544351968914270401000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2566061 |
0.7892841 |
15.6191580 |
4.8816698 |
| ENSG00000165152 |
84302 |
PGAP4 |
protein_coding |
Q9BRR3 |
FUNCTION: Golgi-resident glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-N-acetylgalactosamine transferase involved in the lipid remodeling steps of GPI-anchor maturation. Lipid remodeling steps consist in the generation of 2 saturated fatty chains at the sn-2 position of GPI-anchors proteins (PubMed:29374258). Required for the initial step of GPI-GalNAc biosynthesis, transfers GalNAc to GPI in the Golgi after fatty acid remodeling by PGAP2 (PubMed:29374258). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374258}. |
Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables glycosyltransferase activity. Involved in GPI anchor biosynthetic process. Located in Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84302; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; GPI anchor biosynthetic process [GO:0006506] |
|
ENSMUSG00000039611 |
Pgap4 |
51.675161 |
2.0472467577 |
1.033685 |
0.220771878 |
22.124649 |
0.00000255507894423255984509436161689066580038343090564012527465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008620106335285161755044129605618508094266871921718120574951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
70.7647574 |
8.9989671 |
34.8081917 |
3.5042740 |
| ENSG00000165219 |
26130 |
GAPVD1 |
protein_coding |
Q14C86 |
FUNCTION: Acts both as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) and a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), and participates in various processes such as endocytosis, insulin receptor internalization or LC2A4/GLUT4 trafficking. Acts as a GEF for the Ras-related protein RAB31 by exchanging bound GDP for free GTP, leading to regulate LC2A4/GLUT4 trafficking. In the absence of insulin, it maintains RAB31 in an active state and promotes a futile cycle between LC2A4/GLUT4 storage vesicles and early endosomes, retaining LC2A4/GLUT4 inside the cells. Upon insulin stimulation, it is translocated to the plasma membrane, releasing LC2A4/GLUT4 from intracellular storage vesicles. Also involved in EGFR trafficking and degradation, possibly by promoting EGFR ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. Has GEF activity for Rab5 and GAP activity for Ras. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16410077}. |
Alternative splicing;Endocytosis;Endosome;GTPase activation;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables GTPase activating protein binding activity and guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Involved in regulation of protein transport. Located in cytosol and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26130; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; endosome [GO:0005768]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; GTPase activating protein binding [GO:0032794]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of protein transport [GO:0051223]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
17545148_EGF-stimulated receptor ubiquitination and trafficking are mediated via GAPex-5: GAPex-5-mediated EGFR ubiquitination is independent of Rab5 activation 31358736_The findings suggest that SPIN90, as an adaptor protein, simultaneously binds inactive Rab5 and Gapex5, thereby altering their spatial proximity and facilitating Rab5 activation. 32321936_CRISPR-mediated gene targeting of CK1delta/epsilon leads to enhanced understanding of their role in endocytosis via phosphoregulation of GAPVD1. 33548618_An interdependence between GAPVD1 gene polymorphism, expression level and response to interferon beta in patients with multiple sclerosis. 33917494_Phosphorylation of GAPVD1 Is Regulated by the PER Complex and Linked to GAPVD1 Degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000026867 |
Gapvd1 |
554.567912 |
2.6184211763 |
1.388697 |
0.514533203 |
7.008659 |
0.00811164131593055184876739360788633348420262336730957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015843301021984244891793736087493016384541988372802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
689.4991739 |
246.6583682 |
266.3050086 |
68.5554667 |
| ENSG00000165233 |
84270 |
CARD19 |
protein_coding |
Q96LW7 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in inhibiting the effects of BCL10-induced activation of NF-kappa-B. May inhibit the phosphorylation of BCL10 in a CARD-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15637807}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84270; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; CARD domain binding [GO:0050700]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124] |
15637807_BinCard inhibits BCL10-mediated activation of NF-kappa B. 23633586_the crystal structure of BinCARD reveals that all three cysteines were oxidized 30795865_BinCARD isoform2 (BinCARD2) is a one of CARD proteins involved in apoptosis and inflammation. BinCARD2 knock down suppresses innate immune responses induced by 3pRNA, poly(I:C) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV). 32763502_CARD19, the protein formerly known as BinCARD, is a mitochondrial protein that does not regulate Bcl10-dependent NF-kappaB activation after TCR engagement. |
ENSMUSG00000037960 |
Card19 |
612.870950 |
2.2605533743 |
1.176676 |
0.116143128 |
101.148828 |
0.00000000000000000000000853253945618023951257219203482411658508196588013512782392607750221735773976661221240647137165069580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000087580168548831949013706276539466280582040468097550067877511714188598634933669018209911882877349853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
860.3912700 |
61.5061389 |
383.3826163 |
20.3611519 |
| ENSG00000165271 |
65083 |
NOL6 |
protein_coding |
Q9H6R4 |
FUNCTION: Probably associated with rRNA. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:11895476}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
The nucleolus is a dense subnuclear membraneless organelle that assembles around clusters of rRNA genes and functions in ribosome biogenesis. This gene encodes a nucleolar RNA-associated protein that is highly conserved between species. RNase treatment of permeabilized cells indicates that the nucleolar localization is RNA dependent. Further studies suggest that the protein is associated with ribosome biogenesis through an interaction with pre-rRNA primary transcripts. Alternative splicing has been observed at this locus and two splice variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:65083; |
condensed nuclear chromosome [GO:0000794]; CURI complex [GO:0032545]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; small-subunit processome [GO:0032040]; UTP-C complex [GO:0034456]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; tRNA export from nucleus [GO:0006409] |
34561331_Nucleolar protein 6 promotes cell proliferation and acts as a potential novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. 34607487_NOL6 promotes the proliferation and migration of endometrial cancer cells by regulating TWIST1 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000028430 |
Nol6 |
650.192627 |
2.0829685813 |
1.058641 |
0.092089995 |
131.192369 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000224737310533461367115273313566717126992597970885924551658153230140161555770174665533356339608417329145595431327819824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000029072065762260208939511891723678637168011409275850770662136851280106707853877028024935924577221157960593700408935546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
890.7996218 |
46.5347602 |
430.7264046 |
17.1787855 |
| ENSG00000165288 |
254065 |
BRWD3 |
protein_coding |
Q6RI45 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. Required in the control of cell shape. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. |
Alternative splicing;Bromodomain;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains a bromodomain and several WD repeats. It is thought to have a chromatin-modifying function, and may thus play a role in transcription. Mutations in this gene are associated with a spectrum of cognitive disabilities and X-linked macrocephaly. This gene is also associated with translocations in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:254065; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
17668385_BRWD3 is therefore a new gene implicated in the etiology of XLMR associated with macrocephaly and may cause disease by altering intracellular signaling pathways affecting cellular proliferation. 19377476_Includes the identification of truncating mutations in this gene that segregated with mental retardation in the families tested. 22024541_potential serological biomarker of breast cancer 24462886_A nonsense mutation in BRWD3 in a family with X-linked intellectual disability associated with macrocephaly. 29166413_BCL7A, BRWD3, and AUTS2 demonstrate significantly higher mutation frequencies among AA cases. These genes are all involved in translocations in B-cell malignancies. Moreover, we detected a significant difference in mutation frequency of TP53 and IRF4 with frequencies higher among CA cases. Our study provides rationale for interrogating diverse tumor cohorts to best understand tumor genomics across populations. |
ENSMUSG00000063663 |
Brwd3 |
171.791691 |
2.2669189979 |
1.180733 |
0.243975698 |
22.898319 |
0.00000170801180873264098895902059899176705926038266625255346298217773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005883373231480461924228914094570086490421090275049209594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
235.7449828 |
40.1708512 |
104.4043059 |
12.9463634 |
| ENSG00000165300 |
26050 |
SLITRK5 |
protein_coding |
O94991 |
FUNCTION: Suppresses neurite outgrowth. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Members of the SLITRK family, such as SLITRK5, are integral membrane proteins with 2 N-terminal leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains similar to those of SLIT proteins (see SLIT1; MIM 603742). Most SLITRKs, including SLITRK5, also have C-terminal regions that share homology with neurotrophin receptors (see NTRK1; MIM 191315). SLITRKs are expressed predominantly in neural tissues and have neurite-modulating activity (Aruga et al., 2003 [PubMed 14557068]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:26050; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; synapse [GO:0045202]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; circulatory system development [GO:0072359]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; grooming behavior [GO:0007625]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; skin development [GO:0043588]; striatum development [GO:0021756] |
25426764_This study did not find any evidence supporting the association of Tourette syndrome and SLITRK5. 28085938_Mutation in SLITRK5 gene is Associated with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder 34326333_SLITRK5 is a negative regulator of hedgehog signaling in osteoblasts. 35579188_MUC21 controls melanoma progression via regulating SLITRK5 and hedgehog signaling pathway. 35872846_The Role of SliTrk5 in Central Nervous System. |
ENSMUSG00000033214 |
Slitrk5 |
238.904139 |
0.2053486083 |
-2.283853 |
0.135807151 |
287.795739 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000015026263352914106986974669734427877097774678152264643243406693227179794195774538165119298385668781672256434485034736931068261031556735553384847317473024457754873436932108177188638364896178245544433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004168940734755868951301073712343184066653945117546453163051727918434227561440232399742869589952272944185494964646443709495170049173410195379238818462026502659895088598318579897750169038772583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
91.6354222 |
7.9753648 |
449.7092604 |
23.9469480 |
| ENSG00000165322 |
94134 |
ARHGAP12 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWW6 |
FUNCTION: GTPase activator for the Rho-type GTPases by converting them to an inactive GDP-bound state. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;GTPase activation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of a large family of proteins that activate Rho-type guanosine triphosphate (GTP) metabolizing enzymes. The encoded protein may be involved in suppressing tumor formation by regulating cell invasion and adhesion. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:94134; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; morphogenesis of an epithelial sheet [GO:0002011]; negative regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051058]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11854031_molecular cloning and characterization of ARHGAP12 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18504429_ARHGAP12 inactivates RAC1, thereby impairing cell motility, invasion and adhesion to the extracellular matrix. The gene is transcriptionally suppressed by Hepatocyte Growth Factor in vitro. 18504429_Met-driven invasive growth involves transcriptional regulation of Arhgap12. 18984674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000041225 |
Arhgap12 |
110.799677 |
0.4717384075 |
-1.083941 |
0.227312325 |
22.503241 |
0.00000209789285664047780660484109060970325799644342623651027679443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007159514118847040981127253372884311488633102271705865859985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.5650164 |
11.7985875 |
140.0221455 |
17.9056491 |
| ENSG00000165338 |
143279 |
HECTD2 |
protein_coding |
Q5U5R9 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase which accepts ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfers the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28584101}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Catalyzes ubiquitination of Botulinum neurotoxin A light chain (LC) of C.botulinum neurotoxin type A (BoNT/A). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28584101}. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28584101}. |
Predicted to enable ubiquitin-protein transferase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein ubiquitination. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:143279; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19214206_HECTD2 haplotypes are associated with the susceptibility to human prion diseases. 19754925_The common haplotypes of HECTD2, tagged by rs12249854, are not associated with susceptibility to late onset Alzheimer's disease 21335971_HECTD2 polymorphisms are not associated with genetic susceptibility to sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a Korean population 23770851_A major biological consequence of upregulation of miR-221 is reprogramming of androgen receptor signaling via downregulation of HECTD2 and RAB1A. 34972816_Human gut-microbiome-derived propionate coordinates proteasomal degradation via HECTD2 upregulation to target EHMT2 in colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000041180 |
Hectd2 |
44.551359 |
0.4705265146 |
-1.087652 |
0.276209592 |
15.555071 |
0.00008013641003601868156944881826930782153795007616281509399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000223467487650035105629583997988163446279941126704216003417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.1745710 |
5.1341189 |
58.1166959 |
7.4210952 |
| ENSG00000165379 |
145581 |
LRFN5 |
protein_coding |
Q96NI6 |
FUNCTION: Cell adhesion molecule that mediates homophilic cell-cell adhesion in a Ca(2+)-independent manner. Promotes neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neurons. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18227064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18585462}. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the leucine-rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain-containing family of proteins. A similar protein in mouse, a glycosylated transmembrane protein, is thought to function in presynaptic differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:145581; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043031]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20410109_Expression of SALM family proteins SALM3 and SALM5 in nonneural and neural cells induces both excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic differentiation in contacting axons. 21736948_SALM5/Lrfn5, has recently been implicated in severe progressive autism and familial schizophrenia, pointing to the clinical importance of SALMs.[review] 29348429_Presynaptic differentiation induced by protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type D (PTPdelta)-leucine rich repeat and fibronectin type III domain containing 5 (SALM5) requires the dimeric property of SALM5. 29348579_In the 2:2 heterotetrameric SALM5/PTPdelta complex, a SALM5 dimer bridges two separate PTPdelta molecules. 31152157_we found that chr14.232.a increases expression of LRFN5 in his fibroblasts. Reduced expression of LRFN5 in fibroblasts should be interpreted with caution as these cells might not be representative of expression in brain cells, which are involved in the neurodevelopmental phenotype. 31748543_Identification of novel common variants associated with chronic pain using conditional false discovery rate analysis with major depressive disorder and assessment of pleiotropic effects of LRFN5. 35088940_LRFN5 locus structure is associated with autism and influenced by the sex of the individual and locus conversions. 36266731_CircLRFN5 inhibits the progression of glioblastoma via PRRX2/GCH1 mediated ferroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000035653 |
Lrfn5 |
73.935156 |
4.5662732018 |
2.191017 |
0.283437567 |
58.561880 |
0.00000000000001969965129018758984245874159014820584519224119790514748729037819430232048034667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000130155260986199110924944596183264064687482020055142584169516339898109436035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
123.6869450 |
19.4526422 |
26.9298236 |
3.4703792 |
| ENSG00000165416 |
10910 |
SUGT1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2Z0 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
This gene encodes a highly conserved nuclear protein involved in kinetochore function and required for the G1/S and G2/M transitions. This protein interacts with heat shock protein 90. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes for this gene have been defined on several different chromosomes. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:10910; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; chaperone binding [GO:0051087]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647] |
12746458_Sgt1 binds to S100A6 in a calcium-regulated manner 15346769_SGt1.2 is a splicing variant of SGT1 and widely expressed in human adult tissue. 17420470_Multiple lines of evidence show that SGT1 plays an essential role in signaling pathways linked to Nod1 activation in epithelial lineage cells. 17466273_This suggests that the interaction of Sgt1 with Hsp70 and Hsp90 is regulated by S100A6 in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. 18358234_Sgt1 is a co-chaperone protein with an expression pattern matching that of the well known heat shock proteins. 19398558_protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates Ser(361) on Sgt1, and this phosphorylation inhibits Sgt1 dimerization 20126976_SUGT1 amplification might give rise to promoting transcription of the gene directly subsequent to the progression of colorectal cancer cases with worsening prognosis 20213445_Sgt1 translocates to the nucleus due to heat shock. S100A6 is necessary for nuclear translocation of the Sgt1 protein. 20404110_These findings support a novel role for Hsp90-Sgt1 chaperones in ensuring the fidelity of Mis12 multiprotein complex assembly. 21864708_S100A6-Ca(2+)-mediated Sgt1 dephosphorylation promotes its nuclear translocation, most likely due to disruption of the Sgt1-Hsp90 complex 22869522_Plk1 is required for the kinetochore localization of Sgt1 and phosphorylates serine 331 of Sgt1 at the kinetochores. 23184943_Chp-1 and melusin can interact with cochaperones PP5 and Sgt1 and with each other in an ATP-dependent manner 23440515_our data revealed a previously uncovered role of SGT1 in gastric cancer development, and suggested that SGT1 could be a promising anti-cancer target to against gastric cancer 23935490_Data suggest that SspH2 (ubiquitin ligase effector from Salmonella typhimurium) ubiquitination activity and protein stability is enhanced by SGT1. 26545799_Data (including data from studies using purified proteins/hepatocyte lysates) suggest eEF1A1/Sgt1a interact as multimer; D2/D3 domains of eEF1A1 and TPR domain of Sgt1 are involved in multimer formation; Sgt1 competes with viral RNA to bind to eEF1A. 27591899_Fusion of human SGT1 (hSGT1) to NOD1 LRR significantly enhanced the solubility, and the fusion protein was stabilized by coexpression of mouse Hsp90alpha. 28696259_Data suggest that PHLPP1 plays an important role in assembly of kinetochores by counteracting RNF41-mediated SGT1 degradation. (PHLPP1 = PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 1; RNF41 = ring finger protein 41; SGT1 = suppressor of G2 allele of SKP1) 28816574_the SGT1-HSP90 complex contributes to the E3 ligase activity of the CUL4A complex that is necessary for CENP-A ubiquitylation and CENP-A deposition at the centromere. 30656909_REVIEW: cellular function of S100A6 and its ligands, CacyBP/SIP and Sgt1 32514048_SUGT1 controls susceptibility to HIV-1 infection by stabilizing microtubule plus-ends. |
ENSMUSG00000022024 |
Sugt1 |
328.511896 |
2.1033735148 |
1.072705 |
0.108746531 |
96.547575 |
0.00000000000000000000008712496802929355973094048684118328704956783858924248303725983155754164499739999882876873016357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000853894108972359147527992119515867777657616802817118000455947485205498992399952840059995651245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
427.6499735 |
26.9357748 |
204.4827298 |
9.5933100 |
| ENSG00000165449 |
220963 |
SLC16A9 |
protein_coding |
Q7RTY1 |
FUNCTION: Proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter. May catalyze the transport of monocarboxylates across the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in urate metabolic process. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:220963; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carnitine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015226]; creatine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005308]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; carnitine transmembrane transport [GO:1902603]; creatine transmembrane transport [GO:0015881]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718]; urate metabolic process [GO:0046415] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19503597_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19890391_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20037589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20162742_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20162743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23990105_it has a possible physiological role in urate excretion from human intestinal epithelial cells. 24824278_Strong association of SLC16A9 gene variation with HBsAg loss was identified in Chronic Hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon and adefovir. 31784090_Molecular characterization of the orphan transporter SLC16A9, an extracellular pH- and Na(+)-sensitive creatine transporter. 32566650_SLC1A1, SLC16A9, and CNTN3 Are Potential Biomarkers for the Occurrence of Colorectal Cancer. 33555501_Monocarboxylate transporter 9 (MCT9) is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. 34097251_The tissue expression of MCT3, MCT8, and MCT9 genes in women with breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000037762 |
Slc16a9 |
15.457249 |
3.6366676965 |
1.862617 |
0.446126270 |
18.123357 |
0.00002070460901879630439604597358371762538808980025351047515869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000062648632455398410275385079337695515278028324246406555175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.2753913 |
6.6360127 |
6.7181242 |
1.5367976 |
| ENSG00000165457 |
2350 |
FOLR2 |
protein_coding |
P14207 |
FUNCTION: Binds to folate and reduced folic acid derivatives and mediates delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and folate analogs into the interior of cells. Has high affinity for folate and folic acid analogs at neutral pH. Exposure to slightly acidic pH after receptor endocytosis triggers a conformation change that strongly reduces its affinity for folates and mediates their release. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23934049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2605182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:4066659}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Folate-binding;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the folate receptor (FOLR) family, and these genes exist in a cluster on chromosome 11. Members of this gene family have a high affinity for folic acid and for several reduced folic acid derivatives, and they mediate delivery of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate to the interior of cells. This protein has a 68% and 79% sequence homology with the FOLR1 and FOLR3 proteins, respectively. Although this protein was originally thought to be specific to placenta, it can also exist in other tissues, and it may play a role in the transport of methotrexate in synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2350; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; folic acid binding [GO:0005542]; folic acid receptor activity [GO:0061714]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; folate import across plasma membrane [GO:1904447]; folic acid transport [GO:0015884]; fusion of sperm to egg plasma membrane involved in single fertilization [GO:0007342]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; sperm-egg recognition [GO:0035036] |
12543860_FR-beta gene is a target for multiple coordinate actions of nuclear receptors for ATRA directly and indirectly acting on a transcriptional complex containing activating Sp1/ets and inhibitory AP-1 proteins. 12809644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17035141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19161160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19493349_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951991_study describes that functional FRbeta is specifically expressed by M-CSF-polarized (M2) macrophages as well as by ex vivo isolated tumor-associated macrophages, and that tumors induce its expression in an M-CSF-dependent manner 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20683905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20683905_The rare alleles of specific single nucleotide polymorphisms within the FOLR1, FOLR2, and FOLR3 genes were statistically significant for association with meningomyelocele. 22094710_Expression of folate receptor-beta on activated macrophages holds a promising potential for early diagnosis of atherosclerosis. (Review) 22211358_Functional FR-beta present on osteoarthritis synovial macrophages provides a potential tool for the diagnosis and treatment of this disease. 22350599_High Folate Receptor beta expressing tumor-associated macrophages are associated with pancreatic cancer. 23439585_High FOLR2 mRNA expression is associated with uraemic patients on hemodialysis. 23480364_severe pre-eclampsia is associated with decreased placental expression of FR-beta and a reduction in the number of fetal macrophages (Hofbauer cells) 24206618_The FRalpha gene was expressed in all parathyroid cells analyzed, and the FRbeta gene was expressed by most. 25015955_FR-beta is uniquely expressed on this proinflammatory subpopulation offers a new strategy to suppress migration of inflammatory monocytes into sites of inflammation. 25971554_we confirmed the similarities between epithelial ovarian cancer and fallopian tube, normal and adenocarcinoma using FOLR1, FOLR2, CD68 and CD11b markers 26248049_FR-beta expression was low or absent in the majority of ovarian, breast and colorectal tumor samples. 27534550_Folate receptor beta as a novel CD11b/CD18 regulator for trafficking and homing of a subset of macrophages on collagen. 28948692_We identified eight novel variants in SLC19A1 and twelve novel variants in FOLR1, FOLR2, and FOLR3. Pathogenic variants include c.1265delG in SLC19A1 resulting in an early stop codon, four large insertion deletion variants in FOLR3, and a stop_gain variant in FOLR3 29616859_Study report the expression of both FR-alpha and FR-beta on CD138 + plasma cells isolated from patients with multiple myeloma and the up-regulation of both FR-alpha and FR-beta expression after exposure to all-trans retinoic acid in two model myeloma cell lines. 29955133_we identified and characterised oncogenic fusion genes and their function in CRC, and implicated NAGLU-IKZF3 and RNF121-FOLR2 as novel molecular targets for personalised medicine development. 30280318_Folate receptor beta is expressed on myeloid cells and activated macrophages. FRbeta represents a useful marker for rheumatoid arthritis disease. [review] 30415267_Silencing of the expression of the FOLR2 gene in NCI-H1650 cells reduced cell viability, increased cell apoptosis, and arrested cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, decreased the expression of cyclin D1, upregulated expression of cell cycle inhibitors, p21 and p27, upregulated the expression of Bax/Bcl-2, and inhibited phosphorylation of AKT, mTOR, and S6K1. 31824505_(18)F-AzaFol for Detection of Folate Receptor-beta Positive Macrophages in Experimental Interstitial Lung Disease-A Proof-of-Concept Study. 32296026_Targeting folate receptor beta positive tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer with a folate-modified liposomal complex. 32532019_Folate Receptor beta (FRbeta) Expression in Tissue-Resident and Tumor-Associated Macrophages Associates with and Depends on the Expression of PU.1. 34070369_Folate Receptor Beta as a Direct and Indirect Target for Antibody-Based Cancer Immunotherapy. 34755134_Targeting folate receptor beta on monocytes/macrophages renders rapid inflammation resolution independent of root causes. 35185910_Folate Receptor Beta for Macrophage Imaging in Rheumatoid Arthritis. 35255727_Folate Receptor Expression by Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophage Subtypes and Effects of Corticosteroids. 35394484_FOLR2+ Macrophages Are Associated with T-cell Infiltration and Improved Prognosis. 35545363_Association of periconceptional folate supplements and FOLR1 and FOLR2 gene polymorphisms with risk of congenital heart disease in offspring: A hospital-based case-control study.', trans 'FOLR1FOLR2. |
ENSMUSG00000032725 |
Folr2 |
11.748271 |
0.1719891874 |
-2.539610 |
0.596401227 |
21.282808 |
0.00000396269631282941418230596208882587916377815417945384979248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013061500128933041357543604066293596588366199284791946411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2165213 |
1.3785510 |
18.6160079 |
4.0971889 |
| ENSG00000165458 |
3636 |
INPPL1 |
protein_coding |
O15357 |
FUNCTION: Phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) phosphatase that specifically hydrolyzes the 5-phosphate of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) to produce PtdIns(3,4)P2, thereby negatively regulating the PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) pathways (PubMed:16824732). Required for correct mitotic spindle orientation and therefore progression of mitosis (By similarity). Plays a central role in regulation of PI3K-dependent insulin signaling, although the precise molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways remain unclear (PubMed:9660833). While overexpression reduces both insulin-stimulated MAP kinase and Akt activation, its absence does not affect insulin signaling or GLUT4 trafficking (By similarity). Confers resistance to dietary obesity (By similarity). May act by regulating AKT2, but not AKT1, phosphorylation at the plasma membrane (By similarity). Part of a signaling pathway that regulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling (PubMed:11739414, PubMed:12676785). Required for the maintenance and dynamic remodeling of actin structures as well as in endocytosis, having a major impact on ligand-induced EGFR internalization and degradation (PubMed:15668240). Participates in regulation of cortical and submembraneous actin by hydrolyzing PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 thereby regulating membrane ruffling (PubMed:21624956). Regulates cell adhesion and cell spreading (PubMed:12235291). Required for HGF-mediated lamellipodium formation, cell scattering and spreading (PubMed:15735664). Acts as a negative regulator of EPHA2 receptor endocytosis by inhibiting via PI3K-dependent Rac1 activation (PubMed:17135240). Acts as a regulator of neuritogenesis by regulating PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 level and is required to form an initial protrusive pattern, and later, maintain proper neurite outgrowth (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of the FC-gamma-RIIA receptor (FCGR2A) (PubMed:12690104). Mediates signaling from the FC-gamma-RIIB receptor (FCGR2B), playing a central role in terminating signal transduction from activating immune/hematopoietic cell receptor systems (PubMed:11016922). Involved in EGF signaling pathway (PubMed:11349134). Upon stimulation by EGF, it is recruited by EGFR and dephosphorylates PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 (PubMed:11349134). Plays a negative role in regulating the PI3K-PKB pathway, possibly by inhibiting PKB activity (PubMed:11349134). Down-regulates Fc-gamma-R-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages independently of INPP5D/SHIP1 (By similarity). In macrophages, down-regulates NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription by regulating macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)-induced signaling (By similarity). Plays a role in the localization of AURKA and NEDD9/HEF1 to the basolateral membrane at interphase in polarized cysts, thereby mediates cell cycle homeostasis, cell polarization and cilia assembly (By similarity). Additionally promotion of cilia growth is also facilitated by hydrolysis of (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) to PtdIns(3,4)P2 (By similarity). Promotes formation of apical membrane-initiation sites during the initial stages of lumen formation via Rho family-induced actin filament organization and CTNNB1 localization to cell-cell contacts (By similarity). May also hydrolyze PtdIns(1,3,4,5)P4, and could thus affect the levels of the higher inositol polyphosphates like InsP6. Involved in endochondral ossification (PubMed:23273569). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1PNY0, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P549, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WVR3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11016922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11349134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11739414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12235291, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12676785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12690104, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15668240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15735664, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16824732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17135240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21624956, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23273569, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9660833}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Immunity;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3-binding |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an SH2-containing 5'-inositol phosphatase that is involved in the regulation of insulin function. The encoded protein also plays a role in the regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor turnover and actin remodelling. Additionally, this gene supports metastatic growth in breast cancer and is a valuable biomarker for breast cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:3636; |
basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; inositol-polyphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0004445]; phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0034485]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; establishment of mitotic spindle orientation [GO:0000132]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; immune system process [GO:0002376]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043569]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of actin filament organization [GO:0110053]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; ruffle assembly [GO:0097178] |
12086927_candidate gene for type 2 diabetes 12147234_overexpression strongly reduces the proliferation rate of K562 erythroleukemia cell line 12370370_SHIP phosphorylation by the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-associated Fc gamma RIIa requires Shc phosphorylation, leads to activation of Src kinases, and down-regulates NF-kappa B-induced gene transcription during phagocytosis. 12690104_regulation of FcgammaR-mediated activation of human myeloid cells by the expression and function of the inositol phosphatase SHIP-2 15220217_INPPL1 variants may impact susceptibility to disease and/or to subphenotypes involved in the metabolic syndrome in some diabetic patients. 15316017_Schizosaccharomyces pombe synaptojanin (SPsynaptojanin) and human SH2 domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase SHIP2 comparison: substrate specificity and mechanism study 15492005_SHIP1 and SHIP2 interact preferentially with Tec and inactivate it by de-phosphorylation of local PtdIns 3,4,5-P(3) and inhibition of Tec membrane localization 15557176_A novel regulatory role is suggested for SHIP2 in macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF)-stimulated myeloid cells. 15668240_SHIP2 plays a distinct role in signaling pathways mediated by integrins and growth factor receptors. 15735664_SHIP-2 accumulates transiently at actin-rich regions along the cellular leading edge in HGF-stimulated MDCK cells; overexpression alters HGF-mediated lamellipodium formation 15777721_Findings suggest that SHIP2 gene expression is controlled by the Sp-family of transcription factors. 16302969_Data report the identification of the cytoskeletal protein vinexin as a protein interacting with SHIP2. 16804414_The SNPs in the SHIP2 gene promoter and the 5'-UTR may account partly for the impaired fasting glycemia and may be a marker for the risk of diabetes 16842970_SHIP2 substitutes for PTEN in the acute regulation of PKB in PC3 cells but not other prostate cell lines, where PTEN may share this role with further PIP3-degrading mechanisms. 17219406_SHIP2 tyrosine phosphorylation and Shc association can be regulated by serine/threonine signaling pathways, either indirectly (via PKC), or directly (via T958) 17314030_In a yeast two-hybrid screen for new interaction partners of Arap3, the PI 5'-phosphatase SHIP2 was identified as an interaction partner of Arap3. 17557929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17557929_There was no association of INPPL1 polymorphisms & essential hypertension. Any association may be limited to metabolic syndrome patients with hypertension as part of the phenotype 17671700_ignificance of glucose intolerance in prognosis of male hepaatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients and down-regulation of SHIP2 expression in HCC. 17672824_shift in the balance of lipid signals is the activation of SHIP2 by increased tyrosine phosphorylation, an effect observed in HeLa cells in response to both PTP inhibitors and epidermal growth factor. 17893231_endogenous SHIP2 in MDA-231 breast cancer cells supports in vitro cell proliferation, increases cellular sensitivity to drugs targeting the EGFR and supports cancer development and metastasis 18061583_These data raise the interesting possibility that SHIP2 inhibition exerts proliferative effects in beta-cells and further support the attractiveness of a specific inhibition of SHIP2 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18692052_Thse data provide a molecular link between SHIP2 and ITSN1 which are involved in receptor endocytosis regulation. 18991394_NMR and ITC (isothermal titration calorimetry) studies on the Sam domain of Ship2 revealing its three-dimensional structure and its possible mode of interaction with the Sam domain from the EphA2 receptor 19033458_the corneal epithelial-specific miR-184 can interfere with the ability of miR-205 to suppress SHIP2 levels 19065064_High expression of obesity-linked phosphatase SHIP2 is associated with invasive breast cancer. 19477690_comparison of expression of SHIP-1, SHIP-2, and Syk protein to histamine release from mast cells cultured from the peripheral blood of chronic idiopathic urticaria responder (R), chronic idiopathic urticaria NR, and normal subjects 19518129_SH2 domain of SHIP2, in conjunction with the C-terminus, confers an inhibitory effect to maintain a low basal activity, and signal-induced tyrosine phosphorylations overcome this effect to activate SHIP2 19765305_This binding mode of Ship 2 protein is identical to the association between Ship2-Sam and the Sam domain from the Ephrin A2 receptor. 19825976_data highlight a novel biological role of the PP2A(T130) holoenzyme in EGF signaling through interaction with EGFR and the phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase SHIP2. 19839650_Data suggest that a combination of tissue distribution, specificity, and kinetic differences is likely responsible for SHIP1 and SHIP2 in vivo functional differences. 19880507_SHIP2 (SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase 2) SH2 domain negatively controls SHIP2 monoubiquitination in response to epidermal growth factor. 19895833_Data show that SHIP2 localizes to the nucleus and periphery, and has been shown to translocate to the cell membrane following EGF treatment. 20114020_A recent study now shows that two additional tyrosines within Tir recruit the inositol phosphatase SHIP2 to generate a PI(3,4)P2-enriched membrane platform that stabilizes pedestal assembly. 20114025_The authors demonstrate that Y483 and Y511 within tandem ITIM-like sequences of Escherichia coli Tir are essential for recruiting human SHIP2, a host inositol phosphatase. 20236936_LL5beta directs the translocation of filamin A and SHIP2 to sites of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) accumulation, and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 localization is mutually modified by co-recruited SHIP2. 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530248_Treatment of HEKs and HCEKs with antago-205 increased SHIP2 levels and impaired the ability of these cells to seal linear scratch wounds compared with untreated or irrelevant-antago treatments 20654688_The upregulation of SHIP2 in Zucker rat glomeruli prior to the age of onset of proteinuria suggests a possible role for SHIP2 in the development of podocyte injury. 21770892_The function of SHIP2 is different at the plasma membrane where it recognizes PtdIns(3,4,5)P3, and in the nucleus where it may interact with PtdIns(4,5)P2, particularly in speckles. 21918362_Caveolin-1 knockdown by small interfering RNA reduces H2O2-induced SHP-2 phosphorylation in rat primary astrocytes and in CRT-MG human astroglioma cells. 22079859_results support the hypothesis that SHIP2 may play a critical role in the initiation and progression of LSCC and may serve as both a prognostic marker and a potential therapeutic target in patients with LSCC 22194892_Nephrin ligation resulted in abnormal morphology of actin tails in human podocytes when Ship2, Filamin or Lamellipodin were individually knocked down. 22244754_SHIP2 suppresses ligand-induced activation of EphA2 and promotes receptor coordinated chemotactic cell migration. 22593208_RhoA associates with SHIP2 to regulate cell polarization and migration. 23273567_mutations in inositol polyphosphate phosphatase-like 1 (INPPL1) cause opsismodysplasia with or without renal phosphate wasting. 23273569_INPPL1 mutations in OPS, a severe spondylodysplastic dysplasia with major growth plate disorganization, supports a key and specific role of this enzyme in endochondral ossification. 23552673_INPPL1 is the disease gene for opsismodysplasia; opsismodysplasia has genetic heterogeneity. 24091101_SHIP2 play roles in normal development and at in cell proliferation in some cancer derived cells. [review] 24133597_The results of this research suggested that SHIP2 expression was correlated with malignant phenotypes of non-small cell lung cancer and may thus serve as a poor prognostic factor and valuable oncogene for NSCLC. 24183204_Together, our result was shown that miR-184 might play a part in proliferation of HCC cells by INPPL1 loss and act as antiapoptotic factor in the development of HCC by inhibiting the activities of caspases 3/7. 24228114_SHIP2 expression is correlated with significant characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma, and it may be useful as an unfavorable prognostic factor in HCC. 24313349_Association with SHIP2 and aging might depend on its effect on the insulin/IGF-1 pathway. 24561238_SHIP2 localization in intact cells is dependent on phosphorylation mechanisms on both Ser/Thr and Tyr residues. 24704254_The crystal structures of human SHIP2 in complex with phosphoinositide substrate analogs revealed a membrane interaction patch likely to assist in sequestering substrates from the lipid bilayer. 24802135_In conclusion, SHIP2 plays a key role in breast cancer stem cells of ER-negative breast cancers 25383712_Findings indicate that SHIP2 is a regulator of lymphatic function in humans and that inherited mutations in the INPPL1 gene may act in concert with HGF, and likely MAP3K7, mutations to exacerbate lymphatic phenotypes. 25525286_Kaplan-Meier method and Cox multifactor analysis suggested that high SHIP2 protein level and positive distant metastasis were critically associated with the unfavorable survival of coloretal cancer patients. 25635986_results indicated genotype and allele frequency of SHIP2(+1893CC/AA) locus in Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) Han Chinese patients was significantly different from healthy controls; G allele (+2945A/G) seemed to increase susceptibility to hypertension for T2DM patients 26123392_SHIP2 inhibition was accompanied by an increased Akt and FOXO-1 phosphorylation, whereas overexpression of the wild-type SHIP2 gene had the opposite effects 26188518_investigated the molecular link between SHIP2 expression and metabolic dyslipidemia using overexpression or suppression of SHIP2 gene in HepG2 cells 26201869_Suppression of SHIP2 contributes to tumorigenesis and proliferation of gastric cancer cells via activation of Akt. 26456051_these findings suggest that SHIP2 is an important regulator of hepatic lipogenesis and lipoprotein secretion in insulin resistance state. 26826186_Regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by SHIP2 controls glioblastoma cell migration through the organization of focal adhesions. 26910424_the dissociation process of the EphA2-SHIP2 SAM-SAM domain heterodimer complex the dissociation process of the EphA2-SHIP2 SAM-SAM domain heterodimer complex 27170292_In order to shed light on the role of the C2 related (C2R) domain, immediately C-terminal to the SHIP2 phosphatase domain, molecular cloning, expression, purification and crystallization of the human SHIP2 fragment containing the phosphatase (Ptase) and C2R domains were performed an X-ray crystallographic data analysis was conducted. 27246739_In glioblastoma 1321 N1 cells, we recently identified Myo1c as a new interactor of SHIP2. SHIP2 localization at lamellipodia and ruffles is impaired in Myo1c depleted cells. In the absence of Myo1c, N1 cells tend to associate to form clusters. 27597754_SHIP2 recruits Mena to invadopodia and disruption of SHIP2-Mena interaction in cancer cells leads to attenuated capacity for ECM degradation and invasion in vitro, as well as reduced metastasis in vivo. 27708270_article focuses on the mutations associated with opsismodysplasia and explores the role of INPPL1/ SHIP2 in skeletal development (Review) 27716613_the expression and intrinsic phosphatase activity of the lipid phosphatase SHIP2 is increased in human colorectal cancer, and that increased expression within a large cohort of CRC patient is correlated to a worse patient survival. SHIP2 functions as an oncogene, by enhancing cell migration and invasion, and reducing cell adhesion in colorectal cancer cells. 27926875_HIP2 regulates mitotic spindle alignment. SHIP2 is expressed in G1 phase, whereas Aurora A kinase is enriched in mitosis. SHIP2 binds Aurora A kinase and the scaffolding protein HEF1 and promotes their basolateral localization at the expense of their luminal expression connected with cilia resorption. 28117748_decreased expression of transcription factor Sp1 contributes to suppression of SHIP2 in gastric cancer cells. 28792888_Aiming to uncover interdomain regulatory mechanisms in SHIP2, the authors determined crystal structures containing the 5-phosphatase and a proximal region adopting a C2 fold. This reveals an extensive interface between the two domains, which results in significant structural changes in the phosphatase domain. 28869677_The authors report two novel mutations in the INPPL1 gene and show that cell migration is very much decreased in fibroblasts derived from three opsismodysplasia (OPS) patients as compared with control individuals. In contrast, cell adhesion on fibronectin is increased in OPS fibroblasts. 30061681_FBP17 and CIP4 prime the membrane of resting cells for fast endophilin-mediated endocytosis by recruiting the 5'-lipid phosphatase SHIP2 and lamellipodin to mediate the local production of phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate and endophilin pre-enrichment. 30228226_Data show that inositol phosphatase SHIP2 (SHIP2) recruited src-Family tyrosine kinases Src family kinases to the fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs), which promoted FGFR-mediated phosphorylation. 31498891_Low SHIP2 expression is associated with migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. 31545285_SHIP2 knockdown impairs cell proliferation, invasion, migration and promotes cell apoptosis. 31628071_Phosphoinositide 5-phosphatases SKIP and SHIP2 in ruffles, the endoplasmic reticulum and the nucleus: An update. 31664099_Abeta modulates actin cytoskeleton via SHIP2-mediated phosphoinositide metabolism. 32183047_IQGAP2 Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells via Elevating SHIP2 Phosphatase Activity. 32198795_SH2 domain-containing inositol-5'-phosphatase 2 (SHIP2) binds to the Western CagA-specific EPIYA-C segment or East Asian CagA-specific EPIYA-D segment of Helicobacter pylori in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner. SHIP2 binds more strongly to EPIYA-C than to EPIYA-D. Interaction with CagA tethers SHIP2 to the plasma membrane, where it mediates production of phosphatidylinositol 3,4-diphosphate [PI(3,4)P(2) ]. 32535200_IRSp53 is a novel interactor of SHIP2: A role of the actin binding protein Mena in their cellular localization in breast cancer cells. 32881386_SHIP2 inhibition alters redox-induced PI3K/AKT and MAP kinase pathways via PTEN over-activation in cervical cancer cells. 33421554_Expression, purification and characterization of the RhoA-binding domain of human SHIP2 in E.coli. 34021368_An auxiliary binding interface of SHIP2-SH2 for Y292-phosphorylated FcgammaRIIB reveals diverse recognition mechanisms for tyrosine-phosphorylated receptors involved in different cell signaling pathways. 34314064_A new layer of phosphoinositide-mediated allosteric regulation uncovered for SHIP2. 35421738_OxLDL-stimulated macrophage exosomes promote proatherogenic vascular smooth muscle cell viability and invasion via delivering miR-186-5p then inactivating SHIP2 mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000032737 |
Inppl1 |
1543.307945 |
0.4407106206 |
-1.182096 |
0.085888102 |
185.656478 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000282152952614116119748479794349448491006370493365011975662149478753416891915966860205696555685233026205987788732898469135079722036607563495635986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000049875180605800641060806553497386940829010501569251983721685577079864542416510816392106474527476358882044013554057926285167923197150230407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
952.1014469 |
63.6198118 |
2178.9185209 |
104.2986278 |
| ENSG00000165474 |
2706 |
GJB2 |
protein_coding |
P29033 |
FUNCTION: Structural component of gap junctions (PubMed:17551008, PubMed:19340074, PubMed:21094651, PubMed:26753910, PubMed:16849369, PubMed:19384972). Gap junctions are dodecameric channels that connect the cytoplasm of adjoining cells. They are formed by the docking of two hexameric hemichannels, one from each cell membrane (PubMed:17551008, PubMed:19340074, PubMed:21094651, PubMed:26753910). Small molecules and ions diffuse from one cell to a neighboring cell via the central pore (PubMed:21094651, PubMed:16849369, PubMed:19384972). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16849369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17551008, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19340074, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19384972, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21094651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26753910}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Ectodermal dysplasia;Gap junction;Hearing;Ichthyosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Non-syndromic deafness;Palmoplantar keratoderma;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the gap junction protein family. The gap junctions were first characterized by electron microscopy as regionally specialized structures on plasma membranes of contacting adherent cells. These structures were shown to consist of cell-to-cell channels that facilitate the transfer of ions and small molecules between cells. The gap junction proteins, also known as connexins, purified from fractions of enriched gap junctions from different tissues differ. According to sequence similarities at the nucleotide and amino acid levels, the gap junction proteins are divided into two categories, alpha and beta. Mutations in this gene are responsible for as much as 50% of pre-lingual, recessive deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:2706; |
astrocyte projection [GO:0097449]; cell body [GO:0044297]; connexin complex [GO:0005922]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; gap junction [GO:0005921]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; gap junction channel activity [GO:0005243]; gap junction channel activity involved in cell communication by electrical coupling [GO:1903763]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; aging [GO:0007568]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to glucagon stimulus [GO:0071377]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; epididymis development [GO:1905867]; gap junction assembly [GO:0016264]; gap junction-mediated intercellular transport [GO:1990349]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; response to antibiotic [GO:0046677]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to human chorionic gonadotropin [GO:0044752]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
11073548_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11074495_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11076062_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11134236_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11162081_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11216657_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11313751_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11313763_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11386851_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11409864_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11432967_M34T variant in deafness 11438992_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11438992_mutational analysis in patients with hereditary hearing impairment 11439000_mutations causing sensorineural hearing impairment in Ghana 11445873_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11483639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11493200_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11584050_prevalence of the 30delG mutation and report of two novel mutations in patients with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss in Lebanon 11587277_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11603757_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11668644_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11668644_founder deletion mutation in GJB6 cooperating with a GJB2 mutation in Ashkenazi Jews with non-syndromic deafness 11748849_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11788203_outer hair cell function is affected by the 35delG mutation in Cx26. 11846738_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11872627_Methylation-sensitive single-stranded conformation analysis showed variable methylation in the promoter region CpG island in 11 out of 20 (55%) breast cancer patients 11872644_Transfection with Cx26 cDNA inhibited dedifferentiation, suppressed cell proliferation, and apoptosis was induced. Tumor growth of PLC/Cx26 was retarded. 11912510_Missense mutations in GJB2 encoding connexin-26 cause the ectodermal dysplasia keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. 11935342_Genetics of congenital deafness in the Palestinian population: multiple connexin 26 alleles with shared origins in the Middle East. 11935342_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11960582_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11968091_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11977173_Effective rehabilitation for profoundly deaf individuals with GJB2-related deafness is possible through cochlear implantation. 12042301_overexpression of Cx43 or Cx26 in breast cancer cells down-regulated fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 12064627_Data indicate that, at least in vitro, connexin26 affects the function of human keratinocytes, independently of obvious changes in coupling. 12064630_These results provide evidence as to how heterozygous connexin 26 (cx26) mutations could contribute to autosomal dominant deafness, by resulting in a net loss, and/or alteration, of Cx26 function. 12068628_Frequency of the 35delG mutation of the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) in patients with non-syndromic autosome-recessive deafness from Bashkortostan and in ethnic groups of the Volga-Ural region 12068628_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12081719_analysis of mutations in the GJB2 gene in Brazilian families with either familial or sporadic deafness in order to determine the frequency and type of connexin26 mutations among patients with non-syndromic hearing loss 12107817_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12107817_mutations in the Cx26 gene in cases of familial and sporadic hearing loss by gene sequencing and identifies the allelic frequency of the most common mutation leading to HL (35delG) in the population of Eastern Austria 12110573_conformational changes in surface structures of connexin 26 gap junctions 12111646_Mutations found for prelingual deafness in Taiwan 12111646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12112666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12167443_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12169891_A novel connexin 26 compound heterozygous mutation results in deafness. 12172392_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 12172392_epidemiology studies of the alleles of GJB2, prevalence rates, genotype-phenotype relations, contribution to the incidence of hearing loss, and other issues related to the clinical validity of genetic testing for GJB2 [review] 12172394_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12174613_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12176036_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12176036_frequency of GJB2 mutations in an Italian population affected by hearing loss, and functional analysis of six missense mutations 12176179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12189487_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12189487_Progressive hearing loss, and recurrent sudden sensorineural hearing loss associated with GJB2 mutations in Austria. 12189493_connexin 26 deafness mutations affect the function of gap junction channels 12212857_Connexin 26 gene mutation is implicated in preverbal hearing impairment. 12384501_roles of Met-34, Cys-64, and Arg-75 in assembly 12384781_prevalence of mutation being responsible for commonest form of non-syndromic recessive deafness in Chinese population 12393046_GJB2 gene mutations are responsible for deafness. 12417772_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12420583_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12484567_These findings suggest that expression of Cx26 and Cx43 might be related to the differentiation of the arachnoid villi and meningiomas, and exhibit the different origin of various subtypes of meningiomas. 12490065_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12497637_Detection of disequilibrium between M34T (c.101T>C) and -493del10 in German hearing impaired persons. 12497637_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12501766_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12505163_Loss-of-function and residual channel activity of connexin26 mutations associated with non-syndromic deafness. 12522692_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12522692_The connexin26 gene is responsible for DFNB1 and DFNA3 (Autosomal Recessive Hereditary Nonsyndromic Deafness Locus 1 and Autosomal Dominant Hereditary Nonsyndromic Deafness Locus 3) 12527132_Mutations may impact outer hair cell function among carriers of one or two mutations. Inner hair cells /nerve impairment among homozygotes and compound heterozygotes is variable. 12530196_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12530196_Sensorineural deafness may be the result of 35delG mutation in the GJB2 gene. 12557263_The expression of the tumor suppressor gene connexin 26 is not mediated by methylation in human esophageal cancer cells. 12560944_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12560944_Results were consistent with inheritance of the 235delC mutation from a common ancestor: implications for genetic diagnostic testing for deafness in the Japanese population. 12624506_GJB2 gene is implicated in large vestibular aqueduct syndrome. 12668604_We suggest that cx26 and cx30 form heteromeric connexons in vivo, within the inner ear, with particular properties essential for hearing. 12684873_We identified two single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) immediately upstream of the first exon of GJB2. 12746422_contribution of mutations and founder effect to non-syndromic hearing loss in India 12767933_Permeability and gating properties of connexin 26. 12768774_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12792423_Mutations in GJB2 were determined in Taiwanese patients with prelingual deafness. 12792423_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12810983_To determinate the frequency of digenic (GJB2/GJB6) background of DFNB (autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss), 17 patients with heterozygous 35delG mutation were screened for deletion of 342 kb in GJB6 gene, and none found. 12833397_W24X is a common allele at GJB2 and may be the cause of the autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment in an Indian population. 12835856_Mutations in the GJB2 gene, especially the 35delG mutation, have been established as a major cause of inherited and sporadic nonsyndromic hearing impairment in different populations. 12844145_Data show that during cell invasion, Shigella induces the opening of connexin 26 (Cx26) hemichannels in an actin- and phospholipase-C-dependent manner. 12851846_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12865758_GJB2 and GJB6 may have a causative role in deafness 12865758_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12904681_No significant differences were found between the 15 children where connexin 26 was known to be the cause of deafness and the other 37 children in the study. 12925341_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14505035_235delC is an ancient mutation that arose after the divergence of Mongoloids and Caucasians. 14520102_evaluate the role of the gap junction protein beta-2 gene (GJB2), encoding connexin 26 (Cx26), in children with moderate to profound prelingual nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing impairment 14534413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14556203_235delC mutation of GJB2 was related with Chinese autosomal recessive deafness, and the 232G to A(Ala78Thr) missense mutation was found to be a novel mutation. 14643477_Three different GJB2 mutations were found in Exon 2 of the probands, which were 35delG, 299-300delAT, and 487G > A (M163V). 14660916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14681041_Cx26 mutants exhibit both sensorineural deafness and various skin disease phenotypes 14681046_Cx26 regulates angiogenesis-related molecules by mechanisms that are both GJIC-dependent and -independent 14719096_Forced expression of Cx26 suppresses the growth of prostate cancer cells and decreases the expression of Bcl-2. 14722929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14722929_Ten novel mutations found in GJB2 in non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness affected children in Kenya and Sudan. 14735592_Maternal origin of mutation in connexin 26 gene 14759569_It showed that patients who are compound heterozygous for a 342-kb deletion involving a large portion of the 5'-part of GJB6, encoding connexin 30, and a GJB2 mutation develop NSHL due to a trait with a digenic pattern of inheritance. 14978038_the first extracellular loop is critical for Cx26 transport to the cell surface as well as function of the resulting gap junction channels. 14979964_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14985372_GJB2 genotype has a major impact on the degree of hearing impairment, and identification of mild genotypes 14985372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15025729_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15033936_Equimolar coexpression of M34T Cx26 mutant & wt Cx26 showed that M34T did not significantly reduce Cx26/Cx26 coupling or alter the electrophysiological properties of the wt channels. Overexpression inhibited conductance. M34T localizes to cell junctions. 15064611_connexin 26 mutations are linked to sensorineural hearing loss in children 15113126_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15138772_GJB2 mutations is a major cause of congenital sensorineuarl hearing loss. 15140236_induction of Cx26 and Cx30 near the wound margins in spontaneous wound healing and-even earlier-after the transplantation of keratinocytes. 15146474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15146474_results confirm the importance of GJB2 mutations in the Hungarian population displaying mutation frequencies that are comparable with those in the Mediterranean area 15148174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15219044_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15226564_The prevalence of Connexin 26 gene in the Indian population as found in their study, together with other deafness genes segregating non-syndromic deafness, accounting for approximately 40% of all cases. 15236885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15242756_These results suggest that Cx26-mediated gap junction intercellular communication may play a crucial role in enhancing the barrier function of Caco-2 cell monolayers. 15253766_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15274422_GJB2 gene mutation is connected with sensorineural hearing loss. 15288505_The telencephalic ganglionic eminence is the most common site of bleeding in preterm infants. Connexin 26 involved in forming intercellular gap junctions is expressed in ganglionic eminence cells up to 500 microns from the bleeding. 15334670_mRNA level correlates with cell differentiation, and is predictive of postopoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. 15337980_A new heterozygous point mutation (C119T) in GJB2 that substitutes a valine for alanine at codon 40 (A40V) in the connexin 26 protein disrupts the function of the gap junctions connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent cells critical for tissue homeostasis. 15345117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15345117_We report the first study of GJB2 and GJB6 mutations in Danish patients with NSHI 15359540_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15365987_1,294 deaf patients were screened for GJB2 coding sequence allele variants, del(GJB6-D13S1830), and/or noncoding region mutations. Genotype-phenotype correlations were categorized as either protein truncating or nontruncating. 15365987_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15386363_Our results suggest the inactivation of Cx26 (connexin 26) in lung cancer may be explained by promoter methylation. 15464305_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15464305_The 35delG mutation was found in nine of the probands or in 14 of the mutated alleles. The V37I mutation and the del(GJB6-D13S1830) mutation were also found in two patients, both are compound heterozygote with 35delG mutation. 15464308_Data exclude a digenetic association of del(GJB6-D13S1830) with heterozygous GJB2 mutations as a cause of deafness in a representative sample of the population from Eastern Austria. 15464308_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15479191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15482471_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15482471_pleiotropic GJB2 mutations are responsible for at least 5 overlapping dermatological disorders associated with syndromic hearing loss and cover a wide range of severity and organ involvement. 15502644_Overexpressed connexin26 in pancreatic cancer is a cause of impaired glucose tolerance. 15504600_GJB2 analysis is an important test that identifies a major cause of newborns with bilateral severe-to-profound NSHI screened by universal newborn hearing screening in Northern China. The most common pathologic mutation of GJB2 in studied cases was 235delC 15504600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15547422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15547423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15547683_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15547683_genetic screening for two common mutations in different populations in Hungary 15577772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15592461_the V84L mutation reduces metabolic coupling mediated by Ins(1,4,5)P(3) to an extent sufficient to impair the propagation of Ca(2+) waves and the formation of a functional syncytium 15617546_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15617546_Two frequently detected mutations, 35delG and delE120, were shown to have single origins based on the conserved genotypes of two closely linked microsatellite and five single nucleotide polymorphism markers. 15635064_Heterozygous missense mutation in sensorineural hearing loss, striate palmoplantar hyperkeratosis and knuckle pads. 15638823_Double heterozygosity with mutations in the GJB2 gene is associated with congenital deafness 15656949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15656949_We hereby describe the hearing impairment in Dutch patients with biallelic connexin 26 (GJB2) and GJB2+connexin 30 (GJB6) mutations 15670746_Here, two known variants G79A and G109A in the GJB2 gene were identified in the hearing-impaired and normal hearing matrilineal relatives of this Japanese family. 15700112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15704645_The expression of connexin 26 in the human colon mucosa was to evaluate. 15744158_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15770735_Cytoplasmic presence of Cx26 and its association with apoptotic markers could indicate distinct role from physiological functions of Cx26 in cancer cells. Connexins might be target for modulations of apoptosis with therapeutic implications. 15793769_Data show that the 235delC heterozygous mutation in GJB2 gene may not aggravate the symptoms of hearing loss associated with the A1555G mitochondrial mutation. 15832357_Findings are in contrast with the results obtained in other populations where GJB2 is a major cause of congenital recessive hearing loss. 15832357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15841999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15855033_GJB2 mutations account for about 30% of Turkish patients with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss(ARNSHL). W24X and delE120 occur more than once in the Turkish ARNSHL population with a frequency of about 5%. 15855033_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15857182_Meta-analysis of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15857852_Mutations in GJB2 is associated with hearing loss 15858675_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15870276_existence of internal ribosome entry sites in connexin mRNAs permits connexin expression in density-inhibited or differentiated cells, where cap-dependent translation is generally reduced 15878206_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15895291_Carriers of connexin 26 35delG mutations presented a decrease of hearing principally at 6,000 and 8,000 Hz, a frequency never analysed in previous studies. 15895291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15932734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15954104_A dominant mutation at a highly conserved residue, p.Gly130Val, was found in the family with Vohwinkel syndrome 15964725_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15964725_mutations in the GJB2 gene and the delGJB6-D13S1830 are prevalent in the Argentinean population in sensorineural deafness 15967879_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15996220_Unrelated individuals with autosomal recessive non-syndromic profound hearing loss, from Tunisia and Morocca, were screened for GJB2 mutations. 16012344_The connexin 26 mutations can be associated with saccular defects of the vestibular receptors. 16088916_Findings suggest that a founder effect for W24X mutation is responsible for its high prevalence among Spanish gypsies with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss. 16125251_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16154643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16158474_Finds involvement of 35delG/GJB2 mutation in etiology of confirmed hearing impairment in 2 of 8 newborns analyzed in Croatia. 16222667_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16226720_Functional studies indicated that the mutation T55N produces a protein that, although expressed to levels similar to those of the wt counterpart, is deeply impaired in its intracellular trafficking and fails to reach the plasma membrane. 16243461_significance of Cx26 mutations in Moroccan families who had hereditary and sporadic deafness 16258398_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16283880_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16335400_heterozygous 235delC mutation of the Cx26 gene may not modulate the severity of hearing loss associated with A1555G mutation 16371502_Non-syndromic hearing loss accounts for 80% of genetic hearing loss in children, with mutations in DFNB1/GJB2 being by far the most common cause. 16379178_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16379178_V37I mutation in the GJB2 gene have been reported as polymorphism in Western countries, however in our country it behaved as a potentially disease-causing missense mutation 16379542_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16380907_GJB2 mutations and degree of hearing loss were studied in a multicenter study. 16380907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16406239_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16407179_Cx26 and Cx43 have roles in closed gap junction channel formation 16425640_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16532460_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16570074_SLC26A4 could be the second most frequent gene implicated in nonsyndromic deafness after GJB2 16647893_Detected with RT-PCR profiling in ovarian cancer cells. Sensitivity to paclitaxel maybe associated with connexin 43. 16650419_Audiometric testing revealed five (22.7%) with unrecognized sensorineural hearing loss; however, on genetic evaluation, none harbored a connexin 26 mutation. 16713631_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16773579_This is the first evidence of a deafness-associated regulatory mutation of GJB2 and of potential coregulation of GJB2 and GJB6 16777986_Cx26 expression, independent of the necessity for gap junctional intercellular communication, partially reverted a breast tumor cell line tumorigenesiss and regulated invasiveneess. 16840571_Mutations within the GJB2 gene are associated with slight/mild sensorineural hearing loss. 16849369_These data support the view that M34T is a pathological variant of Cx26 associated with hearing impairment 16877344_The N14Y mutation induces a change in local structural flexibility of the N-terminal domain of Connexin 26, which is important for exerting the activity of the channel function, resulting in impaired gap junctional intercellular communication. 16981465_The homozygous deletion C at position 233-235 of connexin26 cDNA will induce autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hereditary hearing loss. 17029193_Data show that the C-terminal of Nogo protein interacts with CX26. 17036313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17036313_the V37I allele is pathogenic, but produces milder hearing loss compared to nonsense mutations of connexin 26 such as the 35delG mutation 17041897_the GJB2 mutation p.N14D is associated with recessively inherited HI and exhibits a defective phenotype due to diminished expression at the cell surface. 17041943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17041943_carrier rates for GJB2-based hearing loss in various ethnic groups 17203385_Cx26 expression is associated with lymphatic vessel invasion, large tumor size, high histological grade, and poor prognosis in human breast cancers. 17227765_analysis of aminosulfonate modulated pH-induced conformational changes in connexin26 hemichannels 17253936_GJB2 35delG mutation is an important pathogenic mutation for hearing loss in the Greek Cypriot population. 17253936_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17276518_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17290388_derivative may also act on the Cx26 molecules that accumulate in the Golgi/endosome 17299707_Congenital cytomegalovirus infection is an important cause of severe sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), and it has an incidence comparable to that of GJB2-associated SNHL. 17313762_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17357124_GJB2 mutations, GJB6 deletions, and mtDNA mutations may not be significant in African American and Caribbean Hispanic individuals with hearing impairment 17357124_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17365058_association between GJB2 gene mutations, encoding connexin 26 (Cx26), and nonsyndromic hearing loss [review] 17368814_frequency of 35delG was about 18.5%, however, del(GJB6-D13S1830) was not found in the studied patients with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss; results support founder effect regarding these mutations 17369171_Direct DNA sequencing of the whole coding region of GJB2 revealed that a common homozygous mutation 235delC was responsible for most of the affected members in the Nonsyndromic neurosensory hearing impairment family. 17381453_spectrum of GJB2 mutations in keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome; study suggests that patients with the p.Ser17Phe mutation may have a more severe phenotype and could be at higher risk for tongue carcinoma 17394388_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17394388_frequency of the 35delG allele was estimated as 0.0067 in Brazilian population, and comparison between expected and observed genotype frequencies indicates that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium 17406097_A mutation is present in the GJB2 gene and is prevalent in a Turkish population; however, there are no large deletions. 17426645_Although GJB2 mutations were detected in children with and without CMV-related hearing loss, those with hearing loss had a higher frequency of GJB2 mutations 17426645_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17428550_we found a high GJB2 35delG carrier frequency of 2.8% in Gilan province in the north of Iran 17428836_Connexin 26 mutations leading to aberrant hemichannel activity might be a common feature of keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. 17431919_study reports on the severe hearing loss phenotype noted in two deaf siblings who are compound heterozygous for dominant and recessive GJB2 mutations 17444514_Study shows that GJB2 is the major gene for deafness in Turkey. 17455295_findings identify a cohort of 33 probands with pathogenic GJB2 mutations who have additional structural and/or developmental abnormalities beyond the bilateral sensorineural hearing loss , or who already had an established etiology for their hearing loss 17485979_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17505205_Chinese patients with nonsyndromic hearing impairment appear to have a relatively higher 235delC frequency than that of other Asian populations 17505205_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17551008_Three-dimensional structure of CX26 gap junction channel reveals a plug in the vestibule. 17553572_GJB2 gene mutation contributes to prevalence of autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss in Moroccans. 17553572_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17567887_Different mutations in the GJB2 gene were responsible for most of deafness cases. 17567889_Results show 18/49 non-syndromic autosomal recessive deafness individuals with GJB2 mutation. 17568408_Clinical data showed a bilateral sensorineural hearing loss for children with GJB2 35delG/35delG genotype. 17581693_A deafness-associated mutant human connexin 26 improves the epithelial barrier 17614106_Cx26 may contribute to the metastasis of melanoma by facilitating communication between melanoma cells and their surrounding endothelial cells. 17615163_Cx26 and Cx30 form functional heteromeric and heterotypic channels whose biophysical properties and permeabilities are different from their homotypic counterparts 17660464_A novel -3438CT mutation in the GC box at position -81 relative to the transcription start point abolishes the basal promoter activity. In trans with V84M, it causes profound hearing loss by forming non-functional gap junctions in the cochlea. 17661817_Autosomal recessive deafness caused by p.Val37Ile and p.Leu90Pro mutations in Connexin 26. 17666888_findings suggest that loci other than GJB2 and GJB6 contribute to the pathogenesis of autosomal recessive-nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss and that the full spectrum of GJB2 sequence changes is not yet fully elucidated 17672987_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17672988_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17695503_Cx30 expression in head and neck cancer was drastically reduced compared to apparently normal mucosa while Cx26 expression was almost the same. 17786286_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17903576_Although children with CI with DFNB1 show faster gains in Reynell scores, duration of CI use appears to have a greater effect on speech perception than DFNB1 status. Identification of DFNB1 children is useful in counseling of CI outcomes. 17909436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17909436_there is no increased susceptibility in GJB2 35delG carriers for the development of age-related hearing impairment or noise-induced hearing loss 17935238_Mutations in GJB2 is associated with hearing impairment 17935238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17949297_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17989577_Mutations in connexin 26 and 30 genes are rare in patients with chronic or recurrent acute rhinosinusitis and do not seem to play a contributory role in the pathogensis of these disorders. 17989577_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17993581_report on a family with a novel GJB2 mutation (p.His73Arg) causing a syndrome of focal palmoplantar keratoderma with severe progressive sensorineural hearing impairment 18024254_study reports an African family with dizygotic twins suffering from a lethal form of Keratitis-Ichthyosis-Deafness (KID) syndrome; the two patients were heterozygous for the G45E mutation of GJB2, whereas the mutation was not detected in the two parents 18075246_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18089569_review of autosomal dominant mutations of the genes encoding Cx26 and Cx43 [review] 18167282_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18191019_These results suggest that Cx26 may be implicated in the pathogenesis of PTC and FTC and is associated with the biologically aggressive phenotypes of these tumors. 18196482_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18196482_Show progressive hearing loss in subjects with CX26 mutations. 18245526_Aberrant expression of Cx26 plays an essential role in lung metastasis and is thus a therapeutic target for colorectal patients with lung metastasis. 18261328_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18267319_Polarized Caco-2/TC7 cells express significant amounts of Cx26, Cx32 and Cx43. 18274916_19.26% patients carried GJB2 mutations including 10.12% single mutant carriers. 235delC was the most common type, making up 69.18% of all mutants for GJB2. 18274916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18288393_Cx26 expression is upregulated in a considerable percentage of gastrointestinal carc |
ENSMUSG00000046352 |
Gjb2 |
8.575571 |
6.0723634582 |
2.602258 |
0.622576171 |
19.772102 |
0.00000872468809752336725885611679043307731262757442891597747802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027557542546425189332283053889049995177629170939326286315917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.0177823 |
5.8095962 |
2.4908186 |
0.8583756 |
| ENSG00000165490 |
220042 |
DDIAS |
protein_coding |
Q8IXT1 |
FUNCTION: May be an anti-apoptotic protein involved in DNA repair or cell survival. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24214091}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Growth arrest;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage and regulation of DNA stability. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:220042; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:1902230]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of DNA stability [GO:0097752] |
25612832_NOXIN overexpression, as a result of genomic DNA gain or amplification, promotes HCC tumorigenesis by accelerating DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression, where NOXIN functions as a cofactor of DNA polymerase-primase complex 26493727_DDIAS is a target of NFATc1 and is associated with cisplatin resistance in lung cancer cells. 27412911_EGF activates the ERK5/MEF2 pathway, which in turn induces DDIAS expression to promote cancer cell invasion by activating beta-catenin target genes 28079882_these findings indicate that the stability of the DDIAS protein is regulated by CHIP/HSP70-mediated proteasomal degradation and that CHIP overexpression stimulates the apoptosis of lung cancer cells in response to DNA-damaging agents 28618963_Noxin facilitated the expression of Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E1 through activating P38-activating transcription factor 2 signaling pathway, thus enhanced cell growth of breast cancer 29242605_High DDIAS expression suppresses TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting DISC formation and destabilizing caspase-8 in lung and liver cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000030641 |
Ddias |
44.353764 |
2.4990576536 |
1.321384 |
0.279377748 |
22.491701 |
0.00000211053422018970996437594971062434723307887907139956951141357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007197662913585979263140710027180091401532990857958793640136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.7728980 |
12.3211019 |
24.8846670 |
3.8048023 |
| ENSG00000165507 |
11067 |
DEPP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NTK1 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a critical modulator of FOXO3-induced autophagy via increased cellular ROS. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24530860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25261981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28545464}. |
Autophagy;Cytoplasm;Mitochondrion;Peroxisome;Reference proteome |
|
The expression of this gene is induced by fasting as well as by progesterone. The protein encoded by this gene contains a t-synaptosome-associated protein receptor (SNARE) coiled-coil homology domain and a peroxisomal targeting signal. Production of the encoded protein leads to phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor ELK1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11067; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506] |
15977181_Expressed in endothelial cells of peripheral tissues, but not in atrial or ventricular endocardial cells of the heart, unexpected degree of molecular heterogeneity among arterial endothelial cells, up-regulated in subsets of endothelial cells. 16123073_Depp modulates the effects of progesterone during decidualization and in the decidua by affecting gene expression. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937567_DEPP is a novel insulin-regulatory molecule expressed abundantly in insulin-sensitive tissues including white adipose tissue and liver. 20822508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21510935_DEPP is regulated at the level of transcription by FoxO in human vascular endothelial cells 24936657_C10orf10 expression is frequently decreased in breast cancer tissues and is associated with shorter survival times. 25261981_Knockdown of DEPP prevented the primary and secondary reactive oxygen species wave during FOXO3 activation. 31963726_The Expression of Decidual Protein Induced by Progesterone (DEPP) is Controlled by Three Distal Consensus Hypoxia Responsive Element (HRE) in Hypoxic Retinal Epithelial Cells. 34997944_C10orf10/DEPP activates mitochondrial autophagy and maintains chondrocyte viability in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000048489 |
Depp1 |
8.798060 |
0.1643466617 |
-2.605186 |
0.660640345 |
16.823352 |
0.00004102534390648427146605636828269325633300468325614929199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000119387629728563891503591298803854670040891505777835845947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5849293 |
1.1591810 |
15.8569316 |
3.8071489 |
| ENSG00000165516 |
23588 |
KLHDC2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2U9 |
FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of a Cul2-RING (CRL2) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex of the DesCEND (destruction via C-end degrons) pathway, which recognizes a C-degron located at the extreme C terminus of target proteins, leading to their ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:29779948, PubMed:29775578, PubMed:30526872). The C-degron recognized by the DesCEND pathway is usually a motif of less than ten residues and can be present in full-length proteins, truncated proteins or proteolytically cleaved forms (PubMed:29779948, PubMed:29775578, PubMed:30526872). The CRL2(KLHDC2) complex specifically recognizes proteins with a diglycine (Gly-Gly) at the C-terminus, leading to their ubiquitination and degradation (PubMed:29779948, PubMed:29775578, PubMed:30526872). The CRL2(KLHDC2) complex mediates ubiquitination and degradation of truncated SELENOK and SELENOS selenoproteins produced by failed UGA/Sec decoding, which end with a diglycine (PubMed:26138980, PubMed:30526872). The CRL2(KLHDC2) complex also recognizes proteolytically cleaved proteins ending with Gly-Gly, such as the N-terminal fragment of USP1, leading to their degradation (PubMed:29775578, PubMed:30526872). May also act as an indirect repressor of CREB3-mediated transcription by interfering with CREB3-DNA-binding (PubMed:11384994). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11384994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26138980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29775578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29779948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30526872}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Kelch repeat;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29775578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29779948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30526872}. |
Enables ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity. Involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway. Located in nuclear body and nuclear membrane. Is active in Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23588; |
Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031462]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity [GO:1990756]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the C-end degron rule pathway [GO:0140627] |
16964437_Data show that KLHDC1 and KLHDC2 have differential localization and activity in cultured mammalian cells. 30526872_Three crystal structures have been reported of a CRL2 substrate receptor, KLHDC2, in complex with the diglycine-ending C-end degrons of an early terminated selenoprotein, SelK, and the N-terminal proteolytic fragment of USP1. |
ENSMUSG00000020978 |
Klhdc2 |
118.050751 |
0.4991283227 |
-1.002517 |
0.192886165 |
26.924781 |
0.00000021152929053068118378481293241633043322735829860903322696685791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000805929873059590601108942518188138492973848769906908273696899414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
75.9866764 |
13.1914977 |
153.4534453 |
18.9105493 |
| ENSG00000165617 |
51339 |
DACT1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NYF0 |
FUNCTION: Involved in regulation of intracellular signaling pathways during development. Specifically thought to play a role in canonical and/or non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways through interaction with DSH (Dishevelled) family proteins. The activation/inhibition of Wnt signaling may depend on the phosphorylation status. Proposed to regulate the degradation of CTNNB1/beta-catenin, thereby modulating the transcriptional activation of target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway. Its function in stabilizing CTNNB1 may involve inhibition of GSK3B activity. Promotes the membrane localization of CTNNB1. The cytoplasmic form can induce DVL2 degradation via a lysosome-dependent mechanism; the function is inhibited by PKA-induced binding to 14-3-3 proteins, such as YWHAB. Seems to be involved in morphogenesis at the primitive streak by regulating VANGL2 and DVL2; the function seems to be independent of canonical Wnt signaling and rather involves the non-canonical Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway (By similarity). The nuclear form may prevent the formation of LEF1:CTNNB1 complex and recruit HDAC1 to LEF1 at target gene promoters to repress transcription thus antagonizing Wnt signaling. May be involved in positive regulation of fat cell differentiation. During neuronal differentiation may be involved in excitatory synapse organization, and dendrite formation and establishment of spines. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15580286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16446366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17197390, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18936100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22470507}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the dapper family, characterized by the presence of PDZ-binding motif at the C-terminus. It interacts with, and positively regulates dishevelled-mediated signaling pathways during development. Depletion of this mRNA from xenopus embryos resulted in loss of notochord and head structures, and mice lacking this gene died shortly after birth from severe posterior malformations. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:51339; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; synapse [GO:0045202]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; delta-catenin binding [GO:0070097]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; protein kinase A binding [GO:0051018]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; embryonic hindgut morphogenesis [GO:0048619]; negative regulation of beta-catenin-TCF complex assembly [GO:1904864]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030178]; neural tube development [GO:0021915]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0030177]; regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060828]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:2000095]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
15580286_Downregulation of HDPR1 is common in hepatic cellular carcinomas, frequently involves hypermethylation of the promoter region. 16446366_DACT1 antagonizes Wnt signaling by promoting DVL2 degradation. 18936100_Dpr1 negatively modulates the basal activity of Wnt1/beta-catenin signaling in the nucleus by keeping LEF1 in the repressive state. 19073771_Dact1 regulates adipogenesis through coordinated effects on gene expression that selectively alter intracellular and paracrine/autocrine components of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 19733838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20232357_Knockdown of HDPR1 gene enhanced the invasive ability of lung cancer cells, which was dependent on p120ctn and independent of beta-catenin 20844743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21176356_As(2)O(3) induces demethylation of hdpr1 gene from abnormal hypermethylation status and activates its reexpression, thus suppressing the proliferation of Jurkat cells. 21262972_14-3-3beta interacts with human Dapper1, attenuating the ability of hDpr1 to promote Dishevelled (Dvl) degradation, thus enhancing Wnt signaling 21525190_Cytoplasmic HDPR1 protein expression was associated with tumor malignant progression via beta-catenin accumulation. 22470507_DACT1 stabilizes beta-catenin via DACT1-induced effects on GSK-3beta and directly interacts with beta-catenin proteins. 22610794_five missense heterozygote mutations of the DACT1 gene are specifically identified in 167 stillborn or miscarried Han Chinese fetuses with neural tube defects. 23073659_These findings provided insight into the role of DACT1 as a novel functional tumor suppressor in gastric cancer through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 23696638_Data indicate that Sestd1 cooperates with Dact1 in Vangl2 regulation and in the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway during mammalian embryonic development. 24980960_Dpr1 directly interacts with Beclin1 and Atg14L and enhances the Beclin1-Vps34 interaction and Vps34 activity. 25424899_our results suggested that DACT1 was upregulated during human placenta development. 25524937_There was no statistical difference between groups concerning DACT1 and DACT2 either in promoter hypermethylation or transcript levels. Age was associated with DACT2 promoter hypermethylation, especially over 56 years old. 25558878_Overexpression of Dapper-1 allows the translocation of MIZ-1 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. 25825496_Dpr1 promotes the ubiquitination of Dvl2 by pVHL and mediates the protein aggregate-elicited autophagy initiation 26099026_Dact1 has a critical role in the ability support keratinocyte proliferation, by attenuating Wnt/beta catenin signaling. 27714812_Dact1 is up-regulated by TGF-beta1, inducing apoptosis in mesangial cells. 27833078_DACT1alpha plays a pivotal role as a potential tumor suppressor in migration and invasion of gastric cancer. DACT1alpha methylation may serve as a biomarker for the prognosis of gastric cancer. 28054444_Findings suggest that the DACT1 c.1256G>A nonsense variant is causative of a specific genetic syndrome with features overlapping Townes-Brocks syndrome. 28077137_The simultaneous methylation of DACT1 and DACT2 may play important roles in progression of ESCC and may serve as prognostic methylation biomarkers for ESCC patients. 28237722_Dapper1 attenuates hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis in Ttype 2 diabetes. 28839145_We identified DACT1 as a negative regulator in type I EOC, protecting against malignant expansion by inhibiting canonical Wnt signalling and cis-platinum resistance by regulating autophagy. 29037126_An inhibitory role for DACT1 in leukemogenesis. 30547803_This study demonstrates that cyclin G2 suppresses Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and migration through Dapper1. 31978940_Cyclin G2 regulates canonical Wnt signalling via interaction with Dapper1 to attenuate tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. 33843483_DACT1 variants and colorectal cancer. 34350095_Histone Deacetylation Regulated by KDM1A to Suppress DACT1 in Proliferation and Migration of Cervical Cancer. 35121825_M(6)A demethylase FTO-mediated downregulation of DACT1 mRNA stability promotes Wnt signaling to facilitate osteosarcoma progression. 35510412_Disheveled binding antagonist of beta-catenin 1 interacted with beta-catenin and connexin 43 in human-induced pluripotent stem cells-derived cardiomyocytes. |
ENSMUSG00000044548 |
Dact1 |
10.595207 |
2.9402522170 |
1.555940 |
0.521330379 |
9.184793 |
0.00244034177087559030899788226065538765396922826766967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005305559660940302110776478627940377919003367424011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.6956006 |
5.3190625 |
5.7332094 |
1.5087955 |
| ENSG00000165626 |
222389 |
BEND7 |
protein_coding |
Q8N7W2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable DNA binding activity. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:222389; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; DNA binding [GO:0003677] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28300201_These results validated the association of two previously known skin pigmentation genes, SLC24A5 (minimum p = 2.62 x 10(-14), rs1426654) and SLC45A2 (minimum p = 9.71 x 10(-10), rs16891982), and revealed the intergenic region of BEND7 and PRPF18 as a novel locus associated with this trait (minimum p = 4.58 x 10(-9), rs6602666). |
ENSMUSG00000048186 |
Bend7 |
15.910466 |
0.2671812858 |
-1.904109 |
0.486078059 |
15.325847 |
0.00009047019589058841095713381363907501508947461843490600585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000250438876846414992284606260142254541278816759586334228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3029271 |
3.2817332 |
24.2620169 |
8.4766143 |
| ENSG00000165702 |
8328 |
GFI1B |
protein_coding |
Q5VTD9 |
FUNCTION: Essential proto-oncogenic transcriptional regulator necessary for development and differentiation of erythroid and megakaryocytic lineages. Component of a RCOR-GFI-KDM1A-HDAC complex that suppresses, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development and controls hematopoietic differentiation. Transcriptional repressor or activator depending on both promoter and cell type context; represses promoter activity of SOCS1 and SOCS3 and thus, may regulate cytokine signaling pathways. Cooperates with GATA1 to repress target gene transcription, such as the apoptosis regulator BCL2L1; GFI1B silencing in leukemic cell lines markedly increase apoptosis rate. Inhibits down-regulation of MYC and MYB as well as the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CDKN1A/P21WAF1 in IL6-treated myelomonocytic cells. Represses expression of GATA3 in T-cell lymphomas and inhibits GATA1-mediated transcription; as GATA1 also mediates erythroid GFI1B transcription, both GATA1 and GFI1B participate in a feedback regulatory pathway controlling the expression of GFI1B gene in erythroid cells. Suppresses GATA1-mediated stimulation of GFI1B promoter through protein interaction. Binds to gamma-satellite DNA and to its own promoter, auto-repressing its own expression. Alters histone methylation by recruiting histone methyltransferase to target genes promoters. Plays a role in heterochromatin formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12351384, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16177182, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16688220, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16782810, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17156408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17272506, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17420275}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a zinc-finger containing transcriptional regulator that is primarily expressed in cells of hematopoietic lineage. The encoded protein complexes with numerous other transcriptional regulatory proteins including GATA-1, runt-related transcription factor 1 and histone deacetylases to control expression of genes involved in the development and maturation of erythrocytes and megakaryocytes. Mutations in this gene are the cause of the autosomal dominant platelet disorder, platelet-type bleeding disorder-17. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2014]. |
hsa:8328; |
nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of hemopoiesis [GO:1903706]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12351384_This zinc finger protein mediates erythroid expansion and has a role in normal erythropoiesis 15280509_GATA-1 and NF-Y both contribute to erythroid-specific transcriptional activation of the Gfi-1B promoter. 15507521_Gfi-1B acts in the late stage of erythroid differentiation as a transcriptional repressor. 16177182_GATA-1 and Gfi-1B participates in a feedback regulatory pathway in controlling the expression of the Gfi-1B gene. 17272506_E2A proteins prevent lymphoma cell expansion, at least in part through regulation of Gfi1b and modulation of Gata3 expression. 17420275_GATA1 and GFI1B interplay to regulate bcl-X protein transcription. 19360458_suggest that Gfi1b may be an important factor to establish or maintain myeloid leukemia and myeloproliferative diseases 19522008_Data conclude that Gfi-1B behaves as a lineage-affiliated gene with an open chromatin configuration in multipotent progenitors and sustained activation as cells progress throughout erythroid differentiation. 19773260_GFI1B regulatory elements behave as activators and repressors, consistent with a model in which GFI1B binds to its own promoter and to the conserved non-coding elements as its levels rise. 19965638_HMGB2 potentiates GATA-1-dependent transcription of GFI1B by Oct-1 and thereby controls erythroid differentiation. 20124515_repressing TGF-beta type III receptor (TbetaRIotaII) expression, Gfi-1B favors the Smad2/TIF1-gamma interaction downstream of TGF-beta signaling, allowing immature progenitors to differentiate toward the erythroid lineage. 20143233_Results reveal the presence of different protein complexes, including GATA-1 and Oct-1, involved in Gfi1b regulation. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22399799_Gfi-1B p32, a Gfi-1B isoform, is essential for erythroid differentiation 23788109_Silencing of both BCR-ABL siRNA and GFI1B siRNA is associated with an additive antileukemic effect against K562 cells. 23927492_a mutation in GFI1B causes a platelet disorder; GFI1B has a role a critical regulator of platelet shape, number, and function 24325358_Our studies show that GFI1B, in addition to being causally related to the gray platelet syndrome, is key to megakaryocyte and platelet development. 24395799_TAL1 is involved in regulating H3K27me3 variations in collaboration with GFI1B 25043047_results, supported by evidence from mouse models, identify GFI1 and GFI1B as prominent medulloblastoma oncogenes and implicate 'enhancer hijacking' as an efficient mechanism driving oncogene activation in a childhood cancer 26447191_Gfi1b functions as a transcriptional repressor by recruiting histone-modifying enzymes to promoters and enhancers of target genes. Mutations are associated with certain bleeding disorders. Review. 26851695_SPI1-GFI1B transcriptional network is an important regulatory axis in acute myeloid leukemia as well as in the development of erythroid versus myelomonocytic cell fate 27122003_GFI1B is an essential protein for the normal development of the megakaryocyte lineage 27486782_Role for Alternative GFI1B Splice Variants in Human Hematopoiesis 27768697_study demonstrates the significance of Gfi1b regulated Kindlin3-Talin1 expression in driving megakaryocytic differentiation and highlights the contribution of cytoskeletal agents in the developmental progression of these platelet progenitors 28041820_Results demonstrate that alpha-delta platelet storage pool deficiency is associated with either a heterozygous mutation in GFI1B (de novo or familial) abrogating the binding of the zinc fingers with the promoter of its target genes, or by hypomorphic biallelic mutations leading to autosomal recessive inheritance. 28096094_Platelet CD34 expression and alpha/delta-granule abnormalities in GFI1B- and RUNX1-related familial bleeding disorders. 28439885_A novel GFI1B mutation at the first zinc finger domain causes congenital macrothrombocytopenia. 28667074_High GFI1B expression is associated with small-cell lung cancer. 28880435_Disruption of GFI1B non-DNA-binding zinc-finger 1 is associated with mild to moderate thrombocytopenia without alpha-granule deficiency or bleeding symptomatology, indicating that the site of GFI1B mutation has important phenotypic implications. Platelet CD34 expression appears to be a common feature of perturbed GFI1B function. 29326122_Gfi1b functions as an oncosuppressor in MDS and AML development. 30573501_We conclude that Q89fs, C168F, H181Y, and R184P affect GFI1B function, but are not necessarily sufficient to cause bleedings on their own. 30988160_Findings demonstrate the central role of the GFI1B-LSD1 interaction as a determinant of BRAF-histone deacetylase complex recruitment to enable cell fate decisions driven by GFI1B. 31207059_Macrothrombocytopenia associated with a rare GFI1B missense variant confounding the presentation of immune thrombocytopenia. 31912614_Loss of myeloid-specific lamin A/C drives lung metastasis through Gfi-1 and C/EBPepsilon-mediated granulocytic differentiation. 33028609_Human yolk sac-like haematopoiesis generates RUNX1-, GFI1- and/or GFI 1B-dependent blood and SOX17-positive endothelium. 33054086_Dominant negative Gfi1b mutations cause moderate thrombocytopenia and an impaired stress thrombopoiesis associated with mild erythropoietic abnormalities in mice. 33472357_Dysregulation of oncogenic factors by GFI1B p32: investigation of a novel GFI1B germline mutation. 33690840_Specific proteome changes in platelets from individuals with GATA1-, GFI1B-, and RUNX1-linked bleeding disorders. 33993920_The transcription factors GFI1 and GFI1B as modulators of the innate and acquired immune response. 34450246_Characterization of a genomic region 8 kb downstream of GFI1B associated with myeloproliferative neoplasms. 35031421_Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy associated risk variant, rs3768617 in LAMC1 shows allele specific binding of GFI1B. 35804097_GFI1B acts as a metabolic regulator in hematopoiesis and acute myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000026815 |
Gfi1b |
11.307767 |
17.9432034666 |
4.165366 |
0.702150757 |
50.690112 |
0.00000000000108163099224734854067761449238429144774006895879381318081868812441825866699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006424496356366544877325591920261518472622108699709997381432913243770599365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.2727252 |
9.0173936 |
1.0363135 |
0.4742330 |
| ENSG00000165731 |
5979 |
RET |
protein_coding |
P07949 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase involved in numerous cellular mechanisms including cell proliferation, neuronal navigation, cell migration, and cell differentiation upon binding with glial cell derived neurotrophic factor family ligands. Phosphorylates PTK2/FAK1. Regulates both cell death/survival balance and positional information. Required for the molecular mechanisms orchestration during intestine organogenesis; involved in the development of enteric nervous system and renal organogenesis during embryonic life, and promotes the formation of Peyer's patch-like structures, a major component of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue. Modulates cell adhesion via its cleavage by caspase in sympathetic neurons and mediates cell migration in an integrin (e.g. ITGB1 and ITGB3)-dependent manner. Involved in the development of the neural crest. Active in the absence of ligand, triggering apoptosis through a mechanism that requires receptor intracellular caspase cleavage. Acts as a dependence receptor; in the presence of the ligand GDNF in somatotrophs (within pituitary), promotes survival and down regulates growth hormone (GH) production, but triggers apoptosis in absence of GDNF. Regulates nociceptor survival and size. Triggers the differentiation of rapidly adapting (RA) mechanoreceptors. Mediator of several diseases such as neuroendocrine cancers; these diseases are characterized by aberrant integrins-regulated cell migration. Mediates, through interaction with GDF15-receptor GFRAL, GDF15-induced cell-signaling in the brainstem which induces inhibition of food-intake. Activates MAPK- and AKT-signaling pathways (PubMed:28846097, PubMed:28953886, PubMed:28846099). Isoform 1 in complex with GFRAL induces higher activation of MAPK-signaling pathway than isoform 2 in complex with GFRAL (PubMed:28846099). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20064382, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20616503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20702524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21357690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21454698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28846097, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28846099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28953886}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Hirschsprung disease;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane receptor and member of the tyrosine protein kinase family of proteins. Binding of ligands such as GDNF (glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor) and other related proteins to the encoded receptor stimulates receptor dimerization and activation of downstream signaling pathways that play a role in cell differentiation, growth, migration and survival. The encoded receptor is important in development of the nervous system, and the development of organs and tissues derived from the neural crest. This proto-oncogene can undergo oncogenic activation through both cytogenetic rearrangement and activating point mutations. Mutations in this gene are associated with Hirschsprung disease and central hypoventilation syndrome and have been identified in patients with renal agenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2017]. |
hsa:5979; |
axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane protein complex [GO:0098797]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; embryonic epithelial tube formation [GO:0001838]; enteric nervous system development [GO:0048484]; glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035860]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; innervation [GO:0060384]; lymphocyte migration into lymphoid organs [GO:0097021]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; membrane protein proteolysis [GO:0033619]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; neuron cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007158]; neuron maturation [GO:0042551]; Peyer's patch morphogenesis [GO:0061146]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell size [GO:0045793]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001241]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of metanephric glomerulus development [GO:0072300]; positive regulation of neuron maturation [GO:0014042]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0033141]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; posterior midgut development [GO:0007497]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050770]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; response to pain [GO:0048265]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; ureter maturation [GO:0035799]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657] |
10850414_The presence of coiled-coil domains in the ktn1/ret fusion protein (PTC8) suggests ligand-independent dimerization and thus constitutive activation of the ret tyrosine kinase domain. 11238493_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11589684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11692159_Three new somatic cell missense mutations of the RET proto-oncogene associated with sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). 11746981_A germline RET mutation at codon 603 in exon 10 is associated with both medullary and nonmedullary thyroid cancer in a kindred. 11803116_Differentiation of cardiac ganglionic cells is affected, after RETINOIC ACID treatment, by the down-regulation of c-Ret. 11839664_RET oligonucleotide microarray for the detection of RET mutations in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndromes 11883863_The finding of a somatic deletion in RET exon 15 clarified the sporadic nature of a medullary thyroid carcinoma suspected to be familial. A 12 bp deletion within the catalytic domain of the protooncogene RET. 11886862_role in regulating rac activity and lamellipodia formation 11900218_early detection of RET proto-oncogene mutation is crucial for prevention of thyroidectomy in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 children 11927965_if the association between Hashimoto's thyroiditis and thyroid cancer exists, its molecular basis is different from RET/PTC rearrangement 11932300_Familial medullary thyroid carcinoma: clinical variability and low aggressiveness associated with RET mutation at codon 804. 11935126_family in which the MEN 2A and the HSCR phenotypes are associated with a single point mutation in exon 10 of the RET proto-oncogene. polymorphic sequence variants of the RET proto-oncogene. 11949835_germline mutation of the RET proto-oncogene in members of Slovak families with multiple endocrine neoplasia 2 11950855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11953745_Segregation at three loci explains familial and population risk in Hirschsprung disease. We show oligogenic inheritance of S-HSCR, the 3p21 and 19q12 loci as RET-dependent modifiers, and a parent-of-origin effect at RET. 11953748_Dissecting Hirschsprung disease. RET is the main gene conferring susceptibility. 11955539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11955539_These observations lend support to the idea that both RET alleles have a role in pathogenesis of Hirschsprung's disease, in a dose-dependent fashion. We also showed that the c135G/A polymorphism modifies the phenotype. 11973622_Hirschsprung associated GDNF mutations do not prevent RET activation 11979448_the G691S and S904S variants of RET may somehow play a role on the age of onset of MEN 2A 12000816_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12056817_Activation of RET tyrosine kinase regulates interleukin-8 production by multiple signaling pathways 12057919_RET activation closely parallels the morphological changes, that it is restricted to those areas of the tumor with the cytological alterations and that it is detectable in both mono- and polyclonal tumors 12085189_RET codon 691 polymorphism is associated with radiation induced tumors with a C-cell hyperplasia of thyroid tumors 12114746_RET/PTC rearrangement in thyroid tumors. Review 12161537_RET expression in papillary thyroid cancer from patients irradiated in childhood for benign conditions. 12182057_Analysis of mutation of protooncogene RET are presented in patients with thyroid medullary carcinoma 12182058_analysis of RET somatic mutations supports the differentiation between sporadic and inherited medullary thyroid carcinoma 12187076_5'-End RET splicing: absence of variants in normal tissues and intron retention in pheochromocytomas. 12193298_Possible pathogenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma caused by exon 13 and 14 RET mutations that affect the intracellular domain of ret proto-oncogene protein. 12214285_a protective role of this low-penetrant haplotype in the pathogenesis of HSCR and demonstrate a possible functional effect linked to RET messenger RNA expression. 12355085_genetic interaction between mutations in RET and EDNRB is an underlying mechanism for Hirschsprung disease 12439935_relationship between RET oncogene and Chinese patients with Hirschsprung's disease 12466368_A novel Val648Ile substitution in RET protooncogene observed in a Cys634Arg multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A kindred presenting with an adrenocorticotropin-producing pheochromocytoma. 12474140_A founding locus within the RET proto-oncogene may account for a large proportion of apparently sporadic Hirschsprung disease and a subset of cases of sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma 12490841_Patients with RET codon 790/791 mutations seemed to have a less aggressive clinical course compared with patients with classic multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A syndrome. 12519890_Amplification and overexpression of mutant RET in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2-associated medullary thyroid carcinoma. RET germline mutation in codon 634. Tandem duplication.Genomic chromosome 10 abnormalities increase mutant RET mRNA. 12608895_RET proto-oncogene is often stimulated in follicular cell-derived thyroid tumors, not only in papillary carcinoma but also in follicular tumors (follicular adenomas and follicular carcinoma), and may contribute to tumorigenesis of these tumors. 12632375_Not only RET mutations but also RET polymorphic variants may contribute to the occurrence of total intestinal aganglionosis. 12637586_RET/PTC associates with STAT3 and activates it by the specific phosphorylation of the tyrosine 705 residue. STAT3 activation by the RET/PTC tyrosine kinase is one of the critical signaling pathways for the regulation of specific genes. 12670889_High prevalence of BRAF mutations in thyroid cancer is genetic evidence for constitutive activation of the RET/PTC-RAS-BRAF signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 12720173_in RET mutation carriers in Hirschsprung's disease, the gut caliber change was almost identical to the histologic transition in cases of short segment aganglionosis, whereas these were markedly dissociated in cases exhibiting extensive aganglionosis 12720532_RET rearrangements may not play any distinctive role in driving histotype development and cancer progression in papillary thyroid carcinomas. 12767512_A deletion of the chromosomal region including the RET proto-oncogene is involved in the pathogenesis of SCLC 12788868_Specific nucleotide and amino acid exchanges at codon 634 might have a direct impact on tumor aggressiveness in MEN 2A. 12841548_Letter discussing RET mutations in distinguishing between sporadic and familial medullary thyroid carcinoma. 12872262_Four novel intronic mutations that have a strong association with the HSCR phenotype were identified in Hirschsprung disease patients 12872262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12881714_The BRAF(V599E) mutation appears to be an alternative event to RET/PTC rearrangement rather than to RAS mutations, which are rare in PTC. BRAF(V599E) may represent an alternative pathway to oncogenic MAPK activation in PTCs without RET/PTC activation. 12884527_mutations of the RET protooncogene were analyzed in Russian patients with inherited or sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma.The most common mutation affected codon 918 to cause substitution of methionine with threonine and accounted for 31.6% alleles. 12939698_findings support the notion that both RET alleles are involved in the pathogenesis of a subgroup of Hirschsprung disease patients in a dose-dependent fashion 12959980_Shp2 activity required for RetM918T-induced Akt activation. Shp2 downstream mediator of mutated receptors RetC634Y and RetM918T. Shp2 acts as limiting factor in Ret-associated endocrine tumors, in neoplastic syndromes multiple endocrine neoplasia. 14508694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14555929_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14557473_there is a low-penetrance pheochromocytoma susceptibility locus in a region upstream of the putative loci for Hirschprung disease and apparently sporadic thyroid carcinoma. 14586073_Point mutation in exon 14 at codon 804 of the RET proto-oncogene locus in a case of lymph node metastases of medullary and papillary thyroid carcinoma. 14600022_Loss-of-function germline mutations of the RET proto-oncogene are reported in familial and sporadic cases of Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) with a variable frequency 14602786_new missense point mutation in exon 8 of the RET gene (1597G-->T) corresponding to a Gly(533)Cys substitution in the cysteine-rich domain of RET protein 14711813_Mass spectrometric analysis revealed that RET Tyr(806), Tyr(809), Tyr(900), Tyr(905), Tyr(981), Tyr(1062), Tyr(1090), and Tyr(1096) were autophosphorylation sites. 14739491_association of high-level Ret proto-oncogene protein expression with neuronal morphology suggests that the variable overexpression of Ret in pheochromocytomas might in part be an epiphenomenon, reflecting the known phenotypic plasticity of these tumors 14761598_Ret expression is significantly higher in thyroid papillary carcinoma than benign thyroid tissue; and this characteristic can have important diagnostic value. 14766744_Ret tyrosine 981 constitutes the major binding site of the Src homology 2 domain of Src and therefore the primary residue responsible for Src activation upon Ret engagement 14981541_Expression of the mitogenic and invasive phenotype of RET/PTC-transformed thyroid cells is stimulated by osteopontin. 15044950_Data report the crystal structure of GFRalpha1 domain 3, and the effects of specific mutations on GDNF binding and RET phosphorylation. 15129804_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15138456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15142370_association of RET IVS1-126G>T variant with sporadic medullary thyroid cancer in a cohort of 104 patients 15225646_Persephin/GFRalpha4 is unable to recruit RET protein into lipid rafts. 15231654_RET expression leads to increased HSF1 activation, which correlates with increased expression of stress response genes. RET may be directly responsible for expression of stress response proteins and the initiation of stress response. 15240649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15240649_With this study we excluded influence of the G691S polymorphism on RET mRNA expression, development of somatic RET mutation, the linkage with germline RET mutation, younger onset of medullary thyroid carcinoma, and clinical outcome of the disease. 15240857_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15271413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15273715_mutated in papillary thyroid cancer. 15277225_RET point mutants for follicular thyroid cells may account for the occurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma in patients affected by familial medullary thyroid carcinoma 15286081_Dok-6 binds to the phosphorylated Ret Tyr(1062) residue resulting in phosphorylation of tyrosine residue(s) located within the unique C terminus of Dok-6 predominantly through a Src-dependent mechanism 15297606_RET/PTC expression phosphorylates the Y701 residue of STAT1, a type II interferon (IFN)-responsive protein. 15316058_Selective disruption of oncogenic RET signaling in medullary thyroid carcinoma in vitro and in vivo is associated with loss of the neoplastic phenotype of medullary thyroid carcinoma. 15320968_the RET proto-oncogene mutation Y791F, characterized by a low penetrance, occurs comparatively frequently among patients with normal serum calcitonin concentrations 15331579_mechanisms leading to RET oncogenic conversion 15350625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15351743_RET requires coupling of Gab1 to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase for function in human tumor cells 15355438_Germ-Line Mutation in RET proto-oncogene is associated with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia 15469971_All Ret dominant-negative/+ mice died by 1 month of age and had distal intestinal aganglionosis reminiscent of Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) in humans 15491993_critical role of the immunoglobulin domain in regulation of the localization of human PTPmu in bovine cell lines 15502856_Papillary carcinomas with high RET/PTC1 expression showed an association trend for large tumor size. 15523405_The Cys630 RET genotype may have a more vigorous transforming activity than currently thought and can cause medullary thyroid carcinoma in RET gene carriers within the first year of life. 15548547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15583857_RET has roles in neoplastic transformation [review] 15592804_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15632018_Expression of a human Ret proto-oncogene with the MEN 2B mutation does not cause any features of MEN 2B in mice. 15633231_Mutations of RET proto-oncogene may play an important role in the pathogenesis of Chinese patients with Hirschsprung disease. 15643606_A RET haplotype (A-C-A) composed of alleles at three SNPs is associated with reduced RET gene expression in Hirschsprung patients. 15657578_RET signals through focal adhesion kinase in medullary thyroid cancer cells. 15677445_These findings establish a mechanism for the differential down-regulation of RET9 and RET51 signaling that could explain the apparently paradoxical activities of these two RET isoforms. 15716612_RET/PTC and CK19 have roles in progression of papillary thyroid carcinoma 15741265_RET gene mutation may explain the wide clinical variability associated with germline mutations at codon 804 in medullary thyroid carcinoma/multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A patients. 15753666_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the RET oncogene may play a role in sporadic papillary thyroid carcinoma. 15759212_Of these 86 variations, 8 proved to be in regions highly conserved among different vertebrates and within putative transcription factor binding sites. We therefore considered these as candidate disease-associated variants. 15785245_Koreans showed increased RET gene expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 15829955_a common non-coding RET variant within a conserved enhancer-like sequence in intron 1 is significantly associated with Hirschsprung disease susceptibility 15834508_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of RET is associated with Hirschsprung disease 15841388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15844786_medullary thyroid carcinoma manifested in new RET mutation and RET polymorphism. 15933516_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15940252_in the presence of RET oncoproteins, both RAI and GAB 1 are tyrosine-phosphorylated, and the stoichiometry of this interaction remarkably increases 15953945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956201_Substantial discrimination between predicted functional classes of RET mutations and disease severity even for a multigenic disease such as Hirschsprung disease. 15988377_Mutations in medullary thyroid cancer and in multiple endocrine neoplasia 2. 15994200_RET/PTC is able to phosphorylate the Y315 residue of PKB, an event that results in maximal activation of PKB for RET/PTC-induced thyroid tumorigenesis. 16007166_determination of mutation specific gene expression profiles in papillary thyroid carcinoma 16053382_C630R mirrors C634R in penetrance and in early age of onset of medullary thyroid carcinoma 16118333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16127999_PHOX2A, but not PHOX2B, seems to act directly on the c-RET promoter 16144862_The histone acetylation level was evaluated by the chromatin immunoprecipitation method applied to cells displaying different degrees of endogenous RET expression. 16153436_direct interaction between RET and a broad range of effector molecules that may contribute to tumor pathogenesis 16181547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16203990_The RET/PTC1 oncogene activates a proinflammatory program, provide a direct link between a transforming human oncogene, inflammation, and malignant behavior. 16227613_Y1062 is a critical regulator of Ret9 signaling and suggest that Ret51-specific motifs are likely to inhibit the activity of this isoform 16230779_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16230779_significant association of the S691 allele with medullary thyroid carcinoma 16269442_RET enhancer modulates expression in the enteric nervous system consistent with its proposed role in Hirschsprung disease 16314641_Germline mutation on the RET gene was present in patients with pheochromocytoma or functional paraganglioma. 16357163_Single nucleotide polymorphism in ret is associated with the aggressive growth of pancreatic cancers 16384843_The newly identified RET/N777S germline mutation is a low-penetrant cause of medullary thyroid carcinoma. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16388093_possibility that lower-penetrance RET mutations may contribute to the list of causes of familial pheochromocytomas 16419493_new missense point mutation in exon 5 in familial medullary thyroid carcinoma 16441254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16441254_Two Hirschsprung disease-associated haplotypes derive from a single founding locus, extending up to intron 19 and successively rearranged in correspondence with a high recombination rate region located between the proximal and distal end of the RET gene. 16448984_gene expression impairment seems to be at the basis of the association of HSCR disease with several RET polymorphisms, allowing us to define a predisposing haplotype spanning from the promoter to exon 2. 16452504_These results reveal novel roles of key RET-dependent signaling pathways in embryonic kidney development and provide murine models and new insights into the molecular basis for CAKUT. 16469774_Characterization of the R833C substitution suggests that this tyrosine kinase mutation confers a weak activating potential upon RET but introduces an intracellular cysteine which activate RET. 16483615_frequency of RET rearrangements in papillary thyroid carcinoma for the Polish population 16484222_Erk8 has a role as a novel effector of RET/PTC3 and, therefore, RET biological functions 16525712_Mutational screening of RET revealed 9 different mutations, present in 26 of the 114 MEN 2 Spanish patients. 16534860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16551639_Gas1 is related to the GDNF alpha receptors and regulates Ret signaling 16555159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16556802_evaluation of noncoding sequences at the zebrafish ret locus conserved among teleosts, and at the human RET locus, conserved among mammals 16569669_Mutagenesis analysis revealed that Tyr981 within the intracellular domain of RET was crucial for the interaction with SH2-Bbeta. Morphological evidence showed that SH2-Bbeta and RET colocalized in mesencephalic neurons. 16596053_Medullary thyroid carcinoma as part of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 in a family with a mutation in RET proto oncogene. 16628270_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16646689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16732321_strong propensity to self-association in the RET-transmembrane underlies - and may be required for - dimer formation and oncogenic activation of juxtamembrane cysteine mutants of RET 16767674_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16767674_Some patients with apparently sporadic pheochromacytoma were carrier of mutations in RET proto-oncogene. 16773224_In the human digestive and reproductive systems, a subset of epithelial cells exhibited GFRalpha3- and RET-like staining, suggesting co-localization. 16813162_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16816022_Analysis of the RET gene revealed neither linkage nor mutations in Hirschsprung's disease mapping. 16818057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847065_Cell type-specific functions involve a competitive recruitment of different phosphotyrosine binding adaptor molecules by RET that activate selective signaling pathways. 16849523_We show that RA-induced differentiation is mediated by a positive autocrine loop that sustains Ret downstream signaling and depends on glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor expression and release. 16868135_Timing and extent of prophylactic thyroidectomy can be modified by individual RET mutation 16877807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16945332_the RET finger protein has a role in estrogen receptor-mediated transcription in tumor cells 16946010_Ret mutations in thyroid tumorigenesis. 16954442_First molecular studies on a complex germline RET mutation lying in the juxtamembrane region of the receptor are reported in medullary thyroid carcinoma 16979782_RET dysfunction has a crucial role and discusses RET as a potential therapeutic target. 16986122_A variant located in the 3' untranslated region of the RET gene, which slows down mRNA decay in patients with Hirschsprung disease. 17009072_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17049487_These results suggest that RFP is a mediator connecting several MBD proteins and allowing the formation of a more potent transcriptional repressor complex. 17065770_Identification of a heterozygous germ line missense mutation at codon 634 of exon 11 in the RET gene that causes a cysteine to arginine amino acid substitution in a MEN2A patient. 17102080_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17108762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17138574_The molecular basis for HPT has been further elucidated by teh detection of inactivating germline mutations in the CaSR gene in familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia syndrome and in the RET genes in the familial forms of HPT. 17185892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17185892_results indicate a possible association between the presence of lymph node involvement at the time of diagnosis (extent of disease) of medullary thyroid carcinoma and L769L or S836S polymorphism. 17209045_tumor samples from FMTC patients showed strong nuclear staining of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and Ser(727) STAT3; FMTC-RET mutants activate a Ras/ERK1/2/STAT3 Ser(727) pathway, which plays an important role in cell mitogenicity and transformation. 17227125_Copy gain of PDGFB occurs in a subset of tumors showing no evidence of mutated BRAF or rearranged ret, suggesting that copy gain of PDGFB may underlie the increased expression of platelet-derived growth factor described recently in the literature. 17270245_study demonstrated RET amplification in all 3 cases of radiation-associated thyroid cancers(papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) & anaplastic thyroid cancer(ATC) but not in sporadic well-differentiated PTC; RET amplification was observed in all 6 cases of ATCs 17270543_Children of families with RET cysteine mutations may develop early metastatic medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland. 17274802_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17316110_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17384213_the absence of RET alterations in all cases of C-cell hyperplasia 17388787_our results suggest that SPRY2 regulates GDNF-dependent proliferation and differentiation of TGW neuroblastoma cells mediated by RET tyrosine kinase. 17397038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17397038_These data highlight the pivotal role of the RET gene in both isolated and syndromic Hirschsprung disease. 17431108_RET, a receptor tyrosine kinase involved with differentiation, was consistently up-regulated throughout the time course of retinoic acid treatment in the majority of neuroblastic tumor cell lines. 17440194_study demonstrates that the interaction between RET and PHOX2B polymorphisms has a substantial impact on risk of Hirschsprung's disease 17464312_prevalence of BRAF mutation and RET/PTC were determined in diffuse sclerosing variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma; RET/PTC1 and RET/PTC3 were found in |
ENSMUSG00000030110 |
Ret |
247.377737 |
0.4542128215 |
-1.138560 |
0.132984950 |
73.215048 |
0.00000000000000001162659747790209079047517261250990535227457104355342290546992956024041632190346717834472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000092561261474560339175385742556809184868120117875567309795314940856769680976867675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
149.7225813 |
17.4118925 |
331.8898182 |
26.9633841 |
| ENSG00000165732 |
9188 |
DDX21 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR30 |
FUNCTION: RNA helicase that acts as a sensor of the transcriptional status of both RNA polymerase (Pol) I and II: promotes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) processing and transcription from polymerase II (Pol II) (PubMed:25470060, PubMed:28790157). Binds various RNAs, such as rRNAs, snoRNAs, 7SK and, at lower extent, mRNAs (PubMed:25470060). In the nucleolus, localizes to rDNA locus, where it directly binds rRNAs and snoRNAs, and promotes rRNA transcription, processing and modification. Required for rRNA 2'-O-methylation, possibly by promoting the recruitment of late-acting snoRNAs SNORD56 and SNORD58 with pre-ribosomal complexes (PubMed:25470060, PubMed:25477391). In the nucleoplasm, binds 7SK RNA and is recruited to the promoters of Pol II-transcribed genes: acts by facilitating the release of P-TEFb from inhibitory 7SK snRNP in a manner that is dependent on its helicase activity, thereby promoting transcription of its target genes (PubMed:25470060). Functions as cofactor for JUN-activated transcription: required for phosphorylation of JUN at 'Ser-77' (PubMed:11823437, PubMed:25260534). Can unwind double-stranded RNA (helicase) and can fold or introduce a secondary structure to a single-stranded RNA (foldase) (PubMed:9461305). Together with SIRT7, required to prevent R-loop-associated DNA damage and transcription-associated genomic instability: deacetylation by SIRT7 activates the helicase activity, thereby overcoming R-loop-mediated stalling of RNA polymerases (PubMed:28790157). Involved in rRNA processing (PubMed:14559904, PubMed:18180292). May bind to specific miRNA hairpins (PubMed:28431233). Component of a multi-helicase-TICAM1 complex that acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and plays a role in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines via the adapter molecule TICAM1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JIK5, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11823437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14559904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18180292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25260534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25470060, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25477391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28431233, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28790157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9461305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Helicase;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;rRNA processing;Transcription;Ubl conjugation |
|
DEAD box proteins, characterized by the conserved motif Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD), are putative RNA helicases. They are implicated in a number of cellular processes involving alteration of RNA secondary structure such as translation initiation, nuclear and mitochondrial splicing, and ribosome and spliceosome assembly. Based on their distribution patterns, some members of this family are believed to be involved in embryogenesis, spermatogenesis, and cellular growth and division. This gene encodes a DEAD box protein, which is an antigen recognized by autoimmune antibodies from a patient with watermelon stomach disease. This protein unwinds double-stranded RNA, folds single-stranded RNA, and may play important roles in ribosomal RNA biogenesis, RNA editing, RNA transport, and general transcription. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9188; |
B-WICH complex [GO:0110016]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 7SK snRNA binding [GO:0097322]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; miRNA binding [GO:0035198]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; rRNA binding [GO:0019843]; snoRNA binding [GO:0030515]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of histone acetylation [GO:0035066]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of myeloid dendritic cell cytokine production [GO:0002735]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I [GO:0045943]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0045945]; R-loop disassembly [GO:0062176]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
14559904_RNA helicase II/Gualpha silencing inhibits mammalian ribosomal RNA production 16045751_the function of Gu(alpha)in rRNA processing is at least partially dependent on its ability to interact with ribosomal protein L4. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18180292_in addition to its transcriptional effects, c-Jun regulates rRNA processing and nucleolar compartmentalization of the rRNA processing protein DDX21 20873769_Studies indicated that DDX21, HNRNPC, and RCC2 were isolated from Ku86 multicomponent complex in response to DNA damage. 23419719_Data indicate that DDX21, a nucleolar protein, was confirmed to associate with SET8. 24721576_As sequential interaction of PB1 and NS1 with DDX21 leads to temporal regulation of viral gene expression, influenza A virus likely uses the DDX21-NS1 interaction not only to overcome restriction, but also to regulate the viral life cycle. 25260534_DDX21 expression in breast cancer cells can promote AP-1 activity and rRNA processing, and thus, promote tumorigenesis by two independent mechanisms. 25470060_results uncover the multifaceted role of DDX21 in multiple steps of ribosome biogenesis, and provide evidence implicating a mammalian RNA helicase in RNA modification and Pol II elongation control 25477391_Identification of several late-acting snoRNAs that bind pre-40S particles in human cells and show that their association and function in pre-40S complexes is regulated by the RNA helicase DDX21. 27033607_In dengue virus infected cells, DDX21 translocates from nucleus to cytoplasm to active the innate immune response and thus inhibits DENV replication in the early stages of infection. 28472472_DDX21 can suppress the expression of proteins with G4 qudruplexes in the 3 UTR of its mRNA. 28475895_Results report the biogenesis and function of a box H/ACA snoRNA-ended sno-lncRNA, referred to SLERT (snoRNA-ended lncRNA enhances pre-ribosomal RNA transcription). SLERT is different from Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS) sno-lncRNAs and plays a crucial role in rRNA biogenesis by dislodging a previously unknown clamp of DDX21 ring-shaped arrangements on Pol I complexes, thereby liberating Pol I for active rRNA transcription. 28705764_DDX21 is both an ATP-dependent and ATP-independent helicase, and both ATPase and ATP-dependent helicase activities are inhibited by Rev in a dose-dependent manner, although ATP-independent helicase activity is not. A conserved binding interaction between DDX protein's DEAD domain and Rev was identified, with Rev's nuclear diffusion inhibitory signal motif playing a significant role in binding. 28790157_Knockdown of SIRT7 leads to the same phenotype as depletion of DDX21 (i.e., increased formation of R loops and DNA double-strand breaks), indicating that SIRT7 and DDX21 cooperate to prevent R-loop accumulation, thus safeguarding genome integrity. 29906500_can drastically reduce DDX21's affinity for quadruplex, indicating that the recognition of quadruplex and specificity for telomeric repeat containing RNA quadruplex is mediated by interactions with the 2'OH of loop nucleotides 30165191_Data indicate that DEAD-box helicase 21 (DDX21) regulated Snail transcription factors (Snail) expression independent of its helicase activity. 30322617_DDX21 induced gastric cancer cell growth by up-regulating levels of Cyclin D1 and CDK2. 31251802_The findings revealed that enhancer-mediated enrichment of novel JMJD3-DDX21 interaction at ENPP2 locus is necessary for nascent transcript synthesis via the resolution of aberrant R-loops formation in response to inflammatory stimulus. 31351877_Activation of PARP-1 by snoRNAs Controls Ribosome Biogenesis and Cell Growth via the RNA Helicase DDX21. 31554690_DDX21 knockdown prevented viral late gene transcription and consequently impaired HCMV replication. 31653714_Our work identifies the role of DDX21 in regulation at the translational level through biologically relevant RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) and shows that MAGED2 protein levels are regulated, at least in part, by the potential to form rG4 in their 5'-UTRs. 32231306_RNA helicase DDX21 mediates nucleotide stress responses in neural crest and melanoma cells. 32652076_PRL3-DDX21 Transcriptional Control of Endolysosomal Genes Restricts Melanocyte Stem Cell Differentiation. 33328538_DEAD-box RNA helicase protein DDX21 as a prognosis marker for early stage colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability. 33497018_The RNA-helicase DDX21 upregulates CEP55 expression and promotes neuroblastoma. 33604619_DDX21 interacts with nuclear AGO2 and regulates the alternative splicing of SMN2. 33754909_Identification of Prognostic RBPs in Osteosarcoma. 34125604_Caspase-Dependent Cleavage of DDX21 Suppresses Host Innate Immunity. 34326237_lncRNA SLERT controls phase separation of FC/DFCs to facilitate Pol I transcription. 34578346_DDX21, a Host Restriction Factor of FMDV IRES-Dependent Translation and Replication. 34688145_Identification of MDM2, YTHDF2 and DDX21 as potential biomarkers and targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. 34903139_Downregulation of DEAD-box helicase 21 (DDX21) inhibits proliferation, cell cycle, and tumor growth in colorectal cancer via targeting cell division cycle 5-like (CDC5L). 34987058_The Roles of RNA Helicases in DNA Damage Repair and Tumorigenesis Reveal Precision Therapeutic Strategies. |
ENSMUSG00000020075 |
Ddx21 |
691.637239 |
3.1121785665 |
1.637925 |
0.066414607 |
621.698567 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003193932730031063101786932863120970588768552607041123748013900693479231534509575405763329327887890011871423096546280718931846633477902186667913754888922923730658782845763956848446594274375414301 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001820171702519632704120778068782929176497418904770494539392269334811535832459287530364069581011984768120860539145615490966376509787698716091844035564050517656999875669987270466539237192296881575 |
Yes |
No |
1054.7630030 |
40.3400857 |
341.3022329 |
10.7749901 |
| ENSG00000165757 |
57608 |
JCAD |
protein_coding |
Q9P266 |
|
Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes an endothelial cell-to-cell junction protein. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with coronary artery disease, late onset alzheimer disease, and emphysema distribution. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:57608; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903589]; positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0090050]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900748] |
19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21088011_KIAA1462 gene encodes a yet uncharacterized protein, on chromosome 10p11.23 with genome-wide significant association for CAD/MI 21088011_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24349219_Results in this study identify the KIAA1462 locus as a candidate locus for late onset Alzheimer disease in APOE4 carriers. 28705794_JCAD has a redundant functional role in physiological angiogenesis but serves a pivotal role in pathological angiogenic process after birth. 28775168_High JCAD expression is associated with Liver Cancer. 29794114_JCAD negatively regulates Hippo signaling in endothelial cells and contributes to atherosclerosis by regulating YAP activity and endothelial dysfunction. 31539914_The novel coronary artery disease risk gene JCAD/KIAA1462 promotes endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. 31584065_A key role for the novel coronary artery disease gene JCAD in atherosclerosis via shear stress mechanotransduction. |
ENSMUSG00000033960 |
Jcad |
83.420676 |
0.2820381652 |
-1.826038 |
0.223762441 |
67.476321 |
0.00000000000000021323267668392248330958731949009595597635018039868459727159688554820604622364044189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001581564978821455116619227110604898810633148599838482262214256479637697339057922363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.4409712 |
6.0716791 |
133.7735090 |
14.1134401 |
| ENSG00000165810 |
153579 |
BTNL9 |
protein_coding |
Q6UXG8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in T cell receptor signaling pathway and regulation of cytokine production. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in external side of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:153579; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
31039142_Authors investigated the function of BTNL9 in UM proliferation and invasion. BTNL9 mRNAs in adjacent tissues were remarkably higher than in UM tissues. The percentages of BTNL9 low expression and high expression were 56.45% and 43.55%, respectively. 33756341_BTNL9 is frequently downregulated and inhibits proliferation and metastasis via the P53/CDC25C and P53/GADD45 pathways in breast cancer. 35015148_Integrative omics analysis identifies biomarkers of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000040283 |
Btnl9 |
9.154889 |
0.1150124280 |
-3.120138 |
1.053977945 |
7.229633 |
0.00717098708677833124314204837901343125849962234497070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014184370061759337192097696345172153087332844734191894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2916652 |
0.9243035 |
11.9034621 |
5.0775378 |
| ENSG00000165879 |
10023 |
FRAT1 |
protein_coding |
Q92837 |
FUNCTION: Positively regulates the Wnt signaling pathway by stabilizing beta-catenin through the association with GSK-3. May play a role in tumor progression and collaborate with PIM1 and MYC in lymphomagenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556519}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Wnt signaling pathway |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the GSK-3-binding protein family. The protein inhibits GSK-3-mediated phosphorylation of beta-catenin and positively regulates the Wnt signaling pathway. It may function in tumor progression and in lymphomagenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:10023; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; molecular function inhibitor activity [GO:0140678]; beta-catenin destruction complex disassembly [GO:1904886]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; regulation of protein export from nucleus [GO:0046825] |
12556519_CKI epsilon-dependent phosphorylation of Dvl enhances the formation of a complex of Dvl-1 with Frat-1 and this complex leads to the activation of Wnt-3a-induced accumulation of beta-catenin 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16479254_findings support that Wnt/beta-catenin signalling may be aberrantly activated through FRAT1 overexpression in ovarian serous adenocarcinomas 16982607_PKA phosphorylates FRAT1 in vitro as well as in intact cells and may play a role in regulating the inhibitory activity of FRAT1 toward GSK-3. 18498136_Aberrant activation of beta-catenin/TCF pathway in esophageal cancer appears to be due to upstream events such as FRAT1 overexpression, and c-Myc may be an important element in oncogenesis of human ESCC induced by FRAT1. 20041315_Elevated expression of FRAT1 was associated with astrocytomas. 20096670_Our results suggest that FRAT1 may be an important factor in the tumorigenesis and progression of gliomas, and could be used as a potential molecular marker for pathological diagnosis and a target for biological therapy. 21818639_Down-regulation of Frat1 expression reduced invasive ability in A549 cell line, further supporting idea that Frat1 may play crucial role in carcinogenesis, tumor invasiveness and dissemination in human lung cancer. 22528942_The overexpression of Frat1 and beta-catenin was correlated with tumor differentiation, TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis of NSCLC. 23613813_These results highlight the potential role of FRAT1 in tumorigenesis and progression of glioblastoma. 24829151_The mechanism of inhibiting beta-catenin phosphorylation involves the NDRG1-mediated upregulation of the GSK3beta-binding protein FRAT1. 25387569_Positive ROR2 and FRAT1 expression is associated with the progression and poor prognosis of chondrosarcoma. 25922553_FRAT1 overexpression correlates with pathologic grade, proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis in brain gliomas. 26178481_FRAT1 and ABCG2 overexpression is associated with carcinogenesis, progression, and poor prognosis in patients with Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 27599661_The results of the present study suggest that nuclear FRAT1 activates the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and confers an increase in prostate cancer cell growth. 27666874_These data suggest a potential role for targeting FRAT1 in the prevention of hypoxia-induced HCC cancer progression and metastasis mediated by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition 34319909_LncRNA CCAT1 promotes prostate cancer cells proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulation of miR-490-3p/FRAT1 axis. 35059733_FRAT1 promotes the angiogenic properties of human glioblastoma cells via VEGFA. 36153370_The miR-3648/FRAT1-FRAT2/c-Myc negative feedback loop modulates the metastasis and invasion of gastric cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000070526+ENSMUSG00000067199 |
Peg12+Frat1 |
49.317786 |
0.3899748588 |
-1.358547 |
0.226662707 |
36.923333 |
0.00000000122866710277040671147713869060377409048179231376707321032881736755371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005827482788204114005502648612018143370328004948532907292246818542480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.3292192 |
4.1529196 |
70.5575520 |
6.7978960 |
| ENSG00000165915 |
91252 |
SLC39A13 |
protein_coding |
Q96H72 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a zinc-influx transporter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21917916}. |
Alternative splicing;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Golgi apparatus;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the LIV-1 subfamily of the ZIP transporter family. The encoded transmembrane protein functions as a zinc transporter. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the spondylocheiro dysplastic form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Alternate transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:91252; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; connective tissue development [GO:0061448]; zinc ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071577] |
18513683_clinical features of 6 patients from 2 consanguineous families with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome-like features caused by a mutation in the zinc transporter gene SLC39A13 21739577_mutations in the SLC39A13 gene do not account for the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIB phenotype 21917916_Biochemical characterization of human ZIP13 protein: a homo-dimerized zinc transporter involved in the spondylocheiro dysplastic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. 23213233_human ZIP13 releases zinc from vesicular stores 25006035_The spondylocheiro dysplastic form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, in which ZIP13 is defective, is likely due to a failure of iron delivery to the secretory compartments. 25007800_Authors demonstrated that both the ZIP13(G64D) and ZIP13(DeltaFLA) protein levels are decreased by degradation via the valosin-containing protein (VCP)-linked ubiquitin proteasome pathway. 32295219_The Connective Tissue Disorder Associated with Recessive Variants in the SLC39A13 Zinc Transporter Gene (Spondylo-Dysplastic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Type 3): Insights from Four Novel Patients and Follow-Up on Two Original Cases. 34154618_Zinc transporter SLC39A13/ZIP13 facilitates the metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells via activating Src/FAK signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000002105 |
Slc39a13 |
693.705809 |
2.0366500576 |
1.026198 |
0.074394440 |
190.720360 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000022135715120702491652236273156227727088130357996100479946555018400709028285099864024699523092680292028609388352289322199339949293062090873718261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000004013797975203547905069240863784295782703451452514240732536620854267282201231063209134209808278984301865778723528155325084298965521156787872314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
938.7771869 |
48.0307284 |
464.2303506 |
18.1898984 |
| ENSG00000165996 |
9200 |
HACD1 |
protein_coding |
B0YJ81 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Catalyzes the third of the four reactions of the long-chain fatty acids elongation cycle. This endoplasmic reticulum-bound enzymatic process, allows the addition of two carbons to the chain of long- and very long-chain fatty acids/VLCFAs per cycle. This enzyme catalyzes the dehydration of the 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA intermediate into trans-2,3-enoyl-CoA, within each cycle of fatty acid elongation. Thereby, it participates in the production of VLCFAs of different chain lengths that are involved in multiple biological processes as precursors of membrane lipids and lipid mediators. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18554506}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: In tooth development, may play a role in the recruitment and the differentiation of cells that contribute to cementum formation. May also bind hydroxyapatite and regulate its crystal nucleation to form cementum. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22067203}. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Glycoprotein;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18554506}. |
The protein encoded by this gene contains a characteristic catalytic motif of the protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) family. The PTP motif of this protein has the highly conserved arginine residue replaced by a proline residue; thus it may represent a distinct class of PTPs. Members of the PTP family are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes. This gene was preferentially expressed in both adult and fetal heart. A much lower expression level was detected in skeletal and smooth muscle tissues, and no expression was observed in other tissues. The tissue specific expression in the developing and adult heart suggests a role in regulating cardiac development and differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9200; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; 3-hydroxy-arachidoyl-CoA dehydratase activity [GO:0102343]; 3-hydroxy-behenoyl-CoA dehydratase activity [GO:0102344]; 3-hydroxy-lignoceroyl-CoA dehydratase activity [GO:0102345]; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase activity [GO:0018812]; 3R-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase activity [GO:0080023]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; hydroxyapatite binding [GO:0046848]; very-long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase activity [GO:0102158]; cementum mineralization [GO:0071529]; fatty acid elongation [GO:0030497]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0035338]; positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010811]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; very long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042761] |
15829503_A loss-of-function mutation in the canine ortholog of HACD1 that was identified by genetic mapping in a French pedigree of Labrador retrievers causes a congenital myopathy named centronuclear myopathy (CNM) in Labrador retrievers. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19241460_PTPLA SNPs show genotypic association with Alzheimer disease. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20724468_HACD1 is 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase involved in elongation of very long-chain fatty acids. HACD1 (K64Q) exhibits normal enzyme activity, intracellular localization and interaction with other VLCFA enzymes, with no negative effect on VLCFA elongation 22067203_PTPLA-CAP expression was limited to cementum cells; promoted gingival fibroblast attachment. PTPLA-CAP is splice variant of PTPLA, and that, in the periodontium, cementum and cementum cells express this variant. 23071563_Labrador retrievers carrying two copies of a unique canine HACD1 loss-of-function allele that recently disseminated worldwide, are all affected by a congenital myopathy, confirming its role in muscle development. 23933735_These data indicate that HACD1 is necessary for muscle function. 27939133_Longitudinal analyses in myopathic Labrador retrievers reveal several membrane-associated defects, including ultrastructural triads dysmorphogenesis and mitochondrial mislocalization in Labrador retrievers with deficiencies in the canine HACD1 gene. 28784662_Mutations in HACD1 can result in myopathies in humans; knockout mice lacking Hacd1 develop myopathic phenotypes. Data (including data from studies using knockout mice and cultured cells from knockout mice) suggest that HACD1 and HACD2 exhibit overlapping substrate specificities and thus appear to represent redundant activities in skeletal muscle. 33354762_Biallelic loss-of-function HACD1 variants are a bona fide cause of congenital myopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000063275 |
Hacd1 |
12.016329 |
0.2206360114 |
-2.180260 |
0.626613819 |
12.159582 |
0.00048836308485927153264644084984524852188769727945327758789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001201263860004477077719764466223750787321478128433227539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8417242 |
1.9256718 |
17.4011558 |
5.4776157 |
| ENSG00000166046 |
255394 |
TCP11L2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N4U5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in signal transduction. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:255394; |
signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
|
ENSMUSG00000020034 |
Tcp11l2 |
25.523438 |
0.1175543871 |
-3.088600 |
0.406181675 |
64.509773 |
0.00000000000000096054722542347917606971549615230723064299102244983918907905717787798494100570678710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000006885710076372293367265185663595989139599553522513852854558535909745842218399047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8753299 |
1.5783190 |
49.9733673 |
7.0701505 |
| ENSG00000166073 |
11245 |
GPR176 |
protein_coding |
Q14439 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor involved in normal circadian rhythm behavior. Acts through the G-protein subclass G(z)-alpha and has an agonist-independent basal activity to repress cAMP production. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80WT4}. |
Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Members of the G protein-coupled receptor family, such as GPR176, are cell surface receptors involved in responses to hormones, growth factors, and neurotransmitters (Hata et al., 1995 [PubMed 7893747]).[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:11245; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; circadian behavior [GO:0048512]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28502923_Data suggest that Gpr176 is an SCN-(suprachiasmatic nucleus-)enriched orphan GPCR (G-protein-coupled receptor) that sets the pace of circadian behavior. [REVIEW] |
ENSMUSG00000040133 |
Gpr176 |
12.693199 |
2.8927227780 |
1.532428 |
0.496125382 |
9.753631 |
0.00178968881249119454897311687346928010811097919940948486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003992715669947102981318654002507173572666943073272705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.6656607 |
5.5995285 |
6.9245316 |
1.5976364 |
| ENSG00000166104 |
|
|
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.125868 |
10.9845002208 |
3.457397 |
0.545216416 |
40.288916 |
0.00000000021904819763209057748522850636216895148233874124343856237828731536865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001105350904974241711943251205093902839182717912080988753587007522583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.5700236 |
8.5018279 |
2.7211419 |
0.6913421 |
| ENSG00000166106 |
170689 |
ADAMTS15 |
protein_coding |
Q8TE58 |
FUNCTION: Metalloprotease which has proteolytic activity against the proteoglycan VCAN, cleaving it at the 'Glu-1428-|-1429-Ala' site. Cleaves VCAN in the pericellular matrix surrounding myoblasts, facilitating myoblast contact and fusion which is required for skeletal muscle development and regeneration. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P59384}. |
Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. ADAMTS family members share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature enzyme, which may play a role in versican processing during skeletal muscle development. This gene may function as a tumor suppressor in colorectal and breast cancers. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]. |
hsa:170689; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; myoblast fusion [GO:0007520]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
15599946_negative effect of TGFbeta1 on ADAMTS-1, -5, -9, and -15 coupled with increases in their inhibitor, TIMP-3 may aid the accumulation of versican in the stromal compartment of the prostate in BPH and prostate cancer 16152618_ADAMTS8 and ADAMTS15 have emerged as novel predictors of survival in patients with breast carcinoma 19458070_ADAMTS15 may be target of inactivating mutations in human cancer. 20590445_ADAMTS-15 but not ADAMTS-1 expression was downregulated by androgen in LNCaP prostate cancer cells, possibly through androgen response elements associated with the gene 23233679_Versican processing by ADAMTS5 and ADAMTS15 contribute to muscle fiber formation. 25099234_ADAMTS-15 has multiple actions on tumor pathophysiology including modulation of cell-extracellular matrix interactions, which likely involve syndecan-4. 25649796_ADAMTS15 is a candidate gene for intracranial aneurysms 28005267_ADAMTS15 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 28323982_ADAMTS4 and ADAMTS15 were upregulated in symptomatic uterine leiomyomas. 32354091_ADAMTS-15 Has a Tumor Suppressor Role in Prostate Cancer. 35962790_Biallelic variants in ADAMTS15 cause a novel form of distal arthrogryposis. |
ENSMUSG00000033453 |
Adamts15 |
378.953960 |
0.2984411904 |
-1.744481 |
0.090802127 |
380.599744 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000092127197633353123395314207235025843929912022439088745729228094800908195702428904208728129762649074155811794056223159853513139655583033679244985683967688592995293593582540189554570967477070003280572579461467352945902575811487622559070587158203125 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000032845348721456328246220104937889255986376241573477370469381159087269566724220484475145881335963676666664535742072673821010851667488423492913540543490863756578465508950895043105370408176214601219160759641019220467228478810284286737442016601562500 |
Yes |
No |
179.0139843 |
13.0345586 |
605.7245753 |
28.9158419 |
| ENSG00000166128 |
51762 |
RAB8B |
protein_coding |
Q92930 |
FUNCTION: The small GTPases Rab are key regulators of intracellular membrane trafficking, from the formation of transport vesicles to their fusion with membranes. Rabs cycle between an inactive GDP-bound form and an active GTP-bound form that is able to recruit to membranes different sets of downstream effectors directly responsible for vesicle formation, movement, tethering and fusion. That Rab may be involved in polarized vesicular trafficking and neurotransmitter release. May participate in cell junction dynamics in Sertoli cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
RAB proteins, like RAB8B, are low molecular mass monomeric GTPases that localize on the cytoplasmic surfaces of distinct membrane-bound organelles. RAB proteins function in intracellular vesicle transport by aiding in the docking and/or fusion of vesicles with their target membranes (summary by Chen et al., 1997 [PubMed 9030196]).[supplied by OMIM, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:51762; |
cell tip [GO:0051286]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; peroxisomal membrane [GO:0005778]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; trans-Golgi network transport vesicle [GO:0030140]; GDP binding [GO:0019003]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; TPR domain binding [GO:0030911]; antigen processing and presentation [GO:0019882]; cell-substrate junction organization [GO:0150115]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; Golgi vesicle fusion to target membrane [GO:0048210]; positive regulation of cell projection organization [GO:0031346]; positive regulation of corticotropin secretion [GO:0051461]; protein import into peroxisome membrane [GO:0045046]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; regulation of exocytosis [GO:0017157]; vesicle docking involved in exocytosis [GO:0006904] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26471730_Rab8A GTPase Ser(111) phosphorylation is not directly regulated by PINK1 in vitro and demonstrate in cells the time course of Ser(111) phosphorylation of Rab8A, 8B and 13 is markedly delayed compared to phosphorylation of Parkin at Ser(65). 30969072_there is significant upregulation of RAB8B in patients with rs1986112 GG and AG genotype compared to AA genotype, suggesting a role in schizophrenia development 31707148_Rab8 GTPase can regulate Klotho-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling activity by modulating translocation of Klotho onto the cell surface. |
ENSMUSG00000036943 |
Rab8b |
610.981329 |
2.0541081332 |
1.038512 |
0.101732241 |
103.238558 |
0.00000000000000000000000297126645745398303752262184487669071796160456683852169172851254543357701898287359654204919934272766113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000031147651215923854099198234757330253365450713027405248190546214331897445504182542208582162857055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
788.6216330 |
64.8659796 |
386.0049414 |
23.5035396 |
| ENSG00000166165 |
1152 |
CKB |
protein_coding |
P12277 |
FUNCTION: Reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens (e.g. creatine phosphate) (PubMed:8186255). Creatine kinase isoenzymes play a central role in energy transduction in tissues with large, fluctuating energy demands, such as skeletal muscle, heart, brain and spermatozoa (Probable). Acts as a key regulator of adaptive thermogenesis as part of the futile creatine cycle: localizes to the mitochondria of thermogenic fat cells and acts by mediating phosphorylation of creatine to initiate a futile cycle of creatine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation (By similarity). During the futile creatine cycle, creatine and N-phosphocreatine are in a futile cycle, which dissipates the high energy charge of N-phosphocreatine as heat without performing any mechanical or chemical work (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q04447, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8186255, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Kinase;Mitochondrion;Nitration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in energy homeostasis. The encoded protein reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. It acts as a homodimer in brain as well as in other tissues, and as a heterodimer with a similar muscle isozyme in heart. The encoded protein is a member of the ATP:guanido phosphotransferase protein family. A pseudogene of this gene has been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1152; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; creatine kinase activity [GO:0004111]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cellular chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0030644]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to wortmannin [GO:1904568]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; phosphocreatine biosynthetic process [GO:0046314]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762] |
12160938_2D fingerprinting & mass spectrometry reveal specific targets of protein oxidation in Alzheimer's disease brain, including creatine kinase BB, suggesting involvement of oxidatively modified proteins in neurodegeneration. 15996648_Expression of CKB mRNA and CK-B sometimes occurred in blastic transformation of the hematopoietic system 16384981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424007_CKB was expressed in 78% of colon tumors 17036164_GM130 and BB-CK co-localize specifically in a transient fashion during early prophase of mitosis, when GM130 plays an important role in Golgi fragmentation that starts also at early prophase. 18309274_The asymmetric unit contained two molecules of CKB, giving a crystal volume per protein mass (Vm) of 1.80 A3 Da-1 and a solvent content of 31.6%. 18552983_Autoantibodies to EsteD and BB-CK produced in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis -induced mice were also detected in some endogenous uveitis patients, suggesting that these proteins might be autoantigens. 18566107_Using a yeast 2-hybrid it was discovered that the C-terminal domain of KCC3, that is lost in most hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with agenesis of the corpus callosum-causing mutations, directly interacts with brain-specific creatine kinase. 18682038_The Tat-CK fusion protein markedly increased endogenous CK activity levels within PC12 cells. 18793185_Data show that dose-response inactivation by 4HNE (4-hydroxynonenal) of hBAT (human bile acid CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase) and CKBB (cytosolic brain isoform of creatine kinase) is associated with site-specific modifications. 18977227_Three structural aspects of human-brain-type-creatine-kinase were identified by X-ray crystallography: the ligand-free-form at 2.2A; the ADP-Mg2+, nitrate, and creatine complex (transition-state-analogue complex; TSAC); and the ADP-Mg2+-complex at 2.0A. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19337554_Report the effects of prior calcium channel blocker therapy on creatine kinase-MB (myocardial form) levels after percutaneous coronary interventions. 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 20460152_The correlation of CK-BB as a disease biomarker in both CNS and peripheral tissues from Huntington's disease mice and patients may provide a powerful means to assess disease progression and prognosis. 20520825_Phosphocreatine metabolism in the normal appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis is impaired due to decreased CK-B levels. 20588136_A single troponin I value at 3 days from symptom onset is a better predictor of infarct size compared to peak values and CK-MB. 20721618_CKB was up-regulated in women older than 38 years, and its expression in cumulus cells was associated with embryo quality 20923681_These observations suggested that the ability to generate the oxidized form could protect BBCK against the intracellular oxidative stress. 21308735_Data demonstrate that the downregulation of CKB may play an important role in colon cancer progression by promoting EMT. 21931810_The results suggested that the intra- and inter-subunit domain interactions modified the behavior of kinetic refolding. 21980054_Cigarette smoke induced carbonylation and subsequent degradation of creatine kinase B are involved in the regulation of senescence in bronchial epithelial cells. 22088263_de-methylated CKB gene is inherited that leads to high CKB expression levels in myeloic precursor cells in the bone marrow 22418839_His103 and Phe107 in hASB9-2 are essential for binding to CKB. 22623148_study found promoter SNPs of CKB and TPI1 were weakly associated with schizophrenia;in addition, IFNG polymorphisms were associated with schizophrenia; results suggest that IFNG and proteins affected by IFNG may play a role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia 22885020_effects of osmolytes on human brain-type creatine kinase folding 23049898_analysis of SNPs and their effect on creatine kinase structure and function 23876027_Estimation of CK and its CK isoenzyme fractions can aid in quick and accurate diagnosis of tubal ectopic pregnancy. 23882694_We found that most patients with macular telangiectasia-2 possess retinal autoantibodies, the most prevalent of which were directed against AGL, RBP3, and CK-B. 24518563_increased serum Ckbb reflects failure of osteoclasts or suppression of osteoclasts in children with osteogenesis imperfecta during neridronate treatment 25141318_CK-MB levels were higher after ERCP in non-ischemic patients compared with a myocardial ischemia group. Creatine phosphokinase levels did not differ significantly between groups. 25538032_CK-B catalytic activity also helps in the formation of protrusive ruffle structures which are actin-dependent and abundant on the surface of both unstimulated and LPS-activated macrophages. 26460485_SRC, LYN and CKB expression or DNA methylation could be useful markers for predicting tumor progression. 27318991_membrane localization of BCK seems to be an important and regulated feature for the fueling of membrane-located, ATP-dependent processes, stressing again the importance of local rather than global ATP concentrations. 28364583_The data revealed a varying but significant increase of CK activity in CKBE individuals as compared to controls, reaching an almost 800-fold increase in two CKBE individuals which also had increased erythrocyte creatine. 28806770_These findings support increased CK activity as protection against ischaemia-reperfusion injury, in particular, protection via CKMT2 in a cardiac-relevant cell line, which merits further investigation in vivo. 29227081_Association and oligomerization of Prx II could take part in recovery and protection of the CK BB enzyme activity from inactivation during heat-induced stress. 33485312_Clinical impact of creatine phosphokinase and c-reactive protein as predictors of postgastrectomy complications in patients with gastric cancer. 33597756_Creatine kinase B controls futile creatine cycling in thermogenic fat. 34706306_CKB inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prostate cancer progression by sequestering and inhibiting AKT activation. |
ENSMUSG00000001270 |
Ckb |
97.216824 |
4.6307547277 |
2.211247 |
0.241171695 |
85.407892 |
0.00000000000000000002427498231640511082178524394403410533587487155997286774472554427006798505317419767379760742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000217414283367803078800341686578406119700167698669150749372913633550297163310460746288299560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
178.0063760 |
22.6159566 |
39.2306303 |
4.2926895 |
| ENSG00000166173 |
55323 |
LARP6 |
protein_coding |
Q9BRS8 |
FUNCTION: Regulates the coordinated translation of type I collagen alpha-1 and alpha-2 mRNAs, CO1A1 and CO1A2. Stabilizes mRNAs through high-affinity binding of a stem-loop structure in their 5' UTR. This regulation requires VIM and MYH10 filaments, and the helicase DHX9. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20603131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21746880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22190748}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Translation regulation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity and myosin binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process; positive regulation of mRNA binding activity; and positive regulation of translation. Located in nucleus. Part of polysome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55323; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; polysome [GO:0005844]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; mRNA 5'-UTR binding [GO:0048027]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; myosin binding [GO:0017022]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA stem-loop binding [GO:0035613]; sequence-specific mRNA binding [GO:1990825]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of mRNA binding [GO:1902416]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; RNA processing [GO:0006396] |
17383118_These data define Achn as a newly discovered regulatory molecule that presumably mediates a variety of developmental and homeostatic processes in animals. 19889961_Acheron may influence differentiation in part via its control of cell adhesion dynamics. 19917293_LARP6 has a distinctive bipartite RNA binding domain not found in other members of the La superfamily. LARP6 interacts with the two single-stranded regions of the 5' stem-loop. 21387291_Achn enhances human breast tumor growth and vascularization and that this activity is dependent on nuclear localization. 22139627_Acheron regulates vascular endothelial proliferation and angiogenesis together with Id1 during wound healing. 23887937_The results demonstrate that the La modules of the human LARP6 is also active in tRNA-mediated suppression, even in the absence of stable UUU-3'OH trailer protection. 24469459_LARP6 is a critical mediator by which IGF-1 augments synthesis of collagen type I in vascular smooth muscle 25271881_We postulate that collagen mRNAs directly partition to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane prior to synthesis of the signal peptide and that LARP6 and nonmuscle myosin filaments mediate this process. 25488812_The study presents the structure of the La motif and RRM1 of human LARP6 uncovering in both cases considerable structural variation in comparison to the equivalent domains in La and revealing an unprecedented fold for the RRM1. 25692237_Data indicate that LA motif protein LARP6 binding to spliced leader RNA (5'SL) of collagen alpha2(I) mRNA is more stable than the binding to 5'SL of alpha1(I) mRNA. 26932461_Akt mediated phosphorylation of LARP6; critical step in biosynthesis of type I collagen 28112218_Study shows that mTORC1 phosphorylates La ribonucleoprotein domain family, member 6 to stimulate type I collagen expression. 28782243_A cytoplasmic isoform of La protein as well as LARPs 6, 4, and 1 function in mRNA metabolism and translation in distinct but similar ways, sometimes with the poly(A)-binding protein, and in some cases by direct binding to poly(A)-RNA. 34896113_Characterization of Sequence-Specific Binding of LARP6 to the 5' Stem-Loop of Type I Collagen mRNAs and Implications for Rational Design of Antifibrotic Drugs. 35176288_LARP6 Regulates Keloid Fibroblast Proliferation, Invasion, and Ability to Synthesize Collagen. |
ENSMUSG00000034839 |
Larp6 |
33.126075 |
0.1770781204 |
-2.497542 |
0.515656865 |
21.626243 |
0.00000331287958685547271418651328611648665400934987701475620269775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011003173425289553563968802940564728487515822052955627441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.5412484 |
3.2800583 |
54.8078201 |
12.5245701 |
| ENSG00000166224 |
8879 |
SGPL1 |
protein_coding |
O95470 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves phosphorylated sphingoid bases (PSBs), such as sphingosine-1-phosphate, into fatty aldehydes and phosphoethanolamine. Elevates stress-induced ceramide production and apoptosis (PubMed:11018465, PubMed:14570870, PubMed:24809814, PubMed:28165339). Required for global lipid homeostasis in liver and cholesterol homeostasis in fibroblasts. Involved in the regulation of pro-inflammatory response and neutrophil trafficking. Modulates neuronal autophagy via phosphoethanolamine production which regulates accumulation of aggregate-prone proteins such as APP (By similarity). Seems to play a role in establishing neuronal contact sites and axonal maintenance (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R0X7, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9V7Y2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11018465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14570870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24809814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28165339}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Apoptosis;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Membrane;Nitration;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11018465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24809814, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28165339}. |
Enables sphinganine-1-phosphate aldolase activity. Involved in apoptotic signaling pathway; fatty acid metabolic process; and sphingolipid metabolic process. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. Implicated in nephrotic syndrome type 14. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8879; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; sphinganine-1-phosphate aldolase activity [GO:0008117]; androgen metabolic process [GO:0008209]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; ceramide metabolic process [GO:0006672]; estrogen metabolic process [GO:0008210]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; Leydig cell differentiation [GO:0033327]; luteinization [GO:0001553]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040014]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048705]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingolipid catabolic process [GO:0030149]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
14570870_sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase is a dual modulator of sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide metabolism as well as a regulator of cell fate decisions 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17090686_genetic or epigenetic changes affecting intestinal sphingosine-1-phosphate metabolism may correlate with and potentially contribute to carcinogenesis 17373700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18172856_extracellular S1P is dephosphorylated and subsequently converted by cells, which appears to be important for clearance of the signaling molecule S1P in the local tissue environment after infections or injuries 19119317_Data suggest that lymphocyte trafficking is particularly sensitive to variations in sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase (S1PL) activity and suggest that there is a window in which partial inhibition of S1PL could produce therapeutic levels of immunosuppression. 20519401_Overexpression of sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase (SPL), which induces the degradation of sphingosine 1-phosphate, interfered with the amplification of infectious influenza virus. 21184844_high SPL transcription of H1155 cells was regulated by Sp1 and GATA-4/Sp1 complex formation, both of which bind to Sp1 sites of the 5'-SPL promoter. 21304987_S1P(ext) mediated endothelial cell motility is dependent on intracellular S1P production, which is regulated, in part, by SphK1 and S1PL. 21368890_S1P lyase regulates DNA damage responses through a sphingolipid feedback mechanism. 22784711_SPL expression and activity are downregulated in cancerous tissues, there is a relationship between loss of SPL expression and prostate cancer aggressiveness. 24323699_Data show that a easy assay for 2-hydroxyacyl-CoA lyase (HACL1) and sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase (SGPL1) activities was developed. 24468113_results highlight the importance of S1P in AD suggesting the existence of a global deregulation of S1P signaling in this disease from its synthesis by SphK1 and degradation by SPL to its signaling by the S1P1 receptor. 24704119_S1P lyase - by facilitating S1P1 receptor recycling - is essential for S1P-mediated sustained signaling 24825162_The cells expressing SGPL1 in the parenchyma were CD68(+) APCs. 25347472_Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase downregulation promotes colon carcinogenesis through STAT3-activated microRNAs. 25785436_Results show that dissociation of SHP-1 from spinophilin is followed by an increase in the binding of spinophilin to PP1. 26493335_SPHK1:SGPL1 ratio correlated with increased cellular sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), and S1P correlated with drug resistance (IC50). 26886371_increased SK and SPL mRNA expression along with reduced sphingosine 1-phosphate levels were more commonly observed in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 27160553_Data show that sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) was significantly upregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues and low levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SGPL1) mRNA correlated with a worse overall survival, and that sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2) is over-expressed in a subset of tumours, which in part mediates sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)-induced migration of OSCC cells. 27935985_Overexpression of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SGPL1), reverse the interleukin-8 (IL-8) secretion enhancing effect of microRNA miR-125b in trophoblast cell line HTR8/SVneo cells. 28077491_Report a candidate gene (SGPL1) for autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with atypical disease course. Studies in patient-derived biosamples suggested that this phenotype is due to partial loss of SGPL1 function. Neuron-specific downregulation of the Drosophila orthologue impaired the morphology of the neuromuscular junction and caused progressive neurodegeneration 28125641_Exposure to the combination of 100 muM genistein and 10 nM calcitriol reduced the number of proliferative cells to control levels, increased ERb and VDR expression, and reduced extracellular acidification (40%) as well as respiratory activity (70%), primarily in MG-63 cells..strong overexpression SGPL1, which irreversibly degrades sphingosine-1-phosphate thereby, generating ethanolamine 28165339_Mutations in sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase cause nephrosis with ichthyosis and adrenal insufficiency 28165343_Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase mutations cause primary adrenal insufficiency and steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 28181337_Loss of SGPL1 function is associated with congenital nephrotic syndrome (CNS), adrenal calcifications, and hypogonadism. 28600291_results demonstrate that Sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase (SPL) is a host factor that augments type I IFN responses during influenza A virus infection; study delineates the relationship between IKKepsilon and SPL, which provides a mechanistic understanding of the pro-IFN activity of SPL 28706199_High SGPL1 expression is associated with Huntington's disease. 28931805_Study verifies the role of a high-ranked gene in dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism in the disease and demonstrate that inhibiting the enzyme, sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SPL), has neuroprotective effects in Huntington's disease models. 29375197_describe the sequential expression and localization of the endogenous S1P regulators SGPP-1 and SGPL-1 and highlight their contribution to the sphingolipid rheostat in inflammation. 30517686_SGPL1 Deficiency is associated with Primary Adrenal Insufficiency. 31455837_SGPL1321 mutation: one main trigger for invasiveness of pediatric alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. 32630435_Heterogenous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein H1 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression through the Stabilization of mRNA of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Lyase 1. 32971566_S1P Lyase siRNA Dampens Malignancy of DLD-1 Colorectal Cancer Cells. 32998447_Neurodegeneration Caused by S1P-Lyase Deficiency Involves Calcium-Dependent Tau Pathology and Abnormal Histone Acetylation. 33730651_Influenza A virus NS1 induces degradation of sphingosine 1-phosphate lyase to obstruct the host innate immune response. 34073605_S1P Lyase Regulates Intestinal Stem Cell Quiescence via Ki-67 and FOXO3. |
ENSMUSG00000020097 |
Sgpl1 |
226.090033 |
2.4463177820 |
1.290612 |
0.111566573 |
135.498838 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000025681789367012849780176526817786315235992566139493715873431506518080238223930561588734255984434184938436374068260192871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000003452306111631235616008282310178707074947442461062891482179621669055241642247032658741279220748765510506927967071533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
321.8879590 |
23.0000198 |
132.6871710 |
7.5016025 |
| ENSG00000166226 |
10576 |
CCT2 |
protein_coding |
P78371 |
FUNCTION: Component of the chaperonin-containing T-complex (TRiC), a molecular chaperone complex that assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis (PubMed:25467444). The TRiC complex mediates the folding of WRAP53/TCAB1, thereby regulating telomere maintenance (PubMed:25467444). As part of the TRiC complex may play a role in the assembly of BBSome, a complex involved in ciliogenesis regulating transports vesicles to the cilia (PubMed:20080638). The TRiC complex plays a role in the folding of actin and tubulin (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080638, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25467444, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a molecular chaperone that is a member of the chaperonin containing TCP1 complex (CCT), also known as the TCP1 ring complex (TRiC). This complex consists of two identical stacked rings, each containing eight different proteins. Unfolded polypeptides enter the central cavity of the complex and are folded in an ATP-dependent manner. The complex folds various proteins, including actin and tubulin. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:10576; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cell body [GO:0044297]; chaperonin-containing T-complex [GO:0005832]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; zona pellucida receptor complex [GO:0002199]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent protein folding chaperone [GO:0140662]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; chaperone mediated protein folding independent of cofactor [GO:0051086]; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly [GO:0051131]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; positive regulation of establishment of protein localization to telomere [GO:1904851]; positive regulation of protein localization to Cajal body [GO:1904871]; positive regulation of telomerase activity [GO:0051973]; positive regulation of telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body [GO:1904874]; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase [GO:0032212]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; scaRNA localization to Cajal body [GO:0090666]; toxin transport [GO:1901998] |
19332537_The chaperonin CCT is identified as a novel physiological substrate for p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) and p70 ribosomal S6 kinase (S6K). 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20573828_PB2 associates with CCT2 as a monomer and the CCT binding site is located in a central region of the PB2 protein. 23190606_Destruction of the beta-tubulin:CCT-beta complex provokes Hsp90-dependent protein ubiquitination and degradation. 23782473_Increased expression of CCT2 is associated with tumor progression and the clinical behavior of gallbladder carcinoma. 24375412_PDCD5 bound the apical domain of the CCTbeta subunit, projecting above the folding cavity without entering it. Like PDCD5, beta-tubulin also interacts with the CCTbeta apical domain, but a second site is found at the sensor loop deep within the folding cavity. 25704758_A role for the TRiC subunits TCP1 and CCT2, and potentially the entire TRiC complex, in breast cancer. 27645772_the novel LCA mutations in CCTbeta and the impact of chaperon disability by these mutations in cellular biology. 29483666_We applied whole-genome sequencing (WGS) on 9 trios where the probands are sporadically affected with the most severe form of the disorder and harbor no coding sequence variants affecting the function of known Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) genes. We found de novo protein-altering variants in three intolerant to change genes-CCT2, VASH1, and CYP26A1-for which a plausible link with the enteric nervous system (ENS) exists 31462707_we suggest that CCT2 correlates with Gli-1 expression and is an important determinant of survival in the colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. The results reveal that CCT2 can regulate the folding of Gli-1 in relation to hypoxia in CRC 31964905_Investigating Chaperonin-Containing TCP-1 subunit 2 as an essential component of the chaperonin complex for tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000034024 |
Cct2 |
1067.489371 |
2.2262094850 |
1.154589 |
0.053910420 |
462.080449 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000169493006366798480785955841253848357187296636589251004551571778373271310053205449303495204391422860581336915258680823112282325986754608450043174690262733595235112160722500187597218356277932408446587864263183118762302580760047575 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000074901699819579202942593519205207612582513666662740694708456676466997326265336185777333517599819198752454429297933176806410029704156248913091708510741686777839861240903213138160557969402532520662996487667958103635021138329898442 |
Yes |
No |
1498.2064611 |
46.8501148 |
677.9848722 |
16.8298799 |
| ENSG00000166250 |
79827 |
CLMP |
protein_coding |
Q9H6B4 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the cell-cell adhesion. May play a role in adipocyte differentiation and development of obesity. Is required for normal small intestine development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14573622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15563274, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22155368}. |
Cell junction;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein that is localized to junctional complexes between endothelial and epithelial cells and may have a role in cell-cell adhesion. Expression of this gene in white adipose tissue is implicated in adipocyte maturation and development of obesity. This gene is also essential for normal intestinal development and mutations in the gene are associated with congenital short bowel syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:79827; |
bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565] |
12851705_ASAM, IGSF11, CXADR and ESAM are type I transmembrane proteins and members of the same IGSF superfamily. 14573622_CLMP is a novel cell-cell adhesion molecule and a new component of epithelial tight junctions. 15563274_We identified ACAM (adipocyte adhesion molecule), a novel homologue of the CTX (cortical thymocyte marker in Xenopus) gene family, which may be the critical adhesion molecule in adipocyte differentiation and development of obesity. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22155368_Loss-of-function mutations in CLMP cause congenital short bowel syndrome in human beings, likely by interfering with tight-junction formation, which disrupts intestinal development. 22718816_The PDZ1 and PDZ3 domains of MAGI-1 regulate the eight-exon isoform of the CXADR-like membrane protein. 22992863_Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor gene expression is induced in esophageal cancer cells by the HDAC inhibitor trichostatin A. 23460781_The key processes involved in intestinal epithelial development appear to be unaffected by wild type-CLMP or mutant-CLMP. 27352967_Novel inherited variants in CLMP were identified in three congenital short bowel syndrome patients derived from two unrelated families. 27527752_Inhibition of CFTR or histone deacetylase (HDAC) enhanced CAR expression while CFTR overexpression or restoration of the diminished HDAC activity in cystic fibrosis cells reduced CAR expression. 27720179_We describe a newborn presenting CSBS intestinal malrotation and chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome (CIPS), compound heterozygous for two previously unreported heterozygous mutations in Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor-like membrane protein (CLMP) gene. We identified two heterozygous mutations in CLMP, one in intron 1 (c.28+1G>C) from the father, the other on exon 4 (c502C>T, p.R168X) from the mother. 36241608_CLMP Promotes Leukocyte Migration Across Brain Barriers in Multiple Sclerosis. |
ENSMUSG00000032024 |
Clmp |
49.950943 |
3.1761430722 |
1.667276 |
0.265678278 |
39.497979 |
0.00000000032839915943447786779594369485667845059984060185342968907207250595092773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001637557970693545172715933189817524850973029515444068238139152526855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.0541184 |
12.4583311 |
24.3401897 |
3.2057650 |
| ENSG00000166289 |
79156 |
PLEKHF1 |
protein_coding |
Q96S99 |
FUNCTION: May induce apoptosis through the lysosomal-mitochondrial pathway. Translocates to the lysosome initiating the permeabilization of lysosomal membrane (LMP) and resulting in the release of CTSD and CTSL to the cytoplasm. Triggers the caspase-independent apoptosis by altering mitochondrial membrane permeabilization (MMP) resulting in the release of PDCD8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16188880}. |
Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Lysosome;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding activity; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding activity; and phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding activity. Involved in endosome organization; positive regulation of autophagy; and protein localization to plasma membrane. Located in lysosome. Colocalizes with endosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79156; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate binding [GO:0070273]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001244]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; vesicle organization [GO:0016050] |
22115783_The results suggest that in addition to its role in endosome transport, phafin1 is also involved in lysosomal targeting and autophagosome formation. |
ENSMUSG00000074170 |
Plekhf1 |
37.997710 |
3.5253070122 |
1.817749 |
0.309802428 |
35.014015 |
0.00000000327340781112978740887371909430280519925915427847940009087324142456054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014935239348462337841107343858020051197144084653700701892375946044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.5983075 |
10.4320070 |
16.9969524 |
2.4644142 |
| ENSG00000166313 |
322 |
APBB1 |
protein_coding |
O00213 |
FUNCTION: Transcription coregulator that can have both coactivator and corepressor functions (PubMed:15031292, PubMed:18468999, PubMed:18922798, PubMed:25342469, PubMed:33938178). Adapter protein that forms a transcriptionally active complex with the gamma-secretase-derived amyloid precursor protein (APP) intracellular domain (PubMed:15031292, PubMed:18468999, PubMed:18922798, PubMed:25342469). Plays a central role in the response to DNA damage by translocating to the nucleus and inducing apoptosis (PubMed:15031292, PubMed:18468999, PubMed:18922798, PubMed:25342469). May act by specifically recognizing and binding histone H2AX phosphorylated on 'Tyr-142' (H2AXY142ph) at double-strand breaks (DSBs), recruiting other pro-apoptosis factors such as MAPK8/JNK1 (PubMed:19234442). Required for histone H4 acetylation at double-strand breaks (DSBs) (PubMed:19234442). Its ability to specifically bind modified histones and chromatin modifying enzymes such as KAT5/TIP60, probably explains its transcription activation activity (PubMed:33938178). Functions in association with TSHZ3, SET and HDAC factors as a transcriptional repressor, that inhibits the expression of CASP4 (PubMed:19343227). Associates with chromatin in a region surrounding the CASP4 transcriptional start site(s) (PubMed:19343227). Involved in hippocampal neurite branching and neuromuscular junction formation, as a result plays a role in spatial memory functioning (By similarity). Plays a role in the maintenance of lens transparency (By similarity). May play a role in muscle cell strength (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9QXJ1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15031292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18468999, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18922798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19234442, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19343227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25342469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33938178}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Fe65 protein family. It is an adaptor protein localized in the nucleus. It interacts with the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein (APP), transcription factor CP2/LSF/LBP1 and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. APP functions as a cytosolic anchoring site that can prevent the gene product's nuclear translocation. This encoded protein could play an important role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. It is thought to regulate transcription. Also it is observed to block cell cycle progression by downregulating thymidylate synthase expression. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:322; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:0050750]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone H4 acetylation [GO:0043967]; negative regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902807]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939] |
11029529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11065130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11099823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11436125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12653567_The transcriptional activity of the APP intracellular domain-Fe65 complex is inhibited by activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. 12727304_Adjusting for age and sex, we found a slight risk associated with the deletion in intron 13 of the APBB1 gene for subjects less than 65 years. 12727304_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12779321_gamma-Secretase cleavage and binding to FE65 regulate the nuclear translocation of the intracellular C-terminal domain (ICD) of the APP family of proteins. 12888553_APP and Fe65 mediate transactivation with low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 14569203_Abnormal accumulations of the amyloid-beta precursor protein associated with the aging cellular muscle fibers and appear to be the key pathogenic event in iclusion-body myositis. 15037614_Alcadein and amyloid beta-protein precursor regulates FE65-dependent gene transactivation 15044485_Fe65 is activated by the APP intracellular domain during transcriptional transactivation 15647266_p65FE65 may be an intracellular mediator in a signaling cascade regulating alpha-secretion of APP 15816856_The present work provides evidence that FE65 plays a role in the regulation of amyloid precursor protein processing in an in vivo transgenic mouse model. 16223726_multiple interactions of AICD with FE65 and 14-3-3gamma modulate FE65-dependent gene transactivation 16332686_FE65 is the key agent of Gal4DB-mediated transcriptional transactivation, whereas Tip60 is an FE65-associated repressor. 17368826_Notch1 intracellular domain plays the role of a negative regulator in AICD signaling via the disruption of the AICD-Fe65-Tip60 trimeric complex. 17512906_Nek6 binds to Fe65 through its (267)PPLP(270) motif; the protein-protein interaction between Nek6 and Fe65 regulates their subcellular localization and cell apoptosis 17590240_We demonstrated that treatment with EGCG reduced the A beta levels by enhancing endogenous APP nonamyloidogenic proteolytic processing. 17686488_Results describe the crystal structures of the human FE65 WW domain (residues 253-289) in the apo form and bound to the peptides PPPPPPLPP and PPPPPPPPPL, which correspond to human Mena residues 313-321 and 347-356, respectively. 17854420_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17855370_Fe65 regulation of APP proteolysis may be integrally associated with its nuclear signaling function, as all antecedent proteolytic steps prior to release of Fe65 from the membrane are fostered by the APP-Fe65 interaction 18468999_APP-regulated FE65 plays an important role in the early stress response of cells and that FE65 deregulated from APP induces apoptosis. 18480379_Thyroid cancers are characterized by APP upregulation, increased membrane targeting of the APP ectodomain and significantly increased mRNA levels of the APP scaffold proteins JIP1, ShcA and Fe65. 18550529_crystallographic analysis of the human Fe65-phosphotyrosine domain 18777128_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18777128_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in APBB1 gene is associated with nicotine dependence. 18800165_the beta-sheet edge in some natively folded amyloid oligomers is designed positively to prevent beta aggregation 18833287_Study determined the crystal structure of the carboxy-terminal APP intracellular domain in complex with the C-terminal phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain of Fe65; The unique interface involves the NPxY PTB-binding motif and two alpha helices. 18922798_Dexras1 functions as a suppressor of FE65-APP-mediated transcription, and FE65 tyrosine 547 phosphorylation enhances FE65-APP-mediated transcription, at least in part, by modulating the interaction between FE65 and Dexras1 19381069_The protein-protein interaction between the WW domain of Fe65 and the putative binding motif of Nedd4-2 down-regulates Fe65 protein stability and subcellular localization through its ubiquitylation, to contribute to cell apoptosis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20091743_reduced levels of Sp1 resulted in downregulation of endogenous FE65 mRNA and protein 20133016_Both amyloid-beta precursor protein and Fe65 are co-localized in model Hirano bodies associated with Alzheimer's disease. 20405578_The data of this demonstrated that the induction of AICD/Fe65 or transgelin significantly alters actin dynamics and mitochondrial function in neuronal cells 20568118_Fe65 and Dab1 compete for binding to APP. Dab1 significantly decreased the amount of APP bound to LRP and the level of secreted APP and APP-CTF in LRP expressing cells 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21650223_Fe65 binds preferentially to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) carboxyl terminus when phosphorylated at tyrosine-4507 and in complex with amyloid precursor protein (APP). 21824145_A novel FE65 isoform and the regulation of the splicing events leading to its production may contribute to elucidating neuronal specific roles of FE65 and its contribution to Alzheimer's disease pathology. 21968187_Phosphorylation of LRP1 regulates the interaction with Fe65. 22199353_Fe65 carries out different functions depending on its location in the regulation of Notch1 signaling. 22902274_A ternary complex consisting of AICD, FE65, and TIP60 down-regulates Stathmin1. 23572515_FE65 interactions with BLM and MCM proteins may contribute to the neuronal cell cycle re-entry observed in brains affected by Alzheimer's disease. 24284412_The SV2A/FE65 interaction might play a role in synaptic signal transduction. 24619425_Data indicate that Fe65 is a positive estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) transcriptional regulator. 25397632_A novel phosphorylation site was identified within Fe65 which mediates gene transcription. 26166158_Targeted enhancement of the signaling through the Fe65-cortactin pathway, by either HDAC6 inhibition or Tip60 activation, may lead to the development of new therapeutic drugs that are effective for patients with metastatic breast cancers. 26188042_FE65 influences APP degradation via the proteasome, and phosphorylation of FE65 Ser(610) by SGK1 regulates binding of FE65 to APP, APP turnover and processing. 26276215_Jagged1 is a novel binding partner of Fe65, and Fe65 may act as a novel effector of Jagged1 signaling. 27176072_Fe65 Ser289 phosphorylation did not affect the transcriptional activity of the Fe65-APP complex, in contrast to the previously described Ser228 site. 27836546_Our findings imply that APBB1 plays an important role in the maintenance of EMT-associated CSC-like properties and gamma-radiation resistance via activation of IGF1Rbeta/AKT/GSK3beta pathway in lung cancer cells, highlighting APBB1 as a potential target for therapeutic cancer treatment. 28323844_Fe65 is an adaptor protein involved in both processing and signaling of the Alzheimer-associated amyloid-beta precursor protein, APP. Here, the subcellular localization was further investigated using TAP-tagged Fe65 constructs expressed in human neuroblastoma cells. Our results indicate that PTB2 rather than the WW domain is important for the nuclear localization of Fe65. 28963516_The findings reveal a novel mechanism whereby GSK3beta stimulates amyloidogenic processing of APP by phosphorylation of FE65 at threonine 579. 29615491_FE65 is found to activate ELMO1 by diminishing ELMO1 intramolecular autoinhibitory interaction and to promote the targeting of ELMO1 to the plasma membrane, where Rac1 is activated. We also show that FE65, ELMO1, and DOCK180 form a tripartite complex 33047393_ARF6-Rac1 signaling-mediated neurite outgrowth is potentiated by the neuronal adaptor FE65 through orchestrating ARF6 and ELMO1. 33123906_Abeta40 Promotes the Osteoblastic Differentiation of Aortic Valve Interstitial Cells through the RAGE Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000037032 |
Apbb1 |
13.833732 |
0.3136299155 |
-1.672865 |
0.507377761 |
11.007608 |
0.00090738691102705776401343706893953822145704180002212524414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002129934924739086080786032439959853945765644311904907226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9298721 |
2.3720065 |
21.9831942 |
4.6951465 |
| ENSG00000166341 |
8642 |
DCHS1 |
protein_coding |
Q96JQ0 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. Mediates functions in neuroprogenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. In the heart, has a critical role for proper morphogenesis of the mitral valve, acting in the regulation of cell migration involved in valve formation (PubMed:26258302). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26258302}. |
Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the cadherin superfamily whose members encode calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion molecules. The encoded protein has a signal peptide, 27 cadherin repeat domains and a unique cytoplasmic region. This particular cadherin family member is expressed in fibroblasts but not in melanocytes or keratinocytes. The cell-cell adhesion of fibroblasts is thought to be necessary for wound healing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8642; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; catenin complex [GO:0016342]; membrane [GO:0016020]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; adherens junction organization [GO:0034332]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0016339]; cell migration involved in endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003273]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; cell-cell junction assembly [GO:0007043]; cochlea development [GO:0090102]; condensed mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0072137]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; hippo signaling [GO:0035329]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; mitral valve formation [GO:0003192]; neural tube development [GO:0021915]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; ossification involved in bone maturation [GO:0043931]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389]; post-anal tail morphogenesis [GO:0036342]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24056717_findings show that mutations in genes encoding the receptor-ligand cadherin pair DCHS1 and FAT4 lead to a recessive syndrome in humans that includes periventricular neuronal heterotopia 25355906_These findings suggest that Fat and Dachsous self-bend due to the loss of Ca(2+)-binding amino acids from specific EC-EC linkers, and can therefore adapt to confined spaces. 25930014_Study shows that when key regulators during mammalian cerebral cortical development are disrupted due to DCHS1-FAT4 mutations, functional cerebral asymmetries are stronger. 26258302_DCHS1 deficiency in mitral valve prolapse patient mitral valve interstitial cells (MVICs), as well as in Dchs1(+/-) mouse MVICs, result in altered migration and cellular patterning, supporting these processes as aetiological underpinnings for the disease 27074579_In sum, we establish Dchs1 as a component of the membrane domain surrounding the ciliary base. This suggests a specific role of Dchs1 in PCP-dependent organization of ciliary function and a possible role in lung disease. 29224215_p.R2330C and p.R2513H were not identified in this cohort. found eight missense variants including six considered deleterious. This includes one novel variant (p.A2464P) and two rare variants (p.R2770Q and p.R2462Q). These variants are predicted to be deleterious with combined annotation-dependent depletion (CADD) scores greater than 25, which are in the same range as p.R2330C (CADD = 28.0) and p.R2513H (CADD = 24.3). 29505454_The infant was diagnosed with van Maldergem syndrome on the basis of the clinical features and this was subsequently confirmed with genetic analysis, which indicated a homozygous mutation (c.7204G>A p. D2402N ) in the DCHS1 gene 31358536_Fat4 and Dchs1 mutants mimic the craniofacial phenotype of the human Van Maldergem syndrome and Dchs1-Fat4 signalling is essential for osteoblast differentiation. 32295462_DCHS1 DNA copy number loss associated with pediatric urinary tract infection risk. |
ENSMUSG00000036862 |
Dchs1 |
77.393570 |
0.2791503761 |
-1.840886 |
0.421637053 |
17.236437 |
0.00003300451594496664578818820312555715190683258697390556335449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000097293120700560743827761678304000270145479589700698852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.6578678 |
9.1934909 |
121.6091983 |
23.0054804 |
| ENSG00000166349 |
5896 |
RAG1 |
protein_coding |
P15918 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic component of the RAG complex, a multiprotein complex that mediates the DNA cleavage phase during V(D)J recombination. V(D)J recombination assembles a diverse repertoire of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor genes in developing B and T-lymphocytes through rearrangement of different V (variable), in some cases D (diversity), and J (joining) gene segments. In the RAG complex, RAG1 mediates the DNA-binding to the conserved recombination signal sequences (RSS) and catalyzes the DNA cleavage activities by introducing a double-strand break between the RSS and the adjacent coding segment. RAG2 is not a catalytic component but is required for all known catalytic activities. DNA cleavage occurs in 2 steps: a first nick is introduced in the top strand immediately upstream of the heptamer, generating a 3'-hydroxyl group that can attack the phosphodiester bond on the opposite strand in a direct transesterification reaction, thereby creating 4 DNA ends: 2 hairpin coding ends and 2 blunt, 5'-phosphorylated ends. The chromatin structure plays an essential role in the V(D)J recombination reactions and the presence of histone H3 trimethylated at 'Lys-4' (H3K4me3) stimulates both the nicking and haipinning steps. The RAG complex also plays a role in pre-B cell allelic exclusion, a process leading to expression of a single immunoglobulin heavy chain allele to enforce clonality and monospecific recognition by the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) expressed on individual B-lymphocytes. The introduction of DNA breaks by the RAG complex on one immunoglobulin allele induces ATM-dependent repositioning of the other allele to pericentromeric heterochromatin, preventing accessibility to the RAG complex and recombination of the second allele. In addition to its endonuclease activity, RAG1 also acts as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates monoubiquitination of histone H3. Histone H3 monoubiquitination is required for the joining step of V(D)J recombination. Mediates polyubiquitination of KPNA1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Disease variant;DNA recombination;DNA-binding;Endonuclease;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Multifunctional enzyme;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome;SCID;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in activation of immunoglobulin V-D-J recombination. The encoded protein is involved in recognition of the DNA substrate, but stable binding and cleavage activity also requires RAG2. Defects in this gene can be the cause of several diseases. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5896; |
DNA recombinase complex [GO:0097519]; endodeoxyribonuclease complex [GO:1905347]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; histone monoubiquitination [GO:0010390]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070244]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; pre-B cell allelic exclusion [GO:0002331]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; regulation of behavioral fear response [GO:2000822]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; V(D)J recombination [GO:0033151]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
12115231_RAG expression is up-regulated in peripheral IgD+ and VpreB+ B cells of patients with active SLE. 12145704_Multiple PCR-SSCP analysisof RAG-1 showed shifted bands in 5 cases: Philadelphia-positive ALL, MLL, FL, and AML. An A-to-G SNP at 2571 was found. 12200379_B-cell differentiation arrest in bone marrow of RAG-deficient SCID patients corresponds to residual recombination activities of mutated RAG1 and RAG2 proteins. 12355431_RAG1 expression and non-functional TCR rearrangements continuously take place in peripheral mature T cells of all activation/differentiation stages 12757263_Data show that a mature nonmalignant human B cell clone producing IgMlambda-ICA can express RAG-1/RAG-2 transcripts 14500629_RAG1 mRNA splice forms have been identified that are expressed in immature T cells (CD2+CD7+CD3-) of the jejunal mucosa, both intraepithelially and in lamina propria. 14624253_Erk and Abl kinases suppress RAG-1 and -2 gene expression through T cell receptor-independent basal signaling 14726805_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15249552_RAG1 and RAG2 interact with recombination signal sequence DNA in the coding region in pre-and post-cleavage type synaptic complexes 15295705_expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 42% of patients with infectious mononucleosis but not from health control subjects. 15843554_Activated mature CD5-positive human tonsil B cells coexpress both RAG1 and RAG2 mRNA and protein, and display DNA cleavage resulting from their recombinase activity. 16061569_Novel RAG1 mutation in a case of severe combined immunodeficiency. A novel homozygous thymine to cytosine substitution at nucleotide position 2686 16465622_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16738334_novel RAG-1 mutation, E649A, that supports elevated cleavage activity in vitro by preferentially enhancing hairpin formation 16857995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17075247_Ths review focusses on the variation of inherited hypomorphic mutations of recombination activating genes either 1 or 2 (RAG1/2) that have been detected in most Omenn syndrome patients. 17307402_analysis of structure-specific nicking of small heteroduplexes by the RAG complex 17890453_5 unrelated cases of combined immune deficiency due to hypomorphic RAG mutations, demonstrate the absence of invariant NKT cells 17982069_IL-6 initiates the expression of RAG1 in circulating B cells, and extends those in tonsil B cells. 18089566_the RAG-7-mer interaction is a critical step for coding DNA distortion and hairpin formation in the context of the 12/23 rule. 18463379_We describe three girls with a primary immunodeficiency disease associated with hypomorphic mutations in one of the two recombinase activating genes (RAG1 and RAG2). 18579371_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18701881_Results indicate that the novel R776W missense mutation in RAG-1 is causal in the T(-)B(-)NK(+) severe combined immunodeficiency disease phenotype in Athabascan-speaking Dine Indians from the Canadian Northwest Territories 18768869_RAG1 Arg972Qln mutation, located in the primary sequence near catalytic amino acid Glu962, is hypersensitive to certain coding flank sequences in a patient with Omenn syndrome. 18830263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116388_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19118899_Karyopherin alpha 1 is a putative substrate of the RAG1 ubiquitin ligase. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19359154_Studies in B and T lymphocytes demonstrate that the reduction in RAG expression at the immature B and double-positive (DP) T cell stages is mediated through tonic (foreign antigen independent) receptor signaling. 19404965_Two independent signals are required for the induction of RAG gene expression in B cells that infiltrate the synovium of patients with RA. 19458910_RAG1 mutations are associated with severe combined immunodeficiencies. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19859091_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19898481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20122409_RAG1-mediated histone monoubiquitylation activity plays a role in regulating the joining phase of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20489056_Hypomorphic Rag mutations can cause destructive midline granulomatous disease. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20703256_In a subset of acute lymphoblastic leukemia RAG might create one of the initiating double-strand breaks. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20813000_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20956421_These disparate and atypical presentations of hypomorphic RAG1 mutations highlight the role of RAG1 in immune function and autoimmunity and expand the disease spectrum linked to these genes. 21131235_study reports 5 cases of RAG deficiency; genetic defects were heterogeneous and included 6 novel RAG mutations; all missense mutations except for Met443Ile in RAG2 were located in active core regions of RAG1 or RAG2 21481940_study demonstrates that exogenous TCR alpha and beta chains transferred into the human immature RAG(+) T cell line Sup-T1 by lentiviral transduction inhibit RAG expression through tonic signaling 21502542_RAG mutations are associated with Idiopathic CD4+ T lymphopenia without autoimmunity or granulomatous disease. 21624848_In the RAG1 gene we detected two novel mutations: L454Q and 469 fs-4bpdel. In the RAG 2 gene: 3 novel mutations: D65Y, G157V, and E480X. One T-B- SCID patient had a compound heterozygote for new mutations in the adenosine deaminase gene: W264X and R235W. 21625022_IL7R and RAG1/2 genes mutations/polymorphisms in patients with SCID. 21655267_The results indicate that in cancer cells E2A, FOXO1 and FOXP1 regulate RAG1 and RAG2 expression, which initiates Ig gene rearrangement much in the way similar to B lymphocytes. 21771083_We report for the first time 3 children with Omenn syndrome in the Chinese population and identify 3 novel mutations in the RAG1 gene. 22424479_Homozygous mutation of p.R394Q/p.R394Q and p.R776Q, 3047-3049 del GCC mutations are novel and they are causing serious T-B-NK + SCID. 22803080_Expression of recombinase RAG-1 in diabetic patients was detected primarily in alphabetaTCR+CD40+ lymphocytes. 22891626_Mutations to the sequence of the nonamer and deletion of the nonamer-binding domain of RAG1 reinforced the role of the nonamer in the enhancement in RAG cleavage. 22942284_A dual interaction between the DNA damage response protein MDC1 and the RAG1 subunit of the V(D)J recombinase. 22984564_Bidirectional activity of the NWC promoter is responsible for RAG-2 transcription in non-lymphoid cells [NWC] 23630330_genetic association studies in population in China: Data suggest that SNPs in RAG1 (rs2227973, A>G, K820R) and LIG4 (DNA ligase IV, rs1805388, exon 2 54C>T, Thr9Ile) are associated with male infertility. 23716691_Data indicate that the recombination-activating gene 1 protein (RAG1) as a substrate of AMPK. 23755767_Case Report: a girl who developed severe BCGitis and vaccine-derived poliovirus infection was discovered to have a novel deletion of RAG1. 23891352_The cases presented here demonstrate that The clinical spectrum of RAG deficiency must expand to encompass early-onset autoimmunity with preserved B lymphocytes. 24122031_Whole exome sequencing reveals homozygous RAG1 mutations that expand the spectrum of combined immunodeficiency with autoimmunity and granuloma occurring with RAG1 deficiency. 24290284_we demonstrate correlation between recombination activity of RAG1 mutants and the severity of clinical presentation and show that RAG1 mutants can induce specific abnormalities of the VDJ recombination process. 24418478_Similar recombination-activating gene (RAG) mutations result in similar immunobiological effects but in different clinical phenotypes. 24472623_The results indicate that the contribution of immune dysregulatory disease due to RAG1 mutations present in the general population may be much higher than previously estimated. 24666246_This is the first description of the co-existence of large amounts of clonal expanded autologous and transplacental-acquired maternal T cells in RAG1-deficient SCID. 24797073_Observations indicate that the RAG proteins exert fine control over every step of V(D)J cleavage. 24904117_PTEN microdeletions in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia are caused by illegitimate RAG-mediated recombination events. 24996264_A hypomorphic recombination-activating gene 1 (RAG1) mutation resulting in a phenotype resembling common variable immunodeficiency 25135298_direct Ddelta2-Jdelta1 rearrangements are prohibited by a B12/23 restriction and ordered TCR-delta gene assembly requires RUNX1 protein, which binds to the Ddelta2-23RSS, interacts with RAG1, and enhances RAG1 deposition at this site 25327637_Investigate the factors that regulate RAG1 and RAG2 cleavage on non-B DNA structures. We find that RAG binding and cleavage on heteroduplex DNA is dependent on the length of the double-stranded flanking region. 25745109_analysis of regions of RAG1 necessary for interaction with RAG2 and measurement of the RAG1-RAG2 binding affinity 25831509_analysis of individual molecular events of RAG-mediated V(D)J DNA cleavage 25849362_These findings provide insight into the role of this poorly understood region of Rag1 and support the role of Rag1 in a post-cleavage stage of recombination 25869295_This study reports on the prevalence of RAG1 and RAG2 mutations in ten severe combined immunodeficiency disorder patients in Egypt. 25976673_compiled 751 genetic variants in human RAG1 gene using 1092 human genomes 26234156_Study reports that RAG1 associates with chromatin at thousands of active promoters and enhancers in the genome of developing lymphocytes. The mouse and human genomes appear to have responded by reducing the abundance of 'cryptic' recombination signals near RAG1 binding sites. 26596586_most common mutation in East Slavs children with Omenn syndrome; associated with more favorable prognosis after hematopoietic stem cells transplantation 26689875_study reported 4 patients with RAG1 deficiency: classic severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) was seen in 2 patients, Omenn syndrome was observed in 1 patient and atypical SCID was seen in one patient 26996199_molecular and cellular mechanisms that account for the expanding range of clinical and immunological phenotypes of human RAG deficiency (review) 27198500_Our results raise the prospect that RAG is a valuable biomarker in lymphoblastic leukaemia disease surveillance. 27301863_This study compares T-cell development of patients with RAG1-dependent immune deficiencies, and elucidates important differences that help to explain the wide range of immunologic phenotypes that result from different mutations within the same gene of various patients. 27559048_The show that DNA damage caused by RAG1 activity in pre-B cells was able to downmodulate RAG1 expression and activity, confirming the existence of a negative feedback regulatory mechanism. 27609655_Estimated disease incidence of RAG1/2 mutations: A case report and querying the Exome Aggregation Consortium. 27713031_Agammaglobulinemia associated to nasal polyposis due to a hypomorphic RAG1 mutation 27808398_We report two siblings with SCID and an atypical phenotype of osteopetrosis (OP). A biallelic microdeletion encompassing the 5' region of TRAF6, RAG1 and RAG2 genes was identified. TRAF6, a tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated family member, plays an important role in T cell signaling and in RANKL-dependent osteoclast differentiation and activation but its role in human OP has not been previously reported 27863852_the ability of the RAG nuclease to minimize the risks of genome disruption by coupling the breakage and repair steps of the V(D)J reaction. This implies that the RAG genes, derived from an ancient transposon, have undergone strong selective pressure to prohibit transposition in favor of promoting controlled DNA end joining in cis by the ubiquitous DNA damage response and DNA repair machineries. 28083621_mutation c.256_257delAA in RAG1 gene seems to occur quite frequently in the Polish patients with severe combined immunodeficiency and may result in classical OS as well as in severe combined immunodeficiency without clinical and laboratory features of OS when occurred in homozygous state 28216420_Our findings suggest that mutations in RAG1, specifically the p.R474C variant, can be associated with relatively mild clinical symptoms or delayed occurrence of T cell and B cell deficiencies but may predispose to progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. 28552805_Leaky SCID can be caused by hypomorphic mutations in RAG1 and RAG2 that result in only partial loss of enzymatic function of the proteins respectively encoded by these genes. 29743177_This study provides novel insights into how hypomorphic Rag1 mutations alter the primary repertoire of T and B cells, setting the stage for immune dysregulation frequently seen in patients. 30226529_Case Report: SCID with cutaneous lymphoproliferative disease caused by novel compound heterozygous mutations in RAG1. 31012019_Combination of sex steroids with OSM increased the percent of CD4(+)FOXP3(+) cells and enhanced RAG-1 expression in these cells, thus promoting the development of immune tolerance during pregnancy. In the study of Th17, such effect of the hormones and OSM was not detected. 31204924_Monitoring RAG1 expression may provide a new method to evaluate the prognosis of adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients 31838659_A Large Cohort of RAG1/2-Deficient SCID Patients-Clinical, Immunological, and Prognostic Analysis. 31907413_provide evidence for a wave of human T-cell development that originates directly from haemogenic endothelium via a RAG1+ intermediate with multilineage potential 32353821_Co-evolution of mutagenic genome editors and vertebrate adaptive immunity. 32655540_The Clinical and Genetic Spectrum of 82 Patients With RAG Deficiency Including a c.256_257delAA Founder Variant in Slavic Countries. 32886094_Znc2 module of RAG1 contributes towards structure-specific nuclease activity of RAGs. 33796120_The Interplay Between Chromatin Architecture and Lineage-Specific Transcription Factors and the Regulation of Rag Gene Expression. 33954879_Clinical Manifestations, Mutational Analysis, and Immunological Phenotype in Patients with RAG1/2 Mutations: First Cases Series from Mexico and Description of Two Novel Mutations. 33987955_RAG1 co-expression signature identifies ETV6-RUNX1-like B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. 34644584_RAG2 abolishes RAG1 aggregation to facilitate V(D)J recombination. 35902638_Partial RAG deficiency in humans induces dysregulated peripheral lymphocyte development and humoral tolerance defect with accumulation of T-bet(+) B cells. 36166051_Expression and clinical significance of RAG1 in myelodysplastic syndromes. |
ENSMUSG00000061311 |
Rag1 |
83.347773 |
0.0289617609 |
-5.109707 |
1.027553924 |
16.534695 |
0.00004776798702394681250338673295097180471202591434121131896972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000137975633752143841872367380219088772719260305166244506835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.6326461 |
3.2635657 |
157.4906592 |
76.5223149 |
| ENSG00000166387 |
8495 |
PPFIBP2 |
protein_coding |
Q8ND30 |
FUNCTION: May regulate the disassembly of focal adhesions. Did not bind receptor-like tyrosine phosphatases type 2A. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9624153}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the LAR protein-tyrosine phosphatase-interacting protein (liprin) family. The encoded protein is a beta liprin and plays a role in axon guidance and neuronal synapse development by recruiting LAR protein-tyrosine phosphatases to the plasma membrane. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:8495; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; synapse organization [GO:0050808] |
20095854_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21462929_analysis of crystal structure of the central coiled-coil domain from human liprin-beta2 22328529_Knockdown of either Rab17 or liprin-beta2 restores invasiveness of ERK2-depleted cells, indicating that ERK2 drives invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells by suppressing expression of these genes. 26443449_rs12791447 is associated with prostate cancer susceptibility in Asians. mRNA levels of PPFIBP2 are differentially expressed in prostate tumours and paired normal tissues. 26663347_Analysis of the role of liprin-beta1 and liprin-beta2 has shown that while liprin-beta1 contributes positively to tumour cell motility in vitro; liprin-beta2 has a negative effect on both cell motility and invasion. 30043417_germline mutations in a novel gene, PPFIBP2, differentiated risk for lethal prostate cancer from low-risk cases and were associated with shorter survival times after diagnosis. |
ENSMUSG00000036528 |
Ppfibp2 |
42.109681 |
0.3624053555 |
-1.464324 |
0.346243221 |
17.436746 |
0.00002970280878423906247508788636135790284242830239236354827880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000088070200412890441090014992386869607798871584236621856689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
23.8636804 |
6.0125755 |
66.4848961 |
11.9565520 |
| ENSG00000166396 |
8710 |
SERPINB7 |
protein_coding |
O75635 |
FUNCTION: Might function as an inhibitor of Lys-specific proteases. Might influence the maturation of megakaryocytes via its action as a serpin. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Palmoplantar keratoderma;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Serine protease inhibitor |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of proteins which function as protease inhibitors. Expression of this gene is upregulated in IgA nephropathy and mutations have been found to cause palmoplantar keratoderma, Nagashima type. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014]. |
hsa:8710; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072126]; positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor production [GO:0090362]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production [GO:0032914] |
12386281_Mesangial cell-predominant gene, megsin. Genetic manipulation of megsin engenders two elementary mesangial lesions, mesangial expansion and an increase in the number of mesangial cells. 12397041_One positive regulatory motif, an incomplete activator protein-1 binding motif (CTGATTCAC) within the -120 to -112 region. This cis-acting element in the 5'-flanking region of megsin is involved in the activation of the megsin gene in mesangial cells. 15213261_Megsin has a role in susceptibility to immunoglobulin A nephropathy 15788472_in transgenic rats, overexpression of human megsin, a recently discovered serpin located in the kidney, produces renal and pancreatic lesions characteristic of serpinopathies 16431886_In this Chinese population, the 2093C-2180T haplotype at the 3'UTR of MEGSIN gene is associated with more severe forms of IgA nephropathy, and more rapid disease progression 16431886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16550745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16550745_The polymorphism of megsin A23167G is associated with susceptibility and progression of IgA nephropathy in Chinese population. GG genotype is associated with severe histological lesions and progression of the disease. 16796905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18471408_A267G in 5'-untranslated region within the exon of megsin may be one of the substantial genetic basis for differentiating 'deficiency of liver yin and kidney yin' syndrome and 'deficiency of qi and yin' syndrome in primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. 18471408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498720_study found out that the megsin TT haplotype (defined as T-2093, T-2180 alleles) could play a protective role in the progression of IgA nephropathy 18580857_recombinant megsin did not affect the mRNA expressions of TGF- and PAI-1, and did not modify the enzymatic activity of PAI-1 18793525_Megsin 2093T-2180C haplotype at the 3' untranslated region is associated with poor renal survival in Korean IgA nephropathy patients. 18793525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24207119_All of the identified mutants are predicted to cause premature termination upstream of the reactive site, which inhibits the proteases, suggesting a complete loss of the protease inhibitory activity of SERPINB7 in palmoplantar keratosis skin. 24514002_study reports on seven unrelated Chinese patients with Nagashima-Type Palmoplantar Keratosis with four underlying SERPINB7 mutations, of which one is a recurrent variant (c.796C>T) 24575807_megsin 2093C/T C allele may be genetic marker for IgA nephropathy susceptibility [review] 24773080_These data clearly provide further evidence that NPPK is caused by loss-of-function mutations in SERPINB7. 24954659_The mean concentration of serpin B7 at 28-32 weeks was 1.5-fold higher in women with subsequent preterm deliveries compared to controls. 25007157_Megsin 2093C/T TT genotype, and C25663G G allele and GG genotype were associated with the risk of IgAN in Asian population 25940237_Results show splice variants from the two recurrent splice-site mutations in SERPINB7, provide evidence for the pathogenicity of the mutations and suggest an in-frame deletion of exon 3 may cause NPPK and that the CD-loop could affect SERPINB7 function 26763456_Recessive missense mutation of SERPINB7 gene was found in Japanese families diagnosed with palmoplantar keratosis. 26871801_These results indicate that megsin gene variants may play a role in the severity, development, and/or progression of IgAN in Northwest Chinese population 27666198_Direct sequencing of SERPINB7 revealed five homozygous founder mutations (c.796C>T) and four compound heterozygous mutations in nine patients, including one novel mutation (c.122_127delTGGTCC). 27786350_Case Report: striate palmoplantar keratoderma showing transgrediens in a patient with heterozygote nonsense mutations in DSG1 and SERPINB7. 28211129_SERPINB7 mutations are related strictly to the PPKN phenotype. Our study indicates that screening for SERPINB7 mutations is useful to distinguish PPKN from other PPK types and from non-PPK keratinizing diseases with palmoplantar skin lesions. 29106929_mutant SERPINB7 mRNAs harboring r.796c>u were degraded by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Furthermore, the truncated SERPINB7 protein was degraded via a proteasome-mediated pathway 30592269_SERPINB7 may be a valuable candidate for further studies. In the present study, a method for identifying novel key pathogenic skinspecific molecules is presented, which may be used for investigating and treating psoriasis. 31706940_Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis in Finland caused by a SERPINB7 founder mutation. 32406097_SERPINB7 novel mutation in Chinese patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis and cases associated with atopic dermatitis. 34334259_Updated allele frequencies of SERPINB7 founder mutations in Asian patients with Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis/keratoderma. 34379845_Acral peeling in Nagashima type palmo-plantar keratosis patients reveals the role of serine protease inhibitor B 7 in keratinocyte adhesion. 34454985_Uniting biobank resources reveals novel genetic pathways modulating susceptibility for atopic dermatitis. 35178744_Two novel mutations of SERPINB7 in eight cases of Nagashima-type palmoplantar keratosis in the Chinese population. 35864103_SerpinB7 deficiency contributes to development of psoriasis via calcium-mediated keratinocyte differentiation dysfunction. |
ENSMUSG00000067001 |
Serpinb7 |
22.080465 |
25.1191225628 |
4.650714 |
0.613113928 |
95.809764 |
0.00000000000000000000012647041640242642795300252619665578526636611135605370934622691987680997982579356175847351551055908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001231334661015708505080155036039014186382828354598449748674195147746246448150486685335636138916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
43.1332475 |
17.5196762 |
1.7257285 |
0.6781523 |
| ENSG00000166401 |
5271 |
SERPINB8 |
protein_coding |
P50452 |
FUNCTION: Has an important role in epithelial desmosome-mediated cell-cell adhesion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27476651}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Serine protease inhibitor |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the ov-serpin family of serine protease inhibitors. The encoded protein is produced by platelets and can bind to and inhibit the function of furin, a serine protease involved in platelet functions. In addition, this protein has been found to enhance the mechanical stability of cell-cell adhesion in the skin, and defects in this gene have been associated with an autosomal-recessive form of exfoliative ichthyosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:5271; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; epithelial cell-cell adhesion [GO:0090136]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951] |
16493485_PI8 is released by platelets and controls functional responses 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19188865_Data show that SERPINB8 is expressed in normal neuroendocrine cells of several organs as well as in neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas, where it can be used as an additional diagnostic immunohistochemical marker. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20953187_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 27476651_report of mutations in SERPINB8 that are associated with exfoliative ichthyosis and provide evidence that SERPINB8 contributes to the mechanical stability of intercellular adhesions in the epidermis |
ENSMUSG00000026315 |
Serpinb8 |
244.475221 |
2.0828132141 |
1.058533 |
0.104838741 |
103.094883 |
0.00000000000000000000000319475212739821018126912022774672091223137692174637385156918281767929324033161719853524118661880493164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000033442937163402539745576699431304764040682098781289727900398797005854234498656296636909246444702148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
341.1465312 |
21.1997136 |
164.8261371 |
8.1241396 |
| ENSG00000166411 |
3419 |
IDH3A |
protein_coding |
P50213 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic subunit of the enzyme which catalyzes the decarboxylation of isocitrate (ICT) into alpha-ketoglutarate. The heterodimer composed of the alpha (IDH3A) and beta (IDH3B) subunits and the heterodimer composed of the alpha (IDH3A) and gamma (IDH3G) subunits, have considerable basal activity but the full activity of the heterotetramer (containing two subunits of IDH3A, one of IDH3B and one of IDH3G) requires the assembly and cooperative function of both heterodimers. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28139779}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Transit peptide;Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
|
Isocitrate dehydrogenases catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. These enzymes belong to two distinct subclasses, one of which utilizes NAD(+) as the electron acceptor and the other NADP(+). Five isocitrate dehydrogenases have been reported: three NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, which localize to the mitochondrial matrix, and two NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases, one of which is mitochondrial and the other predominantly cytosolic. NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenases catalyze the allosterically regulated rate-limiting step of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Each isozyme is a heterotetramer that is composed of two alpha subunits, one beta subunit, and one gamma subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha subunit of one isozyme of NAD(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3419; |
mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase complex (NAD+) [GO:0005962]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004449]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; NAD binding [GO:0051287]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; isocitrate metabolic process [GO:0006102]; tricarboxylic acid cycle [GO:0006099] |
14555658_for IDH, a normal alpha subunit is required for catalytic activity and alpha-Arg88 likely participates in the isocitrate site, whereas the beta and gamma subunits have roles in the nucleotide functions of this allosteric enzyme 16737955_active sites of the human NAD-IDH are shared between alpha and gamma subunits and between alpha and beta subunits 17432878_Asp181 is essential for nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-specific IDH alpha subunit catalysis and may also facilitate the binding of substrates. 20306291_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25531325_The silencing of IDH3a significantly delayed tumor growth by suppressing the HIF-1-mediated Warburg effect and angiogenesis. 30613765_IDH3alpha is elevated in glioblastoma patient samples compared to normal brain tissue and promotes glioblastoma progression in orthotopic glioma mouse models. On molecular levels, IDH3alpha ablation reduces TCA cycle turnover and shunts energy metabolism. In addition, IDH3alpha affects one-carbon metabolism and regulates nucleotide production as well as DNA methylation through effect on cSHMT. 31012789_This study highlights the importance of including this rarely-mutated gene in the molecular diagnostic set-ups for inherited retinal degenerations, and further delineates the phenotypic spectrum elicited by mutations in IDH3A. 34269949_Association between IDH mutational status and tumor-associated epilepsy or venous thromboembolism in patients with grade II and III astrocytoma. 35463978_Subcellular Proteome Analysis Reveals Apoptotic Vulnerability of T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000032279 |
Idh3a |
354.534762 |
2.1840601818 |
1.127013 |
0.340526192 |
10.662025 |
0.00109357590353264437846303458456986845703795552253723144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002530362178420102019227311274107705685310065746307373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
525.2643566 |
114.8418497 |
241.8700944 |
38.4767575 |
| ENSG00000166428 |
122618 |
PLD4 |
protein_coding |
Q96BZ4 |
FUNCTION: 5'->3' DNA exonuclease which digests single-stranded DNA (ssDNA). Regulates inflammatory cytokine responses via the degradation of nucleic acids, by reducing the concentration of ssDNA able to stimulate TLR9, a nucleotide-sensing receptor. Involved in phagocytosis of activated microglia. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BG07}. |
Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Exonuclease;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable single-stranded DNA 5'-3' exodeoxyribonuclease activity. Predicted to be involved in hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation; phagocytosis; and regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response. Predicted to be located in early endosome and endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Predicted to be active in several cellular components, including endoplasmic reticulum; phagocytic vesicle; and trans-Golgi network membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:122618; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; single-stranded DNA 5'-3' exodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0045145]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900015] |
23124809_We determined that PLD4 is a novel susceptibility gene for sysetmic sclerosis in Japanese, thus confirming the involvement of PLD4 in autoimmunity. 27840999_PLD4 expression in colon cancer tissues 30679154_PLD4 is a genetic determinant to systemic lupus erythematosus. |
ENSMUSG00000052160 |
Pld4 |
712.495253 |
0.2537738133 |
-1.978385 |
0.086340994 |
518.994984 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000070015918915757681155633211265708354390040292978333404833127551518990361545601961436967651360455311370304358244918144090554495656342354251093973971721576829665006777879020048842530700283644624645998784411362125336834 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034913343351235921622046434660271122522869088553031416924114434844878577014571852389508558595477420213433722906082289857415079376221799189937240871695783857365074505104017070654723481918367452361992361360255371576716 |
Yes |
Yes |
278.4857914 |
24.2972643 |
1101.0436915 |
67.0362624 |
| ENSG00000166432 |
84460 |
ZMAT1 |
protein_coding |
Q5H9K5 |
|
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing Cys2-His2 (C2H2)-type zinc fingers, which are similar to those found in the nuclear matrix protein matrin 3. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:84460; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270] |
26191264_Suggest that ZMAT1 transcript variant 2 is a potential diagnostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. 35392973_ZMAT1 acts as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by inducing SIRT3/p53 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000052676 |
Zmat1 |
117.281002 |
0.2329834647 |
-2.101701 |
0.169190197 |
163.691864 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000017663469252195454464140699714903621578716164160560420486094695867947923155496837160922206124140810407086021882605564314872026443481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000002767651870089224091232981711452627446453315772638857358899213971019121426525723522669171952734386288330625802700524218380451202392578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.1212889 |
4.6873156 |
190.7113652 |
11.4731741 |
| ENSG00000166444 |
6764 |
DENND2B |
protein_coding |
P78524 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: May be involved in cytoskeletal organization and tumorogenicity. Seems to be involved in a signaling transduction pathway leading to activation of MAPK1/ERK2. Plays a role in EGFR trafficking from recycling endosomes back to the cell membrane (PubMed:29030480). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:29030480, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9632734}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which may activate RAB9A and RAB9B. Promotes the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound Rab proteins into their active GTP-bound form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937701}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: May block ERK2 activation stimulated by ABL1 (Probable). May alter cell morphology and cell growth (Probable). {ECO:0000305|PubMed:10229203, ECO:0000305|PubMed:9632734}. |
Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene was identified by its ability to suppress the tumorigenicity of Hela cells in nude mice. The protein encoded by this gene contains a C-terminal region that shares similarity with the Rab 3 family of small GTP binding proteins. This protein preferentially binds to the SH3 domain of c-Abl kinase, and acts as a regulator of MAPK1/ERK2 kinase, which may contribute to its ability to reduce the tumorigenic phenotype in cells. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms are identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6764; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374] |
19843505_Using RNA in situ hybridisation in mouse, the authors found that St5 is expressed in the frontal cortex during embryonic development. In adult mouse brain, expression of St5 was especially high in the hippocampal area and cerebellum. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25713415_DENND2B interacts with the Rab13 effector MICAL-L2 at the cell periphery, and this interaction is required for the dynamic remodeling of the cell's leading edge. 29030480_Here, we discover that intersectin-s binds DENND2B, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the exocytic GTPase Rab13, and this interaction promotes recycling of ligand-free EGFR to the cell surface. Our study thus reveals a novel mechanism controlling the fate of internalized EGFR with important implications for cancer. 31707778_Findings provide evidence of suppression of tumorigenicity 5 (ST5) involvement in positive regulation of osteoclastogenesis via src Kinases (Src)/Syk Kinase (Syk)/calcium signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000031024 |
Denn2b |
72.912036 |
0.3730984306 |
-1.422372 |
0.469241473 |
8.806779 |
0.00300113438440361042502946276044895057566463947296142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006431002252293450786868600488332958775572478771209716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.8483624 |
11.5339799 |
82.9204134 |
22.0504810 |
| ENSG00000166503 |
50810 |
HDGFL3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y3E1 |
FUNCTION: Enhances DNA synthesis and may play a role in cell proliferation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10581169}. |
3D-structure;Growth factor;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable double-stranded DNA binding activity; microtubule binding activity; and transcription coregulator activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including microtubule polymerization; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization; and neuron projection development. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:50810; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; microtubule polymerization [GO:0046785]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
15371438_LEDGF/p75 and HRP2 IBDs avidly bind HIV-1 Integrase, share a similar domain organization and have an evident evolutionary and likely functional relationship 19237540_Hepatoma-derived growth factor-related protein-3 interacts with microtubules and promotes neurite outgrowth in mouse cortical neurons 24012673_Depletion of HRP-3 induces apoptosis of radio- and chemoresistant A549 cells. HRP-3 is essential for regulating reactive oxygen species-dependent, p53-induced cell death. 26823754_Glucose deprivation-induced HRP-3 up-regulation potentially plays a major role in protecting hepatocellular carcinoma cells against apoptosis caused by energy pressure. 28854847_The study observed higher expression levels of HDGFRP3 and ID2 in bipolar disorder (BD) patients who favourably respond to lithium. Both of these genes are involved in neurogenesis, and HDGFRP3 has been suggested to be a neurotrophic factor. 31162607_HRP3 PWWP is a new family of minor groove-specific DNA-binding proteins 34714604_A novel function of HRP-3 in regulating cell cycle progression via the HDAC-E2F1-Cyclin E pathway in lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000025104 |
Hdgfl3 |
31.379040 |
0.2541556178 |
-1.976216 |
0.338970210 |
35.224170 |
0.00000000293853862417453045610020713972708461536598179009160958230495452880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000013448939563663897044548123924697508035919213398301508277654647827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.0878461 |
2.9783825 |
51.5037583 |
7.1370355 |
| ENSG00000166532 |
57494 |
RIMKLB |
protein_coding |
Q9ULI2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the synthesis of beta-citryl-L-glutamate and N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate. Beta-citryl-L-glutamate is synthesized more efficiently than N-acetyl-L-aspartyl-L-glutamate. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80WS1}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Ligase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable N-acetyl-L-aspartate-L-glutamate ligase activity and citrate-L-glutamate ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in glutamine family amino acid metabolic process. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57494; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; citrate-L-glutamate ligase activity [GO:0072591]; ligase activity, forming carbon-nitrogen bonds [GO:0016879]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; N-acetyl-L-aspartate-L-glutamate ligase activity [GO:0072590]; glutamine family amino acid metabolic process [GO:0009064]; protein modification process [GO:0036211] |
21454531_ribosomal modification protein rimK-like family member A (Rimkla) gene is a NAAG synthetase (NAAGS-II), which synthesizes the N-acetylated tripeptide N-acetylaspartylglutamylglutamate (NAAG(2)) |
ENSMUSG00000040649 |
Rimklb |
58.139653 |
0.2102936355 |
-2.249523 |
0.377397563 |
33.896736 |
0.00000000581161223452619847519432229820089685912165577974519692361354827880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000025938734980830568832288203062058640213649596262257546186447143554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.0795528 |
5.5340190 |
95.3050079 |
17.6578107 |
| ENSG00000166546 |
146227 |
BEAN1 |
protein_coding |
Q3B7T3 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Reference proteome;Spinocerebellar ataxia;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is one of several proteins that interact with NEDD4, a member of a family of ubiquitin-protein ligases. These proteins have PY motifs in common that bind to the WW domains of NEDD4. NEDD4 is developmentally regulated, and is highly expressed in embryonic tissues. Mutations in this gene (i.e., intronic insertions of >100 copies of pentanucleotide repeats including a (TGGAA)n sequence) are associated with spinocerebellar ataxia type 31. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:146227; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
19878914_SCA31 is associated with 'inserted' pentanucleotide repeats containing (TGGAA)n. 21163552_Our data indicate that SCA31 is absent or rare in the Chinese population on Taiwan. 22049201_This study describes the structure of SCA31 pentanucleotide repeat sequences in a cohort of Caucasian patients with spinocerebellar ataxia. 23607545_we conclude that the RNA foci containing BEAN1-direction transcript (UGGAA)n are associated with Purkinje cell degeneration in Spinocerebellar ataxia type 31 26876577_this study reveals a regulation mechanism of NEDD4-1 stability by O-GlcNAcylation. |
ENSMUSG00000031872 |
Bean1 |
44.952674 |
3.0640207870 |
1.615426 |
0.262464306 |
38.404155 |
0.00000000057509812400909669848420933998124453256917121279911953024566173553466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002805171285649129549934786207994810713906019827845739200711250305175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
64.9017020 |
10.8333177 |
21.3686240 |
2.8554999 |
| ENSG00000166578 |
115811 |
IQCD |
protein_coding |
Q96DY2 |
FUNCTION: Component of the nexin-dynein regulatory complex (N-DRC), a key regulator of ciliary/flagellar motility which maintains the alignment and integrity of the distal axoneme and regulates microtubule sliding in motile axonemes. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A8J0N6}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Flagellum;Reference proteome |
|
Located in ciliary basal body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:115811; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; motile cilium [GO:0031514] |
|
ENSMUSG00000029601 |
Iqcd |
8.179030 |
3.7074614028 |
1.890432 |
0.592933572 |
10.799894 |
0.00101505916081968722460004972418801116873510181903839111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002358298947536373573602430653295414231251925230026245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.1694491 |
4.8930366 |
3.6015569 |
1.1258407 |
| ENSG00000166582 |
201161 |
CENPV |
protein_coding |
Q7Z7K6 |
FUNCTION: Required for distribution of pericentromeric heterochromatin in interphase nuclei and for centromere formation and organization, chromosome alignment and cytokinesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18772885}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Centromere;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Kinetochore;Metal-binding;Methylation;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Predicted to enable carbon-sulfur lyase activity and metal ion binding activity. Involved in pericentric heterochromatin assembly; positive regulation of cytokinesis; and regulation of chromosome organization. Acts upstream of or within ameboidal-type cell migration. Located in several cellular components, including midbody; nucleus; and spindle midzone. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201161; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; midbody [GO:0030496]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; spindle midzone [GO:0051233]; carbon-sulfur lyase activity [GO:0016846]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ameboidal-type cell migration [GO:0001667]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; centromere complex assembly [GO:0034508]; pericentric heterochromatin formation [GO:0031508]; positive regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032467]; regulation of chromosome organization [GO:0033044] |
18772885_Results suggest that CENP-V (nuclear protein p30) is required for centromere organization, chromosome alignment and cytokinesis in human cells |
ENSMUSG00000018509 |
Cenpv |
43.516840 |
0.3039413784 |
-1.718135 |
0.275146580 |
39.321882 |
0.00000000035939109312492605390858664099430416771774332573841093108057975769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001783063036814759216614478335165457079103390469754231162369251251220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.0310043 |
3.9557351 |
59.8316207 |
8.8560992 |
| ENSG00000166592 |
6236 |
RRAD |
protein_coding |
P55042 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in cardiac antiarrhythmia via the strong suppression of voltage-gated L-type Ca(2+) currents. Regulates voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C trafficking to the cell membrane (By similarity). Inhibits cardiac hypertrophy through the calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) pathway. Inhibits phosphorylation and activation of CAMK2D. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056528}. |
3D-structure;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;GTP-binding;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity and calcium channel regulator activity. Predicted to be involved in small GTPase mediated signal transduction. Predicted to be located in cytosol. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. Implicated in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomarker of congestive heart failure. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:6236; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium channel regulator activity [GO:0005246]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901842]; small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0007264] |
16511212_crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of human Rad GTPase 16866878_Crystal structure of the GTPase domain of human Rad in the GDP-bound form at 1.8 A resolution. 17195088_Methylation and gene silencing of the Ras-related GTPase gene is associated with lung and breast cancers 17525370_Evidence from Rad transgenic mice suggests that the Rad-associated signaling pathway may play a role in arrhythmogenesis in diverse cardiac diseases. 17672918_occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 1 18056528_Rad is a novel mediator that inhibits cardiac hypertrophy through the CaMKII pathway 20079427_the implication of oxidative stress in modulating Rad expression, in association with the initiation and progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis muscle atrophy 20460530_It is proposed for the first time that Rad may promote carcinogenesis at least in part by inhibiting GCIP-mediated tumor suppression. 22487779_results indicate that RRAD might act as a functional tumor suppressor and its epigenetic inactivation may play an important role in NPC development 22658652_Rad over expression could be a molecular target to improve bortezomib sensitivity in human leukemia and lymphoma. 23973784_Mouse Rad Q65P (the murine equivalent of human Rad Q66P) inhibits L-type currents conducted by CaV1.2 or CaV1.3 channels as potently as wild-type Rad (>95% inhibition of both channels). 24222170_RRAD hypermethylation is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 24632303_Rad suppresses the NF-Kappa-B mediated transcription and downstream gene activation. Rad can directly bind to RelA/p65 and suppress the interaction of RelA/p65 with the NF-kappa-B response DNA element. 24648519_Ras(V12)-mediated oncogenic transformation induces RRAD epigenetic inactivation, which in turn promotes glucose uptake and may contribute to ovarian cancer 25114038_RRAD expression is frequently decreased in lung cancer. Ectopic expression of RRAD greatly reduces glycolysis whereas knockdown of RRAD promotes glycolysis in lung cancer cells. 25313011_RRAD promotes EGFR-mediated STAT3 activation and induces temozolomide resistance of malignant glioblastoma. 25893381_Data show that Ras-related associated with diabetes protein (RRAD) directly binds to the p65 subunit of the NF-kappa B (NF-kappaB)complex and inhibits the nuclear translocation of p65, which in turn negatively regulates the NF-kappaB signaling 26344687_Brg1 inhibits proliferation and migration of human aortic smooth muscle cells by directly up-regulating RRAD in aortic dissection. 26546438_our study revealed that RRAD expression was decreased in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor tissues and predicted poor clinical outcome for HCC patients and played an important role in regulating aerobic glycolysis and cell invasion and metastasis and may represent potential targets for improving the treatment of HCC 30391675_this study established RRAD to be a biomarker as well as a novel negative regulator of cellular senescence. 31114854_RRAD mutation causes electrical and cytoskeletal defects in cardiomyocytes derived from a familial case of Brugada syndrome. 31857616_RRAD expression in gastric and colorectal cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis. 34001616_Reconstitution of beta-adrenergic regulation of CaV1.2: Rad-dependent and Rad-independent protein kinase A mechanisms. |
ENSMUSG00000031880 |
Rrad |
52.765875 |
22.1146059498 |
4.466928 |
0.390769652 |
199.112411 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000326231365045760687010262866674347659635657063919843302081133815874836010795319463331644749033991809800294085476763186748350165089505026116967201232910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000062051223557673037774617756597852157189882036417699848353963556692707459377233342183993687818695450481281703045566972010149697780434507876634597778320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
103.2525398 |
25.9505339 |
4.6720187 |
1.1338268 |
| ENSG00000166670 |
4319 |
MMP10 |
protein_coding |
P09238 |
FUNCTION: Can degrade fibronectin, gelatins of type I, III, IV, and V; weakly collagens III, IV, and V. Activates procollagenase. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This secreted protease breaks down fibronectin, laminin, elastin, proteoglycan core protein, gelatins, and several types of collagen. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4319; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
15095982_The catalytic domain of human matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) has been expressed in Escherichia coli and its crystal structure solved at 2.1 angstroms resolution. 15288123_Beta-carotene suppresses UVA-induction of MMP-10. 15371548_a tightly regulated expression level of stromelysin-2 is required for limited matrix degradation at the wound site 15375490_Overexpression of MMP-10 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15944607_identified significant interactions between MMP10 (nt+180) polymorphisms and gender in abdominal aortic aneurysm 16054593_zinc finger protein 267 as a negative transcriptional regulator of MMP-10 might promote liver fibrogenesis 16331256_Increased levels of MMP-10 is associated with gastric cancer 16516860_Finally, we found that induction of mmp-3 and mmp-10 gene expression by hypomethylation was cell-specific, suggesting that epigenetic changes may predispose cells to express stromelysin genes. 16580524_C-reactive protein augmented MMP-1 and -10 messenger ribonucleic acid expression in vascular endothelial cells. Might provide a link between inflammation and plaque vulnerability. 17009259_The ability of MMP-10 to superactivate procollagenases that are relevant to cartilage degradation suggests that this activation represents an important mechanism by which this MMP contributes to tissue destruction in arthritis. 17543340_Primary colorectal cancers and metastatic liver lesions showed highly significant differences in MMP-1, -10, -11, and TIMP-1. 17695449_MMP-10 protein levels were higher in the lung tumor tissues than in the adjacent normal tissues. 18035073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18427549_Knockdown of MMP-10 expression blocks anchorage-independent growth and invasion of NSCLC cells and addition of catalytically active MMP-10 to PKCiota- or Par6alpha-deficient cells restores anchorage-independent growth and invasion 18617643_VEGF stimulates HDAC7 phosphorylation and cytoplasmic accumulation modulating MT-MMP1/MMP10 expression and angiogenesis. 19317417_Study showed that MMP-9 and TIMP-2 were highly produced in brain microvessels while MMP-10 was notably increased in neurons of the ischemic brain but not in healthy areas. 19489686_MMP1 and MMP10 were suitable markers for cancer detection with gingiva and margin as controls. Using neck tissue as the control, only MMP10 was suitable for cancer detection 19601983_Results suggest that MMP-10 may be important in the initial stages of squamous cell cancer progression and induced in the stroma relating to the general host-response reaction to skin cancer. 19695094_MMP-10 expression is increased in the symptomatic degenerate intervertebral disc 19762781_circulating MMP-10 levels (P |
|
|
131.742917 |
15.6361860387 |
3.966817 |
0.226847290 |
397.281662 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000021512344919265311414844534507811937424199644954051468301350604311307655958104065033643391196091769284326797118772041520509028594701345827008237176596456233535867942041876105208165211135416195658304554646582676676156049844212958532807533629239 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008079445572731705762476846099973196964051117755239047387544265174210467127714060718528728011961778190663058432624424570229886969352252316678116309364344593086334874817973789151612472744779911398434051223096258060457630634232373267877846956253 |
Yes |
No |
257.6563721 |
36.8856161 |
16.5923280 |
2.2275900 |
| ENSG00000166681 |
27018 |
BEX3 |
protein_coding |
Q00994 |
FUNCTION: May be a signaling adapter molecule involved in p75NTR-mediated apoptosis induced by NGF. Plays a role in zinc-triggered neuronal death (By similarity). May play an important role in the pathogenesis of neurogenetic diseases. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in signal transduction. Predicted to act upstream of or within extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:27018; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0008656]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nerve growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005163]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11830582_Structure-function analysis of NADE: identification of regions that mediate nerve growth factor-induced apoptosis 12739005_suppresses cell growth in vivo, when expressed in cultured cells 16777077_DRG-1 may contribute to the dopamine-induced cell growth, which is negatively regulated by NADE 28083995_Results showed that BEX3 was overexpressed in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), and indicated a unique functional role of BEX3 in mediating the sensitivity of NPC cells to cisplatin. 33100228_Characterization of an eutherian gene cluster generated after transposon domestication identifies Bex3 as relevant for advanced neurological functions. |
ENSMUSG00000046432 |
Bex3 |
162.393325 |
0.3943635118 |
-1.342402 |
0.123054749 |
122.763503 |
0.00000000000000000000000000015710177711107004691980516897740599276822440391950821443241540779345949782217981005594253929302794858813285827636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001919554826290888855153829401651997674194683747243550215284852779257655547469341161814782026340253651142120361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.3762559 |
7.5914824 |
236.0534377 |
12.1953965 |
| ENSG00000166780 |
89927 |
BMERB1 |
protein_coding |
Q96MC5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of cell motility involved in cerebral cortex radial glia guided migration and negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization. Predicted to be located in microtubule cytoskeleton. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:89927; |
microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; cell motility involved in cerebral cortex radial glia guided migration [GO:0021814]; microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007019]; negative regulation of cell motility involved in cerebral cortex radial glia guided migration [GO:0021822]; negative regulation of microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007026] |
Mouse_homologues 25099998_The newly identified migration inhibitory protein (MINP) regulates the radial migration in the developing neocortex. |
ENSMUSG00000044117 |
Bmerb1 |
86.872613 |
2.9135130493 |
1.542760 |
0.245617809 |
38.723109 |
0.00000000048839258992191059782774334078027725358772670460894005373120307922363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002396500873420013495457678821755516385128004230864462442696094512939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
140.3041111 |
22.6117944 |
48.6729402 |
5.9195773 |
| ENSG00000166881 |
23306 |
NEMP1 |
protein_coding |
O14524 |
FUNCTION: Together with EMD, contributes to nuclear envelope stiffness in germ cells (PubMed:32923640). Required for female fertility (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6ZQE4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32923640}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in nuclear membrane organization. Predicted to be located in nuclear inner membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in nuclear envelope. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23306; |
nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear inner membrane [GO:0005637]; nuclear membrane organization [GO:0071763] |
31079234_NEMP1 shows responsibility for the resistance of tamoxifen through regulating NCOA1 in breast cancer cells 31854049_Study observes that TMEM194A overexpression is associated with considerable augmentation of cell proliferation, which strongly supported its oncogenic role in breast cancer cells. TMEM194A functions in separation of centrosomes from the nuclear envelope. However, its expression is negatively regulated by miR-1285 in breast cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000040195 |
Nemp1 |
741.361404 |
2.0076427999 |
1.005503 |
0.057766431 |
305.952452 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001663314201633034658496105963166757369333734298344326133064425567611714574319975105503177148012759240295416343088039724032931136773868042461207896560598189806380623004819843679946700376603985205292701721191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000491010352322071832176381537504688327709997182177809356453427307156025725159046934748426421371781489508679595459236569259193279397241953266162695242258769960103776102550154902814938395749777555465698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
995.0287321 |
34.3764860 |
499.0315731 |
13.5833416 |
| ENSG00000166938 |
115752 |
DIS3L |
protein_coding |
Q8TF46 |
FUNCTION: Putative cytoplasm-specific catalytic component of the RNA exosome complex which has 3'->5' exoribonuclease activity and participates in a multitude of cellular RNA processing and degradation events. In the cytoplasm, the RNA exosome complex is involved in general mRNA turnover and specifically degrades inherently unstable mRNAs containing AU-rich elements (AREs) within their 3' untranslated regions, and in RNA surveillance pathways, preventing translation of aberrant mRNAs. It seems to be involved in degradation of histone mRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20531386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20531389}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Exonuclease;Exosome;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Nuclease;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
The cytoplasmic RNA exosome complex degrades unstable mRNAs and is involved in the regular turnover of other mRNAs. The protein encoded by this gene contains 3'-5' exoribonuclease activity and is a catalytic component of this complex. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]. |
hsa:115752; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasmic exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000177]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000178]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; rRNA catabolic process [GO:0016075] |
20531386_Data show that hDIS3 and hDIS3L are active exonucleases, but only hDIS3 has retained endonucleolytic activity, and suggest that three different ribonucleases can serve as catalytic subunits for the exosome in human cells. 20531389_Data indicate that hDis3L1 is a novel exosome-associated exoribonuclease in the cytoplasm of human cells. 29321365_we screened the susceptibility loci for Myocardial infarction (MI) using exome sequencing and validated candidate variants in replication sets. We identified that three genes (GYG1, DIS3L and DDRGK1) were associated with MI at the discovery and replication stages. |
ENSMUSG00000032396 |
Dis3l |
112.468154 |
0.4497901812 |
-1.152676 |
0.222022487 |
26.363173 |
0.00000028288297872314723741454583691434798708996822824701666831970214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001062430729250293539887091583129308247634980943985283374786376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
70.2067141 |
9.5011675 |
156.7835023 |
14.6456427 |
| ENSG00000166987 |
114785 |
MBD6 |
protein_coding |
Q96DN6 |
FUNCTION: Binds to heterochromatin. Does not interact with either methylated or unmethylated DNA (in vitro). |
Chromosome;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Enables chromatin binding activity. Located in chromocenter; fibrillar center; and nucleoplasm. Implicated in autism spectrum disorder. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114785; |
chromocenter [GO:0010369]; chromosome [GO:0005694]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682] |
20700456_MBD5 and MBD6 are unlikely to be methyl-binding proteins, yet they may contribute to the formation or function of heterochromatin. 23052207_MBD6 is regulated by Ago2 via an interaction with Oct4, which alters self-renewal and gene expression in human adipose tissue-derived stem cells. 23055267_This study demonstrates examples of autistic patients carrying alterations in MBD6. 24634419_We studied and showed that both MBD5 and MBD6 interact with the mammalian PR-DUB Polycomb protein complex in a mutually exclusive manner, and that the MBD of MBD5 and MBD6 is both necessary and sufficient to mediate this interaction. 25638327_Frameshift mutations of MBD6 gene is associated with stomach and colorectal cancers. 27744583_Our findings imply that reduced stability and enhanced dynamics of MBD1 or MBD6 is the origin of ATP7B dysfunction in Wilson disease patients with the G85V or G591D mutation. 31313936_The decreased expression of the MBD6 protein was correlated with the tumor size of uterine leiomyomas |
ENSMUSG00000025409 |
Mbd6 |
354.902627 |
0.3916716293 |
-1.352283 |
0.171803584 |
60.477987 |
0.00000000000000744059144054467869043961739167853544434615142844080537543050013482570648193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000050216337294211003721361111773849991660059830650419954167773539666086435317993164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
179.3846177 |
26.3443398 |
461.7693268 |
48.4631478 |
| ENSG00000167080 |
124872 |
B4GALNT2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NHY0 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the synthesis of the Sd(a) antigen (Sia-alpha2,3-[GalNAc-beta1,4]Gal-beta1,4-GlcNAc), a carbohydrate determinant expressed on erythrocytes, the colonic mucosa and other tissues. Transfers a beta-1,4-linked GalNAc to the galactose residue of an alpha-2,3-sialylated chain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12678917, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14688233}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
B4GALNT2 catalyzes the last step in the biosynthesis of the human Sd(a) antigen through the addition of an N-acetylgalactosamine residue via a beta-1,4 linkage to a subterminal galactose residue substituted with an alpha-2,3-linked sialic acid. B4GALNT2 also catalyzes the last step in the biosynthesis of the Cad antigen (Montiel et al., 2003 [PubMed 12678917]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:124872; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008376]; lipid glycosylation [GO:0030259]; negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022408]; oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0009312]; protein N-linked glycosylation via asparagine [GO:0018279]; UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine metabolic process [GO:0019276]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process [GO:0006047] |
14688233_molecular cloning; cDNA predicts a 566 aa protein showing 66.6% and 39% identity with mouse CT beta4GalNAc-T and human GM2/GD2 synthase 17965433_A putative CpG island encompassing the promoter and exon 1 regions in the human Sd(a) beta4GalNAcT-II gene was identified. 18485915_Epigenetic changes in a group of glycosyltransferases including B4GALNT2 and ST3GAL6 represent a malignant phenotype of gastric cancer caused by silencing of the activity of these enzymes 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24145553_These experiments demonstrate successful transduction of rhesus macaque muscle with rAAVrh74.MCK.GALGT2 after vascular delivery and induction of molecular changes thought to be therapeutic in several forms of muscular dystrophy. 24953560_In normal colon samples a significant relationship between sLe(x) expression and the ratio between FUT6/B4GALNT2 activities exists, demonstrating for the first time a role for B4GALNT2 in sLe(x) inhibition in vivo. 28813663_B4GALNT2 overexpression prevented the infection of every avian influenza virus strain tested, including the H5, H9, and H7 subtypes, which have previously caused disease in humans. 31036568_Results found that demonstrate that EGFR ligands can activate the human GALGT2 promoter. Deletion analysis of the GALGT2 promoter identified a 45-bp region containing a TFAP4-binding site that was required for soluble HB-EGF activation. 32290493_High Expression of the Sd(a) Synthase B4GALNT2 Associates with Good Prognosis and Attenuates Stemness in Colon Cancer. 33662872_The role of the blood group-related glycosyltransferases FUT2 and B4GALNT2 in susceptibility to infectious disease. 33770101_Short-term treatment of golden retriever muscular dystrophy (GRMD) dogs with rAAVrh74.MHCK7.GALGT2 induces muscle glycosylation and utrophin expression but has no significant effect on muscle strength. 33919332_Glycosyltransferase B4GALNT2 as a Predictor of Good Prognosis in Colon Cancer: Lessons from Databases. 34397142_B4GALNT2 Controls Sd(a) and SLe(x) Antigen Biosynthesis in Healthy and Cancer Human Colon. 34500083_Analysis of the proximal promoter of the human colon-specific B4GALNT2 (Sd(a) synthase) gene: B4GALNT2 is transcriptionally regulated by ETS1. 35409292_Glycoproteomic and Phenotypic Elucidation of B4GALNT2 Expression Variants in the SID Histo-Blood Group System. |
ENSMUSG00000013418 |
B4galnt2 |
10.926979 |
0.3082552878 |
-1.697802 |
0.474062300 |
13.600265 |
0.00022615355299737693612477373861224805295933037996292114257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000587060577249610233627197253269969223765656352043151855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3113404 |
1.6382980 |
17.4795277 |
3.0605013 |
| ENSG00000167107 |
80221 |
ACSF2 |
protein_coding |
Q96CM8 |
FUNCTION: Acyl-CoA synthases catalyze the initial reaction in fatty acid metabolism, by forming a thioester with CoA (PubMed:17762044). Has some preference toward medium-chain substrates (PubMed:17762044). Plays a role in adipocyte differentiation (PubMed:16380219). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16380219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17762044}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Fatty acid metabolism;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
Enables medium-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in fatty acid metabolic process. Predicted to be located in mitochondrial matrix. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80221; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; butyrate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047760]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; medium-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031956]; acyl-CoA metabolic process [GO:0006637]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000076435 |
Acsf2 |
37.331167 |
0.4826360234 |
-1.050992 |
0.359533700 |
8.392573 |
0.00376757181302933390198983687469080905430018901824951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007897934946784968684996286469868209678679704666137695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.4873304 |
5.9363640 |
55.6805377 |
8.7039225 |
| ENSG00000167114 |
10999 |
SLC27A4 |
protein_coding |
Q6P1M0 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the levels of long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) in the cell by facilitating their transport across cell membranes (PubMed:10518211, PubMed:12556534, PubMed:20448275, PubMed:21395585, PubMed:22022213). Appears to be the principal fatty acid transporter in small intestinal enterocytes (PubMed:20448275). Also functions as an acyl-CoA ligase catalyzing the ATP-dependent formation of fatty acyl-CoA using LCFA and very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) as substrates, which prevents fatty acid efflux from cells and might drive more fatty acid uptake (PubMed:22022213, PubMed:24269233). Plays a role in the formation of the epidermal barrier. Required for fat absorption in early embryogenesis (By similarity). Probably involved in fatty acid transport across the blood barrier (PubMed:21395585). Indirectly inhibits RPE65 via substrate competition and via production of VLCFA derivatives like lignoceroyl-CoA. Prevents light-induced degeneration of rods and cones (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91VE0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10518211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12556534, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20448275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21395585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22022213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269233}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Ichthyosis;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of fatty acid transport proteins, which are involved in translocation of long-chain fatty acids cross the plasma membrane. This protein is expressed at high levels on the apical side of mature enterocytes in the small intestine, and appears to be the principal fatty acid transporter in enterocytes. Clinical studies suggest this gene as a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Mutations in this gene have been associated with ichthyosis prematurity syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:10999; |
brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; fatty acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015245]; long-chain fatty acid transporter activity [GO:0005324]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; oleate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901480]; oleoyl-CoA ligase activity [GO:0090434]; palmitoyl-CoA ligase activity [GO:0090433]; very long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0031957]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; fatty acid transport [GO:0015908]; glucose import in response to insulin stimulus [GO:0044381]; lipid transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:1990379]; long-chain fatty acid import into cell [GO:0044539]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; medium-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0001579]; negative regulation of all-trans-retinyl-ester hydrolase, 11-cis retinol forming activity [GO:0062003]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; skin development [GO:0043588]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; very long-chain fatty acid catabolic process [GO:0042760] |
14715877_findings propose fatty acid transport protein 4 as a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome 15168018_intra-pair correlations revealed that FATP4 expression was significantly up-regulated in acquired obesity.' 17901542_Data suggest that endogenous FATP4 does not function to translocate fatty acids across the plasma membrane, but functions more as a very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase. 19631310_Mutations in FATP4 gene cause the ichthyosis prematurity syndrome. 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20815031_Mutation in FATP4 in a patient with self-healing congenital verruciform hyperkeratosis.( 20965718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22028793_even though hypoxia regulates the expression of FATP2 and FATP4 in human trophoblasts, mouse Fatp2 and Fatp4 are not essential for intrauterine fetal growth. 22235293_FATP1 and FATP4 proteins perform different functional roles in handling long chain fatty acids in skeletal muscle 23271751_FATP4 plays crucial roles in the development and maturation of both sebaceous and meibomian glands, as well as in the formation and composition of sebum 23290633_FATP4, ichthyin and TGM1 interact in lipid processing essential for maintaining the epidermal barrier function 24120574_the clinical implications of defects in these transporters and relevant animal models, including the FATP4 animal models and ichthyosis prematurity syndrome, a congenital ichthyosis caused by FATP4 deficiency. [review] 24503477_the cell surface protein CD36/FAT directly facilitates fatty acid transport across the plasma membrane, whereas the intracellular acyl-CoA synthetases FATP4 and ACSL1 enhance fatty acid uptake indirectly by metabolic trapping 24889544_We describe two siblings with ichthyosis prematurity syndrome and report a recurrent homozygous mutation (c.1430T>A) that is predicted to lead to a p.Val477Asp substitution in fatty acid transport protein 4. 26341232_SLC27A4 gene mutation is responsible in the diagnosis of ichthyosis prematurity syndrome in a premature infant. 26548558_we resequenced the SLC27A3 and SLC27A4 genes using 267 autism spectrum disorders(ASD) patient and 1140 control samples and detected 47 and 30 variants for the SLC27A3 and SLC27A4, revealing that they are highly polymorphic with multiple rare variants. 26662804_The results have interesting implications that SLC27A4/ATG4B complex might be conducive to the occurrence of autophagy in human cancer cells, which is meaningful investigations toward the aim of developing autophagy-targeting drugs and have significant values in clinical application. 27016784_no association between placental expression and maternal body mass index 27168232_expand the mutational repertory of FATP4 with three undescribed pathogenic mutations in two families 29701233_Case Report: ichthyosis prematurity syndrome caused by novel homozygous mutation in SLC27A4. 30388870_high SLC27A4 is associated with tumor progression in breast cancer cells. 31089396_High FATP4 expression was associated with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 31595490_Impacts of deletion and ichthyosis prematurity syndrome-associated mutations in fatty acid transport protein 4 on the function of RPE65. 32357142_The positive feedback between ACSL4 expression and O-GlcNAcylation contributes to the growth and survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. 32519158_Physical Activity During Pregnancy Is Associated with Increased Placental FATP4 Protein Expression. |
ENSMUSG00000059316 |
Slc27a4 |
207.654610 |
2.1837503133 |
1.126808 |
0.127463776 |
78.404403 |
0.00000000000000000083964788676482586272052580477515844860356074197036378714553706004153355024755001068115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000007037593872032272072927041929182937479666482233180146987905345667968504130840301513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
284.0270076 |
21.3307948 |
131.1829176 |
7.7075029 |
| ENSG00000167173 |
56905 |
C15orf39 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZRI6 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56905; |
cytosol [GO:0005829] |
|
ENSMUSG00000032300 |
1700017B05Rik |
661.337525 |
2.7717605242 |
1.470803 |
0.065704277 |
511.563557 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002897546967606364607953469854279443677603977760713345622609051294042874081492214493520612742191420143089912079648863373704456863675069260721174471832588129520673630969442810626703758650700119786982306818399379246869459 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001430360977988961099561042947327161643883051190209144741584306311407429680112238632763897540485992624503208844126121020395927819723022387439995834727683146247947030385253915545597650146831149182938450040067532481243240 |
Yes |
No |
974.8799268 |
38.1787179 |
354.1557828 |
11.2872568 |
| ENSG00000167196 |
26263 |
FBXO22 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEZ5 |
FUNCTION: Substrate-recognition component of the SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. Promotes the proteasome-dependent degradation of key sarcomeric proteins, such as alpha-actinin (ACTN2) and filamin-C (FLNC), essential for maintenance of normal contractile function. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22972877}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of the ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbxs class and, as a transcriptional target of the tumor protein p53, is thought to be involved in degradation of specific proteins in response to p53 induction. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:26263; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; nucleocytoplasmic transport [GO:0006913]; positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032436]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; protein polyubiquitination [GO:0000209]; regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048742]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
21768309_FBXO22 is a key regulator of histone methylation marks, namely, H3K9 and H3K36 methylation, through the regulation of KDM4A protein levels. 22761574_we determined that the phage-encoded GogB effector protein in Salmonella targets the host SCF E3 type ubiquitin ligase through an interaction with Skp1 and the human F-box only 22 (FBXO22) protein 25336657_FBXO22 protein is required for optimal synthesis of NMDA receptor coagonist D-serine by interacting with serine racemase, activating it, and preventing its targeting to membranes. 26087183_Authors demonstrate that F-box only protein 22 (FBXO22) interacts with and thereby destabilizes KLF4 via polyubiquitination. As a result, FBXO22 could promote HCC cells proliferation. 26868148_Results indicate that SCF(Fbxo22)-KDM4A is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets methylated p53 and regulates key senescent processes. 28117675_Data show that FBXO22 mediated the polyubiquitination and degradation of CD147 by interacting with CD147 intracellular domain (CD147-ICD). 29945959_FBXO22 has two roles in breast cancer: it promotes breast tumor cell proliferation but prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis 30418174_the level of Fbxo22 in tumor tissues defines a new subclass of ER-positive breast cancers for which SCFFbxo22-mediated KDM4B degradation in patients can be a therapeutic target for the next generation of SERMs. 30808376_This study uncovered a new mechanism by which FBXO22 functions as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis and progression by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of p21 30887251_Knockdown of FBXO22 inhibits melanoma cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis via the HIF-1alpha/VEGF pathway. 31138683_SCF(FBXO22) targets HDM2 for degradation and possesses inhibitory effects against breast cancer tumor cell invasion and metastasis. 31217475_FBXO22 is highly expressed in human lung adenocarcinoma and high FBXO22 expression predicts significant poor prognosis. 31948764_Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 promotes osteosarcoma progression via miR-433-3p/FBXO22 axis. 32249768_FBXO22 plays a tumor-promoting role by ubiquitylating and degrading nuclear PTEN. In accordance, FBXO22 is overexpressed in various cancer types, and contributes to nuclear PTEN downregulation in colorectal cancer tissues. 33706682_TP53/p53-FBXO22-TFEB controls basal autophagy to govern hormesis. 34215846_Global identification of phospho-dependent SCF substrates reveals a FBXO22 phosphodegron and an ERK-FBXO22-BAG3 axis in tumorigenesis. 34795058_The ubiquitin E3 ligase FBXO22 degrades PD-L1 and sensitizes cancer cells to DNA damage. 36127346_Fbxo22 promotes cervical cancer progression via targeting p57(Kip2) for ubiquitination and degradation. |
ENSMUSG00000032309 |
Fbxo22 |
161.847822 |
2.1172392606 |
1.082184 |
0.203711595 |
27.847409 |
0.00000013126971086693453268528272281229218876319464470725506544113159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000511629504197505620549375586481044564379772054962813854217529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
205.5267538 |
31.0115815 |
97.7766947 |
10.7891153 |
| ENSG00000167210 |
125336 |
LOXHD1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVV2 |
FUNCTION: Involved in hearing. Required for normal function of hair cells in the inner ear (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19732867}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Deafness;Hearing;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a highly conserved protein consisting entirely of PLAT (polycystin/lipoxygenase/alpha-toxin) domains, thought to be involved in targeting proteins to the plasma membrane. Studies in mice show that this gene is expressed in the mechanosensory hair cells in the inner ear, and mutations in this gene lead to auditory defects, indicating that this gene is essential for normal hair cell function. Screening of human families segregating deafness identified a mutation in this gene which causes DFNB77, a progressive form of autosomal-recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss (ARNSHL). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:125336; |
stereocilium [GO:0032420]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
19732867_A mutation in LOXHD1, which causes DFNB77, a progressive form of autosomal-recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss (ARNSHL), was identified. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21465660_A founder mutation R1572X in the LOXHD1 causes autosomal recessive hearing loss in Ashkenazi Jews 21465660_This is the second reported mutation in the LOXHD1 gene, and its homozygous presence in two of 39 Ashkenazi Jewish families with congenital ARNSHL suggest that it could account for some 5% of the familial cases in this community 22341973_Authors identified a missense change in LOXHD1. Data implicate rare alleles in LOXHD1 in the pathogenesis of FCD and highlight how different mutations in the same locus can potentially produce diverse phenotypes. 25792669_Mutations in LOXHD1 are identified in a Japanese population with sensorineural hearing loss. 26973026_We report a Japanese family carrying compound heterozygotes of truncating and nontruncating mutations in LOXHD1 identified by targeted NGS analysis. The fact of lower degree of hearing impairment in our cases than previously reported and the molecular modeling of the missense mutant provide insight to the genotype-phenotype correlation of DFNB77. 27121161_Analysis of SLC4A11, ZEB1, LOXHD1, COL8A2 and TCF4 gene sequences in a multi-generational family with late-onset Fuchs corneal dystrophy found no evidence for found polymorophisms causing the disease in this specific pedigree. 29676012_We hypothesize that environmental factors or genetic modifiers are responsible for phenotypic differences. No association was found between heterozygous LOXHD1 variants and the occurrence of Fuchs corneal dystrophy in carriers. 29799290_While mutations in ZEB1 contributed to 2% of the late-onset Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD) cases, the exact role of the two variant of uncertain significance (VUS) identified in ZEB1 and LOXHD1 in FECD pathogenesis needs to be studied. 30760222_Results demonstrated that a novel missense variant, LOXHD1: c.5948C > T, was associated with non-progressive Deafness, autosomal recessive 77 in a Chinese family under consanguineous marriage. 31547530_By analyzing the largest number of patients with LOXHD1 related hearing loss yet to be reported, we determined several characteristics of LOXHD1 variations, and recurrent variants 31709873_The LOXHD1 variant c.1828G>A present in the wife had not previously been reported in individuals with congenital hearing loss. 32149082_Five Novel Mutations in LOXHD1 Gene Were Identified to Cause Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss in Four Chinese Families. 33753533_Rising of LOXHD1 as a signature causative gene of down-sloping hearing loss in people in their teens and 20s. 33892339_Recessive LOXHD1 variants cause a prelingual down-sloping hearing loss: genotype-phenotype correlation and three additional children with novel variants. 35705030_Oncofusion-driven de novo enhancer assembly promotes malignancy in Ewing sarcoma via aberrant expression of the stereociliary protein LOXHD1. |
ENSMUSG00000032818 |
Loxhd1 |
105.936652 |
0.0471399069 |
-4.406907 |
0.405238036 |
106.675870 |
0.00000000000000000000000052427154887396123648220617757600946771156308246432302436033793049952045350892149144783616065979003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000005644236368621202314250667635066310063479190244572451437073737888234364890038818884931970387697219848632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9899814 |
2.9154529 |
213.5170914 |
38.9981079 |
| ENSG00000167216 |
83473 |
KATNAL2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYT4 |
FUNCTION: Severs microtubules in vitro in an ATP-dependent manner. This activity may promote rapid reorganization of cellular microtubule arrays. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03025}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Isomerase;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable microtubule-severing ATPase activity. Predicted to be involved in cytoplasmic microtubule organization. Located in cytoplasm; microtubule; and spindle pole. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83473; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; katanin complex [GO:0008352]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; isomerase activity [GO:0016853]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule severing ATPase activity [GO:0008568]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; microtubule severing [GO:0051013] |
22495311_results from de novo events and a large parallel case-control study provide strong evidence in favour of CHD8 and KATNAL2 as genuine autism risk factors 23018867_KATNAL2 methylation correlates with severity of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 34096614_Biallelic mutations in KATNAL2 cause male infertility due to oligo-astheno-teratozoospermia. |
ENSMUSG00000025420 |
Katnal2 |
54.526173 |
0.1918798058 |
-2.381725 |
0.275010652 |
79.199222 |
0.00000000000000000056152190094011369281233471347054434707430909456618442834874294078417733544483780860900878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000004744169008515213700022991291513428485772518968432900215992376047324796672910451889038085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.9424917 |
3.2968958 |
88.9245556 |
10.3093264 |
| ENSG00000167280 |
64772 |
ENGASE |
protein_coding |
Q8NFI3 |
FUNCTION: Endoglycosidase that releases N-glycans from glycoproteins by cleaving the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond in the N,N'-diacetylchitobiose core. Involved in the processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12114544}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a cytosolic enzyme which catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptides and proteins with mannose modifications to produce free oligosaccharides. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:64772; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds [GO:0004553]; mannosyl-glycoprotein endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity [GO:0033925]; protein deglycosylation [GO:0006517]; protein folding [GO:0006457] |
12114544_involved in processing of free oligosaccharides in the cytosol; identification of the gene encoding human cytosolic ENGase 12905469_endo-beta-n-acetylglucosaminidase present in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients, may contribute to the depletion of glycosaminoglycans from cartilage allowing the invasion of synovial cells 18586680_identification of O-GlcNAcase as a caspase-3 substrate with a novel caspase-3 cleavage site and provide insight about O-GlcNAcase regulation during apoptosis. 20026047_Data show that kinetic and X-ray crystallographic analyses of the binding modes with human/bacterial O-GlcNAcases identify some of these as competitive inhibitors. 20413512_O-GlcNAcase expression is increased in erythrocytes from both individuals with pre-diabetes and individuals with less well-controlled diabetes. 20668520_As the generation of the bulk of fOS is unaffected by co-down regulation of Ngly1p and Engase1p, alternative quantitatively important mechanisms must underlie the liberation of these fOS from either LLO or glycoproteins during protein N-glycosylation. 21873561_Serological N-acetyl-glucosaminidase, telomere length, and the UCP2-886G>A variant are independent risk factors for type 2 diabetes. 26923419_In patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, urinary NAGase was correlated with urinary ET-1 which was inversely associated with eGFR and positively correlated with total kidney volume. 33730571_Transcriptome-wide association study reveals two genes that influence mismatch negativity. 34397265_N-acetyl-ss-D-glucosaminidase is predictive of mortality in chronic heart failure: a 10-year follow-up. |
ENSMUSG00000033857 |
Engase |
373.224157 |
0.3404347186 |
-1.554550 |
0.260921837 |
34.043936 |
0.00000000538815752598359237012691641001936593280419174334383569657802581787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000024114373888271020770130331810701673767027841677190735936164855957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
183.5695883 |
35.3168260 |
540.7485482 |
74.5674831 |
| ENSG00000167302 |
146705 |
TEPSIN |
protein_coding |
Q96N21 |
FUNCTION: Associates with the adapter-like complex 4 (AP-4) and may therefore play a role in vesicular trafficking of proteins at the trans-Golgi network. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:22472443, ECO:0000305|PubMed:26542808}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Located in coated vesicle membrane; nucleus; and trans-Golgi network membrane. Is extrinsic component of organelle membrane. Colocalizes with AP-4 adaptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:146705; |
coated vesicle membrane [GO:0030662]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of organelle membrane [GO:0031312]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588] |
26542808_The bivalency of the interactions contributes to a higher avidity of tepsin for AP-4. |
ENSMUSG00000025377 |
Tepsin |
230.699022 |
0.4472285589 |
-1.160916 |
0.137416706 |
71.261090 |
0.00000000000000003129469199112821875116150735618901542233534929932092794047093775589019060134887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000242727090798240937873639262162888913681972618977336630941010753303999081254005432128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
149.7573374 |
16.2712218 |
336.2682584 |
25.2458398 |
| ENSG00000167363 |
64122 |
FN3K |
protein_coding |
Q9H479 |
FUNCTION: Fructosamine-3-kinase involved in protein deglycation by mediating phosphorylation of fructoselysine residues on glycated proteins, to generate fructoselysine-3 phosphate (PubMed:11016445, PubMed:11522682, PubMed:11975663). Fructoselysine-3 phosphate adducts are unstable and decompose under physiological conditions (PubMed:11522682, PubMed:11975663). Involved in intracellular deglycation in erythrocytes (PubMed:11975663). Involved in the response to oxidative stress by mediating deglycation of NFE2L2/NRF2, glycation impairing NFE2L2/NRF2 function (By similarity). Also able to phosphorylate psicosamines and ribulosamines (PubMed:14633848). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ER35, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11016445, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11522682, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11975663, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14633848}. |
Acetylation;ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
A high concentration of glucose can result in non-enzymatic oxidation of proteins by reaction of glucose and lysine residues (glycation). Proteins modified in this way, fructosamines, are less active or functional. This gene encodes an enzyme which catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructosamines which may result in deglycation. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:64122; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; protein-fructosamine 3-kinase activity [GO:0102194]; protein-ribulosamine 3-kinase activity [GO:0102193]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; fructosamine metabolic process [GO:0030389]; fructoselysine metabolic process [GO:0030393]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; post-translational protein modification [GO:0043687]; protein deglycation [GO:0036525] |
11975663_involved in the removal of fructosamine residues from hemoglobin in erythrocytes. 15102834_The aim of this work was to identify the fructosamine residues on hemoglobin that are removed as a result of the action of FN3K in intact erythrocytes. 15381090_These data suggest that FN3K and FN3KRP act as protein repair enzymes and are expressed constitutively in human cells independently of some of the variables altered in the diabetic state. 16037310_Enzyme is a constitutive 'housekeeping' gene and that ig plays an important role in cell metabolism, possibly as a deglycating enzyme. 16523184_No significant correlation between FN3K activity and the levels of HbA1c, total glycated haemoglobin (GHb) and haemoglobin fructoselysine residues, either in the normoglycaemic or diabetic group. 16920277_In this paper we propose a resolution of both these quandaries by proposing that fructosamine-6-phosphates are deglycated by phosphorylation to fructosamine-3,6-bisphosphates catalyzed by FN3KRP and/or possibly FN3K. 19834870_G900C polymorphism associates with the level of HbA (1c) and the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus, but not with either of the diabetic microvascular complications. 19834870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20858683_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21253391_These findings suggest that deglycating enzymes Glyoxalase I and fructosamine-3-kinase may be involved in the malignant transformation of colon mucosa. 21288167_two new mutations and additional variants within the FN3K gene in diabetic patients 23492569_The marginal association of rs1056534 of FN3K is located in exon 6 with diabetic nephropathy progression. 24908234_Report association of rs1056534 and rs3848403 of fructosamine 3-kinase gene with sRAGE in patients with diabetes. 26352355_FN3K could act in concert with other molecular mechanisms and may impact on gene expression and activity of other enzymes involved in deglycation process 27461879_In a multiple regression analysis, FN3K rs1056534, TF polymorphism and presence of diabetes mellitus were predictors for HHV-8 infection. 31398338_FN3K is a targetable modulator of NRF2 activity in cancer. 32636308_A redox-active switch in fructosamine-3-kinases expands the regulatory repertoire of the protein kinase superfamily. 33208304_FN3K expression in COPD: a potential comorbidity factor for cardiovascular disease. |
ENSMUSG00000025175 |
Fn3k |
14.751680 |
0.2178322450 |
-2.198711 |
0.461734583 |
24.504067 |
0.00000074153146633631826406302285648042271759550203569233417510986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002659782367709369785936180177743359820397017756476998329162597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2376014 |
1.9205474 |
24.8764154 |
5.4528596 |
| ENSG00000167378 |
126298 |
IRGQ |
protein_coding |
Q8WZA9 |
|
Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126298; |
GTP binding [GO:0005525] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000041037 |
Irgq |
1303.667618 |
2.0948181834 |
1.066825 |
0.056278885 |
358.130036 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007190615297764243346011239773384261850634335184412521555431693530442326409633003731283359072888487827989219202464514152394417107291474044865409246315914156264962675891988131948466631790920773170238539107046449316840153187513351440429687500000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002401209995361996126218731687423817823938918279477321298497158369541590634854763046181323566882101030927344505736342670230157303065540929476582254820867754561882112608379616293392264960651226370774713458899896068032830953598022460937500000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1778.2161322 |
65.4643970 |
855.4302463 |
23.9092337 |
| ENSG00000167393 |
28227 |
PPP2R3B |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5P8 |
FUNCTION: The B regulatory subunit might modulate substrate selectivity and catalytic activity, and also might direct the localization of the catalytic enzyme to a particular subcellular compartment. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Protein phosphatase 2 (formerly named type 2A) is one of the four major Ser/Thr phosphatases and is implicated in the negative control of cell growth and division. Protein phosphatase 2 holoenzymes are heterotrimeric proteins composed of a structural subunit A, a catalytic subunit C, and a regulatory subunit B. The regulatory subunit is encoded by a diverse set of genes that have been grouped into the B/PR55, B'/PR61, and B''/PR72 families. These different regulatory subunits confer distinct enzymatic specificities and intracellular localizations to the holozenzyme. The product of this gene belongs to the B'' family. The B'' family has been further divided into subfamilies. The product of this gene belongs to the beta subfamily of regulatory subunit B''. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:28227; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein phosphatase type 2A complex [GO:0000159]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; protein phosphatase regulator activity [GO:0019888]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726] |
25007185_Results show the crystal structure of PR48/PR70, at 2.0 A degrees resolution with two domain elongated structure and two Ca2+ binding EF-hands Scattering data. 27974665_PPP2R3B codes for the PR70 protein, a regulatory substrate-recognizing subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. PR70 decreased melanoma growth by negatively interfering with DNA replication and cell cycle progression through its role in stabilizing CDC6-chromatin licensing and CDT1 interaction |
|
|
81.066071 |
0.4927471826 |
-1.021080 |
0.228162954 |
19.976345 |
0.00000784061345101518616951003642911999236275732982903718948364257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024930515841659660547990559620323836043098708614706993103027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.3546463 |
10.3285458 |
94.5187456 |
14.7829105 |
| ENSG00000167524_ENSG00000007202 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
91.193884 |
0.3586056293 |
-1.479530 |
0.544604345 |
6.544025 |
0.01052370061463446006266853061106303357519209384918212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020095143657469855674735370598682493437081575393676757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.1314025 |
22.5035590 |
134.4394342 |
41.9670957 |
| ENSG00000167525 |
147011 |
PROCA1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NCQ7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables cyclin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in arachidonic acid secretion and phospholipid metabolic process. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:147011; |
cyclin binding [GO:0030332]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; arachidonic acid secretion [GO:0050482]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644] |
|
ENSMUSG00000044122 |
Proca1 |
32.402493 |
0.2441861806 |
-2.033947 |
0.349940730 |
34.699309 |
0.00000000384768089112024173698125144066524427888253967466880567371845245361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000017420788329121093282350783899327384407484942130395211279392242431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.7437195 |
2.8998878 |
52.5274261 |
7.3179845 |
| ENSG00000167535 |
784 |
CACNB3 |
protein_coding |
P54284 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the voltage-gated calcium channel that gives rise to L-type calcium currents (PubMed:8119293). Increases CACNA1B peak calcium current and shifts the voltage dependencies of channel activation and inactivation (By similarity). Increases CACNA1C peak calcium current and shifts the voltage dependencies of channel activation and inactivation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54287, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9MZL3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8119293}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cytoplasm;Ion channel;Ion transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a regulatory beta subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel. Beta subunits are composed of five domains, which contribute to the regulation of surface expression and gating of calcium channels and may also play a role in the regulation of transcription factors and calcium transport. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:784; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:1990454]; membrane [GO:0016020]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; calcium channel regulator activity [GO:0005246]; high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0008331]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0005245]; calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel [GO:0061577]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; calcium ion transport into cytosol [GO:0060402]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901843]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential [GO:0098903]; regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901385]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
19917615_in the presence of Pax6(S), beta(3) is translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus;full-length Ca(v)beta may act directly as a transcription regulator independent of its role in regulating Ca(2+) channel activity |
ENSMUSG00000003352 |
Cacnb3 |
22.831746 |
0.1015192841 |
-3.300174 |
0.673450122 |
23.154319 |
0.00000149507000377488714504151199463644061893319303635507822036743164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005182534818158134089639658970138924587445217184722423553466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3954232 |
1.5737627 |
33.7823748 |
9.2243611 |
| ENSG00000167549 |
84940 |
CORO6 |
protein_coding |
Q6QEF8 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Predicted to enable actin filament binding activity. Predicted to be involved in actin filament organization and cell migration. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84940; |
actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell migration [GO:0016477] |
Mouse_homologues 24523531_these findings demonstrate that Coronin 6 is a critical regulator of AChR clustering at the postsynaptic region of the neuromuscular junction |
ENSMUSG00000020836 |
Coro6 |
50.533808 |
0.0815370077 |
-3.616401 |
0.350412422 |
116.441709 |
0.00000000000000000000000000380396916492647251362948433480082478782491373226283254026605565041829455988353636541887681232765316963195800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000044071102727091626089436263893182918859204874053413692689492016749146967649619632823032588930800557136535644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7588486 |
1.7967792 |
96.4092279 |
11.7591106 |
| ENSG00000167552 |
7846 |
TUBA1A |
protein_coding |
Q71U36 |
FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers. Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms. Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Lissencephaly;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Microtubule;Nitration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Microtubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton perform essential and diverse functions and are composed of a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulins. The genes encoding these microtubule constituents belong to the tubulin superfamily, which is composed of six distinct families. Genes from the alpha, beta and gamma tubulin families are found in all eukaryotes. The alpha and beta tubulins represent the major components of microtubules, while gamma tubulin plays a critical role in the nucleation of microtubule assembly. There are multiple alpha and beta tubulin genes, which are highly conserved among species. This gene encodes alpha tubulin and is highly similar to the mouse and rat Tuba1 genes. Northern blot studies have shown that the gene expression is predominantly found in morphologically differentiated neurologic cells. This gene is one of three alpha-tubulin genes in a cluster on chromosome 12q. Mutations in this gene cause lissencephaly type 3 (LIS3) - a neurological condition characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, and early-onset epilepsy caused by defective neuronal migration. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:7846; |
condensed chromosome [GO:0000793]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; cerebellar cortex morphogenesis [GO:0021696]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport [GO:0030705]; dentate gyrus development [GO:0021542]; forebrain morphogenesis [GO:0048853]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; glial cell differentiation [GO:0010001]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; memory [GO:0007613]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; microtubule polymerization [GO:0046785]; microtubule-based process [GO:0007017]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; motor behavior [GO:0061744]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuron projection arborization [GO:0140058]; organelle transport along microtubule [GO:0072384]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807]; response to L-glutamate [GO:1902065]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; startle response [GO:0001964]; synapse organization [GO:0050808]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
16941085_the dipole moments of each tubulin isotype may influence their functional characteristics within the cell, resulting in differences for MT assembly kinetics and stability 17218254_Mutations in alpha-tubulin in mice and humans that affect neuronal migration result in abnormal lamination of brain structures with associated behavioral deficits. 17389232_Given that Spastin engages the MT in two places, we propose that severing occurs by forces exerted on the C-terminal tail of tubulin, which results in a conformational change in tubulin, which releases it from the polymer. 17584854_Retrospective examination of MR images suggests that patients with TUBA1A mutations share not only cortical dysgenesis, but also cerebellar, hippocampal, corpus callosum, and brainstem abnormalities 17914564_Increased expression of tubulin alpha is associated with pulmonary sclerosing hemangioma 18199681_The diminished production of TUBA1A tubulin in R264C individuals is consistent with haploinsufficiency as a cause of the disease phenotype. 18669490_the TUBA1A phenotype is distinct from LIS1, DCX, RELN and ARX lissencephalies. Compared with the phenotypes of children mutated for TUBA1A, these prenatally diagnosed fetal cases occur at the severe end of the TUBA1A lissencephaly spectrum. 18728072_Missense mutations within the TUBA1A gene are associated with specific abnormalities in lissencephaly. 18954413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18954413_mutation analysis in the TUBA1A gene in 46 patients with classical lissencephaly. 19251251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 20466733_LIS-associated mutations of TUBA1A operate via diverse mechanisms that include disruption of binding sites for microtubule-associated proteins. 20510079_The expression of alpha-tubulin and MDR1 may play an important role in the development and progression of human non-small cell lung carcinoma. 20603323_Mutations in TUBA1A result in defects in the tubulin folding and heterodimer assembly. 21094644_Data show that IAV-infected cells contain elevated level of AcTub and alpha-tubulin. 21357695_Alpha2B-adrenergic receptor interaction with tubulin controls its transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell surface 21403111_We report a mutation in TUBA1A as a cause of polymicrogyria. So far, all mutations in TUBA1A have occurred de novo, resulting in isolated cases. This article describes familial recurrence of TUBA1A mutations due to somatic mosaicism in a parent. 22264709_study describes a 14-month-old girl with TUBA1A mutation-associated lissencephaly, and summarize the clinical and neuroradiologic findings of 19 cases in the literature 22565168_Data show that Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity was >50% lower and membrane-associated tubulin content was >200% higher in erythrocyte membranes from diabetic patients. 22633752_We described the clinical course and pathological findings in a child with TUBA1A mutation 22948023_Missense mutations in TUBA1A were found in 3 patients with polymicrogyria. 23361065_TUBA1A and TUBB2B coding regions have been sequenced that are associated with cortical malformations. 23528852_case provides new insight into the wide spectrum of disease phenotypes associated with TUBA1A mutation 23818224_Studies suggest that tubulin-interactive agents have the potential to play a significant role in the fight against cancer. 24392928_The present study confirms that mutations in tubulin genes are responsible for complex brain malformation. 24574051_These findings call attention to PKC-mediated phosphorylation of alpha-tubulin as a novel mechanism for controlling the dynamics of microtubules that result in cell movement. 24914767_These results demonstrated that SelP interacts with tubulin, alpha 1a (TUBA1A). 24940781_Lysine 40 acetylation of alpha-tubulin does not result in significant changes in kinesin-1's landing rate or motility parameters. 25059107_This study show all foetuses with lissencephaly and cerebellar hypoplasia carried distinct TUBA1A mutations. 25602620_Data from studies using peptide fragment of alpha-tubulin (residues 31-49) suggest that Ser38 is crucial for substrate recognition by alpha-tubulin acetylase 1 (ATAT1); Asp39, Ile42, the glycine stretch (residues 43-45), and Asp46 are also involved. 26161965_Data suggest that tubulin functionally interact with the vimentin network in a cell-type specific manner. 26165356_Data show that tubulin phosphorylation and acetylation play important roles in the control of microtubule assembly and stability. 26227334_Studies indicate that alpha-tubulin acetylation and microtubule level is mainly governed by opposing actions of alpha-tubulin acetyltransferase 1 (ATAT1) and histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6). 26307527_Data show that plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) was associated with tubulin in normotensive and hypertensive erythrocytes. 26493046_data suggest that the TUBA1A mutations disrupting lateral interactions have pronounced dominant-negative effects on microtubule dynamics that are associated with the severe end of the lissencephaly spectrum 27228351_Long intergenic non-coding RNA APOC1P1-3 inhibits apoptosis by decreasing alpha-tubulin acetylation in breast cancer. 27431206_induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from the umbilical cord and peripheral blood of two lissencephaly patients with different clinical severities carrying alpha tubulin (TUBA1A) missense mutations, were generated. 28440465_Molecular docking studies revealed that 6f interacted and bound ef fi ciently with the colchicine-binding site of tubulin. In addition, 6f treatment induced G2/M cell cycle arrest dose-dependently and subsequently induced cell apoptosis 28687665_Results show that Tuba1a plays an essential, noncompensated role in neuronal saltatory migration in vivo and highlight the importance of microtubule flexibility in nucleus-centrosome coupling and neuronal-branching regulation during neuronal migration. 28912522_These data unequivocally show that free tubulin dimers represent the preferred HDAC6 substrate, with a K M value of 0.23 microM and a deacetylation rate over 1,500-fold higher than that of assembled microtubules. 29109381_A de novo heterozygous c.320A>G [p.(His 107 Arg)] mutation in TUBA1A was identified in a patient with microcephaly, epileptic seizures, and severe developmental delay. 30249017_Low Tubulin expression is associated with liver cancer. 30429459_Knockdown of either beta3-tubulin or alpha-tubulin via siRNA increased lung cancer cell sensitivity to paclitaxel, indicating that these two proteins help cells increase the drug resistance. 31235911_This study examined the crystal structures of human vasohibin 1 and 2 in complex with small vasohibin-binding protein (SVBP) in the absence and presence of different inhibitors and a C-terminal alpha-tubulin peptide. 31574570_Tubulin mutations in brain development disorders: Why haploinsufficiency does not explain TUBA1A tubulinopathies. 31578588_the palmitoylation level of Rasrelated protein Rab7a (Rab7a) was enhanced by androgen treatment. Palmitoylation of alphatubulin and Rab7a were essential for cell proliferation. Notably, in the supernatant of LNCaP cells, the palmitoylation level of alphatubulin was also increased following androgen treatment. Palmitoylation of alphatubulin may provide a new potential target for the treatment of prostate cancer. 31767681_Structure of spastin bound to a glutamate-rich peptide implies a hand-over-hand mechanism of substrate translocation. 31833200_Microcephaly with a simplified gyral pattern in a child with a de novo TUBA1A variant. 32885602_HDAC6-mediated alpha-tubulin deacetylation suppresses autophagy and enhances motility of podocytes in diabetic nephropathy. 32989326_Mutations disrupting neuritogenesis genes confer risk for cerebral palsy. 33331338_Elevated TUBA1A Might Indicate the Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Gastric Cancer, Being Associated with the Infiltration of Macrophages in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. 33649541_Novel variants in TUBA1A cause congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles with or without malformations of cortical brain development. 34185819_Novel proteins associated with chronic intermittent hypoxia and obstructive sleep apnea: From rat model to clinical evidence. 34508164_alphaTAT1-induced tubulin acetylation promotes ameloblastoma migration and invasion. 35017693_Complementing the phenotypical spectrum of TUBA1A tubulinopathy and its role in early-onset epilepsies. 35511030_TUBA1A tubulinopathy mutants disrupt neuron morphogenesis and override XMAP215/Stu2 regulation of microtubule dynamics. |
ENSMUSG00000072235 |
Tuba1a |
1091.153413 |
2.6137897217 |
1.386143 |
0.051073771 |
749.075836 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000637306320742039452208849536172537534432218260881631589243880686415230109136430271499648479559517200562209027536608896704288895340885250505010769258041083035731770682 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000470332064707625100499437410245105076289436857147587634618032634071884638575189684723100227838073937168602564886994067093635971643478236139018785167277885685250207030 |
Yes |
Yes |
1593.2383817 |
50.3896869 |
614.1233875 |
15.5701723 |
| ENSG00000167553 |
84790 |
TUBA1C |
protein_coding |
Q9BQE3 |
FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers. Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms. Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Methylation;Microtubule;Nitration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity. Predicted to be a structural constituent of cytoskeleton. Predicted to be involved in microtubule cytoskeleton organization and mitotic cell cycle. Located in microtubule cytoskeleton and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84790; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic microtubule [GO:0005881]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport [GO:0030705]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; microtubule-based process [GO:0007017]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278] |
21965743_These results suggest that tubulin alpha-6 chain is one of the candidates for biomarkers for well-differentiated hepatitis C virus-associated human hepatocellular carcinoma. 32599139_Circular RNA TUBA1C accelerates the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by sponging miR-143-3p. 33654196_Tektin4 loss promotes triple-negative breast cancer metastasis through HDAC6-mediated tubulin deacetylation and increases sensitivity to HDAC6 inhibitor. 34517210_TUBA1C expression promotes proliferation by regulating the cell cycle and indicates poor prognosis in glioma. 34845165_Tubulin alpha 1c promotes aerobic glycolysis and cell growth through upregulation of yes association protein expression in breast cancer. 35513790_The oncogenic role of tubulin alpha-1c chain in human tumours. |
ENSMUSG00000043091 |
Tuba1c |
516.156578 |
2.6043486554 |
1.380923 |
0.099595709 |
190.234518 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000028257979155093410802565662809914882567033900753203757165621478261703467311632049598007148174854854526248692288964425856079287768807262182235717773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000005117641378272131274101787378719998894242567332777385266425097837416161563814541806797843738591768667495879828466254224395015626214444637298583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
750.0573968 |
42.5920686 |
290.2084350 |
12.7694972 |
| ENSG00000167566 |
57701 |
NCKAP5L |
protein_coding |
Q9HCH0 |
FUNCTION: Regulates microtubule organization and stabilization. Promotes microtubule growth and bundling formation and stabilizes microtubules by increasing intense acetylation of microtubules (PubMed:26482847, PubMed:26485573). Both tubulin-binding and homodimer formation are required for NCKAP5L-mediated microtubule bundle formation (PubMed:26485573). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26482847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26485573}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in microtubule bundle formation and microtubule depolymerization. Located in centrosome and microtubule plus-end. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57701; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule plus-end [GO:0035371]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; microtubule depolymerization [GO:0007019] |
26485573_These results show that Cep169 targets microtubule tips and regulates stability of microtubules with CDK5RAP2. 26549230_These data suggest that the dissociation of Cep169 from centrosomes is controlled by Cdk1/Cyclin B during mitosis, and that Cep169 might regulate MT dynamics of mitotic spindle. 29269292_Our findings suggest that Cep169 regulates cell growth by interacting with multiple proteins. |
ENSMUSG00000023009 |
Nckap5l |
23.467028 |
0.3784691464 |
-1.401752 |
0.368497148 |
14.493675 |
0.00014063091557560002294036127779008893412537872791290283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000378227462444580264915722223051375294744502753019332885742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2292117 |
3.1306891 |
34.9194561 |
5.3391555 |
| ENSG00000167615 |
114823 |
LENG8 |
protein_coding |
Q96PV6 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114823; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991] |
30216441_genetic polymorphism is associated with pemphigus foliaceus |
ENSMUSG00000035545 |
Leng8 |
1836.651368 |
0.3364038357 |
-1.571734 |
0.084565463 |
334.365779 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001076300531935092562854365928671471988585780001426319619455610881972536096222935269513761333106187500551076390901322668398510831186714296895455326919327418692062261841859671974861107149323835585619235644116997718811035156250000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000340905490372574400098789565080099248640827599372719840648941585790194000317860465192219563569546051997729086556127885074793265595576128900602194894934461916781318702093997356306152163307743307996133808046579360961914062500000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
942.5535067 |
58.6117110 |
2818.5901791 |
124.4809998 |
| ENSG00000167701 |
2875 |
GPT |
protein_coding |
P24298 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible transamination between alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to form pyruvate and glutamate. Participates in cellular nitrogen metabolism and also in liver gluconeogenesis starting with precursors transported from skeletal muscles (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Aminotransferase;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid degradation; L-alanine degradation via transaminase pathway; pyruvate from L-alanine: step 1/1. |
This gene encodes cytosolic alanine aminotransaminase 1 (ALT1); also known as glutamate-pyruvate transaminase 1. This enzyme catalyzes the reversible transamination between alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to generate pyruvate and glutamate and, therefore, plays a key role in the intermediary metabolism of glucose and amino acids. Serum activity levels of this enzyme are routinely used as a biomarker of liver injury caused by drug toxicity, infection, alcohol, and steatosis. A related gene on chromosome 16 encodes a putative mitochondrial alanine aminotransaminase.[provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:2875; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; L-alanine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase activity [GO:0004021]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; biosynthetic process [GO:0009058]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; L-alanine catabolic process [GO:0042853]; positive regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0045722]; response to starvation [GO:0042594] |
12480555_Glucose intolerance is associated with elevated serum aminotransferase independent of obesity, but even a mildly elevated ALT is relatively uncommon in free-living men with glucose intolerance. 12774006_Histology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals with normal ALT values, not significantly different from those with elevated ALT levels, and low normal value does not guarantee freedom from steatohepatitis with advanced fibrosis. 14506613_genotypes of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and beta3-adrenergic receptor were strongly associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase level which increased with the accumulation of components of metabolic syndrome 15306699_mildly elevated in severe acute respiratory syndrome patients during second week after onset of fever. 16652026_In coinfected Hic/hepatitis C patients, normal ALT levels are not an indicator of mild necroinflammation and may not portend a more benign disease course. 17134955_In obesity, elevated ALT activity is associated with increased fasting insulin suggesting that insulin resistance, rather than body mass index alone, plays a role in mediating the increased aminotransferase activity. 17378732_Provides a quantitative analysis of the main impact of the trauma of liver resection, liver ischemia, and other factors on the postoperative evolution of transaminases. 17405346_Insulin resistance in obese patients is associated with alanine aminotransferase activity. 17570354_Data show that OCT/ALT is a potent indicator for the diagnosis and the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 17764776_May serve as a useful marker for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or diabetes risk in Filipino women. 17766001_Weight reduction secondary to a hypocaloric diet were associated with improvement in hypertransaminasemia and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 17877759_PTLP activity is positively associated with serum ALT1, GOT1 and GOT2 in type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. 17907292_In hepatitis C, alterations in the liver tissue as reflected by ALT elevation are mainly associated with periportal bridging/necrosis, viral load and duration of disease. 17907318_Abnormal serum aminotransferase values are uncommon in severely obese children in France. 17934148_Type 2 diabetic patients have 80% more liver fat than age-, weight-, and sex-matched nondiabetic subjects, which is underestimated in type 2 diabetics. 18090161_In obese patients with NAFLD (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease), OSA (obstructive sleep apnea) was associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase levels and a trend toward histologic evidence of progressive liver disease. 18178283_ALAT elevations associate with obesity and diabetes, and provide new evidence that in elderly male patients, ALAT elevations, absent other known liver diseases, may selectively associate with diabetes 18242760_Data revealed higher alanine aminotransferase for women with a family history of diabetes, when adjusted for age and BMI. 18315552_Raised ALT is common in apparently healthy British South Asians, and is significantly associated with an adverse metabolic and atherothrombotic risk profile. 18432999_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18473412_Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common cause of persistently elevated serum alanine aminotransferase level among the general population of Iran. 18508279_Tag-free ALT1 and ALT2 were obtained by cleavage of enterokinase digestion and used for initial characterization of the enzymes. The specific ALT activity of purified fusion or His-tag-removed ALT1 was about 15-fold higher than that of ALT2 18708042_Alanine aminotransferase, alanine/aspartate aminotransferase ratio, and gamma-glutamyl transferase are associated with the MetS but not with angiographically determined coronary atherosclerosis. 18763311_found a strong relationship between alanine aminotransferase levels and metabolic syndrome in metabolic syndrome 18774966_HEV markers (HEV RNA and anti-HEV) were detected in donors with elevated ALT levels who were widely distributed over Japan 19012630_Neither ALT nor GGT concentrations were correlated with ALP concentration, but AST concentration was moderately correlated with ALP concentration. 19065605_Serum levels are an independent risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in subjects without fatty liver or hepatic dysfunction. 19100265_In the US population, elevated gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) was associated with mortality from all causes, liver disease, cancer, and diabetes, while alanine aminotransferase (ALT) was associated only with liver disease mortality. 19159884_alanine aminotransferase may have a role in progression of cardiovascular disease and diabetes in Koreans 19217453_A high proportion of obese children present elevated ALT1 levels. 19232448_High ALT level and low platelet count are closely associated with the development of hepatocarcinogenesis in hepatitis C carrirs. who are thus candidates for antiviral agents. 19303161_approximately 60% of the variation in S-ALT, a marker of liver fat content, is genetically determined 19360321_A clinical method for selective measurement of ALT1 and 2 in human plasma is described. 19370784_Results suggest that alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels and AST/ALT ratio do not seem to be reliable predictors for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. 19393479_the management of patients with pyelonephritis should take into account that moderate and self-limited abnormalities in aminotransferase levels are frequent during the acute phase of the disease 19687577_All metabolic syndrome-related risk factors are significantly correlated with the increase in blood levels of alanine aminotransferase in a population of Japanese men and women. 19938201_Obesity and elevated ALT are associated with insulin resistance 20032584_elevation in GPT in obese children most likely reflects insulin resistance 20190678_No significant relationship between serum hepatitis B virus DNA level and liver histological stage, gender, age, body mass index, or hepatitis B surface antigen was observed in these patients with normal ALT. 20205615_The association of coffee and green tea consumption with serum activities of liver enzymes in free-living Japanese men and women was examined, focusing on sex difference and effect modifications of alcohol and obesity. 20387481_Chronic hepatitis B patients with high non-specific cytotoxic T-Lymphocytes also has the high ALT level. 20433554_Lowering the ALT upper normal reference limit will facilitate earlier detection of risky phenotypes of obesity. 20872970_Data suggest that serum alanine aminotransferase is inadequate for diagnosing lamivudine resistance and has implications where viral resistance testing is suboptimal and for reimbursement of rescue therapy. 20961180_Nrmal levels of ALT are associated with metabolic and androgenic phenotypes, i women of reproductive age. 20972737_liver enzymes, especially ALT, were significantly associated with IR according to direct clamp assessment, which were independent of the traditional risk factors in diabetic patients 21040936_Subjects with metabolic syndrome had significantly higher plasma levels of alanine aminotransferase. 21199427_Study confirmed significant and independent associations of GGT and ALT with MetS in adult Chinese people. 21692932_An hepatitis B virus DNA level of >/=5 log10 copies/mL and an alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level of >20 to =40 IU/L were independent predictors of hepatitis reactivation in a Cox model. 21715038_In a cross-sectional analysis of Taiwanese industrial employees, elevated ALT associated with MS, but in subjects who did not meet MS criteria, elevated ALT by itself did not associate with IFG/T2DM. 21720553_The prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS) and risk factors for and association with elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as markers of hepatic injury in a large Hispanic health disparity cohort with high rates of obesity, was studied. 21987480_discriminates persons infected with hepatitis C virus from those at low risk of liver disease, but would be considered elevated in a large proportion of the U.S. population 22132177_The patterns of interaction between smoking and alcohol consumption or BMI with respect to AST and ALT resembled those observed for gamma-GT. 22140488_The magnitude of the association of PNPLA3 with liver enzymes is driven by the size of abdominal fat. 22158663_alanine aminotransferase levels largely within the normal range, there was an inverse association between ALT and all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events 22177542_In a cross-sectional study, Chinese adolescents and young adults with more metabolic syndrome components were more likely to suffer from elevated ALT 22242166_This study highlights the necessity of intensive follow-up for those with elevated AST and ALT levels and comorbid alcohol use disorder for preventing excessive natural deaths. 22293393_the COMT polymorphism affects serum ALT activity to maintain liver function 22352690_APRI and AST/ALT are independent predictors for significant fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C patients. 22357454_Patients with HLA-DQA1 and DRB1 genotypes have higher alanine aminotransferase elevation, whereas HLA-negative cases have a higher incidence of Gilbert's syndrome. 22389715_An elevated ALT does not accurately predict significant liver injury. Decisions on commencing antiviral therapy should not be heavily based on a particular ALT threshold. 22954960_ALT[Alanine transaminase] may be a marker of an underlying etiology relating to the paradoxical associations of diabetes and IHD at a population level. 22975640_Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome were associated with ALT levels in a male population from southern China. 23119080_Data indicate that ferritin levels and hyperuricemia are two independently significant factors associated with alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation among obese adolescents. 23384374_Among HIV/HCV-coinfected persons, risky drinking was associated with a higher adjusted mean AST (62.2 vs. 51.4 U/L; adjusted ratio of means 1.2, 95% CI [1.07, 1.37], p = .003) and ALT (51.3 vs. 41.6 U/L; compared with non-risky drinking 23403445_Data from cross-sectional study in children/adolescents in Republic of Korea suggest normal ALT/GPT serum reference values; ALT/GPT serum level appears effective as biomarker in predicting cardiovascular/metabolic syndrome risk in population studied. 23522007_Elevated ALT is associated with developing depressive symptoms, suggesting that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease may represent an independent modifiable risk factor for depression. 23667618_Alcohol consumption, smoking status, and metabolic syndrome impact on serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), was determined. 23880909_Elevated serum alanine aminotransferase level was independently associated with an increased risk of intracerebral hemorrhage in East Asian men. 23884827_Role of insulin resistance and adipocytokines on serum alanine aminotransferase in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 24158044_Elevated serum ALT levels are prevalent among elderly agricultural and fishing population workers in Taiwan. 24205292_fibrosis is not rare in Chinese CHB patients with persistent normal alanine aminotransferase, especially HBeAg-positive patients over 30 years old 24275711_elevated ALT is common in the Korean population; it is associated with metabolic disorders (obesity, insulin resistance, or metabolic syndrome) in the majority of patients 24324749_A new model that combines ALT, platelets, CK-18 fragments, and triglycerides was established by logistic regression among nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients. 24349501_Among patients with chronic HCV infection, daily consumption of filtered coffee may have a beneficial effect on the stabilization of ALT levels. 24500143_ALT and visceral adipose tissue affect metabolic risk factors in a middle-aged Japanese population 24691744_PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism is associated with elevated alanine transaminase levels in Mexican indigenous and Mestizo populations. 24819732_A prospective association between ALT levels and metabolic syndrome highlights the value of ALT levels, even mild ALT elevations within the normal range, as a predictor of the MetS risk in male schizophrenia patients. 24849491_Statistically significant differences were observed in the mean values of GPT in type 1 diabetics compared to type 2 and control groups 24937007_Peginterferon alfa-2a is associated with elevations in alanine aminotransferase at the end of treatment in chronic hepatitis C patients with sustained virologic response. 24953204_Alanine aminotransferase showed associations with BMI, glycaemia, lipids, and creatinine. The relationship between alanine aminotransferase and age was best expressed by polynomial regression. 25145475_In nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, adipose tissue insulin resistance (but not hepatic insulin resistance) and liver triglyceride content are major factors in the elevation of plasma aminotransferase levels. 25219834_Serum alanine aminotransferase has limited predictive value for liver disease in chronic hepatitis C 25272068_The aim of this study was to establish the reference intervals (RIs) of total bilirubin (TBIL), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and creatinine (CREA) for apparently healthy elderly (Han ethnicity) in Shuyang, China. 25437895_elevated serum ALT and GGT levels are associated with increased arterial stiffness, independent of the classical atherosclerotic risk factors in Japanese men 25543901_Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase levels were elevated postoperatively in recipients of an orthotopic liver transplant from a brain-dead donor receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. 25874513_ALT was significantly associated with elevated levels of triacylglycerols, hyperglycemia, and obesity. In patients with metabolic syndrome, one must consider liver involvement if the patient has ALT levels in the upper third of the reference range. 26160405_There are significant relationships of elevated ALT levels with cardiometabolic risk factors (obesity, hypertension, hypercholesteremia, hyperuricemia, hypertriglyceridemia) and several sex-related differences in rural Chinese. 26290281_The serum hepcidin, ferritin, alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase, gamma-glutamyltransferase and bilirubin were examined in two independent Chinese cohorts consisted of 3455 individuals. 26446640_Elevated aminotransferase levels, even within the normal range, were significantly associated with increased risk of all external-cause mortalities, including suicide, and injury. 26632395_IBS [irritable bowel syndrome ] may be an important condition in certain patients with elevated ALT levels and MS [ metabolic syndrome ]. 26664483_Age, female gender, and elevated ALT can help identifying cases with biliary etiology of acute pancreatitis. 26791191_Data suggest that, in context of abnormal hepatic lipid accumulation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, circulating GPT1 rises due to up-regulation of hepatic expression of GPT1 associated with greater gluconeogenesis and insulin resistance. 26791408_Liver fat content and serum ALT were inversely correlated with bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly men. 27260292_The data of this study confirmed the genetic heterogeneity of childhood-onset pure HSP, with SPG4/SPAST and SPG3A/ATL1 being the most frequent forms. 27304617_Measurements of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels could be helpful in detecting progression or recurrence in treated patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV) - hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and normal alanine aminotransferase (ALT). 27390880_High serum alanine aminotransferase expression is associated with metabolic syndrome. 27430334_Results indicate that AZD4619 increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT1) protein expression in a dose-dependent manner in human, but not in rat hepatocytes. 27935953_Baseline alanine transaminase (ALT) and a hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) above 1000 IU/ml were independent predictive factors for ALT elevation. 28007909_Our results using Mendelian randomization suggest that ALT reduces the risk of ischaemic heart disease (IHD), probably through reducing triglyceride levels. 28415934_Early abnormal liver enzyme levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase may increase the prevalence of human cytomegalovirus antigenemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 28540298_The detection of ALT, AFP, AFP-L3, and GP73 has a certain guiding significance to predict the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatic cirrhosis patients 28540984_In men with hepatic steatosis, we found that elevated serum ALT levels were associated with lower serum SHBG levels. 28628604_ALT is a more suitable index than AST for developing a regression model. 28796937_Elevated serum GPT (alanine aminotransferase) levels are positively and independently associated with T2DM in large scale study of rural Chinese population over 35 years old. 29192630_HCC [hepatocellular carcinoma] patients who are sero-positive for DCP [Des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin] and sero-negative for AFP[Alpha-fetoprotein] have significantly higher levels of serum ALT[alanine aminotransferase]; serum ALT levels may be of diagnostic importance in AFP-negative, HBV-related HCC [hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma] patients. 29553104_high transaminase elevations do not predict severe complications or reflect remnant ischemic area. 29897928_a relationship between NAFLD with high ALT and lower BMD in the general U.S. population 30134916_Both GGT and ALT are effective markers for identifying Metabolically Unhealthy Obese. 30204299_High Alanine Transaminase expression is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 30333032_A significant joint association of serum uric acid and serum ALT with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence was observed in all participants, which was slightly stronger in men than in women. 30453754_Preoperative elevated serum AST/ALT may be a potential independent predictor of postoperative acute kidney injury in hepatocellular carcinoma patients who have undergone hepatectomy 30566759_Association between serum liver enzymes and all-cause mortality: The Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study. 30946812_effect of alanine transaminase on the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus 30973940_Lowering the current upper limit of normal of serum alanine aminotransferase may help to identify elderly patients at risk of significant liver disease. 32139603_Combined and sequential non-invasive approach to diagnosing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and persistently normal alanine aminotransferase levels. 32157800_Clinical implications of aminotransferase elevation in hospitalised infants aged 8-90 days with respiratory virus detection. 32849256_Association of Alanine Aminotransferase With Different Metabolic Phenotypes of Obesity in Children and Adolescents: The CASPIAN-V Study. 33408301_Eating Fast and Until Full Is Associated with Elevated Alanine Aminotransferase Activity in Japanese Schoolchildren: A Cross-Sectional Study. 33742744_Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is a risk factor for glucose intolerance onset in men regardless of alanine aminotransferase status. 34099767_Aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase ratio is associated with frailty and mortality in older patients with heart failure. 34315874_GWAS of serum ALT and AST reveals an association of SLC30A10 Thr95Ile with hypermanganesemia symptoms. 34355631_Bi-directional and temporal relationship between elevated alanine aminotransferase and hypertension in a longitudinal study of Chinese adults. 35853763_Aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase ratio and the risk of diabetic nephropathy progression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A biopsy-based study. 36107005_Identification of alanine aminotransferase 1 interaction network via iTRAQ-based proteomics in alternating migration, invasion, proliferation and apoptosis of HepG2 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000022546 |
Gpt |
9.947096 |
0.3295401218 |
-1.601474 |
0.572093340 |
8.156120 |
0.00429160874545708639210550572329339047428220510482788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008897899295258688071030839239483611891046166419982910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4787644 |
2.8980959 |
15.7178696 |
5.3256303 |
| ENSG00000167711 |
5345 |
SERPINF2 |
protein_coding |
P08697 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease inhibitor. The major targets of this inhibitor are plasmin and trypsin, but it also inactivates matriptase-3/TMPRSS7 and chymotrypsin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15853774}. |
Acute phase;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal;Sulfation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the serpin family of serine protease inhibitors. The protein is a major inhibitor of plasmin, which degrades fibrin and various other proteins. Consequently, the proper function of this gene has a major role in regulating the blood clotting pathway. Mutations in this gene result in alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor deficiency, which is characterized by severe hemorrhagic diathesis. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:5345; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; fibrinogen complex [GO:0005577]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004866]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048514]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; fibrinolysis [GO:0042730]; maintenance of blood vessel diameter homeostasis by renin-angiotensin [GO:0002034]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; negative regulation of fibrinolysis [GO:0051918]; negative regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010757]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin [GO:2000049]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta production [GO:0071636] |
12549929_Multiple Lys residues within alpha 2-antiplasmin contribute, perhaps in a zipper-like fashion, to its binding to the in-tandem, multikringle array that configures the plasmin heavy chain. 12911586_Alpha2-antiplasmin has an important role in acute pulmonary embolism 16828203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17203182_alpha2-antiplasmin induction inhibits E-cadherin processing mediated by the plasminogen activator/plasmin system, leading to suppression of progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via upregulation of cell-cell adhesion 17317851_the Arg6Trp polymorphism may play a significant role in governing the long-term deposition/removal of intravascular fibrin 17388801_TAFIa, PAI-1 and alpha-antiplasmin: complementary roles in regulating lysis of thrombi and plasma clots 17883703_Fibrinolysis is amplified by converting alpha-antiplasmin from a plasmin inhibitor to a substrate 17890952_Hydroxyethyl starch (HES) dilution enhances fibrinolysis by diminishing alpha2-antiplasmin-plasmin interactions. 17961166_Sequencing analysis revealed the presence of two alpha2-PI gene variations, both in the second half of exon 10: a frameshift mutation and a G to A transition at nucleotide 11337 in codon 407. 18048863_Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and alpha(2)-antiplasmin are not markers for recanalization in patients with ischemic stroke treated with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. 18550704_Identification in human milk of complexes of matriptase with ATIII, A1AT, or A2AP, provides evidence that the proteolytic activity of matriptase, from cells that express no or low levels of HAI-1, may be controlled by secreted serpins. 19073825_Plasmin in nephrotic urine activates the epithelial sodium channel 19492163_deficiency in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive haematologic cancer receiving imatinib mesylate 19691486_FXIIIa substrate, A2AP, sequences suggests that the residue located two positions beyond the reactive glutamine is not conserved. this position makes important contributions to effective FXIIIa-A2AP interactions 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20071328_OPN is highly susceptible to cleavage near its integrin-binding motifs, and the protein is a novel substrate for plasmin and cathepsin D 20112045_Results describe the functional characterization of the unique plasmin(ogen)-binding region of the human alpha(2)-plasmin inhibitor. 20553378_ADAMTS13 inactivation by plasmin as a potential cause of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21251197_fibrinolysis is enhanced by inhibiting enzymatic cleavage of precursor alpha2-antiplasmin 21471521_the antifibrinolytic function of FXIII is independent of fibrin-fibrin cross-linking and is expressed exclusively through alphaAP. 21486949_Truncation of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 by plasmin promotes blood-brain barrier disruption. 21505192_Levels of free full-length alpha2AP were decreased in myocardial infarction (MI); the percentage of C-terminally cleaved alpha2AP was unaltered, and Arg407Lys did not influence alpha2AP levels or MI risk. 21543325_When the C terminus of alpha(2)-antiplasmin was removed, the binding affinity for active site-blocked plasmin remained high, suggesting additional exosite interactions between the serpin core and plasmin. 21707521_Study revealed that plasmin was present in tumor tissue, and that it was responsible for processing progalanin to galanin(1-20) in the extracellular environment. 22205503_Data suggest that decreased amounts of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in plasma vs serum ex vivo may reflect reduced factor XIII (FXIII) in vivo; thus, plasma vs serum alpha2-plasmin inhibitor may be useful diagnostic marker for severe FXIII deficiency. 23992406_protective mediator during gram-negative (pneumo)sepsis, limiting bacterial growth, inflammation, tissue injury, and coagulation 24034420_increased N-terminal cleavage of alpha2AP may have a role in liver cirrhosis 24659849_Two differentially expressed proteins, alpha-1-antitrypsin (SERPINA1) and alpha-2 antiplasmin (SERPINF2) are associated with purpura fulminans. 24818165_Data suggest serum A2AP (SERPINF2) level can serve as biomarker for diabetic retinopathy; levels of A2AP (but not fibrinogen, plasminogen, or plasminogen activator inhibitor 1) are up-regulated in hyperglycemic type 1 diabetes with retinopathy. 25065555_Possession of the alpha2AP 407Lys allele was negatively associated with AAA, and thus changes in alpha2AP may affect aneurysm growth and development. 25331118_FXIII-A has a functional role through exposure on the activated platelet membrane where it exerts antifibrinolytic function by cross-linking alpha2AP to fibrin 25464232_A significant correlation was found between soluble fibroblast activation protein levels and alpha2-antiplasmin cleavage in coronary thrombosis. 26088309_Changes in plasma A2AP are associated with cardiovascular disease event presentation. 26626994_This review presents recent findings regarding the main aspects of the natural heterogeneity of A2AP with particular focus on the functional and possible clinical implications. [review] 26743600_alpha2AP has a profibrotic effect probably not by the action as a plasmin inhibitor, and the blocking of alpha2AP exerts an antifibrotic effect in humans and mice with systemic sclerosis 27861608_Higher plasma concentrations of a-2-AP and PAI-1 in patients with OSA indicated that these patients had increased prothrombotic activity. OSA increases the risk of cardiovascular complications as it enhances prothrombotic activity. 28710283_Data suggest that protein aggregates interact with tissue-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen to efficiently generate plasmin; this aggregate-bound plasmin is shielded from inhibition by alpha-2-antiplasmin and degrades protein aggregates to release smaller, soluble but relatively hydrophobic peptide fragments; these fragments bind to and are cytotoxic to microglia (by not vascular endothelial cells). 29306602_findings suggest that the alpha2AP Arg407Lys polymorphism could be involved in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia and its outcomes 30020241_Studied sex hormone and serpin family F member 2 (SERPINF2) levels in preeclampsia and found a correlation between imbalanced steroid hormone levels and excessive SERPINF2 in early-onset preeclampsia patients. 31129263_Data show that total free alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor (alpha2-PI) in human body fluids can be accurate and fast measured by new sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. 31282989_Abnormal fibrinolysis recognized by thromboelastography in a case of severe bleeding with normal coagulation and platelet function, leads to detection of a novel SERPINF2 variant causing severe alpha-2-antiplasmin deficiency. 31653347_human alpha2-antiplasmin is glycated and acetylated at several sites, with the possible competition between acetylation and glycation at K-182 and K-448; finding suggests possibly relevant alterations to alpha2-antiplasmin function at high glycemia and during aspirin use 32815915_Interaction of glycated and acetylated human alpha2-antiplasmin with fibrin clots. 32945390_Decrease in matrix metalloproteinase3 activity in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts causes alpha2antiplasmin and extracellular matrix deposition, and contributes to fibrosis development. 34830419_Fibrinogen and Antifibrinolytic Proteins: Interactions and Future Therapeutics. |
ENSMUSG00000038224 |
Serpinf2 |
6.094422 |
0.0648309102 |
-3.947174 |
0.970479907 |
24.496421 |
0.00000074448015858204170469916705066282247571507468819618225097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002669710189667379845595033757699177101585519267246127128601074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7704779 |
0.5432897 |
11.9751050 |
3.1235590 |
| ENSG00000167721 |
55720 |
TSR1 |
protein_coding |
Q2NL82 |
FUNCTION: Required during maturation of the 40S ribosomal subunit in the nucleolus. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in endonucleolytic cleavage of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) and maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA). Predicted to be located in nucleolus. Predicted to be part of preribosome, small subunit precursor. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55720; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; preribosome, small subunit precursor [GO:0030688]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; U3 snoRNA binding [GO:0034511]; endonucleolytic cleavage of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000479]; maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000462] |
19584346_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20805244_hTsr1 is involved downstream in nuclear export of the pre-40S particles. 31296287_This study describes the clinical characteristics of the Chinese Han population with Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection and identified TSR1 as a potential causal gene, which might bring about a further progress in diagnosis and treatment of the disorder. 32102773_a novel congenital cataract candidate gene TSR1 was identified by whole genome sequencing and Sanger sequencing in a Chinese congenital cataract family |
ENSMUSG00000038335 |
Tsr1 |
205.080284 |
2.7644165630 |
1.466975 |
0.225729312 |
40.789849 |
0.00000000016951136967851635237610885023168101962132148230466555105522274971008300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000861862837221805443670848107207095242787708855303208110854029655456542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
323.3348453 |
43.7886219 |
118.0898769 |
11.8809833 |
| ENSG00000167740 |
124936 |
CYB5D2 |
protein_coding |
Q8WUJ1 |
FUNCTION: Heme-binding protein which promotes neuronal but not astrocyte differentiation. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable heme binding activity. Predicted to be involved in nervous system development. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of neuron differentiation. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. Predicted to be active in endomembrane system and membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:124936; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane [GO:0016020]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666] |
26692170_alysis of CYB5D2 gene expression and genomic alteration data available from Oncomeinetrade mark detected significant reductions of CYB5D2 mRNA in 40 SCCs and CYB5D2 gene copy number in 107 SCCs. Collectively, we provide evidence that CYB5D2 is a candidate tumor suppressor of cervical tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000057778 |
Cyb5d2 |
44.786660 |
0.4130879559 |
-1.275479 |
0.284397868 |
20.040829 |
0.00000758062207778172102764363549098902694822754710912704467773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024129821407819324833449181610944833664689213037490844726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.0971446 |
6.5972667 |
65.2484511 |
11.0265024 |
| ENSG00000167748 |
3816 |
KLK1 |
protein_coding |
P06870 |
FUNCTION: Glandular kallikreins cleave Met-Lys and Arg-Ser bonds in kininogen to release Lys-bradykinin.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Cleaves Neisseria meningitidis NHBA in saliva; Neisseria is an obligate commensal of the nasopharyngeal mucosa. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31369555}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
Kallikreins are a subgroup of serine proteases having diverse physiological functions. Growing evidence suggests that many kallikreins are implicated in carcinogenesis and some have potential as novel cancer and other disease biomarkers. This gene is one of the fifteen kallikrein subfamily members located in a cluster on chromosome 19. This protein is functionally conserved in its capacity to release the vasoactive peptide, Lys-bradykinin, from low molecular weight kininogen. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3816; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003073]; zymogen activation [GO:0031638] |
9857240_we propose a model to illustrate how the two enhancers may work to regulate the transcription of PSA and hK2. 11130770_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11727832_Tissue kallikrein KLK1 is expressed de novo in endothelial cells and mediates relaxation of human umbilical veins. 11849458_Association of the tissue kallikrein gene promoter with ESRD and hypertension. 11849458_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11912256_Loss-of-function polymorphism of the human kallikrein gene with reduced urinary kallikrein activity. 11912256_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11913965_Kinetic peculiarities of human tissue kallikrein 12581867_endothelial cells synthesize and release an active form of tissue kallikrein - kinin generation on the surface may play an important role in maintenance of circulation homeostasis 12670744_Diminution of kallikrein biosynthesis in African Americans seems to involve mechanisms at or distal to the aldosterone receptor, and perhaps at the level of the kallikrein gene itself. 12887060_essentially unsusceptible to processing by human urinary kallikrein (tissue-type) 14660481_that in the airways, monocytes, neutrophils, and alveolar macrophages may contribute to increased TK activity 14988406_Sustained hyaluronan depolymerization is expected to cause tissue kallikrein activation, EGF release, and EGFR signaling. 15086490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15086490_The K allele of KLK1 promoter and TT genotype of TGF-beta1 may be a genetic KLK1 -130 GN and -128 G-C, and the susceptibility factor contributing to progressive renal deterioration in Taiwanese primary vesicoureteric reflux children. 15167446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15364809_Transduced human tissue kallikrein activated murine Akt-B through Ser-473 phosphorylation providing new information on the pathway involved in hTK-induced neoangiogenesis. 15544850_transgenic rats expressing hKLK1 have an impaired renal response to acute volume expansion 15611141_kallikrein/kinin protects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vivo and in vitro via Akt-Bad.14-3-3 and Akt-GSK-3beta-caspase-3 signaling pathways 15651049_analysis of peptide inhibitor/substrate binding to human apo kallikrein 1 15662224_Induction of KLK1 in carotid arteriosclerosis does not lead to kallikrein-kinins pathway activation. 15765151_Data describe the vascular, hormonal, and renal phenotypes of carriers of the loss-of-function polymorphism of the human tissue kallikrein gene. 15855348_Gene delivery protects against rat diabetic cardiomyopathy by improving cardiac function and promoting glucose utilization and lipid metabo 15905889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905889_There are polymorphisms in regulatory region of human tissue kallikrein gene in Chinese Han people. Differences in both allele and genotype frequencies show association of hypertension with polymorphisms. 16129698_the the kallikrein-kinin system has roles in intramyocardial inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy 16465461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16957554_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17050061_findings suggest the presence of an abnormality in the kallikrein-kinin system in the placentas of women with pregnancy-induced hypertension 17158887_KLK1 may participate in epidermal desquamation through cleavage of desmoglein 1 and regulation by lympho-epithelial Kazal-type-related inhibitor (LEKTI). 17671125_Up-Regulation of kallikrein 11 is associated with ovarian carcinoma 17699431_tissue kallikrein may act as an intrarenal modulator of Ca reabsorption 17761919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17762646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17762646_rs5517 in the KLK1 gene was significantly associated with essential hypertension in a Chinese Han population 17804733_Kallikrein 6 induces E-cadherin shedding and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. 18182238_Protective actions of human tissue kallikrein gene in transgenic rat hearts. 18283336_Proteins such as caveolin-1 (CAV-1) and Akt, Proto-Oncogene Protein, which are known to be altered in colon cancer, affect KLK6 expression and KLK6 secretion 18327081_pTK levels are genetically determined and regulated by Na and K diet 18359858_KLK1 was shown to exhibit both trypsin- and chymotrypsin-like selectivities with Tyr/Arg preferred at site P1, Ser/Arg strongly preferred at P1', and Phe/Leu at P2. 18402547_restoration of the kallikrein-kinin system reduces kidney injury and protects renal function in 5/6-nephrectomized rats via changes in the expression and activation of G protein-coupled receptors including B(2)R 18577888_The kallikrein-kinin system may be one of the more important players in angiogenesis associated with prostate and breast tumours. 18627303_role of KLK1 in arterial function; role of KLK1 in the control of ionic transport in the renal tubule; cardio- and nephro-protective effects of KLK1 and kinins in acute cardiac ischemia, post-ischemic heart failure, and diabetes [review] 18689794_Tissue kallikrein decreased GSK-3beta activity via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway and enhanced VEGF and VEGFR-2 expression in endothelial cells. 18713009_extensive cytoplasmic expression of tissue prokallikrein and plasma prekallikrein was observed, which was similar in small cell and non-small cell lung tumours; however, nuclear labelling for the kallikreins was absent or limited 18725990_factor XII is activated by misfolded proteins in humans, leading to kallikrein formation without initiating coagulation 18844446_S(1)' and S(2)' subsite specificity of KLK1 showed peculiarities that were observed with substrates containing the amino acid sequence of human kininogen 19082699_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19232384_GATA3 was found to bind the site located at -954/-855 and to be a key regulator of abundant KLK1 expression in keratinocyte. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19558318_Combination of KLK2, 3, 13, and 14 and KLK1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 13, and 14 showed very strong discriminatory potential for semen liquefaction and viscosity, respectively. 19578768_Angiogenesis in cervical cancer is mediated by HeLa metabolites through endothelial cell tissue kallikrein. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20143645_elevated plasma levels in patients with hereditary angioedema 20225398_Tissue kallikrein levels are increased in type 2 diabetes, and findings do not support a role for the kallikrein-kinin system in mediating the effects of statin therapy on endothelial function. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20482314_The results indicate differential signaling pathways mediated by TK in promoting prostate cancer cell migration and invasion via PAR(1) activation, and proliferation via kinin B2 receptor stimulation. 20516044_KLK1 gene polymorphisms are not associated with lupus nephritis in a Chinese Han population. 20516044_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20533273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20533273_Results suggested that the rs5517 polymorphism was associated with cerebral hemorrhage, while the rs5516 polymorphism was not in Changsha Han Chinese. 20536386_lung epithelial cells support the assembly and activation of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system by a mechanism dependent on HSP90, and could contribute to KKS-mediated inflammation in lung disease. 20613781_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20613781_rs5516 in the KLK1 gene may be involved in the development of essential hypertension. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21164105_Tissue kallikrein is essential for invasive capacity of circulating proangiogenic cells. 21200088_Neither rs5515 nor rs3212855 SNP is associated with cerebral hemorrhage. 21211543_Increased expression of hK1 by astrocytes co-localized with GFAP was found, contrasting with kinin B1 and B2 receptors, which were co-localized with NeuN in the sclerotic hippocampus 21571276_Suggest that a genetic polymorphism in KLK1 may contribute to the risk of developing later stage abdominal aortic aneurysm. 21679467_Unexpectedly, elevated KLK1 expression and excretion is found in patients with established or incipient acute kidney injury. 21823154_Data suggest that lower plasma tissue kallikrein levels are independently associated with first-ever stroke and are an independent predictor of recurrence after an initial stroke. 23635481_KLK1 promoter polymorphisms are associated with development of AKI and adverse outcomes. Further studies are needed to validate these findings. 23697984_Tissue kallikrein-modified mesenchymal stem cells provide enhanced protection against ischemic cardiac injury after myocardial infarction. 23765970_Polymorphism of the KLK1 A1789G gene is associated with coronary artery stenosis. 23874198_Data suggest factor XII binding/autoactivation are increased on surface of hantavirus-infected vascular endothelium; thus, activation of kallikrein-kinin system during hantavirus infection could have profound implications on capillary permeability. 24005896_allele H is a common polymorphism in Japanese and may contribute to decreased reabsorptions of calcium and sodium in the kidney 24530396_Tissue kallikrein facilitated the activation of EGFR, ERK1/2 and p38 cascade. Not p38 but ERK1/2 phosphorylation was severely compromised in cells depleted of EGFR. Impairment of signaling of ERK1/2 seemed not to be restricted to EGFR phosphorylation. 24586431_Up-regulation of KLK1 in tubular epithelial cells may mediate pro-inflammatory pathway and PAR activation during diabetic nephropathy. 24599937_These data do not support a role for the Tissue kallikrein-kinin system, protective or deleterious, in the development of insulin resistance and diabetes. 24626253_Our findings suggest that higher levels of TK in plasma are associated with the presence of CAD and are a predictor of mild coronary arteriosclerosis. 25100328_Preclinical characterization of recombinant human tissue kallikrein-1 as a novel treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus. 25448306_The kallikrein system in retinal damage/protection 26677174_TK promoted cell survival and beta-catenin degradation in serum-starved SH-SY5Y cells via increasing autophagy. 26884824_KLK1 rs5516 SNP is not related to the incidence of Alzheimer's disease in a Hunan Han Chinese population. 27329205_increasing the serum levels of AngII increased the risk of acute myocardial infarction (AMI); the risk of AMI increased when the serum levels of AngII and KLK1 simultaneously increased; individuals with the combined genotypes of ACE DD and KLK1 GG showed increased risk of AMI compared with those with the combined genotypes of ACE II and KLK1 AA 27618014_Recognition of anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or Kallikrein Inhibitor may lead to therapeutics to enhance existing treatments for patients who do not respond to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapies. 27858843_The rs5516 G allele of KLK1 was significantly associated with aortic aneurysm 28322037_Letter: KLK1 (rs5516) was associated with thoracic aortic dissection. 28621557_Our findings suggest that the A2233C polymorphism of KLK1 may be a marker of evaluation of hypertensive subjects' responses to angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors benazepril. 30618416_these findings showed that oxidative stress, impaired corpus cavernosum endothelial cells, and severe penis fibrosis were involved in the induction of erectile dysfunction by hyperhomocysteinemia in rats, whereas hKLK1 preserved erectile function by inhibiting these pathophysiological changes 30801944_kallikrein has an apple domain disc with a rotated conformation compared to factor XI 30908937_The findings indicate that KLK1 intervenes early in the antiviral defense modulating the severity of influenza infection. Decreased KLK1 expression in Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients could contribute to the worsening of influenza. 31873176_Associations of ACE I/D polymorphism with the levels of ACE, kallikrein, angiotensin II and interleukin-6 in STEMI patients. 33355364_Coexpression of tissue kallikrein 1 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 improves myocardial ischemiareperfusion injury by promoting angiogenesis and inhibiting oxidative stress. 33397811_Kallikrein directly interacts with and activates Factor IX, resulting in thrombin generation and fibrin formation independent of Factor XI. |
|
|
15.377198 |
0.1424050369 |
-2.811928 |
0.485746757 |
40.123816 |
0.00000000023836517915971788973296202767434941172108864293477381579577922821044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001199546554516684692607903620661762011945228323384071700274944305419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0621486 |
1.3308665 |
28.4212536 |
4.4878432 |
| ENSG00000167895 |
147138 |
TMC8 |
protein_coding |
Q8IU68 |
FUNCTION: Probable ion channel. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) is an autosomal recessive dermatosis characterized by abnormal susceptibility to human papillomaviruses (HPVs) and a high rate of progression to squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed skin. EV is caused by mutations in either of two adjacent genes located on chromosome 17q25.3. Both of these genes encode integral membrane proteins that localize to the endoplasmic reticulum and are predicted to form transmembrane channels. This gene encodes a transmembrane channel-like protein with 8 predicted transmembrane domains and 3 leucine zipper motifs. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:147138; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; mechanosensitive ion channel activity [GO:0008381]; protein sequestering activity [GO:0140311]; tumor necrosis factor binding [GO:0043120]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558]; regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:1902041]; zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0055069] |
12426567_Mutations in EVER2 are associated with epidermodysplasia verruciformis. 17711520_study reports a novel nonsense mutation of the TMC8 gene in Brazilian patients with epidermodysplasia verruciformis 18224692_Genetic variation in the EVER2 gene is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the skin 19706093_epidermodysplasia verruciformis in a father and a son with typical histologic and clinical findings that occur in the absence of mutations in EVER1 or EVER2. 21196704_Results underline the possible relevance of the EVER2/TMC8 single nucleotide polymorphism rs7208422 in influencing susceptibility to beta-papillomaviruses and their oncogenic potential. 21387292_Data support the involvement of the TMC6/8 region in cervix cancer susceptibility. 22158547_study describes the presence of two previously unreported homozygous mutations in the EVER2 gene in two Italian epidermodysplasia verruciformis patients, each of whom have already developed more than 10 non-melanoma skin cancers 22761942_EVER proteins appear as key components of the activation-dependent regulation of Zn(2+) concentration in T cells. However, the impact of EVER-deficiency in T cells on EV pathogenesis remains to be elucidated 22903682_EVER2-deficient patients display mild T-cell abnormalities: a significant increase of memory CD4+ and effector memory CD8+ T cells, a bias of the T cell receptor Valphabeta and Vgammadelta repertoires and an increase of skin-homing CD4+ T-cell subsets. 23429285_Ever2 interacts with the N-terminal domain of TRADD, impairs the recruitment of TRAF2 and RIPK1 and promotes apoptosis. 23534907_EV is also a rare autosomal recessive genodermatosis involving susceptibility to human papillomavirus (HPV) infections and squamous cell carcinoma, caused in most cases by homozygous mutations in EVER1 or EVER2. 23535066_We report a case of Merkel cell polyomavirus detection in the skin of a patient with epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EDV) and a family history remarkable for an unusual inheritance pattern for EDV. 24586810_Loss of the HPV-infection resistance EVER2 protein impairs NF-kappaB signaling pathways in keratinocytes. 25220380_TMC8 was found to be localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where it inhibited receptor mediated Ca(2+) release, activation of Ano1 and volume regulated LRRC8-related Cl(-) currents. 25378492_Expression of both EVER1 and EVER2 in B cells is activated immediately after Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, whereas at later stages, it is strongly repressed by latent membrane protein 1-activated NF-kappaB signaling. 25495765_We found a possible correlation between the EVER2 TT genotype and the development of AK, suggesting a potential role of this polymorphism in the development of AK. 25853559_A common genetic variation in TMC8 is associated with high-risk HPV infection and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma etiology. 26126409_Findings suggest that SNPs in EVER2 may be involved in the development of premalignant skin lesions that harbour beta-HPV, perhaps giving rise to SCC tumours that have lost beta-HPV gene expression during progression. 26227733_TMC6/EVER1 and TMC8/EVER2 are known to be involved in the development of EV. 27097911_There were no differences in Ever2 SNPs between head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients with human papilloma virus (HPV)-positive and HPV-negative tumors, and healthy controls. 27899077_The present study did not show any significant association of the EVER1/2 polymorphisms (rs2290907and rs16970849) with cervical cancer. 28646613_The relatively high proportion of EV patients without mutation in TMC6/8 indicates the existence of EV-causing mutations in additional, presently unknown gene(s). However, a homozygous TMC8 splice site mutation in our patients resulted in aberrant transcripts which cannot retain the healthy phenotype 30068544_these findings suggest that the disruption of CIB1-EVER1-EVER2-dependent keratinocyte-intrinsic immunity underlies the selective susceptibility to beta-HPVs of epidermodysplasia verruciformis patients. 32917726_Expression of a TMC6-TMC8-CIB1 heterotrimeric complex in lymphocytes is regulated by each of the components. 34459021_Case of epidermodysplasia verruciformis with a novel mutation of TMC8. 36170758_Establishment of a human induced pluripotent stem cell line, KMUGMCi005-A, from a patient with Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (EV) bearing homozygous splicing donor site mutation in the TMC8 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000050106 |
Tmc8 |
472.368033 |
0.3980178186 |
-1.329095 |
0.251672364 |
27.078415 |
0.00000019536725585424366287746219920939960701389281894080340862274169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000747511569600813573899635369746086155373632209375500679016113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
258.1131300 |
47.6968218 |
652.3908946 |
86.7972842 |
| ENSG00000167912 |
100505501 |
TOX-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.388707 |
0.4005807832 |
-1.319835 |
0.430410449 |
9.348508 |
0.00223167098815181975252075474713819858152419328689575195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004883537996311468516730247557688926463015377521514892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1003687 |
3.6390164 |
25.2268866 |
5.9270868 |
| ENSG00000167978 |
23524 |
SRRM2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UQ35 |
FUNCTION: Required for pre-mRNA splicing as component of the spliceosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19854871, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28076346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28502770, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29301961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29360106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29361316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30705154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9531537}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Spliceosome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables C2H2 zinc finger domain binding activity and protein N-terminus binding activity. Involved in mRNA splicing, via spliceosome. Located in Cajal body and nuclear speck. Part of U2-type catalytic step 2 spliceosome and U2-type precatalytic spliceosome. Biomarker of Parkinson's disease. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23524; |
Cajal body [GO:0015030]; catalytic step 2 spliceosome [GO:0071013]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; U2-type catalytic step 2 spliceosome [GO:0071007]; U2-type precatalytic spliceosome [GO:0071005]; C2H2 zinc finger domain binding [GO:0070742]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398] |
19789211_results suggest multiple functions for Cwc21/SRm300 in the splicing process, including an important role in the activation of splicing in association with Isy1. 19854871_demonstrate that SRm300, the only serine arginine-related protein known to be at the core of human catalytic spliceosomes, is a functional ortholog of Cwc21p, also interacting directly with Prp8p and Snu114p. 20161708_Data show that the consistent dysregulation of the RNA splicing factor SRRM2 in two different PD neuronal sources and in PD blood makes SRRM2 a strong candidate gene for PD and draws attention to the role of RNA splicing in the disease. 26135620_The S346F mutation in SRRM2 predisposes to papillary thyroid carcinoma by affecting alternative splicing of unidentified downstream target genes. 28062851_cellular complexes comprising cactin, DHX8 and SRRM2 sustain precise chromosome segregation, genome stability and cell proliferation by allowing faithful splicing of specific pre-mRNAs. 33095160_SON and SRRM2 are essential for nuclear speckle formation. 33171483_A compound downregulation of SRRM2 and miR-27a-3p with upregulation of miR-27b-3p in PBMCs of Parkinson's patients is associated with the early stage onset of disease. 35567594_Loss-of-function variants in SRRM2 cause a neurodevelopmental disorder. 35929045_SRRM2 organizes splicing condensates to regulate alternative splicing. |
ENSMUSG00000039218 |
Srrm2 |
3800.779045 |
0.4788444455 |
-1.062371 |
0.057940193 |
330.379666 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007945031904986639358608502827677541174001334053221925842093615217830914520503020622112959524602877888220357845039560429882886290948920397476510840322313594321637843564552505515725900828161165634355711517855525016784667968750000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002484505739779720418049991259221607514910593589053981778056276203525889152955840036479673223782331995616729815023880774806770358670574396871829249191762019996179455546837817886537611022923499604075914248824119567871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2472.8352150 |
92.6729355 |
5202.4367762 |
140.0166974 |
| ENSG00000167984 |
197358 |
NLRC3 |
protein_coding |
Q7RTR2 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of the innate immune response (PubMed:15705585, PubMed:22863753, PubMed:25277106). Attenuates signaling pathways activated by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and the DNA sensor STING/TMEM173 in response to pathogen-associated molecular patterns, such as intracellular poly(dA:dT), but not poly(I:C), or in response to DNA virus infection, including that of Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV1) (By similarity) (PubMed:22863753). May affect TLR4 signaling by acting at the level of TRAF6 ubiquitination, decreasing the activating 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination and leaving unchanged the degradative 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitination (PubMed:22863753). Inhibits the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway possibly by directly interacting with the posphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit p85 (PIK3R1/PIK3R2) and disrupting the association between PIK3R1/PIK3R2 and the catalytic subunit p110 (PIK3CA/PIK3CB/PIK3CD) and reducing PIK3R1/PIK3R2 activation. Via its regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, controls cell proliferation, predominantly in intestinal epithelial cells (By similarity). May also affect NOD1- or NOD2-mediated NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:25277106). Might also affect the inflammatory response by preventing NLRP3 inflammasome formation, CASP1 cleavage and IL1B maturation (PubMed:25277106). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5DU56, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15705585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22863753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25277106}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Leucine-rich repeat;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a NOD-like receptor family member. The encoded protein is a cytosolic regulator of innate immunity. This protein directly interacts with stimulator of interferon genes (STING), to prevent its proper trafficking, resulting in disruption of STING-dependent activation of the innate immune response. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:197358; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding [GO:0036312]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045824]; negative regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032687]; negative regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032688]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901223]; negative regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly [GO:1900226]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
15705585_This report describes the first cloning and characterization of a novel CATERPILLER gene, CLR16.2 that is located on human chromosome 16. The protein encoded by this gene has a typical NBD-LRR configuration. 22718770_Post-transcriptional inhibition of luciferase reporter assays by the Nod-like receptor proteins NLRX1 and NLRC3. 22863753_NLRC3 inhibited Toll-like receptor (TLR)-dependent activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB by interacting with the TLR signaling adaptor TRAF6 25277106_overexpression of NLRC3 with NLRP3/cryopyrin inflammasome components suppresses pro-caspase-1 cleavage and IL-1beta processing. 26378020_The extent of NLRC3 and AIM2 gene reduction was correlated with cancer progression. 26763980_NLRX1, NLRP12 and NLRC3 negatively modulate the host immune response following virus exposure. (Review) 28584053_The NLRC3 interferes with the assembly and activity of the NALP3 inflammasome complex by competing with ASC for pro-caspase-1 binding. 28731142_NLRC3 promoted K48-linked polyubiquitination and degradation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1). 30081150_Down-regulated expression of NLRC3 may play an important role in cancer progression and prognosis of HCC by acting as a tumor suppressor. 31303617_expression of NLRC3 was significantly associated with CD8+ T cells infiltration 32584509_NLRC3 silencing accelerates the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cell via IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation. 34533122_[Knockdown of NLRC3 promotes proliferation and invasion of human colon cancer cells]. |
ENSMUSG00000049871 |
Nlrc3 |
22.546621 |
0.3305219401 |
-1.597182 |
0.348812615 |
21.715803 |
0.00000316175935860003995067635251814408547943457961082458496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010536818273410835720255672443013139627510099671781063079833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
11.6144303 |
2.7238717 |
35.4705137 |
5.0601044 |
| ENSG00000167994 |
5866 |
RAB3IL1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TBN0 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which may activate RAB3A, a GTPase that regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Promotes the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound Rab proteins into their active GTP-bound form. May also activate RAB8A and RAB8B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937701}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the ras-related protein Rab3A. The encoded protein binds Rab3a and the inositol hexakisphosphate kinase InsP6K1. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 7. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:5866; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi to plasma membrane transport vesicle [GO:0070319]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
24072714_Intermediates in the guanine nucleotide exchange reaction of Rab8 protein catalyzed by guanine nucleotide exchange factors Rabin8 and GRAB. 30599141_Rab27/Rabphilin3a/GRAB/Rab3 constitutes a signaling module in sperm exocytosis. 33011223_Identification of hub genes in unstable atherosclerotic plaque by conjoint analysis of bioinformatics. |
ENSMUSG00000024663 |
Rab3il1 |
97.167360 |
0.2082552150 |
-2.263575 |
0.200814370 |
132.104270 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000141963428171090109658212502128246984049044049835916042696914915314103822514750865603494478506263476447202265262603759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000018461499557755858657257562407783109245653333061381225370176825360420584571676232837900144545528746675699949264526367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.7333772 |
4.5098573 |
163.1180461 |
13.1205487 |
| ENSG00000167996 |
2495 |
FTH1 |
protein_coding |
P02794 |
FUNCTION: Stores iron in a soluble, non-toxic, readily available form. Important for iron homeostasis. Has ferroxidase activity. Iron is taken up in the ferrous form and deposited as ferric hydroxides after oxidation. Also plays a role in delivery of iron to cells. Mediates iron uptake in capsule cells of the developing kidney (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Iron;Iron storage;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes the heavy subunit of ferritin, the major intracellular iron storage protein in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is composed of 24 subunits of the heavy and light ferritin chains. Variation in ferritin subunit composition may affect the rates of iron uptake and release in different tissues. A major function of ferritin is the storage of iron in a soluble and nontoxic state. Defects in ferritin proteins are associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2495; |
autolysosome [GO:0044754]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; intracellular ferritin complex [GO:0008043]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; ferric iron binding [GO:0008199]; ferrous iron binding [GO:0008198]; ferroxidase activity [GO:0004322]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; cellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879]; immune response [GO:0006955]; intracellular sequestering of iron ion [GO:0006880]; iron ion transport [GO:0006826]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147] |
11783942_gene coding and flanking regions were sequenced and examined for mutations that might modulate the iron burden of individuals harboring the common mutant hemochromatosis HFE genotype or cause hemochromatosis independent of mutations in the HFE gene 11903046_An alternative model of H ferritin promoter transactivation by c-Jun (H ferritin, also called isoferritin) 11964300_activates regulatory T cells by induction of changes in dendritic cells 11988076_mu-1,2-Peroxobridged di-iron(III) dimer formation in human H-chain ferritin 12387819_Analysis of sequence effect on folding efficiency of ferritin heavy and light subunits. 12435735_FTH expression is mediated by Nrf2 in response to xenobiotics and cancer chemopreventive dithiolethiones 14615048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14998975_Placenta immunomodulatory ferritin (PLIF) plays a major role in placentation and embryonic growth. 15727900_Intra-leukocytic hemosiderin inclusions (a complex of ferritin, denatured ferritin and other material) are associated with iron overload and acute infection. 15755449_Data reveal striking differences in iron oxidation and hydrolysis chemistry between human mitochondrial ferritin and human H-chain ferritin despite their similar diiron ferroxidase centers 15967798_H-ferritin mRNA, IL-1beta, and poly(C)-binding proteins may have roles in ferritin translation and iron homeostasis in human liver 17070541_We report the crystallographic structures of four human H apoferritin variants at a resolution of up to 1.5 Angstrom. Crystal derivatives using Zn(II) as redox-stable alternative for Fe(II), allows us to characterize the different metal-binding sites. 17702748_H ferritin regulates folate metabolism through its internal ribosome entry site 17761032_We have detected a significant inverse correlation of -0.565 (PG hepcidin polymorphism genotypes. 25265351_High ferritin expression is associated with malignant phenotype of breast cancer. 25448225_The goals of this study were to evaluate the multilineage differentiation ability of human mesenchymal stem cells expressing an MRI reporter, human ferritin heavy chain (FTH). 26327381_Stopped-flow kinetics assays revealed that human H ferritin has different levels of activity compared with its R. catesbeiana counterpart 26518749_Studies indicate that the the best characterized cytosolic ferritins in mammals are encoded by two genes, FTH and FTL, with four exons and similar structures. 26540556_H-ferritin tissue expression and the number of CD68+/H-ferritin+ cells were increased in the lymph nodes of adult-onset Still's disease patients, and these results correlated significantly with disease severity 26602884_Ferritin light chain and ferritin heavy chain are required for the neural differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells under extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field. 26758041_Among myelodysplastic syndromes patients only, CD163 + macrophage density and HO1 and H-ferritin expression by CD163 + macrophages increased in tandem with marrow iron. High HO1 was significantly associated with shorter overall survival. 26853188_Recombinant human H-chain ferritin nanocages were characterized by transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. These results indicate that H-chain ferritin is able to self-assemble into nanocages with a narrow size distribution. 26886577_Human FTH1 is a general pro-survival sequence. 27566559_ferritin heavy chain has a role in ovarian cancer stem cell expansion and epithelial to mesenchymal transition 27611581_there is no significant relationship between serum ferritin concentrations and depressive symptoms among Chinese adults. 27732930_Report in vivo magnetic resonance imaging of xenografted neuroblastoma tumors using FTH1 reporter gene expression controlled by a tet-on switch. 28289076_fumarate increases ferritin gene transcription by activating the NRF2 (nuclear factor [erythroid-derived 2]-like 2) transcription factor. 28636371_Data suggest that, in homopolymeric H-subunit ferritin (HuHF), iron oxidation proceeds with a 2:1 Fe(II):O(2) stoichiometry at iron level of 2 Fe(II) atoms/H-subunit with generation of H2O2; L-subunit-rich heteropolymeric ferritin also facilitates iron oxidation at the ferroxidase center and additionally promotes oxidation at the mineral surface once iron-binding capacity has been exceeded. 28754384_The H-ferritin could bind up to 24 NCOA4(383-522) fragments forming highly stable and insoluble complexes. The binding was partially inhibited only by Fe(II) among the various divalent metal ions analyzed. The iron-dependent, highly-specific formation of the remarkably stable H-ferritin-NCOA4 complex shown in this work may be important for the characterization of the mechanism of ferritinophagy. 28774348_Findings indicate that induction of EMT, increased migration and survival depend, in MCF-7 and H460 cells, on the release of FHC control on two pathways, namely the iron/ROS metabolism and CXCR4/CXCL12 axis. 28837569_Low levels of FTH-positive tumor cells and microglia/macrophages were associated with poor survival in anaplastic astrocytomas, while high amounts of FTL-positive microglia/macrophages had a negative prognostic value 28960260_this study shows that H-ferritin is increased in the bone marrow of patients affected by macrophage activation syndrome 28993630_iron overload due to impaired ferritinophagy or other cause(s) is likely to initiate prion-like spread of alpha-syn and ferritin, creating retinal iron dyshomeostasis and associated cytotoxicity. Since over-expression of alpha-syn is a known cause of Parkinson's disease. 29046127_High serum ferritin (SF) and the overall survival of allogeneic hematopoietic SF was only significantly associated with prolonged RBC transfusion dependence post-transplantation. 29240947_A critical role of a FTH1 gene:pseudogene:miRNA network in regulating tumorigenesis in prostate cancer, whereby oncogenic miRNAs downregulate the expression of FTH1 and its pseudogenes to drive oncogenesis. 29457657_Human oligodendrocytes undergo apoptosis when exposed to Sema4A and take up H-ferritin for meeting iron requirements and that these functions are mediated via the Tim-1 receptor. H-ferritin can block Sema4A-mediated cytotoxicity. Sema4A is detectable in the CSF of multiple sclerosis patients and HIV-seropositive persons and can induce oligodendrocyte cell death. 29544765_Study demonstrate that the amounts of ferritin heavy subunit are inversely correlated, in K562 cells, to H19/miR-675 levels, and that this phenomenon may be largely attributed to the increase in ROS production induced by the FHC silencing. 29580991_the role of FTH1 in the FIH control of HIF-1 activity, is reported. 29729700_CD16 expression and morphological maturity of neutrophils are associated with higher iron ferritin levels in major beta-thalassemia. 30102404_Data show that piR-FTH1 (ferritin heavy chain 1) knocks down the Fth1 mRNA via the HIWI2 and HILI mediated mechanism. 30274235_Ferritin Heavy Chain (FHC) protein expression inversely correlates with NF-kappaB activation in cancer cell lines. 30325535_This study demonstrated that serum ferritin is a strong and independent prognostic factor associated with early death, induction failure, incidence of relapse, and OS in AML patients treated by intensive chemotherapy. 30518922_Ferritin heavy subunit enhances apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through modulation of miR-125b/p53 axis. 30552136_Ferritin is up-regulated by inflammation and exhibits cytokine-like activity in periodontal ligament cells inducing a signaling cascade through transferrin receptor via ERK/P38 MAPK. 30610587_High FTH expression is associated with prostate cancer. 30700131_H-ferritin inhibits mineralization and osteoblastic differentiation of human valvular interstitial cells, enhances nuclear localization of Sox9, reduces nuclear accumulation of RUNX2, decreases phosphate channel expression, upregulates ENPP2, and decreases TNF-alpha and IL-1beta expression in valvular interstitial cells derived from human calcified stenotic aortic valve. 30720039_A kinetic model is proposed in which the inhibition of the protein's activity is caused by bound iron(III) cations at the ferroxidase center, with the rate limiting step corresponding to an exchange or a displacement reaction between incoming iron(II) cations and bound Fe(III) cations. 30850661_The data account for transferrin-independent binding of ferritin to CD71 and suggest that select pathogens may have adapted to enter cells by mimicking the ferritin access gate. 30873154_Iron and Ferritin Modulate MHC Class I Expression and NK Cell Recognition. 31104064_Overexpression of FTH1 was detected in 890 RCC tissues (15.2904+/-0.63157) compared to 129 normal kidney tissues (14.4502+/-0.51523, p |
ENSMUSG00000024661 |
Fth1 |
15801.157387 |
2.5340704183 |
1.341457 |
0.015817968 |
7191.617827 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
22756.5807466 |
253.8746236 |
9043.5911079 |
77.3456950 |
| ENSG00000168000 |
26580 |
BSCL2 |
protein_coding |
Q96G97 |
FUNCTION: Plays a crucial role in the formation of lipid droplets (LDs) which are storage organelles at the center of lipid and energy homeostasis (PubMed:19278620, PubMed:21533227, PubMed:31708432, PubMed:30293840). In association with LDAF1, defines the sites of LD formation in the ER (PubMed:31708432). Also required for growth and maturation of small nascent LDs into larger mature LDs (PubMed:27564575). Mediates the formation and/or stabilization of endoplasmic reticulum-lipid droplets (ER-LD) contacts, facilitating protein and lipid delivery from the ER into growing LDs (PubMed:31178403, PubMed:27879284). Regulates the maturation of ZFYVE1-positive nascent LDs and the function of the RAB18-ZFYVE1 complex in mediating the formation of ER-LD contacts (PubMed:30970241). Binds anionic phospholipids including phosphatidic acid (PubMed:30293840). Plays an important role in the differentiation and development of adipocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z2E9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19278620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21533227, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27564575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27879284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30293840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30970241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31178403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31708432}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Congenital generalized lipodystrophy;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Lipid degradation;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes the multi-pass transmembrane protein protein seipin. This protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and may be important for lipid droplet morphology. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital generalized lipodystrophy type 2 or Berardinelli-Seip syndrome, a rare autosomal recessive disease characterized by a near absence of adipose tissue and severe insulin resistance. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Naturally occurring read-through transcription occurs between this locus and the neighboring locus HNRNPUL2 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-like 2).[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:26580; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; lipid catabolic process [GO:0016042]; lipid droplet formation [GO:0140042]; lipid droplet organization [GO:0034389]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050995]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162] |
11479539_Alterations in BSCL2 (seipin gene) are responsible for BSCL (OMIM :606158).Predicted human seipin protein sequence. 14602785_Congenital lipodystrophy patients with Seipin mutations have a more severe lack of body fat, which affects both metabolically active and mechanical adipose tissue, compared with patients with mutations in the AGPAT2 gene. 14981520_Heterozygous missense mutations in BSCL2 are associated with distal hereditary motor neuropathy and Silver syndrome. 14981520_seipin is an integral membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) 15126564_We identified a novel nonsense mutation of seipin at codon 275 (R275X). Of four congenital generalized lipodystrophy patients, three were homozygous for R275X. No seipin mutation was found in any exon in one patient. 15181077_mutations in AGPAT2 and Gng3lg are approximately equally represented in congenital generalized lipodystrophy 15732094_Our study indicates that the dominant N88S mutation in the Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy gene 2 leads to a broad spectrum of motor neuron disorders. 16427281_description of two Dutch families with BSCL2 mutations and phenotypic variability of the gene mutation. Features are compatible with Silver syndrome, variant Silver syndrome (foot rather than hand involvement), distal HMN type II, or distal HMN type V. 16435205_mutations in AGPAT2 or Seipin may have roles in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 17420921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17486577_This study reaffirms the clinical phenotype of the disorders associated with a BSCL2 Ser90Leu mutation and describes a genetically proven family with Silver syndrome and dHMN type V in Asia. 17535271_The 669insA mutation in exon 4 of the BSCL2 gene was identified as the major genetic alteration leading to BSCL in a group of 22 patients from the northeastern Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Norte. 17663003_Our data confirm that most likely only two mutations (N88S, S90L) in exon 3 of BSCL2 may lead to dHMN-V or SS phenotypes. 18093937_seipin is found at endoplasmic reticulum lipid droplet junctions and is important for droplet morphology 18155601_Berardinelli-Seip syndrome is a congenital form of generalized lipodystrophy, transmitted as an autosomal recessive trait. It is well documented in medicine and skin. It is a rare disorder caused by mutations of AGPAT2 gene or BSCL2 gene. 18224579_Silver syndrome--related to the N88S mutation in the BSCL2 gene--is characterized by a spectrum of clinical findings 18250201_These results suggest that an evolutionally conserved function of seipin in phospholipid metabolism and LD formation may be functionally important in human adipogenesis. 18458148_Study demonstrates that BSCL2 is an essential, cell-autonomous regulator of adipogenesis. 18585921_The transmembrane domains in seipin are critical for ER retention, ubiquitination, formation of inclusions, and activation of UPR. Seipin expression is detected in neurons in the spinal cord and in the frontal lobe cortex of the brain. 18612770_Here we report the third Italian family with dHMN and SPG17 in which two affected members harbor the heterozygous N88S mutation in the BSCL2 gene. 18690553_Case Report: novel BSCL2 mutation in an Indian patient with congenital generalized lipodystrophy associated with normal intellectual ability. 18698612_A new subtype of congenital generalized lipodystrophy is not associated with the BSCL2 gene. 19226263_BSCL2 gene mutations were found in the homozygous form in four Brazilian kindreds (c.412C>T c.464T>C, c.518-519insA, IVS5-2A>G), and in two kindreds compound mutations were found (c.1363C>T, c.424A>G). 19252810_We describe results of Seipin/BSCL2 mutation screening in sporadic adult-onset upper motor neuron syndromes. 19278620_Study showed that alterations in the pattern of lipid droplets in seipin deficient cells. 19323790_This report suggests that a different type of distal hereditary motor neuropathy could exist within one family carrying N88S mutations in BSCL2. 19396477_These results expand the clinical spectrum of HMN and suggest a digenic inheritance of HMN in this family with a BSCL2 mutation and a chromosome 16 locus likely contributing to the phenotype. 19438831_Japanese CGL patients with BSCL2 mutations presented with severe insulin resistance, even during infancy, prior to the development of diabetes mellitus 19574402_Bscl2 is required for PPARgamma's full activation to initiate the adipogenesis transcription program. 19762912_heterozygous mutation in the seipin gene in congenital lipodystrophy was associated with dystonia, mental retardation and behaviour change. 20598714_DNA sequencing of BSCL2 was performed and a heterozygous N88S missense mutation in BSCL2 gene was detected in all three patients with distal hereditary motor neuropathy type V 20806400_study of an Italian family with a Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 phenotype with pyramidal signs; in the 3 affected siblings an S90L mutation was revealed; confirms variability of phenotypes associated with Ser90Leu mutation 21750110_N88S seipin mutant transgenic mice develop motor neuron disease via endoplasmic reticulum stress. 21957196_the biochemical characteristics of seipin and its mis-sense mutants 22234369_the increased expression of seipin markedly reduced the mass of white adipose tissue and the size of adipocytes and lipid droplets 22427291_This study showed that a A novel polymorphism G-->T was found in the Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2 gene on intron 4 in patient with hereditary motor neuropathy type V in Italy family. 22474068_role of seipin in human disease 23142943_This report expands the variability of the clinical spectrum associated with the BSCL2 gene and describes the first family with the p.S90W mutation. 23470542_The mutant seipin (Bscl2) formed protein aggregates in the CNS neurons of transgenic mice and caused a specific loss of alpha motor neurons in the ventral horn of spinal cord. 23553728_Identification of a known BSCL2 mutation in a family with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. 23564749_Our results suggest that exon 7 skipping in the BSCL2 gene due to the c.985C>T mutation is responsible for a novel early onset, fatal neurodegenerative syndrome involving cerebral cortex and basal ganglia. 23659685_Mutation identified in BSCL2 gene causing congenital generalized lipodystrophy Pakistani population. 23907395_This study analysed the relationship between hepacivirus (HCV) and seipin, a protein involved in lipid droplet maturation, and suggested that the outer surface of lipid droplets is a critical factor for HCV release. 23989774_This study presents potential molecular mechanisms by which different pathogenic mutations in the human lipodystrophy protein seipin may cause severe lipodystrophy. 24778225_Here, we report teratozoospermia syndrome in a lipodystrophic patient with compound BSCL2 mutations, with sperm defects resembling the defects of infertile seipin null mutant mice. 24961962_A homozygous and truncating mutation was identified in the BSCL2 gene suggesting congenital generalized lipodystrophy. 25195639_a brief overview of the genetic association of the CGLs, and focus on the current understanding of differential contributions of distinct seipin domains to lipid storage and adipogenesis. 25219579_A missense mutation was found in BSCL2 N88S, in a patient with Silver syndrome. 25487175_The S90L mutationof BSCL2 is predominantly associated with Silver syndrome 25832430_The mutation of seipin at glycosylation sites disrupt its function in regulating lipid droplet metabolism, and the autophagy acts as an adaptive response to break down abnormal lipid droplets. 25934999_We confirmed reduction of brain volume and number of sperm in human patients with BSCL2 mutation. This is the first report demonstrating that seipin is necessary for normal brain development and spermatogenesis 26282322_Increased aggregation and subsequent impaired oligomerization of Celia seipin leads to cell death. In heterozygous carriers, wildtype seipin might prevent the damage caused by mutant seipin through its sequestration into harmless mixed oligomers. 26815532_BSCL2 mutations account for a small number of patients with inherited neuropathies in Taiwan. The p.R96H mutation is associated with distal hereditary motor neuropathy. 26975546_BSCL2 defines the localization of adipose differentiation-related protein, which has a role in lipid accumulation and adipogenic differentiation 27391332_results suggest that Celia seipin is probably playing an underestimated role in adipocyte maturation, but not in senescence, and its expression can be modified by exogenous factors as fatty acids. 27612026_Data show that all three patients exhibited characteristic features of congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL) due to mutations in the Bernardinelli-Seip congenital (BSCL2) gene. 27806294_These data identify SEIPIN as an evolutionarily conserved regulator of microsomal GPAT. 27838812_Results provide evidence that the hepatic BSCL2 deficiency induces the increase and expansion of lipid droplets potentially via increased SCD1 activity. 27862672_In this Chinese Han population the novel Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease-associated gene mutations BSCL2 was discovered. 27868354_We identified a novel BSCL2 mutation, c.213-1336_c.294 + 1921delinsCA, which is expected to result in p.Thr72Cysfs*2, among classical Berardinelli-Seip syndrome patients in northern Peru. This null mutation was shared by five patients from two pedigrees, indicating the presence of a founder mutation. 27879284_Together, these data suggest that seipin helps to connect newly formed lipid droplets to the endoplasmic reticulum and that by stabilizing endoplasmic reticulum-lipid droplet contacts seipin facilitates the incorporation of protein and lipid cargo into growing lipid droplets in human cells. 28916377_Mutation in BSCL2 gene is associated with Type 2 congenital generalized lipodystrophy. 29336362_SH3TC2, PMP2, and BSCL2 pathogenic variants might be rare in Chinese Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) patients. 29478747_In all patients of Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL), molecular results confirmed BSCL2 mutation. c.782dupG (p.Ile262Hisfs*12) was the most common genotype identified. The findings highlight the uniqueness of the genotype and phenotype in this cohort. 30266686_Seven mutations in BSCL2 were found among congenital generalized lipodystrophy patients, in which splice site mutation c.404+1G > T, nonsense mutation c.402C > G, and frameshift mutation c.759_760delGA were novel. 30447390_this is the first time that BSCL2 transcript expression is mapped in the different regions of human brain. Hypothesize that seipin has specific CNS functions and may play a role in peroxisome biogenesis. 30871963_the effects of SEIPIN on triglyceride and PGC-1alpha are dependent on calcium concentrations, signifying regulatory activity on hepatic lipometabolism through alterations in the intracellular calcium level. 30901948_promethin is indeed an lipid droplet-associated protein that forms a complex with seipin. 30903322_c.974dupG in the BSCL2 gene may be a variant with a role in Celia's encephalopathy 31178403_These results suggest that seipin supports the formation of structurally uniform endoplasmic reticulum lipid droplet (LD) contacts and facilitates the delivery of triglycerides from endoplasmic reticulum to LD. This counteracts ripening-induced shrinkage of small LD. 32094408_Oligomers of the lipodystrophy protein seipin may co-ordinate GPAT3 and AGPAT2 enzymes to facilitate adipocyte differentiation. 32108980_Clinical features of inherited neuropathy with BSCL2 mutations in Japan. 32236581_Novel compound heterozygous variant of BSCL2 identified by whole exome sequencing and multiplex ligationdependent probe amplification in an infant with congenital generalized lipodystrophy. 32320108_Phenotypic correlations in a large single-center cohort of patients with BSCL2 nerve disorders: a clinical, neurophysiological and muscle magnetic resonance imaging study. 33147895_SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis. 33315072_Nuclear lipid droplets form in the inner nuclear membrane in a seipin-independent manner. 33481779_Seipin traps triacylglycerols to facilitate their nanoscale clustering in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 33674387_Seipin accumulates and traps diacylglycerols and triglycerides in its ring-like structure. 34323918_Retinyl esters form lipid droplets independently of triacylglycerol and seipin. 35922214_[Novel MFN2, BSCL2 and LRSAM1 variants in a cohort of Chinese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease]. 36444643_A motor neuron disease-associated mutation produces non-glycosylated Seipin that induces ER stress and apoptosis by inactivating SERCA2b. |
ENSMUSG00000071657 |
Bscl2 |
26.288260 |
0.3450978023 |
-1.534923 |
0.428859003 |
12.569766 |
0.00039203775523604977902916712828584877570392563939094543457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000981257803507562271355668670480554283130913972854614257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.0127627 |
3.6462927 |
35.0411095 |
7.0127041 |
| ENSG00000168003 |
6520 |
SLC3A2 |
protein_coding |
P08195 |
FUNCTION: Component of several heterodimeric complexes involved in amino acid transport (PubMed:11557028, PubMed:9829974, PubMed:9751058, PubMed:10391915, PubMed:10574970, PubMed:11311135, PubMed:30341327). The precise substrate specificity depends on the other subunit in the heterodimer (PubMed:9829974, PubMed:9751058, PubMed:10391915, PubMed:10574970, PubMed:30867591, PubMed:10903140). The complexes function as amino acid exchangers (PubMed:11557028, PubMed:10903140, PubMed:12117417, PubMed:12225859, PubMed:30867591). The heterodimer functions as sodium-independent, high-affinity transporter that mediates uptake of large neutral amino acids such as phenylalanine, tyrosine, leucine, histidine, methionine, tryptophan, valine and isoleucine (PubMed:9751058, PubMed:11557028, PubMed:11311135, PubMed:11564694, PubMed:12117417, PubMed:12225859, PubMed:25998567, PubMed:30867591, PubMed:30341327). The heterodimer with SLC7A5/LAT1 mediates the uptake of L-DOPA (By similarity). The heterodimer formed by SLC3A2 and SLC7A6 or SLC3A2 and SLC7A7 mediates the uptake of dibasic amino acids (PubMed:9829974, PubMed:10903140). The heterodimer with SLC7A5/LAT1 mediates the transport of thyroid hormones diiodothyronine (T2), triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) across the cell membrane (PubMed:11564694, PubMed:12225859). The heterodimer with SLC7A5/LAT1 is involved in the uptake of toxic methylmercury (MeHg) when administered as the L-cysteine or D,L-homocysteine complexes (PubMed:12117417). When associated with LAPTM4B, the heterodimer with SLC7A5/LAT1 is recruited to lysosomes to promote leucine uptake into these organelles, and thereby mediates mTORC1 activation (PubMed:25998567). The heterodimer with SLC7A5/LAT1 may play a role in the transport of L-DOPA across the blood-brain barrier (By similarity). The heterodimer formed by SLC3A2 and SLC7A5/LAT1 or SLC3A2 and SLC7A8/LAT2 is involved in the cellular activity of small molecular weight nitrosothiols, via the stereoselective transport of L-nitrosocysteine (L-CNSO) across the transmembrane (PubMed:15769744). The heterodimer with SLC7A10 translocates small neutral L- and D-amino acids across the plasma membrane. SLC3A2-SLC7A10 preferentially mediates exchange transport, but can also operate via facilitated diffusion (By similarity). Together with ICAM1, regulates the transport activity of SLC7A8/LAT2 in polarized intestinal cells by generating and delivering intracellular signals (PubMed:12716892). Required for targeting of SLC7A5/LAT1 and SLC7A8/LAT2 to the plasma membrane and for channel activity (PubMed:9751058, PubMed:11311135, PubMed:30867591). Plays a role in nitric oxide synthesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) via transport of L-arginine (PubMed:14603368). May mediate blood-to-retina L-leucine transport across the inner blood-retinal barrier (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10852, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q794F9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10391915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10574970, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10903140, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11311135, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11389679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11557028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11742812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12117417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12225859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12716892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14603368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15769744, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15980244, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25998567, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30341327, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30867591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9751058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9829974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9878049}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of hepatitis C virus/HCV infection, the complex formed by SLC3A2 and SLC7A5/LAT1 plays a role in HCV propagation by facilitating viral entry into host cell and increasing L-leucine uptake-mediated mTORC1 signaling activation, thereby contributing to HCV-mediated pathogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30341327}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the solute carrier family and encodes a cell surface, transmembrane protein. The protein exists as the heavy chain of a heterodimer, covalently bound through di-sulfide bonds to one of several possible light chains. The encoded transporter plays a role in regulation of intracellular calcium levels and transports L-type amino acids. Alternatively spliced transcript variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:6520; |
amino acid transport complex [GO:1990184]; anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; apical pole of neuron [GO:0044225]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; aromatic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015173]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium:sodium antiporter activity [GO:0005432]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-leucine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015190]; neutral amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015175]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; isoleucine transport [GO:0015818]; L-alanine import across plasma membrane [GO:1904273]; L-histidine transport [GO:1902024]; L-leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:1903801]; leucine import across plasma membrane [GO:0098713]; leucine transport [GO:0015820]; methionine transport [GO:0015821]; phenylalanine transport [GO:0015823]; proline transport [GO:0015824]; response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0043330]; thyroid hormone transport [GO:0070327]; tryptophan transport [GO:0015827]; tyrosine transport [GO:0015828]; valine transport [GO:0015829]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] |
12181350_Data show that, in vitro, under physiological conditions, CD98 is constitutively associated with beta1 integrins regardless of activation status. 12716892_the interaction of CD98/LAT2 with ICAM-1, found to be expressed to the basolateral domain, and the potential of such interaction on intracellular signal activation in Caco2-BBE cell monolayers 12740424_Involved in process of cell fusion necessary for syncytiotrophoblast formation. During this physiologically important event, amino acid transport activity is also regulated through expression of this membrane protein. 15178563_The heavy chain of the cell surface antigen 4F2 is induced by lysophosphatidylcholine, oxLDL and many oxidation products. It mediates increased cytokine production by endothelial cells. 15485886_results explain how high expression of CD98hc antigen in human cancers contributes to transformation 15556631_iRNA-induced reduction in CD98 expression suppresses cell fusion during syncytialization of placental cell line. 15625115_CD98hc is an integrin-associated protein that mediates integrin-dependent signals, which promote tumorigenesis. 15713750_CD98 is a scaffolding protein that interacts with basolaterally expressed amino acid transporters and beta1 integrins and can alter amino acid transport and cell adhesion, migration and branching morphogenesis 16785209_The 15 carboxy-terminal residues of 4F2hc are required for the transport function of the heterodimer. Mutation of the conserved residue leucine 523 to glutamine in the carboxy terminus reduced the Vmax of arginine and leucine uptake. 17023546_Results demonstrated that a reduction of Sp1 or NF-kappaB expression reduced CD98 protein expression. 17451431_data suggest N-glycosylation of CD98 & subsequent interaction with galectin 3 is critical for aspects of placental cell biology, & provides rationale for observation that in mice truncation of CD98hc extracellular domain leads to early embryonic lethality 17558306_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17611393_CD98hc is a bridge between multidrug resistance phenotype and tumor metastasis 17724034_The structure of human 4F2HC ectodomain provides a model for homodimerization and electrostatic interaction with plasma membrane. 18032696_The transmembrane domain of CD98 heavy chain has an essential role in the stimulation of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin for cell adhesion and motility. 18054915_Altogether, our results support a model whereby CyPB induces integrin-mediated adhesion via interaction with a multimolecular unit formed by the association between CD147, CD98 and beta1 integrins. 18660501_interaction between SLC3A2 and SAT1 suggests that these proteins may facilitate excretion of acetylated polyamines. 18813831_Inhibition of system L (LAT1/CD98hc) reduces the growth of cultured human breast cancer cells. 19018776_CD98 expression in primary and metastatic neoplasms is reported. 19065266_CD98 was phosphorylated in vitro by ecto-protein kinases from Jurkat cells and by the commercial casein kinase 2 (CK2). 19171406_over expression of CD98 is a pathological factor to predict the prognosis in patients with resectable stage I pulmonary adenocarcinoma 19562367_We conclude that arginine transport in human erythroid cells is due to both system y(+) (CAT1 transporter) and system y(+)L (4F2hc/y(+)LAT2 isoform), which mainly contribute, respectively, to the influx and to the efflux of the cationic amino acid. 19777189_High CD98 expression is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer with lymph node metastases. 19808856_4F2hc genes may play important roles in leiomyoma cell proliferation and regulate leiomyoma growth. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19922591_CD98 expression is down-regulated in thyroid papillary carcinoma; this may relate to the better prognosis associated with many of these tumours. 20091333_High expression of 4F2HC is associated with high-grade gliomas. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20811665_CD98 expression was associated with the grade of malignancy and cell cycle control, and was useful for predicting poor outcome in thymic epithelial tumors 21270293_Taken together, these observations indicate that 4F2hc is likely to be involved in GLUT1 stabilization and to contribute to the regulation of not only amino acid but also glucose metabolism. 21282044_CD98hc is involved in integrin trafficking and by consequence, in keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation. 21352957_Folding seems to be directed by the initial formation of hydrophobic clusters within the first strands of the beta-barrel of domain A followed by additional hydrophobic interactions in domain C. 21486766_Compared with the adult cerebral cortex, mRNAs encoding OATP1A2, OATP1C1, OATP3A1 variant 2, OATP4A1, LAT2 and CD98 were reduced in fetal cortex at different gestational ages, whilst mRNAs encoding MCT8, MCT10, OATP3A1 variant 1 and LAT1 were similar. 21670318_The integrin-binding domain of the CD98 heavy chain transgene is required for antigen-driven T cell clonal expansion in the pathogenesis of an autoimmune disease such as experimental type 1 diabetes. mellitus. 21750865_Results suggest that 4F2hc may play a significant role in tumor progression, hypoxic conditions and poor outcome in patients with pulmonary NE tumors. 22077314_study revealed that LAT1 and CD98 expression are positively correlated with breast cancer proliferation and negatively correlated with ER and PgR status; show that LAT1 and CD98 expression are prognostic factors in triple negative breast cancer 22291182_Strategies targeting transgenic CD98 heavy-chain demonstrate clinical application for treating type 1 diabetes and other T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22499670_[REVIEW] Rapid proliferation and resulting clonal expansion are dependent on CD98, a protein whose well-conserved orthologs appear restricted to vertebrates. 23272174_The interaction of galectin 3 and CD98 can induce Eos to release chemical mediators that contributes to the initiation of the intestinal inflammation. 23297381_These findings demonstrate the importance of the extracellular loop of CD98 in the innate host defense response to intestinal infection by attaching and effacing (A/E) pathogens. 23651923_Although extracellular galectin-3 accumulates due to the decrease in MMP-2 activity, galectin-3 signaling events are blocked due to an impaired interaction with 4F2hc, inducing an increased degradation of beta-catenin. 23940088_heteromerization of y+LAT1 and 4F2hc within the cell is not disrupted by any of the tested LPI mutations 24359579_observed a correlation between less differentiated and more aggressive clear cell renal cell cancer and CD98hc expression; found that CD98hc is not only a descriptive marker for aggressive cancers, but bears a major regulatory role of malignant cell function 24484217_We detected elevated levels of antipeptide responses, but failed to detect reactivity against native CD98-expressing HeLa cells in sera of immunized mice. 24516142_The extracellular domain of 4F2hc interacts with LAT2, almost completely covering its extracellular face and stabilizing the solubilized transporter. 24782339_data suggest that genetic variation of rs1059292 in CD98 gene may affect clinical outcome of NSCLC in Chinese population 25041835_Overexpression of CD98, integrin beta1, integrin beta3 and Fak is associated with the progression and liver metastases of colorectal cancer 25084765_High CD98hc expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 25299125_The detergent-induced stabilization of the purified human 4F2hc-LAT2 complex presented here paves the way towards its crystallization and structure determination at high-resolution 25505297_Studied and identified the eukaryotic protein CD98hc as a partner for Brucella T4SS subunit VirB2. 25701737_CAP-D3 down-regulates transcription of genes that encode amino acid transporters (SLC7A5 and SLC3A2) to promote bacterial autophagy by colon epithelial cells. 25995262_HSV-1 recruited cellular fusion regulatory proteins CD98hc and beta1 integrin to the nuclear membrane for viral de-envelopment fusion. 26172215_CD98-mediated phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase may facilitate the assembly of pro-tumorigenic signaling complexes and the subsequent amplification of a positive feedback loop of CD98/integrins/FAK/RhoA/ROCK. 26493331_ubiquitylation and the resulting downregulation of CD98 can limit cell proliferation and clonal expansion. 26540405_Study demonstrated that the mRNA expression levels of the two system xc- subunits, SLC7A11 and SLC3A2, in peripheral white blood cells are lowered in patients with schizophrenia than healthy individuals 26621329_exposure to diesel exhaust particle extract induces functional overexpression of the amino acid transporter LAT1/CD98hc in lung cells 27626312_Data suggest that SLC3A2-NRG1 should be considered a therapeutic target for patients with invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung (IMA). 27834933_Expression levels of CD98 and beta1-integrin-A (the activated form of beta1-integrin) were significantly increased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues relative to those of normal liver tissues. 28052681_The low expression of CD98 is a novel biomarker for predicting poor prognosis in patients with cutaneous angiosarcoma. 28179310_Data suggest that increased CD98 (4F2hc) expression plays an essential role in tumor aggressiveness and metastasis. 28320871_These results demonstrate a novel fundamental role of LAT1 to support the protein expression of 4F2hc via a chaperone-like function in chorionic trophoblasts. 28350098_SLC3A2 is upregulated in osteosarcoma and plays a crucial role in tumor growth. 29545595_SLC3A2 appears to play a role in the aggressive Breast cancer ( BC) subtypes driven by MYC and could act as a potential prognostic marker. Functional assessment is necessary to reveal its potential therapeutic value in the different BC subtypes. 29906411_this study showed that integrin co-receptor, SLC3A2, required for cell proliferation, is expressed at the surface of resting dermal fibroblasts in young patients and is reduced drastically with aging 30300664_LAT1 and 4F2hc were identified as significant independent markers for predicting a worse prognosis in patients with pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma 30341327_these data suggest that SLC3A2 plays an important role in regulating Hepatitis C virus entry 30470261_our findings demonstrated that low expression of miR-490-3p or high expression of PPM1F was positively associated with poor survival and tumor recurrence in patients with HCC, and miR-490-3p suppressed cell proliferation and invasion by targeting PPM1F. 30867591_cryo-electron microscopy structures of human LAT1-4F2hc alone and in complex with the inhibitor 2-amino-2-norbornanecarboxylic acid at resolutions of 3.3 A and 3.5 A, respectively 30958588_This study reports the crystal structure of the murine CD98hc extracellular domain and a comprehensive comparison with its human ortholog, revealing only one conserved surface patch that is neither shielded by glycosylation nor by the cell membrane with an accessible surface area typical for an antibody epitope. 31053148_Sorafenib induced translocation of miR-21 to the nucleus, where it promoted the expression of SNHG1, resulting in upregulation of SLC3A2, leading to the activation of Akt pathway 31092450_LAT1 was closely associated with the expression of 4F2hc and phosphorylation of the mTOR pathway. LAT1 is a significant molecular marker used to predict prognosis after surgical resection of colorectal cancer patients. 31160781_This study reports the cryo-EM structure of the human LAT1-CD98hc heterodimer at 3.3-A resolution. 31276435_SLC3A2/CD98hc, autophagy and tumor radioresistance: a link confirmed. 31282475_SLC7A5 and SLC3A2 structures are analyzed together with lower resolution cryo-EM structure, and multibody 3D auto-refinement against single-particle cryo-EM data was used to characterize the dynamics of the interaction of CD98hc and LAT1. 31575908_CD98hc (SLC3A2) sustains amino acid and nucleotide availability for cell cycle progression. 31701662_Abnormalities in the genes that encode Large Amino Acid Transporters increase the risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder. 32093034_Co-Expression Effect of SLC7A5/SLC3A2 to Predict Response to Endocrine Therapy in Oestrogen-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. 32993041_Sub-Nanometer Cryo-EM Density Map of the Human Heterodimeric Amino Acid Transporter 4F2hc-LAT2. 33066406_The Heavy Chain 4F2hc Modulates the Substrate Affinity and Specificity of the Light Chains LAT1 and LAT2. 33184944_Overexpression of membranal SLC3A2 regulates the proliferation of oral squamous cancer cells and affects the prognosis of oral cancer patients. 33785413_Targeting SLC3A2 subunit of system XC(-) is essential for m(6)A reader YTHDC2 to be an endogenous ferroptosis inducer in lung adenocarcinoma. 34075107_The heavy chain of 4F2 antigen promote prostate cancer progression via SKP-2. 34182526_Expression of LAT1 and 4F2hc in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. 34294905_Plasmodium vivax binds host CD98hc (SLC3A2) to enter immature red blood cells. 34942513_Expression profile of CD98 heavy chain and L-type amino acid transporter 1 and its prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. 35057861_SLC3A2 inhibits ferroptosis in laryngeal carcinoma via mTOR pathway. 35501367_Polarity protein SCRIB interacts with SLC3A2 to regulate proliferation and tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer. 35596131_HCMV-miR-US33-5p promotes apoptosis of aortic vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting EPAS1/SLC3A2 pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000010095 |
Slc3a2 |
1077.864967 |
2.1570090276 |
1.109032 |
0.056513281 |
385.521504 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007813857175391277196498023145397984987939306715462301038901400890790859790789328101014324815828640797570116741891097619837945534194746577146373107660835556548146365637485588106199157084014671518048302919088785555012943717656526132486760616302490 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002826777742862138524448447567382965748852763187769266665522425868617564919437304192061034414971920165319430645200229672868590294640389431257677591142833970650054762589083355154316646673876585483803514171267760868300200627345475368201732635498047 |
Yes |
Yes |
1508.8932817 |
50.2448925 |
704.7562294 |
18.2371311 |
| ENSG00000168010 |
89849 |
ATG16L2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NAA4 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in regulating epithelial homeostasis in an ATG16L1-dependent manner. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6KAU8}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;WD repeat |
|
Predicted to be involved in autophagosome assembly and negative stranded viral RNA replication. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:89849; |
Atg12-Atg5-Atg16 complex [GO:0034274]; autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; phagophore assembly site membrane [GO:0034045]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; negative stranded viral RNA replication [GO:0039689]; protein lipidation [GO:0006497]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
23850713_Three novel risk loci including ATG16L2 were discovered by genome-wide association study in the Korean Crohn's disease population, of which two showed patterns of association in the International Inflammatory Bowel Disease Genetics Consortium dataset. 24406150_Atg16L2 may play an important role in autophagy of T cells and serve as a potential biomarker to predict clinical relapse of Multiple sclerosis 26663301_A novel SNP-systemic lupus erythematosus association was identified between FCHSD2 and P2RY2, peaking at rs11235667 on a 33-kb haplotype upstream of ATG16L2. 27611316_ATG16L2 is a susceptibility gene for Crohn's disease in the Chinese population. The rs11235604 single nucleotide polymorphism is remarkably associated with downregulation of the expression of ATG16L2. 29454863_Patients with the ATG16L2 rs10898880 CC variant genotype had a better LRFS, PFS, and OS (adjusted hazard ratio = 0.59, 0.64, and 0.64; 95% confidence interval: 0.45-0.79, 0.48-0.84, and 0.48-0.86; p = 0.0004, 0.002, and 0.003, respectively), but a greater risk for development of severe RP (adjusted hazard ratio = 1.80, 95% confidence interval: 1.04-3.12, p = 0.037) than did patients with AA/AC genotypes. 31692259_Results found ATG16L2 rs10898880 was significantly associated with the occurrence of grade 3-4 oral mucositis and myelosuppression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients treated with radiotherapy. 33113339_Identification of a novel differentially methylated region adjacent to ATG16L2 in lung cancer cells using methyl-CpG binding domain protein-enriched genome sequencing. 35239457_The role of ATG16L2 in autophagy and disease. |
ENSMUSG00000047767 |
Atg16l2 |
450.153116 |
0.1457227596 |
-2.778702 |
0.191231709 |
193.247977 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000006214392150490994327730615992267223543355999017880898512874661318081706899356547900092270585407683841030464049186993191753458631865214556455612182617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000001138020200263611384610051839774188702653911608574725318742515904029275263968088155283835261742626390525735054388978273465227175620384514331817626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
112.7696303 |
14.9174384 |
779.8528593 |
71.3980477 |
| ENSG00000168016 |
9881 |
TRANK1 |
protein_coding |
O15050 |
|
ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Predicted to enable ATP binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9881; |
|
22182935_The results of this study suggested that significant novel association signals near the genes TRANK1 and provide supportive evidence for the previously reported association signals near ANK3 and within the 3p21.1 locus. 32791513_Independent replications and integrative analyses confirm TRANK1 as a susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder. 33737391_Kleine-Levin syndrome is associated with birth difficulties and genetic variants in the TRANK1 gene loci. 34014031_Impaired blood-brain barrier in the microbiota-gut-brain axis: Potential role of bipolar susceptibility gene TRANK1. 34992606_New Evidence of Gut Microbiota Involvement in the Neuropathogenesis of Bipolar Depression by TRANK1 Modulation: Joint Clinical and Animal Data. |
ENSMUSG00000062296 |
Trank1 |
472.214516 |
0.3594091582 |
-1.476301 |
0.178287165 |
66.572217 |
0.00000000000000033730693221345343759568644811920424182943864326554572752314697936526499688625335693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002475708761546779113323524867222189113458261523065262466047897760290652513504028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
262.1486594 |
29.2648162 |
734.6962879 |
57.9215115 |
| ENSG00000168056 |
4054 |
LTBP3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NS15 |
FUNCTION: Key regulator of transforming growth factor beta (TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3) that controls TGF-beta activation by maintaining it in a latent state during storage in extracellular space. Associates specifically via disulfide bonds with the Latency-associated peptide (LAP), which is the regulatory chain of TGF-beta, and regulates integrin-dependent activation of TGF-beta. {ECO:0000303|PubMed:10743502, ECO:0000303|PubMed:11104663}. |
Alternative splicing;Amelogenesis imperfecta;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;EGF-like domain;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Growth factor binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene forms a complex with transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) proteins and may be involved in their subcellular localization. Activation of this complex requires removal of the encoded binding protein. This protein also may play a structural role in the extracellular matrix. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:4054; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; transforming growth factor beta binding [GO:0050431]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; bone morphogenesis [GO:0060349]; bone remodeling [GO:0046849]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; elastic fiber assembly [GO:0048251]; lung saccule development [GO:0060430]; negative regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030502]; negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032331]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation [GO:2000741]; positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation [GO:1902462]; transforming growth factor beta activation [GO:0036363]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
12154076_These findings indicate that human latent TGF-beta-binding protein-3 (LTBP-3) has an essential role in the secretion and targeting of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1). 16157329_Extracellular matrix is an important site of deposition for LTBP-3 and LTBP-4. 16223572_stimulation of transcriptional activity of promoter is stimulated by TGF-beta 1 18672106_Data show that LTBP-3 play an important regulatory role in TGF-beta activation and autocrine growth control in mesenchymal stem cells. 19344874_homozygous nonsense mutation, Y774X, in a consanguineous Pakistani family where oligodontia is inherited along with short stature in an autosomal-recessive fashion 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19897194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21700711_Latent transforming growth factor beta-binding proteins-2 and -3 inhibit the proprotein convertase 5/6A. 25187517_the mechanism of transcriptional activation of LTBP3 promoter depends on MALAT1 initiated from neighboring gene LTBP3 and involves both the direct interaction of the Sp1 and promoter-specific activation 25669657_Phenotype-genotype correlations between LTBP3 mutations and families with brachyolmia with amelogenesis imperfecta. 25899461_New recessive truncating mutation in LTBP3 has been described in a family with oligodontia, short stature, and mitral valve prolapse. 27068007_LTBP3 is a novel component of the microfibrillar network involved in the acromelic dysplasia spectrum. 29348457_A specific role for LTBP3 in cancer progression toward metastatic disease. 29625025_homozygous LTBP3 pathogenic variants predispose individuals to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, along with the previously described skeletal and dental abnormalities. 30887145_Data indicate that latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 3 (LTBP3) is a disease gene for acromicric dysplasia (ACMICD) and suggest the genotype-phenotype correlation of LTBP3 mutations. 32432408_Bi-allelic loss-of-function novel variants in LTBP3-related skeletal dysplasia: Report of first patient from India. 32452514_Common variants in LTBP3 gene contributed to the risk of hip osteoarthritis in Han Chinese population. 34481123_Latent TGFbeta-binding proteins regulate UCP1 expression and function via TGFbeta2. 34906192_Novel LTBP3 mutations associated with thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. 35352826_Expanding genotypic and phenotypic spectrums of LTBP3 variants in dental anomalies and short stature syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000024940 |
Ltbp3 |
26.964581 |
0.3941597364 |
-1.343148 |
0.489880571 |
7.365471 |
0.00664881646207493657435572131930712203029543161392211914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013242009307816228133591884841280261753126978874206542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2644018 |
3.6726694 |
28.7162020 |
6.2719913 |
| ENSG00000168062 |
116071 |
BATF2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N1L9 |
FUNCTION: AP-1 family transcription factor that controls the differentiation of lineage-specific cells in the immune system. Following infection, participates in the differentiation of CD8(+) thymic conventional dendritic cells in the immune system. Acts via the formation of a heterodimer with JUN family proteins that recognizes and binds DNA sequence 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3' and regulates expression of target genes (By similarity). Selectively suppresses CCN1 transcription and hence blocks the downstream cell proliferation signals produced by CCN1 and inhibits CCN1-induced anchorage-independent growth and invasion in several cancer types, such as breast cancer, malignant glioma and metastatic melanoma. Possibly acts by interfering with AP-1 binding to CCN1 promoter. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20531301}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in defense response to protozoan; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation; and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:116071; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; myeloid dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0043011]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20473897_Decreased expression of BATF2 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 20531301_Inhibition of AP-1 by SARI negatively regulates transformation progression mediated by CCN1. 21867603_BCR-ABL mediates the down-regulation of SARI mRNA expression in K562 cells. 21892628_Data suggest that SARI as a potential therapeutic target in CML. 23049725_Loss of SARI expression initiates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is visualized by repression of E-cadherin and up-regulation of vimentin in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and in clinical lung adenocarcinoma specimens. 24133583_SARI expression may predict a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung patients, and SARI may serve as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for lung cancer. 24252932_BATF2 plays a tumor-suppressor role in the development of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma and BATF2 may serve as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic target for this disease. 24282278_MDA-7/IL-24 has a role in cancer-specific apoptosis through SARI induction 25762344_these novel findings suggest that BATF2, a tumor suppressor gene, is a potent negative regulator of HGF/MET signaling in colorectal cancer 26022579_these findings indicate that BATF2 status could be served as a potential biomarker to predict prognosis in colorectal cancer 26135942_In conclusion, as a tumor suppressor, BATF2 serves as a prognostic biomarker of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and it may be a potential therapeutic target for ESCC treatment. 26339361_Suggest that SARI might play an important role in the occurrence and development of prostate cancer. IFN-beta might inhibit the growth of prostate cancer and promote cellular apoptosis by inducing the expression of SARI. 26376615_Batf2 has a role in infectious diseases and cancer 26808579_Results demonstrate that SARI is a novel target gene of glucocorticoid receptor, and the upregulation of SARI plays an important role in dexamethasone's killing effect on B lymphoma cells. 26977016_BATF2 may exert selective pressure on the recombination machinery via a repetitive motif-based mechanism for the maintenance of heterochromatin stability. 27785591_BATF2 gene was modulated after treatment with zebularine and was a poor prognostic marker, since its low levels were correlated with relapse and a poor prognosis for medulloblastoma patients. 27926863_Gain- and loss-of-function studies uncovered a role for Batf2 in myeloid differentiation in both murine and human systems. We thus demonstrate that chronic infection can deplete HSPCs and identify BATF2 as a mediator of infection-induced HSPC terminal differentiation 28739720_Our findings expanded the understanding of the role of BATF2 in tumors, and also suggested a potential of using BATF2 as a therapeutic target to hinder bevacizumab induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma. 29764370_BATF2 gene expression is associated with tuberculosis in the HIV infected patients. 31140101_BATF2 role in the multidrug resistance of human gastric cancer cells and the regulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 31549215_BATF2 was overexpressed in tissues from patients with non-responsive gastric cancer (GC) and the vincristine resistance cell line, SGC7901/VCR, while levels of c-Fos and c-Jun were reduced. AP-1 down-regulation by BATF2 overexpression or AP-1 knockdown can inhibit drug resistance in GC cells. These findings suggest that BATF2 inhibits DR in vincristine resistance GC cell line by down-regulating AP-1 expression. 32119762_SARI prevents ocular angiogenesis and inflammation in mice. 32166887_miRNA-765 mediates multidrug resistance via targeting BATF2 in gastric cancer cells. 32650804_m(6)A modification-mediated BATF2 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer through inhibition of ERK signaling. 32696470_BATF2 expression as a novel marker for invasive phenotype in malignant melanoma. 33452462_BATF2 prevents glioblastoma multiforme progression by inhibiting recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. 33740622_BATF2 balances the T cell-mediated immune response of CADM with an anti-MDA5 autoantibody. 34565331_Expression and clinical implications of basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor 2 in breast cancer. 34774620_SARI inhibits growth and reduces survival of oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC) by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. |
ENSMUSG00000039699 |
Batf2 |
11.157992 |
0.4818169386 |
-1.053443 |
0.472740173 |
5.057115 |
0.02452503291384226097315846004676131997257471084594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043093986405751398549579533892028848640620708465576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.2523160 |
2.6096137 |
15.1106492 |
3.4840768 |
| ENSG00000168071 |
283234 |
CCDC88B |
protein_coding |
A6NC98 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a positive regulator of T-cell maturation and inflammatory function. Required for several functions of T-cells, in both the CD4(+) and the CD8(+) compartments and this includes expression of cell surface markers of activation, proliferation, and cytokine production in response to specific or non-specific stimulation (By similarity). Enhances NK cell cytotoxicity by positively regulating polarization of microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) to cytotoxic synapse, lytic granule transport along microtubules, and dynein-mediated clustering to MTOC (PubMed:25762780). Interacts with HSPA5 and stabilizes the interaction between HSPA5 and ERN1, leading to suppression of ERN1-induced JNK activation and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis (PubMed:21289099). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4QRL3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21289099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25762780}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Stress response |
|
This gene encodes a member of the hook-related protein family. Members of this family are characterized by an N-terminal potential microtubule binding domain, a central coiled-coiled and a C-terminal Hook-related domain. The encoded protein may be involved in linking organelles to microtubules. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:283234; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; cytoplasmic microtubule organization [GO:0031122]; cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport [GO:0030705]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102] |
21289099_Data show that a novel Girdin family protein, Gipie, is expressed in endothelial cells, where it interacts with GRP78, a master regulator of the UPR, and that Gipie/GRP78 interaction controls the IRE1-JNK signaling pathway. 22837380_A genotype dataset found a sarcoidosis risk locus on chromosome 11q13.1, a risk region for Crohn disease. An allele-dependent expression of CCDC88B was found in bronchoalveolar lavage samples of German, Swedish and Czech patients with sarcoidosis. 25762780_results demonstrate an important role for HkRP3 in regulating the clustering of lytic granules and MTOC repositioning during the development of NK cell-mediated killing. 29030607_A critical function of CCDC88B in colonic inflammation and inflammatory bowel disease |
ENSMUSG00000047810 |
Ccdc88b |
309.339278 |
0.1426343766 |
-2.809606 |
0.234659443 |
130.840013 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000268388440883132132748773941749339661385222341826407888839192197002021398486234929695037898511600360507145524024963378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000034597496833493713753024133376003385467427318926210055190709703882670050158350781577265564692424959503114223480224609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.0374527 |
14.2095192 |
534.9470626 |
69.6152697 |
| ENSG00000168081 |
5368 |
PNOC |
protein_coding |
Q13519 |
FUNCTION: [Nociceptin]: Ligand of the opioid receptor-like receptor OPRL1. It may act as a transmitter in the brain by modulating nociceptive and locomotor behavior. May be involved in neuronal differentiation and development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P55791}.; FUNCTION: [Nocistatin]: Blocks nociceptin action in pain transmission by inhibiting nociceptin-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O62647}.; FUNCTION: [Orphanin FQ2]: Has potent analgesic activity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q64387}. |
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Neuropeptide;Neurotransmitter;Opioid peptide;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate multiple protein products. These products include nociceptin, nocistatin, and orphanin FQ2 (OFQ2). Nociceptin, also known as orphanin FQ, is a 17-amino acid neuropeptide that binds to the nociceptin receptor to induce increased pain sensitivity, and may additionally regulate body temperature, learning and memory, and hunger. Another product of the encoded preproprotein, nocistatin, may inhibit the effects of nociceptin. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:5368; |
axon terminus [GO:0043679]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; neuropeptide hormone activity [GO:0005184]; opioid peptide activity [GO:0001515]; opioid receptor binding [GO:0031628]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; sensory perception [GO:0007600]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11436130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11501941_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12812047_Peripheral blood levels are elevated in Wilson disease 12950177_results show that nociceptin/NociR is present and functional in human neutrophils, and the results identify a novel dialogue pathway between neural and immune tissues 16043263_The presence of two different forms of mature nocistatin (NST-17 and NST-30) and a possible N-terminal methionine cleaved NST-29 have been confirmed by both radioimmunoassay and mass spectrometry. 17910740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17910740_Two SNPs in PNOC showed marginal association with alcoholism and one with illicit drug dependence. 18292431_Peripheral blood mononuclear cells transcribe pre-pro-nociception/orphaninFQ. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19501074_Our results support the concept postulating that chronic ethanol consumption and withdrawal downregulate the PNOC/OPRL1 system, which critically controls alcohol intake. 19560501_Unstable angina is associated with a significant increase in circulating nociceptin/orphanin FQ levels unrelated to intervening transient myocardial ischemia or hemodynamic changes. 19573600_data obtained from neocortex of epileptic patients provide strong evidence that temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with alterations in mu opioid and nociceptin receptor binding and signal transduction mechanisms downstream of these receptors 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20100531_Results showed that vigorous and prolonged hyperventilation changes plasma nociceptin/orphanin FQ levels due to the direct effects of hypocapnic alkalosis or to different sympatho-adrenergic system responses. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20888736_PNOC expression level was 2.99 times higher in vitiligo involved skin when compared to healthy control skin. 21310194_chronic ischemic conditions of atherosclerotic origin are associated with significantly lower plasma nociceptin levels 21547539_activation of NFkappaB by OFQ/Nociceptin suggests a likely mechanism for its modulation of the central nervous and immune systems. 21600132_A high expression of nociceptin in adenomyosis may be one of the casual factors of dysmenorrhea. The severity of dysmenorrhea is positively correlated with the expression of nociceptin in eutopic endometrial tissue. 21744319_The presence of Orphanin, Oxytocin, ANP, eNOS and iNOS proteins was identified in the human umbilical cord.[Orphanin] 22706982_Strong expression of PNOC was seen in neoplastic neurons of 7/7 brainstem gangliogliomas, but was significantly weaker in non-brainstem GGs. 23454174_REVIEW: intracellular localization and physiological role of nociceptin and nocistatin 25677768_Data suggest that nociceptin and nociceptin receptor evolved as one of 4 opioid receptor systems in vertebrates; this system exhibits both analgesic and hyperalgesic effects. [REVIEW] 25677772_Data suggest that nociceptin plays a crucial role in progress of meiosis during spermatogenesis. [REVIEW] 25677773_Opioid neuropeptide systems are important mediators of ovarian steroid signaling that regulate reproduction in female; data suggest that nociceptin and nociceptin receptor system in arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus is such a system. [REVIEW] 25677774_Data suggest that both nociceptin and nocistatin inhibit myometrial contractions and may play roles in perception of pain during delivery. [REVIEW] 25677775_Data suggest that the nociceptin/nociceptin receptor system is involved in modulation of the immune response and in pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. [REVIEW] 25677776_Data suggest that the nociceptin/nociceptin receptor system is involved in modulation of psychological and inflammatory stress responses and in pathogenesis of anxiety. [REVIEW] 25677777_Data suggest that interaction between the nociceptin/nociceptin receptor system and the orexin/orexin receptor system in neurons of the hypothalamus positively and negatively modulate complex and integrated responses to stress. [REVIEW] 25677778_Data suggest that nociceptin/nociceptin receptor signaling in neurons of the hippocampus modulate learning and memory. [REVIEW] 26233486_findings suggest that SNPs in opioid receptors and the PNOC genes are associated with NAS severity. 26349406_Study presents evidence suggesting that the PNOC and OPRL1 are dysregulated in suicide completers, thereby potentially contributing to impaired emotional and behavioral control and, ultimately, to the suicidal crisis 26791055_The presence of the PNOC rs732636 A allele was associated with the worse Neonatal abstinence syndrome outcomes in infants. 27983768_found differences in Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome outcomes depending on PNOC and COMT SNP genotype. 33841428_PNOC Expressed by B Cells in Cholangiocarcinoma Was Survival Related and LAIR2 Could Be a T Cell Exhaustion Biomarker in Tumor Microenvironment: Characterization of Immune Microenvironment Combining Single-Cell and Bulk Sequencing Technology. |
ENSMUSG00000045731 |
Pnoc |
39.668594 |
0.3550992853 |
-1.493706 |
0.250873725 |
36.759221 |
0.00000000133656912276626699552390954819957105681460518553649308159947395324707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006316926113362184645561208312181458723877369720867136493325233459472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.2867941 |
8.9641486 |
49.2370817 |
17.8903024 |
| ENSG00000168152 |
79725 |
THAP9 |
protein_coding |
Q9H5L6 |
FUNCTION: Active transposase that specifically recognizes the bipartite 5'-TXXGGGX(A/T)-3' consensus motif and mediates transposition. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20010837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23349291}. |
DNA integration;DNA recombination;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables sequence-specific DNA binding activity and transposase activity. Involved in DNA integration and transposition, DNA-mediated. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79725; |
DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transferase activity [GO:0016740]; transposase activity [GO:0004803]; DNA integration [GO:0015074]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; transposition, DNA-mediated [GO:0006313] |
23349291_results indicate that human THAP9 is an active DNA transposase that, although 'domesticated,' still retains the catalytic activity to mobilize P transposable elements across species 33854048_THAP9-AS1/miR-133b/SOX4 positive feedback loop facilitates the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 34033475_Oligomerization of THAP9 Transposase via Amino-Terminal Domains. 34072453_THAP9 Transposase Cleaves DNA via Conserved Acidic Residues in an RNaseH-Like Domain. 34691358_THAP9-AS1 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Reduces ROS Generation through the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway by Increasing SOCS3 Promoter Methylation in Osteosarcoma. |
|
|
12.168044 |
0.4052383416 |
-1.303157 |
0.472516008 |
7.721324 |
0.00545723480213019650902905866018954839091747999191284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011064393637285946728199270694403821835294365882873535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6986240 |
2.4019966 |
16.6976511 |
3.8651957 |
| ENSG00000168209 |
54541 |
DDIT4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NX09 |
FUNCTION: Regulates cell growth, proliferation and survival via inhibition of the activity of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Inhibition of mTORC1 is mediated by a pathway that involves DDIT4/REDD1, AKT1, the TSC1-TSC2 complex and the GTPase RHEB. Plays an important role in responses to cellular energy levels and cellular stress, including responses to hypoxia and DNA damage. Regulates p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis in response to DNA damage via its effect on mTORC1 activity. Its role in the response to hypoxia depends on the cell type; it mediates mTORC1 inhibition in fibroblasts and thymocytes, but not in hepatocytes (By similarity). Required for mTORC1-mediated defense against viral protein synthesis and virus replication (By similarity). Inhibits neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth mediated by NGF via its effect on mTORC1 activity. Required for normal neuron migration during embryonic brain development. Plays a role in neuronal cell death. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15545625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15632201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15988001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17005863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17379067, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19557001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20166753, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21460850}. |
3D-structure;Antiviral defense;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable 14-3-3 protein binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus; negative regulation of TOR signaling; and response to hypoxia. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54541; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of intracellular signal transduction [GO:1902532]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010801]; negative regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032007]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048011]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0032984]; reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:0072593]; regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032006]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666] |
14646594_RTP801 might play important roles in Abeta toxicity and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease 15180327_co-transfection with antisense Sp1 oligonucleotide suggests that hypoxia induction of the RTP801 promoter is mediated by Sp1 15592522_REDD1 (RTP801) can act as a transcriptional downstream target of PI 3-kinase signaling in human prostate cancer cells. 15632201_RTP801 and RTP801L work downstream of AKT and upstream of TSC2 to inhibit mTOR functions 15988001_REDD1 as a critical transducer of the cellular response to energy depletion through the TSC-mTOR pathway. 16258273_Stress response gene REDD1 is identified in this review as an essential regulator of checkpoint kinase mTOR activity through the tuberous sclerosis tumor suppressors TSC1/2 complex. 17005863_The elevation of RTP801 we detect in PD substantia nigral neurons may mediate their degeneration. 17307335_These results demonstrate that hypoxic condition-and high cell density-induced expression of Redd1 is mediated by coactivation of Sp1 and HIF-1alpha downstream of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 18796435_unique effect of inhibition of fatty-acid synthase results from negative regulation of the mTOR pathway via DDIT4 18953439_results suggest a novel mechanism by which AMPK activation after hypoxia-induced energy stress may be crucial in regulating REDD1 expression to control the mTOR pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 19114033_The results suggest that REDD1 expression is upregulated during ER stress through a mechanism involving activation of PERK, phosphorylation of eIF2alpha, and increased ATF4 expression. 19127203_REDD1 expression in response to hypoxia and dexamethasone is cell-type specific and that physiologically appropriate levels of PO2 should be used when investigating fetal lung development. 19210572_PKR represents a cognitive decline biomarker able to dysregulate translation via two consecutive targets p53 and Redd1 in Alzheimer disease lymphocytes 19221489_DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 is a key mediator in RAS protein -mediated transformation through an effect on anti-apoptosis. 19557001_REDD1 degradation is crucially required for the restoration of mTOR signalling as cells recover from hypoxic stress. 19996311_Insulin induces REDD1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation in adipocytes. 20166753_Structure/function analyses have led us to identify two segments in REDD1 that are essential for mTORC1 inhibition. 20354178_sertraline exerts antiproliferative activity by targeting the mTOR signaling pathway in a REDD1-dependent manner 20374513_that expression of RTP801 was lower in oral lichen planus than in controls 20473305_Our data support the notion that Rtp801 may represent a major molecular sensor and mediator of cigarette smoke-induced lung injury. 21123297_DDIT4, an inhibitor of mTOR signaling, is a direct target for 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) and VDRE-BP, and functions to suppress cell proliferation in response to vitamin D 21258409_Data show that miR-495 expression was directly modulated by transcription factor E12/E47, and promotes oncogenesis via downregulation of E-cadherin and REDD1. 21266827_In the HER2 overexpression type and triple-negative breast carcer, tumor cell proliferation and survival in the hypoxic tumor environment could possibly be due to disinhibition of the mTOR pathway and HIF-1alpha stabilization by downregulation of REDD1. 21414293_these results provide preliminary evidence that Redd1 inhibits the invasive activity of NSCLC cells via suppression of the mTOR downstream pathway. 21460850_these results collectively demonstrate that TXNIP stabilizes Redd1 protein induced by ATF4 in response to 2-DG, resulting in potentiation of mTOR suppression. 21540236_Metformin increases REDD1 expression in a p53-dependent manner. REDD1 invalidation, using siRNA or REDD1(-/-) cells, abrogates metformin inhibition of mTOR. 21798997_mechanisms have evolved in tumors to escape growth suppressive signals resulting from VHL loss and REDD1 upregulation 21909097_REDD1 is a new host defense factor, and chemical activation of REDD1 expression represents a potent antiviral intervention strategy 22527987_REDD1 expression plays a role in maintaining normal function of placenta, while the increase of REDD1 is related to the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 23193052_An immobilization-induced attenuation of mTORC1 signaling mediated by induction of REDD1/2 and defective p70S6K1 phosphorylation. 23528835_The sustained overexpression of Redd1 leads to mTORC1 inhibition and to consequent Akt activation that is involved in cell survival. 23717519_mTORC1 regulates REDD1 protein stability in a 26S proteasome dependent manner. 24338366_Translocation to the plasma membrane appears to be an inactivation mechanism of REDD1 by G-protein coupled receptors. 24728411_these postmortem and preclinical findings identify REDD1 as a critical mediator of the atrophy of neurons and depressive behavior caused by chronic stress exposure 25056877_the results demonstrate that REDD1 acts not only as a repressor of mTORC1 but also as a constant modulator of the phosphorylation of Akt in response to growth factors and nutrients. 25058423_Caspase 3 cleaved REDD1 during apoptotic activation. 25147182_analysis of ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) by the E3 ligase HUWE1 25255219_MiR-630 reduced apoptosis by downregulating several apoptotic modulators, PARP3, DDIT4, and EP300. 25337238_REDD1 and p-AKT over-expression may serve as a prognostic biomarker in ovarian cancer, but KRAS mutations and REDD1 protein over-expression were not correlated in OC. 25504525_REDD1 knockout (KO) mice, all skin compartments, epidermal stem, and progenitor cells were protected from atrophic effects of glucocorticoids. 26269521_Findings from this study propose a REDD1-regulated mechanism in T2D skeletal muscle that may contribute to whole body insulin resistance and may be a target to improve insulin action in insulin-resistant individuals. 26487002_These data highlight the central role of REDD1 in regulating both protein synthesis and autophagy in skeletal muscle during sepsis. 26827808_findings implicate REDD1 as a crucial regulator of mTORC1 activity in iron-depleted cells 26968249_C/EBPbeta promotes autophagy in PC3 cells by augmenting REDD1 expression. 27094713_a novel STAT3-dependent mechanism of both IL-6-induced activation of mTOR and IL-6-dependent reversion of stress-induced inhibition of mTOR activity, is reported. 27189933_Changes in REDD1 mRNA and protein have been observed in skeletal muscle under various physiological conditions (e.g., nutrient consumption and resistance exercise) and pathological conditions (e.g., sepsis, alcoholism, diabetes, obesity) suggesting a role for REDD1 in regulating mTORC1-dependent skeletal muscle protein metabolism. [Review] 27556956_The production of superoxide anion in nockout-Rtp801 mouse lung fibroblasts (MLF) was lower than that in Rtp801 Wt cells after cigarette smoke extract treatment, and it was inhibited in Wt MLF by silencing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase-4 (Nox4) expression with small interfering Nox4 RNA. 27577706_The HIF-1alpha-REDD1-mTOR pathway was involved in the response to hypoxia in BeWo cells. Hypoxia-induced REDD1 upregulation is mediated by a HIF-1alpha-dependent pathway. Disruption of REDD1 blocked the effects of hypoxia on suppressing mTOR and resulted in additional accumulation of HIF-1alpha in BeWo cells. 27876894_DDIT4 activity is directly linked to regulation of mTOR signalling 28332630_these findings uncover a novel mechanism by which PML loss may contribute to mTOR activation and cancer progression via dysregulation of basal DDIT4 gene expression. 28334504_Expression of key autophagy markers (microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B light chain 3 and autophagy protein 5) was markedly reduced in cultured human chondrocytes with REDD1 depletion. 28342915_REDD1 is overexpressed during Familial Mediterranean fever inflammatory attacks induced by physical or psychological stress 28484222_DDIT4 might serve as a novel prognostic biomarker in several malignancies. 29084921_REDD1 is confirmed as an oncogene in BUC, and antagonizing REDD1 could be a potential therapeutic strategy to sensitize BUC cells to paclitaxel 29115444_This is concurrent with an increase in the expression level of DDIT4, which is an inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. these results provided a novel insight on miR1243p involvement in the biological alterations of male patients with major depressive disorder and suggested that this miRNA may also serve as a malespeci fi c target for antidepressant treatment 29378913_Silencing lncDDIT4 in naive CD4(+) T cells enhanced Th17 differentiation through increased activation of the DDIT4/mTOR pathway. 29447340_Our data suggest that DDIT4 is critical for normal decidualization and the apoptosis of decidual cells. DDIT4 deficiency is likely involved in the development of preeclampsia. 29485721_High expression of RTP801 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 29712770_REDD1 expression, as a mediator linking inflammation, autophagy, and NET release, was also specifically associated with the inflammatory response of UC. 29925665_A microarray analysis revealed that in A3G-transduced Vero cells, several cellular transcripts were differentially expressed, suggesting that A3G regulates the expression of host factors. One of the most upregulated host cell factors, REDD1 (regulated in development and DNA damage response-1, also called DDIT4), reduced MV replication approximately 10-fold upon overexpression in Vero cells. 29976242_Data show that DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) was upregulated in gastric cancer (GC) cells and tissue, and that the mitogen-activated protein kinase and p53 signaling pathways were involved in the suppression of proliferation. 30302791_findings suggest miR-7 as a key regulator of hypoxia-mediated mTOR signaling through modulation of REDD1 expression. These findings contribute new insight into the miRNA-mediated molecular mechanism of the hypoxic response through mTOR signaling, highlighting potential targets for tumor suppression. 30312603_These results suggest that REDD1 might play a pivotal role in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) pathogenesis, thereby potentially providing a new therapeutic target for IDD treatment 30372793_DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) has a role in human squamous cell carcinoma and is a molecular vector for the anti-carcinoma effect of 1,25(OH)2 D3 30428884_REDD1 is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma and may promote ovarian cancer metastasis. 30446641_Cellular metabolism constrains innate immune responses in preterm infants due to perturbations in the expression of PPARgamma, MALT1, DDIT4, and most of the cytokines. 30485138_Inhibition of REDD1 reduced vascular endothelial cell injury, apoptosis and oxidative stress. 30745581_Study identified DDIT4 as a cell-intrinsic regulator for adaptive responses and therapy resistance in glioblastoma cells which may interfere with cell death induction by temozolomide, radiotherapy or hypoxia by inhibiting mTORC1 activity. 30816673_These findings indicate that miR221 might play an important role in human placental development by precisely regulating the DDIT4 expression. 30864724_Study revealed that constitutive overexpression of Redd1 induced HSP27 and HSP70 expression in lung cancer cells. The expression of Redd1, HSP27 and HSP70 was highly increased in lung cancer tissues compared with that in normal lung tissues. Constitutive overexpression of Redd1 led to AKT activation and HSP27 and HSP70 induction, all of which were involved in lung cancer cell survival and resistance to ionizing radiation. 30930273_REDD1 plays a critical role in the process of neuronal damage caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage. 31755224_Up-regulation of DDIT4 predicts poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukaemia. 31914654_A novel nonepigenetic function of HDAC4 induced by dexamethasone, through which it can directly modulate HIF-1a activity and promote the upregulation of the DDIT4 gene and protein expression. 31916238_A Key Role of DNA Damage-Inducible Transcript 4 (DDIT4) Connects Autophagy and GLUT3-Mediated Stemness To Desensitize Temozolomide Efficacy in Glioblastomas. 32151711_LncRNA PSMB8-AS1 acts as ceRNA of miR-22-3p to regulate DDIT4 expression in glioblastoma. 32279996_Loss of heterozygosity for Kras(G12D) promotes REDD1-dependent, non-canonical glutamine metabolism in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 32732871_Synaptic RTP801 contributes to motor-learning dysfunction in Huntington's disease. 32877205_Is REDD1 a metabolic double agent? Lessons from physiology and pathology. 33524531_The stress response protein REDD1 as a causal factor for oxidative stress in diabetic retinopathy. 34131105_RTP801/REDD1 contributes to neuroinflammation severity and memory impairments in Alzheimer's disease. 34211002_High expression of DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) is associated with advanced pathological features in the patients with colorectal cancer. 34310076_DDIT4 S-Nitrosylation Aids p38-MAPK Signaling Complex Assembly to Promote Hepatic Reactive Oxygen Species Production. 34614448_REDD1 attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis via inhibiting of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. 34730176_Helicobacter pylori-induced REDD1 modulates Th17 cell responses that contribute to gastritis. 34941434_Exercise reduces the protein abundance of TXNIP and its interacting partner REDD1 in skeletal muscle: potential role for a PKA-mediated mechanism. 35636256_REDD1 interacts with AIF and regulates mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation in the keratinocyte response to UVB. 35984399_REDD1 Ablation Attenuates the Development of Renal Complications in Diabetic Mice. 36077083_Nutritional Sensor REDD1 in Cancer and Inflammation: Friend or Foe? |
ENSMUSG00000020108 |
Ddit4 |
89.300520 |
4.8988084401 |
2.292431 |
0.203444737 |
133.064562 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000087518854696971038960887605333470712374120399895543951160292743064094724638973354750859368067494870047084987163543701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000011482473736242599022473866640919652213653379839572525614389421363614717856130482964704953019463573582470417022705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
146.1092923 |
16.9445163 |
30.0433220 |
3.0159693 |
| ENSG00000168255 |
|
POLR2J3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H1A7 |
FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB11 is part of the core element with the central large cleft (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring readthrough transcription between the neighboring POLR2J3 (RNA polymerase II subunit J3) and UPK3BL2 (uroplakin 3B like 2) genes on chromosome 7. The readthrough transcript is unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2021]. |
|
RNA polymerase II, core complex [GO:0005665]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II activity [GO:0001055] |
|
|
|
321.957977 |
0.4413825493 |
-1.179899 |
0.155422954 |
56.812111 |
0.00000000000004795042698387835792288354135781299745117144464612302101613749982789158821105957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000310008016768306863006091263042715363445513132578668091809959150850772857666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
197.5870016 |
22.5886647 |
450.9310381 |
36.3560057 |
| ENSG00000168255_ENSG00000170667 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.471405 |
0.2787889023 |
-1.842755 |
0.778623719 |
5.615150 |
0.01780586134463781750048028129640442784875631332397460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032298698961147127850512816849004593677818775177001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0118205 |
1.5319632 |
10.7838901 |
3.4778714 |
| ENSG00000168268 |
64943 |
NT5DC2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H857 |
|
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable 5'-nucleotidase activity. Predicted to be involved in dephosphorylation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64943; |
5'-nucleotidase activity [GO:0008253]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
30978441_Disruption of NT5DC2 in GSCs markedly reduces the expression of Fyn, a Src family proto-oncogene that has been implicated in the regulation of GBM progression. The expression of NT5DC2 strongly correlated with increased aggression of human gliomas, but not that of other brain tumors. 32382041_NT5DC2 promotes tumor cell proliferation by stabilizing EGFR in hepatocellular carcinoma. 32962856_NT5DC2 suppression restrains progression towards metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer through regulation p53 signaling. 32991874_NT5DC2 knockdown inhibits colorectal carcinoma progression by repressing metastasis, angiogenesis and tumor-associated macrophage recruitment: A mechanism involving VEGF signaling. 35894142_Decreased RNAbinding protein IGF2BP2 downregulates NT5DC2, which suppresses cell proliferation, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in diffuse large Bcell lymphoma cells by regulating the p53 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000071547 |
Nt5dc2 |
748.005267 |
2.1278146582 |
1.089372 |
0.064740223 |
285.556957 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000046204094620658064951093038487603278140158051452549708282452942499442055911262591896793486036579556162564687544014834570274582029623991281748923395740385184466379742129760188618092797696590423583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012652549844172782896885289287615490258655728820412953753678640458607959077833537908958146155960524037211344039454658531329943781029872501117223815202887486630611846294414135627448558807373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1034.3604494 |
38.6532683 |
489.5877657 |
14.6586475 |
| ENSG00000168280 |
3800 |
KIF5C |
protein_coding |
O60282 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated force-producing protein that may play a role in organelle transport. Has ATPase activity (By similarity). Involved in synaptic transmission (PubMed:24812067). Mediates dendritic trafficking of mRNAs (By similarity). Required for anterograde axonal transportation of MAPK8IP3/JIP3 which is essential for MAPK8IP3/JIP3 function in axon elongation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28738, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P56536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24812067}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a kinesin heavy chain subunit involved in the transport of cargo within the central nervous system. The encoded protein, which acts as a tetramer by associating with another heavy chain and two light chains, interacts with protein kinase CK2. Mutations in this gene have been associated with complex cortical dysplasia with other brain malformations-2. Two transcript variants, one protein-coding and the other non-protein coding, have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:3800; |
axon cytoplasm [GO:1904115]; axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; ciliary rootlet [GO:0035253]; dendrite cytoplasm [GO:0032839]; distal axon [GO:0150034]; kinesin complex [GO:0005871]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008574]; anterograde axonal protein transport [GO:0099641]; anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex [GO:0098971]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport [GO:0030705]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; mRNA transport [GO:0051028]; organelle organization [GO:0006996]; synaptic vesicle transport [GO:0048489] |
16835241_analysis of the GRIF-1 binding domain of the kinesin, KIF5C, which substantiates a role for GRIF-1 as an adaptor protein in the anterograde trafficking of cargoes 17887960_binding of the kinesin-binding domain of RanBP2 to KIF5B and KIF5C determines mitochondria localization and function 18682247_KIF5C, a member of the kinesin 1 heavy chain family, is a substrate for protein kinase CK2. 19011756_Results identified the motor neuron protein KIF5C as a new binding partner for the protein kinase CK2alpha'. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24812067_Genetic association of KIF4A and KIF5C mutations in intellectual disability and synaptic function. 26954557_Study found that in peripheral blood mononuclear cells the median expression of KIFC3, KIF1B, and KIF5C was much lower than the expression of dynactin subunits DCTN1 and DCTN3, in both sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and healthy cases 29048727_KIF5C mutations are associated with a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by infantile onset epilepsy, and subtle but recognizable types of brain malformations. 30200238_Findings point to a role for Kinesin-2 in the long-range movement of RAB5 endosomes during interphase. At the onset of mitosis, Kinesin-2 mediated transport controls timing of nuclear envelope breakdown and localization of RAB5 endosomes at spindle. 31757889_The adaptor proteins HAP1a and GRIP1 collaborate to activate the kinesin-1 isoform KIF5C. 31844033_Reduced miR-203 predicts metastasis and poor survival in esophageal carcinoma. 32511265_Deletion of the Pseudorabies Virus gE/gI-US9p complex disrupts kinesin KIF1A and KIF5C recruitment during egress, and alters the properties of microtubule-dependent transport in vitro. 34966180_KIF5C deficiency causes abnormal cortical neuronal migration, dendritic branching, and spine morphology in mice. 36122673_Abnormal course of the corticospinal tracts in KIF5C-related encephalopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000026764 |
Kif5c |
20.978630 |
4.0379939878 |
2.013639 |
0.557543959 |
12.516536 |
0.00040336596480925276551540714642385410115821287035942077636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001007902766308544154072457388338079908862709999084472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.9682504 |
13.5763679 |
8.7104363 |
2.5525179 |
| ENSG00000168283 |
648 |
BMI1 |
protein_coding |
P35226 |
FUNCTION: Component of a Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC1-like complex, a complex class required to maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of many genes, including Hox genes, throughout development. PcG PRC1 complex acts via chromatin remodeling and modification of histones; it mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119', rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility (PubMed:15386022, PubMed:16359901, PubMed:26151332, PubMed:16714294, PubMed:21772249, PubMed:25355358, PubMed:27827373). The complex composed of RNF2, UB2D3 and BMI1 binds nucleosomes, and has activity only with nucleosomal histone H2A (PubMed:21772249, PubMed:25355358). In the PRC1-like complex, regulates the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of RNF2/RING2 (PubMed:15386022, PubMed:26151332, PubMed:21772249). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15386022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16359901, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16714294, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21772249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25355358, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26151332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27827373}. |
3D-structure;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a ring finger protein that is major component of the polycomb group complex 1 (PRC1). This complex functions through chromatin remodeling as an essential epigenetic repressor of multiple regulatory genes involved in embryonic development and self-renewal in somatic stem cells. This protein also plays a central role in DNA damage repair. This gene is an oncogene and aberrant expression is associated with numerous cancers and is associated with resistance to certain chemotherapies. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome X. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the upstream COMM domain containing 3 (COMMD3) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:100532731;hsa:648; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; heterochromatin [GO:0000792]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PcG protein complex [GO:0031519]; PRC1 complex [GO:0035102]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; promoter-specific chromatin binding [GO:1990841]; RING-like zinc finger domain binding [GO:0071535]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activator activity [GO:0097027]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; DNA methylation [GO:0006306]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; histone acetylation [GO:0016573]; histone H2A-K119 monoubiquitination [GO:0036353]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001234]; negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic [GO:0045814]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of immature T cell proliferation in thymus [GO:0033092]; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0051443]; regulation of adaxial/abaxial pattern formation [GO:2000011]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; rostrocaudal neural tube patterning [GO:0021903]; segment specification [GO:0007379]; somatic stem cell division [GO:0048103] |
12183433_The Bmi-1 oncogene induces telomerase activity and immortalizes human mammary epithelial cells. 12482990_Bmi-1 extends the replicative life span of human fibroblasts by suppressing the p16-dependent senescence pathway 12829790_BMI-1 binds the MLL repression domain. Recruitment of BMI-1 to the MLL protein may be able to modulate its function. 14536079_E2a-Pbx1 and Bmi-1 are likely to play a role in the pathogenesis of human lymphoid leukemias through downregulation of the INK4A-ARF gene 14732230_modulation of Bmi-1 protein might be involved in human colorectal carcinogenesis by repressing the INK4a/ARF proteins 15009096_BMI-1 is transiently localized with the centromeric region in interphase. 15029199_BMI1 overexpression is an alternative or additive mechanism in the pathogenesis of medulloblastomas 15563468_Activation or overexpression of MAPKAP kinase 3pK resulted in phosphorylation of Bmi1 and other PcG members and their dissociation from chromatin 15931389_Altered expression is associated with therapy failure and death in patients with multiple types of cancer. 16105758_a subgroup of M0 patients has a high expression level of polycomb group gene BMI-1, which may contribute to leukemogenesis 16107895_CALM-AF10+ T-ALL associatd with elevated expression of subset of HOXA genes and some of there transcriptional and functional regulators, as well as specific overexpression of oncogene BMI1 16314526_EZH2 is essential for BMI1 recruitment to the polycomb bodies. 16501599_Critical for the short-term survival of cancer cells, and inhibition has minimal effect on the survival of normal cells. 16537449_p16(INK4a) expression was regulated by the Polycomb group repressor Bmi-1, which is shown as a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc. 16714294_Bmi-1-Ring1B complex stabilizes the interaction of the ubiquitin ligase complex. 16751658_Bmi1 is required for H2A ubiquitylation; H2A ubiquitylation regulates Bmi1-mediated gene expression 16874656_BMI-1 is expressed in gastrointestinal stem cells and may have a role protein in cellular differentiation and stem cell maintenance 16936260_bmi1 expression caused by oxidative stress may be involved in the pathogenesis of cellular senescence of biliary epithelial cells in primary biliary cirrhosis. 16963837_Advanced cell- & animal imaging, expression profiling, stable siRNA-gene targeting, and TMAs of experimental and clinical samples indicate that activation of the BMI1 oncogene-associated PcG pathway plays an essential role in metastatic prostate cancer. 16982619_Bmi-1 regulates the differentiation and clonogenic self-renewal of I-type neuroblastoma cells 17134822_PcG protein BMI1 is associated with adverse pathological features and clinical PSA recurrence of prostate cancer. 17145810_The oncogenic role of Bmi-1 in human primary breast carcinomas is not determined by its capacity to inhibit INK4a/ARF proteins(p16INK4a, p14ARF, or h-TERT) or to induce telomerase activity. 17145814_Bmi1 overexpression was correlated with the malignant grades of human digestive precancerous tissues, which suggests that advanced Bmi1 dysregulation might predict malignant progression. 17148583_ERK5 probably mediates HOXB9 expression by repressing BMI1 in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines 17148591_Bmi-1 and LMP1 down-regulate the ataxia telangiectasia-mutated (ATM) tumor suppressor and conclude that Bmi-1 contributes to LMP1-induced oncogenesis in Hodgkin lymphoma 17151361_Our data suggest that Mel-18 regulates Bmi-1 expression during senescence via down-regulation of c-Myc. 17161394_Our results provide new information on the roles of Bmi-1 and HPV-16 E6 in the multi-step process of oral epithelial carcinogenesis. 17179983_The Bmi-1 may act through p16(INK4A)-independent pathways to regulate cellular proliferation during oral cancer progression. 17233832_many human cell types undergo senescence by activation of the p16(INK4a)/Rb pathway, and that introduction of Bmi-1 can inhibit p16(INK4a) expression and extend the life span of human epithelial cells 17298744_The intensive expression of Bmi-1 in breast cancer is related to tumor progression. 17344414_Study shows that the ability of the oncogene BMI1 to repress the INK4A-ARF locus requires its direct association and is dependent on the continued presence of the EZH2-containing Polycomb-Repressive Complex 2 complex. 17360938_In a cohort of 64 CML patients, the level of BMI1 at diagnosis correlated with time to transformation to blast crisis, and the combination of low BMI1 and high proteinase-3 expression was associated with an improved overall survival 17452456_These results suggest that Bmi-1 and Mel-18 may have overlapping functions in cancer cell growth. 17454639_Bmi-1 seems to play a secondary role in chronic myeloid leukemia transformation 17545584_Mel-18 and Bmi-1 may regulate the Akt pathway in breast cancer cells, and that Mel-18 functions as a tumor suppressor by repressing the expression of Bmi-1 and consequently down-regulating Akt activity. 17557835_BMI1 is a target gene for SALL4 in leukemic cells. 17597110_BMI-1 mediated repression of p16(ink4a) may contribute to an increased aggressive behavior of stem cell-like melanoma cells. 17625597_Bmi-1 may promote maintenance of suprabasal keratinocyte survival to prevent premature death during differentiation. 17666329_Bmi-1 mRNA expression is correlated to differentiation and metastasis of gastric carcinoma and may facilitate its prognostic evaluation. 17711569_Elevated Bmi-1 is associated with breast cancer 17917742_Bmi-1 could be a candidate biomarker for long-term survival in HCC 17974970_Examination of various growth-regulatory pathways suggested that Bmi-1 overexpression together with H-Ras promotes human mammary epithelial cell transformation and breast oncogenesis by deregulation of multiple growth-regulatory pathways. 17989714_BMI1 is an oncogenic candidate in a novel TCRB-associated chromosomal aberration in a patient with TCRgammadelta+ T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 18094618_BMI-1 antibody as a potential marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma may be rational, and could have diagnostic and prognostic value. 18156489_BMI1 is an intrinsic regulator of human stem/progenitor cell self-renewal. 18228133_Bmi-1 expression associated with favorable overall survival only in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients. 18246051_loss of BMI-1 expression was associated with features of aggressive tumors. Low levels of BMI-1 expression were also significantly associated with decreased patient survival. 18264721_Bmi-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in respect to clinicopathological features and therapeutic outcomes 18269588_Neither EGFR nor BMI-1 had significant prognostic impact for basal-like phenotype of breast cancer. 18346113_BMI-1 is a novel independent prognostic marker in oligodendroglial tumours. 18347933_study showed BMI-1 expression was inversely correlated with the differentiation grade of renal clear cell carcinoma; BMI-1 was strongly expressed in both papillary carcinomas and oncocytomas 18427816_BMI1 gene is aberrant at the chromosomal level in a subset of gliomas, and possibly contributes to brain tumour pathogenesis 18438345_Bmi-1 protein is highly expressed in ovarian epithelial cancer tissues, and its expression level correlates with histological grade and clinical phase of the patients. 18439910_Bmi1 can induce multipotency in astrocytes. 18450386_the results suggest that BMI1 does not play a significant prognosticator role ini astrocytic tumors 18475299_Loss of BMI-1 seems to be associated with an aggressive phenotype in endometrial carcinomas. 18565849_BMI-1 measured prior to allo-SCT can serve as a biomarker for predicting outcome in patients with CP-CML receiving allo-SCT 18591938_overexpression associated with the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma 18592462_The relative expression of BMI1 in bladder tumor tissues is greater than 5 times that of nontumor samples and there is a statistically significant correlation between the level of BMI1 expression and the stage of the bladder tumors. 18668134_BMI1 overexpression accompanied with 11q23 rearrangements is associated with acute myeloid leukemias. 18701473_Overexpresion of BMI-1 is associated with ewing sarcoma tumorigenesis 18781299_inhibitors, BMI-1 is presumed to be positively regulated by BCR-ABL and further by posttranscriptional modification in the course of the disease progressio 18817867_Data demonstrate that Bmi1 promotes prostate tumorigenesis, and that Bmi1 expression is associated with a reduction in tumor suppressors p16(INK4A) and p14(ARF). 18829528_An important role for BMI1 in the maintenance of tumor-initiating side population cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19012049_candidate for stem cell marker and renewal factor in nasal mucosa, may contribute to tissue homeostasis and differentiation in the epithelium and submucosal glands of normal nasal mucosa, and may play a role in proliferation of nasal polyps 19021148_dysregulated BMI-1 could indeed lead to keratinocytes transformation and tumorigenesis, potentially through promoting cell cycle progression and increasing cell mobility. 19080002_Overexpression of Bmi-1 and Ki67 protein are significantly correlated with tumorigenesis, metastasis and prognosis of colorectal carcinoma. 19080003_Bmi-1 protein is highly expressed in bladder cancer. 19099625_SALL4 and BMI-1 expressions are up-regulated significantly in acute leukemia. 19228380_Expression of Bmi-1 was greater in bladder cancers than in the adjacent normal tissues. Bmi-1 expression was positively correlated with tumor classification and TNM stage, but not with tumor number. 19233177_A polymorphism in Bmi-1 that reduces levels of this important protein. 19269851_transcripotional control of Th2 memory cell generation 19337376_provides evidence that, in the appropriate context, expression of the SYT-SSX2 oncogene leads to loss of Bmi1 polycomb function 19379548_Suppression of Bmi-1 expression is not able to reduce proliferation of K562 cells. 19386347_Distinct expression of BMI1 in hepatocellular carcinoma is reported. 19389366_The more pronounced effects of Bmi-1 over-expression in culture were largely attributable to the attenuated induction of p16(Ink4a) and p19(Arf) in culture, proteins that are generally not expressed by neural stem/progenitor cells in young mice in vivo. 19452584_Increased Bmi1 mRNA expression was significantly associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression, and the oncoprotein was largely distributed in the cytoplasm of tumor cells. 19543317_BMI1 collaborates with H-RAS to induce an aggressive and metastatic phenotype with the unusual occurrence of brain metastasis. 19556423_BMI1 expression is required for maintenance and self-renewal of normal and leukemic stem and progenitor cells, and expression of BMI1 protects cells against oxidative stress. 19605626_BMI1 is expressed in human GBM tumors and highly enriched in CD133-positive cells. Stable BMI1 knockdown using short hairpin RNA-expressing lentiviruses resulted in inhibition of clonogenic potential in vitro and of brain tumor formation in vivo 19639171_Bmi-1 mRNA might be a new tool to support the diagnosis of breast cancers 19695678_The overexpression of polycomb-group protein Bmi1 is essential for colony formation and cell proliferation, probably by the repression of cellular senescence in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 19778799_The overexpression of Bmi-1 protein was significantly correlated to the tumorigenesis, metastasis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. 19806792_Inhibition of Bmi-1 expression in human gastric carcinoma cells affects cell proliferation and invasiveness. 19884659_upregulation of Bmi-1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and enhanced the motility and invasiveness of nasopharyngeal epithelial cells, whereas silencing endogenous Bmi-1 expression reversed EMT and reduced motility 19903340_Nuclear PTEN reduces BMI1 function independently of its phosphatase activity. 19903841_Bmi-1 protein is downregulated by miR-15a or miR-16 expression and leads to significant reduction in ovarian cancer cell proliferation and clonal growth. 19907431_key role of Bmi-1 downregulation in enforcing aging in primary human keratinocytes 19934271_Bmi1 functions independent of Ink4A/Arf repression in liver cancer development. 19940551_Data show that tumor spheroid cells express ABCG2, Bmi1, WNT5A, CD133, prox1 and VEGFR3. 19956605_Silencing of Bmi1 inhibits drug-induced Top2alpha degradation, increases the persistence of Top2alpha-DNA cleavage complex, and increases Top2 drug efficacy. 19957112_High Bmi1 is associated with colon cancer. 20015867_Although Bmi-1 does not influence the basal level of apoptotic activity, its overexpression protects the tumor cells against the proapoptotic action of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. 20024662_The expression of Bmi-1 was elevated in colon cancer and might serve as an independent prognostic marker. 20035051_Bmi-1 bestows apoptotic resistance to glioma cells through the IKK-NF-kappaB pathway; Bmi-1 as a useful indicator for glioma prognosis. 20085590_Bmi-1 gene is upregulated in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with ATP-binding cassette transporter B1 expression. 20127006_EZH2 and BMI-1 are upregulated in osteosarcoma. EZH2 and BMI-1 may be useful targets for cancer immunotherapy of osteosarcoma, although knock-down of EZH2 and BMI-1 could not prevent osteosarcoma growth. 20145620_Negative Bmi-1 expression is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. 20170541_BMI1 acts as an oncogene and Mel-18 functions as a tumor suppressor via downregulation of BMI1. 20190806_Bmi1 is a MYCN target gene that regulates tumorigenesis through repression of KIF1Bbeta and TSLC1 in neuroblastoma. 20308890_Studies indicate that in the absence of BMI1, reactive oxygen species accumulate, associating with activation of DNA damage response pathways and increased apoptosis. 20377880_Expression of Bmi-1 might be important in the acquisition of an invasive and/or aggressive phenotype of ovarian carcinoma, and serve as a independent biomarker for shortened survival time of patients. 20385206_The study confirmed a direct involvement of Bmi-1 in the regulation of human fetal NSCs self-renewal and proliferation in vitro, and suggested that the Ink4a/Arf locus was a potential downstream target of Bmi-1 pathway. 20426791_BMI1 plays an important role in the late progression of pancreatic cancer and may represent a therapeutic target for treatment of this cancer. 20428793_BMI-1 depletion leads to reduced cell growth and proliferation, and increased cell apoptosis. 20530672_Studies not only highlight Bmi-1 as a cancer-dependent factor in multiple myeloma, but also elucidate a novel antiapoptotic mechanism for Bmi-1 function involving the suppression of Bim. 20551323_the molecular mechanism of Bmi-1-mediated regulation of the p16 gene 20564407_Bmi1 and EZH2 had characteristic and distinctive expression in NSCLCs. 20568112_Loss of BMI1 enhances docetaxel activity and impairs antioxidant response and promotes prostate cancer. 20569464_data suggest that the PS domain of BMI1 is involved in its stability and that it negatively regulates function of BMI1 oncoprotein 20574517_miR-128a has growth suppressive activity in medulloblastoma and that this activity is partially mediated by targeting Bmi-1. 20591222_Bmi-1 downregulation in esophageal carcinoma cells inhibits cell proliferation, cell cycle, and cell migration, while increasing cell apoptosis. 20592341_the BMI-I protein is significantly overexpressed in ovarian, endometrial and cervical cancer 20661663_knockdown of BMI-1 expression can induce cell-cycle arrest and up-regulate p16INK4a, HOXA9 and HOXC13 in HeLa cells 20717685_Our analysis showed correlation between BMI1 and PCGF2 gene's expression and survival in children with medulloblastoma. 20724541_Introduction of BCR-ABL and BMI1 in human cord blood CD34+ cells induces lymphoid leukemia upon transplantation in NOD/SCID mice. 20809956_Overexpression of Bmi-1 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 20818389_Bmi1 and Twist1 act cooperatively to repress expression of both E-cadherin and p16INK4a. 20818602_High BMI1 is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 20921134_BMI1 contributes to histone ubiquitylation and has a role in maintaining genomic stability. 21039844_A direct correlation analysis showed that ubiquitin-specific protease 22 was strongly correlated with BMI-1 and c-Myc at the mRNA level. 21047978_ESFT that do not overexpress BMI-1 represent a novel subclass with a distinct molecular profile and altered activation of and dependence on cancer-associated biological pathways. 21059209_Decreased Mel-18 and increased Bmi-1 mRNA expression was associated with the carcinogenesis and progression of gastric cancer 21113618_C-MYC and BMI-1 expression was detected in stromal cells only 21125401_Overexpression of the EZH2, RING1, and BMI1 genes is common in MDS and indicate poor prognosis. The products of these genes might participate in epigenetic regulation of Myelodysplastic syndrome. 21152871_Bmi-1 may be a potential molecular target for the therapy of breast carcinoma. 21162745_Bmi-1/Mel-18 ratio can be potentially used as a tool for stratifying women at risk of developing breast malignancy. 21164364_Increase of BMI1 is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 21170084_a previously unrecognized link between BMI-1, contact inhibition and the Hippo-YAP pathway 21252986_higher expression of BMI-1 and immune responses to BMI-1 protein is associated with improved outcome following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. 21259057_the aim of this study was to investigate the prognosis and clinicopathologic roles of beta-catenin, Wnt1, Smad4, Hoxa9, and Bmi-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 21276135_WWOX was identified as a Bmi1 target in small cell lung cancer cells 21276221_Bmi-1 promotes invasion and metastasis, and its elevated expression is correlated with an advanced stage of breast cancer 21307872_Bmi-1 elicits radioprotective effects on normal human keratino by mitigating the genotoxicity of ionizing radiation through epigenetic mechanisms. 21309753_BMI1 protein human might be an independent prognostic marker in patient diagnosed with uterine cervical cancer. 21370603_Bmi-1 might participate in the development and progression of uterine cervical cancer and have clinical potential not only as a useful predictor of aggressive phenotype but also a promising prognostic predictor. 21373837_Studies indicate that new targets have recently been investigated as potential modulators in myeloid leukemia pathogenesis, including miR-328, BMI1, FOXOs and IL1RAP. 21383063_BMI1 is recruited to sites of DNA DSBs, where it persists for more than 8 h. BMI1 is required for postdamage ubiquitination of histone H2A at lysine 119 and contributes to efficient homology-mediated repair of DNA breaks. 21428211_Bmi-1 siliencing combined treatment of doxorubicin might be a new strategy for biological treatment on breast cancer. 21430439_F box protein betaTrCP regulates BMI1 protein turnover via ubiquitination and degradation. 21496667_results indicate that dMSCs lose their odontogenic differentiation potential during senescence, in part by reduced Bmi-1 expression. 21572997_DNA methyltransferase controls stem cell aging by regulating BMI1 and EZH2 through microRNAs.( 21638011_A significant association between the expression of Bmi-1 and estrogen receptor was found in primary breast cancers and their metastases. 21656027_Bmi-1 may be associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung squamous cell carcinoma 21678481_It has been clearly established that BMI1 is a bonafide oncogene and plays critical roles in promoting cancer stem cell self-renewal and tumorogenesis. 21685941_Knockdown experiments of Bmi1 in vitro and in vivo demonstrate that Hh signaling not only drives Bmi1 expression, but a feedback mechanism exists wherein downstream effectors of Bmi1 may, in turn, activate Hh pathway genes 21725369_correlated the expression of miR-200b, miR-15b and BMI1 with the clinicopathological status and prognosis of tongue squamous cell carcinoma patients 21732356_Data indicate that the dynamics of recognition of UV-damaged chromatin, and the nuclear arrangement of BMI1 protein can be influenced by acetylation and occur as an early event prior to the recruitment of HPbeta to UV-irradiated chromatin. 21735131_simultaneous activation of USP22 and BMI-1 may associate with GC progression and therapy failure 21755556_BMI1 was required to maintain the proliferative capacity of laryngeal Cancer stem cells. 21772249_Crystallography of a complex of the Bmi1/Ring1b RING-RING heterodimer & UbcH5c shows that UbcH5c interacts with Ring1b only. Bmi1/Ring1b interacts with nucleosomal DNA & an acidic patch on histone H4 to achieve specific monoubiquitination of H2A. 21851624_MicroRNA-194 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition of endometrial cancer cells by targeting oncogene BMI-1. 21856782_dysregulation of the BMI1 gene mediated by MYCN or MYC overexpression, confers increased cell proliferation during neuroblastoma genesis and tumor progression 21865393_Correlating with the loss of H3K27me3, human papillomavirus 16 E6/E7-expressing cells exhibited derepression of specific EZH2-, KMD6A-, and BMI1-targeted HOX genes. 21866458_Bmi1 expression is associated with the clinicopathological characteristics of colorectal cancer. 21883379_Twist1 directly activates Bmi1 expression and that these two molecules function together to mediate cancer stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition--{REVIEW} 21919891_Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness: the Twist1-Bmi1 connection 21960247_a c-Myb-Bmi1 transcription-regulatory pathway is required for p190(BCR/ABL) leukemogenesis. 21999765_Overexpression of BMI-1 correlates with drug resistance in B-cell lymphoma cells through the stabilization of survivin expression. 22009787_ATP-binding cassette, G2 subfamily (ABCG2) and BMI-1, predict the transformation of oral leukoplakia to cancer. 22040961_Expressions of ABCB1, BMI-1, HOXB4 were not detected in the patients with non-malignant hematologic diseases, but were higher in de novo acute leukemia patients and lower in patients in complete remission. 22096526_Results suggest that Bmi1 plays a crucial role in the maintenance of the stem cell pool in postnatal skeletal muscle and is essential for efficient muscle regeneration after injury especially after repeated muscle injury. 22120066_Overexpression of BMI1 confers clonal cells resistance to apoptosis and contributes to adverse prognosis in myelodysplastic syndrome. 22120721_report that BMI1 has a critical role in stabilizing cyclin E1 by repressing the expression of FBXW7, a substrate-recognition subunit of the SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets cyclin E1 for degradation 22132147_Measuring BMI-1 autoantibody levels of patients with cervical cancer could have clinical prognostic value as well as a non-tissue specific biomarker for neoplasms expressing BMI-1. 22170051_Regulation of the potential marker for intestinal cells, Bmi1, by beta-catenin and the zinc finger protein KLF4: implications for colon cancer. 22209830_results indicate that Bmi-1 may play an important role in breast cancer radiosensitivity. 22252887_BMI1, which is upregulated in a variety of cancers, has a positive correlation with clinical grade/stage and poor prognosis. [Review] 22265735_Bmi1 expression profiles show a marked elevation in the proneural glioblastoma subtype. 22293918_Bmi-1 plays a part in autoreactive CD4+ T cell proliferative capability and apoptotic resistance in immune thrombocytopenia patients 22366984_Bmi-1 status in breast cancer is an independent prognostic factor, which also is associated with tumor histological grade and basal-like phenotype. 22384090_Bmi1 is down-regulated in the aging brain and displays antioxidant and protective activities in neurons 22420951_Bmi-1 regulates key pathways involved in the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. 22509111_high expression of p16(INK4a) and low expression of Bmi1 are associated with endothelial cellular senescence in human cornea. 22664532_After cisplatin treatment, Bmi1 is required for the self-renewal of stem-like cells that are important for the expansion of the stem-like cell pool in human A549 cells and that targeting Bmi1 slows down the formation of tumors in vivo. 22725270_expression patterns of ALDH1 and Bmi1 in OE were associated with malignant transformation, suggesting they may be valuable predictors for evaluating risk of oral cancer. 22766604_Both Bmi1 and EZH2, not each alone, could be potent candidates of new target therapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22777769_Bmi-1 represses transcription of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and abrogates IGF-IR signaling in prostate cancer 22825250_Structural alterations of BMI1 and downstream effectors are rare but they do occur in human myeloproliferative neoplasms. 22842564_These results suggest that Bmi-1 plays an important role in tumor radioadaptive resistance under FIR and may be a potent molecular target for enhancing the efficacy of fractionated RT. 22863087_Coexpression of B-lymphoma Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion region-1 (BMI1) and sex-determining region of Y chromosome-related high mobility group box-2 (SOX2) may promote cervical carcinogenesis. 22872929_Bmi-1 siRNA has a role in inhibiting ovarian cancer cell line growth and decreasing telomerase activity 22898137_Cervical cancer with excessive BMI-1 expression possesses high metastases potential and that BMI-1 may be a promising biomarker for predicting metastasis in cervical cancer. 22912356_We found that overexpression of c-Myc was significantly associated with that of BMI1, and that patients who harbored glioblastomas overexpressing c-Myc and BMI1 showed significantly longer overall survival. 22967049_Knockdown of endogenous Bmi-1 reduced the invasiveness and migration of glioma cells. NF-kappaB transcriptional activity and MMP-9 expression and activity were significantly increased in Bmi-1-overexpressing but reduced in Bmi-1-silenced cells. 22982443_miR-200c overexpression resulted in significant down-regulation of BMI-1. 22994774_There was higher Bmi-1 protein expression in intestinal-type carcinomas. 23023333_Our results suggest that CHMP1A serves as a critical link between cytoplasmic signals and BMI1-mediated chromatin modifications that regulate proliferation of central nervous system progenitor cells. 23046527_There was no significant correlation between p16INK4A expression and BMI1 expression. 23057360_The expressions of Bmi1 and hTERT genes may have a close relation to the proliferative capacity of CD34+ cells. 23078618_This study demonstrates that high expression Bmi-1 is associated with esophageal adenocarcinoma and precancerous lesions, which implies that Bmi-1 plays an important role in early carcinogenesis in esophageal adenocarcinoma. 23092893_Akt phosphorylates the transcriptional repressor bmi1 to block its effects on the tumor-suppressing ink4a-arf locus. 23138990_High expression of Bmi1 was associated with hepatocarcinogenesis. 23204235_our results link CSCs, EMT, and CIN through the BMI1-AURKA axis 23239878_A positive feedback loop connected by the WNT signaling pathway regulates BMI1 expression. 23242307_Downregulation of the Bmi1 gene by RNAi can inhibit the proliferation and invasivesness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 23255074_miR-218 suppressed protein expression of BMI-1 downstream targets of cyclin-dependent kinase 4, a cell cycle regulator, while upregulating protein expression of p53. 23308129_BMI1 could be developed as a dual bio-marker (serum and biopsy) for the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer in Caucasian and African-American men. 23383216_Bmi-1 promotes glioma angiogenesis by activating NF-kappaB signaling. 23437065_These results implicate Bmi1 in the invasiveness and growth of pancreatic cancer and demonstrate its key role in the regulation of pancreatic cancer stem cells. 23468063_The Bmi-1 pathway was downregulated in GBM cells. 23525303_siRNA against Bmi-1 significantly suppresses tumor growth and induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. 23559850_BMI-1 might render important oncogenic property of retinoblastomas. 23592496_Authors assessed the functional relevance of two genes, FoxG1 and Bmi1, which were significantly enriched in non-Shh/Wnt MBs and showed these genes to mediate MB stem cell self-renewal and tumor initiation in mice. 23601184_Sp1 and c-Myc are important transcription factors that directly bind to the BMI1 promoter region and regulate gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 23671559_Regulation of TCF4-mediated BCL2 gene expression by BMI1 is universal. 23686310_Upregulation of BMI1 and downregulation of miR-16 in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) side population has a key role in the disease's progression by reducing MCL cell apoptosis. 23700898_Bmi-1 may contribute to malignant cell transformation, and its expression in tissues taken from patients with cervical, breast and ovarian cancer could be a marker for diagnosis and prognosis. 23708658_Data indicate that post-translational phosphorylation of Nanog is essential to regulate Bmi1 and promote tumorigenesis. 23712029_BMI-1 expression plays a role in hTERT-induced immortalisation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 23727134_BMI-1 and RING1B expression was enhanced with the development of embryos in early pregnancy. 23744494_Single nucleotide polymorphism in BMI1-PIP4K2A is associated with Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma. 23807724_These data demonstrate that Bmi-1 plays a vital role in HCC invasion and that Bmi-1 is a potential therapeutic target for HCC 23820733_BMI1 may represent a novel diagnostic marker and a therapeutic target for bladder cancer, and deserves further investigation. 23864317_Bmi1 and FoxF1 may cooperate with hedgehog signaling in non-small-cell lung carcinogenesis. 23873108_Data indicate that B cell-specific Moloney murine leukaemia virus integration site 1 (BMI1) gene was co-regulated with progesterone receptor (PR) in the invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 23873701_Identified a novel t(10;14)(p12;q32)/IGH-BMI1 rearrangement and its IGL variant in six cases of chronic lymphocytic leukemia; this study shows that BMI1 is recurrently targeted by chromosomal aberrations in B-cell leukemia/lymphoma. 23950210_High BMI1 expression is associated with glioma. 23984324_Increased expression of the Bmi-1 in pediatric brain tumors may be important in the acquisition of an aggressive phenotype. 23990442_Bmi-1 was a significant prognostic factor of poor overall survival in lung adenocarcinoma patients. 24039897_MiR-200c and miR-203 overexpression in breast cancer cells downregulated Bmi1 expression accompanied with reversion of resistance to 5-Fu mediated by Bmi1. 24122997_Aberrant EZH2 and BMI1 expression was significantly associated with mode of invasion, but not with lymph node metastasis or survival rate in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24139839_The data of this study suggest for the first time that the combination of Bmi1 and EZH2 overexpression may be a highly sensitive marker for the prognosis in glioma patients. 24145240_Early detection marker distinguishes cancerous from non-cancerous regions in mouth squamous cell carcinoma 24219349_stem renewal factor Bmi-1 was a direct target of miR-203 24252251_miR-15a inhibits cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via the down-regulation of Bmi-1 expression 24292392_Downregulation of BMI-1 inhibits the ability of colorectal cancer-initiating cells to self-renew, resulting in the abrogation of their tumorigenic potential. 24300467_Bmi1 displays higher expression in recurrent than in primary ovarian neoplasms 24312366_findings suggest that TAMs may cause increased Bmi1 expression through miR-30e* suppression, leading to tumor progression 24317363_knockdown of Bmi-1 in PC3 and DU145 cells significantly reduced cell proliferation and upregulated the p16 tumor-suppressor 24337040_Bmi1 knockdown inhibited cell cycle progression through derepression of the p16INK4a/p14ARF locus and caused inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, tumor sphere formation, enhanced sensitivity to cisplatin, and cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase 24342665_The study suggested correlation between increased Bmi-1 expression and clinical progression in ovarian epi |
ENSMUSG00000026739 |
Bmi1 |
205.992053 |
0.3459975138 |
-1.531166 |
0.229761620 |
43.184015 |
0.00000000004982610416274707849309884136211124591037124886838682868983596563339233398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000262842493724855894159853804607058190556667653936528949998319149017333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
104.6816323 |
16.7414949 |
304.4395263 |
33.8653169 |
| ENSG00000168300 |
115294 |
PCMTD1 |
protein_coding |
Q96MG8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein methylation. Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:115294; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0004719] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23505305_Presence of at least one A allele (AG or AA genotype) for rs1015213 was associated with a shallower anterior chamber depth (-0.07 mm, 95% CI -0.01 to -0.14 mm, p=0.028) after adjusting for age and sex (both p=0.001). 23847314_In our study, rs1015213 (located in the intergenic region between PCMTD1 and ST18) was associated significantly with primary angle closure. 24474268_The three genetic susceptibility loci for primary angle-closure glaucoma did not underlie any major phenotypic diversity in terms of disease severity or progression. 27455018_No significant association of PLEKHA7 rs11024102, COL11A1 rs3753841 and PCMTD1-ST18 rs1015213 with primary angle closure glaucoma was found among ethnic Han Chinese from Sichuan 29310965_In this study, 2 of 8 (primary angle-closure glaucoma) PACG-associated loci were associated significantly with PACS status, the earliest stage in the angle-closure glaucoma disease course. The association of these PACG loci with PACS status suggests that these loci may confer susceptibility to a narrow angle configuration. 30377206_This study has identified an increased percentage of IDH1 and PCMTD1 mutations in Squamous Cell Lung Cancers arising in the Appalachian Kentucky residents versus The Cancer Genome Atlas, with population-specific implications for the personalized treatment of this disease. 35486881_Human Protein-l-isoaspartate O-Methyltransferase Domain-Containing Protein 1 (PCMTD1) Associates with Cullin-RING Ligase Proteins. |
ENSMUSG00000051285 |
Pcmtd1 |
315.531991 |
0.4734183638 |
-1.078812 |
0.100257826 |
116.297509 |
0.00000000000000000000000000409085828046493103237519407595146958300295117898128658819198699823118910504082812451542849885299801826477050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000047283530320800615274501168653733518187096039035337538567987188796193928977396048196624178672209382057189941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
209.7097403 |
14.6049006 |
446.2297340 |
21.0106775 |
| ENSG00000168301 |
200845 |
KCTD6 |
protein_coding |
Q8NC69 |
FUNCTION: Probable substrate-specific adapter of a BCR (BTB-CUL3-RBX1) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex mediating the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Promotes the ubiquitination of HDAC1; the function seems to depend on KCTD11:KCTD6 oligomerization. Can function as antagonist of the Hedgehog pathway by affecting the nuclear transfer of transcription factor GLI1; the function probably occurs via HDAC1 down-regulation, keeping GLI1 acetylated and inactive. Inhibits cell growth and tumorigenicity of medulloblastoma (MDB) (PubMed:21472142). Involved in regulating protein levels of ANK1 isoform Mu17 probably implicating CUL3-dependent proteasomal degradation (PubMed:22573887). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21472142, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22573887}. |
Cytoplasm;Growth regulation;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Enables ankyrin binding activity; cullin family protein binding activity; and identical protein binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway and ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:200845; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; M band [GO:0031430]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; cullin family protein binding [GO:0097602]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
21472142_Rescuing KCASHs expression reduces the Hedgehog-dependent medulloblastoma growth, suggesting that loss of members of this novel family of native HDAC inhibitors is crucial in sustaining Hh pathway-mediated tumorigenesis. 22573887_Obscurin and KCTD6 regulate cullin-dependent small ankyrin-1 (sAnk1.5) protein turnover 24307990_A biophysical characterization of the POZ/BTB of KCTD6, is reported. |
ENSMUSG00000021752 |
Kctd6 |
26.717155 |
0.4667409315 |
-1.099306 |
0.310266329 |
12.851516 |
0.00033720600499292409379936685809298069216310977935791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000854448177458465296663092658491223119199275970458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.2889205 |
3.5692530 |
39.5820145 |
4.8299367 |
| ENSG00000168334 |
165904 |
XIRP1 |
protein_coding |
Q702N8 |
FUNCTION: Protects actin filaments from depolymerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15454575}. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a striated muscle protein and belongs to the Xin actin-binding repeat-containing protein (XIRP) family. The protein functions to protect actin filaments during depolymerization. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:165904; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091] |
15454575_Xin and XIRP2 define a novel actin-binding motif 16631741_Here, we identify Xin, the protein encoded by the human gene 'cardiomyopathy associated 1'(CMYA1) as filamin c binding partner at these specialized structures where the ends of myofibrils are attached to the sarcolemma 19151983_Data show that in myofibrillar myopathies Xin protein exhibites significant alterations in their localization. 20657180_Data provide further support that ALS2CL, EPHA3, and CMYA1 are bona-fide tumor-suppressor genes and contribute to the tumorigenesis of HNSCC. 23985323_We identify the SH3 domains of nebulin and nebulette as novel ligands of proline-rich regions of Xin and XIRP2. 24225086_The strong correlation between the degree of muscle damage and Xin immunoreactivity suggests that Xin may be a suitable outcome measure to evaluate disease progression and treatment effects in clinical trials. 24963132_Aciculin interacts with filamin C and Xin and is essential for myofibril assembly. 29176328_Abnormal CMYA1 expression affects the phosphorylation of Cx43 through the protein kinase c signaling pathway, which is involved in the regulation of gap junction intercellular communication. 29306897_Report pathogenic XIRP1/2 rare variants in arrhythmogenic disorders such as sudden unexplained nocturnal death syndrome and Brugada syndrome. 33261556_An interaction of heart disease-associated proteins POPDC1/2 with XIRP1 in transverse tubules and intercalated discs. |
ENSMUSG00000079243 |
Xirp1 |
66.974151 |
27.6009177497 |
4.786644 |
0.395808327 |
268.478094 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000243559677156497529452351226014170031137666026428568463483090507556150592353309392390328681828706379111912099506787826803172756598104205227704577472959586448286728455059346742928028106689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000062738932545024494648151043304981556257900248689451822911215194683803945513830928033116464224591157598090326006752546056071209522929387317559502099291457444252273489837534725666046142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
137.5233849 |
36.1086168 |
5.0152297 |
1.2856854 |
| ENSG00000168348 |
84684 |
INSM2 |
protein_coding |
Q96T92 |
FUNCTION: May function as a growth suppressor or tumor suppressor in liver cells and in certain neurons. {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II; neuron differentiation; and regulation of cell cycle process. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be part of transcription repressor complex. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84684; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010564] |
20091020_insulinoma-associated protein 2 beta (IA-2beta) and zinc transporter-8 may have a role in rapid progression of type 1 diabetes 21343251_Data show that INSM2 is the expressed n fetal pancreas. |
ENSMUSG00000045440 |
Insm2 |
9.674807 |
0.0099841615 |
-6.646143 |
1.095479586 |
59.328497 |
0.00000000000001334302343529447289908296314608592482221273173986775262278570153284817934036254882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000088793068487351851623843280707484389082263104286951715948816854506731033325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.1862519 |
0.1563539 |
18.7951733 |
4.5116829 |
| ENSG00000168389 |
84879 |
MFSD2A |
protein_coding |
Q8NA29 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) symporter, which plays an essential role for blood-brain barrier formation and function (PubMed:24828040, PubMed:34135507, PubMed:32572202). Specifically expressed in endothelium of the blood-brain barrier of micro-vessels and transports LPC into the brain (By similarity). Transport of LPC is essential because it constitutes the major mechanism by which docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an omega-3 fatty acid that is essential for normal brain growth and cognitive function, enters the brain (PubMed:34135507, PubMed:26005868). Transports LPC carrying long-chain fatty acids such LPC oleate and LPC palmitate with a minimum acyl chain length of 14 carbons (By similarity). Does not transport docosahexaenoic acid in unesterified fatty acid (By similarity). Specifically required for blood-brain barrier formation and function, probably by mediating lipid transport (By similarity). Not required for central nervous system vascular morphogenesis (By similarity). Acts as a transporter for tunicamycin, an inhibitor of asparagine-linked glycosylation (PubMed:21677192). In placenta, acts as a receptor for ERVFRD-1/syncytin-2 and is required for trophoblast fusion (PubMed:18988732, PubMed:23177091). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9DA75, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18988732, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21677192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23177091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24828040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26005868, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34135507}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Lipid transport;Membrane;Primary microcephaly;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane protein and sodium-dependent lysophosphatidylcholine transporter. The encoded protein is involved in the establishment of the blood-brain barrier and is required for brain growth and function. Defects in this gene are a cause of a progressive microcephaly syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:84879; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; fatty acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015245]; long-chain fatty acid transporter activity [GO:0005324]; lysophosphatidylcholine flippase activity [GO:0140348]; lysophospholipid:sodium symporter activity [GO:0051978]; oleate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901480]; phospholipid transporter activity [GO:0005548]; brain development [GO:0007420]; carbohydrate transport [GO:0008643]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; cognition [GO:0050890]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; establishment of blood-brain barrier [GO:0060856]; fatty acid transport [GO:0015908]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; lipid transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:1990379]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; lysophospholipid translocation [GO:0140329]; lysophospholipid transport [GO:0051977]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; motor behavior [GO:0061744]; negative regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0031999]; organic substance transport [GO:0071702]; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:0006656]; photoreceptor cell morphogenesis [GO:0008594]; photoreceptor cell outer segment organization [GO:0035845]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0010867]; regulation of dendrite development [GO:0050773]; regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040014]; regulation of neuron projection arborization [GO:0150011]; regulation of phosphatidylcholine metabolic process [GO:0150172]; regulation of phosphatidylethanolamine metabolic process [GO:0150175]; regulation of phosphatidylserine metabolic process [GO:0150178]; retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0060042]; retinal pigment epithelium development [GO:0003406]; transcytosis [GO:0045056]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0034379] |
17145094_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17145094_three additional SNPs in the MFSD2 genes showed ethnic differences in allelic frequencies 18694395_Results identify Mfsd2a (major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 2a) and an additional closely related protein Mfsd2b, and suggest that Mfsd2a plays a role in adaptive thermogenesis. 18988732_MFSD2 is a placenta-specific receptor for the fusogenic, endogenous retrovirus-derived, human syncytin-2, and plays a role in placenta morphogenesis. 20236515_MFSD2A is a novel lung cancer tumor suppressor gene that regulates cell cycle progression and matrix attachment. 21677192_MFSD2A is a putative Tunicamycin transporter at the plasma membrane. 21736709_SNP rs12072037 modulates MFSD2A promoter activity and thus might affect MFSD2A levels in normal lung and in lung tumors. 23177091_Importance of MFSD2a in trophoblast fusion and placenta development. 23349019_Several tagging SNPs and haplotypes in TRIT1, MYCL1 and MFSD2A region are significantly associated with risk and clinicopathological features of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. 26005865_A homozygous mutation affecting a highly conserved MFSD2A residue (p.Ser339Leu) is associated with a progressive microcephaly syndrome characterized by intellectual disability, spasticity and absent speech. 26005868_MFSD2A mutations impair brain lipid transport activity. 26747400_The regulatory role of Mfsd2a deepens our knowledge of the function of the BBB, potentially contributing to the effective drug delivery in the treatments for neurodegenerative diseases, brain tumors, and life-threatening infections in the CNS 26869380_In offspring of women with gestational diabetes mellitus treated either with diet or insulin, higher fetal fat accretion and lower placental MFSD2a contribute to reduce docosahexaenoic acid availability. 26945070_MFSD2A transported structurally related acylcarnitines but not a lysolipid without a negative charge, demonstrating the necessity of a negatively charged headgroup interaction with Lys-436 for transport. 28827082_Levels of DHA-derived epoxides are lower in colon tissues from patients with ulcerative colitis than healthy and resolving mucosa. Production of these metabolites by gut endothelium requires MFSD2A; endothelial progenitor cells that overexpress MFSD2A reduce colitis in mice. 29899523_When compared with placental expression of other genes, alkaline phosphatase expression was positively related to genes including the lysophosphatidylcholine transporter MFSD2A (major facilitator superfamily domain containing 2A, P A; p.Pro402His) in MFSD2A. Both affected individuals had microcephaly, hypotonia, appendicular spasticity, dystonia, strabismus, and global developmental delay. 30292405_Results suggest that major facilitator superfamily domain containing-2A (MFSD2A) might affect angiogenesis and inhibit gastric cancer (GC) development and progression, and may help predict prognosis and could be a therapeutic target in GC. 31584009_The prognostic value of major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 2A in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 31681849_These findings suggest endothelial Mfsd2a as an important pathogenic mediator and supplementation with docosahexaenoic acid as a potential therapeutic option for Zika virus infection. 31861865_This study found a significant and progressive decline of MFSD2a levels in blood of Alzheimer's Disease patients (Control 0.83 +/- 0.13, GDS4 0.72 +/- 0.09, GDS6 0.48 +/- 0.05*, p |
ENSMUSG00000028655 |
Mfsd2a |
3011.164855 |
3.4183743132 |
1.773310 |
0.042649229 |
1710.745941 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4685.7678147 |
120.7157114 |
1380.3149992 |
27.9997432 |
| ENSG00000168404 |
197259 |
MLKL |
protein_coding |
Q8NB16 |
FUNCTION: Pseudokinase that plays a key role in TNF-induced necroptosis, a programmed cell death process (PubMed:22265413, PubMed:22265414, PubMed:22421439, PubMed:24316671). Does not have protein kinase activity (PubMed:22265413, PubMed:22265414, PubMed:22421439, PubMed:24316671). Activated following phosphorylation by RIPK3, leading to homotrimerization, localization to the plasma membrane and execution of programmed necrosis characterized by calcium influx and plasma membrane damage (PubMed:22265413, PubMed:22265414, PubMed:22421439, PubMed:24316671). In addition to TNF-induced necroptosis, necroptosis can also take place in the nucleus in response to orthomyxoviruses infection: following activation by ZBP1, MLKL is phosphorylated by RIPK3 in the nucleus, triggering disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol.following ZBP1 activation, which senses double-stranded Z-RNA structures, nuclear RIPK3 catalyzes phosphorylation and activation of MLKL, promoting disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol (By similarity). Binds to highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates such as inositolhexakisphosphate (InsP6) which is essential for its necroptotic function (PubMed:29883610). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D2Y4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22265413, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22265414, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22421439, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24316671, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29883610}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Necrosis;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. The encoded protein contains a protein kinase-like domain; however, is thought to be inactive because it lacks several residues required for activity. This protein plays a critical role in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced necroptosis, a programmed cell death process, via interaction with receptor-interacting protein 3 (RIP3), which is a key signaling molecule in necroptosis pathway. Inhibitor studies and knockdown of this gene inhibited TNF-induced necrosis. High levels of this protein and RIP3 are associated with inflammatory bowel disease in children. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:197259; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; execution phase of necroptosis [GO:0097528]; necroptotic process [GO:0070266]; necroptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097527]; protein homotrimerization [GO:0070207]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
19844255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22265413_Findings implicate MLKL as a key mediator of necrosis signaling downstream of the kinase RIP3. 22421439_study suggests that MLKL is a key RIP3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrotic cell death 23612963_the importance of the RIP3-MLKL interaction in the formation of functional necrosomes and suggest that translocation of necrosomes to mitochondria-associated membranes is essential for necroptosis signaling. 23720157_Low expression of MLKL is associated with decreased OS in patients with resected PAC and decreased RFS and OS in the subset of patients with resected PAC who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. 24219132_Data suggest that nucleotide- (ATP-) binding residues of human MLKL have divergently evolved from mouse Mlkl and conventional protein kinases; studies include small-angle X-ray scattering, thermal shift of nucleotide binding, and sequence alignment. 24316671_This study reveals a crucial mechanism of MLKL-mediated TNF-induced necroptosis. 24322838_MLKL protein expression is significantly upregulated in children, diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease. 24703947_Report role of MLKL/RIP3 pathway in necrotic membrane disruption. 24813885_Authors demonstrate that the full four-helical bundle domain (4HBD) in the N-terminal region of MLKL is required and sufficient to induce its oligomerization and trigger cell death. 24813885_MLKL binding to phosphatidylinositol phosphates is required for plasma membrane rupture 25220470_MLKL structure determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals how different structural elements of the MLKL N-terminal region contribute to MLKL function and membrane permeation. 25697054_in the absence of caspase-8 activity, 24(S)-Hydroxycholesterol induces a necroptosis-like cell death which is RIPK1-dependent but MLKL-independent. 25748555_High expression of RIP3 in keratinocytes from toxic epidermal necrolysis patients potentiates MLKL phosphorylation/activation and necrotic cell death. 25766324_a novel non-enzymatic function of AChE-R is to stimulate RIPK1/MLKL-dependent regulated necrosis (necroptosis). The latter complements a cholinergic system in the ovary, which determines life and death of ovarian cells. 26165695_MLKL upregulation in SPARC overexpressed cells treated with Ara-C, indicates necrosis as a possible cell death process for the SKM-1 cells under these stringent conditions 26283547_These data reveal a potential role for RIPK3 as a suppressor of MLKL activation and indicate that phosphorylation can fine-tune the ability of MLKL to induce necroptosis. 26704887_Modelling predicts that a C-terminal helix constrains the activity of MLKL1, but not MLKL2 26823841_MLKL was a prognostic biomarker for cervical squamous cell carcinoma 26853145_Results show that upon activation, MLKL undergoes oligomerization mediated by the brace domain, being recruited to the plasma membrane through avidity of N-terminal helix bundle for phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP). 26865533_Necroptosis signaling is modulated by the kinase RIPK1 and requires the kinase RIPK3 and the pseudokinase MLKL. (Review) 26866270_coexpression of Hsp90 increases MLKL oligomerization and plasma membrane translocation and enhances MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Findings demonstrate that an efficient necrotic response requires a functional Hsp90. 26868910_Phosphorylated MLKL leads to a conformational change, exposure of the N-terminal domain, results in MLKL membrane localization, oligomerization and membrane permeabilization. 26933192_Results from interaction proteomics identified MLKL as a novel HSP90 client protein in HT-29 cells. 27033670_MLKL forms cation channels that are permeable preferentially to Mg(2+) rather than Ca(2+) in the presence of Na(+) and K(+). 27411587_In AML, MLKL expression is reduced in specific subsets. This is linked to its function in activating the ASC inflammasome. 27432118_Low expression of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein was associated with decreased overall survival in all patient-group with resected colon cancer. 27473085_Downregulated expression of MLKL is associated with gastric caner. 27756058_results reveal a pathway for MLKL-dependent programmed necrosis that is executed in the absence of RIPK3 and potentially drives the pathogenesis of severe liver diseases. 27920255_MLKL octamer formation depends on alpha-helices 4 and 5. 28130493_this study shows that MLKL is an endogenous activator of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and that MLKL activation provides a mechanism for concurrent processing and release of IL-1beta independently of gasdermin-D 28412393_adhesion-induced eosinophil cytolysis takes place through RIPK3-MLKL-dependent necroptosis, which can be counterregulated by autophagy 28650960_Data suggest that necroptotic cells externalize phosphatidylserine (PS) after translocation of phosphorylated MLKL to cell membrane; necroptotic cells with exposed PS release extracellular vesicles containing MLKL; inhibition of MLKL after PS exposure can reverse process of necroptosis and restore cell viability. 28666573_this study shows that release of phosphorylated MLKL within extracellular vesicles serves as a mechanism for self-restricting the necroptotic activity of this protein 28844856_Thus, activation of MLKL determines cell lysis with release of proinflammatory mediators. We found that pMLKL, the activated form of MLKL, is significantly increased in intestinal epithelial cells expressing RIP3 as well as in bioptic inflamed ileal and colonic tissues from CD and UC patients. 28854080_Biological events and molecular signaling following MLKL activation during necroptosis have been reported. 28878015_these findings demonstrate that Trx1 is a critical regulator of necroptosis that suppresses cell death by maintaining MLKL in a reduced inactive state. 29104146_Data show that phosphatidylinositol transfer protein alpha (PITPalpha) is involved in the function of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) in necroptosis. 29606984_Results demonstrate that MLKL concentrations measured after three days of ICU treatment in critically ill patients predict prognosis during intensive care unit treatment. These data not only suggest a previously unrecognized function of MLKL as a biomarker in critical illness and sepsis but also highlight the clinical relevance of MLKL in the pathophysiology of inflammatory and infectious diseases. 29656768_MLKL expression alters APP metabolism and loss-of-function mutation might contribute to late-onset ApoE varepsilon4-negative AD in the Hong Kong Chinese population. 29883610_Highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates are an additional, crucial requirement for MLKL death effector function acting directly on MLKL to execute necroptosis. 29930286_Following activation, toggling within the MLKL pseudokinase domain promotes 4HB domain disengagement from the pseudokinase domain alphaC helix and pseudocatalytic loop, to enable formation of a necroptosis-inducing tetramer. 30084053_Our studies suggested that chelerythrine (CHE) possibly induces apoptosis through the nuclear translocation of MLKL and *MLKL, which is promoted by a mutual regulation between MLKL and PERK-eIF2alpha pathway in response to ROS formation. The present study clarified the new function of MLKL in apoptosis. 30158627_Necroinflammation driven by RIPK3-MLKL-dependent necroptosis plays a crucial role in the progression of IRI to CKD. 30355688_Data demonstrate that the NS1 protein of influenza A virus (IAV) interacts with MLKL. Coiled-coil domain 2 of MLKL has a predominant role in mediating the MLKL interaction with NS1. The interaction of NS1 with MLKL increases MLKL oligomerization and membrane translocation. Moreover, the MLKL-NS1 interaction enhances MLKL-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. 30509860_REVIEW: recent structural studies of the core machinery of the pathway, the protein kinases receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPK)1 and RIPK3, and the terminal effector, the pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), in shaping our mechanistic understanding of necroptotic signaling 30644439_The bromodomain protein BRD4 positively regulates necroptosis via modulating MLKL expression. 30683918_The lncRNA-FA2H-2-MLKL pathway is essential for regulation of autophagy and inflammation, and suggested that lncRNA-FA2H-2 and MLKL could act as potential therapeutic targets to ameliorate atherosclerosis-related diseases. 30837196_These results suggest that MLKL may modulate PI(3,4,5)P3 production, thereby regulating insulin sensitivity. 31031142_It uncovers mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL's) activating switch in -terminal executioner domain (NED) triggered by a select repertoire of IP metabolites. 31095773_Study found that the phosphorylated mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (pMLKL) was increased in the ageing human testes. Seminal pMLKL expression was decreased in groups with sperm concentration 0-5 and 5-10 million/ml when compared with normal sperm concentration in young men and showed an age-related increased expression in men aged 22-60 years with normal sperm concentration. 31230815_we identify an unexpected role of TAM kinases (Tyro3, Axl, and Mer)as promoters of necroptosis, a pro-inflammatory necrotic cell death. Pharmacologic or genetic targeting of TAM kinases results in a potent inhibition of necroptotic death in various cellular models. We identify phosphorylation of MLKL Tyr376 as a direct point of input from TAM kinases into the necroptosis signaling 31719524_Current translational potential and underlying molecular mechanisms of necroptosis. 31727943_Understanding allosteric interactions in hMLKL protein that modulate necroptosis and its inhibition. 32004572_ID1 overexpression increases gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by activating RIP3/MLKL-dependent necroptosis. 32114297_PI3K mediates tumor necrosis factor induced-necroptosis through initiating RIP1-RIP3-MLKL signaling pathway activation. 32162861_The Trend of ripk1/ripk3 and mlkl Mediated Necroptosis Pathway in Patients with Different Stages of Prostate Cancer as Promising Progression Biomarkers. 32358523_A novel neurodegenerative spectrum disorder in patients with MLKL deficiency. 32621119_MLKL Aggravates Ox-LDL-Induced Cell Pyroptosis via Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. 32788571_Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like Protein Promotes Human Monocyte Cell Adhesion to Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Via Upregulation of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Expression. 32917855_Reduction in MLKL-mediated endosomal trafficking enhances the TRAIL-DR4/5 signal to increase cancer cell death. 33051424_Changes in plasma levels of RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL in patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease and its clinical predictive value.', trans 'RIPK1RIPK3MLKL. 33054864_Increased MLKL mRNA level in the PBMCs is correlated with autoantibody production, renal involvement, and SLE disease activity. 33318170_Locking mixed-lineage kinase domain-like protein in its auto-inhibited state prevents necroptosis. 33531383_Location, location, location: A compartmentalized view of TNF-induced necroptotic signaling. 33616081_Differential role of MLKL in alcohol-associated and non-alcohol-associated fatty liver diseases in mice and humans. 33625952_RIPK3 Activates MLKL-mediated Necroptosis and Inflammasome Signaling during Streptococcus Infection. 33754026_MLKL: Functions beyond serving as the Executioner of Necroptosis. 33767595_MLKL inhibits intestinal tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway. 33795639_A family harboring an MLKL loss of function variant implicates impaired necroptosis in diabetes. 33850121_Conformational interconversion of MLKL and disengagement from RIPK3 precede cell death by necroptosis. 34158471_The MLKL kinase-like domain dimerization is an indispensable step of mammalian MLKL activation in necroptosis signaling. 34217157_Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like Pseudokinase (MLKL) Gene Expression in Human Atherosclerosis with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. 34500630_Positive Charges in the Brace Region Facilitate the Membrane Disruption of MLKL-NTR in Necroptosis. 34647144_Mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase-mediated necroptosis aggravates periodontitis progression. 34811356_Human RIPK3 maintains MLKL in an inactive conformation prior to cell death by necroptosis. 35166320_Rare catastrophes and evolutionary legacies: human germline gene variants in MLKL and the necroptosis signalling pathway. 35264437_Necroptosis-driving genes RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL-p are associated with intratumoral CD3(+) and CD8(+) T cell density and predict prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 35264780_Membrane permeabilization is mediated by distinct epitopes in mouse and human orthologs of the necroptosis effector, MLKL. 35851586_Enhanced nuclear localization of phosphorylated MLKL predicts adverse events in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000012519 |
Mlkl |
63.164235 |
0.1838553404 |
-2.443357 |
0.303174713 |
63.256804 |
0.00000000000000181439808083597208247606964394169334773966139988388146520037480513565242290496826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000012783062373813340462371536103772960422703293403845492548498441465198993682861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
18.2898259 |
3.4409705 |
99.6883430 |
12.1694429 |
| ENSG00000168405 |
8418 |
CMAHP |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
Sialic acids are terminal components of the carbohydrate chains of glycoconjugates involved in ligand-receptor, cell-cell, and cell-pathogen interactions. The two most common forms of sialic acid found in mammalian cells are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) and its hydroxylated derivative, N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc). Studies of sialic acid distribution show that Neu5Gc is not detectable in normal human tissues although it was an abundant sialic acid in other mammals. Neu5Gc is, in actuality, immunogenic in humans. The absense of Neu5Gc in humans is due to a deletion within the human gene CMAH encoding cytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase, an enzyme responsible for Neu5Gc biosynthesis. Sequences encoding the mouse, pig, and chimpanzee hydroxylase enzymes were obtained by cDNA cloning and found to be highly homologous. However, the homologous human cDNA differs from these cDNAs by a 92-bp deletion in the 5' region. This deletion, corresponding to exon 6 of the mouse hydroxylase gene, causes a frameshift mutation and premature termination of the polypeptide chain in human. It seems unlikely that the truncated human hydroxylase mRNA encodes for an active enzyme explaining why Neu5Gc is undetectable in normal human tissues. Human genomic DNA also shows evidence of this deletion which does not occur in the genomes of African great apes. Nonetheless, the CMAH gene maps to 6p21.32 in humans and great apes indicating that mutation of the CMAH gene occurred following human divergence from chimpanzees and bonobos. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
19890979_Data show that CMAH gene expression is significantly upregulated in the adult stem cell populations studied, both of hematopoietic and mesenchymal origin, and identify CMAH as a novel stem cell marker. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23709682_Metabolically reintroducing sialic acid to human T cells (which by mutation of CMAH occurring 2 million years ago lack natural sialic acid) blunts proliferation and activation. 24033743_GGTA1/CMAH knockout pig samples had increased relative amounts of high-mannose, incomplete, and xylosylated N-linked glycans |
|
|
11.236743 |
0.2715486985 |
-1.880717 |
0.532590550 |
12.687706 |
0.00036806745168945273873409296250258648797171190381050109863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000926603374882538333677517439213033867417834699153900146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4255808 |
1.5799713 |
16.4622450 |
3.5796100 |
| ENSG00000168421 |
399 |
RHOH |
protein_coding |
Q15669 |
FUNCTION: Negative regulator of hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation, survival and migration. Critical regulator of thymocyte development and T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signaling by mediating recruitment and activation of ZAP70. Required for phosphorylation of CD3Z, membrane translocation of ZAP70 and subsequent activation of the ZAP70-mediated pathways. Essential for efficient beta-selection and positive selection by promoting the ZAP70-dependent phosphorylation of the LAT signalosome during pre-TCR and TCR signaling. Crucial for thymocyte maturation during DN3 to DN4 transition and during positive selection. Plays critical roles in mast cell function by facilitating phosphorylation of SYK in Fc epsilon RI-mediated signal transduction. Essential for the phosphorylation of LAT, LCP2, PLCG1 and PLCG2 and for Ca(2+) mobilization in mast cells (By similarity). Binds GTP but lacks intrinsic GTPase activity and is resistant to Rho-specific GTPase-activating proteins. Inhibits the activation of NF-kappa-B by TNF and IKKB and the activation of CRK/p38 by TNF. Inhibits activities of RAC1, RHOA and CDC42. Negatively regulates leukotriene production in neutrophils. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11809807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19414807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22850876}. |
Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ras superfamily of guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-metabolizing enzymes. The encoded protein is expressed in hematopoietic cells, where it functions as a negative regulator of cell growth and survival. This gene may be hypermutated or misexpressed in leukemias and lymphomas. Chromosomal translocations in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma occur between this locus and B-cell CLL/lymphoma 6 (BCL6) on chromosome 3, leading to the production of fusion transcripts. Alternative splicing in the 5' untranslated region results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:399; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; GTPase inhibitor activity [GO:0005095]; kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0019210]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell projection assembly [GO:0030031]; cortical cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030865]; engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:0043652]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; mast cell activation [GO:0045576]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043124]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0016601]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of neutrophil migration [GO:1902622]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217] |
15563831_5' end heterogeneity of RhoH mRNAs was observed, due to alternative splicing of some 5' exons and to the use of these different transcription start sites. 16541139_In both Richter's transformation and prolymphocytic transformation, high-levels of AID mRNA expression and high-frequency mutations of RhoH protein genes were detected. 17443219_Aberrant somatic hypermutation of RhoH gene is associated with diffuse large B cell lymphoma 17476282_RHOH mutation is associated with splenic and nodal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas 18559497_Underexpression of RhoH is associated with Hairy Cell Leukemia 18691253_low expression of the RhoH transcript was a predictor of worse prognosis in both overall and disease-free survival. 19414807_RhoH/TTF represents an inducible feedback inhibitor in neutrophils that is involved in the limitation of innate immune responses. 19847197_RhoH has a function in the progression of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a murine model and show RhoH expression is altered in human primary lymphocytic (CLL) samples. 19950172_Data suggest that RhoH function might be regulated by lysosomal degradation of RhoH protein following TCR complex but not BCR activation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20738848_propose that RhoH functions as a negative regulator for IL3-induced signals through modulation of the JAK-STAT pathway 20851766_RhoH is a key adapter protein that maintains LCK in the inactive state, contributing to the regulation of both pre-TCR and TCR signalling during T-cell development. 21473742_Repression of the RHOH gene by JunD 22474251_RhoH plays a critical role in prosurvival chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell-cell and cell-microenvironment interactions with this agent. 22689994_conclude that RhoH expression provides a key molecular determinant that allows T cells to switch between sensing chemokine-mediated go signals and TCR-dependent stop signals 22850876_RHOH deficiency leads to T cell defects and persistent epidermodysplasia verruciformis-HPV infections. 23499578_Our current results indicate differential requirements for RhoH in the development of TCRalphabeta CD8alphaalpha IELs compared to other subsets of T cells including agonist selected T cells. 23850828_Mutations in hematopoiesis-specific Rho GTPases Rac2 and RhoH lead to a wide range of human blood disorders. (Review) 27574848_extracellular microenvironment signals regulate RhoH and Kaiso to modulate actin-cytoskeleton structure and transcriptional activity during T cell migration 27740624_These results highlight a novel negative regulatory role for RhoH in eosinophil differentiation, most likely in consequence of altered GATA-2 levels. 29510700_RhoH promotes prostate cancer cell migration and RhoH expression levels correlate with prostate cancer progression. 31204928_In AML, RhoH expression negatively correlates with recurrence rate, which can be used as a prognostic indicator independently 32959187_Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identifies RHOH and TRAF1 as key candidate genes for psoriatic arthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000029204 |
Rhoh |
32.981011 |
10.4202328149 |
3.381316 |
0.392921355 |
81.730296 |
0.00000000000000000015598397490605800713489031160259908949496396245325058110484106599358256062259897589683532714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001351128796721488413367251142689768508633365121592603656786035770664966548793017864227294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.9140882 |
14.1643886 |
5.6081018 |
1.2057109 |
| ENSG00000168427 |
377007 |
KLHL30 |
protein_coding |
Q0D2K2 |
|
Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:377007; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000026308 |
Klhl30 |
13.548724 |
0.4016165059 |
-1.316110 |
0.423584517 |
9.941480 |
0.00161595583306974413008438862249249723390676081180572509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003635900624406924238479765776332897075917571783065795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7571332 |
2.1113562 |
19.4641129 |
3.2703404 |
| ENSG00000168477 |
7148 |
TNXB |
protein_coding |
P22105 |
FUNCTION: Appears to mediate interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix. Substrate-adhesion molecule that appears to inhibit cell migration. Accelerates collagen fibril formation. May play a role in supporting the growth of epithelial tumors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17033827}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the tenascin family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins. The tenascins have anti-adhesive effects, as opposed to fibronectin which is adhesive. This protein is thought to function in matrix maturation during wound healing, and its deficiency has been associated with the connective tissue disorder Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. It is one of four genes in this cluster which have been duplicated. The duplicated copy of this gene is incomplete and is a pseudogene which is transcribed but does not encode a protein. The structure of this gene is unusual in that it overlaps the CREBL1 and CYP21A2 genes at its 5' and 3' ends, respectively. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7148; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; tenascin complex [GO:0090733]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; collagen fibril binding [GO:0098633]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; collagen metabolic process [GO:0032963]; elastic fiber assembly [GO:0048251]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; positive regulation of cell fate determination [GO:1905935]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of collagen fibril organization [GO:1904028]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation [GO:0010862]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta activation [GO:1901390]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900748]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043506]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641] |
12121677_molecular studies on RCCX haplotypes revealing a unique recombination giving rise to a TNXB/TNXA hybrid gene, CYP21A deletion and CYP21B duplication on one chromosome 12376099_localization and analysis of the principal promoter for human tenascin-X 12746407_chromosomal mapping of a de novo unequal crossover causing a deletion of the steroid 21-hydroxylase gene and a non-functional hybrid tenascin-X gene 14729256_The transmission disequilibrium test did not show allelic association between these two TNXB single nucleotide polymorphisms and schizophrenia, and the rs1009382-rs204887 haplotypes were not associated with the illness either. 15102077_Both elastic fiber abnormalities and reduced collagen content contribute to the observed phenotype in TNX-deficient patients. 15339882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15455729_different distributions of tenascin-C and -X were found around the epithelium and the endomysium of the mental symphyseal region, and affect the specific formation of the mandible during ossification in the fetus 15733269_elastic fiber abnormalities in hypermobility type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome are specific for TNX-haploinsufficient individuals and confirm an important role for TNX in regulating elastic fiber integrity 16567571_Tenascin-X expression is markedly decreased in AAA tissue, and AAA is associated with high serum concentrations of tenascin-X. 17033827_TNX contributes to matrix stability and is possibly involved in collagen fibril formation. 17192952_Association of the TNXB locus or its adjacent region of the NOTCH4 locus with schizophrenia. 17192952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17202312_TNXB and TNC may be involved in the malignant transformation of plexiform neurofibromas 17263730_Multiple species of TNX in blood were identified and characterized. 17453911_TNX is unlikely to be involved in matrix deposition in the early phase of wound healing, but it is required in the later phase when remodeling and maturation of the matrix establishes and improves its biomechanical properties. 18058064_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18058064_TNXB(tenascin XB protein) gene is a candidate gene susceptible to Systemic lupus erythematosus in the Japanese population. 18091320_This study showed different patterns of expression of tenascin and fibronectin along the process of tumorigenesis and tumor progression in pleomorphic adenoma, a fact that might play a role in invasion properties of these tumors. 18155129_Data indicate a complex architecture of the extracellular matrix in the uterosacral ligaments, with marked differences in tenascin and elastin expression between postmenopausal women with or without pelvic organ prolapse. 18335242_TNX-deficient women are at risk of obstetric complications. 18588874_These results indicate that the hypoxia-induced activation of the XB-S promoter is regulated through dissociation of HDAC1 from an Sp1-binding hypoxia-responsive element site. 18679583_These results suggest possible involvement of XB-S in the function of Eg5. 19116923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19143814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19143821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19738457_Tenascin-X may be a new diagnostic marker of malignant mesothelioma in the differential diagnosis of cancers involving the serosal cavities. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19860791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20853426_Three point mutations in TNX gene were found to be associated with hypermobility type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) . The phenotypic effects of V1195M mutation on 7th fibronectin Type III domain (TNXfn7) with regards to EDS were investigated. 21317684_rs204887 itself or a nearby variant is unlikely to play a major role in the development of schizophrenia although a cumulative contribution of rare variants in the TNXB gene cannot be ruled out. 22588153_Combined analysis of tenascin-C expression and the nodule size improved the prediction of malignancy in this patient cohort. 22694956_Genome-wide association study of age-related macular degeneration identifies TNXB, FKBPL and NOTCH4 as candidate susceptibility genes. 22827484_Noticeable decreased expression of tenascin-X in calcific aortic valves. 22991340_no difference in genotype frequency was detected between patients who experienced a re-dislocation after the initial surgery and patients who did not sustain a re-dislocation. 23284009_Tenascin-X haploinsufficiency was associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia 23620400_these results suggest that mutations in TNXB can cause hereditary primary vesicoureteral reflux . 25926574_It plays regulatory roles in collagen functions such as fibril organization and fibrillogenesis in calcific aortic valves. 26090390_We then quantified the tenascin-X level in serum of patients and identified tenascin-X as potent marker for ovarian cancer, showing that secretomic analysis is suitable for the identification of protein biomarkers when combined with protein immunoassay. 26408188_the identification of a rare missense variant in TNXB in combination with a positive family history of VUR and joint hypermobility may represent a non-invasive method to diagnose PVUR and warrants further evaluation in other cohorts 27297501_Study describes a biallelic TNXB variants in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to CYP21A2 deletions resulting in a classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome phenotype with skin hyperextensibility, widened atrophic scars and joint hypermobility. 27367046_Hypermethylated sites at TNXB are associagted with response to starvation in anorexia nervosa. 27582382_patients with the TNX-deficient type EDS typically have generalized joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility and easy bruising. In contrast to the classical type, the inheritance pattern is autosomal recessive and atrophic scarring is absent. Molecular analysis of TNXB in a diagnostic setting is challenging. 29470764_mRNA for tenascin-X gene values was higher in ventricular septal defects. 29917237_Loss of TNXB expression is associated with Gastrointestinal diseases. 30277495_These results suggest that fetal membranes may be a source of amniotic fluid TNX whereby protein and mRNA expression seem to be significantly impacted by inflammation independent of fetal membrane status. 30605228_TNX-deficient patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome have upper gastric dysfunction. 30642396_Data demonstrates gene expression changes in differentially methylated TNXB gene in patients with age-related macular degeneration. 30711938_TNXB is a novel diagnostic biomarker for Malignant Mesothelioma 32056283_Data indicate that tenascin XB protein (TNXB) mRNA expression was downregulated in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC) compared with adjacent normal tissues. 32606567_Differential DNA methylation patterns in human Schlemm's canal endothelial cells with glaucoma. 33332743_A TNXB splice donor site variant as a cause of hypermobility type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. |
ENSMUSG00000033327 |
Tnxb |
64.822357 |
0.0342119984 |
-4.869354 |
0.460838868 |
102.821926 |
0.00000000000000000000000366668887145773573445018825004027970668220618825869312322699041482854109830213928944431245326995849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000038166662724059366259901671657914785937707982377262881060123579732984433476872254686895757913589477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3489999 |
1.8294453 |
92.1144842 |
33.6724547 |
| ENSG00000168495 |
661 |
POLR3D |
protein_coding |
P05423 |
FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Specific peripheric component of RNA polymerase III which synthesizes small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs. Plays a key role in sensing and limiting infection by intracellular bacteria and DNA viruses. Acts as nuclear and cytosolic DNA sensor involved in innate immune response. Can sense non-self dsDNA that serves as template for transcription into dsRNA. The non-self RNA polymerase III transcripts, such as Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs) induce type I interferon and NF- Kappa-B through the RIG-I pathway (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19609254, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631370}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Antiviral defense;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene complements a temperature-sensitive mutant isolated from the BHK-21 Syrian hamster cell line. It leads to a block in progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle at nonpermissive temperatures. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:661; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; RNA polymerase III complex [GO:0005666]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006383] |
22189167_Studies indicate that aatients with anti-RNAP have an increased risk of malignancy within a 5-year timeframe before or after onset of systemic sclerosis (SSc) skin changes. |
ENSMUSG00000000776 |
Polr3d |
273.338606 |
2.3984276958 |
1.262089 |
0.104107387 |
147.734880 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000054210750700391982794082796817147010722474864508466703934255683677894974686427131367941461420612014876496687065809965133666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000007860026329447796814495067553149324942763099843178292308225314596916727968694007006749714661086869682549149729311466217041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
359.5720637 |
26.9735021 |
151.0394229 |
8.6433816 |
| ENSG00000168528 |
347735 |
SERINC2 |
protein_coding |
Q96SA4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in several processes, including phosphatidylserine metabolic process; positive regulation of CDP-diacylglycerol-serine O-phosphatidyltransferase activity; and positive regulation of serine C-palmitoyltransferase activity. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:347735; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phosphatidylserine metabolic process [GO:0006658]; sphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006665] |
21752829_SERINC2 protein localizes in lysosomes in HeLa cells 23455491_In subjects of European descent, SERINC2-NKAIN1 expression of genes is associated with alcohol dependence. 23778322_study concluded that SERINC2 was a replicable and significant risk gene specific for alcohol dependence in individuals of European descent 24424505_TDE2 may have an effect on tumor cell growth by influencing the expression of SREBP and p21. 28935972_Results suggest that the serine incorporator 2 (SERINC2) gene is a novel autism spectrum disorder (ASD) candidate gene. 29268082_In contrast to human SERINC5(S5), we observed that human SERINC2(S2) did not restrict HIV-1, and was inefficiently incorporated into HIV-1 virions when compared to S5. 34288243_SERINC2 increases the risk of bipolar disorder in the Chinese population. |
ENSMUSG00000023232 |
Serinc2 |
21.547834 |
0.3827668876 |
-1.385462 |
0.393739731 |
12.487361 |
0.00040971461598446828151695586761604772618738934397697448730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001022900495928746834525813191874021867988631129264831542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.3548345 |
2.7418202 |
29.9468706 |
4.5233067 |
| ENSG00000168542 |
1281 |
COL3A1 |
protein_coding |
P02461 |
FUNCTION: Collagen type III occurs in most soft connective tissues along with type I collagen. Involved in regulation of cortical development. Is the major ligand of ADGRG1 in the developing brain and binding to ADGRG1 inhibits neuronal migration and activates the RhoA pathway by coupling ADGRG1 to GNA13 and possibly GNA12. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aortic aneurysm;Calcium;Collagen;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes the pro-alpha1 chains of type III collagen, a fibrillar collagen that is found in extensible connective tissues such as skin, lung, uterus, intestine and the vascular system, frequently in association with type I collagen. Mutations in this gene are associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV, and with aortic and arterial aneurysms. [provided by R. Dalgleish, Feb 2008]. |
hsa:1281; |
collagen type III trimer [GO:0005586]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; platelet-derived growth factor binding [GO:0048407]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; aorta smooth muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0060414]; basement membrane organization [GO:0071711]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; elastic fiber assembly [GO:0048251]; endochondral bone morphogenesis [GO:0060350]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; heart development [GO:0007507]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; layer formation in cerebral cortex [GO:0021819]; limb joint morphogenesis [GO:0036022]; lung development [GO:0030324]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of immune response [GO:0050777]; negative regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001223]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; peptide cross-linking [GO:0018149]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; response to angiotensin [GO:1990776]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; skin development [GO:0043588]; supramolecular fiber organization [GO:0097435]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; transforming growth factor beta1 production [GO:0032905]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11577371_mutational analysis in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV 11973338_keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), a key stimulator of epithelial cell proliferation during wound healing, preferentially binds to collagens I, III, and VI. 12140670_COL3A1 mutations appear not to be a major cause of isolated spontaneous cervical artery dissections 12140670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12149201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12149201_variants in the COL3A1 gene modulate the risk of coronary artery disease and could also modulate the response to antithrombotic therapy 12631068_collagen type III was up-regulated by high glucose, but not by TGF-beta1 in renal fibroblasts 12880417_Proportion of collagen III relative to collagen I increased significantly up to 6 weeks after initial injury and remained elevated up to 6 months, at which time the proportion of collagen III was 70% above baseline values 14633859_Although connective tissue growth factor alone had no effect on collagen secretion, combined stimulation with IGF-I enhanced collagen accumulation. 14970208_fibroblasts from Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients, with mutations in COL5A1 and COL3A1, synthesize aberrant types V and III collagen and show defective organization of these proteins into the extracellular matrix and reduction of alpha(2)beta(1) integrin 15193836_Association between COL3A1 collagen gene exon 31 and risk of floppy mitral valve/mitral valve prolapse among the Chinese population of Taiwan 15193836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15227656_The lower collagen content in the endopelvic fascia and skin of women with SUI is not due to reduced collagen synthesis or selective reduction in synthesis of either collagen I or collagen III. 15365990_Predicted rates of AA substitution for Gly are compared with missense mutations known to cause disease. Any Gly replacement causes disease. The level of triple-helix destabilization determines outcome. More destabilizing mutations were seen than expected. 15514164_hnRNP A1 & K ARE positive effectors of collagen synthesis acting at the post-transcriptional level by interaction with the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of 3A1 mRNAs. 15838180_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15894390_characterization of the proximal promoter of the COL3A1 gene; segment from -96 to -34 necessary for activation of transcription; multiple proteins depending on cell types, found to form the DNA-protein complex at -79 to -63 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043429_analysis of binding between collagen type III and integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 16088212_collagen III, and probably fibronectin, are degraded extracellularly in smooth muscle cells from varicose veins by a mechanism involving MMPs, and maybe MMP3 by a direct or an indirect pathway 16259598_Antisense oligodeoxynuclotides down-regulate collagen type III gene expression. 16356540_demonstrates, for the first time, that BIRC3 (anti-apoptotic protein), COL3A1 (matrix protein synthesis), and CXCL3 (chemokine) were up-regulated in the thrombin-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells 16521042_The expression of precursor proteins and mRNA of type I and type III collagens is increased in usual interstitial pneumonia and sarcoidosis, reflecting mainly active synthesis of these collagens in different areas of the lung. 16681691_Type III collagen was expressed significantly higher in valvular cardiomyopathy. 16838047_data showed the complexity of the regulation of the COL3A1 gene (human alpha1(III) collagen) involving several transcription factors. 17146610_Altered expression of decorin mRNA in the different dermal strata and a decrease in the collagen-to-decorin ratio inflicted by both age and ultraviolet irradiation affect collagen bundle diameter and subsequently the mechanical properties of human skin. 17396208_The results suggest that a high level of decorin mRNA might be associated with the reduced content of collagen type III, resulting in a less flexible form of extracellular matrix in the connective tissue in stress urinary incontinence and prolapse. 18089612_COL3A1 was overexpressed in uterine fibroids. 18389341_Case report of a novel COL3A1 gene mutation in patient with aortic dissected aneurysm and cervical artery dissections. 18401458_High glucose levels downregulate mRNA levels in dermal fibroblast cell cultures. 18521510_Data reveal a more critical role for membrane cholesterol in collagen type III-induced than in VWF-induced Ca(2+) signalling. 18642782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18722615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18722615_There may be an association between COL3A1 genotype and risk of pelvic organ prolapse 18805790_the human type III collagen Gly991-Gly1032 cystine knot-containing peptide has both 7/2 and 10/3 triple helical symmetries 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19000145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19000145_the constructs containing the 'G' allele of rs3106796 appear to exert lower transcriptional activity of COL3A1 than the 'A' allele, depending on the promoter types. 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19152942_COL3A1 exon 31 polymorphism may have a role in determining the risk of pelvic organ prolapse in women 19152942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19389097_A dose-dependent increase in viable cells was demonstrated after the IPL irradiation. There was no significant change in mRNA levels of collagen I and fibronectin. 19398000_Results describe the mechanism of interaction and cleavage of human type III collagen by fibroblast MMP-1 by using a panel of recombinant human type III collagens (rhCIIIs) containing engineered sequences in the vicinity of the cleavage site. 19398442_COL3A1 is a disease-associated gene in both paediatric and adult gastroesophageal reflux and COL3A1 is genetically associated with hiatal hernia in adult males. 19398442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19424605_the Aright curved arrow G (Ile1205Val) polymorphism of COL3A1 were associated (PA is a predictor of pelvic organ prolapse 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19639654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19764567_The expression of collagen III and CTGF in pPROM group were decreased significantly when compared to their control groups. The expression of collagen III in pPROM group appeared significantly decreased when compared to that in tPROM group. 19790048_Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha inhibits the fibroblast-like markers type I and type III collagen during hypoxia-induced chondrocyte redifferentiation. 19858036_HGF inhibited TGF-beta1 mRNA expression and reduced collagen III secretion. 19893454_Data show that the expression of collagen types I, III and fibronectin was significantly higher in pancreatic cancer, and the expression of collagen type IV, laminin and vitronectin was significantly lower in pancreatic cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19932771_The catalytic domain of MMP-12 binds to the triple helix and cleaves the typical sites -Gly(775)-Leu(776)- in alpha-2 type I collagen and -Gly(775)-Ile(776)- in alpha-1 type I and type III collagens and at multiple other sites in both collagen types. 20039537_Through alveolar macrophage mediation SiO2 can accelerate the expression of TIMP-1 and collagen III, and inhibit the expression of MMP-1 in human lung fibroblasts. 20063990_Data suggest that integrin alpha(2)beta(1), glycoprotein Ib and vWf interactions with collagen I and III contribute to platelet adhesion under high shear flow. 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227120_Patients presenting a significant increase in maximum ascending aortic aneurysm size have a significantly higher type III procollagen level than those demonstrating no or limited growth in maximum aneurysm diameter. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631730_meprins could be important players in several remodeling processes involving collagen fiber deposition 20648054_Physical and laboratory examinations revealed that true haploinsufficiency of COL3A1, COL5A2, and MSTN, but not that of SLC40A1, leads to a clinical phenotype. 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20699621_In addition, among nondiabetic kidney disease, elevation of u-IVc was observed in patients with membranous nephropathy and ANCA. 20704113_Tendon sheath fibroblasts can transfect with antisense TGF-beta1 gene successfully and can decrease production of collagen I, collagen III, and TGF-beta1, which were factors of tendon adhere formation. 20720362_A novel point mutation is demonstrated at c.2528 G>A (p.Gly843Glu) in the COL3A1 gene of a Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV patient. 21044884_identification of the GVMGFO discoidin domain receptor binding motif on collagen III 21086191_cases of segmental mediolytic arteriopathy and traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage undergo genetic testing for COL3A1 mutations 21343850_Data show that TGF-beta1 stimulated cell proliferation, enhanced the gene expression of type I and III collagen, and alpha-SMA. 21558934_RT-PCR showed that COL3A1 from osteoblasts from Pfeiffer syndrome grown on PLPG acid plates were downregulated after 30 days. 21637106_COL3A1 haploinsufficiency results in a variety of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV with delayed onset of complications and longer life expectancy 21858035_Data suggest that combination of HA, PIIINP, TGF-ss1 may provide a potential useful tool to assess liver fibrosis in adult HCV patients. 21941774_Alveolar macrophages exposed to SiO2 can induce elevated type III procollagen and collagen III expression levels in human lung fibroblasts. 21946467_Type IV, or vascular, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is a life-threatening, autosomal dominant condition. It is caused by mutation of the COL3A1 gene. 22001912_Data show that homozygous and compound heterozygous changes found in PLOD1 and SLC2A10 may confer autosomal recessive effects, and three MYH11, ACTA2 and COL3A1 heterozygous variants were considered as putative pathogenic gene alterations. 22019127_Letter: Describe COL3A1 mutations and clinical features of vascular type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in Italian patients. 22019950_procollagen III N-terminal peptide has a role in HBeAg loss in patients with chronic hepatitis B during entecavir therapy 22238662_Disease-associated mutations prevent GPR56-collagen III interaction. 22241462_study found that allele A of SNP rs1800255 conferred a 1.71-fold increased risk for intracranial aneurysms (IAs) and results in an amino acid change of Ala698Thr, which led to a lower thermal stability of the peptide; results support the view that the functional variant of COL3A1 is genetic risk factors for IAs in the Chinese population 22573319_The minimum type III sequence necessary for cleavage by the MMP1 and MMP13 was 5 GXY triplets, including 4 residues before and 11 residues after the cleavage site (P4-P11'). 22788708_Data suggest that cardiac fibrosis, as assessed by serum extracellular matrix protein biomarkers (including PIIINP, procollagen Type III-N-terminal peptide), develops early in hypertensive patients and is predictive of cardiovascular events or death. 22836729_This study indicates that SP, mediated via NK-1 R, increases collagen remodeling and leads to increased MMP3 mRNA and protein expression that is further enhanced by cyclic mechanical loading. 22851868_IL-17, IL-23 and PIIINP have an inverse correlation with vitamin D in their involvement in the immune response in patients with HCV-4-related liver diseases in Egypt 22884488_The present study reveals that serum levels of PEDF are independently associated with P-III-P levels, suggesting that PEDF level is a novel biomarker of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 23013106_COL3A1 rs1800255, COL6A1 rs35796750 and COL12A1 rs970547 were not significantly associated with sit-and-reach, straight leg raise or total shoulder rotation range of motion 23040566_serum PICP and PIIINP levels correlate with the presence of left atrial fibrosis and may act as predictors for post-operative atrial fibrillation (AF) even in the absence of previous history of AF 23344861_Arteriovenous malformation patients exhibit changes in the Col I/Col III ratio and elastic fibers in the vasculature, which may compromise the structural integrity of cerebral vessels. 23645670_analysis of collagen folding in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome mutations 23688910_Case Report: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV due to a mutation in intron 14 of the COL3A1 gene leading to venous manifestations without affecting arterial vessels at clinical presentation. 23749290_A2AR activation downstream signaling for Col1 and Col3 expression proceeds via two distinct pathways with varying sensitivity to cAMP activation. 24038457_either selective knock-down of S1PR1 or silencing S1PR3 induced collagen alpha1(I) and collagen alpha1(III) expression in mesenchymal stem cells 24088220_The objective of this study was to determine the concentrations of types I, II and III collagen in six distinct regions of the supraspinatus tendon. 24286194_Data indicate that in dedifferentiating chondrocytes, alpha5beta1 integrin was found to be involved in the induction of type I (COL1A1) and type III procollagen (COL3A1) expression. 24361166_results suggest that mitofusin-2 protein may affect the synthesis of procollagen of fibroblasts in postmenopausal patients with pelvic organ prolapse (POP); changes in Mfn2 and procollagen expression may play a role in the development of POP 24421219_The results point to the fact that the injury and/or mandible fracture increase the collagen type III metabolism and its dynamics depends on the type of the used bone fixation. 24503541_Gal-1 decreased the expression of collagen genes COL3A1 and COL5A1 but increased the expression of fibronectin and laminin 5. 24641356_Expression of COL3A1 mRNA encoding key fibrotic extracellular matrix molecules was down-regulated by pre-miRNA-29b. 24650746_Arterial pathology in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome individuals is related to the underlying COL3A1 mutation type. 24664438_Variants of the COL3A1 gene are associated with a risk of stroke recurrence and prognosis. 24700772_As a result of the translocations, COL3A1-PLAG1, the constitutively active promoter of the partner gene drives the ectopic expression of PLAG1. 24760181_rs1800255, COL3A1 2209 G>A polymorphism not associated with pelvic organ prolapse in Dutch population 25073002_The first main finding of this study was that the rare COL3A1 rs1800255 AA genotype was associated with increased risk of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in the Polish cohort but not the South African cohort. 25193015_These results suggest that let-7d may suppress renal cell carcinoma growth, metastasis, and tumor macrophage infiltration at least partially through targeting COL3A1 and CCL7. 25231012_The production and purification of rhCOL3A1 described in this study offer a new method for obtaining high level of rhCOL3A1 in relatively pure form, which is suitable for biomedical materials application. 25344368_During heart valve development, Krox20-mediated activation of fibrillar Col1a1 and Col3a1 genes is crucial to avoid postnatal degeneration of the aortic valve leaflets. 25420629_novel missense mutation c.2176G>C in Chinese family with vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome 25432063_intracellular S1P plays a crucial role in the TGF-beta1-induced expression of Col alpha1(I) and Col alpha1(III), which is required for human fibrosis development. 25559610_Data indicate that N-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen (PIIINP) is a highly effective means to evaluate left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic pressure (EDP) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). 25758994_the clinical phenotype of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients is influenced by the type of COL3A1 variant. 25786138_miR-29a and miR-29b enhance cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by regulating SPARC and COL3A1 gene expression. 25846194_compare reported phenotypes for patients with missense variants in the C-propeptide domain for other human collagen disorders including COL1A1 and COL1A2 (osteogenesis imperfecta). 25893343_Report dysregulated expression of COL3A1 in disc degeneration. 26017485_In familial AAA we found one pathogenic and segregating variant (COL3A1 p.Arg491X), one likely pathogenic and segregating (MYH11 p.Arg254Cys), and fifteen VUS. 26258650_TGFbeta target genes including TGFBI, BAMBI, COL3A1 and SERPINE1 are significantly increased in Diamond Blackfan Anemia induced pluripotent stem cells 26406420_High serum Collagen Type III is associated with ovarian and breast cancer. 26497932_A novel missense mutation in COL3A1 was found in a young patient with cervical artery dissection as the single manifestation of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. 26741506_High COL3A1 expression is associated with colorectal carcinoma. 27363273_Data show that emodin can block pulmonary fibroblast proliferation and differentiation into myofibroblasts, and reduce the synthesis of collagen type 1 (Col1) and collagen type 3 (Col3). 27442361_High serum procollagen type III N-terminal peptide expression is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 27498063_Col3A may be a potential adjunct marker for both differentiating fibroadenoma from phyllodes tumor and assessing malignant potential in PTs. 27636223_Abnormal regulation of COL1 and COL3 may contribute to the early predisposition to POP in premenopausal women. 27648120_The findings indicate the critical role of CatB in regulating the expression of collagens III and IV by fibroblasts via prolonging TLR2/NF-kappaB activation and oxidative stress. 27655637_Kaplan-Meir analysis of GSE7696 indicate that COL3A1 and SNAP91 correlated with survival. 27889474_von Willebrand factor A1 domain-collagen binding is independent of gain- or loss-of-function phenotype and under shear stress, platelet translocation pause times on collagen-bound A1A2A3 are either normal or shorter depending on whether A1 is concertedly bound with the A3 domain to collagen. 28183226_Case Report: pathogenetic heterozygous COL3A1 mutation c.3140 G>A, p. Gly1047Asp in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome vascular type with different phenotypes in the same family. 28258187_Brain MRI in the affected siblings as well as in the two previously reported individuals with bi-allelic COL3A1 mutations showed a brain phenotype similar to that associated with mutations in GPR56. 28367737_Hepatitis C virus/Hepatitis B Virus co-infected patients with significant fibrosis did not show any significant difference (P > 0.05) from HCV mono-infected patients with respect to HCV-NS4, collagen III and MMP-1. 28481042_In conclusion, based on serological collagen formation and degradation makers, penetrating Crohn's disease is associated with increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediated breakdown of type III collagen 28742248_We identified biallelic COL3A1 variants in two unrelated families. In a 3-year-old female with developmental delay the nonsense variant c.1282C>T, p.(Arg428*) was detected in combination the c.2057delC, p.(Pro686Leufs*105) frame shift variant. 29191827_the role of cortisol regenerated by 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 (11beta-HSD1) in collagen III degradation in human amnion fibroblasts, was investigated. 29216800_Case Report: novel missense COL3A1 mutation in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patient presenting with pulmonary complications and iliac arterial dissection. 29263043_Reduced expression of types I and III collagen and TIMP-1 as well as the increased expression of MMP-1 and MMP-8 in the anterior vaginal wall tissues play important roles in the onset of pelvic organ prolapse. 29346445_provide a picture of the gene expression changes in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome skin fibroblasts and highlight that dominant negative mutations in COL3A1 also affect post-translational modifications and deposition into the ECM of several structural proteins crucial to the integrity of soft connective tissues 29376591_Given the high specificity of the polymorphism at the rs1800255 locus of the COL3A1 gene, determined by the Sanger sequencing, it can be concluded that there is an association between this polymorphism and urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women. 29471595_Elevated circulating PIIINP levels are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus individuals with adipose tissue expansion and systemic proinflammatory profile suggestive for adipose tissue dysfunction. 29498185_Analysis of polymorphisms of COL3A1 gene (rs1800255) did not show differences in allele distribution between women with and without SD. 29533249_a variant of COL3A1 (rs3134646) is associated with the risk of developing colonic diverticulosis in white men, whereas rs1800255 (COL3A1) and rs1800012 (COL1A1) were not associated with this condition after adjusting for confounding factors. 30111669_High Aminoterminal Propeptide of Type III Procollagen level is associated with increase in Cardiovascular Events in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. 30213581_Association Between Plasma Level of Collagen Type III Alpha 1 Chain and Development of Strictures in Pediatric Patients With Crohn's Disease. 30229812_Serum levels of collagen Type III and miRNA-98 in patients with osteoarthritis were significantly higher compared to that of healthy volunteers. 30267195_Increased collagen III in the proximal portion of the long head of the biceps tendon is associated with glenohumeral arthritis. 30273997_CITP, PIIINP, and P4NP 7S do not reflect myocardial collagen mRNA expression but presumably reflect extra-cardiac organ injury in heart failure. 30474650_the frequency of COL3A1 mosaicism 30518744_Findings suggested a tumor-suppressor role of the miR-29 family in control of MTX resistance and cell apoptosis through regulating COL3A1 or MCL1. 30545625_a triple helix fragment of hCOL3A1, Gly489-Gly510, contained multiple charged residues, as well as representative Glu-Lys-Gly and Glu-Arg-Gly charged triplets. 30550979_Significant decrease in the expression of the genes HOXA13 and COL3A in the uterosacral ligaments in advanced stages of prolapse, indicates that these gene expressions may play a role in the development of uterine prolapse. 30837697_The three different Glu>Lys variants point toward a new variant type in COL3A1 causative of vEDS, which has consistent clinical features. This is important knowledge for COL3A1 variant interpretation 31041498_Polymorphism rs1800255 from COL3A1 gene and the risk for pelvic organ prolapse. 31075413_Mutations in the COL3A1 gene cause the vascular type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. It is the most serious form of EDS, since patients often die suddenly due to a rupture of large arteries. Most of the glycine mutations lead to the synthesis of type III collagen with reduced thermal stability, which is more susceptible for proteinases. Intracellular accumulation of this normally secreted protein is also found. [review] 31533654_COL3A1 expression was associated with shorter overall survival in the four major histotypes of epithelial ovarian carcinoma patients 31575845_2 novel COL3A1 gene mutations were identified in two vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients. 31600821_Application of the 2017 criteria for vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in 50 patients ascertained according to the Villefranche nosology. 31816141_Human skin fibrosis: up-regulation of collagen type III gene transcription in the fibrotic skin nodules of lower limb lymphoedema. 31833208_Amniotic band sequence in paternal half-siblings with vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. 31903873_Diagnostic role of collagen-III and matrix metalloproteinase-1 for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. 32168427_Extracellular vesicle-mediated crosstalk between NPCE cells and TM cells result in modulation of Wnt signalling pathway and ECM remodelling. 32692893_Collagen I and collagen III polymorphisms in women with pelvic organ prolapse. 32757451_Collagen Type III Alpha 1 chain regulated by GATA-Binding Protein 6 affects Type II IFN response and propanoate metabolism in the recurrence of lower grade glioma. 32945508_Prognostic significance of abnormal matrix collagen remodeling in colorectal cancer based on histologic and bioinformatics analysis. 32999266_COL3A1, COL6A3, and SERPINH1 Are Related to Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Occurrence According to Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. 33280513_Role of COL3A1 and POSTN on Pathologic Stages of Esophageal Cancer. 33472700_Lnc-GULP1-2:1 affects granulosa cell proliferation by regulating COL3A1 expression and localization. 33819468_miR-29a-3p-dependent COL3A1 and COL5A1 expression reduction assists sulforaphane to inhibit gastric cancer progression. 33930075_COL3A1 rs1800255 polymorphism is associated with pelvic organ prolapse susceptibility in Caucasian individuals: Evidence from a meta-analysis. 34047934_Identification of COL3A1 variants associated with sporadic thoracic aortic dissection: a case-control study. 34252356_Data mining-based study of collagen type III alpha 1 (COL3A1) prognostic value and immune exploration in pan-cancer. 34261485_Turnover of type I and III collagen predicts progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 34587764_COL3A1 Missense Variant in a Patient Presenting With Hemoptysis. 34691289_Collagen Family Genes Associated with Risk of Recurrence after Radiation Therapy for Vestibular Schwannoma and Pan-Cancer Analysis. 35047627_COL3A1 and Its Related Molecules as Potential Biomarkers in the Development of Human Ewing's Sarcoma. 35587586_Atypical variants in COL1A1 and COL3A1 associated with classical and vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome overlap phenotypes: expanding the clinical phenotype based on additional case reports. 35598375_Overexpressed COL3A1 has prognostic value in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes the aggressiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activating the NF-kappaB pathway. 35699227_Carriers of COL3A1 pathogenic variants in Denmark: Interfamilial variability in severity and outcome of elective surgical procedures. 35964930_Phenotype of COL3A1/COL5A2 deletion patients. 36148899_COL3A1 Overexpression Associates with Poor Prognosis and Cisplatin Resistance in Lung Cancer |
ENSMUSG00000026043 |
Col3a1 |
5.600849 |
0.0700646262 |
-3.835170 |
1.019497406 |
17.449999 |
0.00002949644392845084036334016297509208470728481188416481018066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000087511057765614946499753423747591796200140379369258880615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7018945 |
0.5113107 |
9.9262445 |
2.7233212 |
| ENSG00000168546 |
2675 |
GFRA2 |
protein_coding |
O00451 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for neurturin. Mediates the NRTN-induced autophosphorylation and activation of the RET receptor. Also able to mediate GDNF signaling through the RET tyrosine kinase receptor.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Participates in NRTN-induced 'Ser-727' phosphorylation of STAT3. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O08842}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) and neurturin (NTN) are two structurally related, potent neurotrophic factors that play key roles in the control of neuron survival and differentiation. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the GDNF receptor family. It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-linked cell surface receptor for both GDNF and NTN, and mediates activation of the RET tyrosine kinase receptor. This encoded protein acts preferentially as a receptor for NTN compared to its other family member, GDNF family receptor alpha 1. This gene is a candidate gene for RET-associated diseases. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:2675; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor receptor activity [GO:0016167]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
12490080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12624147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17522305_Both GFR alpha2a and GFR alpha2c, but not GFR alpha2b, promote neurite outgrowth in transfected Neuro2A cells. 17825269_GFRalpha-2 were observed within sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves, dorsal column nuclei, olivary nuclear complex, reticular formation, pontine nuclei, locus caeruleus, raphe nuclei, substantia nigra, and quadrigeminal plate. 18521090_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19573479_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19860791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20116071_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20116071_This study found nominally-significant evidence for interactions between GFRA1, 2 and 3 associated with schizophrenia and clozapine response, consistent with the locations of these three genes within linkage regions for schizophrenia. 20369355_GFRA2 genetic variants, and age, may play a role in susceptibility to tardive dyskinesia. 20369355_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21723942_Cyclic AMP signalling through PKA but not Epac is essential for neurturin-induced biphasic ERK1/2 activation and neurite outgrowths through GFRalpha2 isoforms. 23881409_The study shows co-localization of RET with GFRA1 and GFRA2 in myenteric ganglia of the adult human colon. 24067900_GFRalpha-2 is associated with severe abdominal pain sensation in pancreatic cancer patients. 24139947_In the cochlea, immunolabeling for GFRalpha-2 receptors was identified mainly in the cell bodies of the spiral neurons than in the nerve fibers. No structures in the organ of Corti were labeled with GFRalpha-2 receptor antibody 24402129_GFRalpha2 is under-expressed in functioning adenomas and over-expressed in non-functioning adenomas, specifically gonadotropinomas 24974787_GFRA2 variants associated with diabetic neuropathic pain. 27396331_The cardiac GFRA2 signaling pathway is distinct from the canonical pathway dependent on the RET tyrosine kinase. 27400681_High GFRalpha2 expression level leads to PTEN inactivation via Mir-17-5p up-regulation, promoting pancreatic tumor cell growth and chemoresistance. 29414779_biophysical results show that the relative concentration of GFRa2 on cell surfaces can affect the functional affinity of NRTN through avidity effects. 29724592_A novel genome-wide significant locus at GFRA2 on chromosome 8p21.3 was identified to be associated with disease risk, and expression analyses showed that the risk-associated allele at rs36196656 decreased GFRA2 mRNA concentrations in GFRA2 tissue. 30722993_GFRA2 was upregulated in human neuroblastoma cells and tissues, and promoted neuroblastoma cell proliferation through interacting with the tumor suppressor PTEN. 31392261_We have reconstituted the complete extracellular region of the RET signaling complex together with Neurturin (NRTN) and GFRalpha2 and determined its structure at 5.7-A resolution by cryo-EM. The proteins form an assembly through RET-GFRalpha2 and RET-NRTN interfaces. |
ENSMUSG00000022103 |
Gfra2 |
7.209444 |
0.2308702262 |
-2.114846 |
0.673795605 |
10.576238 |
0.00114550528794464317669521413733946246793493628501892089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002645127980297705579115774554566087317653000354766845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5333716 |
1.2337471 |
11.0633365 |
2.7758889 |
| ENSG00000168556 |
3622 |
ING2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H160 |
FUNCTION: Seems to be involved in p53/TP53 activation and p53/TP53-dependent apoptotic pathways, probably by enhancing acetylation of p53/TP53. Component of a mSin3A-like corepressor complex, which is probably involved in deacetylation of nucleosomal histones. ING2 activity seems to be modulated by binding to phosphoinositides (PtdInsPs). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11481424, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12859901}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Growth regulation;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene is a member of the inhibitor of growth (ING) family. Members of the ING family associate with and modulate the activity of histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) complexes and function in DNA repair and apoptosis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:3622; |
CCAAT-binding factor complex [GO:0016602]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; Sin3 complex [GO:0016580]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; male germ-line stem cell asymmetric division [GO:0048133]; male meiosis I [GO:0007141]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:1902166]; negative regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902455]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of histone deacetylation [GO:0031065]; positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance [GO:1902459]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000772]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:2001020]; seminiferous tubule development [GO:0072520]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spermatid development [GO:0007286]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
11481424_p33ING2/ING1L is a DNA damage-inducible gene that negatively regulates cell proliferation through activation of p53 by enhancing its acetylation. 15005689_The ING1L gene may be involved in basal cell carcinogenesis. 15748897_P33ING2 cooperates with p53 to regulate apoptosis via activation of both the mitochondrial/intrinsic and death-receptor/extrinsic apoptotic pathways. 16024799_ING2 can act as a cofactor of p300 for p53 acetylation and thereby plays a positive regulatory role during p53-mediated replicative senescence. 16465410_The expression of ING2 was down-regulated in 6 of 7 lung cancer cell lines that had a p53 mutation. 16488987_Observations suggest that p33ING2 is required for the initial DNA damage sensing and chromatin remodeling in the nucleotide excision repair process. 16755297_The data showed that nuclear ING2 expression was significantly reduced in radial growth phase (RGP), vertical growth phase (VGP), and metastatic melanomas compared with dysplastic nevi (P |
ENSMUSG00000063049 |
Ing2 |
70.164852 |
2.4876886869 |
1.314806 |
0.195735424 |
45.902170 |
0.00000000001243081866831621038732293121362529070977887002413808659184724092483520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000068513399381757755110593433348179252459497767802076850784942507743835449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.1113614 |
11.9772898 |
40.5867514 |
3.8988191 |
| ENSG00000168615 |
8754 |
ADAM9 |
protein_coding |
Q13443 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves and releases a number of molecules with important roles in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis, such as TEK, KDR, EPHB4, CD40, VCAM1 and CDH5. May mediate cell-cell, cell-matrix interactions and regulate the motility of cells via interactions with integrins. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61072}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: May act as alpha-secretase for amyloid precursor protein (APP). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12054541}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cone-rod dystrophy;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain) family. Members of this family are membrane-anchored proteins structurally related to snake venom disintegrins, and have been implicated in a variety of biological processes involving cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, including fertilization, muscle development, and neurogenesis. The protein encoded by this gene interacts with SH3 domain-containing proteins, binds mitotic arrest deficient 2 beta protein, and is also involved in TPA-induced ectodomain shedding of membrane-anchored heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:8754; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metalloendopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902945]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:0042987]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033631]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; membrane protein intracellular domain proteolysis [GO:0031293]; monocyte activation [GO:0042117]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of keratinocyte migration [GO:0051549]; positive regulation of macrophage fusion [GO:0034241]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to manganese ion [GO:0010042]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179] |
11831872_ADAM9 is involved in monocyte fusion. 11955914_The downregulated expression of ADAM9 may serve as a marker for anterior polar cataracts. 12054541_cloning of a novel form of human ADAM9 (hADAM9s) which has an alpha-secretase activity for Amyloid Protein Precursor 12484779_First evidence is presented of ADAM9 as an insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) protease produced and secreted by osteoblasts in culture, able to degrade IGFBP-5 with high potency, thereby regulating the critical activity of IGFBP-5. 12535668_The results indicate that ADAM9, ADAM10, and ADAM17, members of the disintegrin and metalloprotease family, catalyze alpha-secretory cleavage and therefore act as alpha-secretases in A172 cells. 12767059_Expression of ADAM-9 mRNA and protein in human breast cancer. 14997207_Cytoplasmic ADAM9 overexpression is associated with poor differentiation in ductal adenocarcinoma 15205330_ADAM9 overexpression enhances cell adhesion and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells via modulation of other adhesion molecules and changes in sensitivity to growth factors, thereby promoting metastatic capacity to the brain. 15856464_In melanoma ADAM-9 protein expression appeared to be restricted to the melanoma cells within the invading front. 16311053_In conclusion, our findings are consistent with the hypothesis that FHL-2 and ADAM-9 are important modulators of IGFBP-5 actions and are, in part, regulated in a coordinated manner in bone 16806063_ADAM9 does not behave as a genuine alpha-secretase but rather acts as an important upstream regulator of ADAM10 activity. 17018608_Intracellular ROS and/or hydrogen peroxide, generated by cell stress, regulate ADAM9 expression. ADAM9 may support prostate cancer cell survival and progression. 17342749_These findings suggest that reactive oxygen species is a common mediator responsible for ADAM9 protein induction in human prostate cancer cells, downstream from androgen receptor, and stress response signaling. 17704059_the ADAM-9 adhesive domain plays a role in regulating the motility of cells by interaction with beta1 integrins and modulates MMP synthesis. 18061337_ADAM9 is overexpressed in prostate cancer cases and is an independent prognostic marker of PSA relapse-free survival following radical prostatectomy. 19003995_ADAM9 plays a crucial role in UV-induced EGFR activation and is overexpressed in skin cancer cell lines 19237226_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19237226_The data of this suggested that promoter polymorphisms which regulate ADAM9 transcription are protective against SAD. 19253070_involved in advanced atherosclerosis, in catalytically active form, most notably associated with cells of monocytic origin 19394555_Cell migration in response to the amino-terminal fragment of urokinase requires epidermal growth factor receptor activation through an ADAM9/10-mediated mechanism. 19409519_ADAM9 is a CRD gene and also is a form of pathology wherein retinal disease first manifests at the POS-RPE junction. 19473694_ADAM9 expression is low in the squamous epithelium of the cervix, but is increased in CIN3 lesions as well as SCCs being the increase in both cases statistically significant. 19505527_the role of the disintegrin domain of the human ADAM9 (ADAM9D) on the adhesion of breast tumor cells and platelets to collagen I 19543729_Data show that the expression levels MMP1, MMP9, ADAM9 and TIMP3 were altered in drug-resistant sublines. 19564338_Experiments revealed that ADAM9 and ADAM10, but not ADAM17, are involved in the shedding of PrP(C) and that ADAM9 exerts its effect on PrP(C) shedding via ADAM10. 20388695_disintegrin and metalloprotease-9 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and can be used as a prognostic marker 20422344_is expressed in adenoid cystic carcinoma-associated metastasis 20672324_ADAM9 plays a crucial role in prostate cancer progression and therapeutic resistance in part by altering E-cadherin and integrin expression. 20736367_Secreted variants of ADAM9 are a key determinant in manifestation of aggressive migratory phenotypes associated with breast cancer progression. 21135106_ADAM-9 expression plays an important role in mediating cell-cell contacts between fibroblasts and melanoma cells and that these interactions contribute to proteolytic activities required during invasion of melanoma cells. 21956108_ADAM10 activity is regulated by inhibition of ADAM9, and this regulation may be used to control shedding of amyloid precursor protein by enhancing alpha-secretase activity, a key regulatory step in the etiology of Alzheimer disease 22064652_The miR-126/ADAM9 axis plays essential role in the inhibition of invasive growth of pancreatic cancer cells. 22480688_Transient transfection of ADAM9 and ACE cDNAs into HEK293 cells demonstrated that ADAM9 requires both membrane anchorage and its catalytic domain to shed ACE. 23106877_ADAM9 expression was low in castration resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), correlated with poor prognosis and might be involved in the succession from hormonal sensitive prostate cancer (HSPC) to CRPC by various functions. 23342005_a novel molecular mechanism of ADAM9 in the regulation of prostate cancer cell proliferation. 23405089_The over-expression of MGAM was confirmed with a 6.6 fold increase in expression at the mRNA level whereas the fold change in ADAM9 demonstrated a 1.6 fold increase. 23429442_ADAM19 was upregulated in patients with ulcerative colitis and, to a lesser extent, in patients with Crohn's disease compared with normal controls. In contrast, ADAM9 and ADAM10 expression did not differ between patients with IBD and controls. 23437250_miR-126&126* restored expressions play a tumor suppressor role by directly regulating ADAM9 and MMP7 in melanoma. 23499592_ADAM9 is an important molecule in the processes of invasion and metastasis. 23857158_The expression of circulating ADAM9 is down-regulated in pulmonary sarcoidosis. 24705471_ADAM9 up-regulates N-cadherin via miR-218 suppression in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 24770635_ADAM9 high expression is correlated positively and significantly with HDGF high expression in non-small cell lung cancer. 24823697_this study describes the role of miR-126 in bladder cancer progression, identifying miR-126 and ADAM9 as potential clinical biomarkers of disease aggressiveness 25060522_Results show how ADAM9 regulates lung cancer metastasis to the brain by facilitating the tPA-mediated cleavage of CDCP1. 25063875_ADAM9 is expressed in an inducible fashion on PMN surfaces where it degrades some ECM proteins, and it promotes alveolar-capillary barrier injury during ALI 25091951_We identified a novel autosomal recessive ADAM9 mutation causing autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy (arCRD), anterior polar and posterior subcapsular cataract in a consanguineous Egyptian family. 25177692_Given the significant correlation between tumor ADAM9 expression and serum RCAS1 concentration in both cervical and endometrial cancer as well as the role for ADAM9 in RCAS1 shedding. 25213697_our data indicated that miR-126 inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of OS cells by downregulating ADAM-9. 25344581_ADAM9 plays an important role in gastric cancer proliferation and invasion, and that while expressed at high levels in some cancer cells that are responsive to functional inhibition and antitumor activity of a catalytic site-directed antibody. 25546566_Whole exome sequencing was performed, which identified a novel, homozygous mutation in ADAM9, c.967delT; p.Ser323Glnfs*33. 25646025_This study has identified tenascin-C as a promoter of the invasiveness of brain tumor-initiating cells through a mechanism involving ADAM-9 proteolysis via the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway. 25778452_ADAM9 silencing inhibits the tumor growth of non-small lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. 26179263_results suggested that miR-203 played tumor suppressive roles by downregulating ADAM9 and HULC and indicated its potential application in cancer treatment 26261534_miR-126 may act as a tumor suppressor via inhibition of cell invasion by downregulating ADAM9 in breast cancer development. 26507842_ADAM9 and ROS1 are direct downstream targets of miR-33a 26553452_ADAM9 enhances CDCP1 protein expression by suppressing miR-218 for lung tumor metastasis 26592768_Activation of ERalpha but not ERbeta increases ADAM9 expression in cultured human neuronal cells. 27026568_Increased ADAM9 mRNA expression is associated with esophageal adenocarcinoma. 27498787_the present study demonstrated the expression and clinical roles of miR-140 in glioma and suggested that miR-140 inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells, partially at least via suppressing ADAM9 expression. Therefore, miR-140 may be a novel candidate target for the development of therapeutic strategies for patients with glioma 27554339_Data show that ADAM9 silencing affected MMP2 and ADAM15 expression. 27571068_The results suggest that ADAM9 mRNA expression is associated with tumor grade and histological type in gliomas and can serve as an independent prognostic factor, specifically in LGG patients. 27770372_data reveal miR-590 as a tumor suppressor in NSCLC, which is at least partially mediated through targeting of ADAM9. Restoration of miR-590 may provide a promising therapeutic strategy for NSCLC. 27827458_Study demonstrates that diabetes-mediated decrease in miR-126 leads to a corresponding increase in its target, ADAM9, which in turn cleaves MERTK (inactivates downstream engulfment signaling), thus resulting in defective macrophage efferocytosis of apoptotic cardiomyocytes. 27878272_ADAM9 is a direct target of miR-20b and that miR-20b decreased the 5-FU resistance of HCT116-R cells. 28209612_miR-520f inhibited tumor cell invasion by directly targeting ADAM9 and the TGFbeta receptor TGFBR2. 28260063_ADAM9 could possibly be regarded as a biomarker for GC diagnosis and prevention. Moreover, as directly targeted by miR-126 in GC, ADAM9 may be a potential target for GC therapeutic treatment which warrants intensive study 28537886_These results revealed that ADAM9 down-regulates miR-1 via activating EGFR signaling pathways, which in turn enhances CDCP1 expression to promote lung cancer progression. 28639884_MiR-126-ADAM9 pathway-based therapeutic targeting may represent a novel approach for the inhibition of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma metastases. 28648644_Mechanistic investigations found that quercetin suppressed Snail-dependent Akt activation by upregulating maspin and Snail-independent a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) 9 expression pathways to modulate the invasive ability of NSCLC cells 28675123_hese results emphasize the critical influence of ADAM9 on lung cancer progression and aggressiveness. ADAM9 should at least be a marker of cancer aggressiveness and a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. 28713950_These findings suggested that miR302a inhibited osteosarcoma cell growth and metastasis by targeting ADAM9. 28849046_miR-543 serves as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma multiforme through ADAM9 regulation. 28928095_ADAM9 is a component of cell-cell junctions. ADAM9 must be expressed by both adjacent cells for cell junction localisation. ADAM9 can self-associate via its ectodomain. The soluble ADAM9 ectodomain inhibits monocyte-endothelial transmigration. 29115634_Collective results suggested that galangin may act as an effective chemotherapeutic agent for glioma cancer depending on its ability to bring about ADAM9 and Erk1/2 activation. 29142101_ADAM9 regulates beta1 integrin endocytosis. Reduced migration of ADAM9-silenced cells is, at least in part, caused by the accumulation and altered activity of beta1 integrin at the cell surface 29247567_Data show that ADAM9 is over-expressed in an activated form in human ovarian clear cell carcinomas, and suggest that it plays a key role in cisplatin resistance. 29432845_our results showed that ADAM9 is an important mediator of IL-6-induced hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion 29550974_Studies indicate that a disintegrin and a metalloprotease 9 (ADAM9) is involved in solid cancers with the different mechanisms which it employ to drive tumor progression [Review]. 29622675_SNX9 knockdown revealed a nonredundant effect on overall ADAM9 protein levels, resulting in increased ADAM9 levels at the cell surface 29879625_miR-129-5p suppressed cell proliferation and invasion ability through regulating ADAM9. 30556643_ADAM9 was also found to foster angiogenesis without an impact on tumor cell proliferation. 30723129_ADAM9 knock-out cells failed to produce viral progeny when incubated with encephalomyocarditis virus. However, bypassing encephalomyocarditis virus entry into cells through delivery of viral RNA directly to the cytosol yielded infectious virions from ADAM9 knock-out cells, suggesting that ADAM9 is not required for encephalomyocarditis virus replication post-entry. 31030477_High ADAM9 expression is associated with Uterine Cervical Cancer. 31153639_The enhancement of circRNA_0020123 in tumor tissues correlated with positive lymph node metastasis, advanced TNM stages, and adverse prognosis for NSCLC patients. For the mechanism, circRNA_0020123 could sponge miR-488-3p to release its inhibition on ADAM9 expression. 31227006_Study finds that ADAM9 is a target of miR-126 in dabrafenib-resistant cells and its silencing impairs melanoma cell proliferation and invasiveness and increases dabrafenib sensitivity. 31381863_Data indicate a novel proteolytic pathway of meprin beta with ADAM proteases 9, 10, and 17 by specific prodomain cleavage. 31409686_Cells lacking ADAM metallopeptidase domain 9 (ADAM9) show reduced Encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) infection efficiency. Inhibition of the metalloproteinase activity of ADAM9 does not affect virus infection. Reconstitution of inactive ADAM9 in knockout cells restores susceptibility to EMCV, pointing to a proteinase-independent role of ADAM9 in mediating EMCV infection. ADAM9 facilitates EMCV attachment to cell surface. 31793719_Aberrant expression of ADAM9 in ovarian cancer and its clinical significance. 31841187_MiR-126 inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting ADAM9 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 31943867_Long noncoding RNA CASC9 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer via sponging miR-488-3p. 32078829_Role of ADAM9 and miR-126 in the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm. 32719332_Stabilization of ADAM9 by N-alpha-acetyltransferase 10 protein contributes to promoting progression of androgen-independent prostate cancer. 33096780_An Overview of ADAM9: Structure, Activation, and Regulation in Human Diseases. 33176868_Analysis of ADAM9 regulation and function in vestibular schwannoma primary cells. 33260155_The emerging role of the MiR-1272-ADAM9-CDCP1 signaling pathway in the progression of glioma. 33786875_Involvement of the A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 9 in oral cancer cell invasion. 33811456_Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 39 promotes human glioma cells migration and invasion by facilitating ADAM9 mRNA maturation. 33911034_ADAM9 enhances Th17 cell differentiation and autoimmunity by activating TGF-beta1. 34055989_mir-126-5p Promotes Cisplatin Sensitivity of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Inhibiting ADAM9. 34187214_Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HOXB-AS3 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating ADAM9 expression through targeting miR-498-5p in endometrial carcinoma. 34528498_Overexpression of ADAM9 decreases radiosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cell by activating autophagy. 34597997_Long non-coding RNA ASMTL-AS1 deteriorates the oncogenicity of osteosarcoma by decoying microRNA-342-3p and consequently raising ADAM9 expression. 34671207_ADAM9 functions as a transcriptional regulator to drive angiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 34698500_Identification of driver genes for critical forms of COVID-19 in a deeply phenotyped young patient cohort. 35080810_Cancer-associated fibroblasts at the unfavorable desmoplastic stroma promote colorectal cancer aggressiveness: Potential role of ADAM9. 35163068_High Glucose Impairs Expression and Activation of MerTK in ARPE-19 Cells. 35740916_Relevance of A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase Domain-Containing (ADAM)9 Protein Expression to Bladder Cancer Malignancy. 35780836_Metalloprotease ADAM9 cleaves ephrin-B ligands and differentially regulates Wnt and mTOR signaling downstream of Akt kinase in colorectal cancer cells. 35880619_Circ_0005714/miR-223-3p/ADAM9 regulatory axis affects proliferation, migration, invasion, and angiopoiesis in trophoblast cells. 36267325_IL-17A Promotes Epithelial ADAM9 Expression in Cigarette Smoke-Related COPD. |
ENSMUSG00000031555 |
Adam9 |
3381.076725 |
2.0436008845 |
1.031113 |
0.028109908 |
1357.988728 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000282922400127111313424599093713351 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000409405355478055236740811810346924 |
Yes |
Yes |
4660.8199728 |
79.7123026 |
2297.2679692 |
30.9116604 |
| ENSG00000168672 |
157638 |
LRATD2 |
protein_coding |
Q96KN1 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Located in cytoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:157638; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
19549893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20158306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25980316_We demonstrated the decreased of circulating FAM84B mRNA and protein after neoadjuvant CRT may predict pCR, and FAM84B protein is overexpressed in ESCC. 26759717_Data suggest that FAM84B protein and the NOTCH pathway are involved in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and may be potential diagnostic targets for ESCC susceptibility. 28186973_High FAM84B expression is associated with prostate cancer progression. 30638658_non-coding RNA (lncRNA) FAM84B-AS promotes resistance of Gastric Cancer to platinum drugs through inhibition of FAM84B expression. 32183428_The Oncogenic Potential of the Centromeric Border Protein FAM84B of the 8q24.21 Gene Desert. 32291380_FAM84B, amplified in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, promotes tumorigenesis through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 32558489_Identification of Hub Genes in Gastric Cancer with High Heterogeneity Based on Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network. 33759248_FAM84B acts as a tumor promoter in human glioma via affecting the Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway. 36419094_FAM84B promotes the proliferation of glioma cells through the cell cycle pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000072568 |
Lratd2 |
68.209677 |
0.3753868789 |
-1.413550 |
0.269892177 |
27.283104 |
0.00000017574034433655950332370330579240258472850655380170792341232299804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000676377625602223206539344042137473778097955801058560609817504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.5531354 |
8.3656554 |
95.1714842 |
15.5089455 |
| ENSG00000168685 |
3575 |
IL7R |
protein_coding |
P16871 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for interleukin-7. Also acts as a receptor for thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP). |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;SCID;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for interleukin 7 (IL7). The function of this receptor requires the interleukin 2 receptor, gamma chain (IL2RG), which is a common gamma chain shared by the receptors of various cytokines, including interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9, and 15. This protein has been shown to play a critical role in V(D)J recombination during lymphocyte development. Defects in this gene may be associated with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:3575; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-7 receptor activity [GO:0004917]; B cell homeostasis [GO:0001782]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; immune response [GO:0006955]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070233]; negative regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001915]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via STAT [GO:1904894]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033089]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; regulation of DNA recombination [GO:0000018]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; T cell homeostasis [GO:0043029]; T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001913] |
12149213_IL-7 may function to regulate the milieu of the microenvironment by modulating IL-6 secretion by the IL-7R-expressing stromal elements 12354940_IL-2 signaling can diminish IL-7Ralpha expression via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent mechanism. 12792903_IL-7R has a role in some human solid malignancies [review] 14607751_Interaction between IL-7 and its receptor has the major role in modulating T-ALL survival within the microenvironment generated by the T-ALL/TEC interaction. 14726805_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15674389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15728501_Expansion of CD8 positive, CD127 negative effector-like T cells is identified as a novel feature of HIV-associated immune perturbation. 15879083_Maturation of memory CD4 and CD8 T cells is associated with a CD127high phenotype and the expression of CD127 serves as a predictor of the functional quality of antiviral T cells. 15947093_Virus-specific IL-7Ralpha+ cells proliferated vigorously in response to IL-7, IL-15, or peptide, whereas IL-7Ralpha- cells required both peptide and helper-cell activation or IL-2 or IL-15 for optimal expansion 16004964_Altogether, we show that gamma(c) is the target of an ubiquitination mechanism and its expression level can be regulated through the activities of a couple of ubiquitin-ligase/ubiquitin-hydrolase enzymes, namely c-Cbl/DUB-2. 16075257_The T cell proliferation gene IL7R (CD127) was also underexpressed in PPMS, but was up-regulated in SPMS compared to the controls. 16357322_Aging affects IL-7Ralpha expression by T cells, leading to impaired signaling and survival responses to IL-7. 16435014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16614257_HIV infection produces the Tat protein, which in turn may up-regulate IL-7R in a paracrine manner, which ultimately promotes early events in HIV replication. 16709829_Transcription of the IL-7R alpha subunit is suppressed in both naive and memory T cells following IL-7 stimulation. 16818676_Cell surface expression of CD127 therefore allows accurate estimation of regulatory T cell numbers and isolation of pure populations for in vitro studies and should contribute to our understanding of regulatory abnormalities in immunopathic diseases. 16818678_CD127 can be used to quantitate regulatory T (Treg) cell subsets in individuals with type 1 diabetes supporting the use of CD127 as a biomarker for human Treg cells. 16837861_CD127 expression on T cells remains low in HIV-infected patients despite antiretroviral therapy 16951331_IL-7 receptor and Notch1 pathways cooperate to synchronize cell proliferation and suppression of non-T lineage choices in primitive intrathymic progenitors. 17045841_CD127 uniquely enables the purification of FOXP3+ Treg cells and, potentially, also 'adaptive' regulatory T-cell subsets from the CD4+CD25- T-cell population. 17079288_A large fraction of peripheral HCV-specific CD8+ T cells were CD127+ and KLRG1-. Intrahepatic virus-specific CD8+ T cells displayed significantly reduced levels of CD127 expression but similar levels of KLRG1 expression compared to the peripheral blood. 17173927_CD4+ regulatory T-cells exhibiting suppressive activity in vitro display distinctly lower surface expression of CD127, irrespective of their level of CD25 expression. 17363735_results confirm that signal transduction via the IL-15R, and hence NK ontogeny, is preferentially retained relative to the IL-7R as gammac expression becomes limiting. 17442928_These findings suggest that DNA methylation is involved in regulating IL-7Ralpha expression in T cells via affecting IL-7Ralpha gene promoter activity. 17504502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17504502_gene encoding the IL-7Ralpha chain is polymorphic, and investigation of inhalation allergic patients compared with controls showed significant association with two alleles at position +1237 and +2087 17579041_A subset of naive CD8-positive cells characterized by low interleukin-7 receptor alpha message and protein expression may encompass cells that have recently received homeostatic signals. 17591854_CD4(+)CD25(+)CD45RO(+)IL-7Ralpha(high) cell population contained allospecific CD4 T cells and secreted effector cytokines. 17609371_Increased constitutive interleukin-7 receptor alpha expression has minimal effects on the numbers or function of effector and memory CD8 T cells formed. 17660530_Alleles of IL2RA and IL7RA and those in the HLA locus are identified as heritable risk factors for multiple sclerosis. 17660530_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660816_Results provide compelling evidence that polymorphisms in IL7R, which encodes the interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7Ralpha), indeed contribute to the non-HLA genetic risk in multiple sclerosis. 17660817_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660817_Results show allelic association of a polymorphism in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) as a significant risk factor for multiple sclerosis in four independent family-based or case-control data sets. 17894415_Immunolocalization of IL-7, IL-7Ralpha, SDF-1alpha, and CXCR4 resulted in a diffuse but specific labeling. RT-PCR analysis confirmed the expression of the above-mentioned transcripts. 17909291_Stimulation of the IL-7 pathway begins with IL-7 binding to unglycosylated and glycosylated forms of its alpha-receptor, IL-7 receptor alpha. 17928869_Haplotypes of the IL7R gene are correlated with altered expression in whole blood cells in multiple sclerosis. 17956896_IL-7 reduced CD127-surface expression and shedding by CD8+ T cells; results support a role for IL-7 in the down-regulation of CD127 expression and impairment of CTL function observed in HIV infection 18025189_We report that loss of CD127 defines terminally differentiated B cell-helping effector T cells in human tonsils. 18272905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18272905_The association between rs6897932 and multiple sclerosis in the Olmsted County collection appeared to be much stronger than anticipated on the basis of recent studies 18292507_Expression of transgenic IL-7 receptor alpha by itself does not support increased survival of effector antigen-specific CD4 or CD8 T cells into the memory phase following infection with Listeria monocytogenes. 18354419_IL2RA and IL7RA genes confer susceptibility for multiple sclerosis in two independent European populations. 18354419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18390701_IL-7- and TCR/CD28-mediated signaling data show that differentially regulate IL-7Ralpha expression on human T cells with a transient and chronic effect, respectively. 18390743_during HIV infection, specific changes in the fraction of CD4(+) T cells expressing CD25 and/or CD127 are associated with disease progression 18563381_Independent replication of the association between the CAPSL and IL7R locus and type 1 diabetes, especially for early-onset type 1 diabetes patients. 18563381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18687755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18721276_Association studies between IL7RA rs6897932 and multiple sclerosis. 18721276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18774388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18847371_Down-regulation of CD127 was mainly associated with T cell activation and reverted only partially after suppression of detectable plasma HIV RNA with HAART 19011158_This suggests a role for gamma(C) cytokines in the pathogenesis of diseases in which CD127 expression is altered on CD8+ T cells such as in progressive viral infections and cancer. 19096522_CD8+ T-cell CD127 expression is significantly higher in children with better HIV disease control, and may have a role as an immunologic indicator of disease status. 19141282_The SCID mutations of IL-7Ralpha locate outside the binding interface with IL-7, suggesting that the expressed mutations cause protein folding defects in IL-7Ralpha 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19231135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19231135_confirm involvement of polymorphisms in the IL7RA and IL2RA genes in multiple sclerosis pathogenesis 19239367_HIV infection results in impaired IL-7 responsiveness, especially in memory CD4+ T cells, and this defect is likely compounded by aging. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19253027_No significant differences were observed between the genotypic distributions of IL-7alphaR polymorphisms and incidence of acute or chronic graft versus host disease. 19253027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19349467_Notch1 controls early T cell development, in part by regulating the stage- and lineage-specific expression of IL-7Ralpha. 19494261_sIL-7Ralpha mRNA is constitutively present among peripheral T lymphocytes and is down-modulated in vitro by IL-7 19505916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19523791_Letter: Analysis of variation in the IL7RA and IL2RA genes in atopic dermatitis. 19525955_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19605492_following the antigen-driven downregulation of IL-7Ralpha seen on all populations in acute IM, in every case, the TLD-specific population recovered expression unusually quickly post-IM 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19626041_Combined analysis of 663 individuals with sarcoidosis and 586 controls provided strong statistical support for a genuine association of IL7R with the risk of sarcoidosis 19626041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19667968_Quantification of CD127( expression in t4 cells is a significant tool for monitoring the outcome course of renal transplant patients. 19690616_This is the first report on the quantification of plasma sCD127 in a population of healthy adults. Soluble CD127 plasma concentrations remained stable over time in a given individual and sCD127 immunoreactivity was resistant to repeated freeze-thaw cycles 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714586_Enhanced expression of IL-7Ralpha and IL-7 in rheumatoid arthritis patients contributes significantly to the joint inflammation by activating T cells, B cells, and macrophages. 19744146_A role of rs6897932 in predisposition to chronic inflammatory arthropathies. 19744146_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19798683_Data show that bound CD4+ T cells had high proliferative activity and increased CD25 and FoxP3 expression, and also expressed CD127. 19834503_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834503_Studies indicate that five SNPs showed genome-wide significant association with MS: HLA-DRA, IL7R, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A. 19865102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19866484_The IL-7Ralpha(high)CD25(+)CD45RO(+)CD4(+)FoxP3(-) T cell population is expanded after liver transplantation. A preexisting HCV infection negatively influences the expansion of this population. 19874827_a marker for regulatory T cell in patients with malignant glioma treated with autologous dendritic cell vaccination 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19940860_CD127(low/-) and FoxP3(+) expression levels characterize different regulatory T-cell populations in human peripheral blood 20035760_Demonstrate that sCD127 is detectable at various levels in the plasma of healthy humans. IL-7 treatment has no impact on sCD127 plasma concentration in patients infected by HIV. 20060740_These findings support a role for the IL-7/IL-7R system in B-cell oncogenesis. 20072139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072142_findings suggest that IL-7Ralpha polymorphisms can influence T cell development and homeostasis, and thereby contribute to the altered immune regulation associated with disease development in patients with multiple sclerosis 20097866_Data suggest that IL-7Ralpha haplotype difference is likely to affect the immunophenotype and disease pathogenesis. 20112030_The association with rs6897932[T244I] in the interleukin-7 receptor alpha chain (IL7RA) gene suggest this variant is likely to be causative rather than a surrogate proxy in Multiple Sclerosis. 20187771_gene polymorphism influences multiple sclerosis susceptibility and response to interferon-beta 20190194_IL-7 triggers rapid IL-7Ralpha endocytosis, which is required for IL-7-mediated signaling and subsequent receptor degradation. 20194581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20194581_We found no significant difference in genotype or allele frequencies interleukin 7 receptor alpha rs6897932 between controls and patients with multiple sclerosis 20219786_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20226540_The IL-7 transcript, lacking exon 4, and not the full length IL-7 represents the dominant IL-7 RNA transcript in human PBMCs and a novel IL-7R splice variant lacking exons 5, 6 and 7. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304824_Recombinant and native sources of soluble CD127 significantly inhibit interleukin (IL)-7-mediated signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 and Akt phosphorylation in CD8(+) T cells. 20368992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20450971_Studies indicate that SNP in IL7RA, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A genes has been consistently associated with MS. 20466416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20539016_Circulating CD4+CD25hiCD127lo Treg-cell levels are not significantly associated with the extent of severity of carotid/coronary atherosclerosis. 20638239_increased expression by CD8-positive Treg populations from primary biliary cirrhosis patients 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20812848_IL-7Ralpha haplotype 2 HIV-infected patients with IL-7Ralpha haplotype 2 had significantly lower soluble IL-7Ralpha levels compared with those of patients without haplotype 2 20812848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20815339_A large favorable entropy change, a global favorable electrostatic component, and glycosylation of the receptor, albeit not at the interface, contribute significantly to the interaction between IL-7 and the IL-7R subunit alpha extracellular domain. 20952689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21129157_sIL-7R is induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines in Rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells 21131424_Activation and proliferation of CD127-positive T regulatory cells (Tregs) is inhibited by a hypocalcemic vitamin D analog TX527, which has immunoregulatory properties. 21159243_The high expression of IL-7 and IL-7R is highly positie correlated with clinic stage, lymph node metastasis, VEGF-D, LVD and poor prognosis in Non-small cell lung cancer. 21161391_The IL7R T244I polymorphism was associated with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. 21190413_Considering allele, genotype and haplotype frequencies, no significant association was observed between multiple sclerosis and IL7Ra polymorphisms 21209878_immunological nonresponders to HIV therapy display elevated BM IL-7/IL-7Ralpha expression but impaired T-cell responsiveness to IL-7, suggesting the activity of a central compensatory pathway targeted to replenish the CD4+ compartment 21211217_The frequency of IL-7R rs6897932 C allele in idiopathic demyelinating optic neuritis patients was significantly greater than in controls. 21287555_screened for multiple sclerosis-associated IL-7RA gene polymorphism rs6897932 21300823_When isolated from multiple sclerosis patients, both nonmature and effector subsets of memory CD127(low) regulatory T cells exhibit kinetically distinct defects in suppression that are evident with CD2 pathway costimulation. 21326139_an association between severe acute graft versus host disease and donor IL-7R[alpha] single nucleotide polymorphism genotypes. 21481848_During chronic HCV infection non-reactive HCV-specific CD8(+) cells targeting the virus are PD-1(+)/CD127(-)/Bim(+) and, blocking apoptosis and PD-1/PD-L1 pathway on them enhances in vitro reactivity. 21536738_Gain-of-function mutations in interleukin-7 receptor-alpha (IL7R) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemias. 21543551_Homozygosity for the IL7R exon 6 rs6897932 C allele is associated with a higher risk for multiple sclerosis in our Dutch population 21562156_Dominant HIV clonotypes are characterized by higher PD-1 expression and lower C127 expression compared with subdominant clonotypes, and TCR avidity positively correlates with PD-1 expression 21625022_IL7R and RAG1/2 genes mutations/polymorphisms in patients with SCID. 21670443_Data reveal a significant association of the SNP rs6897932 of the interleukin-7 receptor alpha gene with non-NMO multiple sclerosis in Japanese populations. 21680796_relationship between CD127 expression, IL-7 signaling and Ig gene rearrangement in pre-B cells 21740271_Infection of PBMCs with HIV in vitro results in the downregulation of CD127 surface expression on CD8(+) T cells. 21757642_Demonstrate an increase in the proportion of CD4+CD25highIL-7Ralphahigh activated T cells in kidney transplant recipients, regardless of the immunosuppressive regimen. 21839739_Results show a downregulation of CD127 expression on T cells including Tregs in patients early post-SCT. 21863001_[review] CD127 has an important role in HIV immunopathogenesis 21892159_IL7R mutational activation is involved in human T-cell leukemogenesis. 21904560_Our data strongly support superiority of combined CD127 and FOXP3 analysis in comparison to CD25 and FOXP3 assessment for further quantification of T(reg) cells in malignant diseases. 21920046_HIV infection of thymocytes did not affect CD127 expression on either total thymocytes or on single positive CD4 or single positive CD8 subsets. 21938017_we did not demonstrate a significant association between IL-7Ralpha haplotype 2 and faster CD4 T-cell recovery in Africans. The IL-7Ralpha SNPs associated with CD4 T-cell recovery following cART differ in African and Caucasian cohorts. 22021616_Though dispensable for autophagy induction, transgenic Vps34 is a critical regulator of naive T cell homeostasis, modulating interleukin (IL)-7 receptor alpha trafficking, signaling, and recycling. 22247488_No difference was found between patients with Vogt Koyanagi-Harada disease and normal controls in the expression of IL-7Ralpha on CD4(+) T cells. 22262655_multiple sclerosis is associated with increased expression of IL-7R-alpha on most CD8+ T cell subsets and with higher frequencies of CD8 effector memory cells coexpressing IL-7R-alpha 22302060_IL-7 and IL-7Ralpha+ T cells were both found to be increased in exocrine glands of Sjogren syndrome patients indicating that IL-7 could contribute to glandular inflammation. 22310831_CD127 expression was significantly reduced in T cells from HIV infected subject. 22312161_IL-7(R)-dependent T cell-driven immune activation plays an important role in inflammation in Sjogren syndrome. 22329520_our comprehensive genetic study revealed three SNPs and a risk of haplotype associated with rapid progression to AIDS in the IL7RA gene and more widely, its role in CD4+ T cell homeostasis. 22425228_The genetic association of IL-7R varients with diseases is discussed in a review. 22471460_Polymorphisms of IL-7R is not associated with Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma. 22640659_Letter: report increased frequency of CD127/CD215 co-expressing CD4(+) T cells in Wegener's granulomatosis. 22661557_IL-7Ralphalow memory CD8+ T cells are significantly elevated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. 22695916_Notch1 controls T-cell development, in part by regulating the stage- and lineage-specific expression of IL-7R. (Review) 22824721_Data indicate that the mean number of CD4(+)CD25(+)CD127(lo) regulatory T cells per mul of whole blood was 48+/-16.9with a range of 18 - 79. 22914435_The soluble IL-7Ralpha levels correlate with the rs6897932 [C] risk allele carriership. 23069254_IL7R mutations may contribute to the development of diverse types of acute leukemias. 23151878_CPSF1 was identified among protein-binding candidates. A consensus polyadenylation signal AAUAAA is present in intron 6 of IL7 receptor directly downstream from the 5' splice site. Mutations to this site and CPSF1 knockdown increased exon 6 inclusion. 23157741_IL-7/IL-7R promotes c-Fos/c-Jun expression and activity in non-small cell lung cancer which further facilitates cyclin D1 expression, and accelerates proliferation of cells and VEGF-D-induced lymphovascular formation. 23207282_IL-7 induces the initial reduction in cell-surface CD127 protein independent of transcriptional suppression, which is delayed by 40-60 min. 23282736_The percentage of CD4+CD25+CD127low/- Treg and Foxp3 in portal hypertension and hypersplenism was significantly increased, suggesting that they may take part in the regulation of immune function and be related to the change of T lymphocyte subsets. 23301543_A low Mcl-1 expression and Bim upregulation after antigen encounter are involved in CD127(low) HCV-specific cytotoxic T cell hyporeactivity during chronic infection. 23329834_Activated IL-7 receptors embedded in membrane microdomains induce actin-microfilament meshwork formation, anchoring microtubules that grow radially from rafted receptors to the nuclear membrane. 23454692_genetic, immunologic, and metabolic factors contribute to a dysregulation of the IL-7/IL-7 receptor pathway in type 1 diabetes and identify a novel hyperglycemia-mediated interference of immune regulatory networks. 23462217_results suggest an association between the IL7Ralpha, rs6897932, T-allele and increased mortality among untreated HIV-infected, Zimbabwean individuals 23610432_IL7Ralpha has a role in potentiating IL-7 bioactivity and in promoting autoimmunity 23628622_Data indicate that both CgammaCR-CD127(+)composed of Interleukin-7 (IL-7) tethered to IL-7Ralpha/CD127, and CgammaCR-CD122(+) CD8(+) T((E/CM)) engraft in mice and persist in an absence of exogenous cytokine administration. 23692589_The rs1494555GG and rs1494558TT IL-7Ralpha genotypes of the donor were associated with the acute and chronic graft versus host disease in the univariate analysis. 23841696_Data indicate that HCV-infected patients with fibrosis presented with a higher proportion of CD4+ T cells expressing CD127 compared with HCV-infected patients without fibrosis. 23888080_In the cord blood of children with respiratory syncytial virus disease there was downregulation of interleukin 7 receptor and chemokine receptor 7, and in the severe disease subcategory, downregulation of Toll-like receptor 4. 23965471_CD127 is downregulated at a transcriptional level in memory CD8 T cells in association with upregulation of Eomes expression in HIV infected patients. 23985573_The findings indicate that genetic variants of IL7RA result in haplotype-associated differential responsiveness to immunological stimuli that influence multiple sclerosis susceptibility not exclusively by varying levels of soluble IL-7RA. 24130709_The IL7R, TNFRSF1A, and GPC5 polymorphisms tended to be associated with having a second event of Multiple sclerosis within a year. 24130718_The IL7R polymorphism was associated with reduced odds of multiple sclerosis attacks involving the brainstem/cerebellum as were the TNFRSF1A and IL12A polymorphisms. 24242875_Il7 receptor SNP rs6897932 may be associated with increased systemic lupus erythematosus risk in Chinese populations. 24337176_the results indicate that the genetic variation of IL7R may be associated with inflammatory demyelinating diseases such as Multiple sclerosis (MS) and neuromyelitis optica (NMO) in the population studied. 24348676_CD127 expression is differentially modulated on CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in the course of T1D. 24465587_CD8 positive T lymphocytes expressing CD127 exhibit increased distribution frequency and distinct functional characteristics that correlate with clinicopathological status in oral neoplasms. 24572742_The IL2RA and IL7RA variants had univariate association in MS and T1D, whereas the MGAT1 and CTLA-4 variants associated with only MS or T1D, respectively. 24678068_Our analysis revealed that none of these 35 samples carried an IL7R mutation in exon 6. Whether differences in the genetic makeup of adult and childhood T-ALL explain the differential response to therapy remains to be determined 24695377_These results strongly suggest that IL-7/IL-7R prevents apoptosis by upregulating the expression of bcl-2 and by downregulating the expression of bax 24708420_Newborns have a higher proportion of circulating thymically derived Helios(+) Treg cells than adults and that S. aureus possess an ability to convert neonatal conventional CD4(+) T cells into FOXP3(+) CD25(+) CD127(low) Treg cells via the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. 24723426_data suggest that lnc-IL7R contributes another layer of complexity in regulation of the inflammatory response 24759676_Early Omenn syndrome can be observed in patients with IL7R mutations, and autoimmune cytopenias could also complicate the clinical course of SCID babies with this type of defect. 24787007_we report noncysteine in-frame mutations in IL7R and CRLF2 located in a region of the transmembrane domain closer to the cytosolic domain in acute lymphoblastic leukemias 24820104_Low-level transient antigenic stimuli during cART were not associated with changes in the thymic function or the IL-7/CD127 system. 24946690_Measurement of the sIL-7R/IL-7 axis will help in guided immune monitoring after HSCT and guided interference with sIL-7R may be explored in GVHD management. 25007250_Sustained virological response correlates with higher expression of CD127, lower T cell exhaustion status and better HIV and HCV proliferative responses at baseline. 25033393_This study then provides evidence that soluble factor(s) are responsible for low CD127 expression on circulating CD8 T-cells in HIV+ individuals and further implicates Tat in suppressing this receptor essential to CD8 T-cell proliferation and function. 25231631_CD127(hi) effluxer CD8(+) T cells represent a novel population of early memory T cells resident in BM with properties required for long-lived memory 25333710_In view of the important role IL-7 plays in lymphocyte proliferation, homeostasis and survival, down regulation of CD127 by Tat likely plays a central role in immune dysregulation and CD4 T-cell decline 25352021_the influence of IL-7 receptor alpha-chain (IL-7Ralpha) gene haplotypes in donors on the outcome of haematopoietic cell transplantation, was investigated. 25366767_Data indicate that individuals carrying the interleukin-7 receptor A/A genotype were more susceptible to diarrhea. 25421942_rs6897932 allele of interleukin-7 receptor alpha is not associated with general inflammation, and reported associations between T-allele in rs6897932 with several autoimmune diseases may be mediated through effects on restricted part of the immune system 25539460_CD4+CD45RO+CD25-/lowCD127+: CD4+CD45RO+CD25hiCD127-/low ratio in peripheral blood indicates heart transplant recipients at risk for cardiac allograft vasculopathy. 25769928_The present study highlights perturbed IL-7/IL-7R T cell signaling through STAT5 as a potential mechanism of T cell exhaustion in chronic T. cruzi infection. 25903732_This study demonstrated that rs6897932 in IL7Ra gene is associated with the progression of multiple sclerosis in Central European Slovak population. 25986373_Substitution of the first 10 Nterminal residues or deletion of residues 17-21 prevented Tat from interacting with and down regulating CD127 from the cell surface. 26100671_Findings indicate that IL7 receptor (IL7R) and c-myc expression as intrinsic biomarkers that can predict the fate of CD8+ T effector cells after adoptive transfer. 26123418_A girl with severe combined immunodeficiency was a compound heterozygote for 2 new frameshift mutations, c.589_598del10 p.P197fsX44 and c.993delA p.Q331fsX2. Each parent carried one of these. 26272555_this study shows that in human CD8 T cells that IL-7 binding to its receptor induces CD127 internalization via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, transport of the receptor from early to late endosomes and ultimately degradation of CD127 by the proteasome. 26333292_A decrease of CD4(+) CD25(+) CD127(low) FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells with impaired suppressive function had been found in untreated ulcerative colitis patients. 26408663_cooperation between IL-7R and alpha2beta1 integrin can represent an important pathogenic pathway in Th17-osteoclast function associated with inflammatory diseases 26425877_Pretransplant recipient circulating CD4+CD127lo/-TNFR2+ Treg cell is potentially a simpler alternative to Treg cell function as a pretransplant recipient immune marker for acute kidney injury. 26499378_Data suggest that the lack of IL-7 receptor alpha chain (IL7Ralpha) expression, associated with hypermethylation of the IL7R promoter, in T cells restricts T-cell development in Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia (SIOD) patients. 26608987_the variant of IL-7RA (rs6897932) was associated with NMO especially NMO-IgG positive patients while the variant of IL-7 (rs1520333) with MS patients. 26852660_Immunophenotyping with CD135 and CD117 predicts the FLT3, IL-7R and TLX3 gene mutations in childhood T-cell acute leukemia. 26974155_results suggest that LNK suppresses IL-7R/JAK/STAT signaling to restrict pro-/pre-B progenitor expansion and leukemia development, providing a pathogenic mechanism and a potential therapeutic approach for B-ALLs with LNK mutations. 26999524_IL7Ralpha level was higher in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic children. 27105585_CD127 is a useful surface marker to isolate donor-antigen-specific-Tregs in operational tolerance after liver transplantation 27188999_This study suggested that the IL7R C allele was associated with an increased risk of MS and larger-scale studies of populations are needed to explore the roles played by the IL7R T244I polymorphism during the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. 27268088_The interleukin-7 receptor alpha (IL-7Ralpha) signaling pathways are prime therapeutic targets because these pathways harbor genetic aberrations in both T-cell ALL and B-cell precursor ALL. Therapeutic targeting of the IL-7Ralpha signaling pathways may lead to improved outcomes in a subset of patients. 27315061_Therefore, generalized CD8+ T-cell impairment in HCV infection is characterized, in part, by impaired IL-7-mediated signalling and survival, independent of CD127 expression. This impairment is more pronounced in the liver and may be associated with an increased potential for apoptosis. This generalized CD8+ T-cell impairment represents an important immune dysfunction in chronic HCV infection that may alter patient health. 27322554_indicate that IL7RhighSH2B3low expression distinguishes a novel subset of high-risk B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia associated with Ikaros dysfunction 27325567_These studies provide in vivo evidence that IL-7Ralpha signals positively regulate normal human B-cell production and proliferation beyond the fetal period and suggest that TSLP can replace IL-7 in providing these signals. 27456877_ |
ENSMUSG00000003882 |
Il7r |
831.525156 |
0.2090118050 |
-2.258344 |
0.083955974 |
714.764343 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018413996800158325153362409434013344709083151528675236558126845714394797686766054358373195042961433968297381436220402144247930217124572450999869014432912909444269865484367004 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012942409179539852391592683409819779232337871328831192659892545419679795043099951497951080501151696365893435059788453335814079185560776948048505141995036073249837506360705593 |
Yes |
Yes |
295.1276926 |
15.9445016 |
1422.4214937 |
49.3963637 |
| ENSG00000168734 |
11142 |
PKIG |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2B9 |
FUNCTION: Extremely potent competitive inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity, this protein interacts with the catalytic subunit of the enzyme after the cAMP-induced dissociation of its regulatory chains. {ECO:0000250}. |
Protein kinase inhibitor;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the protein kinase inhibitor family. Studies of a similar protein in mice suggest that this protein acts as a potent competitive cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, and is a predominant form of inhibitor in various tissues. The encoded protein may be involved in osteogenesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:11142; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004862]; negative regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:2000480]; negative regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042308]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122] |
9218452_Functional studies of the mouse homolog 11742798_Functional studies of the mouse homolog 16870489_These results indicate that the downregulation of PKIgamma may be prerequisite for the PKA activation during the osteoblastic differentiation of precursor cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23963683_Results show that endogenous levels of Pkig reciprocally regulate osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation and that this reciprocal regulation is mediated in part by LIF. |
ENSMUSG00000035268 |
Pkig |
40.873192 |
2.9376316266 |
1.554653 |
0.316189832 |
24.136200 |
0.00000089757040275035566273802850600915803624957334250211715698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003192322685444638444312486294518471652281732531264424324035644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
60.2936843 |
11.0296400 |
20.6594571 |
3.0044046 |
| ENSG00000168778 |
79867 |
TCTN2 |
protein_coding |
Q96GX1 |
FUNCTION: Component of the tectonic-like complex, a complex localized at the transition zone of primary cilia and acting as a barrier that prevents diffusion of transmembrane proteins between the cilia and plasma membranes. Required for hedgehog signaling transduction (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Glycoprotein;Joubert syndrome;Meckel syndrome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a type I membrane protein that belongs to the tectonic family. Studies in mice suggest that this protein may be involved in hedgehog signaling, and essential for ciliogenesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with Meckel syndrome type 8. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:79867; |
ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; MKS complex [GO:0036038]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; protein localization to ciliary transition zone [GO:1904491]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
21462283_a truncating mutation in TCTN2 linked to Meckel Gruber syndrome was shown. 21565611_Network building strategy led to the proposal of candidates for new ciliopathy disease genes, leading to the identification of the first human mutations in the Nephronophthisis gene Ataxin10 (ATXN10) and Joubert syndrome gene Tectonic2 (TCTN2). 29866362_TCTN2 Depletion-Induced IFT88 Lumen Leakage and Ciliary Weakening 31050183_Data suggest that TCTN2 enhances autophagy by targeting the miR-216b-Beclin-1 pathway, thereby ameliorating neuronal apoptosis and relieving spinal cord injury. 32655147_Two novel TCTN2 mutations cause Meckel-Gruber syndrome. 33590725_A founder mutation in TCTN2 causes Meckel-Gruber syndrome type 8 among Jews of Ethiopian and Yemenite origin. |
ENSMUSG00000118662 |
Tctn2 |
47.662571 |
2.2605310669 |
1.176662 |
0.367165322 |
9.986034 |
0.00157731937321580460188708006086244495236314833164215087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003561455399826414860986467658676701830700039863586425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.9485755 |
15.7519416 |
31.0628045 |
5.2425846 |
| ENSG00000168779 |
6474 |
SHOX2 |
protein_coding |
O60902 |
FUNCTION: May be a growth regulator and have a role in specifying neural systems involved in processing somatosensory information, as well as in face and body structure formation. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is a member of the homeobox family of genes that encode proteins containing a 60-amino acid residue motif that represents a DNA binding domain. Homeobox genes have been characterized extensively as transcriptional regulators involved in pattern formation in both invertebrate and vertebrate species. Several human genetic disorders are caused by aberrations in human homeobox genes. This locus represents a pseudoautosomal homeobox gene that is thought to be responsible for idiopathic short stature, and it is implicated in the short stature phenotype of Turner syndrome patients. This gene is considered to be a candidate gene for Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009]. |
hsa:6474; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cardiac pacemaker cell differentiation [GO:0060920]; cardiac right atrium morphogenesis [GO:0003213]; cartilage development involved in endochondral bone morphogenesis [GO:0060351]; chondrocyte development [GO:0002063]; embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis [GO:0048557]; embryonic forelimb morphogenesis [GO:0035115]; embryonic skeletal joint morphogenesis [GO:0060272]; mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0010463]; muscle tissue morphogenesis [GO:0060415]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation [GO:0002053]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048743]; positive regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045880]; positive regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000648]; regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve [GO:2000172]; regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032330]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sinoatrial node cell development [GO:0060931]; sinoatrial node development [GO:0003163]; sinoatrial valve development [GO:0003172]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089] |
19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20858598_work establishes a link between Tbx5, Shox2 and Bmp4 in the pacemaker region of the developing heart 21047392_SHOX2 DNA methylation is found in bronchial aspirates of lung cancer patients 21426551_Frequent gene amplification correlated with hypermethylation of the SHOX2 gene locus. 21694641_SHOX2 DNA methylation is associated with lung cancer. 22108652_A CE marked in vitro diagnostic test kit to quantify SHOX2 DNA methylation in bronchial aspirates was developed and characterized. 22555092_DNA methylation of PITX2 and SHOX2 is an independent prognostic biomarker for disease progression in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. 23038774_Shox2 regulates progression through chondrogenesis at two distinct stages--the onset of early differentiation and the transition to maturation and hypertrophy. 23851611_Elevated SHOX2 expression is associated with tumor recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. 24026539_The combination of EBUS-TBNA and SHOX2 methylation level strongly improves the assessment of the nodal status by identifying additional malignant lesions and confirming benign nodes and therefore avoiding invasive follow-up procedures. 24136974_The assay is based on quantification of methylated Short Stature Homeobox gene two (SHOX2) DNA in the specimen measured via multiplex real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) on bisulfite-converted DNA. 24386354_prognostic value of SHOX2 and SEPT9 DNA methylation in benign, paramalignant and malignant pleural effusions 24421874_SHOX2, like SHOX, regulates NPPB directly whilst activates ACAN via its cooperation with the SOX trio. 24746361_miR-375/SHOX2 functional relationship regulates breast tumorigenesis by controlling the process of EMT. 25331797_SHOX2 DNA methylation identified 66% of the patients with cancer subsequent to a cytological equivocal diagnosis. SHOX2 complements the cytological diagnosis and the methylation marker panel. 25533636_SHOX2 overexpression favors differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiac pacemaker cells, improving biological pacing ability. 25675432_The longitudinal measurement of extracellular plasma mSHOX2 DNA yields information about the response to cytotoxic treatment and allows an early assessment of treatment response for lung cancer patients. 26697824_important role in the process of intervertebral disc degeneration 27036009_Whole-genome microarray mRNA-expression profiles of myofibroblasts and skin fibroblasts revealed four additional genes that are significantly differentially expressed in these two cell types: NKX2-3 and LRRC17 in myofibroblasts and SHOX2 and TBX5 in skin fibroblasts 27138930_these results suggest a genetic contribution of SHOX2 in early-onset atrial fibrillation 27544059_High SHOX2 methylation is associated with Lung cancer. 27660666_Study showed that SHOX2 methylation levels in adenomas and colorectal carcinomas (CRC) were significantly higher compared to those in normal control tissues. Histologic transition from adenomas to CRC was paralleled by amplification of the SEPT9 gene locus. 27840009_We have identified that SHOX2 expression or methylation are potent independent prognostic indicators for predicting LGG patient survival, and have potential to identify an important subset of LGG patients with IDHwt status with significantly better overall survival. 27999621_Study found SHOX2 and SEPT9 frequently methylated in biliary tract cancers. 28069583_Data suggest that the microRNA miR-375/short stature homeobox 2 protein (SHOX2) axis may be a novel therapeutic target for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 28325362_the methylation positive rates of SHOX2 with RASSF1A in stage III were both higher than the other stages of lung cancer 29610456_Post-therapeutic SHOX2 and SEPT9 circulating cell-free DNA(ccfDNA) methylation levels correlated with UICC stage (all P |
ENSMUSG00000027833 |
Shox2 |
1253.138185 |
0.1544097281 |
-2.695164 |
0.054274628 |
2864.775273 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
337.2143704 |
12.2227602 |
2199.7622349 |
40.5185914 |
| ENSG00000168785 |
10098 |
TSPAN5 |
protein_coding |
P62079 |
FUNCTION: Regulates ADAM10 maturation and trafficking to the cell surface. Promotes ADAM10-mediated cleavage of CD44. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26686862}. |
Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Most of these members are cell-surface proteins that are characterized by the presence of four hydrophobic domains. The proteins mediate signal transduction events that play a role in the regulation of cell development, activation, growth and motility. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10098; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein maturation [GO:0051604] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27223087_Tspan5 may serve as a prognostic biomarker for predicting outcome of gastric cancer patients. Tspan5 functions as a tumour suppressor in stomach to control the tumour growth. 28428248_two TspanC8-specific motifs in the large extracellular domain of Tspan5 that are important for ADAM10 interaction and exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. One of the anti-Tspan5 mAbs does not recognize Tspan5 associated with ADAM10, providing a convenient way to measure the fraction of Tspan5 not associated with ADAM10. 28600292_Endothelial Tspan5- and Tspan17-ADAM10 complexes may regulate inflammation by maintaining normal VE-cadherin expression and promoting T lymphocyte transmigration. 29908376_intensity in villi in tubal pregnancy was significantly higher than that in normal intrauterine pregnancy 31665629_TSPAN5 Enriched Microdomains Provide a Platform for Dendritic Spine Maturation through Neuroligin-1 Clustering. 32096299_Data show that gene tetraspanin-5 (TSPAN5) is the target of miR-155 in breast cancer (BC). 32753686_TSPAN5 influences serotonin and kynurenine: pharmacogenomic mechanisms related to alcohol use disorder and acamprosate treatment response. 33955149_Tspan5 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumour metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by activating Notch signalling. |
ENSMUSG00000028152 |
Tspan5 |
57.022871 |
0.3825344022 |
-1.386339 |
0.245260088 |
32.119140 |
0.00000001450017204621593843396667040642269985717405234026955440640449523925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000062071502146794444351877225330565979177777080622036010026931762695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.2397208 |
4.7532959 |
82.2888937 |
8.0362417 |
| ENSG00000168811 |
3592 |
IL12A |
protein_coding |
P29459 |
FUNCTION: Heterodimerizes with IL12B to form the IL-12 cytokine or with EBI3/IL27B to form the IL-35 cytokine (PubMed:8943050, PubMed:8605935). IL-12 is primarily produced by professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as B-cells and dendritic cells (DCs) as well as macrophages and granulocytes and regulates T-cell and natural killer-cell responses, induces the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), favors the differentiation of T-helper 1 (Th1) cells and is an important link between innate resistance and adaptive immunity (PubMed:1673147, PubMed:1674604, PubMed:8605935). Mechanistically, exerts its biological effects through a receptor composed of IL12R1 and IL12R2 subunits (PubMed:8943050). Binding to the receptor results in the rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of cellular substrates including the JAK family kinases TYK2 and JAK2 (PubMed:7528775). In turn, recruited STAT4 gets phosphorylated and translocates to the nucleus where it regulates cytokine/growth factor responsive genes (PubMed:7638186). As part of IL-35, plays essential roles in maintaining the immune homeostasis of the liver microenvironment and functions also as an immune-suppressive cytokine (By similarity). Mediates biological events through unconventional receptors composed of IL12RB2 and gp130/IL6ST heterodimers or homodimers (PubMed:22306691). Signaling requires the transcription factors STAT1 and STAT4, which form a unique heterodimer that binds to distinct DNA sites (PubMed:22306691). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P43431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1673147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1674604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2204066, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22306691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7528775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7638186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8605935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8943050}. |
3D-structure;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Host-virus interaction;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a subunit of a cytokine that acts on T and natural killer cells, and has a broad array of biological activities. The cytokine is a disulfide-linked heterodimer composed of the 35-kD subunit encoded by this gene, and a 40-kD subunit that is a member of the cytokine receptor family. This cytokine is required for the T-cell-independent induction of interferon (IFN)-gamma, and is important for the differentiation of both Th1 and Th2 cells. The responses of lymphocytes to this cytokine are mediated by the activator of transcription protein STAT4. Nitric oxide synthase 2A (NOS2A/NOS2) is found to be required for the signaling process of this cytokine in innate immunity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3592; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; interleukin-12 complex [GO:0043514]; interleukin-12 receptor complex [GO:0042022]; late endosome lumen [GO:0031906]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; interleukin-12 beta subunit binding [GO:0042163]; interleukin-12 receptor binding [GO:0005143]; interleukin-27 binding [GO:0045513]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903588]; negative regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032700]; negative regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050709]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; negative regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900747]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:2000510]; positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation [GO:0050671]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation [GO:0032946]; positive regulation of natural killer cell activation [GO:0032816]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045954]; positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002860]; positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation [GO:0032819]; positive regulation of NK T cell activation [GO:0051135]; positive regulation of NK T cell proliferation [GO:0051142]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0034393]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to UV-B [GO:0010224]; response to virus [GO:0009615] |
11940489_STATE OF ART REVIEW. Malignant B-cells from follicular and marginal zone lymphomas expressed IL-12 p35 and p40 transcripts, whereas only p35 mRNA was detected in mantle cell lymphoma. 12117904_Leishmania priming of human dendritic cells for CD40 ligand-induced interleukin-12p35 secretion is strain and species dependent 12270766_possible role of IL-12 and tissue antioxidants in development and progression of chronic sinusitis 12358856_an alternate mRNA isoform of the human interleukin-12 p35 gene differing from normal p35 transcripts by the deletion of exon 3 is identified 12372421_IL-12 induces expression of the perforin gene in NK cells which is directly regulated by STAT4 12472178_that p35 gene was intact in SLE patients. IL-12 expression in PMN of SLE patients was less prominent than that of the normal controls. 12558814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12576336_results demonstrate that interleukin-12(p35) gene activation in the course of dendritic cell maturation involves selective remodeling of a single positioned nucleosome within the promoter containing critical Sp1-binding sites 12633940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12672403_A key mechanism in the pathogenesis of MS is the increased expression of CD86 and CD40L and the increased production of IL12 during disease progression. 12911539_Renal immune complex deposition can occur in absence of IL-12p35, but structural renal damage requires presence of IL-12p35 or mediators induced by this molecule, such as IFN-gamma. 12944981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14566095_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14629328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14660053_IL-12 can enhance the expression of ICAM-1 in the presence of IFN-gamma and, with IL-18, enhances natural killer anti-tumor activity 14675394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14962816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15051764_IL-12(p35) transcriptional repression in neonatal dendritic cells takes place at the chromatin level. 15087447_IL12 does not activate STAT4 signaling in human vascular endothelial cells 15170937_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15356557_Decreased LPS-induced IL-12(p70) and IL-10 responses were associated with the TLR4 (Asp299Gly) polymorphism and independently with asthma, especially atopic asthma in school-age children 15361128_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15448160_interleukin 12 and interferon gamma are involved in inhibition of cytotrophoblastic cell invasion 15489234_interleukin-12 p35 gene transcription is activated by interferon regulatory factor-1 and interferon consensus sequence-binding protein 15643599_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15741223_TSLP is a major regulatory cytokine for CD40 ligand-induced IL-12 production by DCs, and TSLP-activated DCs could promote the persistence of Th2 inflammation even in the presence of IL-12-inducing signals 15810889_iC3b interferes with monocyte-derived dendritic cell differentiation and IL-12 and IL-10 production is mediated via an ERK MAPK-dependent mechanism 15863393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15937086_IL12A gene polymorphisms may affect the final steps of gastric carcinogenesis in H pylori infected subjects. 15963597_novel anti-inflammatory property of recombinant HBsAg which involves inhibition of interleukin 12. 16230423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16544245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16702372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16754651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16803996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16885196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16938461_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16961803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17002904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17007011_This review summarizes information on the expression and role of IL-12 both in patients with Crohn's diease and experimental models of colitis, thus emphasizing differences between IL-12 and IL-23 activity on the development of intestinal inflammation. 17062130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17152005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17225924_Our results suggest that IL-12 and IL-18 contribute to the establishment of Th1 polarization seen in FMF and play a part in its pathogenesis. 17236132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17257312_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17304101_Interferon-gamma and bacterial lipopolysaccharide act synergistically on human neutrophils enhancing interleukin-8, interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-12 p70 secretion and phagocytosis via upregulation of toll-like receptor 4 17361014_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17444864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17461482_The positive expressions of IL-12 and IL-18 can play an important role in progression and metastasis of gastric cancer, and IL-12 might be an independent factor of poor prognosis in gastric carcinoma. 17509455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17553352_The levels of IFN-gamma, IL-12 and TRAIL in synovium fluid from the patients with RA are higher than those in healthy donors. This result indicates that the pattern of cytokine on course of RA is main of Th1, more typical in synovium fluid than in serum. 17564777_mRNA levels of IL12 subunit p35 in active SLE patients was significantly higher compared with those in the inactive SLE patients 17627763_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17640324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17653830_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17671745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17846855_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17881511_Engagement of gC1qR on dendritic cells by hepatitis C virus core protein limits the induction of Th1 responses by inhibiting TLR-induced IL-12 production and may contribute to viral persistence. 17922692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17947455_Our data suggest that the intestinal microvasculature is responsive to ligands of TLR3 expressed on intestinal endothelial cells, thereby adding to the regulation of adaptive immunity and leukocyte recruitment. 18050195_In primary Sjogren's syndrome, infiltration of the salivary gland by macrophages and dendritic cells and expression of IL-18 and IL-12 play active roles in infiltrative injuries and have a correlation with predictors of lymphoma development. 18092318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18159163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18159163_Single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotype of interleukin-12A are not associated with hepatitis B virus persistence and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. 18190588_an increased expression of IL-12 p40, IL-12 p35 and IL-23 p19 mRNA was observed in bone marrow mononuclear cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with aplastic anemia compared with the corresponding one in normal controls. 18260379_The expression of GATA-3 was negatively correlated to the expression of IL-12 in patients with allergic rhinitis. 18300344_probiotic S. thermophilus and Leuconostoc strains are more potent inducers of Th1 type cytokines IL-12 and IFN-gamma than the probiotic Lactobacillus strains 18311140_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18385764_TAP1 and TAP2 expression restores both antigen presentation and immunogenicity in A375 melanoma cells and concomitantly increases IL-12 and IFN-gamma production in tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 18413324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18419254_These observations suggest that lower measles-specific T-cell immune responses elicited by measles vaccine in infants may be due to diminished levels of IL-12 and IL-15. 18554158_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18566447_anti-CD3/CD28 enhances vaccine efficacy by limiting the regulatory T cell response and promoting expansion of activated effector cells 18588867_The gene expression of IL-12 p35 was significantly higher in periodontitis compared with gingivitis. 18606709_study demonstrates that oxidative stress induced by soluble cigarette smoke components potently inhibits the production of IL-12 and IL-23 by maturing dendritic cells 18628242_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18632425_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18671862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18672993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18717726_IL-12 promotes disease development in acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. 18773331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18805825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18972297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18976327_The elevation of IL-10 and the significant correlation between IL-10 and IL-12, a proinflammatory cytokine, may suggest that immunological disturbances and neuroprotective mechanisms are involved in patients with PD. 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19031096_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19073967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19117745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19118071_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19118071_These findings suggest that IL12A rs568408 and IL12B rs3212227 may individually and jointly contribute to the risk of cervical cancer and may modify cervical cancer risk associated with parity. 19126646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19144161_Results suggest that IL-12, a principal TH1 cytokine with potent anti-angiogenic activity, is the mediator of angiostatin's activity. 19148899_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148899_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in interleukin 12 is associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19200845_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19230467_The production of IL-12, IL-18, and TNF-alpha by alveolar macrophages was increased in patients with both acute and chronic forms of Hypersensitivity pneumonitis in either the absence or presence of lipopolysaccharide compared with controls 19253530_IL-12 p35, ICAM-1 and MCP-3 mRNAs are expressed in primary nasal epithelial cells. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19297619_TLR9 and MyD88 are essential to initiate IL12 and IFNgamma responses and favor host hyperresponsiveness to TLR agonists resulting in overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines and the sepsis-like symptoms of acute malaria. 19299334_A novel model in which IL-12 and IFN-alpha act in a nonredundant manner to regulate the colinear generation of both effector and memory cells. 19332120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19376105_Median IL-10 and IL-12 levels were significantly higher in cancer patients than in healthy controls. 19408823_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19454678_In monocytes, TLR8 was responsible for IL-12 induction upon endosomal delivery of ssRNA oligonucleotides 19458352_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19458352_Our data show significant associations between primary biliary cirrhosis and IL12A 19470040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19505916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19508433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19543959_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19543959_genetic variation in IL-12 A/C (-1188) and IFN-gamma A/T (+874) cytokine genes could be risk factors for MS patients, while IL-2 G/T (-330) and IL-2 G/T (+166) are not 19566870_Both high levels of sHLA-I and low levels of IL-12 could attenuate NK activities after hepatectomy, especially when FFP would be administered. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19594368_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19646340_The IL-12 (-1188 A/C 3UTR) gene polymorphism is not associated with disease susceptibility or severity in three age-related chronic inflammatory syndromes. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19693089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19710469_In the subset of genes that STAT4 programs for expression in Th1 cells, IL-12-induced mRNA levels remain increased for a longer time than mRNA from genes that are not programmed. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19797506_Results desceibe the gene expression of interleukins-17A, -23, and -12 and determine the proximity of IL-17A- and IL-23-producing cells in rheumatoid synovial tissue. 19798410_IL-12 and IL-27 have roles in modulating Th2 polarization of carcinoembryonic antigen specific CD4 T cells from pancreatic cancer patients 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19885559_This study demonstrated an encouraging result of immunomodulative therapy in malignant brain tumors by rAAV2 carrying IL-12 through activating NK cells. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19950173_Data show that the combinatorial signal delivered by R-DC to T cells via B7-H1 and sialoadhesin is crucial for the induction of IL-35(+) Treg. 19956842_exosomes derived from IL-12-anchored renal cancer cells express renal cell carcinoma-associated antigen G250 and GPI-IL-12 20027291_The IL-23 induced cytokines allow for the subsequent production of IL-12 and amplify the IFN-gamma production in the type-1 cytokine pathway. 20054003_Data show that that 4-trifluoromethyl-celecoxib can inhibit secretion but not transcription of IL-12 (p35/p40) and IL-23 (p40/p19 heterodimers), and that this is associated with HERP function in the endoplasmic reticulum. 20060272_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20060272_rs582504 (IVS-798A/T) SNP and the haplotype TA (rs582054 and rs2243151) associated with atopic dermatitis 20061784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20082482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20213229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20231901_SOCS-3 and PIAS-3 upregulation impairs IL-12-mediated interferon-gamma response in CD56 T cells in HCV-infected heroin users 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20350312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20350312_study has shown strong associations between polymorphisms in the genes of IL12A and IL12RB1 and protection from severe malarial anemia in Kenyan children 20372811_Data show that exosomes inhibited the expression of JAK3 and phosphorylation of STAT5 in high doses in T-cells, but not JAK2, while EXO/IL-12 had much less attenuated reduction of the expression of p-STAT5. 20418110_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20521253_IL12A rs568408 may contribute to the risk of HCC and modify HCC risk associated with HBV infection 20521253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20544370_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20551083_Describe the successful construction, characterization and production of the heterodimeric immunocytokine F8-IL12. Engineered tumor-targeting heterodimeric immunocytokine F8-IL12 using different combinations of the two subunits (p35 and p40). 20555355_IL12A is a novel multiple sclerosis susceptibility loci, and it's risk allele seems to be protective for celiac disease. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20581146_In a transgenic model, the IL-12p35/interferon (IFN)-gamma axis promotes antibody-induced joint inflammation by activating natural killer (NK)T cells and suppressing transforming growth factor(TGF)-beta. 20603050_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634089_Hyperglycemia influenced IL-12 response from peripheral mononuclear cells in diabetes mellitus patients to some degree during infection. 20639880_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20714168_Findings in this study suggest that adiponectin, IL-12p70, and IL-13 may play a role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20818961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881642_High IL-10 levels were significantly associated with mucositis. 20960273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21044109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21044109_Results have established an association between IL-12A polymorphism and GD susceptibility in the Chinese population. 21086908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21145044_semiquinone glucoside derivative dose dependent study showed approximately similar level of induction in IL-12p40, IL-12p35, IL-23p19 and RelA proteins expression at all tested concentration (30-90 microg/ml) compared to control 21177981_Lys-des[Arg9]-bradykinin alters migration and production of interleukin-12 in monocyte-derived dendritic cells 21285006_This study demonstrated that interleukin-35 expression could be detected in the CD4(+) T cells from peripheral blood of chronic hepatitis B patients. 21387004_Interferon-alpha-conditioned human monocytes combine a Th1-orienting attitude with the induction of autologous Th17 responses: role of IL-23 and IL-12. 21397857_Data show that MMP-2-conditioned dendritic cells primed naive CD4(+) T cells to differentiate into an inflammatory T(H)2 phenotype through OX40L expression and inhibition of IL-12p70 production. 21402701_IL-23 induction by beta-glucans is due to activation of c-Rel associated with Ser-10-histone H3 phosphorylation in the il23a promoter mediated by MAPK and SAPK or PKA, and inhibition of il12a transcription 21513752_These results suggest that the SNPs in IL-12A rs568404 and IL-12B rs3212227 may individually and jointly contribute to the risk of asthma in a Chinese population. 21518507_The imbalance of T cell subsets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpurapatients is mainly associated with IL-12, but not with IL-23 and IL-17. 21518761_the presence of IL-1 and/or IL-6 during activation of human CD8 T cells attenuates Fas-mediated AICD, whereas IL-12 increases the susceptibility of activated CD8 T cells to this form of cell death 21606320_single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Interleukin 12a gene is associated with neuroendocrine tumor. 21878338_Results show that cryopreservation of monocytes or iDCs leads to an impaired cytokine response for IL-10, TNF-alpha, IL-12p70 and IL-1beta. 22005588_IL12 pathway highlights the interplay between innate and acquired immunity. 22011063_Gene-gene interactions of IL-12A rs2243115 and IL-12B rs3212227 may contribute to brain tumor susceptibility. 22038227_Data suggest that operative injury is associated with increased IL-12 levels, and ischemia and reperfusion with decreased IL-12 levels. 22040814_IL-12 and IL-27 gene polymorphisms may not be involved in susceptibility to colorectal cancer 22133036_We describe a novel effect of MTX reducing the gene expression of IL-12A independently of corticosteroid application in patients. 22438968_in contrast to TGF-beta, IL-35 is not constitutively expressed in tissues but it is inducible in response to inflammatory stimuli 22581790_variation in the IL12B gene, but not IL12A, partly explains inter-individual differences in disease susceptibility and severity 22614250_Genotyped IL12A and IL12B polymorphisms in four hundred-five patients with cervical cancer and four hundred fifty unrelated Showed that the IL12B polymorphism may be a genetic risk factor for cervical cancer. 22656398_Interleukin-27 and interleukin-12 augment activation of distinct cord blood natural killer cells responses via STAT3 pathways. 22691562_We found significant differences on the mean values of IL-12 between the panic disorder and control groups 22734699_IL-12A rs2243115 polymorphism may contribute to genetic susceptibility to COPD in a Chinese population 22819329_Autoimmune diseases appear to cluster in two groups that either show strong associations with the Th1/Th17 pathway (IL12B and IL23R) or the Th1/IL-35 pathway ( polymorphisms in the IL12A gene region). Review 22940148_Data show that SNP of IL-12B gene was associated with significantly increased overall risk of cancers, however, the SNPs of IL-12A gene did not appear to have an influence on cancer susceptibility. 23053983_This study investigates gene expression of interleukin (IL)-12-related (IL-12A, IL-12B, IL-23A) cytokine and IL-10 in stimulated monocytes from colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. 23065210_These findings suggest that the IL-12A and IL-12B independently and jointly be involved in the susceptibility to intracranial aneurysm. 23154182_these results reveal a novel functional role for IL-35 in suppressing cancer activity, inhibiting cancer cell growth, and increasing the apoptosis sensitivity of human cancer cells through the regulation of genes related to the cell cycle and apoptosis. 23285065_The results of the present study show that circulating IL-35 is a potentially novel biomarker for coronary artery disease. 23297419_The p40 subunit of interleukin (IL)-12 promotes stabilization and export of the p35 subunit: implications for improved IL-12 cytokine production. 23388728_These findings suggest that Tim-3-mediated differential regulation of IL-12/IL-23 drives T(H)17 cell development, a milieu favoring viral persistence and autoimmune phenomenon during chronic hepatitis C. 23619469_expressed by trophoblast cells 23657466_Alpha-nac is a potent inducer of a Th1 response via IL12 and TLR2. 23714111_stimulated human peripheral blood T cells of healthy donors produce high amounts of IL-35 protein. However, the biological function of this cytokine remains to be elucidated. 23717436_TGF-beta1 blockade and IL-12p70 production augments antitumor immunity in tumor and dendritic cell fusions. 23734222_Data indicate that IL-12 increased after surgery in 38 of 52 cases. 23752604_Serial determinations of serum IL-10 and IL-12 reflected well the course of STS in children and enabled remission and relapse phases to be distinguished. To avoid G-CSF and sepsis influence. 23755218_Poor nutritional status and frailty in subjects over 75 years were associated with decreased IL-12p70 and IL-23 production. 23778029_IL-12 and IL-18 are elevated during the earlier stages of Chronic kidney disease but are not associated with arterial stiffness. 24012048_Complicated malaria was associated with enhanced expression of IFN-gamma and TGF-beta but lower IL-2 and IL-12alpha in comparison to uncomplicated malaria. 24040445_IL-35 could be a valuable biomarker for assessing colorectal carcinoma progression and prognosis in clinical settings. 24121041_circulating IL-35 in PDAC patients significantly increased, suggesting that regulating the expression of IL-35 may provide a new possible target for the treatment of PDAC patients, especially for the resectable ones. 24130718_The IL7R polymorphism was associated with reduced odds of multiple sclerosis attacks involving the brainstem/cerebellum as were the TNFRSF1A and IL12A polymorphisms. 24145357_Data suggest that IL-15 may improve the cytotoxicity of CIK cells against leukemia cells by upregulating CD3CD56 cells and downregulating Treg cells and IL-35. 24158609_The IL-12A rs568408 and IL-12B rs3212227 polymorphisms were analyzed in relation to anti-hepatitis B antigens development in 602 hemodialysis patients. 24273881_IL-35 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine comprising the p35 subunit of IL-12 and the subunit Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) -induced gene 3(EBI3)--{REVIEW} 24289573_The expression levels of GOLPH2 and IL-12A were negatively correlated. 24376289_The increased expression of IL-35 in chronic and aggressive periodontitis suggests its possible role in pathogenesis of periodontitis. 24782489_ingestion of apoptotic cells by DCs leads to increased expression of IL-12p35 and Ebi3 without affecting IL-12p40. 24970690_The results suggest that the decreased expression of IL-35 could be involved in the pathogenesis of childhood asthma. 24994465_IL-35 levels are dramatically decreased in immune thrombocytopenia patients, suggesting that IL-35 may be involved in the pathogenesis of this disease. 25037175_We investigated the relations of three potentially functional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in IL-12A (rs2243115 and rs568408) and IL-12B (rs3212227) with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 25073578_These results might indicate an important new role for IL-35 as an autocrine growth factor in pancreatic cancer growth. 25139335_the impairment of IL-12p35 expression during the neonatal period might be caused by other epigenetic regulation occurs in the chromatin level. 25179705_Glucose increases the IL-12 production in stimulated PBMCs of diabetes patients through increased IL-12 gene expression 25200154_Data show that dsFvalpha gene and interleukin 12 (IL-12) gene were successfully expressed in the supernatant of transfected cells. 25202013_Medroxyprogesterone acetate differentially regulates interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-10 in a human ectocervical epithelial cell line in a glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-dependent manner 25214710_IL-35 and IL-37 protein expressions were higher in IBD patients compared with controls. 25258182_Study indicated that the rs568408 variation in IL-12A gene could influence disease susceptibility, and was associated with the severity of oral lichen planus in our East Chinese cohort. 25316442_IFN-lambda1-mediated IL-12 production in macrophages induces IFN-gamma production in human NK cells. 25323532_IL-17 and IL-35 may be critically involved in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B-related LC. 25326182_A significant and positive correlation was identified between plasma concentrations of IL-35 and disease severity score in asthmatic patients. 25446896_In human breast cancer, expression of IL12A and cytotoxic effector molecules are predictive of pathological complete response rates to paclitaxel. 25469793_No significant association was observed between rs2243115 in IL-12A and RA 25480413_IL-35 is a promising potential biomarker in prognostication of clinical outcome of NSCLC patients and the regulation of IL-35 expression may provide a new target for the treatment of NSCLC patients 25550844_DN was associated with enhanced Th1 response and suppression of Th2 responses which might be due to inreased levels of IL-12 and decreased levels of IL-33 cytokines respectively. 25563480_IL-12 can induce monocytic tumor cells directional differentiation into macrophage-like cells. 25575066_The levels of EBI3 and IL-12p35 mRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in moderate or hyper-responders were significantly higher than those in non- or hypo-responders. 25577895_NK cell activity in children with IDDM after in vitro stimulation by IL12 inhibits autoimmunity by increased IL10 synthesis. 25611266_IL-35 contributed to the establishment and maintenance of maternal-fetal tolerance during early pregnancy. 25640666_IL35 appears to contribute to the loss of immunological self-tolerance in ITP patients by modulating T cells and immunoregulatory cytokines. 25697137_IL-35 might play an important role in rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 25731770_IL-35 might suppress T cell activation during the peripheral immune responses of rheumatoid arthritis. 25752977_increased serum IL-35 could be directly related to increased levels of IL-35 mRNA in CD4(+) T cells and hepatitis B virus DNA load in chronic hepatitis B patients. 25799145_Genome-wide association study in an admixed case series reveals IL12A as a new candidate in Behcet disease 25820702_we demonstrate that IL-12p35 is required for tolDCs to reach their full suppressive potential. 25854372_IL-35 over-expression is associated with genesis of gastric cancer. 25869609_IL-35 is highly expressed in chronic HBV CD4(+) T-cells and plays an important role in the inhibition of the cellular immune response in chronic HBV. 25935866_IL-35 mRNA and protein were higher in tuberculous pleural effusions than in malignant ones. 25985710_Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from severe asthmatic children release lower amounts of IL-12 and IL-4 after LPS stimulation. 26017027_the distribution of interleukin (IL)-12 (IL12; 1188A/C), IL17 (A7488G) and IL-23 receptor (IL23R; +2199A/C) gene polymorphisms in patients with alopecia areata, was investigated. 26042836_Serum levels of IL-35 increased in normal pregnancy and decreased in recurrent spontaneous abortion. 26044961_IL-35 can effectively suppress the proliferation and IL-4 production of activated CD4+CD25- T cells in allergic asthma, and that IL-35 may be a new immunotherapy for asthma patients. 26062743_Findings demonstrate that IL-12 is increased significantly in chronic hepatitis B patients and that viral protein HBx induces IL-12 expression in hepatocytes through the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. 26085094_Insight into the control of vascular inflammation by IL-35. 26104769_Gene-gene interaction analysis showed that subjects car |
ENSMUSG00000027776 |
Il12a |
8.224607 |
0.1726462605 |
-2.534109 |
0.790714534 |
10.397723 |
0.00126170821388890143886774009018836295581422746181488037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002891741185869594211316213616669301700312644243240356445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.9708847 |
1.1629262 |
11.8295792 |
4.1943156 |
| ENSG00000168872 |
55308 |
DDX19A |
protein_coding |
Q9NUU7 |
FUNCTION: ATP-dependent RNA helicase involved in mRNA export from the nucleus. Rather than unwinding RNA duplexes, DDX19 functions as a remodeler of ribonucleoprotein particles, whereby proteins bound to nuclear mRNA are dissociated and replaced by cytoplasmic mRNA binding proteins. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9UMR2}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Helicase;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity and RNA helicase activity. Predicted to be involved in poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55308; |
cytoplasmic stress granule [GO:0010494]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; RNA helicase activity [GO:0003724]; poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0016973]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043] |
34612147_Silencing of let-7b-5p inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and stemness characteristics by Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp-box helicase 19A. |
ENSMUSG00000015023 |
Ddx19a |
227.403356 |
2.1064315521 |
1.074801 |
0.172084555 |
38.572417 |
0.00000000052759293820220245276436915170953367848483139823656529188156127929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002581130847817204801709557211589554648334399189479881897568702697753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
305.6042985 |
31.0737874 |
145.9046618 |
11.1528523 |
| ENSG00000168938 |
5480 |
PPIC |
protein_coding |
P45877 |
FUNCTION: PPIase that catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and may therefore assist protein folding. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20676357}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Isomerase;Reference proteome;Rotamase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase)) family. PPIases catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and accelerate the folding of proteins. Similar to other PPIases, this protein can bind immunosuppressant cyclosporin A. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5480; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; cyclosporin A binding [GO:0016018]; peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity [GO:0003755]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization [GO:0000413] |
24990953_These findings establish cyclophilin C as an ER cyclophilin, demonstrate the novel involvement of cyclophilins B and C in ER redox homeostasis 26691022_Cyclophilin C participates in cytomegalovirus US2 protein-mediated degradation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. 27801851_Independent validation with glioma patients tissue (n = 70) and normal brain tissue (n = 19) found PPIC, EMP3 and CHI3L1 were up-regulated in glioma tissue. Survival value validation showed that the three genes correlated with patient survival by Kaplan-Meir analysis, including grades, age and therapy. |
ENSMUSG00000024538 |
Ppic |
110.449114 |
0.1717936207 |
-2.541252 |
0.193410353 |
184.906190 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000411412594156398496517268919692649136477153634712829966010096097284562905798698884664049543352429615119088745708864074401844845851883292198181152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000072377233489254376099426694940676186021906084330510028809823791992519169579531749241797932069596404396571130701598661971729598008096218109130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.1364741 |
4.2120080 |
193.8191062 |
13.9166430 |
| ENSG00000168970 |
8681 |
JMJD7-PLA2G4B |
protein_coding |
P0C869 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-dependent phospholipase A1 and A2 and lysophospholipase that may play a role in membrane phospholipid remodeling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10085124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10358058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase. Cleaves the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached to the sn-2 position of phosphatidylethanolamines, producing lysophospholipids that may be used in deacylation-reacylation cycles. Hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholines with low efficiency but is inefficient toward phosphatidylcholines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Calcium-dependent phospholipase A1 and A2 and lysophospholipase. Cleaves the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached to the sn-1 or sn-2 position of diacyl phospholipids (phospholipase A1 and A2 activity, respectively), producing lysophospholipids that may be used in deacylation-reacylation cycles. Can further hydrolyze lysophospholipids enabling complete deacylation. Has no activity toward alkylacyl phospholipids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10085124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10358058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome |
|
This locus represents naturally-occurring readthrough transcription between the neighboring jumonji domain containing 7 (JMJD7) and phospholipase A2, group IVB (cytosolic) (PLA2G4B) genes. Readthrough transcripts encode fusion proteins that share amino acid sequence with each individual gene product, including a partial JmjC domain and downstream C2 and phospholipase A2 domains. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2013]. |
hsa:100137049;hsa:8681; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047498]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; phosphatidyl phospholipase B activity [GO:0102545]; phospholipase A1 activity [GO:0008970]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; parturition [GO:0007567]; phosphatidylcholine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036151]; phosphatidylethanolamine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036152]; phosphatidylglycerol acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036148] |
11741884_circulating human neutrophils express groups V and X sPLA(2) (GV and GX sPLA(2)) mRNA and contain GV and GX sPLA(2) proteins, whereas GIB, GIIA, GIID, GIIE, GIIF, GIII, and GXII sPLA(2)s are undetectable 15274049_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15999343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
191.012052 |
0.2093889181 |
-2.255743 |
0.162956715 |
193.152252 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000006520659498636590745705686318533551501561675307225069297333817227369742339888975517170520562585960416694819813659272922379273040860425680875778198242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000001189677802223437354997362970565846161809816809316308825686756647612759037057281559786700148148135472151828615459956406397168393596075475215911865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
65.9466024 |
9.9456779 |
315.1972317 |
32.1537666 |
| ENSG00000168994 |
221749 |
PXDC1 |
protein_coding |
Q5TGL8 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable phosphatidylinositol binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:221749; |
phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091] |
30204804_We used allele specific expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines from 306 Hutterites related in a single pedigree to provide formal evidence for parent of origin effects. Our approach identified two putative novel imprinted genes, PXDC1 and PWAR6, with asymmetrical parent of origin gene expression. |
ENSMUSG00000021411 |
Pxdc1 |
118.971781 |
3.5257749788 |
1.817940 |
0.154611966 |
143.642789 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000425295060630529231038928220020414311471795643975236730199975859004308216180585540492362431330697347675595665350556373596191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000060012955018227649138405993457073188762307663308590586244902951815761717289649505467294399174704722099704667925834655761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
189.4079004 |
18.2035003 |
54.0833325 |
4.2980729 |
| ENSG00000168995 |
27036 |
SIGLEC7 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y286 |
FUNCTION: Putative adhesion molecule that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. Preferentially binds to alpha-2,3- and alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. Also binds disialogangliosides (disialogalactosyl globoside, disialyl lactotetraosylceramide and disialyl GalNAc lactotetraoslylceramide). The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. Mediates inhibition of natural killer cells cytotoxicity. May play a role in hemopoiesis. Inhibits differentiation of CD34+ cell precursors towards myelomonocytic cell lineage and proliferation of leukemic myeloid cells (in vitro). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10611343}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable sialic acid binding activity. Predicted to be involved in cell adhesion. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:27036; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; sialic acid binding [GO:0033691]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155] |
11774609_Regulation of myeloid cell proliferation and survival by p75/AIRM1 and CD33 surface receptors. 12438315_high resolution crystal structures of this protein; insights into ligand specificity of this family of proteins 12778482_Sialidase unmasking of siglec-7 on NK cells permits it to interact with GD3 on target cells and inhibit killing. This has inplications for tumor escape from NK cells. 14747738_x-ray crystallographic analysis of the saccharide-binding domain of p75/AIRM1 15292262_Siglec-7 and Siglec-9 are capable of negative regulation of TCR signaling and ligand binding is required for optimal activity 15557178_Siglec-7 can inhibit Fc epsilon receptor I-mediated serotonin release from rat basophilic leukemia cells and recruit the tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2. 15703304_upon pervanadate (PV) treatment, Siglec-7 recruited the protein tyrosine phosphatases Src homology-2 (SH2) domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1 and SHP-2 less efficiently than did other inhibitory receptors 16623661_structural analysis of siglec-7 in complex with sialosides 16732727_Siglecs-7 did not interact with sulfate derivatives of LacNAc and sulfated oligosaccharides containing sialic acid. 16828866_The expression levels of Siglec-7 were detectable in bone marrow plasma from AML patients and serum from normal donors. 18331725_The species-specific differences in the expression expression of Siglecs in SIV infection was studied. 19710502_The decreased expression of Siglec-7 represents an early marker of dysfunctional natural killer-cell subsets associated with high levels of HIV-1 viremia. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22933622_Based on upregulated SIGLEC7 expression in blood monocytes during relapse, findings suggest a role for SIGLEC7 in acute disease activity in multiple sclerosis. 23029261_Siglec-7 participates in generating a monocyte-mediated inflammatory outcome following pathogen recognition. 24330394_These results show that Siglec-7 binds HIV-1 via gp120 and contributes to enhance the susceptibility to infection of CD4 positive T cells and monocyte-derived macrophages. 24569453_Expression of Siglec-7 and -9 ligands was associated with susceptibility of NK cell-sensitive tumor cells and, unexpectedly, of presumably NK cell-resistant tumor cells to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. 24810846_Siglec-7 plays a significant role in inhibiting IgE-mediated mast cell activation, but only moderately affects IgE-mediated activation in primary human basophils. 27312286_Siglec-7 defines a highly functional natural killer cell subset and inhibits cell-mediated activities. 28378743_Data reported that Siglec-7 was expressed on beta-cells and down-regulated in type 1 and type 2 diabetes and in infiltrating activated immune cells. Furthermore, Siglec-7 seems to play a critical role in the maintenance of an immune-suppressive anti-inflammatory microenvironment, which is lost in diabetes, and may contribute to the manifestation and progression of this metabolic syndrome. 28786023_CD56bright NK cells from obese subjects had a reduced expression of Siglec-7 29617289_NK cells with Siglec-7neg phenotype possess a high and sustainable killing activity and have the capability to eliminate a NK-resistant leukemia cell and hypersialylated tumor cells 30690753_Siglec-7 is constitutively expressed on human eosinophils and downmodulates eosinophil activation. 32027025_DNA methylation-mediated Siglec-7 regulation in natural killer cells via two 5' promoter CpG sites. 32319079_Reduced Siglec-7 expression on NK cells predicts NK cell dysfunction in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. 32322597_The Roles of Siglec7 and Siglec9 on Natural Killer Cells in Virus Infection and Tumour Progression. 32391973_Targeting glycosylated antigens on cancer cells using siglec-7/9-based CAR T-cells. 32457377_Discovery of a new sialic acid binding region that regulates Siglec-7. 32513821_Decidual glycodelin-A polarizes human monocytes into a decidual macrophage-like phenotype through Siglec-7. 33248687_The conserved arginine residue in all siglecs is essential for Siglec-7 binding to sialic acid. 33495350_Genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal a specific ligand for the glycan-binding immune checkpoint receptor Siglec-7. 33640457_Identification and functional characterization of a Siglec-7 counter-receptor on K562 cells. 34273636_Siglec-7 is an indicator of natural killer cell function in acute myeloid leukemia. 35367830_Siglec-7 mediates varicella-zoster virus infection by associating with glycoprotein B. 35526487_Regulation of Siglec-7-mediated varicella-zoster virus infection of primary monocytes by cis-ligands. 36211376_Siglec-7 represents a glyco-immune checkpoint for non-exhausted effector memory CD8+ T cells with high functional and metabolic capacities. |
ENSMUSG00000030474 |
Siglece |
54.153609 |
7.2685273062 |
2.861663 |
0.347515185 |
68.171373 |
0.00000000000000014988604305014656984499984252595951435402077498316303350023304119531530886888504028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001119594127236924908505145543520560822473133887403062836085609887959435582160949707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
98.1774975 |
18.0453279 |
13.5726901 |
2.1757433 |
| ENSG00000169026 |
84179 |
SLC49A3 |
protein_coding |
Q6UXD7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84179; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857] |
|
ENSMUSG00000029490 |
Mfsd7a |
18.075565 |
0.3491476963 |
-1.518091 |
0.400501977 |
14.829679 |
0.00011766904487753667872193541477088274405105039477348327636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000320856290853951877251742930141631404694635421037673950195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3320983 |
4.4424497 |
23.8349187 |
8.6705635 |
| ENSG00000169047 |
3667 |
IRS1 |
protein_coding |
P35568 |
FUNCTION: May mediate the control of various cellular processes by insulin. When phosphorylated by the insulin receptor binds specifically to various cellular proteins containing SH2 domains such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85 subunit or GRB2. Activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase when bound to the regulatory p85 subunit (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16878150}. |
3D-structure;Diabetes mellitus;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transducer;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein which is phosphorylated by insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Mutations in this gene are associated with type II diabetes and susceptibility to insulin resistance. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:3667; |
caveola [GO:0005901]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; insulin receptor complex [GO:0005899]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005159]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding [GO:0043548]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase adaptor activity [GO:0005068]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0046676]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0032000]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; positive regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010907]; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045725]; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046628]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11287026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11289056_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11522686_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11775217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11874945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11874945_association between the Gly972Arg polymorphism in insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and birth weight in a population-based sample of Brazilian newborns 11877394_Insulin receptor substrate 1 translocation to the nucleus by the human JC virus T-antigen 11978177_Nitric oxide regulates oestrogen-activated signalling pathways at multiple levels through cyclic GMP-dependent recruitment of insulin receptor substrate 1 in human breast cancer cells. 12107745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12107745_insulin sensitivity of glucose disposal and lipolysis: no influence of common genetic variants 12213887_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12213887_Relationship of genotypes to phenotypic features of polycystic ovary syndrome 12351658_IRS-1 is a novel direct substrate for IKK and that phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser(312) (and other sites) by IKK may contribute to the insulin resistance mediated by activation of inflammatory pathways 12354757_PTPL1/FAP-1 has a key role in the apoptotic process in human breast cancer cells independent of Fas but associated with an early inhibition of the insulin receptor substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway 12358865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12370850_genetic variants in the gene appear not to have a major role as modifier genes in familial combined hyperlipidemia 12409308_Data suggest that salicylic acid can reverse the inhibitory effects of TNFalpha on insulin signaling via insulin receptor substrate 1 12414625_Constitutive IRS-1 activation is a common phenomenon in tumors. 12475767_In two cohorts ofobese Caucasian children, we measured insulin sensitivity and genotyped insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 and IRS-2 genes for the Arg972Gly and the Asp1057Gly variants, respectively. 12475767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12477526_Increased frequency of the G972R variant of the insulin receptor substrate-1 (irs-1) gene among girls with a history of precocious pubarche. Sex hormone-binding globulin concentrations were lower among girls heterozygous for G972R variant. 12477526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12493740_inhibition of insulin-stimulated insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway by Grb10 12510059_role in modulating insulin-stimulated degradation by serine 312 phosphorylation 12560071_concluded that the IRS-1 protein is involved in the signalling pathway of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase 12565902_Data describe the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) co-activator 1, PPAR gamma, insulin receptor substrate-1, glucose transporter isoform-4, and mitochondrial uncoupling protein-1 in adipose tissue. 12588284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12606535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12606535_findings suggest a role for Arg(972) IRS-1 in conferring risk for the development of type 1 diabetes 12732844_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12763374_Increased growth caused by IRS-1 over-expression is balanced by constitutive activation of pro-death mechanisms. 12765939_there is an increase of serine 636 phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 in primary culture of skeletal muscle cells from patients with type 2 diabetes. 12819898_Carriers of the Gly972Arg variant of the IRS-1 gene are at a 25% increased risk of having Type 2 diabetes compared with non-carriers. 12819898_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12821935_IRS-1 is stabilized in tumor cells, the IRS-1/Akt/GSK-3 pathway is upregulated, and improved cell survival is seen in the presence of IGF-I 12843189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12843189_the Arg(972) IRS-1 variant could contribute to the risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases associated with type 2 diabetes by producing a cluster of insulin resistance-related metabolic abnormalities. 12910680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12934392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14583092_Protein kinase C delta modulates the ability of the insulin receptor kinase to tyrosine-phosphorylate IRS-1. 14602724_IRS-1 has a role in insulin attenuation of platelet functions by interfering with cAMP suppression along with Gi 14604996_Both of the IRS proteins modulate VPF/VEGF expression in pancreatic cancer cells by different mechanistic pathways. 14633864_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14633864_The association of variants in IRS1 with type 2 diabetes and type 2 diabetes-related phenotypes and the differential expression of IRS1 in adipocytes and skeletal muscle suggest a role of this gene in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. 14642408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14642408_The IRS-1 Gly972Arg polymorphism relates to higher fasting insulin levels and lower triglyceride levels. The impact of this genotype and its modification by overweight may be smaller than suggested previously. 14668342_ETV6-NTRK3.IRS-1 complex formation through the NTRK3 C terminus is essential for ETV6-NTRK3 transformation 14693412_None of the polymorphisms in INSR or IRS1 was associated with metabolic syndrome findings. 14693412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14707024_G972R IRS-1 polymorphism impairs insulin regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. 14966273_These data indicate that both insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and -3, but not IRS-2 or IRS-4, play key roles in the differentiation of brown adipocytes. 14988278_Association of this gene's single nucleotide polymorphism with type 2 diabetes. 15001544_Activation of hexosamine pathway affects glucose-induced phosphorylation of IRS-1. Impairs coupling of IRS-1 and PI 3-kinase and activativates Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin/phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein-1/p70S6 kinase pathway. 15044323_AII, acting via the type 1 receptor, increases IRS-1 phosphorylation at Ser312 and Ser616 via JNK and ERK1/2, respectively, thus impairing the vasodilator effects of insulin mediated by the IRS-1/PI 3-kinase/Akt/eNOS pathway. 15069075_phosphorylation of Ser(318) by PKC-zeta might contribute to the inhibitory effect of prolonged hyperinsulinemia on IRS-1 function. 15127203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15155816_data demonstrate cell-specific alterations in IRS protein concentrations in theca cells from polycystic ovaries consistent with exaggerated amplification of the insulin signal & which may play a role in ovarian hyperandrogenism & thecal hyperplasia 15161794_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15182363_Data show that in adipocytes the insulin receptor is localized to caveolae,and that part of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), the immediate downstream signal mediator, colocalizes with the insulin receptor in the plasma membrane and caveolae. 15209769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15222685_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15222685_a lack of the Arg972 IRS1 polymorphism was found in the Parakana Indian population 15240653_By inducing endothelial dysfunction, the Arg(972) IRS-1 polymorphism may contribute to the genetic predisposition to develop cardiovascular disease. 15247132_Having at least one R allele (GR or RR) for IRS1 G972R was associated with an increased risk of colon cancer [odds ratio 1.4, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 1.1-1.9] 15247132_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15308584_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15316008_SH2-B dramatically enhanced leptin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 and IRS2 in human and mouse cells. 15318176_nuclear IRS-1 interacts with ERalpha and that this interaction might influence ERalpha transcriptional activity 15474880_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15561965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15561965_unable to replicate the association of the IRS-1 G972R polymorphism with type 2 diabetes 15561966_Estimate of the overall contribution of IRS1 variation to type 2 diabetes susceptibility, but current study suggests that previous studies have overestimated the magnitude of this effect. 15561966_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15581831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15582274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15590636_the G972R naturally occurring polymorphism of IRS-1 not only reduces phosphorylation of the substrate but allows IRS-1 to act as an inhibitor of the insulin receptor kinase, producing global insulin resistance 15604215_mTOR/S6K1 overactivation contributes to elevated serine phosphorylation of IRS-1, leading to impaired insulin signaling to Akt in liver and muscle 15634339_pinpoint the signalling dysregulation in type 2 diabetes to be the insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of IRS1 in human adipocytes 15636429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15665022_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15678496_IRS1 G972R GR/RR genotypes were associated with a 2.8-fold increased risk for prostate cancer and also associated with a more advanced Gleason score and AJCC stage. 15678496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15705377_IRS1 variant and CYP21 mutations seem to play a limited role in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome in the population studied. 15705377_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15759454_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15781195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15781195_the PPARgamma and IRS-1 genes have a possible interaction in their effects on adiponectin concentration in blood 15849359_IRS-1 is a novel physiological substrate for pelle-like kinase 15926113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15940190_Carriers of Pro allele compared with carriers of Ala allele of PPARG2 gene had higher frequency of insulin resistance. No association was found between insulin resistance and alleles and genotypes of PPAR and IRS1 genes. 15940190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15965906_Data show that JC polyomavirus T-antigen inhibits homologous recombination DNA repair by binding insulin receptor substrate 1, which then translocates to the nucleus and binds Rad51 at the site of damaged DNA. 15985484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16020478_Phosphorylation of Ser1223 dampens association of IRS-1 with Src homology domain 2 (SH2)-containing phosphatase-2 (SHP-2). 16030120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16037106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16084882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16084882_The Gly972Arg variant of IRS-1 may modulate reproduction by lowering sex hormone-binding globulin in both healthy women and women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 16128672_Insulin induces IRS1 protein levels in humans and rodents 16129678_Ser(318) phosphorylation of IRS-1 is an early physiological event in insulin-stimulated signal transduction, which attenuates the continuing action of insulin 16129690_IRS-1 serine 307 phosphorylation is attenuated in insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes 16233930_Variations in various codons among African Pygmies and Bantus. 16284438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16284649_IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in muscle has a role in insulin resistance 16354680_Raptor directly binds to and serves as a scaffold for mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of IRS-1 on Ser636/639. 16367885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16418171_interleukin-6 has a role in insulin signal transduction via insulin receptor substrate-1 in skeletal muscle cells 16448675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16489531_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16516141_Negative feedback phosphorylation of serine 312 required relatively high concentrations of insulin (EC(50)=3 nM) for a long time (t(1/2) ca. 30 min) and reduced the steady-state tyrosine phosphorylation, without affecting the concentration, of IRS1. 16522427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16603055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16648810_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16752222_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16914728_These studies suggest that, through serine phosphorylation, Raptor-mTOR and S6K1 promote the depletion of IRS1 from specific intracellular pools in pathological states of insulin and IGF-I resistance and in lesions associated with tuberous sclerosis. 16970908_Ser24 is a negative regulatory phosphorylation site in IRS-1. 17020651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17030605_IRS-1 is selectively inactivated in metastatic breast cancer in transgenic mice. 17030631_Transgenic mice overexpressing IRS1 in the mammary gland show progressive mammary hyperplasia, tumorigenesis and metastasis. 17044098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17046546_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17051426_Genetic variation in IRS1 is associated with breast cancer risk 17051426_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17068339_phosphorylation is a mechanism for regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1/2, Akt, and ERK1/2 17075427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17075427_Polymorphism of the insulin receptor substate-1 gene at codon 972, especially Gly/Arg variant, appears to be associated with occurrence of obstructive sleep apnea syndromes in male patients, whereas this polymorphism is not related to severity of OSAS 17124363_IRS-1 gene polymorphisms do not associate with obesity. 17124363_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17179152_hypoxia-mediated suppression of Akt may induce caspase-mediated IRS-1 cleavage. 17222321_We showed that clearance of HCV improves insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and hepatic IRS1/2 expression. 17222824_Overexpression of IRS1 and IRS2 but not of Shc induced DNA synthesis in starved CHO-IR cells independent of exogenous growth factors. 17279354_CRP may cause insulin resistance by increasing IRS-1 phosphorylation at Ser(307) and Ser(612) via JNK and ERK1/2, respectively, leading to impaired insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, GLUT4 translocation, and glycogen synthesis 17332342_IRS-1 activates promoters involved in cell growth and cell proliferation, resulting in a more transformed phenotype. 17360977_Assessment of IRS-1 phosphorylation in vivo shows that insulin has profound effects on IRS-1 serine/threonine phosphorylation in healthy humans. 17361103_This review points out that IRS-1, which is inactivated in metastatic mammary tumors, may be a novel predictive indicator of metastasis. 17374994_This review discusses the roles of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in oncogenic transformation and cancer progression. 17416760_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17443311_Data do not support an association of common variants in IRS1 with type 2 diabetes in populations of European descent. 17443311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17459875_phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling and induces apoptosis is inhibited by energy depletion via AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser-794 17465001_Despite the small sequence divergence of the hepatitis C virus core proteins of genotypes 3a and 1b, the 2 proteins appear to interfere with insulin receptor substrate 1 using genotype-specific mechanisms 17570749_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17575262_phosphorylation is inhibited by RBP4 in diabetic adipocytes 17591841_IRS-1 may act as a repressor of liganded estrogen receptor (ER)alpha and coactivator of unliganded ERalpha. 17638892_PTPN13/PTPL1 induces apoptosis through insulin receptor substrate-1 dephosphorylation 17640984_Understanding the complex phosphorylation patterns of IRS-1 is crucial to elucidating the factors contributing to insulin resistance and, ultimately, the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. 17647275_PMA-induced insulin resistance, through induction of serine phosphorylation of IRS1 mediated by activated JNK and PKCs, increases ApoB secretion in Chang liver cells. 17719609_IRS-1 Gly972Arg polymorphism is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in the Japanese population. 17719609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17721885_Overexpression of Akt1 upregulates glycogen synthase activity and phosphorylation of mTOR in IRS-1 knockdown HepG2 cells.( 17827156_identify miR145 as a micro RNA that down-regulates the IRS-1 protein, and inhibits the growth of human cancer cells 17827393_IGF-1 activates the IGF receptor/IRS/PI3K/PKB pathway, and that PI3Kalpha is essential for the potentiatory effect of IGF-1 on platelet responses 17868644_The results of this study show that triglyceride is a central feature of peripheral insulin resistance, and also suggest that triglyceride-induced ER stress influences insulin resistance. 17898946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17905199_Chimeric IRS1, consisting of the conserved N-terminus of rat IRS1 with the variable C-terminal of human IRS1, did not target the plasma membrane, indicating that subtle sequence differences direct human IRS1 to the plasma membrane. 17908691_Rapamycin inhibits S6K1-dependent IRS-1 serine phosphorylation, increases IRS-1 protein levels, and promotes association of tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS-1 with PI3K. 17914103_Carrying the variant allele of the IRS1 Gly972Arg SNP further decreased the risk for colorectal cancer among the INSR-603G allele carriers. 17914103_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18059035_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18208559_Transgenic mice overexpressing IRS1 show impaired insulin action and insulin secretion. 18216326_nondiabetic carriers of the G972R IRS-1 variant showed increased expression of prothrombotic genes and a decreased expression of fibrinolytic genes 18222120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18264722_agents that block IRS-1 potentiate the effect of mTOR inhibition in the growth of prostate cancer cell xenografts. 18285345_phosphorylation of IRS-1 Ser(357) mediates at least in part the adverse effects of PKC-delta activation on insulin action 18305032_the K1 mutation within the retinoblastoma protein (Rb) binding motif of TAg disrupts not only Rb binding but also IRS1 binding, contributing to the loss of activation of PI3K/Akt signaling. 18316360_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18398029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498745_Results demonstrate a key role for the CUL7 E3 in targeting IRS-1 for degradation, a process that may contribute to the regulation of cellular senescence. 18521741_nuclear IRS-1 is a novel AR regulator 18611262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18615395_Gly972Arg genotype is associated with lower birth weight, body length and head circumference in neonates with adequate gestational age.Gly972Arg polymorphism in the IRS-1 gene was genotyped. 18615395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18615538_None of the components in the IGF-1 pathway including IGFBP3, PI3k, and PTEN influence the relation between IRS-1 genotype and prostate cancer risk. Ther is no association between carriage of the variant IRS-1 gene and prostate cancer risk. 18615538_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18642444_results indicate that IRS-1 plays a significant role in Simian Virus 40 large T antigen activation of cell cycle progression genes 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18710329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18716398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18834857_mir-126, a cell growth suppressor, targets IRS-1. 18851963_IRS-1 may have a more general role in cancer, and could be considered as a protein having the opposite effect of tumor suppressors. 18952604_S6K1 directly phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser-270 to promote insulin resistance in response to TNF-(alpha) signaling through IKK2. 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18992263_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19035139_There is excessive activation of IRS-1 in endometrial carcinoma and atypical hyperplasia. Over-activation of IRS-1 may be an intermediate event linking hyperinsulinemia and endometrial carcinoma. 19038974_During in-vitro decidualization of cultured human ESCs, levels of IRS-1 increased, suggesting a potential involvement of the IGF signalling pathway in the decidualization process. 19053277_There are significant changes in dynamics within the phosphotyrosine-binding domain of IRS1 that have significant consequences for stability and function. 19117011_the nucleus, nuclear interaction between IRS-1 and Rad51, and the inhibition of recombination. 19124510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19140314_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19259821_The differential degradation of IRS-1 and IRS-2 contributes to their distinct modes of action. 19261680_Increased expression of both insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 confers increased sensitivity to IGF-1 stimulated cell migration 19328476_After the action of testosterone solution, the protein expressions of IRS-1mRNA, IRS-1, and GLUT-4 in endometrial glandular epithelial cells all decreased significantly. Metformin may reverse this effect. 19375584_Omental IRS-1 expression was low and unaffected by visceral obesity. Subcutaneous IRS-1 was reduced in visceral obesity. 19391107_Data show that IGF-IR resistant to miR145 is not down-regulated by miR145 but fails to rescue colon cancer cells from growth inhibition, and indicate that down-regulation of IRS-1 plays a significant role in the tumor suppressor activity of miR145. 19418728_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19418728_The association of single and combined polymorphisms Gly972Arg, SNP43, & Pro12Ala, of the genes IRS1, CAPN10, PPARG2, respectively, with the risk of failure to sulphonylurea and metformin therapies was determined in patients with NIDDM. 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19447894_IL-4 can accelerate migration of differentiated airway epithelial cells after injury which requires IRS-1 and/or IRS-2. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19557384_Focusing on early-onset diabetes, which is characterised by a stronger genetic background, may be related to an IRS1 single-nucleotide polymorphism. 19557384_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19561084_IRS-1 lacking the SAIN domain does not interact with Raptor, is not phosphorylated at Ser-636/639, and favorably interacts with PI 3-kinase. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19639489_IGF-I induces a temporally regulated nuclear or cytoplasmic localization of IRS-1 that correlate with the transition from proliferation to chondrogenic differentiation. 19671924_The sites of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification of rat and human IRS-1, were identified. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19716569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19716569_results suggest the participation of Gly972Arg polymorphism of IRS1 in the genetic susceptibility to TD2 in Mexican population. The restriction of including only participants with normal BMI might increase the power to detect genetic determinants of T2D 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19734900_C allele of rs2943641 was associated with reduced basal levels of IRS1 protein and decreased insulin induction of IRS1-associated phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase activity in human skeletal muscle biopsies. 19734900_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19803812_interactions between the molecular expression of SOCS3, IRS-1 and phospho-AKT mediated by the genotype 1b virus 19843326_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19843521_Expression of IRS1 can be directly activated by beta-catenin. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19924529_Nuclear IRS-1 may be a useful marker to predict tamoxifen response in patients with early breast cancer, particularly when assessed in combination with progesterone receptor. 19926323_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19926323_The association of insulin receptor (IotaNSR) and insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) polymorphisms with the risk of developing polycystic ovary syndrome, was investigated. 19956100_Sixteen single-nucleotide polymorphisms(SNPs) were evaluated for IRS1 and 10 for PAX4. Transmission disequilibrium testing neither show type I diabetes association of SNPs in the two genes, nor did haplotype analysis. 20012307_No association of G972S polymorphism in insulin receptor substrate-1 gene with PCOS and insulin resistance was detected and so should not be viewed as major contributor to the development of PCOS or insulin resistance. 20012307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20170352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20170352_insulin receptor substrate 1 Gly972Arg and G protein beta3 subunit C825T polymorphisms are associated neither with polycystic ovary syndrome nor with metabolic syndrome in the Slovak female population 20176643_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20207740_Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells. 20210696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20210696_Only the IRS-1 polymorphism is associated with increased susceptibility to PCOS in a Greek population. 20229450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20229450_The IRS-1 Gly972Arg has the highest frequency reported world-wide for polycystic ovary syndrome women. 20351777_Hepatitis B virus X protein impairs hepatic insulin signaling through degradation of IRS1 and induction of SOCS3 20363874_AMPK functions to inhibit IGF-I-stimulated PI3K pathway activation through stimulation of IRS-1 serine 794 phosphorylation. 20384434_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20416077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20416304_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20437058_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20437825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20490451_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20540360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20540360_The obtained data indicate the possibility of participation of polymorphism in gene IRS1 in formation of predisposition to prostate cancer. 20540670_G972R polymorphism associated with gestational diabetes in Greek women 20540670_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20685959_PKR regulates the upstream central transmitters of insulin signaling, IRS1 and IRS2, through different mechanisms. 20730618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20738937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20824664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20824664_genetic association studies: in a healthy Spanish population of young adults, an SNP in IRS1 (G972R) is associated with insulin resistance/sensitivity; a high-CHO, low-fat diet induces greater peripheral sensitivity to insulin in GR heterozygotes 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20977583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21204696_IRS1 G972R polymorphims is not associated with prostate cancer risk. 21289241_gestational diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance subjects had a persistent impairment in IRS1 activation 21325637_Data show that PDGF-mediated IRS-1/IRS-2 dysregulation resulted in the attenuation of insulin-induced IRS-1/IRS-2-associated PI 3-kinase activity. 21353221_The insulin-resistance and type 2 diabetes locus near the IRS1 gene is a determinant of lower HDL cholesterol among T2D subjects but does not translated into a detectable coronary artery disease risk. 21454638_Pin1 bin |
ENSMUSG00000055980 |
Irs1 |
65.100599 |
0.1496484300 |
-2.740351 |
0.378242976 |
48.198990 |
0.00000000000385086632694800310034709047287325379884531662000313190219458192586898803710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000022022001931713494755862370309274758575085462197762353753205388784408569335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.5513446 |
5.1297309 |
93.6487936 |
22.7127427 |
| ENSG00000169071 |
4920 |
ROR2 |
protein_coding |
Q01974 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor which may be involved in the early formation of the chondrocytes. It seems to be required for cartilage and growth plate development (By similarity). Phosphorylates YWHAB, leading to induction of osteogenesis and bone formation (PubMed:17717073). In contrast, has also been shown to have very little tyrosine kinase activity in vitro. May act as a receptor for wnt ligand WNT5A which may result in the inhibition of WNT3A-mediated signaling (PubMed:25029443). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17717073, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25029443}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Kringle;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Sulfation;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor protein tyrosine kinase and type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the ROR subfamily of cell surface receptors. The protein may be involved in the early formation of the chondrocytes and may be required for cartilage and growth plate development. Mutations in this gene can cause brachydactyly type B, a skeletal disorder characterized by hypoplasia/aplasia of distal phalanges and nails. In addition, mutations in this gene can cause the autosomal recessive form of Robinow syndrome, which is characterized by skeletal dysplasia with generalized limb bone shortening, segmental defects of the spine, brachydactyly, and a dysmorphic facial appearance. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4920; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; coreceptor activity involved in Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:1904929]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding [GO:0031435]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; astrocyte development [GO:0014002]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; macrophage migration [GO:1905517]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation [GO:0045651]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein kinase C activity [GO:1900020]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175]; regulation of synaptic signaling by nitric oxide [GO:0150045]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
12815588_Heterozygous mutations in ROR2 have recently been shown to give rise to autosomal dominant brachydactyly type B1 (BDB1). 12919145_ROR2 is mutated in hereditary brachydactyly with nail dysplasia, but not in Sorsby syndrome. 15388793_identification of human Ror2 as a novel regulator of canonical Wnt signaling in osteoblastic (bone-forming) cells with selective activities, enhancing Wnt1 but antagonizing Wnt3 15654020_The ROR2 protein modulates the growth of neurites as well as their branching pattern in hippocampal neurons. 17095577_Ror2 initiates commitment of MSCs to osteoblastic lineage and promotes differentiation at early and late stages of osteoblastogenesis. 17101003_Brachydactyly type B1: report of a family with de novo ROR2 mutation. 17619808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17619808_The region of the first through the second ROR2 introns is most likely to contain the functional polymorphism/s responsible for hand bone length and BMD. 17665217_The clustering of Robinow-causing mutations in the extracellular frizzled-like cysteine-rich domain of ROR2 suggests a stringent requirement for the correct folding of the domain before export of ROR2 from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. 17717073_Ror2 induces osteogenic differentiation, at least in part, through a release of the 14-3-3beta-mediated inhibition 17996904_In this study, we showed for the first time the connection of ROR2 in Dupuytren's disease 18215320_Ror2 positively modulates Wnt3a-activated canonical signaling in a lung carcinoma, H441 cell line. This activity of Ror2 is dependent on cooperative interactions with Fzd2 but not Fzd7. 18365018_Activation via tyrosine phosphorylation of ROR2 receptor leads to its internalisation into Rab5 positive endosomes. These findings show that BDB mutant receptors are defective in kinase activation as a result of failure to recruit Src 18615587_both Wnt5a and Wnt3a bound Ror2, only Wnt5a induced Ror2 homo-dimerization and tyrosine phosphorylation in U2OS human osteoblastic cells. 18703641_Stimulation of epithelia by the CaSR increased the expression of the tyrosine kinase Ror2, suggesting existence of a unique paracrine relationship for CDX2 homoeostasis in the intestine. 18831060_clinical and molecular findings of two sib pairs from the same extended family with Robinow syndrome due to a novel intragenic ROR2 deletion involving exons 6 and 7 that could not be detected by sequencing 19135982_the interaction of Ror2 with BRIb is specific and independent of post-translational N-glycosylation. 19448672_Expression of MMP2 in RCC cells was suppressed by Ror2 knockdown, placing Ror2 as a mediator of MMP2 regulation in RCC and a potential regulator of extracellular matrix remodeling. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19461659_The deletion represents the second ROR2 mutation associated with a autosomal dominant brachydactyly type B1-syndactyly phenotype. 19533773_Distal symphalangism affecting only 4th finger with ROR2 mutation. 19561643_Results indicate that Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling involves the activation of a SFK, leading to MMP-13 expression, and that constitutively active Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling confers invasive properties on osteosarcoma cells in a cell-autonomous manner. 19640924_Data showed a correlation between the severity of BDB1, the location of the mutation, and the amount of membrane-associated ROR2. 19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19802008_Data show that ROR2 knockdown results in a decrease in signaling downstream of Wnt5A. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20185829_a unique regulation pattern for Ror2 in the VHL-HIF axis that has the potential to be applied to other cancer etiologies. 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20591152_data show the importance of epigenetic alterations of ROR2 in colon cancer, highlighting the close interconnection between canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways in this type of tumour 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21069266_Results suggest that Wnt5a plays the role of a tumor suppressor in leukemogenesis through the Wnt5a/Ror2 noncanonical signaling pathway that inhibits Wnt canonical signaling. 21342370_Results show expression of Wnt5a and Ror2 is induced during Snail-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition or malignant progression of cancer cells and that activated Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling confers highly motile and invasive properties on cancer cells. 21377971_2265C>A mutation in ROR2 gene is associated with Brachydactyly type B1 in Chinese family. 21693067_We report two mentally retarded female siblings and their cognitively normal father, all carrying a similar 5.3 Mb microdeletion at 9q22.2q22.32, involving 30 genes including the ROR2 gene and and SYK gene. 22057548_The present study provides evidence of the significant association between ROR2 variants and the OPG/RANKL ratio in human plasma and also suggests ROR2 association with hand osteoarthritis. 22128168_Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling might also be required for expression of MMP-13 gene during the development of the cartilaginous tissue. 22178368_Molecular analysis of the ROR2 gene in a Lebanese family with a mild form of recessive Robinow syndrome revealed the presence of a previously undescribed missense mutation: p.R272C (c.814C>T), in the cysteine-rich domain of the protein. 22293903_WNT-5a and ROR2 were more highly expressed in more severe disease states, and therefore may play a coordinated role in the occurrence and progression of osteosarcoma 22294416_Results show that ROR2 is a useful prognostic indicator in the clinical management of these soft-tissue sarcomas and may represent a novel therapeutic target. 22490406_Results provided evidence of linkage and association between the ROR2 gene and a gene controlling risk to non-syndromic cleft palate. 22493546_Data suggest that Wnt5a and Ror2 may serve as tumor suppressor genes in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, and may serve as clinicopathologic biomarkers for prognosis in HCC patients. 22781592_High ROR2 expression is involved in the pathophysiology of Multiple myeloma-induced bone disease. 22988987_ROR2 expression was not seen in any of the hematological malignancies studied. 22992069_The unusual Asp-Leu-Gly motif in Ror2 is displaced compared with other inactive kinases, allowing the activation loop to interact directly with the tyrosine kinase domains. 23233346_review will explore the dual role of ROR2 in tumorigenesis and provide an up to date analysis of current literature in this rapidly expanding field 23238279_Sequence analysis of the gene ROR2 indicated a nonsense mutation (c.2278C>T, p.Q760X) in exon 9 in all brachydactyly type B affected individuals of the family. 23278988_This study demonstrated the first attempt to identify Wnt5a and Ror2 as additional mechanisms contributing to dysregulation of the non-canonical WNT signaling pathway in medulloblastoma. Ror2 may play a role as an oncosuppressor in medulloblastoma. 23469623_Our results do not support the relevance of ROR2/Wnt5a as biomarkers in stage 1 pure seminomas 23893409_a new role for Ror2 in conveying a tonic signal to stabilize soluble beta-catenin and create a poised state of enhanced responsiveness to Wnt3a exogenous signals in RCC. 23963164_DEX induces the upregulation of noncanonical Wnt ligand Wnt5a. Recombinant WNT5a protein induces CLAN formation through the noncanonical Wnt receptor ROR2/RhoA/ROCK signaling axis. 24104062_Data shows that ROR1 and ROR2 are inversely expressed in melanomas and negatively regulate each other. Also, hypoxia initiates a shift of ROR1-positive melanomas to a more invasive, ROR2-positive phenotype. 24158497_ROR2 is an epigenetically inactivated tumor suppressor gene that antagonizes both beta-catenin and AKT signaling in multiple various carcinomas. 24932600_this paper reports the findings on three families with recessive Robinow syndrome which were identified in India. Three mutations in ROR2 gene, two novels and one previously known mutation were observed in these patients 24954533_report a three-generation Chinese family with dominant inheritance of the BDB1 limb phenotype. Sequence analysis identified a novel heterozygous base deletion (c.1396-1398delAA) in the gene ROR2 in all affected family members 25029443_Human ROR1 and ROR2 are receptor tyrosine kinase-like pseudokinases. 25209439_High expression of the novel Wnt receptor ROR2 is associated with breast cancer. 25301559_These results suggest that ROR2 expression is correlated with malignant attributes of CRC and may serve as an indicator for poor prognosis in patients with CRC. 25387569_Positive ROR2 and FRAT1 expression is associated with the progression and poor prognosis of chondrosarcoma. 25542006_Mutations in key regions of the kinase domain of Ror2 resulted in the abrogation of increased tumor growth, cell migration, and cell invasion observed with expression of wild-type Ror2. 25755786_These results indicate that ROR2 is significantly correlated with cancer progression and poor prognosis in cervical cancer 26259918_We present strong evidence that ROR2 could be used as an indicator of poor prognosis and could represent a novel therapeutic target for PDAC. 26284319_ROR2 gene mutations are associated with autosomal recessive robinow syndrome. 26305508_Findings suggest that high receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor (ROR) 2 or proto-oncogene protein Wnt-5A (Wnt5a) expression is associated with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 26515598_Data show that silencing receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) ROR2 and ROR1 has a strong inhibitory effect on the ability of ovarian cancer cells to proliferate, migrate and invade. 26559837_These data suggest a mechanism where human cytomegalovirus alters the expression of the Wnt receptor ROR2 to alter Wnt5a-mediated signaling and inhibit trophoblast motility 26596412_results corroborated previous findings of Ryk-mediated Wnt5a effect, and suggested a role for Ror2 in the Wnt5a machinery in glioblastoma 26690702_This study identifies an interaction between ROR1 and ROR2 that is required for Wnt5a signaling that promotes leukemia chemotaxis and proliferation. 26708384_Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling enhances expression and secretion of CXCL16 in mesenchymal stem cells thereby activating CXCR6 expressed on tumor cells to promote proliferation. 26771355_Data show that CD13 anntigen and receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (ROR2) identify a cardiac lineage precursor pool that is capable of successful engraftment into the porcine heart. 26862065_the b-catenin-independent WNT score correlated with reduced overall survival only in the metastasized situation . This is in line with the in vitro results of the alternative WNT receptors ROR1 and ROR2, which foster invasion 27440078_Data show that receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 (ROR2) is epigenetically silenced by promoter hypermethylation in colorectal cancer cell lines and in early stages of colorectal neoplasia tissue. 27631337_found no association between ROR2 staining and poor patient survival 28127051_Ror2 signaling promotes tumor invasiveness and advances the understanding of how Golgi structure and transport can be regulated. 28277191_Knockdown of Ror2 expression in renal cell carcinoma cells significantly reduced cell proliferation and induced apoptosis. 28465645_In squamous/adenosquamous carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder positive ROR2 or WNT5a expression is generally associated with a poor prognosis. 28475014_Our findings suggest that receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 may be an important regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, primarily regulated the non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway in ovarian cancer cells, and may display a promising therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. 28536612_WNT5A and ROR2 are induced by inflammatory mediators through NF-kB and STAT3 transcription factors, and are involved in the migration of human ovarian cancer cell line SKOV-3. 28559016_Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling enhanced tongue SCC cell aggressiveness and promoted production of MMP-2 following DeltaNp63beta-mediated EMT 28618961_On these bases, we identified that miR-208b targets receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 gene by which miR-208b can regulate the development of osteosarcoma. 28681925_Wnt5a suppressed osteoblastic differentiation through Ror2/JNK signaling in periodontal ligament stem cell-like cells. 29151594_Studied physiology of pancreatic cancer in an adipocyte model and found role of WNT and ROR2 signaling in cancer progression. 29395309_ROR1 and ROR2 play distinct roles in endometrial cancer. ROR1 may promote tumor progression, while ROR2 may act as a tumor suppressor in endometrioid endometrial cancer. 29453334_beta-catenin-independent regulation of Wnt target genes by RoR2 and ATF2/ATF4 in colon cancer cells 29465811_CK1epsilon is activated by noncanonical Wnt and identify p120-catenin and CK1epsilon as two critical factors controlling Ror2 function. 30060804_Here, we show that Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) autocrine signaling controls the emergence of cytonemes, and that cytonemes subsequently control paracrine Wnt/beta-catenin signal activation. Upon binding of the Wnt family member Wnt8a, the receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 becomes activated. 30431423_Cytomegalovirus infection increased ROR2 protein expression in trophoblasts, with no effect on ROR1 and RYK expression, hence regulating trophoblast migration. 30957191_lncRNA 430945 promotes vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration by upregulating the expression of ROR2 and activating the RhoA signaling pathway. 31148590_we found that ROR2 exerts a pivotal role in the adhesion of multiple myeloma cells to the bone marrow microenvironment 31617258_Whole-exome sequencing identified compound heterozygous variants in ROR2 gene in a fetus with Robinow syndrome. 31878941_ROR2 induces cell apoptosis via activating IRE1alpha/JNK/CHOP pathway in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. 32048761_ROR2 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating MAPK/p38 signaling pathway in breast cancer. 32052562_The role of WNT5A and Ror2 in peritoneal membrane injury. 32172608_Tomographic Study of the Malformation Complex in Correlation With the Genotype in Patients With Robinow Syndrome: Review Article. 32945438_Knockdown of Ror2 suppresses TNFalphainduced inflammation and apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. 32951408_Upregulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 33048444_Novel pathogenic genomic variants leading to autosomal dominant and recessive Robinow syndrome. 33496066_Clinical and molecular characterization of four patients with Robinow syndrome from different families. 34080643_Oncogenic E6 and/or E7 proteins drive proliferation and invasion of human papilloma viruspositive head and neck squamous cell cancer through upregulation of Ror2 expression. 34278704_Downregulation of ROR2 promotes dental pulp stem cell senescence by inhibiting STK4-FOXO1/SMS1 axis in sphingomyelin biosynthesis. 34763666_ROR1 and ROR2 expression in pancreatic cancer. 35032666_Cellular and molecular mechanisms implicated in the dual role of ROR2 in cancer. 35344616_Phenotypic and mutational spectrum of ROR2-related Robinow syndrome. 36001375_Noncanonical Wnt/Ror2 signaling regulates cell-matrix adhesion to prompt directional tumor cell invasion in breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000021464 |
Ror2 |
30.686980 |
5.9634489342 |
2.576147 |
0.502412248 |
25.113894 |
0.00000054042063096273185112376627806107798335233383113518357276916503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001972942991098174910961178182833286598452104954048991203308105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.1333060 |
15.5571303 |
8.7535480 |
2.0986509 |
| ENSG00000169083 |
367 |
AR |
protein_coding |
P10275 |
FUNCTION: Steroid hormone receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues (PubMed:19022849). Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins like ZBTB7A that recruits NCOR1 and NCOR2 to the androgen response elements/ARE on target genes, negatively regulating androgen receptor signaling and androgen-induced cell proliferation (PubMed:20812024). Transcription activation is also down-regulated by NR0B2. Activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3 and ZIPK/DAPK3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14664718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15563469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17591767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17911242, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18084323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19022849, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19345326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20812024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20980437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25091737}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Lacks the C-terminal ligand-binding domain and may therefore constitutively activate the transcription of a specific set of genes independently of steroid hormones. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19244107}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Lacks the C-terminal ligand-binding domain and may therefore constitutively activate the transcription of a specific set of genes independently of steroid hormones. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19244107}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Lipid-binding;Lipoprotein;Metal-binding;Neurodegeneration;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Pseudohermaphroditism;Receptor;Reference proteome;Steroid-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Triplet repeat expansion;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The androgen receptor gene is more than 90 kb long and codes for a protein that has 3 major functional domains: the N-terminal domain, DNA-binding domain, and androgen-binding domain. The protein functions as a steroid-hormone activated transcription factor. Upon binding the hormone ligand, the receptor dissociates from accessory proteins, translocates into the nucleus, dimerizes, and then stimulates transcription of androgen responsive genes. This gene contains 2 polymorphic trinucleotide repeat segments that encode polyglutamine and polyglycine tracts in the N-terminal transactivation domain of its protein. Expansion of the polyglutamine tract from the normal 9-34 repeats to the pathogenic 38-62 repeats causes spinal bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA, also known as Kennedy's disease). Mutations in this gene are also associated with complete androgen insensitivity (CAIS). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:367; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; androgen binding [GO:0005497]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; POU domain binding [GO:0070974]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor binding [GO:0001091]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; steroid binding [GO:0005496]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; activation of prostate induction by androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0060520]; androgen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030521]; animal organ formation [GO:0048645]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus [GO:0071383]; cellular response to testosterone stimulus [GO:0071394]; epithelial cell differentiation involved in prostate gland development [GO:0060742]; epithelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0003382]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; intracellular receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030522]; intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030518]; lateral sprouting involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060599]; Leydig cell differentiation [GO:0033327]; male genitalia morphogenesis [GO:0048808]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; male somatic sex determination [GO:0019102]; mammary gland alveolus development [GO:0060749]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; morphogenesis of an epithelial fold [GO:0060571]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of integrin biosynthetic process [GO:0045720]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in prostate gland development [GO:0060769]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043568]; positive regulation of integrin biosynthetic process [GO:0045726]; positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033148]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0045945]; prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis [GO:0060740]; prostate gland growth [GO:0060736]; regulation of developmental growth [GO:0048638]; regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903076]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003073]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; seminiferous tubule development [GO:0072520]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; tertiary branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060748]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
11079451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11103816_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11121205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11172827_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11221880_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11231320_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11389183_Androgens induce neuroprotection directly through the androgen receptor. 11397855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11409695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11437399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11456479_Almost all of the amino acids located at the 13-residue C-terminal end of the androgen receptor participate in its ligand binding function and consequently in its transcriptional activation. 11474658_androgen receptor and DXS15-134 markers show a high rate of discordance for germline X chromosome inactivation in patients with breast or ovarian cancer 11543741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11545293_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11547131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11550169_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11564035_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11571725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11571732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11587068_Molecular studies performed on eight individuals with AIS were reported. Exon-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR), single-strand conformation polymorphism, and sequencing analyses, were performed in exons 2 to 8 of the AR gene. 11591412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11591424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11595700_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11600555_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11701709_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11720249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11720249_androgen receptor CAG repeats in both black and white patients do not appear to be a strong indicator of prostatic cancer risk 11751688_The aggregation and localization of the truncated form, with or without an expanded polyglutamine tract, is differentially controlled by Glucocorticoid receptor mutants. 11751884_These results demonstrate that activation of the human AR NTD by IL-6 was mediated through MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways in LNCaP prostate cancer cells 11774215_The AR gene (CAG)n exhibits polymorphism among normal male population and the present work could serve as a basis for further exploration of its pathological and genetic significance. 11779876_The FXXLF motif mediates androgen receptor-specific interactions with coregulators 11788641_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11792931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11803263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11804942_poor reproductive performance observed in women with PCOS may be due to the concomitant increase and elevations in endometrial AR 11818501_Domain interactions between coregulator ARA(70) and the androgen receptor (AR); structure activity relationship 11818512_Missense substitution at M807 is associated with androgen insensitivity syndrome 11845321_stained sections throughout male genital development documented the expression of AR and 5 alpha-reductase type 2 in the phallus. 11847524_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11856748_can promote nuclear translocation of beta-catenin in LNCaP and PC3 prostate cancer cells 11861380_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11875111_function inhibited by the reproductive orphan nuclear receptor DAX-1 11889162_Two de novo mutations in the AR gene cause the complete androgen insensitivity syndrome in a pair of monozygotic twins. 11894977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11894978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11896058_Conformational analysis of the androgen receptor amino-terminal domain involved in transactivation. Influence of structure-stabilizing solutes and protein-protein interactions 11903314_role in blood pressure 11906285_Structural basis for the glucocorticoid response in a mutant human androgen receptor 11923466_presence of both the amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains in the AR is essential for the completion of a transcriptionally active form with coactivators and intranuclear compartmentalization common to the steroid hormone receptors 11927493_CAG/CAA repeat lengths in androgen receptor gene may provide useful marker for clinically significant prostate cancer 11931767_These results suggest a model for the functional coordination between the promoter and enhancer in which communication between these elements is established through shared coactivators in the AR transcription complex. 11935317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11956643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11967956_CAG polymorphic repeat lengths in androgen receptor gene among Japanese prostate cancer patients: potential predictor of prognosis after endocrine therapy. 11967956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11971763_regulation of androgen receptor by PI3 kinase 11971970_Results suggest that the conserved AR acetylation site contributes to a pathway governing prostate cancer cellular survival, as AR acetylation mutants are defective in MEKK1-induced apoptosis. 11981028_androgen receptor has a capacity to activate transcription in a ligand-independent manner 12011088_The binding of HuR, CP1, and CP2 to AR mRNA suggests a role for each of these proteins in the post-transcriptional regulation of AR expression in cancer cells. 12015328_major sites of AR phosphorylation 12031042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12031042_contribution of genetic polymorphism of oestrogen and androgen receptor (AR) genes in male infertility 12036913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12039962_activation function-1 domain of androgen receptor contributes to the interaction between subnuclear splicing factor compartment and nuclear receptor compartment 12039962_identification as a coactivator for the androgen receptor [p102 U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle-binding protein] 12042281_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12050225_An androgen receptor gene mutation (E653K) in a family with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency as well as in partial androgen insensitivity. 12051960_review of NH(2)-terminal and carboxyl-terminal interaction in the androgen receptor 12061774_Stabilization of androgen receptor protein is induced by agonist, not by antagonists. 12083956_significance for endocrine therapy in prostatic cancer (REVIEW) 12085360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12085360_the androgen receptor-CAG alleles may contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma predisposition among women through a mechanism different from that for men 12089361_Our study thus suggests a functional cooperation between AR and Stat5. 12101115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12111704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12111704_Polymorphisms within the gene are biomarkers for the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia and benign prostatic enlargement(SRD5A2) 12115497_DHT may play more important roles than testosterone in the regulation of androgen action in endometrial cancer and normal human endometrium, especially in the secretory phase, in which both AR and 5alpha-reductase are increased 12119296_Androgen Receptor requires proteasome activity in prostate tumor cells 12124798_Characterization of androgen receptor and nuclear receptor co-regulator expression in human breast cancer cell lines exhibiting differential regulation of kallikreins 2 and 3. 12146732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12161010_review: role of androgen receptor CAG repeat polymorphism as modifier of carcinogenesis 12161011_the role of AR in inhibiting E(2) action at genomic level in MCF-7 cells 12163482_Data show that steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) enhanced ligand-independent activation of the AR by IL-6 to the same magnitude as that obtained via ligand-dependent activation, and that activation required MAPK. 12189490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12202660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12213902_Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome is caused by a novel mutation in the ligand-binding domain 12218053_There is a coregulatory role for the TRAP-mediator complex in receptor-mediated gene expression. 12220434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12226080_interactions between AR, Smad3, and Smad4 may result in the differential regulation of the AR transactivation, which further strengthens their roles in the prostate cancer progression 12230620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12370109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12372281_Full binding of androgen to the polyglutamine-expanded N-terminal domain of the mutant AR leads to structural alteration with nuclear translocation that eventually results in the onset of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. 12376473_polymorphic CAG repeats in the gene and prostate cancer risk 12376504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12385020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12390340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12394768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12394768_Our results suggest that short CAG repeats are associated with an increased prostate cancer risk in Hispanic men. 12399527_Comparison of fertile men and those with azoospermia on the basis of CAG repeats revealed that the number of CAG repeats in both groups were similar. 12399527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12404104_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12441355_AR possesses an intrinsic transcriptional repression activity, and AR interacts directly with SMRT 12465595_Review. Molecular genetics & structural analysis allow a better understanding of the structure/function relationship of the androgen & its role in androgen insensitivity syndrome, hormone-resistant prostate cancer, Kennedy's disease & male infertility. 12481545_role in spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy [review] 12482965_a new mechanism for androgen-mediated prostate cancer cell survival that appears to be independent of the activity of the receptor on androgen response element-mediated transcription 12499384_androgen receptor has a site in the ligand binding domain that is involved in estrogen induction of androgen receptor trans-activation 12514133_Data show that stimulation of the RhoA effector protein kinase C-related kinase (PRK) signalling cascade results in a ligand-dependent superactivation of androgen receptors both in vivo and in vitro. 12532157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12532336_Data suggest that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) actions on normal prostate cells may be mediated independently through androgen receptors and vitamin D receptors. 12534937_different populations may show different numbers of CAG repeats 12559985_Chip overexpression reduced the rate of AR degradation, consistent with an effect on AR folding,Chip affected AR folding was further supported by the finding that the effects of exogenous Chip were reproduced by a mutant lacking the U box 12568409_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12569365_interaction with Cdc25B may contribute to prostate cancer development 12573820_Data indicate that growth factors are unable to initiate the nuclear translocation of androgen receptors in the absence of androgens or to induce ligand-independent transcriptional activity. 12582022_AR repeat length may be partly responsible for the increased risk for early-onset breast cancer in women who use OCs. 12582022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12586762_androgens can regulate PTHrP production, and the androgen effect on PTHrP is mediated at least in part by transcriptional regulation via the androgen receptor 12591938_identification of an inhibitory domain located in an 81-amino acid segment lying upstream of the DNA-binding domain (DBD) that interacted directly with DBD and repressed DBD binding to the androgen response element 12593895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12593895_study suggests that the androgen receptor gene microsatellite polymorphism may be a candidate genetic marker for risk of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women 12602902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12602915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12606125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12629350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12632109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12634316_a direct correlation exists between the CAG repeat length in the exon 1 of the AR gene and the risk of being azoospermic. 12637980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12637980_Positive independent correlation of the CAG repeat number with body fat content, leptin and insulin. 12648179_Long CAG repeats in the AR gene are not associated with infertility in Finnish males. 12648179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12649062_DNA interaction in the context of the general mechanisms that dictate the sequence-specificity of DNA-binding and dimerization of the nuclear receptors 12651911_Substantial qualitative and quantitative differences in prostate specific antigen expression and AR occupancy of the prostate specific antigen enhancer were observed when dihydrotestosterone and ligand-independent activations of the AR were compared 12668243_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12682292_FLNa interfered with androgen receptor (AR) interdomain interactions and competed with the coactivator transcriptional intermediary factor 2 to specifically down-regulate AR function. 12712467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714604_data suggest that AR interacting peptides and/or AR coregulators may utilize the (F/W)XXL(F/W) and FXXLY motifs to mediate their interaction with AR and exert their influences on AR transactivation 12727953_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12755998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12755998_certain types of age-related changes in ageing men were associated with the length of the AR gene CAG repeat, suggesting that this parameter may play a role in setting different thresholds for the array of androgen actions in the male. 12767946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12767946_The CAG repeats in exon 1 of the androgen receptor gene are longer in endometrial cancer patients. 12771131_SMRT and DAX-1 repress agonist-dependent activity of androgen receptors 12775722_SWI/SNF function potently regulates core AR target gene promoter activation, with a preference for hBRM-containing complexes. 12779088_The loss of the androgen receptor expression together with the observed loss of other steroid hormone receptors in BRCA1-mutated tumors may lead to a hormone-independent growth or to anti-hormone resistant growth of these tumors. 12788064_Deletion of the polyglutamine repeat positively affected the interactions of the ligand-binding domain with the amino-terminal domain as well as the recruitment of the p160 coactivator SRC-1e to the amino-terminal domain of the AR. 12799378_there is a direct interaction between the AR DNA binding domain (DBD) and Tcf4. 12802043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12804609_AR and PIAS3 regulate the STAT3-mediated transcriptional activity by their physical protein-protein competition on STAT3 12810069_Results suggest that p54(nrb) functions as a coactivator of androgen receptors that potentiates transcription and possibly splicing. 12824190_A polyglutamine-expanded form of androgen receptor regulates its cleavage by caspase-3 and enhances cell death. 12843171_Fifteen different mutations were identified, including five (S119X, T602P, L768V, I898F, and P904V) that have not been described previously 12843184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12843184_earlier presentation may relate to increased androgen sensitivity, indicated by androgen receptor gene CAG repeat length. 12860943_Androgen receptor mutation with antiandrogen withdrawal response or survival rate is not specific. 12877254_An association exists between CAG repeat lengths and impaired spermatogenesis in azoospermic males 12879219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12890669_EGR1 binds to the androgen receptor (AR) in prostate carcinoma cells, and an EGR1-AR complex can be detected 12895004_Androgen receptors were only seen in hair follicle dermal papilla cells and the basal cells of the sebaceous gland. 12908100_exon 5 of the androgen receptor has a role in androgen binding, as shown by analysis of insertion/deletion mutation in the androgen receptor 12923188_androgen can regulate the nuclear export signal and, subsequently, the NLS of the AR, providing a mechanism by which androgen regulates AR nuclear/cytoplasmic shuttling. 12925954_GGC and CAG trinucleotide repeat lengths in the androgen receptor gene polymorphism is associated with esophageal cancer risk 12925954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12949936_Orphan receptor TR2 may function as a negative modulator to suppress AR function in prostate cancer. Further studies on how to control TR2 function may result in ability to modulate AR function in prostate cancer. 12970746_IL-4 enhances PSA expression through activation of the AR and Akt signaling pathways in LNCaP prostate cancer cells 14504193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14504193_These findings support the theory that short trinucleotide repeat genotypes of the AR gene protect against breast cancer. 14511213_We conclude that more numerous CAG repeats do not directly cause oligozoospermia and propose that men with longer CAG repeats might be more prone to develop infertility in response to any pathogen/epigenetic factors. 14511217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14511406_androgen receptor downregulates E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and promotes apoptosis of prostatic cancer cells 14517289_androgen receptor, Hsp70, and Bag-1L are all targeted to the androgen response elements of the gene that encodes prostate-specific antigen 14517714_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14517714_The repeat polymorphisms in the AR gene are associated with bone mass in women with high levels of sex-hormone binding globulin. 14519624_Promoter methylation of AR occurs in a differentiation stage-selective manner in follicular non-hodgkin's lymphoma. 14573323_Androgen receptor CAG repeat polymorphism is associated with cognitive function in older men. 14573323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14585317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14612401_AR acetylation promoted cell survival and growth of prostate cancer cells 14627807_H3-K4 methylation at the human prostate specific antigen (PSA) locus following gene activation and repression via androgen receptor 14641003_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14641003_Results do not support a common role for the androgen receptor gene exon 1 CAG repeat in type 1 diabetes mellitus susceptibility; however, an effect of a disease variant in linkage disequilibrium could be detected. 14645241_androgen receptor transactivation requires activating signal cointegrator-2 and the tumor suppressor retinoblastoma 14652007_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14662770_androgen receptor transactivation and coactivation by TIF2/GRIP1 in recurrent prostate cancer is increased by EGF signaling through MAPK 14663470_S-phase fraction was significantly higher in prostate tumors with high AR density 14664704_Conserved hydrophobic residues are important for receptor-dependent gene transcription and that M244, L246 and V248 are part of the binding interface for TFIIF. 14667136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14667136_The CAG repeat polymorphism in the first exon of the androgen receptor (AR) gene is associated with reduced bone mass and increased risk of osteoporotic fractures in women. 14667996_AR is a functional component of the mechanism through which progesterone antagonists induce endometrial antiproliferative effects in the presence of estrogens 14668339_the androgen receptor mediates non-genomic activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase in androgen-sensitive epithelial cells 14691592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14698481_AR containing 51 glutamine repeats showed a consistent, though minimal, reduction in its ability to inhibit beta-catenin-mediated transcription, in comparison to a non-pathogenic form with 20 repeats. 14713779_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14726805_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, genetic testing, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 14734264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14742287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14743468_In situ shortening of CAG repeat lengths in prostate cancer(PCA), prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, and postatrophic hyperplasia(PAH). Frequency of CAG shortening was significantly higher in PAH than in PCA. 14744796_Androstanediol is a stronge activator of mutant AR in prostate cancer cells and induces more cell proliferation 14755454_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14769635_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14963700_Androgen receptor over-expression is associated with gastric cancer 14966121_AR transcriptional hyperactivity associated with shortened poly(Q) length stems from altered ligand-induced conformational changes that enhance coactivator recruitment 14966297_Data report the identification of Rad9, a key member of the checkpoint Rad protein family, as a coregulator to suppress androgen-androgen receptor transactivation in prostate cancer cells. 14968432_The transactivational activity of AR was shown to be affected by the size of the trinucleotide-repeat-regions (CAG and GGC) within the gene. 14973115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14974091_Novel nonsense mutations that introduce premature termination codons in the AR gene in Australian patients with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome. 14974917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14981536_Pim1 and Etk are required for IL6-induced activation of androgen receptor-mediated transcription in prostate cancer. 14985354_glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta phosphorylates the androgen receptor, thereby inhibiting androgen receptor-driven transcription 14999487_the expression of the Kennedy's disease mutation combined with a second allele with a large but normal CAG repeat sequence may have contributed to the motor neuron degeneration displayed in the heterozygote female. 15013685_review elucidates the molecular functions of the androgen receptor and its role in prostate cancer and examines how the mechanism of androgen action has played a role in the translation of new therapies 15023052_The interaction of the androgen receptor N-terminal activation domain AF1 with the transcription factor TFIIF complex imposes a functional conformation in the AF1 domain, which facilitates the formation of an assembly of proteins with AF1. 15042597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15044606_Data show that the haplotype distribution of CAG and GGC repeat lengths is different in men with idiopathic infertility compared to fertile normozoospermic men. 15044606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15046097_Mutations in androgen receptor is associated with Androgen-Insensitivity Syndrome. 15053245_An R840S mutation on exon 7 of the AR ligand-binding domain was characterized in an X-linked androgen insensitivity syndrome patient. 15061984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15062556_AR N-terminal(1-34) suppressed both androgen-dependent AR N-to-C interaction and prostate specific antigen transcription and also caused delaying translocation to the nucleus and the decreasing stability of the AR were inhibition to enter into S phase 15091318_Coding & splice junctions of the androgen receptor gene were scanned in genomic DNA samples from psychiatric patients. 2 variants affecting protein structure & expression were found: R726L in 1 of 17 scanned alcoholics, & P516S in 1 of 3 phobia patients. 15091318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15107424_AR transcriptional activity is negatively regulated by CHIP, which promotes AR degradation 15109605_Data suggest the ligand-binding domain has a role in maintaining the stability of androgen receptor-DNA complexes. 15117901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15118070_molecular dynamic modeling to create four-dimensional models of each of the mutant receptors 15120698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120698_concluded that AR-CAG repeat length does not constitute an important factor for the genetic predisposition to endometriosis 15123687_Data suggest that acetylation and phosphorylation of the androgen receptor (AR) are linked events and that the conserved AR lysine motif contributes to a select subset of pathways governing AR activity. 15131260_LATS2 may play a role in AR-mediated transcription and contribute to the development of prostate cancer 15136785_Candidate gene for benign prostatic hyperplasia. 15136785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15156193_AR is controlled by a suppressor complex lost in an androgen-independent prostate cancer cell line. 15171708_Results describe a novel mutation in exon 7 of the androgen receptor gene in a patient with partial androgen insensitivity syndrome. 15178691_androgen receptor-mediated transactivation and cell growth is suppressed by the glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in prostate cells 15199155_SENP1's ability to enhance AR-dependent transcription is not mediated through desumoylation of AR, but rather through its ability to deconjugate histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), thereby reducing its deacetylase activity. 15201804_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15205473_PTEN, via distinct mechanisms, differentially regulates androgen receptors in various stages of prostate cancers. 15215582_results suggest that hAR AF-1 recruits co-activators previously known only to interact with the AF-2 domain 15229204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15229204_The |
ENSMUSG00000046532 |
Ar |
394.391957 |
0.3924162090 |
-1.349543 |
0.094945294 |
203.581970 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034530248062233074985826866954466021603203851159550878141359354688158898522021279009293653451944532533779997178525220189598821107779258454684168100357055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006688536238826249455908700162370193508291242927513191367839834709681161054769509801406453410818457049035169490543324688491821916613844223320484161376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
225.2750288 |
13.2303935 |
577.9880150 |
22.0160665 |
| ENSG00000169105 |
113189 |
CHST14 |
protein_coding |
Q8NCH0 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of sulfate to position 4 of the N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) residue of dermatan sulfate. Plays a pivotal role in the formation of 4-0-sulfated IdoA blocks in dermatan sulfate. Transfers sulfate to the C-4 hydroxyl of beta1,4-linked GalNAc that is substituted with an alpha-linked iduronic acid (IdoUA) at the C-3 hydroxyl. Transfers sulfate more efficiently to GalNAc residues in -IdoUA-GalNAc-IdoUA- than in -GlcUA-GalNAc-GlcUA-sequences. Has preference for partially desulfated dermatan sulfate. Addition of sulfate to GalNAc may occur immediately after epimerization of GlcUA to IdoUA. Appears to have an important role in the formation of the cerebellar neural network during postnatal brain development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19661164}. |
Carbohydrate metabolism;Disease variant;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the HNK-1 family of sulfotransferases. The encoded protein transfers sulfate to the C-4 hydroxyl of N-acetylgalactosamine residues in dermatan sulfate. Mutations in this gene have been associated with adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:113189; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; N-acetylgalactosamine 4-O-sulfotransferase activity [GO:0001537]; phosphate ion binding [GO:0042301]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; carbohydrate biosynthetic process [GO:0016051]; dermatan sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030208]; dermatan sulfate proteoglycan metabolic process [GO:0050655] |
11470797_D4ST-1 is encoded by a single exon located on human chromosome 15q14; type II membrane protein of 376 amino acids with a 43-amino acid cytoplasmic domain and a 316-amino acid luminal domain containing two potential N-linked glycosylation sites 12847091_human D4ST-1, C4ST-1, and S4ST-2 have differential roles in dermatan sulfate biosynthesis 19661164_D4ST-1 is a key enzyme and is indispensable in the formation of important functional domains in dermatan sulfate and cannot be compensated by other 4-O-sulfotransferases 20004762_dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 has a role in adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome 20533528_A homozygous CHST14 (carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14) mutation in the two familial cases and compound heterozygous mutations in four sporadic cases of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, were identified. 20842734_Musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (former EDS type VIB) and adducted thumb clubfoot syndrome (ATCS) represent a single clinical entity caused by mutations in the dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 encoding CHST14 gene. 21309034_Loss of dermatan-4-sulfotransferase 1 (D4ST1/CHST14) function represents the first dermatan sulfate biosynthesis defect, 'dermatan sulfate-deficient adducted thumb-clubfoot syndrome'. 22581468_We report on the detailed clinical characterization of two sisters with musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by a homozygous mutation in the CHST14 gene. 26373698_CHST14 gene mutations are associated with musculocontractural type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. 26646600_patients with CHST14/D4ST1 deficiency develop progressive multisystem fragility-related manifestations, establishment of a comprehensive and detailed natural history and health-care guidelines as well as further elucidation of the pathophysiology in view of future etiology-based therapy are crucial 28238810_Dermatan sulfate does not appear in urine of patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by a CHST14/D4ST1 deficiency. 29976758_DS-epi1, DS-epi2, and D4ST1 form homomers and are all part of a hetero-oligomeric complex where D4ST1 directly interacts with DS-epi1, but not with DS-epi2. The cooperation of DS-epi1 with D4ST1 may therefore explain the processive mode of the formation of iduronic acid blocks. 30195269_Patients with musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome-CHST14 are susceptible to develop scoliosis, thoracolumbar kyphosis. 32130795_Delineation of musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome caused by dermatan sulfate epimerase deficiency. 34815299_Clinical and molecular features of 66 patients with musculocontractural Ehlers-Danlos syndrome caused by pathogenic variants in CHST14 (mcEDS-CHST14). |
ENSMUSG00000074916 |
Chst14 |
153.626782 |
0.4872056147 |
-1.037397 |
0.133781604 |
60.800869 |
0.00000000000000631500348935602880886474647989776616162431151571543530565122637199237942695617675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000042874632706023451760377260909572534432264261095024693304367247037589550018310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
101.3316653 |
8.3401496 |
209.4318489 |
11.2300050 |
| ENSG00000169116 |
25849 |
PARM1 |
protein_coding |
Q6UWI2 |
FUNCTION: May regulate TLP1 expression and telomerase activity, thus enabling certain prostatic cells to resist apoptosis. {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of telomerase activity. Located in several cellular components, including Golgi apparatus; endosome; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25849; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; positive regulation of telomerase activity [GO:0051973] |
18027867_Ectopic expression of hPARM-1 in PC3 prostate cancer cells increased colony formation, suggesting a probable role in cell proliferation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22766399_PARM1 does not play a major role in the development of epispadias 23902727_Our results strongly suggest the oncogenic potential of PARM-1. 31297877_Neurexophilin and PC-esterase domain family member 4 (NXPE4) and prostate androgen-regulated mucin-like protein 1 (PARM1) as prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000034981 |
Parm1 |
1294.317537 |
2.5284806467 |
1.338271 |
0.044004277 |
947.082003 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000057153797011831203576758648768231163495498617762937693413699084961539376935499523402942899899136260252466007387627381974313 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000055866890324147588551792068340862963341052502621996572034426519213910575487918820921388511618457103243935011989958934442215 |
Yes |
No |
1881.9608722 |
48.4298392 |
749.5854378 |
15.8084241 |
| ENSG00000169122 |
90362 |
FAM110B |
protein_coding |
Q8TC76 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in tumor progression. |
Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Located in cytosol and mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90362; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule organizing center [GO:0005815]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739] |
17499476_Localizes to centrosomes and accumulates at the microtubule organization center in interphase and at spindle poles in mitosis; ectopic expression impairs cell cycle progression in the G1 phase. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21919029_FAM110B was able to regulate androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells and FAM110B itself was regulated by androgens. FAM110B siRNA inhibited the growth of prostate cancer cells in vitro. |
ENSMUSG00000049119 |
Fam110b |
159.645358 |
0.2438855990 |
-2.035724 |
0.144942025 |
206.676116 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007295750493931929754779745247377124162847881853380213751964864156602682648238805340430675807937293513392773129880449455020308135999584919773042201995849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001441569977114260725296611141332020510128014399641930178245886280323193723550851073445054707300509784815788559312016263447286945620362530462443828582763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.0794856 |
5.7876154 |
260.5210286 |
13.9647432 |
| ENSG00000169136 |
22809 |
ATF5 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2D1 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that either stimulates or represses gene transcription through binding of different DNA regulatory elements such as cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AC][AG]-3'), ATF5-specific response element (ARE) (consensus: 5'-C[CT]TCT[CT]CCTT[AT]-3') but also the amino acid response element (AARE), present in many viral and cellular promoters. Critically involved, often in a cell type-dependent manner, in cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation (PubMed:10373550, PubMed:15358120, PubMed:21212266, PubMed:20654631). Its transcriptional activity is enhanced by CCND3 and slightly inhibited by CDK4 (PubMed:15358120). Important regulator of the cerebral cortex formation, functions in cerebral cortical neuroprogenitor cells to maintain proliferation and to block differentiation into neurons. Must be down-regulated in order for such cells to exit the cycle and differentiate (By similarity). Participates in the pathways by which SHH promotes cerebellar granule neuron progenitor cells proliferation (By similarity). Critical for survival of mature olfactory sensory neurons (OSN), directs expression of OSN-specific genes (By similarity). May be involved in osteogenic differentiation (PubMed:22442021). Promotes cell proliferation and survival by inducing the expression of EGR1 sinergistically with ELK1. Once acetylated by EP300, binds to ARE sequences on target genes promoters, such as BCL2 and EGR1 (PubMed:21791614). Plays an anti-apoptotic role through the transcriptional regulation of BCL2, this function seems to be cell type-dependent (By similarity). Cooperates with NR1I3/CAR in the transcriptional activation of CYP2B6 in liver (PubMed:18332083). In hepatic cells, represses CRE-dependent transcription and inhibits proliferation by blocking at G2/M phase (PubMed:22528486, PubMed:18701499). May act as a negative regulator of IL1B transduction pathway in liver (PubMed:24379400). Upon IL1B stimulus, cooperates with NLK to activate the transactivation activity of C/EBP subfamily members (PubMed:25512613). Besides its function of transcription factor, acts as a cofactor of CEBPB to activate CEBPA and promote adipocyte differentiation (PubMed:24216764). Regulates centrosome dynamics in a cell-cycle- and centriole-age-dependent manner. Forms 9-foci symmetrical ring scaffold around the mother centriole to control centrosome function and the interaction between centrioles and pericentriolar material (PubMed:26213385). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70191, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10373550, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15358120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18332083, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18701499, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20654631, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21212266, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21791614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22442021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22528486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24216764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24379400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25512613, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26213385}. |
Acetylation;Activator;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables several functions, including DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity; and tubulin binding activity. Involved in several processes, including fat cell differentiation; regulation of cell cycle process; and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in centrosome; cytosol; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22809; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; cerebellar granule cell precursor proliferation [GO:0021930]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition [GO:1902750]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; olfactory bulb interneuron development [GO:0021891]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of centrosome cycle [GO:0046605]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
15358120_activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5) is a new interacting partner of cyclin D3 15890932_recruitment of ATFx to the HTLV-1 LTR serves to link viral transcription with critical events in cellular homeostasis 16164412_Overexpression of the bZIP protein ATF5, a transcriptional activator, stimulates asparagine synthetase promoter/reporter gene transcription via the nutrient-sensing response unit. 16170340_The widespread expression of ATF5 in glioblastomas 16300731_ATF5 increases cisplatin-induced apoptosis through up-regulation of Cyclin D3 transcription, which elicits survival signals in HeLa cells 17346882_Contribution of common variations of ATF4 and ATF5 to the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder may be minimal if any. 17346882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18055463_translation of ATF5 is regulated by the alternative 5'-UTR region of its mRNA, and ATF5 may play a role in protecting cells from amino acid limitation or arsenite-induced oxidative stress 18195013_ATF4 contributes to basal ATF5 transcription, and eIF2 kinases direct the translational expression of multiple transcription regulators by a mechanism involving delayed translation reinitiation 18332083_ATF5 is abundant in the liver, activates CYP2B6, and cooperates with the constitutive androstane receptor in sustaining the hepatic-specific expression of this P450 in human hepatocytes and hepatoma cells. 18458088_cisplatin increased ATF5 protein expression via preventing its ubiquitin-dependent degradation, which might be associated with its promoting the nucleus-to-cytoplasm translocation of E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Cdc34 18701499_Loss of ATF5 is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma 18832568_The down-regulation of the SAP gene by ATF5 may represent a common mechanism for the pathogenesis of Hemophagocytic syndrome that is associated with either Epstein-Barr virus infection or immune disorders with dysregulated T-cell activation. 19251251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19285020_These results indicate that ATF5 is targeted for degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, and that cadmium slows the rate of ATF5 degradation via a post-ubiquitination mechanism. 19531563_Identified a novel ATF5 consensus DNA binding sequence. Demonstrate in C6 glioma and MCF-7 breast cancer cells that ATF5 occupies this sequence and that ATF5 activates reporter gene expression driven by this site. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20423929_our studies not only provided molecular basis of ATF5 transcriptional regulation, but also identified ATF5 as a target gene of EBF1 transcription factor. 21212266_BCL-2 is an essential mediator for the cancer-specific cell survival function of ATF5 in glioblastoma and breast cancer cells 21521685_an essential role for HSP70 in maintaining high levels of ATF5 expression in glioma cells and support the conclusion that ATF5 is an important substrate protein of HSP70 that mediates HSP70-promoted cell survival in glioma cells. 21791614_coordinated actions by ATF5, p300, Elk-1, and ERK/mitogen-activated protein kinase are essential for ATF5-dependent Egr-1 activation and cell proliferation and survival 21972289_ATF5 polymorphisms influence ATF function and response to treatment in children with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 22442021_The evidence suggests a role for ATF5 in the regulation of osteogenic differentiation in adipose-derived stem cells. 22528486_a mechanistic link between elevated NPM1 expression and depressed ATF5 in HCC and suggests that regulation of ATF5 by NPM1 plays an important role in the proliferation and survival of HCC. 23018213_demonstrated that interference with the function of ATF5 could markedly increase the apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells and identified B-cell leukemia lymphoma-2 as an ATF5-targeted apoptosis-related gene 23876217_The 5'-untranslated region regulates ATF5 mRNA stability via nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in response to environmental stress. 24302293_ATF5 promotes the proliferation of HSV-1 via a potential mechanism by which ATF5 enhances the transcription of viral genes during the course of an HSV-1 infection 24379400_N-terminal hydrophobic amino acids play an important role in the regulation of ATF5 protein expression in IL-1beta-mediated immune response and that ATF5 is a negative regulator for IL-1beta-induced expression of SAA1 and SAA2 in HepG2 cells. 25294425_Low expression level of ATF5 in hepatocellular carcinoma indicated aggressive tumor behavior and predicted a worse clinical outcome. 25512613_the TAK1-NLK pathway is a novel regulator of basal or IL-1beta-triggered C/EBP activation though stabilization of ATF5 25517360_Report a global loss of 5hmC identified three new genes (ECM1, ATF5, and EOMES) with potential anti-cancer functions that may promote the understanding of the molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. 25682872_Activating transcription factor 5 enhances radioresistance and malignancy in cancer. 26213385_Data show that ATF5 is an essential structural protein that is required for the interaction between the mother centriole and the pericentriolar material. 26365117_This study provides the first evidence that the methylation level of ATF5 decreased, and its mRNA expression was evidently up-regulated in glioma. 26679606_These results suggest that the hepatic functions of the human iPS-HLCs could be enhanced by ATF5, c/EBPalpha, and PROX1 transduction. 27125458_Our results suggest that ATF5 promotes invasion by inducing the expression of integrin-alpha2 and integrin-beta1 in several human cancer cell lines. 27426517_ATF5 expression can rescue UPR(mt) signaling in atfs-1-deficient worms requiring the same UPR(mt) promoter element identified in C. elegans. Furthermore, mammalian cells require ATF5 to maintain mitochondrial activity during mitochondrial stress and promote organelle recovery. Combined, these data suggest that regulation of the UPR(mt) is conserved from worms to mammals. 28861715_Study reports that reduced levels of ATF5 in brain of Huntington's disease patients, probably due to its sequestration into the characteristic PolyQ containing neuronal inclusion bodies, correlates with decreased levels of the antiapoptotic protein MCL1, a transcriptional target of ATF5. Also provides evidence of decreased ATF5 being deleterious by rendering neurons more vulnerable to polyQ-induced apoptosis. 29326161_Data suggest that ATF5 is modified by SUMO2/3 at a conserved SUMO-targeting consensus site; this SUMOylation of ATF5 appears to be required for transport of ATF5 to centrosome. (ATF5 = activating transcription factor-5; SUMO = small ubiquitin-like modifier) 31676720_Dominant-Negative ATF5 Compromises Cancer Cell Survival by Targeting CEBPB and CEBPD. 32342199_ATF5 involved in radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by promoting epithelial-to-mesenchymal phenotype transition. 32603335_Expression of activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5) is mediated by microRNA-520b-3p under diverse cellular stress in cancer cells. 33640883_Maf1 suppression of ATF5-dependent mitochondrial unfolded protein response contributes to rapamycin-induced radio-sensitivity in lung cancer cell line A549. 33959786_Influence of genetic variants in asparaginase pathway on the susceptibility to asparaginase-related toxicity and patients' outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 33980247_ATF5 and HIF1alpha cooperatively activate HIF1 signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. 34262025_ATF5, a putative therapeutic target for the mitochondrial DNA 3243A > G mutation-related disease. 34617722_Human Cytomegalovirus Infection Activates Glioma Activating Transcription Factor 5 via microRNA in a Stress-Induced Manner. |
ENSMUSG00000038539 |
Atf5 |
687.837892 |
2.4208081995 |
1.275489 |
0.081904584 |
241.484021 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000186692480754079408952167932412909868056475345664766705081416139654491641650029331805697358837880869303143586202563657359446119550998701222543907363160542445257306098937988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043258728664524522592091369070965847764123226333260515915042055682143879738462631768659775616669142659419020751665135227670501437185947984920275644071807619184255599975585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
996.4768700 |
50.1750077 |
414.2567542 |
16.0391340 |
| ENSG00000169220 |
10636 |
RGS14 |
protein_coding |
O43566 |
FUNCTION: Regulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling cascades. Inhibits signal transduction by increasing the GTPase activity of G protein alpha subunits, thereby driving them into their inactive GDP-bound form. Besides, modulates signal transduction via G protein alpha subunits by functioning as a GDP-dissociation inhibitor (GDI). Has GDI activity on G(i) alpha subunits GNAI1 and GNAI3, but not on GNAI2 and G(o)-alpha subunit GNAO1. Has GAP activity on GNAI0, GNAI2 and GNAI3. May act as a scaffold integrating G protein and Ras/Raf MAPkinase signaling pathways. Inhibits platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-stimulated ERK1/ERK2 phosphorylation; a process depending on its interaction with HRAS and that is reversed by G(i) alpha subunit GNAI1. Acts as a positive modulator of microtubule polymerisation and spindle organization through a G(i)-alpha-dependent mechanism. Plays a role in cell division. Required for the nerve growth factor (NGF)-mediated neurite outgrowth. Involved in stress resistance. May be involved in visual memory processing capacity and hippocampal-based learning and memory. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15917656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17635935}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;GTPase activation;Membrane;Microtubule;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal transduction inhibitor;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes a member of the regulator of G-protein signaling family. This protein contains one RGS domain, two Raf-like Ras-binding domains (RBDs), and one GoLoco domain. The protein attenuates the signaling activity of G-proteins by binding, through its GoLoco domain, to specific types of activated, GTP-bound G alpha subunits. Acting as a GTPase activating protein (GAP), the protein increases the rate of conversion of the GTP to GDP. This hydrolysis allows the G alpha subunits to bind G beta/gamma subunit heterodimers, forming inactive G-protein heterotrimers, thereby terminating the signal. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been observed but have not been thoroughly characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10636; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; PML body [GO:0016605]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; spindle [GO:0005819]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; G-protein alpha-subunit binding [GO:0001965]; GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity [GO:0005092]; GTPase activating protein binding [GO:0032794]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; cell division [GO:0051301]; chromosome segregation [GO:0007059]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; learning [GO:0007612]; long-term memory [GO:0007616]; long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:0060291]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0031914]; nucleocytoplasmic transport [GO:0006913]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050769]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription in response to stress [GO:0043620]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; spindle organization [GO:0007051]; visual learning [GO:0008542]; zygote asymmetric cell division [GO:0010070] |
15917656_We show that RGS14 is a component of mitotic asters formed in vitro from HeLa cell extracts and that depletion of RGS14 from cell extracts blocks aster formation. 19636837_NMR 1H, 13C and 15N resonances of the RGS domain (residues 56-207) 19878719_RGS14 serves as a novel scaffold to integrate GTP-Binding Protein alpha Subunit and Ras/Raf/MAPkinase signalling events through the action of its GL domain. 20627871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20842066_RGS-14 may facilitate cognitive processing by modulating Cav1 channel-mediated intracellular divalent calcium ion Ca(2)+ transients. 21880739_RGS14 can form complexes with GPCRs in cells that are dependent on Galpha(i/o) and these RGS14.Galpha(i1).GPCR complexes may be substrates for other signaling partners such as Ric-8A 23255434_The RBD region associates with the RGS domain region, producing an intramolecular interaction within RGS14 that enhances the GTPase activating function. 26987813_Data support the notion that the Galpha, but not Gbetagamma, arm of the Gi/o signalling is involved in TRPC4 activation and unveil new roles for RGS and RGS14 in fine-tuning TRPC4 activities. 28776200_The findings of this study suggested new pre- and postsynaptic regulatory functions of RGS14 and RGS14 variants, specific to the primate brain, and provide evidence for unconventional roles of RGS14 in the nuclei of striatal neuron. 30217807_We discovered 154 SNPs from five independent regions associated with FGF23 concentration. A locus strongly associated with variations in FGF23 concentration is rs11741640, within RGS14 and upstream of SLC34A1 (a gene involved in renal phosphate transport). 31754202_The rs1256328 (ALPL) and rs12654812 (RGS14) Polymorphisms are Associated with Susceptibility to Calcium Nephrolithiasis in a Taiwanese population. 33309307_Genetic Polymorphisms of RGS14 and Renal Stone Disease. 33410399_Human genetic variants disrupt RGS14 nuclear shuttling and regulation of LTP in hippocampal neurons. 35307350_RGS14 regulates PTH- and FGF23-sensitive NPT2A-mediated renal phosphate uptake via binding to the NHERF1 scaffolding protein. |
ENSMUSG00000052087 |
Rgs14 |
206.181079 |
0.4512480693 |
-1.148007 |
0.172341870 |
43.891329 |
0.00000000003471232872548897506491523204013368176373832696413046505767852067947387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000185568262219564369640061340858115408042339211647231422830373048782348632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
136.8304422 |
15.1124419 |
305.5941336 |
23.8434593 |
| ENSG00000169231 |
7059 |
THBS3 |
protein_coding |
P49746 |
FUNCTION: Adhesive glycoprotein that mediates cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions. Can bind to fibrinogen, fibronectin, laminin and type V collagen. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the thrombospondin family. Thrombospondin family members are adhesive glycoproteins that mediate cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions. This protein forms a pentameric molecule linked by a single disulfide bond. This gene shares a common promoter with metaxin 1. Alternate splicing results in coding and non-coding transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2011]. |
hsa:7059; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; bone trabecula formation [GO:0060346]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; growth plate cartilage development [GO:0003417]; ossification involved in bone maturation [GO:0043931] |
11943589_Normal human adult corneal keratocytes have mRNA for this protein. 17022822_This is the first report of the THBS3 gene working as a stimulator of tumor progression. 33910854_Pathological Significance and Prognostic Roles of Thrombospondin-3, 4 and 5 in Bladder Cancer. 33961290_Serum levels of the IgA isotype switch factor TGF-beta1 are elevated in patients with COVID-19. 34669362_mRNA Expression of thrombospondin 1, 2 and 3 from proximal to distal in human abdominal aortic aneurysm - preliminary report. |
ENSMUSG00000028047 |
Thbs3 |
180.150367 |
0.1489374494 |
-2.747222 |
0.188599583 |
211.208979 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000748349262809340427213063553502722641071332032804206831620579610983016082366927282172883508295830100527455203034386617866498270235098289049346931278705596923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000151310070124189928473846278590896446065854266225012654508722913154938283791295301567651284846556191577528660175232916827725571096152634709142148494720458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.7261675 |
7.9866441 |
311.8945430 |
35.5670312 |
| ENSG00000169246 |
23117 |
NPIPB3 |
protein_coding |
Q92617 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
26320399_The overexpression of NPIPB3 restored the interferon-beta responses in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus open reading frame 6 (SARS-CoV ORF6) expressing cells, indicating that the interaction of SARS CoV ORF6 and NPIPB3 reduced Type I interferon antagonism by SARS-CoV ORF6. |
|
|
239.314059 |
0.4108160799 |
-1.283435 |
0.134661167 |
90.626428 |
0.00000000000000000000173527026076985184813521387813670767890818961376333589083234901218055767913028830662369728088378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000016282637666219336016198667290985477916757039655176244610183117211832382054126355797052383422851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
140.3618964 |
16.5155238 |
343.0472794 |
28.1490475 |
| ENSG00000169247 |
79628 |
SH3TC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF17 |
|
Alternative splicing;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Disease variant;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;TPR repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein with two N-terminal Src homology 3 (SH3) domains and 10 tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) motifs, and is a member of a small gene family. The gene product has been proposed to be an adapter or docking molecule. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C, a childhood-onset neurodegenerative disease characterized by demyelination of motor and sensory neurons. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:79628; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance [GO:0032287]; regulation of ERBB signaling pathway [GO:1901184]; regulation of intracellular protein transport [GO:0033157] |
11716477_This paper presents an analysis of the SH3TC2 promoter after identifying a read-through transcript of the SH3TC2 and HTR4 loci. Available data suggests HTR4 is a separate locus with its own promoter, and not the product of a bi-cistronic transcript. 14574644_mutations in an uncharacterized transcript, KIAA1985, in 12 families with autosomal recessive neuropathy 16326826_a founder mutation, p.Arg1109X in the CMT4C gene, causes variable peripheral neuropathy phenotypes 17470135_the SH3TC2 p.R1109X mutation is associated with a conserved haplotype and, therefore, may be a private founder mutation for the Gypsy population 18511281_Linkage analysis confirmed that all families are linked to CMT4C locus on chromosome 5q32 (multipoint LOD score of 9.06). Haplotype analysis suggests that two SH3TC2 mutations are present in this cohort 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19272779_Structural alterations to the SH3TC2 gene could possibly predispose to peripheral nerve inflammation. 19744956_Missense mutations in the SH3TC2 causing Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C affect its localization to plasma membrane. 20028792_Mistargeting of SH3TC2 away from the recycling endosome is the fundamental molecular defect that leads to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21291453_Mutations in the SH3TC2 gene are a frequent cause of HMSN I in Czech patients. 22950825_This study presented evidence that mutations c.279G --> A and c.3676-8G -->A in the SH3TC2 gene cause aberrant splicing and are therefore pathogenic and causal for CMT4C. 22978647_Data indicate that the most frequent form is SH3TC2 gene (CMT4C; 57.14%), followed by HK1 gene causative of CMT4G (CMT4G/HMSN-Russe 25%) and NDRG1 p.R148X in CMT type 4D (CMT4D/HMSN-Lom; 17.86%). 24833716_SH3TC2 is regulated by the transcription factors CREB and SOX10, define a regulatory SNP at this disease-associated locus and reveal SH3TC2 as a candidate modifier locus of CMT disease phenotypes. 25429913_The novelty of our data is the relatively high frequency of SH3TC2 and GDAP1 mutations in demyelinating and axonal forms, respectively, of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 25737037_DNA sequence analysis in a French-Canadian family revealed a novel combination of 2 known recessive mutations, p.R904X and p.R954X, in the SH3TC2 gene. 26829735_A homozygous missense mutation c.1894G>A of SH3TC2 is associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C. 27231023_In this series of undiagnosed CMT4 patients, SH3TC2 mutation frequency is 30%, confirming that CMT4C may be the most common AR-CMT type. 27882734_Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C (CMT4C) is an autosomal recessive demyelinating form of CMT characterized clinically by early onset and severe spinal deformities, and is caused by mutations in SH3TC2. 28981955_This present clinical and physiologic features of 5 patients with CMT4C caused by biallelic private mutations of SH3TC2. 29336362_SH3TC2, PMP2, and BSCL2 pathogenic variants might be rare in Chinese Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) patients. 30653784_Mutations in SH3TC2 are responsible for 26% of Greek patients with suspected CMT4C. 31227790_Compound heterozygous mutations of SH3TC2 in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4C patients. 31634715_Implication of the SH3TC2 gene in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease associated with deafness and/or scoliosis: Illustration with four new pathogenic variants. 33587240_Screening for SH3TC2 variants in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in a cohort of Chinese patients. |
ENSMUSG00000045629 |
Sh3tc2 |
64.680108 |
0.2335712041 |
-2.098066 |
0.356292798 |
33.539485 |
0.00000000698318524742228920379811569910458168841671522386604920029640197753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000030878314635096761846487490015683574640092956542503088712692260742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.4473486 |
6.1864284 |
75.5308218 |
18.4255728 |
| ENSG00000169249 |
8233 |
ZRSR2 |
protein_coding |
Q15696 |
FUNCTION: Pre-mRNA-binding protein required for splicing of both U2- and U12-type introns. Selectively interacts with the 3'-splice site of U2- and U12-type pre-mRNAs and promotes different steps in U2 and U12 intron splicing. Recruited to U12 pre-mRNAs in an ATP-dependent manner and is required for assembly of the prespliceosome, a precursor to other spliceosomal complexes. For U2-type introns, it is selectively and specifically required for the second step of splicing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21041408, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9237760}. |
Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ribonucleoprotein;RNA-binding;Spliceosome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes an essential splicing factor. The encoded protein associates with the U2 auxiliary factor heterodimer, which is required for the recognition of a functional 3' splice site in pre-mRNA splicing, and may play a role in network interactions during spliceosome assembly. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8233; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; spliceosomal complex [GO:0005681]; U12-type spliceosomal complex [GO:0005689]; U2AF complex [GO:0089701]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; pre-mRNA 3'-splice site binding [GO:0030628]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380]; spliceosomal complex assembly [GO:0000245] |
19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041408_Data show that through recognition of a common splicing element, Urp facilitates distinct steps of U2- and U12-type intron splicing. 22389253_In univariate analysis, mutated SRSF2 predicted shorter overall survival and more frequent acute myeloid leukemia progression compared with wild-type SRSF2, whereas mutated U2AF1, ZRSR2 had no impact on patient outcome. 25586593_ZRSR2 has a role in RNA splicing; dysregulated splicing of U12-type introns is a characteristic feature of ZRSR2 mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome 25964599_The mutational status of the SRSF2, U2AF1 and ZRSR2 did not affect the response rate or survival in MDS patients who had received first-line decitabine treatment. 28942350_We conclude that the common clinical features of patients with an isolated mutation of ZRSR2 are a macrocytic anemia without leukopenia, thrombocytopenia or an increase in marrow blast percentage 31124956_This meta-analysis indicates a positive effect of SF3B1 and an adverse prognostic effect of SRSF2, U2AF1, and ZRSR2 mutations in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. 31361176_ZRSR2 mutation in a child with refractory macrocytic anemia and Down Syndrome. 33568749_ZRSR2 overexpression is a frequent and early event in castration-resistant prostate cancer development. 34615655_Sex-Biased ZRSR2 Mutations in Myeloid Malignancies Impair Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Activation and Apoptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000044068 |
Zrsr1 |
190.406127 |
3.0661789350 |
1.616442 |
0.447700012 |
12.189035 |
0.00048071246210198113890665894132325774990022182464599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001183933913002709970366255198825911065796390175819396972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
327.7619802 |
120.7202133 |
109.5363589 |
28.9913291 |
| ENSG00000169252 |
154 |
ADRB2 |
protein_coding |
P07550 |
FUNCTION: Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The beta-2-adrenergic receptor binds epinephrine with an approximately 30-fold greater affinity than it does norepinephrine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2831218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7915137}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Hydroxylation;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes beta-2-adrenergic receptor which is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. This receptor is directly associated with one of its ultimate effectors, the class C L-type calcium channel Ca(V)1.2. This receptor-channel complex also contains a G protein, an adenylyl cyclase, cAMP-dependent kinase, and the counterbalancing phosphatase, PP2A. The assembly of the signaling complex provides a mechanism that ensures specific and rapid signaling by this G protein-coupled receptor. This receptor is also a transcription regulator of the alpha-synuclein gene, and together, both genes are believed to be associated with risk of Parkinson's Disease. This gene is intronless. Different polymorphic forms, point mutations, and/or downregulation of this gene are associated with nocturnal asthma, obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2019]. |
hsa:154; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal dense core vesicle [GO:0098992]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; adenylate cyclase binding [GO:0008179]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; beta2-adrenergic receptor activity [GO:0004941]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; norepinephrine binding [GO:0051380]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; activation of transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0007171]; adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway [GO:0071880]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; adrenergic receptor signaling pathway [GO:0071875]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; desensitization of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway by arrestin [GO:0002032]; diet induced thermogenesis [GO:0002024]; endosome to lysosome transport [GO:0008333]; heat generation [GO:0031649]; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040015]; negative regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045986]; norepinephrine-epinephrine-mediated vasodilation involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0002025]; positive regulation of AMPA receptor activity [GO:2000969]; positive regulation of autophagosome maturation [GO:1901098]; positive regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030501]; positive regulation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:2000481]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of lipophagy [GO:1904504]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mini excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0061885]; positive regulation of protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010739]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; regulation of sodium ion transport [GO:0002028]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to psychosocial stress [GO:1990911]; smooth muscle contraction [GO:0006939]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
11039642_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11147800_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11192234_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11229437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11230287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11246538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11258696_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11288039_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11306963_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11371409_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11380082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11434877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11466580_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11706779_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11713122_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11713125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11718682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11718682_the allelic frequency of beta2-adrenergic receptor gene mutation in codons 16 and 27 did not differ between obese subjects and non-obese 11735081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11739457_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11775126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11775127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11778498_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11785682_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11798553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11798846_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11798846_The distribution of the SNP genotype AA, GA and GG at position 1023 in the severe hypertension group was significantly different from that in normal group. 11809767_sequestration caused by Akt and insulin 11809992_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11821707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11821707_The beta2-adrenoceptor (ADRB2) plays a pivotal role in signalling in relation to hypertension and obesity. Polymorphisms of the ADRB2 gene have been shown to be potentially related to essential hypertension and other non-cardiovascular disease phenotypes. 11836685_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11854867_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11879211_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11882399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11884023_Regulation of beta2-adrenergic receptors on CD4 and CD8 positive lymphocytes by cytokines in vitro 11921496_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11941312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11941588_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11942593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11956670_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12008746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12023679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12030897_27Glu polymorphism of the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene interacts with physical activity influencing obesity risk among female subjects 12065131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12075579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12077726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12080445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12080445_the beta2-adrenergic receptor is associated with the propensity to gain weight from childhood to young adulthood in males 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12083963_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12083965_variation in asthma (review article) 12106601_beta1-adrenoceptor and beta2-adrenoceptor couple to Gs-proteins to activate adenylyl cyclase 12111048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140284_role of heterodimerization with beta 1-adrenergic receptor regulates beta 2-adrenergic receptor internalization and ERK signaling efficacy 12142723_polymorphic in cystic fibrosis 12142724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12142724_polymorphic in cystic fibrosis 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12167654_assessment of binding and activation properties of Cys mutants 12215468_linkage analysis of ADRB2 polymorphisms does not support the role of this gene as a major causative gene for the detected linkage of human chromosome 5 with hypertension 12244098_Results indicate that the proportion of homo- and heterodimers between the closely related beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic receptors is determined by their relative levels of expression. 12361188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12390345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12391272_beta(2)AR activation of ERK1/2 does not require PKA phosphorylation of the beta(2)AR, receptor internalization or switching from activation of G(s) to G(i) but clearly requires activation of a Src family member that may be downstream of PKA. 12394950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12409304_identified the Zn2+ binding site responsible for the positive effect of Zn2+ ions on agonist binding to the 2AR 12422339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12428391_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12429837_Data report a novel positioning of Src, mediating signals from insulin to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and to beta(2)-adrenergic receptor trafficking. 12439523_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12439523_data demonstrate that homozygosity for Arg16, which in vitro is associated with decreased down-regulation of the beta(2)AR, protects from preterm delivery 12441217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12442007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12474986_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12502697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12519093_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12527744_Effects of Arg16 Gly polymorphism on forearm blood flow responses to isoproterenol dependent on differences in endothelial generation of nitric oxide. Regional blood flow responses to isoproterenol greater in Gly16 than in Arg16 homozygotes. 12527744_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12563174_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12569260_No evidence of excess allele sharing identity by descent in sib pairs, revealing a lack of linkage between 2q14-q23 or 5q32 (chromosome region harboring the gene. encoding beta 2 adrenergic receptor) and hypertension in our study sample. 12574108_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12605574_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12628991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12629568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12682000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12682000_The Glu27 allele of the beta2-adrenergic receptor was associated with a lower risk of incident coronary events in an elderly population 12716862_Polymorphisms not significantly different in NIDDM compared with normal values. 12727985_lipolytic catecholamine resistance of sc adipocytes in polycystic ovary syndrome is probably due to a combination of decreased amounts of beta(2)-adrenergic receptors, the regulatory II beta-component of protein kinase A, and hormone-sensitive lipase 12740450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12807170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12822042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12824951_b2-AR 27Glu polymorphism has a protective effect against metabolic disorders in obese families from southern Poland. 12832031_lipolysis and fat oxidation promoted by a peak oxygen consumption test appear to be blunted in polymorphic Glu27Glu beta2 adrenergic receptor obese females 12835612_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12869379_agonist-induced desensitization of cardiac beta2ARs is more pronounced in wild type than Thr164Ile polymorphism subjects. 12885990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12888635_Females with polymorphism and higher carbohydrate intake had higher obesity risk. High carbohydrate intake was associated with higher insulin levels among women with Gln27Glu polymorphism. 12888635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12900437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12900437_The association of genetic polymorphisms of ADRB2 with blood pressure-related and obesity-related phenotypes. 12905693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 13680034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14500986_findings show that signaling via the erythrocyte beta2-adrenergic receptor and heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Galphas) regulated the entry of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum 14510910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14510956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14553962_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14557466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14557466_the Arg(16) and Gln(27) variants of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor gene contribute to metabolic syndrome susceptibility in men. 14557486_down-regulation of beta(2)-AR protein with labor may constitute a contributory mechanism by which uterine quiescence is removed at term. 14573333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14610472_Beta2-adrenergic receptor variants are associated with spirometric values and bronchodilator responsiveness, but different regions of the gene provide evidence for association with these phenotypes. 14610528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14615367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14650112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14655898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14657864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14657864_variation in the beta(2)AR gene is associated in the pathogenesis of asthma and acts as a disease modifier in nocturnal asthma 14665698_Arg16/Gly polymorphism is associated with differences in acute pressor responses to sympathoexcitation 14665698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14678342_Meta-analysis of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14678347_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693408_Increased sensitivity to catecholamine-induced lipolysis of Gly allele promotes higher free fatty acids concentrations in portal system, which could enhance higher levels of fasting insulin. 14693408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14709719_Insulin and beta-adrenergic agonists stimulate a rapid phosphorylation and sequestration of the beta2-adrenergic receptors (beta2ARs). 14715679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14715679_the beta2-AR genotype, both independently and interacting with habitual PA levels, is significantly associated with a-vDO2 during exercise in postmenopausal women 14734649_internalization of beta(1)AR is both arrestin- and dynamin-dependent and follows the same clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway as beta(2)AR 14748897_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14981238_3D structure of human beta2 adrenergic receptor predicts ligand-binding sites for epinephrine and norepinephrine. 14981808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15016730_Beta2AR is essential for the adaptive physiological response needed to clear excess fluid from the alveolar airspace of normal and injured lungs. 15069780_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15079793_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15123695_hetero-oligomerization between beta(2)AR and beta(3)AR forms a beta-adrenergic signaling unit that possesses unique functional properties 15126009_Gln27Glu polymorphism was associated with the change in fructosamine level resulting from exercise, but not Arg16Gly polymorphism 15126009_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15147203_Data describe the agonist-induced regulation of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor on living cells by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy using a fluorescence-labeled arterenol derivative. 15153795_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15153795_The beta(2)-adrenergic receptor (ADRB2) does not contribute substantially to susceptibility to asthma, but it is possible that these polymorphisms influence disease activity and drug responses in individuals with asthma. 15155261_Gain of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release is increased in beta2-adrenergic receptor transgenic(TG4) myocytes. Increased gain likely contributes to increased contraction amplitudes in field-stimulated TG4 myocytes. 15166301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166301_body fat response to exercise training in older adults is associated with the combined effects of the Glu12/Glu9 alpha2b-adrenergic receptor, Trp64Arg beta3-adrenergic receptor, and Gln27Glu beta2-adrenergic receptor gene variants 15170877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15212591_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15245435_human melanocytes express functional beta2-AR (4230 receptors per cell) with a Bmax at 129.3 and a KD of 3.19 nM but lack beta1-AR expression. 15248848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15249444_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15282385_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15284533_Beta2-adrenoceptor Thr164Ile polymorphism is associated with markedly decreased vasodilator and increased vasoconstrictor sensitivity 15284533_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15297801_Beta2-adrenoceptor densities are decreased in patients with subjective hypoglycemia unawareness and might contribute to the reduced beta-adrenergic sensitivity in this subgroup of patients. 15323067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15323067_genetic variation in the beta2AR was not associated with blood pressure or with overweight, obesity, and fat distribution. 15329337_functional association between the beta(2)-AR and the BK(Ca) channel in pregnant human myometrium. 15334382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15334382_the ADRB2 Arg(16)-Gly genotype influences total cholesterol and LDL-C levels in an age-specific manner, that it may interact with beta(3)-adrenergic receptor Trp(64)-Arg genotypes 15342173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15355441_Polymorphisms in beta2-adrenergic receptor is associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 15364898_This study revealed an association of LDL-cholesterol with beta2-adrenergic receptor gene haplotype. 15388645_Truncation of beta2-adrenergic receptor C-terminal cytoplasmic tail to a 15-amino acid motif harboring a potential Src homology 2-binding domain at Y350 and an Akt phosphorylation site at S345,346 was sufficient to enable receptor regulation by insulin. 15464701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15479221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15480094_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15480094_variants at the B2AR locus may play a role in the pathophysiology of hypertension in a Chinese population. 15480095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15480095_beta2AR gene polymorphisms participate in the determination of cardiac target organ damage associated with hypertension. 15492118_A significant fraction of B2ARs exists in oligomeric complexes after ligand-induced endocytosis. 15493717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15498794_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15506640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15520258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15520258_Variation in haplotype frequencies for the beta2 adrenergic receptor gene was found to be associated with risk of myocardial infarction. 15542284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15554460_ADRB2 R16G polymorphism may play an important role in diastolic blood pressure response to benazepril treatment in hypertension 15557128_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15563584_beta2-adrenoceptor (beta3-AR)does not regulate the activity of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) chloride channel. 15578262_-367 SNP is probably not causally related to the degree of down-regulation. 15596681_ADRB2 + 79 C/G polymorphism and the haplotypes shown in this study may be involved in the pathogenesis of COPD. 15596681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15618708_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15634674_Binding of beta-arrestin to the receptor is a prerequisite for subsequent receptor desensitization. 15638826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15638826_beta2-Adrenergic receptor gene variations is associated with hypertension 15644445_results suggest PDE4D is an integral component of the beta2AR signaling complex and illustrate a mechanism for fine-tuned betaAR subtype signaling specificity and intensity in the cardiac system 15687340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15703163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15719258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15794198_Beta2 adrenergic receptor gene is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden. 15797659_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15797659_Relative to Gln27 homozygotes, carrying the Glu27 allele was not associated with new-onset hypertension 15806595_No significant relationship between the ADRB2 genotype at positions 16 and 27 and bronchodilator response when defined as 12% improvement in FEV(1). 15806595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15817484_analysis of differences in binding and activation by agonists and partial agonists of the beta2 adrenoceptor 15817638_first demonstration that gating of the iKCa1 potassium channel is regulated by beta2-adrenoceptors 15824464_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15833737_regulation by interleukin-1beta and role os such increase in increasing cyclic AMP accumulation 15833937_evidence for an interaction between the beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors was observed in men for longitudinal change in body mass index and women showed suggestive evidence for an interaction between the beta1- and beta3-adrenergic receptors 15840289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15853829_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15861037_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15861037_beta1AR or the beta2AR polymorphisms do not affect patient response to beta-blockade treatment for stable congestive heart failure 15867853_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15879435_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15917856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15920038_dDespite considerable polymorphism in alpha2-AR genes, such variation is not a major determinant of variability in yohimbine response and by inference, in susceptibility to essential hypertension. 15931235_No evidence that haplotype for two most common polymorphisms in beta2AR are associated with development of myocardial infarction in Swedish hypertensive population, but haplotype may be associated with systolic blood pressure. 15931235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15932670_No difference was observed in beta(2)-adrenergic receptor between patients with heart failure and control subjects. 15939803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15946904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15946904_significant association of heart rate and diastolic pressure with SNPs of the gene encoding beta2AR; Gly16 or Glu27 could aggravate orthostatic tachycardia by excessive venous pooling. 15956122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15956122_the Gly16 allele is related to greater weight gain and blood pressure elevation 15959859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15976384_Genetic variation of the ADRB2 does not influence the immediate response to inhaled beta2-agonist. 15987731_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15994241_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15994241_The influence of polymorphic variants in the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene on the cardiovascular response to sympathoexcitation may have important implications in the development of hypertension and heart failure 16004558_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16009000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16027244_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16027735_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16041242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16041242_in women Thr164Ile heterozygosity is associated with increased diastolic blood pressure 16054001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142389_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16153394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16164442_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16172412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16188057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16188057_probable association between Arg16Gly polymorphism of ADRB2 gene and hypertension 16189366_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16197474_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16205624_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16205624_The present study indicates that the beta-2 adrenoceptor polymorphism does not influence the ocular hypotensive effects of topical beta adrenoceptor antagonists. 16207148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16227135_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16251889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16280290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16280323_the beta2 adrenergic receptor has a role in beta-arrestin-dependent, G protein-independent ERK1/2 activation 16286511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16289313_Beta-2 adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism is associated with lung adenocarcinoma 16289313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16301860_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 16322642_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16338281_Arg16 homozygosity of ADRB2 appears to improve pregnancy outcome after beta(2)-agonist tocolysis. 16338281_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16339181_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16339181_Subjects homozygous for Arg at codon 16 of the beta2AR have reduced and mean arterial pressure (MAP) at rest that persist during exercise with no evidence for differential changes over the course of exercise despite large changes in catecholamines. 16369119_It was the aim of this study to investigate the association between beta(2)-AR genetic polymorphisms and total serum IgE in asthmatic patients of Chinese Han nationality 16369119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369120_The Gly16 polymorphism of beta(2)-AR was overrepresented in nocturnal asthmatic patients and correlated with nocturnal asthma 16374847_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16395068_African american children with status asthmaticus who have the Gln/Glu genotype at amino acid position 27 of the beta-2 adrengergic receptor may benefit from treatment with aminophylline in addition to adrenergic beta agonists. 16395068_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16407241_G protein-coupled receptor kinase site serine cluster has a role in beta2-adrenergic receptor internalization, desensitization, and beta-arrestin translocation 16409205_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16412099_beta-arrestin trafficking differs between human kidney cells and neurons. 16417856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16420563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16448568_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16449022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16461848_Both decreased beta2-adrenoceptor-related vasodilation and beta2-AR polymorphisms may contribute to the hemodynamic diversity of patients with postural tachycardia syndrome. 16461848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16467650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16467650_haplotypes with a Gln27 allele (Gly16Gln27 and Arg16Gln27) conferred a significantly higher risk for hypertension than the Gly16Glu27 haplotype 16493638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16493638_The ADRB2 Arg16Gly variant is associated with obesity-related phenotypes in Brazilian males of European descent. 16537879_Arg16Gly polymorphism of the beta2-adrenoreceptor does not influence airway function during short duration low- and high-intensity exercise. During recovery, the Arg16 genotype is associated with reduced bronchodilation. 16537879_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16551744_The apo-beta2AR shows less dynamic flexibility, whereas the antagonist-beta2AR structure is quite rigid. 16554384_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16563272_Gly16/Gly genotype of beta-2-AR gene +46 A-->G variant is associated with higher level of serum LDL-C in Kazakans, especially in women. 16563272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16569551_Genetic variations of the alpha and beta adrenergic receptors (Beta2 Gln27 allele) were found to be significant predictors of vaospastic angina. 16571957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573811_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16585076_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16596417_Arginine-19Cysteine polymorphism in beta-2 adrenoceptor upstream peptide may play an important role in bronchodilator drug responsiveness in African American asthmatic subjects. 16596417_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16615274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16618831_B2AR plays role in sudden cardiac death(SCD). Study of genetic variation in B2AR gene may help identify those at increased SCD risk. 16618831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16636198_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16651467_A Q27E beta2-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphism was positively associated with increased risk of venous thromboembolism. 16651467_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16670773_EP(1) does not appear to have a significant direct effect on airway tone but acts as a modulator of the beta(2)AR, altering G(alphas) coupling via steric interactions imposed by the EP(1):beta(2)AR heterodimeric signaling complex 16672841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16683069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16685203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16685203_Variants at the ADRB2 locus may play a role in the pathophysiology of hypertension specifically in the Yi minority group. 16714291_the mechanism for the beta-AR antagonist-mediated augmentation of wound repair is due to beta2-AR blockade, preventing the binding of endogenously synthesized epinephrine 16728691_Homozygous beta2AR Gln27Glu predicts cardiac troponin release in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Homozygous deletion of B2AR increases the odds of reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. 16728691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16740612_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16741943_Data suggest that either positive or negative imbalances in ADRB2 function increase the vulnerability to chronic pain c |
ENSMUSG00000045730 |
Adrb2 |
130.251990 |
0.4630168120 |
-1.110864 |
0.140356339 |
63.658988 |
0.00000000000000147932517362071220650669695291807756751828613860089145504161933786235749721527099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000010502568332198996407499033788830795886501618188746398629973555216565728187561035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
81.7792688 |
7.7493117 |
177.7847685 |
11.1086287 |
| ENSG00000169291 |
126669 |
SHE |
protein_coding |
Q5VZ18 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
Predicted to enable phosphotyrosine residue binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126669; |
phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784] |
9315092_Reports data for mouse She and not human. |
ENSMUSG00000046280 |
She |
30.490845 |
0.2221548386 |
-2.170363 |
0.355986102 |
39.399129 |
0.00000000034545105188310277752427434365064835147807187354374036658555269241333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001717365283191174605332149103527512867817250707958010025322437286376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.1866627 |
3.0552685 |
50.7694664 |
8.3059982 |
| ENSG00000169313 |
64805 |
P2RY12 |
protein_coding |
Q9H244 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for ADP and ATP coupled to G-proteins that inhibit the adenylyl cyclase second messenger system. Not activated by UDP and UTP. Required for normal platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11104774, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11196645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502873, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12578987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24670650, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24784220}. |
3D-structure;Blood coagulation;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the family of G-protein coupled receptors. This family has several receptor subtypes with different pharmacological selectivity, which overlaps in some cases, for various adenosine and uridine nucleotides. This receptor is involved in platelet aggregation, and is a potential target for the treatment of thromboembolisms and other clotting disorders. Mutations in this gene are implicated in bleeding disorder, platelet type 8 (BDPLT8). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:64805; |
cell body membrane [GO:0044298]; cell projection membrane [GO:0031253]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled adenosine receptor activity [GO:0001609]; G protein-coupled ADP receptor activity [GO:0001621]; G protein-coupled purinergic nucleotide receptor activity [GO:0045028]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; calcium-mediated signaling using extracellular calcium source [GO:0035585]; cell projection organization [GO:0030030]; cellular response to ATP [GO:0071318]; cytosolic calcium signaling involved in initiation of cell movement in glial-mediated radial cell migration [GO:0021808]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; hemostasis [GO:0007599]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of integrin activation by cell surface receptor linked signal transduction [GO:0033626]; positive regulation of ion transport [GO:0043270]; positive regulation of microglial cell migration [GO:1904141]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900029]; regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050920]; regulation of microglial cell migration [GO:1904139]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; substrate-dependent cell migration, cell extension [GO:0006930]; visual system development [GO:0150063] |
12080041_Characterization and channel coupling of the nucleotide receptor in brain capillary endothelial cells 12560222_identification of the reactive cysteine residues on the human P2Y(12) receptor by site-directed mutagenesis using pCMBS as the thiol reagent 12606772_PI3-K activation is signaled by rapid feedback amplification that involves P2Y(12) receptor-mediated activation of Syk. 12623443_the P2Y(1) purinoceptor and the P2Y(12)receptor appear to be involved in ADP-induced platelet shape change, an early phase of platelet activation that precedes aggregation 12668663_Intercellular calcium communication is primarily mediated by a signaling mchanism operating between this protein, ITGA2B and ITGB3. 12912815_In healthy subjects ADP-induced platelet aggregation is associated with a haplotype of the P2Y12 receptor gene. Carriers of the H2 haplotype may have an increased risk of atherothrombosis and less response to platelet inhibitors 14644082_Supports P2Y(12) as a drug target compared with P2Y(1). 14645014_ADP-mediated P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptor activation supports LPA-induced platelet aggregation. 14662702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14662702_The P2Y12 H2 haplotype is associated with atherosclerosis. 14717977_stimulation of the human P2Y12 receptor stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells activates two major intracellular signaling mechanisms leading either to cell proliferation or to actin cytoskeleton reorganization 15099288_Whereas P2RY1 antagonism did not affect collagen or thrombin-induced thrombin generation, P2RY12 antagonism did decrease both, suggesting that ADP potentiates thrombin generation primarily through the P2Y12 receptor 15142872_GIRK channels are important functional effectors of the P2Y(12) receptor in human platelets. 15187029_the Src family kinase inhibitor PP1 selectively potentiates the contribution to the calcium response by P2Y(12), although inhibition of adenylate cyclase by P2Y(12) is unaffected 15203713_both P2Y12 and P2Y1 contribute to ADP-potentiation of platelet-derived microparticles generation induced by collagen 15284110_ADP signaling through P2Y(1) may contribute to the initial stages of platelet adhesion and activation mediated by immobilized VWF, and through P2Y(12) to sustained thrombus formation. 15304052_platelet ADP receptor P2Y(12) and clusterin are downregulated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 15464998_Results describe the cloning of DNA sequences encoding the murine ortholog of the human P2Y12 receptor, and its expression in the mouse brain. 15483100_P2Y12 receptors could play a key role in the hypersensitivity of platelets in type 2 diabetic patients. 15514209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15602005_Absence of desensitization of the Gi protein-coupled P2Y12 receptor-dependent responses could represent a mechanism to preserve the hemostatic properties in platelets 15665114_both P2Y(1) and P2Y(12) desensitize in human platelets; P2Y(12), but not P2Y(1), desensitization is mediated by GRKs 15795539_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15869601_Galpha(i) signaling downstream of P2Y12 activation, but not Galpha(q) or Galpha(z) signaling downstream of P2Y1 or alpha2A activation, respectively, has a requirement for lipid rafts that is necessary for its function in ADP-mediated platelet activation 15886804_P2Y12 ADP receptor has a role in tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins of 27 and 31 kDa in thrombin-stimulated human platelets 15933261_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15933261_a P2Y12 34C>T polymorphism may have a role in development of ischemic cerebrovascular events in patients with peripheral artery disease 15968399_function in the platelet procoagulant response 16181985_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16181985_There is no association between P2Y12 receptor gene polymorphism and platelet response to clopidogrel in patients with coronary artery disease. 16185654_Identification of 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate and leukotriene E4 as P2Y12 receptor agonists. 16236603_Results suggest that P2Y12 plays a potentiatory role in ADP-induced shape change through regulation of the Rho kinase pathway. 16405973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16581111_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16769602_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16804093_This study therefore is the first to reveal distinct roles for PKC isoforms in the regulation of platelet P2Y receptor function and trafficking. 16837456_Data show that at relatively high concentration of agonist, inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor and of calcium mobilization result in complete inhibition of PAR4-induced aggregation, with no effect on either thrombin or PAR1-mediated platelet aggregation. 16840732_Outside-in signaling via P2Y12 and both PI3Kbeta and PI3Kgamma isoforms is required for maintenance of a platelet aggregate. 17127487_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17337040_No influence of the T744C polymorphism of the P2Y12 receptor gene on clopidogrel response in acute coronary syndrome 17337040_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17707382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17707382_the haplotype H2 of purinergic receptor P2Y G-protein coupled 12 (P2RY12) was significantly associated with a lower risk of incident Deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism as compared to the reference haplotype H1 17803810_Gene sequence variations of the P2Y12 receptor gene are associated with the presence of significant coronary artery disease, particularly in non-smoking individuals 17803810_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17995973_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18004210_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18175333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18175333_common variation in the P2Y12 gene predicts restenosis in percutaneous coronary intervention-treated patients 18213371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18213371_The P2Y(13) Met-158-Thr polymorphism is in tight linkage disequilibrium with the P2Y(12) locus but is not associated with acute myocardial infaction or classical cardiovascular risk factors 18278193_Use VerifyNow P2Y12 assay to measure platelet P2Y12 receptor blockade by prasugrel and clopidogrel. 18485500_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18577829_Coexisting polymorphisms of the genes affecting clopiogrel resistance may influence platelet activation 18577829_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18726826_present data clearly show that P2Y purinoceptor 11 and P2Y purinoceptor 12 are expressed in human pancreatic islets 18755689_the the G(i)-coupled P2Y12 receptor has a role in the regulation of diacylglycerol-mediated events in activated platelets 18787507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18800613_plays a critical role in the regulation of integrin alphaIIb beta3 functions. (review) 18836720_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19012950_T2DM patients with suboptimal clopidogrel response have enhanced platelet procoagulant activity compared to patients with optimal response, which can be down-regulated by more potent platelet P2Y(12) inhibition using high clopidogrel maintenance dosing. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19106083_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19132197_Functional variability of platelet response to clopidogrel correlates with P2Y(12) receptor occupancy. 19229056_severe platelet dysfunction associated with a single base pair deletion in P2Y(12) genes (378delC), resulting in a frame-shift and premature truncation of the protein 19237732_heterozygous mutation, predicting a lysine to glutamate (K174E) substitution in P2Y(12), was identified in one case with mild type 1 von Willebrand disease (VWD) and a VWF defect 19334620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19334620_polymorphisms of the P2Y12 gene identified can be used for determination of the risk group for myocardial infarction in the young males. 19525944_identified a molecular pathway in microglia that converted ATP-driven process extension into process retraction during inflammation: reversal was driven by upregulation of the A(2A) adenosine receptor coincident with P2Y(12) downregulation. 19530321_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19531897_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19552634_P2Y(12) is targeted by ticagrelor via a mechanism that is non-competitive with ADP 19576320_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19740098_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19783848_Decreased P2Y(12) receptor immunoreactivity in proximity to the lesions is directly correlated with the extent of demyelination found in all types of gray matter cortical plaques and subcortical white matter. 19822647_The P2Y12 receptor is required for proinflammatory actions of the stable abundant mediator LTE4. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914687_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20031628_Genetic ariation in P2RY12 is associated with residual on-clopidogrel platelet reactivity in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary interventions. 20031628_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20063989_Data show that ADP significantly increased VEGF, but not endostatin, release from platelets, and that both P2Y(1) and P2Y(12) receptor antagonism inhibited this release. 20068232_Studies indicate that release of ATP and the subsequent activation of P2 receptors help establish the basal level of activation for signal transduction pathways and regulate a wide array of responses. 20126830_Polymorphisms of the P2Y12 receptor gene contribute significantly to the interindividual variability in platelet inhibition after partial in vitro blockade with the P2Y12 antagonist cangrelor 20162250_Genetic variations exist in this protein in platelet function disorders. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20473398_Evaluation of antiplatelet agents in open flow systems demonstrates that inhibition of either ADP by apyrase or antagonism of P2X(1) signaling had no inhibitory effect on platelet accumulation. 20492465_clopidogrel active metabolite formation potentiation by rifampicin leads to greater P2Y12 receptor blockade and inhibition of platelet aggregation after clopidogrel 20589315_Letter: Report vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) ELISA to evaluate P2Y12-ADP receptor activity in coronary artery disease patients taking antiplatelet agents. 20599922_the cytosolic side of TM3 and the exofacial side of TM5 are critical for P2Y(12) receptor function;Arg 256 in TM6 and Arg265 in EL3 appear to play a role in antagonist recognition rather than effects on agonist-induced receptor function 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20630458_Low response to P2Y12 inhibition by clopidogrel is an independent predictor of cardiovascular death in percutaneous coronary angioplasty. 20691446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20695985_vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is phosphorylated in patients with genetic defects of the platelet P2Y(12) receptor for ADP 20873239_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20930120_roles of thrombin receptors (protease-activated receptors, PARs) and the ADP receptor P2RY12 (purinergic receptor P2Y G protein-coupled 12) in platelets ex vivo 20966167_central role played by P2Y in platelet thrombus formation (review) 21071695_Suggest P2Y12 receptor not only is central to ADP-induced platelet activation but also mediates platelet-independent responses, specifically under conditions of enhanced thrombin formation, such as local vessel injury and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. 21153923_This study confirmed significant inter-ethnic differences in CYP3A5 and P2Y12 frequencies between Iranians and other ethnic groups. 21216445_P2Y12 single-nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes revealed a significant association between P2Y12 haplotype, denoted H3, and an increase in the ADP-induced platelet aggregation response relative to that for the reference haplotype H1. 21231822_The P2Y12 receptor, activated by ADP, plays a central role in platelet activation and thrombus formation. Thus, the P2Y12 receptor has been an effective target for antithrombotic drugs. (Review) 21497813_SELP Pro715 allele is linked to low levels of sP-selectin, and both are associated with decreased P2Y12 ADP receptor reactivity in patients on clopidogrel therapy 21524751_In diabetes mellitus patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, impaired inhibition of P2Y12 by clopidogrel is an independent predictor of cardiac death. 21937696_P2Y(12)R function is compromised after deletion or mutation of the 4 amino acids at the extreme C-terminus of this receptor (ETPM), a putative postsynaptic density 95/disc large/zonula occludens-1 (PDZ)-binding motif. 22010907_The P2RY12 variants were associated with lung function in a large family-based asthma cohort. House dust mite exposure caused significant gene-by-environment effects 22079667_functional interaction of A2A and P2Y12 receptors on P2Y1 receptor 22159428_P2Y(12)-receptor gene variation has an effect on outcome of clopidogrel-treated patients undergoing elective coronary stent implantation 22273509_The platelet P2Y12 receptor contributes to granule secretion through Ephrin A4 receptor. 22275393_T744C P2RY12 polymorphism did not significantly affect the risk of VTE in the Korean population. 22440490_Increased residual platelet reactivity assessed by VerifyNow P2Y12 assay is related to post-discharge CV events in subjects with AMI. Prognostic significance is attenuated in patients with stable coronary disease after PCI. 22528678_These studies indicate putative roles of the P2Y(12) receptor in inflammatory states and diseases of the brain, lung, and blood vessels--{REVIEW} 22574824_Data indicate that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in P2RY1 and P2RY12 are associated with on-aspirin platelet reactivity in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). 22610101_Findings suggest a novel model by which arrestin can serve as an adaptor to promote NHERF1 interaction with a GPCR to facilitate effective NHERF1-dependent receptor internalization. 22647518_In patients undergoing nonurgent percutaneous coronary intervention intravenous/oral P2Y12 inhibitor elinogrel did not significantly increase thrombolysis in myocardial infarction or bleeding. 22652599_increased fractalkine levels are associated with decreased endogenous platelet inhibition and impaired response to P2Y12 inhibition with clopidogrel. 22701645_Combined blockade of P2Y12, P2Y1 and PI3-kinase p110beta fully prevents platelet and leukocyte activation during hypothermic extracorporeal circulation. 22704077_reactivity, as assessed by post-treatment P2Y12 mediated reactivity, is heightened after thrombolytic therapy during STEMI management. 22721490_Clopidogrel resistance was not associated with ADP receptor P2Y1 and P2Y12 gene polymorphisms. 22740070_in acute coronary syndrome diabetes mellitus patients undergoing PCI, the extent of P2Y12 inhibition by clopidogrel is not related to glycaemic control but is related to body weight and inflammatory status as assessed by the WBC 22746349_A novel pathway is described for testosterone regulation of P2Y12 expression in a megakaryocytic DAMI cell line. 22916275_Data describe a novel function of ARF6 in the internalization of P2Y purinoceptors and demonstrate the integral importance of this small GTPase upon platelet ADP receptor function. 23054651_In this review, we provide a brief but comprehensive report on P2Y(12), its role on platelet thrombus formation, and the targeting of this receptor as an intervention for cardiovascular disease 23140172_Demonstrate that P2Y(12) activation protects platelets from apoptosis via PI3k-dependent Bak/Bax inactivation. 23299202_This review aims to provide an overview on the state of the art P2Y12 receptor directed inhibition in ACS patients with a focus on patients undergoing a coronary stenting procedure. [review] 23314576_In our cohort, a pre-procedure P2Y12 reaction units value was the strongest independent predictor of all and major perioperative thromboembolic and hemorrhagic complications after Pipeline Embolization Device 23387322_analysis of endosomal sorting of a novel P2Y12 purinoreceptor mutant 23506580_Coexisting polymorphisms of of CYP2C19 and P2Y12 affected clopidogrel responsiveness and clinical outcome more than single polymorphism in Chinese patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. 23568163_Characterized the expression of P2Y12 receptor in breast cancer cell lines and evaluate its role in enhancing the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin. Observed a significant upregulation in P2Y12 expression in 4T1 breast cancer cell line with cisplatin. 23612493_RT-PCR analysis of total RNA extracted from human nasal turbinate, primary cultured human nasal epithelial cells and nasal vascular endothelial cells demonstrated the expression of P2Y12 receptor mRNA. 23751441_Platelet P2Y12 function also appears to be inversely correlated with JAK2V617F allele burden. This compromised P2Y12 function may be a novel mechanism for the bleeding tendency associated with extreme thrombocytosis in MPN. 23751603_study elicited an association between the T744C polymorphism of the P2Y12 ADP receptor gene and platelet reactivity 23844259_Data indicate that the ADP(PGE1) method is a reliable test for monitoring P2Y12 receptor inhibition by platelet aggregation. 23849096_P2Y1 and P2Y12 genes were polymorphic in a Korean population; 3 intronic P2Y12 polymorphisms (i-139C>T, i-744T>C, i-801insA) were in complete linkage disequilibrium but not with the c.52C>T polymorphism; platelet aggregation in response to ADP associated with c.52C>T polymorphism but not with the 3 intronic polymorphisms or the P2Y1 c.1622A>T polymorphism 23850619_Epac agonist 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP affects P2Y12 receptors in blood platelets 23940995_Our results suggest that 18C > T polymorphism of the P2RY12 gene may be an independent predictor of pharmacological response to clopidogrel. 24047499_Bradykinin induces ATP release from human subcutaneous fibroblasts via connexin and pannexin-1-containing hemichannels leading to calcium mobilization through the cooperation of B2 and P2Y12 receptors. 24071464_The data demonstrate nucleoside triphosphates in general act as P2Y12 receptor antagonists and antagonise ADP-, collagen-, and epinephrine-induced platelet aggregation. 24357254_Among patients with stable coronary artery disease, smokers have more P2Y12 receptor binding than nonsmokers and have a higher degree of clopidogrel-mediated platelet inhibition. 24437181_the study revealed no association between the risk of clopidogrel resistance and the presence of polymorphic variants of platelet receptor genes P2RY12 and GpIIIa. 24510678_The findings of this study suggest a potential association between P2Y12-receptor H2/H2 carriers and reduced platelet function mediated by TRAP in healthy volunteers. 24612393_thrombin activates the mTORC1 pathway in human platelets through PKC-mediated ADP secretion and subsequent activation of P2Y(12), in a manner largely independent of the canonical PI3 kinase/Akt pathway 24612435_analysis of a P2Y12 receptor mutation and a function-reducing polymorphism in protease-activated receptor 1 in a patient with chronic bleeding [case report] 24630878_In patients on maintenance prasugrel therapy exposed to a reloading dose (30 or 60 mg) of prasugrel, in vitro cangrelor is associated with further platelet P2Y12 receptor inhibitory effects. 24670650_2.6 A resolution crystal structure of human P2Y12R in complex with a non-nucleotide reversible antagonist, AZD1283 24723492_PAR4-P2Y12 association supports arrestin-mediated sustained signaling to Akt. 24745016_The evidence from our study indicates that P2Y12 methylation may bring new hints to elaborate the pathogenesis of CR. 24747445_Platelet ADP and AA receptor inhibition is a prominent early feature of coagulopathy in traumatic brain injury in humans and rats and is linked to the severity of brain injury in patients with isolated head trauma. 24784220_structures of P2Y12R in complex with agonist 2-methylthio-adenosine-5'-diphosphate (2MeSADP, analogue of endogenous agonist ADP) at 2.5 A resolution, and corresponding ATP derivative 2-methylthio-adenosine-5'-triphosphate (2MeSATP) at 3.1 A resolution 24971933_study reports robust involvement of P2Y12R in inflammatory pain: anti-hyperalgesic effect of P2Y12R antagonism could be mediated by the inhibition of both central and peripheral cytokine production and involves alpha7-receptor mediated efferent pathwaysefferent pathways 25064036_Establish a reliable antiplatelet profile of SAR216471, and support its potential use in clinical practice as an alternative to currently available P2Y12 receptor antagonists. 25075638_Data indicate that SAR216471 is a potent, highly selective, and reversible P2Y purinoceptor 12 (P2Y12) receptor antagonist and by far the most potent inhibitor of ADP-induced platelet aggregation among the P2Y12 antagonists. 25106522_the distribution of the ABCB1, CYP3A5, CYP2C19, and P2RY12 gene polymorphisms distinguishes to the Mexican Mestizos population from other ethnic groups. 25186974_Experiments reveal a surmountable and competitive mode of antagonism of ticagrelor at P2Y12 -receptors activated by either the natural agonist ADP or the synthetic agonist 2-methylthio-ADP. 25247182_Our findings suggest that the regulation of gpiibiiia and P2Y12 levels could be clinically useful to activate platelets to reach hemostasis. 25297118_2 functional single nucleotide polymorphisms of PON1 gene (rs662 and rs854560) and 3 variants of the P2RY12 gene (rs2046934, rs6798347, rs6801273) in samples pooled from average Hungarian Roma and Hungarian population samples, were investigated. 25329809_this is the first study to report that PJ34 could act via a competitive P2Y(12) antagonism. 25428217_Two patients with bleeding diathesis had dysfunctional platelet P2Y12 receptor for ADP, attributable to homozygous His187Gln mutation. 25579761_These data strongly suggest that P2Y12 may represent an important pharmacological target for the treatment of patients with allergic bronchial asthma. [review] 25730082_coexisting polymorphisms of CYP3A5*3 and 2C19*2, but not P2Y12*1, play an important role in the variability of clopidogrel's curative effect 25778862_This is the first study to demonstrate that the genetic polymorphisms of P2RY12 can affect platelet and eosinophil activation in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease after aspirin exposure. 25838093_Leukotriene E4 may play some important roles in allergic mucus secretion partially via activation of P2Y12 receptor 26083990_Baseline platelet aggregation was increased in carriers of the common alleles of P2Y12 SNPs rs1907637, rs2046934, and rs6809699 and rs6787801 TC heterozygotes. 26311415_In non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing PCI a loading dose of ticagrelor or prasugrel given during the procedure provides optimal P2Y12-ADP receptor blockade in 2 h and maximal inhibition within 4 h. 26353776_While there is increasing evidence for the cancer-protective effect of aspirin, this study suggests P2Y12 inhibition may also play a role. 26354056_Report appropriate P2Y12 inhibitor regimen to prevent increased bleeding risk and maintain antiplatelet efficacy in East Asian patients with acute coronary syndrome. in Korean patients 26391841_ADP stimulation of P2Y12 led to cAMP decrease that, in turn, caused changes in phospholipase C phosphorylation by protein kinase A, increase in cytoplasmic calcium level and, consequently, PS+ platelet formation 26663880_P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy and dual antiplatelet therapy inhibit hemostatic system activation to a comparable extent in healthy volunteers. 26743169_Synergistic inhibition of both P2Y1 and P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate receptors by GLS-409 immediately attenuates platelet-mediated thrombosis and effectively blocks agonist-stimulated platelet aggregation irrespective of concomitant aspirin therapy. 26870959_PON1, P2Y12 and COX1 polymorphisms were associated with poorer vascular outcomes in patients with extracranial or intracranial stents. 26885820_The ratio of ADP- to TRAP-induced platelet aggregation quantifies P2Y12-dependent platelet inhibition independently of the platelet count in contrast to conventional ADP-induced aggregation. 26950170_In the presence of loss of function C34T polymorphism of P2Y12 receptor, smoking is associated with increased adverse cardiovascular outcome in coronary artery disease patients. 27028818_upon platelet activation with ADP, the number of GP IIb-IIIa and P2Y12 receptors increases, which may serve as evidence of these proteins being synthesized in the activated platelets 27487748_The present report illustrates an update of dysfunctional platelet P2Y12R mutations diagnosed with congenital lifelong bleeding problems. [review] 27488401_No association was found in genotype frequencies of P2Y12 and responsiveness to clopidogrel in coronary heart disease patients of Han ethnicity. 27494721_P2RY12, the gene related to thrombogenesis was differentially expressed between the left atrium and right atrium in Sinus rhythm and Atrial fibrillation. Therefore, the changes in the expression of these genes were likely involved in the pathophysiology of AF-related thrombus formation. 27566695_P2Y12R gene rs2046934 C>T and rs3732759 A>G polymorphisms might be associated with the risk of coronary artery disease and the efficacy of clopidogrel treatment for CAD. 27628007_Abnormalities of P2Y12 receptor include congenital deficiencies or high activity in diseases like diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease, exposing such patients to a prothrombotic condition. (Review) 27694321_studies describe 2 novel modes of action of ticagrelor, inhibition of platelet ENT1 and inverse agonism at the P2Y12R that contribute to its effective inhibition of platelet activation. 27786340_In patients with type 2 diabetes, the presence of chronic kidney disease is associated with hyperreactive platelets and a dysfunctional status of the P2Y12 receptor signalling pathway. 27795489_The Conundrum of Platelet P2Y12 Inhibition in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. 27862351_The results suggest that P2Y12 is a useful marker for the identification of human microglia throughout the lifespan. Moreover, P2Y12 expression might help to discriminate activated microglia and infiltrating myeloid cells from quiescent microglia in the human CNS. 27975100_miR-223, miR-26b, miR-126 and miR-140 are expressed at a lower level in platelets and megakaryocytes in type 2 diabetics causing up-regulation of P2RY12 and SELP mRNAs that may contribute to adverse platelet function. 28070995_apart from the established association of the CYP2C19 *2 and *3 LOF alleles with high on-treatment platelet reactivity (HTPR), haplotypes of P2RY12 rs6798347, rs6787801, rs6801273, and rs6785930 rather than rs2046934 (T744C) that related to pharmacodynamics of clopidogrel in patients with ACS were independently associated with HTPR 28091702_aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of platelet receptor gene (P2Y12, P2Y1) and glycoprotein gene (GPIIIa) polymorphisms, as well as their interactions, on antiplatelet drug responsiveness and clinical outcomes in patients with acute MIS 28296036_CLEC-2 and P2Y12 are required for CpG ODN-induced platelet activation and thrombosis, and might be targeted to prevent adverse events in patients at risk. 28329746_We documented a different effect of CYP2C19 and P2Y12 receptor polymorphisms on platelet reactivity and cardiovascular outcome in coronary artery disease patients after percutaneous coronary intervention on clopidogrel treatment. Importantly, increased platelet reactivity adversely affects the cardiovascular outcome independently of the studied polymorphisms. 28472364_Polymorphisms of the P2RY12 gene may predict individual differences in both cancer and postoperative pain severity 28652403_Data suggest that PAR4 and P2Y12 heterodimer internalization/endocytosis is required for beta-arrestin-2 recruitment to endosomes and up-regulation of Akt signaling; activation of PAR4 but not of P2Y12 drives internalization of the PAR4-P2Y12 heterodimer. (PAR4 = protease-activated receptor 4; P2Y12 = purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 12 protein; Akt = proto-oncogene protein c-akt) 28753204_Findings offer insight into positive regulation of Akt signaling through P2Y12 phosphorylation as well as MAPK signaling in platelets by ASK1. 28791856_Studies indicate that purinergic receptor P2Y12 (P2Y12 receptor) gene C34T and G52T polymorphism might be a risk factor for the poor response to the platelet in patients on clopidogrel therapy. 28844979_The DHA - naringenin hybrid presented triple antiplatelet activity simultaneously targeting PAR-1, P2Y12 and COX-1 platelet activation pathways 28949406_Downregulation of the P2Y12 receptor in the superior cervical ganglia after myocardial ischemia may improve cardiac function by alleviating the sympathoexcitatory reflex 29117459_This novel dominant negative variant confirms the important role of R265 in EL3 in the functional integrity of P2Y12R, and suggests that pathologic heterodimer formation may underlie this family bleeding phenotype. 29232918_Genomic association study identified deleterious rare variants in P2RY12 in patients with ischemic stroke. 29273052_P2Y12R was associated with an anti-inflammatory phenotype in human microglia in vitro and was expressed at lower levels in active inflammatory MS lesions compared to normal-appearing white matter 29510176_The meta-analysis shows a potential of association between P2RY12 gene polymorphisms and higher risks of composite ischemic events for coronary artery disease patients treated with clopidogrel. [review] 29526844_Expression of platelet hsa-miR-223 increased and P2RY12 mRNA reduced in type 2 diabetic patients following ET non-significantly. 29635252_association of SNPs of PEAR1, P2Y12, and UGT2A1 with platelet reactivity in 290 Chinese patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with aspirin and clopidogrel 29791922_P2Y12 T744C and C34T polymorphisms are significantly associated with adverse clinical events. 29848980_Minor allele frequencies (MAF) in a Puerto Rican population were 46% for PON1 (rs662), 41% for ABCB1 (rs1045642), 14% for CYP2C19*17, 13% for CYP2C19*2, 12% for P2RY12-H2 and 0.3% for CYP2C19*4. No carriers of the CYP |
ENSMUSG00000036353 |
P2ry12 |
25.683094 |
0.1164898853 |
-3.101723 |
0.413981770 |
66.299027 |
0.00000000000000038744993754394199406714364479810387725372319693041556210033604656928218901157379150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002831069840667615843568458951876277675898968978068781510160079051274806261062622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0385234 |
1.4610333 |
43.4189807 |
6.4204672 |
| ENSG00000169330 |
23251 |
MINAR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UPX6 |
FUNCTION: Intrinsically disordered protein which may negatively regulate mTOR signaling pathway by stabilizing the mTOR complex component DEPTOR (PubMed:30080879). Negatively regulates angiogenesis (PubMed:29329397). Negatively regulates cell growth (PubMed:29329397, PubMed:30080879). Negatively regulates neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:D3ZJ47, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29329397, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30080879}. |
Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of TOR signaling; negative regulation of angiogenesis; and negative regulation of protein ubiquitination. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23251; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of TOR signaling [GO:0032007] |
29329397_MINAR1 physically interacts with Notch2 and its binding to Notch2 increases its stability and function. While MINAR1 is highly expressed in the normal human breast, its expression is significantly downregulated in advanced human breast cancer and its re-expression in breast cancer cells inhibited tumor growth. 30080879_Ubtor inhibits mTOR signaling by stabilizing the mTOR complex component DEPTOR. Inhibiting Ubtor function promotes cell growth in neurons and cancer cells. Increasing Ubtor function reduces cancer cell growth. 33728681_Novel functional variants in the Notch pathway and survival of Chinese colorectal cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000039313 |
Minar1 |
11.757896 |
2.2323699206 |
1.158576 |
0.438861818 |
7.117870 |
0.00763193084384697871536129554215222015045583248138427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014993650905787489144294077902941353386268019676208496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.2622995 |
4.3672582 |
7.3287415 |
1.5788850 |
| ENSG00000169344 |
7369 |
UMOD |
protein_coding |
P07911 |
FUNCTION: [Uromodulin]: Functions in biogenesis and organization of the apical membrane of epithelial cells of the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop (TALH), where it promotes formation of complex filamentous gel-like structure that may play a role in the water barrier permeability (Probable). May serve as a receptor for binding and endocytosis of cytokines (IL-1, IL-2) and TNF (PubMed:3498215). Facilitates neutrophil migration across renal epithelia (PubMed:20798515). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20798515, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3498215, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: [Uromodulin, secreted form]: In the urine, may contribute to colloid osmotic pressure, retards passage of positively charged electrolytes, and inhibits formation of liquid containing supersaturated salts and subsequent formation of salt crystals (By similarity). Protects against urinary tract infections by binding to type 1 fimbriated E.coli (PubMed:11134021, PubMed:32616672). Binds to bacterial adhesin fimH which mediates the stable formation of bacterial aggregates, prevents the binding of E.coli to uroplakins UPK1A and UPK1B which act as urothelial receptors for type I fimbriae, and allows for pathogen clearance through micturation (PubMed:11134021, PubMed:32616672). Also promotes aggregation of other bacteria including K.pneumoniae, P.aeruginosa and S.mitis and so may also protect against other uropathogens (PubMed:32616672). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91X17, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11134021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32616672}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nephronophthisis;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is the most abundant protein in mammalian urine under physiological conditions. Its excretion in urine follows proteolytic cleavage of the ectodomain of its glycosyl phosphatidylinosital-anchored counterpart that is situated on the luminal cell surface of the loop of Henle. This protein may act as a constitutive inhibitor of calcium crystallization in renal fluids. Excretion of this protein in urine may provide defense against urinary tract infections caused by uropathogenic bacteria. Defects in this gene are associated with the renal disorders medullary cystic kidney disease-2 (MCKD2), glomerulocystic kidney disease with hyperuricemia and isosthenuria (GCKDHI), and familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy (FJHN). Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:7369; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cilium [GO:0005929]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; membrane [GO:0016020]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; IgG binding [GO:0019864]; antibacterial innate immune response [GO:0140367]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0030644]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0030643]; cellular response to unfolded protein [GO:0034620]; cellular sodium ion homeostasis [GO:0006883]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; citric acid secretion [GO:0046720]; collecting duct development [GO:0072044]; connective tissue replacement [GO:0097709]; creatinine homeostasis [GO:0097273]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; endoplasmic reticulum organization [GO:0007029]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; juxtaglomerular apparatus development [GO:0072051]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; metanephric ascending thin limb development [GO:0072218]; metanephric distal convoluted tubule development [GO:0072221]; metanephric thick ascending limb development [GO:0072233]; micturition [GO:0060073]; multicellular organismal response to stress [GO:0033555]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; neutrophil migration [GO:1990266]; organ or tissue specific immune response [GO:0002251]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0055075]; protein localization to vacuole [GO:0072665]; protein transport into plasma membrane raft [GO:0044861]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of protein transport [GO:0051223]; regulation of urine volume [GO:0035809]; renal sodium ion absorption [GO:0070294]; renal urate salt excretion [GO:0097744]; renal water homeostasis [GO:0003091]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to water deprivation [GO:0009414]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433]; urate transport [GO:0015747]; urea transmembrane transport [GO:0071918] |
11730273_We identified a silent polymorphism in the UMOD gene at codon C174 which co-segregates with autosomal dominant medullary cystic kidney disease in the ADMCKD2 family. 11932463_binds to virulent Bordetella pertussis and reduces its adherence to both renal and pulmonary epithelial cells 11982485_Uromodulin promoter directs high-level expression of biologically active human alpha1-antitrypsin into mouse urine. 12471200_Mutations of the UMOD gene are responsible for medullary cystic kidney disease 2 and familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy 12624657_the effects of Tamm-Horsfall protein on the protection of oxalate induced radical injury may be partly due to its intact glycosylation and its adhesion to the cell membrane. 12832729_Two genes predisposing to dominant MCKD, MCKD1 and MCKD2, have been localized to chromosome 1q21 and 16p12. Review. 14531790_specific role of exon 4 encoded sequence of UMOD in the generation of the medullary cystic kidney disease type 2 renal phenotype. 14569098_this study points to a mutation clustering in exon 4 of UMOD as a major genetic defect in familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy. 14570881_Species variations of the glycomoiety of THP can lead to the differential binding of THP to type 1-fimbriated E. coli. 15033942_degree of conversion of the tetrasaccharidic Sd(a) precursor into the final pentasaccharidic Sd(a) form can be considered to result from a very closely related pattern of glycosylation for genetically homogeneous individuals 15086896_evidence for the mutation of the UMOD gene in the majority of Japanese families with familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy 15253706_individuals with two UMOD mutations are viable, but they do have more severe disease on average than heterozygotes. 15266028_Tamm-Horsfall protein has immunomodulatory role on polymorphpolymorphonuclear leukocyte functions(apoptosis,chemotaxis,phagocytosis). 15327389_the autosomal-dominant gene mutations responsible for UMOD-associated kidney disease cause a profound reduction of THP excretion. 15575003_Excretion of uromodulin is reduced in familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy. 15589826_D8C, a novel domain present in UMOD, mutates in familial juvenile hyperuricemia. 15785410_Tamm-Horsfall protein in a 16-month-old girl with surgical resection of a nephroblastoma after pre-operative chemotherapy 15983957_A novel mutation (Gln316Pro) was found in exon 5. There is provide additional evidence for the existence of a fourth calcium-binding epidermal growth factor-like domain in the structure of Tamm-Horsfall protein. 16164624_We identified a new candidate uromodulin-associated kidney disease locus on chromosome 1q41 16982955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17010121_12 different uromodulin missense mutations were found to lead to defective endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi protein transport, suggesting a common pathogenetic mechanism in medullary cystic kidney disease and familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy. 17065110_a mutation in UMOD gene may lead to familial nephropathy associated with hyperuricemia 17151335_there are different urinary and plasma mutant uromodulin profiles in early and late familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy 17245395_Haplotype analysis showed cosegragation with the phenotype in all eight affected individuals indicating that the uromodulin C744G mutation may be due to a founder effect. 18047931_Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein from renal transplant patients is not only modified in glycosylation but bears an apoptosis-inducing capacity on mononuclear cells and polymorphonuclear neutrophils, leading to an impaired immune function in patients. 18068104_Intact protein core structure of Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein, but not carbohydrate side-chains, is essential for protein-binding and cell-stimulating activities of the molecule. 18351395_Assessed tubular function in diabetic children by measuring Tamm-Horsfall protein and glutathione S-transferase levels in urine. 18375198_Urinary uromodulin is generated by a conserved C-terminal proteolytic cleavage and retains its entire ZP domain. 18409515_mutations in its gene as a cause of familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy 18409531_Mutant uromodulin causes uricemic underexcretion and hyperuricemia 18455532_patients with interstitial cystitis(IC)with decreased uromodulin and kininogen had worsening IC severity.Uromodulin and kininogen were significantly less present in the urine of the IC group vs the AC group. 18600511_Phenotypes of transgenic mice harboring mutant human UMOD gene 18651238_UMOD is a potential biochemical marker of therapeutic response of the kidney to therapy in Fabry disease. 18830570_The finding that LZP might act as a new partner of THP would provide novel insights into renal functions related to THP and LZP, such as the urothelial permeability barrier and the host defense against the adhesion of pathogens. 18846391_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18846391_UMOD mutations do not seem to be a significant cause of congenital anomalies of the kidney and uninary tract in this cohort. 18950917_This novel UMOD sequence variant, which is associated with an immunohistochemical pattern different from previous reports and a histological picture characterized by immature renal structures, suggests a possible role for UMOD in renal development 19203555_genetic analysis of novel D196Y mutation in UMOD gene in family cohort with familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy age-related protein excretion levels 19430482_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19465746_Familial juvenile hyperuricaemic nephropathy-causing uromodulin mutants are impaired in protein maturation and trafficking. 19959715_Elevated uromodulin concentrations precede the onset of chronic kidney disease and associate with a common polymorphism in the UMOD region. 19959715_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075439_The combined analysis of serum and urinary uromodulin provides new insights into the role of uromodulin in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and suggests that uromodulin may be an active player in CKD progression. 20151160_While renal functional decline is slow in individuals with UMOD mutations, it may appear early in life and be associated with marked hyperuricemia. 20172860_UMOD is expressed in the primary cilia of renal tubules in human kidney biopsy samples. 20222955_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20624112_Distal tubular dysfunction was associated with the THP gene and macroalbuminuria in patients with type 1 diabetes. 20624112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20686651_In contrast to CKD, the UMOD variant confers protection against kidney stones when studied in 3,617 Icelandic and Dutch kidney stone cases 20686651_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20948228_[REVIEW] relation of uromodulin concentration in blood and urine to chronic kidney disease 21067798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21081491_THGP modulation of ROMK function confers a new role of THGP on renal ion transport and may contribute to salt wasting observed in FJHN/MCKD-2/GCKD patients. 21082022_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21082022_Studies identified and validated a SNP upstream of the uromodulin (UMOD) gene whose minor allele is associated with a lower risk of hypertension. 21109754_[REVIEW] UMOD analysis is of importance in all conditions with renal involvement and may be useful in the proper classification of renal diseases. 21332338_Using multivariate analysis, patients with chronic kidney disease and gout were associated with lower urinary UMOD excretion than those who have gout alone. 21358122_it is suggested that uromodulin mutation may be responsible for the enhancement of renal androgen action 21546974_With current interest in new urinary biomarkers for CKD, the role of urinary UMOD deserves further investigation. Review. 21738052_present study highlights that the common variant of the UMOD gene is protective against diabetic nephropathy susceptibility and also affects kidney function and blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes 21868615_Hyperuricemia disproportionate to renal function represents the hallmark of renal disease caused by UMOD mutation. 22034507_The indel mutation is associated with a relatively mild clinical UMOD-associated kidney disease (UAKD) phenotype. 22117067_Molecular and cellular effects of Tamm-Horsfall protein mutations and their rescue by chemical chaperones. 22132988_The detection of uromodulin mutants, using the C148W mutant as a target molecule, is reported. 22237754_Both in vitro and in vivo, mutant isoforms partially escaped retention in the endoplasmic reticulum and reached the plasma membrane where they formed large extracellular aggregates that have a dominant-negative effect on coexpressed wild-type protein. 22538938_Mutant uromodulin is secreted in the urine of patients with familial hyperuricemic nephropathy and induces the formation of extracellular aggregates 22592667_It was shown that common variants of uromodulin are associated with diastolic blood pressure in a community-based Chinese cohort. Urinary uromodulin was correlated with urinary sodium. 22693617_association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and urinary uromodulin concentrations with rare variants in UMOD gene 22776760_The present study reported a novel mutation in exon 9 of UMOD in the Chinese Han population, within the GPI anchor signal segment of uromodulin. 22947327_The rs12917707 minor allele showed association with lower risk of end-stage renal disease. 22997256_uromodulin is a NLRP3 agonist handled by antigen-presenting cells as an immunostimulatory nanoparticle 23009031_Data indicate that Tamm-Horsfall Protein (THP) binds to urinary catheters and facilitates the binding of uropathogenic bacteria to catheters. 23344472_UMOD promoter variants seem to initiate a cascade of transcriptional and biochemical changes influencing UMOD secretion, leading to altered plasma uric acid levels. 23586973_RESULTS: rs1260326 in GCKR (beta=1.30, P = 3.23E-03), rs17319721 in SHROOM3 (beta = -1.28, P-value = 3.18E-03) and rs12917707 in UMOD (beta = 2.0, P-value = 8.84E-04) were significantly associated with baseline estimated GFR. 23826568_The UMOD gene was identified a novel heterozygous missense variant (c.187T>C; p.Cys63Arg) in exon 3. 23988501_The novel uromodulin mutations found in the Chinese families lead to misfolded protein, which was retained in the endoplasmic reticulum, finally contributed to the phenotype of familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy. 24185693_Genetic susceptibility link to hypertension and chronic kidney disease to the level of uromodulin expression and uromodulin's effect on salt reabsorption in the kidney. 24577984_Familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy (FJHN) is a rare autosomal-dominant disease caused by mutations in the UMOD gene located at 16p11.2-12 that encodes for uromodulin, or Tamm-Horsfall glycoprotein. 24594405_the set of sequence specific transcription factors that regulate the uromodulin gene UMOD and their upstream binding locations are not well characterized. We built a high resolution map of its transcriptional regulation 24628133_Homozygotes for the common G allele of rs12917707 had a 2.2 times greater risk of post-operative fluid overload after adjustment for clinical variables. A genetic risk score including 14 SNPS independently associated with post-operative fluid overload. 24648000_Suggest that uromodullin may have a renal physiologic function related to its inhibitory effect on the NFkappaB pathway. 24667016_Urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein does not correlate with carotid artery intima media thickness in childhood type1 diabetes. 24697042_Genome-wide association studies identified uromodulin as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease (CKD) and hypertension, and suggested that the level of uromodulin in the urine could represent a useful biomarker for the development of CKD. 24849497_Here, we reviewed the signal transduction pathway of UMOD and its role in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases. [review] 25163389_UMOD does not play a role in IgA nephropathy pathogenesis nor progression. 25436415_Wild-type uromodulin was efficiently trafficked to the cell surface in transfected tsA 201 cells, whereas the mutants were partially retained within the cell, and incompletely processed 25493955_significantly associated with kidney function decline [meta-analysis] 25671765_The main and new finding of this study is the association of bilateral small caliber non-arteriosclerotic renal arteries with hyperuricemia due to a novel UMOD mutation causing intracellular accumulation of UMOD in distal tubular cells. 25840631_Uromodulin has greater immunosuppressive activities than THP and lower inductive property in relation to activation of immune cells. 25935139_lower levels associated with nephrolithiasis 26040415_UMOD: A significant effect of the rare p.V458L variant on the value of estimated glomerular filtration in elderly population was found. 26617860_In essential hypertension there's a close negative relationship between lowered urine UMOD and increased serum inflammatory cytokines. 26673890_These data demonstrate that the membrane-bound serine protease hepsin is the enzyme responsible for the physiological cleavage of uromodulin. 26811476_the crystal structures of polymerization regions of human UMOD and mouse ZP2, an essential sperm receptor protein that is structurally related to UMOD but forms heteropolymers, are reported. 26966016_Data strongly suggest that the uromodulin ancestral allele, driving higher urinary excretion of uromodulin, has been kept at a high frequency because of its protective effect against urinary tract infections 27045027_UMOD gene variants in humans fulfill the criteria for ascribing a gene as causal of Hypertension. 27113631_The uromodulin-CFH interaction enhanced the cofactor activity of CFH for factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b to inactivated C3b. 27315129_UMOD rs13333226 does not appear to be associated with preeclampsia in Han Chinese women. 27448670_Single-nucleotide polymorphism in UMOD gene is associated with type 2 diabetes. 27729211_novel UMOD missense mutation c.457T>G, p.(Cys153Gly) in patients with chronic kidney disease; mutation leads to severely reduced serum uromodulin concentrations 27938332_The frequency of uromodulin single nucleotide polymorphism rs13333226 GG/GA genotype was significantly higher and the frequency of G allele was much higher in the patients with end stage renal disease than in the controls. 27958261_Serum uromodulin concentrations are closely correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate, which is the recommended measure of renal function. As uromodulin is produced exclusively by renal tubular cells, the assessment of uromodulin levels in patients with chronic kidney disease may be an alternative method for evaluating the number of functioning nephrons. 28029393_High urinary uromodulin levels are associated with lower risk for UTI in older community-dwelling adults independent of traditional UTI risk factors. 28182086_These findings suggest that the levels of urinary microvesicle-bound uromodulin are associated with the severity of diabetic kidney disease. 28206617_Low UMOD expression is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus-nephritis and kidney diseases. 28598953_Studied genetic association of uromodulin SNP in kidney function of patients with hypertension and cardiovascular disease. 28605509_Homozygous UMOD mutation did not show a strikingly more severe clinical evolution nor was the near absence of urinary uromodulin associated with urinary tract infections or kidney stones. 28609449_Data show that one SNP (rs183962941), located in a non-coding region of uromodulin protein (UMOD), was nominally associated with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). 28613246_Patients with Acute kidney injury tended to have lower sUMOD. Although sUMOD correlated significantly with kidney function in the early phase of severe acute pancreatitis (AP), measuring sUMOD did not allow to reliably predict AP severity or development 28742158_THP appears to participate directly in complement inactivation by its ability to act as a cofactor for C3b degradation. 28829050_these data support THP as an important negative regulator of neutrophil activation in the urinary tract, with dual functions to counteract bacterial colonization and suppress excessive inflammation within the urinary tract 28858977_low serum concentration linked with chronic kidney disease 28914853_The missense mutation p.142R>R/Q in the uromodulin gene in patients with cast Nephropathy in Multiple Myeloma. 28954491_Allele C of rs11864909 was preferentialy transmitted from parents to the children with chronic tubulointerstinal nephritis. 29180395_Taken together, our data suggest that interstitial THP positively regulates mononuclear phagocyte number, plasticity, and phagocytic activity. In addition to the effect of THP on the epithelium and granulopoiesis, this new immunomodulatory role could explain the protection conferred by THP during AKI. 29511113_Mendelian randomization identified UMOD as a novel, causal mediator of CKD. 29513881_we report a novel UMOD mutation in a Brazilian family with 11 affected members, and we discuss the importance of performing genetic testing in families with inherited kidney disease of unknown cause. 29578190_The frequency of UMOD rs4293393 variant with C allele was significantly higher in individuals with iabetic nephropathy . UMOD rs4293393 T>C variation might have a bearing on susceptibility to nephropathy in north Indian individuals with type 2 diabetes. 29698955_lower serum level associated with greater risk for kidney allograft failure 29779026_Urinary extracellular vesicles (EV) UMOD mRNA levels are progressively elevated from type 2 diabetes to diabetic kidney disease (DKD) groups and correlate with widely used estimated glomerular filtration rate and albumin creatinine ratio diagnostic criteria. An EV mRNA signature could identify DKD with greater than 90% sensitivity and 70% specificity. 30454063_Serum uromodulin is independently associated with an increased risk of incident end-stage kidney disease in chronic kidney disease patients. 30903163_Association of serum uromodulin with mortality and cardiovascular disease in the elderly-the Cardiovascular Health Study. 31253490_Serum uromodulin is associated with urinary albumin excretion in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. 31411505_uromodulin is independently associated with acute kidney injury development after adjusting for clinically relevant parameters such as age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, severity of cirrhosis, and kidney function 31422399_Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease due to UMOD (encoding uromodulin) mutation (ADTKD-UMOD) is a rare hereditary disease. In the present study, we reported 2 ADTKD cases with confirmed UMOD mutations (Arg185His, Trp258Gly) by gene testing. Renal histology showed chronic tubulointerstitial nephropathy with fibrillar inclusions in the cells of distal tubules. 31879271_Peptidomic Analysis of Urine from Youths with Early Type 1 Diabetes Reveals Novel Bioactivity of Uromodulin Peptides In Vitro. 32011449_rs12917707in UMOD showed lack of significant association with the non-diabetic end-stage renal disease 32045104_Importance of glycosylation in the interaction of Tamm-Horsfall protein with collectin-11 and acute kidney injury. 32058862_Serum uromodulin and risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the community-based KORA F4 study. 32113667_SPTB related spherocytosis in a three-generation family presenting with kidney failure in adulthood due to co-occurrence of UMOD disease causing variant. 32291270_Association of Serum Uromodulin with Death, Cardiovascular Events, and Kidney Failure in CKD. 32450155_Clinical and genetic spectra of autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease due to mutations in UMOD and MUC1. 32616672_Architecture and function of human uromodulin filaments in urinary tract infections. 32764816_Serum uromodulin is inversely associated with arterial hypertension and the vasoconstrictive prohormone CT-proET-1 in the population-based KORA F4 study. 32769629_Uromodulin to Osteopontin Ratio in Deceased Donor Urine Is Associated With Kidney Graft Outcomes. 32815518_The cryo-EM structure of the human uromodulin filament core reveals a unique assembly mechanism. 32847529_A novel likely pathogenic variant in the UMOD gene in a family with autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease: a case report. 33196145_Cryo-EM structure of native human uromodulin, a zona pellucida module polymer. 33414784_Extratubular Polymerized Uromodulin Induces Leukocyte Recruitment and Inflammation In Vivo. 34071541_Polymorphism in the GATM Locus Associated with Dialysis-Independent Chronic Kidney Disease but Not Dialysis-Dependent Kidney Failure. 34145125_Study of Uromodulin Gene Polymorphism in Egyptian Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. 34187999_Mechanistic interactions of uromodulin with the thick ascending limb: perspectives in physiology and hypertension. 34593962_Effect of a common UMOD variant on kidney function, blood pressure, cognitive and physical function in a community-based cohort of older adults. 34824175_ASSOCIATION OF GENETIC POLYMORPHISM AND EXPRESSION OF UMOD GENE AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE. 34828293_UMOD Polymorphisms Associated with Kidney Function, Serum Uromodulin and Risk of Mortality among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease, Results from the C-STRIDE Study. 35039253_Correlation of serum uromodulin levels with renal fibrosis and renal function progression in patients with CKD. 35263610_Systematic analysis of modulating activities of native human urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein on calcium oxalate crystallization, growth, aggregation, crystal-cell adhesion and invasion through extracellular matrix. 35273390_Structure of the decoy module of human glycoprotein 2 and uromodulin and its interaction with bacterial adhesin FimH. 35947615_An intermediate-effect size variant in UMOD confers risk for chronic kidney disease. |
ENSMUSG00000030963 |
Umod |
8.199503 |
5.8952202362 |
2.559546 |
0.671608207 |
15.570103 |
0.00007950180341714570156439606529730212969298008829355239868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000221781632666239001284297360783170915965456515550613403320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.7803676 |
6.1158604 |
2.3669095 |
0.8936166 |
| ENSG00000169385 |
6036 |
RNASE2 |
protein_coding |
P10153 |
FUNCTION: This is a non-secretory ribonuclease. It is a pyrimidine specific nuclease with a slight preference for U. Cytotoxin and helminthotoxin. Selectively chemotactic for dendritic cells. Possesses a wide variety of biological activities. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12578357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3458170}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endonuclease;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lyase;Lysosome;Nitration;Nuclease;Reference proteome;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a non-secretory ribonuclease that belongs to the pancreatic ribonuclease family, a subset of the ribonuclease A superfamily. The protein antimicrobial activity against viruses. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014]. |
hsa:6036; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lyase activity [GO:0016829]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; ribonuclease A activity [GO:0004522]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response in mucosa [GO:0002227]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090501] |
9826755_The antimicrobial protein, RNase 2 exhibits antiviral against respiratory syncytial virus. 11876642_atomic resolution structure 11916383_crystal structure of a post-translationally modified form of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) with four extra residues on its N terminus ((-4)EDN) has been solved and refined at atomic resolution (1 A) 11959927_EDN and ECP are paralogs in human and Old World monkeys. 12606041_evidence for glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored neurotoxin on granulocytes 15356558_data suggest that peripheral blood eosinophils from subjects with untreated asthma have increased inflammatory capacity, as reflected by greater intracellular concentrations of EDN 15528350_Results reveal the dendritic cell-activating activity of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and suggest that it is a likely participant of inflammatory and immune responses--an endogenous multifunctional immune alarmin. 15755456_Results describe the crystal structure of placental ribonuclease inhibitor in complex with eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, and a mutational analysis based on this structure. 16014847_May possibly be associated with the development of tropical pulmonary eosinophilia. 16014847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16428483_Elevated glycosylated form of EDN in urine is associated with ovarian cancer 17351112_EGO is a novel ncRNA gene expressed during eosinophil development and is necessary for normal MBP and EDN transcript expression. 17641730_Data show that uEPX/c levels did not correlate with established markers of asthma severity and eosinophilic airway inflammation in atopic asthmatic children. 17927842_MAZ and Sp1 play important roles on the transcriptional activation of the human edn promoter through specific binding to a 34-nt segment present in representative primate eosinophil rnase promoters. 17965582_Urinary concentrations of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin in patients with atopic dermatitis show a significant positive correlation with disease severity. 18195069_EDN can activate myeloid DCs by triggering the Toll-like receptor (TLR)2-myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling pathway 18636464_In three continental population groups (Asia, Europe, Africa), the angiogenin and RNase 2 genes appear to exhibit markedly less genetic heterogeneity with regard to T195C and A238G (ANG) and C425A (RNASE2) SNPs. 18636464_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19014520_No variation in genes encoding eosinophil-derived neurotoxin for Atopic dermatitis pathogenesis in this German cohort. 19014520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19115260_the roles of the six discrete segments in transcription regulation were investigated and the -350/-329 region (ednR2) was shown to be involved in the regulation of edn expression 19717523_ECP and EDN disrupt skin integrity and cause inflammation 21680952_Eosinophil protein X in urine from asymptomatic neonates is a biomarker significantly associated with later development of allergic sensitization, nasal eosinophilia, and eczema during the first 6 years of life 23053729_findings show substantial amounts of EPX/EDN localise in an extra-granular, low equilibrium density compartment of eosinophils 23533305_A higher level of serum EDN was found specifically in patients with ALS, indicating that EDN may participate in the pathophysiology of Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 24814827_mRNA levels of eosinophil granule proteins, rather than sputum eosinophil%, may reflect airway hyperresponsiveness and airflow limitation. 24890227_increased in feces after the ingestion of enterocolitis-causative foods 25221852_RNASE2 gene expression was differentially expressed in rheumatoid arthritis patients considering a sequence polymorphism. 26534742_Serum EDN level may be a useful marker for monitoring persistent airflow limitation in adult patients with asthma who had positive results for house-dust-specific IgE antibodies. 28169973_In healthy children, 95th Percentile values ranged from 1519 mg/kg at 0 months to 54.4 mg/kg at 144 months for fecal calprotectin (fCP) and from 9.9 mg/kg at 0 months to 0.2 mg/kg at 144 months for fecal eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (fEDN). There was a significant association between age and fCP concentrations and age and fEDN concentrations and a significant association between fEDN and fCP. 28866306_EDN serum level could be considered a candidate molecule as a clinical biomarker for evaluating atopic dermatitis activity and a predictor of relapse 30367910_the rs3827907 C-allele appeared to particularly influence inhaled corticosteroid treatment response in the presence of eosinophilic inflammation 32294405_Immune Sensing of Synthetic, Bacterial, and Protozoan RNA by Toll-like Receptor 8 Requires Coordinated Processing by RNase T2 and RNase 2. 32571644_Combined assessment of serum eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and YKL-40 may identify Asthma-COPD overlap. 34615736_Blood eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin are associated with different asthma expression and evolution in adults. 35265065_RNASE2 Mediates Age-Associated B Cell Expansion Through Monocyte Derived IL-10 in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. |
ENSMUSG00000072601+ENSMUSG00000050766+ENSMUSG00000090166+ENSMUSG00000072596+ENSMUSG00000047222+ENSMUSG00000059606+ENSMUSG00000062148 |
Ear1+Ear14+Ear10+Ear2+Rnase2a+Rnase2b+Ear6 |
76.640382 |
0.4713322941 |
-1.085184 |
0.195299499 |
31.213280 |
0.00000002311791882532897134812842029113338915280451146827545017004013061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000097186124141798801904680170545003381477044968050904572010040283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.6911273 |
6.2043941 |
106.2804735 |
8.7263551 |
| ENSG00000169403 |
5724 |
PTAFR |
protein_coding |
P25105 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for platelet activating factor, a chemotactic phospholipid mediator that possesses potent inflammatory, smooth-muscle contractile and hypotensive activity. Seems to mediate its action via a G protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1281995, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1374385, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1656963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1657923}. |
Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor for platelet-activating factor (PAF) that localizes to lipid rafts and/or caveolae in the cell membrane. PAF (1-0-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine) is a phospholipid that plays a significant role in oncogenic transformation, tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, and pro-inflammatory processes. Binding of PAF to the PAF-receptor (PAFR) stimulates numerous signal transduction pathways including phospholipase C, D, A2, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and the phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Following PAFR activation, cells become rapidly desensitized and this refractory state is dependent on PAFR phosphorylation, internalization, and down-regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:5724; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; G protein-coupled purinergic nucleotide receptor activity [GO:0045028]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; lipopolysaccharide immune receptor activity [GO:0001875]; mitogen-activated protein kinase binding [GO:0051019]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; platelet activating factor receptor activity [GO:0004992]; cellular response to 2-O-acetyl-1-O-hexadecyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine [GO:1904317]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to gravity [GO:0071258]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032959]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; parturition [GO:0007567]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of cellular extravasation [GO:0002693]; positive regulation of gastro-intestinal system smooth muscle contraction [GO:1904306]; positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0060732]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; positive regulation of maternal process involved in parturition [GO:1904303]; positive regulation of neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043315]; positive regulation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0010863]; positive regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:1904058]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of transcytosis [GO:1904300]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of voltage-gated chloride channel activity [GO:1902943]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to dexamethasone [GO:0071548]; response to symbiotic bacterium [GO:0009609]; transcytosis [GO:0045056] |
11861812_activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase and induces proliferation of epidermal cells 11928813_Neuroblastoma clone cells show an inverse relationship between invasiveness and differentiative capacity and by the expression of specific cell surface PAF receptors. 12467527_PAF receptor transcripts in five human cancer cell lines derived from the breast (BT20, SKBR3 and T47D cells), the pancreas (Miapaca cells) and the bladder (5,637 cells) confirm the existence of a splice variant of the PAF-R transcript 2. 12601006_a novel pathway whereby the epidermal PAF-R can augment chemotherapy-induced apoptotic effects through an NF-kappaB-dependent process 12713583_the epidermal platelet-activating factor receptor augments staphylococcal alpha-toxin signaling 12756251_platelet-activating factor receptor is desensitized and internalized by coumermycin-gyrase B-induced dimerization 14500680_The C-terminal tail of the PAFR is of critical importance for platelet-activating factor-induced Janus kinase 2 activation. 14500726_PAFR degradation can occur via both the proteasome and lysosomal pathways and ligand-stimulated degradation is ubiquitin-dependent 14617636_platelet-activating factor receptor-mediated signaling has a critical role in differentiated endothelial cell functions, including cell migration and proteolytic activation of MMP2 15115767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15149885_investigated whether the increase of uPA monocyte expression and chemokine releases induced by oxidised low density lipoproteins involved proinflammatory phospholipid products having platelet-activating factor-like activity via the PAFR pathway 15160913_Analysis of 102 B-CLL patients revealed dramatic differences for their membrane PAF-R expression, a result that might be related to their plasma IL-4 levels. 15748960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15748960_the PAFR gene missense mutation has a relation to the susceptibility for multiple sclerosis . 16115894_UVB photo-oxidizes cellular phospholipids, creating PAF analogs that stimulate the PAF receptor to induce further PAF synthesis and apoptosis 16306050_PAF induced CREB and ATF-1 phosphorylation via a PAFR-mediated signal transduction mechanism that required pertussis toxin-insensitive Galphaq protein and adenylate cyclase activity and was antagonized by a cAMP-dependent PKA and p38 MAPK inhibitors. 16793019_presence of functional PAF-R in arterial spindle-shaped smooth muscle cells of synthetic phenotype may be important for their migration from the media into the intima and atherosclerotic plaques formation 16837045_The functional PAF-R are present in blast cells of patients with acute leukemia; a result that could be of physiologic importance regarding the important effect of PAF on leukocytes maturation and functions. 16984258_These studies suggest that SZ95 sebocytes express functional PAF-Rs and PAF-Rs are involved in regulating the expression of inflammatory mediators, including COX-2, PGE(2) and IL-8. 17928889_epidermal PAF-R can modulate UVB-mediated early gene expression 18187960_a lower expression of PAFR in HCC correlated with both poor differentiation and portal venous invasion. 18632638_analysis of PAFR activation and pleiotropic effects on tyrosine phospho-EGFR/Src/FAK/paxillin in ovarian cancer 19474802_cis-urocanic acid stimulates mediator production by a pathway that is independent of these serotonin 2A and PAF receptors in human keratinocytes 19620302_PAFR is localized in lipid rafts and/or caveolae, a position that is important for proper coupling to downstream signaling elements. 19703903_analysis of the cross-talk between protease-activated receptor 1 and platelet-activating factor receptor regulates melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM/MUC18) expression and melanoma metastasis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20007715_conserved proline in TM6 is crucial for intracellular trafficking of PAFR. 20032301_Results reveal that some strains of Gram-positive bacteria exploit hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-regulated platelet-activating factor receptor as a means for translocation through intestinal epithelial cells. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20392487_role in activation of mast cells by PAF. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20637897_The expression of PAF receptor (PAF-R) in early endothelial progenitor cell and the release of PAF under stimulation with factors involved in endothelial dysfunction, were investigated. 21063106_Platelet-activating factor plays a pivotal role in the oxLDL-induced recruitment of hBMSCs through mechanisms involving platelet-activating factor receptor dependent activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases. 21247619_Urban particulate matter (PM) increases adhesion of S. pneumoniae to human airway epithelial cells. PM-stimulated adhesion is mediated by oxidative stress and PAFR. 21615674_Pneumococcal ligands keratin 10, laminin receptor and platelet-activating factor receptor are elevated in aged lungs and contribute to the enhanced susceptibility to pneumonia. 21658861_An implication of platelet-activating factor receptor A224D mutation in the susceptibility to relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis in Tunisian population. 22570511_PAFR may have a role in tumor response mechanisms, such as stress responses caused by chemotherapeutic agents 22577252_recognition of apoptotic cells by phagocytes leads to activation of PAFR pathways, resulting in a microenvironment response favorable to melanoma growth 22595142_Eosinophils use their platelet-activating factor receptors (PAFRs) to interact directly with Staphylococcus aureus. 23070058_Data suggest that expression of PAFR and SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) is down-regulated in endothelial progenitor cells of type 2 diabetic patients with poor glycaemic control compared to those with good glycaemic control. 23911710_Inhibition of platelet aggregation by lipoteichoic acid was blocked using a monoclonal anti-PafR antibody and Ginkgolide B,a well-defined PafR antagonist, demonstrating that the LTA inhibitory signal occurs via PafR. 24062612_oxLDL induces alternative macrophage activation by mechanisms involving CD36 and PAFR 24130805_oxLDL induces the recruitment of PAFR and CD36 into the same lipid rafts, which is important for oxLDL uptake and IL-10 production 24289152_Data suggest PAF/PAF receptor signaling exerts proinflammatory effect on neutrophil via down-regulation of LXRa (liver X receptor alpha) and target genes (ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1, ABC G1, sterol response element binding protein 1c). 24824933_patients presenting elevated PAFR expression had significantly longer survival times compared to those with low PAFR expression (log-rank test, p |
ENSMUSG00000056529 |
Ptafr |
16.635173 |
5.4337041666 |
2.441936 |
0.435402913 |
35.111077 |
0.00000000311424230118773840546614874939378853069271713138732593506574630737304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014235433993660892234523417630709385406362343928776681423187255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.0195921 |
7.4031064 |
5.1925393 |
1.2226481 |
| ENSG00000169413 |
6039 |
RNASE6 |
protein_coding |
Q93091 |
FUNCTION: Ribonuclease which shows a preference for the pyrimidines uridine and cytosine (PubMed:8836175, PubMed:27013146). Has potent antibacterial activity against a range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, including P.aeruginosa, A.baumanii, M.luteus, S.aureus, E.faecalis, E.faecium, S.saprophyticus and E.coli (PubMed:25075772, PubMed:27089320). Causes loss of bacterial membrane integrity, and also promotes agglutination of Gram-negative bacteria (PubMed:27089320). Probably contributes to urinary tract sterility (PubMed:25075772). Bactericidal activity is independent of RNase activity (PubMed:27089320). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25075772, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27013146, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27089320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8836175}. |
3D-structure;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Disulfide bond;Endonuclease;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Nuclease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the ribonuclease A superfamily and functions in the urinary tract. The protein has broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:6039; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; ribonuclease activity [GO:0004540]; antibacterial humoral response [GO:0019731]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; defense response [GO:0006952]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090501] |
25075772_Ribonucleases 6 is an antimicrobial peptide with activity against uropathogens and participates in the maintenance of urinary tract sterility. 27089320_These results indicate that RNase6, as previously reported for RNase3, is able to specifically agglutinate Gram-negative bacteria as a main trait of its antimicrobial activity. 30287244_An RNase6 dual catalytic and extended binding site arrangement facilitates the cleavage of polymeric substrates 35896049_RNASE6 is a novel modifier of APOE-epsilon4 effects on cognition. |
ENSMUSG00000021880 |
Rnase6 |
18.357170 |
4.2656953467 |
2.092781 |
0.394403554 |
30.192260 |
0.00000003912677650420988622156681690025803455057484825374558568000793457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000160553578315857104432973776267368215542319376254454255104064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.1823041 |
7.3847896 |
6.8849167 |
1.4844638 |
| ENSG00000169418 |
4881 |
NPR1 |
protein_coding |
P16066 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the atrial natriuretic peptide NPPA/ANP and the brain natriuretic peptide NPPB/BNP which are potent vasoactive hormones playing a key role in cardiovascular homeostasis. Has guanylate cyclase activity upon binding of the ligand. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1672777}. |
cGMP biosynthesis;Chloride;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GTP-binding;Lyase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Vasoactive |
|
Guanylyl cyclases, catalyzing the production of cGMP from GTP, are classified as soluble and membrane forms (Garbers and Lowe, 1994 [PubMed 7982997]). The membrane guanylyl cyclases, often termed guanylyl cyclases A through F, form a family of cell-surface receptors with a similar topographic structure: an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a single membrane-spanning domain, and an intracellular region that contains a protein kinase-like domain and a cyclase catalytic domain. GC-A and GC-B function as receptors for natriuretic peptides; they are also referred to as atrial natriuretic peptide receptor A (NPR1) and type B (NPR2; MIM 108961). Also see NPR3 (MIM 108962), which encodes a protein with only the ligand-binding transmembrane and 37-amino acid cytoplasmic domains. NPR1 is a membrane-bound guanylate cyclase that serves as the receptor for both atrial and brain natriuretic peptides (ANP (MIM 108780) and BNP (MIM 600295), respectively).[supplied by OMIM, May 2009]. |
hsa:4881; |
ANPR-A receptor complex [GO:1990620]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; guanylate cyclase activity [GO:0004383]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; natriuretic peptide receptor activity [GO:0016941]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; peptide receptor activity [GO:0001653]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; blood vessel diameter maintenance [GO:0097746]; body fluid secretion [GO:0007589]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cGMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006182]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; dopamine metabolic process [GO:0042417]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048662]; positive regulation of cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0010753]; positive regulation of renal sodium excretion [GO:0035815]; positive regulation of urine volume [GO:0035810]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; receptor guanylyl cyclase signaling pathway [GO:0007168]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043114]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11704663_kinetics of internalization, trafficking, and down-regulation of recombinant guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-A (NPRA) 11851379_unlikely that NPR1 is the same as the MCKD1 gene, mutations in which cause the adult form of medullary cystic kidney disease type 1; however, it is presently unknown whether it plays a disease modifying role 12135318_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12483301_This gene codes for natriuretic peptide receptor A, which mediates natriuretic, diuretic, and vasorelaxing actions of the natriuretic peptides. 12506509_The 'deletion 15129' variant might participate in the functional impairment of natriuretic peptide system defining and increased genetic susceptibility to hypertension. 12547834_activation stabilizes a membrane-distal dimer interface 12794112_Human dendritic cells, but not monocytes, express functional ANP receptor GC-A at both mRNA and protein levels. 12855709_NPRA-PKG association may have a role in compartmentation of cGMP-mediated signaling and regulation of receptor sensitivity 12872042_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12872042_The novel Npr1 gene 3C variant and the Npr3 gene C(-55) allele are associated with hypertensive family history 14646971_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14646971_the M341I missense mutation is associated with risk of myocardial infarct (MI) and may be a genetic marker of MI 15459247_NPR-A and NPR-B are desensitized in cells in which they are not internalized. 15911067_discussion of experimental insights into the mechanisms that cells utilize in modulating the delivery and metabolic processing of ligand-bound NPRA into the cell interior [review] 15911069_discussion of the functional significance of the promoter region of Npr1 gene and its transcriptional regulation [review] 15911610_ATP does not activate NPRA and NPRB as has been repeatedly reported. Instead, ATP increases activity primarily by maintaining proper receptor phosphorylation status but also serves a previously unappreciated enzyme stabilizing function. 16262696_interaction of atrial natriuretic peptide with natriuretic peptide receptor-A modulates the binding of ATP to the kinase homology domain 16778132_NPR-A protein localized to cardiomyocytes, endocardial endothelial cells, and smooth muscle of intramyocardial vessels; downregulation in the density of NPR-A in heart and coronary was observed in artery of patients with ischemic heart disease 16875975_ANP/NPRA system significantly contributes to ventricular remodeling in human essential hypertension. 16875975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16986166_Data suggest that natriuretic peptide receptor A (NPR-A) interacts with fibronectin to enhance brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) activation of cyclic GMP and that a small NPR-A-specific RGD peptide augments this action of BNP. 17460430_Nppa and Npr1 gene polymorphisms are not associated with normal-tension glaucoma, suggesting that this gene does not have an important role in the pathogenesis of optic neuropathy in this disease. 17460430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17672826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18306933_In patients with Dukes stage C/D colorectal cancer, the Cox Proportional Hazard Model analysis demonstrated a significant association between increased patient survival and low expression of ITGB2 (p = 0.011) and NPR1 (p = 0.023) genes. 18360023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18383440_Real-time PCR revealed that large adipocytes expressed higher mRNA levels of NPRA, and binding studies showed that large adipocytes expressed more NPR-A on the membrane than small adipocytes. 18436476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18436476_The '4-minus' haplotype of the NPR-A receptor gene is associated with high NT-proBNP values and is a genetic determinant of the interindividual variability in the BNP system in healthy individuals but probably not in patients with cardiovascular disease. 18713751_alternative splicing can regulate endogenous ANP/GC-A signaling 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126660_In the present study conducted in a homogeneous Hellenic population, no associations between Angiotensinogen,angiotensin-converting enzyme, and NPRA gene polymorphisms and hypertension were found. 19126660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19165164_Adipose tissue blood flow responsiveness to nutrient intake is related to the transcription of two genes expressed in adipose tissue and directly involved in vasodilatory actions (eNOS and NPRA). 19326473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19458086_Data indicate that the familial ANP mutation associated with atrial fibrillation has only minor effects on natriuretic peptide receptor interactions but markedly modifies peptide proteolysis. 19563399_These results indicate that the ANP/GC-A system is involved in immune regulation through plasmacytoid dendritic cells in secondary lymphoid organs. 19679847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20024606_Results show that NOGCbeta1 and GC-A interact and that NOGCbeta1 regulates atrial natriuretic peptide signaling in HK-2 cells. 20034689_Midregional pro-A-type natriuretic peptide has a comparable accuracy to brain natriuretic peptide BNP for evaluation of cardiocirculatory exercise limitation. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20529973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20529973_The SS genotype of the AGT gene was related with an increased risk for 3-vessel CAD 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20700369_The data indicates that ANP, BNP, and CNP and natriuretic peptide receptor transcripts are expressed and are functional in human lens epithelial cells. 20977274_we identified and characterized new phosphorylation sites in GC-A and GC-B and provide the first evidence of phosphorylation sites within human guanylyl cyclases. 21366551_Cellular exposure to Go6976 reduced basal and natriuretic peptide-dependent, but not detergent-dependent, GC-A and GC-B activity. 21375691_review attempts to provide insights and to delineate the current concepts in the field of functional genomics and signaling of GC-A/NPRA in hypertension and cardiovascular disease states at the molecular level 21586128_NPRA promotes prostate cancer development in part by regulating macrophage migration inhibitory factor 21828054_Go6976 reduces GTP binding to the catalytic site of GC-A and GC-B and that ATP increases the magnitude of the inhibition. 22001395_Results demonstrate the opposite effects of NPR-A and NPR-C in LPS-mediated endothelial permeability and lung injury. 22133375_human ventricular cardiomyocytes express low levels of GC-A and GC-A in cardiomyocytes from failing human hearts is refractory to ANP stimulation. 22949736_Guanylyl cyclases A and B are asymmetric dimers that are allosterically activated by ATP binding to the catalytic domain. 23186809_ACNP stimulated both human natriuretic peptide receptors (NPRs), NPRA and NPRB, as potent as their native ligands in receptor transfected cells. 24699414_Molecular dynamics analysis indicated decreases in the values of Van der Waals, electrostatic energy and potential energy of NPRB/Vasonatrin peptide compared to NPRA/Vasonatrin peptide. 24885858_High NPR1 expression is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 25117468_Cardiac fibrosis and the endogenous natriuretic peptide system were evaluated in end-stage heart failure to assess the anti-fibrotic actions of the dual GC-A/-B activator. 25631869_NPRA was detected in E11.5 cardiac progenitor cells. 25955817_In this review we highlight the mechanisms by which NPR-A affects signaling pathways involved in inflammation and cancer, and we discuss its potential as a novel target in inflammation, cancer, and cancer-related inflammation 26253614_Data suggest up-regulation of NPRA in skeletal muscle (SM) correlates with whole-body insulin sensitivity; NPRA is down-regulated in SM in obese subjects compared to normal controls; NPRA in SM is up-regulated in response to diet-induced weight loss. 26374856_After ligand binding, NPRA is rapidly internalized and trafficked from the cell surface into endosomes, Res and lysosomes, with concurrent generation of intracellular cyclic GMP in HEK-293 cells. 27634171_The results indicate that the inhibition of NPRA suppresses gastric cancer development and targeting NPRA may represent a promising strategy for the treatment of gastric cancer. 28432261_Data suggest that signaling via ANP/ANPR (atrial natriuretic factor/ANP receptor) in vascular endothelial cells activates PAK4 (p21-activated kinase 4) and CCM2 (cerebral cavernous malformation 2 protein), resulting in phosphorylation of MLC (myosin light chain), cytoskeletal reorganization, and cell spreading; kinase homology domain of ANPRA (guanylyl cyclase-A) activates downstream targets of ANP/ANPR signaling. 28765884_These results of the distinct presence of NPRA and NPRBpositive cells in unstable plaques underlying acute myocardial infarction suggested that natriuretic peptides serve a role in regulating plaque instability in humans. 29409758_It was the aim to investigate the expression of natriuretic peptide receptors NPR-A, NPR-B and NPR-C during adipocyte differentiation (AD), upon stimulation with fatty acids (FA), and in murine and human adipose tissue depots. 30169131_The role of NPR1 signaling in the diabetic complications.[review] 30696704_Data show that all the residues of the ATP-binding site of the are conserved in the phosphorylated pseudokinase domain (PKD) of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor type A (GC-A) and atrial natriuretic factor receptor B (GC-B). 31430210_The minor alleles of rs35479618 (p.E967K, gnomAD non-Finnish European allele frequency 0.017) and rs116245325 (p.L1034F, allele frequency 0.0007) of NRP1 were associated with higher blood pressure. [Meta analysis] 33375031_ANP and BNP Exert Anti-Inflammatory Action via NPR-1/cGMP Axis by Interfering with Canonical, Non-Canonical, and Alternative Routes of Inflammasome Activation in Human THP1 Cells. 34671022_Natriuretic peptide receptor a promotes gastric malignancy through angiogenesis process. 34930837_Discovery of small molecule guanylyl cyclase A receptor positive allosteric modulators. |
ENSMUSG00000027931 |
Npr1 |
7.884296 |
0.1416186254 |
-2.819917 |
0.890986799 |
9.756286 |
0.00178710566441015361767441493867636381764896214008331298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003987792364878200122857432319278814247809350490570068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.9718868 |
1.2028688 |
13.9022300 |
5.0264347 |
| ENSG00000169429 |
3576 |
CXCL8 |
protein_coding |
P10145 |
FUNCTION: Chemotactic factor that mediates inflammatory response by attracting neutrophils, basophils, and T-cells to clear pathogens and protect the host from infection (PubMed:7636208, PubMed:18692776). Also plays an important role in neutrophil activation (PubMed:9623510, PubMed:2145175). Released in response to an inflammatory stimulus, exerts its effect by binding to the G-protein-coupled receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, primarily found in neutrophils, monocytes and endothelial cells (PubMed:1840701, PubMed:1891716). G-protein heterotrimer (alpha, beta, gamma subunits) constitutively binds to CXCR1/CXCR2 receptor and activation by IL8 leads to beta and gamma subunits release from Galpha (GNAI2 in neutrophils) and activation of several downstream signaling pathways including PI3K and MAPK pathways (PubMed:8662698, PubMed:11971003). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11971003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11978786, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1840701, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18692776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1891716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2145175, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2212672, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7636208, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8662698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9623510}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Citrullination;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the CXC chemokine family and is a major mediator of the inflammatory response. The encoded protein is commonly referred to as interleukin-8 (IL-8). IL-8 is secreted by mononuclear macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, T lymphocytes, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts. It functions as a chemotactic factor by guiding the neutrophils to the site of infection. Bacterial and viral products rapidly induce IL-8 expression. IL-8 also participates with other cytokines in the proinflammatory signaling cascade and plays a role in systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). This gene is believed to play a role in the pathogenesis of the lower respiratory tract infection bronchiolitis, a common respiratory tract disease caused by the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The overproduction of this proinflammatory protein is thought to cause the lung inflammation associated with csytic fibrosis. This proinflammatory protein is also suspected of playing a role in coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction. This protein is also secreted by tumor cells and promotes tumor migration, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis. This chemokine is also a potent angiogenic factor. The binding of IL-8 to one of its receptors (IL-8RB/CXCR2) increases the permeability of blood vessels and increasing levels of IL-8 are positively correlated with increased severity of multiple disease outcomes (eg, sepsis). This gene and other members of the CXC chemokine gene family form a gene cluster in a region of chromosome 4q. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. |
hsa:3576; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; CXCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0045236]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; interleukin-8 receptor binding [GO:0005153]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide [GO:0061844]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; embryonic digestive tract development [GO:0048566]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; killing of cells of another organism [GO:0031640]; negative regulation of cell adhesion molecule production [GO:0060354]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; neutrophil activation [GO:0042119]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process [GO:0031328]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of entry of bacterium into host cell [GO:2000535]; regulation of single stranded viral RNA replication via double stranded DNA intermediate [GO:0045091]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; response to molecule of bacterial origin [GO:0002237]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11756416_This lithium-induced up-regulation of NF-kappa B and MAP kinase activation was associated with an enhancement of interleukin-8 mRNA accumulation as well as an increase in interleukin-8 protein release. 11784713_Vascular endothelial growth factor modulates neutrophil transendothelial migration via up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human brain microvascular endothelial cells 11814358_Conformational changes of dimeric IL-8 induced by heparan sulfate, but not by heparin, refer to an 'activation' of the chemokine which is hypothesized to be important for the migration of neutrophils to inflammatory sites. 11854210_IFN-gamma primed CD14(high) human gingival fibroblasts to enhance production of IL-8 in response to LPS through augmentation of the CD14-TLR system 11855786_Increased plasma levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 are observed in beta-thalassaemia major patients and may be relevant in the pathophysiology of beta-thalassaemia 11868823_Human bronchial epithelium releases neutrophil chemotactic factor. 11876744_Lidocaine inhibits secretion of IL-8 and IL-1beta and stimulates secretion of IL-1 receptor antagonist by epithelial cells. Lidocaine inhibits the expression of il-8 mRNA. 11884401_secretion induced by combined effects of protein kinase C and ERK activation with TFF-papetide and TNF-alpha 11884459_TNF-alpha induction of IL-8 in vascular endothelium is down-regulated in vitro via an eotaxin/CCL11-induced acceleration of IL-8 mRNA decay. 11888846_Cushing's syndrome patients have markedly elevated levels of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-8 11896938_The effect of LPS on neutrophils from patients with high risk of type 1 diabetes mellitus in relation to IL-8, IL-10 and IL-12 production and apoptosis in vitro. 11910304_mechanical strain increased interleukin-8 protein expression 11911801_Mycobacterium bovis-mediated upregulation of IL-8 biosynthesis and release by human monocytes involves intracellular protein kinase signaling pathways and transcription factor NF-kappa B. 11950481_process of cervical dilatation during parturition at term is associated with an increased expression of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 mRNA in the lower uterine segment 11956621_Expression of IL8 in primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. 11960393_Secretion levels of sIL-2R, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-alpha, but not IL-4 and IL-12, are elevated in activated T-cells in large granular lymphocytic leukemia associated with autoimmune disorders. 11964077_IL-8 is down regulated in ovarian carcinoma and in serous effusions 11966578_determine the cellular contents and concentrations of interleukin 6 (IL-6), interleukin 8 (IL-8) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in fluids of patients with spermatocele or epididymal cyst 11973337_TF-FVIIa signaling induced increased transcription as well as mRNA stabilization leading to the significant up-regulation of IL-8 protein synthesis 11989790_Inflammatory cytokines mediate C-C (monocyte chemotactic protein 1) and C-X-C (interleukin 8) chemokine expression in human pleural fibroblasts. 11999552_REVIEW: Role of IL8 in leukocytosis and stem cell mobilization. 12027404_IL8 is overexpressed in paclitaxel-resistant human osteosarcoma cells 12033786_Huh7 cells expressing the hepatitis C viral protein NS5A showed an up-regulation of interleukin-8 12034575_expression in airway epithelial cells by interleukin-17 12039947_regulation of secretion in bronchial epithelial cells by phospholipase D activation by sphingosine 1-phosphate 12055326_Weight loss in obese subjects was associated with opposite changes in the secretion and transcription of IL-8 and TNF-alpha in the adipose tissue, as well as in plasma 12056817_IL-8 production by RET tyrosine kinase is regulated by multiple signaling pathways 12060853_Endogenous expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells 12067976_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12081586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12090473_TNFalpha and IL-8 regulate the expression and function of CD44 variant proteins in human colon carcinoma cells. 12091490_Native LDL potentiate TNF alpha and IL-8 production by human mononuclear cells. 12093676_Mycobacterium bovis-mediated upregulation of IL8 in human monocyes is down-regulated by IL10. 12096924_Glutamine decreases production of this and il6 but not nitric oxide and prostaglandins e(2) production by human gut in-vitro. 12096927_Endotoxin-stimulated production is increased in short-term cultures of whole blood from healthy term neonates. 12100025_Anti-CD45 isoform antibodies enhance phagocytosis and gene expression of IL-8 and TNF-alpha in human neutrophils by differential suppression on protein tyrosine phosphorylation and p56lck tyrosine kinase. 12101072_plays a role in the pathogenesis of the otitis media with effusion (review) 12115500_new autocrine function of secreted interleukin-8 and the intracellular signal transduction leading to the regulation of cytosolic calcium and to a migratory tumor cell phenotype 12117737_Simvastatin reduces expression of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-8 in circulating monocytes from hypercholesterolemic patients. 12117926_Leishmania promastigotes release a granulocyte chemotactic factor and induce interleukin-8 release by neutrophil granulocytes 12117969_Induction of IL-8 in THP-1 macrophages and human microvascular endothelial cells during Bartonella henselae infection 12117995_interleukin-8 secretion from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected monocytes is regulated by protein tyrosine kinases 12123753_Induction of interleukin 8 release from the HMC-1 mast cell line: synergy between stem cell factor and activators of the adenosine A(2b) receptor. 12126643_IL-8 gene transcription is induced by p38 MAP kinase via AP-1 in hVMSCs 12133438_The expression of IL-1beta mRNA and IL-8 mRNA was increased significantly in patients with ulcerative colitis UC 12139952_in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis, the proportion of RANTES relative to IL-8 was significantly increases 12149127_stimulation of secretion by sphingosine 1-phosphate 12150710_Mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB regulate Helicobacter pylori-mediated interleukin-8 release from macrophages. 12151316_Results describe a novel action of proteasome inhibitors, possibly through reactive oxygen species production, of targeting the upstream signaling molecules Ras, ERK and JNK, which leads to AP-1 activation and interleukin-8 gene expression. 12151344_expression in colon carcinoma cells exposed to pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate 12163591_human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 repress IL-8 transcription through effects on CREB binding protein/p300 and P/CAF 12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12165085_Normal and SV40 transfected human peritoneal mesothelial cells produce IL-6 and IL-8: implication for gynaecological disease. 12169092_These results demonstrate that Rho family small GTPases RhoA, Rac1 and Cdc42 are novel signal transducers for SP-stimulated IL-8 expression. 12169272_Lymphotoxin beta receptor induces interleukin 8 gene expression via NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation.(AP-1) 12186702_enhances the migration of bone marrow stromal cells 12186913_released from lung epithelial cells rendered necrotic by influenza A virus infection 12187073_The endogenous levels of TPO, IL-6 and IL-8 are elevated in the thrombocytopenic patients with AML and MDS. 12195386_treatment of neutrophils with pneumolysin either alone or in combination with the chemotactic tripeptide, N-formyl-l-methionyl-l-leucyl-l-phenylalanine resulted in a time-dependent increase in synthesis and release of IL-8 12223528_Platelet factor 4 induces human natural killer cells to synthesize and release interleukin-8. 12225945_Regulation of human airway epithelial cell IL-8 expression by MAP kinases. 12239630_human IL8 expression mediates elements of the systemic inflammatory response in pancreatic tumor cell lines 12359770_Elevated expression of IL-8 (and not PTHrP) by MDA-MET cells is a phenotypic change that may be related to their enhanced ability to metastasize to the skeleton. 12364441_plasma IL-8 levels are increased in obese subjects, and are related to fat mass and TNF-alpha system 12366401_Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H infection of human intestinal epithelial cells activates the MAP kinase signaling system and NF-kappa b, leading to secretion of interleukin-8. 12382118_Pressure-induced IL-8 production was inhibited by PKC activity. 12384994_IL-8 increases gap junctional intercellular communication in cultured fibroblasts and induces a more rapid maturation of granulation tissue. 12388718_mediates angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma 12391099_Circulating ICAM-1, IL-8, and MCP-1 in untreated obstructive sleep apnea were significantly greater than in controls. nCPAP therapy could reduce OSAS-induced hypoxia and generation of inflammatory mediators. 12393171_We used specific pharmacologic inhibitors to identify the signalling molecules which lead to interleukin (IL)-8 and MCP-1 production in human monocytes in response to M. tuberculosis infection 12410798_some heat-stable component of P. gingivalis, including LPS, may be responsible for the induction of IL-8 and MCP-1 in HUVECs by a CD14-dependent mechanism 12415593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12453441_Interleukin-8-has a role in proliferation, survival, and MMP production in CXCR1 and CXCR2 expressing HUVECs 12480084_expressed in CSF of children with bacterial or viral meningitis 12485855_Activation of the p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 pathways is required for Fas-induced production in colonic epithelial cells 12496258_mediation of angiogenic effects by CXCR2 12513912_Elevated serusm levels of this protein in advanced non-small cell lung cancer are related to prognosis. 12520365_results revealed that Porphyromonas gingivalis induces the expression of IL-8 and MCP-1 mRNAs in vascular endothelial cells, but bacterial proteases degrade both chemokines 12524080_interleukin 8 induced by IL-1beta via activation of NF-kappaB in granulosa cells may have a role in the periovulatory period of follicular maturation 12529421_the relationship between interleukin (IL)-8, IL-1beta and neutrophils in vaginal fluid obtained from 60 healthy women and 51 women who were bacterial vaginosis positive 12530093_IL-8 is over-expressed in cutaneous melanoma; no direct correlation was found between IL-8 expression and survival; it would appear that IL-8 plays a major role in melanoma development. 12533683_role in inducing CXC chemokine GCP-2/CXCL6 in mesenchymal cells 12543081_Follicular growth & increased capillary vessel densities were seen in rats after hIL-8 injection. IL-8 can participate in follicular development. It may play important roles in ovulation & luteinization among mediators induced by endogenous LH. 12547728_spontaneous release of IL-8 and IL-1ra by airway neutrophils was significantly higher than that from blood neutrophils in cystic fibrosis 12548717_Elevated levels of IL-8 are found in brains of patients with HIV-1 encephalitis; inhibition of long-term potentiation in IL-8-perfused rat hippocampus suggests that it plays a role in cognitive dysfunction associated with HIV-1-associated dementia. 12565901_Data show that hydrogen peroxide induced a time-dependent increase in histone acetylation that was maintained for 12 hours, and was associated with increased IL-8 production. 12573991_Acetylation of H4 mediated by air pollutant particles was associated with the promoter region of the IL-8 gene 12576442_Upregulation of this cytokine by infiltrating macrophages correlates with tumor angiogenesis and patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer. 12584113_Data show that inhibition of endogenous RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 by their respective dominant negative mutants inhibits neurotensin-induced interleukin-8 protein production and promoter activity. 12594001_CSMCs respond to LPS with increased expression of IL-8 mRNA and secreted IL-8, and that expression of matrix metabolizing enzymes in CSMCs is not directly affected by IL-8. IL-8 produced by CSMCs in response to gram-negative infection 12594058_3-aminobenzamide inhibited gene expression of interleukin-8 induced by hydrogen peroxide. 12615831_Concentrations of IL-8 were significantly higher in patients than in controls in luteal phase. Red lesions were associated with significantly increased levels of peritoneal fluid IL-8 only in luteal phase. 12626597_The mechanism of IL-8 regulation of angiogenesis may be in part due to enhanced proliferation and survival of endothelial cells by differential expression of anti-apoptosis genes and in part by activation of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9. 12628493_Neutrophil recruitment to inflammatory sites is mediated by two related receptors: CXCR1 and CXCR2. Both receptors share two ligands, interleukin-8 (CXCL8) and GCP-2 (CXCL6). 12632066_IL-8 regulates MMP-2 activity and plays an important role in the invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer 12633940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12634636_Expression of interleukin-8 in human fallopian tube epithelial and stromal cells differs. Expression in response to inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha varies. May be important in pathogenesis of salpingitis. 12637525_stretch of airway smooth muscle causes production of interleukin-8 by activating CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein and activator protein-1 transcription factor through activation of extracellular regulated kinase-1 and 2 and p38 kinase signaling pathways 12646250_Data show that ergothioneine abolished the transcriptional activation of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in human alveolar epithelial cells. 12653788_There is a significan correlation of IL-8 to age, total fructose, immunoglobulin G (IgG) concentration and leucocyte count. 12654635_binds to heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate in lung tissue 12654834_FliC of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is sufficient to induce IL-8 release in T84 cells and that activation of the Erk and p38 pathways is required for IL-8 induction 12660426_mast cells may play an active role in the angiogenesis of basal cell carcinoma through the production of IL-8 12662377_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12662377_individuals with interleukin-8-251TT and interleukin-10-819TT, a combination presumably causing mild inflammation, have a higher probability of the continuing Helicobacter pylori infection, especially among current smokers. 12702497_results indicate that epithelial TLR5 mediates p38 activation and subsequently regulates flagellin-induced IL-8 expression independently of NF-kappaB, probably by influencing IL-8 mRNA translation 12707271_Pretreatment of monocytic cells with low TNF doses inhibited TNF-induced (restimulation with a high dose) IL-8 promoter-dependent transcription as well as IL-8 production, which was prevented by overexpression of C/EBPbeta, but not p65 or Oct-1. 12720537_IL-8 increased by 30% after weight loss. IL-8 and IL-6 correlated with measures of insulin resistance, and changes in IL-6 but not IL-8 were correlated with improvement in insulin sensitivity after weight loss. 12727029_Candida albicans induce expression of il-8 in cultured epidermal keratinocyttes. 12729795_These observations indicate that von Willebrand factor plays an active role in sequestering interleukin-8 into Weibel-Palade bodies. 12738388_enhanced expression in Helicobacter pylori infection of gastric mucosa; significant association with bacteria load, chronic inflammation and activity 12744776_The role of IL8 in cultured nasal epithelial cells was studied for its ability to synthesize and deliver neutrophil chemotactic factors following TNF-alpha induction. 12748056_Abrogation of MRP-14 activity with a specific antibody reduced the IL-8-stimulating potential of bronchial secretions, suggesting it was a stimulus to IL-8 production in the lung and may amplify neutrophilic inflammation in bronchial disease 12748173_IL-8 regulation by bradykinin involves prostanoid-dependent activation of AP-1 and NF-LI-6 and prostanoid-independent activation of NF-kappaB 12777373_IL8 transcription is induced when oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine binds to a 37-kDa GPI-anchored protein, which interacts with TLR4 12782302_IL-8 is upregulated by neutrophil elastase via toll-like receptor 4 12792476_Stimulation of conjunctival epithelium with TNF-alpha and/or IFN-gamma generated release of the chemotactic factors IL-8 and RANTES, which could act to prolong inflammation. May prolong inflammation by recruiting eosinophils to the ocular surface. 12797546_results indicate that RBC, when interacting with extracellular matrix, may participate in the recruitment of inflammatory cells by stimulating fibroblasts to secrete IL-8. 12802400_Data report the location and level of interleukin (IL)-8 and TGF-beta2 expression in the fimbrial compartment of fallopian tubes and IL-10 expression in the endometrium of women with pyoinflammatory adnexal diseases. 12818188_These results show that cathepsin L is secreted from human fibroblasts in response to external stimuli and plays an important role in IL-8 processing in inflammatory sites. 12820969_IL8 selectively recruited a single NF-kB subunit. 12839933_Bombesin stimulates nuclear factor kappa B activation and expression of this angiogenic factor in prostate cancer cells. 12839942_Common polymorphisms in this protein are associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer. 12839942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12849706_The lack of glutamine increases IL-8 production by Caco-2 cells after LPS stimulation 12850808_Higher cytosol IL8 levels were found in the walls of ruptured aneurysms than in the asmptomatic aneurysms. 12855659_IL-8 is regulated by NF-kappaB and has a role in mediating angiogenesis and metastasis of human bladder cancer 12857601_Serum amyloid A appears to be important mediator of inflammatory process, possibly contributing to pool of IL-8 produced in chronic diseases, which may play a role in degenerative diseases. 12870115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12871882_serum and cyst fluid levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were evaluated in women with endometriomas and compared with those in women with benign or malignant ovarian tumours. 12876073_adipose tissue mRNA of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 was increased in HIV-associated lipodystrophy syndrome subjects 12898436_Relationship of polymorphism at this locus to susceptibility to E. coli-associated diarrhea. 12898448_effects of interleukin (IL)-15 on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMNL) activity against Aspergillus and IL-8 release were investigated 12901801_Significant relationship between IL-8 levels in drainage veins and both gastric tumor size and lymph node metastasis. 12902511_Increased shedding of IL-8 bound to a trimolecular complex with heparan sulfate and syndecan-1 in cultured vascular endothelium is associated with plasmin activity and inhibition of neutrophil transendothelial migration. 12909591_Although an intact promoter NF-kappa B site is crucial to macrophage IL-8 production, only LPS-stimulated production appears to require additional nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B. 12919697_IL-8 is implicated as a potent activator of the bone destruction common in metastatic bone disease. 12933891_Differential interleukin-8 and nitric oxide production in epithelial cells induced by mucosally invasive and noninvasive Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes. 12952969_IL8 is overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects 12960242_Induces human neutrophils to produce IL-8 (more in smokers) through the generation of peroxynitrite and subsequent activation of NF-kappaB. 13129857_Data suggest that the elevated circulating levels of IL-8 in obese subjects is due to the release of IL-8 from nonfat cells in adipose tissue. 14500465_differential IL-8 expression in macrophages infected with M. tuberculosis and M. marinum may be critically associated with distinct host responses in tuberculosis 14500470_Up-regulation of interleukin-8 by novel small cytoplasmic molecules of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae via p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. 14500479_saliva CD14 promoted the invasion of oral epithelial cells by A. actinomycetemcomitans and consequently augmented the production of IL-8, playing an important role in innate immunity in the oral cavity 14530367_Recombinant IL-8 induces articular chondrocyte hypertrophy and calcification through p38 MAP kinase and transglutaminase 2. 14550286_PAI-1 and IL-8 secretion are increased by glucose 14578856_Increase in IL-8 is independent of nuclear factor kappaB activation and is associated with an increase in c-Jun N-terminal kinase and activator protein-1 activity. 14604894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14623984_an aberrant DNA methylation pattern may be responsible for the differences in IL-8 release between high and low metastatic breast carcinoma cell lines 14625302_IL-8 is regulated by MEF (ELF4) in human cells 14630611_Data show that tumor necrosis factor-alpha priming significantly enhanced interleukin (IL)-8 secretion in response to concentrated ambient particles and other urban air particles in HTB54 cells. 14634582_Some levels, such as interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, may fluctuate during normal pregnancy. These spontaneous variations during pregnancy must be taken into account when mucosal immunologic responses to lower genital tract infection are being studied. 14634584_Microvessel endothelium of fetal placental vasculature produces both interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 in umbilical placental vascular disease. May play key role in interaction of endothelial cells of placenta villi with neighboring cells. 14641180_data identified Rac1 as a key intermediate in Yersinia enterocolitica invasin-triggered IL-8 synthesis and demonstrated that maximum IL-8 induction involves several MAP kinase cascades 14645117_both NF-kappa B and C/EBP beta transcription factors were cross-linked to the il-8 promoter after IL-1 treatment 14657869_Cockroach proteases and PAR-2 activation synergistically increase TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 transcription via activation of ERK in bronchial epithelial cells 14669337_The relative IL-8 mRNA expression levels were significantly higher in esophageal mucosa of esophageal reflux patients than in normal controls. 14672330_significant negative correlation between the concentrations of IL-8 and oxygen in ovarian follicular fluid 14675394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14676125_elevated serum interleukin-8 is associated with venous invasion, and advanced pathological tumor-node-metastasis stage of hepatocellular carcinoma 14688120_role of Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin protease (hap) in the induction of IL-8 in intestinal epithelial T84 cells 14714557_minor trauma to skin may induce expression of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and IL-8 14718619_significantly higher in supernatants from Hepatitis C virus-infected primary human macrophage cultures. 14725568_The expression of IL-8 and IL-18 mRNAs was down-regulated from the third or fourth gestational month (GM) until the eighth or ninth GM, respectively, and both increased before the onset of labor 14729508_Anti-IL-8:IL-8 complexes may be involved in the pathogenesis of lung inflammation in clinical acute lung injury. 14730209_Results indicate that neutrophil elastase activates p38 MAP kinase which upregulates NF-kappaB and AP-1 activities, thus inducing interleukin-8 mRNA expression and protein synthesis. 14756945_IL-8 may play an important role in the local gastric and duodenal mucosal inflammatory infiltration with a large number of neutrophils when there is Helicobacter pylori infection. 14767470_IL-8 confers androgen-independent growth and migration of prostatic cells. 14977935_Trichomonas vaginalis-induced neutrophil recruitment may be mediated via the IL-8 expressed by neutrophils in response to activation by live T. vaginalis. 15001458_IL-8 is a primary regulator of monocyte adhesion to EC in response to glucose. It accounts for almost 50% of glucose-mediated monocyte adhesion. The regulation of IL-8 production in EC by glucose does not appear to be through PPAR[alpha]. 15021975_Peripheral blood monocytes upregulated both tumor ENA-78 and IL-8 mRNA and protein. Alveolar macrophages only upregulated ENA-78 mRNA and protein. 15022458_Production of IL-8 in endothelial cells can be regulated by fluid shear stress. 15039334_Reactive oxygen species regulate immune signaling through TLR4 mediated NF-kappa B activation and Il-8 expression 15047831_IL-8 was generated upon exposure of lung organ culture to adenovirus 7 15057743_The mucosal inflammatory response to H. pylori infection is complex and involves different pathways converging on the IL-8 promoter. 15063730_Expression of IL-8 was markedly upregulated by nitric oxide. 15069060_in non-transformed human colonocytes, MEK activation following flagellin/TLR5 engagement is a key modulator for NFkappaB-independent, IL-8 and MIP3alpha expression. 15072962_mRNA abundance of IL-6 and IL-8 appears to be influenced by glycogen availability in the contracting muscle. 15077296_Collagen II-reactive T cells in rheumatoid arthritis joints can increase the production of chemokines such as IL-8, MCP-1, and MIP-1 alpha through interaction with synoviocytes. 15079071_CD28-stimulated T cells actively secrete IL-8, and Bcl-xL up-regulation protects T cells from radiation-induced apoptosis 15085176_haplotype-specific increase in transcription may cause susceptibility to Respiratory Syncytial Virus-induced bronchiolitis 15096327_Data show that oxidant-injured and stressed airway epithelial cells upregulate thioredoxin, but produce little IL-8, which may be important in airway epithelial cell-mediated multistep navigation of neutrophils to sites of oxidant injury. 15102084_Human airway trypsin-like protease might promote PAR-2-mediated IL-8 production to accumulate inflammatory cells in the epidermal layer of psoriasis. 15120188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120188_Promoter polymorphism of the IL-8 gene is associated with Parkinson's disease. 15143062_Ox-PAPC-mediated IL-8 expression in endothelial cells is regulated by the c-src kinase/STAT3 pathway 15146413_MIF may play an important role in the migration of inflammatory cells into the synovium of rheumatoid joints via induction of IL-8. 15152368_concetration in children with acute lymphoblbastic leukemia after chemotherapy 15158775_Both motility and adherence to intestinal epithelial cells (Int407)are possible triggering factors contributing to IL-8 mRNA expression by Vibrio cholera. 15169673_Nitric oxide induction of IL-8 gene expression could be a significant contributing factor in the initiation and induction of inflammatory response in the respiratory epithelium. 15178568_Among apparently healthy men and women, elevated levels of IL-8 are associated with an increased risk of future coronary artery disease. These prospective data support a role for IL-8 in the development of CAD events. 15178703_This is the first evidence of the involvement of ROS and calcium/calcineurin in IgE-dependent IL-8 production. 15181190_Data show that IL-8/CXCL8 is consistently transcribed and expressed in fetal intestinal tissue, in a developmentally regulated inverse relationship with gestational maturation. 15194816_data suggest that cyclic mechanical stretch of the uterine cervix by the presenting part of the fetus during labour may augment both IL-8 and MCP-3 production in the uterine cervix via AP-1 activation. 15196572_Candida albicans and Saccharomyes cerevisiae stimulated Caco-2 cells to produce IL-8 only in the presence of butyric acid, a metabolite produced by intestinal bacteria. S. cerevisiae zymosan and glucan also enhanced IL-8 secretion. Treatment of Caco 15203561_We believe that H. pylori-related cytokine activation becomes concentrated on gastric mucosa and this pathogen-induced local inflammatory cascade does not cause changes in circulatory levels of these cytokines. 15203565_Activation of NF-kappaB is an important signal transduction pathway in M. bovis-induced IL-8 secretion in monocytic or epithelial cells. Calcium influx had a direct effect on IL-8 secretion in U937 cells or HEp-2 cells infected with M. bovis. 15208657_IL-8 gene overexpression in breast cancer requires a complex cooperation between NF-kappaB, AP-1 and C/EBP transcription factors. 15208668_MAPK-AP-1 and ROS-NF-kappaB signaling pathways are involved in the IL-1beta-induced IL-8 expression and that these paracrine signaling pathways induce endothelial cell proliferation 15209388_IL-6 and IL-8 levels in all amniotic fluids and in all supernatants 15214047_downregulation in leukocytes in Crohn's disease 15218164_IL8 production by dengue virus infected monolayers contributes to the virus-induced effect on the cytoskeleton and tight junctions and thereby modifies transendothelial permeability. 15220553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15222686_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15222686_interleukin 8 interleukin 8 precursor emoctakin protein 3-10C LUCT/interleukin-8 CXC chemokine ligand 8 T cell 15265021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15271933_IL-8 production in response to serotype VIII Group B Streptococcus was significantly higher (P |
|
|
3544.075821 |
40.8622757171 |
5.352698 |
0.061959486 |
12335.963631 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6969.4276418 |
285.5130799 |
171.8396099 |
6.7465316 |
| ENSG00000169436 |
169044 |
COL22A1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFW1 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a cell adhesion ligand for skin epithelial cells and fibroblasts. |
Alternative splicing;Collagen;Cytoplasm;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes member of the collagen family which is thought to contribute to the stabilization of myotendinous junctions and strengthen skeletal muscle attachments during contractile activity. It belongs to the fibril-associated collagens with interrupted triple helix (FACIT) subset of the collagen superfamily, which associate with collagen fibers through their C-terminal collagenous domains and mediate protein-protein interactions through their N-terminal noncollagenous domains. The encoded protein is deposited in the basement membrane zone of the myotendinous junction which is present only at the tissue junctions of muscles, tendons, the heart, articular cartilage, and skin. A knockdown of the orthologous zebrafish gene induces a muscular dystrophy by disruption of the myotendinous junction. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:169044; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; endothelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0001886]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198] |
15016833_collagen XXII is the first specific extracellular matrix protein present only at tissue junctions 20222955_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20222955_association between serum creatinine level and polymorphisms in the collagen type XXII alpha 1 (COL22A1) gene, on chromosome 8, and in the synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) gene, on chromosome 12 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24428702_Collage XXII interacts with collagen-binding integrins via the protein motifs GLQGER and GFKGER. 30541770_COL22A1 is required to maintain vascular integrity. These data further suggest that mutations in COL22A1 could be one of the risk factors for intracranial aneurysms in humans. 30678304_COL22A1 mediates fibroblast to myofibroblast transition in systemic sclerosis. Silencing of COL22A1 significantly reduced TGFbeta-induced ACTA2 expression. 33166209_eQTL variants in COL22A1 are associated with muscle injury in athletes. |
|
|
25.876366 |
2.6267841476 |
1.393298 |
0.318325113 |
19.605230 |
0.00000952082420279685967870984819594326609148993156850337982177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000029867665299315974568230419583514390069467481225728988647460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.8810577 |
7.4728151 |
14.5254190 |
2.3109444 |
| ENSG00000169439 |
6383 |
SDC2 |
protein_coding |
P34741 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. Regulates dendritic arbor morphogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Differentiation;Glycoprotein;Heparan sulfate;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane (type I) heparan sulfate proteoglycan and is a member of the syndecan proteoglycan family. The syndecans mediate cell binding, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal organization and syndecan receptors are required for internalization of the HIV-1 tat protein. The syndecan-2 protein functions as an integral membrane protein and participates in cell proliferation, cell migration and cell-matrix interactions via its receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. Altered syndecan-2 expression has been detected in several different tumor types. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6383; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048813]; regulation of dendrite morphogenesis [GO:0048814] |
12036876_Identification of integrin alpha(M)beta(2) as an adhesion receptor on human peripheral blood monocytes for Cyr61 and connective tissue growth factor: immediate-early gene products expressed in atherosclerotic lesions.(integrin alpha(M)beta(2)) 12055189_role in mediating adhesion and proliferation of colon carcinoma cells 12708751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12860416_Ezrin N-terminal domain binds to the syndecan-2 cytoplasmic domain with an estimated K(D) of 0.71 microM and without the requirement of other proteins 12860968_Mechanisms for the regulation of HSPG have been studied. 14527339_Interleukin-8 binds to syndecan-2 on vascular endothelial cells. 14674716_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14674716_the HSPG T allele is a risk factor for the development of severe diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients 15936998_Syndecan-2 induces osteoblastic cell apoptosis through the JNK/Bax apoptotic pathway and the cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-2 is required for this action. 16253987_the transmembrane domains are sufficient for inducing dimerization and transmembrane domain-induced oligomerization is crucial for syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 functions 16440330_PKCdelta acts as a pro-survival kinase and that SYND2 inhibits the anti-apoptotic action of PKCdelta in osteoblast. 16997272_molecular complex most likely to obstruct RACK1 for functional attachment at syndecan-2, as revealed in cells transfected with oncogenic ras 17035092_HSPGs are expressed on the membrane of myeloid leukemic cell lineages. 17261577_heparanase-1 expression and heparan sulphate proteoglycan degradation are induced by estradiol in human endometrium 17457918_these data suggested that both HSPG and CD81 are important for HCV entry. 17516498_HSPG modulation of BMP signaling in myositis ossificans cells is reported. 17623663_syndecan-2 acts as a suppressor for MMP-2 activation, causing suppression of metastasis 18032547_There are pronounced tubulointerstitial HSPG alterations in primary kidney disease, which may affect the inflammatory response. 18093920_syndecan TMD homodimerization and heterodimerization can be mediated by GxxxG motifs and modulated by sequence context 18342939_This study provides evidence for the up-regulation of syndecan-2 and -4 in human primary CD4 T cells during in vitro activation and suggest an inhibitory role for these syndecans in CD4 T cells. 18599487_pleiotrophin (PTN) and syndecan-2 and -3 as direct binding partners of Y-P30. 18716610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19073173_A pivotal role of this heparan sulphate proteoglycan in the formation of new blood vessels. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19179614_HSPGs and HSPG-dependent signaling are affected in both central and peripheral chondrosarcomas. 19288017_SDC2 and CYR61 expression affect the severity of cancer, and the survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 19383343_estradiol affects the expression of syndecan-2, but not of syndecan-4, through ERalpha 19450993_changes in the pattern expression of syndecan-1 and -2 indicate that both molecules may be involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and tumor progression of prostate cancer. 19641225_Syndecan-2 plays a crucial role in the migratory potential of melanoma cells. 19786981_Study results supported the potential role of SDC2 in prostatic carcinogenesis and cancer progression. 19822079_Data report that the bFGF, FGFR1/2 and syndecan 1-4 expressions are altered in bladder tumours. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19962968_these results suggest that syndecan-2 regulates cell migration of colon carcinoma cells through Tiam1-dependent Rac activation in colon cancer cells. 20006588_syndecan's interactions with both CASK and neurofibromin are dependent on syndecan homodimerization. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20683009_Results support a potential role for syndecan-2 in pancreatic carcinogenesis and cancer progression. Expression of syndecan-2 might serve as a prognostic marker. 20929862_RGD-independent cell adhesion via a tissue transglutaminase 2-fibronectin matrix promotes fibronectin fibril deposition and requires syndecan-4/2 and {alpha}5{beta}1 integrin co-signaling. 21036168_syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 regulate the compensatory effect of TG-FN on osteoblast cell adhesion and actin cytoskeletal formation in the presence of RGD peptides. 21148276_These results demonstrate that syndecan-1 and syndecan-2 gene silencing by RNA interference reduces HSV-1 entry, plaque formation and facilitates cell survival. 21289173_The findings demonstrate that LRP1 and HSPG function in a cooperative manner to mediate cellular Abeta uptake and define a major pathway through which Abeta gains entry to neuronal cells. 21317913_syndecan-2 was expressed preferentially in basal cells in benign tissue. In prostate cancer samples, syndecan 2 was expressed in granular-cytoplasmic localisation. 21482826_HIV-1 p17 matrix protein interacts with heparan sulfate side chain of CD44v3, syndecan-2, and syndecan-4 proteoglycans expressed on human activated CD4+ T cells affecting tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 2 production. 21569759_the cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-2 regulates colon cancer cell migration via interaction with syntenin-1. 21813734_Here the protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor CD148 is shown to be a key intermediary in cell adhesion to syndecan-2 extracellular domain, with downstream beta1 integrin-mediated adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. 22170634_a specific glycochain is a receptor for dengue virus strain DEN2 16681 22227189_the data suggest that MMP-7 directly mediates shedding of syndecan-2 from colon cancer cells. 22238310_Syndecan 1 and syndecan 2 are cellular molecules responsible for susceptibility to HTLV-1. 22437834_Notch receptors control their own activity by inducing the expression of syndecan-2, which then acts to propagate Notch signaling by direct receptor interaction. 22471946_SDC-2 is a novel (perineural) invasion-associated gene in PDAC which cooperates with K-ras to induce a more invasive phenotype. 22493442_MC1R regulates melanoma cell migration via inhibition of syndecan-2 expression. 22550000_The repression of syndecan-2 by Wnt/beta-catenin/TCF signaling contributes to the resistance of osteosarcoma cells to doxorubicin. 22745764_Report demonstrates that syndecan-1 enhances malignancy of a mesenchymal tumour cell line, via induction of syndecan-2 expression. 22881146_lower TCR/CD3 surface levels caused by syndecan-2 led to reduced TCR/CD3 responsiveness 23297089_SDC-2 modulates TGFbeta2 transcriptional regulation via Smad2 signaling to facilitate fibrosarcoma cell adhesion. 23333331_Taken together, these results suggest that the extracellular domain of syndecan-2 regulates the interaction of HCT116 human colon carcinoma cells with fibronectin. 23736812_DNA from 4 HPV positive and 4 HPV negative fresh frozen primary HNSCC were subject to comprehensive genome-wide methylation profiling.Pathway analysis of 1168 methylated genes showed 8 signal transduction pathways (SDC2) of which 62% are hypermethylated. 23747112_Clinical validation of SDC2 methylation in serum DNA by quantitative methylation-specific PCR demonstrated a high sensitivity of 87.0% (95% CI, 80.0% to 92.3%) in detecting cancers. 23975428_RKIP, LOX and SDC2 are coordinately regulated and collectively encompass a prognostic signature for metastasis-free survival in ER-negative breast cancer patients 24424718_syndecan 2 shows no changes associated to histological grade of Prostate cancer 24442880_SDC2 is overexpressed in Leri's pleonosteosis. The minor allele of a missense SDC2 variant, p.Ser71Thr, could confer protection against systemic sclerosis. 24447566_RhoA, but not RhoC was shown to be essential for the anchored phenotype of breast carcinoma cells that accompanied siRNA-mediated loss of syndecan-2. 24472179_SDC2 expression was higher in skin melnaoma cells. It enhanced tyrosinase activity by increasing the membrane and melanosome localization of protein kinase CbetaII. UVB-induced up-regulation was required for UVB-induced melanin synthesis. 24613844_Taken together, these data suggest that IL-1alpha regulates extracellular domain shedding of syndecan-2 through regulation of the MAP kinase-mediated MMP-7 expression in colon cancer cells. 24662262_The results demonstrate the importance of PDZ-binding domain of syndecan-2 for controlling LFA-1 affinity and cell adhesion. 24736615_HIV matrix protein p17 is pro-fibrogenic through its interactions both with CXCR2 and syndecan-2 on activated HSCs 24804215_Extracellular matrix proteins expression profiling in chemoresistant variants of the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line. 24956062_Data indicate that the extracellular and cytoplasmic domains of syndecans 1/2/3/4 are intrinsically disordered regions. 25916113_In this review we considered the function of syndecan-2, the structure of syndecan-2 and its role in the formation of amyloid plaques. 27270030_data suggest that syndecan-2 induces extracellular shedding of E-cadherin and supports the acquisition of a fibroblast-like morphology by regulating MMP-7 expression in a colon cancer cell line 28753106_Methylation of SFRP1, SFRP2, SDC2, and PRIMA1 promoter sequences was observed in 85.1%, 72.3%, 89.4%, and 80.9% of plasma samples from patients with Colorectal cancer and 89.2%, 83.8%, 81.1% and 70.3% from adenoma patients, respectively. 28940845_Emerging roles of SDC2 in epithelial and mesenchymal cancer progression has been summarized. (Review) 30562054_SDC2 plays an important role in the invasive properties of lung adenocarcinoma cells. 31311305_Acute inflammation induces syndecan-2 expression predominantly in the proximal colon. 31707342_Syndecan-2 in colorectal cancer plays oncogenic role via epithelial-mesenchymal transition and MAPK pathway. 31930596_LMP1 upregulates SDC2 and SYTL4. 31962098_A novel plasma based early colorectal cancer screening assay base on methylated SDC2 and SFRP2. 32902825_Circular RNA circNFATC3 acts as a miR-9-5p sponge to promote cervical cancer development by upregulating SDC2. 33126908_Robust performance of a novel stool DNA test of methylated SDC2 for colorectal cancer detection: a multicenter clinical study. 33152121_Targeting stromal cell Syndecan-2 reduces breast tumour growth, metastasis and limits immune evasion. 33393623_Stool DNA test targeting methylated syndecan-2 (SDC2) as a noninvasive screening method for colorectal cancer. 34355516_Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived syndecan-2 regulates the immune response during sepsis to foster bacterial clearance and resolution of inflammation. 34360683_Syndecan Transmembrane Domain Specifically Regulates Downstream Signaling Events of the Transmembrane Receptor Cytoplasmic Domain. 34596215_Syndecan-2, negatively regulated by miR-20b-5p, contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer cells via the JNK/ERK signaling pathway. 34769248_Bacteroides fragilis Enterotoxin Upregulates Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Expression through MAPK and AP-1 Activation in Intestinal Epithelial Cells, Leading to Syndecan-2 Release. 35227195_The methylation of SDC2 and TFPI2 defined three methylator phenotypes of colorectal cancer. 35499710_Evaluation of combined detection of multigene mutation and SDC2/SFRP2 methylation in stool specimens for colorectal cancer early diagnosis. 35569509_Plasma membrane proteoglycans syndecan-2 and syndecan-4 engage with EGFR and RON kinase to sustain carcinoma cell cycle progression. |
ENSMUSG00000022261 |
Sdc2 |
10020.938236 |
3.4095932952 |
1.769600 |
0.018542777 |
9285.183490 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15416.9069216 |
253.3590672 |
4555.5671460 |
57.6510650 |
| ENSG00000169446 |
93380 |
MMGT1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N4V1 |
FUNCTION: Part of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex (EMC) that enables the energy-independent insertion into endoplasmic reticulum membranes of newly synthesized membrane proteins (PubMed:30415835, PubMed:29809151, PubMed:29242231, PubMed:32459176, PubMed:32439656). Preferentially accommodates proteins with transmembrane domains that are weakly hydrophobic or contain destabilizing features such as charged and aromatic residues (PubMed:30415835, PubMed:29809151, PubMed:29242231). Involved in the cotranslational insertion of multi-pass membrane proteins in which stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequences become ER membrane spanning helices (PubMed:30415835, PubMed:29809151). It is also required for the post-translational insertion of tail-anchored/TA proteins in endoplasmic reticulum membranes (PubMed:29809151, PubMed:29242231). By mediating the proper cotranslational insertion of N-terminal transmembrane domains in an N-exo topology, with translocated N-terminus in the lumen of the ER, controls the topology of multi-pass membrane proteins like the G protein-coupled receptors (PubMed:30415835). By regulating the insertion of various proteins in membranes, it is indirectly involved in many cellular processes (By similarity). May be involved in Mg(2+) transport (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K273, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29242231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29809151, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30415835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32439656, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32459176}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Magnesium;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Contributes to membrane insertase activity. Involved in protein insertion into ER membrane by stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence and tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane. Is integral component of endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Part of EMC complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:93380; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; EMC complex [GO:0072546]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cobalt ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015087]; ferrous iron transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015093]; inorganic cation transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022890]; magnesium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015095]; copper ion transport [GO:0006825]; magnesium ion transport [GO:0015693]; protein insertion into ER membrane by stop-transfer membrane-anchor sequence [GO:0045050]; tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane [GO:0071816] |
Mouse_homologues 18057121_These experiments suggest that MMgT proteins may provide regulated pathways for Mg(2+) transport in the Golgi and post-Golgi organelles of epithelium-derived cells.(MMgT1 PROTEIN, MOUSE) |
ENSMUSG00000061273 |
Mmgt1 |
278.267557 |
2.4219877902 |
1.276192 |
0.096720665 |
176.547385 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000027498292745206939354648397118059098088445081482631691063198134411448272716731082226779349243775427358510779485278874290088424459099769592285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000004606978444032400051627733399297431734585540772895966407852607287070495423283083846861280105556711497033495206210318428929895162582397460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
410.7644461 |
26.9730056 |
170.8054551 |
8.7498069 |
| ENSG00000169499 |
59339 |
PLEKHA2 |
protein_coding |
E5RHB5 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Binds specifically to phosphatidylinositol 3,4-diphosphate (PtdIns3,4P2), but not to other phosphoinositides. May recruit other proteins to the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12101241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14516276}. |
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
Enables fibronectin binding activity; laminin binding activity; and phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion. Located in cytoplasm and membrane. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
19786618_These findings identify TAPP2 as a novel link between PI3K signaling and the cytoskeleton with potential relevance for leukemia progression. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23460911_This study identified TAPP2 as a novel regulator of malignant B cell migration. |
ENSMUSG00000031557 |
Plekha2 |
993.333315 |
0.4475539246 |
-1.159867 |
0.080131333 |
206.562402 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007724690945208411595191515598528064288455154796589809203031784613959559697037009954205238759453744299029502127031899193741748543828862239024601876735687255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001524283935177488886201387281812618570452773821345734791728414747078650729138653741445874487420327269120793752972260574896079532436488079838454723358154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
646.3085155 |
35.8594795 |
1455.7375796 |
56.5815274 |
| ENSG00000169508 |
1880 |
GPR183 |
protein_coding |
P32249 |
FUNCTION: G-protein coupled receptor expressed in lymphocytes that acts as a chemotactic receptor for B-cells, T-cells, splenic dendritic cells, monocytes/macrophages and astrocytes (By similarity). Receptor for oxysterol 7-alpha,25-dihydroxycholesterol (7-alpha,25-OHC) and other related oxysterols (PubMed:21796212, PubMed:22875855, PubMed:22930711). Mediates cell positioning and movement of a number of cells by binding the 7-alpha,25-OHC ligand that forms a chemotactic gradient (By similarity). Binding of 7-alpha,25-OHC mediates the correct localization of B-cells during humoral immune responses (By similarity). Guides B-cell movement along the B-cell zone-T-cell zone boundary and later to interfollicular and outer follicular regions (By similarity). Its specific expression during B-cell maturation helps position B-cells appropriately for mounting T-dependent antibody responses (By similarity). Collaborates with CXCR5 to mediate B-cell migration; probably by forming a heterodimer with CXCR5 that affects the interaction between of CXCL13 and CXCR5 (PubMed:22913878). Also acts as a chemotactic receptor for some T-cells upon binding to 7-alpha,25-OHC ligand (By similarity). Promotes follicular helper T (Tfh) cells differentiation by positioning activated T-cells at the follicle-T-zone interface, promoting contact of newly activated CD4 T-cells with activated dendritic cells and exposing them to Tfh-cell-promoting inducible costimulator (ICOS) ligand (By similarity). Expression in splenic dendritic cells is required for their homeostasis, localization and ability to induce B- and T-cell responses: GPR183 acts as a chemotactic receptor in dendritic cells that mediates the accumulation of CD4(+) dendritic cells in bridging channels (By similarity). Regulates migration of astrocytes and is involved in communication between astrocytes and macrophages (PubMed:25297897). Promotes osteoclast precursor migration to bone surfaces (By similarity). Signals constitutively through G(i)-alpha, but not G(s)-alpha or G(q)-alpha (PubMed:21673108, PubMed:25297897). Signals constitutively also via MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3U6B2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16540462, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21673108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21796212, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22875855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22913878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22930711, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25297897}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene was identified by the up-regulation of its expression upon Epstein-Barr virus infection of primary B lymphocytes. This gene is predicted to encode a G protein-coupled receptor that is most closely related to the thrombin receptor. Expression of this gene was detected in B-lymphocyte cell lines and lymphoid tissues but not in T-lymphocyte cell lines or peripheral blood T lymphocytes. The function of this gene is unknown. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1880; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; oxysterol binding [GO:0008142]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell activation involved in immune response [GO:0002312]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; dendritic cell homeostasis [GO:0036145]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; immune response [GO:0006955]; leukocyte chemotaxis [GO:0030595]; mature B cell differentiation involved in immune response [GO:0002313]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; regulation of astrocyte chemotaxis [GO:2000458]; T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010818]; T follicular helper cell differentiation [GO:0061470] |
16540462_Based on the constitutive signaling and cellular expression pattern of EBI2, it is suggested that it may function in conjunction with BILF1 in the reprogramming of the cell during EBV infection 18628402_Structural motifs of importance for the constitutive activity of EBI2: analysis of receptor activation in the absence of an agonist. 21261596_REVIEW: functional properties and in vivo biology 22875855_Molecular characterization of oxysterol binding to the Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 2 (GPR183). 22913878_Data indicate that EBI2 expression modulates CXCL13 binding affinity to CXCR5. 22930711_This model of ligand docking yields important structural insight into the molecular mechanisms mediating EBI2 function. 23473835_Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps is characterized by B-cell inflammation and EBV-induced protein 2 expression. 24480442_EBI2 is expressed in primary human monocytes and macrophages. 25297897_These results demonstrate a role for EBI2 in astrocyte function and suggest that modulation of this receptor may be beneficial in neuroinflammatory disorders. 26898310_Studies provide evidence that EBI2 and oxysterols are important players not only in the immune system but also in the central nervous system. Proper functioning of the EBI2/oxysterol system seems crucial for healthy physiology and prevention of the onset or progression of several neurodegenerative diseases. [review] 27902324_this study concludes that EBI2 expression is directly influenced by EBV infection and that BRRF1 is necessary and sufficient for EBI2 upregulation during infection. 28003273_Human EBI2 (GPR183) expression in mice leads to an abnormally expanded CD5+ B1a B-cell subset and chronic lymphocytic leukemia-like B-cell malignancies. 28052250_These data suggest a significant role for EBI2 in human CD4(+) T cell migration, notably in patients with multiple sclerosis. 28125291_On ligand engagement, EBI2 typically signals via inhibitory G-protein subunit alpha to induce intracellular calcium mobilization, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation, and cell proliferation. 30742043_these data implicate the EBI2-oxysterol axis in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis 31550518_Orphan G-protein coupled receptor 183 (GPR183) potentiates insulin secretion and prevents glucotoxicity-induced beta-cell dysfunction. 33240287_GPR183 Regulates Interferons, Autophagy, and Bacterial Growth During Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection and Is Associated With TB Disease Severity. 33511653_A single nucleotide polymorphism in the gene for GPR183 increases its surface expression on blood lymphocytes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. 34229205_EBI2-expressing B cells in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with AQP4-IgG: Association with acute attacks and serum cytokines. 35351968_EBI2 is a negative modulator of brown adipose tissue energy expenditure in mice and human brown adipocytes. 35875859_Abnormal lower expression of GPR183 in peripheral blood T and B cell subsets of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. |
ENSMUSG00000051212 |
Gpr183 |
255.746293 |
7.4679809456 |
2.900718 |
0.126646432 |
591.109821 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014371681087621470321310084830234564209379240092417324815382618090726786799840972102111947086161689107961062680901093481302659750005022579141196591644452105223638313514302596209969248893430385449323324 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007856518994566403829038395578744253085916256987494177451982044024570110182561566391463525216681478023271758468236300702856805998516650971394763694697522231986405393727091113878740297561502300750489637 |
Yes |
No |
454.7008929 |
35.2382821 |
61.3371599 |
4.2520902 |
| ENSG00000169548 |
129025 |
ZNF280A |
protein_coding |
P59817 |
FUNCTION: May function as a transcription factor. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a zinc finger protein. The encoded protein contains 4 C2H2-type zinc fingers, which are commonly found in transcription factors. A variety of functions may be performed by this type of zinc finger protein, including the binding of DNA or RNA. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:129025; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
33414445_ZNF280A promotes lung adenocarcinoma development by regulating the expression of EIF3C. |
|
|
22.161210 |
0.1241531454 |
-3.009807 |
0.436093249 |
56.221860 |
0.00000000000006473777283839280701706296717254270643769707010983793793457152787595987319946289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000415628328444835928254962299207267409817574688180030761941452510654926300048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7262661 |
1.4013641 |
38.3613576 |
5.7116261 |
| ENSG00000169683 |
201255 |
LRRC45 |
protein_coding |
Q96CN5 |
FUNCTION: Component of the proteinaceous fiber-like linker between two centrioles, required for centrosome cohesion. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24035387}. |
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Leucine-rich repeat;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Located in several cellular components, including centrosome; cytosol; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201255; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
24035387_LRRC45 is a critical component of the proteinaceous linker between two centrioles and is required for centrosome cohesion. |
ENSMUSG00000025145 |
Lrrc45 |
89.329787 |
0.4857450223 |
-1.041729 |
0.215431573 |
23.326739 |
0.00000136686534965677132105819468338436806220670405309647321701049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004763856158709796486490015143822063237166730687022209167480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.3467005 |
8.3492114 |
125.1242245 |
12.0004167 |
| ENSG00000169684 |
1138 |
CHRNA5 |
protein_coding |
P30532 |
FUNCTION: After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Ligand-gated ion channel;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit and a member of a superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels that mediate fast signal transmission at synapses. These receptors are thought to be heteropentamers composed of separate but similar subunits. Defects in this gene have been linked to susceptibility to lung cancer type 2 (LNCR2).[provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:1138; |
acetylcholine-gated channel complex [GO:0005892]; dopaminergic synapse [GO:0098691]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; synapse [GO:0045202]; acetylcholine receptor activity [GO:0015464]; acetylcholine-gated cation-selective channel activity [GO:0022848]; excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005231]; ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0015276]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; transmitter-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:1904315]; behavioral response to nicotine [GO:0035095]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; membrane depolarization [GO:0051899]; nervous system process [GO:0050877]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; synaptic transmission, cholinergic [GO:0007271] |
17135278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17559419_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18163978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18165968_From a panel of 59 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located on 11 candidate genes, we identify four SNPs (one each on CHRNA5 and CHRNA2 and two on CHAT) that appear to have pharmacogenetic relevance in smokin cessation therapy. 18165968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18227835_A common haplotype in the CHRNA5/CHRNA3 gene cluster on chromosome 15 contains alleles, which predispose to nicotine dependence. 18227835_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18385676_CHRNA5 and CHRNA3 are promising candidate genes in the region of 15q25.1 for lung cancer. 18385676_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18385738_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18414406_Functional studies in human brain reveal that the variants associated with alcohol dependence are also associated with altered steady-state levels of CHRNA5 mRNA. 18414406_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18450646_Environmental tobacco smoke and nicotine up-regulated the levels of alpha5 and alpha7 expression in a time-dependent fashion 18519132_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18519524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18559515_Increased levels of cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 5 is associated with squamous cell lung carcinoma 18618000_In the 2,827 long-term smokers examined, common susceptibility and protective haplotypes at the CHRNA5-A3-B4 locus were associated with nicotine dependence severity. 18759969_Correlated SNPs in the cholinergic nicotinic receptor gene cluster CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4, in a case-control study of cocaine dependence composed of 504 European-American and 583 African-Americans. 18780872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18783506_A non-synonymous coding SNP in CHRNA5 was associated with case status and, in Caucasians, with experiencing a pleasurable rush or buzz during the first cigarette; these sensations were associated highly with current smoking (OR = 8.2, P = 0.0001). 18783506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18957677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18957677_The CHRNA5-A3 region on chromosome 15q24-25.1 is a risk factor both for nicotine dependence and for lung cancer.( 18978134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18978134_the association between the alpha5 subunit nicotinic acetylcholine receptor single nucleotide polymorphism and lung cancer may, in part, be confounded by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 18996504_CHRNA5 seem to exert no relevant influence on smoking cessation probability in heavy smokers in the general population. 18996504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19005185_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19010884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19010884_smokers who carry the CHRNA3 and CHRNA5 variants are expected to be at increased risk for lung cancer compared with smokers who do not carry these alleles. 19029397_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19029397_Two distinct variant groups in the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene cluster are strongly associated with heavy smoking. The snp rs16969968 alters the coding sequence of these genes. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19132693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19132693_The alpha5 and alpha3 subunits play a significant role in both nicotine dependence and alcohol abuse/dependence. 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19223495_D398N polymorphism of the CHRNA5 gene was associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 19223495_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247474_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19259974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19300482_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19300482_The CHRNA 3/5 and the HHIP loci make a significant contribution to the risk of COPD. 19390575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19429911_Genetic variant in the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene cluster is associated with smoking cessation during pregnancy. 19429911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19436041_The CHRNA5-A3-B4 haplotypes are associated with a broad range of nicotine dependence phenotypes, but these associations are not consistently moderated by age at initial smoking. 19443489_Two distinct mechanisms conferring risk for nicotine dependence and lung cancer: altered receptor function caused by a D398N amino acid variant in CHRNA5 and variability in CHRNA5 mRNA expression. 19482438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19482438_There was no evidence of association of CHRNA5 rs16969968 with smoking status (p=0.28) or, among daily smokers, of association with cotinine levels (p=0.49). 19577767_Although CHRNA5 polymorphism is rare from Japanese lung cancer, polymorphism status might be correlated with shorter survival. 19628476_Genetic variation at CHRNA5/CHRNA3/CHRNB4 cluster influences blood nicotine level. 19628476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19641473_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19641473_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in CHRNA5 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 19671882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19696770_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19706762_CHRNA5 SNP rs16969968 is the most significant SNP associated with nicotine dependence 19706762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19733931_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19776245_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19859904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19859904_These results indicate that variants within CHRNA3 and among CHRNA5, CHRNA3, and CHRNB4 contribute significantly to the etiology of ND through gene-gene interactions. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20381163_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20381163_This study suggested that the possibility that the wide individual variability in response, and sequent sensitization to nicotine are due to both a variant Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in rs16969989 and early life stress. 20395203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20418889_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485328_The data of this study supported the importance of variants in the CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster as mediators of the genetic risk for substance dependence. 20548021_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20564069_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20564069_Smoking behavior and COPD are mediators of the association between the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs1051730 and the risk of lung cancer. 20584212_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20624154_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20631687_Genetic variation in CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene cluster influences cognitive flexibility differently in African Americans and European Americans. 20631687_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20643934_Data suggest that both CHNA5 Asp398Asn and CHRNA3 rs578776 are associated with smoking. 20643934_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20656943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20656943_The CHRNA3/5 locus was associated with increased smoking intensity and emphysema in individuals with COPD 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20685379_This review focuses on the clustered nicotinic acetylcholine receptor genes CHRNalpha5/alpha3/beta4 and evaluates their role in nicotine addiction and lung cancer. 20691427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20700147_The enhancer region and the nonsynonymous polymorphism rs16969968 generate three main haplotypes that alter the risk of developing nicotine dependence. 20725741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20733116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20733116_Study identified four genetic variations in the CHRNA5 promoter region that define three haplotypes affecting activity of the promoter of this gene, thus modulating CHRNA5 transcript levels in normal lung tissue. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20736995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20808433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20808433_associations of variants in the CHRNA5/A3/B4 cluster with smoking initiation, smoking quantity and smoking cessation 20840187_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20854418_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881005_A variation in the alpha5 subunit of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors increases the risk of nicotine dependence and lung cancer. 20886544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20886544_evidence that CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene cluster variants,particularly CHRNA5 variant rs16969968, could be associated with cognitive performance possibly mediating in part risk for developing nicotine dependence 21168125_CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 is involved in the transition toward heavy smoking in mid-adulthood and in smoking persistence. 21228559_Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) CHRNA5 on chromosome 15 is not associated with Parkinson's disease risk in the overall anaylsis or after stratifying on smoking status. 21248747_Variant A of the rs1051730 SNP of CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene cluster was significantly associated with smoking quantity in 2 Italian populations, Val Borbera and Cilento, no association was found in Carlantino population. 21321393_nAChR7-specific antibodies are able to penetrate the brain upon inflammation, with resulting decreases of brain nAChR7 receptor and worsening episodic memory. 21385908_This study demonstrates the additive and independent association of the nicotine metabolite ratio and SNPs in the CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster with smoking rate in treatment-seeking smokers. 21418140_The Asp398Asn risk allele is significantly associated with smoking severity independently in schizophrenia patient smokers and control smokers. 21436384_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in CHRNA5 is associated with smoking persistence in African Americans. 21440309_This study demonistreated that CHRNA5 polymorphism(16969968) are more common among Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. 21448929_Results indicate that the CHRNA5 gene with under-activated or over-activated promoter activity may be protective against lung cancer, implying a complex role of the CHRNA5 gene in lung cancer. 21559498_CHRNA3-CHRNA5 variation impacts indirectly on lung cancer risk 21586512_results demonstrate a role for CHRNA5 in modulating adhesion and motility in bronchial cells, as well as in regulating p63, a potential oncogene in squamous cell carcinoma 21593077_Common variation in the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene region (chromosome 15q25) IS ASSOCIATED WITH SMOKING QUANTITY AND THE GENOTYPE MAY BE associated with BMI in smokers 21646606_Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor polymorphisms are associated with additional increased risk of lung cancer, bladder cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after adjustment for smoking. 21747048_Variation in CHRNA5-A3-B4 was independently and additively associated with increased smoking, nicotine dependence, and lung cancer risk. 21748402_CHRNA3 and CHRNA5 have roles in different forms of tobacco dependence, but the specific genetic variants do not account for much fo the total genetic variance for predisposition to nicotine dependence 21764527_nicotine-dependent smokers lacking the rs16969968 A allele are more likely to recall smoking-related memories and engage in habitual responding to smoking cues than A allele smokers 21765098_CHRNA5 and CYP2A6 genotypes appeared to be independent, with each approximately doubling the odds of being a regular smoker by age 18 years. 21810735_Women with the variant AA genotype of CHRNA5 rs16969968 or variant CC genotype of LOC123688 rs8034191 were at significantly increased risk of heavy smoking. 21858091_Data show that luciferase expression was equivalent among CHRNA3 haplotypes, but the combination of deletion at rs3841324 and variation at rs503464 decreased CHRNA5 promoter-derived luciferase activity. 21873428_analysis of how nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) alpha5 subunits and/or variants modulate function of alpha6*-nAChR 21955800_Relationship between the polymorphism of the CHRNA5 gene and the strength of nicotine addiction measured by multiple factors including the Fagerstrom test score. 22008662_results confirm the involvement of the CHRNA5 gene in the amount of nicotine use and further suggest involvement of the BDNF gene in smoking behavior 22012472_This study provides evidence of a sex-specific gene x environment effect of CHRNA5 and childhood adversity on the risk for nicotine dependence 22017462_An interaction between tobacco smoke exposure and a CHRNA3/5 polymorphism was found for BHR in children, but CHRNA3/5 was not associated with asthma or lung function. 22024278_Two specific aspects of executive functioning related to drug addiction--impulsivity and working memory--are demonstrated in transgenic mice overexpressing alpha3/alpha5/beta4 nicotinic receptor subunits. 22042234_This study examines whether the CHRNA5/CHRNA3/CHRNB4 locus is correlated also with externalizing behaviors in three independent longitudinally assessed adolescent samples 22101982_vivo evidence of the involvement of the CHRNA5, CHRNA3 and CHRNB4 genomic cluster in nicotine addiction 22223462_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in CHRNA5 gene is associated with nicotine dependence. 22241830_Genetic variation within the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene cluster is associated with nicotine dependence. 22336398_The genetic risks of nicotine dependence associated with the CHRNA5-A3-B4 subunit genes are specific, and not shared among commonly comorbid psychiatric disorders 22382680_Collectively, the presence of alpha7 and beta4 nAChRs in PDLSCs supports a key role of Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) in the modulation of nicotine-induced apoptosis 22382757_study provides evidence for a general role of the CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster in substance use initiation that is not limited to nicotine and alcohol. 22406075_The A allele of the single nucleotide polymorphism rs16969968 (alpha5, G > A), which correlates with the development of lung cancer, shows a non-significant trend to be associated with cervical lesions. 22459873_transgenic mice with human alpha 5, alpha 3, beta 4 subunit genes drank less ethanol than wild-type in a two-bottle (ethanol vs. water) preference test 22461431_A replication of association between two SNPs previously associated with COPD (CHRNA3/5 and IREB2), as well as an association with COPD of one locus initially associated with lung function (ADCY2). 22665477_The alpha5 variant-induced change in alpha3beta4alpha5 nAChR function may underlie some of the phenotypic changes associated with this polymorphism. 22820273_alpha3beta4alpha5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, expressing the the N398 variant of CHRNA5, exhibits a reduced response to agonists when extracellular calcium is high and it may lead to distinct downstream cellular signaling. 22837378_Results suggest important role for CHRNA5 variants as genetic risk factor for airflow obstruction that may be independent of smoking status. 22868939_The genetic risk of heavy smoking (as measured by the rs16969968 A allele) is greater in early-onset smokers (onset of smoking at A at rs503464 of CHRNA5 may be associated with reduced risk of lung cancer, thus representing a susceptibility allele in Chinese individuals. 23358500_The present study investigated the association of CHRNA5 polymorphisms and smoking topography. 23430818_our findings provide evidence for the presence of multiple CHRNA5 mRNA isoforms that may modulate the multimeric nicotine receptor and cis-regulatory variations in the CHRNA5 locus that act in vivo in the control of CHRNA5 mRNA expression 23458267_Rare genetic variation in the CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene cluster contributes modestly to the level of response to alcohol. 23576140_Evaluated the association between CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene cluster variants (rs667282 and rs3743073, two variants modifying lung cancer risk) and risk of gastric cancer. 23692359_Genetic variants in the CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene cluster alter nicotine intake and body mass index in a population of Alaska Native people, who have a distinct haplotype structure, smoking behaviors and prevalence of obesity. 23729684_SNP rs1051730 associated with smoking and body mass index 23843950_Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits alpha4 and alpha5 associated with smoking behavior and lung cancer are regulated by upstream open reading frames. 23844051_CHRNA5-A3-B4 rs667282 TT/TG genotypes were associated with significantly increased risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 23943838_Level of cigarettes per day during adolescence and young adulthood is associated with CHRNB3A6, CHRNA5A3B4, and CHRNA2 24033696_The effect of nicotine replacement on continuous abstinence is moderated by the combined genetic risks from CYP2A6 and CHRNA5. 24184962_the alpha5 subunit can occupy the position of a nonbinding subunit, or replace a beta2 subunit participating in a canonical binding site. 24303001_substance dependence associated variants have a direct cis-regulatory effect on CHRNA5 transcript levels in human frontal cortices of African and European ancestry. 24588897_Investigated associations between neuroticism and 13 SNPs in the CHRNA5 and CHRNA3 genes in young adult Mexican American men and women. 24682045_in African-Americans, variants (common or rare) in genes other than CHRNA5 most likely contribute toward the nicotine-dependent phenotype. 24719457_Increased expression of NeuroD1 subsequently leads to regulation of expression and function of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit cluster of alpha3, alpha5, and beta4. 24727484_Among smokers who are hospitalized with acute myocardial infarction, the high-risk CHRNA5 allele was associated with lower likelihood of quitting before hospitalization and significantly less abstinence 1 year after hospitalization with MI. 24733007_Among African Americans, CHRNA5-A3-B4 variants are not associated with smoking but can influence smoking abstinence. 24793809_Silencing of alpha5-nAChR significantly inhibits nicotine-induced cell proliferation in tumor cell lines. 24819610_Data found that DRD2 rs1076560 and CHNRA5 rs16969968 interact to modulate cognitive function, prefrontal physiology during working memory, and prefrontal gray matter volume. 24934182_CHRNA5 SNPs predicted nicotine deprivation-induced reduction in cognitive control. 25051068_Four SNPs in the CHRNA3/5 locus are associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease risk. [Meta-analysis] 25072098_Genetic variation in CHRNA5 protein influence smoking behaviors and the level of carbon monoxide. 25073833_The CHRNA5 genetic risk synergized the effect of partner smoking, producing an especially low likelihood of successful smoking reduction in two complementary studies. 25187487_Single nucleotide polymorphism in CHRNA5 is associated with lung cancer. 25293386_In Mendelian randomisation analyses, there was no strong evidence that the minor allele of rs16969968/rs1051730 was associated with depression, anxiety or psychological distress in current or former smokers. [Meta-analysis] 25297392_Suggest no relationship between these smoking-related SNPs in the CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster and psoriasis vulgaris in Chinese Han population. 25329654_CHRNA5 rs3841324 combined variant genotypes (ins/del+del/del) had a >1.5-fold elevated risk for nasopharyngeal carcinoma 25384568_Study provides new evidence that the overexpression of the CHRNA5/A3/B4 region disrupts pyramidal neuronal structure in the hippocampus, and thus affecting the cognitive capacities 25471942_focus on the CHRNA5/A3/B4 gene cluster and its role in nicotine dependence (review) 25474695_CHRNA5-A3-B4 genotype associates with body mass index in never smokers. 25652844_A low to moderate level of Nicotine Dependence in the Kashubians, of Poland, influenced by age, sex, as well as the CHRNA5 rs16969968 variant was demonstrated 25674902_Results indicate that the minor alleles of both polymorphisms modulate response speed in a sex-dependent, diametrically opposed manner. 25941207_Preventive interventions in adolescents reduced the genetic risk for smoking from rs16969968 CHRNA5. 26010901_Data suggest that CHRNA5-A3-B4 gene variants do not exhibit a robust association with smoking cessation and are unlikely to be useful for clinically optimizing smoking cessation pharmacotherapy for Caucasian smokers. 26184988_In non-Hispanic White participants, a novel association between rs1289899 in the CHRNA5 gene and posttraumatic stress disorder was observed. 26220977_A novel regulatory SNP association with nicotine dependence was found. Previously observed differences in CHRNA5 mRNA expression and nicotine dependence risk were connected to underlying DNA methylation differences. 26228411_This study showed that CHRNA5(rs16969968) interacted with chronic low family support in association with child mental health status 26239294_Study showed that multiple rare, low frequency and common variants in the CHRNA5 gene contribute to the development of nicotine dependence 26434895_Our meta-analysis provided statistical evidence for a strong association between rs16969968 polymorphism and the risk of lung cancer, especially in smokers and Caucasians. 26689306_suggest that gene variance in the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 cluster is associated with an increased risk of death, incidence of COPD and tobacco-related cancer in smokers 26751916_The minor allele increased the risk of COPD when compared to the population at large. Homozygosity for the risk allele was associated in both cohorts with all-cause mortality, with any type of cancer among the COPD patients and with the number of pack-years among the male smokers. 26757861_No associations were found between the analyzed variants and smoking, however, there was an association among non-smoking subjects between the A allele of rs16969968 and high body mass index. 26909550_These results suggest that exposure to nicotine might negatively impact the apoptotic potential of chemotherapeutic drugs and that alpha5-nAChR/AKT signaling plays a key role in the anti-apoptotic activity of nicotine induced by cisplatin. 26942719_two SNPs (rs6495308 and rs11072768) in CHRNA5-A3-B4 have a indirect effect on lung cancer through smoking behaviors 26981579_rs2036527 is a risk factor for smoking exposure and lung cancer association in African-Americans. 27050379_Our present study suggested that rs667282 in CHRNA5-A3 may modify the prognosis of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer 27072204_There was no association of rs16969968 polymorphism at CHRNA5 with cancer risk in the overall pooled analysis 27127891_the association of 3 selected single-nucleotide polymorphisms (CHRNA3 rs1051730, rs6495308, and CHRNA5 rs55853898) with nicotine dependence in an isolated population of Kashubians from Poland, is reported. 27302872_The results of this study suggests a pleiotropic role of Chr15q25 CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene cluster with complex influences in ADHD, tobacco smoking and cognitive performance. 27355804_Polymorphisms in the CHRNA5 and NRXN1 genes, influenced greater consumption of cigarettes in a Mexican Mestizo population. 27541642_We determined that the other patients harbored mutations in genes that have not previously been linked to RTT or other neurodevelopmental syndromes, such as the ankyrin repeat containing protein ANKRD31 or the neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-5 (CHRNA5). 27543155_quitting smoking is highly beneficial in reducing lung cancer risks for smokers regardless of their CHRNA5 rs16969968 genetic risk status. Smokers with high-risk CHRNA5 genotypes, on average, can largely eliminate their elevated genetic risk for lung cancer by quitting smoking- cutting their risk of lung cancer in half and delaying its onset by 7years for those who develop it. 27645992_This study shows that unorthodox acetylcholine binding sites can form at the alpha5/alpha4 and beta3/alpha4 interfaces in (alpha4beta2)2alpha5 and (alpha4beta2)2beta3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) and at the alpha4/alpha5 in (beta2alpha4)2alpha5 nAChRs. 27698409_Glutamatergic N398 neurons responded to lower nicotine doses (0.1 muM) with greater frequency and amplitude but they also exhibited rapid desensitization, consistent with previous analyses of N398-associated nicotinic receptor function 27758088_our results show that a genomic region with functionally related genes, such as the CHRNA5/CHRNA3/CHRNB4 cluster, is under coordinated regulatory control. 27835950_The data replicate previous result suggesting CHRNA5 as a candidate gene for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and rs8040868 as a risk variant for the development of COPD in the Swedish population. 28442398_RP11-650L12.2 rs149941240 polymorphism was associated with the risk of colorectal cancer. 28474623_The rs13180 (IREB2), rs16969968 (CHRNA5) and rs1051730 (CHRNA3) were significantly associated with Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in additive model [Padj =0.00001, odds ratio (OR)=0.64; Padj =0.0001, OR=1.41 and Padj =0.0001, OR=1.47]. The C-G haplotype by rs13180 and rs1051730 was a protective factor for COPD in our population (Padj =0.0005, OR=0.61). 28520984_The CHRNA5 gene is significantly associated with heavy smoking in a Hispanic/Latino cohort. 28857330_Increased habenula-striatum functional connectivity may be modulated by the nicotinic receptor variant rs16969968 and may lead to increased Opioid use. 29196725_Four SNPs in the CHRNA5 locus (e.g. rs503464, rs55853698, rs55781567 and rs16969968) were found to be significantly associated with nicotine dependence. 29609626_Frequency of the cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 5 (CHRNA5) rs16969968-A allele and cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 3 (CHRNA3) rs1051730-T allele were significantly higher in lung cancer than in normal controls. 29688464_Smoking and genotype were not independently associated with surgery in ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn's disease (CD). However, interaction between rs16969968 and smoking in predicting surgery was observed for both UC and CD. The CHRNA5 rs16969968 A variant interacts with smoking to influence IBD-related surgery. 29993116_CHRNA3/5 polymorphisms are associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Mexicans. 30097758_A common haplotype of CHRNA5 that results in reduced cardiac expression of CHRNA5 and attenuated macrophage inflammasome activation is associated with lower mortality after acute myocardial infarction. 30202994_Genome-wide variants shared between smoking quantity and schizophrenia contribute to a common pathophysiology underlying these traits involving altered CHRNA5 expression in the brain. 30366711_To examine the association between CHRNA5 and schizophrenia and its clinical features adjusted for smoking status in early-onset schizophrenia patients. The study provides strong evidence that rs16969968 on CHRNA5 is tightly linked to genetic susceptibility and cognitive deficits in early-onset schizophrenia in the Chinese population. 30453884_Results indicate rs4887074 is associated with nicotinic receptor CHRNB4 expression, and along with two regulatory variants of nicotinic receptors CHRNA3 and CHRNA5, modulates the effect of rs16969968 on nicotine dependence risk. 30543688_Cholinergic Receptor Nicotinic Alpha 5 (CHRNA5) RNAi is associated with cell cycle inhibition, apoptosis, DNA damage response and drug sensitivity in breast cancer 30550855_Further investigation indicated that nicotine-induced Ca(2+) response and TRPC3 up-regulation was reversibly blocked by small interfering RNA (siRNA) suppression of alpha5-nAChR. 30829278_this study shows that CHRNA5 polymorphism is not associated with tobacco-related oral squamous cell carcinoma 31072760_Exposure to smoking in adolescents, even at low doses, is linked to volume changes in t |
ENSMUSG00000035594 |
Chrna5 |
15.065489 |
2.1603396472 |
1.111258 |
0.387555005 |
8.413397 |
0.00372466021972961544225788621531592070823535323143005371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007821309552313148588664759586208674591034650802612304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.7000879 |
5.1927951 |
9.6543546 |
1.9346596 |
| ENSG00000169704 |
2815 |
GP9 |
protein_coding |
P14770 |
FUNCTION: The GPIb-V-IX complex functions as the vWF receptor and mediates vWF-dependent platelet adhesion to blood vessels. The adhesion of platelets to injured vascular surfaces in the arterial circulation is a critical initiating event in hemostasis. GP-IX may provide for membrane insertion and orientation of GP-Ib. |
3D-structure;Bernard Soulier syndrome;Blood coagulation;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a small membrane glycoprotein found on the surface of human platelets. It forms a 1-to-1 noncovalent complex with glycoprotein Ib, a platelet surface membrane glycoprotein complex that functions as a receptor for von Willebrand factor. The complete receptor complex includes noncovalent association of the alpha and beta subunits with the protein encoded by this gene and platelet glycoprotein V. Defects in this gene are a cause of Bernard-Soulier syndrome, also known as giant platelet disease. These patients have unusually large platelets and have a clinical bleeding tendency. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:2815; |
glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex [GO:1990779]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway [GO:0007597]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; positive regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010572]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209] |
11686325_Both the high affinity thrombin receptor (GPIb-IX-V) and GPIIb/IIIa are implicated in expression of thrombin-induced platelet procoagulant activity. 11812775_Lateral clustering of platelet GP Ib-IX complexes leads to up-regulation of the adhesive function of integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 12036872_The cysteine knot of platelet GPIb beta is critical for the interaction of GPIb beta with GPIX. 12361948_PKA-mediated phosphorylation of GPIbbeta at Ser(166) negatively regulates VWF binding to GPIb-IX and is one of the mechanisms by which PKA mediates platelet inhibition 12447957_Novel nonsense mutation is associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome. 12463594_structure-activity relationship of mutations found in Bernard-Soulier syndrome 12517745_factor XI is localized to GPIb in membrane rafts and this association is important for promoting the activation of factor XI by thrombin on the platelet surface 15351858_findings indicate that the Ala14-->Thr mutation in the transmembrane region of GP IX does not induce intracellular GP Ib/IX complex degradation, but prevents its insertion in the cytoplasmic membrane of platelets and CHO cells 15477207_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17763149_3 families from Iran with Bernard-Soulier syndrome were investigated; the presence of the same GpIX Phe55Ser missense mutation in two families and of a single base insertion (GP1BA C3221 ins) in the third family were demonstrated 17804902_the first non-Caucasian Turkish Bernard-Soulier syndrome case due to GPIX N45S and is likely the result of a recurrent mutational event. 17922811_The transmembrane domain of GPIX plays an important role in expression and assembly of the GPIb-IX complex by interacting with its counterparts of GPIb. 18057877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18057877_Polymorphisms in human platelet alloantigen (HPA)-1 and HPA-3 (GPIIb/IIIa), HPA-2 (GPIb/IX), HPA-4 (GPIIIa) and HPA-5 (GPIa/IIa) were found to be associated with the symptoms and recurrence of ischemic stroke. 18450753_laminin supports platelet adhesion depending on the interaction of VWF and GPIb-IX-V under pathophysiological high shear flow 18612104_glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex contributes to tissue factor-independent thrombin generation by recombinant factor VIIa on the activated platelet surface 18638089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18674540_Data demonstrate the native-like heteromeric interaction among the isolated Ibalpha, Ib beta and IX TM peptides, which provides support for the four-helix bundle model of the TM domains in the glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. 19377075_Findings point to a role of the GPIb-V-IX complex intrinsic to megakaryocytes at the stage of proplatelet formation and suggest a functional link with the underlying microtubular cytoskeleton in platelet biogenesis. 19404517_Homozygous missense mutation in position 1829 (A(R)G) of the GPIX gene causes Bernard-Soulier syndrome in a Swiss family. 19558434_14-3-3beta, 14-3-3gamma, 14-3-3epsilon, 14-3-3eta and 14-3-3theta isoforms interact with the GPIb-IX complex in platelets 19566547_the putative convex surface of the LRR domain in GPIX is sufficient, in the context of full-length subunit, to mediate its association with GPIbbeta 19874464_Raft association and cytoskeletal linkage of the platelet GPIb-IX-V complex are interrelated and are required for optimal receptor function, by attracting signaling proteins and membrane skeletal association allows proteins to move to new locations. 21507943_GP Ibbeta/GP IX mediates the disulfide-linked GP Ibalpha localization to the GEMs, which is critical for vWf interaction at high shear 21529934_GPIIb/IIIa is the primary receptor set involved in platelet adhesion to adsorbed fibrinogen and serum albumin irrespective of their degree of adsorption-induced unfolding, while the GPIb-IX-V receptor complex plays an insignificant role. 21699652_Report glycoprotein Ib/IX complex mutations found in Bernard-Soulier syndrome in Indian patients. 21908432_GPIbbeta missense mutations from Bernard-Soulier syndrome were examined for changes to GPIb-IX complex surface expression. Mutations A108P and P74R were found to maintain normal secretion/folding of GPIbbeta(E) but were unable to support GPIX surface expression 23143686_GPIX increased the expression of GPIba by promoting the formation of a disulfide bond between GPIba and GPIbb in transfected CHO-K1 cells. 23929303_Studies indicate that platelets from Bernard-Soulier syndrome (BSS) are defective in glycoprotein (GP)Ib-IX-V, a platelet-specific adhesion-signaling complex, composed of GPIbalpha disulfide linked to GPIbbeta, and noncovalently associated with GPIX and GPV. 23995613_genetic association study in population in western India: Data suggest novel mutations in platelet glycoprotein Ib (GP1BA, GP1BB) and GP9 are associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome in subjects studies; of 12 mutations identified, ten were novel. 26203189_Data show that localization of the GP Ib-IX complex to the lipid domain is mediated by GP Ibbeta and GP IX transmembrane domains. 28561420_Case Report: suggest that alloantibodies directed against Cab4b, the first human platelet antigen carried by glycoprotein IX, can induce severe neonatal thrombocytopenia. 28603902_ERK5 associates with CKII to play essential roles in GPIb-IX-mediated platelet activation via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. 33550613_Oxidation shuts down an auto-inhibitory mechanism of von Willebrand factor. |
ENSMUSG00000030054 |
Gp9 |
15.654778 |
0.1174875396 |
-3.089420 |
0.507019792 |
47.746156 |
0.00000000000485134633328186701438223896475548978582392756209173967363312840461730957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000027530131441461112254425438093101039752769176871538547857198864221572875976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1583568 |
1.1167231 |
27.0939522 |
4.3579006 |
| ENSG00000169783 |
84894 |
LINGO1 |
protein_coding |
Q96FE5 |
FUNCTION: Functional component of the Nogo receptor signaling complex (RTN4R/NGFR) in RhoA activation responsible for some inhibition of axonal regeneration by myelin-associated factors (PubMed:14966521, PubMed:15694321). Is also an important negative regulator of oligodentrocyte differentiation and axonal myelination (PubMed:15895088). Acts in conjunction with RTN4 and RTN4R in regulating neuronal precursor cell motility during cortical development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D1T0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14966521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15694321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15895088}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Intellectual disability;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable epidermal growth factor receptor binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within generation of neurons and protein kinase B signaling. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in extracellular matrix and extracellular space. Implicated in autosomal recessive non-syndromic intellectual disability and glaucoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84894; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; epidermal growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005154] |
14686891_The LERN1 expression pattern is specific to the central nervous system, highly and broadly expressed during early stages of development and gradually restricted to forebrain structures as development proceeds(LERN1) 17005555_the Lingo-1 ectodomain is a module implicated in central nervous system repair inhibition 17239012_the ternary complex of NgR/TROY/LINGO-1 expressed on astrocytes, macrophages/microglia and neurones, by interacting with Nogo-A on oligodendrocytes, might modulate glial-neuronal interactions in demyelinating lesions of multiple sclerosis 17726113_inhibitory agents of LINGO-1 activity can protect dopaminergic neurons against degeneration 19182806_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19182806_Variant in the sequence of the LINGO1 gene confers risk of essential tremor. 19254717_Quick identification of essential N-glycosylation sites of a heavily glycosylated neuroglycoprotein Lingo-1, which are sufficient for the support of its surface expression. 19363035_WNK1 is a novel signaling molecule involved in regulation of LINGO-1 mediated inhibition of neurite extension. 19553813_the LINGO1 gene is associated with an increased risk for essential tremor 19720553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19720553_Thisdy demonstrateda significant association between LINGO1 rs9652490 and essential tremor (P = 0.014) and Parkinson disease (P = 0.0003), thus providing the first evidence of a genetic link between both diseases. 19805735_LINGO1 variant increases risk of familial essential tremor. 19908305_In this study, SNPs rs9652490, rs11856808, and rs7177008 of LINGO1 were genotyped in a total of 694 Austrian subjects (349 PD, 345 controls). No association could be found between genotype or allele counts and Parkinson disease. 19908305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20117178_LINGO1 SNP (rs9652490) is not associated with sporadic PD in our Polish cohort. 20117178_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20310002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20310002_Our study gives further evidence that LINGO1 acts as a susceptibility gene for essential tremor. 20369371_LINGO1 and LINGO2 variants are associated with essential tremor and Parkinson disease 20369371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20372186_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20372186_The LINGO1 gene is a risk factor for essential tremor in a Caucasian population in North America. 20468067_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20600614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20600614_The two markers rs9652490 and rs11856808 were not strongly related to the essential tremor,late onset sporadic Parkinson's disease, but the rs9652490G allele might be a protective factor for the early onset Parkinson's disease in Chinese population. 20659559_LINGO-1 inhibits multiple aspects of oligodendrocyte differentiation independently of the LRRs via a process that requires p75(NTR) signalling 20951767_No significant differences are found in genotype and allele distribution in the rs9652490 variant of LINGO1 in either Chinese or Caucasian Parkinson disease patients. 20951767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20957646_LINGO1 variant rs9652490 (A > G) is unlikely to play a major role in Parkinson's disease in Chinese populations. 21158743_while there were no significant differences in the Lingo1 minor allele frequency and genotype frequency between Chinese essential tremor and controls, pooled analysis showed a higher proportion of GG genotype in tremor patients 21219542_LINGO1 variants are not a major risk factor for developing familial essential tremor in this population, which suggests the existence of other genetic risk factors responsible for familial essential tremor in this movement disorder clinic population. 21264305_genotyping results lead us to conclude that no association exists between the key variant rs9652490 and Essential tremor (P(corr) = 1.00). 21506150_This study demonistrated that LINGO1 variants could increase risk of PD, specifically those presenting the non-rigid-akinetic phenotypes, which suggests that LINGO1 may have a role in the etiology of tremor in PD at least in the Spanish population. 21741293_There were no significant differences in frequencies for all alleles between the essential tremor (ET) group and controls; however, an association of genotype A/G of the SNP rs9652490 with the familial ET phenotype was found. 21752692_Single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP)s of LINGO1 play a role in the development of Parkinson's disease in the Italian population. 21955595_This study showed that LINGO1 rs9652490 and rs11856808 are not associated with the risk of Parkinson's disease. 22133804_the N-terminal region containing the leucine-rich repeats along with the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of LINGO-1 are not required for self-interaction or interaction with amyloid precursor protein 22425540_Results of a meta-analysis suggest a relationship between LINGO1 rs11856808 polymorphism and risk of essential tremor (ET) and familial ET, while rs9652490 polymorphism is only associated with the risk for familial ET. 22514275_LINGO-1, a transmembrane signaling protein, inhibits oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination through intercellular self-interactions 22710005_the present meta-analysis does not support the notion that LINGO1 rs9652490 SNP is a major genetic risk factor for parkinson disease.[meta-analysis] 23482566_LINGO-1 potentiates neuronal apoptosis, likely by inhibiting WNK3 kinase activity. 23574883_This study demonistrated that theLINGO1 rs9652490 and rs11856808 polymorphisms are not associated with risk for multiple sclerosis. 23682623_This review found that several gene variants in the LINGO1 gene may increase the risk of essential tremor. 23754655_LINGO1 variants are associated with essential tremor in Chinese Han female patients. 24448210_Lingo-1 signaling is altered in the schizophrenia brain. 24531928_The results of this study show Increased LINGO1 in the cerebellum of essential tremor patients. 24583087_LINGO-1 can directly bind to ErbB2, block ErbB2 translocation into lipid rafts, and inhibit its phosphorylation. 25666623_Data indicate that leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 1 (LINGO-1) is intracellular and competes with Nogo-66 receptor (NgR) for binding to p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR). 26254004_LINGO1 rs11856808 plays a protective role by decreasing the risk for PD, but not for MSA, in Chinese population. 26979953_LINGO1 protein acts as a gateway protein internalizing into the tumor cells when engaged by antibody and can carry antibody conjugated with drugs to kill Ewing sarcoma cells. 28837161_We identified homozygous missense variants in LINGO1, p.(Arg290His) in family F162 and p.(Tyr288Cys) in family PKMR65. Both variants were predicted to be pathogenic, and segregated with the phenotype in the respective families. Molecular modeling of LINGO1 suggests that both variants interfere with the glycosylation of the protein. 30064229_LINGO1 might be a positive primary glioblastoma prognostic gene and C7orf31 and VEGFA might be negative prognosticators. 31932443_LINGO1 is a regulator of BK channels. 33830473_LINGO-1 shRNA protects the brain against ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB and JAK2/STAT3. |
ENSMUSG00000049556 |
Lingo1 |
23.245657 |
6.2736650005 |
2.649308 |
0.390870006 |
50.258861 |
0.00000000000134744869195214043955664706224237432957008264722276180691551417112350463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007936289981330243882231205178346691245933053338035279011819511651992797851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.7190348 |
9.8288949 |
6.5431779 |
1.3768392 |
| ENSG00000169855 |
6091 |
ROBO1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6N7 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for SLIT1 and SLIT2 that mediates cellular responses to molecular guidance cues in cellular migration, including axonal navigation at the ventral midline of the neural tube and projection of axons to different regions during neuronal development (PubMed:10102268, PubMed:24560577). Interaction with the intracellular domain of FLRT3 mediates axon attraction towards cells expressing NTN1 (PubMed:24560577). In axon growth cones, the silencing of the attractive effect of NTN1 by SLIT2 may require the formation of a ROBO1-DCC complex (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of cell migration via its interaction with MYO9B; inhibits MYO9B-mediated stimulation of RHOA GTPase activity, and thereby leads to increased levels of active, GTP-bound RHOA (PubMed:26529257). May be required for lung development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O89026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10102268, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24560577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26529257, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chemotaxis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
Bilateral symmetric nervous systems have special midline structures that establish a partition between the two mirror image halves. Some axons project toward and across the midline in response to long-range chemoattractants emanating from the midline. The product of this gene is a member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily and encodes an integral membrane protein that functions in axon guidance and neuronal precursor cell migration. This receptor is activated by SLIT-family proteins, resulting in a repulsive effect on glioma cell guidance in the developing brain. A related gene is located at an adjacent region on chromosome 3. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:6091; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; axon guidance receptor activity [GO:0008046]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; LRR domain binding [GO:0030275]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; aorta development [GO:0035904]; aortic valve morphogenesis [GO:0003180]; axon midline choice point recognition [GO:0016199]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; chemorepulsion involved in postnatal olfactory bulb interneuron migration [GO:0021836]; endocardial cushion formation [GO:0003272]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070100]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033600]; negative regulation of negative chemotaxis [GO:0050925]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; outflow tract septum morphogenesis [GO:0003148]; positive regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050772]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway involved in heart induction [GO:0035481]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900748]; pulmonary valve morphogenesis [GO:0003184]; Roundabout signaling pathway [GO:0035385]; ventricular septum morphogenesis [GO:0060412] |
12082532_Tumour specific promoter region methylation of ROBO1 in human cancers 16254601_a slight disturbance in neuronal axon crossing across the midline between brain hemispheres, dendrite guidance, or another function of ROBO1 may manifest as a specific reading disability in humans 16636676_Both medulloblastoma and glioma tumors express Robo1. 16685377_Expression of Robo1 is mainly in tumor cells, whereas Robo4 is primarily in endothelial cells of tumor vessels. Therefore, the Robo proteins provide potential target structures for the anti-tumorigenic and anti-angiogenic therapy of colorectal carcinoma. 16740745_The ROBO1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and shed into serum in humans. These observations suggest that ROBO1 is a potential new serologic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma and may represent a new therapeutic target. 17062560_heparin/HS is an integral component of the minimal Slit-Robo signaling complex and serves to stabilize the relatively weak Slit-Robo interaction 17671114_Dutt1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in lung cancer 17671369_The minimal Robo1-binding region required for Slit activation has been mapped to the N-terminal immunoglobulin (Ig)1-2 domains. 17848514_the crystal structures of the first two Ig domains of Robo1 (Ig1-2), and the minimal complex between these proteins (Slit2 D2-Robo1 Ig1). 17968499_a chemorepulsive effect mediated by interaction of Slit2 and Robo1 participates in glioma cell guidance in the brain. 18270976_mRNA expression of ROBO1 in lymphocytes was significantly reduced in the autistic group 18387595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18948384_Robo1 is essential for Robo4-mediated filopodia induction 19023125_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19104841_Inactivation of ROBO1/DUTT1 could be used as molecular signature for early detection and prognosis of the head and neck cancer. 19706539_Data uncover a previously unknown function of USP33 and reveal a new player in Slit-Robo signaling in cancer cell migration. 20029409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20300657_These results describe a Slit-miR-218-Robo1 regulatory circuit whose disruption may contribute to gastric cancer metastasis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20438712_these findings reveal that through interacting with Robo1, Slit2 is a novel and potent lymphangiogenic factor and contributes to tumor lymphatic metastasis. 20471383_ROBO1 may function beyond the receptor through stepwise cleavages and translocation to the nucleus. 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20949370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20949370_While replication will be critical, the present results strongly support ROBO1 as the first gene discovered to be associated with language deficits affecting normal variation in language ability. 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21060114_This study proposed that the expression of ROBO1 in the anterior neocortex may mark the early location of the human motor cortex, including its corticospinal projection neurons, allowing further study of their early differentiation. 21283129_Engagement of Robo1 by Slit2 recruits Hakai to E-cad, culminating in E-cad ubiquitination and lysosomal degradation. 21385904_Data show direct interaction between miR-218 and the 3'UTR of mRNAs encoding ROBO1, survivin (BIRC5), and connexin43 (GJA1). 21465248_three major members (Slit2/3 and Robo1) of Slit/Robo family are widely expressed in the human normal and malignant ovarian tissues; but Slit/Robo signaling may not play an important role in regulating human ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration 21686327_SLIT-ROBO signaling potentially contributes to the development of diabetic retinopathy. 21857494_studies demonstrate a novel role for Slit2/Robo1 axis in HIV replication and may contribute to the understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis 21875486_Robo1 expression correlates negatively with invasive ductal carcinoma brain metastasis, and correlates positively with the age and prognosis of IDC patients. 21998696_distinct ROBO1 variants may influence the risk of wet and dry AMD, and the effects of ROBO1 on AMD risk may be modulated by RORA variants. 22262894_The results of this study indicated that normal crossing of the auditory pathways requires an adequate ROBO1 expression level. 22719878_data suggests the importance of abrogation of SLIT2-ROBO1 and SLIT2-ROBO2 interactions in the initiation and progression of CACX and also for early diagnosis and prognosis of the disease 22826604_we report that the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells is determined by an interaction between the Robo1 receptor and its ligand Slit2 22898079_breast cancer cell migration and invasion was promoted when miRNA- 218 was significantly down regulated, in the way of up-regulation of Robo1. 23119100_Data indicate that slit2N alters the localization and binding of Robo1 to WASp and LSP1 in HIV-1-gp120-treated immature dendritic cells (iDCs). 23733161_Downregulation of miRNA-218 and upregulation of ROBO-1 were first demonstrated in pancreatic cancer. 23953227_Low Robo1 expression was associated with cell proliferation and migration in ICC and was one of the adverse prognostic factors in patients with these tumors. 23954868_No genetic association of ROBO1 with developmental dyslexia was found in Indian population. 24247621_Frameshift mutations of ROBO1 and ROBO2 genes and alteration of ROBO2 expression in gastric and colorectal cancers suggest that both genes might play roles in the pathogenesis of both cancers. 24430574_ROBO1 contributs to the deficits in developmental dyslexia and its correlated phenotypes. 24612512_Family-based analysis shows association of SNPs in ROBO1 with reading diasbilities. 24673457_Full-length Robo1 is present almost exclusively as a dimer; parallel studies demonstrate the biological activity of Slit2 and its interaction with Robo1. 24752651_Lower expression of ROBO1 is associated with prostate cancer disease progression. 24777535_In this review, we summarize recent findings demonstrating that the neuronal guidance cues, Slit and Roundabout (Robo), prevent the migration of multiple leukocyte subsets towards diverse inflammatory chemoattractants. 24777813_prognostic implications of SLIT and ROBO1 expression in gallbladder cancer 24981056_Data show that ubiquitin specific peptidase 33 (USP33) mediates nerve tissue proteins Slit-Robo signaling in lung cancer cell migration. 25010661_ROBO1 was a functional target of miRNA-218's downstream pathway involving in cell invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer. 25465073_Inactivation of SLIT2 and/or ROBO1 is one of the early events in development of dysplastic lesions of head and neck and has prognostic importance. 25605242_Slit2/Robo1 signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through Src-mediated activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 25752613_identify two separate binding sites for heparin interaction with Robo1: one binding site at the previously identified site for heparin dp8 and a second binding site at the N terminus of Robo1 that is disordered in the x-ray crystal structure 25786906_Data indicate that SLIT2, miR-218-1, RET/PLAG1 and SLIT2/ROBO1 pathway involved in Hirschsprung's disease. 25955714_miR29a inhibits cell migration and invasion in breast cancer cells, at least in part, by directly targeting Robo1. 26022159_Robo1 promoted cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) expression in HUVECs, and a distorted actin cytoskeleton in HUVECs was observed when Robo1 expression was suppressed. In conclusion, Robo1 promoted angiogenesis in HCC mediated by Cdc42. 26081620_these studies demonstrate that miR-219-5p inhibited cancer cell growth and invasion by direct targeting ROBO1, implicating miR-219-5p as an attractive candidate for cancer therapy. 26252416_miR-29a markedly inhibits the protein expression of Robo1 in mesenchymal stem cells. 26264936_Significantly increased serum Slit2 levels and hepatic expression of Slit2 and Robo1 were observed in patients with liver fibrosis. 26282852_expression pattern in extravillous trophoblasts associated with the remodeling events of the tubal pregnancy 26400100_our findings indicated that Slit2/Robo1 axis possibly be regarded as a significant clinical parameter for predicting brain metastasis in breast cancer patients. 26427657_ROBO1 deletion in a putative transcriptional regulatory region 26608094_ROBO1 somatic mutation is associated with myelodysplastic syndrome progression. Overexpression of ROBO1 produces anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in leukaemia cells. However, this effect was lost in ROBO mutants. 26713366_These results suggest that Slit2/Robo1 binding exerts an effect on cell migration, which is negatively regulated by Robo4, and Robo1 may function by interacting with CdGAP in HUVECs. 26745454_human placental multipotent mesenchymal stromal cell express Slit2 and both Robo1 and Robo4 are present in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 26889813_Over-expression of miR-218 in glioma cells may inhibit the proliferation and tumorigenicity through targeting Robo1, suggesting that miR-218 could be a potential target for developing therapies in treating glioma. 26975850_A SLIT2/ROBO1 signaling circuit as a key regulatory mechanism. 27176045_We postulate that Robo1 promotes tumor invasion partly by the upregulation of MMP2 after activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Notably, Slit2 knockdown caused the upregulation of Robo1 expression both at the mRNA and protein levels. Thus, the stimulatory effects of Slit2 knockdown on tumor progression can be ascribed, at least in part, to the upregulation of Robo1 and its positive role in tumor progression. 27240594_Results demonstrate that human ROBO1 may be involved in the regulation of the structure and connectivity of posterior part of corpus callosum. 27431199_Slit2-Robo1 signaling promoted the adhesion, invasion and migration of tongue carcinoma cells by upregulating the expression levels of MMP2 and MMP9 and, downregulating the expression of E-cadherin. 27659325_Results indicate the importance of SLIT2-ROBO1-CDC42 signaling pathway in predicting tumor progression. 27916173_High Slit2 expression is associated with glioma. 28004534_Differential expression levels and methylation status of ROBO1 in mantle cell lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. 28240421_These findings offer direct evidence supporting ROBO1-callosum association in humans and also provide valuable insight into the functions of ROBO1 and the gene-to-brain mechanisms that underlie human reading. 28323002_ROBO1 mediated the inhibitory effect of miR-218 on angiogenesis in gastric cancer. 28402530_ROBO1 gene mutation is responsible for the development of pituitary stalk interruption syndrome. 28406573_The findings indicate that the migration of human neural progenitor cells from the fetal subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb is partially regulated by the Slit2-Robo1 axis. 28485101_SLIT2/ROBO1 signalling may regulate trophoblast differentiation and invasion causing restricting beta human chorionic gonadotrophin (beta-hCG) production, shallow trophoblast invasion and inhibiting placental angiogenesis in missed and threatened miscarriage during the first trimester. 28592524_we show that variants in ROBO1 are associated with CHD involving septal defects and tetralogy of Fallot. 28738960_Overexpression of miR-218 and inhibition of Robo1 reduced the number of the invased cells of HCC4006. 28924964_High ROBO1 expression is associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion. 28936884_miR-218 inhibits human lung adenocarcinoma cell migration and invasion via the suppression of Ecop and Robo1 expression 28973045_The alteration of Slit2 and Robo1 expression in the retinas of diabetic rats and patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy suggests a role for the Slit-Robo signal in the various stages diabetic retinopathy. 29194579_Exome sequencing identified ROBO1 variants in one family and a GREB1L variant in another family. GREB1L and ROBO1 were added to our kidney-gene panel and additional variants were identified. Next-generation sequencing substantially contributes to identifying causes of fetal kidney anomalies. 29299781_findings indicate that in a diabetic-like environment, in addition to mesangial cells, autocrine activation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling of HRGECs may contribute to angiogenesis of HRGECs through PI3K/Akt/VEGF pathway. 29520710_The results suggest that Robo1 exists in two conformations that differ by their compactness and capability to interact with Heparan Sulfate. The results also suggest that the highly flexible interdomain hinge region connecting the Ig1 and Ig2 domains of Robo1 plays an important functional role in promoting the Robo1-Slit interaction. 29523788_SLIT2 and ROBO1promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and contributes to the Warburg effect in osteosarcoma. 29693114_the expression of hsa_circRNA0054633 has a protective effect against high glucoseinduced endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting ROBO1 and HO1. 29864155_Robo1 expression might counteract migration and also radiation-induced migration of glioblastoma cells, a process that might be connected to mesenchymal-epithelial transition. 30019121_Nuclear Localization of Robo is Associated with Better Survival in Bladder Cancer. 30077386_ROBO1 was associated with Autism Spectrum Disorders, Dyslexia and Speech Sound Disorder. 30157923_MiR-218 modulates the osteogenic differentiation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) fibroblast-like synovial cells (FLS) through the roundabout guidance receptor 1 (ROBO1)/Dickkopf-1 protein (DKK-1) axis. 30427759_Arl4A participates in Slit2/Robo1 signaling to modulate cell motility by regulating Cdc42 activity. 30530901_Familial ROBO1 deletion is associated with ectopic posterior pituitary, duplication of the pituitary stalk and anterior pituitary hypoplasia. 30842157_SLIT2 induced motility and a SLIT2 gradient induced chemotaxis of breast cancer cells, which was amplified by heparin. ROBO1 was abundantly expressed in BMs of breast and colon cancer as well as in PM of ovarian cancer. Together, this suggests that ROBO-expressing tumor cells are attracted to the brain and peritoneum by SLIT2-mediated chemotaxis. 30896071_Our study reveals the inhibitory function of Slit-Robo signalling in gastric cancer (GC) and uncovers a role of USP33 in suppressing cancer cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by enhancing Slit2-Robo1 signalling. USP33 represents a feasible choice as a prognostic biomarker for GC. 31194736_SLIT2-ROBO1 signaling was linked with regulation of genes involved in inflammation, pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein genes, decidualization and fetal growth. We propose that this receptor-ligand couple is a component of the signaling network that promotes Spontaneous preterm birth (SPTB). 31393085_The mRNA levels of SLIT2 and ROBO1 were higher in the basal plate of SPTB placentas when compared to those of infants born at term or from elective preterm deliveries 31791578_Engagement of Robo1 by Slit2 induces formation of a trimeric complex consisting of Src-Robo1-E-cadherin for E-cadherin phosphorylation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 31811830_R5, a neutralizing antibody to Robo1, suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis by inhibiting angiogenesis via down-regulating filamin A. 32213157_A Study Based on the Correlation Between Slit2/Robo1 Signaling Pathway Proteins and Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis. 32620618_Photosensitizer treatment with illumination robustly enhanced the antitumor effect of the IT-ROBO1 immunotoxin. 32687658_Identifying and treating ROBO1(-ve) /DOCK1(+ve) prostate cancer: An aggressive cancer subtype prevalent in African American patients. 33037408_PRRG4 promotes breast cancer metastasis through the recruitment of NEDD4 and downregulation of Robo1. 33236535_Crosstalk between the activated Slit2-Robo1 pathway and TGF-beta1 signalling promotes cardiac fibrosis. 33318575_Structural insights and evaluation of the potential impact of missense variants on the interactions of SLIT2 with ROBO1/4 in cancer progression. 33714986_Roundabout homolog 1 inhibits proliferation via the YY1-ROBO1-CCNA2-CDK2 axis in human pancreatic cancer. 33767589_LncRNA-NONHSAT024778 promote the proliferation and invasion of chordoma cell by regulating miR-1290/Robo1 axis. 34021307_Circular RNA_0001495 increases Robo1 expression by sponging microRNA-527 to promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells. 34268498_ROBO1 Promotes Homing, Dissemination, and Survival of Multiple Myeloma within the Bone Marrow Microenvironment. 34414975_Expression of the axon guidance factor Slit2 and its receptor Robo1 in patients with Hirschsprung disease: An observational study. 34490644_Ductular reaction promotes intrahepatic angiogenesis through Slit2-Roundabout 1 signaling. 35227688_Biallelic pathogenic variants in roundabout guidance receptor 1 associate with syndromic congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. 35236289_miR-152-3p impedes the malignant phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing roundabout guidance receptor 1. 35348658_Novel dominant and recessive variants in human ROBO1 cause distinct neurodevelopmental defects through different mechanisms. 35534675_Identification of non-synonymous variations in ROBO1 and GATA5 genes in a family with bicuspid aortic valve disease. 35584116_An ancient founder mutation located between ROBO1 and ROBO2 is responsible for increased microtia risk in Amerindigenous populations. 36029493_MiR-218 Targeted Regulation of Robol Expression Regulates Proliferation, Invasion and Migration of Glioma Cells. 36042257_NMR analysis suggests the terminal domains of Robo1 remain extended but are rigidified in the presence of heparan sulfate. 36277474_Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-29b Reduces Angiogenesis in Pancreatic Cancer by Silencing ROBO1 and SRGAP2. |
ENSMUSG00000022883 |
Robo1 |
469.060960 |
2.6395554419 |
1.400295 |
0.103341102 |
182.703423 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000001245022326827272461861703189811180496016201870307877377824985437152813157576868750590257078009594079881657523178883906211922294460237026214599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000216960207130702978384136175740230158931644155702044852442988786947906809710821843054566363337687068897543379852876910263148602098226547241210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
696.6242706 |
68.6461884 |
266.0806558 |
19.6448858 |
| ENSG00000169885 |
163688 |
CALML6 |
protein_coding |
Q8TD86 |
|
Calcium;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity and enzyme regulator activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:163688; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; enzyme regulator activity [GO:0030234] |
15621662_a novel human gene, CAGLP (calglandulin-like protein) was predicted, and subsequently isolated from human skeleton muscle 30699354_The EF-hand protein calmodulin-like 6 (CALML6) directly bound to the phosphorylated serine-rich (SR) region of IRF3 and impaired its dimerization and nuclear translocation. |
|
|
7.906358 |
0.1474806352 |
-2.761403 |
0.851030458 |
10.352933 |
0.00129269141111460232271279657823015440953895449638366699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002957700391885216290727145249661589332390576601028442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1308996 |
1.3735217 |
14.5843543 |
5.5213383 |
| ENSG00000169896 |
3684 |
ITGAM |
protein_coding |
P11215 |
FUNCTION: Integrin ITGAM/ITGB2 is implicated in various adhesive interactions of monocytes, macrophages and granulocytes as well as in mediating the uptake of complement-coated particles and pathogens (PubMed:9558116, PubMed:20008295). It is identical with CR-3, the receptor for the iC3b fragment of the third complement component. It probably recognizes the R-G-D peptide in C3b. Integrin ITGAM/ITGB2 is also a receptor for fibrinogen, factor X and ICAM1. It recognizes P1 and P2 peptides of fibrinogen gamma chain. Regulates neutrophil migration (PubMed:28807980). In association with beta subunit ITGB2/CD18, required for CD177-PRTN3-mediated activation of TNF primed neutrophils (PubMed:21193407). May regulate phagocytosis-induced apoptosis in extravasated neutrophils (By similarity). May play a role in mast cell development (By similarity). Required with TYROBP/DAP12 in microglia to control production of microglial superoxide ions which promote the neuronal apoptosis that occurs during brain development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05555, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20008295, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21193407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28807980, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9558116, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Integrin;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Systemic lupus erythematosus;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes the integrin alpha M chain. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. This I-domain containing alpha integrin combines with the beta 2 chain (ITGB2) to form a leukocyte-specific integrin referred to as macrophage receptor 1 ('Mac-1'), or inactivated-C3b (iC3b) receptor 3 ('CR3'). The alpha M beta 2 integrin is important in the adherence of neutrophils and monocytes to stimulated endothelium, and also in the phagocytosis of complement coated particles. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:3684; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; integrin alphaM-beta2 complex [GO:0034688]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane raft [GO:0044853]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; complement component C3b binding [GO:0001851]; heat shock protein binding [GO:0031072]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; amyloid-beta clearance [GO:0097242]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway involved in cell-cell signaling [GO:1905114]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0098742]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; complement-mediated synapse pruning [GO:0150062]; ectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0010668]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; negative regulation of dopamine metabolic process [GO:0045963]; phagocytosis, engulfment [GO:0006911]; positive regulation of hippocampal neuron apoptotic process [GO:0110090]; positive regulation of microglial cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:1904151]; positive regulation of neuron death [GO:1901216]; positive regulation of neutrophil degranulation [GO:0043315]; positive regulation of prostaglandin-E synthase activity [GO:2000363]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; positive regulation of superoxide anion generation [GO:0032930]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; vertebrate eye-specific patterning [GO:0150064] |
11881155_Mac-1 molecules mediated cell adhesion predominantly to fibrinogen, and its early degradation products, fragments X and Y 11893077_CD11b-mediated adhesion of myeloid leukemia cells in the course of induced monocytic differentiation is crucial for cell attachment, development of a monocytic phenotype and subsequent survival. 11937770_Respiratory syncytial virus enhances the expression of CD11b molecules by human eosinophils primed with platelet-activating factor 11953106_CD11b may play an important role in pathogenic process(in COPD) 12009501_fibroblasts prostaglandin-E2 is elevated in Alzheimer's disease (prostaglandin-E2, PGE2) 12036876_Identification of integrin alpha(M)beta(2) as an adhesion receptor on human peripheral blood monocytes for Cyr61 and connective tissue growth factor: immediate-early gene products expressed in atherosclerotic lesions.(integrin alpha(M)beta(2)) 12107753_Impaired neutrophil actin assembly causes persistent expression and reduced primary granule exocytosis in Type II diabetes 12145463_Increased expression of CD11b/CD18 adhesion molecules was obtained in PV and ET patients, which could be associated with increased leukocyte adehesiveness contributing to the hypercoagulable state. 12165526_mediates type I phagocytosis under nonopsonic conditions and type II under opsonic conditions 12208882_The junctional adhesion molecule 3 (JAM-3) on human platelets is a counterreceptor for the leukocyte integrin Mac-1. 12234260_Histoplasma capsulatum inhibits apoptosis and Mac-1 expression in leucocytes. 12244179_Mac-1 (CD11b) is required for neutrophil-Fc alpha RI binding of secretory IgA and subsequent neutrophil activation. 12377763_investigation of molecular basis for broad ligand recognition 12377937_iIgA promotes neutrophil apoptosis through a mechanism dependent on Mac-1(CD11b) cooperation, which involves the activation of the respiratory burst 12390020_The mechanism that regulates the unmasking of the integrin alpha M cryptic binding site in the gamma C-domain of fibrinogen has been identified. 12393547_recognition of uPA by alpha(M)beta(2) allows for formation of a multicontact trimolecular complex, in which a single uPA ligand may bind to both uPAR and alpha(M)beta(2); interaction of uPA with each receptor influences cell adhesion and migration 12393719_ZBP-89 is a repressor of the human beta 2-integrin CD11b gene during differentiation of monocytes into macrophages 12444150_The same lectin domain within CD11b regulates both the cytotoxic and adhesion functions of Mac-1/CR3. 12466503_Stabilizing the integrin alpha M inserted domain in alternative conformations with a range of engineered disulfide bonds. 12485936_Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) is crucial for effective Fc receptor-mediated immunity to melanoma. 12495676_Leptospira interrogans binds to the CR3 receptor on neutrophils 12516552_Adhesion of dendritic cells derived from CD34+ progenitors to resting human dermal microvascular endothelial cells is down-regulated upon maturation and partially depends on CD11a-CD18, CD11b-CD18 and CD36. 12576754_Level of expression of the adhesion molecule/complement receptor CD11b/CD18 and the chemokine receptor IL-8 receptor-A was also higher after vaginal delivery. 12600815_the expression of ICAM-1 might involve both p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB activities, whereas the regulation of CD11b, CD18, and ICAM-3 expressions might be mediated through p38 MAPK but not NF-kappaB. 12665127_uPAR up-regulated the Mac-1 adhesion to fibrinogen, and focal adhesion kinase and MAPK were involved in this regulation 12694184_ICAM-4 binds to the I domain of this integrin. 12731070_Fibrinogen-CD11b/CD18 interaction activates the NF-kappa B pathway and delays apoptosis in human neutrophils. 12760968_Our results indicate that induction of Ca2+ entry by the depletion of Ca2+ from intracellular stores upregulates CD11b/CD18 expression on eosinophils and primes eosinophil transmigration across lung epithelium. 12816955_three separate domains of alpha M beta 2 (the alpha MI-domain, the alpha M beta-propeller, and the beta 2I-domain) function together and contribute to the formation of the C3bi-binding site 12847278_The extracellular, membrane-proximal region of the CD11b receptor subunit plays an important role in integrin activation and therefore could be targeted by certain cell surface proteins as a conduit to control the integrin 'inside-out' signaling process. 12960243_Interaction of proteinase 3 with CD11b/CD18 (beta2 integrin) on the cell membrane of human neutrophils. 14532278_cooperative engagement of CR3 on both the lectin-like site involved in beta-glucan binding and the I-domain involved in C3bi binding produces AA release 14751053_CD11b expression with the whole blood flow cytometry seemed feasible and reliable in the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. 14769799_assembly of Plg and uPA on integrin alpha(M)beta(2) regulates Plm activity and plays a crucial role in neutrophil-mediated thrombolysis 15004192_The interaction between Mac-1 and Thy-1 is involved in the adhesion of leukocytes to activated endothelial cells as well as in subsequent transendothelial migration of leukocytes into the perivascular tissue. 15073035_Some anti-Mart antibodies interfere with Mac-1-dependent cellular functions of neutrophils. 15217824_platelet-activating factor or interleukin 8 acted in concert with P-selectin for further enhancing the activation of alphaMbeta2 15277376_Myeloid-related proteins-induced increased adhesion of monocytes to Fibronectin and upregulation of CD11b contribute to a facilitated accumulation of monocytes 15294914_BAP31 may play a role in regulating intracellular trafficking of CD11b/CD18 in neutrophils 15304494_studies of the interaction of the ligand binding alphaMI-domain of alphaMbeta2 with the D fragment of fibrinogen, which has multiple binding sites for integrin alphaMbeta2 15454120_we have shown here that eosinophils from atopic children express Mac-1 and demonstrated that this expresion may be up regulated by fMLP. 15485828_each subunit of alphaMbeta2 contributes distinct properties to alphaMbeta2 and that, in most but not all cases, the response of the integrin is a composite of the functions of its individual subunits 15585684_CD11b is increased on circulating phagocytes as an early sign of late-onset sepsis in extremely low-birth-weight infants 15615722_the beta2I domain of integrin alphaMbeta2 has a site which supports ICAM-1 binding to alpha(M)beta(2) and controls the open and closed conformation of the alpha(M)beta(2) receptor 15641787_A novel binding region within the central domain of the fibrinogen gamma-module localizes within gamma chain residues 228-253 and has been identified as the integrin alpha M subunit of Mac-1. 15718918_elastase binds to the beta(2)-integrin CD11b and induces a conformational alteration of CD11b 15730520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15741160_The alphaM lectin domain (but not the alpha M I domain) mediates integrin alphaMbeta2-dependent phagocytosis of chilled platelets by myeloid cells. 15778383_findings reveal that mycobacteria promote their uptake through a process of 'inside-out' signaling involving CD14, TLR2, PI3K, and cytohesin-1. This converts low avidity CR3 into an active receptor leading to increased bacterial internalization 15976367_Patients with higher peripheral CD11b expression showed a markedly augmented increase in dialysate glucose in adipose tissue during oral glucose tolerance testing and increased adipose tissue lipolysis as well. 16037628_In DVT subjects, at baseline, the phenotypical expression of CD11b was decreased and that of CD11c was increased, and upon PMN activation in DVT subjects CD11b, CD11c and CD18 increased, while CD11a expression did not show any change 16239529_studies suggest that the activation and surface expression of CR3, FHA expression, and the efficiency of ACT internalization all influence whether B. pertussis will be phagocytosed and ultimately killed by neutrophils 16249234_We demonstrate that cell movement in response to IL-8 is mediated by Mac-1, whereas LFA-1 is required for directional migration. By contrast, chemotaxis to fMLP requires Mac-1 for cell movement. 16260637_Has been implicated in the firm adhesion and transmigration of leukocytes at sites of platelet deposition. 16357311_Monocytes exposed to nonesterified fatty acids demonstrated a significant increase in CD11b message expression 16389569_CRP induces CD11b expression in monocytes through a peroxide independent pathway involving both Syk phosphorylation and [Ca(2+)](i) release. 16508260_Both hypoxia and heat shock prevented the lipopolysaccharide-induced increase in adult CD11b. 16614246_While tolerogenic DCs are not induced via alphavbeta5, coligation of CR3 and alphavbeta5 maintains the DC's tolerogenic profile. 16782049_Mac-1 subunits take different conformation when expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) and human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells, respectively 16915040_telmisartan inhibits the expression of the pro-inflammatory beta2-integrin MAC-1 expression in lymphocytes independently of angiotensin II 17172930_Increased levels of cellular adhesion molecules in patients with coronary artery ectasia may be an indicator of endothelial activation and inflammation and are likely to be in the causal pathway leading to coronary artery ectasia. 17202372_demonstrated the role of DC-SIGN in complement opsonized virus uptake and infection 17202407_These results establish for the first time at least two distinct roles for talin during CR3/alpha(M)beta(2)-mediated phagocytosis, most noticeably activation of the CR3/alpha(M)beta(2) receptor and phagocytic uptake. 17228360_We conclude that in vivo transmigrated leukocytes from patients on biocompatible high-flux hemodiafiltration or high-flux hemodialysis have a preserved capacity to express CD11b at the site of interstitial inflammation. 17346796_PLD-synthesised PtdOH stimulates the generation of PtdIns(4,5)P(2), which in turn mediates talin binding to, and activation of, CD11b/CD18 required for neutrophil stable adhesion and migration. 17372166_observations identify interaction of CD40L and Mac-1 as an alternative pathway for CD40L-mediated inflammation; this novel mechanism expands understanding of inflammatory signaling during atherogenesis 17445870_both AGE-BSA and MG induce a dose-dependent expression of the adhesion molecule Mac-1 on the surface of neutrophils 17721605_review focuses on the non-receptor tyrosine kinase Syk as an important downstream signaling component of beta2 integrins (CD11/CD18) that is required for the control of different PMN functions including adhesion, migration and phagocytosis. 17927697_We report that Bordetella persussis ACT ( adenylate cyclase toxin) induces COX-2 in HEK293T cells expressing Mac-1. 17957461_Mannitol upregulates monocyte HLA-DR, monocyte and neutrophil CD11b, and inhibits neutrophil apoptosis. 18065787_HD patients with a low P(HCO3) exhibited low neutrophil pHi that in turn increased the expression of CD11b/CD18. This increased expression of CD11b/CD18 on the uraemic neutrophils may contribute to the pHi-mediated phagocytosis. 18096476_IL1R2 was greatly decreased with future rejection and FLT3, ITGAM, and PDCD1 showed borderline changes in future cardiac rejections. 18156711_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18164590_TNF-alpha unveils a previously unknown capacity of neutrophils to migrate to CCL3 through the intervention of Mac-1. 18204098_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204098_identified and confirmed through replication two new genetic loci for SLE: a promoter-region allele associated with reduced expression of BLK and increased expression of C8orf13 and variants in the ITGAM-ITGAX region 18204446_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18204446_study presents four new regions having genetic associations with systemic lupus erythematosus in women of European descent: ITGAM, KIAA1542, PXK and rs10798269 18204448_A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M)(encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic luopus erythematosus. 18204448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18375764_Bordetella pertussis CyaA binding to CD11b/CD18 18414903_Cancer patients with infection had higher blood neutrophil and monocyte CD11b/CD18 expression levels than patients with neoplastic fever, those with advanced cancer without infection, or healthy controls 18495781_Myeloid zinc factor-1 is involved in a calcitriol-induced signaling pathway leading to myeloid cell differentiation and activation of CD11b and CD14. 18496641_Diabetic microangiopathy is accompanied by increase in CD11b expression and decrease in CD62L expression on peripheral blood neutrophils. 18509085_cooperation of the alpha(M)beta(2)/GPIbalpha and to PSGL-1/P-selectin systems regulates the prothrombotic properties of PMN-derived microparticles and MP-induced platelet activation 18541300_The differential involvement of CD11c and CD11b in adhesion and subsequent cytoskeletal changes in monocytes exposed to different conditions. 18617697_Myeloperoxidase independent of its catalytic activity through signaling via the adhesion molecule CD11b/CD18 rescued human neutrophils from constitutive apoptosis and prolonged their life span. 18644795_analysis of conformational changes in the alpha(M)beta(2) headpiece and reorientation of its transmembrane domains when alpha(M)beta(2) interacts with uPAR 18676132_Down regulation of CD11b and CD18 expression in children with hypercholesterolemia: a preliminary report. 18678668_Streptococcus gordonii DL1 surface protein Hsa binds to the host cell membrane glycoproteins CD11b, CD43, and CD50 18684982_A versatile beta 2 integrin adhesion molecule, CD11b, expressed by eosinophils plays a key role in recognizing and/or interacting with beta-glucan that is present on the surface of the fungus Alternaria alternata. 18685529_Neutrophil chemotaxis and polarization were found to be impaired 24 h postexercise. Adherence was impaired 24 h postexercise as well, but the expression of the adhesion molecule CD11b/CD18 was not affected 18714035_closely related alpha(M)beta(2) ligands, plasminogen and angiostatin, derived from plasminogen, as well as fibrinogen and its two derivative alpha(M)beta(2) recognition peptides, P1 and P2-C, differed markedly in their effects on neutrophil apoptosis. 18762778_Interleukin-33 enhances adhesion, CD11b expression and survival in human eosinophils 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18941116_Both uPAR small-interference RNA (siRNA) and soluble anti-beta(1)/-beta(2) monoclonal antibodies abolished the anti-HIV effects of uPA, whereas CD11b siRNA reversed the anti-HIV effect of M25, but not that induced by uPA 19052753_Fibromyalgia patients showed a significantly decreased expression of CD11b on neutrophils. 19073595_the heparan sulfate proteoglycan form of epithelial CD44v3 plays a critical role in facilitating PMN recruitment during inflammatory episodes via directly binding to CD11b/CD18. 19086264_the role of protein kinase C zeta (PKCzeta) in interleukin (IL)-8-mediated activation of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) in human neutrophils 19110536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19129174_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19129174_These results demonstrate that the coding variant, rs1143679, best explains the ITGAM-systemic lupus erythematosus association, especially in European- and African-derived populations, but not in Asian populations. 19135988_Data confirmed the increased monocyte alphaL, alphaM and beta2 integrin subunits in diabetes mellitus. 19246218_Changes in external anion composition, not internal chloride or increases in Cl(-) efflux, are responsible for Mac-1 activation and increased adhesion to ICAM-1. 19250688_These changes in gene expression may reflect changes in the types of macrophages that populate the lesions in anti-CD11d mAb-treated rats. 19286673_ITGAM was associated with disease susceptibility of systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese and Thai populations. 19286673_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19387459_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19387459_Study showed that ITGAM is associated as a risk factor for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Hispanic Americans. 19480860_Findings indicate that the proposed CRP/CD11b ratio test could potentially assist physicians in determining an appropriate antibiotic treatment in patients with severe bacterial infection. 19546439_Data show that CD45, CD11b, CD15, and CD56 were diagnostic parameters with flow cytometry. 19550115_The positive rates of both CD11b and CD14 in HL-60 cells were over 90% after 5-day treatment (2 micromol/L ATRA or 10 micromol/L NSC67657. 19572148_Findings suggest the important role of the CD11b+/CD14/CD15+/CD33+ MDSCs in mediating immunosuppression in NSCLC. 19578722_histone modification including PRC2-mediated repressive histone marker H3K27me3 and active histone marker acH4 may involve in CD11b transcription during HL-60 leukemia cells reprogramming to terminal differentiation 19587009_suppressed ability of DCs to induce T cell proliferation was dependent on adhesive interactions between DCs and lymphatic endothelial cells that were mediated by the binding of Mac-1 on DCs to ICAM-1 on LECs. 19747912_ATRA-induced increase of Vav1 expression and phosphorylation may be involved in recruiting PU.1 to the CD11b promoter and in regulating CD11b expression during the late stages of neutrophil differentiation of APL-derived promyelocytes. 19748962_study found no evidence from a combined analysis of 3336 cases and 3502 controls to support association, of the ITGAM variant, R77H, with rheumatoid arthritis in the Caucasian population 19800635_The combination of high environmental stress and low CNS serotonin lead to increased expression of the beta(2)-integrins CD11b and CD11c on monocyte cell surfaces. 19811837_Dectin-1, although indispensable for recognition of beta-glucan-bearing particles in mice, is not the major receptor for yeast particles in human neutrophils. 19833726_CCL2 and interleukin-6 promote survival of human CD11b+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells and induce M2-type macrophage polarization 19863185_The CR3(CD11b/CD18) on PMNs was measured in NLF sample via chemiluminescence, and the technique shows promise as a diagnostic method for measuring upper airway LPS exposure. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19939855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19939855_results show a strong association between the risk allele (A) at rs1143679 of ITGAM and renal disease, discoid rash and immunological manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. 20185670_The immunomodulatory effects of ketamine are mediated via reduced interleukin-8 production in whole blood and expression of CD11b and CD16 on neutrophils. 20190138_These results demonstrate a role of PKCdelta in alpha(M)beta(2)-mediated Foxp1 regulation in monocytes. 20228269_High CD11b is associated with therapy resistance- and minimal residual disease in precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 20423844_Kidney-Tonifying plus Blood-Promoting Recipe regulates CD11b/CD18 and Bcl-2/Bax expression in blood leukocytes and improves microcirculatory status in aged patients with kidney deficiency and blood stasis syndrome. 20483667_The blockade of IL-1beta with anakinra and its effects on interleukin 8 (IL-8) levels and CD11b integrin expression in monocytes of type 1 diabetics are reported. 20580686_uPAR acts as a cofactor for iC3b binding to CR3 and regulates CR3-mediated phagocytosis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20629846_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20629846_This meta-analysis demonstrates a significant association between ITGAM gene polymorphism and SLE in multiple ethnic populations. 20665668_Rap1-mediated activation of alpha(M)beta(2) in macrophages shares both common and distinct features from Rap1 activation of alpha(IIb)beta(3) expressed in CHO cells. 20666624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20666624_an association of the ITGAM 77His or 858Val variants with systemic lupus erythematosus incidence and some clinical manifestation of this autoimmune disorder 20706761_The alteration of CD11b expression of PMN caused by garenoxacin at 0.5, 5.0, and 100.0 mg/l is not considered to hamper the function of these first-line-defense phagocytes. 20800911_Stent-induced activation of macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) on the surface of neutrophils might trigger their MMP-9 release, possibly leading to the mobilization of bone marrow-derived stem cells. 20824631_Our results identify Fc block treatment, dead cells, and cell doublets exclusion as simple but crucial steps for the proper analysis of tumor-infiltrating CD11b(+) cell populations. 20826754_we show that shedding of human CD11/CD18 complexes is a part of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis but not in osteoarthritis 20848568_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881011_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21068098_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21135163_Involvement of CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) in fibrin(ogen)-mediated melanoma-neutrophil aggregations is defined in a study of cell interactions linked to thrombosis, inflammation, and cancer metastasis under venous flow conditions. 21151989_Polymorphisms of the ITGAM gene confer higher risk of discoid cutaneous than of systemic lupus erythematosus in Swedish and Finnish populations 21252155_alphaMbeta integrin activation prevents alternative activation of human and murine macrophages and impedes foam cell formation. 21263017_study shows that P. gingivalis activates Rac2 and Cdc42 and upregulates CD11b/CD18 and its high-affinity epitope on neutrophils 21273385_Mycobacterial hypersensitivity pneumonitis requires TLR9-MyD88 in lung CD11b+ CD11c+ cells 21362770_Two large cohorts of systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients of European Caucasian ancestry do not support the implication of ITGAM, ITGAX, and CD58 genes in the genetic susceptibility of SSc, although they were identified as autoimmune disease risk genes. 21403131_Kinetic studies showed that the cleavage of CD11b is positively correlated with PMN detachment and subsequent transmigration. 21454473_the systemic lupus erythematosus-associated R77H substitution in the CD11b chain of the Mac-1 integrin compromises leukocyte adhesion and phagocytosis 21551251_PMN sialidase could be a physiologic source of the enzymatic activity that removes sialyl residues on beta2 integrin and ICAM-1, resulting in their enhanced interaction, and may be an important regulator of the recruitment of these cells to inflamed sites. 21571730_a potential influence of ITGAM rs1143679 in vascular lesion as part of pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis 21610569_Data found that blocking CD11b, CD18, or CD54 on the endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) surface with monoclonal antibodies protected EPCs, enhancing its survival. 21676865_low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) interacts with integrin alphaMbeta2 at specific binding sites 21840425_The aim of this study is to examine whether the ITGAM variant is also associated with other than systemic lupus erythematosus autoimmune diseases. 21874872_The data obtained suggest that spontaneous cell adhesion to fibrinogen is mediated to a greater extent by CD11b/CD18 integrins, while chemokine-stimulated adhesion and migration is mostly dependent on CD11c/CD18 molecules. 22052909_structures and interaction analyses of integrin alphaMbeta2 cytoplasmic tails 22053606_Morbidly obese individuals had significantly increased levels CD11b expression on monocytes as compared to controls. 22095715_Denticity of the Asp/Glu ligand of integrin CD11b/CD18 can modify divalent cation (calcium or magnesium) selectivity at the metal ion-dependent adhesion site in neutrophils, and hence integrin function. 22229891_conclude that IL-8 is the major factor regulating the expression of CD11b activation epitope in neutrophils 22251373_Data indicate the simultaneous analysis of CD64 together with CD304 (Neuropilin-1) or the combination of CD11b and CD38 was suitable for the identification of rheumatoid arthritis (RA)patients with high current activity in synovitis. 22552879_This study demonstrated regulation of alpha(M)-integrin on circulating mononuclear cells in Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS), as well as an important role for alpha(M)-integrin-ICAM-1 interactions in pathogenic GBS patient leukocyte trafficking at the blood-nerve barrier in vitro 22586164_The R77H variant of ITGAM impairs a broad range of CR3 effector functions in human monocytes and may predispose to systemic lupus erythematosus. 22722613_The early signaling requirements for the CD11b/CD203c compartment expression and CD63 degranulation provide support for the hypothesis that CD11b and CD203c reside in a similar compartment. 22893614_CD11b suppressed induction of NFATc1 by the complementary mechanisms of downregulation of RANK expression and induction of recruitment of the transcriptional repressor B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) to the NFATC1 gene. 23092917_CD11b expression correlates with monosomal karyotype and predicts an extremely poor prognosis in cytogenetically unfavorable acute myeloid leukemia. 23184931_macrophage interleukin-13 receptor has a role in foam cell formation through alphaMbeta2 integrin interference 23257917_integrin alpha9beta1/CD11B levels in circulating neutrophils are significantly elevated in pneumonia patients 23269830_Motility assays and time-lapse video microscopy showed that pneumococcal stimulation of macrophage motility required RrgA and complement receptor 3. 23334594_This study did not find an upregulation of CD11b in brain in patient with multiple sclerosis. 23398146_Allele frequencies were determined in the blood donor population as follows: 0.318 for HNA-1a, 0.668 for HNA-1b, 0.014 for HNA-1c, 0.768 for HNA-3a, 0.232 for HNA-3b, 0.882 for HNA-4a, 0.118 for HNA-4b, 0.736 for HNA-5a and 0.264 for HNA-5b. 23451151_findings demonstrate that the reduction in CR3-mediated phagocytosis associated with the 77H CD11b variant is not macrophage-restricted but demonstrable in other CR3-expressing professional phagocytic cells 23452299_There was no difference in neutrophil or monocyte CD11b expression among 4 study groups (sepsis (S), septic shock (SS), traumatic brain injury (TBI), controls (C)). Lymphocyte CD11b showed lower values in SS compared to C and TBI or S. 23469114_the 3D structure of the alphaA-containing ectodomain of the leukocyte integrin CD11b/CD18 (alphaMbeta2) in its inactive state 23479224_The progression of diapedesis may be regulated by spatial and temporal cleavage of Mac-1, which is triggered upon interaction with endothelium. 23514737_Binding kinetics differences between Mac-1 and lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1 are quantified and insight provided into their distinct functions in the inflammatory cascade of activated neutrophils. 23573259_Coronary artery disease patients blood samples showed a significantly higher L-selectin, but not CD11b response to TLR stimulation than controls. 23671673_The expression of CD11b, TLR4 and TLR2 is increased in monocyte-derived macrophages in IQ memory-discrepant individuals. 23686079_Hyperglycemic patients with type 2 diabetes have significantly higher levels of CD11b on granulocytes and monocytes compared to expression values of healthy controls. 23708937_The altered expression levels of ITGAM and FCgammaRIIIA mRNA in systemic lupus erythematosus patients and their correlations with clinical data suggest that ITGAM and FCgammaRIIIA may play a role in this disease. 23720274_LPS-induced Mac-1 expression on monocytes was significantly inhibited by pre-treatment with U-75302, a BLT1-receptor antagonist, suggesting a pivotal role of 5-LO-derived leukotrienes stop 23727038_Rhinovirus colocalizes with CD68- and CD11b-positive macrophages following experimental infection in humans. 23753600_studies of ITGAM genetic variants which are linked to systemic lupus erythematosus(SLE) have revealed that the R77H variant of the CD11b/Mac-1 receptor displays functional defects which may be relevant to SLE development 23754403_Staphylococcus aureus LukAB directly interacts with neutrophil CD11b by binding to the I domain, a property that determines the species specificity exhibited by this toxin. 23812215_Expression of CD11b and CD162 on monocytes has a temperature-dependent regulation, with decreased expression during hypothermia. 23880611_PGE2 may be involved in regulation of CD11b expression on eosinophils by aspirin administration. 23918739_The nonsynonymous ITGAM variants rs1143679 and rs1143678/rs113683 contribute to altered Mac-1 function on neutrophils. 23981064_Distribution of integrin beta(2) is also markedly altered in M. tuberculosis-infected DCs. A corresponding reduction in the alphaL (CD11a) and alphaM (CD11b) subunits that associate with integrin beta(2) was also observed. 24264377_In vivo engagement of B cell receptors in CD11b-deficient mice leads to increased autoantibody production and kidney immunoglobulin (Ig) deposition, thereby maintaining autoreactive B cell tolerance. 24269694_genetic polymorphism is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Brazilian patients 24373176_CD11b expression on polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with ankylosing spondylitis stimulated with lipopolysaccharide is not different to that of healthy controls. 24608226_The transcript levels of ITGAM significantly decreased for the systemic lupus erythematosus risk allele (A) relative to the non-risk allele (G), in a dose-dependent fashion. 24726062_Complement receptor 3 (CR3) inhibition impairs phagocytosis of serum-opsonized zymosan but has little impact on phagocytosis of unopsonized zymosan in the absence or presence of lipopolysaccharide. 24782118_Although CD11b was more frequently expressed in blast cells of patients with intermediate and unfavorable cytogenetic risk groups, this feature did not translate into different clinical outcome. 24829201_circulating trisomy 12 CLL cells also have increased expression of the integrins CD11b, CD18, CD29, and ITGB7, and the adhesion molecule CD323. 24886912_Results show the functional importance of integrin alpha M (ITGAM) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathogenesis through impaired phagocytosis. 24945596_The HNA-1b allotype influences the Fc gamma RIIIb cooperation with Fc gamma RIIa, but not with CR3. 25005557_hnRNP K in PU.1-containing complexes recruited at the CD11b promoter: a distinct role in modulating granulocytic and monocytic differentiation of AML-derived cells. 25024378_This suggests that FcgammaRIIIb signals in association with macrophage-1 Ag. 25136078_A negative correlation was found between CD11b percentage and postinfarct left ventricular ejection fraction. 25231265_beta2 integrins-mediated chemosensory adhesion and migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes on the vascular graft surface, bacterial cellulose. 25238263_Il-6-induced recruitment of CD11b+ CD14+ HLA-DR- myeloid-derived suppressor cells is associated with progression and poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. 25305756_A new genome-wide significant association between ITGAM-ITGAX and IgA nephropathy. 25315704_The rs1143679 polymorphism is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in different ethnic groups and with lupus nephritis in Europeans. No association was found with rheumatoid arthritis. [Meta-Analysis] 25365491_role of CD11b/CD18 in priming of human leukocytes by endotoxin glycoforms from Escherichia coli 25461401_Data indicate that Candida albicans beta-Glucan induces high IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) levels, independently from Dectin-1/complement receptor 3 (CR3). 25554420_Examination of CR3 ( CD11b/CD18)mutant variants and mass spectrometry analysis of the N-glyc |
ENSMUSG00000030786 |
Itgam |
1869.839852 |
0.2641910842 |
-1.920346 |
0.091497842 |
416.520862 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001395497685231402596610481799239936128673588549652938527659825572262905098845926301865712125748346038498947167757940686017571134508446542049395465574143865250963538888787414097469534655720579079887457205653218836920554673142365331717229537 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000539202770523966044741908142520884289479139370945256348798767386853178830409966827089582831440743667901652141136282874775651102099614338137630549239603738184561732945796345939327980194253594381411777922389514054875564853883812554968812947 |
Yes |
No |
779.3572898 |
57.5990423 |
2977.9637841 |
156.9581687 |
| ENSG00000169902 |
8460 |
TPST1 |
protein_coding |
O60507 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the O-sulfation of tyrosine residues within acidic motifs of polypeptides, using 3'-phosphoadenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as cosubstrate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28821720, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9501187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9733778}. |
3D-structure;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables protein homodimerization activity and protein-tyrosine sulfotransferase activity. Involved in peptidyl-tyrosine sulfation. Is integral component of Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8460; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-tyrosine sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008476]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate metabolic process [GO:0050427]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; peptidyl-tyrosine sulfation [GO:0006478] |
12032733_results exclude TPST1 as the causative gene for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome 12056800_Shear stress-dependent downregulation of TPST1 in human endothelium involves protein kinase C 12169668_Tyrosine sulfation of CCR5 N-terminal peptide follows a discrete pattern and temporal sequence 16244708_Affinity purified salivary TPST showed a single band of 50-54 kDa and is the first report characterizing a tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase in secretory fluid from the parotid gland 16859706_Human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase may be functional as homodimer/oligomer in the trans-Golgi compartment. 18672380_The kinetic parameters of tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-1 and -2, catalyzing tyrosine sulfation of CCR8 peptides, were determined using liquid chromatography electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23472069_up-regulation of TPST-1 and tyrosine sulfation of CXCR4 by LMP1 might be a potential mechanism contributing to nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis 25079514_TPST1 rs3757417T>G polymorphisms are associated with colorectal cancer. 26238632_TPST1 was significantly negatively correlated with the expression of cMet in lung cancer and may be a negative prognostic biomarker of lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000034118 |
Tpst1 |
261.086233 |
2.5674993925 |
1.360364 |
0.117313005 |
134.870195 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000035247539738186375388325194959002827172595570004013363995927656668582990768968791258503037155946913117077201604843139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000004716715199779064907101045635360801720082637786742699607290469019795268356670518185291829382776995771564543247222900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
369.3895974 |
24.1819158 |
144.8838920 |
7.5756600 |
| ENSG00000169962 |
83756 |
TAS1R3 |
protein_coding |
Q7RTX0 |
FUNCTION: Putative taste receptor. TAS1R1/TAS1R3 responds to the umami taste stimulus (the taste of monosodium glutamate). TAS1R2/TAS1R3 recognizes diverse natural and synthetic sweeteners. TAS1R3 is essential for the recognition and response to the disaccharide trehalose (By similarity). Sequence differences within and between species can significantly influence the selectivity and specificity of taste responses. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11917125, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12892531}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Signal;Taste;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a G-protein coupled receptor involved in taste responses. The encoded protein can form a heterodimeric receptor with TAS1R1 to elicit the umami taste response, or it can bind with TAS1R2 to form a receptor for the sweet taste response. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:83756; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sweet taste receptor complex [GO:1903767]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; taste receptor activity [GO:0008527]; detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sweet taste [GO:0001582]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; sensory perception of sweet taste [GO:0050916]; sensory perception of umami taste [GO:0050917] |
11894099_sequence differences in T1R receptors within and between species (human and mouse) can significantly influence the selectivity and specificity of taste responses 12706725_The mechanism of interaction of the sweet protein monellin with T1R2-T1R3 receptor. 15299024_cysteine-rich region of T1R3 has a role in determining responses to intensely sweet proteins 15353592_findings demonstrate the different functional roles of T1R3 and T1R2 and the presence of multiple ligand binding sites on the sweet taste receptor 15585941_An immunohistochemistry study to determine whether and where T1R3 may be localized in the liver and pancreas. 15668251_transmembrane domains of human T1R3 bind with lactisole to inhibit sweet taste 16633339_water rinses remove the inhibitor from the heteromeric sweetener receptor TAS1R2-TAS1R3, which activates cells and results in the perception of strong sweetness from pure water 17499612_Although T1R2-T1R3 is known to have multiple potential ligand-binding sites to receive a wide variety of sweeteners, the present study is apparently the first to identify the ATD of hT1R3 as a new sweetener-binding region. 17928076_These results show that T1R2 and T1R3 receptors, in addition to their role in taste perception, may also have a role in intrahepatic cholangiocytes. 17935609_Some of the amino acid positions crucial for activation of hTAS1R2+hTAS1R3 by neohesperidin dihydrochalcone are involved in the binding of allosteric modulators in other class C GPCRs 18539481_Expressed in the sweet/umami gustatory pathways in taste receptor cells and trigeminal neural pathways in transgenic mice. 19083128_The heteromeric G-protein-coupled receptor T1R2:T1R3 responds to a vast array of chemically diverse natural and artificial sweeteners. 19146926_Taken together, these results suggest that Tas1R1-Tas1R3 receptor variants found in human fungiform papillae might contribute to inter-individual differences of sensitivity to L-glutamate. 19559618_Allelic polymorphism within the TAS1R3 promoter is associated with human taste sensitivity to sucrose. 19559618_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19571223_In our sample of subjects, the frequencies of 2 nsSNPs, C329T in tas1r1 and C2269T in tas1r3, were significantly higher in [glutamate] nontasters than expected, whereas G1114A in tas1r1 was more frequent in tasters. 19587085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19587085_Variations in perception of umami taste correlated with variations in the human TAS1R3 gene. 19664591_Interactions between the human sweet-sensing T1R2-T1R3 receptor and sweeteners detected by saturation transfer difference NMR spectroscopy. 20302879_Results from mutagenesis and chimeras of the receptor indicated that brazzein interacts with both T1R2 and T1R3 and that the Venus flytrap module of T1R2 is important for brazzein agonism. 21324568_The sweet taste receptors (alpha-gustducin and T1R3) are involved in glucose-stimulated secretion of GLP-1 and PYY. 21422378_amino acid substitutions (F749S and R757C), located in the transmembrane domain of T1R3, severely impair receptor functions in vitro 21540445_T1R2/T1R3 is involved in glucose-dependent secretion of satiation peptides 22427794_Data show that that Tas1r1 and Tas1r3 are expressed in murine and human spermatozoa. 22450161_Overexpressed the human N-terminal domain of T1R3 in E. coli and found that the refolded protein behaves as a dimer; showed that hT1R3-NTD is functional and capable of binding sucralose with an affinity in the millimolar range. 22773945_T1R3 is a receptor responsible for the detection of calcium by taste. 23370115_Five amino acid residues in cysteine-rich domain of human T1R3 were involved in the response for sweet-tasting protein, thaumatin 24068707_effects of artificial sweeteners on adipose tissue may be largely independent of the classical sweet taste receptors, T1R2 and T1R3 24214976_A complex molecular mechanism involving changes in the properties of both the orthosteric and non-orthosteric sites of T1R1 underlies the determination of ligand specificity in mammalian T1R1/T1R3. 25029362_human and mouse membrane trafficking systems for sweet taste receptors T1r2 and T1r3 25924601_TAS1R3 gene rs307355 polymorphism found independent risk factor for dental caries experience by logistic regression & increased risk of caries. Moderate caries (4-7 caries) found to be associated w/TAS1R3 rs307355 heterozygous genotype 26168276_The transcripts of TAS1R3 and UCN2 in peripheral blood cells may be considered potential biomarkers of consumption of sugary and fatty food, respectively, to complement data of food-intake questionnaires. 26422579_T1R3 gene expression in the tongue is suppressed by chemotherapy. 27936499_The molecular anatomy of sweet taste receptor dimers T1R2-T1R3 has been presented. 28228527_We observe that binding of agonists to VFD2 of TAS1R2 leads to major conformational changes to form a TM6/TM6 interface between TMDs of TAS1R2 and TAS1R3, which is consistent with the activation process observed biophysically on the metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 homodimer. 29110749_Regarding 'consumption of carbohydrates (% energy) and higher amount of sweet foods, respectively...no associations were found for the TAS1R3 alleles.' 30353220_These studies are the first to demonstrate a protective effect of an artificial sweetener, through the sweet taste receptor T1R3, on VEGF-induced vasculogenesis in a retinal microvascular endothelial cell line. 30518043_Studied association of taste 1 receptor member 1 (TAS1R1) and taste 1 receptor member 3 (TAS1R3) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with food choices at a buffet meal. and found certain TAS1R1 and TAS1R3 SNPs to be associated with fat and savoury-tasting and protein-rich food choices following a laboratory buffet in humans. 30723160_The data further reveal that the C terminus of the extracellular cysteine-rich domain needs to be properly folded for T1R3 dimerization and co-trafficking, but not for surface expression of T1R2 alone. These results guided the modeling of the T1R2-T1R3 dimer in living cells. 30883570_Structural insights into the differences among lactisole derivatives in inhibitory mechanisms against the human sweet taste receptor. 30893427_Conserved Residues Control the T1R3-Specific Allosteric Signaling Pathway of the Mammalian Sweet-Taste Receptor. 31092329_Using homology modeling, molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, this study investigates the effects of five natural umami ligands on the structural dynamics of T1R1-T1R3. 31553164_Modeling and Structural Characterization of the Sweet Taste Receptor Heterodimer. 32551626_Binding Hotspot and Activation Mechanism of Maltitol and Lactitol toward the Human Sweet Taste Receptor. 32580504_Artificial Sweeteners Disrupt Tight Junctions and Barrier Function in the Intestinal Epithelium through Activation of the Sweet Taste Receptor, T1R3. 32607758_Current Progress in Understanding the Structure and Function of Sweet Taste Receptor. 33654187_Polymorphic variants in Sweet and Umami taste receptor genes and birthweight. 35565677_TAS1R3 and TAS2R38 Polymorphisms Affect Sweet Taste Perception: An Observational Study on Healthy and Obese Subjects. |
ENSMUSG00000029072 |
Tas1r3 |
8.545792 |
0.1783781993 |
-2.486989 |
0.623046320 |
18.009087 |
0.00002198529893238220514961253626573522979015251621603965759277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000066333403974235766805030156678668618042138405144214630126953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3705020 |
0.9785807 |
13.4181216 |
2.8583692 |
| ENSG00000170017 |
214 |
ALCAM |
protein_coding |
Q13740 |
FUNCTION: Cell adhesion molecule that mediates both heterotypic cell-cell contacts via its interaction with CD6, as well as homotypic cell-cell contacts (PubMed:7760007, PubMed:15496415, PubMed:15048703, PubMed:16352806, PubMed:23169771, PubMed:24945728). Promotes T-cell activation and proliferation via its interactions with CD6 (PubMed:15048703, PubMed:16352806, PubMed:24945728). Contributes to the formation and maturation of the immunological synapse via its interactions with CD6 (PubMed:15294938, PubMed:16352806). Mediates homotypic interactions with cells that express ALCAM (PubMed:15496415, PubMed:16352806). Acts as a ligand for the LILRB4 receptor, enhancing LILRB4-mediated inhibition of T cell proliferation (PubMed:29263213). Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow (PubMed:24740813). Mediates attachment of dendritic cells onto endothelial cells via homotypic interaction (PubMed:23169771). Inhibits endothelial cell migration and promotes endothelial tube formation via homotypic interactions (PubMed:15496415, PubMed:23169771). Required for normal organization of the lymph vessel network. Required for normal hematopoietic stem cell engraftment in the bone marrow. Plays a role in hematopoiesis; required for normal numbers of hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow. Promotes in vitro osteoblast proliferation and differentiation (By similarity). Promotes neurite extension, axon growth and axon guidance; axons grow preferentially on surfaces that contain ALCAM. Mediates outgrowth and pathfinding for retinal ganglion cell axons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P42292, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15048703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15294938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15496415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16352806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24945728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29263213, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7760007}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Inhibits activities of membrane-bound isoforms by competing for the same interaction partners. Inhibits cell attachment via homotypic interactions. Promotes endothelial cell migration. Inhibits endothelial cell tube formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15496415}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), also known as CD166 (cluster of differentiation 166), which is a member of a subfamily of immunoglobulin receptors with five immunoglobulin-like domains (VVC2C2C2) in the extracellular domain. This protein binds to T-cell differentiation antigene CD6, and is implicated in the processes of cell adhesion and migration. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:214; |
axon [GO:0030424]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048846]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; neuron projection extension [GO:1990138]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12481253_ALCAM expression up-regulated in low-grade prostate tumors and down-regulated in high-grade tumors; may play role in progression of prostate cancer 12843199_ALCAM is expressed on human endometrial epithelial cells and blastocysts. 15140234_the intact cell adhesion function of ALCAM may both favor primary tumor growth and represent a rate-limiting step for tissue invasion from vertical growth phase melanoma. 15169840_PKCA has a major role in cytoskeleton-dependent avidity modulation of ALCAM. 15496415_a novel soluble isoform of ALCAM may have ALCAM-dependent and ALCAM-independent functions 16024937_Overexpression of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule is associated with tumor invasion and nodal metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 16204050_Data attribute a novel signaling role to ALCAM in regulation of proteolysis and support its previously postulated sensor function in invasive growth. 16650408_Localization of ALCAM specifically at cell-cell junctions in endothelial cells supported its role in transendothelial migration 16818742_Engagement of CD6 with CD166 on tumor cells plays an important role in gammadelta T cell activation by tumor cells sensitized with nonpeptide antigens endogenously or exogenously. 16818773_the CD6-ALCAM interaction results in activation of the three MAP kinase cascades, likely influencing the dynamic balance that determines whether resting or activated lymphocytes survive or undergo apoptosis. 16865058_The above results indicate that ALCAM-ALCAM interactions are crucial to the survival and primary site maintenance of breast cancer cells. 17624664_HLA-A *0201 restricted ALCAM peptides primed autologous CD8(+) T cells to elicit cytotoxic response against ALCAM(+) human cancer cells. 17971418_These results indicate that homotypic and heterotypic ALCAM-mediated adhesion are governed by significantly distinct kinetic and mechanical properties. 18157132_These findings indicate an important function for ALCAM in the recruitment of leukocytes into the brain. 18171982_disruption of ALCAM-mediated adhesion is a relevant step in ovarian cancer cell motility, and ADAM17/TACE takes part in this process, which may be relevant to invasive potential 18172759_activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM/CD166) may have a role in breast cancer 18202807_This study has, for the first time, shown that patients who develop skeletal metastasis tend to have the lowest levels of ALCAM transcripts in their breast cancers. 18279810_Over the past decade, alterations in expression of ALCAM have been reported in several human tumors (melanoma, prostate cancer, breast cancer, colorectal carcinoma, bladder cancer, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma). 18347173_Decreased/lost ALCAM membrane expression is a marker of poorer outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer. 18483249_ALCAM coordinates tissue growth and cell migration in a process involvnig L1CAM 18810438_Higher ALCAM expression showed a positive correlation with estrogen receptor status and is a useful predictive marker for the response to taxane-free chemotherapy. 19142865_Increased ALCAM expression in the cytoplasm is associated with oral cancer 19322904_Elevated levels of ALCAM in serum is associated with breast cancer. 19337990_upregulation of CD166 in a von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor gene defective renal cell carcinoma cell line. 19603023_ALCAM overexpression is a relevant independent prognostic marker for poor survival and early tumour relapse in pancreatic cancer. 19626493_Report prognostic significance of the cancer stem cell markers CD133, CD44, and CD166 in colorectal cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20180536_Data show that compounds 17 and 18 were discovered as new potential inhibitors, with a nanomolar activity for ADAM-17 isolated enzyme and soluble ALCAM release in cancer cells. 20208136_ALCAM is expressed in neuroblastoma primary tumors with diverse patterns of subcellular localization. 20220571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364042_examined ALCAM expression levels in primary breast cancer and distant metastases of the same patient within 29 autopsy cases to better understand the underlying mechanisms of metastases and the role of adhesion molecules in this process 20530423_Loss of ALCAM in breast cancer cells facilitates the invasive behaviour of breast cancer and high levels of ALCAM in the cells have a suppressive role in the aggressive nature of breast cancer cells. 20606680_Prognostic impact of this and other cancer stem cell markers expression in colorectal cancer. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20726988_Data show that CD6-ALCAM interaction in vitro induced a synergistic co-stimulation of normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 20826154_CD166 is highly expressed within the endogenous intestinal stem cell niche 20929568_Data suggests that loss of ALCAM expression, due in part to DNA methylation of extensive segments of the promoter, significantly impairs the ability of circulating tumor cells to adhere to each other, and may therefore promote metastasis. 20952758_involvement of ALCAM in the pathogenesis of different types of tumors [review] 20972617_ALCAM expression was associated with estrogen receptor-positive phenotype, nodal involvement and breast tumor cells in bone marrow. Strong ALCAM expression in ductal carcinomas correlated with shorter recurrence-free intervals/overall survival. 21119604_Both transfection of mimics of microRNA-192 or -215 and ALCAM knockdown by an ALCAM-specific siRNA significantly increased the migration of HFE145 cells 21126364_There is a lineage-specific silencing of ALCAM in bi-potential erythromegakaryocytic progenitor cell lines. 21293922_polymorphisms in ALCAM gene is associated with breast cancer. 21364949_ALCAM may have an important role in thyroid tumor biology. 21430457_High ALCAM expression is associated with the development of endometrioid carcinoma. 21440089_cholesterol-induced apoptosis in monocytes is accompanied by reduced expression of ALCAM and attenuated monocyte migration 21670959_ALCAM is expressed at high levels in breast cancer membranes resulting in weakened adherent ability and metastasis. 21683980_Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule protein (CD166) is almost always expressed in prostate cancer and decreased levels of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule expression may lead to an aggressive behavior of tumor cells. 21757661_ALCAM levels measured at admission of acute ischemic stroke are associated with long-term mortality. 21816001_The impact of ALCAM in wound healing may thus be somewhat due to its impact on cell migration and growth. 21858815_increased ALCAM expression found in majority of esophageal cancer(EC)lesions; expression was not associated with histopathology parameters except tumor grading; ALCAM-positive patients had worse survival; increased ALCAM expression in primary malignant lesions and elevated serum-ALCAM level are prognostic markers of poor survival in EC 21915031_We sought to determine if ezrin, KBA.62, p-Akt, CD166, and nestin, may be helpful in distinguishing melanoma from nevi and atypical melanocytic lesions 21935604_Two SNPs in the ALCAM gene were associated with breast cancer-specific survival. 22130902_Increased expression of CD44, CD166 and CD133 from normal mucosa samples to adenoma and carcinoma was linked to tumor progression in tumors of the ampulla of Vater. 22166264_High ALCAM expression is associated with glioblastoma invasion. 22304788_our findings indicate that activated leukocyte adhesion molecule expression levels in gliomas are probably linked to other mechanisms than its supposed role as regulator of matrix metalloproteinase 2. 22482754_positive prognostic marker for overall survival of colorectal cancer patients 22555284_sALCAM levels differed between patients and healthy controls (median 24.2 vs. 18.9 ng/ml, p |
ENSMUSG00000022636 |
Alcam |
3322.169418 |
3.0240024570 |
1.596459 |
0.027617971 |
3475.383224 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5079.7449381 |
86.6512079 |
1691.7054663 |
23.9485393 |
| ENSG00000170027 |
7532 |
YWHAG |
protein_coding |
P61981 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein implicated in the regulation of a large spectrum of both general and specialized signaling pathways. Binds to a large number of partners, usually by recognition of a phosphoserine or phosphothreonine motif. Binding generally results in the modulation of the activity of the binding partner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16511572}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene product belongs to the 14-3-3 family of proteins which mediate signal transduction by binding to phosphoserine-containing proteins. This highly conserved protein family is found in both plants and mammals, and this protein is 100% identical to the rat ortholog. It is induced by growth factors in human vascular smooth muscle cells, and is also highly expressed in skeletal and heart muscles, suggesting an important role for this protein in muscle tissue. It has been shown to interact with RAF1 and protein kinase C, proteins involved in various signal transduction pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7532; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005159]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein kinase C inhibitor activity [GO:0008426]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11824616_Aberrant expression of signaling-related proteins 14-3-3 gamma and RACK1 in fetal Down syndrome brain (trisomy 21). 11996670_Results show that three 14-3-3 isoforms, beta, gamma and eta, are DAL-1/Protein 4.1B-binding proteins. 12364343_TSC2 associates with 14-3-3 in vivo 12482592_14-3-3 binds to the IGF-1 receptor after IGF1R's serine autophosphorylation 15057270_14-3-3 suppresses importin alpha/beta-dependent nuclear localization of Thr157-phosphorylated p27, suggesting implications for cell cycle disorder in Akt-activated cancer cells. 16223726_multiple interactions of AICD with FE65 and 14-3-3gamma modulate FE65-dependent gene transactivation 17109079_Interaction of human 14-3-3gamma with the small heat shock protein Hsp20 was analyzed by means of size-exclusion chromatography and chemical crosslinking. 17284169_Both single marker and haplotype analyses were negative for the Ywhag gene association with smoking initiation and nicotine dependence. 17394238_our data indicate that 14-3-3gamma may contribute to tumorigenesis by promoting genomic instability. 17611984_Detection of only 2 (14-3-3 eta and gamma) out of 7 different isoforms in synovial fluid suggests they are specific to the site of joint inflammation 18054924_Report reduced expression of 14-3-3 gamma in uterine leiomyoma as identified by proteomics. 18426801_human 14-3-3gamma binds to the ERK1/2 molecular scaffold KSR1, which is mediated by the C-terminal stretch of 14-3-3gamma 18843201_These results suggest that the override of checkpoint observed in 14-3-3gamma knockdown cells is due to failure to inhibit cdc25C function. 19034380_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the temporal lobe from patients with schizophrenia. 19173300_changes in the expression of five 14-3-3 isoforms (beta, gamma, epsilon, tau, and zeta) during the apoptosis of JURL-MK1 and K562 cells. 19558434_14-3-3beta, 14-3-3gamma, 14-3-3epsilon, 14-3-3eta and 14-3-3theta isoforms interact with the GPIb-IX complex in platelets 19772960_Abundant level of the phosphorylated FOXO1, its impaired nucleocytoplasmic shuttling, and the lowered expression of 14-3-3 protein in leiomyoma induces a shift in the cellular machinery toward a prosurvival execution program. 19801645_analysis of the interaction between 14-3-3 proteins, the N-terminal region of tyrosine hydroxylase, and negatively charged membranes 20146355_Zebrafish gene knockdowns imply roles for human YWHAG in infantile spasms and cardiomegaly. 20381070_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the anterior cingulate cortex from patients with schizophrenia 20388496_14-3-3 eta, beta, gamma and sigma isoforms were negatively expressed in meningioma. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639859_14-3-3 protein gamma forms a complex with Checkpoint kinase 1 phosphorylated at Ser296, but not at ATR sites (Ser317 and Ser345). 20870266_Elevated expression of 14-3-3gamma in human hepatocellular carcinoma predicts extrahepatic metastasis and worse survival 21109226_data do not exclude the possibility that YWHAG loss of function is also sufficient to cause neurological phenotypes 21148311_a new role for 14-3-3gamma in protecting p21 from MDMX-mediated proteasomal turnover, which may partially account for DNA damage-induced elevation of p21 levels independent of p53. 21416292_Data indicate that gene analysis revealed an up-regulation of all four 14-3-3 isoforms beta, eta, gamma, and sigma. 21420405_results support that membrane binding involves the non-conserved, convex area of 14-3-3gamma, and that Trp residues do not intercalate in the bilayer. 21867493_Increased expression of 14-3-3 gamma in lung cancer coincides with loss of functional p53. 22366688_description of a protein complex that mediates carrier formation and contains budding and fission molecules, as well as other molecules, such as the adaptor protein 14-3-3gamma 22537031_miR-141/YWHAG and miR-520e/RAB11A are two potential miRNA/protein target pairs associated with severe obesity. 22556425_hypoxia can activate p53 through inactivation of MDMX by the ATR-Chk1-MDMX-14-3-3gamma pathway. 22658894_Increased expression of 14-3-3gamma in breast cancer is associated significantly with tumor progression and poor prognosis. 22856523_14-3-3gamma protein binds strongly to long DNA targets and shows very strong preference for supercoiled DNA. 23115241_Using individual amino acid substitutions within the 14-3-3gamma VRII, we identified two residues required for and two contributing to the gamma-specific phenotypes. 23189152_The peripheral binding of 14-3-3gamma to membranes involves isoform-specific histidine residues. 23500129_high 14-3-3gamma expression is associated with poor survival in NPC patients. Thus, this study has identified that the 14-3-3gamma involves in the carcinogenesis of NPC. 23695676_Mitotic Plk1 activity is regulated not only by Plk1-Thr210 phosphorylation, but also by Plk1 binding to 14-3-3gamma following Plk1-Ser99 phosphorylation downstream of the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway. 23851690_14-3-3gamma was induced in B cells by T-dependent and T-independent primary CSR-inducing stimuli in vitro. 23977325_physiological changes in phosphate anions concentration can modulate affinity and specificity of interaction of 14-3-3 with its multiple targets and therefore the actual phosphointeractome of 14-3-3. 24055376_The region surrounding pSer19 of Tyrosine hydroxylase adopts an extended conformation in the 14-3-3gamma-bound state, whereas adopts a bent conformation when free in solution. 24269678_Data indicate that 14-3-3 zeta, gamma, epsilon, and tau isoforms but not the sigma protein hydrolyze ATP. 24284060_The normalisation capability of 14-3-3 gamma was superior to traditional LC in quantifying Western blot signals of the platelet AD-biomarker Monoamine Oxidase B of patient versus controls. 24870749_High 14-3-3gamma expression was seen in 59.5% of non-small cell lung cancers. 24947669_Proteomics analysis show that Ser40 of TH protein does not significantly contribute to the binding of 14-3-3gamma, and rather has reduced accessibility in the TH:14-3-3gamma complex. 25047048_These results showed that the cell surface expression of TRPM4 channels is mediated by 14-3-3gamma binding. 25154416_Data show that two isoforms of the 14-3-3 family, 14-3-3epsilon and 14-3-3 gamma, can stabilize Cdt2 independent of each other when overexpressed. 25224486_Changes for CRMP2, TCP1epsilon, TPM2 and 14-3-3gamma were confirmed in experimental tumors and in a series of 28 human SI-NETs. 25384678_Loss of p53 function may result in upregulation of 14-3-3gamma in lung cancers 25947081_14-3-3 protein expression was quantitatively analyzed in cerebrospinal fluid of 231 sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and 2035 control patients. 27100507_hypermethylation of the 14-3-3 gene promoter accounts for the decreased 14-3-3 gamma in uterine leiomyomas and that such a low level of expression may be involved in the pathogenesis of leiomyomas 27102539_Data suggest that miR-181b-3p functions as a metastasis activator by promoting Snail-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells by directly targeting YWHAG. 27212225_Study identified 14-3-3gamma as a binding partner for segment a of ANO1 and enhanced the surface expression of ANO1. In addition, its gene silencing of 14-3-3gamma inhibited migration and invasion of these glioblastoma cell lines. 27253419_Study demonstrated a mechanism by which 14-3-3gamma restricts centrosome duplication to once per cell cycle, by inhibiting cdc25C and cdk1 activation resulting in decrease phosphorylation of T199 in NPM1. Also, loss of 14-3-3gamma causes centrosome over-duplication, centrosome clustering and tumor formation in mice. 27288018_Study found that the overexpression of 14-3-3gamma in utero in the developing mouse cortex results in delays in pyramidal neuron migration. 27894843_The present study revealed the tumor suppressive role of miR-509-5p in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by targeting YWHAG, suggesting that miR-509-5p/YWHAG axis might be considered as a novel and potential target for clinical diagnosis and therapeutics of NSCLC. 28126486_MiR-217 directly targeted 3'UTR of YWHAG and suppressed the expression of YWHAG. 28412242_14-3-3gamma regulates the differentiation ability of CPNE1 through the binding with C2A domain of CPNE1 in HiB5 cells. 28745316_Data indicate angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) as a key player that coordinates an increase in cellular energy flux crucial for EMT via an ANGPTL4/14-3-3gamma signaling axis. 28777935_YWHAG de novo mutations cause early onset epilepsy, including epileptic encephalopathies and intellectual disability. 29253567_These results suggest that a major role of 14-3-3gamma in desmosome assembly is to transport PG to the cell border leading to the initiation of desmosome formation. 29382566_Overexpression of 14-3-3gamma in uterine leiomyoma cells resulted in reductions in the phosphorylations of multiple signaling molecules, including AKT, pan, ERK1/2, GSK-3 alpha/beta, MEK1/2, Foxo1 and Vimentin and may have causal effect of the growth of uterine leiomyoma. 29649512_14-3-3gamma protein directly interacts with the kinase domain of CaMKK2 and the region containing the inhibitory phosphorylation site Thr(145) within the N-terminal extension. CaMKK isoforms differ in their 14-3-3-mediated regulations and the interaction between 14-3-3 protein and the N-terminal 14-3-3-binding motif of CaMKK2 might be stabilized by small-molecule compounds. 29678907_14-3-3gamma associated primarily with cytoplasmic PKP1 phosphorylated at S155 and destabilized intercellular cohesion of keratinocytes by reducing its incorporation into desmosomes. 29771442_miR-222 inhibits cell proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells by down-regulating YWHAG expression. 29772231_14-3-3 beta and gamma function as positive regulators of GR transactivation and glucocorticoid-mediated hepatic gluconeogenesis. 29848704_Findings indicate the roles and molecular mechanisms of 14-3-3GAMMA protein (14-3-3gamma) in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration, and neoplasm invasion. 30570871_Decreased expression of miR-182 in ESCC cells was accompanied by decreased cell invasion and proliferation, promotion of cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. Dual-luciferase and western blot confirmed YWHAG as a target gene of miR-182. 30653408_YWHA/14-3-3 proteins recognize phosphorylated TFEB by a noncanonical mode for controlling TFEB cytoplasmic localization and its activity. 30830684_The role of 14-3-3gamma in breast cancer invasiveness to promote cell motility. Inhibition of 14-3-3gamma could, therefore, become a novel target of therapy to prevent invasion and metastasis in patients with breast cancers expressing 14-3-3gamma. 31180055_The results in this report demonstrate that 14-3-3 epsilon and 14-3-3 gamma form a complex with Centrin2 and that the binding site is located in the N-terminal EF hand in Centrin2, EF1. 31926053_Expanding the genotype-phenotype correlation of de novo heterozygous missense variants in YWHAG as a cause of developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. 31961068_14-3-3 protein binding blocks the dimerization interface of caspase-2. 32535685_Functional genetic variants in centrosome-related genes CEP72 and YWHAG confer susceptibility to gastric cancer. 32633081_Molecular basis for the recognition of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by the 14-3-3 protein family. 33075494_Human adipocyte differentiation and composition of disease-relevant lipids are regulated by miR-221-3p. 33159816_The 14-3-3/SLP76 protein-protein interaction in T-cell receptor signalling: a structural and biophysical characterization. 33349918_Genetic diagnosis of infantile-onset epilepsy in the clinic: Application of whole-exome sequencing following epilepsy gene panel testing. 33393734_Epilepsy and electroencephalogram evolution in YWHAG gene mutation: A new phenotype and review of the literature. 33813791_14-3-3gamma prevents centrosome duplication by inhibiting NPM1 function. 34413451_14-3-3 proteins inactivate DAPK2 by promoting its dimerization and protecting key regulatory phosphosites. 34709972_Long non-coding RNA NORAD protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury induced brain damage, cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation by regulating miR-30a-5p/YWHAG. 34915349_Myoclonic epilepsy of infancy related to YWHAG gene mutation: towards a better phenotypic characterization. 36243722_A heterozygous missense variant in the YWHAG gene causing developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 56 in a Chinese family. |
ENSMUSG00000051391 |
Ywhag |
2026.384398 |
2.2469555080 |
1.167972 |
0.038155419 |
944.449997 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000213393400335923360399386962138769902845360749594293541457307554468190973831590266513570739850287386368481231917648741391082 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000207216222957778213732750201332172711213889053845642892633949341167833181148758766478697879408871040780472021527565554246458 |
Yes |
No |
2834.1552844 |
61.3315433 |
1270.5496135 |
21.8580959 |
| ENSG00000170085 |
375484 |
SIMC1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NDZ2 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Inhibits the protease activity of CAPN3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23707407}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Inhibits the protease activity of CAPN3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23707407}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome |
|
Enables SUMO polymer binding activity and peptidase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of peptidase activity. Located in sarcomere. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:375484; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; peptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0030414]; SUMO polymer binding [GO:0032184]; negative regulation of peptidase activity [GO:0010466] |
23707407_Authors found that PLEIAD also interacts with CTBP1 (C-terminal binding protein 1), a transcriptional co-regulator, and CTBP1 is proteolyzed in COS7 cells expressing CAPN3. |
ENSMUSG00000043183 |
Simc1 |
121.568970 |
0.4080525871 |
-1.293173 |
0.174190665 |
55.078486 |
0.00000000000011581161748026911505119237819225377821648510778818064181905356235802173614501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000730504048721697459985684123420154607430471171980457256722729653120040893554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.7470761 |
8.7213345 |
171.9358799 |
14.7293623 |
| ENSG00000170122 |
2298 |
FOXD4 |
protein_coding |
Q12950 |
|
DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the forkhead/winged helix-box (FOX) family of transcription factors. FOX transcription factors play critical roles in the regulation of multiple processes including metabolism, cell proliferation and gene expression during ontogenesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with a complex phenotype consisting of dilated cardiomyopathy, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and suicidality. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:2298; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding, bending [GO:0008301]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
17273782_The W148R mutation disrupts an extremely highly conserved tryptophan residue in the forkhead domain of FOXD4, possibly resulting in reduced DNA binding capacity and altered transcriptional activity. 22876580_FOXd4 encodes forkhead box D4 protein. |
ENSMUSG00000051490 |
Foxd4 |
48.777402 |
0.3174993123 |
-1.655175 |
0.247156660 |
46.333795 |
0.00000000000997289008115584820106217983666163575014185216360829144832678139209747314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000055359104023264502939040622088264008253399861558818884077481925487518310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.7788326 |
3.7083296 |
75.3610032 |
7.1217509 |
| ENSG00000170153 |
57484 |
RNF150 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULK6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57484; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25609945_rs10007052 in the RNF150 gene is significantly associated with the risk of COPD in Chinese populations of Hainan province. |
ENSMUSG00000047747 |
Rnf150 |
6.943372 |
0.3333173604 |
-1.585032 |
0.596434935 |
7.388502 |
0.00656421408638070431190714160152310796547681093215942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013082338632862434979475807494964101351797580718994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0668515 |
1.3461446 |
9.4936571 |
2.3542780 |
| ENSG00000170275 |
10491 |
CRTAP |
protein_coding |
O75718 |
FUNCTION: Necessary for efficient 3-hydroxylation of fibrillar collagen prolyl residues. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17055431}. |
Disease variant;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is similar to the chicken and mouse CRTAP genes. The encoded protein is a scaffolding protein that may influence the activity of at least one member of the cytohesin/ARNO family in response to specific cellular stimuli. Defects in this gene are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta, a connective tissue disorder characterized by bone fragility and low bone mass. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10491; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; chaperone-mediated protein folding [GO:0061077]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; negative regulation of post-translational protein modification [GO:1901874]; peptidyl-proline hydroxylation to 3-hydroxy-L-proline [GO:0018400]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
17055431_complexes with prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 (P3H1) to decrease prolyl 3 hydroxylation; dysregulation of prolyl 3 hydroxylation is a mechanism for connective tissue disease 18566967_Screening of 78 subjects diagnosed with osteogenesis imperfecta type II or III, identified three probands with mutations in CRTAP and 16 with mutations in LEPRE1. 18996919_Mutations in CRTAP and LEPRE1 are found in 3 patients with type II osteogenesis imperfecta. 19550437_CRTAP mutations not described earlier were identified in 10 individuals who had a clinical diagnosis of lethal and severe osteogenesis imperfecta. 19727905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727905_SNP rs7623768 and the haplotype G-C of rs4076086-rs7623768 in CRTAP were associated with femoral neck bone mineral density (p = 0.009 and p = 0.003, respectively). 19846465_CRTAP and P3H1 are mutually stabilized in the collagen prolyl 3-hydroxylation complex in endoplasmic reticulum. 19862557_Null mutations in LEPRE1 and CRTAP cause severe recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. 19895918_CRTAP deficiency results in higher bone mineral content of the bone matrix in osteogenesis imperfecta type VII. 20425614_Importantly, human mutations in the CRTAP gene have been associated with recessive forms of OI. 24043621_An additional function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum protein complex prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1.cartilage-associated protein.cyclophilin B: the CXXXC motif reveals disulfide isomerase activity in vitro. 26634552_This study enhances our knowledge about the mutational pattern of the LEPRE1, CRTAP, and PPIB genes. LEPRE1 should be the first gene analyzed in mutation detection studies in patients with recessive OI. 27901313_To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to exclude potential correlations between heterozygous variants in CRTAP and milder skeletal impairments in a large number of patients 30389107_Osteogenesis imperfecta caused by COL1A1, CRTAP and LEPRE1 mutations. Report of 2cases.', trans 'Osteogenesis imperfecta causada por mutacion en los genes COL1A1, CRTAP y LEPRE1. Estudio de 2casos. 35703132_Novel BMP1, CRTAP, and SERPINF1 variants causing autosomal recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. |
ENSMUSG00000032431 |
Crtap |
1043.378028 |
0.4842778652 |
-1.046093 |
0.064210655 |
265.126295 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001309626126154807787547829857826267643117711281198824192671715754509837424757575529334957104408724496089769925002814293316560312858182018850305248646066769158124998284620232880115509033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000332703642375989028091253410018880619627905779356971741643593334703080047268618298486936932203903859538337701193623071584261793913026135814864966272486057619062194135040044784545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
700.5410640 |
36.9639088 |
1457.9729870 |
53.4665179 |
| ENSG00000170293 |
152189 |
CMTM8 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZV2 |
|
Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the chemokine-like factor gene superfamily, a novel family that is similar to the chemokine and the transmembrane 4 superfamilies. This gene is one of several chemokine-like factor genes located in a cluster on chromosome 3. This gene acts as a tumor suppressor, and plays a role in regulating the migration of tumor cells. The encoded protein is thought to function as a a negative regulator of epidermal growth factor-induced signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:152189; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; structural constituent of myelin sheath [GO:0019911]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; myelination [GO:0042552] |
12782130_Bioinformatics based on CKLF2 cDNA and protein sequences in combination with experimental validation identified CKLFSF1-8 gene clusters, between the SCY and the TM4SF gene families. The 8 family members were cloned and characterized. 16263120_These results identify CKLFSF8 as a novel regulator of EGF-induced signaling and indicate that the association of EGFR with four transmembrane proteins is critical for EGFR desensitization. 16806010_Cell proliferation and expression of EGFR of tumor cells can be inhibited by transfection of CKLFSF8. 17149703_These data implicate CMTM8 as a negative regulator of epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced signaling. 17681841_The cloning and sequencing of an alternative splice form of CMTM8, obtained from a human blood cDNA library, that utilizes apoptotic pathways distinct from CMTM8, is reported. 19308021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22337876_Down-regulation of CMTM8 also promoted an epithelial mesenchymal transition-like change in MCF-10A cells, indicating a broader role for CMTM8 in regulating cellular transformation. 25551557_This study identified CMTM8 as a new candidate tumor suppressor gene and GPR177 as a new candidate oncogene in osteosarcoma. 26503336_overexpression of CMTM8 in bladder cancer results in reduced malignant cell growth, migration and invasion, which could make it a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of bladder cancer. 26574634_This is the first extensive study of CMTM8 expression in both normal and tumorous human tissues. Our findings strongly supported the potential role of CMTM8 as a novel tumor suppressor and may shape further functional studies on this gene 26615421_our data suggested that CMTM8 is an important tumor suppressor gene in human bladder cancer and qualified as a useful prognostic indicator for patients with bladder cancer. 32268840_CMTM8 Is a Suppressor of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation and Promoter of Proliferation Via EGFR Signaling. 33395025_Influence of CMTM8 polymorphisms on lung cancer susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. 33978454_Downregulated CMTM8 Correlates with Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer Patients. 34978519_MicroRNA-582-5p promotes triple-negative breast cancer invasion and metastasis by antagonizing CMTM8. 35429970_Identification and validation of EMT-immune-related prognostic biomarkers CDKN2A, CMTM8 and ILK in colon cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000041012 |
Cmtm8 |
6.467084 |
0.1176875672 |
-3.086966 |
0.780073518 |
20.190219 |
0.00000701105157324778601466222505145253762748325243592262268066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000022432933280107809079564895604619323421502485871315002441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3436164 |
0.7386850 |
11.5843198 |
2.7419586 |
| ENSG00000170323 |
2167 |
FABP4 |
protein_coding |
P15090 |
FUNCTION: Lipid transport protein in adipocytes. Binds both long chain fatty acids and retinoic acid. Delivers long-chain fatty acids and retinoic acid to their cognate receptors in the nucleus. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04117}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Lipid-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
FABP4 encodes the fatty acid binding protein found in adipocytes. Fatty acid binding proteins are a family of small, highly conserved, cytoplasmic proteins that bind long-chain fatty acids and other hydrophobic ligands. It is thought that FABPs roles include fatty acid uptake, transport, and metabolism. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2167; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; fatty acid binding [GO:0005504]; hormone receptor binding [GO:0051427]; long-chain fatty acid binding [GO:0036041]; long-chain fatty acid transporter activity [GO:0005324]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; cellular response to lithium ion [GO:0071285]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; fatty acid transport [GO:0015908]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; white fat cell differentiation [GO:0050872] |
12417276_observations suggest that oxLDL-mediated increase in gene expression accelerate cholesterol ester accumulation, and that this is an important component of the genetic program regulating conversion of macrophages to foam cells 15015141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15015141_fatty acid binding protein 4 and PPARgamma work together to influence a biologic pathway affecting insulin sensitivity and body composition 15168018_intra-pair correlations revealed that FATP4 expression was signifcantly up-regulated in acquired obesity. 15456755_a pre-lipolysis complex containing at least AFABP and HSL exists 15734831_Loss of expression of A-FABP is associated with progression of bladder carcinoma. 16313911_ALBP gene expression accelerates cholesterol and triglyceride accumulation in macrophage foam cells and affects some key gene expression for lipid metabolism. 16641093_Data demonstrate a significant genetic variation in humans that results in decreased adipose tissue aP2 expression due to alteration of the CAAT box/enhancer-binding protein binding and reduced transcriptional activity of the aP2 promoter. 16641093_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16750515_FABP4 protein is expressed within the skeletal muscle fibers & FABP4 mRNA & protein are more abundant in the endurance trained subjects.[fatty acid binding protein 4] 16952017_Expression occurs not only in mature adipocytes, but has a wider embryonic expression pattern than previously appreciated. 17322100_the metallothionein genes, adipophilin (ADFP), CD36, adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (FABP4), ATP binding cassette protein A1 (ABCA1), and liver X receptor (LXR[alpha]) all emerged as strongly positively correlated with PPAR[gamma] expression. 17396233_These data indicate for the first time that human macrophage aP2 promoter is a direct target for the regulation by LXR/RXR heterodimers. 17425064_genetic variability at the FABP4 locus has been shown to be associated with plasma lipid levels, type 2 diabetes, and coronary heart disease risk 17428383_There were not significant difference A-FABP expression between ductal infiltrating carcinoma and benign tissue in human breast cancer. 17535427_Changes in DNA methylation at adipogenic promoters during cellular aging. 17553506_thiazolidinedione increases FABP4 plasma concentrations in diabetic patients, reflecting PPARgamma activation 17826730_Hypoxia enhances the expression of FABP4 in term human trophoblasts, suggesting that fatty acid binding proteins support fat accumulation in the hypoxic placenta. 18024526_FABP4 concentrations should be taken into consideration as an early marker of kidney damage in patients with type 2 diabetes. 18417367_human epicardial adipose and ascending aorta tissues express fatty-acid-binding protein 4 and that its level of expression in epicardial adipose tissues of metabolic syndrome patients is elevated 18421072_High FABP4 & low adiponectin levels are independent predictors of atherogenic dyslipidemia. FABP4 plasma concentrations hold strong potential for development as a clinical biomarker for atherogenic dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetic subjects. 18437151_Maternal AFABP serum concentrations are significantly increased in preeclampsia. 18535557_A-FABP serum levels are positively associated with body weight and fat mass 18564921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18657008_Serum FABP levels were unchanged in patients with AN and were not related to any of parameters studied 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18710473_Exercise training with weight loss induced a significant reduction in circulating A-FABP levels in obese Korean women. 18820256_Mapping of the hormone-sensitive lipase binding site on the adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (AFABP). Identification of the charge quartet on the AFABP/aP2 helix-turn-helix domain. 18835952_Serum A-FABP is significantly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes, independent of body size, blood lipids and c-reactive protein. 18931100_May be a biomarker for progression of diabetic nephropathy and its cardiovascular risk. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19001529_Serum FABP4 levels increased as the numbers of stenotic coronary artery increased, although these differences were attenuated after adjustment for age and fasting glucose levels 19115207_A-FABP is a candidate progression marker of human transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder that is differentially regulated by PPAR in urothelial cancer cells 19181913_Adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein may play a role in obstructive sleep apnoea and metabolic dysfunction 19197257_Examine adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein as a determinant of insulin sensitivity in morbid-obese women. 19368945_Serum A-FABP concentrations were significantly correlated with BMI and waist circumference 19421706_results indicate that variation in A-FABP plasma levels reflect alterations in nutritional status in patients with anorexia nervosa 19573524_Increased circulating AFABP and RBP-4 concentrations were demonstrated in patients with preeclampsia, suggesting it be an important pathophysiology of preeclampsia. 19608978_the release of FABP4 from adipocytes may be involved in the development of cardiac contractile dysfunction of obese subjects. 19625659_FABP4 emerged as a novel target of the VEGF/VEGFR2 pathway and a positive regulator of cell proliferation in endothelial cells. 19842034_Study reveals that high A-FABP serum levels are associated with obesity, breast cancer risk, and adverse tumor characteristics. 19844814_An association between FABP4 gene polymorphisms and the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. 19844814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19911253_Interaction between PTEN to FABP4 suggests a role for this phosphatase in the regulation of lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20009357_Among coronary artery disease patients the fasting level of FABP4 positively correlated with metabolic syndrome and serum levels of FABP4 correlated with a number of MetS criteria. 20111020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20111020_our finding from a multiethnic cohort of postmenopausal women did not support the notion that common genetic variants in the FABP4 gene may trigger increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus 20156355_FABP4 may have a role in cardiometabolic risk in childhood obesity 20156355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20193950_Increased serum A-FABP was significantly associated with a greater coronary plaque burden. 20231079_A-FABP levels correlated positively with total-cholesterol [total-C] in both preterm and fullterm infants). In addition to total-C, weight gain correlated independently with a-FABP levels in preterm infants 20388924_a hyperlipidemic mechanism of familial combined hyperlipidemia different from similar metabolic conditions where fat mass is strongly related to FABP4 and hypertriglyceridemia 20413122_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20452069_Co-expression of A- and E-FABP is detected in cultured human aortic endothelial cells, which is the critical cellular component in the development of atherosclerosis. 20579864_Serum A-FABP levels were significantly higher in the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease group than the non-NAFLD group. 20587710_significant association between serum osteocalcin and A-FABP in metabolic syndrome 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20723896_Fatty acid-binding protein 4 may have a role in endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes 20870707_obese patients who lost weight showed a decrease in A-FABP (a mean 2% reduction in BMI was associated with a mean 29% decrease in A-FABP 21063874_Olmesartan ameliorated arterial stiffness in patients with hypertension, which may be involved in the reduction of serum A-FABP. 21073559_expression of FABP4/aP2 is increased at the mRNA level in unstable carotid plaques. Immunohistochemical analyses showed localization of FABP4/aP2 to macrophage populations. 21106915_A-FABP predicts the development of the metabolic syndrome independently of pubertal status, adiposity, and insulin resistance in Korean boys. 21159847_Circulating A-FABP, adiponectin, and leptin levels were shown to be associated with vascular inflammation 21167393_Data show that metabolic syndrome was positively correlated with fasting FABP4 levels in chronic hemodialysis patients. 21176857_Data found high serum A-FABP4 but unchanged RBP4 concentrations and their associations with renal function and early diabetic nephropathy in type 2 DM. 21257725_Results indicate that serum FABP4 is associated with inflammatory factors related to obesity and MS in non-diabetic morbidly obese women. 21376375_Expression of aP2 is similar in all studied lipomatous tumors 21407103_investigation of intraindividual changes in AFABP in breast milk during 12 months of lactation; levels correlated negatively with infants' body weight during 1st month of lactation; decreasing trend until 3rd month, subsequent increase till 12 month 21421494_Elevated serum A-FABP is closely related to glucose metabolism disorder. 21492859_while both serum A-FABP and E-FABP levels are associated with MetS, only A-FABP is significantly associated with increased risk of CAD in Chinese adults 21552513_Serum A-FABP is closely associated with the presence and severity of CAD in Chinese women 21562251_Serum A-FABP is significantly associated with ischemic stroke in this case-control study and serves as a useful prognostic indicator for early mortality. 21600061_Increased plasma A-FABP in non-elderly men had a significant association with the presence of coronary artery disease, independent of established CAD risk factors. 21664182_Childhood obesity and obstructive sleep apnea are associated with higher plasma FABP4 levels and thus promote cardiometabolic risk. 21720879_Data indicate that expression of FABP4 in granulosa cells is higher in polycystic ovary syndrome patients than in control subjects; same for serum FABP4. FABP4 expression is up-regulated in granulosa cells by testosterone, insulin, or rosiglitazone. 21775757_It is suggested that fetal tissues are the main source of cord arterial serum AFABP, and in GDM fetuses AFABP values correlate with adiposity markers. 21966368_Data show that LPL, FABP4, LRP1 and ASP expression in visceral adipose tissue was higher in lean controls, while in subcutaneous adipose tissue, LPL and FABP4 expression were also higher in lean controls. 22102888_High serum FABP4 is associated with cardiovascular events in end-stage renal disease. 22174896_FABP4 is linked to atherogenesis, plaque instability and adverse outcome in patients with carotid atherosclerosis and acute ischemic stroke. 22188744_Maternal serum FABP4 levels are elevated before the clinical onset of preeclampsia, and this increase occurs independently of maternal body mass index. 22396741_Common variants of the liver fatty acid binding protein genes 1-4 influence the risk of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance in Spanish population 22476608_Fatty acid binding protein 4 is significantly overexpressed in cerebellar liponeurocytomas. 22562362_These data unravel a novel pro-angiogenic role for endothelial cell-FABP4 and suggest that it could be exploited as a potential target for diseases associated with pathological angiogenesis 22584136_Plasma FABP4 was positively associated with incident diabetes in older adults, and such association was statistically significant in lean men only. 22617714_Circulating adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels were paradoxically lower in chronic pancreatitis patients and did not depend on pancreatic diabetes. 22679309_Circulating A-FABP levels are associated with long-term prognosis in patients with coronary heart disease and may represent an important pathophysiological mediator of atherosclerosis. 22706792_Our data showed a positive association between plasma fatty acid binding protein 4 but not 3 and the risk of diabetes in US male physicians 22709426_FABP4 can modulate the insulin-signalling pathway in endothelial cells and, consequently, decrease eNOS activation and NO production. 22717543_FABP4 contributes to blood pressure elevation and atherogenic metabolic phenotype in hypertensives, and the elevation of FABP4 is predisposed by a family history of hypertension. 22855337_Circulating levels of fetuin-A, RBP4, and FABP4 are associated with insulin resistance and with distinct components of metabolic syndrome consistent with the multifactorial pathogenesis of metabolic dysregulation. 22918198_Increased A-FABP levels were found in the patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, which were correlated significantly with left ventricular mass index and myocardial performance index. 23013043_Increased A-FABP may be causally related to the pathogenesis of heart dysfunction in humans. 23052058_Data suggest that up-regulation of FABP4 promotes insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, and atherosclerosis. [REVIEW] 23068962_Data from a longitudinal study suggest that FABP4 and TNF-alpha are significant predictors for glycemic progression (progression from normoglycemia to prediabetes to type 2 diabetes). 23139800_FABP4 expression in adipose and hepatic tissues in the settings of obesity and insulin resistance, was analyzed. 23183502_Weight reduction in type 1 diabetic patients is associated with a desirable decrease of body fat and transiently increased FABP 23183506_Contribution of A-FABP in the process of endothelial dysfunction could help to explain the role of obesity in cardiovascular damage. 23224329_High serum A-FABP levels were significantly associated with complex coronary lesions in patients with stable CAD, suggesting that high A-FABP levels may be involved in coronary plaque vulnerability. 23357154_Data suggest that the reduction of FABP4 serum levels may contribute to the preventive effect of lipoprotein apheresis on cardiovascular events. 23372061_Increased AFABP expression promotes human arterial smooth muscle cell growth and migration via reactive oxygen species-mediated activation. 23375099_Critically ill patients have higher serum A-FABP concentrations. 23387955_High Fabp4 expression is associated with atherosclerotic lesion. 23391391_FABP4 promotes VEGF-induced airway angiogenesis. 23480783_Insulin sensitizing and lipid lowering therapies do not affect free fatty acid binding (RBP)4 levels in polycystic ovary syndrome patients. 23525430_Circulating A-FABP level predicts the development of cardiovascular disease after adjustment for traditional risk factors in a community-based cohort. 23598540_In overweight and obese women, FABP4 showed an independent association with parameters of left ventricular remodelling. 23642261_FABP4 is associated with the clinical manifestations and biomarkers of heart failure (HF), and is associated with obesity and diabetes in HF patients. It exhibits a parallel evolution with the circulating levels of NT-proBNP in HF patients. 23714112_we found the increased expression of FABP4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue, synovial fluid and in the blood circulation. These increased FABP4 levels positively correlated with serum cholesterol levels, independent of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. 23805908_The inhibition of macrophage FABP4 expression can be attributed to the antiatherogenic properties of tamoxifen. 23866022_Serum A-FABP levels not only were associated with myocardial perfusion abnormalities and left ventricular function, but also predicted the presence of heart failure in patients with coronary artery disease. 23979787_Fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels increased and retinol-binding protein 4 levels did not change during moderate weight loss in obese women with metabolic syndrome. 24043587_Associations of common single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes in the FABP4 gene with lower plasma FABP4 but higher fasting glucose levels. 24044564_A-FABP seems to be a valuable predictor of atherogenic risk profile 24075747_FABP4 is upregulated in response to PUFA oxidation end-products in human macrophages in a pathway involving Akt and ERK/Nrf2 24150574_Among individuals aging more than 65 years included in the study, serum A-FABP was inversely associated with liver steatosis. 24182337_Cardiac surgery increased A-FABP mRNA expression in peripheral monocytes. 24214285_Data suggest that two adipokines, adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (FABP4) and lipocalin-2 (LCN2), function as pivotal modulators of vascular function and may be involved in pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in obese subjects. [REVIEW] 24240026_Results suggestive of bi-directional interaction between FABP4 and PPARgamma pathways that may be driving aggressive tumor cell behavior in bone. 24266781_Serum a-FABP is positively correlated to body fat content, especially to trunk fat in HIV infected children on highly-active-antiretroviral-therapy. 24312381_results demonstrate that the FABP4-induced DNA synthesis and cell migration are mediated primarily through a MAPK-dependent pathway that activates the transcription factors c-jun and c-myc in HCASMCs 24319114_found that FABP4 level was higher and PPARgamma level was lower in human visceral fat and mouse epididymal fat compared with their subcutaneous fat 24352293_FABP4 is actively released from human adipocytes in vitro via a non-classical, calcium-dependent mechanism. 24390652_Circulating FABP4 is involved in the metabolic disturbances of systemic lupus erythematosus, affecting lipid metabolism and IR, and it could be a biomarker of atherosclerosis in this population. 24397811_A strong association was found between adipocyte fatty acid binding protein and FGF 21 levels in metabolic syndrome individuals. 24425381_FABP4 plays an important role in the cell growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma through the MAPK pathway. 24491219_Serum A-FABP levels were not different between patients with essential hypertension and normal controls. 24740818_FABP4 overexpression is associated with prostate cancer progression. 24756370_High expression level of FABP4 is associated with increased incidence of residual disease in high-grade serous ovarian cancer after surgery. 24842767_Serum A-FABP concentrations correlate significantly with visceral fat area, metabolic syndrome, and predicted significant myocardial ischemia on single-photon emission computed tomography . 24865546_Fatty acid binding protein 4 expression is detected in arteriovenous malformations and cavernous malformations in a subset of endothelial cells and some perivascular fibroblast-like vimentin-positive cells. 24939870_It also provides a link between DLL4-NOTCH and FOXO1-mediated regulation of endothelial gene transcription, and it shows that DLL4-NOTCH is a nodal point in the integration of pro-angiogenic and metabolic signaling in endothelial cells. 24971341_A-FABP is more strongly associated with some cardiometabolic risk factors in premenopausal than in postmenopausal women. 25122052_FABP4 rs77878271 is a novel variant affecting serum total cholesterol levels and cardiovascular risk 25123032_The serum level of A-FABP is not a predictor of a positive SPECT result 25127012_Serum A-FABP levels independently and positively correlate with subclinical atherosclerosis in pre- and postmenopausal Chinese women with normal glucose tolerance after adjustments for the traditional risk factors 25130095_Serum FABP4 concentration and systolic blood pressure after 10 min standing in an orthostatic test at 24 weeks are associated with subsequent development of pregnancy-induced hypertension in overweight women. 25142635_Elevation of circulatng FABP4 levels was associated with left ventricular dysfunction in a general population. 25369469_AP2 is a negative regulator of osteoblast differentiation and mineralization. 25506691_Urinary FABP4 level is independently correlated with level of albuminuria and possibly predicts yearly decline of estimated glomerular filtration rate. Urinary FABP4 would be a novel biomarker of glomerular damage. 25572488_FABP4 is functionally expressed in endometrial epithelium and is necessary for maintaining the cell function of epithelial cells of endometrium. 25603556_Palmitate activation by FATP4 triggers hepatocellular apoptosis via altered phospholipid composition and steatosis by acylation into complex lipids. 25606668_Gene-environment interactions studies found significance association between selenium and rs2290201 in FABP4 for total and LDL cholesterol levels and rs1800774 in CETP for elevated LDL cholesterol. 25659997_Increased plasma levels of FABP4 and PTEN is associated with more severe insulin resistance in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. 25664790_The binding of FABP4 towards a group of small molecules structurally related to the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen was analyzed through X-ray crystallography. 25719934_Serum A-FABP levels were associated with fat mass, and were also influenced by visceral fat area after menopause in Chinese women without diabetes mellitus. 25897794_FABP4 inhibition suppresses PPARgamma activity and VLDL-induced foam cell formation in IL-4-polarized human macrophages. 25923423_Biological network analysis of differentially regulated genes revealed that FABP4, ADIPOQ and RBP4 were most down regulated genes, sharing strong connection with the other molecules of lipid metabolism pathway. 25953897_we identify adipocyte-type fatty acid-binding protein (A-Fabp) and other members of the fatty acid-binding protein (Fabp) family as interaction partners of Cgi-58. 25958041_Our data suggest that FABP4 in glomerular mesangial cells is up-regulated in diabetic nephropathies and FABP4 mediates apoptosis via the ER stress in human mesangial cells. 26069234_Circulating FABP4 may prove useful as a prognostic biomarker in risk stratification of patients with acute coronary syndrome. 26343611_These findings indicate that exogenous FABP4 interacts with plasma membrane proteins, specifically CK1. 26687459_our findings set up a novel mechanism for FABP4, adipsin and adiponectin through gut microbiota mediating expression in gut Paneth cells. 26752184_Serum irisin might exert antagonistic effects on FABP4 in the middle-aged Chinese population. 26823558_results underline a gender difference in FABP4 secretion in stable COPD patients. 26887419_Increased FABP4 level showed increased risk for reduced lung function in subjects with normal ventilatory function. 26959740_Results suggested that the expression of a lipid metabolism-related gene and an important SNP in the 3'-UTR of FABP4 are associated with TNBC prognosis. 26992681_The increase in placental FABP4 expression in preeclampsia may affect the function of trophoblast, and this increase may have a role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 27013610_FABP4 locally produced by epicardial/perivascular fat and macrophages in vascular plaques contributes to the development of coronary atherosclerosis. 27061264_Exogenous FABP4 plays a key role in tumor proliferation and activates the expression of fatty acid transport proteins in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. 27089280_High FABP expression is associated with Sepsis. 27155388_eFABP4 induces ER stress and potentiates the effect of linoleic acid in HepG2 cells, suggesting that FABP4 could be a link between obesity-associated metabolic abnormalities and hepatic insulin resistance mechanisms 27181269_Study found that the fasting insulin and age-adjusted AFABP concentrations were significantly higher in the gestational diabetes mellitus group of women compared with the normal glucose tolerance participants in the mid- and late stages of pregnancy. 27221153_FABP4 DNA hypomethylation induced by Hcy may be involved in the overexpression of FABP4, thereby inducing cholesterol accumulation in macrophages. 27236410_Findings in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia provide evidence of altered proteins involved in synaptic function (FABP4), cytoarchitecture organization (NEFH), and circadian molecular clock signaling (CSNK1E), which may be contributing to the cognitive and/or negative symptoms in this disorder. FABP4, CSNK1E and NEFH could become potentially useful biomarkers for schizophrenia. 27241838_FABP4 level was independently associated with gender, adiposity, renal dysfunction, and levels of cholesterol. 27270834_The present study demonstrated that the androgen was correlated with the serum A-FABP levels negatively in men, but positively in women. 27294862_FABP4 over-expression in cardiomyocytes can aggravate the development of cardiac hypertrophy through the activation of ERK signal pathway. 27323829_our research demonstrated that high FABP3 or FABP4 expression had strong prognostic value for overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer 27534843_serum A-FABP levels were increased significantly in normoglycemic individuals with a first-degree family history of diabetes; the use of serum A-FABP as a biomarker in the first-degree relatives of patients with diabetes may result in overestimation of the risk of obesity-induced metabolic disease and cardiovascular disease 27563749_Taken together, PPAR gamma and FABP4 gene expression levels in PBMCs [peripheral blood mononuclear cells] may be indicators of metabolic factors and body composition components. 27568980_High FABP4 expression is associated with ovarian cancer. 27609367_Elevated levels of FABP4 are associated with higher cardiovascular mortality among men with type 2 diabetes. 27630211_Increased second-trimester FABP4 independently predicted pre-eclampsia in women with type 1 diabete and significantly improved reclassification and discrimination. 27712128_The distribution of genotype frequencies in the assessed women (PON1 Q192R polymorphism) was QQ = 20%, QR = 48% and RR = 32%. Significantly higher serum FABP4 levels were found in women with genotype QR/RR (20.6 +/- 2.20 ng/mL), when compared with the levels found in the QQ group (12.8 +/- 1.70 ng/mL) (p = .004). 27819006_In multiple linear regression stepwise analysis, BMI, HbA1C, and HOMA-IR were significantly independent determinants for A-FABP. BMI, HbA1C, and HOMA-IR are independently associated with A-FABP in obese subjects with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. A-FABP may be related to insulin resistance and inflammation in type 2 diabetes and concomitant obesity. 27856250_These genes should be at the downstream of signal pathways and be regulated by the 23 genes identified before. Our findings may provide a unique new model for studying the molecular control of cattle cross-talk between adipose and skeletal muscle. 27864793_Results show that serum FABP4 levels were significantly increased in patients with psoriasis. 27914823_mTOR/FABP4 signaling pathway directly regulates the proliferation of endothelial cells in hemangioma. Rapamycin and inhibitors of FABP4 have therapeutic potential for treating infantile hemangiomas. 27936164_secreted FABP4 and FABP5 from adipocytes as adipokines differentially affect transcriptional and metabolic regulation in ADSC near adipocytes 27991582_ubiquitylation destabilizes the fold of two proteins, FKBP12 and FABP4 28042581_higher serum A-FABP level is positively associated with MetS in type 2 DM patients 28088613_Circulating levels of AFABP and EFABP are not decreased in Lipodystrophy despite adipose tissue loss in contrast to other adipokines including leptin and adiponectin. 28108519_High FABP4 expression is associated with Acute Monocytic Leukemia. 28303680_High serum A-FABP concentration is associated with peripheral arterial disease in women, but not men, with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 28324040_AFABP levels were higher in neonates compared with adults. Preterm infants had higher AFABP levels compared with full-term infants. Among full-term infants, AFABP levels in SGA infants were lower, compared with appropriate for gestational age and large for gestational age infants. 28620819_findings reveal a pro-angiogenic role of FABP4 in first trimester placental trophoblast cells and its regulation may have impact in placental physiology. 28654680_We found that serum FABP4 concentration were associated with insulin resistance and secretion in type 2 diabetes mellitus. This suggests that FABP4 may play an important role in glucose homeostasis. 28660445_Compared with the low arterial stiffness group, the high arterial stiffness group had higher values for age, systolic blood pressure, pulse pressure, duration of kidney transplantation and serum A-FABP 28701570_Compared to control group, breast cancer patients show higher FABP4 and FABP5 blood levels. Our data suggest that, particularly, circulating FABP4 levels could be considered a new independent breast cancer biomarker. Our work translates basic science data to clinic linking the relationship between adipose tissue and lipid metabolism to breast cancer. 28781090_High levels of FABP4 are significantly related to stroke risk and severity, independent from other traditional and emerging risk factors, suggesting that they may play a role in stroke pathogenesis. 28801883_Elevation of FABP4 is associated with an increased risk of death and poor functional outcome events in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute ischemic stroke and is independent of other established clinical risk predictors and biomarkers 28808264_Inhibition of MIR31HG reduced the enrichment of active histone markers, histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) and acetylation (AcH3), in the promoter of the adipogenic-related gene, fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4). 28860092_Elevated A-FABP concentration could be a predictor for MetS and arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients 28893569_the function of FABP4 in cervical cancer and the underlying molecular mechanisms, were investigated. 28903937_Ectopic expression and secretion of FABP4 in vascular endothelial cells contribute to neointima formation after vascular injury. 29017449_A-FABP concentration was an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in patients with stable angina undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. 29171144_Patient serum analysis demonstrated significantly increased FABP4 in those with underlying liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. This suggests FABP4, an FABP not normally expressed in the liver, can be synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes and HCC cells, and that FABP4 may play a role in regulating tumour progression in the underlying setting of obesity. 29237483_FABP4 from adipocytes mediate adipocyte-cholangiocarcinoma interactions that are crucial for the invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cholangiocarcinoma cells 29264639_Increased FABP4 blood level is a biomarker of lead exposure in women. 29304747_Blood FABP4 is a biomarker for metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease independently of HIV status and antiretroviral therapy. 29305311_FABP4 shows potential as a novel biomarker for diabetic retinopathy prediction in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM), and strict glycemic control and more frequent retinal examination should be highlighted for T2DM patients with the highest quartile range of FABP4. 29394285_Increased second trimester plasma FABP4 independently predicted GH/PE in GDM patients 29437708_These findings identify A-FABP as a functional marker for protumor macrophages, thus offering a new target for tumor immunotherapy 29445067_FABP4 concentration is an independent predictor of the progression of carotid atherosclerosis. 29454748_Thus, FABP4 overexpression in hepatic stellate cells may contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis in patients with metabolic risk factors by modulation of inflammatory pathways. 29733540_these results indicate that FABP4 low-expression plays a critical role in the proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells, and maybe a biomarker for HCC diagnosis and prognosis, and may provide an emerging therapeutic target for HCC in future. 29850615_intermittent high glucose potentiates A-FABP activation and inflammatory responses via TLR4/p-JNK signalin |
ENSMUSG00000062515 |
Fabp4 |
325.777431 |
0.0795479586 |
-3.652031 |
0.149300865 |
665.303835 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001049270497625319037420105090365179519251427080222524380824247812114790532630347971877170161527397006952953054461478571287984128586160924834202006387096939253560516339319061778242784303 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000661847544655970442400266294106313439002119674964237262827300171150464262322643084184976760915818571947933566509071096107244319274782445340137398077411553339486623086543591317106037718 |
Yes |
No |
48.5632725 |
5.4551285 |
613.7036835 |
39.6297706 |
| ENSG00000170379 |
285966 |
TCAF2 |
protein_coding |
A6NFQ2 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Negatively regulates the plasma membrane cation channel TRPM8 activity. Involved in the recruitment of TRPM8 to the cell surface. Promotes prostate cancer cell migration stimulation in a TRPM8-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25559186}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Enables transmembrane transporter binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of anion channel activity; positive regulation of cell migration; and positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane. Located in cell junction and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:285966; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; negative regulation of anion channel activity [GO:0010360]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; regulation of anion channel activity [GO:0010359] |
25559186_Report novel TRP channel-associated factors that modulate TRPM8 activity. 34433829_Evidence for opposing selective forces operating on human-specific duplicated TCAF genes in Neanderthals and humans. |
ENSMUSG00000029851 |
Tcaf2 |
11.131910 |
2.1910652310 |
1.131632 |
0.505387884 |
4.967433 |
0.02582895006407559534977735893335193395614624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.045095257031672088265938924678266630508005619049072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.3992923 |
4.6577609 |
7.1166452 |
1.6902696 |
| ENSG00000170396 |
91752 |
ZNF804A |
protein_coding |
Q7Z570 |
|
Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a zinc finger binding protein. Polymorphisms in this gene, especially rs1344706, are thought to confer increased susceptibility to schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and heroin addiciton. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:91752; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendritic microtubule [GO:1901588]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance [GO:1902952]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010975] |
18677311_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18677311_genome-wide association study of schizophrenia; meta-analysis provided strongest evidence for association around ZNF804A (P = 1.61 x 10(-7)) and this strengthened when the affected phenotype included bipolar disorder (P = 9.96 x 10(-9)) 19407193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407193_healthy carriers of rs1344706 risk genotype show no changes in regional activity but pronounced gene dosage-dependent alteration in functional coupling of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex across hemispheres & with hippocampus & abnormal coupling of amygdala 19844207_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19844207_This study suggested that there is a consistent link between the A allele of rs1344706, increased expression of ZNF804A and risk for schizophrenia. 20048749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20048749_ZNF804A variants examined in this study confer risk of more than one category of disease. Rs1344706[T] is associated with both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, and the copy number variants identified here suggest a connection with anxiety as well. 20231838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368704_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20368704_The allelic association at the ZNF804A locus is now one of the most compelling in schizophrenia to date, and supports the accumulating data suggesting overlapping genetic risk between schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20458322_This study further evidence for a positive association between the ZNF804A locus and schizophrenia, and support previous findings implicating that ZNF804A is likely a true susceptibility locus for schizophrenia. 20538430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538430_This study suggested that significant association between ZNF804A status and the clinical symptomatology based on lifetime severity score for mania. 20603450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20664580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20664580_ZNF804A is predicted to have a role in phenotypes reflecting altered neural connectivity. 20688871_We conclude that ZNF804A is robustly, if modestly, associated with schizophrenia risk, with much work still remaining to elucidate its role in schizophrenia biology. 20862696_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20862696_results do not support the hypothesis that moderately rare non-synonymous variants at the ZNF804A locus are involved in schizophrenia susceptibility 20934520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20934520_These data are consistent with our earlier behavioral data and suggest that ZNF804A is delineating a schizophrenia subtype characterized by relatively intact brain volume 20946959_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20946959_Our findings confirm a key role for disturbed functional connectivity in the genetic risk architecture of schizophrenia 20957649_data suggest that rs1344706 may be related to memory dysfunction in schizophreni 21040459_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21040459_genome-wide supported psychosis risk variant of ZNF804A is associated with altered executive control (larger conflict effect), which is a potential endophenotype of psychotic disorders 21349497_The results if this study suggested that a clinical and molecular modulation by sex of the association of ZNF804A ingle Nucleotide Polymorphism rs7597593 and risk of schizophrenia. 21457757_These results suggest that the genetic variation in ZNF804A might increase susceptibility not only for schizophrenia but also for schizotypal personality traits in healthy subjects. 21525856_The ZNF804A risk variant rs1344706 identifies neural mechanisms common to both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder through its potential effects on cortical thickness, white matter tract integrity, and cognitive function. 21663974_This study demonistrated that variation in ZNF804A contribute to the etiology or clinical schizophrenia in Chinese Han population. 21767209_nominal association of SNP rs1344706 with bipolar disorders and psychosis subphenotype 21810628_SNP rs1344706 associated with abnormal dorsolateral prefrontal cortex functional connectivity with other brain areas in schizophrenia 21876541_The results of this study demonistrated that ZNF804A was significantly associated with variation in interpersonal attributions in healthy participants but not in patients. 21890790_Our results suggest that ZNF804A is a common risk gene for schizophrenia in world populations and that the newly identified functional SNP (rs359895) is likely a risk SNP for schizophrenia. 21892778_The results of this study provided the further evidence that ZNF804A is of functional relevance to schizophrenia and indicates that ZNF804A may be a novel target for pharmacological interventions. 21911029_The ZNF804A variant may confer risk for schizophrenia by exerting its effects on the white matter in the left prefrontal lobe together with other risk factors for schizophrenia. 21988329_using a PCR-RFKP method an association between ZNF804A rs1344706 variant and schizophrenia in a Turkish population was replicated 21993378_present study adds new evidence for an association between the conserved mammalian region of the ZNF804A gene and schizophrenia 22042765_The present data support fronto-hippocampal dysconnectivity as intermediate phenotype linking rs1344706 genotype for ZNF804A to psychosis 22080834_gene ontology analysis of differentially expressed genes indicated a significant effect of ZNF804A knockdown on expression of genes involved in cell adhesion, suggesting a role for ZNF804A in processes such as neural migration, neurite outgrowth and synapse formation 22328493_ZNF804A risk variant influence white matter integrity involving cortico-limbic brain regions in schizophrenia. 22373944_these results indicated that IQ may modulate the role of rs1344706 in the etiology of both schizophrenia and its cognitive impairments 22384243_ZNF804a regulates expression of the schizophrenia-associated genes PRSS16, COMT, PDE4B, and DRD2 22775511_The ZNF804A rs1344706 variant was not associated with schizophrenia in the Romanian population from Cluj Napoca . 22781169_The present study provides evidence that ZNF804A might have a role in cognitive traits of relevance to reading and spelling. 22840435_analysis of a genomewide supported psychosis variant in ZNF804A and white matter integrity in the human brain 22871346_The results of this study that supporting the association between ZNF804A and schizophrenia in our Han Chinese sample. 22887939_ZNF804A may also contribute to schizophrenia susceptibility in Asians although the risk SNP is different from that in Europeans. 22945618_growing body of evidence suggests that the risk allele of rs1347706 is associated with a distinctive set of phenotypic features in healthy volunteers and individuals with schizophrenia. 22948380_The findings of this study suggested that ZNF804A is associated with a subtype of schizophrenia with better cognitive and neurological functioning 23010486_This study have identified a novel transcriptional variant of ZNF804A in human LCLs and postmortem brain samples. 23032874_results show that ZNF804A modulates mechanisms underlying cognitive control. 23147122_no association between the ZNF804A (rs1344706) and white matter connectivity was found 23155182_ZNF804A variation is associated with a schizotypy phenotype. 23212061_rs1344706 associated with decrease in ZNF804A expression during second trimester of fetal brain development, evidence for schizophrenic risk mechanism 23295962_This study demonistrated that ZNF804A genotype modulates neural activity in prefrontal cortex during working memory for faces. 23351715_showed no significant association of ZNF804a rs1344706 with ADHD in UK and Taiwanese sample 23434502_This study demonistratedt that ZNF804A regulate the gene expression involved in TGF-beta signaling. 23562677_The resukts of this study show no significant associations in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. 23590871_Thr results of this study concluded that rs1344706 or a yet unknown polymorphism in linkage disequilibrium is also involved in conferring susceptibility to schizophrenia in samples with different (Asian) ancestral backgrounds. 23776546_Meta-analysis indicates that the European GWAS-identified risk SNP rs1344706 within ZNF804A is not associated with schizophrenia in Han Chinese population. 23815973_This study suggests that rs1366842 is associated with schizophrenia in Han Chinese. 24066410_No evidence found that the ZNF804A SNP rs1344706 is a susceptibility locus for SZ in Han Chinese. 24078172_In schizophrenic patients, AA carriers had thicker prefrontal and temporal cortex and less disturbed cortical folding; the opposite was seen in controls. The A allele was associated with lower prefrontal ZNF804A expression in schizophrenic patients. 24123948_ZNF804A is one of a handful of genes so far identified to have been strongly associated with risk for both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. 24247043_findings confirm the effects of the psychosis risk variant in ZNF804A on the dysfunction of the Theory of Mind network 24315717_The data of this study does not preclude the possibility of other functional variants in ZNF804A, it provides evidence that the rs1344706 SZ risk allele is the cis-regulatory variant directly. 24424391_Significant associations found between ZNF804A genotype and variation in the auditory P300 response in schizophrenia. 24424392_ZNF804A has pleiotropic effects on risk for SZ and neural mechanisms that are indexed by the novel P300b ERP component. 24462263_This study demonistrated that Allelic imbalance associated with the schizophrenia risk SNP rs1344706 indicates a cis-acting variant in ZNF804A. 24636489_No significant associations were found between rs1344706 and the cognitive traits of intelligence, memory, inhibition, or with white matter microstructure. 24685285_The present study indicates that the ZNF804A schizophrenia risk gene may affect regional white matter microstructure, including white matter regions that have been found compromised in schizophrenia patients. 24828433_Epistasis increases the risk variation explained above the contribution of the polygenic score in the ZNF804A pathway, showing its role in intelligence (IQ), memory and social cognition in cases with psychosis. 24866414_Results suggest that ZNF804A could have a pivotal role in mediating the intermediate phenotypes associated with verbal traits in individuals with autism 25065377_Our findings demonstrate effects of ZNF804A genetic variation on brain structure, with diverging regional effects in schizophrenia patients and healthy controls in frontal and temporal brain areas. 25162540_SNP rs1344706 influences the expression of novel splice variant ZNF804A(E3E4)in fetal brain and may be part of mechanism by which allelic variation in ZNF804A affects risk of psychosis 25217366_This study showed that no effect of schizophrenia risk genes ZNF804A on macroscopic brain structure 25526981_Single nucleotide polymorphism rs1344706 of ZNF804A is associated with schizophrenia. 25708696_Several ZNF804A variants were significantly associated with the risk of heroin addiction, and these variants affected decision making and gray matter volume in heroin abusers compared with controls. 25757652_Study found a significant decrease in intrahippocampal theta (using MEG) and greater coactivation of the superior frontal gyrus with the hippocampal network (using fMRI) in risk versus nonrisk ZNF804A rs1344706 homozygotes 25896933_P3b latencies were more variable for AA carriers than C carriers. Intra-subject variability, was not associated with genotype. Results suggest that this risk gene is associated with an attenuated form of an endophenotype associated with the psychosis. 25905630_findings suggest that ZNF804A may affect a differentiating neuron's response to inflammatory cytokines 25921517_ZNF804A rs1344706 may aggravate the risk for schizophrenia by exerting its effects on cortical thickness, surface area, and cortical volume in these brain regions. 25935703_These findings provided supportive evidence for the involvement of ZNF804A rs1344706 in Bipolar disorder, especially in BD-I. 26164821_This study demontrated that ZNF804A expression in developmental brain. 26382569_SNPs have also been implicated for regulating ZNF804A expression in human brain. In this independent replication study, we tested the rs7597593 and rs1344706 SNP genotypes and their corresponding haplotypes for association with heroin addiction 26654932_ZNF804A SNP rs1344706 was associated with the functional connectivity between right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and left hippocampal formation 26670283_The single-nucleotide polymorphism rs1344706 (A/C) at the second intron of gene ZNF804A on 2q32.1 is the most widely supported of all the genome-wide association studies-identified risk factors in schizophrenia. 26866941_rs1344706 and rs1366842 of ZNF804A might confer a small but detectable risk of schizophrenia (and bipolar disorder) in Asians. 26934312_results did not support the association of rs1344706 with schizophrenia in Han Chinese 27759212_ZNF804A variants found to be associated with Bipolar disorder or Schizophrenia in other populations are also associated with Bipolar disorder risk in Latinos. 27784192_ZNF804A SNPs are involved in the susceptibility of major mood disorders 27790829_Authors assessed the effect across the human brain of the CACNA1C rs1006737 genotype on FA, in a Caucasian clinical sample as well as in health, and whether this genotype effect was different between diagnostic groups and whether it interacted with the ZNF804A rs1344706 genotype. 27837918_data reveal a novel subcellular distribution for ZNF804A within somatodendritic compartments and a nanoscopic organization at excitatory synapses. Moreover, results suggest that ZNF804A plays an active role in neurite formation, maintenance of dendritic spines, and activity-dependent structural plasticity. 28078547_Study provides evidence for an epistatic interaction between ZNF804A rs1344706 and COMT rs4680 on the grey matter volume of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which may improve our understanding on the biological mechanism underlying the genome-wide supported variant ZNF804 rs1344706 of schizophrenia on the prefrontal anatomy. 28120939_rs1344706 showed marginal allelic association with bipolar disorder. Positive association of rs1344706 with schizophrenia was observed in Northern Chinese. 28544350_Genetic variants in ZNF804A are associated with susceptibility to both Schizophrenia and Bipolar I Disorder. 28648753_The combination of tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) with genotyping can be powerful to unveil the role of white matter in bipolar disorder, in conjunction with risk genes, ANK3 and ZNF804A. 28740209_Single nucleotide polymorphism in ZNF804A gene is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. 28924186_Among the transcripts associated with ZFP804A, a SZ risk gene, neurogranin (NRGN), is one of ZFP804A targets. Interestingly, downregulation of ZFP804A decreases NRGN expression and overexpression of NRGN can ameliorate ZFP804A-mediated migration defect. 28931092_An association between ZNF804A single nucleotide polymorphism rs7597593 and both schizotypy and psychotic-like experiences 29112096_We found that rs12476147 (P=0.0078) was associated significantly with schizophrenia, but no SNPs showed statistically significant associations with major depressive disorder after Bonferroni correction. Moreover, we also found that haplotype block 2, which included rs12476147 and rs1344706, was associated significantly with schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. 29247760_Study provides evidence to suggest that rs1344706 variation is not associated with gray matter alterations in a relatively large case-control cohort of schizophrenia cases and healthy individuals, when using either standard univariate or novel multivariate analytical approaches. 29257977_Effects of ZNF804A rs1344706 on verbal fluency functional connectivity in psychosis. 29527501_The results of this study elucidated the contribution of rs1344706 to functional connectivity within the brain network, and may have important implications for our understanding of this risk gene's role in functional dysconnectivity in schizophrenia. 29611035_This study demonstrated that schizophrenic patients who were homozygous for the rs1344706 risk allele (AA) exhibited a lower strength of resting-state functional connectivity between the bilateral hippocampus and the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. 30079586_ZNF804A-rs1344706 is associated with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. ZNF804A and CACNA1C polymorphisms are epistatically implicated in psychiatric diagnosis. 30118824_Study provides evidence that the ZNF804A gene has a certain effect on psychosis risk, measured as schizotypal traits in healthy subjects. In addition, findings suggest, for the first time, that genetic variation in the ZNF804A gene may modulate the relationship between the lifetime cannabis use and psychotic proneness. 30597088_Convergent Evidence That ZNF804A Is a Regulator of Pre-messenger RNA Processing and Gene Expression. 30670685_The variant rs10497655 was significantly associated with autism spectrum disorder in Han Chinese, which had a significant effect on ZNF804A expression, with the T risk allele homozygotes related with reduced ZNF804A expression in human fetal brains. 30852803_ZNF804A rs1344706 nonlinearly modulated spontaneous regional brain activity in bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in healthy individuals by interaction with COMT rs4680. ZNF804A rs1344706 and COMT rs4680 are associated with brain activity of corticolimbic neural circuitry. 31076262_Associations of schizophrenia risk gene ZNF804A with schizotypy and attention deficit in healthy subjects. 31122238_No significant association was found between the two SNPs (rs1344706 and rs7603001) in ZNF804A and autism in Han Chinese population. 31994908_The expression of zinc finger 804a (ZNF804a) and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) genes is related to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 32544854_Effect of ZNF804A gene polymorphism (rs1344706) on the plasticity of the functional coupling between the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the contralateral hippocampal formation. 32626976_Schizophreniaassociated microRNA148b3p regulates COMT and PRSS16 expression by targeting the ZNF804A gene in human neuroblastoma cells. 32941385_Genetic impact of ZNF804A on cognitive function in patients with bipolar I disorder. 33395218_Ethnicity-dependent effects of Zinc finger 804A variant on schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. 33446247_Schizophrenia risk ZNF804A interacts with its associated proteins to modulate dendritic morphology and synaptic development. 34329479_Schizophrenia-associated variation at ZNF804A correlates with altered experience-dependent dynamics of sleep slow waves and spindles in healthy young adults. 34364876_Schizophrenia risk candidate protein ZNF804A interacts with STAT2 and influences interferon-mediated gene transcription in mammalian cells. 35447233_Genetic analysis of the ZNF804A gene in Mexican patients with schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder and bipolar disorder. 35728455_Study of a functional SNP rs13423388 in a novel enhancer element of schizophrenia-associated ZNF804A. 35796825_A functional neuroimaging association study on the interplay between two schizophrenia genome-wide associated genes (CACNA1C and ZNF804A). |
ENSMUSG00000070866 |
Zfp804a |
88.314648 |
2.4567905290 |
1.296775 |
0.196917343 |
43.674345 |
0.00000000003878226602082545797823239018368990382867877997341565787792205810546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000206279728456714859019844672474860384353556597147871798370033502578735351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
128.6980476 |
14.2611110 |
52.8251205 |
4.6444173 |
| ENSG00000170412 |
55890 |
GPRC5C |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ84 |
FUNCTION: This retinoic acid-inducible G-protein coupled receptor provide evidence for a possible interaction between retinoid and G-protein signaling pathways. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the type 3 G protein-coupled receptor family. Members of this superfamily are characterized by a signature 7-transmembrane domain motif. The specific function of this protein is unknown; however, this protein may mediate the cellular effects of retinoic acid on the G protein signal transduction cascade. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55890; |
cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] |
28228611_Data suggest that agents (such as all-trans retinoic acid) that activate GPRC5C restore and/or maintain functional insulin-secreting cells; GPRC5C appears to play role in regulation of expression of genes controlling apoptosis, cell survival, and cell proliferation in insulin-secreting cells. |
ENSMUSG00000051043 |
Gprc5c |
39.814833 |
2.1726883450 |
1.119481 |
0.301702380 |
13.860841 |
0.00019685775299306993118934883124637735818396322429180145263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000516462928222131620326074141757999313995242118835449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
51.3765570 |
9.7706733 |
23.7622209 |
3.5987699 |
| ENSG00000170425 |
136 |
ADORA2B |
protein_coding |
P29275 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for adenosine. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an adenosine receptor that is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. This integral membrane protein stimulates adenylate cyclase activity in the presence of adenosine. This protein also interacts with netrin-1, which is involved in axon elongation. The gene is located near the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:136; |
glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; G protein-coupled adenosine receptor activity [GO:0001609]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; mast cell degranulation [GO:0043303]; positive regulation of cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0010753]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of chronic inflammatory response to non-antigenic stimulus [GO:0002882]; positive regulation of guanylate cyclase activity [GO:0031284]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043306]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; relaxation of vascular associated smooth muscle [GO:0060087]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11906291_1,8-disubstituted xanthine derivatives: synthesis of potent A2B-selective adenosine receptor antagonists 12080047_A2BR binds to E3KARP and Ezrin upon agonist stimulation. 12600879_Mast cell-mediated stimulation of angiogenesis: cooperative interaction between A2B and A3 adenosine receptors. 12939345_Selectively up-regulated by hypoxia (>5-fold increase in mRNA), and antagonists neutralize ATP-mediated endothelial permeability 15187156_demonstrated induction of IgE synthesis by the interaction between adenosine-stimulated mast cells and B lymphocytes involves up-regulation of IL-4 and IL-13 mediated by A(2B) receptors 15550390_Interferon-gamma down-regulates adenosine 2b receptor-mediated signaling and inhibits the expression of adenylate cyclase 15637124_adenosine A2B receptors mediate the adenosine-induced contraction vasomotor effect in human chorionic vessels and that this involves synthesis of a thromboxane receptor activator or a related prostanoid. 15769552_The PKC delta and epsilon isoforms are also involved in adenosine receptor A(2b) dependent upregulation of IL-6 expression. 16103269_A(2B) receptors may play role in regulating glomerular remodeling associated with glomerular mesangial cell proliferation. Activation of A(2B) receptors may prevent glomerular remodeling associated with renal disease, hypertension, and diabetes. 16631311_A2bR signals through adenylate cyclase (AC) 6 isoform in intestinal epithelial cells 16707627_A(2B) receptors up-regulate IL-4 through G(q) signaling that is potentiated via cross-talk with G(s)-coupled pathways. 16778150_Data indicate that adenosine increases the release of IL-19 from bronchial epithelial cells via activation of adenosine A(2B) receptors, and IL-19 in turn activates human monocytes to release TNF-alpha, which upregulates A(2B) receptor expression. 17077301_Transcriptional coordination of adenosine a2B receptor by HIF-1alpha and amplified adenosine signaling during hypoxia. 17301835_adenosine treatment of dermal papilla cells upregulates FGF-7 expression via the A2b adenosine receptor and that cAMP acts as one of the second messengers in this pathway 17428235_Adenosine is not a direct GHSR agonist. In human embryonic kidney 293s (HEK) cells expressing GHSR, adenosine activates endogenously expressed A(2B)R resulting in calcium mobilization. 17565009_Epac1 activation in HUVEC results in ERK1/2 activation, and this protein, at least in part, mediates response to the physiologically relevant event of A(2B)AR stimulation 18004767_Short-term TNF-alpha cell treatment caused A(2B) AR phosphorylation inducing, in turn, impairment in A(2B) AR-G protein coupling and cAMP production 18056839_Pharmacologic and genetic evidence for vascular A2BAR signaling as central control point of hypoxia-associated vascular leak. 18215420_The results herein provide initial evidence that the inhibitory effect of hypoxia on MMP-9 by mature dendritic cells requires the activation of A(2b) in a cAMP/PKA-dependent pathway. 18351132_our findings revealed the role of adenosine receptors in breast cancer cell lines on growth modulation role of A3 and functional form of A2B, although its involvement in cell growth modulation was not seen 18367727_A(2B)-R are required for ASL volume homeostasis in human airways, and therapies directed at inhibiting A(2B)-R may lead to a cystic fibrosis-like phenotype with depleted ASL volume and mucus stasis. 18703227_A2B adenosine receptors may differentially modulate hENTs in hPMEC, which could be a mechanism attempting to re-establish physiological extracellular adenosine levels in pre-eclampsia. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19019667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19794965_Data suggest that adenosine receptor modulation may be useful for refining the use of chemotherapeutic drugs to treat human cancer more effectively. 19841638_Hypoxic mature dendritic cells predominantly express adenosine receptor A2b. 19883624_Studies indicate that adenosine mediates its actions by means of activation of specifiic G protein-coupled receptors, for which 4 subbtypes: A1R, A2AR, A2BR and A3R have 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20008542_Oxidative/nitrosative stress selectively altered A(2B) adenosine receptors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 20011598_Development of Chlamydia trachomatis is reversibly retarded by prolonged exposure of infected cells to extracellular adenosine mediated by the A2b adenosine receptor. 20029460_demonstrated that hypoxia-induced apoptosis of T cells was mediated by A(2a )and A(2b) receptors. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20388705_TNF-alpha-induced A(2B)AR expression in colonic epithelial cells is post-transcriptionally regulated by miR27b and miR128a 20619442_ADORA2B was overexpressed in colorectal carcinomas grown under a hypoxic state, presumably promoting cancer cell growth. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20926384_Adenosine A2A receptor is involved in cell surface expression of A2B receptor 21030693_The results of this study suggest that deterioration of structure in the extracellular domains of GPCRs compromises overall receptor structure with profound consequences for receptor activation and constitutive activity. 21109603_Adenosine A(B) receptors mediate an early induction of NR4A1 and a decrease in cell proliferation via the cAMP/Epac pathway in coronary artery smooth muscle cells. 21242513_The ability of transgenic A2BR blockade to reduce circulating interleukin (IL)-6 levels by 24 hr may be explained by the reduction of bacterial load, and reflects that transgenic mice are going to live. 21335481_[review] There is evidence that the ADORA2B receptor has cardioprotective effects upon its activation. However, controversy remains regarding the precise timing of activation required to induce cardioprotection. 21480628_The main differences between the general dynamic behaviors of the A(2A)AR receptors and A(2B)AR receptors explored can be explained in terms of their particular sequences, loops lengths, and disulfide bridges. 21506953_Inhibition of human mast cell activation would be a mechanism for A AR antagonists, but not A(2B) AR antagonists. 21590734_Adenosine receptor expression and activation during the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cell to osteoblasts and adipocytes, was investigated. 21620804_Only the disulfide bond of the adenosine A2B receptor is essential for ligand binding and receptor activation. 21622827_2',3'-cAMP inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells from the aorta and coronary arteries. This effect is due in part to metabolism of 2',3'-cAMP to adenosine, with engagement of the A2B receptor. 21730968_data show that expression of A1Rs induced adipocyte differentiation, whereas A2bR expression inhibited adipogenesis and stimulated an osteoblastic phenotype 21966389_IL-4 amplifies the pro-inflammatory effect of adenosine in human mast cells by increasing expression levels of adenosine receptors A2B and decreasing A2A 22119961_A2B receptors are expressed in neuroendocrine tumors during cellular stress, damage and hypoxia. 22217884_adenosine stimulates human endothelial progenitor cells migration by activating A2A and A, but not A2B, receptors and provides evidence to support a role of adenosine in modulating angiogenic capacity of hEPC 22504483_studies identify adenosine-elicited stabilization of Per2 in the control of HIF-dependent cardiac metabolism and ischemia tolerance and implicate Per2 stabilization 22679008_ADORA2B is a candidate gene known to modify the severity of sickle cell disease. 22767505_Binding of A(2B)AR to specific sites on p105 prevents polyubiquitylation and degradation of p105 protein. 22848385_study identified the A2bAR as a significant regulator of HFD-induced hallmarks of T2D, thereby pointing to its therapeutic potential. 22867902_A(1) and A(2B)adenosine receptors could be potential biomarkers to provide an early indication of SA risk and their stimulation may turn out to improve fetoplacental perfusion by increasing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and nitric oxide (NO). 22963436_The most recent evidence concerning the role of ADORA2B and its potential therapeutic relevance is discussed. [Review Article] 23045479_A(2B)ARs mediate C. difficile toxin-induced enteritis and disease. 23286920_Distinct interactions of structurally diverse ligands with the human A(2B) receptor and differences between closely related receptor subtypes. 23483055_Identification of a pharmacologically tractable Fra-1/ADORA2B axis promoting breast cancer metastasis. 23584256_CD73 promotes the production of renal adenosine that is a prominent driver of renal hypertension by enhanced ADORA2B signaling-mediated endothelin-1 induction in a hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha-dependent manner. 23638125_Hypoxia induced serotonin synthesis and secretion is amplified by ADORA2B signaling via MAPK/CREB and TPH-1 activation. 23682121_Adenosine regulates bone metabolism via A1, A2A, and A2B receptors. 23716716_High concentrations of extracellular adenosine in the tumor microenvironment can chronically activate A2B receptors to suppress Rap1B prenylation and signaling at the cell membrane, resulting in reduced cell-cell contact and promoting cell scattering. 23855769_increased expression levels of the adenosine A2B receptor and a heightened deposition of hyaluronan (a component of the extracellular matrix) in remodeled vessels of patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD 24136993_an important role of the A2B receptor-dependent upregulation of JunB in VEGF production and possibly other AP-1-regulated events. 24391213_ADORA2B was induced in lung cells after cyclic mechanical stress. A prominent region within the ADORA2B promoter conveys stretch responsiveness and has a binding site for HIF-1. 24434023_Data indicate that hypoxia regulates prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) through hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha (HIF2alpha) and from stimulated A2B adenosine receptors. 24464644_Activation of the adenosine A2B receptor is regulated by the C-terminus of G protein alpha-subunits. 24502579_the adenosine A2b receptor was shown to be the only one of the adenosine receptors whose cardiac expression is induced by ischemia in both mice and humans and whose function is implicated in ischemic pre- or post-conditioning 24584483_After myocardial infarction, A2B receptor signaling regulates myocardial repair and remodeling. 24589267_Studies indicate that adenosine signaling through the adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) and A2B receptor (A2BR) were involved in sickle cell disease (SCD). 24652540_The effects of extracellular cAMP on monocytes are mediated by CD73 ecto-5'-nucleotidase and A2A and A2B adenosine receptors, as selective antagonists could reverse its effects. 24877077_HUVECs from preeclampsia exhibit elevated protein level of A2BAR and impairment of A2BAR-mediated NO/VEGF signaling pathway. 24928509_study implicates the A2bAR as a regulator of adipocyte differentiation and the A2bAR-KLF4 axis as a potentially significant modulator of adipose biology. 24966910_Findings support a potentially destructive role for A2BAR under intestinal ischemia/reperfusion and acute hypoxic conditions. 25002363_A2B receptor activation blunts trophoblast migration possibly as a result of reduced activation of the MAPK signaling pathway and lower proMMP-2 levels. 25087184_Data indicate adenosine receptor ADORA2B as the specific receptor and signalling pathway for the metabolite 5'-methylthioadenosine (MTA). 25429616_Stimulation of A1AR and A2BAR had a prominent anti-proliferative/pro-apoptotic effect on the glioblastoma stem cells. 25587035_the A2B adenosine receptor (ADORA2B) is essential for adenosine-induced SphK1 activity in human and mouse normal and sickle erythrocytes in vitro 25629231_The rs7208480 of ADORA2B as well as the haplotypes were not found to be associated with chronic heart failure susceptibility. 25765819_our data suggest that adenosine A2b signaling represses CIITA transcription in VSMCs by manipulating the interaction between STAT1 and the epigenetic machinery. 25966978_the A2B AR activation-driven angiogenesis via cAMP-PKA-CREB mediates VEGF production and PI3K/AKT-dependent upregulation of eNOS in HMEC-1 26228921_Data show that ADORA2B mRNA and protein were significantly up-regulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and that ADORA2B controls cellular proliferation via HIF-1alpha activation, suggesting it may be a key regulator of tumoral progression in OSCCs. 26478435_ADORA2B is a target gene of miR-128b.MiR-128b represses cell proliferation, migration and invasion and promotes apoptosis by targeting ADORA2B in gastric cancer. 26748211_A2B receptor activation is critically required for the stimulatory effect of adenosine on IL-10 production and suppression of nitric oxide release. 27199507_Findings suggest that, in obese status, the lower expression level of A2bAR, KLF4, and KLF15 of visceral adipose tissue may correlate with obese-dyslipidemia induced inflammation in Uygur population. 27208173_Actinin-1 binds to the C-terminus of A2B adenosine receptor (A2BAR) and enhances A2BAR cell-surface expression 27226580_cells lacking A2b do not respond in this manner to hypoxia or ATP but transfection of A2b restores this response, that Epac1 is critically involved, and that Rap1B is important for the relative positioning of the centrosome and nucleus. 27482003_erythrocyte AMP-activated protein kinase was activated in humans at high altitude. It is a key protein functioning downstream of the A2B adenosine receptor, phosphorylating and activating BPG mutase and thus inducing 2,3-BPG production and O2 release from erythrocytes. 27693637_The A2b adenosine receptor antagonist PSB-603 promotes oxidative phosphorylation and ROS production in colorectal cancer cells via adenosine receptor-independent mechanism. 27729268_Studies show that A2b receptor is overexpressed in various tumor lines and biopsies from patients with different cancers. This suggests that A2b receptor can be used by tumor cells to promote progression. [review] 28137910_the effects of TNF-alpha were investigated on the expression/responsiveness of the A2B adenosine receptor (A2BAR), a Gs-coupled receptor that promotes mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation into osteoblasts. 28169986_CD73-depedent elevation of plasma adenosine signaling via ADORA2B-mediated protein kinase A phosphorylation, ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of erythrocyte ENT1 is a novel feed-forward signaling network underlying initial hypoxic adaptation and retention upon re-exposure. 28701304_findings suggest that hypoxia, through HIF1A, contributes to the development and progression of pulmonary fibrosis through its regulation of ADORA2B expression on alternatively activated macrophages, cell differentiation, and production of profibrotic mediators 28921456_this study demonstrated that the Haemophilus influenzae infection stimulated A2A and A2B adenosine receptors. 29524036_monocyte-derived macrophages from ankylosing spondylitis patients expressed increased levels of A2AAR and reduced levels of A1 and A2BAR compared to healthy controls 30020825_ADO inhibits oxalate transport by reducing PAT1 surface expression as shown by biotinylation studies. We conclude that ADO inhibits oxalate transport by lowering PAT1 surface expression in C2 cells through signaling pathways including the A2B AR, PKC, and phospholipase C 30157211_A2B adenosine receptor in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells diminishes ERK1/2 phosphorylation by activation of MAPK-phosphatase-1 30242135_hypoxia increased expression of adenosine receptor 2B (A2BR) in human breast cancer cells through the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. 30664911_Activation of ADORA2B associates with an anti-inflammatory response in several tissue and diseases. In tissues from pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus, ADORA2B is overexpressed and correlates with hyperglycaemia and oxidative stress. ADORA2B shows low affinity for adenosine and its activation results in triggering intracellular signaling cascades lowering the inflammatory response. [review] 31234425_Reciprocal positive regulation of HIF and the A2B receptor in a hypoxic microenvironment thus enhances glycolytic and mitochondrial metabolism in osteoclasts to drive increased bone resorption. 31263105_APIP is crucial for cardioprotection against myocardial infarction by virtue of binding to and stabilizing ADORA2B, thereby dampening ischemic heart injury. 31278195_ADORA2B-AMPK signaling cascade-induced 2,3-biphosphoglycerate production promotes O2 delivery by erythrocytes to counteract kidney hypoxia and progression of chronic kidney disease 31678144_Our results indicate that A2B receptors contribute to radiation resistance in a cancer-cell-specific manner, and may be a promising target for radiosensitizers in cancer radiotherapy. 31846065_Adenosine receptor 2B activity promotes autonomous growth, migration as well as vascularization of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. 31980601_Cancer associated fibroblasts-CD73 expression is enhanced via an adenosine-A2B receptor-mediated feedforward circuit triggered by tumor cell death, which enforces the CD73-checkpoint. 32076070_Cysteine redox state regulates human beta2-adrenergic receptor binding and function. 32348778_Characterization of cancer-related somatic mutations in the adenosine A2B receptor. 32419057_Tumor-derived exosomes promote angiogenesis via adenosine A2B receptor signaling. 32589947_Adenosine/A2B Receptor Signaling Ameliorates the Effects of Aging and Counteracts Obesity. 33096224_Insulin requires A2B adenosine receptors to modulate the L-arginine/nitric oxide signalling in the human fetoplacental vascular endothelium from late-onset preeclampsia. 33268695_Involvement of CD73 and A2B Receptor in Radiation-Induced DNA Damage Response and Cell Migration in Human Glioblastoma A172 Cells. 33524770_Systematic deletion of adenosine receptors reveals novel roles in inflammation and pyroptosis in THP-1 macrophages. 34070360_Adenosine and Cordycepin Accelerate Tissue Remodeling Process through Adenosine Receptor Mediated Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway Stimulation by Regulating GSK3b Activity. 35562985_Adenosine Receptor A2B Negatively Regulates Cell Migration in Ovarian Carcinoma Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000018500 |
Adora2b |
18.344568 |
3.8817146537 |
1.956694 |
0.446145912 |
19.804519 |
0.00000857796135991398749727140926601975934318033978343009948730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027134742750177980117731041387330037650826852768659591674804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.0578607 |
7.6008396 |
7.9226362 |
1.6791260 |
| ENSG00000170439 |
196410 |
METTL7B |
protein_coding |
Q6UX53 |
FUNCTION: Thiol S-methyltransferase that catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosyl-l-methionine to hydrogen sulfide and other thiol compounds including dithiothreitol, 7alpha-thiospironolactone, L-penicillamine, and captopril. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33649426}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid droplet;Membrane;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Signal;Transferase |
|
Enables thiol S-methyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in methylation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:196410; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase activity [GO:0008757]; thiol S-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018708]; methylation [GO:0032259] |
31121562_Results indicate that METTL7B may promote metastasis of thyroid cancer through EMT and may therefore be considered as a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of thyroid carcinoma. 33484445_Low Molecular Pectin Inhibited the Lipid Accumulation by Upregulation of METTL7B. 33649426_Human METTL7B is an alkyl thiol methyltransferase that metabolizes hydrogen sulfide and captopril. 33858297_circ-PSD3 promoted proliferation and invasion of papillary thyroid cancer cells via regulating the miR-7-5p/METTL7B axis. 35034026_Prognostic Potential of METTL7B in Glioma. 35144642_Methyltransferase like 7B is a potential therapeutic target for reversing EGFR-TKIs resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. 35254598_METTL7B contributes to the malignant progression of glioblastoma by inhibiting EGR1 expression. 35397445_Potent necrosis effect of methanethiol mediated by METTL7B enzyme bioactivation mechanism in 16HBE cell. 35603523_Methyltransferase like 7B is upregulated in sepsis and modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response and macrophage polarization. |
ENSMUSG00000025347 |
Mettl7b |
41.571524 |
0.2044008778 |
-2.290527 |
0.278969354 |
73.398468 |
0.00000000000000001059482914146060803975449983380002988528006338807578232130701678670448018237948417663574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000084575272108144178798430291516869658171513404818896847414677608867350500077009201049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.5259573 |
2.7642639 |
71.6383625 |
7.6727638 |
| ENSG00000170458 |
929 |
CD14 |
protein_coding |
P08571 |
FUNCTION: Coreceptor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide (PubMed:1698311, PubMed:23264655). In concert with LBP, binds to monomeric lipopolysaccharide and delivers it to the LY96/TLR4 complex, thereby mediating the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (PubMed:20133493, PubMed:23264655, PubMed:22265692). Acts via MyD88, TIRAP and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response (PubMed:8612135). Acts as a coreceptor for TLR2:TLR6 heterodimer in response to diacylated lipopeptides and for TLR2:TLR1 heterodimer in response to triacylated lipopeptides, these clusters trigger signaling from the cell surface and subsequently are targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway (PubMed:16880211). Binds electronegative LDL (LDL(-)) and mediates the cytokine release induced by LDL(-) (PubMed:23880187). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16880211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1698311, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20133493, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22265692, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23264655, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23880187, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8612135}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;GPI-anchor;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a surface antigen that is preferentially expressed on monocytes/macrophages. It cooperates with other proteins to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide, and to viruses. This gene has been identified as a target candidate in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients to potentially lessen or inhibit a severe inflammatory response. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:929; |
endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lipopolysaccharide receptor complex [GO:0046696]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; lipoteichoic acid binding [GO:0070891]; opsonin receptor activity [GO:0001847]; peptidoglycan immune receptor activity [GO:0016019]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to diacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071726]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to lipoteichoic acid [GO:0071223]; cellular response to molecule of bacterial origin [GO:0071219]; cellular response to triacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071727]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031666]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034145]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032481]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to magnesium ion [GO:0032026]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612]; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034142] |
11062291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11199329_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11257272_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11282774_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11343243_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11732288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11779220_CD14-dependent activation of NF-kappaB by filarial parasitic sheath proteins 11825494_Data suggest that soluble lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 (sCD14) elevation is associated with the development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) after major burns. 11841490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11841490_results suggest that the enhanced CD14 expression in psoriasis is not attributable to functional variants of CD14 (-159C/T) 11843056_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11854210_IFN-gamma primed CD14(high) human gingival fibroblasts to enhance production of IL-8 in response to LPS through augmentation of the CD14-TLR system 11876746_The important host receptor CD14 is partially implicated in TNF, IL-1, IL-6 and MCP-1 production, while CD14-independent pathways seem to be responsible for IL-8 production after S. suis stimulation. 11932927_Though Cd14 is known to faciitate binding of several bacterial ligands to TLR, no role could be found for CD14 in C. pneumoniae binding. 11935032_No association between the CD14 C(-260)T and CD18 codon 441 gene polymorphisms and the incidence of stroke was found in a large, prospective, matched case-control sample from the Physicians' Health Study. 11935032_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11985523_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12006789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12011764_CD14 polymorphism is associated with smoking dependence 12011764_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12067299_Human proteinase 3 can inhibits LPS-mediated TNF-alpha production through CD14 degradation 12075251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12101079_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12103253_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12117913_plasma factor LBP and cell surface receptor CD14 were necessary for LPS activation of p38, which was tightly associated with LPS priming of the PMN respiratory burst 12126249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12140663_TT genotype of CD14 associated with risk of atherosclerotic or microangiopathic stroke 12171914_CD14 has a role in mediating signaling responses to Aspergillus fumigatus 12174084_Data show that the TLR4-mediated LPS response in bladder epithelial cells also uses the co-receptor CD14 for efficient LPS signalling. 12185442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12207338_Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae activate human peripheral blood monocytes utilizing TLR2, CD14 and CD11a/CD18 as cellular receptors. 12324469_Lipopolysaccharide rapidly traffics to and from the Golgi apparatus with the toll-like receptor 4-MD-2-CD14 complex 12404174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12410798_some heat-stable component of P. gingivalis, including LPS, may be responsible for the induction of IL-8 and MCP-1 in HUVECs by a CD14-dependent mechanism 12438323_lipopolysaccharide may induce proliferation of periodontal epithelial cells by upregulating keratinocyte growth factor 1 expression via the CD14 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway 12450609_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12492251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12566518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12580907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12594207_innate immune recognition of LTA via LBP, CD14, and TLR-2 represents an important mechanism in the pathogenesis of systemic complications in the course of infectious diseases brought about by Gram-positive pathogens. while TLR-4 and MD-2 are not involved. 12624278_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12624278_The CD14 -159C/T polymorphism is associated with increased common carotid artery intima-media thickness in smokers 12663765_Human cytomegalovirus activates inflammatory cytokine responses via CD14 and Toll-like receptor 2 12679473_first study to suggest an effect of a genetic polymorphism of the CD14 gene on both insulin sensitivity (healthy subjects and type 2 diabetic patients) and endothelial dysfunction (sICAM-1 levels) in type 2 diabetes mellitus 12700637_CD14 is not critical for phosphatidylserine-induced apoptosis in human macrophages 12731067_a new functional role of CD55 as a member of a multimeric LPS receptor complex. 12754215_data support the hypothesis that lipopolysaccharide binding protein can inhibit cell responses to lipopolysaccharide(LPS) by inhibiting LPS transfer from membrane CD14 to the Toll-like receptor 4-MD-2 signaling receptor 12756848_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12757265_data suggest that peripheral blood cells are of negligible importance in LPS-induced production of inflammatory mediators in vivo and that LPS may activate genes via a CD14-independent pathway that is slower and less efficient 12825176_A significant association between the CD14 TT genotype and C. pneumoniae infection was found. 12825176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12832426_there may be a resistive exercise training-induced reduction in TLR4/CD14 expression in older women 12853157_results provided experimental evidence for existence of close association between CD14 and HIV coreceptor CXCR4 on human monocytic cells 12885845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12897754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12897754_The TT genotype of -159 C-->T CD14 is associated with nonatopic asthma and food allergy, particularly in white subjects. Thus CD14 is a candidate gene specifically for nonatopic asthma and not for asthma in general 12911501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911501_The polymorphic maeker C-159T of CD14 was associated with serum total IgE concentration in atopic Chinese children. 12938192_increased serum levels in chronic Hepatitis B and C patients and inversely correlated with HBsAg in chronic Hepatitis B 12940436_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12942028_Results show that the surface receptors TLR2/4 and CD14 are essential for in vitro cellular activation induced by Neisseria meningitidis lipopolysaccharide-containing outer membrane vesicles and purified lipopolysaccharides. 12960274_A marker on monocytes that can differentiate into several distinct mesenchymal cell lineages. 14500479_saliva CD14 promoted the invasion of oral epithelial cells by A. actinomycetemcomitans and consequently augmented the production of IL-8, playing an important role in innate immunity in the oral cavity 14508193_soluble CD14 is associated with aortic stiffness independently of age, BP and atherosclerosis in humans. 14510720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14517492_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14517492_the CD14-159 C --> T polymorphism may be an important genetic trait, related to the ability of CD14 to bind and transport lipids, such as cholesterol 14517520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14587643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14617510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14624155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14648231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14648231_association between the C(-260)T polymorphism in the CD14 promoter and acute myocardial infarction 14672339_CD14 promoter region polymorphism in women with idiopathic recurrent miscarriage 14672339_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14673018_CD14 and TLR2 but not TLR4 play a major role in lipoteichoic acid -mediated effects on PMN and granulocytes 14706103_downregulated by Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection in monocytes 14720421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14739370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14996480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15034063_CD14 can be considered a type 2 acute phase protein (APP) in vivo. Serum levels of CD14 in patients with arthropathies correlates with those of C-reactive protein, an APP, and IL-6, a cytokine known to regulate the synthesis of APP in the liver. 15039096_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15069085_Involvement of CD14/TLR4, CR3, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the degradation of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase in response to LPS. 15080833_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15080833_The lack of association between CD14 genotypes and IgE as well as atopic outcomes in this large German study population seems to indicate that CD14 genotypes may not directly be involved in the development of allergies during childhood. 15081257_Comparison of the genotypes of 242 patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) and 210 healthy subjects shows that polymorphisms in CD14 do not confer susceptibility to GBS and are not associated with Campylobacter jejuni infection. 15081257_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15116260_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15116260_concluded that the -159T/C polymorphism in the CD14 monocyte receptor gene was not associated with progression of coronary atherosclerosis in this population nor did it influence the efficacy of pravastatin in the treatment of atherosclerosis. 15120158_this study provides evidence that Porphyromonas gingivalis outer membrane vesicles contribute to the loss of membrane-bound CD14 receptors from the surface of macrophage-like cells and that gingipains degrade this LPS receptor 15132789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15143473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15164100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166925_in a study of 2558 unrelated Caucasians, it is concluded that the C159T variant has no important effect on plasma cholesterol levels 15175649_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15190267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15207785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15257175_Although (C260T) polymorphism in CD14 gene in this study is associated with expression of sCD14, no significant association was found between this polymorphism and early markers of atherosclerosis. 15257175_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15269840_CD14 and CD16 in monocytes may have a role in development of coronary atherosclerosis and expression of TNF-alpha 15273551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15292769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15356557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15358661_the presence of the membrane-anchored, but not the soluble, form of CD14 is a strong factor in IL-8 induction in bladder epithelial cells in response to bacterial components 15369724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15373760_Most interestingly, sCD14 levels were regulated differentially by the same genetic variants in plasma and milk 15373760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15378299_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15378299_Polymorphism of the CD14 gene is associated with atopic asthma 15491315_C -159T promoter polymorphism was associated in female but not in male patients with periodontal disease 15491315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15516360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15520404_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15558232_The monocytic CD14 expression and serum levels of C-reactive protein, IL-6 and soluble adhesion molecules were higher in the diabetes group than in the group with normal glucose tolerance. 15591473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15591473_The polymorphism of CD14 gene may play an important role in the development of airway obstruction among adult male farmers. 15599151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15602630_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15602630_The CD14/-2984 polymorphism but not the CD14/-159 is associated with IgE level in Taiwanese asthmatic children. 15619435_CD14 is commonly expressed in melamona-infiltrating monocytes/macrophages 15640605_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15647432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15655821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15655821_co-existence of a mutation in either the TLR4 or CD14 gene, and in NOD2/CARD15 is associated with an increased susceptibility to developing Crohn disease compared to ulcerative colitis 15670766_These results indicate that the CD14 region spanning amino acids 57-64 is critical for interacting with TLR2 and enhancing TLR2-mediated peptidoglycan signaling. 15686783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15714129_There was no significant correlation between CD14-159 promoter polymorphism and the severity of pancreatitis 15741437_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15753758_CD14 polymorphism associated with increased prevalence of gram-negative bacterial infection in critically ill adults 15753758_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15764151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15764151_There was no association found between the CD14-159T allele and Crohns disease or ulcerative coltis nor any interaction with the CARD15 or TNF-alpha alleles. 15777548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15778383_findings reveal that mycobacteria promote their uptake through a process of 'inside-out' signaling involving CD14, TLR2, PI3K, and cytohesin-1. This converts low avidity CR3 into an active receptor leading to increased bacterial internalization 15842262_gene polymorphism is associated with chronic periodontitis in Caucasian subjects of a north European origin 15854776_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15867866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15879416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15932345_studies suggest that SP-A could contribute to modulate Re-LPS responses by altering the competence of the LBP-CD14 receptor complex 15940135_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15946916_An altered immune response to lipopolysaccharides with influence on the anti-inflammatory therapy seems to play a role in the genetic predisposition to ulcerative colitis for CD14 gene 15946916_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15966209_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15975149_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15975149_Those with the CD14 -159CC genotype had a significantly increased risk of early infection with P.aeruginosa suggesting that CD14 C-159T plays a role in determining the risk of early infection with P.aeruginosa. 16038043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16038043_The frequencies of IL-1beta+3 594T, IL-10-1082G and CD14-159T allele were similar in patients with mild or severe pancreatitis and in controls. 16046876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16051275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16061600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16061600_the single-nucleotide polymorphism at CD14/-159 is associated with the development of biliary atresia and idiopathic neonatal cholestasis 16085746_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16101942_CT genotype of promotor polymorphism C159T in the CD14 gene is associated with lower prevalence of atopic dermatitis and lower IL-13 production. 16109674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16137548_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16142747_Finds that CD14 polymorphisms influence regulators of the inflammation induced by endotoxin in organic dusts 16142747_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16148556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16159630_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16165702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16165702_The genetic determination of the defense mechanisms in Crohn's disease appears to be not associated with the polymorphism of the CD14 genes. 16174094_The important role of CD14 in innate immunity is reviewed here. 16174099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16194368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16239565_CD14 and TLR2 remained upregulated throughout the experimental period following exposure to Staphylococcus aureus PepG 16246938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16266379_CD14-C159T promoter variant influences total IgE levels and also indicates that the T allele has a more profound effect on total IgE in children with atopic asthma 16266379_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16273620_C-T (-159) polymorphism in the promoter region of the CD14 gene in patients with alcoholic liver disease and chronic hepatitis C virus infection 16273620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16273622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16273622_The C allele may be associated with the pathogenesis of alcoholic pancreatitis, and alcoholic patients with acute pancreatitis and cirrhosis of liver are probably two different subpopulations. 16275943_The lipopolysaccharide-binding function characteristic of CD14 enables effective host responses to pathogens. 16283111_In patients with community-acquired infection, low on-admission level of monocyte CD14 is related to fatal outcome 16290232_Maternal allergy status may affect allergic risk in offspring through a decreased expression of fetal CD14. 16292464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16331574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16331574_The T allele of the C-159T polymorphism of CD14 gene may be a risk factor for myocardial infarction. 16337421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16368002_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16368002_The role of the CD14 -260 C>T polymorphism in the susceptibility to and severity (defined as subfertility and/or tubal pathology) of C. trachomatis infection in women is reported. 16385250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16386288_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16387800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16387800_Subjects with CD14 -159CC were more likely to have moderate or severe acute asthma. 16409569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16427140_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16433727_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16437636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16437636_significant increase of the combined carriership of the CD14 -260T and TLR9 -1237C alleles in the chronic relapsing pouchitis group suggests that these markers identify a subgroup of patients with a risk of developing chronic or refractory pouchitis 16443672_In conclusion, our results strongly support an important role for endothelial membrane CD14 in the activation of endothelium for leukocyte recruitment. 16444757_Results identify a new lipopolysaccharide-binding domain of CD14 with a strong lipopolysaccharide-neutralizing activity. 16446545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16467036_No association between the CD14/C-159T polymorphism and increased risk for the development of rheumatoid arthritis. 16467036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16492974_Results suggest that the presence of intact breast milk soluble CD14 in the upper digestive system could promote innate immunity in this low bacteria density lumen. 16509825_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16512634_Significantly elevated serum concentrations of LBP and sCD14 are found in severe sepsis patients. 16520888_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16538169_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16552356_Ciprofloaxin suppressed the expression of CD14 induced by lipopolysaccharides in monocytes. 16611358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16611358_The IL-6 -174 G/C, IL-10 -1082 G/A and CD14 -260 C/T SNPs may alter risk for sepsis in ventilated VLBW infants 16614348_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16625214_Multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) test was applied to detect epistasis, and identified single-IL4R(Q576R)- and three-IL4R(Q576R), IL5RA(-80), CD14(-260)- locus association models that predict multiple sclerosis risk with 75-76% accuracy. 16625214_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16698680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16706818_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16706818_findings indicated that the polymorphism of CD14 but not TLR4 Asp299Gly mutation was associated with Chinese patients with colorectal cancer, and the CD14 gene may contribute to the predisposition to colorectal cancer 16749413_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16751411_Pathogen recognition receptor CD14 is involved in activation of immature monocyte-derived dendritic cells by the envelope protein surface unit (ENV-SU) of multiple sclerosis-associated retroviral element (MSRV) of human endogenous retrovirus. 16785528_New insights are provided into the importance of stoichiometry among the components of the TLR4/MD-2/CD14 complex; supraoptimal CD14 levels do not suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling. 16815140_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16836908_This study revealed a significant increase in the expression of CD14 and TLR4 in inflamed human dental pulp tissue. 16848791_This study suggests that CD14 directly binds to triacylated lipopeptides and facilitates recognition of the lipopeptides by the TLR2/TLR1 complex without binding to the receptor complex. 16860318_description of a novel feedback mechanism in apoptotic signaling pathway for SGLT-1-dependent cytoprotection; observation suggests new function for CD14 on enterocytes involving induction of caspase-dependent SGLT-1 activity which leads to cell rescue 16873708_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16879054_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16890863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16893989_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16916546_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16933467_A mutation in CD14 is associated with sarcoidosis. 16933467_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16950285_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16950521_CD14/-159 polymorphism may play a role in the development of perennial allergic rhinitis in Korean children. 16950521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17003960_CD14 plays a role in IgE-mediated allergic diseases, and its gene polymorphisms can be important for manifestation of these disorders 17003960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17007028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17007028_These findings show the role of a single-nucleotide polymorphism at CD14/-159 on the development of chronic hepatitis B. Endotoxin susceptibility may play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B. 17030237_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17046070_serum sCD14 levels are increased in MS and correlate inversely with disease activity in relapsing multiple sclerosis patients 17052752_A marker that may be used used to detect macrophages and in the anatomical plane of the fetomaternal junction. 17056323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17062130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17067484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17075287_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17086894_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17086894_no association of CD14 or TLR4 polymorphisms with H. pylori-related gastric malignancy. 17087609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17087609_further evidence is provided for the role of CD14 C(-260)--> T promoter polymorphism as a genetic susceptibility marker of atherosclerosis 17098305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17098305_pathogenetic role of the CD14 C-260T polymorphism in atherosclerosis as -260TT genotype may favour increased inflammation in atheroma promoting possible worsening atherosclerosis 17126402_PI3 kinase effectors PKB and PKC(zeta) are also activated by PI3 kinase in a CD14 dependent manner in lipopolysaccharides stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. 17187267_CD14-C159T polymorphism is not associated with familial Mediterranean fever or development of amyloidosis in the population studied 17187267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17196641_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17201240_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17205552_Signaling by soluble CD14 was TLR2 dependent. CD14-triggered TLR2-mediated response in astrocytes lead to the production of CXCL8, IL-6, and IL12p40, whereas typical TLR-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines were not produced at detectable levels. 17207357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17217435_We considered the effects of a common promotor polymorphism of the lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 associated with increased transcriptional activity upon the development of posttransplant rejection and graft survival. 17259806_CD14-159 and -550 polymorphisms might not play a major role in the pathogenesis of food allergy in Japanese children 17259806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17264400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17274987_CD14 is a novel ligand for alpha4beta1, exhibiting similar activation-state dependent binding characteristics as other alpha4beta1 ligands. 17304102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17304102_reduced signaling through CD14/toll-like receptor 4 in response to challenge by gram-negative bacteria after burns results in a blunted innate immune response and subsequent increased likelihood for systemic infection and death 17309585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17309585_Promoter polymorphisms of the CD14 gene did not influence susceptibility to inflammatory periodontitis in the population cohorts studied. 17436151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17436151_Reports of progression of atherosclerosis in CD14 gene polymorphism in different populations are conflicting. Screening for CD14 159C/T polymorphism is unlikely to be a useful tool for risk assessment of MI at young age. 17438094_Functional polymorphism in CD14 is associated with greater risk of H. pylori-related gastric carcinoma, which might be mediated by elevated CD14. 17438094_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17448042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17448042_an evident association exists between the carriage of the T-containing genotype and and the extent periodontal disease 17456337_CD14/-159 SNP is associated with atopic diseases in Chinese Han ethnic group children. 17456337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17471431_CD14 -550 C/T, which is related to the serum level of sCD14, is associated with the development of respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in the Japanese population. 17511783_Association of CD14, IL1B, IL6, IL10 and TNFA functional gene polymorphisms with symptomatic dental abscesses. 17511783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17515856_CD14 polymorphism (-159 cytosine/thymine) might partly explain the difference in predisposition to develop complications of infectious diseases in different patients. 17515856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17565650_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17565650_The existence of a mutation in the CD14 gene is associated with an increased susceptibility to ulcerative colitis. 17600225_In unstable angina patients oxidized LDL may contribute to upregulating CD14 expression in monocytes 17617027_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17617027_There was no association between IL-10 and CD14 polymorphisms and myocardial infarction occurrence 17653770_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17653770_functional promoter polymorphism, -260 C > T, of CD14 that is a main receptor of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. the frequencies of CD14 TT genotype was higher in Buerger disease. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17802898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17846597_c |
ENSMUSG00000051439 |
Cd14 |
509.526039 |
2.3691692299 |
1.244381 |
0.074355972 |
283.227731 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000148672849135252749913159195832933091805803520029107277735656561821959471288925988992003221453090548630133044052437150988140700578415175508671852657633639623654259187546244902478065341711044311523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040117207554594709247588094852778962541085927649724918931425798046655465061592375875887674337415334928834687761948996992640004717421964588217870235060491350409517252728619496338069438934326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
724.4576115 |
31.0904022 |
308.0276095 |
10.5857101 |
| ENSG00000170525 |
5209 |
PFKFB3 |
protein_coding |
Q16875 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes both the synthesis and degradation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10077634, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17499765, ECO:0000305|PubMed:16316985}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Hydrolase;Kinase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of bifunctional proteins that are involved in both the synthesis and degradation of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, a regulatory molecule that controls glycolysis in eukaryotes. The encoded protein has a 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity that catalyzes the synthesis of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F2,6BP), and a fructose-2,6-biphosphatase activity that catalyzes the degradation of F2,6BP. This protein is required for cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis. It functions as a regulator of cyclin-dependent kinase 1, linking glucose metabolism to cell proliferation and survival in tumor cells. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:5209; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity [GO:0003873]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 2-phosphatase activity [GO:0004331]; brain development [GO:0007420]; fructose 2,6-bisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0006003]; fructose metabolic process [GO:0006000] |
12935880_The results show the expression of the pfkfb3 gene in and its downregulation during myogenic cell differentiation, the decrease of uPFK-2 isozyme levels, product of pfkfb3 gene, is due to its degradation through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway 12963966_PFKFB3 cloning and characterization 15466858_pfkfb3 is a hypoxia-inducible gene that is stimulated through HIF interaction with the consensus HRE site in its promoter region 15896703_kinase activity of human brain 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase is regulated via inhibition by phosphoenolpyruvate 16115917_Findings support a potential role for the phosphorylation of PFKFB3 protein in the progression of cancer and angiogenesis. 16306349_Insulin induces the phosphorylation of PFKFB3 protein, expanding the role of these structurally unique iPFK-2/PFKFB3 isoforms in the metabolic regulation of adipocytes. 16311927_Our results clearly demonstrated the existence of splice isoform of PFKFB-4 mRNA in the DB-1 melanoma cells and its overexpression under hypoxic conditions. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16698023_The results obtained highlight the importance of uPFK-2 on the regulation of glycolysis, on cell viability and proliferation and also on anchorage-independent growth. 17143338_PFKFB-4 and PFKFB-3 genes are expressed in gastric and pancreatic cancer cells, they strongly respond to hypoxia via a HIF-1alpha dependent mechanism and possibly have a significant role in the Warburg effect which is found in malignant cells 17499765_Results show a direct substrate-substrate interaction in the kinase domain of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFKFB3). 18039179_PFK-2/FBPase-2 protein rather than its product fructose 2,6-P(2) is the over-riding determinant of glucose-induced insulin secretion through regulation of glucokinase activity or subcellular targeting. 19473963_ectopic expression of PFKFB3 increased the expression of several key cell cycle proteins, including cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)-1, Cdc25C, and cyclin D3 and decreased the expression of the cell cycle inhibitor p27 19490427_Our results demonstrate that the splice variant UBI2K4 impedes the tumour cell growth and might serve as a tumour suppressor in astrocytic tumours. 20080744_Glycolysis-promoting enzyme 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase, isoform 3 (PFKFB3), is degraded by the E3 ubiquitin ligase APC/C-Cdh1. 20453422_Interleukin 6 enhances glycolysis through expression of the glycolytic enzymes hexokinase 2 and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3. 21402913_Data demonstrate that PFKFB3 is essential for cell division and that it is regulated by APC/C-Cdh1 and SKP1-CUL1-F (SCF)-beta-TrCP. 21860432_inducible PFKFB3 is required for increased growth, metabolic activity and is regulated through active JAK2 and STAT5. 21987444_The allelic deletion of PFKFB3 resulted in a decrease of PFKFB3 mRNA level accompanied by a lower PFKFB3 protein level. 22106309_The breakdown of PFKFB3 during S phase occurs specifically via a distinct residue (S(273)) within the conserved recognition site for SCF-beta-TrCP. 22275052_Low bisphosphatase activity of PFKFB3 is solely due to the presence of a serine at residue 302. 23548149_Stress stimuli affect PFKFB3 transcriptional regulation and kinase activation by protein phosphorylation and glycolysis in cancer cells. 23911327_Study showed that endothelial cells (ECs)relied on glycolysis rather than on oxidative phosphorylation for ATP production and that loss of the glycolytic activator PFKFB3 in ECs impaired vessel formation. 24043759_Phosphofructokinase deficiency impairs ATP generation, autophagy, and redox balance in rheumatoid arthritis T cells. 24204309_Because deregulation of endometrial SRC-2 expression has been associated with common gynecological disorders of reproductive-age women, this signaling pathway, involving SRC-2 and PFKFB3 24295899_PFKFB3 regulates oxidative stress homeostasis via its S-glutathionylation in cancer. 24332967_blockade of PFKFB3 by the small molecule 3-(3-pyridinyl)-1-(4-pyridinyl)-2-propen-1-one (3PO) reduced vessel sprouting. 24515104_estrogen receptor directly promotes PFKFB3 mRNA transcription 24633012_Reduced methylation of PFKFB3 shifted glucose utilization from glycolysis toward the pentose phosphate pathway. 24700124_PFKFB3 is a promising target for the reduction of endothelial glycolysis and its related pathological angiogenesis 25032860_PFKFB3 promotes cell cycle progression and suppresses apoptosis via Cdk1-mediated phosphorylation of p27. 25359860_Shear stress-mediated repression of endothelial cell metabolism via KLF2 and PFKFB3 controls endothelial cell phenotype. 25672572_A binding site for miR-26b was predicted in the 3'UTR of PFKFB3. miR-26b overexpression repressed PFKFB3 mRNA and protein levels. 26093295_study demonstrated that miR-206 regulated PFKFB3 expression in breast cancer cells, thereby stunting glycolysis, cell proliferation and migration 26171876_Shh regulates PFKFB3 activation in breast cancer cells. 26322680_Data show that inhibition of AMP-Activated kinase (AMPK) or 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase-fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) results in enhanced cell death in mitosis. 26337471_Data indicate that 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase3 (PFKFB3) and phosphofructokinase (PFK1) expression allows discrimination between induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) and cancer stem cells (CSCs). 26530697_Our data suggest that chronic inflammation promotes the development of CRC by stimulating aerobic glycolysis and IL-6 is functioning, at least partly, through regulating PFKFB3 at early stage of colorectal cancer (CRC). 26681033_MicroRNA-26b inhibits osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by down-regulating PFKFB3 expression 26718307_a novel role of PFKFB3 in glycolytic metabolism and ER stress of OA cartilage explants and chondrocytes 26827442_Insulin resistance in obese boys leads to up-regulation of INSIG2 gene expression as well as to down-regulation of PFKFB1, PFKFB3, and HK2 genes in the blood cells as compared to obese patients with normal insulin sensitivity. 27146014_Data suggest that hepatic glucokinase activity is regulated by reversible binding to specific inhibitor protein glucokinase regulatory protein (GKRP) and by binding to activator proteins such as 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose 2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK2/FBP2); changes in glucokinase expression and activity are associated with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. [REVIEW] 27262815_the novel role of PFKFB3 in induction of paclitaxel resistance by raising lactate production and activating TLR4 signaling, was characterized. 27373212_The targeting of MCT1 and PFKFB3 regulated cell proliferation. 27491040_we investigate the crosstalk between PFKFB3 and TIGAR (TP53-Induced Glycolysis and Apoptosis Regulator), a protein known to protect cells from oxidative stress. Our results show consistent TIGAR induction in HeLa cells in response to PFKFB3 knockdown 27491149_The expression of PFKFB3, PFKFB4, NAMPT, and TSPAN13 is strongly up-regulated in pediatric glioma. 27799347_PFK-2 seems to be a strategic element that links NADPH oxidase activation and glycolysis modulation, and, as such, is proposed as a potential therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. 27901115_data suggesting that p53 promotes nucleotide biosynthesis in response to DNA damage by repressing the expression of the phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK2) isoform 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3), a rate-limiting enzyme that promotes glycolysis. 27983531_Knockdown of PFKFB3 by siRNAs significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration abilities of gastric cancer cells. Our data suggest that PFKFB3 might be a potential biomarker for gastric cancer and anti-neoplastic targeting gene. 28082200_PFKFB3 was a novel downstream substrate of mTOR signaling pathway as PFKFB3 level was augmented after knocking down TSC2 in THP1 and OCI-AML3 acute myeloid leukemia cells. 28152500_This work has uncovered a novel function of the enzymes PFKFB3 and PFKFB4 in ovarian cancer cells during mitotic arrest 28161638_Taken together, our study identifies PFKFB3 as a key TGFbeta1 effector protein that mediates TGFbeta1's effect on Snail expression, invasion, and glycolysis. 28857200_Study provides evidence that PFKFB3 overexpression occupied a dominant position in sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 29327288_conclude that PFKFB3 bears an oncogene-like regulatory element in lung adenocarcinoma progression 29335521_PFKFB3 is a hub for coordinating cell cycle and glucose metabolism. Combined targeting of PFKFB3 and CDK4 may be new strategy for breast cancer treatment. 29393396_Results indicate that PFKFB3 is involved in the proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenesis of breast cancer. 29435871_PI3K-Akt pathway inhibitors, Akti-1/2 and LY294002, reduced PFKFB3 gene induction by PHA, as well as Fru-2,6-P2 and lactate production. Moreover, both inhibitors blocked activation and proliferation in response to PHA, showing the importance of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the antigen response of T-lymphocytes. 29511345_Data showed that PFKFB3 was among the most upregulated candidate genes in tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKIs)-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) samples. PFKFB3 was required for TKIs-resistant CML to compensate the TKIs-inhibited proliferation of CML and the increase of apoptosis. In addition, PFKFB3 was upregulated by transcription factor PU.1 in TKI-resistance CML cells. 29559632_PFKFB3 expression promotes HCC growth through the PFKFB3/AKT/ ERCC1 signaling pathway to enhance the ability of DNA repair and its pro-tumor effects during glycolysis. The expression of PFKFB3 was correlated with a poor prognosis for HCC patients. 30171427_glycolytic enzyme PFKFB3 plays a critical role in TNF-alpha-induced endothelial inflammation. 30250201_Study identifies PFKFB3 as a critical factor in homologous recombination repair of ionizing radiation induced DNA double-strand breaks. 30785217_Tissue array revealed that the expression of LT-alpha in HNSCC samples positively correlated with microvessel density, lymphocytes infiltration and endothelial PFKFB3 expression. 30819197_This study aims to characterise the expression and phosphorylation of isozymes of the key glycolytic regulatory protein, 6-phosphofructokinase-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase (PFK-2/FBPase-2), in urinary exosomes of subjects with pre-eclampsia . 30822195_nine molecules were picked out as potential PFKFB3 inhibitors. The stability of PFKFB3-lead complexes was verified by 40 ns molecular dynamics simulation. 31026442_The PRKD3 up-regulated 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) and activated glycolysis as shown by increased glucose consumption and lactate production. 31126985_PFKFB3 is an essential target of EGFR signaling and that PFKFB3 activation is required for glycolysis stimulation upon EGFR activation. PFKFB3 has a key role in mediating glucose metabolism and survival of NSCLC cells in response to EGFR signaling. 31209811_PFKFB3 may promote angiogenesis and tumor progression and metastases by regulating the CD163 expression by tumor-associated macrophages infiltrating oral squamous cell carcinoma. 31410981_miR-488 inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation and glycolysis by targeting PFKFB3, and thus, miR-488 may be a novel therapeutic candidate for prostate cancer 31413316_In breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs), there is an inverse relationship between Pfkfb3 expression and autophagy, which reduces Pfkfb3 expression and elicits cellular dormancy. Disrupting autophagy and this event enables Pfkfb3 to drive dormant BCSCs and metastatic lesions to recur. 31471554_we demonstrate here that inhibition with siRNA against the glycolytic genes PFKFB3 or LDHA, respectively, prevents the proliferation of HUVECs and inhibits vessel formation in vitro as well as in vivo. 31562297_PFKFB3 inhibition reprograms malignant pleural mesothelioma to nutrient stress-induced macropinocytosis and ER stress as independent binary adaptive responses. 31668919_TTP may contribute to suppression of glycolysis and energy production of cancer cells in part by downregulating PFKFB3 expression. 31671668_Study finds that oxaliplatin (Oxa) induces autophagy of colon cancer (CC) cells with a concomitant promotion of PFKFB3 expression at both mRNA and protein levels suggesting that PFKFB3 is involved in Oxa-resistance of CC cells. 31720731_Activation of the HIF1alpha/PFKFB3 stress response pathway in beta cells in type 1 diabetes. 31862780_Reactive Oxygen Species Drive Proliferation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia via the Glycolytic Regulator PFKFB3. 31958214_Upregulation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3) by hyperactivated mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 is critical for tumor growth in tuberous sclerosis complex. 32051533_PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PFKFB3 pathway mediated lung fibroblast aerobic glycolysis and collagen synthesis in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary fibrosis. 32169429_CPEB4 Increases Expression of PFKFB3 to Induce Glycolysis and Activate Mouse and Human Hepatic Stellate Cells, Promoting Liver Fibrosis. 32198345_Long noncoding RNA AGPG regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming. 32209481_c-Src Promotes Tumorigenesis and Tumor Progression by Activating PFKFB3. 32282711_high levels of protein and gene expression closely related to the occurrence, development, and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 32620030_Small molecule 3PO inhibits glycolysis but does not bind to 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 (PFKFB3). 32990355_Mir-488 alleviates chemoresistance and glycolysis of colorectal cancer by targeting PFKFB3. 33307155_Inhibition of glycolytic activator PFKFB3 suppresses tumor growth and induces tumor vessel normalization in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33390824_Long non-coding RNA MSC-AS1 facilitates the proliferation and glycolysis of gastric cancer cells by regulating PFKFB3 expression. 33400016_YAP promotes ocular neovascularization by modifying PFKFB3-driven endothelial glycolysis. 33420377_Inhibition of PFKFB3 induces cell death and synergistically enhances chemosensitivity in endometrial cancer. 33516882_PFK activation is essential for the odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. 33684599_PFKFB3 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced excessive inflammation and cellular dysfunction in HTR-8/Svneo cells: Implications for the role of PFKFB3 in preeclampsia. 33931981_Positive regulation of PFKFB3 by PIM2 promotes glycolysis and paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. 34020913_Increased expression of PFKFB3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its association with lymphangiogenesis. 34044589_Genetic Variation in PFKFB3 Impairs Antifungal Immunometabolic Responses and Predisposes to Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis. 34110658_PFKFB3-dependent glucose metabolism regulates 3T3-L1 adipocyte development. 34193800_A Potential Oncogenic Role for PFKFB3 Overexpression in Gastric Cancer Progression. 34227742_Increased glycolysis in skeletal muscle coordinates with adipose tissue in systemic metabolic homeostasis. 34234350_Functional diversity of PFKFB3 splice variants in glioblastomas. 34303764_Fascin promotes lung cancer growth and metastasis by enhancing glycolysis and PFKFB3 expression. 34359849_PFKFB3 Inhibition Impairs Erlotinib-Induced Autophagy in NSCLCs. 34612136_KLF9 (Kruppel Like Factor 9) induced PFKFB3 (6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2, 6-Biphosphatase 3) downregulation inhibits the proliferation, metastasis and aerobic glycolysis of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. 34907156_Long noncoding RNA GSEC promotes neutrophil inflammatory activation by supporting PFKFB3-involved glycolytic metabolism in sepsis. 35087090_Aberrant upregulation of the glycolytic enzyme PFKFB3 in CLN7 neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 35094634_Hyperglycemia induces miR-26-5p down-regulation to overexpress PFKFB3 and accelerate epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. 35107852_Targeting of PFKFB3 with miR-206 but not mir-26b inhibits ovarian cancer cell proliferation and migration involving FAK downregulation. 35444287_Glycometabolic reprogramming-mediated proangiogenic phenotype enhancement of cancer-associated fibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinoma: role of PGC-1alpha/PFKFB3 axis. 35794237_PFKFB3 works on the FAK-STAT3-SOX2 axis to regulate the stemness in MPM. 35804016_PFKFB3 regulates cancer stemness through the hippo pathway in small cell lung carcinoma. 35918720_PFKFB3-mediated glycometabolism reprogramming modulates endothelial differentiation and angiogenic capacity of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 36064579_ALK fusion promotes metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells by transcriptionally upregulating PFKFB3. 36405760_Increased stromal PFKFB3-mediated glycolysis in inflammatory bowel disease contributes to intestinal inflammation. |
ENSMUSG00000026773 |
Pfkfb3 |
190.418925 |
2.1453649125 |
1.101223 |
0.141508396 |
60.646890 |
0.00000000000000682878642114110083816009925370384739086248400072309827635308465687558054924011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000046256488102819023952620889259060551705192865928895074034699064213782548904418945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
252.2265197 |
20.8027041 |
118.3022169 |
7.5708052 |
| ENSG00000170537 |
79905 |
TMC7 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z402 |
FUNCTION: Probable ion channel. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable mechanosensitive ion channel activity. Predicted to be involved in ion transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79905; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; mechanosensitive ion channel activity [GO:0008381] |
|
ENSMUSG00000042246 |
Tmc7 |
13.101713 |
2.4725227952 |
1.305984 |
0.447309475 |
8.776823 |
0.00305082179322877736910024637495553179178386926651000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006524214672277131067679167841788512305356562137603759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.4227634 |
5.3503638 |
8.0154355 |
1.7764654 |
| ENSG00000170542 |
5272 |
SERPINB9 |
protein_coding |
P50453 |
FUNCTION: Granzyme B inhibitor. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Serine protease inhibitor |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the serine protease inhibitor family which are also known as serpins. The encoded protein belongs to a subfamily of intracellular serpins. This protein inhibits the activity of the effector molecule granzyme B. Overexpression of this protein may prevent cytotoxic T-lymphocytes from eliminating certain tumor cells. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 6. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
hsa:5272; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043027]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; immune response [GO:0006955]; mast cell mediated immunity [GO:0002448]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951]; protection from natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042270] |
12036886_Expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins caspase 3, Bcl-2, and PI9 predict clinical outcome in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 12517944_The presence and subcellular localization of proteinase inhibitor 9 in leukocytes and dendritic cells are consistent with a protective role against ectopic or misdirected granzyme B during an immune response. 15458434_a high expression of PI-9 by tubular epithelial cells can serve as one of the factors protecting renal allografts from rejection in spite of the presence of inflammatory cell infiltrates. 15494398_proteinase inhibitor 9 was effectively hydrolyzed and inactivated by human granzyme M, raising the possibility that this orphan granzyme bypasses proteinase inhibitor 9 inhibition of granzyme B 15531453_Since PI-9 considerably alters GrzB and killer cell sensitivity, it may strongly influence the efficacy of GvL(graft-versus-leukemia) effects 16144945_Over expression of SERPINB9 is associated with metastatic melanoma 16267761_Soluble SERPINB9 circulates in blood and increases on primary Cytomegalovirus infection in post renal transplantation patients 16306080_Estrogen induction of PI-9 may reduce the ability of cytolytic lymphocytes-mediated immune surveillance to destroy newly transformed cells 16310039_up-regulated expression of PI-9 in gestational trophoblastic diseases contributes to disease pathogenesis via immune evasion 17077322_loss of PI9 expression in tumor cells may reflect some mechanism associated with progression 17479112_PI9 inhibited apoptotic death by directly interacting with the intermediate active forms of caspase-8 and -10. This indicates that PI9 can regulate pro-apoptotic apical caspases. 18191723_The data suggest that PI-9 is tightly linked to maturation and may allow dendritic cells to exert their function in a potentially hostile environment. 18669594_A significant population consumes levels of genistein in soy products that may be high enough to induce PI-9, perhaps potentiating the survival of some preexisting breast cancers by enabling them to evade immunosurveillance. 19956856_upregulated expression of PI-9 in NSCLC cells may serve to protect them from apoptosis induced by GrB 21296596_Reduced proteinase inhibitor 9 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells is associated with atherosclerotic disease progression. 21795594_constitutive expression of serine protease inhibitor 9 (PI-9) on human peripheral blood-and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells is a major defense mechanism against granzyme B-mediated destruction by NK cells 21919028_Inhibition of Granzyme B by PI-9 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis. 22090449_PI-9 induction within human mononuclear phagocytes by virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis serves to protect these primary targets of infection from elimination by apoptosis and thereby promotes intracellular survival of the organism. 22167597_SerpinB9 expression in human renal tubular epithelial cells is induced by triggering of the viral dsRNA sensors TLR3, MDA5 and RIG-I during subclinical rejection. 22387007_lung cancer cells utilise their increased PI-9 expression to protect from granzyme B-mediated cytotoxicity as an immune evasion mechanism 23892923_Suppression of granzyme B initiated apoptosis in protease inhibitor-9-expressing leukemia cells. 24445365_Increased intracellular PI-9 activity in mononuclear phagocytes from HIV-infected patients contributes to successful intracellular infection by virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 24488096_The GrB-Sb9 nexus may therefore represent an additional mechanism of limiting lymphocyte lifespan and populations. 26318431_We filtered four OSCC genes including SERPINB9, SERPINE2, GAK, and HSP90B1 through the gene global prioritization score (P |
ENSMUSG00000021404+ENSMUSG00000057726+ENSMUSG00000062342+ENSMUSG00000038327+ENSMUSG00000054266+ENSMUSG00000045827+ENSMUSG00000021403+ENSMUSG00000071452 |
Serpinb9c+Serpinb9g+Serpinb9e+Serpinb9f+Serpinb9d+Serpinb9+Serpinb9b+Serpinb9h |
16.425798 |
3.6648142627 |
1.873740 |
0.408126449 |
22.204685 |
0.00000245075092106553118456897799593008357987855561077594757080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008298482127764909190427260188283042907642084173858165740966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.5321729 |
6.4993781 |
7.3076523 |
1.5174522 |
| ENSG00000170545 |
57228 |
SMAGP |
protein_coding |
Q0VAQ4 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in epithelial cell-cell contacts. May play a role in tumor invasiveness and metastasis formation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15986429}. |
Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sialic acid;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in cell junction; nucleoplasm; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57228; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
33049294_SMAGP knockdown inhibits the malignant phenotypes of glioblastoma cells by inactivating the PI3K/Akt pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000053559 |
Smagp |
88.600451 |
4.1541951300 |
2.054569 |
0.203362027 |
103.021166 |
0.00000000000000000000000331586678352443993331044399688222428817297990078140747818645050603442170356061069469433277845382690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000034661610286700233774088626463815851941861744331854324469694393628937945095458417199552059173583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
134.3446316 |
16.2696949 |
32.5631962 |
3.2054856 |
| ENSG00000170571 |
133418 |
EMB |
protein_coding |
Q6PCB8 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the outgrowth of motoneurons and in the formation of neuromuscular junctions. Following muscle denervation, promotes nerve terminal sprouting and the formation of additional acetylcholine receptor clusters at synaptic sites without affecting terminal Schwann cell number or morphology. Delays the retraction of terminal sprouts following re-innervation of denervated endplates. May play a role in targeting the monocarboxylate transporters SLC16A1 and SLC16A7 to the cell membrane (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane glycoprotein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. The encoded protein may be involved in cell growth and development by mediating interactions between the cell and extracellular matrix. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:133418; |
axon [GO:0030424]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; cell-cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098632]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; dendrite self-avoidance [GO:0070593]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; plasma membrane lactate transport [GO:0035879] |
2963822_Reports the original cloning of the mouse embigin gene, referred to as gp70, from embryonal carcinoma cells. 21787388_Data show that Gp70 (embigin) was negative in all normal, adjacent non-neoplastic and PIN lesions and only a very small percentage of cases. 25773908_Study reports elevated expression of Embigin in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and shows its novel functions in regulating cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. 26090721_embigin is regulated by HOXC8 and its loss plays an important role in the progression of breast tumors 30446621_This study analyzed the direct interaction between CAIV and the two Monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) chaperones basigin (CD147) and embigin (GP70). 32213169_Rare and common variants analysis of the EMB gene in patients with schizophrenia. |
ENSMUSG00000021728 |
Emb |
988.001748 |
0.3384524682 |
-1.562975 |
0.054914834 |
831.657173 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000706946880965731712126309862835952056752694582594845700332103836917004366710349549388952704113427933092914538695703817818022253401497601578789954583 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000592871361537170433609402777265065191929434648444543996819212831531493855638072615920099065005138663638551351635808309797386386188170902117299669014 |
Yes |
No |
503.2445617 |
17.5054928 |
1497.2375340 |
32.4512056 |
| ENSG00000170791 |
79145 |
CHCHD7 |
protein_coding |
Q9BUK0 |
|
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disulfide bond;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be located in mitochondrial intermembrane space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79145; |
mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex assembly [GO:0033108] |
16736500_CHCHD7 is a newly identified member of a ubiquitously expressed multifamily of proteins containing a conserved (coiled coil 1)-(helix 1)-(coiled coil 2)-(helix 2) domain; it has not been previously associated with neoplasia. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22842048_Molecular interactions guiding the protein recognition between Mia40 and the disulfide-reduced CHCHD5 and CHCHD7. |
ENSMUSG00000042198 |
Chchd7 |
433.687079 |
0.4104277032 |
-1.284800 |
0.094003023 |
187.821650 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000095023704073652545560709160414287705726264016902034490171017848009949367820215745741780937841088900112934299488354206175699800951406359672546386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000016918575055815580862877969193414455871521007574127934178523802229521067605135061850864355506862139860691472692533210420151590369641780853271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
258.6368203 |
25.5618120 |
634.3627520 |
43.9661379 |
| ENSG00000170801 |
94031 |
HTRA3 |
protein_coding |
P83110 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease that cleaves beta-casein/CSN2 as well as several extracellular matrix (ECM) proteoglycans such as decorin/DCN, biglycan/BGN and fibronectin/FN1. Inhibits signaling mediated by TGF-beta family proteins possibly indirectly by degradation of these ECM proteoglycans (By similarity). May act as a tumor suppressor. Negatively regulates, in vitro, trophoblast invasion during placental development and may be involved in the development of the placenta in vivo. May also have a role in ovarian development, granulosa cell differentiation and luteinization (PubMed:21321049, PubMed:22229724). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9D236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21321049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22229724}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal |
|
Enables endopeptidase activity; identical protein binding activity; and serine-type peptidase activity. Involved in proteolysis. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:94031; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; serine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008236]; negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030514]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12513693_We cloned the full-length sequences of two forms (long and short) of human HtrA3 mRNA, located the gene on chromosome 4p16.1, determined its genomic structure and revealed how the two mRNA variants are produced through alternative splicing 16251496_Upregulation of HTRA3 expression in association with placental development was revealed by a significant elevation of this protein in the maternal serum during the first trimester 16650464_RT-PCR analysis showed a significant reduction of HTRA1 and HTRA3 mRNA in endometrial cancer compared to normal endometrium. HTRA1 and HTRA3 protein showed a similar pattern of expression in EC tissue. 17962403_Structural and functional analysis of the PDZ domains of human HtrA1 and HtrA3 18241672_In ovarian cancer there is a dramatic decrease of HtrA3 mRNA and protein levels in all ovarian tumor groups; HtrA3 may function as a tumor suppressor. 19359045_critical for normal placental development; different expression profile during abnormal pregnancy 19424634_HtrA3 was down-regulated in endometrial cancers. 19951697_these data indicate that 15dPGJ2 is able to stimulate the expression of HtrA3 through an indirect mechanism involving the MEK/ERK pathway but independent of PPARgamma. 20068077_cigarette smoke-induced methylation of HtrA3 could contribute to the etiology of chemoresistant disease in smoking-related lung cancer. 20154083_HtrA3 may be a previously uncharacterized mitochondrial cell death effector whose serine protease function may be crucial to modulating etoposide- and cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cell lines. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20469960_role of HtrA3 (along with HtrA1 and HtrA2) in development/progression of cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and arthritic diseases [REVIEW] 21035848_inhibitor of trophoblast invasion during placental development 21047919_Abnormally high levels of serum HtrA3 at approximately 13-14 wk of gestation is associated with preeclampsia 21321049_decidual HtrA3 negatively regulates trophoblast invasion 21555518_HTRA3 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 22923201_results suggest that HtrA3 variants may play different roles in cancer development, and that the increased HtrA3-L levels in thyroid tissue could be correlated with the development of malignant lesions 23049902_HtrA3 may have a role as an early marker for preeclampsia 23812730_Data indicate that in breast cancers with no lymphatic metastasis, the expression of HtrA3 was lower in patients with estrogen receptor (ER)- and progesterone receptor (PR)-positive tumors. 25002585_HtrA1 and HtrA3 are crucial for trophoblast-decidual cell interaction in the control of trophoblast invasion. 25274382_Data indicate that the levels of high temperature requirement factor A3 (HtrA3)protein were lower in all subtypes of ovarian cancer and the lowest levels of HtrA3 were in epithelial ovarian cancer. 25456008_HtrA3 is likely to be associated with the acquisition of the invasive phenotype in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and may be a potential prognostic marker for oral cance 26110759_New insights into the structure and function of DeltaN-HtrA3, which seems to have a unique combination of features among human HtrA proteases. 27166271_HTRA3 suppresses tumor cell invasiveness and may serve as a prognostic biomarker for postoperative recurrence or survival in NSCLC 28642151_Removal of the 6 additional LB loop residues caused a complete loss of the proper trimeric structure. Impairing their interactions with the PDZ domain decreased the amount of the trimers. The LB loop helps stabilize the DeltaN-HtrA3L oligomer structure suggesting involvement of the LB-PDZ interactions in the stabilization. A monomeric form of the DeltaN-HtrA3L is proteolytically inactive. 28676687_Study demonstrated that in women serum levels of HtrA3 during early pregnancy were significantly lower in IUGR pregnancies, establishing an association between lower HtrA3 levels and placental insufficiency. 28716573_HtrA3 expression in the peritumoral stroma of patients with stage II colorectal cancer is associated with high-grade tumor budding and may be a novel marker of poor outcome. 28860718_Our findings demonstrated a novel pro-apoptotic role of HTRA3 in pancreatic cancer cells via inducing Bax. 29266444_The HtrA1-PDZ and HtrA4-PDZ as well as HtrA2-PDZ and HtrA3-PDZ respond similarly to different halogen substitutions of peptide; -Br substitution at R2-position and -I substitution at R4-position are most effective in improving peptide selectivity for HtrA1-PDZ/HtrA4-PDZ and HtrA2-PDZ/HtrA3-PDZ, respectively; -F substitution would not address substantial effect on peptide selectivity for all the 4 domains 29477555_results indicate that actin, beta-tubulin, vimentin, and TCP1alpha are HtrA3 cellular partners and suggest that HtrA3 may influence cytoskeleton dynamics. 30139517_Hypoxia is responsible for the reduction of HtrA3 which in turn promotes endometrial cancer progression. 30940659_Low HTRA3 expression is associated with Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 31013509_Low expression of HtrA3 at 15 weeks is associated with, and may be useful for, the early detection of late-onset preeclampsia development and small for gestational age birth. 31180543_Knockdown of linc00467 altered the expression of downstream genes, including HtrA serine peptidase 3 (HTRA3), and RNA immunoprecipitation and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays indicated that linc00467 recruited EZH2 to the HTRA3 promoter to inhibit its expression. 31260151_HtrA3 isoforms stimulate drug-induced apoptotic death of lung cancer cells via XIAP cleavage. 31280864_This study reports allosteric modulation of Human HtrA3 (High temperature requirement protease A3) enzyme activity for the first time. A novel non-classical allosteric ligand binding pocket mediates allostery in HtrA3. 31899476_Our study also reports an intricate ligand-induced allosteric switch, which redefines the existing hypothesis of HtrA3 activation besides opening up avenues for modulating protease activity favorably through suitable effector molecules. 32486357_Expression of HTRA Genes and Its Association with Microsatellite Instability and Survival of Patients with Colorectal Cancer. 33462352_Hsa-miR-494-3p attenuates gene HtrA3 transcription to increase inflammatory response in hypoxia/reoxygenation HK2 Cells. 35035835_Study on the Correlation between the Levels of HtrA3 and TGF-beta2 in Late Pregnancy and Preeclampsia. |
ENSMUSG00000029096 |
Htra3 |
8.327474 |
3.0584125598 |
1.612783 |
0.572110970 |
8.146165 |
0.00431523148033662474337690539982759219128638505935668945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008941852681421953719098638657669653184711933135986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1515501 |
4.2120028 |
4.0195311 |
1.1484596 |
| ENSG00000170802 |
3344 |
FOXN2 |
protein_coding |
P32314 |
FUNCTION: Binds to the purine-rich region in HTLV-I LTR. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a forkhead domain binding protein and may function in the transcriptional regulation of the human T-cell leukemia virus long terminal repeat. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3344; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21531217_HLTF methylation may exist in gastric cardia dysplasia stages and may play important role in the development of gastric cardia adenocarcinoma. 26802049_HTLF is a RUNX1 target whose down-regulation promotes genomic instability and correlates with complex cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia patients. 29396548_The Ser365 and Ser369 sites in a conserved DSGYAS motif are critical for the degradation of FOXN2 by beta-Trcp and RSK2. Moreover, gain-of-function and loss-of-function studies show that FOXN2 impairs cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo and enhances the radiosensitivity of lung cancer. 30720155_The WT1-AS was under-expressed in cervical carcinoma and suppresses cervical cancer cell growth and aggressiveness via a miR-203a-5p/FOXN2 axis. 33577027_FOXN2 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 35008435_HOXC6-Mediated miR-188-5p Expression Induces Cell Migration through the Inhibition of the Tumor Suppressor FOXN2. |
ENSMUSG00000034998 |
Foxn2 |
235.096767 |
2.2195361698 |
1.150258 |
0.107148480 |
116.707065 |
0.00000000000000000000000000332758933519709335827984585797536958916614562296221968923886754027180695340859539754774232278577983379364013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000038734399516963013338080536616174823170691836611744521793023288437347699530999278749732184223830699920654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
330.0184358 |
21.8418212 |
149.6826526 |
7.8067031 |
| ENSG00000170909 |
126014 |
OSCAR |
protein_coding |
Q8IYS5 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of osteoclastogenesis which plays an important bone-specific function in osteoclast differentiation. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Osteoclasts are multinucleated cells that resorb bone and are essential for bone homeostasis. This gene encodes an osteoclast-associated receptor (OSCAR), which is a member of the leukocyte receptor complex protein family that plays critical roles in the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses. The encoded protein may play a role in oxidative stress-mediated atherogenesis as well as monocyte adhesion. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:126014; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; collagen receptor activity [GO:0038064]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316] |
15155468_hOSCAR thus represents a novel class of molecule expressed by dendritic cells involved in the initiation of the immune response. 15650060_ligation of OSCAR promotes dendritic cell survival by an ERK- and PI3K-dependent pathway, linked to expression of the Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) antiapoptotic molecules 15905516_Human OSCAR mediates the rescue from apoptosis and the cooperation between dendritic cells and antigen-specific T cells that is prevented by CD85j receptor. 16007331_Promoter variant in OSCAR gene (OSCAR-2322A>G) might be one of genetic determinants of bone density in postmenopausal women. 16109714_analysis of a positive feedback circuit of TRANCE-induced activation of NFATc1, involving NFATc1-mediated OSCAR expression and its subsequent activation of NFATc1, necessary for efficient differentiation of osteoclasts 16493074_OSCAR is a functional receptor on monocytes and neutrophils, involved in the induction of the primary proinflammatory cascade and the initiation of downstream immune responses. 18821671_OSCAR (osteoclast associated immunoglobulin-like receptor)is expressed by erosion front osteoclasts and by synovial microvessels mononuclear cells. OSCAR is induced in monocytes of rheumatod arthritis patients, facilitating osteoclast differentiation 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21172874_This review discusses the structure-function relationship, expression pattern, and physiological role of OSCAR in osteoimmunology and summarizes its potential implications for human diseases. 21841309_Data suggest that OSCAR is a collagen receptor that binds to specific collagen motifs and costimulates osteoclastogenesis in DAP12-deficient humans and mice. 22009730_OSCAR is expressed in vascular endothelial cells and is regulated by oxLDL involving NFATc1 22949349_Rotative stress in mouse cells results in increased levels of Oscar transcription. 22985931_endothelial cell-derived OSCAR was found to be involved in the STAT signaling pathway and to affect monocyte adhesion. 23146195_Data indicate that osteoclast associated receptor (OSCAR) was strongly expressed by the vasculature of active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. 24448348_Plasma OSCAR level was higher in the serum of RA patients than controls, and higher in patients with destructive RA rather than non-destructive RA. 25716998_OSCAR is a receptor for surfactant protein D that activates TNF-alpha release from human CCR2+ inflammatory monocytes. 26552697_Each domain of OSCAR binds a collagen triple-helical peptide; the primary site is on the C-terminal domain in contrast to GPVI and LAIR-1. 26786702_OSCAR can play a proinflammatory role in monocyte-derived cells and may contribute crucially on multiple levels to rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 28555364_regulation of OSCAR by TNF-alpha and receptor activator of NF kappa beta ligand (RANKL) in pre-osteoclasts/osteoclasts 32246488_Sex-biased ceRNA networks reveal that OSCAR can promote proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma in women. 32859940_Osteoclast-associated receptor blockade prevents articular cartilage destruction via chondrocyte apoptosis regulation. |
ENSMUSG00000054594 |
Oscar |
43.683798 |
3.8429827783 |
1.942227 |
0.304745038 |
40.800075 |
0.00000000016862665900502412112209364852279634694465215716263628564774990081787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000857660057516938706120819910515328324263073511701804818585515022277832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.5948396 |
12.3849996 |
18.7325177 |
2.6729670 |
| ENSG00000170962 |
80310 |
PDGFD |
protein_coding |
Q9GZP0 |
FUNCTION: Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, survival and chemotaxis. Potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin. Plays an important role in wound healing. Induces macrophage recruitment, increased interstitial pressure, and blood vessel maturation during angiogenesis. Can initiate events that lead to a mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis, including influx of monocytes and macrophages and production of extracellular matrix (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11331881, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15271796}. |
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Mitogen;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a core motif of eight cysteines, seven of which are found in this factor. This gene product only forms homodimers and, therefore, does not dimerize with the other three family members. It differs from alpha and beta members of this family in having an unusual N-terminal domain, the CUB domain. Two splice variants have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:80310; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; growth factor receptor binding [GO:0070851]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus [GO:0036120]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of cell division [GO:0051781]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072126]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of monocyte extravasation [GO:2000439]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell chemotaxis [GO:0071673]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050730] |
11980634_Platelet-derived growth factor D: tumorigenicity in mice and dysregulated expression in human cancer 12427128_we localized PDGF-D in human kidneys suggesting that PDGF-D may have a role in kidney development. 14514732_PDGF-D plays an important role in the pathogenesis of tubulointerstitial injury through binding of PDGF-Rbeta in both human obstructive nephropathy 15271796_full-length PDGF-D is activated in tissues and is capable of increasing interstitial fluid pressure and macrophage recruitment and the maturation of blood vessels in angiogenic processes. 15988036_PDGF D is activated and processed by urokinase plasminogen activator and they colocalize in human prostate carcinoma. 16189269_Sp1, like Ets-1, induces PDGF-D transcription and mRNA expression; H2O2 stimulates Ets-1, but not Sp1, and activates D3-dependent PDGF-D transcription 18187181_PDGF-D is present in the neointima of the arteriopathy of Chronic allograft nephropathy, where it can engage PDGF-Rbeta to promote mesenchymal cell migration, proliferation, and neointima formation. 18258854_All 3 residues in Sp1 (Thr668, Ser670, and Thr681) are required for Sp1-dependent platelet-derived growth factor-D activation in response to angiotensin II 18403754_PDGF-D promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transitiion and thus could be a novel therapeutic target for the prevention and/or treatment of prostate cancer. 18471357_Compared with control group, levels of PDGF-D and PDGF-B were progressively elevated in blood and urine of IgA nephropathy children. 18573494_PDGF-C and PDGF-D, like PDGF-A and PDGF-B, play important roles in atherosclerosis by stimulating MMP activity and influencing monocyte migration 18600092_Association of platelet-derived growth factor-D gene polymorphism with ischemic stroke in a Chinese case-control study 18600092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18997817_uPA not only generates active PDGF-DD, but also regulates its spatial distribution, provides novel insights into the biological function of PDGF-DD. 19028801_PDGF-DD, a novel mediator of smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation, is upregulated in endothelial cells exposed to atherosclerosis-prone flow patterns. 19357108_PDGF-DD serum levels in patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) were significantly higher (1.67 +/- 0.45 ng/ml) and in patients with lupus nephritis significantly lower (0.66 +/- 0.86 ng/ml) compared to healthy controls. 19544444_PDGF-D-induced acquisition of the EMT phenotype in PC3 cells is, in part, a result of repression of miR-200. 19733850_LH significantly increased PDGF-D messenger RNA (mRNA) expression but suppressed PDGF-B and PDGF-C mRNA in human granulosa-luteal cells 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20406896_human umbilical cord blood tropism toward glioma cells are partially dependent on the PDGF/PGGFR system. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21098708_Study unveiled a novel signaling axis of matriptase/PDGF-D/beta-PDGFR in PCa, providing new insights into functional interplay between serine protease and growth factor signaling networks. 22289441_The results of this study suggested that PDGFD -858A/C variant is probably associated with risk for non-hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. 22415093_PDGF-D promotes malignant mesothelioma cell chemotaxis through PDGF-betabeta receptor signaling pathways along a PI3 kinase/PDK1/Akt/Rac1/ROCK axis and relevant to ERK activation 22471482_High PDGFD expression promotes ovarian cancer invasion by regulating matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 22689130_Taken together with our previous finding that matriptase is a proteolytic activator of PDGF D, this study provides a molecular insight into signal amplification of the proteolytic network and PDGF signaling loop during cancer progression. 22704460_Meta-analysis showed that single nucleotide polymorphism rs974819 of PDGFD gene was significantly associated with an increasing risk of coronary heart disease (OR=1.08, 95% CI=1.05 - 1.11) in both Europeans and South Asians including Han Chinese. 23187740_Down-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-D expression blockades NF-kappaB pathway to inhibit cell proliferation and invasion as well as induce apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 23505219_Platelet-derived growth factor-D and Rho GTPases regulate recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts in cholangiocarcinoma. 24158561_PDGF-D is highly expressed in gemcitabine resistant (GR) liver neoplasm cells. Furthermore, down-regulation of PDGF-D in GR cells led to partial reversal of the EMT phenotype. 24646915_Data suggest that targeting platelet-derived growth factor-D as a strategy for endometrial cancer treatment. 24870786_Compared with matched normal endometrial cases, PDGF-D was up-regulated in endometrial cancer. Expression of PDGF-D protein, found in 78% of the cases, was associated with nonendometrioid histologic type. 24938433_PDGF-DD secreted by gastric cancer derived mesenchymal stem cells is capable of promoting gastric cancer cell progression in vitro and in vivo. 25332166_PDGF-D is highly expressed by ASCs, where it acts as a potent mitogenic factor. 25333347_PDGFD, CDH1 and SLIT2 are upregulated in low grade meningiomas and schwannomas compared with healthy tissue. 25391964_PDGFD-PDGFRbeta signalling is required for human neocortical development and local production of growth factors by radial glia supports the expanded germinal region and progenitor heterogeneity of species with large brains 25760076_PDGF-D expression is associated with miR-106a and Twist1 in HCC patients 26157007_Novel findings reveal a new paradigm in matriptase activation involving PDGF-D-specific signal transduction leading to extracellular acidosis. 26362023_polymorphism of rs7950273 in the PDGFD gene is not associated with ischaemic stroke in the Chinese Han population 26924050_upregulated in kidney fibrosis, may mediate renal scarring, and is dispensable for normal kidney development and physiological functions 27507215_This study suggested that epithelial-mesenchymal transition process can be triggered by the PDGF-D/PDGFRb axis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma, and then involved in the tumor cell invasion via activation of p38/AKT/ERK/ epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway. 27585990_No specific genotype of rs974819 of Platelet-derived growth factor D demonstrated increased cardiovascular mortality in the total population, however, the male group with genotypes A/A and G/A demonstrated an increased risk that persisted in a multivariate evaluation where adjustments were made for well-known cardiovascular risk factors. 28035069_PDGF-D promotes tumor growth and aggressiveness of colorectal carcinoma. Down-regulation of PDGF-D inactivates Notch1/Twist1 axis, which could reverse epithelial mesenchymal transformation and prevent CRC progression. 28267575_There are four platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) genes (PDGFA, PDGFB, PDGFC and PDGFD) that reside on chromosomes 7, 22, 4 and 11. 28346846_significant correlations between DNA methylation of the PDGFD gene promoter and the risk of developing either IA or BAVM 28965749_Numerous studies have shown that PDGF-C and PDGF-D are critical regulators of the cardiovascular system as angiogenic and survival factors. PDGF-C and PDGFD are widely expressed in many different types of cells with pleotropic effects. [review] 29079201_PDGF-C and PDGF-D are relatively new members of the PDGF family and are potent angiogenic and survival factors. Recent studies have demonstrated their important roles in different types of eye diseases. [review] 29240605_PDGF-D overexpression is an independent predictor of platinum-based chemotherapy resistance and it may also be a potential biomarker for targeted therapy and poor prognosis. 29955147_We report the first recurrent molecular variant of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans involving PDGFD 30836770_PDGF-D and its PDGF receptor beta (PDGFR-beta) are expressed in colorectal cancer. 32186759_PDGFD induces ibrutinib resistance of diffuse large Bcell lymphoma through activation of EGFR. 32452055_Identification of a four immune-related genes signature based on an immunogenomic landscape analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 33640869_Inhibiting PDGF-D alleviates the symptoms of HELLP by suppressing NF-kappaB activation. 33971972_Rare variant analysis of 4241 pulmonary arterial hypertension cases from an international consortium implicates FBLN2, PDGFD, and rare de novo variants in PAH. 34539622_A Transcriptional Signature of PDGF-DD Activated Natural Killer Cells Predicts More Favorable Prognosis in Low-Grade Glioma. 35027451_PDGF-D-PDGFRbeta signaling enhances IL-15-mediated human natural killer cell survival. 35472332_E3 ligase HUWE1 promotes PDGF D-mediated osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by effecting polyubiquitination of beta-PDGFR. 36308081_ZNF561 antisense RNA 1 contributes to angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma through upregulation of platelet-derived growth Factor-D. |
ENSMUSG00000032006 |
Pdgfd |
154.497726 |
0.1217453203 |
-3.038062 |
0.169735090 |
371.945547 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007056529987717739886744169611806134306460730298057641078276462980165693045255681524538240566812929744401274281102862362919812858101512958957071540769064704082355500089577815721658096636502861023631128379457466692770140070933848619461059570312500000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002450691355734443220375551784686939351994932065080532050246266801930456314584014349820428882590803110609149480451410020851224953286042707573805236948742983257657530904257816357689612678529762699035799561331216978032898623496294021606445312500000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.1359218 |
3.8967891 |
282.0883958 |
16.5071401 |
| ENSG00000171045 |
203062 |
TSNARE1 |
protein_coding |
Q96NA8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable SNAP receptor activity and SNARE binding activity. Predicted to be involved in intracellular protein transport; vesicle docking; and vesicle fusion. Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be part of SNARE complex. Predicted to be active in endomembrane system. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:203062; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; membrane [GO:0016020]; SNARE complex [GO:0031201]; SNAP receptor activity [GO:0005484]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278]; vesicle fusion [GO:0006906] |
24166486_GWAS meta analysis identifies TSNARE1 as a novel Schizophrenia / Bipolar susceptibility locus 25471352_Study provides the first evidence that the minor allele of TSNARE1 rs10098073 is significantly associated with a reduced risk of schizophrenia in a Han Chinese population, suggesting TSNARE1 may represent a susceptibility gene for this disease |
|
|
119.572955 |
0.3993215997 |
-1.324377 |
0.341284279 |
14.458631 |
0.00014327181896756045211514807302677354527986608445644378662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000384909364390460958203765695628817411488853394985198974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.9313542 |
20.2201556 |
160.1144397 |
35.9274724 |
| ENSG00000171056 |
83595 |
SOX7 |
protein_coding |
Q9BT81 |
FUNCTION: Binds to and activates the CDH5 promoter, hence plays a role in the transcriptional regulation of genes expressed in the hemogenic endothelium and blocks further differentiation into blood precursors (By similarity). May be required for the survival of both hematopoietic and endothelial precursors during specification (By similarity). Competes with GATA4 for binding and activation of the FGF3 promoter (By similarity). Represses Wnt/beta-catenin-stimulated transcription, probably by targeting CTNNB1 to proteasomal degradation. Binds the DNA sequence 5'-AACAAT-3'. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18819930}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors involved in the regulation of embryonic development and in the determination of the cell fate. The encoded protein may act as a transcriptional regulator after forming a protein complex with other proteins. The protein may play a role in tumorigenesis. A similar protein in mice is involved in the regulation of the wingless-type MMTV integration site family (Wnt) pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:83595; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; endoderm formation [GO:0001706]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060828]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
11691915_gene expression, chromosome mapping, transactivation, interference with Wnt signaling 18682240_stable endoderm progenitors can be established from human ES cells by constitutive expression of SOX7 producing extraembryonic endoderm progenitors 18819930_Sox7 is a tumor suppressor that functions as an independent checkpoint for beta-catenin transcriptional activity. Inactivation of Sox7 could promote the development of a majority of colorectal tumors and approximately half of prostate tumors. 18940723_stable expression induces a stable expandable extra embryonic endoderm phenotype in hESCs 19108950_SOX7, down-regulated in colorectal cancer, induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. 22171135_Data show that SOX7 is upregulated by aspirin and is involved in aspirin-mediated growth inhibition of human colorectal cancer SW480 cells. 22706399_The methylation of the CpG island of the SOX7 gene can be used as a predictive factor for the development and prognosis of myelodysplastic syndrome patients. 22777918_Association of SOX7 protein expression with clinical outcomes was evaluated. SOX7 mRNA expression was significantly down-regulated in lung adenocarcinoma compared with matched adjacent normal tissues. 23295859_Sox7 is a negative regulator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway through impeding the transcriptional machinery of beta-catenin/TCF/LEF-1 transcriptional complex, and the loss of expression may be involved in the pathogenesis of endometrial cancer. 23557216_SOX7 is a novel tumor suppressor gene silenced in the majority of NSCLC samples. 24012678_SOX7 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. 24558429_miR-184 represents a potential onco-miR and plays an important role in HCC progression by suppressing SOX7 expression 24788044_Decreased expression of Sox7 correlates with the upregulation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and the poor survival of gastric cancer patients. 24816720_SOX7 plays an important inhibitory role in hepatocarcinogenesis, and might be a novel target for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. 25073511_Low SOX7 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 25297608_The expression of SOX7 correlates with tumor progression as a tumor suppressor, possibly through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in ovarian cancers, suggesting that SOX7 may be a promising prognostic marker. 25407488_Ectopic expression of miR-492 led to downregulation of SOX7 protein. 25940713_The results provided unequivocal evidence for a novel tumor suppressor role of SOX7 in acute myeloid leukemia 26515813_The results suggest that miR-664 functions as an oncogene miRNA and has an important role in promoting human osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration by suppressing SOX7 expression. 26944317_the HMG-box is a key domain of SOX7 for negatively regulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway when functioning as a tumor suppressor in a glioma. 27044823_miR-935 contributed to cell proliferation of gastric cancer through targeting SOX7. 27133048_miR-595 played a critical role in carcinogenesis by suppression of SOX7. 27150562_SOX7 transcription factor mediates PDGF-BB-induced IL-33 expression. 27188720_Consistent with bioinformatics predictions, SOX7 was correlated positively with AXIN2 and negatively with beta-catenin, suggesting that SOX7 and AXIN2 might play important roles as co-regulators through the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway in the breast tissue to affect the carcinogenesis process. 27459612_Aberrant methylation of the promoter regions of the SOX7 gene in patients with acute myeloid leukemias. 27697092_Overexpression of miR-935 inhibited SOX7 expression. 28266181_miR-9 was up-regulated and SOX7 was down-regulated in human non-small-cell lung cancer tissues and cell lines. 28586005_The results indicate that SOX7 may inhibit the progression of liver carcinoma and that SOX7 downregulation may accurately predict poor prognosis in liver carcinoma patients. 28765960_Mechanistically, SOX7 was confirmed to be the downstream target of miR-616 in NSCLC cells. Forced expression of SOX7 prevented the promoting effects of miR-616 overexpression on the proliferation and metastasis of NSCLC cells, while knockdown of SOX7 reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-616 knockdown on the proliferation and metastasis of NSCLC cells. 29231262_These results provide the first clue that miR-24-3p could play a role as an oncomiR in Lung cancer by regulating SOX7. 29271667_SOX7 inhibits oncogenic beta-catenin-mediated transcription by disrupting the beta-catenin/BCL9 interaction. 29271996_miR-616 acted as a tumor promoter in glioma, and its oncogenic roles were involved in the regulation of SOX7 and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 29444818_Sox7 promotes tumor growth via vessel abnormalization, and its level determines the therapeutic outcome of VEGFR2 inhibition in High-grade glioma. 29757932_we have identified an array of potential target genes of SOX7 and examined four of them for their roles in SOX7-mediated tumor suppression. We found that SOX7 could both activate and repress its target genes; and achieve its antiproliferative function through regulating multiple genes simultaneously. 29957056_Low SOX7 expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 30381030_MiR-494-3p promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration, and invasion by directly targeting Sox7. 30488457_inactivation of canonical SRY-box transcription factor 7( Sox7 )is responsible for the upregulated expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) in non-metastatic prostate cancer 30554866_Our findings demonstrated that SOX7 methylation conferred adverse prognosis in myelodysplastic syndrome patients and was associated with leukemia progression. 31332289_An unappreciated role of SOX7 in regulation of cellular apoptosis through control of MAPK/ERK-BIM signaling. 31683462_LncRNA HAND2-AS1 sponging miR-1275 restrains proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cells by regulating SOX7 expression. 31955140_SOX7 is involved in polyphyllin D-induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest through down-regulation of cyclin D1. 32521870_Effects of miR-492 on migration, invasion, EMT and prognosis in ovarian cancer by targeting SOX7. 32808728_ACTA2-AS1 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression via sequestering miR-378a-3p and miR-4428 to elevate SOX7 expression. 33733517_SOX7 blocks vasculogenic mimicry in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 33835399_CircUBQLN1 Promotes Proliferation but Inhibits Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress of Hippocampal Neurons in Epilepsy via the miR-155-Mediated SOX7 Upregulation. 33846290_The transcription factor Sox7 modulates endocardiac cushion formation contributed to atrioventricular septal defect through Wnt4/Bmp2 signaling. 34570228_A dominant-negative SOX18 mutant disrupts multiple regulatory layers essential to transcription factor activity. 34728626_Endothelial deletion of SHP2 suppresses tumor angiogenesis and promotes vascular normalization. 35222878_miR-146a Inhibited Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation by Targeting SOX7. 35260939_Predisposition to atrioventricular septal defects may be caused by SOX7 variants that impair interaction with GATA4. 35645102_SOX7 modulates the progression of hepatoblastoma through the regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 35718188_The mechanism by which crocetin regulates the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-125b-5p/SOX7 molecular axis to inhibit high glucose-induced diabetic retinopathy. |
ENSMUSG00000063060 |
Sox7 |
15.913086 |
0.2423666583 |
-2.044737 |
0.416822457 |
26.210486 |
0.00000030615561603305166434363707682331234849471002235077321529388427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001144883935304748583344867235433994778759370092302560806274414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1756508 |
1.7298413 |
25.6488408 |
4.0352720 |
| ENSG00000171115 |
155038 |
GIMAP8 |
protein_coding |
Q8ND71 |
FUNCTION: Exerts an anti-apoptotic effect in the immune system and is involved in responses to infections. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q75N62}. |
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Mitochondrion;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein belonging to the GTP-binding superfamily and to the immuno-associated nucleotide (IAN) subfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins. In humans, the IAN subfamily genes are located in a cluster at 7q36.1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:155038; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070232] |
20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000064262 |
Gimap8 |
668.099072 |
18.0186288127 |
4.171417 |
0.107773037 |
1868.764095 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1279.4458685 |
81.4823172 |
71.5149487 |
4.3277174 |
| ENSG00000171121 |
27094 |
KCNMB3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPA1 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the calcium activated potassium KCNMA1 (maxiK) channel. Modulates the calcium sensitivity and gating kinetics of KCNMA1, thereby contributing to KCNMA1 channel diversity. Alters the functional properties of the current expressed by the KCNMA1 channel. Isoform 2, isoform 3 and isoform 4 partially inactivate the current of KCNBMA. Isoform 4 induces a fast and incomplete inactivation of KCNMA1 channel that is detectable only at large depolarizations. In contrast, isoform 1 does not induce detectable inactivation of KCNMA1. Two or more subunits of KCNMB3 are required to block the KCNMA1 tetramer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10766764, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10864947}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
MaxiK channels are large conductance, voltage and calcium-sensitive potassium channels which are fundamental to the control of smooth muscle tone and neuronal excitability. MaxiK channels can be formed by 2 subunits: the pore-forming alpha subunit and the modulatory beta subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is an auxiliary beta subunit which may partially inactivate or slightly decrease the activation time of MaxiK alpha subunit currents. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009]. |
hsa:27094; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calcium-activated potassium channel activity [GO:0015269]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; action potential [GO:0001508]; detection of calcium ion [GO:0005513]; neuronal action potential [GO:0019228]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813] |
16958040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16958040_The frequency of the delA750 mutation was significantly increased in idiopathic generalized epilepsy (7.9%) compared to that in the controls (5.5%; P = 0.016, one-sided; OR = 1.52; 95%-CI: 1.05-2.21). 18591419_The KCNMB3 isoforms beta3a-d may have unique functions in primates. 19204046_Report beta subunit (KNMB1-4)-specific modulations of BK channel function by a Slo1 mutation associated with epilepsy and dyskinesia. 23826284_Single-nucleotide polymorphism in KCNMB3 gene is associated with Insulin Resistance. 31364720_The results from the present study suggested that BK channels modulated the activation state of spinal microglia, and that KCNMB3 is a potential therapeutic target for neuropathic pain. |
ENSMUSG00000091091 |
Kcnmb3 |
41.635783 |
0.4526714349 |
-1.143464 |
0.347430757 |
10.693065 |
0.00107537866093433990763439389581890281988307833671569824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002490208508847012534165310526645953359548002481460571289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.7686775 |
6.0221637 |
54.5708536 |
9.1640501 |
| ENSG00000171132 |
5581 |
PRKCE |
protein_coding |
Q02156 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays essential roles in the regulation of multiple cellular processes linked to cytoskeletal proteins, such as cell adhesion, motility, migration and cell cycle, functions in neuron growth and ion channel regulation, and is involved in immune response, cancer cell invasion and regulation of apoptosis. Mediates cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix via integrin-dependent signaling, by mediating angiotensin-2-induced activation of integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) in cardiac fibroblasts. Phosphorylates MARCKS, which phosphorylates and activates PTK2/FAK, leading to the spread of cardiomyocytes. Involved in the control of the directional transport of ITGB1 in mesenchymal cells by phosphorylating vimentin (VIM), an intermediate filament (IF) protein. In epithelial cells, associates with and phosphorylates keratin-8 (KRT8), which induces targeting of desmoplakin at desmosomes and regulates cell-cell contact. Phosphorylates IQGAP1, which binds to CDC42, mediating epithelial cell-cell detachment prior to migration. In HeLa cells, contributes to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced cell migration, and in human corneal epithelial cells, plays a critical role in wound healing after activation by HGF. During cytokinesis, forms a complex with YWHAB, which is crucial for daughter cell separation, and facilitates abscission by a mechanism which may implicate the regulation of RHOA. In cardiac myocytes, regulates myofilament function and excitation coupling at the Z-lines, where it is indirectly associated with F-actin via interaction with COPB1. During endothelin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, mediates activation of PTK2/FAK, which is critical for cardiomyocyte survival and regulation of sarcomere length. Plays a role in the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy via persistent phosphorylation of troponin I (TNNI3). Involved in nerve growth factor (NFG)-induced neurite outgrowth and neuron morphological change independently of its kinase activity, by inhibition of RHOA pathway, activation of CDC42 and cytoskeletal rearrangement. May be involved in presynaptic facilitation by mediating phorbol ester-induced synaptic potentiation. Phosphorylates gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit gamma-2 (GABRG2), which reduces the response of GABA receptors to ethanol and benzodiazepines and may mediate acute tolerance to the intoxicating effects of ethanol. Upon PMA treatment, phosphorylates the capsaicin- and heat-activated cation channel TRPV1, which is required for bradykinin-induced sensitization of the heat response in nociceptive neurons. Is able to form a complex with PDLIM5 and N-type calcium channel, and may enhance channel activities and potentiates fast synaptic transmission by phosphorylating the pore-forming alpha subunit CACNA1B (CaV2.2). In prostate cancer cells, interacts with and phosphorylates STAT3, which increases DNA-binding and transcriptional activity of STAT3 and seems to be essential for prostate cancer cell invasion. Downstream of TLR4, plays an important role in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immune response by phosphorylating and activating TICAM2/TRAM, which in turn activates the transcription factor IRF3 and subsequent cytokines production. In differentiating erythroid progenitors, is regulated by EPO and controls the protection against the TNFSF10/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, via BCL2. May be involved in the regulation of the insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of AKT1. Phosphorylates NLRP5/MATER and may thereby modulate AKT pathway activation in cumulus cells (PubMed:19542546). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11884385, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1374067, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15355962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16757566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17603037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17875639, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17875724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19542546}. |
3D-structure;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell cycle;Cell division;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Immunity;Kinase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine- and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by calcium and the second messenger diacylglycerol. PKC family members phosphorylate a wide variety of protein targets and are known to be involved in diverse cellular signaling pathways. PKC family members also serve as major receptors for phorbol esters, a class of tumor promoters. Each member of the PKC family has a specific expression profile and is believed to play a distinct role in cells. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the PKC family members. This kinase has been shown to be involved in many different cellular functions, such as neuron channel activation, apoptosis, cardioprotection from ischemia, heat shock response, as well as insulin exocytosis. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this kinase is important for lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated signaling in activated macrophages and may also play a role in controlling anxiety-like behavior. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5581; |
cell periphery [GO:0071944]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; 14-3-3 protein binding [GO:0071889]; actin monomer binding [GO:0003785]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity [GO:0004698]; calcium-independent protein kinase C activity [GO:0004699]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; ethanol binding [GO:0035276]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase C activity [GO:0004697]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; signaling receptor activator activity [GO:0030546]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; cellular response to ethanol [GO:0071361]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; insulin secretion [GO:0030073]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; locomotory exploration behavior [GO:0035641]; macrophage activation involved in immune response [GO:0002281]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; mucus secretion [GO:0070254]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; negative regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:2000650]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010811]; positive regulation of cellular glucuronidation [GO:2001031]; positive regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032467]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024]; positive regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050996]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of mucus secretion [GO:0070257]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0032230]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0061178]; regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050730]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; response to morphine [GO:0043278]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0051932]; TRAM-dependent toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0035669] |
11740573_Isoforms of protein kinase C and their distribution in human adrenal cortex and tumors 11809819_PKCepsilon mediates neurite induction by increased association to the cytoskeleton during neuronal differentiation. 11877428_Switch chimeras, containing the C1B from epsilonPKC in the context of deltaPKC (delta(epsilonC1B)) and vice versa (epsilon(deltaC1B)), were generated and tested for their translocation in response to ceramide and arachidonic acid. 11884385_Direct phosphorylation of capsaicin receptor VR1 by protein kinase Cepsilon and identification of two target serine residues 11934885_The anchoring protein RACK1 links protein kinase Cepsilon to integrin beta chains. 11956211_Protein kinase C epsilon-dependent regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator involves binding to a receptor for activated C kinase (RACK1) and RACK1 binding to Na+/H+ exchange regulatory factor. 11964154_The contribution of PKCepsilon kinase activity in controlling the phosphorylation of Thr(566) and Ser(729)of PKCE. 11994357_No thyroid papillary carcinoma, follicular adenoma, or anaplastic carcinoma harbored the PKCalpha 881A>G mutation. 11997513_Critical role of diacylglycerol- and phospholipid-regulated protein kinase C epsilon in induction of low-density lipoprotein receptor transcription in response to depletion of cholesterol. 12093536_REVIEW:Interaction of protein kinase C isozymes with membranes containing anionic phospholipids utilizing fluorescent phorbol esters to probe the properties of the C1 domains 12121973_promotes survival of lung cancer cells by suppressing apoptosis through dysregulation of the mitochondrial caspase pathway 12185081_role in regulating caveolin-1 expression and secretion 12198125_activation inhibited TNF-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 cells 12205039_Protein kinase C-epsilon mediates bradykinin-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human airway smooth muscle cells 12372810_PKCepsilon-mediated inhibition of Cl-/OH- exchange activity in Caco-2 cells 12372816_PKCepsilon as the key isoform responsible for actin disruption in T84 cells 12385023_Protein kinase C epsilon plays a role in lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-12 synthesis in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. 12505875_absence of protein kinase C-epsilon allows increased expression of potassium(V) channels (like Kv3.1b) to occur in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, which likely contributes to decreased hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction 12505880_selective modulation of novel PKC epsilon may regulate TNF-R1 signaling in intestinal epithelium. 12536241_Il-2 and polysaccharide K increased expression of protein kinase C epsilon. 12783114_The novel varepsilon and eta and atypical zeta, but not the conventional alpha and beta and the novel delta PKCs, may be involved in the signaling pathways involved in thrombin-induced human platelet P-selectin expression 12970744_our data suggest that an association of PKCepsilon with Bax may neutralize apoptotic signals propagated through a mitochondrial death-signaling pathway. 14532285_PKC-epsilon is specifically required in the signaling pathway leading to the induction of hsp90 beta gene in response to heat shock. 14643884_PKC epsilon (epsilon) was recently found to be a critical component of TLR-4 signaling pathway and thereby to play a key role in macrophage and dendritic cell (DC) activation in response to LPS [review] 14656938_PKCdelta and PKCepsilon may offer novel targets for development of cancer preventive or therapeutic agents that selectively inactivate PKCepsilon or stimulate PKCdelta. 14709334_A putative Rac1/Cdc42/PKC-alpha pathway is convergent with the PKC-epsilon/MEK1/2 pathway in terms of the activation of JNK by PMA. 14720513_Induction of neurites by the regulatory domain of PKCE is counteracted by PKC catalytic activity and RhoA GTP-binding protein metabolism. 14739299_intramolecular within epsilon PKC is critical and rate limiting in the process of PKC translocation 15190080_protein kinase Cepsilon has a role in phosphorylation of the activation loop of protein kinase D 15233804_Results suggest that the involvement of protein kinase C alpha in carbachol-induced soluble amyloid precursor protein (sAPPalpha) release is negligible, but PKC epsilon may be important in coupling cholinergic receptors with APP metabolism. 15284224_Use of PKC agonists and isozyme-specific pseudosubstrate peptide antagonists suggested a role for PKCalpha and -epsilon in VEGF-mediated DAF up-regulation, mediating A cytoprotective pathway in ECs. 15364951_PKCepsilon plays a critical role in the regulation of ADAM12 cell-surface expression 15467757_a mutually reinforcing signaling loop sustains the activation of beta1 integrins, PKCepsilon, and PKB/Akt in adherent prostate cancer cells 15499829_We analyzed the dependence of the expression of some selected protein kinase C isoenzymes on the availability and/or action of androgens. 15509588_central role of PKC isoforms and the negative regulatory function of c-Src in the control of stromelysin 3 expression 15559761_PAR1 seems to be the responsible receptor for thrombin-induced migration and adhesion of human colon carcinoma cells including PKCepsilon as an essential signal transducer 15572354_diacylglycerol-responsive PKC isoforms differentially influence CaR agonist-induced release of Ca2+ from internal stores 15627650_two fatty acids inhibited the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced plasma membrane translocation of protein kinase C (PKC)-alpha and -epsilon 15632189_DGK interacts selectively with and is phosphorylated by PKCepsilon and -eta and peptide agonist-induced selective activation of PKCepsilon directly leads to DGK translocation 15691837_Results demonstrate that a branched signaling pathway involving MEK, ERK, PKCepsilon, PKCalpha, and caveolin-1 regulates collagen expression in normal lung tissue and is perturbed during fibrosis. 15698833_PKC epsilon and delta are the main PKC isozymes involved in G alpha(q)-mediated signaling in human atria 15718244_A highly conserved sequence N-terminal of the C1b domain is identified that is crucial for neurite induction by PKC epsilon, indicating that this motif may be critical for some morphological effects of PKC. 15784626_post-receptor signaling of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is through protein kinase c epsilon-dependent expression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) 15809302_fMLP-induced activation of NF-kappaB utilizes a signaling pathway requiring activity of PKCepsilon, a signaling component downstream of RhoA in cytokine gene transcription stimulated by a chemoattractant 15827341_protein kinase C epsilon has a role in regulating sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells 15967991_intracellular M. leprae activates Erk1/2 directly by p56Lck by means of a PKCepsilon-dependent and MEK-independent signaling pathway 16079188_The predominant pathway for thrombin-induced DAF expression involves transactivation of PAR2 by PAR1 and signaling via PKC-epsilon/MAPK. 16266318_insulin-like growth factor-1 can protect human VSMC via multiple signals, including PKC-epsilon, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways 16637058_In conclusion, our results provide evidence for PKCepsilon-mediated differential ERK activation and growth regulation in Panc-1C cells. 16698938_increased neuronal PKCepsilon activity can promote Abeta clearance and reduce AD neuropathology through increased endothelin-converting enzyme activity 16785234_PKCepsilon activates Akt via DNA-PK to mediate its antiapoptotic function 16793902_Thus, PAR2 activates PKCepsilon and PKA in sensory neurons, and thereby sensitizes TRPV1 to cause thermal hyperalgesia. 16930532_Cdc42 is an important downstream factor in the pathway through which PKC mediates morphological and cytoskeletal effects 17018591_PKC epsilon is involved in a coordinated regulation of RhoA and RhoC activation, possibly through direct post-translational phosphorylation. 17038313_PKC-mediated activation of NCKX2 is sensitive to mutation of multiple PKC consensus sites via a mechanism that may involve several phosphorylation events 17215072_results firmly establish that angiotensin II activates p44/42 MAPK through protein kinase C epsilon in H295R cells 17382347_Residues in the PKCepsilon C1b domain, in particular Asn49, that are essential for neurite outgrowth. 17434141_Since HMGA1 regulates IR promoter activity, expression of IR gene was impaired causing reduction of IR on cell surface and that compromises with insulin sensitivity. 17561374_Cellular knockdown of protein kinase Cepsilon (PKCepsilon) leads to decreased activation of PLCgamma1 by epidermal growth factor (EGF). EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of PKCepsilon as well as its association with EGF receptor and PLCgamma1. 17569788_PKCepsilon levels negatively interfere with megakaryocytic differentiation. 17616661_PKC epsilon exerts its oncogenic activity through deregulation of the cell cycle via a p21/Cip1-dependent mechanism 17628663_These data show that angiotensin II attenuates Ca2+ uptake predominantly into mitochondria that do not colocalize with endoplasmic reticulum, by a mechanism involving p38 MAPK and a novel-type PKC. 17668322_These results suggest that PKCepsilon mediates its effects on TNFalpha- based apoptosis partly by preventing activation and translocation of Bax to the mitochondria. 17678893_The modulation of claudin-4 activity by PKCepsilon may not only provide a mechanism for disrupting TJ function in ovarian cancer, but may also be important in the regulation of TJ function in normal epithelial cells. 17785460_Study demonstrates that PKCepsilon forms a signaling complex and acts co-operatively with Akt to protect human vascular endothelial cells against apoptosis through induction of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and inhibition of caspase-3 cleavage. 17851107_Regulation of the subcellular localisation of Tat-interactive protein 60 kDa via phosphorylation provides a novel means of controlling Tat-interactive protein 60 kDa function. 17991733_PLCgamma-mediated activation of PKCepsilon and PKCbetaI and intracellular calcium is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions from acetaldehyde-induced insult 18171914_conclude that dopamine receptor D4 (D4R) augmented aldosterone synthesis/secretion induced by angiotensin II mediated through enhancing protein kinase c-epsilon phosphorylation and calcium elevation 18172602_Cx43Hc electrical conductance is inhibited after PKC activation. Inhibition is predominantly mediated by PKC-epsilon. Partial inhibition may be provided by PKC-beta II/PKC-delta. 18184679_Moraxella catarrhalis infection activates protein kinase C and its isoforms alpha, epsilon and theta, which differentially regulate interleukin-8 transcription in human pulmonary epithelial cells. 18237277_identify three new phosphorylation sites that contribute to the isoform-specific function of PKCepsilon and highlight a novel and direct means of cross-talk between different members of the PKC superfamily 18292183_Probiotic-secretory proteins protect the intestinal epithelium from hydrogen peroxide-induced insult by a PKC beta1/epsilon- and ERK1/2-dependent mechanism. 18296444_Protein kinase C-epsilon regulates sphingosine 1-phosphate-mediated migration of human lung endothelial cells through activation of phospholipase D2, protein kinase C-zeta, and Rac1 18317451_PKC epsilon mediates TRAIL resistance by Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Hdm2 resulting in suppression of p53 expression and downregulation of Bid in breast cancer cells 18319301_Data identify PKCepsilon as regulators of EC lumenogenesis in 3D collagen matrices. 18398416_Preconditioning signaling cascade involves STAT3 activation after varepsilonPKC and ERK1/2 activation 18408015_PKCepsilon through its interaction with peripherin facilitates its aggregation and subsequent cell death 18436431_Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate -induced NF-kappaB-dependent transcription is driven by novel PKC isoforms, particularly PKCdelta and epsilon. 18458086_scaffold protein MyD88 as the link coupling TLR2,4 to PKCepsilon recruitment, phosphorylation, and downstream signaling. 18462068_activation of prostaglandin F2alpha receptor in vivo modulate uveoscleral outflow through the PKCepsilon-dependent secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 18556656_UDP-glucuronosyltransferase chemical detoxifying system requires regulated phosphorylation supported by protein kinase C 18663158_caveolin-dependent internalization is involved in PKC-epsilon-mediated inhibition of vascular K(ATP) channels (Kir6.1 and SUR2B) by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate or angiotensin II 18844064_Sera from aplastic anemia patients could upregulate the expression of protein kinase C epsilon. 18947333_Our results argue for the involvement of galectin-1 in the PKCepsilon/vimentin-controlled trafficking of integrin-beta1 18988868_Phorbol ester-induced PKCepsilon down-modulation sensitizes AML cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis and cell differentiation. 19030108_demonstrate a reciprocal relationship in levels of the novel PKC isoforms delta and epsilon in human and mouse platelets and a selective role for PKCepsilon in signalling through GPVI. 19168130_Protein kinase C epsilon can induce distinctly different signaling from the Golgi and from the plasma membrane. 19244118_miR-205 exerts a tumor-suppressive effect in human prostate by counteracting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reducing cell migration/invasion, at least in part through the down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. 19248786_In human myocardium, cardioprotection can be achieved by either inhibiting PKC-delta or activating PKC-varepsilon at the onset of reperfusion. 19324950_PKC(alpha) and PKC(epsilon) differentially regulate Legionella pneumophila-induced GM-CSF 19429675_3CTS contact targeting sequence is involved in the modulation of translocation via its 14-3-3-binding site, in cytoplasmic desequestration via the alpha-helix, and in selective PKCepsilon targeting at the cell-cell contact via Glu-374 19432558_An allosteric alcohol-binding site was identified in protein kinase C epsilon. 19435802_Data reveal a multicomponent kinase signaling pathway downstream of integrin-matrix interactions and Cdc42 activation involving PKCepsilon, Src, Yes, Pak2, Pak4, B-Raf, C-Raf and ERK1/2 to control EC lumen formation in 3D collagen matrices. 19542546_MATER protein interacts with tPKCepsilon in cumulus cells under physiological conditions. 19573263_Report expression of protein kinase A and C subunits in post-mortem prefrontal cortex from persons with major depression and normal controls. 19577658_involved in ionizing radiation induced bystander response 19633292_Results indicate that HA binding to CD44 promotes PKCepsilon activation, increases the phosphorylation of the stem cell marker, Nanog, leads to microRNA-21 (miR-21) production and PDCD4 reduction. 19635931_The cascade of events initiated by hog dust exposure is mediated by PKC-alpha/-epsilon and ultimately results in the release of TNF-alpha. 19655190_PKCalpha- and PKCepsilon-mediated phosphorylation of cMyBP-C and cTnI as well as cTnT decrease myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity and may thereby reduce contractility and enhance relaxation of human myocardium. 19662078_Study reports the crystal structure of 14-3-3zeta bound to a synthetic diphosphorylated PKCepsilon V3 region revealing how a consensus 14-3-3 site and a divergent 14-3-3 site cooperate to bind to 14-3-3 and so activate PKCepsilon. 19815625_Report PKCepsilon-dependent and -independent effects of taurolithocholate on PI3K/PKB pathway and taurocholate uptake in HuH-NTCP cell line. 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20072156_phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate(PMA)downregulates onzin expression through PKCepsilon-ERK2 signaling pathway, which favors monocytic differentiation of leukemic cells. 20171211_the binding of filamin A to vimentin and protein kinase C epsilon is an essential regulatory step for the trafficking and activation of beta1 integrins and cell spreading on collagen 20198332_PKCepsilon regulates Bcl-2 induction through activation of the transcription factor CREB in breast cancer cells. 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20350291_[review] overview of the biology of PKCepsilon and methods for substrate identification, and discussion of substrate categories 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20471435_Two isoforms of PKCs are involved in the regulation of the PDCD4 protein expression related to the proteasomal degradation pathway. 20566643_PKCepsilon modulates survival in prostate cancer cells via multiple pathways. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20732874_PKC{delta} and PKC{epsilon}-regulated NKCC1 surface expression plays an important role in the regulation of chloride secretion 20965248_Protein Kinase C epsilon acts as negative allosteric modulator of Epidermal Growth Factor receptor signalling 21081127_Results show that both PKC epsilon and PKC zeta isoforms are involved in the formation of ROS by C2-ceramide and the opening of the mPTP. 21124804_Data show that inhibition of cellular factors required for early steps in the infection cycle including PKCepsilon can block RVFV infection, and may represent a starting point for the development of anti-RVFV therapeutics. 21236337_The study shows a correlation between fatty acids, protein kinase C epsilon phosphorylation and downregulation of insulin receptor. 21277149_Resistin-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell migration was associated with increased MMP expression, which was dependent on PKCepsilon activation. 21283634_the tumor suppression in SMMC-7721 by C/EBPbeta 3'UTR RNA is due to the inhibition of protein kinase Cepsilon activity through direct physical interaction between C/EBPbeta 3'UTR RNA and protein kinase Cepsilon. 21411725_study identified PKCepsilon as the isoform involved in VIP-dependent F508del-CFTR membrane insertion 21423656_PKCepsilon as the PKC isoform involved in smoke-induced TACE activation and hyperproliferation of lung cells. 21465464_These data demonstrate that TRAIL and PKCepsilon must be reciprocally regulated to ensure physiological colon epithelial cell differentiation starting from the stem cell pool. 21489985_partial blockade of PKC potentiates aggregation and dense granule secretion by ADP in association with increased Ca(2+) 21532342_Enhanced PKCepsilon mediated phosphorylation of connexin43 at serine 368 by a carboxyl-terminal mimetic peptide is dependent on injury. 21596133_Suppression of protein kinase C epsilon activity alters mitochondrial homeostasis. 21649687_The polymorphisms of PRKCE in families wtih Carney syndrome are reported. 21858203_Data indicate that RhoA, PKCdelta and PKCepsilon modulated uPA-induced cell adhesion and polarization, whereas only RhoA and PKCepsilon were also responsible for the redirection of virions in intracellular vesicles. 21955404_Overexpression of protein kinase C epsilon is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 21964026_PKCepsilon controls cell proliferation but not cell activation of CD4-positive T lymphocytes; for the first time, increased expression of PKCepsilon is found in CD4-positive T cells of Hashimoto thyroiditis patients. 21996750_PKCvarepsilon is required for non-small cell lung carcinoma cell survival and maintenance of tumor growth 22158047_protein kinase C-epsilon is directly regulated by miR-107 in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 22162761_C-peptide increases Na,K-ATPase expression via PKC- and MAP kinase-dependent activation of transcription factor ZEB in human renal tubular cells 22304920_The ability of ATF2 to reach the mitochondria is determined by PKCepsilon, which directs ATF2 nuclear localization. Genotoxic stress attenuates PKCepsilon effect on ATF2; enables ATF2 nuclear export and localization at the mitochondria. 22326427_These results suggest that PKCdelta and epsilon specifically regulate the morphology of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. 22384062_Non-small cell lung carcinoma cell motility, rac activation and metastatic dissemination are mediated by protein kinase C epsilon 22475757_SZ95 sebocytes express the conventional cPKCalpha; the novel nPKCdelta, epsilon, and eta; and the atypical aPKCzeta 22712879_Ciliated cell detachment is associated with PKCepsilon autodownregulation in bronchial epithelium. 22773829_activated GR can inhibit p53-dependent apoptosis through induction of the anti-apoptotic factor PKCepsilon. 22849349_study concludes that PKCepsilon plays an essential role in endothelial homoeostasis, acting as an upstream co-ordinator of gene expression through activation of ERK1/2, inhibition of JNK and diversion of the NF-kappaB pathway to cytoprotective gene induction 22927445_the intracellular interaction of IL-32alpha with PKCepsilon and STAT3 promotes STAT3 binding to the IL-6 promoter by enforcing STAT3 phosphorylation, which results in increased production of IL-6. 22955280_a molecular link between PKCepsilon and RelA-nuclear factor kappa B that controls key responses implicated in prostate cancer progression. 23071564_data suggest that platelet generations produced before the acute event retain PKCepsilon-mRNA that is not down-regulated during terminal megakaryocyte differentiation. 23123196_Report metabolic cooperation between the EGFR/PKC-epsilon/NF-kappaB pathway in PKM2 upregulation and tumorigenesis. 23266964_Studies indicate that protein kinase C isoform epsilon (PKCepsilon) is differentially regulated in erythrocyte and megakaryocyte progenitors, suggesting an addressing role toward maturation of either lineage. 23349801_Data indicate that the phosphorylation of GSK-3beta was reduced by siRNA of PKCdelta, PKCepsilon, and PKCzeta. 23364795_MiR-31 directly targets PRKCE and thereby suppresses NF-kappaB activity and induces apoptosis and sensitivity to anti-cancer treatments via down-regulation of BCL2 expression. 23457043_High PRKCE expression is associated with papillary thyroid tumor development. 23524339_PKC epsilon plays central role in mediating HGF-induced fluctuant ERK-paxillin signaling, probably via the regulation of endosomal degradation of c-Met for the migration of HepG2. 23562764_Upregulation of PKCeta contributes to breast cancer cell growth and targeting either PKCepsilon or PDK1 triggers PKCeta downregulation 23564461_Phosphorylation of serine 779 in fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 and 2 by protein kinase C(epsilon) regulates Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and neuronal differentiation. 23589174_Data indicate that small molecules that block the oncogenic addiction to PKCepsilon signaling by promoting ATF2 nuclear export, resulting in mitochondrial membrane leakage and melanoma cell death. 23612973_similar to Ser-428/431 (in LKB1(L)), Ser-399 (in LKB1(S)) is a PKCzeta-dependent phosphorylation site essential for nucleocytoplasmic export of LKB1(S) and consequent AMPK activation. 23824184_This study identifies PKCzeta as a novel key upstream regulator of BA-regulated SHP function, revealing the role of Thr-55 phosphorylation in epigenomic regulation of liver metabolism. 23824807_This study identifies PKCalpha, PKCepsilon, and vimentin as key factors affecting efficient infection and transduction by echovirus 1 and baculovirus, respectively. 23967087_our results identify a novel regulatory pathway involving the interplay between ZO-1, alpha5-integrin and PKCepsilon in the late stages of mammalian cell division. 23977066_Cysteinyl leukotrienes signaling downstream of CysLT1R in mast cells is differentially regulated by two distinct PKCalpha and PKC epsilon. 23977398_These results provide further support for the contribution of PKCs in Niemann Pick Type C1 disease pathogenesis. 24070896_MiR-143 specifically targets the 3'-UTR of PRKCE and regulates its expression. 24166186_activated in compressive load-cultured nucleus pulposus cells 24298017_PKCepsilon may negatively regulate adverse myocardial remodeling by cooperating with calcineurin to downregulate fibrosis and induce transcription of cardioprotective wound healing genes, including COX-2 24312401_PKCepsilon activation in late passage NP cells may represent a molecular basis for aggrecan availability, as part of an PKCepsilon/ERK/CREB/AP-1-dependent transcriptional program that includes upregulation of both chondrogenic genes and microRNAs 24338688_Vascular endothelial tight junctions and barrier function are disrupted by 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid partly via protein kinase C epsilon-mediated zona occludens-1 phosphorylation at threonine 770/772. 24515280_HepaCAM may prevent the translocation of PKCepsilon from cytosolic to particulate fractions, resulting in the inhibition of 786-0 cell proliferation. 24788249_VIP regulates CFTR membrane expression and function in Calu-3 cells by increasing its interaction with NHERF1 and P-ERM in a VPAC1- and PKCepsilon-dependent manner. 24815185_PKC epsilon regulates the interaction between Cx43 and Kir6.1 in the cardiomyocyte mitochondria and this interaction prevents hypoxia induced cell death. 24825907_RNAi silencing of Sp1 and STAT1 in breast cancer cells reduced PKC mRNA and protein expression, as well as PRKCE promoter activity. 24848988_PKCepsilon activation may have therapeutic efficacy for AD by reducing neurotoxic Abeta accumulation as well as having direct anti-apoptotic and synaptogenic effects 24872409_a novel mechanism by which a PKC-Rab5a-Rac1 axis regulates cytoskeleton remodeling and T-cell migration, both of which are central for the adaptive immune response. 24888992_Knockdown of PKCepsilon expression inhibited proliferation, induced apoptosis and decreased invasiveness of human glioma cell lines, and suppressed the growth of U87 cell-derived tumors in nude mice. PKCepsilon physically interacts with Stat3. 25178676_Data suggest that interleukin-32alpha (IL-32alpha) associates with leukemia zinc finger (PLZF) and protein kinase c epsilon (PKCvarepsilon), and then inhibits PLZF sumoylation, resulting in suppression of the transcriptional activity of PLZF. 25245533_IL-32alpha inhibits BCL6 SUMOylation by activating PKCepsilon, resulting in the modulation of BCL6 target genes and cellular functions of BCL6. 25308712_MicroRNA-146a controls Th1-cell differentiation of human CD4-positive T-lymphocytes by targeting PKCepsilon. 25322815_Suggest distinct role of PKCepsilon in controlling cell fate and immune response of monocyte subsets. 25372487_PKC-delta activates p38/MAPK, responsible for the inhibition of MMP-2 and -9 secretion, PKC-epsilon activates a pathway made of ERK1/2, mTOR and S6K responsible for the inhibition of NHE1 activity and cell migration. 25483024_PKCepsilon-mediated regulation has a role in protection from loss of chromosome integrity in cells failing to resolve catenation in G2 25778903_Depletion of PKCepsilon not only enhanced HGF-induced phosphorylation of JNK and paxillin (Ser178) but also prevented c-Met degradation. 25788289_miR-34a regulates blood-tumor barrier (BTB) function by targeting PKCepsilon; after phosphorylation, PKCepsilon is activated and contributes to regulation of the expression of tight junction-related proteins, ultimately altering BTB permeability. 25883219_PKCepsilon-CREB-Nrf2 signalling induces HO-1 in the vascular endothelium and enhances resistance to inflammation and apoptosis. 26023164_PKCepsilon is a key factor for driving the formation of bone metastasis by prostate cancer cells and is a potential therapeutic target for advanced stages of the disease. 26821209_Docosahexaenoic acid increase the efficacy of docetaxel in mammary cancer cells by downregulating Akt and PKCepsilon/delta-induced ERK pathways. 27037060_PKCepsilon down-regulation suppresses sorting and the cancer stem-like phenotype of renal cell carcinoma 769P side population cells through the regulation of ABCB1 transporter and the PI3K/Akt, Stat3 and MAPK/ERK pathways that are dependent on the phosphorylation effects. 27081176_PKCdelta and PKCepsilon work as a functional couple with opposite roles on thrombopoiesis, and the modulation of their balance strongly impacts platelet production. 27312950_PRKCE plays two major roles in cardiac muscle cells: it takes part in regulating cardiac muscle contraction via targeting the sarcomeric proteins, as well as it modulates cardiac cell energy production and metabolism by targeting cardiac mitochondria. (Review) 27330081_These results indicate that PKC promotes synaptogenesis by activating PSD-95 phosphorylation directly through JNK1 and calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II and also by inducing expression of PSD-95 and synaptophysin. 27573736_Resistin-associated vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction and intimal hyperplasia are related to PKCepsilon-dependent Nox activation and ROS generation 27776404_Curcumin inhibited phorbol ester-induced membrane translocation of protein kinase C-epsilon (PKCepsilon) mutants, in which the epsilonC1 domain was replaced with alphaC1, but not the protein kinase C-alpha (PKCalpha) mutant in which alphaC1 was replaced with the epsilonC1 domain, suggesting that alphaC1 is a determinant for curcumin's inhibitory effect. 27793751_protein kinase C-epsilon regulation, phospholipase D1 protects retinal pigment epithelium cells from lipopolysaccharide-induced damage 28004745_PKCvarepsilon directly modulates the Aurora B-dependent abscission checkpoint by phosphorylating Aurora B at S227. This phosphorylation invokes a switch in Aurora B specificity, with increased phosphorylation of a subset of target substrates, including the CPC subunit Borealin. 28056995_epsilonPKC phosphorylation and its coevolution with ALDH2 play an important role in the regulation and protection of ALDH2 enzyme activity. 28223364_NF-kappaB signaling thus appears to play a critical role in promoting both castration resistance and enzalutamide resistance in PKC/Twist1 signaling in prostate cancer. 28286252_PKCepsilon is a key upstream mediator in resistin-induced inflammation that may interact synergistically with TLR4 to promote NF-kB activation in macrophages. 28402859_we demonstrate that PKCepsilon cooperates with the loss of the tumor suppressor Pten for the development of prostate cancer in a mouse model. Mechanistic analysis revealed that PKCe overexpression and Pten loss individually and synergistically upregulate the production of the chemokine CXCL13, which involves the transcriptional activation of the CXCL13 gene 28476658_Protein kinase C acts as a tumor suppressor.Cancer-associated mutations in protein kinase C are generally loss-of-function mutations.[review] 28492560_results imply that an intimate correlation between miR-218-5p and PRKCE/MDR1 axis abnormal expression is a key determinant of gemcitabine tolerance, and suggest a novel miR-218-5p-based clinical intervention target for Gallbladder cancer patients. 28591572_These results demonstrate the relevance of hepatic diacylglycerol-induced PKCepsilon activation in the pathogenesis of NAFLD-associated hepatic insulin resistance in humans. 28765889_The downregulation of mi143 promoted cell proliferation by regulating PKCepsilon in the hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 29038521_Data show that protein kinase C epsilon (PKCepsilon) phosphorylates migration and invasion inhibitory protein (MIIP) at Ser303 and promotes its binding to RelA/p65, facilitating colorectal cancer metastasis. 29127121_This study uncovers a previously unrecognized role for PKCepsilon in supporting AML cell survival and disease progression by regulating mitochondrial ROS biology and positions mitochondrial redox regulators as potential therapeutic targets in AML 29280140_PKCepsilon interacts with Stat3 during Th17 differentiation and its overexpression results in an enhanced expression of Stat3 and pStat3(Ser727); conversely, when PKCepsilon is forcibly downregulated, CD4+ -T cells show lower levels of pStat3(Ser727) expression and defective in vitro expansion into the Th17-lineage. 29439667_Results indicate an important role of protein kinase C epsilon (PKCepsilon) in autophagy and as a therapeutic target. 29452158_PKCepsilon isoenzyme mediates the inhibitory action of Angiotensin II on slowly activating delayed rectifier K(+) curren and by phosphorylating distinct sites in KCNQ1/KCNE1, cPKC and PKCepsilon isoenzymes produce the contrary regulatory effects on t |
ENSMUSG00000045038 |
Prkce |
18.523416 |
0.1881078232 |
-2.410368 |
0.472922016 |
27.033551 |
0.00000019995452174689488811384040223284586090812808834016323089599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000763846609787203709828601588122110044309920340310782194137573242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9074345 |
1.5838144 |
20.2801811 |
5.1604549 |
| ENSG00000171174 |
64080 |
RBKS |
protein_coding |
Q9H477 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribose at O-5 in a reaction requiring ATP and magnesium. The resulting D-ribose-5-phosphate can then be used either for sythesis of nucleotides, histidine, and tryptophan, or as a component of the pentose phosphate pathway. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03215, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17585908}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Potassium;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate metabolism; D-ribose degradation; D-ribose 5-phosphate from beta-D-ribopyranose: step 2/2. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03215}. |
This gene encodes a member of the carbohydrate kinase PfkB family. The encoded protein phosphorylates ribose to form ribose-5-phosphate in the presence of ATP and magnesium as a first step in ribose metabolism. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:64080; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ribokinase activity [GO:0004747]; D-ribose catabolic process [GO:0019303]; pentose-phosphate shunt [GO:0006098] |
17585908_Identification and characterization of human ribokinase. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25749547_Asn199 and Glu202 play an important role in the regulation of human ribokinase activity. |
ENSMUSG00000029136 |
Rbks |
22.887829 |
0.4743814272 |
-1.075881 |
0.313836008 |
11.963995 |
0.00054238448940999790977290917481923315790481865406036376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001322801563729604848451693044353305594995617866516113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.8242732 |
2.9958920 |
31.4761947 |
4.0499233 |
| ENSG00000171208 |
81831 |
NETO2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NC67 |
FUNCTION: Accessory subunit of neuronal kainate-sensitive glutamate receptors, GRIK2 and GRIK3. Increases kainate-receptor channel activity, slowing the decay kinetics of the receptors, without affecting their expression at the cell surface, and increasing the open probability of the receptor channels. Modulates the agonist sensitivity of kainate receptors. Slows the decay of kainate receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs), thus directly influencing synaptic transmission (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a predicted transmembrane protein containing two extracellular CUB domains followed by a low-density lipoprotein class A (LDLa) domain. A similar gene in rats encodes a protein that modulates glutamate signaling in the brain by regulating kainate receptor function. Expression of this gene may be a biomarker for proliferating infantile hemangiomas. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 8. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:81831; |
glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; ionotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035255]; neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0099645]; regulation of kainate selective glutamate receptor activity [GO:2000312]; regulation of neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0098696]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0098962] |
15340161_Determination of the neuropilin and tolloid-like protein 2 signal peptide cleavage site by N-terminal sequencing. 19217376_Rat neto2 plays a role in glutamate signaling in the brain by modulating the function of kainate receptors. 26277340_Results suggested that the extracellular N-terminal region including the two CUB domains was largely responsible for the distinct regulatory effects of Neto1 and Neto2 on the desensitization properties of GluK1 homomeric receptors 26699544_NETO2 upregulation could serve as a potential biomarker for the prediction of advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis in patients with colorectal carcinoma. 29297384_NETO2 may be involved in colorectal cancer progression, but is not directly associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition 29989576_upregulation of NETO2 gene is first stipulated by the isoform 1 (NM_018092.4), and the probable mechanism of its activation is associated with the increased expression of SAP30 transcription factor. 30770791_NETO2 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells and represents a novel prognostic indicator as well as a potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer. 30975469_NETO2 expression is up-regulated in Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) clinical specimens and cell lines. NETO2 down-regulation reduces proliferation, migration and invasion in irradiated NPC cell lines. 33157203_Neuropilin and tolloid-like 2 regulates the progression of osteosarcoma. 33390848_NETO2 promotes esophageal cancer progression by inducing proliferation and metastasis via PI3K/AKT and ERK pathway. 34552241_Kainate receptor modulation by NETO2. |
ENSMUSG00000036902 |
Neto2 |
250.019410 |
3.6248576110 |
1.857924 |
0.208794628 |
75.869135 |
0.00000000000000000303100941122326030622763128338611226095852796804178130862794660060899332165718078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000024799167910008492013913387309714843548949452404031069951972909848336712457239627838134765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
383.4640277 |
48.7452991 |
106.2522787 |
10.1752817 |
| ENSG00000171223 |
3726 |
JUNB |
protein_coding |
P17275 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in regulating gene activity following the primary growth factor response. Binds to the DNA sequence 5'-TGA[GC]TCA-3'. Heterodimerizes with proteins of the FOS family to form an AP-1 transcription complex, thereby enhancing its DNA binding activity to an AP-1 consensus sequence and its transcriptional activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P09450}. |
Acetylation;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleoplasm. Part of transcription factor AP-1 complex. Biomarker of Hodgkin's lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:3726; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; transcription factor AP-1 complex [GO:0035976]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; decidualization [GO:0046697]; embryonic process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060136]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; labyrinthine layer blood vessel development [GO:0060716]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033687]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; osteoclast proliferation [GO:0002158]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation [GO:2000319]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; trophectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0001829]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
11726656_JunB is an important regulator of erythroid differentiation 12080089_JunB potentiates function of BRCA1 activation domain 1 (AD1) through a coiled-coil-mediated interaction 12145210_Aberrantly expressed c-Jun and JunB are a hallmark of Hodgkin lymphoma cells, stimulate proliferation and synergize with NF-kappa B. 12371906_demonstrated that a functional AP-1 site mediates MMP-2 transcription in cardiac cells through the binding of distinctive Fra1-JunB and FosB-JunB heterodimers. The synthesis of MMP-2 is considered to be independent of the AP-1 transcriptional complex 12393503_results have revealed, for the first time, amplification and expression patterns of JUNB in primary cutaneous lymphomas 12506033_Real-time RT-PCR gave further insights into the role of JunB in human CML. The expression levels were significantly impaired in CML cases. In the promoter area, most of the CpG sites were methylated only in CML cases. 12522006_C/EBPalpha and PKC/delta affect expression of this gene and monocyte differentiation. 12592382_Expression of junB was induced by TPA and Saikosaponin a during 30 min to 6 h of treatment. 12907453_JunB was strongly expressed in T-cell lymphomas, but non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas do not or only weakly express JunB. 12907627_Transcription factor c-Jun plays a principal role in down-regulation of mdr-1 expression and induction of apoptosis in salvicine-treated human MDR K562/A02 cells. 15507668_c-jun, junD, junB, and c-fos and Notch2 are expressed in splenic marginal zone lymphoma 16552541_The IGFBP3, hRas, JunB, Egr-1, Id1 and MIDA1 genes were up-regulated in psoriatic involved skin compared with uninvolved skin. 16880520_5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole sensitivity-inducing factor (DSIF)- and NELF-mediated transcriptional pausing has a dual function in regulating immediate-early expression of the human junB gene. 17204476_JunB and JunD contribute opposing effects; JunB activated whereas JunD repressed heme oxygenase-1 expression in human renal epithelial cells 17306025_results suggest that HTLV-I HBZ-SP1- mediated sequestration of JunB to the HBZ-SP1 nuclear bodies may be causing the repression of JunB activity in vivo 17495958_Coordinated down- and up-regulation of the various AP-1 subunits in the course of epidermal wound healing is important for its undisturbed progress, putatively by influencing inflammation and cell-cell communication. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17681951_Dimerization with the Jun proteins inhibits c-Fos nuclear exit. 17690253_JunB is a critical target of mTOR and is translationally regulated in NPM-ALK-positive lymphomas. 17965727_constitutive action of aberrantly expressed JunB on hypomethylated CD30 CpG islands of lymphocytes triggers CD30 induction and initiates activation of the JunB-CD30-JunB loop, essential to the pathogenesis of HL and ALCL 18391017_JunB levels, which are high in S phase, drop during mid- to late G2 phase due to accelerated phosphorylation-dependent degradation by the proteasome, and are required for subsequent reduction of cyclin A2 levels in prometaphase 18424718_sumoylation of JunB regulates its ability to induce cytokine gene transcription and likely plays a critical role in T cell activation. 18628455_JunB plays an important role in controlling prostate carcinogenesis and may be a new target for cancer prevention and therapy. 18843287_results establish a role for JunB in normal erythropoiesis and indicate that JunB may play a major role in the development of JAK2 V617F myeloproliferative disorders. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19151755_confirmed the downregulation of the FOS-JUNB pathway at transcriptional and protein level 19409613_JUNB downregulation is a DNA methylation-independent phenomenon encountered in chronic lymphocytic leukemia only in advanced phases. 19666408_When p53 dysfunction and low expression of JunB are simultaneous, they may play an important role in down-regulating the expression of KAI1 by synergism in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19923172_Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays confirmed that JunB/Fra-1 proteins interact in vivo with the beta4-integrin promoter and that JunB/Fra-1 promoter occupancy is reduced during keratinocyte differentiation as well as in HPV8 E2 positive keratinocytes 20006998_This analysis shows that the overwhelming majority of JUNB alleles in both chronic phase and blast crisis samples remain unmethylated 20030915_The methylation of JunB and CDH13 gene promoters probably plays a role in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukemia and may have clinical significance in predicting prognosis of CML. 20056077_JunB functions as a transcriptional factor and up-regulates the expression of VEGF. 20132737_The increase in JunB expression attenuated nuclear relocation of apoptosis-inducing factor and mitochondrial Bcl-2 reduction that occurred following hydrogen peroxide exposure. 21225234_Monoammonium glycyrrhizinate highly stimulated JUNB expression in a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. 21289643_JunB and c-Jun have opposite roles in human epidermal neoplasia and that their functional specificities are dependent on both N- and C-terminal domains. 21326808_JunB is a direct transcriptional activator of GzB and that GzB transcription is also promoted by NPM-ALK. 21393445_JunB activates aromatase promoters by maintaining JunD expression 22020339_Study confirmed that JunB was upregulated in VHL-defective clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma (ccRCC) specimens by immunostaining. Short-hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown of JunB in 786-O and A498 VHL null ccRCC cells suppressed their invasiveness. 22252121_up-regulation of JunB induced by HGF might play an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation and cell invasion through MMP-9 expression. 22328780_Different mechanisms preserve translation of programmed cell death 8 and JunB in poliovirus-infected endothelial cells. 22710716_A novel mechanism by which mitosis progression and chromatid cohesion are regulated through GSK3/SCF(FBXW7)-mediated proteolysis of JunB. 23259178_Apoptosis rate of HepG2 cells transformed with pEGFP-C1-wtp53/JunB was significantly higher. 23297064_JunB is shown to be regulated at a post-transcriptional level during EC activation. In activated EC, the AP-1 transcription factor JunB, is regulated on a post-transcriptional level. 23308222_JunB regulates visceral smooth muscle cell contractility through effects on both myosin and the actin cytoskeleton. 23749999_Data indicate that the C-terminal JunB caspase cleavage product functions as a potent inhibitor of AP-1-dependent transcription. 24107296_Data demonstrate that S100A14 is transcriptionally regulated by JunB and involved in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell differentiation. 24136993_an important role of the A2B receptor-dependent upregulation of JunB in VEGF production and possibly other AP-1-regulated events. 24200694_JUNB was specifically expressed in human immune cells during acute liver injury. 24780198_JunB expression was significantly increased while cyclin-D1 expression was significantly down-regulated in pre-eclampsia relative to control placental mesenchymal stromal cells. 24858691_These results demonstrate a unique induction of JUNB in response to kinase inhibitor therapies that may be among the earliest events in the progression to treatment resistance. 25145835_findings uncover the oncogenic role of the JUNB/CD30 axis and its potential as therapeutic target in ALK+ ALCL. 25662951_The MAPK pathway plays a primary role in the control of JUNB gene expression. 25753664_Caveolin 2 disengages repressed Egr-1 and JunB promoters from lamin A/C through disassembly of H3K9me3 in the inner nuclear membrane. 26217035_JunB is likely to be a key target of c-Abl in expression of p21 in Adriamycin-induced DDR. 26318166_PDK1 functions as a tumor promoter in human gallbladder cancer by upregulating JunB, promoting epithelial mesenchymal transformation, and cell migration. 26658840_Highly recurrent mutation of JUNB is associated with nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. 26725775_Our findings demonstrate that miRNA-149* may serve as an oncogenic regulator in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia by negatively regulating JunB 26747248_CARMA1- and MyD88-dependent activation of Jun/ATF-type AP-1 complexes is a hallmark of ABC diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. 26754630_Results suggested that JunB could play an important role in promoting cell invasion, migration and distant metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via pathways other than epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 26860974_VEGF-induced endothelial migration is mediated primarily by induction of JunB whereas the promotion of endothelial proliferation by VEGF is mediated by JunB-independent AP-1 family members. 26926107_ETS2, HNF4A and JUNB are synergistic master regulators of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. 27147707_BATF/JUN-B and BATF/C-JUN complexes play important roles in OA cartilage destruction through regulating anabolic and catabolic gene expression in chondrocytes. 27245101_JunB neddylation mediated by Itch promotes its ubiquitination-dependent degradation. 27591797_It has been shown that the AP-1 family member JunB and retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARa) mediate catalase transcriptional activation and repression, respectively, by controlling chromatin remodeling through a histone deacetylases-dependent mechanism. 27890927_a specific role for AP-1/JunB in multiple myeloma cell proliferation, survival and drug resistance. 29083110_MVIH and Jun-B have a synergistic effect on the regulation of angiogenesis and cell proliferation. 29186616_JUNB governs a feed-forward network of TGFB signaling that aggravates breast cancer invasion. 29895215_RAC2 and JUNB were upregulated in non-small cell carcinoma tissues, and that their upregulations were associated with poor prognoses for non-small cell carcinoma patients. 29899166_IL-6-induced JunB expression contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition changes in uveal melanoma cells. 30227324_LINC00657 might be involved in regulating esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC's) response to radiation; and it functioned as an oncogene in ESCC by targeting miR-615-3p and JunB. 31641227_ETS2 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal fibrosis by targeting JUNB transcription. 31806366_Promotion of cellular senescence by THG-1/TSC22D4 knockout through activation of JUNB. 31982139_The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 contributes to Transforming Growth Factor-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells through the regulation of JUNB. 32299901_miR-939 acts as tumor suppressor by modulating JUNB transcriptional activity in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 32382040_PKCtheta-JunB axis via upregulation of VEGFR3 expression mediates hypoxia-induced pathological retinal neovascularization. 32406953_Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer progression via exosome-mediated miR-95 transfer. 32510596_JunB can enhance the transcription of IL-8 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 32582999_Activating transcription factor 3 inhibits endometrial carcinoma aggressiveness via JunB suppression. 32945523_miR3133 inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis by targeting the JUNB/VEGF pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 33450132_JUNB-FBXO21-ERK axis promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting autophagy. 34007044_JunB is a key regulator of multiple myeloma bone marrow angiogenesis. 34519628_Circular RNA PUM1 (CircPUM1) attenuates trophoblast cell dysfunction and inflammation in recurrent spontaneous abortion via the MicroRNA-30a-5p (miR-30a-5p)/JUNB axis. 34921867_Skp2 promotes APL progression through the stabilization of oncoprotein PML-RARalpha and the inhibition of JunB expression. 35616875_AP-1 Subunit JUNB Promotes Invasive Phenotypes in Endometriosis. 35726195_FGF7/FGFR2-JunB signalling counteracts the effect of progesterone in luminal breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000052837 |
Junb |
773.311133 |
3.7890774119 |
1.921847 |
0.063823225 |
941.878299 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000773052132685670244597347790330023566291812264105487002226386209871890802415631075708505429080449858376598432487365957155155 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000745767939767352451730719058372262743349223931277706048099095190250279224971406852652076891071424861234532733370693159349237 |
Yes |
No |
1241.5889820 |
44.5591554 |
330.0241584 |
10.0966928 |
| ENSG00000171236 |
116844 |
LRG1 |
protein_coding |
P02750 |
|
Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The leucine-rich repeat (LRR) family of proteins, including LRG1, have been shown to be involved in protein-protein interaction, signal transduction, and cell adhesion and development. LRG1 is expressed during granulocyte differentiation (O'Donnell et al., 2002 [PubMed 12223515]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:116844; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0034713]; type II transforming growth factor beta receptor binding [GO:0005114]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; keratinocyte migration [GO:0051546]; leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell [GO:0061756]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in wound healing [GO:0060054]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010838]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells [GO:0035313] |
12223515_cDNA clones for human leucine-rich alpha2-glycoprotein were isolated. LRG expression was up-regulated during neutrophil differentiation but down-regulated during monocytic differentiation. The hLRG gene was localized to chromosome 19p13.3. 16699948_Mass spectrometry analysis identified the serum inhibitory factor as leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein-1 in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay . 17194537_These results also indicate that the CSF level assay of TGF-beta1, TbetaR-II and LRG is useful for the diagnosis of patients with INPH, and TGF-beta1, TbetaR-II and LRG may be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. 17583700_Several indirect lines of evidence suggest a role for LRG in implantation/decidualization. 19324010_These results strongly suggest that LRG was a secretory type 1 acute-phase protein whose expression was up-regulated by the mediator of acute-phase response. 19851871_Serum LRG when bound to extracellular Cyt c that is released from apoptotic cells acts as a survival factor for lymphocytes and possibly other cells that are susceptible to the toxic effect of extracellular Cyt c. 20442399_autologous Cyt c is an endogeneous ligand for LRG and PLIbeta and these serum proteins neutralize the autologous Cyt c released from the dead cells 21282491_LRG1 was identified as a serum biomarker that accurately identifies patients with heart failure. 21557262_Screened for NSCLC-related proteins in urinary exosomes by comparing urinary exosomes proteome of normal controls and NSCLC patients. The LRG1 was found to be expressed at higher levels in urinary exosomes and lung tissue of NSCLC patients. 22116432_This study demonistrated that LRG expression in resident astrocytes increased with age. 22277732_Increased plasma levels of the APC-interacting protein MAPRE1, LRG1, and IGFBP2 precede a diagnosis of colorectal cancer in women 22374925_High Serum leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein is associated with ulcerative colitis. 23284758_Overexpression of serum LRG1 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 24058569_Human LRG (hLRG) concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was measured and hLRG expression in post-mortem human cerebral cortex and mouse LRG (mLRG) in the brain were examined. 24760273_LRG1 potentially offered clinical value in directing personal treatment for endometrial carcinoma patients 25058884_Results suggest that serum LRG-1 is a promising biomarker for pancreatic cancer. 25277046_The blood proteins IGF1, IGF2, IBP2, IBP3 and A2GL have been proposed as indirect biomarkers for detection of GH administration and as putative biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis. 25589464_silencing the expression of LRG1 suppresses the growth of glioblastoma U251 cells in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that LRG1 may play a critical role in glioblastoma development, and it may have potential clinical implications in glioblastoma therapy. 25636050_Higher LRG1 is a significant predictor for arterial stiffness, endothelial function, and peripheral arterial disease. 25799488_Data found LRG1 as a promising candidate marker for detection of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) and the combination of LRG1 and CA125 showed improved performance to distinguish EOC including early stage EOC from non-cases compared to CA125. 25814288_LGR1 is involved in the inhibition of HCC metastasis. 26049667_Findings suggest that LRG1 promotes invasion and migration of glioma cells through TGF-beta signaling pathway. 26425690_Two of these proteins were verified in a separate patient cohort: values of CRP and LRG1 combined gave a highly significant indication of extended survival post one week of radiotherapy treatment. 26448929_Reanalysis of a total of 47 MDS patients revealed biomarker candidates, with alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein and leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein as the most promising candidates. 26517349_Data show that leucine-rich-alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 (LRG1) is markedly up-regulated and serves as an independent factor of poor outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 26856989_Results provided evidence for LRG1 function as a novel inducer of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer, which was at least partially through promotion of HIF-1alpha expression. 27378305_LRG1 may be a key regulatory factor of allergic responses. 27491861_the expression of 3 miRs and 9 mRNAs associate with the PIK3CA status. Expression of LRG1 is independent of luminal (A or B) subtype, decreased after neo-adjuvant aromatase inhibitor treatment. 27611322_These findings suggest that sputum LRG is a promising biomarker of local inflammation in asthma. 28098902_Downregulation of LRG1 is associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 28179066_Serum leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein (LRG) levels were significantly elevated in psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis compared with healthy controls. Serum LRG correlated positively with CRP levels in patients with psoriasis vulgaris and in patients with psoriatic arthritis. These results indicate that serum LRG concentrations can be a useful alternative biomarker for psoriasis. 28202345_combination of modified whole blood LRG1 mRNA levels, plasma LRG1 protein and Alvarado score at the ED may be useful to diagnose simple and complicated acute appendicitis from other causes of abdominal pain 28358372_This study shows that TNF-alpha is the predominant proinflammatory cytokine that induces the secretion of LRG1. LRG1 contributes to angiogenesis-coupled de novo bone formation by increasing angiogenesis and recruiting MSCs in the subchondral bone of osteoarthritis joints. 28376129_LRG1 plays a crucial role in the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) by regulating RUNX1 expression. LRG1 may be a potential detection biomarker as well as a marker for monitoring recurrence and therapeutic target for CRC. 28697446_The detection of LRG1 in accordance with the DeltaRct value (electron-transfer resistance at the electrode surface) of the sensor layer incorporating LRG1 BP3 peptides showed a statistically significant difference (p |
ENSMUSG00000037095 |
Lrg1 |
74.697688 |
0.2715189423 |
-1.880875 |
0.210521015 |
82.360122 |
0.00000000000000000011341916255437292608301978128487178941507577836525998658812053321298662922345101833343505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000988816798170433778534815137257809662557909359767460179269082942710156203247606754302978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.0338831 |
4.3323221 |
118.5969156 |
9.7240551 |
| ENSG00000171241 |
79801 |
SHCBP1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEM2 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in signaling pathways governing cellular proliferation, cell growth and differentiation. May be a component of a novel signaling pathway downstream of Shc. Acts as a positive regulator of FGF signaling in neural progenitor cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z179}. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable SH2 domain binding activity. Predicted to be involved in fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway and regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm; midbody; and spindle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79801; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; midbody [GO:0030496]; spindle [GO:0005819]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008543]; regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:2000177] |
23804634_The central region of SHCBP1 was found to bind to measles virus C protein, as well as the phosphoprotein, but the two viral proteins did not compete for SHCBP1 binding. 24289556_Knockdown of SHCBP1 induced cell cycle delay. 25486361_This study gives novel insight into the role of SHCBP in cytokinesis completion. 27129942_Immunohistochemical analysis revealed SHCBP1 was significantly up-regulated in breast cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues (82 of 128, 64%). Over-expressed SHCBP1 was correlated with advanced clinical stage and poorer survival. Ablation of SHCBP1 inhibited the proliferation in vitro. 27572315_Data indicate that the oncogene SS18-SSX1 promotes tumorigenesis by increasing the expression of SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1 (SHCBP1), which normally acts as a tumor promoting factor. 29020987_SHCBP1 was found highly expressed in SS cell lines and tissues, which was linked to the poor clinical prognosis and was implicated in SS aggressive progression. SHCBP1 regulated invasion and metastasis by modulating the TGF-beta1/Smad signaling pathway and promoting the EMT in SS. 29745440_SHCBP1, a member of Src homolog and collagen homolog (Shc) family, was significantly overexpressed in glioma tissues and glioma cell lines compared to the corresponding normal tissues and cells. Ectopic overexpression of SHCBP1 promoted glioma cell migration and invasion, whereas knockdown of endogenous SHCBP1 had the opposite effects. SHCBP1 promoted aggressiveness in gliomas by activating the NF-kappaB signaling path... 30177836_study establishes a novel convergence between EGFR and beta-catenin pathways and highlights a potential significance of SHCBP1 as a prognostic biomarker and a therapeutic target. 30592290_Study revealed that SHCBP1 may play a role in cell growth and metastasis and may be a potential diagnosis biomarker and therapeutic target for gastric cancer. 31472149_High SHCBP1 expression is associated with cisplatin induced apoptosis resistance, migration and invasion through activating Wnt pathway in lung cancer. 32003010_SOX2-induced upregulation of lncRNA LINC01561 promotes non-small-cell lung carcinoma progression by sponging miR-760 to modulate SHCBP1 expression. 32351983_PART1 and hsa-miR-429-Mediated SHCBP1 Expression Is an Independent Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Glioma Patients. 32447485_SHCBP1 was significantly upregulated in PCa tissues compared with BPH tissues. Patients with a higher expression of SHCBP1 were associated with poor survival outcomes than those with a lower expression of SHCBP1. 32769441_SHCBP1 Promotes the Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via the TGFbeta Pathway. 32791092_A four-gene signature in the tumor microenvironment that significantly associates with the prognosis of patients with breast cancer. 33515675_SHCBP1 interacting with EOGT enhances O-GlcNAcylation of NOTCH1 and promotes the development of pancreatic cancer. 33990570_Hyperactivation of HER2-SHCBP1-PLK1 axis promotes tumor cell mitosis and impairs trastuzumab sensitivity to gastric cancer. 34247545_Long Non-Coding RNA TP53TG1 Upregulates SHCBP1 to Promote Retinoblastoma Progression by Sponging miR-33b. 35013128_EGF-induced nuclear translocation of SHCBP1 promotes bladder cancer progression through inhibiting RACGAP1-mediated RAC1 inactivation. |
ENSMUSG00000022322 |
Shcbp1 |
259.938444 |
2.1089245072 |
1.076507 |
0.159260354 |
45.220801 |
0.00000000001760255076196483473189018235767412841330514794435657677240669727325439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000096120476968775790488198133319162333107477103055771294748410582542419433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
366.9331705 |
36.1601814 |
175.0089229 |
12.8794308 |
| ENSG00000171246 |
4884 |
NPTX1 |
protein_coding |
Q15818 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in mediating uptake of synaptic material during synapse remodeling or in mediating the synaptic clustering of AMPA glutamate receptors at a subset of excitatory synapses. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
NPTX1 is a member of the neuronal pentraxin gene family. Neuronal pentraxin 1 is similar to the rat NP1 gene which encodes a binding protein for the snake venom toxin taipoxin. Human NPTX1 mRNA is exclusively localized to the nervous system. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4884; |
glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic cleft [GO:0043083]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; cellular response to potassium ion [GO:0035865]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; mitochondrial fragmentation involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043653]; mitochondrial transport [GO:0006839]; neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane [GO:0099645]; postsynaptic density assembly [GO:0097107]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0098962] |
16115696_The purpose of the present study was to assess the toxic effect of taipoxin in SCLC-cell lines and to determine if toxicity correlates to NPR and NP1 and NP2 expression levels. 17151277_Neuronal pentraxin 1 transgene is a key factor for the synapse loss, the neurite damage, and the apoptotic neuronal death evoked by amyloid-beta protein, which regulates NP1 expression. 24529709_NPTX1 binds and inhibits TDGF1, and reduces both Nodal and BMP signaling. 25029423_Long acting progestin contraceptive-enhanced NPTX1 secretion and reactive oxygen species generation in endometrial stromal cells impair endometrial endothelial cells survival resulting in a loss in vascular integrity. 25053281_NPTX1 was significantly associated with bipolar disorder. 25498504_Taken together, these results demonstrate that NP1 gene is a target of as hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and it regulates NP1 expression by binding to hypoxia responsive elements in its promoter region. 25646694_These results suggest that NPTX1 hypermethylation and consequent mRNA changes might be an important molecular mechanism in lung cancer. 26038830_findings suggest that lower NARP mRNA expression contributes to lower excitatory drive onto parvalbumin interneurons in schizophrenia. 29345391_NPTX1 is down-regulated in colon cancer. In addition, NPTX1 inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells via decreasing cyclin A2 and CDK2. 29501530_Relative to normal elderly, plasma NP1 was elevated in patients with mild cognitive impairment and elevated further in the subset that progressed to early-stage Alzheimer's disease. 31113871_Findings indicate that neuronal pentraxin 1 (NPTX1) is a potential clinical therapeutic target. 31118494_MiR-4295 facilitates cell proliferation and metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by targeting NPTX1. 32255252_Long non coding RNA SLC26A4-AS1 exerts antiangiogenic effects in human glioma by upregulating NPTX1 via NFKB1 transcriptional factor. 34212686_Downregulation of NPTX1 induces cell cycle progression through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in breast cancer. 34788392_NPTX1 mutations trigger endoplasmic reticulum stress and cause autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia. 35216489_Tryptophan Metabolites Regulate Neuropentraxin 1 Expression in Endothelial Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000025582 |
Nptx1 |
97.928165 |
0.4339236971 |
-1.204487 |
0.174654470 |
48.254773 |
0.00000000000374285963721116519103381332274292614924193767222959650098346173763275146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000021454216794266719499414103636972055676179760297372922650538384914398193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.3864143 |
6.5835895 |
142.4441340 |
9.7787744 |
| ENSG00000171365 |
1184 |
CLCN5 |
protein_coding |
P51795 |
FUNCTION: Proton-coupled chloride transporter. Functions as antiport system and exchanges chloride ions against protons (PubMed:20466723). Important for normal acidification of the endosome lumen. May play an important role in renal tubular function. The CLC channel family contains both chloride channels and proton-coupled anion transporters that exchange chloride or another anion for protons. The absence of conserved gating glutamate residues is typical for family members that function as channels (Probable). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20466723, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiport;ATP-binding;CBS domain;Cell membrane;Chloride;Disease variant;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Ion transport;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the ClC family of chloride ion channels and ion transporters. The encoded protein is primarily localized to endosomal membranes and may function to facilitate albumin uptake by the renal proximal tubule. Mutations in this gene have been found in Dent disease and renal tubular disorders complicated by nephrolithiasis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:1184; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; antiporter activity [GO:0015297]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; solute:proton antiporter activity [GO:0015299]; voltage-gated chloride channel activity [GO:0005247]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; renal system process [GO:0003014] |
12631345_ClC-5 mutations are associated with modifications in the polarity and expression of H+-ATPase, but not ultrastructural alterations in kidney proximal tubule cells 12631358_crucial role for the interaction between the two subunits at the interface of the homodimeric hCLC-5. 12637640_CLCN5 gene mutation in spanish patients with Dent's disease is associated with this renal tubulopathy. 12886045_Dent's disease phenotype may be explained by mutations that affect so far unknown regulating elements of the CLCN5 gene or another gene(s), probably encoding CLC-5 accessory protein(s) 12904289_interaction between the C-terminal tail of ClC-5 and cofilin, an actin-associated protein that is crucial in the regulation of albumin uptake by the proximal tubule 13679301_ClC-5 channel activity can be restored for specific Dent's mutations by expression of the missing portion of the ClC-5 molecule. 14569459_the first report of a retrotransposon insertion in the CLCN5 gene associated with Dent's disease 14675051_The segmental expression of ClC-5 and H+-ATPase is essentially achieved during early nephrogenesis, in parallel with the onset of glomerular filtration 15086899_mutation analysis of the coding region of CLCN5 by DNA sequencing in X-linked nephrolithiasis 15571186_Genetic analysis that confirmed the diagnosis pf Dent's disease and revealed a novel mutation in the CLCN5 gene. 15692680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15702377_We conclude that overexpression of ClC-5, specifically amino acids 347-647, can alter the normal translation or trafficking of ENaC and other ion transport proteins by a mechanism that is independent of the chloride conductance of ClC-5. 15719255_first report to characterize mutations in the CLCN5 gene in Korean patients with Dent's disease; a novel mutation, E609X was reported 16034421_coupled Cl-/H+ transport of ClC-4 and ClC-5 is of significant magnitude in vivo 16686597_both nucleotides induce an increase in thermal stability of ClC-5 Ct, supporting the suggestion that both nucleotides interact with and modify the biophysical properties of this prot 16807762_CLCN5 mutation should be considered irrespective of the presence of hypercalciuria in a patient with low molecular weight proteinuria. 16822791_Dent's disease is an inherited tubulopathy caused by CLCN5 gene mutations. 17195847_Study reports the structures of the cytoplasmic domain of the human transporter ClC-5 in complex with ATP and ADP; the nucleotides bind to a specific site in the protein. 17262170_Missense mutation W547G can also alter the expression levels of a CLCN5 mRNA splicing variant. 18019214_abnormalities in the CLCN5 and OCRL1 genes in Dent's disease [review] 18025833_A novel G333R CLCN5 mutation caused defective expression of megalin, cubilin, and Dab2 in a patient with Dent's disease 18184518_CLCN5 mutation in Dent's disease 18322545_CAIII expression is upregulated in kidney cortex samples from the end-stage kidney of a patient with Dent's disease owing to the G506E mutation of CLCN5 18540256_Frameshift mutation in CLCN5 protein is associated with Dent disease. 19019917_three classes of Dent's disease-causing CLC-5 mutations: class 1 leads to endoplasmic reticulum retention and degradation of CLC-5; class 2 causes defects in endosomal acidification; class 3 alters endosomal distribution of CLC-5 19131966_Nitrate uncoupled proton transport but mutating the highly conserved serine 168 to proline in ClC-5, led to coupled NO3(-)/H+ exchange. 19546586_six different truncating mutations cause premature termination of protein translation and result in a non-functional truncated protein 19546591_Studies showed that three novel CLC-5 mutations were identified, and mutations in OCRL1, CLC-4 and cofilin excluded in causing Dent's disease. 19657328_Report novel CLCN5 mutations in patients with Dent's disease result in altered ion currents or impaired exchanger processing. 19673950_Novel mutations of the CLCN5 gene including a complex allele and A 5' UTR mutation in Dent disease 1. 19713962_show that the direct application of ATP, ADP and AMP in inside-out patch experiments potentiates the current mediated by ClC-5 with similar affinities. The nucleotides increase the probability of ClC-5 to be in an active, transporting state. 19806368_A nonsense codon of CLCN5 was found in four unrelated young males with Dent's disease. Focal glomerusclerosis was also confirmed after kidney biopsy. 19940036_Interaction with KIF3B alters CLC-5 cell surface expression, chloride current, and alters albumin endocytosis. Interaction with KIF3B facilitates microtubular transport and endocytosis of CLC-5-containing vesicles away from cell surface. 20049483_We discuss the putative role of ClC-5 in receptor-mediated endocytosis and protein uptake by the proximal renal tubule and the possible molecular and cellular consequences of disease-causing mutations[review] 20421284_Suggest that CLC-5 is directly involved in endosomal acidification by exchanging endosomal Cl(-) for H(+). 20501796_data suggest that voltage sensing is an intrinsic property of the CLC-5 protein and that permeant anions, particularly Cl(-), modulate a voltage-dependent transition to an activated state from which Cl(-)/H(+) exchange can occur 20513761_Propose that protons bind to the extracellular gating glutamate E211 in CLC-5 to block transport. 20680351_A novel CLCN5 mutation is reported in a boy with Bartter-like syndrome and partial growth hormone deficiency. 21173145_ATP induces conformational changes in the carboxyl-terminal region of ClC-5. 21305656_Heterogeneity in the processing of CLCN5 mutants related to Dent disease. 22267722_protonation of the gating glutamate 211 at the central anion-binding site of ClC-5 is mediated by the proton glutamate 268. 22824269_The molecular events underlying the transient currents of ClC-5 emerging from these results can be explained by an inward movement of the side chain of Glu(ext), followed by the binding of extracellular Cl(-) ions. 23029130_ClC-5 overexpression found in biopsies of proteinuric patients suggests that proteinuria may play a part in its expression and that podocytes are likely to have a key role in albumin handling in proteinuric states 23211344_Case Report: computer simulation analysis of CIC-5 missense mutations in Dent's disease. 23566014_Certain misprocessing mutations in CLC-5 chloride channels alter intramolecular interactions within the full-length protein, ensuring that they do not elicit the unfolded protein response. 23572577_Dent disease-causing CLC-5 mutations have differing effects on endosomal acidification and receptor-mediated endocytosis that may not be coupled. 24081861_Dent disease is caused by mutations in at least two genes, i.e. CLCN5 and OCRL1, and its genetic background and phenotypes are common among European countries and the USA. 24099800_These results elucidate the biophysical properties of ClC-5 and contribute to the understanding of its physiological role. 24428215_study described a single Chinese family with Dent disease, and findings suggest that a novel frameshift mutation (c. 246delG) in exon 5 of the CLCN5 gene was responsible for Dent disease in this case 25001568_structural complexity of the CLCN5 5'UTR region 25124980_A novel mutation in the CLCN5 gene was identified in our patient with Dent's disease. 25907713_Previously reported mutations and their associated phenotype in 377 male patients with Dent disease are reviewed and described phenotype and novel and recurrent mutations in a large cohort of 117 Dent disease patients belonging to 90 families. 27117801_we carefully investigated the functional effects of four CLC-5 mutations, including three missense mutations (S244L, R345W, T657S) and one nonsense mutation (Q629X) 27174143_A diagnosis of Dent disease was established in 19 boys from 16 families by the presence of loss of function/deleterious mutations in CLCN5 or OCRL1. 28348980_These data suggest that ClC-5 enhances the cytotoxic action of Clostridium difficile toxins TcdA and TcdB by accelerating the acidification and maturation of vesicles of the early and early-to-late endosomal system. 28383812_Novel CLCN5 (c.1205G>A, p.W402*) and FGF23 (c.526C>G, p.R176G) mutations were found in two patients from the remaining two families 28815356_We demonstrated that most Polish patients with DD carry CLCN5 mutations, and they usually present with proteinuria and hypercalciuria. 28899456_Low CLC5 expression is associated with chemoresistance in Multiple Myeloma. 29058463_Expression of ClC-5 carrying Dent's disease-associated mutations in HEK293 cells had varying effects: (1) no detectable expression of mutant protein; (2) retention of a truncated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum; or (3) diminished protein expression with normal distribution in early endosomes. 30044661_ittle, if any, active H(+) transport, supported by ATP, occurred. Major transporters include cariporide-sensitive NHE1 in basolateral membranes and ClC3 and ClC5 in apical osteoblast membranes. The mineralization inhibitor levamisole reduced bone formation and expression of alkaline phosphatase, NHE1, and ClC5. 30852663_Prevalence of low molecular weight proteinuria and Dent disease 1 CLCN5 mutations in proteinuric cohorts. 31054069_ClC-5 upregulation ameliorates renal fibrosis via inhibiting NF-kappaB/MMP-9 pathway signaling activation, suggesting that ClC-5 may be a novel therapeutic target for treating renal fibrosis and chronic kidney disease. 31674016_Multicenter study of the clinical features and mutation gene spectrum of Chinese children with Dent disease. 31852738_Cl(-) and H(+) coupling properties and subcellular localizations of wildtype and disease-associated variants of the voltage-gated Cl(-)/H(+) exchanger ClC-5. 32019767_CLCN5 5'UTR isoforms in human kidneys: differential expression analysis between controls and patients with glomerulonephritis. 32201916_Functional analysis of suspected splicing variants in CLCN5 gene in Dent disease 1. 32495484_Phenotypic spectrum and antialbuminuric response to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin receptor blocker therapy in pediatric Dent disease. |
ENSMUSG00000004317 |
Clcn5 |
109.453465 |
2.5432153470 |
1.346654 |
0.168620357 |
64.269237 |
0.00000000000000108527091780362646297639156495704319953073059730475069528665699181146919727325439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000007757190676407518771045985136048910097892293558086151961106224916875362396240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
160.4876108 |
16.0307089 |
63.5354477 |
5.0727941 |
| ENSG00000171368 |
11076 |
TPPP |
protein_coding |
O94811 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of microtubule dynamics that plays a key role in myelination by promoting elongation of the myelin sheath (PubMed:31522887). Acts as a microtubule nucleation factor in oligodendrocytes: specifically localizes to the postsynaptic Golgi apparatus region, also named Golgi outpost, and promotes microtubule nucleation, an important step for elongation of the myelin sheath (PubMed:31522887, PubMed:33831707). Required for both uniform polarized growth of distal microtubules as well as directing the branching of proximal processes (PubMed:31522887). Shows magnesium-dependent GTPase activity; the role of the GTPase activity is unclear (PubMed:21995432, PubMed:21316364). In addition to microtubule nucleation activity, also involved in microtubule bundling and stabilization of existing microtubules, thereby maintaining the integrity of the microtubule network (PubMed:17105200, PubMed:17693641, PubMed:18028908, PubMed:26289831). Regulates microtubule dynamics by promoting tubulin acetylation: acts by inhibiting the tubulin deacetylase activity of HDAC6 (PubMed:20308065, PubMed:23093407). Also regulates cell migration: phosphorylation by ROCK1 inhibits interaction with HDAC6, resulting in decreased acetylation of tubulin and increased cell motility (PubMed:23093407). Plays a role in cell proliferation by regulating the G1/S-phase transition (PubMed:23355470). Involved in astral microtubule organization and mitotic spindle orientation during early stage of mitosis; this process is regulated by phosphorylation by LIMK2 (PubMed:22328514). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17105200, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17693641, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18028908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20308065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21316364, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21995432, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22328514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23093407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23355470, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26289831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31522887}. |
Cell cycle;Cell division;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Mitosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Enables several functions, including GTPase activity; magnesium ion binding activity; and protein homodimerization activity. Involved in several processes, including microtubule cytoskeleton organization; negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation; and positive regulation of protein polymerization. Located in several cellular components, including mitochondrion; mitotic spindle; and perinuclear region of cytoplasm. Colocalizes with microtubule and microtubule bundle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:11076; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; postsynaptic Golgi apparatus [GO:0150051]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; tubulin binding [GO:0015631]; astral microtubule organization [GO:0030953]; cell division [GO:0051301]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; microtubule nucleation by microtubule organizing center [GO:0051418]; microtubule polymerization [GO:0046785]; myelin assembly [GO:0032288]; negative regulation of tubulin deacetylation [GO:1904428]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048709]; positive regulation of myelination [GO:0031643]; positive regulation of protein polymerization [GO:0032273]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0070507] |
15564385_TPPP/p25 has a role in stabilization of physiological microtubular ultrastructures and cell survival 15590652_perhaps p25alpha plays a pro-aggregatory role in the common neurodegenerative disorders hall-marked by alpha-synuclein aggregates 16879710_Recombinant TPPP plays an important role for tubulin-related transport in developing, myelinating oligodendrocytes. 17027006_identified glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a new interacting partner of TPPP/p25 within the alpha-synuclein positive Lewy body 17693641_ERK2 can regulate TPPP activity via the phosphorylation of Thr(14) and/or Ser(18) in its unfolded N-terminal tail 17823288_Myelin basic protein and p25alpha colocalize in myelin in normal human brains. 18025801_data suggest that gain of 5p15.33 (TPPP and ZDHHC11) may become a potential biomarker identifying high-risk patients with disease progression in bladder cancer. 18028908_LIMK1 phosphorylation of p25 blocks p25 activity, thus promoting microtubule disassembly. 18204489_we review evidence pertaining to the role of GSK3 in the myocardium and discuss effects of genetic manipulation of GSK3 activity in vivo--REVIEW 18311157_GSK-3 is involved in the regulation of, and cross-talk between, two major forms of synaptic plasticity, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor dependent long-term potentiation and NMDAR-dependent long-term depression--REVIEW 18728964_contribution of GSK3 in growth regulation of myeloma cells 19382230_Data suggest that the intracellular level of TPPP/p25 influences the cell differentiation, proliferation and the formation of protein aggregates, and consequently, the etiology of central nervous system diseases. 19698783_The RING domain of XIAP (and probably cIAP-1 and cIAP-2) associates with GSK3, GSK3 acts upstream of the apoptosome to promote intrinsic apoptosis, and the association between XIAP and GSK3 may block the pro-apoptotic function of GSK3. 20308065_TPPP/p25 promotes tubulin acetylation by inhibiting histone deacetylase 6 20849899_Although serine-129 phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein facilitates TPPP-mediated alpha-SYN oligomerization, this modification does not seem to play an inevitable role in the early step of alpha-SYN oligomer formation in a cellular model of multiple system atrophy. 21565174_these investigations suggest the CSF-TPPP/p25 level could become diagnostic marker of MS and other demyelination-related diseases. 21616478_This study demonistrated that p25 is generated during spatial memory formation. 21832049_Interactions of pathological hallmark proteins: tubulin polymerization promoting protein/p25, beta-amyloid, and alpha-synuclein. 21857997_Data show that TPPP may work as a protective factor for cells against the damage effects of the accumulation of abnormal forms of PrPs, besides its function as an agent for dynamic stabilization of microtubular ultrastructures. 21900749_GSK3 has a significant role in maintaining repression of growth factor-inducible genes during quiescence. CREB, NFkB and AP-1 mediate this regulation of gene expression by GSK-3. 21995432_Binding of Zn(2) bivalent cation to structurally disordered TPPP/p25 influences TPPP/p25-promoted tubulin polymerization and GTPase activity. 22083140_Wnt induces the phosphorylation of LRP6 which consequently access the catalytic pocket of GSK3 as pseudo-substrates, thus directly blocking its activity against beta-catenin. 22326478_The authors conclude that the modest structural changes that p25alpha undergoes can promote weak intermolecular contacts and that polyanions such as heparin play a central role in stabilizing these aggregates. 22328514_The RhoA-ROCK-LIMK2-TPPP pathway controls metaphase spindle-orientation; TPPP colocalizes with LIMK2 at the mitotic spindle. 23161404_GSK3 promotes the mitochondrial translocation of p53, enabling its interaction with Bcl2 to allow Bax oligomerization and the subsequent release of cytochrome C. 23355470_dual Rock and Cdk phosphorylation of Tppp1 inhibits its regulation of the cell cycle to increase cell proliferation 23727580_results suggest that ROCK regulates beta-catenin stability in cells via preventing TPPP1-mediated inhibition of HDAC6 activity, to reduce its acetylation and degradation via phosphorylation by CK1 and GSK3beta 24655651_Epigenetic changes in TPPP, in combination with experiences of maltreatment, may confer risk for depression in children. 25445539_suggest that the zinc as a specific divalent cation could be involved in the fine-tuning of the physiological TPPP/p25 level counteracting both the enrichment and the lack of this protein leading to distinct central nervous system diseases 26289831_the central folded domain of TPPP/p25 following binding to microtubules can drive s homotypic protein-protein interactions leading to bundled microtubules. 26317805_Results reveal a link between p25 and BACE1 in Alzheimer disease (AD) brains and suggest that upregulated Cdk5 activation by p25 accelerates AD pathogenesis by enhancing BACE1 activity via phosphorylation. 27258419_This study demonstrated that the AAV9-mediated p25 overexpression mouse model, which is a practical model exhibiting neurodegeneration-like pathological and behavioral changes. 27630306_TPPP may have a role in poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma 27671864_TPPP/p25 is co-enriched and co-localized with alpha-synuclein in brain inclusions of Parkinson's disease patients. Interaction of alpha-synuclein with various deletion mutants and fragments of TPPP/p25 were characterized. 28074911_The objective of this paper is to highlight a critical point of a recently published Skoufias's paper in which the crucial role of the microtubules in TPPP/p25 dimerization leading to microtubule bundling was suggested. 28271739_The knowledge accumulated so far underlines the key roles of the multifunctional TPPP/p25 in both physiological and diverse pathological processes, consequently its validation as drug target sorely needs a new innovative strategy that is briefly reviewed here. 31505170_The binding of TPPP/p25 to a new binding site of DYNLL/LC8, outside the canonical binding groove, counteracted the TPPP/p25-derived hyperacetylation of the microtubule network. 31522887_These results demonstrate that TPPP on Golgi outposts are important for local microtubule nucleation and myelin sheath elongation. 31631174_This study revealed the low expression level of TPPP in pancreatic cancer cells. In addition, the high expression of TPPP promotes the invasion, migration and angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer cells. 34831132_Anti-Aggregative Effect of the Antioxidant DJ-1 on the TPPP/p25-Derived Pathological Associations of Alpha-Synuclein. 35062349_HERV-W Envelope Triggers Abnormal Dopaminergic Neuron Process through DRD2/PP2A/AKT1/GSK3 for Schizophrenia Risk. |
ENSMUSG00000021573 |
Tppp |
9.118900 |
0.3945400857 |
-1.341756 |
0.535317582 |
6.429435 |
0.01122442736276716562793254183816316071897745132446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021322078233519094203618493565954850055277347564697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0481266 |
1.9255839 |
12.9908567 |
3.1621211 |
| ENSG00000171408 |
27115 |
PDE7B |
protein_coding |
Q9NP56 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes (PubMed:10814504, PubMed:10872825). May be involved in the control of cAMP-mediated neural activity and cAMP metabolism in the brain (PubMed:10814504). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10814504, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10872825}. |
cAMP;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; 3',5'-cyclic AMP degradation; AMP from 3',5'-cyclic AMP: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10814504, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10872825}. |
The 3',5'-cyclic nucleotides cAMP and cGMP function as second messengers in a wide variety of signal transduction pathways. 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) catalyze the hydrolysis of cAMP and cGMP to the corresponding 5'-monophosphates and provide a mechanism to downregulate cAMP and cGMP signaling. This gene encodes a cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase, a member of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase family.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
hsa:27115; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; synapse [GO:0045202]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cAMP catabolic process [GO:0006198]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
19033455_higher levels than in normal B-cell of PDE7B are found in chronic lymphocytic leukemia 19850283_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20798984_As a first exploitation of this unique cohort, we identify three novel candidate dyslexia genes, ZNF280D and TCF12 at 15q21, and PDE7B at 6q23.3, by molecular mapping of the familial translocation with the 15q21 breakpoint. 21120911_High PDE7B is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 21362230_PDE7B mRNA expression is obviously higher in mantle cell lymphoma patients compared with normal controls and significantly correlates with unfavorable cytogenetic characteristics. 21383644_Genetic variation in the phosphodiesterase 7B is associated with bioavailability of testosterone enanthate. 21796143_The low frequency of this 5' untranslated region variant indicates that it does not explain the higher PDE7B expression in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) but it has the potential to influence other settings that involve a role for PDE7B. 23453122_higher expression of PDE7B might be a novel unfavorable prognostic indicator in MCL, which possess important clinical significance. 27092952_PDE7B polymorphisms were not associated with schizophrenia risk. 30209363_both low miR-200c and high PDE7B expression were correlated with poor survival of breast cancer patients. Our study supports a critical role of miR-200c/PDE7B relationship in triple-negative breast cancer tumorigenesis. 30323354_We have identified three novel loci (PDE7B, UBL3, and a new independent marker in CDKN2B-AS1) associated with BRCAX, and replicated previously reported SNPs (24 of 92) and moderate/high-penetrance (seven of 23) genes for Korean BRCAX. For the novel candidate loci, evidence supported their roles in regulatory function 31740742_The Prognostic Significance of PDE7B in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000019990 |
Pde7b |
17.279072 |
0.1064443809 |
-3.231828 |
0.511559904 |
49.234734 |
0.00000000000227093782417735027266328587153619664607689943025548018340487033128738403320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000013227719922990407172772909472568091115984856287468574009835720062255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.7373158 |
0.9819926 |
25.7870507 |
4.5266336 |
| ENSG00000171425 |
51545 |
ZNF581 |
protein_coding |
Q9P0T4 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51545; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
25.863091 |
2.0144298456 |
1.010372 |
0.335814823 |
9.111901 |
0.00253951804522403864691759700633610918885096907615661621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005507388531811168233542908012623229296877980232238769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.6573036 |
7.1635374 |
17.8255553 |
2.7767116 |
| ENSG00000171425_ENSG00000213015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
140.429122 |
0.3056999130 |
-1.709812 |
0.160488881 |
115.411031 |
0.00000000000000000000000000639653420120759190278671697230384397811484473076285433742874330663349393896743855236763920402154326438903808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000073301898144273339924743910477052724414068117438409511322767438786711467063605951466342958156019449234008789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.5391912 |
6.6726094 |
215.6519844 |
13.7769993 |
| ENSG00000171444 |
4163 |
MCC |
protein_coding |
P23508 |
FUNCTION: Candidate for the putative colorectal tumor suppressor gene located at 5q21. Suppresses cell proliferation and the Wnt/b-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Inhibits DNA binding of b-catenin/TCF/LEF transcription factors. Involved in cell migration independently of RAC1, CDC42 and p21-activated kinase (PAK) activation (PubMed:18591935, PubMed:19555689, PubMed:22480440). Represses the beta-catenin pathway (canonical Wnt signaling pathway) in a CCAR2-dependent manner by sequestering CCAR2 to the cytoplasm, thereby impairing its ability to inhibit SIRT1 which is involved in the deacetylation and negative regulation of beta-catenin (CTNB1) transcriptional activity (PubMed:24824780). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18591935, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19555689, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22480440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24824780}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene is a candidate colorectal tumor suppressor gene that is thought to negatively regulate cell cycle progression. The orthologous gene in the mouse expresses a phosphoprotein associated with the plasma membrane and membrane organelles, and overexpression of the mouse protein inhibits entry into S phase. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4163; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010633]; negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050680]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
11173969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18591935_MCC is a nuclear, beta-catenin-interacting protein that can act as a potential tumor suppressor in the serrated colorectal cancer pathway by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction. 19555689_Results identify MCC as a potential scaffold protein regulating cell movement and able to bind Scrib, beta-catenin and NHERF1/2. 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21279955_observed a significant association of the rs11283943 SNP with increased breast cancer risk in an Indian population 22213290_Promoter methylated MCC is associated with inflammatory bowel disease in colorectal cancer. 22480440_MCC regulates lamellipodia formation by binding to Scrib and its downstream partner Myosin-IIB in a multiprotein complex. 22542170_we have shown that promoter methylation of the APC gene does not extend to the neighbouring MCC gene in lung cancer, but LOH is found at both loci. 23913442_targeted by miR-494, which is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma 24824780_cytoplasmic MCC-DBC1 interaction sequesters DBC1 away from the nucleus, thereby removing a brake on DBC1 nuclear targets, such as SIRT1 25200342_Our results indicate that in sharp contrast to its tumor suppressive role in colorectal cancer, MCC functions as an oncogene in B cells 27208794_Alterations (deletion/methylation/mutation/expression) of MCC and CTNNBIP1 were analyzed in breast cancer patients (N=120) followed by expression/mutation analysis of beta-catenin. The alterations of MCC/CTNNBIP1 showed significant correlation with increased nuclear beta-catenin/p-beta-catenin(Y654) expression. 27226254_MCC might confer alterative genetic susceptibility to colorectal cancer in individuals with schizophrenia promising to shed more light on the relationship between schizophrenia and cancer progression. 28638476_Significantly, miR-4260 was increased in human colorectal cancer tissues with simultaneous downregulation of MCC and SMAD4. 29035389_Study described a novel tumor suppressor function of MCC in the regulation of E-cadherin mediated cell-cell adhesion in colorectal cancer cells. 29144123_Data suggest that millisecond dynamic changes in PDZ1 domain conformation are responsible for higher affinity of scribble PDZ1 for phosphorylated ligands; oligopeptide fragments of RPS6KA2 and MCC were used as ligands in these nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shift experiments. (RPS6KA2 = ribosomal protein S6 kinase 2; MCC = mutated in colorectal cancer protein) 29695640_This study provided new evidence of epistatic association of VAMP5 and MCC with increased risk of Hirschsprung disease |
ENSMUSG00000071856 |
Mcc |
21.720558 |
2.0037360875 |
1.002693 |
0.342591939 |
8.643123 |
0.00328298173264963662545956601945817965315654873847961425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006968192461016486059788288542904410860501229763031005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.4425412 |
5.7479904 |
14.7796242 |
2.2865340 |
| ENSG00000171451 |
92126 |
DSEL |
protein_coding |
Q8IZU8 |
|
Glycoprotein;Isomerase;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity. Predicted to be involved in chondroitin sulfate metabolic process and dermatan sulfate metabolic process. Predicted to be located in Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92126; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity [GO:0047757]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; chondroitin sulfate metabolic process [GO:0030204]; dermatan sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030208]; dermatan sulfate metabolic process [GO:0030205] |
20358601_DSEL was selected for study in 125 patients with diaphragmatic hernias, as it is involved in the synthesis of decorin, a protein that is required for normal collagen formation and that is upregulated during myogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000038702 |
Dsel |
10.722562 |
4.6314842920 |
2.211475 |
0.527788155 |
19.032300 |
0.00001285243640680507358270076578854457238776376470923423767089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000039811534389180037736121614555528935852635186165571212768554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.5438252 |
5.7371857 |
3.6359482 |
1.0774737 |
| ENSG00000171466 |
54811 |
ZNF562 |
protein_coding |
Q6V9R5 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54811; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000053211+ENSMUSG00000000103 |
Zfy1+Zfy2 |
126.587498 |
2.4232379480 |
1.276936 |
0.230052826 |
29.880145 |
0.00000004595951759785393054702975633614425721162888294202275574207305908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000186876716183009371363783128298929891997204322251491248607635498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
126.5633677 |
49.4172384 |
53.3865209 |
15.0016732 |
| ENSG00000171509 |
59350 |
RXFP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBX9 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for relaxins. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins leading to stimulation of adenylate cyclase and an increase of cAMP. Binding of the ligand may also activate a tyrosine kinase pathway that inhibits the activity of a phosphodiesterase that degrades cAMP. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the leucine-rich repeat-containing subgroup of the G protein-coupled 7-transmembrane receptor superfamily. The encoded protein plays a critical role in sperm motility, pregnancy and parturition as a receptor for the protein hormone relaxin. Decreased expression of this gene may play a role in endometriosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:59350; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; activation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007190]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; lung connective tissue development [GO:0060427]; myofibroblast differentiation [GO:0036446]; nipple morphogenesis [GO:0060658]; parturition [GO:0007567] |
11809971_capable of mediating the action of relaxin through an adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent pathway 14742692_Gene expression pattern and protein localization of LGR7 receptor in human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle. 15240635_Binding to and gene expression of the LGR7 relaxin receptor changes markedly with the phases of the menstrual cycle, suggesting a specific role for the hormone in the physiology of the human uterus. 15465925_Substitution of the relaxin-3 A-chain with the A-chain from insulin-like peptide 5 results in a chimeric peptide that selectively activates GPCR135 and GPCR142 over LGR7. 15566402_mouse and rat LGR7 share 85.2 and 85.7% identity with human LGR7 15695505_Data describe the conformation of the relaxin-binding site of the leucine-rich G-protein-coupled receptor 7. 15722441_Relaxin receptor (LGR7) increases the transcription of IGFBP-1 and prolactin in decidual and endometrial stromal cells through the promoter region containing multiple CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP) binding sites. 15956684_human LGR7 LDL-A module NMR studies; demonstration that calicum is required for the module to form a stable and correctly folded structure 15956698_increase in LGR7 expression and H2 relaxin binding in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle suggests a specific role for relaxin after ovulation in the human uterus 15956719_Amino acid sequence analysis of the LGR7 C-terminal tail and intracellular loops revealed multiple putative phosphorylation sites, suggesting that signal switching from Gs to Gi may occur after receptor phosphorylation 16051677_LGR7.10 splice variant is expressed at the cell surface, LGR7.2 is predominantly retained within cells and LGR7.1 is partially secreted. None stimulates cAMP production. 16303766_Relaxin stimulates leukocyte adhesion and migration through a relaxin receptor LGR7-dependent mechanism 16963451_The essential role of the LDLa module in LGR7 and LGR8 function is reported. 17148455_Specific residues in the N-terminal region of the RXFP1 receptor low density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLa) module play a key role in receptor activation. 17158203_The LDL-A module of LGR7 influences receptor maturation, cell surface expression, and relaxin-activated signal transduction. 18079195_The dominant-negative effects of the LGR7 splice variants expressed in the chorion and decidua could be functionally significant in the peripartal period. 18434306_analysis of truncated human relaxin-2 and -3 (H2 and H3) relaxin peptides and their binding and cAMP activities on RXFP1, RXFP2, and RXFP3 18533687_N-glycosylation at Asn-303 of RXFP1 was required for optimal intracellular cAMP signaling 18723073_RXFP1 is a constitutive dimer with negative cooperativity in ligand binding, and dimerization occurs through the 7TM domain, and that the ectodomain has a stabilizing effect on this interaction. 18843967_Decrease in the expression of relaxin receptor in the placenta is related with the occurrence and development of preeclampsia. 19116340_The autocrine/paracrine actions of relaxin in the decidua are under additional controls at the level of expression of its receptor on the surface of its target cells. 19279230_The apparent lack of classical regulation for RXFP1 and RXFP2 provides the molecular basis for the prolonged signaling and physiological actions of relaxin and related peptides 19416160_Point mutations of conserved residues or complete deletion of the LDL-A module resulted in loss of the cAMP response to relaxin 19416161_Ligand-mediated activation of RXFP1 and RXFP2 is a complex process involving various domains of the receptors 19416162_Relaxin binds to RXFP2 with high affinity, although INSL3 has a very poor affinity for RXFP1 19416175_Data tested the hypothesis that relaxin plays a role in endometriosis by comparing the expression of relaxin mRNA and its LGR7 (RXFP1) receptor mRNA in normal human endometrium to those in samples from patients with endometriosis. 19416177_The data suggest that luteal LGR7 mRNA expression may be regulated by relaxin and/or LH and that the corpus luteum is a target organ for relaxin. 19416186_Data show the expression of the relaxin receptor RXFP1 on the acrosome of human spermatozoa. 19416214_Data show that connective tissues as diverse as ligaments and basal lamina keratinocytes express RXFP1. These data lend support to our contention that relaxin affects ligament integrity and wound healing. 19416222_The expression of RXFP1, evaluated by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR, was downregulated in uterine fibroid tissues. 19416223_Data showm an accelerated progression of prostate cancer in TRAMP males with transgenic relaxin overexpression and a longer survival of TRAMP, RXFP1-deficient males. 19712722_These results suggest that relaxin activates PPARgamma activity and increases the overall response in the presence of PPARgamma agonists, and that this activation is dependent on the presence of RXFP1. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20655530_Endometrial expression of relaxin and relaxin receptor in endometriosis. 20664520_Uncovered is a pre-assembled, constitutively active G-protein-coupled receptor signalosome, that couples the relaxin receptor, relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1), to cAMP following receptor stimulation with sub-picomolar concentrations of peptide. 21324453_LGR7 is constitutively expressed in human endometrium, and an increased LGR7 immunostaining is demonstrated in the secretory phase, confirming the involvement of relaxin in the physiology of endometrium and suggesting its role in implantation. 22180889_[review] The relaxin receptor RXFP1 localizes in the acrosomal region of sperm. 22737225_relaxin-2 and its receptors RXFP1 and RXFP2 are expressed in GSV and their expression is significantly decreased in varicose GSV 22973049_These results provide new mechanistic insights into the binding and activation events of RXFP1 and RXFP2 by their native hormone ligands. 23024363_Identification of key residues essential for the structural fold and receptor selectivity within the A-chain of human gene-2 (H2) relaxin 23043266_The decreased cellular expression of relaxin-2 receptor RXFP1 in scleroderma skin might represent a pro-fibrotic factor and contribute to the substantial inefficacy of relaxin treatment in systemic sclerosis, as reported in the literature. 23212924_The development of a quantitative high-throughput platform for an RXFP1 agonist screen. 23302396_Report increased expression of RXFP1 in placenta of patients with placenta accreta. 23926099_the RXFP1 receptor lacking the LDLa module binds ligand normally but cannot signal through any characterized G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway 24640555_To create a tool to investigate the low-affinity interaction, a protein scaffold system displaying exoloops 1 and 2 from RXFP1 was designed. 24640556_RXFP1, is a complex G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)and has a rhodopsin-like 7 transmembrane helix region and a large ecto-domain containing Leucine-rich repeats and a Low Desnsity Lipoprotein Class-A module at the N-terminus. 24640558_We have developed and assessed four microRNA against human RXFP1. 24797570_RXFP-1 receptors are present at the ligament, cartilage, and synovium of the TM joint, indicating that it is a potential target for relaxin. This suggests that circulating relaxin may impact joint stability. 25389293_Using cells stably expressing RXFP1, we found that relaxin regulation of PPARgamma activity requires accumulation of cAMP and subsequent activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). 25547165_H2 relaxin amide is fully active at the relaxin receptor RXFP1 and thus dimerization is not required for biological activity. 25685807_Synthetic covalently linked dimeric form of H2 relaxin retains native RXFP1 activity and has improved in vitro serum stability. 26238605_RXFP1 gene expression was dysregulated in the anterior cingulate of bipolar patients. 26761440_The decreased expression of the endometrial RLX receptor in women with implantation failures, both in vitro fertilization failure and recurrent pregnancy loss, suggests that RLX may play a crucial role in the structural and functional changes of the endometrium during the window of implantation. 27088579_The complex binding mode of the peptide hormone H2 relaxin to its receptor RXFP1 has been deciphered. 27310652_Binding of relaxin to RXFP1 recruits G proteins with subsequent activation of adenylyl cyclase and elevation of cAMP. 28076930_Hormone receptor expression was concentrated in the fibroblasts, and RXFP1 was also evident in blood vessels and nerves 30709904_Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis lung fibroblasts transfected with anti-miR-144-3p had increased RXFP1 expression and reduced alpha-smooth muscle actin expression. 31419161_In mice expressing human RXFP1 gene treated with carbon tetrachloride, ML290 significantly reduced collagen content, alpha-smooth muscle actin expression, and cell proliferation around portal ducts. 32297670_The anti-fibrotic actions of relaxin are mediated through AT2 R-associated protein phosphatases via RXFP1-AT2 R functional crosstalk in human cardiac myofibroblasts. 34454945_Structural Insights into the Unique Modes of Relaxin-Binding and Tethered-Agonist Mediated Activation of RXFP1 and RXFP2. 34972106_Identification of a distal RXFP1 gene enhancer with differential activity in fibrotic lung fibroblasts involving AP-1. 36443381_Characterization of a new potent and long-lasting single chain peptide agonist of RXFP1 in cells and in vivo translational models. |
ENSMUSG00000034009 |
Rxfp1 |
215.937970 |
0.2711599119 |
-1.882784 |
0.118328963 |
266.162593 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000778533193282544355506212018438426690004837566190753763172257112071778072557720064671496662762913630882412077490635184646155783357487996909908414551026306638092933098960202187299728393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000198808822367653196092420473604839927601526147175879828664070452457578385532051758267305746998334417315698404612570553435409370866108413298682698958086412233114970149472355842590332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.5704978 |
7.6102530 |
350.9195510 |
17.1495502 |
| ENSG00000171522 |
5734 |
PTGER4 |
protein_coding |
P35408 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G(s) proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. Has a relaxing effect on smooth muscle. May play an important role in regulating renal hemodynamics, intestinal epithelial transport, adrenal aldosterone secretion, and uterine function. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor family. This protein is one of four receptors identified for prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). This receptor can activate T-cell factor signaling. It has been shown to mediate PGE2 induced expression of early growth response 1 (EGR1), regulate the level and stability of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA, and lead to the phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this receptor may be involved in the neonatal adaptation of circulatory system, osteoporosis, as well as initiation of skin immune responses. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5734; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; prostaglandin E receptor activity [GO:0004957]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of eosinophil extravasation [GO:2000420]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of integrin activation [GO:0033624]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051492]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to nematode [GO:0009624]; T-helper cell differentiation [GO:0042093] |
11782353_Involvement of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP(4) in colon carcinogenesis. 11876748_Placentally derived prostaglandin E2 acts via the EP4 receptor to inhibit IL-2-dependent proliferation of CTLL-2 T cells. 11948128_Increased PGE(2) synthesis in the adjacent stroma and its biological effect via EP(4) on the carcinoma cells may contribute to tumor growth and progression of gallbladder carcinoma. 12149218_effects of PGE2 on monocyte-derived dendritic cells were mediated through increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate by 2 of the known PGE2 receptors, EP2 and EP4 12215436_endogenous PGE(2) may modulate inflammation during atherogenesis and other inflammatory diseases by suppressing macrophage-derived chemokine production via the EP4 receptor 12228765_Activation of prostaglandin E2-receptor EP2 and EP4 pathways induces growth inhibition in human gastric carcinoma cell lines. 12566441_activation of PI3K/ERK signaling by the EP(4) receptors induces the functional expression of early growth response factor-1 (EGR-1). 14517215_COX-2 induction by bradykinin in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells is mediated by the cyclic AMP response element through a novel autocrine loop involving endogenous prostaglandin E2, EP2 receptor, and EP4 receptor 14709160_both beta-arrestin1 recruitment and the presence of Ser/Thr residues in the distal half of the C-terminal domain were necessary for maximal agonist-induced internalization 15100359_Vascular COX-2 was colocalized with prostaglandin E(2) EP4 receptors but not with EP2 receptors in kidney 15290741_EP3 and EP4 mediate different actions of PGE2 on mature human osteoclasts. Activation of EP4 receptors inhibits actin ring formation and activation of EP3 receptors increases number of lamellipodia. 15347673_Endothelin-1-induced prostaglandin E2-EP2 and EP4 signaling regulates vascular endothelial growth factor production and ovarian carcinoma cell invasion 15528329_Prostaglandin (PG)E2 induces an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP concentration in the T-leukemic cell line Jurkat via the E-prostanoid (EP)3 receptor. 15970595_PGE2 increases VEGF transcriptionally and involves the Sp-1 binding site via a cAMP-dependent mechanism involving EP2 and EP4 receptors 16020747_EP4 overexpression is associated with enhanced inflammatory reaction in atherosclerotic plaques 16428339_We concluded that PGE2 stimulates the BNP promoter mainly via EP4, PKA, Rap, and p42/44 MAPK. 16574793_seminal plasma and PGE(2) can promote the expression of tumorigenic and angiogenic factors, in cervical adenocarcinoma cells via the EP4 receptor, EGFR, and ERK1/2 signaling pathways 16857763_Presumably plays a key role for active patency of the human ductus arteriosus in the third trimester. 17046175_The EP4 receptor mediates IL-1 beta-induced catabolic metabolism via the p38 MAP kinase pathway in human tendon fibroblasts and may play a major role in the tendon's degenerative changes often seen in the later stages of tendinopathy. 17130837_Elevated activity in colorectal cancer cells increases resistance to spontaneous apoptosis and promotes anchorage-independent growth, but has no effect on proliferation. 17290397_EP4 mRNA was significantly higher in normal colon tissue compared with tumor tissue. 17447842_Genetic variants associated with Crohn disease risk in a locus modulating cis-acting regulatory elements of PTGER4. 17496729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17525067_participates in placentation through EVT invasion by up-regulating PGE2 production and PGE2 receptor expression in first trimester extravillous trophoblasts 17611676_Results show co-expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 receptors EP1, 2 and 4 in non-small cell lung cancer cells concomitant with the synthesis of PGE2. 17631291_Results reveal that egr-1 is a target gene of PGE(2) in HCA-7 cells and is regulated via the newly identified EP4/ERK/CREB pathway. 17877755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18005048_Expression of prostaglandin E(2) receptors (EP(2), EP(3), EP(4)), prostaglandin D(2) receptor (DP(2)), prostanoid thromboxane A(2) receptor (TP) and to a lesser extent EP(1) were observed in several hair follicle compartments. 18086382_herpes simplex virus type 1 infected mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells demonstrated a dramatic down-regulation of the expression of the EP2 and EP4 receptors 18254372_mRNA expressions of EP4 receptors observed in NCI-H292 cells and human nasal epithelial cells. 18270204_PGE(2)-EP4 signaling augments NF-kappaB1 p105 protein stability through EPRAP after proinflammatory stimulation, limiting macrophage activation. 18319253_CCR7 and the EP2/EP4 receptor signaling pathway are down-stream targets for COX-2 to enhance the migration of breast cancer cells toward LECs and to promote lymphatic invasion 18516068_Of the 4 EP receptor subtypes, smooth muscle cells in the human pulmonary vein express the EP4 and EP1 receptor subtypes. The relaxations induced by PGE2 in this vessel result from the activation of the EP4 receptor. 18797183_level of exptression in nasal polyps reversely correlates with chronic rhinosinusitis associated with bronchial asthma 18802112_The catabolic effects of prostaglandin E2 in osteoarthritis (OA) are specifically mediated via engagement of the EP4 receptor; of the four PGE2 receptors, only EP4 is up-regulated in OA vs normal cartilage. 18829529_PGE(2) induces angiogenesis in prostate cancer through EP2 and EP4. 19227010_EP4 is directly involved in regulation of proliferation and invasion of inflammatory breast cancer cells 19273625_PGE2 acts via prostaglandin receptor EP2- and EP4-mediated signaling and cyclic AMP pathways to up-regulate IL-23 and IL-1 receptor expression. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19407222_EP2 and EP4 receptor inhibition induces apoptosis of human endometriotic cells through suppression of ERK1/2, AKT, NFkappaB, and beta-catenin pathways and activation of intrinsic apoptotic mechanisms 19407341_PGE(2)-stimulated production of Abeta involves EP(4) receptor-mediated endocytosis of PS-1 followed by activation of the gamma-secretase, as well as EP(2) receptor-dependent activation of adenylate cyclase and PKA 19444759_These results suggest that IL-1beta induces EP4 receptor expression in chondrocytes by an autocrine mechanism that increases PGE2 production, whereas it reduces the expression of EP1 and EP2 via direct action. 19445930_The EP4 agonist PF-04475270 is a novel ocular hypotensive compound which is bioavailable following topical dosing and effectively lowers intraocular pressure. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19558693_PGE2 expression is mediated by EP4 receptor and may have a role in colorectal cancer 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19879194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014019_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20018632_PGE2 potently inhibits secretion of IFN-alpha by TLR-activated plasmacytoid dendritic cells, an effect mainly mediated by PG receptors E-prostanoid 2 and E-prostanoid 4 20086108_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20145136_EP4 overexpression, via AR activation, supports an important mechanism for castration-resistant progression of prostate cancer. 20222910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20353998_Increased expression of PGE2 in the lung tumor microenvironment may initiate a mitogenic signaling cascade composed of EP4, betaArrestin1, and c-Src which mediates cancer cell migration. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484658_EP1 and EP4 subtypes of prostaglandin E receptors (but not EP2 and EP3 receptors) may be involved in regulation of paracellular permeability in differentiated Caco-2 cell cultures. 20503412_regulate activities exhibited by IBC cells that have been associated with the aggressive phenotype. ep4 regulate invasion 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20551148_Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP2 and EP4 regulated gene expression profiling in ciliary smooth muscle cells. 20561984_Data seem to rule out a major influence of these polymorphisms on UC or RA predisposition. 20587336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20846217_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20970516_chronic activation of the EP receptor is associated with increased production of mediators likely to increase the pro-inflammatory milieu of airway epithelial cells. 21052031_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21071691_Results are suggestive of platelet EP4 receptor activation as a novel antithrombotic strategy. 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21081469_miR-16 and miR-21 are directly regulated by the transcription factor NF-kappaB and yet nicotine-promoted cell proliferation is mediated via EP2/4 receptors. 21111772_Data show that inhibition of PGE2 receptors EP2 and EP4 suppresses expression and/or activity of MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP7 and MMP9 proteins and increases expression of TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, and TIMP4 proteins. 21365278_EP4 receptors are expressed by human eosinophils, and are also present on infiltrating leukocytes in inflamed human nasal mucosa. 21424266_The role of PGE(2) in human atherosclerotic plaque on platelet EP(3) and EP(4) receptor activation and platelet function in whole blood. 21589857_found that PGE(2) and hypoxia independently induce expression of PTGER4 indicating two independent pathways regulating prostanoid receptor expression 21600299_Prostaglandin EP4 receptor enhances BCR-induced apoptosis of immature B cells 21681739_Data suggest that PGE(2) -EP4 signaling might be protective against allergic responses by inhibiting the interaction of eosinophils with the endothelium and might hence be a useful therapeutic option for controlling inappropriate eosinophil infiltration. 21683675_Prostaglandin E2 produced by Entamoeba histolytica signals via EP4 receptor and alters claudin-4 to increase ion permeability of tight junctions 21723865_findings indicate early divergence in the signaling pathways stimulated by strain and establish PGE2/EP4 as the pathway used by strain to regulate Sost expression. 21832044_Human kidney cells evidence increased EP4 and decreased Rap1GAP expression levels in the malignant compared with benign samples. 22037551_We identified new susceptibility loci for non-cardia gastric cancer at 5p13.1: rs13361707 in the region including PTGER4 and PRKAA1 22080750_PGE(2) enhances IL-8 production via EP4 receptor coupled to G(s) protein in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells 22276108_Neuroblastoma express all four forms of PGE(2) receptors. 22353936_EP-4 receptor expression is modulated at the post-transcriptional level by miR-101. 22362924_With HO as a model oxidant stress, stimulation of CFTR seems to involve PGE production and likely EP receptor activation in Calu-3 airway epithelial cells. 22580611_Targeted interference of EP2/EP4 signal to RalA.GTP may provide benefit to patients diagnosed with advanced kidney cancer. 22695889_The PTGER4 -1254 G allele demonstrated a higher frequency in aspirin-intolerant chronic urticaria (AICU)patients and lower promoter activity with decreased expression of PTGER4 and contributes to the development of AICU. 22704539_Activation of E-type prostanoid (EP) 4 receptor by PGE(2) or an EP4-selective agonist (ONO AE1-329) enhanced the barrier function of human microvascular lung endothelial cells. 22706114_This review article presents a short overview of experimental approaches aimed at manipulation of signaling via EP2 and EP4 receptors that could have therapeutic utility. 22732652_different EP receptors (EP(1-4)) to PGE(2)-induced anion secretion in human and mouse colon mucosa 22924768_PGE(2) -mediated NF-kappaB activation by simultaneous stimulation of EP(1) and EP(4) receptors induces maximal IL-8 promoter activation and IL-8 mRNA and protein induction 23090667_Data indicate that PGE2 regulates pancreatic stellate cell profibrotic activities via EP4 receptor, thus suggesting EP4 receptor as useful therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer to reduce desmoplasia. 23242524_Loss of function of EP2- and EP4-mediated PGE2 signaling inhibits adhesion of human endometriotic epithelial and stromal cells through integrin-mediated mechanisms. 23300802_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the PTGER4 gene regulatory sequences are strongly associated with Crohn's disease susceptibility. 23337716_PGE(2) coordinates control of IL-23 release in a dose-dependent manner by differential use of EP(2) and EP(4) receptors in LPS-activated MoDCs. 23364535_Human prostate cancer is associated with EP4 and EP2 overexpression and reduced EP3 expression. 23613969_This is the first report to demonstrate that Lymphocytic colitis is associated with increased TNF-alpha, INF-gamma and IL-8 concurrent with a marked up-regulation of EP4. 23619266_PGE2 induces MUC2 and MUC5AC expression in intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells via EP4-p38MAPK signaling. 23759445_PGE2 production induced by pathogen recognition receptors/p38 MAPK signaling is up-regulated by EP4-triggered signaling to maintain an effective PGE2 concentration. 24069348_JARID1A, JMY, and PTGER4 polymorphisms are related to ankylosing spondylitis in Chinese Han patients. 24133193_potential relevance of the COX-2/mPGES-1/EP-4 axis in the AAA-associated hypervascularization 24146253_Elastogenesis is spatially regulated by PGE-EP4 signaling in the ductus arteriosus. 24467603_Four single nucleotide polymorphisms in two genes in the PGE2 family, PTGES2 and PTGER4, were significantly associated with primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. 24793213_The PTGER4 modulating variant rs7720838 increases susceptibility for Crohn's disease and might resemble a risk factor for stricturing disease behavior. 24876670_the microsomal PGE2-synthase-1/PGE-receptor-4 axis is increased by smoking in human abdominal aortic aneurysms 24980222_mediates inhibitory effect of Prostaglandin E2 on nasal fibroblast migration 25109834_PGE2 upregulates c-myc in hepatocellular carcinoma via PTGER4 signaling. 25329458_data show a protective role for the PGE2 receptors EP(2) and EP(4) following osmotic changes, through the reduction of human mast cell activity caused by calcium influx impairment and MAP kinase inhibition. 25531811_Altered inhibitory function of the EP4R in eosinophils and monocytes from aspirin-intolerant patients 25670004_Gene expression analysis revealed that three gene BACH2, PTGER4 and ZFP36L1, are down-regulated in MS patients' blood cells compared to healthy subjects. 25690101_TGF-beta2 therefore promotes the adhesion and invasiveness of virulent macrophages by modulating COX2, EP4, and PKIG transcription to initiate a prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)-driven autostimulatory loop that augments PKA and EPAC activities. 25733698_miRNA 526b is a COX-2 upregulated, oncogenic miRNA promoting stem-like cells, the expression of which follows EP4 receptor-mediated signaling. 26188701_IP and EP4 receptors have a role in prostanoid regulation of angiogeneis 26538147_The PTGER4 gene is a candidate risk factor for radiological progression in rheumatoid arthritis 26689593_The cross-talk between SP1 and p65, and the positive feedback regulatory loop of PI3-K/Akt signaling by EP4 contribute to the overall responses of solamargine in this process 27010855_GW627368X therefore effectively inhibits cervical cancer survival, motility, proliferation and angiogenesis by blocking EP4/EGFR interactive signaling. 27230680_Findings suggest SUMO-1 protein and PGE2 receptor subtype 4 (EP4) as two potential targets for new therapeutic or prevention strategies for endometrial cancers. 27450806_These results indicate that the blockage of PGE2-EP4 signaling prevents the bone destruction required for prostate cancer metastases, and that this is, in part due to the abrogation of bone cell responses. The study provides further evidence that an EP4 antagonist is a candidate for the treatment of prostate cancer in the blockade of bone metastasis. 27506158_Reprogramming of mammary epithelial cells can result from EP4 -mediated stem cell property transfer by extracellular vesicles/exosomes containing caveolae-associated proteins, between mammary basal and luminal epithelial cells. 27544059_High PTGER4 methylation is associated with Lung cancer. 27616330_in breast cancer cells overexpression of S1P3 and its activation by S1P has pro-inflammatory and pro-metastatic potential by inducing COX-2 expression and PGE2 signaling via EP2 and EP4. 27869171_EP4 expression can promote the development of resistance to aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer 28094049_The results show that stimulation with the selective EP4 agonist CAY10598 or PGE2 promotes invadopodia-mediated degradation of the ECM, as well as the invasion of breast cancer cells in in vitro models. 28108433_Case Report: elevated EP4 expression in pulmonary hypertension patient with dissecting pulmonary aneurysm. 28432343_Collectively, these results indicate that COX-1/PGE2/EP4 upregulates the beta-arr1 mediated Akt signaling pathway to provide mucosal protection in colitis. 28899736_discovery of recurrent PTGER4 amplification implies a potential of exploring targeting therapy to the prostaglandin synthesis pathways in a subset of these tumors 29401596_results indicate that PGE2 inhibits hCAP18/LL-37 expression, especially VD3-induced cathelicidin and autophagy, which may reduce host defense against Mtb. Accordingly, antagonists of EP4 may constitute a novel adjunctive therapy in Mtb infection. 29491476_COLEC12 integrates H. pylori, PGE2-EP2/4 axis and innate immunity in gastric diseases 29658109_High EP4 expression is associated with chemoresistant breast carcinoma. 30053598_Data indicates that PGE2 suppression of TNF-alpha by human monocytic cells occurs via EP2R and EP4R expression. However EP4Rs also control their own expression and that of EP2 whereas the EP2R does not affect EP4R expression. This implies that EP4 receptors have an important master role in controlling inflammatory responses. 30191681_Data imply an upregulated expression of PTGER4 and PSCA as well as a downregulated expression of MBOAT7 in gastric tissue as risk-conferring gastric cancer patho-mechanisms. 30455960_Study demonstrated that the expression of EP4 receptors was up-regulated by c-Myc by binding to Sp-1 under low cellular density conditions but was down-regulated under high cellular density conditions via the increase in the expression levels of HIF-1alpha protein, which may pull out c-Myc and Sp-1 from DNA-binding. 30835912_These results suggest that PGE2 regulates human brain endothelial cell migration via cooperation of EP2, EP3, and EP4 receptors. 30917001_EP2 and EP4 receptors play different roles in the regulation of COX-2 expression in human amnion fibroblasts. 30980797_butyrate uptake reduces expressions of prostanoid EP4 receptors and their mediation of cyclooxygenase-2 induction in HCA-7 human colon cancer cells 31167696_SHOX2 and PTGER4 methylation detection in blood plasma has certain value in the early diagnosis of lung cancer 31217077_a role for EP2/EP4 signaling in regulating IGF-1-induced cell proliferation, in which EP2/EP4 signaling represses IGF-1-induced GGCT expression, is reported. 31253169_Prostaglandin receptor EP4 expression by Th17 cells is associated with high disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. 31455205_This work has generated a set of novel homology models of the rEP4 and hEP4 receptors. 32321307_Dysregulated prostaglandin E receptor 4 overexpression in vascular smooth muscle cells promotes inflammatory monocyte/macrophage infiltration leading to abdominal aortic aneurysm exacerbation. 32438662_Concerted EP2 and EP4 Receptor Signaling Stimulates Autocrine Prostaglandin E2 Activation in Human Podocytes. 32464244_3 SNPs were found to be significantly associated with CD/UC/IBD: IRF5 rs4728142 (UC: OR = 1.21, 95% CI = 1.09-1.35, P = 0.0003; OR = 1.30, 95% CI = 1.08-1.57, P = 0.006 in Asian), PTGER4 rs4613763 (CD: the overall OR = 1.28, 95% CI = 1.01-1.64, P = 0.04; IBD: OR = 1.31, 95% CI = 1.04-1.65, P = 0.02), IL12B rs6887695 (CD: the overall OR = 1.17, 95% CI = 1.06-1.30, P = 0.002; UC: the overall OR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.01-1.26. 32846747_Association between PTGER4 polymorphisms and inflammatory bowel disease risk in Caucasian: A meta-analysis. 33038299_Prostaglandin D2 strengthens human endothelial barrier by activation of E-type receptor 4. 33053354_Prostaglandin E2-EP4 Axis Promotes Lipolysis and Fibrosis in Adipose Tissue Leading to Ectopic Fat Deposition and Insulin Resistance. 33158942_Prostanoid Receptors of the EP4-Subtype Mediate Gene Expression Changes in Human Airway Epithelial Cells with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity. 33264604_Cryo-EM Structure of the Prostaglandin E Receptor EP4 Coupled to G Protein. 33600772_Whole-genome sequencing of African Americans implicates differential genetic architecture in inflammatory bowel disease. 33662689_DNA methylation of PTGER4 in peripheral blood plasma helps to distinguish between lung cancer, benign pulmonary nodules and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. 34262017_CD147 receptor is essential for TFF3-mediated signaling regulating colorectal cancer progression. 34475053_Pathological Roles of Prostaglandin E2-specific E-type Prostanoid Receptors in Hormone-sensitive and Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. 34502044_Prostaglandin E2 Receptor 4 (EP4) Affects Trophoblast Functions via Activating the cAMP-PKA-pCREB Signaling Pathway at the Maternal-Fetal Interface in Unexplained Recurrent Miscarriage. 34529833_Prostaglandin E2 directly inhibits the conversion of inducible regulatory T cells through EP2 and EP4 receptors via antagonizing TGF-beta signalling. 34740924_Single-Cell Analysis Reveals EP4 as a Target for Restoring T-Cell Infiltration and Sensitizing Prostate Cancer to Immunotherapy. 35549670_Nanomolar EP4 receptor potency and expression of eicosanoid-related enzymes in normal appearing colonic mucosa from patients with colorectal neoplasia. 35914351_PARP14 regulates EP4 receptor expression in human colon cancer HCA-7 cells. 36078128_The Prostaglandin E2 Receptor EP4 Promotes Vascular Neointimal Hyperplasia through Translational Control of Tenascin C via the cAPM/PKA/mTORC1/rpS6 Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000039942 |
Ptger4 |
1002.645260 |
2.5014363937 |
1.322757 |
0.069979171 |
354.281568 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000049520315726293666555083472390281617255907243288939222533317005453913635997062886055006064310407413309571799738936154795378146153358720615091744876710582041704845323452198974904783851288104476765991601716621062223566696047782897949218750000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000016425165395957178512489058908893129611891449981803689135300210611510685047569763489038977934520948353790826494595034461558366702052751900230054417426039514118683854166076679949286567418843645060899660848008352331817150115966796875000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1467.0810431 |
55.9642956 |
590.5768566 |
17.5659436 |
| ENSG00000171611 |
171558 |
PTCRA |
protein_coding |
Q6ISU1 |
FUNCTION: The pre-T-cell receptor complex (composed of PTCRA, TCRB and the CD3 complex) regulates early T-cell development. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a single-pass type I membrane protein that is found in immmature but not mature T-cells. Along with TCRB and CD3 complex, the encoded protein forms the pre-T-cell receptor complex, which regulates early T-cell development. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:171558; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process [GO:0070244] |
11891328_Combined expression of pTalpha and Notch3 in T cell leukemia identifies the requirement of preTCR for leukemogenesis 14500629_High levels of pre-T cell receptor alpha-chain mRNA splice forms have been demonstrated in immature CD2+CD7+CD3- T cells of the jejunal mucosa, both intraepithelially and in lamina propria. 17823309_identified a polyproline-arginine sequence in the pTalpha cytoplasmic tail that interacted in vitro with SH3 domains of the CIN85/CMS family of adaptors, and mediated the recruitment of multiprotein complexes involving all (CMS, CIN85, and CD2BP3) members 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33652347_Generation of self-reactive, shared T-cell receptor alpha chains in the human thymus. |
ENSMUSG00000036858 |
Ptcra |
153.098020 |
0.1942924271 |
-2.363698 |
0.151470801 |
264.409407 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001876727189147225396577895662432442825640496438763282311483670937516357787497269881107860730172252261390303873823893895583976039129642381991385329518574887064374934197985567152500152587890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000474323515613237102050501918032289663778426537269955305013312819897333360922233159221816121731099231508132776232038845418504825173706072767904518179549189227373062749393284320831298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.6429967 |
4.9048616 |
257.3200547 |
14.1602877 |
| ENSG00000171657 |
27197 |
GPR82 |
protein_coding |
Q96P67 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an orphan G protein-coupled receptor of unknown function. The encoded protein is a member of a family of proteins that contain seven transmembrane domains and transduce extracellular signals through heterotrimeric G proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:27197; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930] |
Mouse_homologues 22216272_GPR82-deficient mice showed decreased serum triacylglyceride levels, increased insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, most pronounced under Western diet |
ENSMUSG00000047678 |
Gpr82 |
217.158337 |
2.0914294828 |
1.064489 |
0.119123806 |
80.522449 |
0.00000000000000000028742097043795344838327336373349966105676422507403920420659959589215759478975087404251098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000002462178481523037164087395782685930964793202042989960463825749314992208383046090602874755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
302.7604167 |
21.4597916 |
145.7893123 |
8.1626686 |
| ENSG00000171714 |
203859 |
ANO5 |
protein_coding |
Q75V66 |
FUNCTION: Does not exhibit calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23047743}. |
Cell membrane;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Membrane;Osteogenesis imperfecta;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the anoctamin family of transmembrane proteins. The encoded protein is likely a calcium activated chloride channel. Mutations in this gene have been associated with gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:203859; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; intracellular calcium activated chloride channel activity [GO:0005229]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; chloride transmembrane transport [GO:1902476]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
20096397_Recessive mutations were identified in ANO5 that result in a proximal limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD2L) in three French Canadian families and in a distal non-dysferlin Miyoshi myopathy (MMD3) in Dutch and Finnish families. 20692837_mutation in patients with a distal myopathy;(a new separate clinical, genetic and histopathologic entity) 21186264_A founder mutation in Anoctamin 5 is a major cause of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. 22336395_The c.191dupA mutation, already reported as a founder mutation in Caucasian patients with anoctamin myopathies, was found in our family in a heterozygous state. 22402862_Mutations are distributed all over the gene, indicating that muscular dystrophy caused by ANO5 can be expected to occur in all populations 22499103_This study identified four novel mutations in the ANO5 gene cause high lever Creatine Kinase and limb girdle muscular weakness and Miyoshi type of muscular dystrophy. 22742934_occurrence and molecular epidemiology of LGMD2L, caused by mutations in the anoctamin 5 (ANO5) gene, in a Italian cohort differed from those observed in other European countries. 22980764_This study demonistrayed that anoctamin 5 mutations associate to distal muscular dystrophy. 23041008_Dilated cardiomyopathy is associated with mutations in the ANO5 gene. 23047743_By sequencing the entire ANO5 gene coding region and untranslated regions in a large Italian gnathodiaphyseal dyplasia family, a novel missense mutation causing the p.Thr513Ile substitution, was found. 23055322_A family is described in which 2 mutations in ANO5 segregate with marked creatine kinase-type hypercreatinemia, demonstrating that recessively inherited ANO5 mutations not only lead to muscular dystrophy but may also cause bone disease. 23606453_investigated the prevalence and spectrum of ANO5 gene mutations and related clinical phenotypes; study confirmed that ANO5 gene mutations are responsible for about one fourth of cases of undiagnosed muscular dystrophy in the population studied 23607914_a diagnosis of ANO5 causing Muscular Dystrophy, Limb-Girdle, Type 2L, in 16% of the families (11/68) in a well-defined limb girdle muscular dystrophy cohort in the Netherlands 23663589_ANO5 mutations can be associated with amyloid deposition in muscle 23670307_A high prevalence of ANO5 deficiency was found among patients with unclassified recessive limb girdle muscular dystrophy 2 23843187_This study showed that TMEM16E possesses distinct function other than chloride channel activity, and another protein-stabilizing machinery toward the TMEM16E proteins should be considered for the on-set regulation of their phenotypes in tissues. 24232312_The present report describes an association between LGMD2L consequent upon mutation in ANO5 and macular dystrophy in one affected person. 24639367_supervised aerobic exercise training is safe and effective in improving oxidative capacity and muscle function in patients with anoctamin 5 deficiency 25891276_Study screened the ANO5 gene in 786 myopathic patients and 52 controls by combining NGS and Sanger sequencing. In the cohort of patients, thirty-three are homozygous or compound heterozygous for causative mutations in ANO5 26911675_Here we show that Ano5-deficient mice have reduced capacity to repair the sarcolemma following laser-induced damage, exhibit delayed regeneration after cardiotoxin injury and suffer from defective myoblast fusion necessary for the proper repair and regeneration of multinucleated myotubes. these data suggest that ANO5 plays an important role in sarcolemmal membrane dynamics. 27216912_A heterozygous mutation in the ANO5 gene c.1067G > A (p.Cys356Tyr) was identified in both affected individuals in a Russian family with giant cementoma and bone fractures consistent with a diagnosis of gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia. 27911336_Study characterized 12 newly identified and 2 previously identified patients with ANO5 mutations from 11 families. Material was genetically homogeneous with most patients homozygous for the Finnish founder variant c.2272C>T (p.Arg758Cys). In one family, study found a novel p.Met470Arg variant compound heterozygous with p.Arg758Cys. 28176803_After Ano5 gene knock-down with shRNA in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast precursors the authors saw elevated expression of osteoblast-related genes such as Col1a1, osteocalcin, osterix and Runx2 as well as increased mineral nodule formation in differentiating cells. The data suggest that ANO5 plays a role in osteoblast differentiation. 28187523_Asymptomatic, sometimes mild hyperCKemia or exercise intolerance is a presentation of ANO5-related myopathy. 28902351_Results show that ANO5 is downregulated in thyroid cancer and, negatively associated with lymph node metastasis. Its inhibition promotes the migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells suggesting it as a tumor marker. 29124309_First direct demonstration of Ca(2+)-dependent Phospholipid scrambling activity for TMEM16E; this suggests a gain-of-function phenotype related to a Gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia mutation. 30235762_The Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2L family was characterized by mild chronic myopathy and bilateral gastrocnemius hypertrophy with obviously increased creatine kinase levels. Pathological changes included atrophy of fibers with interstitial connective tissues hyperplasia. The pathogenic allele was a c.220C> T mutation in the ANO5 gene. 30257928_ANO5-mediated phospholipid scrambling or ionic currents play an important role in muscle repair. 30554457_Through whole-genome sequencing, the novel mutation c.1067G>T (p.C356F) in ANO5 is responsible for the atypical gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia observed in our patients. GDD should be included in the differential diagnosis for patients with fibro-osseous lesions. 30672373_elucidating TMEM16E function 30996299_A novel missense mutation p.C356W in anoctamin 5 (ANO5) gene was successfully identified as the pathogenic mutation by whole-exome sequencing (WES). 31395899_ANO5 mutations in the Polish limb girdle muscular dystrophy patients: Effects on the protein structure. 32027096_Genetic association analysis identifies a role for ANO5 in prostate cancer progression. 32112655_TMEM16E/ANO5 mutations related to bone dysplasia or muscular dystrophy cause opposite effects on lipid scrambling. 32367299_Persistent asymptomatic or mild symptomatic hyperCKemia due to mutations in ANO5: the mildest end of the anoctaminopathies spectrum. 32399949_Anoctamin 5 (ANO5) muscular dystrophy-three different phenotypes and a new histological pattern. 32902009_ANO5-associated Gnathodiaphyseal dysplasia with calvarial doughnut lesions: First report in an Asian Indian with an expanded phenotype. 32925086_Phenotypic Spectrum of Myopathies with Recessive Anoctamin-5 Mutations. 33496727_ANO5 ensures trafficking of annexins in wounded myofibers. 33818761_Novel ANO5 intronic Roma variant alters splicing causing muscular dystrophy. 34145687_Muscle involvement assessed by quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in patients with anoctamin 5 deficiency. 34238763_Anoctamin 5 promotes osteosarcoma development by increasing degradation of Nel-like proteins 1 and 2. 34550615_Muscle biopsy and MRI findings in ANO5-related myopathy. 36157935_Anoctamin 5 regulates the cell cycle and affects prognosis in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000055489 |
Ano5 |
29.388556 |
0.4496090088 |
-1.153257 |
0.276821368 |
17.848638 |
0.00002391904229705152463221658198921915072787669487297534942626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000071669724787754872700161479226466099134995602071285247802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.2771964 |
3.6083190 |
45.5452679 |
5.0148659 |
| ENSG00000171793 |
1503 |
CTPS1 |
protein_coding |
P17812 |
FUNCTION: This enzyme is involved in the de novo synthesis of CTP, a precursor of DNA, RNA and phospholipids. Catalyzes the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either L-glutamine or ammonia as a source of nitrogen. This enzyme and its product, CTP, play a crucial role in the proliferation of activated lymphocytes and therefore in immunity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16179339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24870241}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Glutamine amidotransferase;Immunity;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Pyrimidine biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Pyrimidine metabolism; CTP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; CTP from UDP: step 2/2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16179339, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24870241}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme responsible for the catalytic conversion of UTP (uridine triphosphate) to CTP (cytidine triphospate). This reaction is an important step in the biosynthesis of phospholipids and nucleic acids. Activity of this proten is important in the immune system, and loss of function of this gene has been associated with immunodeficiency. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:1503; |
cytoophidium [GO:0097268]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; CTP synthase activity [GO:0003883]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; 'de novo' CTP biosynthetic process [GO:0044210]; B cell proliferation [GO:0042100]; CTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006241]; glutamine metabolic process [GO:0006541]; nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006139]; pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process [GO:0019856]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098] |
16179339_CTP synthetase is phosphorylated by protein kinase A 17463002_Data indicate that protein kinase C phosphorylation at Ser(462) stimulates human CTP synthetase 1 activity, whereas phosphorylation at Thr(455) inhibits activity. 17681942_analysis of phosphorylation and regulation of human CTPS1 in human cells shows that GSK3 is a novel regulator of CTPS activity 18600551_studies provide novel information on the potential interacting proteins that may regulate CTPS1 function or intracellular localization 20739275_analysis of the kinetic properties of hCTPS1 and hCTPS2, and determination that Ser(68) is a major site of CTPS2 regulation by phosphorylation 24477477_Rods and rings (RR) are protein assemblies composed of CTPS1 and IMPDH2. Glutamine deprivation initiates reversible assembly of mammalian rods and rings. 24870241_results highlight a key and specific role of CTPS1 in the immune system by its capacity to sustain the proliferation of activated lymphocytes during the immune response 28459447_The filament structures elucidate allosteric mechanisms of assembly and regulation that rely on a conserved conformational equilibrium. The findings may provide a mechanism for increasing human CTP synthase activity in response to metabolic state and challenge the assumption that metabolic filaments are generally storage forms of inactive enzymes. 29097181_CTP synthase forms the cytoophidium in human hepatocellular carcinoma. 32161190_Impaired lymphocyte function and differentiation in CTPS1-deficient patients result from a hypomorphic homozygous mutation. 33576499_Energy deficiency caused by CTPS downregulation in decidua may contribute to pre-eclampsia by impairing decidualization. 34991621_CTPS1 promotes malignant progression of triple-negative breast cancer with transcriptional activation by YBX1. 35912542_CTPS1 inhibition suppresses proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000028633 |
Ctps |
1822.870282 |
2.7940746688 |
1.482371 |
0.057752503 |
646.918058 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010456235427670307557325488239056565439262792062376287377204897293700926441260692292743471441511040845557216519242533773315398556174565230928014060895791899489789128903641945152220235316996 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006325165365262857864688997646726963657835300375607135649444089217065791954984701428506130790396052678605719665861419382700729462372244583672918110422285074820459679678250364491633954657996 |
Yes |
Yes |
2656.6610503 |
103.2811308 |
958.1700963 |
27.9860129 |
| ENSG00000171860 |
719 |
C3AR1 |
protein_coding |
Q16581 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the chemotactic and inflammatory peptide anaphylatoxin C3a. This receptor stimulates chemotaxis, granule enzyme release and superoxide anion production. |
Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sulfation;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
C3a is an anaphylatoxin released during activation of the complement system. The protein encoded by this gene is an orphan G protein-coupled receptor for C3a. Binding of C3a by the encoded receptor activates chemotaxis, granule enzyme release, superoxide anion production, and bacterial opsonization. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]. |
hsa:719; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; complement component C3a receptor activity [GO:0004876]; complement receptor activity [GO:0004875]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; blood circulation [GO:0008015]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; complement receptor mediated signaling pathway [GO:0002430]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575] |
12511407_results indicate that normal human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells express functional C3aR and that the C3aR-C3a axis sensitizes the responses of these cells to SDF-1 12871936_Sulfation of tyrosine 174 in the human C3a receptor is essential for binding of C3a anaphylatoxin. 15039137_determination of whether the levels of complement factors C3a, C4a, and C5a are elevated at the site of inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and in asthma 15067069_Complement receptor 3 (CR3) is involved in the binding of Leishmania promastigote surface antigen-2 leucine-rich repeat motifs to macrophages, an interaction which can be blocked by anti-CR3 antibodies. 15278436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15356170_C3a receptor is highly expressed in primary renal proximal tubular epithelial cells in studies that define a new pathway by which complement activation may directly modulate the renal response to immunologic injury. 16778800_C3aR is expressed on plasmacytoid dendritic cells. 17234193_endothelial cells and subendothelial smooth muscle cells express both C3aR and C5aR 17472841_C3a receptor may be used as a unique biomarker of diagnosis and disease activity in patients with lupus nephritis. 17498719_In stenotic valves, expression of C3aR mRNA was upregulated 18538384_on the basis of the location of C3aR and C5aR, C5aR may play a role in activation of inflammatory cells, whereas C3aR may mediate mucus secretion and mucosal swelling in allergic nasal mucosa, especially severe persistent allergic nasal mucosa 19005416_Significantly more transcripts encoding alternative pathway components factor B, C3 and properdin, and C3a receptor and C5a receptor were detected in grade 3 versus grade 0 or 1 biopsies of human cardiac allografts. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21371235_Mutant gonococci lacking the pilin glycan did not bind to the I-domain when it is in a closed, low-affinity conformation and cannot induce an active conformation to complement receptor 3 during pex cell challenge. 21589858_shows that both beta-arrestin-1 and beta-arrestin-2 play a novel and shared role in inhibiting G protein-dependent ERK1/2 phosphorylation. These findings reveal a new level of complexity for C3aR regulation by beta-arrestins in human mast cells 21799898_a new level of complexity for C3aR regulation 22868393_Complement C3a receptor activation contributes to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 22901903_significantly decreased expression of C3aR mRNA and protein expression in placentas with preeclampsia compared to controls 23077507_study demonstrates that although C3a causes phosphorylation of its receptor at multiple sites, Ser459, Thr463, Ser465, Thr466 and Ser470 participate in C3aR desensitization 23284683_functional regulation of C3aR by NHERFs in human mast cells 24321396_C3aR and CD46 activation via intrinsic generation of their respective ligands is an integral part of human Th1 (but not Th2) immunity. 24327134_In patients with IgAN, urinary and renal C3a and C5a and renal expression of C3aR and C5aR are significantly correlated with the activity and severity of renal injury. 24743347_The obesity-induced down-regulation of complement C3 and C3aR which is specific to subcutaneous adipose tissue. 25426664_High C3aR1 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia-M2. 25465103_these findings suggest a critical role for C3a through autocrine/paracrine induction of C3aR in the pathogenesis of cigarette smoke-induced sterile inflammation and provide new therapeutic targets for the treatment of emphysema. 25544179_Observed a positive correlation between the expression of anaphylatoxin-receptors C3aR and C5aR with platelet activation in patients with coronary artery disease. 25603857_Medulloblastoma cells express C3aR, and siRNA-mediated knockdown of C3aR inhibits proliferation of these cells in vitro. 28576324_Studies indicate that the complement response lie the active fragments, C3a and C5a, acting through their specific receptors, C3aR, C5aR1 and C5aR2 to direct the cellular response to inflammation. 29138505_This study aimed to investigate the role of C3aR and C5aR in these two diseases...Our data indicates that increased C3aR expression may lead to over activation of the Th17 cell response and may therefore contribute to the pathogenesis of Behcet's disease (BD) and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease (VKH). 29802205_Anaphylatoxin C3a has novel roles involved in regulating platelet function and thrombus formation. 30032131_this study shows that C3AR1 expression on M2 macrophages is down-regulated by stimulating the histamine H4 receptor and the IL-4 receptor 30168657_C3aR-positive cells are found more often in patients with inflammatory cardiomyopathy. The relevance of C3aR-positive cells in patients with non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy should be further evaluated as potential predictors or modulators of adverse cardiac remodelling, the substrate of progressive heart failure. 30415998_This study demonstrate a crucial role for activation of the C3-C3aR network in mediating neuroinflammation and tau pathology. 30597512_C3aR has roles in platelet function, thrombus formation and in vivo hemostasis 31102134_The Role of Complement C3a Receptor in Stroke. 31484069_Peptide/Receptor Co-evolution Explains the Lipolytic Function of the Neuropeptide TLQP-21. 31798904_Deficiency of C3a receptor attenuates the development of diabetic nephropathy. 31931851_Results found that C3a-C3aR signaling in carcinoma associated fibroblasts (CAFs) facilitates the metastasis of breast cancer. Mechanically, C3a-C3aR signaling augments pro-metastatic cytokine secretion and extracellular matrix components expression of CAFs via the activation of PI3K-AKT signaling. 32159364_The validation experiments showed that those variants in CCR5 and C3AR1 significantly increased the rise of intracellular calcium and the variant in CCR5 profoundly enhanced proliferative capacity of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 33176600_Down-Regulation of C3aR/C5aR Inhibits Cell Proliferation and EMT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33306149_Changes in VGF and C3aR1 gene expression in human adipose tissue in obesity. 33446393_Autoantibodies against C5aR1, C3aR1, CXCR3, and CXCR4 are decreased in primary Sjogren's syndrome. 33539329_High Expression of the Component 3a Receptor 1 (C3AR1) Gene in Stomach Adenocarcinomas Infers a Poor Prognosis and High Immune-Infiltration Levels. 33746964_Mitochondrial C3a Receptor Activation in Oxidatively Stressed Epithelial Cells Reduces Mitochondrial Respiration and Metabolism. 34162127_Identification and characterization of prognosis-related genes in the tumor microenvironment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35220210_The Complement C3a-C3a Receptor Axis Regulates Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Activating the ERK Pathway in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000040552 |
C3ar1 |
400.422464 |
7.4867130612 |
2.904332 |
0.169248034 |
272.885420 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000026672063708481180580550236884491097073147645280041431170394493874268998918851157000279805826767725059401612866669160322536189040604550441351817029604393156916319895799460937269032001495361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006992533931388671250525715860384667319364380787069273371048250378849076252593642448403056670087006896739308992117614013202730952183050932861287641542809290218229989477549679577350616455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
704.9701265 |
75.8032753 |
94.7120924 |
7.9703313 |
| ENSG00000171988 |
221037 |
JMJD1C |
protein_coding |
Q15652 |
FUNCTION: Probable histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' of histone H3, thereby playing a central role in histone code. Demethylation of Lys residue generates formaldehyde and succinate. May be involved in hormone-dependent transcriptional activation, by participating in recruitment to androgen-receptor target genes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Dioxygenase;Iron;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene interacts with thyroid hormone receptors and contains a jumonji domain. It is a candidate histone demethylase and is thought to be a coactivator for key transcription factors. It plays a role in the DNA-damage response pathway by demethylating the mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1) protein, and is required for the survival of acute myeloid leukemia. Mutations in this gene are associated with Rett syndrome and intellectual disability. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015]. |
hsa:221037; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; histone deacetylase complex [GO:0000118]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; dioxygenase activity [GO:0051213]; histone H3K9 demethylase activity [GO:0032454]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; histone H3-K9 demethylation [GO:0033169]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17290275_TRIP8 gene codes for a protein predicted to be a transcriptional regulator associated with nuclear thyroid hormone receptors. Positional candidate gene for autism. 17353003_the discovery of a new Receptors, Androgen coactivator which belongs to the JmjC containing enzyme family as a novel variant of JMJD1C 17549425_Human JMJD1C variant 2 with TRI8H1, TRI8H2, and JmjC domains showed 85.7% total-amino-acid identity with mouse Jmjd1c. 18940312_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19936222_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20526338_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20648472_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23593242_No evidence for JMJD1C histone demethylase activity towards H3K9. 24240613_JMJD1C regulates the RAP80-BRCA1 branch of this DNA-damage response (DDR) pathway. 24318875_JMJD1C represses neural differentiation of hESCs at least partially by epigenetically sustaining miR-302 expression 24501218_Depletion of JMJD1C impairs expansion and colony formation of leukemic cell lines, with the strongest effect observed in the MLL-rearranged ALL cell line SEM. 26181491_Our findings indicate that mutations in JMJD1C contribute to the development of Rett syndrome and intellectual disability. 26414697_genetic variants in the androgen-related genes CYP17A1 and JMJD1C might be associated with risk of Barrett's esophagus (BE) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). 26494788_JMJD1C is directly recruited by RUNX1-RUNX1T1 to its target genes and regulates their expression by maintaining low H3K9 dimethyl (H3K9me2) levels 26608785_Histone modifier genes (JMJD1C, RREB1, MINA, KDM7A) alter conotruncal heart phenotypes in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. 27064872_JMJD1C is one of the target genes of hsa-miR-590- 3p. 28406950_Study provides evidence that SNPs of JMJD1C and KCNQ1 are prospectively associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in Korean population. Additionally, CDKAL1 may not be associated with T2D onset over the age of 40. 29222425_Polymorphisms in JMJD1C are associated with pubertal onset in boys and reproductive function in men 29804699_JMJD1C is the autosomal gene where variants have been demonstrated to be associated with Testosterone (one of Cardiovascular disease risk factors) at genome-wide significance. 30622285_High JMJD1C expression is associated with increased metabolic dysregulation and leukemogenesis. 31954878_Jumonji domain containing 1C (JMJD1C) sequence variants in seven patients with autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability and seizures. 32034158_JMJD1C activates lipogenic gene transcription in liver.JMJD1C demethylates histone H3 K9 lysine at lipogenic promoters.JMJD1C is phosphorylated at the threonine T505 by mTOR. 33075016_JMJD1C knockdown affects myeloid cell lines proliferation, viability, and gemcitabine/carboplatin-sensitivity. 33591602_Finding underlying genetic mechanisms of two patients with autism spectrum disorder carrying familial apparently balanced chromosomal translocations. 34475205_AR-negative prostate cancer is vulnerable to loss of JMJD1C demethylase. 34586733_Histone demethylase JMJD1C promotes the polarization of M1 macrophages to prevent glioma by upregulating miR-302a. 35468015_JMJD1C-regulated lipid synthesis contributes to the maintenance of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. 35777757_Histone demethylase KDM3C regulates the lncRNA GAS5-miR-495-3p-PHF8 axis in cardiac hypertrophy. 36429088_JMJD1C Regulates Megakaryopoiesis in In Vitro Models through the Actin Network. |
ENSMUSG00000037876 |
Jmjd1c |
665.938670 |
0.4504386805 |
-1.150597 |
0.085390873 |
179.365496 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000006667446410547823235038769890790417327511373749694723444385298052674911629577981234198701095412779266493642771340688568670884706079959869384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000001136391559118774473057574019612290554582235046775766002096936104800892700012721276736315720016191823001083793798215992865152657032012939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
420.8302990 |
67.9849847 |
943.5325523 |
110.0445791 |
| ENSG00000172031 |
253152 |
EPHX4 |
protein_coding |
Q8IUS5 |
|
Hydrolase;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable hydrolase activity. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:253152; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787] |
20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20723587_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22798687_The identification of two human epoxide hydrolases: EH3 and EH4. 34066758_Relative Importance of Soluble and Microsomal Epoxide Hydrolases for the Hydrolysis of Epoxy-Fatty Acids in Human Tissues. |
ENSMUSG00000033805 |
Ephx4 |
85.770829 |
0.4801610853 |
-1.058410 |
0.174783012 |
37.183922 |
0.00000000107496413348699741997664057176556373640607944253133609890937805175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005129799744671219910909004864336263596058529401489067822694778442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.9571047 |
6.6405625 |
115.2185786 |
9.2732786 |
| ENSG00000172081 |
126308 |
MOB3A |
protein_coding |
Q96BX8 |
FUNCTION: May regulate the activity of kinases. {ECO:0000250}. |
Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126308; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
35046109_MOB3A Bypasses BRAF and RAS Oncogene-Induced Senescence by Engaging the Hippo Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000003348 |
Mob3a |
1189.197265 |
2.6295020007 |
1.394790 |
0.055758457 |
627.067836 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000217041372498581429506937531061375565797018699788700343168829458673497299541036683372433377639867615441627401968496539563891491844615654502994366087251169520714561192003223023557947010590265244 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000124650998368835102551127059124126317620095965472846192624999764087723639343607535248615369053056424845855384608861791624441931496779299582171317595545433491237862557233380083413005425354751286 |
Yes |
No |
1718.9124365 |
59.2824005 |
658.8662225 |
17.8177216 |
| ENSG00000172115 |
54205 |
CYCS |
protein_coding |
P99999 |
FUNCTION: Electron carrier protein. The oxidized form of the cytochrome c heme group can accept an electron from the heme group of the cytochrome c1 subunit of cytochrome reductase. Cytochrome c then transfers this electron to the cytochrome oxidase complex, the final protein carrier in the mitochondrial electron-transport chain.; FUNCTION: Plays a role in apoptosis. Suppression of the anti-apoptotic members or activation of the pro-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family leads to altered mitochondrial membrane permeability resulting in release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. Binding of cytochrome c to Apaf-1 triggers the activation of caspase-9, which then accelerates apoptosis by activating other caspases. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Apoptosis;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Electron transport;Heme;Iron;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a small heme protein that functions as a central component of the electron transport chain in mitochondria. The encoded protein associates with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where it accepts electrons from cytochrome b and transfers them to the cytochrome oxidase complex. This protein is also involved in initiation of apoptosis. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal dominant nonsyndromic thrombocytopenia. Numerous processed pseudogenes of this gene are found throughout the human genome.[provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:54205; |
apoptosome [GO:0043293]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; respirasome [GO:0070469]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097202]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process by cytochrome c [GO:0008635]; cellular respiration [GO:0045333]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; mitochondrial electron transport, cytochrome c to oxygen [GO:0006123]; mitochondrial electron transport, ubiquinol to cytochrome c [GO:0006122]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280] |
11839755_galectin-3 is enriched in the mitochondria and prevents mitochondrial damage and cytochrome c release 16934433_non-rare allelic variants of the Cyt c protein are absent in the populations analyzed in this study 18345000_Mutation of human cytochrome c enhances the intrinsic apoptotic pathway and causes thrombocytopenia 18417609_MICS1 individually functions in mitochondrial morphology and cytochrome c release. 18825408_Serum cyto-c is a potent tumor marker as a predictor for malignant potential in several different types of cancer. 19029908_Both neurons and cancer cells strictly inhibit cytochrome c-mediated apoptosis by a mechanism dependent on glucose metabolism. 19172527_In 77 Italian patients with inherited thrombocytopenia and clinical and laboratory features similar to those of patients with the CYCS missense (Gly41Ser) mutation, no alterations of the open reading frame were identified. 19172527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19404857_there was no evidence of somatic mutations of CYTOCHROME C in the cancers 19640329_No difference in the serum level of cytochrome c was seen among the the groups of patients with type 2 diabetes, controls or in subjects with IGT. 19770576_Data show that sorafenib initiated lethal apoptotic process through the release of cytochrome c and caspase 3/7 activation. 19851871_Serum LRG when bound to extracellular Cyt c that is released from apoptotic cells acts as a survival factor for lymphocytes and possibly other cells that are susceptible to the toxic effect of extracellular Cyt c. 19875445_Membrane-associated XIAP induces mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization leading to cytochrome c and Smac release, which is dependent on Bax and Bak. 19895853_NOA36/ZNF330 is translocated from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm when apoptosis is induced and that it contributes to cytochrome c release. 20227384_it is the specific nitration of solvent-exposed Tyr74 which enhances the peroxidase activity and blocks the ability of cytochrome c to activate caspase-9, thereby preventing the apoptosis signaling pathway 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21192676_heme electronic structure change may ultimately be responsible for the enhanced proapoptotic activity of G41S mutated human cyt c 21448217_Cerebrospinal fluid Bcl-2 and cytochrome C levels are elevated in adults after severe traumatic brain injury. 21706253_Tyrosine phosphorylation turns alkaline transition into a biologically relevant process and makes human cytochrome c behave as an anti-apoptotic switch. 21712378_Resveratrol induces p53-independent, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP)-mediated Bax protein oligomerization on mitochondria to initiate cytochrome c release and caspase activation. 21751259_Data show that G-Rh2 and Bet A cooperated to induce Bax traslocation to mitochondria and cytochrome c release, and enhanced cleavage of caspase-8 and Bid. 21869827_Translocation of ARTS initiates a first wave of caspase activation leading to the subsequent release of additional mitochondrial factors, including cytochrome C and SMAC/Diablo. 22102269_Studies indicate that the CYCS mutation in TP Cargeegis a glycine 41 replacement by serine, which yields a cytochrome C variant with enhanced apoptotic pathway activity in vitro. 22157762_mitochondrial import and direct electron transfer from cytochrome c to Rac1 modulates mitochondrial H(2)O(2) production in alveolar macrophages pulmonary fibrosis. 22184220_Dynamic changes in cytochrome c distribution at the Raman band of 750 cm(-1) were observed after adding an apoptosis inducer to the cells. 22192356_Specific nitration of tyrosines 46 and 48 makes cytochrome c assemble a non-functional apoptosome. 22320973_The levels of cellular apoptosis-associated proteins such as Smac/DIABLO, Cyto C, and the activated fragment of caspase-3 increased in pancreatic cancer cells, but the expression of XIAP was significantly decreased after 24 h treatment with the combination of TRAIL and gemcitabine. 22363611_CCN1 promotes the activation of p53 and p38 MAPK, which mediate enhanced cytochrome c release to amplify the cytotoxicity of TNFalpha. 23070294_structural characterization of cytochrome c in micelle 23150584_Spectroscopic analyses of HCCS alone and complexes of HCCS with site-directed variants of cytochrome c revealed the fundamental steps of heme attachment and maturation. 23207240_Data indicate that the formation of cytochrome c-Apaf-1 apoptosome and the presence of Smac are absolutely required for PSAP-induced apoptosis. 23334161_results suggest the impact of residue 41 on the conformation of cytochrome c influences its ability to act in both of its physiological roles, electron transport and caspase activation 23443079_G-Rh2 causes rapid and dramatic translocation of both Bak and Bax, which subsequently triggers mitochondrial cytochrome c release and consequent caspase activation. 24099549_a mechanism of multiple radical formations in the cytochrome c-phospholipid complexes under H2O2 treatment, consistent with the stabilization of the radical in the G41S mutant, which elicits a greater peroxidase activity from cytochrome c 24326104_Data indicate a novel missense mutation (Y48H) of the cytochrome c (CYCS) gene responsible for thrombocytopenia. 24329121_proposed that mutation of residue 41, and interaction with cardiolipin, increase peroxidase activity by altering the 40-57 Omega loop and its hydrogen bond network with the propionate of haem ring A; these changes enhance access of hydrogen peroxide and substrate to the haem 25028650_In vitro ultrastructural changes of MCF-7 for metastasise bone cancer and induction of apoptosis via mitochondrial cytochrome C released by CaCO3/Dox nanocrystals 25275009_The mitochondrial metalloprotease OMA1 was activated in a Bax- and Bak-dependent fashion. 25578497_Monitoring of serum cytochrome c might also serve as a sensitive apoptotic marker in vivo reflecting chemotherapy-induced cell death burden in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 26216969_These findings establish a framework for understanding the molecular basis of cytochrome c-mediated blocking of SET/TAF-Ibeta. 27461282_This work reveals a direct conformational link between the 40-57 Omega-loop of cytochrome c in which residue 41 resides and the dynamical properties of the axial ligand to the heme iron. 28317242_ROCK activation phosphorylated Rac1b at Ser71 and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels by facilitating the interaction between Rac1b and cytochrome c. Conversely, ROCK inactivation abolished their interaction, concomitant with ROS reduction. 28598148_Data suggest that the stronger effect of K72A mutation on the peroxidase activity of human versus yeast cytochrome c results from relief of steric interactions between side chains at positions 72 and 81 (Ile in human vs Ala in yeast), which suppresses the dynamics of omega-loop D necessary for the intrinsic peroxidase activity of cytochrome c. 28617588_Data suggest that although HCCS mediates heme attachment to N-terminal cysteine in heme-attachment site (CXXXH) of cytochrome C variants, up to 50% of cytochrome C produced is modified in an oxygen-dependent manner, resulting in a mixed population of cytochrome c. [HCCS = holocytochrome c synthase] 28888620_The caspase-8/Bid/cytochrome c axis links signals from death receptors to mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. 29083920_The naturally occurring Y48H variant of cytochrome c in its oxidized heme state is more peroxidatic than either the Wild Type protein or the G41S variant that is also implicated in thrombocytopenia. 29257225_Cytochrome c was upregulated in the primary Sjogren's syndrome patients, indicating the potential role of cytochrome c in the pathogenesis and development of primary Sjogren's syndrome. 29949346_In this study, site-directed variants at the 41 and 48 positions in the 40-57 Omega-loop and at the 81 and 83 positions in the 71-85 Omega-loop reveal that conformational transitions in the 71-85 Omega-loop, leading to the alkaline or peroxidatic conformers, are controlled by the 40-57 Omega-loop. The variants causing thrombocytopenia, G41S and Y48H, lower the p Ktrigger and increase p Ka2. 30051457_This study clearly demonstrates that thrombocytopenia can result from CYCS loss-of-function variants. 30515402_Upon positive validation on a larger set of patients, combined quantification of Bcl-2 and cytochrome c might be considered as an adjunct in differential diagnosis of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of colon and rectum 30632703_our study identified three mRNAs (TBX21, TGIF2, and CYCS) that were significantly altered between high- and low-risk patients with breast cancer. The three-mRNA model was independent and predicted the prognosis of patients robustly. Furthermore, this model could predict survival probability precisely in patients with or without metastasis. 31150218_I81A and V83G variants of human cytochrome c were prepared. These results show that the I81A substitution significantly influences the thermodynamics and kinetics of access to alternate conformers of human cytochrome c, while the V83G substitution has a more modest effect on these properties. 31678591_Important role for lysine residues of Cyt c and nucleotides in the regulation of apoptosome-dependent apoptotic cell death as well as demonstrate how these mutations and nucleotides may have a pivotal role in human diseases such as cancer. 31760234_Comparison of the structural dynamic and mitochondrial electron-transfer properties of the proapoptotic human cytochrome c variants, G41S, Y48H and A51V. 32244917_Distal Unfolding of Ferricytochrome c Induced by the F82K Mutation. 32717223_Physical contact between cytochrome c1 and cytochrome c increases the driving force for electron transfer. 32848065_Spin cascade and doming in ferric hemes: Femtosecond X-ray absorption and X-ray emission studies. 33480393_Altered structure and dynamics of pathogenic cytochrome c variants correlate with increased apoptotic activity. 33680287_VDAC1 Conversely Correlates with Cytc Expression and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Human Breast Cancer Patients. 33916826_Lysine 53 Acetylation of Cytochrome c in Prostate Cancer: Warburg Metabolism and Evasion of Apoptosis. 34224685_Influence of cysteine-directed mutations at the Omega-loops on peroxidase activity of human cytochrome c. 34229541_Declined expressions of vast mitochondria-related genes represented by CYCS and transcription factor ESRRA in skeletal muscle aging. |
|
|
857.776784 |
2.1714037209 |
1.118628 |
0.057810008 |
377.026912 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000552402749576919495409944061549045506757415894804715125868003618226373725645675614705350851901979105292605792261894730007713357860700865717180457903982134245173705822047986938450119779107900181027482108668015536867557102596038021147251129150390625 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000194593426819936322213548835891577025518235255445047558706536513899744111112155647379117198832377994660455095318833324747869011542107363387008980726747088916588527749242502276078361553153546629646401399001132137556169254821725189685821533203125000 |
Yes |
No |
1142.8000035 |
38.2389724 |
530.0090644 |
13.9159808 |
| ENSG00000172164 |
6641 |
SNTB1 |
protein_coding |
Q13884 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein that binds to and probably organizes the subcellular localization of a variety of membrane proteins. May link various receptors to the actin cytoskeleton and the dystrophin glycoprotein complex. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calmodulin-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Dystrophin is a large, rod-like cytoskeletal protein found at the inner surface of muscle fibers. Dystrophin is missing in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patients and is present in reduced amounts in Becker Muscular Dystrophy patients. The protein encoded by this gene is a peripheral membrane protein found associated with dystrophin and dystrophin-related proteins. This gene is a member of the syntrophin gene family, which contains at least two other structurally-related genes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6641; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex [GO:0016010]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; synapse [GO:0045202]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936] |
16192269_beta1-syntrophin acts through a class-I PDZ interaction with the C terminus of ABCA1 to regulate the cellular distribution and activity of the transporter 24975899_SNTB1 and MCPH1 are located on chromosome 8, which may be involved in neuroticism, avoidant personality and depression. 28595731_SNPs within the SNTB1 gene are associated with increased risk of oral cancer. 28848321_Our study confirms that the two susceptibility loci ZFHX1B and SNTB1 are associated with moderate to high myopia in a Han Chinese population, as well as in a European population, when both SNPs are combined. 31300455_Association of the ZC3H11B, ZFHX1B and SNTB1 genes with myopia of different severities. 32452213_Association of SNTB1 with High Myopia. |
ENSMUSG00000060429 |
Sntb1 |
1164.626519 |
0.4827678201 |
-1.050599 |
0.053937185 |
380.600952 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000092071409957072947394677716329915089204685686062129519838743509398363422271693696680254955315106599632252878743740274775493228622121818428799643137896517519561231577196860521398026205821124674670411349312383088305811185136917629279196262359619141 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000032845348721456328246220104937889255986376241573477370469381159087269566724220484475145881335963676666664535742072673821010851667488423492913540543490863756578465508950895043105370408176214601219160759641019220467228478810284286737442016601562500 |
Yes |
Yes |
769.0681524 |
25.8230558 |
1604.2322199 |
35.8866874 |
| ENSG00000172175 |
10892 |
MALT1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UDY8 |
FUNCTION: Protease that enhances BCL10-induced activation: acts via formation of CBM complexes that channel adaptive and innate immune signaling downstream of CARD domain-containing proteins (CARD9, CARD11 and CARD14) to activate NF-kappa-B and MAP kinase p38 pathways which stimulate expression of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (PubMed:11262391, PubMed:18264101, PubMed:24074955). Mediates BCL10 cleavage: MALT1-dependent BCL10 cleavage plays an important role in T-cell antigen receptor-induced integrin adhesion (PubMed:11262391, PubMed:18264101). Involved in the induction of T helper 17 cells (Th17) differentiation (PubMed:11262391, PubMed:18264101). Cleaves RC3H1 and ZC3H12A in response to T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation which releases their cooperatively repressed targets to promote Th17 cell differentiation (By similarity). Also mediates cleavage of N4BP1 in T-cells following TCR-mediated activation, leading to N4BP1 inactivation (PubMed:31133753). May also have ubiquitin ligase activity: binds to TRAF6, inducing TRAF6 oligomerization and activation of its ligase activity (PubMed:14695475). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q2TBA3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11262391, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14695475, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18264101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24074955, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31133753}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Hydrolase;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
This gene encodes a caspase-like protease that plays a role in BCL10-induced activation of NF-kappaB. The protein is a component of the CARMA1-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signalosome that triggers NF-kappaB signaling and lymphoctye activation following antigen-receptor stimulation. Mutations in this gene result in immunodeficiency 12 (IMD12). This gene has been found to be recurrently rearranged in chromosomal translocations with other genes in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas, including a t(11;18)(q21;q21) translocation with the baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 3 (also known as apoptosis inhibitor 2) locus [BIRC3(API2)-MALT1], and a t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation with the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus (IGH-MALT1). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2018]. |
hsa:10892; |
CBM complex [GO:0032449]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; polkadots [GO:0002096]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; small molecule binding [GO:0036094]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; B-1 B cell differentiation [GO:0001923]; defense response [GO:0006952]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; nuclear export [GO:0051168]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of T cell cytokine production [GO:0002726]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 cell differentiation [GO:2000321]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process [GO:0051603]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050856]; response to fungus [GO:0009620]; T cell proliferation [GO:0042098]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
11960389_REVIEW: Genetic alterations involving MALT1 underlying the pathogenesis of MALT lymphoma 12651604_Fuses with API2 and defines a distinctive clinicopathologic subtype in pulmonary extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. 12931213_translocations t(11;18)(q21;q21) and t(14;18)(q21;q32) represent the main structural aberrations involving MLT/MALT1 in MALT lymphomas, whereas true amplifications of MLT/MALT1 occur rarely in MZBCL 14562112_copy numbers of API2-MALT1 do not reflect tumor cell proportions, and that the number of copies of API2-MALT1 in a tumor cell is different for each clinical sample. 14760068_MALT1 chromosome rearrangements have a role in MALT gastric lymphomas in patients with Sjogren's syndrome 15191563_Translocation breakpoint never exceeded 2.5% in B-cell lymphoma 15363040_Detection of API2-MALT1 fusion transcripts is useful for evaluating the prognosis and clinical behavior of the MALT lymphoma. 15598810_NF-kappa B signaling, once activated in a CD40-dependent immune response, is maintained and enhanced through deregulation of MALT1 or formation of an API2-MALT1 fusion. 15696476_API2-MALT1 transcript was confirmed to be associated with the levels of apoptosis and API2 of MALT lymphoma. 15982633_Taken together, our results strongly indicated that API2-MALT1 possesses a novel mechanism of self-activation by up-regulating its own expression in t(11;18)(q21;q21)-carrying MALT lymphomas. 16123224_nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of MALT1 and BCL10 complex may indicate that these molecules are involved not only in the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway but also in other biologic functions in lymphocytes 16341151_Study further supports the close interaction between the MALT1 and BCL10 proteins in the pathogenesis of MALT lymphomas. 16395399_Common translocation in MALT lymphoma results in a fusion of the cIAP2 region on chromosome 11q21 with the MALT1 gene on chromosome 18q21. 16395405_Chromosomal translocations leads to upregulation of either BCL10 or MALT1 or the generation of a fusion protein, cIAP2-MALT1. 16630178_This study demonstrates that translocations involving MALT1, including IGH/MALT1, are uncommon in cutaneous MALT lymphomas and primary cutaneous DLBCL. 16804917_MALT1-MAP4 fusion does not result in activation of NF-kappa B as with other MALT1-associated translocations. 16891304_the t(11, 18)(q21;q21) translocation creating the c-IAP2.MALT1 fusion protein activates NF-kappaB independently of TRAF1 AND TRAF2 and contributes to human malignancy in the absence of signaling adaptors that might otherwise regulate its activity 17101977_CARMA3/Bcl10/MALT1-dependent NF-kappaB activation mediates angiotensin II-responsive inflammatory signaling in hepatocytes. 17145608_In vivo data indicate an effect of API2-MALT1 expression on the normal immune response of transgenic mice. 17199743_Our results suggest that MALT1-specific translocations and FOXP1 rearrangements are not commonly involved in pathogenesis. 17894851_careful observation for development of gastric carcinoma and disease progression is essential during follow-up of API2-MALT1-positive MALT lymphoma when patients decline second-line treatment. 17948050_Upon T-cell activation, Malt1 is ubiquitinated, which is critical for the engagement of Carma1-Bcl10-Malt1 and IKK complexes, thereby directing T cell receptor signals to the NF-kappaB pathway. 18231929_BCL10 and MALT1 might not only reflect the lymphocytic origin of H-RS cells, but autonomous activity of this crippled antigen receptor pathway might confer NFB activity and apoptosis resistance 9 at least in those cases of HL expressing wild-type IB. 18367485_chromosome region 18q21 gain including the MALT1 gene is associated with the activated B-cell-like gene expression subtype and increased BCL2 gene dosage and protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 18625728_Data show that the protein kinase C-responsive inhibitory domain of CARD11 functions in NF-kappaB activation to regulate the association of multiple signaling cofactors that differentially depend on Bcl10 and MALT1 for association. 18691973_Caspase-8 undergoes limited activation upon antigenic stimulation, and this activation is dependent on the paracaspase MALT1. 18806265_analysis of protein domains that mediate interaction between Bcl10 and MALT1 19060847_Methylation and API2/MALT1 fusion in colorectal extranodal marginal zone lymphoma. 19112107_components of the CBM complex, Carma3, Bcl10, and Malt1 are key mediators of the CXCL8/IL8-induced NFkappaB activation and VEGF up-regulation. 19234489_TRAF2 interaction is critical for c-IAP2/MALT1-mediated increases in the NF-kappaB activity, increased expression of endogenous NF-kappaB target genes and resistance to apoptosis. 19279678_data suggest that this inherent instability of MALT1-API2 prevents its accumulation and renders a potential effect on MALT lymphoma development via destabilization of BCL10 unlikely 19394813_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19394813_data does not support the hypothesis that germline variations of MALT1 may play a role as genetic risk factors in the development of primary gastric lymphoma. 19444310_T-cell activation triggers the recruitment of the COP9 signalosome (CSN) to the Carma1-Bcl10-Malt1 (CBM) complex, and CSN downregulation impairs TCR-induced IKK activation. 19494296_A20 functions as a Malt1 deubiquitinating enzyme and proteasomal degradation and de novo synthesis of A20 contributes to balance T cell receptor/CD28-induced IKK/NF-kappaB signaling 19841089_These results indicate a growth-promoting role for MALT1 paracaspase activity in activated B cell like-diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 19897720_Results demonstrate a key role for MALT1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) of the activated B-cell subtype, and provide a rationale for the development of pharmacological inhibitors of MALT1 in DLBCL therapy. 19965626_The molecular characterization of the IGH-MALT1 fusion products in 5 new cases of t(14;18)-positive mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas, is reported. 20079017_API2-MALT1 fusion gene is a distinctive genetic aberration in MALT lymphomas, and is not present in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 20695076_activation of NF-kappaB by CXCR4 occurs through Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1 (CBM) complex in OSCC. loss of components of CBM complex in HNSCC can inhibit SDF-1 alpha induced phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaBalpha. 20804738_A20 is cleaved by MALT1 with the realease of the hA20p50 and hA20p37 fragments. 21055028_The presence of 3 copies of bcl-6 and MALT1 genes are the commonest genetic abnormalities observed in ocular MALT lymphomas. 21273489_study shows API2-MALT1 fusion oncoprotein induces proteolytic cleavage of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK); resulting deregulated NIK activity is associated with constitutive noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling, enhanced B cell adhesion and apoptosis resistance 21283787_Thus, dectin-1 and dectin-2 control adaptive T(H)-17 immunity to fungi via Malt1-dependent activation of c-Rel. 21448133_MALT1 proteolytic activity plays a role in T-cell receptor-induced JNK activation through cleavage of CYLD protein. 21757570_the detection of MALT1 gene rearrangements in BALF cells is useful for the diagnosis of pulmonary MALT lymphoma, as it is a specific method that is less invasive than surgical biopsy. 21873235_a central role for Malt1-dependent RelB cleavage in canonical NF-kappaB activation and thereby provide a rationale for the targeting of Malt1 in immunomodulation and cancer treatment. 21966355_Data show that the tandem Ig-like domains of MALT1 exists as a mixture of dimer and tetramer in solution. 22309193_MALT1 has many similarities to caspase 8, even cleaving the putative target protein CYLD with comparable efficiencies, but with diametrically opposite primary substrate specificity. 22366302_Authors provide biochemical and structural evidence that MALT1 activation is dependent on its dimerization and show that mutations at the dimer interface abrogate activity in cells. 22574776_The catalytic activity of MALT1 promotes activation of canonical and non-canonical NF-kappaB as well as other signalling pathways. 22689981_work establishes a molecular link between MALT lymphoma and ABC-DLBCL, and provides mouse models to test MALT1 inhibitors. Finally, our results suggest that hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells may be involved in the pathogenesis of human B-cell lymphomas 22752732_Absence of the carcinoma cell-specific mutation suggests that the inactivation of MALT1 expression but not the mutation promotes oral carcinoma progression 23018871_Report t(14;18)(q32;q21) involving IGH-MALT1 in extranodal diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the breast and testis. 23238016_A selected lead compound, MI-2, featured direct binding to MALT1 and suppression of its protease function. 23238017_These phenothiazines selectively inhibit cleavage activity of recombinant and cellular MALT1 by a noncompetitive mechanism. 23264041_USP2a plays an important role in TCR signaling by deSUMOylating TRAF6 and mediating TRAF6-MALT1 interaction 23358872_Overexpression of MALT1 partially rescues HECTD3 depletion-induced apoptosis. 23416615_monoubiquitination of MALT1 is essential for its catalytic activation and is therefore a potential target for the treatment of ABC-DLBCL and for immunomodulation. 23770847_our study implicates RIP1 ubiquitination as a critical component of API2-MALT1-dependent lymphomagenesis 23778523_observations demonstrate MALT1 represses genes activating the aggressive phenotype of carcinoma cells, and MALT1 acts as a tumour suppressor and the loss of expression stimulates oral carcinoma progression 23799590_Taken together, loss of MALT1 expression alters keratin expression and enhances proliferation of carcinoma cells, and may progress oral carcinomas into the advanced state. 23946259_In the crystal structure of human MALT1casp-Ig3 in complex with the tricyclic phenothiazine derivative thioridazine the inhibitor is bound in a hydrophobic pocket far from the active site. 23977204_Glutamate 549 at the dimerization interface is required for the formation of the enzymatically active, monoubiquitinated form of MALT1. 24004675_This review highlights the recent advances in the normal and disease-related functions of MALT1 24074955_Structure-guided mutagenesis confirmed the observed interfaces in Bcl10 filament assembly and MALT1 activation in vitro and NF-kappaB activation in cells. 24332264_Combined immunodeficiency associated with homozygous MALT1 mutations. 24971370_The MALT1 and MALT1-V1 variant expression level was downregulated in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 25105596_MALT1 auto-proteolysis is essential for NF-kappaB-dependent gene transcription in activated lymphocytes. 25285878_This is q review of the understanding of MALT1 function and regulation, and the development of small molecule MALT1 inhibitors for therapeutic applications. 25384343_Overexpression of CARMA-BCL10-MALT in T-ALL may contribute to the constitutive cleavage and inactivation of A20, which enhances NF-kappaB signaling and may be related to T-ALL pathogenesis. 25500259_MALT1 exerts its effect upon immune response through the initiation of cellular miR-2909 RNomics. 25502755_The strongest hypermethylation signal in type 2 diabetes mellitus is in the promoter of the MALT1 gene, involved in insulin and glycemic pathways, and related to taurocholate levels in blood. 25569716_API2-MALT1 induces paracaspase-mediated cleavage of the tumour suppressor protein LIMA1. 25748427_data demonstrate that MALT1 ubiquitination is critical for the engagement of CBM and IKK complexes, thereby directing platelet signals to the NF-kappaB pathway. 25982276_MALT1-dependent NF-kappaB activation is crucial for the development of EGFR-associated solid-tumor progression 25996250_MALT1 uses multiple strategies to ensure NF-kappaB activation and target gene expression. (Review) 26377317_Comparative analysis of the active site suggests that paracaspases constitute one of the several subclasses of metacaspases that have evolved several times independently. 26386283_Studies indicate that t(11;18)(q21;q21) translocation involves MALT1 (MALT lymphoma translocation protein 1) gene. 26507244_An overview of the present understanding of MALT1's function is presented. [review] 26525107_By regulating linear ubiquitination, MALT1 is both a positive and negative pleiotropic regulator of the human canonical NF-kappaB pathway. 26540570_Data show that Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)inhibitor Ibrutinib augments MALT lymphoma associated translocation protein (MALT1) inhibition by S-Mepazine in CD79 antigen mutant activated B cell-subtype (ABC) of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). 26573773_The MALT1-mediated HOIL-1 cleavage provides a gain-of-function mechanism that is involved in the negative feedback regulation of NF-kappaB signaling. 26668357_Data show that caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 11/B-cell CLL/lymphoma 10/mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1 signaling drives lymphoproliferation through NF-kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. 26716947_The MALT1 is a key player in the activation of the NF-kappa B upon antigen receptor stimulation and lymphocyte activation. 26767426_MALT1 protease activity has a central role in keratinocyte immunity 26787500_Targeting MALT1 proteolytic activity in autoimmune disease and B-cell lymphoma might not be a successful strategy. (Review) 26788853_Backbone Assignment of the MALT1 Paracaspase by Solution NMR. 27006117_results unveil HOIL1 as a negative regulator of lymphocyte activation cleaved by MALT1. 27068814_TCR-induced alternative splicing augments MALT1 scaffolding to enhance downstream signalling and to promote optimal T-cell activation. 27071417_Psoriasis mutations disrupt CARD14 autoinhibition promoting BCL10-MALT1-dependent NF-kappaB activation 27113748_MALT1 deficiency or pharmacological inhibition of MALT1 catalytic activity inhibits pathogenic mutant CARD14-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in human primary keratinocytes. 27253662_A missense mutation in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation 1 gene (MALT1) was identified in a family with siblings with IPEX-Like Syndrome. MALT1 deficiency should now be considered as a possible cause of IPEX-like syndrome associated with immunodeficiency. 27538487_These results demonstrate a key role for the proteolytic activity of MALT1 in PEL, and provide a rationale for the pharmacological targeting of MALT1 in PEL therapy. 27681433_Thrombin-mediated MALT1 protease activation triggers acute disruption of endothelial barrier integrity via CYLD cleavage. 27813118_Taken together, this present study indicates that miR-649 promotes herpes simplex virus type 1 replication through regulation of the MALT1-mediated antiviral signaling pathway and suggests a promising target for antiviral therapies. 27939769_CARD14/MALT1-mediated signaling in keratinocytes has a role in psoriasis [review] 28278699_Mutations in the translocated MALT1 allele is associated with IGH-MALT1-positive MALT lymphoma. 28286260_Authors utilized transcriptomic data and experimental evidences to prove that miR-181d was a novel regulator of NFkappaB signaling pathway by directly repressing MALT1, leading to induced PN markers and reduced MES genes. 28717989_The results suggest that the involvement of MALT1 in DNA damage-induced NF-kappaB is through the recruitment of TRAF6. 29259013_High MALT1 expression is associated with Breast Cancer. 29359407_this first report show that MALT1 integrates several T-cell activation pathways and indirectly controls gamma-chain receptor dependent survival, to impact on T-cell expansion 29382759_MALT1 and TRAF6 cooperatively interact with CARMA1-BCL10 filaments and form CARMA1-BCL10-MALT1-TRAF6 signalosome. 29913212_MALT1 paracaspase also targets MCPIP1 and degrade MCPIP1 protein in endothelial cells. 29953499_These findings suggested that cleavage at R781 of MALT1 played a role in the survival of activated B-cell like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. 30024860_Specific covalent inhibition of MALT1 paracaspase suppresses B cell lymphoma growth. 30214442_review of recent advances in the understanding of the molecular function of the protease MALT1 and summarize how MALT1 scaffold and protease function contribute to the transmission of CBM signals. 30279415_MALT1 C-terminal region covering the Ig2-paracaspase-Ig3 domain is flexibly attached to the BCL10-MALT N-terminal death domain core filaments 30283440_Data indicate the importance of 'tuning' caspase recruitment domain family member 11 (CARD11 or CARMA1)-B cell CLL/lymphoma 10 (BCL10)-MALT1 paracaspase (MALT1) complex (CBM) signaling to preserve immune homeostasis [Review]. 30336982_MALT1 activation by TRAF6 in lymphocytes needs neither BCL10 nor CARD11. 30446641_Cellular metabolism constrains innate immune responses in preterm infants due to perturbations in the expression of PPARgamma, MALT1, DDIT4, and most of the cytokines. 30514565_Deregulated CARD11, BCL10 or MALT1 (CBM) expression or CBM signaling have been associated with immunodeficiency, autoimmunity and cancer. (Review) 30825465_Our findings support a genotype-phenotype relationship that implicates the MALT1 pathway in the allergic immune pathogenesis of peanut allergy. 30898647_Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 sponged miR-195 to regulate proliferation, apoptosis and migration and immune escape abilities of DLBCL by regulation of PD-L1. 31037583_Two patients harboring a novel MALT1 mutation presented with signs of immune deficiency and dysregulation and were found to have an abnormal T cell receptor repertoire. These findings reinforce the link between MALT1 deficiency and combined immunodeficiency. 31133753_Following activation of CD4(+) T cells, NEDD4-binding protein 1 (N4BP1) undergoes rapid cleavage at Arg 509 by the paracaspase mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation 1 (MALT1). MALT1-mediated inactivation of N4BP1 facilitates the reactivation of latent HIV-1 proviruses. 31420608_High MALT1 expression is associated with PAR1-driven NF-kappaB activation and metastasis in osteosarcoma and breast cancer. 31474984_MALT1 Proteolytic Activity Suppresses Autoimmunity in a T Cell Intrinsic Manner. 31556968_Results suggest possibilities regarding targeting of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein-1 (MALT1)-Jun proto-oncogene (c-Jun)-glutaminase (GLS1) axis as a potential therapeutic strategy against activated B cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL). 31644910_MALT1 Phosphorylation Controls Activation of T Lymphocytes and Survival of ABC-DLBCL Tumor Cells. 31774199_Blocking MALT1 protease activity increases the endo-lysosome abundance, impairs autophagic flux, and culminates in lysosomal-mediated cell death 31791579_Domain structures of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation 1 protein for nuclear localization in oral carcinoma cells and the proliferation inhibition. 31961340_GRK2 suppresses lymphomagenesis by inhibiting the MALT1 proto-oncoprotein. 31980531_Studied MALT1 (mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation gene 1) ubiquitination; results found the MALT1 Ig3 domain interacts directly with ubiquitin and was identified as a novel ubiquitin-binding domain, providing insight into the molecular requirements for MALT1 activation. 32213560_MALT1 Protease Plays a Dual Role in the Allergic Response by Acting in Both Mast Cells and Endothelial Cells. 32388054_TAK1 lessens the activity of the paracaspase MALT1 during T cell receptor signaling. 32452133_MALT1 is a potential therapeutic target in glioblastoma and plays a crucial role in EGFR-induced NF-kappaB activation. 32785655_Identification of MALT1 feedback mechanisms enables rational design of potent antilymphoma regimens for ABC-DLBCL. 32831293_GLS1-mediated glutaminolysis unbridled by MALT1 protease promotes psoriasis pathogenesis. 32858082_Human immune disorder associated with homozygous hypomorphic mutation affecting MALT1B splice variant. 33419765_Intrinsic Abnormalities of Keratinocytes Initiate Skin Inflammation through the IL-23/T17 Axis in a MALT1-Dependent Manner. 34273195_MALT1 positively correlates with Th1 cells, Th17 cells, and their secreted cytokines and also relates to disease risk, severity, and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke. 34559885_Progressive B cell depletion in human MALT1 deficiency. 34721419_MALT1-Dependent Cleavage of HOIL1 Modulates Canonical NF-kappaB Signaling and Inflammatory Responsiveness. 34753803_MALT1 Is a Targetable Driver of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Claudin-Low, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. 34788483_Blood MALT1, Th1, and Th17 cells are dysregulated, inter-correlated, and correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients; meanwhile, MALT1 decline during therapy relates to treatment outcome. 34802389_Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HOXD-AS2 promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating the miR-3681-5p/MALT1 signaling pathway. 35079916_Expanding the Clinical and Immunological Phenotypes and Natural History of MALT1 Deficiency. 35262976_Aberrant blood MALT1 and its relevance with multiple organic dysfunctions, T helper cells, inflammation, and mortality risk of sepsis patients. 35353938_MALT1 in asthma children: A potential biomarker for monitoring exacerbation risk and Th1/Th2 imbalance-mediated inflammation. 35500150_Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 in rheumatoid arthritis: Longitudinal change after treatment and correlation with treatment efficacy of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. 35622982_MALT1 positively relates to Th17 cells, inflammation/activity degree, and its decrement along with treatment reflects TNF inhibitor response in ankylosing spondylitis patients. 35727133_A nucleation barrier spring-loads the CBM signalosome for binary activation. 35895897_The Gab2-MALT1 axis regulates thromboinflammation and deep vein thrombosis. 35967391_MALT1 regulates Th2 and Th17 differentiation via NF-kappaB and JNK pathways, as well as correlates with disease activity and treatment outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. 36094731_Assignment of IVL-Methyl side chain of the ligand-free monomeric human MALT1 paracaspase-IgL3 domain in solution. 36314929_Blood MALT1 deficiency is common and relates to unfavorable induction therapy response and survival profile in acute myeloid leukemia patients. |
ENSMUSG00000032688 |
Malt1 |
411.431484 |
3.1847142551 |
1.671164 |
0.132867824 |
154.920913 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000001457057661553558340062188097254023538275116989543701379231133180584186749052609783029069796724680463384515860525425523519515991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000217894337229285936441801930699221473860697233999633455305334142106845727507926727156722284187151394974080176325514912605285644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
627.8968144 |
47.7948693 |
198.4451533 |
11.7081074 |
| ENSG00000172183 |
3669 |
ISG20 |
protein_coding |
Q96AZ6 |
FUNCTION: Interferon-induced antiviral exoribonuclease that acts on single-stranded RNA and also has minor activity towards single-stranded DNA. Exhibits antiviral activity against RNA viruses including hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis A virus (HAV) and yellow fever virus (YFV) in an exonuclease-dependent manner. May also play additional roles in the maturation of snRNAs and rRNAs, and in ribosome biogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11401564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12594219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16033969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21036379}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Manganese;Metal-binding;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;rRNA processing |
|
Enables 3'-5' exonuclease activity and RNA binding activity. Involved in defense response to virus; negative regulation of viral genome replication; and nucleobase-containing compound catabolic process. Located in cytoplasm and nuclear lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:3669; |
Cajal body [GO:0015030]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; exonuclease activity [GO:0004527]; exoribonuclease II activity [GO:0008859]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; single-stranded DNA 3'-5' exodeoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0008310]; U1 snRNA binding [GO:0030619]; U2 snRNA binding [GO:0030620]; U3 snoRNA binding [GO:0034511]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA catabolic process, exonucleolytic [GO:0000738]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364] |
15527770_ISG20has distinctive residues, Met14 and Arg53, to accommodate hydrogen bonds with the 2'-OH group of the UMP ribose, and these residues may be responsible for the preference of ISG20 for RNA substrates 18278447_ISG20 has a role in reducing the synthesis of HBV proteins 21036379_ISG20 inhibited infections by hepatitis C virus, bovine viral diarrhea virus and hepatitis A virus. Moreover, ISG20 demonstrated cell-type specific antiviral activity against yellow fever virus, a classical flavivirus. 23830076_The results suggest that hantavirus infection interferes with DAXX-mediated apoptosis, and expression of interferon-activated Sp100 and ISG-20 proteins may indicate intracellular intrinsic antiviral attempts. 27342813_these data provide a detailed explanation for the specific antiviral action of ISG20 and suggest that ISG20 may act as a promising antiviral drug candidate against IAV. 27626689_Interferon-stimulated gene of 20 kDa protein (ISG20) acts as an innate anti-HBV effector that selectively degrades hepatitis B virus (HBV) RNA and blocks replication of infectious HBV particles. 27764096_We discovered two genome-wide significant SNPs. The first was novel and near ISG20. The second was in TRIOBP, a gene previously associated with prelingual nonsyndromic hearing loss. Motivated by our TRIOBP results, we also looked at exons in known hearing loss genes, and identified two additional SNPs, rs2877561 in ILDR1 and rs9493672 in EYA4 (at a significance threshold adjusted for number of SNPs in those regions). 28521375_Variation at rs12913965 may affect the risk for shoulder dislocation by affecting the activity of either TICRR or ISG20. 29195126_we have identified a novel mechanism involving ISG20 induction by T3 via the IL-8/p-JAK2/p-STAT3 signaling pathway to promote tumor angiogenesis in HCC. 29899085_In conclusion, the authors identified that the influenza A virus-upregulated Long noncoding RNA lnc-ISG20 is a novel interferon-stimulated gene that elicits its inhibitory effect on influenza A virus replication by enhancing ISG20 expression. They demonstrated that lnc-ISG20 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to bind miR-326 to reduce its inhibition of ISG20 translation. 33147372_ISG20 and nuclear exosome promote destabilization of nascent transcripts for spliceosomal U snRNAs and U1 variants. 33830434_Host Interferon-Stimulated Gene 20 Inhibits Pseudorabies Virus Proliferation. 33896836_High expression of ISG20 predicts a poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. 33969602_Interferon-induced degradation of the persistent hepatitis B virus cccDNA form depends on ISG20. 34405956_Placenta-derived interferon-stimulated gene 20 controls ZIKA virus infection. 36177004_The regulation of ISG20 expression on SARS-CoV-2 infection in cancer patients and healthy individuals. |
ENSMUSG00000039236 |
Isg20 |
162.452314 |
3.4366682125 |
1.781011 |
0.338751986 |
26.220900 |
0.00000030450903461956225732755573938626003638319161836989223957061767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001139015040796943387555405745314995868966434500180184841156005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
228.8192728 |
60.7118037 |
66.2285676 |
12.8007957 |
| ENSG00000172216 |
1051 |
CEBPB |
protein_coding |
P17676 |
FUNCTION: Important transcription factor regulating the expression of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses (PubMed:1741402, PubMed:9374525, PubMed:12048245, PubMed:18647749). Also plays a significant role in adipogenesis, as well as in the gluconeogenic pathway, liver regeneration, and hematopoiesis. The consensus recognition site is 5'-T[TG]NNGNAA[TG]-3'. Its functional capacity is governed by protein interactions and post-translational protein modifications. During early embryogenesis, plays essential and redundant roles with CEBPA. Has a promitotic effect on many cell types such as hepatocytes and adipocytes but has an antiproliferative effect on T-cells by repressing MYC expression, facilitating differentiation along the T-helper 2 lineage. Binds to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokines genes and plays a role in the regulation of acute-phase reaction and inflammation. Also plays a role in intracellular bacteria killing (By similarity). During adipogenesis, is rapidly expressed and, after activation by phosphorylation, induces CEBPA and PPARG, which turn on the series of adipocyte genes that give rise to the adipocyte phenotype. The delayed transactivation of the CEBPA and PPARG genes by CEBPB appears necessary to allow mitotic clonal expansion and thereby progression of terminal differentiation (PubMed:20829347). Essential for female reproduction because of a critical role in ovarian follicle development (By similarity). Restricts osteoclastogenesis: together with NFE2L1; represses expression of DSPP during odontoblast differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21272, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12048245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18647749, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829347, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9374525, ECO:0000303|PubMed:25451943}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Essential for gene expression induction in activated macrophages. Plays a major role in immune responses such as CD4(+) T-cell response, granuloma formation and endotoxin shock. Not essential for intracellular bacteria killing. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28033}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Acts as a dominant negative through heterodimerization with isoform 2 (PubMed:11741938). Promotes osteoblast differentiation and osteoclastogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21272, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28033, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11741938}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Alternative initiation;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Glycoprotein;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This intronless gene encodes a transcription factor that contains a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain. The encoded protein functions as a homodimer but can also form heterodimers with CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins alpha, delta, and gamma. Activity of this protein is important in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses, among other processes. The use of alternative in-frame AUG start codons results in multiple protein isoforms, each with distinct biological functions. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2013]. |
hsa:1051; |
C/EBP complex [GO:1990647]; CHOP-C/EBP complex [GO:0036488]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; condensed chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000779]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; chromatin DNA binding [GO:0031490]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; histone acetyltransferase binding [GO:0035035]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding [GO:0035259]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000979]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding [GO:0044389]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; embryonic placenta development [GO:0001892]; granuloma formation [GO:0002432]; hepatocyte proliferation [GO:0072574]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033598]; memory [GO:0007613]; myeloid cell development [GO:0061515]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; ovarian follicle development [GO:0001541]; positive regulation of biomineral tissue development [GO:0070169]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; positive regulation of sodium-dependent phosphate transport [GO:2000120]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:1990440]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of dendritic cell differentiation [GO:2001198]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032675]; regulation of odontoblast differentiation [GO:1901329]; regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045670]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; T-helper 1 cell activation [GO:0035711]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
1934061_Demonstration of alternative translation initiation in mouse 10921906_mutational studies of the rat and chick orthologs demonstrating alternative translational initiation 11452034_mutational studies of mouse ortholog demonstrating alternative translational initiation 11466389_The activities of several functional C/EBPbeta responsive elements in the promoter region and in the intron of CCR5 suggest regulatory roles for C/EBPbeta in CCR5 gene expression and in the pathogenesis of HIV disease. 11741938_These findings provide new insight into the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 promoter by an interplay between two opposite beta isoforms and p300 co-activator. 11751971_PGE(2) induces HIV-1 LTR activity in t cells through a complex interplay between C/EBPbeta and CREB 11756662_CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta is a mediator ofkeratinocyte survival and skin tumorigenesis involving oncogenic Ras signaling. 11825899_C/EBP beta binding to the C/EBP site, which is in part mediated via activation of RSK, can primarily explain the TPA responsiveness of the IGF-I gene promoter 11893744_cooperation with cyclic AMP-induced forkhead transcription factor in differentiating human endometrial stromal cells 11997389_Conserved amino acids regulationregulate phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) gene expression. 12036869_Conditional expression of C/EBP alpha induced the C/EBP family members C/EBP beta and C/EBP epsilon and subsequent granulocyte differentiation. 12071851_Decreased activity and enhanced nuclear export of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein beta during inhibition of adipogenesis by ceramide. 12151100_Organization of the promoter regions involved in transcriptional activation of the human NF-IL6 gene 12213825_both phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of C/EBPbeta in response to growth hormone coordinately modulate its ability to activate transcription by modulating its DNA binding activity and its transactivation capacity 12242300_Calreticulin interacts with C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta mRNAs and represses translation of C/EBP proteins. 12367750_Regulates HIV-1 transcription in activated Jurkat T cells 12393563_IL-1 induces CRP expression through 2 overlapping response elements, the binding sites for CCAAT-box/enhancer-binding protein-beta (C/EBP-beta) and p50-nuclear factor-kappaB (p50-NFkappaB). 12410800_5'-region from -252 to -175, containing a consensus site for CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins alpha,beta (C/EBPalpha,beta), was essential for SAA1 induction in HASMCs. 12482935_IRF-1-CEBPbeta complex activate the promoter of IL-18 binding protein. 12493739_the level of basal as well as cAMP-stimulated IL-10 transcription depends on the expression of C/EBP alpha and beta and their binding to three motifs in the promoter/enhancer region 12496392_A C/EBP beta element in the FasL promoter, identified by a functionally significant single-nucleotide polymorphism, affects FasL expression in vitro and ex vivo and is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in African American patients. 12505790_MEK2 and p38 in IFN-gamma-mediated signal transduction and induction of C/EBP beta expression and activity associated with interleukin-6 (IL-6) secretion in colon epithelial cells. 12618752_Positively functioning NF-IL6 (C/EBPbeta)is not constitutively multiubiquinated by the proteasome. Deletion of leucine zipper domain in NF-IL6 caused the loss of its homodimerization activity & its degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. 12631601_C/EBP-beta may have a role in promoting tumor invasiveness 12665574_HMGI-Y physically interacts with Sp1 and C/EBP beta and facilitates the binding of both factors to the insulin receptor promoter 12670924_There are high levels of FGF-BP expression in invasive human breast cancer, relative to normal breast and in situ carcinoma, and in MDA-MB-468 human breast cancer cells. 12692227_Papillomavirus E2 protein binds to C/EBP factors and may contribute to enhancing keratinocyte differentiation, which is suppressed by the viral oncoproteins E6 and E7 in HPV-induced lesions 12707271_Pretreatment of monocytic cells with low TNF doses inhibited TNF-induced (restimulation with a high dose) IL-8 promoter-dependent transcription as well as IL-8 production, which was prevented by overexpression of C/EBPbeta, but not p65 or Oct-1. 12748173_transcriptional activation of the interleukin-8 promoter by bradykinin involves the prostanoid-independent activation of nuclear factor-kappaB, and prostanoid-dependent activation of activating protein-1 and nuclear factor-interleukin-6 12825852_Expression levels of C/EBPbeta isoforms in breast tumors were correlated with clinicopathological tumor parameters, expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors (ER, PR), Ki67 immunostaining, and expression of 7 cell-cycle regulatory proteins. 12900520_These results suggest that CSF-induced and HIV-1-mediated regulation of Hck and C/EBPbeta represent the heterogeneous susceptibility of tissue macrophages to HIV-1 infection. 12947119_study provides strong evidence that early growth response 1 regulates low density lipoprotein receptor transcription via a novel mechanism of protein-protein interaction with CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta 12970736_We conclude that C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta contribute to the deregulated expression of Bcl-2 in t(14;18) lymphoma cells 14530280_isoform LAP* is the primary isoform of C/EBP beta that regulates, through a redox switch, the LPS-induced expression of the IL-6 gene. 14670999_Overexpression of C/EBP beta was sufficient to increase basal expression of a Dlx3 reporter gene in a dose-dependent manner. 14728809_Transfection of NF-IL63'UTR nduced tumor suppression in a human hepatoma cell line. 14729647_Calcitrio may signal cell differentiation of HL 60 cells which in turn regulates expresson of CEBPB 14759369_Ras-induced structural alteration of C/EBPbeta determines differential gene activation through selective interaction with distinct Mediator complexes 14976428_CEBPbeta could be an important gene in acute promyelocytic leukemia pathogenesis 15044620_mechanisms of MDR1 activation by C/EBPbeta include C/EBPbeta binding of the chromatin of the MDR1 gene and interactions of C/EBPbeta with the Y box and Y box-associated proteins. 15082764_Data show that epidermal growth factor receptor signaling results in phosphorylation of CUG-BP1, and leads to increased binding of CUG-BP1 to CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta (C/EBP beta) mRNA and elevated expression of the C/EBPbeta LIP isoform. 15102854_CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta gene expression is activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress through an unfolded protein response element downstream of the protein coding sequence 15381907_The specific expression pattern of C/EBP-beta in gestational trophoblastic disease indicate that C/EBP-beta could potentially be an additional marker of such lesions. 15385533_ATF3-FL and C/EBPbeta act as transcriptional suppressors for the ASNS gene to counterbalance the transcription rate activated by ATF4 following amino acid deprivation 15561713_NF-kappaB- and C/EBPbeta-driven interleukin-1beta gene expression and PAK1-mediated caspase-1 activation play essential roles in interleukin-1beta release from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages 15688424_Direct interaction between the IL6 promoter and the C/EBP beta protein in myxoid lipoarcoma. 15710476_C/EBP beta is identified as a new partner for HIV-1 Tat in stimulating monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) transcription in astrocytes. 15762841_Defective thermoregulation owing to the lack of C/EBPbeta is associated with the reduced capacity to supply fatty acids as fuels to sustain brown fat thermogenesis. 15777639_C/EBPbeta is involved in the down-regulating of trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) gene expression. 15777798_Activation by C/EBP alpha and beta did not depend on their binding to the C/EBP site, since they still activated IGFBP-5 promoter. 15778453_A new distal enhancer site is identified in the CYP3A4 gene where C/EBPbeta-LAP binds and activates transcription, whereas the truncated form, C/EBPbeta-LIP (liver inhibitory protein), antagonizes LAP activity and causes gene repression. 15785238_This factor plays important roles in the regulation of thyroid specific genes and processes, and its functions are altered in human thyroid carcinoma. 15879117_Transactivators C/EPB-beta and GATE-binding factor 1 (GBF1) physically interact to induce interferon-gamma-regulated transcription; an intact GTPS motif in C/EBP beta regulatory domain 2 is required for an interaction with GBF1. 16009338_Together this shows that glucocorticoids increase DNA-binding activity of C/EBPbeta via post-translational mechanism(s) involving phosphorylation. 16026328_findings show that expression of C/EBPbeta, which contributes to the regulation of amino-acid-responsive genes, is itself controlled by amino acid availability through transcription 16227626_negative cross-talk between p53 and C/EBPbeta is likely to impact expression of their respective target genes 16307770_C/EBPbeta is involved in enhancing transcription from the P670 promoter of HPV16 during keratinocyte differentiation 16318580_GBF1 is recruited to the endogenous IRF-9 promoter, and interacts with C/EBP-beta, IL-1, and IL-6 16399783_C/EBPbeta plays an essential constitutive role in the expression of COX-2, but may not be directly involved in its regulation in association with human labour. 16418324_Identification of the CEBPB gene as a target of translational regulation in myeloid precursor cells transformed by the BCR/ABL oncogene. 16453302_demonstrate a novel role for C/EBP-beta in interleukin-1beta-induced connective tissue disease and define a new nuclear target for the Extracellular Signal-Regulated MAP Kinases pathway in matrix metallopeptidase 1 gene activation 16458921_Several DNA:transcription factor complexes were formed with the conserved regulatory regions identified in multi-species sequence alignment. 16465418_Data imply that the comparison of C/EBP beta expression could be a prognostic marker for patients with glioma. 16563127_identifies new function of C/EBPbeta in LDLR transcription as an oncostatin M-induced transactivator by itself in addition to its role as an EGR-1 co-activator 16608438_ATRA triggers an increase in the translation of C/EBPbeta-LIP that antagonizes C/EBP transactivators by interacting with their binding sites in the albumin promoter 16709933_constitutive expression of C/EBPbeta in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma and its relationship to NPM-ALK 16785565_C/EBP beta is an essential signaling component for inhibition of NF-kappa B-mediated transcription in TNF-tolerant monocytic cells. 16820889_COX-2 is downregulated by PC-SPES via inhibition of NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta in non-small cell lung cancer cells 16959612_C/EBPbeta plays a key role in the coordination of TGFbeta cytostatic gene responses, and its malfunction may trigger evasion of these responses in breast cancer 17203171_CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins alpha and beta have roles in growth and differentiation of hepatoblastomas 17251582_Our data suggest that Tat-C/EBPbeta association is mediated through cdk9, and that phosphorylated C/EBPbeta may influence AIDS progression by increasing expression of HIV-1 genes. 17303761_CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta is a mediator of PPAR delta-dependent 14-3-3 epsilon gene regulation in human endothelial cells. 17335903_c-Rel((1-300)) binding to C/EBPbeta increases the affinity of C/EBPbeta for the C/EBP binding site at -53 on the CRP promoter 17504763_diacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 expression is regulated by CAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) and C/EBPalpha during adipogenesis 17513780_A switch between C/enhancer-binding protein (CEBP) zeta and CEBP beta operates at the CEBP site on the C-reactive protein (CRP)promoter to regulate CRP transcription. 17540774_Important constitutive gene regulatory functions for C/EBPbeta in differentiated macrophages but not in human blood monocytes. 17570496_data demonstrated that chronic inflammation appeared to play roles in induction of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta expression in prostate epithelium which was associated with increased Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and androgen receptor downregulation 17583490_C/EBPbeta is essential for the transcription of the 17beta-HSD8 gene in the liver 17596295_KGF increased integrin alpha(5) expression by phosphorylating C/EBP-beta 17616429_CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta may play a major role in interleukin-6-mediated inhibition of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha gene expression. 17620318_Results identify in Italians a suggestive linkage of early-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D) to chromosome 12q15, in the region of the CHOP gene, but no link to C/EBPbeta. 17652082_IL-17 is a potent inducer of CRP expression via p38 MAPK and ERK1/2-dependent NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta activation. 17675296_C/EBP-beta participates in insulin-responsive expression of the F7 gene. 17705277_The evidence is presented indicating that PDX-1 triggers hepatic dedifferentiation by repressing the key hepatic transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta. 17785586_PPARgamma agonists have diverging and overlapping mechanisms blocking transactivation of transcription factors NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta. 17921324_IL-17 induces MMP-1 in human cardiac fibroblasts directly via p38 MAPK- and ERK-dependent AP-1, NF-kappaB, and C/EBP-beta activation. 17928076_C/EBPbeta was identified as the transcription factor regulating Tas1r3 promoter activity in HuCCT1 cells. 17989362_The effect of cell density and inflammatory conditions on the expression, compartmentalization, activation, and the anti-proliferative function of the GR in primary human lung fibroblast cultures, was studied. 18182446_C/EBPbeta, which binds to multiple cis-regulatory elements in promoter I.3/II, is a key factor in the transcriptional complex controlling aromatase expression in uterine leiomyoma cells. 18198130_Pyk2 is induced and involved in monocyte differentiation and C/EBPbeta is a critical regulator of the Pyk2 expression. 18294142_Lysophosphatidic acid-induced transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E(2) release via C/EBPbeta in human bronchial epithelial cells. 18339625_ERK-regulated site in Med1 protein is also essential for up-regulating interferon-induced transcription although not critical for binding to C/EBP-beta 18512730_C/EBP beta overexpression significantly upregulated promoter activities of IL-8, COX-2, and anti-apoptotic Bfl-1 genes in prostate cancer cells. 18647749_C/EBPbeta as a direct substrate of G9a-mediated post-translational modification that alters the functional properties of C/EBPbeta during gene regulation. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18682709_Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) showed decreased expression of HNF3 beta/FoxA2 and TTF-1 mRNA in papillary thyroid carcinoma cell lines, when compared with normal thyroid cells 18703796_C/EBPbeta was found to have an important role in epithelial cell ICAM-1 regulation, while the adjacent NF-kappaB sequence binds the RelA/p65 and NF-kappaB1/p50 members of the NF-kappaB family to induce ICAM-1 expression in response to H. influenzae. 18786141_NRAMP1 proximal region binds CCAAT enhancer binding proteins alpha or beta and is crucial for transcription 18809921_These data indicate that NF-IL6 is a natural inhibitor of APOBEC3G that facilitates HIV-1 replication. 18852215_ERalpha is involved in the transcriptional regulation of HSD17B8 gene in response to E2 through its interaction with C/EBPbeta. 19014341_the interplay between NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta has an impact on the ability of C/EBPbeta to stimulate TGF-beta1 transcription 19043455_C/EBPbeta regulates bcl-xl gene expression in human breast cancer cells in response to cigarette smoke condensate treatment 19064995_P. aeruginosa induces IL-8 promoter expression and protein production in conjunctival epithelial cells by activating RelA and C/EBPbeta and by promoting the cooperative binding of these transcription factors to the IL-8 promoter 19088256_Tumor necrosis factor-alpha upregulates 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta in HepG2 cells. 19109189_Regulates cytokine production in mature neutrophils; nuclear C/EBPbeta is rapidly phosphorylated upon cell stimulation, suggesting that it can activate cytokine promoters. 19116245_Two CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family members [C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) and C/EBPbeta] enhanced V2 transcription via different pathways. 19126543_a composite enhancer binding both PPARgamma and C/EBPa,b factors confers adipocyte-specific expression to Retn in mouse, and its absence from the human gene may explain the lack of adipocyte expression in humans. 19133313_C/EBPbeta is a mediator of the deleterious effects of unsaturated free fatty acids on beta-cell function. 19169276_Ha-Ras transformation of MCF10A cells leads to repression of Singleminded-2s through NOTCH and C/EBPbeta. 19222842_C/EBP beta is cyclically regulated during the human menstrual cycle and could have a role in endometrial receptivity. 19248099_C/EBPbeta directly binds to the MMP-13 promoter region and stimulates the expression of MMP-13 in chondrocytes in inflammatory arthritis. 19335620_Results demonstrate that intracellular galectin-9 transactivates inflammatory cytokine genes in monocytes through direct physical interaction with NF-IL6. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19487031_Both CBF1 and C/EBP-beta bind the CR2 promoter in B cells raising the possibility that these factors facilitate or respond to alterations in chromatin structure to control the timing and/or level of CR2 transcription. 19489038_C/EBPbeta regulated cell growth and conferred TNF-alpha resistance to prostate cancer cells, in part, via regulation of metastatic gene expression 19523687_Results suggest that the C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta transcription factors enhance expression of the TNFR1 protein in cells. 19592659_C/EBP-beta binds to the CCAAT box in the CD1d promoter, required for its expression in keratinocytes 19632992_Data show that PU.1 participates in the regulation of MD-2 in nonmyeloid cells cooperatively with C/EBPbeta. 19641492_data indicate that the PRDM16-C/EBP-beta complex initiates brown fat formation from myoblastic precursors 19652226_analysis of activation of trophoblast-specific PLAC1 in breast cancer by CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) isoform 2 19690170_Daxx is a new negative regulator of C/EBPbeta with a possible role in acute promyelocytic leukemia 19717648_C/EBPB is up-regulated in multiple myeloma; it directly influences expression of IRF4, BLIMP1, and BCL2 19717648_C/EBPbeta directly bound to the promoter region of IRF4, BLIMP1, and BCL2. 19723873_Found that MMP-1 mRNA levels were maximal following 16 hours of IL-1beta stimulation and that this correlated with the expression of the transcription factor CCAAT enhancer-binding protein-beta (CEBPB). 19733238_Results indicate that regulation of the IkappaBalpha level is one of the underlying mechanisms by which C/EBP-beta controls NF-kappaappaB-associated signalling. 19734226_Elevated chemoattractant CXCL8 hypersecretion in airway smooth muscle cells of patients with asthma is caused by increased binding of CEBPB, nuclear factor NF-kappaB p65, and RNA polymerase II to the CXCL8 promoter. 19747512_Thus C/EBPbeta negatively regulates JCV, which together with NF-kappaB activation, may control the balance between JCV latency and activation leading to progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). 19806478_IL-1beta induces the expression of 11beta-HSD1 mRNA in the fetal lung tissue through mechanisms that involve C/EBPbeta binding to the promoter. 19811452_Data show that C/EBPalpha replaces C/EBPbeta and C/EBPdelta as a regulator of SREBP1c expression in maturing adipocytes. 19903813_Microbial infection promotes the formation of a NFkappaB p50-C/EBPbeta silencer complex in the regulatory sequence of microRNA let-7i. 19962993_These data show that c/EBPbeta is a major regulatory element driving transcription of the CXCL12 gene in response to cytokines and cell confluence. 20004457_Here the authors show that G protein coupled receptor protein of human herpesvirus 8 induces CCL2 in endothelial cells via activation of C/EBPbeta. 20015877_Interference with CEBPbeta expression results in a dramatic decrease in cell proliferation in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells. 20032975_In human glioma, expression of C/EBPbeta and STAT3 correlates with mesenchymal differentiation and predicts poor clinical outcome 20099975_Down regulation of CEBPB is associated with cervical squamous cell carcinoma. 20209087_C/EBP-beta regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered cell death in mouse and human models 20224108_A robust induction of C/EBPbeta indicates that it is a biomarker of endometrial receptivity and plays a conserved functional role during implantation. 20225273_proposed a model in which C/EBPbeta plays an important role in the osteolytic characteristics and pathological causes of giant cell tumor of bone 20351173_Results identify four novel C/EBPbeta-activating modifications, including RSK-mediated phosphorylation of a bifunctional residue in the leucine zipper that regulates DNA binding and homodimerization and thereby promotes cell cycle arrest. 20385540_C/EBPbeta is able to up-regulate CDH3 promoter activity in breast cancer cells; the expression of C/EBPbeta linked with a worse prognosis of breast cancer patients 20452968_CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein beta DNA binding is auto-inhibited by multiple elements that also mediate association with p300/CREB-binding protein 20460359_Common allelic variants in CEBPB could influence abdominal obesity and related metabolic abnormalities associated with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in healthy White Northern European families. 20460359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20583135_Data show that IGFBP5 expression is down-regulated during 4HPR-induced neuronal differentiation of human RPE cells through a MAPK signal transduction pathway involving C/EBPbeta. 20605485_C/EBPbeta is a critical regulator of the immunosuppressive environment created by growing cancers. 20638476_HSD17B10 is regulated by several isoforms of C/EBP-beta in HepG2 cells. 20690902_Transcription of hHSS triggered by EGF (epidermal growth factor) and the role of C/EBPbeta (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta) as a potential core factor responsible for hHSS transcription in HepG2 cells, was investigated. 20699097_C/EBPbeta isoform, LIP, is another member of the group of transcription factors, including E2F1 and p53, which are capable of playing a role in autophagy. 20702408_CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein {beta} and NF-{kappa}B mediate high level expression of chemokine genes CCL3 and CCL4 by human chondrocytes in response to IL-1{beta}. 20797423_Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers suppression of AMPK while increasing C/EBPbeta and pCREB expression which activates PEPCK gene transcription. 20818427_we show that C/EBPbeta1 induces senescence. Taken together, degradation of C/EBPbeta1 by Ras activation may represent a mechanism to bypass OIS. 20948428_UA can promote the monocytic differentiation of HL60 cells and increase the expression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta by activating the ERK pathway 21048943_Knock-down of C/EBP-beta abrogated CSC-mediated activation of LOC554202. Over-expression of miR-31 significantly enhanced proliferation and tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells; knock-down of miR-31 inhibited growth of these cells 21098707_Findings reveal a novel mechanism through which HER2 silences tumor suppression in a concerted manner by switching expression of C/EBPss isoforms. 21145827_used the opposing transcriptional effects driven by LAP and LIP to determine the genuine C/EBPbeta molecular signature in the Hep3B cell line. We subsequently investigated the role of each of the LAP and LIP isoforms in drug-induced Hep3B cell death. 21283634_the tumor suppression in SMMC-7721 by C/EBPbeta 3'UTR RNA is due to the inhibition of protein kinase Cepsilon activity through direct physical interaction between C/EBPbeta 3'UTR RNA and protein kinase Cepsilon. 21302301_these studies reveal how the C/EBPbeta factor, known to have a key role during osteogenesis, contributes to regulating the expression of Runx2, the master regulator of osteoblast differentiation. 21303932_CEBPbeta, CYP1B1, and FOS mRNA and protein expression was increased in Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cellss derived from pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. 21308746_Results suggest that the p38alpha, MAPK, and MKK6 play prominent roles in IL-1beta and C/EBP-beta-mediated C3 gene expression in astrocytes. 21326902_Studies indicate that the CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins alpha and beta (C/EBPalpha,beta) are founding members of the C/EBP-transcription factor family. 21343335_this thus demonstrates that C/EBPbeta is indeed regulated at the posttranscriptional level by HuR in ALK(+) anaplastic large cell lymphomas. 21344389_CEBPB is both necessary and sufficient to activate MMP-1 gene expression in a chondrosarcoma cell line via ERK MAP kinases and p90 ribosomal S6 kinases. 21345218_TGFbeta1 induced MAD1 expression by recruitment C/EBPalpha/beta heterodimers, SP1, and SMAD3 binding to promoter of the MAD1. 21389327_We could demonstrate that C/EBPbeta protein expression is under eIF4E-translational control in multiple myeloma 21447826_C/EBPbeta mediates the activation of EBV lytic gene expression associated with bortezomib and another UPR inducer. 21471847_C/EBP-beta may be involved in mediating PGE2-induced IL-8 activation in astrocytomas 21545825_A striking activity of C/EBP is imaged predominantly in the brain of living C/EBP-luc transgenic mice in response to lipopolysaccharide, showing for the first time in vivo that C/EBP mediates the brain response to inflammation. 21558273_C/EBPbeta reduces monocytic proliferation by affecting the retinoblastoma/E2F/cyclin E pathway and that it may contribute to, but is not directly required for, macrophage morphology. 21595849_hyperplastic parathyroid cells in nodules have an autonomous proliferation mechanism similar to that of cancer, in which C/EBPb is upregulated and phosphorylated to interact with the oncogenic Ras/MAPK pathway 21612443_The -110 to -79 sequence segment upstream from the transcription initiation site of Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a TPA responsive element (TRE), and its induction is controlled by CCAAT-Enhancer-Binding Protein-beta. 21689417_study demonstrates that the Src/Stat3 and C/EBP signaling pathways positively regulate the expression of the Jab1 oncogene; results show that Stat3 and LAP2 (C/EBP-beta2) are the two major transcription factors that contribute to Jab1 overexpression that leads to increased proliferation of breast cancer cells 21804532_3'UTR inhibition and Cebpb mRNA compartmentalization were absent in primary fibroblasts, allowing Ras-induced C/EBPbeta activation and oncogene-induced senescence to proceed. 21854628_CCAAT-enhancer binding protein beta expression and elevations in LIP play an important role in regulating cellular survival via suppression of anoikis 21883217_Mutation of the C/EBP-beta response element abrogates C/EBP-beta- and glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transactivation of norepinephrine transporter. 21899882_The ERK_CEBP/beta intracellular signaling is a key inflammatory pathway that links phagocytosis of wear particles to inflammatory gene expression in osteoprogenitors. 21917825_data demonstrate that C/EBPbeta is involved in expression of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and ADAMTS-5 in arthritic synovium and cartilage 21980398_Sumolylation of C/EBPbeta1 in breast cancer cells may be a mechanism to circumvent oncogene-induced senescence. 21988375_Altered PRKRA signalling and C / EBPbeta expression is associated with HLA-B27 expression in monocytic cells. 21998664_RSK-C/EBPbeta phosphorylation pathway may contribute to the development of lung injury and fibrosis 22013073_C/EBP is a newly identified transcriptional activator of the LMP1 gene, independent of the EBNA2 coactivator 22080951_amino-acid changes in the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta (CEBPB, also known as C/EBP-beta) in the stem-lineage of placental mammals changed the way it responds to cyclic AMP/protein kinase A (cAMP/PKA) signalling 22095691_findings show that C/EBPbeta and RUNX2, with MMP-13 as the target and HIF-2alpha as the inducer, control cartilage degradation 22152057_finding that raised CEBPB expression in circulating leukocyte-derived RNA samples in vivo is associated with greater muscle strength and better physical performance in humans 22242598_Physical interaction is confirmed between human remodeling subunit RSF proteins C/EBPbeta, chromatin remodeling protein SNF2H, and apobec-1 complementation factor ACF1. 22374303_C/EBP-beta target genes in monocytic cells are summarized and resulting functions are described, including regulation of proliferation and differentiation as well as orchestration of processes of mainly the innate immune response. [review] 22379085_knockdown of C/EBPbeta isoforms blocks activation of human papillomavirus (HPV) late gene expression from complete viral genomes upon differentiation. 22538425_both expanded limbal NCs and HUVEC rejoined with LEPC to form spheres to upregulate expression of DeltaNp63alpha, CK15, and CEBPdelta, the former but not the latter abolished expression of CK12 keratin. 22689263_Data show that C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta promote Dio2 expression in the trophoblastic cell line JEG3 through a conserved CCAAT element, which is a novel key component of the Dio2 promoter code that confers tissue-specific expression of D2 in these cells. 22728165_In prostate cancer cells, S100A8 expression is stimulated by prostaglandin E2 via EP2 and EP4 receptors through activation of the protein kinase A signaling pathway and stimulation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding-protein-beta binding to the S100A8 promoter. 22763786_We showed that C/EBPbeta interacts with the proximal promoter of the gene ABCC6. 22818222_C/EBPbeta regulates interleukin (IL)-1beta astrocytic inflammatory genes. 22860016_The LIP isoform of CEBPB mediates a non-apoptotic cell death process via engulfment of neighboring cells. 22911498_we identified the differentiation-associated transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta as a critical regulator of CCL20 gene expression in normal human keratinocytes. 22921787_these results provide evidence that the cancer cell growth suppression by this 62nt RNA containing AU-rich elements may be due to competitive binding to HuR. 22955269_hepatitis C virus induced an increase in activation of the major gluconeogenic transcription factors including CEBPB, promoting gluconeogenic gene expression. 23097472_these findings revealed a novel functional link between C/EBPbeta and STAT3 that is a critical regulator of endometrial differentiation in women. 23314288_Authors conclude the regulation of both C/EBPbeta gene expression and C/EBPbeta-LIP and C/EBPbeta-LAP protein turn-over plays an important role for the expression of adipogenic regulators and/or adipocyte differentiation genes in early adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stromal/progenitor cells and at later stages in human immature adipocytes. 23560079_USF2 functionally interacts with YY1 blocking its inhibitory activity, in favor of CEBPB transactivation. 23711709_Study was done to identify target genes of transcription factor CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta (CEBPB) in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by all-trans retinoic acid. 23741337_C/EBPbeta-regulated proteins BCL2A1, G0S2 and DDX21 play a crucial role in survival and proliferation of ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells. 23770848_loss of BRM epigenetically induces C/EBPbeta transcription, which then directly induces alpha5 integrin transcription to promote the malignant behavior of mammary epithelial cells 23782703_data provide evidence for CS/GH-V dysregulation in acute HFD-induced obesity in mouse pregnancy and chronic obesity in human pregnancy and implicate C/EBPbeta, a factor ass |
ENSMUSG00000056501 |
Cebpb |
264.042042 |
2.3689455498 |
1.244245 |
0.111460620 |
124.911100 |
0.00000000000000000000000000005322662026340033310049685967643550781637897984975466306990402680804704924218649642053691195542342029511928558349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000661300433575579866882132394298921618460285710149609501146679847886558764255560127764965727692469954490661621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
376.1181658 |
22.5230213 |
160.0133689 |
7.6663853 |
| ENSG00000172232 |
566 |
AZU1 |
protein_coding |
P20160 |
FUNCTION: This is a neutrophil granule-derived antibacterial and monocyte- and fibroblast-specific chemotactic glycoprotein. Binds heparin. The cytotoxic action is limited to many species of Gram-negative bacteria; this specificity may be explained by a strong affinity of the very basic N-terminal half for the negatively charged lipopolysaccharides that are unique to the Gram-negative bacterial outer envelope. It may play a role in mediating recruitment of monocytes in the second wave of inflammation. Has antibacterial activity against the Gram-negative bacterium P.aeruginosa, this activity is inhibited by LPS from P.aeruginosa. Acting alone, it does not have antimicrobial activity against the Gram-negative bacteria A.actinomycetemcomitans ATCC 29532, A.actinomycetemcomitans NCTC 9709, A.actinomycetemcomitans FDC-Y4, H.aphrophilus ATCC 13252, E.corrodens ATCC 23834, C.sputigena ATCC 33123, Capnocytophaga sp ATCC 33124, Capnocytophaga sp ATCC 27872 or E.coli ML-35. Has antibacterial activity against C.sputigena ATCC 33123 when acting synergistically with either elastase or cathepsin G. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1399008, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1937776, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2312733}. |
3D-structure;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Chemotaxis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Membrane;Reference proteome;Serine protease homolog;Signal;Zymogen |
|
Azurophil granules, specialized lysosomes of the neutrophil, contain at least 10 proteins implicated in the killing of microorganisms. This gene encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate a mature azurophil granule antibiotic protein, with monocyte chemotactic and antimicrobial activity. It is also an important multifunctional inflammatory mediator. This encoded protein is a member of the serine protease gene family but it is not a serine proteinase, because the active site serine and histidine residues are replaced. The genes encoding this protein, neutrophil elastase 2, and proteinase 3 are in a cluster located at chromosome 19pter. All 3 genes are expressed coordinately and their protein products are packaged together into azurophil granules during neutrophil differentiation. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:566; |
azurophil granule [GO:0042582]; azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extrinsic component of membrane [GO:0019898]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding [GO:0043395]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; toxic substance binding [GO:0015643]; antimicrobial humoral response [GO:0019730]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular extravasation [GO:0045123]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; glial cell migration [GO:0008347]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; monocyte activation [GO:0042117]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; neutrophil-mediated killing of bacterium [GO:0070944]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of fractalkine production [GO:0032724]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process [GO:0045348]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; protein kinase C signaling [GO:0070528]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043114] |
11861296_Secretion of heparin-binding protein (CAP37) from human neutrophils is determined by its localization in azurophilic granules and secretory vesicles 11891183_CAP37 is localized within the vascular endothelium associated with atherosclerotic plaques. CAP37 is induced in endothelial cells in response to inflammatory mediators 11994286_Azurocidin 1 displays antimicrobial activity against E. coli, S. faecalis, and C. albicans. 12054586_structural analysis of N-glycans 12135665_A comparison of proforms and mature forms of azurocidin in regulating granulopoiesis 12438368_arginine-rich residues of CAP37 amplify lipopolysaccharide-induced monocyte activation 12826073_CAP37 is a neutrophil-derived inflammatory mediator that augments leukocyte adhesion to endothelial monolayers 14515154_Azurocidin 1 (cationic antimicrobial protein 37)is a multifunctional inflammatory mediator causing an increase of vascular permeability [review]. 15020208_Due to its localization to atherosclerotic plaques and its ability to modulate smooth muscle cells, CAP37 may play a role in the progression of this disease. 15879141_Secretion of CAP37, a neutrophil granule protein accumulating on the endothelial cell surface and promoting arrest of monocytes, could contribute to the recruitment of monocytes at inflammatory loci. 18346022_HBP appears to be one of the primary effector molecules of antibody-mediated nonhemolytic transfusion reactions including transfusion acute lung injury 18787642_HBP and human neutrophil peptides 1-3 triggered macrophage release of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma, which acted in an autocrine loop to enhance expression of CD32 and CD64 and thereby enhance phagocytosis[heparin-binding protein, HBP] 19151333_Data show that human neutrophils challenged with leukotriene B(4) release heparin-binding protein as determined by Western blot analysis. 19590686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20083497_The TAASC motif in a cyclizised 20-44 amino acid peptide is part of the ligand in HBP responsible for activation of the HBP receptor on monocytes. Monocytes release HBP constitutively in small amounts and more so in the presence of lipopolysaccharide. 20107486_group A streptococci induce contact activation and HBP release during skin infection, which likely contribute to the symptoms seen in erysipelas: fever, pain, erythema, and edema 20399025_Proliferating bile ductules may play a role in the inflammatory response in biliary atresia through expression of CAP37. 22207392_Heparin-binding protein is elevated in patients with shock from septic and non-septic etiologies. 22278372_AZU1 exhibited high affinity binding to PTX3 in a calcium ion-dependent manner 23808364_Low levels of azurocidin in maternal serum in the first trimester were associated with subsequent preterm prelabor rupture of membranes. 23883488_Plasma levels of heparin-binding protein were significantly higher in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. 25412625_identified a multifunctional bioactive peptide, based on CAP37, that induces cell migration, possesses antibacterial and LPS-binding activity, and is effective at healing infected and noninfected corneal wounds in vivo. 26170148_Neuronal CAP37 may modulate the neuroinflammatory response in Alzheimer disease. 29288710_the patterns of HBP regulation of the expression of the adhesion molecular VCAM-1 were similar to those seen in MCP-1 after pretreatment with inhibitors 31608993_patients with chronic periodontitis displayed 3.6 times mean higher levels of azurocidin in gingival crevicular fluid than healthy controls 32156261_Heparin-binding protein measurement improves the prediction of myocardial injury-related cardiogenic shock. 33454168_The Dynamics of Heparin-Binding Protein in Cardiothoracic Surgery-A Pilot Study. 33868298_Serum Heparin-Binding Protein as a Potential Biomarker to Distinguish Adult-Onset Still's Disease From Sepsis. 34151489_Combined detection of procalcitonin, heparin-binding protein, and interleukin-6 is a promising assay to diagnose and predict acute pancreatitis. 34418081_Azurocidin is loaded into small extracellular vesicles via its N-linked glycosylation and promotes intravasation of renal cell carcinoma cells. 34495248_Diagnostic value of heparin-binding protein in the cerebrospinal fluid for purulent meningitis in children. 34965528_The Dynamics of Circulating Heparin-Binding Protein: Implications for Its Use as a Biomarker. 35024012_Application Value of Blood Heparin-Binding Protein in the Diagnosis of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 35220703_[Changes of heparin-binding protein in severe burn patients during shock stage and its effects on human umbilical vein endothelial cells and neutrophils]. 35628475_Human Platelets Contain, Translate, and Secrete Azurocidin; A Novel Effect on Hemostasis. 36195852_Clinical value of serum sTREM-1 and HBP levels in combination with traditional inflammatory markers in diagnosing hospital-acquired pneumonia in elderly. 36245028_Increased CAP37 Expression in Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. |
|
|
405.150702 |
0.1243295184 |
-3.007759 |
0.106396220 |
913.776518 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000993107707447951786798620252720555959968189179638847747024442685632743151399795425308227843662314325354972159002951986138992074599 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000910451538008184377633439879564418282008580827954137164858113777621262144192379313800905530452333400462940392384907206008073974308 |
Yes |
No |
90.2444736 |
6.1917428 |
731.4861049 |
25.0221213 |
| ENSG00000172243 |
64581 |
CLEC7A |
protein_coding |
Q9BXN2 |
FUNCTION: Lectin that functions as pattern recognizing receptor (PRR) specific for beta-1,3-linked and beta-1,6-linked glucans, which constitute cell wall constituents from pathogenic bacteria and fungi (PubMed:11567029, PubMed:12423684). Necessary for the TLR2-mediated inflammatory response and activation of NF-kappa-B: upon beta-glucan binding, recruits SYK via its ITAM motif and promotes a signaling cascade that activates some CARD domain-BCL10-MALT1 (CBM) signalosomes, leading to the activation of NF-kappa-B and MAP kinase p38 (MAPK11, MAPK12, MAPK13 and/or MAPK14) pathways which stimulate expression of genes encoding pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (By similarity). Enhances cytokine production in macrophages and dendritic cells (By similarity). Mediates production of reactive oxygen species in the cell (By similarity). Mediates phagocytosis of C.albicans conidia (PubMed:17230442). Binds T-cells in a way that does not involve their surface glycans and plays a role in T-cell activation. Stimulates T-cell proliferation. Induces phosphorylation of SCIMP after binding beta-glucans (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6QLQ4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11567029, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12423684, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17230442}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Lectin;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. The encoded glycoprotein is a small type II membrane receptor with an extracellular C-type lectin-like domain fold and a cytoplasmic domain with an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif. It functions as a pattern-recognition receptor that recognizes a variety of beta-1,3-linked and beta-1,6-linked glucans from fungi and plants, and in this way plays a role in innate immune response. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. This gene is closely linked to other CTL/CTLD superfamily members on chromosome 12p13 in the natural killer gene complex region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:64581; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; (1->3)-beta-D-glucan binding [GO:0001872]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; MHC protein binding [GO:0042287]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; antifungal innate immune response [GO:0061760]; carbohydrate mediated signaling [GO:0009756]; cell activation [GO:0001775]; cell recognition [GO:0008037]; cellular response to molecule of fungal origin [GO:0071226]; defense response to protozoan [GO:0042832]; detection of fungus [GO:0016046]; detection of molecule of fungal origin [GO:0032491]; detection of yeast [GO:0001879]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; phagocytosis, recognition [GO:0006910]; positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050850]; positive regulation of cell maturation [GO:1903431]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900017]; positive regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production [GO:0002732]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of interleukin-23 production [GO:0032747]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of killing of cells of another organism [GO:0051712]; positive regulation of lymphocyte activation [GO:0051251]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production [GO:0071639]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of respiratory burst [GO:0060267]; positive regulation of superoxide anion generation [GO:0032930]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:2000318]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070884]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; response to yeast [GO:0001878]; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002223]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
12423684_Dectin-1b cDNA encodes for a transmembrane protein of the C-type lectin-like receptor family. It is selectively expressed in several purified DC subpopulations but not in monocytes and is up-regulated upon stimulation with lipopolysaccharide. 14707091_Uptake of zymosan particles can occur by beta glucan receptor (or SIGNR1) and results in TNF-alpha production by macrophages. 15956283_Dectin-1 activates Syk tyrosine kinase in macrophages for reactive oxygen production 16870151_hDectin-1E was not secreted and it mainly resided in the cytoplasm. The binding of hDectin-1E and RanBPM was further confirmed in vivo by co-immunoprecipitation assay and confocal microscopic analysis. 17182550_CD37 is important for dectin-1 stabilization in APC membranes and controls dectin-1-mediated IL-6 production. 17698636_hDectin-1 is involved in the uptake and cross-presentation of cellular antigens. 18549457_dectin-1 synergizes with both TLR2 and TLR4 pathways for the production of TNF-alpha in human primary PBMCs and in monocyte-derived macrophages. 19122653_dectin-1 activates two independent signaling pathways, one through Syk and one through Raf-1, to induce immune responses. 19134118_Our results demonstrate that TLR2, TLR4 and Dectin-1 actively sense, internalize and respond in an innate way to Mycobacterium ulcerans in human epidermal keratinocytes. 19223162_co-stimulation of dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor and Dectin-1 induces the metabolism of arachidonic acid 19358895_Collectively, these findings identify Dectin-1 as a key receptor influencing critical biological functions of DC in response to C. albicans leading to T cells response alteration. 19614557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19614557_This study suggests a crucial role played by dectin-1 in the mucosal antifungal mechanisms in immunocompromised hosts. 19633936_demonstrate the novel induction of Dectin-1 in type II airway epithelial cells and its critical role in the innate immune response against Mtb in non-phagocytic cells 19773555_Dectin-1 engagement by Mtb enables DC to promote a Th1/Th17 response, whereas DC-SIGN and MR costimulation limits dectin-1-dependent Th17 generation and favors a Th1 response, probably by interfering with release of cytokines. 19811837_Dectin-1, although indispensable for recognition of beta-glucan-bearing particles in mice, is not the major receptor for yeast particles in human neutrophils. 19864674_mutated form of dectin-1 was poorly expressed, did not mediate beta-glucan binding, and led to defective production of cytokines...higlights specific role of dectin-1 in human mucosal antifungal defense 19888805_Results demonstrate a decrease of TLRs and dectin-1 expression mainly on monocytes as opposed to neutrophils, as soon as 30 minutes after Paracoccidioides brasiliensis stimulation. 19915667_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19915667_dectin-1 expression is elevated on macrophages, neutrophils, and other immune cells involved in the inflammatory reaction in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but is not the major susceptibility factor for IBD. 20158887_loss of one functional allele of DECTIN-1 is not associated with either susceptibility to or severity of rheumatoid arthritis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20299682_the MTB-induced IL-17A response relies strongly on the endogenous IL-1 pathway and IL-1R signaling. TLR4 and dectin-1 are the main receptors responsible for mediating the signals responsible for IL-17A production by MTB. 20360401_distinct roles of CR3, Dectin-1, and sialic acids in the interaction with Histoplasma and suggested that multiple receptor use might be important to host defense against Histoplasma. 20421639_beta-glucans are recognized by membrane-associated dectin-1 and cytoplasmic NLRP3 inflammasome 20452827_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452827_The effects of the dectin-1 Y238X polymorphism on graft-versus-host disease and Candida sp. colonization in stem cell transplantation patients are reported. 20577092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20608913_Mast cells from atopic eczema patients have impaired upregulation of the fungal recognition receptor Dectin-1. 20631729_A remarkably high expression of dectin-1 mRNA was observed in psoriatic epidermis 20700596_Dectin-1, a pattern recognition receptor involved in antifungal immunity, polymorphisms in the gene may play a role in human disease (Review) 20807886_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20807886_role for Dectin-1 in antifungal immunity that is the ability to control both resistance and tolerance to the fungus contingent on hematopoietic/nonhematopoietic compartmentalization 21242599_dectin-1 Y238X heterozygosity has a limited influence on susceptibility to invasive aspergillosis and may be important in susceptible non-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients; this is partly due to redundancy inherent in innate immune system 21283787_Thus, dectin-1 and dectin-2 control adaptive T(H)-17 immunity to fungi via Malt1-dependent activation of c-Rel. 21296999_Regulation of dectin-1-mediated dendritic cell activation by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligand troglitazone. 21426724_TLR2 and Dectin-1 were expressed by endothelial cells in response to Aspergillus fumigatus stimulation. 21515468_Expressions of TLR2, TLR4 and dectin-1 increased in HaCaT cells in response to Trichophyton rubrum exposure. 21531876_results define the dectin-1/inflammasome pathway as the mechanism that enables the host immune system to mount a protective Th17 response and distinguish between colonization and tissue invasion by Candida albicans 21876553_Mycobacterium abscessus activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via dectin-1/Syk-dependent signaling and the cytoplasmic scaffold protein p62/SQSTM1 in human macrophages. 21881131_genetic variation in DECTIN-1 was not associated with susceptibility to candidemia. 21985303_We demonstrate that heterozygosity for the Y238X DECTIN-1 polymorphism in HIV-infected patients predisposes to bacterial infections, and in particular to pneumonia. 22199280_Yeast-derived beta-glucan lacks cytotoxic effects towards B-lymphoma cells but up-regulation of CD86 suggests maturation of the cells via dectin-1 by the carbohydrate 22267217_dectin-1 acted as an extracellular sensor for pathogens that induced both IL-1beta production and maturation through a noncanonical caspase-8-dependent inflammasome for protective immunity 22384201_Dectin-1 and DC-SIGN polymorphisms are associated with invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis infection 22562430_Dectin-1 contributes to the Aspergillus fumigatus-induced chemokine synthesis in human bronchial epithelial cells. 22674328_identified a polymorphism in the gene for Dectin-1 (CLEC7A) that is strongly linked to a severe form of ulcerative colitis 22952831_Antibody constant region peptides can display immunomodulatory activity through activation of the Dectin-1 signalling pathway 23097038_Expression and function of dectin-1 is defective in monocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. 23239982_These data demonstrate that MBL has an ability to mediate the opsonophagocytosis of Candida albicans by human neutrophils independent of complement activation, which is coupled with intracellular Dectin-1-triggered ROS production 23332664_Results suggest that dectin-1 may play a role in the development of nasal polyps, and may participate in the inflammatory reaction in nasal polyps. 23374272_nonsense mutation in the CLEC7A gene, p.Tyr238X, rs16910526 and a novel homozygous frameshift variant in exon 27 of the DOCK8 gene, c.3193delA were identified in brothers with an immunodeficiency syndrome characterized by severe eczema, milk and egg allergies, infections, diarrhea, failure to thrive and, in two of the three, lymphoma lymphoma 23475217_beta-glucan primes the response to components of human microbiota through the dectin-1 and noncanonical Raf-1 kinase pathway. 23674515_Vimentin is an endogenous, activating ligand for Dectin-1. Its presence in areas of artery wall inflammation and O production suggests that vimentin activates Dectin-1 and contributes to lipid oxidation and cholesterol accumulation in atherosclerosis. 23745599_Melatonin synthesis in human colostrum mononuclear cells enhances dectin-1-mediated phagocytosis by mononuclear cells. 23787127_interaction of Dectin-1 with TLR2 seemed to require that both receptors are from the same species 24068891_we found that secretory IgA is taken up by M cells via the Dectin-1 receptor, with the possible involvement of Siglec-5 acting as a co-receptor. 24094722_Levels of expression of C-type lectin maybe associated with the pathogenesis of otitis media with effusion. 24440830_The superoxide induction with whole glucan particle was concluded to be Dectin-1-mediated and required Src family kinases, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and protein kinase B/Akt. 24721111_this study investigated the role of dectin-1 expressed by keratinocytes in wound healing 24808366_The unconventional protein secretion triggered by the dectin-1 pathway is dependent on inflammasome activity and an active autophagic process. 24835401_Induction and activation of human Th17 by targeting antigens to dendritic cells via dectin-1. 24864436_dectin-1 expression in conjunctival epithelial cells (CECs) was demonstrated, and expression of both dectin-1 and BAFF in CECs is thought to be involved in pathologic aggravation of allergic inflammatory in patients with vernal keratoconjuctivitis 25008994_The result of this study suggests that there is no correlation between Dectin-1 Y238X Gene polymorphism and RVVC. 25161190_Dectin-1 expressed on human pulmonary epithelial cells has a considerable impact on the Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae triggered immune response. 25251945_IECs may respond to beta-glucans by the secretion of pro-inflammatory chemokines in a Dectin-1- and Syk-dependent pathway 25267792_CARD9 regulates H-Ras activation by linking Ras-GRF1 to H-Ras, which mediates Dectin-1-induced extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) activation and proinflammatory responses when stimulated by their ligands. 25461401_Data indicate that Candida albicans beta-Glucan induces high IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) levels, independently from Dectin-1/complement receptor 3 (CR3). 25883525_The analysis of Dectin-1 gene polymorphisms showed no significant association with fungal keratitis in the northern Han Chinese population. 26123355_this study provides novel and opposing functions of hDectin-1 expressed on the two major human DC subsets, pDCs and mDCs 26156997_This study demonstrated that Toll-Like Receptors and Dectin-1, a C-Type Lectin Receptor, Trigger Divergent Functions in CNS Macrophages. 26352598_Our data suggest that the genetic diversity of CLEC7A gene influences the autism spectrum disorders (ASD) phenotype by behaving as a disease specifier and imply that the genetic control of innate immune response could determine the ASD phenotype. 26709456_Dectin-1 is essential for efficient immune response against Mycobacteria. 26739065_dectin-1 has a role in glycyrrhetinic acid inhibition of contact hypersensitivity induced by trichophytin 26963509_study represents the first analysis demonstrating that harbouring polymorphisms of Dectin-1 (rs7309123) or TLR2 (rs5743708) represents an independent risk factor of developing IFD in patients with AML undergoing induction chemotherapy. 26963514_TREM-1 and Dectin-1 function concurrently in the corneal innate immune response by regulating inflammatory cytokine expression in fungal keratitis. 27449326_this study shows that curdlan inhibits tumor growth via activating dendritic cells through dectin-1 signaling 27600310_high tumoral dectin-1 expression was an independent predictor of adverse clinical outcome in ccRCC patients. This molecule and established nomograms might help clinicians in future decision making and therapeutic developments 28303575_Unique cytokine secretion and varying expression levels of n Dectin-1 isoforms on monocyte-derived cells may indicate distinct isoform usage as a cell type-specific mechanism of regulating anti-fungal immunity. 28335387_Dectin-1-mediated activation of the Syk, MAPKs, PI3K and NF-kappaB signaling pathways contributes to F. proliferatum-stimulated CXCL-8 release from BEAS-2B cells and provides an important basis for developing novel therapeutic strategies in clinical allergy. 28394331_Dectin 1 is highly expressed on macrophages in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 28454101_theses data suggest miR-146a may play the potent negative feedback regulator in inflammatory response following Dectin-1 stimulation 28614714_Dectin-1 may have therapeutic implications as a biomarker for metabolic dysregulation in humans. 28848046_These results suggest that the intracellular domain, not ligand-binding domain, of Dectin-1 determines the species-specific ligand profile. 28873980_Dectin-1 is expressed on mDCs and is down-regulated after contact with A. fumigatus, indicating that mDCs recognize A. fumigatus via this receptor. Blocking of Dectin-1, followed by stimulation with depleted zymosan diminished the up-regulation of the T-cell co-stimulatory molecules CD40, CD80, HLA-DR and CCR7 on mDCs and led to decreased release of the cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-8, IL-1beta and IL-10. 28926773_this study shows that Dectin-1 is essential for IL-1beta production through JNK activation and apoptosis in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis 29110339_Dectin-1 receptor blockage decreased the IL-12, IL-17, IL-10 and TNF-alpha levels indicating the participation of such receptor in the induction of these cytokines. 29475849_The invertebrate tropomyosin presented in the context of impaired dectin-1 function, as observed in allergic individuals, leads to unrestrained IL-33 secretion and skewing of immune responses toward type 2 immunity. 29668708_Dectin-1/Dectin-2-induced autocrine PGE2 signaling licenses dendritic cells to prime Th2 responses. 30517524_A significant association between polymorphisms in the gene that encode dectin-1 and invasive aspergillosis (systematic review). 30882002_These results show the involvement of the Dectin-1 receptor in fungal recognition and its consequent participation in the induction of the killing mechanisms against P. brasiliensis 30944411_Dectin-1-induced RIPK1 and RIPK3 activation protects host against Candida albicans infection. 31139177_Dendritic Cell-Derived TSLP Negatively Regulates HIF-1alpha and IL-1beta During Dectin-1 Signaling. 31371767_Human thioredoxin, a damage-associated molecular pattern and Malassezia-crossreactive autoallergen, modulates immune responses via the C-type lectin receptors Dectin-1 and Dectin-2. 31613800_Dectin-1 genetic deficiency predicts chronic lung allograft dysfunction and death. 31696220_Association between dectin-1 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms and fungal infection: a systemic review and meta-analysis. 31845221_Study demonstrates that Dectin-1 rs3901533 and rs7309123 polymorphisms increase the susceptibility to pulmonary invasive fungal disease in acute myeloid leukemia patients in a Chinese Han population. 31964711_RHOA-mediated mechanical force generation through Dectin-1. 32234475_Divergent Roles for Macrophage C-type Lectin Receptors, Dectin-1 and Mannose Receptors, in the Intestinal Inflammatory Response. 32476786_Genetic association analysis of CLEC5A and CLEC7A gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms and Crohn's disease. 32493087_The relationship between dectin-1 and mast cells in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. 33552998_Interaction Between Dendritic Cells and Candida krusei beta-Glucan Partially Depends on Dectin-1 and It Promotes High IL-10 Production by T Cells. 33982290_Epigenetic regulation of epithelial dectin-1 through an IL-33-STAT3 axis in allergic disease. 34305908_Dectin-1 Controls TSLP-Induced Th2 Response by Regulating STAT3, STAT6, and p50-RelB Activities in Dendritic Cells. 34329585_Commensal bacteria and fungi differentially regulate tumor responses to radiation therapy. 36139454_Dectin-1 as a Potential Inflammatory Biomarker for Metabolic Inflammation in Adipose Tissue of Individuals with Obesity. 36377664_Human Dectin-1 deficiency impairs macrophage-mediated defense against phaeohyphomycosis. |
ENSMUSG00000079293 |
Clec7a |
47.106862 |
2.1686117318 |
1.116772 |
0.260386686 |
18.302335 |
0.00001884760445015532426445148406202179103274829685688018798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000057217326549628257721831492421671327974763698875904083251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.4010817 |
11.5225491 |
29.4889564 |
4.0154904 |
| ENSG00000172260 |
257194 |
NEGR1 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z3B1 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in cell-adhesion. May function as a trans-neural growth-promoting factor in regenerative axon sprouting in the mammalian brain (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including feeding behavior; locomotory behavior; and positive regulation of neuron projection development. Predicted to be located in extracellular region and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:257194; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; feeding behavior [GO:0007631]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051963] |
19079261_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19164386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19746409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19812171_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19851340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19910938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20215397_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20386550_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20520848_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20724581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20725061_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21427694_Data suggest that in addition to its reported role in the brain, NEGR1 is also expressed in subcutaneous adipose tissue and acts as a central 'hub' in an obesity-related transcript network. 21624008_The results of these studies provide supporting evidence for MYEOV and NEGR1 as gene targets of 11q13 gains and 1p31 deletions in a neuroblastoma subset. 21750520_Meta-analysis of 4992 subjects revealed seven SNPs near four loci, including NEGR1, TMEM18, SH2B1 /ATP2A1 and MC4R, showing significant association at 0.005 22179955_Gene-treatment interactions were observed for long-term (NEGR1 rs2815752, Pmetformin*SNP = 0.028; FTO rs9939609, Plifestyle*SNP = 0.044) weight loss. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22443470_Our study supports earlier reports of SH2B1 to be of importance in insulin sensitivity and, in addition, suggests potential roles of NEGR1 and MTCH2. 23229156_Results imply a regulatory role for TMEM18, BDNF, MTCH2 and NEGR1 in adipocyte differentiation and biology. In addition, we show a variation of MAF expression during adipogenesis, while NPC1, PTER and SH2B1 were not regulated. 23950990_Data indicate strong associations with severe obesity for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs9939609 within the FTO gene and SNP rs2815752 near the NEGR1 gene. 25072390_First study to find an association between an obesity risk gene and differences in white matter integrity. As our subjects were young and healthy, our results suggest that NEGR1 has effects on brain structure independent of its effect on obesity. 25245582_NEGR1 could be an important locus influencing certain personality dimensions in BN patients. 25370040_We observed novel selection signals in CDKAL1 and NEGR1, well-known diabetes and obesity susceptibility genes 25640768_Genetic variants associated with BMI and WHR in adults influence growth patterns and general and abdominal fat development from early childhood onwards. 27005443_Significant associations were identified at 3.5 years old for TMEM18 rs6548238, NEGR1 rs2815752, BDNF rs10767664 and rs6265 (1 year old and 3.5 years old) with anthropometric phenotypes 27479909_Single nucleotide polymorphism in NEGR1 gene is associated with major depressive disorder. 27940359_NEGR1 interacts with NPC2 and increases its protein stability; it has a role in obesity 28428959_Our results indicate a possible contribution of CNVs in LEPR, NEGR1, ARHGEF4, and CPXCR1 and the intergenic regions 12q15c, 15q21.1a, and 22q11.21d to the development of obesity, particularly abdominal obesity in Mexican children. 28969442_NEGR1, strong candidate gene, associated with clinical features of Depression (e.g., earlier age at onset and recurrent and more severe forms of Depression). Gene expression patterns in the prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex most closely matched the genetic findings. 31510847_Placental NEGR1 DNA methylation is associated with BMI and neurodevelopment in preschool-age children. 32090785_Integrating genome-wide association study and expression quantitative trait loci data identifies NEGR1 as a causal risk gene of major depression disorder. 32209393_1p31.1 microdeletion including only NEGR1 gene in two patients. 32375678_analysis of genomic information from multiple non-cancer cohorts showed that both the NEGR1 promoter deletion and the BTNL3-8 deletion were CNVs occurring at high frequencies in the general population. Intriguingly, the upstream NEGR1 CNV deletion was homozygous in ~ 40% of individuals in the non-cancer population. 32419576_Association of the NEGR1 rs2815752 with obesity and related traits in Pakistani females. 32552051_Polymorphisms in Neuronal Growth Regulator 1 and Otoancorin Alternate the Susceptibility to Lung Cancer in Chinese Nonsmoking Females. 32710982_Highly Conserved Molecular Features in IgLONs Contrast Their Distinct Structural and Biological Outcomes. 32958118_Na/K-ATPase beta1-subunit associates with neuronal growth regulator 1 (NEGR1) to participate in intercellular interactions. 33296963_Depression in multiple sclerosis patients associated with risk variant near NEGR1. 34739656_CircDLGAP4 overexpression relieves oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury by elevating NEGR1 through sponging miR-503-3p. 35090585_Harnessing tissue-specific genetic variation to dissect putative causal pathways between body mass index and cardiometabolic phenotypes. |
ENSMUSG00000040037 |
Negr1 |
21.710631 |
0.2330611621 |
-2.101219 |
0.705706729 |
7.506291 |
0.00614838364678100147281414322719683696050196886062622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012323484875948883740526262897674314444884657859802246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4134375 |
6.3499214 |
56.3444136 |
17.6235833 |
| ENSG00000172379 |
9915 |
ARNT2 |
protein_coding |
Q9HBZ2 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that plays a role in the development of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis, postnatal brain growth, and visual and renal function (PubMed:24022475). Specifically recognizes the xenobiotic response element (XRE). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24022475}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Methylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the basic-helix-loop-helix-Per-Arnt-Sim (bHLH-PAS) superfamily of transcription factors. The encoded protein acts as a partner for several sensor proteins of the bHLH-PAS family, forming heterodimers with the sensor proteins that bind regulatory DNA sequences in genes responsive to developmental and environmental stimuli. Under hypoxic conditions, the encoded protein complexes with hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in the nucleus and this complex binds to hypoxia-responsive elements in enhancers and promoters of oxygen-responsive genes. A highly similar protein in mouse forms functional complexes with both aryl hydrocarbon receptors and Single-minded proteins, suggesting additional roles for the encoded protein in the metabolism of xenobiotic compounds and the regulation of neurogenesis, respectively. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:9915; |
aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex [GO:0034751]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; aryl hydrocarbon receptor binding [GO:0017162]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; brain development [GO:0007420]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666] |
12210012_There is no association of ARNT2 gene with cleft palate only (n = 45) and cleft lip/palate (n = 37). 17826745_We thus propose that NDN regulates neuronal function and hypoxic response by regulating the activities of the ARNT2:SIM1 and ARNT2:HIF1alpha dimers, respectively. 17899366_a possible use of ARNT2 and GST A1 as prognostic breast cancer biomarkers. 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20706985_promotes differentiation of IL-22-producing CD4(+) T-cells 21512513_In white males, rs4072568 in ARNT2 was also associated with BMI (P = 9 x 10(-4)) and % body fat (P = 0.001). 21945317_ARNT2 might play an important role in the modulation of HIF-1-regulated signaling and metabolism. 24022475_mutation of ARNT2 results in absence of detectable levels of ARNT2 transcript and protein from patient fibroblasts compared with controls, consistent with nonsense-mediated decay of the mutant transcript and loss of ARNT2 function. 24465693_These results provide insight into the mechanisms of NPAS4/ARNT dimerisation and transcriptional activation. 24635660_nominal associations were found between autism spectrum disorder scores and single-nucleotide polymorphisms in OXT, ARNT2 and CD38 24814368_Data suggest that selected human SIM1 (single-minded homolog 1) variants exhibit poor dimerization with ARNT2 and anomalous intracellular localization; these data were used to predict 'hot-spot' in SIM1/SIM2 (residues 290-326) critical for function. 25613063_Attenuated ARNT2 expression in HCC827 cells greatly promoted tumor growth. 29149419_Immunohistochemistry confirmed ARNT2 expression in cell sub-populations within proliferative zones of patients' glioblastoma. Decreased ARNT2 expression was consistently observed in non-tumorigenic glioblastoma cells, compared to tumorigenic cells. Moreover, ARNT2 expression correlated with a tumorigenic molecular signature at both the tissue level within the tumor core and at the single cell level in the patients' tumors 29194499_The single nucleotide polymorphisms rs4778599 in the gene encoding aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 2 (ARNT2), showed an association that survived correction for multiple testing with emotion recognition of audio-visual stimuli in women 29948506_Low expression of ARNT2 is associated with gastric cancer. 31964743_The meta-analysis of both populations showed that carriers of the ARNT2 rs1374213G, CX3CR1 rs7631529A, and CX3CR1 rs9823718G alleles (where the RefSeq identifier appears as a subscript) had a significantly increased risk of developing invasive aspergillosis according to a log-additive model. 36343253_Structures of NPAS4-ARNT and NPAS4-ARNT2 heterodimers reveal new dimerization modalities in the bHLH-PAS transcription factor family. |
ENSMUSG00000015709 |
Arnt2 |
765.712587 |
2.2308915651 |
1.157620 |
0.077646538 |
220.608652 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006662264106746101001214652835424498889587887351221607599554913591874851565193756295565628985722389240293117030210982711820846997874401296257929061539471149444580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001414892348425502736961970396632653185900313864045101765118223275261784267613589829074698292837877069667599355915139302489625522385452427442942280322313308715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1090.6491200 |
48.5239206 |
492.2543100 |
16.7967514 |
| ENSG00000172382 |
83886 |
PRSS27 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQR3 |
|
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This gene is located within a large protease gene cluster on chromosome 16. It belongs to the group-1 subfamily of serine proteases. The encoded protein is a secreted tryptic serine protease and is expressed mainly in the pancreas. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:83886; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12441343_structure and activity of the human enzyme, a serine peptidase found in the pancreas 18948266_Marapsin's restricted expression, localization, and cytokine-inducible expression suggest a role in the terminal differentiation of keratinocytes in hyperproliferating squamous epithelia. 23447538_Mutational tail loss is an evolutionary mechanism for liberating marapsins and other type I serine proteases from transmembrane anchors. 33452606_Expression Status of Serine Protease 27: A Prognostic Marker for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Preoperative Chemotherapy/Chemoradiotherapy. |
ENSMUSG00000050762 |
Prss27 |
11.288198 |
0.2075635381 |
-2.268375 |
0.574401658 |
15.983064 |
0.00006391168236642125297271299633194985290174372494220733642578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000181341105676350954458223019294393907330231741070747375488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3970465 |
1.5626471 |
20.6175210 |
4.0504490 |
| ENSG00000172399 |
51778 |
MYOZ2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPC6 |
FUNCTION: Myozenins may serve as intracellular binding proteins involved in linking Z line proteins such as alpha-actinin, gamma-filamin, TCAP/telethonin, LDB3/ZASP and localizing calcineurin signaling to the sarcomere. Plays an important role in the modulation of calcineurin signaling. May play a role in myofibrillogenesis. |
Cardiomyopathy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a family of sarcomeric proteins that bind to calcineurin, a phosphatase involved in calcium-dependent signal transduction in diverse cell types. These family members tether calcineurin to alpha-actinin at the z-line of the sarcomere of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, and thus they are important for calcineurin signaling. Mutations in this gene cause cardiomyopathy familial hypertrophic type 16, a hereditary heart disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:51778; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; FATZ binding [GO:0051373]; protein phosphatase 2B binding [GO:0030346]; telethonin binding [GO:0031433]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; skeletal muscle fiber adaptation [GO:0043503]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] |
17347475_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17347475_Two missense mutations, S48P substitution and I246M affecting highly conserved amino acids were linked to hereditary Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy characterized by early onset of symptoms, pronounced cardiac hypertrophy, and cardiac arrhythmias. 17434779_Mutations in MYOZ1 and MYOZ2 are at least very rare events as an underlying disease mechanism for idiopathic or familial DCM 18591919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19472918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22987565_The cardiac phenotype in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by MYOZ2 mutations might be independent of calcineurin activity in the heart. 28296734_may play a modifying role in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy by affecting the penetrance or degree of performance of the MYH7 gene 30280773_Study found that MYOZ2 can be used as prognostic factor for gastric cancer. MYOZ2 is highly expressed in gastric cancer (GC) tissues, and its expression is associated with lymph node metastasis, TNM staging and poor patients survival. These results suggest that MYOZ2 gene may play an important role in the occurrence and development of gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000028116 |
Myoz2 |
44.999110 |
0.2707090451 |
-1.885185 |
0.257855664 |
56.330326 |
0.00000000000006126322035642733406531101324257133829706903349610058739926898851990699768066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000393834988005604304844741637743603045152766123360166261591075453907251358032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.9031211 |
3.4117624 |
73.8989994 |
7.5094725 |
| ENSG00000172508 |
57571 |
CARNS1 |
protein_coding |
A5YM72 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the synthesis of carnosine and homocarnosine. Carnosine is synthesized more efficiently than homocarnosine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20097752}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Ligase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
CARNS1 (EC 6.3.2.11), a member of the ATP-grasp family of ATPases, catalyzes the formation of carnosine (beta-alanyl-L-histidine) and homocarnosine (gamma-aminobutyryl-L-histidine), which are found mainly in skeletal muscle and the central nervous system, respectively (Drozak et al., 2010 [PubMed 20097752]).[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:57571; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; carnosine synthase activity [GO:0047730]; homocarnosine synthase activity [GO:0102102]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; carnosine biosynthetic process [GO:0035499]; histidine catabolic process [GO:0006548] |
20097752_carnosine synthase is identified as ATP-grasp domain-containing protein 1 26206726_CNDP1 and CARNS are expressed in glomeruli and tubular cells; TauT is expressed in renal epithelial cells; CDNP1 may have a role in diabetic neuropathy 33533160_Combining bioinformatics analysis and experiments to explore CARNS1 as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000075289 |
Carns1 |
87.159592 |
0.1845028544 |
-2.438285 |
0.342489776 |
47.712152 |
0.00000000000493622397329649990061998279517614370091177500299295388686005026102066040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000028001024537223803228251468144947204739342305757077156158629804849624633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1985868 |
6.7315221 |
125.6220542 |
25.1952791 |
| ENSG00000172543 |
1521 |
CTSW |
protein_coding |
P56202 |
FUNCTION: May have a specific function in the mechanism or regulation of T-cell cytolytic activity.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Plays a role during influenza virus infection in lungs cells ex vivo. Acts at the level of virus entering host cytoplasm from late endosome. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15340161}. |
Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Thiol protease;Zymogen |
|
The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the peptidase C1 family, is a cysteine proteinase that may have a specific function in the mechanism or regulation of T-cell cytolytic activity. The encoded protein is found associated with the membrane inside the endoplasmic reticulum of natural killer and cytotoxic T-cells. Expression of this gene is up-regulated by interleukin-2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1521; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; cysteine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008234]; immune response [GO:0006955]; proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process [GO:0051603] |
11490002_Endogenous cathepsin W is expressed predominantly in NK cells, is up-regulated by IL-2, and is mainly targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum. 12437118_Cathepsin W-positive cells had a 'lymphocyte phenotype', but the relative portion of cathepsin W-positive cells among the infiltrating leukocytes in gastrointestinal disease differed remarkably. 15358123_a genetic variant and a novel isoform of cathepsin W are present in about 14% and 12%, respectively, within the Caucasian population 19100676_Despite being expressed in the effector subset of CD8(+) and NK cells and of being released during target cell killing, our functional inhibition studies exclude an essential role of CatW in the process of cytotoxicity. 22050231_The predominant expression of wildtype form by infiltrating immune cells was confirmed in 116 patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and 27 reflux-negative individuals demonstrating that cathepsin W expression is not altered in this disease. 26060270_These results establish CtsW as an important host factor for entry of influenza A virus into target cells and suggest that CtsW could be a promising target for the development of future antiviral drugs. 35867415_Proteomic Identification of Potential Target Proteins of Cathepsin W for Its Development as a Drug Target for Influenza. |
ENSMUSG00000024910 |
Ctsw |
232.687813 |
4.3799738299 |
2.130922 |
0.112771526 |
383.246155 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000024447251646974731069872303930801526442071997301851345224924153852872877905438528257760294540601354151913973600514274322208981939875507418516884492334818937597805248397291945916988530419746983690454001022249273106234923602642084006220102310180664 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008779596941833261408654219964581784021330977675170185487593986632744041226966848959955859595467362164098910578977934649934192849290417959132757094010869629733594592740557400929764814385720143975900900954519728847103010593855287879705429077148438 |
Yes |
No |
384.9188366 |
26.6170086 |
88.5152794 |
5.2711382 |
| ENSG00000172748 |
169270 |
ZNF596 |
protein_coding |
Q8TC21 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:169270; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
30653506_a genome-wide search of association between European ancestry and Multiple sclerosis (MS) revealed a region of interest close to the ZNF596 gene on chromosome 8 in Hispanics; cases had a significantly higher proportion of European ancestry compared to controls. |
|
|
40.393950 |
0.3678689786 |
-1.442736 |
0.253664233 |
32.882984 |
0.00000000978762545360691138081849713972401594297423343959962949156761169433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000042665490754647966228138550705620279934748850791947916150093078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.3569628 |
4.3386815 |
63.6132225 |
7.8711597 |
| ENSG00000172794 |
326624 |
RAB37 |
protein_coding |
Q96AX2 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Rab proteins are low molecular mass GTPases that are critical regulators of vesicle trafficking. For additional background information on Rab proteins, see MIM 179508.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2006]. |
hsa:326624; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endosome [GO:0005768]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
18687502_Promoter/exon1 methylation is the predominant mechanism in down-regulation of the hRAB37, and can serve as a potential prediction biomarker of NSCLC progression. 19148500_the TMEM22/RAB37 complex is likely to play a crucial role in growth of renal cell carcinoma 23372429_Rab37 mRNA was specifically expressed in some ESCC cell lines but its genetic polymorphisms were not associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 23826383_Results identify Rab37 as an additional component of the machinery governing exocytosis of beta-cells and suggest that impaired expression of this GTPase may contribute to defective insulin release in pre-diabetic and diabetic conditions. 25183545_RAB37 regulates the exocytosis of TIMP1 in a nucleotide-dependent manner to inactivate MMP9 migration axis in vitro and in vivo and to suppress tumor metastasis. 28151721_Our findings suggest that Rab37-mediated TSP1 secretion in cancer cells suppresses metastasis and angiogenesis via a cross-talk with endothelial cells and reveal a novel component of the vesicular exocytic machinery in tumor microenvironment and tumor progression 29229996_results demonstrate a role of RAB37 in autophagosome formation through a molecular connection of RAB37, ATG5-12, ATG16L1 up to LC3B, suggesting an organiser role of RAB37 during autophagosomal membrane biogenesis. 29717487_Low RAB37 expression is associated with lung cancer. 30131385_This study shows that RAB37 hypermethylation is involved in NPC metastasis and chemoresistance, and that our prognostic model can identify patients who are at a high risk of distant metastasis and might benefit from for docetaxel IC. 30158579_Rab37-mediated SFRP1 secretion suppresses cancer stemness. 30165196_Findings indicate that patients with low vesicle associated membrane protein 8 (VAMP8)/low rab GTP-binding protein RAB37 (RAB37) expression profile showed significantly high risk of death even after adjusting for tumor metastasis parameter. 32926650_Methionine represses the autophagy of gastric cancer stem cells via promoting the methylation and phosphorylation of RAB37. |
ENSMUSG00000020732 |
Rab37 |
11.757248 |
0.2568752162 |
-1.960860 |
0.495320256 |
17.039683 |
0.00003660671892316322392942062879939157937769778072834014892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000107080941954179422229663509735786419696523807942867279052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3123587 |
1.4256816 |
16.8962888 |
3.0705902 |
| ENSG00000172817 |
9420 |
CYP7B1 |
protein_coding |
O75881 |
FUNCTION: A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in the metabolism of endogenous oxysterols and steroid hormones, including neurosteroids (PubMed:10588945, PubMed:24491228). Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR; NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase) (PubMed:10588945, PubMed:24491228). Catalyzes the hydroxylation of carbon hydrogen bonds of steroids with a preference for 7-alpha position (PubMed:10588945, PubMed:24491228). Usually metabolizes steroids carrying a hydroxy group at position 3, functioning as a 3-hydroxy steroid 7-alpha hydroxylase (PubMed:24491228). Hydroxylates oxysterols, including 25-hydroxycholesterol and (25R)-cholest-5-ene-3beta,26-diol toward 7-alpha hydroxy derivatives, which may be transported to the liver and converted to bile acids (PubMed:9802883, PubMed:10588945). Via its product 7-alpha,25-dihydroxycholesterol, a ligand for the chemotactic G protein-coupled receptor GPR183/EBI2, regulates B cell migration in germinal centers of lymphoid organs, thus guiding efficient maturation of plasma B cells and overall antigen-specific humoral immune response (By similarity). 7-alpha hydroxylates neurosteroids, including 3beta-hydroxyandrost-5-en-17-one (dehydroepiandrosterone) and pregnenolone, both involved in hippocampus-associated memory and learning (PubMed:24491228). Metabolizes androstanoids toward 6- or 7-alpha hydroxy derivatives (PubMed:24491228). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10588945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24491228, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9802883}. |
Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Heme;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Intrahepatic cholestasis;Iron;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Microsome;Monooxygenase;Neurodegeneration;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; bile acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10588945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9802883}.; PATHWAY: Steroid hormone biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24491228}. |
This gene encodes a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. The cytochrome P450 proteins are monooxygenases which catalyze many reactions involved in drug metabolism and synthesis of cholesterol, steroids and other lipids. This endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein catalyzes the first reaction in the cholesterol catabolic pathway of extrahepatic tissues, which converts cholesterol to bile acids. This enzyme likely plays a minor role in total bile acid synthesis, but may also be involved in the development of atherosclerosis, neurosteroid metabolism and sex hormone synthesis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG5 or HSP), an autosomal recessive disorder. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:9420; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; 24-hydroxycholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase activity [GO:0033782]; 25-hydroxycholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase activity [GO:0033783]; 27-hydroxycholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase activity [GO:0047092]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxysterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase activity [GO:0008396]; steroid hydroxylase activity [GO:0008395]; B cell chemotaxis [GO:0035754]; bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006699]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050673]; intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030520]; negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033147]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; prostate gland epithelium morphogenesis [GO:0060740]; sterol metabolic process [GO:0016125] |
14521990_In Alzheimer's disease (AD). CYP7B mRNA was significantly decreased (approximately 50% decline; PT p.R112X), 1 amino acid changing (c.440 G>A p.G147D) and 1 duplication (c.945_947 dupGGC p.A316AA) 24491228_21-hydroxy-pregnenolone was identified as a new substrate, and overall low activity toward pregnanes could be related to the increased potency of 7-hydroxy derivatives produced by CYP7B1. 24519355_enduring sensory ataxia can be a pivotal sign in SPG5, and expands the phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations in CYP7B1 24641183_Spastic paraplegia type 5 has a higher frequency in Taiwanese than in other ethnic groups, associated with a CYP7B1 founder mutation and its phenotype is characterized by pronounced dorsal column sensory loss, with cerebellar ataxia in some patients. 24658845_The patient was homozygous for a mutation (c.1249C>T) in CYP7B1 that alters a highly conserved residue in oxysterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase previously reported in a family with hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5 25915148_Using an agnostic omics approach to focus on the association of CWP with body mass index, we have confirmed a steroid hormone association and identified a genetic variant upstream of the CYP genes, which likely controls this response. 26370385_The two novel variants cosegregated with pyramidal signs and autoimmune diseases suggesting that they might be susceptibility factors. 26374131_SPG11 and CYP7B1 were the most common cause of autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia in Greece. 26399852_Data indicated that the two GWAS-defined variants in the CYP7B1 region do not strongly influence HIV-1 infection susceptibility. 26714052_Data indicate two novel homozygous mutations (one frameshift and one missense mutation) detected in CYP7B1 (SPG5A), while no disease-causing mutation was identified for PNPLA6 (SPG39) and C19orf12 (SPG43). 27278684_miR17 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with the cancer stem cell phenotype by regulating CYP7B1 expression in colon cancer. 30710743_This study provides evidence for CYP7B1 as a key regulator of three vital intracellular regulatory oxysterol levels. 31337596_AKR1D1 and CYP7B1 mutations in patients with inborn errors of bile acid metabolism: Possibly underdiagnosed diseases. 32202070_Clinical characteristics of Taiwanese patients with Hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5. 33771085_Description of clinical features and genetic analysis of one ultra-rare (SPG64) and two common forms (SPG5A and SPG15) of hereditary spastic paraplegia families. 34946825_Phenoconversion from Spastic Paraplegia to ALS/FTD Associated with CYP7B1 Compound Heterozygous Mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000039519 |
Cyp7b1 |
878.763901 |
0.0992228519 |
-3.333184 |
0.337259522 |
82.239991 |
0.00000000000000000012052643103040825978073581194964693042427137113062248765724127075316118862247094511985778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001048921062505203941793701901019768462215199590127114037674260771382250823080539703369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
171.5857759 |
33.3573543 |
1739.9682317 |
242.1389140 |
| ENSG00000172824 |
283848 |
CES4A |
protein_coding |
Q5XG92 |
FUNCTION: Probable carboxylesterase. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine esterase;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the carboxylesterase large family. The family members are responsible for the hydrolysis or transesterification of various xenobiotics, such as cocaine and heroin, and endogenous substrates with ester, thioester, or amide bonds. They also participate in fatty acyl and cholesterol ester metabolism, and may play a role in the blood-brain barrier system. This gene, also called CES6, encodes a secreted enzyme, and may play a role in the detoxification of drugs and xenobiotics in neural and other tissues of the body and in the cerebrospinal fluid. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been reported, but the full-length nature and/or biological validity of some variants have not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:283848; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; carboxylic ester hydrolase activity [GO:0052689] |
|
ENSMUSG00000060560 |
Ces4a |
33.304566 |
0.3922496120 |
-1.350156 |
0.262837018 |
27.282615 |
0.00000017578486258876207770133711684457100687950514839030802249908447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000676377625602223206539344042137473778097955801058560609817504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.1924488 |
3.9227079 |
52.2093945 |
6.4985864 |
| ENSG00000172830 |
54961 |
SSH3 |
protein_coding |
Q8TE77 |
FUNCTION: Protein phosphatase which may play a role in the regulation of actin filament dynamics. Can dephosphorylate and activate the actin binding/depolymerizing factor cofilin, which subsequently binds to actin filaments and stimulates their disassembly (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
The ADF (actin-depolymerizing factor)/cofilin family (see MIM 601442) is composed of stimulus-responsive mediators of actin dynamics. ADF/cofilin proteins are inactivated by kinases such as LIM domain kinase-1 (LIMK1; MIM 601329). The SSH family appears to play a role in actin dynamics by reactivating ADF/cofilin proteins in vivo (Niwa et al., 2002 [PubMed 11832213]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:54961; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008138]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; negative regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030837]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
17848544_Expression of phosphatase-dead versions of SSH proteins, SSH1, SSH2 & SSH3 results in phosphorylation/inactivation of cofilin, changes in cytoskeleton organization, loss of cell polarity, and assembly of aberrant arrays of laminin-332 in keratinocytes. 33275222_SSH3 promotes malignant progression of HCC by activating FGF1-mediated FGF/FGFR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000034616 |
Ssh3 |
235.733681 |
0.3801526746 |
-1.395349 |
0.169552337 |
66.486585 |
0.00000000000000035228296493933885035388348726610779130186533350359290306386128577287308871746063232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002580494571962601341627956612057977105043120270508327784853008779464289546012878417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
129.2425155 |
15.4185145 |
342.8507497 |
28.4228295 |
| ENSG00000172889 |
51162 |
EGFL7 |
protein_coding |
Q9UHF1 |
FUNCTION: Regulates vascular tubulogenesis in vivo. Inhibits platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB-induced smooth muscle cell migration and promotes endothelial cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix and angiogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23386126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23639441}. |
Angiogenesis;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a secreted endothelial cell protein that contains two epidermal growth factor-like domains. The encoded protein may play a role in regulating vasculogenesis. This protein may be involved in the growth and proliferation of tumor cells. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2012]. |
hsa:51162; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
14592969_is the first identified inhibitor of mural cell migration specifically produced by endothelial cells. 17934064_Human EGFL7 may protect endothelial cell from hyperoxia-induced apoptosis by inhibition of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway. 18193184_Intronic miRNAs from tissue-specific transcripts, or their natural absence, make cardinal contributions to cellular gene expression and phenotype. 18521848_The lack of association between expression of miRNA and its host gene EGFL7 suggests their regulation by independent stimuli in colon cancer. 19116145_Mature miR-126 can be generated from three different transcripts of EGFL7 with each one having its own promoter. 19824075_Egfl7 promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by enhancing cell motility through EGFR-dependent FAK phosphorylation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20034472_miR-126 can inhibit proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells through one of its targets, EGFL7. 20213100_EGFL7 may be used as a predictive marker for glioma prognosis and as a potential therapeutic target for malignant glioma. 20423846_miR-126 can downregulate EGFL7 expression at the protein level in ECV-304 cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20837907_Epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 suppresses intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression in response to hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in human coronary artery endothelial cells. 20953557_Studies indicate that two biologically active miRNAs miR-126 and its complement miR-126*, which are encoded by intron 7 of the egfl7 gene, have been described to mediate vascular functions. 22013081_Two angiogenesis-associated transcripts (Egfl7 and Acvrl1) showed lower expression in early-onset PE versus late-onset pre-eclampsia and versus gestational age-matched controls. 22018271_Heterogeneous methylation in the promoter region of EGFL7 was associated with cancer progression in non-small cell lung cancer. 22037871_Human breast cancer lesions expressing high levels of Egfl7. 22160377_Studies indicate that Egfl7 controls blood vessel development by promoting endothelial cell migration and proliferation. 23280513_Early-onset intrauterine growth restriction at 20-24 weeks' gestation is associated with higher values of EGFL7 expression in maternal plasma. 23386126_Data indicate that EGFL7 and integrin alphavbeta3 integrin colocalized in vesicular structures in uman umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). 23404186_Egfl7 expression is thus associated with better prognosis factors and with the absence of lymph node invasion in human breast cancer lesions. 23558933_Egfl7 is significantly upregulated in human epithelial tumor tissues, suggesting Egfl7 to be a potential biomarker for human epithelial tumors, especially liver and breast cancer. 23922111_study provides clinical data indicating a relationship between miRNA-126 and the clinical outcome of metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with chemotherapy combined with anti-VEGF-A, whereas the impact of EGFL7 is more speculative 24286167_The loss of EGFL7 expression play a role in the development and progression of systemic sclerosis. 24595089_egfl7 is initially expressed in all endothelial cells and then is progressively restricted to veins and to their neighbouring capillaries. 24696719_malignant glioma cells and glioma vascular endothelial cells highly express VE-statin/Egfl7, which is significantly correlated with the degree of malignancy. 24751645_demonstrate significantly reduced Egfl7 expression in pre-eclampsia placentas, concurrent with a downregulation of Notch target genes 24815445_EGFL7 promotes growth of Renal cell carcinoma by facilitating migration and tube formation of endothelial cells. These effects were produced by EGFL7-mediated focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation through combination with epidermal growth factor receptor. 24945379_EGFL7 enhances EGFR-AKT signaling, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and metastasis of gastric cancer cells. 25140000_EGFL7 may predict response to first-line chemotherapy and bevacizumab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer 25592646_The aim of the present descriptive study was to analyse the intra-tumoural expressions of epidermal growth factor-like domain 7 (EGFL7) and microRNA-126 (miRNA-126) in primary tumours from patients with stage II-IV colorectal cancer. 25601205_Endothelial cells control pancreatic cell fate at defined stages through EGFL7 signaling. 25667199_Data suggest that, in trophoblast cells, EGFL7 regulates cell migration and invasion/placentation by activating multiple signaling pathways via MAPK, PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase), and NOTCH1 (translocation-associated notch protein 1). 25730089_EGFL7, OPN, and PGE2 may have a role in recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma 25987088_High EGFL7 expression promotes migration and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in pancreatic Cancer. 26288231_EGFR mutational analysis is useful in the diagnosis of non-small-cell-lung cancer. 26504055_Loss of EGFL7 expression is associated with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. 26542361_The preferential expression of EGFL7 in less differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma compared to VEGF, suggests a possible important role of this angiogenic factor in a later oncogenic and infiltrative/metastatic phase. 26722408_By regulating endothelial cell adhesion, EGFL7 plays a key role in the regulation of glioma angiogenesis. 26799121_A gene expression study was conducted to investigate the levels of Egfl7 and miRNA126-5p in human carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques 27259812_Up-regulated MALAT1 promoted the invasion and metastasis of GC, and the increase of EGFL7 expression was a potential mechanism via altering its H3 histone acetylation level 27611944_In conclusion, miR-126 could inhibit tumor proliferation and angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating EGFL7 expression 27650497_Egfl7 is thus an endogenous and constitutive repressor of blood vessel endothelial cell activation in normal and inflammatory conditions and participates in a loop of regulation of activation of these cells by pro-inflammatory cytokines. 27725228_Oncogenic activation of EGFRwt in GBM is likely maintained by a continuous EGFL7 autocrine flow line. 27766530_These findings suggest that the stimulating effect of EGFL7-ESCs on fibroblast proliferation and migration may provide a useful strategy for wound healing. 28275117_This phase II trial evaluated the efficacy of parsatuzumab (also known as MEGF0444A), a humanized anti-EGFL7 IgG1 monoclonal antibody, in combination with modified FOLFOX6 (mFOLFOX6) (folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin) bevacizumab in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer 28533390_Levels of both EGFL7 mRNA and EGFL7 protein are increased in blasts of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) compared with normal bone marrow cells. High EGFL7 mRNA expression associates with lower complete remission rates, and shorter event-free and overall survival in older (age >/=60 y) and younger (age |
ENSMUSG00000026921 |
Egfl7 |
222.125710 |
0.2519450427 |
-1.988819 |
0.137718100 |
212.870523 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000324802119352990705062556648899659566453669090329614680587779138919985914198926689457418370311065046145344458521014002338068299424733709201973397284746170043945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000066125231471036447644798088484899940615853830718969146493701632365332895796837581749223581024219722176495302902279915021471756730875313223805278539657592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
91.5804592 |
7.8453533 |
366.6196871 |
19.0021608 |
| ENSG00000172890 |
55191 |
NADSYN1 |
protein_coding |
Q6IA69 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the final step of the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) de novo synthesis pathway, the ATP-dependent amidation of deamido-NAD using L-glutamine as a nitrogen source. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12547821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31883644}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Ligase;NAD;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Cofactor biosynthesis; NAD(+) biosynthesis; NAD(+) from deamido-NAD(+) (L-Gln route): step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12547821}. |
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme in metabolic redox reactions, a precursor for several cell signaling molecules, and a substrate for protein posttranslational modifications. NAD synthetase (EC 6.3.5.1) catalyzes the final step in the biosynthesis of NAD from nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NaAD).[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. |
hsa:55191; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; glutaminase activity [GO:0004359]; NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing) activity [GO:0003952]; 'de novo' NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0034627]; NAD biosynthetic process [GO:0009435] |
19724895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20418485_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22390397_several SNPs related to calcium metabolism are associated with height, in particular rs3829251 at the DHCR7/NADSYN1 gene. 22785457_findings suggest that VDR, NADSYN1, and GC polymorphisms may be linked to the manifestation of vitamin D deficiency in Japanese children 23636220_Data indicate that SNPs in the DHCR7/NADSYN1 locus showed evidence of positive association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 24642724_NADSYN1/DHCR7 locus (rs12785878 and rs1790349) polymorphisms have an effect on plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and coronary artery disease incidence 26149120_Polymorphisms in CYP2R1-rs10766197 and DHCR7/NADSYN1-rs12785878 are associated with vitamin D deficiency in Uygur and Kazak ethnic populations 31883644_Bi-allelic Mutations in NADSYN1 Cause Multiple Organ Defects and Expand the Genotypic Spectrum of Congenital NAD Deficiency Disorders. 31911602_Homo sapiens NAD(+) synthetase (hsNadE) lacks substrate specificity for glutamine over ammonia. 32938288_Genetic variants of vitamin D metabolism-related DHCR7/NADSYN1 locus and CYP2R1 gene are associated with clinical features of Parkinson's disease. 34681008_Disruptive NADSYN1 Variants Implicated in Congenital Vertebral Malformations. 35491967_Further description of two patients with biallelic variants in NADSYN1 in association with cardiac and vertebral anomalies. |
ENSMUSG00000031090 |
Nadsyn1 |
509.607459 |
0.3290681745 |
-1.603542 |
0.390333535 |
15.889513 |
0.00006714977964624157255948966316339010518277063965797424316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000189835423784433178669150965589551560697145760059356689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
250.1992476 |
57.1007483 |
753.9566500 |
124.1195877 |
| ENSG00000172893 |
1717 |
DHCR7 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBM7 |
FUNCTION: 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway reducing the C7-C8 double bond of cholesta-5,7-dien-3beta-ol (7-dehydrocholesterol/7-DHC) and cholesta-5,7,24-trien-3beta-ol, two intermediates in that pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25637936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9465114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9634533}. |
Cholesterol biosynthesis;Cholesterol metabolism;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis;Steroid metabolism;Sterol biosynthesis;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; cholesterol biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25637936, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9634533}. |
This gene encodes an enzyme that removes the C(7-8) double bond in the B ring of sterols and catalyzes the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to cholesterol. This gene is ubiquitously expressed and its transmembrane protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane and nuclear outer membrane. Mutations in this gene cause Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS); a syndrome that is metabolically characterized by reduced serum cholesterol levels and elevated serum 7-dehydrocholesterol levels and phenotypically characterized by cognitive disability, facial dysmorphism, syndactyly of second and third toes, and holoprosencephaly in severe cases to minimal physical abnormalities and near-normal intelligence in mild cases. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2009]. |
hsa:1717; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear outer membrane [GO:0005640]; 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase activity [GO:0047598]; NADP binding [GO:0050661]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-CH group of donors [GO:0016627]; sterol delta7 reductase activity [GO:0009918]; brassinosteroid biosynthetic process [GO:0016132]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via desmosterol [GO:0033489]; cholesterol biosynthetic process via lathosterol [GO:0033490]; regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0045540]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126] |
11161831_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11503168_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11767235_This protein catalyses the last step of endogenous cholesterol synthesis. SLOS is caused by a biochemical enzymatic defect. 11857552_identified a new mutation in DHCR7 12116246_Mutation analysis demonstrated a novel mutation in the DHCR7 gene, present in homozygous form in the two affected individuals available for testing, and heterozygous in the parents. 12833423_SLOS is a recessive gene disorder. A fetus was found to have renal agenesis. 14981719_Our identification of a single haplotype associated with the T93M mutation in patients whose ancestors originate in the region of the Mediterranean Sea basin suggests a founder effect. 15286151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15521979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15776424_DHCR7 mutations have a role in the Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome 15954111_identification of nine novel missense mutations of the DHCR7 gene 15979035_Mutational analysis of the DHCR7 gene led to the identification of seven distinct mutations, three of which are new (F174S, H301R, and Q98X) for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. 16497572_In Polish individuals with SLOS two DHCR7 mutations, c.452G>A (p.Trp151X) and c.976G>T (p.Val326Leu), account for 65.2% of all observed DHCR7 mutations. 16497572_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17441222_DHCR7 mutation is a rapid and reliable method for prenatal diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. 17595012_DHCR7 gene mutations is associated with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. 17855807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17965227_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17965227_it appears that a combination of founder effects, recurrent mutations, and drift have shaped the present frequency distribution of DHCR7 mutations in Europe 18006960_The study identified compound heterozygous mutations ([p.Arg352Trp] + [p.Lys376ArgfsX37]) in a Korean girl with clinical and laboratory features typical of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. 18249054_DHCR7 mutation is associated with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19365639_The p.G366V is a novel mutation of the DHCR7 gene with guanine by thymine nucleotide exchange resulting in glycin by valin amino acid exchange in the dehydrocholesterol reductase enzyme. 19390132_study determined the mutational spectrum of DHCR7 gene in 17 Slovak Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome patients; 6 different mutations were identified: nonsense mutation W151X and missense mutations V326L, L109P, G410S, R352Q, Y432C 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19940018_LBR mutant variants and sterol reductases can severely interfere with the regular organization of the nuclear envelope and the endoplasmic reticulum. 20418485_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20541252_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20635399_Mutations of the 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase gene is associated with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. 21441443_Study confirms that variation in DHCR7 is associated with predisposition to autoimmune disease type 1 diabetes. 21696385_Two previously reported N287K (861 C>A) and R352Q (1055 G>A) and a novel R352L (1055 G>T) mutations were identified in the DHCR7 gene in these patients. 21972121_GC and NADSYN1/DHCR7 loci individually and collectively contribute to variation in plasma vitamin D levels in Chinese Hans. 22130326_ANKRD55 and DHCR7 are novel multiple sclerosis risk loci. 22182693_This study demonistrated that the accumulation of an immediate cholesterol precursor, 7-DHC and its oxysterol metabolite, 3beta,5alpha-dihydroxycholest-7-en-6-one (DHCEO)in DHCR7 knockout mice. 22211794_The p.Thr93Met is the most frequent mutation in Turkish SLOS patients showing that there might be a founder in East Mediterranean regions 22390397_several SNPs related to calcium metabolism are associated with height, in particular rs3829251 at the DHCR7/NADSYN1 gene. 22576297_Our study is the first to confirm the association of variants in DHCR7 and CYP2R1 with 25(OH)-vitamin D levels in patients with chronic liver diseases. Results also showed an association between DHCR7 and liver stiffness. 22801813_we found that the two variant genotypes of DHCR7/NADSYN1 (rs3829251, rs12785878) were both associated with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. 23321614_Studies suggest DHCR7 mutation for the diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome. 23377224_Genetic variation in DHCR7 associated with lower serum 25(OH)D has a decreased risk of aggressive prostate cancer. 23636220_Data indicate that SNPs in the DHCR7/NADSYN1 locus showed evidence of positive association with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 23730842_In patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C, GG homozygosis for DHCR7 gene and lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are independently associated with the severity of liver fibrosis. 23734184_Data indicate that the same nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) genotypes of CYP2R1, GC and DHCR7 that are associated with reduced 25(OH)D3 serum levels were found to be associated with hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 24184224_This study provides evidence that the DHCR7 gene is involved in the susceptibility to ocular Behcet disease. 24642724_NADSYN1/DHCR7 locus (rs12785878 and rs1790349) polymorphisms have an effect on plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and coronary artery disease incidence 24663808_rs3829251 (DHCR7) influenced progression of subclinical atherosclerosis in a manner dependent on type 2 diabetes status but independent of 25(OH)D levels. The SNP modulates DHCR7 mRNA levels in aortic adventitia. 24974252_In this mendelian randomisation study, we generated an allele score (25[OH]D synthesis score) based on variants of genes that affect 25(OH)D synthesis or substrate availability (CYP2R1 and DHCR7) 25040602_This study shows that Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome patients who are heterozygous/homozygous for one pathogenic mutation and only one parent carrying that mutation are candidates for DHCR7 gene (partial) deletions. 25637936_physical and functional interaction between DHCR24 and DHCR7 26038244_Allelic variations in CYP2R1 and GC affect vitamin D levels, but variant alleles on VDR and DHCR7 were not correlated with vitamin D deficiency. 26149120_Polymorphisms in CYP2R1-rs10766197 and DHCR7/NADSYN1-rs12785878 are associated with vitamin D deficiency in Uygur and Kazak ethnic populations 26383826_The aim of this study was to investigate the association of three polymorphisms in the GC gene (rs7041 and rs4588) and CYP2R1 gene (rs10741657) on 25-(OH) VD serum concentration among Jordanians. 26685159_In this study, we demonstrate that the prevalent c.964-1G>C Dhcr7 mutation perturbs SMO cilia localization and SHH pathway activation as a consequence of reduced cholesterol biosynthesis 26887953_these findings highlight DHCR7 as an important regulatory switch between cholesterol and vitamin D synthesis. 27052530_Genetic variations in ABCG5, CYP7A1, and DHCR7 may contribute to differing responses of serum cholesterol to dairy intake among healthy adults. 27401223_Review: DHCR7 activity should be considered during drug development and prenatal toxicity assessment. 27520299_phosphorylation modulates DHCR7 activity in cells, and contributes to the overall synthesis of cholesterol, and probably vitamin D 28369852_DHCR7 mutations for 2 female fetuses with Smith-Lemli- Opitz syndrome and metatarsal bony syndactyly were analyzed. 28415985_The DHCR7 polymorphism may be a pre-treatment predictive marker for response to PEG-IFN-based therapy in chronic HCV genotype 1 infection. 28706201_DHCR7 polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. 29300326_pathogenic mutations in DHCR7 protein are located either within the transmembrane region or are near the ligand-binding site, and are highly conserved among species. 29433144_The study detected Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS) mutations in only 0.7% of stillbirths. This does not support a strong association between unrecognized DHCR7 mutations and stillbirth. 29920211_SNPs rs6720173 (ABCG5), rs3808607 (CYP7A1), and rs760241 (DHCR7) may work in conjunction with each other to amplify individual genotyping impacts on serum cholesterol responses to dairy consumption. 30139224_aim of this study was to determine the association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of PNPLA3 (rs738409), COX-2 (rs689465) and DHCR7 (rs12785878) and advanced liver fibrosis in Thai patients 30475961_A genetic risk score (GRS) was calculated based on 3 genetic variants [i.e., 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7) rs12785878, cytochrome P450 2R1 (CYP2R1) rs10741657 and group-specific component globulin (GC) rs2282679] related to circulating vitamin D levels. We found a significant interaction between dietary fat intake and vitamin D GRS on 2-y changes in whole-body bone mineral density. 30796319_Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphism and DHCR7 Contribute to the Abnormal Interplay Between Vitamin D and Lipid Profile in Rheumatoid Arthritis. 31357732_DHCR7 rs12785878 minor allele was associated with thyroid cancer in Portuguese population. 31882361_The authors propose that the DHCR7 inhibitors and 7-dehydrocholesterol are potential therapeutics against emerging or highly pathogenic viruses. 31911440_Twin enzymes, divergent control: The cholesterogenic enzymes DHCR14 and LBR are differentially regulated transcriptionally and post-translationally. 32055014_Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: what is the actual risk for couples carriers of the DHCR7:c.964-1G>C variant? 32517587_Genetic Variation in Cytochrome P450 2R1 and Vitamin D Binding Protein Genes are associated with Vitamin D Deficiency in Adolescents. 32629226_Occurrence of c.976 G>T (p.Val326Leu) and c.452 G>A (p.Trp151Ter) variants in DHCR7 gene in population of polish women with recurrent miscarriage. 32764491_Vitamin D Pathway Genetic Variation and Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Association Study. 32938288_Genetic variants of vitamin D metabolism-related DHCR7/NADSYN1 locus and CYP2R1 gene are associated with clinical features of Parkinson's disease. 33179238_[Clinical and genetic analysis of a Chinese pedigree affected with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome]. 33961971_Vitamin D pathway gene polymorphisms, vitamin D level, and cytokines in children with type 1 diabetes. 34093899_Association of Polymorphisms in Vitamin D-Metabolizing Enzymes DHCR7 and CYP2R1 with Cancer Susceptibility: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 36164611_High DHCR7 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis for Cervical Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000058454 |
Dhcr7 |
344.498302 |
4.2745494787 |
2.095772 |
0.096972276 |
490.883194 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000091546029845747101211841914427714875717569160243514971402488723335851209890435384968414637600937771090362334807872654776831821846602263984099301450655968603148089652489782044657626822046884324908581045153194235660989892145 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000042625217682120733000755064448009190387653188715086892038496895056146061700341957314982359616152133364469438608887859311956604426607171466215667635536939531857385298177767161118038177822007530899061402107479852574511994443 |
Yes |
No |
569.7295112 |
33.2530129 |
134.2612498 |
6.6660029 |
| ENSG00000172927 |
26579 |
MYEOV |
protein_coding |
Q96EZ4 |
|
Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:26579; |
|
12202983_Epigenetic inactivation of myeov is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinomas 16275643_MYEOV protein synthesis is regulated by upstream open reading frames 16552434_The putative role for MYEOV genes may provide important targets for intervention in Gastric adenocarcinoma, evidenced by their role in promoting invasion and proliferation, key phenotypic hallmarks of cancer cells. 16678123_These data suggest that ETV4 and Myeov may provide novel targets for therapeutic intervention. 17390055_Both myeov and hst (fgf4) are normally situated approximately 475-kb apart at band 11q13, a region that is frequently amplified and overexpressed in various tumours. 20569498_High MYEOV is associated with colon cancer cell migration. 20854874_MYEOV expression is a prognostic factor for patients with multiple myeloma, in part through a role of MYEOV in the control of MMC proliferation. 21624008_The results of these studies provide supporting evidence for MYEOV and NEGR1 as gene targets of 11q13 gains and 1p31 deletions in a neuroblastoma subset. 30181549_experiments demonstrated that the MYEOV ceRNA sequestered miR-30c-2-3p from binding its targets TGFBR2 and USP15 mRNAs, which in turn leading to constitutive activation of TGF-beta signaling and tumor progression in Non-small cell lung cancer. 32420813_Overexpression of MYEOV predicting poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 32879444_MYEOV increases HES1 expression and promotes pancreatic cancer progression by enhancing SOX9 transactivity. 33278551_High expression of MYEOV reflects poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. 34930894_The MYEOV-MYC association promotes oncogenic miR-17/93-5p expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. |
|
|
120.646152 |
8.8517474846 |
3.145962 |
0.232907910 |
188.801056 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000058081638112816702310417809192030928989843364249232926622318369176748265577596907467231394035754366239866178667911045252481017087120562791824340820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000010391333073274843041866674876856145861098451654484632292929093212771605608217571721702747146320506138334870821493538528557110112160444259643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
214.7313692 |
35.3538439 |
24.4801363 |
3.3519405 |
| ENSG00000172995 |
10777 |
ARPP21 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBL0 |
FUNCTION: Isoform 2 may act as a competitive inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent enzymes such as calcineurin in neurons. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Calmodulin-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein. The encoded protein is enriched in the caudate nucleus and cerebellar cortex. A similar protein in mouse may be involved in regulating the effects of dopamine in the basal ganglia. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:10777; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24127197_Interstitial deletion of 3p22.3p22.2 encompassing ARPP21 and CLASP2 is a potential pathogenic factor for a syndromic form of intellectual disability. 31653410_Mutation analysis of GLT8D1 and ARPP21 genes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients from mainland China. 33581934_Genetic analysis of GLT8D1 and ARPP21 in Australian familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 34047500_Mechanism of ARPP21 antagonistic intron miR-128 on neurological function repair after stroke. |
ENSMUSG00000032503 |
Arpp21 |
74.929799 |
0.0596974568 |
-4.066187 |
0.625337055 |
34.877483 |
0.00000000351118132910775439187370583807822066457760001867427490651607513427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015941260048486757062653196011063616577274615337955765426158905029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2113046 |
3.4768657 |
138.5581507 |
39.6452878 |
| ENSG00000173083 |
10855 |
HPSE |
protein_coding |
Q9Y251 |
FUNCTION: Endoglycosidase that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) into heparan sulfate side chains and core proteoglycans. Participates in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and remodeling. Selectively cleaves the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying either a 3-O-sulfo or a 6-O-sulfo group. Can also cleave the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying a 2-O-sulfo group, but not linkages between a glucuronic acid unit and a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid moiety. It is essentially inactive at neutral pH but becomes active under acidic conditions such as during tumor invasion and in inflammatory processes. Facilitates cell migration associated with metastasis, wound healing and inflammation. Enhances shedding of syndecans, and increases endothelial invasion and angiogenesis in myelomas. Acts as procoagulant by increasing the generation of activation factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activation factor VII. Increases cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), independent of its enzymatic activity. Induces AKT1/PKB phosphorylation via lipid rafts increasing cell mobility and invasion. Heparin increases this AKT1/PKB activation. Regulates osteogenesis. Enhances angiogenesis through up-regulation of SRC-mediated activation of VEGF. Implicated in hair follicle inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12213822, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12773484, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15044433, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16452201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18557927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18798279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19244131, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20097882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20181948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20309870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20561914, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21131364}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Magnesium;Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are major components of the basement membrane and extracellular matrix. The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans to permit cell movement through remodeling of the extracellular matrix. In addition, this cleavage can release bioactive molecules from the extracellular matrix. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:10855; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; heparanase complex [GO:1904974]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; beta-glucuronidase activity [GO:0004566]; heparanase activity [GO:0030305]; syndecan binding [GO:0045545]; angiogenesis involved in wound healing [GO:0060055]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:0061028]; Factor XII activation [GO:0002542]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan catabolic process [GO:0030200]; heparin metabolic process [GO:0030202]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030194]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0090091]; positive regulation of hair follicle development [GO:0051798]; positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033690]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; protein transmembrane transport [GO:0071806]; proteoglycan metabolic process [GO:0006029]; regulation of hair follicle development [GO:0051797]; response to organic substance [GO:0010033]; vascular wound healing [GO:0061042] |
11759110_Erythromycin and clarithromycin modulation of growth factor-induced expression of heparanase mRNA on human lung cancer cells in vitro. 11798780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11973358_Activation, processing and trafficking of extracellular heparanase by primary human fibroblasts. 12027584_REVIEW: Heparinase: involvement in cancer metastasis, angiogenesis and normal development 12029075_Results indicate consistent expression of heparanase in normal and abnormal placenta, in small fetal vessels and in a variety of trophoblast subpopulations with different invasive potentials. 12065771_It was concluded that heparanase might play an important role in the development of invasion and metastasis of the gastric cancer. 12097647_Cell surface expression and secretion markedly promote tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. 12213822_structural recognition plays critical roles in tumor metastasis; specificity of the purified recombinant human heparanase 12219030_Heparanase-1 expression is associated with the metastatic potential of breast cancer 12509917_Heparanase participates in the structure damage and remodeling of abdominal aorta at matrix level, which contributes to abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) formation. 12679316_reduced heparanase mRNA expression may result in abnormal cell growth and correlate with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression 12824922_Expression correlates with tumor invasiveness patterns in human oral squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in SCID mice. 12837765_Intracellular processing of the heparin proteoglycan polysaccharide chains is catalyzed by heparanase. 12904690_results suggest that the expression of heparanase may influence different malignant behaviors in endometrial cancer 12927802_heterodimer formation is necessary and sufficient for heparanase enzymatic activity in mammalian cells 14522979_heparanase gene transcription is regulated in activated T cells by early growth response 1 14558943_NF-kappaB is an essential factor in the regulatory mechanisms of heparanase gene transcription. 14573609_glycosylation affected the kinetics of endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transport and of secretion of the enzyme 14633698_Heparanase activates signal transduction pathways and, depending on its expression levels, may modulate tumor progression in glioma cells. 14676122_Increased HPR1 expression is associated with thyroid tumor malignancy and may significantly contribute to thyroid tumor metastases 14769819_characterization of the hpa-tg mice emphasizes the involvement of heparanase and heparan sulfate in processes such as embryonic implantation, food consumption, tissue remodeling, and vascularization 14967027_Tobacco etch virus protease cleavage sites of heparanase are engineered to provide evidence that proteolytic processing at both junctions between residues 109 and 110 and 157 and 158 leads to activation of the 65 kDa heparanase precursor. 14989983_Heparanase gene expression may play some roles in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, and it may participate the regulation of menstrual cycle and may be an important target of the trentment for endometriosis. 15034597_heparanase is translocated into the cell nucleus where it may degrade the nuclear heparan sulfate and thereby affect nuclear functions that are thought to be regulated by heparan sulfate 15040016_Heparanase, CD44v6 and nm23 may play important roles in the invasive infiltration and lymph node metastasis in gastric carcinomas. 15100255_In sites relatively remote from inflammatory foci, within blood vessels and extravascular tissues, heparanase can act as a T cell cytokine that is involved in regulating cell activation and behavior. 15109255_Inflammatory cytokines and fatty acids regulate endothelial cell heparanase expression. 15144715_Heparanase mRNA may be important to the loss of glomerular negative charge in GBM and lead to proteinuria in steroid responsive nephrotic syndrome. 15292202_Heparan sulfate is not only a substrate for, but also a regulator of, heparanase. 15334672_Point mutation may be one of the causes for enhanced heparanase mRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. 15368349_one of the roles CREB plays in the acquisition of melanoma cells metastatic phenotype is affecting HPSE-1 activity 15471949_Heparanase is a critical determinant of myeloma dissemination and growth in vivo. 15610235_dysregulated heparanase expression may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome, possibly through an abnormality in post-translational control of latent heparanase activation 15625607_Expression of heparanase was significantly more frequent in tumors of higher TNM stage, higher Dukes stage, higher vascular infiltration, higher lymph vessel infiltration and poor survival. 15645118_HPSE-1 likely plays important roles in regulating the in vivo growth and progression of melanoma 15659389_Results suggest that proheparanase processing at site 2 is brought about by cathepsin L-like proteases. 15682491_NF-kappaB RelA (p65) activation was related with increased heparanase gene expression and correlated with poor clinicopathological characteristics in gastric cancers. 15728796_Heparanase plays a role in ovarian tissue remodeling during folliculogenesis and corpus luteum formation and regression. 15737842_HPR1 was expressed at a significantly higher frequency in the invasive comedo and DCIS with microinvasion subtypes than in the noninvasive subtypes. HPR1 expression was inversely associated with HS deposition in the extracellular basement membrane. 15760902_identified three potential heparin binding domains and provided evidence that one of these is mapped at the N terminus of the 50-kDa active heparanase subunit 15983219_Loss of heparan sulfsate in the glomerular basement membrane in diabetic nephropathy is attributable to accelerated heparan sulfate degradation by increased HPR1 expression. 16007175_expression during the pathogenesis of bladder cancer is due to promoter hypomethylation and transcription factor EGR1 16093249_EGR1 regulates heparanase transcription in tumor cells and importantly, can have a repressive or activating role depending on the tumor type 16097072_The expression of heparanase mRNA in an esophageal cancer cell line can be inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which can inhibit metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma or other tumors by inhibiting the expression of heparanase. 16112651_In summary, we have characterized a link between leukomogenic factors and the downregulation of heparanase in myeloid leukemic cells. 16217746_results emphasize the significance and clarify the involvement of heparanase in primary breast cancer progression by generating a supportive microenvironment that promotes tumor growth, angiogenesis and survival 16288472_Brain-metastatic melanoma cells (B16B15b) showed augmenting levels of HPSE-1 protein expression in a time-dependent manner. Secondly, B16B15b cells pre-treated with HPSE-1 showed a significant increase in the number of cells that invaded into the brain . 16391819_heparanase may play a novel role for cyclooxygenase 2 mediated tumor angiogenesis in breast-cancer progression 16429446_HPSE-1 activity may represent a physiological mechanism involved in neural cellular differentiation 16514606_proteoglycans tonically suppress osteoblast function and that this inhibition is alleviated by heparan sulfate degradation with heparanase 16709798_Heparanase is a key enzyme in dendritic cell transmigration through the extracellular matrix. 16759020_Hypoxia plays an important role in the augmentation of the heparanase expression and the invasiveness of human laryngeal carcinomas. 16790442_Heparanase resides in and accumulates in the lysosomal compartment, where it may participate in normal turnover of heparan sulfate. The secreted enzyme facilitates cell invasion associated with cancer metastasis, angiogenesis, and inflammation. 16826429_Expressions of p75(NTR) and HPSE-1 correlated with each other in medulloblastoma. 16855356_REVIEW of heparanase involvement in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis 16867222_heparanase modifies FGF2 binding, signaling, and angiogenesis in metastatic melanoma cells 16890383_This hypothesis indicates a possible novel function of heparanase and its link to HIF1alpha and Cox-2, and therefore this function would give us a clue about potential new strategies for cancer therapy. 16982797_HPSE 'off/on switch': Lacritin targets the deglycanated core protein of SDC1 and not HS chains or SDC2 or SDC4. Binding requires partial or complete removal of HS chains by endogenous HPSE. This limits lacritin activity to HPSE release sites. 17051139_HPSE is involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria in overt diabetic nephropathy by degradation of heparan sulfates 17095861_4 Israeli Jewish populations (Ashkenazi, North African, Mediterranean and Near Eastern) were examined for 7 HPSE gene SNPs. Four out of 7 SNPs (rs4693608, db11099592, rs4364254, db6856901) were found to be polymorphic. 17095861_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17141400_The higher expression of Hpa and Ang-2 in ectopic and eutopic endometrium may play an important role in the pathogenesis and development of endometriosis. 17208203_Splice 5 escaped proteolytic cleavage, was devoid of HS degradation activity and exhibited diffused rather than granular cellular localization. 17217623_Nuclear localization of heparanase predicts a favorable outcome in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 17261577_heparanase-1 expression and heparan sulphate proteoglycan degradation are induced by estradiol in human endometrium 17284253_we speculate that nuclear translocation of enzymatically active heparanase may be involved in cellular differentiation. 17339423_Heparanase influences expression and shedding of syndecan-1 17419711_The CGC HSPE-1 haplotype associates with stage in ovarian cancer. This haplotype may affect splicing of the HSPE-1 gene, as in silico it alters the presence of a splicing motif. 17437011_The combined effects of heparanase and HSULF could account for the lack of biologically active HS in tumour cells rather than deficiencies in the biosynthetic enzymes. 17467664_Genetic downregulation of the expression of heparanase may serve as an efficient cancer therapeutic for human HCC. 17481627_There is no significant difference in heparanase-1 expression in the eutopic endometrium from women with or without endometriosis. 17519955_This review focuses on the role of heparanase in heparan sulfate degradation in proteinuric diseases and the possibility/feasibility of heparanase inhibitors 17524042_High expression of heparanase, combined with NF-kappaB p65, may contribute to the highly invasive and metastatic behavior of gallbladder carcinoma. 17611567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17611567_certain HPSE gene SNPs may contribute to basal heparanase gene expression; alterations in this gene are an important determinant in the pathogenesis of ALL, AML and MM 17634531_Heparanase induction by estrogen receptors represents an important pathway in breast tumorigenesis and may be responsib, for failure of tamoxifen therapy in some patients. 17715045_Heparanase and NF-kappaB p65 proteins were found in 30 (62.5%) and 22 (45.9%) tumor specimens, respectively, a rate significantly higher than that in the adjacent tissues. 17989358_HPSE plays a role in extracellular matrix remodeling and in increasing heparin-binding growth factor release during embryo implantation. 18064313_Heparanase pro-enzyme reverses the anti-coagulant activity of unfractionated heparin on the coagulation pathway and on thrombin activity. Heparanase pro-enzyme abrogated the factor X inhibitory activity of low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH). 18167611_Accumulating evidence suggests that small inhibitory genetic molecules targeting heparanase are of value for control and treatment of human malignancies. 18212251_Heparanase directly contributes to prostate tumor growth in bone and its ability to metastasize to distant organs. 18217145_Heparanase facilitates blood coagulation by dissociation of TFPI from the vascular surface shortly after local elevation of heparanase levels, and subsequent induction of TF expression. 18246800_The high expression of HPA mRNA and HIF-1alpha protein is correlated with carcinogenesis, progression, invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 18288398_The coexpression of heparanase and vascular endothelial growth factor in atypical melanocytes and melanoma cells suggests their function in cell migration and invasion. 18305555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18329709_Trophoblast heparanase is not required for invasion in vitro. Its abundant expression suggests another role during pregnancy, perhaps in controlling the availability of ECM-bound growth factors or acting as a transcription factor. 18357711_The expression of HPSE is significantly increased in squamous carcinomas of head and neck, and is directly related to the clinical stage and lymph node metastasis. 18390199_Hpa may up-regulate the expression of C-erbB-2 in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. 18450756_Cathepsin L has a role in processing and activation of proheparanase through multiple cleavages of a linker segment 18487013_heparanase overexpression can facilitate tumor invasion and accelerate bone destruction caused by prostate cancer bone metastasis. 18512775_Heparanase (HPSE) activity was dramatically higher in Synovial fluid (SF) and Synovial tissue (ST)of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients than in SF and ST from Osteoarthritis patients and asymptomatic donors;HPSE RNA was upregulated in ST of RA patients 18545691_pro-adhesive properties of heparanase are mediated by its interaction with cell surface HS proteoglycans, and utilized the KKDC peptide to examine this possibility 18557927_Heparanase 1 is a key actor of inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis. 18609704_Strong heparanase expression is related with the degradation of basement membrane which allows or accelerates tumor invasion and metastasis. 18618498_findings suggest that heparanase expression and cellular localization are decisive for lung cancer patients' prognosis, most likely because of heparanase-mediated tumor cell dissemination by blood and lymph vessels. 18646256_Overexpressed heparanase and its splice variant localize to the endoplasmic reticulum independent of glycosylation in COS-7 cells. 18647407_Results indicate that heparanase has pleiotropic effects on tumor cells. 18662687_The hydrophobic C-terminus region of heparanase is a determinant for its intracellular trafficking to the Golgi apparatus, followed by secretion, activation, and tumor cell migration. 18704599_Heparanase seems to be significantly associated with lymph node metastasis as well as dedifferentiation. We assume that HPSE plays a crucial role for the aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer. 18773863_The overexpression of heparanase may play an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis, progression, and metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma. 18798279_heparanase plays a unique dual role in tumor metastasis, facilitating tumor cell invasiveness and inducing VEGF C expression, thereby increasing the density of lymphatic vessels that mobilize metastatic cells 18809970_heparanase plays an important role in invasion and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma 18812315_heparanase acts as a master regulator of the aggressive tumor phenotype by up-regulating protease expression and activity within the tumor microenvironment 19096032_role for heparanase in the regulation of arterial structure, mechanics, and repair 19157148_The expression of heparanase was associated with invasion, metastasis and prognosis of nasopharyngeal cancer. 19180921_Hypoxia promotes the expression of HPA and the invasiveness of SKOV3 cells through the HIF-1alpha pathway. 19305494_Results show that heparanase alters the level of nuclear syndecan-1. 19401035_mRNA and protein are detected in inflammatory sinus mucosa and nasal polyps but not in normal sinus mucosa 19406828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19406828_The current study indicates that rs4693608 and rs4364254 SNPs are involved in the regulation of heparanase expression and provides the basis for further studies on the association between HPSE gene SNPs and disease outcome. 19437318_Changes in plasma HP levels correlated with response to treatment for children diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma 19452723_The expressions of HGF and Hpa in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma are higher than that in nonmalignant tissues, and correlate with lymph node metastasis, clinical stages and pathological grading. 19715595_HPSE gene expression is involved in rhabdomyosarcoma tumor invasion. 19749739_Heparanase expression is already induced in Barrett's epithelium without dysplasia, and is further increased during progression through distinct pathological stages, namely, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia, and adenocarcinoma. 19802384_syndecan-1 and FGF-2, but not FGFR-1 share a common transport route and co-localize with heparanase in the nucleus, and this transport is mediated by the RMKKK motif in syndecan-1 19835469_Glioma tissues contain increased levels of heparanase 19916174_heparanase has a role in invasiveness, metastasis and angiogenesis, but not proliferation of human gastric cancer cells 19955948_The gene expression of heparanase in cervical cancer enhances growth, invasion, and angiogenesis of the tumor. 19956890_up-regulation of Hpa by hypoxia is NF-kappaB-dependent in MIA PaCa-2 cells 20007507_T5 is a novel functional splice variant of human heparanase endowed with protumorigenic characteristics 20075159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20075159_The present study indicates a highly significant correlation of HPSE gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms rs4693608 and rs4364254 and their combination with the risk of developing acute graft-versus-host disease. 20097882_pathway driven by heparanase expression in myeloma cells: elevated levels of VEGF and shed syndecan-1 form matrix-anchored complexes that together activate integrin and VEGF receptors on adjacent endothelial cells thereby stimulating tumor angiogenesis 20164500_Altogether, these findings support the notion that HPSE is a critical downstream target of HER2 mechanisms driving BMBC and is potentially relevant for BMBC therapeutic interventions. 20193112_Decreased expression of Syndecan-1 mRNA and the increased expression of HPA-1 mRNA can promote the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 20309870_HPSE expresses and functions in human osteoblasts. It may mediate osteoblastogenesis through regulation of osteogenic gene expression and histone H3 modification. 20339231_may facilitate the function of heparan sulfate-binding growth factors that elicit an angiogenic response and favor osteoclastogenesis in ameloblastomas 20388348_HPSE, HIF-1alpha and VEGF play a role in tumor angiogenesis and promote malignant progress of retinoblastoma. 20403028_results indicate that aberrant expression of EGR1 in gastric cancer is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis, and heparanase transcription 20434010_The results support the notion that heparanase is a modulator of blood coagulation, and suggest a novel mechanism by which heparanase regulates tissue factor and TFPI levels in endothelial and cancer cells. 20578081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20578081_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the HPSE gene is associated with gastric cancer. 20619346_Recent progress in heparanase research emphasizing the molecular mechanisms that govern its pro-tumorigenic and pro-adhesive properties. 20634491_heparanase is a potential modulator of blood hemostasis, and suggest a novel mechanism by which heparanase increases the generation of activated factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activated factor VII. 20653782_Preferential up-regulation of heparanase and cyclooxygenase-2 in carcinogenesis of Barrett's oesophagus and intestinal-type gastric carcinoma. 20660327_Serum heparanase and vascular endothelial growth factor were identified as independent predictive factors for hepatocellular carcinoma 20798248_The results suggest that loss of the adenine (A)/uracil (U)-rich consensus element is an important regulatory mechanism contributing to heparanase induction in human cancer. 21029368_Heparanase expression is induced in Ewing's sarcoma. 21076620_Data show that BRAF knockdown led to suppression of the expression of the GABPbeta, which involved in regulating HPR1 promoter activity. 21131364_a novel mechanism driving the HGF pathway whereby heparanase stimulates an increase in both HGF expression and syndecan-1 shedding to enhance HGF signaling. 21153652_Heparanase expression was found to be insignificant among the various stages in the endometrial pathway to cancer. 21257720_SST0001, a chemically modified heparin, inhibits myeloma growth and angiogenesis via disruption of the heparanase/syndecan-1 axis 21364956_Heparanase levels are elevated in the urine and plasma of type 2 diabetes patients and associate with blood glucose levels. 21385059_Overexpression of heparanase influenced expression of most genes involved in heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis, albeit to a different degree in the cortex and thalamus of the transgenic mice. 21415391_findings uncover a new level of regulation governing sVEGF-R1 retention versus release and suggest that manipulations of the heparin/heparanase system could be harnessed for reducing unwarranted release of sVEGF-R1 in pathologies such as preeclampsia 21424539_HPR1 production is increased in endothelial cells from rat models of diabetes, and in macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions of diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Increased HPR1 production may contribute to pathogenesis and progression of atherosclerosis. 21461610_Advanced glycation end-products induce heparanase expression in endothelial cells 21464728_Heparanase expression was present in 57 (67.8%) of the 84 endometrial carcinomas, and was significantly associated with the endometrioid histotype 21483695_Over-expression of heparanase demonstrates the importance of heparan sulfate proteoglycans for the uptake of intestinal derived lipoproteins and its role in the formation of fatty streaks 21490396_heparanase generates a vicious cycle that powers colitis and the associated tumorigenesis: heparanase, acting synergistically with the intestinal flora, stimulates macrophage activation 21505182_Multiple antigenic peptides of human heparanase elicit a much more potent immune response against tumors 21600934_analyzed the involvement of heparanase, a heparan sulfate glycosidase, in the homeostasis of proximal tubular epithelial cells in the diabetic milieu 21671176_Targeted silencing of heparanase gene by siRNA could dramatically inhibit the invasiveness and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. 21706269_Study found positive staining for HPA-1 in 15% of adrenocortical adenomas and 91.67% of human adrenocortical carcinomas. 21757697_Heparanase-mediated loss of nuclear syndecan-1 enhances histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity to promote expression of genes that drive an aggressive tumor phenotype 21780097_Molecular model of human heparanase with proposed binding mode of a heparan sulfate oligosaccharide and catalytic amino acids. 21965756_Elevated serum CL, Hpa, and MMP-9 levels are correlated with malignant invasion and progression in ovarian cancer. 22001963_heparanase expression is associated with histone modifications and promoter DNA methylation plays a role in the control of gene silencing in glioblastoma 22005029_Hyperpigmentation in human solar lentigo is promoted by heparanase-induced loss of heparan sulfate chains at the dermal-epidermal junction. 22009724_heparanase enhances pituitary cell viability and proliferation and may thus contribute to pituitary tumor development and progression. 22020734_Findings indicate the prominent presence of heparanase in the epithelial component of radicular cysts versus sparse or no expression in periapical granulomas. 22102278_Heparanase and syndecan-1 interplay orchestrates fibroblast growth factor-2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells. 22133010_heparanase over-expression is associated with clear cell renal cell cancer. 22194600_Heparanase enhances the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT5b but not STAT5a in head and neck cancers. 22227299_study demonstrates a role for heparanase in modulation of acute localized inflammation and mast cell activity, accordingly affecting inflammatory pain 22260074_Heparanase can induce angiogenesis to promote tumor growth by releasing bFGF and VEGF in nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. 22276173_SNPs in HPSE play an important role in gastric cancer progression and survival, and perhaps may be a molecular marker for prognosis and treatment values. 22331282_Role for heparanase in sustaining immune cell-epithelial crosstalk that underlies intestinal inflammation and the associated cancer. Review. 22363633_These results suggest that small RNAs targeting transcription start site can induce transcriptional gene silencing of heparanase via interference with transcription initiation. 22488243_the expression levels of HPSE and miR-1258 in NSCLC tissue are closely related. In HPSE-positive samples, the expression levels of miR-1258 were relatively low; in HPSE-negative samples, the expression levels of miR-1258 were relatively high. 22575501_Heparanase and COX-2 might play complementary roles in the stepwise progression of oral epithelial dysplasia to carcinoma. 22682139_Taking into account the pro-metastatic and pro-angiogenic functions of heparanase, with over-expression in human malignancies and abundance in platelets and placenta. 22692572_data indicate that intact heparan sulfate chains are required to mediate neuroinflammatory responses, and point to heparanase as a modulator of this process, with potential implications for Alzheimer's disease 22719918_demonstrated that artificial miRNAs against HPSE might serve as an alterative mean of therapy to low HPSE expression and to block the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of melanoma cells 22952874_The results in this study demonstrate that genetic alteration and reduction of HPSE expression are associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 22956610_Heparanase is upregulated and associated with the VEGF expression in hypoxia-induced retinal diseases. 23028487_Elevated urine heparanase levels are associated with proteinuria and decreased renal allograft function. 23048032_Heparanase enhances the insulin receptor signaling pathway to activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase in multiple myeloma 23162016_Heparanase activates macrophages, resulting in marked induction of cytokine expression associated with plaque progression toward vulnerability. 23241438_heparanase plays essential roles in regulating the invasion, proliferation, and angiogenesis of A549 cells 23251556_T5, a novel splice variant of heparanase, is a functional, pro-tumorigenic entity. 23288725_These results suggest that heparanase participates in tumor growth of cervical cancer by influencing the proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells 23313782_study did not find any significant difference in heparanase promoter methylation between colon carcinoma and normal colonic mucosa, suggesting that heparanase overexpression in colon carcinoma is mediated by other mechanisms 23370684_Data indicate that the overexpression of HPSE1 and HPSE2 in the intervertebral degenerated discs suggests a role for these factors in mediating extracellular matrix remodeling in degenerative discs during disease development. 23415719_MiR-1258 may play an important role in breast cancer development and progression by regulating the expression of HPSE, and they might be potential prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer. 23430739_Heparanase regulates secretion, composition, and function of tumor cell-derived exosomes 23499526_Heparanase is critically involeved in inflammation, diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. (Review) 23499527_Heparanase mediates unexpected intracellular effects on T cell differentiation and insulin-producing beta cell survival in T cell-dependent autoimmune Type 1 diabetes mellitus. (Review) 23499528_Induction of heparanase prior to the appearance of malignancy was reported in essentially all inflammatory conditions. (Review) 23499529_The plastic substrate specificity suggests a complex role of heparanase in regulating the structures of heparan sulfate in matrix biology. (Review) 23499530_Heparanase is up-regulated in atherosclerosis and other vessel wall pathologies. (Review) 23504321_Targeting of heparanase-modified syndecan-1 by prosecretory mitogen lacritin requires conserved core GAGAL plus heparan and chondroitin sulfate as a novel hybrid binding site that enhances selectivity. 23504323_Characterization of heparanase-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT activation and its integrin dependence. 23511033_Elevation of serum heparanase is associated with Crohn's disease. 23649655_CCL19/CCR7 may upregulate the expression of heparanase via Sp1 and contribute to the invasion of A549 cells. 23704979_The prognostic role of FLT1/VEGFR1, heparanase and epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in patients with resected cholangiocarcinoma, was investigated. 23771368_The relative Heparanase mRNA expression level in hepatocellular carcinoma was lower than that in noncancerous tissue. 23794232_Heparanase is frequently expressed in oral mucosal melanoma. 23907942_The study suggest that one of the causes of unexplained miscarriages may result from the impaired expression of heparanase and heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. 23982701_role of HPSE in tumor invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer and concluded that either the expression of HPSE in cancer and/or the serum concentration of HPSE may be a useful biomarker for the evaluation of surgery effects and prognosis prediction. 23984412_the function of heparan sulfate proteoglycans and heparanase in breast cancer behavior and progression, is discussed. 24169805_Involvement of heparanase in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and a role for the enzyme in facilitating abnormal interactions between immune and epithelial cell subsets of the affected skin. 24189015_results revealed that dialysis treatments induce change in the transcriptomic pattern of biosynthetic proteoglycans in PBMCs with an up-regulation of HPSE. 24286246_HPV16 oncogene E6 is capable of inducing overexpression of heparanase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 24291708_this study describes (1)H NMR spectroscopic studies of the hydrolysis of the pentasaccharide substrate fondaparinux by heparanase, and provide conclusive evidence that heparanase hydrolyses its substrate with retention of configuration and is thus established as a retaining glycosidase 24319286_the importance of rs4693608 SNP for HPSE gene expression in activated MNCs, indicating a role in allogeneic stem cell transplantation, including postconditioning, engraftment, and GVHD. 24465803_Heparanase potentiates the bioactivity of resistin in its standard bioassay. 24632672_DNA methylation play the regulation role in heparanase gene in different stages of breast cancer 24699306_We found that heparanase induction is associated with decreased levels of CXCL10, suggesting that this chemokine exerts tumor-suppressor properties in myeloma. 24740543_Together, these data indicate a role for heparanase in inflammatory cell trafficking in vivo that appears to require enzymatic activity. 24747732_Heparanase was localized to the cytoplasm and nucleus of tumor cells and to cells within the microenvironment in different types of lung cancer. 24753252_Because HS with unsubstituted glucosamine residues accumulates in heparanase-expressing breast cancer cells, we assumed that these HS structures are resistant to heparanase and can therefore be utilized as a heparanase inhibitor. 24766948_High heparanase expression is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 24861922_serum levels of HPSE were significantly higher in breast cancer patients than in benign breast disease and in healthy controls. 24862152_Taking into account the prometastatic, pro-angiogenic and pro-coagulant functions of heparanase, ove |
ENSMUSG00000035273 |
Hpse |
210.730159 |
0.4854025309 |
-1.042746 |
0.126443723 |
68.368220 |
0.00000000000000013564613833079736781051742900326444437378665605880428968177398019179236143827438354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001016313198864248316444620231222055678030566383020227849698358113528229296207427978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.8566577 |
12.7928631 |
298.2814828 |
17.9862760 |
| ENSG00000173145 |
64318 |
NOC3L |
protein_coding |
Q8WTT2 |
FUNCTION: May be required for adipogenesis. {ECO:0000250}. |
Coiled coil;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in DNA replication initiation. Predicted to act upstream of or within fat cell differentiation. Located in mitochondrion; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64318; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; DNA replication initiation [GO:0006270]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444] |
15564382_Fad24, a mammalian homolog of Noc3p, is a positive regulator in adipocyte differentiation. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22796266_Results indicate the importance of four gastric cancer susceptibility polymorphisms of IL-10, NOC3L, PSCA and MTRR in the Chinese Han population. 24146276_We found PLCE1, C11orf92-C11orf93, and NOC3L associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility 30741601_Knockdown of human NOC3 in HeLa cells abrogates the chromatin association of other pre-RC proteins including hCDC6 and hMCM, leading to DNA replication defects and eventual apoptosis in an abortive S-phase. Human NOC3 physically interacts with multiple human pre-replicative complex (pre-RC) proteins and associates with known replication origins throughout the cell cycle. |
ENSMUSG00000024999 |
Noc3l |
101.115931 |
3.9442676927 |
1.979757 |
0.199494995 |
98.898148 |
0.00000000000000000000002658279218837005561280329058836438593288551612613424313530114794640324404895181942265480756759643554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000266008144203621731043132645274165122919673657868286194218450380066798288680729456245899200439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
160.9995973 |
20.4658802 |
41.2888245 |
4.2221323 |
| ENSG00000173166 |
65059 |
RAPH1 |
protein_coding |
Q70E73 |
FUNCTION: Mediator of localized membrane signals. Implicated in the regulation of lamellipodial dynamics. Negatively regulates cell adhesion. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the Mig10/Rap1-interacting adaptor molecule/Lamellipodin family of adapter proteins, which function in cell migration. Members of this family contain pleckstrin-homology domains, Ras-association domains, and proline-rich C-termini. The protein encoded by this gene regulates actin dynamics through interaction with Ena/Vasodilator proteins as well as direct binding to filamentous actin to regulate actin network assembly. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:65059; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; axon extension [GO:0048675]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15609301_RMO1 is expressed and deleted in osteosarcoma 18076380_proline-rich peptides organize the 4 subunits of BChE into a 340 kDa tetramer, by interacting with the C-terminal BChE tetramerization domain 19000833_Consistently, in HeLa cells, lamellipodin was required for EGF-induced proliferation. 21115820_Data show that profilin1 negatively regulates lamellipodin targeting to the leading edge; profilin1 depletion increases lamellipodin concentration at the lamellipodial tip (where it binds Ena/VASP), and this mediates the hypermotility. 22194892_Nephrin ligation resulted in abnormal morphology of actin tails in human podocytes when Ship2, Filamin or Lamellipodin were individually knocked down. 22915108_results of this study suggested that that PI(3,4)P2, Lpd, and Ena/VASP are involved in the process movement of multipolar migrating cells. 23483482_The crystal structure of Lpd cc-RA-PH presents a molecular model of Lpd enhances actin polymerization by oligomerization via two intermolecular contact sites. 24057252_The results suggest that although the RAPH1 gene was deleted or amplified in all samples, the Lpd does not seem to play a major role in tumorigenesis of mammary carcinomas. 24076656_this study suggests a novel mechanism in which Lpd mediates EGFR endocytosis via Mena downstream of endophilin. 26169271_These data indicate a possible role for Lpd in the actin-based movement and the cell-to-cell spread of L. monocytogenes. 26295568_The authors propose that Lpd delivers Ena/VASP proteins to growing barbed ends and increases their actin polymerase activity by tethering them to actin filaments. 26419705_Disruption of the RIAM/lamellipodin-integrin-talin complex markedly impairs cell migration. 26726010_these studies demonstrate an insight into how the Lpd-PH domain regulates cellular signals in a PI(3,4)P2 dependent manner. 27346732_The human RAPH1 gene is the CHE2 locus. 30056565_High RAPH1 expression is correlated with aggressive breast cancer phenotypes and provides independent prognostic value in invasive breast cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000026014 |
Raph1 |
68.501350 |
2.1765162697 |
1.122021 |
0.191956986 |
34.661824 |
0.00000000392248798652242569570667055610380113961355164065025746822357177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000017748596775312999260045313497380359279986805631779134273529052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
91.6368476 |
14.5925073 |
42.5421625 |
5.1956535 |
| ENSG00000173209 |
130872 |
AHSA2P |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable ATPase activator activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of ATPase activity and protein folding. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
32345988_Gene expression network analysis of lymph node involvement in colon cancer identifies AHSA2, CDK10, and CWC22 as possible prognostic markers. |
|
|
552.648106 |
0.3202421044 |
-1.642765 |
0.167534503 |
92.689958 |
0.00000000000000000000061163146365847822879104529822314459948493855859817981735252704483807306701237394008785486221313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000005824309937805896633334724818411807685732136734937934607111292839576321966887917369604110717773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
257.5596292 |
31.1590005 |
810.0788239 |
69.6796803 |
| ENSG00000173218 |
81839 |
VANGL1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TAA9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the tretraspanin family. The encoded protein may be involved in mediating intestinal trefoil factor induced wound healing in the intestinal mucosa. Mutations in this gene are associated with neural tube defects. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010]. |
hsa:81839; |
lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; pigmentation [GO:0043473]; Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:0060071] |
11956595_Molecular cloning and characterization of Strabismus 2 16410243_VANGL protein may serve as an effector mediating the intestinal trefoil factor (ITF) healing response of the intestinal mucosa. 17409324_In a protein-protein interaction assay V239I abolished interaction of VANGL1 protein with its binding partners, disheveled-1, -2, and -3. These findings implicate VANGL1 as a risk factor in human neural-tube defects. 19166844_VANGL1 increases invasion and migration of mouse squamous cancer cells and promotes pulmonary metastasis in a mouse squamous tumor model. 19319979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19319979_role of VANGL1 as a risk factor in the development of spinal neural tube defects 20043994_This study demonstrates a high degree of functional conservation of VANGL genes across evolution and provides a model system for studying potential variants identified in human neural tube defects. 20944126_KITENIN plays an important role in human gastric cancer progression by AP-1 activation. 21142127_Loss of membrane targeting of Vangl1 and Vangl2 proteins causes neural tube defects. 21291170_a compact membrane-associated portion with very short predicted extra- and intracellular loops, while the protein harbors a large intracellular domain 21418393_KITENIN is associated with human colorectal cancer progression including invasion and metastasis. 22179838_NOS1AP colocalizes with both SCRIB and VANGL1 along cellular protrusions in metastatic breast cancer cells, but does not colocalize with either SCRIB or VANGL1 at cell junctions in normal breast cells 22840317_KITENIN is associated with tumor invasiveness and metastasis in human oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. 24407469_The rs4839469 allele of VANGL1 was obviously associated with neural tube defects (NTDs). And genotype GC increased the risk of NTDs, changes in the three-dimensional protein structure may have impacted its biological functions. 24452931_The results show that the Vangl1 amino terminus lacks PM targeting determinants, and these are restricted to the carboxy terminus, including the predicted PDZBM motif at the C-terminus 24893630_Elevated KITENIN expression is associated with drug resistance in colorectal cancer. 24909917_Findings identify that KITENIN-targeting miR-124, miR-27a, and miR-30b function as endogenous inhibitors of colorectal cancer cell motility and demonstrate that miR-124 plays a suppressor role in colorectal tumorigenesis. 25068569_These results strongly suggest that R181 and R274 play critical roles in Vangl protein function and that their mutations cause neural tube defects in humans. 25208524_VANGL1 mutations are associated with neural tube defects. 25605251_High levels of KITENIN increased glioma invasiveness and progression, and are associated with the up-regulation of EMT and stemness markers. 25874746_Authors silenced VANGL1 gene expression in the HepG2 HCC cell line by stable transfection with a vector containing siRNA template for VANGL1 and investigated the change in cell invasion and motility. 26496979_Results found that KITENIN is associated with tumor progression by enhancing angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. 26735870_a novel and ultrasensitive sandwich-type immunosensor was fabricated to detect Vangl in human serum using C60-templated AuPt as labels and rGO-TEPA-PTC-NH2 as the platform. 26914375_We first propose the use of a DNA biosensor to detect the missense single nucleotide polymorphism (rs4839469 c.346G>A p.Ala116Thr) of the vangl1 gene 27648936_Study provides evidence that KITENIN functions in the maintenance of a higher expression level of ErbB4 in advanced colorectal cancer tissues, independent of ubiquitin-mediated degradation via Nrdp1. 27755493_two rare missense mutations in VANGL1, encoding a receptor involved in WNT/PCP signaling, may be associated with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis 29189642_VANGL1 gene is not associated with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in the Chinese population 29366806_High KITENIN expression is associated with cholangiocarcinoma. 30146736_Circular RNA circ-VANGL1 is a competing endogenous RNA which contributes to bladder cancer progression by regulating miR-605-3p/VANGL1 pathway. 30360226_ErbB4/KITENIN-Mediated Signaling is Activated in Cetuximab-Resistant Colorectal Cancer Cells. 30779060_Circ-VANGL1 promotes the development of Osteoporosis via binding to miRNA-217 to downregulate RUNX2 expression. 31076544_Data suggest that circular RNA VANGL1 (circVANGL1) functions as an oncogene to promote non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression partly through miR-195/BCL2 apoptosis regulator (Bcl-2) axis, which might be a therapeutic target for NSCLC patients. 31758655_Silencing circular RNA VANGL1 inhibits progression of bladder cancer by regulating miR-1184/IGFBP2 axis. 32356230_Somatic mutations in planar cell polarity genes in neural tissue from human fetuses with neural tube defects. 33228740_Up-regulation of VANGL1 by IGF2BPs and miR-29b-3p attenuates the detrimental effect of irradiation on lung adenocarcinoma. 34750955_Knockdown of circular RNA VANGL1 inhibits TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in melanoma cells by sponging miR-150-5p. 35028616_Deletions in VANGL1 are a risk factor for antibody-mediated kidney disease. 35713047_Myelomeningocele among Pakistani population. |
ENSMUSG00000027860 |
Vangl1 |
191.422429 |
0.4898524059 |
-1.029581 |
0.108894944 |
91.050858 |
0.00000000000000000000140026455587517973079476977656206340668041296658161621089102102932777427213295595720410346984863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000013181061763212788337586013629564910107022361940856988282277234558748091330926399677991867065429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
125.5633156 |
8.8318891 |
258.0831172 |
11.7679424 |
| ENSG00000173227 |
91683 |
SYT12 |
protein_coding |
Q8IV01 |
FUNCTION: Synaptic vesicle phosphoprotein that enhances spontaneous neurotransmitter release but does not effect induced neurotransmitter release (By similarity). Unlike other synaptotagmins, it does not bind Ca(2+) or phospholipids (By similarity). Essential for mossy-fiber long-term potentiation in the hippocampus (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97610, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q920N7}. |
Cytoplasmic vesicle;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the synaptotagmin gene family and encodes a protein similar to other family members that mediate calcium-dependent regulation of membrane trafficking in synaptic transmission. Studies of the orthologous gene in rat have shown that the encoded protein selectively modulates spontaneous synaptic-vesicle exocytosis and may also be involved in regulating calcium independent secretion in nonneuronal cells. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. The gene has previously been referred to as synaptotagmin XI but has been renamed synaptotagmin XII to be standard with mouse and rat official nomenclature.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2010]. |
hsa:91683; |
exocytic vesicle [GO:0070382]; hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse [GO:0098686]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; clathrin binding [GO:0030276]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; calcium-ion regulated exocytosis [GO:0017156]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:0060291]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis [GO:0017158]; regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0014059]; regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0046928]; spontaneous exocytosis of neurotransmitter [GO:0048792]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
17190793_Studies of the orthologous gene in rat have shown that spontaneous synaptic-vesicle exocytosis is selectively modulated by synaptotagmin 12. 32108133_Synaptotagmin 12 (SYT12) Gene Expression Promotes Cell Proliferation and Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma and Involves the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000049303 |
Syt12 |
42.101560 |
17.4740988636 |
4.127146 |
0.414277645 |
112.476125 |
0.00000000000000000000000002810287940154667802979270986405688876928258420100047974193917598998890793049465486319604679010808467864990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000314718133510492375399158844039530459335352389417102800119812773673800068707784305388486245647072792053222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
78.1183865 |
19.6107660 |
4.5431574 |
1.0303578 |
| ENSG00000173258 |
158399 |
ZNF483 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF39 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:158399; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000038630 |
Zkscan16 |
9.826900 |
0.3884840445 |
-1.364073 |
0.539190373 |
6.309161 |
0.01201156548279670895074122682899542269296944141387939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022659855128588882178242158715875120833516120910644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8534776 |
2.2008256 |
15.1193645 |
3.6822295 |
| ENSG00000173262 |
144195 |
SLC2A14 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDB8 |
FUNCTION: Hexose transporter that can mediate the transport of glucose and dehydroascorbate across the cell membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28971850}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Members of the glucose transporter (GLUT) family, including SLC2A14, are highly conserved integral membrane proteins that transport hexoses such as glucose and fructose into all mammalian cells. GLUTs show tissue and cell-type specific expression (Wu and Freeze, 2002 [PubMed 12504846]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:144195; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0055056]; dehydroascorbic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0033300]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; hexose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015149]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; dehydroascorbic acid transport [GO:0070837]; glucose import [GO:0046323]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659]; monosaccharide transmembrane transport [GO:0015749]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
22421804_SLC2A14 polymorphism has a possible role in changing the genetic susceptibility to late Alzheimer disease age of onset in a Han Chinese population. 26183839_High expression of GLUT-14 was associated with Gastric Adenocarcinoma. 27460888_report presents an expanded SLC2A14 gene locus and a more diverse tissue expression, concurring with the existing evidence for disease associations 28971850_Three alleles in the SLC2A14 gene associated independently with inflammatory bowel disease. 30885992_Under hypoxia and HIF1 blockade, cancer cells adapt their energy metabolism via upregulation of the GLUT14 glucose transporter and creatine metabolism providing new avenues for drug targeting. |
|
|
6.675434 |
0.0272369726 |
-5.198290 |
1.111023617 |
34.291384 |
0.00000000474477756868325622119568108652799820479373238413245417177677154541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000021351499059074652581790258612862154485867449693614616990089416503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3542674 |
0.3032143 |
13.1269126 |
3.4553921 |
| ENSG00000173366 |
|
|
protein_coding |
H0Y858 |
|
Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Lysosome;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
|
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; response to molecule of bacterial origin [GO:0002237]; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034162]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224] |
|
|
|
9.824285 |
110.6356823382 |
6.789673 |
1.101652909 |
60.105396 |
0.00000000000000899115321178239846508946742552741011619105940960716694121401815209537744522094726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000060515012040997813609142204566104395472214347306838533313566586002707481384277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.4319113 |
28.4400210 |
0.1757559 |
0.2012750 |
| ENSG00000173451 |
83591 |
THAP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0W7 |
|
3D-structure;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA binding activity and metal ion binding activity. Located in nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:83591; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
|
ENSMUSG00000020137 |
Thap2 |
44.142037 |
2.5605148056 |
1.356434 |
0.384153461 |
11.654826 |
0.00064036196269524209030016281829489344090688973665237426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001544150068515238180891224750723722536349669098854064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
54.5159411 |
13.0663745 |
21.5319669 |
3.7624194 |
| ENSG00000173530 |
8793 |
TNFRSF10D |
protein_coding |
Q9UBN6 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL (PubMed:9430226). Contains a truncated death domain and hence is not capable of inducing apoptosis but protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis (PubMed:9537512). Reports are contradictory with regards to its ability to induce the NF-kappa-B pathway. According to PubMed:9382840, it cannot but according to PubMed:9430226, it can induce the NF-kappa-B pathway (PubMed:9382840, PubMed:9430226). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9382840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9430226, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9537512}. |
Apoptosis;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor contains an extracellular TRAIL-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a truncated cytoplamic death domain. This receptor does not induce apoptosis, and has been shown to play an inhibitory role in TRAIL-induced cell apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8793; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; TRAIL binding [GO:0045569]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11844843_TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is not constitutively expressed in the human brain, whereas both apoptosis-mediating and apoptosis-blocking TRAIL receptors are found on neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes 12421985_Enhanced expression of DcR2 promotes peripheral blood eosinophil survival in the airways of allergic asthmatics following segmental antigen challenge. 12488957_Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by TRAIL to beta-cell lines CM were inhibited competitively by soluble TRAIL receptors, R1, R2, R3 or R4. 12808117_likely to be involved in chronic pancreatitis; pancreatic stellate cells may directly contribute to acinar regression by inducing apoptosis of parenchymal cells in a TRAIL-dependent manner 12915532_Respiratory syncytial virus infection strongly up-regulated the expression of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its functional receptors death receptor 4 (DR4) and DR5. 14999791_Our results demonstrate that DcR1 and DcR2 genes are frequently methylated in various tumor types and aberrant methylation was the cause for silencing of DcR1 and DcR2 expression. 15301860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15538968_The DcR2 was found to have a truncated and non-functional death domain. 15916713_TRAIL-R4 but not TRAIL-R3 is the decoy receptor which appeared to influence TRAIL sensitivity in breast cancer cells 15919363_CD8+ lymphocytes and NKT lymphocytes, but not CD4+ lymphocytes, express TRAIL-R4 15921376_Resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells is associated with expression of TRAIL-R4. 16319225_Preligand assembly domain-mediated ligand-independent association between TRAIL receptor 4 (TR4) and TR2 regulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 16799475_DCR2 was found positive in 81 and 33% normal, 46 and 10% nodular hyperplasia, 74 and 36% PIN tissues, 87 and 89% low-grade carcinomas, and 100 and 93% high-grade carcinomas 16934748_TRAIL-R4-beta is a new splice variant of TRAIL-receptor 4 lacking the cysteine rich domain 1 16980609_The specificity of DcR1- and DcR2-mediated TRAIL inhibition reveals an additional level of complexity for the regulation of TRAIL signaling. 17522430_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17545522_CASP8, DCR2, and HIN-1 methylation leads to progression of neuroblastoma 18460741_These data strongly support a recent proposal that a segment at 8p21.3 contains crucial prostate cancer tumor suppressors. 18980997_DCR2-methylated patients showed significantly poorer 5-year event-free survival in the whole neuroblastoma group (43% 18981952_High TRAIL death receptor 4 and decoy receptor 2 expression correlates with significant cell death in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19730199_Results indicate that disc cells, after herniation, undergo apoptotic cell death via the DR5/TRAIL pathway. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948942_Higher levels of TRAIL and the TRAIL decoy receptor, TRAIL R4, were expressed by leukocytes in inflamed human periodontal tissues. 20018172_these results demonstrated that hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha played a crucial role in regulating the transcription of DcR2. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20799941_TRAIL receptor-4 expression profiles on T cells might be important in revelation of rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20875141_ANT2 shRNA treatment sensitized MCF7, T47 D, and BT474 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by up-regulating the expression of TRAIL death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4 and DR5) and down-regulating the TRAIL decoy receptor 2 (DcR2). 22028813_transcript levels of UCHL1, COL1A2, THBS1 and TNFRSF10D were inversely correlated with promoter methylation 23584885_The membrane expression of the TRAIL receptors DR4, DR5, DcR1 and DcR2 is greater in normal endometrium than endometrioid adenocarcinoma (EAC). The level of the receptors in EAC is not dependent on grading and staging and does not predict survival. 24211571_the results presented here claim for a relevant impact of aberrant methylation of decoy receptors in melanoma and allow to understand how the silencing of DcR1 and DcR2 is related to melanomagenesis. 24649804_membrane expression more common in endometrioid endometrial cancer than in normal endometrium 25003639_This study identified TNFRSF10D DNA methylation status as an independent prognostic biomarker for relapse-free survival and overall mortality in non-metastatic melanoma patients. 26050621_DcRs regulate TRAIL sensitivity at a supracellular level 26542757_Results identified epigenetic inactivation of TNFRSF10C and TNFRSF10D in majority of cervical cancer cases. 28356293_Urinary DcR2 could potentially serve as a novel biomarker for tubulointerstitial injury and may reflect senescence of renal proximal tubular cells in diabetic nephropathy. 28962588_results suggest that CD264 is a surface marker of cellular age for bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 29879421_The high-dose hook effect was apparent during ELISA testing of uDcR2 in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients, yet dilution of the urine samples neutralized this effect. However, the use of a four-fold dilution of urine for uDcR2/cre testing may eliminate the high-dose hook effect and make it possible to effectively monitor the severity of TII in CKD patients. 31183506_data suggest that the determination of intracellular co-expression patterns of TRAIL-R1, TRAIL-R2, and TRAIL-R4 provides an innovative and robust method for risk stratification in breast cancer patients beyond conventional prognostic markers. 31612990_Survival of aging CD264(+) and CD264(-) populations of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells is independent of colony-forming efficiency. |
ENSMUSG00000045362+ENSMUSG00000037613+ENSMUSG00000010751 |
Tnfrsf26+Tnfrsf23+Tnfrsf22 |
124.008657 |
2.5767187683 |
1.365535 |
0.201047475 |
45.791196 |
0.00000000001315534456763260417566662686575357883375647638501959590939804911613464355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000072344592331690475642590551784471067375825725775939645245671272277832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
179.7022810 |
20.8285315 |
70.2178035 |
6.3077391 |
| ENSG00000173531 |
4485 |
MST1 |
protein_coding |
G3XAK1 |
|
Disulfide bond;Kringle;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;Serine protease homolog;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains four kringle domains and a serine protease domain, similar to that found in hepatic growth factor. Despite the presence of the serine protease domain, the encoded protein may not have any proteolytic activity. The receptor for this protein is RON tyrosine kinase, which upon activation stimulates ciliary motility of ciliated epithelial lung cells. This protein is secreted and cleaved to form an alpha chain and a beta chain bridged by disulfide bonds. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:4485; |
vacuole [GO:0005773]; histone kinase activity [GO:0035173]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; mammary duct terminal end bud growth [GO:0060763]; negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process [GO:1904036]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0033601]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010758]; regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046425]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
12177064_These results suggest that activation of RON by macrophage-stimulating protein inhibits LPS-induced macrophage Cox-2 expression. 12919677_Data show that macrophage stimulating protein (MSP) and its receptor (Ron) induce phosphorylation of both Ron and alpha6beta4 integrin, and result in activation of alpha3beta1 integrin. 14597639_macrophage-stimulating protein-responsive cell growth in culture is suppressed by the ron-sema domain 15764806_Macrophage stimulating protein and its receptor RON are involved in the pathophysiology of endometriosis. 16170349_repression of MSP gene expression by mutant p53 may contribute to oncogenesis in a cell type-specific manner 17456594_overexpression of MSP, MT-SP1, and MST1R was a strong independent indicator of both metastasis and death in human breast cancer 18438406_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18480548_Cell migration and production of inflammatory cytokines by the brain are enhanced by MSP stimulation in primary microglia. 18700007_The five gene transcripts (aldolase B, elafin, MST-1, simNIPhom and SLC6A14) were changed in patients with ulcerative colitis, and were related to the disease activity. 19079170_Gene-centric association mapping of chromosome 3p implicates MST1 in IBD pathogenesis. 19456860_Results suggest that hepatocyte growth factor activator is a major serum activator of pro-macrophage-stimulating protein. 19657358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657358_The effect of BSN-MST1 locus on Crohn's disease predisposition was replicated, but no influence on ulcerative colitis or multiple sclerosis predisposition could be detected 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19944697_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20014019_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20024904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20307617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21081472_results suggest that MSP induces uPAR expression via MAPK, AP-1 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways 21249150_the oncogenic effect of BRAF(V600E) is associated with the inhibition of MST1 tumor suppressor pathways, and that the activity of RASSF1A-MST1-FoxO3 pathways determines the phenotypes of BRAF(V600E) tumors. 21619683_MSP-induced RSK2 activation is a critical determinant linking RON signaling to cellular EMT program. 21723047_considerable number of Merkel cell carcinoma cases expressed both RON and MSP, while Merkel cells do not express these molecules 21875933_These findings suggest that the MSP/RON signaling pathway may be regulated by hepsin in tissue homeostasis and in disease pathologies, such as in cancer and immune disorders. 21931648_Studies indicate that the cylindromatosis/turban tumor syndrome gene (CYLD) ranked highest, followed by acylaminoacyl-peptidase (APEH), dystroglycan (DAG1), macrophage-stimulating protein (MST1) and ubiquitin-specific peptidase 4 (USP4). 22087277_the missense SNP impairs MSP function by reducing its affinity to RON and perhaps through a secondary effect on in vivo concentration arising from reduced thermodynamic stability, resulting in down-regulation of the MSP/RON signaling pathway. 22245154_HAT cleaves proMSP at the physiological activation site 22554193_The present results refine the known genetic architecture in primary sclerosing cholangitis by confirming MST1 locus association. 23011677_MSP may be one of the major determinants that affects the properties of tumor stroma and that produces a permissive microenvironment to promote cancer metastasis 23422030_Results suggest that the [AA] genotype of the common MST1 variant rs3197999 enhances genetic risk of sporadic extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma irrespective of primary sclerosing cholangitis status. 23928732_Mst1 has an important role in inhibiting the growth of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo; its antiproliferative effect is associated with induction of apoptosis. 24409221_functional consequences of the macrophage stimulating protein 689C inflammatory bowel disease risk allele 25193665_These results support the hypothesis that the alpha-chain of MSPalphabeta mediates RON dimerization. 25315688_MSP appears to promote the migration of fibroblasts, enhances collagen synthesis and remodeling, and effectively improves wound healing. 25551685_Identify MST1/MSP as a mitogen for tracheal basal cells. 25704570_Elevated serum levels of MST1 were found in subjects with excessive alcohol use. 27609031_These data suggest that MSP is an effective inhibitor of inflammation and lipid accumulation in the stressed liver, thereby indicating that MSP has a key regulatory role in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. 29441677_Our analysis suggests that MST1 might interact with key susceptibility genes involved in autophagy and bacterial recognition. These findings provide insight into the genetic architecture of Crohn's disease in Chinese and may partially explain the disparity of genetic signals in Crohn's disease susceptibility across different ethnic populations by highlighting the contribution of gene-gene interactions. 30212651_Legionella pneumophila effector protein LegK7(lpg1924) hijacks the conserved Hippo signaling pathway by molecularly mimicking host Hippo kinase (MST1 in mammals), which is the key regulator of pathway activation. 30981108_Mst1 overexpression inhibits mitophagy activity via suppressing the ERK-Mfn2 pathway, ultimately augmenting IL-24-inducd esophageal cancer death via enhanced mitochondrial stress. 31254927_Comparative characterization of the HGF/Met and MSP/Ron systems in primary pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 32156191_Macrophage stimulating 1-induced inflammation response promotes aortic aneurysm formation through triggering endothelial cells death and activating the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 32692720_Mst1 promotes mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in oxidative stress-induced rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. 33070035_Macrophage-stimulating protein is decreased in severe preeclampsia and regulates the biological behavior of HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells. 33109096_circCRAMP1L is a novel biomarker of preeclampsia risk and may play a role in preeclampsia pathogenesis via regulation of the MSP/RON axis in trophoblasts. |
ENSMUSG00000032591 |
Mst1 |
96.279710 |
0.2567972162 |
-1.961299 |
0.311609506 |
38.251838 |
0.00000000062178477424824240796443508921494992824907654949129209853708744049072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003018928706547387702535283272213886829327122995891841128468513488769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.1865800 |
11.7684187 |
166.1771815 |
32.2568297 |
| ENSG00000173546 |
1464 |
CSPG4 |
protein_coding |
Q6UVK1 |
FUNCTION: Proteoglycan playing a role in cell proliferation and migration which stimulates endothelial cells motility during microvascular morphogenesis. May also inhibit neurite outgrowth and growth cone collapse during axon regeneration. Cell surface receptor for collagen alpha 2(VI) which may confer cells ability to migrate on that substrate. Binds through its extracellular N-terminus growth factors, extracellular matrix proteases modulating their activity. May regulate MPP16-dependent degradation and invasion of type I collagen participating in melanoma cells invasion properties. May modulate the plasminogen system by enhancing plasminogen activation and inhibiting angiostatin. Functions also as a signal transducing protein by binding through its cytoplasmic C-terminus scaffolding and signaling proteins. May promote retraction fiber formation and cell polarization through Rho GTPase activation. May stimulate alpha-4, beta-1 integrin-mediated adhesion and spreading by recruiting and activating a signaling cascade through CDC42, ACK1 and BCAR1. May activate FAK and ERK1/ERK2 signaling cascades. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10587647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11278606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15210734}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Tissue remodeling;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
A human melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan plays a role in stabilizing cell-substratum interactions during early events of melanoma cell spreading on endothelial basement membranes. CSPG4 represents an integral membrane chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expressed by human malignant melanoma cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1464; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; glial cell migration [GO:0008347]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; ruffle assembly [GO:0097178]; substrate-dependent cell migration [GO:0006929]; tissue remodeling [GO:0048771] |
12220645_identified a novel repeat named CSPG in the central ectodomain 14573520_Data suggest that MCSP is a novel marker for epidermal stem cells that contributes to their patterned distribution by promoting stem cell clustering. 15009727_MCSP coexpression with a subset of beta 1 integrin basal keratinocytes within the epidermis suggests that MCSP colocalizes with epidermal stem cells, MSCP expression within the hair follicle was more complex 15210734_MCSP may facilitate primary melanoma progression by enhancing the activation of key signaling pathways important for tumor invasion and growth. 15504744_PKC-alpha-mediated NG2 phosphorylation at Thr(2256) is a key step for initiating cell polarization and motility 16169245_MCSP/NG2 proteoglycan may be considered an important receptor mediating COL6-sarcolemma interactions, a relationship that is disrupted by the pathogenesis of UCMD muscle. 16253523_tumour cells can regulate both the function and structure of the host-derived tumour vasculature through NG2 expression 16365873_Co-expression and interaction of NG2 and galectin-3 in human glioma cells establish a molecular basis for the NG2/galectin-3 interaction. 16455987_dendritic cell-based immunization represents an effective strategy to implement T cell-based immunotherapy targeting high molecular weight-melanoma-associated antigen (HMW-MAA) in patients with HMW-MAA-bearing tumors [HMW-MAA] 16625365_NG2 is abundantly distributed in the intestinal subepithelial myofibroblasts layer of the mouse and human intestines. 17268261_Colocalization of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (NG2) with type VI collagen in the pericellular area suggests that NG2 may play an important role in cell-matrix interactions. 17591920_Differential phosphorylation of NG2 proteoglycan by ERK and PKCA helps balance cell proliferation and cell movement. 17592550_NG2 expression was uniformly positive on a cell line derived from angiomyolipoma. 17851550_NG2 antigen diagnosis of MLL rearrangements in pediatric patients 18292781_Data show that NG2 and integrin alpha4 oppositely regulate anoikis in fibroblasts, and that NG2 and integrin alpha4 regulate FAK phosphorylation by PKCalpha-dependent and -independent pathways, respectively. 18469852_High NG2/MPG expression correlated with multidrug resistance mediated by increased activation of alpha3beta1 integrin/PI3K signaling and their downstream targets, promoting cell survival 18519770_High molecular weight-melanoma-associated antigen is more sensitive and specific than MART-1, S-100p, and HMB-45 for immunohistochemistry-based detection of malignant melanoma sentinel lymph nodes micrometastases 18634019_NG2 has a role in metastasis formation in soft-tissue sarcoma patients 18767415_the coexpression of KOR-SA35443 (kappa opioid receptor) and NG2 (chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan) in result of karyotype abnormal changes may predict a poor prognosis in Pro-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia 18829565_A Lm-based vaccine against HMW-MAA can trigger cell-mediated immune responses to this antigen that can target not only tumor cells but also pericytes in the tumor vasculature. 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19462316_NG2 expression on culture-expanded mesenchymal stromal cells was investigated by flow cytometry. 19604403_NG2 was present in the evolving astroglial scar after human traumatic spinal cord injury, and, therefore, might play an important role in the blockade of successful CNS regeneration. 19776755_Human skin aging is associated with reduced expression of the stem cell markers beta1 integrin and MCSP 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20448346_Staining intensity of HMW-MAA in acral lentiginous melanoma lesions was weaker than in superficial spreading melanoma where it was found to be higher than previously reported. 20455858_in squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck and in basal breast carcinoma, CSPG4 is expressed by cancer stem cells 20805128_Results showed the expression of MCSP and PRAME in conjunctival melanoma and benign conjunctival nevi and showed that MCSP and PRAME were differentially expressed in both and can help to differentiate the lesions diagnostically. 21070915_Functional and clinical relevance of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4. 21092857_In regions of spinal cord neurodegeneration of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis model mice, NG2-positive cells exhibit enhanced proliferation and accelerated differentiation into oligodendrocytes but remained committed to the oligodendrocyte lineage. 21123584_Cells that express NG2 proteoglycan act predominantly as a reservoir of new oligodendrocytes in the demyelinated spinal cord. 21658254_Cell surface P-selectin binding depends on CHST11 gene expression. CSPG4 serves as a P-selectin ligand through its CS chain and participates in P-selectin binding to the highly metastatic breast cancer cells. 21798846_High NG2 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 22004131_REVIEW outlines recent advances in our understanding of CSPG4-associated cell signaling, describing the central role it plays in melanoma tumor cell growth, motility, and survival, and explores how modifying CSPG4 function and protein-protein interactions may provide us with novel combinatorial therapies for the treatment of advanced melanoma 22021902_Findings define the CSPG4-specific fully human scFv-FcC21 antibody as a candidate therapeutic agent to target the many types of tumors that express CSPG4. 22699001_NG2 mediates activation of Rho leading to amoeboid invasiveness in sarcoma cell line. 22999866_Although transgenic nestin-GFP-expressing progenitor cells share morphological and molecular markers with NG2-glia, they do not express other pericyte markers nor do they differentiate into the muscle lineage. 23359523_NG2-positive adipose stem cells loaded on scaffolds fabricate skeletal muscle tissue in vivo without the need of a myogenic pre-differentiation step in vitro. 23474192_tThis study demonistrated taht human infants, Western blot analyses exhibited trends for lower NG2 levels in the germinal matrix and white matter of infants with Intraventricular hemorrhage relative to controls without Intraventricular hemorrhage. 23559515_NG2-Col VI interplay as putatively involved in the regulation of the cancer cell-host microenvironment interactions sustaining sarcoma progression 23804106_cell polarity complexes as new effectors of NG2 signaling in the establishment of front-rear polarity 23925489_NG2 knockdown results in loss of beta1 integrin activation in endothelial cells, revealing a mechanism for NG2-dependent cross talk between pericytes and endothelial cells. 23953863_data suggest that locally produced CSPG4 stimulates human extravillous trophoblast migration and invasion and suggests that IL11 and LIF regulate villous cytotrophoblast differentiation towards the invasive phenotype at least in part via CSPG4. 23995070_Transgenic NG2-positive glia are identified as the major central nervous system cellular target of IL-17 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. 24177010_This study showed that high CSPG4 expression correlates with disease recurrence and overall survival in breast cancers. 24334762_T-cells transduced with a CSPG4-specific chimeric antigen receptor inhibit the growth of CSPG4-expressing tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. 24386429_The results highlight an unprecedented, complex pattern of NG2/CSPG4 isoform expression in foetal and neoplastic CNS 24740185_Reduced promoter methylation and increased expression of CSPG4 are associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. 24932730_Low CSPG4 expression is associated with pancreatic tumors. 25016058_Describe CSPG4-specific immunotoxin that kills rhabdomyosarcoma cells and binds to primary tumor tissues. 25166220_MMP-13 overexpression or exogenous MMP-13 reduces anoikis by more effectively shedding NG2. 25503117_NG2 expression in pediatric brain tumors differs depending upon type and, unlike adult glioma, includes expression on lower-grade tumors. 25713464_These data are consistent with the concept that expression of inhibitory CSPG within the injury scar is an important impediment to regeneration but that NG2+ progenitors derived from ESNLCs can modify the microenvironment 26074703_The up-regulation of NG2 is associated with poor prognosis in HCC. 26340347_The NG2 proteoglycan protects oligodendrocyte precursor cells against oxidative stress via interaction with OMI/HtrA2. 26689475_A positive CSPG4 stain may be associated with an increased risk of metastasis and mortality from chordoma. 26792897_These data suggest the possible involvement of GD3 and NG2 in pre/pro-tumorigenic events occurring in the complex microenvironment of the tissue surrounding glioblastoma 26890881_the ratio of serum proteoglycan 4 to protease C1 inhibitor may be used for screening of early breast cancer. 27292772_The results indicate that CSPG4/NG2 has roles in regulating chondrosarcoma cell function in relation to growth, spread and resistance to chemotherapy. 28098860_CSPG4 is a cell surface proteoglycan regulated by interleukin 11 in human endometrial epithelial cancer cells. the data suggest that CSPG4 inhibition may impair endometrial cancer progression by reducing cancer cell proliferation, migration and potentially epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. 28715802_Both tumor cell and vascular NG2 expression were shown to be present in a significant number of patients with colorectal cancer and this makes NG2 a double target for anti-tumor therapies. 28842504_In addition to establishing the binding region for CSPG4, this work ascribes for the first time a role in TcdB CROPs in receptor binding and further clarifies the relative roles of host receptors in TcdB pathogenesis. 28945172_of NG2/CSPG4 rather than changes in CD44 or Ki-67 expression is associated with low overall survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients 28964848_NG2 may represent a promising target for the modulation of ICAM-1-mediated immune responses. 29054751_Study suggests that CSPG4 and progranulin may engage in mutual cell-to-cell communications orchestrating regenerative processes, which may enhance the repair capacity of the adult brain. CSPG4 might engage with PTPRs as cell bound ligand or as soluble molecule after its shedding, possibly regulating thereby adhesion and synaptic strength, which contribute to the rebuilding of connectivity after injury. [review] 29196603_Ng2/Cspg4 deletion altered the expression of genes regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis. 29291617_DNA methylation status of blood leukocytes may be associated with susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer . The MCSM-H of blood leukocytes may be associated with CRC risk, especially in younger people. 29302076_We observed familial segregation of two rare missense mutations in Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4) (c.391G > A [p.A131T], MAF 7.79 x 10(-5) and c.2702T > G [p.V901G], MAF 2.51 x 10(-3)). The CSPG4(A131T) mutation was absent from the Swedish Schizophrenia Exome Sequencing Study (2536 cases, 2543 controls), while the CSPG4(V901G) mutation was nominally enriched in cases (11 cases vs. 3 controls) 29462330_This study revealed that CSPG4 interacted with perlecan to support cell adhesion and actin polymerization and the data suggest a novel mechanism by which CSPG4 expressing cells might attach to perlecan-rich matrices so as those found in connective tissues and basement membranes. 30213051_NG2/CSPG4 expression has been demonstrated in oligodendrogliomas, astrocytomas, and glioblastomas (GB), and it correlates with malignancy 30590711_High NG2 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 33255261_Receptor Binding Domains of TcdB from Clostridioides difficile for Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 and Frizzled Proteins Are Functionally Independent and Additive. 33649790_Expression of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4) in melanoma cells is downregulated upon inhibition of BRAF. 33727640_NG2/CSPG4, CD146/MCAM and VAP1/AOC3 are regulated by myocardin-related transcription factors in smooth muscle cells. 34078123_CSPG4 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. 34344877_Identification of a germline CSPG4 variation in a family with neurofibromatosis type 1-like phenotype. 36221119_CSPG4 expression in soft tissue sarcomas is associated with poor prognosis and low cytotoxic immune response. |
ENSMUSG00000032911 |
Cspg4 |
1109.590479 |
4.5593272449 |
2.188821 |
0.054330256 |
1718.469573 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1833.1821062 |
60.3494545 |
405.0204902 |
11.3990575 |
| ENSG00000173588 |
51134 |
CEP83 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y592 |
FUNCTION: Component of the distal appendage region of the centriole involved in the initiation of primary cilium assembly. May collaborate with IFT20 in the trafficking of ciliary membrane proteins from the Golgi complex to the cilium during the initiation of primary cilium assembly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23348840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23530209}. |
Alternative splicing;Ciliopathy;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Nephronophthisis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a centriolar protein involved in primary cilium assembly. Defects in this gene have been associated with infantile nephronophthisis and intellectual disability. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:51134; |
centriole [GO:0005814]; ciliary transition fiber [GO:0097539]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; establishment of centrosome localization [GO:0051660]; protein localization to centrosome [GO:0071539]; vesicle docking [GO:0048278] |
23530209_CCDC41 is required for the docking of ciliary vesicles 24882706_We have identified mutations in CEP83, another distal appendages component encoding gene, as a cause of infantile nephronophthisis associated with central nervous system abnormalities in half of the individuals. 31455668_The results reveal a molecular mechanism of kinase regulation in ciliogenesis and identify CEP83 as a key substrate of TTBK2 during cilia initiation. 33938610_Beyond nephronophthisis: Retinal dystrophy in the absence of kidney dysfunction in childhood expands the clinical spectrum of CEP83 deficiency. 36222666_The centrosomal protein 83 (CEP83) regulates human pluripotent stem cell differentiation toward the kidney lineage. |
ENSMUSG00000020024 |
Cep83 |
51.729545 |
3.1555291761 |
1.657882 |
0.476918472 |
11.435460 |
0.00072055640129913976939246555986073872190900146961212158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001720940531258139489720337955702689214376732707023620605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.8537024 |
24.2474251 |
24.7254687 |
5.7153016 |
| ENSG00000173599 |
5091 |
PC |
protein_coding |
P11498 |
FUNCTION: Pyruvate carboxylase catalyzes a 2-step reaction, involving the ATP-dependent carboxylation of the covalently attached biotin in the first step and the transfer of the carboxyl group to pyruvate in the second. Catalyzes in a tissue specific manner, the initial reactions of glucose (liver, kidney) and lipid (adipose tissue, liver, brain) synthesis from pyruvate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9585002}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Biotin;Disease variant;Gluconeogenesis;Ligase;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Manganese;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Pyruvate;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate biosynthesis; gluconeogenesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:9585002}. |
This gene encodes pyruvate carboxylase, which requires biotin and ATP to catalyse the carboxylation of pyruvate to oxaloacetate. The active enzyme is a homotetramer arranged in a tetrahedron which is located exclusively in the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate carboxylase is involved in gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, insulin secretion and synthesis of the neurotransmitter glutamate. Mutations in this gene have been associated with pyruvate carboxylase deficiency. Alternatively spliced transcript variants with different 5' UTRs, but encoding the same protein, have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5091; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; biotin binding [GO:0009374]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; pyruvate carboxylase activity [GO:0004736]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; NADH metabolic process [GO:0006734]; NADP metabolic process [GO:0006739]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation by host of viral process [GO:0044794]; pyruvate metabolic process [GO:0006090]; viral release from host cell [GO:0019076]; viral RNA genome packaging [GO:0019074] |
12112657_IVS15+2-5delTAGG results in the retention of intron 15 during pre-mRNA splicing and frameshift mutations. 12437512_expression and characterization of a variant by retroviral gene transfer 16325442_1 deficiency patient survived from neonatal lactic acidemia and shows an unusual subcortical leucodystrophic process. 18297087_The crystal structures at 2.8-A resolution of full-length PC from Staphylococcus aureus and the C-terminal region (missing only the BC domain) of human PC, is reported. 18676167_Eight novel mutations were identified in PC from 8 pyruvate carboxylase deficiency patients. 19296078_The activities of pyruvate carboxylase (PC) were decreased by 65% in pancreatic islets of patients with type 2 diabetes. 19306334_Nine novel mutations of the PC gene, in five unrelated patients, are reported. 20807508_PC protein is easily detectable by streptavidin blot and the presence of considerable amounts of PC in cultured human myotubes and in human muscle tissue was shown. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23294723_Increased PC expression is correlated with the malignant progression of GC, which might be a potential target for GC biotherapy. 23383084_characterization of PC distal promoter 25243911_PC and PDH may be an important part of cellular adaptation to the IDH1 mutation and may serve as potential therapeutic targets 25607840_These findings indicate that PC-mediated anaplerosis in early-stage NSCLC is required for tumor survival and proliferation. 26906558_Pyruvate carboxylase activates the RIG-I-like receptor-mediated antiviral immune response by targeting the MAVS signalosome. 27732858_breast cancer cells proliferating as lung metastases activate PC-dependent anaplerosis in response to the lung microenvironment. 27890529_PC enzyme activity is much higher in the highly invasive breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 than in less invasive breast cancer cell lines. Strong PC suppression lowered glucose incorporation into downstream metabolites of oxaloacetate, the product of the PC reaction, including malate, citrate and aspartate. 30005601_Our studies indicate that PC is specifically required for the growth of breast cancer that has disseminated to the lungs. Overall, these findings point to the potential of targeting PC for the treatment of pulmonary metastatic breast cancer 30870574_Study compares type A and type C patients with pyruvate carboxylase deficiency (PCD). Type C PCD is not associated to homozygous variants in PC. In silico modeling found that variants lead to type A or type C phenotype based on the destabilization between the two major enzyme conformers. 33109566_Overexpression of Pyruvate Carboxylase Is Correlated With Colorectal Cancer Progression and Supports Growth of Invasive Colon Cancer HT-29 Cell Line. 33177242_Integrated analysis of transcriptomic and metabolomic data demonstrates the significant role of pyruvate carboxylase in the progression of ovarian cancer. 33435350_Rethinking the Citric Acid Cycle: Connecting Pyruvate Carboxylase and Citrate Synthase to the Flow of Energy and Material. 33880999_Expression of pyruvate carboxylase in cultured human astrocytoma, glioblastoma and neuroblastoma cells. 34245978_Pyruvate carboxylase supports basal ATP-linked respiration in human pluripotent stem cell-derived brown adipocytes. 34632533_Protective effects of all-trans retinoic acid against gastric premalignant lesions by repressing exosomal LncHOXA10-pyruvate carboxylase axis. 34764457_Fibroblast pyruvate carboxylase is required for collagen production in the tumour microenvironment. 35907054_The ubiquitous expression of pyruvate carboxylase among human prostate tumors. |
ENSMUSG00000024892 |
Pcx |
123.879350 |
2.3997149494 |
1.262863 |
0.142045662 |
80.944863 |
0.00000000000000000023210410848849535484030543203808695189386963654745558733455412792068273120094090700149536132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001995257216825970491230454967950743939971291168232014716366062856423013727180659770965576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
185.7116876 |
15.9658834 |
77.7155415 |
5.4561692 |
| ENSG00000173641 |
27129 |
HSPB7 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBY9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Chaperone;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Stress response |
|
This gene encodes a small heat shock family B member that can heterodimerize with similar heat shock proteins. Defects in this gene are associated with advanced heart failure. In addition, the encoded protein may be a tumor suppressor in the p53 pathway, with defects in this gene being associated with renal cell carcinoma. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:27129; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; aggresome [GO:0016235]; Cajal body [GO:0015030]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; filamin binding [GO:0031005]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; heart development [GO:0007507]; regulation of heart contraction [GO:0008016]; response to unfolded protein [GO:0006986] |
19464326_HSPB7 constitutively localized to SC35 splicing speckles, driven by its N-terminus. Unlike HSPB1 and HSPB5, that chaperoned heat unfolded substrates and kept them folding competent, HSPB7 did not support refolding. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20038796_Cardiac signaling genes exhibit unexpected sequence diversity in sporadic cardiomyopathy, revealing HSPB7 polymorphisms associated with disease. 20124441_The rs1738943 shows that although this SNP is located within HSPB7, it resides in a block of high LD that spans HSPB7 and a nearby gene, CLCNKA, which encodes a voltage-sensitive chloride channel expressed mainly in the kidney. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20975947_Data show a significant association between a SNP in HSPB7 gene (rs1739843, minor allele frequency 39%) and idiopathic DCM. 20975947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21731611_Overexpression of HSPB1, as well as HSPB6, HSPB7 and HSPB8 independently protect against tachycardia remodeling by attenuation of the RhoA GTPase pathway at different levels. 22785082_HSPB7 is a potential early biomarker after MI and serves as an independent risk factor of ACS in patients with acute chest pain. 24585183_Results imply that HSBP7 is likely to be a tumor suppressor gene regulated by p53 and its downregulation by hypermethylation may play a critical role in renal carcinogenesis. 25889438_HSPB7 loci is associated in the pathophysiologuy of ischemic heart failure. 27441470_Patients with central sleep apnea and congestive heart failure had higher T allele frequencies in the HSPB7 gene. 28827800_our findings characterize HSPB7 as an intercalated disc protein and suggest it has an essential role in maintaining intercalated disc integrity and conduction function in the adult heart. 29331499_Loss of Hspb7 in zebrafish or human cardiomyocytes stimulated autophagic pathways and expression of the sister gene encoding Hspb5. Inhibiting autophagy caused FilaminC aggregation in HSPB7 mutant human cardiomyocytes and developmental cardiomyopathy in hspb7 mutant zebrafish embryos. 29577611_SRARP and HSPB7 are tumor suppressors that are commonly inactivated in malignancies. 30660137_HSPB7 Gene Polymorphism Associated with Anthropometric Parameters of Obesity and Fat Intake in a Central European Population. 33097082_HSPB7 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells via ERK signaling pathway. 33827396_Cardio-Vascular Heat Shock Protein (cvHsp, HspB7), an Unusual Representative of Small Heat Shock Protein Family. 35977674_Is the small heat shock protein HSPB7 (cvHsp) a genuine actin-binding protein? |
ENSMUSG00000006221 |
Hspb7 |
32.853526 |
0.3859769096 |
-1.373414 |
0.286750823 |
23.380251 |
0.00000132936330917509010070786095586425901160509965848177671432495117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004637533075732529214011204410361699501663679257035255432128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.1241704 |
3.3854978 |
44.8276580 |
5.6762847 |
| ENSG00000173706 |
57493 |
HEG1 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULI3 |
FUNCTION: Receptor component of the CCM signaling pathway which is a crucial regulator of heart and vessel formation and integrity. May act through the stabilization of endothelial cell junctions. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction; negative regulation of Rho-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity; and negative regulation of membrane permeability. Located in cell-cell junction. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57493; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cardiac atrium morphogenesis [GO:0003209]; cardiac muscle tissue growth [GO:0055017]; cell-cell junction assembly [GO:0007043]; endothelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0001886]; heart development [GO:0007507]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; lung development [GO:0030324]; lymph circulation [GO:0003017]; lymph vessel development [GO:0001945]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of membrane permeability [GO:1905709]; negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035024]; negative regulation of Rho-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:2000299]; pericardium development [GO:0060039]; positive regulation of fibroblast growth factor production [GO:0090271]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; protein localization to cell junction [GO:1902414]; regulation of body fluid levels [GO:0050878]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; venous blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048845]; ventricular septum development [GO:0003281]; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis [GO:0003222] |
14680629_Identification of the zebrafish heart of glass (heg) gene. Description of HEG's role in the regulation of concentric heart growth in zebrafish. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23814056_These data show that HEG1 can recruit the Rap1-KRIT complex to the plasma membrane. 24643410_Human patients with cerebral cavernous malformations who lack exonic mutations in krev interaction trapped protein (KRIT)1, cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) protein 2, or programmed cell death (PDCD)10 protein do not have mutations in HEG. 26780829_These studies establish that the binding of HEG1 to Rasip1 mediates Rap1-dependent recruitment of Rasip1 to and stabilization of endothelial cell cell-cell junctions. 28361969_Study shows that HEG homolog 1 is a novel mucin-like membrane protein that serves as a diagnostic and therapeutic target for malignant mesothelioma. 30250045_he specific detection of mesothelioma with SKM9-2 can thus be performed by the recognition of sialylated glycan modification in the specific region of HEG1 31278131_HEG1 overexpression significantly promotes HCC cell migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32205484_HEG1 Is a Highly Specific and Sensitive Marker of Epithelioid Malignant Mesothelioma. 32284171_HEG1-responsive microRNA-23b regulates cell proliferation in malignant mesothelioma cells. 33774129_LncRNA SNHG12 promotes proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting HEG1 via miR-516a-5p. 34240508_Membranous HEG1 expression is a useful marker in the differential diagnosis of epithelioid and biphasic malignant mesothelioma versus carcinomas. |
ENSMUSG00000075254 |
Heg1 |
517.535920 |
2.2334357278 |
1.159265 |
0.078537314 |
219.025612 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014754500210714616853134426836085325717915419330687247918619549643355148284665530178978291752063190545933080473106816856373210526676142961832738365046679973602294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003115542533764631144418032985630553776575819555614172046639445320430598902040205382694745728748794168417153167794855236167814171999168593174545094370841979980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
702.7783425 |
44.9983023 |
316.5677880 |
15.3566338 |
| ENSG00000173744 |
3267 |
AGFG1 |
protein_coding |
P52594 |
FUNCTION: Required for vesicle docking or fusion during acrosome biogenesis (By similarity). May play a role in RNA trafficking or localization. In case of infection by HIV-1, acts as a cofactor for viral Rev and promotes movement of Rev-responsive element-containing RNAs from the nuclear periphery to the cytoplasm. This step is essential for HIV-1 replication. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10613896, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14701878, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15749819}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Glycoprotein;Metal-binding;mRNA transport;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Spermatogenesis;Transport;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is related to nucleoporins, a class of proteins that mediate nucleocytoplasmic transport. The encoded protein binds the activation domain of the human immunodeficiency virus Rev protein when Rev is assembled onto its RNA target, and is required for the nuclear export of Rev-directed RNAs. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:3267; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; acrosome assembly [GO:0001675]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; mRNA export from nucleus [GO:0006406]; spermatid nucleus differentiation [GO:0007289] |
14701878_hRIP is an essential cellular Rev cofactor, which acts at a previously unanticipated step in HIV-1 RNA export. 18775314_Study demonstrates that the clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the SNARE VAMP7 is directly mediated by Hrb, a clathrin adaptor and ArfGAP. 18819912_HRB is involved in clathrin-dependent endocytosis and recruits TI-VAMP in this process 19262425_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21439320_Association ofalpha-synuclein with Rab attachment receptor protein and soluble sensitive factor attachment receptors (SNAREs) highlights a key role for membrane transport defects in alpha-synuclein-mediated pathology. 21752912_The authors show that cells lacking functional HRB have significantly reduced production of influenza virus progeny and that this defect results from impaired viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) delivery to the plasma membrane. 23984888_The top primary GWAS association of Airway hyperresponsiveness was in rs6731443 (P-value 2.5E-06) located within the AGFG1 genes. 24577083_Selenite caused CYLD upregulation via LEF1 and cIAP downregulation, both of which contribute to the degradation of ubiquitin chains on RIP1 and subsequent caspase-8 activation and colorectal tumor cell apoptosis. 26701340_HRB knock-down affected CD4 downregulation induced by Nef but not by HIV-1 Vpu. 27518435_Necroptotic RIP1 phosphorylation and ubiquitination seem to be tightly coordinated: inhibition or absence of RIP1 kinase activity blocks necroptotic RIP1 ubiquitination, whereas mutation of RIP1 necroptosis-associated ubiquitination site (K115R) dampens RIP1 kinase activity during necroptotic signaling. 30682089_human miR-186, 210 and 222 directly regulate the human genes Dicer1, HRB and HIV-EP2, thus may be filling key roles during HIV-1 replication and miRNA biogenesis. 31243884_Analyses indicated that circAGFG1 acts as a sponge for miR-203 to repress the effect of miR-203 on its target, ZNF281. In conclusion, study suggests that circAGFG1 promotes NSCLC growth and metastasis though a circAGFG1/miR-203/ZNF281 axis. 31703640_CircAGFG1 promoted RAF1 expression by sponging miR-370-3p and further activated RAF/MEK/ERK pathway to regulate cervical cancer progression. 32141537_CircAGFG1 aggravates the progression of cervical cancer by downregulating p53. |
ENSMUSG00000026159 |
Agfg1 |
592.200652 |
3.0481062463 |
1.607913 |
0.512106817 |
9.294671 |
0.00229821453283069951356587523605412570759654045104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005017252847889531845726462933043876546435058116912841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
794.2845263 |
229.3437370 |
262.5692916 |
54.7567330 |
| ENSG00000173890 |
26996 |
GPR160 |
protein_coding |
Q9UJ42 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable G protein-coupled receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. Located in plasma membrane. Part of receptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26996; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930] |
19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26871479_Our data suggest that the expression level of endogenous GPR160 is associated with the pathogenesis of prostate cancer 27259691_these findings suggest an important role of GPR160 in regulating the entry of BCG into macrophages by targeting the ERK signaling pathway. 34168114_GPR160 is a potential biomarker associated with prostate cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000037661 |
Gpr160 |
21.211134 |
0.4094776222 |
-1.288143 |
0.383531701 |
11.331782 |
0.00076191763821269978696620883695800330315250903367996215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001812101891720826508935804355360232875682413578033447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.7656777 |
3.2042846 |
33.7418537 |
4.9406727 |
| ENSG00000173918 |
114897 |
C1QTNF1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXJ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Collagen;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Enables collagen binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of platelet aggregation; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion; and positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration. Located in extracellular space. Is integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114897; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; negative regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010544]; negative regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:0090331]; positive regulation of aldosterone secretion [GO:2000860]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010906] |
12409230_molecular cloning, gene expression, and subcellular localization of GIP 16386877_The review describes the potential role of C1qTNF1 as an intracellular regulator of signal transduction 16806199_These findings indicate that CTRP1 expression may be associated with a low-grade chronic inflammation status in adipose tissues. 18171693_CTRP1 enhances the production of aldosterone. CTRP1 was highly expressed in obese subjects as well as up-regulated in hypertensive patients, CTRP1 may be a newly identified molecular link between obesity and hypertension. 18783346_CTRP1 may be considered a novel adipokine, providing an important framework to further address the physiological functions and mechanisms of the action of this family of secreted glycoproteins in normal and disease states. 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23000311_CTRP1 level was significantly higher in subjects with metabolic syndrome compared to healthy subjects. 24827430_CTRP1 is a novel adipokine associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in humans. 24945145_The levels of circulating CTRP1 are associated with coronary artery disease in men. 24965225_Increased plasma CTRP1 was independently associated with type 2 diabetes. Profiling of plasma adipokines such as CTRP1 is particularly important to obtain a greater understanding of their contribution to the type 2 diabetic state. 25635749_The variation of plasma CTRP-1 and IL-6 concentrations may play an important role in reflecting the degree of inflammation in CHD and the severity of coronary arterial atherosclerosis. 25767880_the strong association of CTRP1 with insulin resistance in NAFLD 27169633_Increased serum CTRP 1 levels were closely associated with the prevalence and severity of CAD, it might be regarded as a marker for myocardial infarction. 27175610_CTRP1 has a role in linking dysregulation of lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses in macrophages 28207876_High serum CTRP1 level is associated with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. 28625919_In cultured endothelial cells, treatment of CTRP1 led to increased permeability to fluorescent-labelled dextran and apparent formation of paracellular holes as observed after disturbed flow exposure, which was evidently reduced in the presence of a CTRP1-specific neutralizing antibody. 29360808_CTRP1 may participate in the process of vasculitis and blood coagulation during the acute phase of Kawasaki Disease 29953821_A single bout of high-intensity interval exercise may stimulate CTRP1 and CTRP9 secretions in healthy men. 30103635_serum levels significantly elevated in both early-onset and late-onset pre-eclampsia 31081425_High serum CTRP1 levels are associated with coronary artery disease. 31183364_These findings suggest that CTRP1 potentially indicates poor prognosis in Glioblastoma (GBM) and promotes the progression of human GBM. 31965030_Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein superfamily in patients with coronary artery disease. 32081468_Hypomethylation of C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-1 promoter region in whole blood and risks for coronary artery aneurysms in Kawasaki disease. 32383048_Methylation of CpG sites in C1QTNF1 (C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 1) differs by gender in acute coronary syndrome in Han population: a case-control study. 32569781_C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-1 attenuates microglia autophagy and inflammatory response by regulating the Akt/mTOR pathway. 33060724_CTRP-1 levels are related to insulin resistance in pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus. 34288211_CTRP1 decreases ABCA1 expression and promotes lipid accumulation through the miR-424-5p/FoxO1 pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. 34840267_C1q Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein 1: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis. 35172300_Novel Adipokines CTRP1, CTRP9, and FGF21 in Pediatric Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. 35202556_C1q/TNF-related protein-1: Potential biomarker for early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder. 36195912_CTRP1 prevents high fat diet-induced obesity and improves glucose homeostasis in obese and STZ-induced diabetic mice. |
ENSMUSG00000017446 |
C1qtnf1 |
18.335103 |
117.9041926748 |
6.881471 |
1.065346235 |
101.899612 |
0.00000000000000000000000584079673184520493892585934622919496490575445060332454578966087732974643564887173852184787392616271972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000060286825008416239852005149555332669393574869024304785902464241115206178278640436474233865737915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.9340429 |
28.4110616 |
0.3081733 |
0.2394401 |
| ENSG00000173928 |
126074 |
SWSAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6NVH7 |
FUNCTION: ATPase which is preferentially stimulated by single-stranded DNA and is involved in homologous recombination repair (HRR). Has a DNA-binding activity which is independent of its ATPase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21965664}. |
DNA damage;DNA recombination;DNA repair;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Enables single-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in double-strand break repair via homologous recombination and protein stabilization. Part of Shu complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126074; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; Shu complex [GO:0097196]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821] |
21965664_the human Shu complex (hSWS1.SWSAP1) has an evolutionarily conserved function in homologous recombination 30926776_SWSAP1 protects RAD51 filaments by antagonizing the anti-recombinase, FIGNL1. 31665741_our study uncovers a protein complex, which consists of SWS1, SWSAP1, SPIDR and PDS5B, involved in DNA repair and provides insight into Shu complex function and composition. |
ENSMUSG00000051238 |
Swsap1 |
16.612444 |
0.3739824000 |
-1.418958 |
0.471863801 |
9.104478 |
0.00254984465458465677303867558123329217778518795967102050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005528159092489649123480788261986162979155778884887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.8674289 |
2.6373421 |
23.8811155 |
4.5859346 |
| ENSG00000174013 |
200933 |
FBXO45 |
protein_coding |
P0C2W1 |
FUNCTION: Component of E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes. Required for normal neuromuscular synaptogenesis, axon pathfinding and neuronal migration (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of neurotransmission at mature neurons (By similarity). May control synaptic activity by controlling UNC13A via ubiquitin dependent pathway (By similarity). Specifically recognizes TP73, promoting its ubiquitination and degradation. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19581926}. |
Acetylation;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Developmental protein;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Synapse;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Members of the F-box protein family, such as FBXO45, are characterized by an approximately 40-amino acid F-box motif. SCF complexes, formed by SKP1 (MIM 601434), cullin (see CUL1; MIM 603134), and F-box proteins, act as protein-ubiquitin ligases. F-box proteins interact with SKP1 through the F box, and they interact with ubiquitination targets through other protein interaction domains (summary by Jin et al., 2004 [PubMed 15520277]).[supplied by OMIM, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:200933; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; postsynaptic cytosol [GO:0099524]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic cytosol [GO:0099523]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; synapse [GO:0045202]; anterior commissure morphogenesis [GO:0021960]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cerebral cortex radially oriented cell migration [GO:0021799]; cerebral cortex tangential migration [GO:0021800]; corticospinal tract morphogenesis [GO:0021957]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:2000300]; synapse assembly involved in innervation [GO:0060386]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
16012741_FBXO45 gene consisting of 3 exons, and the vicinity of the transcriptional start site had several estrogen receptor binding consensus sequences. 19581926_FBXO45 promotes the proteasome-dependent degradation of p73. 24878430_Study found that the R108C mutation in FBXO45 is a rare variant with a modest effect on schizophrenia risk that may disrupt the structure and function of the FBXO45 protein 24992930_Fbxo45 is the substrate-receptor subunit of a functional E3 ligase for Par-4 that has a critical role in cancer cell survival. 25460509_Data show that epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-transcription factors can be dynamically degraded by an atypical ubiquitin E3 ligase complex Skp1-Pam-Fbxo45 (SPFFbxo45). 28011490_Relatively low FBXO45 expression in gastric cancer tissues is associated with cancer progression and constitutes an independent prognostic factor 29665250_Genetic variations in FBXO45 are associated with emotional expression. 29997255_FBXO45 does not simply function in substrate recognition but is important for assembly of the PAM/FBXO45/SKP1 complex. 31285543_FBXO45-MYCBP2 regulates mitotic cell fate by targeting FBXW7 for degradation. 31644309_A SNP at the rs6583331 locus 3q29 is associated with the susceptibility of vitiligo in the Chinese Han population. The T allele of the locus within the FBXO45-NRROS gene (3q29) was significantly associated with vitiligo (odds ratio = 1.22, 95% confidence interval: 1.10-1.36, p = 0.0001). Association at the genotype level was strong (p = 0.0007). 33966034_DNAJB9 suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by promoting FBXO45-mediated degradation of ZEB1. 34779401_Elevated FBXO45 promotes liver tumorigenesis through enhancing IGF2BP1 ubiquitination and subsequent PLK1 upregulation. 35098525_MiR-30a-5p hampers proliferation of lung squamous cell carcinoma through targeting FBXO45. 35279684_Fbxo45 facilitates pancreatic carcinoma progression by targeting USP49 for ubiquitination and degradation. 35838331_Fbxo45-mediated NP-STEP46 degradation via K6-linked ubiquitination sustains ERK activity in lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000035764 |
Fbxo45 |
176.508343 |
2.0202874013 |
1.014561 |
0.119678503 |
72.505139 |
0.00000000000000001665975236294740838021235977124562951277627267519972076303957919662934727966785430908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000131145570601121998769031696119245595524574818499172201846647567435866221785545349121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
239.0069002 |
16.7067662 |
119.1515379 |
6.5805448 |
| ENSG00000174021_ENSG00000117151 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
115.026977 |
0.4562730625 |
-1.132031 |
0.141811121 |
65.022095 |
0.00000000000000074062944017065138938049165810616716170668367199420023538891655334737151861190795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000005332531969228690003539539938364403564288122438358241694800199184101074934005737304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.8045090 |
7.4114678 |
164.5829480 |
10.7124793 |
| ENSG00000174080 |
8722 |
CTSF |
protein_coding |
Q9UBX1 |
FUNCTION: Thiol protease which is believed to participate in intracellular degradation and turnover of proteins. Has also been implicated in tumor invasion and metastasis. |
3D-structure;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Thiol protease;Zymogen |
|
Cathepsins are papain family cysteine proteinases that represent a major component of the lysosomal proteolytic system. Cathepsins generally contain a signal sequence, followed by a propeptide and then a catalytically active mature region. The very long (251 amino acid residues) proregion of the cathepsin F precursor contains a C-terminal domain similar to the pro-segment of cathepsin L-like enzymes, a 50-residue flexible linker peptide, and an N-terminal domain predicted to adopt a cystatin-like fold. The cathepsin F proregion is unique within the papain family cysteine proteases in that it contains this additional N-terminal segment predicted to share structural similarities with cysteine protease inhibitors of the cystatin superfamily. This cystatin-like domain contains some of the elements known to be important for inhibitory activity. CTSF encodes a predicted protein of 484 amino acids which contains a 19 residue signal peptide. Cathepsin F contains five potential N-glycosylation sites, and it may be targeted to the endosomal/lysosomal compartment via the mannose 6-phosphate receptor pathway. The cathepsin F gene is ubiquitously expressed, and it maps to chromosome 11q13, close to the gene encoding cathepsin W. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8722; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process [GO:0051603] |
15184381_cathepsin F has a role in modifying low density lipoprotein particles 15989693_cathepsin F, matrix metalloproteinases 11 and 12 are upregulated in cervical cancer 16963053_data demonstrate a novel proatherogenic role for AngII, namely its ability to enhance secretion of lysosomal cathepsin F by monocyte-derived macrophages 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23297359_Homozygous and compound heterozygous missense mutations in CTSF are associated with adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 24255036_Small hairpin RNA silencing of proteinases overexpressed in diabetic corneas enhanced corneal epithelial and stem cell marker staining and accelerated wound healing. 25576872_Disease-causing cathepsin-F mutants fail to cleave LIMP-2. Our findings provide evidence that LIMP-2 represents an in vivo substrate of cathepsin-F with relevance for understanding the pathophysiology of type-B-Kufs-disease. 27524508_Biallelic mutations in this gene have been shown to cause Type B Kufs disease, an adult-onset neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis with some cases resembling the impairment seen in AD. 28474574_The CTSF gene may function as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer 30561534_Clinical distinction of type A (progressive myoclonus epilepsy) and type B (dementia with motor disturbance) Kufs disease was supported by molecular diagnoses. Type A is usually caused by recessive pathogenic variants in CLN6 or dominant variants in DNAJC5. Type B Kufs is usually associated with recessive CTSF pathogenic variants. 33236952_Long noncoding RNA LINC00982 upregulates CTSF expression to inhibit gastric cancer progression via the transcription factor HEY1. 35447134_Cathepsin F genetic mutation is associated with familial papillary thyroid cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000083282 |
Ctsf |
115.578719 |
0.2000427331 |
-2.321620 |
0.172645066 |
194.890410 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000002722259601748582931456430510685146786827856875510633955208414711091066984907675405357911124949699518207350940036080844119936728020547889173030853271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000502256896522613540150125151300245845881949421029898270920718783995894389781545534850252608012360042272871152660429494574145792284980416297912597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.2958342 |
4.4888512 |
192.8922327 |
13.0541404 |
| ENSG00000174125 |
7096 |
TLR1 |
protein_coding |
Q15399 |
FUNCTION: Participates in the innate immune response to microbial agents. Specifically recognizes diacylated and triacylated lipopeptides. Cooperates with TLR2 to mediate the innate immune response to bacterial lipoproteins or lipopeptides (PubMed:21078852). Forms the activation cluster TLR2:TLR1:CD14 in response to triacylated lipopeptides, this cluster triggers signaling from the cell surface and subsequently is targeted to the Golgi in a lipid-raft dependent pathway (PubMed:16880211). Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16880211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21078852}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;NAD;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This gene is ubiquitously expressed, and at higher levels than other TLR genes. Different length transcripts presumably resulting from use of alternative polyadenylation site, and/or from alternative splicing, have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7096; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; Toll-like receptor 1-Toll-like receptor 2 protein complex [GO:0035354]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lipopeptide binding [GO:0071723]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; Toll-like receptor 2 binding [GO:0035663]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cell activation [GO:0001775]; cellular response to bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071221]; cellular response to triacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0071727]; detection of triacyl bacterial lipopeptide [GO:0042495]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; macrophage activation [GO:0042116]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway [GO:0034137]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; toll-like receptor 1 signaling pathway [GO:0034130]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224] |
11932926_The extracellular, but not cytoplasmic domain of TLR1 inhibits Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in endothelial cells. TLR1 might restrain the dangerous innate response to LPS by binding to TLR4 and preventing the formation of active signaling complexes. 12091878_These data indicate that TLR1 and TLR2 are required for lipoprotein recognition and hat defects in the TLR1/2 signaling pathway may account for human hyporesponsiveness to Borrelia burgdorferi OspA vaccination. 12600829_All nine patients expressed all of the TLRs studied, whereas only five out of the nine patients had any granulomas positive for IL-4.The associations between TLRs 1, 5, and 9 were different in IL-4-negative compared with IL-4-positive patients. 12975352_TLR1 and TLR2 are required for ara-lipoarabinomannan- and tripalmitoyl cysteinyl lipopeptide-stimulated cytokine secretion from mononuclear cells. Confocal microscopy revealed that TLR1 and TLR2 cotranslationally form heterodimeric complexes 14966134_Toll-like receptor 2 dimerized with Toll-like receptor 6 or 1 is activated by saturated fatty acid and inhibited by polyunsaturated fatty acid 15790341_The surface expression of TLR1 by FACS analysis after the stimulation of JAR cells with different TLR ligands. 15793154_TLR2-TLR1 coactivation serves as the underlying mechanism for the proinflammatory toxicities associated with Amphotericin B 15812078_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15812078_The observed multiple associated SNPs at the TLR6-TLR1-TLR10 gene cluster were dependent and suggest the presence of a founder prostate cancer risk variant on this haplotype background. 16002719_Diminished expression and function of TLR1 is a likely consequence of chronic filarial antigen stimulation and could serve as a novel mechanism underlying the dysfunctional immune response in lymphatic filariasis 16081826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16081826_Reduced signaling via TLR-2/TLR-1 heterodimers protects from late stage Lyme disease in individuals with heterozygous Arg753Gln polymorphism of Tlr-2 16177110_Activation of NF-kappa B in monocytic THP-1 cells by a lipid-associated membrane protein (LAMP) from Mycoplasma pneumoniae is mediated by TLR2. 16374251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16455995_Toll-Like Receptor 2 (TLR2) recognizes PorB through direct binding, and that PorB-induced cell activation is mediated by a TLR2/TLR1 complex 16461792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16461792_Presence of TLR1 239G > C (Arg80 > Thr) or the presence of both TLR1 743A > G (Asn248 > Ser) and TLR6 745C > T (Ser249 > Pro) single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with invasive aspergillosis following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. 16537705_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16848791_This study suggests that CD14 directly binds to triacylated lipopeptides and facilitates recognition of the lipopeptides by the TLR2/TLR1 complex without binding to the receptor complex. 16880211_TLR-2/6 and TLR2/1 heterodimer sorting at the cell surface determines heterotypic associations with CD36 and intracellular targeting 16893894_In vitro functional studies involving TLR1 Gly676Ala and TLR1 Gly676Leu results in reduced NF-kappa B activation of signal-deficient mutants. 16971956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17172927_These data suggest that Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 expression correlates with the extent and severity of coronary artery disease. 17202359_Diminished TLR1/2 signaling may contribute to the increased infection-related morbidity and mortality and the impaired vaccine responses observed in aging humans 17314700_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17395901_Intestinal enteroendocrine cells express TLRs which may be involved in innate immune responses. 17475868_TLR1 single nucleotide polymorphism P315L may predispose certain individuals to infectious diseases for which the sensing of microbial cell components by TLR1 is critical to innate immune defense. 17548585_We report that I602S, a common single nucleotide polymorphism within TLR1, is associated with aberrant trafficking of the receptor to the cell surface and diminished responses of blood monocytes to bacterial agonists. 17595233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17595679_variation in the inflammatory response to bacterial lipopeptides is regulated by a common TLR1 transmembrane domain polymorphism 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17889651_Propose that formation of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer brings the intracellular TIR domains close to each other to promote dimerization and initiate signaling. 17932345_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17932345_We genotyped 19 common (>5%) haplotype-tagging SNPs chosen from the SNPs discovered in a resequencing study spanning TLR6, TLR1, and TLR10 to test for the association between sequence variants cluster and prostate cancer. 18006661_activation of NF-kappaB by beta-defensin 3 depends on the expression of both TLR1 and TLR2 18056480_Heterodimerization of TLR2 with TLR1 or TLR6 evolutionarily has developed to expand the ligand spectrum to enable the innate immune system to recognize the numerous, different structures of various bacterial lipopolysaccharides. 18091991_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18292749_TLR1, 2, and 4 protein colocalized with adiponectin in human adipocytes. 18451040_The lipoproteins from U. parvum were found to activate NF-kappaB through TLR1, TLR2 and TLR6. 18461142_Findings suggest that TLR1 deficiency influences adaptive immunity during leprosy infection to affect clinical manifestations such as nerve damage and disability. 18461142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18474641_the results show that MG149, a triacylated lipoprotein from M. genitalium, activates NF-kappaB through TLR1 and TLR2. 18547625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18547625_These results suggest that functional relevant TLR1 and TLR6 variants are directly involved in asthma development. 18635889_Hypermorphic genetic variation in TLR1 (toll-like receptor 1) is associated with increased susceptibility to organ dysfunction, death, and gram-positive infection in sepsis. 18684966_Through cooperation of TLR1 and TLR2 signaling, TLR5 is stored intracellularly in neutrophils and is up-regulated in a protein synthesis-independent manner. 18686608_Human epidermal keratinocytes constitutively express all TLR 1-10 mRNA, which may enable human keratinocytes to respond to a wide range of pathogenic micro-organisms. 18752252_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18752252_common haplotype in the TLR10-TLR1-TLR6 gene cluster influences prostate cancer risk and clearly supports the need for further investigation of TLR genes in other populations 18776592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19029192_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19200604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19254290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19456232_Altered TLR1 function, or at least a TLR1 N248S-linked trait, may affect the progression from leprosy infection to disease as well as the disease course and the risk of debilitating reactional episodes. 19503839_the IL-1beta and VDR activation pathways have roles in human TLR2/1-induced antimicrobial responses 19505919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19543401_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19543401_polymorphisms in TLRs 1, 4, and 5 are associated with altered risks of urinary tract infections in adult women 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19627277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19771452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19818630_Studies provide molecular model for TLR and NLR signalling pathways. 20016852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20100933_Studies show substantial decreases in older compared with young individuals in cytokine production in response to TLR1/2, TLR6, TLR3, TLR5, and TLR8, TLR7 and TLR9 in DCs. 20207250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20348427_TLR10 is most related to TLR1 and TLR6, both of which independently cooperate with TLR2 in the sensing of a variety of microbial and fungal components; TLR10 shares a number of microbial agonists with TLR1, but not TLR6, and uses TLR2 as a coreceptor. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20448286_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20459687_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20478407_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20478407_TLR-1 is involved in the recognition of P.falciparum and has a role in susceptibility to and manifestation of malaria in pregnancy. 20497180_Transfection experiments with human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells and antibody-mediated inhibition of TLR signalling in human macrophage-like (THP-1) cells suggested that TLR2 interacts with TLR1 to recognize curli amyloid fibrils. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20560984_Studies indicate that TLR1/2 heterodimer recognizes the envelope proteins of HCMV leading to the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20595247_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20616560_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20617178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20650298_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20797905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20815312_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819670_The concentrations of TLR1, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 appeared to be increased in bacterial pleural effusion compared to non-bacterial pleural effusions. 20977567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21048935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048935_results partially replicate and extend previous findings, supporting that variants of TLR1 gene are determinants of severe complications during sepsis 21078852_M. tuberculosis lipoproteins LprG and LpqH participate in the regulation of adaptive immunity by inducing cytokine secretion and costimulatory molecules and by directly regulating the activation of memory T lymphocytes via Toll-like receptors 1 and 2. 21105983_Results indicate that Neisseria lactamica plays an important role in suppressing pathogen-induced inflammation in the nasopharyngeal mucosa, mediated through TLR-1/2 stimulation, by activating PPAR-gamma and inhibiting NF-kappabeta activity. 21108742_These findings suggest that TLR1 gene polymorphisms may affect immunoglobulin A nephropathy susceptibility in Korean children. 21642391_the role of TLR1 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis defense and provide the first evidence that TLR1 variants are associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis in a low-incidence country 21646294_Notably, among myeloid differentiation transgene MyD88-dependent TLR, only stimulation via TLR1/2 consistently educates spleen dendritic cells with gut-homing imprinting capacity. 21852947_TLR1/6 polymorphisms modulate TH1 T-cell polarization through genetic regulation of monocyte IL-10 secretion in the absence of IL-12. 21952587_After stimulation with agonists recognized by TLR1/2, IL-8 secretion by neonatal neutrophils (whether term or preterm) substantially exceeded that of adult neutrophils. 21998742_a dominant role for TLR1/TLR2 heterodimers in the induction of the early inflammatory response by Borrelia spirochetes in humans 22150367_absence of the common haplotype in the TLR10-TLR1-TLR6 gene cluster increases the risk of developing chronic disease in patients already affected by sarcoidosis. 22200569_Our findings showed slight differences in the distribution of T1805G variants in women with pregnancy loss. 22219617_No TLR1 polymorphisms were detected in Korean subjects. 22238472_Among African American women with pelvic inflammatory disease, variants in the TLR1 and TLR4 genes, which may increase signaling, were associated with increased Chlamydia trachomatis infection. 22246581_The TLR1-1805GG polymorphism in B burgdorferi RST1-infected patients was associated with stronger Th1-like inflammatory responses, an environment that may set the stage for antibiotic-refractory arthritis. 22280448_Women with microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity and histological chorioamniotis had higher amniotic fluid sTLR1, 2 and 6 levels. 22301633_3 TLR1 polymorphisms are associated with an increased susceptibility for candidemia in white patients. 22447933_a mechanism for the differential trafficking of TLR1 I602S variants, and highlight the distinct roles for PRAT4A and PRAT4B in the regulation of TLR1 surface expression. 22703024_The results showed that the genetic markers in TLR1, TLR4, TLR5 TLR6, and TLR10 were associated with the occurrence of acute Graft-versus-host disease following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation 22842950_This work thus shows a re-localization of TLR 1 and 2 expression sites with decreased grade of expression in lichen planu lesions. 22998942_TLR1, TLR2 and NOD2 were the main pattern recognition receptors responsible for recognition of B. fragilis 23067142_These results suggest that the nonfunctional TLR1 602S/S genotype is associated with a reduced risk of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric diseases, probably via diminished Th1 responses. 23151486_The study shows that genetic variation within the TLR10/1/6 locus is the major common genetic factor explaining interindividual variation in TLR1/2-mediated cytokine responses. 23255565_Compared to white women, African American women with clinically suspected pelvic inflammatory disease were more likely to carry variants in the TLR1, TLR2, and TIRAP genes. 23403223_Toll like receptor 1 single nucleotide polymorphism I602S may play a role in the pathogenesis of M. abscessus lung infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. 23430250_Human lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) and CD14 independently deliver triacylated lipoproteins to Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1) and TLR2 and enhance formation of the ternary signaling complex 23478521_Genetic variation in TLR1 is associated with increased mortality in patients with sepsis after traumatic injury. 23547143_SNP N248S associated with increased risk for leprosy 23575331_TLR1 1805G allele and the GG genotype influence susceptibility to PTB in a well-conserved population of northern Spain. 23626692_The 663leucine and 688aspragine residues outside of the BB loop are essential for the responsiveness of TLR2/2, TLR2/1 and TLR2/6, but the 681proline residue inside of the BB loop exhibits divergent roles in TLR2/2, TLR2/1 and TLR2/6 signal transduction. 23652523_GWAS meta-analysis identified an association between TLR1 and H. pylori seroprevalence; if confirmed, genetic variations in TLR1 may help explain some of the observed variation in individual risk for H. pylori infection. 24002163_Interestingly, 602Ser, which shows signatures of selection, inhibits TLR1 surface trafficking and subsequent activation of NFkappaB upon recognition of a ligand. This suggests that reduced TLR1 activity may be beneficial for human health. 24112285_T1805G polymorphism not associated with severity of bronchiolitis or risk of postbronchiolitis wheezing 24240055_Triggering the TLR2/1 complex with Pam3CSK4 initiates human platelet activation by engaging tyrosine kinases of the src family and Syk, the adaptor protein LAT, as well as the key mediator PLCgamma2. 24351080_Expression of toll-like receptors 1-5 but not TLR 6-10 is elevated in livers of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 24392083_the genetic architecture of TLR1 variation differs substantially in southeast Asians compared to other populations and common variation in TLR1 in Thais is not associated with outcome from melioidosis. 24440818_These results suggest that TLR2/1 signaling and S1P cooperate in pro-inflammatory cytokine production and myofibroblast differentiation and promote cell migration of skin fibroblast 24445834_Authors demonstrated that TLR1 rs5743618 was associated with asthma and atopic eczema during the first 6 years of life after early bronchiolitis and TLR6 rs5743810 was associated with present atopy at preschool age. 24511099_In the genetic association analysis, polymorphisms in TLR1 (S248N and R80T), TLR2 (P631H), and TLR6 (P249S) were associated with an increased susceptibility to complicated skin and skin structure infections. 24581860_Four genes showed increased expression in the epithelium of OLP patients: CD14, CXCL1, IL8, and TLR1, and at least two of these proteins, TLR1 and CXCL1, were expressed at substantial levels in oral keratinocytes. 24612386_TLR2 and its co-receptors, TLR1 and TLR6, contribute to the pathogenicity of aPLA; aPLA are internalized via clathrin- and CD14-dependent endocytosis; and endocytosis is required for NF-kappaB activation 24629739_The expression of TLR1 was the lowest and expression of TLR4 was the highest on leukocytes in acute otitis media children. 24780078_rs4833095 of TLR1 may be associated with the susceptibility for alopecia areata in the Korean population 24922103_A common TLR1 polymorphism (T-->G mutation at position 1805) is associated with an increased risk of laboratory-defined neurosyphilis 24984237_No association was observed for either TLR1 1805 T>G or TLR6 745 C>T polymorphism and pulmonary tuberculosis. 25028161_Genetic variation rs5743565 in TLR1 might be associated with the decreased susceptibility to Graves disease, whlie polymorphisms in TLR6 and TLR10 did not reach the statistical significance. 25033332_This review summarizes current knowledge of the multiple roles of toll-like receptors in bacterial lung infections and highlights the mechanisms used by pathogens to modulate or interfere with TLR signaling in the lungs. 25128583_Data indicate that single nucleotide polymorphism of toll-like receptor TLR1 was significantly associated with a reduced risk of coronary artery disease (CAD). 25253287_Data show that a total of nine single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TLR1, TLR4, TLR6 and TLR8 in Caucasians, and two other SNPs, one each in Toll-like receptors TLR4 and TLR8, in African Americans were significantly associated with HIV status. 25261617_SNPs in the exons of TLR1 and TLR6 are associated with susceptibility to type 1 diabetes in the Chinese population. 25320195_TLR1 expression in periprosthetic tissues most accurately predicted periprosthetic joint infection. 25378593_TLR1 polymorphisms could influence immune-related disease through Teff resistance to Treg suppression. 25544311_Toll-like receptor 1 Gene SNP rs5743618 is associated with increased risk for tuberculosis in Han Chinese children. 25553878_These results clarify the importance of TLR2/1 and FcgammaRII in platelet adhesion and activation, and strengthen the role of platelets as an active player in sensing bacterial infections. 25605403_T1805G genotype associated with reduced risk of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin osteitis following infant vaccination 25687912_TLR1 rs4833095 and TLR10 rs10004195 may play crucial roles in H. pylori susceptibility and gastric pathogenesis. 25722298_Polymorphisms in TLR1 (R80T), NOD2 (L1007fsX1), and MYD88 (-938C>A) are associated with predisposition to development of chronic Q fever. 25784560_Data suggest that the TLR2 Arg753Gln and TLR1 Ile602Ser SNPs influence the risk of developing leptospirosis and its severity. 25825356_These data suggest that the TLR1 N248S polymorphism might play a role in Th1/Th2 differentiation, and the determination of serum IgE levels. 25850295_The correlation between TLR1, TLR6, and TLR10 polymorphisms and the development of atopic dermatitis in the Republic of Bashkortostan has been found. 25857934_SNP TLR1-248N is associated with TB protection in an Indian population and exhibits an increased immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis lysate in vitro. 25969543_Activation of MyD88-dependent TLR1/2 signaling by misfolded alpha-synuclein, a protein linked to neurodegenerative disorders. 26470427_Frequencies of TLR1-TLR6 two-locus haplotypes in major populations of South Urals were determined for the first time. 26559190_concluded that TLR-1 rs4833095 and TLR10 rs10004195 confer susceptibility to development of gastroduodenal disease, especially GC in H.pylori disease 26633000_a case-control study of 504 Papua New Guinean children with severe malaria showed that a genetic variant in TLR1 may contribute to the low severe malaria case fatality rates in this region through a reduced pro-inflammatory cellular phenotype. 26729809_a novel mechanism of action for TLR1 SNP rs5743618 in modulating polymorphonuclear leukocytes priming responses. 26738805_The data suggest that genetic variation in TLR1 has effects on the host response to Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Asian populations. 27196764_Our data suggest that TLR1 rs5743618 could serve as a predictor of clinical response to FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in patients with mCRC. 27214039_Association analyses yielded a significant result for the TLR1 variant rs3923647, conferring strong protection against Tuberculosis (Odds ratio [OR] 0.21, CI confidence interval [CI] 0.05-0.6, Pnominal 1 x 10-3) when applying a recessive model of inheritance. 27277333_We found lower expression levels of TLR1, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and TLR9 in PBMCs from patients with ALL compared with those from control patients. We also observed that the PBMCs from patients with Pre-B and B ALL had lower TLR4 expression than controls 27369862_genetic polymorphism is associated with transplant-related mortality in hematologic malignancies 27727278_2 single nucleotide polymorphisms in toll like receptor 1 were significantly associated with Treponema denticola. 27755461_Studied the relationship between polymorphisms in MBL, TLR1, TLR2 and TLR6 encoding genes and stimulated IFN-gamma and IL-12 ex vivo production in BCG osteitis survivors. Found that variant genotypes of the MBL2 gene (if homozygous) and variant genotypes of the TLR2 gene (only heterozygotes present) are associated with low IFN-gamma production. 27806314_Suggest that the TLR1 rs4833095 polymorphism may play a role in the development and progression of IgA nephropathy in a Chinese Han population. 27998389_rs5743551 and rs5743618 polymorphisms affected the risk of pulmonary tuberculosis in an Iranian population 28123183_Study concludes that genetic variation in the TLR10-TLR1-TLR6 gene cluster mediates responsiveness to organic dust, but indicates different signaling pathways for IL-6 and TNF-alpha. These studies provide new insight into the role of the TLR10-TLR1-TLR6 gene cluster and the innate immune response to organic dust. 28327786_data indicates that different TLR genes may actually play a role in the IL-17 production. In addition, different markers of TLR1, 2 and 4 appeared associated with serum levels of other important cytokines and chemokines that take part in the leprosy pathogenesis 28368946_Study findings suggest that TLR1 rs4833095 and TLR10 rs10004195 may play crucial roles in H. pylori susceptibility and gastric pathogenesis in the Thai population. 28474755_Significant correlations with atherosclerosis susceptibility were found for the toll like receptor 1 (TLR1) rs5743551 polymorphism and toll like receptor 6 (TLR6) rs5743810 polymorphism. 28692144_rs5743618 polymorphism increased the the risk of needing inhaled corticosteroids at 11-13 years of age for postbronchiolitis asthma 29175392_mean proportions of European ancestry differed significantly between the genotypes of the TLR6 (P249S) gene in a population of the Atlantic Forest, Sao Paulo, Brazil 29454979_Studied association of genetic variants of toll like receptor 1 (TLR1) with susceptibility to tuberculosis (TB) in Chinese peopulations; results suggest that SNPs of the TLR1 gene were associated with TB susceptibility in the Chinese Tibetan population. 29566186_Intake of red and processed meat interacted with TLR1, TLR10, so that variant carriers of wild type alleles were at increased risk of colorectal cancer. 30028533_association of rs5743618 with BCG osteitis not found 30289892_Heterozygous genotype of the TLR1 single nucleotide polymorphism rs4833095 showed a statistically significant association with an increased protection from leprosy in Brazilian women. 30574617_TLR1 rs4833095 SNP was associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer but not atrophic gastritis in a European population. 30577800_Whole-genome sequencing reveals possible role of deleterious mutation of TLR1 in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the thoracic spine in the Chinese population. 30866782_Study identifies TLR1 as a gene associated with a severe phenotype of bacteremic melioidosis. The TLR1 variant rs76600635, common in East Asian populations, may be associated with poor outcomes from melioidosis. This variant has not been previously associated with outcomes in sepsis. 30924193_Toll-like receptor 1 and 10 variations increase asthma risk and review highlights further research directions. 31017904_Authors demonstrated that these differences relied on diverse signaling pathways activated by TLR1/2. MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways were engaged by TLR1, whereas the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway was activated by TLR2. 31314777_Toll-like receptor 1 may have a role in favorable prognosis in pancreatic cancer 31454983_we also investigated the association of breastfeeding duration with DNA methylation at two sites in the promoter of the toll-like receptor-1 (TLR1) gene, as well as the association between DNA methylation of the toll-like receptor-1 (TLR1) gene and susceptibility to different diseases. 33725589_Altered tonsillar toll-like receptor (TLR)-1 and TLR-2 expression levels between periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis and cervical adenitis (PFAPA), and group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal (GAbetaHS) recurrent tonsillitis patients. 34354705_Association of Immune and Inflammatory Gene Polymorphism With the Risk of IgA Nephropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 45 Studies. 34429510_Modulation of Toll-like receptor 1 intracellular domain structure and activity by Zn(2+) ions. 34464323_Are Pattern Recognition Receptors Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma? 34497333_Toll-like receptor 1 as a possible target in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 34928049_Landscape of Cell Communication in Human Dental Pulp. 35031300_Toll-Like Receptor 1 Locus Re-examined in a Genome-Wide Association Study Update on Anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG Titers. |
ENSMUSG00000044827 |
Tlr1 |
660.879837 |
2.8610604036 |
1.516550 |
0.085134687 |
313.875049 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031267120338423033478872815192527570790261036860756060919108982644106199706469406086564961474908189717487046940878168488879404175913961944632927301382673715326627602165615376836327321541375567903742194175720214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009361109456290548075372252052559942877182470855313224114378869051768546743247655920339199228703666501995861066910004307738141367589939541016763252581572510525710687612861368722683153009711531922221183776855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
923.9768702 |
56.5047683 |
325.4700248 |
15.0440930 |
| ENSG00000174173 |
54931 |
TRMT10C |
protein_coding |
Q7L0Y3 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial tRNA N(1)-methyltransferase involved in mitochondrial tRNA maturation (PubMed:18984158, PubMed:21593607, PubMed:23042678, PubMed:27132592). Component of mitochondrial ribonuclease P, a complex composed of TRMT10C/MRPP1, HSD17B10/MRPP2 and PRORP/MRPP3, which cleaves tRNA molecules in their 5'-ends (PubMed:18984158). Together with HSD17B10/MRPP2, forms a subcomplex of the mitochondrial ribonuclease P, named MRPP1-MRPP2 subcomplex, which displays functions that are independent of the ribonuclease P activity (PubMed:23042678, PubMed:29040705). The MRPP1-MRPP2 subcomplex catalyzes the formation of N(1)-methylguanine and N(1)-methyladenine at position 9 (m1G9 and m1A9, respectively) in tRNAs; TRMT10C/MRPP1 acting as the catalytic N(1)-methyltransferase subunit (PubMed:23042678). The MRPP1-MRPP2 subcomplex also acts as a tRNA maturation platform: following 5'-end cleavage by the mitochondrial ribonuclease P complex, the MRPP1-MRPP2 subcomplex enhances the efficiency of 3'-processing catalyzed by ELAC2, retains the tRNA product after ELAC2 processing and presents the nascent tRNA to the mitochondrial CCA tRNA nucleotidyltransferase TRNT1 enzyme (PubMed:29040705). In addition to tRNA N(1)-methyltransferase activity, TRMT10C/MRPP1 also acts as a mRNA N(1)-methyltransferase by mediating methylation of adenosine residues at the N(1) position of MT-ND5 mRNA (PubMed:29072297). Associates with mitochondrial DNA complexes at the nucleoids to initiate RNA processing and ribosome assembly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18984158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21593607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23042678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24703694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27132592, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29040705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29072297}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Methyltransferase;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion nucleoid;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Transit peptide;tRNA processing |
|
This gene encodes the precursor of a subunit of the mitochondrial ribonuclease P, which is involved in 5' processing of mitochondrial tRNAs. The encoded protein may confer RNA-binding capacity to mitochondrial ribonuclease P and may be essential for transcript processing, RNA modification, translation and mitochondrial respiration. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:54931; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; mitochondrial ribonuclease P complex [GO:0030678]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; tRNA methyltransferase complex [GO:0043527]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; mRNA (adenine-N1-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0061953]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; tRNA (adenine-N1-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016429]; tRNA (guanine(9)-N(1))-methyltransferase activity [GO:0052905]; tRNA (guanine-N1-)-methyltransferase activity [GO:0009019]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; mitochondrial RNA 5'-end processing [GO:0000964]; mitochondrial tRNA 3'-end processing [GO:1990180]; mitochondrial tRNA 5'-end processing [GO:0097745]; mitochondrial tRNA methylation [GO:0070901]; mitochondrial tRNA processing [GO:0090646]; mRNA methylation [GO:0080009]; positive regulation of mitochondrial translation [GO:0070131] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21857155_MRPP1 is essential for transcript processing, RNA modification, translation and mitochondrial respiration. 22028365_We also identify the 5' and 3' transcript ends of the three lncRNAs and show that mitochondrial RNase P protein 1 (MRPP1) is important for the processing of these transcripts. 23755257_Inhibition of mitochondrial RNase P by beta-amyloid is an unspecific effect and is not mediated by beta-amyloid interaction with SDR5C1. 27132592_identifying mutations in TRMT10C as a cause of mitochondrial disease and highlighting the importance of RNA processing for correct mitochondrial function 29040705_in addition to being an essential component of the RNase P reaction, MRPP1/2 serves as a processing platform for several down-stream tRNA maturation steps in human mitochondria. 29880640_This study proposes low-resolution models of the MRPP1-MRPP2 and MRPP1-MRPP2-MRPP3 complexes that suggest the overall architecture, stoichiometry, and orientation of subunits and tRNA substrates. 32833542_m(1)A Regulator TRMT10C Predicts Poorer Survival and Contributes to Malignant Behavior in Gynecological Cancers. 33380464_Disease-associated mutations in mitochondrial precursor tRNAs affect binding, m1R9 methylation, and tRNA processing by mtRNase P. 34489609_Structural basis of RNA processing by human mitochondrial RNase P. |
ENSMUSG00000044763 |
Trmt10c |
176.401747 |
2.0411078860 |
1.029352 |
0.119952036 |
74.261186 |
0.00000000000000000684359311264003182403156309226132036833206700801048548432614637704318738542497158050537109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000055142579310530723333364165271793870403834989283534812054554663518501911312341690063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
237.2540512 |
16.9158964 |
117.2272361 |
6.5959184 |
| ENSG00000174327 |
201232 |
SLC16A13 |
protein_coding |
Q7RTY0 |
FUNCTION: Proton-linked monocarboxylate transporter. May catalyze the transport of monocarboxylates across the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:12739169}. |
Cell membrane;Diabetes mellitus;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in monocarboxylic acid transport. Located in Golgi apparatus and cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201232; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; monocarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008028]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; monocarboxylic acid transport [GO:0015718] |
23945395_Data identified three new loci for type 2 diabetes with genome-wide significance: MIR129-LEP, GPSM1 and SLC16A13. 34257700_The Association between the rs312457 Genotype of the SLC16a13 Gene and Diabetes Mellitus in a Chinese Population. |
ENSMUSG00000044367 |
Slc16a13 |
15.181342 |
0.3822371605 |
-1.387460 |
0.450470327 |
9.536735 |
0.00201399744139063282058477177827171544777229428291320800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004443518450888757354011460165565949864685535430908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6665253 |
2.3841735 |
22.8773904 |
3.9555544 |
| ENSG00000174370 |
219833 |
KCNJ5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
Q8TAV5 |
|
Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
extracellular region [GO:0005576] |
|
|
|
72.935131 |
0.2881793889 |
-1.794961 |
0.618589378 |
7.465018 |
0.00629094134437636117590519901909829059150069952011108398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012585293337353632009412152115146454889327287673950195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.1286416 |
19.3138137 |
120.8036873 |
46.6313823 |
| ENSG00000174483 |
582 |
BBS1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFJ9 |
FUNCTION: The BBSome complex is thought to function as a coat complex required for sorting of specific membrane proteins to the primary cilia. The BBSome complex is required for ciliogenesis but is dispensable for centriolar satellite function. This ciliogenic function is mediated in part by the Rab8 GDP/GTP exchange factor, which localizes to the basal body and contacts the BBSome. Rab8(GTP) enters the primary cilium and promotes extension of the ciliary membrane. Firstly the BBSome associates with the ciliary membrane and binds to RAB3IP/Rabin8, the guanosyl exchange factor (GEF) for Rab8 and then the Rab8-GTP localizes to the cilium and promotes docking and fusion of carrier vesicles to the base of the ciliary membrane. The BBSome complex, together with the LTZL1, controls SMO ciliary trafficking and contributes to the sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway regulation. Required for proper BBSome complex assembly and its ciliary localization (PubMed:17574030, PubMed:22072986). Plays a role in olfactory cilium biogenesis/maintenance and trafficking (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3V3N7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17574030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22072986}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Obesity;Olfaction;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transport;Vision |
|
Mutations in this gene have been observed in patients with the major form (type 1) of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. The encoded protein may play a role in eye, limb, cardiac and reproductive system development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:582; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; BBSome [GO:0034464]; centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; patched binding [GO:0005113]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; smoothened binding [GO:0005119]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; brain morphogenesis [GO:0048854]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; cellular lipid metabolic process [GO:0044255]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport [GO:0043001]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; hormone metabolic process [GO:0042445]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:0061351]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; non-motile cilium assembly [GO:1905515]; olfactory behavior [GO:0042048]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; photoreceptor cell morphogenesis [GO:0008594]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; regulation of cilium beat frequency involved in ciliary motility [GO:0060296]; sensory perception of smell [GO:0007608]; striatum development [GO:0021756]; ventricular system development [GO:0021591]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12524598_This protein has amino acid sequence homolgy with mice. Missense mutation accounts for about 80% of all BBS1 mutations on a similar genetic background across populations. 12567324_Identification of a novel Bardet-Biedl syndrome protein, BBS7, that shares structural features with this protein. 12677556_BBS1 participates in complex inheritance and in different families, mutations in BBS1 can interact genetically with mutations at each of the other known BBS genes, as well as at unknown loci, to cause the phenotype 12837689_The presence of three mutant alleles in the BBS family correlates with a more severe Bardet-Biedl phenotype. 14993910_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15517396_disease-associated alleles occur at relatively high frequencies in normal haplotypes 17065520_The cardinal feature of retinal degeneration in BBS1 can show a wide spectrum of disease expression. 18669544_A novel BBS1 mutation was identified, most probably a founder mutation, further confirming the Faroe Islands as a genetic isolate. 18766993_Although neither proband fulfilled the typical criteria for BBS, this diagnosis was confirmed on mutation analysis. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21520335_this report describes the identification and characterization of a splice donor site mutation that leads to missplicing of BBS1 transcripts in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 22410627_Patients with BBS1 mutations had a milder phenotype than did patients with mutations in other BBS genes. 22940089_Our findings confirm the consistent pathogenicity of the BBS1 M390R mutation in Bardet-Biedl syndrome in patients homozygous for the common M390R mutation in the BBS1 gene. 23143442_Variants in BBS1 are significantly associated with nonsyndromic autosomal recessive RP and relatively mild forms of BBS. 23432027_Novel mutations (c.1110G>A and c.39delA (p.G13fs*41)) in BBS1 found in Tunisian families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 23559858_Exome sequencing identified a novel homozygous mutation (c.47+1G>T) in BBS1 that inactivates the splice donor site at the end of exon 1. 24611592_novel BBS1 mutations in Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients in Spain 24611735_Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients with missense mutations in BBS1 have lower biochemical cardiovascular disease markers compared with patients with BBS10 and other BBS1 mutations. 24681783_mediates endosomal recycling, sorting and signal transduction of Notch receptors 24691443_loss of BBS1, BBS4, or OFD1 led to decreased NF-kappaB activity and concomitant IkappaBbeta accumulation and that these defects were ameliorated with SFN treatment. 24939912_Results show that BBS1 and BBS3 regulates the ciliary traficking of PC1. 25494902_A homozygous BBS1 p.M390R mutation is associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 26022370_We report a case in which whole-exome sequencing in a patient previously suspected to have Usher syndrome revealed disease-causing mutations in BBS1 and SLC26A4. 26103456_M390R mutation in BBS1 reduces surface expression of insulin receptor in fibroblasts derived from BBS patients. 26254420_BBS1 emerged as a novel predictor of overall survival in MPM. 27434533_Importantly, one Japanese and one Omani families carried compound biallelic mutations in two distinct genes (TMEM67/RPGRIP1L and TMEM138/BBS1, respectively). 30484961_Retrotransposon insertion in exon 13 was identified in a female with Bardet-Biedl syndrome carrying the most common BBS1 mutation (BBS1: Met390Arg). 31997113_Novel biallelic splice-site BBS1 variants in Bardet-Biedle syndrome: a case report of the first Japanese patient. 32759308_The BBSome assembly is spatially controlled by BBS1 and BBS4 in human cells. 33169370_A BBS1 SVA F retrotransposon insertion is a frequent cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 33572860_BBS Proteins Affect Ciliogenesis and Are Essential for Hedgehog Signaling, but Not for Formation of iPSC-Derived RPE-65 Expressing RPE-Like Cells. 33630762_Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins regulate intracellular signaling and neuronal function in patient-specific iPSC-derived neurons. 33910932_BBS1 branchpoint variant is associated with non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa. 34423835_The Bardet-Biedl syndrome complex component BBS1 controls T cell polarity during immune synapse assembly. 34940782_Comparative Natural History of Visual Function From Patients With Biallelic Variants in BBS1 and BBS10. |
ENSMUSG00000006464 |
Bbs1 |
48.670539 |
0.4047761393 |
-1.304804 |
0.472195796 |
7.451218 |
0.00633935383261862578363476927734154742211103439331054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012678707665237251567269538554683094844222068786621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.0358629 |
9.2472711 |
71.8993200 |
15.7560562 |
| ENSG00000174501 |
400986 |
ANKRD36C |
protein_coding |
Q5JPF3 |
|
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
|
ion channel inhibitor activity [GO:0008200] |
33184803_Exome Sequencing Identifies Abnormalities in Glycosylation and ANKRD36C in Patients with Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. |
|
|
62.399396 |
0.1717723098 |
-2.541431 |
0.793837345 |
8.918290 |
0.00282328789379426457403776673515949369175359606742858886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006079026887294433634245649500371655449271202087402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.9892434 |
9.8885820 |
104.8878860 |
40.6055008 |
| ENSG00000174669 |
3177 |
SLC29A2 |
protein_coding |
Q14542 |
FUNCTION: Mediates equilibrative transport of purine, pyrimidine nucleosides and the purine base hypoxanthine. Very less sensitive than SLC29A1 to inhibition by nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR), dipyridamole, dilazep and draflazine. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9396714}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The uptake of nucleosides by transporters, such as SLC29A2, is essential for nucleotide synthesis by salvage pathways in cells that lack de novo biosynthetic pathways. Nucleoside transport also plays a key role in the regulation of many physiologic processes through its effect on adenosine concentration at the cell surface (Griffiths et al., 1997 [PubMed 9396714]).[supplied by OMIM, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:3177; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; neurotransmitter transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005326]; nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005337]; purine nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015211]; uridine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015213]; adenine transport [GO:0015853]; adenosine transport [GO:0032238]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; guanine transport [GO:0015854]; hypoxanthine transport [GO:0035344]; lactation [GO:0007595]; neurotransmitter transport [GO:0006836]; neurotransmitter uptake [GO:0001504]; nucleoside transmembrane transport [GO:1901642]; nucleoside transport [GO:0015858]; purine nucleoside transmembrane transport [GO:0015860]; pyrimidine-containing compound transmembrane transport [GO:0072531]; thymine transport [GO:0035364]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104]; uridine transport [GO:0015862]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855] |
9478986_Functional nucleoside transporter in stable and transient transfection studies in mammalian cells. 12006583_role in functional and molecular characterization of nucleobase transport 12527552_hENT1 and hENT2 on the basolateral membrane function with concentrative nucleoside transporters on the apical membrane to mediate active reabsorption of nucleosides within the kidney. 12590919_an analysis of function by site-directed glycosylation mutagenesis 12820662_Equilibrative nucleoside transporters (hENT1, hENT2) together with adenosine kinase and 5'-nucleotidase play a crucial role in the regulation of CFTR through an adenosine-dependent pathway in human airway epithelia. 15386342_Only a few endometrial carcinomas (15%) were found to be negative for hCNT1, but they all retained hENT1 and hENT2 expression. 15644498_residue 33 resides in an extracellular domain as predicted by the current hENT2 topology model and suggested that it is a functionally important component of both the permeant and dipyridamole binding sites. 15649894_the corresponding residues in TMs 1 and 11 of hENT1, hENT2, and CeENT1 are important for dipyridamole interactions and nucleoside transport. 16214850_The low overall genetic diversity in SLC29A2 makes it unlikely that variation in the coding region contributes significantly to clinically observed differences in drug response. 16924660_Data show that insulin restores glucose inhibition of adenosine transport by increasing the expression and activity of the equilibrative nucleoside transporter 2 in human umbilical vein endothelium. 17921321_Human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells rely on ENT1 for nucleoside transport with little contribution from ENT2. 17926640_These data suggest that selected genes of the SLC28 and SLC29 families are not only targets of HIV-1 infection, but might also contribute to the development of adipose tissue alterations leading to lipodystrophy. 18635603_Report expression and hepatobiliary transport characteristics of ENT2 in sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes. 18703227_hPMEC from pre-eclampsia exhibit increased total transport (hENT1+hENT2), and maximal velocity (Vmax) for hENT2- (2-fold), but reduced Vmax for hENT1-mediated adenosine transport 18945750_correlation between the recently described p53-inducible apoptosis gene TIGAR and both sensitivity to fludarabine and hENT2 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. 19105964_HIF-1alpha-dependent repression of ENT2 increases mucosal adenosine signaling and attenuates hypoxia-associated inflammation of the intestine. 19297449_This evidence suggested that apical CNT3 and basolateral ENT2 are involved in proximal tubular reabsorption of adenosine and some nucleoside drugs and that apical ENT1 is involved in proximal tubular secretion of 2'-deoxyadenosine. 20392501_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21156465_Studies show that ABCC4 and SLC29A2 expression were predictive of achieving CR, and the high expression of GSTP1 suggests that this may be a therapeutic target for relapsed AML. 21822668_Data show that ENT1, ENT2, ENT4 and CNT3 protein was detected on ovarian carcinoma cells in all effusions, with expression observed in 1-95% of tumor cells. 23590299_these findings reveal the transcriptional repression of ENT1,2 as an innate protective response during acute pulmonary inflammation. 23639800_Data suggest that SLC29A2 is localized to apical membrane of adult Sertoli cells. In contrast, SLC29A1 is located on basolateral membrane of Sertoli cells; SLC29A1 is primarily responsible for basolateral nucleoside uptake into Sertoli cells. 27160886_Direct evidence for apical localization of ENT1 and integral expression of ENT2 in intestinal epithelial cells. 27271752_two novel functional splice variants of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 2 (ENT2), which are present at the nuclear envelope, were identified. 28218790_Results showed that both SLC29A1 and SLC29A2 were expressed at lower levels in colon cancer cell lines originating from metastatic sites than from primary sites. 31601121_Hypoxia did not change expression of either hENT1, hENT2, or TK1. 33994542_Exosomes secreted from cancer-associated fibroblasts elicit anti-pyrimidine drug resistance through modulation of its transporter in malignant lymphoma. 34503974_Remdesivir and EIDD-1931 Interact with Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporters 1 and 2: Implications for Reaching SARS-CoV-2 Viral Sanctuary Sites. |
ENSMUSG00000024891 |
Slc29a2 |
19.107946 |
0.3529753447 |
-1.502361 |
0.426859684 |
12.372359 |
0.00043573678095797574102987503863460005959495902061462402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001082922190089193785825227855923458264442160725593566894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7846754 |
2.5994397 |
27.9272717 |
4.7796997 |
| ENSG00000174705 |
285590 |
SH3PXD2B |
protein_coding |
A1X283 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein involved in invadopodia and podosome formation and extracellular matrix degradation. Binds matrix metalloproteinases (ADAMs), NADPH oxidases (NOXs) and phosphoinositides. Acts as an organizer protein that allows NOX1- or NOX3-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and ROS localization. Plays a role in mitotic clonal expansion during the immediate early stage of adipocyte differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12615925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19755710, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20609497}. |
Cell junction;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes an adapter protein that is characterized by a PX domain and four Src homology 3 domains. The encoded protein is required for podosome formation and is involved in cell adhesion and migration of numerous cell types. Mutations in this gene are the cause of Frank-ter Haar syndrome (FTHS), and also Borrone Dermato-Cardio-Skeletal (BDCS) syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2015]. |
hsa:285590; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; podosome [GO:0002102]; phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0080025]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate binding [GO:0010314]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; adipose tissue development [GO:0060612]; bone development [GO:0060348]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; eye development [GO:0001654]; heart development [GO:0007507]; podosome assembly [GO:0071800]; protein localization to membrane [GO:0072657]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] |
19228371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20137777_These findings establish a role for TKS4 in Frank-Ter Haar syndrome and embryonic development. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20609497_Tks4 and Tks5 directly bind to NoxA1. The integrity of the N-terminal PRR of NoxA1 is essential for this direct interaction with the Tks proteins. 20943948_The Nox1-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species is dependent on Src phosphorylation of NoxA1 and Tks4. Blockage of phosphorylation of NoxA1 and Tks4 decreases Nox1-dependent ROS generation and blocks SrcYF-induced invadopodia formation. 21886807_SH3PXD2B is a scaffold protein that plays a key role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton via Src and cortactin. 22829589_a new function for Tks4 in the regulation of growth factor-dependent cell migration. 26183326_Misfolded Frank-ter Haar syndrome protein Tks4(R43W) is transported via the microtubule system to the aggresomes. 27802184_Suggest the importance of Tks adaptor proteins in melanoma growth and metastasis in vivo is likely via functional invadopodia formation. 29100834_We report a sibling pair with Frank-ter Haar syndrome (FTHS) caused by a homozygous, novel mutation pLys133Glnfs*13 in the SH3PXD2B gene. 29928795_The interaction of Tks4 with Src may result in the long term stabilization of the kinase in its active conformation, leading to prolonged Src activity following epidermal growth factor stimulation. 30962481_Significance of the Tks4 scaffold protein in bone tissue homeostasis. 31591456_Enhanced endothelial motility and multicellular sprouting is mediated by the scaffold protein TKS4. 31671862_Absence of the Tks4 Scaffold Protein Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Like Changes in Human Colon Cancer Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000040711 |
Sh3pxd2b |
94.728181 |
2.5533844966 |
1.352411 |
0.202034604 |
44.851980 |
0.00000000002125058626479999476774644014329243351876796985777673398843035101890563964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000115400534683019841875115146980222734576781995485816878499463200569152832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
133.9483905 |
15.6903258 |
52.7318923 |
4.8794203 |
| ENSG00000174788 |
126006 |
PCP2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVA1 |
FUNCTION: May function as a cell-type specific modulator for G protein-mediated cell signaling. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within rhodopsin mediated signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in neuronal cell body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126006; |
guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085] |
16298104_The data demonstrate that PCP-2 is a comparatively weak GoLoco motif protein that exhibits highest affinity interactions and GDI activity toward Galphai1, Galphai2, and Galphai3 subunits. 18768681_characterization of the mouse 136 aa conserved isoform, Ret-PCP2 |
ENSMUSG00000004630 |
Pcp2 |
7.415298 |
0.0817975669 |
-3.611798 |
0.918589223 |
18.844025 |
0.00001418547286039407718779073452886052564281271770596504211425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000043729653178658432722755722288354718330083414912223815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0513318 |
0.7041364 |
13.0707705 |
3.9488191 |
| ENSG00000174804 |
8322 |
FZD4 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULV1 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for Wnt proteins (PubMed:30135577). Most frizzled receptors are coupled to the beta-catenin (CTNNB1) canonical signaling pathway, which leads to the activation of disheveled proteins, inhibition of GSK-3 kinase, nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin (CTNNB1) and activation of Wnt target genes (PubMed:30135577). Plays a critical role in retinal vascularization by acting as a receptor for Wnt proteins and norrin (NDP) (By similarity). In retina, it can be activated by Wnt protein-binding and also by Wnt-independent signaling via binding of norrin (NDP), promoting in both cases beta-catenin (CTNNB1) accumulation and stimulation of LEF/TCF-mediated transcriptional programs (By similarity). A second signaling pathway involving PKC and calcium fluxes has been seen for some family members, but it is not yet clear if it represents a distinct pathway or if it can be integrated in the canonical pathway, as PKC seems to be required for Wnt-mediated inactivation of GSK-3 kinase. Both pathways seem to involve interactions with G-proteins. May be involved in transduction and intercellular transmission of polarity information during tissue morphogenesis and/or in differentiated tissues. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30135577}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene is a member of the frizzled gene family. Members of this family encode seven-transmembrane domain proteins that are receptors for the Wingless type MMTV integration site family of signaling proteins. Most frizzled receptors are coupled to the beta-catenin canonical signaling pathway. This protein may play a role as a positive regulator of the Wingless type MMTV integration site signaling pathway. A transcript variant retaining intronic sequence and encoding a shorter isoform has been described, however, its expression is not supported by other experimental evidence. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8322; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; Wnt receptor activity [GO:0042813]; Wnt-protein binding [GO:0017147]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cerebellum vasculature morphogenesis [GO:0061301]; extracellular matrix-cell signaling [GO:0035426]; locomotion involved in locomotory behavior [GO:0031987]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0010812]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0035567]; Norrin signaling pathway [GO:0110135]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of neuron projection arborization [GO:0150012]; progesterone secretion [GO:0042701]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030947]; retina vasculature morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0061299]; retinal blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0061304]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055]; Wnt signaling pathway, calcium modulating pathway [GO:0007223] |
12172548_Functions in retinal angiogenesis. Mutations disrupts angiogenesis in vitreoretinopathy. 14737064_High-resolution genotyping and haplotype analysis excluded FZD4 as the defective gene in a family previously linked to the EVR1 locus. 15024691_Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy has mutations in a second gene at the EVR1 locus, low-density-lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5), a Wnt coreceptor 15223780_Eight mutations have been identified in the FZD4 gene in a cohort of 40 unrelated patients with FEVR (familial exudative vitreoretinopathy) 15370539_FZD4 mutations are associated with autosomal dominant familial exudative vitreoretinopathy 15488808_A novel missense mutation in the FZD4 gene was identified in Japanese patients with FEVR (familial exudative vitreoretinopathy). 15981244_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15981244_mutations in the LRP5 and/or FZD4 genes may have roles in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy 17093393_Mutations in FZD4 were observed in 5.6% of studied clinically diagnosed familial exudative vitreoretinopathy in Indian population. Could play vital role in pathogenesis and provide greater insight in to genotype/phenotypic functions of FZD4 gene. 17386109_Fz4 expression may play a critical role in responses to Wnt signaling in the tumor microenvironment. 18156211_sFRP-1 can interact with Wnt receptors Frizzled 4 and 7 on endothelial cells to transduce downstream to cellular machineries requiring Rac-1 activity in cooperation with GSK-3beta 18161623_Homozygous state for the FZD4 gene is possibly involved in the severity of the familial exudative vitreoretinopathy phenotype 18787502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020754_Report activation of Wnt signalling in acute myeloid leukemia by induction of Frizzled-4. 19172507_The clinical features in the three children and their relatives with a documented FZD4 mutation support the previous reports of a high degree of intrafamilial and interfamilial variability in familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR). 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20008721_Mutations occurring in the FZD4 gene affect patients diagnosed with both autosomal-dominant familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (AdFEVR) or retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) 20008721_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20141357_Mutations in the FZD4 gene in this group of premature infants supports a role for the FZD4 pathway in the development of severe retinopathy of prematurity. 20340138_Studies report 21 novel variants for FZD4, LRP5, and NDP. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20713528_Results provide mechanistic insights to ERG oncogenesis in prostate cancer, involving activation of WNT signaling through FZD4, leading to cancer-promoting phenotypic effects, including EMT and loss of cell adhesion. 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20938005_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20938005_The profile of the mutations obtained in FZD4 further illustrates the complexity of familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR)and provides a better understanding of the genotype-phenotype correlations. 21097938_FZD4 mutation screening can be a useful tool especially in mild or atypical cases of familial exudative vitreoretinopathy & Germ-line mutations in FZD4 do not appear to be a common cause of Coats disease. 21363911_Frizzled 4 is a member of the Wnt signaling family that governs both stemness and invasiveness of glioma stem cells, and that it may be a major cause of GBM recurrence and poor prognosis. 22057916_miR-493 is a new tumor suppressor miRNA in bladder cancer and inhibits cell motility through downregulation of RhoC and FZD4. 22574936_Genetic analysis revealed that all affected family members of one pedigree carried an exon 2 mutation of COL2A1, and in the second pedigree, all affected members carried an FZD4 mutation. 23077402_Five mutations have been found in the FZD4 gene in six Chinese families with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 23441120_Six different nonsynonymous DNA variants are identified in the coding region of either the FZD4 gene (p.H69Y, p.R127H, and p.Y211H) or the LRP5 gene (p.R1219H, p.H1383P, and p.T1540M) in seven patients with advanced retinopathy of prematurity 24386373_Polymorphisms in several genes involved in the Wnt signaling pathway were associated with hepatic fibrosis or inflammation risk in HCV-infected males. 24744206_Defective trafficking resulting in haploinsufficiency is a major cellular mechanism for several missense FEVR-causing FZD4 mutants. 25751279_analysis of allosteric ligands of Frizzled4 26119001_The relatively high prevalence of the p.[P33S(;)P168S] variant in ROP (retinopathy of prematurity) and intrauterine growth restriction suggests that it also may be a marker for increased risk of developing ROP and preterm birth. 26158506_These structural, biophysical and cellular data, map Fz4 and putative Lrp5/6 binding sites to distinct patches on Norrin, and reveal a GAG binding site spanning Norrin and Fz4 cysteine-rich domain. 26244290_Mutations of FZD4 accounted for the largest proportion, which could be directly applied to the testing strategy to start with screening for FZD4 mutations. 26277630_Letter: FZD4+ and FZD4- melanocytes were significantly lower in hair follicles of patients with rhododenol-induced leukoderma. 26530129_Two were novel mutations: p.E134* and p.T503fs of FZD4 lead to the loss of FZD4 activity. 27316669_Several novel mutations (missense, non-stop and insertion) were detected in the coding regions of FZD4, TSPAN12 and ZNF408 genes among the unrelated familial exudative vitreoretinopathy probands. The mutations in FZD4 and TSPAN12 were involved in autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive families and further validates the involvement of these gene in exudative vitreoretinopathy development. 27458145_human FZD4 assembles-in a DVL-independent manner-with Galpha12/13 but not representatives of other heterotrimeric G protein subfamilies. 27510711_novel role of let-7b/Fzd4 axis through wnt signaling 27555740_Seven novel mutations found in this study have broadened the spectrum of mutations in FZD4 known to cause familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR), providing a deeper understanding of this disease. The results show that mutations in FZD4 are associated with the phenotypes of retinal folds or ectopic macula in FEVR 27668459_The findings in this family support the concept that some mutated FZD4 alleles can be associated with recessive rather than dominant disease. 28211206_Three affected individuals within a family with FEVR presented with variable disease severity. All three affected family members harboured mutation c.349T>C (p.Cys117Arg) in FZD4. 28245136_FZD4 down-regulation leads to loss of WNT/beta-catenin signal activity and subsequently to reduced alveolar epithelial cell wound repair capacity and impaired expression of elastogenic components. 28494495_Among the detected mutations, LRP5 accounted for the largest proportion with a mean mutation rate of 16.1% (5/31, 16.1%), followed by NDP (3/31, 9.7%), FZD4 (2/31, 6.5%), TSPAN12 (1/31, 3.2%), and KIF11 (1/31, 3.2%). All the novel changes were predicted to be pathogenic by a series of bioinformatics analyses. 28546512_Study shows that WNT5A stimulates dimerization of membrane-anchored FZD4 CRDs and oligomerization of full-length FZD4, which requires the integrity of CRD palmitoleoyl-binding residues. These results suggest that FZD receptors may form signalosomes in response to Wnt binding through the CRDs and that the Wnt palmitoleoyl group is important in promoting these interactions. 28577497_FZD4 was confirmed to be a downstream target of miR-505, and found to be up-regulated in cervical cancer patients. 28658627_Accessory proteins in Frizzled (FZD) receptor complexes are thought to determine ligand selectivity and signaling amplitude. 28668722_FZD4 Tyrosine 250(2.39) is crucial for DVL2 interaction and DVL2 translocation to the plasma membrane. 28671046_his study showed that Let7b modulates the proliferation, invasiveness, and migration of liver cancer cell and reduces the proportion of cancer stem cells in liver cancer cell by inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway via downregulated Frizzled4. 28831115_Findings suggest that the novel epidemiological miR-SNP (rs713065) loci in the 3'UTR of FZD4 may significantly influence overall survival in early stage NSCLC patients by specifically and differentially interacting with miRNAs such as miR-204 which modulates FZD4 expression and cellular function in the Wnt/FZD4-signaling driven tumor cell proliferation and progression pathways. 28982955_The screening of candidate genes namely NDP, FZD4 and TSPAN12 led to the identification of six major coding region variants in 36 ROP probands. 29135315_Mutation in FZD4 gene is associated with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 29293331_FzM1.8 is an allosteric agonist of FZD4. In the absence of any WNT ligand, FzM1.8 binds to FZD4, promotes recruitment of heterotrimeric G proteins, and biases WNT signaling toward a noncanonical route that involves PI3K. In colon cancer cells, the FZD4/PI3K axis elicited by FzM1.8 preserves stemness and promotes proliferation of undifferentiated cells. 29465286_rs61749246:C>A of the FZD4 gene is associated with retinopathy of prematurity. 29566281_Downregulation of miR-3127-5p promotes EMT through activating the Wnt/FZD4/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 30097784_This is the first study to report a group of patients with digenic familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR). In most affected eyes, the stage was more severe than stage 3. We speculate that the phenotype of FEVR is more severe in patients with digenic rather than monogenic variants of FEVR-related genes. 30135577_atomic-resolution crystal structure of the human Frizzled 4 receptor (FZD4) transmembrane domain in the absence of a bound ligand 30173892_circular RNA 100290 has a role in promoting colorectal cancer progression through miR-516b-induced downregulation of FZD4 expression and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling [circRNA_100290] 30513533_Our data indicate FEVR status is associated with a significantly smaller FAZ, decreased vascular density in the fovea. In addition, patients with the LRP5 mutation had a milder phenotype than those with the FDZ4 or TSPAN12 mutations. 30820142_Variable reduction in Norrin signaling activity caused by novel mutations in FZD4 identified in patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 30849938_these results demonstrate that during the course of evolution, FZD4 has acquired new functions or epistasis via complex patter of gene duplications, sequence divergence and conformational remodeling. 31237656_The positive rate for pathogenic mutations in the known FEVR-associated genes was 38.9% (21/54). Among the mutations, LRP5 mutation was the predominant, accounting for 66.7% (14/21) of genetic positive patients. Patients with FEVR-RRD due to LRP5 mutations have less retinal vascular leakage or neovasculization than do patients with FEVR-RRD due to TSPAN12/FZD4 mutations. 31359032_WNT2b Activates Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition Through FZD4: Relevance in Penetrating Crohn s Disease. 31618077_Secreted Wnt6 binds to FZD4 to activate the canonical Wnt6 signaling pathway, which is upstream of ROCK1 and 14-3-3sigma, and that this is the cell signaling pathway underlying diabetes-associated centrosome amplification. 31765079_Identification of novel variants in the FZD4 gene associated with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy in Chinese families. 31957812_MicroRNA-1286 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to promote the progression of osteoporosis via regulating FZD4 expression. 31985040_Frizzled-4 is required for normal bone acquisition despite compensation by Frizzled-8. 31999491_Identification of Novel Mutations in the FZD4 and NDP Genes in Patients with Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy in South India. 32420371_Role of NDP- and FZD4-Related Novel Mutations Identified in Patients with FEVR in Norrin/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. 32828883_Up-Regulation of Nfat5 mRNA and Fzd4 mRNA as a Marker of Poor Outcome in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. 32889247_An induced pluripotent stem cell line (EHTJUi002-A) derived from a neonate with c.678G>A mutation in the gene FZD4 causing exudative vitreoretinopathy. 33302760_Novel FZD4 and LRP5 mutations in a small cohort of patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR). 34021822_Circ_0001955 Acts as a miR-646 Sponge to Promote the Proliferation, Metastasis and Angiogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 34199009_Whole-Gene Deletions of FZD4 Cause Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy. 35022017_Ocular phenotype and genetical analysis in patients with retinopathy of prematurity. 35352610_Circ_0088036 facilitates the proliferation and inflammation and inhibits the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through targeting miR-326/FZD4 axis in rheumatoid arthritis. 35394490_FZD4 in a Large Chinese Population With Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy: Molecular Characteristics and Clinical Manifestations. |
ENSMUSG00000049791 |
Fzd4 |
46.738852 |
0.3569753108 |
-1.486104 |
0.262963583 |
32.396419 |
0.00000001257179278548917266169971035990465813014793639013078063726425170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000054225500150152013251594261241186889499488188448594883084297180175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.6408581 |
4.0509476 |
69.4288170 |
7.1974994 |
| ENSG00000174842 |
11146 |
GLMN |
protein_coding |
Q92990 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Regulatory component of cullin-RING-based SCF (SKP1-Cullin-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes (PubMed:22405651, PubMed:22748924). Inhibits E3 ubiquitin ligase activity by binding to RBX1 (via RING domain) and inhibiting its interaction with the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme CDC34 (PubMed:22405651, PubMed:22748924). Inhibits RBX1-mediated neddylation of CUL1 (PubMed:22405651). Required for normal stability and normal cellular levels of key components of SCF ubiquitin ligase complexes, including FBXW7, RBX1, CUL1, CUL2, CUL3, CUL4A, and thereby contributes to the regulation of CCNE1 and MYC levels (By similarity). Essential for normal development of the vasculature (PubMed:11845407). Contributes to the regulation of RPS6KB1 phosphorylation (PubMed:11571281). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BZM1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11571281, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11845407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22405651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22748924}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a phosphorylated protein that is a member of a Skp1-Cullin-F-box-like complex. The protein is essential for normal development of the vasculature and mutations in this gene have been associated with glomuvenous malformations, also called glomangiomas. Multiple splice variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:11146; |
Cul2-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031462]; Cul3-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031463]; Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031464]; cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0031461]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; hepatocyte growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005171]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; ubiquitin-protein transferase inhibitor activity [GO:0055105]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; epigenetic regulation of gene expression [GO:0040029]; muscle cell differentiation [GO:0042692]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0032434]; vasculogenesis [GO:0001570] |
11845407_Describes the characterizations of 14 different mutations in the glomulin gene in patients with glomuvenous malformations. 12604780_FAP48-FKBP complexes increase IL2 production 22092580_A novel GLMN mutation is described in an Italian family with glomuvenous malformations in which some members present with the less commonly observed phenotype of solitary lesions. 22280104_These data identify glomulin as a permissivity factor for VACV infection and as a potential therapeutic target for inhibition of vaccinia virus (VACV) infection. 22405651_The glomuvenous malformation protein Glomulin binds Rbx1 and regulates cullin-1 RING ligase-mediated turnover of Fbw7. 22678819_FAP48 adipocyte expression plays a key role in HIV-associated lipodystrophy. 22748924_Structural and biochemical analyses reveal that GLMN adopts a HEAT-like repeat fold that tightly binds the E2-interacting surface of RBX1, inhibiting CRL-mediated chain formation by the E2 CDC34. 24961656_Our report contributes to document the possible association between the c.395-1G>C mutation of GLMN gene and glomuvenous malformations. 30325312_In summary, we present a case of congenital plaquetype GVM and a case of familial disseminated cutaneous GVM, both with the same glomulin gene mutation (c.157_161delAAGAA), but with different clinical expression. 35732373_GLMN causing vascular malformations: the clinical and genetic differentiation of cutaneous venous malformations. |
ENSMUSG00000029276 |
Glmn |
223.026904 |
0.4875505723 |
-1.036376 |
0.132040591 |
61.382405 |
0.00000000000000469991941723339475745295130831890390560567341213249470399659912800416350364685058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000032250493072229153102717394973580902527230795245882788435665133874863386154174804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
152.4912448 |
15.1222492 |
314.8251412 |
22.0774229 |
| ENSG00000174851 |
10897 |
YIF1A |
protein_coding |
O95070 |
FUNCTION: Possible role in transport between endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15990086}. |
Acetylation;Endoplasmic reticulum;ER-Golgi transport;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to be involved in endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport. Located in Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10897; |
COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle [GO:0030134]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0006888]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
15990086_Human Yip1A (YIPF5) interacts with and localizes human Yif1 (YIF1A) to the Golgi apparatus. 18718466_YIF1A is involved in the maintenance of the Golgi structure. |
ENSMUSG00000024875 |
Yif1a |
213.827478 |
2.0783243499 |
1.055421 |
0.115832877 |
83.696451 |
0.00000000000000000005768870935019187309826417683190496445421396985860865852524526076194888446480035781860351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000511709945918769323787533735411132840432069098478962522816293478911120473640039563179016113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
303.8090503 |
20.6546324 |
147.4194642 |
7.9907542 |
| ENSG00000174945 |
155185 |
AMZ1 |
protein_coding |
Q400G9 |
FUNCTION: Probable zinc metalloprotease. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8TXW1}. |
Alternative splicing;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity and metallopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:155185; |
metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
|
ENSMUSG00000050022 |
Amz1 |
10.291709 |
3.1011215192 |
1.632790 |
0.547114766 |
9.073924 |
0.00259280117128099073936509100235525693278759717941284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005616340664530000519050201290838231216184794902801513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8635356 |
4.3536075 |
4.5003174 |
1.1702260 |
| ENSG00000175040 |
9435 |
CHST2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y4C5 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the transfer of sulfate to position 6 of non-reducing N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residues within keratan-like structures on N-linked glycans and within mucin-associated glycans that can ultimately serve as SELL ligands. SELL ligands are present in high endothelial cells (HEVs) and play a central role in lymphocyte homing at sites of inflammation. Participates in biosynthesis of the SELL ligand sialyl 6-sulfo Lewis X and in lymphocyte homing to Peyer patches. Has no activity toward O-linked sugars. Its substrate specificity may be influenced by its subcellular location. Sulfates GlcNAc residues at terminal, non-reducing ends of oligosaccharide chains. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11042394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11726653}. |
Alternative initiation;Carbohydrate metabolism;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; carbohydrate sulfation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11726653}. |
This locus encodes a sulfotransferase protein. The encoded enzyme catalyzes the sulfation of a nonreducing N-acetylglucosamine residue, and may play a role in biosynthesis of 6-sulfosialyl Lewis X antigen. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:9435; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; N-acetylglucosamine 6-O-sulfotransferase activity [GO:0001517]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; keratan sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0018146]; N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process [GO:0006044]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; sulfur compound metabolic process [GO:0006790] |
12855678_is distributed throughout the Golgi apparatus and orchestrates the biosynthesis of L-selectin ligands 16897186_A novel tumor antigen that is specifically expressed in ovarian mucinous, clear cell and papillary serous adenocarcinomas. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19571171_report the sites at which N-Acetylglucosamine-6-sulfotransferase-1 is modified with N-linked glycans and the effects that each glycan has on enzyme activity, specificity, and localization.[N-Acetylglucosamine-6-sulfotransferase-1] 19898482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041608_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24799377_A method for O-GlcNAc detection using in vitro sulfation with two N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)-specific sulfotransferases, carbohydrate sulfotransferase 2 and carbohydrate sulfotransferase 4. 28320965_GlcNAc6ST1 is up-regulated in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. 30093410_mRNA transcript analyses on the genes involved in synthesizing GlcNAc-6-O-sulfated glycans in human colon cancer tissues indicated that GlcNAc6ST-2 (CHST4) is preferentially expressed in cancer cells ... GlcNAc6ST-3 (CHST5) was only expressed in nonmalignant epithelial cells, whereas GlcNAc6ST-1 (CHST2) was expressed equally in both cancerous and nonmalignant epithelial cells. 35939855_Site-selective sulfation of N-glycans by human GlcNAc-6-O-sulfotransferase 1 (CHST2) and chemoenzymatic synthesis of sulfated antibody glycoforms. |
ENSMUSG00000033350 |
Chst2 |
204.841566 |
2.5163266659 |
1.331319 |
0.124799107 |
114.727361 |
0.00000000000000000000000000902964012032917537809778314292521350442573095570428593675183900018845666382572012764740065904334187507629394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000103076170283107992789098481574820432037233671459653917649880230651519841256202880686032585799694061279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
295.9031565 |
19.8790857 |
118.4959283 |
6.4392460 |
| ENSG00000175048 |
79683 |
ZDHHC14 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZN3 |
FUNCTION: Palmitoyltransferase that could catalyze the addition of palmitate onto various protein substrates. May have a palmitoyltransferase activity toward the beta-2 adrenergic receptor/ADRB2 and thereby regulate G protein-coupled receptor signaling (PubMed:27481942). May play a role in cell differentiation and apoptosis (PubMed:21151021, PubMed:24407904). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21151021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24407904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27481942}. |
Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables palmitoyltransferase activity. Involved in peptidyl-L-cysteine S-palmitoylation. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79683; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0016409]; protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0019706]; peptidyl-L-cysteine S-palmitoylation [GO:0018230]; protein palmitoylation [GO:0018345]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612] |
24407904_Identify ZDHHC14 as a novel tumour suppressor gene that is commonly down-regulated in testicular germ cell tumours and prostate cancer. 24807047_Results indicate that ZDHHC14 is involved in tumor progression in patients with scirrhous type gastric cancer. 33185190_The palmitoyl acyltransferase ZDHHC14 controls Kv1-family potassium channel clustering at the axon initial segment. |
ENSMUSG00000034265 |
Zdhhc14 |
232.755107 |
0.2395480104 |
-2.061613 |
0.288396728 |
45.842371 |
0.00000000001281612801203861527640762697742368042032323760537337875575758516788482666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000070531711207192380718033951168951731225398305014095967635512351989746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.6405367 |
24.6601804 |
410.8676167 |
71.9524265 |
| ENSG00000175106 |
201158 |
TVP23C |
protein_coding |
Q96ET8 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in protein secretion and vesicle-mediated transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be integral component of Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100533496;hsa:201158; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000014177 |
Tvp23b |
23.244729 |
3.5340039509 |
1.821304 |
0.567518052 |
9.623928 |
0.00192058486039845119006108653536557540064677596092224121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004259629232078307979614262279710601433180272579193115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
39.7214206 |
18.4690658 |
10.8667348 |
3.6509468 |
| ENSG00000175130 |
65108 |
MARCKSL1 |
protein_coding |
P49006 |
FUNCTION: Controls cell movement by regulating actin cytoskeleton homeostasis and filopodium and lamellipodium formation (PubMed:22751924). When unphosphorylated, induces cell migration (By similarity). When phosphorylated by MAPK8, induces actin bundles formation and stabilization, thereby reducing actin plasticity, hence restricting cell movement, including neuronal migration (By similarity). May be involved in coupling the protein kinase C and calmodulin signal transduction systems (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P28667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22751924}. |
Actin-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) family. Members of this family play a role in cytoskeletal regulation, protein kinase C signaling and calmodulin signaling. The encoded protein affects the formation of adherens junction. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on the long arm of chromosomes 6 and 10. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:65108; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284] |
22751924_Gene knockdown in prostate cancer cells or in neurons reveals a critical role for MARCKSL1 in migration that is dependent on the phosphorylation state. 22772381_Patients with high expression of PPH3 and high MARCKSL1 protein had a lower survival rate versus patients with low MARCKSL1 and high PPH3 expression. 24863880_MARCKSL1 suppresses LOXL2-induced oncogenesis. 26555156_MARCKSL1 showed potent anti-angiogenic activity and reduced the levels of VEGF and HIF-1alpha expression. MARCKSL1 decreased VEGFinduced phosphorylation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway components. 29588366_High MARCKSL1 expression is associated with liver tumor. 30856208_Validation study of MARCKSL1 as a prognostic factor in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. 31155484_Direct Reprogramming of Human Neurons Identifies MARCKSL1 as a Pathogenic Mediator of Valproic Acid-Induced Teratogenicity. 34586620_METTL14-Mediated miR-30c-1-3p Maturation Represses the Progression of Lung Cancer via Regulation of MARCKSL1 Expression. 35864549_MARCKSL1-2 reverses docetaxel-resistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells by recruiting SUZ12 to suppress HDAC1 and elevate miR-200b. 36374807_IncRNA TYMSOS Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in Thyroid Carcinoma through Regulating MARCKSL1 and Activating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000047945 |
Marcksl1 |
799.282554 |
6.3757939856 |
2.672605 |
0.069406981 |
1626.309246 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1392.2489000 |
56.7846831 |
219.9648169 |
7.9952948 |
| ENSG00000175147 |
200197 |
TMEM51-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.093120 |
0.1944167261 |
-2.362776 |
0.475539699 |
25.158566 |
0.00000052804569255937082751235604749506791222302126698195934295654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001931587217391899238361305940481216225634852889925241470336914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2787085 |
1.5544650 |
27.1053529 |
4.6822405 |
| ENSG00000175155 |
388403 |
YPEL2 |
protein_coding |
Q96QA6 |
|
Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be located in nucleolus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388403; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
19107206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056645_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33022222_Structural Variants Create New Topological-Associated Domains and Ectopic Retinal Enhancer-Gene Contact in Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa. |
ENSMUSG00000018427 |
Ypel2 |
116.507443 |
0.3783026695 |
-1.402387 |
0.161520887 |
76.888806 |
0.00000000000000000180859353415373543905200353567159649596093162902314763901268079848705383483320474624633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000014946719240822584261055691126605013331856358917387565810042104885724256746470928192138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
64.9880513 |
7.5316048 |
173.1388198 |
13.1709826 |
| ENSG00000175175 |
22843 |
PPM1E |
protein_coding |
Q8WY54 |
FUNCTION: Protein phosphatase that inactivates multifunctional CaM kinases such as CAMK4 and CAMK2 (By similarity). Dephosphorylates and inactivates PAK. May play a role in the inhibition of actin fiber stress breakdown and in morphological changes driven by TNK2/CDC42. Dephosphorylates PRKAA2 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11864573}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Manganese;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the PPM family of serine/threonine-protein phosphatases. The encoded protein is localized to the nucleus and dephosphorylates and inactivates multiple substrates including serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1, 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and the multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
hsa:22843; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0004722]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; peptidyl-threonine dephosphorylation [GO:0035970]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
11864573_The p21-activated kinase PAK is negatively regulated by POPX1 and POPX2, a pair of serine/threonine phosphatases of the PP2C family. (POPX1; POPX2) 20801214_The Ppm1E contributes to dephosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase. 27661114_Data show that miR-135b selectively targets the AMPK phosphatase Ppm1e. 27793001_miR-135b-5p expression downregulates Ppm1e to activate AMPK signaling, which inhibits LPS-induced TNFalpha production via suppressing ROS production and NFkappaB activation. 28423719_Ppm1E upregulation in human gastric cancer is important for cell proliferation, possible via regulating AMPK-mTOR signaling. 28460435_our results suggest that miR-135b-induced Ppm1e silence induces AMPK activation to inhibit osteoblastoma cell proliferation. 34556632_CircHAS2 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating PPM1E mediated by hsa-miR-944. |
ENSMUSG00000046442 |
Ppm1e |
56.469017 |
3.4917012629 |
1.803930 |
0.239003956 |
58.105566 |
0.00000000000002484224806706721914683795085469404223725109308318348411148690502159297466278076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000163328098650294923378294216905243437540449363831740470232034567743539810180664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
88.7769989 |
13.8267456 |
25.5522996 |
3.2234662 |
| ENSG00000175262 |
148345 |
C1orf127 |
protein_coding |
K7EPZ7 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in heart development. Predicted to act upstream of or within determination of left/right symmetry. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
Mouse_homologues determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; heart development [GO:0007507] |
|
ENSMUSG00000070577 |
Gm572 |
12.688114 |
0.1759824218 |
-2.506497 |
0.515085423 |
27.070527 |
0.00000019616601894779960991859488281946477528094874287489801645278930664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000750300709942866644877536470847889660262808320112526416778564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2655673 |
1.1286445 |
18.8774137 |
3.2666791 |
| ENSG00000175265 |
23015 |
GOLGA8A |
protein_coding |
A7E2F4 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in maintaining Golgi structure. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
The Golgi apparatus, which participates in glycosylation and transport of proteins and lipids in the secretory pathway, consists of a series of stacked, flattened membrane sacs referred to as cisternae. Interactions between the Golgi and microtubules are thought to be important for the reorganization of the Golgi after it fragments during mitosis. The golgins constitute a family of proteins which are localized to the Golgi. This gene encodes a golgin which structurally resembles its family member GOLGA2, suggesting that they may share a similar function. There are many similar copies of this gene on chromosome 15. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:23015; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
26738811_The microarray analysis and the validation study revealed an increase in Golgin A8 Family, Member A (GOLGA8A) mRNA and protein levels in Intracerebral hemorrhage. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
1208.839147 |
0.4099555735 |
-1.286461 |
0.053928760 |
572.531046 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000158033193147228434995204321193286419057317858390094994924116064465332173092391311139070217508327929390835707086270215024963879470463849800981916800388337429271227669112765622753734444421563953102571578303 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000085442122009270762442513780306338770873958230158534420451551706126273493336807358822463168326560754569300362009800430015303132320793022004861845740021892383985917209270722619831839591780142847719217048393 |
Yes |
No |
707.2452901 |
24.1595430 |
1737.6093658 |
39.0908441 |
| ENSG00000175274 |
9537 |
TP53I11 |
protein_coding |
O14683 |
|
Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of cell population proliferation. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9537; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285] |
12883691_PIG11, as a downstream target of p53, is involved in apoptosis of gastric cancer cells 15225615_Overexpression of PIG11 could induce cell apoptosis in the low levels and enhanced the apoptotic effects of arsenic trioxide 16170329_Jasmonates can circumvent drug resistance induced by p53 mutations. 17482569_PIG11 protein may play an important role by interaction with other biological molecules in the regulation of apoptosis and provided us a novel angel of view to explore the possible function of PIG11 in vivo. 19096915_PIG11 is considered to be a new candidate liver tumour suppressor gene. 30376610_TP53I11 functions as a mediator to balance activation of AKT and AMPK to adapt cells to different cellular contexts such as extracellular matrix-attachment and -detachment. 30940320_Findings showed that hypoxic treatment upregulated the expression of HIF1alpha, but reduced TP53I11 protein levels and TP53I11 overexpression reduced HIF1alpha expression under normal culture and hypoxicconditions, and in xenografts of MDA-MB-231 cells. 32572880_MiR-645 promotes proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting TP53I11. 36190397_Overexpression of hsa_circ_0006470 inhibits the malignant behavior of gastric cancer cells via regulation of miR-1234/TP53I11 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000068735 |
Trp53i11 |
493.331436 |
0.3072120780 |
-1.702693 |
0.076659395 |
508.792755 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011611200416393201451480441313003685805744508656876404493083314336973700454210469188363460560739147756815402187517912687786134950169717219514171700057646382474794757136071145035358488406337523490856924491090516865561667 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005656149113728173287081183390676543022460598496748009846080327434865978084582479769667848173283410114194693301656070485995533927010893574426986569007119283226624064152430852990502785226113764928958239343310394701243269 |
Yes |
Yes |
235.1201063 |
12.2191288 |
770.9792452 |
25.3657484 |
| ENSG00000175294 |
117144 |
CATSPER1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NEC5 |
FUNCTION: Voltage-gated calcium channel that plays a central role in calcium-dependent physiological responses essential for successful fertilization, such as sperm hyperactivation, acrosome reaction and chemotaxis towards the oocyte. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21412338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21412339}. |
Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Flagellum;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Calcium ions play a primary role in the regulation of sperm motility. This gene belongs to a family of putative cation channels that are specific to spermatozoa and localize to the flagellum. The protein family features a single repeat with six membrane-spanning segments and a predicted calcium-selective pore region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:117144; |
CatSper complex [GO:0036128]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sperm principal piece [GO:0097228]; calcium activated cation channel activity [GO:0005227]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0005245]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; regulation of cilium beat frequency involved in ciliary motility [GO:0060296]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
3530540_Overview of the complications of diabetes. 14688170_Potential role for CatSper in sperm motility and fertility in mouse and human. CatSper is therefore implicated as a potential target to explore the molecular mechanisms of male infertility. 16625279_CATSPER1 is meiotically and post-meiotically expressed in human testis tissue. 16740636_CatSper1 and CatSper2 can associate with and modulate the function of the Ca(v)3.3 channel, which might be important in the regulation of sperm function. 18976756_CatSper1 may be a potential target for immunocontraception, and the antibody may be a tool to study the function of ion channels in sperm. 19344877_sequence analysis of CATSPER1 in heritable forms of nonsyndromic male infertility revealed two separate insertion mutations (c.539-540insT and c.948-949insATGGC) that are predicted to lead to frameshifts and premature stop codons 20648059_Studies indicate that CATSPER channel represents a novel human male fertility factor. 21404705_The decreased or abnormal expression of the CatSper1 protein may be a factor involved in the pathogenesis of idiopathic asthenozoospermia. 21412338_progesterone activates the sperm-specific, pH-sensitive CatSper Ca(2+) channel 21412339_human CatSper is synergistically activated by elevation of intracellular pH and extracellular progesterone 22354039_It was shown that odorants directly activate CatSper without involving G protein-coupled receptors and cAMP. Membrane-permeable analogues of cyclic nucleotides activated CatSper directly via an extracellular site. 23313885_The immediate upstream region and the first exon in the human CATSPER1 gene negatively regulate transcriptional activity. 23313885_This work reports the cloning and characterization of the promoter regions in the human and murine Catsper1 genes. The immediate upstream region and the first exon in the human CATSPER1 gene negatively regulate transcriptional activity. The mouse Catsper1 promoter exhibited transcriptional activity in both orientations and displayed significant expression levels in mouse testis in vivo. 23344959_CatSper activation can elicit functionally different behaviors according to the sensitivity of the Ca(2+) store, which may be regulated by capacitation and NO from the cumulus. 23530196_CatSper is indeed the principal Ca2+ channel of human spermatozoa, and that it is strongly potentiated by progesterone. 23623968_Progesterone via CatSper activates the PI3K-AKT pathway required for motility and hyperactivation but not for acrosome reaction. 25101494_Sox5 and Sox9 cause a significant increase in transactivation of the Catsper1 promoter. 26354096_The role of CATSPER1 in idiopathic asthenospermia pathogenesis: exonal SNP rs1893316 in CATSPER1 significantly correlated with idiopathic asthenospermia risk 26453676_Sperm with a near absence of CatSper current failed to respond to activation of CatSper by progesterone and there was fertilization failure at IVF. 27134080_Electrophysiological studies showed a significant increase in Cd(2+) and manganese (Mn(2+)) currents through the CaV3.1 mutants as well as a reduction in the inhibitory effect of Cd(2+) on the Ca(2+) current. 28507119_explored whether steroid hormones to which human spermatozoa are exposed in the male and female genital tract influence CatSper activation via modulation of ABHD2 30017233_The human CATSPER1 promoter is positively regulated in vitro by CREB-A in HEK293 and GC1-spg cells. Both lines showed differential transcriptional regulation, which was defined by the factors and coactivators present in each cell line as well as the context in which the CRE sites were found in the promoter. 30203545_Catsper1 tyrosine phosphorylation functions as an intracellular sensor for Ca (2+) entry in human sperm through regulation of cytoplasmic pH. 30379860_results show that the transcriptional factor SRY specifically binds to different sites in the promoter sequence and has the ability to control CATSPER1 gene transcription. 32712386_CatSper: The complex main gate of calcium entry in mammalian spermatozoa. 33456575_Roles of CatSper channels in the pathogenesis of asthenozoospermia and the therapeutic effects of acupuncture-like treatment on asthenozoospermia. 34440724_CRISP2, CATSPER1 and PATE1 Expression in Human Asthenozoospermic Semen. |
ENSMUSG00000038498 |
Catsper1 |
72.016807 |
0.2856636434 |
-1.807611 |
0.203586489 |
82.453074 |
0.00000000000000000010820888550568709333973627260761091034522663132581591304524903929262791280052624642848968505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000944508072184471581232859513935597246470113295754183514729707127344227046705782413482666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.0260902 |
4.7128864 |
113.0917705 |
10.3506668 |
| ENSG00000175309 |
85007 |
PHYKPL |
protein_coding |
Q8IUZ5 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent breakdown of 5-phosphohydroxy-L-lysine, converting it to ammonia, inorganic phosphate and 2-aminoadipate semialdehyde. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22241472}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Lyase;Mitochondrion;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome |
|
This is a nuclear gene encoding a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 5-phosphonooxy-L-lysine to ammonia, inorganic phosphate, and 2-aminoadipate semialdehyde. Mutations in this gene may cause phosphohydroxylysinuria. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:85007; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lyase activity [GO:0016829]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; transaminase activity [GO:0008483] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23242558_Phosphohydroxylysinuria is due to mutations in the AGXT2L2 gene and the resulting lack of activity of phosphohydroxylysine phospholyase in vivo. |
ENSMUSG00000020359 |
Phykpl |
200.555745 |
0.3951902868 |
-1.339381 |
0.116479118 |
134.671294 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000038961489260493179116528954314707412388947107245887183344852033067212877664534380513228217779442275059409439563751220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000005204509746745377759014055623253367193048396030353323134789211750947497796282188026184556406406045425683259963989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
110.2517253 |
9.2545754 |
280.4295089 |
15.4775066 |
| ENSG00000175463 |
374403 |
TBC1D10C |
protein_coding |
Q8IV04 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits the Ras signaling pathway through its intrinsic Ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) activity. Acts as a negative feedback inhibitor of the calcineurin signaling pathway that also mediates crosstalk between calcineurin and Ras. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17230191}. |
Alternative splicing;GTPase activation;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has an N-terminal Rab-GTPase domain and a binding site at the C-terminus for calcineurin, and is an inhibitor of both the Ras signaling pathway and calcineurin, a phosphatase regulated by calcium and calmodulin. Genes encoding similar proteins are located on chromosomes 16 and 22. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:374403; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; B cell activation [GO:0042113]; calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0033173]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; negative regulation of B cell activation [GO:0050869]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] |
17230191_Carabin inhibits calcineurin and Ras and was identified by a yeast-two-hybrid screen with calcineurin 17230191_Carabin is a negative feedback inhibitor of the calcineurin signalling pathway that also mediates crosstalk between calcineurin and Ras 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23109291_Carabin as a new negative regulator of B-cell function, whose deficiency in B cells speeds up early B-cell responses 29437589_identify prolyl 4-hydroxylase 2 (P4HA2) as a specific proline hydroxylase of Carabin. Carabin hydroxylation leads to its proteasomal degradation, thereby activating the Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway and increasing B-cell lymphoma proliferation. 35425695_Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis Identifies TBC1D10C as a New Prognostic Biomarker for Breast Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000040247 |
Tbc1d10c |
86.763543 |
0.1679826669 |
-2.573616 |
0.214196712 |
154.506221 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000001795150095665507359507432160236620610446636095233388989651644010733529714564574235889455255336250028008748813590500503778457641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000267911177067976641745507946773964171246852362969197156325194898597103472190916704528631424667151073037985042901709675788879394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.1724335 |
3.7247013 |
144.8966636 |
13.3058701 |
| ENSG00000175471 |
79772 |
MCTP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6DN14 |
FUNCTION: Calcium sensor which is essential for the stabilization of normal baseline neurotransmitter release and for the induction and long-term maintenance of presynaptic homeostatic plasticity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A1ZBD6}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including modulation of chemical synaptic transmission; negative regulation of endocytosis; and negative regulation of response to oxidative stress. Is integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79772; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045806]; negative regulation of response to oxidative stress [GO:1902883]; regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048168]; regulation of neurotransmitter secretion [GO:0046928] |
15528213_MCTPs are evolutionarily conserved C2 domain proteins that are unusual in that the C2 domains are anchored in the membrane by two closely spaced transmembrane regions and represent Ca(2+)-binding but not phospholipid-binding modules 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26195140_MCTP1 was observed on synaptic vesicles in neuronal cell bodies and pre-synaptic axon terminals. 28040410_This Gene-based tests suggest evidence of association with related genes, ZEB2, RND3, MCTP1, CTBP2, and beta EEG. 33571139_The DNA methylation-regulated MCTP1 activates the drug-resistance of esophageal cancer cells. 33826368_Multiple C2 domain-containing transmembrane proteins promote lipid droplet biogenesis and growth at specialized endoplasmic reticulum subdomains. |
ENSMUSG00000021596 |
Mctp1 |
43.551422 |
2.1264356521 |
1.088437 |
0.431747279 |
6.158280 |
0.01307983460930701655189345444796344963833689689636230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024478047271886849145516862336080521345138549804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.1853090 |
15.9551918 |
27.3864732 |
5.5124834 |
| ENSG00000175489 |
126364 |
LRRC25 |
protein_coding |
Q8N386 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the inhibition of RLR-mediated type I interferon signaling pathway by targeting RIGI for autophagic degradation. Interacts specifically with ISG15-associated RIGI to promote interaction between RIGI and the autophagic cargo receptor p62/SQSTM1 to mediate RIGI degradation via selective autophagy (PubMed:29288164). Also plays a role in the inhibition of NF-kappa-B signaling pathway and inflammatory response by promoting the degradation of p65/RELA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12384430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29044191, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29288164}. |
Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126364; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630] |
28536942_LRRC25, a potential leukocyte differentiation antigen, is a key regulator of all-trans retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation 29044191_Our study has not only identified LRRC25 as a novel inhibitor of NF-kappaB signaling pathway, but also uncovers a new mechanism of crosstalk between NF-kappaB signaling and autophagy pathways. 29288164_The findings identify a previously unrecognized role of LRRC25 in type I interferon signaling activation by which LRRC25 acts as a secondary receptor to assist RIG-I delivery to autophagosomes for degradation in a p62-dependent manner. 30340835_LRRC25 as a critical molecular switch whose down-regulation resulted in cardiac hypertrophy in a TGF-beta1- and NF-kappaB-dependent manner. |
ENSMUSG00000049988 |
Lrrc25 |
511.841321 |
3.7141859187 |
1.893046 |
0.077177009 |
627.471287 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000177335176503195832510619478435737054690173271319778929958361838170814173809590405840156462993634477386451166321269768197553469535982376143729926186238796943734277834621328993998121674653869297 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000102645772752438054135554391075627522503413997726027048939773750319817957957634917334521594069660442946788266397481623929024396998708235723620016703436873905039888913446462603689494921901986627 |
Yes |
No |
814.0195955 |
36.7092237 |
220.7144637 |
8.4459124 |
| ENSG00000175538 |
10008 |
KCNE3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6H6 |
FUNCTION: Ancillary protein that assembles as a beta subunit with a voltage-gated potassium channel complex of pore-forming alpha subunits. Modulates the gating kinetics and enhances stability of the channel complex. Assembled with KCNB1 modulates the gating characteristics of the delayed rectifier voltage-dependent potassium channel KCNB1 (PubMed:12954870). Associated with KCNC4/Kv3.4 is proposed to form the subthreshold voltage-gated potassium channel in skeletal muscle and to establish the resting membrane potential (RMP) in muscle cells. Associated with KCNQ1/KCLQT1 may form the intestinal cAMP-stimulated potassium channel involved in chloride secretion that produces a current with nearly instantaneous activation with a linear current-voltage relationship. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JJV7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10646604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12954870}. |
3D-structure;Brugada syndrome;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, isk-related subfamily. This member is a type I membrane protein, and a beta subunit that assembles with a potassium channel alpha-subunit to modulate the gating kinetics and enhance stability of the multimeric complex. This gene is prominently expressed in the kidney. A missense mutation in this gene is associated with hypokalemic periodic paralysis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10008; |
basolateral part of cell [GO:1990794]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body membrane [GO:0032809]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; cellular chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0030644]; membrane repolarization during action potential [GO:0086011]; membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098915]; negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:1902260]; negative regulation of membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:1905025]; negative regulation of potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:1903765]; negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:1903817]; potassium ion export across plasma membrane [GO:0097623]; regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction [GO:0086091]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization [GO:0060307]; sodium ion transport [GO:0006814]; ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086005] |
11956246_Ectopic expression of KCNE3 accelerates cardiac repolarization and abbreviates the QT interval. 14504341_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15037716_The authors found MiRP2-R83H in 3 of 321 control subjects and in 5 unaffected related individuals. Provocation of an unaffected carrier with glucose or KCl did not induce weakness. 15212652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16308347_interaction of MiRP2-72 with KCNQ1-338; and MinK-59,58 with KCNQ1-339, 340 16374062_The result indicates that 112G/A SNP in the KCNE1 gene and 198T/C SNP in the KCNE3 gene could determine an increased susceptibility to develop MD. 16449802_The characterization of a missense mutation in MiRP2 that affects its phosphorylation and consequent interactions with Kv3.4 is reported. 16782062_KCNE3 also inhibits currents generated by Kv4.3 in complex with the accessory subunit KChIP2 17495071_Up-regulation and incrased activity of KV3.4 channels and their accessory subunit Mirp2 induced by amyloid peptide are involved in apoptotic neuronal death. 18209471_Abnormalities in the KCNE3 gene is a potential genetic risk factor for initiation and/or maintenance of atrial fibrillation. 19077539_KCNE variants reveal a critical role of the beta subunit carboxyl terminus in PKA-dependent regulation of the IKs potassium channel, KCNQ1. 19122847_KCNE3 plays a functional role in the modulation of I(to) in the human heart and suggest that mutations in KCNE3 can underlie the development of BrS. 19306396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19961415_The KCNE3 protein within the micellesis in monomeric form and acquires mainly alpha-helical conformation. 20034061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20034061_data show that SNPs in KCNE1 and KCNE3 are not associated with Meniere disease in Caucasians 20040519_2 of the 8 MiRP2 extracellular domain acidic residues (D54 and D55) are important for KCNQ1-MiRP2 constitutive activation. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21899751_Allele frequencies are studied for 11 known variants of KCNE3 gene, of which two (F66F and R83H) are polymorphic but are not associated with chronic tinnitus. 22190306_The results of this study indicated that Kv7.5 contributes to the spatial regulation. 22987075_A KCNE3 T4A mutation was identified in a Japanese patient presenting Brugada-pattern ECG and neurally mediated syncope. 26410412_KCNE1 and KCNE3: The yin and yang of voltage-gated K(+) channel regulation 26668384_Data show that voltage-gated potassium channel KCNE3 directly affects the S4 movement in potassium channel KCNQ1. 26718405_KCNQ1/KCNE3 channels make only a small contribution to basolateral conductance in normal colonic crypts, with increased channel activity in UC appearing insufficient to prevent colonic cell depolarization in this disease. 26890422_Based on current evidence from published studies, neither of the two variants from KCNE was significantly associated with the risk of Meniere's disease--{REVIEW} 27162025_Reported here are previously undiscovered protein-coding regions in exon 1 of hKCNE3 and hKCNE4 that extend their encoded extracellular domains by 44 and 51 residues, which yields full-length proteins of 147 and 221 residues, respectively. 27626070_Structural, computational, biochemical, and electrophysiological studies lead to an atomically explicit integrative structural model of the KCNE3-KCNQ1 complex that explains how KCNE3 induces the constitutive activation of KCNQ1 channel activity, a crucial component in K(+) recycling. 27922120_Regulation of human cardiac potassium channels by full-length KCNE3 and KCNE4 has been reported. 35716725_Comparing the structural dynamics of the human KCNE3 in reconstituted micelle and lipid bilayered vesicle environments. |
ENSMUSG00000035165 |
Kcne3 |
40.144095 |
0.3419667435 |
-1.548072 |
0.352414161 |
18.865719 |
0.00001402505835571263042205105570081613564070721622556447982788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000043262024301199372190458031228743607243814039975404739379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.8112691 |
6.1949879 |
63.0704039 |
12.0221209 |
| ENSG00000175592 |
8061 |
FOSL1 |
protein_coding |
P15407 |
|
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The Fos gene family consists of 4 members: FOS, FOSB, FOSL1, and FOSL2. These genes encode leucine zipper proteins that can dimerize with proteins of the JUN family, thereby forming the transcription factor complex AP-1. As such, the FOS proteins have been implicated as regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and transformation. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:8061; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; learning [GO:0007612]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cell cycle [GO:0045787]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation [GO:2000144]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to cAMP [GO:0051591]; response to corticosterone [GO:0051412]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to gravity [GO:0009629]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; vitellogenesis [GO:0007296] |
11912197_Molecular mechanism of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1-induced glutathione depletion in alveolar epithelial cells. Involvement of AP-1/ARE and Fra-1. 12209953_upregulation of cyclin D1 and Fra-1 in human colorectal adenocarcinomas is driven by abnormally expressed beta-catenin 12692267_The regulation by Akt3 was found to be due to two specific regions in the Fra-1 regulatory sequence which match Sp1 consensus sites 13679379_cooperative interactions between factors binding to multiple cis-elements of the -379/-283 promoter region appear to regulate TPA-induced fra-1 transcription in human cells 15608675_Fra-1 expression is associated with a more malignant cell phenotype and suggest that Fra-1 could have a pivotal role in breast cancer progression. 15615716_Delayed recruitment of Fra-1 to the IL-8 promoter provides an example how AP-1 subunits may dampen excessive chemokine synthesis. 15831677_Fra-1 may likely play an important role in the maintenance/progression of malignant gliomas 16490785_PI3K through p21-activated kinase 1 regulates FRA-1 proto-oncogene induction by cigarette smoke and the subsequent activation of the Elk1 and cAMP-response element-binding protein transcription factors 17192200_Overexpression of Fra-1, leading to a persistent high cytoplasmic accumulation, may play a role in the process of breast carcinogenesis. 17371847_Data report that the intrinsic instability of Fra-1 depends on a single destabilizer contained within the C-terminal 30 to 40 amino acids. 17572495_The activation of MMP-9 promoter is dependent upon interactions of Fra-1/c-Jun with Stat3. 17616677_FRA-1 can promote motility, invasion, and anchorage-independent growth of lung epithelial cells in vitro, but is insufficient for tumor formation 17872495_Data suggest that HGF-induced effects in some mesothelioma cells are mediated via activation of a novel PI3K/ERK5/Fra-1 feedback pathway 17882273_a large multiprotein complex, which includes Fra-1, p300, P/CAF, junD, junB, and Sp1 acts at the AP1-5 site to produce a synergistic increase in hINV gene expression 18096084_Fra-1 is associated with cell migration in human MMs and that Fra-1 modulation of CD44 may govern migration of selected MMs. 18098284_In colon cells, the induction of epithelial mesenchymal transition by oncogenic Ha-RAS could occur through the overexpression of proteins like FRA-1 and vimentin. 18172271_IL-13R alpha 2, EphA2, and Fra-1 are attractive therapeutic targets representing molecular denominators of high-grade astrocytomas. One hundred percent of GBM tumors overexpress at least one of these proteins. 18288638_Data suggest that Fra-1 enhances lung cancer epithelial cell motility and invasion by inducing the activity of matrix metalloproteinases, in particular MMP-2 and MMP-9, and EGFR-activated signaling. 18435914_A prominent role for ERK1/2 was shown in the TPA-induced activation of c-Jun regulating the Fra1 promoter. 19160107_Fra-1 might play a role in the progression and prognosis of NSCLC. 19384981_study found surface parameters for Fra-1 are similar in general to those of c-Fos and c-Jun; differences were found in the interactions of the three proteins with phospholipids 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19923172_Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays confirmed that JunB/Fra-1 proteins interact in vivo with the beta4-integrin promoter and that JunB/Fra-1 promoter occupancy is reduced during keratinocyte differentiation as well as in HPV8 E2 positive keratinocytes 20198886_Expression of the FOSL1 gene proved to substantially increase in both psoriatic lesions of the skin and atherosclerotic lesions of vessels as compared with nonlesion samples. 20353950_AP-1 (Fra-1/c-Jun)-mediated induction of expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 is required for 15S-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid-induced angiogenesis 20511396_in tumor tissue derived from highly metastatic basal-like MDA-MB231 cells, high levels of c-Jun/Fra1 complexes were detected 20663135_High FOSL1 is associated with melanoma. 21088499_FRA1 takes part in a control of architecture and migratory nature of GBM cells. It is a phosphorylated factor that transactivates JunB with which it makes effectively AP-1 pairs. 21371080_A high frequency of Fra-1 in DCIS tumours may be associated with early events in breast carcinogenesis. Although Fra-1 expression correlated with features of a more aggressive phenotype in IDC, no relationship with overall survival was found. 21460858_Fra-1 is an important mediator of interstitial lung disease following gefitinib treatment 21526963_Activated nuclear factor kappaB and Fos-related antigen 1 are elevated in epithelial cells in lung tissues of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. 21558934_RT-PCR showed that FOSL1 from osteoblasts from Pfeiffer syndrome grown on PLPG acid plates were upregulated after 30 days. 21640141_Two AP-1 components, c-Jun and Fra-1, were phosphorylated, and bound to the AP-1 binding site of the MMP-1 promoter in 143B cells. 21708480_study shows that YAP could promote cell proliferation by activating transcription factor Fra-1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 21822309_study reports Fra-1 is highly expressed in the muscle-invasive form of bladder cancer and to a lesser extent in superficial bladder cancer; gene coding for AXL tyrosine kinase is directly upregulated by Fra-1 in bladder cancer and other cell lines; data demonstrate that AXL mediates the effect of Fra-1 on tumour cell motility but not on cell proliferation 21840727_data suggest the involvement of an injury-induced Fra-1 transcription factor as a regulator of keratinocyte gene expression, which might act as an antagonistic player to restrict epithelial-driven angiogenic responses during normal skin flap integration. 21969367_Molecular characterization of the microRNA-138-Fos-like antigen 1 (FOSL1) regulatory module in squamous cell carcinoma. 22028113_This study demonstrated ESCC patients positive for Fra-1 to be associated with poor prognosis. The findings also suggest that Fra-1 regulation may play an important role in the progression of ESCC. 22198213_identified Fra-1 as a new target of miR-34a and demonstrated that miR-34a inhibits Fra-1 expression at both protein and messenger RNA levels; p53 indirectly regulates Fra-1 expression via a miR-34a-dependant manner in colon cancer cells 22235402_Enhanced FOSL1 expression significantly correlated with high psoriasis area and severity index. High level of FOSL1 gene expression was proposed to be a marker of pathological process activity in psoriasis. 22286759_PKCtheta signalling as an important regulator of Fra-1 accumulation in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cells. 22411068_the molecular data suggest that the functional outcome of the 11q12 rearrangements is deregulated expression of FOSL1. 22461694_Rhinovirus-induced MMP-9 expression is dependent on Fra-1, which is modulated by formoterol and dexamethasone. 22514348_Fra-1 was induced by Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A and is essential for LMP2A-triggered MMP9 expression. 22911824_Fra-1 mediates anti-fibrotic effects in the lung through the modulation of proinflammatory, profibrotic and fibrotic gene expression. 23001043_MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. 23301044_Fra-1 and c-Fos have roles in supporting growth of human malignant breast tumors by activating membrane biogenesis at the cytoplasm 23483055_Identification of a pharmacologically tractable Fra-1/ADORA2B axis promoting breast cancer metastasis. 23625206_Data indicate that estrogen induced the expression of c-Jun, Fra-1, c-Fos, cyclin D1 and cyclin E1 while tamoxifen (TMX) decreased the expression. 24084233_we review the current knowledge of av and b3 transcriptional regulation in endothelial cells and discuss the role of FOSL1 in angiogenesis 24604526_CD44 dysregulated the activation of the Fra1 gene. The interaction of Fra-1 and CD44 may therefore be important in cervical carcinoma. 24652774_These results suggest that FOSL1 may be related to IgAN severity. 24658684_FRA1 plays an important role in mediating cross talk between oncogenic RAS-ERK and TGFbeta signaling networks during tumor progression. 25175497_Fra1 promotes the growth of HaCaT cells in vitro by arresting the cell cycle and inhibiting cell apoptosis. 25301070_Fra-1 induces critical changes in the expression of tgfb1 and Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition transcription factors through direct binding to the tgfb1, zeb1 and zeb2 genomic regulatory regions. 25651840_Results suggested that Fra-1 expression is low in cervical cancer tissues and promotes apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by p53 signaling pathway. 25666264_High Fra-1 expression significantly correlates with shorter overall survival. 25750173_Intense immunohistochemical staining of Fra-1 was observed at the tumor marginal area adjacent to inflammatory cells and in parallel with IL-6 secretion and STAT3 activation in colorectal cancer tissues. 26330014_We identified and confirmed that Fra-1 affected the expression level of CTTN and EZR in vitro through LC-MS/MS analyses and western blot technology. 26337460_miR-195 can repress the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells via regulating Fra-1 26549498_Results suggest that Fra-1 is upregulated in lung cancer tissues and functions by affecting the P53 signaling pathway. 26646695_Our results demonstrate that Fra-1 is an important determinant of the metastatic potential of human colon cancer cells, and that the Fra-1 classifier can be used as a prognostic predictor in colon cancer patients. 26975631_SIRT1 expression correlated positively with Fra-1 expression, metastasis and overall survival in patients with colorectal cancer 27002720_Up-regulation of Fra-1 appeared in retinal ganglion cells following light-induced retina damage. 27134167_HGF-induced FRA1 activation is associated with the fibrosis-dependent development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 27144339_the results indicate that FRA1 promotes cancer growth through AKT, and enhances cancer cell migration through JNK/c-Jun, pinpointing FRA1 as a key integrator of JNK and AKT signaling pathways and a potential therapeutic target for squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 27220889_MUC1 enhancement of ERK activation influences FRA-1 activity to modulate tumor migration, invasion and metastasis in a subset of pancreatic cancer cases 27685628_a Fra-1-miR-134 axis drives a positive feedback loop that amplifies ERK/JNK signaling and reduces chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells. 27816489_PKCtheta;-induced phosphorylations control the ability of Fra-1 to stimulate gene expression and breast cancer cell migration. 27882471_High FRA1 expression is associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 28169308_Our findings indicated that functional SNP rs1892901 in FOSL1 might affect the expression of FOSL1, and ultimately increase the risk of gastric cancer. 28220783_High FOS-like antigen 1 (FOSL1) expression with mutant KRAS protein lung and pancreatic cancer patients showed the worst survival outcome. 28232512_These findings indicate that an aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin signalling leads to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance of glioma via Fra1 induction, which suggests novel therapeutic strategies for the malignant disease. 28386843_constitutive activation and non-regulation of Fra-1 by bicalutamide in PC-3 cells suggested that Fra-1, probably a key component, involved in transition of aggressive androgen-independent PC-3 cells with poor prognosis. 28481878_Study shows that FOSL1 is the main immediate early AP-1 member induced by melanoma oncogenes; found that FOSL1 is involved in melanoma cell migration as well as cell proliferation and anoikis-independent growth. 28653890_Multivariate analysis identified Fra-1 as an independent prognostic factor. Fra-1 may be involved in the progress of hepatocellular carcinoma and could be a promising molecular candidate in the diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. 28790303_High expression of c-Jun or Fra-1 was associated with poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. 29112457_FOSL1 is a determinant of lung cancer in vivo and regulates tumor cell proliferation and survival, largely in the context of KRAS mutations through amphiregulin and cell survival gene regulation. 29257201_Fra1 inhibited the protein levels of Bcl2, cMyc, Survivin, and BclxL. Fra1 overexpression in intestinal mucosal epithelial cells may restrain damage repair after intestinal mucosal injury in inflammatory bowel disease remittent period through weakening the protective effect of intestinal mucosa, thus increasing the risk of recurrence. 29305863_Taken together, our results indicated that miR-449 overexpression inhibited osteogenic differentiation of HG-FFA-treated hBMSCs through the Sirt1/Fra-1 signal pathway. 29382358_Transient knockdown of urokinase/plasminogen activator urokinase receptor (uPAR) in basal-like breast cancer cells grown on vitronectin reduces FRA-1 phosphorylation and stabilization; and uPAR and FRA-1 are required for vitronectin-induced cell invasion 29384218_results reveal that miR-130a directly targets FOSL1 and suppresses the inhibition of ZO-1, thus inhibiting cancer cell migration and invasion, in triple-negative breast cancer. 29807388_the overexpression of Fra1 disrupted inflammatory cytokine secretion by medullary thymic epithelial cells in the myasthenia gravis thymus 29914371_Findings suggest that fos-related antigen 1 (Fra-1) transcription factor leads to the production of interleukin 11 (IL-11) protein in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients. 29993138_This study revealed for the first time that Fra-1, c-Jun and c-Fos were overexpressed in odontogenic keratocysts and had a close correlation with proliferation and anti-apoptosis potential of odontogenic keratocysts. 30318470_FRA1-overexpressing keratinocytes produce elevated amounts of proinflammatory cytokines and active matrix metalloproteases, leading to the induction of the autoinflammatory loop and paracrine activation in neighbor cells. Therefore, the elevated expression of FRA1 and its altered transcriptional regulation in the skin of patients with psoriasis is an important driving factor in the development of psoriatic plaques. 30563891_Id1 was regulated by the KRAS oncogene through JNK, and loss of Id1 resulted in downregulation of elements of the mitotic machinery via inhibition of the transcription factor FOSL1 and of several kinases within the KRAS signaling network. 30575900_FOSL1 can promote the occurrence and progression of prostate cancer by altering the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process of cells. 30782279_mRNA expression of Fra-1 was significantly lower in the ideal efficacy group than in the poor efficacy group 30807813_These results demonstrate that the upregulation of FRA-1 in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells plays a key role in the carcinogenic process. 30935763_FOSL1 is an independent prognostic biomarker of gastric cancer 30990796_the Fra-1/ARG1 ratio in synovial macrophages was related to RA disease activity. In conclusion, these data suggest that Fra-1 orchestrates the inflammatory state of macrophages by inhibition of Arg1 expression and thereby impedes the resolution of inflammation. 31015574_reveal a role for DDX5 as a regulatory protein of Fra-1 signaling and suggest DDX5 as a potential therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer 31248836_Postoperative detection of TCF7, c-Myc, and FOSL1 may be useful for stratifying patients with a high risk of unfavorable prognosis, and suppressing TCF7 or its downstream effectors may be a promising strategy for the treatment of Perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (PHCC) 31612408_This review presents a detailed description of the regulatory factors and functions of FRA1, as well as the expression and function of FRA1 in various tumors. 31672492_Our results show that the loss of miR-4516 from CAF-derived exosomes is associated with FOSL1-dependent triple negative breast cancer progression and suggest that miR-4516 can be used as an anti-cancer drug for triple negative breast cancer. 31937587_Estrogen-induced FOS-like 1 regulates matrix metalloproteinase expression and the motility of human endometrial and decidual stromal cells. 32124141_All-trans retinoic acid enhances the effect of Fra-1 to inhibit cell proliferation and metabolism in cervical cancer. 32271412_HOXA10 promotes the development of bladder cancer through regulating FOSL1. 32305558_ETV4 is a theranostic target in clear cell renal cell carcinoma that promotes metastasis by activating the pro-metastatic gene FOSL1 in a PI3K-AKT dependent manner. 32385348_The nuclear oncoprotein Fra-1: a transcription factor knocking on therapeutic applications' door. 32661324_AR-induced long non-coding RNA LINC01503 facilitates proliferation and metastasis via the SFPQ-FOSL1 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 32753701_FOSL1 is a novel mediator of endotoxin/lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary angiogenic signaling. 32945473_Xanthohumol targets the ERK1/2Fra1 signaling axis to reduce cyclin D1 expression and inhibit nonsmall cell lung cancer. 33389529_FRA-1 suppresses apoptosis of Helicobacter pylori infected MGC-803 cells. 33450386_FOSL1 promotes tumorigenesis in colorectal carcinoma by mediating the FBXL2/Wnt/beta-catenin axis via Smurf1. 33456361_Lipopolysaccharide Affects the Proliferation and Glucose Metabolism of Cervical Cancer Cells Through the FRA1/MDM2/p53 Pathway. 33533919_Fra-1 regulates its target genes via binding to remote enhancers without exerting major control on chromatin architecture in triple negative breast cancers. 33705609_SOX9 in prostate cancer is upregulated by cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote tumor progression through HGF/c-Met-FRA1 signaling. 33794365_FOSL1 promotes metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through super-enhancer-driven transcription program. 33887357_FOSL1 promotes cholangiocarcinoma via transcriptional effectors that could be therapeutically targeted. 34230127_FosL1 Regulates Regional Metastasis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Promoting Cell Migration, Invasion, and Proliferation. 34282187_The role of FOSL1 in stem-like cell reprogramming processes. 34320363_SMAD4 represses FOSL1 expression and pancreatic cancer metastatic colonization. 34399888_NF1 regulates mesenchymal glioblastoma plasticity and aggressiveness through the AP-1 transcription factor FOSL1. 34420141_Silent FOSL1 Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Glioma Stem Cells by Down-Regulating miR-27a-5p. 34432948_Pharmacological Inhibition of Core Regulatory Circuitry Liquid-liquid Phase Separation Suppresses Metastasis and Chemoresistance in Osteosarcoma. 34907034_Transcription Factor FOSL1 Enhances Drug Resistance of Breast Cancer through DUSP7-Mediated Dephosphorylation of PEA15. 35163444_Role of the Transcription Factor FOSL1 in Organ Development and Tumorigenesis. 35484756_Fos-Related Antigen 1 May Cause Wnt-Fzd Signaling Pathway-Related Nephroblastoma in Children. 35511484_A systematic comparison of FOSL1, FOSL2 and BATF-mediated transcriptional regulation during early human Th17 differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000024912 |
Fosl1 |
79.559487 |
2.9483318037 |
1.559899 |
0.186989827 |
71.809981 |
0.00000000000000002369507132339038485619848032034174658026910653891346919541760485117265488952398300170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000184851613495371074163694281790910844237423184656735064557153691566782072186470031738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
121.6676286 |
13.3671945 |
41.4885241 |
3.7985460 |
| ENSG00000175697 |
165829 |
GPR156 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFN8 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large superfamily of cell surface receptors characterized by 7 helical transmembrane domains, together with N-terminal extracellular and C-terminal intracellular domains.[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:165829; |
G protein-coupled receptor heterodimeric complex [GO:0038039]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled GABA receptor activity [GO:0004965]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway [GO:0007214] |
20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000046961 |
Gpr156 |
6.106831 |
6.9308617642 |
2.793035 |
0.774659823 |
15.457937 |
0.00008436192850727269681131159639875249922624789178371429443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000234365154294625466831897275810092651227023452520370483398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.3193879 |
5.5602146 |
1.6555773 |
0.7459846 |
| ENSG00000175745 |
7025 |
NR2F1 |
protein_coding |
P10589 |
FUNCTION: Coup (chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter) transcription factor binds to the ovalbumin promoter and, in conjunction with another protein (S300-II) stimulates initiation of transcription. Binds to both direct repeats and palindromes of the 5'-AGGTCA-3' motif. Represses transcriptional activity of LHCG. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10644740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11682620}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear hormone receptor and transcriptional regulator. The encoded protein acts as a homodimer and binds to 5'-AGGTCA-3' repeats. Defects in this gene are a cause of Bosch-Boonstra optic atrophy syndrome (BBOAS). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:7025; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; retinoic acid-responsive element binding [GO:0044323]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11811951_Inhibit aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene expression 11934895_Regulation of retinoic acid-induced inhibition of AP-1 activity by orphan receptor chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor. 12093745_Formation of an hER alpha-COUP-TFI complex enhances hER alpha AF-1 through Ser118 phosphorylation by MAPK. 12551987_regulates transcription of hepatitis B virus 12972613_Transcription of the LHR gene is repressed by EAR3. 15157742_COUP-TF may be involved in repression of the human MGP gene promoter at the myoblast stage 17009409_findings show that enhancer II of HBV genotype A is also repressed by COUP-TF1; in contrast, two different enhancer II constructs of HBV genotype D were activated by COUP-TF1 17674191_COUP-TFI selectively regulates the expression of endogenous E2-target genes and consequently modifies ER alpha positive mammary cells response to E2. 18199540_Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor D by hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha and chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factors 1 and 2. 19112178_A chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor I (COUP-TFI) complex represses expression of the gene encoding tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8). 19526345_study identifies two unique corticotroph tumor populations which differ in their expression of COUP-TFI, the presence of which occurs more frequently in macroadenomas. 19578876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20007910_Transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms involving NR2F1 and IRE1beta ensure low microsomal triglyceride transfer protein expression in undifferentiated intestinal cells and avoid apolipoprotein B lipoprotein biosynthesis. 20111703_provide detailed experimental validation of each step and, as a proof of principle, utilize the methodology to identify novel direct targets of the orphan nuclear receptor NR2F1 (COUP-TFI) 20306291_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22357705_a novel mechanism of MTP repression that involves binding of NR2F1 to the DR1 element and recruitment of corepressors 23975195_COUP-TFI and related NRs such as the COUPTFs and PNR can selectively associate with the developmental corepressor BCL11A via a conserved motif F/YSXXLXXL/Y within the RID1 and RID2 domains. The interaction with BCL11A facilitates COUP-TFII-mediated repression of the RARb2 gene. 23975195_Interaction of NSD1 with the NR2E/F subfamily including COUP-TFI, COUP-TFII, EAR2 and TLX requires an F/YSXXLXXL/Y motif. Interactions of NSD1 with liganded NRs require an overlapping LXXLL motif. 24462372_NR2F1 has an important role in the development of the visual system and that haploinsuffiency can lead to optic atrophy with intellectual impairment. 24906407_our mechanistic in vitro assays and in vivo results suggest that a reduction in chemokine CXCL12 expression, with an enhancement of CXCR4 expression, provoked by COUP-TFI, could be associated with an increase in the invasive potential of breast cancer 25787832_COUP-TFII is expressed in a diverse subset of GABAergic interneurons predominantly innervating small dendritic shafts originating from both interneurons and pyramidal cells. 26986877_Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome (BBSOAS)encompasses a broad range of clinical phenotypes. Functional studies help determine the severity of novel NR2F1 variants. Some genotype-phenotype correlations seem to exist, with missense mutations in the DNA-binding domain causing the most severe phenotypes 28922831_fifth of COUP-TFI cells also co-expressed COUP-TFII, and cells expressing either transcription factor followed posterior or anterio-lateral pathways into the cortex 28963436_Whole-exome sequencing identified a novel missense NR2F1 variant in each case, Cys86Phe in the DNA-binding domain in Case 1, and a Leu372Pro in the ligand-binding domain in Case 2. Using molecular modeling we are also able to demonstrate the putative effect of the two missenses on protein function, generating a hitherto undescribed molecular model for the ligand-binding domain of NR2F1 in the process. 30322396_Findings from basic biological analysis of disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) dormancy to the clinical situation and supports further clinical studies of nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member 1 (NR2F1) as a marker of dormancy. 30445268_functional studies on NR2F1 transfected cells, during osteoblast differentiation in combination with TGFbeta1 and BMP-2, showed that TGFb1 does not recover osteoblast differentiation, whereas BMP-2 rescues osteoblast differentiation in NR2F1 siRNA transfected cells. Thus, our results showed that BMP-2 could intervene in NR2F1 down-regulated signaling pathways to recover osteoblast differentiation. 31357956_NR2F1 may be an underlying mechanism of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma recurrence and metastasis via regulating tumor cell dormancy through CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway. 31530388_The NR2F1-induced NR2F1-AS1 promotes ESCC progression through activation of Hedgehog signaling pathway. 31729143_Clinical and neurocognitive issues associated with Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome: A case study. 31913971_Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf Optic Atrophy Syndrome Presenting as New-Onset Psychosis in a 32-Year-Old Man: A Case Report and Literature Review. 31994002_lncRNA NR2F1-AS1 Regulates miR-17/SIK1 Axis to Suppress the Invasion and Migration of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. 32275123_Phenotypic expansion of Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome and further evidence for genotype-phenotype correlations. 32484994_NR2F1 regulates regional progenitor dynamics in the mouse neocortex and cortical gyrification in BBSOAS patients. 33661352_Dynamic expression of NR2F1 and SOX2 in developing and adult human cortex: comparison with cortical malformations. 34475402_Long non-coding RNA NR2F1-AS1 induces breast cancer lung metastatic dormancy by regulating NR2F1 and DeltaNp63. 34686322_The Parkinson's-disease-associated mutation LRRK2-G2019S alters dopaminergic differentiation dynamics via NR2F1. 34738863_Long noncoding RNA NR2F1-AS1 plays a carcinogenic role in gastric cancer by recruiting transcriptional factor SPI1 to upregulate ST8SIA1 expression. 34812843_An NR2F1-specific agonist suppresses metastasis by inducing cancer cell dormancy. 34837429_NR2F1 database: 112 variants and 84 patients support refining the clinical synopsis of Bosch-Boonstra-Schaaf optic atrophy syndrome. 35462433_Metabolic Switch Under Glucose Deprivation Leading to Discovery of NR2F1 as a Stimulus of Osteoblast Differentiation. 35471456_NR2F1 Is a Barrier to Dissemination of Early-Stage Breast Cancer Cells. 35936005_METTL3 inhibits inflammation of retinal pigment epithelium cells by regulating NR2F1 in an m(6)A-dependent manner. |
ENSMUSG00000069171 |
Nr2f1 |
29.923771 |
0.2464563976 |
-2.020596 |
0.376369053 |
28.591523 |
0.00000008937260648985462740936035978128737511383405944798141717910766601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000354226549889971579788148017819970903019566321745514869689941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.9418888 |
2.7200008 |
45.1141460 |
6.9887456 |
| ENSG00000175866 |
10458 |
BAIAP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UQB8 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein that links membrane-bound small G-proteins to cytoplasmic effector proteins. Necessary for CDC42-mediated reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and for RAC1-mediated membrane ruffling. Involved in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by WASF family members and the Arp2/3 complex. Plays a role in neurite growth. Acts syngeristically with ENAH to promote filipodia formation. Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in response to bacterial infection. Participates in actin bundling when associated with EPS8, promoting filopodial protrusions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11130076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11696321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14752106, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17115031, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19366662}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
The protein encoded by this gene has been identified as a brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor (BAI1)-binding protein. This adaptor protein links membrane bound G-proteins to cytoplasmic effector proteins. This protein functions as an insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate and suggests a role for insulin in the central nervous system. It also associates with a downstream effector of Rho small G proteins, which is associated with the formation of stress fibers and cytokinesis. This protein is involved in lamellipodia and filopodia formation in motile cells and may affect neuronal growth-cone guidance. This protein has also been identified as interacting with the dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy gene, which is associated with an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:10458; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine cytoplasm [GO:0061846]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; neuron projection branch point [GO:0061845]; neuron projection terminus [GO:0044306]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic cytosol [GO:0099524]; postsynaptic density, intracellular component [GO:0099092]; presynaptic cytosol [GO:0099523]; rough endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005791]; ruffle [GO:0001726]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; cytoskeletal anchor activity [GO:0008093]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; proline-rich region binding [GO:0070064]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; transcription coregulator binding [GO:0001221]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus [GO:0071364]; cellular response to L-glutamate [GO:1905232]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008286]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061003]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; protein localization to synapse [GO:0035418]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of modification of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton [GO:1905274]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
14596909_LIN7B is a partner of IRSp53 anchoring the actin-based membrane cytoskeleton at cell-cell contacts. 14752106_IRSp53, when activated by small GTPases, participates in F-actin reorganization not only in an SH3-dependent manner but also in a manner dependent on the activity of the IRSp53/MIM homology domain 15635447_IRSp53 comprises a central SH3 domain, which binds to proline-rich regions of a wide range of actin regulators, and a conserved N-terminal IRSp53/MIM homology domain that harbours F-actin-bundling activity. Presents crystal structure of this novel domain 15673667_These results suggest that PSD-95 interaction is an important determinant of synaptic IRSp53 localization and that the SH3 domain of IRSp53 links activated Rac1/Cdc42 to downstream effectors for the regulation of spine morphogenesis. 16702231_Therefore, IRSp53 optimizes the activity of the WAVE2 complex in the presence of activated Rac and PIP(3). 17003044_The mechanism of membrane deforamtion induced by the IRSp53 RCB domain is reported. 17115031_These results support a model whereby the synergic bundling activity of the IRSp53-Eps8 complex, regulated by Cdc42, contributes to the generation of actin bundles, thus promoting filopodial protrusions. 17371834_Together, these data reveal that interplay between actin dynamics and a novel membrane-deformation activity promotes cell motility and morphogenesis. 18417251_tyrosine 310 as a primary site of tyrosine phosphorylation in response to insulin signalling and we have shown that although IRSp53 is tyrosine phosphorylated in response to epidermal growth factor receptor signalling, tyrosine 310 is not crucial. 19054385_LIN7-IRSp53 association plays a role during assembly of functional tight junctions and surface polarization in epithelial cells 19193906_Both spatial learning and novel object recognition are impaired in transgenic mice deficient of IRSp53 expression. 19286134_The authors show that IRSp53 family members, key regulators of membrane and actin dynamics, directly interact with both Tir and EspF(U).[Tir & EspFU] 19460367_SPIN90 and IRSp53 positively cooperated to mediate Rac activation, and co-expression of SPIN90 and IRSp53 in COS-7 cells led to the complex formation of SPIN90-IRSp53 in the leading edge of cells 19733838_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19733838_this study support the participation of BAIAP2 in the continuity of ADHD across life span,in some of the populations analyzed, suggest that genetic factors potentially influencing abnormal cerebral lateralization may be involved in this disorder. 19762983_The authors demonstrated that the association between the enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 EspFu and IRSp53 induces dynamic membrane remodeling in epithelial cells. 19933840_this work does not conform to current views that the inverse-BAR domain or Cdc42 controls IRSp53 localization but provides an alternative model of how IRSp53 is recruited (and released) to carry out its functions at lamellipodia and filopodia. 20360004_IRSp53 and spinophilin regulate localized Rac activation by T-lymphocyte invasion and metastasis protein 1 20418908_IRSp53, through its interaction with Eps8, not only affects cell migration but also dictates cellular growth in cancer cells. 20621182_Suppression of IRSp53 expression inhibited IGF-I-induced membrane targeting and local accumulation of WAVE2 at the leading edge of cells. 20678498_Cdc42 regulates the activity of IRSp53 by regulating the IRSp53-WIRE interaction as well as localization of the complex to plasma membrane to generate filopodia. 20888579_The results of this study and the supporting evidence highlighted previously suggest that the BAIAP2 gene may be involved in autism susceptibility. 21542353_A molecular dynamics study of the interaction between domain I-BAR of the IRSp53 protein and negatively charged membranes 21814501_Studied generation of filopodia with regards to the dynamic interaction established by Eps8, IRSp53 and VASP with actin filaments. 21893288_Structural basis for complex formation between human IRSp53 and the translocated intimin receptor Tir of enterohemorrhagic E. coli 22179776_mDia1 and WAVE2 are important Src homology 3 domain partners of IRSp53 in forming filopodia. 22767515_LIN7 is a novel regulator of IRSp53. 24377651_These above results indicated the possible involvement of BAIAP2 in the etiology of attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity, especially ADHD-I. 24392092_BAIAP2 is related to emotional modulation of human memory strength. 24584464_IRSp53 adopts a closed inactive conformation that opens synergistically with the binding of human Cdc42 to the CRIB-PR and effector proteins, such as the tumor-promoting factor Eps8, to the SH3 domain. 25031323_determined the alpha-synuclein-binding domain of beta-III tubulin and demonstrated that a short fragment containing this domain can suppress alpha-synuclein accumulation in the primary cultured cells 26275848_Results suggest the hypothesis that defective actin/membrane modulation in IRSp53-deficient dendritic spines may lead to social and cognitive deficits through N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor dysfunction. 26469246_dimers sense negative membrane curvature, display a non-monotonic sorting with curvature, and expand the membrane tube at high imposed tension while constricting it at low tension 27320196_Overexpression of LIN7 or IRSp53 did not prevent the formation of hyperfused mitochondria in cells coexpressing the Drp1 K38A mutant, thus suggesting that LIN7-IRSp53 complex requires functional Drp1 to regulate mitochondrial morphology. 28195572_BAIAP2 is a candidate gene for mediating dendritic spine density abnormalities in schizophrenia. Data suggest that altered DNA methylation in schizophrenia may be a mechanism for schizophrenia-related dendritic spine density reductions. 28938222_A BAIAP2 polymorphism, rs8079626, affects medial frontal gyrus and inferior parietal lobe connectivity in attention deficit hyperactivity order adults. 29743604_Coincident with the loss of PICK1 by GBF1-activated ARF1, CDC42 recruitment leads to the activation of IRSp53 and the ARP2/3 complex, resulting in a burst of F-actin polymerisation potentially powering scission. 30696821_IRSp53 heterodimer with only one subunit is phosphorylated, and each subunit of IRSp53 independently binds one 14-3-3 dimer. 30893014_Phosphorylation-dependent inhibition of IRSp53 by 14-3-3 counters activation by Cdc42 and cytoskeletal effectors, resulting in down-regulation of filopodia dynamics and cancer cell migration. In serum-starved cells, increased IRSp53 phosphorylation triggers 14-3-3 binding, which inhibits filopodia formation and dynamics, irrespective of whether IRSp53 is activated by Cdc42 or downstream effectors (Eps8, Ena/VASP). 32388796_BAIAP2 rs8079781, postnatal smoking exposure, and emotional problems in Japanese children aged 5 years: the Kyushu Okinawa Maternal and Child Health Study. 32535200_IRSp53 is a novel interactor of SHIP2: A role of the actin binding protein Mena in their cellular localization in breast cancer cells. 33506012_Insulin Receptor Substrate p53 Ameliorates High-Glucose-Induced Activation of NF-kappaB and Impaired Mobility of HUVECs. 34523824_Genetic variation in genes regulating skeletal muscle regeneration and tissue remodelling associated with weight loss in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 34839189_Impaired prepulse inhibition in mice with IRSp53 deletion in modulatory neurotransmitter neurons including dopamine, acetylcholine, oxytocin, and serotonin. |
ENSMUSG00000025372 |
Baiap2 |
140.331092 |
2.0579205732 |
1.041187 |
0.188851981 |
29.951772 |
0.00000004429269721692828537732539682936216962616526870988309383392333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000180497021237399646272203516429721847913469900959171354770660400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
187.4933816 |
21.6970384 |
91.7242942 |
7.9469268 |
| ENSG00000175874 |
200407 |
CREG2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IUH2 |
|
Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to be located in Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:200407; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794] |
12408961_CREG2 are putative secreted glycoproteins and may be novel neuronal extracellular molecules. |
ENSMUSG00000050967 |
Creg2 |
27.493012 |
0.3012811740 |
-1.730818 |
0.364582335 |
23.166007 |
0.00000148601051991737795496489969032660738434969971422106027603149414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005154762696587660833133504034719862829660996794700622558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8885586 |
2.8291734 |
36.3434190 |
5.8538042 |
| ENSG00000175946 |
340359 |
KLHL38 |
protein_coding |
Q2WGJ6 |
|
Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:340359; |
|
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 34050138_KLHL38 involvement in non-small cell lung cancer progression via activation of the Akt signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000022357 |
Klhl38 |
11.616792 |
0.4071767486 |
-1.296273 |
0.483452566 |
7.357909 |
0.00667684033332734388349605225698724098037928342819213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013290649132826917733218863304500700905919075012207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
6.4523793 |
2.6076191 |
15.8006719 |
4.1226395 |
| ENSG00000176049 |
9832 |
JAKMIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q96AA8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is reported to be a component of the Golgi matrix. It may act as a golgin protein by negatively regulating transit of secretory cargo and by acting as a structural scaffold of the Golgi. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:9832; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017] |
17572408_NECC 1 & 2 proteins primarily expressed in (neuro)endocrine tissues in vertebrates thus supporting a role for these proteins in the regulated secretory pathway. 19845895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 30796769_individuals with SNP62 (rs12653715 G/C) who were GG homozygous had a significantly increased risk of Graves' disease. The transmission disequilibrium test (TDT) indicated that SNP62 (rs12653715) and SNP63 (rs12653081) loci in the Janus kinase and microtubule interacting protein 2 (JAKMIP2) gene showed dominant transmission from heterozygous parents to the affected offspring. |
ENSMUSG00000024502 |
Jakmip2 |
13.274330 |
8.6294422317 |
3.109267 |
0.845615643 |
11.116328 |
0.00085571027270384353389381937304847269842866808176040649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002019875839614381895364969565775936644058674573898315429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.3049372 |
8.8259091 |
1.7641014 |
0.6957869 |
| ENSG00000176124 |
10301 |
DLEU1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11406609_Leu1 seems to be only one of the smallest splicing variants of a large gene termed BCMS. 19260139_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19347735_propose that the underlying pathomechanism of CLL involves co-regulation of miRNA genes miR-16-1 and miR-15a by the two long non-coding RNA genes DLEU1 and DLEU2. 23593011_we describe an example where two lncRNA genes (DLEU1 and DLEU2) are epigenetically deregulated together with a cluster of neighboring protein-coding tumor suppressor genes in almost all patients suffering from chronic lymphocytic leukemia 28427156_Data suggest that DLEU1 may in part function as a tumor suppressor gene and confer chemoimmunotherapy resistance in children and adolescents with Burkitt lymphoma. 28598010_It has been suggested that through interaction with miR-490-3p DLEU1 may influence the expression of CDK1, CCND1 and SMARCD1 protein, subsequently promoting the development and progression of ovarian carcinoma. 29738550_In two cohorts with available data, we identified one intronic SNP (rs13361131) in myosin X gene (MYO10) associated with C17:0 level (P = 1.37x10-8), and two intronic SNP (rs12874278 and rs17363566) in deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 1 (DLEU1) region associated with C19:0 level (P = 7.07x10-9) 29745433_lncRNA DLEU1 combines with mTOR and then increases the expression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to promote endometrial carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression. Silence of mTOR after up-regulation of lncRNA DLEU1 resulted in decrease of cell viability, migration, and invasion and increase of apoptosis. 30001771_Our findings indicate that DLEU1 contributes to endometrial cancer development by sponging miR-490 to regulate SP1 expression 30098595_Data found that DLEU1 was up-regulated in CRC tissues. Its overexpression promoted CRC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. DLEU1 co-localized with SMARCA1 in CRC, and is indispensable for the deposition of SMARCA1 at the promoter of KPNA3 gene. Collectively, DLEU1 recruited SMARCA1 to epigenetically activate KPNA3, thereby promoting proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer. 30382579_Long noncoding RNA DLEU1 aggravates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis via the miR-381/CXCR4 30551552_DLEU1 promoted tumorigenesis and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. 30793303_Up regulation of DLEU1 expression by epigenetic modification promotes tumorigenesis in human cancer 31257517_Small interfering RNA demonstrated that silencing DLEU1 downregulated TRAF4. The viability of Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)cells was significantly decreased following RNA interference with DLEU1 and TRAF4 production. 31379208_Long noncoding RNA DLEU1 aggravates osteosarcoma carcinogenesis via regulating the miR-671-5p/DDX5 axis 31702026_these results indicated a prooncogenic role of DLEU1 in the progression and development of renal cell carcinoma via modulation of the Akt pathway and EMT phenotype. 31713587_SP1-DLEU1-miR-4429 feedback loop promotes cell proliferative and anti-apoptotic abilities in human glioblastoma. 31841195_LncRNA DLEU1/microRNA-300/RAB22A axis regulates migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. 33113626_[Deleted in lymphocytic leukemia 1 promoted proliferation and apoptosis of nephroblastoma cells through regulating miR-513a-5p and RANBP2 pathway]. 33170430_Silencing of lncRNA DLEU1 inhibits tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer via regulating miR-429/TFAP2A axis. 33880596_Knockdown of lncRNA DLEU1 inhibits the tumorigenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of miR1495p/CDK6 axis. 34650128_DLEU1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression by activating interferon-stimulated genes. 34738190_Overexpression of lncRNA DLEU1 in Gastric Cancer Tissues Compared to Adjacent Non-Tumor Tissues. 34740384_LncRNA DLEU1 is overexpressed in premature ovarian failure and sponges miR-146b-5p to increase granulosa cell apoptosis. 35014679_Survivalrelated DLEU1 is associated with HPV infection status and serves as a biomarker in HPVinfected cervical cancer. 35619131_DLEU1 promotes cell survival by preventing DYNLL1 degradation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35647200_lncRNA DLEU1 Modulates Proliferation, Inflammation, and Extracellular Matrix Degradation of Chondrocytes through Regulating miR-671-5p. 35853854_Long non-coding RNA DLEU1 promotes malignancy of breast cancer by acting as an indispensable coactivator for HIF-1alpha-induced transcription of CKAP2. 35864972_YY1-induced DLEU1/miR-149-5p Promotes Malignant Biological Behavior of Cholangiocarcinoma through Upregulating YAP1/TEAD2/SOX2. 36039933_LncRNA DLEU1 facilitates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by miR-126-5p/GAB1 axis. |
|
|
184.140652 |
5.0739812338 |
2.343118 |
0.377189291 |
35.328289 |
0.00000000278556459375465057600017614914972990947106268322386313229799270629882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012788470732136436229221518377872218730217923621239606291055679321289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
248.9219085 |
61.0176685 |
49.4711825 |
8.8261810 |
| ENSG00000176155 |
284001 |
CCDC57 |
protein_coding |
Q2TAC2 |
FUNCTION: Pleiotropic regulator of centriole duplication, mitosis, and ciliogenesis. Critical interface between centrosome and microtubule-mediated cellular processes. Centriole duplication protein required for recruitment of CEP63, CEP152, and PLK4 to the centrosome. Independent of its centrosomal targeting, localizes to and interacts with microtubules and regulates microtubule nucleation, stability, and mitotic progression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32402286}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in several processes, including G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle; cilium assembly; and microtubule cytoskeleton organization. Located in centriolar satellite; centriole; and spindle microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284001; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; spindle microtubule [GO:0005876]; centriole replication [GO:0007099]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; microtubule nucleation [GO:0007020]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045931] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 32402286_CCDC57 Cooperates with Microtubules and Microcephaly Protein CEP63 and Regulates Centriole Duplication and Mitotic Progression. |
ENSMUSG00000048445 |
Ccdc57 |
226.617559 |
2.6619137617 |
1.412464 |
0.422396409 |
10.772285 |
0.00103031254682163942587580507392885920125991106033325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002391854858617080761828965762560983421280980110168457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
444.4473026 |
122.7343214 |
168.3096709 |
33.4949434 |
| ENSG00000176170 |
8877 |
SPHK1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NYA1 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to form sphingosine 1-phosphate (SPP), a lipid mediator with both intra- and extracellular functions. Also acts on D-erythro-sphingosine and to a lesser extent sphinganine, but not other lipids, such as D,L-threo-dihydrosphingosine, N,N-dimethylsphingosine, diacylglycerol, ceramide, or phosphatidylinositol (PubMed:20577214, PubMed:23602659, PubMed:29662056, PubMed:24929359, PubMed:11923095). In contrast to proapoptotic SPHK2, has a negative effect on intracellular ceramide levels, enhances cell growth and inhibits apoptosis (PubMed:16118219). Involved in the regulation of inflammatory response and neuroinflammation. Via the product sphingosine 1-phosphate, stimulates TRAF2 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, and promotes activation of NF-kappa-B in response to TNF signaling leading to IL17 secretion (PubMed:20577214). In response to TNF and in parallel to NF-kappa-B activation, negatively regulates RANTES induction through p38 MAPK signaling pathway (PubMed:23935096). Involved in endocytic membrane trafficking induced by sphingosine, recruited to dilate endosomes, also plays a role on later stages of endosomal maturation and membrane fusion independently of its kinase activity (PubMed:28049734, PubMed:24929359). In Purkinje cells, seems to be also involved in the regulation of autophagosome-lysosome fusion upon VEGFA (PubMed:25417698). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11923095, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16118219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20577214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23602659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23935096, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24929359, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25417698, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28049734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29662056}.; FUNCTION: Has serine acetyltransferase activity on PTGS2/COX2 in an acetyl-CoA dependent manner. The acetyltransferase activity increases in presence of the kinase substrate, sphingosine. During neuroinflammation, through PTGS2 acetylation, promotes neuronal secretion of specialized preresolving mediators (SPMs), especially 15-R-lipoxin A4, which results in an increase of phagocytic microglia. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CI15}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Coated pit;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transferase |
|
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to form sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a lipid mediator with both intra- and extracellular functions. Intracellularly, S1P regulates proliferation and survival, and extracellularly, it is a ligand for cell surface G protein-coupled receptors. This protein, and its product S1P, play a key role in TNF-alpha signaling and the NF-kappa-B activation pathway important in inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and immune processes. Phosphorylation of this protein alters its catalytic activity and promotes its translocation to the plasma membrane. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2017]. |
hsa:8877; |
clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; acetyltransferase activity [GO:0016407]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; D-erythro-sphingosine kinase activity [GO:0017050]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; lipid kinase activity [GO:0001727]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein phosphatase 2A binding [GO:0051721]; sphinganine kinase activity [GO:0008481]; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor activity [GO:0038036]; blood vessel development [GO:0001568]; brain development [GO:0007420]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0071363]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; DNA biosynthetic process [GO:0071897]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:1900060]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045931]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; positive regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031398]; positive regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045987]; protein acetylation [GO:0006473]; regulation of endocytosis [GO:0030100]; regulation of endosomal vesicle fusion [GO:1905364]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903978]; regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150077]; regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050764]; regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010803]; response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0034612]; sphingoid catabolic process [GO:0046521]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingolipid metabolic process [GO:0006665]; sphingosine biosynthetic process [GO:0046512]; sphingosine metabolic process [GO:0006670] |
11777919_These findings show a role for SphK in the signal transduction by TRAF2 specifically leading to activation of NF-kappa B and antiapoptosis. 11915350_synthesize sphingosine 1-phosphate,a lipid mediator in intracellular signaling system 12080051_results indicate that SPHK1-interacting protein(SKIP) is a novel protein likely to play a regulatory role in the modulation of SPHK1 activity 12124383_activation and translocation to cell membrane dependent on protein kinase C 12393916_characterization of the nucleotide-binding site of human sphingosine kinase 1 through a combination of site-directed mutagenesis and affinity labeling with the ATP analogue, FSBA 12444147_role for sphingosine kinase in the regulation of neutrophil priming 12847068_Resting tone and myogenic responses of isolated hamster resistance arteries increased with forced expression of human Sphk1 in smooth muscle cells 14532121_Activation of this enzyme in mediated by ERK1/2 phoshporylation 14575709_results provide the first evidence of the active nuclear export of SPHK1 and suggest it is mediated by a CRM1-dependent pathway 14742298_Data show that respiratory syncytial virus stimulates sphingosine kinase activity in lung epithelial cells, leading to activation of antiapoptotic sphingosine 1-phosphate and subsequently activation of Akt and extracellular signal-related kinase. 14988393_SK1 is down-regulated by genotoxic stress, and basal SK1 function may be necessary for the maintenance of tumor cell growth 15052627_hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy is not caused by point mutations of sphingosine kinase 1 15191888_SphK1 mediates TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 gene expression through a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway and may participate in oscillatory flow-mediated proinflammatory signaling pathway in the vasculature. 15265705_PI3K and ERK/MAPK mediated the activation of sphingosine kinase and would be involved in the HGF-induced migration of endothelial cells. 15302883_SPHK plays an important role in the immune-inflammatory pathologies triggered by anaphylatoxins in human neutrophils 15585953_Comparison of base sequence of SPHK1/Sphk1 in human, mouse, and rat. 15632208_role for SK in the regulation of vascular phenomena that occur under conditions of stress 15693752_SK1 has marked effects on cell function, with plasma membrane-associated SK having a potent inhibitory effect on the G1-S phase transition [SK1] 15710602_SK1 down-regulation by TNF is dependent on the lysosomal pathway of apoptosis and specifically on cathepsin B, which functions as an SK1 protease in cells 15749892_model in which M.tuberc. inhibits both the activation and phagosomal translocation of sphingosine kinase 1 to block the localized Ca2+ transients required for phagosome maturation 15855330_IL-1beta and TNF-alpha induced an early and sustained increase in SPHK activity in INS-1 cells and isolated islets. 16038795_Findings demonstrate a role of SPHK1 activation in proinflammatory signalling and of SPHK1 basal activity in survival of A549 lung carcinoma cells. 16194537_results suggest that SphK1 may be critical for growth, metastasis and chemoresistance of human breast cancers 16243846_the specific plasma membrane localization and activation of SK1 is mediated largely by specific lipid-protein interactions 16507765_For the first time endogenous SK1 is implicated as an important survival enzyme in MCF-7 cells. The biological consequences of knocking down the enzyme are linked to its biochemical role as a regulator of sphingolipid metabolism. 16516161_These findings strongly suggest that high expression and up-regulation of SPHK1 and S1P receptors protect PC3 cells from the apoptosis induced by CPT. 16529909_These findings uncover a new functional role for Sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1), which can control survival/death balance by targeting sphingolipid de novo biosynthesis. 16571380_Data show that protein kinase C-alpha activation in endothelial cells leads to upregulation of sphingosine kinase-1 expression and activity, which is critically involved in the mechanism of endothelial cell migration. 16623665_results suggest that export of Sphk-1a isoform occurs under physiological conditions and may contribute to the establishment of the vascular S1P gradient. 17064696_SK1 is cleaved by cathepsin B in a sequential manner after basic amino acids, and the initial cleavages at the two identified sites, histidine 122 and arginine 199, occur independently of each other. 17114809_SphK-dependent Akt activation plays a significant role in TNF-alpha-induced cyclin D expression and cell proliferation 17388800_IGFBP-3 induces angiogenesis through IGF-I- and SphK1-dependent mechanisms 17482291_the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is involved in regulation of SphK1, with AKT2 playing a key role in PDGF-induced SphK1 expression 17519232_the localization and activity of SK1 are coordinately regulated with actin dynamics during macrophage activation 17599053_BCR/ABL induces SPK1 expression and increases its cellular activity, leading to upregulation of Mcl-1 in CML cells. 17641298_These data suggested that SPHK1 activation by TGF-beta1 leads to Rho-associated myofibroblasts differentiation mediated by transactivated S1P receptors in the lung fibrogenic process. 17822721_the SKase pathway, through the generation of S1P, is critically involved in mediating globular adiponectin-induced endothelial cell activation 18058224_High expression of sphingosine kinase 1 is associated with estrogen receptor negative breast breast cancer. 18178871_These data suggest that differential formation of sphingosine-1-phosphate by SphK1 and SphK2 has distinct and important actions in human mast cells. 18192241_Activation of sphingosine kinase-1 mediates induction of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. 18199826_Ang-1-induced inhibition of leakiness is mediated through activation of SK-1, defining a new signaling pathway in the Ang-1 regulation of permeability. 18261991_The hypoxia-stimulated SK-1 upregulation was functionally coupled to increased migration since the selective depletion of SK-1, but not of SK-2, by siRNAs abolished the migratory response. 18263879_a novel mechanism of regulation of both SK1 and SK2 that is mediated by their interaction with eEF1A. 18362204_apoptotic cells may up-regulate SphK1 to produce and secrete sphingosine-1-phosphate that serves as a 'come-and-get-me' signal for scavenger cells to engulf them in order to prevent necrosis 18401414_SphK1 is inolved in regulating imatinib-induced apoptosis and SphK1 is a downstream effector of the Bcr-Abl/Ras/ERK pathway inhibited by imatinib but upstream regulator of Bcl-2 family members 18426913_Sphingosine kinases and sphingosine-1-phosphate are critical for transforming growth factor beta-induced ERK1 and ERK2 activation and promotion of migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells 18644866_Datas suggest that filamin A links sphingosine kinase 1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to locally influence the dynamics of actin cytoskeletal structures at lamellipodia to promote cell movement. 18718048_Chronic myelogenous leukemia cells express SphK-1 and different S1P receptor, and P210(bcr/abl) fusion protein in CML cells can activate SphK-1. 18824518_SphK1/sphingosine-1-phosphate pathway contributes to colon carcinogenesis 18849324_the crucial role of activation of the SPHK1S1PS1P1 signaling pathway in response to inflammatory mediators in endothelial cells in regulating endothelial barrier homeostasis. 18852266_PP2A appears to function as an endogenous regulator of SK1 phosphorylation 18922940_Sphingosine kinase 1 is a new modulator of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha during hypoxia in human cancer cells. 18980995_SPHK1 in astrocytoma cell lines was elevated at both mRNA and protein levels, and the SPHK1 mRNA and protein were significantly up-regulated by up to 6.8- and 40-fold, respectively, in primary astrocytomas 19017993_Anti-inflammatory effects of sphingosine kinase modulation in inflammatory arthritis 19074142_SphK1 expression is transcriptionally regulated by IL-1 in glioblastoma cells, and this pathway may be important in regulating survival and invasiveness of glioblastoma cells. 19116345_Evidence suggesting that SPHK enhances migration of ML-1 cells by an autocrine mechanism and that the S1P-evoked migration is dependent on protein kinase C alpha, ERK1/2, and SPHK. 19162217_SPHK1 inhibition is a novel way to block PAR-1 mediated signalling. 19238330_The sphingosine kinase 1 signaling pathway is activated in Rheumatoid Arthritis, suggesting that manipulation of sphingosine kinase 1 activity in diseases of aberrant inflammation and angiogenesis may be beneficial. 19240026_Results indicate that SPHK1 and 2 isoforms and neutral sphingomyelinase contribute to the regulation of chemosensitivity by controlling ceramide formation and the downstream Akt pathway in human colon cancer cells. 19633297_IGFBP-3 in MCF-10A cells requires SphK1 activity and S1P1/S1P3, suggesting that S1P, the product of SphK activity and ligand for S1P1 and S1P3 19657322_Transforming growth factor-beta2 upregulates sphingosine kinase-1 activity, which in turn attenuates the fibrotic response to TGF-beta2 by impeding CTGF expression. 19706837_Inhibition of SphK1 activity restored the antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of tamoxifen in TamR cells. 19782042_Direct evidence shows that the plasma membrane lipid raft microdomain is the major site of action for SphK1 to overcome serum-deprived cell growth inhibition. 19815712_Data show that under basal conditions, sphingosine kinase-1, integrin alpha(v)beta(3), and CD31 exist as a heterotrimeric complex which is required in SK-1-mediated endothelial cell survival. 19830907_SphK1 is an important effector of Gq-coupled receptors, linking them via cross-activation of S1P receptors to G(i) and G12/13 signalling pathways. 19854831_CIB1 interacts with SK1 in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner at the previously identified 'calmodulin-binding site' of SK1. 19914200_evidence indicates that the COOH-terminal region of SphK1 encompasses a structural element that is necessary for the increase in catalytic activity in response to PMA treatment and that its deletion renders SphK1 active with respect to PMA treatment 19956567_Sphingosine kinase-1 is central to androgen-regulated prostate cancer growth and survival 20053797_The effect of isoflurane on caveolae formation in proximal tubule cells via transforming growth factor beta-1 release is reported. 20104488_CXCL4 induces SphK1 enzyme activity as well as its translocation to the cell membrane. SphK1 as a central regulator of acute and delayed monocyte activation 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20386061_Data suggest that the localization of sphingosine kinase 1 influences the substrate pools that it has access to and that S1P can rapidly translocate from the site where it is synthesized to other intracellular sites. 20404323_Sphingosine kinase mediates resistance to the synthetic retinoid N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide in human ovarian cancer cells 20519401_Overexpression of sphingosine 1-phosphate-producing sphingosine kinase 1 heightened the cells' susceptibility to influenza virus infection. 20520628_conversion of sphingosine to sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) protects keratinocytes from UVB-induced cell death 20606403_results demonstrate that SPHK1 is upregulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and provide clues of the role SPHK1 might play in tumor progression 20634980_Data implicate Sphk-1 in HBD-2 regulation in oral keratinocytes which also involves the activation of PI3K, AKT, GSK-3beta and ERK 1/2. 20661259_TLR4-mediated SphK1 activation was found to be critical for the redox-dependent activation of HIF-1alpha and ASK1, and the prevention of lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of caspase 3 and the expression interleukin-6. 20838377_study defines the mechanism regulating eEF1A-mediated SK1 activation, and also establishes SK1 as being integral for PTI-1-induced oncogenesis 20846391_Overexpression of sphingosine kinase 1 is associated with salivary gland carcinoma progression. 20889557_These results support a model in which the interaction between sphingosine kinase 1, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1 and/or 3, and ERK-1/2 might drive breast cancer progression 20926375_the ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of SK1 is an important mechanism controlling cell survival 21075134_Data suggest that whereas sphingosine kinase localization does not affect downstream metabolism of sphingosine-1-phosphate, localization has an important effect on the pools of substrate to which this key signaling enzyme has access. 21075214_The PP2A-B'alpha holoenzyme appears to function as an important endogenous regulator of SK1. 21209394_SphK1/S1P signaling may play important roles in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma carcinogenesis 21304987_S1P(ext) mediated endothelial cell motility is dependent on intracellular S1P production, which is regulated, in part, by SphK1 and S1P lyase. 21392092_Melatonin inhibited the stability of HIF-1alpha in a time- and concentration- dependent manners. Also, melatonin decreased SPHK1 activity in PC-3 cells during hypoxia. 21418911_SphK1 plays an important role in regulating the MUC5AC expression in airway epithelial cells under the induction of TNF-alpha. 21464128_Comparisons with the SK1 inhibitor, SKi or siRNA knockdown of SK1 indicated that (S)-FTY720 vinylphosphonate and FTY720 behave as typical SK1 inhibitors in preventing sphingosine 1-phosphate-stimulated rearrangement of actin in MCF-7 cells. 21575515_SphK1 potently enhances the prolieration, migration and invasion of colon cancer HT-29 cells, and suppresses cell apoptosis. 21625639_Increased SPHK1 expression is associated with glioma. 21672077_over-expression of sphingosine kinase-1 in human endothelial cells promotes, in part, their de-differentiation to a progenitor cell phenotype 21696364_[review] SK and the sphingolipid rheostat are important for both islet function and beta cell survival as a common therapeutic target that protects the beta cell from diabetogenic insults and ultimately improves pancreatic islet function. 21756066_Data show that nilotinib induces apoptosis through upregulating ceramide synthase genes and downregulating SK-1 in CML cells in addition to inhibition of BCR/ABL. 21769916_results showed that in TGW cells, GDNF increased SPHK1 transcription, leading to the production and secretion of S1P 21936950_SPHK1 is implicated in the metastasis of esophageal cancer. 21940753_Study has identified SphK1 as a proproliferative oncogenic kinase, an Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin activator, and probably a biomarker for thyroid cancer as well. 22016563_activation of phospholipase C and protein kinase C-beta 2 by the IGF-II/mannose-6-phosphate receptor are required for the activation of sphingosine kinase 1. 22155656_SphK1 activity is important for insulin synthesis and secretion 22227192_These data suggest that SPK1 acetylation plays a key role in cell growth, cell size, and cell-cycle control. 22315056_data suggest that decrease in circulating Sphingosine-1-phosphate during prostate cancer progression may stem from a significant downregulation of erythrocyte sphingosine kinase-1 activity which may be a potential mechanism of cancer-induced anaemia. 22322056_The expression of SPHK1 in gastric cancer is significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and a poor prognosis. 22322303_These findings demonstrate a key role for sphingosine kinase-1 in histamine-induced rapid P-selectin up-regulation and associated leukocyte rolling, and suggest that endothelial SK-1 is an important contributor to allergic inflammation 22331716_Results that antineoplastic agents induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells by downregulating the antiapoptotic SK-1 and GCS genes that may result in accumulation of apoptotic ceramides. 22422617_Data suggest that sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 transactivation is dependent on SPHK1, is upstream of MAP kinase signaling system, and is required for LDL-regulated expression of connective tissue growth factor in mesangial cells. 22450659_miR-124 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer through down-regulation of SPHK1. 22460268_findings highlight an important role for S1P(4) and SK1 in ER(-) breast cancer progression. 22684547_SphK1 promoting the secretion of MMP-2/9 and uPA via activation of ERK1/2 and suppression of p38 MAPK pathways maybe the molecular mechanisms for its regulation of the malignant behavior of colon cancer cell. 22733311_findings identify a novel role for the nuclear localization of sphingosine kinase 1 combined with either ERK-1/2 or SFK or LYN or AKT or NF-kappaB, which significantly shortens disease-specific survival and/or recurrence in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer 22781898_Overexpression of SphK1 and NF-kappaB may be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of colon carcinoma. 22833671_Oncogenic K-Ras regulates bioactive sphingolipids in a sphingosine kinase 1-dependent manner 22961081_Data have identified that the enzyme SphK1 is an important regulator of lipid partitioning and insulin action in skeletal muscle under conditions of increased lipid supply. 23166225_a correlation between SphK1 expression and cetuximab response was found in colorectal cancer patients. 23232649_SphK1 regulates tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion, which ultimately contributes to tumor progression and malignancy phenotype in colon cancer. FAK pathway, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 may play critical roles in this SphK1mediated effect. 23314175_Sphingosine kinase 1 functions to increase the stability of c-Myc and suppresses Ap3A formation, which might maintain the Warburg effect and cell survival. 23359503_The function of SphK1 and SphK2 can be interchangeable in mast cells and is species and cell type determined. 23426175_SPHK1 contributes toward the regulation of CD44 protein expression through the ERK signaling pathway through sphingosine-1-phosphate in human colon cancer cells. 23462226_We are herein provide the first evidence of increased SPHK-1 expression in post-labor amnions, and that sphingosine-1-phosphate increases the PTGS-2 expression in amnion cells 23466305_key role of Sphk1, S1PR1 and S1PR3 in angiogenesis underlying the liver fibrosis process 23576579_SPHK1 overexpression modulates intestinal cell proliferation through increased c-Myc translation. 23602659_SphK1 recognizes the lipid substrate and catalyzes ATP-dependent phosphorylation. 23651497_The H2O2-induced src/PDGFRbeta/SK1 signaling cascade was impaired in nSMase2-deficient fro/fro cells and was rescued by exogenous C2Cer that activated src/PDGFRbeta/SK1. 23658376_In carotid artery plaque, expression of SPHK1 was observed at smooth muscle cell-rich sites and was co-localized with intraplaque FX/FXa content. 23839903_Demonstrate that HPPCn attenuated oxidative injury and fibrosis induced by ethanol feeding and that the SphK1/S1P/S1PRs signalling pathway contributes to this protective effect. 23861887_the SPHK rheostat does not play a major role in tumor cell viability, and that SPHKs might not be attractive targets for pharmacological intervention in the area of oncology. 23893239_SPHK1 expression was increased in cancer versus non-cancer tissue in patients with cutaneous melanoma and this corroborates previous reports showing that the levels of SPHK1 mRNA and protein are higher in malignant tumors than in healthy tissues. 23928990_High sphingosine kinase 1 is associated with breast cancer. 23939980_We propose that the reduction in SphK1 activity late in DENV-2-infected cells is a consequence of DENV-2 out-competing SphK1 for eEF1A binding and hijacking cellular eEF1A for its own replication strategy. 23955546_SphK1 may be a predictive factor for treatment outcome after neoadjuvant treatment in luminal type breast cancers. 24092575_increased expression of SPHK1 may be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of bladder cancer 24137500_SK is a key pro-viral factor regulating multiple cellular signal pathways triggered by influenza virus infection 24276247_these findings suggest that TFR1 has an important role in sphingosine kinase 1-mediated oncogenesis. 24337110_suggest that combined inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and sphingosine kinase-1 has potential as an anticancer therapy in triple-negative breast cancer in which insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 expression is high. 24422628_IGF1R mediates insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of both SphK1 and SphK2. 24452756_Endogenously liberated amyloid Beta peptides significantly decreases expression and activity of SPK1. 24468113_The results highlight the importance of S1P in AD suggesting the existence of a global deregulation of S1P signaling in this disease from its synthesis by SphK1 and degradation by SPL to its signaling by the S1P1 receptor. 24473437_this study delineates a novel role for sphingosine kinase 1 (SK1) in metabolic disorders associated with obesity 24503067_Sphingosine kinase 1 regulates measles virus replication. 24816639_Knockdown of SPHK1 expression inhibits the PI3K/AKT activation, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression, and human RA-FLS migration and invasion in vitro. Potentially, SPHK1 may be a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. 24903384_Data show that sphingosine kinase SphK1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors S1P1, S1P2, S1P3, and S1P5 were expressed from primary, up to recurrent and secondary glioblastomas, with sphingosine kinase SphK2 levels were highest in primary tumors. 25109605_SphK1 confers resistance to apoptosis in gastric cancer cells via the Akt/FoxO3a/Bim pathway. 25176316_oxLDL induced angiogenesis requires SPHK1/S1P signalling both in vitro in a HMEC-1 tube formation model and in vivo in the murine Matrigel plug model 25260803_Sacral chordoma patients with high expression of SPHK1 possessed shorter continuous disease-free survival time. 25310737_these data indicated that Sphk1 inhibition plays an important role in caspase-dependent apoptotic neuronal death in an experimental Parkinson's disease model 25319495_This establishes that sphingosine kinase, in addition to producing sphingosine-1-phosphate as a signaling molecule, also consumes dihydrosphingosine to regulate ceramide synthesis. 25404266_Data suggest that sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) is involved in the regulation of small cell lung cancer multi-drug resistance, and a target gene to evaluate the chemosensitivity and clinical prognostic for small cell lung cancer (SCLC). 25411162_E2F7 directly increases the transcription and activity of the Sphk1/S1P axis resulting in activation of AKT and subsequent drug resistance. 25417698_induced pluripotent stem cell derived human Niemann-Pick type C disease neurons are generated and the abnormalities caused by VEGF/SphK inactivity in these cells are corrected by replenishment of VEGF. 25481644_Our findings demonstrate that leptin-induced STAT3 is partially cross activated through SK1-mediated IL6 secretion and gp130 activation. Positive correlations in human tissues suggest the potential significance of this pathway in ER-negative breast cancer 25587035_the A2B adenosine receptor (ADORA2B) is essential for adenosine-induced SphK1 activity in human and mouse normal and sickle erythrocytes in vitro 25671829_SPHK1 might represent a novel and useful prognostic marker of hepatocellular carcinoma progression in patients with portal vein tumor thrombus. 25778867_results suggest for the first time that SPHK1 is involved in the development and progression of NPC, which can be used as a useful prognostic marker for NPC patients and may be an effective target for treating NPC 25786072_In contrast to the SK activity, S1PP activity was homogeneous across the peripheral blood NK cells, suggesting a bias in the SK pathway towards proliferation and migration, activities supported by S1P. 25805832_SK1 is overexpressed in 786-0 renal carcinoma cells lacking functional VHL, with concomitant high sphingosine 1-phosphate levels that appear to be HIF-2alpha mediated. 25892494_A novel chimeric aequorin fused with caveolin-1 reveals a sphingosine kinase 1-regulated Ca(2) microdomain in the caveolar compartment. 26045781_Resveratrol-induced proliferation inhibition of K562 cells might be mediated through its modulation activity of SphK1 pathway by regulating S1P and ceramide levels, which then affected the proliferation and apoptosis process of leukemia cells. 26071354_results indicate that miR-101 exerts its anti-CRC activities probably through down-regulating SphK1 26073327_Hepatitis B virus X protein is able to elevate the expression of SPHK1 in hepatoma cells by upregulating transcription factor AP2 alpha. 26264277_The silencing of SphK1 potentiated the apoptotic effects of the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate. 26311741_SPHK1 is involved in tumor development and progression of cervical cancer 26376826_In summary, this study demonstrates a link between SphK1/sphingosine-1-phosphate and TGF-beta-induced miR-21 in renal tubular epithelial cells. 26493335_High SPHK1 protein correlated with resistance to cisplatin (IC50) in an independent gastric cancer cell line panel and with survival of patients treated with chemotherapy prior to surgery but not in patients treated with surgery alone. 26540633_Data show that long non-coding RNA HULC promotes tumor angiogenesis in liver cancer through microRNA miR-107/E2F1 transcription factor (E2F1)/sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) signaling. 26549227_MiR-506 suppresses the angiogenesis of liver cancer by inhibiting SPHK1. 26590717_Results reveal an lncRNA- and E2F1-driven regulatory loop in which E2F1-dependent induction of antisense RNA leads to changes in chromatin structure, facilitating E2F1-dependent expression of SPHK1 and restriction of E2F1-induced apoptosis. 26662312_SphK1 is associated with the proliferation and invasiveness of CRC cells and the SphK1 gene may contribute to a novel therapeutic approach against CRC. 26673009_SphK1 expression is functionally associated to cellular proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and mitotane sensitivity of adrenocortical carcinoma. 26716409_High SPHK1 expression is associated with ovarian cancer. 26842184_Sphk1 plays an important role in the malignant transformation of breast epithelial cells and modulates breast cancer metastasis through the regulation of Ecadherin expression. 26855418_low oxLDL concentration triggers sprouting angiogenesis that involves ROS-induced activation of the neutral sphingomyelinase-2/sphingosine kinase-1 pathway, and is effectively inhibited by GW4869. 26877098_Found that upregulation of SphK1 expression in the stiff substrate is dominant in metastatic cancer cells but not in primary cancer cells. These results suggest that alterations in the mechanical environment of the extracellular matrix surrounding the tumor cells actively regulate cellular properties such as secretion, which in turn, may contribute to cancer progression. 26886371_increased SK and SPL mRNA expression along with reduced sphingosine 1-phosphate levels were more commonly observed in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 26912347_In conclusion, these data suggested that HuR bound to SphK1 mRNA and played a crucial role in TGF-beta1-induced hepatic stellate cell activation. 26937138_SPHK1 mRNA is up-regulation in colorectal cancer. 27021309_The analysis suggests that the catalytic function and regulation of SPHK1 and SPHK2 might be dependent on their conformational mobility. (Review) 27065335_we identified sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) as a novel target of miR-506, the expression of which inhibited the SPHK1/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway, which is activated in pancreatic cancer. High SPHK1 expression was significantly associated with poor survival in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer specimens. 27099350_SphK1 is regulated by PDGF-BB in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells via the transcription factor Egr-1, promoting cell proliferation. 27160553_Data show that sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) was significantly upregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues and low levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SGPL1) mRNA correlated with a worse overall survival, and that sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2) is over-expressed in a subset of tumours, which in part mediates sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)-induced migration of OSCC cells. 27467777_SPHK1 mediated autophagy is different in neurons and neuroblastoma cells 27562371_Butyrate and bioactive proteolytic form of Wnt-5a regulate colonic epithelial proliferation and spatial development 27621003_high expression associated with higher levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate, which in turn is associated with lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer 27697999_The combination of FTY720 with the SPHK1 inhibitor SKI-II results in synergistic inhibition of MM growth. CXCR4/CXCL12-enhanced expression correlates with reduced MM cell sensitivity to both FTY720 and SKI-II inhibitors, and with SPHK1 coexpression in both cell lines and primary MM bone marrow (BM) samples, suggesting regulative cross-talk between the CXCR4/CXCL12 and SPHK1 pathways in MM cells 27801960_Melatonin-treated cells also exhibited an inhibition of the SphK1/S1P axis. Antifibrogenic effect of SphK1 inhibition was confirmed by treatment of LX2 cells with PF543. Abrogation of the lipid signaling pathway by the indole reveals novel molecular pathways that may account for the protective effect of melatonin in liver fibrogenesis. 27811358_Sphk1 induced NF-kappaB-p65 activation, increased expression of cyclin D1, shortened the cell division cycle, and thus promoted proliferation of breast epithelial cells. 27811359_Inhibiting SPHK1 using specific siRNAs or the pharmacological inhibitor FTY720 led to potent anti-cancer activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells/ 27821815_Everolimus sensitizes prostate cancer cells to docetaxel by down-regulation of HIF-1alpha and sphingosine kinase 1 expression. 27942860_demonstrated the roles played by miR-144-3p and FN1 in mediating the oncogenic function of SphK1, which enhanced the understanding of the etiology of PTC 27956387_Inhibition of SPHK1 in human acute myeloid leukemia cells induces MCL1 degradation and caspase-dependent cell death. 28049734_These results highlight the importance of sphingosine and its conversion to sphingosine-1-phosphate by SphK1 in endocytic membrane trafficking. 28108260_SphKs/Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling is critical for the growth and survival of estrogen receptor positive MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. 28178265_By simulating therapeutic strategies that target multiple nodes of the pathway such as Raf and SphK1, we conclude that combination therapy should be much more effective in blocking VEGF signaling to EKR1/2. The model has important implications for interventions that target signaling pathways in angiogenesis relevant to cancer, vascular diseases, and wound healing. 28206952_High SPHK1 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 28258651_Sphingosine kinase-1 (SK1) plays a crucial role in the metabolic reprogramming of human ovarian cancer cells. 28351953_Data indicate that the mitotic kinase Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) was an important effector of S1P-S1P5 signaling, and a new function of the SphK1-S1P pathway specifically in the control of mitosis in HeLa cells. 28364399_SphK1 may be novel targets for inhibiting lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 28405684_our data suggest that SphK1 modulates the expression of EMT-related markers and cell migration by regulating the expression of p-FAK in CRC cells. Thus, SphK1 may play a functional role in mediating the EMT process in CRC. 28521610_the blockage of SPHK1 activity to attenuate autophagy may be a promising strategy for the prevention and treatment of patocellular carcinoma 28583134_SphK1 expression regulates the early stage of colon carcinogenesis and tumor growth, thus inhibition of SphK1 may be an effective strategy for colon cancer chemoprevention. 28615679_Study shows that both in prostate and breast cancers vascular endothelial growth factor and sphingosine-kinase-1 are independently regulated by mammalian target of rapamycin 1. 28706199_Low SPHL1 expression is associated with Huntington's disease. 28729416_High SPHK1 expression is associated with ovarian Cancer. 28733250_SK1 activation is renoprotective via induction of autophagy in the fibrotic process 28778177_Immuno |
ENSMUSG00000061878 |
Sphk1 |
211.137678 |
3.0449352617 |
1.606412 |
0.116135951 |
196.648802 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000001125041282575977427185466006842751552650335669641262847775491066518950430769868033103353192705564213276449758889541374884402102907188236713409423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000209666784480068513279600887036820621044469839488999868944048084248446279943994254413975360853954417278384388155856865587622905877651646733283996582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
319.3236972 |
22.0400085 |
105.7026271 |
6.0095621 |
| ENSG00000176463 |
28232 |
SLCO3A1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UIG8 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the Na(+)-independent transport of organic anions such as prostaglandins (PG) E1 and E2, thyroxine (T4), deltorphin II, BQ-123 and vasopressin (PubMed:16971491, PubMed:19129463). Also displays a low transport activity of estrone 3-sulfate (PubMed:10873595, PubMed:16971491, PubMed:19129463). Shows a pH-sensitive substrate specificity towards T4 and estrone 3-sulfate which may be ascribed to the protonation state of the binding site and leads to a stimulation of substrate transport in an acidic microenvironment (PubMed:19129463). Hydrogencarbonate/HCO3(-) acts as the probable counteranion that exchanges for organic anions (PubMed:19129463). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10873595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16971491, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19129463}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity. Involved in positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation; and prostaglandin transport. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:28232; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; organic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008514]; prostaglandin transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015132]; sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015347]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; prostaglandin transport [GO:0015732]; sodium-independent organic anion transport [GO:0043252]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
14631946_OATP-D plays an important role in translocating prostaglandins in specialized tissues and cells. 16971491_Further evidence is provided for the involvement of OATPs in oligopeptide transport. OATP3A1 variants might be involved in the regulation of extracellular vasopressin concentration in human brain. 18521091_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19330903_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21278488_tissue-specific localization of OATP2B1, OATP3A1 and OATP5A1 has been analyzed in normal mammary tissue and corresponding breast cancer tissues. 21486766_Compared with the adult cerebral cortex, mRNAs encoding OATP1A2, OATP1C1, OATP3A1 variant 2, OATP4A1, LAT2 and CD98 were reduced in fetal cortex at different gestational ages, whilst mRNAs encoding MCT8, MCT10, OATP3A1 variant 1 and LAT1 were similar. 22377092_Single nucleotide polymorhpisms of SLCO3A1 were associated with nicotine dependence. 24945726_SLCO3A1, a novel Crohn's disease-associated gene, mediates inflammatory processes in intestinal epithelial cells through NF-kappaB transcription activation. 26349991_our results revealed altered OATP3A1 and OATP4A1 mRNA levels and novel mechanisms that might be involved in their regulation in colorectal cancer 30063921_OATP3A1 functions as a bile acid efflux transporter that is up-regulated as an adaptive response to cholestasis. 34971708_Tumor necrosis factor alpha upregulates the bile acid efflux transporter OATP3A1 via multiple signaling pathways in cholestasis. |
ENSMUSG00000025790 |
Slco3a1 |
287.915120 |
2.3252973346 |
1.217415 |
0.183799207 |
43.083535 |
0.00000000005245182618770676939353050459046887924602353692193901224527508020401000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000276397341853106759882877638796554696509755189026691368781030178070068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
405.3405111 |
44.4189235 |
175.3812231 |
14.4403323 |
| ENSG00000176472 |
284346 |
ZNF575 |
protein_coding |
Q86XF7 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284346; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30925934_Results found DNA methylation of the ZNF575 gene in infant cord blood to be associated with maternal antidepressant use in pregnancy in two independent cohorts. This association persists into early childhood. |
ENSMUSG00000066721 |
Zfp575 |
21.883360 |
0.4662876998 |
-1.100708 |
0.404594117 |
7.371463 |
0.00662670084073417858111509914920134178828448057174682617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013203307830620474375149520085415133507922291755676269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3209863 |
3.5555132 |
28.8676764 |
5.1536730 |
| ENSG00000176533 |
2788 |
GNG7 |
protein_coding |
O60262 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction. Plays a role in the regulation of adenylyl cyclase signaling in certain regions of the brain. Plays a role in the formation or stabilzation of a G protein heterotrimer (G(olf) subunit alpha-beta-gamma-7) that is required for adenylyl cyclase activity in the striatum (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
Predicted to enable G-protein beta-subunit binding activity. Predicted to be involved in G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway and regulation of adenylate cyclase activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within behavioral fear response; locomotory behavior; and receptor guanylyl cyclase signaling pathway. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2788; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277] |
18219292_GNG7 suppression represents a new prognostic indicator in cases of oesophageal cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20543539_Reduced expression of G-gamma 7 is associated with the histological grade of EHCC and may prove to be a useful marker for predicting the prognosis of human EHCC. 22183866_Loss of GNG7 protein expression is a frequent event in head and neck cancer with hypermethylation of the promoter region of GNG7 being probably the mechanism for the observed inactivation. 23403885_GNG7 is a highly specific promoter methylated gene associated with head and neck cancer. 30945310_GNG7 is a tumor suppressor gene in Clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression. 33139493_Elevated MicroRNA 183 Impairs Trophoblast Migration and Invasiveness by Downregulating FOXP1 Expression and Elevating GNG7 Expression during Preeclampsia. 33864871_G protein gamma 7 suppresses progression of lung adenocarcinoma by inhibiting E2F transcription factor 1. 34635014_MicroRNA miR-19b-3p mediated G protein gamma subunit 7 (GNG7) loss contributes lung adenocarcinoma progression through activating Hedgehog signaling. 34650124_GNG7 and ADCY1 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic adenocarcinoma through bioinformatic-based analyses. 35240924_Long non-coding RNA LINC00472 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-4311/GNG7 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000048240 |
Gng7 |
88.812341 |
0.2065459645 |
-2.275465 |
0.240175573 |
89.287881 |
0.00000000000000000000341343739101727225556002826034322551646491084457789285191726263990474876663938630372285842895507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000031627329498691112850748030325207576667779708252890825091740989449817789136432111263275146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.4871134 |
7.2403018 |
154.3476674 |
24.1356625 |
| ENSG00000176595 |
9920 |
KBTBD11 |
protein_coding |
O94819 |
|
Kelch repeat;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:9920; |
|
29267898_Our study highlighted the high colorectal cancer risk of people carrying MYC rs6983267 G and KBTBD11 rs11777210 C alleles |
ENSMUSG00000055675 |
Kbtbd11 |
74.651829 |
0.4462786733 |
-1.163983 |
0.193700166 |
36.558411 |
0.00000000148159290897729393527392542992534782420044336959108477458357810974121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006982219456099890954582978390722744488350315350544406101107597351074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.4827475 |
5.5697262 |
105.0352896 |
8.0951718 |
| ENSG00000176597 |
84002 |
B3GNT5 |
protein_coding |
Q9BYG0 |
FUNCTION: Beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase that plays a key role in the synthesis of lacto- or neolacto-series carbohydrate chains on glycolipids, notably by participating in biosynthesis of HNK-1 and Lewis X carbohydrate structures. Has strong activity toward lactosylceramide (LacCer) and neolactotetraosylceramide (nLc(4)Cer; paragloboside), resulting in the synthesis of Lc(3)Cer and neolactopentaosylceramide (nLc(5)Cer), respectively. Probably plays a central role in regulating neolacto-series glycolipid synthesis during embryonic development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11283017, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11384981}. |
Developmental protein;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
This gene encodes a member of the beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase family. This enzyme is a type II membrane protein. It exhibits strong activity to transfer GlcNAc to glycolipid substrates and is identified as the most likely candidate for lactotriaosylceramide synthase. This enzyme is essential for the expression of Lewis X epitopes on glycolipids. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:84002; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; beta-galactosyl-N-acetylglucosaminylgalactosylglucosyl-ceramide beta-1,3-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008457]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; lactosylceramide 1,3-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0047256]; UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0008499]; brain development [GO:0007420]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; glycolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0009247]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
18483624_Helicobacter pylori induces beta3GnT5 in human gastric cell lines, modulating expression of the SabA ligand sialyl-Lewis x 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22411838_bone marrow samples of acute myeloid leukemia patients had 16-fold higher expression of B3GNT5 than those of healthy donors 32677340_B3GNT5 is a novel marker correlated with stem-like phenotype and poor clinical outcome in human gliomas. |
ENSMUSG00000022686 |
B3gnt5 |
55.596854 |
0.4581050221 |
-1.126250 |
0.247403105 |
20.874194 |
0.00000490457743678941131932561697803762967851071152836084365844726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000015984005954297132360121883043468926643981831148266792297363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.0245749 |
5.4513641 |
74.7598977 |
7.9974749 |
| ENSG00000176641 |
220441 |
RNF152 |
protein_coding |
Q8N8N0 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase mediating 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of RRAGA in response to amino acid starvation. Thereby, regulates mTORC1 signaling and plays a role in the cellular response to amino acid availability (PubMed:25936802). Also mediates 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of target proteins and their subsequent targeting to the proteasome for degradation. Induces apoptosis when overexpressed (PubMed:21203937). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21203937, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25936802}. |
Apoptosis;Lysosome;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25936802}. |
Enables small GTPase binding activity and ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to amino acid starvation; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling; and protein polyubiquitination. Located in lysosomal membrane. Is integral component of organelle membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:220441; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; organelle membrane [GO:0031090]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to amino acid starvation [GO:0034198]; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904262]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936]; protein K63-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070534]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21203937_RNF152 is a lysosome localized E3 ligase with pro-apoptotic activities 25936802_A mechanism for regulation of mTORC1 signaling by RNF152-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination of RagA. 32486221_The Role of Tissue-Specific Ubiquitin Ligases, RNF183, RNF186, RNF182 and RNF152, in Disease and Biological Function. |
ENSMUSG00000047496 |
Rnf152 |
21.560526 |
0.1027182409 |
-3.283236 |
0.474914274 |
56.542671 |
0.00000000000005499195698586280680968721572716424707082507120081693585689208703115582466125488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000354600823552352588536942680333201577804001086713370227698760572820901870727539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3613971 |
1.1303548 |
32.9731506 |
5.6932909 |
| ENSG00000176659 |
284756 |
LINC02910 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
97.758013 |
2.3601245466 |
1.238863 |
0.241925591 |
25.747733 |
0.00000038908382232565757402560418717896162377201108029112219810485839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001441847154789531966476482348349374973395242705009877681732177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
128.3753050 |
20.4513645 |
54.7427871 |
6.4524176 |
| ENSG00000176681 |
9884 |
LRRC37A |
protein_coding |
A6NMS7 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9884; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
ENSMUSG00000034239+ENSMUSG00000078632 |
Gm884+Lrrc37a |
32.997508 |
0.3402334239 |
-1.555403 |
0.516032058 |
8.702630 |
0.00317751259464018557393538699784585332963615655899047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006761834760220464257685080156079493463039398193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.6920795 |
4.2742009 |
39.0624529 |
8.3062281 |
| ENSG00000176695 |
81099 |
OR4F17 |
protein_coding |
Q8NGA8 |
FUNCTION: Odorant receptor. {ECO:0000305}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Membrane;Olfaction;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose, to initiate a neuronal response that triggers the perception of a smell. The olfactory receptor proteins are members of a large family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) arising from single coding-exon genes. Olfactory receptors share a 7-transmembrane domain structure with many neurotransmitter and hormone receptors and are responsible for the recognition and G protein-mediated transduction of odorant signals. The olfactory receptor gene family is the largest in the genome. The nomenclature assigned to the olfactory receptor genes and proteins for this organism is independent of other organisms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:81099; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; olfactory receptor activity [GO:0004984] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
ENSMUSG00000108891+ENSMUSG00000108908+ENSMUSG00000061195 |
Olfr1291-ps1+Olfr1293-ps+Olfr1289 |
27.276207 |
0.4667581060 |
-1.099253 |
0.300139194 |
13.667013 |
0.00021825489638413242193468177809734243055572733283042907714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000567655025661637771192125079267043474828824400901794433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.5760915 |
3.4273254 |
37.8706159 |
4.7463391 |
| ENSG00000176697 |
627 |
BDNF |
protein_coding |
P23560 |
FUNCTION: Important signaling molecule that activates signaling cascades downstream of NTRK2 (PubMed:11152678). During development, promotes the survival and differentiation of selected neuronal populations of the peripheral and central nervous systems. Participates in axonal growth, pathfinding and in the modulation of dendritic growth and morphology. Major regulator of synaptic transmission and plasticity at adult synapses in many regions of the CNS. The versatility of BDNF is emphasized by its contribution to a range of adaptive neuronal responses including long-term potentiation (LTP), long-term depression (LTD), certain forms of short-term synaptic plasticity, as well as homeostatic regulation of intrinsic neuronal excitability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11152678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12553913, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29909994}.; FUNCTION: [BDNF precursor form]: Important signaling molecule that activates signaling cascades downstream of NTRK2. Activates signaling cascades via the heterodimeric receptor formed by NGFR and SORCS2 (PubMed:24908487, PubMed:29909994). Signaling via NGFR and SORCS2 plays a role in synaptic plasticity and long-term depression (LTD). Binding to NGFR and SORCS2 promotes neuronal apoptosis. Promotes neuronal growth cone collapse (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P21237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24908487, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29909994}. |
3D-structure;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the nerve growth factor family of proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protein. Binding of this protein to its cognate receptor promotes neuronal survival in the adult brain. Expression of this gene is reduced in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's disease patients. This gene may play a role in the regulation of the stress response and in the biology of mood disorders. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:627; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; nerve growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005163]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; brain-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0031547]; collateral sprouting [GO:0048668]; memory [GO:0007613]; modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0050804]; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001234]; negative regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010832]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; nerve development [GO:0021675]; nerve growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038180]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; positive regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0031550]; positive regulation of collateral sprouting [GO:0048672]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of receptor binding [GO:1900122]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000008]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11244490_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11782995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840487_Mutation is associated with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome, suggesting the syndrome is genetic. 11935372_Results support the involvement of NGF, BDNF, leptin, and mast cells in human coronary atherosclerosis and metabolic syndrome, implying neuroimmune and adipoimmune pathways in the pathobiology of these cardiovascular disorders. 12008958_Platelets appear to bind, store and release BDNF upon activation at the site of traumatic injury to facilitate the repair of peripheral nerves or other tissues that contain TrkB. 12130635_role in regulating surface expression of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazoleproprionic acid receptors by enhancing the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor/GluR2 interaction in developing neocortical neurons 12140770_a candidate gene in stress and affective disorders 12140781_BDNF as a potential risk allele associated with bipolar disorder 12161822_The brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder: evidence from a family-based association study. 12192623_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12192623_that the BDNF C-270T polymorphism is a relevant risk factor for AD particularly in patients lacking the ApoE epsilon4 allele in this German sample. 12397373_The gene expression of this protein was studied in the developing human tooth. 12480128_BDNF mRNA levels in prefrontal cortex increase from infancy to adulthood, i.e. they are low during infancy and adolescence, peak during young adulthood, and are stable throughout adulthood and aging. 12524161_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12531456_BDNF modulates cytokine mRNA expression in immune cells. (BDNF) 12553913_role for BDNF and its val/met polymorphism in human memory and hippocampal function; val/met mutation exerts these effects by impacting intracellular trafficking and activity-dependent secretion of BDNF 12568867_Ovarian levels of this factor are present in follicular fluid from normally cycling women. 12694935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12694935_Single base pair (bp) polymorphism at position 240 in non-coding region of BDNF gene and at position 480 within proBDNF sequence analyzed. Frequency of 240T allele found to be significantly increased in partial epilepsy patients. 12719654_This review discusses the importance of BDNF/neurotrophic tyrosine kinase type 2 receptor signaling pathway interactions in memory processes. 12738784_identified a functional cAMP-response element (CRE) in the BDNF gene promoter III and established that it participated in the modulation of BDNF expression in NT2/N neurons via downstream signaling from the D1 class of dopamine receptors. 12742659_Thirty minutes of moderate exercise significantly induced BDNF production in multiple sclerosis patients and controls, but no differential effects are seen. 12753507_mRNA for BDNF is detectable in PBMC. Levels in relapsing-remitting MS are increased by about 60% compared with patients with other neurological diseases or healthy subjects, suggesting a potentially neuroprotective facet of autoimmune inflammation. 12836135_Sequence variants of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene are strongly associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder. 12842310_Low BDNF levels may play a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorders and antidepressants may increase BDNF in depressed patients. 12851636_reduction in BDNF in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics, and suggests that intrinsic cortical neurons, afferent neurons, and target neurons may receive less trophic support in this disorder. 12888803_the BDNF Met66 variant may be a susceptibility factor to eating disorders, mainly to anorexia nervosa restricted type and low body mass index. 12890761_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12890761_The relationship of the BDNF val66met genotype and hippocampal activity during episodic memory processing using blood oxygenation level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging and a declarative memory task in healthy individuals was studied 12900521_Data suggest that activation of bronchial eosinophils by neurotrophins (nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophins-3 and -4) might play a role in the regulation of eosinophilic inflammation in allergic asthma. 12912764_Messenger RNA levels of BDNF and trk B were significantly reduced, independently and as a ratio to neuron-specific enolase, in both prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in suicide subjects, as compared with those in control subjects. 12921913_Observed immunohistochemical differences in BDNF between schizophrenic and normal cases may indicate the existence of BDNF dysfunction in schizophrenic brain, and this dysfunction may be one of the factors involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. 12951204_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14582140_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14623369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14623369_We investigated a novel polymorphism of single nucleotide substitution (C270T) of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene in schizophrenia patients (n=101) and in controls (n=68). 14636373_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14642442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14673216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14681916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14730194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14730195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14730195_These results suggest that genetic variants of the BDNF gene may play a role in specific cognitive functions, but not in overall intelligence. 14997020_A strong association between the APOE-epsilon4 polymorphism and late-onset Alzheimer's was observed, but there was no significant association between this BNDF polymorphism and affected patients. 14997020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15084795_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15084795_the current study does not demonstrate any significant difference in Val66Met BDNF genotype or allele frequencies between Alzheimer's disease patients and controls 15094483_BDNF levels were progressively decreased by 1 Hz rTMS in healthy subjects; there was no effect of 1 Hz rTMS on BDNF plasma levels in ALS patients, an effect probably due to the loss of motor cortex pyramidal cells. 15108194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15108194_Study suggests that the BDNF 196G/A gene polymorphism might be associated with a susceptibility to eating disorders. 15115760_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15115760_support for a role for BDNF in the susceptibility to aberrant eating behaviors 15118353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120095_Data indicate the possibility of linkage disequilibrium between the C270T variation and a mutation in coding region of the BDNF gene and suggest that this gene may play a role in the development of familial Parkinson's disease. 15120095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15177062_In nigra, increased numbers of BDNF-IR and, less frequently, NT-3-IR ramified glia surrounded fragmented neurons 15274036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15279867_Genetic factor other than BDNF is involved in the etiology of febrile seizures. 15279867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15336520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15337270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15375678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15384083_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15457498_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15459944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15526143_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15537879_The variation in the BDNF gene (val66met)affects the anatomy of the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, identifying a genetic mechanism of variation in brain morphology related to learning and memory. 15541709_This review focuses on the role of BDNF expression and secretion related to the structural and functional changes of hippocampal synapses during late-phase long term potentiation, in the context of long-term memory. 15543516_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15544837_Monocytes, produce, store and release nerve growth factor, BDNF and neurotrophin 3 15547445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15567073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15596541_The Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays an important role in synaptic plasticity and rapidly recruits full-length TrkB (TrkB-FL) receptor into cholesterol-rich lipid rafts from nonraft regions of neuronal plasma membranes. 15626819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15626819_This study did not provide evidence supporting an association between BDNF and COMT genes and declarative memory phenotypes. 15626824_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15630410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15630410_The val66met SNP showed significant association for valine with schizophrenia but not bipolar disorder (BP). Haplotype analysis of val/met SNP revealed highly significant underrepresentation of the met or met-1 haplotype in schizophrenia. 15635706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15635706_Results did not find a significant association between the three BDNF SNPs studied and Alzheimer's disease when evaluated individually or with haplotype analysis. 15647480_We investigated the involvement of signaling mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its receptor tyrosine kinase TrkB in producing the altered GABA-related gene expression in schizophrenia. 15657181_MM cells express TrkB, and respond to BDNF by activating MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling cascades 15657604_Alterations in BDNF gene is associated with anorexia nervosa and bulimia 15665077_Enzyme inhibitors blocked the BDNF-induced effects on the epileptic GABA currents. 15710474_Unstimulated human peripheral blood monocytes, but not lymphocytes, constitutively secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). 15719396_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15726264_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15768049_Val66met, a functional and abundant missense polymorphism in the coding region of the BDNF gene, was associated with variance in the volume of the hippocampal formation in 19 patients with first-episode schizophrenia. 15770238_BDNF variation and mood disorders: a novel functional promoter polymorphism and Val66Met are associated with anxiety. 15770238_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15772739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15772739_The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism has a gender specific influence on planning ability in Parkinson's disease. 15816823_human scalp hair follicles are both a source and target of bioregulation by BDNF, which invites to target TrkB-mediated signaling for therapeutic hair growth modulation. 15837123_BDNF essentially increased during the first 2 postnatal weeks in the hippocampus and hypothalamus, with no close correlation to its mRNA levels. 15838855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15838855_The distribution of the 240 C/T polymorphism was significantly different between AD patients and controls. 15843069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15866349_confirmation that the BDNF gene is the true susceptibility gene for eating disorders could lead to rapid therapeutic progress in treating these disorders--REVIEW 15896483_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15896496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15899246_BDNF polymorphisms are neither robust genetic risk factors nor determinants of BDNF protein levels in Alzheimer's disease 15899246_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15900221_There are two single nucleotide polymorphisms that are not associated with either anorexia nervosa or schizophrenia. 15913870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15913964_No association between BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and genetic risk for schizophrenia in Chinese subjects. Significant relationship between BDNF genotype and logical memory. 15918078_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15935057_These results demonstrate that the reduction of BDNF occurs early in the course of AD and correlates with loss of cognitive function, suggesting that BDNF plays a role in synaptic loss and cellular dysfunction underlying cognitive impairment in AD. 15940292_BDNF polymorphism is involved in the pathogenesis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. 15940299_BDNF variants affect liability to juvenile-onset mood disorders, supported by data from two independent samples. 15949651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15970929_In three case control studies Val66Met polymorphism is not associated with late onset Alzheimer's disease. 15987945_A mechanism to understand the defect associated with variant BDNF and provide a framework two ligands for BDNF and NT-4. 16005437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16005437_The BDNF may be a susceptibility gene for MDD and schizophrenia-in particular, in a subgroup of patients with schizophrenia with a lifetime history of depressive symptoms. 16039058_BDNF plays some role in the neurotoxicity of methamphetamine 16043130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16046000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16046000_The BDNF-Val66Met polymorphism: implications for susceptibility to multiple sclerosis and severity of disease. 16054753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16054753_These results suggest that the BDNF GG genotype has a protection effect from AD development in females. The BDNF GG genotype may reduce the effect of APOEepsilon4 on AD risk in females. 16056149_Interaction of the functional Val66Met polymorphism of the BDNF gene with DR# ser9gly polymorphism influencinf age at onset in schizophrenia. 16105728_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16109452_Genetic polymorphism (Val66Met) may contribute to substance abuse vulnerability. 16109452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16139165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16139165_Results do not in favour an implication of BDNF in unipolar affective disorder. 16152572_BDNF Val66Met allele increases risk for bipolar I disorder in patients of European descent. 16152572_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16152573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16152573_The significant association of BDNF variants with nicotine dependence (ND) implies that this gene plays a role in the etiology of ND in European-Americans and that the involvement of BDNF is gender specific 16166223_BDNF plays role as anorexigenic factor in dorsal vagal complex. BDNF may constitute common downstream effector of leptin and CCK, possibly involved in their synergistic action. 16172806_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16186425_Tissue levels of BDNF have an important role in atherogenesis and plaque instability via the activation of NAD(P)H oxidase. 16222333_The val allele of BDNF may be associated with predisposition to bipolar illness but in bipolar patients gives better performance on complex cognitive tests. 16301096_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16314750_Genetic polymorphism is not associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder. 16343697_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16343697_The BDNF valine66methionine (Val66Met) polymorphism is a relevant risk factor for geriatric depression. 16344533_Homozygosity for a rare allele of the functional BDNF variant was associated with a 5.3-year older onset age for Parkinson disease, suggesting that BDNF may influence PD onset age. 16344533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16356643_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16388065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16388901_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16388901_The Val66Met polymorphism of bdnf may impact on age-related changes of the brain, and genotype effects of the BDNF gene on brain morphology might differ in female from in male. 16389585_Finding suggests that the investigated BDNF polymorphism plays an important role in the phenotype of schizophrenia, but not in the performance of tests of prefrontal cognitive functions analyzed in these patients. 16389585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16391475_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16406671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16441896_Human bronchial smooth muscle cells can express NGF, BDNF and NT-3. Expression may be differently regulated by inflammatory cytokines. Might have potential role in airway inflammation. 16442082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16442082_The presence of the met-BDNF allele was found associated with a reduced volume of the hippocampal formation in healthy volunteers. 16446138_This study provide in vivo evidence for a functional interaction between Mecp2 and Bdnf and demonstrate the physiological significance of altered BDNF expression/signaling in RTT disease progression. 16446742_BDNF genotype was significantly associated with later life Raven scores, controlling for sex, age 11 MHT score and cohort. BDNF genotype was significantly associated with age 79 MHT score, controlling for sex and age 11 MHT score. 16446742_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16458264_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16458264_There was a significant three-way interaction between BDNF(variant val66met) genotype, 5-HTTLPR, and maltreatment history in predicting depression. 16472361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16472361_This study investigates the relationship between Val66Met polymorphisms of the BDNF gene and prefrontal cognitive function in 129 patients with schizophrenia and 111 patients with bipolar mood disorder. 16497333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16513879_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16533563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16533563_Our investigation indicates that the BDNF gene Val66Met polymorphism is related to the onset age of schizophrenia and the levels of clinical symptoms that remain after long-term antipsychotic treatment. 16538178_Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism might not greatly contribute to the efficacy of lithium in bipolar disorder. 16538178_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16541456_obsessive-compulsive disorder and Tourette syndromemay have distinct genetic risk factors related to BDNF polymorphism. 16565926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16568151_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16568151_The BDNF-linked complex polymorphic region is a functional variation that confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder and affects transcriptional activity of the BDNF gene. 16581172_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16604191_Cystamine and cysteamine increase brain levels of BDNF in Huntington disease via HSJ1b and transglutaminase 16606648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16623937_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16627933_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16631352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16633140_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16648150_Results revealed the expression of BDNF mainly in oocytes and, in a minority of samples, also in the granulosa cells (GCs). 16648236_These novel data demonstrate that neurotrophins influence ASM [Ca(2+)](i) and force regulation and suggest a potential role for neurotrophins in airway diseases. 16649215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16649215_There was a nominally higher frequency of the G-712A G-allele and the G/G genotype in subjects with substance dependence than in controls. 16680163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16698101_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16707914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16707914_These findings suggest a possible relationship between Val66Met polymorphism and BMI in healthy adults. 16713371_BDNF is likely to play roles not only in early growth but also in maintenance of neurons throughout life. 16740142_A significant interaction effect between 'MS-status' and the BDNF genotype was found for GM volumes, with the result that patients carrying the BDNF Met-allele showed a higher risk of developing global GM atrophy than the homozygous Val/Val. 16741916_BDNF gene variation may influence brain morphology. 16741916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16741941_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16741941_Results are consistent with previous studies pointing to a role for BDNF in susceptibility to mood disorders. 16786155_Light and electron microscopy immunohistochemistry showed that tonsillar samples were positive for BDNF. 16787706_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16797081_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16807663_levels of BDNF and beta-TG in blood of Alzheimers patients is decreased; BDNF and beta-TG are associated with degree of platelet activation 16818862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16823800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16824691_Several strategies to decrease central BDNF activity that have potential use in the treatment of drug addiction are proposed. [REVIEW] 16846718_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16848784_BDNF V166M polymorphism is not associated with variation in working memory in healthy adolescents. 16848784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16854566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16869232_In the human BDNF gene, resulting in a valine to methionine substitution in the prodomain (Val66Met), has been shown to lead to memory impairment and susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disorders. 16872631_results support an association between the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and sense of coherence such that study participants who were Met carriers were found to have an increased likelihood of a weaker sense of coherence 16876305_No correlations between BDNF levels and clinical variables in autistic patients, but serum levels are lower in autistic patients compared with a control group. 16890377_BDNF is a stress-responsive intercellular messenger modifying hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis activity 16890377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16890384_It is proposed that p11 may act through the tPA/plasminogen/BDNF pathway to achieve its antidepressant effect. 16897602_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16899999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16901635_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16901635_These results suggest that the 196G/A SNP of the human BDNF gene does not contribute to the genetic susceptibility to BN and BED, but may predispose those patients to a more severe binge eating behavior. 16905325_After correction for the predominant effect of the CAG expansion, no multiple regression model provided evidence of association between the BDNF Val66Met genotype and variation in HD age-at-onset. 16905325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16962724_Zinc sulfate could be potential agent for the treatment of Rett syndrome through increasing central BDNF levels. 16979146_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16979146_The Val66Met BDNF polymorphism is associated with citalopram efficacy, with M-allele carriers responding better to citalopram treatment. Moreover, the Val66Met polymorphism was correlated with improvements in core, activity, and psychic anxiety symptoms. 17006024_The role of BDNF in depression is discussed. 17010953_In contrast to short duration aerobic exercise immediately after a following short duration high-intensity exercise to exhaustion, there is a transient augmentation of serum BDNF. 17012654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17036259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17044097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17044097_role of two common BDNF variants (Val66Met, C270T) in two samples of ADHD probands from the United Kingdom (n = 180) and Taiwan (n = 212) 17092970_BDNF G196A polymorphism in part determines the antidepressant effect of both milnacipran and fluvoxamine. 17092970_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17096834_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17096834_neither sequence variations in nor near the BDNF gene contribute significantly to the variance of age at onset in Huntington disease 17130481_A de novo chromosomal inversion, 46,XX,inv(11)(p13p15.3) caused hyperphagia and severe obesity, impaired cognitive function, and hyperactivity in a young girl 17151862_Decreased BDNF may be a pathogenetic factor involved not only in dementia and depression, but also in type 2 diabetes. 17161975_Serum BDNF may be a useful marker of disease activity in atopic dermatitis. Both activated T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and eosinophils are major cellular sources of serum BDNF. 17167336_Single nucleotide polymorphisms are not associated with aggression in childhood and adolescence. 17186223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17196936_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17197106_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17210134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17210134_The sexual abuse scale were negatively associated with memory performance. Furthermore, the low-activity Met allele of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene interacted with sexual abuse scores to result in reduced memory test performance. 17216343_Two exons within BDNF represent potential functional variants that may be causing the observed associations of this protein with attention deficit with hyperactivity. 17217930_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17217930_The study confirms the association of Val66Met to substance-related disorders, eating disorders, and schizophrenia. 17219016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17219016_We did not find support for an involvement of the Val66 allele of the Val66Met polymorphism of BDNF in the pathogenesis of ADHD 17222482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17222482_The BDNF val66met polymorphism may modify the association between stroke and depression. 17229524_In conclusion, our results do not provide statistically significant evidence that common genetic variability in BDNF would associate with the risk for PD in the Caucasian populations studied here. 17229524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17239400_The better functioning val66val allele of BDNF appears to be associated with an increased risk for bipolar disorder and perhaps early onset or rapid cycling. [REVIEW] 17241828_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17267117_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17267117_results do not support a significant role for the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in the development of schizophrenia in Asian populations (Review; Meta-analysis) 17284422_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17284422_SNPs in BDNF gene showed no statistical significance in bipolar disorder. 17289348_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17289348_population-based study and meta-analysis demonstrate that the BDNF C-270T and Val66Met polymorphisms do not play major roles in the susceptibility to schizophrenia in either Caucasian or Asian populations 17293537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17293537_Two SNPs are found between exons VI and VII, while the Val66Met polymorphism is located in the coding exon VIII; the total distance for the three SNPs is 14308 base pairs in Alzheimer disease. 17349978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17349978_Results suggest that BDNF has a possible role in the pathogenesis of autism through its neurotrophic effects on the serotonergic system. 17366345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373693_Observational study of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17375136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17375136_our data provide no support for association in this large OCD patient sample and point toward the need to examine other genes as candidates for risk determinants in OCD. 17376155_Altered BDNF levels modulated by BDNF gene variability are associated with the susceptibility to eating disorders, providing physiological evidence that BDNF plays a role in the development of anorexia nervosa and bulemia nervosa. 17392738_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17392738_The results of this study support the notion that allelic variation at the BDNF locus--in interaction with other gene variants--influences anxiety- and depression-related personality traits. 17401528_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17401528_The combination of 5-HT1A GG and BDNF GA + AA genotypes is associated with an increased risk of depression. 17404118_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17404118_findings suggest that Met-BDNF a |
ENSMUSG00000048482 |
Bdnf |
10.319595 |
6.8467837906 |
2.775426 |
0.589826406 |
25.438141 |
0.00000045679698746485066556942433203813980213681134046055376529693603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001681796840853378822313690492407101118033097009174525737762451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5007019 |
7.0336766 |
2.7265234 |
0.9133212 |
| ENSG00000176714 |
79635 |
CCDC121 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZUS5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:79635; |
|
|
|
|
15.208753 |
0.3418031800 |
-1.548762 |
0.531333145 |
8.438041 |
0.00367451873899333819259438449478238908341154456138610839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007725911194806506232524156985164154320955276489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5570471 |
2.5906778 |
22.5550731 |
4.8230322 |
| ENSG00000176749 |
8851 |
CDK5R1 |
protein_coding |
Q15078 |
FUNCTION: p35 is a neuron specific activator of CDK5. The complex p35/CDK5 is required for neurite outgrowth and cortical lamination. Involved in dendritic spine morphogenesis by mediating the EFNA1-EPHA4 signaling. Activator of TPKII. The complex p35/CDK5 participates in the regulation of the circadian clock by modulating the function of CLOCK protein: phosphorylates CLOCK at 'Thr-451' and 'Thr-461' and regulates the transcriptional activity of the CLOCK-BMAL1 heterodimer in association with altered stability and subcellular distribution. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24235147}. |
3D-structure;Biological rhythms;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene (p35) is a neuron-specific activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5); the activation of CDK5 is required for proper development of the central nervous system. The p35 form of this protein is proteolytically cleaved by calpain, generating a p25 form. The cleavage of p35 into p25 results in relocalization of the protein from the cell periphery to nuclear and perinuclear regions. P25 deregulates CDK5 activity by prolonging its activation and changing its cellular location. The p25 form accumulates in the brain neurons of patients with Alzheimer's disease. This accumulation correlates with an increase in CDK5 kinase activity, and may lead to aberrantly phosphorylated forms of the microtubule-associated protein tau, which contributes to Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8851; |
axon [GO:0030424]; contractile fiber [GO:0043292]; cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; protein kinase 5 complex [GO:0016533]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; beta-tubulin binding [GO:0048487]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0061575]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; ionotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035255]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein kinase activator activity [GO:0030295]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axonal fasciculation [GO:0007413]; brain development [GO:0007420]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching [GO:0009792]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; G1 to G0 transition involved in cell differentiation [GO:0070315]; hippocampus development [GO:0021766]; ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0035235]; layer formation in cerebral cortex [GO:0021819]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; neuron cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007158]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; neuron migration [GO:0001764]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0018107]; positive regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process [GO:0045348]; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031116]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; positive regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:2000273]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061001]; regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016241]; regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045664]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511]; serine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042501]; superior olivary nucleus maturation [GO:0021722] |
9010203_Performed functional studies in mouse. 11784720_Like p25, p29 was more stable than p39 and caused redistribution of Cdk5 in cortical neurons. Our data suggest that neurotoxic insults lead to calpain-mediated conversion of p39 to p29, which might contribute to deregulation of Cdk5. 12226093_cleavage of p35 to p25 greatly enhances the kinase activity of CDK5 and increases the phosphorylation of Ser(202)/Thr(205) and may play a pivotal role in neuronal cell death in Alzheimer's disease 12230554_a short peptide (amino acid residues 154-279; Cdk5 inhibitory peptide; CIP), derived from p35, specifically inhibits Cdk5 activity in vitro and in HEK293 cells cotransfected with the peptide and Cdk5/p25, but had no effect on endogenous cdc2 kinase 12826674_p25-Cdk5 is responsible for the mitotic-like phosphoepitopes present in neurofibrillary tangles 12859671_Neither the CDK5 activator p25 immunoreactivity nor the p25/p35 ratio was elevated in Alzheimer disease brains or in other tauopathies (n = 34) compared with controls (n = 11) 14976144_Expression of p35 and CDK5 in insulin-producing beta-cellsis new signaling pathway controlled by glucose, and its functional role may comprise regulation of various biological processes in beta-cells, such as expression of the insulin gene. 15123618_These results suggest that Cdk5/p35 and p25 are novel players in digoxin-triggered prostate cancer cell apoptosis and, therefore, become potential therapeutic targets. 15175076_significantly lower levels of cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 (p35) gene transcripts were detected in gangliogliomas compared to controls 15342635_CK2 acts as an inhibitor of Cdk5 in the brain 15492003_data suggest that Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5)-Cdk5 activator p35 is required to elicit the maximum GTP-induced secretory response from neutrophils 15536496_Cdk5 activity and p35 translocation in the ventral striatum were upregulated in methamphetamine sensitized rats. 15741232_an early event in neuronal cell death is p25/Cdk5-mediated retinoblastoma phosphorylation 15917097_role of the CDK5 molecular complex in the genetic etiology of early-onset Alzheimer disease; a yet unknown functional variant in CDK5 or in a nearby gene might lead to increased susceptibility for early onset Alzheimer disease 16407256_molecular analysis of the CDK5/p25 and CDK2/cyclin A systems 16425041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16425041_novel mutations and novel polymorphisms in coding regions and 3'UTR were detected in patients with with non-syndromic mental retardation 16678793_Cdk5 and Erk1/2 kinases share some common substrates but impact of their cross talk on tau phosphorylation has not previously been demonstrated. 17036052_nestin is a survival determinant whose action is based upon a novel mode of Cdk5 regulation, affecting the targeting, activity, and turnover of the Cdk5/p35 signaling complex 17060323_p35 employs pathways distinct from that used by Cdk5 for transport to the nucleus 17121855_phosphorylation of Thr(138) predominantly defines the susceptibility of p35 to calpain-dependent cleavage and dephosphorylation of this site is a critical determinant of Cdk5-p25-induced cell death associated with neurodegeneration 17491008_p35 is a microtubule-associated protein that modulates microtubule dynamics 17493033_Increased expression of Cdk5 was seen in stroke-affected tissue, with about a third showing increased p35 and p25 cleaved fragment. Increased Cdk5-, p-Cdk5- and p35-positive neurons and microvessels occurred in stroke-affected regions. 17496813_This experiment demonstrate increased immunoreactivity for the activators of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in post-mortem human hippocampi affected by the neurodegenerative condition hippocampal sclerosis. 18053171_the involvement of 3'-UTR in the modulation of CDK5R1 expression 18247371_Data demonstrate that a decrease in the level of Egr-1, one of the targets for MAPK, by Tat has a negative impact on the level of p35 expression in NGF-treated neural cells. 18325333_p35 co-expression targets E-cadherin to lysosomes and p35-triggered disappearance of E-cadherin precursor can be blocked specifically by lysosomal protease inhibitors, indicating p35 induces endocytosis and subsequent degradation of precursor E-cadherin 18829967_p25 and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 play important roles as mediators of dopamine and glutamate in the neurotoxicity associated with Huntington's disease. 19154537_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19154537_Subjects carrying both the CDK5R1 (3'-UTR, rs735555) AA genotype and the GSK-3beta (-50, rs334558) CC genotype had a 12.5-fold decrease in Alzheimer disease risk suggesting synergistic effects (epistasis) between both genes 19638632_a role for Cdk5-p35 as a survival factor in countering MPP+-induced neuronal cell death. 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20097924_These are the first quantitative and site-specific measurements of phosphorylation of p35 20354813_CDK5/p35 may represent a biomarker for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer 20518484_both proteasomal degradation and calpain cleavage of p35 and p39 are stimulated by membrane association, which is in turn mediated via myristoylation of their p10 regions. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21130530_The present study dissects the role of 3 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs334558 and rs6438552 of GSK3B, and rs735555 of CDK5R1) in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis among eastern Indians. 21220307_Study reveals a unique role of Cdk5/p35 in activation of the major noncanonical function of EPRS, namely translational control of macrophage inflammatory gene expression. 21544067_The decrease in membrane-associated p35 in socially isolated transgenic mice reduces associated levels of p35, alpha-CaMKII, and GluR1 and leads to endocytosis of AMPA receptors. 21625387_findings indicate that miR-103 and miR-107 regulate CDK5R1 expression, allowing us to hypothesize that a miRNA-mediated mechanism may influence CDK5 activity and the associated molecular pathways 21772061_This study suggested that reduced p35 expression in schizophrenia has an impact on synaptic protein expression and cognition and that these deficits can be rescued, at least in part, by the inhibition of histone deacetylase 1. 22964075_Reduced p35 basal content and down--regulation of CDK5/p35/p25 by antipsychotics are demonstrated in postmortem prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic subjects. 23151508_p10, the N-terminal domain of p35, protects against CDK5/p25-induced neurotoxicity. 24085300_Structural basis for the different stability and activity between the Cdk5 complexes with p35 and p39 activators. 24550687_Expression of p35 is upregulated in human pituitary adenomas. 24725413_These results reveal a physiological role of p25 production in synaptic plasticity and memory and provide new insights into the function of p25 in Abeta-associated neurotoxicity and Alzheimer's disease-like pathology. 24802945_Cdk5/p35 is required for motor learning and involved in long-term synaptic plasticity. 25391294_Under cell-free in vitro conditions, p35 is covalently modified by SUMO1. SUMO2 is conjugated to p35 in cells. The 2 major SUMO acceptor lysines in p35 are K246 and K290. Different degrees of oxidative stress resulted in differential p35 sumoylation. 26657932_the minor allele of CDK5R1 3'-UTR rs735555 polymorphism was associated with increased risk for NS-ID. In conclusion, our data suggest that mutations and polymorphisms in CDK5 and CDK5R1 genes may contribute to the onset of the NS-ID phenotype 27343180_the downregulation of the miR-15/107 family might have a role in the pathogenesis of AD by increasing the levels of CDK5R1/p35 and consequently enhancing CDK5 activity. 27387995_It is shown that p5 binds the kinase at the same CDK5/p25 and CDK5/p35 interfaces, and is thus a non-selective competitor of both activators, in agreement with available experimental data in vitro. 29997370_Study demonstrated that NEAT1 and HOTAIR negatively regulate CDK5R1 mRNA levels, while MALAT1 has a positive effect. 30718749_The Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5 Inhibitor Peptide Inhibits Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Replication. 33346796_Elevated CDK5R1 predicts worse prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on TCGA data. |
ENSMUSG00000048895 |
Cdk5r1 |
53.823949 |
0.4957863406 |
-1.012210 |
0.234533925 |
18.760332 |
0.00001482181420273090110000142882729079474302125163376331329345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000045548610791652734044315797845570159552153199911117553710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.3878207 |
5.2252394 |
73.7903176 |
7.1466726 |
| ENSG00000176788 |
10409 |
BASP1 |
protein_coding |
P80723 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Isopeptide bond;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a membrane bound protein with several transient phosphorylation sites and PEST motifs. Conservation of proteins with PEST sequences among different species supports their functional significance. PEST sequences typically occur in proteins with high turnover rates. Immunological characteristics of this protein are species specific. This protein also undergoes N-terminal myristoylation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]. |
hsa:10409; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; PML body [GO:0016605]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; diaphragm development [GO:0060539]; gonad development [GO:0008406]; mesenchymal to epithelial transition [GO:0060231]; metanephric mesenchyme development [GO:0072075]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; podocyte differentiation [GO:0072112]; positive regulation of heart growth [GO:0060421]; positive regulation of metanephric ureteric bud development [GO:2001076]; substantia nigra development [GO:0021762]; thorax and anterior abdomen determination [GO:0007356] |
14701728_BASP1 can confer WT1 cosuppressor activity in transfection assays, and elimination of endogenous BASP1 expression augments transcriptional activation by WT1. 18268500_proteomic assessments of membrane microdomains in prefrontal cortex and validation in two brain series, strongly implicates LAMP, STXBP1 and BASP1 in schizophrenia and supports the view of a neuritic and synaptic dysfunction in the neuropathology 18949357_Identification of novel aberrant methylation of BASP1 and SRD5A2 for early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by genome-wide search. 19376485_BASP1 and TPPsig-BASP1 genes were not involved in the etiology of Mobius syndrome. 19956849_BASP1 and SRD5A2 are methylated in early hepatocellular carcinoma 21269271_Results suggest that BASP1 and WT1 play concerted, central roles in directing cell fate during differentiation. Here, BASP1/WT1 work to divert K562 cells away from blood cell lineage toward neuron phenotype. 22939983_Repression of transcription by WT1-BASP1 requires the myristoylation of BASP1 and the PIP2-dependent recruitment of histone deacetylase. 24166496_Findings provide new insights into the function of prohibitin in transcriptional regulation and uncover a BASP1-prohibitin complex that plays an essential role in the PIP2-dependent recruitment of chromatin remodeling activities to the promoter. 24350992_Sequestration by BASP1 renders cells increasingly resistant to abrin toxicity. 25919928_Data suggest methylation status of gene promoters for BASP1 (brain abundant membrane attached signal protein 1) and CDH11 (cadherin 11) in tumor, skin, and metastatic tumor tissue may serve as prognostic biomarkers in patients with advanced melanoma. 27270539_Downregulation of BASP1 expression may play a role in the tumorigenesis of thyroid cancer. 28212542_we uncover a novel polymorphism, rs187843643 (OR = 1.96; 95% CI = [1.54, 2.48]; P = 3.53 x 10-8), associated with melanoma. The SNP rs187842643 lies within a noncoding RNA 177kb downstream of BASP1 (brain associated protein-1). We find that BASP1 expression is suppressed in melanoma as compared with benign nevi, providing additional evidence for a putative role in melanoma pathogenesis. 28492543_data have identified BASP1 as an ERalpha cofactor that has a central role in the transcriptional and antitumourigenic effects of tamoxifen. 29674693_data suggest that BASP1 silencing via promoter methylation may be involved in A/E-mediated leukemogenesis and that BASP1 targeting may be an actionable therapeutic strategy in t(8;21) AML. 30982764_Bioinformatic analysis and clinical data from our study suggest that BASP1 and its putative interaction partner WT1 can be used as biomarkers for predicting outcomes in pancreatic cancer patients. 31944520_The brain acid-soluble protein 1 (BASP1) interferes with the oncogenic capacity of MYC and its binding to calmodulin. 33042262_Targeting positive feedback between BASP1 and EGFR as a therapeutic strategy for lung cancer progression. 33247706_Overexpression of BASP1 Indicates a Poor Prognosis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 34266955_Cholesterol is required for transcriptional repression by BASP1. 34531104_BASP1 is up-regulated in tongue squamous cell carcinoma and associated with a poor prognosis. |
ENSMUSG00000045763 |
Basp1 |
279.184982 |
2.0328023069 |
1.023470 |
0.114650978 |
79.485469 |
0.00000000000000000048578504388119284550456620561335908336532466630241925212296827396585285896435379981994628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000004123166904937553634418338912653538408153306749781173354274521614115656120702624320983886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
378.3281954 |
24.1861277 |
187.2911037 |
9.2748934 |
| ENSG00000176809 |
374819 |
LRRC37A3 |
protein_coding |
O60309 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374819; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
ENSMUSG00000034239+ENSMUSG00000078632 |
Gm884+Lrrc37a |
52.713254 |
0.4089966326 |
-1.289839 |
0.441189385 |
8.256953 |
0.00405962146471078050985470397904464334715157747268676757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008454919263317499725229886564648040803149342536926269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.0830854 |
8.1377642 |
72.2079853 |
13.9779338 |
| ENSG00000176845 |
284207 |
METRNL |
protein_coding |
Q641Q3 |
FUNCTION: Hormone induced following exercise or cold exposure that promotes energy expenditure. Induced either in the skeletal muscle after exercise or in adipose tissue following cold exposure and is present in the circulation. Able to stimulate energy expenditure associated with the browning of the white fat depots and improves glucose tolerance. Does not promote an increase in a thermogenic gene program via direct action on adipocytes, but acts by stimulating several immune cell subtypes to enter the adipose tissue and activate their prothermogenic actions. Stimulates an eosinophil-dependent increase in IL4 expression and promotes alternative activation of adipose tissue macrophages, which are required for the increased expression of the thermogenic and anti-inflammatory gene programs in fat. Required for some cold-induced thermogenic responses, suggesting a role in metabolic adaptations to cold temperatures (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Hormone;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable hormone activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including brown fat cell differentiation; energy homeostasis; and positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284207; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0090336]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to muscle activity [GO:0014850] |
24393292_Results show that Subfatin is a novel adipokine regulated by adipogenesis and obesity, with tissue distribution different from its homologue Meteorin 26307585_Data suggest that there is no correlation between serum Metrnl levels and BMI (body mass index) in humans. 27716826_Overexpression of METRNL inhibited mineralized nodule formation. 27748745_downregulation of METRNL during adipogenesis and functional induction of increased proliferation in stromal vascular fraction cells with concomitant inhibition of adipocyte differentiation may result in hypertrophic AT accumulation 30212581_Lower serum levels of Metrnl in patients with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus are negatively associated with insulin resistance and inflammatory cytokines. 30394666_Serum Metrnl is associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease in Chinese patients. 30463448_Serum levels of subfatin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with vascular adhesion molecules. 30825562_Low Serum Metrnl is associated with worsening of glucose tolerance, impaired endothelial function and atherosclerosis. 31442362_Myokines in skeletal muscle physiology and metabolism: Recent advances and future perspectives. 31635130_Data shows elevated METRNL plasma levels in individuals with T2D, further exacerbated with obesity. Additionally, a strong positive association was observed between METRNL and irisin. 32068104_Maternal and umbilical cord blood subfatin and spexin levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. 32330176_Circulating levels of Meteorin-like protein in polycystic ovary syndrome 33126870_Characterization of the serum levels of Meteorin-like in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and its association with inflammatory cytokines. 33248913_Potential emerging roles of the novel adipokines adipolin/CTRP12 and meteorin-like/METRNL in obesity-osteoarthritis interplay. 35709278_Meteorin-like promotes heart repair through endothelial KIT receptor tyrosine kinase. 36036749_Decreased serum interleukin-41/Metrnl levels in patients with Graves' disease. 36084603_Elevated levels of Metrnl in rheumatoid arthritis: Association with disease activity. |
ENSMUSG00000039208 |
Metrnl |
583.823408 |
2.0773186082 |
1.054723 |
0.068823807 |
236.729035 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002032085517897793280706494856382716507787421385659751432003716657963816941966039758466556892295240002198882891110215518419164450353590813808102311099901271518319845199584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000462150727953334779096426989947424122341923114172099366785664397186971717498979475644818644645355998168849837506178817478508489581794788092494741249538492411375045776367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
797.0372623 |
33.5605186 |
386.2667481 |
12.7633912 |
| ENSG00000176868 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.271533 |
0.0242369169 |
-5.366650 |
2.142091960 |
5.119714 |
0.02365551103071036193048470863686816301196813583374023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.041730051728610606520675219144322909414768218994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6107058 |
6.5212588 |
62.6968728 |
130.9119185 |
| ENSG00000176953 |
84901 |
NFATC2IP |
protein_coding |
Q8NCF5 |
FUNCTION: In T-helper 2 (Th2) cells, regulates the magnitude of NFAT-driven transcription of a specific subset of cytokine genes, including IL3, IL4, IL5 and IL13, but not IL2. Recruits PRMT1 to the IL4 promoter; this leads to enhancement of histone H4 'Arg-3'-methylation and facilitates subsequent histone acetylation at the IL4 locus, thus promotes robust cytokine expression (By similarity). Down-regulates formation of poly-SUMO chains by UBE2I/UBC9 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84901; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein sumoylation [GO:0016925] |
20410506_ZBTB25 functions as a negative regulator of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-AT) activation, such that RNA interference mediated knockdown resulted in enhanced activation of target genes. 29693310_interactions of fat intake with the genetic (rs11150675) and transcriptional (ILMN_1725441) variations at the NFATC2IP locus on 2-year weight change. cis-DNA methylation at cg26663590 of the NFATC2IP locus showed an opposite impact on weight-loss in response to high-fat vs low-fat diet. baseline methylation at cg26663590 causally mediated 52.8% of the effect of rs11150675 on 2-year weight-loss in the high-fat diet group 31666531_Targeted deletion of NFAT-Interacting-Protein-(NIP) 45 resolves experimental asthma by inhibiting Innate Lymphoid Cells group 2 (ILC2). 34265397_Calcium channel TRPV6 promotes breast cancer metastasis by NFATC2IP. |
ENSMUSG00000030722 |
Nfatc2ip |
467.250143 |
0.4363757053 |
-1.196357 |
0.305544185 |
14.203300 |
0.00016408249739699733399204972794649393108556978404521942138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000436770764758930289846372563289378376794047653675079345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
270.1668894 |
52.4527476 |
622.7685743 |
87.2281832 |
| ENSG00000177105 |
391 |
RHOG |
protein_coding |
P84095 |
FUNCTION: Required for the formation of membrane ruffles during macropinocytosis. Plays a role in cell migration and is required for the formation of cup-like structures during trans-endothelial migration of leukocytes. In case of Salmonella enterica infection, activated by SopB and ARHGEF26/SGEF, which induces cytoskeleton rearrangements and promotes bacterial entry. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15133129, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17074883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17875742, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20679435}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Rho family of small GTPases, which cycle between inactive GDP-bound and active GTP-bound states and function as molecular switches in signal transduction cascades. Rho proteins promote reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and regulate cell shape, attachment, and motility. The encoded protein facilitates translocation of a functional guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) complex from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane where ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 is activated to promote lamellipodium formation and cell migration. Two related pseudogene have been identified on chromosomes 20 and X. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:391; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell projection assembly [GO:0030031]; cortical cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030865]; engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:0043652]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; Rac protein signal transduction [GO:0016601]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of neutrophil migration [GO:1902622]; regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900027]; Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0007266] |
12376551_RhoG function is mediated by signals independent of Rac1 and Cdc42 activation and instead by direct utilization of a subset of common effectors 12545154_we show a novel function for the small GTPase RhoG on the regulation of the interferon-gamma promoter and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) gene. RhoG also promotes T-cell spreading on fibronectin 15199069_C-terminal basic tail of RhoG specifically assists the recruitment of the TrioN-PH domain to specific membrane-bound phospholipids 16339170_Results suggest that RhoG contributes to the regulation of Rac1 activity in migrating cells. 16568096_RhoG is involved in caveolar trafficking. Such translocation is associated with changes in RhoG GDP/GTP levels and is highly dependent on lipid raft integrity and on the function of the GTPase dynamin2. 16621998_define RhoG as a critical component of G protein-coupled receptor-stimulated signaling cascades in murine neutrophils 17027967_Taken together, these results suggest that Dock4 plays an important role in the regulation of cell migration through activation of Rac1, and that RhoG is a key upstream regulator for Dock4. 17570359_RhoG protects cells from apoptosis caused by the loss of anchorage through a PI3K-dependent mechanism, independent of its activation of Rac1. 17875742_These results identify a new signaling pathway involving RhoG and its exchange factor SGEF downstream from ICAM1 that is critical for leukocyte trans-endothelial migration. 19208761_Results suggest that RhoG is a central target of the Yersinia stratagem and a major upstream regulator of Rac1 during different phases of the Yersinia infection cycle. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20679435_The activation of RhoG recruits its effector ELMO2 and a Rac GEF Dock4 to form a complex with EphA2 at the tips of cortactin-rich protrusions in migrating breast cancer cells. 22251971_The authors show that enteropathogenic Escherichia coli translocates EspH, which inactivates mammalian RhoGEFs and triggers cytotoxicity. 22383878_The invasive capacity of HPV transformed cells requires the hDlg-dependent enhancement of SGEF/RhoG activity. 22683270_several Rho family small GTPases activate PI3K by an indirect cooperative positive feedback that required a combination of Rac, CDC42, and RhoG small GTPase activities 24106269_RhoG is expressed and activated in platelets, plays an important role in GPVI-Fc receptor gamma-chain complex-mediated platelet activation, and is critical for thrombus formation in vivo. 26746014_This study describes the regulation of EMT in RPE cells by TGF-beta1/miR-124/RHOG signaling and suggests that the supplement of miR-124 exogenously would be a valuable therapeutic approach for the prevention or treatment of proliferative vitreoretinopathy. 27437949_yrosine phosphorylation of SGEF suppresses its interaction with RhoG, the elevation of RhoG activity, and SGEF-mediated promotion of cell migration. We identified tyrosine 530 (Y530), which is located within the Dbl homology domain, as a major phosphorylation site of SGEF by Src, and Y530F mutation blocked the inhibitory effect of Src on SGEF 27539661_These data suggest a novel link between Tiam1 and RhoG/ILK /ELMO2 pathway as upstream effectors of the Rac1-mediated phagocytic process in trabecular meshwork cells. 27832197_These results suggest that the levels of RhoG and RhoB GTPases and their negative regulator RhoGDI3 might be linked to the aggressiveness of the pancreatic cancerous cell lines. It is possible that RhoGDI3 could induce the downregulation of RhoG and RhoB. 28202690_RhoG and SGEF modulate the phosphorylation of paxillin, which plays a key role during invadopodia disassembly. 29454349_High RHOG expression is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 30781697_siRNA-mediated depletion of RHOG strongly inhibits tube formation in vascular endothelial cells (ECV cells), an effect reversed by transfecting dominant active constructs of CDC42 or RAC1 in the RHOG-depleted cells. 30914742_The small GTPase RhoG regulates microtubule-mediated focal adhesion disassembly. 31793126_RhoG/Rac1 signaling pathway was involved in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma (SACC) cell migration and invasion. RhoG/Rac1 at least partially mediated epiregulin/Src/AKT/ERK1/2 signaling to promote SACC cell migration and invasion. 32963317_Regulation of Ras homolog family member G by microRNA-124 regulates proliferation and migration of human retinal pigment epithelial cells. 33513601_RhoG deficiency abrogates cytotoxicity of human lymphocytes and causes hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. 33649803_miR1243p inhibits the viability and motility of glioblastoma multiforme by targeting RhoG. |
ENSMUSG00000073982 |
Rhog |
628.906192 |
2.1447435526 |
1.100805 |
0.076234481 |
208.216573 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003364857768545989480204728090750878087456778000810283405028836843829899745340781527136761943370057388529061474891448425827977786184419528581202030181884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000672060902080362742839653156198498314684334239511827796277305550378869094512287750578902064246712589027219183801146280485272477278613223461434245109558105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
864.8742139 |
35.9917145 |
406.1493288 |
13.2149974 |
| ENSG00000177150 |
125228 |
FAM210A |
protein_coding |
Q96ND0 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in the structure and strength of both muscle and bone. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BGY7}. |
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:125228; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29618611_Genetic variation near FAM210A, a gene of previously unknown function, was strongly associated with both appendicular and whole body lean mass, as well as bone mineral density. |
ENSMUSG00000038121 |
Fam210a |
92.995443 |
2.0366213447 |
1.026178 |
0.203468179 |
25.360386 |
0.00000047558487053396296395996385199256284437296926626004278659820556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001748351852822239978649883525296804265281025436706840991973876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
127.9085548 |
18.4763341 |
63.2339969 |
6.8658432 |
| ENSG00000177191 |
374907 |
B3GNT8 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z7M8 |
FUNCTION: Beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase that plays a role in the elongation of specific branch structures of multiantennary N-glycans. Has strong activity towards tetraantennary N-glycans and 2,6 triantennary glycans. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15620693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15917431}. |
Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000305}. |
Enables protein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity. Involved in poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374907; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; protein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0016262]; UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0008499]; UDP-glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0008194]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0030311] |
15486459_highly expressed in lung, throat and ileum, whereas the expression level was low in tongue, breast, uteri, testis. In addition, it was also demonstrated that B3GALT7 is differentially transcribed in human tumor cell lines. 15620693_The cloning of a novel beta1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase that is upregulated in a human colon cancer cell line. 18826941_up-regulation of beta3Gn-T8 in differentiated cells increases poly-N-acetyllactosamine chains by activating intrinsic beta3Gn-T2. 20963502_These results reveal a new mechanism by which beta3Gn-T8 can regulate MMP-2 and TIMP-2. 21468598_The down-regulation of beta3Gn-T8 caused significant inhibition of tumor cell growth in vitro. 22901175_High beta3Gn-T8 expression is associated with laryngeal carcinoma. 24573103_we suggest that beta3GnT8 plays a key role in the metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by altering the beta1,6-branched polylactosamine sugars of CD147. 24715095_The results demonstrated a critical role of beta3GnT8 in the metastatic potential of glioma cells, indicating that manipulating beta3GnT8 expression may have therapeutic potential for the treatment of malignant glioma. 24970053_Study shows that beta3GnT8 is involved in the regulation of CD147 N-glycosylation and further influences MMP-2 expression in tumor cells suggesting that it may play an important role in the CD147 signaling as an upstream modulator of MMP-2 in tumor cells. 25269761_In conclusion, the alteration of b3GnT8 in colorectal cancer cells correlates with tumor sensitivity to the chemotherapeutic drug and has significant implication for the development of new treatment strategies. 27459970_Cjun plays a significant role in regulating the expression of beta3GnT8 in the SGC7901 cell line. 29393491_These results revealed that b3GnT8 may play a key role in the development of oxaliplatin resistance in colon cancer cells possibly through the alteration of the glycosylation of integrin beta1. These findings may be valuable for overcoming drug resistance in colon cancer 32945502_Nglycosylation and receptor tyrosine kinase signaling affect claudin3 levels in colorectal cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000059479 |
B3gnt8 |
80.719361 |
0.2176014146 |
-2.200240 |
0.919708263 |
5.110375 |
0.02378318009864331325498021385556057794019579887390136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.041940231571801107890440363235029508359730243682861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.4406232 |
15.7654457 |
146.5004424 |
50.4622169 |
| ENSG00000177238 |
493829 |
TRIM72 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMU5 |
FUNCTION: Muscle-specific protein that plays a central role in cell membrane repair by nucleating the assembly of the repair machinery at injury sites. Specifically binds phosphatidylserine. Acts as a sensor of oxidation: upon membrane damage, entry of extracellular oxidative environment results in disulfide bond formation and homooligomerization at the injury site. This oligomerization acts as a nucleation site for recruitment of TRIM72-containing vesicles to the injury site, leading to membrane patch formation. Probably acts upstream of the Ca(2+)-dependent membrane resealing process. Required for transport of DYSF to sites of cell injury during repair patch formation. Regulates membrane budding and exocytosis. May be involved in the regulation of the mobility of KCNB1-containing endocytic vesicles (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Exocytosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-nitrosylation;Transport;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including cellular protein metabolic process; plasma membrane repair; and protein homooligomerization. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway; and negative regulation of myotube differentiation. Predicted to be located in cytoplasmic vesicle membrane. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and sarcolemma. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:493829; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; muscle system process [GO:0003012]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0043569]; negative regulation of myotube differentiation [GO:0010832]; plasma membrane repair [GO:0001778]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
19129174_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19967786_Crystal structure of PRY-SPRY domain of human TRIM72. 21343302_membrane-delimited interaction between MG53 and PTRF contributes to initiation of cell membrane repair 21412170_MG53, annexin A1, and dysferlin localize to the t-tubule network and show enriched labeling at longitudinal tubules of the t-system in overstretch 22253476_data reveal NM-IIA as a key cytoskeleton motor protein that facilitates vesicle trafficking during MG53-mediated cell membrane repair 23699904_MG53/TRIM72 protein can be directly applied as a therapeutic agent to increase membrane repair capacity of many cell types. 24344130_MG53 induces FAK ubiquitination with the aid of UBE2H during skeletal myogenesis. 25869134_Zn(2+) interacts with MG53 in protection against injury to the cell membrane 26306047_MG53 is a facilitator of rapid injury repair, a mediator of cell migration, and a modulator of myofibroblast differentiation during wound healing 26790476_MG53 is an effective biomarker of myocardial injury and dysfunction in murine hearts. However, MG53 is not expressed in human heart and therefore does not hold utility as a clinical biomarker of myocardial injury 29268030_CRIg is a novel interacting partner of TRIM72 in the lung. 29806630_serum TRIM72 may be a potential biomarker for the diagnosis and the prognosis of colon cancer. 30852740_TRIM72 Immunohistochemical Expression Can Predict Relapse in Colorectal Carcinoma. 31779687_MG53 enhances the efficacy of hUC-MSCs in the recovery of TBI, indicating that such adjunctive therapy may provide a novel strategy to lessen damage and optimize recovery for brain injury. 32471489_TRIM72 promotes alveolar epithelial cell membrane repair and ameliorates lung fibrosis. 32681036_MG53 suppresses interferon-beta and inflammation via regulation of ryanodine receptor-mediated intracellular calcium signaling. 33000676_MG53/CAV1 regulates transforming growth factor-beta1 signaling-induced atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation. 33566837_MG53 is not a critical regulator of insulin signaling pathway in skeletal muscle. 33744959_Functional and Adaptive Significance of Promoter Mutations That Affect Divergent Myocardial Expressions of TRIM72 in Primates. 34521423_MG53 suppresses tumor progression and stress granule formation by modulating G3BP2 activity in non-small cell lung cancer. 34958003_Ubiquitination and degradation of MGMT by TRIM72 increases the sensitivity of uveal melanoma cells to Dacarbazine treatment. 35324524_TRIM72 exerts antitumor effects in breast cancer and modulates lactate production and MCT4 promoter activity by interacting with PPP3CA. 35438597_MG53 represses high glucose-induced inflammation and angiogenesis in human retinal endothelial cells by repressing the EGR1/STAT3 axis. 36053137_Cryo-EM structure of human MG53 homodimer. |
ENSMUSG00000042828 |
Trim72 |
20.123556 |
0.4908747338 |
-1.026573 |
0.336078133 |
9.483823 |
0.00207291595677018460758267437427093682345002889633178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004561156756399511839894511666670950944535434246063232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2698144 |
2.9516366 |
27.3329852 |
3.9209558 |
| ENSG00000177272 |
3738 |
KCNA3 |
protein_coding |
P22001 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a potassium-selective channel through which potassium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Potassium channels represent the most complex class of voltage-gated ion channels from both functional and structural standpoints. Their diverse functions include regulating neurotransmitter release, heart rate, insulin secretion, neuronal excitability, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume. Four sequence-related potassium channel genes - shaker, shaw, shab, and shal - have been identified in Drosophila, and each has been shown to have human homolog(s). This gene encodes a member of the potassium channel, voltage-gated, shaker-related subfamily. This member contains six membrane-spanning domains with a shaker-type repeat in the fourth segment. It belongs to the delayed rectifier class, members of which allow nerve cells to efficiently repolarize following an action potential. It plays an essential role in T-cell proliferation and activation. This gene appears to be intronless and it is clustered together with KCNA2 and KCNA10 genes on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3738; |
axon [GO:0030424]; calyx of Held [GO:0044305]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005251]; outward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0015271]; voltage-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005244]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; optic nerve development [GO:0021554]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] |
12150982_role in apoptosis induced by actinomycin D 12604782_distribution of FLAG epitope-tagged Kv1.3 channels (Kv1.3/FLAG) significantly differs from the stochastic Poisson distribution in the plasma membrane of human T lymphoma cells 12632187_manipulation of membrane cholesterol changed both the kinetic properties of Kv1.3 and steady-state parameters of activation by modifying lipid-protein interactions. 12807917_Fas ligand increases Kv1.3 channel activity through the same canonical apoptotic signaling cascade that is required for potassium efflux, cell shrinkage, and apoptosis 12850541_In different glioma samples investigated for expression of KV1.3 potassium channels, no correlation of expression with glioma entities and malignancy grades is evident for KV1.3. 12909584_Of 13 voltage-gated K+ (Kv) potassium channels sought, only Kv1.3 mRNA was present. Kv1.3 sets the resting potential of the cells, but it is not required for Fc receptor-mediated phagocytosis. 14745040_Localization of Kv1.3 channels in the IS might open an unrevealed possibility in the regulation of ion channel activity by signaling molecules accumulated in the immune synapse. 15632141_study of the mitochondrial localization of Kv1.3 16043714_Kv1.3 is highly expressed in postmortem multiple sclerosis brain inflammatory infiltrates. 16317062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16729292_functional role of K(v)1.5 and K(v)1.3 on activated human dendritic cells 17088564_T cells with other antigen specificities from these patients, or autoreactive T cells from healthy individuals and disease controls, express low levels of Kv1.3 and are predominantly naive or central-memory (T(CM)) cells 17160583_The influence of extracellular pH and zinc ions (Zn(2+)) on the steady-state inactivation of Kv1.3 channels expressed in human lymphocytes, was investigated. 17242956_Cholesterol depletion causes significant, reversible alterations in the Kv1.3 channel function in Jurkat cells. 17579055_Defective temporal and spatial Kv1.3 channel distribution may contribute to the abnormal functions of T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. 17582781_Ketanserin acts directly on the open state of the Kv1.3 channel, reducing current flow. Augmentation of extracellular [K] enhances current flow through the channel. 17854350_The Kv1.3 potassium channel, postsynaptic density protein 95, and insulin receptor serine kinase co-localize to regulate membrane excitability and synaptic transmission at critical locations in the olfactory bulb. 17878353_Specific Kv1.3 blockers may be beneficial in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis in which effector memory T cells are found in the target organ 18611390_The stimulation of CD28 in addition to CD3 strongly inhibits Kv1.3 current and this additive inhibition is mediated by CD45 activation. 18818304_These findings suggest that Bax mediates cytochrome c release and mitochondrial depolarization in lymphocytes, at least in part, via its interaction with mitochondrial Kv1.3. 19104661_The effects of clofazimine provide the first line of experimental evidence in support of a causal relationship between Kv1.3 and calcium oscillation in human T cells. 19295169_novel inhibitory effects of phosphoinositides and SDF-1alpha on Kv1.3 current may have a significant function as a downregulation mechanism of Kv1.3 activity for the maintenance of T lymphocyte activation in immune responses 19371328_Conclude that the wild-type hK(v)1.3 channel undergoes at least two different conformational changes before finally closing with a low verapamil affinity in one open state and a high verapamil affinity in the other open state. 19409928_Tregs from multiple sclerosis patients had fewer K(V)1.3 channels than naive cells and there was no difference in the membrane capacitance or channel density between the two subtypes of cells. 19465885_Methylation of KV1.3 gene promoter could explain the decrease of KV1.3 expression in pancreatic adenocarcinomas. 19489042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19489042_Study found evidence for Kv1.3 role in olfactory function & possible diabetes link: olfactory impairment found in homozygous carriers of Kv1.3 polymorphism rs2821557; then, olfactory dysfunction correlates with higher HbA1c & fasting plasma glucose. 19574640_preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the tetramerization domain 19590190_DNA methylation is responsible for a decrease of K(v)1.3 gene expression in breast adenocarcinoma and is associated with poorly differentiated tumors and younger patients. 19712592_The expression level of Kv1.3 in each stage of breast cancer using mRNA isolated from breast cancer patients and in immortalized and tumorigenic human mammary epithelial cells, was evaluated. 19841189_upon Ag presentation, membrane-incorporated Kv1.3 channels move along the plasma membrane to localize in the IS. 19850126_Given that glutamate is present in plasma and that both mGluRs and K(V)1.3 channels regulate T-lymphocyte responsiveness, our finding may account for the presence of immune-associated alterations in AD. 19959227_trafficking abnormalities contribute to defective signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus T cells 19961728_Kv1.3 channels of peripheral CD4(+)T cell and CD28(null)/CD28(+)T cells from acute coronary syndrome patients significantly increased after activation. 20060838_investigation of native Kv1.3 channel, including transmembrane and linker segments synthesized in sequence. These native segments form helices vectorially (N- to C-terminus) only in a permissive vestibule located in the last 20 A of the tunnel. 20114030_role of this channel in the sequence of events leading to Bax-induced cytochrome c release 20371822_Release of granzyme B impairs neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation through the expression of potassium channel subunit Kv1.3. 20601376_higher expression on major T-lymphocyte subsets of newborns compared to adult ones except for T(h)1 lymphocytes 20603149_increased impact on T-lymphocyte activation in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients 20798505_A comparison of the expression patterns of Kv1.3 and Kv1.5 in the human fetus. 20865378_Kv1.3 contributes an unusual nonconducting role - the detection of metabolic state. 20884640_K(V)1.3 potassium channels are functional in proliferating mouse and human vascular smooth muscle cells and have positive effects on cell migration. Blockers of the channels may be useful as inhibitors of neointimal hyperplasia. 21087602_treatment with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against Kv1.3, significantly blocked A549 cells' proliferation 21220411_A mutation in Kv1.3 (A413C) doubles the stoichiometry of emopamil but not verapamil for blocking the channel. 21586699_findings are not supportive of a role for Kv1.3 in the modulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity 21726550_PDZ binding domain-dependent interactions affect both Kv1.3 localization (plasma membrane vs. golgi complex) and electrophysiological function. PDZ interactions affect localization and function via independent mechanisms. 21834013_regulatory switch of Kv1.3 activity in peripherally induced Tregs may constitute an important contributing factor in the signaling rewiring associated with the development of these cells 22045429_Our findings provide the first evidence that KCNA3 is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis and suggest that KCNA3 may influence the risk for autoimmune pancreatitis 22110135_Functional blockade of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 mediates reversion of T effector to central memory lymphocytes through SMAD3/p21cip1 signaling. 22134923_hypoxia disrupts AP1/clathrin-mediated forward trafficking of Kv1.3 from the trans-Golgi to the plasma membrane thus contributing to decreased Kv1.3 surface expression in T lymphocytes. 22169811_CD4+CD28null T cells expressed small numbers of the voltage-gated Kv1.3 and intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel KCa3.1 when quiescent, but increased Kv1.3 expression 4-fold with little change in KCa3.1 levels upon activation. 22192444_Data suggest that rituximab induces apoptosis of malignant B lymphocytes by stimulating FcgammaRIIB receptors and inhibiting Kv1.3 channels. 22360360_expression of Kv1.5 and Kv1.3 increased in skeletal muscle tumorigenesis in a close relationship with malignancy. 22378744_Selective knockdown of protein kinase A 1(PKAI) eliminates modulation of Kv1.3 channels by PKAI activation. 22547057_and immunocytochemistry experiments revealed an association between K(v)1.5, K(v)beta1.3, the receptor for activated C kinase (RACK1), PKCbetaI, PKCbetaII, and PKCtheta. 22931594_Diclofenac can significant down-regulate the expression of Kv1.3 and Kir2.1 channels in human macrophages, lower their membrane potential and inhibit the process of foam cell formation. 22952817_GrB released from T cells induced neurotoxicity by interacting with the membrane bound Gi-coupled PAR-1 receptor and subsequently activated Kv1.3 and Notch-1 23099443_role of Kv1.3 in modulating cholesterol-metabolism-associated molecules in human acute monocytic leukemia cell-derived macrophages (THP-1 macrophages) and human monocyte-derived macrophages exposed to oxidized LDL 23300077_MMP23-PD suppresses the voltage-gated potassium channel KV1.3, but not the closely related KV1.2 channel, by trapping the channel intracellularly. 23335746_CMYA5 is a new potential substrate of Kcna3 in human heart 23382885_diseases. Our present results indicate a critical role for Kv1.3 in the conversion of CD8+ T cells into potential pathogenic effector cells with cytotoxic function. 24055377_Authors show the helical transmembrane S3b-S4 hairpin ('paddle') of a voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel, a critical region of the Kv voltage sensor, forms in the ribosomal vestibule. 24114469_We show the structure of the T1 domain derived from the voltage-dependent potassium channel K(v)1.3 of Homo sapiens sapiens at 1.2 A resolution crystallized under near-physiological conditions. 24594979_results revealed that the deficient expression of Kv1.3 channel would cause the less Ca2+ signal, leading to the less efficiency in secretion 24939846_Targeting the ion channel Kv1.3 with scorpion venom peptides engineered for potency, selectivity, and half-life 25175978_the small molecule Kv1.3 blocker PAP-1 dose-dependently inhibited proliferation and suppressed IL-2 and IFN-gamma production. 25208915_Kv1.3 channels modulate human vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation independently of mTOR signaling pathway. 25301362_Treatment with Acacetin for 24 h significantly inhibited Kv1.3 protein expression. 25362031_This study demonstrated that Potassium channel Kv1.3 is highly expressed by microglia in human Alzheimer's disease. 25644777_JAK2 participates in the signalling, regulating the voltage-gated K(+) channel KCNA3. 25688010_The inhibition of Kv1.3 channels might be involved in antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of the compounds observed in cancer cell lines expressing these channels. 25739456_actin dynamics regulates the membrane motility of Kv1.3 channels. 25829491_These results demonstrate that Kv1.3 channels are primarily localized in the nucleus of several types of cancer cells and human brain tissues where they are capable of regulating nuclear membrane potential and activation of transcription factors 25944908_The increment and decrement of the basic residue number in a positively charged S4 sensor of Kv1.3 channel yields conductance-voltage relationship curves in the positive direction by approximately 31.2 mV and 2-4 mV 26148969_Findings reveal that alpha-defensins are endogenous inhibitors of potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 3 (Kv1.3) with distinct interaction mechanisms. 26156069_the association between Kv1.3 and the COPII cargo adaptor subunit isoform Sec24a 26393354_Results contribute to the characterization of leukemic B cells, as it shows that upregulation of Kv1.3 in pathologic B lymphocytes is linked to the oncogenic B-RAF signaling. 26634786_The implication of Kv1.3 in a wide repertoire of human pathologies indicates this channel is an important therapeutic target. 26655221_Data suggest that C-terminus is necessary for Kv1.3-induced cell proliferation; the mechanism involves accessibility of key docking sites at the C terminus; phosphorylation of Tyr-447 by MAP kinase signal cascade appears crucial. 26748289_concluded that Kv1.3 may stimulate macrophage migration through the activation of ERK. 26931497_results identify a caveolin-binding domain in Kv1 channels and highlight the mechanisms that govern the regulation of channel surface localization during cellular processes 26994905_we report that Kv1.3-NPs reduced NFAT activation and CD40L expression exclusively in CD45RO(+) T cells. Furthermore, Kv1.3-NPs suppressed cytokine release and induced a phenotype switch of T cells from predominantly memory to naive. 27802162_the tertiary structure of the C-terminal domain of Kv1.3 is necessary and sufficient for Kv1.3- KCNE4 interaction. 28248292_T-cell dependency on Kv1.3 or KCa3.1 might be irreversibly modulated by antigen exposure. 28472608_Kv1.3 methylation may serve as diagnostic and prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. 29415410_In this work, we showed that although both Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels are expressed in U87 (glioblastoma), MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer) and LS174 (colon adenocarcinoma) cells, these respond differently to KAaH1 or KAaH2, two homologous Kv1 blockers from scorpion venom 29650988_These results demonstrate that the C-terminal region of Kv1.3 immediately proximal to the S6 helix is required for the activation gating and conduction, whereas the presence of the distal region of the C-terminus is not exclusively required for trafficking of Kv1.3 to the plasma membrane. 31141130_High KV1.3 Expression is associated with Active Ulcerative Colitis. 31536992_Expression of the Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel Kv1.3 in Lesional Skin from Patients with Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma and Benign Dermatitis. 31597447_Kv1.5 downregulation upon PM leaves Kv1.3 as the dominant Kv1 channel expressed in dedifferentiated cells. We demonstrated that the inhibition of Kv1.3 channel function with selective blockers or by preventing Kv1.5 downregulation can represent an effective, novel strategy for the prevention of intimal hyperplasia and restenosis of the human vessels used for coronary angioplasty procedures. 31661467_beta1-Integrin- and KV1.3 channel-dependent signaling stimulates glutamate release from Th17 cells. 32056271_A common genetic variant rs2821557 in KCNA3 is linked to the severity of multiple sclerosis. 32562800_Pregnancy-induced hypertension decreases Kv1.3 potassium channel expression and function in human umbilical vein smooth muscle. 32597830_Kv1.3 modulates neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. 32910509_The Kv1.3 ion channel acts as a host factor restricting viral entry. 33038663_Mutual regulation between beta-TRCP mediated REST protein degradation and Kv1.3 expression controls vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switch. 33230847_Voltage-dependent conformational changes of Kv1.3 channels activate cell proliferation. 33649184_Unique molecular characteristics and microglial origin of Kv1.3 channel-positive brain myeloid cells in Alzheimer's disease. 33828089_Kv1.3 voltage-gated potassium channels link cellular respiration to proliferation through a non-conducting mechanism. 34196606_A novel mitochondrial Kv1.3-caveolin axis controls cell survival and apoptosis. 34554500_The Kv1.3 K(+) channel in the immune system and its ''precision pharmacology'' using peptide toxins. 35091471_Rearrangement of a unique Kv1.3 selectivity filter conformation upon binding of a drug. 35328733_Role of C-Terminal Domain and Membrane Potential in the Mobility of Kv1.3 Channels in Immune Synapse Forming T Cells. 35788586_Structures of the T cell potassium channel Kv1.3 with immunoglobulin modulators. |
ENSMUSG00000047959 |
Kcna3 |
23.400679 |
5.5891613889 |
2.482632 |
0.406892765 |
39.422748 |
0.00000000034129771989027302062670386565421728336522377844630682375282049179077148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001698067308332703449097179702442349941149402070550422649830579757690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.6450137 |
9.9527986 |
7.3481565 |
1.5435895 |
| ENSG00000177406 |
100049716 |
NINJ2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
107.104092 |
0.2645484499 |
-1.918396 |
0.418504473 |
17.877103 |
0.00002356391396594271079776260202631732454392476938664913177490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000070663017094131337983431428995118039892986416816711425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.4807089 |
11.5901711 |
163.9483735 |
30.9022891 |
| ENSG00000177427 |
125170 |
MIEF2 |
protein_coding |
Q96C03 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial outer membrane protein involved in the regulation of mitochondrial organization (PubMed:29361167). It is required for mitochondrial fission and promotes the recruitment and association of the fission mediator dynamin-related protein 1 (DNM1L) to the mitochondrial surface independently of the mitochondrial fission FIS1 and MFF proteins. Regulates DNM1L GTPase activity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21508961, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23283981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23530241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23921378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29361167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29899447}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Phosphoprotein;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an outer mitochondrial membrane protein that functions in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology. It can directly recruit the fission mediator dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) to the mitochondrial surface. The gene is located within the Smith-Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:125170; |
mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; dynamin family protein polymerization involved in mitochondrial fission [GO:0003374]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; positive regulation of mitochondrial fission [GO:0090141]; positive regulation of protein targeting to membrane [GO:0090314]; regulation of mitochondrion organization [GO:0010821] |
15517828_Smith-Magenis syndrome is caused by a de novo deletion on chromosome 17. 21508961_MiD49/51 are new mediators of mitochondrial division affecting Drp1 action at mitochondria. 21508961_Mitochondrial outer membrane protein that recruits fission mediator Drp1 to the mitochondrial surface. 23283981_we find that either MiD49 or MiD51 can mediate Drp1 recruitment and mitochondrial fission in the absence of Fis1 and Mff. 23880462_MIEF1 and MIEF2 are differentially expressed in human tissues during development 23921378_MiD49 and MiD51 can act independently of Mff and Fis1 in Drp1 recruitment and suggest that they provide specificity to the division of mitochondria. 26564796_These findings and data showing MARCH5-dependent degradation of MiD49 upon stress support the possibility that MARCH5 regulation of MiD49 is a novel mechanism controlling mitochondrial fission and, consequently, the cellular response to stress. 26903540_The results indicate that Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission through MiD49/MiD51 regulates cristae remodeling during intrinsic apoptosis. 27660309_MiD49 and MiD51 recruit inactive forms of Drp1 in mitochondrial fission. [review] 28137654_Knockdown of MIEF2 reduces DOX-induced mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes and in vivo. Also, knockdown of MIEF2 protects heart from DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Our study identifies a novel pathway composed of Foxo3a and MIEF2 that mediates DOX cardiotoxicity. 29431643_In health, MiD49 regulate Drp1-mediated fission, whereas in disease, epigenetic upregulation of MiD49 increases mitotic fission, which drives pathological proliferation and apoptosis resistance 29899447_cryo-electron microscopy structure of full-length human DRP1 co-assembled with MID49 and an analysis of structure- and disease-based mutations 32068312_An epigenetic increase in mitochondrial fission by MiD49 and MiD51 regulates the cell cycle in cancer: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. 32236517_Mitochondrial fragmentation enables localized signaling required for cell repair. 33317572_MIEF2 over-expression promotes tumor growth and metastasis through reprogramming of glucose metabolism in ovarian cancer. 33414447_MIEF2 reprograms lipid metabolism to drive progression of ovarian cancer through ROS/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000018599 |
Mief2 |
29.550900 |
0.4608356162 |
-1.117676 |
0.300573562 |
13.799378 |
0.00020340352315822567445466328983627590787364169955253601074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000532500177689856522486588907838722661836072802543640136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.0547373 |
5.3383001 |
36.7172463 |
8.0658690 |
| ENSG00000177432 |
266812 |
NAP1L5 |
protein_coding |
Q96NT1 |
|
Coiled coil;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein that shares sequence similarity to nucleosome assembly factors, but may be localized to the cytoplasm rather than the nucleus. Expression of this gene is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinomas. This gene is located within a differentially methylated region (DMR) and is imprinted and paternally expressed. There is a related pseudogene on chromosome 4. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:266812; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; nucleosome assembly [GO:0006334] |
20622171_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000055430 |
Nap1l5 |
27.061561 |
2.8407126036 |
1.506253 |
0.340587285 |
19.790597 |
0.00000864067027057857778011944194229698723574983887374401092529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027315547910417606699466988584568127862439723685383796691894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.8499405 |
8.1150354 |
14.4787115 |
2.3285702 |
| ENSG00000177453 |
167359 |
NIM1K |
protein_coding |
Q8IY84 |
|
ATP-binding;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Enables ATP binding activity; magnesium ion binding activity; and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in protein phosphorylation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:167359; |
ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
|
ENSMUSG00000095930 |
Nim1k |
28.979889 |
0.0385518117 |
-4.697058 |
0.543706234 |
123.584846 |
0.00000000000000000000000000010384925402125695291239028719642203963517822311958277462566461997078508087705844831205581613176036626100540161132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001275220457033072035144576287326661337866851126826489647119906507293577151585656226373544086527545005083084106445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1496469 |
0.8514082 |
56.6978616 |
8.7711417 |
| ENSG00000177468 |
167826 |
OLIG3 |
protein_coding |
Q7RTU3 |
FUNCTION: May determine the distinct specification program of class A neurons in the dorsal part of the spinal cord and suppress specification of class B neurons. |
Coiled coil;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in neuron differentiation and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II; spinal cord motor neuron cell fate specification; and spinal cord motor neuron migration. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:167826; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spinal cord motor neuron cell fate specification [GO:0021520]; spinal cord motor neuron migration [GO:0097476] |
20353580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20439292_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20921970_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20921970_SNP within the OLIG3/TNFAIP3 locus (rs6920220) was associated with being less likely to maintain MTX monotherapy 30157244_Two identified variants revealed novel candidate genes for hip and knee osteoarthritis. OLIG3 and FIP1L1 have specific roles in transcription and may effect expression of other genes. Identified variants in these genes may thus have a role in the regulatory events leading to osteoarthritis. |
ENSMUSG00000045591 |
Olig3 |
28.093058 |
0.1017134728 |
-3.297417 |
0.398673501 |
86.969211 |
0.00000000000000000001102238375322590616582367932416093363851509365792772594046418366264816768307355232536792755126953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000099932668426053062725900413702998899153043942676789130035580610567080839246045798063278198242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1974038 |
1.4361866 |
51.5714643 |
6.6554282 |
| ENSG00000177469 |
284119 |
CAVIN1 |
protein_coding |
Q6NZI2 |
FUNCTION: Plays an important role in caveolae formation and organization. Essential for the formation of caveolae in all tissues (PubMed:18056712, PubMed:18191225, PubMed:19726876). Core component of the CAVIN complex which is essential for recruitment of the complex to the caveolae in presence of calveolin-1 (CAV1). Essential for normal oligomerization of CAV1. Promotes ribosomal transcriptional activity in response to metabolic challenges in the adipocytes and plays an important role in the formation of the ribosomal transcriptional loop. Dissociates transcription complexes paused by DNA-bound TTF1, thereby releasing both RNA polymerase I and pre-RNA from the template (By similarity) (PubMed:18056712, PubMed:18191225, PubMed:19726876). The caveolae biogenesis pathway is required for the secretion of proteins such as GASK1A (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54724, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056712, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18191225, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19726876}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Congenital generalized lipodystrophy;Cytoplasm;Diabetes mellitus;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;rRNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Transcription termination;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that enables the dissociation of paused ternary polymerase I transcription complexes from the 3' end of pre-rRNA transcripts. This protein regulates rRNA transcription by promoting the dissociation of transcription complexes and the reinitiation of polymerase I on nascent rRNA transcripts. This protein also localizes to caveolae at the plasma membrane and is thought to play a critical role in the formation of caveolae and the stabilization of caveolins. This protein translocates from caveolae to the cytoplasm after insulin stimulation. Caveolae contain truncated forms of this protein and may be the site of phosphorylation-dependent proteolysis. This protein is also thought to modify lipid metabolism and insulin-regulated gene expression. Mutations in this gene result in a disorder characterized by generalized lipodystrophy and muscular dystrophy. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:284119; |
caveola [GO:0005901]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA primary transcript binding [GO:0042134]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; rRNA transcription [GO:0009303]; termination of RNA polymerase I transcription [GO:0006363]; transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter [GO:0006361] |
15242332_Caveolae of human adipocytes are proposed to function in targeting, relocation and proteolytic control of PTRF and other PEST-domain-containing signalling proteins 17026959_The findings indicate also a novel extranuclear function for PTRF in the control of lipolysis. 19068216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19726876_identified PTRF mutations in 5 nonconsanguineous patients who presented with both generalized lipodystrophy and muscular dystrophy 20300641_PTRF-CAVIN deficiency thus presents the phenotypic spectrum caused by a quintessential lack of functional caveolae. 20427576_These data demonstrate a new function for PTRF/cavin-1, a new functional interaction between caveolin-1 and Rab8 and that actomyosin interactions can induce tension on caveolin-1-containing membranes. 20684003_mutations in PTRF result in a novel phenotype that includes generalized lipodystrophy with mild metabolic derangements, myopathy, cardiac arrhythmias, atlantoaxial instability, and pyloric stenosis 20732728_PTRF/cavin-1-expressing PC3 cells exhibit decreased migration, and that this effect is mediated by reduced MMP9 production. 21152401_Findings suggest that Cav-1 and PTRF/Cavin could represent two relevant and distinct targets to modulate IGF-IR function. 21343302_membrane-delimited interaction between MG53 and PTRF contributes to initiation of cell membrane repair 21445100_PTRF expression is increased in senescent human fibroblasts. 21683594_This study identified no pathogenic mutations in BAG3, MATR3, PTRF or TCAP in Australian muscular dystrophy. 21705337_PTRF/cavin-1 is a novel regulator of oxidative stress-induced premature senescence by acting as a link between free radicals and activation of the p53/p21(Waf1/Cip1) pathway. 21913217_The cavin family protein Polymerase 1 and transcript release factor, SRBC and serum deprivation response protein were down regulated in breast cancer cell lines and breast tumor tissue. 22461895_Data show that two proteins, PTRF/cavin-1 and MIF, which are differentially expressed between normal lung and non-small cell lung cancer. 23214712_PTRF/cavin-1 is essential for multidrug resistance in cancer cells via the fortification of lipid rafts. 23404184_PTRF and Cav-1 can bind IGF-IR and regulate IGF-IR internalization and plasma membrane replacement, mechanisms frequently deregulated in cancer cells.[review] 23770857_The tumor-promoting role of cavin-1 in pancreatic cancer was found to be largely dependent on caveolin-1. 23934189_caveolin-1 in advanced prostate cancer is present outside of caveolae, because of the lack of cavin-1 expression 23938946_In this review stromal PTRF expression decreases with progression of prostate cancer disease. 24473072_Rather than forming a single coat complex containing the three cavin family members, single-molecule analysis reveals an exquisite specificity of interactions between cavin1, cavin2 and cavin3. 24747515_PTRF acts as a modulator in GBM chemoresistance 24812087_In human adipose tissue, PTRF mRNA levels positively correlated with markers of lipolysis and cellular senescence. A negative relationship between telomere length and PTRF mRNA levels was observed in human subcutaneous fat. 25588833_cavin3 is recruited to the caveolae coat by cavin1 to interact with caveolin1 and regulate the duration time of caveolae at the plasma membrane. 25721873_this study presents a novel mutation of PTRF from Saudi Arabia and our findings broaden the mutation spectrum of PTRF in the familial CGL4 phenotype. 25822667_Using in silico and in vitro analysis we show that Cavin-1 is expressed in myogenic Rhabdomyosarcoma tumors and human and primary mouse RMS cultures. Cavin-1 or Cav-1 knockdown led to impairment of cell proliferation and migration. 25904680_The presence of caveolae as an anatomic structure is not sufficient to ensure their proper function in patient with PTRF mutation. 25942420_Our data support a role for PTRF/cavin-1, through caveolae formation, as an attenuator of the non-caveolar functionality of Cav1 in Gal3-Cav1 signalling and regulation of focal adhesion dynamics and cancer cell migration. 26086560_Cavin-1 and cavin-2 are strongly expressed within caveolae-like structures within liver sinusoidal endothelial cells of the hepatitis C-related cirrhotic liver and cavin-1 would play a critical role in regulating aspects of caveolin-1. 26725982_This study reports an unanticipated function of ROR1 as a scaffold of cavin-1 and caveolin-1, two essential structural components of caveolae. 27167729_A homozygous PTRF mutation was identified in patient-1. Congenital generalized lipodystrophy type 4 was caused by homozygous PTRF c.481-482insGTGA (p.Lys161Serfs*41) mutation in patient-2. 27203393_PTRF inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Future studies need to define the role of PTRF in the regulation of chemo-resistance in colorectal cancer cells and in colorectal cancer stem cells. 27634346_The expression of the PTRF protein was significantly weaker than that in the adjacent normal lung tissues using immunohistochemical staining. The findings revealed that miR187 promotes cell growth and invasion by targeting PTRF and miR187 may be a new prognostic factor for nonsmall cell lung cancer 27834731_Purified Cavin1 60S complexes were analyzed structurally in solution and after liposome reconstitution by electron cryotomography. Cavin1 adopted a flexible, net-like protein mesh able to form polyhedral lattices on phosphatidylserine-containing vesicles. Mutating the two coiled-coil domains in Cavin1 revealed that they mediate distinct assembly steps during 60S complex formation. 27894957_DNA methylation profiling identifies PTRF/Cavin-1 as a novel tumor suppressor in Ewing sarcoma when co-expressed with caveolin-1, which PTRF, disrupts the MDM2/p53 complex, leading to apoptosis. 28393200_Results show that PTRF is a direct target of miR-187. PTRF plays crucial roles in miR-187-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells. 28698382_Data suggest that the predominant plasmalemmal anionic lipid phosphatidylserine is essential for proper caveolin/cavin clustering, caveola formation, and caveola dynamics; membrane scrambling (by using other phospholipids) can perturb caveolar stability; these studies involved caveolin-1 and cavin-1 as models of caveolin/cavin clustering. 29556340_Overexpressing PTRF induced the malignancy of nearby cells in vivo, suggesting that PTRF alters the microenvironment through intercellular communication via exosomes in glioblastoma. 29869069_Data suggest that PTRF is present in the bloodstream and associates with exosomes; visceral adipose tissue may be a source of plasma PTRF; PTRF is rapidly processed inside adipocytes and promotes glucose absorption in adipocytes. 30949900_High CAVIN1 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 31267558_Overexpression of PTRF led to MAPK inhibitors (MAPKi) resistance in melanoma, increased cell adhesion and sphere formation. In addition, immunohistochemistry of patient samples showed that PTRF expression levels were a significant biomarker of poor progression-free survival. 31332168_Data evaluate the interaction between one candidate interactor protein, protein phosphatase 1 alpha (PP1alpha), and Cavin-1 and -3 and show that UV treatment causes release of Cavin3 from caveolae allowing interaction with, and inhibition of, PP1alpha. 31448673_CAV1-CAVIN1-LC3B-mediated autophagy regulates high glucose-stimulated LDL transcytosis. 31605605_PTRF/CAVIN1, regulated by SHC1 through the EGFR pathway, is found in urine exosomes as a potential biomarker of ccRCC. 31706570_The p.Glu176Argfs mutation imparts high positive charge to the cavin-1 LZD2 domain. The mutation imparts high membrane-binding propensity to this region. The peptide stretch displays preferential binding to the negatively-charged liposomes. Binding to the cholesterol/sphingomyelin-rich domain is also enhanced. 32065471_A role for caveola-forming proteins caveolin-1 and CAVIN1 in the pro-invasive response of glioblastoma to osmotic and hydrostatic pressure. 32493699_Stromal CAVIN1 Controls Prostate Cancer Microenvironment and Metastasis by Modulating Lipid Distribution and Inflammatory Signaling. 32550897_Homotrimer cavin1 interacts with caveolin1 to facilitate tumor growth and activate microglia through extracellular vesicles in glioma. 33496726_Caveolin-1 and cavin1 act synergistically to generate a unique lipid environment in caveolae. 35069587_PTRF/Cavin-1 as a Novel RNA-Binding Protein Expedites the NF-kappaB/PD-L1 Axis by Stabilizing lncRNA NEAT1, Contributing to Tumorigenesis and Immune Evasion in Glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000004044 |
Cavin1 |
20.594933 |
0.4333622033 |
-1.206355 |
0.421263870 |
8.217190 |
0.00414954108446406386145888234295853180810809135437011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008623940637382369184260610950332193169742822647094726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.4100447 |
3.7018479 |
28.8929061 |
5.7911418 |
| ENSG00000177556 |
475 |
ATOX1 |
protein_coding |
O00244 |
FUNCTION: Binds and deliver cytosolic copper to the copper ATPase proteins. May be important in cellular antioxidant defense. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Chaperone;Copper;Copper transport;Ion transport;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a copper chaperone that plays a role in copper homeostasis by binding and transporting cytosolic copper to ATPase proteins in the trans-Golgi network for later incorporation to the ceruloplasmin. This protein also functions as an antioxidant against superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, and therefore, may play a significant role in cancer carcinogenesis. Because of its cytogenetic location, this gene represents a candidate gene for 5q-syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:475; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; copper chaperone activity [GO:0016531]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; copper-dependent protein binding [GO:0032767]; cuprous ion binding [GO:1903136]; metallochaperone activity [GO:0016530]; cellular copper ion homeostasis [GO:0006878]; copper ion transport [GO:0006825]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
12029094_transfers copper to the NH2-terminal domain of the Wilson's disease protein and regulates its catalytic activity 12594858_Gene structure of ATOX1. 12679332_A copper-dependent interaction of Atox1 with the metal binding sites of menkes protein was observed 12686548_X-ray absorption spectroscopy of this copper chaperone reveals a copper center capable of formation with exogenous thiols and phosphines 12763797_Regulates the function of ATP7B in Wilson's disease 14709553_handling of copper by Atox1 and copper transfer between Atox1 and WND are under kinetic rather than thermodynamic control 15476398_Detailed structural and dynamic characterization of the behavior of human HAH1 in solution, in the physiologically relevant reduced apo and copper(I)-bound forms 15670166_interaction between the human copper(I) chaperone, HAH1, and one of its two physiological partners, the Menkes disease protein (ATP7A), was investigated in solution using heteronuclear NMR 15761197_Atox1 functions not only as a copper chaperone for SOD3 but also as a positive regulator for SOD3 transcription and may have an important role in modulating oxidative stress in the cardiovascular system. 16172131_a three-domain construct of ATP7A interacts with copper(I) and copper(I)-HAH1 16571664_Wilson disease protein is an acceptor of oopper from HAH1 protein. 17545667_localization of ATP7A between the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane may be regulated by the accumulation of the adducts with HAH1, whereas the main role of domains 5 and 6 is to assist copper(I) translocation 17616150_The results from the quantum mechanical (QM) and MD simulations suggest that either a two- or three-coordinate exchange reaction is preferred and that it is unlikely that a four-coordinate Cu(I) species plays a role in copper exchange. 17881304_Divergent energetic properties of Atox1 apo- and holo-forms may be linked to conformational changes that facilitate copper transfer to the target. 18245776_Atox1 functions as a novel transcription factor that, when activated by copper, undergoes nuclear translocation, DNA binding, and transactivation, thereby contributing to cell proliferation. 18416466_No major role can be attributed to Atox1 in the pathophysiology or clinical variation of Wilson disease. 18416466_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18558714_Forms a ocomplex with some domains of ATP7B, an interesting property of this class of proteins which have a signaling role in the function of the ATPases. 18685091_Conserved residues modulate copper release in human copper chaperone Atox1. 19146392_Atox1 residues have been conserved to ensure backbone-loop flexibility, electrostatic copper site stabilization, and proper core packing. 19453293_The interaction between the human copper(I)-chaperone HAH1 (human ATX1 homologue) and a metal-binding domain in one of its partners, namely the P-type copper-transporting ATPase, ATP7A, was characterized. 21258123_Unification of the copper(I) binding affinities of the metallo-chaperones Atx1, Atox1, and related proteins: detection probes and affinity standards. 21482801_By binding to Atox1 in the cytoplasm, cisPt transport to DNA may be blocked. In agreement with this model, cell line studies demonstrate a correlation between Atox1 expression levels, and cisplatin resistance. 22574136_thermodynamic parameters of copper (Cu) transfer from the human copper chaperone Atox1 to the fourth metal-binding domain of the Wilson disease protein 22648419_GSSG oxidizes copper-coordinating cysteines of Atox1 with formation of an intramolecular disulfide. GSH alone is sufficient to reduce the disulfide, restoring the ability of Atox1 to bind copper; glutaredoxin 1 facilitates this reaction when GSH is low 22677543_No major role can be attributed to Atox1 and COMMD in the pathophysiology or clinical variation of Wilson disease. 23169585_different effects of ATX1 unfolding on Cu(I) affinity 23553875_Based on structural analysis, this work determines that the protein possesses two distinct conformations referred to as 'in' and 'out' due to the relative positioning of Cys12 (one of Cu(I) binding residues). 23624903_Knockdown of ATOX1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells was associated with reduction in copper-stimulated cell proliferation. These findings suggest that ATOX1 plays an important role in copper-stimulated proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells. 23751120_Binding of free cisplatin and reaction with the cisplatin-loaded Atox1 produce the same protein-bound platinum intermediate in the transfer of metal-binding domain (repeat) (MBD)2 from Atox1. 23778981_the primary coordination site of Atox1 for interaction wtih cisplatin is at the cysteine residues in the Cu(I)-binding sequence Cys(12)GlyGlyCys(15) 24036897_Atox1 contains positive residues that mediate membrane association and aid subsequent copper loading. 24343031_CTR1 silencing increased the protein levels of copper chaperone ATOX1 and copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase 1 (CCS-1), but decreased copper chaperone for cytochrome c oxidase (COX17). 24445997_Atox1 has a role in copper transport to tumor cell nuclei. 24469739_These results indicate that the roles of Atox1 in the regulation of cellular trafficking of platinum drugs are dependent on the coordination configurations. 24522867_Human Grx1 can catalyse reduction of Atox1 by glutathione but only in the presence of Cu(I). 24824562_The Cu-binding motif in Atox1, as well as in target Cu-binding domains of ATP7A/B, consists of a MX1CXXC motif where X1 = T. 24837030_The data collected here shows that the Atox1 keeps its dimer nature also in the presence of the CTR1 c-terminal domain; however, two geometrical states are assumed by the Atox1. 25111319_Cisplatin is one of the most used anticancer drugs. Its cellular influx and delivery to target DNA may involve the copper chaperone Atox1 protein. 25673218_Human cytoplasmic copper chaperones Atox1 and CCS exchange copper ions in vitro 25962064_Studied the localization of Atox1 in HeLa cells using fluorescence imaging in combination with in vitro binding experiments to fluorescently labeled DNA duplexes harboring the proposed promotor sequence. 26213915_To identify new interactions partners of Atox1, a yeast two-hybrid screen with a large human placenta library of cDNA fragments using Atox1 as bait, was performed. 26437801_Cu chaperone function of Atox1 mediated through Cu transporter ATP7A is required for VEGF-induced angiogenesis via activation of Cu enzyme lysyl oxidase. 26745413_C-Terminus of Human Copper Importer Ctr1 Acts as a Binding Site and Transfers Copper to Atox1 26745464_In addition to Atox1, the human cytoplasm also contains Cu chaperones for loading of superoxide dismutase 1 (i.e. CCS) and cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria (i.e. Cox17). [review] 26784148_results suggest the possibility of a therapy with copper-chelating or ionophore drugs in subtypes of tumors showing specific alterations in ATOX1 expression 26866891_Multiple genetic models identified genetic associations with systolic blood pressure and ATOX1. 26879543_Upon neuronal differentiation, transitions in redox states upregulates expression of ATOX1 and its partner ATP7A, producing higher flux of copper through the secretory pathway. 27305454_Since full occupancy of the tetrahedral cavity is a common feature of all Atox1 dimeric structures obtained with other metal ions (Cu(+), Cd(2+), and Hg(2+)), we propose that in the case of platinum, where the occupancy is only 0.4, the remaining cavities are occupied by Cu(+) ions 28027931_Cu chaperone Atox1 has a role in breast cancer cell migration 28294521_Highlighted in this review are unique redox properties of Atox1 and other copper chaperones. Also, summarized are the redox nodes in the cytosol which potentially play dominant roles in the redox regulation of copper chaperones 28543811_The structural flexibility of the human copper chaperone Atox1 has been reported based on insights from combined pulsed EPR studies and computations. 28549213_It show that copper(I) and glutathione form large polymers with a molecular mass of approximately 8 kDa, which can transfer copper to Atox1. 28900031_Data suggest that N-terminal segment of metal-binding domains (MBDs) 1-3 of ATOX1 interact with nucleotide-binding domain of ATP7B, thus physically coupling the domains involved in copper binding and those involved in ATP hydrolysis; interactions with MBDs 1-3 of ATOX1 activate ATP7B ATP hydrolysis. (ATOX1 = copper transport protein ATOX1; ATP7B = Cu-binding P type ATPase ATP7B) 29168020_Copper chaperone Atox-1 is involved in the induction of SOD3 in a monocyte cell line. 30824611_Here, we show that DCAC50, a recently developed small-molecule inhibitor of the intracellular copper chaperones, ATOX1 and CCS, reduces cell proliferation and elevates oxidative stress, triggering apoptosis in a panel of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. 30980273_we found four novel variants viz. c.6 + 30G > A, c.207 + 32dup, c.207 + 43G > A, and c.40G > A, p.(Gly14Ser) in ATOX1 in Indian Wilson disease patients. p.(Gly14Ser) located in the second exon appears to aggravate the effect of ATP7B mutation p.(Ile1102Thr), probably by restricting the downstream flow of copper. 31317143_Genetic deletion of ATOX1 decreased MAPK pathway activation in BRAF V600E mutant melanoma. 31553645_Cu-dependent Atox1 binding to TRAF4 plays an important role in Atox1 nuclear translocation and ROS-dependent inflammatory responses in TNF-alpha-stimulated vascular endothelial cells. 31898157_Evaluation of copper chaperone ATOX1 as prognostic biomarker in breast cancer. 31932435_High Atox1 expression is associated with breast cancer cell migration. 31961892_The authors findings represent a functional role for Atox1 in colorectal cancer metastasis. 32396355_Cu(I) Controls Conformational States in Human Atox1 Metallochaperone: An EPR and Multiscale Simulation Study. 32748830_An EPR Study on the Interaction between the Cu(I) Metal Binding Domains of ATP7B and the Atox1 Metallochaperone. 34550632_APEX2-based Proximity Labeling of Atox1 Identifies CRIP2 as a Nuclear Copper-binding Protein that Regulates Autophagy Activation. 35315340_Copper enhances genotoxic drug resistance via ATOX1 activated DNA damage repair. 36067318_Memo1 binds reduced copper ions, interacts with copper chaperone Atox1, and protects against copper-mediated redox activity in vitro. 36208051_Copper coordination states affect the flexibility of copper Metallochaperone Atox1: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations. 36291703_Crystal Structure of the Human Copper Chaperone ATOX1 Bound to Zinc Ion. |
ENSMUSG00000018585 |
Atox1 |
155.388689 |
3.4612107026 |
1.791277 |
0.167621735 |
113.345367 |
0.00000000000000000000000001812816441304940290851673070242950687370738985321937422636235800458735182433267496548978670034557580947875976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000204253211249319995543322341686769031916375957564460702651365706637200114759167490774416364729404449462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
235.5457531 |
22.2579489 |
68.2749129 |
5.1301549 |
| ENSG00000177570 |
401474 |
SAMD12 |
protein_coding |
Q8N8I0 |
|
Epilepsy;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to be active in cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane. Implicated in familial adult myoclonic epilepsy 1. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:401474; |
cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29507423_Abnormal expansions of TTTCA and TTTTA repeats in intron 4 of SAMD12 cause benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy. Single-molecule, real-time sequencing of BAC clones and nanopore sequencing of genomic DNA identified two repeat configurations in SAMD12. 30194086_We identified the pentanucleotide repeat expansion in SAMD12 as the causative mutation in Chinese FCMTE pedigrees. 31406141_LncRNA SAMD12-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by interacting with NPM1. 31483537_identified a novel expanded intronic (TTTGA)n insertion at the same site as the previously reported (TTTCA)n insertion in SAMD12 31646576_LncRNA SAMD12-AS1 down-regulates P53 to promote malignant progression of glioma. 32203200_Familial adult myoclonic epilepsy type 1 SAMD12 TTTCA repeat expansion arose 17,000 years ago and is present in Sri Lankan and Indian families. 32973343_Founder effect of the TTTCA repeat insertions in SAMD12 causing BAFME1. 33040085_DNA analysis of benign adult familial myoclonic epilepsy reveals associations between the pathogenic TTTCA repeat insertion in SAMD12 and the nonpathogenic TTTTA repeat expansion in TNRC6A. 33681653_Clinical and genomic analysis of a large Chinese family with familial cortical myoclonic tremor with epilepsy and SAMD12 intronic repeat expansion. |
ENSMUSG00000058656 |
Samd12 |
62.323629 |
0.4328372024 |
-1.208104 |
0.219910133 |
30.509811 |
0.00000003321823088095858937763096320472389066935647861100733280181884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000137531861936311029520895203234753800813905399991199374198913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9156952 |
5.7226627 |
88.1023440 |
8.7909935 |
| ENSG00000177575 |
9332 |
CD163 |
protein_coding |
Q86VB7 |
FUNCTION: Acute phase-regulated receptor involved in clearance and endocytosis of hemoglobin/haptoglobin complexes by macrophages and may thereby protect tissues from free hemoglobin-mediated oxidative damage. May play a role in the uptake and recycling of iron, via endocytosis of hemoglobin/haptoglobin and subsequent breakdown of heme. Binds hemoglobin/haptoglobin complexes in a calcium-dependent and pH-dependent manner. Exhibits a higher affinity for complexes of hemoglobin and multimeric haptoglobin of HP*1F phenotype than for complexes of hemoglobin and dimeric haptoglobin of HP*1S phenotype. Induces a cascade of intracellular signals that involves tyrosine kinase-dependent calcium mobilization, inositol triphosphate production and secretion of IL6 and CSF1. Isoform 3 exhibits the higher capacity for ligand endocytosis and the more pronounced surface expression when expressed in cells.; FUNCTION: After shedding, the soluble form (sCD163) may play an anti-inflammatory role, and may be a valuable diagnostic parameter for monitoring macrophage activation in inflammatory conditions. |
Acute phase;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) superfamily, and is exclusively expressed in monocytes and macrophages. It functions as an acute phase-regulated receptor involved in the clearance and endocytosis of hemoglobin/haptoglobin complexes by macrophages, and may thereby protect tissues from free hemoglobin-mediated oxidative damage. This protein may also function as an innate immune sensor for bacteria and inducer of local inflammation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:9332; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953] |
11688984_soluble CD163 inhibits phorbol ester-induced lymphocyte proliferation 11865982_haptoglobin-dependent HbSR/CD163 scavenging system for hemoglobin clearance prevents toxic effects of hemoglobin in plasma and kidney 12208511_has at least two distinct functions: the clearance of hemoglobin in its cell-bound form and participation in anti-inflammation as a soluble factor, exhibiting cytokine-like functions 12377940_a metalloproteinase is responsible for LPS-mediated shedding of CD163 14656926_CD163 mediates an anti-inflammatory pathway involving interleukin-10 release and heme oxygenase-1 synthesis. 14962251_sCD163 may be a valuable laboratory parameter in monitoring diseases such as Gaucher. 15146432_Increased numbers of CD163+ macrophages in SpA synovium and local production of sCD163 are associated with global inflammation as well as impairment of T cell activation, suggesting a dual role for CD163+ macrophages in Spondylarthropathy synovitis. 15448162_SRCR domain 3 of CD163 is an exposed domain and a critical determinant for the calcium-sensitive coupling of haptoglobin.hemoglobin complexes 15479433_sCD163-NMMHCA complexes were present in activated T lymphocytes after incubation with shed sCD163 15613100_Serum levels of soluble CD163 were highly increased in reactive hemophagocytic syndrome, suggesting a macrophage-specific marker. 15624762_in HIV encephalitis, expression of CD163 was far more widespread in grey matter ramified microglia than was expression of HLA-DR 15846794_CD163 specifically reveals perivascular macrophages(PVM) in the normal human CNS. In MS lesions, CD163 staining reveals expression on foamy macrophages and microglia, besides an upregulation of the amount of PVM stained. 16189277_results identify CD163 as a scavenger receptor for native Hb and small-molecular-weight Hb-based blood substitutes after Hp depletion 16507898_CD163 identifies perivascular macrophages in normal and viral encephalitic brains and potential precursors to perivascular macrophages in blood. 16517975_AM-3K, an anti-macrophage antibody, recognizes CD163, a molecule associated with an anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype. 16522161_These data suggest that hemoglobin may mediate a stimulatory effect on erythropoiesis through the activation of CD163 on hematopoietic progenitor cells. 17095719_symptomatic plaques show a more pronounced induction of CD163 and HO-1 in response to plaque hemorrhages. 17102136_only the beta-chain of haptoglobin is involved in CD163 receptor recognition 17117055_The increased free-hemoblobin, haptoglobin, and sCD163 in chronic renal failure suggested 8-isoprostane-mediated suppression of Hb catabolism through CD163 receptor shedding 17460152_CD163-mediated Hb-Hp uptake by peripheral blood monocytes constitutes an Hb-Hp clearance pathway, which acts at the site of intravascular hemolysis to reduce Hb-Hp circulation time and toxicity 17525367_Individuals with diabetes mellitus and a haptoglobin 2.2 genotype demonstrate lower CD163 scavenger receptor levels and an impaired hemoglobin clearance capacity, with increased incidence of myocardial infarction. 17548657_CD163 either acts as a TWEAK scavenger in pathological conditions or serves as an alternate receptor for TWEAK in cells lacking Fn14/TweakR. 17629586_Activated macrophages are involved in ALF resulting in a 10-fold increase in sCD163. A high level (>26mg/l) of sCD163 was significantly correlated with fatal outcome and might be used with other parameters to determine prognosis. 17947394_CD163 and HCP-1 constitute a linked pathway for Hb catabolism and heme-iron recycling in human macrophages. 18078989_DC-sign+ CD163+ macrophages expressing hyaluronan receptor LYVE-1 are located within chorion villi of the placenta. 18276779_CD163, a marker of perivascular macrophages, is up-regulated by microglia in simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis after haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex stimulation and is suggestive of breakdown of the blood-brain barrier. 18316565_High-level expression of CD163 is associated with leiomyosarcomas 18320015_Data show that in cardiac surgical patients the expression of scavenger molecule CD163 on monocytes is significantly higher in 'on-pump' patients than that of 'off-pump' patients. 18410276_studied gene expression profile of brain lesions of a patient with Neuromyelitis optica by using DNA microarray; found marked up-regulation of interferon gamma-inducible protein 30 (IFI30), CD163, and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1, osteopontin) 18542032_Helpful for evaluation of a monocytic component in acute myeloid leukemias. 18563533_Casein kinase II activity is increased by the binding of haptoglobin 1-1-hemoglobin to CD163. 18604302_Data show that CD64 indexes for neutrophils and monocytes, and CD163 index for neutrophils can all be used for discrimination of SIRS and sepsis in critically ill neonates and children. 18849484_during bacterial infection, CD163 on resident tissue macrophages acts as an innate immune sensor and inducer of local inflammation 19040468_CD163 is a useful adjunct in distinguishing AFX from other malignant cutaneous spindle cell tumors and offers improved specificity in identifying cutaneous histiocytic/dendritic lesions. 19040468_CD163 is of diagnostic value in cutaneous spindle cell lesions. 19131549_Hp protects hemoglobin (Hb) when oxidatively challenged with H(2)O(2) preserving CD163-mediated Hb clearance under oxidative stress conditions. 19473660_The CD163-expressing macrophages recognize and internalize TWEAK: potential consequences in atherosclerosis. 19528371_Results show that both serum levels of sCD163 and the presence of CD68(+) macrophage infiltration at the tumor invasive front are independent predictors of survival in AJCC stage I/II melanoma. 19582880_High CD163 expression is associated with rectal cancer. 19885719_findings show that CD163 only interacts with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in early endosomes 19910578_CXCL4 may promote atherogenesis by suppressing CD163 in macrophages, which are then unable to upregulate the atheroprotective enzyme heme oxygenase-1 in response to hemoglobin. 19961729_Expression level of CD163 was significantly increased in patients with coronary heart disease and positively correlated with disease severity and serum CRP and LDL-C. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20299688_The sCD163/sTWEAK plasma ratio may be associated with atherothrombosis burden in peripheral arterial disease. We hypothesize that an imbalance between TWEAK and CD163 could reflect the progression of atherothrombosis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20472850_CD163 expression was seen in all xanthogranulomas and reticulohistiocytomas, 4 epithelioid cell histiocytomas, 2 cases of Langerhans cell histiocytosis, and 8 xanthomas but was absent in atypical fibroxanthomas and Spitz nevi. 20807704_Tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme (TACE/ADAM17) mediates ectodomain shedding of the scavenger receptor CD163. 21120485_Soluble CD163 is a useful marker for systemic sclerosis (SSc), reflecting activation of M2-type macrophages in SSc. 21692033_De novo expression of CD163 by activated microglia/macrophages and CD163+ infiltrating monocytes are neither restricted to nor predominant in hemorrhagic brain lesions. 21737148_In acute active lesions and at the rim of chronic active lesions of multiple sclerosis, strong accumulation of CD163-positive macrophages/microglia is seen. 21766094_Antibodies from a patient with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease bind to macrophages that express the scavenger receptor CD163. 21799753_Cell proteins associated with M1 and M2 macrophages are also expressed by other cell types in the tumour islets and stroma of patients with non-small cell lung cancer 21813065_Plasma levels of macrophage derived sCD163 are associated with disease activity and predict radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. 21839737_in humans neither visceral fat nor fatty liver are major sources of sCD163 21933102_histological chorioamnionitis associated with increase of umbilical cord blood sCD163 21962403_Decreased sTWEAK concentration, and increased sCD163/sTWEAK ratio were significantly and independently associated with long-term cardiovascular mortality in patients with lower-extremity peripheral arterial disease. 22044760_CD68 and CD163 are prognostic factors for Korean patients with Hodgkin lymphoma 22060747_This review summarizes the current knowledge on the regulation of sCD163 in normal and pathological states. [Review] 22098563_Monocyte/macrophage activation, as reflected by CD163 levels, is associated with HOMA-IR in normal-weight and obese subjects after controlling for known mediators of insulin resistance. CD163 adds to standard risk markers for predicting insulin resistance 22211334_CD163 is not a sensitive marker for identification of atypical fibroxanthoma. 22279103_CD163-L1 is highly expressed and colocalizes with CD163 on large subsets of macrophages, but in contrast to CD163 the expression is low or absent in monocytes and in alveolar macrophages, glia, and Kupffer cells. 22289504_CD163 staining is lower than CD68, with less non-specific staining of background inflammatory cells and Hodgkin cells, therefore is a better marker for Hodgkin lymphoma associated macrophages. 22290142_increased plasma concentrations of heme, haptoglobin , heme oxygenase-1, and sCD163 were associated with susceptibility to malaria. 22309204_invading bacterial fibronectins are a novel ligand for the soluble form of scavenger receptor CD163 in the innate immune response 22354894_the expression of hemoglobin scavenger receptor CD163 on monocytes of cardiac surgical patients is induced by methylprednisolone present in cardiopulmonary bypass fluid 22362417_we show a strong association between CD163 mRNA expression in bladder cancer biopsies and poor patient outcome. 22450890_Macrophage-specific sCD163 was strongly associated with insulin resistance independently of TNF-alpha and other predictors. 22453843_Serum sCD163 levels were elevated in scleroderma patients compared with normal controls 22504842_Letter/Case Report: describe CD163 positive xanthogranuloma arising from a radiation port in Merkel cell carcinoma treated with radiotherapy. 22540373_The presence of histological chorioamnionitis affected the number of CD163(+) cells in the placental chorionic plate and in the subchorionic fibrin but not in the fetal membranes. 22682876_Data show that erum concentrations of HO-1, sCD163 and IL-10 in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (s-JIA) patients were markedly elevated in the active phase. 22807450_alpha(1)-Acid glycoprotein up-regulates CD163 via TLR4/CD14 protein pathway: possible protection against hemolysis-induced oxidative stress. 22884782_The numbers of CD163(+) macrophages in lesional skin and serum CD163 levels were associated with disease progression of cutaneous T cell lymphoma. 22911680_Serum sCD163 is superior to PCT and CRP for the diagnosis of sepsis and differentiate the severity of sepsis. 22937125_men with diabetes mellitus type 1 have higher serum concentrations of CD163 than controls. 22948049_Increased CD163 expression was associated with Hodgkin lymphoma 22949100_Higher numbers of CD163+ macrophages and metalloproteinase-9+ cells were detected in invasive extramammary Paget's disease. 23011084_High correlation of sCD163 with IL-12 and CXCL10 suggests the association of their well-known anti-inflammatory function in long-standing rheumatoid arthritis patients. 23013330_Measurement of urine soluble CD163 levels is valuable for identifying sepsis and diagnosing acute kidney injury. 23149357_Serum soluble CD163 levels were significantly higher in Influenza-associated encephalopathy patients with poor outcomes than in those without neurological sequelae. 23150181_This study hallmarks the association of elevated sCD163 with organ dysfunction and adverse outcome of critical illness and may point to the liver as a potential source. 23165891_Letter/Case Report: CD163 proinflammatory macrophages and interleukin-17-producing cells in pigmented necrobiosis lipoidica accompanied by insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. 23224400_Serum CD163 and TARC as disease response biomarkers in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 23289476_Multivariate analysis identified the density of CD163-positive cells as well as the ratio of CD163/CD68 expression as negative predictors for survival of epithelial ovarian cancer patients. 23326413_An increased number of CD163(+) chondrocytes with enhanced phagocytic activity were discovered within degraded joint cartilage, indicating a role in eliminating degraded tissues. 23463035_Case Report: atypical fibrous histiiocytoma positive for CD163/CD44. 23539121_CD163 Overexpression is associated with meningioma. 23555776_CD68 has a role in poor recurrence-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma, but CD163 is more related to active hepatitis 23557330_CD163 expression in macrophages was strongly induced by direct contact with ATN-1 cells. 23589619_These findings suggest that CD163 and IgG collaborate to engage monocytes and endothelial cells in a two-pass detoxification mechanism to mount a systemic defense against Hb-induced oxidative stress. 23595052_Our study shows that elevated serum sCD163 levels were associated with poor prognosis in patients with ovarian cancer. 23640944_peripheral blood mononuclear cells from systemic sclerosis release significantly greater amounts of sCD163 than do PBMC from healthy subjects 23660665_We suggest that atheroma plaques show a more pronounced induction of CD163 and HO-1. 23671278_analysis of the contact region between CD163 and its high affinity ligand Hp-Hb reveals a mechanism of Ca2+-dependent coupling and uncoupling of ligand 23687420_CD163 expression may be related to disease severity and prognosis in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure patients. 23692821_Studied levels of soluble CD163 as a predictive biomarker of myocardial infarction in HIV infected individuals and found sCD163 did not prove to be a useful biomarker for prediction of first-time MI in a HIV-infected population. 23792028_Serum M65 has the potential as a new diagnostic parameter for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and serum CD163 is a new prognostic parameter in HCC patients. 23800379_CD163-TWEAK interactions might play a role in the pathogenesis of Systemic sclerosis 23873589_The impact of anti-inflammatory cytokines provoked by CD163 positive macrophages on ventricular functional recovery after myocardial infarction. 23922818_Inflammatory bowel disease mucosa is abundantly infiltrated with CD163-positive cells, which could contribute to amplify the inflammatory cytokine response. 24118665_soluble CD163 promotes a specific defence of the immune system against fibronectin-binding protein A-mediated inflammatory activation enabling successful pathogen elimination, tissue recovery and resolution of inflammation. 24138337_We report significantly increased levels of the macrophage markers neopterin and sCD163 in a cohort of patients with acute liver injury, predominantly triggered by paracetamol poisoning. 24423341_sCD163 correlates with CD163 mRNA expression in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue and with whole-body insulin sensitivity in the steady-state condition. 24489836_CD163 expression was associated with angiogenesis and shortened survival in patients with uniformly treated classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 24498098_There was a significant negative correlation between the number of CD163(+), CD204(+) or CD206(+) alveolar macrophages. 24515766_Our study confirms previous reports of a prognostic role of tumor-infiltrating macrophages in classical Hodgkin lymphoma, but only for CD163. 24548423_Patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension present altered serum soluble TWEAK and soluble CD163 levels. 24577568_SP induces higher levels of CD163 in monocytes and that high expression of CD163 is associated with increases HIV infection in macrophages. 24597777_liver myofibroblasts play a direct role in regulating the expression of CD163 on monocytes in human liver tissues and thereby may regulate monocyte function during hepatitis B induced liver failure. 24612259_propose the serum sCD163 value 1.8 mg/L as a cutoff concentration for survival analysis in patients with multiple myeloma, which should be validated in future studies 24612419_Findings suggest a positive association among intraleaflet hemorrhage, neovascularization, and enhanced expression of CD163 and HO-1 as a response to intraleaflet hemorrhage in stenotic aortic valves in AS patients undergoing HD. 24619759_Coexpression of CSF- 1R and CD163 can be used to identify a subgroup of patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma at high risk of recurrence or progression who may benefit from aggressive chemotherapy. 24623375_Increased soluble CD163 is associated with the severity of disease in chronic viral hepatitis and predicts fibrosis. 24637679_The macrophage-specific markers CD163, soluble CD163, and soluble MR are increased in septic patients. 24858806_The scavenger receptor CD163 has been found to be over-expressed in Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 24883329_Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that OSCC patients overexpressing CD163 had significantly worse overall survival (P |
ENSMUSG00000008845 |
Cd163 |
240.794726 |
4.8604574483 |
2.281092 |
0.291481792 |
56.374851 |
0.00000000000005989152248605989195152056001559500144552743161607821775760385207831859588623046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000385520659352047135584101712950748319338242081633083557790087070316076278686523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
399.8586991 |
71.4883156 |
82.3392121 |
11.0285735 |
| ENSG00000177595 |
55367 |
PIDD1 |
protein_coding |
Q9HB75 |
FUNCTION: Component of the DNA damage/stress response pathway that functions downstream of p53/TP53 and can either promote cell survival or apoptosis (PubMed:10973264, PubMed:15073321, PubMed:16360037, PubMed:17159900). Associated with CRADD and the CASP2 caspase, it forms the PIDDosome a complex that activates CASP2 and triggers apoptosis (PubMed:15073321, PubMed:17159900). Associated with IKBKG and RIPK1, it enhances sumoylation and ubiquitination of IKBKG which is important for activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B (PubMed:16360037, PubMed:17159900). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10973264, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15073321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16360037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17159900}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Hydrolase;Intellectual disability;Leucine-rich repeat;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains a leucine-rich repeat and a death domain. This protein has been shown to interact with other death domain proteins, such as Fas (TNFRSF6)-associated via death domain (FADD) and MAP-kinase activating death domain-containing protein (MADD), and thus may function as an adaptor protein in cell death-related signaling processes. The expression of the mouse counterpart of this gene has been found to be positively regulated by the tumor suppressor p53 and to induce cell apoptosis in response to DNA damage, which suggests a role for this gene as an effector of p53-dependent apoptosis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:55367; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endopeptidase complex [GO:1905369]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; death receptor binding [GO:0005123]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest [GO:0006977]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein autoprocessing [GO:0016540]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15073321_activation of caspase-2 occurs in a complex that contains PIDD, whose expression is induced by p53, and RAIDD; increased PIDD expression resulted in spontaneous activation of caspase-2 and sensitization to apoptosis by genotoxic stimuli 16360037_PIDD plays a critical role in DNA-damage-induced NF-kappaB activation, controlling the balance between life and death upon DNA damage. 16982033_The functional consequences of the identified PIDD/nucleolin interaction remain to be elucidated, but may be related to a recently discovered new role for PIDD in the activation of NF-kappaB upon genotoxic stress. 17159900_PIDD autoproteolysis marks the bifurcation between pro-death caspase-2 and pro-survival NF-kappaB pathway 17329820_PIDD death domain (DD) and RAIDD DD assemble into an oligomeric complex. Within the PIDDosome, the interaction between PIDD and RAIDD is mediated by a homotypic interaction between their death domains. 17437012_No correlation between Pidd expression and the p53 mutation status of oral squamous cell carcinoma, suggesting that Pidd expression may be regulated by p53-independent mechanisms. 17637755_PIDD isoforms are capable of activating nuclear factor-kappaB in response to genotoxic stress, but only isoform 1 interacts with RIP-associated ICH-1/CED-3 homologous protein with a death domain and activates caspase-2. 18238895_p53-mediated apoptosis occurs by a PIDD- and caspase 2-dependent mechanism, and p53's full transcriptional regulatory functions may be required only for events that are downstream of cytochrome c release 20208132_Total caspase-2 is upregulated during tumour progression in renal cell carcinomas. 20406701_point mutations on RAIDD (R147E) and on PIDD (Y814A) exert a dominant negative effect on the formation of the PIDDosome, and that this effect cannot be applied after the PIDDosome has been formed 20966961_Hsp90 has a major role in controlling PIDD functional activity. 21371439_a new splicing variant of PIDD named PIDD4 is reported. 21415862_PIDD performs key functions upon UV irradiation, including TLS, NHEJ, NF-kappaB activation and cell death. 22854598_The ATM phosphorylation of the PIDD DD enables a binary switch through which cells elect to survive or die upon DNA injury. 25936804_By sequestering PIDD at the kinetochore, BubR1 acts to delay PIDDosome formation until the next cycle, defining a new mechanism by which cells evade apoptosis during mitosis. 26846109_PIDD expression was lower in HCC tissues and HCC cell lines, compared with the adjacent non-tumorous tissues and LO2 normal hepatocytes. PIDD could serve as an independent prognostic factor to predict the survival of HCC patients. PIDD facilitated cell cycle progression and accelerated cell proliferation in HepG2 cells, while overexpression of PIDD resulted in cell cycle arrest at G1 phase in Hep3B cells. 28432080_NPM1-dependent nucleolar PIDDosome is a key initiator of the caspase-2 activation cascade. 28686357_Whole exome sequencing (WES) of an affected fetus, and subsequent Sanger sequencing of the second fetus, revealed a homozygous frameshift variant in CRADD, which encodes an adaptor protein that interacts with PIDD and caspase-2 to initiate apoptosis 31455821_PIDD interaction with KEAP1 as a new mutation-independent mechanism to promote NRF2 stabilization and chemoresistance in NSCLC. 31582733_Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder risk alleles correlated with increased expression (and decreased methylation) of ARTN and PIDD1 and with a decreased expression (and increased methylation) of C2orf82. 32194167_ATR signalling mediates the prosurvival function of phospho-NPM against PIDDosome mediated cell death. 33414379_Biallelic mutations in the death domain of PIDD1 impair caspase-2 activation and are associated with intellectual disability. 34163010_Pathogenic variants in PIDD1 lead to an autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder with pachygyria and psychiatric features. |
ENSMUSG00000025507 |
Pidd1 |
215.582504 |
0.4885415904 |
-1.033447 |
0.175564102 |
34.165115 |
0.00000000506284668467862437184996362996361463082450882211560383439064025878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000022727377453119375187034107181280329079697821725858375430107116699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
137.6574999 |
16.9866381 |
284.5423347 |
24.3601319 |
| ENSG00000177614 |
79605 |
PGBD5 |
protein_coding |
Q8N414 |
FUNCTION: Transposase that mediates sequence-specific genomic rearrangements (PubMed:26406119, PubMed:28504702). Can induce genomic rearrangements that inactivate the HPRT1 gene (PubMed:27491780). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26406119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27491780, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28504702}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Endonuclease;Hydrolase;Nuclease;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transposition |
|
The piggyBac family of proteins, found in diverse animals, are transposases related to the transposase of the canonical piggyBac transposon from the moth, Trichoplusia ni. This family also includes genes in several genomes, including human, that appear to have been derived from the piggyBac transposons. This gene belongs to the subfamily of piggyBac transposable element derived (PGBD) genes. The PGBD proteins appear to be novel, with no obvious relationship to other transposases, or other known protein families. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:79605; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; endonuclease activity [GO:0004519]; transposase activity [GO:0004803]; non-replicative transposition, DNA-mediated [GO:0098038] |
26406119_DNA transposition catalyzed by PGBD5 in human cells occurs genome-wide, with precise transposon excision and preference for insertion at TTAA sites. 28504702_Previously undefined genomic rearrangements in rhabdoid tumors involved PGBD5-specific signal (PSS) sequences at their breakpoints and recurrently inactivated tumor-suppressor genes. PGBD5 physically associated with genomic PSS sequences mediating PGBD5-induced DNA rearrangements in rhabdoid tumor cells. In immortalized cells, PGBD5 sufficed for transformation via specific catalytic residues in the transposase domain. 33450253_The C-terminal Domain of piggyBac Transposase Is Not Required for DNA Transposition. 34232995_Cognate restriction of transposition by piggyBac-like proteins. |
ENSMUSG00000050751 |
Pgbd5 |
82.134929 |
2.8775229040 |
1.524827 |
0.295070774 |
25.844076 |
0.00000037013892035410053960980394580082553090960573172196745872497558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001375094504008689651335952362776193780291578150354325771331787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
113.1528665 |
19.2408113 |
39.4411267 |
5.0901744 |
| ENSG00000177666 |
57104 |
PNPLA2 |
protein_coding |
Q96AD5 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the initial step in triglyceride hydrolysis in adipocyte and non-adipocyte lipid droplets (PubMed:15550674, PubMed:15364929, PubMed:16150821, PubMed:17603008, PubMed:16239926, PubMed:34903883). Exhibits a strong preference for the hydrolysis of long-chain fatty acid esters at the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone and acts coordinately with LIPE/HLS and DGAT2 within the lipolytic cascade (By similarity). Also possesses acylglycerol transacylase and phospholipase A2 activities (PubMed:15364929, PubMed:17032652, PubMed:17603008). Transfers fatty acid from triglyceride to retinol, hydrolyzes retinylesters, and generates 1,3-diacylglycerol from triglycerides (PubMed:17603008). Regulates adiposome size and may be involved in the degradation of adiposomes (PubMed:16239926). May play an important role in energy homeostasis (By similarity). May play a role in the response of the organism to starvation, enhancing hydrolysis of triglycerides and providing free fatty acids to other tissues to be oxidized in situations of energy depletion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BJ56, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15364929, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15550674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16150821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16239926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17032652, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17603008, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34903883}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Lipid degradation;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
PATHWAY: Glycerolipid metabolism; triacylglycerol degradation. |
This gene encodes an enzyme which catalyzes the first step in the hydrolysis of triglycerides in adipose tissue. Mutations in this gene are associated with neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:57104; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; acylglycerol O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0016411]; diolein transacylation activity [GO:0051265]; lipoprotein lipase activity [GO:0004465]; mono-olein transacylation activity [GO:0051264]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; retinyl-palmitate esterase activity [GO:0050253]; triglyceride lipase activity [GO:0004806]; acylglycerol acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036155]; diacylglycerol biosynthetic process [GO:0006651]; lipid droplet disassembly [GO:1905691]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; negative regulation of sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0010891]; positive regulation of triglyceride catabolic process [GO:0010898]; triglyceride catabolic process [GO:0019433] |
15364929_iPLA2epsilon (adiponutrin), iPLA2zeta (TTS-2.2), and iPLA2eta (GS2) are three novel TAG lipases/acylglycerol transacylases that likely participate in TAG hydrolysis and the acyl-CoA independent transacylation of acylglycerols 15550674_reported that adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), catalyzes the initial step in triglyceride hydrolysis; ATGL and hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) coordinately catabolize stored triglycerides in adipose tissue [ATGL] 16239926_Results show that adipose triglyceride lipase has an important role in lipid droplet/adiposome turnover 16644682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16644682_Polymorphisms indicate potential role of ATGL in pathways involved in components of the metabolic syndrome. 16679289_CGI-58 interacts with adipose triglyceride lipase, stimulating its TG hydrolase activity up to 20-fold 16752181_PNPLA2 is not regulated by obesity and exhibits low in vitro triglyceride hydrolase activity. 17032652_identified a novel PEDF-R gene in the retina for a phospholipase-linked membrane protein with high affinity for PEDF, suggesting a molecular pathway by which ligand/receptor interaction on the cell surface could generate a cellular signal 17187067_Neutral lipid storage disease subgroup characterized by mild myopathy, absence of ichthyosis and mutations in both alleles of adipose triglyceride lipase. 17327373_Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) is less important than hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) in regulating catecholamine-induced lipolysis. Both lipases regulate basal lipolysis in human adipocytes. ATGL expression is not influenced by obesity or PCOS. 17356053_In obese subjects, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia are strongly associated with ATGL and HSL mRNA and protein expression, independent of fat mass 17609260_The lack of correlation between ATGL protein content and in vitro TG lipase activity indicates that small decrements in ATGL protein expression are not responsible for the reduction in TG lipase activity observed in obesity. 17631826_Deficient in lipid storage diseases. 17657808_In the present study a novel homozygous PNPLA2 mutation c.475_478dupCTCC (p.Gln160ProfsX19) in the patatin domain, the ATGL active site, was detected in a woman with NLSD and severe myopathy. 18072017_mRNA expression is closely related to individual and regional differences in adipocyte size; impaired insulin sensitivity is associated with decreased aadipose triglyceride lipase mRNA expression. 18191271_There is a novel role for PEDF in hepatic triglyceride homeostasis through binding to ATGL. Both localize to adiposomes in hepatocytes. 18224330_ATGL expression in skeletal muscle fibers, slow-twitch, is demonstrated. 18445597_the C-terminal region of ATGL is essential for proper localization of the enzyme and suppresses enzyme activity 18445677_The lack of the C-terminal domain of adipose triglyceride lipase causes neutral lipid storage disease through impaired interactions with lipid droplets. 18952067_Two novel homozygous mutations in exon 5 of PNPLA2 gene were found in patients with neutral lipid storage disease associated with myopathy. 18952573_review of adipose triglyceride lipase and the lipolytic catabolism of cellular fat stores [review] 19010445_Review focuses on the importance of ATGL as TG lipase within the 'lipolytic machinery' and the current knowledge of molecular mechanisms that regulate ATGL activity. 19061969_Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome: deficiency in CGI-58, a lipid droplet-bound coactivator of lipase. (Review) 19106247_ATGL in addition to hormone sensitive lipase may be important for human skeletal muscle lipolysis 19208393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19390624_No association between genetic variants in PNPLA2 genes and childhood and adolescent obesity 19390624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401457_review summarizes recent findings with the goal of relating structural variants of ATGL and CGI-58 to functional consequences in lipid metabolism [review] 19433586_results suggest that ATGL/CGI-58 acts independently of HSL and precedes its action in the sequential hydrolysis of triglycerides in human hMADS adipocytes 19692632_critical sites in the N-terminal region of desnutrin and the requirement of the C-terminal region for TAG hydrolysis in cultured cells 19695247_TNFalpha decreased ATGL and HSL protein content and triglycerides (TG)-hydrolase activity but increased basal lipolysis due to a marked reduction in perilipin protein content 20167152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237999_The results suggest a molecular pathway by which PEDF ligand/receptor interactions on the cell surface could generate a cellular signal. 20370797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20832801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20832801_variants within PNPLA2 may modulate the TG component of the familial combined hyperlipidemia trait, thus implicating PNPLA2 as modifier gene in this lipid disorder 21073837_A novel homozygous mutation IVS2+1G > A in the PNPLA2 gene was identified in 2 cases causing neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy (NLSDM.) 21129760_Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) levels were inversely correlated with body mass index and positively correlated with insulin sensitivity index. In muscle, ATGL mRNA had a strong positive relationship with carnitine palmitoyltransferase I mRNA. 21170305_1 out of 13 healthy individuals carried at least one rare mutation of PNPLA2. 21393244_interaction of ATGL with CGI-58 increased lipolysis, whereas interaction of ATGL with perilipin 5 decreased lipolysis. 21498783_Data indicate that altered ATGL and HSL expression in skeletal muscle could promote DAG accumulation and disrupt insulin signaling and action. 21543206_Resveratrol increased adipose triglyceride lipase gene and protein expressions, an effect that was not observed for hormone-sensitive lipase in human SGBS adipocytes. 21544567_Four novel and two previously reported mutations were detected, affecting different parts of the PNPLA2 gene in 6 patients with neutral lipid storage disease 21613358_findings are compatible with the notion that the ATGL-G0S2 complex is an important long-term regulator of lipolysis under physiological conditions such as fasting in humans 21680814_total lipase, ATGL and HSL activities were higher in visceral white adipose tissue of cancer patients compared with individuals without cancer and higher in cancer patients with cachexia compared with cancer patients without cachexia 21757733_the C terminus sequesters ABHD5 and thus inhibits basal ATGL activity 21789191_GBF1 and ATGL interact directly and in cells, through multiple contact sites on each protein. 21828047_ATGL knockdown increased monocyte adhesion to the endothelium through enhanced TNFalpha-induced ICAM-1 expression via activation of NFkappaB and PKC. 22183409_We have mapped the epitope of the antibody that detects PEDF-R to the coding region of exon 4. 22535977_Reduced mRNA and protein content of Plin and G0S2 and borderline increased ATGL protein in sc adipose tissue from poorly controlled type 2 diabetic subjects. 22713505_The results demonstrated that adipose triglyceride lipase Ser(404) phosphorylation is not increased in mixed skeletal muscle during moderate-intensity exercise and that AMPK does not appear to be an activating kinase for ATGL Ser(404) in skeletal muscle. 22815850_These data suggest that elevated levels of ATGL are involved in the exercise-induced enhancement of lipolysis in primary adipocytes. 22832386_PNPLA2 gene mutations are responsible for neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy in Chinese Han patients. 22990388_Contribution of novel ATGL missense mutations to the clinical phenotype of NLSD-M: a strikingly low amount of lipase activity may preserve cardiac function. 23232698_Data indicate that PNPLA2 mutations in neutral lipid storage sisease with myopathy (NLSD with myopathy). 23297223_UBXD8-mediated recruitment of p97/VCP to LDs increases lipid droplet (LD) size by inhibiting the activity of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), the rate-limiting enzyme in triacylglycerol hydrolysis. 23818523_PEDF receptor is a transmembrane phospholipase that is required for the survival and antiapoptotic effects of PEDF on retina cells. It has determinants for PEDF binding within its L4 ectodomain that are critical for enzymatic stimulation. 23824421_In humans, ATGL has a remarkable effect on cellular lipid droplet handling, and its lack causes both perivisceral, skeletal muscle, and pancreas fat accumulation; in contrast, the impact on whole-body insulin sensitivity and fatty acid metabolism is minor 23827855_The pathophysiological impact due to defective lipolysis by ATGL deficiency on mitochondrial dysfunction. [Review] 24332944_In patients with TGCV, even when hydrolysis of intracellular TG is defective, the marked up-regulation of PPARgamma and related genes may lead to increased uptake of LCFAs, the substrates for TG synthesis. 24440819_our results suggest that inhibition of the major lipolytic enzymes ATGL and HSL by long-chain acyl-CoAs could represent an effective feedback mechanism controlling lipolysis 24742676_Data indicate that fat-specific protein 27 (FSP27) increases the inhibitory effect of transcription factor Egr1 on the adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) promoter. 25054327_PLIN5 was significantly colocated with ATGL, mitochondria and CGI-58, indicating a close association between the key lipolytic effectors in resting skeletal muscle. 25114172_Data suggest that PNPLA2 hydrolyzes arachidonic acid from triglycerides in mast cell (MC) lipid droplets; PNPLA2 appears to regulate substrate availability of AA for eicosanoid (PGD2/LTC4) generation/secretion upon MC activation with IgE. 25177954_Results indicate that the serum adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) level may be closely related to obesity. 25258314_Data indicate that the peptide corresponding to residues Lys-20 to Ala-52 from G0S2 Inhibits ATGL in the nanomolar range. 25700221_Data suggest that pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) and adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) may serve as therapeutic targets for managing vascular hyperpermeability in sepsis. 25956450_Study reports the clinical and genetic findings of a neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy family of Italian origin with 3 affected siblings. to highlight the effect that different gene mutations may have on ATGL lipase activity, authors performed a functional characterization of the novel PNPLA2 missense mutations identified in their patients 25985012_Distinct cardiac phenotype between two homozygotes born in a village with accumulation of a genetic deficiency of adipose triglyceride lipase. 26318046_Data indicate that a tumor suppressor mechanism by which G0/G1 switch gene 2 product (G0S2) directly inhibits activity of a key intracellular adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL). 26330055_Authors show that rat ATGL, coactivated by rat CGI-58, efficiently hydrolyzes triglycerides and retinyl ester. 26500201_Although we found evidence for moderate association between PNPLA2 tagSNPs and anthropometric and metabolic parameters in our cohort, no evidence for association between polymorphisms in the PNPLA2 gene and the presence and severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease was identified. 26569053_ANGPTL8 is a stress-response protein that down-regulates expression of ATGL. 26600210_PNPLA2 mutations were associated with an extended phenotype, including brain involvement in cases of neutral lipid-storage disease with myopathy. 26803235_A novel deletion was identified in PNPLA2 protein from a patient with complete deficiency of adipose triglyceride lipase. 26882978_Rab32 controls intracellular lipid accumulation through inducing lipolysis via enhancing ATGL expression indirectly. 26922712_A missense mutation in PNPLA2 is the rare cause of severe dilated cardiomyopathy secondary to neutral lipid storage disease. 27213586_The ATGL gene was frequently deleted in various forms of human cancers and was associated with poor prognosis. 27559856_ABHD5 possesses a PNPLA2-independent function in regulating autophagy and tumorigenesis. 27635633_Oxidative stress decreased the levels of PNPLA2 transcripts with no effect on ALOX5 expression. Exogenous additions of P1 peptide or overexpression of the PNPLA2 gene decreased both LTB4 levels and death of RPE cells undergoing oxidative stress. 27851965_a Snail1-ATGL axis that regulates adipose lipolysis and fatty acid release, is reported. 28179319_Results suggest that increased adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) expression is associated with increased adiposity and stromal proliferation in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). 28391974_Study reports the derivation of iPSCs from fibroblasts of two Neutral Lipid Storage Disease with Myopathy (NLSDM)patients carrying different ATGL mutations. These iPSCs exhibited defects in neutral lipid metabolism similar to those of NLSDM fibroblasts. NLSDM-iPSCs were able to undergo directed differentiation into cardiomyocytes. 29072982_No difference in the genotype frequency of rs7925131 or rs7942159 in PNPLA2 between the normal free fatty acids (FFA) group and the high FFA group in a Chinese Han population. 29146190_Thus, ATGL in leucocytes may be an important biomarker for the diagnosis of TGCV and our assay may provide insights into pathophysiology and elucidate the underlying mechanism of TGCV and related disorders. 29320510_Non-cardiac ATGL-mediated modulation of the cardiac lipidome may play an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic heart failure. 29457907_loss of ATGL may thus increase cancer aggressiveness by activation of pro-oncogenic signaling via SRC kinase and increased levels of bioactive lipids. 29472527_ATGL-PPAR-alpha axis play roles in cancer development and progression. [review] 29539587_Gene analysis for PNPLA2 revealed an identical homozygous mutation c.757+1G>T in all patients 29764424_ATGL is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and predicts a poor prognosis. ATGL promotes HCC cell growth by maintaining elevated levels of diacylglycerol and free fatty acids in vitro and in vivo. 30367149_Evidence for a previously uncovered tumor-suppressor function of ATGL in hepatocellular carcinoma, with the outlined molecular mechanisms shedding light on new potential targets for anticancer therapy. 30754064_Association of the PNPLA2, SCD1 and Leptin Expression with Fat Distribution in Liver and Adipose Tissue From Obese Subjects. 30918066_PNPLA2 influences TRL secretion, but is not involved in lipid-droplet homeostasis in human hepatoma cells, a physiological role that is quite distinct from the metabolic function of PNPLA2 in nonhepatic tissues. 30926171_PEDF promotes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of ATGL in hepatocytes through COP1.PEDF enhances nuclear import of predominantly cytosolic ATGL protein for its subsequent proteasomal degradation in the nucleus. 31147543_Obese patients had a decrease in ATGL expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue. 31404588_Protein-protein interactions regulate the activity of Adipose Triglyceride Lipase in intracellular lipolysis. 31476254_These results indicated that ATGL promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells proliferation through upregulation of the AKT signaling pathway. 31525260_The homozygous variant c.245G > A/p.G82D in PNPLA2 is associated with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy phenotypic manifestations. 31610914_Rab18 plays a role upstream of the cytosolic lipolytic enzyme adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) and that recruitment of ATGL by Rab18 is mediated by elements of the Arf/GBF1 machinery. We find that Arf4-GFP is accumulated on the subset of lipid droplets associated with Rab18. 31757217_The role of ATGL and its deficiency in lipid and glucose homeostasis in humans and transgenic mice has been discussed. (Review) 32404277_Adipose triglyceride lipase activity regulates cancer cell proliferation via AMP-kinase and mTOR signaling. 32542055_The ATGL lipase cooperates with ABHD5 to mobilize lipids for hepatitis C virus assembly. 32685558_Association between PNPLA2 Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Diabetic Kidney Disease in a Chinese Han Population with Type 2 Diabetes. 32777979_Burkholderia pseudomallei interferes with host lipid metabolism via NR1D2-mediated PNPLA2/ATGL suppression to block autophagy-dependent inhibition of infection. 32818550_Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible gene 2 (HIG2)/HILPDA, and intracellular lipolysis in cancer. 33064888_Downregulation of adipose triglyceride lipase by EB viral-encoded LMP2A links lipid accumulation to increased migration in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 33160079_Decoration of myocellular lipid droplets with perilipins as a marker for in vivo lipid droplet dynamics: A super-resolution microscopy study in trained athletes and insulin resistant individuals. 33205054_The Role of Adipose Triglyceride Lipase and Cytosolic Lipolysis in Cardiac Function and Heart Failure. 33445064_Dietary fat content and adipose triglyceride lipase and hormone-sensitive lipase gene expressions in adults' subcutaneous and visceral fat tissues. 33621408_Adipose triglyceride lipase promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells via enhancing the lipolytic pathway. 33675111_Resting skeletal muscle PNPLA2 (ATGL) and CPT1B are associated with peak fat oxidation rates in men and women but do not explain observed sex differences. 33824421_Loss of ephrin B2 receptor (EPHB2) sets lipid rheostat by regulating proteins DGAT1 and ATGL inducing lipid droplet storage in prostate cancer cells. 34387896_Hepatocyte-specific deletion of adipose triglyceride lipase (adipose triglyceride lipase/patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 2) ameliorates dietary induced steatohepatitis in mice. 35676490_ATGL is a biosynthetic enzyme for fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids. |
ENSMUSG00000025509 |
Pnpla2 |
594.597089 |
0.4163543604 |
-1.264116 |
0.100206720 |
156.759464 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000577710754734878218126022915163445176044564918182251799199104678689200642062353671239542741489871036097980550039210356771945953369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000087366913318512311682382260322541836251857382167341172397325937529626842698390422814800184217465250924306019442155957221984863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
359.5664220 |
31.6148565 |
871.5888450 |
54.5073230 |
| ENSG00000177685 |
283229 |
CRACR2B |
protein_coding |
Q8N4Y2 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20418871}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Involved in store-operated calcium entry. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:283229; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; regulation of store-operated calcium entry [GO:2001256]; store-operated calcium entry [GO:0002115] |
|
ENSMUSG00000048200 |
Cracr2b |
156.567566 |
0.1280863219 |
-2.964812 |
0.187399122 |
266.817178 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000560539655893907880694855793555718073243837723081123006669554307500813963664415691147402419580279964150772228683208800048717920438265275579185780872523703344256773561937734484672546386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000143888092539027482886877424528384886655744329524029923713146353732443500419150286619475333467390963942407930330963878690975198811541772772327725873897641406529146479442715644836425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.7442333 |
4.8674735 |
313.1825798 |
21.0545402 |
| ENSG00000177699 |
100129540 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.645671 |
3.6211487698 |
1.856447 |
0.525790959 |
12.463714 |
0.00041493408153666142381202353028868401452200487256050109863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001034706376665166975906129387396958918543532490730285644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.5690749 |
7.5245605 |
6.8486292 |
1.6964533 |
| ENSG00000177707 |
25945 |
NECTIN3 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQS3 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in cell-cell adhesion through heterophilic trans-interactions with nectin-like proteins or nectins, such as trans-interaction with NECTIN2 at Sertoli-spermatid junctions. Trans-interaction with PVR induces activation of CDC42 and RAC small G proteins through common signaling molecules such as SRC and RAP1. Also involved in the formation of cell-cell junctions, including adherens junctions and synapses. Induces endocytosis-mediated down-regulation of PVR from the cell surface, resulting in reduction of cell movement and proliferation. Plays a role in the morphology of the ciliary body. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16216929}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the nectin family of proteins, which function as adhesion molecules at adherens junctions. This family member interacts with other nectin-like proteins and with afadin, a filamentous actin-binding protein involved in the regulation of directional motility, cell proliferation and survival. This gene plays a role in ocular development involving the ciliary body. Mutations in this gene are believed to result in congenital ocular defects. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:25945; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical junction complex [GO:0043296]; cell-cell contact zone [GO:0044291]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse [GO:0098686]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density membrane [GO:0098839]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; establishment of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0061951]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0002089]; protein localization to cell junction [GO:1902414]; retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0060042]; spermatid development [GO:0007286] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22926846_Data suggest that expression of nectin-3 is up-regulated in eutopic endometrium of patients with endometriosis as compared with control subjects and up-regulated in all endometriotic lesions investigated compared with eutopic endometrium. 24116228_Nectin-3 trans-interacts with Nectin-2 to promote lymphocyte and monocyte extravasation. 24386110_Nectin-3 is associated with the formation of cell junctions and be a putative suppressor molecule to the invasion of breast cancer cells. 25690753_Expression of nectin-3 in pancreatic cancer can be a prognostic factor. 26038560_PVRL3 is a physiologically relevant binding partner that can serve as a target for the prevention of TcdB-induced cytotoxicity in C. difficile infection. 26602083_Data suggest that 3 independent regions of TcdB (Clostridium difficile toxin B; 1372-1493, 1493-1848, 1851-2366) contribute to binding and entry of TcdB into mammalian cells; residues 1372-1493 are sufficient for interaction with PVRL3. 28689229_Nectin-3 mutation in men with severe teratospermia 30469078_Nectin-3 expression was associated with ovarian cancer, and a greater expression level of nectin-3 was related to poor overall survival. 31855317_Loss of nectin-3 expression as a marker of tumor aggressiveness in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. |
ENSMUSG00000022656 |
Nectin3 |
79.345898 |
6.2287875765 |
2.638951 |
0.224325623 |
145.307167 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000183995462811232700945326092041119781223810770319682614735175125273020127602113926910628628752508717525415704585611820220947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000026214025396658249858929359717965513480343661203635610475185253341173003253568261623589197295558506084489636123180389404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
131.8407965 |
20.9339238 |
21.3679259 |
2.7774913 |
| ENSG00000177721 |
389289 |
ANXA2R |
protein_coding |
Q3ZCQ2 |
FUNCTION: May act as a receptor for annexin II on marrow stromal cells to induce osteoclast formation. |
Receptor;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:389289; |
signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023] |
16895901_analysis of the annexin II receptor on human marrow stromal cells 18636554_annexin II and its receptor axis play a central role in prostate cancer metastasis, and prostate cancer utilizes the hematopoietic stem cell homing mechanisms to gain access to the niche. 22223826_Results show that AXII and AXIIR play important roles in multiple myeloma (MM) and that targeting the AXII/AXIIR axis may be a novel therapeutic approach for MM. 23640736_AXIIR acts as a novel inducer of apoptosis in human cells, partially through activating Caspase-8. 25633185_these subsequent effects might be via suppressing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and matrix metalloproteinase 9. ... AXIIR participates in angiogenesis, and may be a potential therapeutic target for angiogenesis related diseases 27183438_Data highlighted the crucial role of AXIIR in reducing Mum2C cell viability through inducing apoptosis, while autophagy played a protective role in this process. 29694949_Overexpression of AX2R significantly inhibited cell proliferation, migration and tube formation in both types of endothelial cells and increased the expression of KLF2, mediating VEGF and VEGFR2. |
|
|
16.584896 |
0.1119496304 |
-3.159078 |
0.513015758 |
46.107638 |
0.00000000001119312057455645165820025354764258784454056261381538206478580832481384277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000061807130445362224949229950559330794626622385123937419848516583442687988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2599372 |
1.1790750 |
29.3462693 |
5.2659895 |
| ENSG00000177732 |
6666 |
SOX12 |
protein_coding |
O15370 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that binds to DNA at the consensus sequence 5'-ACCAAAG-3' (By similarity). Acts as a transcriptional activator (By similarity). Binds cooperatively with POU3F2/BRN2 or POU3F1/OCT6 to gene promoters, which enhances transcriptional activation (By similarity). Involved in the differentiation of naive CD4-positive T-cells into peripherally induced regulatory T (pT reg) cells under inflammatory conditions (By similarity). Binds to the promoter region of the FOXP3 gene and promotes its transcription, and might thereby contribute to pT reg cell differentiation in the spleen and lymph nodes during inflammation (By similarity). Plays a redundant role with SOX4 and SOX11 in cell survival of developing tissues such as the neural tube, branchial arches and somites, thereby contributing to organogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q04890}. |
Activator;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Members of the SOX family of transcription factors are characterized by the presence of a DNA-binding high mobility group (HMG) domain, homologous to the HMG box of sex-determining region Y (SRY). Forming a subgroup of the HMG domain superfamily, SOX proteins have been implicated in cell fate decisions in a diverse range of developmental processes. SOX transcription factors have diverse tissue-specific expression patterns during early development and have been proposed to act as target-specific transcription factors and/or as chromatin structure regulatory elements. The protein encoded by this gene was identified as a SOX family member based on conserved domains, and its expression in various tissues suggests a role in both differentiation and maintenance of several cell types. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:6666; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein-DNA complex [GO:0032993]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell fate commitment [GO:0045165]; positive regulation of regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0045591]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510] |
185058_Functional analysis of the orthologous mouse gene. 24019301_SOX12 and NRSN2 were identified as candidate genes that may be involved in the developmental defects in 20p13 microdeletion. 24920608_This genome-wide screen has identified two novel metastatic suppressors: TMED3 and SOX12, the knockdown of which increases metastatic growth after direct seeding. 25704764_Up-regulated Sox12 induced by FoxQ1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis by transactivating Twist1 and FGFBP1 expression. 26998831_In this study we screened the transcriptional profiles of 70 MCL patients for SOXC cluster and miR17, miR18a, miR19b and miR92a, from the miR-17-92 cluster. Gene expression analysis showed higher SOX11 and SOX12 levels compared to SOX4 (P = 0.0026). Moreover we found a negative correlation between the expression of SOX11 and SOX4 27858992_SOX12 may be involved in leukemia progression by regulating the expression of beta-catenin and then interfering with TCF/Wnt pathway, which may be a target for AML. 28975985_SOX12 can increase the expression of CDK4 and IGF2BP1, which confer malignant phenotypes to HepatocellularCarcinoma. 29127951_Data found that, in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines, Sox12+ HCC cells generated significantly more tumor spheres in culture, were more chemo-resistant to cisplatin, were detected in circulation more frequently, and formed distal tumor more frequently compared to Sox12- HCC cells. Moreover, Sox12 appeared to functionally contribute to the stemness of HCC cells. 30858360_Overexpression of SOX12 promoted colorectal cancer (CRC) cell proliferation and metastasis, whereas downregulation of SOX12 hampered CRC aggressiveness. 30922917_SOX12 overexpression increased gastric cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis, whereas SOX12 downregulation decreased these behaviors. 31782868_SOX12 was identified as a target of miR-296 which suppressed it expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 31904384_SOX12 promotes the growth of multiple myeloma cells by enhancing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 32019439_Low SOX12 Expression Is Correlated With Poor Prognosis in Patients With Gastric Cancer. 32196581_MicroRNA-370 suppresses SOX12 transcription and acts as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer. 32592199_LncRNA SNHG1 contributes to the regulation of acute myeloid leukemia cell growth by modulating miR-489-3p/SOX12/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 33340249_Long noncoding RNA DUXAP10 promotes the stemness of glioma cells by recruiting HuR to enhance Sox12 mRNA stability. 33416144_SOX12 contributes to the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and malignant transformation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 34789303_LncRNA MNX1-AS1 promotes ovarian cancer process via targeting the miR-744-5p/SOX12 axis. 34868396_Identification of SOX6 and SOX12 as Prognostic Biomarkers for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study Based on TCGA Database. 35022519_LncRNA UCA1 promotes SOX12 expression in breast cancer by regulating m(6)A modification of miR-375 by METTL14 through DNA methylation. 35256570_LINC01063 functions as an oncogene in melanoma through regulation of miR-5194-mediated SOX12 expression. 36266695_LncRNA CASC9 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma through targeting miR-874-3p/SOX12 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000051817 |
Sox12 |
250.429350 |
0.3018849407 |
-1.727929 |
0.129156296 |
180.194242 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000004395511673540402446357079491301996628837961346489534473847290333180755641045381877383137864490070172103280618514098421201197197660803794860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000756150959224432920157527352250736902492333771409361409476584247854758855828109254245402077319784372305688791016109462361782789230346679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
118.8841745 |
9.4033085 |
396.6182253 |
19.8302214 |
| ENSG00000177738 |
648987 |
ANXA2R-OT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33858283_Long Non-Coding RNA LOC648987 Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis of Renal Cell Carcinoma by Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. |
|
|
46.532257 |
0.3072187971 |
-1.702662 |
0.245888454 |
50.675790 |
0.00000000000108955316565986926452968169478818154325555633832323110254947096109390258789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006468947998849425567194382826913007667607447004343157459516078233718872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
20.0831641 |
3.2475663 |
65.8416774 |
6.1954826 |
| ENSG00000177791 |
58529 |
MYOZ1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NP98 |
FUNCTION: Myozenins may serve as intracellular binding proteins involved in linking Z-disk proteins such as alpha-actinin, gamma-filamin, TCAP/telethonin, LDB3/ZASP and localizing calcineurin signaling to the sarcomere. Plays an important role in the modulation of calcineurin signaling. May play a role in myofibrillogenesis. |
3D-structure;Cell projection;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is primarily expressed in the skeletal muscle, and belongs to the myozenin family. Members of this family function as calcineurin-interacting proteins that help tether calcineurin to the sarcomere of cardiac and skeletal muscle. They play an important role in modulation of calcineurin signaling. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:58529; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; pseudopodium [GO:0031143]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; FATZ binding [GO:0051373]; protein serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004865]; telethonin binding [GO:0031433]; myofibril assembly [GO:0030239]; negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070885]; negative regulation of skeletal muscle tissue regeneration [GO:0043417]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; skeletal muscle fiber adaptation [GO:0043503]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
16076904_Our findings provide evidence for a novel connection between the Z-disc protein calsarcin-2 and the sarcolemma via filamins and beta1 integrins. 17254821_Mutations in PDLIM3 and MYOZ1, encoding myocyte Z line proteins, do not play any significant role in the genetic etiology of idiopathic DCM. 17434779_Mutations in MYOZ1 and MYOZ2 are at least very rare events as an underlying disease mechanism for idiopathic or familial DCM 19472918_A large number of variations were found in many of the genes (myozenin 1, gamma-filamin, kinectin-1) in patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophies and controls. 19472918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24177373_Our results implicate MYOZ1 as the causative gene at the chromosome 10q22 locus for AF. |
ENSMUSG00000068697 |
Myoz1 |
25.796090 |
0.2072405019 |
-2.270622 |
0.360141389 |
42.763969 |
0.00000000006175929707461774311612592568165348849706930423053563572466373443603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000323940023035308451781447744677018898973308580480079399421811103820800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.7401202 |
2.4904932 |
42.4345819 |
7.4082376 |
| ENSG00000177943 |
158056 |
MAMDC4 |
protein_coding |
Q6UXC1 |
FUNCTION: Probably involved in the sorting and selective transport of receptors and ligands across polarized epithelia. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q63191}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to be involved in protein transport. Predicted to be located in membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:158056; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; protein transport [GO:0015031] |
7829488_PMID:7829488 describes studies in rat, however, the human MAMDC4 gene product appears to be a homolog of rat apical early endosomal glycoprotein. 25956157_Results suggest that it is the presence of rare syntenic SEC16A and MAMDC4 deletions that increases susceptibility to axial spondyloarthritis in family members who carry the HLA-B*27 allele. 27821716_Expression is localized to the apical surface of the neonatal enterocyte and decreases over time in association with bacterial colonization of the intestine |
ENSMUSG00000026941 |
Mamdc4 |
68.282366 |
0.1825472134 |
-2.453658 |
0.730954667 |
7.953115 |
0.00480046908533345289410432243926152295898646116256713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009856019432399745067163721046199498232454061508178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
21.4589616 |
10.1867876 |
118.5197710 |
39.8374555 |
| ENSG00000178026 |
388886 |
LRRC75B |
protein_coding |
Q2VPJ9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Leucine-rich repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388886; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737] |
Mouse_homologues 27633041_Data show that leucine rich repeat containing 75B (Lrrc75b) is a suppressor of C2C12 myoblast myogenic differentiation. |
ENSMUSG00000046807 |
Lrrc75b |
36.393794 |
0.4194083607 |
-1.253572 |
0.336429818 |
13.701586 |
0.00021427349861272737313773462108912326584686525166034698486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000557791329722020492662415414031329419231042265892028808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.8690396 |
3.7433934 |
45.7501282 |
5.9430867 |
| ENSG00000178038 |
259173 |
ALS2CL |
protein_coding |
Q60I27 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for Rab5 GTPase. Regulates the ALS2-mediated endosome dynamics. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15388334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16473597, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17239822}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;GTPase activation;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Acts upstream of or within endosome organization. Predicted to be located in cytoplasmic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:259173; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087] |
15388334_These results suggest that amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 C-terminal like (ALS2CL), a novel ALS2 homologue, modulates Rab5-mediated endosome dynamics in HeLa cells. 17239822_ALS2CL is a novel ALS2-interacting protein implicated in ALS2-mediated endosome dynamics. 20657180_Data provide further support that ALS2CL, EPHA3, and CMYA1 are bona-fide tumor-suppressor genes and contribute to the tumorigenesis of HNSCC. 23425335_This supports the notion that de novo mutations in ALS2CL are extremely rare in schizophrenia |
ENSMUSG00000044037 |
Als2cl |
153.264960 |
0.0664233612 |
-3.912165 |
0.212105147 |
396.167267 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000037608176859655245393568304375897865421485528104064102360814612419555317365208446551144605108484083860927389000513020004522462315992818501639174149801285648392792598260238004625484953689181136962245557265332063668489270824579762120265513658524 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014017593193144228802648803746591746045551039144475846776454192034901295462650855556249894779132302571557045440110559998148475459859279139435289935054273586383372377598737496581016565729676543954498207454821518758505960455806871323147788643837 |
Yes |
Yes |
19.3564756 |
2.9192190 |
293.4618730 |
23.3588315 |
| ENSG00000178053 |
4291 |
MLF1 |
protein_coding |
P58340 |
FUNCTION: Involved in lineage commitment of primary hemopoietic progenitors by restricting erythroid formation and enhancing myeloid formation. Interferes with erythropoietin-induced erythroid terminal differentiation by preventing cells from exiting the cell cycle through suppression of CDKN1B/p27Kip1 levels. Suppresses COP1 activity via CSN3 which activates p53 and induces cell cycle arrest. Binds DNA and affects the expression of a number of genes so may function as a transcription factor in the nucleus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15861129}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell projection;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes an oncoprotein which is thought to play a role in the phenotypic determination of hemopoetic cells. Translocations between this gene and nucleophosmin have been associated with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:4291; |
ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; myeloid progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002318]; regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition [GO:1902806]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796] |
12176995_phosphorylation of 14-3-3 binding site by MADM 14506644_These findings suggest that an NPM/MLF1 fusion is the primary molecular abnormality in t(3;5) MDS and AML with multilineage dysplasia, and that cases with NPM/MLF1 may be clinically distinct from other MDS-associated disease 17854834_Over-expression of MLF1 has little impact on skeletal muscle function in mice; progressive formation of protein aggregates in muscle are not necessarily pathogenic; MLF1 and MRJ may function together to ameliorate the toxic effects of mutant proteins. 17967869_shuttling of MLF1 is critical for the regulation of cell proliferation and a disturbance in the shuttling balance increases the cell's susceptibility to oncogenic transformation 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20471513_MLF1 gene rearrangement is associated with acute myeloid leukemia. 22151054_Data present the high-resolution crystal structure of this binding motif [MLF1(29-42)pSer34] in complex with 14-3-3epsilon and analyse the interaction with isothermal titration calorimetry. 22193965_changes in the subcellular localization of NPM, due to alterations in the relative abundance of NPM and NPM-MLF1 proteins, may contribute to the enhanced myeloid progenitor activity of Npm +/- cells 23271436_The subcellular localization of full-length human MLF1 is 14-3-3epsilon-independent. 23403313_Data indicte that acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with NPM1-MLF1 and AML with NPM1 mutations showed similar immunophenotypical and molecular features, including gene mutation patterns and gene expression profiling (GEP). 27840155_Mutation in HTT causes Huntington's disease (HD); aggregates of mutated HTT cause apoptosis in neurons of HD patients. Data suggest that both MLF1 and MLF2 preferentially interact with mutated N-terminal HTT; MLF1/MLF2 reduce number of neurons (Neuro2A cell line) containing mutant HTT aggregates and subsequent apoptosis. (HTT = Huntingtin protein; MLF = myeloid leukemia factor) 27984043_These findings suggest that MLF and the associated co-chaperones play a direct role in modulating gene transcription. 28137643_The data indicate that MLF1 serves as a proapoptotic antagonist that interacts with the HAX1/HtrA2-OMI/PARL (HOP) mitochondrial complex to modulate cell survival. 28545128_SNP associated with neuroblastoma resides upstream of the MLF1. Gene silencing of MLF1 in neuroblastoma cells results in significant growth inhibition. 31675375_the abnormal gene regulation imposed by NPM-MLF1 can be characterized by the enhanced recruitment of NuRD to gene regulatory regions. Thus, different mechanisms would orchestrate the dysregulation of NPM function in NPMc+- versus NPM1-MLF1-associated leukemia. 32703400_CRL4(DCAF8) and USP11 oppositely regulate the stability of myeloid leukemia factors (MLFs). |
ENSMUSG00000048416 |
Mlf1 |
38.041709 |
2.3158966182 |
1.211571 |
0.344346317 |
12.304318 |
0.00045191167593382290104328524726895466301357373595237731933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001119351625571946007298151926079299300909042358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.8340317 |
9.9087190 |
21.9799000 |
3.3430056 |
| ENSG00000178104 |
9659 |
PDE4DIP |
protein_coding |
Q5VU43 |
FUNCTION: Functions as an anchor sequestering components of the cAMP-dependent pathway to Golgi and/or centrosomes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUJ3}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 13]: Participates in microtubule dynamics, promoting microtubule assembly. Depending upon the cell context, may act at the level of the Golgi apparatus or that of the centrosome (PubMed:25217626, PubMed:27666745, PubMed:28814570, PubMed:29162697). In complex with AKAP9, recruits CAMSAP2 to the Golgi apparatus and tethers non-centrosomal minus-end microtubules to the Golgi, an important step for polarized cell movement (PubMed:27666745, PubMed:28814570). In complex with AKAP9, EB1/MAPRE1 and CDK5RAP2, contributes to microtubules nucleation and extension from the centrosome to the cell periphery, a crucial process for directed cell migration, mitotic spindle orientation and cell-cycle progression (PubMed:29162697). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25217626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27666745, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28814570, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29162697}. |
Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene serves to anchor phosphodiesterase 4D to the Golgi/centrosome region of the cell. Defects in this gene may be a cause of myeloproliferative disorder (MBD) associated with eosinophilia. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:9659; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; myofibril [GO:0030016]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; astral microtubule organization [GO:0030953]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; positive regulation of microtubule nucleation [GO:0090063]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of Golgi organization [GO:1903358] |
17143517_MMGL-antibody is significantly with a favorable prognosis. Consequently, MMGL-anatibodies may be a useful tumor marker to diagnose and establish a prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21767579_A role of the SANS-myomegalin complex in microtubule-dependent inner segment cargo transport towards the ciliary base of photoreceptor cells. 25961151_PDE4DIP genetic variation was associated with increased risk for ischemic stroke. 29162697_A specific isoform of myomegalin, termed 'SMYLE,' promotes microtubule assembly and function. 30030436_analysis of the recurrent homozygous deletion of DROSHA and microduplication of PDE4DIP in pineoblastoma 32471155_Bioinformatic Analysis Reveals Phosphodiesterase 4D-Interacting Protein as a Key Frontal Cortex Dementia Switch Gene. 34260267_Myomegalin regulates Hedgehog pathway by controlling PDE4D at the centrosome. 34289528_Epistatic interaction of PDE4DIP and DES mutations in familial atrial fibrillation with slow conduction. |
ENSMUSG00000038170 |
Pde4dip |
108.781212 |
3.3390242404 |
1.739427 |
0.185598214 |
87.151630 |
0.00000000000000000001005121528843755324167088960361526712540598309134114979172293369291679709931486286222934722900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000091183735499285970617815714201957241415074221136684138764791351938754360162420198321342468261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
156.7322627 |
21.7406292 |
47.3322572 |
4.9498337 |
| ENSG00000178115 |
727909 |
GOLGA8Q |
protein_coding |
H3BV12 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues ;mmu:99412; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
65.600840 |
0.0954532859 |
-3.389061 |
0.420188443 |
61.881072 |
0.00000000000000364839688099407089258529478892698587711525184257288501044058648403733968734741210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000025194544707524745494081489038850180955009423755530661992452223785221576690673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6150414 |
3.9747175 |
106.0505271 |
28.8033120 |
| ENSG00000178150 |
163071 |
ZNF114 |
protein_coding |
Q8NC26 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:163071; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
|
|
|
12.370335 |
0.4531329447 |
-1.141994 |
0.465667578 |
6.144085 |
0.01318523827192033710808960478289009188301861286163330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024650299796522376349905414372187806293368339538574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8251508 |
2.2738198 |
17.4063872 |
3.1594251 |
| ENSG00000178175 |
167465 |
ZNF366 |
protein_coding |
Q8N895 |
FUNCTION: Has transcriptional repression activity. Acts as corepressor of ESR1; the function seems to involve CTBP1 and histone deacetylases. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17085477}. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables estrogen receptor binding activity and transcription corepressor activity. Involved in negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II; and response to estrogen. Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:167465; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033147]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627] |
16393996_DC-SCRIPT consists of a proline-rich region, 11 C2H2-type zinc fingers, and an acidic region. Localization studies reveal that DC-SCRIPT resides in the nucleus and that nuclear localization is critically dependent on the zinc fingers. (DC-SCRIPT) 17085477_Results indicate that ZNF366 may play an important role in regulating the expression of genes in response to estrogen. 19525478_Identification of ZNF366 and PTPRD as novel determinants of plasma homocysteine in a family-based genome-wide association study 19525478_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20478364_DC-SCRIPT can act as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development.[review] 21122099_study provides a higher level of evidence that DC-SCRIPT is indeed an independent, pure prognostic, factor for primary breast cancer and shows that DC-SCRIPT mRNA expression is most informative for either ESR1-positive and/or ESR2-low pT1 tumors 22473304_DC-SCRIPT is a key regulator of androgen receptor and vitamin d receptor that play an opposite role in prostate cancer etiology and loss of DC-SCRIPT may be involved in the onset of prostate cancer. 22615205_DC-SCRIPT has a primary role in the regulation of interleukin (IL)-10 production by monocytes. 23440419_DC-SCRIPT serves an important role in regulating GR function in DCs, corepressing GR-dependent upregulation of the tolerance-inducing transcription factor GILZ. 25663546_these data show that DC-SCRIPT acts as a novel regulator of CDKN2B and induces cell cycle arrest in ESR1-positive breast cancer cells. 26170389_These data demonstrate that besides nuclear receptor regulation, DC-SCRIPT also modulates activation of NF-kappaBp65 after TLR activation in human DCs. |
ENSMUSG00000050919 |
Zfp366 |
48.855925 |
2.0136620582 |
1.009822 |
0.251863902 |
15.908367 |
0.00006648415408296539015099713143541748650022782385349273681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000188206005804481983417417167991914084268501028418540954589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.3204206 |
10.4957852 |
34.0726905 |
4.0120699 |
| ENSG00000178188 |
25970 |
SH2B1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NRF2 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein for several members of the tyrosine kinase receptor family. Involved in multiple signaling pathways mediated by Janus kinase (JAK) and receptor tyrosine kinases, including the receptors of insulin (INS), insulin-like growth factor I (IGF1), nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs). In growth hormone (GH) signaling, autophosphorylated ('Tyr-813') JAK2 recruits SH2B1, which in turn is phosphorylated by JAK2 on tyrosine residues. These phosphotyrosines form potential binding sites for other signaling proteins. GH also promotes serine/threonine phosphorylation of SH2B1 and these phosphorylated residues may serve to recruit other proteins to the GHR-JAK2-SH2B1 complexes, such as RAC1. In leptin (LEP) signaling, binds to and potentiates the activation of JAK2 by globally enhancing downstream pathways. In response to leptin, binds simultaneously to both, JAK2 and IRS1 or IRS2, thus mediating formation of a complex of JAK2, SH2B1 and IRS1 or IRS2. Mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 and IRS2, resulting in activation of the PI 3-kinase pathway. Acts as positive regulator of NGF-mediated activation of the Akt/Forkhead pathway; prolongs NGF-induced phosphorylation of AKT1 on 'Ser-473' and AKT1 enzymatic activity. Enhances the kinase activity of the cytokine receptor-associated tyrosine kinase JAK2 and of other receptor tyrosine kinases, such as FGFR3 and NTRK1. For JAK2, the mechanism seems to involve dimerization of both, SH2B1 and JAK2. Enhances RET phosphorylation and kinase activity. Isoforms seem to be differentially involved in IGF-I and PDGF-induced mitogenesis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11827956, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14565960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15767667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16569669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17471236, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9694882, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9742218}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain |
|
This gene encodes a member of the SH2-domain containing mediators family. The encoded protein mediates activation of various kinases and may function in cytokine and growth factor receptor signaling and cellular transformation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:25970; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase adaptor activity [GO:0005068]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060391]; regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000278] |
15767667_SH2-B or APS homodimerization and SH2-B/APS heterodimerization thus provide direct mechanisms for activating and inhibiting Janus kinase 2 17228025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17471236_overexpression of SH2B1beta, by enhancing phosphorylation/activation of RET transducers, potentiates the cellular differentiation and the neoplastic transformation thereby induced, and counteracts the action of RET inhibitors. 19079260_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19079261_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19164386_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19342444_SH2B1beta functions as an adapter protein that cross-links actin filaments, leading to modulation of cellular responses in response to JAK2 activation. 19692490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19746409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19910938_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20215397_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20386550_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20616199_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20724581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20725061_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20808231_Deletions of the 16p11.2 SH2B1-containing region were identified in 31 patients with developmental delay and obesity. 20816152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20816195_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21566085_Adapter protein SH2B1beta binds filamin A to regulate prolactin-dependent cytoskeletal reorganization and cell motility 21750520_Meta-analysis of 4992 subjects revealed seven SNPs near four loci, including NEGR1, TMEM18, SH2B1 /ATP2A1 and MC4R, showing significant association at 0.005 21796141_Our results suggest that there is a visceral fat area (VFA)-specific genetic factor and that a polymorphism in the SH2B1 gene influences the risk of visceral fat accumulation. 21907990_Variability at the SH2B1 obesity locus is associated with myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetic patients and with reduced insulin-stimulated nitric oxide synthase activity in human endothelial cells. 22248999_With the current study we were able to replicate and confirm that the SH2B1 gene locus is significantly associated with complex obesity in a Caucasian population. 22443470_Our study supports earlier reports of SH2B1 to be of importance in insulin sensitivity and, in addition, suggests potential roles of NEGR1 and MTCH2. 22901222_High SH2B1 expression was associated with lymph node metastasis, and recurrence in non-small cell lung cancer. 22942098_The known, obesity related, sh2b1 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms rs4788102 and rs7498665 are associated with plasma triglyceride levels. 23054017_Demonstration of the additive effect of four polymorphisms on the LRP5, LEPR, near MC4R and SH2B1 genes on metabolic syndrome risk. 23121087_Data show the synthetic effect of SNPs on the indices of adiposity and risk of obesity in Chinese girls, but failed to replicate the effect of five separate variants of SEC16B rs10913469, SH2B1 rs4788102, PCSK1 rs6235, KCTD15 rs29941 and BAT2 rs2844479. 23160192_SH2B1 plays a critical role in the control of human food intake and body weight and is implicated in maladaptive human behavior. 23190452_Studies indicate that insulin receptor (IR) and IGF Type 1 Receptor (IGFR) have been identified as important partners of Grb10/14 and SH2B1/B2 adaptors. 23270367_The rare coding mutation betaThr656Ile/gammaPro674Ser (g.9483C/T) in SH2B1 was exclusively detected in overweight or obese individuals. 23519644_The obesity risk alleles of non-synonymous SNPs at SH2B1 and APOB48R have no strong effect on weight loss-related phenotypes in overweight children after a 1-year lifestyle intervention. 23640704_Common variants near BDNF and SH2B1 show nominal evidence of association with snacking behavior in European populations. 23825611_rare missense mutations of FTO and SH2B1 did not confer risks of obesity in Chinese Han children in our cohort 24103803_Data (from in excess of six genetic association studies) suggest that an SNP in SH2B1 (rs4788102) is not associated with abnormal glucose homeostasis in obese subjects of European ancestry. [META-ANALYSIS] 24621099_This study highlighted the importance of two candidate genes, SH2B1 and FAIM2, in the risk of overweight/obesity. 24736401_SH2B1 can enhance neurite outgrowth and accelerate the maturation of human induced neurons under defined conditions. 24971614_4 novel variants in SH2B1 were identified in individuals with obesity and insulin resistance. 25234362_We report evidence that the 16p11.2 deletion may influence specific obesity-associated disinhibited eating behaviors 25471250_The rs7359397 (SH2B1) was associated with the body weight, body mass index, and truncal fat mass reduction. 26031769_Mutation analysis has demonstrated that variation in the SH2B1 gene is frequent in both lean and obese groups, with distinctive variations being present on either side of the weight spectrum. 26077624_that SH2B1 is a key positive mediator of pathological cardiac hypertrophy 27164951_Results identified SH2B as a functional target of miR-361 which down-regulation suppresses lung cancer progression and metastasis through regulation of SH2B1. 27530450_SH2B1 polymorphisms are associated with HbA1c, largely independent of BMI, in European American young adults. 27802221_This study is the first to show that neuronal SH2B1, a key protein in insulin signaling, may have a role in the accumulation of Abeta42 in an animal model of Alzheimer's Disease. 28039048_SH2B1 fine-tunes global-local chromatin states. 28544142_Chromosome microarray analysis was performed on both twins and their parents. An identical 244 kb microdeletion on 16p11.2 including 9 Refseq genes, including SH2B1, was identified in the twins. 28694205_SH2B1 and RABEP1 genetic variants are associated with worsening of LDL and glucose parameters in patients treated with psychotropic drugs 29127727_The high-resolution structure of the SH2 domain of SH2B1 further reveals conformationally plastic protein loops that may contribute to the ability of the protein to recognize dissimilar ligands. Together, numerous hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions, in addition to backbone conformational flexibility, permit the recognition of diverse peptides by SH2B1. 29380446_Data reported that SH2B1 expression levels were significantly upregulated and positively associated with EMT markers and poor patient survival in lung adenocarcinoma (LADC) specimens. Further results reveal that SH2B1 has a major role in LADC progression and that SH2B1 is a critical activator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 29631267_The increased expression of genes in leptin (JAK/STAT or AKT) signaling implies that the main mode of action for human SH2B1 mutations might affect leptin signaling rather than insulin signaling. 30370521_Hsa_circ_0136666 promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer through miR-136/SH2B1 axis. 30518945_Copy number variations in SH2B1 gene is associated with distal syndromes with intellectual disability. 31439647_These studies demonstrate that the PH domain plays a crucial role in how SH2B1 controls energy balance and glucose homeostasis. 31739166_provide a mini overview of the roles of SH2B1 in cancer. 31984680_BBOX1-AS1 contributes to colorectal cancer progression by sponging hsa-miR-361-3p and targeting SH2B1. 32251290_Mice with LepR neuron-specific or adult-onset, hypothalamus-specific ablation of Sh2b1 develop obesity, insulin resistance, and liver steatosis. Hypothalamic overexpression of human SH2B1 protects against high fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndromes. Results unravel an unrecognized LepR neuron Sh2b1/ sympathetic nervous system/brown adipose tissue /thermogenesis axis that combats obesity and metabolic disease. 32365683_Association of the SH2B1 rs7359397 Gene Polymorphism with Steatosis Severity in Subjects with Obesity and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. 33356989_Hsa_circ_0075960 Serves as a Sponge for miR-361-3p/SH2B1 in Endometrial Carcinoma. 34689140_Genetic Obesity in Children: Overview of Possible Diagnoses with a Focus on SH2B1 Deletion. |
ENSMUSG00000030733 |
Sh2b1 |
435.730283 |
0.3378288133 |
-1.565636 |
0.197919092 |
60.334706 |
0.00000000000000800239139897841329501109474740379626845384729988408523126963700633496046066284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000053933925593114787656406022738699025293493231891783779019533540122210979461669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
202.4705887 |
38.5241628 |
603.4013393 |
82.0629137 |
| ENSG00000178201 |
57191 |
VN1R1 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZP7 |
FUNCTION: Putative pheromone receptor. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Pheromone response;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Pheromones are chemical signals that elicit specific behavioral responses and physiologic alterations in recipients of the same species. The protein encoded by this gene is similar to pheromone receptors and is primarily localized to the olfactory mucosa. An alternate splice variant of this gene is thought to exist, but its full length nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57191; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; pheromone receptor activity [GO:0016503]; response to pheromone [GO:0019236]; sensory perception of chemical stimulus [GO:0007606] |
17627382_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17627382_The human VN1R1 gene are unlikely to be associated with gender and hence to contribute to distinct gender-specific behavior. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22355687_Structure and function analyses of the purified GPCR human vomeronasal type 1 receptor 1 28440809_the reported association in this study suggests that, as a result of genetic variation, naturally occurring endogenous modulation of VN1R1 function affects women's socio-sexual behavior, and that humans thus communicate via chemo-signaling. |
|
|
6.761771 |
0.3620085732 |
-1.465904 |
0.639597616 |
5.401176 |
0.02012319164090210776851819218791206367313861846923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036059039531348202611837905351421795785427093505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7131824 |
1.7037522 |
10.3521138 |
2.9684088 |
| ENSG00000178209 |
5339 |
PLEC |
protein_coding |
Q15149 |
FUNCTION: Interlinks intermediate filaments with microtubules and microfilaments and anchors intermediate filaments to desmosomes or hemidesmosomes. Could also bind muscle proteins such as actin to membrane complexes in muscle. May be involved not only in the filaments network, but also in the regulation of their dynamics. Structural component of muscle. Isoform 9 plays a major role in the maintenance of myofiber integrity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12482924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21109228}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epidermolysis bullosa;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
Plectin is a prominent member of an important family of structurally and in part functionally related proteins, termed plakins or cytolinkers, that are capable of interlinking different elements of the cytoskeleton. Plakins, with their multi-domain structure and enormous size, not only play crucial roles in maintaining cell and tissue integrity and orchestrating dynamic changes in cytoarchitecture and cell shape, but also serve as scaffolding platforms for the assembly, positioning, and regulation of signaling complexes (reviewed in PMID: 9701547, 11854008, and 17499243). Plectin is expressed as several protein isoforms in a wide range of cell types and tissues from a single gene located on chromosome 8 in humans (PMID: 8633055, 8698233). Until 2010, this locus was named plectin 1 (symbol PLEC1 in human; Plec1 in mouse and rat) and the gene product had been referred to as 'hemidesmosomal protein 1' or 'plectin 1, intermediate filament binding 500kDa'. These names were superseded by plectin. The plectin gene locus in mouse on chromosome 15 has been analyzed in detail (PMID: 10556294, 14559777), revealing a genomic exon-intron organization with well over 40 exons spanning over 62 kb and an unusual 5' transcript complexity of plectin isoforms. Eleven exons (1-1j) have been identified that alternatively splice directly into a common exon 2 which is the first exon to encode plectin's highly conserved actin binding domain (ABD). Three additional exons (-1, 0a, and 0) splice into an alternative first coding exon (1c), and two additional exons (2alpha and 3alpha) are optionally spliced within the exons encoding the acting binding domain (exons 2-8). Analysis of the human locus has identified eight of the eleven alternative 5' exons found in mouse and rat (PMID: 14672974); exons 1i, 1j and 1h have not been confirmed in human. Furthermore, isoforms lacking the central rod domain encoded by exon 31 have been detected in mouse (PMID:10556294), rat (PMID: 9177781), and human (PMID: 11441066, 10780662, 20052759). The short alternative amino-terminal sequences encoded by the different first exons direct the targeting of the various isoforms to distinct subcellular locations (PMID: 14559777). As the expression of specific plectin isoforms was found to be dependent on cell type (tissue) and stage of development (PMID: 10556294, 12542521, 17389230) it appears that each cell type (tissue) contains a unique set (proportion and composition) of plectin isoforms, as if custom-made for specific requirements of the particular cells. Concordantly, individual isoforms were found to carry out distinct and specific functions (PMID: 14559777, 12542521, 18541706). In 1996, a number of groups reported that patients suffering from epidermolysis bullosa simplex with muscular dystrophy (EBS-MD) lacked plectin expression in skin and muscle tissues due to defects in the plectin gene (PMID: 8698233, 8941634, 8636409, 8894687, 8696340). Two other subtypes of plectin-related EBS have been described: EBS-pyloric atresia (PA) and EBS-Ogna. For reviews of plectin-related diseases see PMID: 15810881, 19945614. Mutations in the plectin gene related to human diseases should be named based on the position in NM_000445 (variant 1, isoform 1c), unless the mutation is located within one of the other alternative first exons, in which case the position in the respective Reference Sequence should be used. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:5339; |
axon [GO:0030424]; brush border [GO:0005903]; costamere [GO:0043034]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; hemidesmosome [GO:0030056]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; myelin sheath [GO:0043209]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; sarcoplasm [GO:0016528]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; ankyrin binding [GO:0030506]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; dystroglycan binding [GO:0002162]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; actomyosin contractile ring assembly actin filament organization [GO:2000689]; adherens junction organization [GO:0034332]; cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0055013]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; cellular response to fluid shear stress [GO:0071498]; cellular response to hydrostatic pressure [GO:0071464]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; establishment of skin barrier [GO:0061436]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; hemidesmosome assembly [GO:0031581]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization [GO:0045104]; intermediate filament organization [GO:0045109]; keratinocyte development [GO:0003334]; leukocyte migration involved in immune response [GO:0002522]; mitochondrion morphogenesis [GO:0070584]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; myoblast differentiation [GO:0045445]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; nucleus organization [GO:0006997]; peripheral nervous system myelin maintenance [GO:0032287]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein-containing complex organization [GO:0043933]; regulation of ATP citrate synthase activity [GO:2000983]; regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043114]; respiratory electron transport chain [GO:0022904]; response to food [GO:0032094]; sarcomere organization [GO:0045214]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741]; skeletal myofibril assembly [GO:0014866]; T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010818]; tight junction organization [GO:0120193]; transmission of nerve impulse [GO:0019226]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11441066_During polarization of peripheral blood T lymphocytes, plectin redistributes to the uropod associated with vimentin and fodrin. This vimentin-plectin-fodrin complex provides a continuous linkage from the nucleus (lamin B) to the cortical cytoskeleton. 12136158_The structure was solved by the molecular-replacement method. In addition, the preparation of selenomethionine-derivative crystals is described. 12791251_Data report the crystal structure of the actin binding domain of plectin and show that this region is sufficient for interaction with F-actin or the cytoplasmic region of integrin alpha6beta4. 14966116_propose a previously unrecognized function of plectin as cytoskeletal regulator of PKC signaling (dislocation of PKCdelta and elevated enzymatic activity), and possibly other signaling events, through sequestration of the scaffolding protein RACK1 15500642_the involvement of desmoplakin (DP), plectin, and periplakin in the destruction of epithelial cell integrity ensures the efficient elimination of cytoskeleton, but also provides specificity for selectively targeting individual adhesion molecules 15654962_homozygous mutations in the plectin gene (PLEC1)in epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia 15810881_discussion of phenotypic spectrum of plectin mutations [review] 15817481_the CH1 domain of the plectin-ABD associates with the groove between the two FNIII domains of beta4 16507904_Co-localization, co-immunoprecipitation, and in vitro overlay analyses demonstrated direct interaction of plectin and GFAP. 17397861_Results describe the crystal structure of an N-terminal fragment of the plakin domain of plectin to 2.05 A resolution. 17515952_PLEC1 was differeentially expressed in sclerotic hippocampi compared to non-sclerotic ones. 17662978_A novel functional co-localisation is identified between two plakin cytolinker proteins. 18084872_results reveal that plectin is up-regulated in colorectal adenocarcinoma as well as in bizarre glands and locally invasive tumor nests in tubular adenoma, compared with normal colorectal mucosa 18155192_Thus, plectin appears to interact with CXCR4 and plays an important role in CXCR4 signaling and trafficking and HIV-1 infection. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19366731_Data show that intermediate filament recruitment to focal adhesions in endothelial cells requires beta3 integrin, plectin and the microtubule cytoskeleton, and is dependent on microtubule motors. 19709076_BRCA2-plectin interaction plays an important role in the regulation of centrosome localization and also that displacement of the centrosome may result in genomic instability and cancer development. 20016501_missense mutation causes structure of plectin amino terminus alteration so binding to actin and costameric proteins are attenuated 20052759_Plectin expression patterns determine two distinct subtypes of epidermolysis bullosa simplex 20447487_Autosomal recessive forms of epidermolysis bullosa simplex associated with extracutaneous manifestations, such as muscular dystrophy (MIM 226670) or pyloric atresia (MIM 612138), have been linked to genetic mutations in the gene for plectin 20471030_This protein has been found differentially expressed in thalami from patients with schizophrenia. 20665883_Plectin deficiency can indeed lead to both muscular dystrophy and pyloric atresia in an individual epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS) patient. 21109228_data show that isoform 1f of plectin plays a key role in skeletal muscle function and that disruption of the plectin 1f can cause the LGMD2 phenotype without any dermatologic component as was previously reported with mutations in constant exons of PLEC 21175599_mutational analysis of PLEC1 revealed a homozygous 36 nucleotide insertion (1506_1507ins36) that results in a reduced expression of PLEC1 mRNA and plectin in patients with epidermolysis bullosa simplex and congenital myasthenic syndrome. 21288893_The structure of the plakin domain of plectin reveals a non-canonical SH3 domain interacting with its fourth spectrin repeat. 21420381_degradation of plectin induced by staurosporine-treatment in liver cells resulted in cytoskeleton disruption and induced morphological changes in these cells by affecting the expression and organization of cytokeratin 18. 21424933_plectin deficiency might play an important role in the transformation of human liver cells 21469503_plectin expression was deficient in hepatocellular carcinoma and was probably through post-translational modification 21743296_novel esophageal squamous cell carcinoma marker plectin 1 was identified by mass spectrometry and immunohistochemical analysis 21821021_plectin participates in actin assembly and invasiveness in carcinoma cells in an isoform-specific manner 22240165_The novel FUS-plectin interaction offers new perspectives for understanding the role of FUS and plectin mutations in the pathogenesis of FUS associated diseases 22245045_findings suggest that plectin promotes the migration and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells through activation of Erk 1/2 kinase and is a potential prognostic biomarker of HNSCC. 22333906_A linker region in the COOH-terminal end and serine residue at position 4645 may be important for the binding of plectin to intermediate filaments. 23289980_results confirm epidermolysis bullosa simplex-pyloric atresia is linked to mutations in distal exons 1-30 and 32 of PLEC; while epidermolysis bullosa simplex-muscular dystrophy is linked to PLEC mutations in all exons, in most cases one of the mutations affects exon 31 23717685_this study is the first to demonstrate that up-regulation of vimentin and plectin expression positively correlates with the invasion and metastasis of androgen-independent PCA 23774525_Six of sicteen epidermolysis bullosa simplex probands had dominant PLEC missense mutations. 23921385_the potential importance of the endophilin B2-plectin complex in the biological functions depending on nuclear migration and positioning. 24218614_Mislocated Plectin is necessary for exosome formation and produces exosomes that are capable of promoting pancreatic tumor growth and aggression. 24940650_plectin interacts with keratins 5 and 14 in a process associated with epidermolysis bullosa simplex 25556389_Report of a non-consanguineous Iranian family with two affected sisters showing limb-girdle muscular dystrophy and myasthenic symptoms without any skin involvement, caused by plectinopathy. 25712130_The dominant expression of the P1a isoform in epidermal basal cell layer and cultured keratinocytes suggests that mutations in the first exon of isoform 1a cause skin-only epidermolysis bullosa simplex without extracutaneous involvement. 26527396_data demonstrate that plectin is an essential regulator of nuclear morphology in vitro and in vivo and protects the nucleus from mechanical deformation. 27413182_The Structure of the Plakin Domain of Plectin Reveals an Extended Rod-like Shape. 27566071_lectin and cytoskeletons were not detected in the nuclei of liver cells compared to the results of confocal microscopy. Despite the absence of nuclear plectin and cytoskeletal filaments, the evidence provided support that nuclear pleomorphism of cancer cells is correlated with the cytoplasmic disorganization of cytoskeleton. 27813154_We present two cases of Epidermolysis bullosa with significant urologic involvement resulting from mutations in plectin. 28447722_These findings extend current knowledge of the mutation spectrum of the PLEC gene associated with limbgirdle muscular dystrophy 2Q. 29761480_Three of them [PLEC (OR = 6.28, p = 6.42 x 10(-23) ) (p.Arg2016Trp), EXO5 (OR = 3.37, p = 4.82 x 10(-09) ) (p.Arg344AlafsTer10) and DNAH7 (OR = 1.64, p = 0.048)] were replicated as potential candidates. 29797489_The study has identified two mutations in two large consanguineous pedigrees. Identification of novel variants in the LAMA3 and PLEC genes will expand the mutation spectrum and also help in genetic counselling of patients in the Pakistani population. 30161220_40/359 arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) patients carried 1+ rare PLEC variants but rare variants also seem to occur frequently in the control population and no difference was found in the prevalence of rare PLEC variants in ARVC patients with/without desmosomal likely pathogenic/pathogenic variant. Decreased plectin junctional localization in myocardial tissue was found in 5 variant ARVC patients. 30730609_PLEC encodes plectin, a cytoskeletal protein that maintains tissue integrity. GRINA encodes TMBIM3, which regulates cell survival. We hypothesized that in a joint predisposed to Osteoarthritis (OA), expression of these genes alters to combat aberrant biomechanics and is epigenetically regulated. However, carriage of the OA risk-conferring allele at this locus hinders this response and contributes to disease development. 30991875_High PLEC expression is associated with squamous cell carcinoma in Paranasal Sinus Neoplasms. 31184804_We conclude that the phenotype caused variants in PLEC1 and ITGB4 can be markedly dominated by ACC. Especially if pyloric atresia is present, but also if it is absent, these genes should be considered in newborns with marked and widespread ACC. 32580029_Multi-tissue epigenetic analysis of the osteoarthritis susceptibility locus mapping to the plectin gene PLEC. 32605089_Four Individuals with a Homozygous Mutation in Exon 1f of the PLEC Gene and Associated Myasthenic Features. 33219316_Plectin is a regulator of prostate cancer growth and metastasis. 34571895_Plectin in Cancer: From Biomarker to Therapeutic Target. 35080691_Autophagosome-lysosome fusion is facilitated by plectin-stabilized actin and keratin 8 during macroautophagic process. 35139142_Plectin-mediated cytoskeletal crosstalk controls cell tension and cohesion in epithelial sheets. 35579050_Clinical heterogeneity in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with plectin (PLEC) mutations-A study of six unrelated families from India. |
ENSMUSG00000022565 |
Plec |
4233.563902 |
5.4457466822 |
2.445130 |
0.034783433 |
5009.197125 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
7271.6869498 |
156.3534428 |
1345.1796627 |
23.9579095 |
| ENSG00000178226 |
146547 |
PRSS36 |
protein_coding |
Q5K4E3 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease. Hydrolyzes the peptides N-t-Boc-Gln-Ala-Arg-AMC and N-t-Boc-Gln-Gly-Arg-AMC and, to a lesser extent, N-t-Boc-Ala-Phe-Lys-AMC and N-t-Boc-Val-Leu-Lys-AMC. Has a preference for substrates with an Arg instead of a Lys residue in position P1. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
Enables serine-type endopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:146547; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
15536082_analysis of post-translational processing mechanisms of polyserase-2 revealed that this novel polyprotein is a secreted enzyme whose three protease domains remain as an integral part of a single polypeptide chain |
ENSMUSG00000070371 |
Prss36 |
74.549442 |
0.1538405199 |
-2.700493 |
0.397725040 |
43.681696 |
0.00000000003863686411592545404160490659758639929444168359395916922949254512786865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000205580430551932132970787037912262316258216188202823104802519083023071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.8747025 |
14.0267832 |
112.7319768 |
60.8279054 |
| ENSG00000178297 |
360200 |
TMPRSS9 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z410 |
FUNCTION: Serase-1 and serase-2 are serine proteases that hydrolyze the peptides N-t-Boc-Gln-Ala-Arg-AMC and N-t-Boc-Gln-Gly-Arg-AMC. In contrast, N-t-Boc-Ala-Phe-Lys-AMC and N-t-Boc-Ala-Pro-Ala-AMC are not significantly hydrolyzed. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine protease;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane-bound type II serine polyprotease that is cleaved to release three different proteases. Two of the proteases are active and can be inhibited by serine protease inhibitors, and one is thought to be catalytically inactive. This gene enhances the invasive capability of pancreatic cancer cells and may be involved in cancer progression. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:360200; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
12886014_Polyserase-I is a human polyprotease with the ability to generate independent serine protease domains from a single translation product 16872279_The isolation and characterization of serase-1B, a splice variant of polyserase-1, is reported (accession AB109390.1). 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 23229837_SNP rs4806846 in TMPRSS9 gene is associated with neuroticism in a European sample. 24756697_These effects were mediated by the efficient conversion of pro-uPA to active uPA and high phosphorylation levels of ERK detected in the PANC-1 cells expressing exogenous polyserase-1. 31943016_Combination of whole exome sequencing and animal modeling identifies TMPRSS9 as a candidate gene for autism spectrum disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000059406 |
Tmprss9 |
11.332394 |
0.2494658537 |
-2.003086 |
0.748826186 |
6.495390 |
0.01081545706617900205748217246082276687957346439361572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020606189014689822724957224409081391058862209320068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.2794835 |
2.2335261 |
17.6061377 |
6.0675218 |
| ENSG00000178386 |
7766 |
ZNF223 |
protein_coding |
Q9UK11 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing a Kruppel-associated box domain and multiple zinc finger domains. The function of this protein has yet to be determined. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:7766; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
47.722385 |
0.4387198436 |
-1.188628 |
0.375599539 |
9.549071 |
0.00200050606812887101990106053506224270677193999290466308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004418295610591371769260149449110031127929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.4192925 |
7.8891479 |
72.0566548 |
12.6993134 |
| ENSG00000178573 |
4094 |
MAF |
protein_coding |
O75444 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional activator or repressor. Involved in embryonic lens fiber cell development. Recruits the transcriptional coactivators CREBBP and/or EP300 to crystallin promoters leading to up-regulation of crystallin gene during lens fiber cell differentiation. Activates the expression of IL4 in T helper 2 (Th2) cells. Increases T-cell susceptibility to apoptosis by interacting with MYB and decreasing BCL2 expression. Together with PAX6, transactivates strongly the glucagon gene promoter through the G1 element. Activates transcription of the CD13 proximal promoter in endothelial cells. Represses transcription of the CD13 promoter in early stages of myelopoiesis by affecting the ETS1 and MYB cooperative interaction. Involved in the initial chondrocyte terminal differentiation and the disappearance of hypertrophic chondrocytes during endochondral bone development. Binds to the sequence 5'-[GT]G[GC]N[GT]NCTCAGNN-3' in the L7 promoter. Binds to the T-MARE (Maf response element) sites of lens-specific alpha- and beta-crystallin gene promoters. Binds element G1 on the glucagon promoter. Binds an AT-rich region adjacent to the TGC motif (atypical Maf response element) in the CD13 proximal promoter in endothelial cells (By similarity). When overexpressed, represses anti-oxidant response element (ARE)-mediated transcription. Involved either as an oncogene or as a tumor suppressor, depending on the cell context. Binds to the ARE sites of detoxifying enzyme gene promoters. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12149651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14998494, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15007382, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16247450, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19143053}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Cataract;Chromosomal rearrangement;Deafness;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Dwarfism;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a DNA-binding, leucine zipper-containing transcription factor that acts as a homodimer or as a heterodimer. Depending on the binding site and binding partner, the encoded protein can be a transcriptional activator or repressor. This protein plays a role in the regulation of several cellular processes, including embryonic lens fiber cell development, increased T-cell susceptibility to apoptosis, and chondrocyte terminal differentiation. Defects in this gene are a cause of juvenile-onset pulverulent cataract as well as congenital cerulean cataract 4 (CCA4). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:4094; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; inner ear development [GO:0048839]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:0070306]; megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0030219]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; regulation of chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0032330]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366] |
12939343_results suggest that Tc-mip plays a critical role in Th2 signaling pathway and represents the first proximal signaling protein which links TCR-mediated signal to the activation of c-maf Th2 specific factor 14688382_The short form of the proto-oncogene c-maf is highly induced in minimal change nephrotic syndrome T cells during relapse, where it translocates to the nuclear compartment and binds to the DNA responsive element. 14692531_High levels of c-maf mRNA is associated with multiple myeloma 14998494_c-maf transforms plasma cells by stimulating cell cycle progression and by altering bone marrow stromal interactions 15749884_role of c-Maf in the transcriptional regulation of IL-10 and the underlying molecular mechanism in macrophages 16424013_results suggest that c-Maf might cause a type of T-cell lymphoma in both mice and humans and that ARK5, in addition to cyclin D2 and integrin beta(7), might be downstream target genes of c-Maf leading to malignant transformation 16470690_Findings expand the mutation spectrum of MAF in association with congenital cataract and highlight the genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity of congenital cataract. 16498264_Segmental allergen challenge in asthmatics leads to increased GATA-3, c-maf and T-bet expression in BAL cells but not in bronchial biopsies 17044113_OPN is significantly upregulated in MM patients with maf translocations, particularly in the fraction lacking bone disease 17490615_Taken together, these data establish beta7 ITG as a new molecular target of PAHs, whose up-regulation by these environmental contaminants most likely requires activation of co-operative pathways involving both AhR and c-maf. 17823980_c-Maf is capable of interactions with c-Myb that lead to reduced promoter binding and decreased Bcl-2 expression, rendering CD4 T cells more prone to apoptosis. 17875642_the differential DNA binding specificity between Maf homodimers and Nrf2-Maf heterodimers establishes the differential gene regulation by these dimer-forming transcription factors 17897790_CD13 transcription is regulatd by MAF via an atypical response element. 17901057_Pax-6 and c-Maf interact with G1 to activate basal expression of the glucagon gene 17982426_MAF mutation p.Arg299Ser is the third mutation identified in association with the CCMC phenotype, and all three mutations are located in the basic region of the DNA binding domain in the MAF protein (OMIM 177075). 18059226_Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma(AILT) shows c-Maf expression and provide new insight into the pathogenesis of AILT suggesting c-Maf to be a useful diagnostic marker. 18585411_MafG-mediated nuclear retention may enable Nrf2 proteins to evade cytosolic proteasomal degradation and consequently stabilize Nrf2 signaling 18616618_The exclusion of these genes as likely candidates supports the hypothesis that the ocular phenotype associated with peters' anomaly segregating in this family is a distinct, new, autosomal dominant entity in the anterior segment dysgenesis spectrum. 19151714_In addition to FTO and MC4R, we detected significant association of obesity with three new risk loci in NPC1 (endosomal/lysosomal Niemann-Pick C1 gene), near MAF (encoding the transcription factor c-MAF) and near PTER (phosphotriesterase-related gene). 19215682_c-maf may be important in chondrocyte hypertrophy and terminal differentiation, and may be involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis 19687312_detection of c-Maf may be of particular value in the differential diagnosis of small cell lymphomas. 19844255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19883431_we determined the significance of loss or downregulation of CD79a, overexpression of cyclinD1, and c-maf expression in bone marrow specimens with plasma cell myeloma 20067416_Taken together, these studies demonstrate a new level of transcriptional regulation of MMP-13 expression by the c-maf. 20080955_novel role for MAF as a transcriptional repressor, preventing expression of blood vessel endothelial cells-specific genes, thereby maintaining the differentiation status of lymphatic endothelial cells 20127678_c-Maf interacts with Ubc9 & PIAS1. c-Maf can be SUMOylated at Lys-33 in vitro. SUMOylation attenuates its transcriptional activity. 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20668459_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20712903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21163924_the MEK-ERK pathway regulates MAF transcription 21209279_Monocyte-derived macrophages with CD14 of high-antigen positivity display increased expression of c-Maf, which upregulates production of two key factors (hyaluronan and interleukin-10) that promote growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 21216956_Hepatitis C virus impairs the induction of cytoprotective Nrf2 target genes by delocalization of small Maf proteins. 21362551_Methionine adenosyltransferase II serves as a transcriptional corepressor of Maf oncoprotein 21767287_Data indicate that genetic variants near the KCNQ1 and MAF/WWOX genes are associated with reduced insulin secretion, and the PTPRD genetic variant appears to be associated with progression to diabetes in Han Chinese. 21876034_we studied the mechanisms underlying IL-2 regulation of C-MAF expression in human T cells 22345400_findings show that the transcription factor c-Maf/c-MAF is crucial for mechanosensory function; sensitivity to high-frequency vibration is reduced in humans carrying a dominant mutation in the c-MAF gene 22427637_Bcl6 and Maf collaborate to orchestrate a suite of genes that define core characteristics of human Tfh cell biology. 22875803_c-Maf increases human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 expression in interleukin (IL)-4-producing CD4 T cells by binding the proximal HIV-1 long terminal repeat region (LTR) and augmenting HIV-1 transcription. 23229156_Results imply a regulatory role for TMEM18, BDNF, MTCH2 and NEGR1 in adipocyte differentiation and biology. In addition, we show a variation of MAF expression during adipogenesis, while NPC1, PTER and SH2B1 were not regulated. 23512105_All four of the genes originally identified as showing genome-wide significance (IRF6, ABCA4 and MAF, plus the 8q24 region) were confirmed in this independent sample of trios (who were primarily of European and Southeast Asian ancestry). 23840443_Polymorphisms rs9939609 (FTO gene) and rs1424233 (MAF gene) were genotyped using allelic discrimination assays in a prospective multicenter cohort study; these polymorphisms did not show associations with birth weight, BMI and Ponderal Index at discharge, and weight gain, neither testing for a dominant, additive nor for a recessive model. 24509877_MAF has a role in mediating crosstalk between Ras-MAPK and mTOR signaling in NF1 24982420_LPS promotes PDCD4 degradation via a pathway involving PI3K and mTOR, releasing Twist2, which induces IL-10 via c-Maf. 25064449_Differential effect of cataract-associated mutations in MAF on transactivation of MAF target crystalline genes. 25448412_Study added a novel insight for c-MAF ubiquitination and degradation, suggesting that c-MAF stability is strictly regulated. 25865493_Disease-causing mutations were demonstrated to impair proper MAF phosphorylation, ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, perturbed gene expression in primary skin fibroblasts, and induced neurodevelopmental defects in an in vivo model. 26376684_Results suggest that MAF is a mediator of breast cancer bone metastasis. 16q23 gain or MAF protein overexpression in tumors may help to select patients at risk of bone relapse. 26496036_Findings implicate the strong effects of ROS on multiple stem cell functions with a central role for c-Maf in stem cell senescence. 26694163_Data suggest miR-1290 as the new oncomiR involved in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma pathogenesis probably through downregulation of its target genes MAF and ITPR2. 26719333_Collectively, these studies show that FGF signaling up-regulates expression of alphaA-crystallin both directly and indirectly via up-regulation of c-Maf. 26969892_interplay between MATalpha1, c-Myc, and Maf proteins, and their deregulation during chronic cholestasis may facilitate cholangiocarcinoma oncogenesis 27097296_Epidermal differentiation gene regulatory networks are controlled by MAF and MAFB. 27793878_These results define the role of MAF and GSK3 in the resistance of t(14;16) multiple myeloma to proteasome inhibitors. 28235765_Our results argued that increased expression of sIL6R from myeloid cells and subsequent c-Maf induction were adverse events for counteracting tumor-specific Th1 generation. Overall, this work provides a mechanistic rationale for sIL6R targeting to improve the efficacy of T-cell-mediated cancer immunotherapy 28300844_The interaction between c-Maf and RORgammat, and Blimp-1. 28673317_UBE2O mediates c-Maf polyubiquitination and degradation, induces MM cell apoptosis, and suppresses myeloma tumor growth, which provides a novel insight in understanding myelomagenesis and UBE2O biology. 28745329_MAF overexpression contributes to PMF pathogenesis. 28813657_this study shows that genes associated with MAF-binding enhancers are suppressed in macrophages isolated from rheumatoid-arthritis patients, revealing a disease-associated signature of IFN-gamma-mediated repression 28849415_we identified two heterozygous rare variants in genes that are involved in early cataract development; the novel c.809C>A; p.(Ser270Tyr) in MAF and the c.168C>G; p.(Tyr56 *) variant in CRYGD, previously reported as pathogenic 29080939_common variant , rs889472, of c-MAF is associated with gout susceptibility. 29467225_This study highlights that TMEPAI decreases c-Maf stability by recruiting the ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 to c-Maf for proteasomal degradation in myeloma cells. 30201991_Our results identify c-MAF as a relevant factor that drives two highly divergent post-activation fates of human TH17 cells 30659945_A novel MAF mutation was identified in a Chinese family with congenital non-syndromic bilateral nuclear cataracts.This novelp.Val271Glu mutation impairs the transcriptional activity of crystallins by MAF. 31218784_CCND1, NSD2, and MAF gene rearrangements were estimated accurately by IHC, suggesting that conventional FISH assays can be replaced by IHC. 31536480_PD-1hiCXCR5- T peripheral helper cells promote B cell responses in lupus via MAF and IL-21. 31564713_Maf expression may be a marker for the macrophage population in humans. 31600839_Skeletal abnormalities are common features in Ayme-Gripp syndrome. 31822558_The deubiquitinase USP7 stabilizes Maf proteins to promote myeloma cell survival. 33309247_16q23/MAF Gene Deletion Is a Frequent Cytogenetic Abnormality in Multiple Myeloma Associated With IgH Deletion but Significantly Lower Incidence of High-Risk Translocations. 33312178_MAFB and MAF Transcription Factors as Macrophage Checkpoints for COVID-19 Severity. 33528093_Ayme gripp syndrome in an Indian patient. 33833231_Aberrant TGF-beta1 signaling activation by MAF underlies pathological lens growth in high myopia. 34280251_Germinal Center T follicular helper (GC-Tfh) cell impairment in chronic HIV infection involves c-Maf signaling. 34356658_Loss of the MAF Transcription Factor in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 34377934_MAF Amplification and Adjuvant Clodronate Outcomes in Early-Stage Breast Cancer in NSABP B-34 and Potential Impact on Clinical Practice. 34852950_Association between WWOX/MAF variants and dementia-related neuropathologic endophenotypes. 35359922_Molecular Mechanisms Driving IL-10- Producing B Cells Functions: STAT3 and c-MAF as Underestimated Central Key Regulators? 35383094_Transcription Factor c-Maf Promotes Immunoregulation of Programmed Cell Death 1-Expressed CD8(+) T Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. 35395181_c-Maf: The magic wand that turns on LSEC fate. 35467036_c-Maf enforces cytokine production and promotes memory-like responses in mouse and human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. 35613277_Differential metabolic requirement governed by transcription factor c-Maf dictates innate gammadeltaT17 effector functionality in mice and humans. |
ENSMUSG00000055435 |
Maf |
414.615970 |
0.3589535471 |
-1.478131 |
0.085822566 |
302.808865 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008050515321157644529849295290400403339999095383159434345825018304653785200772543874742745006413573404726901653686608195823032834884391875892513784460017329254718894079347057957107836045906879007816314697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002343700318348852749645751968690914279019607020336248876387289359157101886279279616799084969183938838481210847037576696863264175856905490351989891609689735734546383802423541453663347056135535240173339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
220.9153366 |
12.2935084 |
620.4964059 |
21.8000271 |
| ENSG00000178623 |
2859 |
GPR35 |
protein_coding |
Q9HC97 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a receptor for kynurenic acid, an intermediate in the tryptophan metabolic pathway. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G-proteins that elicit calcium mobilization and inositol phosphate production through G(qi/o) proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16754668}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables C-X-C chemokine receptor activity. Involved in several processes, including chemokine-mediated signaling pathway; negative regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity; and positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration. Is integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2859; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; C-X-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016494]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of neuronal action potential [GO:1904456]; negative regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901386]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025] |
17940199_The results of the study demonstrate the coupling of GPR35 to endogenous G proteins that modulate neuronal Ca2+ channel and thereby provide evidence for a potential role of GPR35 in regulating neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission 18271057_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20361937_These results strongly suggest that 2-acyl lysophosphatidic acid is an endogenous ligand for GPR35. 20599711_human iNKT cells express GPR35 functionally active in reducing IL-4 release. 20919992_screening assays used to identification of small MW agonists; some compounds are species-specific agonists; agonists/ligands include zaprinast, cromolyn & dicumarol 22820167_This review presents a summary of what is known about the G-protein coupled receptors GPR35 and GPR55 and their potential characterization as lysophospholipid or cannabinoid receptors, respectively--{REVIEW} 22821403_GPR35 shows associations in both ulcerative colitis (UC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), whereas TCF4 represents a PSC risk locus not associated with UC. Both loci may represent previously unexplored aspects of PSC pathogenesis. 24347166_results clearly show that R4.60, R(164), R(167), and R6.58 play crucial roles in the agonist initiated activation of GPR35. 25411203_This article shows that GPR35 is the receptor of CXCL17. 25489960_Single-nucleotide polymorphism in GPR35 gene is associated with Crohn's disease. 27064272_Small molecules that stimulate or block GPR35 activity can modulate vascular proliferation and migration. 28425521_We performed a label-free kinome short hairpin RNA screen and identified a putative signaling network of GPR35 in HT-29 cells, some of which was validated using gene expression, biochemical and cellular assays. The results showed that GPR35 induced hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, and was involved in synaptic transmission, sensory perception, the immune system, and morphogenetic processes. 28943434_GPR35 interacts with CXCL17 in breast cancer cells. 28961156_Using exome array data, we identified GPR35 as a novel susceptibility gene associated with chronic AIC in pediatric cancer patients 30043283_The histology of colon sections from GPR35(-/-) mice with dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis showed extensive pathological changes including submucosal edema, diffuse ulcerations, and evidence of complete loss of crypts compared to wild-type mice with DSS-induced colitis. 30445046_Immunoreactivity for GPR35 was detected in normal corneas, keratoconus and Fuchs' dystrophy, mainly in the corneal epithelium and endothelium. In corneas with Fuchs' dystrophy, less intensive immunoreactivity for GPR35 in endothelium was revealed. 31250711_high level expression of G protein-coupled receptor 35 V2/3 mRNA in regional lymph nodes of colon cancer patients is a sign of poor prognosis. 32999316_Activation of the G-protein coupled receptor GPR35 by human milk oligosaccharides through different pathways. 33724219_Inflammatory bowel disease susceptible gene GPR35 promotes bowel inflammation in mice. 33839412_GPR35 regulates osteogenesis via the Wnt/GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 34790192_GPR35 in Intestinal Diseases: From Risk Gene to Function. 35276691_Expression and clinical significance of CXCL17 and GPR35 in endometrial carcinoma. 35622222_The GPR35 expression pattern is associated with overall survival in male patients with colorectal cancer. 35926043_Mitochondrial remodeling and ischemic protection by G protein-coupled receptor 35 agonists. |
ENSMUSG00000026271 |
Gpr35 |
150.034412 |
7.1764840828 |
2.843277 |
0.185863657 |
240.018839 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000389580980942786822057647814390410242197172238963199725428210789735229764837697135687745784198859076857512468143818881455399343225983778415955072205179021693766117095947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000089706946625827353829018629398379140561814926207391931195158588211846579628497947359826784740381661856456560167627290880239583032254059580257177231032983399927616119384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
258.5674091 |
25.8293004 |
36.2023338 |
3.1574285 |
| ENSG00000178695 |
115207 |
KCTD12 |
protein_coding |
Q96CX2 |
FUNCTION: Auxiliary subunit of GABA-B receptors that determine the pharmacology and kinetics of the receptor response. Increases agonist potency and markedly alter the G-protein signaling of the receptors by accelerating onset and promoting desensitization (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Synapse |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in protein homooligomerization. Predicted to act upstream of or within regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. Predicted to be located in cell projection. Predicted to be part of receptor complex. Predicted to be active in postsynaptic membrane and presynaptic membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:115207; |
cell projection [GO:0042995]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260] |
15357420_novel human gene, designated PFET1 (predominantly fetal expressed T1 domain) present in a variety of fetal organs, with highest expression levels in the cochlea and brain 18210030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18347171_Pfetin is a powerful prognostic marker for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. 19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20386566_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20386566_This study provided that kctd12 are associated with Bipolar I in the Han Chinese population. 23290008_KCTD12 is a useful and reliable biomarker for both the diagnosis and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumor. 23996491_N-terminal domain of KCTD12 assumes an alpha/beta structure, whereas the C-terminal domain is predominantly characterized by a beta-structure. 26847701_Studies determined that KCTD12 plays an important role in the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer progression via activation of the ERK signaling pathway. 28000887_Low KCTD12 expression is associated with uveal melanoma. 28869606_our study demonstrate that KCTD12 binds to CDC25B and activates CDK1 and Aurora A to facilitate the G2/M transition and promote tumorigenesis and that Aurora A phosphorylates KCTD12 at serine 243 to trigger a positive feedback loop, thereby potentiating the effects of KCTD12. Thus, the KCTD12-CDC25B-CDK1-Aurora A axis has important implications for cancer diagnoses and prognoses. 30157793_KCTD12 may exert its inhibitory role in ESCC through the suppression of WNT /NOTCH, stem cell factors, and chromatin remodelers and can be introduced as an efficient therapeutic marker. 30886212_association of KCTD12 gene and miR-383-binding genes with rumination 32207860_KCTD12 promotes G1/S transition of breast cancer cell through activating the AKT/FOXO1 signaling. 32961112_Bayesian Genome-wide TWAS Method to Leverage both cis- and trans-eQTL Information through Summary Statistics. |
ENSMUSG00000098557 |
Kctd12 |
913.646692 |
2.7072781168 |
1.436843 |
0.056627275 |
654.889250 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000193108612888416933287308813283500551149820514660484854753810486435045292700428895730594028164182561683661694520885388862040661203886678869327240474443368116985288679282827770948847727832 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000118761796926376422222575398257960457496491810288517265412884621315290584421852014854039187757733400738684967551960354966036220569347176330509403326716668628354139643249450250587267662478 |
Yes |
No |
1342.6773727 |
44.3630016 |
499.5925143 |
13.3995882 |
| ENSG00000178718 |
54913 |
RPP25 |
protein_coding |
Q9BUL9 |
FUNCTION: Component of ribonuclease P, a ribonucleoprotein complex that generates mature tRNA molecules by cleaving their 5'-ends (PubMed:12003489, PubMed:16723659, PubMed:30454648). Also a component of the MRP ribonuclease complex, which cleaves pre-rRNA sequences (PubMed:28115465). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12003489, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16723659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28115465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30454648}. |
3D-structure;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;rRNA processing;tRNA processing |
|
Enables ribonuclease P RNA binding activity. Contributes to ribonuclease P activity. Involved in tRNA 5'-leader removal. Located in centriolar satellite and nucleoplasm. Part of multimeric ribonuclease P complex and ribonuclease MRP complex. Biomarker of autistic disorder. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54913; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; multimeric ribonuclease P complex [GO:0030681]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ribonuclease MRP complex [GO:0000172]; ribonuclease P activity [GO:0004526]; ribonuclease P RNA binding [GO:0033204]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; tRNA 5'-leader removal [GO:0001682] |
20215441_analyses of interactions with deletion mutant proteins indicate that the Alba-type core domain of both Rpp20 and Rpp25 contains most of the determinants for mutual association and P3 RNA recognition. 20632321_Taken together, these findings suggest a potential role for the RPP25 gene transcript in the neurobiology of developmental brain disorders. 23587095_Rpp25 is a major target of autoantibodies to the Th/To autoantigen complex 29625199_Study showed the crystal structure of Rpp20/Rpp25 complex, and confirmed that Rpp20 and Rpp25 exhibit similar molecular structures to one another, to their yeast homologs (Pop7 andPop6, respectively), and to archaeal Alba proteins. These proteins do not seem to undergo significant conformational change upon RNA binding, suggesting that they interact with their cognate RNAs via a pre-formed binding surface. 31942724_LINC00319 promotes migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in cervical cancer by regulating miR-3127-5p/RPP25 axis. 33571640_Crystal structure of human RPP20-RPP25 proteins in complex with the P3 domain of lncRNA RMRP. |
ENSMUSG00000062309 |
Rpp25 |
203.796088 |
2.9786840015 |
1.574675 |
0.131426630 |
145.066380 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000207705862242783361354422093939030355348506512290480351069629944752928542321003155021849791161958620477889780886471271514892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000029563534490872540955323602045704363213164812569745149671590809488853483311525924043163676691037267119099851697683334350585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
304.7777726 |
22.8298320 |
102.9933986 |
6.2616335 |
| ENSG00000178764 |
22882 |
ZHX2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y6X8 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional repressor (PubMed:12741956). Represses the promoter activity of the CDC25C gene stimulated by NFYA (PubMed:12741956). May play a role in retinal development where it regulates the composition of bipolar cell populations, by promoting differentiation of bipolar OFF-type cells (By similarity). In the brain, may promote maintenance and suppress differentiation of neural progenitor cells in the developing cortex (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C0C0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12741956}. |
3D-structure;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The members of the zinc fingers and homeoboxes gene family are nuclear homodimeric transcriptional repressors that interact with the A subunit of nuclear factor-Y (NF-YA) and contain two C2H2-type zinc fingers and five homeobox DNA-binding domains. This gene encodes member 2 of this gene family. In addition to forming homodimers, this protein heterodimerizes with member 1 of the zinc fingers and homeoboxes family. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:22882; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; mRNA catabolic process [GO:0006402]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; retinal bipolar neuron differentiation [GO:0060040]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019] |
12741956_identification as a transcriptional repressor 16952470_ZHX2, a transcriptional repressor, may participate in globin gene regulation. 17056598_ZHX proteins 1, 2 and 3 are major transcriptional mediators of podocyte disease 17447851_High ZHX2 is associated with metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 18194454_These data support the idea that ZHX2 contributes to AFP repression in the liver after birth and may also be involved in AFP reactivation in liver cancer. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21443521_There was no significant difference in high and low percentage of HbF in GG, GA, and AA bearing individuals showing that ZHX2 gene variant has no role in ameliorating the severity of beta-thalassemia major in the South Indian population from Andhra Pradesh. 21987443_Expression profiling of L-1236 cells following siRNA-mediated knockdown of ZHX2 showed inhibition of genes regulating differentiation and apoptosis, suggesting tumor suppressor activity of ZHX2. 22078940_results demonstrate multiple mechanisms decreasing expression of tumor suppressor gene ZHX2 in Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines 22661463_simultaneous application of ZFN and rescue DNA induced gene repair of the disease-causing mutation on the genomic level, resulting in recovery of protein expression. 22984075_Expression of a constitutively active Raf transgene enhances lymphoproliferation, indicating a role for the Ras-MAPK pathway in linker for activation of T cells (LAT)-mediated autoimmune hyperproliferation. 25195714_Data indicate that zinc-fingers and homeoboxes 2 (ZHX2) suppresses glypican 3 (GPC3) transcription by binding with its core promoter. 25473899_Data show that Zinc-fingers and homeoboxes 2 (ZHX2) represses nuclear transcription factor Y alpha (NF-Y)-mediated activation of multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1) transcription. 25746325_Two novel markers, rs7840785 (PINX1) and rs7844465 (ZHX2), are significantly associated with carotid intima-media thickness. 26679602_These results indicated that ZHX2 plays a critical role in the proliferation and osteo/odontogenic differentiation of SCAPs. 28152006_ZHX2 expression in renal cell carcinoma 28258223_Zhx2 is a novel regulator of Mup expression; Zhx2 activates as well as represses expression of target genes 29580980_Remarkably, ZHX2 significantly decreased hepatitis B virus antigen expression, pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) and hepatitis B virus core particle DNA production both in vitro and in mouse livers supporting. 29752719_data indicate that HCC-promoting properties of HBV may include ZHX2 silencing via a miR-155 dependent pathway and suggests a novel therapy for HBV-related HCC 30026228_These studies reveal ZHX2 as a potential therapeutic target for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 30784286_the expression profiles of ZHX2 and PTEN were positively correlated in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues 31683461_ZHX2 could inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis of lung cancer cells by inhibiting p38MAPK signaling pathway. 31740790_Tumor suppressor ZHX2 inhibits NAFLD-HCC progression via blocking LPL-mediated lipid uptake. 32059999_The zinc fingers and homeoboxes 2 protein ZHX2 and its interacting proteins regulate upstream pathways in podocyte diseases. 32114388_ZHX2 restricts hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing stem cell-like traits through KDM2A-mediated H3K36 demethylation. 32382017_ZHX2 drives cell growth and migration via activating MEK/ERK signal and induces Sunitinib resistance by regulating the autophagy in clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 32770671_ZHX2 inhibits SREBP1c-mediated de novo lipogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via miR-24-3p. 33542193_HNRNPD interacts with ZHX2 regulating the vasculogenic mimicry formation of glioma cells via linc00707/miR-651-3p/SP2 axis. 33837660_Upregulation of ZHX2 predicts poor prognosis and is correlated with immune infiltration in gastric cancer. 34279541_Transcription factor Zhx2 restricts NK cell maturation and suppresses their antitumor immunity. 36037364_USP13 promotes deubiquitination of ZHX2 and tumorigenesis in kidney cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000071757 |
Zhx2 |
59.187000 |
0.4796721068 |
-1.059880 |
0.240099363 |
19.386993 |
0.00001067314978545500577140903164519158963230438530445098876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000033347944714927154502039086114706378793925978243350982666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.6460189 |
5.7736724 |
83.1383251 |
8.0011481 |
| ENSG00000178773 |
27132 |
CPNE7 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBL6 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein that may play a role in calcium-mediated intracellular processes. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99829}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a member of the copine family, which is composed of calcium-dependent membrane-binding proteins. The gene product contains two N-terminal C2 domains and one von Willebrand factor A domain. The encoded protein may be involved in membrane trafficking. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2008]. |
hsa:27132; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629] |
25453951_These results suggest Cpne7 is a diffusible signaling molecule that is secreted by preameloblasts, and regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal cells of dental or non-dental origin into odontoblasts. |
ENSMUSG00000034796 |
Cpne7 |
246.465328 |
0.0698119599 |
-3.840382 |
0.233761314 |
261.548731 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007887392571199564557392017627816181139861495728878213778358613574180281693812007837994395520092359458500459947467929935394605404562814971263675473643617319652321384637616574764251708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001983269409725818900943373495523278260352111444077217926234078229128050087366396724506107397181390597477393734803345069533032567656206719995453865990064912239176919683814048767089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.3014992 |
5.3189804 |
480.5613629 |
46.2730333 |
| ENSG00000178860 |
9242 |
MSC |
protein_coding |
O60682 |
FUNCTION: Transcription repressor capable of inhibiting the transactivation capability of TCF3/E47. May play a role in regulating antigen-dependent B-cell differentiation. |
DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional repressor capable of binding an E-box element either as a homodimer or as a heterodimer with E2A in vitro. The encoded protein also forms heterodimers with E2A proteins in vivo. This protein is capable of inhibiting the transactivation capability of E47, an E2A protein, in mammalian cells. This gene is a downstream target of the B-cell receptor signal transduction pathway. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9242; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; branchiomeric skeletal muscle development [GO:0014707]; cardiac conduction system development [GO:0003161]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; diaphragm development [GO:0060539]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] |
15052269_role in repressing lymphotoxin alpha 18368067_ABF-1 is frequently silenced by promoter methylation in follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt's lymphoma. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25070843_results demonstrate that ABF-1 facilitates formation of memory B cells but prevents plasma cell differentiation. 28612433_this study shows that musculin inhibits human T-helper 17 cell response to interleukin 2 by controlling STAT5B activity 31101622_These findings identify a novel recurrent MSC mutation as a key driver of the CD30-IRF4-MYC axis and cell cycle progression in a unique subset of anaplastic large cell lymphomas 31675985_Results found that MSC hypermethylation was more common in non-superficial type gastric cancer (GC) than those without MSC hypermethylation. 34992594_The Pathogenic Roles of IL-22 in Colitis: Its Transcription Regulation by Musculin in T Helper Subsets and Innate Lymphoid Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000025930 |
Msc |
217.953293 |
4.7248209550 |
2.240260 |
0.291709917 |
53.716995 |
0.00000000000023155156318187778660726699854451656346993049240268192079383879899978637695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001439032030553480541824532418680339650738156387355104470771038904786109924316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
350.0196903 |
60.2152904 |
73.9740565 |
9.5833539 |
| ENSG00000178896 |
54512 |
EXOSC4 |
protein_coding |
Q9NPD3 |
FUNCTION: Non-catalytic component of the RNA exosome complex which has 3'->5' exoribonuclease activity and participates in a multitude of cellular RNA processing and degradation events. In the nucleus, the RNA exosome complex is involved in proper maturation of stable RNA species such as rRNA, snRNA and snoRNA, in the elimination of RNA processing by-products and non-coding 'pervasive' transcripts, such as antisense RNA species and promoter-upstream transcripts (PROMPTs), and of mRNAs with processing defects, thereby limiting or excluding their export to the cytoplasm. The RNA exosome may be involved in Ig class switch recombination (CSR) and/or Ig variable region somatic hypermutation (SHM) by targeting AICDA deamination activity to transcribed dsDNA substrates. In the cytoplasm, the RNA exosome complex is involved in general mRNA turnover and specifically degrades inherently unstable mRNAs containing AU-rich elements (AREs) within their 3' untranslated regions, and in RNA surveillance pathways, preventing translation of aberrant mRNAs. It seems to be involved in degradation of histone mRNA. The catalytic inactive RNA exosome core complex of 9 subunits (Exo-9) is proposed to play a pivotal role in the binding and presentation of RNA for ribonucleolysis, and to serve as a scaffold for the association with catalytic subunits and accessory proteins or complexes. EXOSC4 binds to ARE-containing RNAs. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16912217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17545563, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18172165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20368444, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21255825}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Exosome;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding;rRNA processing |
|
Enables mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding activity. Involved in nucleic acid metabolic process and positive regulation of cell growth. Acts upstream of or within defense response to virus. Located in cytosol; nucleoplasm; and transcriptionally active chromatin. Part of exosome (RNase complex). [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54512; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000177]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; euchromatin [GO:0000791]; exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000178]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nuclear exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0000176]; nucleolar exosome (RNase complex) [GO:0101019]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 3'-5'-exoribonuclease activity [GO:0000175]; mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding [GO:0035925]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; DNA deamination [GO:0045006]; histone mRNA catabolic process [GO:0071044]; maturation of 5.8S rRNA [GO:0000460]; nuclear mRNA surveillance [GO:0071028]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process [GO:0000956]; nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, exonucleolytic, 3'-5' [GO:0034427]; polyadenylation-dependent snoRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0071051]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; RNA catabolic process [GO:0006401]; RNA processing [GO:0006396]; rRNA catabolic process [GO:0016075]; rRNA processing [GO:0006364]; U4 snRNA 3'-end processing [GO:0034475] |
12419256_Protein-protein interactions between human exosome components support the assembly of RNase PH-type subunits into a six-membered PNPase-like ring. 17545563_Knock-down of hRrp41p or hRrp4p but not PM/Scl-100 or PM/Scl-75 leads to codepletion of other subunits. 30155936_Findings show that EXOSC4 is highly expressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors and cell lines and demonstrate its oncogenic role in development and progression of CRC. 35008922_RNA Exosome Component EXOSC4 Amplified in Multiple Cancer Types Is Required for the Cancer Cell Survival. |
ENSMUSG00000034259 |
Exosc4 |
152.368009 |
2.6275007454 |
1.393691 |
0.135270674 |
108.155307 |
0.00000000000000000000000024852095514751139331152005431469838131024200568585505095003529570877459642375129078573081642389297485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000002701155594975897286982540015154205759439434582698978830421347626907294103837386956001864746212959289550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
222.4109166 |
17.1716702 |
85.2128461 |
5.3656893 |
| ENSG00000178917 |
285346 |
ZNF852 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMS4 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:285346; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
34957631_Zinc finger protein 852 is essential for the proliferation, drug sensitivity, and self-renewal of gastric cancer cells. |
|
|
39.800004 |
0.0401066990 |
-4.640013 |
0.531111954 |
65.202274 |
0.00000000000000067591470609951799112790777002412709828902033244030223002596358128357678651809692382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004884181729596067029079745577581092066322856863613832700821149046532809734344482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.4629572 |
1.5922533 |
111.3084369 |
26.8918681 |
| ENSG00000178919 |
2304 |
FOXE1 |
protein_coding |
O00358 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that binds consensus sites on a variety of gene promoters and activate their transcription. Involved in proper palate formation, most probably through the expression of MSX1 and TGFB3 genes which are direct targets of this transcription factor. Also implicated in thyroid gland morphogenesis. May indirectly play a role in cell growth and migration through the regulation of WNT5A expression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12165566, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16882747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20094846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20484477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21177256, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24219130, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25381600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9697705}. |
Congenital hypothyroidism;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This intronless gene encodes a protein that belongs to the forkhead family of transcription factors. Members of this family contain a conserved 100-amino acid DNA-binding 'forkhead' domain. The encoded protein functions as a thyroid transcription factor that plays a role in thyroid morphogenesis. Mutations in this gene are associated with the Bamforth-Lazarus syndrome, and with susceptibility to nonmedullary thyroid cancer-4. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2016]. |
hsa:2304; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cranial skeletal system development [GO:1904888]; embryonic organ morphogenesis [GO:0048562]; hair follicle morphogenesis [GO:0031069]; hard palate development [GO:0060022]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; pharynx development [GO:0060465]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; soft palate development [GO:0060023]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; thyroid gland development [GO:0030878]; thyroid hormone generation [GO:0006590] |
11580993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11762722_Compared with normal thyroids, transcripts were more abundant in 24% of thyroid lesions 12165566_Loss of function mutation of TTF-2 is associated with congenital hypothyroidism, thyroid agenesis and cleft palate 12165566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14611701_By means of a polyclonal antibody, TTF2 is identified in adult human thyroid and hair follicles and prepubertal testis. 14654228_a basic amino acid stretch present at both ends of the DNA-binding domain is a bona fide nuclear localization signal, able to bind the nuclear import receptor importin alpha 15140221_a putative role of FOXE1 in mediating hedgehog signaling in the human epidermis downstream of GLI2. 15320969_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15320969_no genetic alteration was present in the TTF-2 gene of congenital hypothyroid and cleft palate patients, suggesting that defects in the TTF-2 gene are a rare event. 15367491_FOXE1 is required for hair follicle morphogenesis. 15367491_Foxe1 expression in the hair follicle is dependent on the Shh pathway. Loss of Foxe1 expression in skin causes aberrant hair formation with disoriented, misalignment and aberrantly shaped hair follicles. 16327884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16481406_Results provided evidence to suggest that variation in FOXE1 polyalanine tract length predisposes to premature ovarian failure. 16584930_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17318017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17717707_FOXE1 through its alanine containing stretch modulates significantly the risk of thyroid dysgenesis occurrence, enhancing a mechanism linking an alanine containing transcription factor to disease. 17717707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19192046_A novel homozygous polymorphism that prevented the binding of MYF-5 to FOXE1 promoter and affected the FOXE1 expression was found in 45% nonsyndromic cleft palate. 19192046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19198613_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19730683_USF1 and USF2 regulate transcriptional activity of the FOXE1 promoter. 19779022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19779022_These data indicate that FOXE1 is a major gene for cleft lip with or without cleft palate and provides new insights for improved counseling and genetic interaction studies. 19845668_given the seemingly relevant role that FOXE1 plays in the development of cutaneous SCC, these results may lead to the development of novel therapies that replace or mimic FOXE1 function to treat this form of cancer. 19930442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19930442_results imply that another tumour suppressor gene at this locus may be more important than FOXE1 in skin carcinogenesis and suggest that variation in the FOXE1 polyalanine tract length predisposes to cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. 20094846_Binding ability of mutant FOXE1 protein to the human thyroperoxidase promoter is reduced compared with the wild-type FOXE1 in patients with thyroid diseases. 20094846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20157192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20350937_FOXE1 is unlikely to be the only key player in radiation-related thyroid carcinogenesis. 20350937_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453517_Review. Describes spectrum of human Foxe1/TTF2 mutations. 20544801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20572854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21177256_MSX1 and TGF-beta3 are direct targets of FOXE1. 21311165_FOXE1-polyAla tract expansion may contribute to the molecular background of familial but not sporadic forms of thyroid hemiagenesis. 21367965_Effects of genetic variation in FOXE1 on serum free thyroxine (FT4) levels in Caucasian populations are demonstrated, as well as borderline significant effects on serum thyroid hormone (TSH) levels. 21462296_Polymorphisms in TIMP2 and WNT9B are novel loci predisposing to cleft palate. 21730105_Both FOXE1 and NKX2-1 were associated with the increased risk of sporadic Japanese PTC. 21896990_these results excluded the association of poly (Ala) polymorphism with autoimmune thyroid diseases; however it confirms the involvement of FOXE1 in the genesis of thyroid carcinoma. 22177572_Polyalanine repeat expansions in FOXE1 is associated with the genetic aetiology of POF in Chinese women. 22493691_Novel associations for hypothyroidism and autoimmune risk loci include SNPs near the FOXE1 gene. 22521644_these data suggest that TTF-2 may modulate the function of ERalpha as a corepressor and play a role in ER-dependent proliferation of mammary cells. 22736773_coding polyalanine expansion in FOXE1 may be responsible for the observed association between FOXE1 and papillary thyroid cancer 22753311_FOXE1 genes suggest a role for orofacial clefting in hispanic polulation. 22882326_study showed evidence of association between forkhead box E1 (FOXE1) variants and thyroid cancer risk in the Portuguese population 23327367_Nuclear FOXE1 expression in tumor cells in vicinity of the PTC border is associated with presence of a risk allele of rs1867277 (c.-238G>A) in the 5' untranslated region of the FOXE1 gene, as well as with pathological characteristics of PTC. 23512105_In addition, eight genes classified as 'second tier' hits in the original study (PAX7, THADA, COL8A1/FILIP1L, DCAF4L2, GADD45G, NTN1, RBFOX3 and FOXE1) showed evidence of linkage and association in this replication sample. 23715628_the FOXE1 gene exhibits significant differential expression levels between PTC tissues and adjacent non-tumor thyroid tissues. 24105688_Significant association with PTC was found for rs1801516 (D1853N) in ATM and rs1867277 in the promoter region of FOXE1 (OR = 1.55, 95% CI 1.03, 2.34). 24127282_single nucleotide polymorphisms at 9q22.33 near FOXE1 showed convincing evidence of association with nonmedullary thyroid carcinoma risk in high-risk families 24252547_study identifies probable susceptibility variants of FOXE1 for oral clefts in the Thai population 24280874_FOXE1 and SYNE1 hypermethylation markers demonstrated significantly increased expression in neoplastic tissue. 24325646_genetic association studies in population in Germany: Data suggest that an SNP in FOXE1 (rs965513) is associated with increased risk for differentiated thyroid cancer (of an aggressive nature) in the population studied. 24489898_Common variations of FOXE1 are a risk factor associated with increased thyroid cancer susceptibility. 24563486_These results strongly support the FOXE1 locus as a risk factor for nsOFC. With the data of the initial study, there is now considerable evidence that this locus is the first conclusive risk factor shared between nsCL/P and nsCPO. 24646064_A tissue-dependent differentially methylated regions (DMR) in the FOXE1 promoter. This DMR contains two consecutive CpG dinucleotides, which are epigenetic modifiers of FOXE1 expression in nontumoral tissues. 24744143_three common variations on FOXE1 is a risk factor associated with increased thyroid cancer susceptibility, but these associations vary in different ethnic populations 24756757_The current meta-analysis provided evidence that FOXE1 genetic polymorphisms may contribute to increased papillary thyroid carcinoma risk..ATM genetic polymorphisms may not be important dominants of susceptibility to this neoplasm. 24852370_Findings suggest that the SNPs in XKR4 and near FOXE1 are involved in the regulation of TSH levels. 25251503_critical role in the regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma development 25303483_Our data suggest a role for PTCSC2, FOXE1, and TSHR in the predisposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma. 25381600_FOXE1 germline rare variant is involved in familal non-medullary thyroid carcinoma. 25538088_our data suggest that SYNE1 and FOXE1 are promising markers for colorectal cancer detection. 25652407_Causal mutations for orofacial clefting and thyroid diseases occur within cis-regulatory elements at the human FOXE1 locus. 25950909_analysis of novel somatic mutations of FOXE1 in papillary thyroid cancer 26013125_In pancreatic cancer cells, AF6 is expressed at reduced levels, causing Dvl2 to be upregulated and available to bind and enhance FOXE1-induced trans-activation of Snail, which promotes proliferation and metastasis. 26100861_this study shows that FOXE1 polymorphism is strongly associated with non-syndromic cleft lip and palate in populations in northeast China 26206751_genetic susceptibility to thyroid cancer seems likely to be associated with the risk alleles at rs1867277, rs965513, rs1443434, and rs907580 26356687_Mutations of TTF2 is associated with risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer in Chinese. Patients with Multiplendular goiter and no metastasis are more likely to suffer PTC. G/A mutation of TTF2 had a high correlation with PTC in the overall population. 26370671_High Levels of mRNA of both FOXE1 are associated with benign than in malignant thyroid lesions. 26722557_Our findings suggest that FOXE1 variations generate a higher risk for poor histopathological features of papillary thyroid carcinoma 26728781_Taken together, this study showed that rs7043516 may be considered as a potentially susceptible marker of cleft lip only among Chinese Han populations. 27191655_The rs965513 polymorphism is a risk factor for thyroid cancer.[meta-analysis] 27207655_We confirmed associations with papillary thyroid cancer and SNPs in FOXE1/HEMGN, SERPINA5 (rs2069974), FTO (rs8047395), EVPL (rs2071194), TICAM1 (rs8120) and SCARB1 (rs11057820) genes. We found associations with SNPs in FOXE1, SERPINA5, FTO, TICAM1 and HSPA6 and and follicular thyroid cancer 27271927_methylation-mediated silencing of FOXE1 expression may contribute to the progression of CRC. 27474100_FOXE1 polyalanine repeat polymorphisms are associated with thyroid cancer, but only for tumours larger than 1 cm, suggesting a role in disease progression. 27604706_Our results implicate FOXE1 as an important locus whose polymorphic variation increases risks for all types of isolated clefts, and opens a new biological pathway to investigate in efforts to understand genetic factors underlying human clefting. 27610545_In a Cuban population, differentiated thyroid cancer risk was positively and strongly associated with the number of copies in the minor allele (A) for SNP rs965513 near FOXE1 among people who consumed less iodine than the median. 27755953_FOXE1 was the only gene which was over-expressed in six out of eight lung cancer cell lines and human cancer tissue specimens and is an important regulator by targeting autophagy and Matrix Metalloproteinases pathways in lung cancer development. 27824288_The functional variants rs965513 and rs1867277 independently contribute to genetic predisposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma, while a contributing role of the FOXE1 poly-Ala polymorphism could not be confirmed. 27852061_FOXE1 interacts with ELK1 on thyroid relevant gene promoters, establishing a new regulatory pathway for its role in adult thyroid function. Co-regulation of TERT suggests a mechanism by which allelic variants in/near FOXE1 are associated with thyroid cancer risk. 28049826_Report that PTCSC2 binds myosin-9 (MYH9). In a bidirectional promoter shared by FOXE1 and PTCSC2, MYH9 inhibits the promoter activity in both directions. This inhibition can be reversed by PTCSC2, which acts as a suppressor. 28054174_In the analysis of all OFCs combined, SNPs near FOXE1 reached genome-wide significance 28398607_We identified a FOXE1: c.532_537delGCCGCC p.(Ala178_Ala179del) variant that predisposes to thyroid ectopia. Taken together, this is the first report of mosaic 11p13 deletion in association with thyroid dysgenesis 28660995_Patient-related factors modify the predisposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma by increasing the risk for rs944289 (near the NKX2-1 locus) per year of age, and by enhancing the protective effect of the FOXE1 GGT haplotype in men. 28727628_replication confirmed at genome-wide significance the association of loci at FOXE1 with hypothyroidism, and PDE8B, CAPZB and PDE10A with serum TSH. A total of 12 SNPs seemed to explain nearly 7% of the serum TSH variation 29509083_We confirmed the association of FOXE1 gene and cleft lip with or without cleft palate by a family based study. For the first time, rs1867277 was significantly associated with cleft lip with or without cleft palate 29788924_The meta-analysis revealed that common variations of FOXE1 (rs965513, rs944289 and rs1867277) were risk factors associated with increased DTC susceptibility. 30793770_Gli2 promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of TPC-1 cells by activating Wnt/beta-catenin and FOXE1 is involved in this process. 30941771_MiR-524-5p targeting on FOXE1 and ITGA3 prevents thyroid cancer progression through different pathways including cell cycling and autophagy. 31129275_Results indicate that high expression of FOXE1 may function as a tumor suppressor in the early stage of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and restrain the proliferation, migration and invasion of PTC by negatively regulating PDGFA expression. Thus, FOXE1 could serve as a prognostic biomarker for PTC. 31345669_A systematic review and meta-analysis on protective role of forkhead box E1 (FOXE1) polymorphisms in susceptibility to non-syndromic cleft lip/palate. 31564061_GRHL3 SNPs interact with FAM49A, FOXE1, NTN1, and VAX1 in the pathogenesis of non-syndromic oral clefts in the Brazilian population. 31846430_FOXE1 regulates migration and invasion in thyroid cancer cells and targets ZEB1. 31918722_FOXE1 represses cell proliferation and Warburg effect by inhibiting HK2 in colorectal cancer. 31944555_the polymorphism of FOXE1 rs10217225 was correlated with an increased risk of cleft lip with or without cleft palate, and the polymorphism of FOXE1 rs4460498 was a protective factor for non-syndromic cleft lip (Meta-Analysis) 32986379_Network-Based Analysis Reveals Association of FOXE1 Gene Polymorphisms in Thyroid Cancer Patients; A Case-Control Study in Southeast of Iran. 33798911_YY1-induced up-regulation of FOXE1 is negatively regulated by miR-129-5p and contributes to the progression of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. 34643920_Genetic predisposition of SNPs in miRNA-149 (rs2292832) and FOXE1 (rs3758249) in thyroid Cancer. 36308369_The Effect of LL37 Antimicrobial Peptide on FOXE1 and lncRNA PTCSC 2 Genes Expression in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) and Normal Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000070990 |
Foxe1 |
15.794380 |
0.4166759162 |
-1.263002 |
0.538098736 |
5.223633 |
0.02228195005505632930731252372424933128058910369873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.039510041183641451956187751193283475004136562347412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6866134 |
3.2680766 |
23.0682436 |
5.1779356 |
| ENSG00000178922 |
81888 |
HYI |
protein_coding |
Q5T013 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible isomerization between hydroxypyruvate and 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate (also termed tartronate semialdehyde). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Isomerase;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a putative hydroxypyruvate isomerase, which likely catalyzes the conversion of hydroxypyruvate to 2-hydroxy-3-oxopropanoate, and may be involved in carbohydrate transport and metabolism. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:81888; |
hydroxypyruvate isomerase activity [GO:0008903]; glyoxylate metabolic process [GO:0046487] |
22490543_Protein HYI may closely bind with protein P311 by an alpha helix in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts. |
|
|
125.900039 |
0.4490990844 |
-1.154894 |
0.238908413 |
23.092252 |
0.00000154411707581099377615705889321695565286063356325030326843261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005350039445767667932321934309847222266398603096604347229003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
75.6064883 |
11.7034765 |
169.7442324 |
17.5935357 |
| ENSG00000179057 |
283284 |
IGSF22 |
protein_coding |
Q8N9C0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Immunoglobulin domain;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:283284; |
|
|
|
|
14.167829 |
0.4994036444 |
-1.001722 |
0.410928164 |
6.018320 |
0.01415812077487547428200631571826306753791868686676025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026266196912664907525680746402940712869167327880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.2044151 |
2.9227226 |
20.6050901 |
3.8830187 |
| ENSG00000179104 |
160335 |
TMTC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N394 |
FUNCTION: Transfers mannosyl residues to the hydroxyl group of serine or threonine residues. The 4 members of the TMTC family are O-mannosyl-transferases dedicated primarily to the cadherin superfamily, each member seems to have a distinct role in decorating the cadherin domains with O-linked mannose glycans at specific regions. Also acts as O-mannosyl-transferase on other proteins such as PDIA3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28973932}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28973932}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The encoded protein contains many tetratricopeptide repeats, sequences known for being involved in protein-protein interactions. This protein binds both the calcium uptake pump SERCA2B and the carbohydrate-binding chaperone calnexin, and it appears to play a role in calcium homeostasis in the ER. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:160335; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; dolichyl-phosphate-mannose-protein mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0004169]; mannosyltransferase activity [GO:0000030]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; protein O-linked mannosylation [GO:0035269] |
18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19386601_TMTC2 expression induced by HIF-2alpha. 19625618_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24764305_findings provide an important link between aneuploidy and the stress pathways activated by Aurora B inhibition and also support the use of Aurora B inhibitors in combination therapy for treatment of cancer. 27311106_A previously uncharacterized gene, TMTC2, has been identified as a candidate for causing progressive sensorineural hearing loss in humans. This finding identifies a novel locus that causes autosomal dominant SNHL. 30729851_Polymorphism rs7961953 in TMTC2 gene is not associated with primary open-angle glaucoma. 31094927_Metastasizing pleomorphic adenomas with recurrent PLAG1/HMGA2 gene rearrangements and a novel HMGA2-TMTC2 fusion. 33436046_Conserved sequence motifs in human TMTC1, TMTC2, TMTC3, and TMTC4, new O-mannosyltransferases from the GT-C/PMT clan, are rationalized as ligand binding sites. |
ENSMUSG00000036019 |
Tmtc2 |
174.700782 |
0.3122350603 |
-1.679296 |
0.165526574 |
102.037084 |
0.00000000000000000000000544920546945921989933503971081964201426817579602200834204894851035827496588126450660638511180877685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000056402715798890658874189893283949070388793001195454061261455092936289990035447772243060171604156494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.3240038 |
9.5512193 |
277.9509935 |
20.5065238 |
| ENSG00000179240 |
100506127 |
GVQW3 |
protein_coding |
Q3ZCU0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:100506127; |
|
|
|
|
21.988900 |
0.3266877482 |
-1.614016 |
0.360871554 |
20.831555 |
0.00000501498530786321425323486672409600828359543811529874801635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000016325801310997140232145891092230272079177666455507278442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.9613387 |
2.4883687 |
33.8764739 |
4.5102620 |
| ENSG00000179331 |
54734 |
RAB39A |
protein_coding |
Q14964 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the maturation and acidification of phagosomes that engulf pathogens, such as S.aureus and M.tuberculosis. Plays a role in vesicular trafficking. Plays a role in the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes. Negatively regulates LPS-induced autophagosome formation in macrophages possibly by implicating PI3K (PubMed:24349490). May be involved in multiple neurite formation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BHD0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21255211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24349490}. |
Autophagy;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable GTPase activity. Involved in phagosome acidification and phagosome-lysosome fusion. Located in phagocytic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54734; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; phagosome acidification [GO:0090383]; phagosome-lysosome fusion [GO:0090385]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; Rab protein signal transduction [GO:0032482]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
19833722_Results show that Rab39a interacts with caspase-1 and suggest that Rab39a functions as a trafficking adaptor linking caspase-1 to IL-1beta secretion. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26163492_our findings indicate that Rab39a favours chlamydial replication and infectivity. This is the first report showing that a late endocytic Rab GTPase is involved in chlamydial infection development. 27494456_C9ORF72 causes suboptimal autophagy 29648608_Molecular pathways regulated by RAB39A are transcriptionally maintained by the formation of molecular complex with RXRB, NCOR and HDAC that also contribute to cancer stemness. |
ENSMUSG00000055069 |
Rab39 |
29.695050 |
2.7790981158 |
1.474617 |
0.319798879 |
21.627640 |
0.00000331046721165362109104684379401462024361535441130399703979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011000111671320902267685176711964345486194361001253128051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.5595708 |
8.7923869 |
15.7629706 |
2.5454852 |
| ENSG00000179344 |
3119 |
HLA-DQB1 |
protein_coding |
A2AAZ0 |
|
Adaptive immunity;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Lysosome;MHC II;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
HLA-DQB1 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogs. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DQA) and a beta chain (DQB), both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (APC: B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages). The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and it contains six exons. Exon 1 encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DQ molecule both the alpha chain and the beta chain contain the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities, resulting in up to four different molecules. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow transplantation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:14961; |
endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; MHC class II protein complex [GO:0042613]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0002504] |
10998087_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11024583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11027344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11034591_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11045836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11053637_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11064106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11082515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11082516_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11082517_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11097225_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11098934_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11115839_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11118029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11120931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11124840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11157139_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11158011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11165717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11165718_Observational study of gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11169240_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11169241_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11169242_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11171832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11179016_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11181188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11182227_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11195230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11218373_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 11229460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11233253_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11239517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11246532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11250044_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11250046_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11257148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11260508_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11285127_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11285131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11288988_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11291046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11294566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11296153_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11317658_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11318984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11327387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11334675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11334677_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11345587_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11347740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11393660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11424637_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11454644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11469465_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11474874_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11476905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11476906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11477477_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11484084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11495087_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11502807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11532022_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11543893_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11555411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11556984_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11580849_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11588129_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11592043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11600541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11672906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11678027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11678832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11679920_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11683403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11704285_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11723075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11724418_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11724419_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11736906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11752507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11756990_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11776098_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11776160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11780465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11782272_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11782273_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11783381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11802942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11802952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11804200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11812768_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11839711_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11841366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11841486_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11841486_association of TNF alleles with HLA-DR, -DQ and -B alleles in 216 healthy individuals from the north of England 11845225_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11862400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11864433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11872662_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11881821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11888582_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11894970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11895223_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11900275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11903620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11904677_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11914751_A retroviral long terminal repeat adjacent to the gene modifies type I diabetes susceptibility on high risk DQ haplotypes. 11914753_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11916167_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11916169_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11916169_Relative and absolute HLA-DQA1-DQB1 linked risk for developing type I diabetes before 40 years of age in the Belgian population 11920855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11923913_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11929589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11929590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11929591_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11934390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11935333_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11950806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11953202_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11953202_Relationship between HLA-DQA1, -DQB1 genes polymorphism and susceptilibity to bronchial asthma among Northern Hans 11972875_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11972877_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11972882_Lack of evidence for association of HLA-DQB1 genes and gastric cancer carcinogenesis or H. pylori infection. 11972882_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11978563_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11984513_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11985790_HLA-DQB1 alleles are associated with susceptibility or resistance to gastric cancer and also influence its clinical features 11985790_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11994765_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11997714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12010826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12021129_HLA-DRB1, DQB1, and DQA1 allele profile in Brazilian patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. 12021129_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12021131_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12021132_Molecular modeling of eluted peptides from DQ6 molecules (DQB1*0602 and DQB1*0604) negatively and positively associated with type 1 diabetes 12021137_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12021139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12021143_The combination of several polymorphic amino acid residues in the DQalpha and DQbeta chains forms a domain structure pattern and is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. 12021150_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12021152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12027934_genotype influences the relative risk of type 1 diabetes conferred by dietary factors 12028537_Association of HLA-DRB1*1502-DQB1*0501 haplotype with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus 12028537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12039527_HLA DQA1-DQB1 genotypes in Bedouin families with celiac disease. 12050583_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12070003_The high frequency of HLA-DRB1*1501-DQA1*0102-DQB1*0602 haplotype in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria(PNH), including AA-PNH syndrome, and aplastic anemia (AA) patients.(DQB1) 12071546_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12072047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12074713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12077712_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12083823_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12089669_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12090587_Women carrying the HLA-DQB1*0301 allele have an increased risk of developing CIN when infected by HPV 16, although there was not an increased frequency of recurrent disease among women carrying this allele. 12100571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12107223_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12109964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12121676_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12124873_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12125959_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12134251_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12137324_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12139680_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12144621_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12144622_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12144623_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12144625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12144632_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12145745_HLA class II haplotypes containing DRB1 and DQB1 alleles are strong risk factors for human systemic lupus erythematosus 12149602_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12150008_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12151439_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12170471_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12196893_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12209103_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12209609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12233873_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12235085_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12235090_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12270547_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12296785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12356573_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12358854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12358858_Six different variants, including a novel polymorphic site, were detected in exon 1. 12362498_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12364437_Observational study of gene-disease association and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12364641_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12366783_DQB1*0604 was found to be strongly associated with non-obstructive azoospermia and haplotype analysis suggested that the DQB1*0604 allele may play a decisive role in the pathogenesis of non-obstructive azoospermia. 12366783_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12366785_the major histocompatibility complex region's conferred susceptibility to CD is very similar to that observed for DM1, with shared risk and protective haplotypes. 12370403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12373032_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12392858_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12405606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12405608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12410803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12410803_macrophages from DQB1*0201/*0302 type 1 diabetes patients are sensitized to secrete both cytokines and PGE-2 following nonantigenic stimulation 12443029_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12445309_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12445315_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12445316_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12447731_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12453977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12453977_There is an association of HLA-DQ genotype in autoantibody-negative and rapid-onset type 1 diabetes. 12455817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12464650_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12472657_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12493453_polymorphic in acute rejection development in liver transplantation 12507821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12507826_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12513847_HLA-DQB1*06 allele is associated with pathogenesis of the major beta-thalassemia in Guangdong area. 12513847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12515291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12542740_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12543794_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12556916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12556916_specific DQB1 genes are implicated in disorders of motor control during sleep. 12574360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12579512_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12590979_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12594107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12605834_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12618908_Exon 2 and intron 2 of the HLA DQB1 gene from 20 individuals were cloned and sequenced and eight alleles were obtained. Results indicated that different regions of intron 2 in the DQB1 gene had different evolutionary patterns. 12622778_Association of DQB1 haplotypes with susceptibility for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 12639765_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12648278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12648281_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12651073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12651074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12656131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12665835_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12666382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12687342_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12694584_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12694585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12694588_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12694588_Polymorphism of HLA-DRB1, DQB1 and DPB1 in unrelated healthy volunteers from the Naxi ethnic group. The distribution characteristics of the HLA class II alleles revealed that the Naxi ethnic group belonged to the Southern group of Chinese. 12721173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12721936_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12721936_Reduced frequency in children with diabetes mellitus type 1, associated with enterovirus RNA. 12734793_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12753657_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12753667_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12757179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12765483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12770797_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12771724_Observational study of gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12774051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12778461_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12786999_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12787001_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12788886_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12788886_TNF alpha and DQB1*02 alleles in linkage disequilibrium in IDDM and NIDDM; TNF alpha promoter polymorphism associated with insulin-deficient phenotype in NIDDM only together with DQB*02 12793199_A significant number of rheumatoid arthritis Hungarian patients carried DR4 haplotypes on DQB1*0302 (54%) relative to DQB1*0301 which was present on 36% of the haplotypes. 12793199_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12794545_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12820696_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12823769_Dravidian-speaking castes of southern India were typed for polymorphism at this allele. 12823769_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12825172_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12835080_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12878355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12878360_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12878363_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12887819_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12890388_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12911285_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12917799_Association between diabetes type 1 and DQB1 alleles in a tri-racial (Caucasian, Black and Indo-American) mixed population in Uruguay. 12917799_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12921878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12941076_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12948297_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12956878_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12974555_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12974796_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14504973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14508706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14510801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14514946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14551034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14562382_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14567462_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14581805_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14592217_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14602216_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14617034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14623754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14648147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14655281_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14662898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14669136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14669136_The HLA-DRB1 or the HLA-DQB1 gene is within the susceptibility haplotype for multiple sclerosis amoung African Americans. 14675393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14677183_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14679080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14680508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14686115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693734_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14694619_HLA-DRB1 * 1401 and DQB1 * 05 may be the susceptible genes and HLA-DRB1 * 09 the protection gene of silicosis. 14694619_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14700595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14700596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14718045_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14740435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14752708_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14762600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14769912_MHC class II molecule DQ0602 confers strong susceptibility to narcolepsy but dominant protection against type 1 diabetes: the crystal structure of DQ0602 reveals the molecular features underlying these contrasting genetic properties 14964841_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14967485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14988284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14990915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14995006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15003812_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009181_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15009387_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15013978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15013978_association of specific HLA-DR and -DQ alleles and haplotypes with type 1 diabetes may underline several characteristics that distinguish Bahraini patients from other Caucasians patients. 15014429_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15016191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15019597_No evidence of polymorphism with severe retinopathy in younger Type 1 diabetic patients. 15019597_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15030582_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15037989_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15041165_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15049049_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15055351_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15057902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15059369_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15061705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15070884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083289_Results confirm the positive association of the DR2 haplotype with multiple sclerosis, particularly the allele DQB1*0602, in the population studied in Malaga, southern Spain. 15089899_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15089901_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15095040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15096192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15104683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15107633_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15109436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15112906_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15116308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120190_The association of HLA-DQB1 polymorphisms and genetic susceptibility to celiac disease. 15120191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15120192_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15122136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15128924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15128924_association between microchimerism and maternal compatibility at the class II DRB1 and/or DQB1 HLA loci and with the maternal HLA-DQB1*0301 allele. 15144462_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15144476_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15149287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15149287_the DQB1*0602 allele, which has been negatively associated in African-Americans in previous reports, was not detected in the present Kuwaiti schizophrenia patients or controls 15157381_HLA-DQB1 is a susceptibility gene for narcolepsy. 15164528_Crohn disease not associated with HLA-DQB1 in Asian Indians. 15174785_A high prevalence of HLA-DQB1 susceptibility haplotypes for coeliac disease was observed both in serum IgA endomysial antibodies-negative diabetics and in those with associated coeliac disease . 15174785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15185301_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15191519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15191529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15194283_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15194331_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15194331_Presence of microchimerism may be associated with acceptance, tolerance and survival of liver all |
ENSMUSG00000073421 |
H2-Ab1 |
33.284959 |
2.6827914289 |
1.423735 |
0.433077198 |
10.494436 |
0.00119734549999559532380832838072137747076340019702911376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002753204483554289906666046050531804212369024753570556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
47.2848357 |
14.5161259 |
17.7986258 |
4.0353686 |
| ENSG00000179388 |
1960 |
EGR3 |
protein_coding |
Q06889 |
FUNCTION: Probable transcription factor involved in muscle spindle development. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a transcriptional regulator that belongs to the EGR family of C2H2-type zinc-finger proteins. It is an immediate-early growth response gene which is induced by mitogenic stimulation. The protein encoded by this gene participates in the transcriptional regulation of genes in controling biological rhythm. It may also play a role in a wide variety of processes including muscle development, lymphocyte development, endothelial cell growth and migration, and neuronal development. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:1960; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; synapse [GO:0045202]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002042]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus [GO:0035924]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; endothelial cell chemotaxis [GO:0035767]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; neuromuscular synaptic transmission [GO:0007274]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033089]; regulation of gamma-delta T cell differentiation [GO:0045586]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11909874_HIV Tat binds Egr proteins and enhances Egr-dependent transactivation of the Fas ligand promoter 14525795_Vascularendothelial growth factor induces expression of NR4A nuclear receptors and Egr3 via KDR and KDR-mediated signaling mechanisms. 15171706_data suggest that Egr3 is a target for the estrogen receptor alpha 15173177_Egr-2 and Egr-3 transcription is enhanced by Hepatitis B virus X protein, which induces fasL gene expression 17360599_These findings support the previous genetic association of altered calcineurin signaling with schizophrenia pathogenesis and identify EGR3 as a compelling susceptibility gene. 18059339_findings indicate that Egr3 has an essential downstream role in VEGF-mediated endothelial functions leading to angiogenesis and may have particular relevance for adult angiogenic processes involved in vascular repair and neovascular disease 19124717_Enforced expression of Egr3 transgene, from the CD2 antigen promoter, facilitates development of RAG2-deficient double-negative (DN) stage 3 thymocytes to the DN4 stage and subsequently to the double-positive stage of development. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19822898_Data show that VEGFR1 promoter binding sites for ELF-1, CREB and EGR-1/3 play a positive role in gene transcription in endothelial cells. 19839995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965691_Egr-3 is a critical determinant of VEGF signaling in activated endothelial cells 20144677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20379146_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20506119_Results suggest that in many cells of neuroectodermal and epithelial origin EGR1, EGR2, and EGR3 activate NAB2 transcription which is in turn repressed by NAB2, thus establishing a negative feedback loop. 20537399_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20537399_This study demoistrated that ERG3 are not genetic risk factors for schizophrenia in japanese. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20687139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20687139_SNP rs35201266 in intron 1 of the EGR3 gene showed a significant association with schizophrenia 21421043_EGR3 bound to the TREM-1 promoter. 22276163_Study supports the association of EGR3 with schizophrenia in Han Chinese sample. 22370066_EGR3, a gene that translates environmental stimuli into long-term changes in the brain, may be associated with risk for child bipolar disorder 1. 22425949_EGR3 gene may play an important role in schizophrenia susceptibility 23342084_Egr3 mRNA expression reveals that Egr3 mRNA expression is increased in tumor cells of non-relapsed samples compared to normal prostate cells, but is significantly lower in relapsed samples compared to non-relapse. 23460371_Decreased EGR3 expression might play a critical role in the differentiation, proliferation, metastasis and progression of gastric cancer cells. 23485457_EGR2 and EGR3 are regulated by NFkappaB and MAPK signalling pathways downstream of TNFalpha stimulation in breast adipose fibroblasts, and this in turn is upstream of CYP19A1 transcription via PI.4 23904169_Our results suggest that Egr-3 is a transcription factor associated with TGF-beta1 expression and in vivo regulatory activity 23906810_These results provide the first evidence that Egr-3, is up-regulated in scleroderma and is necessary and sufficient for profibrotic responses. 23935197_These data suggest that type I IFN stimulation induces a rapid recruitment of a repressive Egr3/Nab1 complex that silences transcription from the ifngr1 promoter. 23962955_Genetic variation in EGR3 may affect prefrontal function through neurodevelopment 24886494_Data shows association of Egr3 genetic polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in the Uygur and Han of China 25633035_EGR3 promotes excessive production of IL6 and IL8 observed during the progression of prostate cancer. 26474411_These findings support previously reported associations between EGR3 and schizophrenia. 27667480_In the PPI network, genes may be involved in Down syndrome (DS) by interacting with others, including nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 (NR4A2)early growth response (EGR)2 and NR4A2EGR3. Therefore, RUNX1, NR4A2, EGR2, EGR3 and ID4 may be key genes associated with the pathogenesis of DS. 27856665_Egr2 and Egr3 have emerged as regulatory molecules that suppress excessive immune responses. Mice deficient for Egr2 and Egr3 develop a lupus-like disease with dysregulated activation of effector T cells. Egr2 and Egr3 confer suppressive activity to CD4(+) T cells and regulate the production of inhibitory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-beta1. 28070994_miR-718 acts as a tumor suppressive microRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating the expression of EGR3, which may provide a new diagnostic marker and treatment target for HCC 28098878_EGR3 contributes to cell growth inhibition via upregulation of FasL in Hepatocellular carcinoma. 28847731_KSRP decreased EGR3 mRNA stability in an ARE-independent manner. 31081063_Study demonstrated that EGR3 expression was enhanced in prostate cancer (PC) tissues. EGR3 was proposed as a possible target of miR335, and was negatively regulated by miR335. Silencing EGR3 suppressed the viability and angiogenesis of PC cell line. 32138690_Silencing of miRNA-210 inhibits the progression of liver cancer and Hepatitis B virus-associated liver cancer via up-regulating EGR3. 32518380_Expression and prognostic value of the transcription factors EGR1 and EGR3 in gliomas. 33113163_Schizophrenia risk candidate EGR3 is a novel transcriptional regulator of RELN and regulates neurite outgrowth via the Reelin signal pathway in vitro. 33485349_HELQ and EGR3 expression correlate with IGHV mutation status and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 34243729_XIST promotes apoptosis and the inflammatory response in CSE-stimulated cells via the miR-200c-3p/EGR3 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000033730 |
Egr3 |
32.768350 |
20.0686744967 |
4.326873 |
0.499476122 |
97.383196 |
0.00000000000000000000005712881388314432350858863898542735796805174762829751924217620319412791474178447970189154148101806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000564783183466316355719054266742591767796216698858505433111548872660012676760743488557636737823486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.9925389 |
19.2593526 |
3.2172240 |
0.9265207 |
| ENSG00000179399 |
2262 |
GPC5 |
protein_coding |
P78333 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Heparan sulfate;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2262; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; regulation of protein localization to membrane [GO:1905475] |
12721791_GPC5 is a possible target for the 13q31-q32 amplification detected in lymphoma cell lines. 17846126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18195134_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19010793_Independent replication confirms GPC5 as a genetic risk factor for multiple sclerosis. 19010793_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19022413_ZIC2, SPRY2, and GPC5 genes are candidate genes suspected to explain the malformations associated with cerebral anomalies in the hypothesis of a contiguous gene syndrome in 13q deletion syndrome 19174780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19556317_Confirm the association of polymorphisms within GPC5 with response to interferon-beta therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis. 19556317_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19590514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19865102_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20304703_GPC5 polymorphism associated with susceptibility to lung cancer in never smokers 20304703_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360844_GPC5 is a novel genetic locus protective against sudden cardiac arrest 20360844_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20688270_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20688270_No association between GPC5rs2352028 variant and lung cancer in never smokers in meta-analysis of 7 genome-wide association studies under the random effects model. 20692050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20692050_This study supports that multiple sclerosis susceptibility at 13q31-32 may localize to the Glypican-5 gene. 20886065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20944657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20966902_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21339334_GPC5 stimulates Hh signaling by facilitating/stabilizing the interaction between Hh and Ptc1. 22236185_findings suggested that SNP rs2352028 in GPC5 might confer a slight risk to lung cancer/adenocarcinoma 23223018_GPC5 is a gene required for normal neural tube development. 23867465_Shh binds to HSPG co-receptors containing a glypican 5 core and 2-O-sulfo-iduronic acid to promote neural precursor proliferation. 23962560_Data suggest that glypican-5 (GPC5) is a metastasis suppressor gene in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and may be a potential biomarker that predicts NSCLC metastasis. 24130709_The IL7R, TNFRSF1A, and GPC5 polymorphisms tended to be associated with having a second event of Multiple sclerosis within a year. 24135429_These results indicate that GPC5 polymorphisms would be useful genetic indicators for Inflammatory demyelinating diseasess, including neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis . 24456789_Variants in the 50-upstream region of GPC5 confer risk of lung cancer in never smokers 24682381_GPC5, a tumor suppressor, is regulated by miR-620 in lung adenocarcinoma. 24943672_gene variants in IRF5, IRF8 and GPC5 were not associated with risk of relapse or disease progression in multiple sclerosis 25818666_miR-709 may positively regulate invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through targeting GPC5. 25999661_Results suggest a potential association between CRP and GPC5 variants with lung cancer risk; variation in GKN1 is associated with chemotherapy response in the Chinese Han population. 26631038_GPC5 protein expression showed a close correlation with the tumorigenesis and tumor progression of prostate cancer, and that might be applied as a novel biomarker for the prediction of diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer. 27157618_GPC5 is a novel epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor, which inhibits tumor growth by suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. 27554041_These results suggest that miR-297 acted as an oncogenic miRNA, partly by targeting GPC5, adenocarcinoma of the lung. 27806326_Suggest that GPC5 is able to suppress the lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by competitively binding to Wnt3a and inactivating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 28893348_Our results showed that GPC5 was lowly expressed in PCa cell lines. 29407175_Taken together, our results suggest GPC5 as a tumor suppressor in PDAC and its expression is possibly regulated by miR-4295. Our study indicates that the miR-4295/GPC5 axis may play an important role in the pathogenesis of PADC and has potential applications for the development of PDAC therapy. 30557546_Hotair promoted Gastric Cancer development by promoting GCP5 expression via sponging miR-217. 30951720_miR-301b represses the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells by up-regulating GPC5 expression 33512817_Glypican-1, -3, -5 (GPC1, GPC3, GPC5) and Hedgehog Pathway Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 33606708_Subcellular localization of glypican-5 is associated with dynamic motility of the human mesenchymal stem cell line U3DT. 34079082_GPC5 suppresses lung cancer progression and metastasis via intracellular CTDSP1/AhR/ARNT signaling axis and extracellular exosome secretion. |
ENSMUSG00000022112 |
Gpc5 |
31.853727 |
0.4651624220 |
-1.104194 |
0.384698928 |
8.184657 |
0.00422461619179754273994964464122858771588653326034545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008766390410646945907657823227054905146360397338867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.1169829 |
4.9663445 |
48.0051537 |
7.2231804 |
| ENSG00000179406 |
285908 |
LINC00174 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29729381_oncogenic role of LINC00174 in clinical colorectal cancer specimens and cellular experiments. 31492194_LINC00174 accelerated carcinogenesis of glioma via sponging miR-1523-3p and increasing the SLC2A1 expression, which could be considered as a molecular target for glioma diagnosis and therapy. 32128852_LINC00174 is an oncogenic lncRNA of hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates miR-320/S100A10 axis. 32390602_LINC00174 is a favorable prognostic biomarker in glioblastoma via promoting proliferative phenotype. 33161413_LINC00174 is a novel prognostic factor in thymic epithelial tumors involved in cell migration and lipid metabolism. 34226413_LINC00174 Facilitates Proliferation and Migration of Colorectal Cancer Cells via MiR-3127-5p/ E2F7 Axis. 34787848_LINC00174 triggers the malignant development of breast cancer by negatively regulating miR-1827 level. 35451652_Downregulated long intergenic non-coding RNA 00,174 represses malignant biological behaviors of lung cancer cells by regulating microRNA-584-3p/ribosomal protein S24 axis. 35616230_LINC00174 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in renal clear cell carcinoma by regulating miR-612/FOXM1 axis. 36060149_Long Intergenic Nonprotein Coding RNA 00174 Aggravates Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via MicroRNA-185-5p/Nuclear Factor IX axis. |
|
|
93.947514 |
0.2809760268 |
-1.831481 |
0.190372283 |
95.539674 |
0.00000000000000000000014495696679147719848270236180353097329809966522387810661359731044528498244972070096991956233978271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001407608440685660206902615148427886582733031521955527808688838839468182584369060350582003593444824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.9408014 |
6.1408845 |
150.1848854 |
14.0885606 |
| ENSG00000179431 |
24147 |
FJX1 |
protein_coding |
Q86VR8 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an inhibitor of dendrite extension and branching. {ECO:0000250}. |
Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is the human ortholog of mouse and Drosophila four-jointed gene product. The Drosophila protein is important for growth and differentiation of legs and wings, and for proper development of the eyes. The exact function of this gene in humans is not known. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:24147; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; retina layer formation [GO:0010842] |
25150169_FJX1 does not influence the levels of FAT1 ectodomain phosphorylation. 28673206_The results of our Western blot analysis reveal a significant positive correlation between FJX1 and HIF1alpha proteins in endometrium of women with and without endometriosis. 31236144_FJX1 transcript and protein level is upregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissue samples. FJX1 promotes cell proliferation, anchorage-dependent growth, and cellular invasion in vitro. 32159255_MicroRNA-1249 targets four-jointed box kinase 1 and reduces cell proliferation, migration and invasion of colon adenocarcinoma. 32354225_FOXD3-AS1 Contributes to the Progression of Melanoma Via miR-127-3p/FJX1 Axis. 35278814_MiR-532-3p suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion of colon adenocarcinoma via targeting FJX1. |
ENSMUSG00000075012 |
Fjx1 |
445.836378 |
0.1644557868 |
-2.604228 |
0.150057380 |
285.806802 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040760437979805882376248020634288329755068264388291194952813507359963209042951630097622040725352845425235581662167663202423044405307552855495926641717899154698789843109807407017797231674194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011182603430890981238367506458150259097534440717279548117229107166419584258972262083491131578640591548070135631325000680476896909473295079901277812015858675702417723840653707156889140605926513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
131.9527575 |
16.2909739 |
805.3588092 |
68.3693242 |
| ENSG00000179523 |
645212 |
EIF3J-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31421822_EIF3J-AS1 promotes CTNND2 expression via sponging miR-122-5p. Hypoxia-induced EIF3J-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulating CTNND2. 31709617_H3K27 acetylation-induced lncRNA EIF3J-AS1 improved proliferation and impeded apoptosis of colorectal cancer through miR-3163/YAP1 axis. 32811869_LncRNA EIF3J-AS1 enhanced esophageal cancer invasion via regulating AKT1 expression through sponging miR-373-3p. 33764843_Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) EIF3J-DT induces chemoresistance of gastric cancer via autophagy activation. |
|
|
29.791874 |
0.2811123110 |
-1.830781 |
0.307554713 |
35.923047 |
0.00000000205266317329958425500805372883924432292346295980678405612707138061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000009557510548234027897367082128501220017469108825025614351034164428710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.1335644 |
2.7730977 |
47.1397501 |
6.3930207 |
| ENSG00000179528 |
85474 |
LBX2 |
protein_coding |
Q6XYB7 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q804R0}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including muscle cell differentiation; positive regulation of convergent extension involved in gastrulation; and positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Predicted to be part of chromatin. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:85474; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; muscle cell differentiation [GO:0042692]; positive regulation of convergent extension involved in gastrulation [GO:1904105]; positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000052]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
29669692_LBX2 was identified as a pathogenic gene in Chinese patients with atrial septal defect. 32559617_LncRNA LBX2-AS1 facilitates abdominal aortic aneurysm through miR-4685-5p/LBX2 feedback loop. 32567804_Identification of LBX2 as a novel causal gene of lung adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000034968 |
Lbx2 |
22.633341 |
0.1890970320 |
-2.402801 |
0.495802453 |
23.172329 |
0.00000148113344439212487812997272318416008829444763250648975372314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005139052571515694475541395636053465523218619637191295623779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4495684 |
2.0686406 |
33.8552866 |
6.9717382 |
| ENSG00000179532 |
144132 |
DNHD1 |
protein_coding |
Q96M86 |
FUNCTION: Essential for the normal assembly and function of sperm flagella axonemes. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:34932939}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Flagellum;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable dynein intermediate chain binding activity; dynein light intermediate chain binding activity; and minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity. Predicted to be involved in cilium movement. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:144132; |
dynein complex [GO:0030286]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; inner dynein arm [GO:0036156]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; sperm flagellum assembly [GO:0120316] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 34932939_Bi-allelic variants in DNHD1 cause flagellar axoneme defects and asthenoteratozoospermia in humans and mice. |
ENSMUSG00000030882 |
Dnhd1 |
124.364417 |
0.1530711200 |
-2.707726 |
0.262179749 |
100.477122 |
0.00000000000000000000001197724784909764841981850804208100352060292915440755834306543986360338305274808590183965861797332763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000122088520892735702803147529409878045095576150151377684659198411334934952776620775694027543067932128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.9224287 |
6.5690037 |
208.7131026 |
29.5793644 |
| ENSG00000179598 |
201164 |
PLD6 |
protein_coding |
Q8N2A8 |
FUNCTION: Presents phospholipase and nuclease activities, depending on the different physiological conditions (PubMed:17028579, PubMed:21397847, PubMed:28063496). Interaction with Mitoguardin (MIGA1 or MIGA2) affects the dimer conformation, facilitating the lipase activity over the nuclease activity (PubMed:26711011). Plays a key role in mitochondrial fusion and fission via its phospholipase activity (PubMed:17028579, PubMed:24599962, PubMed:26678338). In its phospholipase role, it uses the mitochondrial lipid cardiolipin as substrate to generate phosphatidate (PA or 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate), a second messenger signaling lipid (PubMed:17028579, PubMed:26711011). Production of PA facilitates Mitofusin-mediated fusion, whereas the cleavage of PA by the Lipin family of phosphatases produces diacylgycerol (DAG) which promotes mitochondrial fission (PubMed:24599962). Both Lipin and DAG regulate mitochondrial dynamics and membrane fusion/fission, important processes for adapting mitochondrial metabolism to changes in cell physiology. Mitochondrial fusion enables cells to cope with the increased nucleotide demand during DNA synthesis (PubMed:26678338). Mitochondrial function and dynamics are closely associated with biological processes such as cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation (PubMed:21397848). Mediator of MYC activity, promotes mitochondrial fusion and activates AMPK which in turn inhibits YAP/TAZ, thereby inducing cell growth and proliferation (PubMed:26678338). The endonuclease activity plays a critical role in PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis during spermatogenesis (PubMed:21397847, PubMed:21397848). Implicated in spermatogenesis and sperm fertility in testicular germ cells, its single strand-specific nuclease activity is critical for the biogenesis/maturation of PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA). MOV10L1 selectively binds to piRNA precursors and funnels them to the endonuclease that catalyzes the first cleavage step of piRNA processing to generate piRNA intermediate fragments that are subsequently loaded to Piwi proteins. Cleaves either DNA or RNA substrates with similar affinity, producing a 5' phosphate end, in this way it participates in the processing of primary piRNA transcripts. piRNAs provide essential protection against the activity of mobile genetic elements. piRNA-mediated transposon silencing is thus critical for maintaining genome stability, in particular in germline cells when transposons are mobilized as a consequence of wide-spread genomic demethylation (By similarity). PA may act as signaling molecule in the recognition/transport of the precursor RNAs of primary piRNAs (PubMed:21397847). Interacts with tesmin in testes, suggesting a role in spermatogenesis via association with its interacting partner (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5SWZ9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17028579, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21397847, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21397848, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24599962, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26678338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26711011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28063496}. |
Differentiation;Endonuclease;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Meiosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nuclease;Reference proteome;Spermatogenesis;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables cardiolipin hydrolase activity and protein homodimerization activity. Involved in mitochondrial fusion. Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of mitochondrial fusion. Located in mitochondrial outer membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201164; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; cardiolipin hydrolase activity [GO:0035755]; endoribonuclease activity, producing 5'-phosphomonoesters [GO:0016891]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; DNA methylation involved in gamete generation [GO:0043046]; lipid catabolic process [GO:0016042]; meiotic cell cycle [GO:0051321]; mitochondrial fusion [GO:0008053]; P granule organization [GO:0030719]; piRNA processing [GO:0034587]; positive regulation of mitochondrial fusion [GO:0010636]; spermatid development [GO:0007286] |
17028579_PLD6, aka MitoPLD, encodes an N-terminal mitochondrial localization sequence, localizes to the outer mitochondrial surface, generates phosphatidic acid, a signaling lipid, and triggers trans-mitochondrial association; involved in mitochondrial fusion. 21397848_Data suggest that mitochondrial-surface phosphatidic acid generated by MitoPLD/Zuc recruits or activates nuage components critical for piRNA production. 22281006_MitoPLD performs a critical function in a pathway that creates a specialized form of RNAi required by developing spermatocytes to suppress transposon mobilization during meiosis. 26711011_Propose that MIGA proteins promote mitochondrial fusion by regulating mitochondrial phospholipid metabolism via MitoPLD. 34326815_Decreased piRNAs in Infertile Semen Are Related to Downregulation of Sperm MitoPLD Expression. |
ENSMUSG00000043648 |
Pld6 |
64.470502 |
2.7556662679 |
1.462401 |
0.201567518 |
54.114015 |
0.00000000000018918706161835077122664864668036467941535441750211532507819356396794319152832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001180220215336795024290899317476731013309976248137900256551802158355712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
97.7262297 |
11.5391068 |
35.7459319 |
3.4594795 |
| ENSG00000179630 |
144811 |
LACC1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IV20 |
FUNCTION: Purine nucleoside enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorolysis of adenosine, guanosine and inosine nucleosides, yielding D-ribose 1-phosphate and the respective free bases, adenine, guanine and hypoxanthine (PubMed:31978345). Also catalyzes the phosphorolysis of S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine into adenine and S-methyl-5-thio-alpha-D-ribose 1-phosphate (PubMed:31978345). Also has adenosine deaminase activity (PubMed:31978345). Acts as a regulator of innate immunity in macrophages by modulating the purine nucleotide metabolism, thereby regulating the metabolic function and bioenergetic state of macrophages (PubMed:31978345). Enables a purine nucleotide cycle between adenosine and inosine monophosphate and adenylosuccinate that prevents cytoplasmic acidification and balances the cytoplasmic-mitochondrial redox interface (PubMed:31978345). The purine nucleotide cycle consumes aspartate and releases fumarate in a manner involving fatty acid oxidation and ATP-citrate lyase activity (PubMed:31978345). Participates in pattern recognition receptor (PRR)-induced cytokines in macrophages: associates with the NOD2-signaling complex and promotes optimal NOD2-induced signaling, cytokine secretion and bacterial clearance (PubMed:28593945, PubMed:31875558). Localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum upon PRR stimulation of macrophages and associates with endoplasmic reticulum-stress sensors, promoting the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response (UPR) (PubMed:31875558). Does not show laccase activity (PubMed:27959965, PubMed:31978345). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27959965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28593945, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31875558, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31978345}. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hydrolase;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Peroxisome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes an oxidoreductase that promotes fatty-acid oxidation, with concomitant inflammasome activation, mitochondrial and NADPH-oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species production, and bactericidal activity of macrophages. The encoded protein forms a complex with fatty acid synthase on peroxisomes and is thought to be modulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signaling events. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with inflammatory bowel disease, Behcet's disease, leprosy, ulcerative colitis, early-onset Crohn's disease, and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2017]. |
hsa:144811; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; adenosine deaminase activity [GO:0004000]; copper ion binding [GO:0005507]; guanosine phosphorylase activity [GO:0047975]; purine-nucleoside phosphorylase activity [GO:0004731]; S-methyl-5-thioadenosine phosphorylase activity [GO:0017061]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway [GO:0070431]; pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002221]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; regulation of cellular pH [GO:0030641]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of purine nucleotide metabolic process [GO:1900542] |
19068216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20018961_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20473688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25220867_There is an association of a mutation in LACC1 with a monogenic form of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 25367361_Association between leprosy and tag SNPs at NOD2 (rs8057431) and CCDC122-LACC1 (rs4942254). 27098602_LACC1 common SNPs represent genetic risk factors also for JIA and ulcerative colitis. 27881174_The results show that a frameshift mutation in LACC1 leads to a similar juvenile arthritis phenotype as previously described. This mutations strongly supports the significance of these gene variants in the development of juvenile arthritis 27959965_FAMIN is a peroxisome-associated protein with primary role(s) in macrophages and other immune cells, where its metabolic functions may be modulated by PPAR signaling events 28593945_LACC1 is critical for amplifying PRR-induced outcomes, an effect that is attenuated by the LACC1 disease-risk variant. 29706348_mRNA expression levels of both HIF1A and LACC1 were upregulated in the skin lesions of individuals with leprosy. 29717096_Our findings confirm that LACC1 variants can be responsible for the recessive form of juvenile arthritis. 31875558_LACC1 Required for NOD2-Induced, ER Stress-Mediated Innate Immune Outcomes in Human Macrophages and LACC1 Risk Variants Modulate These Outcomes. 33493343_A novel loss-of-function mutation in LACC1 underlies hereditary juvenile arthritis with extended intra-familial phenotypic heterogeneity. 33606008_LACC1 deficiency links juvenile arthritis with autophagy and metabolism in macrophages. 35179464_[Macrophage involvement in juvenile arthritis onset: LACC1 bridges the gap?]', trans 'Role des macrophages dans le developpement de l'arthrite juvenile - LACC1 fait-il le lien ? 35978195_LACC1 bridges NOS2 and polyamine metabolism in inflammatory macrophages. |
ENSMUSG00000044350 |
Lacc1 |
749.611445 |
11.7885873953 |
3.559319 |
0.744319546 |
18.742020 |
0.00001496482531343768573113724162926274630081024952232837677001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000045930717743052656867712435495576528410310856997966766357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1411.3534060 |
603.4022299 |
120.6051494 |
37.1232480 |
| ENSG00000179698 |
340390 |
WDR97 |
protein_coding |
A6NE52 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
The function and protein-coding potential of this gene is unknown. The exon combination is based on AB058778.1 for which two possible open reading frames can be predicted (with start codons at nucleotide 26 or 2614). The position of the first ORF stop codon is consistent with a prediction of nonsense-mediated decay. Given the observation of the first ORF and its length, a predicted translation of the second ORF is inconsistent with the translation leaky scanning theory. Therefore, this gene is represented as a non-protein-coding transcript. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:340390; |
|
|
|
|
33.816005 |
0.2371984471 |
-2.075834 |
0.351536108 |
35.480858 |
0.00000000257569427420431960676850764908624863425146145345934201031923294067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011872969233996175176731097849255197607121203873248305171728134155273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.1701926 |
3.2075822 |
60.0294879 |
8.4492217 |
| ENSG00000179761 |
51268 |
PIPOX |
protein_coding |
Q9P0Z9 |
FUNCTION: Metabolizes sarcosine and L-pipecolic acid. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10642506}. |
Acetylation;FAD;Flavoprotein;Oxidoreductase;Peroxisome;Reference proteome |
|
Enables L-pipecolate oxidase activity and sarcosine oxidase activity. Involved in L-lysine catabolic process to acetyl-CoA via L-pipecolate. Located in peroxisome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51268; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; peroxisomal matrix [GO:0005782]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; L-pipecolate oxidase activity [GO:0050031]; sarcosine oxidase activity [GO:0008115]; L-lysine catabolic process to acetyl-CoA via L-pipecolate [GO:0033514]; lysine catabolic process [GO:0006554] |
20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000017453 |
Pipox |
103.125466 |
0.2639064196 |
-1.921902 |
0.197375780 |
95.985298 |
0.00000000000000000000011573978631339036543247428370239086362001746043465256483180657667841906288686004700139164924621582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001127603462696793144044480621217114140616188513979231514171904654508793441891612019389867782592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.2100491 |
5.5533783 |
160.7291610 |
13.4180850 |
| ENSG00000179813 |
144809 |
FAM216B |
protein_coding |
Q8N7L0 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:144809; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000045655 |
Fam216b |
8.100511 |
12.4055763828 |
3.632917 |
0.794724222 |
27.009876 |
0.00000020241858604298230437182077451341299934028938878327608108520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000772613997929769512256555248630451870894830790348351001739501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.2591324 |
7.9808993 |
1.2442596 |
0.6041924 |
| ENSG00000179855 |
126326 |
GIPC3 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF64 |
FUNCTION: Required for postnatal maturation of the hair bundle and long-term survival of hair cells and spiral ganglion. {ECO:0000250}. |
Deafness;Disease variant;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the GIPC family. Studies in mice suggest that this gene is required for postnatal maturation of the hair bundle and long-term survival of hair cells and spiral ganglion in the ear. Mutations in this gene are associated with autosomal recessive deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:126326; |
|
11836571_Molecular cloning and characterization of human GIPC3, a novel gene homologous to human GIPC1 and GIPC2 17690910_DFNB72 is telomeric to DFNB68, the only other known deafness locus with statistically significant support for linkage to chromosome 19p. 18066515_A maximum 2-point LOD score of 3.08 was obtained for the marker D19S586. The region overlaps with the recessive locus DFNB15. 18950845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21326233_Gipc3 plays a pivotal role in acoustic signal acquisition and propagation in cochlear hair cells, while mutations are associated with audiogenic seizures and sensorineural hearing loss. 21660509_Haplotype analysis excluded GIPC3 from the obligate linkage interval in this family and defined a novel locus spanning 4.08 Mb and 104 genes. 23510777_This study identified a novel causative mutation in GIPC3 for congenital nonsyndromic hearing loss in a consanguineous family from Saudi Arabia. 25296581_This study expands the mutational spectrum of GIPC3 in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. 29605370_This study is the first report of the contribution of theGIPC3 gene to hearing loss in the Iranian population 33168789_Low incidence of GIPC3 variants among the prelingual hearing impaired from southern India. 34071867_Genetic Variant c.245A>G (p.Asn82Ser) in GIPC3 Gene Is a Frequent Cause of Hereditary Nonsyndromic Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Chuvash Population. |
ENSMUSG00000034872 |
Gipc3 |
385.001565 |
0.2704748390 |
-1.886434 |
0.096816388 |
390.099867 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000787292350094715349135752394172226252291871479475878802721899666123111831721589858768619150567204155932540638116383329505892198617428152072673744976728828674700224617927397452884649981002247294517789158279655813924696738936859219393227249383926 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000289786411157057312530994230907572134651465456206425545685361515581776965903141560091531426709314892272860316311397559182168933258794335459495637308368898047477049794823330745087408044723921289191637106223611158872799364871752914041280746459961 |
Yes |
No |
165.9538889 |
10.3370590 |
617.8264961 |
23.6401973 |
| ENSG00000179938 |
653073 |
GOLGA8J |
protein_coding |
A6NMD2 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:653073; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
17.281522 |
0.0244046727 |
-5.356699 |
0.965102201 |
53.568647 |
0.00000000000024971294600465371434950554897161073515188603466619099435774842277169227600097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001547339665419264931716398966051752815464848112014806247316300868988037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.4339922 |
0.4321007 |
23.2051660 |
11.9382634 |
| ENSG00000179954 |
284297 |
SSC5D |
protein_coding |
A1L4H1 |
FUNCTION: Binds to extracellular matrix proteins. Binds to pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) present on the cell walls of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and fungi, behaving as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR). Induces bacterial and fungal aggregation and subsequent inhibition of PAMP-induced cytokine release. Does not possess intrinsic bactericidal activity. May play a role in the innate defense and homeostasis of certain epithelial surfaces (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable fibronectin binding activity; laminin binding activity; and scavenger receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in defense response; detection of bacterial lipoprotein; and negative regulation of interleukin-8 production. Predicted to act upstream of or within regulation of interleukin-8 production. Predicted to be located in collagen-containing extracellular matrix. Predicted to be active in extracellular matrix and extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284297; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; laminin binding [GO:0043236]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; defense response [GO:0006952]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; detection of bacterial lipoprotein [GO:0042494]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032717] |
Mouse_homologues 21217009_Group B scavenger receptor protein S5D-SRCRB might play a role in innate defense and homeostasis of certain specialized epithelial surfaces. 24641504_the results indicate that S5D-SRCRB is an integral component of the urogenital tract involved in innate immune functions. |
ENSMUSG00000035279 |
Ssc5d |
18.733275 |
0.2372118681 |
-2.075752 |
0.791651702 |
6.171277 |
0.01298408211364418356204009086241057957522571086883544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024329700647123034956686993268704100046306848526000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6241285 |
3.6211153 |
28.3652514 |
10.5393652 |
| ENSG00000180015 |
|
|
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.678259 |
10.5447846252 |
3.398458 |
0.897292352 |
16.517671 |
0.00004819876337469646476394102840856703551253303885459899902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000139138225583907641346587125141809337947051972150802612304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.3226906 |
6.5995634 |
1.1045966 |
0.5782814 |
| ENSG00000180066 |
|
LINC02870 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.995280 |
0.3544039531 |
-1.496533 |
0.358916552 |
17.702420 |
0.00002582977712892013406192903701708019070792943239212036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000077097575414127638760743155277310734163620509207248687744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.9527624 |
3.4237316 |
39.6548443 |
6.2778928 |
| ENSG00000180071 |
253650 |
ANKRD18A |
protein_coding |
Q8IVF6 |
|
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:253650; |
|
23131552_These results suggest that ANKRD18A hypermethylation and consequent mRNA alterations might be a vital molecular mechanism in lung cancer. |
|
|
11.510235 |
0.3323770779 |
-1.589107 |
0.452099790 |
12.922697 |
0.00032462172402069185096415426805549486743984743952751159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000824117070269248614897139582069485186366364359855651855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7541433 |
1.7960308 |
17.5767118 |
3.2697002 |
| ENSG00000180229 |
283755 |
HERC2P3 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.193790 |
0.4447609580 |
-1.168898 |
0.421995562 |
7.525899 |
0.00608181802839921712561244149242156709078699350357055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012204980842851454250763687525704881409183144569396972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3718578 |
6.1382572 |
29.7430322 |
9.5183168 |
| ENSG00000180318 |
8092 |
ALX1 |
protein_coding |
Q15699 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific DNA-binding transcription factor that binds palindromic sequences within promoters and may activate or repress the transcription of a subset of genes (PubMed:9753625, PubMed:8756334). Most probably regulates the expression of genes involved in the development of mesenchyme-derived craniofacial structures. Early on in development, it plays a role in forebrain mesenchyme survival (PubMed:20451171). May also induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) through the expression of SNAI1 (PubMed:23288509). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20451171, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23288509, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8756334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9753625}. |
Acetylation;Activator;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The specific function of this gene has yet to be determined in humans; however, in rodents, it is necessary for survival of the forebrain mesenchyme and may also be involved in development of the cervix. Mutations in the mouse gene lead to neural tube defects such as acrania and meroanencephaly. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8092; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis [GO:0048704]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010718]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20451171_Disruption of CART1 (ALX1) causes extreme microphthalmia and severe facial clefting. 20932315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23288509_ALX1 upregulated expression of the key EMT regulator Snail (SNAI1) and that it mediated EMT activation and cell invasion by ALX1. 24081945_hypermethylation of HIST1H4F, PCDHGB6, NPBWR1, ALX1, and HOXA9 was significantly associated with shorter survival in stage 1 Non-small-cell lung cancer 25736924_we found that depletion of ALX1 caused a dramatic cell cycle arrest, followed by massive apoptotic cell death, and eventually resulted in a significant decrease in migration and invasion of the osteosarcoma cell line studied. 26722397_we identify critical roles of ALX1 in lung cancer development and progression 27053613_Knockdown of the CART1 gene significantly inhibited cell invasion and proliferation and induce cell cycle arrest in S phase. 27324866_Our study concludes that the splice site variant identified in the ALX1 gene causes mild form of Frontonasal dysplasia. 29936472_According to our analysis, three proteins, namely aristaless-like homeobox1 isoform X1 (ALX1), major histocompatibility complex polypeptide-related sequence A (MICA), and uncharacterized protein C14orf105 isoform X12 were found to be potential markers for Opisthorchis viverrini (OV)- infection, as they were predominantly found in all OV-infected groups 30773258_ALX1 is highly expressed in human melanoma tissues and cell lines. Knockdown of ALX1 suppressed the proliferation and invasion of melanoma cells. 34104082_Promoter Methylation-mediated Silencing of the MiR-192-5p Promotes Endometrial Cancer Progression by Targeting ALX1. |
ENSMUSG00000036602 |
Alx1 |
8.781867 |
0.1472346638 |
-2.763811 |
0.707113332 |
16.474783 |
0.00004930146478057845937535350056002414476097328588366508483886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000142043650236450927663509058440638455067528411746025085449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3760066 |
1.0906944 |
16.0407506 |
3.7907895 |
| ENSG00000180354 |
222166 |
MTURN |
protein_coding |
Q8N3F0 |
FUNCTION: Promotes megakaryocyte differentiation by enhancing ERK and JNK signaling as well as up-regulating RUNX1 and FLI1 expression (PubMed:24681962). Represses NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity by inhibiting phosphorylation of RELA at 'Ser-536' (PubMed:24681962). May be involved in early neuronal development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7ZX36, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24681962}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity; positive regulation of MAPK cascade; and positive regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:222166; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0045654]; regulation of signaling [GO:0023051] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31552488_High MTURN expression is associated with lung cancer. 33506033_C7ORF41 Regulates Inflammation by Inhibiting NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. 33528492_PKCalpha/ERK/C7ORF41 axis regulates epidermal keratinocyte differentiation through the IKKalpha nuclear translocation. |
ENSMUSG00000038065 |
Mturn |
121.765265 |
0.2741506182 |
-1.866959 |
0.165764704 |
134.526789 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000041902914239501401938498305736938738257553994827692916247620911658585982088348783052705881502220108814071863889694213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000005571955082658024191490252747494830219206456318780970762103688839901092737832608535464284926774780615232884883880615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.6155020 |
6.6446521 |
171.6994803 |
15.7217200 |
| ENSG00000180425 |
54494 |
C11orf71 |
protein_coding |
Q6IPW1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Located in nuclear body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54494; |
nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634] |
|
ENSMUSG00000042293 |
Gm5617 |
35.804802 |
0.3654535627 |
-1.452240 |
0.274814403 |
28.634169 |
0.00000008742581304990877085165317363427139873977012030081823468208312988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000346789841606195489697865878483962198686185729457065463066101074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.2618434 |
3.8823757 |
53.0752487 |
6.9005441 |
| ENSG00000180539 |
401563 |
LINC02908 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35196780_[The role and mechanism of lncRNA C9ORF139 targeting miR-24-3P/TAOK1 in regulating the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells]. |
|
|
195.434781 |
0.1080344499 |
-3.210437 |
0.152691060 |
477.993579 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000058389973510827951620926541263395480389742654756518060943837255711705154970492110059527339675647078312533956966008215470203932268336451205127580790981897772368248736446913406125346432860309029584301621429860897009613745337540 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000026599876821599401473730507080875143116892976040086621397821147173818192426922941697479015218134546185492880710186386016889861091426983617681732271111425757030752663488044049013469841170984381056770306997994882223538273202586 |
Yes |
Yes |
36.9791805 |
6.6194291 |
342.0230330 |
41.4388916 |
| ENSG00000180592 |
387640 |
SKIDA1 |
protein_coding |
Q1XH10 |
|
Alternative initiation;Isopeptide bond;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
|
hsa:387640; |
|
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000054074 |
Skida1 |
21.011439 |
0.1487210355 |
-2.749319 |
0.470469290 |
36.425798 |
0.00000000158590191617773667889107643940967487528048707190464483574032783508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007447633561178299336808988553989760439399958613648777827620506286621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7358584 |
1.5890300 |
32.0667680 |
6.2944144 |
| ENSG00000180616 |
6752 |
SSTR2 |
protein_coding |
P30874 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for somatostatin-14 and -28. This receptor is coupled via pertussis toxin sensitive G proteins to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. In addition it stimulates phosphotyrosine phosphatase and PLC via pertussis toxin insensitive as well as sensitive G proteins. Inhibits calcium entry by suppressing voltage-dependent calcium channels. Acts as the functionally dominant somatostatin receptor in pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells where it mediates the inhibitory effect of somatostatin-14 on hormone secretion. Inhibits cell growth through enhancement of MAPK1 and MAPK2 phosphorylation and subsequent up-regulation of CDKN1B. Stimulates neuronal migration and axon outgrowth and may participate in neuron development and maturation during brain development. Mediates negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling through PTPN6. Inactivates SSTR3 receptor function following heterodimerization. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15231824, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18653781, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19434240, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22495673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22932785}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Somatostatin acts at many sites to inhibit the release of many hormones and other secretory proteins. The biologic effects of somatostatin are probably mediated by a family of G protein-coupled receptors that are expressed in a tissue-specific manner. SSTR2 is a member of the superfamily of receptors having seven transmembrane segments and is expressed in highest levels in cerebrum and kidney. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6752; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; neuropeptide binding [GO:0042923]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; somatostatin receptor activity [GO:0004994]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; cellular response to estradiol stimulus [GO:0071392]; cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus [GO:0071385]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; peristalsis [GO:0030432]; regulation of muscle contraction [GO:0006937]; response to starvation [GO:0042594]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
11753241_SSTR transcripts are expressed and functional in retroorbital fibroblasts. SSTR1 is expressed in Grave's disease and octreotide inhibits retroorbital cell growth, explaining the SRIH therapeutic effect. 11839658_Quantitative evaluation of somatostatin receptor subtype 2 expression in sporadic colorectal tumor and in the corresponding normal mucosa 11920268_Somatostatin modulates G-CSF-induced but not interleukin-3-induced proliferative responses in myeloid 32D cells via activation of somatostatin receptor subtype 2. 12021920_SSTRs 1-5 are heterogeneously expressed in gastroenteropancreatic endocrine tumors 12210479_expression of SSTR2 transcripts up-regulated in prostatic carcinoma cells; SSTR2 agonists may have role in treatment of prostate cancer 12414882_somatostatin receptor transcripts were found in lymphocytes both from Graves' ophthalmopathy retroorbital tissues and blood samples, with levels of expression of SST1, -2, and -4 mRNA higher than those of the SST3 and -5 transcripts 12474541_localization and expression in human prostatic tissue and prostate cancer cell lines 12490654_sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells to death ligand-induced apoptosis 12675130_Presence and intracellular localization of the spliced variant SSR2(a) and its endogenous ligand SS in the cultured human neuroblastoma (NB) cell line, SH-SY5Y. 12684217_study demonstrates for the first time a selective and inducible expression of the recently discovered cortistatin, as well as somatostatin receptor 2, in human monocyte-derived cells 14572771_Expression of somatostatin receptor 2 by human pancreatic cancer causes significant slowing of tumor growth by a mechanism independent of exogenous somatostatin 14576502_Activation of SSTR 2 by SSTR 2 agonist significantly suppressed insulin secretion. 14602773_Sst2 and sst5 were expressed in 70%, sst1 in 50%, and sst3 and sst4 subtypes only in 15-20% of insulinomas 14671213_The receptor from somatostatinoma was completely phosphorylated. Only unphosphorylated sst2A was present in human tumors not exposed to autocrine stimulation. 14695784_SST2R gene together with p53 and ras genes may participate in pancreatic cancerous angiogenesis. 14760765_Expression of reintroduced human SSTR2 gene exerts its antiangiogenic effects by down-regulating expressions of factors involved in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis, suggesting SSTR2 gene transfer as new strategy of gene therapy for pancreatic cancer. 15118275_The degree (or level) of sst2 and sst5 expression is critical for the ultimate GH response of somatotropinomas to endogenous SRIF tone and exogenous SRIF analogue therapy. 15153427_Epithelial sst2A cells, identified as neuroendocrine, gastrin-producing cells, were found in large numbers in the antrum and the duodenum, but not in the gastric corpus. 15205362_SSTR2 provides an anti-angiogenic effect on pancreatic cancer xenografts, susgesting gene transfer as a promising strategy of gene therapy for pancreatic cancer. 15231824_human somatostatin receptor 2 dimers have a role in receptor trafficking 15257106_Expression of the SSTR2 gene in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells induces apoptosis, which may be mediated via down-regulation of Bcl-2 & up-regulation of Bax (alteration of Bcl-2/Bax ratio) & inhibits tumor angiogenesis, inhibiting of tumor growth. 15754023_gene transfer into pancreatic neoplasm cells resulted in no apoptosis, but a significant cell proliferation inhibition 15914528_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15914528_SSTR2 and SSTR5 variants seem to have a minor role in determining the responsiveness to somatostatin analogs in acromegaly 16115892_activation of the IKK/NFkappaB signaling cascade by SSTR2 requires a complicated network consisting of Galpha(14), protein kinase C, CamkII, ERK, and c-Src 16214911_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16254490_In the temporal lobe epilepsy, dentate gyrus, sst2 receptor mRNA expression was strongly increased in the granule cell layer, sst2 receptor-binding sites and immunoreactivity was preserved in the inner but decreased in the outer molecular layer. 16601140_the subtype 2 receptor-mediated antiproliferative effect of SRIH on TT cell proliferation may be exerted through a decrease in cyclin D1 and cdk4 levels 16606630_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16645635_Sst2 sensitized NIH3T3 cells to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis, enhanced TNFalpha-mediated activation of NF-kappaB, resulting in JNK inhibition and subsequent executioner caspase activation and cell death. 16917505_Physical interaction between a sst2 and p85, revealing a novel mechanism for negative regulation by ligand-activated GPCR of PI3K-dependent survival pathways, which may be an important molecular target for antineoplastic therapy. 16954443_Cytostatic action exerted by SSTR2 analogs might account for the tumor shrinkage observed in acromegalic patients treated with long-acting somatostatin analogs. 16996150_results show that Somatostatin receptor 2 is predominantly expressed on thyroid tissue and is a valid target for treatment of thyroid tumours 17546456_We conclude that the somatostatin receptor plays a role in the total renal uptake of radiolabelled somatostatin analogues. 17603546_Somatostatin caused rapid sst(2a) receptor phosphorylation and desensitization of epithelial antisecretory responses. 17678886_17q gain and promoter polymorphisms can play a role into the regulation of sst2 expression in neuroblastomas 17706924_The functional interactions between human somatostatin receptor 2 (hSSTR2) and human dopamine receptor 2 (hD2R) in both co-transfected CHO-K1 or HEK-293 cells as well as in cultured neuronal cells which express both the receptors endogenously. 17848636_Analysis of orbital tissues reveals upregulation of SSTR1 and -2 in a group of Graves' ophthalmopathy (GO) patients. Adipogenesis, a process occurring in GO orbits, provides one possible explanation for some of the observed increase. 18196892_Sst(2) is the best target for visualization of neuroendocrine tumors(NE) tumors, whereas noradrenaline transporter is only a useful target in a subpopulation of NE tumors. 18234910_This study was undertaken to investigate molecular mechanism of transcriptional regulation of the human sst2 gene, for which an additional exon (exon 1) in the 5'-untranslated region was recently found. 18292657_sst2 was expressed in 67% of the patients with HCC 18325993_Existence of a novel upstream promoter for the hSSTR2 gene that is regulated by epigenetic modifications, suggesting for complex control of the hSSTR2 transcription. 18599562_SSTR2 is the predominant mediator of functional ocular antiangiogenic effects. 18617261_Somatostatin regulates early trophoblast functions mainly through an interaction with SSTR2. 18653781_Data show that human somatostatin receptors (SSTR)2 and SSTR5 heterodimerize, and that selective activation of SSTR2 and not SSTR5, or their costimulation, modulates the association. 18682975_SSTR2 is not suited as prognostic marker or therapeutic target in uveal melanoma 18695896_High somatostatin receptor 2 expression is associated with neo-angiogenesis and high grade meningiomas. 18697876_Rabbit monoclonal antibody UMB-1 may prove of great value in the assessment of sst2A status in human neuroendocrine tumors during routine histopathological examination. 18808065_sst2 mRNA and receptor levels were significantly higher in the meningothelial subtype than in the fibroblastic subtype of meningiomas 18852217_Results show that glucocorticoids selectively downregulate somatostatin type 2, but not dopamine D2 and only to a minor degree sst5 receptors in human neuro-endocrine BON and TT cells. 18936524_Immunohistochemistry stufy of SSTR2 in prostate tissue from patients with bladder outlet obstruction showed that the majority of cells showed a weak intensity. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19106227_An autocrine and paracrine role of SST in the lacrimal system and at the ocular surface and a role of SST in corneal immunology. 19148511_SSTR2 could be a promising candidate for gene therapy for SSTR2-positive and SSTR2-negative tumors 19318729_Both SSTR1 and 2 mRNA levels in SCA were greater than Cushing disease, while SSTR1 mRNA levels, but not SSTR2, in silent corticotroph adenoma were also greater than non-functioning pituitary tumor. 19324939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19324939_Variants in SSTR2 may influence pathways of insulin sensitivity to modulate glucose homeostasis. 19330452_SSTR2 had higher expression in patients that had normalized GH and IGF-I. There was a positive correlation between the percentage of tumor reduction by octreotide-lar and SSTR2 expression. 19389921_Site specificity of agonist and second messenger-activated kinases for somatostatin receptor subtype 2A (Sst2A) phosphorylation. 19423539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19434240_Somatostatin sst2A receptor participates in the development and maturation of specific neuronal populations during rat and human brain ontogenesis. 19575008_Data suggest that enhanced SSTR2 expression plays an antiproliferative role in MCF-7 cells through inducing apoptosis and G(1)/S cell cycle arrest, and by decreasing EGFR expression, thereby counteracting the growth-stimulating effect of EGF. 19671855_hSSTr2 restoration mediated by oncolytic adenovirus enhances TRAIL-induced antitumor efficacy against pancreatic cancer. 19748526_heterodimerisation between hSSTR2 and hSSTR5 is potentiated in the absence of receptor-stimulation 19759190_Overexpression of SSTR type 2A was associated with metastatic carcinoids in pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours. 19805200_The upregulation of both sst2 and TSP-1 tumor suppressors may function as an early negative feedback to restrain pancreatic carcinogenesis. 19885591_down-regulation of MDR genes MDR1, MRP2, and LRP is responsible for the improvement in the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of hSSTR2-expressing pancreatic cancer cells 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20182388_Studies show that this study may be the basis for further functional studies to evaluate the role of somatostatin receptors sst1 to sst5 in the diabetic state. 20228164_sst(2) receptors can be internalized in sst(2)-expressing neuroendocrine tumors in patients under octreotide therapy. 20233796_Data indicate that OcF showing high-affinity binding to the sstr2. 20422506_The association between SST immunostaining and tracer uptake in [(111)In]-DTPA octreotide (DTPAOC) scintigraphy and [(68)Ga]-DOTA-D-Phe(1)-Tyr(3)-octreotide (DOTATOC) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT). 20450431_SSTR2 expression is inhomogeneous in thyroid disease, with the highest density detected in cold thyroid nodules 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20717067_Data show that the mRNA levels of SSTR1, SSTR2, SSTR3, and SSTR5 were high in PET compared with AC, whereas the expression of SSTR4 was low in PET and AC. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20810604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20942237_Lower expression of SSTR2 and activation of STAT3 in olfactory neuroblastoma cells might contribute to the development of ONB. 20948194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20948194_polymorphism in the SSTR2 gene is associated with obesity, food intake and nutrient intake in the Mediterranean population 21215273_Mean cortical SSTR2 mRNA levels were significantly (19%) lower in the subjects with schizophrenia compared to controls. 21287294_The co-expression of sstrs and D2R in a significant number of the studied cases offers a potential therapeutic alternative for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 21330405_pasireotide activates the somatostatin receptor 2 via a molecular switch that is structurally and functionally distinct from that turned on during octreotide-driven sst(2A) activation 21383526_differential gene expression profiles revealed more abundant mRNA expression in ectopic ACTH syndrome than in Cushing disease of SSTR-2 21503779_mRNA levels of SSTR2a, SSTR3 and SSTR5 in neuroendocrine lung cancer affected patients, were determined. 21667819_we investigated expression of SSTR2 and SSTR5 in the human thoracic duct 22213295_High somatostatin receptor 2 is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma. 22419713_Determination of the expression of SSTR2 in an attempt to establish correlations and/or associations with clinical characteristics of patients with nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. 22472799_Low somatostatin receptor subtype 2, but not dopamine receptor subtype 2 expression is associated with the lack of biochemical response of somatotropinomas to treatment with somatostatin analogs 22495673_Data show that the aspartic acid changes at position 89 to either Ala, Leu, or Arg generated mutant somatostatin receptor subtype 2 (SSTR2) with varying expression profiles and a complete inability to bind somatostatin-14 (SST). 22592599_Results suggest that targeting adenoviral vectors to sstr2A could provide a new strategy for the efficient transfer of genes to glioblastoma cells. 22640914_Report down-regulation of SSTR-2 expression in operable hepatocellular carcinomas. 22932785_Data suggest that somatostatin-14 inhibits secretion from alpha and beta pancreatic cells by activating GIRK (G protein-coupled inwardly-rectifying potassium channel) and inhibiting exocytosis; these effects are mediated by SSTR2 in both cell types. 23677175_The analyses of this study demonstrated specific upregulation of sst 2 mRNA in medulloblastoma 23794313_Somatostatin receptor-2 positivity, either focal or diffuse, does not seem to predict prognosis in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. 23828624_We genotyped two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes of importance for respiratory control: P2RY1 (adenosine diphosphate/adenosine triphosphate receptor) and SSTR2 (somatostatin receptor). 24060005_Because of its diffuse strong expression and widespread availability, immunohistochemistry for SSTR2A is useful to confirm the diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors in an appropriate setting particularly if material is limited. 24098585_ZAC1 and SSTR2 are down-regulated in non-functioning pituitary adenomas but not in somatotropinomas. 24182563_We studied the expression of SSTR(2A) and SSTR(5) with new procedures in 108 pituitary tumors 24189142_Whereas sst2 receptors might play a primary role in the differentiation and regulation of TSH, LH, and FSH cells, sst5 receptors appear to be mainly involved in GH regulation from birth onward 24565507_SSTR2 is overexpressed in gastric and duodenal neuroendocrine tumors 24565897_agonist-selective sst2 receptor internalization is regulated by multi-site phosphorylation of its carboxyl-terminal tail. 24828612_Filamin A is involved in SST2 stabilization and signaling in tumoral somatotrophs, playing both a structural and functional role. 24967740_SSTR 5 was shown to be the main receptor subtype in the analysed differentiated or anaplastic thyroid malignancies, whereas SSTR 2 was found only in a small percentage. 25008035_SSTR2 expression was tested in GH-secreting adenomas from 60 patients with acromegaly who had undergone pituitary surgery, 36 of whom had received octreotide with varying levels of response. Its expression was not correlated with baseline or post-octreotide GH or IGF-1 levels or tumor volume. 25010045_SSTR2 expression seems an important factor in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer 25554089_SSTR2A and SSTR3 are more likely to be expressed in SDH-deficient pheochromocytomas/paragangliomas compared with tumors demonstrating normal SDHB staining pattern. 25591947_Somatostatin type 2 receptor, a clinically crucial molecular target, shows variable and unpredictable expression in neuroendocrine neoplasms irrespective of tumor grade. 25635370_Relationships between SSTR2A and breast or prostate cancer showed low concordance between CpGs methylation grade and cancer. 25676386_This study indicated that SSTR2 may be associated with the selective vulnerability of the noradrenergic system in Alzheimer's disease. 25765179_Somatostatin receptors were expressed in a high proportion of merkel cell carcinomas, although expression was heterogeneous between tumours and was not associated with disease severity. 25808161_Data indicate that somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS) and immunohistochemical results for somatostatin and dopamine receptors sstr2, sstr3, sstr5 and D2R were compared in neuroendocrine neoplasms tissues. 25872131_In pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, the primary tumor and metastases differ significantly in their SSTR2A expression. 25872132_Study demonstrates the first evidence of SST2R expression and somatostatin receptor scintigraphy positivity in pancreatic serous cystadenomas. 25879040_e hSSTr2 gene can act as not only a reporter gene for in vivo imaging, but also a therapeutic gene for local radionuclide therapy. 25890201_Low SSTR2 expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 25906124_although the limited number of cases with adequate term follow-up, SSTR-2A expression could be a prognostic factor and somatostatin analogs therapeutic candidate for SmCCs of the bladder as these tumors show high percentage of SSTR-2A expression 25925002_SSTR2 and SSTR5 protein levels were induced as compared to any agent alone. 25962406_An immunohistochemical investigation of the expression of somatostatin receptor subtypes 26036598_mir-185 regulates the expression of SSTR2 in GH-secreting pituitary adenoma. The staining intensity of SSTR2 is stronger in adenoma samples than controls. 26095613_sST2 is proposed as a biomarker for progressive vascular fibrosis, and the involvement of sST2 in the pathogenesis of limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis may be exploited therapeutically. 26158180_The expression of VEGF and SSTR2 were associated with progression and prognosis of gastric cancer. 26211366_VPA was observed to stimulate the expression of somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2). 26238605_SSTR2 gene expression was dysregulated in the anterior cingulate of bipolar patients. 26259237_there is an elevation in CXCR4 and a decrease in SSTR2A expression with increasing malignancy in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms 26339384_CD56 marker is a useful alternative that is comparable to SSTR2A for the diagnosis of phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors. 26391562_Results show that histological subtyping of pituitary tumor correlated with SSTR2, E cadherin and p27kip protein levels and these may serve as useful biomarkers for prognosis. 26474434_Data showed that the distribution of somatostatin receptor (SSTR) subtypes among the 199 pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) was: SSTR2 (54.8%), SSTR1 (53.3%), SSTR4 (51.8%), SSTR5 (33.7%), and SSTR3 (28.6%). 26531719_Combination treatment increased both SSTR2 and SSTR5 mRNA and protein levels in DU-145 cells. The data suggest that this combination therapy may be a good candidate for patients with advanced metastatic Prostate cancer (PCa) do not respond to androgen deprivation. 26733502_Filamin-A is required to mediate SSTR2 effects in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours 26796520_SSTR2 promoter hypermethylation might be associated with the risk and progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma in males. 26978232_The number of SSTR-2-expressing cells was significantly smaller in the patients with Crohn's disease than that in those with the unchanged mucosa and in those with indeterminate (unclassified) colitis. 27402219_expression of MDM2, somatostatin receptor 2A, and PD-L1 in follicular dendritic cell sarcoma 27455094_The results of this study showed the SSTR2 expression was lower in patients pretreated with LA-SSA/PEGV compared to the drug-naive acromegalic patients. 28120505_This study investigated the presence of progenitor/stem cells in non-functioning pituitary tumors (NFPTs) and tested the efficacy of dopamine receptor type 2 (DRD2) and somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2) agonists to inhibit in vitro proliferation 28467778_SSTR2A expression is infrequent in astrocytomas and negative in the majority of glioblastomas where it is of no prognostic significance. In contrast, oligodendrogliomas show intense membranous and cytoplasmic SSTR2A expression. 28782576_SSTR2 was significantly hypermethylated in colorectal cancer tissues when compared with adjacent normal colorectal tissues. 29807052_Olfactory neuroblastoma demonstrate high SSTR2a expression regardless of their differentiation. 30128959_SSTR2A expression is correlated with longer OS in medullary thyroid carcinoma, especially for stage IV patients, suggesting that SSTR2A expression might be a useful prognostic factor in medullary thyroid carcinoma. 30152518_SSTR2 is a poor prognostic biomarker in SCLC and potential future therapeutic signaling target. 30193580_In this cohort showed that most IDH-wild type gliomas did not express SSTR2A protein and a significant overexpression of SSTR2A protein was observed in the IDH-mutant gliomas 30334904_Patients with neuroblastoma, including relapsed or progressive disease, showed SSTR2 expression at diagnosis 30531706_This study indicates a down-regulation of SSTR2 expression as small intestinal neuroendocrine tumors progress through the intestinal wall, which might signify underlying biological processes of importance for SI-NET invasion behavior. 30585825_SSTR2a may be helpful to distinguish follicular dendritic cell sarcomas from inflammatory pseudotumor-like follicular dendritic cell sarcomas ... and may be a potential therapeutic target for treatment of follicular dendritic cell sarcomas 30609928_study suggests that SSTR2 might play a critical role in the aetiopathogenesis of periodontitis 30822353_Reaults indicate that endosomal trafficking of somatostatin receptor 2 (SSTR2) is dependent on numerous regulatory mechanisms controlled by its C terminus and the retromer machinery. 31208995_Minute pulmonary meningothelial-like nodules cells closely resemble SSTR2a-positive meningothelial cells. 32328798_Expression of potential therapeutic target SSTR2a in primary and metastatic non-keratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 32576907_Enhancing the anti-tumour activity of (177)Lu-DOTA-octreotate radionuclide therapy in somatostatin receptor-2 expressing tumour models by targeting PARP. 33132215_SSTR2a is constantly expressed in lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma with squamous differentiation other than that with glandular differentiation. 33313679_The PDZ Domain Protein SYNJ2BP Regulates GRK-Dependent Sst2A Phosphorylation and Downstream MAPK Signaling. 33402692_Somatostatin receptor 2 expression in nasopharyngeal cancer is induced by Epstein Barr virus infection: impact on prognosis, imaging and therapy. 33491286_Predictive and prognostic significance of tumour subtype, SSTR1-5 and e-cadherin expression in a well-defined cohort of patients with acromegaly. 33598797_The potential of somatostatin receptor 2 as a novel therapeutic target in salivary gland malignant tumors. 33828200_Understanding the influence of lipid bilayers and ligand molecules in determining the conformational dynamics of somatostatin receptor 2. 33886620_Octreotide inhibits secretion of IGF-1 from orbital fibroblasts in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy via inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. 34040115_A potential role for somatostatin signaling in regulating retinal neurogenesis. 34320691_The prognostic significance of neuroendocrine markers and somatostatin receptor 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34601710_The immunohistochemical expression of SSTR2A is an independent prognostic factor in meningioma. 35184184_Diagnostic Utility of Somatostatin Receptor 2A Immunohistochemistry for Tumor-induced Osteomalacia. 35264912_Somatostatin Receptor 2: A Potential Predictive Biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. |
ENSMUSG00000047904 |
Sstr2 |
27.430659 |
4.3032738375 |
2.105435 |
0.329572411 |
43.551928 |
0.00000000004128572101402471690117866571318946955493345285503892228007316589355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000219200446822663600936925023801506596382582259252558287698775529861450195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.9372109 |
8.8827468 |
10.0689375 |
1.7790463 |
| ENSG00000180628 |
84333 |
PCGF5 |
protein_coding |
Q86SE9 |
FUNCTION: Component of a Polycomb group (PcG) multiprotein PRC1-like complex, a complex class required to maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of many genes, including Hox genes, throughout development. PcG PRC1 complex acts via chromatin remodeling and modification of histones; it mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119', rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility (PubMed:26151332). Within the PRC1-like complex, regulates RNF2 ubiquitin ligase activity (PubMed:26151332). Plays a redundant role with PCGF3 as part of a PRC1-like complex that mediates monoubiquitination of histone H2A 'Lys-119' on the X chromosome and is required for normal silencing of one copy of the X chromosome in XX females (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UK78, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26151332}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in Golgi apparatus; centrosome; and nucleoplasm. Part of PcG protein complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84333; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PcG protein complex [GO:0031519]; PRC1 complex [GO:0035102]; X chromosome [GO:0000805]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; histone H2A-K119 monoubiquitination [GO:0036353]; inactivation of X chromosome by genomic imprinting [GO:0060819]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000024805 |
Pcgf5 |
153.437188 |
2.4195140211 |
1.274717 |
0.249697600 |
25.451317 |
0.00000045368794163826762546522122603043225552710282499901950359344482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001671183932762872318656083119037258910566379199735820293426513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
218.6883483 |
35.0218941 |
91.0485490 |
10.8448375 |
| ENSG00000180720 |
1132 |
CHRM4 |
protein_coding |
P08173 |
FUNCTION: The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is inhibition of adenylate cyclase. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The muscarinic cholinergic receptors belong to a larger family of G protein-coupled receptors. The functional diversity of these receptors is defined by the binding of acetylcholine and includes cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degeneration, and potassium channel mediation. Muscarinic receptors influence many effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. The clinical implications of this receptor are unknown; however, mouse studies link its function to adenylyl cyclase inhibition. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1132; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor activity [GO:0016907]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0004993]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007197]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; regulation of locomotion [GO:0040012]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12505680_relative to other muscarinic receptor subtypes, the M(4) receptor could be the subtype which is selectively compromised in Alzeheimer's disease 15263021_M4 increases expression of 'migratory' integrins; M4 effects resulted from inhibition of the inhibitory pathway involving the adenylyl cyclase-cyclic AMP-protein kinase A pathway 17373692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18282687_In progressive supranuclear palsy: there were no changes in M4 muscarinic receptor density 18337477_Regions in i3 including Leu272-Arg338 and Val373-Ala393 are involved in internalization of the M4 receptor; the region including Val373-Ala393 is indispensable for its recycling, whereas the other regions are dispensable for internalization and recycling. 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406819_analysis of allosteric agonism and modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 21295605_Use of HM4- and green fluorescent protein-expressing trangenic mice as tissue donors in cell-based therapy validates a rodent model of Huntington disease. 23490763_The data of this study suggested that the rs2067482 polymorphism may help to predict susceptibility to schizophrenia and/or therapeutic responsiveness. 24074052_Data indicate that compounds derived from VU0152100 showed M4 muscarinic receptor (M4 mAChR) direct agoinst properties. 24768300_This study identify suppression of the PVHSIM1-->PAGvl/DR circuit connection as sufficient to induce overeating behavior. 24807966_[(3)H]LY2119620 to probe specifically the human M2 and M4 muscarinic receptor allosteric binding sites. 26025056_This study demonstrated that CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressed M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors which density were significantly increased in asthmatic children in comparison with controls. 26958838_crystal structures of the M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors bound to the inverse agonist, tiotropium 27269905_the association of the African-specific CHRM4 SNP with cocaine dependence survived correction for multiple testing 31211471_Authors discuss how M4 activity regulates DA release and signaling, the potential sources of ACh that can regulate M4 activity, and the implications of targeting M4 activity for the treatment of the motor symptoms in movement disorders. [Review] 32234387_Group II muscarinic acetylcholine receptors attenuate hepatic injury via Nrf2/ARE pathway. 34806612_Muscarinic Receptors Expression in the Peripheral Blood Cells Differentiate Dementia with Lewy Bodies from Alzheimer's Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000040495 |
Chrm4 |
8.993404 |
0.0913520774 |
-3.452419 |
0.746525265 |
27.229267 |
0.00000018070247536526826936672618460072436974428455869201570749282836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000694032926461451851240581131102791445641742029692977666854858398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6036806 |
0.8682394 |
17.6315453 |
4.4100813 |
| ENSG00000180758 |
80045 |
GPR157 |
protein_coding |
Q5UAW9 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor that promotes neuronal differentiation of radial glial progenitors (RGPs). The activity of this receptor is mediated by a G(q)-protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C206}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Developmental protein;Differentiation;G-protein coupled receptor;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable G protein-coupled receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway and radial glial cell differentiation. Predicted to be located in ciliary membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80045; |
ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; circadian behavior [GO:0048512]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; radial glial cell differentiation [GO:0060019] |
Mouse_homologues 27142930_Thus, GPR157-Gq protein signaling at the primary cilia of radial glial progenitors is activated by the cerebrospinal fluid and contributes to neurogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000047875 |
Gpr157 |
75.757690 |
6.0096406245 |
2.587279 |
0.325150859 |
59.855961 |
0.00000000000001020597748009018405231708653741326911150541934675262112364180211443454027175903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000068472830730059597513457912503976675363116626005233200658040004782378673553466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
134.6254822 |
26.5345739 |
22.3151089 |
3.4950901 |
| ENSG00000180769 |
404201 |
WDFY3-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32275336_USF1-induced overexpression of long noncoding RNA WDFY3-AS2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via targeting miR-491-5p/ZNF703 axis. 32401758_WDFY3-AS2, BDNF-AS and AFAP1-AS1 as potential prognostic factors for patients with triple-negative breast tumors 32536038_LncRNA WDFY3-AS2 suppresses proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-2355-5p/SOCS2 axis. |
|
|
23.201921 |
0.4419842982 |
-1.177933 |
0.375537229 |
9.792917 |
0.00175185348897424764125219098787056282162666320800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003916001438324987968253587666822568280622363090515136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8173443 |
3.4674330 |
28.7497300 |
5.1518881 |
| ENSG00000180773 |
120103 |
SLC36A4 |
protein_coding |
Q6YBV0 |
FUNCTION: Uniporter that mediates the transport of neutral amino acids like L-tryptophan, proline and alanine (PubMed:21097500). The transport activity is sodium ions-independent, electroneutral and therefore functions via facilitated diffusion (PubMed:21097500). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21097500}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
SLC36A4 belongs to the SLC36 family of amino acid transporters based on sequence similarity with other family members (e.g., SLC36A1; MIM 606561). SLC36 proteins contain about 500 amino acids and have 9 to 11 transmembrane domains. Unlike other SLC36 family members, which are proton-coupled amino acid transporters, SLC36A4 is a high-affinity/low-capacity non-proton-coupled amino acid transporter (Pillai and Meredith, 2011 [PubMed 21097500]).[supplied by OMIM, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:120103; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; L-alanine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015180]; L-amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015179]; L-proline transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015193]; L-tryptophan transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015196]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; amino acid transmembrane transport [GO:0003333]; L-alanine transport [GO:0015808]; L-proline import across plasma membrane [GO:1904271]; L-tryptophan transmembrane transport [GO:1904556]; proline transport [GO:0015824]; tryptophan transport [GO:0015827] |
20498635_SLC36A4 has a similar in vivo growth regulatory activity to fly SLC36 family members when expressed in Drosophila and is also required for amino acid-dependent mTORC1 activation, and mTORC1-regulated proliferation in human cells. 21097500_SLC36A4 (hPAT4) is a high affinity amino acid transporter when expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. 26434594_Data predict that colorectal cancer cells with high PAT4 expression will be more resistant to depletion of serine and glutamine, allowing them to survive and outgrow neighbouring normal and tumorigenic cells. |
ENSMUSG00000043885 |
Slc36a4 |
256.249424 |
3.0920707673 |
1.628573 |
0.220859516 |
52.255729 |
0.00000000000048723583678845127244212750774224703802575686673037580476375296711921691894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002963555155731120847104886178294256052732913442326889708056114614009857177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
368.6596441 |
50.4472618 |
119.9852322 |
12.1389486 |
| ENSG00000180817 |
5464 |
PPA1 |
protein_coding |
Q15181 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPase) family. PPases catalyze the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate to inorganic phosphate, which is important for the phosphate metabolism of cells. Studies of a similar protein in bovine suggested a cytoplasmic localization of this enzyme. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5464; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; inorganic diphosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0004427]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphate-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006796] |
17494625_Neither human hexokinase-1 nor human inorganic pyrophosphatase expression segregated concordantly with human cytoplasmic glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase expression. 20206270_Data are consistent with the postsynaptic gephyrin scaffold acting as a platform for protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), which regulates gephyrin cluster size by dephosphorylation of gephyrin- or cytoskeleton-associated proteins. 21317537_IRBIT opposes the effects of WNKs and SPAK by recruiting PP1 to the complex to dephosphorylate CFTR and NBCe1-B, restoring their cell surface expression, in addition to stimulating their activities 21514157_PP1gamma is the major histone H3 phosphatase acting on the mitotically phosphorylated residues H3T3ph, H3S10ph, H3T11ph, and H3S28ph. 22797819_Pyrophosphatase overexpression is associated with invasion, metastasis and recurrence in gastric cancer 23215877_Results identify PP1 as a novel regulator of Cl(-)-HCO3(-) anion exchangers activity which, in concert with CFTR, coordinates events at both apical and basolateral membranes, crucial for efficient HCO3(-) secretion from Calu-3 cells. 23718219_PPP1R42 regulation of PP1 function in centrosome separation. 25011105_The human PP1 interaction with the measles V protein is mediated by a conserved PP1-binding motif in the C-terminal region of the V protein. 25011106_Measles virus binding to DC-SIGN leads to inhibition of PP1 phosphatase activity and hence inhibition of RIG-I and Mda5 dephosphorylation. 25028520_findings indicate that brain PP-1I associates with and is regulated by the associated protein kinases C-TAK1 and PFTK1 26378044_PP-1 and Akt have roles in AR-v7 protein expression and activities when AR is functionally blocked 26722435_PPA1 may serve as a potential biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer 26869028_The Newcastle disease virus-induced translation shutoff at late infection times was attributed to sustaining phosphorylation of eIF2a, which is mediated by continual activation of PKR and degradation of PP1. 26948660_Proteomic profiling identifies the inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPA1) protein as a potential biomarker of metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 26981768_Thus, the Ska complex, specifically the Ska1 C-terminal domain, recruits PP1 to kinetochores to oppose spindle checkpoint signaling kinases and promote anaphase onset. 27509921_enhanced NEK2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) promotes HCC progression and drug resistance by promoting PP1/Akt and Wnt pathway activation, which may represent a new therapeutic target for HCC. 27666431_Results show that PPA1 expression is significantly higher in many tumors, especially those of lung and ovarian origin, which suggests that PPA1 plays an important role in carcinogenesis and in the development of some tumors. 28202851_PPA1 serves as a potential prognostic biomarker for patients with Ovarian serous carcinoma. 29222185_The p37 controls cortical NuMA levels via the phosphatase PP1 and its regulatory subunit Repo-Man, but it acts independently of Galphai, the kinase Aurora A, and the phosphatase PP2A. 29764992_Study identified phosphorylation of RV[S/T]F motifs in known and previously unidentified PP1 regulatory proteins as a cell cycle-dependent event and shows that Aurora B was the primary kinase responsible for this phosphorylation event during mitosis. 29898919_PP1-NIPP1 expression resulted in the build up of RNA-DNA hybrids (R-loops), enhanced chromatin compaction and a diminished repair of DNA double-strand breaks. 31433993_PP1 and PP2A Use Opposite Phospho-dependencies to Control Distinct Processes at the Kinetochore. 31494926_CDK1-counteracting phosphatases PP1 and PP2A-B55, together with Aurora and Polo kinases, contribute to the temporal regulation and order of events in the different stages of mitotic exit from anaphase to cytokinesis. (Review) 32755477_PP1 promotes cyclin B destruction and the metaphase-anaphase transition by dephosphorylating CDC20. 33238888_The PP1 regulator PPP1R2 coordinately regulates AURKA and PP1 to control centrosome phosphorylation and maintain central spindle architecture. 33537097_Mutation of SPINOPHILIN (PPP1R9B) found in human tumors promotes the tumorigenic and stemness properties of cells. 33583053_Crystallographic and modeling study of the human inorganic pyrophosphatase 1: A potential anti-cancer drug target. 33991172_PP1, PKA and DARPP-32 in breast cancer: A retrospective assessment of protein and mRNA expression. 34634305_Basolateral protein Scribble binds phosphatase PP1 to establish a signaling network maintaining apicobasal polarity. |
ENSMUSG00000020089 |
Ppa1 |
210.114196 |
2.7518950103 |
1.460425 |
0.111012643 |
177.585698 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000016314719130719948279564859397308751195745981951564728773475585202978094321077484551801867956173615277536484424736329401639522984623908996582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000002755208860062087584034362846226009379913990034063453259510912344378926466412958409868101140538862317899693188394394383067265152931213378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
313.9138032 |
22.3120519 |
114.8269850 |
6.6016578 |
| ENSG00000180828 |
27319 |
BHLHE22 |
protein_coding |
Q8NFJ8 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits DNA binding of TCF3/E47 homodimers and TCF3 (E47)/NEUROD1 heterodimers and acts as a strong repressor of Neurod1 and Myod-responsive genes, probably by heterodimerization with class a basic helix-loop-helix factors. Despite the presence of an intact basic domain, does not bind to DNA (By similarity). In the brain, may function as an area-specific transcription factor that regulates the postmitotic acquisition of area identities and elucidate the genetic hierarchy between progenitors and postmitotic neurons driving neocortical arealization. May be required for the survival of a specific population of inhibitory neurons in the superficial laminae of the spinal cord dorsal horn that may regulate pruritis. Seems to play a crucial role in the retinogenesis, in the specification of amacrine and bipolar subtypes. Forms with PRDM8 a transcriptional repressor complex controlling genes involved in neural development and neuronal differentiation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C6A8}. |
Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a protein that belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors that regulate cell fate determination, proliferation, and differentiation. A similar protein in mouse is required for the development of the dorsal cochlear nuclei, and is thought to play a role in in the differentiation of neurons involved in sensory input. The mouse protein also functions in retinogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:27319; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12213201_Segregates with Duane syndrome. Brain-specific expression with the highest abundance in the cerebellum. 35806162_BHLHE22 Expression Is Associated with a Proinflammatory Immune Microenvironment and Confers a Favorable Prognosis in Endometrial Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000025128 |
Bhlhe22 |
2050.429443 |
0.4955220981 |
-1.012979 |
0.034074191 |
897.872256 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002846867349985947799685630817149315570059107080991101269170361305491474504680033119680636578318739907262811167009075707298745175803322 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002546652247623793356294007011754292023991212311589397206190701559826528987143213015219430792172551068602410090832351265509349216444922 |
Yes |
No |
1372.2683542 |
30.3659530 |
2789.1478268 |
40.2685434 |
| ENSG00000180871 |
3579 |
CXCR2 |
protein_coding |
P25025 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for interleukin-8 which is a powerful neutrophil chemotactic factor (PubMed:1891716). Binding of IL-8 to the receptor causes activation of neutrophils. This response is mediated via a G-protein that activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system (PubMed:8662698). Binds to IL-8 with high affinity. Also binds with high affinity to CXCL3, GRO/MGSA and NAP-2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1891716, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8662698}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the G-protein-coupled receptor family. This protein is a receptor for interleukin 8 (IL8). It binds to IL8 with high affinity, and transduces the signal through a G-protein activated second messenger system. This receptor also binds to chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1/MGSA), a protein with melanoma growth stimulating activity, and has been shown to be a major component required for serum-dependent melanoma cell growth. This receptor mediates neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation. The angiogenic effects of IL8 in intestinal microvascular endothelial cells are found to be mediated by this receptor. Knockout studies in mice suggested that this receptor controls the positioning of oligodendrocyte precursors in developing spinal cord by arresting their migration. This gene, IL8RA, a gene encoding another high affinity IL8 receptor, as well as IL8RBP, a pseudogene of IL8RB, form a gene cluster in a region mapped to chromosome 2q33-q36. Alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]. |
hsa:3579; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; mast cell granule [GO:0042629]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; C-C chemokine binding [GO:0019957]; C-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016493]; C-X-C chemokine receptor activity [GO:0016494]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; interleukin-8 binding [GO:0019959]; interleukin-8 receptor activity [GO:0004918]; acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002438]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; interleukin-8-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038112]; metanephric tubule morphogenesis [GO:0072173]; midbrain development [GO:0030901]; negative regulation of neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0033030]; neutrophil activation [GO:0042119]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010666]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043117]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12164325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12239185_Phagocytosing neutrophils down-regulate its expression 12442335_CXCR1 and CXCR2 internalization and recycling are tightly regulated by receptor domains and by actin-related kinases. 12496258_role in mediating angiogenic effects of interleukin effects in intestinal microvascular endothelial cells 12628493_Neutrophil recruitment to inflammatory sites is mediated by two related receptors: CXCR1 and CXCR2. Both receptors share two ligands, interleukin-8 (CXCL8) and GCP-2 (CXCL6). 12870115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12888558_functions as a dimer and truncated receptors negatively modulate receptor activities competing for the formation of wild type dimers 12975484_a potentiation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 generation in the presence of coactivation of P2Y2 nucleotide receptors and CXCR2 would be sufficient for additional Ca2+ release. 14713106_the data suggest that constitutive expression of CXCR1 and CXCR2 play an important role regulating the IL-8-mediated metastatic phenotype in human malignant melanoma cells. 14967163_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15028716_neutrophil migration in response to CXCR1 or CXCR2 agonists is not dependent on endocytosis of CXCR1 or CXCR2 15063762_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15265017_extra- and intracellular CXCR1 and CXCR2 are differentially expressed and regulated on T lymphocytes and mast cells 15358660_The results support the hypothesis of bacterial propagation through CXCR2 neutrophil recruitment and confirm that tissue injury is unrelated to A. phagocytophilum tissue load. 15364949_Arrestin has a role in regulating MAPK activation and preventing NADPH oxidase-dependent death of cells expressing CXCR2 15454487_IL-8 and CXCR2 participate in the altered megakarocyte growth that features myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis 15479720_membrane-bound activated Cdc42 and Rac1 localize to the leading edge of cells expressing wild-type CXCR2 receptor, but not in cells expressing mutant CXCR2 15545821_Activation of neutrophils and down-regulation of CXCR2 were predominantly caused by IL-8 15598788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15618253_In eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis, significant increase in both proliferative and secretory phases for epithelial CXCR2 expression, and in proliferative phase for CXCR1 expression. May be involved in pathogenesis of endometriosis. 15626158_neutrophils from transgenic mice were found to express hCXCR2 and to respond to CMV vCXCL-1 15630732_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15772681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793866_the relative expression levels of CXCR-1 and -2 mRNA were rather lower than expected in the affected esophageal mucosa of patients with reflux esophagitis 15946947_CXCR1-CXCR2 heterodimers are as likely to form in cells co-expressing these two chemokine receptors as the corresponding homodimers. 16086366_We propose that the concurrence of CXCR2 on oligodendrocytes and induced CXCL1 on hypertrophic astrocytes in MS provides a novel mechanism for recruitment of oligodendrocytes to areas of damage, an essential prerequisite for lesion repair. 16098254_Gene polymorphisms active in the EGFR pathway may be associated with the sensitivity of colorectal cancer patients to platinum-based chemotherapy. 16260092_neutrophil migration induced by artocarpin involves binding to CXCR2 16272353_increased expression of ELR+ CXC chemokines and their interaction with CXCR2 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of post-lung transplantation cold ischemia-reperfusion injury 16406804_in CXCR2-expressing cells FAK phosphorylation was adhesion-dependent and was stimulated by fibronectin.Overall, several aspects of CXCL8-induced FAK phosphorylation and migration are regulated in a receptor-specific manner. 16411061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16679868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16702372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16793206_No significant association existed between CXCR2 +1208 C/T polymorphism and multiple sclerosis susceptibility. 16793206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16897191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16987681_CXCR-1 and CXCR-2 chemokine receptors of synovial fluid neutrophils may have diverse functions in the course of inflammatory arthritides 16990258_analysis of the LLKIL motif in CXCR2, which is required for full IL-8 ligand-induced activation of Erk, Akt, and chemotaxis in HL60 cells 17003486_TNF-alpha and IL-1beta enhance IL-8 expression in term decidual cells, suggesting that these cytokines are important regulators of chorioamnionitis-related decidual neutrophil infiltration. 17142783_most circulating human CD4+ T cells store the inflammatory chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR1 within a distinct intracellular compartment 17204468_data herein indicate that the second extracellular loop (2ECL) of the receptors CXCR1,CXCR2, and CXCL8 is critical for the distinct rate of internalization of each 17272812_CXCR2 receptor is important the homing of circulating endothelial progenitor cells. 17295203_Mesenchymal stem cells express chemokine receptor CXCR2 and migrate upon stimulation with IL-8. 17360650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17435771_By activating CXCR2, macrophage migration inhibitory factordisplays chemokine-like functions and acts as a major regulator of inflammatory cell recruitment and atherogenesis. 17604950_Findings indicate that beta-endorphin and Met-enkephalin are contained in primary granules of PMN, and that CXCR1/2 ligands induce p38-dependent translocation and release of these opioid peptides to inhibit inflammatory pain 17630697_The N-loop residues in IL-8 (H18 and F21) and the receptor N-termini are the major structural determinants regulating the rate of receptor internalization, which in turn controlls the activation profile of ERK1/2. 17672867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17709521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17939034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17949231_CXCR2 +1208C/T polymorphism may affect the disease progression. 17949231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17996233_Intracellular cross-talk between the GPCR CXCR1 and CXCR2: role of carboxyl terminus phosphorylation sites 18025257_Cyr61 promotes interleukin-8-dependent chemotaxis, transendothelial migration, and intravasation by induction of CXCR1/CXCR2 through integrin alphavbeta3/Src/PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway. 18199703_CXCR2 signaling promotes liver cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. 18208820_Abnormal CXCR2 modulation and impaired expression cause systemic lupus erythematosis-neutrophil hyporesponsiveness to IL-8 stimulation in vitro. 18244953_The allergen-induced levels of beta(c) mRNA and CCR3 mRNA in sputum-derived cells were inhibited by TPI ASM8, with no significant effects on the cell surface protein expression of CCR3 and beta(c). 18292390_There is a novel mechanism via CXCR2 induction by PPAR-gamma that can enhance the immune response in human macrophages. 18307412_Data show that CXCR2 chemokine receptor antagonism enhances delta opioid receptor (DOP) function via allosteric regulation of the CXCR2-DOP receptor heterodimer. 18462836_These data suggest that CXCR2 overexpression in peripheral T cells is intracerebral microglial TNF-alpha-dependent and TNF-alpha primes T cells transendothelial migration in Alzheimer's diseases. 18555777_Study reports that knocking down the chemokine receptor CXCR2 (IL8RB) alleviates both replicative and oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) and diminishes the DNA-damage response. 18633131_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18676870_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18755694_the type I PDZ ligand of CXCR2 acts to both delay lysosomal sorting and facilitate proper chemotactic response. 18780829_induction of autocrine CXCR2 signaling is a novel mode of resistance to oxaliplatin 18852457_identify a pseudo-(E)LR motif as the structural determinant for MIF's activity as a non-canonical CXCR2 ligand 19010874_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19012493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19026125_No significant association was found between +2607 IL-8RA polymorphisms and nationality or in Behcets disease or health controls. 19035451_PaCa-derived CXCL8 and fibroblast-derived CXCL12 and corresponding receptors CXCR2 and CXCR4 cooperatively induce angiogenesis in vitro by promoting HUVEC proliferation, invasion, and tube formation 19057948_single nucleotide polymorphisms in pancreatic cancer (Review) 19067586_findings unravel new mechanisms involving the CXCR2 receptor in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and pose it as a potential target for developing novel therapeutics for intervention in this disease 19118103_epitope mapping providesinformation about the relative location of amino acids on the surfaces of hCXCR1 and hCXCR2 interacting with hCXCL8 19147552_Studies show the importance of host CXCR2-dependent CXCL-8-mediated angiogenesis in the regulation of melanoma growth and metastasis. 19151925_Data show that CXCL8 stimulation leads to paxillin phosphorylation in normal neutrophils, and that both CXCL8 receptors (CXCR1 and CXCR2) mediate CXCL8-induced paxillin phosphorylation. 19155217_RPS19 significantly compromised CXCR2-dependent MIF-triggered adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells under flow conditions. We, therefore, propose that RPS19 acts as an extracellular negative regulator of MIF. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19401689_CXCR1 and CXCR2 play essential role in growth, survival, motility and invasion of human melanoma. 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19435808_Data provide the first demonstration that direct interaction of VASP with CXCR2 is essential for proper CXCR2 function and demonstrate a crucial role for VASP in mediating chemotaxis in leukocytes. 19435811_Results indicate that EGR-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB mediate GRO/CXCR2 proliferative signaling in esophageal cancer and may represent potential target molecules for therapeutic intervention. 19549892_Data show that expression of CXCL1 and its receptor, CXCR2, are elevated in cancer tissue compared with normal endometrium. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19585580_Data demonstrate that CXCR1 and CXCR2 expression play a critical role in melanoma tumor progression and, functional blockade of CXCR1 and CXCR2 could be potentially used for future therapeutic intervention in malignant melanoma. 19634663_CXCR1 and CXCR2 are important factors in mediating the migration of endothelial cells induced by shear stress. 19750480_LL-37 may act as a functional ligand for CXCR2 on human neutrophils. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19887480_Snail upregulation plays a role in non-small cell lung carcinoma by promoting tumor progression mediated by CXCR2 ligands 19890050_In human neutrophils and in cell lines that coexpress the chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2, we used fluorescence resonance energy transfer techniques to show that these two receptors form homo- and heterodimers 19904283_We focus on the involvement of two chemokine networks, namely CCL2/CCR2 and CXCL8/CXCR2, in promoting macrophage and neutrophil infiltration, respectively, into the lesioned parenchyma after focal traumatic brain injury--REVIEW 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20005738_This is the first study to show that IL-8 and IL-8 receptors are upregulated in both pancreatic adenocarcinomas and neuroendocrine tumours, and indicate this signalling pathway may modulate tumour behaviour through autocrine and/or paracrine loops. 20016196_The CXCR-1 receptor, but not the CXCR-2 receptor was found to be expressed in human small airway epithelial cells. 20016852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20018298_CXCR2 was able to promote invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma 20044480_CMV uses the UL146 gene product expressed in infected endothelial cells to attract neutrophils by activating their CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors, whereby neutrophils can act as carriers of the virus to uninfected endothelial cells 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20070156_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20070156_The CXCR2 +1440(G/A) single-nucleotide polymorphism and some haplotypes are associated with periodontitis in Brazilian individuals. 20089160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20419088_LASP-1 interaction with CXCR2 is critical for CXCR2-mediated chemotaxis 20429924_Above median expression of CXCR2, CXCR3 and CCR1 in the tumour islets is associated with increased survival in non-small cell carcinoma, and expression of CXCR3 correlates with increased macrophage and mast cell infiltration in the tumour islets. 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20505188_CXCR2 thus has potential as a therapeutic target and for use in ovarian cancer diagnosis and prognosis 20519647_CXCR2 signaling is critical in transgenic mice with C-rel-deficient/NFkappaB1-deficient/heterozygous Rela+/- neutrophilia causing spontaneous inflammation. 20540789_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20540789_Results indicate that the polymorphisms in IL-8 and CXCR2 genes are associated with increased breast cancer risk, as well as disease progression. 20568250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20580690_These data suggest that HpHSP60 enhances angiogenesis via CXCR2/PLCbeta2/Ca2+ signal transduction in endothelial cells. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20630874_Data propose that the CXC motif in CXCL8 functions as a conformational switch that couples Site-I and Site-II interactions for both CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors. 20635912_lower percentages of positive leukocytes in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802378_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21036625_CXCR1 and CXCR2 are novel mechano-sensors mediating laminar shear stress-induced endothelial cell migration. 21042230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21106938_the N-like loop in MIF is critical for MIF's noncognate interaction with CXCR2 and proatherogenic functions; the 2-site binding model that explains chemokine receptor activation also applies to MIF 21214373_The results of this study suggest that polymorphisms of CXCL8 are associated with increased susceptibility to IgAN, and polymorphisms of CXCR2 with the pathological progression of childhood IgAN. 21343381_The expression of CXCL1 and CXCR2 was higher in gastric cancer tissues compared with adjacent noncancerous tissues. 21441140_CXCR2 mediates the atherogenic activity of environmental pollutants, such as dioxins, and contributes to the development of atherosclerosis through the induction of a vascular inflammatory response by activating the AhR-signaling pathway. 21555225_Data demonstrate that blocking megakaryopoiesis by simultaneous inhibition of CXCR1 and CXCR2 can enhance differentiation of UCB CD133(+) cells into megakayocytic progenitors. 21670971_These data suggests an important role for CXCR2 receptors in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 21749879_CXCR1 and CXCR2 silencing modulates CXCL8-dependent endothelial cell proliferation, migration and capillary-like structure formation. 21876773_IQGAP1 is a novel essential component of the CXCR2 'chemosynapse'. 21915051_mRNA levels for CXCR1 and CXCR2 are increased in blood in males with obstructive CAD and decreased in patients with improved perfusion. 21948388_A novel allosteric binding cavity in the transmembrane domain of CXCR2 is identified at the same interface postulated as the ligand entry channel in the opsin receptor. 21989491_synergistic effect of CXCR1 and CXCR2 in shear-stress-induced endothelial cell migration 22076427_The data do not support the hypothesis that bronchoepithelial expression of CXCR2 facilitates transepithelial migration of neutrophils 22088968_It was shown that four SNPs in CXCR1 and three in CXCR2 strongly correlated with age-adjusted lung function in cystic fibrosis patients. SNPs comprising haplotypes CXCR1_Ha and CXCR2_Ha were in high linkage disequilibrium. 22117410_the role of the IL8RA gene in atopic bronchial asthma. 22152684_Data show that expression of CXCR1 and CXCR2 on neutrophils was significantly decreased in AAV patients compared to healthy controls (HC). 22171941_association between CXCR1/CXCR2 variants and visceral leishmaniasis 22203670_PDZ scaffold protein NHERF1 couples CXCR2 to its downstream effector phospholipase C (PLC)-beta2, forming a macromolecular complex 22231733_Our data implicate IL-8/CXCR2 signaling pathway in the progression and regulation of angiogenesis in astrocytomas and provide a rationale for CXCR2 therapeutic exploitation in these tumors 22242662_The N-terminal element of the CXCR2 receptor, when attached to the N-terminus of the stabilized B1 domain, binds to IL-8. This binding is characterized by a small favorable enthalpy change and a larger favorable entropy change. 22274915_expression of CXCR2 is associated with the development and progression of expression of CXCR2 is associated with the development and progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). 22325052_Polymorphisms within genes encoding interleukin-8 and its receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 participate in genetic predisposition to acute pyelonephritis. 22389383_p53 mutation leads to inactivation of the IL8-CXCR2-p53 signaling pathway, resulting in the loss of an important growth inhibitory mechanism and the hyper-proliferation of neuroendocrine cells in small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma 22482416_Data suggest that CXCR1 and IL-8 may contribute to hepatic inflammation. 22617157_our study demonstrates the critical roles of the tumour microenvironment-encoded IL-8/CXCR2 in colon cancer pathogenesis 22626766_This is the first report of the expression of IL-8 receptors in endometrial carcinoma and the results show an association between IL-8 and IL-8 receptors and the pathogenesis of endometrial carcinoma. 22661400_We failed to suggest that IL-8, IL-18, and CXCR2 have been associated with the risk of silicosis in an occupational group from Iran. 22763041_These findings suggest a protective role of CXCL8 (-251) A in the CXCR2 (+1208) TT and TC genotypes and an increased risk of CXCL8 (-251) A in association with the CXCR2 (+1208) CC genotype in systemic sclerosis patients. 22763101_Expression levels of CXCR2 and IL-6Ralpha were not changed in comparison with normal fallopian tubes in tubal pregnancy. 22850671_Staphopain A is an important immunomodulatory protein that blocks neutrophil recruitment by specific cleavage of the N-terminal domain of human CXCR2 22885102_IFN-gamma-induced apoptosis of human embryonic stem cell is restricted by CXCR2 signaling. 22893608_These results indicate that macrophage-derived Cxcr2 ligands may be important for promoting mammary tumor formation regulated by FGFR signaling. 22904195_HIV-1 matrix protein p17 promotes angiogenesis via chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2. 22986777_A biologically active natural product, triptolide, mediates a protective effect by inhibiting CXCR2 activity. 23023221_Data show that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) directly regulate T cell proliferation by induction of CXCL3 chemokine and its receptor, CXCR2 on the surface in T cells. 23029099_Glioblastoma cell-secreted interleukin-8 induces brain endothelial cell permeability via CXCR2. 23052840_The silencing of the pro-angiogenic chemokine GRO-alpha is proportionally correlated with decreased expression of CXCR2 in pro-inflammatory cytokine-stimulated SGEC indicating the GRO-alpha/CXCR2 complex as a novel therapeutic target for Sjogren's syndrome. 23204236_CXCR2 axis gene expression profiles in human NSCLC cell lines and lung adenocarcinomas defined a cluster driven by CXCL5 and associated with smoking, poor prognosis, and RAS pathway activation. 23293110_VEGFR-2 and PAR-1 polymorphisms predicted longer disease-free survival and overall survival in pancreatic carcinoma. CXCR-2 polymorphism was a negative predictor for disease-free survival. 23389772_findings of the current study suggest a broad involvement of the chemokine GRO-alpha/CXCR2 system in Sjogren's syndrome pathogenesis that is mediated by the involvement of ADAM17 23403077_Gene knockdown of MIF, CXCR2 or CXCL8 disrupts the growth nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumor spheres. 23479735_Chemokine CXCL1 dimer is a potent agonist for the CXCR2 receptor. 23548249_the CXCR-2 +1208 C>T polymorphism is an independent prognostic marker in patients with squamous cell lung carcinoma and is associated with aggressive tumor biology and shorter disease-free survival 23615182_these results indicated that polymorphism in CXCL12G801A and CXCR2(+1208)C/T showed high risk for end-stage renal disease in North Indian population. 23727325_IL-8 and IL-8 receptors were expressed in all types of tumors with variable intensity and subcellular distribution. There was a statistically significant correlation between levels of expression and tumor stage and tumor type. 23758411_CCR6 and CXCR2 were higher in the colorectal metastasis group than in the non-metastasis group, but there was no difference between the lung and liver metastasis subgroups. CXCR4 was not different between the metastasis and non-metastasis groups. 23869868_the cellular senescence caused by CXCR2 upregulation depends on p53 and is mediated by p38 activation. 23912333_Dual antagonism of CXCR2 inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in alveolar macrophages from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. 23972657_overexpression of both CXCL-8 and CXCR-2 may be a useful marker for predicting the outcome in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 24161763_Data indicate that anti-cancer drugs increase the fraction of side population (SP) cells and the production of IL-8 and its receptor in hepatoma cells. 24332572_Data indicate that three genes, namely Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 2 (CXCR2), C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2) and E1A-Binding Protein P400 (EP400), were able to identify HCC individually with accuracies of 82.4%, 78.4% and 65%, respectively. 24338377_High expression of CXCR2 correlates with lymph node metastasis in esophageal carcinoma. 24339979_New conformational state of NHERF1-CXCR2 signaling complex captured by crystal lattice trapping. 24376747_augmentation of proinflammatory chemokines CXCL1/2, by potentiating NF-kappaB activation through EGFR-transactivated Akt, contributes to CXCR2-driven ovarian cancer progression 24430363_polymorphism in CXCR2C1208T and CXCL12G801A showed high risk for breast cancer in north Indian population. However, CCR532 exhibited no association. 24450359_Expression of AP2-sigma2 V88D and V98S dominant negative mutants resulted in loss of CXCR2 mediated chemotaxis 24462138_CXCR1 and CXCR2 (rs4674258C/T, rs1008563C/T, rs6723449T/C) were analyzed for association with IL8 levels and with myocardial infarct risk. 24510965_these results indicate that GRK6 complexes with AGS3-Galphai2 to regulate CXCR2-mediated leukocyte functions at different levels, including downstream effector activation, receptor trafficking, and expression at the cell membrane. 24582495_Blockage of CXCR2 suppresses tumor growth of intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma. 24593195_CXCR2 signaling contributes to the metastatic immunophenotype of renal cell carcinoma cells. 24642259_This study provides an understanding of the structural basis for the PDZ-mediated NHERF1-PLCbeta3 interaction that could prove valuable in selective drug design against CXCR2-related cancers. 24678812_Studies suggest that CXCL8 and CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptorsr may contribute significantly to disease-associated processes, including tissue injury, fibrosis, angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. 24736615_HIV matrix protein p17 is pro-fibrogenic through its interactions both with CXCR2 and syndecan-2 on activated HSCs 24768637_the structural basis for the PDZ domain-mediated NHERF1-CXCR2 interaction 24777453_analysis of mutations in CXCR2 and their role in hematological traits 24883303_IL-8 and CXCR2 expression was distinctly uncommon as opposed to IL-6, VEGF and SOCS-3, which were detected in the vast majority of cases. 24946112_No association was found between the studied genes (IL-8, CXCR1, and CXCR2) and COPD susceptibility but three polymorphisms in the IL-8 gene appear to be involved in a worse progression of the disease. 24972913_The higher expression of IL-8R2 was found in early esophageal carcinoma, which may indicate that IL-8R2 plays an important role and is better prognostic factor in esophageal cancer development. 24989774_Pro-inflammatory cytokines activate CXC receptor-2 stimulated by IL-8 and CXCL1 to induce neutrophil transmigration. 25022956_levels of CXCR1 and CXCR2 proteins were associated with the capacity of gastric cancer cell migration, while knockdown of their expression inhibited gastric cancer cell migration and invasion abilities in vitro. 25172501_In TPA-induced skin inflammation, MIF is released from damaged keratinocytes and then triggers the chemotaxis of CD74(+)CXCR2(+) NKT cells for IFN-gamma production. 25339290_CXCR2 ubiquitination on K327 residue modulates agonist-activated CXCR2 cell sorting and intracellular signaling. 25349304_miR141-CXCL1-CXCR2 signaling-induced Treg recruitment regulates metastases and survival of non-small cell lung cancer. 25412626_ADAM17 induction down-regulates the receptor in an irreversible manner and may serve as a master switch in controlling CXCR2 function. 25456886_our results reveal that circulating concentrations of IL-8 and IL-12 increase along with important vascular threatening traits as fasting serum glucose and VLDL-c, respectively 25462858_our data showed that the CXCR2/CXCL5 axis contributes to EMT of HCC cells through activating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta/Snail signaling, and it may serve as a potential therapeutic target. 25480945_3'UTR SNP modulates CXCR2 expression, signaling, and susceptibility to lung cancer 25484047_Data indicate that the antibodies bound specifically to CXC chemokine receptor-2 (CXCR2) expressing cells. 25484064_Data indicate the antibodies recognized distinct epitopes of CXC chemokine receptor-2 (CXCR2). 25580640_CXCL7/CXCR2 signalling pathways are a predictive factor of poor outcome in metastatic colon cancer. 25620445_we investigated the changes in promoter methylation patterns using methylation arrays and observed that the promoters of immunomodulatory factors, COX2 and PTGES, and migration-related factors, CXCR2 and CXCR4, were hypomethylated after 5-aza treatment 25622052_Data revealed a critical role of a PDZ-based CXCR2 macromolecular complex in EPC homing and angiogenesis. 25682075_Our results demonstrated that resistance to anti-proliferative effects of CXCR2 may also arise from feedback increases in MIP-2 secretion. 25757087_data demonstrate that CXCR2 regulates bone marrow blood vessel repair/regeneration and haematopoietic recovery, and clinically may be a therapeutic target for improving bone marrow transplantation. 25794662_TLR3 stimulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells from human tonsils into follicular dendritic cell-like cells and induces chemokine secretion, possibly by recruiting C-X-C chemokine receptor 2-expressing immune cells. 25837197_The results showed that H. pylori induced the activation of Jak1/Stat3 and IL-8 production, which was inhibited by a Jak/Stat3 specific inhibitor AG490 in AGS cells in a dose-dependent manner 26038959_IL-10 rs1800896,CXCR2 rs1126579 and selected clinical features can be used as markers for septic shock development, but not for decreased survival. 26058729_Study shows that CXCL5 expression is elevated in positive correlation to bladder cancer grade and promotes cell migration and invasion via binding to its receptor CXCR2. 26060478_we found the mRNA level of NF-kappaB and IL-8 was higher in gastric ulcer patients, especially in patients with H.pylori-positive gastric ulcer. 26087179_G31P blockage of CXCR1 and CXCR2 can inhibit human lung cancer cell growth and metastasis 26111149_Data suggest that IL4 and IL8RB loci may have a small-effect genetic impact on the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. 26188847_CXCR2 is a potential independent adverse prognostic biomarker for recurrence and survival of patients with non-metastatic ccRCC after nephrectomy. 26231560_CXCR2 positivity combined with postoperative complications is associated with subsequent tumor recurrence in esophageal cancer. 26267317_Inhibition of IL-8 signalling can enhance response in platinum sensitive and resistant high grade serous ovarian carcinoma. 26287498_CXCR2 expression is enriched in human atherosclerotic coronary artery. 26297794_Serum amyloid A1alpha induces paracrine IL-8/CXCL8 via TLR2 and directly synergizes with this chemokine via CXCR2 and formyl peptide receptor 2 to recruit neutrophils. 26302999_The results showed that the expression of N-Ac-PGP receptors (CXCR1 and CXCR2) in CESCs was upregulated by N-Ac-PGP. 26364720_Data show that long ncRNAs MALAT1 silencing downregulated the expression of the microRNA miR-22-3p target gene CXCR2 and AKT pathway. 26503598_CXCR2-CXCL1 axis is correlated with neutrophil infiltration and predicts a poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma 26519257_Studied the expression of CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathway, its impact on cell proliferation and cytokine expression in human colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells. 26521741_These studies provide direct evidence linking the activation of IL8, DNA demethylation and the induction of the OA process with important therapeutic implications therein for patients with this debilitating disease. 26559818_Data show that trefoil factor-3 (TFF3) secreted from mammary carcinoma cells promotes de novo angiogenesis via interleukin-8 (IL-8)/IL-8 receptor CXCR2. 26648969_The results of this study show that the CXCR2 rs1126579 polymorphism is significantly associated with ischemic stroke, both individually and in combination with the genotype and/or alleles of other chemokine genes. 26771140_High CXCR2 expression is associated with pancreatic cancer. 26827264_Letter: cold temperatures up regulate CXCR2 ligand Il8 in microvascular endothelial cells which may contribute to neutrophil recruitment and inflammation in skin from patients with livedo vasculopathy with winter ulcerations. 26837773_Our findings suggest that CXCL3 and its receptor CXCR2 are overexpressed in prostate cancer cells, prostate epithelial cells and prostat |
ENSMUSG00000026180 |
Cxcr2 |
35.716177 |
0.4673230736 |
-1.097508 |
0.312206128 |
12.387570 |
0.00043220137459793980284905590139032938168384134769439697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001075040830648060514312946978066065639723092317581176757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1042201 |
4.4543294 |
49.7367124 |
6.3079278 |
| ENSG00000180881 |
84698 |
CAPS2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXY5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Calcyphosine-2 is a calcium-binding protein with 2 EF-hand motifs (Wang et al., 2002 [PubMed 11846421]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:84698; |
calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] |
Mouse_homologues 11846421_Discusses cloning of the human homolog of mouse Caps2 (GeneID: 353025). 19238500_The CAPS2-deficient mice show reduced secretion of BDNF and NT-3. And the cerebella of these mice exhibit developmental deficits, such as delayed development. 20302894_CAPS2 KO mice will be a useful animal model to study the aspects of the neuropathology and behavior characteristics of neurodevelopmental disorders 21173225_CAPS2 promotes activity-dependent brain-derived neurotrophic factor secretion during the postnatal period that is critical for the development of hippocampal GABAergic networks. 22111578_CAPS family proteins exert dual roles in DCV trafficking, mediating trafficking at both the secretion site for exocytosis and at the Golgi complex for biogenesis 23615300_possible association of the dense-core vesicle secretion-related gene,CAPS2 with autism specturum disorder. (review) 25437547_Naturally occurring splice variants of CAPS2 in CAPS1/CAPS2-deficient cells were studied and found that CAPS2 primes vesicles independently of its MUN domain. 25754523_These results suggest that Caps2 KO mice have altered endocrine responses to CORT administration, while maintaining CORT-induced anxiety/depressive-like behavior. 28963059_that CAPS2 deficiency strongly impairs hippocampal adult neurogenesis and maturation of newborn neurons 30389842_Epigenetic tuning of CAPS variants may allow modulation of endocrine adrenaline and noradrenaline release 33846232_CAPS2 Deficiency Impairs the Release of the Social Peptide Oxytocin, as Well as Oxytocin-Associated Social Behavior. |
ENSMUSG00000035694 |
Caps2 |
13.040589 |
0.3791876096 |
-1.399016 |
0.450401085 |
9.680624 |
0.00186221364339029908652189959639144944958388805389404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004137629591516004019802199564992406521923840045928955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7633050 |
1.3927080 |
12.7057466 |
2.4502155 |
| ENSG00000180902 |
728294 |
D2HGDH |
protein_coding |
Q8N465 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the oxidation of D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D-2-HG) to alpha-ketoglutarate (PubMed:15070399, PubMed:15609246, PubMed:16037974, PubMed:20020533, PubMed:33431826). Also catalyzes the oxidation of other D-2-hydroxyacids, such as D-malate (D-MAL) and D-lactate (D-LAC) (PubMed:33431826). Exhibits high activities towards D-2-HG and D-MAL but a very weak activity towards D-LAC (PubMed:33431826). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15070399, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15609246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16037974, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20020533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33431826}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;FAD;Flavoprotein;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes D-2hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, a mitochondrial enzyme belonging to the FAD-binding oxidoreductase/transferase type 4 family. This enzyme, which is most active in liver and kidney but also active in heart and brain, converts D-2-hydroxyglutarate to 2-ketoglutarate. Mutations in this gene are present in D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria, a rare recessive neurometabolic disorder causing developmental delay, epilepsy, hypotonia, and dysmorphic features. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:728294; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase activity [GO:0051990]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; 2-oxoglutarate metabolic process [GO:0006103]; malate metabolic process [GO:0006108]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; response to cobalt ion [GO:0032025]; response to manganese ion [GO:0010042]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043] |
16037974_Two novel pathogenic mutations in D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase gene in patient with a mild presentation and asymptomatic siblings with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria with a splice error (IVS4-2A-->G) and a missense mutation (c.1315A-->G;p.Asn439Asp). 19283509_This enzyme assay will have utility in differentiating patients with 2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria and in assessing the residual activities linked to pathogenic mutations in the D2HGDH gene 20727073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20727073_We did not find evidence for mutations in the genes D2HGDH and L2HGDH as an alternative mechanism for raised 2-hydroxyglutarate levels in brain tumours 21625441_D2HGDH mutation is not associated with glioblastoma. 26178471_D2HGDH elevates alpha-KG levels via IDH2 expression modulation, influencing histone and DNA methylation, and HIF1alpha hydroxylation. D2HGDH mutants found in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are enzymatically inert. 27322736_D2HGDH-GAL3ST2 is more frequently seen in prostate cancer samples, and seems to be enriched in African Americans. 30908763_Study presents the functional characterization of 31 D2HGDH missense variants, and the identification of 10 novel variants in a large cohort of patients with D-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria Type I. The functional tests proved effective in classifying missense variants associated with severely impaired D-2-HGDH activity. 31349060_hD2HGDH directly reduces recombinant human ETF, thus establishing a metabolic link between the oxidation of D-2-hydroxyglutarate and the mitochondrial electron transport chain. 32101699_MYC Regulation of D2HGDH and L2HGDH Influences the Epigenome and Epitranscriptome. 32386320_Adult diffuse glioma GWAS by molecular subtype identifies variants in D2HGDH and FAM20C. 34296423_D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase in breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic marker associated with proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000073609 |
D2hgdh |
68.237332 |
0.3761355913 |
-1.410675 |
0.408529409 |
11.390184 |
0.00073833236301981469348887365811151539674028754234313964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001759978307198395344052022082337316533084958791732788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.4292142 |
10.8647864 |
103.3972842 |
20.3637009 |
| ENSG00000180914 |
5021 |
OXTR |
protein_coding |
P30559 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for oxytocin. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor family and acts as a receptor for oxytocin. Its activity is mediated by G proteins which activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. The oxytocin-oxytocin receptor system plays an important role in the uterus during parturition. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5021; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; microvillus [GO:0005902]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; oxytocin receptor activity [GO:0004990]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; peptide hormone binding [GO:0017046]; vasopressin receptor activity [GO:0005000]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; eating behavior [GO:0042755]; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070371]; estrous cycle [GO:0044849]; female pregnancy [GO:0007565]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; heart development [GO:0007507]; lactation [GO:0007595]; maternal behavior [GO:0042711]; maternal process involved in parturition [GO:0060137]; memory [GO:0007613]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; negative regulation of gastric acid secretion [GO:0060455]; positive regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045777]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of norepinephrine secretion [GO:0010701]; positive regulation of penile erection [GO:0060406]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0032230]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; positive regulation of uterine smooth muscle contraction [GO:0070474]; positive regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045907]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by vasopressin [GO:0001992]; response to amphetamine [GO:0001975]; response to anoxia [GO:0034059]; response to cocaine [GO:0042220]; response to cytokine [GO:0034097]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sleep [GO:0030431]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; sperm ejaculation [GO:0042713]; suckling behavior [GO:0001967]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537] |
11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11955056_The role of the N-terminus of the oxytocin receptor in high-affinity agonist binding has been characterized in detail, revealing that a single residue, Arg34, provides the agonist-specific epitope within this domain. 12126740_oxytocin receptors are present on human osteoblast-like cells; when oxytocin binds, it decreases IL-6 production, which may affect bone metabolism in humans 12161007_identification, localization and functional activity of oxytocin receptors in epididymis 12166628_estradiol and progesterone not only regulate oxytocin receptor expression and binding in normal mammary myoepithelium but also in malignant mammary cell lines 12270111_expressed in osteoclast cell cultures 12810550_oxytocin receptor activation of a Gbetagamma-mediated pathway as a consequence of Galpha(q) activation in myometrium and OTR-COSM6 cells that results in increased ERK1/2-P. 12843193_Oxytocin receptor is spatially regulated, with significantly greater expression in the fundal region of the uterus at term 12955084_depending on their localization, oxytocin receptors transactivate EGFR and activate ERK1/2 using different signalling intermediates. The final outcome is a different temporal pattern of EGFR and ERK1/2 phosphorylation 14664707_Oxytocin receptor forms homodimers and oligomers in the cell model used and that these oligomers are present at the cell surface. 14691010_Oxytocin receptor is expressed in penis ata concentration similar to that present in other portions of male genital tract and mediates corpus cavernosum contractility. 14749664_Oxytocin receptor antagonist reduced peak tension to 43%+/-12% of its original value without affecting peak calcium. 15035619_Three amino acids in the hydrophilic face of helix 8 of OTR are important to its role in preserving the receptor conformation that is necessary for ligand binding and stimulation of G-protein-mediated phospholipase C activation. 15044599_Data demonstrate that the dynamics of oxytocin receptor expression can be modulated by stimulation with estradiol and oxytocin in both the pregnant and non-pregnant uterus. 15089975_the oxytocin receptor localization in lipid rafts enriched in caveolin-1 turns the inhibition of cell growth into a proliferative response, eliciting different epidermal growth factor receptor/mitogen-activated protein kinase activation patterns. 15089977_the human oxytocin receptor forms dimeric and oligomeric complexes in vivo in intact living cells, and that these complexes exist at the cell surface level. 15093695_OT and OT-receptor mRNAs are expressed throughout the GI tract 15591449_Oxytocin receptor is highly expressed in the penis during fetal life and modulates migration and proliferation of its smooth muscle cells. 15705593_atosiban acts as a 'biased agonist' of the human oxytocin receptors 15831296_Oxytocin receptor is expressed in smooth muscle cells and epithelial cells of peritoneal endometriotic lesions and ovarian endometriotic cysts 15992526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16042376_The oxytocin receptor DRY motif, besides playing a crucial role in receptor activation, may also be implicated in receptor promiscuity 16333859_molecular dynamics analysis of mechanism of desmopressin binding in vasopressin V2 receptor versus vasopressin V1a and oxytocin receptors 16888077_results suggest elevation of IL1 in myometrium at the end of pregnancy initiates process of down-regulation of oxytocin receptors in advanced labour resulting in desensitization of the myometrium to elevated levels of oxytocin in blood during lactation 16966388_increasing cell cholesterol levels is not sufficient per se to affect OTR signaling 17148753_Specific amino acids in the RVSSVKL segment in the COOH-terminal region of the third intracellular domain of oxytocin receptor influence the ability of OTR to activate G protein-mediated actions. 17383819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17383819_These findings provide support for association of OXTR with autism in a Caucasian population. 17492653_Changes in prostatic concentrations of oxytocin (OT) that occur with aging and malignant disease may act to facilitate cell proliferation. Localization of oxytocin receptor within the plasma membrane modulates OT's proliferative response in the prostate. 17726073_Melatonin, like oxytocin, can negatively regulate oxytocin receptor transcription in human myometrial cells via modulation of protein kinase C signaling 17728669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17893705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17893705_This study showing that SNPs and haplotypes in the OXTR gene confer risk for ASD. 17939166_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17939166_study is the first to report associations between AVPR1A and OXTR genetic variation with life history traits in humans 17952758_OTR staining occurred in most of these cells in myomas, while controls contained only scattered cells positive for OTR 18082926_A lower oxytocin receptor gene expression at mid-cycle could be involved in the aetiology of primary dysmenorrhoea. 18207134_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18207134_The resulting pattern of findings confirmed the hypotheses of the significance of the genes involved in the development of affiliative behaviors in the manifestation of ASD, the strongest results were obtained for allelic associations with the OXTR genes. 18312604_Androgen dependent prostate growth in benign prostate hyperplasia may be linked to the interaction of androgen binding protein and oxytocin receptor, associated with caveolin 1 19001515_Melatonin synergizes with oxytocin to promote myometrial cell contractions in vitro, which in vivo would promote coordinated and forceful contractions of the late term pregnant uterus necessary for parturition. 19015103_Controlling for maternal education, depression and marital discord, OXTR genes were significantly associated with maternal sensitivity. Mothers with OXTR AA or AG genotypes were less sensitive than mothers with the GG genotype. 19015103_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126785_OTRs are capable of very efficient and complete resensitization due to receptor recycling via the rab4/rab5 short cycle 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19347709_Oxytocin, its receptor and the PGF(2alpha) receptor are involved in the regulation of labour through a paracrine mechanism. 19376182_A role is supported for oxytocin receptor haplotypes in the generation of affectivity, emotional loneliness and intelligence quotient. 19376182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423652_oxytocin receptor responsiveness is regulated by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 in human myometrial smooth muscle 19461999_The gene encoding the related oxytocin receptor (OXTR) was tested for association with the Dictator Game and a related paradigm, the Social Values Orientation (SVO) task. 19515497_A significant novel association of the SNPs 6930G>A and 9073G>A within the OXTR gene with unipolar depressive disorder was found. 19515497_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19777562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19777562_genetic variation in the OXTR gene might be relevant in the etiology of autism on high-functioning level 19845972_These data provide further evidence for the role of OXTR and the oxytocin signaling pathway in the etiology of autism and, for the first time, implicate the epigenetic regulation of OXTR in the development of the disorder. 19934046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934046_a naturally occurring genetic variation of the oxytocin receptor relates to both empathy and stress profiles 19943975_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20094064_OXTR has a significant role in conferring the risk of autism spectrum disorder in the Japanese population. 20094064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20096818_OTR and TRPV1 may be involved in dysmenorrhea and its severity in adenomyosis 20097922_Immunoreactive OTR was found in the corpus luteum and granulosa cells of large and, surprisingly, also small pre-antral follicles of the ovary. 20196918_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20196918_The variants in the OXTR were nominally associated with severity of overall symptoms accessed using the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (rs237885, rs237887) as well as on the improvement of the positive symptoms (rs11706648, rs4686301, rs237899). 20303388_Data presented here does not support the role of common genetic variation in OXTR in the aetiology of autism spectrum disorders in Caucasian samples 20303388_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20347913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20347913_Oxytocin receptor polymorphisms were associated with social cognitive impairments in attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. 20400491_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20400491_This is the first study to suggest effects of OXTR genotype on physiological reactivity to infant crying. 20413116_Possible roles of oxytocin receptor and vasopressin-1alpha receptor in the pathomechanism of dysperistalsis and dysmenorrhea in patients with adenomyosis uteri. 20436377_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20488544_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20488544_The findings suggest that an OXTR haplotype is associated with a discrete depressive temperament. Clarification of the biological basis of this temperamental trait may help to elucidate the pathophysiology of depressive disorder. 20547007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20547038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20585395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20647384_present multimodal imaging data implicating OXTR in hypothalamic-limbic circuits critical for emotion regulation and sociality in humans. 20670427_Inflammatory cytokines modulate the expression of functional oxytocin receptors in airway smooth muscle. 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20708845_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20708845_The potential importance of this OXTR gene polymorphism in the etiology of depression and anxiety disorders. 20711752_Significantly different oxytocin baseline concentrations and oxytocin receptor expressions between fertile and infertile men strongly suggest that oxytocin/oxytocin receptor system is likely to be linked with male infertility 20724662_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20724662_findings suggest that OXTR rs53576 is sensitive to input from the social environment, specifically cultural norms regarding emotional social support seeking 20832055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20832055_The rs2254298A allele of OXTR was significantly associated with larger bilateral amygdala volume and larger the number of rs2254298A alleles an individual had, the larger their amygdala volume. 20926803_The increased ability of human amnion to produce prostaglandins in response to OXT treatment suggests a complementary role for the OXT/OXTR system in the activation of human amnion and the onset of labor. 21090345_Significant differences in the content of OT and expression of OTR between fertile and infertile men suggested an association of OT with male infertility. 21208749_Girls homozygous for the G allele were characterized by smaller volumes of both left and right amygdala than were carriers of the A allele. 21561435_Cholesterol induced both a changed orientation and a decreased distance of the receptor-bound ligands, suggesting a more compact receptor state in association with cholesterol. 21734268_The synergistic regulation of human oxytocin receptor promoter by CCAAT/ enhancer-binding protein and RELA may play a role in the regulation of genes involved in the labor process. 21876222_Comparative analysis of human and canine OXTR amino acid sequence revealed that the biggest difference between the two proteins is a five-amino-acid fragment, which is present in the human but absent in the canine receptor. 21896752_The effects of OXTR on depressive symptoms may be largely mediated by the influence of OXTR on psychological resources. 21934640_concluded that in this sample, 10 SNPs in the OXTR gene were not significantly associated with conduct disorder 21963428_physical interactions between oxytocin receptor and beta(2)adrenergic receptor in the context of a new heterodimer pair lie at the heart of observed allosteric effects 21964067_The present demonstration of a novel beta(2)adrenergic receptor-coupled signalling pathway that is dependent on oxytocin receptor co-expression is suggestive of a molecular interaction between the two receptors 21984889_[review] The distribution of the OT receptor (OTR) system in both the brain and periphery is far-reaching and its expression is subject to changes over the course of development. 22015110_results suggest an association between variation in OXTR and human pair-bonding and other social behaviors. 22084107_Individuals homozygous for the G allele of OXTR were judged to be more prosocial than carriers of the A allele. 22123970_A common single nucleotide polymorphism (rs53576) in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) might interact with stress-protective effects of social support. 22146101_Oxytocin receptor A carrier males had higher levels of resting sympathetic cardiac control as compared to their G/G counter parts. However, G/G participants displayed significantly higher levels of sympathetic reactivity topsychological stress. 22212599_Oxytocin receptor (OXTR) is not associated with optimism 22294460_However, the haplotype consisting of the OXTR_rs237885 A allele and OXTR_rs2268493 A allele was associated with significantly higher callous-unemotionals cores than other haplotypes. 22296985_participants were genotyped for a functional polymorphism (rs2268498) in the promoter region of the OXTR gene. carriers of the C-allele rated accidentally committed harm as significantly more blameworthy than non-carriers 22336563_Reduced plasma oxytocin and both OXTR and CD38 risk alleles were related to less parental touch 22357335_natural variants of OXTR associated with trait empathy; specifically, individuals with certain OXTR genotype did perform better on trait empathy, while others did not 22372486_OXTR single nucleotide polymorphisms rs6770632 and rs1042778 may be associated with extreme, persistent and pervasive aggressive behaviours in females and males, respectively. 22421562_the region of the OXTR gene including both the rs4564970 and the rs1488467 polymorphisms may be involved in the regulation of the relationship between alcohol and aggression as well as between alcohol and the propensity to react to situations with anger. 22457427_greater perceived threat predicted engagement in fewer charitable activities for individuals with A/A and A/G genotypes of OXTR rs53576, but not for G/G individuals 22487732_We did not observe any association between the genotypes or alleles of the selected SNPs within COX-2 and OXTR genes and treatment resistance, response and remission in the whole sample 22510359_The present review article seeks to further strengthen the argument in favour of the differential susceptibility theory by incorporating findings from behavioural and neuroanatomical studies in relation to genetic variation of the oxytocin receptor gene. [Review] 22563705_Mothers with the GG genotype of OXTR rs53576 show greater differential maternal sensitivity across varying levels of interparental conflict. 22651577_Oxytonergic gene variants appear to be involved in schizophrenia vulnerability. 22763666_Infants' faces were more strongly preferred following oxytocin inhalation; this effect was only observed for participants homozygous for the OXTR rs53576G genotype 22809402_This study adds further evidence to the hypothesis that genetic variations in the OXTR modulate mind-reading and social behaviour. 22882465_study found a heterozygote effect on one SNP in the oxytocin receptor gene (rs75775), so that individuals heterozygous for this SNP had elevated risk for premature ejaculation symptoms compared with carriers of either homozygote 22892716_Decrease in DNA methylation of the OXTR and subsequent increase in expression may be a potential mechanism supporting physiological recovery after acute stress on an epigenetic level. 22986294_this mini-review integrates recent accumulating evidence about human behavioral and neural correlates of OXTR--REVIEW 22999795_Oxytocin receptor overexpression in myometrial smooth muscle cells may be responsible for increased uterine contractility and adenomyosis-associated dysmenorrhea. 23040540_We conclude that molecular studies are warranted to elucidate functional consequences of OXTR variants that have shown stable associations with sociobehavioral phenotypes 23089921_A combination of three oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms is associated with an increased risk for preterm birth. 23219106_supportive evidence for the association between OXTR and the clinical phenotypes of autism spectrum disorders 23252931_The present study did not provide supportive evidence for the contribution of OXTR to susceptibility to schizophrenia in a Japanese population. 23284802_Our preliminary findings support hypotheses about an involvement of OXTR rs2254298 in emotional empathy in schizophrenic and healthy individuals, warranting independent replication. 23354128_Oxytocin receptor gene and prosocial behavior interaction modulates the association between stress and physical health. 23355275_Oxytocin receptor, but not connexin-43, expression is related to BMI, suggesting an alteration in oxytocin receptor expression or function related to obesity 23470776_The functioning of females was most affected by negative social environments regardless of stress, whereas the functioning of males was differentially susceptible to stress depending on OXTR genotype and negative social environments 23547247_Study revealed that three specific haplotypes on OXTR were associated with emotional reactions after an experimental betrayal of trust in an iterated Prisoner's Dilemma Game 23562248_Initial evidence that the capacity to respond to suggestions for altered internal experience (hypnosis) is influenced by the oxytocin receptor gene. 23637833_OXTR SNP rs237885 did not associate with maternal behavior, but it did associate with pre-natal (but not post-natal) depression score. 23653389_Dysfunctional labor patterns and increased oxytocin utilization seen in obese women may not be due to differences in OXTR expression. 23678036_Data from cultured myometrial cells from pregnant women undergoing elective cesarean section suggest that PGF2alpha increases expression of OTR in lower segment of uterus and decreases expression of OTR in the upper segment. 23684879_Our findings identify gender-dependent mechanisms of OXTR rs53576 gene variation impacting the functional connectivity of the hypothalamus in healthy individuals 23708061_The results of this study highlight possible neural pathway by which a naturally occurring variation of the OXTR gene may affect an anxiety-related temperamental trait in female subjects by modulating prefrontal-amygdala functional connectivity. 23731038_The continuity of attachment security from infancy into young adulthood is moderated by OXTR genetic variation. 23838880_The relations between OXTR and loneliness were examined, as well as interactions between OXTR and sex, parental support, 5-HTTLPR genotype, and DRD2 genotype. 23863476_Genotype differences in a polymorphism in the oxytocin receptor gene rs1042778 predicted creative ideation in young adults 23889750_Maternal OXTR missense single nucleotide polymorphisms rs4686302 and rs237902 may have gestational age-dependent effects on prematurity. 23915847_Recent progress in molecular biology has augmented our knowledge about OTR regulation in the uterus at the transcription level, although the totality of preparation for labor through OTR expression is still obscure. 23921259_Two of the most intensively studied OXTR SNPs (rs53576 and rs2254298) failed to explain a significant part of human social behavior. 23946005_These results show that decreased volume of the insula is a neuroanatomical correlate of ALTs and a potential intermediate phenotype linking autistic-like traits with OXTR in male subjects. 23974948_The results of this study the OXTR as potential biomarkers for research on disorders of social dysfunction and the neurobiology of empathy. 24059750_We conclude that polymorphic variation of the OXTR characterizes children with high levels of callous-unemotional traits and conduct problems. 24120094_Findings suggest that the OXTR-genotype rs237915 moderates risk for social and emotional problems after stressful experiences and that this effect is partly mediated by genotype-dependent sensitivity to the reinforcement value of negative social cues 24128365_Carriers of the T-allele exhibited more accurate recognition skills than subjects carrying the CC-genotype 24209975_A significant gender-heterogeneous effect was identified in one OXTR SNP on dichotomized social connectedness; rs4686302 T allele was nominally associated with social connectedness in men, whereas the association direction was opposite in women 24223720_A relation was found between the OXTR rs53576 variant and state loneliness, in girls only. 24295535_These findings support the importance of the oxytocin receptor variation in emotional and physiological reactions to the affective experiences of other conspecifics 24367110_A common SNP in the oxytocin receptor (rs237887) was strongly associated with recognition memory in combined probands, parents, and siblings after correction for multiple comparisons. 24393355_findings obtained from an imaging-genetics approach provided preliminary evidence for the association between OXTR and neuronal function in the MTL in ASD individuals. 24454713_gene-behavior association analysis suggests that oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms have an impact in both breeds on (i) proximity seeking towards an unfamiliar person, as well as their owner, and on (ii) how friendly dogs behave towards strangers 24458227_results do not contradict the hypothesis of associations between personality traits and oxytocin-related gene variants; however, there are no statistically significant associations after correcting for multiple testing. 24523928_Epigenetic misregulation of the OXTR gene may be implicated in anorexia nervosa 24618689_Early caregiving combined with genetic liability along the axis of vasopressin-oxytocin gene pathways: G x E contributions to PTSD. 24621820_personality, behavior and environmental features associated with OXTR genetic variants 24660771_Women, but not men, with high levels of poststressor OT and the GG genotype of rs53576 felt the most positive affect after the stressor. 24703166_OXTR genotype may partially account for the transmission of maternal depression to youth and support the role of dysfunctional social processes 24749639_Mothers and GG allele carriers of the OXTR gene showed an early latency (~100 ms) differential frontal ERP response to strong intensity facial expressions, and mothers also showed modulation of the posterior EPN waveform by negative valence. 24814480_the combination of rs2254298(A/G) and rs53576(G/G)in oxytocin receptor gene confers a deleterious effect on social cognition 24836510_study does not support the contribution of rare non-synonymous OXTR variations to ASD susceptibility in the Japanese population. 24916666_variability in rs11131149 was significantly associated with social cognition. 25001970_OXTR rs53576 is connected with the striatal Dopamine transporter availability in vivo and modulates the interactions between the oxytocinergic and dopaminergic systems. 25003328_OXTR polymorphism interacts with social stress to predict antisocial outcomes in at-risk adolescents. 25047302_In children with borderline personality symptoms, there were significant maltreatment X OXTR X gender interactions. 25092245_This current meta-analysis demonstrated that the association of OXTR with autism spectrum disorder and the findings suggest directions for future studies of the etiology of autism spectrum disorder. 25199917_First longitudinal study to examine the role of environmental risk exposure and OXTR methylation in the development of callous-unemotional traits for youth low vs high in internalizing problems 25244972_The findings of this study provided preliminary support for the involvement of genetic variants of the OXTR in social cognitive impairments in schizophrenia. 25262417_These results support the hypothesis that the oxytocin system plays a role in the pathophysiology of mood and anxiety disorders 25309987_Carriers of both the T allele of OXTR rs1042778 and the C allele of clock rs1801260 showed the lowest total prosocial tendency scores compared with the other groups. the clock gene and OXT/AVP systems are intertwined and contribute to human prosociality. 25326040_OXTR variation modulates levels of social support via proximal impacts on individual temperament. 25403479_Our findings suggest an association between genetic variation in OXTR and endorsement of prosocial behavior indirectly through prosocial tendencies, and that the pathway is dependent on the type of prosocial behavior and gender. 25419912_Mothers' OXTR genotype predicted her warmth toward her children, even after controlling for child genotype. This association was not found for fathers. 25476609_examined associations between polymorphisms in OXTR and AVPR1a and individual differences in emotional and cognitive empathy 367 young adults; emotional empathy was associated solely with OXTR, whereas cognitive empathy was associated solely with AVPR1a 25563749_Results suggest that OXTR hypomethylation is associated with social anxiety disorder (SAD) and social phobia-related traits potentially reflecting a decreased oxytocin tone to be pathogenetically relevant in SAD 25564674_The data support the view that the presence of the G allele of OXTR not only promotes prosocial behaviors but also favors sensitivity to a negative social stressor 25593022_OXT activation of the OXTR occurs in the posterior retina and that this may serve as a paracrine signaling pathway that contributes to communication between the cone photoreceptor and the RPE. 25622005_boys and girls of depressed mothers who carried the Oxytocin Receptor rs53576 GG genotype exhibited increased sensitivity for sad faces and decreased sensitivity for happy faces. 25627343_In normal uteri, the expression of oxytocin The expression pattern of oxytocin receptor in the normal junctional zone of the uterus is disrupted in women with adenomyosis. 25637390_two variants of OXTR rs53576 are associated with racial ingroup bias in brain activities that are linked to implicit attitude and altruistic motivation 25640833_Religion impacts self-control in a social context, and whether this effect differs depending on the genotype of an oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) polymorphism (rs53576). 25646574_The present study investigated the association between the rs2268498 polymorphism on the OXTR gene and social perception abilities as measured by the interpersonal perception. 25675509_variability in OXTR methylation impacts social perceptual processes often linked with oxytocin, such as perception of facial emotions. 25680993_there were stronger associations between interdependence and empathic neural responses in the insula, amygdala and superior temporal gyrus in G/G compared with A/A carriers. 25687563_Fetal membranes from preterm birth show differences in OXTR methylation, regulation and expression. Epigenetic alteration of this gene in preterm birth fetal membrane may be indicating an in utero programing and a link to autism spectrum disorders. 25773927_a positive association between the G allele of OXTR rs53576 and bulimia nervosa 25890851_This study suggests that OXTR exon 1 methylation in particular is associated with phenotype traits such as depression. 25935637_variation in the OXTR gene was found to interact with 2D:4D to predict men's (but not women's) performance in a cognitive empathy task. 25968600_Study identified, in OXTR and AVPR1A genes, signatures of balancing selection in the cis-regulative acting sequences such as transcription factor binding and enhancer sequences, as well as in a transcriptional repressor sequence motif. Additionally, in the intron 3 of the OXTR gene, the SNP rs59190448 appears to be under positive directional selection. 25977357_Using a family-based association design, it was suggestive that a particular OXTR variant (rs11131149) interacted with maternal cognitive sensitivity on children's ToM 26061800_Low maternal care in childhood was associated with greater DNA methylation in an OXTR target sequence in blood cells in adulthood. 26106053_OXTR polymorphisms may be a useful intermediate endophenotype to consider in the treatment of patients with anorexia nervosa. 26110343_data suggest that G allele carriers of the OXTR might be more vulnerable to panic and major depressive disorder. 26121678_genetic variation in the rs53576 influences general sociality; however, the study did not detect significant genetic association between rs53576 and close relationships (Cohen's d = 0.01, p = .64)(Meta-Analysis) 26178189_sex differences in oxytocin effects on social cooperation are specific to individuals with OXTR rs53576 GG genotype. 26228411_The oxytocin receptor (OXTR, rs53576) was associated with increased risk for comorbid depressive and disruptive behavior disorders. 26241486_The study tested the hypothesis that variation in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR rs53576) and self-report of rejection sensitivity are associated with adrenocortical reactivity to social stress. 26365303_In this study, authors examine the association between the OXTR gene and a specific social phenotype within ASD 26389606_there was no evidence that OXTR rs53576 moderated the association between attachment security during early childhood and overall coherence of mind ('security') during the Adult Attachment Interview at age 18 years. 26390829_the rs7632287 AA genotype was associated with higher frequency of antisocial behavior in boys. We conclude that the rs7632287 and rs4564970 polymorphisms in OXTR may independently influence antisocial behavior in adolescent boys. 26406593_Results show that genetic variants in the oestrogen receptor alpha and the oxytocin receptor may be associated with an increased risk of oesophageal adenocarcinoma and Barrett's oesophagus. 26444016_results indicate that the OXTR genotype affects attitudinal trust as part of an individual's relatively stable disposition, and further affects behavioral trust through changes in attitudinal trust. 26477647_The found of this study underscore a series of relations among a common oxytocin receptor gene variant, early life stress exposure, and structure and function of the amygdala in early life. 26488131_The OXTR rs53576 genotype and attachment style are on social anxiety possibly constituting a targetable combined risk marker of social anxiety disorder. 26506050_Variants of OXTR have been linked to individual differences in psychological and physiological response patterns to stress and social information. 26599592_These findings suggest that genetic variations in the oxytocin receptor gene may not explain a significant part of alexithymia in patients with obsessive-compulsive disord |
ENSMUSG00000049112 |
Oxtr |
9.361279 |
0.3887637247 |
-1.363034 |
0.515329652 |
7.060220 |
0.00788143121264520477020631972209230298176407814025878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015434513028876637591446652209015155676752328872680664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5555512 |
1.8363338 |
14.4044089 |
2.8739028 |
| ENSG00000180938 |
137209 |
ZNF572 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z3I7 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:137209; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
9.966089 |
0.3625787300 |
-1.463634 |
0.561917863 |
6.837706 |
0.00892533950676916397470872510666595189832150936126708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017263531793986746504243612321261025499552488327026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1953994 |
1.9380414 |
14.3047609 |
3.3886332 |
| ENSG00000180998 |
283554 |
GPR137C |
protein_coding |
Q8N3F9 |
FUNCTION: Lysosomal integral membrane protein that may regulate MTORC1 complex translocation to lysosomes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31036939}. |
Glycoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of TORC1 signaling. Located in lysosomal membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:283554; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; positive regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904263] |
|
ENSMUSG00000049092 |
Gpr137c |
19.337107 |
0.3854266313 |
-1.375472 |
0.350908897 |
15.908842 |
0.00006646748782622002426484497661363093357067555189132690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000188194920451756678419358292941865329339634627103805541992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.7526267 |
2.8625860 |
30.6549647 |
4.7461600 |
| ENSG00000181004 |
166379 |
BBS12 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZW61 |
FUNCTION: Component of the chaperonin-containing T-complex (TRiC), a molecular chaperone complex that assists the folding of proteins upon ATP hydrolysis. As part of the TRiC complex may play a role in the assembly of BBSome, a complex involved in ciliogenesis regulating transports vesicles to the cilia (PubMed:20080638). Involved in adipogenic differentiation (PubMed:19190184). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19190184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20080638}. |
Bardet-Biedl syndrome;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Obesity;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex that is involved in membrane trafficking. The encoded protein is a molecular chaperone that aids in protein folding upon ATP hydrolysis. This protein also plays a role in adipocyte differentiation. Defects in this gene are a cause of Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 12. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:166379; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly [GO:0051131]; eating behavior [GO:0042755]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; intraciliary transport [GO:0042073]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of stem cell differentiation [GO:2000737]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863] |
17160889_BBS12 accounts for approximately 5% of all BBS cases and defines a novel branch of the type II chaperonin superfamily 19190184_the BBS10 and BBS12 proteins are located within the basal body of this primary cilium and inhibition of their expression impairs ciliogenesis, activates the GSK3 pathway, and induces PPAR nuclear accumulation, hence favoring adipogenesis 20472660_Using sequence analysis, the role of BBS6, 10 and 12 was assessed in a Bardet-Biedl syndrome patient population comprising 93 cases from 74 families. 20827784_Mutation in BBS12 accounts for Bardet-Biedl syndrome and termination of pregnancy of a fetus. 22958920_BBS12 inactivation increases glucose absorption by mature human adipocytes, increases insulin sensitivity, enhances glucose absorption and increases triglyceride content. 24611592_novel BBS12 mutations in Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients in Spain |
ENSMUSG00000051444 |
Bbs12 |
16.358330 |
2.7596743167 |
1.464498 |
0.414436307 |
12.701850 |
0.00036529395863397015218818064674621837184531614184379577636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000920091950415938492416345617641582066426053643226623535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.2585072 |
6.5043478 |
8.8514846 |
1.8974693 |
| ENSG00000181007 |
284406 |
ZFP82 |
protein_coding |
Q8N141 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284406; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
22580414_ZNF545 acts as a functional tumour suppressor in gastric cancer by inhibiting rRNA transcription. 25360542_ZNF545 inhibits breast tumor cell proliferation through inducing apoptosis and is disrupted by promoter methylation in breast cancer. 25714013_These findings indicated that the methylated CpG sites of the ZNF545 promoter could be used for the clinical prediction of the prognosis of gastric cancer 28677721_the results suggested that ZNF545 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer and is frequently inactivated by promoter methylation. 30211622_ZFP82 is a tumor suppressor and is disrupted by promoter CpG methylation during esophageal carcinogenesis. 31165610_ZNF545 protein promoted the apoptosis of myeloma cells. |
ENSMUSG00000098022 |
Zfp82 |
80.730288 |
5.4589420317 |
2.448621 |
0.946686081 |
5.962326 |
0.01461474806893216411840530355448208865709602832794189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027018401049354188320217318164395692292600870132446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.3556483 |
53.6711345 |
10.8268135 |
6.5888720 |
| ENSG00000181026 |
64782 |
AEN |
protein_coding |
Q8WTP8 |
FUNCTION: Exonuclease with activity against single- and double-stranded DNA and RNA. Mediates p53-induced apoptosis. When induced by p53 following DNA damage, digests double-stranded DNA to form single-stranded DNA and amplifies DNA damage signals, leading to enhancement of apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16171785, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18264133}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;DNA damage;Exonuclease;Hydrolase;Nuclease;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Enables exonuclease activity. Involved in intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator and response to ionizing radiation. Located in nuclear membrane; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:64782; |
nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; exonuclease activity [GO:0004527]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator [GO:0042771]; response to ionizing radiation [GO:0010212] |
18264133_AEN is an important downstream mediator of p53 in apoptosis induction in cancer. 20429933_identification of ISG20L1 as a p53 family target and discovery that modulation of this target can regulate autophagic processes further strengthens the connection between p53 signaling and autophagy |
ENSMUSG00000030609 |
Aen |
235.974807 |
2.8895450839 |
1.530842 |
0.105302558 |
217.137501 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000038087787739247733025778350540264078916901460785817667669861102465477602265445743517800568749741453477859019319965953192814317462833173522085417062044143676757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007962829278063689448194856469402593512110340006945487826800533386866044733653707033126693456824149439837397904042883939020394667984703573893057182431221008300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
356.9636789 |
22.3408287 |
124.4085989 |
6.3787904 |
| ENSG00000181045 |
284129 |
SLC26A11 |
protein_coding |
Q86WA9 |
FUNCTION: Exhibits sodium-independent sulfate anion transporter activity that may cooperate with SLC26A2 to mediate DIDS-sensitive sulfate uptake into high endothelial venules endothelial cells (HEVEC). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12626430}. |
Anion exchange;Cell membrane;Ion transport;Lysosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the solute linked carrier 26 family of anion exchangers. Members of this family of proteins are essential for numerous cellular functions including homeostasis and intracellular electrolyte balance. The encoded protein is a sodium independent sulfate transporter that is sensitive to the anion exchanger inhibitor 4,4'-diisothiocyanostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:284129; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; anion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008509]; secondary active sulfate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008271]; sulfate transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015116]; ion transport [GO:0006811]; sulfate transport [GO:0008272] |
21752829_SLC26A11 protein localizes in lysosomes in HeLa cells |
ENSMUSG00000039908 |
Slc26a11 |
65.202439 |
2.6814837545 |
1.423032 |
0.256181516 |
30.732566 |
0.00000002961526539795278693584747371249366043599593467661179602146148681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000123224452580780174740113447687250847195628011832013726234436035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.3783895 |
16.3312639 |
37.4290177 |
4.7392226 |
| ENSG00000181104 |
2149 |
F2R |
protein_coding |
P25116 |
FUNCTION: High affinity receptor for activated thrombin coupled to G proteins that stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis. May play a role in platelets activation and in vascular development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10079109}. |
3D-structure;Blood coagulation;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Coagulation factor II receptor is a 7-transmembrane receptor involved in the regulation of thrombotic response. Proteolytic cleavage leads to the activation of the receptor. F2R is a G-protein coupled receptor family member. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:2149; |
caveola [GO:0005901]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet dense tubular network [GO:0031094]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; G-protein alpha-subunit binding [GO:0001965]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; thrombin-activated receptor activity [GO:0015057]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell-cell junction maintenance [GO:0045217]; connective tissue replacement involved in inflammatory response wound healing [GO:0002248]; dendritic cell homeostasis [GO:0036145]; establishment of synaptic specificity at neuromuscular junction [GO:0007529]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of glomerular filtration [GO:0003105]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of renin secretion into blood stream [GO:1900134]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; platelet dense granule organization [GO:0060155]; positive regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030194]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051281]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; positive regulation of smooth muscle contraction [GO:0045987]; positive regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045907]; protein kinase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007205]; regulation of blood coagulation [GO:0030193]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; trans-synaptic signaling by endocannabinoid, modulating synaptic transmission [GO:0099553] |
11816709_Though PAR1 is insufficient to induce metastasis in cells with low TF expression, it enhances the metastatic potential of cells with high TF expression, indicating a possible synergy between TF and PAR1 in promoting metastasis. 11888681_Proteolytic activation of PAR1 is required for thrombin stimulation and the control of angiogenic processes in tissue repair. 11907122_When expressed in respiratory epithelial cells and cell lines, protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR1)induces the release of IL-6, IL-8, and PGE2. 11964083_PAR-1 is upregulated in pancreatic cancer 11986954_CLL B cells consistently express thrombin receptor mRNA; co-expression of angiogenic molecules and receptors suggest autocrine pathways of stimulation. 12023853_Role of thrombin and its major cellular receptor, protease-activated receptor-1, in pulmonary fibrosis. Review. 12039967_a novel role for Go proteins in the signal transduction of thrombin receptors in HMECs (human microvascular endothelial cells) that regulates calcium signaling 12052963_target for endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR)-dependent activated protein C(APC) signaling, suggesting a role for this receptor cascade in protection from sepsis 12058063_down-regulation is controlled by sorting nexin 1 12084570_These data suggest that an untranslated RNA plays a role in PAR-1 gene expression during embryonic growth. 12195707_Both PAR1 and PAR2 upregulate COX-2, but not COX-1, expression in HUVEC cells 12370395_PAR1-mediated proinflammatory cytokine release from respiratory epithelial cells in vitro is inhibited by pretreatment with house dust mite allergen Der p 1. 12372769_stimulation of PAR-1 or PAR-2 on HUR leads to iPLA(2)-catalyzed phospholipid hydrolysis, resulting in the production of metabolites that may mediate inflammation or provide cytoprotection to the bladder. 12406873_The number of PAR-1 receptors on the platelet surface is associated with the intervening sequence IVSn-14 A/T intronic variation, and it was also found to govern the platelet response to the SFLLRN agonist in terms of aggregation & P-selectin expression. 12505789_Thrombin upregulates COX-2-derived prostaglandin E2 synthesis by both catalytic cleavage of PAR1 and bFGF-dependent noncatalytic activity 12534282_PAR1 is a primary mediator of RhoA activation, signaling, and cytoskeletal reorganization when expressed on LNCaP prostate cancer cells. 12586611_data suggest that activated protein C regulates calcium concentration in human brain endothelium and in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by binding to endothelial protein C receptor and signaling via protease activated receptor-1 12594292_Activation and up-regulation of PAR1 is tightly coupled to brain inflammation and neuronal damage during HIV-1 infection. 12637343_Review. PAR1 expression correlates with the invasion properties of breast carcinoma. Part of the molecular mechanism of PAR1 invasion involves the formation of focal contact complexes on PAR1 activation. 12707033_the aberrant expression of the functional thrombin receptor PAR-1 in colon cancers and its important involvement in cell proliferation and motility 12737439_gastric epithelial cells express thrombin receptors and that these receptors may play a protective role in the gastric mucosa. 12789289_This review focuses on the role of the thrombin receptor in melanoma and its regulation by AP-2. 12805069_differentiation of human monocytes is associated with differential expression of functionally active PARs that mediate distinct regulatory functions in inflammation and atherogenesis. 12832443_PAR1 could be clearly detected on the surface of eosinophils, however thrombin had no effect on eosinophil function 12883880_PAR-1 mediates the proliferation-modulating effects of thrombin on prostate cancer cells. 12975361_analysis of the PAR-1 promoter regions bp -365 to -329 and bp -206 to -180 demonstrated that Sp1 was predominantly bound to the PAR-1 promoter in metastatic cells, whereas AP-2 was bound to the PAR-1 promoter in nonmetastatic cells. 13680213_Our data suggest that thrombin/PAR-1 may inhibit Sp1-dependent HCMV replication, which might be an important regulatory mechanism for HCMV persistence and replication in RPE 14507634_PAR1 is the predominant thrombin receptor on invasive extravillous trophoblasts;findings support a role for PAR1, and potentially PAR2 and PAR3 in the invasive phase of human placentation 14521606_PAR-1 and PAR-4 have roles in activating GPIb translocation into the cytoskeleton in platelets 14623891_PAR-1 signaling, along with thrombin, has a role in up-regulating the synthesis of TFPI-2 via a MAPK/COX-2-dependent pathway 14632180_PAR-1 mRNA was expressed specifically in the mesenchymal portions, including dermal papilla and connective tissue sheath, of anagen hair follicles. 14642534_thrombin disarms PAR-1 from further proteolytic activation, but leaves the receptor responsive for non-tethered ligands 14961162_stroke patients exhibited significant cleavage and internalization of PAR-1 and failed to respond to thrombin in vitro, indicating that high concentrations of thrombin occur with acute cerebrovascular ischemic events in vivo 14966279_Results reveal that a novel alteration in trafficking of activated protease-activated receptor 1 causes persistent signaling, and may contribute to breast carcinoma cell invasion. 14982936_the information that specifies PAR1 shedding resides within its N-terminal exodomain rather than its heptahelical segment; and ADAM17/TACE or a metalloproteinase with similar properties mediates PAR1 shedding 15023990_internalization of activated PAR1 is controlled by multiple regulatory mechanisms involving phosphorylation and a highly conserved tyrosine-based motif, YXXL 15045135_evidence that only one of the thrombin platelet receptors, PAR1 or PAR4, is sufficient to induce intracellular signaling leading to the cleavage of the beta3 cytoplasmic domain 15078882_PAR-1 and PAR-4 signal Rap1B activation, the ability of thrombin to activate this GTPase independently of secreted ADP involves costimulation of both receptors as well as binding to GPIb-IX-V. 15099288_results suggest stimulation of both the PAR1 & PAR4 receptors are necessary for thrombin-induced procoagulant activity, & the P2Y(12) receptor, but not the P2Y(1) receptor, is responsible for potentiation of agonist-induced platelet procoagulant activity 15183114_The inactivation of PAR1 due to proteolytic removal of the ligand region may contribute to the termination of the intracellular signaling initiated by thrombin in the vascular endothelial cells. 15191806_PAR1 is most intensely expressed in astrocytes of white and gray matter and moderately expressed in neurons. PAR1 and GFAP co-localization demonstrates that PAR1 is expressed on the cell body and on astrocytic endfeet that invest capillaries. 15247268_role in chemotaxis in conjuction with plasmin 15280447_data confirm a role for PAR1 in migration and metastasis and demonstrate an unexpected role for PAR2 in thrombin-dependent tumor cell migration and in metastasis 15313016_Sustained stimulation of platelet TR is associated with tyrosine dephosphorylation of a novel p67 peptide in a manner regulated by extracellular calcium 15383630_PAR1 activation induced a matrix metalloproteinase-dependent release of transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-alpha), activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). 15455382_Overexpression of protease activated receptor 1 is associated with ovarian carcinoma 15522964_thrombin via PAR1 induced the internalization of endoglin and type-II TGF-beta receptor (TbetaRII) but not type-I receptors in human ECs 15548541_the crystal structure of thrombin bound to heparin shows that the asymmetric unit is composed of two thrombin dimers, each sharing a single heparin octasaccharide chain 15550696_In vitro factor Xa stimulated interleukin-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 release and RNA expression by activation of protease-activated receptor 1. 15559761_PAR1 seems to be the responsible receptor for thrombin-induced migration and adhesion of human colon carcinoma cells including PKCepsilon as an essential signal transducer 15561975_cause activation of a Ca(2+)-independent PLA(2)in bladder microvascular endothelial cells 15563688_PGE(2) downregulated expression of all three PARs in pulmonary fibrosis 15582715_PAR3 receptors and analogues can mediate cell signaling by interaction with PAR1-type thrombin receptors 15625067_Low levels of protease-activated receptor-1 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck 15626732_cross-communication between the prototypical barrier-protective S1P and barrier-disruptive PAR1 pathway 15707890_MMP-1 in the stromal-tumor microenvironment can alter the behavior of cancer cells through PAR1 to promote cell migration and invasion. 15755869_findings imply that the thrombin/protease-activated receptor 1 system system might be involved in the pathophysiology of endometriosis, stimulating inflammatory responses of endometriotic cells and their mitogenic activity 15769747_by signaling through the same receptor PAR1, APC, and thrombin can exert distinct biological effects in perturbed endothelium 15821019_May stimulate PGE2 in pulmonary fibrosis by airway epithelium 15860737_Rac1 plays a critical role in maintaining the surface expression of PAR1 and the responsiveness to thrombin in vascular smooth muscle cells 15869604_FVIIa induces PRIM1 and ensuing cellular proliferation via a TF- and of the PARs entirely PAR-2-dependent pathway, in distinction to that of thrombin which is PAR-1-dependent and TF-independent 15878870_analysis of protease-activated receptor-1 selectivity for G protein signaling by agonist peptides and thrombin 15891109_leukocyte elastase mediates apoptosis of human lung epithelial cells through PAR-1-dependent modulation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway via alterations in mitochondrial permeability and by modulation of JNK and Akt 15923186_mapped for the first time the epitopes of thrombin recognizing a macromolecular ligand, hirudin, in the S and F forms 16021575_a role for PAR-1 in the initial phases of melanoma development as well as in tumor progression and metastasis 16052512_Data show that stimulation of PAR1 results in increased DNA binding of the NFkappaB p65 subunit, and that activation of PAR1 attenuates docetaxel induced apoptosis through the upregulation of Bcl-xL. 16087677_Plasmin and thrombin accelerate shedding of syndecan-4 ectodomain, which generates cleavage sites at Lys(114)-Arg(115) and Lys(129)-Val(130) bonds 16141404_PAR-1 activation promotes cell proliferation and CXCR4-dependent migration and differentiation, leading to a proangiogenic effect 16194864_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16341594_Data show that membrane transport of p42(IP4) induced by epidermal growth factor is inhibited by stimulation of phospholipase C-coupled thrombin receptor. 16354200_A blocking antibody to PAR-1 abolishes activated protein C effects on keratinocytes. 16354660_the transmembrane 7-8th helix-i1 loop may move in a coordinated manner to transfer the signal from PAR1 to G protein. 16359518_PAR1 and also PAR2 can mediate barrier protection in endothelial cells and FXa can use either receptor to enhance barrier integrity 16407403_These findings establish an essential role for endogenous SNX1 in sorting activated PAR1 to a distinct lysosomal degradative pathway that is independent of retromer, Hrs, and Tsg101. 16409451_Significant thrombin generation can occur on vascular tissue in the absence of platelets or platelet microparticles and on the surface of non-apoptotic SMC. 16606835_Because LTD4 and thrombin are likely to be formed concomitantly in vivo, cysLT2-R and PAR-1 may cooperate to augment vascular injury. 16709572_protease-activated receptor-1 has a role in calcium influx, which activates a feed-forward mechanism of TRPC1 expression via nuclear factor-kappaB activation in endothelial cells 16803467_PAR-1 activation did not modify the number of colonies or the day of emergence, in keeping with the lack of induction of angiopoietin 1 gene expression; PAR-1 activation also enhanced migration toward angiopoietin 1 16837456_Data show that at relatively high concentration of agonist, inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor and of calcium mobilization result in complete inhibition of PAR4-induced aggregation, with no effect on either thrombin or PAR1-mediated platelet aggregation. 16839349_the role of thrombin in myocardial damage after coronary artery bypass grafting 16946713_Loss of AP-2 is a crucial event in the progression of human melanoma and contributes to the acquisition of the metastatic phenotype via upregulation of PAR-1. 16952995_new class of cell-penetrating inhibitors, termed pepducins, that provide insight into previously unidentified roles of PAR1 and PAR4 in protease signaling. 17015787_PAR-1 agonism causes platelet activation, venous constriction, arterial dilatation, and tPA release in vivo in humans. 17267663_These data revealed that PAR1 can be part of a preassembled complex with Galpha(i1) protein, resulting either from a direct interaction between these partners or from their colocalization in specific microdomains. 17294805_The antiproliferative effect was more pronounced in cell cultures displaying higher expression of PAR1. 17303701_This study has identified an important role for the direct activation of G(i/o) by PAR1 in human platelets 17323377_cooperative PAR(1)/PAR(4) signaling network that contributes to thrombin-mediated tumor cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma 17347481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17373694_PARs (PAR-1, PAR-2, and PAR-4) are overexpressed in prostate cancer and may serve as potential predictors of recurrence. The data suggest potential role of PARs in autocrine and paracrine mechanisms of prostate cancer. 17374729_These results altogether identify PAR1 as a survival factor that protects cells from undergoing apoptosis. 17376866_PAR3 has a role in allosterically regulating PAR1 signaling governing increased endothelial permeability 17384202_roles of PAR1 and PAR2 and F7 in tissue factor mobilization and endocytosis 17414212_REVIEW: the signaling and regulatory mechanisms of protease-activated receptors in various tissues 17470200_factor VIIa-tissue factor, PAR1 and PAR2 have roles in transcription in tumor cell lines 17492768_Activation of PAR1-induced dynamic cytoskeletal reorganization and reduced PC-3 binding to collagen I, collagen IV, and laminin (P |
ENSMUSG00000048376 |
F2r |
244.569601 |
0.4525070330 |
-1.143988 |
0.107958873 |
113.994772 |
0.00000000000000000000000001306524958358124603783080649411384495011151006250746973325945632658827769145837294217926682904362678527832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000147999296894596469624965926561255724642295455734656247731985143030247406570332202591089298948645591735839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
156.5069651 |
88.0506323 |
347.5521744 |
138.6385140 |
| ENSG00000181195 |
5179 |
PENK |
protein_coding |
P01210 |
FUNCTION: [Met-enkephalin]: Neuropeptide that competes with and mimic the effects of opiate drugs. They play a role in a number of physiologic functions, including pain perception and responses to stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7057924}.; FUNCTION: [Leu-enkephalin]: Neuropeptide that competes with and mimic the effects of opiate drugs. They play a role in a number of physiologic functions, including pain perception and responses to stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7057924}.; FUNCTION: [Met-enkephalin-Arg-Phe]: Met-enkephalin-Arg-Phe neuropeptide acts as a strong ligand of Mu-type opioid receptor OPRM1. Met-enkephalin-Arg-Phe-binding to OPRM1 in the nucleus accumbens of the brain increases activation of OPRM1, leading to long-term synaptic depression of glutamate release. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P22005}.; FUNCTION: [PENK(114-133)]: Increases glutamate release in the striatum and decreases GABA concentration in the striatum. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04094}.; FUNCTION: [PENK(237-258)]: Increases glutamate release in the striatum. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P04094}. |
3D-structure;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Endorphin;Neuropeptide;Opioid peptide;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate multiple protein products. These products include the pentapeptide opioids Met-enkephalin and Leu-enkephalin, which are stored in synaptic vesicles, then released into the synapse where they bind to mu- and delta-opioid receptors to modulate the perception of pain. Other non-opioid cleavage products may function in distinct biological activities. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:5179; |
axon terminus [GO:0043679]; cell body fiber [GO:0070852]; chromaffin granule lumen [GO:0034466]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; neuronal dense core vesicle lumen [GO:0099013]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; symmetric synapse [GO:0032280]; synaptic vesicle lumen [GO:0034592]; neuropeptide hormone activity [GO:0005184]; opioid peptide activity [GO:0001515]; opioid receptor binding [GO:0031628]; aggressive behavior [GO:0002118]; aging [GO:0007568]; behavioral fear response [GO:0001662]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; cellular response to vitamin D [GO:0071305]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; general adaptation syndrome, behavioral process [GO:0051867]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; locomotory exploration behavior [GO:0035641]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of behavioral fear response [GO:2000987]; regulation of long-term synaptic depression [GO:1900452]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to epinephrine [GO:0071871]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to morphine [GO:0043278]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; sensory perception [GO:0007600]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; startle response [GO:0001964]; synaptic signaling via neuropeptide [GO:0099538] |
11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12000709_Results suggest that methylation-related inactivation of the ppENK gene is an intermediate or late event during pancreatic carcinogenesis. 16406203_Proenkephalin peptide F has varying immunoreactivity in different circulatory biocompartments after exercise 16621157_Proenkephalin A 119-159 is a stable proenkephalin A precursor fragment identified in human circulation 17074347_The discrete cell-phenotype localization and timing of the changes in the level of PEA and of piGABA-R mRNA. 17198183_Smoking was not associated with p16 or ppENK hypermethylation in pancreatic cancer patients 17503481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17599100_study provides evidence that the growth-responsive nuclear protein, proenkephalin (Penk), is required, in part, for apoptosis induction, in response to activation or overexpression of p53 and RelA(p65) 18082911_It found widespread expression of preproenkephalin (pPENK) mRNA and production of the enkephalin precursor protein proenkephalin (PENK) in rat and mouse tissues, as well as in tissues and cells from humans and pigs. 18184800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184800_analysis of polymorphisms of proenkephalin (PENK) and prodynorphin (PDYN) genes in relation to heroin abuse and gene expression in the human striatum and the relevance of genetic dopaminergic tone 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20207019_indicate alterations of the cerebral PENK A- and PTA-system in both, dementia and acute neuroinflammatory disorders 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628265_we demonstrated reduced ppE expression in patients with elevated psychological distress. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21810780_found higher levels for MOR mRNA (+27%) in schizophrenia but no differences in DOR or proenkephalin mRNAs 22102294_Differential tertiary conformations of PE subdomains undergo ordered proteolytic processing to generate active enkephalin peptides for cell-cell communication in the nervous and endocrine systems. 22391864_Expression of preproenkephalin is significantly decreased in brain from HIV-1 infected patients compared to HIV-1 negative subjects. 22393040_Findings indicate the unique function of cathepsin V for producing enkephalin and neuropeptide Y (NPY) neuropeptides required for neurotransmission in health and neurological diseases. 22745721_The findings suggest an important role for Neuroticism as an endophenotype linking PENK polymorphisms to cannabis-dependence vulnerability synergistically amplifying the apparent genetic risk. 23395721_Peptide F is bound to white blood cells in the blood. Exercise alters Peptide F in the plasma and white blood cell blood fractions. 23937196_Data from women undergoing hysterectomy for uterine fibroids suggest that uterine isthmian-cervical region exhibits nerve fibers expressing enkephalin (ENK); uterine fundus/corpus myoma pseudocapsules do not exhibit nerve fibers expressing ENK. 24289328_Promoter methylation of WIF1, PENK and NPY is associated with colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC) diagnosis and can be used to CRC from other cancers. 24496384_EPS led to the discovery of two novel immunomodulatory proteins, MFAP5 and PENK that when administered to mice subjected to endotoxemic shock, reversed the cytokine storm and provided a significant survival benefit 24937654_increased plasma PENK-A levels are associated with disease severity and in-hospital mortality after acute intracerebral hemorrhage. 24937655_enhanced plasma proenkephalin A could be a useful, complementary tool to predict short- or long-term clinical outcome after severe traumatic brain injury. 25891176_BSP demonstrated that emodin, to a certain degree, affected the demethylation of tumor-suppressor genes P16, RASSF1A, and ppENK in the pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1. 26164485_The PENK polymorphism-and potentially opioid neurotransmission more generally-modulates functioning and structural integrity of brain regions. 26218633_Serum PENK-A levels were not associated with all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and its association with cardiovascular mortality was strongly attenuated after accounting for all traditional risk factors. 26634308_Nav1.7 deletion has profound effects on gene expression, leading to an upregulation of enkephalin precursor Penk mRNA and met-enkephalin protein in sensory neurons. 28263851_These data indicate that in untrained women exercise training will not change resting of plasma Peptide F concentrations unless both forms of exercise are performed but will result in significant increases in the immediate post-exercise responses. 29030229_The concentration of PENK 143-183 was significantly greater in patients with Moyamoya disease (MMD) than control patients and decreased in an age-dependent manner in MMD. 29466891_High PENK is associated with increased risk of CKD defined by eGFR in men, but not in women. No association of PENK with CKD defined by urinary albumin excretion UAE was observed. 29673232_These results demonstrate that proinflammatory molecules and endogenous enkephalin have opposite gene regulation during Dry eye disease. 31091993_The opioid system, reflected by PENK (proenkephalin), is not only independently associated with glomerular dysfunction, but also with tubular damage in heart failure. 31973568_PENK-A was neither independently associated with functional outcome (OR: 1.29, 95% CI: 0.16-10.35) nor mortality 32334633_PENK inhibits osteosarcoma cell migration by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000045573 |
Penk |
35.120358 |
0.4394665475 |
-1.186175 |
0.280587673 |
18.135015 |
0.00002057824151740137959883808482786093918548431247472763061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000062304583548070642333958912839619870283058844506740570068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.5763097 |
3.8780773 |
49.4404527 |
5.7406983 |
| ENSG00000181409 |
9625 |
AATK |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMQ8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in neuronal differentiation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10837911}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains a tyrosine kinase domain at the N-terminus and a proline-rich domain at the C-terminus. This gene is induced during apoptosis, and expression of this gene may be a necessary pre-requisite for the induction of growth arrest and/or apoptosis of myeloid precursor cells. This gene has been shown to produce neuronal differentiation in a neuroblastoma cell line. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011]. |
hsa:9625; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; brain development [GO:0007420]; peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:0038083]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
14521924_Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase is a Cdk5 activator p35 binding protein. 17651901_This paper deals with the mouse ortholog. 27485693_ATKK was validated as a target gene of miR-558, and upregulation of miR-558 was observed in radioresistant lung cancer cells. Additionally, ectopic overexpression of ATKK partially but significantly reduced the miR-558-induced radioresistance. 34523681_Lemur tail kinase 1 (LMTK1) regulates the endosomal localization of beta-secretase BACE1. |
ENSMUSG00000025375 |
Aatk |
36.539775 |
0.2706570564 |
-1.885462 |
0.372866295 |
25.343635 |
0.00000047973273086753842217952069001962733807431504828855395317077636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001762722207519259846626030752148039937310386449098587036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.0882254 |
4.3892643 |
70.8076630 |
10.6036076 |
| ENSG00000181444 |
168544 |
ZNF467 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z7K2 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that promotes adipocyte differentiation and suppresses osteoblast differentiation in the bone marrow. Enhances the osteoclast-supporting ability of stromal cells. Binds with STAT3 the consensus sequence 5'-CTTCTGGGAAGA-3' of the acute phase response element (APRE). Transactivates several promoters including FOS, OSM and PPARG. Recruits a histone deacetylase complex (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a zinc finger protein whose function has not yet been elucidated in humans. However, the mouse ortholog of this protein enhances adipocyte differentiation and suppresses osteoblast differentiation in bone marrow. The mouse protein also is a transcription factor for several genes and can help recruit histone deacetylase complexes. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:168544; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
17848547_These results identify EZI as a novel cargo protein for importin-7 and demonstrate a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling mechanism that is mediated by importin-7-dependent nuclear localization and CRM1-independent nuclear export. 22700861_ZNF467 gene DNA methylation is importants in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 32032745_demonstrate that PCBP2 and ZNF467 impact adipogenic but not osteogenic differentiation, further supporting evidence that AMSCs and BMSCs appear to be adapted to their microenvironment |
ENSMUSG00000068551 |
Zfp467 |
183.695503 |
0.1470039803 |
-2.766073 |
0.146846065 |
396.746161 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000028135958768206802676330266974583791573351395240649153867714349830757738923515757765098808109026836647345488106706168721338852507720070627881043079833803507598702642839231768928344719400586060305270065599640741903480350982746927002153825014830 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010513588643512213085536789484994144990164962365676748584592733665386189728896753603532465167384756210505796424726752684630790019151128298986286689134992677911080169530033049933689246383312649539639885526936093421146445336944452719762921333313 |
Yes |
No |
48.3210515 |
5.0393320 |
331.2405538 |
19.4820390 |
| ENSG00000181513 |
79777 |
ACBD4 |
protein_coding |
Q8NC06 |
FUNCTION: Binds medium- and long-chain acyl-CoA esters and may function as an intracellular carrier of acyl-CoA esters. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Lipid-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the acyl-coenzyme A binding domain containing protein family. All family members contain the conserved acyl-Coenzyme A binding domain, which binds acyl-CoA thiol esters. They are thought to play roles in acyl-CoA dependent lipid metabolism. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]. |
hsa:79777; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; fatty-acyl-CoA binding [GO:0000062]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631] |
21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28463579_acyl-CoA binding domain protein 4 (ACBD4) as a tail-anchored peroxisomal membrane protein which interacts with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) protein, vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein-B (VAPB) to promote peroxisome-ER associations. |
ENSMUSG00000056938 |
Acbd4 |
44.697149 |
0.3184220590 |
-1.650988 |
0.263082036 |
40.532996 |
0.00000000019332367222659807457400225070079380351728559617185965180397033691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000979223542232185250718823219190714568505029546940932050347328186035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.1572700 |
3.5840076 |
70.5962047 |
6.6830947 |
| ENSG00000181577 |
221416 |
C6orf223 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.401071 |
13.3589758835 |
3.739738 |
0.572729674 |
50.759042 |
0.00000000000104430385896173140713100793301780846999982088618708075955510139465332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006207782907078193475785898397109735242886674466689100881922058761119842529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.9884430 |
12.2991121 |
2.7823353 |
0.8754560 |
| ENSG00000181634 |
9966 |
TNFSF15 |
protein_coding |
O95150 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for TNFRSF25 and TNFRSF6B. Mediates activation of NF-kappa-B. Inhibits vascular endothelial growth and angiogenesis (in vitro). Promotes activation of caspases and apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10597252, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11911831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11923219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9872942}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein is abundantly expressed in endothelial cells, but is not expressed in either B or T cells. The expression of this protein is inducible by TNF and IL-1 alpha. This cytokine is a ligand for receptor TNFRSF25 and decoy receptor TNFRSF21/DR6. It can activate NF-kappaB and MAP kinases, and acts as an autocrine factor to induce apoptosis in endothelial cells. This cytokine is also found to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation, and thus may function as an angiogenesis inhibitor. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:9966; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity [GO:0007250]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; immune response [GO:0006955]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11739281_Vascular endothelial growth inhibitor is an endothelial cell-specific gene and inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and tumor growth; mediates G1 arrest in G0/G1 cells responding to growth stimuli, and apoptosis in cell division 12882979_TL1A-induced NF-kappaB activation and c-IAP2 production prevent DR3-mediated apoptosis 14568967_TL1A mRNA and protein expression is up-regulated in inflammatory bowel disease, particularly in involved areas of Crohn's disease (CD) in gut mucosa cell types other than endothelial, including lamina propria lymphocytes as well as tissue macrophages. 15207783_Expression of TL1A and its receptor DR3 by lamina propria mononuclear cells (LPMC) could have significant influence on the severity of mucosal inflammation. 15760679_TL1A and DR3 is involved in atherosclerosis via the induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines 16061878_VEGI is an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis 16221758_Genetic variations in the TNFSF15 gene contribute to the susceptibility to inflammatory bowel diseases in Japanese and European populations. 16221758_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16604264_It can be concluded that VEGI72-251 is able to increase the level of human IL-2 production by the activation of T lymphocytes 16966713_a significant association between TNFSF15 and Crohn's disease 17030188_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17371957_The induction of TL1A on APCs via specific pathway stimulation suggests a role for TL1A in Th1 responses to pathogens, and in CD. 17513783_Mononuclear phagocytes are a major source of TL1A in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as revealed by their strong TL1A expression in either synovial fluids or synovial tissue of rheumatoid factor (RF)-seropositive RA patients, but not RF-negative/RA patients. 17663424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17663424_TNFSF15 is an ethnic-specific IBD susceptibility gene. Five SNPs that comprise the 2 common haplotypes were genotyped in 599 Caucasian patients with Crohn's dis, 382 Caucasian patients with ulcerative colitis, and 230 controls. 17935696_TL1A forms a homotrimer with each monomer assuming a jellyroll beta-sandwich fold. The CD loop in TL1A is the longest among the TNF ligand members with known structure and the AA' loop in TL1A is the second longest after that in TRAIL. 18287561_TL1A may contribute to renal inflammation and injury through DR3-mediated activation of NF-kappaB and caspase-3 18338776_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18338776_Variants in TNFSF15 contribute to overall CD susceptibility in European populations, although to a lesser extent than that seen in the Japanese. 18422820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18422820_TNFSF15 genotypes play an important role in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease in Koreans. 18757243_TL1A may serve as an inflammatory marker in rheumatoid arthritis. Interactions between TL1A and its receptors may be important in the pathogenesis of rheumatois arthritis. 19124533_The allelic expression imbalance of TNFSF15 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was examined to reveal the effects of the single nucleotide polymorphisms on the transcriptional activity of TNFSF15. 19174806_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19174806_confirms that TNFSF15 or a closely linked gene is involved in the genetic predisposition to CD 19251437_sodium butyrate has different effects on lung vascular TNFSF15 (TL1A) expression in pulmonary artery and microvascular endothelial cells 19262684_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19262684_TL1A gene variation exacerbates induction of TL1A in response to FcgammaR stimulation in Jewish CD patients and this may lead to chronic intestinal inflammation via overwhelming T cell responses 19422935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19522538_Results provide insights into the structure and function of TL1A and provide the basis for the rational manipulation of its interactions with cognate receptors. 19543369_A haplotype strongly associated with predisposition to spondyloarthritis is located near to TNFSF15. 19760754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19786547_these data suggest that TL1A secretion in lymphoid organs might contribute to rheumatoid arthritis initiation by promoting autoantibody production. 19815424_Data suggest that lipopolysaccharide induces TL1A expression through the transcriptional activation via a NF-kappa B pathway. 19839006_Our findings suggest a role for TL1A in pro-inflammatory APC-T cell interactions 19885571_VEGI functions as a negative regulator for aggressiveness during the development and progression of prostate cancer. 20018961_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20125169_critically involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis 20150621_VEGI functions as a negative regulator of aggressiveness during development and progression of bladder cancer. 20176734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20349123_TL1A increased cytotoxicity of IL-12/IL-18-activated NK cells against target cells dependent on NK activation for lysis and could function in vivo as a key co-activator of NK cytotoxicity. 20367632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20410491_TL1A promotes foam cell formation in human macrophages in vitro by increasing low density lipoprotein uptake, by enhancing intracellular total and esterified cholesterol levels and reducing cholesterol efflux. 20473688_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20675196_The TL1A/DcR3 ligand/receptor pair is upregulated in active ulcerative colitis. 20848476_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20863486_TL1A can regulate the inflammatory processes through modulation of the betaig-h3 expression through two separate pathways, one through PKC and PI3K and the other through ERK, which culminates at NF-kappaB activation. 20886065_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21153332_role in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis 21153333_role of TNFRSF25:TNFSF15 in disease and health 21217782_studies for the first time establish the regulatory axis of AMPK-LITAF-TNFSF15 and also suggest that LITAF may function as a tumor suppressor 21228792_neither TNFSF15 nor IL23R variants contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility in Koreans 21300286_Decoy Receptor 3 (DcR3)neutralizes three different TNF ligands: FasL, LIGHT, and TL1A. Crystal structure of DcR3 reported here provides a mechanistic basis for the broadened specificity required to support the decoy function of DcR3. 21368235_Substance P- and hemokinin-1-stimulated monocytes potentiate T helper type (Th)17 cell generation in vitro through IL-1beta, IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor-like (TNF)1A expression. 21537832_DcR3 may act as an inducer, and membrane-bound TL1A may act as a receptor in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. 21636646_susceptibility gene for irritable bowel syndrome and irritable bowel syndrome constipation 21672030_in active psoriasis, we observed abundant immunostaining for TL1A and significant upregulation of its receptors DR3 and DcR3 21730793_the TNFSF15 genotype is positively associated with isolated colonic (L2) Crohn disease. 22210436_Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) produced by cancer cells and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) produced mainly by tumor-infiltrating macrophages and regulatory T cells effectively inhibits TNFSF15 production by endothelial cells. 22641456_Protein expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-like ligand 1A (TL1A) and death-domain receptor (DR)3 is upregulated in the aged bladder tissues. 22684480_Polymorphisms in TNFSF15 were associated with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. 23000144_Two significant susceptibility loci, TNFSF15 (rs4979462) and POU2AF1 (rs4938534) (combined odds ratio [OR] = 1.56, p = 2.84 x 10(-14) for rs4979462. 23204549_TL1A is up-regulated in ankylosing spondylitis (AS), associates with disease activity and is influenced by anti-TNF treatment, suggesting that TL1A may be of pathogenic and potentially of therapeutic importance in AS patients. 23250276_increased expressiojn in gut tissue , but not in the peripheral blood, from inflammatory bowel disease patients 23382586_VEGI192 and VEGI174 expression is markedly decreased in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma and are linked to pathological grade and stage. 23404494_attenuated S. typhimurium carrying the dual function plasmid VEGI151/survivin cannot only be specifically enriched in the tumor tissue, but also showed a synergistic antitumor effect in vivo. 23545578_this suggests that VEGI functions mainly through inhibition of angiogenesis and is a negative regulator of aggressiveness during the development and progression of renal cell carcinoma . 23598291_Circulating levels of TL1A correlate with the progression of atheromatous lesions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 23642711_Response elements regulating TNFSF15 in primary human myeloid cells, were analyzed. 24005100_It has been identified as a new disease susceptibility gene among Japanese. Though different from Europeans, it is indicated that a T lymphocyte differentiation route (Th1/Th17) shares a common disease developing process. [Review] 24016146_may play an important role in the pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis 24023314_VEGI, possibly via DR3, suppresses the aggressive nature of pituitary tumours and its expression level is closely linked to the invasion and destruction of the suprasellar and sella regions 24141405_Tumor-infiltrating natural killer and CD4(+) T cells under the influence of cancer cells significantly increase the production of IFNgamma, which in turn inhibits TNFSF15 expression in vascular endothelial cells. 24220298_Our data demonstrate a key role for TL1A in promoting ILC2s at mucosal barriers. 24269700_genetic polymorphism is associated with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis in Hungarians 24384427_ADAMTS 8, CCL23, and TNFSF15 are implicated in anti-angiogenic activities 24783249_Combining the genetic marker TNFSF15 with ASCA IgA increased the power of predicting stenosis/perforating phenotype in Crohn's disease patients with TNFSF15 but not with a NOD2 genetic background 24814505_The SNP rs7848647 associated with the TNFSF15 gene is associated with surgical diverticulitis. 24832108_These results suggested that TL1A could promote Th17 differentiation in rheumatoid arthritis via the activation of RORc, and this effect may be mediated by the binding of TL1A with DR3. 24835165_TNFSF15 SNPs, rs6478108 and rs4574921, may be independent genetic predictive factors for the development of stricture/non-perianal penetrating complications and perianal fistula, respectively. 25028192_This meta-analysis indicated that most of the seven TNFSF15 polymorphisms (except for rs4263839) were risk factors contributed to CD and UC susceptibility. The differences in ethnicity did not influence the risk obviously. 25148371_TL1A increases expression of CD25, LFA-1, CD134 and CD154, and induces IL-22 and GM-CSF production from effector CD4 T-cells 25197060_Mechanisms mediating TNFSF15:DR3 contributions to pattern recognition receptor outcomes included TACE-induced TNFSF15 cleavage to soluble TNFSF15; soluble TNFSF15 then led to TRADD/FADD/MALT-1- and caspase-8-mediated autocrine IL-1 secretion. 25200589_Soluble TL1A synergized with IL-23 to stimulate peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with psoriasis vulgaris to produce IL-17. 25251497_Results show that subjects with TNFSF15 -358CC genotype were at higher risks for developing gastric adenocarcinoma in the Helicobacter pylori infected group. 25399326_DR3 is expressed in some interstitial vascular endothelial cells (EC) in human kidney in situ; these EC also respond to its ligand TL1A by activating NF-kappaB. 25501099_associations exist between TNFSF15 gene polymorphisms and IBD (both CD and UC) in the Indian population 25647275_study has defined the increased serum and SF samples levels of TL1A and DcR3 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA); findings support the hypothesis that TL1A and DcR3 may contribute to the pathogenesis of RA 25664710_This is the first report of the association between early Crohn's disease and the TNFSF15 single nucleotide polymorphisms. 25778932_This study indicates that the HDAC inhibitor may be exploited as a therapeutic strategy modulating the soluble VEGI/DR3 pathway in osteosarcoma patients 25899471_Human primary biliary cirrhosis-susceptible allele of rs4979462 enhances TNFSF15 expression by binding NF-1. 25908025_TL1A blood levels are elevated in psoriasis patients; TL1A expression is higher in psoriatic lesions than in normal skin 25929716_Plasma levels of TL1A were significantly higher in newly diagnosed SLE patients compared with controls, and were positively associated with SLE disease activity index. 25998826_There were significant associations of rs3810936, rs6478108, rs6478109, rs7848647 with CD in Korean pediatric patients (P = 6.5x10(-8), P = 1.3x10(-8), P = 3.7x10(-8), P = 2.9x10(-8), respectively). 26046454_Addition of TL1A to IL-1beta + IL-23 also augmented ILC3 proliferation 26072972_The data indicate that TL1A may contribute to pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases via local but not systemic induction of IL-17A but not IL-4, IL-13 or IFN-gamma. 26200500_This study shows an association between TNFSF15-rs3810936 and AAU and suggests that the TL1A/DR3 pathway may be implicated in the pathogenesis of this disease. 26393680_Higher TL1A levels were associated with early stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 26509650_TL1A-induced cell death is directly mediated through DR3. 26768609_(188)Re-NGR-VEGI has the potential as a theranostic agent. 26810853_Biologics beyond TNF-alpha inhibitors and the effect of targeting the homologues TL1A-DR3 pathway in chronic inflammatory disorders. 26823868_Rs3810936 of TNFSF15 were related to the risk of ankylosing spondylitis 26945876_Patients with mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) exhibited higher VEGI levels than those with moderate and severe TBI. 27081759_the blocking of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) decreased TL1A-stimulated IL-6 production by rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 27188743_miRNA-31 can directly bind to the 3-UTR of TNFSF15, thereafter negatively regulating its expression in Caco2 cells. 27507062_Results provide evidence that variance within TNFSF15 has the potential to affect cytokine expression across a range of tissues and thereby contribute to protection from infectious diseases such as leprosy, while increasing the risk of immune-mediated diseases including Crohn's disease and primary biliary cholangitis. 27665176_These results raise the possibility for involvement of TL1A/DR3/DR3-mediated mechanisms in epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and the development of inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease. 27733581_TL1A differentially induces expression of TH17 effector cytokines IL-17, -9, and -22 and provides a potential target for therapeutic intervention in TH17-driven chronic inflammatory diseases. 28062298_the DR3/TL1A pathway directly enhances human OC formation and resorptive activity, controlling expression and activation of CCL3 and MMP-9. 28197769_results support an idea that the genetic susceptibility of TNFSF15 to CD may be confounded, in part, by the increase of Prevotella 28337757_Data suggest that human regulatory T-lymphocytes express DR3 and demonstrate DR3/TL1A-mediated activation of signaling via MAP kinases and NFkappaB. (DR3 = death receptor 3; TL1A/TNFSF15 = tumor necrosis factor [ligand] superfamily, member 15) 28362712_The expression of VEGI and E-cadherin was significantly lower in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) tissues compared with normal kidney tissues (P |
ENSMUSG00000050395 |
Tnfsf15 |
72.003411 |
5.0705459140 |
2.342141 |
0.212269939 |
132.088575 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000143090238897761487476369011246496137848724085840775524703748504668774027514174525081702693540819382178597152233123779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000018591654279321827732402589262684504430030335648576962978674244785915506949505130590560852965609228704124689102172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
104.1167682 |
38.9012933 |
19.9997171 |
5.5326453 |
| ENSG00000181649 |
7262 |
PHLDA2 |
protein_coding |
Q53GA4 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in regulating placenta growth. May act via its PH domain that competes with other PH domain-containing proteins, thereby preventing their binding to membrane lipids (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is located in a cluster of imprinted genes on chromosome 11p15.5, which is considered to be an important tumor suppressor gene region. Alterations in this region may be associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, adrenocortical carcinoma, and lung, ovarian, and breast cancer. This gene has been shown to be imprinted, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in placenta and liver. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:7262; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of embryonic development [GO:0045995]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of glycogen metabolic process [GO:0070873]; regulation of growth hormone activity [GO:1903547]; regulation of spongiotrophoblast cell proliferation [GO:0060721] |
9328465_PHLDA2 gene is imprinted, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in placenta and liver. 15952111_Transcripts of TSSC3 could not be detected in human oocytes and preimplantation embryos. 16584773_Exposure of trophoblasts to hypoxia in vitro markedly reduced the expression of PHLDA2. 17180344_association with low birth weight 17303335_Up-regulation of TSSC3 occurred in Dicer knockdown cells. 20201924_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20484977_Expression levels of PHLDA2 gene were upregulated in the first trimester pregnancy 21555518_PHLDA2 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 22021909_TSSC3 has a potent tumor suppressor role in osteosarcoma, probably by inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis via the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. 22100507_The results suggest that placental PHLDA2 may provide a biomarker for suboptimal skeletal growth in pregnancies uncomplicated by overt fetal growth restriction. 22444668_A luciferase reporter assay was used to identify in the PHLDA2 promoter a 15 bp repeat sequence variant that significantly reduces PHLDA2-promoter efficiency. Maternal inheritance of the variant resulted in a significant increase in birth weight. 22610481_TSSC3 inhibits osteosarcoma tumorigenicity through reducing stemness and promoting apoptosis of tumor inducing cells 24268429_TSSC3 overexpression suppressed osteosarcoma cell growth and increased apoptosis through caspase-3 upregulation, suggesting that TSSC3 may play a pro-apoptosis role to maintain the normal balance of growth 24703004_results suggest upregulated pleckstrin homology-like domain family A member 2 (PHLDA2) in placenta of monozygotic twins may be associated with the pathogenesis of singleton intrauterine growth restriction 24953163_elevated expression in placenta of growth restricted pregnancies [review] 24986528_The gene expression pattern of CDKN1C, H19, IGF2, KCNQ1 and PHLDA2 genes was evaluated using RT-PCR. 26218012_PHLDA2 may promote the occurrence/development of preeclampsia by inhibiting proliferation/migration/invasion of trophoblasts. 26845447_TSSC3 downregulation promotes the Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) of osteosarcoma cells by regulating EMT markers via a signal transduction pathway that involves Snail, Wnt-beta-catenin/TCF, and GSK-3beta 26935516_PHLDA2 plays an important role in the occurrence and development of pregnancy complications by promoting trophoblast apoptosis and suppressing cell invasion. 26944942_Placental PHLDA2 expression was significantly 2.3 fold higher in reduced fetal movements pregnancies resulting in delivery of a growth restricted compared with a normal birth weight infant. 27044808_TSSC3 was a prognostic marker in osteosarcoma. 28032865_RanBP9/TSSC3 complex cooperatively suppress metastasis via downregulation of Src-dependent Akt pathway to expedite mitochondrial-associated anoikis. 30092789_Authors demonstrated that TSSC3 was an independent prognostic marker for overall survival in osteosarcoma, and positive ATG5 expression associated with positive TSSC3 expression suggested a favorable prognosis for patients. Then, we showed that TSSC3 overexpression enhanced autophagy via inactivating the Src-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in osteosarcoma. 31194812_Increased CDKN1C and PHLDA2 and reduced IGF-2 abundances in placental tissue were related to BW and early period catch-up growth in full-term SGA infants. 32062476_PHLDA2 gene polymorphisms and risk of HELLP syndrome and severe preeclampsia. 32385195_PHLDA2 regulates EMT and autophagy in colorectal cancer via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 33179538_Prognostic and predictive value of Pleckstrin homology-like domain, family A family members in breast cancer. 34006890_PHLDA3 promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and invasion via activation of the Wnt signaling pathway. 34284400_Tumor-Suppressing STF cDNA 3 Overexpression Suppresses Renal Fibrosis by Alleviating Anoikis Resistance and Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt Pathway. 34475057_HGF-mediated Up-regulation of PHLDA2 Is Associated With Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer. 35841528_RhoGDI1 interacts with PHLDA2, suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells, and participates in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 35894264_Knockdown of PHLDA2 promotes apoptosis and autophagy of glioma cells through the AKT/mTOR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000010760 |
Phlda2 |
51.777070 |
2.7368549211 |
1.452519 |
0.241304673 |
36.713128 |
0.00000000136854734276958922007041460748317379669813931286626029759645462036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006457723394910210615086195102066413120667220937320962548255920410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
77.5109714 |
11.0281970 |
28.4990726 |
3.2731863 |
| ENSG00000181656 |
54112 |
GPR88 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZN0 |
FUNCTION: Probable G-protein coupled receptor implicated in a large repertoire of behavioral responses that engage motor activities, spatial learning, and emotional processing. May play a role in the regulation of cognitive and motor function. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EPB7, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ESP4}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a G protein-coupled receptor found almost exclusively in the striatum, a brain structure that controls motor function and cognition. Defects in this gene have been associated with chorea, speech delay, and learning difficulties, as well as some neuropsychiatric disorders. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:54112; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytoskeletal motor activity [GO:0003774]; G protein-coupled photoreceptor activity [GO:0008020]; cellular response to light stimulus [GO:0071482]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; motor learning [GO:0061743]; neuromuscular process controlling balance [GO:0050885]; neuronal action potential [GO:0019228]; phototransduction [GO:0007602] |
27499251_Study designed and synthesized a series of 2-PCCA analogues bearing a variety of substituents at the phenyl ring of the aniline moiety to determine the structure-activity relationship (SAR) in this region; SAR studies suggested that there is a hydrophobic pocket in the GPR88 binding site interacting with the aniline region of 2-PCCA 35501348_Activation and allosteric regulation of the orphan GPR88-Gi1 signaling complex. |
ENSMUSG00000068696 |
Gpr88 |
22.816707 |
0.1601638931 |
-2.642379 |
0.399448420 |
49.362588 |
0.00000000000212764801756189317652372195434697809855381644972283083916408941149711608886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000012417589853386137059951809618424753032736584934525581047637388110160827636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6406888 |
1.7542807 |
41.6508858 |
5.6519265 |
| ENSG00000181690 |
5324 |
PLAG1 |
protein_coding |
Q6DJT9 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor whose activation results in up-regulation of target genes, such as IGFII, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation: when overexpressed in cultured cells, higher proliferation rate and transformation are observed. Other target genes such as CRLF1, CRABP2, CRIP2, PIGF are strongly induced in cells with PLAG1 induction. Proto-oncogene whose ectopic expression can trigger the development of pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary gland and lipoblastomas. Overexpression is associated with up-regulation of IGFII, is frequently observed in hepatoblastoma, common primary liver tumor in childhood. Cooperates with CBFB-MYH11, a fusion gene important for myeloid leukemia. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11888928, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14695992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14712223}. |
Acetylation;Activator;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;DNA-binding;Dwarfism;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Pleomorphic adenoma gene 1 encodes a zinc finger protein with 2 putative nuclear localization signals. PLAG1, which is developmentally regulated, has been shown to be consistently rearranged in pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary glands. PLAG1 is activated by the reciprocal chromosomal translocations involving 8q12 in a subset of salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5324; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; gland morphogenesis [GO:0022612]; multicellular organism growth [GO:0035264]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; prostate gland growth [GO:0060736]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
11882654_Identification of a karyopherin alpha 2 recognition site in PLAG1, which functions as a nuclear localization signal 11894114_overexpression of PLAG1 does not depend on chromosomal rearrangements in radiation associated pleomorphic adenomas 14695992_PLAG1 regulates promoter P3-dependent transcription of IGF2 in hepatoblastomas. 15208321_a direct repression of the transactivating capacity of the oncoprotein PLAG1 by SUMOylation 15262430_PLAG1 amplification is associated with malignant mixed tumor of salivary gland 15585652_Plag1 and Plagl2 are novel leukemia oncogenes that act by expanding hematopoietic progenitors expressing CbF beta-SMMHC. 15642402_fusion with HAS2 in lipoblastoma 15920557_Finding reinforces the role of PLAG1 on the tumorigenesis of benign and malignant pleomorphic adenoma. 15930271_Results establish the in vivo tumorigenic capacity of PLAG1 and indicate that the transgenic mice constitute a valuable model for pleomorphic salivary gland tumorigenesis and potentially for other glands as well. 16108035_Overexpression of PLAG1 is associated with pleomorphic adenomas in transgenic mice 16736500_PLAG1 protein is overexpressed in epithelial, myoepithelial, and mesenchymal-like tumor cells in tumors with fusions to CHCHD7 and TCEA1. 17332914_The importance and versatility of the PLAG1 oncogene in tumourigenesis is discussed. 17693184_PLAG1 gene rearrangements is associated with pleomorphic adenoma 18059337_Molecular analyses in salivary gland tumors revealed that ring formation consistently generated novel FGFR1-PLAG1 gene fusions in which the 5'-part of FGFR1 is linked to the coding sequence of PLAG1 18269579_Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) demonstrated rearrangements of the PLAG1 region in lipoblastoma in adolescencts and young adults. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19347935_overexpression of PLAG1 is associated with pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary gland. 19692702_a significant regulation of PLAG1 by miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-107, and miR-424. 20189936_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20522588_Overexpression in transgenic mice causes hypereinsulinemic normoglycemia and insulin resistance. 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20687796_Overexpression of the oncogene PLAG1 is associated with the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 21394649_present results also suggest that overexpression of PLAG1 is essential for the tumorigenesis of pleomorphic adenomas, although the mechanisms mediating PLAG1 overexpression seem to be variable. 21927843_close relationship between cutaneous mixed tumors and pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary gland. However, the mechanism of PLAG1 expression in cutaneous mixed tumors appears to be possibly different from that of pleomorphic adenomas. 22038920_myoepithelial tumors with PLAG1 alteration share a common morphologic phenotype with salivary gland-like morphology and are genetically related to their salivary gland counterpart 22192798_PLAG1 immunohistochemistry is useful for distinguishing lipoblastoma from other lipomatous tumors including liposarcoma. 22485045_We conclude that most Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma, regardless of morphologic subtype,carry altered PLAG1 genes 22593475_PLAG1 is evidently not involved in the development of myoepithelial tumours. The proportion of 8q12-alterations in myoepithelial tumours was very low. 23023303_PLAG1 binding to the IGF2 P3 promoter and IGF2 expression is cell type-specific, and that the PLAG1 transcription factor acts as a transcriptional facilitator that partially overrides the insulation by the H19 ICR. 23404581_These results suggest that PLAG1 and CYLD do not play a role in ACC tumorigenesis. 23554918_miR-141 contributes to fetal growth restriction by regulating PLAG1 expression. 23630011_A subset of cutaneous and soft tissue ME tumors appears genetically linked to their salivary gland counterparts, displaying frequent PLAG1 gene rearrangements and occasionally LIFR-PLAG1 fusion. 23690029_PLAG1 not only activates genes that promote cell proliferation and tumor formation but also genes that inhibit these cellular processes. 23738717_Ten cases of salivary duct carcinoma had PLAG1 rearrangement/amplification (22.7%) and eight had HMGA2 (18.2%) rearrangement/amplification. 23958548_a marker with good specificity for salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas 24185117_Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma of the vulva with PLAG1 gene activation: molecular genetic characterization of 2 cases 24433523_Report illustrates two different tumorigenic pathways implicating PLAG1 in lipoblastoma: amplification through multiple copies of a small marker chromosome derived from chromosome 8, and a paracentric inversion of the long arm of chromosome 8. Review. 24468654_Lacrimal and salivary gland PAs and Ca-ex-PAs have similar genomic profiles and frequently overexpress the PLAG1 oncoprotein. Copy number gains involving 9p23-p22.3 (NFIB) and 22q12-qter (PDGFB) may be of importance for disease progression. 24516594_Altogether, these data suggest that HMGA2 is an upstream activator of PLAG1. 24700772_lipoblastoma is a group of lipomatous tumors with PLAG1 rearrangement and overexpression. 25060425_The nuclear import of PLAG1 by KPNA2 is essential for the role of KPNA2 in HCC cells. 25439740_Fluorescence in situ hybridization for PLAG1 or HMGA2 can be used to distinguish between pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma and their morphologic mimics. 25786906_Data indicate that SLIT2, miR-218-1, RET/PLAG1 and SLIT2/ROBO1 pathway involved in Hirschsprung's disease. 26492619_The Thr34 of PLAG1 is critical for LpMab-10 recognition. 26882287_High PLAG1 expression is associated with pleomorphic adenoma. 27381214_expression of PLAG1 can be considered a valuable diagnostic marker for recurrent pleomorphic adenoma 27463119_The sensitivity (55%) and specificity (75%) of PLAG1 in diagnosing PA in FNAs is relatively modest thus limiting its diagnostic utility. 27473265_Plag1 expression is lost in malignant transformation from pleomorphic adenoma to carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. 28012286_MiR-26a can facilitate occurrence of pituitary tumor and invasiveness, probably via inhibiting PLAG1 expression. 29135520_HRAS mutations were more common in epithelial-myoepithelial carcinomas (EMCAs) with intact PLAG1 and HMGA2. Most EMCAs arose ex pleomorphic adenoma (PA)and the genetic profile of EMCA varies with the absence or presence of preexisting PA and its cytogenetic signature. Progression to higher grade EMCA with intact PLAG1 and HMGA2 correlates with the presence of TP53, FBXW7 mutations, or SMARCB1 deletion. 29437290_Rearrangement of PLAG1 and HMGA2 and expression of the corresponding proteins are frequent and specific findings in lacrimal gland pleomorphic adenoma (PA) and ca-ex-PA. 29641991_PLAG1 and USF2 cooperation is thus an important contributor to stem cell-specific expression of MSI2 and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell-specific transcriptional circuitry. 29735329_Proliferation and apoptosis assays demonstrated that miR-181a/135a/302c function as tumor suppressors via repressing PLAG1/IGF2 signaling. 30026293_PLAG1 is a microRNA target gene that is overexpressed in Wilms tumors with mutations in microRNA processing genes. 30307055_The presence of PLAG1 fusion was associated with specific histological features in pleomorphic adenoma 30489320_PLAG1 rearrangements resulting in PLAG1 expression underpin ~25% of uterine myxoid leiomyosarcomas and may serve as a useful diagnostic biomarker 30839344_Differential Expression of PLAG1 in Apocrine and Eccrine Cutaneous Mixed Tumors: Evidence for Distinct Molecular Pathogenesis. 31094927_Metastasizing pleomorphic adenomas with recurrent PLAG1/HMGA2 gene rearrangements and a novel HMGA2-TMTC2 fusion. 31442350_Transcriptomic analysis showed that Plag1 increases the expression of a set of neuronal genes in NPCs. 31614359_The mechanisms of PLAG1 transcriptional upregulation in lipoblastoma pathogenesis. 31757836_Bayesian Modeling Identifies PLAG1 as a Key Regulator of Proliferation and Survival in Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. 31796335_Undifferentiated myxoid lipoblastoma with PLAG1 gene rearrangement in infant. 31922228_PLAG1 silencing promotes cell chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer via the IGF2 signaling pathway. 32572900_MicroRNA-21-5p promotes the inflammatory response after spinal cord injury by targeting PLAG1. 33027073_Molecular Profiling of Clear Cell Myoepithelial Carcinoma of Salivary Glands With EWSR1 Rearrangement Identifies Frequent PLAG1 Gene Fusions But No EWSR1 Fusion Transcripts. 33097826_Lipoblastomas presenting in older children and adults: analysis of 22 cases with identification of novel PLAG1 fusion partners. 33230916_Recent advances in smooth muscle tumors with PGR and PLAG1 gene fusions and myofibroblastic uterine neoplasms. 33291420_Novel Variant in PLAG1 in a Familial Case with Silver-Russell Syndrome Suspicion. 33300192_Pediatric fibromyxoid soft tissue tumor with PLAG1 fusion: A novel entity? 34063412_Methylation and Expression of FTO and PLAG1 Genes in Childhood Obesity: Insight into Anthropometric Parameters and Glucose-Lipid Metabolism. 34223693_Further heterogeneity in Silver-Russell syndrome: PLAG1 deletion in association with a complex chromosomal rearrangement. 34292619_Some pleomorphic adenomas of the breast share PLAG1 rearrangements with the analogous tumour of the salivary glands. 34390320_Malignant transformation of salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma: proof of principle. 34455363_The histological and molecular spectrum of lipoblastoma: A case series with identification of three novel gene fusions by targeted RNA-sequencing. 34684585_FTO and PLAG1 Genes Expression and FTO Methylation Predict Changes in Circulating Levels of Adipokines and Gastrointestinal Peptides in Children. 34906590_Pleomorphic adenoma: detection of PLAG1 rearrangement-positive tumor components using whole-slide fluorescence in situ hybridization. 35639948_PLAG1 dampens protein synthesis to promote human hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal. |
ENSMUSG00000003282 |
Plag1 |
149.107616 |
0.4302467902 |
-1.216764 |
0.174045651 |
48.212542 |
0.00000000000382434307656021772917442779789317860994479758574016159400343894958496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000021904270007772146550401172471370201278589862070589333598036319017410278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.5076826 |
10.0745539 |
204.7488991 |
16.0784890 |
| ENSG00000181722 |
26137 |
ZBTB20 |
protein_coding |
Q9HC78 |
FUNCTION: May be a transcription factor that may be involved in hematopoiesis, oncogenesis, and immune responses (PubMed:11352661). Plays a role in postnatal myogenesis, may be involved in the regulation of satellite cells self-renewal (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K0L9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11352661}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene, which was initially designated as dendritic cell-derived BTB/POZ zinc finger (DPZF), belongs to a family of transcription factors with an N-terminal BTB/POZ domain and a C-terminal DNA-bindng zinc finger domain. The BTB/POZ domain is a hydrophobic region of approximately 120 aa which mediates association with other BTB/POZ domain-containing proteins. This gene acts as a transcriptional repressor and plays a role in many processes including neurogenesis, glucose homeostasis, and postnatal growth. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Primrose syndrome as well as the 3q13.31 microdeletion syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:26137; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; positive regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045821]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0046889]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19850283_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19955470_Misexpression of Zbtb20 in transgenic mice converts the normal cytoarchitectonic organization of the subiculum, postsubiculum, and granular retrosplenial cortex to a CA1-like stratum pyramidale. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21702992_ZBTB20 mRNA & protein expression were elevated significantly in HCC tissues compared with the paired non-tumor tissues & normal liver. HCC recurrence or metastasis increased & disease-free survival decreased with high ZBTB20 expression. 22037551_We identified new susceptibility loci for non-cardia gastric cancer at 3q13.31: rs9841504 in ZBTB20 23283686_This study disclosed Zbtb20-mediated transcriptional repressor mechanism may be involved in development of the human archicortex. 23861218_Polymorphism in ZBTB20 gene is associated with gastric cancer. 24694013_Major depressive disorder is associated with significant hypermethylation within the coding region of ZBTB20. 25017102_Missense mutations in ZBTB20 underlie Primrose syndrome. 25062845_3q13.31 microdeletion-based dosage imbalance of ZBTB20 linked to a range of neurodevelopmental, cognitive and psychiatric disorders, likely mediated by dysregulation of multiple ZBTB20 target genes. 25311537_important role for ZBTB20 in controlling NSCLC development 26893361_High ZBTB20 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 27061120_We report a boy with intellectual disability carrying two de novo missense mutations in the last exon of ZBTB20 (Ser616Phe and Gly741Arg; both previously unreported). One of them, Ser616Phe, affects an amino acid located in one of the C2H2 zing-fingers involved in DNA-binding and close to other missense mutations already described. Reverse phenotyping showed that this patient presents with classic features of Primrose syn 27646774_ZBTB20 rs9841504 polymorphism is a protective factor for gastric cancer rather than esophageal cancer. 29681083_we report novel de novo ZBTB20 mutations in three independent cases with characteristic features of Primrose syndrome including constant CCA. 29737001_Our data document that both mutations have dominant negative impact on wild-type ZBTB20, providing further evidence of the specific behavior of Primrose syndrome (PS)-causing mutations on ZBTB20 function. 30099442_ZBTB20 knockdown inhibited glioblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. 30217971_ZBTB20 is a candidate susceptibility gene for seasonal affective disorder 30281617_Two ZBTB20 single nucleotide variants, located at the N-terminal and central regions of the protein and potentially conferring autism risk, altered dendritic spine morphology. In contrast, a single nucleotide variant identified in patients with intellectual disability and located at the C-terminus of ZBTB20 affected dendritic arborization and dendritic length but had no effect on dendritic spine morphology 31539138_Long non-coding RNA LINC00641 promotes cell growth and migration through modulating miR-378a/ZBTB20 axis in acute myeloid leukemia. 31556767_an important role for ZBTB20 in controlling gastric cancer development 31821719_Primrose syndrome associated with unclassified immunodeficiency and a novel ZBTB20 mutation. 32071410_Primrose syndrome: a phenotypic comparison of patients with a ZBTB20 missense variant versus a 3q13.31 microdeletion including ZBTB20. 32238402_The diagnostic challenges and clinical course of a myeloid/lymphoid neoplasm with eosinophilia and ZBTB20-JAK2 gene fusion presenting as B-lymphoblastic leukemia. 32266967_Primrose syndrome: Characterization of the phenotype in 42 patients. 32319639_HBV DNA integrates into upregulated ZBTB20 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 32936247_Prediction of gastric cancer risk: association between ZBTB20 genetic variance and gastric cancer risk in Chinese Han population. 33275231_LncRNA SNHG8 promotes cell migration and invasion in breast cancer cell through miR-634/ZBTB20 axis. 33777314_ZBTB20 Positively Regulates Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Fission, and Inflammatory Responses of ox-LDL-Induced Macrophages in Atherosclerosis. 34285142_An association study in the Taiwan Biobank elicits three novel candidates for cognitive aging in old adults: NCAM1, TTC12 and ZBTB20. 34825699_Circ-SFMBT2 facilitates the malignant growth of acute myeloid leukemia cells by modulating miR-582-3p/ZBTB20 pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000022708 |
Zbtb20 |
43.784814 |
0.1559659034 |
-2.680697 |
0.634212231 |
16.071448 |
0.00006099679323945318454606653868488308489759219810366630554199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000173504079440032566231111310628421051660552620887756347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7037393 |
5.4355229 |
62.1170546 |
24.1826770 |
| ENSG00000181744 |
205428 |
DIPK2A |
protein_coding |
Q8NDZ4 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in cardiomyocyte proliferation through paracrine signaling and activation of the PPI3K-AKT-CDK7 signaling cascade. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23784961}. |
Alternative splicing;Autism;Autism spectrum disorder;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Involved in several processes, including cardiac muscle cell proliferation; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process; and positive regulation of protein kinase C activity. Located in Golgi membrane and extracellular space. Part of COPI vesicle coat. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:205428; |
COPI vesicle coat [GO:0030126]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0034392]; positive regulation of protein kinase C activity [GO:1900020]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014066] |
21264219_results support a model where the DIA1 and DIA1R regulate molecular traffic through the cellular secretory pathway or affect the function of secreted factors, and functional deficits cause disorders with ASD-like symptoms and/or mental retardation 28096202_HASF (C3orf58) is a novel ligand of IGF1R. 31251111_DIPK2A promotes STX17- and VAMP7-mediated autophagosome-lysosome fusion by binding to VAMP7B. |
ENSMUSG00000045414 |
Dipk2a |
195.234387 |
0.4798846035 |
-1.059241 |
0.118867107 |
80.122310 |
0.00000000000000000035193624815178398087790170447428225157324287522214527855479726525800288072787225246429443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000003004383471787352246297114754520016719872071859614168568008985005235444987192749977111816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
129.6423768 |
11.4925822 |
272.3790066 |
16.3564878 |
| ENSG00000181773 |
2827 |
GPR3 |
protein_coding |
P46089 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor with constitutive G(s) signaling activity that activate cyclic AMP. Has a potential role in modulating a number of brain functions, including behavioral responses to stress (By similarity), amyloid-beta peptide generation in neurons and neurite outgrowth (By similarity). Maintains also meiotic arrest in oocytes (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19213921}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor family and is found in the cell membrane. G protein-coupled receptors, characterized by a seven transmembrane domain motif, are involved in translating outside signals into G protein mediated intracellular effects. The encoded protein activates adenylate cyclase and modulates amyloid-beta production in a mouse model, suggesting that it may play a role in Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2012]. |
hsa:2827; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; positive regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043950]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0051480]; regulation of meiotic nuclear division [GO:0040020]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222] |
12649592_control of gene expression in vascular endothelial cells in the presence of fluid shear stress and classifies it as a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor. 15591206_GPR3 is expressed in the ovary and testes, and is necessary for the regulation of meiosis in mouse. 17953967_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17953967_We conclude that perturbations in GPR3 are not a common explanation for POF in this population. 20158988_Mutations in GPR3 are not a common cause of premature ovarian failure in Chinese women. 23732663_GPR3 is a key factor in the regulation of the nervous system and follicle development.[review] 23826079_Results demonstrate that GPR3 signals at the plasma membrane and can be silenced by GRK2/beta-arrestin overexpression. These results also strongly implicate the serine and/or threonine residues in the third intracellular loop in the regulation of GPR3 activity. 24069330_Gpr3 stimulates Abeta production via interactions with APP and beta-arrestin2. 30038319_these results suggest an important role of the allosteric sodium binding site for GPR3 activity and open a possible avenue for the modulation of Abeta production in the Alzheimer's Disease. 31516076_Development of a High-Throughput Screening-Compatible Assay for Discovery of GPR3 Inverse Agonists Using a cAMP Biosensor. 34048700_Lipolysis drives expression of the constitutively active receptor GPR3 to induce adipose thermogenesis. 34302056_Silencing the G-protein coupled receptor 3-salt inducible kinase 2 pathway promotes human beta cell proliferation. |
ENSMUSG00000049649 |
Gpr3 |
24.787968 |
3.0763569222 |
1.621223 |
0.321803459 |
26.433804 |
0.00000027272567212324086298772755215802376937972439918667078018188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001025848858445217858946681144249879480412346310913562774658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.6253090 |
7.4174654 |
12.6665470 |
2.0235034 |
| ENSG00000181785 |
219447 |
OR5AS1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N127 |
FUNCTION: Odorant receptor. {ECO:0000305}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Olfaction;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose, to initiate a neuronal response that triggers the perception of a smell. The olfactory receptor proteins are members of a large family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) arising from single coding-exon genes. Olfactory receptors share a 7-transmembrane domain structure with many neurotransmitter and hormone receptors and are responsible for the recognition and G protein-mediated transduction of odorant signals. The olfactory receptor gene family is the largest in the genome. The nomenclature assigned to the olfactory receptor genes and proteins for this organism is independent of other organisms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:219447; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; odorant binding [GO:0005549]; olfactory receptor activity [GO:0004984] |
|
ENSMUSG00000075158 |
Olfr1111 |
12.357325 |
0.4885107189 |
-1.033538 |
0.426036296 |
5.929885 |
0.01488621580448254953787934340425636037252843379974365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027485682421086118226716266121911758091300725936889648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4558917 |
2.3985496 |
17.3121381 |
3.1412099 |
| ENSG00000181790 |
575 |
ADGRB1 |
protein_coding |
O14514 |
FUNCTION: Phosphatidylserine receptor which enhances the engulfment of apoptotic cells (PubMed:24509909). Also mediates the binding and engulfment of Gram-negative bacteria (PubMed:26838550). Stimulates production of reactive oxygen species by macrophages in response to Gram-negative bacteria, resulting in enhanced microbicidal macrophage activity (PubMed:26838550). In the gastric mucosa, required for recognition and engulfment of apoptotic gastric epithelial cells (PubMed:24509909). Promotes myoblast fusion (By similarity). Activates the Rho pathway in a G-protein-dependent manner (PubMed:23782696). Inhibits MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of DLG4/PSD95, promoting DLG4 stability and regulating synaptic plasticity (By similarity). Required for the formation of dendritic spines by ensuring the correct localization of PARD3 and TIAM1 (By similarity). Potent inhibitor of angiogenesis in brain and may play a significant role as a mediator of the p53/TP53 signal in suppression of glioblastoma (PubMed:11875720). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:C0HL12, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UHD1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11875720, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23782696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24509909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26838550}.; FUNCTION: [Vasculostatin-120]: Inhibits angiogenesis in a CD36-dependent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15782143, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19176395}.; FUNCTION: [Vasculostatin-40]: Inhibits angiogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22330140}. |
Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Myogenesis;Neurogenesis;Phagocytosis;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
Angiogenesis is controlled by a local balance between stimulators and inhibitors of new vessel growth and is suppressed under normal physiologic conditions. Angiogenesis has been shown to be essential for growth and metastasis of solid tumors. In order to obtain blood supply for their growth, tumor cells are potently angiogenic and attract new vessels as results of increased secretion of inducers and decreased production of endogenous negative regulators. BAI1 contains at least one 'functional' p53-binding site within an intron, and its expression has been shown to be induced by wildtype p53. There are two other brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor genes, designated BAI2 and BAI3 which along with BAI1 have similar tissue specificities and structures, however only BAI1 is transcriptionally regulated by p53. BAI1 is postulated to be a member of the secretin receptor family, an inhibitor of angiogenesis and a growth suppressor of glioblastomas [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:575; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipopolysaccharide binding [GO:0001530]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; engulfment of apoptotic cell [GO:0043652]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of protein ubiquitination [GO:0031397]; peripheral nervous system development [GO:0007422]; phagocytosis, recognition [GO:0006910]; positive regulation of myoblast fusion [GO:1901741]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903428]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11875720_brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 over-expression suppresses tumour angiogenesis 12074842_BAI1 was expressed in cerebral neurons but not astrocytes. It was localized in the cytoplasm and cell membrane. BAI1 protein may play an important role in synapse formation and signal transduction 12507886_BAI1 was widely expressed in normal brain but was absent in 28 glioma cell lines and in the majority of human glioblastoma investigated. BAI1 expression did not correlate with TP53 status 21724586_MBD2 overexpression during gliomagenesis may drive tumor growth by suppressing the antiangiogenic activity of a key tumor BAI1. 22330140_Proprotein convertases, primarily furin, activate latent matrix metalloproteinase-14, which then directly cleaves BAI1 to release the bioactive fragment. 23595754_The results of this study indicated that BAI1 plays an important role in synaptogenesis that is mechanistically distinct from its role in phagocytosis. 23782696_findings demonstrate that BAI1 is a synaptic receptor that can activate both the Rho and ERK pathways, with the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the receptor playing key roles in the regulation of BAI1 signaling activity 24509909_recognition of apoptotic cells by BAI1 contributes to their clearance in the human gastric mucosa and this is associated with anti-inflammatory effects 25376607_Results show that lower BAI1 expression correlates with poorer patient survival, and high Nestin expression is associated with an increased probability of metastases in breast cancer patients. 26129954_BAI1 may be involved in the negative regulation of bladder transitional cell carcinoma microvascular proliferation, and its expression may be associated with a reduction in p53 mutations. 26710850_Data suggest agonist-induced signal transduction via either BAI1/ADGRB1 or GPR56/ADGRG1 does not require conserved membrane-proximal stalk region; thus, it appears GAIN domain cleavage via autoproteolysis is not necessary for receptor activation. 27852701_We have uncovered a new role for BAI1 in facilitating macrophage anti-viral responses. We show that arming oHSV with antiangiogenic Vstat120 also shields them from inflammatory macrophage antiviral response, without reducing safety 29894688_Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1) prevents proto-oncogene Protein c-mdm2 (Mdm2)-mediated tumor supressor p53 (p53) polyubiquitination, and its loss substantially reduces p53 levels. 31582835_EZH2 targeting reduces medulloblastoma growth through epigenetic reactivation of the BAI1/p53 tumor suppressor pathway. 32255478_BAI1 acts as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer A549 cells by inducing metabolic reprogramming via the SCD1/HMGCR module. 32614850_Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 is expressed in the Myo/Nog cell lineage. 33934543_BAI1 nuclear expression reflects the survival of nonsmoking non-small cell lung cancer patients. 34475070_BAI1 as a Prognostic Marker of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC). 35738517_Maternal exposure to atmospheric PM2.5 and fetal brain development: Associations with BAI1 methylation and thyroid hormones. |
ENSMUSG00000034730 |
Adgrb1 |
61.479228 |
0.1335561364 |
-2.904482 |
0.290717351 |
104.025662 |
0.00000000000000000000000199712495563097276988150408535358961588909519537532239922241191301156837401009624954895116388797760009765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000021010380858954495852347958049312552566807399205360380584198037520748947315496479859575629234313964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.1154374 |
3.1665762 |
121.4663352 |
13.8748842 |
| ENSG00000181885 |
1366 |
CLDN7 |
protein_coding |
O95471 |
FUNCTION: Plays a major role in tight junction-specific obliteration of the intercellular space. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the claudin family. Claudins are integral membrane proteins and components of tight junction strands. Tight junction strands serve as a physical barrier to prevent solutes and water from passing freely through the paracellular space between epithelial or endothelial cell sheets, and also play critical roles in maintaining cell polarity and signal transductions. Differential expression of this gene has been observed in different types of malignancies, including breast cancer, ovarian cancer, hepatocellular carcinomas, urinary tumors, prostate cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancers, thyroid carcinomas, etc.. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:1366; |
apicolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016327]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; lateral plasma membrane [GO:0016328]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; calcium-independent cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell-adhesion molecules [GO:0016338]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0007162]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471] |
12673207_Loss of claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, providing insight into the potential role of CLDN-7 in the progression and ability of breast cancer cells to disseminate. 14502431_2 forms of claudin-7, a full-length form with 211 AA residues and a C-terminal truncated form with 158 AA residues, are able to regulate the expression of a tissue-specific protein, prostate-specific antigen, in the LNCaP prostate cancer cell line. 15475928_Loss of claudin-1 expression proved to be a strong predictor of disease recurrence and poor patient survival in stage II colon cancer. 15790437_Claudin-1 and claudin-7 may play a significant role in tumor progression of cervical neoplasia and may represent useful markers for malignant transformation of cervical squamous cells. 16049341_Overexpression of claudin-7 is associated with gastric tumorigenesis 17060315_induction of claudin7 expression by ELF3 appears critical to the formation of the epithelial structures in biphasic synovial sarcoma 17103306_Claudin tight junction proteins in endoscopy biopsy samples showed Barrett's metaplasia contains more claudin-2 and claudin-3 than found in normal esophageal mucosa, but markedly lower claudins 1 and 5, indicating very different tight junction barriers. 17418912_When compared, adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas revealed significant differences in CLDN7 expression. 17579117_claudin-7-associated EpCAM is recruited into (tetraspanin-enriched membrane microdomains) and forms a complex with CO-029 and CD44v6 that facilitates metastasis formation 17611659_Results show show that claudin 7 expression changed with the gastric carcinogenic process and that this is implicated in cancer characteristics. 17922590_Claudin-7 to be a candidate expression marker for distinguishing chromophobe renal cell carcinoma from other renal tumor subtypes, including the morphologically similar oncocytoma. 17962811_Reduced claudin-7 expression correlates with loss of differentiation in thyroid neoplasms. 18298564_CLDN-7 is significantly overexpressed in all main histologic types of epithelial ovarian cancer 18349130_The role of extracellular loop domains of claudin-1 in determining tight junctions function, is studied. 18357381_a reduced expression of the claudin-7 gene might lead to venous invasion and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. 18439941_Claudin-3 and claudin-7 expression in effusions independently predicts poor survival in ovarian cancer. 18519685_claudin-7 overexpression promotes a loss of tumor cell polarization and contributes to tumorigenesis 18550469_neither occludin nor claudin-7 expression was associated with clinicopathologic findings in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. 18560860_Claudin-1 plays a crucial role in recruiting occludin to tight junctions, and occludin is involved in intercellular barrier function. 18667601_Aspirin induces gastric epithelial barrier dysfunction by activating p38 MAPK via claudin-7. 18799195_claudin-7 and claudin-8 have potential use as immunohistochemical biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma 18981000_claudin-1 expression is an independent prognosticator of shortened disease-specific patient survival in clinically relevant subgroups of clear cell renal cell carcinoma 19120888_Down-regulation of claudin-7 might lead to altered tight junction structure and be related to the impaired epithelial function in active ulcerative colitis. 19194274_Expression pattern of claudins 5 and 7 distinguishes solid-pseudopapillary from pancreatoblastoma, acinar cell and endocrine tumors of the pancreas. 19231096_claudin-4, in addition to 1 and 5, might be a useful differential diagnostic marker of lung cancer in Korean people. 19661441_is altered in early-stage psoriasis 19960275_Claudins 6, 7, and 9 expressions are closely related to gastric carcinogenesis. 20204275_Claudin-1 was expressed in all 18 cases of Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma studied 20478039_Claudin-1, -3, -4, -5, and -7 are expressed in developing human lung from week 12 to week 40 with distinct locations and in divergent quantities. 20874001_Increased expression of claudin-6, claudin-7, or claudin-9 is sufficient to enhance tumorigenic properties of a gastric adenocarcinoma cell line. 20926780_These data suggest that proteasomes regulate claudin-1 localization at the plasma membrane, which changes upon proteasomal inhibition to a Rab5a-mediated endosomal localization. 21083599_Claudin-7 down-regulation is an important feature in oral squamous cell carcinoma 21184237_Analysis of staining intensities of CLDN 1 and 3 is useful as an auxiliary diagnostic and prognostic tool in patients with salivary gland mucoepidermoid carcinoma. 21193919_transcriptional activity of claudin 7 gene not a useful marker of laryngeal tumor 21310043_Claudin-7 mRNA level is decreased already as an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis, probably contributing to the compromised epithelial barrier in adenomas. 21480761_Claudin-7 and tricellulin were markedly reduced at all stages of tumor development. In situ hybridization analysis showed no correlation between HPV infection and altered expression of the tight junction proteins. 21641901_The claudin-7 inhibits cell migration and invasion through ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in response to growth factor stimulation in human lung cancer cells. 21645451_down-regulation of Claudin-7 and overexpression of Slug in lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma 21789222_Claudin-7 is significantly upregulated in epithelial ovarian cancer. 21956537_CD24+ (P=0.07) and claudin-7 positivity (P=0.05) were associated with reduced time of recurrence, suggesting a contribution of these markers to aggressiveness of breast cancer. 22941467_Increased expression of claudin-1 contributes to an anti-apoptotic role in TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. 23146509_Survival analysis showed a trend toward a better prognosis among patients with overexpression of claudin-7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 23433123_Claudin-7 was phosphorylated at serine 204 by protein kinase C. 23953778_lack of claudin-7 expression in the tumour centre may be used to identify patients with increased risk for regional recurrence 24333468_Evaluated expression of claudins in gastric cancer and determined their significance for patient outcome. Claudin-3 and claudin-7 were expressed in 25.4% and 29.9% of gastric cancer tissues; 51.5% of gastric cancer tissues had reduced claudin-18. 24358122_These results suggest aberrant Claudin 7, alpha - and beta-catenin expression and/or localisation patterns may be putative markers for distinguishing localised prostate cancer from aggressive metastatic disease when used collectively. 24479816_the CLDN7 rs4562 (c.590C>T) genotype had a higher risk of lymph node involvement and a lower degree of tumor differentiation 24696415_Increased expression of claudin-7 is associated with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. 24727741_This study suggests the possibility that EpCAM, together with CD44v6 and claudin-7 as well as ALDH1, may be involved in the development of the aggressive phenotype of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. 24737165_Data show that claudin-4 and claudin-7 were observed in hepatocytes of severely damaged mouse and human livers. 24815833_The present study demonstrates that high expression of claudins 1, 4, 5 and down-regulation of claudin-7 are positive prognostic markers and are associated with good outcome and increased survival rates. 24997475_these results confirm the role of claudin-1 as a promoter of colon tumorigenesis and further identify the role of the dysregulated antigen-tumor interaction and inflammation in claudin-1-dependent upregulation of colon tumorigenesis. 25038829_Claudin 1, 4, and 7 are important building blocks of paracellular adhesion molecules; their decreased expression in colorectal cancer seems to have critical effects on cell proliferation, motility, invasion, and immune response against the tumor. 25078758_The increased claudin-1 expression was significantly associated with the high pathologic grade, the presence of microscopic perineural invasion, vascular invasion, nodal metastasis, and advanced clinical stage of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 25500541_Loss of claudin-7 potentiates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition to promote colon cancer, in a manner dependent on Rab25. 25514462_Data indicate that claudin-7 knockdown cells display decreased anchorage-independent growth. 25759378_A variant, rs222857, in the CLDN7 locus, predicted adiponectin increases within intensive lifestyle intervention. 25778318_Icreased claudin 7 expression was related to decreased survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 26054340_CLDN-7 palmitoylation prohibits tight junction integration and fosters glycolipid-enriched membrane domains recruitment. Via associated molecules, palmitoylated CLDN-7supports motility and invasion. 26081244_we identified a previously unrecognized function of claudin-7 in regulating cell proliferation and maintaining epithelial cell attachment through engaging integrin beta1. 26216285_We identified hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha as a regulatory factor that bound endogenous CLDN7 promoter in differentiating intestinal epithelial cells and stimulated CLDN7 promoter activity. 26319240_claudin 1 and claudin 4 are differentially involved in atopic dermatitis pathogenesis 26340953_localization of Cldn3, Cldn7 and Cldn10 proteins in the different compartments of murine endometrium up to day 8.5 of pregnancy (dpc) as well as in human endometrium and first trimester decidua 26464708_The expression of claudin-7 has no obviously difference between cervical carcinoma tissues and adjacent non-neoplastic tissues. 26872891_These results suggested that increase of Cldn4-expression may be involved in early molecular events during carcinogenesis of adenocarcinoma, whereas increase of Cldn7-expression may be associated with tumor invasion or progression. 26982264_that the dysregulated expression of these miRNAs, in conjunction with the high claudin 1 levels, could serve as a useful biomarker that identifies a subset of tumors within the poorly characterized basal-like subtype of breast cancer 27444172_that claudins-4 and -7 might be valuable markers for distinguishing hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma and that cholangiolocellular carcinoma might arise from hepatic ductal cells 27884700_suggest that the reduction of CLDN5, 7, and 18 expression loses the suppressive ability of interaction between PDK1 and Akt and causes sustained phosphorylation of Akt, resulting in the disordered proliferation in lung squamous carcinoma cells 28055967_Cycling hypoxia could induce significant changes in CLDN1 and CLDN7 expression in nasopharyngeal cancer cells, indirectly regulation P18 expression and affecting cell invasion/proliferation. 28094766_These results identify EpCAM as a substrate of matriptase and link HAI-2, matriptase, EpCAM, and claudin-7 in a functionally important pathway that causes disease when it is dysregulated. 28295005_84/118, 64/118, 52/118 reaction with claudin-1, claudin-3 and claudin-4 in cancer and colon polyps had a membrane localization, respectively.Mislocalization claudin-3 to nucleus in colon cancer and mislocalization claudin-4 to nucleus in adenomas of the colon were detected for the first time. 28832026_this paper shows that TGF-beta1 alters esophageal epithelial barrier function by attenuation of claudin-7 in eosinophilic esophagitis 29031421_these results suggest that Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide induces TLR2 expression in the gastric adenocarcinoma cells, and that the longer the exposure to lipopolysaccharide, the greater the expression of TLR2 in the cell membrane; consequently the expression of claudin-4, -6, -7 and -9 also increases 29422769_In addition to replicating a previously identified genome-wide significant locus for corneal astigmatism near the PDGFRA gene, gene-based analysis identified three novel candidate genes, CLDN7, ACP2, and TNFAIP8L3, that warrant further investigation to understand their role in the pathogenesis of corneal astigmatism. (Meta-analysis) 29482498_Immunohistochemical expression levels of cytoplasmic claudins 3 and 7 appear to be novel prognostic factors in triple-negative breast cancer. 29512497_DICFM approach may be applied as an appropriate approach to quantify the immunohistochemical staining of claudin-7 on the cell membrane and claudin-7 may serve as a marker for identification of lung cancer 29788731_CLDN7 expression is significantly elevated in gastric cancer tissues, and the overexpression of CLDN7 is closely related to lymph node metastasis. CLDN7 executes an oncogenic function, promoting cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 29901188_the present study revealed the distinct expression profiles of claudin5, 7 and 8 in nonneoplastic mucosal tissues and gastric carcinoma tissues. Furthermore, the expression of these claudin proteins was highly associated with metastatic progression and prognosis in patients with gastric carcinoma 30044945_In the salivary gland ducts from patients with IgG4-related disease there was significant infiltration of IgG-positive plasma cells, and expression of GBP-1, CLDN-7 and LSR was increased. 30243087_The mechanism involved in the modulation of serine phosphorylated claudin-7. 30416041_CLDN7 may be expressed in the rapidly proliferating and dominant cell population in human pancreatic cancer tissues. 30428910_Authors have demonstrated a previously undescribed role of CLDN7 as a ccRCC suppressor and suggest that loss of CLDN7 potentiates EMT and tumor progression. 30528239_Decreasing expression of Claudin-7 may promote the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 30945750_Results how that cancer-initiating cell (CIC) -tumor exosomes (TEX) rescue Claudin7 (cld7)-knockdown (kd) (cld7kd) tumor progression. 31115553_the findings of the present study demonstrated that the expression levels of CLDN1, 3, 7 and 8 varied between laryngeal squamous carcinoma tissues and nonneoplastic tissues 31298324_Long noncoding RNA DDX11-AS1 induced by YY1 accelerates colorectal cancer progression through targeting miR-873/CLDN7 axis. 31737127_Claudin-7 is frequently expressed in the chromophobe renal cell carcinoma with high specificity. 32749148_Claudin-7 Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis in Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Through Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling. 32992138_The p53-inducible CLDN7 regulates colorectal tumorigenesis and has prognostic significance. 33441633_Reduced occludin and claudin-7 expression is associated with urban locations and exposure to second-hand smoke in allergic rhinitis patients. 33483086_Titanium dioxide particles modulate epithelial barrier protein, Claudin 7 in asthma. 34281572_Claudin-7 deficiency promotes stemness properties in colorectal cancer through Sox9-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. 34571860_A Claudin-Based Molecular Signature Identifies High-Risk, Chemoresistant Colorectal Cancer Patients. 34763991_Claudin-7 in keratinocytes is downregulated by the inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase and is highly expressed in the stratum granulosum of the psoriatic epidermis. 34774484_N-glycosylation status of Trop2 impacts its surface density, interaction with claudin-7 and exosomal release. 36275703_Matrix metalloproteinase 7 contributes to intestinal barrier dysfunction by degrading tight junction protein Claudin-7. |
ENSMUSG00000018569 |
Cldn7 |
90.761668 |
0.2638861785 |
-1.922012 |
0.251831794 |
57.483177 |
0.00000000000003408824198970690893264627094155157152334219630707146109216409968212246894836425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000222925322006235723929020331361736497518405419882014939503278583288192749023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.8414595 |
5.7012253 |
136.6647351 |
14.2875666 |
| ENSG00000181982 |
91050 |
CCDC149 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZUS6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:91050; |
|
17457313_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000045790 |
Ccdc149 |
96.509511 |
2.8974422430 |
1.534780 |
0.526895391 |
7.897305 |
0.00495084941020147804163764604368225263897329568862915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010132354034189380159736160180727893020957708358764648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
156.1132122 |
54.9095698 |
54.2765745 |
13.6885629 |
| ENSG00000182022 |
51363 |
CHST15 |
protein_coding |
Q7LFX5 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that transfers sulfate from 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) to the C-6 hydroxyl group of the GalNAc 4-sulfate residue of chondroitin sulfate A and forms chondroitin sulfate E containing GlcA-GalNAc(4,6-SO(4)) repeating units. It also transfers sulfate to a unique non-reducing terminal sequence, GalNAc(4SO4)-GlcA(2SO4)-GalNAc(6SO4), to yield a highly sulfated structure similar to the structure found in thrombomodulin chondroitin sulfate. May also act as a B-cell receptor involved in BCR ligation-mediated early activation that mediate regulatory signals key to B-cell development and/or regulation of B-cell-specific RAG expression; however such results are unclear in vivo. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11572857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12874280}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Chondroitin sulfate (CS) is a glycosaminoglycan which is an important structural component of the extracellular matrix and which links to proteins to form proteoglycans. Chondroitin sulfate E (CS-E) is an isomer of chondroitin sulfate in which the C-4 and C-6 hydroxyl groups are sulfated. This gene encodes a type II transmembrane glycoprotein that acts as a sulfotransferase to transfer sulfate to the C-6 hydroxal group of chondroitin sulfate. This gene has also been identified as being co-expressed with RAG1 in B-cells and as potentially acting as a B-cell surface signaling receptor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:51363; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate binding [GO:0050656]; N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase activity [GO:0050659]; chondroitin sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030206]; hexose biosynthetic process [GO:0019319] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23349846_Findings indicate that GalNAc4S-6ST mRNA expressed by astrocytic tumor cells is associated with poor patient prognosis. 26642349_The direct action of CHST15 on the proliferation. 27410685_blockade CHST15 represses colonic fibrosis 30963568_The expression of HOTAIR closely correlated with the level of CHST15 protein. 31746400_Results showed that CHST15 is highly expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) TE1 cell line and tissues. Its knockdown inhibited TE1 cell growth and proliferation, but induced cell apoptosis. These findings indicate that CHST15 may play an essential role in mediating the tumorigenicity of ESCC cells. 34922539_circCHST15 is a novel prognostic biomarker that promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis through the miR-125a-5p/EIF4EBP1 axis. 35798703_CHST15 gene germline mutation is associated with the development of familial myeloproliferative neoplasms and higher transformation risk. |
ENSMUSG00000030930 |
Chst15 |
301.274919 |
0.4282215124 |
-1.223571 |
0.120219326 |
103.017782 |
0.00000000000000000000000332153579455908664106372071369857961132036652370819612592971583134304758289090386824682354927062988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000034696297471827397363362366096134813893780119525694490161308279618790351150892092846333980560302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
190.6306926 |
14.3581367 |
447.6914029 |
22.6137308 |
| ENSG00000182050 |
25834 |
MGAT4C |
protein_coding |
Q9UBM8 |
FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase that participates in the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) to the core mannose residues of N-linked glycans. Catalyzes the formation of the GlcNAcbeta1-4 branch on the GlcNAcbeta1-2Manalpha1-3 arm of the core structure of N-linked glycans. Essential for the production of tri- and tetra-antennary N-linked sugar chains (By similarity). Does not catalyze the transfer of GlcNAc to the Manalpha1-6 arm to form GlcNAcBeta1-4Manalpha1-6 linkage ('GnT-VI' activity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10962001}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
Predicted to enable acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein N-linked glycosylation. Predicted to be located in Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25834; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; alpha-1,3-mannosylglycoprotein 4-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008454]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; viral protein processing [GO:0019082] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 33581268_Association of MGAT4C with major neurocognitive disorder in the Mexican population. |
ENSMUSG00000019888 |
Mgat4c |
120.337923 |
73.3750550771 |
6.197218 |
0.329829618 |
444.309486 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001248953222239759365493336942833013528659795691237076087086330294727478621404034991574502245975514189390609798285259126349539497859497228275548528654009575500186554544417963839634767365851399489848818554927532062658120785847545948659 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000519283086204474584799748808976528248945602124198514507464685761071460342574169116687499939409755035124425360020998797023084062296723709113636653252318771159636482843748863923334699347869294714679923421528140017532298548044097997772 |
Yes |
No |
175.8748955 |
38.6131828 |
2.4107816 |
0.4801098 |
| ENSG00000182132 |
30820 |
KCNIP1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZI2 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of Kv4/D (Shal)-type voltage-gated rapidly inactivating A-type potassium channels. Regulates channel density, inactivation kinetics and rate of recovery from inactivation in a calcium-dependent and isoform-specific manner. In vitro, modulates KCND1/Kv4.1 and KCND2/Kv4.2 currents. Increases the presence of KCND2 at the cell surface. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10676964, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11423117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12829703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17187064}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a member of the family of cytosolic voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel-interacting proteins (KCNIPs), which belong to the neuronal calcium sensor (NCS) family of the calcium binding EF-hand proteins. They associate with Kv4 alpha subunits to form native Kv4 channel complexes. The encoded protein may regulate rapidly inactivating (A-type) currents, and hence neuronal membrane excitability, in response to changes in the concentration of intracellular calcium. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:30820; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; voltage-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005244]; regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901379] |
15358149_Data show that KChIP1, KChIP2.1, and KChIP2.2 could form homo- as well as hetero-oligomers, and that this oligomerization did not perturb their interaction with Kv4.2 potassium channel. 17057713_X-ray crystallographic and small-angle X-ray scattering data that show that the KChIP1-Kv4.3 N-terminal cytoplasmic domain complex is a cross-shaped octamer bearing two principal interaction sites. 18393943_These results reveal a new role for KChIP3 in the regulation of calcium regulated secretion and also suggest that the functions of each of the KChIPs may be more specialized than previously appreciated. 19550036_EF-hands 3 and 4 of KChIP1 are functionally involved in a specific association with PS on the membrane 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21129448_our findings suggest that KChIP1 interacts with Kv4.3 in interneurons at the stratum lacunosum-moleculare/radiatum junction 24681403_Protein aggregation due to nsSNP resulting in P56S VABP protein is associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 24792378_V234I-VAPB induces ubiquitin aggregation followed by cell death; proposed that V234I-VAPB exhibits the characteristics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in spite of not having the typical aggregation property of different mutations in various neurodegenerative diseases 24886904_KCNIP1 from copy number variations study might function as a type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene whose dysregulation alters insulin production. 26831368_These studies showed that a common copy number variation in KCNIP1 gene is a genetic predictor of atrial fibrillation risk possibly pointing to a functional pathway. 28132811_Study shows that the VAPB-PTPIP51 tethers regulate autophagy and demonstrates that overexpression of VAPB or PTPIP51 to tighten endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria contacts impairs, whereas small interfering RNA-mediated loss of VAPB or PTPIP51 to loosen contacts stimulates, autophagosome formation. 29176790_the current study provides evidence that genetic variants of Kv accessory proteins may contribute to the susceptibility of Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. 29491224_This is the first copy number variation association study of the KCNIP1 gene in Chinese population, and these data indicated that KCNIP1 might function as a type 2 diabetes-susceptibility gene whose dysregulation alters insulin production. |
ENSMUSG00000053519 |
Kcnip1 |
34.748166 |
0.2959101129 |
-1.756769 |
0.281990054 |
41.600493 |
0.00000000011196503106959077898785952325837124606000561044538699206896126270294189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000577228033037778503626053257501713270039012115830701077356934547424316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.6803990 |
3.2063970 |
56.7401294 |
6.2338999 |
| ENSG00000182134 |
11022 |
TDRKH |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2W6 |
FUNCTION: Participates in the primary piRNA biogenesis pathway and is required during spermatogenesis to repress transposable elements and prevent their mobilization, which is essential for the germline integrity. The piRNA metabolic process mediates the repression of transposable elements during meiosis by forming complexes composed of piRNAs and Piwi proteins and govern the methylation and subsequent repression of transposons. Required for the final steps of primary piRNA biogenesis by participating in the processing of 31-37 nt intermediates into mature piRNAs. May act in pi-bodies and piP-bodies by transferring piRNA precursors or intermediates to or between these granules. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80VL1}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Isopeptide bond;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;RNA-mediated gene silencing;Spermatogenesis;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in fertilization; gamete generation; and piRNA metabolic process. Predicted to be located in mitochondrion; pi-body; and piP-body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:11022; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; P granule [GO:0043186]; pi-body [GO:0071546]; piP-body [GO:0071547]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; male meiotic nuclear division [GO:0007140]; P granule organization [GO:0030719]; piRNA processing [GO:0034587]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
15955813_Tudor domain proteins interact with arginine-glycine-rich motifs in a methylarginine-dependent manner. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29118143_Unlike most other Tudor domains TDRD2 preferentially recognizes an unmethylated arginine-rich sequence from PIWIL1. 30503856_TDRKH missense mutation segregates with dominant distal hereditary motor neuropathy in a four generation pedigree. |
ENSMUSG00000041912 |
Tdrkh |
17.664359 |
2.2879728549 |
1.194070 |
0.348869141 |
11.991631 |
0.00053439984472198947748622366304971365025267004966735839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001305269188829482826519345906035596271976828575134277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.7394027 |
5.1193272 |
9.9777427 |
1.8224926 |
| ENSG00000182179 |
7318 |
UBA7 |
protein_coding |
P41226 |
FUNCTION: Activates ubiquitin by first adenylating with ATP its C-terminal glycine residue and thereafter linking this residue to the side chain of a cysteine residue in E1, yielding a ubiquitin-E1 thioester and free AMP. Catalyzes the ISGylation of influenza A virus NS1 protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16254333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20133869}. |
ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11157743}. |
The modification of proteins with ubiquitin is an important cellular mechanism for targeting abnormal or short-lived proteins for degradation. Ubiquitination involves at least three classes of enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes, or E1s, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, or E2s, and ubiquitin-protein ligases, or E3s. This gene encodes a member of the E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme family. The encoded enzyme is a retinoid target that triggers promyelocytic leukemia (PML)/retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARalpha) degradation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia, where it is involved in the conjugation of the ubiquitin-like interferon-stimulated gene 15 protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7318; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ISG15 activating enzyme activity [GO:0019782]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; ISG15-protein conjugation [GO:0032020]; modification-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0019941]; protein modification by small protein conjugation [GO:0032446]; protein modification process [GO:0036211] |
11891284_UBE1L is a retinoid target that triggers PML/RARalpha degradation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia 14976209_RA treatment of APL and other RA-responsive leukemic cells induced expression of UBE1L and ISG15 as well as intracellular ISG15 conjugates. A physical association was found between UBE1L and ISG15 in vivo. 18583345_Ube1L was required for transfer of ISG15 to UbcH8 and for binding of Ube1L to UbcH8 19074853_UBE1L-ISG15 preferentially inhibits cyclin D1 in lung cancer 20307617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20601676_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21670151_the cellular effects of progerin expression in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome are transduced, at least in part, through reduced function of the Ran GTPase and E2 SUMOylation pathways. 29743376_RNF170, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated ubiquitin E3 ligase, interacted with pUL50 and promoted pUL50-mediated UBE1L degradation via ubiquitination. 31428903_TNF-alpha, similar to the response by IFN-beta, could directly induce expression of ISG15 and its conjugation machinery, UbE1L and UbcH8, in human lung carcinoma. 31974171_Type I Interferon Regulates a Coordinated Gene Network to Enhance Cytotoxic T Cell-Mediated Tumor Killing. |
ENSMUSG00000032596 |
Uba7 |
810.520504 |
0.1644392203 |
-2.604374 |
0.093972924 |
747.039293 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001766719067760456451824892223617518051232648554691198120727071172889495667154491433026976594390900102404571829118450243724520654671700353342328607604260923806599480278 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001290929378224967150152647176684065118489534713058570945294875957153477714354555895770039117061241608689227196774972769310524244806299658477667167956176619698453790930 |
Yes |
Yes |
231.1996902 |
16.0944478 |
1418.2234182 |
65.5444343 |
| ENSG00000182199 |
6472 |
SHMT2 |
protein_coding |
P34897 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the cleavage of serine to glycine accompanied with the production of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, an essential intermediate for purine biosynthesis (PubMed:24075985, PubMed:29364879, PubMed:33015733 PubMed:25619277, PubMed:33015733). Serine provides the major source of folate one-carbon in cells by catalyzing the transfer of one carbon from serine to tetrahydrofolate (PubMed:25619277). Contributes to the de novo mitochondrial thymidylate biosynthesis pathway via its role in glycine and tetrahydrofolate metabolism: thymidylate biosynthesis is required to prevent uracil accumulation in mtDNA (PubMed:21876188). Also required for mitochondrial translation by producing 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate; 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate providing methyl donors to produce the taurinomethyluridine base at the wobble position of some mitochondrial tRNAs (PubMed:29452640, PubMed:29364879). Associates with mitochondrial DNA (PubMed:18063578). In addition to its role in mitochondria, also plays a role in the deubiquitination of target proteins as component of the BRISC complex: required for IFNAR1 deubiquitination by the BRISC complex (PubMed:24075985). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18063578, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21876188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24075985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25619277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29364879, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29452640, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33015733}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cardiomyopathy;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion nucleoid;Nucleus;One-carbon metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Pyridoxal phosphate;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide |
PATHWAY: One-carbon metabolism; tetrahydrofolate interconversion. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:25619277, ECO:0000305|PubMed:33015733}. |
This gene encodes the mitochondrial form of a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction of serine and tetrahydrofolate to glycine and 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate. The encoded product is primarily responsible for glycine synthesis. The activity of the encoded protein has been suggested to be the primary source of intracellular glycine. The gene which encodes the cytosolic form of this enzyme is located on chromosome 17. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:6472; |
BRISC complex [GO:0070552]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; glycine hydroxymethyltransferase activity [GO:0004372]; L-allo-threonine aldolase activity [GO:0008732]; mRNA 5'-UTR binding [GO:0048027]; mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity [GO:0000900]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; pyridoxal phosphate binding [GO:0030170]; serine binding [GO:0070905]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; folic acid metabolic process [GO:0046655]; glycine biosynthetic process from serine [GO:0019264]; glycine metabolic process [GO:0006544]; L-serine biosynthetic process [GO:0006564]; L-serine catabolic process [GO:0006565]; L-serine metabolic process [GO:0006563]; one-carbon metabolic process [GO:0006730]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; protein K63-linked deubiquitination [GO:0070536]; protein tetramerization [GO:0051262]; purine nucleobase biosynthetic process [GO:0009113]; regulation of aerobic respiration [GO:1903715]; regulation of mitochondrial translation [GO:0070129]; regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0002082]; response to type I interferon [GO:0034340]; tetrahydrofolate interconversion [GO:0035999]; tetrahydrofolate metabolic process [GO:0046653] |
9573390_This paper compares the mitochondrial and cytoplasmic forms of this enzyme and suggests that the two genes are a result of a single gene duplication. 11386852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18988749_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19048631_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19513116_SHMT1 and SHMT2 are functionally redundant in nuclear de novo thymidylate biosynthesis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22220685_The present study not only describes individual genetic variation that directly affects SHMT1 and SHMT2 activity, but provided insight into the overall regulation of the Folate and Methionine Cycles. 25619277_SHMT1 exists in solution as a tetramer, both in the absence and presence of PLP, while SHMT2 undergoes a dimer-to-tetramer transition. 25855294_SHMT2 is required for glioblastoma multiforme cells to adapt to the tumour environment, but also renders these cells sensitive to glycine cleavage system inhibition 26103880_The SHMT-2 is the direct targets of miR-370 and miR-373, respectively, in human articular chondrocytes. 26662310_our results for the first time showed that miR-615-5p prevents proliferation and migration through negatively regulating SHMT2 in HCC. 26975021_High SHMT2 expression increases glycine-dependent nucleotide synthesis leading to bladder cancer growth. 27391339_Data suggest that serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2) may be a potential target in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 27530298_Site-directed mutagenesis experiments on SHMT1 demonstrate that selective enzyme inhibition relies on the presence of a cysteine residue at the active site of SHMT1 (Cys204) that is absent in SHMT2. 27666119_These results indicate that SHMT2 may be a valuable prognostic biomarker in ER-negative breast cancer cases 27836973_High SHMT2 expression is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 29020998_Our data confirm the heterogeneity of breast tumors at a functional proteomic level and dissects the relationship between metabolism-related proteins, pathological features and patient survival. These observations highlight the importance of SHMT2 and ASCT2 as valuable individual prognostic markers and potential targets for personalized breast cancer therapy 29073064_The one-carbon donor formate generally rescues cells from SHMT inhibition, but paradoxically increases the inhibitor's cytotoxicity in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL); this effect is rooted in defective glycine uptake in DLBCL cell lines, rendering them uniquely dependent upon SHMT enzymatic activity to meet glycine demand. 29180469_SHMT2 Desuccinylation is associated with Cancer Cell Proliferation. 29323231_Findings support the hypothesis that age-associated respiration defects in fibroblasts of elderly humans are caused not by mtDNA mutations but by epigenetic regulation of nuclear genes including SHMT2. 30367038_serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2) is acetylated at K95 in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. SHMT2-K95-Ac disrupts its functional tetramer structure and inhibits its enzymatic activity. SHMT2-K95-Ac promotes its degradation via the K63-ubiquitin-lysosome pathway in a glucose-dependent manner. SHMT2-K95-Ac is decreased in human CRC samples which is correlated with poorer postoperative overall survival. 30500180_Characterized the serine hydroxymethyltransferase reaction catalyzed by SHMT1 and SHMT2, with a focus on pH dependence and substrate inhibition. SHMT2 maintains a pronounced tetrahydrofolate substrate inhibition even at the alkaline pH characteristic of the mitochondrial matrix, whereas with SHMT1 this is almost abolished. At this pH, SHMT2 also shows a catalytic efficiency that is much higher than that of SHMT1. 31142841_metabolic control of BRISC-SHMT2 assembly regulates immune signaling; data reveal a mechanism in which metabolites regulate deubiquitylase activity and inflammatory signalling 31379360_Increased expression of SHMT2 is a negative prognostic biomarker in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Expression of the SHMT2 gene promoted the proliferation and migration of HepG2 HCC cells 31500219_Chronic inflammation might thus prime the transition of PCa cells towards more advanced stages, and SHMT2 could represent a missing factor to further understand the molecular mechanisms responsible for the transition of prostate cancer towards a more aggressive phenotype. 31773687_High expression of SHMT2 is correlated with tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in gastrointestinal tumors. 32203214_Serine-dependent redox homeostasis regulates glioblastoma cell survival. 32330411_Loss of PYCR2 Causes Neurodegeneration by Increasing Cerebral Glycine Levels via SHMT2. 32903271_Cancer proteome and metabolite changes linked to SHMT2. 33015733_Impairment of the mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism enzyme SHMT2 causes a novel brain and heart developmental syndrome. 33066813_Evaluating the clinical significance of SHMT2 and its co-expressed gene in human kidney cancer. 33142801_BRCA1-A and BRISC: Multifunctional Molecular Machines for Ubiquitin Signaling. 33456583_Cytoplasmic SHMT2 drives the progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by inhibiting beta-catenin degradation. 33569544_The serine hydroxymethyltransferase-2 (SHMT2) initiates lymphoma development through epigenetic tumor suppressor silencing. 33894044_Interaction analysis of gene variants related to one-carbon metabolism with chronic hepatitis B infection in Chinese patients. 33928169_Identification of SHMT2 as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Correlating with Immune Infiltrates in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 33990700_The loss of SHMT2 mediates 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by upregulating autophagy. 34166228_Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 expression promotes tumorigenesis in rhabdomyosarcoma with 12q13-q14 amplification. 34624079_SHMT2 inhibition disrupts the TCF3 transcriptional survival program in Burkitt lymphoma. 35018218_Induction of serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis in neuroblastoma. 35211429_SHMT2 Drives the Progression of Colorectal Cancer by Regulating UHRF1 Expression. 35333683_Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2) potentiates the aggressive process of oral squamous cell carcinoma by binding to interleukin enhancer-binding factor 2 (ILF2). 35798250_SHMT2 promotes the tumorigenesis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating the m6A modification of PPAT. 36206102_Exosome-mediated transfer of circ_0063526 enhances cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via regulating miR-449a/SHMT2 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000025403 |
Shmt2 |
441.520535 |
2.0441106844 |
1.031473 |
0.119467961 |
73.834217 |
0.00000000000000000849610129809947054667855215841747716911377803186873614027518897273694165050983428955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000068079508773044615041036128042627803654992256802373079560553037481440696865320205688476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
566.8075706 |
39.0540632 |
279.2405481 |
14.3517840 |
| ENSG00000182223 |
326340 |
ZAR1 |
protein_coding |
Q86SH2 |
FUNCTION: Essential for female fertility. May play a role in the oocyte-to-embryo transition (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Reference proteome |
|
This maternal effect gene is oocyte-specific and encodes a protein that is thought to function in the initiation of embryogenesis. A similar protein in mouse is required for female fertility. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:326340; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; translation [GO:0006412] |
12773403_The carboxyl-termini of these ZAR1 proteins contain an important functional domain that is conserved through vertebrate evolution and that may be necessary for normal female reproduction in the transition from oocyte to embryonic life. 16551357_Zygote arrest 1 (ZAR1) could be implicated in regulation of meiosis and post meiotic differentiation of male and female germ cells through expression of shorter splicing variants. Central role of this gene in early reproductive processes. 20654783_we identified a frequently aberrant methylated region within the Zygote arrest 1 (ZAR1) gene in melanoma and demonstrated a distinct methylation pattern between melanoma and nevus.The involvement of ZAR1 in the carcinogenesis of melanoma remains unclear. 21206179_Findings indicate that non-promoter hypermethylation of ZAR1 is extremely frequent in diffuse gliomas and pituitary adenomas, but methylation-related aberrant ZAR1 expression is far less likely to be related to glioma tumorigenesis. 23583134_Hypermethylation of ZAR1 regions is extremely frequent in neuroblastomas and correlates with established markers of progressive disease and outcome. 24787227_ZAR1 and SFRP4 qMSP could be used as potential biomarker for CC diagnosis 25227574_A decreased methylation level at CpG sites of ZAR1 exon 1/intron 1. CpGi could serve as a biomarker for invasive bladder cancer. 28588743_Study shows for the first time the lung tumor-specific epigenetic inactivation of ZAR1 due to DNA methylation of its CpG island promoter. Furthermore, ZAR1 was characterized by the ability to block tumor growth through the inhibition of cell cycle progression in cancer cell lines. 28791558_ZAR1 has oncogenic effects in neuroblastoma by suppressing cell differentiation via regulation of MYCN expression.Elevated ZAR1 expression level is closely related to poor prognosis of patients with neuroblastoma. 31801617_Study presents evidence that ZAR1, which harbors tumor suppressive properties, is a prognostic and diagnostic cancer biomarker for lung and kidney. ZAR1 suppresses tumor cell line growth in part through p53 and strongly depending on its functional zinc-finger. 32700283_Variation Screening of Zygote Arrest 1(ZAR1) in Women with Recurrent Zygote Arrest During IVF/ICSI Programs. 32828887_The ZAR1 protein in cancer; from epigenetic silencing to functional characterisation and epigenetic therapy of tumour suppressors. |
ENSMUSG00000063935 |
Zar1 |
13.011798 |
0.3118788315 |
-1.680942 |
0.463846756 |
13.729352 |
0.00021112895958978248711450376173814902358571998775005340576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000550330097589021632539796335947812622180208563804626464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3720176 |
1.9924991 |
20.6245229 |
3.8831553 |
| ENSG00000182253 |
23336 |
SYNM |
protein_coding |
O15061 |
FUNCTION: Type-VI intermediate filament (IF) which plays an important cytoskeletal role within the muscle cell cytoskeleton. It forms heteromeric IFs with desmin and/or vimentin, and via its interaction with cytoskeletal proteins alpha-dystrobrevin, dystrophin, talin-1, utrophin and vinculin, is able to link these heteromeric IFs to adherens-type junctions, such as to the costameres, neuromuscular junctions, and myotendinous junctions within striated muscle cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11353857, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16777071, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18028034}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Intermediate filament;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an intermediate filament (IF) family member. IF proteins are cytoskeletal proteins that confer resistance to mechanical stress and are encoded by a dispersed multigene family. This protein has been found to form a linkage between desmin, which is a subunit of the IF network, and the extracellular matrix, and provides an important structural support in muscle. Two alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23336; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; costamere [GO:0043034]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton [GO:0045111]; neurofilament cytoskeleton [GO:0060053]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; intermediate filament binding [GO:0019215]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; vinculin binding [GO:0017166]; fast-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction [GO:0031443]; intermediate filament cytoskeleton organization [GO:0045104] |
11454237_Genomic organization and single-nucleotide polymorphism map of desmuslin, a novel intermediate filament protein on chromosome 15q26.3. 12669240_Expression of the intermediate filament protein synemin in myofibrillar myopathies and other muscle diseases. 12887813_the default of KIAA0353 gene may play a role in the occurrence and development of varicose great saphenous vein in PDVI patients. 14552890_The colocalization of Synemin [syn] with vimentin, GFAP, or neurofilament supports the idea that Syn is a key cross-linking protein in morphogenesis that connects different cytoskeletal structures 15318345_Based on its localization and its expression pattern, beta-synemin functions as a structural protein involved in maintaining muscle integrity through its interactions with alpha-dystrobrevin, desmin, and other structural proteins. 15657940_synemin is associated with ruffled membranes in addition to being distributed along the intermediate filament network 16476617_Desmuslin is down-regulated in incompetent saphenous veins. 16777071_Mammalian synemin is also shown to colocalize with dystrophin within muscle cell cultures 17564317_The stability of DMN was analyzed under the action of low-level laser therapy. 18028034_alpha-synemin, but not beta-synemin, interacts with both vinculin and metavinculin 18084875_results revealed that synemin was modulated nearly in all human human hepatocellular carcinoma cases 18342854_Results suggest human alpha-synemin plays an essential role in linking the heteropolymeric intermediate filament to adherens-type junctions, such as the costameres within mammalian striated muscle cells, via its interaction with talin. 19853601_The LIM domain protein zyxin was identified as an interaction partner for human synemin. 20199207_The differences in human syncoilin and beta-synemin mRNA ratios between Duchenne muscular dystrophy and normal muscles were not statistically significant 20543860_SYNM could represent a novel putative breast tumor suppressor gene that is prone to epigenetic silencing. SYNM promoter methylation may become a useful predictive biomarker to stratify breast cancer patients' risk for tumor relapse. 20573469_Desmuslin expression is required for the maintenance of vascular smooth muscle phenotype. Decreased desmuslin expression may affect differentiation of VSMCs and ultimately contribute to the development of varicose veins. 21144834_Synemin knock-down did not influence the cytoskeleton expression and organization of human Chang liver cells 22337773_synemin positively regulates glioblastoma cell proliferation by helping sequester PP2A away from Akt, thereby favoring Akt activation. 23594359_Immunohistochemistry of synemin in reactive astrocytes and Rosenthal fibers in two patients with Alexander disease. There was an abundance of GFAP-positive Rosenthal fibers and widespread reactive gliosis in the white matter and subpial regions. 25447537_alpha-Synemin localizes to the M-band of the sarcomere through interaction with the M10 region of titin 27470516_LMOD1, SYNPO2, PDLIM7, PLN, and SYNM down-regulation reflect the altered phenotype of smooth muscle cells in vascular disease and could be early sensitive markers of SMC dedifferentiation. 30276801_a novel heterozygous missense mutation p.(Trp538Arg) of SYNM was identified and cosegregated with the affected members in a Chinese family 31461342_Synemin is a target of myocardin family coactivators. 33019757_c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Is Regulated Downstream of the Cytoskeletal Protein Synemin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Radioresistance and DNA Repair. 35361267_A risk model of gene signatures for predicting platinum response and survival in ovarian cancer. 35769011_Synemin promotes pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch in shunt-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. |
ENSMUSG00000030554 |
Synm |
253.578209 |
0.3949521790 |
-1.340250 |
0.135011578 |
97.645963 |
0.00000000000000000000005002904943159643508512681581587895565045085990113725734396073760792966744759269204223528504371643066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000494925448800511671688375711822274868888428106573791652046776130824401462859896128065884113311767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
149.0275419 |
12.4107390 |
380.5373185 |
21.3405451 |
| ENSG00000182257 |
|
PRR34 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.453196 |
0.2507070308 |
-1.995926 |
0.565423287 |
13.490222 |
0.00023980979616254372325731547554994449455989524722099304199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000620436913472242760128616545500790380174294114112854003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3396407 |
1.3176374 |
13.4533314 |
3.0196236 |
| ENSG00000182287 |
8905 |
AP1S2 |
protein_coding |
P56377 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of clathrin-associated adaptor protein complex 1 that plays a role in protein sorting in the late-Golgi/trans-Golgi network (TGN) and/or endosomes. The AP complexes mediate both the recruitment of clathrin to membranes and the recognition of sorting signals within the cytosolic tails of transmembrane cargo molecules. |
Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Golgi apparatus;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Adaptor protein complex 1 is found at the cytoplasmic face of coated vesicles located at the Golgi complex, where it mediates both the recruitment of clathrin to the membrane and the recognition of sorting signals within the cytosolic tails of transmembrane receptors. This complex is a heterotetramer composed of two large, one medium, and one small adaptin subunit. The protein encoded by this gene serves as the small subunit of this complex and is a member of the adaptin protein family. Transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:8905; |
AP-1 adaptor complex [GO:0030121]; AP-type membrane coat adaptor complex [GO:0030119]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; melanosome assembly [GO:1903232]; platelet dense granule organization [GO:0060155]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
17617514_A mutation in the 3d intron causes skipping of exon 3 yielding a protein with 3 new AAs terminating at codon 64. A new nonsense mutation p.Gln66X was found in exon 3. Without AP1S2, defective membrane protein trafficking alters brain neural cell fate. 18428203_absence of an AP-1 defect in peripheral tissues is due to functional redundancy among AP-1 subunits 23756445_The AP1S2 c.426+1 G>T mutation segregates with the disease in the Pettigrew syndrome family. 24928897_sigma1B adaptin regulates adipogenesis by mediating the sorting of sortilin in adipose tissue. 30714330_Four generations in Chinese pedigree with Pettigrew syndrome resulting from a novel splice site mutation in AP1S2. AP1S2 mutations appear to be an important cause of Mental retardation,delayed in walking, abnormal speech, hypotonia, dysmorphic features, abnormal behavior and brain. 31712557_Long noncoding RNA LINC00518 acts as a competing endogenous RNA to promote the metastasis of malignant melanoma via miR-204-5p/AP1S2 axis. |
ENSMUSG00000031367 |
Ap1s2 |
1846.576984 |
2.0140974702 |
1.010134 |
0.040163976 |
634.948830 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004192787307885935919156761680428769448618376994439354725152265711436922299778826589719451348038221283729929062983584715829772897109835537261993179626850078982168071109586737985044231619748341 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002455775423190333890178717033393845860411502728555240740891704534841335279676513907402622657372302248373119243747222616870644408838735027929586913713422687217779752485906457468753577954196327 |
Yes |
No |
2503.0150557 |
73.4152715 |
1251.3962385 |
27.8992736 |
| ENSG00000182326 |
716 |
C1S |
protein_coding |
P09871 |
FUNCTION: C1s B chain is a serine protease that combines with C1q and C1r to form C1, the first component of the classical pathway of the complement system. C1r activates C1s so that it can, in turn, activate C2 and C4. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Complement pathway;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Hydroxylation;Immunity;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine protease;Signal;Sushi |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a serine protease, which is a major constituent of the human complement subcomponent C1. C1s associates with two other complement components C1r and C1q in order to yield the first component of the serum complement system. Defects in this gene are the cause of selective C1s deficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:716; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; complement component C1 complex [GO:0005602]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; complement activation, classical pathway [GO:0006958]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
14674770_Interaction with the prime side residues at the cleavage point in C1s enhances the affinity of the enzyme for complement 2 and complement 4 substrates; these prime subsite residues mediate positive cooperativity in the cleavage of the substrate. 16169853_full specificity of the enzyme using a randomized phage display library 18062908_There are splice variants of C1s mRNA transcripts in normal human cells 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20008834_Detailed mapping of post-translational modifications and insights into the C1r/C1s binding sites. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20592021_These results provide further structural insights into the architecture of the C1 complex, and the interactions between C1r and C1s. 22855709_Four positively charged amino acids on the serine protease domain appear to form a catalytic exosite that is required for efficient cleavage of C4 in the classical pathway of complement. 23592783_A molecular switch governs the interaction between the human complement protease C1s and its substrate, complement C4. 23650384_Analysis of its interaction properties by surface plasmon resonance shows that rC1q retains the ability of serum C1q to associate with the C1s-C1r-C1r-C1s tetramer, to recognize physiological C1q ligands such as IgG and pentraxin 3 23989031_Data indicate that complement C1s mRNA level was low in ICR-derived glomerulonephritis (ICGN) mice liver as compared with age-matched ICR mice. 24695853_TNT003, an inhibitor of the serine protease C1s, prevents complement activation induced by cold agglutinins. 26231209_C1q exists as the C1 complex (C1qC1r2C1s2), and C1q binding to ligands activates the C1r/C1s proteases. Incubation of nucleoli with C1 caused degradation of the nucleolar proteins nucleolin and nucleophosmin 1. T 27745832_Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome in at least the great majority of cases results from specific classes of heterozygous mutations in C1R and C1S. 28104818_The serine protease domains of C1r and C1s are at the periphery of the C1r2s2 tetramer both when alone or within the nonactivated C1 complex. The C1 complex adopts a conformation incompatible with intramolecular activation of C1. Instead, intermolecular proteolytic activation between neighboring C1 complexes bound to a complement-activating surface occurs. Many structurally unrelated molecular patterns can activate C1. 31921203_Two Different Missense C1S Mutations, Associated to Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Lead to Identical Molecular Outcomes. 33804666_The Impact of Complement Genes on the Risk of Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease. 34155115_C1q binding to surface-bound IgG is stabilized by C1r2s2 proteases. |
ENSMUSG00000038521+ENSMUSG00000079343 |
C1s1+C1s2 |
10.566370 |
0.1109096892 |
-3.172543 |
0.920643112 |
11.581898 |
0.00066596917453245942780659660797937249299138784408569335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001602756402429333232317887336648709606379270553588867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8076340 |
1.2770781 |
16.0700263 |
6.0944446 |
| ENSG00000182372 |
2055 |
CLN8 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBY8 |
FUNCTION: Could play a role in cell proliferation during neuronal differentiation and in protection against cell death. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19431184}. |
Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane protein belonging to a family of proteins containing TLC domains, which are postulated to function in lipid synthesis, transport, or sensing. The protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and may recycle between the ER and ER-Golgi intermediate compartment. Mutations in this gene are associated with a disorder characterized by progressive epilepsy with cognitive disabilities (EPMR), which is a subtype of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCL). Patients with mutations in this gene have altered levels of sphingolipid and phospholipids in the brain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:2055; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; ceramide binding [GO:0097001]; adult walking behavior [GO:0007628]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; cellular macromolecule catabolic process [GO:0044265]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; ceramide metabolic process [GO:0006672]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; glutamate reuptake [GO:0051935]; lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008610]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; lysosome organization [GO:0007040]; mitochondrial membrane organization [GO:0007006]; musculoskeletal movement [GO:0050881]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045861]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neurofilament cytoskeleton organization [GO:0060052]; neuromuscular process controlling balance [GO:0050885]; neuromuscular process controlling posture [GO:0050884]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; regulation of cell size [GO:0008361]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; retinal rod cell apoptotic process [GO:0097473]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; somatic motor neuron differentiation [GO:0021523]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
17129765_patients with CLN8 mutations from Italy. In these patients, the onset of epilepsy occurred between 3 and 6 years of age, with myoclonic, tonic-clonic, and atypical absence seizures. Electroencephalograms revealed focal and/or generalized abnormalities. 19201763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19431184_CLN8 plays a role in cell proliferation during neuronal differentiation and in protection against cell death. 19807737_a novel, large CLN8 gene deletion c.544-2566_590del2613 in a Turkish family with a slightly more severe phenotype of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinose was described. 22388998_CLN8 is a candidate modifier gene for GD1. Increased expression may protect against severe GD1.It may function as a protective sphingolipid sensor and/or in glycosphingolipid trafficking. 22964447_A missense mutation at the CLN8 gene (763C>G)has been identified in 3 consanguineous Israeli-Arab patients. The phenotype in 2 of them is milder than that of their cousin who has typical neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 23160995_This study highlights a close interaction between CLN5/CLN8 proteins, and their role in sphingolipid metabolism. Our findings suggest that CLN5p/CLN8p most likely are positive modulators of CerS1 and/or CerS2. 26443629_Novel missense mutation in CLN8 in late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis 26657971_This study does not support a contribution of rare missense CLN8 variations to ASD susceptibility in the Japanese population. 27844444_Whole-exome sequencing and homozygosity mapping revealed a novel homozygous CLN8 mutation, c.677T>C (p.Leu226Pro in 5 relatives from a large Turkish consanguineous family 30397314_CLN8 recruits lysosomal soluble proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), delivers them to the Golgi apparatus via COPII-coated vesicles, and recycles back to the ER via COPI-coated vesicles. CLN8 interacts with the lysosomal soluble proteins through its large luminal loop. The export signal of CLN8 (261VDWNF265) is localized in its cytosolic C-terminus. CLN8 deficiency results in depletion of enzymes at the lysosome. 30453012_the phosphorylation levels of several substrates of PP2A, namely Akt, S6 kinase, and GSK3beta, were decreased in CLN8 disease patient fibroblasts. 30919163_The Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses-Linked Loss of Function CLN5 and CLN8 Variants Disrupt Normal Lysosomal Function. 32597833_CLN8 associates with CLN6 to form the EGRESS complex (ER-to-Golgi Relaying of Enzymes of the lySosomal System), the functional unit responsible for the recruitment of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum and their transfer to the Golgi complex. 34044364_miR-3074-5p/CLN8 pathway regulates decidualization in recurrent miscarriage. 34201538_CLN8 Mutations Presenting with a Phenotypic Continuum of Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis-Literature Review and Case Report. |
ENSMUSG00000026317 |
Cln8 |
276.146210 |
3.1639901956 |
1.661745 |
0.161451649 |
102.978091 |
0.00000000000000000000000338875163783905870570296661900988779596450056840210636457376853483344780748609537113225087523460388183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000035348391642759368008554388171094744656365568335798868804930184927409753115057355898898094892501831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
413.4772234 |
42.4343850 |
131.5771163 |
10.2032453 |
| ENSG00000182389 |
785 |
CACNB4 |
protein_coding |
O00305 |
FUNCTION: The beta subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels contributes to the function of the calcium channel by increasing peak calcium current, shifting the voltage dependencies of activation and inactivation, modulating G protein inhibition and controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11880487}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Ion channel;Ion transport;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a member of the beta subunit family of voltage-dependent calcium channel complex proteins. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of alpha-1, alpha-2/delta, beta, and gamma subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. Various versions of each of these subunits exist, either expressed from similar genes or the result of alternative splicing. The protein encoded by this locus plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the alpha-1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Certain mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE), juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), and episodic ataxia, type 5. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:785; |
cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0009898]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic cytosolic calcium levels [GO:0099626]; adult walking behavior [GO:0007628]; cAMP metabolic process [GO:0046058]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; detection of light stimulus involved in visual perception [GO:0050908]; gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion [GO:0014051]; gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway [GO:0007214]; muscle cell development [GO:0055001]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; neuronal action potential propagation [GO:0019227]; Peyer's patch development [GO:0048541]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleolus [GO:1904751]; positive regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901387]; regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:2000300]; regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901385]; spleen development [GO:0048536]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852]; thymus development [GO:0048538] |
16866717_The novel nucleotide substitution T87C (D29D)in CACNB4 was observed in 2 migrainous vertigo patients and was not present in control DNA samples. 18446307_No pathogenic mutation were identified in CACNB4. 18712068_plays a role in neurotransmitter release. 18755274_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18755274_proband identified with severe myoclonic epilepsy in infancy heterozygous for de novo SCN1A nonsense mutation & CACNB4 missense mutation (R468Q); greater Ca(v)2.1 currents caused by the mutation may increase neurotransmitter release in excitatory neurons 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21220418_The Ca2+ channel beta4c subunit interacts with heterochromatin protein 1 gama via a PXVXL binding motif. 21297076_CACNB4 is associated with acute lung injury in mice 22892567_Cacnb4 directly couples electrical activity to gene expression, a process defective in juvenile epilepsy 23756480_Genome-wide association studies identify CACNB4 mutation releated to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. 24875574_The nuclear targeting properties of the truncated beta(4b(1-481)) subunit in tsA-201 cells, skeletal myotubes, and in hippocampal neurons, were investigated. 32176688_The homozygous CACNB4 p.(Leu126Pro) variant underlies the severe neurological phenotype in the two siblings. |
ENSMUSG00000017412 |
Cacnb4 |
430.882102 |
0.4774625578 |
-1.066540 |
0.089637128 |
141.992320 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000976249210800953271359161870124003170018865457703517329316595463375106096816793330151178914588783186445652972906827926635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000136582354041915351253487074969456567878052787555589343142316227951497454439350594202970401447316817211685702204704284667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
279.0708162 |
17.8949984 |
588.5354409 |
25.9189864 |
| ENSG00000182511 |
2242 |
FES |
protein_coding |
P07332 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts downstream of cell surface receptors and plays a role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, microtubule assembly, cell attachment and cell spreading. Plays a role in FCER1 (high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor)-mediated signaling in mast cells. Acts down-stream of the activated FCER1 receptor and the mast/stem cell growth factor receptor KIT. Plays a role in the regulation of mast cell degranulation. Plays a role in the regulation of cell differentiation and promotes neurite outgrowth in response to NGF signaling. Plays a role in cell scattering and cell migration in response to HGF-induced activation of EZR. Phosphorylates BCR and down-regulates BCR kinase activity. Phosphorylates HCLS1/HS1, PECAM1, STAT3 and TRIM28. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11509660, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15302586, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15485904, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16455651, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17595334, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18046454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19001085, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19051325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20111072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2656706, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8955135}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Transferase;Tumor suppressor;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
This gene encodes the human cellular counterpart of a feline sarcoma retrovirus protein with transforming capabilities. The gene product has tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity and that activity is required for maintenance of cellular transformation. Its chromosomal location has linked it to a specific translocation event identified in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia but it is also involved in normal hematopoiesis as well as growth factor and cytokine receptor signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants encoding different isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:2242; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; immunoglobulin receptor binding [GO:0034987]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cardiac muscle cell proliferation [GO:0060038]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to vitamin D [GO:0071305]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; microtubule bundle formation [GO:0001578]; myoblast proliferation [GO:0051450]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000251]; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031116]; positive regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045657]; positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045639]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045595]; regulation of cell motility [GO:2000145]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043304]; regulation of vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0060627]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11994747_Closing in on the biological functions of Fps/Fes and Fer. A review. 12653561_Fes naturally adopts an inactive conformation in vivo, and maintenance of the inactive structure requires the coiled-coil and SH2 domains. 12871378_Fps/Fes and Fer are expressed in human and mouse platelets, and are activated following stimulation with collagen and collagen-related peptide (CRP), suggesting a role in GPVI receptor signaling 15003822_Fes transduces inductive signals for terminal macrophage and granulocyte differentiation, and this biological activity is mediated through the activation of lineage-specific transcription factors. 15099290_FPS mediates enhanced sensitization to VEGF and PDGF signaling in ECs; this hypersensitization contributes to excessive angiogenic signaling and underlies the observed hypervascular phenotype of human myristoylated FPS expressed in transgenic mice. 15485904_c-Fes is a regulator of the tubulin cytoskeleton and may contribute to Fes-induced morphological changes in myeloid hematopoietic and neuronal cells 15630569_NMR assignment of the SH2 domain 15713745_PEDF downregulates Fyn through Fes, resulting in inhibition of FGF-2-induced capillary morphogenesis of endothelial cells 15929003_NMR analysis of Src homology 2 domain from the human feline sarcoma oncogene Fes 16455651_FES has a growth suppressive function in colorectal neoplasms. 16792528_A novel Fes-KAP-1 interaction is reported, suggesting a dual role for KAP-1 as both a Fes activator and downstream effector. 17521372_These novel results indicate the involvement of Fes in VEGF-A-induced cellular responses by cultured endothelial cells. 17595334_shows a major function of FES downstream of activated KIT receptor and thereby points to FES as a novel target in KIT-related pathologi 18046454_Ezrin/Fes interaction at cell-cell contacts plays an essential role in hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell scattering and implicates Fes in the cross-talk between cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion. 18775312_The SH2 and catalytic domains of active Fes and Abl pro-oncogenic kinases form integrated structures essential for effective tyrosine kinase signaling. 19001085_study shows Fes phosphorylates C-terminal tyrosine residues in HS1 implicated in actin stabilization; coordinated action of F-BAR & SH2 domains of Fes allow for coupling to FcepsilonRI signaling & potential regulation of actin reorganization in mast cells 19051325_Study of promoter methylation as important mechanism responsible for downregulation of FES gene expression in colorectal cancer cells. Treatment with DNA methyltransferase inhibitor resulted in expression of functional FES transcripts in CRC cell lines. 19082481_Downregulation of the c-Fes protein-tyrosine kinase inhibits the proliferation of renal carcinoma. 19382747_c-Fes oligomerization is independent of activation; data suggest that conformational changes, rather than oligomerization, govern c-Fes kinase activation and downstream signaling in vivo. 19464057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19865112_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19885553_FGF-2 activates Fes via the second coiled-coil domain, leading to lamellipodium formation and chemotaxis by endothelial cells 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20030920_c-fes gene expression was found in myeloid leukemias, whereas low or no expression in lymphocytic leukemias. 20117079_FES kinase is a mediator of wild-type KIT signalling implicated in cell migration. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23404507_analysis of the JAK-Fes-phospholipase D signaling pathway that is enhanced in highly proliferative breast cancer cells 31573955_Identification of FES as a Novel Radiosensitizing Target in Human Cancers. 31746983_This study supports the critical role of FER and FES tyrosine kinase fusions in the pathogenesis of follicular T-cell lymphoma and provides additional evidence that these can drive follicular T-cell lymphoma in the absence of RHOA mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000053158 |
Fes |
295.574861 |
0.1504884793 |
-2.732275 |
0.173459606 |
238.151418 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000994913242802419505001194719160168999997756120696697335608515917753818230468896490191106031375353150226677158334858298028875880854348182080748586031404556706547737121582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000226619127527217787472846479798048284179791082220924017289498783026064437768867991680583801883253481154530049941632393689835092443493960723266411605436587706208229064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
85.6198250 |
11.0964106 |
571.5339805 |
49.1451192 |
| ENSG00000182557 |
201305 |
SPNS3 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMD2 |
FUNCTION: Sphingolipid transporter. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Lipid transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in lipid transport and transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201305; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; lipid transport [GO:0006869] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 34608834_Bioinformatics-based identification of SPNS3 (Spinster homolog 3) as a prognostic biomarker of apoptosis resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. 35249471_Upregulation of FHL1, SPNS3, and MPZL2 predicts poor prognosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients with FLT3-ITD mutation. |
ENSMUSG00000020798 |
Spns3 |
84.892684 |
0.1129778042 |
-3.145889 |
0.222734235 |
227.671318 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000191955374815635138131356259770014709508356514384189485840636392558586722043875055433700696739907305986207461925808014008333567102480843313827563179074786603450775146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000042477681143609813760266801014973165814509153978636613120511059567565121574512884214768281888877363411823583229289263960499263995257424042506499972660094499588012695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
18.6164575 |
2.9048405 |
165.2877283 |
14.2450565 |
| ENSG00000182568 |
6304 |
SATB1 |
protein_coding |
Q01826 |
FUNCTION: Crucial silencing factor contributing to the initiation of X inactivation mediated by Xist RNA that occurs during embryogenesis and in lymphoma (By similarity). Binds to DNA at special AT-rich sequences, the consensus SATB1-binding sequence (CSBS), at nuclear matrix- or scaffold-associated regions. Thought to recognize the sugar-phosphate structure of double-stranded DNA. Transcriptional repressor controlling nuclear and viral gene expression in a phosphorylated and acetylated status-dependent manner, by binding to matrix attachment regions (MARs) of DNA and inducing a local chromatin-loop remodeling. Acts as a docking site for several chromatin remodeling enzymes (e.g. PML at the MHC-I locus) and also by recruiting corepressors (HDACs) or coactivators (HATs) directly to promoters and enhancers. Modulates genes that are essential in the maturation of the immune T-cell CD8SP from thymocytes. Required for the switching of fetal globin species, and beta- and gamma-globin genes regulation during erythroid differentiation. Plays a role in chromatin organization and nuclear architecture during apoptosis. Interacts with the unique region (UR) of cytomegalovirus (CMV). Alu-like motifs and SATB1-binding sites provide a unique chromatin context which seems preferentially targeted by the HIV-1 integration machinery. Moreover, HIV-1 Tat may overcome SATB1-mediated repression of IL2 and IL2RA (interleukin) in T-cells by binding to the same domain than HDAC1. Delineates specific epigenetic modifications at target gene loci, directly up-regulating metastasis-associated genes while down-regulating tumor-suppressor genes. Reprograms chromatin organization and the transcription profiles of breast tumors to promote growth and metastasis. Promotes neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells in the adult subventricular zone, possibly by positively regulating the expression of NEUROD1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q60611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10595394, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11463840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12374985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12692553, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1505028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15618465, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15713622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16377216, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16630892, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17173041, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17376900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18337816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19103759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19247486, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19332023, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19430959, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33513338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9111059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9548713}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Chromosomal rearrangement;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Host-virus interaction;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a matrix protein which binds nuclear matrix and scaffold-associating DNAs through a unique nuclear architecture. The protein recruits chromatin-remodeling factors in order to regulate chromatin structure and gene expression. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:6304; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; double-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003690]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; chromatin remodeling [GO:0006338]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
11937547_Two strong SATB1 binding sites, located 4.5 kb apart, have been detected in strong matrix attachment regions of the candidate regulatory region of the CD8 gene complex. 12374985_SATB1 targets chromatin remodelling to the IL-2Ralpha ('interleukin-2 receptor alpha') gene 14605447_SATB1 makes a complex, mainly with p300, regardless of the presence of DNA; SATB1/p300 complex binding to the 5' upstream AT-rich region in the bp -115 to bp -106 segment and represses the gp91(phox) promoter activity 15618465_SATB1 family protein expressed in the erythroid progenitor cells may have a role in globin gene expression during early erythroid differentiation. 15851481_SATB1-mediated transcriptional repression is regulated by nuclear matrix binding 15970696_SATB1 N-terminal residues 20-40 represent a novel determinant of nuclear targeting 16371359_SATB1 possesses a DNA-binding mode similar to that of the POU-specific DNA-binding domain, which is known to share structural similarity to the four-helix CUT domain 16377216_SATB1 formed special three-dimensional network distributions during early apoptosis. The distribution change of SATB1 was associated with cleavage of the protein and accompanied by the nuclear architecture collapse. 16630892_Phosphorylation of SATB1 acts as a molecular switch regulating its transcriptional activity in vivo. 17173041_Our studies identify PML and SATB1 as a regulatory complex that governs transcription by orchestrating dynamic chromatin-loop architecture. 17343824_Results show for the first time that forced-expression of SATB1 in K562 cells triggers SPARC up-regulation by binding to a 17bp DNA sequence in the third intron. 17376900_SATB1-mediated assembly of chromatin in T cells may play a role in integration site selection by HIV-1. 17652321_Determination of the crystal structure of the complex of the CUT domain of SATB1 and a matrix attachment region DNA, in which the third helix of the CUT domain deeply enters the major groove of DNA in the B-form. 18337816_SATB1 reprogrammes chromatin organization and the transcription profiles of breast tumours to promote growth and metastasis; this is a new mechanism of tumour progression 18408014_SATB1 has a role in controlling transcription in immune cells during normal cell functions or in assisting in efficient and rapid clearance of nonfunctional or potentially damaging immune cells through its action with SUMO 19072498_SATB1 is a master regulator in the metastasis of breast cancer and, therefore, can be considered as an independent prognostic factor and a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer 19103759_role of SATB1-CtBP1 interaction in the repression and derepression of SATB1 target genes during Wnt signaling in T cells 19304547_The expression of SATB1 mRNA was 13-fold higher in non-small cell lung cancer tissues than in normal lung tissues. 19332023_These results indicate that SATB1 regulates beta-like globin genes at the nuclear level interlaced with chromatin and DNA level, and emphasize the nuclear matrix binding activity of SATB1 to its regulatory function. 19860849_Overexpression and involvement of special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 in multidrug resistance in human breast carcinoma cells. 20126258_SATB1 orchestrates T(H)2 lineage commitment by mediating Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. 20351170_Data show that regulation of SATB1 sumoylation and caspase cleavage is controlled by SATB1 phosphorylation; specifically, PIAS1 interaction with SATB1 is inhibited by phosphorylation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20584685_SATB1 expression can be associated with the development and metastasis of bladder urothelial carcinoma. 20595686_In contrast to previous studies, we found that SATB1 expression did not promote breast cancer progression and was not associated with breast cancer outcome. 20811679_overexpression of SATB1 correlated with metastatic potential of human gastric cancer 20980149_use of SATB1 as target or prognostic marker for breast cancer should be viewed with caution and a possible confounding effect of the estrogen receptor status of the tumor should be taken into account when analysing new markers as SATB1. 21232178_SATB1 is a bona fide EZH2 target gene in HeLa cells and the repression of SATB1 by EZH2 may be mediated by trimethylation modification on H3K 21270445_Deficiency in SATB1 expression in Sezary cells plays an important role in Sezary syndrome pathogenesis by causing apoptosis resistance. 21355308_SATB1 and BRMS1 might play an important role in the development and lymph node metastasis of ovarian cancer. 21597389_Loss of special AT-rich binding protein 1 expression is associated with lung cancer. 21743493_We have identified a feed-forward regulatory loop in which FOXP3 suppresses the expression of the oncogene SATB1 21764697_SATB1 mRNA expression is associated with the postoperative recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 21767935_SATB1 may have a role in metastasis of cutaneous malignant melanoma 21799257_Clustering of expression data revealed that 600 out of 19000 genes analysed were significantly upregulated upon overexpression of the PDZ-like domain. 21841785_Repression of the genome organizer SATB1 in regulatory T cells is required for suppressive function and inhibition of effector differentiation. 21870058_SATB1 may play an important role in the progression of human rectal cancer. 22088470_Study provided the gene expression profile of HBV-related HCC and presented differential expression patterns of SATB-1, TM4SF-1 and ST-14 between cancerous and noncancerous tissues in patients with HBV-related HCC. 22583549_The expression of SATB1 was high in human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue and liver cancer cell lines with high metastatic potential. SATB1 promoted cell cycle progression and cell proliferation and prevented apoptosis. 22683624_miR-191 overexpression is sufficient to induce senescence in HEKn cells and that the direct targets, involved in this process, are the Special AT-rich Binding protein 1 (SATB1) and the Cyclin Dependent Kinase 6 (CDK6) mRNAs. 22710879_Studies indicate that the regulation of the activity of SATB1 has a critical role in driving two important differentiation pathways in T cells. 22771615_Perspectives on SATB1 function in higher-order chromatin structure and gene regulation, and its role in metastasis of breast cancer and other tumor types. [review] 22782115_Genome wide mapping of SATB1 binding sites and chromatin packaging. [Review] 22820583_SATB1 expression levels differ distinctly between hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with different invasive capacities. 22839214_SATB1 may have an important role as a positive regulator of glioma development and progression, and that SATB1 might be a useful molecular marker for predicting the prognosis of glioma 22864778_SATB1 expression seems to be a potential prognosis factor confirming the inner heterogeneous features of Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas 22879953_These results reveal a novel role of SATB1 in cell type-specific regulation of replication timing along the chromosome. 22935204_SATB1 expression is a factor of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. 22998183_This review evaluates the potential of SATB1 as a molecular target for cancer therapy. 23076250_SATB1 functions in the promotion of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. cases positive for SATB1 and Bcl-2 were associated with poor prognosis. 23188721_expression level of the SATB1 gene in gastric mucosa of dyspeptic patients in relation to Helicobacter pylori infection, a family history of gastric cancer, and histopathological changes 23251624_These data indicate a novel role for ATM as a suppressor of SATB1-induced malignancy in breast epithelial cells. 23278463_study found 1 mutation in 38 hepatocellular carcinoma cases; the mutation was missense mutation: a AGT to AAT transition at codon 354 (S354N); S354N was found in exon 7A located within the MAR domain of the SATB1 gene 23308245_SATB1 has ability to promote prostate cancer aggressiveness through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 23317753_SATB1 might be a useful molecular marker for predicting the prognosis of patients with astrocytoma 23326301_Findings suggest that SATB1 (Special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 1)is involved in the carcinogenesis, development and progression of colorectal cancer. 23437226_We have identified a novel HLA-A*02-restricted SATB1-derived peptide epitope recognized by CD8(+) T cells, which, in turn, recognizes and kills HLA-A*02(+) SATB1(+) tumor cells 23516037_Over-expression of SATB1 is responsible for abnormal proliferation of mesenchymal derived human osteosatcoma U2OS cells. 23613626_SATB1 acts as a potential growth and metastasis promoter in colorectal cancer 23642278_SATB1 has a role in metastatic prostate cancer cell growth and invasion 23686316_p16 mutations collaborate with the oncogenic activity of SATB1 23696028_SATB1 is overexpressed in bladder cancer and regulates malignant cell growth and apoptosis. 23894778_Patients with family history of gastric cancer and H. pylori infection, with reversible histopathological changes of gastric mucosa, have higher levels of SATB1 and c-Myc gene expression as compared to patients without family history of gastric cancer. 24009715_SATB1 and PML may play an important role in up regulating HLA class I expression in EBV+ cHL. 24047082_EBV LMP-1-mediated over-expression of SATB1 is associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression. 24118100_Loss of SATB1 nuclear expression correlates with poor survival and a less favourable response to adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer 24176859_Data conclude that phospho-SATB1, but not SATB1 mRNA expression, is associated with the progression and prognosis of glioma 24260116_Plakoglobin represses SATB1 expression and decreases in vitro proliferation, migration and invasion. 24370885_SATB1 expression was strongly down-regulated in the tumor U251 cells. 24696710_SATB1 may be involved in nasopharyngeal carcinoma development and progression. 24715035_SATB1 gene expression show considerable changes with diabetic complications of bone diseases. 24729451_SATB1 overexpression is associated with colon carcinoma. 24747435_this study highlights a novel SATB1-p21 axis that plays an important role in the disease progression of cutaneous CD30+LPDs, which provides novel molecular insights into this disease and possibly leads to new therapies in the future. 24938377_SATB1 is indispensable for lymphocyte differentiation and stem cell development. (Review) 24966956_SATB1 may be a valuable predictor in assessing the metastasis, recurrence, and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 24971456_Expression of SATB1 promotes the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer. 25257341_the co-expression of SATB1 and S100A4 may be a significant prognostic indicator for the 5-year overall survival rate in patients with colorectal carcinoma. 25323550_Immunohistochemical expression of SATB1 and SATB2 was analysed in tissue microarrays with primary tumours and a subset of paired lymph node metastases from 175 patients operated with pancreaticoduodenectomy for periampullary adenocarcinoma. 25326863_We found SATB1 to be an independent prognostic factor in patients with a radically resected adenocarcinoma in the upper gastrointestinal tract 25347096_Overexpression of special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 1 is associated with endometrial cancer. 25384658_Moderate and high expression of SATB1 correlate with significantly better prognosis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma patients. 25496125_High SATB1 expression is associated with recurrence in rectal cancer. 25543122_This review will discuss the four major findings regarding SATB1/2 in colorectal cancer studies.[review] 25586771_expression of SATB1 may increase the size of the BCSC population via the activation of the Notch signaling pathway and by increasing expression levels of Snail1 and Twist1. 25619478_our data provide compelling evidence that miR-23a functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma, and its inhibitory effect on tumor are mediated chiefly through downregulation of SATB1. 25706386_results suggest that SATB1 plays a crucial role in the progression of bladder cancer by regulating genes controlling EMT processes 25762622_Up-regulation of histidine-rich calcium binding protein promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma and is mediated by SATB1. 25874491_SATB1 mRNA, protein, and immunoreactivity levels did not correlate with patients' clinicopathological data and their overall survival, but the latter analysis was limited by a relatively short period of follow 25896016_Data suggest that SATB1 expression is down-regulated during activation of hepatic stellate cell (as seen in liver fibrosis); up-regulation of SATB1 expression appears to reduce collagen synthesis and cell activation/proliferation/migration. 25951709_High SATB1 expression in was detected in 48.3% of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and 7.8% of normal esophagus tissues. 25956130_SATB1 and HER2 expression correlated with poorly differentiated breast cancer and indicated an unfavorable prognosis. 25966097_SATB1 protein expression showed an increasing trend in advancing stages of breast cancer development. 26084613_replicative oncolytic adenovirus armed with SATB1 shRNA exhibits effective antitumor effect in human prostate cancer. Our study provides the basis for the development of ZD55-SATB1 for the treatment of prostate cancer 26108419_SATB1 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer, promoting cancer cell proliferation and invasion through the activation of MYC. 26165840_SATB1 reprograms the expression of tumor growth- and metastasis-associated genes to promote tumorigenesis and functionally overlaps with Wnt signaling critical for colorectal cancer tumorigenesis. 26422397_SATB1 as a Dual Regulator of Anti-Apoptotic BCL2 and Pro-Apoptotic NOXA Genes 26512778_Findings indicate that high Ki67 antigen/ SATB1 protein ratio was an independent predictor of worse overall survival (OS), while Ki67 and SATB1 did not reach statistical significance as single predictors. 26528635_radiation decreases SATB1 expression and sensitizes cancer cells to confer clinical benefit of patients, suggesting that SATB1 is predictive of response to preoperative RT and clinical outcome in rectal cancer. 26563145_Our results highlight the significance of SATB1 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 26678884_SATB1 expression was decreased in ATL cells compared with normal controls. Knockdown of SATB1 expression significantly enhanced invasion of Jurkat cell in vitro. SATB1 knockdown enhanced beta-catenin nuclear accumulation and transcriptional activity and thus may increase the invasiveness of Jurkat cells through the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in vitro. 26701851_High expression of SATB1 is associated with colorectal cancer. 26810818_Results suggested that high expression of SATB1 is significantly correlated with poor differentiation of CRC. SATB1 might promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by increasing the aberrant expression of beta-catenin. 26876172_Tumor-driven, unremitting expression of Satb1 in activated Zbtb46+ inflammatory dendritic cells that infiltrate ovarian tumors results in an immunosuppressive phenotype characterized by increased secretion of tumor-promoting Galectin-1 and IL-6. 27044805_modulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by SATB1 may contribute to prostate cancer metastasis. 27052102_Results suggest that SATB1 is activated to bind to chromatin at S/MARs after exposure to Abeta 1-42, resulting in alternative utilization and movement of 82-kDa ChAT to these regions demonstrating that both proteins play critical roles in the response of neural cells to acute Abeta-exposure. 27107063_Decreased expression of SATB1 in ccRCC may result from over-expressed miR-21-5p. Our data suggest that SATB1 may have a potential value as a prognostic marker in ccRCC. 27179949_Logistic regression revealed that four variants in NR3C1 and SATB1 were significantly associated with lung cancer risk after false discovery rate (FDR) correction [For NR3C1, rs9324921: odds ratio (OR)=1.23, P for FDR=0.029; rs12521436: OR=0.85, P for FDR=0.040; rs4912913: OR=1.17, P for FDR=0.040; For SATB1, rs6808523: OR=1.33, P for FDR=0.040]. 27462121_combination of the sequence-specific and nonspecific DNA-binding modes of SATB1 should be advantageous in a search for target loci during transcriptional regulation 27466515_overexpression of SATB1 was an independent poor prognostic factor in stage I-III, especially in stage II colorectal cancer (CRC). SATB1 may play an important role in LNM of CRC. SATB1 may be a biomarker of LNM and of recurrence after surgery for CRC 27472393_SATB2 can induce dedifferentiation by inducing stemness and may have a role in pancreatic carcinogenesis 27590341_SATB1 interacts directly with OGG1, increases its binding to 8-oxoG-containing DNA, promotes Schiff base formation, and stimulates its glycosylase and apyrimidinic/apurinic lyase enzymatic activities. 27637333_revealed more than 170 NFAT-associated proteins, half of which are involved in transcriptional regulation. Among them are many hitherto unknown interaction partners of NFATc1 and NFATc2 in T cells, such as Raptor, CHEK1, CREB1, RUNX1, SATB1, Ikaros, and Helios. 27697109_SATB1 binds to the upstream region of UCA1 that its promoter activity increases with SATB1 depletion and SATB1 repressed the expression of oncogenic UCA1 suppressing growth and survival. 27783844_These findings suggest SATB1 may play an important role in OSCC invasiveness and metastasis. 27883059_HBx upregulated hepatic SATB1. 28049521_High SATB1 expression is associated with glioblastoma. 28147311_This paper provides evidence that SATB1 plays an oncogenic role in esophageal cancer by up-regulation of FN1 and PDGFRB. 28205095_These data implied that SATB1 might regulate gene expression through its different oligomerization state. 28345457_Silencing of special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 inhibited the proliferation of KYSE450 and EC9706 cells which have a relatively high level of special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1, and the ability of migration and invasion of KYSE450 and EC9706 cells was distinctly suppressed. 28636989_Invasion and metastasis of GIN in Chinese patients correlates with SATB1 overexpression in tumor tissues, most profoundly in gastric cancer. 28801365_High SATB1 expression is associated with Immunosuppressive Function of Regulatory T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B. 29079132_Study results in bladder cancer are consistent with the conflicting data reported in other cancers, and that SATB1 might have different roles in cancer dependent on genetic background and stage of the cancer. The role of SATB1 is dependent on multiple factors, its use as a biomarker limited and as a therapeutic target likely highly variable among patients. 29306014_Studies indicate Special AT-rich Sequence Binding Protein 1 (SATB1) to affect proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, cell morphology / cell polarity, EMT and multidrug-resistance as well as tumor formation, growth, invasion and metastasis [Review]. 29307244_gradually reduced expression observed during gestation, and lower expression detected in placenta of pre-eclampsia compared to normal pregnancy 29334836_Study shows that SNF5 is an upstream regulator of SATB1 in several conditions and that both are deficient in Sezary cells. SNF5 also utilizes SATB1 to recruit itself to specific sites. Overexpression of SNF5 induces SATB1 expression and partially reverse apoptosis resistance phenotype in Sezary cells. These results suggest that both SNF5 and SATB1 may regulate apoptosis-related genes in Sezary syndrome. 29374696_High SATB1 expression was associated with a better overall survival of patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma.ATB1 level correlates with Ki-67 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. 29510190_SATB1 activated the expression of T-helper 17 cytokines while repressing T-helper 1-related genes. The heterogeneity in SATB1 expression across CD30+ LPDs was associated with the extent of promoter DNA methylation. Hence, SATB1 expression defines a subtype of CD30+ LPDs with characteristic pathobiology and prognosis. 29546272_SATB1expression in the human placenta is affected by oxidative stress and might regulate the migration and invasion of trophoblasts via beta-catenin signaling. 29751003_Study reports disease stage-associated decrease of SATB1 expression in mycosis fungoides and an inverse expression of STAT5 and SATB1 in tumor cell lines. STAT5 inhibited SATB1 expression through induction of MIR155 providing mechanistic link between the proto-oncogenic JAK3/STAT5/MIR155 pathway, SATB1, and cytokines linked to cutaneous T-cell lymphoma severity and progression. 29932248_Results show that knockdown of LUCAT1 significantly repressed the SATB1 expression, whereas SATB1 expression was partially rescued after inhibition of miR-495, demonstrating that the LUCAT1 has a pivotal role in clear cell renal cell carcinoma progress by regulating SATB1 mediated by miR-495. 29936452_The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of p16 and SATB1 proteins in regard to expression of the Ki-67 antigen and available clinicopathological data (i.a. receptor status, staging and grading 30082769_The PAK5-mediated special AT-rich binding protein-1 (SATB1) phosphorylation on Ser47 initiated EMT cascade and promoted migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells. 30132561_SATB1 may reprogram energy metabolism in ovarian cancer by regulating lactate dehydrogenase and MCT1 levels to promote metastasis. 30337520_Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote progression and gemcitabine resistance via the SDF-1/SATB-1 pathway in pancreatic cancer. 30368875_High SATB1 expression is associated with tumor growth and invasion of gastric cancer. 30720170_miR-122-5p was significantly downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cell lines. Additionally, it was demonstrated that special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 1 (SATB1) was targeted by miR-122-5p. Results revealed that miR-122-5p inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation, cell migration and cell invasion by targeting SATB1. Data suggested that miR-122-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in NPC. 30803026_study has implications for understanding the role of SATB1 in human health and disease and suggests an approach for modulating PD-1 in T cells, highly relevant to human malignancies or chronic viral infections. 31001272_the promoter switch might play a crucial role in fine-tuning of SATB1 protein expression in a cell type specific manner. 31147803_SATB1 and hepatitis B virus X protein play a role in promoting anoikis resistance and metastasis in hepatitis B virus-associated liver cancer. 31290787_SATB1 Expression of Colorectal Adenomatous Polyps is Higher than that of Colorectal Carcinomas. 31497998_important roles of DRAIC-miR-122-SATB1 axis in NPC 31543366_Loss of SATB1 Induces p21-Dependent Cellular Senescence in Post-mitotic Dopaminergic Neurons. 31724324_MiR-191-5p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma by repressing SATB1 to inhibit Wnt pathway. 31737131_SATB1 protein is overexpressed in the gastric adenocarcinomas. 31830989_The data show that SATB1 is essential for establishing secretory ameloblast cell polarity and for EMP secretion. In line with the deformed apical architecture, amelogenin transport to the apical secretory front and secretion into enamel space were impeded in Satb1(-/-) SABs resulting in a massive cytoplasmic accumulation of amelogenins and a thin layer of hypomineralized enamel. 32525527_MicroRNA-448 targets SATB1 to reverse the cisplatin resistance in lung cancer via mediating Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. 32562536_Special AT-rich Sequence Binding-Protein 1 (SATB1) Correlates with Immune Infiltration in Breast, Head and Neck, and Prostate Cancer. 32669713_N(6)-methyladenine in DNA antagonizes SATB1 in early development. 32771472_Differential SATB1 Expression Reveals Heterogeneity of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. 32862579_miR-449a regulates biological functions of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting SATB1. 33285627_SATB-1 and Her2 as predictive molecular and immunohistochemical markers for urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. 33356851_SATB1-mediated chromatin landscape in T cells. 33390772_SATB1 Knockdown Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion and Decreases Chemoradiation Resistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Reversing EMT and Suppressing MMP-9. 33513338_Mutation-specific pathophysiological mechanisms define different neurodevelopmental disorders associated with SATB1 dysfunction. 33564000_Global chromatin organizer SATB1 acts as a context-dependent regulator of the Wnt/Wg target genes. 33955522_SATB1 protein is associated with the epithelialmesenchymal transition process in nonsmall cell lung cancers. 34031799_Trisomy X syndrome with dystonia and a pathogenic SATB1 variant. 34576286_Increased Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Levels at the Onset of Sjogren's Syndrome in SATB1-Conditional Knockout Mice. 34621503_Study on the Mechanism of miR-34a Affecting the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Human Keloid Fibroblasts by Regulating the Expression of SATB1. 34961766_SATB1, genomic instability and Gleason grading constitute a novel risk score for prostate cancer. 35113413_Expression of SATB1 is a prognostic indicator for survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. 35353722_Elevated Expression of SATB1 Predicts Unfavorable Clinical Outcomes in Colon Adenocarcinoma. 35460833_Downregulation of SATB1 by miRNAs reduces megakaryocyte/erythroid progenitor expansion in preclinical models of Diamond-Blackfan anemia. 35611599_MicroRNA-409 regulates the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cell lines by targeting special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 1 (SATB1). 36058862_[Exploring new molecules that regulate hematopoietic stem cells and early stages of lymphoid hematopoiesis: the functional significance of ESAM and SATB1]. 36376298_The 3D enhancer network of the developing T cell genome is shaped by SATB1. |
ENSMUSG00000023927 |
Satb1 |
1002.461517 |
0.2344976898 |
-2.092354 |
0.080415016 |
667.169707 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000412203978310839531948017205643965476348393727387477946524759803705015362472113661921962513355845292810457822547565659992100180362583754808610342994054338381833475234542224678050408190 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000262247013787413427088176743594462039011504886409285828760372472837039912955331296574573332981968952065201883542907915653182979012235678500020495722724769748620298526727040653980026340 |
Yes |
Yes |
384.2408852 |
23.0699715 |
1650.8251992 |
66.6391338 |
| ENSG00000182578 |
1436 |
CSF1R |
protein_coding |
P07333 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts as cell-surface receptor for CSF1 and IL34 and plays an essential role in the regulation of survival, proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic precursor cells, especially mononuclear phagocytes, such as macrophages and monocytes. Promotes the release of pro-inflammatory chemokines in response to IL34 and CSF1, and thereby plays an important role in innate immunity and in inflammatory processes. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoclast proliferation and differentiation, the regulation of bone resorption, and is required for normal bone and tooth development. Required for normal male and female fertility, and for normal development of milk ducts and acinar structures in the mammary gland during pregnancy. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, regulates formation of membrane ruffles, cell adhesion and cell migration, and promotes cancer cell invasion. Activates several signaling pathways in response to ligand binding, including the ERK1/2 and the JNK pathway (PubMed:20504948, PubMed:30982609). Phosphorylates PIK3R1, PLCG2, GRB2, SLA2 and CBL. Activation of PLCG2 leads to the production of the cellular signaling molecules diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, that then lead to the activation of protein kinase C family members, especially PRKCD. Phosphorylation of PIK3R1, the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, leads to activation of the AKT1 signaling pathway. Activated CSF1R also mediates activation of the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and/or MAPK3/ERK1, and of the SRC family kinases SRC, FYN and YES1. Activated CSF1R transmits signals both via proteins that directly interact with phosphorylated tyrosine residues in its intracellular domain, or via adapter proteins, such as GRB2. Promotes activation of STAT family members STAT3, STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Promotes tyrosine phosphorylation of SHC1 and INPP5D/SHIP-1. Receptor signaling is down-regulated by protein phosphatases, such as INPP5D/SHIP-1, that dephosphorylate the receptor and its downstream effectors, and by rapid internalization of the activated receptor. In the central nervous system, may play a role in the development of microglia macrophages (PubMed:30982608). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12882960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15117969, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16170366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16337366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16648572, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17121910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18467591, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18814279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19193011, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19934330, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20489731, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30982608, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30982609, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7683918}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Kinase;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is the receptor for colony stimulating factor 1, a cytokine which controls the production, differentiation, and function of macrophages. This receptor mediates most if not all of the biological effects of this cytokine. Ligand binding activates the receptor kinase through a process of oligomerization and transphosphorylation. The encoded protein is a tyrosine kinase transmembrane receptor and member of the CSF1/PDGF receptor family of tyrosine-protein kinases. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a predisposition to myeloid malignancy. The first intron of this gene contains a transcriptionally inactive ribosomal protein L7 processed pseudogene oriented in the opposite direction. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Expression of a splice variant from an LTR promoter has been found in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), HL cell lines and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:1436; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; CSF1-CSF1R complex [GO:1990682]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor activity [GO:0005011]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cell-cell junction maintenance [GO:0045217]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0036006]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; forebrain neuron differentiation [GO:0021879]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:0038145]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060603]; microglial cell proliferation [GO:0061518]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; olfactory bulb development [GO:0021772]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; phosphatidylinositol metabolic process [GO:0046488]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation by host of viral process [GO:0044794]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell motility [GO:2000147]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of macrophage proliferation [GO:0120041]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061098]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:2000249]; regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045124]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; ruffle organization [GO:0031529]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11852791_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11891846_AP-1 proteins, GR and associated co-factors regulate transcription from the c-fms first promoter in breast carcinoma cells. 12031912_upregulated significantly in acute myeloid leukemia patients with a white blood cell count higher than 30 x 10(9)/L cells 12130514_DNA binding to and transactivation of the M-CSF receptor promoter were deficient in acute myeloid leukemia PU.1 mutants that affected the DNA-binding domain, contibuting to the block in differentiation in AML. 12372416_CSF-1 and its receptor are regulated by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) and its analogue tacalcitol in human monocytes which parallels the inhibition of differentiation into dendritic cells without altering survival 12381783_These observations correlate CSF-1R expression with changes in the growth and development of the normal and neoplastic prostate 12529666_C-fms expression correlates with monocytic differentiation in PML-RAR alpha+ acute promyelocytic leukemias 12773394_In t(8;21) leukaemic cells expressing the aberrant fusion protein AML1-ETO, we demonstrate that this protein is part of a transcription factor complex binding to extended sequences of the c-FMS intronic regulatory region rather than the promoter. 14654075_findings of co-expression of KIT and/or FMS with their respective ligands implies these receptors might contribute to leukemogenesis in some patients with AML through autocrine, paracrine, or intracrine interactive stimulation. 14738146_Lower expression of CSF1R is associated with acute myeloid leukemia-M2 and higher expression of CSF1R is associated with acute myeloid leukemia-M5 15117969_data suggest that colony-stimulating factor receptor-1R (CSF-1R) disrupts cell adhesion by uncoupling adherens junction complexes from the cytoskeleton and promoting cadherin internalization through a Src-dependent mechanism 15144560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15297464_CSF-1-mediated wild-type (WT)-CSF-1R phosphorylation was not markedly affected by Src-family kinases (SFK) inhibition, indicating that lack of SFK binding is not responsible for diminished Y559F phosphorylation. 15626739_HIV-1 Nef interferes with M-CSF receptor signaling through Hck activation and thereby inhibits M-CSF functions in monocytes/macrophages. 16034075_In c-fms transgenic mice it is determined that although the c-fms promoter is inactive in dendritic cell (DC) precursors, it is up-regulated in all DC subsets during differentiation 16170366_the CSF1R mutation of Asp-802 to Val confers resistance to kinase inhibitor imatinib 16631474_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16648572_Inhibitory activity of lead compounds and drug candidates, such as ABT-869, against the CSF-1R protein in situ. 16708222_No evidence that CSF1R 2033T variant was a major risk factor for Crohn's disease in New Zealand. 16823860_Creation of a conditional allele of the Csf1r by placing LoxP sites around Exon 5 of the Csf1r gene in mice. 17292918_2.7 A resolution crystal structure of the cytosolic domain of c-Fms that comprises the kinase domain and the juxtamembrane domain 17360941_method revealed the presence of an activated colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) kinase in the acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) cell line MKPL-1, essential for the growth and survival of MKPL-1 cells. 17420255_tyrosine 559 is the major mediator of receptor activation and cell death, intracellular signaling, and cell proliferation and that the tyrosine residues at positions 697 and 807 play lesser roles in these events 17675037_We thus conclude that Ox-LDL induces monocyte differentiation to macrophages in vivo and this phenomenon involves activation of the M-CSF-receptor. 17880962_The results suggest that the growth factor M-CSF might have an important role in ovarian function. 17893228_Nef perturbs the intracellular maturation and the trafficking of nascent Fms, through a unique mechanism that required both the activation of Hck and the aberrant spatial regulation of the active Hck 17960171_c-KIT but not CSF1R mutations play a role in the leukemogenesis of childhood CBF-AML. 17981568_analysis of the transcriptional regulation of the Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (csf1r) gene during hematopoiesis [review] 18294963_CSF-1 receptor RIPping can be activated by various intracellular signal transduction pathways and that RIPping is likely to play an important role during macrophage activation. 18510570_Expression of M-CSF, CSF-1R and CD3 is a significant prognostic factor in primary prostatic cancers by predicting the development of metastases. 18565574_VEGF expression was statistically correlated to c-fms and COX-2 expression in high-grade CIN. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18788612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18814279_c-Fms signals are blocked by imatinib mesylate inhibition of osteoclasts, which suppresses bone metastases of breast cancer 18971950_mutant CSF1R was constitutively phosphorylated, but rapidly dephosphorylated on exposure to imatinib, in cell line derived from a patient with an atypical myeloproliferative neoplasms, as being responsive to imatinib. 18997822_CSF1R may be a critical factor facilitating hTERT immortalization of epithelial cells. 19017797_Calorimetric data indicate that M-CSF cannot dimerize FMS without receptor-receptor interactions mediated by FMS domains D4 and D5 19151756_findings suggest that HuR plays a supportive role for c-fms in breast cancer progression by binding a 69-nt element in its 3'UTR, thus regulating its expression 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19321746_Genes for Fra2, Id2, and CSF1-receptor are deregulated, regardless of whether the in anaplastic large cell lymphoma contains the t(2;5). 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19375163_study evaluated the prevalence of the activating mutations of C-FMS in a series of 85 patients with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; no mutations in codons 301 and 969 of the C-FMS gene were detected in any of the 85 samples 19377443_CSF1R plays a relevant role in clear cell renal cell carcinoma carcinogenesis 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19585521_This finding establishes an intriguing link between the pathogenesis of Nef and a newly emerging concept that the Golgi-localized Src kinases regulate the Golgi function. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19762488_These results reveal a novel proteolytic regulation of M-CSF receptor expression in monocytes to control M-CSF signaling and monocytic differentiation into macrophage/osteoclast-lineage cells or dendritic cells. 20098615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20181277_c-Fms plays a central role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by mediating the differentiation and priming of monocyte lineage cells 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20504948_The different spatiotemporal expression of IL-34 and CSF-1 allows for complementary activation of the CSF-1R in developing and adult tissues. 20574656_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574656_the minor allele at CSF1R +22693T>C may have a susceptibility effect in the development of asthma, via increased CSF1R protein and mRNA expression in inflammatory cells 20974809_identified a competition for binding the 69-nt sequence, through which vigilin and HuR exert opposing effects on c-fms expression, suggesting a role for vigilin in suppression of breast cancer progression 21041311_CSF-1-mediated receptor dimerization leads to a Tyr-559/SFK/c-Cbl pathway resulting in receptor ubiquitination that permits full receptor tyrosine phosphorylation of this class III RTK in macrophages 21049007_data reveal quantitative site-specific changes in tyrosine phosphorylation induced by CSF-1R activation in epithelial cells and identify many candidate SRC-dependent substrates phosphorylated downstream of an RTK 21063905_Inhibition of the c-fms proto-oncogene autocrine loop and tumor phenotype in glucocorticoid stimulated human breast carcinoma cells. 21466808_Data indicate that blood treated with EDTA and refrigerated maintained CD115 stability. 21880693_Data suggest that sunitinib binds preferentially to the inactive form, preventing the activation of CSF-1R. 22052465_results suggest that budding RCC stimulates the proximal adjacent microenvironment in the kidney to release mediators of CSF-1, CSF-1R, and epidermal growth factor expression in RCCs 22084313_p110delta-dependent translocation of exogenous CSF-1 to the nucleus-associated CSF-1Rs, correlating with a prominent role of p110delta in activation of the Rab5 GTPase, a key regulator of endocytic trafficking 22096574_Data demonstrate that c-Jun, cyclin D1 and c-Myc, known for their involvement in cell proliferation, are downstream CSF-1R in breast cancer cells. 22153499_Studies by small-angle X-ray scattering of unliganded hCSF-1R point to large domain rearrangements upon CSF-1 binding, and provide structural evidence for the relevance of receptor predimerization at the cell surface 22186992_Studies indicate that Macrophage-colony stimulating factor (CSF-1) signaling through its receptor (CSF-1R) promotes the differentiation of myeloid progenitors. 22197934_Genome-wide linkage analysis plus exome sequencing identified 14 different mutations affecting the tyrosine kinase domain of the colony stimulating factor 1 receptor in 14 families with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids. 22365076_Suggest that CSF-1 and its receptor, C-FMS, are involved in the genesis of early endometriotic lesions and that endometriotic lesions contribute to elevated CSF-1 levels in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. 22375015_Macrophage proliferation is regulated through CSF-1 receptor tyrosines 544, 559, and 807 22955918_CSF1R and cd68 gene expression is an independent predictor for progression-free survival of Hodgkin lymphoma patients. 23038421_exome sequencing identified heterozygous CSF1R mutations (p.I794T and p.R777W) in 2 families with autosomal dominantly inherited leukoencephalopathy; mutational analysis of CSF1R in 21 sporadic cases revealed no mutations; another novel CSF1R mutation, p.C653Y, was identified in 1 patient with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids 23052599_This study showed that Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids and pigmented glia with CSF1R mutation. 23116709_One mechanism of RANK inhibition by 1,25(OH)2D3 is down-regulation of the M-CSF receptor c-Fms, which is required for the expression of RANK. 23392676_Targeting the activity of CSF1R inhibits microglial proliferation and slows neuronal damage and disease progression. 23408870_Sequencing in this study establishes that CSF1R mutations observed in hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy (HDLS) also cause familial pigmented orthochromatic leukodystrophy (POLD). 23418320_CSF1/CSF1R signaling is important in the recruitment of tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells that can limit the efficacy of radiotherapy 23649896_CSF1R mutations are responsible for a significant proportion of clinically and pathologically proven hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathies with spheroids. 23744080_Data suggest that CSF-1R-independent actions of IL-34 via receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase zeta (PTP-zeta) might be considered in evaluating IL-34 roles in development and disease. 23787135_Our report emphasizes the presence of atypical Parkinsonism in Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids due to CSF1R mutations 23816250_This study showed that a novel A781V mutation in the CSF1R gene causes hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids. 23889897_our study indicates that pathogenic mutations in CSF1R are an unlikely cause of multipel sclerosis in the Canadian population 23924795_Data indicate that anti-CD115 monoclonal antibody H27K15 exerts partial inhibitory effects on CD115 signaling, but inhibits monocyte chemotactic protein-1 secretion and reduces interleukin-6 production. 24034409_diagnosis of HDLS or a de novo mutation in CSF1R must be considered in patients with bilateral symmetric changes in ukodystrophies. 24120500_These results indicate that all of the Fms mutations tested severely impair the kinase activity and most of the mutations also impair the trafficking to the cell surface, further suggesting that hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids is caused by the loss of Fms function. 24145216_CSF1R mutations in hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids are loss of function. 24336230_CSF-1R signaling by haploinsufficiency may play a role in microglial dysfunction leading to the pathogenesis of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids 24362524_CSF-1R mayact as a transcriptional regulator on proliferation-related genes in breast cancer. 24532199_CSF1R gene analysis was performed in 15 patients with undefined leukoencephalopathy and progressive cognitive decline 24619759_Our data demonstrate that a high number of non-Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells expressing CSF-1R are correlated with an increased tumor macrophage content and worse survival in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 24682770_The identified isoform of CSF-1R mRNA may interfere with the expression of full-length CSF-1R mRNA, thereby affecting the biological activity of the ligand/receptor signaling axis in Sprague-Dawley rats. 24706185_We report three patients with HDLS who carried missense mutations in the CSF1R gene, two of them novel (p.L582P and p.V383L). 24722292_The survival of CSF1R(pos) cells requires active AKT (v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1) signaling, which contributed to increased levels of nuclear, transcriptionally competent beta-catenin. 24807373_haploinsufficiency of CSF-1R is sufficient to cause Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids [review] 24828813_CSF-1R D802V and KIT D816V homologous mutations have differential effects on receptor tertiary structure and allosteric communication. 24955855_Our results provide new insights into the molecular physiology of the CSF-1 receptor and contribute to our understanding of substrate selection by TACE and gamma-secretase. 25012610_The first report of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids due to a novel CSF1R missense mutation. 25088194_Autocrine CSF1R signaling is essential in maintaining low claudin expression. 25144241_results suggest that CSF1R SNP rs10079250 may contribute to lung cancer susceptibility in never-smoking females 25534203_C/EBPalpha-C(m)-mediated downregulation of Csf1r has a negative, rather than positive, impact on the progression of AML involving C/EBPalpha-C(m), which might possibly be accelerated by additional genetic and/or epigenetic alterations inducing Csf1r upregulation 25854167_Determination of CSF1 and CSF1R expression may be useful as a prognosticator of the clinical course and/or outcomes of Pigmented villonodular synovitis . 25863088_A missense mutation c.2563C>A (p.P855T) of the CSF1R gene has been identified to associated with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy. 25913741_CSF1R gene had variations in genic regions that affected the association of RORalpha with its target binding site in vivo 25935893_CSF1R mutations account for 10% of idiopathic adult onset leukodystrophies. 26066800_CSF1R pathway activation was evident in the cHL and inactivation of this pathway could be a potential therapeutic target in cHL cases. 26179200_Report treatment of diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumour of the soft tissue using CSF1R inhibition with emactuzumab. 26235028_Data show crystal structures of CSF1-CSF1R ternary complexes, and propose a mechanism for their cooperative action that relies on the adoption by dimeric CSF-1 of an active conformational state and homotypic receptor interactions. 26437001_Assessing serum levels of WFA(+) -CSF1R has diagnostic value for predicting carcinogenesis and the survival of LC patients. 26443621_All 4 hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids patients had a different single nucleotide mutation in the cytoplasmic part of the gene. Different mutations lead to different levels of depletion of nonclassical slan-positive monocytes. 26467457_High CSF-1R expression is associated with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 26642091_peripheral nerve injury induced de novo expression of colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) in injured sensory neurons. CSF1 was transported to the spinal cord, where it targeted the microglial CSF1 receptor (CSF1R). 26743272_The aim of this study was to compare the expression of CSF-1R in nasopharyngeal carcinoma to nasopharyngitis. 27190017_findings suggest that expression of wild-type CSF1R in some cells, whether achieved by mosaicism or chimerism, may confer benefit in hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids. 27239844_The frequencies of the rare alleles of CCR2, ITGB3, and 3'UTR of c-fms in the Old Believers are lower than in the sample of Novosibirsk Russians, and the rare allele of DBH is more frequent 27334834_CSF-1R is a novel therapeutic target. 27338940_This review showed that CSF1R mutation is related to Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids. 27568101_CSFIR mutation is associated with Metaplastic Breast Cancer. 27602954_Hypoxia promotes glioma-associated macrophage infiltration via periostin and subsequent M2 polarization by upregulating TGF-beta and M-CSFR. 27680516_The phenotype of adult-onset leukoencephalopathy axonal spheroids and pigmented glia caused by CSF1R mutations is affected by sex 28449811_Results suggest that TP63 rs7631358 G > A and CSF1R rs10079250 A > G may affect the risk and prognosis of lung cancer in never-smoking females. 28655719_study, therefore, provided insights into the sequence-structure-function relationships of the M-CSF/c-FMS interaction and of ligand/receptor tyrosine kinase interactions in general. 28724665_this is the first study to demonstrate CSF1R genetic variant regulates the CSF-1R signaling and sensitivity to CSF-1R inhibitors. 28827005_Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia.(S39-S41) is a subtype of dominantly inherited leukoencephalopathy caused by CSF1R mutations. 28875266_Concerning pigmented villonodular synovitis , clinical trials assessing CSF-1R inhibitors have revealed promising initial outcomes. Blocking CSF-1/CSF-1R signaling represents a promising immunotherapy approach and several new potential combination therapies for future clinical testing. 28921817_To verify its sensitivity and specificity, we retrospectively applied our criteria to 83 axonal spheroids and pigmented glia cases who had CSF1R mutations 29544907_Adult-onset Mendelian leukodystrophy genes are not common factors implicated in Alzheimer's disease, but there is a potential pathogenic link between NOTCH3, CSF1R, and sporadic late-onset Alzheimer's disease. 29665011_High CSF-1R expression is associated with chemoresistant neuroblastoma. 29719257_CSF1R(+) Macrophages Sustain Pancreatic Tumor Growth through T Cell Suppression and Maintenance of Key Gene Programs that Define the Squamous Subtype. 29767252_Study find elevated expression of CSF1R in primary gastric cancer tissue (GC) to be significantly associated with the presence of lymph node and peritoneal metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and poor survival. In vitro analysis also revealed a functional role for the CSF1R in GC development, and a prognostic and predictive biomarker for GC. 30067976_CSF1R regulates microglia density and may contribute to leukodystrophy pathogenesis. 30075184_These data suggest that CSF-1R has the potential to reduce sensitivity to gefitinib and may be involved in resistance development. 30136118_The detection of the CSF1R mutation outside of the region-encoding TKD may extend the genetic spectrum of adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia (ALSP) with CSF1R mutations. Mutational analysis of all the coding exons of CSF1R should be considered for patients clinically suspected of having ALSP. 30541986_M-CSFR inhibition suppressed programmed death-1 and -2 ligand in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) cells and macrophages stimulated with conditioned medium from ATL-T cells. 30702078_CSF1R was significantly overexpressed in pancreatic cancer cells. 30729751_A novel gain-of-function mutation was identified as a cause of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids. 30899951_IL-6, IL-34 and M-CSFR may be closely related to the development of chronic periodontitis. 30940906_Targeting the CSF1R abrogated MvarphiMCL-dependent MCL survival. 30982608_Homozygous Mutations in CSF1R are associated with Pediatric-Onset Leukoencephalopathy resulting in Congenital Absence of Microglia. 30982609_Bi-allelic CSF1R Mutations are associated with Skeletal Dysplasia of Dysosteosclerosis-Pyle Disease Spectrum and Degenerative Encephalopathy with Brain Malformation. 31028249_When monocytes are differentiated into macrophages with CSF-1, CSF-1R is redirected to transcription starting sites, colocalizes with H3K4me3, and interacts with ELK and YY1 transcription factors. 31093799_A novel CSF-1R mutation in a family with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids misdiagnosed as hydrocephalus. 31149782_Polymorphisms in MAPK9 (rs4147385) and CSF1R (rs17725712) are associated with the development of inhibitors in patients with haemophilia A. 31520500_Factors predictive of the presence of a CSF1R mutation in patients with leukoencephalopathy. 31636099_Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (CSF1R) Activates AKT/mTOR Signaling and Promotes T-Cell Lymphoma Viability. 31768065_In this study, we uncovered activating mutations in CSF1R and rearrangements in RET and ALK that conferred dramatic responses to selective inhibition of RET (selpercatinib) and crizotinib, respectively, in patients with histiocytosis. 32118593_Is CSF1R Expression Localization Crucial for its Prognostic Value in Colorectal Cancer? 32238382_CSF1R Is Required for Differentiation and Migration of Langerhans Cells and Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis. 32304779_Characterization of a p53/miR-34a/CSF1R/STAT3 Feedback Loop in Colorectal Cancer. 32379601_Abnormal expression of colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) and transcription factor PU.1 (SPI1) in the spleen from patients with major psychiatric disorders: A role of brain-spleen axis. 32430064_Loss of homeostatic microglial phenotype in CSF1R-related Leukoencephalopathy. 32847933_Immunomodulatory Activity of a Colony-stimulating Factor-1 Receptor Inhibitor in Patients with Advanced Refractory Breast or Prostate Cancer: A Phase I Study. 33097690_CSF1R signaling is a regulator of pathogenesis in progressive MS. 33153411_CSF1R and HCST: Novel Candidate Biomarkers Predicting the Response to Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 33197935_SSBP2-CSF1R is a recurrent fusion in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia with diverse genetic presentation and variable outcome. 33350588_Attenuated CSF-1R signalling drives cerebrovascular pathology. 33731849_The receptor of the colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1R) is a novel prognostic factor and therapeutic target in follicular lymphoma. 33737586_Exploring dementia and neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis genes in 100 FTD-like patients from 6 towns and rural villages on the Adriatic Sea cost of Apulia. 33749994_Further expanding the mutational spectrum of brain abnormalities, neurodegeneration, and dysosteosclerosis: A rare disorder with neurologic regression and skeletal features. 33764399_CSF1/CSF1R-mediated Crosstalk Between Choroidal Vascular Endothelial Cells and Macrophages Promotes Choroidal Neovascularization. 33774864_Expression of CD1 molecules and colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor in indeterminate cell histiocytosis. 33800170_Interleukin-34-CSF1R Signaling Axis Promotes Epithelial Cell Transformation and Breast Tumorigenesis. 33841415_Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-2 (TREM2) Interacts With Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (CSF1R) but Is Not Necessary for CSF1/CSF1R-Mediated Microglial Survival. 33948764_A novel mutation in CSF1R associated with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids. 34069563_Tumor-Associated Macrophage Promotes the Survival of Cancer Cells upon Docetaxel Chemotherapy via the CSF1/CSF1R-CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. 34135456_From HDLS to BANDDOS: fast-expanding phenotypic spectrum of disorders caused by mutations in CSF1R. 34155128_Regulation of closely juxtaposed proto-oncogene c-fms and HMGXB3 gene expression by mRNA 3' end polymorphism in breast cancer cells. 34298983_Transfection of Vitamin D3-Induced Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells for the Silencing of Potential Tolerogenic Genes. Identification of CSF1R-CSF1 Signaling as a Glycolytic Regulator. 34510422_Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor blockade attenuates inflammation in inflamed gingival tissue explants. 34652888_Clinical and genetic characterization of adult-onset leukoencephalopathy caused by CSF1R mutations. 34830445_CD40 Pathway and IL-2 Expression Mediate the Differential Outcome of Colorectal Cancer Patients with Different CSF1R c.1085 Genotypes. 35040698_CSF1 receptor inhibition of tenosynovial giant cell tumor using novel disease-specific MRI measures of tumor burden. 35290551_Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling in the central nervous system and the potential of its pharmacological inhibitors to halt the progression of neurological disorders. 35597882_M-CSFR expression in the embryonal component of hepatoblastoma and cell-to-cell interaction between macrophages and hepatoblastoma. 35917184_Lysosomal acid lipase, CSF1R, and PD-L1 determine functions of CD11c+ myeloid-derived suppressor cells. |
ENSMUSG00000024621 |
Csf1r |
5034.010659 |
4.0958825682 |
2.034174 |
0.027447321 |
5653.334622 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
8275.6179079 |
128.4850204 |
2034.8461333 |
26.8086448 |
| ENSG00000182580 |
2049 |
EPHB3 |
protein_coding |
P54753 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase which binds promiscuously transmembrane ephrin-B family ligands residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. The signaling pathway downstream of the receptor is referred to as forward signaling while the signaling pathway downstream of the ephrin ligand is referred to as reverse signaling. Generally has an overlapping and redundant function with EPHB2. Like EPHB2, functions in axon guidance during development regulating for instance the neurons forming the corpus callosum and the anterior commissure, 2 major interhemispheric connections between the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. In addition to its role in axon guidance also plays an important redundant role with other ephrin-B receptors in development and maturation of dendritic spines and the formation of excitatory synapses. Controls other aspects of development through regulation of cell migration and positioning. This includes angiogenesis, palate development and thymic epithelium development for instance. Forward and reverse signaling through the EFNB2/EPHB3 complex also regulate migration and adhesion of cells that tubularize the urethra and septate the cloaca. Finally, plays an important role in intestinal epithelium differentiation segregating progenitor from differentiated cells in the crypt. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15536074}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Kinase;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into two groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. This gene encodes a receptor for ephrin-B family members. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:2049; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; axon guidance receptor activity [GO:0008046]; ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005003]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005005]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axonal fasciculation [GO:0007413]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis [GO:0021952]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; dendritic spine development [GO:0060996]; dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0060997]; digestive tract morphogenesis [GO:0048546]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050770]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022407]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; retinal ganglion cell axon guidance [GO:0031290]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; thymus development [GO:0048538]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; urogenital system development [GO:0001655] |
11956217_RYK, a catalytically inactive receptor tyrosine kinase, associates with EphB2 and EphB3 but does not interact with AF-6. 15536074_while catalytic activity of EphB3 is required for inhibition of integrin-mediated cell adhesion, a distinct signaling pathway to Rho GTPases shared by WT- and KD-EphB3 receptor mediates inhibition of directional cell migration 18978678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19483190_EphB3-ephrin-B interaction promotes mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) by re-establishing epithelial cell-cell junctions and such an MET-promoting effect contributes to EphB3-mediated tumor suppression. 19607727_EPHB3, MASP1 and SST map to 3q26.2-q29 and may have roles in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21106840_Ephrin B3 receptor regulates the synthesis and release of D-serine in astrocytes, which may have important implications on synaptic transmission and plasticity. 21266352_EphB3 provides critical support to the development and progression of NSCLC by stimulating cell growth, migration, and survival. 21804545_Data show that EphB receptors interact with E-cadherin and with the metalloproteinase ADAM10 at sites of adhesion. 22039307_Our work shows that EphB3 is consistently expressed by malignant T lymphocytes, most frequently in combination with EphB6, and that stimulation with their common ligands strongly suppresses Fas-induced apoptosis in these cells. 22314363_EphB3 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis via a PP2A/RACK1/Akt signalling complex 24707046_These results uncover enhancer decommissioning as a mechanism for transcriptional silencing of the EPHB3 tumor suppressor. 25277775_results identify EPHB3 as a novel target of SNAIL1 and suggest that disabling EPHB3 signaling is an important aspect to eliminate a roadblock at the onset of EMT processes. 26930615_Study found up-regulated expression of ephrinB3/EphB3 in intractable temporal lobe epilepsy patients and experimental temporal lobe epilepsy rats, which suggested that ephrinB3/EphB3 might be involved in the pathogenesis of temporal lobe epilepsy 27986811_work suggested that EphB3 acted as a tumor promoter in Papillary Thyroid Cancer by increasing the in vitro migration as well as the in vivo metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Cancer cells through regulating the activities of Vav2 and Rho GTPases in a kinase-dependent manner. 28120491_These results show that EphB3 protein is lost in ovarian serous carcinoma and is associated with tumor grade and FIGO stage, which indicate that EphB3 protein may play a role in carcinogenesis of ovarian serous carcinoma and may be used as a molecular marker for prognosis. 29620230_These results indicated the suppressive effect of Form on colon carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion, possibly via miR149induced EphB3 downregulation and the inhibition of the PI3K/AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways. 29789713_FOXD2-AS1 acted as a tumor inducer in GC partly through EphB3 inhibition by direct interaction with EZH2 and LSD1. 29970482_Data suggest that receptor-tyrosine kinase HEK2 (EphB3) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic alpha polypeptide (PIK3CA) are cooperating oncogenes that contribute toward its pathogenesis. 30044964_phosphorylation of mTOR through signaling by EphB3 is a potential mechanism of AZD4547 resistance in GC cells 30408551_EZH2-mediated epigenetic suppression of EphB3 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by affecting E-cadherin and vimentin expression. 30535864_Receptor Tyrosine Kinase EphB3: a Prognostic Indicator in Colorectal Carcinoma. 32294981_Expression Profile and Prognostic Significance of EPHB3 in Colorectal Cancer. 34296545_Low Expression of EphB2, EphB3, and EphB4 in Bladder Cancer: Novel Potential Indicators of Muscular Invasion. |
ENSMUSG00000005958 |
Ephb3 |
44.225320 |
3.3626972942 |
1.749619 |
0.267243402 |
43.698923 |
0.00000000003829825281549118558185592959141761628533151551323499006684869527816772460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000203852221982203340667553541029101416004465363585040904581546783447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.3780287 |
13.2396080 |
18.9601508 |
3.0654476 |
| ENSG00000182621 |
23236 |
PLCB1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NQ66 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the hydrolysis of 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and mediates intracellular signaling downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (PubMed:9188725). Regulates the function of the endothelial barrier. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z1B3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9188725}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Epilepsy;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. This reaction uses calcium as a cofactor and plays an important role in the intracellular transduction of many extracellular signals. This gene is activated by two G-protein alpha subunits, alpha-q and alpha-11. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23236; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; postsynaptic cytosol [GO:0099524]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lamin binding [GO:0005521]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phospholipase C activity [GO:0004629]; activation of meiosis involved in egg activation [GO:0060466]; cellular response to fluoride [GO:1902618]; cellular response to glyceraldehyde [GO:1905631]; cellular response to ionomycin [GO:1904637]; cellular response to vasopressin [GO:1904117]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007213]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007215]; inositol trisphosphate metabolic process [GO:0032957]; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048009]; interleukin-1-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070498]; interleukin-12-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0035722]; interleukin-15-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0035723]; learning [GO:0007612]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of monocyte extravasation [GO:2000438]; phosphatidylinositol catabolic process [GO:0031161]; phosphatidylinositol metabolic process [GO:0046488]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of acrosome reaction [GO:2000344]; positive regulation of CD24 production [GO:2000560]; positive regulation of developmental growth [GO:0048639]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of embryonic development [GO:0040019]; positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:1900087]; positive regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0032024]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045663]; postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099170]; regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903140]; regulation of fertilization [GO:0080154]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; regulation of retrograde trans-synaptic signaling by endocanabinoid [GO:0099178]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12213492_detailed analysis of the human PLC beta1 gene showing the existence of alternative splicing; complete determination of the exon/intron structure of the gene spanning 250 kb of DNA 12821674_PLC beta 3 and PLC beta 1 bind to calmodulin 15085153_The myelodysplastic syndrome patients, bearing the deletion, rapidly evolved to acute myeloid leukemia. 16136505_This review summarizes current knowledge about nuclear PI-PLC-beta 1, its localization, activity changes during cell cycle phases, and possible involvement in the progression of myelodisplastic syndrome to acute myeloid leukemia. 16860758_alternative pathway operates in the absence of Lck-dependent tyrosine-phosphorylation events and was initiated by the T cell receptor-dependent activation of raft-enriched heterotrimeric Galpha11 proteins 17041247_These results support the model that activation of selected PLC isoforms at the cleavage furrow controls progression of cytokinesis through regulation of PIP2 levels 17335878_New data in this review hints at the fact that the imbalance of nuclear versus cytoplasmic phosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C beta 1 signaling could affect the cell cycle progression of hematopoietic cells. 17363325_These results demonstrate that two waves of nuclear PI-PLCbeta(1b) activity occur in serum-stimulated cells during G(1) phase of the cell cycle and that the later increase in the PLC activity is equally important for the progression into the S phase. 17393430_PC-PLC and ROS were involved in chicken blastodisc differentiation to vascular endothelial cells. PC-PLC was an important factor in the blastodisc cell survival and differentiation, and it might perform its function associated with ROS. 17620288_Spontaneous calcium oscillations and nuclear translocation of PLC-beta1 may reflect some degree of oocyte maturity. 18203956_PC-PLC activation through CCR5 is specifically induced by gp120, since triggering CCR5 through its natural ligand CCL4 (MIP-1beta) does not affect PC-PLC cellular distribution and enzymatic activity, as well as CCL2 secretion 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18692062_Ins(1,4,5)P(3) and IP(3)-receptor (type 2) regulate PLCbeta1 and thereby maintain levels of Ins(1,4,5)P(3), which implies some functional significance for Ins(1,4,5)P(3) in the heart 18957514_PLCb1 localization is regulated by its own substrate, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate. 19114693_The association between the presence of phosphoinositide-phospholipase C beta1 (PI-PLCbeta1) mono-allelic deletion with the clinical outcome of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) patients was evaluated. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19491339_An extracellular PI-PLC enzyme activity that may be acutely involved in the regulation of PtdIns levels in lung surfactant, was identified. 19519170_Data show that PI(3,4,5)P3 potentiates Ca(2+)-stimulated phospholipase C-beta activitiy. 19729020_Dilated atria from human and mouse showed heightened expression of PLCbeta1b. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20171262_These findings suggest that PLC/CAMK IV-NF-kappaB is involved in RAGE mediated signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21091263_data confirm that phospholipase C beta 1 transcript levels are decreased in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from subjects with schizophrenia. However, the changes in levels of mRNA do not translate into a change at the level of protein. 21338571_These studies suggest that Protein kinase C phosphorylation regulates the level of PLCB1 cytosolic and nuclear activity by regulating its cellular compartmentalization. 21663700_For the first time it is shown that SHP-2 and PLCbeta1 are present as a preformed complex. Complex PLCbeta1 is tyr-phosphorylated basally. Ang II increased SHP-2-PLCbeta1 complexes and caused complex associated PLCbeta1 tyr-phosphorylation to decline. 22076473_PI-PLCbeta1 gene amplification seems to be correlated to clinicopathological parameters. 22286107_Alpha-synuclein protects the integrity of PLCbeta1 and its ability to be activated by Galpha q, which may in turn impact calcium signaling. 22459146_PLCbeta1 expression is a key player in myoblast differentiation, functioning as a positive regulator in the correction of delayed differentiation of skeletal muscle in myotonic dystrophy myoblasts 22507702_existence of a susceptibility locus on the short arm of chromosome 20 moved us to analyse PLCB1, the gene codifying for PI-PLC beta1 enzyme, which maps on 20p12 22690784_case report - homozygous deletion associated with malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy 22889834_Data show a novel role of phospholipase Cbeta1 (PLCbeta1) in gene regulation through translin-associated factor X (TRAX) association. 23006664_PLCbeta1 is enriched at the plasma membrane. 23058275_Nuclear signaling elicited by phospholipase C beta1 plays an important role in the control of the balance between cell cycle progression and apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome cells. (Review) 23555755_a concerted gp120-mediated signaling involving both PC- and PI-specific phospholipase C beta1 is required for the expression of CCL2 in macrophages 23656785_PLCbeta1 positively targets cyclin D3, likely through a PKCalpha mediatedpathway, and that, as a downstream effect of its activity, K562 cells undergo to an accumulation in the S phase of the cell cycle, leading to a decrease of cell proliferation. 23659438_A peptide that mimics part of the alpha-synuclein binding site to PLCbeta prevents aggregation. PLCbeta1 can reduce cell damage under oxidative stress and offers a potential site that might be exploited to prevent alpha-synuclein aggregation. 23793622_Cholesterol regulates HERG K+ channel activation by increasing phospholipase C beta1 expression 23916604_Interaction between PLCbeta1 and TRAX affect the function of TRAX as part of the machinery involved in RNA interference. [review] 24035496_PLCbeta1-linked signaling pathways may be involved in the neural system in schizophrenia. [review] 24076015_PLC-beta1 and DAGL-alpha are detected in discrete brain regions, with a marked predominance of pyramidal morphologies of positive cortical cells.[review] 24296032_nuclear PI-PLCb1 signalling is involved in diseases showing an altered myogenic differentiation and affecting the hematopoietic system.[review] 24315024_Novel variations in PLCB1 do not allow prediction of functional phenotypes that might explain, at least in part, the symptoms of malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy (MMPSI). 24338081_The selectivity of PLCbeta toward certain genes lies in the rate at which the RNA is hydrolyzed by C3PO. 24475116_Phospholipase C-beta1 and beta4 contribute to non-genetic cell-to-cell variability in histamine-induced calcium signals in HeLa cells. 24684524_PLCB1 is now reported in a number of different EIEE (early infantile epileptic encephalopathy) phenotypes and our report provides further evidence for phenotypic pleiotropy encountered in early infantile epilepsy syndromes. 25160985_Our data indicate that the amplification of PLCb1a expression, following treatment with kinamycin F, confers a real advantage to K562 cells viability and protects cells themselves from apoptosis. 25192965_one specific Egr-1 binding site was identified at nt-451/-419 and PLCB1 promoter activity was increased more than 5-fold 25649181_The rs6108160 polymorphism in the PLCB1 gene reached statistical significance after antidepressant drug use. 25977289_results show that PI-PLCbeta1 quantification in MDS predicts the response to azacitidine and is associated with an increased myeloid differentiation. 26434682_Polymorphism of the PLCB4/B1 genes might be involved in the coronary artery aneurysm pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. 26525203_PI-PLCbeta1 is a modulator of hematopoiesis. [review] 26614510_PLCbeta1 is a candidate signature gene for proneural subtype high-grade glioma. 26620550_Reduction in plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 abundance by PTPRN2 and PLCbeta1 releases the PI(4,5)P2-binding protein cofilin from its inactive membrane-associated state into the cytoplasm where it mediates actin turnover dynamics. 26639088_Dysregulation of primary PLC signaling is linked to several brain disorders including epilepsy, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, Huntington's disease, depression and Alzheimer's disease. (Review) 26746047_Phospholipase C beta connects G protein signaling with RNA interference. (Review) 28106288_The role of PLCb1 nuclear isoform is being analyzed in relation to the cell cycle regulation, the cell differentiation, and different physiopathological pathways focusing on the importance of the nuclear localization from both molecular and clinical point of view. (Review) 28860459_rs1047383 in the PLCB1 gene is associated with cocaine dependence. PLCB1 expression is upregulated in the nucleus accumbens of cocaine abusers. 29895226_this study revealed the important role of circ-PRKCI-miR-1324-PLCB1 regulatory network in Hirschsprung disease (HSCR), providing a novel insight for the pathogenesis of HSCR. 29897006_The intronic PLCB1 InDel is the first variant found in familial multiple papilloid adenomata-type multinodular goiter and in a subset of patients with sporadic multinodular goiter. 30420274_During osteogenic differentiation, PLC-beta1 expression varies concomitantly with cyclin E expression and the two proteins interact. 31883110_Three novel patients with epileptic encephalopathy due to biallelic mutations in the PLCB1 gene. 34580062_A PLCB1-PI3K-AKT Signaling Axis Activates EMT to Promote Cholangiocarcinoma Progression. 35303162_Impact of phospholipase C beta1 in glioblastoma: a study on the main mechanisms of tumor aggressiveness. 35469845_Elevation of phospholipase C-beta1 expression by amyloid-beta facilitates calcium overload in neuronal cells. 35608718_MicroRNA-1297 participates in the repair of intestinal barrier injury in patients with HIV/AIDS via negative regulation of PLCbeta1. |
ENSMUSG00000051177 |
Plcb1 |
47.282281 |
0.2103343748 |
-2.249243 |
0.439197292 |
25.056576 |
0.00000055672561886007584750098425158126858036666817497462034225463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002027896584363104803507742504575794839638547273352742195129394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.5308625 |
5.3556697 |
83.6513613 |
16.7880268 |
| ENSG00000182667 |
50863 |
NTM |
protein_coding |
Q9P121 |
FUNCTION: Neural cell adhesion molecule. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Immunoglobulin domain;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the IgLON (LAMP, OBCAM, Ntm) family of immunoglobulin (Ig) domain-containing glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell adhesion molecules. The encoded protein may promote neurite outgrowth and adhesion via a homophilic mechanism. This gene is closely linked to a related family member, opioid binding protein/cell adhesion molecule-like (OPCML), on chromosome 11. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009]. |
hsa:50863; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; neuron recognition [GO:0008038] |
12819783_NTM shows close linkage to OPCML on chromosome 11q25. 15379248_Human neurotrimin is expressed on the surface of CHO cells and could strengthen their aggregation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21036197_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21036197_The finding of this study provided evidence that NTM at 11q25 chromosome regions affecting IQ. 22661486_A quantitative analysis of central corneal thickness and a subsequent analysis of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), SNPs in two cell adhesion molecules, NTM and CNTNAP4, were identified and may increase POAG susceptibility in a subset of cases. 23054244_A translocation breaks intron 1 of a splicing isoform of Neurotrimin at 11q25 in a family with intracranial and thoracic aortic aneurysm. 24616287_The generation and cardiac phenotype of single and double heterozygous gene-targeted OPCML and Neurotrimin knockout mice. 25819087_Both the AFF3 and NTM triglyceride associations were replicated among Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis study participants (P = 1.00 x 10(-7) and 8.00 x 10(-5), respectively). 26334118_NTM is not a susceptibility gene for autism spectrum disorders. 32033718_Neurotrimin, a neural cell adhesion molecule, is increased in leiomyoma compared to myometrium in patient tissue after estrogen and progesterone treatment. 32710982_Highly Conserved Molecular Features in IgLONs Contrast Their Distinct Structural and Biological Outcomes. |
ENSMUSG00000059974 |
Ntm |
15.996529 |
3.1477176883 |
1.654306 |
0.418607353 |
15.684552 |
0.00007483287590961040444681451333508448442444205284118652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000209947395633121005253593494010999620513757690787315368652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.6130973 |
7.6523537 |
7.5577308 |
1.8734316 |
| ENSG00000182676 |
116729 |
PPP1R27 |
protein_coding |
Q86WC6 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits phosphatase activity of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) complexes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19389623}. |
ANK repeat;Protein phosphatase inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Enables phosphatase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of catalytic activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:116729; |
phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein phosphatase inhibitor activity [GO:0004864] |
|
ENSMUSG00000025129 |
Ppp1r27 |
6.212635 |
0.0891721647 |
-3.487263 |
0.871051504 |
21.183667 |
0.00000417305762013981709735669506367017334014235530048608779907226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013711190198313106075015017915053050501228426583111286163330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0745404 |
0.6975875 |
12.6609062 |
3.5046661 |
| ENSG00000182685 |
283870 |
BRICD5 |
protein_coding |
Q6PL45 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be involved in regulation of cell population proliferation. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:283870; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127] |
Mouse_homologues 30721158_An SFTPC BRICHOS mutant links epithelial ER stress and spontaneous lung fibrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000045744 |
Bricd5 |
21.360240 |
0.3641801095 |
-1.457276 |
0.388612085 |
14.124115 |
0.00017113571713075700648359900313266734883654862642288208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000454064926271791047783510375523974289535544812679290771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.9363789 |
3.5468904 |
30.0330705 |
6.6106801 |
| ENSG00000182685_ENSG00000184207 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.784545 |
0.2187339710 |
-2.192751 |
0.676581579 |
9.777665 |
0.00176644463923513578805513102309987516491673886775970458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003944436138443359156358081207827126490883529186248779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.9717103 |
6.1046497 |
59.7134896 |
19.3863000 |
| ENSG00000182718 |
302 |
ANXA2 |
protein_coding |
P07355 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-regulated membrane-binding protein whose affinity for calcium is greatly enhanced by anionic phospholipids. It binds two calcium ions with high affinity. May be involved in heat-stress response. Inhibits PCSK9-enhanced LDLR degradation, probably reduces PCSK9 protein levels via a translational mechanism but also competes with LDLR for binding with PCSK9 (PubMed:18799458, PubMed:24808179, PubMed:22848640). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18799458, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22848640, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24808179}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Binds M.pneumoniae CARDS toxin, probably serves as one receptor for this pathogen. When ANXA2 is down-regulated by siRNA, less toxin binds to human cells and less vacuolization (a symptom of M.pneumoniae infection) is seen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25139904}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Annexin;Basement membrane;Calcium;Calcium/phospholipid-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Extracellular matrix;Host-virus interaction;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Secreted;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the annexin family. Members of this calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein family play a role in the regulation of cellular growth and in signal transduction pathways. This protein functions as an autocrine factor which heightens osteoclast formation and bone resorption. This gene has three pseudogenes located on chromosomes 4, 9 and 10, respectively. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Annexin A2 expression has been found to correlate with resistance to treatment against various cancer forms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2019]. |
hsa:302; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; AnxA2-p11 complex [GO:1990665]; azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; basement membrane [GO:0005604]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cornified envelope [GO:0001533]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; membrane [GO:0016020]; midbody [GO:0030496]; myelin sheath adaxonal region [GO:0035749]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PCSK9-AnxA2 complex [GO:1990667]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane protein complex [GO:0098797]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; Schmidt-Lanterman incisure [GO:0043220]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098641]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; phospholipase A2 inhibitor activity [GO:0019834]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; S100 protein binding [GO:0044548]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; virion binding [GO:0046790]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; fibrinolysis [GO:0042730]; membrane raft assembly [GO:0001765]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor catabolic process [GO:0032804]; negative regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002091]; osteoclast development [GO:0036035]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance [GO:1905581]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding [GO:1905597]; positive regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905599]; positive regulation of plasma membrane repair [GO:1905686]; positive regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010756]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:1905602]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of vacuole organization [GO:0044090]; positive regulation of vesicle fusion [GO:0031340]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; vesicle budding from membrane [GO:0006900] |
11781322_identification of a hetereotetramer as a plasmin reductase 12468550_amino acids critical for tissue-type plasminogen activator-annexin A2 interaction 12629510_results suggest that annexin II, and, likely, annexin I, may be endogenous suppressors of prostate cancer cell migration and their reduced or lost expression may contribute to prostate cancer development and progression 12699894_virtual Northern blots to analyze expression of NACA and ANX2 in progenitor cultures of nine children with Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and five healthy individuals 12730231_analysis of annexin A2 interaction with tissue plasminogen activator, plasminogen, and plasmin 13679511_annexin 2/S100A10 complex functions in the intracellular positioning of recycling endosomes and that both subunits are required for this activity 14504107_annexin II-mediated assembly of plasminogen and t-PA on monocyte/macrophages contributes to plasmin generation, matrix remodeling, and directed migration 14522961_annexin II binds to CEACAM1 in breast neoplasms 14613585_possible mechanistic and regulatory role of Anx-II in prostate cancer progression 14672933_ANXA2 is a Ca(2+)-dependent RNA-binding protein that interacts with the mRNA of the nuclear oncogene, c-myc 14991775_AII does not bind 1,25-D(3) in a physiologically relevant manner 14995994_Western blotting of endothelial cell surface of a number of sites showed higher amounts of tissue plasminogen activator annexin II on cerebral endothelial cell. In contrast, expression of u-PA receptor was the same for all ECs 15051937_Lipocortin II may be a marker or contribute to asthma exacerbation. 15064349_Annexin I serves as both ligand and receptor in promoting phagocytosis. 15070701_E2A-HLF induces annexin II by substituting for cytokines that activate downstream pathways of Ras 15211578_Reduced Annexin 2 expression is associated with osteosarcoma metastases 15226372_Experiments using individual subunits identify annexin 2 as a PtdIns(4,5)P(2)-binding entity 15257287_siRNA-mediated downregulation of annexin A2/S100A10 and disruption of the complex by microinjection of peptide competitors result in a marked reduction in von Willebrand Factor 15302870_Temperature stress-induced annexin 2 translocation is dependent on both expression of protein p11 tyrosine phosphorylation of annexin 2. 15471954_observations suggest a novel pathway for endothelial activation induced by APLA/anti-beta2GPI antibodies that is initiated by cross-linking or clustering of annexin A2 on the endothelial surface 15526283_Human colon adenocarcinoma cell differentiation is associated with an up-regulation of AnxA1, AnxA2, and AnxA5 and with a subcellular relocation of these proteins 15567461_investigation undertaken to identify the significance of annexin II expression and regulation in leukaemia do not fully support the concept of the coagulopathy associated with APL being caused by hyperfibrinolysis alone 15574370_S100A10 and annexin A2 play an important role in plasmin regulation and in cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis [review] 15784727_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15784727_several single nucleotide polymorphisms in bone morphogenic protein 6, annexin A2, and klotho were associated with sickle cell osteonecrosis 15788416_S100A4 protein alone or in a complex with annexin II accelerated tissue plasminogen activator-mediated plasminogen activation in solution and on the endothelial cell surface 15849182_complex with S100A10 is a substrate of thioredoxin 15940368_AX-II, in addition to inducing GM-CSF expression, increases membrane-bound RANKL synthesis by marrow stromal cells through MAPK-dependent pathway. 15944914_Results show that progression from prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia to prostate cancer is characterized by a reduction of ANX2 and suggest that downregulation of these proteins could represent an important event in prostate carcinogenesis. 16100712_annexin A1 and A2 may have roles in dysferlin deficiency and in muscular dystrophies 16177123_Annexin A2 is part of the putative cell surface vitamin D binding protein binding site complex and functions to mediate the chemotactic cofactor effect. 16230353_analysis of the structural determinant of the PtdIns(4,5)P2 selectivity of A2t (annexin II-p11 heterotetramer), which may be involved in the regulation of PtdIns(4,5)P2 clustering in the cell 16331566_The experimental data suggest that the ANNEXIN A2 gene may relate to cellular apoptosis induced by p53 gene. 16493010_anti-A2 antibodies contribute to the prothrombotic diathesis in antiphospholipid syndrome 16501079_novel gag-binding protein essential for the proper assembly of HIV in monocyte-derived macrophages. 16524621_annexin 2 mediated fibrinolysis on the transitional cell carcinoma cells may play a role in inducing hemorrhagic disorder in vascular intimal carcinomatosis 16643892_Annexin II-dependent localized plasmin generation is associated with angiogenesis and metastasis in breast cancer 16709165_Review discusses a role for annexin 2 in the regulation of ecto-5'-nucleotidase activity, which is dependent upon the stability of the membrane rafts. 16797773_Real-time RT-PCR confirmed up-regulation of IL-8, osteopontin, and TNFRSF14 and down-regulation of SAMeS and CD209 in AH. 16882661_analysis of calcium-dependent heparin binding to annexin A2 16963080_Results describe the design, production, biophysical characterization and binding properties of a soluble mutant form of annexin A2 domain IV that adopts a partially folded conformation. 16984913_that Annexin2 is required for strong binding of S100A10 to the C-terminal domain of the protein Ahnak. 16989986_we further showed that LMP1 increased the serine, but not tyrosine, phosphorylation of annexin A2 by activating a novel signaling pathway, the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway. 17065584_The median of anti-annexin A2 IgM titer from preterm infants who were delivered with high-grade chorioamnionitis (CAM) was significantly higher than those from preterm infants without CAM and with low-grade CAM. 17239928_demonstration of an angiostatin receptor (ANX2) in vascular endothelial tumors including angiosarcoma; diffuse and strong reactivity signified the absence of any down-regulation of ANX2 in both benign and malignant tumors 17441315_Cellular DNA synthesis is significantly reduced in small interference RNa transfected a prostatic cancer cell line. 17513451_following injury, N-glycosylation events and AII presentation on the cell surface of airway epithelial cells are important mediators in repair 17581860_The anx 2-S100A10/CFTR complex is important for CFTR function across epithelia. 17626749_Elevated or reduced expression of Annexin II may be correlated to reverse or progression of carcinogenesis, respectively. 17709546_uPA plays a major role in inducing MMP-1 production in activated human monocytes, which is mediated by a plasmin-dependent mechanism involving signaling through the annexin A2 heterotetramer. 17711622_The increase of annexin II and its expression levels, and the increase of core-fucosylation might all be related to HCC metastatic ability. 17824845_analysis of the pH-induced membrane binding of annexins A6 and A2-S100A10 17971878_p11/S100A10 light chain of annexin A2 is dispensable for annexin A2 association to endosomes and functions in endosomal transport 17999956_the annexin II-S100A10 complex, which regulates exocytosis, forms a ternary complex with TrpRS. 18008140_These results suggested that Annexin A2 may play roles in p53 induced apoptosis and it is also involved in regulation of cell proliferation. 18084608_IRF-1 silencing with siRNA produced upmodulation of the Annexin-II protein in THP-1 cells. 18164291_analysis of translocation and assembly at the plasma membrane; heterogeneous assembly formation was shown between annexins A5 and A2 18174463_it is proposed that annexin 2 acts as a receptor for factor Xa on the surface of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and that annexin 2 facilitates factor Xa activation of PAR-1 but does not enhance coagulant function of factor Xa 18211896_The findings suggest annexin 2 externalization is coupled to lipid efflux in prostate epithelium and that IFNgamma induces down-regulation of the protease-binding anx2(t) scaffold at the cell surface. 18262347_Annexin A2 localizes to the basal epithelial layer and is down-regulated in dysplasia and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 18289715_The effect of alcohol on fibrinolysis and plasmin is mediated in part by ANXA2. Alcohol directly influences hepatic pathways of fibrinolysis that may contribute to ALD. 18332131_Rab14 also co-localized in part with annexin A2 and lamellar bodies in alveolar type II cells 18384219_Annexin II and beta(2)-tubulin down-regulation is important in nasopharyngeal carcinoma formation and may represent potential targets for further investigations. 18389276_annexin-2 is required for cAMP-induced AQP2 exocytosis in renal cells 18434302_Within the endothelial cell, p11 is required for Src kinase-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of A2, which signals translocation of both proteins to the cell surface. 18494762_annexin II is a novel HSP27-interacted protein which is involved in UVC resistance in human cells 18502476_Expression of ANAX2 in human atheroslerotic abdominal aortic aneurysms is reported. 18565825_a tyrosine phosphorylation switch in annexin A2 is an important event in triggering Rho/ROCK-dependent and actin-mediated changes in cell morphology associated with the control of cell adhesion 18636554_annexin II and its receptor axis play a central role in prostate cancer metastasis, and prostate cancer utilizes the hematopoietic stem cell homing mechanisms to gain access to the niche. 18712570_Annexin II overexpression may induce gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer resulting in rapid recurrence. 18799458_identification of the minimal inhibitory sequence of AnxA2 should pave the way toward the development of PCSK9 inhibitory lead molecules for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia 18924133_Annexin A2 has a role in malignant phenotype and secretion of IL-6 in DU145 prostate cancer cells 18990701_phosphorylation of Tyr-23 is essential for proper endosomal association and function of AnxA2, perhaps because it stabilizes membrane-associated protein via a conformational change. 19016789_EspL2 of E. coli O157:H7 Sakai bound F-actin-aggregating annexin 2 directly, increasing its activity.[EspL2] 19020748_Annexin A2 expression and phosphorylation are up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. 19022301_These observations are consistent with a role for annexin A2 as an actin nucleator on PI(4,5)P2-enriched membranes. 19176991_Via its receptor annexin II on endothelial surface, tPA regulates intravascular fibrin deposition. Review. 19289089_actin patches are nucleated on early endosomes via annexin A2 and Spire1, and these patches control endosome biogenesis, presumably by driving the membrane remodeling process 19325895_Anx2, by interacting with Gag at the membranes that support viral assembly, functions in the late stages of HIV-1 replication 19339807_fatty acid-binding protein-5, squamous cell carcinoma antigens 2, alpha-enolase, annexin II, apolipoprotein A-I and albumin were detected at a high level in Atopic dermatitis skin lesions, but scarcely in the normal controls 19380152_This study found that patients with Posttraumatic stress disorder had lower levels of p11 mRNA than control subjects, while those with major depression disorder, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia had significantly higher p11 levels than the controls. 19513064_ANX2 expression in the primary kidney tumours showed significant associations with a higher stage, a higher nuclear grade. ANX2 expression is an independent predictor for metastasis. 19549357_Annexin II participates in invasion and infiltration of hematologic malignancies probably through enhancing the degradation of extracellular matrix by cells of hematologic malignancies. 19556289_Annexin A2 is associated with receptivity in the human endometrium. 19585213_AnxA2 is overexpressed in MM patients and myeloma cell lines U266 and RPMI8226, and AnxA2 overexpression appeared to affect the proliferation, apoptosis, invasive potential and production of pro-angiogenic factors 19605586_In this study, rabbit vesivirus (RaV) virions were shown to bind annexin A2 (ANXA2) in a membrane protein fraction from HEK293T cells. 19642359_Abnormally high levels of Annexin II and u-PAR expression in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells may contribute to the increased production of plasmin, leading to primary hyperfibrinolysis. 19656851_Studies show that GSK-3 and Omi/HtrA2 synergistically cause annexin A2 cleavage and then cell cycle inhibition or apoptosis. 19724273_S100A6 binds to annexin 2 in pancreatic cancer cells and promotes pancreatic cancer cell motility. 19764771_Results showed that expression of Anxa2 is enhanced when cancer cells acquire drug resistance and it plays an essential role in MDR-induced tumor invasion. 19823170_Inducible ANXA2 expression in cholangiocytes may play a compensatory role for the impaired anion exchanger activity of cholangiocytes in primary biliary cirrhosis. 19885616_A sandwich ELISA system for ANXA2 was developed for the detection of ANXA2 in human samples. The serum ANXA2 concentrations of the patients with hepatocellular carcinoma were significantly elevated when compared with those of normal individuals. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19951950_Data show that identification of annexin-II as one of the fH ligands on apoptotic cells together with the fact that autoantibodies against annexin-II are found in systemic lupus erythematosus provides further insight in the pathogenesis of this disease. 19954599_Thalidomide can inhibit the expression of AnxA2 mRNA and protein in RPMI8226 and HMEC-1 cells. 20015551_the upregulated expression of annexin A2 by SARS-associated cytokines and the cross-reactivity of anti-SARS-CoV S2 antibodies to annexin A2 may have implications in SARS disease pathogenesis. 20018898_Study identify annexin A2 as a novel binding partner for TM601 in multiple human tumor cell lines and human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC). 20047591_annexin II promotes the invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro, and annexin II and HAb18G/CD147 interact with each other in the same signal transduction pathway working as a functional complex in tumor progression. 20079732_Annexin II may be an attractive target for therapeutic strategies aimed to inhibit angiogenesis and breast cancer. 20093721_CFTR function by annexin A2-S100A10 complex has roles in health and disease [review] 20093722_endothelial annexin A2 has a role in vascular fibrinolysis [review] 20121258_the interaction of AnxA2 with STAT6 20225235_This study identified 22 differentially expressed proteins related to liver fibrosis, and verified a potential biomarker (ANXA2) for non-invasive diagnosis of immune liver fibrosis. 20229030_Levels of anti-A2 autoantibody are higher in antiphospholipid patients and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with thrombosis, which may be helpful in identifying potential cases of antiphospholipid syndrome. 20335258_identify ANXA2 as a novel host factor contributing, with NS5A, to the formation of infectious HCV particles. NS5A specifically recruits ANXA2 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20407807_Shear stress especially induced sustained increases in the expression of Annexin A2 and GAPDH in a comparative proteome analysis of effect of shear stress on HMSCs. 20493868_The metabolism of annexin A2 in for Opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma is reported; its use as a neoplasm marker is discussed. 20540360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561442_Bortezomib may down-regulate the expression of VEGF in endothelial cells through regulating the activity of HIF-1alpha and the expression of Annexin A2. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20702651_These results indicate that plasminogen promotes influenza A virus replication in an annexin 2-dependent fashion in the absence of viral neuraminidase. 20826156_Annexin A2 expression is required for the biologic effects of progastrin in vivo and in vitro. 20847146_Annexin II mediates the binding of anti-dsDNA antibodies to mesangial cells, contributing to the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis. 20947498_annexin 2 regulates endothelial morphogenesis through an adherens junction-mediated pathway upstream of Akt. 20970165_Annexin A2 expression is reduced in intestinal-type sinonasal adenocarcinoma, and this loss of expression is associated to the more aggressive histopathological types. 21033036_Expression of ANXA2 was high in glioma samples and was correlated with pathological grades. 21122411_The benign lesions with positive ANXA1 and/or ANXA2 expression showed mild to severe atypical hyperplasia of the gallbladder epithelium. The positive rates of ANXA1 and/or ANXA2 were significantly lower in the well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. 21132403_results suggest that annexin-1, annexin-2, and annexin-3 are identified as potential biomarkers associated with lymph node metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma 21146216_High annexin II is associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia. 21193750_Anti-annexin A2 autoantibodies are significantly associated with cerebral venous thrombosis. 21237296_ANXA2 plays a role in regulating proliferation in dasatinib-sensitive WM-115 cells and could potentially play a role in sensitivity to dasatinib in melanoma cells. 21330046_altered expression levels of proteins involved in brush border formation, such as ezrin and keratin 19 support the notion that annexin II is a key player in cell differentiation and an indispensable element of apical membrane domain. 21491466_MBD1-containing chromatin associated factor 2, epithelial malignancy-related vimentin and exocytosis-related annexin A2 were changed upon exposure to airborne nanoparticle PM(0.056). 21572519_Data show that ANXA2 is part of a novel molecular pathway underlying PDA metastases and a new target for development of PDA therapeutics. 21603851_Aberrant expression of Annexin A2 and Cdc42 play a role in carcinogenesis, differentiation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 21645192_Data suggest that although annexin A2 is not an exclusive marker of APPL1/2 endosomes, it has an important function in membrane recruitment of APPL proteins, acting in parallel to Rab5. 21809360_results suggest that the interaction of HAb18G/CD147 with annexin II is involved in the interconversion between mesenchymal and amoeboid movement of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 21817168_this study identified a novel osteoporosis susceptibility gene ANXA2, and suggested a novel pathophysiological mechanism, mediated by ANXA2, for osteoporosis in humans 21849434_Both the annexin A2 and p11 subunits of calpactin I coimmunoprecipitate with human papillomavirus type 16 E5 in COS cells and in human epithelial cell lines, and an intact E5 C terminus is required for binding. 21886777_Cochlin interacts with TREK-1 and annexin A2. 21900167_In this study, the authors showed that human annexin II (Anx2) protein could bind to the enterovirus type 71 virion via the capsid protein VP1. 21908427_The role of the annexin A2 heterotetramer in vascular fibrinolysis. 21918681_Results suggest that ANXA2 is a cellular RBP that can modulate the frameshifting efficiency of viral RNA, enabling it to act as an anti-viral cellular protein, and hinting at roles in RNA metabolism for other cellular mRNAs. 21928315_Interferon-gamma stimulates p11-dependent surface expression of annexin A2 in lung epithelial cells to enhance phagocytosis. 21976520_The levels of expression of annexin A2 in human glioma samples correlate with their degree of malignancy. 22044461_Selective disruption of the fibrinolytic activity of ANX II may provide a novel strategy for specific inhibition of neoangiogenesis in human breast cancer. 22141411_Bcl-xL to Bax protein ratios, an index of survival activity in cells exposed to lethal stresses, were increased in the cells that had been precultured in rANX II for 24 h prior to UVC irradiation 22223826_Results show that AXII and AXIIR play important roles in multiple myeloma (MM) and that targeting the AXII/AXIIR axis may be a novel therapeutic approach for MM. 22230505_Overexpression of AnnexinII in the Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma(ccRCC) is closely correlated with the ccRCC development. 22235123_a novel interaction involving K17 and AnxA2 and identify AnxA2 as a potential regulator of keratin filaments. 22301157_Anxa2 recruits HCV NS proteins and enriches them on the lipid raft to form the HCV replication complex. 22452176_This review retraces the current state of knowledge on Annexin A2 and A5 functions causing thrombophilia. [review] 22452352_Anxa2 might influence proliferation, migration and invasion of MCF-7 cells by increasing expression of c-myc and cyclin D1 via activation of Erk1/2 signalling pathways. 22493182_ANXA2 has a dual role in the pathogenesis of human adenomyosis through conferring endometrial cells both metastatic potential and proangiogenic capacity. 22587461_AnxA2 and NHERF2 form a scaffold complex that links adjacent Tir molecules at the plasma membrane forming a lattice that could be involved in retention and dissemination of other effectors at the bacterial attachment site. 22645245_ANXA2 may act upstream of the RhoA/ROCK pathway by regulating F-actin remodeling and is a key factor in human endometrial adhesiveness 22679123_the M2 haplotype of the ANXA5 gene confers a risk of delivering small-for-gestational age babies 22681645_Upregulated expression of annexin II is associated with gastric cancer. 22705595_ANXA2 exemplifies an interesting class of targetable bone-remodeling factors expressed by normal and malignant plasma cells and the BM microenvironment that have a significant impact on survival of myeloma patients. 22792315_Depletion of annexin A1 or A2 alters the retrograde transport of shiga toxin but not ricin, without affecting toxin binding or internalization. 22822523_presenting application of the PCR-RFLP technique for determination of the ANXA2 gene single nucleotide polymorphism frequency and their clinical association among Indian sickle cell patients 22830395_Annexin A2 anchors S100A10 to the cell surface and, in doing so, allows S100A10 to play a prominent role in the activation of plasminogen in angiogenesis and oncogenesis. 22848640_AnxA2 acts as an endogenous regulator of PCSK9-induced LDLR degradation 22859294_a novel role for ANXA2 in NSCLC cell proliferation by facilitating the cell cycle partly through the regulation of p53 via JNK/c-Jun. 22879587_Annexin A2 and A5 serve as new ligands for C1q on apoptotic cells 22913982_Protein expression analysis found downregulation of annexin II in human coronary artery endothelial cells 22917188_Results suggest that abnormal ubiquitination and/or degradation of annexin A2 may lead to presence of annexin A2 at high level, which may further promote metastasis and infiltration of the breast cancer cells. 22939813_the ANXA2 N-terminal domain does not appear to be the target antigen for anti-ANXA2 antibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome. 22940583_The AHNAK peptide adopts a coil conformation that arches across the heterotetramer contacting both annexin A2 and S100A10 protomers with tight affinity. 22957061_AnxA2 has a role in EGFR-Src membrane bound signaling complex and ligand induced activation of downstream signaling pathways 23091277_N-terminal acetylation of AnxA2 is required for S100A10 binding 23091278_AnxA2 has an inhibitory effect on actin polymerization, and a modification with WithfA significantly increases this inhibitory role of AnxA2 23131771_Partial knockdown of Annexin A2 and PSF showed decrease in p53 IRES activity and reduced levels of both the p53 isoforms. 23139605_The characteristics and distribution of ANXA2 expression has good diagnostic potential for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. 23148505_an annexin A2 niche in cell fate regulation 23174572_Up-regulated expression of ANXA2 is closely related to the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. 23188673_Annexin A2 may serve as a discriminative serological marker for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 23226323_nuclear translocation of annexin A2 in response to genotoxic agents and its role in mitigating DNA damage 23275167_Binding of AHNAK peptide to the surface of AnxA2 is governed by several hydrophobic interactions between side chains of AHNAK and pockets on S100A10. 23334362_shRNA-mediated knockdown of either ANXA2, FYN, LCK or S100A10, all led to inhibition of annexin A2 phosphorylation and resulted in marked sensitization to prednisolone 23391921_Annexin II is involved in fibroblast resistance to UV B light. 23494179_Annexin II up-regulation was associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 23522334_ANXA2 deletion in caco2 cells induced the pseudopodia shorted and spared, non-stained areas increased, mitochondria decreased, and the expression and polymerization of F-actin and beta-tubulin changed. 23529818_Elevated expression of annexin II was associated with lymph node metastatic lung cancers. 23558678_an important role of AnxA2 in controlling dynamics of beta1 integrin at the cell surface that in turn is required for the active turnover of cell-matrix associations, cell migration, and wound closure. 23572070_annexin A2 has a role in preventing hyperglycemia-induced loss of human endothelial cell surface fibrinolytic activity 23637395_Annexin A2 and S100A10 regulate human papillomavirus type 16 entry and intracellular trafficking in human keratinocytes. 23696646_extracellular C-1-P, acting through the extracellular annexin a2-p11 heterotetrameric protein, can mediate vascular endothelial cell invasion. 23713052_Perfomed proteomic analysis on a transgenic mouse model of severe cardiac hypertrophy; compared data to dataset of heart failure found MYH7, IGFBP7, ANXA2, and DESM to be biomarker candidates for heart failure. 23721211_Plasminogen stimulates autocrine cytokine production in human airway smooth muscle cells in a manner mediated by plasmin and annexin A2. 23757730_complex formation of AnxA2 with S100A10 is a central regulatory mechanism in the acute release of VWF in response to cAMP-elevating agonists 23792445_data provide evidence for AnxA2 as a mediator of EGFR endocytosis and signaling in breast cancer via regulation of cofilin activation 23840117_Annexin A2 silencing inhibits invasion, migration, and tumorigenic potential of hepatoma cells. 23861394_annexins such as AnxA2 can efficiently induce membrane deformations after lipid segregation, a mechanism possibly underlying annexin functions in membrane trafficking. 23886630_The regulation of S100A4, S100A6 and ANXA2 in primary human thyrocytes, was investigated. 23931152_Authors show here that AnxA2, p11 and AHNAK are required for type 3 secretion system-mediated Salmonella invasion of cultured epithelial cells. 23950866_ANXA2 enhances the migration and invasion potential of HCC cells in vitro by regulating the trafficking of CD147-harboring membrane microvesicles. 23994525_an annexin A2-S100A10 molecular bridge participates in cell-cell interactions, revealing a hitherto unexplored function of this protein interaction 24019232_Studied secreted protein biomarkers in invasive breast cancer; identified annexin II as a novel secretory biomarker candidate for invasive breast cancer, especially estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. 24111848_Plasminogen stimulates airway smooth muscle cell proliferation in a manner mediated by urokinase and annexin A2. 24239898_By associating with P-glycoprotein, Anxa2 promotes invasion of multidrug resistant breast cancer cells. 24402284_annexin A2 may participate in keloid formation by inhibiting keloid fibroblast proliferation. 24591759_With some cancers, ANXA2 can be used for the detection and diagnosis of cancer and for monitoring cancer progression. [Review] 24626613_the present study demonstrated that ANXA2 and SOD2 are potential target genes of HOXA13 and their coexpression predicts the poor prognosis of Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 24668792_Annexin A2 was identified as down-regulated in the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues after 2-DE Gel coupled with MALDI-TOF-MS identification. 24719459_HPV16 suppresses LC maturation through an interaction with A2t, revealing a novel role for this protein. 24806074_metastatic cancer cells have elevated rate of cell injury and they rely on the S100A11-ANXA2 complex to enable cell membrane repair. S100A11 in a complex with Annexin A2 helps reseal the plasma membrane. 24808179_data revealed a plausible new role of AnxA2 in the reduction of PCSK9 protein levels via a translational mechanism. 24819400_Annexin A2 is a key molecule in the DDR-2/annexin A2/MMP-13 loop, the activation of which contributes to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis, mainly through promoting invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. 24884814_Urinary calreticulin, annexin A2, and annexin A3 are very likely a panel of biomarkers with potential value for upper tract urothelial carcinoma diagnosis. 24968947_Data suggest that S100A4 and Annexin A2 proteins could be useful prognostic markers to predict tumor progression and prognosis in urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. 25034653_This study shows that ANXA2 and GAL3 deregulated expression was associated with an invasive phenotype in gastric cancer cell lines and may contribute to metastasis in gastric cancer patients. 25139904_CARDS toxin binds selectively to annexin A2; it serves as a distinct receptor for CARDS toxin binding and internalization and enhances CARDS toxin-induced vacuolization in mammalian cells 25150310_ANXA2 is involved in gastric cancer multi-drug-resistance (MDR) through regulating p38MAPK and AKT pathways as well as certain MDR factors 25219463_ANXA2 effectively predicted those endometrioid endometrial carcinomas that finally recurred. 25233429_Data suggest that calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol 4,5-diphosphate- (PI(4,5)P2-) binding proteins (such as ANXA2, PRKCA [protein kinase C alpha], and SYT1 [synaptotagmin I]) interactions with membrane microdomains are tightly regulated. [REVIEW] 25284003_Study points out the regulatory function of Anxa2 in RCC cell motility and provides a molecular-based mechanism of Anxa2 positivity in the progression of RCC. 25287627_findings indicate a significant decrease in Anx A2 expression in colon cancer patients compared to healthy controls and in parallel with tumor progression 25290763_These data indicate a novel functional role of AnxA2 in the negative post-transcriptional regulation of type I collagen synthesis in human fibroblasts. 25303710_Annexin A2 complexes with S100 proteins: structure, function and pharmacological manipulation 25344575_Results show the transcriptional repression of ANXA2 by ERG in prostate epithelial cells plays a critical role in abrogating differentiation, promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and in the inverse correlation of expression seen in prostate tumor. 25347736_Data indicate that annexin A2 overexpression in microsatellite instability (MIN) cells induces disassembly and colocalization of coilin with centromeres. 25355205_Our results support a model whereby AnxA2 limits the availability of TRPA1 channels to regulate nociceptive signaling in vertebrates. 25362534_HE4 and annexin II binding interaction promoted ovarian cancer cell invasion. 25402728_annexin A2 (ANXA2) on nasopharygeal carcinoma cells is a ligand for DC-SIGN on dendritic cells 25416440_Consistently, double-labeling immunofluorescence experiments illustrated co-localization of ANXA2 and Lewis y antigen within the same area. In conclusions, ANXA2 contains Lewis y antigen. 25418092_Results reveal that AnxA2 and its derivatives bind cooperatively to membranes containing cholesterol, phosphatidylserine, and/or phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, thus providing a mechanistic model for the lipid clustering activity of AnxA2 25476478_The present meta-analysis results indicated that ANXA2 overexpression might be associated with poor outcomes in patients with malignant tumors. 25500542_Mir206 targets ANXA2 a |
ENSMUSG00000032231 |
Anxa2 |
2405.780931 |
3.6347507730 |
1.861856 |
0.054850271 |
1122.161509 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000503791357807024259712530498684274423451879458622278657195536188613817335704987615519 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000585508696159974671994162553044462763915165319399232459845702920769547199846254928017 |
Yes |
No |
3831.4589673 |
121.4598613 |
1061.1266929 |
26.1348788 |
| ENSG00000182749 |
164091 |
PAQR7 |
protein_coding |
Q86WK9 |
FUNCTION: Plasma membrane progesterone (P4) receptor coupled to G proteins (PubMed:23763432). Seems to act through a G(i) mediated pathway (PubMed:23763432). May be involved in oocyte maturation (PubMed:12601167). Involved in neurosteroid inhibition of apoptosis (PubMed:23161870). Also binds dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), pregnanolone, pregnenolone and allopregnanolone (PubMed:23161870). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12601167, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23161870, ECO:0000303|PubMed:23763432}. |
Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Oogenesis;Receptor;Reference proteome;Steroid-binding;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable steroid binding activity and steroid hormone receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in response to steroid hormone. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:164091; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; steroid binding [GO:0005496]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; response to steroid hormone [GO:0048545] |
17082257_cDNAs for the mPR alpha subtypes from spotted seatrout (st-mPRalpha) and humans (hu-mPRalpha) encode progestin receptors that display many functional characteristics of G protein-coupled receptors. 18603275_Heterologous expression of MPRA in yeast confirms its ability to function as a membrane progesterone receptor. 19071147_mPRalpha is an intermediary in progestin stimulation of sperm motility in humans by a mechanism involving G-protein activation 21761364_Data show abundant mPRalpha (PAQR7), mPRbeta (PAQR8), and mPRgamma (PAQR5), but not classical nuclear PR (A or B isoforms) mRNA expression and mPRalpha protein expression in a panel of commonly used ovarian cancer cell lines. 27115344_Utilizing both genetic and pharmacologic approaches, the authors establish that sex steroid effects on human melanin synthesis are mediated by the membrane-bound, steroid hormone receptors G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), and progestin and adipoQ receptor 7 (PAQR7). 27340667_The effects of progesterone treatment on the expression levels of progesterone receptor membrane component 1 (PGRMC1), plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 RNA-binding protein (PAIRBP1), and progestin and adipoQ receptor 7 (PAQR7) on both mRNA and protein levels were investigated in spheroids derived from human glioma cell lines U-87 MG and LN-229. 31416049_The results suggest that progesterone induces vascular smooth muscle cell relaxation by reducing cellular calcium levels through mPRalpha-induced alterations in multiple signaling pathways. 33930460_Membrane progesterone receptor alpha (mPRalpha/PAQR7) promotes migration, proliferation and BDNF release in human Schwann cell-like differentiated adipose stem cells. 35007844_Establishment of a steroid binding assay for membrane progesterone receptor alpha (PAQR7) by using graphene quantum dots (GQDs). 35974286_Membrane Progesterone Receptor alpha (mPRalpha/PAQR7) Promotes Survival and Neurite Outgrowth of Human Neuronal Cells by a Direct Action and Through Schwann Cell-like Stem Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000037348 |
Paqr7 |
90.959438 |
0.0391308379 |
-4.675550 |
1.343608007 |
8.680385 |
0.00321653111525779973611793849386231158860027790069580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006836981460427005337365802262183933635242283344268798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6790961 |
5.8860024 |
167.7891373 |
100.6047745 |
| ENSG00000182782 |
338442 |
HCAR2 |
protein_coding |
Q8TDS4 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a high affinity receptor for both nicotinic acid (also known as niacin) and (D)-beta-hydroxybutyrate and mediates increased adiponectin secretion and decreased lipolysis through G(i)-protein-mediated inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. This pharmacological effect requires nicotinic acid doses that are much higher than those provided by a normal diet. Mediates nicotinic acid-induced apoptosis in mature neutrophils. Receptor activation by nicotinic acid results in reduced cAMP levels which may affect activity of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and phosphorylation of target proteins, leading to neutrophil apoptosis. The rank order of potency for the displacement of nicotinic acid binding is 5-methyl pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid = pyridine-3-acetic acid > acifran > 5-methyl nicotinic acid = acipimox >> nicotinuric acid = nicotinamide. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17932499}. |
Apoptosis;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable nicotinic acid receptor activity. Involved in neutrophil apoptotic process and positive regulation of neutrophil apoptotic process. Located in cell junction and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:338442; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; nicotinic acid receptor activity [GO:0070553]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050995]; neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0001781]; positive regulation of adiponectin secretion [GO:0070165]; positive regulation of neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0033031] |
12646212_HM74b has high similarity to HM74 is a receptor for nicotinic acid [HM74b] 16018973_Our results provided direct evidence indicating that HM74A, but not HM74, was sufficient to mediate anti-lipolytic effect of niacin in adipose tissue. 16674924_However, the synergistic effects of HM74A were not dramatically affected by co-treatment with both inhibitors, indicating the cross-talk occurred at the receptor level. 17932499_neutrophils express functional GPR109A receptors,which might be involved in the regulation of neutrophil numbers 18639743_Data show that the high-affinity niacin receptor HM74A is significantly down-regulated in the anterior cingulate cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. 18787507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19136666_Data show that many phenolic acids, including those from the hydroxybenzoic and hydroxycinnamic acid classes, can bind and activate GPR109A (HM74a/PUMA-G), the receptor for the antidyslipidemic agent nicotinic acid. 19141678_GPR109A receptor plays an important role in the dual regulation of adiponectin secretion and lipolysis 19502010_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19633298_Data show that the coordinated PPARgamma-mediated regulation of the GPR81, GPR109A and GPR109B presents a novel mechanism by which TZDs may reduce circulating free fatty acid levels and perhaps ameliorate insulin resistance in obese patients. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20184326_Data show that Mk-6892 was discovered as full and potent niacin receptor (GPR109A) agonist. 20380810_these results demonstrate that GPR109A and GPR109B dimerization is a constitutive process occurring early during biosynthesis. 20460384_The agonist-induced internalization of GPR109A receptors is regulated by GRK2 and arrestin3 in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner and that internalized receptor recycling is independent of endosomal acidification. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20655299_niacin-mediated activation of GP109A in liver lowers ABCA1 expression leading to reduced hepatic cholesterol efflux to high density lipoprotein. 21655214_In contrast, in a squamous cell carcinoma derived cell line, both GPR109A and GPR109B show a more diffuse cellular localization and the receptors are nearly non-functional. 21768093_upon binding to niacin GPR109A receptors initially activate G(i), leading to dissociation of the Gbetagamma subunit from activated G(i), and subsequently induce ERK1/2 activation via two distinct pathways. 22267479_Nicotnic acid displays a range of effects that are lipoprotein-independent and potentially antiatherogenic. These effects are mediated by GPR109A. 22962331_A sequence from residues 329 to 343 in the C-terminal tail of HCA plays a crucial role in keeping HCA in an inactive conformation. 23526298_Review of the role of GPR109A and its downstream effects in the context of atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation, along with insights into strategy for future drug development. [Review Article] 23658787_despite NA's anti-inflammatory effect on human macrophages, it has no effect on foam cells in reverse cholesterol transport; due to GPR109A down-regulation 23770183_These studies provide key insights into mechanisms by which GPR109A may influence cholesterol efflux in macrophages. 24215154_Although its functional role is still unknown, HCA2 may be potentially involved in the pathogenesis of various retinopathies and may offer a new therapeutic target. 24371223_GPR109A is a tumor suppressor in mammary gland. 24662263_the promiscuous activity exerted by niacin via both GPR109A and GPER may open new avenues towards a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in its biological action exerted in different pathophysiological conditions, including malignant diseases. 25329911_GPR109A expression is upregulated in blood and substantia nigra in Parkinson disease patients. 25361930_The results of this study suggested that GPR109A signaling is associated with T2DM, playing a role in regulation of the inflammatory cytokines. 25375133_These results suggest that the PKC pathway and PDGFR/EGFR transactivation pathway play important roles in HCA2-mediated Akt activation. 25463108_niacin, at a relatively low concentration, preserves the ability of HMVEC to form tubes under conditions of saturated fatty acid excess, and may elicit this effect through activation of GPR109A 25690651_Results suggest that the atypical motif asparaging-cysteine-systeine Asn(17)-Cys(18)-Cys(19) is crucial for the normal surface trafficking and function of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2 protein hGPR109A. 26656756_new insights into the G protein coupling profiles of the HCA receptors and the function of the receptor's C terminus 27570060_These results demonstrate that GPR109A is functionally expressed in both human and murine islet beta-cells. 29263047_GPR109A may inhibit inflammatory cytokine production, induced by palmitic acid, by MIN6 cells possibly via inhibiting the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. 30659164_These results indicate that during aging, GPR109A modulates de novo lipid accumulation in liver and adipose tissue, and its dysregulation can lead to age-associated obesity and hepatic steatosis. 31617441_This review summarizes the use of niacin in treatment of dyslipidemia, the pharmacogenetics of niacin response and the potential role of HCAR2 signaling in the treatment of a variety of inflammatory and metabolic diseases. 31734354_C. butyricum decreased the fecal secondary BA contents, increased the cecal SCFA quantities, and activated G-protein coupled receptors (GPRs), such as GPR43 and GPR109A. The analysis of clinical specimens revealed that the expression of GPR43 and GPR109A gradually decreased from human normal colonic tissue to adenoma to carcinoma 31858105_Niacin Ameliorates Hepatic Steatosis by Inhibiting De Novo Lipogenesis Via a GPR109A-Mediated PKC-ERK1/2-AMPK Signaling Pathway in C57BL/6 Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. 32039055_Hydroxycarboxylic Acid Receptor 2 Is a Zika Virus Restriction Factor That Can Be Induced by Zika Virus Infection Through the IRE1-XBP1 Pathway. 34777363_GPR Expression in Intestinal Biopsies From SCT Patients Is Upregulated in GvHD and Is Suppressed by Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics. 34852802_Rare and potentially pathogenic variants in hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor genes identified in breast cancer cases. |
ENSMUSG00000045502 |
Hcar2 |
10.020217 |
2.7728568292 |
1.471373 |
0.517960014 |
8.269783 |
0.00403103303851806878121966093431183253414928913116455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008402492253710872743832638320782280061393976211547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.9987202 |
5.2591642 |
5.4652811 |
1.5220335 |
| ENSG00000182796 |
440104 |
TMEM198B |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36038663_Dual role of pseudogene TMEM198B in promoting lipid metabolism and immune escape of glioma cells. |
|
|
121.211962 |
0.2515368000 |
-1.991159 |
0.163861803 |
155.347955 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000001175318033998728744184706645741063468291396420734275976099319233647152985150488786231563563934934824040112744114594534039497375488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000175940103263907065265172533995282479475532178607135884247213781411893887808703229174860137654090586067923140944913029670715332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.7641078 |
5.4866251 |
199.0111227 |
13.1622174 |
| ENSG00000182853 |
284013 |
VMO1 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z5L0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284013; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615] |
|
ENSMUSG00000020830 |
Vmo1 |
10.237649 |
0.2563436587 |
-1.963849 |
0.511366974 |
16.016832 |
0.00006278182086026336868739283758600322471465915441513061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000178203783826439885427939113782258573337458074092864990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1008277 |
1.3821169 |
16.1034282 |
2.9955479 |
| ENSG00000182873 |
100506504 |
PRKCZ-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31939714_PRKCZ-AS1 promotes the tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma via sponging miR-766-5p to modulate MAPK1. |
|
|
7.738665 |
0.2036275929 |
-2.295995 |
0.629253131 |
14.614430 |
0.00013190065167593324909310614767576907979673705995082855224609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000356044919300800056811279192814367888786364346742630004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.7883686 |
1.6020090 |
13.1421721 |
4.7385911 |
| ENSG00000182890 |
2747 |
GLUD2 |
protein_coding |
P49448 |
FUNCTION: Important for recycling the chief excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, during neurotransmission. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Mitochondrion;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is localized to the mitochondrion and acts as a homohexamer to recycle glutamate during neurotransmission. The encoded enzyme catalyzes the reversible oxidative deamination of glutamate to alpha-ketoglutarate. This gene is intronless.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:2747; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; glutamate dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0004352]; glutamate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0004354]; glutamate dehydrogenase [NAD(P)+] activity [GO:0004353]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; leucine binding [GO:0070728]; glutamate biosynthetic process [GO:0006537]; glutamate catabolic process [GO:0006538]; glutamate metabolic process [GO:0006536] |
11950837_identify the structural basis for allosteric differences of GlUD1 and GLUD2 15044002_These results suggest that the Ser443 residue plays an important role in the different thermal stability of human glutamate dehydrogenase isozymes (hGDH1 and hGDH2). 15378063_GLUD2 originated by retroposition from GLUD1 in the hominoid ancestor less than 23 million years ago. 15750346_results suggest that cysteine 323 plays an important role in catalysis by human GDH isozymes; C323 is not directly involved in allosteric regulation. 17924438_amino acid changes, acting in concert with Arg443Ser and Gly456Ala, ought to be responsible the unique properties of the brain-specific human isoenzyme 18688271_Mitochondrial targeting specificity of GLUD2 is due to an amino acid substitution in the mitochondrial targeting sequence soon after the duplication event in the hominoid ancestor approximately 18-25 million years ago. 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19393024_study of molecular mechanisms regulating hGDH2 function by creating & analyzing mutants with single amino acid substitutions in the regulatory domain (antenna, pivot helix) of the protein 19428807_GDH2 localizes mainly to mitochondria and to a lesser extent to the endoplasmic reticulum of cells 19448744_Hence, while most of the hGDHs translocate into the mitochondria (a process associated with cleavage of the signal sequence), part of the protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum, probably serving additional functions 19826450_A gain-of-function rare polymorphism in hGDH2 hastens the onset of Parkinson's disease in hemizygous subjects. 19826450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20194501_GLUD2 glutamate dehydrogenase is expressed in neural and testicular supporting cells 21420458_[review] Whereas GDH2 in most mammals is encoded by a single functional GLUD1 gene expressed widely, humans have acquired through retroposition an X-linked GLUD2 gene that encodes a highly homologous isoenzyme GDH2 expressed in testis and brain. 21621574_Human GDH1 appears to act like bovine GDH1, but human GDH2 does not show the same enhancement of branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex enzyme activities. 22360420_A protein encoded by this locus was found to be differentially expressed in postmortem brains from patients with atypical frontotemporal lobar degeneration. 22658952_first N-terminal alpha helical structure is crucial for the mitochondrial import of hGDH2 and these findings may have implications in understanding the evolutionary mechanisms that led to the large mitochondrial targeting signals of human GDHs 22709669_first N-terminal alpha helical structure is crucial for the mitochondrial import of hGDH2 and these findings may have implications in understanding the evolutionary mechanisms that led to the large mitochondrial targeting signals of human GDHs 24352816_hGDH2 can operate efficiently in the relatively acidic environment that prevails in astrocytes following glutamate uptake [review] 25225364_IDH1(R132H) exhibits a growth-inhibitory effect that is abrogated in the presence of glutamate dehydrogenase 2 (GLUD2), a hominoid-specific enzyme purportedly optimized to facilitate glutamate turnover in human forebrain. 26241911_Study of the expression of the GDH1/2 in human steroidogenic organs revealed that, while GDH2 was expressed specifically in steroid-synthesizing cells, GDH1 was expressed both in the cells that produce steroids and in those that lack endocrine function. 26399640_hGDH2 evolution bestowed large human neurons with enhanced glutamate metabolizing capacity, thus strengthening cortical excitatory transmission. 27118840_Notably, the introduction of GLUD2 did not affect glutamate levels in mice, consistent with observations in the primates. Instead, the metabolic effects of GLUD2 center on the tricarboxylic acid cycle, suggesting that GLUD2 affects carbon flux during early brain development, possibly supporting lipid biosynthesis. 27422263_The expression of GLUD2 was identified in the cellular and subcellular compartments of numerous tissues. 28032919_This study demonstrated that hGDH2 expression increases capacity for uptake and oxidative metabolism of glutamate, particularly during increased workload and hypoglycemia. 29146184_This proliferation requires glutamate dehydrogenase 2, which synthesizes glutamate from ammonia and alpha-ketoglutarate and is expressed in MCF7 and T47D cells. Our findings provide insight into how cancer cells survive under glutamine deprivation conditions and thus contribute to elucidating the mechanisms of tumor growth. 29943084_In HEK293 cell lines GDH2 and GDH1 were over-expressed and found to be co-localized in subcellular fractions. 30045961_The autoantibodies to GluD2 are common in patients with OMAS, bind to surface determinants, and are potentially pathogenic. 30314897_GLUD2 overexpression inhibited Glioblastoma (GBM) cell growth suggesting a novel potential drug target for control of GBM progression. The possibility to enhance GLUD2 activity in GBM could result in a blocked/reduced proliferation of GBM cells without affecting the survival of the surrounding neurons. 31400387_present data, showing that GLUD2 expression in Tg mice improves in vivo glucose homeostasis by boosting fasting serum insulin levels, suggest that evolutionary adaptation of hGDH2 has enabled humans to achieve narrow-range euglycemia by regulating glutamate-mediated basal insulin secretion 32917661_Ammonia inhibits energy metabolism in astrocytes in a rapid and glutamate dehydrogenase 2-dependent manner. 33093440_Functional validation of a human GLUD2 variant in a murine model of Parkinson's disease. 33421122_Crystal structure of glutamate dehydrogenase 2, a positively selected novel human enzyme involved in brain biology and cancer pathophysiology. |
ENSMUSG00000021794 |
Glud1 |
20.223114 |
0.4336719648 |
-1.205324 |
0.379033058 |
10.212100 |
0.00139522227333306971831794474070420619682408869266510009765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003176535670892505040796560678018067847006022930145263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.9622106 |
3.3203364 |
27.7885446 |
5.1290383 |
| ENSG00000182912 |
|
TSPEAR-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.658712 |
0.2654259795 |
-1.913619 |
0.544336090 |
12.988039 |
0.00031348716624467366917081156962865406967466697096824645996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000797908358987995097039158665097602352034300565719604492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8565117 |
1.7950936 |
18.5769940 |
3.9407781 |
| ENSG00000182950 |
161753 |
ODF3L1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IXM7 |
|
Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to be active in cytoskeleton. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:161753; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856] |
|
ENSMUSG00000045620 |
Odf3l1 |
10.806250 |
3.4441437567 |
1.784145 |
0.508425948 |
12.744765 |
0.00035700706616947794303992824715976439620135352015495300292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000900448444405586856387202487894683144986629486083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.3797649 |
5.4337982 |
5.0169741 |
1.3073308 |
| ENSG00000182957 |
221178 |
SPATA13 |
protein_coding |
Q96N96 |
FUNCTION: Acts as guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for RHOA, RAC1 and CDC42 GTPases. Regulates cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly through a RAC1, PI3K, RHOA and AKT1-dependent mechanism. Increases both RAC1 and CDC42 activity, but decreases the amount of active RHOA. Required for MMP9 up-regulation via the JNK signaling pathway in colorectal tumor cells. Involved in tumor angiogenesis and may play a role in intestinal adenoma formation and tumor progression. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17145773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17599059, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19151759, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19893577, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19934221}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Enables guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity and identical protein binding activity. Involved in cell migration; plasma membrane bounded cell projection assembly; and regulation of cell migration. Located in several cellular components, including filopodium; lamellipodium; and ruffle membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:221178; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; filopodium assembly [GO:0046847]; lamellipodium assembly [GO:0030032]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] |
17599059_These results suggest that similar to Asef, Asef2 plays an important role in cell migration, and that Asef2 activated by truncated mutant APC is required for aberrant migration of colorectal tumor cells. 19151759_Asef2, Neurabin2 and APC cooperatively regulate actin cytoskeletal organization and are required for HGF-induced cell migration. 19910543_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19934221_Asef2 activates Rac1 to modulate adhesion and actin dynamics and thereby regulate cell migration. 24144700_A new role for Rac activation, promoted by Asef2, in modulating actomyosin contractility. 24874604_Phosphorylation of S106 modulates Asef2 guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity and Asef2-mediated cell migration and adhesion turnover. 32339198_Mutations in SPATA13 cause primary angle closure glaucoma. |
ENSMUSG00000021990 |
Spata13 |
99.376546 |
2.7098590268 |
1.438218 |
0.179884088 |
64.742013 |
0.00000000000000085374964150137297713748308976304882822337189622954878309712967165978625416755676269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000006135026635131580060702520498807264935379264698955825707571420934982597827911376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
145.7075874 |
16.0684091 |
54.1481495 |
4.7648341 |
| ENSG00000183010 |
5831 |
PYCR1 |
protein_coding |
P32322 |
FUNCTION: Housekeeping enzyme that catalyzes the last step in proline biosynthesis. Can utilize both NAD and NADP, but has higher affinity for NAD. Involved in the cellular response to oxidative stress. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16730026, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19648921}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Amino-acid biosynthesis;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Mitochondrion;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Proline biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Stress response |
PATHWAY: Amino-acid biosynthesis; L-proline biosynthesis; L-proline from L-glutamate 5-semialdehyde: step 1/1. |
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the NAD(P)H-dependent conversion of pyrroline-5-carboxylate to proline. This enzyme may also play a physiologic role in the generation of NADP(+) in some cell types. The protein forms a homopolymer and localizes to the mitochondrion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:5831; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase activity [GO:0004735]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; L-proline biosynthetic process [GO:0055129]; negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death [GO:1903206]; proline biosynthetic process [GO:0006561]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881] |
16730026_Mutagenesis and kinetic studies reveal the pivotal roles of the dinucleotide-binding Rossmann motif and residue Glu221 in the human enzyme Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase(P5CR). 19576563_In Autosomal-recessive cutis laxa type 2, a single nucleotide change leads to a missense mutation adjacent to a splice junction in the gene encoding PYCR1. 19648921_Mutations in PYCR1 cause cutis laxa with progeroid features. 21204221_The phenotype caused by PYCR1 mutations corresponds to geroderma osteodysplasticum rather than ARCL2B. 21487760_Mutation analysis revealed the presence of disease-causing variants in PYCR1, including a novel deletion of the entire PYCR1 gene in one family, and in each of the other patients the homozygous missense mutations. 21567914_A novel mutation in PYCR1 causes an autosomal recessive cutis laxa with premature aging features in a family. 22052856_The findings presented here suggest a mutation screening of PYCR1 and cardiovascular survey in patients with De Barsy syndrome (DBS). 23531708_Identification of two new mutations in the PYCR1 gene in patients with autosomal recessive cutis laxa, type 2. 23743200_Data suggest that DJ-1 and PYCR1 are on the same pathway of anti-oxidative stress protection of the cells. 24035636_our current study presents the second largest group of patients with PYCR1-related ARCL and expands the clinical and genetic spectrum. 24431009_confirming that indeed PYCR1 generates L-pipecolic acid from Delta(1)-piperideine-6-carboxylate 26733354_Silencing of both PYCR1 and PYCR2 completely abolished anti-oxidation activity of RRM2B, demonstrating a functional collaboration of these metabolic enzymes in response to oxidative stress. 27677826_Results indicate that single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-derived mutations, R119G and G206W, enhance the rigidity of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase (P5CR) structure. 28078560_Authors found that PYCR1 was highly expressed in prostate cancer tissues and then knocked down PYCR1 in PCa cell lines (DU145, PC-3 and LNCap) via lentivirus-mediated gene delivery and analyzed its biological function. 28194412_experimental results indicate the R119G mutation could be an involving pathomechanism for Autosomal recessive cutis laxa . 28258219_PYCR1 forms a concentration-dependent decamer in solution, consistent with the pentamer-of-dimers assembly seen crystallographically 28379297_these findings revealed that the mRNA and protein PYCR1 levels were significantly related to the poor outcome in either ER-negative or ER-positive breast cancer. PYCR1 could serve as a prognostic biomarker, therapeutic target and predictive biomarker for breast cancers. 29562167_Authors describe a biosynthetic pathway exhibited by cells expressing mutant IDH1. By virtue of a change in cellular redox homeostasis, IDH1-mutated cells synthesize excess glutamine-derived proline through enhanced activity of pyrroline 5-carboxylate reductase 1 (PYCR1), coupled to NADH oxidation. 30450527_we firmly establish biallelic mutations in POLR3A as the genetic cause of a recognizable, neonatal, Wiedemann-Rautenstrauch-like progeroid syndrome. Thus, we suggest that POLR3A mutations are causal for a portion of under-diagnosed early-onset segmental progeroid syndromes 30605882_PYCR1 is negatively regulated by miR-488 and then promotes the occurrence and development of non-small-cell lung cancer and activates p38 MAPK pathway. 30916574_High PYCR1 expression is associated with migration and Invasion of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. 31108370_acetylation of PYCR1 at K228 inhibits cell proliferation, while deacetylation of PYCR1 mediated by SIRT3 increases PYCR1's activity. Our findings on the regulation of PYCR1 linked proline metabolism with SIRT3, CBP and cell growth, thus providing a potential approach for cancer therapy. 31606203_PYCR1 plays a role in the proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance by regulating STAT3-mediated p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB signalling pathways in the colorectal cancer cells.PYCR1 is highly espressed in tissues and cells of the colorectal cancer patients. 31619254_PYCR1 interference inhibits cell growth and survival via c-Jun N-terminal kinase/insulin receptor substrate 1 (JNK/IRS1) pathway in hepatocellular cancer. 31987921_Mitochondrial oxidative stress by Lon-PYCR1 maintains an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that promotes cancer progression and metastasis. 32133692_High PYCR1 expression is associated with lung adenocarcinoma. 32213586_Oncogenic Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) K1 oncoprotein interacted with and activated PYCR enzyme, increasing intracellular proline concentration. Consequently, the K1-PYCR interaction promoted tumor cell growth in 3D spheroid culture and tumorigenesis in nude mice. This study demonstrates that an increase of proline biosynthesis induced by K1-PYCR interaction is critical for KSHV-mediated tumorigenesis. 33461172_Dysregulation of USP18/FTO/PYCR1 signaling network promotes bladder cancer development and progression. 33689096_PYCR1 promotes bladder cancer by affecting the Akt/Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 33706104_MiR-328-3p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma-genesis by downregulation PYCR1. 34239351_Deciphering the effects of PYCR1 on cell function and its associated mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma. 34461437_MiR-1207-5p targets PYCR1 to inhibit the progression of prostate cancer. 34696668_MicroRNA hsa-miR-150-5p inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinogenesis by suppressing PYCR1 (pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1). 35108535_Proline synthesis through PYCR1 is required to support cancer cell proliferation and survival in oxygen-limiting conditions. 35760868_Cancer-associated fibroblasts require proline synthesis by PYCR1 for the deposition of pro-tumorigenic extracellular matrix. 36104652_The role of PYCR1 in inhibiting 5-fluorouracil-induced ferroptosis and apoptosis through SLC25A10 in colorectal cancer. 36227136_SENP3 affects the expression of PYCR1 to promote bladder cancer proliferation and EMT transformation by deSUMOylation of STAT3. |
ENSMUSG00000025140 |
Pycr1 |
81.246249 |
2.1136963506 |
1.079768 |
0.178197016 |
37.051070 |
0.00000000115075425702411283410239647837696244647709420405590208247303962707519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005473777903214922904067871021636590422865253913187189027667045593261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
110.0485106 |
11.2554366 |
52.5612296 |
4.2931171 |
| ENSG00000183019 |
199675 |
MCEMP1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IX19 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a single-pass transmembrane protein. Based on its expression pattern, it is speculated to be involved in regulating mast cell differentiation or immune responses. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:199675; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802] |
26846866_The expression of the gene MCEMP1 had the strongest association with stroke of 11,181 genes tested. |
ENSMUSG00000013974 |
Mcemp1 |
68.293319 |
0.2980207041 |
-1.746516 |
0.211720184 |
70.267946 |
0.00000000000000005177215403549133315622197901725874579327576845665104254834432140341959893703460693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000397377531754473256478906250536583003065149054993179800199243345559807494282722473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.3377197 |
4.1289540 |
105.8415411 |
8.3317844 |
| ENSG00000183111 |
389337 |
ARHGEF37 |
protein_coding |
A1IGU5 |
FUNCTION: May act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). {ECO:0000250}. |
Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
Predicted to enable guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:389337; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085] |
30926623_ArhGEF37 was identified as a constituent of clathrin-mediated endocytosis: ArhGEF37 accumulated at dynamin 2-rich late endocytic sites. Endocytosis rates increased in the presence of ArhGEF37. |
ENSMUSG00000045094 |
Arhgef37 |
6.415364 |
0.2409813895 |
-2.053006 |
0.756678171 |
6.750781 |
0.00937066721076841059601125749622951843775808811187744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018062991102626831108057814390122075565159320831298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6391856 |
1.0256923 |
6.4541949 |
2.2899373 |
| ENSG00000183208 |
390637 |
GDPGP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZNW5 |
FUNCTION: Specific and highly efficient GDP-D-glucose phosphorylase regulating the levels of GDP-D-glucose in cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21507950}. |
Cytoplasm;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Hydrolase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
Enables GDP-D-glucose phosphorylase activity. Involved in glucose metabolic process. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:390637; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; GDP-D-glucose phosphorylase activity [GO:0080048]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006] |
21507950_C15orf58 in humans and C10F3.4 in C. elegans display GDP-hexose phosphorylase activity but the major reaction catalyzed by these enzymes is the phosphorolysis of GDP-D-glucose to GDP and D-glucose 1-phosphate |
ENSMUSG00000050973 |
Gdpgp1 |
30.801756 |
0.4229374648 |
-1.241484 |
0.302596015 |
16.976461 |
0.00003784612581510345596848970961545433056016918271780014038085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000110549934104675826583054354390611706548952497541904449462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.1447643 |
4.2559275 |
45.2462293 |
6.6296604 |
| ENSG00000183281 |
5343 |
PLGLB1 |
protein_coding |
Q02325 |
FUNCTION: May bind noncovalently to lysine binding sites present in the kringle structures of plasminogen. This may interfere with the binding of fibrin or alpha-2-antiplasmin to plasminogen and may result in the localization of activity at sites necessary for extracellular matrix destruction. |
Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable serine-type endopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5342;hsa:5343; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit binding [GO:0036313]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043553]; negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014067] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
61.648080 |
0.1800346001 |
-2.473654 |
0.357828922 |
45.374312 |
0.00000000001627551162644154045163912884766296319816181181749925599433481693267822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000089137867015316197400452192563794677829247525835398846538737416267395019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5608156 |
6.4201152 |
101.3931478 |
24.1081552 |
| ENSG00000183386 |
2275 |
FHL3 |
protein_coding |
Q13643 |
FUNCTION: Recruited by SOX15 to FOXK1 promoters where it acts as a transcriptional coactivator of FOXK1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R059}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Activator;Cytoplasm;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a family of proteins containing a four-and-a-half LIM domain, which is a highly conserved double zinc finger motif. The encoded protein has been shown to interact with the cancer developmental regulators SMAD2, SMAD3, and SMAD4, the skeletal muscle myogenesis protein MyoD, and the high-affinity IgE beta chain regulator MZF-1. This protein may be involved in tumor suppression, repression of MyoD expression, and repression of IgE receptor expression. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:2275; |
focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; stress fiber [GO:0001725]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transcription coregulator activity [GO:0003712]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517] |
12681290_Data show that FHL3 (human four-and-a-half LIM-only protein 3) interacts with human phosphatase CDC25B in the cell nucleus. 15117962_FHL2 and FHL3, respectively, are colocalized with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin receptor at the periphery of Z-discs, suggesting a role in mechanical stabilization of muscle cells 15453830_MZF-1 and FHL3 formed a complex of high molecular mass with some additional proteins in the nucleus. Transcriptional repression of FcepsilonRI by MZF-1 required FHL3. 17389685_FHL3 association with MyoD may contribute to the regulation of MyoD-dependent transcription of muscle genes and thereby myogenesis 19139564_Human four-and-a-half LIM family members suppress tumor cell growth through a TGF-beta-like signaling pathway. 20586194_the second zinc finger motif in LIM4 was responsible for the auto-activation of FHL3. 22219185_FHL3 does not bind to HIF-1alpha or p300, indicating that it regulates transactivation by a novel molecular mechanism. 22362714_FHL3 suppressed anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of human breast cancer cells. 22633874_findings suggest that the interaction between Ang and FHL3 may provide some clues to the mechanisms of Ang-regulated cell growth and apoptosis 23616667_FHL3 enhances Tax1-mediated activation of the Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat (LTR) without affecting basal activity and regulates NF-kappaB activation by Tax1 in a cell-specific manner. 24690879_These findings suggest that functional interactions between FHL3 and MT-1X may provide some clues to the mechanisms of FHL3-regulated cell proliferation. 24998228_PCBP2 could bind to FHL3 mRNA 3'UTR-A and inhibited the expression of FHL3 in T98G glioms cells 25659096_the present study established a link between Ang and FHL3 proteins and identifies a new pathway for regulating astrocytoma progression. 29955125_these findings highlight the role of FHL3 as a stemness-suppressor in regulation of the Smad2/3-SOX4-SOX2 axis in glioma 31693182_PCBP2 promotes the development of glioma by regulating FHL3/TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. 35249471_Upregulation of FHL1, SPNS3, and MPZL2 predicts poor prognosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients with FLT3-ITD mutation. |
ENSMUSG00000032643 |
Fhl3 |
50.542632 |
0.4705912888 |
-1.087453 |
0.262086802 |
17.164765 |
0.00003427348743276854761002914173673161712940782308578491210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000100671975026400749124444455873117476585321128368377685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.7473969 |
5.1204237 |
68.0713159 |
7.1791361 |
| ENSG00000183506 |
375133 |
PI4KAP2 |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process and phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
176.717187 |
0.3282544734 |
-1.607113 |
0.216473068 |
53.835573 |
0.00000000000021798989476696111119657668408864745353790970394669557208544574677944183349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001357607952219555336145280129740646577092555435939402741496451199054718017578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.6004845 |
12.8939742 |
277.9078211 |
27.3148280 |
| ENSG00000183569 |
253190 |
SERHL2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H4I8 |
FUNCTION: Probable serine hydrolase. May be related to cell muscle hypertrophy. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Peroxisome;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable hydrolase activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasmic vesicle. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:253190; |
perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000058586 |
Serhl |
32.300533 |
0.3529162363 |
-1.502602 |
0.377983871 |
15.470876 |
0.00008378636300985221299804373007447111376677639782428741455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000233029342005920241933866754457937986444449052214622497558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
18.0414982 |
4.0678530 |
52.1129041 |
7.6087437 |
| ENSG00000183578 |
388121 |
TNFAIP8L3 |
protein_coding |
Q5GJ75 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a lipid transfer protein. Preferentially captures and shuttles two lipid second messengers, i.e., phosphatidylinositol 4,5- bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate and increases their levels in the plasma membrane. Additionally, may also function as a lipid-presenting protein to enhance the activity of the PI3K-AKT and MEK-ERK pathways. May act as a regulator of tumorigenesis through its activation of phospholipid signaling. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TBL6}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Lipid transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable phosphatidylinositol binding activity and phosphatidylinositol transfer activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including inositol lipid-mediated signaling; positive regulation of intracellular signal transduction; and positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388121; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphatidylinositol transfer activity [GO:0008526]; inositol lipid-mediated signaling [GO:0048017]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644]; phospholipid transport [GO:0015914]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216] |
25242044_human cancers have markedly upregulated TIPE3 expression. Knocking out TIPE3 diminishes tumorigenesis, whereas enforced TIPE3 expression enhances it in vivo 25479791_TIPE3 protein is highly expressed in most human carcinoma cell lines. These results suggest that TIPE3 may play important roles in carcinogenesis and cell secretion. 27783229_Further MD simulations confirmed the dynamic stability of these lipids in the TH domain. This computational analysis thus provides insight into the binding mode of phospholipids in the TH domain of the TIPE family of proteins. 28388580_TIPE3 protein was upregulated in breast cancer tissues and positively correlated to invasion and metastasis of human breast cancer cells by activating AKT and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 29422769_In addition to replicating a previously identified genome-wide significant locus for corneal astigmatism near the PDGFRA gene, gene-based analysis identified three novel candidate genes, CLDN7, ACP2, and TNFAIP8L3, that warrant further investigation to understand their role in the pathogenesis of corneal astigmatism. (Meta-analysis) 29510688_High TIPE3 expression in the plasma membrane is associated with non-small-cell lung cancer. 30217224_TIPE3 downregulation correlates with its CpG island hypermethylation in several solid cancers. TIPE3 acts as a tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), providing a further insight into NPC progression and representing a potential prognostic biomarker for NPC 30639532_TIPE3 inhibits p38 phosphorylation and blocks p38 nuclear translocation to inhibit glioblastoma cell apoptosis. 31140050_TNFAIP8L3 is highly expressed in human cancer cells and promotes carcinogenesis. Silence of TNFAIP8L3 diminished Gastric Cancer cells migration mediated by miR-9-5p. 31978770_Effects of the long and short isoforms of TIPE3 on the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer. 35041835_Loss of TIPE3 reduced the proliferation, survival and migration of lung cancer cells through inactivation of Akt/mTOR, NF-kappaB, and STAT-3 signaling cascades. |
ENSMUSG00000074345 |
Tnfaip8l3 |
52.382644 |
3.7074970709 |
1.890446 |
0.229853206 |
71.256013 |
0.00000000000000003137532557752706076633166511019379758945485576300191143950257810502080246806144714355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000243224687775367360753669349153179405388545627781510249931784528598655015230178833007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
79.7804014 |
11.3393019 |
21.6741580 |
2.6077267 |
| ENSG00000183579 |
84133 |
ZNRF3 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULT6 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that acts as a negative regulator of the Wnt signaling pathway by mediating the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of Wnt receptor complex components Frizzled and LRP6. Acts on both canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Acts as a tumor suppressor in the intestinal stem cell zone by inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway, thereby resticting the size of the intestinal stem cell zone (PubMed:22575959). Along with RSPO2 and RNF43, constitutes a master switch that governs limb specification (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08D68, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22575959}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation pathway;Wnt signaling pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Enables frizzled binding activity and ubiquitin-protein transferase activity. Involved in cellular protein metabolic process and negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway. Is integral component of plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84133; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; frizzled binding [GO:0005109]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; limb development [GO:0060173]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:2000051]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway [GO:2000095]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511]; Wnt receptor catabolic process [GO:0038018]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20935629_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22575959_study provides new mechanistic insights into the regulation of Wnt receptor turnover, and reveals ZNRF3 as a tractable target for therapeutic exploration 23504200_ZNRF3 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth and promotes cell apoptosis by affecting the Wnt/beta-catenin/TCF4 signalling pathway. 23670221_Genes within recently identified loci associated with waist-hip ratio (WHR) exhibit fat depot-specific mRNA expression, which correlates with obesity-related traits. Adipose tissue (AT) mRNA expression of 6 genes (TBX15/WARS2, STAB1, PIGC, ZNRF3, GRB14 24225776_Signalling potency of R-spondin proteins depends on their ability to recruit ZNRF3 or RNF43 via Fu1 into a complex with LGR receptors, which interact with Rspo via Fu2 24349440_ZNRF3 binds RSPO1 and LGR5-RSPO1 with micromolar affinity via RSPO1 furin-like 1 (Fu1) domain. 25891077_Data indicate Dishevelled (DVL) as a dual function adaptor to recruit negative regulators ZNRF3/RNF43 to Wnt receptors to ensure proper control of pathway activity. 25923840_ZnRF3 negatively influences both the Wnt and Hedgehog proliferative pathways and probably this way it negatively regulates cancer progression 26423400_miR-93/ZNRF3/Wnt/beta-catenin regulatory network contributes to the growth of lung carcinoma. 26549292_Report shows that miR-146b participated in migration, invasion and chemoresistance in osteosarcoma via downregulation of ZNRF3. 27352324_ZnRF3 negatively influences both the Wnt and Hedgehog proliferative pathways, and probably this way it negatively regulates cancer progression. 27448298_Data indicate that clinical specimens showed a significant inverse correlation between zinc and ring finger 3 (ZNRF3) and beta-catenin mRNA levels. 27661107_Data suggest that inactivation of RNF43 and ZNRF3 is important in serrated tumorigenesis and has identified a potential therapeutic strategy for this cancer subtype. 27733215_ZNRF3 inhibited the metastasis and tumorigenesis via suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in NPC cells. 29497989_The ZNRF3 is ubiquitinated by beta-TRCP in both CKI-phosphorylation- and degron-dependent manners. 29735715_Missense variants of ZNRF3 are associated with Disorders of Sex Development. 29769720_results establish that RSPO2, without the LGR4/5/6 receptors, serves as a direct antagonistic ligand to RNF43 and ZNRF3, which together constitute a master switch that governs limb specification; these findings have direct implications for regenerative medicine and WNT-associated cancers 30348125_The present study suggests rs7290117 in ZNRF3 may be involved in the regulation of axial length, though our results do not support a contribution of the SNPs we tested in ZNRF3, HGF and MFRP to primary angle-closure glaucoma in northern Chinese people 30816445_miR106b3p promotes cell proliferation and invasion, partially by downregulating ZNRF3 and inducing EMT via Wnt/betacatenin signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. 31934854_The tumor suppressor PTPRK promotes ZNRF3 internalization and is required for Wnt inhibition in the Spemann organizer. 33367931_MicroRNA301a/ZNRF3/wnt/betacatenin signal regulatory crosstalk mediates glioma progression. 33513905_Low Protein Expression of both ATRX and ZNRF3 as Novel Negative Prognostic Markers of Adult Adrenocortical Carcinoma. 34273374_RSPO2 silence inhibits tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by ZNRF3/Hedgehog-Gli1 signal pathway. 34590584_A MET-PTPRK kinase-phosphatase rheostat controls ZNRF3 and Wnt signaling. 34657141_A positive feedback loop of lncRNA-RMRP/ZNRF3 axis and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates the progression and temozolomide resistance in glioma. 34716314_Somatic driver mutation prevalence in 1844 prostate cancers identifies ZNRF3 loss as a predictor of metastatic relapse. 35039505_RNF43/ZNRF3 loss predisposes to hepatocellular-carcinoma by impairing liver regeneration and altering the liver lipid metabolic ground-state. |
ENSMUSG00000041961 |
Znrf3 |
59.449600 |
2.1538844644 |
1.106941 |
0.194720384 |
32.951119 |
0.00000000945053452441482992657193764555328963083979942894075065851211547851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000041256991890080713979473950227955247882505318557377904653549194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83.1544928 |
10.3340420 |
38.8952067 |
3.8348340 |
| ENSG00000183621 |
220929 |
ZNF438 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z4V0 |
FUNCTION: Isoform 1 acts as a transcriptional repressor. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription factor activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:220929; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17669267_The transcriptional activity of ZNF438 was studied by transfecting recombinant pM-ZNF438 into mammalian cells. The subsequent analysis based on the duel luciferase assay system showed that ZNF438 was a transcriptional repressor. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000050945 |
Zfp438 |
47.166926 |
2.4497172475 |
1.292615 |
0.447857832 |
8.053718 |
0.00454103719051964383607300490552916016895323991775512695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009362440135782922751017665063955064397305250167846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.8026563 |
22.2150946 |
20.8763824 |
6.4559600 |
| ENSG00000183638 |
94137 |
RP1L1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWN7 |
FUNCTION: Required for the differentiation of photoreceptor cells. Plays a role in the organization of outer segment of rod and cone photoreceptors (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Microtubule;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Vision |
|
This gene encodes a member of the doublecortin family. The protein encoded by this gene contains two N-terminal doublecortin domains, which bind microtubules and regulate microtubule polymerization, and two C-terminal large repetitive regions, both of which contain a high percentage of glutamine and glutamic acid residues. This protein is a retinal-specific protein. Its exact length varies among individuals due to the presence of a 16aa repeat in the first C-terminal repetitive region. The 16aa repeat is encoded by the highly polymorphic 48-bp repeat, and 1-6 copies of the 16aa repeat have been identified in normal individuals. The current reference sequence shown here has a single copy of the 16aa repeat. This protein and the RP1 protein, another retinal-specific protein, play essential and synergistic roles in affecting photosensitivity and outer segment morphogenesis of rod photoreceptors. Mutations in this gene cause occult macular dystrophy (OMD). [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:94137; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; photoreceptor connecting cilium [GO:0032391]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; axoneme assembly [GO:0035082]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; photoreceptor cell development [GO:0042461]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12724644_The RP1L1 gene encodes a large, highly polymorphic, retinal-specific protein. No RP1L1 disease-causing mutations were identified in any of the samples tested. 20826268_Amino acid substitution of p.Arg45Trp in retinitis pigmentosa 1-like 1 (RP1L1) was found in three occult macular dystrophy (OMD)families and p.Trp960Arg in a remaining OMD family. 22466457_The abnormalities in the multifocal electroretinograms and optical coherence tomography observed in the occult macular dystrophy patients of different durations strongly support the contribution of RP1L1 mutation to the presence of this disease. 22504327_The clinical phenotypes differed between the proband and her mother and were indistinguishable from other sporadic or RP1L1-unassociated OMD patients, suggesting that mutation-dependent clinical features may not be present. 23229695_Occult macular dystrophy is a genetically heterogeneous disorder in a white family of European descent, screened for genetic mutations in the RP1L1 gene. 23281133_RP1L1 mutations are associated with retinal diseases, including retinitis pigmentosa and occult macular dystrophy. 23619761_These findings indicate that the phenotype in some cases of occult macular dystrophy with an Arg45Trp mutation in the RP1L1 gene can be unilateral for a considerable period. 23745001_Our study revealed that the previously identified mutation in the retinitis pigmentosa 1L1 gene from Japanese families, R45W3, also was found in Korean occult macular degeneration patients. 24838559_We describe in detail a case of bilateral chronic subfoveal serous retinal detachment in an atypical occult macular dystrophy patient carrying a novel heterozygous RP1L1 mutation (p.S1199P) 25692141_findings indicate that a homozygous p.S1210P exchange in the RP1L1 gene can cause cone dystrophy 26782618_A p.Arg45Trp mutation in the RP1L1 gene was identified in the Occult macular dystrophy patient, in the two symptomatic offspring and also in two of the asymptomatic siblings of the patient. 27029556_We propose that the combination of heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in these genes drives syndromic retinal dystrophy, likely through the genetic interaction of at least two loci. 27623337_A unique motif including six amino acids (1196-1201) downstream of the doublecortin domain could be a hot spot for RP1L1 pathogenic variants. The significant association of the morphologic phenotypes and genotypes indicates that there are two types of pathophysiology underlying the occult macular dysfunction syndrome 29196766_the presence of pathogenic RP1L1 variants is significantly associated with characteristic abnormalities of the photoreceptor layer in the macular region (e.g., blurring of the ellipsoid zone [EZ] and absence of the interdigitation zone 30025130_Autosomal dominant occult macular dystrophy (OCMD) phenotype showed consistent clinical findings including classical microstructural changes on SD-OCT. An important hallmark of RP1L1-related OCMD is the dominant family history with reduced penetrance. 31833436_Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in RP1L1 gene is associated with retinitis pigmentosa. 32176261_Two recurrent RP1L1 variants are related to occult macular dystrophy in the Chinese population. 32940107_A variant in the RP1L1 gene in a family with occult macular dystrophy in a predicted intrinsically disordered region. 34865606_RP1L1 rs3924612 gene polymorphism and RP1L1 protein associations among patients with early age-related macular degeneration. |
ENSMUSG00000046049 |
Rp1l1 |
16.034628 |
0.1231908888 |
-3.021033 |
0.482470595 |
47.254251 |
0.00000000000623506082663093315401143073642454292635634027774926835263613611459732055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000035125762519493350223682064300886472747731392729519939166493713855743408203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5890902 |
0.9301607 |
20.9507317 |
4.0069071 |
| ENSG00000183696 |
7378 |
UPP1 |
protein_coding |
Q16831 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the reversible phosphorylytic cleavage of uridine and deoxyuridine to uracil and ribose- or deoxyribose-1-phosphate (PubMed:7488099). The produced molecules are then utilized as carbon and energy sources or in the rescue of pyrimidine bases for nucleotide synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7488099, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Glycosyltransferase;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Pyrimidine metabolism; UMP biosynthesis via salvage pathway; uracil from uridine (phosphorylase route): step 1/1. {ECO:0000305}. |
This gene encodes a uridine phosphorylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible phosphorylation of uridine (or 2'- deoxyuridine) to uracil and ribose-1-phosphate (or deoxyribose-1-phosphate). The encoded enzyme functions in the degradation and salvage of pyrimidine ribonucleosides. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:7378; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; deoxyuridine phosphorylase activity [GO:0047847]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; thymidine phosphorylase activity [GO:0009032]; uridine phosphorylase activity [GO:0004850]; cellular response to glucose starvation [GO:0042149]; CMP catabolic process [GO:0006248]; dCMP catabolic process [GO:0006249]; dTMP catabolic process [GO:0046074]; dUMP catabolic process [GO:0046079]; nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006139]; UMP catabolic process [GO:0046050]; UMP salvage [GO:0044206]; uridine catabolic process [GO:0006218] |
11807789_The expression level of UPase gene may be an independent prognostic marker in human breast carcinoma 12084455_Characterization of the promoter region of UPase has indicated a direct regulation of its expression by the tumor suppressor gene p53. Review. 12115385_Uridine phosphorylase overexpression is associated with lymph node metastasis in oral neoplasms 16798057_Thymidine phosphorylase and uridine phosphorylase were both responsible for converting 5'dFUrd/5FU into 5FU/FUrd, respectively 19291308_The presented structures confirm that hUPP1 is dimeric. They also reveal the mechanism by which 5-benzylacyclouridine engages the active site of the protein and disables the enzyme by locking the protein in a closed conformation. 19714313_Data show that enhanced cytotoxicity of 5-FU by bFGF through modulating the expression of UPP1 at the transcription level. 20856879_The dimeric enzyme is capable of a large hinge motion facilitating ligand exchange. 28163244_there are inter-ethnic differences for uridine phosphorylase 1 (UPP1) and zinc finger-SWIM containing 4 (ZSWIM4) in response to 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 31496029_Uridine phosphorylase 1 associates to biological and clinical significance in thyroid carcinoma cell lines. 32583596_Uridine phosphorylase 1 is a novel immune-related target and predicts worse survival in brain glioma. 32864839_Metabolites modulate the functional state of human uridine phosphorylase I. |
ENSMUSG00000020407 |
Upp1 |
635.162078 |
3.3771048122 |
1.755787 |
0.116189203 |
220.928817 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005672659772521194524091955643202010228122491367063326896608805806095428046080067515280233938406940125548261567344651397198625284584716510494217800442129373550415039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001206461934328715072080863939534918059706996889344386849774694344983033145978640598298163816651200530430102978457362035907352373897971631322434404864907264709472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
993.9296085 |
65.3965747 |
296.1115589 |
14.7862211 |
| ENSG00000183718 |
84851 |
TRIM52 |
protein_coding |
Q96A61 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase (PubMed:27667714). Positively regulates the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway (PubMed:27667714, PubMed:28073078). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27667714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28073078}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Exhibits antiviral activity against Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). Ubiquitinates the viral non-structural protein 2 (NS2A) and targets it for proteasome-mediated degradation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27667714}. |
Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
Enables transcription coactivator activity and ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Involved in several processes, including positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity; and protein autoubiquitination. Located in cytosol and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84851; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
28073078_these data suggested that TRIM52 was a positive regulator of the NF-kappaB pathway. 29089476_TRIM52 can promote cell proliferation and HBx may regulate TRIM52 expression via the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 29898761_Our findings suggest that TRIM52 up-regulation promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC cells through the ubiquitination of PPM1A. 30185771_TRIM52 plays an oncogenic role in ovarian cancer development. 31002351_Based on these data, it was speculated that TRIM52 is critical for lung cancer progression and that downregulation of TRIM52 could inhibit cell proliferation by blocking cell cycle progression. 31133683_A repetitive acidic region contributes to the extremely rapid degradation of the cell-context essential protein TRIM52. 32898524_TRIM52 positively mediates NF-kappaB to promote the growth of human benign prostatic hyperplasia cells through affecting TRAF2 ubiquitination. 35676608_Long non-coding RNA TRIM52-AS1 sponges microRNA-577 to facilitate diffuse large B cell lymphoma progression via increasing TRIM52 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000040365 |
Trim41 |
97.416303 |
0.4176457161 |
-1.259648 |
0.154457142 |
68.357838 |
0.00000000000000013636212990403610344615949033028166271535546567265223538711893525032792240381240844726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001020641499687410199138189007739905663748862670557604470644719185656867921352386474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.3602004 |
5.9798802 |
135.7618675 |
9.2442617 |
| ENSG00000183762 |
83999 |
KREMEN1 |
protein_coding |
Q96MU8 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Cooperates with DKK1/2 to inhibit Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by promoting the endocytosis of Wnt receptors LRP5 and LRP6. In the absence of DKK1, potentiates Wnt-beta-catenin signaling by maintaining LRP5 or LRP6 at the cell membrane. Can trigger apoptosis in a Wnt-independent manner and this apoptotic activity is inhibited upon binding of the ligand DKK1. Plays a role in limb development; attenuates Wnt signaling in the developing limb to allow normal limb patterning and can also negatively regulate bone formation. Modulates cell fate decisions in the developing cochlea with an inhibitory role in hair cell fate specification. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q90Y90, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q99N43}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Ectodermal dysplasia;Glycoprotein;Kringle;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a high-affinity dickkopf homolog 1 (DKK1) transmembrane receptor that functionally cooperates with DKK1 to block wingless (WNT)/beta-catenin signaling. The encoded protein is a component of a membrane complex that modulates canonical WNT signaling through lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6). It contains extracellular kringle, WSC, and CUB domains. Mutations in this gene result in ectodermal dysplasia. This protein has also been found to be a functional receptor for Coxsackievirus A10 and may be an alternative entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2021]. |
hsa:83999; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell communication [GO:0007154]; limb development [GO:0060173]; negative regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048681]; negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090090]; negative regulation of ossification [GO:0030279]; regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060828]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12050670_Functional characterization of related Kremen proteins in mouse. 18502762_Kremen may not be essential for Dkk1-mediated Wnt antagonism and Kremen may only play a role when cells express a high level of LRP5/6 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20153141_This study demonstrated that a representative tSNP of KREMEN1 might modulate the risk of schizophrenia in the Japanese population. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20846389_The mRNA expression levels of DKK-1 binding receptor LRP5/6 and Krm1/2 in SCs from patients with MM were significantly higher than those in myeloma cells and in SCs from healthy donors. 20935629_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23041840_Six Dkk-1, three Sost, one Kremen-1 and 10 LRP-5 polymorphisms were significantly associated with radiological progression of rheumatoid arthritis joint destruction. 26206087_Kremen1 has a pro-apoptotic activity that is decreased upon Dkk1 binding or by cancer mutations. 27049303_Ectodermal dysplasia including oligodontia is due to homozygosity for KREMEN1 p.F209S (c.626 T>C). 27524201_Structure of the dual-mode Wnt regulator Kremen1 and insight into ternary complex formation with LRP6 and DKK1 have been presented. 29526031_Thai family study that has identified the second and third mutations found in KREMEN1 confirms that KREMEN1 is a human disease gene for autosomal recessive ectodermal dysplasia 13, hair/tooth type. Agenesis of permanent maxillary lateral incisors and mandibular anterior teeth could be a unique manifestation of KREMEN1 mutations. 29925589_Dkk4 CRD2 mediates high-affinity binding to both the E1E2 region of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6 E1E2) and the Kremen1 (Krm1) extracellular domain. 31447119_MiR-137 repressed KREMEN1 expression in neuronal cells. 31911601_CV-A10 mature virus alone and in complex with KRM1 as well as of the CV-A10 A-particle. 32521004_Replication of 15 loci involved in human plasma protein N-glycosylation in 4802 samples from four cohorts. 32690697_Molecular basis of Coxsackievirus A10 entry using the two-in-one attachment and uncoating receptor KRM1. 34028942_Novel homozygous KREMEN1 mutation causes ectodermal dysplasia. 34837059_Receptome profiling identifies KREMEN1 and ASGR1 as alternative functional receptors of SARS-CoV-2. 34903854_Novel SARS-CoV-2 receptors: ASGR1 and KREMEN1. |
ENSMUSG00000020393 |
Kremen1 |
205.340342 |
4.9198610895 |
2.298618 |
0.254097958 |
77.159013 |
0.00000000000000000157733206070007914685579323290538462747856755321755389473437070080308330943807959556579589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000013079450121310768227484971988953977130009208888685324351230931938516732770949602127075195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
360.1544607 |
55.6937222 |
73.4911499 |
8.8151444 |
| ENSG00000183773 |
150209 |
AIFM3 |
protein_coding |
Q96NN9 |
FUNCTION: Induces apoptosis through a caspase dependent pathway. Reduces mitochondrial membrane potential. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15764604}. |
2Fe-2S;3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Electron transport;FAD;Flavoprotein;Iron;Iron-sulfur;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable several functions, including 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding activity; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding activity; and metal ion binding activity. Involved in execution phase of apoptosis. Located in cytosol; endoplasmic reticulum; and mitochondrial inner membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:150209; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding [GO:0051537]; flavin adenine dinucleotide binding [GO:0050660]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H [GO:0016651]; execution phase of apoptosis [GO:0097194] |
15764604_AIFL has 598 amino acids, with a characteristic Rieske domain and a pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase domain (Pyr_redox). AIFL shares 35% homology with AIF, mainly in the Pyr_redox domain. 16001080_AIF maintains the transformed state of colon cancer cells through its NADH oxidase activity, by mechanisms that involve complex I function. 19166416_H. pylori triggers apoptosis in AGS cells via interaction with death receptors in the plasma membrane, leading to the cleavage of procaspase-8, release of cytochrome c and AIF from mitochondria, and activation of subsequent downstream apoptotic events 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22387901_AIFM3 is a direct target of miR-210 in human hepatoma cells. 22550867_The expression of apoptosis-inducing factor was identified in pineal gland and thymus, but it did not change with age. 27473083_Upregulated expression of AIFM3 is associated with cholangiocarcinoma. 31088422_AIFM3 was significantly more expressed in breast cancer tissues than in normal tissues. There was a significant association of AIFM3 expression with tumor size, lymph node metastasis, molecular typing and TNM staging. Lymph node metastasis and TNM stage were independent factors of AIFM3 expression. High AIFM3 expression was related to a shorter OS and DFS. 32664187_Apoptosis-Inducing Factor, Mitochondrion-Associated 3 (AIFM3) Protein Level in the Sera as a Prognostic Marker of Cholangiocarcinoma Patients. 34502088_CRKL, AIFM3, AIF, BCL2, and UBASH3A during Human Kidney Development. 34949658_Bioinformatic Prediction of Novel Signaling Pathways of Apoptosis-inducing Factor, Mitochondrion-associated 3 (AIFM3) and Their Roles in Metastasis of Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000022763 |
Aifm3 |
33.759882 |
0.2362193305 |
-2.081801 |
0.326443048 |
42.134996 |
0.00000000008518503607310545594863448107185812697983440244797748164273798465728759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000442566396493853053336349361349903036577657644556893501430749893188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.7312029 |
2.7298182 |
54.4293741 |
7.0758677 |
| ENSG00000183784 |
157983 |
DOCK8-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44.281615 |
0.3619310471 |
-1.466213 |
0.233224695 |
41.234843 |
0.00000000013499458748030408564479506807755847253016412423676229082047939300537109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000692328044200586604037987310372162172433796456516574835404753684997558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.2423557 |
4.1722434 |
67.4255577 |
7.3744078 |
| ENSG00000183785 |
51807 |
TUBA8 |
protein_coding |
Q9NY65 |
FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers. Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms. Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the alpha tubulin protein family. Alpha tubulins are one of two core protein families (alpha and beta tubulins) that heterodimerize and assemble to form microtubules. Mutations in this gene are associated with polymicrogyria and optic nerve hypoplasia. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2010]. |
hsa:51807; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278]; spermatid development [GO:0007286] |
16380905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19896110_Mutation of the variant alpha-tubulin TUBA8 results in polymicrogyria with optic nerve hypoplasia. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20466094_TUBA8 is expressed at low levels in the developing human brain. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21872825_TUBA8 can play a role in the regulation of cell growth, proliferation, and cell migration in a cell-specific manner in vitro. 28063004_Data provide evidence for a role of TUBA8 in hepatic fibrogenesis and malignancies making it a novel player in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma pathology. 30627818_Low TUBA8 expression is associated with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. 35126370_Dysregulation of SAA1, TUBA8 and Monocytes Are Key Factors in Ankylosing Spondylitis With Femoral Head Necrosis. |
ENSMUSG00000030137 |
Tuba8 |
123.295109 |
0.1552333359 |
-2.687490 |
0.369173613 |
48.284257 |
0.00000000000368700413266626377133076520898683479422752728993373239063657820224761962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000021150478429130994971919314072852198130997303238132190017495304346084594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.1258351 |
9.2974429 |
197.7827799 |
42.6454956 |
| ENSG00000183853 |
55243 |
KIRREL1 |
protein_coding |
Q96J84 |
FUNCTION: Required for proper function of the glomerular filtration barrier. It is involved in the maintenance of a stable podocyte architecture with interdigitating foot processes connected by specialized cell-cell junctions, known as the slit diaphragm (PubMed:31472902). It is a signaling protein that needs the presence of TEC kinases to fully trans-activate the transcription factor AP-1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31472902}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
NEPH1 is a member of the nephrin-like protein family, which includes NEPH2 (MIM 607761) and NEPH3 (MIM 607762). The cytoplasmic domains of these proteins interact with the C terminus of podocin (NPHS2; MIM 604766), and the genes are expressed in kidney podocytes, cells involved in ensuring size- and charge-selective ultrafiltration (Sellin et al., 2003 [PubMed 12424224]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:55243; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; myosin binding [GO:0017022]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-cell junction maintenance [GO:0045217]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; renal protein absorption [GO:0097017] |
16968734_A striking finding in this study is the lack of contribution of NEPH1, NPHS1, and NPHS2 genes in 15 Asian families with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 17968527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17968527_common variants in LRRC7, KIRREL, NPHS2 and ACTN4 do not appeear to contribute to susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy in Finnish patients with type 1 diabetes 18258597_Neph1 but not nephrin specifically binds to adaptor protein Grb2 and tyrosine kinase Csk in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. 18562307_Neph1-Nephrin proteins bind the Par3-Par6-atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) complex to regulate podocyte cell polarity 18922801_tyrosine phosphorylation of Neph1 mediated by Fyn results in significantly increased Neph1 and ZO-1 binding, suggesting a critical role for Neph1 tyrosine phosphorylation in reorganizing the Neph1-ZO-1 complex. 20507940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21402783_Localization of Neph1 to the podocyte cell membrane is altered in the presence of mutant Myo1c, and is actin dependent. Knockdown of Myo1c inhibits Neph1 membrane localization. Neph1 is critical for the maintenance of glomerular function. 22262837_Neph1-CD adopts a global shape in solution, and its interaction with ZO-1 involves multiple sites. 24554715_maintaining high levels of Neph1 at the membrane using a podocyte cell line overexpressing chimeric Neph1 increased the ability of podocytes to resist PAN-induced injury and PAN-induced albumin leakage 27044863_Analysis of interaction surfaces between NEPH1 and MYO1c led to the identification of a critical residue in Neph1 involved in binding to Myo1c. Indeed, a point mutant from this site abolished interaction between Neph1 and Myo1c. 31472902_Mutations in KIRREL1, a slit diaphragm component, cause steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. 32534710_Overexpression of kin of IRRE-Like protein 1 (KIRREL) as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. 35177623_Cell adhesion molecule KIRREL1 is a feedback regulator of Hippo signaling recruiting SAV1 to cell-cell contact sites. 36044856_Transmembrane protein KIRREL1 regulates Hippo signaling via a feedback loop and represents a therapeutic target in YAP/TAZ-active cancers. |
ENSMUSG00000041734 |
Kirrel |
325.386614 |
0.4531699179 |
-1.141876 |
0.090535864 |
161.586487 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000050936646324264370430520033235803857050212076378200974717256079674105422722934863981874013312165991318458679870673222467303276062011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000007905624603008854450493867395998478010181203242874928734871895878566220420533878675216672032334541686537932037026621401309967041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
204.8473096 |
13.1616482 |
455.1510448 |
19.4073501 |
| ENSG00000184007 |
8073 |
PTP4A2 |
protein_coding |
Q12974 |
FUNCTION: Protein tyrosine phosphatase which stimulates progression from G1 into S phase during mitosis. Promotes tumors. Inhibits geranylgeranyl transferase type II activity by blocking the association between RABGGTA and RABGGTB. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14643450}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Prenylation;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to a small class of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are cell signaling molecules that play regulatory roles in a variety of cellular processes. PTPs in this class contain a protein tyrosine phosphatase catalytic domain and a characteristic C-terminal prenylation motif. This PTP has been shown to primarily associate with plasmic and endosomal membrane through its C-terminal prenylation. This PTP was found to interact with the beta-subunit of Rab geranylgeranyltransferase II (beta GGT II), and thus may function as a regulator of GGT II activity. Overexpression of this gene in mammalian cells conferred a transformed phenotype, which suggested its role in tumorigenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Related pseudogenes exist on chromosomes 11, 12 and 17. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]. |
hsa:8073; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; prenylated protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004727]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008138]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
14643450_PRL phosphatases increase cell proliferation by stimulating progression from G1 into S phase 16832410_PRL-2 mRNA expression was not significantly higher in malignant compared to benign breast tissue. 16957164_PRL-2 was expressed heavily in almost every tissue and cell type examined. Widespread expression of PRL-2 in multiple organ systems suggests an important functional role for these enzymes in normal tissue homeostasis. 17440740_Colonic adenocarcinoma cells have the ability to produce PTP4A1, PTP4a2, and PTP4A3, which may relate to the lymph node metastasis of colonic adenocarcinoma. 17666324_PRL-2 can promote cell adhesion and invasion activity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 20226699_Mouse pre-B-cells transfected with human PRL-2 had higher growth responses to Epo or IL-3, shorter cell cycle, less Epo requirement for survival, more cell migration, less cell adhesion, change to an immature cell morphology, & more Bmi-1 expression. 20841483_Overexpression of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PRL-2 correlates with breast tumor formation and progression. 21765462_Results suggest a model in which PRL-2 promotes cell migration and invasion through an ERK1/2-dependent signaling pathway. 21993571_PRL-2 plays an important role in lung cancer and can be a biomarker of lung cancer, substituting for the function of other PRLs. 22413991_Studies indicate that PRL-1 and PRL-2 and PRL-3 are oncogenes and belong to the few phosphatases that lead to the development of cancer. 23362275_Results suggest that TRP32 maintains the reduced state of PRL and thus regulates the biological function of PRL. 23568563_PTP4A2 expression is correlated with overall survival in progestin receptor-positive breast carcinomas. 25193986_Our findings highlight the important role of miR-29c in regulating CRC EMT via GSK-3b/b-catenin signaling by targeting GNA13 and PTP4A and provide new insights into the metastatic basis of colorectal cancer 27872499_study identified a critical role for PRL2 phosphatase in the proliferation and survival of human T-ALL cells; demonstrated that PRL2 is important for the leukemogenic potential of oncogenic NOTCH1 in vivo 28220038_identified a critical role for PRL2 phosphatase in the proliferation and survival of human AML cells. Further, we demonstrated that PRL2 is essential for the leukemogenic potential of AML1-ETO9a in vivo 30718434_altered PRL-2 expression leads to metabolic reprogramming of the cells. These findings uncover a magnesium-sensitive mechanism controlling PRL expression, which plays a role in cellular bioenergetics 32733084_A FRET-based screening method to detect potential inhibitors of the binding of CNNM3 to PRL2. 32788364_Mechanism of PRL2 phosphatase-mediated PTEN degradation and tumorigenesis. 34992672_Downregulated Expression of miRNA-130a-5p Aggravates Hepatoma Progression via Targeting PTP4A2. |
ENSMUSG00000028788 |
Ptp4a2 |
1632.405564 |
2.0519969857 |
1.037029 |
0.056995380 |
328.581447 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000019577266435758234232613584937363392006066522693056770446555973405892886893660825256001238341956105751281995266134632665303832441844568071063640218148739794120610472508499428494243340542757536582030297722667455673217773437500000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006083377949300874767882149265026253448526126028080339195576202147987088684318380357419712816552668430667229664659811572364656898215564692458768096339200551647616620155954969247427688294749259512173011898994445800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2194.9327395 |
100.6938889 |
1078.3628429 |
36.5205174 |
| ENSG00000184154 |
120356739 |
LRRC51 |
protein_coding |
Q8WZ04 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the O-methylation, and thereby the inactivation, of catecholamine neurotransmitters and catechol hormones (By similarity). Required for auditory function (PubMed:18794526). Component of the cochlear hair cell's mechanotransduction (MET) machinery. Involved in the assembly of the asymmetric tip-link MET complex. Required for transportation of TMC1 and TMC2 proteins into the mechanically sensitive stereocilia of the hair cells. The function in MET is independent of the enzymatic activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A1Y9I9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18794526}. |
Alternative splicing;Catecholamine metabolism;Cytoplasm;Deafness;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hearing;Membrane;Methyltransferase;Neurotransmitter degradation;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the leucine-rich repeat containing family. The encoded protein contains a transmembrane domain and two leucine-rich repeat domains. Unlike in mouse and other mammals, readthrough transcription is observed in primates between this gene and the adjacent transmembrane O-methyltransferase (Tomt) gene. Previously, this locus was annotated as a single gene representing the readthrough transcripts as well as the two different transcript species that encoded different proteins. It has since been split into three genes, including the two stand-alone genes and a third gene representing the readthrough transcription. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2022]. |
hsa:220074; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; catechol O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016206]; L-dopa O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0102084]; O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0008171]; orcinol O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0102938]; auditory receptor cell development [GO:0060117]; catecholamine catabolic process [GO:0042424]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; dopamine catabolic process [GO:0042420]; dopamine metabolic process [GO:0042417]; methylation [GO:0032259]; neurotransmitter catabolic process [GO:0042135]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
|
ENSMUSG00000064307 |
Lrrc51 |
21.049046 |
0.4156032258 |
-1.266721 |
0.532059707 |
5.310160 |
0.02120140485929115220509189043696096632629632949829101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.037780120212862172701662188956106547266244888305664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.0668934 |
3.0500139 |
22.6717444 |
5.1136732 |
| ENSG00000184156 |
3786 |
KCNQ3 |
protein_coding |
O43525 |
FUNCTION: Associates with KCNQ2 or KCNQ5 to form a potassium channel with essentially identical properties to the channel underlying the native M-current, a slowly activating and deactivating potassium conductance which plays a critical role in determining the subthreshold electrical excitability of neurons as well as the responsiveness to synaptic inputs. Therefore, it is important in the regulation of neuronal excitability. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11159685, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14534157, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16319223, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9872318}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Ubl conjugation;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes a protein that functions in the regulation of neuronal excitability. The encoded protein forms an M-channel by associating with the products of the related KCNQ2 or KCNQ5 genes, which both encode integral membrane proteins. M-channel currents are inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and are activated by retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant drug. Defects in this gene are a cause of benign familial neonatal convulsions type 2 (BFNC2), also known as epilepsy, benign neonatal type 2 (EBN2). Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:3786; |
axon initial segment [GO:0043194]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; membrane [GO:0016020]; node of Ranvier [GO:0033268]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated potassium channel complex [GO:0008076]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0005251]; voltage-gated potassium channel activity [GO:0005249]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; membrane hyperpolarization [GO:0060081]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] |
12524525_A cytoplasmic carboxy-terminal subunit interaction domain (sid) suffices to transfer assembly properties between KCNQ3 and KCNQ1. 12640002_specific parts of the C-terminus enable the interaction between KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 channels and that different parts of the KCNQ3 C-terminus are important for regulating current amplitude 12832524_Coexpressed KCNQ2 plus KCNQ3 cDNAs generate channels with 1:1 (KCNQ2:KCNQ3) stoichiometry in CHO cells and that native M channels in SCG neurons adopt the same conformation during development 12928862_There may be a genetic contribution of this gene in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy in a South Indian population. 15304482_Src associates with KCNQ2-5 subunits but phosphorylates only KCNQ3-5. 15483133_After KCNQ2/3 heteromerization, current levels can augment as much as 10-fold, and we have discovered that there are three processes underlying this potentiation. 16235065_the KCNQ2 mutation is responsible for the benign familial neonatal convulsion phenotype, possibly because of haplo-insufficiency, whereas the KCNQ3 variant is functionally silent 16319223_Mutagenesis and electrophysiological studies of the second site, located in the S4-S5 intracellular loop of all KCNQ subunits, reveal a mechanism of channel inhibition 16721610_the diacylglycerol produced during activation of phospholipase c, any activation of protein kinase C that it may stimulate, and downstream products of its metabolism are not essential players in the acute muscarinic modulation of KCNQ2/3 channels 16735477_Several BFNC mutations of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 disrupt surface expression or polarized surface distribution of KCNQ channels, thereby revealing impaired targeting of KCNQ channels to axonal surfaces as a benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC) etiology. 16990515_depletion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate suffices to suppress KCNQ current fully, and other second messengers are not needed 18089837_ICA-27243 is a novel and selective KCNQ3 potassium channel activator. 18166285_The expression of KCNQ3 increased in late fetal life to infancy in brain. 18249525_This study identified a novel missense mutation of KCNQ3, c.988C>T located within exon 6. c.988C>T led to the substitution Cys for Arg in amino acid position 330 (p.R330C) in KCNQ3 potassium channel. 18425618_A three-dimensional homology model in the W309R mutant indicated that the R side chain of pore helices is too far from the Y side chain of the selectivity filter to interact via hydrogen bonds with each other and stabilize the pore structure. 18625963_Sequence variations of the KCNQ2 (and KCNQ3)genes may contribute to the etiology of common idiopathic epilepsy syndromes. 18676988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18786918_among the allowed assembly conformations are KCNQ3/4 and KCNQ4/5 heteromers. 18790849_most wild-type channels are functionally silent, with rearrangements of the pore-loop architecture induced by the presence of a hydroxyl-containing residue at the 315 position 'unlocking' the channels into a conductive conformation 19464834_mutations in the SCN1A gene are differentially involved in the pathogenesis of and sequence variations of the KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 genes may contribute to the etiology of rare and common idiopathic epilepsy syndromes [review] 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20610766_This study reported that the presence of this uncommon residue at position 315 has a strong impact on the stability of the homotetramers and on channel trafficking. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21730298_Data show that KCNQ3 and KCNE5 mRNA expressions were significantly upregulated in preeclampsia. 21976501_Different structural determinants, identified at the N and C termini of KCNQ3, prevent the effects of syntaxin 1A and calmodulin, respectively. 21980481_constitutive tethering of calmodulin is not required for Kv7 channel function 22334706_the Kv7.2-Kv7.3 heteromer assembles as a tetramer with a predominantly 2:2 subunit stoichiometry and with a random subunit arrangement. 22447848_This study demonistrated that benign neonatal sleep myoclonus can show autosomal dominant inheritance but not allelic to KCNQ3. 23002961_A medium-throughput assay reliably detects changes in the biophysical properties of three classes of KCNQ2/3 channels and peak current amplitude and therefore may serve as a reliable assay to evaluate KCNQ2/3 openers and blockers. 23209695_the single KCNQ channel in Drosophila (dKCNQ) has similar electrophysiological properties to neuronal KCNQ2/3 23360469_KCNQ3 mutations might be involved in families with infantile seizures. 24375629_We described clinical, genetic, and functional data from 17 families with a diagnosis of benign familial neonatal epilepsy caused by KCNQ2 or KCNQ3 mutations and we showed that some mutations lead to a reduction of Q2 channel regulation by syntaxin-1A. 24843134_We monitored KCNQ2/3 channel currents and translocation of PHPLCdelta1 domains as real-time indicators of PM PI(4,5)P2, and translocation of PHOSH2x2, and PHOSH1 domains as indicators of plasma membrane and Golgi PI(4)P, respectively. 25041603_In bipolar disorder patients' prefrontal cortex, Kcnq3 expression was decreased, DNA methylation was decreased, and Kcnq3 mRNA was decreased compared to controls. 25278462_the clinical and EEG features of this patient further on expand the phenotypic variability of KCNQ3 gene mutations 25524373_mutations in KCNQ3, similarly to KCNQ2, can be found in patients with more severe phenotypes including intellectual disability 25740509_the present results suggest that gain-of-function mutations in Kv7.2/3 currents may cause human epilepsy with a severe clinical course 25998125_Phosphorylation of KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 anchor domains by protein kinase CK2 augments binding to AnkG. 26627826_a structural mechanism for the gating of the Kv7.3 PM and for the site of action of RTG as a Kv7.2/Kv7.3 K(+) current activator. 26692086_Carboxyl terminus helix C-D linker residues play a role in KCNQ3 current amplitudes by controlling the exit of the KCNQ3 channel from the endoplasmic reticulum. 26969140_Tannic acid activates Kv7.4 and Kv7.3/7.5 K(+) channels resulting in vasodilation. 27445338_USP36 actions extend beyond TrkA because the presence of USP36 interferes with Nedd4-2-dependent Kv7.2/3 channel regulation. 27607834_In the present work, a pharmacophore-based 3D-QSAR model was generated for a series of N-pyridyl and pyrimidine benzamides possessing KCNQ2/Q3 opening activity. The pharmacophore model generated contains one hydrogen bond donor (D), one hydrophobic (H), and two aromatic rings (R). They are the crucial molecular write-up detailing predicted binding efficacy of high affinity and low affinity ligands for KCNQ2/Q3 opening a 29474891_An optimum cholesterol level in the plasma membrane is required for the proper functioning of Kv7.2/Kv7.3 channels. 29748663_Phylogenetic analysis, electrostatic potential mapping, in silico docking, electrophysiology, and radioligand binding assays reveal that the anticonvulsant binding pocket evolved to accommodate endogenous neurotransmitters including gamma-aminobutyric acid, which directly activates KCNQ5 and KCNQ3 via W265. 30348901_PIP2 modulates KCNQ3 channel function by interacting synergistically with a minimum of four cytoplasmic domains 30578330_Epilepsy-associated R230C mutation allows S4 movement but shifts the open/closed transition of the gate to very negative potentials. 30885609_a tight spatial and functional relationship between the DAT/GLT-1 transporters and the Kv7.2/7.3 potassium channel that immediately readjusts the membrane potential of the neuron, probably to limit the neurotransmitter-mediated neuronal depolarization 31177578_Patients with recurrent de novo variants in KCNQ3 exhibited global developmental delay and autistic features. 32580997_Heteromeric Assembly of Truncated Neuronal Kv7 Channels: Implications for Neurologic Disease and Pharmacotherapy. 33037390_The identification of two pathogenic variants in a family with mild and severe forms of developmental delay. 35384780_Phenotypic Spectrum in a Family Sharing a Heterozygous KCNQ3 Variant. |
ENSMUSG00000056258 |
Kcnq3 |
263.026695 |
0.1817829375 |
-2.459711 |
0.299930482 |
61.199969 |
0.00000000000000515623486578090650736598075611844046356772256617384542209947539959102869033813476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000035250591301031115865018938225677985314745685463400093340169405564665794372558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
72.7361996 |
34.1194949 |
411.1612420 |
137.2761895 |
| ENSG00000184206 |
643707 |
GOLGA6L4 |
protein_coding |
A6NEF3 |
|
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:643707; |
|
|
|
|
20.661056 |
0.2406799096 |
-2.054812 |
0.439953782 |
22.231385 |
0.00000241690558403913549267928891073342612116903183050453662872314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008193276623890132930082622064738018252683104947209358215332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5728932 |
2.3092231 |
31.3085773 |
5.9757836 |
| ENSG00000184220 |
84319 |
CMSS1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQ75 |
|
Alternative splicing;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84319; |
RNA binding [GO:0003723] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000022748 |
Cmss1 |
89.588537 |
2.6798797492 |
1.422168 |
0.178630545 |
64.167947 |
0.00000000000000114252461392474317542129035243415193535784942207439440764460414357017725706100463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000008158521190870444577953474039878662373210561897796111452407785691320896148681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
130.2726123 |
15.8402265 |
48.8525379 |
4.6520719 |
| ENSG00000184224 |
100505621 |
NDUFV1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23964515_Our data confirm the possibility of gain of new protein-coding genes during human evolution due to simple accumulation of point mutations |
|
|
10.839522 |
0.3757140201 |
-1.412293 |
0.561005928 |
6.320754 |
0.01193329089475843492185180849673997727222740650177001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022534144017750886573869806284164951648563146591186523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3111463 |
2.2194106 |
16.5416643 |
3.6686547 |
| ENSG00000184226 |
5101 |
PCDH9 |
protein_coding |
Q9HC56 |
FUNCTION: Potential calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the protocadherin family, and cadherin superfamily, of transmembrane proteins containing cadherin domains. These proteins mediate cell adhesion in neural tissues in the presence of calcium. The encoded protein may be involved in signaling at neuronal synaptic junctions. Sharing a characteristic with other protocadherin genes, this gene has a notably large exon that encodes multiple cadherin domains and a transmembrane region. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:5101; |
cell-cell contact zone [GO:0044291]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22300792_Our results suggest that PCDH9 might function as a tumor suppressor during cancer development and progression 25172662_Protocadherin 9 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration through activating GSK-3beta in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25869928_Loss of PCDH9 is associated with the differentiation of tumor cells and metastasis in gastric cancer 28055966_miR-215-5p up-regulation and PCDH9 down-regulation occurs in glioma samples. miR-215-5p could inhibit the mRNA and protein levels of PCDH9 in glioma cell lines by targeting its promoter and 3' UTR at the same time. 28791409_PCDH9 acts as a potential tumor suppressor gene, and that the loss of PCDH9 expression appears be a driver in a significant fraction of hepatocarcinogenesis cases. 28990594_convergent lines of evidence suggest that PCDH9 is likely a novel risk gene for MDD. 31059116_This review discusses the role and potential use as biomarkers of semaphorin 3A (SEMA3A), protocadherin 9 (PCDH9), and S100 calcium binding protein A3 (S100A3) in carcinogenesis and chemoresistance of various tumors, including ovarian cancer. 35084653_COP1 Acts as a Ubiquitin Ligase for PCDH9 Ubiquitination and Degradation in Human Glioma. |
ENSMUSG00000055421 |
Pcdh9 |
52.106099 |
3.8703676078 |
1.952471 |
0.392205592 |
23.193064 |
0.00000146524877125589072805115879727377858898762497119605541229248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005088722791467517573443281320155762159629375673830509185791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.6918534 |
17.2108243 |
19.0975149 |
3.3370798 |
| ENSG00000184232 |
220323 |
OAF |
protein_coding |
Q86UD1 |
|
Reference proteome;Signal |
|
|
hsa:220323; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000032014 |
Oaf |
633.226398 |
0.2437450926 |
-2.036555 |
0.072961924 |
817.115528 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001025382898963810627332553723149063165559544256812201843961485401862003741982071035566737266960731786847102978569702999051845742885908666831817391289458 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000827030141459335798367032089973566666413833189060863084645916509531140110298334457357464712680583981637640085953758071338686264058027425182688632670425 |
Yes |
No |
252.3028741 |
13.1396661 |
1043.1251940 |
33.6362376 |
| ENSG00000184261 |
56660 |
KCNK12 |
protein_coding |
Q9HB15 |
FUNCTION: Probable potassium channel subunit. No channel activity observed in heterologous systems. May need to associate with another protein to form a functional channel (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium channel;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
This gene encodes one of the members of the superfamily of potassium channel proteins containing two pore-forming P domains. The product of this gene has not been shown to be a functional channel, however, it may require other non-pore-forming proteins for activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:56660; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; outward rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:0015271]; potassium ion leak channel activity [GO:0022841]; potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0071805]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; stabilization of membrane potential [GO:0030322] |
18209473_THIK-1 and THIK-2 are abundantly expressed in the proximal and distal nephron of the mammalian kidney. 18676988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24163367_The cytoplasmic amino-terminal region of THIK2 (Nt-THIK2) contains an arginine-rich motif (RRSRRR) that acts as a retention/retrieval signal. 25148687_In cell and tissues co-expressing THIK1 and THIK2, heterodimeric channels may contribute to cell excitability. |
ENSMUSG00000050138 |
Kcnk12 |
14.134761 |
0.2463981255 |
-2.020937 |
0.540848363 |
14.085999 |
0.00017463891926968022464718155450924541582935489714145660400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000462611351116381933675641979775150502973701804876327514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9009176 |
2.2864409 |
20.4396410 |
6.4336057 |
| ENSG00000184307 |
254887 |
ZDHHC23 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYP9 |
FUNCTION: Palmitoyltransferase that could catalyze the addition of palmitate onto various protein substrates and be involved in a variety of cellular processes (Probable). Palmitoyltransferase that mediates palmitoylation of KCNMA1, regulating localization of KCNMA1 to the plasma membrane. May be involved in NOS1 regulation and targeting to the synaptic membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22399288, ECO:0000305|PubMed:22399288}. |
Acyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity. Involved in protein localization to plasma membrane and protein palmitoylation. Predicted to be located in Golgi membrane. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:254887; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0019706]; peptidyl-L-cysteine S-palmitoylation [GO:0018230]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein palmitoylation [GO:0018345]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612] |
|
ENSMUSG00000036304 |
Zdhhc23 |
37.571893 |
0.4796139509 |
-1.060054 |
0.270202476 |
15.423774 |
0.00008590076556461078371128292641145662855706177651882171630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000238326184160461506224629180117347004852490499615669250488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
23.8115737 |
4.1278987 |
49.7479132 |
5.7582335 |
| ENSG00000184313 |
374977 |
MROH7 |
protein_coding |
Q68CQ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374977; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000047502 |
Mroh7 |
153.011307 |
0.0566774138 |
-4.141082 |
0.233199321 |
384.248306 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014792841023034162604587404308375955211462109261568826664833664956010664033686337797109424530815387289181079418634235523816239770494570788152874188776729013654640126410130607015048537969001371269204511234898183000274762832759734010323882102966309 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005325422768292298651950204679242842097704714164698873544531118866443705173639665929722656421767358991649990776725527753492151752715448306957088844188014320028274674848651142721968875406449019757759208014858548496661683202546555548906326293945312 |
Yes |
No |
14.2894468 |
9.5198128 |
254.9765922 |
117.2815394 |
| ENSG00000184371 |
1435 |
CSF1 |
protein_coding |
P09603 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that plays an essential role in the regulation of survival, proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic precursor cells, especially mononuclear phagocytes, such as macrophages and monocytes. Promotes the release of pro-inflammatory chemokines, and thereby plays an important role in innate immunity and in inflammatory processes. Plays an important role in the regulation of osteoclast proliferation and differentiation, the regulation of bone resorption, and is required for normal bone development. Required for normal male and female fertility. Promotes reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, regulates formation of membrane ruffles, cell adhesion and cell migration. Plays a role in lipoprotein clearance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16337366, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19934330, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20504948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20829061}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Growth factor;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that controls the production, differentiation, and function of macrophages. The active form of the protein is found extracellularly as a disulfide-linked homodimer, and is thought to be produced by proteolytic cleavage of membrane-bound precursors. The encoded protein may be involved in development of the placenta. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:1435; |
CSF1-CSF1R complex [GO:1990682]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor binding [GO:0005157]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060444]; cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus [GO:0071374]; developmental process involved in reproduction [GO:0003006]; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue [GO:0048873]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:0038145]; macrophage differentiation [GO:0030225]; macrophage homeostasis [GO:0061519]; mammary duct terminal end bud growth [GO:0060763]; mammary gland fat development [GO:0060611]; microglial cell proliferation [GO:0061518]; monocyte activation [GO:0042117]; monocyte differentiation [GO:0030224]; monocyte homeostasis [GO:0035702]; myeloid leukocyte migration [GO:0097529]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; neutrophil homeostasis [GO:0001780]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; ossification [GO:0001503]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; osteoclast proliferation [GO:0002158]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor signaling pathway [GO:1902228]; positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010744]; positive regulation of macrophage differentiation [GO:0045651]; positive regulation of macrophage migration [GO:1905523]; positive regulation of macrophage proliferation [GO:0120041]; positive regulation of microglial cell migration [GO:1904141]; positive regulation of monocyte differentiation [GO:0045657]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071677]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell proliferation [GO:0032946]; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040018]; positive regulation of odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042488]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; positive regulation of protein metabolic process [GO:0051247]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010743]; regulation of ossification [GO:0030278]; response to ischemia [GO:0002931]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11792569_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor and receptor activator NF-kappaB ligand fail to rescue osteoclast-poor human malignant infantile osteopetrosis in vitro. 11843897_High M-CSF levels may correlate with cellular or organ damage in patients treated with peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for hematologic diseases. 12032835_Opposite effects of different doses of MCSF on ERK phosphorylation and cell proliferation in macrophages. 12372416_CSF-1 and its receptor are regulated by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) and its analogue tacalcitol in human monocytes which parallels the inhibition of differentiation into dendritic cells without altering survival 12393446_IFN-gamma shifts monocyte differentiation to macrophages rather than DCs through autocrine M-CSF and IL-6 production. 12456016_in human tumor cells, HGF and M-CSF stimulate osteopontin production (which is subsequently used as a substrate for cell adhesion) 12501178_Time-dependent folding events reveal that recombinant MCSF beta molecules pass through both monomeric and dimeric intermediate states, suggesting that the denatured and dimeric bond-reduced protein folds via multiple pathways. 12548211_macrophage colony-stimulating factor increased platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase secretion by decidual macrophages 12684699_Results suggest that macrophage colony-stimulating factor may autoregulate functional cellular subpopulations of human endometrial stromal cells in an autocrine or a paracrine manner. 12865350_findings directly support the conclusion that membrane-bound colony stimulating factor-1 is functionally active in bone in vivo 12890905_Serum VEGF concentration was increased in arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO) and thromboangitis obliterans, but increased concentration of M-CSF was seen only in ASO. 12894871_CSF1 has a role in regulating macrophage activation [review] 12928417_Monocytes promote angiogenesis via M-CSF-induced vascular endothelial growth factor production. 12929928_sCSF-1 is a key determinant of bone cell activity in the corticoendosteal envelope 14605992_increased levels of serum macrophage colony stimulating factor markedly precede the development of clinical manifestations of preeclampsia 14634568_Increase in serum M-CSF levels precedes development of preeclampsia. Elevation of serum M-CSF supports M-CSF elevation in placenta. This elevation at 18 weeks of gestation may be related to placental hypoxia, considered cause of preeclampsia. 14654075_findings of co-expression of KIT and/or FMS with their respective ligands implies these receptors might contribute to leukemogenesis in some patients with AML through autocrine, paracrine, or intracrine interactive stimulation. 15001836_The serum M-CSF concentration could be of interest as a tumor marker in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. 15116247_red blood cells from diabetic patients induced an increase in MCSF and VCAM1 expression in HUVEC cells, mediated by AGE-RAGE interaction 15256272_Expreeeion of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human osteoblast-like cells is suppressed by arginine-vasopressin. 15261158_results suggest that nuclear actin plays a role in regulating CSF-1 gene transcription, and this role does not depend on actin polymerization 15358207_In vitro human osteoclastogenesis is dependent on M-CSF and the stimulatory effects of GM-CSF are mediated by M-CSF. 15494511_Crystal structures of HLA-B*3501 in complex with 14-mer macrophage-colony stimulating factor peptide reveal that the antigenic peptide follows the general rules of major histocompatibility complex binding. 15576295_The MGFS mRNA expression in these cell lines and recent studies have demonstrated that HCs can stimulate tumor progression. 15624698_Interferon-gamma stimulates transcription of the CSF-1 gene through this sequence, which binds STAT1 15640942_A significant serum tumor marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 15728521_Serum M-CSF levels are markedly increased in Langerhans cell histiocytosis patients who, in addition to bone disease, also show skin or lymph node involvement. 15820145_indicate novel roles of M-CSF in articular cartilage metabolism in collaboration with CTGF/CCN2, particularly during an inflammatory response 15866728_The M-CSF gene was cloned into baculovirus transfer vector pVL1392 under the control of polyhedrin promoter and expressed in the Sf9 cells (Spodoptera frugiperda). 15919699_Uncreased macrophage colony stimulating factor is associated with the process of atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients 15944252_M-CSF enhances tumor growth in mice by increasing endothelial progenitor cells and activating angiogenesis; the effects of M-CSF are largely based on the induction of systemic VEGF from skeletal muscles. 16204228_catalase has a critical role in CSF-independent survival of human macrophages via regulation of the expression of BCL-2 and BCL-XL 16267391_INI1/hSNF5/BAF47 functions in activation of the colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) promoter in HeLa cells. 16318581_MCP-1 and M-CSF, critical for monocyte recruitment, activation, and differentiation, differentially regulate VEGF-A expression and may play an important role in monocyte/macrophage- mediated tumor angiogenesis 16320327_Nurse-like cells are involved in rheumatoid arthritis-induced bone destruction by maintaining osteoclast precursors via production of M-CSF. 16407111_Fusion with COL6A3 overexpresses CSF1, found in some but not all cells in tenosynovial giant-cell tumor and pigmented villonodular synovitis. 16673212_at 35 and 38 weeks, the Macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) levels were significantly higher in twin pregnancy than in singleton pregnancy 16844084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16844084_three polymorphisms located in the colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) gene showed a positive association with aggressive periodontitis 16859503_IL-10 may contribute to the inflammatory process by facilitating monocyte differentiation into TNF-alpha-responsive macrophages in the presence of M-CSF in rheumatoid arthritis. 16951369_Different individual CSF-1 isoforms regulate the frequency of activated macrophages in the kidney during experimental unilateral ureteral obstruction. 17108334_CSF1 is involved in regulating macrophage trafficking at the fetal-maternal interface 17192722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17192722_These data do not support the hypothesis that genetic variability of CSF1 influences the risk for Alzheimer's disease (AD). 17243911_significantly higher levels of macrophage-colony stimulating factor is associated with pancreatic cancer 17355643_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17368603_Significantly higher macrophage-colony stimulating factor level is associated with lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer patients 17420255_a combination of the Src family kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt, phospholipase C, and ERK pathways mediates macrophage proliferation in response to M-CSF 17431224_macrophage colony-stimulating factor(M-CSF) contributes to the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis in patients with IPF through the involvement of mononuclear phagocytes and CCL2 production. 17443671_Increased and prolonged ERK activation led to M-CSF-mediated macrophage differentiation but not to proliferation. 17516513_M-CSF modulates osteoclast-resorbing activity, but is not required for cell survival 17532041_We have shown for the first time that a homeobox gene, HLX1, is a downstream effector gene of CSF-1, that HLX1 regulates placental cell proliferation and that CSF-1 acts, at least in part, through HLX1 to control cell proliferation. 17589498_Monocytopoiesis is controlled by a circuitry involving sequentially miRNA 17-5p-20a-106a, AML1 and M-CSFR, whereby miRNA 17-5p-20a-106a function as a master gene complex interlinked with AML1 in a mutual negative feedback loop. 17916748_M-CSF-driven generation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and conventional dendritic cells in vitro and in vivo was independent of endogenous Flt-3 ligand 17918257_Csf1 fusion with collagen type VI alpha-3 gene is associated with tenosynovial giant cell tumors. 17922812_Human cardiac cells constitutively express M-CSF and its expression is up-regulated by TNF-alpha. 17967422_CSF-1 and TPA use independent pathways to initiate RIPping, and that the intracellular domain is targeted for degradation through ubiquitination 18219369_Differential constitutive and cytokine-modulated expression of Toll-like receptors in primary neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages is reported. 18322228_CSF-1 stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) activation in macrophages. 18435789_Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from periodontitis patients do not need priming by M-CSF to become osteoclast-like cells, suggesting that PBMCs from periodontitis patients are present in the circulation in a different state of activity. 18467591_Discovered IL-34 and its receptor CSF1 by functional screening of the extracellular proteome. 18510570_Expression of M-CSF, CSF-1R and CD3 is a significant prognostic factor in primary prostatic cancers by predicting the development of metastases. 18619508_nuclear c-Abl kinase can activate CSF-1 gene transcription by regulating AP-1 activity in the signaling events induced by L-selectin ligation. 18632616_mM-CSF may be a critical linker between macrophages and malignant cells in the development of hematopoietic malignancies 18668547_CCL23, M-CSF, TNFRSF9, TNF-alpha, and CXCL13 are predictive of rheumatoid arthritis disease activity and may be useful in the definition of disease subphenotypes and in the measurement of response to therapy in clinical studies. 18676750_CSF1, EGFR, and CA IX have roles in increasing survival in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the lung 18708368_GAPDH, a multifunctional protein, now adds regulation of mRNA stability to its repertoire. 18718581_Report clinical use of colony-stimulating factor-1 in ovulation induction for poor responders. 18724005_These results suggest that orthodontic tooth movement causes an increase in VEGF and M-CSF levels, which may induce bone remodeling via osteoclastic bone resorption. 18751872_The close correlation between serum M-CSF and serum thyroid hormone levels suggests that high circulating levels of thyroid hormones may directly or indirectly potentiate the production of M-CSF in patients with GD. 18852899_ability of M-CSF to recruit mononuclear phagocytes, increase VEGF levels, and enhance angiogenesis 18996518_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor is involved in follicle development and ovulation and could be an additional predictor for in vitro fertilization outcome. 19004987_CSF-1 represents a further link between inflammation and cardiovascular disease. 19008293_CRP up-regulates M-CSF release from human monocyte-derived macrophages and human aortic endothelial cells and increased macrophage proliferation. 19017797_Calorimetric data indicate that M-CSF cannot dimerize FMS without receptor-receptor interactions mediated by FMS domains D4 and D5 19196448_renal tubular cell derived m-CSF is a stimulus for monocyte activation 19432671_CSF-1 derived from tumor tissues induces macrophages to shift toward the M2 phenotype, which is considered to promote tumor growth 19443701_CSF1 may play an important role in the clinical behavior of leiomyosarcoma 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19561083_CSF-1-induced WASP activation was fully Cdc42-dependent. 19641137_M-CSF inhibits differentiation of murine bone marrow-derived macrophages into prefusion osteoclasts (pOC) in vitro, but induces fusion of pOCs to form multinucleated osteoclasts, making the osteoclast capable of bone resorption. 19711348_Studies demonstrated that increased CSF-1 production by host cells enhances TAM recruitment and NB growth. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19926892_serum and urine CSF-1 levels correlated with lupus activity, and intrarenal CSF-1 expression correlated with the histopathology activity index of lupus nephritis 19950360_possible local and systemic involvement of M-CSF in humans during fracture healing 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436471_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436471_These studies provide new insights into the pathogenesis of PDB and identify OPTN, CSF1 and TNFRSF11A as candidate genes for disease susceptibility. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20455868_Macrophage colony-stimulating factor in CSF appears to be a biomarker for diagnosis of mild cognition disorder. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20504948_The different spatiotemporal expression of IL-34 and CSF-1 allows for complementary activation of the CSF-1R in developing and adult tissues. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20839008_genetic risk for Paget's disease of bone is associated with variants close to CSF1, OPTN, TM7SF4, and TNFRSF11A genes; most significant results are found in the CSF1 gene region 20839921_Increased prevalence of M-CSF in the setting of HIV infection could contribute to neuronal injury and may be predictive of cognitive impairment. 20925194_These results indicate that nuclear NFAT can activate CSF-1 gene transcription by connecting with the CSF-1 promoter in the signaling events induced by L-selectin ligation. 21239715_M-CSF enhances dendritic cell DC-SIGN (CD209) expression on in vitro derived anti-inflammatory macrophages; M-CSF mediates induction of DC-SIGN by fibroblast- and tumor cell-conditioned media. 21481374_CSF-1, in an autocrine fashion, has a direct effect on endometrial epithelial cell proliferation and attachment to peritoneal mesothelial cells, early steps in endometriosis lesion formation on the peritoneum. 21717212_These observations may indicate a pathogenetic role of Macrophage colony-stimulating factor in Hodgkin lymphoma. 21791433_Humanized CSF-1 mice will be a valuable experimental model to study human myeloid cell biology. 21854753_These findings suggest an important role for CSF1 and the resulting tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in the pathological neovascularization of leiomyosarcoma. 21895511_findings demonstrate that NF-kappaB induces M-CSF expression on a promoter level via multiple functional NF-kappaB binding sites 21938481_Treatment of differentiating cells with alendronate or pamidronate decreases the expression of M-CSF, which enhances preosteoclast formation. These results suggest a new mechanism by which BPs inhibit osteoclastogenesis. 21945122_Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein are elevated in sera of intrinsic asthmatics compared to normal controls. 22028782_CSF-1 dependent Erk activation and proliferation are regulated differentially in progenitors and differentiated cells 22052465_results suggest that budding RCC stimulates the proximal adjacent microenvironment in the kidney to release mediators of CSF-1, CSF-1R, and epidermal growth factor expression in RCCs 22082370_In this review, shedding of macrophage-CSF receptor c-Fms inhibits osteoclastogenesis. 22186992_Studies indicate that Macrophage-colony stimulating factor (CSF-1) signaling through its receptor (CSF-1R) promotes the differentiation of myeloid progenitors. 22365076_Suggest that CSF-1 and its receptor, C-FMS, are involved in the genesis of early endometriotic lesions and that endometriotic lesions contribute to elevated CSF-1 levels in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis. 22678116_Our results reveal a novel mechanism for the therapeutic function of fish oil diet that blocks miR-21, thereby increasing PTEN levels to prevent expression of CSF-1 in breast cancer. 23061794_M-CSF was shown to interact with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BARF1 via the protruding N-terminal loops involving Val38 and Ala84. 23233531_miR-148b controls malignancy by coordinating a novel pathway involving over 130 genes and, in particular, it directly targets players of the integrin signaling, such as ITGA5, ROCK1, PIK3CA/p110alpha, and NRAS, as well as CSF1 23260168_the feline CSF-1R was cloned and the responsiveness to CSF-1 and IL-34 from a range of species, was examined. 23285029_The percentage of CD14(high)CD16(+) monocytes after trauma correlated strongly with plasma C-reactive protein (CRP) transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) levels. 23471483_Nucleolin mediates microRNA-directed CSF-1 mRNA deadenylation but increases translation of CSF-1 mRNA. 23520016_The expression of CSF2 (but not CSF1) was highly up-regulated in glioblastoma patients and we found an inverse correlation between CSF2 expression and patient survival. 23684409_This study is the first to illustrate downstream transcriptional profiles and pathways of IL-34 in comparison with CSF-1 and identify notable differences in CCR2 expression. 23688065_The results indicate usefulness of VEGF and M-CSF in diagnostics of breast cancer patients, especially in combination with CA 15-3. 23870818_high expression correlates with shorter metastasis-free survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients 23924854_GPNMB expression was regulated by EpCAM and CSF-1 partly through their common downstream product c-myc 24016870_Elevated CSF1 serum level is associated with early breast cancer. 24157873_Regulation of immediate-early gene response by THOC5, a member of mRNA export complex contributes to the M-CSF-induced macrophage differentiation. 24178511_genetic polymorphism is associated with platelet counts 24592910_None of SNPs among rs333967, rs2297706 and rs1058885 in CSF-1 was found statistically significantly associated with CP in Han Chinese with Shanghai origin. haplotype T-C-G showed statistically significant association with decreased risk in males. 24604026_Findings suggest the replacement of the 3'-UTR of CSF1 with other sequences in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. 24748497_The findings of this study regarding the unique functional interplay between M-CSF and IL-32 increase our understanding of the mechanisms that regulate the survival and M1/M2 ratio of macrophages, as well as HIV-1 replication in macrophages. 24769444_In a cohort of 453 human breast tumors, NCOA1 and CSF1 levels correlated positively with disease recurrence, higher tumor grade, and poor prognosis. 24956020_The aim of the present study was to assess the effect of soluble mediators produced by breast cancer cells on human osteoclast maturation in a co-culture model. 25066464_potent profibrotic factor in hepatitis C virus liver fibrosis 25138985_macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) may be involved in the regulation of epiphyseal plate injury and repair in Kashin-Beck disease. 25196912_expression and release, from osteoblasts of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), which is indispensable for osteoclast differentiation, was inhibited by uPAR loss. 25313137_results presented herein suggest a potential cross-talk between cancer cells and the microenvironment controlled by CSF1/Vav1 signaling pathways. 25418473_RGC-32 expression on M2-polarized and tumor-associated macrophages is M-CSF-dependent and enhanced by tumor-derived IL-4. 25420919_FoxO1 is highly expressed in M-CSF-derived (M2-like) macrophage subsets, and this M2-like macrophages showed a preferential FoxO1 enrichment on the IL-10 promoter but not in GM-CSF-derived (M1-like) macrophages 25721620_Colony Stimulating Factors 1, 2, 3 and early pregnancy 25854167_Determination of CSF1 and CSF1R expression may be useful as a prognosticator of the clinical course and/or outcomes of Pigmented villonodular synovitis . 25891874_Our findings also suggest that next generation sequencing may help explore the pathogenesis and aid the diagnosis of Juvenile Paget's disease. 25935153_These findings suggest a high usefulness of M-CSF in diagnosing the serous sub-type of epithelial ovarian cancer and in discriminating between cancer and non-carcinoma lesions 26029847_These findings highlight an essential role for PRKAA1-mediated autophagy during differentiation of human monocytes. 26095744_findings demonstrated that M-CSF binds to IL-34; molecular docking studies predicted the formation of a heteromeric M-CSF/IL-34 cytokine 26235028_Data show crystal structures of CSF1-CSF1R ternary complexes, and propose a mechanism for their cooperative action that relies on the adoption by dimeric CSF-1 of an active conformational state and homotypic receptor interactions. 26245897_study shows up-regulation of MCSF in GBM via a SYK-PI3K-NFkappaB-dependent mechanism and identifies IGFBP1 released by microglial cells as a novel mediator of MCSF-induced angiogenesis 26359491_By identifying the M-CSFM residues critical for M-CSF-c-FMS interactions, we have laid down the basis for a deeper understanding of the M-CSF . c-FMS signaling mechanism 26376111_In patients with CLE, 100 and 150 mg PD-0360324 (monoclonal antibody against MCSF) every 2 weeks for 3 months suppressed a subset of circulating monocytes. 26642091_peripheral nerve injury induced de novo expression of colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) in injured sensory neurons. CSF1 was transported to the spinal cord, where it targeted the microglial CSF1 receptor (CSF1R). 26686751_This can be achieved by either blocking the EGF or CSF-1 receptors or supressing the EGF or CSF-1 signal. 27013192_Therefore, our findings indicate that CSF1 signaling is oncogenic during gliomagenesis through a mechanism distinct from modulating glioma-associated microglia/macrophage polarization status 27038418_M-CSF macrophage conversion into foam cells reduces their proinflammatory responses to classical M1-polarizing activation 27107415_miR-1207-5p and CSF1 expression levels and their relationship with lung cancer survival and metastasis status were assayed by means of a lung cancer tissue microarray. 27173404_Upregulation of GM-CSF and M-CSF production by endothelial cells, an effect that appears to be mediated by NF-kappaB and to be independent of IL-1, may be an additional mechanism through which IL-33 contributes to inflammatory activation of the vessel wall. 27445439_M-CSF has been shown to be comparable to CA15-3 and VEGF, specificity, and AUC values only in stages III and IV of BC. 27599777_High CSF1 expression is associated with breast cancer. 28131007_Nucleolin both forms an mRNP complex with the eIF4G and CSF-1 mRNA, and is co-localized with the eIF4G in the cytoplasm further supporting nucleolin's role in translational regulation. 28273887_Results suggest that monocytes from Crohn's disease patients in remission produced high levels of CSF-1 that upregulate CCR5 expression. Consequently, monocytes differentiated in these conditions had a characteristic phenotype and lower production of inflammatory cytokines. 28655719_study, therefore, provided insights into the sequence-structure-function relationships of the M-CSF/c-FMS interaction and of ligand/receptor tyrosine kinase interactions in general. 28656272_It was demonstrated that MCSF and folliclestimulating hormone stimulated the production of estradiol (E2) in luteinized granulosa cells. MCSF may be important in regulating the response of luteinized granulosa cells to gonadotropin and may have a promotive effect in the early phase of follicular development. 28687620_High CSF-1 expression is associated with Breast Cancer. 28779164_study found that age, smoking, periodontitis, manifest caries, and the presence of tumors are associated with the salivary levels of CSF-1. 28875266_Concerning pigmented villonodular synovitis , clinical trials assessing CSF-1R inhibitors have revealed promising initial outcomes. Blocking CSF-1/CSF-1R signaling represents a promising immunotherapy approach and several new potential combination therapies for future clinical testing. 29323162_Data showed that single expression of M-CSF or IL-34 can be observed in lung cancer tissues and correlated with poor survival. Additionally, their high co-expression correlates with disease stages and poor survival. Thus, evaluating the expression of both M-CSF and IL-34 may help to estimate disease progression and malignant degree in lung cancer patients. 29363207_These results highlight heterogeneous effects of M-CSF isoforms on acute myeloid leukemia progression. 29422647_In glioblastoma, colony-stimulating factor-1 and angiocrine IL-6 induce robust arginase-1 expression and macrophage alternative activation, mediated through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-dependent transcriptional activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha. 29734839_The functional rs2050462 in CSF-1 might have a substantial influence on the renal cell carcinoma susceptibility and evolution in the Chinese population. 29767252_Study find elevated expression of CSF1 in primary gastric cancer tissue (GC) to be significantly associated with the presence of lymph node and peritoneal metastasis, advanced TNM stage, and poor survival. In vitro analysis also revealed a functional role for the CSF1 in GC development, and a prognostic and predictive biomarker for GC. 29801457_at 3 months after cardiopulmonary bypass, monocytes continued to express a new macrophage-like milieu that was associated with the persistent activation of the PU.1/M-CSF pathway. 30012324_Elevated CSF1 levels were identified as a causal risk factor for Coronary Artery Disease with consistent epidemiological results. Furthermore, genetically predicted CSF1 levels were associated with CAD in the UK Biobank 30052166_High M-CSF expression is associated with cervical cancer. 30317027_data unveil a novel epigenetic mechanism whereby a BRG1-centered complex mediates transcriptional activation of CSF1 by Ang II in vascular endothelial cells. 30342176_CSF-1 mRNA decay can be regulated at an epigenetic level, and alteration of the N1methylation status leads to phenotypic changes in cancer cell behavior. 30580386_Expression of M-CSF is related to macrophage activity and tumor progression in sporadic vestibular schwannomas. 30592292_Cytoplasmic MCSF suppressed apoptosis in MCF7 human breast cancer cells by inhibiting the HIF1alpha/BNIP3/Bax signalling pathway, which potentiated the dissociation of Bcl2 from Bcl2BNIP3 compounds and the formation of Bcl2Bax compounds. 30816518_These results suggested that the interaction between CSF1 and its receptor served an important role in promoting macrophage infiltration and progression of EC. 31028249_When monocytes are differentiated into macrophages with CSF-1, CSF-1R is redirected to transcription starting sites, colocalizes with H3K4me3, and interacts with ELK and YY1 transcription factors. 31035945_Data indicate a possible clinical applicability and a high diagnostic power for the combination of macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), CA 125 and SCC-Ag in the diagnosis of both studied types of cervical cancer. 31107544_The frequent deletion of CSF1 exon 9 in the fusion transcripts. 31217507_A Selective FGFR inhibitor AZD4547 suppresses RANKL/M-CSF/OPG-dependent ostoclastogenesis and breast cancer growth in the metastatic bone microenvironment. 31469468_Sequencing confirmed CSF1 breakpoints in 28 cases; in all 28 the breakpoint was found to be downstream of exon 5, replacing or deleting a long 3' UTR containing known miRNA and AU-rich element negative regulatory sequences. 31536655_CSF1-associated decrease in endometrial macrophages may contribute to Asherman's syndrome. 31786501_Who's in charge here? Macrophage colony stimulating factor and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor: Competing factors in macrophage polarization. 31859421_Schwann cells orchestrate peripheral nerve inflammation through the expression of CSF1, IL-34, and SCF in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 31911555_miR-149 Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis by Blocking Paracrine Interactions with Macrophages. 31994318_miR-1254 inhibits progression of glioma in vivo and in vitro by targeting CSF-1. 32149159_Genetic Association and Expression Correlation between Colony-Stimulating Factor 1 Gene Encoding M-CSF and Adult-Onset Still's Disease. 32178869_The alternative spliced 3'-UTR mediated differential secretion of macrophage colony stimulating factor in breast cancer cells. 32264887_MiR-423-5p may regulate ovarian response to ovulation induction via CSF1. 32356483_Diagnostic Values of miR-21, miR-124, and M-CSF in Patients With Early Cervical Cancer. 32487125_Oct4 promotes M2 macrophage polarization through upregulation of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in lung cancer. 33652607_The Presence of Colony-Stimulating Factor-1 and Its Receptor in Different Cells of the Testis; It Involved in the Development of Spermatogenesis In Vitro. 33764399_CSF1/CSF1R-mediated Crosstalk Between Choroidal Vascular Endothelial Cells and Macrophages Promotes Choroidal Neovascularization. 34069563_Tumor-Associated Macrophage Promotes the Survival of Cancer Cells upon Docetaxel Chemotherapy via the CSF1/CSF1R-CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. 34298983_Transfection of Vitamin D3-Induced Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells for the Silencing of Potential Tolerogenic Genes. Identification of CSF1R-CSF1 Signaling as a Glycolytic Regulator. 34627193_CircCDC45 promotes the malignant progression of glioblastoma by modulating the miR-485-5p/CSF-1 axis. 35075211_M-CSF supports medullary erythropoiesis and erythroid iron demand following burn injury through its activity on homeostatic iron recycling. 35260161_CSF-1-induced DC-SIGN(+) macrophages are present in the ovarian endometriosis. 35468468_MiR-145 participates in the development of lupus nephritis by targeting CSF1 to regulate the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. 36071257_Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: a clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 39 tumors, with evidence for a CSF1-producing ''null cell'' population. 36177809_Determining the expression levels of CSF-1 and OCT4, CREM-1, and protamine in testicular biopsies of adult Klinefelter patients: Their possible correlation with spermatogenesis. 36221069_LARRPM restricts lung adenocarcinoma progression and M2 macrophage polarization through epigenetically regulating LINC00240 and CSF1. |
ENSMUSG00000014599 |
Csf1 |
141.890291 |
5.3254166935 |
2.412894 |
0.222060490 |
114.530375 |
0.00000000000000000000000000997268760209401452554198027025508163048359633039449172680116143138945392770944309290825913194566965103149414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000113665535912670000824681770704079989045445548576397485040689152625565522258810347011603880673646926879882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
243.2667858 |
30.2921336 |
45.7865198 |
4.6074504 |
| ENSG00000184381 |
8398 |
PLA2G6 |
protein_coding |
O60733 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-independent phospholipase involved in phospholipid remodeling with implications in cellular membrane homeostasis, mitochondrial integrity and signal transduction. Hydrolyzes the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached at sn-1 or sn-2 position of phospholipids (phospholipase A1 and A2 activity respectively), producing lysophospholipids that are used in deacylation-reacylation cycles (PubMed:9417066, PubMed:10092647, PubMed:10336645, PubMed:20886109). Hydrolyzes both saturated and unsaturated long fatty acyl chains in various glycerophospholipid classes such as phosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidates, with a preference for hydrolysis at sn-2 position (PubMed:10092647, PubMed:10336645, PubMed:20886109). Can further hydrolyze lysophospholipids carrying saturated fatty acyl chains (lysophospholipase activity) (PubMed:20886109). Upon oxidative stress, contributes to remodeling of mitochondrial phospholipids in pancreatic beta cells, in a repair mechanism to reduce oxidized lipid content (PubMed:23533611). Preferentially hydrolyzes oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acyl chains from cardiolipins, yielding monolysocardiolipins that can be reacylated with unoxidized fatty acyls to regenerate native cardiolipin species (By similarity). Hydrolyzes oxidized glycerophosphoethanolamines present in pancreatic islets, releasing oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acids such as hydroxyeicosatetraenoates (HETEs) (By similarity). Has thioesterase activity toward fatty-acyl CoA releasing CoA-SH known to facilitate fatty acid transport and beta-oxidation in mitochondria particularly in skeletal muscle (PubMed:20886109). Plays a role in regulation of membrane dynamics and homeostasis. Selectively hydrolyzes sn-2 arachidonoyl group in plasmalogen phospholipids, structural components of lipid rafts and myelin (By similarity). Regulates F-actin polymerization at the pseudopods, which is required for both speed and directionality of MCP1/CCL2-induced monocyte chemotaxis (PubMed:18208975). Targets membrane phospholipids to produce potent lipid signaling messengers. Generates lysophosphatidate (LPA, 1-acyl-glycerol-3-phosphate), which acts via G-protein receptors in various cell types (By similarity). Has phospholipase A2 activity toward platelet-activating factor (PAF, 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine), likely playing a role in inactivation of this potent pro-inflammatory signaling lipid (By similarity). In response to glucose, amplifies calcium influx in pancreatic beta cells to promote INS secretion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A3L7I2I8, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97570, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10092647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10336645, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18208975, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20886109, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23533611, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9417066}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform Ankyrin-iPLA2-1]: Lacks the catalytic domain and may act as a negative regulator of the catalytically active isoforms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9417066}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform Ankyrin-iPLA2-2]: Lacks the catalytic domain and may act as a negative regulator of the catalytically active isoforms. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9417066}. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Chemotaxis;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Dystonia;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Parkinson disease;Parkinsonism;Pharmaceutical;Phospholipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an A2 phospholipase, a class of enzyme that catalyzes the release of fatty acids from phospholipids. The encoded protein may play a role in phospholipid remodelling, arachidonic acid release, leukotriene and prostaglandin synthesis, fas-mediated apoptosis, and transmembrane ion flux in glucose-stimulated B-cells. Several transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been described, but the full-length nature of only three of them have been determined to date. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:8398; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; pseudopodium [GO:0031143]; 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase activity [GO:0003847]; ATP-dependent protein binding [GO:0043008]; calcium-independent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047499]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; myristoyl-CoA hydrolase activity [GO:0102991]; palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase activity [GO:0016290]; phosphatidyl phospholipase B activity [GO:0102545]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; serine hydrolase activity [GO:0017171]; antibacterial humoral response [GO:0019731]; cardiolipin acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0035965]; cardiolipin biosynthetic process [GO:0032049]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; maternal process involved in female pregnancy [GO:0060135]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051967]; phosphatidic acid metabolic process [GO:0046473]; phosphatidylcholine catabolic process [GO:0034638]; phosphatidylethanolamine catabolic process [GO:0046338]; platelet activating factor metabolic process [GO:0046469]; positive regulation of arachidonic acid secretion [GO:0090238]; positive regulation of ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:2000304]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0035774]; positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090037]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0090200]; regulation of store-operated calcium channel activity [GO:1901339]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; urinary bladder smooth muscle contraction [GO:0014832]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
12208880_activation during apoptosis promotes the exposure of membrane lysophosphatidylcholine leading to binding by natural immunoglobulin M antibodies and complement activation 12423354_stimulation of three isoforms of PLA2 by thapsigargin liberates free AA that, in turn, induces capacitative calcium influx in human T-cells 14749286_Arachidonic acid produced by iPLA(2)beta-catalyzed hydrolysis of their substrates induces release of Ca(2+) from ER stores, an event thought to participate in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. 15052324_The GVIB iPLA2 is widely expressed in human tissues but is enriched in heart, placenta, and skeletal muscle. 15249229_Here we show that the C-terminal region of human iPLA(2)gamma is responsible for the enzymatic activity. 15252038_iPLA2 may be dispensable for the apoptotic process to occur 15318030_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15364929_iPLA2epsilon (adiponutrin), iPLA2zeta (TTS-2.2), and iPLA2eta (GS2) are three novel TAG lipases/acylglycerol transacylases that likely participate in TAG hydrolysis and the acyl-CoA independent transacylation of acylglycerols 15385540_truncated iPLA(2) proteins associate with active iPLA(2) and down-regulate its activity during G(1) 15573142_Detailed characterization of group VIA phospholipase A2 beta suggests that the pancreatic islet beta-cells express multiple isoforms of iPLA2beta; the hypothesis in this review is that these isozymes participate in different cellular functions. 16585943_This study reviews the evidence and discusses the potential roles of phospholipase A2 Group 6A for schizophrenia with particular emphasis on published association studies. 16783378_mapped a locus for infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) and neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) to chromosome 22q12-q13 and identified mutations in PLA2G6, encoding a group VI phospholipase A2, in NBIA, INAD and Karak syndrome 16943248_Increase in iPLA(2) and accumulation of membrane phospholipid-derived metabolites in HCAEC exposed to hypoxia or thrombin have important implications in inflammation and arrhythmogenesis in atherosclerosis/thrombosis and myocardial ischemia. 16966332_iPLA2-VIA is a novel regulator of endothelial cell S phase progression, cell cycle residence, and angiogenesis 17003039_The role of calcium influx factor and PLA2G6 in the activation of CRAC channels and calcium entry in rat tumor cell lines is reported. 17033970_The disease gene was mapped to a 1.17-Mb locus on chromosome 22q13.1. 17082190_Transient receptor potential subfamily M member 8 (TRPM8) channel is stimulated by the Ca2+-independent phospholipase A2 (iPLA2) signaling pathway with its end products, lysophospholipids, acting as its endogenous ligands. 17188740_human coronary artery endothelial cells exposed to thrombin or tryptase stimulation demonstrated an increase in iPLA2 activity and arachidonic acid release 17254819_Cerebellar atrophy without cerebellar cortex hyperintensity in infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD) due to PLA2G6 mutation. 17275398_Secretion and activity of sPLA(2) were found to be similar in granulocyte-like PLB cells expressing or lacking cPLA(2)alpha, indicating that they are not under cPLA(2)alpha regulation. 17459165_oxytocin stimulation of uterine PGF2alpha production is mediated, at least in part, by up-regulation of PLA2G6 expression and activity 18208975_iPLA(2)beta and cPLA(2)alpha regulate monocyte migration from different intracellular locations, with iPLA(2)beta acting as a critical regulator of the cellular compass. 18562188_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18570303_PLA2G6 mutations are associated with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy and have been reported previously to cause early cerebellar signs, and the syndrome was classified as neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (type 2). 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18775417_This review discusses the role of iPLA2 in cell growth with special emphasis placed on its role in cell signaling; the putative lipid signals involved are also discussed. 18790994_Tryptase stimulation of human small airway epithelial cells increased membrane-associated, calcium-independent phospholipase A(2)gamma (iPLA(2)gamma) activity, resulting in increased arachidonic acid and PGE(2) release. 18799783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18799783_PLA2G6 mutations are associated with nearly all cases of classic infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. 18826942_H2O2-mediated hyperoxidation of Prdx6 induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M transition through up-regulation of iPLA2 activity. 19059366_iPLA2 activity is responsible for membrane phospholipid hydrolysis in response to tryptase or thrombin stimulation in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells 19087156_Different and even identical PLA2G6 mutations may cause neurodegenerative diseases with heterogeneous clinical manifestations, including dystonia-parkinsonism. 19138334_The nine novel mutations identified in this study suggest the uniqueness of the PLA2G6 mutation spectrum in Chinese patients 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19225567_Chromofungin or Catestatin , penetrate into PMNs, inducing extracellular calcium entry by a CaM-regulated iPLA2 pathway. 19556238_The region with the greatest change upon lipid binding in phospholipase A2 group VI was region 708-730. 19578365_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20053941_iPLA2 expression is increased in neutrophils from people with diabetes and mediates superoxide generation, presenting an alternate pathway independent of protein kinase C and phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase-1 hydrolase signaling. 20171194_These data demonstrate the novel findings that iPLA2 inhibition activates p38 by inducing reactive species, and further suggest that this signaling kinase is involved in p53 activation, cell cycle arrest and cytostasis. 20186954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20186954_Our data suggest that PLA2G6 mutations are unlikely to be an important cause of the common garden variety of Parkinson's disease patients with dystonia or a positive family history 20219570_Results characterize a pathway leading to NOX2 activation in which iPLA(2)-regulated p38 MAPK activity is a key regulator of S100A8/A9 translocation via S100A9 phosphorylation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20464283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20584031_Compound heterozygosity for a large intragenic deletion and a nonsense mutation was found in one patient with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy while the other is carrying two novel splice-site mutations 20619503_This report further defines the clinical features and neuropathology of PLA2G6 related childhood and adult onset dystonia-parkinsonism . 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20629144_Genetically determined NBIA cases from the Indian subcontinent suggest presence of unusual phenotypes of PANK2 and novel mutations 20647408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20669327_We identified genetic deficits in PLA2G6 that were associated with Levodopa responsive parkinsonism with pyramidal signs. 20813170_This study demonistrated that pLA2G6 has a dynamic expression pattern both in terms of the location of expression and the differentiation state of expressing cells. 20881058_The A isoform of PLA2G6 was shown to play a role in controlling the architecture of the endoplasmic reticulum-golgi intermediate compartment proteins in a way that impacts transport. 20886109_Catalytic function of PLA2G6 impaired by mutations is associated with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. 20938027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20938027_The results of this study suggested that PLA2G6 mutations should be considered in patients with early-onset l-dopa-responsive parkinsonism and dementia with frontotemporal lobar atrophy. 21191104_These results indicate that cardiac endothelial cell PAF production is dependent on iPLA(2)beta activation and that both iPLA(2)beta and iPLA(2)gamma may be involved in PGI(2) release. 21368765_PLA2G6 mutations are unlikely to be the major causes or risk factors of Parkinson's disease at least in Asian populations 21482170_data indicate that PLA2G6 mutation may not play a major role in general frontotemporal type of dementia 21700586_tHIS STUDY DEMONISTRATED THAT the PLA2G6 gene allocated PARK14 locus and is associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. 21812034_A possible involvement of calcium-independent group VI phospholipase A2 (iPLA2-VI) in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease has been proposed. 22213678_PLA2G6 mutations are associated with PARK14-linked young-onset parkinsonism and sporadic Parkinson's disease 22218592_acts as an inhibitory modulator of NKCC2 activity in thick ascending limb 22406380_Our result indicated that PLA2G6 mutations might not be a main cause of Chinese sporadic early-onset parkinsonism. 22459563_The results of this study suggested that PLA2G6 is not a susceptibility gene for parkinson disease in our population. 22549787_These data confirm the role of iPLA(2)beta as an essential mediator of endogenous store operated calcium entry. 22680611_The present study confirms the involvement of iPLA(2)-VIA in efficient retinal pigment epithelium phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments. 22903185_Neuronal phospholipid deacylation is essential for axonal and synaptic integrity through the action of iPLA2 and NTE. (Review) 23007400_membrane composition and the presence of nucleotides play key roles in recruiting and modulating GVIA-iPLA(2) activity in cells 23043102_Orai1 and PLA2g6 are involved in adhesion formation, whereas STIM1 participates in both adhesion formation and disassembly. 23074238_Findings reveal for the first time expression of iPLA(2)beta protein in human islet beta-cells and that induction of iPLA(2)beta during endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to human islet beta-cell apoptosis. 23182313_identified four rare PLA2G6 mutations in 250 PD patients in Chinese population with Parkinson's disease 23196729_Mutations in PLA2G6 is often associated with rapidly progressive parkinsonism and with additional features including pyramidal signs, cognitive decline and loss of sustained Levodopa responsiveness. 23277130_The association with bipolar disorder of the iPLA2beta (PLA2G6) its genetic interaction with type 2 transient receptor potential channel gene TRPM2, was examined. 23587695_This study demonistrated that PLA2g8 expression was significantly decreased in patients treated with antipsychotic drug. 24130795_the phenotype of neurodegeneration associated with PLA2G6 mutations 24512906_our findings indicate that PRDX6 promotes lung tumor growth via increased glutathione peroxidase and iPLA2 activities 24522175_clinical findings may be helpful in distinguishing PLA2G6-related neurodegeneration from the other major cause of NBIA, recessive PANK2 mutations. 24745848_Novel PLA2G6 mutations were identified in all patients with Phospholipase A2 associated neurodegeneration. 24791136_The significance of calcium-independent phospholipase A, group VIA (iPLA2-VIA), in retinal pigment epithelial cell survival, was investigated. 24858037_The loss of PS2 could have a critical role in lung tumor development through the upregulation of iPLA2 activity by reducing gamma-secretase. 25004092_IL-1beta and IFNgamma induces mSREBP-1 and iPLA2beta expression and induce beta-cell apoptosis. 25207958_genetic association studies in a population of Han Chinese: Data suggest that SNPs in PLA2G6 (rs132984; rs2284060) are associated with type 2 diabetes and hypertriglyceridemia in the population studied. [Meta-Analysis included] 25348461_A homozygous novel mutation at position c.2277-1G>C in PLA2G6 gene presumed to give rise to altered splicing, was detected, thus confirming the diagnosis of infantile Neuroaxonal Dystrophy (INAD). 25482049_Stimulation of adrenoreceptors causes increased iPLA2 expression via MAP kinase/ERK 1/2. 25668476_Mutations in PANK2 and CoASY lead, respectively, to PKAN and CoPAN forms of Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation . Mutations in PLA2G6 lead to PLAN. Mutations in C19orf12 lead to MPAN 26001724_our findings demonstrate that loss of normal PLA2G6 gene activity leads to lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction and subsequent mitochondrial membrane abnormalities. 26160611_Results demonstrated no significant impact of PLA2G6 and PLA2G4C gene polymorphisms on attenuated niacin skin flushing in schizophrenia patients. 26446356_Three catalytically active cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 are expressed in different areas within the human spermatozoon cell body. Spermatozoa with a significant low motility showed strong differences both in terms of total specific activity and of different intracellular distribution, compared with normal spermatozoa. Phospholipases could be potential biomarkers of asthenozoospermia. 26525102_genetic association study in Quebec City population: Data suggest total plasma n-6 fatty acid phospholipid levels and C-reactive protein are modulated by SNPs in PLA2G4A and PLA2G6 alone or in combination with fish oil dietary supplementation. 26668131_Mutations in PLA2G6 altered Golgi morphology, O-linked glycosylation and sialylation of protein in patients with neurodegeneration 26755131_Analysis of the cells from idiopathic Parkinson's disease patients reveals a significant deficiency in store-operated PLA2g6-dependent Ca(2+) signalling 27030050_This study demonstrated that elevated expression of alphaSyn/PalphaSyn in mitochondria appears to be the early response to PLA2G6-deficiency in neurons. 27196560_PLA2G6 mutations in Indian patients with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy and atypical late-onset neuroaxonal dystrophy 27196560_PLA2G6 were identified in patients with a spectrum of neurodegenerative conditions, such as infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy, atypical late-onset neuroaxonal dystrophy and dystonia parkinsonism complex in Indian families 27268037_Finding suggest the broadness of the clinical spectrum of group VI phospholipases A2 (PLA2G6)-related neurodegeneration. 27317427_These results strongly suggest that PNPLA9, -6 and -4 play a key role in GPL turnover and homeostasis in human cells. A hypothetical model suggesting how these enzymes could recognize the relative concentration of the different GPLs is proposed 27513994_This study identifies a novel PLA2G6 mutation that is the possible genetic cause of FCMTE in this Chinese family. 27709683_This exome sequencing in a family and identified compound-heterozygous PLA2G6 mutations in 2 affected sisters. 27942883_Study performed direct sequencing and investigated copy number variations (CNVs) of this gene in 109 Japanese patients with parkinsonism. Results suggest that CNV in PLA2G6 is rare in parkinsonism, at least in the Japanese population, in contrast to the reports of its frequency in neurodegeneration associated with brain iron accumulation. 28091863_performed a longitudinal brain volumetry study in a couple of bicorial twins with PLA2G6-positive infantile neuronal axonal dystrophy 28150298_PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration was caused by paternal isodisomy of the chromosome 22 (carrying c.680C>T mutation) following in vitro fertilization 28213071_the association of PLA2G6 with the pathogenesis of idiopathic PD, in addition to PARK14. 28295203_PLA2G6 gene mutations in 3 families, are reported. 28651698_We found no significant influence of the PLA2G6 and PLA2G4C polymorphisms on mean age at first hospital admission (P > 0.05) and that the investigated polymorphisms significantly influenced the clinical psychopathology only in male patients. The PLA2G4C polymorphism accounted for approximately 12% of negative symptom severity. 28821231_A novel missense mutation in PLA2G6 gene (c.3G > T:p.M1I) in one and half-year-old boy with muscle weakness and neurodevelopmental regression (speech, motor and cognition). 29325618_This study showed that PANK2 genes account for disease of patients diagnosed with an Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation disorder. 29342349_A lipidomics-based LC/MS assay was used to define the specificity of cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 toward a variety of phospholipids. A unique hydrophobic binding site for the cleaved fatty acid dominates each enzyme's specificity rather than its catalytic residues and polar headgroup binding site. 29454663_PLA2G6 mutations are associated with a continuous clinical spectrum from phospholipase A2-associated neurodegeneration to hereditary spastic paraplegia. 29472584_The catalytic domains of iPLA2beta form a tight dimer and surrounded by ankyrin repeat domains that adopt an outwardly flared orientation, poised to interact with membrane proteins. 29739362_A novel variant (NM_003560.2 c.1427 + 2 T > C) acting on a splice donor site and predicted to lead to skipping of exon 10 was found in PLA2G6 in two siblings diagnosed with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. This mutation seems to be pathogenic and was found in a homozygous state in the two patients and homozygous reference or heterozygous in five healthy family members. 29753029_PLA2G6 inherited genotype may influence melanoma BRAF/NRAS subtype development. 29909971_This study shows a hereto unknown role of PLA2G6/PARK14 in sphingolipid homeostasis and endolysosomal function. The suppression of PLA2G6 expression causes a reduction in Vps26 and Vps35 and leads to an elevation of ceramides and other sphingolipid intermediates in neuroblastoma cell line cells. 30232368_Two missense variants, p.R53C and p.T319M in PLA2G6 gene may contribute to Parkinson's disease susceptibility in Chinese population. 30302010_PLA2G6 mutation is associated with neurodegeneration presenting as a complicated form of hereditary spastic paraplegia. 30707893_Impaired iPLA2beta activity affects iron uptake and storage without iron accumulation: An in vitro study excluding decreased iPLA2beta activity as the cause of iron deposition in PLAN. 30772976_report a PLA2G6 compound complicated mutation in an atypical neuroaxonal dystrophy Chinese family, that is the p. A80T and p.D331Y mutation 31196701_A novel compound heterozygous mutation of the PLA2G6 gene, c.1648delC and c.991G>T, is associated with adult onset ataxia. 31277247_Proportion of calcium-independent (i)PLA2beta-containing mucosal mast cells (MCs) and the expression intensity of sPLA2-IIA was increased in Crohn's disease (CD). In vitro study showed that (i)PLA2beta is involved in the secretion of secretory phospholipases (sPLA2) from human MC line HMC-1. These results suggest that iPLA2beta-mediated release of sPLA2 from intestinal MCs may contribute to CD pathophysiology. 31492433_Study demonstrated significant, though weak, effects of the PLA2G6 polymorphism on the risk of nicotine dependence, as well as a significant, though weak, influence of the PLA2G6-smoking interaction on age of schizophrenia onset, with both effects manifested in a gender-specific fashion. 31493991_Genetic testing of the PLA2G6 confirmed presence of compound heterozygous novel mutations in Malaysian siblings with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy 1 31506141_immunohistochemistry showed a reduction in the protein expression of PLAG6 in the muscular tissue of this child 31689548_Infantile onset progressive cerebellar atrophy and anterior horn cell Degeneration-A novel phenotype associated with mutations in the PLA2G6 gene. 31922589_The compound variants of c.668C>A (p.Pro223Gln) and c.2266C>T (p.Gln756Ter) of the PLA2G6 gene probably underlies infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy in the child 32771225_PLA2G6 variants associated with the number of affected alleles in Parkinson's disease in Japan. 33080873_Metabolic Effects of Selective Deletion of Group VIA Phospholipase A2 from Macrophages or Pancreatic Islet Beta-Cells. 33087576_PLA2G6 guards placental trophoblasts against ferroptotic injury. 33279242_Association of rare heterozygous PLA2G6 variants with the risk of Parkinson's disease. 33576074_Whole genome sequencing reveals biallelic PLA2G6 mutations in siblings with cerebellar atrophy and cap myopathy. 33766980_Typical MRI features of PLA2G6 mutation-related phospholipase-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN)/infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD). 34131139_iPLA2beta-mediated lipid detoxification controls p53-driven ferroptosis independent of GPX4. 34207793_iPLA2beta Contributes to ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis during Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. 34622992_Dissecting the Phenotype and Genotype of PLA2G6-Related Parkinsonism. 35092705_Novel insertion mutation in the PLA2G6 gene in an Iranian family with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. 35247231_Genome sequencing reveals novel noncoding variants in PLA2G6 and LMNB1 causing progressive neurologic disease. |
ENSMUSG00000042632 |
Pla2g6 |
87.751511 |
0.2231324094 |
-2.164028 |
0.433118119 |
22.911738 |
0.00000169612924054762747745335287052892425663230824284255504608154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005845171046108563959716256097642883560183690860867500305175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
34.2923161 |
10.8747809 |
153.9338266 |
33.9035884 |
| ENSG00000184465 |
253769 |
WDR27 |
protein_coding |
A2RRH5 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein with multiple WD repeats. Proteins with these repeats may form scaffolds for protein-protein interaction and play key roles in cell signalling. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, but the full-length structure of some of these variants cannot be determined. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:253769; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000046991 |
Wdr27 |
174.779044 |
0.3562471894 |
-1.489049 |
0.176134953 |
70.094785 |
0.00000000000000005652220819198617426842297117403413347440446236596284235176312904513906687498092651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000433611118978022813489245450150030895115200562902127434661281313310610130429267883300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.3752260 |
10.8866937 |
247.8233845 |
21.3045584 |
| ENSG00000184489_ENSG00000289263 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.207907 |
0.2901418409 |
-1.785170 |
0.561959718 |
9.611367 |
0.00193376622903117028826058820811795158078894019126892089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004286287661886180148929081923370176809839904308319091796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.3850972 |
15.5356020 |
86.6456864 |
37.1000493 |
| ENSG00000184492 |
200350 |
FOXD4L1 |
protein_coding |
Q9NU39 |
|
DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene is a member of the forkhead/winged-helix (FOX) family of transcription factors with highly conserved FOX DNA-binding domains. Members of the FOX family of transcription factors are regulators of embryogenesis and may play a role in human cancer. This gene lies in a region of chromosome 2 that surrounds the site where two ancestral chromosomes fused to form human chromosome 2. This region is duplicated elsewhere in the human genome, primarily in subtelomeric and pericentromeric locations, thus mutiple copies of this gene have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:200350; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
Mouse_homologues 27092474_We demonstrate that mouse and human homologs of Foxd4l1 have similar functional domains compared to the frog protein, as well as conserved transcriptional activities when expressed in Xenopus embryos and blastomere explants. |
ENSMUSG00000051490 |
Foxd4 |
13.370751 |
0.2704322503 |
-1.886661 |
0.494783592 |
15.140634 |
0.00009979211904229095392564879984931280887394677847623825073242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000274391146994078715878884189294240059098228812217712402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6855247 |
2.4849607 |
21.1779639 |
6.0099885 |
| ENSG00000184517 |
162239 |
ZFP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6P2D0 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene belongs to the zinc finger protein family. Some members of this family bind to DNA by zinc-mediated secondary structures called zinc fingers, and are involved in transcriptional regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:162239; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19844255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000055835 |
Zfp1 |
124.169854 |
7.0823409680 |
2.824226 |
0.842721268 |
8.901335 |
0.00284962259841235309582030410524566832464188337326049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006128169469104262530312343670857444521971046924591064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
173.0458343 |
138.6732702 |
24.6484757 |
13.7759397 |
| ENSG00000184545 |
1850 |
DUSP8 |
protein_coding |
Q13202 |
FUNCTION: Has phosphatase activity with synthetic phosphatase substrates and negatively regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase activity, presumably by catalysing their dephosphorylation. Expected to display protein phosphatase activity toward phosphotyrosine, phosphoserine and phosphothreonine residues. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O09112}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Protein phosphatase;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual specificity protein phosphatase subfamily. These phosphatases inactivate their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues. They negatively regulate members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase superfamily (MAPK/ERK, SAPK/JNK, p38), which is associated with cellular proliferation and differentiation. Different members of the family of dual specificity phosphatases show distinct substrate specificities for various MAP kinases, different tissue distribution and subcellular localization, and different modes of inducibility of their expression by extracellular stimuli. This gene product inactivates SAPK/JNK and p38, is expressed predominantly in the adult brain, heart, and skeletal muscle, is localized in the cytoplasm, and is induced by nerve growth factor and insulin. An intronless pseudogene for DUSP8 is present on chromosome 10q11.2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1850; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; MAP kinase tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0017017]; myosin phosphatase activity [GO:0017018]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0004721]; protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:0004725]; protein tyrosine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008330]; dephosphorylation [GO:0016311]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
13129832_DUSP8 is genetically linked to alcohol dependence and was found on chromosome 11p15.5 15899389_Because this variant of hVH-5 lacked intronic sequences in its genomic structure, we suggest it might be a processed pseudogene of hVH-5. 22100391_The phosphorylation of the M3/6 phosphatase by JNK in response to stress stimuli results in attenuation of phosphatase activity and acceleration of JNK activation. 33131190_Diabetes type 2 risk gene Dusp8 is associated with altered sucrose reward behavior in mice and humans. 35428675_Dual-specificity phosphatase 8 (DUSP8) induces drug resistance in breast cancer by regulating MAPK pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000037887 |
Dusp8 |
27.788201 |
2.1895229927 |
1.130617 |
0.305107678 |
13.756557 |
0.00020809321780509011353202386551686231541680172085762023925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000543444859730857275474658063529886931064538657665252685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.9840114 |
8.6699020 |
17.1800973 |
3.1260891 |
| ENSG00000184557 |
9021 |
SOCS3 |
protein_coding |
O14543 |
FUNCTION: SOCS family proteins form part of a classical negative feedback system that regulates cytokine signal transduction. SOCS3 is involved in negative regulation of cytokines that signal through the JAK/STAT pathway. Inhibits cytokine signal transduction by binding to tyrosine kinase receptors including IL6ST/gp130, LIF, erythropoietin, insulin, IL12, GCSF and leptin receptors. Binding to JAK2 inhibits its kinase activity and regulates IL6 signaling. Suppresses fetal liver erythropoiesis. Regulates onset and maintenance of allergic responses mediated by T-helper type 2 cells (By similarity). Probable substrate recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin BC-CUL2/5-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins (PubMed:15601820). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35718, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15601820}. |
Growth regulation;Pharmaceutical;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Signal transduction inhibitor;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a member of the STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), also known as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), family. SSI family members are cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. The expression of this gene is induced by various cytokines, including IL6, IL10, and interferon (IFN)-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to JAK2 kinase, and inhibit the activity of JAK2 kinase. Studies of the mouse counterpart of this gene suggested the roles of this gene in the negative regulation of fetal liver hematopoiesis, and placental development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9021; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; miRNA binding [GO:0035198]; phosphotyrosine residue binding [GO:0001784]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; branching involved in labyrinthine layer morphogenesis [GO:0060670]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to interleukin-17 [GO:0097398]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046426]; negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042532]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0046854]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; positive regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045597]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0007259] |
11727828_active MKK6 in HepG2 cells enhanced basal activity or IL-6-induced transcriptional activation of a SOCS3 promoter 12027890_evidence for pY429pY431 being a new high affinity binding site for SOCS-3 on the EpoR 12198248_SOCS-3 is a major regulator of growth hormone signaling in insulin-producing cells 12351404_chronic expression confers resistance to IFN-alpha in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells 12403768_These data suggest, that there are two, largely distinct modes of negative regulation of gp130 activity, despite the fact that both SOCS3 and SHP2 are recruited to the same site within gp130. 12459551_translational control plays an important role in stabilization and function of SOCS3 12560330_SOCS-3 may have a role in IL-6-mediated insulin resistance in liver 12565872_Results describe the cloning and characterization of the promoter region of the human SOCS-3 gene. 12626585_Data showing that SOCS3 is not recruited to phosphotyrosine motifs of the IL-10 receptor complex suggest that IL-10 signaling is less sensitive than IL-6 signaling to inhibition by SOCS3. 12654831_induction of SOCS3 by Leishmania donovani provides a potent inhibitory mechanism by which intracellular microorganisms may suppress macrophage activation and interfere with the host immune response 12688541_SOCS-3 plays an important role in the suppression of cytokine signaling by GH in down-regulating the acute phase response after injury. 12783885_acceleration of degradation by tyrosine phosphorylation 12847520_These data indicate that SOCS-3 has an important role in regulating the onset and maintenance of T(H)2-mediated allergic immune disease. 14617776_hypermethylation in CpG islands of the functional SOCS-3 promoter that correlates with its transcription silencing in primary lung cancer tissue samples 15163721_rapidly induced in amnion FL cells in HSV-1 infection and appears to be mainly responsible for suppression of IFN signaling and IFN production during the HSV-1 infection. 15217536_Frequent hypermethylation of the functional SOCS-3 promoter correlates with its transcription silencing in NSCLC cell lines and primary lung cancer tissue samples; methylation silencing of SOCS-3 may be used as a marker for early detection of NSCLC 15240148_Our results demonstrate that SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 proteins inhibit IFN-alpha-induced activation of the Jak-STAT pathway and expression of the antiviral proteins 2',5'-OAS and MxA. 15249995_Homozygosity for the A-allele of the C -920-->A promoter polymorphism of the SOCS3 gene may be associated with increased whole-body insulin sensitivity. 15249995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15300962_Leptin resembles immune molecules called cytokines, which another protein, Socs3, inhibits. Colleagues wondered whether Socs3 also suppresses leptin and promotes resistance to the hormone. 15308667_interleukin-1beta regulates interleukin-6-induced suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 expression 15331532_SOCS-3 expression in human skeletal muscle in vivo is not related to insulin resistance in the presence of elevated IL-6 concentrations suggesting that cytokine action could differ in type 2 diabetic patients and nondiabetic obese subjects. 15361843_SOCS1 and SOCS2 but not SOCS3 suppressed the growth of ovarian and breast cancer cells. 15385932_overexpression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 is associated with anaplastic large cell lymphoma 15589317_The insertion of amino acid exchanges into the kinase inhibitory regions of SOCS-3 demonstrated a requirement of these domains for a proper inhibitory function. 15607366_The SOCS3 mRNA expression in bone marrow cells from CML patients who responded well to IFN-alpha therapy was significantly lower than that in cells from healthy volunteers and patients who were resistant to IFN-alpha therapy. 15618960_SOCS-3 is not a tumour suppressor but rather a protector of tumour cells. 15629435_SOCS3/CIS3 regulates hepatocyte growth factor-induced keratinocyte migration by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 phosphorylation 15939448_The induction of SOCS3 by HSV-1 occurs via STAT3 activation immediately after HSV-1 infection. 16007169_promoter methylation and subsequent transcript downregulation of SOCS-3 transcripts and, to a much lesser extent, SOCS-1 are involved in the multistep carcinogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 16007195_loss of SOCS-3 by the associated DNA methylation confers cells advantage in growth and migration 16055089_estrogen receptor 1 directly regulates human SOCS-3 promoter activity in human breast cancer cells 16210657_Inhibition of function in dominant-negative SOCS3 transgenic mice clearly reduces the severity of allergic conjunctivitis 16374465_this study suggests a potential novel function of SOCS-3 in regulating keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation in vitro and during skin repair in vivo. 16402267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16410555_Results suggest a novel interaction between the SOCS1 and SOCS3 proteins and the FGFR3 signaling pathway. 16543409_SOCS-3 inhibits IL-1 signal transduction by inhibiting ubiquitination of TRAF6, thus preventing association and activation of TAK1. 16568091_Able to repress the activity of the Brk non-receptor tyrosine kinase. 16709613_role for IL-11 via pSTAT3 and SOCS3 in initiating and progressing decidualization 16805839_Our data also show that SOCS3 promoted maintenance of neural stem cells 16822822_Data demonstrate that SOCS3 inhibits leptin activation of AMPK and suggest this impairment of leptin signaling in skeletal muscle may contribute to the aberrant regulation of fatty acid metabolism observed in obesity. 16831601_Deletion of the SOCS3 gene in hepatocytes promotes the activation of STAT3, resistance to apoptosis, and an acceleration of proliferation, resulting in enhanced hepatitis-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. 16914720_These data argue for the existence of a novel cAMP/Epac/Rap1/SOCS-3 pathway for limiting IL-6 receptor signaling in Endothelial Cells and illuminate a new mechanism by which cAMP may mediate its potent anti-inflammatory effects. 16920065_Decreased SOCS3 expression in obese adipose tissue may reflect a defective leptin signaling pathway. 16943387_The increase in mRNA for SOCS-3, which correlates with elevated levels of SOCS protein and positive immunostaining in M. avium/HIV-1 co-infected tissues. 17001312_elevated expression of SOCS genes is a specific lesion of breast-cancer cells that may confer resistance to proinflammatory cytokines and trophic factors, by shutting down STAT1/STAT5 signaling that mediate essential functions in the mammary gland 17083795_Upon LPS stimulation, expression of SOCS-3 mRNA is increased in cord blood lymphocytes. 17138568_SOCS3 binds the phosphorylated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) of sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (siglec) 7 and targets it for proteasomal-mediated degradation. 17148681_Collectively, our results show that SOCS-3 antagonizes regulation of cellular events by cAMP and is expressed in human prostate cancer. 17241887_SOCS-3 epigenetic silencing is responsible for sustained IL-6/STAT-3 signaling and enhanced Mcl-1 expression in cholangiocarcinoma 17264307_Using RT-PCR, we demonstrated for the first time that neutrophils express mRNA for SOCS-3. It is interesting that IL-4 increased expression of SOCS-3 at the mRNA and protein levels. 17273770_inactivation of the SOCS3 gene by hypermethylation may be involved in the promotion of malignant behavior of melanomas 17297444_SOCS3 overexpression reduced proliferation. 17325857_a defect in expression of SOCS-2 and SOCS-3 genes may be crucial for the IGF-I hypersensitivity and progressive increase in erythroid cell population size characteristic of Polycythemia vera. 17363902_This is the first demonstration of SOCS-mediated ubiquitination and routing of a cytokine receptor and its impact on maintaining an appropriate signaling output. 17374732_SOCS3 may possibly play a role in IL-6 resistance in at least a fraction of tumors. 17438093_Altered SOCS gene expression leads to increased cell signaling through the ERK-MAPK pathway and may play a role in disease pathogenesis by enhancing glioblastoma multiforme radioresistance. 17445271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17445271_our data do not suggest evidence for a major role of the respective SNPs in SOCS3 in the pathogenesis of extreme obesity in our study groups 17530721_Interleukin-6 (IL-6) was expressed in monocytes and B cells, IL-10 in monocytes, and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 in monocytes and T cells from patients with active disease. 17589943_Increased expression of mucosal SOCS3, but not of SOCS1, may play a critical role in the development of the colonic inflammation of ulcerative colitis. 17605868_SOCS-3 expression of naive T cells was up-regulated significantly after IL-2 stimulation; expression was down-regulated markedly after OVA(323 - 329) antigen stimulation. 17636039_This study details a novel mechanism of SOCS3 up-regulation by PGE2 in breast cancer cells that appears to be STAT independent and involve Sp1 binding to the promoter. 17668875_SOCS3 expression may influence the response to antiviral therapy and genotype 1b hepatitis C virus might induce its up-regulation. This may account for the different responses to therapy between genotype 1-infected and genotype 2-infected patients. 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17881539_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17895321_SOCS3 remained significantly unchanged in polycystic ovarian syndrome women 17935223_The infection of cells with adenovirus CN305 (AdCN305)-SOCS3 and AdCN305-cpp-SOCS3 resulted in dramatic cytotoxicity in liver tumor cells. 18045952_SOCS-3 inhibits androgen-stimulated proliferation by influencing cell cycle regulation in a prostate cancer cell line. 18055217_We conclude that endogenous SOCS3 inhibits AP-1 activity through blocking of JNK phosphorylation. 18097573_Reduced expression of SOCS-3 is closely related to lymph node metastasis. Therefore, SOCS-3 may be a good predictor for lymph node metastasis. 18199397_SOCS-3 may cause tissue damage indirectly in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. 18240972_Human sarcopenia reveals an increase in SOCS-3 and myostatin and a reduced efficiency of Akt phosphorylation. 18250407_SOCS3 and SOCS1 critically regulate influenza A virus-triggered innate immune responses by inhibiting type I interferon alphabeta receptor (IFNAR)1 antiviral signaling and differentially modulating inflammatory signaling pathways. 18414649_Data found that the level of TLR2 and SOCS-3, genes associated with atopy in the children, were significantly downregulated by presence of S. haematobium infection. 18440067_The methylation status of CpG islands of SOCS3 genes in chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms. 18507841_SOCS3 negatively regulates cell motility and decreased SOCS3 induced by methylation may confer a migration advantage to A549 cells. This suggest a negative role of SOCS3 in PYK2 signaling: previously unidentified regulatory mechanism for PYK2 function. 18538318_the lymphadenitis due to M. tuberculosis was associated with activated lysozymes and SOCS-3 but not SOCS-1 compared to controls, which may play a role in the long-term bacterial replication and altered immune modulation characteristic of the disease. 18549612_There is a statistically significant difference in the expression level of socs3 mRNA in myelo-proliferative disease patients between jak2v617f mutation positive group and negative group. 18571793_Oncostatin M stimulation of astrocytes leads to induction of SOCS-3 expression and activation of ERK1/2 and JNK pathways. 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18656467_monocyte SOCS3 correlated with glomerular filtration rate, urea and diastolic blood pressure 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18687693_SOCS-3 acts as a negative regulator of the cell cycle progression under E2F/DP-1 control by interfering with heterodimer formation between DP-1 and E2F 18752121_Constitutive and altered SOCS-3 expression may have potential roles in a subset of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. 18770864_The methylation of SOCS3 may be involved in the pathogenesis of glioblastoma multiforme and in the resistance of this neoplasm to conventional treatment. 18815196_SOCS3 promoter methylation iss detected in 32% of patients with idiopathic myelofibrosis suggesting a role for SOCS3 methylation in this disorder. 18820827_difference in SOCS1, SOCS2 and SOCS3 transcript levels between normal individuals and SLE patients is not statistically significant 18941624_SOCS3 expression in skeletal muscle is not up-regulated in women, despite very high serum leptin concentrations compared to men 18952062_SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-1beta-induced MUC8 gene expression. 18971287_CCL11 induces SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression in murine macrophages, human monocytes, and dendritic cells and inhibits GM-CSF-mediated STAT5 activation and IL-4-induced STAT6 activation in a range of hematopoietic cells. 18986700_increased ratio of sgp130/sIL-6R production and/or reduced sIL-6R production combined with down-regulation of IL-6R and SOCS-3 expression in trophoblasts may lead to less cytokine inhibitory activity in preeclampsia placentas 18989459_influenza A viruses not only suppress IFNbeta gene induction but also inhibit type I IFN signaling through a mechanism involving induction of the SOCS-3 protein 19027008_These results suggest that the interaction of SOCS3 with MAP1S and the integrity of the microtubule cytoskeleton play an important role in the negative regulation of SOCS3 on IL-6 signaling. 19036437_Enhanced SOCS-3 gene expression could promote IL-10 production by placental trophoblast cells, suggesting that SOCS-3 may play an important role in regulation of cytokine induced anti-inflammatory response in placental trophoblasts. 19052638_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19052638_There is no strong effect of the common genetic variation within the SOCS3 gene on the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19083014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19083014_SOCS3 genetic variants play a role in human obesity. 19115200_SOCS3 is a tumor suppressor in breast cancer cells that is regulated by PRL 19129540_Inhibition of cytokine response by IL-25 occurred via a p38 Map kinase-driven Socs-3-dependent mechanism 19164812_Suppressors of cytokine signaling modulate JAK/STAT-mediated cell responses during atherosclerosis. 19225535_SOCS3 inhibits TPO-induced megakaryocytic proliferation in normal and primary myelofibrosis but not the spontaneous growth in primary myelofibrosis 19229050_SOCS3 tyrosine phosphorylation may be a novel bio-marker of myeloproliferative neoplasms resulting from a JAK2 mutation, JAK2 H538QK539L or JAK2 F537-K539delinsL mutations 19231005_Liver expression of SOCS3 is a stronger baseline predictor of antiviral response than viral genotype in determining response to hepatitis c. 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19524687_SOCS3, as negative regulators of cytokine signaling, might maintain homeostasis by regulating multiple signaling pathways and reverse cell malignant behavior. 19543316_SOCS-mediated downregulation of mutant Jak2 (V617F, T875N and K539L) counteracts cytokine-independent signaling. 19592492_a role for SOCS1 and -3 in the seemingly paradoxical hyperresponsive state in cells deficient in IL-18Ralpha, supporting the concept that IL-18Ralpha participates in both pro- and anti-inflammatory responses 19595407_These results suggest that RSV infection escapes the innate antiviral response by inducing SOCS1, SOCS3 or CIS expression in epithelial cells. 19617629_adiponectin augmented the expression of A20, suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 3, B-cell CLL/lymphoma (BCL) 3, TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 1, and TNFAIP3-interacting protein (TNIP) 3. 19634073_Our results show that androgenic -regulation of SOCS-3 leads to inhibition of prolif-eration and secretion in human prostate cancer. 19643162_The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of SOCS-3 on TNFalpha-induced signalling in beta cells. 19737863_overexpression of SOCS3 in T cells reduces IL-17 and accelerates atherosclerosis. 19803812_interactions between the molecular expression of SOCS3, IRS-1 and phospho-AKT mediated by the genotype 1b virus 19913854_Dysregulation of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c in livers of morbidly obese women is associated with altered suppressor of cytokine signaling-3. 19951849_findings suggest that overexpression of p-STAT3 (Tyr705) occurs in urothelial carcinoma, and that pathways other than SOCS3 may contribute to its activation in this cancer 20005910_SOCS3 expression was increased in liver from patients with HBV-infection and this correlated with the severity of liver inflammation. 20067961_Saturated fat and carbohydrates, components of the high fat meal, known to induce oxidative stress and inflammation, also induce an increase in LPS, TLR-4, and SOCS3 20130595_Forced expression of SOCS3 and SHP-1 inhibits IFN-alpha signaling in psoriatic T cells. 20136974_Probiotic administration increased expression of SOCS-2 and SOCS-3 in Helicobacter pylori infection to limit inflammatory signaling. 20137421_Up regulation of SOCS1 and SOCS5 expression and down-regulation of SOCS3 and CIS may correlate with the development of a Th1 mediated immune response in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. 20155426_Deficient expression of SOCS3 is associated with an aggressive phenotype and portends a poor clinical outcome in breast carcinoma. 20231901_SOCS-3 and PIAS-3 upregulation impairs IL-12-mediated interferon-gamma response in CD56 T cells in HCV-infected heroin users 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20335309_SOCS-3 is a novel modulator of FGF-2-regulated cellular events in prostate cancer. 20351777_Hepatitis B virus X protein impairs hepatic insulin signaling through degradation of IRS1 and induction of SOCS3 20372794_SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression attenuates Lck-mediated cellular transformation 20375166_SOCS3 suppresses hepatitis C virus replication in an mTOR-dependent manner. 20398276_Data demonstrate that SOCS proteins are expressed in human melanoma cell lines and their modulation can influence the responsiveness of melanoma cells to IFN-alpha and IFN-gamma. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20433750_Higher mRNA expression levels of SOCS1, 3, 4 and 7 are significantly associated with earlier tumour stage and better clinical outcome in human breast cancer. 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20478455_results suggest that pro-inflammatory cytokines induced SOCS-3 expression. SOCS-3 induction suggests playing important role in negative feedback, suppressing serious destruction of periodontal tissue through a chemokine-dependent mechanism. 20484656_Interferon-gamma-induced SOCS3 expression leads to inhibition of IL-6-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 activation and interleukin (IL)-6-dependent expression of anti-, but not pro-inflammatory, target genes. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20504769_oral administration of HA900 modulates Th-1-type autoimmune disease and inflammation by up-regulating SOCS3 expression and down-regulating pleiotrophin expression via TLR-4 in intestinal epithelial cells 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20631305_Data suggest that SOCS3 may allow HIV-1 to evade the protective innate immune response within the CNS, allowing the recurrence of viral replication and, ultimately, promoting progression toward HAD. 20673263_Authors detected differential expression of SOCS3 between TB patients and LTBIs, but not between TB patients and NIDs, and decreased expression of SOCS3 in T-cells from LTBIs as compared with NIDs. 20689596_Data propose that EBV protein Zta activates SOCS3 protein as an immune escape mechanism that both suppresses optimal IFNalpha secretion by human monocytes and favors a state of type I IFN irresponsiveness in these cells. 20690084_Data conclude that SOCS-3 polymorphism is not a genetic risk factor for RA in Chinese patients. 20690084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20717995_SOCS3 hypermethylation may be involved in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer and could identify a tumor subset with an aggressive behavior. 20840058_increased expression in kidney and liver of patients who died of anaphylactic shock 20934424_SOCS1 and 3 may control chemotaxis and adhesion 21029588_SOCS3 expression is reduced in placenta of women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. 21042758_Insights into the development of applications of SOCS3 gene therapy for lung cancer and, possibly, other human cancers. 21173340_Data suggest that increased plasma soluble gp130/soluble IL-6R/IL-6 ratio and reduced membrane transsignaling gp130 expression could contribute to decreased SOCS-3 expression and subsequent reduction in SOCS-3 antiinflammatory activity in preeclampsia. 21190606_High glucose could produce morphological and ultrastructural changes in renal tubular epithelial cells and induce up-regulation of SOCS-1/3 expression. 21263153_SOCS3 overexpression in K562 cells and in primary erythroid cells recapitulated the growth inhibition induced by Sox6, which demonstrates that SOCS3 is a relevant Sox6 effector. 21275162_Huatan Tongluo Granule upregulates SOCS3 and downregulates TNFa patients with acute cerebral infarction. 21308719_SOCS-3 may be one of proteins which influence ability of TRAIL and resveratrol to cause programmed cell death in prostate cancer. 21325601_Serum amyloid A overrides Treg anergy via monocyte-dependent and Treg-intrinsic, SOCS3-associated pathways. 21337543_found higher levels of SOCS-1/3 mRNA levels in CD4(+) T cells of HIV-infected patients than in healthy controls 21354254_suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 regulates cardiac cell signaling crosstalk, between NF-kappaB and p-STAT3, under hypoxic stress 21360047_Suppressor of cytokine signalling protein SOCS3 expression is increased at sites of acute and chronic inflammation 21385272_Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS3) balance controls cytotoxicity and IL-10 expression in decidual-like natural killer cell line NK-92. 21451109_In this study, we describe a unique signaling pathway responsible for the SOCS3-mediated downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines 21478033_SOCS3 influences myoblast differentiation. 21481788_data describe the involvement of IL-6 transsignaling/Stat3/Socs3 in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia progression and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma development 21490101_Our study demonstrates that the alpha-IFN resistance of HCV core mutants is attributable to upregulated overexpression of the cellular interferon signal attenuator SOCS3 and that this upregulation is caused by overexpression of interleukin-6. 21545585_gene expression induced by live non-pathogenic Lactobacillus and Streptococcus 21547863_concurrent strength and endurance training reduces fat mass and serum leptin and the ratio leptin/fat mass without significant effects on vastus lateralis OB-Rb protein expression; training does not increase the basal expression of SOCS3 protein in humans 21590492_our findings suggest that SOCS3 inactivation by promoter hypermethylation is mutually exclusive to EGFR activation in gliomas and preferentially promotes glioma cell invasion through STAT3 and FAK activation. 21734367_SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 can prevent tubulointerstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TEMT, which may be connected with the activation of STAT1 and STAT3 21765854_Eosinophils are able to transcribe and translate SOCS3 protein and can contribute to the regulation of the Th1/Th2 balance through SOCS3 production. 21876460_Deregulated expression of pSTAT3 and SOCS3 might possess potential roles in the development and progression of human cutaneous melanoma. 21892197_The polymorphism rs4969168 within or near the SOCS3 gene has a significant effect in the Han nationality, while rs9892622 was associated with obesity in Uygur and Kazakh nationalities in Xinjiang of China. 21898505_Glucocorticoids interfere with IL-6-induced expression of the feedback inhibitor SOCS3, thereby leading to enhanced expression of acute-phase genes in hepatocytes. 21934357_Epigenetic dysregulation of the SOCS3 gene may interfere with the cellular response to the complex cytokine network thus supporting survival and expansion of multiple myeloma cells. 22075701_SOCS3 transgene expression in immature B cells regulates both the maintenance of the germinal center and IgE affinity maturation during a T cell-dependent immune response. 22084247_a new biological activity for CUEDC2 as the regulator of JAK1/STAT3 signaling and the mechanism by which SOCS3 has been linked to suppression of the JAK/STAT pathway 22093833_SOCS3 is an important factor for lipid metabolism and a potential drug-target for treatment of widespread obesity. 22260693_One important aspect of SOCS-3 functionality is its role as the specificity determinant within an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex which targets cellular substrates for polyubiquitylation and proteasomal degradation. [Review] 22266116_TNF-alpha inhibits insulin signaling by increased phosphorylation of IRS-1(Ser307) and insulin receptor(Tyr960), and by increasing SOCS3 levels, all of which block normal insulin signal transduction. 22294695_keratinocytes have a cell type-specific impaired capacity to up-regulate SOCS3 which may crucially determine the course of chronic inflammatory skin diseases. 22311708_ERK-dependent regulation of transcriptional activity that requires codependent activation of multiple transcription factors within the same region of the SOCS-3 gene promoter. 22342841_SOCS3 bound and directly inhibited the catalytic domains of JAK1, JAK2, and TYK2 but not JAK3 via an evolutionarily conserved motif unique to JAKs. Mutation of this motif led to the formation of an active kinase that could not be inhibited by SOCS3. 22425648_SOCS3 expression in the paraventricular nucleus was inversely related to serum leptin. 22487676_SOCS1 and SOCS3 mRNA and protein expression was significantly increased in the nasal mucosa and mononuclear leukocytes of patients with mild and moderate/severe persistent perennial allergic rhinitis. 22488585_SOCS3 epigenetic silencing was occasionally detected in immunodeficiency-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. 22532676_IFN-gamma-induced phosphorylation of STAT-1 and transcription of CIITA were suppressed in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-inoculated endothelial cells via a mechanism involving SOCS3 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 3). 22535619_High SOCS3 expression is associated with mucosal relapse in ulcerative colitis. 22547065_Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 inhibits breast tumor kinase activation of STAT3. 22560881_results suggest modulation of SOCS3 expression may represent a novel mechanism through which FXR activation could selectively affect cytokine bioactivity in inflammation response 22574771_review of biology and mechanism of action of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 [review] 22575502_these results demonstrate that in results demonstrate that in human endothelial cells resistin up-regulates SOCS3 expression and activates STAT3 transcription factor. 22576756_both SOCS-3 mRNA and SOCS-3 protein are expressed in human arthritic chondrocytes and affect cellular responses involved in cartilage pathology. 22587677_no significant difference in mRNA expression in adipose and placental tissue obtained from pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes mellitus 22591635_SOCS3 protein is an important regulator of cytokine signaling associated with inflammatory bowel disease and IBD-colorectal cancer[review] 22613986_present study demonstrates that Ang II induces angiogenic factors production partly via AT1/ JAK2/STAT3/SOCS3 signaling pathway in MHCC97H cells 22739025_induction of DNMT1 expression in the chronically inflamed colon may release IL-6 signaling towards signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 from inhibition through SOCS3 increasing the propensity to malignant transformation 22739986_the depletion of SOCS3, as well as the chemical inactivation of PI3K activity in psoriatic keratinocytes, definitively unveils the role of PI3K/AKT cascade on the resistance of diseased keratinocytes to apoptosis. 22745793_The results demonstrate that SOCS1 and SOCS3 each play a functionally distinct role in modulating TLR3, JAK/STAT, and CXCR4/CXCR7 signaling in hMSC. 22768656_High SOCS3 is associated with idiopathic short stature. 22787435_Bcr-Abl may critically requires tyrosine phosphorylation of SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 to mediate tumorigenesis when these SOCS proteins are present in cells. 22820139_Over-expression of SOCS-3 mRNA from peripheral blood of NHL patients correlates with advanced disease and poor response to treatment. 22848642_LPS induces upregulation of MCP-1 in DSCs, which may play a critical role in inhibiting the cytotoxicity of NK cells partly by promoting SOCS3 expression 22925925_SOCS3 is involved in repressing the M1 proinflammatory phenotype, thereby deactivating inflammatory responses in macrophages. 22951153_Obese subjects showed a decreased ability to produce IFN-alpha and IFN-beta in response to TLR ligands; this response was associated with increased basal levels of SOCS3 but not SOCS1. 22957141_Reduced expression of miR122 contributes to decreased SOCS3 expression via promoter methylation. 23028842_SOCS3 functions as a tumor suppressor gene in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with relevance on proliferation and invasion processes. 23030674_SOCS3 expression is increased in human bladder epithelial cells when stimulated with a uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain. 23033269_Higher SOCS3 expression in human T cells favors T helper type 17 cells. Therefore, increased SOCS3 expression in human tuberculosis may reflect polarization toward IL-17-expressing T cells as well as T-cell exhaustion marked by reduced proliferation. 23046072_results suggested that there is no marked association between SOCS3 gene promoter region polymorphisms and the risk of developing metastatic colorectal cancer 23108375_Using two renal cellular models&SOCS-3 siRNA knockdown,we studied SOCS-3 effects on oncostatin M-induced STAT activation, differentiation and proliferation.SOCS-3 knockdown resulted in enhanced pSTAT1/3 phosphorylation & epithelial diff'n. 23111066_Data indicate that knockdown of HDAC8 resulted in the increased expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3, and overexpression of SOCS1 and SOCS3 significantly inhibited cell growth and suppressed JAK2/STAT signaling. 23133602_In HCV-HIV coinfected patients treated with PegIFNalpha and ribavirin, SVR is associated with IL28B rs8099917 polymorphism; HCV treatment-induced neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are associated with SOCS3 rs4969170 polymorphism 23152563_SOCS3 profoundly enhances Fas signal-induced apoptosis by suppression of NF-kappaB-dependent Bfl-1 expression. 23154639_The colon epithelial cell line Caco-2 was stimulated with interferon gamma, interleukin -4 prostaglandin E(2) to allow correlations between SOCS3 expression with STAT1, STAT6 and cyclic amp signaling. 23164156_Intrahepatic SOCS1/3 mRNA levels are associated with cirrhosis but do not predict virological response to therapy in chronic hepatitis C. 23185530_Myocardial infarction is distinguished by the up-regulation of SOCS3 and FAM20A genes within first days in the vast majority of patients. 23206599_In this review SOCS3 (and PTEN) were found to act as negative regulators in such processes as cytoskeleton assembly and axon regeneration. 23226414_The present study investi |
ENSMUSG00000053113 |
Socs3 |
57.150214 |
14.7198665589 |
3.879693 |
0.366307904 |
126.469868 |
0.00000000000000000000000000002426582221530477488773681461957017863657730641500549040764148576792326173341652825743430810234713135287165641784667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000305339757798719935783963298493008313511367623579132342093025413326920597628481857110926966925035230815410614013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
109.1861620 |
23.8939368 |
7.4871587 |
1.4980582 |
| ENSG00000184574 |
57121 |
LPAR5 |
protein_coding |
Q9H1C0 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), a mediator of diverse cellular activities. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the rhodopsin class of G protein-coupled transmembrane receptors. This protein transmits extracellular signals from lysophosphatidic acid to cells through heterotrimeric G proteins and mediates numerous cellular processes. Many G protein receptors serve as targets for pharmaceutical drugs. Transcript variants of this gene have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:57121; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; behavioral response to pain [GO:0048266]; positive regulation of CREB transcription factor activity [GO:0032793] |
16774927_GPR92 is proposed as a fifth LPA receptor, LPA5, which likely has distinct physiological functions in view of its expression pattern. 18499677_FPP and NAG play a role in the sensory nervous system through activation of GPR92 19366702_Four residues involved in ligand recognition in LPA(5) were identified as follows: R2.60N mutant abolished receptor activation, whereas H4.64E, R6.62A, and R7.32A greatly reduced receptor activation. 19860625_Data show that CLL cells express LPA receptors LPA(1-5) and VEGF receptors, and the plasma levels of VEGF are elevated in CLL patients. 20069565_LPA4 and LPA5 receptors induce osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells 21464938_LPA5 is a bona fide LPA receptor on human mast cells responsible for the majority of LPA induced MIP-1beta release. 21832242_It was shown that lysophosphatidic acid 5 receptor transactivated the epidermal growth factor receptor and that inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor blocked lysophosphatidic acid 5 receptor-dependent activation of NHE3. 24632199_These results suggest that LPA5 may act as a negative regulator of cellular responses in mouse fibroblast 3T3 cells, similar to the case for LPA1. 24676544_MMP-2 and MMP-9 were found in HT1080L5 cells, in comparison with control cells. These results suggest that LPA signaling via LPA5 negatively regulates the cell motile and invasive activities of human sarcoma cells. 25294670_Down-regulation of LPA receptor 5 contributes to aberrant LPA signalling in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 25849892_These results suggest that the diverse roles of LPA4, LPA5 and LPA6 are involved in the activation of tumor progression in pancreatic cancer cells. 29309788_These results suggest that the cell motile activity is regulated through the induction of LPA5 by phorbol ester and anticancer drug treatments in A375cells. 29409686_It signaling may play a key role in the mechanisms underlying neuropathic pain following demyelination in the brain. 30093116_LPAR2 and LPAR5 regulate cellular functions during tumor progression in fibrosarcoma HT1080 cells. 31231367_LPA5 Is an Inhibitory Receptor That Suppresses CD8 T-Cell Cytotoxic Function via Disruption of Early TCR Signaling. 31362892_LPAR5 expression was elevated in A375cells treated with anticancer drugs. The high cell survival of highly migratory A375cells is associated with the low LPAR5 expression. The cell survival of A375cells treated with anticancer drugs was increased by LPA5 knockdown. 31902939_Downregulation of LPAR5 expression can inhibit the physiological process of PTC, and this phenomenon is related to the PI3K/AKT pathway and EMT. 32920014_Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 5 transactivation of TGFBR1 stimulates the mRNA expression of proteoglycan synthesizing genes XYLT1 and CHST3. 32964980_LPAR5 stimulates the malignant progression of non-small-cell lung carcinoma by upregulating MLLT11. 33452232_Lysophosphatidic acid mediates the pathogenesis of psoriasis by activating keratinocytes through LPAR5. 33540491_LPAR5 promotes thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by activating class IA PI3K catalytic subunit p110beta. 33975030_Control of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability by Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 5. 34662522_Interference with lysophosphatidic acid receptor 5 ameliorates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury by inactivating NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome signaling. 36199069_LPAR5 confers radioresistance to cancer cells associated with EMT activation via the ERK/Snail pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000067714 |
Lpar5 |
88.299569 |
3.1948057177 |
1.675728 |
0.190740785 |
78.267784 |
0.00000000000000000089977386336353634548750159750758048144495243163423032692338487947836256353184580802917480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000007532990483973793734833005590613708061945430172711129362950188692593656014651060104370117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
134.7333032 |
16.2697344 |
42.4033758 |
4.1012180 |
| ENSG00000184584 |
340061 |
STING1 |
protein_coding |
Q86WV6 |
FUNCTION: Facilitator of innate immune signaling that acts as a sensor of cytosolic DNA from bacteria and viruses and promotes the production of type I interferon (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta) (PubMed:18724357, PubMed:18818105, PubMed:19433799, PubMed:19776740, PubMed:23027953, PubMed:23910378, PubMed:23747010, PubMed:29973723, PubMed:30842659, PubMed:35045565). Innate immune response is triggered in response to non-CpG double-stranded DNA from viruses and bacteria delivered to the cytoplasm (PubMed:26300263). Acts by binding cyclic dinucleotides: recognizes and binds cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP), a second messenger produced by bacteria, and cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), a messenger produced by CGAS in response to DNA virus in the cytosol (PubMed:21947006, PubMed:23258412, PubMed:23707065, PubMed:23722158, PubMed:26229117, PubMed:23910378, PubMed:23747010, PubMed:30842659). Upon binding of c-di-GMP or cGAMP, STING1 oligomerizes, translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum and is phosphorylated by TBK1 on the pLxIS motif, leading to recruitment and subsequent activation of the transcription factor IRF3 to induce expression of type I interferon and exert a potent anti-viral state (PubMed:22394562, PubMed:25636800, PubMed:29973723, PubMed:30842653, PubMed:35045565). In addition to promote the production of type I interferons, plays a direct role in autophagy (PubMed:30568238, PubMed:30842662). Following cGAMP-binding, STING1 buds from the endoplasmic reticulum into COPII vesicles, which then form the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) (PubMed:30842662). The ERGIC serves as the membrane source for WIPI2 recruitment and LC3 lipidation, leading to formation of autophagosomes that target cytosolic DNA or DNA viruses for degradation by the lysosome (PubMed:30842662). The autophagy- and interferon-inducing activities can be uncoupled and autophagy induction is independent of TBK1 phosphorylation (PubMed:30568238, PubMed:30842662). Autophagy is also triggered upon infection by bacteria: following c-di-GMP-binding, which is produced by live Gram-positive bacteria, promotes reticulophagy (By similarity). Exhibits 2',3' phosphodiester linkage-specific ligand recognition: can bind both 2'-3' linked cGAMP (2'-3'-cGAMP) and 3'-3' linked cGAMP but is preferentially activated by 2'-3' linked cGAMP (PubMed:26300263, PubMed:23910378, PubMed:23747010). The preference for 2'-3'-cGAMP, compared to other linkage isomers is probably due to the ligand itself, whichs adopts an organized free-ligand conformation that resembles the STING1-bound conformation and pays low energy costs in changing into the active conformation (PubMed:26150511). May be involved in translocon function, the translocon possibly being able to influence the induction of type I interferons (PubMed:18724357). May be involved in transduction of apoptotic signals via its association with the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3TBT3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18724357, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18818105, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19433799, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19776740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21947006, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22394562, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23027953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23258412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23707065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23722158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23747010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23910378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25636800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26150511, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26229117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26300263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29973723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30568238, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30842653, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30842659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30842662, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35045565}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Antiviral activity is antagonized by oncoproteins, such as papillomavirus (HPV) protein E7 and adenovirus early E1A protein (PubMed:26405230). Such oncoproteins prevent the ability to sense cytosolic DNA (PubMed:26405230). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26405230}. |
3D-structure;Autophagy;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a five transmembrane protein that functions as a major regulator of the innate immune response to viral and bacterial infections. The encoded protein is a pattern recognition receptor that detects cytosolic nucleic acids and transmits signals that activate type I interferon responses. The encoded protein has also been shown to play a role in apoptotic signaling by associating with type II major histocompatibility complex. Mutations in this gene are the cause of infantile-onset STING-associated vasculopathy. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2014]. |
hsa:340061; |
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; endosome [GO:0005768]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; peroxisome [GO:0005777]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; serine/threonine protein kinase complex [GO:1902554]; STING complex [GO:1990231]; 2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP binding [GO:0061507]; cyclic-di-GMP binding [GO:0035438]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; activation of innate immune response [GO:0002218]; autophagosome assembly [GO:0000045]; cellular response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0071360]; cellular response to interferon-beta [GO:0035458]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0002230]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; positive regulation of protein binding [GO:0032092]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type I interferon production [GO:0032481]; positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060340]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; reticulophagy [GO:0061709] |
18724357_STING (TMEM173) is an endoplasmic reticulum adaptor protein that facilitates innate immune signaling 18724357_identification, following expression cloning, of a molecule (STING; stimulator of interferon genes) that appears essential for effective innate immune signalling processes 18818105_results suggest MITA is a critical mediator of virus-triggered IRF3 activation and IFN expression and further demonstrate the importance of certain mitochondrial proteins in innate antiviral immunity. 19240791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19285439_E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF5 interacted with MITA in a viral-infection-dependent manner 19433799_dimerization of ERIS was critical for self-activation and subsequent downstream signaling 21170271_Cellular reactive oxygen species inhibit MPYS induction of IFNbeta 21248775_R71H-G230A-R293Q haplotype MPYS exhibits a > 90% loss in the ability to stimulate IFNbeta production 21892174_DDX41 is an additional DNA sensor that depends on STING to sense pathogenic DNA. 22312431_a new mechanism used by CoVs in which CoV PLPs negatively regulate antiviral defenses by disrupting the STING-mediated IFN induction 22394560_study now shows that in response to cytosolic double-stranded DNA, the C-terminal tail of STING provides a scaffold to assemble IRF3 and TBK1, which leads to TBK1-dependent phosphorylation of IRF3 22394562_results suggest that STING functions as a scaffold protein to specify and promote the phosphorylation of IRF3 by TBK1. 22470840_results indicate that interaction between the pattern recognition receptor RIG-I and the adapter molecule STING, is a major contributor to elicit immunological responses involving the type 1 interferons in neurons following JEV infections 22705373_We elucidate the structural features of the cytosolic c-di-GMP binding domain (CBD) of STING and its complex with c-di-GMP 22706339_virus-cell fusion is sensed by the innate immune system and activates a STING-dependent signaling pathway that leads to the production of type I interferon and molecules encoded by interferon-stimulated genes 22728658_Guanines of c-di-GMP stack against the phenolic rings of a conserved tyrosinein STING, and mutations at the c-di-GMP binding surface reduce nucleotide binding and affect signaling 22728659_report here the crystal structures of the STING cytoplasmic domain and its complex with c-di-GMP, thus providing the structural basis for understanding STING function 22728660_In response to c-di-GMP binding, two surface loops, which serve as a gate and latch of the cleft formed by the dimeric STING(CTD), undergo rearrangements to interact with the ligand 22745133_TRIM32 protein modulates type I interferon induction and cellular antiviral response by targeting MITA/STING protein for K63-linked ubiquitination 22761576_we identified MITA as a novel host target of dengue virus protease 22911572_Hepatitis C virus NS4B suppresses RIG-I-mediated IFN-beta production signaling through a direct protein interaction with STING. 23055924_study describes the mechanism of inhibition of type I IFN production by Dengue virus in primary cells and identify the adaptor molecule STING as a target of the DENV NS2B3 protease complex 23478444_STING instigates cytoplasmic DNA-mediated cellular defense gene transcription and facilitates adoptive responses that are required for protection of the host. 23542348_Mechanistic studies indicated that NS4B disrupts the interactions between STING/MITA and TBK1, an additional mechanism for HCV evasion of host interferon responses. 23585680_study identified STING as a direct receptor for 6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA) leading to TANK-binding kinase 1 and IFN regulatory factor 3 signaling; the ability to sense DMXAA was restricted to murine STING; human STING failed to bind to or signal in response to DMXAA 23631912_Chlamydia induces STING-mediated IFN responses through the detection of c-di-AMP in the host cell cytosol and propose that c-di-AMP is the ligand predominantly responsible for inducing such a response in Chlamydia-infected cells. 23707065_The hSTING variants have evolved to distinguish conventional (3'-5') cyclic dinucleotides from the noncanonical cyclic dinucleotide produced by mammalian cGAS. 23722158_cGAS produces a 2'-5'-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING 23910378_Study shows that human hSTING(H232) adopts a 'closed' conformation upon binding c[G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] and its linkage isomer c[G(2',5')pA(2',5')p], as does mouse mSting(R231) on binding c[G(2',5')pA(3',5')p], c[G(3',5')pA(3',5')p] 24116191_Data indicate that cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is important for the stimulator of interferon genes (STING)-dependent immune activation 24119841_After activation and trafficking, STING is phosphorylated by UNC-51-like kinase (ULK1). This occurs following ULK1 dissociation from its repressor AMPK and was found to be triggered by cGAS-generated cyclic dinucleotides. 24139400_This study provides a mechanistic explanation for abortive HTLV-1 infection of monocytes and reports a link between SAMHD1 restriction, HTLV-1 reverse transcription intermediate sensing by STING, and initiation of IRF3-Bax driven apoptosis. 24204993_Single nucleotide polymorphisms of human STING is associated with innate immune response to cyclic dinucleotides. 24239807_Data indicate that NF-kappaB leads to elevated expression of TNF-alpha sensitizing mediator of IRF3 activation (MITA) induced cell death. 24391220_An alternatively spliced isoform of MITA lacking exon 7, shares the N-terminal portion aa 1-253 with MITA but has a unique 30-aa sequence at the carboxyl terminal. MRP is as a dominant negative regulator of MITA-mediated induction of IFN production. 24449861_STING is stable in cancer-derived HEp-2 or HeLa cells infected with wild-type HSV-1 but is degraded in cells infected with mutants lacking the genes encoding functional infected cell protein 0 (ICP0), ICP4, or the US3 protein kinase. 24614210_This study demonstrates that E2 proteins of high risk human papillomavirus reduce STING and IFN-kappa transcription. 24929887_the molecular mechanisms of MITA-mediated signal transduction and regulation 25007740_The mechanism of double-stranded DNA sensing through the cGAS-STING pathway. 25029335_STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI) is an autoinflammatory disease caused by gain-of-function mutations in TMEM173. 25212897_antagonism of STING signalling during RNA virus infection. 25297994_The cGAS/STING/TBK1/IRF3 cascade was not a direct target of viral antihost strategies, and authors found no evidence that adenovirus stimulation of the cGAS/STING DNA response had an impact on viral replication efficiency. 25299331_In an expression screen for proteins that can activate the IFNB1 promoter, authors identified the ER-associated protein ZDHHC1 as a positive regulator of virus-triggered, MITA/STING-dependent immune signaling. 25311841_PLP2-TM interacts with the key autophagy regulators, LC3 and Beclin1, and promotes Beclin1 interaction with STING, the key regulator for antiviral IFN signaling, to negatively regulate antiviral innate immunity. 25401470_These findings highlight the key role of STING in activating both the innate and adaptive immune responses and implicate aberrant STING activation in features of human lupus. 25425575_Studies in THP-1 knockout cells revealed that the recognition of RNA:DNA hybrids is completely attributable to the cGAS-STING pathway. 25459004_STING (for stimulator of interferon genes) has been found to be seminal for controlling cytosolic-DNA induced cytokine production, and may be responsible for a wide variety of inflammatory diseases 25505063_Hepatitis B virus Pol has a role in suppression of IFN-beta production by direct interaction with STING and subsequent disruption of its K63-linked ubiquitination, providing a new mechanism to counteract the innate DNA-sensing pathways. 25636800_findings show MAVS and STING harbor 2 conserved serine and threonine clusters that are phosphorylated by IKK and/or TBK1 in response to stimulation; results reveal phosphorylation of innate adaptor proteins is an essential and conserved mechanism that selectively recruits IRF3 to activate the type I IFN pathway 25639870_STING constitutes a critical component of the host early response to intestinal damage and is essential for invigorating tissue repair pathways that may help prevent tumorigenesis. 25790474_Data identifies a single amino acid change in STING that leads to its constitutive activation of downstream signaling, by increasing its propensity to dimerize and associate with TBK1. 25792739_stimulation of STING-dependent IRF3 activation by UV is due to apoptotic signaling-dependent disruption of ULK1 (Unc51-like kinase 1), a pro-autophagic protein that negatively regulates STING 25815785_findings demonstrate a novel regulatory circuit in which STING and TBK1 reciprocally regulate each other to enable efficient antiviral signaling activation, and PPM1A dephosphorylates STING and TBK1 25947293_Results reveal a critical role of STING in regulating dsDNA-triggered activation of the JAK1-STAT1 signaling in B cells and highlight the close associations of STING low-expression with JAK1-STAT1 signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus B cells. 26058929_Chronic HBV infected patients were unable to express appropriate levels of STING. 26150511_Cyclic GMP-AMP, but not its linkage isomers, adopts an organized free-ligand conformation that resembles the STING-bound conformation and pays low entropy and enthalpy costs in converting into the active conformation. 26199418_Gammaherpesviruses encode inhibitors that block cGAS-STING-mediated antiviral immunity. 26311870_Knockout of cGAS and STING Rescues Virus Infection of Plasmid DNA-Transfected Cells. 26315534_Studies suggest that the transmembrane protein 173 (STING) pathway is the main innate immune pathway involved in sensing of tumors, and its endogenous activation in APCs leads to subsequent T cell priming against tumor-associated antigens. 26468527_These results demonstrate a novel hepatitis C virus genotype-specific inhibition of the STING-mediated host antiviral immune response via the viral NS4B protein. 26471009_The cGAS-STING signaling pathway is required for not only the innate immune response against HBV but also the suppression of HBV assembly. 26593864_The study demonstrates the lack of association between the presence of systemic autoimmune diseases and mutations in exon 5 of the TMEM173 gene. 26603901_Studies indicate that the STING (stimulator of interferon genes)-controlled innate immune pathway has provided insight for treating autoinflammatory disease and cancer. 26738286_STING(sv) inhibited the activity of the interferon (IFN)-beta promoter. 26867174_cGAS and STING are intracellular sensors that activate the interferon pathway in response to virus infection. [review] 26893169_A STING-dependent, cGAS-independent pathway important for full interferon production and antiviral control of enveloped RNA viruses. 26980676_STING-regulated pathways underlie the pathogenesis of many diseases including infectious diseases and cancers. It has also become evident from these studies that STING is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer. 27125983_These results suggest that pDCs sense cytosolic DNA and cyclic dinucleotides via the cGAS-STING pathway and that targeting this pathway could be of therapeutic interest. 27190175_These data uncover a promycobacterial role for STING-dependent OASL production during Mycobacterium leprae infection that directs the host immune response toward a niche that permits survival of the pathogen. 27234299_Human herpesvirus 1 ICP27 interacted with TBK1 and STING in a manner that was dependent on TBK1 activity and the RGG motif in ICP27 and inhibited type I IFN induction through the cGAS-STING-TBK1 pathway in human macrophages. 27324217_Immune activation of STING requires palmitoylation at the Golgi. 27334590_Primary human endothelial cells mount robust type I interferon responses to human cytomegalovirus that are dependent upon cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), STING, and interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) signaling. 27362340_We discuss three newly described monogenic autoinflammatory diseases [deficiency of adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2), a subtype of macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), and stimulator of interferon genes (STING)-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI)], discuss the possibilities of somatic mosaicism and digenic inheritance, and give an update on new concepts in pathways involved in familial Mediterranean fever 27512060_The regulation of STING via RIG-I-mediated innate immune sensing. 27553710_Studied association of genetic variants of the MAVS, MITA and MFN2 genes with leprosy in Han Chinese from Southwest China; found no association between the variants and susceptibility to leprosy. 27554814_Efficacy of the Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib in the treatment of vasculopathy associated with TMEM173-activating mutations in 3 children. 27566796_A heterozygous gain-of-function mutation in STING can cause familial chilblain lupus. 27696330_cGAs recognizes bacterial/viral DNA, and is a strong activator of STING that can further activate IRF3 and subsequent type I interferon production. (Review) 27706894_Essential roles of the cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway. [review] 27814372_Multivariate analysis supported TMEM173 as an independent prognostic factor. 27835584_these studies demonstrate that transcription factors CREB and c-Myc maintain the transcriptional activity of STING 27902332_cGAS-STING pathway plays a role in the surveillance of hepatitis B virus infection. 27927967_We conclude that the R71H-G230A-R293Q (HAQ) of TMEM173 is a null TMEM173 allele. 28077645_In the present study, the authors found that herpes simplex virus 1 tegument protein UL41 was involved in counteracting the cGAS/STING-mediated DNA-sensing pathway. 28087229_Structural analysis indicates that the 3 disease-associated mutations at positions 206, 281, and 284 of the STING protein define a novel cluster of amino acids with functional importance in the regulation of type I interferon signaling 28119118_Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 Tax protein impairs K63-linked ubiquitination of STING and disrupted the interactions between STING and TBK1 to evade host innate immunity. 28132838_Human Cytomegalovirus tegument protein UL82 negatively regulates STING-mediated signaling. 28194029_Data show that both cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) and interferon-gamma inducible protein 16 (IFI16) are required for the activation of membrane protein STING (STING) and an innate immune response to exogenous DNA and DNA viruses. 28254948_a critical role of p38-mediated USP21 phosphorylation in regulating STING-mediated antiviral functions and identifies p38-USP21 axis as an important pathway that DNA virus adopts to avoid innate immunity responses. 28302626_The mitochondrial damage-cGAS-STING-IRF3 pathway is critically involved in metabolic stress-induced endothelial inflammation. 28366813_In the current study, we studied the role of MITA (Mediator of IRF3 Activation), a regulator of innate immunity, in the regulation of autophagy and its implication in cell death of breast cancer cells. Here, we report that MITA inhibits the fusion of autophagosome with lysosome as evident from different autophagy flux assays 28475463_TheTREX1 and STING, which are opposing regulators of the cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. 28484079_STING, a critical innate sensor, also functions intrinsically in cells of the adaptive immune system to inhibit proliferation. 28592536_The authors found that the herpes simplex virus 1 UL46 protein interacts with and colocalizes with STING. 28625530_this review summarizes important features of the STING activation pathway and recent highlights about the role of STING in bacterial infections by Chlamydia, Listeria, Francisella, Brucella, Shigella, Salmonella, Streptococcus, and Neisseria genera, with a special focus on mycobacteria. 28639100_summarize recent findings that have pointed towards the STING pathway as an innate immune sensing mechanism driving type I interferon production in the tumor context 28647346_our data provide an important insight into STING-mediated induction of type I and III IFNs and subsequent antiviral signaling pathways that regulate VZV replication in human dermal cells. 28704551_STING activated an antiviral/type I interferon response with live but not killed S. aureus. 28717041_pharmacological activation of STING in macrophages and hepatocytes induces host innate responses that can efficiently control hepatitis B virus replication. Hence, despite not playing a significant role in host innate immune response to HBV infection of hepatocytes, STING is potentially a valuable target for immunotherapy of chronic hepatitis B. 28720717_The DNA binding domain of Ku70 was essential for formation of the Ku70-STING complex. Knocking down STING in primary human macrophages inhibited their ability to produce IFN-lambda1 in response to transfection with DNA or infection with the DNA virus HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus-2); STING mediates the Ku70-mediated IFN-lambda1 innate immune response to exogenous DNA or DNA virus infection. 28724326_STING serves to detect - and promote immune defense against - DNA viruses and intracellular bacteria, as described in its initial discovery. The role of STING has since been expanded to include tumor surveillance and immune responses to cancer; indeed, defective STING responses are associated with certain cancers. 28806404_both IL-6 and RIG-I are downstream molecules of STING along the DNA sensor pathway. 28939760_NEMO was critically involved in the cGAS-STING pathway. 28947539_study identifies the AIM2 inflammasome and cGAS/IFI16-STING-type I IFN pathway as a novel mechanism for host innate immunity to the ALVAC vaccine vector. 29106945_STING-IRF3 pathway promotes hepatocyte injury and dysfunction by inducing inflammation and apoptosis and by disturbing glucose and lipid metabolism. 29135982_using a murine HNSCC model that does not express STING, we demonstrate that STING ligands are an effective therapy regardless of expression of STING by the cancer cells 29143896_an electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) attach to the GAS motif on the human STING promoter region. This indicates that IFN-gamma/Janus kinases/STAT1 signaling is essential for the STING upregulation in human keratinocytes. 29263110_Cells of human individuals carrying HAQ TMEM173, which encodes a common hypomorphic variant of STING, were largely or partly defective in inducing type I IFNs and proinflammatory cytokines upon infection. 29263267_C11 depends on signaling through STING to produce antiviral type I interferon, which further supports its potential as a therapeutic drug or research tool. 29263269_This study demonstrates that the HCMV tegument protein pp65 inhibits IFN-beta production by binding and inactivating cGAS early during infection. In addition, this inhibitory activity specifically targets cGAS, since it can be bypassed via the addition of exogenous cGAMP, even in the presence of pp65. Notably, STING proteasome-mediated degradation was observed in both the presence and absence of pp65. 29298342_The cGAS-STING cascade contributes to antibacterial defense against L. pneumophila in mice and men, and provides important insight into how the common HAQ TMEM173/STING variant affects antimicrobial immune responses and susceptibility to infection. 29317664_Data show that human cytomegalovirus (HCMV; human betaherpesvirus 5) glycoprotein US9 inhibits the IFN-beta response by targeting the mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) and stimulator of interferon genes (STING)-mediated signaling pathways. 29367762_The STING signaling pathway may be recurrently suppressed by a number of mechanisms in a considerable variety of malignant disease and be a requirement for cellular transformation. 29456253_recent progress on the regulation of the cGAS-MITA/STING-mediated innate immune response to DNA viruses at the organelle-trafficking, post-translational and transcriptional levels. 29491158_STING is shown to mediate immune activation in response to MVA, but not in response to virulent poxvirus vaccinia virus strains or other virulent poxviruses, which prevent STING activation and DNA sensing during infection and after DNA transfection. 29496741_Here, we report that the ubiquitin-binding selective autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1 is essential for DNA- and cGAMP-stimulated degradation of STING. 29547894_A novel transcript isoform of STING designated STING-beta that sequesters cGAMP and dominantly inhibits innate nucleic acid sensing. 29581256_PUMA promotes the cytosolic release of mitochondrial DNA and activation of the DNA sensors DAI/Zbp1 and STING, leading to enhanced RIP3 and MLKL phosphorylation in a positive feedback loop. 29632140_The HAQ/HAQ TMEM173 genotype may contribute to the slower disease progression characteristic of LTNPs. 29662124_STAG2 deficiency induces interferon responses via cGAS-STING pathway and restricts virus infection. 29694889_Pro-inflammation Associated with a Gain-of-Function Mutation (R284S) in the Innate Immune Sensor STING. 29769207_SOX2 dampens the immunogenicity of HNSCC by targeting the STING pathway for degradation. The nanosatellite vaccine offers a novel and effective approach to enhance the adjuvant potential of STING agonist and break cancer tolerance to immunotherapy. 29793952_This study demonstrated that HSV-1 tegument protein VP22 counteracts the cGAS/STING-mediated DNA-sensing antiviral innate immunity signaling pathway by inhibiting the enzymatic activity of cGAS. 29899553_We present physiological evidence that UBXN3B positively regulates stimulator-of-interferon genes (STING) signaling. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that UBXN3B interacts with both STING and its E3 ligase TRIM56, and facilitates STING ubiquitination, dimerization, trafficking, and consequent recruitment and phosphorylation of TBK1. 29915078_data demonstrate that numerous RNA viruses evade cGAS/STING-dependent signaling and affirm the importance of this pathway in shaping the host range of ZIKV. 29976662_Our studies indicate that the (extracellular vesicles) EVs released by HSV-1-infected cells carry innate immune components such as STING and other host and viral factors; they can activate innate immune responses in recipient cells and inhibit HSV-1 replication. The implication of these data is that the EVs released by HSV-1-infected cells could control HSV-1 dissemination promoting its persistence in the host. 30061387_identified nitro-fatty acids as endogenously formed inhibitors of STING signaling and propose for these lipids to be considered in the treatment of STING-dependent inflammatory diseases. 30193098_This non-canonical activation of STING is mediated by the DNA binding protein IFI16, together with the DNA damage response factors ATM and PARP-1. 30297358_Ectopic expression of STING in KRAS - LKB1 (KL) mutant cells engages IRF3 and STAT1 signaling downstream of TBK1 and impairs cellular fitness, due to the pathologic accumulation of cytoplasmic mitochondrial dsDNA associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. 30355498_IFNalpha-mediated deregulation of mitochondrial metabolism and impairment of autophagic degradation, leading to cytosolic accumulation of mtDNA that is sensed via stimulator of interferon genes (STING) to promote induction of autoinflammatory dendritic cells. 30368497_STING Allele 293Q Is Associated with Protection from Aging-Associated Diseases. 30463579_this study demonstrated that the Increased levels of STING are detected following traumatic brain injury. 30540941_TMED2 associates with MITA only upon viral stimulation, and this process potentiates MITA activation by reinforcing its dimerization and facilitating its trafficking. 30643259_Loss of STIM1 induced spontaneous activation of the STING-TBK1-IRF3 pathway to activate type I IFN responses under sterile conditions in both murine and human cells. Mechanistically, STIM1 directly interacted with STING to retain it in an inactive state on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Accordingly, strong resistance to viral infections observed in STIM1 knockout cells and animals. 30705050_Unlike acute pancreatitis, STING activation is protective in CP. STING signalling is important in regulating adaptive immune responses by diminishing generation of IL-17A during CP and presents a novel therapeutic target for CP. 30728498_vaccinia virus poxin is critical for evasion of cGAS-STING immunity 30816302_STING signaling remodels the tumor microenvironment by antagonizing myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion. 30842659_cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length STING from human and chicken in the inactive dimeric state (about 80 kDa in size), as well as cGAMP-bound chicken STING in both the dimeric and tetrameric states 30842662_Autophagy induction via STING trafficking is a primordial function of the cGAS pathway 30886058_This data uncover a critical IFN-independent function of STING that regulates calcium homeostasis, ER stress, and T cell survival. 30919991_cAIMP administration in humanized mice induces a chimerization-level-dependent STING response. 30952515_This study identifies a new function for IL-1beta in the onset or enhancement of cell-intrinsic immunity, with important implications for cGAS-STING in integrating inflammatory and microbial cues for host defense 31026807_In silico analysis revealed that the human intron-exon gene architecture of TMEM173 (splice sites included) is preserved in other mammal species, predominantly primates, stressing the relevance of alternative splicing in regulating STING antiviral biology. 31118511_a conserved PLPLRT/SD motif within the C-terminal tail of STING mediates the recruitment and activation of TBK1 31121492_our findings disclose that STING deficiency could alleviate LPS-induced SIC in mice. Hence, targeting STING in cardiomyocytes may be a promising therapeutic strategy for preventing SIC. 31221625_The SAVI model we have generated, based on the activity of a mutant human STING protein, represents not only a model system for dissecting mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of SAVI but will also serve as a useful preclinical tool for the in vivo evaluation of therapeutics aimed at curtailing abnormal STING activity. 31332347_targeting of the HER2-AKT1 cascade augments damage-induced cellular senescence and apoptosis, and enhances STING-mediated antiviral and antitumour immunity 31346090_Identification of TMEM203 sheds light into the control of STING-mediated innate immune responses. 31362682_Aligned Expression of IFI16 and STING Genes in RRMS Patients' Blood. 31391232_YIPF5 positively regulates STING-mediated innate immune responses. 31462408_STING Signaling in Melanoma Cells Shapes Antigenicity and Can Promote Antitumor T-cell Activity. 31475926_It is shown that no Mg atoms are needed for STING and cyclic dinucleotides interaction; in fact, magnesium can in some cases obstruct the binding of a cyclic dinucleotide to STING. 31527250_Our findings reveal that PTPN1/2-mediated dephosphorylation of MITA/STING and its degradation by the 20S proteasomal pathway is an important regulatory mechanism of innate immune response to DNA virus. 31665637_STING-Mediated IFI16 Degradation Negatively Controls Type I Interferon Production. 31665638_Mitochondrial Damage Causes Inflammation via cGAS-STING Signaling in Acute Kidney Injury. 31705453_STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy in Three Children with New Clinical Aspect and Unsatisfactory Therapeutic Responses to Tofacitinib. 31745210_STING expression in monocyte-derived macrophages is associated with the progression of liver inflammation and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 31866997_Novel TMEM173 Mutation and the Role of Disease Modifying Alleles. 31874109_HPV16 drives cancer immune escape via NLRX1-mediated degradation of STING. 31896590_Relative Contributions of the cGAS-STING and TLR3 Signaling Pathways to Attenuation of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Replication. 31899324_The STING pathway in response to chlamydial infection. 31903134_Targeting the STING pathway in tumor-associated macrophages regulates innate immune sensing of gastric cancer cells. 31937780_A proapoptotic secretory phenotype is induced by activation of cGAMP synthase/stimulator of interferon response cGAMP interactor 1 (cGAS/STING) in cancer cells treated with antimitotic, accumulate micronuclei and maintain mitochondrial integrity despite intrinsic apoptotic pressure. cGAS/STING-dependent apoptotic effects are required for paclitaxel response in vivo, and are amplified by sequential adding BH3 mimetics. 31941397_Beneficial bacteria activate type-I interferon production via the intracellular cytosolic sensors STING and MAVS. 31968013_identified USP44 as a positive regulator of MITA; USP44 is recruited to MITA following DNA virus infection and removes K48-linked polyubiquitin moieties from MITA at K236, therefore prevents MITA from proteasome mediated degradation 31991682_findings show STING transcription is suppressed in 293T cells but is not driven by SV40 LT; SV40 LT does inhibit cGAS-STING interferon induction but through a mechanism distinct from other DNA virus oncogenes; results indicate that while SV40 LT can inhibit cGAS-STING interferon induction, it does so in an unanticipated ma 32046461_Epithelial Cells in Endometriosis and Adenomyosis Upregulate STING Expression. 32050879_STING expression levels in naturally immunized individuals were approximately 10% higher than those in chronic hepatitis B patients 32169869_Potent STING activation stimulates immunogenic cell death to enhance antitumor immunity in neuroblastoma. 32201077_CSK promotes innate immune response to DNA virus by phosphorylating MITA. 32238587_Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL94 Targets MITA to Evade the Antiviral Immune Response. 32240121_Hair follicle stem cell replication stress drives IFI16/STING-dependent inflammation in hidradenitis suppurativa. 32376795_Obesity and STING1 genotype associate with 23-valent pneumococcal vaccination efficacy. 32482869_Selective reactivation of STING signaling to target Merkel cell carcinoma. 32485908_Hepatitis B Virus DNA is a Substrate for the cGAS/STING Pathway but is not Sensed in Infected Hepatocytes. 32532954_The interactions between cGAS-STING pathway and pathogens. 32541831_Redox homeostasis maintained by GPX4 facilitates STING activation. 32619407_Telomere Stress Potentiates STING-Dependent Anti-tumor Immunity. 32661021_Attenuation of cGAS/STING activity during mitosis. 32668227_Structures and Mechanisms in the cGAS-STING Innate Immunity Pathway. 32673614_A novel STING1 variant causes a recessive form of STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI). 32678307_Deubiquitinase USP35 restrains STING-mediated interferon signaling in ovarian cancer. 32690950_STEEP mediates STING ER exit and activation of signaling. 32725126_A defect in COPI-mediated transport of STING causes immune dysregulation in COPA syndrome. 32753499_PPP6C Negatively Regulates STING-Dependent Innate Immune Responses. 32763501_Regulation of an adaptor protein STING by Hsp90beta to enhance innate immune responses against microbial infections. 32768338_Loss of HPV type 16 E7 restores cGAS-STING responses in human papilloma virus-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas cells. 32796076_Baculovirus Transduction in Mammalian Cells Is Affected by the Production of Type I and III Interferons, Which Is Mediated Mainly by the cGAS-STING Pathway. 32812343_Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 targeting STING transcription promotes bronchopulmonary dysplasia through regulation of CREB. 32814898_C9orf72 in myeloid cells suppresses STING-induced inflammation. 32854711_Comprehensive elaboration of the cGAS-STING signaling axis in cancer development and immunotherapy. 32887628_cGAS-STING pathway in cancer biotherapy. 32917214_Overcoming immunotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) - novel approaches and future outlook. 32926474_EGFR-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of STING determines its trafficking route and cellular innate immunity functions. 33031745_TDP-43 Triggers Mitochondrial DNA Release via mPTP to Activate cGAS/STING in ALS. 33040406_Association of homozygous variants of STING1 with outcome in human |
ENSMUSG00000024349 |
Sting1 |
530.642222 |
0.2900312605 |
-1.785720 |
0.102843076 |
298.699718 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000063250066287621366050731433637281154237846768996970288542983910433229666685568148825789039602777352275704734592668299202700260821801836970986290940636118558247058519215799687884782542823813855648040771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018305313302064536372591127511046616044886034743975827511999440808197827798444384467402706006072039713757261857855022635970191905039730522330287467906424221287154004145225627553372760303318500518798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
244.7416536 |
21.9659110 |
849.7887797 |
52.7979730 |
| ENSG00000184588 |
5142 |
PDE4B |
protein_coding |
Q07343 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes (PubMed:15260978). May be involved in mediating central nervous system effects of therapeutic agents ranging from antidepressants to antiasthmatic and anti-inflammatory agents. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10846163, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15003452, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15260978}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;cAMP;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; 3',5'-cyclic AMP degradation; AMP from 3',5'-cyclic AMP: step 1/1. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:15260978, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8392015, ECO:0000305|PubMed:9371714}. |
This gene is a member of the type IV, cyclic AMP (cAMP)-specific, cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) family. The encoded protein regulates the cellular concentrations of cyclic nucleotides and thereby play a role in signal transduction. Altered activity of this protein has been associated with schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:5142; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; excitatory synapse [GO:0060076]; gamma-tubulin complex [GO:0000930]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; cAMP binding [GO:0030552]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; cAMP catabolic process [GO:0006198]; cellular response to epinephrine stimulus [GO:0071872]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; negative regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway involved in heart process [GO:0140199]; negative regulation of relaxation of cardiac muscle [GO:1901898]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; neutrophil homeostasis [GO:0001780]; positive regulation of interleukin-2 production [GO:0032743]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell contraction [GO:0086004]; regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901841]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
11839681_Inhibition of PDE3B augments PDE4 inhibitor-induced apoptosis in a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia 14585965_TCR-dependent signaling activates PDE4B2 and enhances interleukin-2 production in T cells. 15331441_clinically relevant PDE4 and PI3K/AKT inhibitors might be useful in the treatment of Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and additional B-lymphoid malignancies with increased PDE4B expression 16293762_a mechanistic model whereby DISC1 sequesters phosphodiesterase 4B in resting cells and releases it in an activated state in response to elevated cAMP 16997058_Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction confirmed increased expression of GADD45A, BTG2, PDE4B, and CEBPD and downregulation of TOB1 in skeletal muscle intradialysis. 17088426_Compartmentalized PDE4B acts as a sink to drain cAMP from discrete locations, resulting in multiple domains with different cAMP concentrations. 17417055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17417055_PDE4B haplotype alters the genetic risk of schizophrenia in the Scottish population complements the known participation of this gene in biological processes associated with mental illness 17481393_Behavioral phenotypes of Disc1 missense mutations in mice and consequences for PDE4B 17519386_A super-short, brain specific isoform of human PDE4B, PDE4B5, was identified. It has cAMP hydrolyzing activity and is inhibited by PDE4 inhibitors. PDE4B5 bind to DISC1. The 16 N-terminal residues are identical to the corresponding residues of PDE4D6. 17823207_Altered DISC1-PDE4B interaction may thus underlie the symptoms of some cases of schizophrenia and depression.(Review) 18329668_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18329668_Our result suggests that variations at the PDE4B locus may play a significant role in the etiology of SZ in the Japanese population. 18394866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18394866_the present observations suggest that dysregulation of intracellular signaling mediated by PDE4B is a significant factor in the cause and expression, respectively, of schizophrenia. 18785206_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18785206_the PDE4B gene itself does not link to major depressive disorder (MDD) but the elevated mRNA levels of PDE4B might be implicated in the pathophysiology of MDD. 18983980_NDE1, NDEL1 and LIS1, together with their binding partner dynein, associate with DISC1, PDE4B and PDE4D within the cell, and provide evidence that this complex is present at the centrosome. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19251251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19350560_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506219_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632097_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19632097_There was no strong evidence for association with PDE4B in schizophrenia. 19728060_phosphodiesterase 4B2 gene is an effector of Toll-like receptor signaling in astrocytes, and that its up-regulation at the protein level is controlled by complex mechanisms 19834503_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20436352_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20436352_results do not support a genetic association between tardive dyskinesia and PDE4B 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21184794_found a significant association between PDE4B and PD in the haplotype analysis. Sex-specific analyses demonstrated that PDE4B was associated with PD in females. results suggest PDE4B may play a role in the pathophysiology of PD in the Japanese population. 21520048_these data allow the assignment of different PDE4 subtypes to distinct functions of human lung fibroblasts and highlight the predominant role of PDE4B in controlling pathophysiological processes of human lung fibroblasts. 21595828_Molecular dynamic simulations (with data from crystal structure of catalytic domain of PDE4B with cAMP bound) are used to investigate the catalytic mechanism of PDE4B in the hydrolysis of cAMP. 21742807_Overexpression of the PDE4B in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) impinge on the same genes/pathways that are abnormally active in GC-resistant tumors. 21854221_The reported anti-inflammatory activity of bresol might be attributed to its abilities to inhibit PDE4B and thus elevate cAMP levels in human monocytes. 22160351_a study of Northwestern Han Chinese found that rs472952 is significantly associated with schizophrenia (SCZ) and rs7537440 is associated with SCZ in females; results provide further evidence that PDE4B may play important roles in the etiology of SCZ 22529021_PDE4B was downregulated and the protein kinase A pathway was activated in castration-resistant LNCaP prostate cancer cells. PDE4B expression was reduced in advanced prostate cancer and PDE4B knockdown promoted castration-resistant growth of LNCaP cells. 22610099_PDE4B mediates ERK-dependent up-regulation of mucin MUC5AC by S. pneumoniae by inhibiting cAMP-PKA-dependent MKP-1 pathway. 22832604_Short Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia (DISC)1 splice variants show reduced or no binding to nudE nuclear distribution E homolog (NDEL)1 and PDE4B proteins but fully interact with fasciculation/elongation zeta (FEZ)1 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 GSK3beta. 23451206_PDE4B was found to be highly expressed in CD4+ lymphoid cancer cells, which suggests that it may represent a physiological role unique to the CD8+ and lymphoid cancer cells and thus might represent a target for treatment of certain lymphoid diseases 23575688_ototopical post-inoculation administration of a PDE4 inhibitor suppresses inflammation in this animal model, thus demonstrating the therapeutic potential of targeting PDE4 25546171_PDE4B gene may be involved in the testicular abnormalities of men with DS and cryptorchidism. 25831493_analysis of the mechanism underlying synergistic up-regulation of PDE4B2 via a cross-talk between PKA-Cbeta and p65 25926551_Our results support previously reported association of PDE4B variations with schizophrenia in other populations. 26011935_Our results suggest that PDE4B does not play an important role during the chemotactic response of human neutrophils 26756575_This meta-analysis suggests that PDE4B SNPs are genetically associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia. 28263187_HTT forms a ternary protein complex with the scaffolding protein DISC1 and cAMP-degrading phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) to regulate PDE4 activity. 28356347_Low PDE4B expression is associated with sepsis. 29100790_Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, interacts with PDE4B and attenuates liver fibrosis through miR-132 mediated CTGF inhibition. 29752424_Data suggest that maternal glycemic response during pregnancy is associated with lower DNA methylation of 4 CpG sites within PDE4B gene in placenta (collected after term birth); 3 additional CpG sites are differentially methylated relative to maternal glucose response within TNFRSF1B, LDLR, and BLM genes. (TNFRSF1B = TNF receptor superfamily member-1B; LDLR = low density lipoprotein receptor; BLM = Bloom syndrome protein) 30181004_in psoriatic arthritis, dysregulated miR-23a expression contributes to synovial inflammation through enhanced synovial fibroblasts activation, via PDE4B signalling 30188895_Study combined mutational analysis in the Apc mutated mice with published studies of frank colon cancer in patients to deduce that Pde4b has two strong biological functions. It negatively regulates colonic adenomagenesis in Apc mutated mice. In patients, PDE4B is most commonly inactivated by an epigenetic process. 30229893_PDE4B gene may play a role in the pathogenesis of OLP. 31116379_Genetic Variants Associated With Anxiety and Stress-Related Disorders: A Genome-Wide Association Study and Mouse-Model Study. 31138843_These findings suggest that the disruption of the Myc-PDE4B circuitry can be exploited in the treatment of B cell malignancies. 31324945_PDE4 genetic polymorphisms impact individual susceptibility to beta2-adrenergic receptor targeted therapy in patients with preterm labor. 32264695_Cardiac Overexpression of PDE4B Blunts beta-Adrenergic Response and Maladaptive Remodeling in Heart Failure. 33522352_Long non-coding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) sponges microRNA-124-3p to up-regulate phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B) to accelerate the progression of Parkinson's disease. 34039624_circPDE4B prevents articular cartilage degeneration and promotes repair by acting as a scaffold for RIC8A and MID1. 34985972_Glioblastoma stem cells reprogram chromatin in vivo to generate selective therapeutic dependencies on DPY30 and phosphodiesterases. 35046895_qPCR Analysis Reveals Association of Differential Expression of SRR, NFKB1, and PDE4B Genes With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. 35266293_Population genetics of PDE4B (phosphodiesterase-4B) in neglected Native Americans: Implications for cancer pharmacogenetics. |
ENSMUSG00000028525 |
Pde4b |
16.531981 |
0.4947172878 |
-1.015324 |
0.380704455 |
7.207450 |
0.00726015621506038988375308917966322042047977447509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014339610027337261824453840119986125500872731208801269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7548599 |
2.6745584 |
21.9702229 |
3.5432105 |
| ENSG00000184602 |
8303 |
SNN |
protein_coding |
O75324 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in the toxic effects of organotins (PubMed:15269288). Plays a role in endosomal maturation (PubMed:27015288). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15269288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27015288}. |
3D-structure;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in response to toxic substance. Located in cytoplasm. Is integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8303; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636] |
29058661_The authors show that stannin interacts with human papillomavirus 16 L1 major capsid protein and impairs the interaction of the L2 minor capsid protein with retromer, which is required for virus trafficking to the trans-Golgi network. |
ENSMUSG00000037972 |
Snn |
102.726166 |
0.3567181333 |
-1.487144 |
0.175667720 |
72.773607 |
0.00000000000000001454084907586822420697840973643307008424095784309120621413669027788273524492979049682617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000115079320300168883762801081145224095763417659042671115088296573958359658718109130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.3099732 |
6.2230147 |
156.0172469 |
11.1124551 |
| ENSG00000184619 |
124751 |
KRBA2 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZNG9 |
|
Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable nucleic acid binding activity. Predicted to be involved in DNA integration and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:124751; |
nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; DNA integration [GO:0015074]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
|
|
|
29.428235 |
0.3346642987 |
-1.579213 |
0.357599266 |
19.603704 |
0.00000952842788203501235555752807426799222412228118628263473510742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000029878817832767535952716644875870599662448512390255928039550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.8856422 |
4.3966522 |
50.4535658 |
8.3366094 |
| ENSG00000184702 |
5413 |
SEPTIN5 |
protein_coding |
Q99719 |
FUNCTION: Filament-forming cytoskeletal GTPase (By similarity). May play a role in cytokinesis (Potential). May play a role in platelet secretion (By similarity). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000305}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cell division;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;GTP-binding;Methylation;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene is a member of the septin gene family of nucleotide binding proteins, originally described in yeast as cell division cycle regulatory proteins. Septins are highly conserved in yeast, Drosophila, and mouse and appear to regulate cytoskeletal organization. Disruption of septin function disturbs cytokinesis and results in large multinucleate or polyploid cells. This gene is mapped to 22q11, the region frequently deleted in DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes. A translocation involving the MLL gene and this gene has also been reported in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. The presence of a non-consensus polyA signal (AACAAT) in this gene also results in read-through transcription into the downstream neighboring gene (GP1BB; platelet glycoprotein Ib), whereby larger, non-coding transcripts are produced. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:5413; |
cell division site [GO:0032153]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; septin complex [GO:0031105]; septin ring [GO:0005940]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; adult behavior [GO:0030534]; cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis [GO:0061640]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; regulation of exocytosis [GO:0017157]; regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis [GO:2000300]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; synaptic vesicle targeting [GO:0016080] |
14530399_CDCrel-1 overexpression exerts dopamine-dependent neurotoxicity and may contribute to the development of autosomal-recessive juvenile parkinsonism 15214843_We studied the assembly of three human septins, SEPT4, SEPT5 and SEPT8, with each other (heterotypic) and with themselves (homotypic) using a yeast two-hybrid system. 16179808_the high expression levels of PNUTL1 in human pancreatic endocrine cells that suggests a similar role of this protein in islet cells to that demonstrated in neuronal tissues, and warrants further functional studies of this protein. 17625225_Our finding suggests a role for members of the septin family in the development of proliferative retinal membranes. 18398426_HSP70 and constitutively active HSF1 mediate protection against CDCrel-1-mediated toxicity 31814881_The expression levels of miR-185, SEPT5, LRRK2, and PARK2 genes were measured at a mRNA level in dopaminergic areas of rats' brains and SHSY-5Y cells using the SYBR Green Real-Time PCR Method. 33203136_Presynaptic Vesicle Protein SEPTIN5 Regulates the Degradation of APP C-Terminal Fragments and the Levels of Abeta. |
ENSMUSG00000072214 |
Septin5 |
19.415382 |
0.3777665869 |
-1.404433 |
0.443015607 |
10.157430 |
0.00143720817218956180283395696051229606382548809051513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003265075053335067360726906571244398946873843669891357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.4944677 |
4.1923673 |
25.4911783 |
7.6495352 |
| ENSG00000184752 |
55967 |
NDUFA12 |
protein_coding |
Q9UI09 |
FUNCTION: Accessory subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), that is believed not to be involved in catalysis. Complex I functions in the transfer of electrons from NADH to the respiratory chain. The immediate electron acceptor for the enzyme is believed to be ubiquinone. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27626371}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Electron transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Primary mitochondrial disease;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein which is part of mitochondrial complex 1, part of the oxidative phosphorylation system in mitochondria. Complex 1 transfers electrons to ubiquinone from NADH which establishes a proton gradient for the generation of ATP. Mutations in this gene are associated with Leigh syndrome due to mitochondrial complex 1 deficiency. Pseudogenes of this gene are located on chromosomes 5 and 13. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:55967; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I [GO:0005747]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity [GO:0008137]; aerobic respiration [GO:0009060]; mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled electron transport [GO:0042775]; mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I assembly [GO:0032981]; proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis [GO:0042776]; respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system [GO:0007585]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24717771_NDUFA3, NDUFA5 and NDUFA12 supernumerary subunits are necessary for complex I activity and biogenesis. 32335026_NDUFS4 deletion triggers loss of NDUFA12 in Ndufs4(-/-) mice and Leigh syndrome patients: A stabilizing role for NDUFAF2. 33715266_Novel NDUFA12 variants are associated with isolated complex I defect and variable clinical manifestation. |
ENSMUSG00000020022 |
Ndufa12 |
122.200427 |
2.0707371242 |
1.050144 |
0.137183166 |
59.344812 |
0.00000000000001323285654184087087669419660423827151161458096084722058094484964385628700256347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000088139423536810127426224062826186301990855076482489494082983583211898803710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
164.2626712 |
14.1246609 |
79.8865097 |
5.4021316 |
| ENSG00000184786 |
6991 |
DYNLT2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZS6 |
FUNCTION: May be an accessory component of axonemal dynein and cytoplasmic dynein 1 (PubMed:11278908, PubMed:12584439). Candidate for involvement in male sterility (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P11985, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11278908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12584439}. |
Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Dynein;Membrane;Microtubule;Motor protein;Reference proteome;Transport |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable dynein intermediate chain binding activity. Predicted to be involved in microtubule-based movement. Predicted to be located in cytosol and sperm flagellum. Predicted to be extrinsic component of membrane. Predicted to be part of cytoplasmic dynein complex. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:6991; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic dynein complex [GO:0005868]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
21085971_Because TCTE3 encodes a putative light chain of the outer dynein arm of cilia and human diseases caused by ciliary dysfunction show various phenotypes including skeletal defect, TCTE3 may be a genetic candidate influencing CDH. 21085971_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 29079176_TCTE3 is a useful marker of pancreatobiliary differentiation and may aid in the diagnosis of pancreatobiliary adenocarcinomas. 32749594_Study of Linc00574 Regulatory Effect on the TCTE3 Expression in Sperm Motility. |
ENSMUSG00000079707+ENSMUSG00000116780+ENSMUSG00000079710 |
Dynlt2a1+Dynlt2a3+Dynlt2a2 |
18.005263 |
0.2518269861 |
-1.989495 |
0.416657652 |
24.070955 |
0.00000092850274181035660558481206749981140546879032626748085021972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003299157551545706449063616316763614122464787214994430541992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.3009093 |
2.0064729 |
29.2401444 |
4.6703552 |
| ENSG00000184788 |
340562 |
SATL1 |
protein_coding |
Q86VE3 |
|
Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable N-acetyltransferase activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:340562; |
N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0008080] |
|
ENSMUSG00000025527 |
Satl1 |
9.428383 |
0.2365112190 |
-2.080019 |
0.539844324 |
16.381735 |
0.00005178182115937222067389086865851766106061404570937156677246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000148580808769893874324297122768712142715230584144592285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7652143 |
1.3657529 |
16.1097042 |
3.1436947 |
| ENSG00000184828 |
201501 |
ZBTB7C |
protein_coding |
A1YPR0 |
FUNCTION: May be a tumor suppressor gene. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9427755}. |
Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Tumor suppressor;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of cell population proliferation. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:201501; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045600]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:1903025]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
17932560_Adm and APM-1 protect endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in sepsis. 22253232_our findings define KR-POK as a transcriptional repressor with a pro-oncogenic role that relies upon binding to p53 and inhibition of its transactivation function. 26542693_ZBTB7C genetic variations were significant for susceptibility to ischemic injury in cerebral ischemia. 28571744_Repression of Kr-POK inhibited tumor growth. 32193444_Identification of Novel Alzheimer's Disease Loci Using Sex-Specific Family-Based Association Analysis of Whole-Genome Sequence Data. 33946045_The prognostic and immunological effects of ZBTB7C across cancers: friend or foe? |
ENSMUSG00000044646 |
Zbtb7c |
26.577645 |
0.4136992947 |
-1.273346 |
0.512509830 |
5.837857 |
0.01568491857574058970237196319885697448626160621643066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028797790023187736646592682632217474747449159622192382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.9159081 |
6.7394606 |
38.3448940 |
11.1482355 |
| ENSG00000184838 |
51334 |
PRR16 |
protein_coding |
Q569H4 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of cell size that promotes cell size increase independently of mTOR and Hippo signaling pathways. Acts by stimulating the translation of specific mRNAs, including those encoding proteins affecting mitochondrial functions. Increases mitochondrial mass and respiration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24656129}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in positive regulation of cell size and positive regulation of translation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51334; |
positive regulation of cell size [GO:0045793]; positive regulation of translation [GO:0045727] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24656129_Largen, the product of a gene PRR16, increases cell size upon overexpression in human cells. |
ENSMUSG00000073565 |
Prr16 |
181.859218 |
3.5278235560 |
1.818778 |
0.387291161 |
20.041266 |
0.00000757888874727775599941153109040392621409409912303090095520019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024129507745862741594812528322933076196932233870029449462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
299.0797066 |
75.9390574 |
84.9423767 |
15.9454635 |
| ENSG00000184898 |
375287 |
RBM43 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZSC3 |
|
Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:375287; |
RNA binding [GO:0003723] |
32632220_RNA-binding motif protein 43 (RBM43) suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulation of cyclin B1 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000036249 |
Rbm43 |
54.065030 |
0.4652544012 |
-1.103908 |
0.225220028 |
24.215749 |
0.00000086125114770163523314857505555619532344735489459708333015441894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003066103941166458029859900186187005033389141317456960678100585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.3209711 |
5.2183716 |
74.2446049 |
7.4208353 |
| ENSG00000184916 |
3714 |
JAG2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y219 |
FUNCTION: Putative Notch ligand involved in the mediation of Notch signaling. Involved in limb development (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Membrane;Notch signaling pathway;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The Notch signaling pathway is an intercellular signaling mechanism that is essential for proper embryonic development. Members of the Notch gene family encode transmembrane receptors that are critical for various cell fate decisions. The protein encoded by this gene is one of several ligands that activate Notch and related receptors. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3714; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; growth factor activity [GO:0008083]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; auditory receptor cell fate commitment [GO:0009912]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; epithelial cell apoptotic process involved in palatal shelf morphogenesis [GO:1990134]; gamma-delta T cell differentiation [GO:0042492]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; morphogenesis of embryonic epithelium [GO:0016331]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; respiratory system process [GO:0003016]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; thymic T cell selection [GO:0045061] |
11700865_expression required for spermatogenesis in humans and rats 15292061_JAG2 was found to be overexpressed in malignant plasma cells from MM patients; coculture assay demonstrated that JAG2 induced the secretion of IL-6, VEGF, and IGF-1 in stromal cells; JAG2 overexpression may be an early event in the pathogenesis of MM 16327884_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16899352_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18439488_The upregulation of Jagged2 expression on BMEC was observed upon TNF-alpha activation. Similarly,activation of endothelial cells in Tie2-tmTNF-alpha mice was characterized by increased expression of Jagged2. 19049519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19049519_Results indicate JAG2 may be involved in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate etiology in different populations. 19054571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19417136_SMRT function restoration induces JAG2 down-regulation as well as multipe myeloma apoptosis. 20040020_Notch signaling may participate in controlling cell differentiation and proliferation in normal bone and COF of the jaws. Notch signaling disorder may be a molecular incident in COF occurrence and development. 20133585_JAG2 is a direct Myc target and Jagged2 and Notch signaling participate in P493-6 lymphomagenesis. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20572854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20819128_Expression of Notch3 and Jagged2 were highly correlated in tongue carcinoma tissues. 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21372153_we have investigated their influence on early human hematopoiesis and show that Jagged2 affects hematopoietic lineage decisions very similarly as Delta-like-1 and -4, but very different from Jagged1 21402725_hypoxic induction of JAG2 in tumor cells mediates a hypoxia-regulated cross-talk between tumor and endothelial cells. 21499308_hypoxia-induced Jagged2 activation in both tumor invasive front and normal bone stroma has a critical role in tumor progression and metastasis 21602525_The stromal cell-mediated antiapoptotic effect on B- ALL cells is mediated by Notch-3 and -4 or Jagged-1/-2 and DLL-1 in a synergistic manner. 21892607_This study is the first illustration of Notch-1 and Jagged-2 expression in human tissues from non-cancerous disease. 22030773_Notch-1 and Jagged-2 are not expressed in spastic colon segments, which may be associated with the pathogenesis of Hirschsprung disease. 22341562_JAG2 is often expressed by CD138(+) primary cells. Our results indicate that spontaneous clonogenic growth of myeloma cells requires the expression of JAG2. 22691042_Immunohistochemistry showed a reverse correlation between MUC2 and Notch3 or Jagged1 (P = 0.033 and P = 0.005, respectively) and between MUC5AC and Jagged1 or Hes1 23074278_JAG2-mediated Notch activation confers phenotypic and functional aspects of Langerhans cell histiocytosis to dendritic cells. 24228105_Jagged2 expression status was closely correlated with important histopathologic characteristics (grades and stages) and the recurrence and metastasis of bladder urothelial carcinomas. 24708907_This study demonistrated that NOTCH ligands JAG1 and JAG2 as critical pro-survival factors in childhood medulloblastoma. 24907271_Although Jag1 shares a high degree of homology with Jag2 in the ectodomain region, BACE1 fails to cleave Jag2 effectively, indicating a selective cleavage of Jag1. 25257302_silencing prevents Notch2-driven osteoclast development and bone destruction in multiple myeloma 25351917_Results show that tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis are dependent on JAGGED2 independently of NOTCH activation. 25576913_Increased expression of JAG2, a target of miR-1280, is associated with high metastatic dissemination at diagnosis and a poor outcome in medulloblastoma. 26151095_In CL+/-P Malay patients, the prevalence of mutations in the Jagged2 gene was 12.5%. Three variants (g.19779C>T, g.19547G>A, and g.19712C>T) were identified in the Jagged2 gene among nonsyndromic CL+/-P and noncleft patients. Only g.19712C>T showed a significant association with nonsyndromic CL+/-P patients (P = .039). 26412454_Jagged-2 enhances immunomodulatory activity in adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells 28111308_these results show that the Notch signaling pathway in T cells is crucial for the induction of TH2-mediated allergic airway inflammation in an house dust mite -driven asthma model but that expression of Jagged 1 or Jagged 2 on DCs is not required 28572448_The authors present novel structures of human ligands Jagged2 and Delta-like4 and human Notch2, together with functional assays, which suggest that ligand-mediated coupling of membrane recognition and Notch binding is likely to be critical in establishing the optimal context for Notch signalling. 30280784_Results showed that Jagged2 was highly expressed in paclitaxel-resistant triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) tissues and cells. Jagged2 expression was found to be associated with cancer stem cell (CSC) properties of TNBC cells. Jagged2 maintains CSC properties of TNBC cells and paclitaxel resistance via regulating microRNA-200. 30296338_CD14(+) monocytes serve as Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) cell precursor and JAG2-mediated activation of the Notch signaling pathway initiates a differentiation of monocytes toward LCH cells. 30473216_Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) ENST00000455974 was significantly associated with TNM stage and distant metastasis in patients with DNA mismatch repair-proficient colon cancer. ENST00000455974 was gradually increased across the colonic normal-adenoma-carcinoma-metastasis sequence. ENST00000455974 was mainly located in the nucleus of colon cancer cells and it promoted growth and metastasis through up-regulating JAG2. 31922603_The CT genotype of rs741859 could significantly reduce the risk for NSCLP to 65% (P |
ENSMUSG00000002799 |
Jag2 |
175.831611 |
0.2447070969 |
-2.030872 |
0.231075726 |
73.849851 |
0.00000000000000000842907893830595147777074078020348979917781280475153407594213206266431370750069618225097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000067579144556977637733222234621853084330594722513915056927302771327958907932043075561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.9796138 |
10.7154851 |
272.4141101 |
30.6085083 |
| ENSG00000184922 |
752 |
FMNL1 |
protein_coding |
O95466 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in the control of cell motility and survival of macrophages (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. Required in the cortical actin filament dynamics and cell shape. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a formin-related protein. Formin-related proteins have been implicated in morphogenesis, cytokinesis, and cell polarity. An alternative splice variant has been described but its full length sequence has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:752; |
bleb [GO:0032059]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; GTPase activating protein binding [GO:0032794]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; actin filament severing [GO:0051014]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
14592423_Western blot analysis demonstrated that the protein encoded by this gene is overexpressed in lymphoid malignancies, cancer cell lines and peripheral blood leukocyte from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients. 19815554_Results describe N-myristoylation as a regulative mechanism of FMNL1 responsible for membrane trafficking potentially involved in a diversity of polarized processes of hematopoietic lineage-derived cells. 20617518_Our data suggest that FRL1 is responsible for modifying actin at the macrophage podosome and may be involved in actin cytoskeleton dynamics during adhesion and migration within tissues. 21148482_after Rac-dependent activation of FMNL1, srGAP2 mediates a potent mechanism to limit the duration of Rac action and inhibit formin activity during rapid actin dynamics. 23182705_constitutively activated form of FMNL1 (FMNL1gamma) induces localization of AHNAK1 to the cell membrane. 23460512_Results suggest that macrophage coiling phagocytosis is a complex process involving several actin nucleation/regulatory factors. They also point specifically to the formins mDia1 and FMNL1 as novel regulators of spirochete uptake by human immune cells. 23801653_FMNL1 contributes to leukemogenesis and could act in part through Rac1 regulation. 29283461_Results indicated that FMNL1 is a susceptibility gene for leprosy. 30013189_High expression of FMNL1, resulted from decreased miR-16 and/or MTA1 amplification. 30977161_The carboxy-terminus of the formin FMNL1 bundles actin to potentiate adenocarcinoma migration. 31001854_miR-143 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via targeting FMNL1 based on clinical and radiologic findings. 31387165_Suppressing FMNL1 expression could inhibit bone metastasis in NSCLC through blocking TGF-beta1 signaling. 31861134_Formin-like 1 protein (FMNL1) is a promising therapeutic target for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) progression. |
ENSMUSG00000055805 |
Fmnl1 |
2584.367584 |
2.1545330007 |
1.107375 |
0.049137075 |
503.092297 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000201907760417044026260930715916971979603172900481128013402326747595450557656762515491995237517941273523850920165204739198555997932284221795593515148371722716055919532769337141253227108469376143130458885171267729419768362 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000096134146572760304724967097572236560942392585007489198820244142921807529741668893327330330676135807321948544870443760482113432470658196658568996489420930604450838117331012062805401511746046535221317509870037278887067105 |
Yes |
Yes |
3568.5131095 |
109.4964951 |
1667.3935970 |
38.5822787 |
| ENSG00000184939 |
146198 |
ZFP90 |
protein_coding |
Q8TF47 |
FUNCTION: Inhibits the transcriptional repressor activity of REST by inhibiting its binding to DNA, thereby derepressing transcription of REST target genes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21284946}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Acts as a bridge between FOXP3 and the corepressor TRIM28, and is required for the transcriptional repressor activity of FOXP3 in regulatory T-cells (Treg). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23543754}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the zinc finger protein family that modulates gene expression. The encoded protein derepresses the transcription of certain fetal cardiac genes and may contribute to the genetic reprogramming that occurs during the development of heart failure. Genome wide association studies have identified this gene among ulcerative colitis risk loci. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. |
hsa:146198; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043392]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 31641208_A 16q22.1 variant confers susceptibility to colorectal cancer as a distal regulator of ZFP90. 33796098_Assessing the Function of the ZFP90 Variant rs1170426 in SLE and the Association Between SLE Drug Target and Susceptibility Genes. |
ENSMUSG00000031907 |
Zfp90 |
151.704209 |
0.2813842926 |
-1.829386 |
0.500812640 |
11.999330 |
0.00053219693790353855052804865621851604373659938573837280273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001300534238982819319405126456956622860161587595939636230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.0303357 |
24.2643581 |
264.3349231 |
62.2839901 |
| ENSG00000184949 |
646851 |
FAM227A |
protein_coding |
F5H4B4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:646851; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000042564 |
Fam227a |
18.909899 |
3.0305345830 |
1.599572 |
0.421359550 |
14.110041 |
0.00017242091585453517450787774833997900714166462421417236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000457310461457850715369377603281009214697405695915222167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.2346212 |
6.8674593 |
8.1347532 |
1.7113907 |
| ENSG00000184979 |
11274 |
USP18 |
protein_coding |
Q9UMW8 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the negative regulation of the inflammatory response triggered by type I interferon (PubMed:28165510, PubMed:27325888). Upon recruitment by STAT2 to the type I IFN receptor subunit IFNAR2 interferes with the assembly of the ternary interferon-IFNAR1-IFNAR2 complex and acts as a negative regulator of the type I IFN signaling pathway (PubMed:28165510). Also regulates protein ISGylation. Can efficiently cleave only ISG15 fusions including native ISG15 conjugates linked via isopeptide bonds. Necessary to maintain a critical cellular balance of ISG15-conjugated proteins in both healthy and stressed organisms (PubMed:11788588). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788588, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27325888, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28165510}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Has enzymatic activity similar to isoform 1 and interferes with type I interferon signaling. Major deISGylation enzyme for nuclear proteins (PubMed:22170061). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22170061}. |
Alternative initiation;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Protease;Reference proteome;Thiol protease;Ubl conjugation pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ubiquitin-specific proteases (UBP) family of enzymes that cleave ubiquitin from ubiquitinated protein substrates. It is highly expressed in liver and thymus, and is localized to the nucleus. This protein efficiently cleaves only ISG15 (a ubiquitin-like protein) fusions, and deletion of this gene in mice results in a massive increase of ISG15 conjugates in tissues, indicating that this protein is a major ISG15-specific protease. Mice lacking this gene are also hypersensitive to interferon, suggesting a function of this protein in downregulating interferon responses, independent of its isopeptidase activity towards ISG15. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:11274; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cysteine-type deubiquitinase activity [GO:0004843]; cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004197]; ISG15-specific peptidase activity [GO:0019785]; negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060339]; protein deubiquitination [GO:0016579]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617]; response to stilbenoid [GO:0035634]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
15342634_UBP43 protein levels are regulated by proteolysis via the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase 17374743_Ubp43 deficiency increases the resistance to oncogenic transformation by BCR-ABL 19551150_Epstein-Barr virus independent dysregulation of UBP43 expression alters interferon-stimulated gene expression in Burkitt lymphoma 20068173_Findings suggest that USP18 may significantly limit operation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway triggered by type I IFN and drugs. 20935222_Findings define the ubiquitin protease UBP43 as a novel candidate drug target for APL treatment. 21592959_a model in which Usp18 inhibition promotes up-regulation of miR-7, which in turn inhibits EGFR expression and the tumorigenic activity of cancer cells. 22100648_Inhibition of R. conorii-induced ISG15 by RNA interference results in significant increase in the extent of rickettsial replication, whereas UBP43 knockdown yields a reciprocal inhibitory effect. 22170061_the existence of an N-terminal truncated isoform of USP18, whose expression is controlled on translational level by two independent mechanisms providing translational flexibility 22677194_USP18 is up-regulated in liver samples of patients with chronic hepatitis C that did not respond to therapy, but not in patients with acute hepatitis C. 22683641_although UBP43 depletion can cause hypersensitivity to interferon-alpha/beta-mediated apoptosis in a broad range of cell types, the downstream pathway may vary depending on the cell type. 22731491_USP18 establishes the transcriptional and anti-proliferative interferon alpha/beta differential 22752428_A direct relationship was found between UBP43 and cyclin D1 (but not cyclin E) expression. 23152055_USP18 inhibition induces inflammation by increasing the STAT signaling and exacerbates IFN-induced beta cell apoptosis. 23291318_Usp18 upregulation was associated with Wilms Tumor. 23700969_USP18 expression levels induced by IFNbeta did not differ amongst multiple sclerosis patients carrying different rs2542109 genotypes 24955730_increased expression in the HIV+/HCV+ female patients group compared with HIV-/HCV+ and HIV+/HCV- groups 26008745_Dimerization of IFNAR1 and IFNAR2 and the limiting role of IFNAR1 binding affinity in complex assembly is modulated by USP18. 26046984_Data suggest that USP18 (Ubiquitin-like specific protease 18) sensitive cellular functions include activity of the peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2. 26240016_USP18 negatively regulates NF-kappaB signaling by targeting TAK1 and NEMO for deubiquitination through distinct mechanisms. 27009955_findings show that multiple inflammatory stimuli can modulate interferon stimulated gene expression and thus inhibit hepatocyte interferon signaling via USP18 induction 27227879_results indicated that USP18 modulates the anti-HBV activity of IFN-F via activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in Hepg2.2.15 cells. 27325888_These findings add USP18 deficiency to the list of genetic disorders collectively termed type I interferonopathies 27434537_We show that IRF-7 siRNA knockdown enhanced LPS-induced IL-10 production in human monocyte-derived macrophages, and USP-18 overexpression attenuated LPS-induced production of IL-10 in RAW264.7 cells. Quantitative PCR confirmed upregulation of USP18, USP41, IL10, and IRF7. An independent cohort confirmed LPS induction of USP41 and IL10 genes 27605457_High expression levels of USP18 in the muscles of dermatomyositis patients. 27980214_this study identified PTEN as a previously unrecognized substrate of the ISGylation post-translational modification pathway. The deconjugase USP18 serves as a novel regulator of PTEN stability. This indicates inhibition of ISGylation is therapeutically relevant in cancers. 28165509_USP18's ISG15 specificity is mediated by a small interaction interface. 28165510_STAT2 recruits USP18 to the type I IFN receptor subunit IFNAR2 via its constitutive membrane-distal STAT2-binding site. 28369997_study preliminary elucidated the role of USP18 in hepatitis B virus replication and explored the potential key genes in USP18-mediated signaling pathway 28630501_These results demonstrate that virus-induced IFN-lambda4 potently blocks IFN-alpha signalling by inducing high protein levels of ISG15 and USP18. Moreover, the data clearly demonstrate that DAA therapy restores IFN-alpha responsiveness in HCV-infected cells. 28709980_that Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 directly bind to BCL2L1 and positively regulated its expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 28718215_associates with and deubiquitinates TAK1 to protect against hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and the inflammatory response 28881486_The structures of ubiquitin-specific protease 18 (USP18) and a USP18-Interferon-stimulated 15-KDa protein (ISG15) complex indicate the molecular basis of the specificity of the protease and its interaction with the type I interferon receptor [Review]. 29749454_The role of USP18 in breast cancer provides a novel insight into the clinical application of the USP18/AKT/Skp2 pathway. 30068654_The authors have found that USP18 has the novel ability to inhibit the antiviral function of p21 in differentiated THP-1 cells. USP18 enhanced reverse transcription of HIV-1 by downregulating p21 expression and upregulating intracellular dNTP levels. 30126853_In this review, we summarise our current knowledge of protease-dependent and -independent functions of USP18 and discuss the structural basis of its dual activity 30858391_USP18 and ISG15 coordinately impact on SKP2 and cell cycle progression. 31074081_We demonstrated that clinical outcome of IFN-alpha therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients is associated with the transcriptional response of USP18 to IFN-alpha in in vitro cultured PBMCs. 31455647_This work clarifies the function and consequences of p53 modification by ISG15 and implicates USP18 in HIV-1 infection and potentially in carcinogenesis. 31658294_The authors establish a direct role for type I IFN/USP18 signaling in the maintenance of total and virus-specific Memory CD4 T-cells and provide a new mechanism for the reduced survival of these populations during primary HIV-1 infection. 31886294_we observed increased USP18 and IL2RA expressions after one and six months of INH therapy and decreased IFNA, CCL4, and CXCL11 expressions after six months of LTBI treatment. These results might facilitate the use of mRNA expression as a tool for monitoring INH treatment and may have the potential for monitoring new alternative LTBI regimens. 32248821_The USP18 cysteine protease promotes HBV production independent of its protease activity. 32527992_Relationship Between Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 18 and Hypertension in Polish Adult Male Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. 33214684_Deletion of the deISGylating enzyme USP18 enhances tumour cell antigenicity and radiosensitivity. 33461172_Dysregulation of USP18/FTO/PYCR1 signaling network promotes bladder cancer development and progression. 33533212_[Interferon-regulating activity of the celagrip antiviral drug and its influence on formation of reactive oxygen species and expression of innate immunity genes in the follicular lymphoma patients]. 34001679_Downregulation of USP18 reduces tumor-infiltrating activated dendritic cells in extranodal diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. 34016972_USP18 positively regulates innate antiviral immunity by promoting K63-linked polyubiquitination of MAVS. 34743935_USP18 promotes tumor metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas via deubiquitinating ZEB1. 34759076_Downregulated Expression of USP18 Is Associated with a Higher Recurrence Risk of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. 35063764_The USP18-FBXO6 axis maintains the malignancy of ovarian cancer. 35180471_USP18 reduces paclitaxol sensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer via autophagy. 35258551_A partial form of inherited human USP18 deficiency underlies infection and inflammation. 35387560_Loss of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 destabilizes 14-3-3zeta protein and represses lung cancer metastasis. 35696596_USP18 contributes to the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells by regulating the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. 36376024_Clinical and genetic analysis of familial neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in Chinese: associated with ubiquitin-specific peptidase USP18 gene variants. |
ENSMUSG00000030107 |
Usp18 |
107.067670 |
0.4799566894 |
-1.059024 |
0.179816767 |
34.898659 |
0.00000000347320041866173609539626531827073013802831269458692986518144607543945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015778528217743067511945055355140898889487743872450664639472961425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.7010792 |
7.6629456 |
146.2362277 |
10.6221066 |
| ENSG00000185022 |
23764 |
MAFF |
protein_coding |
Q9ULX9 |
FUNCTION: Since they lack a putative transactivation domain, the small Mafs behave as transcriptional repressors when they dimerize among themselves (PubMed:8932385). However, they seem to serve as transcriptional activators by dimerizing with other (usually larger) basic-zipper proteins, such as NFE2L1/NRF1, and recruiting them to specific DNA-binding sites. Interacts with the upstream promoter region of the oxytocin receptor gene (PubMed:8932385, PubMed:16549056). May be a transcriptional enhancer in the up-regulation of the oxytocin receptor gene at parturition (PubMed:10527846). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10527846, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16549056, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8932385}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Stress response;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that lacks a transactivation domain. It is known to bind the US-2 DNA element in the promoter of the oxytocin receptor (OTR) gene and most likely heterodimerizes with other leucine zipper-containing proteins to enhance expression of the OTR gene during term pregnancy. The encoded protein can also form homodimers, and since it lacks a transactivation domain, the homodimer may act as a repressor of transcription. This gene may also be involved in the cellular stress response. Multiple transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:23764; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; parturition [GO:0007567]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of epidermal cell differentiation [GO:0045604]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914] |
12490281_MafF/NFE2 hetrodimers act as weak transcriptional activators, and, in particular, are able to stimulate activity of the GCS1 promoter. 16371591_In myometrial cells we observed an important induction by interleukin 1 beta and a weaker upregulation by tumor necrosis factor, whereas interleukin 6 treatment had no effect. 16549056_Expression of hMafF or MIP alone did not alter basal reporter transcription activity, whereas co-expression of hMafF and MIP activated transcription efficiently. 19723544_Only in the presence of both MIP and hMafF could the nUS2-pLacZi reporter in yeast genome be activated. 24118457_MAF genes have different levels of biological and genetic relevance. Besides, MAFF and MAFG could be associated with the susceptibility to develop CML. 29757260_These results suggest that MAFB and MAFF play critical roles in the antitumor effects of retinoids by regulating the expression of retinoid target genes such as TFPI2 and can be promising for developing therapies to combat HCC invasion. 30669188_CXCL1 and CSF3 levels are controlled by MAFF in myometrial cells. 32339354_Alternative splicing related genetic variants contribute to bladder cancer risk. 33488846_Responsive Expression of MafF to beta-Amyloid-Induced Oxidative Stress. 33626882_Transcription Factor MAFF (MAF Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor F) Regulates an Atherosclerosis Relevant Network Connecting Inflammation and Cholesterol Metabolism. 33980595_MafF Is an Antiviral Host Factor That Suppresses Transcription from Hepatitis B Virus Core Promoter. 34262028_The HIF target MAFF promotes tumor invasion and metastasis through IL11 and STAT3 signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000042622 |
Maff |
229.748521 |
3.9181722495 |
1.970181 |
0.113937344 |
314.388646 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000024166239652263791268696258204570290474497495295211188447393782214467930500952092083133373243201664081782398555250661461201627040576336189856232928011667160341847580893296807899583988898939423961564898490905761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007264637418888260112659278242717050511577551295806263866185886278227854739578319785472322624146524710276005619340399004432711065096392231240178938316251700669667527794680708663754842291382374241948127746582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
369.4219207 |
25.3022802 |
94.9258132 |
5.5130261 |
| ENSG00000185100 |
122622 |
ADSS1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N142 |
FUNCTION: Component of the purine nucleotide cycle (PNC), which interconverts IMP and AMP to regulate the nucleotide levels in various tissues, and which contributes to glycolysis and ammoniagenesis. Catalyzes the first committed step in the biosynthesis of AMP from IMP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26506222}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Ligase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Purine biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; AMP biosynthesis via de novo pathway; AMP from IMP: step 1/2. {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03126, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26506222}. |
This gene encodes a member of the adenylosuccinate synthase family of proteins. The encoded muscle-specific enzyme plays a role in the purine nucleotide cycle by catalyzing the first step in the conversion of inosine monophosphate (IMP) to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Mutations in this gene may cause adolescent onset distal myopathy. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2016]. |
hsa:122622; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; adenylosuccinate synthase activity [GO:0004019]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphate ion binding [GO:0042301]; 'de novo' AMP biosynthetic process [GO:0044208]; AMP biosynthetic process [GO:0006167]; immune system process [GO:0002376]; IMP metabolic process [GO:0046040] |
15786719_A novel muscle isozyme of adenylosuccinate synthetase, human AdSSL1, is identified from human bone marrow stromal cells. 26506222_Mutations in ADSSL1 are the novel genetic cause of autosomal recessive adolescent onset distal myopathy. 28268051_Study investigated the clinical manifestation in Korean patients with ADSSL1 mutations. Patients with ADSSL1 mutations demonstrated distal muscle weakness in adolescence, followed by quadriceps muscle weakness in the early 30s. All patients had mild facial weakness and two patients complained of easy fatigue while eating and chewing. Muscle biopsies and whole body muscle MR imaging findings are discussed. 32646962_ADSSL1 myopathy is the most common nemaline myopathy in Japan with variable clinical features. |
ENSMUSG00000011148 |
Adssl1 |
25.111489 |
0.1787632547 |
-2.483878 |
0.478509454 |
27.230649 |
0.00000018057336613509962681876311763745635019517976616043597459793090820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000693717564850096346264738973036445557340812229085713624954223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0417181 |
2.8274499 |
45.3723063 |
10.0534979 |
| ENSG00000185101 |
338440 |
ANO9 |
protein_coding |
A1A5B4 |
FUNCTION: Has calcium-dependent phospholipid scramblase activity; scrambles phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylcholine and galactosylceramide (By similarity). Does not exhibit calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) activity (PubMed:22178883). Can inhibit the activity of ANO1 (PubMed:20056604, PubMed:22946059). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P86044, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20056604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178883, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22946059}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Lipid metabolism;Lipid transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TMEM16 (anoctamin) family of proteins, some of which form integral membrane calcium-activated chloride channels. The function of the encoded protein has yet to be elucidated, although it may have channel-forming abilities and also may have phospholipid scramblase activity. This gene has been observed to be upregulated in stage II and III colorectal cancers. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:338440; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; intracellular calcium activated chloride channel activity [GO:0005229]; phospholipid scramblase activity [GO:0017128]; calcium activated galactosylceramide scrambling [GO:0061591]; calcium activated phosphatidylcholine scrambling [GO:0061590]; calcium activated phosphatidylserine scrambling [GO:0061589]; chloride transmembrane transport [GO:1902476]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; negative regulation of intracellular calcium activated chloride channel activity [GO:1902939]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22223854_These results demonstrate a strong association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the PKP3-SIGIRR-TMEM16J gene region and tuberculosis in discovery and validation cohorts. 26317553_Suggest role for up-regulation of ANO9 in progression and metastasis of stage II and III colorectal carcinoma. 26872154_Children with low 25-hydroxyvitamin D and TMEM16J rs7111432-AA or PKP3 rs10902158-GG polymorphisms were at increased risk for tuberculosis or death. 29024940_Our results showed that ANO9 is overexpressed in most pancreatic cancer cell lines tested and in B30% of tissue samples obtained from patients with pancreatic cancer. Moreover, high ANO9 expression was associated with increased proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells and poor survival in patients with pancreatic cancer. 29604966_ANO9 is a cation channel activated by a cAMP/PKA pathway and could play a role in intestine function. 32227267_ANO9 Regulated Cell Cycle in Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 33404124_ANO9 regulates PD-L2 expression and binding ability to PD-1 in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000054662 |
Ano9 |
25.432594 |
0.0084104616 |
-6.893599 |
1.040564485 |
67.882072 |
0.00000000000000017357222704995909026820005308530460989036634628871619279166793603508267551660537719726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001291293382690219910842907169315424792830552906675034563477311166934669017791748046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.4225687 |
0.3250334 |
50.6370393 |
12.8697219 |
| ENSG00000185112 |
131583 |
FAM43A |
protein_coding |
Q8N2R8 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:131583; |
|
Mouse_homologues 19542019_We have shown the participation of a novel transcript (named somitovasculin) in circulatory vessel development |
ENSMUSG00000046546 |
Fam43a |
52.974641 |
0.4788971816 |
-1.062212 |
0.210698547 |
25.833851 |
0.00000037210498267475732156114864856988333485787734389305114746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001381008183122810806760303974083381461923636379651725292205810546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.8241585 |
4.7741796 |
73.1425984 |
6.4682255 |
| ENSG00000185158 |
114659 |
LRRC37B |
protein_coding |
Q96QE4 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Glycoprotein;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:114659; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
19291764_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000034239+ENSMUSG00000078632 |
Gm884+Lrrc37a |
46.778552 |
0.3034195375 |
-1.720614 |
0.310715529 |
29.893198 |
0.00000004565114686195897457281762227797317077460093059926293790340423583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000185673994952470235659649296262874162977141168084926903247833251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.4945068 |
4.8137985 |
78.7273620 |
10.7354481 |
| ENSG00000185168 |
|
LINC00482 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.356938 |
0.0272666510 |
-5.196719 |
1.018937388 |
41.491894 |
0.00000000011836070509056271136893169144738060388766243136160483118146657943725585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000608712197608608274210610085641582830962015293607692001387476921081542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5011261 |
0.3963922 |
18.3495960 |
5.2419120 |
| ENSG00000185187 |
59307 |
SIGIRR |
protein_coding |
Q6IA17 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a negative regulator of the Toll-like and IL-1R receptor signaling pathways. Attenuates the recruitment of receptor-proximal signaling components to the TLR4 receptor, probably through an TIR-TIR domain interaction with TLR4. Through its extracellular domain interferes with the heterodimerization of Il1R1 and IL1RAP. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12925853, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14715412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15866876, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25963006}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable NAD+ nucleosidase activity. Involved in negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:59307; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; negative regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032682]; negative regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001960]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031665]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
15866876_SIGIRR inhibits IL-1R and TLR4-mediated signaling through different mechanisms 16432636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19200604_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19699681_regulatory functions in inflammation and Th1/Th2 cell polarization (Review) 20130217_Data show that Sigirr overexpression depresses NF-B-mediated diverse TLR responses. 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20364327_SIGIRR can inhibit TLR4, 5, and 9-mediated immune responses in human airway epithelial cells. 20506350_SIGIRR/TIR-8 is an inhibitor of Toll-like receptor signaling in primary human cells and regulates inflammation in models of rheumatoid arthritis 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21077278_SIGIRR is expressed constitutively in intestinal epithelial cells to maintain gut innate immunity and then down-regulated during inflammation by inhibition of an SP1-mediated pathway. 21187075_These results suggest that PALM3 may function as an adaptor in the LPS- Toll-like receptor 4 signaling and the interaction of SIGIRR with PALM3 may partly account for the mechanism of the negatively regulatory effect of SIGIRR. 22223854_These results demonstrate a strong association of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the PKP3-SIGIRR-TMEM16J gene region and tuberculosis in discovery and validation cohorts. 22634523_the tested variations of IRAK-M and SIGIRR genes do not confer a relevant role in the susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in European-descent populations 22952899_The present study was undertaken to characterize responses of B cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients to TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation and to explore the potential role of SIGIRR. 24821721_Lipopolysaccharide decreases SIGIRR expression by suppressing specificity protein 1 Sp1 via the TLR4-p38 pathway in monocytes and neutrophils. 24826913_An association was found in the SIGIRR rs7396562 polymorphism and systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in a Chinese population. 25287661_decreased numbers of SIGIRR-positive CD4+ T cells in SLE patients and its correlation with SLEDAI score as well as the clinical data suggest that SIGIRR may be involved in the pathogenesis of SLE. 25654981_IL-37 acts as an extracellular cytokine by binding to the IL-18 receptor but using the IL-1R8 for its anti-inflammatory properties. 25729923_IL-37 requires the receptors IL-18Ralpha and IL-1R8 to carry out its multifaceted anti-inflammatory program upon innate signal transduction. 25963006_To the best of our knowledge, this is one of the first reports of a phenotype associated with SIGIRR in humans. Our data provide novel mechanistic insight into the probable causation of necrotizing enterocolitis 26344057_Levels of SIGIRR are lower in human colorectal tumors, compared with nontumor tissues; tumors contain the dominant-negative isoform SIGIRR(DeltaE8). 26344417_SIGIRR predicts biochemical recurrence in patients with low Gleason score and low pathological stage prostate cancer. 26561030_Tir8/SIGIRR acts anti-inflammatory on different immune responses,its function in allergic asthma is a controversial issue, since anti- as well as pro-inflammatory effects have been reported 26634342_SIGIRR plays an important role in the negative regulation of LPS response and tolerance in human bladder epithelial cells, possibly through its impact on TLR-mediated signaling. 27297888_show by flow cytometry analysis, western blot, confocal microscopy, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction that IL-1R8 is expressed on human and mouse platelets at high levels and on megakaryocytes. IL-1R8-deficient mice show normal levels of circulating platelets 28533483_Our results indicate that high IL-1R8 expression acts as a novel immunomodulatory mechanism leading to dysregulated immunity with important implications for breast cancer immunotherapy. 28869081_SIGIRR is both a negative regulator of TLR4 and a positive regulator of TLR7/8. 29558695_Specificity protein 1 modulates TGFbeta1/Smad signaling and negatively regulates SIGIRR protein production by macrophages after substance P stimulation. 31149943_The anti-inflammatory IL-37/SIGIRR axis is functionally compromised in HIV infection. 32210474_Immune response against Chlamydia trachomatis via toll-like receptors is negatively regulated by SIGIRR 32945488_Single immunoglobulin and Tollinterleukin1 receptor domain containing molecule protects against severe acute pancreatitis in vitro by negatively regulating the Tolllike receptor4 signaling pathway: A clinical and experimental study. 33123603_Negative Effects of SIGIRR on TRAF6 Ubiquitination in Acute Lung Injury In Vitro. 33155227_MiR-340 suppresses CCl4-induced acute liver injury through exerting anti-inflammation targeting Sigirr. 33391457_IL-37 exerts therapeutic effects in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through the receptor complex IL-1R5/IL-1R8. 34036103_Single Immunoglobulin IL-1-Related Receptor (SIGIRR) Gene rs7396562 Polymorphism and Expression Level in Rheumatoid Arthritis. 34083516_IL-37b alleviates endothelial cell apoptosis and inflammation in Kawasaki disease through IL-1R8 pathway. 34563711_SIGIRR Mutation in Human Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Disrupts STAT3-Dependent microRNA Expression in Neonatal Gut. |
ENSMUSG00000025494 |
Sigirr |
129.021639 |
0.1776717422 |
-2.492714 |
0.220745790 |
126.775076 |
0.00000000000000000000000000002080676718867367354641095210728221989000573948664529779671321358924579953889174785408577861289813881739974021911621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000262485370687883242994686757802599749418103945014457267855722121792992648065499794451937987105338834226131439208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.3868116 |
5.3127056 |
211.6228133 |
18.6485957 |
| ENSG00000185201 |
10581 |
IFITM2 |
protein_coding |
Q01629 |
FUNCTION: IFN-induced antiviral protein which inhibits the entry of viruses to the host cell cytoplasm, permitting endocytosis, but preventing subsequent viral fusion and release of viral contents into the cytosol (PubMed:33563656, PubMed:26354436). Active against multiple viruses, including influenza A virus, SARS coronaviruses (SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2), Marburg virus (MARV), Ebola virus (EBOV), Dengue virus (DNV), West Nile virus (WNV), human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) (PubMed:33563656, PubMed:26354436, PubMed:33270927, PubMed:33239446). Can inhibit: influenza virus hemagglutinin protein-mediated viral entry, MARV and EBOV GP1,2-mediated viral entry, SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 S protein-mediated viral entry and VSV G protein-mediated viral entry (PubMed:33563656). Induces cell cycle arrest and mediates apoptosis by caspase activation and in p53-independent manner. In hepatocytes, IFITM proteins act in a coordinated manner to restrict HCV infection by targeting the endocytosed HCV virion for lysosomal degradation (PubMed:26354436). IFITM2 and IFITM3 display anti-HCV activity that may complement the anti-HCV activity of IFITM1 by inhibiting the late stages of HCV entry, possibly in a coordinated manner by trapping the virion in the endosomal pathway and targeting it for degradation at the lysosome (PubMed:26354436). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19544527, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20064371, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20534863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20943977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21177806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21253575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22479637, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26354436, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33239446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33270927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33563656}. |
Acetylation;Antiviral defense;Cell membrane;Endosome;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Interferon-induced transmembrane (IFITM) proteins are a family of interferon induced antiviral proteins. The family contains five members, including IFITM1, IFITM2 and IFITM3 and belong to the CD225 superfamily. The protein encoded by this gene restricts cellular entry by diverse viral pathogens, such as influenza A virus, Ebola virus and Sars-CoV-2. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2021]. |
hsa:10581; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; cellular response to interferon-beta [GO:0035458]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of viral entry into host cell [GO:0046597]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035455]; response to interferon-beta [GO:0035456]; response to type II interferon [GO:0034341]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] |
19544527_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in 1-8D is associated with neoplasms. 20534863_IFITM2 and IFITM3, disrupted early steps (entry and/or uncoating) of the viral infection, viperin, ISG20, and double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase, inhibited steps in west nile virus and dengue virus viral proteins and/or RNA biosynthesis. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21177806_IFITM1, IFITM2, and IFITM3 inhibit HIV-1 replication through interfering with virus entry. 23376165_Although their inhibitory activities were modest when compared to that of tetherin, IFITMs, but not tetherin, directly reduced the expression of HIV-1 proteins including Gag, Vif and Nef. 23720721_Authors show that interferon-induced transmembrane protein 1 (IFITM-1), IFITM-2, and IFITM-3 exhibit a broad spectrum of antiviral activity against several members of the Bunyaviridae family. 24992036_G3BP1, G3BP2 and CAPRIN1 are required for translation of interferon stimulated mRNAs and are targeted by a dengue virus non-coding RNA. 25422070_In virus-producing cells, IFITMs coalesce with forming virions and are incorporated into HIV-1 viral particles. 25464829_Incorporation of IFITM1, IFITM2 and IFITM3 into HIV-1 virions impair viral fusion and spread. 25552713_Host IFITM3,IFITM2 and IFITM1 facilitate morphogenesis of the human cytomegalovirus assembly. 26354436_propose that the IFITM proteins act in a coordinated manner to restrict HCV infection by targeting the endocytosed HCV virion for lysosomal degradation and demonstrate that the actions of the IFITM proteins are indeed virus and cell-type specific 26387945_IFITM2 and IFITM3 specifically antagonize the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (Env), thereby inhibiting viral infection. 27219333_These results indicate that IFITM2 protein can restrict alphavirus infection by inhibiting viral fusion with cellular membranes. 28223169_IFITM2 promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis via IGF1/IGF1R/STAT3 signaling pathway. 28356532_findings show that the sensitivity of influenza A viruses to the IFN-induced antiviral state and IFITM2 and IFITM3 proteins depends on the pH value at which the viral HA undergoes a conformational transition and mediates membrane fusion 28511927_The transcriptional regulation of IFITM1, 2 and 3 expression. 28630320_Delta20 IFITM2 may serve as a major contributor to the gatekeeping mechanism that explains restriction of X4 viruses in the early stage of HIV-1 infection 30087232_overexpression of IFITM1, 2 and 3 suppressed entry of CXCR4 and CCR5 tropic viruses; entry of transmitted founder HIV-1 in U87 cells is more sensitive to inhibition by IFITM2 and IFITM3 than by IFITM1 30266929_These studies identify a novel role for IFITM1, 2, and 3 in inhibiting HIV replication at the level of translation. 31735710_IFITM2 knockdowns in BeWo trophoblasts increased their spontaneous fusion and allowed fusion in the presence of IFN while also making the cells more susceptible to virus infection. 31792954_IFITM1-IFITM3 are expressed by T cells and are directly involved in adaptive immunity; they regulate CD4+ T helper cell differentiation in a T-cell-intrinsic manner. (Review) 33270927_Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection. 33308825_Predicative value of IFITM2 in renal clear cell carcinoma: IFITM2 is associated with lymphatic metastasis and poor clinical outcome. 34319159_IFITM Proteins That Restrict the Early Stages of Respiratory Virus Infection Do Not Influence Late-Stage Replication. 34321474_IFITM proteins promote SARS-CoV-2 infection and are targets for virus inhibition in vitro. 34933450_Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins Inhibit Infection by the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and the Related Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus in a Cell-Specific Manner. 35543509_SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Hijack IFITM2 for Efficient Replication in Human Lung Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000025492+ENSMUSG00000060591+ENSMUSG00000025491+ENSMUSG00000065968 |
Ifitm3+Ifitm2+Ifitm1+Ifitm7 |
137.734819 |
0.4883394603 |
-1.034044 |
0.187327528 |
30.278833 |
0.00000003741871244551695661240914921215339195015303630498237907886505126953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000154015670857732946912016904275621875797241955297067761421203613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
80.7639121 |
9.7698324 |
166.8653377 |
13.6705456 |
| ENSG00000185215 |
7127 |
TNFAIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q03169 |
FUNCTION: May play a role as a mediator of inflammation and angiogenesis. |
Angiogenesis;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene was identified as a gene whose expression can be induced by the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF) in umbilical vein endothelial cells. The expression of this gene was shown to be induced by retinoic acid in a cell line expressing a oncogenic version of the retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion protein, which suggested that this gene may be a retinoic acid target gene in acute promyelocytic leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7127; |
exocyst [GO:0000145]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; exocyst localization [GO:0051601]; exocytosis [GO:0006887] |
19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20157331_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21057457_TNFAIP2 is a cell migration-promoting protein and its expression predicts distant metastasis. Our data suggest that TNFAIP2 may serve as an independent prognostic indicator for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 21555518_TNFAIP2 is a target gene of the BACH1 transcription factor according to ChIP-seq analysis in HEK 293 cells. 21921781_TNFAIP2 may serve as a useful new marker of dendritic and histiocytic sarcomas. 21934093_A functional variant at the miR-184 binding site in TNFAIP2 is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. 23724109_The TNFAIP2 miRNA binding site rs8126 T>C single nucleotide polymorphism may be a marker for susceptibility to gastric cancer. 23975427_the regulation of TNFAIP2 and its role in promoting NPC tumor progression 25383966_A functional TNFAIP2 3'-UTR rs8126 genetic polymorphism contributes to risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 26189798_findings collectively suggest that TNFAIP2 is a direct KLF5 target gene, and both KLF5 and TNFAIP2 promote breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through Rac1 and Cdc42 26347487_data suggest that TNFAIP2 is a novel inhibitor of NF-kappa-B that acts as an autoinhibitor of the TNFalpha response during septic shock. 26701136_A polarized secretion assay suggested that the silencing of endothelial myeloid-secretory impairs T effector transendothelial migration by reducing the preferential secretion of endothelial-produced CCL2. 27130431_Taken together, genome-wide chromatin analysis of Legionella pneumophila-infected macrophages demonstrated induction of TNFAIP2, a NF-kappaB-dependent factor relevant for bacterial replication. 28393234_Data indicate that TNFAIP2 overexpression may facilitate proliferation and metastasis via activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 29596155_Study investigates the role of miR-221 in the inflammatory response and neuronal apoptosis following spinal cord I/R and the potential participation of TNFAIP2 signaling in oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD)-stressed neuronal cell lines. TNFAIP2 overexpression reversed the inflammatory response and cell apoptosis induced by miR-221 under OGD stress. 30145807_The expression of TNFAIP2 is frequently abnormal in human cancers and in infectious diseases. Due to its significant functions in cell proliferation, angiogenesis, migration and invasion, TNFAIP2 could be a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer. 30877198_ERp29-MSec interaction appeared to require the presence of other bridging protein(s), perhaps triggered by post-translational modification of ERp29 31263157_Knockdown of TNFAIP2 resulted in upregulation of E-cadherin expression and downregulation of TWIST1 expression, which decreased motile function in platinum-resistant urothelial cancer cells. 31392347_we establish TNFAIP2 as a novel target of uORF-mediated translational regulation. Furthermore, our findings suggest that during macrophage differentiation a major uORF-dependent translational switch occurs. 32650782_M-Sec facilitates intercellular transmission of HIV-1 through multiple mechanisms. 33109108_Genetic polymorphisms of PGF and TNFAIP2 genes related to cervical cancer risk among Uygur females from China. 34112215_STAT1 epigenetically regulates LCP2 and TNFAIP2 by recruiting EP300 to contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. 36243694_Pan-cancer analysis of oncogenic TNFAIP2 identifying its prognostic value and immunological function in acute myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000021281 |
Tnfaip2 |
576.697633 |
2.4221144383 |
1.276267 |
0.118024852 |
114.603322 |
0.00000000000000000000000000961249107798107141021367140924289198183565781095342314092166137458843463634017290075917117064818739891052246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000109644797767388425050943889308662591052478866668032928849454469785208721166469558738754130899906158447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
783.4381658 |
57.0841591 |
326.2428410 |
17.8060006 |
| ENSG00000185271 |
123103 |
KLHL33 |
protein_coding |
A6NCF5 |
|
Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:123103; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000090799 |
Klhl33 |
9.362849 |
0.3988059918 |
-1.326241 |
0.584656841 |
5.158954 |
0.02312681957277669397843311571705271489918231964111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.040864242157626677609538745628015021793544292449951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8286738 |
1.8362312 |
11.9772882 |
2.9563649 |
| ENSG00000185291 |
3563 |
IL3RA |
protein_coding |
P26951 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor for IL3 expressed on hematopoietic progenitor cells, monocytes and B-lymphocytes that controls the production and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells into lineage-restricted cells (PubMed:10527461). Ligand stimulation rapidly induces hetrodimerization with IL3RB, phosphorylation and enzyme activity of effector proteins such as JAK2 and PI3K that play a role in signaling cell proliferation and differentiation. Activation of JAK2 leads to STAT5-mediated transcriptional program (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P26952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10527461, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29374162}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an interleukin 3 specific subunit of a heterodimeric cytokine receptor. The receptor is comprised of a ligand specific alpha subunit and a signal transducing beta subunit shared by the receptors for interleukin 3 (IL3), colony stimulating factor 2 (CSF2/GM-CSF), and interleukin 5 (IL5). The binding of this protein to IL3 depends on the beta subunit. The beta subunit is activated by the ligand binding, and is required for the biological activities of IL3. This gene and the gene encoding the colony stimulating factor 2 receptor alpha chain (CSF2RA) form a cytokine receptor gene cluster in a X-Y pseudoautosomal region on chromosomes X or Y. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:3563; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; interleukin-3 receptor activity [GO:0004912]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221] |
12351411_Elevated expression in acute myelogenous leukemia is associated with enhanced blast proliferation, increased cellularity, and poor prognosis 12384414_Bioinformatic study of IL-3 Ralpha & GM Ralpha subunits found a tripeptide sequence near the conserved proline-rich domain which was a key difference between them. Cross-exchange of equivalent subunits altered function compared to wild-type receptors. 12504125_Analysis of the 5' promoter of the hIL-3Ra gene. 12943658_IL-3Ralpha mRNA is upregulated by IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF in human eosinophils 14500898_IL-3 receptor activation is not essential for BCR-ABL-induced myeloproliferative diseases 14671644_REVIEWS overexpression of the IL-3Ralpha chain as one of the mechanisms contributing to the development of a highly malignant leukemic phenotype and evidence that IL-3Ralpha is a marker of leukemic stem cells 15795318_Therefore, these data provide strong evidence that integrin-dependent STAT5A activation controls IL-3-mediated proliferation. 16007196_role in modulating tumor neovascularization in conjunction with VEGFR (KDR) 17522711_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17522711_Sequencing of interleukin 3 receptor alpha in an independent case-control cohort revealed both common intronic haplotypes and several novel, rare missense variants associated with schizophrenia. 18047539_variants in the gene coding for its receptor (IL-23R) are strongly associated with Crohn's disease 18547720_A small but significant contribution of the IL3RA polymorphism to susceptibility to schizophrenia, suggesting that the IL3 pathway may be involved in schizophrenia. 18547720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18555589_CD123+ MDCs were an early-stage immature DC subset, with a significant tumor-inhibiting activity partially via involvement of enhanced cytoplasmic TRAIL. 19257981_Data show high expression of CD86 and CD11C, moderate expression of CD1a and CD123, low levels of CD83 on dendritic cells after induction by GM-CSF and IL-4. 19281803_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19281803_our family-based association study revealed a small but significant contribution of the IL3RA variants to susceptibility to schizophrenia in a Chinese population (Han) 19454491_overexpression of CD123 is an aberrant phenotype present in a subset of precursor-B ALL with hyperdiploid genotype 19614769_Progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in immunosuppressed patients is associated with reduced CD123+ and FOXP3+ cells in the perineoplastic inflammatory infiltrate. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19762535_the less mature hematogones (dim CD45+) that express CD34 lack CD123 expression, whereas the more mature hematogones (moderate CD45+) lack CD34 but always express CD123. 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20809502_assessment of CD123 expression is useful for supporting the diagnosis of classical Hodgkin lymphoma 20819538_CD123 was highly expressed in the bone marrow of the patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, significantly correlated with the proportion of bone marrow blasts, and thus might be the marker of MDS malignant clone. 20888334_Expression of dendritic cell markers CD11c/BDCA-1 and CD123/BDCA-2 in coronary artery disease upon activation in whole blood. 21176354_Over expression of IL-3Ralpha and truncated mutation of hbetac may be involved in proliferation and differentiation block in NB4 cells. 21330473_Interleukin 3 receptor alpha is a cell-surface marker present on leukemia-initiating cells of patients with Fanconi anemia-acute myeloid leukemia, and may be a promising therapeutic target for these patients. 21917686_These findings support the usefulness of CD123 and CD103 to aid in the differential diagnosis of B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders 21933861_High levels of CD34+CD38low/-CD123+ blasts are predictive of an adverse outcome in acute myeloid leukemia 21955314_The pattern of CD123 staining can be a useful feature to distinguish hypertrophic lupus erythematosus, squamous cell carcinoma and hypertrophic actinic keratosis. 22719258_we report that IL3 receptor alpha (IL3Ralpha) and NOTCH play integral roles in the host cell type-specific regulation of PROX1 by Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus 22914610_CD123 expression in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with underlying FLT3 and NPM1 mutations. 23470050_We recommend immunohistochemical analyses for CD123, CD56 and CD4 inblastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm patients, particularly in cases where the initial bone marrow study indicates normal morphology. 23791208_CD123 is a useful immunohistochemical marker to facilitate diagnosis of acute graft-versus-host disease in colon. 24030378_Results suggest that CD123 results suggest that CD123 chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) T cells are a promising immunotherapy for the treatment of high-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML). 24152218_We conclude the hMICL/CD123-based MFC assay is a promising MRD tool in AML. 24751333_In the present study we analyzed the expression of four cell surface antigens relevant to human hematopoiesis-CD90, CD96, CD117, and CD123-in bone marrow from pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients and normal control subjects. 24846193_Increases in CD34(+)CD38(-)CD123(+) cells may reflect malignant clonal cells with aberrant differentiation, overproliferation, and decreased apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome, which were similar to acute myeloid leukemia. 24927407_87.8% of AMLs express CD33. Additionally, 9.4% of AMLs express CD123 without concomitant CD33 expression. 25381130_High interleukin-3 receptor alpha is associated with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. 25406851_CD123+ plasmacytoid dendritic cells contribute to the sarcoidal granulomas associated with injected permanent fillers. 25640886_High CD123 expression is associated with systemic mastocytosis. 25779340_Human BDCA2+CD123+CD56+ dendritic cells (DCs) related to blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm represent a unique myeloid DC subset. 25906118_CD123 positivity represents a marker that can facilitate identification of the early T-cell precursor leukemia subtype, but the lack of sensitivity by immunohistochemistry limits the diagnostic utility. 25957287_Our results suggest that the CD34/CD25/CD123/CD99(+) LAIP is strictly associated with FLT3-ITD-positive cells. 26474588_Data indicate that CD123 was preferentially expressed among CD33/CD117-positive precursor-T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). 26642704_CD96 and CD123 are expressed in bone marrow cells of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes 26678095_CD123 expression is associated with systemic mastocytosis. 27443880_IL-3 hardly down-regulates the alpha-chain of its receptor without depleting the common beta-chain, which enables extraordinarily sustained signaling events, predominantly the activation of Stat5. 27465508_the oncogenic events of FLT3/ITD happen at a cell stage possessing CD123 28096272_Our data define the mechanisms by which SL-101 targets acute myeloid leukemia (AML)and warrant further investigation of the clinical application of SL-101 and other CD123-targeting strategies in AML. 28233860_Family-based whole genome analysis of a family with hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis revealed a homozygous deletion that disrupts CSF2RA, CRLF2, and IL3RA gene in the pseudoautosomal region of the X chromosome in the affected child and one of asymptomatic siblings. 29238040_High IL3RA expression is associated with breast cancer. 29374162_Data show that the N-terminal domain (NTD) of interleukin 3 receptor subunit alpha (IL3Ralpha) exhibits exquisite flexibility and a dynamic transition from a high to a low mobility state upon cytokine binding. 30847774_CD123 expression may thus be useful for assessing AML patients' prognoses. At the time of diagnosis, CD123 expression analysis using IHC may represent a clinically useful assessment for de novo AML patients. 31244444_CD123: A Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Treatment of Leukemia. 31261288_Coexpression of TCF4 and CD123 is a highly reliable feature of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms. 31449667_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells in keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma: A blinded study of CD123 as a diagnostic marker. 31758553_Prognostic relevance of CD123 expression in adult AML with normal karyotype. 31839040_expression of CD44, CD87 and CD123 in different phenotype of acute leukemia are different, which correlateds with prognosis 31990690_The RNFT2/IL-3Ralpha axis regulates IL-3 signaling and innate immunity. 32111969_CD28/4-1BB CD123 CAR T cells in blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. 32417762_Clinical value of CD25/CD123 co-expression in acute myeloid leukemia patients. 32460405_FLT3-ITD DNA and mRNA levels in AML do not correlate with CD7, CD33 and CD123 expression. 33129747_CD123 Expression in Philadelphia Chromosome-like B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma. 33358743_Overexpression of CD200 and CD123 is a major influential factor in the clinical course of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. 34034609_Quantitative analyses of CD7, CD33, CD34, CD56, and CD123 within the FLT3-ITD/NPM1-MUT myeloblastic/monocytic bulk AML blastic populations. 34372571_Improved Activity against Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-NK-92 Cells Designed to Target CD123. 34731593_Two New Neutrophil Subsets Define a Discriminating Sepsis Signature. 34855461_CD123 Expression Is Associated With High-Risk Disease Characteristics in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group. 35384878_The Expressions of CD30 and CD123 of Mastocytosis in Taiwan. 36227664_Expression of CD123 Related Long Non-coding RNA in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Bone Marrow Mononuclear Cells and Its Clinical Significance. |
|
|
144.693656 |
0.4656754415 |
-1.102603 |
0.322419159 |
11.379717 |
0.00074250445573513415131045034556223072286229580640792846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001768780788678273258388018440712130541214719414710998535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
77.5177188 |
26.1446730 |
163.7187497 |
39.2801226 |
| ENSG00000185304 |
729857 |
RGPD2 |
protein_coding |
P0DJD1 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Predicted to contribute to GTPase activator activity. Predicted to be involved in NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus. Predicted to be part of nuclear pore. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:729857; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus [GO:0006607]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790] |
|
|
|
346.421524 |
0.3841038603 |
-1.380432 |
0.093037850 |
223.358907 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001673959723722833277477920134314264172647923194445791432404204398060811902931859382825486447984876166099455049531320523137066535492023522380122813046909868717193603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000361751764599546409794843009642189433016907715427852323645101753546501149472152736428376452004561831408015219963625321925515185284005781340965768322348594665527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
195.4911502 |
12.5650076 |
512.7305597 |
21.6678618 |
| ENSG00000185420 |
64754 |
SMYD3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H7B4 |
FUNCTION: Histone methyltransferase. Specifically methylates 'Lys-4' of histone H3, inducing di- and tri-methylation, but not monomethylation (PubMed:15235609, PubMed:22419068). Also methylates 'Lys-5' of histone H4 (PubMed:22419068). Plays an important role in transcriptional activation as a member of an RNA polymerase complex (PubMed:15235609). Binds DNA containing 5'-CCCTCC-3' or 5'-GAGGGG-3' sequences (PubMed:15235609). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15235609, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22419068}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Cytoplasm;Metal-binding;Methyltransferase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a histone methyltransferase which functions in RNA polymerase II complexes by an interaction with a specific RNA helicase. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:64754; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; histone lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0018024]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II complex binding [GO:0000993]; RNA polymerase II intronic transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001162]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; histone lysine methylation [GO:0034968]; myotube cell development [GO:0014904]; negative regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0006469]; nucleosome assembly [GO:0006334]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944] |
15235609_SMYD3 encodes a histone methyltransferase involved in the proliferation of cancer cells. 16081583_SMYD3-NY is a novel transcript variant of the SMYD3 gene, and SMYD3-NY protein may influence transcriptional regulation during spermatogenesis via HTMase activity 16155568_The common variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism in SMYD3 is a susceptibility factor for some types of human cancer. 16441421_Enhanced SMYD3 expression is associated with growth of breast cancer 17431393_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17431393_study shows that SMYD3 polymorphism is not associated with the occurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese population 17963297_The proliferation, migration induction and apoptosis inhibition activities of SMYD3 in hepatocellular carcinoma may be mediated through RIZ1 CpG promoter hypermethylation. 17998933_A cleaved form lacking the amino-terminal 34 amino acids is higher in methyltransferase activity in cancer cells. 18027872_data indicate that the SMYD3 genotype is not related to the risk of developing NSCLC 18294291_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18294291_VNTR polymorphism in the promoter region of SMYD3 gene may be a susceptibility factor for human cancers such as ESCC by interacting with tobacco carcinogens. 18452649_SMYD3 plays crucial roles in HeLa cell proliferation and migration/invasion, and that it may be a useful therapeutic target in human cervical carcinomas. 19321255_SMYD3 has a role in regulation of c-Met expression and in cell migration and invasion induced by HGF 19403031_HBx may induce the expression of histone methyltransferase SMYD3, which in turn stimulates cell proliferation and blocks apoptosis in HepG2 cells. 19509295_The results presented here identify SMYD3 as a new coactivator for estrogen receptor-mediated transcription, providing a possible link between SMYD3 overexpression and breast cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20725992_presence of activating KRAS mutations is significantly correlated to an upregulation of 13 genes (adjusted P-value |
ENSMUSG00000055067 |
Smyd3 |
214.784621 |
0.4035815763 |
-1.309068 |
0.118557780 |
123.299752 |
0.00000000000000000000000000011989596033465739743706398738277089520272908588392530440138446189055349141387024625160506730026099830865859985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001469820909085999369648773010335659009246612646134694786503101658574700399875062606369624518265482038259506225585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
128.1640917 |
9.3555235 |
320.0661903 |
15.1950742 |
| ENSG00000185432 |
25840 |
METTL7A |
protein_coding |
Q9H8H3 |
FUNCTION: Putative methyltransferase. {ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) May be involved in the assembly and release stages of hepatitis C virus (HCV) life cycle and thus play a crucial role in HCV propagation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26185986}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Host-virus interaction;Lipid droplet;Membrane;Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable methyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in methylation. Located in lipid droplet. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25840; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; membrane [GO:0016020]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; methylation [GO:0032259] |
26185986_AAM-B is predominantly localized in lipid droplets and may be involved in recruitment of NS4B protein in the proximity of lipid droplets. 28416772_Results revealed that the methylation level of METTL7A was downregulated in thyroid cancer, and determined the methylation level of one CpG site at the exon of the METTL7A gene body impacted the transcriptional activity. 31955862_Quantitative proteomic analysis identifies novel regulators of methotrexate resistance in choriocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000058057+ENSMUSG00000056487+ENSMUSG00000054619 |
Mettl7a3+Mettl7a2+Mettl7a1 |
1025.668543 |
4.8420182708 |
2.275609 |
0.069486532 |
1081.813158 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000296292688214514274500006200705838193692667061233840369587827774728674163882882847754186693225 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000336406159849710004014822079494500827275140438410062030475404284645892194655958054271093564381 |
Yes |
No |
1710.6961701 |
65.4012181 |
355.5122354 |
11.4515707 |
| ENSG00000185436 |
163702 |
IFNLR1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IU57 |
FUNCTION: The IFNLR1/IL10RB dimer is a receptor for the cytokine ligands IFNL2 and IFNL3 and mediates their antiviral activity. The ligand/receptor complex stimulate the activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway leading to the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISG), which contribute to the antiviral state. Determines the cell type specificity of the lambda interferon action. Shows a more restricted pattern of expression in the epithelial tissues thereby limiting responses to lambda interferons primarily to epithelial cells of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and reproductive tracts. Seems not to be essential for early virus-activated host defense in vaginal infection, but plays an important role in Toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced antiviral defense. Plays a significant role in the antiviral immune defense in the intestinal epithelium. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12469119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12483210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12521379}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the class II cytokine receptor family. This protein forms a receptor complex with interleukine 10 receptor, beta (IL10RB). The receptor complex has been shown to interact with three closely related cytokines, including interleukin 28A (IL28A), interleukin 28B (IL28B), and interleukin 29 (IL29). The expression of all three cytokines can be induced by viral infection. The cells overexpressing this protein have been found to have enhanced responses to IL28A and IL29, but decreased response to IL28B. Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:163702; |
interleukin-28 receptor complex [GO:0032002]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine receptor activity [GO:0004896]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; mucosal immune response [GO:0002385]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; positive regulation of cellular respiration [GO:1901857]; regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0050691]; response to type III interferon [GO:0034342]; type III interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038196] |
12469119_IL-28 and IL-29 interact with a heterodimeric class II cytokine receptor that consisted of IL-10 receptor beta (IL-10Rbeta) and an orphan class II receptor chain, designated IL-28Ralpha. 12483210_distinct receptor complex that is utilized by all three IFN-lambda proteins for signaling and is composed of two subunits, a receptor designated CRF2-12 (also designated as IFN-lambdaR1) and a second subunit, CRF2-4 (also known as IL-10R2) 15166220_interleukin (IL)-28 receptor tyrosine residues have roles in antiviral and antiproliferative activity of IL-29/interferon-lambda 1 16819289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16819289_Results suggested that the g.32349 G>A polymorphism of IL-28RA might be associated with susceptibility to allergic rhinitis. 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724244_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19798076_study supports that IFN-lambdas do not influence every type of cell and that membrane-associated variant IFN-lambda R1 expression is not sufficient to ensure cellular sensitivity toward these cytokines. 20057073_Although the IFN-lambda1(Bac)-IFN-lambda1R1 and IFN-lambda1(Ins)-IFN-lambda1R1 complexes differed only in the nature of the expression system used for the ligand, their crystallization conditions and crystal forms were quite different 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20934432_IFN-lambdaR1 consists of two distinct domains having fibronectin type III topology. 20953190_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21742059_two SNPs in IL28RA are correlated with susceptibility to HCV infection and spontaneous viral clearance, which implicates a primary role of IL28RA in the outcomes of HCV infection 22386267_No consistent association is found between IL28RA and multiple sclerosis in a Basque-Spanish population. 22891284_Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are major producers of IFN-lambda2 (a type III interferon) in response to viral stimulation and also express functional receptors for this cytokine. 23565619_The rs12980275 AG/GG genotype and rs10903035 G allele remained independently associated with early pegylated interferon and ribavirin failure of hepatitis C in hepatitis C/HIV coinfected patients. 24144988_Results show that the distribution of IL10RB and IL28RA genotypes among the Hepatitis C virus-infected and control groups did not differ significantly. 24409098_Epigenetic reprogramming of IFNLR1-mediated response potentiates antiviral activity and suppresses tumor growth. 24438680_IL28RA polymorphism (rs10903035) seems to be implicated in the glucose homeostasis because AA genotype increases the likelihood of IR, but this association was different depending on hepatic fibrosis and HCV genotype. 24510368_This study is the first to show the activation of a type III interferon response in low-risk human papillomavirus positive cervical cells and suggests that the lack of this response may be related to lesion progression. 24752298_IFN-lambda receptor 1 expression is induced in chronic hepatitis C and correlates with the IFN-lambda3 genotype and with nonresponsiveness to IFN-alpha therapies. 25911176_expression of IL-28RA mRNA may be correlated with the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus 26400298_Polymorphism within the IL-28R1, but not in IL-28B, is associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms in Chinese. 27133025_Results show that IFNLR1 box1 and box2 motifs are required for stable complex formation with JAK1 and the crystal structure of JAK1 reveals IFNLR1 box1 binding site in the FERM domain. Also, structure-based mutagenesis reveals IFNLR1 PxxLxF motif that is essential for binding. Structure of JAK1 with IL10RA box1 indicates conservation among class II receptors. 27166550_Selective expression of IFNlambdaR1 was considered to be a plus point towards the targeted anti-viral activity of IFNlambdas but artificial control on its expression will surely make IFNlambdas a better drug with enhanced activity. 27725180_In this structure, the receptor peptide forms an 85-A-long extended chain, in which both the previously identified box1 and box2 regions bind simultaneously to the FERM and SH2-like domains of JAK1. 29080269_Significant associations were observed for 4 variants in IFNAR2, IFNLR1 with hepatitis B virus infection, and IFNLR1-rs4649203 was associated with hepatitis B recovery. Moreover, the authors demonstrated the clear relevance of 5 polymorphisms in IFNA1, IFNA2, IFNL4 with hepatocellular carcinoma. 29453195_This study was designed to explore the genetic etiology of deafness in a large Chinese family with autosomal dominant, nonsyndromic, progressive sensorineural hearing loss (ADNSHL). Inner ear expression of Ifnlr1 was investigated by immunostaining in mice. ifnlr1 Morpholino knockdown Zebrafish were constructed to explore the deafness mechanism.. IFNLR1 mutations are associated with ADNSHL 29549834_Interferon lambda receptor 1 (IFNLR1) mRNA is increased in human rhinovirus (HRV) bronchiolitis infants. Increased IFNLR1 transcript levels characterized HRV-infected infants with more severe bronchiolitis and blood eosinophilia. IFNLR1 transcript is increased in infants infected with HRVC species. 30247785_IFN-lambda4 suppressed HIV infection of macrophages. This IFN-lambda4-mediated HIV inhibition was compromised by the antibodies against IFN-lambda receptor complex, IFN-lambdaR1/IL-10R2. 31366248_Genetic Polymorphisms of the IFNLR1 Gene Correlate with HCV Infection and Biochemical Features of Chronic HCV Patients in Yunnan, China. 31799654_Significance of IL28RA in diagnosis of early pancreatic cancer and its regulation to pancreatic cancer cells by JAK/STAT signaling pathway - effects of IL28RA on pancreatic cancer. 32353085_Differential expression of interferon-lambda receptor 1 splice variants determines the magnitude of the antiviral response induced by interferon-lambda 3 in human immune cells. 33269531_Interferon III-related IL28RA variant is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus and specific disease sub-phenotypes. 33751344_Association of TNFRSF1A and IFNLR1 Gene Polymorphisms with the Risk of Developing Breast Cancer and Clinical Pathologic Features. 34195850_Downregulated expression of IL28RA is involved in the pathogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000062157 |
Ifnlr1 |
14.433487 |
2.3129133016 |
1.209711 |
0.464895745 |
6.763138 |
0.00930599729530724555093268435257414239458739757537841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017950407746828926647264523808189551346004009246826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.5158408 |
5.3090137 |
8.9656125 |
1.8414014 |
| ENSG00000185477 |
285513 |
GPRIN3 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZVF9 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in neurite outgrowth. {ECO:0000250}. |
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in neuron projection development. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:285513; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175] |
22833210_Functional compensation could occur to counteract the loss of one allele in GRIN2C and GRIN3 family genes. 33254176_miR-6838-5p Affects Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion by Targeting GPRIN3 via the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Gastric Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000045441 |
Gprin3 |
322.130253 |
5.3034625940 |
2.406935 |
0.106248188 |
548.015235 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034021893998564451423594846450780987408916908946654379252038705867888414686637069858675437790854183956682320003851202446359991807429914318023225495151319307460307561937282797302241681610531776441086035599873292 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000017998679405692163351067118138753495278870529737852210636078170939790123458088073100187225779786001867519935373657743662360538717627363538333667995032873046857440239620723686054772378238029323844698797699255149 |
Yes |
No |
551.2607530 |
34.3254324 |
104.7205599 |
5.6830527 |
| ENSG00000185482 |
246329 |
STAC3 |
protein_coding |
Q96MF2 |
FUNCTION: Required for normal excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle and for normal muscle contraction in response to membrane depolarization. Required for normal Ca(2+) release from the sarcplasmic reticulum, which ultimately leads to muscle contraction. Probably functions via its effects on muscle calcium channels (PubMed:23736855, PubMed:29078335). Increases CACNA1S channel activity, in addition to its role in enhancing the expression of CACNA1S at the cell membrane. Has a redundant role in promoting the expression of the calcium channel CACNA1S at the cell membrane (By similarity). Slows down the inactivation rate of the calcium channel CACNA1C (PubMed:29078335). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BZ71, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23736855, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29078335}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the excitation-contraction coupling machinery of muscles. This protein is a member of the Stac gene family and contains an N-terminal cysteine-rich domain and two SH3 domains. Mutations in this gene are a cause of Native American myopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2013]. |
hsa:246329; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; synapse [GO:0045202]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; neuromuscular synaptic transmission [GO:0007274]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901387]; skeletal muscle contraction [GO:0003009]; skeletal muscle fiber development [GO:0048741] |
23736855_A mutation in human STAC3 is the genetic basis of the debilitating Native American myopathy. 28777491_STAC3 mutation is associated with overlapping features of Carey-Fineman-Ziter syndrome and Moebius syndrome. 30168660_Study reports patients with congenital myopathy carrying either a homozygous, heterozygous p.(Trp284Ser) STAC3 variant or a novel splice site change (c.997-1G > T). The patients have distinctive dysmorphic features in addition to a malignant hyperthermia-like in some. These variants showed a defective excitation-contraction which is not a result of CaV 1.1 sarcolemma mislocation or impaired interaction with CaV 1.1. 30543836_recent identification of the adaptor protein STAC3 as fourth essential component of skeletal muscle EC coupling prompted vigorous research to reveal its role in this signaling process. 31559918_Bayesian statistics predicted CACNA1S variant p.Thr1009Lys and RYR1 variants p.Ser1728Phe and p.Leu4824Pro are likely pathogenic, and novel STAC3 variant p.Met187Thr has uncertain significance. Nearly a third of MHS subjects had only benign variants. Bayesian method provides new approach to predict MH pathogenicity of genetic variants 31859625_Unexpected discoveries in the case reported here in a Kuwaiti family, via Next Generation Sequencing, identifying the STAC3 mutation as the underlying cause of a Native American Myopathy phenotype. 32492370_Multiple Sequence Variants in STAC3 Affect Interactions with CaV1.1 and Excitation-Contraction Coupling. 36030003_STAC3 related congenital myopathy: A case series of seven Comorian patients. |
ENSMUSG00000040287 |
Stac3 |
155.328857 |
0.3781949514 |
-1.402798 |
0.131211659 |
117.019722 |
0.00000000000000000000000000284227150662093103405805491040520141815108466337723295393745155497482450957652533318764653813559561967849731445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000033189816010858340446087090725370475321063009976284056926073293144834573664692101147011271677911281585693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.7506382 |
7.2111527 |
225.5862615 |
12.1194421 |
| ENSG00000185513 |
26013 |
L3MBTL1 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y468 |
FUNCTION: Polycomb group (PcG) protein that specifically recognizes and binds mono- and dimethyllysine residues on target proteins, therey acting as a 'reader' of a network of post-translational modifications. PcG proteins maintain the transcriptionally repressive state of genes: acts as a chromatin compaction factor by recognizing and binding mono- and dimethylated histone H1b/H1-4 at 'Lys-26' (H1bK26me1 and H1bK26me2) and histone H4 at 'Lys-20' (H4K20me1 and H4K20me2), leading to condense chromatin and repress transcription. Recognizes and binds p53/TP53 monomethylated at 'Lys-382', leading to repress p53/TP53-target genes. Also recognizes and binds RB1/RB monomethylated at 'Lys-860'. Participates in the ETV6-mediated repression. Probably plays a role in cell proliferation. Overexpression induces multinucleated cells, suggesting that it is required to accomplish normal mitosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17540172, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18408754, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20870719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20870725}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromatin regulator;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene represents a polycomb group gene. The encoded protein functions to regulate gene activity, likely via chromatin modification. The encoded protein may also be necessary for mitosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:26013; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; chromatin lock complex [GO:0061793]; condensed chromosome [GO:0000793]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; methylated histone binding [GO:0035064]; nucleosome binding [GO:0031491]; SAM domain binding [GO:0032093]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; heterochromatin formation [GO:0031507]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation [GO:0045652]; regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0007088] |
12588862_The ability of TEL to repress TEL-responsive promoters is enhanced by the presence of H-L(3)MBT, an effect dependent on the H-L(3)MBT and the TEL interacting domains, which are mapped to their respective SPM/SAM domains. 15123827_represents a previously undescribed imprinted locus, a vertebrate Polycomb group gene shown to be regulated by this mechanism, and has implications for the pathogenesis of myeloid malignancies associated with 20q deletions 15334543_L3MBTL may have a role in myeloid leukemia 17540172_The MBT domain is related to protein domains that directly bind methylated histone residues and study found that L3MBTL1 MBT domains compact nucleosomal arrays dependent on mono- and dimethylation of histone H4 lysine 20 and of histone H1b lysine 26. 18026117_An unexpected mode of peptide-mediated dimerization suggests a possible mechanism for chromatin compaction by L3MBTL1 18042461_The structural and binding studies of the two modules provide insights into the molecular principles governing the decoding of lysine methylation states, thereby highlighting a methylation state-specific layer of histone mark readout. 18408754_H4K20 monomethylation and PR-SET7 are important for L3MBTL1 function 20585043_haploinsufficiency of L3MBTL1 contributes to some (20q-) myeloproliferative neoplasms, especially polycythemia vera, by promoting erythroid differentiation 20870725_SET8-mediated methylation of p53 at Lys-382 promotes the interaction between L3MBTL1 and p53 in cells. 21149733_Data suggest that the loss of L3MBTL1 contributes to the development of 20q(-) hematopoietic malignancies by inducing replicative stress, DNA damage, and genomic instability. 21341991_depletion of L3MBTL1 does not affect hESC self-renewal, rather it enhances differentiation toward extra-embryonic trophoblast tissues 21837478_High expression of L3MBTL1 was associated with low grade and hormone receptor-positive tumors, as well as low risk of disease recurrence and breast cancer death. 24243547_Data indicate that germline genes, some of which drive oncogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster, are similarly ectopically activated in a wide range of human cancers. 25754204_The polycomb group protein L3MBTL1 represses a SMAD5-mediated hematopoietic transcriptional program in human pluripotent stem cells. 27553422_Loss of the paternally derived allele of the imprinted L3MBTL1 gene is associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. 29737552_results revealed that the three RNAs-based biomarker network (long non-coding intergenic RNA-[lncRNA RP11-909B2.1], Homo sapiens microRNA-595 [hsa-miRNA-595], and L3MBTL1 mRNA), had high sensitivity and specificity for discriminating CRC from healthy controls and also from benign colorectal neoplasm. 33515207_Expression and DNA Methylation Status of the Imprinted Genes PEG10 and L3MBTL1 in the Umbilical Cord Blood and Placenta of the Offspring of Assisted Reproductive Technology. |
ENSMUSG00000035576 |
L3mbtl1 |
24.917267 |
0.3510966506 |
-1.510060 |
0.423434092 |
12.231391 |
0.00046992147228937139165697023379664187814341858029365539550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001159873065383130834316016688489980879239737987518310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.2283677 |
4.1495880 |
39.8909249 |
7.5814823 |
| ENSG00000185522 |
256329 |
LMNTD2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IXW0 |
|
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be a structural constituent of chromatin. Predicted to be involved in regulation of chromatin assembly. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome. Predicted to be active in lamin filament. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:256329; |
lamin filament [GO:0005638]; structural constituent of chromatin [GO:0030527]; chromatin organization [GO:0006325] |
|
ENSMUSG00000025500 |
Lmntd2 |
77.841207 |
0.0893691274 |
-3.484080 |
0.301242675 |
148.730380 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000032845517097434380118008680444576886763684394110085609061293946296489532148142470879159009536363278414228261681273579597473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000004799998340179519444398510456853420932332076248366941869209519532877114799332424069713831649153235048288479447364807128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.0440245 |
2.4650295 |
136.1370104 |
14.7372398 |
| ENSG00000185551 |
7026 |
NR2F2 |
protein_coding |
P24468 |
FUNCTION: Ligand-activated transcription factor. Activated by high concentrations of 9-cis-retinoic acid and all-trans-retinoic acid, but not by dexamethasone, cortisol or progesterone (in vitro). Regulation of the apolipoprotein A-I gene transcription. Binds to DNA site A. May be required to establish ovary identity during early gonad development (PubMed:29478779). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18798693, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1899293, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29478779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9343308}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the steroid thyroid hormone superfamily of nuclear receptors. The encoded protein is a ligand inducible transcription factor that is involved in the regulation of many different genes. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010]. |
hsa:7026; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; retinoic acid binding [GO:0001972]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0048514]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; female gonad development [GO:0008585]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; interneuron migration [GO:1904936]; lymphatic endothelial cell fate commitment [GO:0060838]; maternal placenta development [GO:0001893]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045736]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010596]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; placenta blood vessel development [GO:0060674]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003084]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; radial pattern formation [GO:0009956]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519]; trophoblast giant cell differentiation [GO:0060707] |
12614160_COUP-TFII represses the alpha-subunit of mitochondrial F1F0 ATP synthase (ATPA) complex and inhibits the USF2-dependent transactivation of the ATPA promoter through competition for an overlapping bindng site in the ATPA cis-acting regulatory element 1. 12843196_DAX-1 and COUP-TFII may play a role in the modulation of Ad4BP/SF-1-dependent transcription of steroidogenic enzymes in different cell types and follicular stages in normal cycling human ovaries. 15265774_GR stimulates COUP-TFII-induced transactivation by attracting cofactors via its activation function-1, while COUP-TFII represses the GR-governed transcriptional activity by tethering corepressors ... 17455195_the DR motif site of the renin gene functions as a negative regulatory element involved in a twofold repression of transcription; nucleic receptors bind the site and are important in renin gene expression; one of the binding proteins may be COUP-TFII. 18199540_Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor D by hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 alpha and chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factors 1 and 2. 18765665_COUP-TFII antagonizes the repression of the PED/PEA-15 gene by HNF-4alpha. 18798693_Data demonstrate that COUP-TFII is a ligand-regulated nuclear receptor, in which ligands activate the receptor by releasing it from the autorepressed conformation. 18815287_venous endothelial cell fate regulator COUP-TFII is expressed in lymphatic cells throughout development and physically interacts with Prox1 to form a stable complex in various cell types 19082449_COUP-TFII may represent a biomarker for good prognosis in colorectal cancer. 19154418_COUP-TFII was investigated as a possible regulator of lymphangiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression. 19210544_The present study shows that COUP-TFII plays important roles in the regulation of the function of Prox1. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20147377_Novel and distinct cell-intrinsic mechanisms mediated by COUP-TF genes to direct the specification and differentiation of progenitor cells; COUP-TFs are crucial for dorsalization of the eye. 20195529_Results strongly suggest that NR2F2 is involved in villous CTB cell differentiation and that NR2F2 acts, at least in part, by directly activating TFAP2A gene expression and by potentiating the transactivation of TFAP2A by RARA and RXRA. 20351309_Data suggest a novel model that the endothelial cell fate regulators, Notch, COUP-TFII, and Prox1, are under an exquisite feedback control mechanism and dynamically regulate each other in LECs. 20386594_role for the TGFbeta pathway and COUP-TFII in mediating the endothelial transdifferentiating properties of retinoic acid 20549515_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20585627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21151097_NR2F2 plays a crucial role in the activation of neural genes during early differentiation in humans. 22178710_In summary, COUP-TFII is expressed in the human fetal forebrain in GABAergic cells, according to its possible role in migration of cortical interneurons. 22493443_COUP-TFII negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation via interaction with Runx2, and during the differentiation state, BMP2-induced Runx2 represses COUP-TFII expression and promotes osteoblast differentiation. 22606236_The C-allele at rs3743462 was associated with increased NR2F2 binding and decreased NR2F2 gene expression. 22693611_nucleolin plays a coregulatory role in transcriptional regulation of the tumor suppressor RARB2 by COUP-TFII 22734039_COUP-TFII regulates vein identity by suppressing the Notch signal pathway. 23136034_MiR-302 inhibits NR2F2 and promotes pluripotency through indirect positive regulation of OCT4. 23201680_findings reveal that the destruction of the TGF-beta-dependent barrier by COUP-TFII is crucial for the progression of PTEN-mutant prostate cancer into a life-threatening disease 23345397_COUP-TFII orchestrates venous and lymphatic endothelial identity by homo- or hetero-dimerisation with PROX1 23458092_COUP-TFII-V2 negatively regulates the function of COUP-TFII by inhibiting its binding to DNA, decreasing Cyp7a1 expression. 23690307_Data suggest that NR2F2 is expressed in stromal cells of healthy ovary with little/no expression in epithelial cells; this pattern is markedly disrupted in ovarian cancers with decreased NR2F2 in stroma and ectopic NR2F2 expression in epithelium. 23704310_Data suggest that NR2F2 and CTNNB1 (catenin beta-1) are aberrantly expressed in uterine fibroid tissue compared with matched myometrium, with strong blood vessel-specific localization. 23744056_Hey2 and COUP-TFII have an important role in arteriovenous differentiation of human endothelial cells. 23975195_COUP-TFII and related NRs such as the COUPTFs and PNR can selectively associate with the developmental corepressor BCL11A via a conserved motif F/YSXXLXXL/Y within the RID1 and RID2 domains. The interaction with BCL11A facilitates COUP-TFII-mediated repression of the RARb2 gene. 23975195_Interaction of NSD1 with the NR2E/F subfamily including COUP-TFI, COUP-TFII, EAR2 and TLX requires a F/YSXXLXXL/Y motif. NSD1 interaction with liganded NRs is mediated by an overlapping LXXLL motif. 24058409_Using several human red opsin enhancer/promoter-luciferase reporter constructs, the study found that COUPTFII suppressed intron 3-4 region-dependent luciferase activities. 24122412_In vitro silencing of COUP-TFII reduces the cell growth. 24141032_These data indicate a novel role for COUP-TFII in suppression of NFkappaB activity. 24176914_COUP-TFII plays a role in controlling the expression of inflammatory cytokines. 24702954_showed that all six coding sequence variants observed in individuals significantly alter the activity of NR2F2 on target promoters 25032732_Overexpression of COUP-TFII was required for cancer cells to metastasise in vivo. 25129343_TGF-beta inhibited the expression of NR2F2. 25372459_These data demonstrate that Nr2f2 is a direct target of POU4F3 in vitro and that this regulatory relationship may be relevant to hair cell development and survival. 25687954_COUP-TFII (NR2F2) induces down-regulation of cadherin-6 and up-regulation of cadherin-11 in cultured cell lines.high expression of COUP-TFII in some gastric and oesophageal adenocarcinomas, correlated with abnormal cadherin-11 expression. 26261604_Positive COUP-TF II expression levels has significant value in determining CRC stage and metastasis and cooperates with negative Smad4 expression contributing to assess prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. 26800338_NR2F2 is a Direct Target Gene of miR-382 in colorectal cancer. 26895100_Low COUPTFII expression is associated with prostate cancer. 27108958_COUP-TFII is a critical factor controlling metastatic gene networks to promote prostate cancer metastasis. 27193872_Results indicate that COUP-TFII may play an oncogenic role in RCC, and COUP-TFII may promote tumor progression through inhibiting BRCA1. 27314877_NR2F2 mediates BMMSCinduced proliferation of Reh cells, partially via regulation of VEGFA. Disrupting microenvironmental support by targeting NR2F2 may be a potential therapeutic strategy for ALL. 27345768_Studied the role of Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group F member 2 (NR2F2) in MSC chondrogenesis in bioprinted cartilage. NR2F2 over-expressed MSCs showed significantly enhanced chondrogenesis while NR2F2 knockdown cells demonstrated the exactly opposite behavior. 27363585_We conclude that COUP-TFII mutations can cause diaphragmatic hernias, and should be included in the differential diagnosis of CDH patients, particularly those with comorbid congenital heart defects. 27748848_miR-382 inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting COUPTFII. 27844448_MicroRNA-27b was targeted and down-regulated by NR2F2 in human gastric cancer tissues and cells. 27866920_We showed that the orphan receptor COUP-TFII is an important player in hepatic neoangiogenesis. COUP-TFII expression in hepatic stellate cells (HSC) controls the crosstalk between hepatic HSC and endothelial cells coordinating vascular remodelling during liver injury. 27905023_Dividing COUP-TFII+ progenitor cells were localized to ventral CGE 28192117_NR2F2 could promote TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal carcinoma cells and inhibit Smad7 expression via transactivation of miR-21. 28922831_fifth of COUP-TFI cells also co-expressed COUP-TFII, and cells expressing either transcription factor followed posterior or anterio-lateral pathways into the cortex 29026152_Genetic and Epigenetic Profiling Reveals EZH2-mediated Down Regulation of OCT-4 Involves NR2F2 during Cardiac Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. 29207189_The results of the present study suggest that COUPTFII functions as a significant regulatory suppressor of gastric cancer growth and metastasis, and suggests that COUPTFII may serve as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer metastasis. 29222010_NR2F2 loss-of-function mutation is associated with increased susceptibility to double outlet right ventricle and ventricular septal defect . 29478779_heterozygous frameshift mutations in NR2F2, encoding COUP-TF2, were identified in three children. 29544697_High COUP-TFII expression is associated with increased lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in prostate adenocarcinoma. 29663647_A pathogenic NR2F2 variant (c.856dupG, p.Val286Glyfs*23) caused syndromic forms of congenital heart defect. 29982401_Under hypoxia, endometriotic stromal cells produce more angiogenin, a potent and noncanonical angiogenic factor, by suppressing the transcription repressor, COUP-TFII to promote angiogenesis. 30481528_The interaction is known to control gluconeogenesis, principally through direct binding of COUP-TFII/Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) complexes to the promoters of gluconeogenic enzyme genes. 30592135_NR2F2-AS1 may influence the NSCLC cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis through regulating miR-320b targeting BMI1. 30720060_These findings suggested NR2F2 as a novel susceptibility gene of human congenital bicuspid aortic valve. 30968145_Study results revealed that COUPTFII knockdown significantly inhibited colorectal cancer invasion and migration. Expression of miR34a was revealed to be inversely correlated with COUPTFII expression. High COUP-TFII expression competitively inhibited miR-34a transcription, thereby promoting the epithelialmesenchymal transition process. These results indicated that COUP-TFII and miR-34a may regulate each other. 31000673_A genome-wide association study implicates NR2F2 in lymphangioleiomyomatosis pathogenesis. 31368079_Orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII is an oncogenic gene in renal cell carcinoma. 31588232_Cooperativity of co-factor NR2F2 with Pioneer Factors GATA3, FOXA1 in promoting ERalpha function. 31886265_Increased COUP-TFII expression mediates the imbalance of Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation and progression to osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients. 31892566_COUP-TFII knock-down promoted proliferation and invasion via activation of Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin and up-regulation of FOXC1. 32065070_Genomic Characterization of Endothelial Enhancers Reveals a Multifunctional Role for NR2F2 in Regulation of Arteriovenous Gene Expression. 32107331_The Coup-TFII orphan nuclear receptor is an activator of the gamma-globin gene. 32109138_LncRNA NR2F2-AS1 Upregulates Rac1 to Increase Cancer Stemness in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. 32320667_Imbalance of Excitatory/Inhibitory Neuron Differentiation in Neurodevelopmental Disorders with an NR2F1 Point Mutation. 32579581_Elevated COUP-TFII expression in dopaminergic neurons accelerates the progression of Parkinson's disease through mitochondrial dysfunction. 32631390_NR2F2 plays a major role in insulin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells. 32819587_DNA methylation at CpG island shore and RXRalpha regulate NR2F2 in heart tissues of tetralogy of Fallot patients. 33166992_COUP-TFII promotes metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through upregulating Snail in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 33200800_miR-194-5p serves a suppressive role in human keloid fibroblasts via targeting NR2F2. 33239293_Regeneration of the pulmonary vascular endothelium after viral pneumonia requires COUP-TF2. 33244044_The absence of (TCAGGG)n repeats in some telomeres, combined with variable responses to NR2F2 depletion, suggest that this nuclear receptor plays an indirect role in the alternative lengthening of telomeres. 33664454_YAP1 overexpression contributes to the development of enzalutamide resistance by induction of cancer stemness and lipid metabolism in prostate cancer. 34070923_The miR-106b/NR2F2-AS1/PLEKHO2 Axis Regulates Migration and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer through the MAPK Pathway. 34084171_Decidual NR2F2-Expressing CD4(+) T Cells Promote TH2 Transcriptional Program During Early Pregnancy. 34315577_Exome sequencing of fetuses with congenital diaphragmatic hernia supports a causal role for NR2F2, PTPN11, and WT1 variants. 34619368_Expanding the clinical spectrum of pathogenic variation in NR2F2: Asplenia. 34910830_Abnormal hsa_circ_0003948 expression affects chronic periodontitis development by regulating miR-144-3p/NR2F2/PTEN signaling. 35666805_The nuclear receptors SF1 and COUP-TFII cooperate on the Insl3 promoter in Leydig cells. |
ENSMUSG00000030551 |
Nr2f2 |
150.647390 |
5.6620016221 |
2.501312 |
0.252299500 |
92.267630 |
0.00000000000000000000075712641387832497836623238537668565427600033660868150959101594704714344175044971052557229995727539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000007172776552531499933633114484722496611560521261441736317904932507261150931299198418855667114257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
251.7083182 |
47.0154998 |
45.0629955 |
6.4014103 |
| ENSG00000185561 |
727910 |
TLCD2 |
protein_coding |
A6NGC4 |
FUNCTION: Regulates the composition and fluidity of the plasma membrane (PubMed:30509349). Inhibits the incorporation of membrane-fluidizing phospholipids containing omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) and thereby promotes membrane rigidity (PubMed:30509349). Does not appear to have any effect on LCPUFA synthesis (PubMed:30509349). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30509349}. |
Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in several processes, including membrane assembly; phospholipid homeostasis; and regulation of membrane lipid distribution. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:727910; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; membrane assembly [GO:0071709]; phospholipid homeostasis [GO:0055091]; plasma membrane organization [GO:0007009]; regulation of membrane lipid distribution [GO:0097035] |
30509349_inhibition of FLD-1 or TLCD1/2 prevents lipotoxicity by allowing increased levels of membrane phospholipids that contain fluidizing long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. |
ENSMUSG00000038217 |
Tlcd2 |
13.543023 |
0.3605377668 |
-1.471778 |
0.447719330 |
11.108365 |
0.00085939223760939098539779479324351996183395385742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002026622372122481325479315117377154820133000612258911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4289620 |
2.0740820 |
20.7530251 |
3.4868107 |
| ENSG00000185567 |
113146 |
AHNAK2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IVF2 |
|
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a large nucleoprotein. The encoded protein has a tripartite domain structure with a relatively short N-terminus and a long C-terminus, separated by a large body of repeats. The N-terminal PSD-95/Discs-large/ZO-1 (PDZ)-like domain is thought to function in the formation of stable homodimers. The encoded protein may play a role in calcium signaling by associating with calcium channel proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2017]. |
hsa:113146; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; regulation of RNA splicing [GO:0043484] |
24675079_Periaxin and AHNAK nucleoprotein 2 form intertwined homodimers through domain swapping 28423668_AHNAK2 is overexpressed in PDAC tissues and is an independent prognostic factor in patients with PDAC. 28435451_The authors reveal that AHNAK2 is upregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells and hypoxic upregulation of AHNAK2 can drive tumorigenesis and progression by supporting EMT and cancer cell stemness. 31011849_Linkage analysis and whole exome sequencing reveals AHNAK2 as a novel genetic cause for autosomal recessive CMT in a Malaysian family. 31621397_Results illustrated that AHNAK2 was upregulated in UM and plays a promoting role in the proliferation and migration of UM cells possibly via regulating PI3K signaling pathway. 32904605_AHNAK2 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Cell Migration in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 33000678_Down-Regulation of AHNAK2 Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion Through Inactivating the MAPK Pathway in Lung Adenocarcinoma. 33168407_Correlation between prognostic indicator AHNAK2 and immune infiltrates in lung adenocarcinoma. 33218938_AHNAK2 is a novel prognostic marker and correlates with immune infiltration in papillary thyroid cancer: Evidence from integrated analysis. 34374294_Silencing of AHNAK2 restricts thyroid carcinoma progression by inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 34627772_AHNAK2 promotes thyroid carcinoma progression by activating the NF-kappaB pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000118667 |
Ahnak2 |
107.875406 |
2.0868181717 |
1.061305 |
0.175420902 |
36.470808 |
0.00000000154969847057155941012223452621148975238973832802003016695380210876464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007282250692657185499955506819943010232698554773378418758511543273925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
148.1043753 |
14.4576339 |
71.2992058 |
5.3730733 |
| ENSG00000185585 |
169611 |
OLFML2A |
protein_coding |
Q68BL7 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable extracellular matrix binding activity and identical protein binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within extracellular matrix organization. Predicted to be located in extracellular matrix and extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:169611; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
22913984_Three neuronal proteins (Huntingtin interacting protein 1, neurofascin, and olfactomedin-like 2a) are novel components of podocyte major processes and their expression in glomerular crescents supports their role in crescent formation. |
ENSMUSG00000046618 |
Olfml2a |
11.349050 |
5.3083125005 |
2.408253 |
0.644806483 |
14.188116 |
0.00016541193132220034117153828479018784491927362978458404541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000440064907410900698399996988641191819624509662389755249023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.8607919 |
6.4702570 |
3.5904739 |
1.0678988 |
| ENSG00000185614 |
389119 |
INKA1 |
protein_coding |
A0A499FIG1 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Inhibitor of the serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK4. Acts by binding PAK4 in a substrate-like manner, inhibiting the protein kinase activity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q96EL1}. |
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
Enables protein kinase binding activity and protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within neural tube development. Located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues mmu:68176; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0030291]; neural tube development [GO:0021915] |
26607847_Inka1 is an endogenous inhibitor of PAK4 that binds to the catalytic domain and forms crystals with PAK4 in cells. 30796022_A competitive in vivo gain-of-function screen identifies C3orf54/INKA1 as a gene regulating leukemia stem cells (LSCs) repopulation kinetics. INKA1 overexpression stalls LSC transiently in G0 without abolishing regenerative potential; silencing has the opposite effect. |
ENSMUSG00000042106 |
Inka1 |
67.078642 |
0.1936138827 |
-2.368746 |
0.218112942 |
130.870387 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000264313061033609247462396131631257024282500983448390004416382029758810619977465973182151337539380620000883936882019042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000034101929902588046099366848609482560559717990381235667010754272186142774557016457692704136661632219329476356506347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.8181509 |
3.2033245 |
113.5273995 |
9.1437757 |
| ENSG00000185634 |
399694 |
SHC4 |
protein_coding |
Q6S5L8 |
FUNCTION: Activates both Ras-dependent and Ras-independent migratory pathways in melanomas. Contributes to the early phases of agrin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of CHRNB1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17409413}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;Synapse |
|
Predicted to enable receptor tyrosine kinase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including apoptotic process; positive regulation of cell population proliferation; and stem cell differentiation. Predicted to be located in postsynaptic membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:399694; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; receptor tyrosine kinase binding [GO:0030971]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; stem cell differentiation [GO:0048863]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
17452444_A new member of the Shc family of docking proteins is characterised, which may mediate a specific aspect of signaling downstream of the MuSK receptor. 20078941_ShcD binds to TrkC in a kinase-activity-dependent manner through its PTB and SH2 domains. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20663410_ShcD interacts with TrkB in a kinase-activity-dependent manner. 24036217_ShcD can exist within the nucleus, and its CH2 domain has a critical role in nuclear export of ShcD. 24430869_The ShcD signaling adaptor facilitates ligand-independent phosphorylation of the EGF receptor. 28213521_ShcD binds to active Ret, TrkA, and TrkB neurotrophic factor receptors predominantly via its phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain. 28724758_ShcD appears to possess several molecular permutations that actively govern the EGFR, which may have implications in development and disease. 33495401_Adaptor Protein ShcD/SHC4 Interacts with Tie2 Receptor to Synergistically Promote Glioma Cell Invasion. |
ENSMUSG00000035109 |
Shc4 |
17.136635 |
0.2207863678 |
-2.179277 |
0.424716885 |
26.262496 |
0.00000029802022623857179635704244859140121803875445039011538028717041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001115308960264026349006711257005886039905817597173154354095458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6523384 |
2.3991339 |
34.4896286 |
7.2268013 |
| ENSG00000185684 |
|
EP400P1 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
110.555572 |
0.3283165776 |
-1.606840 |
0.301149430 |
27.723200 |
0.00000013997393075187275693513583394583799091037690232042223215103149414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000544117781906147405032855499107391494817420607432723045349121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.2331683 |
10.5259566 |
172.7065153 |
22.3331492 |
| ENSG00000185745 |
3434 |
IFIT1 |
protein_coding |
P09914 |
FUNCTION: Interferon-induced antiviral RNA-binding protein that specifically binds single-stranded RNA bearing a 5'-triphosphate group (PPP-RNA), thereby acting as a sensor of viral single-stranded RNAs and inhibiting expression of viral messenger RNAs. Single-stranded PPP-RNAs, which lack 2'-O-methylation of the 5' cap and bear a 5'-triphosphate group instead, are specific from viruses, providing a molecular signature to distinguish between self and non-self mRNAs by the host during viral infection. Directly binds PPP-RNA in a non-sequence-specific manner. Viruses evolved several ways to evade this restriction system such as encoding their own 2'-O-methylase for their mRNAs or by stealing host cap containing the 2'-O-methylation (cap snatching mechanism). Exhibits antiviral activity against several viruses including human papilloma and hepatitis C viruses. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19008854, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19416887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21976647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23334420}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antiviral defense;Cytoplasm;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;TPR repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing tetratricopeptide repeats that was originally identified as induced upon treatment with interferon. The encoded protein may inhibit viral replication and translational initiation. This gene is located in a cluster on chromosome 10 with five other closely related genes. There is a pseudogene for this gene on chromosome 13. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012]. |
hsa:3434; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; host cell [GO:0043657]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; cellular response to exogenous dsRNA [GO:0071360]; cellular response to type I interferon [GO:0071357]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; intracellular transport of viral protein in host cell [GO:0019060]; negative regulation of helicase activity [GO:0051097]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; regulation of defense response to virus [GO:0050688]; response to virus [GO:0009615] |
12708317_The expression of interferon-induced genes IFI-54K and IFI-56K in the infected cells was found to increase 50-100-fold 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16973618_We observed that, although double-stranded RNA or Sendai virus infection induced the two genes with similar kinetics, their induction kinetics in response to interferon-beta were quite different. 19008854_The authors present evidence that P56 (ISG56 protein), the expression of which is strongly induced by IFN, double-stranded RNA and viruses, mediates the anti-HPV effect of IFN. 19416887_ISG56 is a mediator of negative-feedback regulation of virus-triggered induction of type I IFNs and cellular antiviral responses 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21129252_Expression of ifi56 is enhanced significantly when the differentiation of APL cells was induced by all-trans retinoic acid. 21612406_ISG56 interacts with ribosomal protein L15 in gastric cancer cells. 21642987_IFIT1 bound PPP-RNA antagonizes viruses by sequestering specific viral nucleic acids. 21976647_Hepatitis C virus infection suppresses the upregulation of a subset of effector molecules, including ISG56 and IFITM1. 23052390_Data suggested that PIV5 mRNAs are methylated at the 2'-hydroxyl group and that ISG56/IFIT1 inhibits the translation of PIV5 mRNA by some unrecognized mechanism. Also ISG56/IFIT1 is primarily responsible for the IFN-induced inhibition of PIV5. 23334420_crystal structures of human IFIT5, its complex with PPP-RNAs, and an amino-terminal fragment of IFIT1 23363937_ISG56 may play a role in immune and inflammatory reactions induced by toll-like receptor 3 signaling in human mesangial cells. 23529855_protein expression is inhibited by hepatitis C virus 23684765_TLR4 signaling, induced by LPS, increases the expression of melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) and interferon 23785202_Results indicate that miR-203 is an interferon-inducible miRNA that can negatively regulate a number of cellular mRNAs, including an interferon-stimulated gene target, IFIT1/ISG56, by destabilizing its mRNA transcript. 23867918_Data show that interferon-induced proteins with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 and 2 (IFIT1 and IFIT2) contribute to the regulation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication, likely at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional steps. 24098121_The specificity of IFIT1 for 2'O-unmethylated RNA serves as potent antiviral mechanism against viruses lacking 2'O-methyltransferase activity and at the same time allows unperturbed progression of the antiviral program in infected cells. 25905045_Reovirus T3D infection induced STAT-1, ISG-15, IFIT-1, Mx1, and IFIT-3 expression. 26157117_IFIT1 is not a dominant restriction factor against three different families of negative-sense RNA viruses. 26423178_there is a positive feedback loop between phosphorylated STAT1 and ISG56, ISG54 or ISG60. 26980050_Glioblastoma patients with high IFIT1 and low MGMT expression have an improved prognosis. 27240734_Human IFIT1 and mouse IFIT1B have divergent antiviral specificities: only IFIT1 proteins inhibit a virus encoding a cap 2'O-methyltransferase. 27512068_All the rubulaviruses tested were sensitive to the antiviral action of ISG56/IFIT1. 27589693_Taken together, this study revealed that IFIT1 played an important antiviral role in human cytomegalovirus infected fetal astrocytes. 27707917_IFIT1 significantly inhibited human parainfluenza virus type 3, whereas IFIT2, IFIT3, and IFIT5 were less effective or not at all. 27956805_IFIT1 is involved in the regulation of IFNalpha treatment for chronic hepatitis B and its polymorphism rs303218 can predict the end point virological response. 29554348_IFIT1 and IFIT3 interact through a C-terminal motif. IFIT3 stabilizes IFIT1 protein expression, promotes IFIT1 binding to a cap0 Zika virus reporter mRNA and enhances IFIT1 translation inhibition. 29629559_Induction of IFIT1 in response to H9N2 virus infection or viral particle inoculation was more sensitive in HUVECs than in BEAS-2Bs. Data offers new insight into the innate immune response of endothelial cells to H9N2 virus infection. 30282041_Beyond the well-studied role of cytosolic IFIT1 in restricting viral replication, data demonstrate a function for nuclear IFIT1 in differential transcriptional regulation of separate branches of the LPS-induced gene program. 30626937_A statistically positive correlation of p-EGFR(Y1068) expression with IFIT1 and IFIT3 in OSCC tumors. 30702423_HEV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) binds to IFIT1, thereby protecting the viral RNA from IFIT1-mediated translation inhibition. 31444947_Intrahepatic immune changes after hepatitis c virus eradication by direct-acting antiviral therapy. 31502557_The results uncovered a large ensemble of RNA secondary structures of diverse size and shape in the different viruses, which showed little correspondence to the phylogeny of the viruses. Unexpectedly, the 50UTR of several viral genomes in this family did not fold into any structure, suggesting either their extreme sensitivity to IFIT1 or the existence of alternative viral mechanisms of subverting IFIT1 function. 31977029_IFIT1 and IFITM3 were overexpressed in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and indicated poor prognoses for patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 32363951_ISG56 is involved in CXCL10 expression induced by TLR3 signaling in BEAS-2B bronchial epithelial cells. 32962861_Development of bis-ANS-based modified fluorescence titration assay for IFIT/RNA studies. 34763233_Comprehensive analysis of the prognosis and biological significance for IFIT family in skin cutaneous melanoma. 34791638_IFIT1 modulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. |
|
|
8.418358 |
4.3524820806 |
2.121838 |
0.559545621 |
15.757046 |
0.00007201919824247231326046214672231826625647954642772674560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000202553995056953375962852104130718089436413720250129699707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.9478111 |
4.6953281 |
3.2321849 |
0.9562320 |
| ENSG00000185818 |
339983 |
NAT8L |
protein_coding |
Q8N9F0 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the synthesis of N-acetylaspartate acid (NAA) from L-aspartate and acetyl-CoA (PubMed:19524112, PubMed:19807691, PubMed:20385109). Promotes dopamine uptake by regulating TNF-alpha expression (By similarity). Attenuates methamphetamine-induced inhibition of dopamine uptake (PubMed:20385109). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UGX3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19524112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19807691, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20385109}. |
Acyltransferase;Cytoplasm;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Microsome;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a single-pass membrane protein, which contains a conserved sequence of the GCN5 or NAT superfamily of N-acetyltransferases and is a member of the N-acyltransferase (NAT) superfamily. This protein is a neuron-specific protein and is the N-acetylaspartate (NAA) biosynthetic enzyme, catalyzing the NAA synthesis from L-aspartate and acetyl-CoA. NAA is a major storage and transport form of acetyl coenzyme A specific to the nervous system. The gene mutation results in primary NAA deficiency (hypoacetylaspartia). [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:339983; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; aspartate N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0017188]; N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0008080]; aspartate family amino acid metabolic process [GO:0009066] |
19807691_Results indicated that NAT8L, but not NAT14, catalysed the synthesis of NAA from L-aspartate and acetyl-CoA. 21936773_The aim of the present study was to determine which regions of the protein are important for its catalytic activity and its subcellular localization. 24155240_Nat8l impacts on the brown adipogenic phenotype 24246274_This study demonistrated that the human NAT8L gene related to reward dependence, a personality trait, and grey matter volume in the caudate nucleus in healthy subjects, suggesting that NAT8L might also affect human personality 26511490_NAA is produced specifically in NSCLC tumors through NAT8L overexpression, and its extracellular secretion can be detected in blood 26550943_Characterization and recombinant expression of the nat8l gene that codes for ANAT. 27348532_Nat8l CpG island methylation ratios were lower in the patients with schizophrenia than in the healthy controls. 31924153_A Single Medical Marker for Diagnosis of Methamphetamine Addiction - DNA Methylation of SHATI/NAT8L Promoter Sites from Patient Blood. 32612069_Investigating DNA Methylation of SHATI/NAT8L Promoter Sites in Blood of Unmedicated Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000048142 |
Nat8l |
118.888031 |
0.4163648940 |
-1.264080 |
0.172533227 |
53.390556 |
0.00000000000027340805209322923832985432967883717867915716048798913107020780444145202636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001690617029281970334133744387478126975895079131539944228279637172818183898925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
70.8635611 |
7.2303831 |
171.3324394 |
11.5682270 |
| ENSG00000185838 |
54584 |
GNB1L |
protein_coding |
Q9BYB4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
This gene encodes a G-protein beta-subunit-like polypeptide which is a member of the WD repeat protein family. WD repeats are minimally conserved regions of approximately 40 amino acids typically bracketed by gly-his and trp-asp (GH-WD), which may facilitate formation of heterotrimeric or multiprotein complexes. Members of this family are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell cycle progression, signal transduction, apoptosis, and gene regulation. This protein contains 6 WD repeats and is highly expressed in the heart. The gene maps to the region on chromosome 22q11, which is deleted in DiGeorge syndrome, trisomic in derivative 22 syndrome and tetrasomic in cat-eye syndrome. Therefore, this gene may contribute to the etiology of those disorders. Transcripts from this gene share exons with some transcripts from the C22orf29 gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:54584; |
Mouse_homologues cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; social behavior [GO:0035176] |
18003636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18003636_markers associated with psychosis are also correlated with alterations in GNB1L expression, raising the hypothesis that the risk to develop psychosis at this locus could be mediated in a dose sensitive manner via gene expression 18755269_GbetaL is involved in the negative regulation of TNFalpha-stimulated NF-kappaB signaling through a direct interaction with IKK. 19011233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19011233_The present findings support assertions that GNB1L is one of the genes in the 22q11DS region responsible for increasing the risk of schizophrenia. 20538345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538345_The results of this study suggested that GNB1L is linked with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia and not with major depressive disorder. 20860462_Beta-blocker therapy and heart rate control during exercise testing in the general population: role of GNB1L variant. 24831436_mRNA expression results implies that the GNB1L high-expression allele is the risk allele for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in the Han Chinese population. 33932639_Sequencing of the coding regions of GNBIL on chromosome 22q11.2 as a risk gene of schizophrenia. |
ENSMUSG00000000884 |
Gnb1l |
22.716627 |
0.4818066195 |
-1.053474 |
0.328011350 |
10.148028 |
0.00144455667792058018404632857567548853694461286067962646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003281264476163091043520170231317933939862996339797973632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
14.4116342 |
4.1944071 |
30.3762570 |
6.2957699 |
| ENSG00000185842 |
127602 |
DNAH14 |
protein_coding |
Q0VDD8 |
FUNCTION: Force generating protein of respiratory cilia. Produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP. Involved in sperm motility; implicated in sperm flagellar assembly (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Dynein;Glycoprotein;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Dyneins are microtubule-associated motor protein complexes composed of several heavy, light, and intermediate chains. Two major classes of dyneins, axonemal and cytoplasmic, have been identified. DNAH14 is an axonemal dynein heavy chain (DHC) (Vaughan et al., 1996 [PubMed 8812413]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:127602; |
axonemal dynein complex [GO:0005858]; dynein complex [GO:0030286]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018] |
29323929_Genetic variants within DNAH6, DNAH14, and DNAAF3 are associated with variation in lung function among persons with cystic fibrosis. 33577779_Clinical and Genetic Spectrum of Children With Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in China. 35438214_DNAH14 variants are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. |
ENSMUSG00000047369 |
Dnah14 |
99.516894 |
3.1233782700 |
1.643107 |
0.467616448 |
11.737748 |
0.00061245089983944780639979477143697295105084776878356933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001481687474451769950464785630117603432154282927513122558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.5432887 |
63.5959969 |
33.3813295 |
14.1705807 |
| ENSG00000185864 |
440345 |
NPIPB4 |
protein_coding |
C9JG80 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
196.224589 |
0.4218183821 |
-1.245306 |
0.174518278 |
50.361182 |
0.00000000000127899274316673624396851084102395083841839651395133614641963504254817962646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007560245450196646458995440776750868909841796217108367272885516285896301269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
113.7370467 |
12.6865130 |
271.6709209 |
20.9842115 |
| ENSG00000185897 |
2865 |
FFAR3 |
protein_coding |
O14843 |
FUNCTION: G protein-coupled receptor that is activated by a major product of dietary fiber digestion, the short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and that plays a role in the regulation of whole-body energy homeostasis and in intestinal immunity. In omnivorous mammals, the short chain fatty acids acetate, propionate and butyrate are produced primarily by the gut microbiome that metabolizes dietary fibers. SCFAs serve as a source of energy but also act as signaling molecules. That G protein-coupled receptor is probably coupled to the pertussis toxin-sensitive, G(i/o)-alpha family of G proteins. Its activation results in the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, the mobilization of intracellular calcium, the phosphorylation of the MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2 kinases and the inhibition of intracellular cAMP accumulation (PubMed:12711604). Activated by SCFAs and by beta-hydroxybutyrate, a ketone body produced by the liver upon starvation, it inhibits N-type calcium channels and modulates the activity of sympathetic neurons through a signaling cascade involving the beta and gamma subunits of its coupled G protein, phospholipase C and MAP kinases. Thereby, it may regulate energy expenditure through the control of the sympathetic nervous system that controls for instance heart rate. Upon activation by SCFAs accumulating in the intestine, it may also signal to the brain via neural circuits which in turn would regulate intestinal gluconeogenesis. May also control the production of hormones involved in whole-body energy homeostasis. May for instance, regulate blood pressure through renin secretion. May also regulate secretion of the PYY peptide by enteroendocrine cells and control gut motility, intestinal transit rate, and the harvesting of energy from SCFAs produced by gut microbiota. May also indirectly regulate the production of LEP/Leptin, a hormone acting on the CNS to inhibit food intake, in response to the presence of short-chain fatty acids in the intestine. Finally, may also play a role in glucose homeostasis. Besides its role in energy homeostasis, may play a role in intestinal immunity. May mediate the activation of the inflammatory and immune response by SCFAs in the gut, regulating the rapid production of chemokines and cytokines by intestinal epithelial cells. Among SCFAs, the fatty acids containing less than 6 carbons, the most potent activators are probably propionate, butyrate and pentanoate while acetate is a poor activator (PubMed:12496283, PubMed:12711604). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12496283, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12711604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18801738, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23066016}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables G protein-coupled receptor activity. Involved in adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway and cellular response to fatty acid. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2865; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; mucosal immune response [GO:0002385]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; positive regulation of acute inflammatory response to non-antigenic stimulus [GO:0002879]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002720]; regulation of hormone biosynthetic process [GO:0046885]; regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046626]; regulation of norepinephrine secretion [GO:0014061]; regulation of peptide hormone secretion [GO:0090276] |
12711604_characterization of GP41 in human tissue as a receptor for short chain fatty acids 14722361_C2-C6 short-chain fatty acids, ligands of an orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR41, stimulate leptin expression in both a mouse adipocyte cell line and mouse adipose tissue in primary culture 16887331_GPR41 and 43 mediate SCFA signaling in mammary epithelial cells and thereby play an important role in their stress management. 18801738_analysis of conserved polar residues in transmembrane domains V, VI, and VII of free fatty acid receptor 2 and free fatty acid receptor 3 are required for the binding and function of short chain fatty acids 19574715_Results suggest that GPR41 expressed in human colonic mucosa may function as a sensor for luminal short-chain fatty acids. 19630535_Study presents evidence showing that the six amino acid differences, including that R/W174 are polymorphisms rather than gene-specific differences between GPR41 and GPR42. 21220428_Selective orthosteric free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFA2) agonists: identification of the structural and chemical requirements for selective activation of FFA2 versus FFA3. 22493486_GPR41 gene expression is mediated by internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation of bicistronic mRNA encoding GPR40 and GPR41 proteins 22712802_Propionate-stimulated GPR41 strongly coupled to ERK1/2 activation, while the coupling of linoleic acid-activated GPR40 and acetate-activated GPR43 was weaker. 22884094_GPR41 activation inhibits histone acetylation and cell growth. 23066016_Extracellular ionic locks determine variation in constitutive activity and ligand potency between species orthologs of the free fatty acid receptors FFA2 and FFA3 24325907_a significant correlation between a higher body mass index and lower methylation in the promoter region of FFAR3 in type 2 diabetes and obesity patients 25581519_FFAR3 is expressed in pancreatic beta cells and mediates an inhibition of insulin secretion by coupling to Gi-type G proteins. 26260360_Our data suggest that GPR42 be reclassified as a functioning gene and that recognition of sequence and copy number polymorphism of the FFAR3/GPR42 complex be considered during genetic and pharmacological investigation of these receptors. 28075383_a single dose of soluble fibre was able to significantly reduce airway inflammation in stable asthma by downregulating GPR43 and GPR41 28322790_Short-chain fatty acids lowered TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression by reducing phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK in a GPR41/GRP43-dependent manner in renal cortical epithelial cells. 28835131_Data suggest that cytokines TNFalpha and interleukin-1b markedly reduce GPR120/FFAR4 expression in adipocytes; in contrast, these cytokines induce expression of GPR84 and GPR41/FFAR3 in adipocytes. These studies were conducted in adipocytes cultured from subcutaneous adipose tissue. (GPR = G-protein coupled receptor; FFAR = free fatty acid receptor) 28883043_FFAR2 and FFAR3 interact to form a heteromer in primary monocytes and macrophages via proximity ligation assay, and during heterologous expression in HEK293 cells via bimolecular fluorescence complementation and fluorescence resonance energy transfer. FFAR2 and FFAR3 may interact to form a receptor heteromer with signaling that is distinct from the parent homomers. 31487233_Metabolic and physiological role of FFAR1 (GPR40), FFAR4 (GPR120), FFAR3 (GPR41) and FFAR2 (GPR43) is REVIEWED. 32209026_The short-chain free fatty acid receptor FFAR3 is expressed and potentiates contraction in human airway smooth muscle. 33020504_FFA2-, but not FFA3-agonists inhibit GSIS of human pseudoislets: a comparative study with mouse islets and rat INS-1E cells. 35408893_Genetic Inactivation of Free Fatty Acid Receptor 3 Impedes Behavioral Deficits and Pathological Hallmarks in the APPswe Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model. 35628613_Regulator of G-Protein Signaling-4 Attenuates Cardiac Adverse Remodeling and Neuronal Norepinephrine Release-Promoting Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFAR3 Signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000019429 |
Ffar3 |
6.433108 |
4.4615624420 |
2.157549 |
0.928906993 |
5.284336 |
0.02151809369654638509627986309169500600546598434448242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.038293593315773408192193016930104931816458702087402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8965090 |
8.7839635 |
2.3963345 |
1.4543696 |
| ENSG00000185909 |
200942 |
KLHDC8B |
protein_coding |
Q8IXV7 |
FUNCTION: Involved in pinching off the separated nuclei at the cleavage furrow and in cytokinesis (PubMed:20107318). Required for mitotic integrity and maintenance of chromosomal stability. Protects cells against mitotic errors, centrosomal amplification, micronucleus formation and aneuploidy. Plays a key role of midbody function involving abscission of the daughter cells during cytokinesis and appropriate chromosomal and nuclear segregation into the daughter cells (PubMed:22988245, PubMed:23713010). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20107318, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22988245, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23713010}. |
Cell cycle;Cell division;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Kelch repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein which forms a distinct beta-propeller protein structure of kelch domains allowing for protein-protein interactions. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Hodgkin lymphoma. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:200942; |
cellularization cleavage furrow [GO:0110070]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; midbody [GO:0030496]; mitotic cytokinetic process [GO:1902410]; mitotic nuclear division [GO:0140014]; nuclear chromosome segregation [GO:0098813] |
19706467_Depletion of KLHDC8B through RNA interference leads to an increase in binucleated cells, implicating its reduced expression in the formation of classical Hodgkin lymphoma's signature Reed-Sternberg cell. 20107318_Deficiency of KLHDC8B leads to binucleated cells, implicating its involvement in Reed-Sternberg cell formation 22988245_kelch protein KLHDC8B guards against mitotic errors, centrosomal amplification, and chromosomal instability |
ENSMUSG00000032609 |
Klhdc8b |
43.675845 |
0.0757195683 |
-3.723190 |
0.388376856 |
102.651698 |
0.00000000000000000000000399568902077373675229223889067738874144896386339262070603993047199220534082542144460603594779968261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000041561923852445635424866352232690158749237289580962457738652073794410890528183699643705040216445922851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6737292 |
1.8606525 |
75.1329063 |
14.5612992 |
| ENSG00000185920 |
5727 |
PTCH1 |
protein_coding |
Q13635 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a receptor for sonic hedgehog (SHH), indian hedgehog (IHH) and desert hedgehog (DHH). Associates with the smoothened protein (SMO) to transduce the hedgehog's proteins signal. Seems to have a tumor suppressor function, as inactivation of this protein is probably a necessary, if not sufficient step for tumorigenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21537345}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Holoprosencephaly;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the patched family of proteins and a component of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Hedgehog signaling is important in embryonic development and tumorigenesis. The encoded protein is the receptor for the secreted hedgehog ligands, which include sonic hedgehog, indian hedgehog and desert hedgehog. Following binding by one of the hedgehog ligands, the encoded protein is trafficked away from the primary cilium, relieving inhibition of the G-protein-coupled receptor smoothened, which results in activation of downstream signaling. Mutations of this gene have been associated with basal cell nevus syndrome and holoprosencephaly. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:5727; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; caveola [GO:0005901]; ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; dendritic growth cone [GO:0044294]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; midbody [GO:0030496]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; cholesterol binding [GO:0015485]; cyclin binding [GO:0030332]; hedgehog family protein binding [GO:0097108]; hedgehog receptor activity [GO:0008158]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; patched binding [GO:0005113]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; smoothened binding [GO:0005119]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; brain development [GO:0007420]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; cell differentiation involved in kidney development [GO:0061005]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; cell proliferation involved in metanephros development [GO:0072203]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; commissural neuron axon guidance [GO:0071679]; dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning [GO:0021904]; dorsal/ventral pattern formation [GO:0009953]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; embryonic organ development [GO:0048568]; epidermal cell fate specification [GO:0009957]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; hindlimb morphogenesis [GO:0035137]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0043616]; limb morphogenesis [GO:0035108]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060603]; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060644]; metanephric collecting duct development [GO:0072205]; negative regulation of cell division [GO:0051782]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation [GO:0010839]; negative regulation of multicellular organism growth [GO:0040015]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0045879]; negative regulation of stem cell proliferation [GO:2000647]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neural plate axis specification [GO:0021997]; neural tube closure [GO:0001843]; neural tube patterning [GO:0021532]; pharyngeal system development [GO:0060037]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epidermal cell differentiation [GO:0045606]; prostate gland development [GO:0030850]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0008589]; response to chlorate [GO:0010157]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to retinoic acid [GO:0032526]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; smooth muscle tissue development [GO:0048745]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; somite development [GO:0061053]; spermatid development [GO:0007286]; spinal cord motor neuron differentiation [GO:0021522]; stem cell proliferation [GO:0072089] |
11836379_No germline PTCH mutations have been identified in 8 subjects with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome, suggesting that PTCH should be excluded as a candidate gene for BHD. 12007715_Mutations for basal cell carcinoma (BCC), were screened in 15 cases of sporadic BCCs that developed in sun-exposed skin region in a Korean population 12192414_results suggest that the Ptc tumour suppressor functions normally as a transmembrane molecular transporter, which acts indirectly to inhibit Smo activity 12241103_Patched expression in human astrocytic tumors inversely correlates with histological malignancy 12407090_odontogenic keratocysts arise with heterozygous mutations of the gene 12516098_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12516098_The patched polymorphism Pro1315Leu (C3944T) may modulate the association between use of oral contraceptives and breast cancer risk 12925203_Nineteen novel mutations and five new polymorphisms were identified 15308259_mutations are probably related not only to basal cell nevus-associated odontogenic keratocysts but also to sporadic odontgenic keratocysts 15459969_thirteen novel mutations identified in the mutational screening of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients in Italy 15492847_cDNA microarray analysis performed on cell lines derived from ovarian dermoid cysts did not show any significant alteration in the expression of the analyzed target genes of PTCH signaling. 15502856_Papillary carcinomas with high RET/PTC1 expression showed an association trend for large tumor size. 15534865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15565302_No phenotype-genotype relationships were found in the Japanese nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients 15581634_Data show that in both human and mouse a novel Patched homolog 1 first exon (1C) is expressed. 15592520_ptc1 mutations and truncation are responsible for the majority of basal cell carcinoma (BCC) cases. 15598212_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15712338_9 new mutations wew found: c.1436T>G p.L479R; c.1138G>T p.E380X; c.323_324ins2; c.2011_2012dup; c.2535_2536dup; c.2577_2583del, c.3000_3005del; c.3050_3051del; & c.6552A>T. 15780749_Seven isoforms of human PTCH mRNA were identified. 15888139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15905200_Elevated expression of hedgehog target genes human patched gene 1 (PTCH1) or Gli1 occurs in 63 of the 99 primary gastric cancers. 16088933_analysis of missense mutations in the PTCH gene which may be responsible for Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome 16109989_possible relationship between the CGG8 allele in PTCH1 and the risk for ameloblastoma 16203740_Isoforms - novel exon, exon 12b, was specifically expressed in the brain and heart, especially in the cerebellum. Also, disease-associated aberrant splicings found in two patients with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. 16322088_Patched-expressing cells have been identified among endodermally lineage-restricted, murine embryonic stem cells as well as in livers of fetal and adult Ptc-lacZ mice. 16419085_analysis of PTCH mutations in nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome [review] 16645598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16645598_Our data show that MC1R and PTCH variants are associated with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) risk in the French population. 16675912_Germline mutations on PTCH can cause isolated odontogenic cyst, and this PTCH gene responsible for nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome plays an important role in the formation of odontogenic cyst. 16777989_alteration of both p53 and PTCH genes is likely to play a role in radiation-induced basal cell carcinogenesis 16780502_novel insertion mutation in exon 6 of the PTCH gene was identified in a Korean family with naevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome 16804411_aberrant expressions of PTCH and Smo were common in pancreatic carcinoma tissues & were associated with low-level differentiation of tumor tissue & hyperglycemia; this indicated that these molecules played a fundamental role in pancreas tumorigenesis 16867986_the upstream part of the Hedgehog pathway involving Hedgehog interaction with Patched, regulation of Smoothened by Patched, and Smoothened enrichment at the plasma membrane is highly conserved between Drosophila and humans 16931872_defects are associated with the pathogenesis of syndromic as well as a subset of non-syndromic keratocysts 16934747_Patched-1 containing exon 12b is a dominant negative isoform and is expressed in medulloblastomas 17258529_Mutation screening identified a novel nonsense mutation in PTCH (c.1136C > G; p.Ser383X), the gene associated with Gorlin syndrome. 17295047_Reduced expression of PTCH is associated with breast cancer 17461467_Shh-Ptch1-Gli1 signaling pathway may play a role in the progression of colorectal tumor. 17487419_Patched gene is epigenetically regulated in ovarian dermoids and fibromas, but not in basocellular carcinomas. 17597182_PTCH mutations are not mainly involved in the pathogenesis of sporadic trichoblastomas 17597822_a (UV-) mutated PTCH gene is important for sporadic BCC formation independent of clinical phenotype and the IVS16-80G/C and/or IVS17+21G/A SNP site might be important for tumorigenesis in certain BCC patients 17950424_A patient with nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome and West syndrome. The patient had a heterozygous mutation (insertion of TGGC) in the PTCH gene. 18059486_prevalence of PTCH and p53 mutations for basal cell carcinoma is 63% and 46% in psoralen /UVA associated cancer 18068337_A novel PTCH1 mutation in a patient of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. 18068533_there was no evidence of methylation in the PTCH1-1B promoter in the MB cases examined, nor was there methylation in the control cerebellum samples. 18272036_one 3-bp deletion in PTCH gene was the cause of nevoid basal cell carcinoma in a Chinese family through affecting the conformation and function of PTCH protein. 18302678_Frequent germline PTCH mutations detected in this series provide further evidence for the crucial role of PTCH in the pathogenesis of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome in Chinese. 18391952_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18436435_A novel germ-line mutation of the PTCH1 gene in a Japanese family with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome is reported. 18502968_mutations are frequent in PTCH1 in sporadic and nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated keratocystic odontogenic tumors 18538319_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18538319_PTCH is involved in early stage tumor development and the Hh pathway in Chinese HCC is activated by ligand expression but not by mutation. 18543049_Constitutive activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway in chondrosarcoma is rarely caused by PTCH-1 mutation. 18679421_The physiological impact of constitutive heterozygous PATCHED mutations in primary human keratinocytes; mechanism of haploinsufficiency leading to cancer proneness. 18754037_Hh target genes GLI1 and PTCH1 are not expressed in lesional psoriatic skin 18854826_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18854826_azathioprine exposure may be associated with PTCH mutations 18990233_Differential association of alterations in FANCC and PTCH1 with that of PHF2, XPA and two breast cancer susceptibility genes (BRCA1/BRCA2) in the two age groups suggests differences in their molecular pathogenesis. 19002359_study reports three cases of naevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome in a family with two mutations and one single nucleotide polymorphism in PTCH1 19008023_2 novel PTCH1 mutations (3146A-->T, 1686C-->T) were identified in all 5 affected members. The mutation, 3146A-->T in exon 17, is predicted to lead to different PTCH protein translations. 1686C-->T mutation in exon 11 is a nonsense mutation. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19077462_survival analysis revealed that Ptc expression in grade 2 and PDX-1 expression in grade 3 carcinomas are independent survival factors. 19213072_Ptc1 loss of function is complete, but achieved at the protein level in cerebellar tumor development 19221557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287498_data indicate that the PTCH1(+/-) genotype of healthy NBCCS fibroblasts results in phenotypic traits highly reminiscent of those of BCC associated fibroblasts, a clue to the yet mysterious proneness to non photo-exposed BCCs in NBCCS patients 19287961_p16 and PTCH have roles in pathogenesis of melanoma and basal cell carcinoma 19351817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19362041_results suggest that PTCH1 mutations, particularly those causing protein truncations, are associated with a subgroup of OKCs showing increased proliferative activity and thus may relate to a phenotype of higher recurrent tendency. 19414732_We report a case of medulloblastoma associated with novel PTCH mutation as primary manifestation of Gorlin syndrome. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19465923_Data suggest that in the absence of its ligand Shh the dependence receptor Patched serves as the anchor for a caspase-activating complex that includes DRAL, and caspase-9. 19473442_This study found that the majority of all types of lesions, ranging from the benign but locally aggressive ameloblastoma through the varieties of odontogenic keratocysts, expressed PTCH throughout the width of the epithelial component. 19521425_PTCH genes were analyzed by direct sequencing of the PCR product from DNA, and previously unreported mutations were identified in Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome patients. 19557015_These data indicated that all the six families who were diagnosed with Basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS) had mutations in the PTCH1 gene and that a single copy of a PTCH1 mutation causes BCNS. 19564910_Studies suggest that Hh binding to Ptc leads to the de-repression of the GPCR-related protein Smo. 19618880_Our detection rate of PTCH1 mutations, i.e., 86%, was much higher than those previously reported from other countries. The differences may be derived either from ethnicity or the detection methods. 19673023_Data show that methylation of PTCH1a transciptional regulation region is present in a subset of gastric cancers and correlated negatively with PTCH1 expression. 19728145_The mutation of 3146A-->T may be the cause of high expression of GLI and permit SMO to transmit signal to the nucleus through SHH/PTCH/SMO pathway. 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010835_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20012784_Screening for BRAF, RET, KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS mutations, as well as RET-PTC1 and RET-PTC3 rearrangements, was performed on cases of Hashimoto thyroiditis with a dominant nodule 20050020_PTCH1 is preferentially expressed by human bulge cells, compared to differentiated hair follicle keratinocytes 20068110_PTCH1 gene alternation may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome and the related sporadic tumors. 20346027_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20346027_results do not support the hypothesis that common polymorphisms in the proximal 5' regulatory region of the PTCH1 gene could represent an important risk factor for basal cell carcinoma after organ transplantation. 20371205_These results are the first to implicate the Sonic hedgehog pathway in the pathogenesis of the calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor through sequencing. 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20546211_Derangements in the hedgehog signalling pathway in the form of mutations in PTCH1 cause Gorlin syndrome, and it is now evident that derangements in this and other members of this pathway are involved in sporadic basal cell carcinoma development. 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561215_proteins of the SHH signaling pathway are predominantly located within the epithelial components of GOCs and DCs. SHH signaling pathway may play a role in epithelial lining formation. 20583170_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20609239_PTCH germ line mutation is associated with Gorlin syndrome associated with small bowel carcinoma. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20690502_4 novel and 2 known mutations were identified in 2 sporadic and 3 syndromic cases, 2 of which being germline mutations (c.2179delT, c.2824delC) and 4 somatic mutations (c.3162dupG, c.1362-1374dup, c.1012 C>T, c.403C>T). 20858761_These data confirm the role of Ptch1 as a negative regulator of epidermal progenitor turnover and that Ptch1 plays a role in the differentiation of the hair follicle 20937227_The expression level of SMO in NPC is generally high, but the expression level of PTCH-1 was relatively low. 21059263_sonic hedgehog-GLI1 downstream target genes PTCH1, Cyclin D2, Plakoglobin, PAX6 and NKX2.2 are differently regulated in medulloblastoma and astrocytoma 21127038_High PTCH1 is associated with chemoradiotherapy sensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 21129534_Activation of the Hh signaling pathway in neuroblastoma & ganglioneuroblastoma may be associated with the differentiation. 79% of the cases were positive for Ptch1 expression. 21138481_There was loss in at least 1 locus in 5/7 KOT and 4/7 OOC. present finding demonstrates despite existence of clinical, morphological, immunohistochemical, biological behavior differences between OOC and KOT, both have similar genetic alterations at 9q. 21188540_both PTCH1 and SUFU play a key role in the sonic hedgehog signalling pathway, PTCH1 does not make an appreciable contribution to non-familial sporadic medulloblastoma. 21188685_A novel nonsense mutation in the PTCH gene was found. We report the occurrence of epiretinal membranes and the persistence of myelinated nerve fibers. 21206974_Methylation of the PTCH promoter is not a high-prevalence feature of squamous cell cervical cancer or ovarian cancer. 21210781_analyzed 32 nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome families and identified entire deletions of PTCH1 in 5 families 21234763_Our results did not reveal any clearly deleterious inactivating PTCH1 mutations in our collection of colorectal serrated adenocarcinomas 21266456_Ptch1 overexpression underlies derangement of the sonic hedgehog pathway in trisomic neural precursor cells with consequent proliferation impairment 21368767_Five novel PTCH1 mutations induce truncation of the PTCH1 protein or could induce nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. 21389835_Neither CYLD nor PTCH germline mutations were found in the 5 patients with Multiple familial trichoepitheliomas 21424326_High patched protein expression is associated with colon cancer. 21507611_mutation causes one highly conserved glycine residue transit to arginine on the 10th transmembrane region of PTCH protein. 21514272_the 897G-A mutation in the PTCH1 gene is the cause of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome in the Chinese family and works by altering the protein activity of PTCH1, which then activates the Shh/Gli signaling pathway. 21618411_The PTCH1 pathway activity in ERMS tumors did not correlate with a unique clinical phenotype. 21651513_Haploinsufficiency of PTCH may be contributory to the cranial and thoracic neural tube defects in a family with Gorlin syndrome by allowing other genetic or environmental factors to be expressed. 21699520_Mutations found in the PTCH1 gene and neighboring repetitive sequences may have contributed to the development of the studied basal cell carcinomas. 21861228_deregulations of the FANCC-mediated DNA damage repair pathway and the PTCH1-associated sonic hedgehog pathway are associated with the development of early dysplastic head and neck lesions. 21861243_High PTCH1 protein is associated with bladder cancer progression. 21889114_2 genes of loss, CDKN2B and PTCH1, are associated with poor overall survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and may be useful as prognostic markers 21931618_Patched may contribute to cholesterol efflux from cells 22007994_we found a novel missense mutation in exon 8 of the PTCH1 gene, which is located on the transmembrane domain of the Patched receptor. 22069255_in both mouse and human pancreas, expression of the inhibitory Ptch1 receptor occurs in delta cells 22077640_Brooke-Spiegler syndrome: report of two cases not associated with a mutation in the CYLD and PTCH tumor-suppressor genes. 22183980_No somatic mutations were identified in the PTCH1, MLL2, and MLL3 genes in our cohort of hepatoblastoma samples 22201935_LOH of PTCH1 gene is often found in a series of different tumors, for example basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and ovarian carcinoma (OC 22221699_our findings suggest that loss of heterozygosity in the PTCH region may be relevant to the pathogenesis of ameloblastoma but may target a different gene than PTCH. 22313357_Mutations and LOH in PTCH1 were also highly prevalent in Chinese sporadic BCCs. However, UV light plays a less role in causing these mutations, suggesting other potential mechanisms in the development of sporadic BCC in Chinese patients 22340170_Enhanced PTCH1 expression and activation of the sonic hedgehog pathway are involved in brainstem glioma. 22357618_results indicated that miR-212 was involved in tumorigenesis, and the oncogenic activity of miR-212 in non-small cell lung cancer cells was due, in part, to suppression of PTCH1 22407314_Expressions of Shh, Ptch1 and Gli1 were significantly correlated with stage, lymph node metastasis, venous invasion, hepatic infiltration, survival rate, and lymphatic invasion in gallbladder carcinoma. 22456124_PTCH1 expression in the sonic hedgehog pathway was possibly involved in gastric cancer progression and could be an indicator for the prognosis of the disease. 22797776_Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) protein stimulates cell proliferation and induces internalization of the Patched (Ptch) protein 22829011_PTCH1 germline mutation is associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome associated with meningioma. 22911366_High PTCH1 mRNA expression is associated with recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. 22945423_Aberrant methylation of the PTCH1 promoter may be an early, initiating event of colon carcinogenesis. 22952776_novel mutation in patients with keratocystic odontogenic tumors screened for nevoid basal cell carcinoma (NBCC) syndrome 23169491_These findings strongly suggest that patients with constitutional 9q22.3 microdeletion have an increased risk of WT, and that PTCH1 have a role in the pathogenesis of nephroblastomas. 23313819_PTCH1 gene polymorphisms is associated with ovarian tumors. 23317547_All Keratocystic odontogenic tumors with PTCH1 mutations presented the criteria of pathological aggressiveness 23349881_SMO and/or PTCH1 mutations are present at low frequency in different histologic subtypes of gastric tumors and these do not appear to be driver mutations. 23371028_PTCH1 overexpression was an independent prognostic factor for survival and SMO overexpression which was found in 12.0 % of GC patients. 23440386_The data demonstrated that loss of expression of HHIP and PTCH is associated with the methylation of gene promoters 23493353_Data indicate that Shh, Ptch1, Gli1, and Gli2 mRNA expressions were markedly increased in intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma (ICC). 23761049_Increased risk for spina bifida was observed with the G allele of c.3944C>T and the T allele of c.1729trade mark2350G>A in female Chinese patients. 23766265_These results suggest that pathological low flow stimulates smooth muscle cell growth in vitro and vascular remodeling in vivo via Ptc-1 regulation of Notch signaling. 23780909_Our studies identified functionally relevant aberrations at the PTCH1 locus in three of five fetal rhabdomyomas tumours surveyed. 23935859_Data indicate that the Shh signaling transduction is facilitated by binding of Shh to its receptor protein, Ptch, and show the complex structure of Shh-Hhip. 23951062_Data indicate a significant role of hedgehog receptor PTCH1 and SUFU in the pathogenesis of keratocystic odontogenic tumor (KCOT). 24073265_Variations of PTCH1 gene is associated with Hirschsprung disease. 24131384_a noncoding mutation in PTCH-1 may predispose to basal cell carcinoma (case report) 24204797_Mutations in the PTCH1 transmembrane domain 2 are closely related to the development of sporadic keratocystic odontogenic tumors. 24335643_Case Report: identical PTCH1 mutations in epithelial and sarcomatoid primary tumor components and sarcomatoid metastasis of basal cell carcinosarcoma. 24368541_Authors report a loss-of-function mutation of PTCH1, a tumor suppressor in the Hh pathway, in a colorectal cancer that exhibits transcriptional upregulation of the downstream Hh gene GLI1. 24369017_Protein profiles in the fibroblast conditioned media revealed statistically significant differences between two different types (missense versus nonsense) of PTCH1 mutations. 24517962_Germline PTCH1 mutations are linked to nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. 24612059_Serrated colorectal carcinoma as proposed to arise from serrated adenoma is characterized by down regulation of PTCH. 24659465_Two altered PTCH1 transcripts were identified in patients with Gorlin syndrome 24668667_Variants of the PTCH1 and COL17A1 genes may contribute to the development of Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. 24710823_High Ptch-1 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancers. 24733827_The expression of PTCH1 in 50 human cholangiocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma cell line, and vivo growing tumors was measured by quantitative PCR 24805933_Results found that PTCH1 is highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 24840883_our data suggest that the non-canonical Hh pathway mediated through ptch1 and cyclin B1 is involved in the pathogenesis of NBCCS-associated KCOTs. 24942795_germline single base deletion of PTCH1 (c.2613 delC) is a first hit and the LOH of the wild-type allele is a second hit, implying that all 16 BCCs detected in these NBCCS sisters fit the standard two-hit model 24961235_MiR-212 may facilitate pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression and metastasis through targeting PTCH1. 25027328_Ptc1-Gli1 signaling deregulation resulting in abnormal loss of glial precursor cells may contribute to a cognition decline in Alzheimer's disease brains. 25092867_The C-terminal domain of PTCH1 interacts with and is ubiquitylated on K1413 by the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy homolog Itch. 25292199_Results show that XIAP binds to the C terminus of Ptch1 and mediates the death-dependent function of Ptch1. 25330948_our data suggests that activation of the Hedgehog pathway due to PTCH1 inactivation along with HPV infection is important in cervical cancer development. 25395299_Frequent inactivating PTCH1 mutations were found in oesophageal basaloid squamous cell carcinoma. These changes activate the Hedgehog pathway, which has been shown to cross-talk with the Wnt signalling pathway. 25403219_suggest childhood brain magnetic resonance imaging surveillance is justified in SUFU-related, but not PTCH1-related, Gorlin syndrome 25458233_results suggest that the PTCH1 gene plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of sporadic KCOTs, which is comparable to that observed in NBCCS patients 25595896_Data indicate microRNA-9 (miR-9) as the target of patched protein 1 (PTCH1) in resistant glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells with concomitant activation of sonic hedgehog SHH signaling. 25600101_Naevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS) is a rare autosomal dominantly inherited disorder with primary mutations in the Patched (PTCH1) gene 25727044_In this study we presented two cases with Gorlin syndrome. Molecular analysis of the patients showed two frameshift and one nonsense mutations in PTCH1 gene (two germline and one somatic), all of them novel. 25826662_PTCH1 expression is regulated by different 5' untranslated region cis-regulatory elements. 26038600_results indicate that whereas ciliary localization of Patched is essential for suppression of Smoothened activation, the primary event enabling Smoothened activation 26126827_Calcitriol represents a possible endogenous transmitter of Ptch/Smo interaction. 26189965_Melittin induces PTCH1 expression by down-regulating MeCP2 and blocking Shh signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 26290144_The results do not support our hypothesis that common germline genetic variants in the PTCH1 genes is associated with the risk of developing medulloblastoma. 26733130_A genome-wide association study of bone mineral density (BMD) found a new BMD locus that harbors the PTCH1 gene, that associates with reduced spine BMD and the RSPO3 associates with increased spine BMD. 26782978_This is the first report describing a GS-associated ovarian tumor carrying a second hit in the PTCH1 region. 26885983_suggest that CUL2-based E3 ligase complex may play a role in Shh- and Ptc1-dependent signaling pathways 26890308_This study indicates that germline PTCH1 heterozygous mutations play a major role in bone metabolism in patients with NBCCS, in particular in those with PTCH1 protein truncation mutations. SPARC may represent an important downstream modulator of PTCH1 mediation of bone metabolism. 26893459_PTCH1 mutations contribute to as much as 10% of ODA, identify the SHH signaling pathway as a novel effector of SOX2 activity during human ocular development, and indicate that ODA is likely the result of overactive SHH signaling in humans harboring mutations in either PTCH1 or SOX2. 26997450_Increased SHH, PTCH, and GLI1 protein correlated positively with tumor grade, tumor depth and lymph node metastasis in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. 27125030_The Cytoskeletal Protein Zyxin Interacts with the Hedgehog Receptor Patched 27245001_after 20 years of the molecular and epidemiological research of RET/PTC in thyroid radiogenic carcinomas the comprehensive evidence of the dose-effect dependence existence indicating a real relationship between the studied parameters and radiation factor 27325696_These data reveal an interaction between the cytoplasmic domains of Ptch1 and that these domains modulate Ptch1 activity but are not essential for regulation of the Hh pathway. 27386018_In Nigerian patients with ameloblastoma, moderate and strong expressions for PTCH in ameloblast and stellate reticulum were 78.6% and 60.7% respectively 27561271_Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome caused by splicing mutations in the PTCH1 gene. 27588491_PVT1 epigenetically down-regulates PTCH1 expression via competitively binding miR-152, contributing to EMT process in liver fibrosis 27630290_epigenetic silencing of PTCH is a mechanism contributing to chronic lymphocytic leukemia tumorigenesis 28069693_the significant increase of blunt-ended, double-stranded DNA breaks, but not other types of DNA breaks, in normal cells from patients with RET/PTC-driven tumors suggests that blunt-ended double-stranded DNA breaks are a preferred substrate for rearrangement formation, and implicate involvement of the non-homologous end joining pathway in the formation of RET/PTC rearrangements. 28332184_Demonstrate altered cytoplasmic expression of Ptc1 and reduced number and length of primary cilia, where Ptc1 is located, in fibroblasts from Niemann-Pick type C patients. 28390897_Thus, our study clearly demonstrated the unique involvement of the two novel PTCH1 splice variants in HH signal transduction. 28596197_Patients with missense variants in PTCH1 were diagnosed later and less likely to have developed at least 10 basal cell carcinomas and jaw cysts. Patients with identified PTCH1 variants were more likely to be diagnosed earlier, have developed jaw cysts and have bifid ribs or any skeletal abnormality. 28627087_The authors results suggest that PTCH1 germline polymorphisms may potentially be involved in an undetermined, complex pathway influencing the development of multiple PRAs, seborrhoeic keratoses and ICBCCs 28704552_PTCH1 expression is a promising molecular marker for predicting the imatinib response in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in chronic phase. 28733979_This study contributes to increase the pool of clinical manifestations of NBCCS, as well as increasing the number of pathogenic mutations identified in PTCH1 predisposing to the condition. The inconsistencies found between phenotype and genotype suggest the involvement of other modifying factors, genetic, epigenetic or environmental 29230040_Combined heterozygous germline mutations in PTCH1 and PTCH2 were identified in a patient with embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. 29277811_The authors found 15 germline PTCH1 mutations, uniformly distributed across the PTCH1 gene among patients with Basaloid Follicular Hamartoma and Basal Cell Carcinoma. Therefore, Basaloid Follicular Hamartoma and Basal Cell Carcinoma may be the same genetic entity and not two distinctive syndromes. 29309307_Report recurrent GLI1-PTCH gene fusions in a group of malignant mesenchymal neoplasms involving soft tissue, and occasionally bone, with an often nested epithelioid phenotype and strong S100 immunoreactivity. 29339090_High expression of Patched 1 in malignant prostate epithelium was found to be an independent predictor of biochemical recurrence in high-risk PCa patients. 29498494_This is, to our knowledge, the first Gorlin syndrome-causing mutation that has been reported four independent times in distant geographical locations. Therefore, we propose the location of the described mutation as a potential hot spot for mutations in PTCH1. 29544218_Study identified a novel frameshift mutation in exon 9 of the PTCH1 gene in a nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome case with medulloblastoma and the affected father. This frameshift mutation causes premature stop codon and is responsible for the clinical features. 29545091_MiR-155 worsened high glucose-induced EPC function by downregulating PTCH1. 29575684_Authors have established a locus-specific database for the PTCH1 gene using the Leiden Open Variation Database (LOVD). The database provides an open collection for both clinicians and researchers and is accessible online at http://www.lovd.nl/PTCH1. 29908092_Our findings suggest that c.1175C>T in PTCH1 (NM_000264) may be the causative mutation of this pedigree. Our results add to the evidence that PTCH1 variants play a role in the pathogenesis of orofacial clefts. 29930296_report a patient with a novel, isoform 1b specific mutation in PTCH1 and thereby distinguish PTCH1 isoform 1b as the major transcript in the development of Basal cell nevus syndrome. 29954986_this study reports the structures of human Ptch1 alone and in complex with the N-terminal domain of human Sonic hedgehog (ShhN) at resolutions of 3.9 and 3.6 angstroms, respectively, as determined by cryo-electron microscopy. 29995851_atomic insights into the recognition of the N-terminal domain of Sonic Hedgehog (HH-N) by PTCH1, offers a structural basis for cooperative binding of HH-N to various receptors and serves as a molecular framework for HH signalling and its malfunction in disease 30139912_3.5-angstrom resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of native Sonic Hedgehog (SHH-N) in complex with PTCH1 at a physiological calcium concentration reconciles previous disparate findings and demonstrates that one SHH-N molecule engages both epitopes to bind two PTCH1 receptors in an asymmetric manner. 30172247_Results demonstrate that the patched 1 protein (PTCH1) rs10512248 and DNA repair and recombination protein RAD54B (RAD54B) rs12681366 were significantly associated with non-syndromic orofacial clefts (NSOC) in a Northern Chinese population. 30181650_Co-occurrence of mutations in FOXP1 and PTCH1 in a girl with extreme megalencephaly, callosal dysgenesis and profound intelle |
ENSMUSG00000021466 |
Ptch1 |
222.055014 |
3.2407541766 |
1.696330 |
0.434554220 |
14.432433 |
0.00014527861400684215610959459930029424867825582623481750488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000389740110669320840349610923780687699036207050085067749023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
247.1957724 |
76.7485422 |
77.2396106 |
17.3833869 |
| ENSG00000185946 |
55599 |
RNPC3 |
protein_coding |
Q96LT9 |
FUNCTION: Participates in pre-mRNA U12-dependent splicing, performed by the minor spliceosome which removes U12-type introns. U12-type introns comprises less than 1% of all non-coding sequences. Binds to the 3'-stem-loop of m(7)G-capped U12 snRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16096647, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19447915, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24480542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29255062}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Dwarfism;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;RNA-binding;Spliceosome |
|
Two types of spliceosomes catalyze splicing of pre-mRNAs. The major U2-type spliceosome is found in all eukaryotes and removes U2-type introns, which represent more than 99% of pre-mRNA introns. The minor U12-type spliceosome is found in some eukaryotes and removes U12-type introns, which are rare and have distinct splice consensus signals. The U12-type spliceosome consists of several small nuclear RNAs and associated proteins. This gene encodes a 65K protein that is a component of the U12-type spliceosome. This protein contains two RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), suggesting that it may contact one of the small nuclear RNAs of the minor spliceosome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:55599; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; U12-type spliceosomal complex [GO:0005689]; pre-mRNA intronic binding [GO:0097157]; U12 snRNA binding [GO:0030626]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; RNA splicing [GO:0008380] |
16096647_U11/U12-65K contribute to di-snRNP formation and intron bridging in the minor prespliceosome 24480542_Exome analysis of one proband revealed missense (c.1320C>A, p.P474T) and nonsense (c.1504C>T, p.R502X) mutations in the RNPC3 gene. 27510544_Study shows that the C-terminal RNA recognition motif of p65 binds to the distal 3' stem-loop of U6atac. By using a binary splice site mutation suppressor assay, results demonstrate that p65 protein-binding apical stem-loop of U12 snRNA can be replaced by this U6atac distal 3' stem-loop. 29255062_The authores propose that both the C-RRM folding defect and nonsense-mediated decay (NMD)-mediated decrease in the levels of the U11/U12-65K protein reduce formation of the U12-type intron recognition complex and missplicing of a subset of minor introns leading to pituitary hypoplasia and a subsequent defect in growth hormone secretion. 32462814_Expanding the phenotype of biallelic RNPC3 variants associated with growth hormone deficiency. 33650182_Establishing intellectual disability as the key feature of patients with biallelic RNPC3 variants. 34906446_Pathogenic variants in RNPC3 are associated with hypopituitarism and primary ovarian insufficiency. |
ENSMUSG00000027981 |
Rnpc3 |
429.401840 |
0.3075978570 |
-1.700883 |
0.120210494 |
196.548188 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000001183386703314737597709038970415545664116400627953612585305570752569760908846336405970405574333308614347631696015611391104016547615174204111099243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000220262140490864151538382974447433439972760931696413722869807819402981230924555297115211687114277022830441957407590636286442986602196469902992248535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
198.4313269 |
20.8188285 |
651.7311120 |
47.6063474 |
| ENSG00000185947 |
10308 |
ZNF267 |
protein_coding |
Q14586 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:10308; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
15814297_The binding site for NF-Y is critical for ZNF267 gene regulation and, herewith, the activation of this transcriptional factor plays an important role in the activation process of hepatic stellate cells and in liver fibrosis 16054593_ZNF267 as a negative transcriptional regulator of matrix metallopeptidase 10 might promote liver fibrogenesis 21840307_ZNF267 promotes proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro 22076166_Report increased expression of zinc finger protein 267 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 35001816_Knockdown of zinc finger protein 267 suppresses diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progression, metastasis, and cancer stem cell properties. |
|
|
400.832857 |
2.0368705578 |
1.026354 |
0.090139718 |
129.872158 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000437038018055698416750671550408186026256528237832321246492238562973687077871593267830441220667125890031456947326660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000056141698402977440073536922589076801898011564962253738569765940771646570617205845854513768244942184537649154663085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
542.8151257 |
27.8294763 |
268.4094560 |
10.7217127 |
| ENSG00000186056 |
100129196 |
MATN1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31667976_MATN1-AS1 promotes glioma progression through regulating miR-200b/c/429-CHD1 axis, suggesting MATN1-AS1 as a probable target for glioma treatment. 34542816_LncRNA MATN1-AS1 for Prediction of Prognosis in Osteosarcoma Patients and Its Cellular Function. |
|
|
11.827507 |
0.3284383537 |
-1.606305 |
0.526357776 |
9.024058 |
0.00266449189629490304845327308669311605626717209815979003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005762329727371833833216019371548100025393068790435791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8607859 |
1.6851311 |
15.1410498 |
3.3073648 |
| ENSG00000186086 |
653149 |
NBPF6 |
protein_coding |
Q5VWK0 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene is a member of the neuroblastoma breakpoint family (NBPF) which consists of dozens of recently duplicated genes primarily located in segmental duplications on human chromosome 1. This gene family has experienced its greatest expansion within the human lineage and has expanded, to a lesser extent, among primates in general. Members of this gene family are characterized by tandemly repeated copies of DUF1220 protein domains. Gene copy number variations in the human chromosomal region 1q21.1, where most DUF1220 domains are located, have been implicated in a number of developmental and neurogenetic diseases such as microcephaly, macrocephaly, autism, schizophrenia, cognitive disability, congenital heart disease, neuroblastoma, and congenital kidney and urinary tract anomalies. Altered expression of some gene family members is associated with several types of cancer. This gene family contains numerous pseudogenes. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2013]. |
hsa:653149; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737] |
|
|
|
25.184364 |
2.0046590573 |
1.003357 |
0.371602527 |
7.246785 |
0.00710280796215693836781479575392950209788978099822998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014064588881330346639697559396608994575217366218566894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.3782342 |
7.1206171 |
17.2758540 |
2.7695575 |
| ENSG00000186088 |
54103 |
GSAP |
protein_coding |
A4D1B5 |
FUNCTION: Regulator of gamma-secretase activity, which specifically activates the production of amyloid-beta protein (amyloid-beta protein 40 and amyloid-beta protein 42), without affecting the cleavage of other gamma-secretase targets such has Notch. The gamma-secretase complex is an endoprotease complex that catalyzes the intramembrane cleavage of integral membrane proteins such as Notch receptors and APP (amyloid-beta precursor protein). Specifically promotes the gamma-cleavage of APP CTF-alpha (also named APP-CTF) by the gamma-secretase complex to generate amyloid-beta, while it reduces the epsilon-cleavage of APP CTF-alpha, leading to a low production of AICD. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20811458}. |
Alternative splicing;Golgi apparatus;Reference proteome |
|
Accumulation of neurotoxic amyloid-beta is a major hallmark of Alzheimer disease (AD; MIM 104300). Formation of amyloid-beta is catalyzed by gamma-secretase (see PSEN1; MIM 104311), a protease with numerous substrates. PION, or GSAP, selectively increases amyloid-beta production through a mechanism involving its interaction with both gamma-secretase and its substrate, the amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP; MIM 104760) C-terminal fragment (APP-CTF) (He et al., 2010 [PubMed 20811458]).[supplied by OMIM, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:54103; |
trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; regulation of proteolysis [GO:0030162] |
20811458_A gamma-secretase activating protein (GSAP) that selectively increases amyloid-beta production via interactions with both gamma-secretase and its substrate, the amyloid precursor protein carboxy-terminal fragment. 21718343_Aberrant regulation of gamma-secretase activating protein expression plays a key role in acceleration of gamma-cleavage of beta-secretase-cleaved C-terminal fragment of amyloid precursor protein and accumulation of Abeta in AD brains 22681044_Protocols for recombinant bacterial expression and purification of potentially important protein GSAP are not successful in generating soluble forms of GSAP that contain well-ordered and homogeneous tertiary structure. 23209290_gamma-secretase activating protein (GSAP) and imatinib have roles in the regulation of gamma-secretase activity and amyloid-beta generation 25037285_Its promoter variant contributes to Alzheimer's disease liability. 26076991_GSAP cleavage via caspase-3 is regulated and depend upon the availability of 5-Lipoxygenase in Alzheimer's disease. 28743126_These data demonstrate that GSAP proteins are differentially dysregulated in severe Alzheimer Disease, but only the full-length form was associated with cognitive test scores in Alzheimer Disease. 34156424_GSAP regulates lipid homeostasis and mitochondrial function associated with Alzheimer's disease. |
ENSMUSG00000039934 |
Gsap |
117.109507 |
3.2520143505 |
1.701334 |
0.241730002 |
48.063465 |
0.00000000000412644111397530304821062470084940584490879045276301440026145428419113159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000023543204809538260470988439900082102220618684995656622049864381551742553710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
177.8268708 |
25.7479085 |
55.0898535 |
6.0879687 |
| ENSG00000186230 |
388567 |
ZNF749 |
protein_coding |
O43361 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Acetylation;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388567; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000055150 |
Zfp78 |
30.578965 |
2.1327861382 |
1.092739 |
0.311583457 |
12.314219 |
0.00044952075471912537668259246537161288870265707373619079589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001113803313690496987406475248860715510090813040733337402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.2177393 |
7.9997403 |
20.3161586 |
2.9112902 |
| ENSG00000186235 |
151174 |
LINC02610 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.717577 |
0.3786615216 |
-1.401019 |
0.547358169 |
6.280156 |
0.01220973793788772236712514285272845881991088390350341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022995148921432628091876537723692308645695447921752929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.9873981 |
3.8459742 |
29.7511711 |
7.0013513 |
| ENSG00000186272 |
7565 |
ZNF17 |
protein_coding |
P17021 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7565; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
15.678328 |
2.0369194960 |
1.026389 |
0.414237733 |
6.103790 |
0.01348922393968318006463036340392136480659246444702148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025135834534746083479550549100167700089514255523681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1063283 |
5.5938822 |
11.5018920 |
2.3077506 |
| ENSG00000186301 |
|
MST1P2 |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52.019848 |
0.2829959662 |
-1.821147 |
0.239129723 |
60.959840 |
0.00000000000000582510373571275401971337223746372855182442448279678259837055520620197057723999023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000039621442921253573970340493621058611913769795936923756585201772395521402359008789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.3846404 |
3.5654266 |
83.4968220 |
7.4696705 |
| ENSG00000186314 |
153768 |
PRELID2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N945 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable phosphatidic acid transfer activity. Predicted to be involved in phospholipid transport. Predicted to be active in mitochondrial intermembrane space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:153768; |
mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; phosphatidic acid transfer activity [GO:1990050]; phospholipid transport [GO:0015914] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000056671 |
Prelid2 |
26.449732 |
0.4848052145 |
-1.044523 |
0.318330806 |
10.868758 |
0.00097800096157495933386905040407555134152062237262725830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002277938171508031919842984791557682910934090614318847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.7295729 |
4.3810365 |
34.7530753 |
6.3235225 |
| ENSG00000186318 |
23621 |
BACE1 |
protein_coding |
P56817 |
FUNCTION: Responsible for the proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Cleaves at the N-terminus of the A-beta peptide sequence, between residues 671 and 672 of APP, leads to the generation and extracellular release of beta-cleaved soluble APP, and a corresponding cell-associated C-terminal fragment which is later released by gamma-secretase (PubMed:10656250, PubMed:10677483, PubMed:20354142). Cleaves CHL1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P56818, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10656250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10677483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20354142}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Aspartyl protease;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Lipoprotein;Lysosome;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase A1 family of aspartic proteases. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This transmembrane protease catalyzes the first step in the formation of amyloid beta peptide from amyloid precursor protein. Amyloid beta peptides are the main constituent of amyloid beta plaques, which accumulate in the brains of human Alzheimer's disease patients. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:23621; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi-associated vesicle lumen [GO:0070931]; hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse [GO:0098686]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; multivesicular body [GO:0005771]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; aspartic-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004190]; beta-aspartyl-peptidase activity [GO:0008798]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; amyloid fibril formation [GO:1990000]; amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:0042987]; amyloid-beta formation [GO:0034205]; amyloid-beta metabolic process [GO:0050435]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to copper ion [GO:0071280]; cellular response to manganese ion [GO:0071287]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050966]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; prepulse inhibition [GO:0060134]; presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0099171]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to lead ion [GO:0010288]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; signaling receptor ligand precursor processing [GO:0140448] |
11234778_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11466313_BACE1 is in the distal Golgi membrane with a minor presence in the endoplasmic reticulum, endosomes, and plasma membrane in human neuroblastoma SHEP cells and in mouse Neuro-2a cell lines 11684351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11714100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11741910_BACE has a loose substrate specificity and the substrate recognition site in BACE extends over several amino acids 11744168_beta-Secretase cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein mediates neuronal apoptosis caused by familial ALzheimer's disease mutations. 11847218_Intracellular localization of BACE affects sleavage site specificity; processing in the trans-Golgi network preferentially generates truncated amyloid species that accumulate in Alzheimer's disease brain 11860271_Our data are consistent with a role for the cytoplasmic domain in regulating BACE trafficking and localization. 11922623_A model of the three-dimensional structure of the beta-secretase zymogen has been constructed. 12054507_BACE1 interacts with nicastrin 12054559_Splice variants of the beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme BACE1 are found in human brain and pancreas (BACE1) 12093293_Specificity of memapsin 1 and its implications on the design of memapsin 2 (beta-secretase) inhibitor selectivity 12112088_Results show an increase in protein expression of BACE in the cortex of Alzheimer's disease patients compared to age-matched controls 12135764_endocytosis and intracellular transport of memapsin 2, mediated by its cytosolic domain, may involve the binding of GGA1 and GGA2 12206667_Crystal structure analysis of memapsin-2 catalytic unit complexed with its inhibitor OM00-3 defines locations and functions of new binding pockets S3' and S4'. 12223024_Activity levels are increased in brain regions affected by amyloid deposition and remain increased despite significant neuronal and synaptic loss in Alzheimer disease 12270690_Oxidative stress induces increased BACE protein levels and activity in NT2 neurons accompanied by an increase in amyloid beta protein precursor. 12438920_BACE mRNA amounts were similar in the hippocampus and cerebellum of Alzheimer's patients and controls. 12445809_Results describe a decrease in alpha-secretase (81% of normal) and a large increase in beta-secretase activity (185%) in sporadic Alzheimer's disease temporal cortex. 12471021_An isoenzyme specifically truncates amyloid beta-peptide after its presenilin-dependent generation. 12514700_elevated expression and enzymatic activity in the brain of sporadic Alzheimer disease patients 12535780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12535780_The association of beta-site APP cleaving enzyme (BACE) C786G polymorphism with Alzheimer's disease. No significant association of this polymorphism with the occurrence of AD can be established. 12586838_Identification of domains for PLSCR1 and BACE binding and their colocalization in the Golgi area and endosomal compartments suggest involvement of PLSCR1 in the intracellular distribution and/or recruitment of BACE into the lipid raft. 12618121_BACE1 and BACE2 (a) are expressed in normal adult muscle at the postsynaptic domain of neuromuscular junctions, and in cultured human muscle; (b) accumulate in the form of plaque-like inclusions in myositis vacuolated and necrotic muscle fibers 12665519_gamma-secretase cleavage of CT99 is a prerequisite for BACE-mediated processing at Abeta-34 site and therefore, BACE and gamma-secretase activity can be mutually dependent. 12707937_sequence variation in the BACE1 or BACE 2 gene is not a significant risk factor for AD; but, a combination of a specific BACE1 allele and APOE epsilon 4 may increase the risk for Alzheimer disease over and above that attributed to APOE epsilon 4 alone. 12801932_antagonistic effect with beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 2 on beta-amyloid peptide production in cells 12824768_BACE exon 5 polymorphism plays an important role in the development of Alzheimer's disease, possibly by influencing Abeta(42) protein levels. 12857759_BACE1 sheddase is distinct from alpha-secretase and, inhibition of BACE1 shedding does not influence amyloid precursor protein processing at the beta-site 12928915_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12928915_These data suggest a possible genetic relation between BACE1 and AD. 14507929_acts on the P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1, which mediates leukocyte adhesion in inflammatory reactions 14681914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14699153_BACE 1 cleavage regulates a common function of APP and APLPs in neurons 14701757_BACE1 gene expression is tightly regulated at the transcriptional level, and transcription factor Sp1 plays an important role in regulation of BACE1 to process APP generating Abeta in Alzheimer's disease. 14748006_Homology models of alternatively spliced isoforms B (BACEI-476), C (BACEI-457) and D(BACEI-432) suggest that these should have diminished enzyme activity due to the the loss of key complexing residues 14748707_beta-Secretase activity is enhanced by cellular targeting into intracellular cholesterol-rich microdomains 14978286_BACE elevation may lead to increased amyloid beta peptide production and enhanced deposition of amyloid plaques in sporadic Alzheimer disease patients. 14991462_BACE overexpression is not sufficient to produce beta-amyloid plaques, but simultaneous expression of BACE and its substrate (SwAPP) leads to an accelerated amyloid plaque formation. 15034149_Alternative splicing in the BACE-1 5'UTR affects the efficiency of translation initiation 15059975_promotor and 5' UTR sequence analysis 15059977_transcription response element analysis of 5' flanking region 15096037_The major structural difference in the bound and unbound memapsin 2 is a large movement of the flap of about 4.5 angstroms at the tip; the flap in the unbound memapsin 2 appears in a novel 'open' position permitting access to the active-site cleft. 15197182_memapsin 2 and APP, immunoprecipitated together from cell lysates, suggested that the interaction of these two proteins is part of the native cellular processes [memapsin-2] 15211591_Stimulation of cells with muscarinic agonists increased BACE1 expression up to twofold over basal levels. Similar effects of BACE1 up-regulation were observed when protein kinase C was directly activated by phorbol esters. 15213451_NMR structure of the 45.3 kDa catalytic domain of human BACE1 15234966_processing of APP by BACE1 is dependent on a mutual structural compatibility in addition to the sequence feature 15247262_homodimerization of BACE may help the enzyme to acquire specific mechanisms to associate with its substrates to exert catalytic activity. 15451669_Results describe the apo structure of BACE (beta-secretase) to 1.75 A, and the structure of a hydroxyethylamine inhibitor complex derived by soaking. 15452128_transgenic mice overexpressing both human BACE1 and APP show specific alterations in APP processing and age-dependent Abeta deposition suggesting that modulation of BACE1 activity may play a significant role in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis 15466887_serine phosphorylation of BACE is a physiologically relevant post-translational modification that regulates trafficking in the juxtanuclear compartment by interaction with GGA1 15485862_Dimerization of BACE might facilitate binding and cleavage of physiological substrates 15584902_Recombinant BACE1 can recognize and cleave APP peptide substrates at the postulated beta'-cleavage site. It does not appear to be a significant species specificity to this cleavage. 15592644_review of the structural features of the catalytic/specificity apparatus, transmembrane domain, cytosolic domain and the implications of these features in the physiological and pathological roles of this protease 15615712_GGA proteins funstion with the phosphorylated ACDL in the memasin 2-recycling pathway from endosomes to trans Golgi on the way back to the cell surface. 15671026_Data show that the C-terminal domain of PAR-4 is necessary for forming a complex with the cytosolic tail of BACE1. 15784960_BACE1 gene polymorphism C786G might act as an APOE epsilon4 allele-dependent risk factor for developing late onset Alzheimer's disease in Chinese 15784960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15824102_BACE1 and gamma-secretase use beta subunits of voltage-gated sodium channels as substrates 15857888_data indicate that despite being homologous in amino acid sequence, beta-site beta amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 2(BACE2) and BACE1 have distinct functions and transcriptional regulation 15880353_the mechanism of IL-1beta-induced-sAPP(alpha) release is dependent on MEK1/2- and JNK-activated alpha-secretase cleavage in neuroglioma U251 cells 15886016_GGA1 regulates the retrograde transport of internalized BACE1 from endosomal compartments to the TGN by direct interaction in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. 15931081_BACE1-G allele appeared to increase risk of developing Alzheimer's disease 15931081_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16027115_high levels of BACE1 activity are sufficient to elicit neurodegeneration and neurological decline in vivo 16033761_BACE is transported to the late endosomal/lysosomal compartments where it is degraded via the lysosomal pathway and that the di-leucine motif plays a role in sorting BACE to lysosomes 16181410_M2 acetylcholine receptor down-regulation in brains with Alzheimer's disease(AD) affects expression of several genes and proteins with major functions in the pathology of AD, including beta-secretase BACE1 and several modulators of tau protein. 16243299_These findings suggest that the release of BACE1 holoproteins may be a physiologically relevant cellular process. 16246054_Evidence for alterations in beta-secretase activity, and/or alterations in BACE expression, in post-mortem brain tissue and platelets from individuals with Alzheimer disease. (review) 16249081_X-ray crystallographic analysis of BACE1 with macrocyclic peptidomimetics 16279945_Overexpression of secretase in HEK293 cells increased the release of neurotrophic soluble APLP2 severalfold. 16342950_fully processed BACE1 represents a high quality well-folded protein which is highly stable over a long period of time, and is suitable for evaluation of inhibitor binding by NMR for drug intervention 16354928_BACE1 processing pathways are critical for cognitive, emotional, and synaptic functions 16449801_Lower BACE transcription is responsible for the minority of APP undergoing the amyloidogenic pathway and relatively lower Abeta production in the normal conditions, and that a slight increase in BACE1 can induce a dramatic elevation in Abeta production. 16605258_These results suggest that the precision of cleavage by the PS/gamma-secretase complex may be physiologically regulated by the subcellular location and conditions. 16611980_Alterations of the leaky scanning and reinitiation in BACE1 gene expression could play an important role in AD pathogenesis. 16679558_Results suggest that BACE1 gene promoter activity is differentially regulated, and the 91-bp fragment represents a novel promoter region for cell type-specific regulation. 16716081_results strongly suggest that heparin stimulates the partially active BACE1 zymogen, and we propose that the activation is mediated by high-affinity binding of heparin to the pro domain 16757811_Results describe the functional domains of the BACE1 and BACE2 promoters and mechanisms of transcriptional suppression of the BACE2 promoter in normal neuronal cells. 16769154_the increase of BACE1 activity occurring in sporadic alzheimer's disease is likely the effect, rather the cause, of ABeta accumulation and oxidative stress. 16816111_Novel molecular mechanism by which Alzheimer's disease(AD) develops in Down syndrome(DS) and support the therapeutic potential of inhibiting BACE1 in AD and DS. 16897184_Affects glycosylation not only by directly cleaving glycosyltransferases but also by modifying the secretion of glycosyltransferases via some other mechanisms. 16908986_two enzymatic activities are required to generate the pathogenic beta-amyloid; both activities are carried out by two unusual aspartyl proteases known as beta- and gamma-secretase--{review} 16979658_Results describe the mapping of interaction domains mediating binding between BACE1 and RTN3/Nogo proteins. 17113083_These results indicate that increased V(max) for beta-secretase is a feature of AD pathogenesis and this increase does not correlate directly with levels of BACE1, the principal beta-secretase in brain. 17174011_Platelet membrane beta-secretase activity (expressed as initial rate) varied over fourfold between individuals. 17293612_altered cholesterol metabolism and amyloid precursor protein trafficking mediated by ABC transporter 8 may contribute to the accelerated onset of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology in Down syndrome 17307738_BACE1 and BACE2 may act as alternative alpha-secretase-like proteases in proteolytic processing of IL-1R2 and APP 17331621_These results suggest that while excess Abeta is functionally pathological, BACE1-mediated processing of APP and other substrates play a role in 'normal' learning, memory and sensorimotor processes. 17409228_Transgenic BACE1 elevation is triggered by an accumulation of amyloid plaques and may drive a positive-feedback loop in an Alzheimer's disease model. 17425515_Lysine acetylation is necessary for nascent BACE1 to leave the endoplasmic reticulum and move ahead in the secretory pathway, and for the molecular stabilization of the protein. 17511654_SOD1 activity, cytosolic copper and ectodomain cleavage of APP are linked through BACE1. 17576410_Endogenous beta2 processing and Na(v)1.1 protein levels are elevated in brains of BACE1-transgenic mice and Alzheimer's disease patients with high BACE1 levels. 17596706_BACE1 expression and activity is relevance in Alzheimer's disease. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17699523_the membrane topology of RTN3 has an effect on binding of RTN3 to BACE1 17854420_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17897958_soluble ST6Gal I produced by BACE1 plays, at least in part, a role in the sialylation of soluble glycoproteins 17961921_The I-127 isoform of BACE is regulated by both nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and proteasome-dependent degradation.(I-127) 18039469_Taken together, our results not only suggest that bis(7)-tacrine may reduce the biosynthesis of Abeta mainly by directly inhibiting BACE-1 activity, but also provide new insights into the rational design of novel anti-Alzheimer's dimers. 18163181_The expression levels of BACE1 was increased, but did not reach statistical significance. But BACE1 was comparable between DS and controls in adult brain. 18177262_The kinetic constants (kcat, Km, kcat/Km) for cleaving peptides with beta-sites of the WT or the mutated Swedish families (SW) APP by human BACE 1 and cathepsin D were determined and found to be similar. 18182389_amyloid precursor protein (APP) ectodomain are regulated by the loop region and affect beta-secretase cleavage of APP 18182766_Data suggest that BACE1 polymorphism in exon 5 influences risk for late-onset Alzheimer's disease in those carrying the ApoE epsilon4 allele. 18182766_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18255190_our data suggest that the cellular responses to oxidative stress are closely related to the positive feedback loop existing between gamma-secretase and BACE1 18263584_wild-type or Swedish mutated betaAPP overexpression modulates BACE1 promoter transactivation and activity via an NFkappaB-dependent pathway. 18307033_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18374657_BACE and APP come into close proximity within the cell, but probably not on the cell surface. 18378702_The crystal structure of the catalytically active form of BACE1 was reported. 18393796_we review the basic biology of BACE1, focusing on the regulation, structure and function of this enzyme--REVIEW 18434550_Loss of specific miRNAs can contribute to increased BACE1 and Abeta levels in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. 18581272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18581272_Our results suggest that common BACE1 polymorphisms and putatively functional variants have no significant influence on genetic susceptibility to AD, or platelet beta-secretase activity, in this Caucasian Northern Irish population. 18587408_Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer disease and drives feed-forward regulation of BACE1. 18632981_analysis of the consequences of individual N-glycan deletions and of proteasomal inhibition on secretion of active BACE 18650447_Proteolytic shedding of ST6Gal-I by BACE1 regulates the glycosylation and function of alpha4beta1 integrins 18660751_Data show that the serine protease PCSK9 (proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9) contributes to the disposal of non-acetylated BACE1. 18695061_Elevated BACE1 activity may contribute to the amyloidogenic process in sporadic Alzheimer's disease and is associated with the intensity of axonal degeneration. 18790604_Levels of [(3)H]4-DAMP binding, SP1 and BACE1 were not altered in subjects with the disorder 18798280_that the activated conformation of BACE1 is important for protein transport and localization to lipid rafts. 18805488_study demonstrated that caspase-3 inhibition attenuated ischemia-induced beta-amyloid formation by reducing BACE1 production and activity 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19011241_Both ATase1 and ATase2 regulate the steady-state levels of BACE1 19056495_findings show that BACE1 alters sodium channel gating not only through the cleavage of beta subunits, but also through a direct, non-proteolytic interaction with the alpha subunit 19057901_Downregulation of Notch1 signaling by gamma-secretase inhibitors caused neither cell cycle block nor cell death in T-ALL cells 19074428_post-translational S-palmitoylation of BACE1 is not required for APP processing, and that BACE1 can efficiently cleave APP in both raft and non-raft microdomains. 19106624_analysis of translation of BACE1 mRNA 19153172_results suggest an involvement of BACE1 in the multiple sclerosis disease process 19196715_effect of presenilin 1 mutations on BACE1 may contribute to determine the wide clinical and pathological phenotype of early onset familial Alzheimer disease 19251705_Overexpression of RanBP9 resulted in the enhancement of APP interactions with LRP and BACE1 and increased lipid raft association of APP. 19302194_we have for the first time found evidence of a regulatory site involved in BACE1 alternative splicing 19344981_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344981_This present study, neither ADAM10 nor BACE1 present with any evidence to suggest that they are major candidate genes involved in conferring risk for Alzheimer's disease . 19372755_REVIEW: role of BACE1 in neuronal trafficking associated with Alzheimer disease 19405102_The two-transmembrane-domain tertiary structure of RTN proteins is critical for the ability of RTNs to modulate BACE1 activity, whereas N-terminal, C-terminal and loop regions are not essential for this function. 19429494_BACE1 cleaves and activates Neuregulin-1 and is thus directly involved in myelination of the peripheral nervous system during early postnatal development 19462468_While the exact role of the patient-specific miRNA variants within the 3' UTR region of APP and BACE1 demands further analyses, this study does not support a major contribution of miRNA genetic variability to AD pathogenesis 19508864_constitutive JAK2/STAT1 activation mediates endogenous BACE1 expression in neurons; inhibition of JAK2/STAT1 signaling abrogates basal levels of BACE1 expression and Abeta generation. 19682432_this data suggested that a complex system of cis and trans-acting domains regulates splicing of intron 3 and restricts BACE activity at physiological conditions. 19815556_seladin-1 downregulation increases BACE1 levels and activity through enhanced GGA3 depletion during apoptosis 19827607_It plays a role in membrane protein shedding and produces amyloid beta proteins, which accumulation in central nervous system causes Alzheimer disease. 19889475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19968762_BACE1 likely accounts for most of the Abeta produced in the human brain, and that BACE2 activity is not a likely contributor 20041192_Quantitative proteomic analysis of two human epithelial cell lines stably expressing BACE1 was performed and 68 putative beta-secretase substrates were identified. 20066010_A molecular mechanism for the formation of a DOR/secretase complex that regulates the specificity of secretase for Amyloid beta production. 20080541_show that morphological and functional endocytic abnormalities in fibroblasts from individuals with down syndrome are reversed by lowering the expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) or BACE-1 using short hairpin RNA constructs. 20089133_the results of this study demonstrated that BACE1+/- deletion can rescue multiple forms of synaptic and memory failure in 5XFAD mice 20127045_Data show that the interaction of amyloid precursor protein and beta -site amyloid cleavage enzyme 1 is enhanced during the aging process, and the APP-BACE1 complex accumulates in the endosome. 20164582_This study shows that increased BACE1 activity in CSF is related to markers of ADpathology, suggesting a direct link between BACE1 ac-tivity and amyloid plaques and tangles in the brain. 20212127_findings may connect NRG1, ErbBs, Akt, and DISC1 in a common pathway, which may regulate neurodevelopment and contribute to susceptibility to schizophrenia 20236612_in sporadic inclusion-body myositis biopsies BACE1-antisense and BACE1 transcripts were significantly increased 20354142_SNX6 modulates the retrograde trafficking and basal levels of BACE1, thereby regulating BACE1-mediated APP processing and Abeta biogenesis 20455082_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20455082_Screening of 2.6 kb of the human BACE1 gene promoter region from late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and found that there was no significant association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms and AD cases. 20468060_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20484053_GGA3 tightly and inversely regulate BACE1 levels via interaction with ubiquitin sorting machinery 20607864_Elimination of Niemann-Pick type C protein Npc1 significantly increases BACE1 levels in the hippocampus only in 10-week-old Npc1-deficient mice, whereas in the cerebellum the increase is apparent both in 7- and 10-week-old Npc1-deficient mice. 20685197_Over-expression of BACE1 in beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP)-transfected cells is decreased by simultaneous low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) over-expression. 20726888_This study showed that in Alzheimer's disease cerebral cortices, BACE1 elevation occurs in the swollen and sprouting axonal terminals of the neuritic plaques. 20806954_molecular modeling study aimed to locate and provide the full structural characteristics of the exosite binding site of the BACE1 20849576_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20853423_The substrate-binding cleft of memapsin 2 accommodates 12 subsite residues, from P(8) to P(4)'. We have determined the hydrolytic preference as relative k(cat)/K(M) (preference constant) in all 12 subsites. 20930275_This study demonistrated that in down's syndrome is associated with increased bace-1 activity and accumulation of insoluble amyloid beta proteon. 20930286_This analysis suggested that increased BACE1 mRNA expression in remaining neuronal cells may contribute to the increased BACE1 protein levels and activity found in brain regions affected by Alzheimer disease. 20946940_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20946940_Significant associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms are found in BACE1 in subjects with Down syndrome and dementia of Alzheimer's disease. 21209097_Inhibition of beta-secretase in vivo via antibody binding to unique loops (D and F) of BACE1 21245145_BACE1 retrograde trafficking is uniquely regulated by the cytoplasmic domain of sortilin. 21321391_Nerve growth factor shifts amyloid-beta protein precursor (AbetaPP) processing towards the alpha-secretase (non-amyloidogenic) pathway in rat PC12 cells. 21329555_Results demonstrate that NF-kappaB signalling facilitates BACE1 gene expression and APP processing, and increased BACE1 expression mediated by NF-kappaB signalling in the brain could be a mechanism underlying the development of Alzheimer's disease 21354237_The dynamic transition of BACE1 is studied using normal mode analysis and a simplified elastic network model; van der Waals interaction is found to be the main driving force that guides the ligand induced conformational switching to the closed conformer. 21440067_Subcellular fractionation of Alzheimer's disease cortex with low levels of Golgi localized GGA proteins shows an alteration of BACE distribution and extensive co-localization with amyloid beta precursor protein APP. 21500352_Functional analysis revealed that this E682K mutation in APP blocked the beta'-site and shifted cleavage of APP by BACE1 to the beta-site, causing increased Abeta production. 21565331_Overexpression of microRNA-29c in transgenic mice downregulates BACE1 protein levels. 21576249_Cleavage of neuregulin-1 by BACE1 or ADAM10 protein produces differential effects on myelination 21585286_Human cathepsin S cleaves the WT beta-site (k(cat)/K(m): 54 700 m(-1) s(-1)) 1170-fold faster than BACE1 and cathepsins B and L are 440- and 74-fold faster than BACE1, respectively. 21642424_elevation in Abeta secretion by BACE1-GPI is mainly attributed to preferential cleavage at the beta-site and failure to detect +11 Abeta species secreted by cells expressing WTBACE1 21695060_proteolytic cleavage sites of the amyloid precursor-like protein 2 by the proteases ADAM10, BACE1 and gamma-secretase 21707077_Data show that Compound 59 with an IC(50) value of 11 nM on BACE1 and cellular activity of 80 nM. 21712774_SUMO negatively regulates the BACE expression and SP1 is involved in the process 21726644_SREBP2, which can be modulated by the impairment of cerebral cholesterol homeostasis, has a direct role on BACE1 expression 21779381_rs1047964 in BACE1 appeared to be associated with CVD death among women with any migraine. 21795680_Although PrP(C) exerts no control on cleavage of APP(Swe) by BACE1, it has a profound influence on the cleavage of APP(WT), suggesting that PrP(C) may be a key protective player against sporadic Alzheimer disease. 21825135_These results demonstrate a spatial separation between APP and BACE1 during surface-to-endosome transport, suggesting subcellular trafficking as a regulatory mechanism for this proteolytic processing step. 21942621_The conformational dynamics and free energy surfaces of BACE at three steps of the catalytic cycle are studied here by explicit solvent molecular dynamics simulations (multiple runs for a total of 2.2 mus). 22045484_The BACE1 has an ancient role in response to low oxygen/oxidative stress. 22052506_NRG1 processing is impaired but not abolished in BACE1 null mutants. 22122287_In this review, beta-site amyloid precursor protein (APP) cleaving enzyme-1 (BACE1) is implicated in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis, given that BACE1 cleavage of APP is the initiating step in the formation of amyloid beta (Abeta). 22122349_Dysregulation of BACE1 gene expression at the transcription and translation level could play an important role in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. 22150401_This review suggests that therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's disease that are targeted at Abeta-cleaving enzymes (BACE1)should modulate rather than inhibit Abeta generation. 22178568_miR-124 may work as a basilic regulating factor to alleviate cell death in the process of Alzheimer's disease by targeting BACE1 22194329_Detailed analysis of all of the crystal structures of BACE1 deposited in the PDB revealed that flexibility of all three of these regions is a general phenomenon 22223639_Abeta42 may increase the BACE1 level independently of either Cdk5 or caspase 3 and that Cdk5 inhibition for AD may cause BACE1 elevation, a potentially negative therapeutic outcome. 22267734_Biochemical inhibition of the acetyltransferases ATase1 and ATase2 reduces beta-secretase (BACE1) levels and Abeta generation. 22275252_Overexpression of 12/15-Lipoxygenase leads to increased levels of beta-secretase-1 mRNA and protein, a significant elevation in amyloid beta levels and deposition, and a worsening of memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. 22299711_Site-directed mutagenesis at Lys(203) and Lys(382) of BACE1 abolished the proteasomal degradation of BACE1 and affected APP processing at beta site and Abeta production. 22303960_heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H, was found to regulate BACE1 exon 3 alternative splicing and in a manner dependent on the G-rich sequence. 22306812_findings provide a new translational regulation of BACE1, under the control of double-stranded RNA dependant protein kinase in oxidative stress, where eIF2-alpha phosphorylation regulates BACE1 protein expression 22351782_H component of CUTA as a novel BACE1-interacting protein that mediates the intracellular trafficking of BACE1 and the processing of APP to Abeta 22450048_Here we found that M1 Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M1 mAChR), an important G protein-coupled receptor involved in cholinergic neuronal activity, can interact with BACE1 and mediate its proteosomal degradation. 22491325_Soluble amyloid precursor protein-alpha modulates BACE1 activity and amyloid-beta generation. 22553349_Data show that cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by beta-site amyloid precursor protein (APP)-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) occurs in post-endoplasmic reticulum (ER) compartments. 22709416_SNX12 interacts with BACE1 and downregulation of sorting nexin 12 accelerates BACE1 endocytosis and decreases steady-state level of cell surface BACE1. 22721728_In HEK293 cells, miR-195 regulates the BACE1 mRNA translation or decay process, through the 3'-UTR binding site 1 without affecting transcription. 22726800_Low protein levels of Uch-L1 are associated with high protein levels of BACE1 in sporadic AD brains. 22728099_BACE1 mRNA levels were increased in aged Alzheimer's disease mice as well as in Alzheimer's disease patient peripheral blood mononuclear cells 22775589_we found that BACE1 levels were significantly lower in AD compared to CN subjects. 22796214_BACE-1 protein expression and promoter activity is altered following altered prion protein expression. 22846573_Abeta-activated NFAT4 proteins were associated with astrocytic BACE1 gene expression via direct interaction with the BACE1 promoter region. 22879628_Differential gene expression of BACE1 and PSEN1 in the knockdown cells, which is possibly a consequence of MAT2A deregulation and may indicate a self regulatory mechanism. 22940630_Results show that the inverse coupling of APP cleavage by ADAM10 and BACE1 depends on the cellular model 22952813_a possible association of a common synonymous BACE1 polymorphism (rs638405) with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease 22975420_BACE1 is increased by SUMO1, interacting via a dileucine motif in BACE1. 22988240_BACE1(-/-) axon guidance defects are likely the result of abrogated BACE1 processing of CHL1 and BACE1 deficiency produces a CHL1 loss-of-function phenotype 23021373_analysis of biological aspects of BACE1, and the effects of several natural products that modulate BACE1-processing of APP [review] 23023105_A novel membrane assay comprising full-length BACE-1 with measurable activity at pH 6.0. 23024787_dyn1 affects amyloid generation through regulation of BACE-1 subcellular localization and therefore its enzymatic activities. 23036023_Our data suggest that brain BACEl levels may be influenced by the apolipoprotein E genotype before the onset of Alzheimer' |
ENSMUSG00000032086 |
Bace1 |
520.905349 |
0.3933344200 |
-1.346172 |
0.103724136 |
166.949759 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000003430869419886476925628073376361886016316398994428303095236334810851258257333384554877146070184842224781718300619104411453008651733398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000550667605760252477807100607110265627630810722457495604806003989790486916017657486440012016393847835149522040865122107788920402526855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
295.6899188 |
24.7233061 |
757.1855286 |
44.1926413 |
| ENSG00000186340 |
7058 |
THBS2 |
protein_coding |
P35442 |
FUNCTION: Adhesive glycoprotein that mediates cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions. Ligand for CD36 mediating antiangiogenic properties. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20714802}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the thrombospondin family. It is a disulfide-linked homotrimeric glycoprotein that mediates cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions. This protein has been shown to function as a potent inhibitor of tumor growth and angiogenesis. Studies of the mouse counterpart suggest that this protein may modulate the cell surface properties of mesenchymal cells and be involved in cell adhesion and migration. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7058; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; platelet alpha granule [GO:0031091]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965] |
11943589_Normal human adult corneal keratocytes have mRNA for this protein. 12058057_inhibits microvascular endothelial cell proliferation by a caspase-independent mechanism 12358136_All adrenal tissues (control adrenals, nonfunctional adenomas and ACTH-dependent aldosterone-producing adenomas) expressed both TSP1 and TSP2 mRNAs.both TSP1 and TSP2 mRNAs. Correlated closely with the expression of ACTH receptor. 12482844_Homozygosity for the THBS-2 variant allele is significantly associated with a lower risk of premature myocardial infarction. 12482844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12824879_Decreased thrombospondin-2 expression is associated with human salivary gland carcinomas 12861025_Thrombospondin 2 regulates cell proliferation induced by Rac1 redox-dependent signaling 12909644_thrombospondin-1 and thrombospondin-2 have N-terminal regions for binding to alpha6beta1 integrin 15121769_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15347840_results indicate that transforming growth factor TGFbeta1 treatment may regulate angiogenesis in pituitary cells by initially increasing levels of pro-angiogenic growth factor VEGF-A and then stimulating anti-angiogenic thrombospondin -1 and 2 levels 16186819_The 2.6-A-resolution crystal structure of the glycosylated signature domain of human THBS2 was discribed. 16246837_biophysical analysis of roles of signature domains of thrombospondin-4 and thrombospondin-2 in calcium binding, fine structure, and inter-modular interactions 17182969_Gene-expression changes in human evolution that involve specific brain regions, including portions of cerebral cortex. 17202846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17334638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17620335_two mAbs that recognize epitopes that are optimally present when three elements of signature domains of TSP-1 and TSP-2, the EGF-like modules, wire, and the lectin-like module, are in the same protein. 17638877_EWS/FLI1 has a role in regulating tumor angiogenesis in Ewing's sarcoma via suppression of thrombospondins TSP1 and TSP2 18032585_TSP1 and TSP2, together with the VLDLR, initiate a nonapoptotic pathway for maintenance of the normal adult vascular endothelium in a quiescent state. 18089612_TSP-2 was inconsistently expressed in uterine fibroids. 18178577_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18178577_The meta-analysis included 6388 (TSP-1), 4930 (TSP-2), and 6978 (TSP-4) cases; none of the polymorphisms was found to be linked with the risk of myocardial infarction. 18455130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18455130_regulation of intervertebral disc ECM metabolism by the THBS2-MMP system plays an essential role in the etiology and pathogenesis of LDH. 18600213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18600213_The variant allele of THBS2 is a risk factor for TAA in hypertensive patients, whereas the variant alleles of HSPA8, GPX1, AGT, and TNF are protective against this condition. 18682400_Mutations targeting intermodular interfaces or calcium binding destabilize the thrombospondin-2 signature domain. 18718009_TSP-2 was found to be present in some, but not all, annulus cells of the human annulus and the mouse annulus. 18720079_The expression of metastasis inhibitor genes PTEN and thrombospondin 2 was down-regulated in the supraglottic carcinoma tissue with lymph node metastasis. 18955754_A significant correlation between microvessel density and the expression of trombospondin-2 (p=0.009) was found. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19282863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19592030_When TSP-2 expression was reduced in tumor- derived pancreatic stellate cells using selective siRNAs, pancreatic cancer cell invasion was inhibited. 19631562_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19631562_the thrombospondin gene 2 T>G single nucleotide polymorphism is decreased only in plaque erosion, with no difference in frequency between other coronary disease and controls 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227257_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20472562_LRP1 and TSP2 stimulate Notch activity by driving trans-endocytosis of the Notch ectodomain into the signal-sending cell 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20485444_Single-nucleotide polymorphism in THBS2 is associated with coronary atherosclerosis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21682699_In patients with preeclampsia, we demonstrated 1.7-fold higher tsp-2 compared with control group. 21762961_Data suggests that the presence of thrombospondin-1 (rs2228262) and thrombospondin-2 (rs8089) variants need not be considered a risk for coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction among South Indians. 21949402_Endothelial nitric oxide synthase controls the expression of the angiogenesis inhibitor thrombospondin 2 22035575_Calcific aortic stenosis in associated with upregulation of TSP-2 expression, and inactivation of Akt and NF-kappaB. 22308237_TSP-2 has a protective role against cardiac inflammation, injury, and dysfunction in acute viral myocarditis. 23387388_Upregulation of TSP-2 may be a protective mechanism against inflammation and angiogenesis associated with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). 23470460_TSP2 is down-regulated at PCa tissues and cell lines, especially at stroma compartment, which could be related to prostate cancer progression. 23660684_human cytomegalovirus infection induced time-dependent decreases in mRNA and protein expressions of both TSP1 and TSP2 in astrocytes 23807322_Although no SNPs in THBS2 were associated with lumbar spinal stenosis, two haplotypes were significantly associated with disease progression in the Korean population, whereas another haplotype may play a protective role. 23843355_TSP-2 haschondrogenic effects on chondroprogenitor cells via PKCA ERK, p38/MAPK, and Notch signaling pathways. 23875975_Variants within the thrombospondin 2 (THBS2) gene are not associated with Achilles tendinopathy 24374826_Estrogen receptor alpha in cancer-associated fibroblasts suppresses prostate cancer invasion via modulation of thrombospondin 2 and matrix metalloproteinase 3. 24500070_TSP-2 is a potentially useful biomarker for assessment of disease severity and prognosis in HFrEF. 24708169_THBS2 is a salivary biomarker of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. 24764155_THBS2 protein, human is predicting lymph node metastases in OSCC, overall survival and disease-free survival. 25262009_Study suggests THBS2 is aberrantly expressed in gastric cancer and plays a critical role in cancer progression. 25771974_Patients whose MPM tissues expressed elevated mRNA levels of BIRC5, DSP, NME2, and THBS2 showed a statistically significant shorter overall survival. 25976449_No association was observed between the THBS2 3' untranslated region polymorphism and coronary artery disease risk. 26168731_determined if structural differences of the TSPs imparted different effects on vascular smooth muscle cell functions critical to the formation of neointimal hyperplasia 26235673_The level of THBS2 in differentiating stem cells, influences chondrogenic differentiation potential. 27157622_we report microRNA-135b (miR-135b), a key regulator of the malignancy, highly expressed in the RC component and promoting MLS cell invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo through the direct suppression of thrombospondin 2 (THBS2). 27160021_THBS2 and THBS4 mRNA are overexpressed in gastric cancer in a Southeast Chinese population. 27513329_High THBS2 expression is associated with lung cancer. 27632935_THBS2 could be considered as a novel prognostic marker in colorectal cancer. 27997896_THBS2, but not COL1A2 and SPP1, may serve as an indicator of gastric cancer prognosis. 28039493_the tissue levels of THBS2 and LECT-2 may correlate with the stage of atherosclerosis. 28122633_TSP-2 enhances the migration of PCa cells by increasing MMP-2 expression through down-regulation of miR-376c expression. 28216224_STMN1,COF1 and PAIRBP1 thus represent proteins associated with proliferative and aggressive tumors of high grades, while TSP2 and POSTN were connected to low grade tumors with better prognosis 28701476_the combination of THBS2 and CA19-9 yielded a sensitivity of 87% for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in the phase 2b study. 28739842_By testing for THBS2 and another marker, CA19-9, researchers identified blood samples from patients with the disease with 98% specificity and 87% sensitivity. 29467494_Data revealed a particularly high expression of a short TSP2 transcript containing only the last 9 (3') exons of the full-length TSP2 transcript. It lacked the anti-angiogenic thrombospondin type 1 repeats domain. The study proposes that sTSP2 expressed by tumor-associated vessels might compete with stromal TSP2 for binding to anti-angiogenic receptors and thus diminish the anti-angiogenic effects of TSP2. 29480856_Study found that 2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs6422747 and rs6422748) in the THBS2 gene were associated with susceptibility of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) but not severity of IDD in a Chinese Han population; results indicated that THBS2 gene polymorphisms might be the risk factors for IDD. 30031810_TSP-2 expression was associated with MMP-13 expression and poor prognosis in lung cancer. 30168023_These findings identify TSP-2 as a new FGF2 ligand that shares with TSP-1 the same molecular requirements for interaction with the growth factor and a comparable capacity to block FGF2 interaction with proangiogenic receptors. 30338785_Knockdown of thrombospondin 2 inhibits metastasis by modulating PI3K signaling pathway in uveal melanoma cells. 30513279_Collectively, our data disclosed that the downregulation of miR-20a triggered reduced proliferation, decreased autophagy and increased apoptosis by targeting THBS2 in cervical cancer (CC) cells, deepening our understanding on etiology of CC and providing some candidate targets for the therapy of CC. 30569296_High TSP2 expression is associated with Pancreatic Cancer. 30570855_High THBS2 expression is associated with colorectal cancer. 30993566_cervical squamous cell carcinoma exosomes transport miR-221-3p from cancer cells to vessel endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis by downregulating THBS2. 31063715_TSP2 acts as a suppresser of cell invasion, migration and angiogenesis in medulloblastoma by inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway. 31075265_TSP-2 knockdown inhibited lung cancer osteolytic metastasis in vivo. 31092423_the pathological roles of 4N1K-peptide are different from those of TSP-2, and 4N1K-peptide would be a more useful predictive marker and potential therapeutic target compared to TSP-1 and TSP-2 in patients with Bladder Cancer 31233787_A population-based study identifies an association of THBS2 with intervertebral disc degeneration. 31296790_Serum thrombospondin-2 is a candidate diagnosis biomarker for early non-small-cell lung cancer. 31298364_MiR-93-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting THBS2/MMPS signal pathway. 31545460_The protein expression of THBS2 was found to be notably upregulated in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues compared with that in the adjacent tissues. 31589839_the role of TSP-2 might be distinct from that of TSP-1 in the regulation of the TM cell ECM environment. TSP-2 may be involved in the pathogenesis of POAG and contribute to increased IOP levels by increasing the deposition of fibronectin within the ECM in response to TGFbeta2. 33021341_Thrombospondin-2 stimulates MMP-9 production and promotes osteosarcoma metastasis via the PLC, PKC, c-Src and NF-kappaB activation. 33067248_THBS2/CA19-9 Detecting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma at Diagnosis Underperforms in Prediagnostic Detection: Implications for Biomarker Advancement. 33345281_Bioinformatics analysis identifies COL1A1, THBS2 and SPP1 as potential predictors of patient prognosis and immunotherapy response in gastric cancer. 33372257_Circulating Levels of Thrombospondin-1 and Thrombospondin-2 in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Before and After Surgery. 33386676_Serum thrombospondin 2 is a novel predictor for the severity in the patients with NAFLD. 33759165_Circulating Levels of Thrombospondin-1 and Thrombospondin-2 in Patients with Common Brain Tumors. 33794141_Distribution of serum Thrombospondin-2, a novel tumor marker, in general population and cancer patients in China. 34105780_Transcriptomics Identify Thrombospondin-2 as a Biomarker for NASH and Advanced Liver Fibrosis. 34183428_Circulating Thrombospondin-2 as a Novel Fibrosis Biomarker of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. 34454032_Cautions should be taken when using cell models for gastric cancer research. 34471634_Prognostic and Immunological Role of THBS2 in Colorectal cancer. 34638915_miR-29a-3p/THBS2 Axis Regulates PAH-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis. 34669362_mRNA Expression of thrombospondin 1, 2 and 3 from proximal to distal in human abdominal aortic aneurysm - preliminary report. 34763455_Correlation analysis between TSP2, MMP-9 and perihematoma edema, as well as the short-term prognosis of patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. 34784607_MicroRNA 1228 Mediates the Viability of High Glucose-Cultured Renal Tubule Cells through Targeting Thrombospondin 2 and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. 35044104_Circ_0007580 knockdown strengthens the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer via the miR-598-dependent regulation of THBS2. 35277867_Circ-OPHN1 suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion of trophoblast cells through mediating miR-558/THBS2 axis. 35315209_THBS2 promotes cell migration and invasion in colorectal cancer via modulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 35982904_Tsp2 Facilitates Tumor-associated Fibroblasts Formation and Promotes Tumor Progression in Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma. 36335340_Prospective associations of circulating thrombospondin-2 level with heart failure hospitalization, left ventricular remodeling and diastolic function in type 2 diabetes. 36377223_Identification of BGN and THBS2 as metastasis-specific biomarkers and poor survival key regulators in human colon cancer by integrated analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000023885 |
Thbs2 |
92.361917 |
0.0108796158 |
-6.522229 |
0.581275463 |
214.647564 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000133030295116141398458027299768481053338740977630719305169953373437622275210048128184553035944604384048045298604507838950055179094711377274506958201527595520019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000027423563630087246038902775488697569931751953723495412463073196254455418723395533368339216604374755064872797528707564981842459417293866863474249839782714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0372659 |
0.8571949 |
189.5059506 |
29.6427391 |
| ENSG00000186352 |
353322 |
ANKRD37 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z713 |
|
ANK repeat;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
Located in cytosol; mitochondrion; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:353322; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; male germ cell nucleus [GO:0001673]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634] |
19491311_ANKRD37 is a direct HIF-1 target that is highly induced in hypoxia. |
ENSMUSG00000050914 |
Ankrd37 |
10.977986 |
4.0991339111 |
2.035319 |
0.690390647 |
8.482948 |
0.00358490732111234420426137958770596014801412820816040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007556874044504170197245063178570489981211721897125244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.3385970 |
7.2637959 |
4.2449139 |
1.4196352 |
| ENSG00000186399_ENSG00000289397 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
62.901165 |
0.0608318364 |
-4.039030 |
1.304242289 |
7.506388 |
0.00614805568914796908563946686854251311160624027252197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012323484875948883740526262897674314444884657859802246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5088832 |
6.3838646 |
87.4692848 |
67.0062031 |
| ENSG00000186431 |
2204 |
FCAR |
protein_coding |
P24071 |
FUNCTION: Binds to the Fc region of immunoglobulins alpha. Mediates several functions including cytokine production. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12768205}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;IgA-binding protein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is a member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily and encodes a receptor for the Fc region of IgA. The receptor is a transmembrane glycoprotein present on the surface of myeloid lineage cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils, where it mediates immunologic responses to pathogens. It interacts with IgA-opsonized targets and triggers several immunologic defense processes, including phagocytosis, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and stimulation of the release of inflammatory mediators. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2204; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; IgA binding [GO:0019862]; IgA receptor activity [GO:0019766]; cellular response to granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus [GO:0097011]; cellular response to interferon-alpha [GO:0035457]; cellular response to interleukin-6 [GO:0071354]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; Fc receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038093]; immune response [GO:0006955]; neutrophil activation [GO:0042119]; neutrophil mediated immunity [GO:0002446]; positive regulation of neutrophil apoptotic process [GO:0033031]; positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced cell death [GO:1903209] |
11281451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11801662_CD89 circulates in a high molecular mass form in complex covalently linked to IgA and contributes to the formation of polymeric serum IgA. 12560105_study suggests that expression of the FcR splice isoform DeltaEC2 but not Delta66EC2 is differentially regulated in a cell type-specific manner and in response to inflammatory and/or infectious processes 12594283_The Fc alpha receptor 5'-flanking region from -102 to -64 relative to the ATG translation initiation codon is essential for promoter activity and contains two functional binding motifs for C/EBP and Ets family members at -74 and -92, respectively. 12634059_there is a bivalent, pH-dependent interaction between FcalphaRI and IgA with important implications for cytokine-dependent phagocytosis of IgA and the FcalphaRI-mediated degradation or recycling of IgA 12768205_crystal structures of human FcalphaRI alone and in a complex with the Fc region of IgA1 (Fcalpha) 12783876_Crystal structure of the ectodomain of human FcalphaRI 12791088_expression pattern of CD89 and its signalling subunit, the FcR gamma chain, on circulating myeloid cells and in various tissues 15371488_FcalphaRI expressed by interstitial-type dendritic cells could play a critical role to sample IgA-recognized antigens and also during dendritic cell activation. 15564774_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16293625_Pathogenic group A and group B streptococci are well known to produce virulence factors that block the binding of IgA to the leukocyte IgA receptor, Fc alphaRI, thereby inhibiting IgA-mediated immunity. 16627486_Fc receptor gamma RI interacts with the unrelated immunoreceptors FcalphaRI and FcepsilonRI [FCalphaRI, also called CD89] 16876821_These results indicate that GPVI is unique amongst the receptors of its family as it uses different structural domains to interact with several agonists and provide evidence that different sites on GPVI constitute targets to develop antagonists of GPVI. 16990604_On monomeric targeting, FcalphaRI functions as an FcRgamma ITAM-dependent apoptotic module that may be fundamental for controlling inflammation and tumor growth. 17008591_Carriers of 92Asn polymorphism in the myeloid IgA Fc receptor had increased risk of myocardial infarction in CARE and increased odds of coronary heart disease in WOSCOPS study groups. 17008591_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17033823_FCAR promoter SNPs may be related to chronic HCV infection and disease progression in Japanese chronic hepatitis C. 17033823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17339498_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17393381_Fc alpha receptor type I activation mediates glomerulonephritis progression by initiating a cytokine/chemokine cascade that promotes leukocyte recruitment and kidney damage in transgenic mice. 17548632_Pathogen selection by bacterial decoy proteins drives FcalphaRI and IgA-Fc coevolution. 17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18700185_results suggest an endogenous mechanism by which FcalphaR functionality is down-regulated in an 'allergic environment' where FcepsilonRI is co-expressed and extensively cross-linked on FcalphaR-expressing effector cells 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19497711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19555692_Immunoglobulin A: Fc(alpha)RI interactions induce neutrophil migration through release of leukotriene B4. 19859085_Endocytosis of FcalphaR is clathrin- and dynamin-dependent, but is not regulated by Rab5, and the endocytic motif is not located in the cytoplasmic domain of FcalphaR. 19892918_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20811333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20811333_There is an association between the levels of sCD89-IgA complexes in serum and the severity of IgA nephropathy, and a possible genetic component in regulating the production or expression of sCD89. 21037509_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21159834_Data show that the Fc(alpha)RI 844 A>G polymorphism is not associated with systemic sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis sceptibility. 21273231_Genetic variation at the promoter region of IgA receptor is associated with IgA nephropathy. 21383176_FcalphaRI defines a function for pentraxins in inflammatory responses involving neutrophils and macrophages. It also highlights the innate aspect of otherwise humoral immunity-associated antibody receptors. 21653835_In this study, human mammary carcinoma cells are efficiently killed when incubated with human neutrophils and tumor-specific FcalphaRI bispecific or immunoglobulin A antibodies. 21750160_FCAR polymorphism is not associated with high susceptibility to IGA nephropathy in caucasians. 21784854_Glycosylation of the CH2/CH3 interface inhibits interaction with the pathogen IgA binding protein SSL7, while maintaining binding of pIgR, essential to the biosynthesis and transport of SIgA. 21866091_Abnormally glycosylated IgA1 and soluble CD89-IgA and IgA-IgG complexes, features of primary IgA nephropathy, are also present in alcoholic cirrhosis. 21985370_These results suggest a role of anti-FcaRI Fab as a negative regulator in controlling the magnitude of the innate immune response 24732061_this study examined the expression of IL-4 mRNA, IFN-c mRNA and FcaRI mRNA in tonsillar mononuclear cells of IgA nephropathy9(IgAN) patients and non-IgAN patients. 25339672_induces different forms of neutrophil death, depending on the inflammatory microenvironment 25907714_Findings suggest a basis for the use of Fc receptor I for IgA (FcalphaRI) as a molecular target for the treatment of lupus. 27437939_In transgenic mice, IgAN pathogenesis involves impaired clearance of abnormal IgA via CD89, primarily by the Kupffer cells. Conditional IgAN progression in CD89 transgenic mice thus reveals important aspects of IgAN pathogenesis. 28103138_a novel Fcar splice variant termed variant APD isolated from a healthy volunteer that lacks only the IgA-binding EC1 domain, is reported. 29491406_FcalphaRI-induced cytokine production is orchestrated via upregulation of cytokine translation and caspase-1 activation, which is dependent on glycolytic reprogramming. 32076466_Serum Soluble CD89-IgA Complexes Are Elevated in IgA Nephropathy without Immunosuppressant History. |
|
|
84.785890 |
3.5407628906 |
1.824060 |
0.214578939 |
73.122409 |
0.00000000000000001218531458489431173768664864826994089933736695234795313624864832036109874024987220764160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000096957004459859861740461449166011632179243892311164276787138760482775978744029998779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
136.4384120 |
18.2928813 |
38.7641349 |
4.1962942 |
| ENSG00000186469 |
54331 |
GNG2 |
protein_coding |
P59768 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as a modulator or transducer in various transmembrane signaling systems. The beta and gamma chains are required for the GTPase activity, for replacement of GDP by GTP, and for G protein-effector interaction (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell membrane;Host-virus interaction;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Prenylation;Reference proteome;Transducer |
|
This gene encodes one of the gamma subunits of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Such proteins are involved in signaling mechanisms across membranes. Various subunits forms heterodimers which then interact with the different signal molecules. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:54331; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; heterotrimeric G-protein complex [GO:0005834]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G-protein beta-subunit binding [GO:0031681]; adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007191]; cellular response to catecholamine stimulus [GO:0071870]; cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus [GO:0071380]; fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048144]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] |
15105422_Data show that G protein inhibition of N-type calcium channels is critically dependent on two separate but adjacent approximately 20-amino acid regions of the Gbeta subunit, as examined with Gbetas 1 and 5 and Ggamma2. 15747776_10 genes were down-regulated following treatment of the T-ALL cells with 0.15 and 1.5 microg/mL of metal ores at 72 h 17492941_Fission of transport carriers at the trans-Golgi network is dependent on specifically PLCbeta3, which is necessary to activate PKCeta and PKD in that Golgi compartment, via diacylglycerol production. 18045877_signaling pathway by which G(i)-coupled receptor specifically induces Rac and Cdc42 activation through direct interaction of Gbetagamma with FLJ00018. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20007712_Data show that activation of PLCbeta(2) by alpha(q) and beta1gamma2 differ from activation by Rac2 and from each other. 20181083_Data implicate the domain I-II linker region as an important contributor to voltage dependent Gbeta1/Ggamma2 modulation of Cav2.2 calcium channels. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21679469_Gbetagamma inhibits Epac-induced Ca 2+ elevation in melanoma cells. Cross talk of Ca 2+ signaling between Gbetagamma & Epac plays a major role in melanoma cell migration. 22957104_presence of Gng2 and Netrin-G2 immunoreactive elements in the insular cortex, but not in the putamen, suggests a possible common ontogeny of the claustrum and insula 23031273_increased protein expression level of GNG2 alone inhibits proliferation of malignant melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo 24462769_Data indicate that endogenous mTOR interacts with Gbetagamma. 25367286_Alteration of gene expression profiling including GPR174 and GNG2 is associated with vasovagal syncope. 25941381_G-protein betagamma subunits are positive regulators of Kv7.4 and native vascular Kv7 channel activity. 28818508_High GNG2 expression is associated with alcoholic hepatitis. 30928649_this paper shows that GNG2 gene polymorphism is associated with IgA nephropathy risk in Chinese Han population 31730405_Low GNG2 expression is associated with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. 34212982_Interference with KCNJ2 inhibits proliferation, migration and EMT progression of apillary thyroid carcinoma cells by upregulating GNG2 expression. |
ENSMUSG00000043004 |
Gng2 |
15.958655 |
5.8364084824 |
2.545081 |
0.505083046 |
26.895574 |
0.00000021475013427343451435003098687337441674571891780942678451538085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000817357396048451063999280407496028644231955695431679487228393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.2051315 |
8.8609424 |
4.5324202 |
1.2839503 |
| ENSG00000186480 |
3638 |
INSIG1 |
protein_coding |
O15503 |
FUNCTION: Oxysterol-binding protein that mediates feedback control of cholesterol synthesis by controlling both endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport of SCAP and degradation of HMGCR (PubMed:12202038, PubMed:12535518, PubMed:16168377, PubMed:16399501, PubMed:16606821, PubMed:32322062). Acts as a negative regulator of cholesterol biosynthesis by mediating the retention of the SCAP-SREBP complex in the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby blocking the processing of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) SREBF1/SREBP1 and SREBF2/SREBP2 (PubMed:12202038, PubMed:16399501, PubMed:32322062). Binds oxysterol, including 25-hydroxycholesterol, regulating interaction with SCAP and retention of the SCAP-SREBP complex in the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:32322062). In presence of oxysterol, interacts with SCAP, retaining the SCAP-SREBP complex in the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby preventing SCAP from escorting SREBF1/SREBP1 and SREBF2/SREBP2 to the Golgi (PubMed:15899885, PubMed:32322062). Sterol deprivation or phosphorylation by PCK1 reduce oxysterol-binding, disrupting the interaction between INSIG1 and SCAP, thereby promoting Golgi transport of the SCAP-SREBP complex, followed by processing and nuclear translocation of SREBF1/SREBP1 and SREBF2/SREBP2 (PubMed:32322062). Also regulates cholesterol synthesis by regulating degradation of HMGCR: initiates the sterol-mediated ubiquitin-mediated endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) of HMGCR via recruitment of the reductase to the ubiquitin ligases AMFR/gp78 and/or RNF139 (PubMed:12535518, PubMed:16168377, PubMed:22143767). Also regulates degradation of SOAT2/ACAT2 when the lipid levels are low: initiates the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of SOAT2/ACAT2 via recruitment of the ubiquitin ligases AMFR/gp78 (PubMed:28604676). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12202038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12535518, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15899885, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16168377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16399501, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16606821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22143767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28604676, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32322062}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cholesterol metabolism;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Isopeptide bond;Lipid metabolism;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein that regulates cholesterol metabolism, lipogenesis, and glucose homeostasis. The encoded protein has six transmembrane helices which contain an effector protein binding site. It binds the sterol-sensing domains of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase), and is essential for the sterol-mediated trafficking of these two proteins. It promotes the endoplasmic reticulum retention of SCAP and the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of HMG-CoA reductase. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:3638; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; SREBP-SCAP-Insig complex [GO:0032937]; oxysterol binding [GO:0008142]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to sterol [GO:0036315]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cranial suture morphogenesis [GO:0060363]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; middle ear morphogenesis [GO:0042474]; negative regulation of cargo loading into COPII-coated vesicle [GO:1901303]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0045717]; negative regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0070862]; negative regulation of steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0010894]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; SREBP signaling pathway [GO:0032933]; SREBP-SCAP complex retention in endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0036316]; sterol biosynthetic process [GO:0016126]; triglyceride metabolic process [GO:0006641] |
12115587_INSIG1 and p41 Arp2/3 complex (p41-Arc)reduced expression might be involved in gastric cancer development or progression 12242342_INSIG-1 plays a role in regulating cholesterol concentration in human cells 12535518_Data show that Insig-1 appears to play an essential role in the sterol-mediated trafficking of two proteins with sterol-sensing domains, HMG CoA reductase and SCAP. 12869692_insig-1 expression restricts lipogenesis in mature adipocytes and blocks differentiation in preadipocytes 14660594_data indicate that short segments at the N and C termini of insulin induced gene 1(Insig-1) face the cytosol with most of the protein buried within the membrane, forming six transmembrane segments 15085196_nSREBPs are essential for high levels of lipid synthesis in the liver and indicate that Insig's modulate nSREBP levels by binding and retaining SCAP in the ER. 15247248_Insig-1 has a role in feedback control of lipid synthesis in cultured cells 15304479_Insig-1 has a role in activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein induced by cellular stress 15899885_Insig is required for sterol-mediated inhibition of Scap/SREBP binding to COPII proteins in vitro 16168377_Results identify gp78 as the E3 that initiates sterol-accelerated degradation of reductase, and Insig-1 as a bridge between gp78/VCP and the reductase substrate. 16399501_Under conditions of mild steroid depletion, the failure to ubiquinate Insig-1 causes a delay in release of the Scap/sterol regulatory element binding protein-2, but it does not abolish it. 16549805_degradation of ubiquitinated Insigs is controlled by serine residues flanking the sites of ubiquitination 16606821_These studies identify a aspartic acid residue that is crucial for the function of Insig1 and Insig2 proteins in regulating cholesterol homeostasis in mammalian cells. 17043353_Insig-1 sterol-regulated degradation is mediated by the membrane-bound ubiquitin ligase gp78 17106696_Population studies demonstrate that INSIG1 plays a role in glucose homeostasis. 18187584_Activation of CAR and PXR in mouse liver results in activation of Insig-1 along with reduced protein levels of the active form of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 (Srebp-1). 18195716_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18835813_Unsaturated fatty acid-mediated stabilization of Insig-1 enhances the ability of sterols to inhibit proteolytic activation of SREBP-1, which activates transcription of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis 18989534_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18989534_The INSIG1 gene, not the INSIG2 gene, associated with coronary heart disease: tagSNPs and haplotype-based association study. 19638338_Studies define Insig-1 and Insig-2 as the minimal requirement for sterol-accelerated degradation of the membrane domain of reductase. 19740467_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19815544_These data suggest that p97 recruits proteasomes to polytopic ER proteins, such as Insig-1, even before they are extracted from membranes. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19965593_From genetic association studies, SNPs in INSIG1 (including the promoter region) influence hypertriglyceridemia. 19965593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20444954_Common variation in INSIG1 is unlikely to have a major effect on risk of type 2 diabetes risk in white Europeans. 20444954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877301_No significant associations were found between polymorphisms of INSIG1 gene and metabolic syndrome; however, INSIG1 and INSIG2 interactions were found in the significant 3-locus and 4-locus gene-gene interaction models. 20877301_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 24371122_Data show the essential role of PPARgamma and PPARgamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) in up-regulating Insig-1/2 expression, defining a mechanistic pathway triggered by CD36, and leading to cholesterol depletion in hepatocytes. 24484994_Our results indicated that the dysregulation of INSIG1 and SREBF1 caused by ART were observed not only in the fetus but also in the placenta, primarily in the ICSI group 25028659_identified interaction of three genes in INSIG-SCAP-SREBP pathway on risk of obesity, revealing that these genes affect obesity more likely through a complex interaction pattern than single gene effect. 26927283_INSIG1 variation may contribute to statin-induced changes in plasma triglycerides in a sex-specific manner. 28146316_Our findings suggest that miR-92a may affect cholesterol metabolism by repressing insig1, resulting in raised intracellular cholesterol levels and Golgi volume and hence enhanced protein secretion. 28928276_argue that precursor miR-122 molecules modulate polyadenylation site usage in Insig1 mRNAs, resulting in down-regulation of Insig1 protein abundance 30118702_Knock down of FADS1 did not significantly change cholesterol efflux (p=0.70), but knockdown of INSIG1 and LDLR resulted in highly significant reduction of the efflux to HDL (67% and 75% of control, respectively, p |
ENSMUSG00000045294 |
Insig1 |
1780.301044 |
8.2437303671 |
3.043297 |
0.052306300 |
3723.953591 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3209.1045019 |
96.5495774 |
391.8686773 |
10.6618255 |
| ENSG00000186510 |
1187 |
CLCNKA |
protein_coding |
P51800 |
FUNCTION: Voltage-gated chloride channel. Chloride channels have several functions including the regulation of cell volume; membrane potential stabilization, signal transduction and transepithelial transport. May be important in urinary concentrating mechanisms. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Bartter syndrome;Calcium;CBS domain;Chloride;Chloride channel;Deafness;Disease variant;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene is a member of the CLC family of voltage-gated chloride channels. The encoded protein is predicted to have 12 transmembrane domains, and requires a beta subunit called barttin to form a functional channel. It is thought to function in salt reabsorption in the kidney and potassium recycling in the inner ear. The gene is highly similar to CLCNKB, which is located 10 kb downstream from this gene. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1187; |
chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; voltage-gated chloride channel activity [GO:0005247]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; renal absorption [GO:0070293]; transepithelial chloride transport [GO:0030321] |
15044642_Combined impairment of ClC-Ka and ClC-Kb results in phenotype that mimics neonatal Barrter's syndrome with deafness 16849430_Barttin modulates trafficking and function of ClC-K1 and ClC-Kb channels 17510212_CLCNKA genetic variants may have roles in salt-sensitive hypertension 17510212_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17562318_The structure of the cytoplasmic domain of CLCNKA reveals a conserved interaction interface. 17652939_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18094726_Disruption of the gene encoding Barttin, BSND, results in a 'double knockout' of the functions of both ClCKA and ClCKB, manifesting as Bartter syndrome type IV with sensorineural deafness and an especially severe salt-losing phenotype. 18648499_ClC-Ka and ClC-Kb differ in how conformational changes are translated to the extracellular domain, despite the fact that the cytoplasmic domains share the same quaternary structure 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20805576_Identify a protein region that is involved in calcium binding and that is likely undergoing conformational changes underlying the complex gating of CLC-K channels. 21248228_The variant CLCNKA risk allele, telegraphed by linked variants in the adjacent HSPB7 gene, uncovers a previously overlooked genetic mechanism affecting the cardio-renal axis. 23850580_following variables were significantly associated with an estimated glomerular filtration rate: age, type 2 diabetes, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and the CLCNKA GG genotype 24863058_HEK293 cells the potentiating effect of niflumic acid (NFA) on CLC-Ka/barttin and CLC-Kb/barttin channels seems to be absent while the blocking efficacy of niflumic acid and benzofuran derivatives observed in oocytes is preserved 25919862_Single loci of tag Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of CLCNKA_B are not enough to increase the Essential Hypertension susceptibility, the combination of CLCNKA SNP, salt, marine products, meat, edible oil consumption is associated with elevated risk. 26013830_R8W and G47R, two naturally occurring barttin mutations identified in patients with Bartter syndrome type IV, reduce barttin palmitoylation and CLC-K/barttin channel activity. 29674316_Increasing expression of barttin over that of ClC-K partially recovered this insufficiency, indicating that N-terminal modifications of barttin alter both binding affinities and gating properties 32581267_Role of PKC in the Regulation of the Human Kidney Chloride Channel ClC-Ka. |
ENSMUSG00000006216+ENSMUSG00000033770 |
Clcnkb+Clcnka |
19.477861 |
0.0910698913 |
-3.456882 |
0.553288639 |
43.263759 |
0.00000000004783619476695902036922257356707467376710773976355994818732142448425292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000252616184171847983920867615381298208754312639712225063703954219818115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9119103 |
1.3820655 |
33.2198713 |
9.2918199 |
| ENSG00000186567 |
56971 |
CEACAM19 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z692 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:56971; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; membrane [GO:0016020]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157] |
20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23525470_Our results suggest that CEACAM19 mRNA expression represents a promising, novel and clinically useful tissue biomarker for breast cancer management. 27909883_In conclusion, CEACAM19 showed high expression in tumor samples compared to normal mammary tissue. 30217308_High CEACAM19 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 32659328_Identification and expression analysis of novel splice variants of the human carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 19 (CEACAM19) gene using a high-throughput sequencing approach. |
ENSMUSG00000049848 |
Ceacam19 |
61.993279 |
5.3625518197 |
2.422920 |
0.598136167 |
14.523145 |
0.00013844805436991706993309081408227712017833255231380462646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000372628242614875303598265254834132065298035740852355957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.0800538 |
19.0666797 |
7.9399881 |
2.7175477 |
| ENSG00000186583 |
375686 |
SPATC1 |
protein_coding |
Q76KD6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable gamma-tubulin binding activity. Located in centrosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:375686; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737] |
20542897_Speriolin is a novel centrosomal protein present in the connecting piece region of human sperm that is transmitted to the zygote and can be detected throughout the first mitotic division. |
ENSMUSG00000049653 |
Spatc1 |
11.407170 |
0.2685309861 |
-1.896840 |
0.519169079 |
14.215040 |
0.00016306201641964483727356705067279563081683591008186340332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000434204467319855276583734360329458468186203390359878540039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2803831 |
1.8088195 |
19.7433393 |
3.7260452 |
| ENSG00000186652 |
5553 |
PRG2 |
protein_coding |
P13727 |
FUNCTION: Cytotoxin and helminthotoxin. Also induces non-cytolytic histamine release from human basophils. Involved in antiparasitic defense mechanisms and immune hypersensitivity reactions. The proform acts as a proteinase inhibitor, reducing the activity of PAPPA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10913121}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Antibiotic;Antimicrobial;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Heparin-binding;Immunity;Lectin;Nitration;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is the predominant constituent of the crystalline core of the eosinophil granule. High levels of the proform of this protein are also present in placenta and pregnancy serum, where it exists as a complex with several other proteins including pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPPA), angiotensinogen (AGT), and C3dg. This protein may be involved in antiparasitic defense mechanisms as a cytotoxin and helminthotoxin, and in immune hypersensitivity reactions. The encoded protein contains a peptide that displays potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and fungi. It is directly implicated in epithelial cell damage, exfoliation, and bronchospasm in allergic diseases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]. |
hsa:5553; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring compression resistance [GO:0030021]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to nematode [GO:0002215]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production [GO:0010936]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753] |
319906_This protein contains a peptide that displays strong antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and fungi. 12202480_Transcription is regulated by novel combinatorial interactions of GATA-1, PU.1, and C/EBPepsilon isoforms. 12370176_IGF bioactivity is regulated by reversible cell surface binding of PAPP-A, which in turn is regulated by proMBP 12421832_MBP's structure is described, and its ability to bind to pregnancy-associated plasma protein A explained 12534990_Deposits of eosinophilic MBP are found on the surface of eosinophils and damaged muscle fibers surrounded by eosinophils in patients with idiopathic eosinophilic myositis. 14500673_MBP stimulates a Src kinase-dependent activation of class I(A) phosphoinositide 3-kinase and, in turn, activation of protein kinase C zeta in neutrophils, which contributes to the activation of NADPH oxidase and resultant superoxide production. 14988014_Proform of MPB forms a covalent complex with PAPPA in which PAPPA is inhibited. 15647258_the proform of eosinophil major basic protein inhibits the proteolytic activity of PAPP-A 16940047_two regions shown previously to contain the cytotoxic and cytostimulatory properties of MBP are accessible for ligand interaction in cell surface-bound MBP 17082653_Compared to MBP1, which is present in eosinophils, basophils, and a human mast cell line, homologous MBP2 is present only in eosinophils and may be a useful biomarker for eosinophil-associated diseases. 17223728_Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A is involved in processes preceding vulnerable plaque development in acute coronary syndrome. 18476621_MBP and NE collaborated to cause the pathological effects of nasal polyps. 18720885_The expression of MBP in nasal mucus obtained from chronic rhinosinusitispatients was obviously higher than that of nasal mucus obtained from controls. 18852884_knockdown of endogenous MBP-1 is involved in cellular senescence of HFF through p53-p21 pathway. 19014520_No variation in genes major basic protein for Atopic dermatitis pathogenesis in this German cohort 19039208_The significantly elevated levels of proMBP in myelofibrosis patients implies that proMBP could be an important stromal cytokine in bone marrow fibrosis. 19398958_addition to granule-stored MBP, even unstimulated eosinophils contained appreciable amounts of MBP within secretory vesicles 19626619_The proMBP is a novel first trimester serum marker for adverse pregnancy outcome. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20849415_novel transcript was alternatively transcribed from intron III of the ENO1 gene and was feasible for MBP-1 production 20977431_Combinations of respiratory syncytial virus and MBP synergistically induced cell death in pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells (A549). 23033876_During pregnancy, the proform of eosinophil major basic protein-angiotensinogen constitutes the major form in late pregnancy. 24112102_Eosinophil major basic protein activates human cord blood mast cells primed with fibroblast membranes by integrin-beta1. 24814827_mRNA levels of eosinophil granule proteins, rather than sputum eosinophil%, may reflect airway hyperresponsiveness and airflow limitation. 25266917_free protein in nasal mucus can be used as a biomarker to diagnose chronic rhinosinusitis 25728769_MBP-1 aggregation is important for innate immunity and immunopathology mediated by eosinophils.MBP-1 toxicity is restrained via crystallization in eosinophil secretory granules. 29936783_Low PRG2 expression is associated with drug resistance in Chronic myeloid leukemia. 31595373_Mechanism of atopic cataract caused by eosinophil granule major basic protein. 33689807_Development and application of novel immunoassays for eosinophil granule major basic proteins to evaluate eosinophilia and myeloproliferative disorders. 33982062_PRG2 and AQPEP are misexpressed in fetal membranes in placenta previa and percretadagger. |
ENSMUSG00000027073 |
Prg2 |
48.242073 |
0.4541701623 |
-1.138695 |
0.235087630 |
23.848380 |
0.00000104229533907813401406253911440913384467421565204858779907226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003678689432040472741681624152532137372872966807335615158081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.2842742 |
8.3655214 |
68.8613256 |
12.8192776 |
| ENSG00000186654 |
55615 |
PRR5 |
protein_coding |
P85299 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of mTORC2, which regulates cell growth and survival in response to hormonal signals. mTORC2 is activated by growth factors, but, in contrast to mTORC1, seems to be nutrient-insensitive. mTORC2 seems to function upstream of Rho GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton, probably by activating one or more Rho-type guanine nucleotide exchange factors. mTORC2 promotes the serum-induced formation of stress-fibers or F-actin. mTORC2 plays a critical role in AKT1 'Ser-473' phosphorylation, which may facilitate the phosphorylation of the activation loop of AKT1 on 'Thr-308' by PDK1 which is a prerequisite for full activation. mTORC2 regulates the phosphorylation of SGK1 at 'Ser-422'. mTORC2 also modulates the phosphorylation of PRKCA on 'Ser-657'. PRR5 plays an important role in regulation of PDGFRB expression and in modulation of platelet-derived growth factor signaling. May act as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15718101, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17599906}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene encodes a protein with a proline-rich domain. This gene is located in a region of chromosome 22 reported to contain a tumor suppressor gene that may be involved in breast and colorectal tumorigenesis. The protein is a component of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2), and it regulates platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor beta expression and PDGF signaling to Akt and S6K1. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in transcripts encoding different isoforms. Read-through transcripts from this gene into the downstream Rho GTPase activating protein 8 (ARHGAP8) gene also exist, which led to the original description of PRR5 and ARHGAP8 being a single gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:55615; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; TORC2 complex [GO:0031932]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to nutrient levels [GO:0031669]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014065]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; positive regulation of cell growth [GO:0030307]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; TORC2 signaling [GO:0038203] |
15718101_mRNA expression analyses revealed PRR5 overexpression in a majority of colorectal tumors but substantial downregulation of PRR5 expression in a subset of breast tumors and reduced expression in two breast cancer cell lines 17461779_It was demonstrated that immunoprecipitation of Protor-1 or Protor-2 results in the co-immunoprecipitation of other mTORC2 subunits, but not Raptor, a specific component of mTORC1. 17599906_The inhibition of Akt and S6K1 phosphorylation by PRR5 knock down correlates with reduction in the expression level of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRbeta). 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29391396_Fusion protein PRR5-ARHGAP8 plays a role in bipolar disorder with binge eating behavior. |
ENSMUSG00000036106 |
Prr5 |
58.678061 |
0.2334406458 |
-2.098872 |
0.239900323 |
80.471200 |
0.00000000000000000029497288442134419305656200218955164733812253132797193220376863465048700163606554269790649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000002525405901426357381560794593621075872942322182530187728299875260518092545680701732635498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.7817724 |
3.6978822 |
102.1902689 |
9.1367801 |
| ENSG00000186814 |
100101467 |
ZSCAN30 |
protein_coding |
Q86W11 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100101467; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
229.730531 |
0.4943189527 |
-1.016486 |
0.127970762 |
63.334768 |
0.00000000000000174398766501454185324891432481051301327616145312587869753429004049394279718399047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000012311126730428965926860392386252979159803086321722798146538480068556964397430419921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
153.7231171 |
12.6889827 |
313.2137326 |
17.4810816 |
| ENSG00000186862 |
79955 |
PDZD7 |
protein_coding |
Q9H5P4 |
FUNCTION: In cochlear developing hair cells, essential in organizing the USH2 complex at stereocilia ankle links. Blocks inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity mediated by ADGRV1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q9W7}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Chromosomal rearrangement;Cilium;Deafness;Disease variant;Non-syndromic deafness;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Usher syndrome |
|
This gene encodes a ciliary protein homologous to proteins which are mutated in Usher syndrome patients, and mutations and translocations involving this gene have been associated with two types of Usher syndrome. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:79955; |
cilium [GO:0005929]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; stereocilia ankle link [GO:0002141]; stereocilia ankle link complex [GO:0002142]; stereocilium [GO:0032420]; stereocilium tip [GO:0032426]; USH2 complex [GO:1990696]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; auditory receptor cell development [GO:0060117]; auditory receptor cell stereocilium organization [GO:0060088]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound [GO:0050910]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; inner ear receptor cell differentiation [GO:0060113]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605] |
19028668_PDZD7 is a new autosomal-recessive deafness-causing gene and a prime candidate gene for Usher syndrome. 20440071_PDZD7 is a modifier of retinal disease and a contributor to digenic Usher syndrome. 23055499_PDZD7 is a scaffolding component of the ankle-link complex in stereocilia and is associated with the Usher syndrome protein network. 24962568_overexpression of another Usher syndrome protein, PDZD7, decreased the AC inhibition of the VLGR1 beta-subunit 25406310_Both WHRN and PDZD7 are required for the complex formation with USH2A and GPR98. 26416264_Mutations in PDZD7 cause autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss. 26849169_PDZD7 is confirmed as a bona fide autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss gene. 29048736_This is the first report to identify PDZD7 as an ARNSHL-associated gene in the Chinese population. Our finding could expand the pathogenic spectrum and strengthens the clinical diagnostic role of the PDZD7 gene in ARNSHL patients. 30786928_Lnc-PDZD7 promotes stemness properties and suppresses chemosensitivity though the miR-101/EZH2/ATOH8 pathway. 31129248_Three mutations in PDZD7 gene linked to autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss (ARNSHL) were identified in a Chinese pedigree. The findings expand not only our knowledge of genetic causes of ARNSHL, but also PDZD7 genes mutation spectrum of the disease. They will aid personalized genetic counseling, molecular diagnostics and clinical management of this condition. 31454969_PDZD7 can be an important causative gene for moderate to severe ARNSHL in Koreans. Moreover, at least some, if not all, p.Arg164Trp alleles in Koreans could exert a potential founder effect and arise from diverse haplotypes as a mutational hot spot. 35715776_Novel homozygous variant in the PDZD7 gene in a family with nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss. |
ENSMUSG00000074818 |
Pdzd7 |
28.884133 |
0.2191241422 |
-2.190180 |
0.370867981 |
35.316878 |
0.00000000280193266415116777239620749623272288886255410034209489822387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012855618937790251249426653969328004922800801068660803139209747314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9370169 |
2.4246747 |
45.6681909 |
6.8123275 |
| ENSG00000186918 |
55893 |
ZNF395 |
protein_coding |
Q9H8N7 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in papillomavirus genes transcription. |
Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in cytosol and nuclear speck. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55893; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
14625278_HDBP1 and HDBP2 are novel transcription factors shuttling between nucleus and cytoplasm and bind to the specific GCCGGCG, which is an essential cis-element for HD gene expression in neuronal cells 15289353_PBF is an osteosarcoma-associated antigen recognized by autologous cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clone in the context of HLA-B*5502. 17531190_PBF is a new cellular factor mediating the effects of PI3K/Akt signaling and 14-3-3 on cell growth 17897615_PBF binds to SAP30 and represses transcription via recruitment of the HDAC1 co-repressor complex 19018758_colocalization of PBF and Scythe/BAT3 in the nucleus might be an important factor for survival of osteosarcoma cells. 23142027_ZNF395 coordinate the transcriptional regulatory pathway with PPARG2, which may be necessary for the genesis of adipocytes. 23760207_Studies indicate that ZNF395 was strongly expressed in adipocytes, and suggest a role for ZNF395 as a modulator of adipogenesis. 24086395_IkBalpha kinase (IKK)-signaling is necessary to allow ZNF395 to activate transcription and simultaneously enhances its proteolytic degradation. 24599008_miR-525-3p promotes liver cancer cell migration and invasion by directly targeting ZNF395. 28316371_The transcriptional activation of CXCL10 and CXCL11 by ZNF395 was abolished after inhibition of IKK by BMS-345541, which increased the stability of ZNF395. ZNF395 encodes at least two motifs that mediate the enhanced degradation of ZNF395 in response to IKK activation. Thus, IKK is required for ZNF395-mediated activation of transcription and enhances its turn-over to keep the activity of ZNF395 low. 28893800_epigenomic profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) establishes a compendium of somatically altered cis-regulatory elements, uncovering new potential targets including ZNF395. Loss of VHL, a ccRCC signature event, causes pervasive enhancer malfunction, with binding of enhancer-centric HIF2a and recruitment of histone acetyltransferase p300 at preexisting lineage-specific promoter-enhancer complexes 33794543_Downregulation of ZNF395 Drives Progression of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma through Enhancement of Growth Potential. |
ENSMUSG00000034522 |
Zfp395 |
73.193622 |
0.3263194438 |
-1.615643 |
0.204914761 |
64.585281 |
0.00000000000000092443340776580046317341196005466939270318470385501274932948945206589996814727783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000006633270344493540790585677863253532826852269018574892456285851949360221624374389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.6279737 |
5.8925309 |
103.9220486 |
11.9241676 |
| ENSG00000186951 |
5465 |
PPARA |
protein_coding |
Q07869 |
FUNCTION: Ligand-activated transcription factor. Key regulator of lipid metabolism. Activated by the endogenous ligand 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine (16:0/18:1-GPC). Activated by oleylethanolamide, a naturally occurring lipid that regulates satiety. Receptor for peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the ACOX1 and P450 genes. Transactivation activity requires heterodimerization with RXRA and is antagonized by NR2C2. May be required for the propagation of clock information to metabolic pathways regulated by PER2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10195690, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24043310, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7629123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7684926, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9556573}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;DNA-binding;Lipid-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Peroxisome proliferators include hypolipidemic drugs, herbicides, leukotriene antagonists, and plasticizers; this term arises because they induce an increase in the size and number of peroxisomes. Peroxisomes are subcellular organelles found in plants and animals that contain enzymes for respiration and for cholesterol and lipid metabolism. The action of peroxisome proliferators is thought to be mediated via specific receptors, called PPARs, which belong to the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. PPARs affect the expression of target genes involved in cell proliferation, cell differentiation and in immune and inflammation responses. Three closely related subtypes (alpha, beta/delta, and gamma) have been identified. This gene encodes the subtype PPAR-alpha, which is a nuclear transcription factor. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene, although the full-length nature of only two has been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5465; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding [GO:0097371]; NFAT protein binding [GO:0051525]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; nuclear steroid receptor activity [GO:0003707]; phosphatase binding [GO:0019902]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription coactivator binding [GO:0001223]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; behavioral response to nicotine [GO:0035095]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; enamel mineralization [GO:0070166]; epidermis development [GO:0008544]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; gluconeogenesis [GO:0006094]; heart development [GO:0007507]; hormone-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0009755]; lipid localization [GO:0010876]; lipoprotein metabolic process [GO:0042157]; negative regulation of appetite [GO:0032099]; negative regulation of blood pressure [GO:0045776]; negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development [GO:0061052]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of glycolytic process [GO:0045820]; negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process [GO:1903944]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:1903038]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; negative regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902894]; negative regulation of neuron death [GO:1901215]; negative regulation of protein binding [GO:0032091]; negative regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051898]; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process [GO:1903427]; negative regulation of sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0010891]; negative regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:2000272]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process [GO:2001171]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0032000]; positive regulation of fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0045923]; positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation [GO:0046321]; positive regulation of gluconeogenesis [GO:0045722]; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0046889]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; regulation of cellular ketone metabolic process [GO:0010565]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0019217]; regulation of fatty acid transport [GO:2000191]; regulation of lipid metabolic process [GO:0019216]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to lipid [GO:0033993]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11119019_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11409711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11466580_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11668221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11840500_polymorphism is unrelated to schizophrenia or alcoholism. 11845213_crystal structure of a ternary complex containing the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha ligand-binding domain bound to the antagonist GW6471 and a SMRT co-repressor motif 11852057_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARalpha and PPARgamma) agonists decrease lipoprotein lipase secretion and glycated LDL uptake by human macrophages. 11864924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11864924_Variation in the PPAR gene influences human left ventricular growth in response to exercise and hypertension 11897617_cPLA(2) plays a critical role in PPAR-mediated gene transcription in HepG2 cells 11897821_A Val227Ala polymorphism in the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) gene is associated with variations in serum lipid levels. 11914252_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11934839_activation of PPARalpha in human CD4-positive T cells limits the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IFNgamma 11940516_The results suggest that homocysteine may enhance vascular constrictive remodeling by inactivating PPAR-alpha and -gamma in ECs and PPAR-gamma in SMCs. 11980898_differential regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in bladder cancer cells (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, beta) 11981036_the organization of the 5'-flanking and untranslated region of the hPPARalpha gene was characterized and the hPPARalpha promoter region has been identified 12006394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12006394_PPARA L162V polymorphism is associated with increase in plasma LDL cholesterol levels. 12023905_PPARalpha binds to apolipoprotein a enhancers and influences estrogen-mediated transcription 12042669_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12048138_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12055195_regulation of human ASBT gene by PPARalpha 12118000_turnover is predicted by the ubiquitin-proteasome system which controls the ligand-induced expression level of its target genes 12118038_redundancy in the functions of PPARs alpha and delta as transcriptional regulators of fatty acid homeostasis and suggest that in skeletal muscle high levels of the delta-subtype can compensate for deficiency of PPAR alpha 12161442_PPARalpha is regulated by fatty acids in human cells 12163133_PPARalpha binding characteristics by FRET. 12203367_Our results established the presence of PPARalpha in human breast cancer cell lines and showed for the first time that activation of PPARalpha in human breast cancer cells promoted proliferation. 12395215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12408750_5'-flanking region of this gene is transcriptionally active and binds PPARalpha, we characterized the peroxisome proliferator-responsive element in the proximal promoter of the CPT II gene, which appears to be a novel PPRE. 12468272_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12468272_PPARA gene is a modifier of the familial combined hyperlipidemia phenotype 12544508_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12554753_These results provide molecular evidence for a cross-talk between the FXR and PPARalpha pathways in humans. 12594295_The PPAR alpha subtype localizes to the nuclear and perinuclear regions of human airway smooth muscle cells. 12594814_Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in human urinary bladder carcinoma and growth inhibition by its agonists. 12615366_TR2 and TR4 can have distinct functions. Existence of differential and bi-directional regulation between PPAR alpha and TR2/TR4. Possible roles in PPAR alpha signaling pathway in human keratinocytes. 12655356_decrease in cardiac PPARalpha transcription factor gene expression observed in the failing human heart could play an important role in a reduction in fatty acid utilisation by the adult heart during cardiac hypertrophy 12709436_PPARalpha regulates the human apolipoprotein AV gene 12745064_Molecular characterisation of six alternatively spliced variants and a novel promoter in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. 12810707_PPARA has a role as an important modulator of the metabolism of endobiotics and xenobiotics in human hepatocytes 12835617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12835617_There seems to be an association between the polymorphism of the PPARA gene and decreased fasting serum triglyceride levels in glucose tolerant subjects. 12847522_These results identify hepatic activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha as a mechanism underlying glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance. 12855749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12855749_peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha V162 allele is associated with reduced adiposity 12897377_ARA70, a coactivator of the androgen receptor and PPARgamma, was identified as a ligand-enhanced coactivator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in a prostate cancer cell line. 12914524_PPARalpha/RXRalpha complex was counteracted by the expression of ERRalpha in HeLa cells. 12938026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14515181_agonists of PPAR alpha increased basal and insulin-stimulated PAI-1 antigen release with a mechanism involving gene transcription and requiring signaling through the ERK1/2 signaling pathway 14519597_In humans skeletal muscle PPARalpha expression and genes regulating lipid metabolism are tightly linked, but there was no association between both insulin sensitivity and BMI with PPARalpha expression in skeletal muscle. 14523052_PPARalpha transcription factor as a major factor governing hepatic CoA levels by specific modulation of PANK1alpha gene expression 14633846_Increases in PGC-1 and PPAR-alpha levels may play an important role in changes in muscle mitochondria content, oxidative phenotype, and sensitivity to insulin induced by endurance training. 14641801_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14671555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14677049_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14730379_In type 2 diabetes there is a significant gene to gene interaction between the Ala55Val polymorphism in the uncoupling protein 2 gene ( UCP2) and the 161C>T polymorphism in the exon 6 of ppargamma. 14764586_chronic treatment with the PPARalpha agonist fully prevents the acute phase response gene expression in wild-type but not in PPARalpha-deficient mice 15001458_PPARalpha protects EC from glucose-mediated monocyte adhesion, in part through regulation of IL-6 production. 15001550_Only SRC-2 serves as a true coactivator for PPARdelta, whereas all SRC members could enhance PPARalpha-induced transcriptional activation. 15051727_PPARalpha and CITED2 proteins may participate in signaling cascades of hypoxic response and angiogenesis 15067378_PPARalpha and HNF-4 competitively affect the human angiotensinogen promoter through the C region 15083308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15083308_Our findings argue against a significant contribution of PPARalpha variations to the genetic basis of psoriasis. 15111510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15128052_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15131257_PPARalpha S179A-S230A protein displays an impaired ligand-induced transactivation activity and an enhanced trans-repression activity 15196699_Genistein activated transcriptional activity of PPARalpha in fatty acid catabolism. 15199365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15199365_data suggest that the PPARalpha polymorphism L162V might protect against the development of atherosclerosis or coronary heart disease in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 15231516_The antiinflammatory effects of fish oil may result from the inhibitory effects of oxidized omega-3 fatty acids on NF-kappaB activation via a PPARalpha-dependent pathway. 15258199_BF may enhance the capacity of human hepatocytes to direct PC into bile canaliculi via PPARalpha-mediated redistribution of ABCB4 to the canalicular membrane 15309680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15318936_PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma ligands induced apoptotic and antiproliferative responses in human breast cancer cell lines, respectively, which were associated with specific changes in gene expression. 15456881_Data suggest that ERRalpha serves as a nodal point in the regulatory circuitry downstream of PGC-1alpha to direct the transcription of genes involved in mitochondrial energy-producing pathways in cardiac and skeletal muscle. 15497675_This paper focuses on the functions of PPAR-alpha in fatty acid beta-oxidation, lipid metabolism, and vascular inflammation. PPAR-alpha genetics, the clinical use of PPAR-alpha activators and their future perspective are also discussed. 15500444_CLOCK plays an important role in lipid homoeostasis by regulating the transcription of a key protein, PPARalpha 15521013_new cytochrome P450 1A1 induction pathway involving peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and 2 peroxisome proliferator response element sites. 15539630_PPAR-alpha activation increases intracellular concentrations of ROS, through the activation of NADPH oxidase. 15549499_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15608561_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15608561_Response to procetofen is associated with PPARA in subjects with type 2 diabetes. 15642120_Activation of both PPARgamma and PPARalpha may contribute to the improvement in insulin sensitivity 15677519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15677519_PPARalpha gene intron variants influence age at diagnosis of typw 2 diabetes. 15685545_PPARalpha is one mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of hepatitis C infection. 15699244_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15699916_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15735069_Effect of the L162V polymorphism on plasma TG and apoC-III concentrations depends on the dietary PUFA, with a high intake triggering lower TG in carriers of the 162V allele. 15735069_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15759454_Clinical trial of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15797250_PPARalpha has a role in CYP4X1 regulation, and the glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors have roles in CYP4Z1 gene activation 15811118_Less likely to occur in squamous cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis than in normal skin. 15888456_the ligand-independent tight control of the position of the PPAR helix 12 provides an effective alternative for establishing an interaction with CoA proteins 15935279_Phe273Ala mutation dramatically reduced the binding affinity of ligands to PPARalpha; solvent effect may be concluded as the major source of the decrease of binding affinity and thereby of the decrease of its transcriptional activation activity 15940190_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16043164_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16043164_variant frequencies of ICAM1, APOE, PPARA and PAI-1 genes in coronary artery disease patients and healthy blood donors; specific arrangement of polymorphic variants which differentiate both groups 16162941_NPC1 and NPC2 mRNA depletion using small interfering RNA, abolished ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux induced by PPARalpha activators 16221474_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16221474_a L162V polymorphism at the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha locus modulates the risk of cardiovascular events associated with insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus 16226051_Data show that estrogen receptor alpha (ERa) reduces levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARa) in breast cancer cell lines, and that reduction of ERa by sodium butyrate results in an increase in PPARa expression. 16239970_PPAR alpha controls vascular smooth muscle cell-cycle progression at the G1/S transition by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and tumor suppressor p16INK4a 16271724_a conserved functional PPAR responsive element downstream of the transcriptional start site of the human CPT1A gene is localized; this sequence is fundamental for fatty acids or PGC1-induced transcriptional activation of the CPT1A gene 16275545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16285997_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16288935_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16288935_Our findings implicate PPARalpha in the lipid lowering associated with diets high in PUFA and suggests that genetic variation at the PPARA locus may determine the lipid response to changes in PUFA intake 16288986_data show that PPARalpha activation causes an increased nephrin expression by a dual action, on the one hand by stimulating nephrin promoter activity and on the other hand by reducing nephrin mRNA degradation 16297361_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16309557_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16377806_structural differences between human and mouse PPARalpha are responsible for the differential susceptibility to the peroxisome proliferator-induced hepatocarcinogenesis 16416313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16492688_Thioredoxin inhibited the binding of PPARalpha to the PPAR-response element. 16506057_In conclusion, PPARalpha intron 7 G/C polymorphism was associated with physical performance in Russian athletes/ 16506057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16511589_This review focuses on the mechanisms of action of PPAR alpha in metabolic diseases and their associated vascular pathologies. 16630553_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16637234_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16652134_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16763159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16822823_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16847426_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16847426_PPARalpha-V227A is a major polymorphism in the Japanese population, and its activity may be greater compared to wild-type, but decreased by alcohol drinking. 16875506_Diminished lymphocytic expression of PPAR alpha and its activity may contribute to the inflammatory processes that are observed in cystic fibrosis. 16956579_myeloperoxidase is regulated by LXR and PPARalpha ligands 17001213_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17008383_metabolism of a parent compound, beta-carotene, may alternatively activate (9-cisRA) or inhibit (beta-apo-14'-carotenal) specific RXR and PPAR responses 17084382_In conclusion, CEOOH present in oxidized LDL increase CD36 gene expression in a pathway involving PPARalpha. 17129741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17150915_Selected genes (long-chain fatty-acid-CoA ligase (FACL1), carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (CPT1A), adipose differentiation-related protein (ADRP) and aquaporin 3 (AQP3) were down-regulated by PPARalpha siRNA in a kidney tumor cell line. 17181634_Differential transcription occurring early in atopic dermatitis skin was indicated for CCL18, CCL13, IFNalpha2, PPARalpha and PPARgamma. 17184146_PPAR-alpha agonist fenofibrate did not significantly affect insulin sensitivity or resistin/adiponectin concentrations in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 17200111_Residues in PPAR alpha AF-2 transcription factor domain determine the positioning of helix 12 in the active conformation in the absence of a ligand. 17244467_The PPAR-alpha Val227Ala polymorphism is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 17272748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17300045_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17317762_Single nuscleotide polymorphisms of PPARA increase the risk of type 2 diabetes alone and in combination with the SNPs of other genes acting closely with PPAR-alpha. 17331954_PPARalpha transgenic mice that target constitutively activated PPARalpha specifically to hepatocytes do not develop hepatocellular carcinomas, even though they exhibit peroxisome proliferation and hepatocyte proliferation. 17342071_Combined with abdominal obesity, epistasis in the VLDL pathway (lipoprotein lipase, apolipoprotein CIII, hepatic lipase, PPARalpha, PPARgamma, and apo E genes) has a deleterious effect on fasting triglycerides and coronary artery disease risk profile 17355223_Data suggest that activator protein 2alpha and peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor alpha may be especially involved in the ozone-inducible up-regulation mechanism of bombesin receptor subtype 3 expression. 17356846_REVIEW: PPARalpha has been shown to control transcriptional expression of key enzymes that are involved in fatty acid (FA) uptake and oxidation, triglyceride synthesis, mitochondrial respiration uncoupling, and glucose metabolism. 17363697_Transgenic mice with cardiac-restricted overexpression of PPAR alpha exhibit myocyte lipid accumulation and cardiac dysfunction. 17363837_Data suggest that PPARalpha variants may modulate the risk of cardiovascular disease by influencing both fasting and postprandial lipid concentrations. 17431031_Cytochrome P450 eicosanoids are agonists of PPAR alpha. 17436029_Formation of a ligand for the nuclear receptor PPARalpha may be one possibility by which 12R-LOX and eLOX3 contribute to epidermal differentiation. 17492134_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/gamma ligands can down-regulate iNOS DNA methylation 17608096_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17616429_Interleukin-6 inhibits human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha gene expression via CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins in hepatocytes. 17646210_PPARalpha controls gene expression in human white adipocytes 17655842_PPAR-alpha is not involved in the early regulation of delta5 desaturase gene by simvastatin, in THP-1 cells. 17700210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17705849_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17705849_Our results on association of PPARalpha and triglycerides in males showed a much larger effect of the V allele than previously reported in older and less healthy populations 17850927_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17850927_We found no significant differences in genotype or allele distributions between AD patients and controls. None of the PPAR-alpha gene variants influenced markers for AD. 17926914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17951966_Finds influence of drinking, aging or exercise on TC, LDL-C and HDL-C levels in A227 carriers may be different from those in PPARA-WT subjects in Japan. 17951966_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17962186_PPARalpha ligands not only serve as PPARalpha agonists but possibly act as CAR antagonists. 17963696_Hence the anti-inflammatory effect of PPARalpha overrides the pro-inflammatory effect of AhR. 17991667_PBMC gene expression profiles reflect nutrition-related metabolic changes such as fasting and that part of the fasting-induced changes are likely regulated by PPARalpha. 17998026_PPAR-alpha mRNA expression is down-regulated in the liver of rats with chronic kidney failure and this down-regulation may play a role in the development of dyslipidemia. 18003597_Ethanol and acetaldehyde inhibited PPAR-alpha transactivation. 18004978_PPARalpha,gamma DNA methylation induced by Hcy may represent an important mechanism to explain atherosclerosis. 18061194_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18061194_Two PPARA SNPs, L162V and rs4253728 (intronic), are less prevalent in African-Americans than in Caucasians and in African-Americans only are associated with higher apoCIII and TG levels. 18172578_Both mouse and human melanoma cells produced more PPARalpha and PPARgamma protein compared to melanocytes. 18182682_review of role of activation of PPARalpha, -beta/delta, or -gamma or LXRs in skin physiology and cytology and disease 18184928_Hepatic PPARalpha activation may provide an explanation for telmisartan's antidyslipidemic actions observed in recent clinical trials. 18219093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18245819_fibrates simultaneously decreased PCSK9 expression while increasing PC5/6A and furin expression, indicating a broad action of PPARalpha activation in proprotein convertase-mediated lipid homeostasis. 18255343_Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate inhibits endothelial inflammatory processes by a PPAR-alpha mechanism. 18268046_PPAR alpha and PPAR gamma activation stimulates neoangiogenesis in umbilical veins through a VEGF-dependent mechanism. 18292238_investigation of the functional significance of the V227A substitution affecting PPARalpha hinge region; results provide first indication that defective function of a natural PPARalpha variant was due at least partially to increased corepressor binding 18313368_Current findings of PPARalpha and gamma open up the possibility of developing new therapeutic agents that modulate these nuclear receptors to control various inflammatory diseases. 18336366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18388689_polymorphisms in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are critical susceptibility risk factors for dyslipidemias and diabetes [review] 18394939_Stable structures and electronic properties for the complexes of PPARalpha and phthalate as well as adipate esters, were investigated. 18398047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18440986_Overexpression of human truncated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha induces apoptosis in HL-1 cardiomyocytes. 18518955_PPARalpha in human PBMCs regulates fatty acid and amino acid metabolism and PBMCs are a suitable model to study changes in PPARalpha activation in healthy humans. 18541586_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18541586_PPARA 3'UTR SNPs modulate the association between lipid concentrations and dietary n-6 fatty acid intake in whites and long-chain n-3 fatty acid intake in blacks. 18549840_Gene-wide variations in PPARA and TLR4 genes were associated with MI. The minor allele of the PPARA SNP, rs4253623, was associated with a higher risk of MI. 18549840_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18586686_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18586686_variants of PPARA modify the association between breast cancer and aspirin use. 18652775_Results show that a persistent upregulation of PPAR-alpha binding activity and protein expression occurred in injured cortex after traumatic brain injury, which peaked 24 - 72 hours post-injury. 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18680716_FGF21 circulates in human plasma and increases by extreme fasting and PPARalpha activation. 18713766_Report activation of human PPARalpha by perfluoroalkyl acids of different functional groups and chain lengths. 18725353_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18725353_The results of genetic variants analysis revealed that L162V PPARalpha polymorphism would not be present among Senegalese black population, and consequently, should not be involved in diabetes onset. 18726867_L162V SNP does not have a strong impact on the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes or obesity 18726867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18727927_PAR-5359, a well-balanced PPARalpha/gamma dual agonist, exhibits equivalent antidiabetic and hypolipidemic activities in vitro and in vivo. 18786524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18786524_PPAR-alpha and PGC-1A polymorphisms are associated with alcohol consumption in the Mediterranean population 18787507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18797151_lower transactivity of PPAR delta for arachidonic acid in Caco-2 cells, compared with PPAR alpha, is associated with the binding activity of p300 to the receptor 18848838_stimulation of PPARalpha in human macrophages might reduce arterial inflammation through differential regulation of the Trx-1 and VDUP-1 gene expression 18853997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18853997_PPAR-alpha val227ala polymorphism may be involved in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and play a protective role in obesity. 18855529_Interaction between PPARA genotype and beta-blocker treatment influences clinical outcomes following acute coronary syndromes. 18855529_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18955051_Endogenous PPARalpha regulates PDZK1 expression. 18977277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18981151_the response of the pleural mesothelium to LTB4 is the result of a balance between the activation of receptors for LTB4 with a proinflammatory outcome (BLT2) and the activation of a different receptor for LTB4 with an anti-inflammatory outcome (PPAR). 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19070893_Term human labour is associated with changes in expression and activity of PPAR isoforms and its transcription partner, RXRalpha. 19115207_A-FABP is a candidate progression marker of human transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder that is differentially regulated by PPAR in urothelial cancer cells 19118026_PPARgamma will preferentially bind with retinoid X receptor alpha and signal antiproliferative, antiangiogenic, and prodifferentiation pathways in several tissue types, thus making it a highly useful target for down-regulation of carcinogenesis 19119483_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha L162V polymorphism tends to occur in HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma and is absent in HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. 19141539_The present data indicate that down-regulation of MMP and proteasome activities constitutes a novel mechanism of PPAR-induced protections against HIV-induced disruption of brain endothelial cells. 19157507_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor expression in effusions from ovarian carcinomais associated with poor response to chemotherapy at disease recurrence and poor survival 19208777_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19217440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19217440_Polymorphsms may increase risk of myocardial infarct. 19223982_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19254215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19255064_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19279199_Report PPAR/RXRalpha dysregulation in preterm and infection-driven infection labor. 19357976_Dynamic Bayesian transcriptome networks to reveal PPARalpha-dependent and -independent pathways. 19362162_These findings are consistent with the presence of a functional PPAR-binding element in the promoter of the human APOA5 gene; this element is however degenerate and non-functional in the corresponding mouse Apoa5 sequence. 19367093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19386311_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha has a role in obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease [review] 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19422369_P633H, a novel dual agonist at peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma, with different anti-diabetic effects in db/db and KK-Ay mice. 19422653_Data indicate that a higher frequency of the PPAR alpha GG genotype may be associated with top-level endurance athletes. 19422653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19433068_results indicate that human apoA-IV is regulated directly by PPARalphavia the -2979/-2967 PPRE 19451226_Transcriptional profiling demonstrated that Bcl3 activates genes involved in diverse pathways including a subset involved in cellular energy metabolism known to be regulated by PGC-1alpha, ERRalpha, and a second nuclear receptor, PPARalpha. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19458633_Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha is a functional target of p63 in adult human keratinocytes. 19527689_PPARalpha and PPARbeta/delta do not appear to modulate the alternative differentiation of human macrophages. 19560472_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19628794_Shear stress induces synthetic-to-contractile phenotypic modulation in smooth muscle cells via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta activations by prostacyclin released by sheared endothelial cells. 19653005_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19660836_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19681917_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19706994_The regulation and adjustment of PPARalpha activation underlying the balance of molecular cascades might resolve the progression of alcoholic liver diseases (Review) 19710929_results suggest that PPARalpha activation has a major impact on gene regulation in human hepatocytes. Importantly, the role of PPARalpha as master regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism is generally well-conserved between mouse and human 19733654_liver up-regulation of SREBP-1c and down-regulation of PPAR-alpha occur in obese patients, with enhancement in the SREBP-1c/PPAR-alpha ratio associated with n-3 LCPUFA depletion and IR 19748481_PPARalpha regulates the expression of human SLC25A20 via the peroxisome proliferator responsive element. 19776627_The PPARalpha L162V polymorphism may contribute to the interindividual variability in the cardiovascular disease risk factor response to n-3 PUFAs. 19780876_Identified the effect of post-transcriptional regulation of miRNA-10b on PPAR-alpha expression to influence steatosis level in hepatocytes, which may contribute to pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. 19789836_Levels of mRNA and protein of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor a, which regulates b-oxidation of fatty acid, were lower in Japanese patients infected with hepatitis C virus with steatosis than in those without steatosis 19822141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19823578_CYP2J2 activates the nuclear receptor PPARalpha in vitro and in vi |
ENSMUSG00000022383 |
Ppara |
60.743831 |
0.4410494640 |
-1.180988 |
0.323563224 |
13.057702 |
0.00030203976078479116218825084594357122114161029458045959472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000770898645890284836719452687958664682810194790363311767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.9042033 |
7.6903683 |
79.4794983 |
12.1753203 |
| ENSG00000187037 |
353345 |
GPR141 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z602 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
GPR141 is a member of the rhodopsin family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPRs) (Fredriksson et al., 2003 [PubMed 14623098]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:353345; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930] |
25672891_GPR141-NME8 locus had strong genetic effect on susceptibility to generalized periodontitis in Japanese individuals with history of smoking. identified suggestive loci for periodontitis in Japanese population. |
ENSMUSG00000053101 |
Gpr141 |
120.816024 |
38.0272792185 |
5.248963 |
0.847244964 |
27.839538 |
0.00000013180487056195512785574080593525847504565717827063053846359252929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000513579696276255963668748698996990853515853814315050840377807617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
204.1895233 |
163.1688188 |
5.7247179 |
3.2616213 |
| ENSG00000187068 |
285382 |
C3orf70 |
protein_coding |
A6NLC5 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in neuronal and neurobehavioral development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q1LY84}. |
Neurogenesis;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in circadian behavior and nervous system development. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:285382; |
circadian behavior [GO:0048512]; nervous system development [GO:0007399] |
33204364_An Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Preoperative Nomogram for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Bladder Cancer (BLCA). |
ENSMUSG00000043391 |
2510009E07Rik |
20.689983 |
2.7960547878 |
1.483393 |
0.426394360 |
12.160978 |
0.00048799777684986286353796547388128601596690714359283447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001200674643491244546547602745079075248213484883308410644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.0634088 |
7.4348899 |
11.1938342 |
2.1423440 |
| ENSG00000187091 |
5333 |
PLCD1 |
protein_coding |
P51178 |
FUNCTION: The production of the second messenger molecules diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) is mediated by activated phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C enzymes (PubMed:9188725). Essential for trophoblast and placental development (By similarity). Binds phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PubMed:7890667, PubMed:9188725). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R3B1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7890667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9188725}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transducer |
|
This gene encodes a member of the phospholipase C family. Phospholipase C isozymes play critical roles in intracellular signal transduction by catalyzing the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into the second messengers diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3). The encoded protein functions as a tumor suppressor in several types of cancer, and mutations in this gene are a cause of hereditary leukonychia. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:5333; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTPase activating protein binding [GO:0032794]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding [GO:0005546]; lipid catabolic process [GO:0016042]; phosphatidylinositol metabolic process [GO:0046488]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644] |
11960991_Mechanism of 17-beta-estradiol-induced Erk1/2 activation in breast cancer cells. A role for HER2 AND PKC-delta 12761218_Pleckstrin homology domains of phospholipases C-beta and -delta confer activation through a common site 14550290_the PLC-delta1 promoter is under the control of NF-kappaB, which mediates the expression of PLC-delta due to Abeta42 15037625_PLCdelta(1) and PLCdelta(4) are probably differentially regulated in distinct cellular compartments by PI(4,5)P(2) 15509571_results support a model in which PLCbeta2 suppresses the basal catalytic activity of PLCdelta1, which is relieved by binding of Gbetagamma subunits to PLCbeta2 allowing for amplified calcium signals 15809301_Nuclear translocation of phospholipase C-delta1 is linked to the cell cycle and nuclear phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 15817490_the Ral-CaM complex defines a multifaceted regulatory mechanism for PLC-delta1 activation 16240320_In this review, recent findings regarding the molecular machineries and mechanisms of the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of PLCdelta1 will be discussed. 17041247_These results support the model that activation of selected PLC isoforms at the cleavage furrow controls progression of cytokinesis through regulation of PIP2 levels 18006814_PLC delta 1 plays an important suppressive role in the development and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 18434237_Human ARHGAP6 protein possessing GTPase stimulating activity for RhoA on the catalytic properties of PLC-delta1, was studied. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344632_Data are consistent with the idea that phospholipase C d1 and d3 isoforms support the growth and migration of normal and neoplastic mammary epithelial cells in vitro. 19448674_PLCD1 acts as a functional tumor suppressor involved in gastric carcinogenesis. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20018811_After PLC-delta 1 treatment with small interfering RNA, angiotensin II type 1 receptor-stimulated inositol phosphate formation is attenuated. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530480_Rac1 activates phospholipase Cdelta1 through phospholipase Cbeta2 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20657189_PLCD1 is silenced by promoter methylation in breast cancer. Silencing of PLCD1 is reversed by demethylation which leads to the disruption of cell cycle at G2/M phase in breast cancer, indicating that PLCD1 functions as a tumor suppressor in this tumor. 21665001_these data show that mutations in PLCD1 underlie hereditary leukonychia, revealing a gene involved in molecular control of nail growth. 21909432_Significantly deregulated pathways in colorectal cancer were identified and repression of PLCD1 and PLCE1 expression, was validated. 22078044_Mutations in this gene cause hereditary porcelain nails. Review. 22265909_Increased PLC-delta1 activity causes enhanced coronary vasomotility such as that seen in patients with coronary spastic angina. 22458588_A novel mutation in the PLCD1 gene, which leads to an aberrant splicing event, underlies autosomal recessive leuconychia. 22576628_PLCD1 acts as a functional tumor suppressor and may serve as a biomarker for possible early detection and prognosis of chronic myeloid leukemia. 23149345_Genotyping using microsatellite markers linked the families to the gene PLCD1 on chromosome 3p22.2. Sequence analysis of the gene detected one novel (p.Ser740ArgfsX19) and one previously reported mutation (p.Arg437X). 23388389_Provide evidence for intramolecular interactions in the PLC-delta1 PH domain. 23948486_PLCdelta1 is required for maintenance of homeostasis in skin and metabolic tissues. [review] 24903829_Neuropeptide Y decreased PLCD1 expression in HUVECs. 25477137_PLC-delta1 and TRPV6 are critical actor of Ca(2+) homeostasis in CF human bronchial epithelial cells. 25655282_Ectopic expression of PLCD1 inhibits breast tumor cell proliferation in vivo by inducing apoptosis and suppressed tumor cell migration by regulating cytoskeletal reorganization. 25995263_Both unsaturated and saturated dioleoyl-phosphatidylinositol-(4,5)-bisphosphate successfully recruited PHPLCdelta1 to cell membranes. 26755577_slow phase of Gi/o-mediated TRPC4 activation was diminished by inhibiting RhoA or enhancing PLCdelta function 28112359_High PLC delta expression is associated with breast cancer. 28375666_Phospholipase C delta 1 is both a KLF15-regulated gene and a novel repressor of airway smooth muscle hypertrophy. 28423710_PLCD1 acts as a tumour suppressor, by KIF3A-mediated suppression of ERK1/2/beta-catenin/MMP7 signalling, at least in part, in breast cancer. 28430185_A loss of epidermal PLCdelta1 impairs epidermal barrier function through dysregulation of Ca2+ and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling. This study also reveals a possible link among PLCdelta1 downregulation, p38 MAPK hyperactivation, and barrier defects in psoriasis-like skin inflammation. 28528980_The PLCdelta1 negatively regulates autophagy, and PLCdelta1 suppression contributes to the tolerance of CRC cells harboring KRAS mutations to nutrient deprivation and anti-cancer drug treatment. 29122566_Nine of the 32 (28.1%) iCCA patients had gene mutations at chromosome 3p, totaling 11 mutations across five genes. Those included five (15.6%) BAP1 mutations, two each (6.3%) of CACNA2D3 and RASSF1 mutations, and one each (3.1%) of ATG7 and PLCD1 mutations. Six (18.8%) cases had concurrent loss of chromosome 3p and gene mutations. 30003652_For the first time, a hereditary leukonychia case with PLCD1 mutation has been described in Chinese Han pedigree. This finding suggests the PLCD1 mutation maybe involved in hereditary leukonychia. 30618183_tumor-specific methylation of PLCD1 could be used as a novel biomarker for early detection and prognostic prediction in colorectal cancer. 30791982_Epidermal loss of phospholipase C delta 1 attenuates croton oil - induced irritant contact dermatitis. 32236884_PLCD1 Suppressed Cellular Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration via Inhibition of Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 32265483_Hereditary Trichilemmal Cysts are Caused by Two Hits to the Same Copy of the Phospholipase C Delta 1 Gene (PLCD1). 32795530_Germline Mutation of PLCD1 Contributes to Human Multiple Pilomatricomas through Protein Kinase D/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase1/2 Cascade and TRPV6. 33236921_Phospholipase C controls chloride-dependent short-circuit current in human bronchial epithelial cells. 33786625_Identification of two novel mutations in the PLCD1 gene in Chinese patients with hereditary leukonychia. 34727930_The tumor suppressor activity of DLC1 requires the interaction of its START domain with Phosphatidylserine, PLCD1, and Caveolin-1. |
ENSMUSG00000010660 |
Plcd1 |
16.528499 |
0.3325328644 |
-1.588431 |
0.572291985 |
7.200930 |
0.00728658066179898623870858642703751684166491031646728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014382178465920438317771079539397760527208447456359863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2493122 |
3.1923069 |
25.2090488 |
6.6587183 |
| ENSG00000187164 |
57698 |
SHTN1 |
protein_coding |
A0MZ66 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the generation of internal asymmetric signals required for neuronal polarization and neurite outgrowth. Mediates netrin-1-induced F-actin-substrate coupling or 'clutch engagement' within the axon growth cone through activation of CDC42, RAC1 and PAK1-dependent signaling pathway, thereby converting the F-actin retrograde flow into traction forces, concomitantly with filopodium extension and axon outgrowth. Plays a role in cytoskeletal organization by regulating the subcellular localization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) activity at the axonal growth cone. Also plays a role in regenerative neurite outgrowth. In the developing cortex, cooperates with KIF20B to promote both the transition from the multipolar to the bipolar stage and the radial migration of cortical neurons from the ventricular zone toward the superficial layer of the neocortex. Involved in the accumulation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) in the growth cone of primary hippocampal neurons. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0MZ67, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K2Q9}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Developmental protein;Direct protein sequencing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of neuron migration. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57698; |
axon [GO:0030424]; axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule associated complex [GO:0005875]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinesin binding [GO:0019894]; actin filament bundle retrograde transport [GO:0061573]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; Cdc42 protein signal transduction [GO:0032488]; cytoplasmic actin-based contraction involved in cell motility [GO:0060327]; endoplasmic reticulum polarization [GO:0061163]; netrin-activated signaling pathway [GO:0038007]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of neuron migration [GO:2001224]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of establishment of cell polarity [GO:2000114]; substrate-dependent cell migration, cell extension [GO:0006930] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26293343_Rnaset2 inhibits melanocyte outgrowth through interacting with shootin1, and this effect may be associated with vitiligo pathogenesis. 30411541_SHTN1 might be associated with the development of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 32371045_Putative Coiled-Coil Domain-Dependent Autoinhibition and Alternative Splicing Determine SHTN1's Actin-Binding Activity. |
ENSMUSG00000041362 |
Shtn1 |
329.600605 |
0.2174114162 |
-2.201500 |
0.802610331 |
6.884161 |
0.00869628744514500985618443706925972946919500827789306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016862480647706300923571731686934072058647871017456054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
127.9542444 |
60.1260124 |
592.4041981 |
198.5118816 |
| ENSG00000187187 |
339327 |
ZNF546 |
protein_coding |
Q86UE3 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:339327; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
54.865134 |
0.4438588995 |
-1.171827 |
0.274863965 |
18.070956 |
0.00002128231962266100392921694406389576670335372909903526306152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000064317575272415317068526452448651298254844732582569122314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.2514676 |
10.3020293 |
79.4040252 |
16.3460928 |
| ENSG00000187210 |
2650 |
GCNT1 |
protein_coding |
Q02742 |
FUNCTION: Glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the transfer of an N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) moiety in beta1-6 linkage from UDP-GlcNAc onto mucin-type core 1 O-glycan to form the branched mucin-type core 2 O-glycan (PubMed:1329093, PubMed:23027862). The catalysis is metal ion-independent and occurs with inversion of the anomeric configuration of sugar donor (By similarity). Selectively involved in synthesis of mucin-type core 2 O-glycans that serve as scaffolds for the display of selectin ligand sialyl Lewis X epitope by myeloid cells, with an impact on homeostasis and recruitment to inflammatory sites (By similarity). Can also act on glycolipid substrates. Transfers GlcNAc moiety to GalGb4Cer globosides in a reaction step to the synthesis of stage-specific embryonic antigen 1 (SSEA-1) determinant (By similarity). Can use Galbeta1-3GalNAcalpha1- and Galbeta1-3GalNAcbeta1- oligosaccharide derivatives as acceptor substrates (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1329093, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23027862}. |
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1329093}.; PATHWAY: Glycolipid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q09324}. |
This gene is a member of the beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase gene family. It is essential to the formation of Gal beta 1-3(GlcNAc beta 1-6)GalNAc structures and the core 2 O-glycan branch. The gene coding this enzyme was originally mapped to 9q21, but was later localized to 9q13. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2650; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi cisterna [GO:0031985]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008375]; beta-1,3-galactosyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0003829]; cell adhesion molecule production [GO:0060352]; glycoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0009101]; kidney morphogenesis [GO:0060993]; leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:0050901]; O-glycan processing [GO:0016266]; O-glycan processing, core 2 [GO:0016268]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; tissue morphogenesis [GO:0048729] |
12600830_EGF suppressed C2GnT activity in a time- and dose-dependent fashion, and also suppressed core 4 beta1,6 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (C4GnT) activity 12626388_presence of multiple tissue-specific promoters for the C2GnT I gene 12765965_elevated glucose increases the activity of core 2 GlcNAc-T and adhesion of human leukocytes to retinal capillary endothelial cells, in a dose-dependent manner, through diabetes-activated serine/threonine protein kinase C beta2-dependent phosphorylation 15026421_core 2 beta1-6-N-glucosaminyltransferase and dimerization of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 have roles in rolling on P-selectin 15483269_C2GnT-1 regulates sLeX expression level during differentiation of pre-B cells 15591039_upregulated by all-trans retinoic acid (RA) and by IL-4 and IL-13 in the H292 airway epithelial cell line 15882971_A/G polymorphism in enzyme is associated with the susceptibility to prostate cancer in a Japanese population 15926890_A differential functional impact of N-glycosylation on C2GnT-1 and FucT-VII and disclose that a strongly reduced FucT-VII activity retains the ability to fucosylate PSGL-1 on the core2-based binding site(s) for the three selectins. 15932919_Core2GnT is an extremely useful prognostic marker for prostate cancer progression. Acquiring Core2GnT in prostate carcinoma cells facilitates adhesion to type IV collagen and laminin causing aggressive tumor formation by prostate cancer cells. 16179912_C2GnT-1 regulates selectin ligand expression; downregulation of the selectin ligand expression level inhibits tissue infiltration of BCP-leukemia cells 16778138_glycosyltransferase haploinsufficiency results in altered cellular glycosylation and resistance to cell death, identifying a new survival mechanism for T-lymphoma cells 17530395_2 beta1,6 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-I transcription is regulated by Sp1 in lymphocytes and epithelial cells 17947642_regulation of O-glycosylation controls sLe(x) expression, and also suggest that O-glycans may have a function in dendritic cells migration 18815556_Pancreas carcinoma antigen, C2GnT, fused to invariant chain elicits T-cell response and tumor growth inhibition. 19267921_15-fold increase in C2GnT1 mRNA levels in colorectal adenocarcinomas compared to normal colorectal tissues 19524017_Data show that a short glycopeptide Galbeta1-3GalNAcalpha-TAGV was identified as an efficient C2GnT substrate. 20017138_Overexpression of C2GnT-1 enhances the metastatic potential of testicular germ cell tumor. 20841351_Core2 O-glycan structure is essential for expression of SI and DDP-IV during intestinal cell differentiation. 21081110_Data show that the reconstituted membrane system in cells expressing C2GnT-I led to the lipid vesicles exhibiting an enzyme activity 11 times higher than that found in microsomal membranes. 21712812_In C2GnT-expressing bladder tumour cells galectin-3 bound the NKG2D-binding site of MICA, reducing the affinity of MICA for NKG2D on natural killer cells and hence severely impairing natural killer cell activation. 22056345_The X-ray crystal structure (2.3 A resolution) of a mutant form of C2GnT-L (C217S) in complex with UDP was solved. C2GnT-L exists in an 'open' conformation and a 'closed' conformation. 22534569_Down-regulation of C2GnT1 is correlated with breast cancer 23027862_GOLPH3 can regulate cell-cell interaction by controlling Golgi retention of C2GnT1. 23165940_C2GnT-expressing prostate cancer cells evade NK cell immunity and survive longer in the host blood circulation, thereby resulting in the promotion of prostate cancer metastasis. 23617619_Immunohistochemical expression of core 2 beta1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase 1 (C2GnT1) in endometrioid-type endometrial carcinoma may be a novel potential prognostic factor. 23990450_NMIIA is the master regulator of Golgi fragmentation induced by heat shock or inhibition/depletion of HSP70/90 through interaction with gylosyltransferases. 24854630_GCNT1 is over-expressed in prostate cancer and is associated with higher levels of core 2 O-sLe(x) in PSA, PAP and MUC1 proteins. 25086069_Results show that ST3Gal1 uses GM130-GRASP65 and giantin, whereas C2GnT-L uses only giantin for Golgi targeting and defective giantin dimerization in PC-3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells causes fragmentation of the Golgi and prevents its targeting. 26390303_GCNT1 expression in prostate cancer positively correlates with cancer progression and prostate-specific antigen recurrence. 26768364_GCNT1 expression in prostate biopsy specimen is a significant and independent predictor of recurrence after radical prostatectomy, which can be used in pre-treatment decision making for the patient. |
ENSMUSG00000038843 |
Gcnt1 |
319.098672 |
0.2669847760 |
-1.905171 |
0.759110553 |
5.863342 |
0.01545941147744669084962421123918829835020005702972412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028426674150630767273773003012138360645622014999389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
125.8711781 |
57.1300140 |
479.5814308 |
154.7276539 |
| ENSG00000187479 |
387763 |
C11orf96 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z7L8 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:387763; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000087006 |
Gm13889 |
34.046839 |
0.0229314108 |
-5.446531 |
0.661529749 |
120.396169 |
0.00000000000000000000000000051808689676010803875616121604196900814137391078761771653612021221401473286723160516231700967182405292987823486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000006196890272430465649226454753585090082924274525520522788322503906446208406938458423951487930025905370712280273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5993160 |
0.7528610 |
70.8845962 |
10.9967420 |
| ENSG00000187583 |
84069 |
PLEKHN1 |
protein_coding |
Q494U1 |
FUNCTION: Controls the stability of the leptin mRNA harboring an AU-rich element (ARE) in its 3' UTR, in cooperation with the RNA stabilizer ELAVL1 (PubMed:29180010). Decreases the stability of the leptin mRNA by antagonizing the function of ELAVL1 by inducing its atypical recruitment from the nucleus to the cytosol (By similarity). Binds to cardiolipin (CL), phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P) and phosphatidylserine (PS) (PubMed:18191643). Promotes apoptosis by enhancing BAX-BAK hetero-oligomerization via interaction with BID in colon cancer cells (PubMed:29531808) (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8C886, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18191643, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29180010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29531808}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Enables phospholipid binding activity. Involved in 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization; positive regulation of apoptotic process; and response to hypoxia. Located in cytoskeleton and mitochondrial membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84069; |
cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cardiolipin binding [GO:1901612]; phosphatidic acid binding [GO:0070300]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; 3'-UTR-mediated mRNA destabilization [GO:0061158]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666] |
|
ENSMUSG00000078485 |
Plekhn1 |
41.056649 |
0.0246989699 |
-5.339405 |
1.419868347 |
7.679106 |
0.00558638223713912255435909415268724842462688684463500976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011307597616589884145787969771390635287389159202575683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9865820 |
2.4450719 |
109.0475335 |
58.8748153 |
| ENSG00000187634 |
148398 |
SAMD11 |
protein_coding |
Q96NU1 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in photoreceptor development. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable several functions, including histone binding activity; protein domain specific binding activity; and protein self-association. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:148398; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892] |
23978614_SAMD11 was found to be widely expressed in many cell lines and ocular tissues and its transcription was not regulated by CRX, OTX2 or NR2E3 proteins. 26204995_SEZ6L, HISPPD1, FEZF1, SAMD11 gene variants may be associated with autism spectrum disorder. 27734943_analysis of a homozygous nonsense mutation in SAMD11 in five individuals diagnosed with adult-onset retinitis pigmentosa; SAMD11 interacts with CRX and is expressed in retina 34546569_CircSAMD11 facilitates progression of cervical cancer via regulating miR-503/SOX4 axis through Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000096351 |
Samd11 |
13.263058 |
0.0070517959 |
-7.147794 |
1.141877878 |
55.094892 |
0.00000000000011484899749632311777308180182895286372481320757987788283571717329323291778564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000724741856795950978750651579823077621904381384609905580873601138591766357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2089791 |
0.1782455 |
29.7072480 |
7.5683452 |
| ENSG00000187650 |
400673 |
VMAC |
protein_coding |
Q2NL98 |
|
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in type III intermediate filament. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:400673; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; type III intermediate filament [GO:0045098] |
|
ENSMUSG00000054723 |
Vmac |
46.464428 |
0.3487665557 |
-1.519666 |
0.256371476 |
35.997670 |
0.00000000197553661318329248276011787896922627938423033810977358371019363403320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000009215840837732426121408732424926391058050967330927960574626922607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.2325039 |
3.9442774 |
69.9950540 |
7.1119858 |
| ENSG00000187678 |
81848 |
SPRY4 |
protein_coding |
Q9C004 |
FUNCTION: Suppresses the insulin receptor and EGFR-transduced MAPK signaling pathway, but does not inhibit MAPK activation by a constitutively active mutant Ras (PubMed:12027893). Probably impairs the formation of GTP-Ras (PubMed:12027893). Inhibits Ras-independent, but not Ras-dependent, activation of RAF1 (PubMed:12717443). Represses integrin-mediated cell spreading via inhibition of TESK1-mediated phosphorylation of cofilin (PubMed:15584898). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12027893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12717443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15584898}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;Disease variant;Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism;Kallmann syndrome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of cysteine- and proline-rich proteins. The encoded protein is an inhibitor of the receptor-transduced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Activity of this protein impairs the formation of active GTP-RAS. Nucleotide variation in this gene has been associated with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism 17 with or without anosmia. Alternative splicing results in a multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2014]. |
hsa:81848; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; protein kinase inhibitor activity [GO:0004860]; animal organ development [GO:0048513]; cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor [GO:1990830]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0040037]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; negative regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900025] |
12027893_interacts with the dual specificity kinase TESK1; maps to 5q31.3 12717443_Sprouty4 suppresses vascular epithelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced, Ras-independent activation of Raf1 but does not affect epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced, Ras-dependent activation of Raf1. 14977631_Core promoter activity is located within proximal 0.4-kb region. Minimal ERK-inducible promoter activity is between -69 and -31. Core promoter region of hSpry4 gene exhibits significant homology to 5'-flanking region of mouse gene. 16388505_Sprouty4 expression is down regulated in human prostate cancer by DNA methylation and this decreased expression may contribute to increased cell migration. 16465403_Human, chimpanzee, rat and mouse SPRY4 orthologs, consisting of three exons, were well conserved 16877379_the Sprouty/Caveolin-1 interaction modulates signaling in a growth factor- and Sprouty isoform-specific manner 18298822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18298822_SPRY4 gene was found to be associated with schizophrenia. 19483682_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19483682_These results demonstrate that common genetic variants affect TGCT risk and implicate KITLG and SPRY4 as genes involved in Testicular germ cell tumors susceptibility. 19761767_cell adaptation to activated FGFR3 include Sprouty4 activity, which silences the premature receptor signaling and suppress apoptosis. 20482313_The Spry4 might be involved in the timely restriction of MAPK signals under hypoxic conditions, similar to its role in mitogen-regulated processes. 20501643_Spry4 is a downstream target of Wnt7A/Fzd 9 signaling and may have efficacy in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. 22072546_The SPRY4 (rs4324715) variants were significantly associated with germ cell tumors only in the adolescent age group. 23074222_siRNA-mediated knockdown of Spry1, Spry2, or Spry4 promotes IFN-inducible antileukemic effects in vitro and results in enhanced suppressive effects on malignant hematopoietic progenitors from patients with polycythemia vera. 23554919_Spry1 and Spry4 have opposing roles in VSMC phenotypic modulation, and Spry1 maintains the VSMC differentiation phenotype in vitro in part through an Akt/FoxO/myocardin pathway. 23640991_results validated previously reported genetic associations with testicular germ cell tumor in a Scandinavian population, and observed suggestive evidence of a parent-of-origin effect in SPRY4. 23831057_Sprouty2 (but not Sprouty4) has a role in inhibition of cell proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells 23955631_Overexpressed Spry4 in endothelial cells inhibited migration and vitronectin adhesion. Spry4 knockdown enhanced these. Overexpression decreased integrin beta3 protein post-transcriptionally by modulating its tyrosine phosphorylation by c-Src. 24402575_Sprouty4 expression negatively influences cell migration. 24554542_involvement of PAX9, EDA, SPRY2, SPRY4, and WNT10A as risk factors for MLIA. uncovered 3 strong synergistic interactions between MLIA liability and MSX1-TGFA, AXIN2-TGFA, and SPRY2-SPRY4 gene pairs. 1st evidence of sprouty genes in MLIA susceptibility. 24681741_Downregulation of Dusp6, Sprouty4, and Sef--negative modulators of FGF2/ERK1/2 signaling--was present in eutopic endometria of adenomyosis, which may play critical roles in the development of adenomyosis. 24732356_Overexpression of Sprouty4 or pharmacological inhibition of ERK upregulated IL-1R1 expression in primary T cells.Sprouty4 and ERK play a critical role in developing iTh17 cells in Th17 cell-driven autoimmune diseases. 24810925_demonstrated that knockdown of SPRY4-IT1 reduced cell proliferation, invasiveness, and migration 24811094_SPRY4 may function as a tumor suppressor in endometrial adenocarcinoma. 25344859_these results suggest the possibility that SPRY4-IT1 knockdown may induce apoptosis via lipin 2-mediated alterations in lipid metabolism leading to cellular lipotoxicity. 25630587_Sprouty 2 protein, but not Sprouty 4, is an independent prognostic biomarker for human epithelial ovarian cancer. 25742952_ZNF703 was a target of SPRY4-IT1. 25957915_Specific protein 1 plays a crucial role in the regulation of Sprouty4 in response to serum. 26204823_SPRY4 is often deleted in secondary acute myeloid leukemia. 26286024_Data show that proto-oncogene protein B-raf (BRAF) inhibition induces c-Jun N-terminal kinase (c-JUN) expression and c-JUN abundance and activation by down-regulating SPRY2/4 protein expression. 26392417_Results identify the tumor suppressor SPRY4 as a novel molecular effector of MT1-MMP affecting melanoma cell motility. 26768617_Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown of SPRY4 attenuated the AREG-induced down-regulation of E-cadherin. 26982001_These findings suggest that SPRY4-IT1 plays a direct role in the regulation of metastasis and progression of osteosarcoma. 27956498_results found that histone methylation mediated by CCAT1 could also contribute to the lower expression of SPRY4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 27997895_SPRY4 is involved in the development and progression of colorectal cancer. 28064312_Polymorphisms of KITLG, SPRY4, and BAK1 genes in patients with testicular germ cell tumors and individuals with infertility associated with AZFc deletion of the Y chromosome 28275056_mechanistic evidence that KSRP promotes the down-regulation of Spry4 by a previously unidentified mechanism, i.e. post-transcriptional mRNA regulation. 28295819_Studied BAK1, SPRY4 and GAB2 SNPs in pediatric germ cell tumors(GCT); found a variant in SPRY4 was associated with reduced risk of GCT; a variant in BAK1 was positively associated with GCT with a strong estimated effect for testis tumors; and a SNP in GAB2 was associated with increased risk for GCT. 28940816_Our data indicate that KMT2C ELs are associated with specific genetic features and that SPRY4 ELs may add prognostic information. 29048686_Results show that SPRY4 expression level was significantly decreased in glioma tissues, associated with short survival time, and a key target gene of miR-1908. 29410498_The findings indicate that SPRY4 and SPRY4-IT1 may act as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors via activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 30390072_miR-411-5p/3p are required for Non small cell lung carcinoma development by suppressing SPRY4 and TXNIP; thus, the miR-411-SPRY4-AKT axis might act as a promising target for lung cancer therapy clinically. 30651601_Ectopic introduction of SPRY4 recapitulated the growth arrest phenotype of dual BRAF(V600E)/NRAS(Q61) expression while SPRY4 depletion led to a partial rescue from oncogenic antagonism. 30982407_The transient downregulation of the SPRY4 expression via small interfering RNA (siRNA) showed significant enhancement of the osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. 31374860_The authors demonstrated that Spry4 functions as tumor-suppressing protein in cancerogenesis of brain malignancies. 31645544_SPRY4 is responsible for pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis by contributing to osteogenic differentiation and melatonin response of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. 31761616_High expression of SPRY4 was an independent biomarker of favorable prognosis in PHCC 32196809_SPRY4 regulates trophoblast proliferation and apoptosis via regulating IFN-gamma-induced STAT1 expression and activation in recurrent miscarriage. 32389901_Prevalence and associated phenotypes of DUSP6, IL17RD and SPRY4 variants in a large Chinese cohort with isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. 33670044_A Sprouty4 Mutation Identified in Kallmann Syndrome Increases the Inhibitory Potency of the Protein towards FGF and Connected Processes. 33757566_Long non-coding RNA SPRY4-IT1 as a promising indicator for three field lymph-node dissection of thoracic esophageal carcinoma. 33879635_SPRY4 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by repressing oncogene EZH2. 33906393_Identification of SPRY4 as a Novel Candidate Susceptibility Gene for Familial Nonmedullary Thyroid Cancer. 34048471_Sprouty4 negatively regulates ERK/MAPK signaling and the transition from in situ to invasive breast ductal carcinoma. 34339801_Coupling HDAC4 with transcriptional factor MEF2D abrogates SPRY4-mediated suppression of ERK activation and elicits hepatocellular carcinoma drug resistance. 36082406_SPRY4 promotes adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells through the MEK-ERK1/2 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000024427 |
Spry4 |
363.766395 |
8.1021027914 |
3.018296 |
0.566858201 |
23.655163 |
0.00000115236331437463937158599287108318165451237291563302278518676757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004049733933373732654766724570194469379202928394079208374023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
632.1931394 |
314.9294895 |
70.8642928 |
25.2613722 |
| ENSG00000187688 |
51393 |
TRPV2 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5S1 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-permeable, non-selective cation channel with an outward rectification. Seems to be regulated, at least in part, by IGF-I, PDGF and neuropeptide head activator. May transduce physical stimuli in mast cells. Activated by temperatures higher than 52 degrees Celsius; is not activated by vanilloids and acidic pH. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10201375}. |
3D-structure;ANK repeat;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes an ion channel that is activated by high temperatures above 52 degrees Celsius. The protein may be involved in transduction of high-temperature heat responses in sensory ganglia. It is thought that in other tissues the channel may be activated by stimuli other than heat. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51393; |
axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; cell body [GO:0044297]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; growth cone membrane [GO:0032584]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; cation channel activity [GO:0005261]; ion channel activity [GO:0005216]; ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015075]; calcium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098703]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; positive regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090280]; positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120162]; response to heat [GO:0009408]; response to temperature stimulus [GO:0009266]; sensory perception [GO:0007600] |
15249591_TRPV2 and PKA have roles as a signaling module for transduction of physical stimuli in mast cells 16533525_It is concluded that PI3-kinase induces or modulates the activity of recombinant TRPV2 channels; in contrast to the previously proposed mechanism, activation of TRPV2 channels by PI3-kinase is not due to channel translocation to the plasma membrane. 16777226_Both TRPV1 and TRPV2 are found in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. 16882997_The TRPV2 ARD provides the first structural insight into a domain that coordinates nociceptive sensory transduction and is likely to be a prototype for other TRPV channel ARDs 17977643_A progressive loss of s-TRPV2 accompanied by an increase of hTRPV2 expression was found in high-grade and -stage UC. 18787888_Messenger RNA transcripts of TRPVs 1 through 4 are detected for the first time in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 18983665_relative gene expression ofTRPV1-4 in leukocytes is: TRPV3 |
ENSMUSG00000018507 |
Trpv2 |
342.080733 |
3.2847956400 |
1.715804 |
0.267028545 |
39.122390 |
0.00000000039805276901849687031016513153423852511281211263849399983882904052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001965626922286053721030737662035965673812398790687439031898975372314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
544.6036231 |
92.4937306 |
167.4077791 |
21.0531544 |
| ENSG00000187713_ENSG00000176058 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65.543267 |
0.0014834701 |
-9.396808 |
3.296661799 |
4.795932 |
0.02852701999108314678821329835045617073774337768554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.049344757420413366821865253086798475123941898345947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2073190 |
1.3222030 |
139.9324960 |
405.6594414 |
| ENSG00000187730 |
2563 |
GABRD |
protein_coding |
O14764 |
FUNCTION: GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Chloride;Chloride channel;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain where it acts at GABA-A receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels. Chloride conductance of these channels can be modulated by agents such as benzodiazepines that bind to the GABA-A receptor. The GABA-A receptor is generally pentameric and there are five types of subunits: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and rho. This gene encodes the delta subunit. Mutations in this gene have been associated with susceptibility to generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures, type 5. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene, but their biological validity has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2563; |
axon [GO:0030424]; chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; GABA-A receptor complex [GO:1902711]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; synapse [GO:0045202]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005231]; GABA-A receptor activity [GO:0004890]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; transmitter-gated ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:1904315]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; chloride transmembrane transport [GO:1902476]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; nervous system process [GO:0050877]; regulation of membrane potential [GO:0042391]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
16023832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19289452_Lower delta mRNA levels in schizophrenia might reflect a reduced number of alpha(1)beta(x)delta GABA(A) receptors that could contribute to deficient tonic inhibition and prefrontal cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia. 19874574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561060_These findings point to the GABRD gene as a susceptibility gene for COMD. 21795619_In recombinant human cDNA experiments in HEK293 cells, delta subunit coexpression leads to receptors activated by nanomolar THIP concentrations. 23756480_Genome-wide association studies identify GABRD mutation releated to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 24249596_Considering our Argentinean ASD sample, it can be inferred that GABRB3 would be involved in the etiology of autism through interaction with GABRD. These results support the hypothesis that GABAR subunit genes are involved in autism. 29020412_This study found that increased methylation of the promoter of the delta subunit GABAA receptor was associated with reduced mRNA and protein levels in the cerebellum of alcohol use disorder subjects. 31545245_In IDH wild-type diffuse low-grade glioma patients preserved GABRD expression was independently associated with longer overall survival and reduced tumor infiltration macrophages(TIM). CpG methylation of cg13916816 showed a moderately negative correlation with GABRD expression. 33887383_Association between GABA receptor delta subunit gene polymorphisms and heroin addiction. 34194536_Research for Expression and Prognostic Value of GABRD in Colon Cancer and Coexpressed Gene Network Construction Based on Data Mining. 34633442_Gain-of-function variants in GABRD reveal a novel pathway for neurodevelopmental disorders and epilepsy. |
ENSMUSG00000029054 |
Gabrd |
19.077409 |
0.1128194685 |
-3.147912 |
0.494165192 |
47.889661 |
0.00000000000450893115954608362593522327239905990621526843398214623448438942432403564453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000025646174919036684903196903483971473731994894507124627125449478626251220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9407613 |
1.3903014 |
35.2863659 |
6.3248399 |
| ENSG00000187775 |
8632 |
DNAH17 |
protein_coding |
Q9UFH2 |
FUNCTION: Force generating protein component of the outer dynein arms (ODAs) in the sperm flagellum. Produces force towards the minus ends of microtubules. Dynein has ATPase activity; the force-producing power stroke is thought to occur on release of ADP (Probable). Plays a major role in sperm motility, implicated in sperm flagellar assembly and beating (PubMed:31178125). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31178125, ECO:0000305|PubMed:31178125}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Dynein;Flagellum;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Dyneins are microtubule-associated motor protein complexes composed of several heavy, light, and intermediate chains. DNAH17 is a heavy chain associated with axonemal dynein (Milisav and Affara, 1998 [PubMed 9545504]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:8632; |
axonemal dynein complex [GO:0005858]; axoneme [GO:0005930]; dynein complex [GO:0030286]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; outer dynein arm [GO:0036157]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; dynein intermediate chain binding [GO:0045505]; dynein light intermediate chain binding [GO:0051959]; microtubule motor activity [GO:0003777]; minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity [GO:0008569]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; microtubule-based movement [GO:0007018]; outer dynein arm assembly [GO:0036158] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30575322_We found that overexpression of DNAH17 by down-regulation of methylation levels might contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) initiation and progression. In addition, the hypomethylation status of the DNAH17 gene, both in tumor tissue and adjacent non-cancerous tissue, could be a promising biomarker for tumor thrombosis in HCC. 31178125_Mutations in DNAH17 Cause Isolated Male Infertility Due to Asthenozoospermia. 31658987_A DNAH17 missense variant causes flagella destabilization and asthenozoospermia. 31841227_DNAH17 is associated with asthenozoospermia and multiple morphological abnormalities of sperm flagella. 33070343_Novel loss-of-function variants in DNAH17 cause multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella in humans and mice. 33423959_Novel compound heterozygous variants in dynein axonemal heavy chain 17 cause asthenoteratospermia with sperm flagellar defects. |
ENSMUSG00000033987 |
Dnah17 |
33.962918 |
0.1476945617 |
-2.759311 |
0.518655424 |
25.292582 |
0.00000049259957286750826112336392251234151729022414656355977058410644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001808649177991149798082272555366234456641905126161873340606689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3483545 |
3.9520433 |
58.4400864 |
19.4083547 |
| ENSG00000187801_ENSG00000260920 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
501.710994 |
4.3213999880 |
2.111499 |
0.205166937 |
99.270869 |
0.00000000000000000000002202237220303713411207576270526301933303613676000756371513923962887626650797301408601924777030944824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000221423851305741216705740051885138767233847035770556718891504711932416427089265198446810245513916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
826.2616211 |
124.9030614 |
192.8862785 |
21.5427116 |
| ENSG00000187808 |
347454 |
SOWAHD |
protein_coding |
A6NJG2 |
|
ANK repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:347454; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000044400 |
Sowahd |
11.786742 |
0.3169158232 |
-1.657828 |
0.491021021 |
11.872467 |
0.00056969893301013442218905247216298448620364069938659667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001385897522166264521012446486736280348850414156913757324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7592282 |
1.8510216 |
18.2791114 |
3.5308682 |
| ENSG00000188004 |
284677 |
SNHG28 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Enables RNA binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
17.918926 |
0.3006844060 |
-1.733678 |
0.714609940 |
5.368237 |
0.02050669340328944642570796474956296151503920555114746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036688338743339661551789987470328924246132373809814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
7.3826144 |
3.7561574 |
24.4090984 |
9.0978369 |
| ENSG00000188042 |
10123 |
ARL4C |
protein_coding |
P56559 |
FUNCTION: Small GTP-binding protein which cycles between an inactive GDP-bound and an active GTP-bound form, and the rate of cycling is regulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEF) and GTPase-activating proteins (GAP). GTP-binding protein that does not act as an allosteric activator of the cholera toxin catalytic subunit. May be involved in transport between a perinuclear compartment and the plasma membrane, apparently linked to the ABCA1-mediated cholesterol secretion pathway. Recruits CYTH1, CYTH2, CYTH3 and CYTH4 to the plasma membrane in the GDP-bound form. Regulates the microtubule-dependent intracellular vesicular transport from early endosome to recycling endosome process. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15147902, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17398095, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19409876}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
ADP-ribosylation factor-like 4C is a member of the ADP-ribosylation factor family of GTP-binding proteins. ARL4C is closely similar to ARL4A and ARL4D and each has a nuclear localization signal and an unusually high guanine nucleotide exchange rate. This protein may play a role in cholesterol transport. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10123; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; alpha-tubulin binding [GO:0043014]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
17398095_Study shows that three related Arf-like GTPases Arl4a, Arl4c, and Arl4d, are able to recruit ARNO and other cytohesins to the plasma membrane by binding to their PH domains irrespective of whether they are in the diglycine or triglycine form. 19409876_ARL7 might modulate the intracellular vesicular transport via interaction with microtubules. 21187453_an important role of LXRs in the coordinated regulation of lipid metabolic and inflammatory gene programs in macrophages 25486429_Arl4c is involved in tumorigenesis and might represent a novel therapeutic target for suppressing proliferation and invasion of colorectal and lung cancer cells. 26756615_Results indicated that overexpression of Arl4c might contribute to the tumorigenesis and might play a pivotal role in the progression of CRC. 27835592_ARL4C is expressed due to hypomethylation in the 3'-UTR for certain types of cancers and that ARL4C methylation status is involved in squamous cell carcinoma cell function. 28053143_Arl4c as a novel Wnt signal target molecule that links epithelial tubulogenesis to tumourigenesis. 29270876_High ARL4C expression was associated with the depth of invasion and Peritoneal Dissemination in Gastric Cancer. 29432742_We demonstrate that ARL4C knockdown likely attenuates osteogenesis of hASCs through inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway. These results provide new insights into the mechanisms of osteogenic differentiation and provide a potential molecular target for bone tissue engineering. 30357833_ARL4C stabilized by AKT/mTOR pathway promotes the invasiveness of PTEN-deficient glioblastoma cells. 30556117_High ARL4C expression is associated with Peritoneal Dissemination in Gastric Cancer. 30594917_High ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 4C (ARL4C) expression in endometriosis-associated ovarian cancer is a significantly independent predictive factor for worse 5-year overall survival and 5-year progression-free survival. 30647122_ARL4C antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) accumulated in cancer cells more efficiently than the surrounding normal cells in the liver and decreased ARL4C expression in the tumor. These results suggest that ARL4C ASO represents a novel targeted nucleic acid medicine for the treatment of primary and metastatic liver cancers. 31925985_ARL4C is involved in the initiation of the premalignant stage. 33724652_ARL4C might serve as a prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target for gastric cancer: bioinformatics analyses and biological experiments. 34622442_RAF1-MEK/ERK pathway-dependent ARL4C expression promotes ameloblastoma cell proliferation and osteoclast formation. 35718975_Identification of Neural Progenitor Cell-associated Chemoradiotherapy Resistance Gene Set (ARL4C, MSN, TNFAIP6) for Prognosis of Glioma. 36366750_ARL4C depletion suppresses the resistance of ovarian cancer to carboplatin by disrupting cholesterol transport and autophagy via notch-RBP-Jkappa-H3K4Me3-OSBPL5. |
ENSMUSG00000049866 |
Arl4c |
1604.990387 |
2.0133867414 |
1.009624 |
0.042055468 |
580.039672 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003676641109542897031795282971901913044228828975698075430038749861416339988638171644073947121140423063253731654606235144514740944542175029227549032652008434141286859005444600744458022672688886685121459313 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001995118484443130994080270993569513541504114981542602143944630972603432151417714600235894517653001040635131124414614650331246352648555604651251922283680900675141647833138377311790258093385910549668244446 |
Yes |
No |
2174.7443418 |
56.2741436 |
1087.9853201 |
21.8772998 |
| ENSG00000188051 |
100130519 |
TMEM221 |
protein_coding |
A6NGB7 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100130519; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000043664 |
Tmem221 |
33.915169 |
0.3211141174 |
-1.638842 |
0.341244912 |
22.959099 |
0.00000165485074105572562245278309817075879095682466868311166763305664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005713589927013452800241832818528564530424773693084716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.4179205 |
3.5484751 |
48.2158592 |
7.1728968 |
| ENSG00000188070 |
65998 |
ZFTA |
protein_coding |
C9JLR9 |
|
Chromosomal rearrangement;Isopeptide bond;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:65998; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892] |
23672313_Based on a recurrent translocation t(11;16)(q13;p13), the C11orf95-MKL2 fusion gene has been found in eight further cases of chondroid lipomas. 24562983_C11orf95-RELA fusions represent a unique novel mechanism leading to pathological activation of NF-kappaB signaling in supratentorial ependymomas. 25388523_C11orf95-RELA fusion transcript is thought to be the driver genetic alteration leading to activation of the NFkB pathway in supratentorial ependymomas. 33221956_Ependymoma with C11orf95-MAML2 fusion: presenting with granular cell and ganglion cell features. 33576087_Ependymoma-like tumor with mesenchymal differentiation harboring C11orf95-NCOA1/2 or -RELA fusion: A hitherto unclassified tumor related to ependymoma. 33685520_C11orf95-RELA fusion drives aberrant gene expression through the unique epigenetic regulation for ependymoma formation. |
ENSMUSG00000053080 |
Zfta |
181.822640 |
0.4660428211 |
-1.101466 |
0.147507105 |
55.714508 |
0.00000000000008379759176918732479095841880374785519468381483898511419283750001341104507446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000533816337726890277755897282961112612783248498882215926641947589814662933349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
114.6331674 |
10.6208583 |
247.5345846 |
15.5581886 |
| ENSG00000188158 |
4810 |
NHS |
protein_coding |
Q6T4R5 |
FUNCTION: May function in cell morphology by maintaining the integrity of the circumferential actin ring and controlling lamellipod formation. Involved in the regulation eye, tooth, brain and craniofacial development. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20332100}. |
Alternative splicing;Cataract;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction |
|
This gene encodes a protein containing four conserved nuclear localization signals. The encoded protein functions in eye, tooth, craniofacial and brain development, and it can regulate actin remodeling and cell morphology. Mutations in this gene have been shown to cause Nance-Horan syndrome, and also X-linked cataract-40. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]. |
hsa:4810; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; nuclear body [GO:0016604]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; lens development in camera-type eye [GO:0002088] |
14564667_key functions in the regulation of eye, tooth, brain, and craniofacial development 15466011_independent identification of the gene (NHS)causative for Nance-Horan syndrome and extends the number of mutations identified 15623749_X-linked families with cataract should be carefully examined for both ocular and nonocular features, to exclude Nance-Horan syndrome. 16675532_We demonstrate the differential expression of the two NHS isoforms, NHS-A and NHS-1A, and differences in the subcellular localization of the proteins encoded by these isoforms. 17417607_identification of the frequency and distribution of NHS gene mutations and comparison of genotype with Nance-Horan phenotype in five North American NHS families; this report extends the number of unique identified NHS mutations to 14 18949062_This study aimed to identify the causative mutations in new patients diagnosed with Nance-Horan syndrome and to investigate the effect of mutations on subcellular localization of the NHS-A protein. 19414485_Four novel protein truncation mutations and a large deletion of the NHS gene lead to Nance-Horan syndrome. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20332100_these data identify NHS as a new regulator of actin remodelling. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21559051_Direct sequencing of NHS sequences in a Tunisian family identified the first missense mutation (P551S) and a reported SNP-polymorphism (L1319F) in exon 6, a reported UTR-SNP (c.7422 C>T) and a novel one (c.8239 T>A) in exon 8. 22229851_Lens opacities centered around the posterior Y-suture in the context of certain facial features were sensitive and specific clinical signs of carrier status for NHS mutation in asymptomatic females. 23566852_Identification of a previously unreported frameshift mutation (c.558insA) in exon 1 of the NHS gene in a Turkish family with Nance-Horan Syndrome. 24968223_mutations in NHS are the common cause of congenital cataract 25091991_A nonsense mutation c.322G>T (E108X) co-segregated with the disease in a family. Multiple sequence alignments showed that codon 108, where the mutation (c.322G>T) occurred, was located within a phylogenetically conserved region. 25266737_Our findings broaden the spectrum of NHS mutations causing Nance-Horan syndrome and phenotypic spectrum of the disease in Chinese patients. 28061824_Results revealed a novel splice site mutation (NM_198270: c.1045 + 2T > A) in the 5' consensus donor site of intron 4 in the NHS gene in a Chinese family. This mutation led to aberrantly spliced mRNA, which is likely to result in a truncated NHS protein. 28464487_Here, we report a microdeletion of 170,6 Kb at Xp22.13 (17.733.948-17.904.576) (GRCh37/hg19).The microdeletion harbors the NHS, SCLML1, and RAI2 genes and results in a phenotype consistent with Nance-Horan syndromesyndrome and developmental delay. 28557584_Our study expands the repertoire of NHS mutations and the related phenotype, including newly described anterior Y-sutural cataract and dental findings. 28922055_This is the first report of Nance-Horan syndrome due to a skewed X chromosome inactivation resulting from a balanced translocation t(X;1) that disrupts the NHS gene expression, with important implications for clinical presentation and genetic counseling. 29402928_A novel small deletion in the NHS gene is associated with Nance-Horan syndrome in a Chinese pedigree. 30642278_Nance-Horan syndrome (NHS) is an X-linked inheritance disorder characterized by bilateral congenital cataracts, and facial and dental dysmorphism. This disorder is caused by mutations in the NHS gene. However, NHS may be difficult to detect in individuals with subtle facial dysmorphism and dental abnormalities in whom congenital cataracts are the primary clinical manifestations. 31755796_Deleterious NHS mutations are associated with Nance Horan syndrome. 32303606_Low grade mosaicism in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia identified by bidirectional whole genome sequencing reads through the 100,000 Genomes Project clinical diagnostic pipeline. |
ENSMUSG00000059493 |
Nhs |
17.882008 |
0.4572307944 |
-1.129006 |
0.369580298 |
9.468358 |
0.00209046352187083938137246441613115166546776890754699707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004597711456238055133249886807789152953773736953735351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.6111142 |
2.9108695 |
25.6524691 |
4.0939099 |
| ENSG00000188185 |
|
LINC00265 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.735256 |
0.4524282120 |
-1.144239 |
0.452082308 |
6.227648 |
0.01257706607423296832348746931984351249411702156066894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.023624013140198348720266707800874428357928991317749023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2716666 |
3.9848124 |
29.5537874 |
6.0996053 |
| ENSG00000188211 |
374383 |
NCR3LG1 |
protein_coding |
Q68D85 |
FUNCTION: Triggers NCR3-dependent natural killer cell activation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19528259}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
B7H6 belongs to the B7 family (see MIM 605402) and is selectively expressed on tumor cells. Interaction of B7H6 with NKp30 (NCR3; MIM 611550) results in natural killer (NK) cell activation and cytotoxicity (Brandt et al., 2009 [PubMed 19528259]).[supplied by OMIM, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:374383; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; regulation of immune response [GO:0050776] |
19528259_DKFZp686O24166 was designated the gene B7-H6; identification as a tumor cell surface molecule that binds NKp30, a receptor which triggers antitumor NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion 21422170_The NKp30-B7-H6 structure revealed that this NK cell activating complex is distinct from the CTLA4-B7 and PD-1-PD-L T cell inhibitory complexes in both overall organization and detailed atomic interactions that mediate binding and specificity. 23066150_B7-H6:7D8 represents the first Ab-based molecule stimulating NKp30-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity for therapeutic purposes 23687088_These findings reveal that B7-H6 is not only implicated in tumor immunosurveillance but also participates in the inflammatory response in infectious conditions. 24242703_B7-H6-positive carcinomas were significantly associated with a higher differentiation. 24275655_Data indicate that the ectodomain of NKp30 forms functional homo-oligomers that mediate high affinity binding to its corresponding cellular ligand B7-H6. 24780758_this study identified ectodomain shedding of B7-H6 by the metalloproteases 'a disintegrin and metalloproteases' (ADAM)-10 and ADAM-17 from the cell surface of tumor cells as a crucial mechanism of expression regulation of B7-H6. 25001651_Allogeneic and xenogeneic anti-tumor effect of callithrix jacchus natural killer cells is dependent on NKp30 and B7-H6 interaction. 25400778_Study suggests that B7-H6 has a limited value as a prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer patients. 25877893_the interaction between NKp30 and B7-H6 may contribute to the fate of neuroblastoma patients 26241657_Our results suggest that NKP30-B7-H6 interaction can aggravate hepatocyte damage, probably through up-regulation of IL-32 expression in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure 26464699_our present data revealed that higher B7-H6 expression in ovarian cancer tissues was positively correlated with tumor metastasis and cancer progression 26472927_study not only reveals the possibility that tumor therapeutics work as stress inducers to enhance tumor sensitivity to NK cell cytolysis but also suggests that B7-H6 could be a potential target for tumor therapy in the future 26582946_NKp30-B7-H6 interaction is a novel cell contact mechanism that mediates activation of Group 2 innate lymphoid cells and identifies a potential target for the development of novel therapeutics for atopic dermatitis and other atopic diseases. 26891663_Study confirms that B7-H6 is widely expressed in B-cell lymphomas and demonstrates its important role in the pathogenesis and chemosensitivity of lymphoma. 27216712_B7H6-derived peptides trigger TNF-alpha-dependent immunostimulatory activity of lymphocytic NK92-MI cells. 28415577_Data suggest that B7-H6 play an important role in the regulation of the biological behavior of glioma cells. 28928446_Data indicate a sequence of events driven by tumour-derived prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) associated with engagement of the natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 3 (NKp30)-B7H6 antigen (B7H6) pathway leading to significant group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) activation and expansion. 29055565_these studies find that soluble B7H6 is constitutively expressed during pregnancy 29679856_B7-H6 was expressed in gliomas and correlated with glioma progression. Knockdown of B7-H6 inhibited glioma cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion via upregulation of E-cadherin and Bax, and downregulation of vimentin, N-cadherin, MMP-2, MMP-9 and survivin. 30325780_Altogether, these data suggested that the defective expression of NKp30 may be induced by the chronic engagement of this receptor by B7-H6 expressed on HIV-2-infected target cells. This represents a novel mechanism by which the chronic ligand exposure by the viral environment may subvert NK-cell-mediated function to establish persistent HIV-2 infection. 31792298_The prognostic value of B7-H6 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 31904350_Immunological role and underlying mechanisms of B7-H6 in tumorigenesis. 32138659_Positive staining of the immunoligand B7-H6 in abnormal/transformed keratinocytes consistently accompanies the progression of cervical cancer. 32322592_Preferential Expression of B7-H6 in Glioma Stem-Like Cells Enhances Tumor Cell Proliferation via the c-Myc/RNMT Axis. 33220098_Dual role of B7-H6 as a novel prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33483421_Large remodeling of the Myc-induced cell surface proteome in B cells and prostate cells creates new opportunities for immunotherapy. 33523715_NCR3LG1 (B7-H6) is a potential prognostic factor for bladder cancer patients. 33671836_Secreted Ligands of the NK Cell Receptor NKp30: B7-H6 Is in Contrast to BAG6 Only Marginally Released via Extracellular Vesicles. 33824367_Immune checkpoint molecules B7-H6 and PD-L1 co-pattern the tumor inflammatory microenvironment in human breast cancer. 34280008_B7-H6 as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
|
|
18.604653 |
2.8344182755 |
1.503053 |
0.381819138 |
15.910990 |
0.00006639209035306465407806630896203614611295051872730255126953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000188017508367466299867148959990004186693113297224044799804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.7530486 |
6.5927617 |
9.5434524 |
1.9067109 |
| ENSG00000188215 |
123879 |
DCUN1D3 |
protein_coding |
Q8IWE4 |
FUNCTION: Contributes to the neddylation of all cullins by transferring NEDD8 from N-terminally acetylated NEDD8-conjugating E2s enzyme to different cullin C-terminal domain-RBX complexes and may play a role in the cell cycle progression by regulating the SCF ubiquitin E3 ligase complex, after UV damage (PubMed:23201271, PubMed:19617556, PubMed:27542266, PubMed:18823379). At the cell membrane, can promote and as well inhibit cullins neddylation (PubMed:19617556, PubMed:26906416, PubMed:25349211). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18823379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19617556, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23201271, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25349211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26906416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27542266}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleus;Palmitate;Reference proteome |
|
Enables cullin family protein binding activity. Involved in several processes, including negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; regulation of protein neddylation; and response to UV-C. Located in nucleus; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:123879; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0000151]; cullin family protein binding [GO:0097602]; ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding [GO:0031624]; ubiquitin-like protein binding [GO:0032182]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of protein neddylation [GO:2000435]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of protein neddylation [GO:2000436]; positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0051443]; protein neddylation [GO:0045116]; regulation of cell cycle process [GO:0010564]; regulation of protein neddylation [GO:2000434]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to UV-C [GO:0010225] |
18823379_DCUN1D3 is a novel UVC-response gene involved in cell cycle regulation and cell survival. 25349211_SCCRO3 functions as a tumor suppressor by antagonizing the neddylation activity of SCCRO 27542266_DCUN1D3 has a role in activating SCFSKP2 ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through cullin-1 neddylation and cell cycle progression in tumor cells with UV damage |
ENSMUSG00000048787 |
Dcun1d3 |
66.692791 |
2.3893487878 |
1.256617 |
0.271782898 |
20.915533 |
0.00000479986587507172206279459913957907701842486858367919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000015663502170253949872906484852563835374894551932811737060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
93.9256201 |
16.1962821 |
39.8009547 |
5.1684287 |
| ENSG00000188283 |
163087 |
ZNF383 |
protein_coding |
Q8NA42 |
FUNCTION: May function as a transcriptional repressor, suppressing transcriptional activities mediated by MAPK signaling pathways. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15964543}. |
Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a KRAB-related zinc finger protein that inhibits the transcription of some MAPK signaling pathway genes. The repressor activity resides in the KRAB domain of the encoded protein. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
hsa:163087; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
15964543_Overexpression of ZNF383 in cells inhibits the transcriptional activities of AP-1 and SRE, suggesting that ZNF383 may act as a negative regulator in MAPK-mediated signaling pathways. 35835334_19q13.12 KRAB zinc-finger protein ZNF383 represses p53 signaling pathway by interacting with p53. |
ENSMUSG00000099689 |
Zfp383 |
89.001068 |
0.4943488162 |
-1.016399 |
0.279528112 |
12.993234 |
0.00031261851387283379199999444608693011105060577392578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000795834643801832846213284433645185345085337758064270019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.9058663 |
10.2008217 |
101.7886532 |
14.9301896 |
| ENSG00000188305 |
374872 |
PEAK3 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZS72 |
FUNCTION: Probable catalytically inactive kinase (Probable). Interacts with CRK-II and antagonizes CRK-II-signaling. Prevents the formation of CRK-II-dependent membrane ruffling and lamellipodia-like extensions (PubMed:31311869). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:31311869, ECO:0000305|PubMed:31311869}. |
Reference proteome |
|
Enables protein self-association. Involved in regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization and regulation of cell shape. Predicted to be active in actin cytoskeleton and focal adhesion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374872; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
31311869_by binding to CrkII, PEAK3 prevents the formation of CrkII-dependent membrane ruffling. |
|
|
43.434108 |
0.3576152104 |
-1.483520 |
0.287560626 |
26.736505 |
0.00000023317447640598331534521206812038407463205658132210373878479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000883381743262914192246076927617082219512667506933212280273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.7185149 |
4.2389346 |
64.0920748 |
7.7378739 |
| ENSG00000188312 |
401541 |
CENPP |
protein_coding |
Q6IPU0 |
FUNCTION: Component of the CENPA-CAD (nucleosome distal) complex, a complex recruited to centromeres which is involved in assembly of kinetochore proteins, mitotic progression and chromosome segregation. May be involved in incorporation of newly synthesized CENPA into centromeres via its interaction with the CENPA-NAC complex. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16622420}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Centromere;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
CENPP is a subunit of a CENPH (MIM 605607)-CENPI (MIM 300065)-associated centromeric complex that targets CENPA (MIM 117139) to centromeres and is required for proper kinetochore function and mitotic progression (Okada et al., 2006 [PubMed 16622420]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:401541; |
chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000775]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; CENP-A containing chromatin assembly [GO:0034080] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23028590_Data propose that CENP-P/O/R/Q/U self-assembles on kinetochores with varying stoichiometry and undergoes a pre-mitotic maturation step that could be important for kinetochores switching into the correct conformation for microtubule-attachment. 36071244_A novel nonsense variant in the CENPP gene segregates in a Swiss family with autosomal dominant low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. |
ENSMUSG00000021391 |
Cenpp |
66.179059 |
2.4406939201 |
1.287291 |
0.461715147 |
7.144559 |
0.00751917615727344321174818730924016563221812248229980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014793793665869903880549784958020609337836503982543945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.3636940 |
31.8934875 |
35.2834330 |
9.3716123 |
| ENSG00000188483 |
389792 |
IER5L |
protein_coding |
Q5T953 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:389792; |
|
30599213_The results suggest that IER2, IER5, and IER5L proteins are target protein-specific regulators of PP2A (protein phosphatase 2A) activity and modulate cell proliferation through CDC25A (cell division cycle 25A protein) activity. |
ENSMUSG00000089762 |
Ier5l |
425.656080 |
2.2746458112 |
1.185642 |
0.082248792 |
209.568382 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001706212036385189776606339060955446750208027219747395787014466247637463674651878547126967197256176370938300775295375658275123798013339637691387906670570373535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000342635233429189107233427234778644770762452610747019748681522536097703110062369572487319075422999051464143936022511190836459249453582742717117071151733398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
596.2076996 |
27.8040649 |
264.1647822 |
9.8293461 |
| ENSG00000188549 |
388115 |
CCDC9B |
protein_coding |
Q6ZUT6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables RNA binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388115; |
RNA binding [GO:0003723] |
|
ENSMUSG00000045838 |
Ccdc9b |
61.530403 |
0.1959156920 |
-2.351695 |
0.300902557 |
59.506542 |
0.00000000000001218882497577692447022102508633196652661754601221222316098646842874586582183837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000081442759910578274210077309166396550938697013188871665079204831272363662719726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.6512235 |
4.1152128 |
106.8340307 |
13.6945291 |
| ENSG00000188626 |
653720 |
GOLGA8M |
protein_coding |
H3BSY2 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:653720; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
191.458463 |
0.0166073317 |
-5.912036 |
0.518846976 |
110.883877 |
0.00000000000000000000000006274019915563782490706788077136843323605644870555991447133030570164216946360546955929748946800827980041503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000693147709234441772261790491757341775141561015821184380191368483621356527679679970788129139691591262817382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3642374 |
3.3887350 |
339.4209424 |
139.7696585 |
| ENSG00000188687 |
57835 |
SLC4A5 |
protein_coding |
Q9BY07 |
FUNCTION: Mediates sodium- and bicarbonate-dependent electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransport, with a Na(+):HCO3(-) stoichiometry varying from 1:2 to 1:3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26447209}. |
Alternative splicing;Anion exchange;Cell membrane;Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sodium;Sodium transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (NBC) family, part of the bicarbonate transporter superfamily. Sodium bicarbonate cotransporters are involved in intracellular pH regulation and electroneural or electrogenic sodium bicarbonate transport. This protein is thought to be an integral membrane protein. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, but the biological validity of some variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57835; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sodium:bicarbonate symporter activity [GO:0008510]; solute:inorganic anion antiporter activity [GO:0005452]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; bicarbonate transport [GO:0015701]; cerebrospinal fluid secretion [GO:0033326]; epithelial cell development [GO:0002064]; ion homeostasis [GO:0050801]; mitochondrion distribution [GO:0048311]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of intracellular pH [GO:0051453]; regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003073]; renal system process [GO:0003014]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085] |
12063394_Genomic organization of the DCTN1-SLC4A5 locus encoding both NBC4 and p150(Glued). 16365189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16365189_These results additionally confirm the involvement of SLC4A5 with blood pressure control, although the mechanism is still unclear. 19384345_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19384345_Summarizing, the observed associations with resting and submaximal-exercise cardiovascular and metabolic traits in the HERITAGE Family Study are likely due to neither variation in the promoter nor known coding SNPs of SLC4A5 19487301_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22764636_The additive effect of rs10177833 of SLC4A5 on systolic blood pressure is statistically different between women with dark skin color and women with medium skin color (P = .0153). 22987918_Data indicate that 2 SNPs in SLC4A5 (rs7571842 and rs10177833) showed highly significant results and large effects sizes. 26136555_we summarize the potential function of NBCe2 in the regulation of blood pressure, acid-base, and K(+) and Ca(2+) transport in the distal nephron--{REVIEW} 26447209_NBCe2 could be important in proximal kidney tubule apical sodium and bicarbonate cotransport under high-salt conditions. 29642240_NBCe2 activity is stimulated by an increase in intracellular sodium and is hyper-responsive in hRPTCs carrying HV SLC4A5 rs7571842 through an aberrant HNF4A-mediated mechanism |
ENSMUSG00000068323 |
Slc4a5 |
13.755322 |
0.2843814585 |
-1.814101 |
0.521636616 |
11.824141 |
0.00058467672166026942240368846626097365515306591987609863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001419846727822569355803583590613925480283796787261962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
8.0232378 |
2.8364468 |
28.5331675 |
7.1144605 |
| ENSG00000188706 |
51114 |
ZDHHC9 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y397 |
FUNCTION: Palmitoyltransferase that could catalyze the addition of palmitate onto various protein substrates (Probable). The ZDHHC9-GOLGA7 complex is a palmitoyltransferase specific for HRAS and NRAS (PubMed:16000296). May have a palmitoyltransferase activity toward the beta-2 adrenergic receptor/ADRB2 and therefore regulate G protein-coupled receptor signaling (PubMed:27481942). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16000296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27481942}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Through a sequential action with ZDHHC20, rapidly and efficiently palmitoylates SARS coronavirus-2/SARS-CoV-2 spike protein following its synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). In the infected cell, promotes spike biogenesis by protecting it from premature ER degradation, increases half-life and controls the lipid organization of its immediate membrane environment. Once the virus has formed, spike palmitoylation controls fusion with the target cell. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:34599882}. |
Acyltransferase;Disease variant;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Intellectual disability;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an integral membrane protein that is a member of the zinc finger DHHC domain-containing protein family. The encoded protein forms a complex with golgin subfamily A member 7 and functions as a palmitoyltransferase. This protein specifically palmitoylates HRAS and NRAS. Mutations in this gene are associated with X-linked cognitive disability. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode the same protein.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:51114; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; palmitoyltransferase complex [GO:0002178]; palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0016409]; protein-cysteine S-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0019706]; Ras palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0043849]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; peptidyl-L-cysteine S-palmitoylation [GO:0018230]; positive regulation by host of viral process [GO:0044794]; protein palmitoylation [GO:0018345]; protein targeting to membrane [GO:0006612] |
16000296_Data show that H- and N-Ras are palmitoylated by a human protein palmitoyltransferase encoded by the ZDHHC9 and GCP16 genes. 17519897_DHHC9 is a gastrointestinal-related protein highly expressed in microsatellite stable colorectal cancers. 21388813_Studies indicate that mutations in DHHC9 were associated with X-linked mental retardation. 22230506_MMSA-1 may play a pivotal role in multiple myeloma proliferation and osteolysis destruction. 24248599_Data indicate that sp-Erf2/zDHHC9 palmitoylates Ras proteins in a highly selective manner in the trans-Golgi compartment to facilitate PM targeting via the trans-Golgi network, a role that is most certainly critical for Ras-driven tumorigenesis. 24811172_Two missense mutation, R148W and P150S,of zDHHC9, affecting the autopalmitoylation is associated with the X-linked intellectual disability. 26358559_ZDHHC9 gene mutation is associated with Lujan-Fryns syndrome. 26493349_Report demonstrated that MMSA-1 is specifically expressed in multiple myeloma patients and its upregulation is associated with unfavorable clinical features and poor prognosis. 26493479_studies suggest that ZDHHC9 may serve as a safe and effective target for developing therapies against NRAS-driven cancers 27747153_Data demonstrate that ZDHHC9 mutations are associated with reductions in cortical thickness and white matter microstructural integrity, particularly in regions and networks known to contribute to language function. 28168288_The results demonstrate that a mutation in a ZDHHC9 mutation impacts upon white matter organization across the whole-brain, but also shows regionally specific effects, according to variation in gene expression. 28687527_De novo ZDHHC9 mutation was identified in a patient with X-linked intellectual disability. 34620861_DHHC9-mediated GLUT1 S-palmitoylation promotes glioblastoma glycolysis and tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000036985 |
Zdhhc9 |
154.702470 |
3.4102765789 |
1.769889 |
0.155430639 |
130.915467 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000258378176719624552102591214642706960636504272184760751342454114093515301439510454400982908396144921425729990005493164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000033365370851983011482682763107606332481232507112140298762043902428515298406444186674058016706112539395689964294433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
245.8061600 |
20.7471424 |
72.4560247 |
5.0273129 |
| ENSG00000188732 |
340277 |
FAM221A |
protein_coding |
A4D161 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:340277; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000047115 |
Fam221a |
22.471526 |
0.4782981578 |
-1.064018 |
0.479738017 |
4.774487 |
0.02888444546792655678868477764353883685544133186340332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.049901276060487144425881211873274878598749637603759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4306244 |
4.5103131 |
27.8401003 |
6.5372659 |
| ENSG00000188738 |
401024 |
FSIP2 |
protein_coding |
Q5CZC0 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in spermatogenesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:30137358}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein associated with the sperm fibrous sheath. Genes encoding most of the fibrous-sheath associated proteins genes are transcribed only during the postmeiotic period of spermatogenesis. The protein encoded by this gene is specific to spermatogenic cells. Copy number variation in this gene may be associated with testicular germ cell tumors. Pseudogenes associated with this gene are reported on chromosomes 2 and X. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:401024; |
sperm connecting piece [GO:0097224]; sperm end piece [GO:0097229]; sperm midpiece [GO:0097225]; sperm principal piece [GO:0097228]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; protein localization to cilium [GO:0061512]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30745215_Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in FSIP2 cause male infertility with asthenoteratospermia 33162809_FSIP2 can serve as a predictive biomarker for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma prognosis. 33631238_Novel mutations in FSIP2 lead to multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella and poor ICSI prognosis. |
ENSMUSG00000075249 |
Fsip2 |
14.288150 |
0.1490602272 |
-2.746033 |
0.571733057 |
24.846451 |
0.00000062083238594082014472910150543194518490963673684746026992797851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002249260190595607747008309595937447511460050009191036224365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6602026 |
1.4334037 |
24.7928932 |
5.3387302 |
| ENSG00000188747 |
10811 |
NOXA1 |
protein_coding |
Q86UR1 |
FUNCTION: Functions as an activator of NOX1, a superoxide-producing NADPH oxidase. Functions in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which participate in a variety of biological processes including host defense, hormone biosynthesis, oxygen sensing and signal transduction. May also activate CYBB/gp91phox and NOX3. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12657628, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12716910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14617635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14978110, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15181005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15824103, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17602954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19755710}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;TPR repeat |
|
This gene encodes a protein which activates NADPH oxidases, enzymes which catalyze a reaction generating reactive oxygen species. The encoded protein contains four N-terminal tetratricopeptide domains and a C-terminal Src homology 3 domain. Interaction between the encoded protein and proteins in the oxidase regulatory complex occur via the tetratricopeptide domains. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:10811; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; NADPH oxidase complex [GO:0043020]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase activator activity [GO:0016176]; regulation of hydrogen peroxide metabolic process [GO:0010310]; regulation of respiratory burst [GO:0060263]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801] |
17602954_These studies demonstrate that, in reconstituted NOX1/NOXO1/NOXA1 systems, the NOXA1 SH3 domain is not required for function but, when present, can critically modulate the activity of the enzyme system. 17913709_PKA-phosphorylated NoxA1 is a new binding partner of 14-3-3 protein; this forms the basis of a novel mechanism regulating the formation of ROS by Nox1 and, potentially, other NoxA1-regulated Nox family members 18568954_Essential role of NOXA1 in generation of reacgtive oxygen species induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein in endothelial cells is reported. 18606821_a novel, inhibitory function for Noxa1 in Duox1 regulation. 20083677_NoxA1 is the functional homolog of p67phox in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) that regulates redox signaling and VSMC phenotype. 20230789_these results demonstrate that phosphorylation of NoxA1 is a part of the feedback mechanism that functions through activation of Rac with a net outcome of negative modulation of Nox1 activity. 20454568_The first quantitative characterization of the interactions made between the cytosolic regulators NOXO1 and NOXA1 and membrane-bound p22(phox), is presented. 20609497_Tks4 and Tks5 directly bind to NoxA1. The integrity of the N-terminal PRR of NoxA1 is essential for this direct interaction with the Tks proteins. 20943948_The Nox1-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species is dependent on Src phosphorylation of NoxA1 and Tks4. Blockage of phosphorylation of NoxA1 and Tks4 decreases Nox1-dependent ROS generation and blocks SrcYF-induced invadopodia formation. 22244833_Noxa1 has quite different kinetic properties from p67(phox) and suggest that Noxa1 may function as a moderate activator of Nox2. 23957209_Phosphorylation of Thr341 allows Noxo1 to sufficiently interact with Noxa1, an interaction that participates in Nox1 activation 24187133_A NOXA1 peptide blocked NOXA1-Nox1 binding. The finding identifies a NOXA1-activating domain and an isoform-specific Nox1 inhibitor. 28625920_Data from pull-down assay between the Noxo1 and Noxa1 showed that the SH3 domains (Noxa1) is responsible for interaction with Noxo1 C-terminal tail harboring proline rich region. 29374147_both caspase-8-dependent and -independent apoptotic mechanisms are activated in triple-negative breast cancer cells undergoing sustained endoplasmic reticulum stress. 31285435_mitochondrial targeting domain peptide induces necrotic cell death by interaction with the VDAC2 protein. 31727958_These results identify NOXA mRNA destabilization/MCL-1 adaptation as a non-genomic mechanism that limits apoptotic responses. 32015503_MARCH5-dependent degradation of MCL1/NOXA complexes defines susceptibility to antimitotic drug treatment. 32094511_MARCH5 requires MTCH2 to coordinate proteasomal turnover of the MCL1:NOXA complex. 32847975_The Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, OBP-801, Induces Apoptosis in Rhabdoid Tumors by Releasing the Silencing of NOXA. |
ENSMUSG00000036805 |
Noxa1 |
39.133347 |
0.0824607540 |
-3.600149 |
0.370205346 |
120.517850 |
0.00000000000000000000000000048726372544641414234624116076504655420605867375389689116407992317502300555487337874183140229433774948120117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000005842414774645875648470009928030786011024054323553640255334951001803787690863645210015420161653310060501098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1945052 |
1.7839719 |
73.4945037 |
11.1583771 |
| ENSG00000188766 |
399473 |
SPRED3 |
protein_coding |
Q2MJR0 |
FUNCTION: Tyrosine kinase substrate that inhibits growth-factor-mediated activation of MAP kinase (By similarity). Inhibits fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-induced retinal lens fiber differentiation, probably by inhibiting FGF-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (By similarity). Inhibits TGFB-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lens epithelial cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P6N5}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Methylation;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein with a C-terminal Sprouty-like cysteine-rich domain (SRY) and an N-terminal Ena/Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) homology-1 (EVH-1) domain. The encoded protein is a member of a family of proteins that negatively regulates mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling, particularly during organogenesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:399473; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0010719]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of lens fiber cell differentiation [GO:1902747]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512] |
12646235_The finding of Spred-3 revealed the presence of a novel family of regulators for the Ras/MAP kinase pathway, each member of which may have different specificities for extracellular signals. [Spred-3] 16478641_Eve-3 may act as an inhibitor of proliferation pathways in the mature liver and be involved in modulating the unique regenerative capacity of this organ |
ENSMUSG00000037239 |
Spred3 |
9.216351 |
0.2593750432 |
-1.946888 |
0.710421399 |
6.818326 |
0.00902271188912515814672943292862328235059976577758789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017435876863509731926615842212413554079830646514892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3936322 |
1.6970223 |
12.4054559 |
3.9885915 |
| ENSG00000188786 |
4520 |
MTF1 |
protein_coding |
Q14872 |
FUNCTION: Zinc-dependent transcriptional regulator of cellular adaption to conditions of exposure to heavy metals (PubMed:8065932). Binds to metal responsive elements (MRE) in promoters and activates the transcription of metallothionein genes like metallothionein-2/MT2A (PubMed:8065932). Also regulates the expression of metalloproteases in response to intracellular zinc and functions as a catabolic regulator of cartilages (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q07243, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8065932}. |
Acetylation;Activator;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a transcription factor that induces expression of metallothioneins and other genes involved in metal homeostasis in response to heavy metals such as cadmium, zinc, copper, and silver. The protein is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein that accumulates in the nucleus upon heavy metal exposure and binds to promoters containing a metal-responsive element (MRE). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4520; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; histone acetyltransferase binding [GO:0035035]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cartilage homeostasis [GO:1990079]; cellular response to zinc ion [GO:0071294]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to metal ion [GO:0010038]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979] |
11923282_role in regulating metallothionein transcription 12716893_MTF1 transactivation potential is affected by chromium levels 12805380_mediates transcriptional hyperactivation along with heat and heavy metal stress 14610091_MTF-1 contains a cysteine-rich cluster, -632Cys-Gln-Cys-Gln-Cys-Ala-Cys638-, which appears to be specifically required for MTF-1 to activate transcription in the presence of inducing heavy metal ions. 15318808_The MTF-1 serves targeted disruption of the MTF-1 gene results in death at embryonic day 14 due to liver degeneration and under hypoxic-anoxic stress, MTF-1 helps to activate the transcription of the gene PIGF. 17503480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18990686_SP1 and MTF-1 represent new targets in the development of key therapeutics toward modulating the expression of the cellular prion protein and ultimately the prevention of prion disease 19022893_Findings suggest that MTF-1 is involved in hypoxia-dependent regulation of PlGF in trophoblast-derived cells. 19058789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19286843_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19797083_show that the acidic activation domain of hMTF-1 can work as a zinc-inducible activation domain independent of the full-length protein context. 19913599_Genetic regulation via sequences downstream of promoters highlights a new direction for identifying previously unrecognized target genes for MTF-1. 19956853_Loss of LI-cadherin results in up-regulation of MTF-1 and PlGF, thereby regulating angiogenesis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 20026331_Data show that hepcidin transcription involves interactions between functional metal response elements (MREs) in its promoter, and the MRE-binding transcription factor-1. 20688958_Zinc and cadmium can activate FPN1 transcription through the MTF-1. 21386983_Transcriptional regulation of the beta-synuclein 5'-promoter metal response element by metal transcription factor-1. 21798283_Variations in the ability of LAT1/DMT1/MTF1/MT1a to process and transport Hg may not play a significant role in the etiology of autism. 22021037_It is concluded that SUMO conjugation and the SIM on MTF-1 do not play a critical role in suppressing transcriptional activity. Instead, MTF-1 forms complexes with cellular factors through SIM and SUMO moiety in the cytoplasm 22057392_Results identify a cysteine cluster that mediates homodimerization of human MTF-1, and show that dimer formation in vivo is important for basal and especially metal-induced transcriptional activity. 23368743_The zinc-sensing cytoplasmic transcription factor MTF-1 plays a key role in cellular zinc homoeostasis. 25162517_Zn-responsive proteome profiling and time-dependent expression of proteins are regulated by MTF-1 in human alveolar epithelial cells. 25618524_Human ZnT2 expression is regulated by MTF-1. 26336656_MTF-1 has a role in regulating zinc dependent cellular processes at the molecular level [review] 26529669_Forty-one single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the MTF1 gene region. 26824222_MTF1 heads a hierarchy of zinc sensors, and through controlling the expression of a raft of metallothioneins and other key proteins involved in controlling intracellular zinc levels (e.g. ZnT1) alters zinc buffering capacity and total cellular zinc content. |
ENSMUSG00000028890 |
Mtf1 |
201.214283 |
2.1693583611 |
1.117268 |
0.171722429 |
41.574512 |
0.00000000011346290627561882794568076152471247305952850581434177001938223838806152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000584541883639837296317395666316561742004154211826971732079982757568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
291.6569988 |
31.1336049 |
135.1252785 |
10.7566329 |
| ENSG00000188825 |
100130581 |
LINC00910 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.645147 |
0.4162674630 |
-1.264417 |
0.400317265 |
9.809216 |
0.00173639504457102846098071058378309317049570381641387939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003884387823259833130706830672806972870603203773498535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.5432656 |
5.1166352 |
50.1940357 |
8.2774740 |
| ENSG00000188878 |
85302 |
FBF1 |
protein_coding |
Q8TES7 |
FUNCTION: Keratin-binding protein required for epithelial cell polarization. Involved in apical junction complex (AJC) assembly via its interaction with PARD3. Required for ciliogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18838552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23348840}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Involved in apical junction assembly and establishment of epithelial cell polarity. Acts upstream of or within cilium assembly. Located in centriole; centrosome; and spindle pole. Part of ciliary transition fiber. Colocalizes with apical junction complex and keratin filament. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:85302; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; centriole [GO:0005814]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; ciliary transition fiber [GO:0097539]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; spindle pole [GO:0000922]; apical junction assembly [GO:0043297]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; establishment of epithelial cell polarity [GO:0090162] |
18838552_Keratins and the keratin-binding protein Albatross are important for epithelial cell polarization. 27583843_These results suggest that rs1135889 in FBF1 is not associated with leukoaraiosis (LA) risk in the Chinese population. However, the association of rs1135889 (FBF1) with LA before Bonferroni correction and Sidak correction is worth highlighting. 30318703_Albatross is a novel protein that spatiotemporally integrates different aspects of centrosome function, namely ciliogenesis, centriole duplication, and centrosome separation. 34348145_FBF1 deficiency promotes beiging and healthy expansion of white adipose tissue. |
ENSMUSG00000020776 |
Fbf1 |
70.795985 |
0.4480793445 |
-1.158174 |
0.320007077 |
12.815959 |
0.00034367519500226801406478349676376637944485992193222045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000869348051111135545349073439069798041600733995437622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
40.7455828 |
9.1293660 |
91.4686125 |
14.6092103 |
| ENSG00000188931 |
257177 |
CFAP126 |
protein_coding |
Q5VTH2 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of cilium basal body docking and positioning in mono- and multiciliated cells. Regulates basal body docking and cilia formation in multiciliated lung cells. Regulates kinocilium positioning and stereocilia bundle morphogenesis in the inner ear. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q6P8X9}. |
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in cilium organization. Predicted to be located in apical plasma membrane and cilium. Predicted to be active in ciliary basal body. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:257177; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; axonemal microtubule [GO:0005879]; ciliary basal body [GO:0036064]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cilium organization [GO:0044782] |
Mouse_homologues 17971504_1700009P17Rik is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. 22153975_Fltp(T2AiCre): a new knock-in mouse line for conditional gene targeting in distinct mono- and multiciliated tissues. 25296022_The uncharacterized gene Flattop (Fltp) is transcriptionally activated during planar cell polarity acquisition in ciliated tissues. |
ENSMUSG00000026649 |
Cfap126 |
8.624790 |
0.3925548353 |
-1.349034 |
0.537681928 |
6.462100 |
0.01101993142257396383898448988247764646075665950775146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020960591210978311849100208519303123466670513153076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8100364 |
1.6873773 |
12.2574041 |
2.6591532 |
| ENSG00000188938 |
158293 |
FAM120AOS |
protein_coding |
Q5T036 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Differences in the expression level of this gene are associated with the survival rate of those with glioma. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:158293; |
|
|
|
|
452.663067 |
0.3686692864 |
-1.439601 |
0.536563259 |
6.927894 |
0.00848615562741866433227322374932555248960852622985839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016489686290244800342952302685262111481279134750366210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
248.3726489 |
79.7774219 |
676.7903514 |
156.5091239 |
| ENSG00000189001 |
374897 |
SBSN |
protein_coding |
Q6UWP8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374897; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062] |
22792300_BORIS induces demethylation of the SBSN CpG island and disruption and activation of chromatin around the SBSN transcription start site, resulting in an increase in SBSN expression. 23144906_These results support suprabasin as novel oncogene candidate in salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. 25283635_Findings suggest that SBSN is involved in the angiogenic potential of tumor endothelial cells (TEC) and may be a novel TEC marker. 25935274_SCARA5 and SBSN shown to have modest effects on cell proliferation or collagen gel contraction and maybe associated with peripheral vein graft patency. 26899563_we demonstrated that upregulation of suprabasin activated the Wnt/b-catenin signaling pathway and led to nuclear localization of b-catenin and upregulation of Cyclin D1 and c-Myc. Together, our results suggest that suprabasin plays an important oncogenic role in promoting proliferation and tumorigenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma . 30919591_SBSN expression was observed in human clinical specimens of colon and ovarian carcinomas, as well as in circulating tumour cells and metastases of the 4T1 mouse model. The association of SBSN expression with progressive stages of cancer development indicates its role in cancer evolution and therapy resistance. 31399284_Epidermal SBSN expression was decreased in atopic dermatitis (AD) lesional skin compared to healthy skin. The SBSN serum levels were significantly lower in AD patients than in normal subjects. Study results suggested that SBSN regulates normal epidermal barrierand has an anti-apoptotic activity, and its deficiency is involved in the pathogenesis of AD. 32696549_Aberrantly elevated suprabasin in the bone marrow as a candidate biomarker of advanced disease state in myelodysplastic syndromes. 33477529_Suprabasin-A Review. 34775572_Suprabasin: Role in human cancers and other diseases. 36316443_Extracellular vesicles-transferred SBSN drives glioma aggressiveness by activating NF-kappaB via ANXA1-dependent ubiquitination of NEMO. |
ENSMUSG00000046056 |
Sbsn |
5.811511 |
8.9542289740 |
3.162569 |
0.866015345 |
17.261760 |
0.00003256755901423267178388179510228894741885596886277198791503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000096081785138931480208350499605529648761148564517498016357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2892102 |
6.9020579 |
1.2864431 |
0.7222466 |
| ENSG00000189013 |
3805 |
KIR2DL4 |
protein_coding |
Q99706 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for non-classical major histocompatibility class Ib HLA-G molecules. Recognizes HLA-G in complex with B2M/beta-2 microglobulin and a nonamer self-peptide (peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M). In decidual NK cells, binds peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M complex and triggers NK cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype as a molecular switch to promote vascular remodeling and fetal growth in early pregnancy (PubMed:23184984, PubMed:29262349, PubMed:16366734). May play a role in balancing tolerance and antiviral-immunity at maternal-fetal interface by keeping in check the effector functions of NK, CD8+ T cells and B cells (PubMed:10190900, PubMed:16366734). Upon interaction with peptide-bound HLA-G-B2M, initiates signaling from the endosomal compartment leading to downstream activation of PRKDC-XRCC5 and AKT1, and ultimately triggering NF-kappa-B-dependent pro-inflammatory response (PubMed:20179272). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10190900, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16366734, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20179272, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23184984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29262349}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several 'framework' genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response. This gene is one of the 'framework' loci that is present on all haplotypes. Alternate alleles of this gene are represented on multiple alternate reference loci (ALT_REF_LOCs). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, some of which may not be annotated on the primary reference assembly. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:3805; |
early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; MHC class Ib receptor activity [GO:0032394]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0045953]; positive regulation of cellular senescence [GO:2000774]; positive regulation of natural killer cell cytokine production [GO:0002729]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11489965_Crosslinking of KIR2DL4 with a mAb induces interferon-gamma production, but not cytotoxicity, by resting NK cells in the absence of cytokines. 11754000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11994457_The single tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)in the cytoplasmic domain of KIR2DL4 efficiently inhibits natural cytotoxicity responses and recruits SHP-2 protein tyrosine phosphatase (but not SHP-1) to the 2DL4 cytoplasmic domain in NK cells. 12055234_KIR2DL4 has the potential for both activating and inhibitory functions. 12538663_NK clones express both 2DL4 alleles and either one or both alleles of the clonally restricted KIR 3DL1 and 3DL2 genes. 12559621_All genotypes seen included genes for KIR2DL4. 12616484_NK cell receptor, KIR2DL4:HLA-G interaction is not essential for human reproduction. 12794136_The promoter for KIR2DL4 is expressed by all natural killer (NK) cell clones and drives reporter gene expression only in NK cells. 12826375_isolated 3 distinct KIR2DL4 allele clones in each individual with multiple copies of KIR3DL/S1; assumption that unequal crossover event occurred between differing KIR haplotypes resulting in the duplication of the 2DL4, 3DS1/3DL1 genes 12902476_KIR2DL4 transmembrane exon genotype influences both levels of membrane expression and activation of cytotoxic function. 14500636_Appropriate engagement of KIR2DL4 can selectively stimulate NK cells to elicit a strong IFN-gamma response, which has the potential to contribute significant biological benefits, but only in individuals capable of expressing this receptor. 14700593_Specific amplification of the D0 & D2 domains permit PCR discrimination of KIR2DL4 alleles & their frequencies in various cell lines and human populations. 15333596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15580659_4.5% of the individuals of a Caucasoid population bear a recombinant allele of KIR3DP1, officially designed KIR3DP1*004, that associates tightly with gene duplications of KIR3DP1, KIR2DL4 and KIR3DL1/KIR3DS1 15670976_report that ILT2 receptor, ILT3 receptor, ILT4 receptor, and KIR2DL4 receptor expression is up-regulated by HLA-G histocompatibility antigen in antigen-presenting cells, natural killer cells, and T cells 15730517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15778339_evidence that FcepsilonRI-gamma (gamma) associates with 2DL4 to promote surface expression and provide signal transducing function. 15778373_an inhibitory element was identified in the KIR2DL4 promoter and an activating element was found in the KIR3DL3 promoter; AML-2 acts as a repressor of expression of both KIR2DL4 and KIR3DL3 in mature NK cells 15853895_KIR2DL4 alleles may explain the high frequency of this variation in the population. 15896204_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16366734_KIR2DL4 was constitutively internalized into Rab5-positive compartments in NK cells via dynamin-dependent process. Chemokine secretion induced by KIR2DL4 transfection into 293T cells occurred only with recombinant forms of KIR2DL4 trafficked to endosomes. 16403292_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17171757_New insights are provided into the mechanisms by which genetic polymorphism of the KIR2DL4 gene influences its expression. 17200871_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17490516_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17498266_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17610421_8 known KIR2DL4 alleles were observed in individuals involved in bone marrow transplantation; 3 new alleles, KIR2DL4*00203, *00502, *0080104, differering from known alleles at the nucleotide but not the protein sequence level were also identified 17868255_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18074414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18082267_Three new alleles of KIR2DL4 have been identified, among those one allele showed alternatively spliced products. 18186800_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18292514_Signaling pathways are specifically activated by engagement of killer receptor KIR2DL4 transmembrane association with the FcepsilonRI-gamma (FCER1G) receptor in natural killer (NK) cells. 18314122_Human leukocyte antigen-G, a ligand for the natural killer receptor KIR2DL4, is expressed by eutopic endometrium only in the menstrual phase. 18347914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18571006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18586981_Increased competency of T cells to express KIR2DL4 with aging is conferred by a selective increase in H3-Lys 4 dimethylation and limited DNA demethylation 18643961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18668235_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18718052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18778326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18848853_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18945643_The role of DNA methylation in regulating of the genes, KIR2DL2 and KIR2DL4, was characterized;these genes are normally suppressed in part by promoter methylation in non-expressing T cells. 18945962_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19000141_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19032228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19046302_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19134329_Decreased KIR2DL4 expression in placenta may participate in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 19134329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19169284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19218127_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19279038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19304328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19304328_Whereas 26% of the study population has a genotype corresponding to a lack of any functional membrane-bound form of the molecule, no association of the KIR2DL4 transmembrane alleles with susceptibility to MS was observed. 19304799_Cross-linking with anti-LILRB1 on CD14(+) macrophages or anti-KIR2DL4 on CD56(+) NK cells resulted in up-regulation of a small subset of mRNAs including those for IL-6, IL-8, and TNFalpha 19309280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19326408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19394279_Data showed that the CD70, perforin and KIR2DL4 promoters are demethylated in CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells, and that DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) and Dnmt3a levels are decreased in this subset. 19450876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19489269_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19509110_The study confirms that expression of KIR2DL4 by dNK is dependent on the 9A/10A polymorphism and that this polymorphism influences IFNgamma secretion by dNK cells. 19527230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19589363_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19630074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19675166_Stimulatory molecule KIR2DL4 triggers interferon-gamma release by lupus T cells, and production is proportional to disease activity. 19679155_Expression patterns of KIR2DL4 were tightly linked with 9 and 10 poly-adenine polymorphism in exon 7. 19679155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19683555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19700612_KIR2DL4 itself is not associated with preeclampsia, but it may modulate the effect of HLA-G*0106 on risk for preeclampsia. 19700612_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19761533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19846535_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19861144_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19875891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19897003_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19926642_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19968064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20082482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20082646_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20173784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20173792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20179272_The sequential requirement for DNA-dependent protein kinase, Akt, and NF-kappaB in signaling by CD158d delineates a previously uncharacterized endosomal signaling pathway for a proinflammatory response in natural killer cells. 20193031_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20200544_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20210918_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20210919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331834_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20356536_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20371502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20426625_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20483367_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20492596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20519398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20580654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20600442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20643584_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20650299_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20652381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20670355_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20878400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21092455_The expression of KIR2DL4 on NK cells in acute rejection group was statistically lower than that in stable kidney function group after renal transplantation. 21270397_By promoting polyubiquitylation and degradation, E3 ubiquitin ligase Triad3A is identified as an interaction partner for the KIR2DL4 cytoplasmic domain. 21607693_The frequencies of alleles of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genes, KIR3DL3 and KIR3DL2, and the carrier frequency of KIR2DL4 alleles have been determined from a population of African Americans by DNA sequencing of the coding regions. 21623736_KIR2DL4 gene may not be essential for fertility, as shown in a fertile Caucasian woman missing KIR2DL4 [case report] 22320834_Significant differences in the frequency of KIR genes were found between the two populations despite being separated by only 300 km 22467658_Differential transcription factor use by the KIR2DL4 promoter under constitutive and IL-2/15-treated conditions. 23184984_Sustained activation through CD158d induced morphological changes in NK cell shape and size, and survival in the absence of cell-cycle entry, all hallmarks of senescence. 23228393_Beta Microglobulin-free HLA-G activates NK cells via engagement of KIR2DL4 receptors. 23952617_Array CGH showed a 95 Kb de novo duplication on chromosome 19q13.4 encompassing four killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genes. 24033084_Genetic polymorphism of KIR2DL4, a putative NK cell receptor for HLA-G, does not influence susceptibility to asthma. 24127555_KIR2DL4 was found to directly interact with HS/heparin, and the D0 domain of KIR2DL4 was essential for this interaction. 24337374_Abs to KIR2DL4 and HLA-G did not block NK cell IFN-gamma production. 25451741_Results show that HLA-E and KIR2DL4 demonstrate evidence of positive selection between human, chimpanzee and gorilla suggesting a main role for immunological adaptations linked to embryo deep invasion of the maternal endometrium during pregnancy. 25735953_the KIR2DL4 on human mast cells facilitates HLA-G-expressing cancer invasion and the subsequent metastasis. 25759384_The unique functional properties of KIR2DL4 may be mediated by self-association of the receptor. 25818657_Among 438 Polish people, a weak difference was seen between males and females in 9769 C/A genotypes and alleles. Fertile women had a high frequency of homozygosity for the defective 9A variant, so KIR2DL4 is not absolutely necessary for reproduction. 25855135_The 9620 9A/10A (rs11410751) polymorphism in exon 7 did not influence the risk of NSCLC. 26823774_Decreased level of KIR2DL4 rather than its single nucleotide polymorphism is correlated with the susceptibility of pre-eclampsia 26973020_a woman's heterozygosity in HLA-G and LILRB1 might be an advantage for a success of reproduction, but the partner's heterozygosity in 9A/10A KIR2DL4 alleles might not 27491653_Data show the alignment of different KIR2DL4 receptor alleles with ADOMA. 27893413_KIR 2D (L1, L3, L4, S4) and KIR 3DL1 expression was correlated with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma patients. 28445138_Data show that most of the Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)cases were positive for KIR2DL4, suggesting that KIR2DL4 may serve as a marker for LCH diagnosis. 28817184_Serum levels of soluble HLA-G were similar in CMV- and CMV+ subjects but levels in culture supernatants were significantly higher in cells from CMV+ than from CMV- subjects stimulated with CMV antigens. The HLA-G ligand KIR2DL4 was mainly expressed on NK cells and CD56+ T cells with no differences between CMV+ and CMV- subjects. 29419875_The allelic diversity of the KIR2DL4 receptor locus showed no significant association with leukemia among ethnic Hans from southern China. 30482463_Have higher frequencies of the KIR2DL4 positive population. 32023940_Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor 2DL4 (CD158d) Regulates Human Mast Cells both Positively and Negatively: Possible Roles in Pregnancy and Cancer Metastasis. 32246154_Family-based exome sequencing identifies rare coding variants in age-related macular degeneration. 32711226_Possible roles of HLA-G regulating immune cells in pregnancy and endometrial diseases via KIR2DL4. 32998620_Altered oxidative stress markers in relation to T cells, NK cells & killer immunoglobulin receptors that are associated with disease activity in SLE patients. 33305671_Expression of HLA-G and KIR2DL4 receptor in chorionic villous in missed abortion. 34158475_Interaction between HLA-G and NK cell receptor KIR2DL4 orchestrates HER2-positive breast cancer resistance to trastuzumab. 35063466_KIR2DL4 promotes the proliferation of RCC cell associated with PI3K/Akt signaling activation. 35185887_Roles of HLA-G/KIR2DL4 in Breast Cancer Immune Microenvironment. 35848898_Clinical significance and immune landscape of KIR2DL4 and the senescence-based signature in cutaneous melanoma. |
ENSMUSG00000031424+ENSMUSG00000057439 |
Kir3dl1+Kir3dl2 |
9.644378 |
0.1055066007 |
-3.244595 |
0.664323443 |
31.557149 |
0.00000001936560758218398890368854839069689965924681018805131316184997558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000081972001122178286938598195787014644153600784193258732557296752929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8961792 |
0.8871564 |
18.2171640 |
3.6008868 |
| ENSG00000189042 |
163081 |
ZNF567 |
protein_coding |
Q8N184 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:163081; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
57.594832 |
0.3159440703 |
-1.662259 |
0.669872225 |
5.745120 |
0.01653452601558383014412889622235525166615843772888183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.030215377490406997856853266171128780115395784378051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.0340237 |
18.3500031 |
74.7019632 |
41.4106287 |
| ENSG00000189195 |
284697 |
BTBD8 |
protein_coding |
Q5XKL5 |
FUNCTION: Involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis at the synapse. Plays a role in neuronal development and in synaptic vesicle recycling in mature neurons, a process required for normal synaptic transmission. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q80TK0}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse |
|
Predicted to be involved in clathrin-dependent synaptic vesicle endocytosis; neuron projection development; and synaptic vesicle budding from endosome. Located in nucleoplasm. Colocalizes with AP-2 adaptor complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:284697; |
axon [GO:0030424]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; presynapse [GO:0098793] |
14654994_expression pattern of BTBD8 shows it may have a function related to brain development |
ENSMUSG00000111375 |
Btbd8 |
96.237518 |
0.2728016361 |
-1.874076 |
0.214211182 |
76.482707 |
0.00000000000000000222149795149961965422241712451594449653750032857982884409997481611753755714744329452514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000018267024938236426691606463563610417200846586273919359977302434572266065515577793121337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.5429532 |
6.1160226 |
149.6492476 |
14.9563101 |
| ENSG00000189409 |
8510 |
MMP23B |
protein_coding |
O75900 |
FUNCTION: Protease. May regulate the surface expression of some potassium channels by retaining them in the endoplasmic reticulum (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene (MMP23B) encodes a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family, and it is part of a duplicated region of chromosome 1p36.3. Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. This gene belongs to the more telomeric copy of the duplicated region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8510; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; metallopeptidase activity [GO:0008237]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; reproduction [GO:0000003] |
11328856_Compares rat and human proteins, describes unique Type II membrane topology, and suggests a role in reproductive processes. 30052775_There is evidence of MMP23B secretion in plasma and urine, suggesting a role of this poorly characterized metalloproteinase in urinary bladder cancer as a potential non-invasive biomarker for this cancer |
ENSMUSG00000029061 |
Mmp23 |
12.380235 |
0.3567426708 |
-1.487044 |
0.531235040 |
7.696148 |
0.00553388069176304325108572967906184203457087278366088867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011204400412952335297500638944256934337317943572998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.2393827 |
2.6347531 |
20.0536197 |
4.5927860 |
| ENSG00000196074 |
10388 |
SYCP2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BX26 |
FUNCTION: Major component of the axial/lateral elements of synaptonemal complexes (SCS) during meiotic prophase. Plays a role in the assembly of synaptonemal complexes. Required for normal meiotic chromosome synapsis during oocyte and spermatocyte development and for normal male and female fertility. Required for insertion of SYCP3 into synaptonemal complexes. May be involved in the organization of chromatin by temporarily binding to DNA scaffold attachment regions. Requires SYCP3, but not SYCP1, in order to be incorporated into the axial/lateral elements. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CUU3}. |
Cell cycle;Cell division;Chromosome;DNA-binding;Meiosis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The synaptonemal complex is a proteinaceous structure that links homologous chromosomes during the prophase of meiosis. The protein encoded by this gene is a major component of the synaptonemal complex and may bind DNA at scaffold attachment regions. The encoded protein requires synaptonemal complex protein 3, but not 1, for inclusion in the synaptonemal complex. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10388; |
lateral element [GO:0000800]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; synaptonemal complex [GO:0000795]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell division [GO:0051301]; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death [GO:0035234]; female meiotic nuclear division [GO:0007143]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; male genitalia morphogenesis [GO:0048808]; male meiotic nuclear division [GO:0007140]; meiotic nuclear division [GO:0140013]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of developmental process [GO:0051093]; negative regulation of reproductive process [GO:2000242]; synaptonemal complex assembly [GO:0007130] |
20378615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26334652_SYCP2 may contribute to genetic instability during HPV-associated cancer development 31866047_SYCP2 Translocation-Mediated Dysregulation and Frameshift Variants Cause Human Male Infertility. |
ENSMUSG00000060445 |
Sycp2 |
13.868932 |
0.1185665941 |
-3.076231 |
0.612949581 |
26.737593 |
0.00000023304318006276132528121829926709418501218351593706756830215454101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000883110998132569171346179740661463952733356563840061426162719726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5381816 |
1.2578229 |
20.7595143 |
6.1399574 |
| ENSG00000196083 |
3556 |
IL1RAP |
protein_coding |
Q9NPH3 |
FUNCTION: Coreceptor for IL1RL2 in the IL-36 signaling system (By similarity). Coreceptor with IL1R1 in the IL-1 signaling system. Associates with IL1R1 bound to IL1B to form the high affinity interleukin-1 receptor complex which mediates interleukin-1-dependent activation of NF-kappa-B and other pathways. Signaling involves the recruitment of adapter molecules such as TOLLIP, MYD88, and IRAK1 or IRAK2 via the respective TIR domains of the receptor/coreceptor subunits. Recruits TOLLIP to the signaling complex. Does not bind to interleukin-1 alone; binding of IL1RN to IL1R1, prevents its association with IL1R1 to form a signaling complex. The cellular response is modulated through a non-signaling association with the membrane IL1R2 decoy receptor. Coreceptor for IL1RL1 in the IL-33 signaling system. Can bidirectionally induce pre- and postsynaptic differentiation of neurons by trans-synaptically binding to PTPRD (By similarity). May play a role in IL1B-mediated costimulation of IFNG production from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells (Probable). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10799889, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9371760, ECO:0000305|PubMed:10653850, ECO:0000305|PubMed:19836339}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Associates with secreted ligand-bound IL1R2 and increases the affinity of secreted IL1R2 for IL1B; this complex formation may be the dominant mechanism for neutralization of IL1B by secreted/soluble receptors (PubMed:12530978). Enhances the ability of secreted IL1R1 to inhibit IL-33 signaling (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12530978}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Unable to mediate canonical IL-1 signaling (PubMed:19481478). Required for Src phosphorylation by IL1B. May be involved in IL1B-potentiated NMDA-induced calcium influx in neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19481478}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Membrane;NAD;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a component of the interleukin 1 receptor complex, which initiates signalling events that result in the activation of interleukin 1-responsive genes. Alternative splicing of this gene results in membrane-bound and soluble isoforms differing in their C-terminus. The ratio of soluble to membrane-bound forms increases during acute-phase induction or stress. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2018]. |
hsa:3556; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-1 receptor activity [GO:0004908]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; interleukin-33 receptor activity [GO:0002114]; NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity [GO:0050135]; NAD+ nucleotidase, cyclic ADP-ribose generating [GO:0061809]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of interleukin-13 production [GO:0032736]; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production [GO:0032753]; positive regulation of interleukin-5 production [GO:0032754]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of postsynaptic density assembly [GO:0099151]; regulation of presynapse assembly [GO:1905606]; synaptic membrane adhesion [GO:0099560]; trans-synaptic signaling by trans-synaptic complex [GO:0099545] |
11880380_Identification of essential regions in the cytoplasmic tail of interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein critical for interleukin-1 signaling 12393699_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12530978_soluble form of IL-1R AcP contributes to the antagonism of IL-1 action by the type II decoy receptor 12781872_The dramatic changes in levels of IL-1RAcP mRNAs suggest important functions in regulating sensitivity to IL-1 during stress and may play a role in oncogenic processes that are engaged during chronic inflammation. 14734551_IL-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP in Jurkat cells 15528363_Specific destabilization of membrane-bound IL-1 receptor accessory protein mRNA in HepG2 hepatoma cells is mediated by its 2.8-kilobase 3'-untranslated region. 15849357_Analysis of a three-dimensional docking model of the TIR-TIR interaction between MyD88 and IL1RAcP 16519819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17507369_IL-1RAcP, MyD88, and IRAK-4 are the stable components of the endogenous type I interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor signaling complex 17889143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17949817_IL-1RAcP687 functions in the IL-1 signal transduction and response. Furthermore, IL-1RAcP687 can associate with proteins involved in the upstream IL-1 signaling pathway such as IL-1RI, Tollip, and MyD88. 18156980_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18299313_IL-1ra is associated with preserved beta-cell capacity in type 1 diabetes. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19481478_an isoform of the IL-1 receptor accessory protein (termed AcPb) was identified that is expressed exclusively in the CNS. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20730440_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20805474_identifies IL1RAP as a unique cell surface biomarker distinguishing Ph(+) from Ph(-) candidate chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) stem cells and opens up a previously unexplored avenue for therapy of CML 21272866_This study showed a significant downregulation of soluble interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein expression in the endometrium of women with endometriosis. 21373837_Studies indicate that new targets have recently been investigated as potential modulators in myeloid leukemia pathogenesis, including miR-328, BMI1, FOXOs and IL1RAP. 21958553_decreased protein levels in the peritoneal fluid of women with endometriosis 22251538_The genetic polymorphisms of IL-1ss-2023 C allele, IL- 1RAcP -8261 T allele and -8183 A allele are probable host factors for persistent HBV infection. 22723552_Knockdown of IL1RAP decreased clonogenicity and increased cell death of AML cells. 22778412_Interleukin-1R3 mediates interleukin-1-induced potassium current increase through fast activation of Akt kinase. 22904187_MARCH8-mediated polyubiquitination and degradation of IL1RAP is an important mechanism for negative regulation of IL-1beta-induced signaling pathways. 23980170_Combined crystallography and small-angle X-ray-scattering studies reveal that ST2 possesses hinge flexibility between the D3 domain and D1D2 module, whereas IL-1RAcP exhibits a rigid conformation in the unbound state in solution. 24915116_Plasma sIL1RAP levels are reduced in obesity and can potentially act as biomarkers of obesity. 24935223_Data suggest serum levels of soluble IL1RAP (from alternative splicing) are down-regulated in endometriosis throughout menstrual cycle; IL1RAP levels (which peak in proliferative phase in fertile women) exhibit minor variations in endometriosis. 25517029_The SNP rs4624606 in IL-1RAcP was nominally associated with CAD risk. 26268530_The findings of this study support IL1RAP as a novel potential Alzheimer's disease target and highlight the use of amyloid PET as a valuable Alzheimer's disease endophenotype, particularly in a longitudinal framework. 27031441_Reconstitution of ST2 (IL-1R4) specific for IL-33 activity; no suppression by IL-1Ra though a common chain IL-1R3 (IL-1RAcP) shared with IL-1. 27307043_single nucleotide polymorphism A471T in the Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain (TIR) of the IL-1Rrp2 that is present in approximately 2% of the human population, down-regulated IL-36R signaling by a decrease of interaction with IL-1RAcP. 27621309_These results provide novel insights into the role of IL1RAP in CML and a strong rationale for the development of an IL1RAP antibody therapy to target residual CML stem cells. 29238884_Expression level of sIL1RAP may become one of the potential indexes for determining the prognosis of low-grade gliomas 29424312_IL1RAP Polymorphism is Associated With acute Anterior Uveitis. 29773641_This study provides a new mechanistic basis for the efficacy of IL1RAP targeting in acute myeloid leukemia. 30370628_A regulatory network in the PSG10P/miR-19a-3p/IL1RAP pathway may contribute to preeclampsia pathogenesis during pregnancy. 30792413_Association of IL1RAP-related genetic variation with cerebrospinal fluid concentration of Alzheimer-associated tau protein. 31427775_in diseases driven by multiple cytokines, blocking IL-1R3 is a therapy to limit activities from six members of the IL-1 family. 31897507_Associations of IL1RAP and IL1RL1 gene polymorphisms with obesity and inflammation mediators. 31954058_Biallelic variants/mutations of IL1RAP in patients with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. 32829106_IL1RAP regulated by PRPRD promotes gliomas progression via inducing neuronal synapse development and neuron differentiation in vitro. 32871771_The Role of SNPs in IL1RL1 and IL1RAP Genes in Age-related Macular Degeneration Development and Treatment Efficacy. 33602046_The Potential Role of IL1RAP on Tumor Microenvironment-Related Inflammatory Factors in Stomach Adenocarcinoma. 34021002_Proteomic Screens for Suppressors of Anoikis Identify IL1RAP as a Promising Surface Target in Ewing Sarcoma. 35181481_Novel IL1RAP mutation associated with schizophrenia interferes with neuronal growth and related NF-kappaB signal pathways. 35606824_Innate immune mediator, Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), is expressed and pro-tumorigenic in pancreatic cancer. 35803613_Chimeric antigen receptor T-cells targeting IL-1RAP: a promising new cellular immunotherapy to treat acute myeloid leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000022514 |
Il1rap |
71.656150 |
2.6821226268 |
1.423375 |
0.191843776 |
56.108175 |
0.00000000000006859131443375215643720167482560366171344488211980561231939645949751138687133789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000439986006537236744147860549208364158311947850199530307691020425409078598022460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.0559749 |
12.1096069 |
39.7114058 |
3.6786487 |
| ENSG00000196118 |
90835 |
CFAP119 |
protein_coding |
A1A4V9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Flagellum;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:90835; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; sperm principal piece [GO:0097228] |
|
ENSMUSG00000057176 |
Ccdc189 |
25.724002 |
0.4147986208 |
-1.269517 |
0.352369391 |
13.012560 |
0.00030940864062164991467665520197272144287126138806343078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000788751560548454737353818444489661487750709056854248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.9843108 |
3.7408883 |
38.7293671 |
6.1329157 |
| ENSG00000196139 |
8644 |
AKR1C3 |
protein_coding |
P42330 |
FUNCTION: Cytosolic aldo-keto reductase that catalyzes the NADH and NADPH-dependent reduction of ketosteroids to hydroxysteroids. Acts as a NAD(P)(H)-dependent 3-, 17- and 20-ketosteroid reductase on the steroid nucleus and side chain and regulates the metabolism of androgens, estrogens and progesterone (PubMed:10622721, PubMed:11165022, PubMed:7650035, PubMed:9415401, PubMed:9927279). Displays the ability to catalyze both oxidation and reduction in vitro, but most probably acts as a reductase in vivo since the oxidase activity measured in vitro is inhibited by physiological concentration of NADPH (PubMed:14672942, PubMed:11165022). Acts preferentially as a 17-ketosteroid reductase and has the highest catalytic efficiency of the AKR1C enzyme for the reduction of delta4-androstenedione to form testosterone (PubMed:20036328). Reduces prostaglandin (PG) D2 to 11beta-prostaglandin F2, progesterone to 20alpha-hydroxyprogesterone and estrone to 17beta-estradiol (PubMed:15047184, PubMed:20036328, PubMed:10622721, PubMed:11165022, PubMed:10998348, PubMed:19010934). Catalyzes the transformation of the potent androgen dihydrotestosterone (DHT) into the less active form, 5-alpha-androstan-3-alpha,17-beta-diol (3-alpha-diol) (PubMed:10998348, PubMed:14672942, PubMed:11165022, PubMed:7650035, PubMed:9415401, PubMed:10557352). Also displays retinaldehyde reductase activity toward 9-cis-retinal (PubMed:21851338). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10557352, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10622721, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10998348, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11165022, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14672942, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15047184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19010934, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20036328, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21851338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7650035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9415401, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9927279}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipid metabolism;NAD;NADP;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Steroid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14672942}. |
This gene encodes a member of the aldo/keto reductase superfamily, which consists of more than 40 known enzymes and proteins. These enzymes catalyze the conversion of aldehydes and ketones to their corresponding alcohols by utilizing NADH and/or NADPH as cofactors. The enzymes display overlapping but distinct substrate specificity. This enzyme catalyzes the reduction of prostaglandin (PG) D2, PGH2 and phenanthrenequinone (PQ), and the oxidation of 9alpha,11beta-PGF2 to PGD2. It may play an important role in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases such as asthma, and may also have a role in controlling cell growth and/or differentiation. This gene shares high sequence identity with three other gene members and is clustered with those three genes at chromosome 10p15-p14. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2011]. |
hsa:8644; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; 15-hydroxyprostaglandin-D dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0047020]; 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0044594]; 5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047024]; alditol:NADP+ 1-oxidoreductase activity [GO:0004032]; aldo-keto reductase (NADP) activity [GO:0004033]; androstan-3-alpha,17-beta-diol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047044]; androsterone dehydrogenase activity [GO:0047023]; bile acid binding [GO:0032052]; delta4-3-oxosteroid 5beta-reductase activity [GO:0047787]; dihydrotestosterone 17-beta-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0035410]; geranylgeranyl reductase activity [GO:0045550]; ketoreductase activity [GO:0045703]; ketosteroid monooxygenase activity [GO:0047086]; NAD-retinol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004745]; NADP-retinol dehydrogenase activity [GO:0052650]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H, quinone or similar compound as acceptor [GO:0016655]; phenanthrene 9,10-monooxygenase activity [GO:0018636]; prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase activity [GO:0036131]; prostaglandin H2 endoperoxidase reductase activity [GO:0036130]; prostaglandin-F synthase activity [GO:0047017]; retinal dehydrogenase activity [GO:0001758]; steroid dehydrogenase activity [GO:0016229]; testosterone 17-beta-dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0047045]; testosterone dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0047035]; cellular response to cadmium ion [GO:0071276]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; cellular response to corticosteroid stimulus [GO:0071384]; cellular response to jasmonic acid stimulus [GO:0071395]; cellular response to prostaglandin D stimulus [GO:0071799]; cellular response to prostaglandin stimulus [GO:0071379]; cellular response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0034614]; cellular response to starvation [GO:0009267]; cyclooxygenase pathway [GO:0019371]; daunorubicin metabolic process [GO:0044597]; doxorubicin metabolic process [GO:0044598]; farnesol catabolic process [GO:0016488]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; macromolecule metabolic process [GO:0043170]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; negative regulation of retinoic acid biosynthetic process [GO:1900053]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000353]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000379]; progesterone metabolic process [GO:0042448]; prostaglandin metabolic process [GO:0006693]; regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048385]; regulation of testosterone biosynthetic process [GO:2000224]; renal absorption [GO:0070293]; response to nutrient [GO:0007584]; retinal metabolic process [GO:0042574]; retinoid metabolic process [GO:0001523]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; testosterone biosynthetic process [GO:0061370] |
13678667_Glaucomatous optic nerve head astrocytes express a higher level of 3 alpha-HSD isoform AKR1C3 and its mRNA than normal astrocytes. 14671194_expression and activity of type 5 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and type 3 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in female subcutaneous tissue and omental adipose tissue and in preadipocytes 14979715_On the basis of crystal structures, a detailed catalytic mechanism of prostaglandin F synthase is proposed and compared to that of AKR1C1 and AKR1C3. 14997212_Overexpression of hPGFS is associated with primary squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and tumour cell lines derived from respiratory and digestive organs 15212687_Expression of SRD5A1 (5alphaR1) and SRD5A2 (5alphaR2) is elevated, and expression of AKR1C1 (20alpha-HSO), AKR1C2 (3alpha-HSO3) and AKR1C3 (3alpha-HSO2) is reduced in tumorous as compared to normal breast tissue. 15284179_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15284179_Single nucleotide polymorphism may play a role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer in this population, particularly among heavily exposed women. 15582534_enzyme distribution differs between normal and hormonal dependent malignancies of the breast and prostate 15781210_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15814298_Members of the Sp family of transcription factors play an important role in regulating constitutive and stimulated expression of the HSD17B5 gene in H295R cells. 16263811_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16302261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16337083_AKR1C3 protects the mineralocorticoid receptor from activation by deoxycorticosterone in mineralocorticoid target cells of the kidney and colon. 16338060_The expression of AKR1C1 and AKR1C3 in endometrial cancer will govern the ratio of P:E2. 16475787_Based on model structures & inhibition, catalytic mechanism of PGH2 9,11-endoperoxide reductase of PGFS is proposed.Formation of PGF(2alpha) from PGH2 may involve hydride transfer from bound NADPH to PGH2 endoperoxide without specific amino acid residues. 16480815_Type 5 17beta-HSD (AKR1C3) differs significantly from the type 1 enzyme by possessing a spacious and flexible steroid-binding site. 16601286_Elevated expression of AKR1C3 is highly associated with prostate carcinoma 16983398_Glu77Gly AKR1C3 polymorphism is associated with lower testosterone levels in serum. 16983398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17071532_report the clinical history, endocrine evaluation and molecular genetics of a prepubertal girl affected by 17beta-HSD3 deficiency, in whom an erroneous diagnosis of androgen insensitivity syndrome was made 17149600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17166832_analysis of human type 5 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase conformation and binding to inhibitors 17220347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17507624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17583494_HSD17B5 single nucleotide polymorphisms predicted to have functional effects do not appear to be a risk factor for precocious pubarche in girls from Barcelona, despite these girls being at high risk of developing androgen excess in adulthood 17583494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17697149_Carbonyl reductase-1 (CBR1), microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 and 2 (mPGES-1, mPGES-2), cytosolic prostaglandin E synthase (cPGES), aldoketoreductase (AKR1C1) and prostaglandin F synthase (AKR1C3) were all expressed in hair follicles. 17940109_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17940109_Polymorphisms in the HSD17B5 gene are not associated with risk of polycystic ovary syndrome or elevated testosterone levels. 18306354_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18339682_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18339682_The maternal methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase A1298C polymorphism was found to be an effect modifier of the maternal intron 4 polymorphism of the AKR1C3 gene and the childhood leukemia risk. 18552976_Among gene transcripts elevated in depressed episodes were prostaglandin D synthetase (PTGDS) and prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3), both involved in hibernation. We hypothesized them to account for some of the rapid cycling symptoms. 18574251_A strong immunoreactivity was detected not only in classically hormone-associated tissues such as prostate and testis but also in non-hormone-associated tissues such as kidney and bladder in humans and rats. 18632753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18632753_genetic variation in carcinogen-metabolizing genes, particularly AKR1C3, could be associated with bladder cancer risk. 18641923_Data suggest that adipose tissue AKR1C3 expression may be affected by metabolic disease, and its levels are significantly reduced in response to diet-induced weight loss and correlate with leptin levels. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18692800_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18692800_The -71G HSD17B5 variant is not a major component of the molecular pathogenetic mechanisms of PCOS, although it might contribute to the severity of hyperandrogenemia in women with PCOS and biochemical hyperandrogenism. 18984855_Higher mRNA levels of enzymes synthesizing and inactivating androgens are found in differentiated adipocytes, consistent with higher androgen-processing rates in these cells. 18996480_17beta-HSD type 5 was expressed in 56% of breast cancer specimens. decrease in 17beta-HSD type 5 expressions in breast cancer may play a role in the development &/or progression of cancer by modifying the intratumoral levels of estrogens & androgens. 19162045_This is the first study that addresses whether AKR1C3 mediates carcinogen activation within intact living cells following manipulation of AKR1C3 by molecular intervention. 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19273550_By western blot analysis, AKR1C3 is present in human liver obtained at autopsy. By western blot analysis, AKR1C3 is barely detectible in human brain obtained at autopsy. 19320734_AKR1C subfamily genes are stress-inducible and might function as survival factors in keratinocytes. 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19336506_AKR1C3, through its ability to convert androstenedione to testosterone, is likely responsible for adrenal testosterone production. 19423521_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19460435_There is no difference in catalytic properties between variants of 17beta-HSD types 7 and 12 and wild-type enzymes, while variants p.Glu77Gly and p.Lys183Arg in 17beta-HSD type 5 showed a slightly decreased activity. 19487289_AKR1C isoforms as a novel target of jasmonates in cancer cells. 19574343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19846565_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19846565_The researchers found an increased risk of breast cancer in women with AKR1C3 who carried 1 or 2 alleles and who used estrogen-progesterone therapy. 19942269_AKR1C3 expression occurs in a Tanner stage dependent-fashion. Pre- and peri-pubertal changes appear to promote expression in Leydig cells. The pediatric cryptorchid testis reveals AKR1C3 expression in Sertoli cells 20036328_AKR1C3 expression increased steroid conversion by MCF-7 cells, leading to a pro-estrogenic state. Expression of AKR1C3 also reduced the anti-proliferative effects of PGD(2) on MCF-7 cells. 20086173_Data indicate that enzymes CYP17A1 and HSD3B1 showed low expression, while AKR1C3 and SRD5A1 were abundantly expressed. 20126582_Expression of AKR1C3 in renal cell carcinoma, papillary urothelial carcinoma, and Wilms tumor is reported. 20145130_A population level survey of AKR1C3 expression in 2,490 individual cases across 19 cancer types using tissue microarrays revealed marked upregulation of AKR1C3 in a subset. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20634197_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20661409_These findings suggest that AKR1C3 may play important roles in the physiology of endometrial cells 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21039282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21039282_Our data suggest that there is no association of HSD17B6 and HSD17B5 variants with the occurrence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in the Chinese population 21151387_AKR1C3 is expressed in both sex hormone-dependent and hormone-independent malignancies. 21232532_enhanced metabolism of progesterone by SRD5A1 and the 20alpha-HSD and 3alpha/beta-HSD activities of AKR1C1, AKR1C2 and AKR1C3 21323680_Evidence of association of two alleles for alcohol dependence (AD) is found in SRD5A1 and AKR1C3, mediating a protective effect of the minor allele at each AD marker based on the genotype of the second marker. 21365123_Data show that steroidogenic enzymes (AKR1C3, HSD17B2, UGT2B15 and UGT2B17) and stem/progenitor cell markers CK5 and ABCG2 were upregulated in castration resistant prostate cancer. 21444150_PTHrP stimulates prostate cancer cell growth and upregulates aldo-keto reductase 1C3 21521174_role of AKR1C3 in the metabolism of testosterone and progesterone via the 5beta-reductase pathway. 21851338_the pro-proliferative action of AKR1C3 in HL-60 cells involves the retinoic acid signalling pathway and that this is in part due to the retinaldehyde reductase activity of AKR1C3 22170488_AKR1C3 functions in differentiation-associated gene regulation and also has a role in supporting inflammation in atopic dermatitis. 22505408_determined the X-ray crystal structure of AKR1C3 with the cofactor NADP+ and the drug-like inhibitor 3-phenoxybenzoic acid bound at a resolution of 1.68 A degrees in space group P212121 22670171_AKR1C3 immunoreactivity was extensively present in both adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma arising from the lung and the gastroesophageal junction, but not in small cell carcinoma. 23024260_Activin A stimulates AKR1C3 expression and growth in human prostate cancer 23116553_Correlation of aldo-ketoreductase (AKR) 1C3 genetic variant with doxorubicin pharmacodynamics in Asian breast cancer patients. 23165153_The involvement of up-regulated AKR1C1, AKR1C3 and proteasome in CDDP resistance of colon cancers. 23183084_Affect further reduction of 3-keto and 20-keto groups catalyzed by AKR1C2 and AKR1C3. 23196782_AKR1C3 can be considered a therapeutic target in a subgroup of patients with high AKR1C3 expression. 23519145_AKR1C3-mediated radioresistance in lung cancer cells is correlated with an arrest in the G2/M cell cycle and a decreased induction of apoptosis. 23748150_examine the evidence that supports the vital role of AKR1C3 in CRPC and recent developments in the discovery of potent and selective AKR1C3 inhibitors 24012099_Data indicate that fallopian tube and the epithelial component of Brenner tumours (BTs) expressed AKR1C3 and androgen receptor, but the tumour stromal cells showed strong expression of calretinin, inhibin and steroidogenic factor 1 in the majority of BTs. 24228104_Report expression of AKR1C3 in neuroendocrine tumors and adenocarcinomas of pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and lung. 24244276_Significantly higher levels of SRD5A1, AKR1C2, AKR1C3, and HSD17B10 mRNA were however found in bone metastases than in non-malignant and/or malignant prostate tissue 24316309_Silencing of AKR1C3 increases LCN2 expression and inhibits metastasis in cervical cancer. 24571686_AKR1C3 can serve as a promising biomarker for the progression of prostate cancer 24832494_Data suggest that reduction of daunorubicin/idarubicin is catalyzed by AKR1C3 and contributes to resistance of carcinoma cells to these anthracyclines; expression of AKR1C3 is induced in carcinoma cells following exposure to daunorubicin/idarubicin. 24838369_AKR1C3 2 G allele carriers exhibited greater increases in heart rate and stimulant and sedative effects of alcohol than C allele homozygotes 24917395_Aldo-keto reductase 1C3 is overexpressed in skin squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). AKR1C3 affects SCC growth via prostaglandin metabolism. 25419901_Findings indicate the potential involvement of aldo-keto reductase AKR1C3 in the acquired radioresistance by AKR1C3 overexpression. 25446850_Higher expression of PLA2G2A, PTGS2, AKR1B1, AKR1C3 and ABCC4 was seen in 22-B endometriosis cells. 25514466_P450c17 and AKR1C3 inhibition may be an effective combinatorial treatment strategy. 25522430_AKR1C3 mRNA expression did not differ between bipolar disorder patients in any affective state or in comparison with healthy control subjects. 25649766_AKR1C3 activation is a critical resistance mechanism associated with enzalutamide resistance. 25661377_AKR1C3 mediated doxorubicin resistance might be resulted from the activation of anti-apoptosis PTEN/Akt pathway via PTEN loss. 25754347_and AKR1C3 may serve as a valuable therapeutic target in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer 25849402_In the present study, crystal structures of complexes of HSD17B5 with structurally diverse inhibitors derived from high-throughput screening were determined. 26160177_A catalysis-independent role for AKR1C3 on AR activity via Siah2 has been identified. 26170067_these results indicated that the actions of AKR1C3 can produce FP receptor ligands whose activation results in carcinoma cell survival in breast cancer. 26308156_aldo-keto reductase 1C3-mediated prostaglandin D2 metabolism has a role in keloids 26429394_AKR1C3 expression is elevated in prostate cancer cell lines and primary prostate cancer, suggesting a link between AKR1C3 levels and the epigenetic status in prostate cancer cells. 27019068_The results suggest that decreased expression of AKR1C3 may be involved in development of gastric cancer and can be restored by Sodium Butyrate. 27055738_AKR1C3 is the primary enzyme and CBR1 is a minor enzyme responsible for warfarin reduction in human liver cytosol. 27082632_a variant in the promoter region of HSD17B5 related to fetal androgen synthesis influences the genital phenotype in 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency females. 27085562_We identified strong associations between the studied AKR1C3 variants and UBC risk. The homozygous variant genotype of rs12529 was found to be inversely associated with UBC, and rs1937920 was shown to be associated with increased risk of UBC. None of the genotypes were found to be significantly associated with tumor characteristics. 27111237_Five common AKR1C3 polymorphisms were associated with decreased rates of exemestane catalysis. 27385003_Overexpression of AKR1C3 could result in the accumulation of prostaglandin F2alpha (PGF2alpha), which can not only promote prostate cancer cell 's proliferation but also could enhance prostate cancer cells resistance to radiation. 27485119_If our these findings can be reproduced in larger homogeneous cohorts, a genetic stratification based on the AKR1C3 rs12529 single nucleotide polymorphism, can minimize androgen deprivation therapy-related health-related quality of life effects in prostate cancer patients 28025170_The replacement of C154 with a residue possessing a bulky aromatic side-chain impairs the folding of the alpha-helix containing C154 and its neighboring secondary structures, leading to low thermostability of AKR1C3. 28259989_the present study suggests that AKR1C1, AKR1C2, AKR1C3, and AKR1C4 are closely associated with drug resistance to both CDDP and 5FU, and that mefenamic acid, an inhibitor of AKR1C, restores sensitivity through inhibition of drug-resistance in human cancer cells. 28359237_AKR1C3 transcriptional regulation and its role in prostate cancer progression [review] 28457968_Data suggest that, in breast cancer cells, expression of HSD17B5 and expression of GRP78 (an apoptosis inhibitor) are strongly but negatively correlated; GRP78 knockdown decreases breast cancer cell viability whereas HSD17B5 knockdown increases cell viability and cell proliferation. (HSD17B5, 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 5; GRP78, 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein) 29777907_The GG genotype of AKR1C3 rs10508293 is associated with decreased risk for preeclampsia. 29920533_Genotype data on the AKR1C3 rs12529 SNP indicates that all three prostate cancer groups (New Zealanders, African Americans, and Caucasian Americans) have similar genotype and allele frequencies. The highest percentage of high-risk PC as a percentage of all PC were recorded for ever-smoker AA men with the AKR1C3 rs12529 CC genotype while the lowest was recorded for never-smoker NZ men with the CG+GG genotypes. 30139661_AKR1C3 is a novel epithelial-mesenchymal transition driver in prostate cancer metastasis through activating ERK signaling. 30367463_OPSCC with integrated HPV16 show upregulation of AKR1C1 and AKR1C3 expression. 31125365_Age dependent PSA thresholds in prostate cancer screening were valid only in men carrying the AKR1C3 rs12529 CG and GG genotypes in this New Zealand cohort. 31253396_Results suggest that aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and aldo-keto reductase (AKR) 1C3 (AKR1C3) expression were positively correlated in human breast cancer. 31294486_Study demonstrated that AKR1C3 detection in tissues from prostate re-Bx at mCRPC was associated with early resistance to ABI but not DOC. 31308078_the AKR1C3/AR-V7 complex collaboratively confers resistance to AR-targeted therapies in advanced prostate cancer. 31780644_Aldo-keto reductases protect metastatic melanoma from ER stress-independent ferroptosis. 32003543_Microproteomics and Immunohistochemistry Reveal Differences in Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member C3 in Tissue Specimens of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease. 32902124_The AKR1C3/AR-V7 complex maintains CRPC tumour growth by repressing B4GALT1 expression. 33096057_Significance of aldo-keto reductase 1C3 and ATP-binding cassette transporter B1 in gain of irinotecan resistance in colon cancer cells. 33211282_AKR1C3 is a biomarker and druggable target for oropharyngeal tumors. 33258507_AKR1C3 mediates pan-AR antagonist resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer. 33361392_A Positive Feedback Loop of AKR1C3-Mediated Activation of NF-kappaB and STAT3 Facilitates Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33493134_Diagnostic and prognostic values of AKR1C3 and AKR1D1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33675863_AKR1C2 and AKR1C3 expression in adipose tissue: Association with body fat distribution and regulatory variants. 33984486_AKR1C3 decreased CML sensitivity to Imatinib in bone marrow microenvironment via dysregulation of miR-379-5p. 34676395_Development of cisplatin resistance in breast cancer MCF7 cells by up-regulating aldo-keto reductase 1C3 expression, glutathione synthesis and proteasomal proteolysis. 34830394_Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals AKR1C1 and AKR1C3 Mediate Cisplatin Resistance in Signet Ring Cell Gastric Carcinoma via Autophagic Cell Death. 34997089_Assessment of factors associated with PSA level in prostate cancer cases and controls from three geographical regions. 35257428_ARID3A promotes the chemosensitivity of colon cancer by inhibiting AKR1C3. 35489629_Characterization of the major single nucleotide polymorphic variants of aldo-keto reductase 1C3 (type 5 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase). 36067250_Plasma Exosomal AKR1C3 mRNA Expression Is a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. |
|
|
5.624412 |
0.1230534631 |
-3.022643 |
0.864080111 |
16.101902 |
0.00006002372567834180351435680034200004229205660521984100341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000170966845042903317283822239858182001626119017601013183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1895235 |
0.7527179 |
9.8844488 |
2.5098102 |
| ENSG00000196150 |
58500 |
ZNF250 |
protein_coding |
P15622 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity and sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:58500; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000054967 |
Zfp647 |
84.129696 |
0.3536697163 |
-1.499525 |
0.586882697 |
5.673347 |
0.01722455918076682551687284217223350424319505691528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031363742105615391442263728549733059480786323547363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.1707704 |
20.1683505 |
100.0203754 |
36.6125759 |
| ENSG00000196155 |
25894 |
PLEKHG4 |
protein_coding |
Q58EX7 |
FUNCTION: Possible role in intracellular signaling and cytoskeleton dynamics at the Golgi. |
Alternative splicing;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene can function as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) and may play a role in intracellular signaling and cytoskeleton dynamics at the Golgi apparatus. Polymorphisms in the region of this gene have been found to be associated with spinocerebellar ataxia in some study populations. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:25894; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051056] |
12796826_Spinocerebellar ataxia type 4 (SCA4) is mapped to chromosome 16q22.1 in northern germany.Haplotype analyses refined the gene locus to a 3.69 cM interval between D16S3019 and D16S512. 15148151_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15455264_the autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia that we have characterized is allelic with SCA4 and Japanese 16q-linked ADCA type III. 16001362_puratrophin-1 has a role in intracellular signaling and actin dynamics at the Golgi apparatus 16491300_Mutations of the puratrophin1 gene on chromosome 16q22.1 are not a common genetic cause of cerebellar ataxia in a European population. 16491300_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16780885_We found the C-to-T substitution in the puratrophin-1 gene in 20 patients with ataxia (16 heterozygotes and four homozygotes) and four asymptomatic carriers in 9 of 24 families with an unknown type of ADCA. 17357132_among 686 autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxia families in our cohort, 57 families were identified to have 65 affected individuals, who carried the C-to-T substitution of the puratrophin-1 gene 17611710_Disease locus of 16q-autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia was definitely confined to a 900-kb genomic region between the SNP04 and the -16C>T substitution in the puratrophin-1 gene in 16q22.1. 18482007_Rac1 activation specifically in membrane ruffles by the guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor FLJ00068 is sufficient for insulin induction of glucose uptake into skeletal-muscle cells. 19065522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19065522_The mutation of c.-16C to T of the PURATROPHIN-1 gene might be rare in SCA patients in China. 20424877_(TGGAA)(n) repeats in the insertion mutation of PLEKHG4 are related to the pathogenesis of SCA31 21357611_This letter suggested cerebellar ataxia due to a pentanucleotide repeat (TAGAA) expansion on the puratrophin-1 (PLEKHG4) gene on chromosome 16q-22.1. 25025572_Role of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor in Akt2-mediated plasma membrane translocation of GLUT4 in insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle. |
ENSMUSG00000014782 |
Plekhg4 |
77.946327 |
0.3534707503 |
-1.500337 |
0.250576112 |
35.681945 |
0.00000000232307023877762739415496564567269882628508526067889761179685592651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000010762246303941551798575501370635459919000709305691998451948165893554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.0797864 |
7.3849803 |
119.8177914 |
13.9530979 |
| ENSG00000196187 |
9725 |
TMEM63A |
protein_coding |
O94886 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an osmosensitive calcium-permeable cation channel (PubMed:30382938, PubMed:31587869). Mechanosensitive ion channel that converts mechanical stimuli into a flow of ion (PubMed:30382938, PubMed:31587869). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91YT8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30382938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31587869}. |
Calcium;Cell membrane;Disease variant;Ion channel;Ion transport;Leukodystrophy;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Enables mechanosensitive ion channel activity. Predicted to be involved in cation transmembrane transport. Located in centriolar satellite and lysosomal membrane. Implicated in hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9725; |
centriolar satellite [GO:0034451]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; calcium activated cation channel activity [GO:0005227]; mechanosensitive ion channel activity [GO:0008381]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; osmolarity-sensing cation channel activity [GO:1990760] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 33785861_Spinal cord involvement and paroxysmal events in ''Infantile Onset Transient Hypomyelination'' due to TMEM63A mutation. |
ENSMUSG00000026519 |
Tmem63a |
669.818588 |
0.4266759840 |
-1.228787 |
0.094971372 |
164.813387 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000010047899758320314817600651285999108891085390632125839249989083804047199559878578979287917967173210387343829097517300397157669067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001586171127623613378438293823533717051625760381330137144155978632212569583629253018555214392918371879570571536532952450215816497802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
428.0179110 |
28.9689400 |
1008.8736702 |
48.0089201 |
| ENSG00000196189 |
64218 |
SEMA4A |
protein_coding |
Q9H3S1 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor for PLXNB1, PLXNB2, PLXNB3 and PLXND1 that plays an important role in cell-cell signaling (By similarity). Regulates glutamatergic and GABAergic synapse development (By similarity). Promotes the development of inhibitory synapses in a PLXNB1-dependent manner and promotes the development of excitatory synapses in a PLXNB2-dependent manner (By similarity). Plays a role in priming antigen-specific T-cells, promotes differentiation of Th1 T-helper cells, and thereby contributes to adaptive immunity (By similarity). Promotes phosphorylation of TIMD2 (By similarity). Inhibits angiogenesis (By similarity). Promotes axon growth cone collapse (By similarity). Inhibits axonal extension by providing local signals to specify territories inaccessible for growing axons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62178}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Cone-rod dystrophy;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Reference proteome;Retinitis pigmentosa;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the semaphorin family of soluble and transmembrane proteins. Semaphorins are involved in numerous functions, including axon guidance, morphogenesis, carcinogenesis, and immunomodulation. The encoded protein is a single-pass type I membrane protein containing an immunoglobulin-like C2-type domain, a PSI domain and a sema domain. It inhibits axonal extension by providing local signals to specify territories inaccessible for growing axons. It is an activator of T-cell-mediated immunity and suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated endothelial cell migration and proliferation in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. Mutations in this gene are associated with retinal degenerative diseases including retinitis pigmentosa type 35 (RP35) and cone-rod dystrophy type 10 (CORD10). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:64218; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; semaphorin receptor binding [GO:0030215]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; negative regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance [GO:0048843]; neural crest cell migration [GO:0001755]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of excitatory synapse assembly [GO:1904891]; positive regulation of inhibitory synapse assembly [GO:1905704]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010594]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; T-helper 1 cell differentiation [GO:0045063] |
16199541_Mutations within the SEMA4A gene cause various retinal degnerative diseases. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 22491253_Dendritic cell-derived SEM4A is not only critical for T helper type (Th)1 cells but also for Th17 cell differentiation, and multiple sclerosis patients with high Sema4A levels exhibit Th17 cell skewing. 22956603_mutations in SEMA4A may cause susceptibility to light exposure, oxidative stress, and ER stress, which may be involved in the progression and pathology of RP. 23007237_Sema4A plays an inhibitory role in T helper (Th)2-type allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, in a fraction of Sema4a-deficient transgenic mice. 23360997_These results indicate the importance of the Sema4A protein conformation in human and mouse retina homeostasis. 25307848_Germline variants in SEMA4A predispose to familial colorectal cancer type X. 25515530_PACAP released from retinal neural cells (photoreceptors or optic nerve cells) may regulate Sema4A expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells and thereby contribute to the maintenance of retinal structure and function. 26303122_Data suggest that increased expression of semaphorin 4A (Sema4A) is required to promote inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 26648031_Sema4A activated the Akt pathway via Plexin D1 receptor in lung fibroblasts.Lung fibroblasts show elevated levels of Sema4A expression in systemic sclerosis patients. 27554682_In this review, we summarized the current findings on neuroimmune Sema4A and Sema4D molecules in chronic inflammation underlying many diseases and discussed their positive or negative impacts on the implicated molecular and cellular processes 27697528_SEMA 4A confers doxorubicin resistance on hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing epithelialemesenchymal transition. 28007914_Suggest a role for Plexin-B1 as a ligand and Sema4A as a receptor and characterize a reverse signaling pathway downstream of Sema4A regulating cell migration via Scrib. 28805479_Here we show three families with retinal degeneration in which unaffected family members are either homozygous or heterozygous for the variant. The p.R713Q variant in SEMA4A is insufficient to cause either autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa and is unlikely to be pathogenic. 29457657_Human oligodendrocytes undergo apoptosis when exposed to Sema4A and take up H-ferritin for meeting iron requirements and that these functions are mediated via the Tim-1 receptor. H-ferritin can block Sema4A-mediated cytotoxicity. Sema4A is detectable in the CSF of multiple sclerosis patients and HIV-seropositive persons and can induce oligodendrocyte cell death. 29467366_ILT-4 is a receptor for hSEMA4A)on activated CD4(+) T cells. hSEMA4A is highly expressed in human asthmatic lung tissue. 29763494_Advanced peri-implantitis lesions showed higher levels of gene expression for Sem3A and Sem4D and lower levels of Sem4A in comparison to tissues obtained from a healthy dental implant. 30270262_Hypoxic induction of Sema4A contributes to the abnormal proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells. 30342889_In this study, we found that the levels of sSEMA4A were significantly elevated in patients with CRSwNPs and asthma, and that SEMA4A was especially highly expressed in eosinophils in nasal polyps. We also demonstrated that SEMA4A in eosinophils can be cleaved by ADAMTS4, suggesting that eosinophils are a major source of SEMA4A in serum from these patients. 30685700_this study shows that semaphorin 4A acts in a feed-forward loop with NF-kappaB pathway to exacerbate catabolic effect of IL-1beta on chondrocytes 31012544_Sema4A plays direct and dual roles in promoting inflammation and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. 31236543_Sema4A exerts a Treg cell phenotype-stabilizing effect, defined as an increase in percentage and numbers of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ cells, on human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells populations, and CD4+ T cells. 31876207_T-cell specific upregulation of Sema4A as risk factor for autoimmunity in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. 32169103_Sema4A is implicated in the acceleration of Th17 cell-mediated neuroinflammation in the effector phase. 32244055_Sema4D and 4A seem to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of some autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. 32971928_Semaphorin4A-Plexin D1 Axis Induces Th2 and Th17 While Represses Th1 Skewing in an Autocrine Manner. 33460983_Semaphorin 4A restricts tumor progression by inhibiting angiogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. 35328445_Identifying Function Determining Residues in Neuroimmune Semaphorin 4A. 35460904_The possible involvement of sema3A and sema4A in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. |
ENSMUSG00000028064 |
Sema4a |
153.839540 |
10.0581719463 |
3.330296 |
0.227107881 |
218.192672 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022418948316501687203762440672811617859442584942099111026968673415343832987827596979013679617683945181505452144977678071363158887607802682850888231769204139709472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004707022434588405672492592736029129664883013001187599842307387104070331142665899805070376603978148235641543004539973560265003760250124287267681211233139038085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
293.1811838 |
37.2369583 |
28.9423628 |
3.2495978 |
| ENSG00000196295 |
|
GARS1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
368.965324 |
0.2848202303 |
-1.811876 |
0.152174548 |
137.494887 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000009398495034506862729130721831012806180868919134314821877507629243080094234844535879859483973319811411784030497074127197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000001273845607982748348421837209532455308181651711509745537780058359198589398417509688590798511143020732561126351356506347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
155.5167236 |
17.0489591 |
549.9043444 |
41.8474115 |
| ENSG00000196305 |
3376 |
IARS1 |
protein_coding |
P41252 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the specific attachment of an amino acid to its cognate tRNA in a 2 step reaction: the amino acid (AA) is first activated by ATP to form AA-AMP and then transferred to the acceptor end of the tRNA. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8052601}. |
Acetylation;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAS, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. Isoleucine-tRNA synthetase belongs to the class-I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family and has been identified as a target of autoantibodies in the autoimmune disease polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:3376; |
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase multienzyme complex [GO:0017101]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; aminoacyl-tRNA editing activity [GO:0002161]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; isoleucine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004822]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; isoleucyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006428]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27426735_Biallelic IARS Mutations Cause Growth Retardation with Prenatal Onset, Intellectual Disability, Muscular Hypotonia, and Infantile Hepatopathy 27891590_bi-allelic mutations in cytosolic isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase (IARS) have been described in three individuals with growth delay, hepatic dysfunction, and neurodevelopmental disabilities. Here we report an additional subject with this condition identified by whole-exome sequencing. Our findings support the association between this disorder and neonatal cholestasis with distinct liver pathology 29052218_Our report presents new evidence that recessive mutations inIARSgene are associated with characteristic clinical phenotype suchas infantile hepatopathy, growth retardation, facial dysmorphism,hypotonia, intellectual disability with no speech . |
ENSMUSG00000037851 |
Iars |
755.848729 |
2.2804662511 |
1.189329 |
0.083594656 |
200.726991 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000144939773861995334046924931276795453198081407568883174276415512533758889497825567392204236820530793465450466179340015260290641663232236169278621673583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000027711283189158692375334943669064486714134544192144239792900069674417555387845881276994370032913952586661537961761417325767808961245464161038398742675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1065.9897021 |
51.3232332 |
470.9997747 |
17.3195019 |
| ENSG00000196329 |
55340 |
GIMAP5 |
protein_coding |
Q96F15 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in T lymphocyte development and the optimal generation of CD4/CD8 double-positive thymocytes (By similarity). Inhibitor of GSK3A, possibly by sequestering GSK3A in cytoplasmic vesicles and impairing its translocation to the nucleus. Consequently, impairs GSK3A-dependent transcriptional program and regulation of the DNA damage response occurring during T cells proliferation (PubMed:29382851). Required for the survival of peripheral T cells, natural killer (NK) and NK T-cell development and the maintenance of normal liver function (By similarity). May promote the survival of mature T lymphocytes upon cytokine withdrawal (By similarity). May regulate Ca(2+) homeostasis by modulating lysosomal Ca(2+) stores, preventing its accumulation in the absence of T cell activation (By similarity). May play a role in mitochondrial DNA segregation in hematopoietic tissues (By similarity). Is a regulator of liver endothelial cell homeostasis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BWF2, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K3L6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29382851}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Endosome;GTP-binding;Lysosome;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a protein belonging to the GTP-binding superfamily and to the immuno-associated nucleotide (IAN) subfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins. In humans, the IAN subfamily genes are located in a cluster at 7q36.1. This gene encodes an antiapoptotic protein that functions in T-cell survival. Polymorphisms in this gene are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the neighboring upstream GIMAP1 (GTPase, IMAP family member 1) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:55340; |
lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; multivesicular body membrane [GO:0032585]; GTP binding [GO:0005525] |
17220214_A significant increase in systemic lupus erythematosus risk associated with the most common GIMAP5 haplotype was found (odds ratio 1.26, 95% CI 1.02 to 1.54, p = 0.0033). 17220214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17369194_Resutls show that Gimap5 is located in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the endogenous Gimap5 mRNA is up-regulated in activated T-cells. 17641683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17641683_These data suggest that the GIMAP5 gene is associated with islet autoimmunity in type I diabetes and add to recent findings implicating the same single nucleotide polymorphism in another autoimmune disease. 19762377_Data show that IAN5 polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to Systemic lupus erythematosus and the development of clinical disease manifestations in a strictly Korean population. 19762377_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20190135_These data establish Gimap5 as a key regulator of hematopoietic integrity and lymphocyte homeostasis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20817506_Notch signalling protects T-ALL cells from apoptosis by upregulating the expression of GIMAP5. 23098229_Data indicate that overexpression of GTPase of the immune-associated nucleotide-binding protein 5 (GIMAP5) in HEK (human embryonic kidney)-293 cells resulted in increased Ca2+ accumulation within the mitochondria. 25944983_gimap5 has a role in maintaining peripheral tolerance and T cell homeostasis in the gut [review] 27667392_These data,demonstrating the downregulation of the mRNA and protein expression levels of GIMAP5 and GIMAP6 in the tumor tissues and blood of patients with HCC, suggested the involvement of GIMAP5 and GIMAP6 in the pathogenesis of HCC, and indicate their possible use as diagnostic markers for HCC. 29382851_GIMAP5 loss-of-function mutation results in T cell deficiencies. |
ENSMUSG00000039264+ENSMUSG00000043505 |
Gimap3+Gimap5 |
59.583831 |
2.3328435809 |
1.222090 |
0.203457170 |
36.550570 |
0.00000000148756464025711375996071813128602059905780663484620163217186927795410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007008124510116501379898952078751836469727720668743131682276725769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.4416804 |
11.4712859 |
36.5781265 |
3.8919533 |
| ENSG00000196372 |
79754 |
ASB13 |
protein_coding |
Q8WXK3 |
FUNCTION: May be a substrate-recognition component of a SCF-like ECS (Elongin-Cullin-SOCS-box protein) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex which mediates the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation pathway |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing (ASB) family of proteins. They contain ankyrin repeat sequence and a SOCS box domain. The SOCS box serves to couple suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS) proteins and their binding partners with the elongin B and C complex, possibly targeting them for degradation. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants, both protein-coding and not protein-coding, have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:79754; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000033781 |
Asb13 |
58.422249 |
0.4845234538 |
-1.045362 |
0.285571344 |
13.323430 |
0.00026211022509999026570276514647162002802360802888870239257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000674585339577307143907325404086350317811593413352966308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.1882639 |
8.8791934 |
81.8454251 |
13.1853731 |
| ENSG00000196405 |
51466 |
EVL |
protein_coding |
Q9UI08 |
FUNCTION: Ena/VASP proteins are actin-associated proteins involved in a range of processes dependent on cytoskeleton remodeling and cell polarity such as axon guidance and lamellipodial and filopodial dynamics in migrating cells. EVL enhances actin nucleation and polymerization. |
Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3-binding |
|
Predicted to enable SH3 domain binding activity and profilin binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of epithelial cell migration; negative regulation of ruffle assembly; and positive regulation of stress fiber assembly. Located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51466; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; membrane [GO:0016020]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; profilin binding [GO:0005522]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; actin nucleation [GO:0045010]; actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008154]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; negative regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010633]; negative regulation of ruffle assembly [GO:1900028]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030838]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289] |
15939738_Ena/VASP proteins regulate actin polymerization at actin filament barbed ends in vitro in the presence and absence of barbed end capping proteins. 16336193_the interaction of the alphaII-spectrin SH3 domain with EVL 16376568_Data suggest that ena/VASP binding to F-actin allows for gephyrin recruitment to the leading edge of uncapped actin filaments. 17998398_EVL is required for endothelial barrier function in vivo. 18264139_A microRNA encoded in an intron of the gene EVL, is commonly suppressed in human colorectal cancer. 18357390_EVL may be implicated in invasion and/or metastasis of human breast cancer. 19329439_EVL protein is a novel recombination factor that may be required for repairing specific DNA lesions, and that may cause tumor malignancy by its inappropriate expression. 19725871_EVH2 domain, which is highly conserved among the ENA/VASP family proteins, may be responsible for the recombination function of EVL. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20639531_EVL, with either E. coli topoisomerase I or human topoisomerase IIIalpha, catalyzed ssDNA catenation. 21398369_ENA/VASP-family proteins are functionally redundant in homologous recombination, and MENA, VASP and EVL may be involved in the DSB repair pathway in humans 28630144_Identify CRMP-1 as a novel regulator of actin filament elongation and reveal a surprisingly important role for CRMP-1, EVL, and actin polymerization in maintaining the structural integrity of epithelial sheets. 29242101_EVL/miR-342 methylation was preferentially detected in IgD multiple myeloma 34550860_Exercise effects on DNA methylation in EVL, CDKN2A (p14, ARF), and ESR1 in colon tissue from healthy men and women. |
ENSMUSG00000021262 |
Evl |
1536.961833 |
0.4890657657 |
-1.031900 |
0.088117045 |
135.314712 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000028177264313862335421760737987098860890533435450377207345116991622823828309149160609159423529490595683455467224121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000003780876557023709543688286616521119298984815980898414647363615165501301177154703202221153190976110636256635189056396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1031.8758436 |
59.1377693 |
2125.7146940 |
86.4452726 |
| ENSG00000196415 |
5657 |
PRTN3 |
protein_coding |
P24158 |
FUNCTION: Serine protease that degrades elastin, fibronectin, laminin, vitronectin, and collagen types I, III, and IV (in vitro) (PubMed:3198760, PubMed:2033050, PubMed:28240246). By cleaving and activating receptor F2RL1/PAR-2, enhances endothelial cell barrier function and thus vascular integrity during neutrophil transendothelial migration (PubMed:23202369). May play a role in neutrophil transendothelial migration, probably when associated with CD177 (PubMed:22266279). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:2033050, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22266279, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23202369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28240246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:3198760}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
Enables enzyme binding activity; serine-type endopeptidase activity; and signaling receptor binding activity. Involved in several processes, including mature conventional dendritic cell differentiation; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis; and neutrophil extravasation. Located in azurophil granule lumen; cytosol; and plasma membrane raft. Colocalizes with plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5657; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; plasma membrane raft [GO:0044853]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; serine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008236]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; antimicrobial humoral response [GO:0019730]; cell-cell junction maintenance [GO:0045217]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; mature conventional dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097029]; membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0006509]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; neutrophil extravasation [GO:0072672]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
11115080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11389039_PR-3 is responsible for the extracellular generation of antimicrobial peptides in human neutrophils 11714826_Neutrophil proteinase 3 combined with LPS induces bioactive IL-18 secretion by IFN-gamma-primed gingival epithelial cells via a caspase-1-independent pathway. 12067299_Human proteinase 3 can inhibits LPS-mediated TNF-alpha production through CD14 degradation 12114510_Proteinase 3 plays a role in neutrophil response to inflammation 12135665_A comparison of proforms and mature forms of proteinase 3 in regulating granulopoiesis 12140766_Proteinase-3, a serine protease which mediates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in the HL-60 leukemia cell line, is downregulated in its doxorubicin-resistant variant 12191967_PR3 expression on the membrane of neutrophils plays a role in the pathophysiology of PR3-ANCA associated vasculitis. 12200377_CD8 T-cell responses to Wilms tumor gene product WT1 and proteinase 3 were observed in patients with acute myeloid leukemia, and not in controls. 12354776_Cleavage of p21waf1 by proteinase-3, a myeloid-specific serine protease, potentiates cell proliferation 12393722_Interferon-alpha, but not the ABL-kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571), induces expression of myeloblastin in chronic myeloid leukemia 12444202_Protease entry results in direct cleavage of p65 NF-kappaB in the N-terminal region by PR3 and in the C-terminal region by human neutrophil elastase (HNE). PR3 and HNE have specific, fundamental roles in endothelial responses during inflammation. 12506139_Wegener granulomatosis patients have a higher percentage of membrane proteinase 3 expressing neutrophils. Expression is influenced by genetic variance. 12538645_comparison of the action of this enzyme and neutrophil elastase on model substrates 12832446_PR-3 is able to degrade matrigel componenets and denatured collagen and to directly activate secreted but not membrane-bound pro-MMP-2 12894870_Wegener's disease results from the breakdown of self tolerance to PR3 [review] 12960243_Interaction of proteinase 3 with CD11b/CD18 (beta2 integrin) on the cell membrane of human neutrophils. 14525959_PR3 originates from two distinct pools, the granular pool mobilized following degranulation or a plasma membrane pool mobilized upon apoptosis. 14675038_the granulocyte protease, PR3, is an exogenous caspase-like molecule that can sidestep intracellular caspase functions at sites of inflammation. 15331626_relation between membrane expression of PR3 on nonprimed neutrophils of patients with Wegener granulomatosis and their susceptibility for relapses 15686586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15879139_A potential novel role is described for proteinase 3, which can mediate compartmentalized caspase-3 activation in resting neutrophils, in the context of neutrophil survival mechanisms or terminal differentiation. 15916759_The Proteinase 3 (PR3), the target autoantigen of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in the autoimmune vasculitis, Wegener's granulomatosis, is a serine proteinase stored in granules of human neutrophils. 15975933_p21 is one specific target of PR3; PR3-mediated p21 cleavage prevents monocytic differentiation 16167885_This review discusses the expression of proteinase 3 (PR3) in non-hemopoietic cells and its critical involvement in the regulation of immune function through direct modulation of cell signaling, the cytokine network and innate immunity. 16263417_CFU-GM S-phase arrest is mediated by the first four N-terminal amino acids of PR3, andthis activity is dependent on the configuration of the proform providing the correct presentation of this N-terminal motif 16478888_Wegener autoantigen interacts with a 'gateway' receptor (PAR-2) on iDCs in vitro triggering their maturation and licenses them for a T helper 1 (Th1)-type response potentially favoring granuloma formation in Wegener granulomatosis. 16598772_FcgammaRIIIb acts as a membrane adaptor for PR3 16792675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17088257_analysis of human neutrophil protease 3 and elastase active site charge distribution 17158864_glycosylation occurs at both sites in native neutrophil PR3 and in wild type recombinant PR3 (rPR3) expressed in HMC-1 cells. glycosylation at Asn-147, but not at Asn-102, is critical for thermal stability, and for optimal hydrolytic activity of PR3. 17244676_PR-3 and NB1 coimmunoprecipitated from and colocalized on the neutrophil plasma membrane. 17412886_The primary granule proteins elastase (ELA2) and proteinase 3 (PR3) both contain the nonapeptide PR1, which can induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against chronic myeloid leukemia 17452051_These results suggest that anti-PR3 Abs prime human monocytic cells to produce cytokines upon stimulation with various bacterial components by up-regulating the TLR and NOD signaling pathway. 17534941_Rheumatoid arthritis phenotype can be subclassified according to the presence or absence of ACPAs. 17634439_In plasma, anti-PR3 antibodies poorly recognized suspended neutrophils, whereas they bound to mPR3 on adherent cells 17681950_proteinase 3 has a critical role in annexin 1 cleavage in activated neutrophils 17712045_PR3 externalization depended on PLSCR1 17785293_there are a number of (auto)molecules that bind to PR3, some of them even competitive and each binding interaction seems to have specific implications 18023421_Murine and human proteinase 3 complexes have different interaction patterns with peptidic substrates. 18076025_Computational prediction is made of the binding site of PRTN3 to the plasma membrane. 18596726_About half of the patients were found to have CD4+TH1 memory cells responsive to the cPR3(138-169)-peptide; while only a third of the patients had HI-PR3 protein responsive T cells 18854317_The NB1-bound PR3 was active and was cleared from the surface by alpha-1-protease inhibitor 19185066_elevated expression levels of membrane-bound form in Wegener's Granulomatosis patients 19447886_This suggests that constitutive mPr3 is enzymatically inactive or its active site is not accessible to the substrate 19490915_Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) testing of routine sera varies in different laboratories but concordance is greater for cytoplasmic fluorescence (proteinase3/C-ANCA) and myeloperoxidase specificity (MPO-ANCA). 19494315_Neutrophil-derived PR3 can proteolyze high-molecular weight kininogen and liberate PR3-kinin, thereby initiating kallikrein-independent activation of the kinin pathway 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20059480_Epitope shift of proteinase-3 anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in patients with small vessel vasculitis. 20155833_Transcription of PR3 and related myeloid differentiation genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells may represent novel markers of disease activity in Wegener's granulomatosis. 20412702_mPR3high status is associated with generalised not local Wegener granulomatosis and correlates with disease activity and ANCA status 20412704_PR3 and PAR-2- agonists did not induce maturation of human ex vivo DC-like monocytes in Wegener granulomatosis and controls 20423453_REVIEW: structural basis for the different ligand specificities and membrane binding mechanisms of human proteinase 3 and neutrophil elastase 20491791_The increased membrane expression of PR3 found in ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis is not linked directly to circulating PR3 or PR3 gene transcription, but is dependent upon CD177 expression and correlated with the transcription of the CD177 gene. 20530264_cANCAs from Wegener's granulomatosis patients at least in part recognize similar surface structures as do mouse monoclonal antibodies and compete with the binding of alpha1-protease inhibitor to PR3. 20592714_healthy individuals have masked circulating, noncross-reactive, antigen-specific natural autoantibodies against MPO, PR3, and GBM in their serum and IgG fraction 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20828556_The trafficking of precursor NE (proNE) and precursor PR3 (proPR3), was compared. 21193404_neutrophil elastase (NE) and proteinase-3 are capable of almost complete degradation of hemoglobin in vitro 21193407_pivotal role of the NB1-Mac-1 receptor interaction for PR3-ANCA-mediated neutrophil activation 21470489_Suggest that in Wegener's granulomatosis and Churg-Strauss syndrome the cytokine response of the total CD4+ T-cell population and PR3-specific cells is influenced by the underlying disorder. 21700341_membrane-bound PR3 acts as a non-opsonic phagocytosis receptor for bacteria probably by activating PAR2 in neutrophils 22138257_Proteinase 3 carries small unusual carbohydrates and associates with alphalpha-defensins. 22210048_the activity of myeloblastin was significantly altered in the lung adenocarcinoma biopsies harboring a KRAS gene mutation. 22266279_PR3 expression and activity are significantly increased on transmigrating neutrophils; PR3 and NB1/CD177 interactions may play a role in aiding neutrophil transmigration. 22270365_the dual functions (activation/termination) of PR3 in IL-33 biological activity. 22510451_Early plasma exchange in addition to cyclophosphamide/glucocorticoid treatment improves outcome in PR3-ANCA-positive renal vasculitis. 22791638_Some anti-PR3 responses are highly variable across donors. 22844112_Membrane PR3 expressed on apoptotic neutrophils might amplify inflammation by affecting the anti-inflammatory 'reprogramming' of macrophages. 22936713_Proteinase 3 may play a greater role in alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency and COPD 22952809_PAR signaling and serine protease-induced alterations in endothelial function modulate glomerular inflammation via parallel but independent pathways 23202369_Neutrophil proteinase 3 plays a significant role in promoting vascular integrity by signaling through endothelial cell PAR-2. 23380137_Changes in proteinase 3 anti-neutrophil cytoplasm autoantibody levels in early systemic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's) may reflect treatment rather than disease activity. 23911525_It reports the synthesis and enzymatic studies on a new proteinase 3 intermolecular quenched substrate with enhanced selectivity over neutrophil elastase. 23957616_The presence of ANCA in the bile of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a novel finding and highly suggestive of PSC. Biliary IgG ANCA correlates with the severity of bile duct strictures. 24052258_Neutrophil elastase and proteinase-3 trigger G protein-biased signaling through proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1). 24271323_Proteinase 3-anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels are used as a marker for the more severe form of hypertrophic pachymeningitis. 24291125_Lateral flow assay for the determination of IgG-autoantibodies to Pr3. 24719228_Anti-PR3 autoantibodies not detected in sera of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. 24929239_These in vivo data provide, for the first time, compelling evidence of the collateral involvement of cathepsin G, NE, and proteinase 3 in cigarette smoke-induced tissue damage and emphysema 24949444_Elevated levels of GCF proteinase 3 in CP, G-AgP, and gingivitis might suggest that proteinase 3 plays a role during inflammatory periodontal events in host response. 24993595_The data shows that the neutrophil protease PR3 is a direct modulator of human platelets and causes shape change through activation of the Rho/Rho kinase and Ca(2+) signaling pathways. 25092677_Circulating protein levels and enzymatic activity of PRTN3 are markedly elevated in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, and are correlated with increased autoantibodies against beta-cell antigens. 25180606_Proteinase 3-mediated caspase-3 activation controls neutrophil spontaneous death 25416382_these results highlight a potentially important role for proteinase 3 in emphysema. 25461407_Data suggest that targeting proteinase-3 (PR3) specific effector memory cells, to prevent relapse, and instituting anti IL-17 therapy, or modulating Tregs could be newer forms of therapy for granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA). 25788529_miR-634 mimics induced a proinflammatory phenotype in monocyte-derived macrophages, with enhanced expression and release of ADAM17 and IL-6 in Proteinase-3 ANCA-Associated Vasculitis 25927497_ACPA negative rheumatoid arthritis shares the genetic susceptibility loci with ACPA positive disease. 26436651_The PR3-induced microenvironment facilitated recruitment of inflammatory cells, such as macrophages, plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), and neutrophils, which were observed in close proximity within granulomatous lesions in the lungs of GPA patients. 26873743_Report prognostic value of proteinase-3-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody in patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. 26939803_The levels of both NE and PR3 correlated with absolute neutrophil counts and are reduced in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. 26961880_Molecular simulations suggest that PR3 interacts with phosphatidylserine via a small number of amino acids, which engage in long lasting interactions with the lipid heads. As phosphatidylserine is a major component of microvesicles (MVs), this study also examined the consequences of this interaction on MV production and function. 27559009_Studies indicate that the premature activation of proteinase 3 (PR3) would seriously harm the cell by its protease activity. 27752292_Study shows that MPO and PRTN3 in neutrophils of Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) patients with active disease have a distinct pattern of histone modifications, which implicates epigenetic mechanisms in regulating expression of autoantigen genes and suggests that the epigenome may be involved in AAV pathogenesis. 27821628_Changes in the DNA methylation status of the PRTN3 promoter may predict the likelihood of stable remission and explain autoantigen gene regulation 28029757_PRTN3 variants are associated with ANCA-associated vasculitis risk. 28240246_Characterization of the CD177 interaction with the ANCA antigen proteinase 3 responsible for autoimmune diseases has been reported. 28339364_Clinical manifestations varied ANCA-associated vasculitis categories, and neither MPO-ANCA nor PR3-ANCA significantly affected relapse of AAV. 28428279_Our findings demonstrate how RAGE-PR3 interactions between human prostate cancer cells and the bone marrow microenvironment mediate bone metastasis during prostate cancer progression 28546501_unique structural and functional characteristics of PR3 might be key contributors to the systemic inflammation and to the immune dysregulation observed in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. 29079698_this study shows that transgenic mice expressing human Proteinase 3 exhibit sustained neutrophil-associated peritonitis 29132840_A few peptides bound to proteinase 3 (PR3) hydrophobic pockets and inhibited PR3 binding to lipids, while the (KFF)3K d-peptide inshowed a significant affinity for the lipids. 29621735_Our results demonstrate that in the early stage of sepsis, JMJD3 contributes to high levels of neutrophil mPR3 expression and thereby to the production of the inflammatory cytokine IL-1beta 30017196_The lung extracellular matrix is vulnerable to pathological structural changes upon upregulation of serine proteases, including cathepsin G (CG) and proteinase 3 (PR3). 30021768_findings demonstrate a novel mechanism whereby PMN- and AML-associated mP3 inhibits T cell proliferation via direct LRP1 and mP3 interaction, and we identify P3 as a novel target to modulate immunity in myeloid leukemia and autoimmune disease. 30236095_PR3 is involved in triggering inflammatory pathways, disrupting cellular signalling, degrading key structural proteins, and pathogen response.PR3 dysfunction may play a critical role in many processes central to the pathophysiology of COPD and other chronic neutrophilic human diseases. 30880498_The data show that a low P4HA2 and high PRTN3 expression correlates with poor survival in patients with pancreatic cancer, indicating the involvement of collagen deposition in the restraint of the tumor. 30938436_PR3-ANCA-associated vasculitis is strongly associated with the HLA-DPB1 alleles HLA-DPB1*04:01, -DPB1*04:02 and -DPB1*23:01, which share amino acid sequences crucial for the peptide-binding groove. 31125555_Knockdown of PR3 inhibits IkappaBalpha cleavage and enhances the sensitivities of AML cells to differentiation inducers. The level of PR3 mRNA was relatively higher in newly diagnosed AML patients than in those patients with complete remission. PR3 expression and its involvement in IkappaBalpha cleavage might be closely associated with AML. 31490025_A large-scale transcriptome analysis identified ELANE and PRTN3 as novel methylation prognostic signatures for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 31963828_Potent and Broad but not Unselective Cleavage of Cytokines and Chemokines by Human Neutrophil Elastase and Proteinase 3. 31995266_Human proteinase 3 resistance to inhibition extends to alpha-2 macroglobulin. 32303641_Local structural plasticity of the Staphylococcus aureus evasion protein EapH1 enables engagement with multiple neutrophil serine proteases. 32794199_Proteinase 3 Autoreactivity in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated vasculitis-Immunological versus clinical features. 33023023_Immunopathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. 33679731_Pathogenicity of Proteinase 3-Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody in Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: Implications as Biomarker and Future Therapies. 34292081_Proteinase 3 contributes to endothelial dysfunction in an experimental model of sepsis. 35063507_Competitively disrupting the neutrophil-specific receptor-autoantigen CD177:proteinase 3 membrane complex reduces anti-PR3 antibody-induced neutrophil activation. 35341779_Increased Neutrophil elastase and proteinase 3 are closely associated with occurrence and severity of stroke and acute myocardial infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 35602671_Human Proteinase 3, an important autoantigen of c-ANCA associated vasculitis, shares cross-reactive epitopes with serine protease allergens from mites: an in silico analysis. 35672132_Immunological Interaction of HLA-DPB1 and Proteinase 3 in ANCA Vasculitis is Associated with Clinical Disease Activity. |
ENSMUSG00000057729 |
Prtn3 |
35.022556 |
0.0974061269 |
-3.359844 |
0.356083477 |
117.391904 |
0.00000000000000000000000000235596680430114932220068394908741111848504027682090643715174316090759309375718411061484403035137802362442016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000027554730611319303693111113417871964212262696257751592141756074143548078947407731220664572902023792266845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1598993 |
1.5198827 |
63.6751446 |
7.1146450 |
| ENSG00000196436 |
440348 |
NPIPB15 |
protein_coding |
A6NHN6 |
|
Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440348; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
26.554484 |
0.3976058627 |
-1.330589 |
0.494435240 |
7.079536 |
0.00779691767577726183718889174656396789941936731338500976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015283201181204832119764347453383379615843296051025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.5987403 |
4.4704255 |
28.8413854 |
7.7096910 |
| ENSG00000196440 |
100131755 |
ARMCX4 |
protein_coding |
Q5H9R4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The product of this gene belongs to the armadillo repeat-containing family of proteins, which interact with other proteins in a variety of cellular processes. The function of this family member is currently unknown. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2012]. |
hsa:100131755; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
Mouse_homologues 32376790_Human X chromosome exome sequencing identifies BCORL1 as contributor to spermatogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000049804 |
Armcx4 |
108.654887 |
0.3604048124 |
-1.472310 |
0.271949529 |
28.065445 |
0.00000011728134022423385983581586508583960437590576475486159324645996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000459730074986725890600985054701421717027187696658074855804443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.6751290 |
10.9743536 |
160.0531251 |
21.3133148 |
| ENSG00000196449 |
79693 |
YRDC |
protein_coding |
Q86U90 |
FUNCTION: Cytoplasmic and mitochondrial threonylcarbamoyl-AMP synthase required for the formation of a threonylcarbamoyl group on adenosine at position 37 (t(6)A37) in tRNAs that read codons beginning with adenine (PubMed:29760464, PubMed:31481669, PubMed:34545459). Catalyzes the conversion of L-threonine, HCO(3)(-)/CO(2) and ATP to give threonylcarbamoyl-AMP (TC-AMP) as the acyladenylate intermediate, with the release of diphosphate (PubMed:29760464). Participates in t(6)A37 formation in cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNAs (PubMed:29760464). May regulate the activity of some transporters (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3U5F4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29760464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31481669, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34545459}. |
Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transit peptide |
|
Predicted to enable nucleotidyltransferase activity and tRNA binding activity. Acts upstream of or within negative regulation of transport. Predicted to be located in membrane and mitochondrion. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79693; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; double-stranded RNA binding [GO:0003725]; L-threonylcarbamoyladenylate synthase [GO:0061710]; nucleotidyltransferase activity [GO:0016779]; tRNA binding [GO:0000049]; negative regulation of transport [GO:0051051]; regulation of translational fidelity [GO:0006450]; tRNA threonylcarbamoyladenosine modification [GO:0002949] |
12730717_a novel cDNA that encodes a putative human protein with yrdC domain 19279227_hIRIP expression can regulate cargo assembly and function of efflux transporters, including P-glycoprotein, which mediates one of the most common mechanisms of the multidrug resistance 30978526_YrdC promoted the progression of HCC. 31481669_Mutations in YRDC cause an extremely severe form of Galloway-Mowat syndrome (GAMOS), an autosomal recessive disease characterized by early-onset steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome and microcephaly. 34545459_Biallelic variants in YRDC cause a developmental disorder with progeroid features. |
ENSMUSG00000028889 |
Yrdc |
186.684289 |
2.3754712027 |
1.248214 |
0.116970301 |
115.882650 |
0.00000000000000000000000000504269776184047407507611093287794385643472656898489225777079063570555489577629248998391631175763905048370361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000058103215429168935940041395292338492290777598517604697359424035092668667235038526541757164523005485534667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
263.9583629 |
20.9472871 |
112.0264454 |
6.9994751 |
| ENSG00000196466 |
90576 |
ZNF799 |
protein_coding |
Q96GE5 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90576; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
25.908443 |
0.3641663706 |
-1.457330 |
0.456349510 |
10.008817 |
0.00155792521366952905342850854708558472339063882827758789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003520357647544740918588157541080363444052636623382568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.0826042 |
3.8597909 |
36.0242437 |
7.2121376 |
| ENSG00000196476 |
140680 |
C20orf96 |
protein_coding |
Q9NUD7 |
|
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:140680; |
|
Mouse_homologues 17971504_6820408C15Rik is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. |
ENSMUSG00000032680 |
6820408C15Rik |
137.354288 |
0.2276920659 |
-2.134844 |
0.167570812 |
170.451677 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000589544367435076712021000443004337726518686570598999300437390751188283781026194701853443987605568198280547864698064586264081299304962158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000096151103462339586836970153311240886545316104567753619568137335990335128081720767776601568796988623449850663860161148477345705032348632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.9120937 |
5.6563290 |
225.5277630 |
14.7653665 |
| ENSG00000196497 |
79711 |
IPO4 |
protein_coding |
Q8TEX9 |
FUNCTION: Nuclear transport receptor that mediates nuclear import of proteins, such as histones, RPS3A, TNP2 and VDR (PubMed:11823430, PubMed:16207705, PubMed:17682055, PubMed:21454524). Serves as receptor for nuclear localization signals (NLS) in cargo substrates (PubMed:11823430, PubMed:16207705). Is thought to mediate docking of the importin/substrate complex to the nuclear pore complex (NPC) through binding to nucleoporin and the complex is subsequently translocated through the pore by an energy requiring, Ran-dependent mechanism (PubMed:11823430, PubMed:16207705). At the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC, Ran binds to the importin, the importin/substrate complex dissociates and importin is re-exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where GTP hydrolysis releases Ran (PubMed:11823430). The directionality of nuclear import is thought to be conferred by an asymmetric distribution of the GTP- and GDP-bound forms of Ran between the cytoplasm and nucleus (PubMed:11823430). Mediates the nuclear import of the histone H3-H4 dimer when in complex with ASF1 (ASF1A or ASF1B) (PubMed:21454524, PubMed:29408485). Mediates the ligand-independent nuclear import of vitamin D receptor (VDR) (PubMed:16207705). In vitro, mediates the nuclear import of human cytomegalovirus UL84 by recognizing a non-classical NLS (PubMed:12610148). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11823430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12610148, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16207705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17682055, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21454524, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29408485}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Nucleus;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable nuclear import signal receptor activity and nuclear localization sequence binding activity. Involved in DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly; DNA replication-independent chromatin assembly; and protein import into nucleus. Located in chromatin. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79711; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; nuclear import signal receptor activity [GO:0061608]; nuclear localization sequence binding [GO:0008139]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; protein localization to nucleus [GO:0034504] |
16207705_demonstrated that vitamin D receptor (VDR) has two nuclear import systems: ligand-dependent & ligand-independent pathways, & that importin 4 fulfills the ligand-independent nuclear transport through the interaction with the amino terminus of VDR 19788888_importins 4 and 7 accomplish nuclear import of HIF-1alpha more efficiently than the classical importin alpha/beta NLS receptor. 20805509_report a function of IPO4 and nuclear import in the Fanconi anemia pathway of DNA repair 27528606_Importins, Impbeta, Kapbeta2, Imp4, Imp5, Imp7, Imp9, and Impalpha, show the H3 tail binding more tightly than the H4 tail. The H3 tail binds Kapbeta2 and Imp5 with KD values of 77 and 57 nm, respectively, and binds the other five Importins more weakly. 28254634_Study identified a core region encompassing nt - 118 to + 108 of IPO4 gene that is necessary for its promoter activity. Transcription factors binding to this region were screened, resulting in the identification of two members of the Ets family, Ets-like transcription factor-1 and GA binding protein, which repress or activate its promoter activity, respectively. 30861176_Importin-4 functions as a driving force in human primary gastric cancer. 32661323_Inhibiting Importin 4-mediated nuclear import of CEBPD enhances chemosensitivity by repression of PRKDC-driven DNA damage repair in cervical cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000002319 |
Ipo4 |
224.557471 |
2.3938079857 |
1.259307 |
0.110704395 |
132.849537 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000097530383983220998421930777924221026760791721831905795982396407070746224502526505566180059503267330001108348369598388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000012773278328237283953284000244974213618488671461065081220635281519642133119386666340044911294171470217406749725341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
321.9712732 |
22.3886005 |
135.5399879 |
7.7009565 |
| ENSG00000196502 |
6817 |
SULT1A1 |
protein_coding |
P50225 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the sulfate conjugation of a wide variety of acceptor molecules bearing a hydroxyl or an amine groupe. Sulfonation increases the water solubility of most compounds, and therefore their renal excretion, but it can also result in bioactivation to form active metabolites. Displays broad substrate specificity for small phenolic compounds. Plays an important role in the sulfonation of endogenous molecules such as steroid hormones and 3,3'-diiodothyronin (PubMed:16221673, PubMed:12471039, PubMed:22069470, PubMed:21723874, PubMed:10199779, PubMed:7834621). Mediates the sulfate conjugation of a variety of xenobiotics, including the drugs acetaminophen and minoxidil (By similarity). Mediates also the metabolic activation of carcinogenic N-hydroxyarylamines leading to highly reactive intermediates capable of forming DNA adducts, potentially resulting in mutagenesis (PubMed:7834621). May play a role in gut microbiota-host metabolic interaction. O-sulfonates 4-ethylphenol (4-EP), a dietary tyrosine-derived metabolite produced by gut bacteria. The product 4-EPS crosses the blood-brain barrier and may negatively regulate oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination, affecting the functional connectivity of different brain regions associated with the limbic system. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P17988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10199779, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12471039, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16221673, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21723874, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22069470, ECO:0000269|PubMed:35165440, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7834621}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Catecholamine metabolism;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Lipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Transferase |
|
Sulfotransferase enzymes catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs, and xenobiotic compounds. These cytosolic enzymes are different in their tissue distributions and substrate specificities. The gene structure (number and length of exons) is similar among family members. This gene encodes one of two phenol sulfotransferases with thermostable enzyme activity. Multiple alternatively spliced variants that encode two isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6817; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate binding [GO:0050656]; aryl sulfotransferase activity [GO:0004062]; flavonol 3-sulfotransferase activity [GO:0047894]; steroid sulfotransferase activity [GO:0050294]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate metabolic process [GO:0050427]; amine metabolic process [GO:0009308]; catecholamine metabolic process [GO:0006584]; estrogen metabolic process [GO:0008210]; ethanol catabolic process [GO:0006068]; flavonoid metabolic process [GO:0009812]; sulfation [GO:0051923]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
11156380_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11207031_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11219777_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11692076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11692076_The high activity SULT1A1*1 allozyme protects against dietary and/or environmental chemicals involved in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. 11804685_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11804685_genetic polymorphism in SULT1A1 gene may be associated with increased lung cancer risk 12162852_7-OH-flavone sulfotransferase followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics 12165038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12165038_The SULT1A1 R213H polymorphism is not linked with colorectal cancer in an elderly Australian population. 12402313_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12419790_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12419790_There is an an association between genotype and survival of breast cancer patients receiving tamoxifen therapy 12419832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12455060_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12455060_SULT1A1 his(213) allele is important in the development of esophageal cancer in men. 12468438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12469224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12469224_the relationship among the polymorphisms of this enzyme and SULT1A2 in different types of cancers in Taiwanese 12471039_the crystal structure of SULT1A1 provides the molecular basis for substrate inhibition and how the enzyme sulfonates a wide variety of lipophilic compounds 12725421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12761191_the differential substrate specificity of the two enzymes M-PST and P-PST for the thirteen drug compounds tested 12814450_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12867416_study of arginine residues in the active site of human phenol sulfotransferase 12867492_P. 1038 '...clearly expressed...SULT1A1...' P. 1040 '...SULT1A1...which belongs to phase II metabolism,...significantly expressed in HepG2.' 14520706_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14618622_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14618622_We conclude that smoking increases risk of colorectal adenomas and that SULT1A1 and NAT2 only modestly modify this association. 14642079_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14643027_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14643027_Sulfotransferase 1A1 polymorphism is associated with bladder cancer 14648207_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14648207_SULT1A1 slow acetylator genotype might modulate the effect of carcinogenic arylamines contained in tobacco smoke, and has a tendency to present a higher risk for highly differentiated tumors among heavy-smokers. 14688021_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14688021_SULT1A1 polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to lung cancer in relation to tobacco smoking 14871892_In SULT1A1, substrate inhibition occurs with pNP as the substrate but not with dopamine; residue Phe-247 of SULT1A1, which interacts with both p-nitrophenol molecules in the active site, is important for substrate inhibition 14973106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15090717_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15093672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15093672_SULT1A1 His allele was positively associated with the risk of breast cancer in Chinese women 15122594_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15318931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15377847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15383623_SULT1A1 promoter was shown to be dependent on the presence of Sp1 and Ets transcription factor binding sites. 15455371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15516026_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15604994_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15632378_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15743503_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15894657_No significant association found for breast cancer risk. 15894657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15949571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15952058_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15970794_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15987423_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16080486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16103451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16133548_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16133548_SULT1A1*2 and SULT1A2*2 are the major allelic variants in the Korean population. 16137826_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16141802_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16175316_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16175316_Postmenopausal women carrying the variant SULT1A1 His allele may be more susceptible to estrogen-induced carcinogenesis in mammary tissue. 16221673_x-ray crystallographic structure of human SULT1A1 with estradiol 16232327_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16272171_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16280036_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16284375_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16317586_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16317586_SULT1A1 genotype did not correlate with any prognostic or predictive markers associated with breast cancer. 16328031_Progressive SULT1A1 methylation within the promoter area of the gene occurs during breast carcinogenesis. 16380991_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16395669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16402077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16418064_Sulfation of resveratrol in human liver: evidence of a major role for the sulfotransferases SULT1A1. 16425401_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16504378_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16575574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16637266_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16875543_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16926176_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16985032_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16985250_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16985250_The SULT1A1*2 allele and long-term use of estrogen replacement therapy were associated with statistically significantly higher risk of endometrial cancer 17013894_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17074589_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17074589_Results indicate that the SULT1A1 genotype may play an important role in the risk of developing lung cancer, especially in cigarette smokers. 17189289_The presence of SULT1A1 gene deletions and duplications, representing an additional source of variability in the metabolic activity of this enzyme, is demonstrated. 17244352_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17274372_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17293380_Apigenin, epicatechin, and resveratrol exhibited SULT1a1 allele-specific variation in sulfation, with SULT1A1*1 and *3 acting as normal-activity allozymes and SULT1A*2 as low-activity allozyme. 17372239_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17372243_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17479406_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17603900_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17605044_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17605044_SULT1A1 polymorphism is associated with primary brain tumors 17619904_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17619904_SULT1A1 polymorphism is associated with urothelial cancer 17912498_Increased generation of urinary 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine was found in betel-quid chewers with SULT1A1 and GSTP1 genotypes that affect susceptibility to DNA damage. 17912498_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17947222_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17996038_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18006944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18259693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18259693_SULT1A1/SULT1A2 gene complex showed suggestive haplotypic association in the family-based cardiovascular disease study, with the greatest increase in risk conferred by the SULT1A2 235T allele 18264785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18318428_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18318428_a decreased single nucleotide polymorphism of CYP1A1 and an increased single nucleotide polymorphism for SULT1A1 and SULT1E1 genes may be risk factors for endometrial cancer in Caucasians. 18365755_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18365755_The aim of the study was to investigate NAT1, NAT2, GSTM1, GSTT1, GSTP1, SULT1A1, XRCC1, XRCC3 and XPD genetic polymorphisms, coffee consumption and risk of bladder cancer (BC) through a hospital-based case-control study. 18368507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18368507_The study showed a null association of SULT1A1 polymorphism with familial prostate cancer risk in the Japanese population. 18447907_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18497059_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18497059_SULT1A1 polymorphism is associated with ovarian cancer 18499698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18499698_The CYP1A2 and NAT1 but not SULT1A1 and NAT2 genotypes showed significant interactions with heavy smoking in women not men 18632753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18794456_SULT1A1 mRNA is expressed in human skin, at similar levels in men and women. SULT1A1 levels are not altered by topical 17-beta-estradiol treatment. 18854828_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18854828_The SULT1A1*2 revealed contrasting risk association for upper aerodigestive tract cancers and conferred significant increased risk of breast cancer to Asian but not Causcasian women in patients with multiple tobacco-related cancers 18990750_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18990750_Red meat intake was associated with increased colorectal cancer regardless of genotype, but the SULT1A1-638G>A variant modified the association between meat doneness and cancer risk. 19120511_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19120511_SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism is associated with the development of urothelial cancer, especially among cigarette smokers exposed to hazardous chemicals. 19126640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19126640_SULT1A1 gene is a risk modifier on environmental carcinogen in OSCC and the association of SULT1A1 haplotypes with the risk of OSCC might be modified by betel quid chewing. 19237513_he importance of human SULT1A1 as a homodimer was to maintain its structural stability, and the change of secondary structure was responsible for alternating its quaternary structure 19307236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19322015_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19322015_SULT1A1 genetic polymorphisms might modify the arsenic methylation profile and urothelial carcinoma progression. 19339270_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19350537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19350537_The variant SULT1A1 genotype (SULT1A1*1/SULT1A1*2 or SULT1A1*2/SULT1A1*2) was associated with a significantly increased lung cancer risk in cases. 19424794_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19484729_human CYP2E1 and SULT1A1 activate an endogenous cellular molecule or a medium component to become mutagenic 19575027_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19706609_para-Nitrophenyl sulfate activation of human sulfotransferase 1A1 is consistent with intercepting the E[middle dot]PAP complex and reformation of E[middle dot]PAPS. 19776291_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19863350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19904771_study demonstrates that the loss of SULT1A1 appears to be a characteristic molecular signature of hepatocellular carcinoma. 19906068_The interaction between SULT1A1 and CYP1A2 can play an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis in the Chinese population. 19949855_Meta-analysis did not find a significant general relationship between SULT1A1 R213H polymorphism & the risk of breast cancer, but ethnic population analysis revealed a significantly increased breast cancer risk for HH allele carriers among Asians. 19949855_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19956635_Uncategorized study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20032816_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20142249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20192879_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20204402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20214802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20309015_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20417180_the structures of SULT1A2 and an allozyme of SULT1A1, SULT1A1 *3, bound with 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate at 2.4 and 2.3A resolution, respectively, were determined. 20437850_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20505544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20505990_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20528568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20529763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20565970_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20620409_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628863_Only NAT1 showed a significant lower DNA methylation rate in the control group than in the tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer group, and no significant difference in methylation was found in COMT, CYP1A1, CYP2D6, and SULT1A1 genes. 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20663177_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20663177_Polymorphism of SULT1A1 Arg213His is associated with breast cancer. 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881232_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20881232_SULT1A1 1/2 does not contribute to the variation in SULT1A1 enzymatic activity when the 3'-UTR SNPs are included in the statistical model 20936502_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20936502_the statistical hypothesis that SULT1A1 and SULT1A2 alleles are independently distributed was rejected; a strongly positive linkage was detected between SULT1A1*2 and SULT1A2*2 alleles in Turkey population 21072184_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21111704_mechanism of SULT1A1-catalyzed sulfation of adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate by para-nitrophenyl sulfate 21670965_SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism, ethnicity, and smoking may modulate environment-related cancer risk. 21695180_This meta-analysis demonstrates that there is no association between the SULT1A1 R213H polymorphism and colorectal cancer. 21977969_Women in Siberia with SNPS in CYP1A1 gene, in CYP1A2 gene,and in the SULT1A1 gene have an increased risk of development of breast cancer . 22011087_SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism is associated with breast cancer. 22081606_Stp1 is important for appropriate regulation of Stk1 function, hemolysin activity, autolysis, and GBS virulence 22524828_Arg213His polymorphism is not associated with lung cancer. 22678655_discussion of possible association between lower-activity of SULT1A1 with sudden cardiac death (both holiday sudden cardiac death in older adults and sudden infant death syndrome) [REVIEW] 22708928_We observed a previously unreported association between the SULT1A1 rs9282861 genotype and overall survival of breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy or tamoxifen. 23080433_The functional significance of the single nucleotide polymorphisms/haplotypes located upstream of the SULT1A1 start codon. 23157889_SULT1A1 variant allele increases breast cancer risk among subjects who were exposed to high smoked meat intake. 23358261_resequenced the SULT1A2 and SULT1A2 genes and identified 51 variations in ethnic Koreans, including 9 that were previously unknown. Allele frequencies, haplotype structures, LD blocks, and haplotype-tagging SNPs were determined. 23711090_Association between BRCA2 mutation and SULT1A1 gene deletion in male breast cancer emerged. 24010997_The SULT1A1 genetic variability is associated with cancer risk and response to therapy (review). 24039991_Data indicate that protein-ligand interaction energy by using docking Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships(QSAR) models showed accuracy of 67.28%, 78.00% and 75.46%, for the isoforms SULT1A1, SULT1A3 and SULT1E1, respectively. 24307569_The SNP rs9282861 with GG genotype of SULT1A1 was associated with an elevated risk of total neural tube defects. 24763827_The results of this meta-analysis indicate that the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism is associated with the risk bladder cancer under a recessive model. 25103078_The present study provided epidemiological evidence for a significantly increased risk of UCB in ever smokers with the Ala/Ala genotype of the GSTO1 gene and the Arg/Arg genotype of the SULT1A1 gene. 25194687_that SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism is associated with bladder cancer risk. 25225888_the SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism may contribute UADT cancer risk, but didn't show any association with breast cancer. 25314023_3'-Phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate binds antisynergistically to the subunits of the SULT1A1 dimer. 25370010_SULT1A1 is responsible for bioactivation of food genotoxicants 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfuryl alcohol. 25385181_Results indicate that SULT1A1 Arg(213)His may act as a low-penetrance risk allele for developing MBC and could be associated with a specific tumor subtype associated with HER2 overexpression. 25654087_The aim of the study was to assess whether selected single nucleotide polymorphisms of CYP1A1 and 2E1, GSTM1, GSTT1, and SULT1A1 influence susceptibility towards hepatocellular carcinoma. 25771868_Sulfo-conjugation of the multi-hydroxylated metabolites of benzene by human SULT1A1 may represent an important detoxifying pathway. 25819444_Data suggest that the substrate specificities of SULT1E1 and SULT1A1*1 include metabolites of tamoxifen (endoxifen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, and N-desmethyltamoxifen); these metabolites are weak inhibitors of sulfation of estradiol by SULT1E1/SULT1A1*1. 26022216_Higher SULT1A1 levels were observed in rats as well as in humans exposed to high altitude, when compared to sea-level controls 26067475_A systematic analysis showed that three of the twelve human SULTs, SULT1A1, SULT1A3 and SULT1C4, displayed the strongest sulphating activity towards acetaminophen. 26169578_It metabolizes breast cancer drugs like afimoxifene and endoxifen by sulfation. 26340710_Sulfotransferase 1A1 Substrate Selectivity: A Molecular Clamp Mechanism. 26455829_The polymorphism of SULT1A1*2 is not associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk. 26906565_Cytosolic sulfotransferase 1A1 regulates HIV-1 minus-strand DNA elongation in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages. 27207664_We conclude from these studies that SULT1A1 is involved in the bioactivation of AA-I through the sulfonation of AL-I-NOH, contributing significantly to the toxicities of AA observed in vivo. 27221864_SULT1A1 high Copy Number Variation on high Estrogen Concentration and Tamoxifen-Associated Adverse Drug Reactions in Premenopausal Thai Breast Cancer. 27300114_SULT1A1 gene copy number affected the minor allele frequency for each single nucleotide polymorphisms tested. Before administration of exogenous hormones, increasing number of G alleles at rs9282861 was associated with earlier age at menopause, lower frequency of night sweats, and less severe insomnia. Variability in onset of menopause and symptoms before initiation of hormone therapy is partly due to SULT1A1 variation. 27356022_Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) displays high affinity and specificity for SULT1A1. The allosteric network is shown to involve 14 distinct complexes. ECGG binds both the allosteric site and, relatively weakly, the active site of SULT1A1. 28160022_SULT1A1 role in the metabolic detoxification of heterocyclic aromatic amines 28326452_The importance of SULT1A1 genotype for hepatic methyleugenol DNA adducts in humans, and a strong impact of SULT1A1 copy number variations on SULT1A1 hepatic phenotype. 28523759_Silencing the SULT1A1 gene led to changes in resveratrol metabolism, with higher intracellular accumulation of the nonmetabolized resveratrol. 28589969_the NQO1 Pro187Ser or SULT1A1 Arg213His polymorphism combination with smoking significantly confer susceptibility to BC. [META-ANALYSIS] 28867356_SULT1A1 copy number variation was negatively correlated with estrone-sulfate to estrone ratio predominantly in males (E1S/E1; p=0.03, r=-0.21) and may be associated with increased risk for common allergies. 28887105_No significant difference was observed in the RNA levels of CYP1A1 and SULT1A1 between the two groups. The frequency of expression of the CYP17 T/C variant tended to be higher and the A allele of COMT polymorphism together with down-regulation of its mRNA expression may be more frequent in Chinese women with idiopathic POI 29110586_This study demonstrates that the presence of His allele and Gln allele in case of SULT1A1 rs9282861 and XRCC1 rs25487, respectively, involve in lung cancer prognosis in Bangladeshi population. 29233949_SULT1A1 Arg213His (rs9282861) polymorphism might be associated with breast cancer risk, especially among Asian population. 29790428_Different ethnic and racial populations have varying degrees of SULT1A1-mediated sulfation activity. 29908303_Suggest SULT1A1/1A2 play a central role in furfuryl alcohol bioactivation and the formation of hemoglobin adducts. 30120701_Patients were categorized in three groups depending on the decreased SULT1A1 activity due to rs6839 and rs1042157: low activity group (rs6839 (GG) and rs1042157 (TT)); high activity group (rs6839 (AA) and rs1042157 (CC)); and medium activity group (all the other combinations of rs6839 and rs1042157). Associations between SULT1A1 phenotypes and clinical outcome (RFS) were explored 31671219_Prediagnostic circulating inflammation biomarkers and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A case-cohort study in Japan. 31835852_These findings highlight the key insights of structural consequences caused by R213H mutation, which would enrich the understanding regarding the role of SULT1A1 mutation in cancer development. 32152050_Interaction of the Brain-Selective Sulfotransferase SULT4A1 with Other Cytosolic Sulfotransferases: Effects on Protein Expression and Function. 33049293_Evaluation of a conserved tryptophanyl residue in donor substrate binding and catalysis by a phenol sulfotransferase (SULT1A1). 33297275_Investigating the molecular mechanism of hydroxylated bromdiphenyl ethers to inhibit the thyroid hormone sulfotransferase SULT1A1. 34162941_Insights into the substrate binding mechanism of SULT1A1 through molecular dynamics with excited normal modes simulations. |
ENSMUSG00000000739 |
Sult5a1 |
75.537020 |
0.3372502776 |
-1.568108 |
0.245357473 |
40.714473 |
0.00000000017617752295396652411559189043148594688847907718809437938034534454345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000894523645958220117002513618057130476146632247491652378812432289123535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.8804316 |
6.0221506 |
104.1364922 |
11.8922103 |
| ENSG00000196507 |
85012 |
TCEAL3 |
protein_coding |
Q969E4 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the transcription elongation factor A (SII)-like (TCEAL) gene family. Members of this family contain TFA domains and may function as nuclear phosphoproteins that modulate transcription in a promoter context-dependent manner. Multiple family members are located on the X chromosome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding a single isoform. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:85012; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; WW domain binding [GO:0050699] |
10051408_Characterizes TCEAL1, another member of the human TCEAL gene family. |
ENSMUSG00000044550+ENSMUSG00000031409+ENSMUSG00000054034 |
Tceal3+Tceal6+Tceal5 |
47.382621 |
0.4575480367 |
-1.128005 |
0.303827656 |
13.756499 |
0.00020809961701888924343918640946782261380576528608798980712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000543444859730857275474658063529886931064538657665252685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.7485019 |
5.8336961 |
65.3593503 |
8.7243015 |
| ENSG00000196535 |
399687 |
MYO18A |
protein_coding |
Q92614 |
FUNCTION: May link Golgi membranes to the cytoskeleton and participate in the tensile force required for vesicle budding from the Golgi. Thereby, may play a role in Golgi membrane trafficking and could indirectly give its flattened shape to the Golgi apparatus (PubMed:19837035, PubMed:23345592). Alternatively, in concert with LURAP1 and CDC42BPA/CDC42BPB, has been involved in modulating lamellar actomyosin retrograde flow that is crucial to cell protrusion and migration (PubMed:18854160). May be involved in the maintenance of the stromal cell architectures required for cell to cell contact (By similarity). Regulates trafficking, expression, and activation of innate immune receptors on macrophages. Plays a role to suppress inflammatory responsiveness of macrophages via a mechanism that modulates CD14 trafficking (PubMed:25965346). Acts as a receptor of surfactant-associated protein A (SFTPA1/SP-A) and plays an important role in internalization and clearance of SFTPA1-opsonized S.aureus by alveolar macrophages (PubMed:16087679, PubMed:21123169). Strongly enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity (PubMed:27467939). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9JMH9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16087679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18854160, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19837035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21123169, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23345592, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25965346, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27467939}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Golgi apparatus;Motor protein;Myosin;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene can bind GOLPH3, linking the Golgi to the cytoskeleton and influencing Golgi membrane trafficking. The encoded protein is also part of a complex that assembles lamellar actomyosin bundles and may be required for cell migration. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:399687; |
actomyosin [GO:0042641]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; myosin filament [GO:0032982]; myosin II complex [GO:0016460]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; ADP binding [GO:0043531]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA [GO:0008094]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; actomyosin structure organization [GO:0031032]; asymmetric Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090164]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; DNA metabolic process [GO:0006259]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; Golgi ribbon formation [GO:0090161]; Golgi vesicle budding [GO:0048194]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of opsonization [GO:1903028]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; regulation of macrophage activation [GO:0043030] |
12829915_Expression of TIAF-1 in the lymphocytes during chronic allograft rejection may be related to the predominance of a Th2 response in this condition and may protect these cells from apoptosis 14965474_TIAF1 and p53 functionally interact in regulating apoptosis, and TIAF1 is likely to participate in the nuclear translocation of activated p53. 15835906_this dimeric myosin might stably cross-link actin filaments by two ATP-insensitive actin-binding sites at the N-terminal domains for higher-order organization of the actin cytoskeleton 16087679_MyoXVIIIA constitutes a novel receptor for SP-A 18443188_These findings support the hypothesis that SP-A, via SP-R210, suppresses cell-mediated immunity against M. tuberculosis via a mechanism that up-regulates secretion of IL-10 and TGF-beta1.[SP-A receptor] 19006078_Study used a DNA-based long-distance inverse PCR (LDI-PCR) to identify a new MYO18A-PDGFRB fusion gene in an Eos-MPN (eosinophilia-associated atypical myeloproliferative neoplasms) with associated t(5;17)(q33-34;q11.2). 19837035_GOLPH3 bridges phosphatidylinositol-4- phosphate and actomyosin (via MYO18A) to stretch and shape the Golgi to promote budding. 19923322_MYO18A is a novel binding partner of the PAK2/betaPIX/GIT1 complex and suggest that MYO18A may play an important role in regulating epithelial cell migration via affecting multiple cell machineries. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21368882_TIAF1 undergoes self-aggregation in response to TGF-Beta1. 21751808_Myo18aalpha as a novel binding partner of ezrin; the Myo18aalpha/ezrin complex may facilitate B cell receptor-mediated signaling 22534828_In vitro induction of TIAF1 self-association upregulated the expression of tumor suppressors Smad4 and WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WOX1 or WWOX), and WOX1 in turn increased the TIAF1 expression. 23345592_GOLPH3L differs critically from GOLPH3 in that it is largely unable to bind to MYO18A; data demonstrate that despite their similarities, unexpectedly, GOLPH3L antagonizes GOLPH3/MYO18A at the Golgi 23990465_PDZ module mediates direct binding of myosin-18A to GOLPH3, and this interaction in turn modulates the actin binding properties of the N-terminal extension. Thus, myosin-18A can act as an actin cross-linker with multiple regulatory modulators 24485452_Identification of the DNA-damage-induced Golgi response reveals an unexpected pathway through DNA-PK, GOLPH3, and MYO18A that regulates cell survival following DNA damage. 27528748_Studies indicate that MYO18A is overexpressed in metastatic prostate cancer (PC-3) cells. 28942352_a high proportion of MYO18A is found in complex with GOLPH3 at the trans Golgi, where it functions to promote vesicle budding for Golgi-to-plasma membrane trafficking. |
ENSMUSG00000000631 |
Myo18a |
764.337635 |
0.4698296885 |
-1.089790 |
0.079818506 |
185.777376 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000265516802615396444574821276487476730385930456253417323445577647980577372440420682331485604314896423815169751968257028096331850974820554256439208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000046990743484451452723861367722648479519950571479677993835940373228912766879420914627300594595420559783957407951060503137341584078967571258544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
491.6168474 |
39.1134169 |
1053.8308413 |
59.5450111 |
| ENSG00000196547 |
4122 |
MAN2A2 |
protein_coding |
P49641 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the first committed step in the biosynthesis of complex N-glycans. It controls conversion of high mannose to complex N-glycans; the final hydrolytic step in the N-glycan maturation pathway. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
Predicted to enable alpha-mannosidase activity. Predicted to be involved in N-glycan processing and protein deglycosylation. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:4122; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; alpha-mannosidase activity [GO:0004559]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing N-glycosyl compounds [GO:0016799]; mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,3-1,6-alpha-mannosidase activity [GO:0004572]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; mannose metabolic process [GO:0006013]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491]; protein deglycosylation [GO:0006517]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
33141432_High glucose-ROS conditions enhance the progression in cholangiocarcinoma via upregulation of MAN2A2 and CHD8. |
ENSMUSG00000038886 |
Man2a2 |
269.869188 |
0.2883169829 |
-1.794272 |
0.331778779 |
27.142565 |
0.00000018899059322886020987240990928052175590323713549878448247909545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000724545754820253645917015657834658881597533763851970434188842773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
119.6110420 |
26.0180614 |
415.5717186 |
64.4824473 |
| ENSG00000196549 |
4311 |
MME |
protein_coding |
P08473 |
FUNCTION: Thermolysin-like specificity, but is almost confined on acting on polypeptides of up to 30 amino acids (PubMed:6349683, PubMed:6208535, PubMed:15283675, PubMed:8168535). Biologically important in the destruction of opioid peptides such as Met- and Leu-enkephalins by cleavage of a Gly-Phe bond (PubMed:6349683, PubMed:17101991). Catalyzes cleavage of bradykinin, substance P and neurotensin peptides (PubMed:6208535). Able to cleave angiotensin-1, angiotensin-2 and angiotensin 1-9 (PubMed:6349683, PubMed:15283675). Involved in the degradation of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) and brain natriuretic factor (BNP(1-32)) (PubMed:2531377, PubMed:2972276, PubMed:16254193). Displays UV-inducible elastase activity toward skin preelastic and elastic fibers (PubMed:20876573). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15283675, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17101991, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20876573, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2531377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27588448, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2972276, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6208535, ECO:0000269|PubMed:6349683}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Myristate;Neurodegeneration;Neuropathy;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Spinocerebellar ataxia;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein and a common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen that is an important cell surface marker in the diagnosis of human acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). The encoded protein is present on leukemic cells of pre-B phenotype, which represent 85% of cases of ALL. This protein is not restricted to leukemic cells, however, and is found on a variety of normal tissues. The protein is a neutral endopeptidase that cleaves peptides at the amino side of hydrophobic residues and inactivates several peptide hormones including glucagon, enkephalins, substance P, neurotensin, oxytocin, and bradykinin. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:4311; |
axon [GO:0030424]; brush border [GO:0005903]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection terminus [GO:0044306]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; synapse [GO:0045202]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; cardiolipin binding [GO:1901612]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; exopeptidase activity [GO:0008238]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; oligopeptidase activity [GO:0070012]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; phosphatidylserine binding [GO:0001786]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; aging [GO:0007568]; amyloid-beta clearance [GO:0097242]; amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process [GO:0150094]; amyloid-beta metabolic process [GO:0050435]; bradykinin catabolic process [GO:0010815]; cellular response to cytokine stimulus [GO:0071345]; cellular response to UV-A [GO:0071492]; cellular response to UV-B [GO:0071493]; creatinine metabolic process [GO:0046449]; hormone catabolic process [GO:0042447]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; lung development [GO:0030324]; neuropeptide processing [GO:0061837]; peptide metabolic process [GO:0006518]; placenta development [GO:0001890]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; positive regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050769]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; replicative senescence [GO:0090399]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; substance P catabolic process [GO:0010814] |
9857225_We describe the down-regulation of neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (NEP) protein expression in RCC of the clear cell/chromophilic type when compared with renal parenchyma, and show for the first time the lack of enzyme activity of NEP in RCC. 11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11849775_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11906289_Toward an optimal joint recognition of the S1' subsites of endothelin converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), and neutral endopeptidase (NEP). 12070597_stromal expression of CD10 in breast cancer is an important novel prognostic factor 12087466_a marker for cycling cells with propensity for apoptosis in childhood ALL 12102663_expressed at high levels in sebaceous glands of acne patients 12105192_Abeta 42-induced increase in neprilysin is associated with prevention of amyloid plaque formation in vivo 12140380_CD10 antigen is upregulated during the process of metastasis in melanomas. It is rare in primary melanomas. 12150966_role of two C-terminal cysteines in proper folding 12203213_CD10 expression is an integral part of colorectal carcinogenesis and seems to contribute to the invasion and thus probably facilitates metastasis 12387451_Expression declines in Alzheimer disease vasculature; possibly involved in cerebral amyloid angiopathy 12393702_CD10 expression in hematopoitic cells denotes commitment to B-cell and natural killer cells lineages. 12447961_CD5-negative, CD10-negative small B-cell leukemia: variant of chronic lymphocytic leukemia or a distinct entity 12485446_elevated neutral endopeptidase activity in the skin and chronic ulcers of subjects with diabetes combined with peripheral neuropathy may contribute to deficient neuroinflammatory signaling and may impair wound healing in subjects with diabetes. 12527400_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12527400_no association between polymorphisms in the promoter region and Swedish Alzheimer's disease patients 12657655_In transgenic mouse models of amyloidosis, unilateral intracerebral injection of Lenti-Nep reduced amyloid-beta deposits and ameliorated neurodegenerative alterations in the frontal cortex and hippocampus 12754344_nep gene polymorphism is associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. 12785004_The modulator effect of vitamin E and C on NEP membrane enzyme activity after exposure to fatty acid stimulation suggests that lipid oxidation may activate NEP. 14550292_Independent signals determine the subcellular localization of NEP in prostate cancer cells 14673956_Activity of NEP in prostate cancer cells is regulated by bombesin and il-1beta with IL-1beta acting as modulator of cellular differentiation. 14739539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14739539_the GT-repeat polymorphism in the promoter region of the neprilysin gene or some other unknown polymorphisms, which are in a linkage disequilibrium, confer a susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease 14747736_x-ray crystallographic study of neprilysin 14749444_Gene transfer of human neprilysin abolished the increase in Abeta levels in the hippocampus of neprilysin-deficient mice and also reduced the increase in young mutant amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice and to retard development of amyloid pathology 14767532_CD10 has a role in preventing proliferation or differentiation of non-neoplastic and neoplastic hepatocytes 14968440_NEP mRNA and protein are expressed mainly by the epithelial cells and to a minor extent by the stromal cells of human prostate glands. 15100223_endogenous targeting signal in wild-type neprilysin is well optimized for the overall neuronal clearance of Abeta 15205682_CD10 expression was found significantly higher in metastatic than in primary tumors. 15217945_decreased NEP expression might contribute to progression of prostate cancer; methylation is an important mechanism of NEP protein silencing 15283675_We have examined the kinetics of angiotensin peptide cleavage by full-length human ACE, the separate N- and C-domains of ACE, the homologue of ACE, ACE2, and NEP (neprilysin). 15286660_Statistical analysis showed significant association of CD10-positive tumors with clinicopathologic aggressiveness and mitotic figures. 15294904_A three-dimensional model of the neprilysin 2 active site based on the X-ray structure of neprilysin. 15464186_truncating mutations in MME gene in fetomaternal alloimmunisation and antenatal membranous glomerulopathies. 15469471_CD10-stained bile canalicular pattern becomes increasingly reduced with the advance of fibrosis or the presence of severe lobular inflammation or extensive metastases 15502805_CD10 was found in the majority of clear cell renal cell carcinomas. 15548496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15578072_CD10 is a superior marker for distinguishing between a hemangioblastoma and a metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 15720419_CD10 positivity was associated with an excellent 8-year overall survival in the low-risk IPI (International Prognostic Index) patients. 15785408_Expressed in a case of microvillous atrophy. 15860464_Genetic variation close to Neprilysin gene may influence the susceptibility to Alzheimer disease in Chinese population. 15860464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15870909_Dexamethasone is a potent modulator of NEP on immature B-lymphocytes. 15945081_Results conclude that CD10 has limited value in confirming the diagnosis of primary conventional renal-cell adenocarcinoma because of its low specificity. 16123216_data identify CD10- cytoplasmic immunoglobulin-positive pre-B ALL as a rare (2.2%) but distinct immuno-subtype of adult ALL that is characterized by a high MLL rearrangement rate and a worse outcome 16226260_Significant decrease in neprilysin mRNA levels in both Alzheimer's disease and normal elderly subjects with amyloid plaques compared to control cases was found. 16400325_CD10 expression may serve as an additional discriminating criterion. 16652149_NEP is implicated as a major regulator of neuropeptide-stimulated RhoA kinase signaling in prostate cancer cells; NEP inhibits neuropeptide activation of RhoA. 16700740_expression can, perhaps, have an important role in tumor invasion, probably facilitating the occurrence of metastases 16722930_CD10 expression is significntly greater in mucinous cystdenomas than in intraductal papillary mucinous adenomas. 16857799_CD10 may have a role in progression of endometrioid neoplasms of the female genital tract 16877296_the accumulation of Tat-derived proteolytic fragments may serve to inhibit neprilysin and increase amyloid beta peptide levels 16900210_biphasic pattern of CD10 epression in differentiating B cells is not controlled by methylation of the promoter 16900384_Careful monitoring of anti-NEP Ab titer and subclass is mandatory in NEP-deficient mothers during their pregnancies. 16940054_neprilysin proteolytically inactivates fibroblast growth factor-2, resulting in negative regulation of angiogenesis 16943769_Neprilysin activity and amyloid beta concentrations displayed converse changes in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. 16948517_CD10 is a useful additional immunostain for the discrimination of renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the skin and cutaneous adnexal neoplasms with eccrine and apocrine differentiation 16984256_This review summarizes the current body of knowledge concerning the qualitative and quantitative POMC peptide processing with respect to the action and specificity of NEP and ACE and discusses relevant recent analytical method 17207277_NEP overexpression, which seems to be largely driven by increased transcription, is rare in primary melanoma and occurs late in melanoma progression. 17294442_NEP/CD10 is differentially expressed in pancreatic tumors and might be involved in the proliferative activity of pancreatic cancer cells 17296585_MUM1 expression dichotomises follicular lymphoma (FL) into low-grade FL of CD10+/Bcl-6+/MUM1-/Ki-67low phenotype, and high-grade FL of CD10+/- /Bcl-6+/weak/MUM1+/ Ki-67high phenotype 17335564_Expression of CD10 by prostate cancer corresponds to a more aggressive phenotype with a higher malignant potential. 17342744_The function of CD10 in prostate cancer is largely unknown. In the C4-2 CaP cell line, CD10 was found to interact with both HSP27 and HSP70. 17363457_NEP and ACE significantly contribute to the endothelial cell processing of stress hormones (ACTH) and antiinflammatory peptides (alpha-MSH). 17591969_These findings demonstrate an important role for proteolysis in determining the levels of Abeta and Abeta-associated neuropathology in vivo and support the hypothesis that primary defects in Abeta clearance can cause or contribute to LOAD pathogenesis 17662271_Expression is frequenty decreased in chronic myelogenous leukemia. 17712175_Spacio-temporal expression of two endopeptidases, ECE-1 and NEP, involved in the synthesis and degradation of ET-1, might regulate ET-1 action in human endometrium. 17845760_CD10 and CD9 expression correlates with the invasiveness and metastatic potential of malignant melanoma. 17876294_Liver CD10 in childhood appears to undergo reduced synthesis or rapid degradation, which persists in AGS. Absence of CD10 expression thus may limit NEA as a marker of cholestasis in young patients and in AGS. 17885484_CD10 may play a useful role in aiding the differential between endometrial stromal tumors in the ovary and SCST and stromal tumors 17906676_The NEP mRNA and protein levels gradually increased during the time-course of pre-adipocyte differentiation, but did not play a major role in the regulation of ANP-mediated lipolysis.. 17928142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17928142_involvement of neprilysin in the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease 17953966_Enkephalin-degrading enzymes are present in human semen and may be involved in the control of sperm motility, mainly by the regulation of endogenous opioid peptides. 18042078_an immunohistochemical panel including CK7,CD10 and mesothelin is optimal for distinguishing between ovarian and renal clear cell carcinoma. 18092952_Prognostic value of neoplastic CD10 expression in bladder carcinoma and its possible importance in facilitating tumour invasion and metastasis. 18182043_We hypothesize that, in h-IBM muscle, hyposialylated NEP has a role in hampering the cellular Abeta clearing system, thus contributing to its abnormal accumulation within vulnerable fibers and possibly promoting muscle degeneration. 18292286_AITL is a morphologically heterogeneous T-cell lymphoma commonly expressing CXCL13 and CD10; high level of CD10 and CXCL13 did not affect survival. 18370954_CD10 expression was detected in more than half of the cases og non-polypoid growth colorectal neoplasms. 18393807_increasing neprilysin levels in the brain leads to a decrease in brain amyloid beta peptide levels--REVIEW 18518902_Expression of CD10 by mantle cell lymphoma is often associated with other variant morphological, immunophenotypic or genetic features, but does not reflect derivation from germinal centre B cells. 18539150_NEP2 substrate specificity and inhibitor binding was distinct from that of human NEP, suggesting that NEP and NEP2 play distinct physiological roles in humans. 18545147_CD10 can be used as positive marker of Atypical fibroxanthoma. 18602473_This finding suggests that resistance to NEP-mediated proteolysis may underlie the pathogenicity associated with the beta-amyloid A21G mutation. 18605079_Demonstrates expression of immune system in granulocytes after heart surgery. 18619643_This study demonstrated differences in the CD10 immunoreactivity or immunostaining pattern between the stromal components of atypical polypoid adenomyoma and myoinvasive endometrial carcinoma. 18806483_Superficial acral fibromyxoma frequently expresses CD10 and occasionally can have a lipomatous component. 19019493_Insulin degrading enzyme is linked with aggregated Abeta40 isoform while neprilysin negatively correlates with amyloid angiopathy. 19047112_CD10 expression is an unfavorable independent risk factor in prostate cancer 19057576_chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis also reveals amyloid precursor protein binding to the NEP promoter in rat primary neurons but not in HUVEC cells 19127446_Results indicate that the decrease of neprilysin, caused by the decline of estrogen or androgen with aging, may be an important factor leading to amyloid-beta accumulation and Alzheimer's disease. 19152193_CD10 is not a specific marker for diagnosing clear cell renal cell carcinoma 19196432_This study demonstrates that NEP can be inactivated by HNE-adduction, which is associated with, at least partly, reduced Abeta cleavage and enhanced Abeta accumulation. 19250583_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19250583_Our results suggest that -204G/C and 159C/T polymorphisms of the NEP gene may not be associated with SAD. 19287335_Data suggest that CD10 and CK20 may be used for the differential diagnosis of MCN and IPMN-BD. 19326964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19326964_Patients that developed amyloid-beta plaques following brain injuries had a polymorphism in the neprilysin gene. 19437324_CD34 and CD10 expression may have prognostic value and is associated with a better clinical outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. 19448593_The expression of CD10, Bcl-6, MUM1/IRF4, Bcl-2, and FOXP1 was determined immunohistochemically from 88 samples of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated uniformly with R-CHOP 19515046_stromal CD10 expression is associated with malignant transformation of keratinocytes together with infiltration of dermal macrophages and loss of Langerhans cells 19575892_Expressions of CXCL13, CD10 and bcl-6 were significantly higher in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma patients than in peripheral T-cell lymphoma patients. 19606063_This study demenostrated that neprilysin is increased in Alzheimer disease in relation to disease severity. 19656156_in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) treated with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and prednisolone the high expression of CD10 was associated with better overall survival. 19661328_High CD10 is associated with malignant peripheral sheath tumors and their metastases. 19752720_expressed in myoepithelial cells of salivary neoplasms 19787248_Stratification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with respect to combined expression profiles of CD10, Bcl-6 and MUM-1 revealed six groups showing significant differences in survival 19816087_CD10 is associated substantially with liver metastasis of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and might be a molecular target of CRC treatment 19817893_CD10+ fibroblasts are more involved in the progression of hilar and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma than of peripheral intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 19864659_Here we show that a combination of risk genotypes for NEP and IDE genes leads to a higher susceptibility to AD 19864659_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19897485_Estrogen stimulates degradation of beta-amyloid peptide by up-regulating neprilysin. 19925052_Studies illustrated tools for cut-off level determination with prognostic tumor-related biomarkers Bcl-2, Bcl-6, CD10, FOXP1, MUM1, and Cyclin E in DLBCL. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19961253_Data show there is a growing list of tumors that show expression of CD10. 20014550_CD10 and CK7 were consistently positive in the stromal and epithelial components, respectively, in all cases on cell block sections. 20051779_review of role of dna methylation om controlling CD10 genetic transcription and function 20051780_Structural evidence of dense methylation in the CD10 gene promoter suggested that methylated transcription factor binding sites contribute to CD10 silencing as an epigenetic mechanism in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia 20061637_A potential mechanism underlies the neuroprotective effects of antioxidants that spare neprilysin from oxidative modification in pathologic aging. 20079015_The expression of CD10 differs in follicular lymphoma and reactive follicular hyperplasia. Loss of CD10 expression is seen mainly in follicular lymphoma. 20105452_NEP gene does not seem to be a major risk factor for CRPS. 20175824_Myxofibrosarcomas commonly present in the skin and may be difficult to distinguish from atypical fibroxanthoma and CD10 positivity may confound the diagnostic difficulty. 20184665_CD10 positivity is relatively specific in the differential diagnosis of Atypical fibroxanthoma 20204382_CD10 expression is a significant risk factor for liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer and is correlated with prognosis. 20376800_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20376800_The NEP and ApoE gene polymorphisms may be associated with sporadic Alzheimer's disease. 20390424_CD10 does not seem to be a useful marker for discriminating clear cell renal cell carcinomas from adrenocortical tumors since CD10 expression does not rule out the possibility of adrenocortical tumors. 20459800_Results support the pivotal role for DPP IV and neprilysin in the malignant transformation pathways of renal tumors and point to these peptidases as potential diagnostic markers. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506111_demonstrate that the protease activity of CD10 and the adhesion function of beta1-integrin are required to prevent differentiation of mammary progenitors. 20546336_Stromal CD10 expression with associated aggressive features might be related to aberrant beta-catenin expression 20574156_in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) patients a significant association was observed between recurrence status and time to recurrence with expression of CD10 and SPARC;stromal CD10 and SPARC expression are new markers of increased risk for DCIS recurrence 20663017_These findings provide additional support for NEP as the major protease involved in Abeta degradation 20685603_CD10(+) pancreatic stellate cells enhance the progression of pancreatic cancer cells. 20711432_in vitro invasive properties and in vivo tumor growth of CD133+ colon cancer cells are enhanced in the presence of specific cancer-associated fibroblasts, CD10+ fibroblasts 20716621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20856894_decrease of CD10 expression in myoepithelial cells is associated with a higher risk of relapse in ductal carcinoma in situ 20858953_In Lewy body disease, cerebrospinal fluid levels of neprilysin activity are associated with dementia, probably via the amyloid-beta pathway. 20886092_The level of CD10 corresponds to commitment and progression in the B lymphoid lineage. 20947507_increased NF-kappaB activity leads to increased miR-155, which results in decreased PU.1, and consequently reduced CD10 mRNA and protein. 20957047_expression of a pseudophosphorylated NEP variant (Ser6Asp) abrogates the inhibitory effect of NEP on insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) stimulated activation of Akt 21052031_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21076839_fibroblastic CD10 expression may down-regulate skin inflammation by degrading SP or reducing its level in the dermal microenvironment 21225496_CD10 may be useful for the differential diagnosis between basal cell carcinoma and benign tumours of cutaneous appendages originating from hair follicle. 21315759_Suggest that lead acetate causes both the overexpression of beta-amyloid precursor protein and repression of neprilysin resulting in the buildup of amyloid beta. 21365649_data suggest that histone acetylation may facilitate partial re-activation of NEP expression in advanced prostate cancer cells 21425402_Review of the characteristics, main functions, and mechanism of action of CD10. 21499231_circulating neoplastic T cells correspond more often to a CD10-positive subset than to an ICOS-positive subset in Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma 21585282_Data show that expression of the CD10 antigen was noted in less than one-third of the cases, which may therefore be considered as possible FL. 21609487_In dentigerous cyst , high CD10 and osteopontin expression may indicate the neoplastic potentiality of certain areas 21651905_possible participation of angiotensin-converting enzyme, neutral endopeptidase and aminopeptidase P as an inactivation pathway of bradykinin 21677537_Immunohistochemical and histologic features supporting the diagnosis of SPNs over PanNETs include CD10 and nuclear beta-catenin labeling. 21681600_High CD10 expression in stromal cells of non-small cell lung carcinoma is associated with recurrence and metastasis. 21775056_Data show that CD99 combined with E-cadherin/beta-catenin and CD10 can be used as a relatively specific expression profile of SPTs. 21804528_CD10 immunostaining identifies normal enteric mucosa with 100% specificity, but negative staining does not definitively exclude small intestinal mucosa in the setting of active enteritis, a common condition in ileal pouch mucosa. 21835428_High CD10 expression predicts favorable outcome in surgically treated lymph node-positive bladder cancer patients. 21877416_in a controlled human exposure study, observed significant increases in soluble NEP in sputum after acute exposure to diesl exhaust emissions, with an average net increase of 31%. 21883368_CD10 alone should not be relied upon in the distinction of atypical fibroxanthoma from sarcomatoid (spindle cell) squamous cell carcinoma. 21988858_Immunostaining for HGAL was more frequently positive than that for BCL6 and CD10 in follicular lymphomas 21989348_Our findings suggest that absence of CD10 expression in strips of atypical biliary epithelial cells may be a phenotype associated with malignant transformation 22006372_The expression of CD10 can be used to predict the occurrence of distant metastasis in phyllodes tumors of the breast. 22014058_Gastrointestinal stromal tumours occasionally show CD10 immunopositivity 22183801_This study shown that cholesterol regulates the localization of mature NEP in lipid rafts. 22257901_Report immunohistochemical staining for CD10 in differential diagnosis of epithelioid and spindle cell tumors of the skin. 22261707_Report Divergent expression of MUC5AC, MUC6, MUC2, CD10, and CDX-2 in dysplasia and intramucosal adenocarcinomas with intestinal and foveolar morphology and roles in neoplastic progression. 22272689_strong expression in all stages of kidney development 22286396_Low CD10 expression is an adverse prognostic factor for biochemical relapse after radical prostatectomy in localized prostate cancer, which is also associated with high NF-kappaB expression. 22300665_There was a significant relation between CD10 expression as well as Ki67 labelling index and recurrence of ameloblastoma 22371247_research led to the identification of neutral endopeptidase, the M-type receptor for secretory phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)R1) and cationic bovine serum albumin as target antigens of circulating and deposited antibodies in membranous nephropathy. 22384224_analysis of how active site mutations change the cleavage specificity of neprilysin 22410801_the expression of CD10 and p53 was significantly correlated with HER2 positivity in patients with gastric cancer 22417750_These findings suggest that IL-1alpha and GM-CSF are intrinsic cytokines secreted by UVB-exposed keratinocytes that stimulate expression of NEP by fibroblasts. 22464152_Nearly half of the soft tissue sarcomas were found to express CD10. 22492182_Computational prediction and experimental assessment of an HLA-A*0201-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope from neutral endopeptidase. 22572771_Tissue and serum levels of substance P were increased in chronic pancreatitis, while neprilysin levels remained unaltered. 22767595_Cell surface expression of the major amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta)-degrading enzyme, neprilysin, depends on phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK) and dephosphorylation by protein phosphatase 1a. 22880404_Variants of gastric carcinomas according to immunohistochemical mucins and CD10 expressions 22898766_Neprilysin protected against beta cell cytotoxicity induced by exogenously added or endogenously produced human IAPP. 22994707_Positive expression of BCL-6, CD10, CD138 and MUM-1 was shown in 78%, 61%, 39% and 91% of the cases. 23063927_verify amplification and/or deletion in the ACHE, BCHE, EPHB4 and MME genes in 32 samples of sporadic breast cancer 23065018_In keratoconus, corneal epithelium with higher expression of FasL may evoke apoptosis in keratocytes, while neprilysin could prevent possible rescue of keratocytes from apoptosis. 23138928_hypoxia negatively regulates the tumor suppressor function of NEP in prostate cancer 23219141_CD10 expression in melanoma tumor cells remained associated with an increased risk of death and more rapid disease progression. 23339695_Increased expression of CD10 in transitional and squamous cell carcinoma (TCC/SCC) tumor and stromal cells, and decreased expression of E-cadherin in TCC tumor cells, are correlated with tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis in human bladder cancer. 23348903_Prostate cancer biomarkers, AGR2 and CD10, can be used in combination to stratify prostate cancer patients for clinical outcome. 23356903_Case Report: not otherwise specified-type sarcoma with CD10 expression in the left breast in a 45-year-old female was presented. 23360525_study suggests that the severity of periodontal disease may be associated with the expression of metalloendopeptidase genes, including NEP, ECE1 and ADAM17, in the buccal mucosal epithelium. 23509938_The use of three distinct anti-bcl-2 antibodies together with CD10 expression data and FISH analysis for bcl-2 and bcl-6 rearrangements allowed subclassification of follicular lymphoma into four distinct subgroups. 23566254_MUC1 (CD227) expression was associated with infiltration of CD10 myeloid cells, TGF-beta1 expression, and tumor budding grade. 23575921_Correlation between CD10 stromal expression and disease-free survival rate in breast cancer patients. 23653392_CD10 might be involved in the development of endometriosis due to its influence on CD44-dependent cell adhesion. 23686701_Combined expression of CD10/CD26 had a better prognostic value than other features. 23827863_MME expression level was differentially altered in Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis patients. 23838604_Results show that variants in MME gene may be associated with ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. 23857215_only seminomas and intratubular germ cell neoplasia, the precursors of germ cell tumours, express CD10 23863409_The altered expression of enzymes regulating the activity of ET-1, NEP and ECE-1, during parturition is controlled by inflammatory cytokines. 24040464_Case Report: sporadic renal hemangioblastoma expressing CD10. 24099862_Data indicate an important, previously neglected, role of NEP for regulation of luminal factors in the epididymis and suggest a novel role for CNP/guanylyl cyclase B in the epididymal epithelium. 24460801_A direct up-regulation of stroma fibroblast MME expression under hypoxia might contribute to enhanced aggressiveness of hypoxic cancers. 24603459_Overexpression of membrane metalloendopeptidase inhibits substance P stimulation of cholangiocarcinoma growth. 24754336_CD10 strongly labelled only the gastrointestinal cells, with a well-defined apical membrane signal 24825898_the recombinant brain-targeted neprilysin, ASN12, may be an effective treatment for AD and warrant further investigation in clinical trials. 24848988_PKCepsilon activation may have therapeutic efficacy for AD by reducing neurotoxic Abeta accumulation as well as having direct anti-apoptotic and synaptogenic effects 24874475_Expression of CD10 is associated with therapeutic resistance and cancer stem cell-like properties of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 24895167_High CD10 expression is associated with squamous cell carcinoma. 24972738_Serum CD10 levels might serve as a useful marker of synchronous and metachronous liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. 25125048_This meta-analysis indicates that rs3736187 (A/G) polymorphisms may be a potential beneficial single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), which are associated with a decreased risk in Alzheimer disease. 25279712_Immunohistochemical distinction of renal cell carcinoma from other carcinomas with clear-cell histomorphology: utility of CD10 and CA-125 in addition to PAX-2, PAX-8, RCCma, and adipophilin. 25282623_E-cadherin and CD10 in endometrial lesions is not correlated, but reduced expression of both molecules could be critical for progression of endometrial carcinoma 25308002_This study gives substantial proof to the various models/research papers explaining the role of CD10 in breast cancer pathogenesis. 25452160_The expression of neprilysin is increased in glioma cells following 5-HT2C activation. 25608772_High tumoral CD10 expression correlates with aggressive histology in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. 25713420_Letter: suggest that CD10 is not a useful marker to differentiate seminoma from non-seminomatous germ cell tumours. 25733581_Follicular lymphoma CD10(pos) follicular helper T cells specifically display an IL-4(hi)IFN-gamma(lo) cytokine profile and encompass the malignant B-cell-supportive follicular helper T cells subset. 25759539_Evaulate CD10 and mucin expression in relation to microsatellite instability/mismatch repair proteins in 47 cases of small bowel adenocarcinoma. 25921112_High CD10 expression is associated with Phylloides Tumors. 26124315_CD10 expression is related to a distinct gene expression signature in mantle cell lymphoma cases, but is without clinical or biological implications. 26141216_In stage I lung adenocarcinoma, tumoral CD10 correlated with high-grade histology and was an independent predictor of recurrence in intermediate-grade tumors. 26362309_In this meta-analysis of the Han Chinese population, neprilysin confers genetic susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease in Han Chinese populations. 26414904_CD10 gene expression plays a role in the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 26562027_CD10 positivity is luminal/membranous in most benign apocrine breast lesions, the staining being nonuniversal and sometimes focal; analogous staining in apocrine malignancies seems rarer in DCIS and even rarer in invasive apocrine carcinomas, but atypical cytoplasmic positivity may also occur 26573127_CD10 and Bcl2 expression in tumor cells could give convincing diagnostic value to distinguish squamous cell carcinoma from seborrheic keratosis 26609034_This study reveals some unusual findings in otherwise classical disease entity, like absence of palpable spleen, presence of lymphadenopathy, normal or elevated leukocyte counts, expression of CD10, which at times could be diagnostically challenging. 26830028_Case Report: endometrial mixed carcinoma with the neuroendocrine component expressing CD10 that showed a long survival. 26846903_the dynamic behavior of human NEP and NEP2 proteins was monitored by conducting molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. 26881775_These findings indicate that CD10 may promote tumor progression by regulating the expression profiles of genes related to cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and resistance to apoptosis. 26991897_Loss-of-function MME mutations are the most frequent cause of adult-onset autosomal-recessive Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2 in Japan. 27039776_High CD10 expression is associated with Basal cell carcinoma of the skin. 27096746_The peptide qf-Abeta(12-18)C (sequence VHHQKLVC) was cleaved by multiple Abeta-degrading enzymes, including NEP, ACE, and ECE-1, whereas the redesigned peptide qf-Abeta(12-16)AAC (sequence VHHQKAAC) was sensitive to NEP and ACE only. 27513891_CD10 down expression in follicular lymphoma correlates with gastrointestinal lesion involving the stomach and large intestine 27588448_Rare Variants in MME, Encoding Metalloprotease N |
ENSMUSG00000027820 |
Mme |
8.244436 |
8.7345856112 |
3.126739 |
0.958555165 |
9.904222 |
0.00164900043603300947014922428479621885344386100769042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003704603719307035265134731005787216417957097291946411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.0920716 |
9.7680430 |
1.8310386 |
0.9727390 |
| ENSG00000196569 |
3908 |
LAMA2 |
protein_coding |
P24043 |
FUNCTION: Binding to cells via a high affinity receptor, laminin is thought to mediate the attachment, migration and organization of cells into tissues during embryonic development by interacting with other extracellular matrix components. |
3D-structure;Basement membrane;Cell adhesion;Coiled coil;Congenital muscular dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Laminin EGF-like domain;Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Laminin, an extracellular protein, is a major component of the basement membrane. It is thought to mediate the attachment, migration, and organization of cells into tissues during embryonic development by interacting with other extracellular matrix components. It is composed of three subunits, alpha, beta, and gamma, which are bound to each other by disulfide bonds into a cross-shaped molecule. This gene encodes the alpha 2 chain, which constitutes one of the subunits of laminin 2 (merosin) and laminin 4 (s-merosin). Mutations in this gene have been identified as the cause of congenital merosin-deficient muscular dystrophy. Two transcript variants encoding different proteins have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3908; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; protein complex involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098637]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; synaptic cleft [GO:0043083]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2001046]; positive regulation of muscle cell differentiation [GO:0051149]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic [GO:0032224]; regulation of basement membrane organization [GO:0110011]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of embryonic development [GO:0045995]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
11584042_case series and review of laminin alpha2(merosin) deficiency phenotypes and abnormalities 11938437_A number of mutations are identified in association with congenital muscular dystrophies. 12100448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12467726_Merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy with mental retardation and cerebellar cysts, unlinked to the LAMA2 locus in three Tunisian patients. 12552556_In nine congenital muscular dystrophy patients with abnormal white-matter signal at brain MRI and partial deficiency of muscle laminin alpha 2, three novel missense and two splice-site mutations were found. 12609502_However, dy(W)/dy(W) mice, expressing the human laminin alpha2 under the control of the striated muscle-specific portion of the desmin promoter, still developed muscular dystrophy. 15452315_A mild case of autosomal recessive congenital muscular dystrophy is associated with a homozygous out-of-frame deletion in exon 56 of the LAMA2 gene. 16084089_DNA analysis can be used to provide accurate prenatal diagnosis of thecongenital muscular dystrophy, and have an essential role in genetic counseling. 16216942_identified 9 new LAMA 2 mutations 16226104_A relocalization of LAMA2 was noted in the subepithelial basement membrane in a group of Hirschsprung patients. 16504180_suggest that LNalpha1 chain in part ameliorates the development of LNalpha2 chain deficient muscular dystrophy by retaining the binding sites for integrin alpha7Bbeta1D and alpha-dystroglycan, respectively 17426950_Study summarizes recent progress concerning the molecular mechanisms of laminins in development and disease. 18053718_intron mutation is responsible for complete exon 17 skipping in severe congenital muscular dystrophy 18700894_the first fully characterized gross deletion in the LAMA2 gene, encompassing exon 56 (c.7750-1713_7899-2153del), detected in 31% of congenital muscular dystrophy type 1A patients 19294599_In patient 1, a double mutation, c.[9101_9104dupAACA:3412G>A] p.[H3035QfsX4:V1138M] was detected, Patient 2 had a novel homozygous nonsense mutation, c.2907C>A (p.Cys969X), in exon 21. 19553699_Crystal structure shows that the three LG domains adopt typical beta-sandwich folds, with canonical calcium binding sites in LG1 and LG2. LG2 and LG3 interact through a substantial interface, but LG1 is completely dissociated from the LG2-3 pair. 19692349_Ku70 is a regulator of Bax-mediated pathogenesis in laminin-alpha2-deficiency muscle cells. 19893454_Data show that the expression of collagen types I, III and fibronectin was significantly higher in pancreatic cancer, and the expression of collagen type IV, laminin and vitronectin was significantly lower in pancreatic cancer. 20207543_This large study identified novel LAMA2 mutations and highlights the role of immunohistochemical studies for merosin status in predicting clinical severity of MDC1A. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20477750_A single base deletion at position 8005 in the LAMA2 gene is associated with a severe form of classical congenital muscular dystrophy and partial merosin deficiency in congenital muscular dystrophy type 1A. 20607928_LAMA2 mutations were found in three different Russian families with congenital muscular dystrophy. 21953594_This largest series of patients with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy due to laminin alpha2-deficiency expands the clinical phenotype associated with LAMA2 mutations. 22006699_This is the first report to describe dilated cardiomyopathy with conduction defects and merosin deficiency in a patient carrying LAMA2 gene mutations. 22038115_Aberrant methylation at target CpG sites in GABRA1 and LAMA2 was observed with high frequency in tumor tissues. 22654118_Identification of cell adhesive sequences in the N-terminal region of the laminin alpha2 chain. 24225367_Genetic association studies identified two pathogenic mutations in the LAMA2 gene in patients with congenital muscular dystrophy. 24534542_2 patients with partial laminin-alpha2 deficiency and atypical phenotypes, one with almost exclusive central nervous system involvement and second with cardiac dysfunction, rigid spine syndrome and limb-girdle weakness; both have 2 heterozygous LAMA2 variants sharing a potentially pathogenic missense mutation c.2461A>C located in exon 18 24556084_Homozygous truncating mutations in POMK lead to congenital muscular dystrophies with secondary merosin deficiency, hypomyelination and intellectual disability. 24628934_children with LAMA2 congenital muscular dystrophy may be at nogreater risk of developing malignant hyperthermia than the general population 24804215_Extracellular matrix proteins expression profiling in chemoresistant variants of the A2780 ovarian cancer cell line. 25159915_Data find high frequency mutations in LAMA2 protein in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. Its lower expression levels correlate with tumor progression, poor survival and higher chance of cancer recurrence. 25500573_This report widens the clinical spectrum of cerebral manifestations related with mutations in LAMA2 25663498_This study demonstrates a wide clinical spectrum of LAMA2-related muscular dystrophy and its prevalence in an LGMD2 cohort, which indicates that LAMA2 muscular dystrophy should be included in the LGMD2 nomenclature. 25958202_Data showed miR-29a/c as novel regulators of LAMA2 in ependymoma based on miRNA-mRNA covariation and sequence-based target predictions. 25962468_Crystal structure of LAMM L4 domain 26104111_Next generation sequencing was found to be useful for molecular diagnosis of a confirmed case of merosin deficient congenital muscular dystrophy. 26304763_By analyzing the gene test we found that compound heterozygous LAMA2 mutation inherited from the parents. One coming from the father was a gross deletion expanding from exon 36 to exon 65. The from the mother was a missense mutation c.1358G>C 26756417_Differential protein expression of collagen IV, laminin alpha2, and nidogen-1 indicated basal lamina remodeling develops in ischemic failing versus nonfailing human hearts. 26984843_did not find positive association signals of the four single nucleotide polymorphisms in the LAMA2 and EGR1 genes with high myopia 27914711_Using high-throughput technology identify LAMA-2 as a candidate medullary sponge kidney disease biomarker possibly employable in future for the early diagnosis of this disease. 29191403_Data provide evidence that LAMA2 mutations cause congenital muscular dystrophy (MD). There are severe, non-ambulatory or milder, ambulatory variants, the latter resulting from reduced LAMA2 expression and/or deficient function. In LAMA2 MD, Lm-411 replaces Lm-211; however, Lm-411 lacks the ability to polymerize and bind to receptors. This results in a weakened basement membrane leading to the disease. [Review] 29335257_we identified LAMA2 as the coreceptor for staphylococcal superantigens 29369589_It was established that the frequency of individuals with the COL13A1*D/*D genotype was higher in the senile age period. The LAMA2*I/*D genotype was predisposing to longevity among women. 29376585_Although laminin alpha2 related congenital muscular dystrophy with white matter abnormalities is known, the association with occipital cortex dysplasia has been not well recognized. 29465610_The LAMA2 Mutation Congenital Muscular Dystrophy showed demyelinating polyneuropathy white matter changes on brain. 29566247_we demonstrate that a deregulated polyamine metabolism is a characteristic feature of severely affected lower limb muscles in LAMA2- congenital muscular dystrophy. Targeted modulation of this pathway represents a novel therapeutic avenue for this devastating disease 29707938_Merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy (MDC1A) is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disease that occurred due to novel mutations in the LAMA2 gene 30301903_the data highlight our approach, a modified next-generation sequencing assay, as a robust and sensitive tool to detect LAMA2 variants; the assay identifies 85.7% of breakpoint junctions directly alongside sequence information. 31371375_lm-alpha2 roll in controlling cell cycle exit and survival in the midbrain dopaminergic neuron neuron lineage 32213190_LAMA2 regulates the fate commitment of mesenchymal stem cells via hedgehog signaling. 32444167_Clinical and genomic characteristics of LAMA2 related congenital muscular dystrophy in a patients' cohort from Qatar. A population specific founder variant. 32792503_Mex3a interacts with LAMA2 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via PI3K/AKT pathway. 32904964_Limb girdle muscular dystrophy due to LAMA2 gene mutations: new mutations expand the clinical spectrum of a still challenging diagnosis. 32910545_LAMA2-related muscular dystrophy: Natural history of a large pediatric cohort. 32936536_Novel mutation identification and copy number variant detection via exome sequencing in congenital muscular dystrophy. 34156282_Immune-related genes LAMA2 and IL1R1 correlate with tumor sites and predict poor survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. 34565340_LAMA2 and LOXL4 are candidate FSGS genes. 36362280_Alu Deletions in LAMA2 and CDH4 Genes Are Key Components of Polygenic Predictors of Longevity. |
ENSMUSG00000019899 |
Lama2 |
20.994121 |
2.2792611517 |
1.188566 |
0.516915933 |
4.908905 |
0.02671858064405158508791693350303830811753869056701660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.046516424900471975423243975455989129841327667236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.7846005 |
9.5044395 |
12.9427035 |
3.0642914 |
| ENSG00000196597 |
158431 |
ZNF782 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMW2 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:158431; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19030899_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19030899_The present results suggest that the genomic region containing the ZNP510 and ZNP782 genes is an ethnic specific locus associated with stature variation in Chinese. |
|
|
30.850176 |
0.3665339238 |
-1.447981 |
0.321040989 |
20.561503 |
0.00000577457627178968516660660312278530170715384883806109428405761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000018630108365380490905620705643919166050181956961750984191894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.3137378 |
4.4378497 |
42.6066840 |
8.3379983 |
| ENSG00000196611 |
4312 |
MMP1 |
protein_coding |
P03956 |
FUNCTION: Cleaves collagens of types I, II, and III at one site in the helical domain. Also cleaves collagens of types VII and X (PubMed:2557822, PubMed:2153297, PubMed:1645757). In case of HIV infection, interacts and cleaves the secreted viral Tat protein, leading to a decrease in neuronal Tat's mediated neurotoxicity (PubMed:16807369). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1645757, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16807369, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2153297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2557822}. |
3D-structure;Autocatalytic cleavage;Calcium;Collagen degradation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This secreted protease breaks down the interstitial collagens, including types I, II, and III. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. Mutations in this gene are associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4312; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to UV-A [GO:0071492]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; protein metabolic process [GO:0019538]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
11489811_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11528521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11546917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11586041_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11691799_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11705862_Patients with detectable concentrations of urinary MMP-1 had higher rates of disease progression and death from bladder cancer than patients with undetectable urinary MMP-1. 11751876_members of the forkhead family of transcription factors play a role in regulation of the collagenase promoter and increased activity of forkhead transcription factors underlie the increase in collagenase expression observed during replicative senescence 11762702_17beta-estradiol represses MMP-1 synthesis, and this effect may contribute to its action on the inhibition of bone resorption 11824952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11831026_role in degradation of extracellular matrix and joint destruction 11836255_induction in fibroblasts by basic calcium phosphate crystals 11875051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11875051_These data suggest that polymorphisms in the MMP1 and MMP12 genes, but not MMP9, are either causative factors in smoking-related lung injury or are in linkage disequilibrium with causative polymorphisms 11918701_Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase regulates cellular invasiveness and survival in cutaneous epidermal cells. 11934016_in the late healing period of radiation-impaired wounds, increased expression of MMP1 may be related to overdegradation of matrixes and difficulty in granulation tissue formation 12005449_A newly identified single nucleotide polymorphism at position -519 in the promoter region of the MMP-1 gene is reported. This polymorphism consists in a guanine to adenine substitution. A linkage between polymorphisms -519A/G and -1607 1G/2G was studied. 12009332_Reduction of cytokine-induced expression and activity of MMP-1 and MMP-13 by mechanical strain in MH7A rheumatoid synovial cells 12032154_Accessory elements, flanking DNA sequence, and promoter context play key roles in determining the efficacy of insulin and phorbol ester signaling through the enzyme motifs 12034345_destruction of the surrounding matrix by endometriosis might be caused by various MMPs, which are mainly produced in stromal cells. 12050187_Oxidized low-density and high-density lipoproteins regulate the production by activated monocytes 12054564_lack of expression in Ewing sarcoma may be due to loss of accessibility of regulatory element to the specific fusion protein in vivo 12060661_Activation of p38 alpha MAPK enhances its expression by mRNA stabilization 12071839_Activation of protein kinase CK2 is an early step in the ultraviolet B-mediated increase in interstitial collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1; MMP-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) protein levels in human dermal fibroblasts. 12145314_Results demonstrate that generation of the 44-kDa membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) autolysis product regulates collagenolytic activity and subsequent invasive potential. 12177784_keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions are mediated by multiple stimulating agents acting on specific receptors to induce signalling through different mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways leading to altered expression of key biological functions. 12225803_Association of a polymorphism of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene with bone mineral density.Bone density for the distal radius was significantly lower in postmenopausal women with the GG/GG genotype. 12225803_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12229968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12364729_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12393408_MMP1 may play a pivotal role in the formation of capillarylike tubular structures in a collagen-containing fibrin matrix in vitro and may be involved in angiogenesis in a fibrinous exudate in vivo. 12432557_Genotyping was carried out using PCR-RFLP and direct sequencing. In the MMP-1 gene polymorphism, the frequency of the 2G/2G genotype that is associated with higher enzyme activity was significantly increased in colorectal cancer patients 12432557_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12473595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12515907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12517806_viral LMP1 and Zta proteins regulate the expression and activity of MMP-1; first evidence that viral proteins are capable of regulating MMP-1 and clues for the role of EBV in nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression 12528113_A novel promoter element was detected in the human MMP1 gene, and the inflammation-responsive transcription factor SAF-1 was found to interact with it in osteoarthritis 12572877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12622858_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12622858_a polymorphism in the promoter region is associated with the severe chronic periodontitis phenotype in non-smokers 12651627_expression and regulation by intestinal myofibroblasts in inflammatory bowel disease 12667140_catalytic activity on the cell surface is regulated through a vacuolar H(+)-ATPase-dependent degradation process 12676763_MMP-1 induces progressive adult-onset emphysema by the selective degradation of type III collagen within the alveolar wall. 12692352_Gene expression for MMP-1 after UVA1 irradiation was induced in all fibroblasts, but the induction rate was greater in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts than in normal ones. 12706853_MMP1 has a role in tumor invasion [review] 12767235_MT1-MMP-catalyzed release of beta-amyloid precursor protein leads to reduction of the extracellular matrix-associated gelatinase A inhibitor, sAPP, thus making it feasible for gelatinase A to exert proteolytic activity only near its activator, MT1-MMP 12784383_MMP-1 epitope increased interleukin 4 (IL-4) production of rheumatoid arthritis lymphocytes and decreased IL-4 production by control lymphocytes 12787920_These data provide evidence that tissue factor pathway inhibitor-2 does not bind to matrix metalloproteinases-2, -9 or -1, or regulate matrix metalloproteinase-1, in the extracellular matrix. 12788533_Hypoxia may be responsible for delayed wound healing by inducing an increase of MMP-1 synthesis. 12837283_MMP1 is a senescence-associated gene in normal human oral keratinocytes. 12845675_A single nucleotide polymorphism in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter is associated with renal cell carcinoma 12845675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12861139_study showed no change in metalloproteinase-1 production in response to varying estrogen levels in fibroblasts that were derived from incontinent women 12873541_Patients with deteriorating heart failure have increased expression of TIMP1 and MMP1 mRNA. Correlation with pro-inflammatory cytokines suggests common pathways of regulation and potential activation by IL-6 and IL1-beta. 12949792_Upregulation of mmp-1 ia assiciated with neoplasm invasiveness in Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancers 12960156_monocyte matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -9 are differentially regulated by interferon gamma through tumor necrosis factor-alpha and caspase 8 12969782_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12969782_reported association between the matrix metalloproteinase 1 promoter polymorphism and ovarian cancer risk was not supported by our 13129650_Cultured vascular smooth muscle cells infected with Chlamydia pneumoniae secreted increased quantities of MMP-1 protein. 14499230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14512169_Postmortem brain tissue analysis demonstrates accumulation of MMP-1 in macrophages/microglial cells in Durck's granulomas of patients with cerebral malaria. 14515149_Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (interstitial collagenase)is upregulated in endothelial cells by prostaglandin-J2. 14550555_EWS-ER81 and EWS-Fli-1 interact with and thereby activate the MMP-1 promoter, which is potentiated by the cofactor p300 and the proto-oncoprotein c-Jun. 14550952_We found a correlation between promoter polymorphism and MMP-1 expression, and that this SNP was correlated with the clinical stage of cervical cancer. 14558091_catabolic role of ET-1 in osteoarthritis cartilage via MMP-1 and MMP-13 up-regulation. 14581488_MIF is involved in the up-regulation of UVA-induced MMP-1 in dermal fibroblasts through PKC-, PKA-, Src family tyrosine kinase-, MAPK-, c-Jun-, and AP-1-dependent pathways. 14626631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14659851_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14669348_Overexpressed in ulcerative colitis and serve as biological markers. 14679206_results suggest that matrix metalloproteinase-1 can stimulate dephosphorylation of Akt protein and neuronal death through a non-proteolytic mechanism that involves changes in integrin alpha2beta1 signaling 14692651_High levels of MMP-1 expression, which may contribute to the invasive potential of these breast cancer cells 14705229_stimulated expression of MMP-1 and MMP-9 may contribute to the invasive activity and the bone and cartilage loss in pigmented villonodular synovitis 14707126_induction by calveolin 1 14707454_Low levels of MT1-MMP, MMP-1 and AI were found to be favourable markers significantly associated with longer survival in advanced colorectal carcinoma. 14729059_Mutant MMP1 lacking the cytoplasmic tail is recruited to membrane microdomains in breast carcinoma cells. 14730602_Rb protein negatively regulates p38 activation, leading to decreased MMP-1 secretion in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. 14764579_MMP-1 is ERK dependent and is upregulated after cigarette smoke exposure 14962105_general role for elevated MT1-MMP in promoting both the selective invasion and increased growth of malignant melanoma in vivo. 14982353_polymorphism in the promoter region may be associated with early implant failure 14986114_A single nucleotide polymorphism in the MMP-1 promoter is correlated with histological differentiation of gastric cancer 14986114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15127970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15142265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15149160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15149160_a matrix metalloproteinase 1 promoter gene polymorphism may be associated with lymphnode metastasis in patients with breast cancer 15182858_peroxidation and the production of peroxides are important events in the signalling pathway of MMP-1 activation by ultraviolet A rays 15184373_collagenase-1 (MMP-1) levels increase during melanoma progression through mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway 15194213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15200479_2G genotype in MMP-1 promoter was associated with the risk of oral squamous cell carcinoma 15200479_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15257748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15274394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15274394_The presence of the MMP1-2G and MMP3-6A alleles seemed to be associated with decreased risk of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma but mainly when they were carried by the same haplotype. 15288123_Beta-carotene suppressed UVA-induction of MMP-1. 15288468_No general associations of MMP-1 and MMP-3 genes to primary sclerosing cholangitis(PSC) or ulcerative colitis(UC) among Norwegians, but specific alleles were associated to subsets of PSC patients with UC and cholangiocarcinoma. 15288468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15291299_matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) has been suggested to be involved in skin photodamage. 15308634_PHGPx modulates the induction of MMP-1 and collagenase. 15312099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15312099_polymorphisms do not influence susceptibility to periodontitis in Japanese patients 15319295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15319295_Polymorphisms in MMP-1 is associated with renal cell carcinoma 15337261_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15350133_MMP-1 is found to be less efficient at processing triple-helical peptidase substrates than is MMP-14, which may explain the relative collagen specificity of MMP-1. 15375490_Overexpression of MMP-1 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 15383690_Intra-articular hyaluronic acid may rescue inflamed joints from bone and cartilage destruction by reducing the production of MMP-1. 15459390_results show that activated collagenase (MMP-1) moves processively on the collagen fibril; the mechanism of movement is a biased diffusion with the bias component dependent on the proteolysis of its substrate, not adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis 15467742_overexpression of p21SNFT in HepG2 cells leads to repression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 by 70-80% 15476622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15499569_The specific reduction of invasive behavior by human chondrosarcoma cells transfected with matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) siRNA supports the hypothesis that MMP-1 is involved in initiation of chondrosarcoma metastasis. 15528217_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15534109_MMP1 single nucleotide polymorphism does not appear to have a role in the progression of chondrosarcoma 15610507_heat shock-induced expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3 is mediated via an IL-6-dependent autocrine mechanism 15611040_The catalytic metalloproteinase domain and the C-terminal hemopexin domain show the classical MMP-fold, but the structure has revealed new features in surface properties 15612581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15617836_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15638833_Functional polymorphisms of MMP1 acting in cis is associated with allelic expression imbalance in nornal lung 15654517_gene expression regulation in Lyme disease 15654971_the level of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 mRNA expression was markedly increased in fibroblasts receiving keratinocyte releasable stratifin 15661214_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15688379_Single nucleotide polymorphism in Ets binding site of the matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter is associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma 15701845_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15701845_Polymorphism in the promoter region of the MMP-1 is associated with colorectal cancer 15707890_MMP-1 in the stromal-tumor microenvironment can alter the behavior of cancer cells through PAR1 to promote cell migration and invasion. 15718477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15728253_MMP-1 expression is maintained at a low level by Cdc42 via a repression of the Rac1 and ERK1/2 pathways when cell/extracellular-matrix interactions via integrins induce cytoskeleton organization 15737206_essential role for soluble factors, mainly IL-1alpha and bFGF, in the stimulation of dermal fibroblasts by human melanoma cells to secrete MMP-1. 15754326_Over expression of MMP-1 is associated with lymphatic metastasis of nonsmall cell lung carcinoma 15767330_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15804950_The expression of MMP-1 was significantly increased in the Crohn's disease 15817699_Cytokine-stimulated monocytes release Angiotensin II, which is an integral component of the signal transduction pathway that leads to MMP-1 production. 15818737_in hepatocellular carcinoma cells, fibril- and fixed-collagen have opposite effects on MMP-1 production without affecting TIMP production 15832405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15832405_The 2G or 1G SNP in the MMP1 promoter might not modify the risk of esophageal squamous carcinoma and gastric cardiac adenocarcinoma development 15855654_These observations strongly suggest that intracellular association of MMP-1 to mitochondria and nuclei confers resistance to apoptosis and may explain the well-known association of this enzyme with tumor cell survival and spreading. 15864312_MMP-1 is a candidate marker that may be useful for identification of breast lesions that can develop into cancer. 15866608_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15879464_MMP1 promoter SNP haplotype may modify susceptibility to endometriosis. 15879464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15930517_results demonstrate that EPA can inhibit UV-induced MMP-1 expression by inhibiting the MEK1/ERK/c-Fos and SEK1/JNK/c-Jun pathways 15939478_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15955221_MMP-1 gene polymorphisms account for some of the variability in the progression of HCV-related chronic liver diseases. 15955221_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15957163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15965045_in affected tissues the oxidative stress-elicited overexpression of MMP1, and probably other matrix metalloproteinases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling, may play an important role in the pathogenesis 16076963_MMP-1 expression by latanoprost requires prior up-regulation of COX-2 16080875_MMP-1 and MMP-3 promoter polymorphism is not associated with the susceptibility to ovarian cancer. 16080875_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16098031_stratifin stimulates fibroblast MMP-1 levels through the activation of c-fos and MAPK pathway 16103692_The capability of ANG II to induce functionally active MMP in human smooth muscle cells may contribute to the altered plaque composition seen in complicated stages of atherosclerosis 16168111_Monocyte and macrophage cells in the breast tumor microenvironment play an important role in the modulation of MMP-1. 16191276_Data show that the expression of MMP-1 at the acute phase of Kawasaki disease was significantly elevated, especially in Kawasaki disease patients with coronary artery lesions. 16202315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16210018_In both endometrial glands and corresponding endometriotic epithelium, the distribution of MMP-1 is correlated with estrogen receptor beta. 16210545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16213873_Although MMP-1 is not detected in patients with persistent ovarian cysts, MMP-2 and MMP-9 are expressed in all of the cysts 16214204_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16248458_In chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps tissues the expression of TGF-beta1, MMP-7, MMP-9, TIMP-1 protein was significant increased compared to controls. 16256416_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16267613_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16267613_Polymorphisms of the promoter regions of matrix metalloproteinases genes MMP-1 is associated with breast cancer 16273295_These results demonstrate that UVB-irradiated keratinocytes promoted MMP-1 production in UVA-irradiated fibroblasts in a paracrine manner while IL-1Ra reduced MMP-1 production through inhibiting c-Jun mRNA expression. 16278009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16278291_overexpression of SphK1 up-regulated MMP1 protein, MMP1 mRNA, and MMP1 promoter activity, and this action of SphK1 required activation of the ERK1/2-Ets1 and NF-kappaB pathways 16288711_results suggest that gingival fibroblast are stimulated by monocytes resulting in enhanced expression of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 and that the enhanced MMP-1 expression, in contrast to TIMP-1, is partly mediated by ICAM-1 and the signal pathway p38 MAPK 16301860_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 16302919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16311244_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16311244_matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 12 haplotypes may associated with development of lung cancer, particularly among never smokers and men 16321971_in gastric epithelial cells, H. pylori up-regulates MMP-1 in a type IV secretion system-dependent manner via JNK and ERK1/2 16353148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16356191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16359987_The active MMP-1 and MMP-9 plasma levels were found to vary in the menstrual cycle 16386110_expression of MMP-1 was repressed significantly and consistently at the RNA, the protein, and the secretory levels in uninfected newborns of HIV-1 infected mothers as compared to newborns of non-infected mothers 16405530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16410344_Coordinated down-regulation of collagen & TIMP-1 and up-regulation of MMP-1 occurs in fibroblasts exposed to proteasome inhibitors, indicating the proteasome's role in fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodeling. 16424284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16453302_demonstrate a novel role for CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta in interleukin-1beta-induced connective tissue disease and define a new nuclear target for the Extracellular Signal-Regulated MAP Kinases pathway in MMP-1 gene activation 16532917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16538639_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16569638_matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression is regulated by JNK through Ets and AP-1 promoter motifs 16580524_C-reactive protein augmented MMP-1 and -10 messenger ribonucleic acid expression in vascular endothelial cells. Might provide a link between inflammation and plaque vulnerability. 16623785_There was a clear increase in the number of MMP-1-reactive capillaries and fibroblasts in congenital diaphragmatic hernia lungs compared with controls. 16638593_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16676616_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16676616_the association between the functional polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and the development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) 16681691_MMP-1 showed only slight variation between the dilated, ischaemic and valvular cardiomyopathy. 16714289_Pge2 abolished the MEKK1-induced MMP-1 promoter luciferase activity. 16739355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16767672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16767672_The -1607(1G>2G) in promoter region of MMP1 is associated with susceptibility to lung cancer in Northwestern Chinese population of Han nationality. 16767840_Matrix metalloproteinase-I genetic variants may play a role in myocardial infarction 16774538_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16774538_This study suggests that a single nucleotide polymorphism in the MMP-1 promoter region of -1607bp may be associated with severe chronic periodontitis in a Chinese population. 16807369_decrease in Tat-induced neurotoxicity and HIV transactivation is due to Tat's enzymatic cleavage by MMP-1 16850107_Significantly higher mRNA expression of MMP-1 was found in brain-seeking 231-breast cancer clones in comparison to bone-seeking and parental cells. 16877347_These results suggest that CXCL12/CXCR4 interaction transduces the two signaling pathways to promote Natural Killer-cell invasion, which stimulates pericellular degradation of extracellular matrix proteins by membrane-associated MMP-1. 16890240_Results describe the crystal structure of the active form of human matrix metalloproteinase-1 at 2.67 A resolution. 16899023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16912186_MMP-1 expression was confirmed by using specific PI3K inhibitors in metastatic prostatic cancr. 16921111_MMP1 plays a pathogenic role in human emphysema. 16921115_Individuals with the 2G insertion polymorphsim who smoke may be predisposed to enhanced MMP-1 expression in the lung, contributing to the development of COPD. 16937230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16945025_No association between polymorphism and gingival enlargement was revealed in kidney transplant patients who were administered cyclosporin A as a principal immunosuppressive agent 16945025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16967187_All these findings suggested that the fused expressed His-DR inhibited the activity of natural DDR2, and relevant MMP-1 and MMP-2 expression in synoviocytes and NIH3T3 cells provoked by collagen II. 16972255_Data show that UVB irradiation increases PTEN/Akt phosphorylation in dermal fibroblasts, and inhibition of PTEN and activation of Akt by phosphorylation are involved in UVB-induced MMP-1 and -3 secretions through upregulation of AP-1 activity. 16972994_MMPs play a key role in regulating the balance of structural proteins of the articular cartilage matrix according to local mechanical demands 16990034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17000679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17009408_Excessive expression of MMP-1 and TIMP-1 in the diseased colonic mucosa causes excessive hydrolysis of the extracellular matrix (ECM) and ulceration in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients. 17033924_No convincing evidence was found to support the association of MMP1 SNPs with increased breast cancer risk or survival. 17033924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17035633_Screening for Wnt5a-regulated genes in cultured endothelial cells identified several encoding angiogenic regulators, including matrix metalloproteinase-1, an interstitial collagenase, and Tie-2, a receptor for angiopoietins. 17050530_analysis of the catalytic domain of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in complex with the inhibitory domain of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 17077200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17109104_High levels of MMP-1 in tumour and mucosa as well as MMP-2 in plasma may be correlated to risk of developing distant metastases. 17125518_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17125518_These data show a relationship betweeen MMP1 polymorphism and risk of small adenomas associated with colorectal neoplasms. 17145822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17151781_nicotine stimulates bone matrix turnover by increasing production of tPA and MMP-1, 2, 3, and 13, thereby tipping the balance between bone matrix formation and resorption toward the latter process 17178858_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17245132_Emphasis of this review is on membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)-induced chromosome instability which leads to the transition from normalcy to malignancy. 17303772_simvastatin, by inhibiting Rac1 activity, reduces MMP1 expression and collagen degradation in human smooth muscle cells. 17311017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17311017_colorectal carcinoma patients with the 2G/2G genotype for the MMP-1 single nucleotide polymorphisms had significantly better 5-year survival compared to patients with a 1G allele (P |
ENSMUSG00000043089+ENSMUSG00000041620 |
Mmp1a+Mmp1b |
7464.991515 |
3.9226867672 |
1.971842 |
0.020772668 |
9372.147780 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12045.3111597 |
150.2117004 |
3093.2372295 |
32.4115642 |
| ENSG00000196628 |
6925 |
TCF4 |
protein_coding |
P15884 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that binds to the immunoglobulin enhancer Mu-E5/KE5-motif. Involved in the initiation of neuronal differentiation. Activates transcription by binding to the E box (5'-CANNTG-3'). Binds to the E-box present in the somatostatin receptor 2 initiator element (SSTR2-INR) to activate transcription (By similarity). Preferentially binds to either 5'-ACANNTGT-3' or 5'-CCANNTGG-3'. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;Corneal dystrophy;Differentiation;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Primary microcephaly;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes transcription factor 4, a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. The encoded protein recognizes an Ephrussi-box ('E-box') binding site ('CANNTG') - a motif first identified in immunoglobulin enhancers. This gene is broadly expressed, and may play an important role in nervous system development. Defects in this gene are a cause of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. In addition, an intronic CTG repeat normally numbering 10-37 repeat units can expand to >50 repeat units and cause Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different proteins have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:6925; |
beta-catenin-TCF complex [GO:1990907]; beta-catenin-TCF7L2 complex [GO:0070369]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; beta-catenin binding [GO:0008013]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; TFIIB-class transcription factor binding [GO:0001093]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein-DNA complex assembly [GO:0065004]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
15351717_dHAND/E-protein (E2A, ME2, and ALF1) heterodimers have distinct DNA binding specificities 16126178_Competitive RT-PCR-based promoter activity assay showed that over-expression of ITF2B protein inhibited the expression of IL-2Ralpha gene in Jurkat cells in an NRE-dependent manner 17478476_haploinsufficiency of TCF4 causes PHS and suggest that D. rerio is a valuable model to study the molecular pathogenesis of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome and the role of TCF4 in brain development 18222743_Interstitial deletion involving TCF4 is associated with severe developmental delay and multiple abnormalities. 18371301_Protein sequence alignment of the closely related bHLH transcription factors ITF-2B, HeLa E box protein (HITF4), and the E2A proteins E12 and E47 revealed the presence of a highly conserved protein domain. 18627065_Gene disruption of TCF4 is associated with mental retardation but not always associated with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. 18635522_based on results, it is proposed that the observed frequent epigenetic-mediated TCF4 silencing plays a role in tumor formation and progression 18781613_Nine novel deletion mutations in TCF4 in Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome are described. 18792017_findings suggest that the concurrent action of Spi-B and E2-2 controls the development of progenitor cells into the plasmacytoid dendritic cell lineage 18854153_These results identify E2-2 as a specific transcriptional regulator of the plasmacytoid dendritic cells lineage in mice and humans and reveal a key function of E proteins in the innate immune system. 19235238_Studies delineate an underdiagnosed mental retardation syndrome, highlighting TCF4 function during development and facilitating diagnosis within the first year of life. 19394332_ITF-2B is a tumor suppressor that has an important function at the adenoma to carcinoma transition. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19571808_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19635457_This data support the notion that the ITF2 gene on chromosome 18q is a tumor suppressor gene. 19938247_a genotype-phenotype correlation of increased seizure activity with TCF4 missense mutations was proposed in patients with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. 20205897_The diagnosis of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, an underdiagnosed cause of mental retardation, was based on clinical and genetic findings. Searching for TCF4 mutations is highly recommended when others overlapping syndromes was excluded. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20421335_These data suggest that TCF4, NRXN1, and CNTNAP2 may participate in a biological pathway that is altered in patients with schizophrenia and other neuropsychiatric disorders. 20585880_Inactivation of TCF4 by promoter methylation is associated with the early stage of gastric carcinoma progression. 20603605_Data suggest that that ITF2 is one of the CXCR4 targets, which is involved in CXCR4-dependent tumor growth and invasion of breast cancer cells. 20673877_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20673877_This study confirmed that common risk factors in the major histocompatibility complex region and TCF4 gene are associated with schizophrenia in Han Chinese. 20825314_Genetic variation in TCF4 contributes to the development of Fuch's corneal dystrophy. 20825314_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21037240_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21228604_VDM function is influenced by the TCF4 gene in schizophrenia patients. However, the elevated risk for schizophrenia is not conferred by TCF4-mediated VDM impairment. 21245398_The authors report the first independent replication of rs613872 conferring risk of late-onset Fuchs endothelial dystrophy 21533127_study presents evidence to support the role of the intronic TCF4 single nucleotide polymorphism rs613872 in late-onset FECD through both association and linkage studies 21543597_Sensorimotor gating is modulated by TCF4 genotype, indicating an influential role of TCF4 gene variations in the development of early information-processing deficits in schizophrenia. 21659310_Polymorphisms within TCF4, a gene which has been implicated in Fuch's corneal dystrophy susceptibility among Europeans, was also found to be strongly associated in Chinese 21671075_TCF4 (+/+) individuals were only moderately developmentally delayed while TCF4 (+/-) individuals failed to reach developmental milestones beyond those typically acquired by 12 months of age. 21722264_these findings suggest that FAM96B acts as a regulator of E2-2 through the control of its protein expression. 21789225_Usage of numerous 5' exons of the human TCF4 gene potentially yields in TCF4 protein isoforms with 18 different N-termini. 21791550_Common variants at TCF4 show genome-wide significant association with schizophrenia. 21812098_Association between schizophrenia and TCF4 is not mediated by a relatively common non-synonymous variant, or by a variant that alters mRNA expression as measured in adult human brain. 22045651_No obvious difference was observed between patients harboring truncating, missense mutations, or deletions, further supporting TCF4 haploinsufficiency as the molecular mechanism underlying Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. 22146553_We were unable to detect an association between TCF4 rs613872 genotype and the variation in corneal endothelial cell density or variation in cell morphology in a healthy young adult population. 22234156_variation in TCF4, genes are associated with Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy in Caucasian Australian cases 22383159_report on the screening of the TCF4 and MEF2C genes in a cohort of 81 classical, atypical, and incomplete atypical Rett syndrome (RTT) patients; results suggest that these genes are not commonly associated with RTT 22451930_Finding suggests that sensory gating is modulated by an interaction of TCF4 genotype with smoking, and both factors may play a role in early information processing deficits also in schizophrenia. 22460224_different Pitt-Hopkins syndrome-associated mutations impair the functions of TCF4 by diverse mechanisms and to a varying extent, possibly contributing to the phenotypic variability of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome patients. 22777675_TCF4 may modulate the expression of NRXN1 and CNTNAP2 thereby defining a regulatory network in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. 22821403_GPR35 shows associations in both ulcerative colitis (UC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), whereas TCF4 represents a PSC risk locus not associated with UC. Both loci may represent previously unexplored aspects of PSC pathogenesis. 22832956_Common TCF4 variants are involved in psychosis pathology, probably related to abnormal neurodevelopment. 22998502_We have shown that SNP rs613872 in the TCF4 gene is highly associated with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. 23110055_Association of FECD grade with TCF4 was highly significant (OR= 6.01 at rs613872; p = 4.8x10(-25)), and remained significant when adjusted for changes in central corneal thickness. 23129290_The schizophrenia-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms are in linkage disequilibrium with common variants within putative DNA regulatory elements, suggesting that regulation of expression may underlie association with schizophrenia. 23165966_A mosaic TCF4 point mutation can result in a significantly milder phenotype. 23185296_The TGC trinucleotide repeat expansion in TCF4 is strongly associated with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. 23249814_A single nucleotide polymorphism in TCF4 gene is associated with cognitive function in schizophrenic patients and healthy controls. 23671559_Regulation of TCF4-mediated BCL2 gene expression by BMI1 is universal. 23758498_Our results showed that there was no significant association between any of five reported SNPs of TCF4 and PTPRG genes and the occurrence of Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy; only rs7640737 in PTPRG showed an increased risk for corneal dystrophy. 24027308_mRNA isoforms of TCF4 is associated with Epstein-Barr virus lytic trans-activator BZLF1. 24058414_Knockdown of human TCF4 affects multiple signaling pathways involved in cell differentiation and survival in addition to a subset of clinically important mental retardation genes. 24094747_That AGBL1 interacts biochemically with the FCD-associated protein TCF4. 24210665_There is little genetic variation in non-coding region of TCF4 in schizophrenic patients. 24255041_That was the first independent replication of the expanded CTG 18.1 allele conferring significant risk for FECD (>30-fold increase). 24275585_The rs9960767 (C) of TCF4 appears to be associated with neurocognitive deficits in the Reasoning/Problem-Solving cognitive domain, in patients with episode psychosis. 24339136_results suggest that a schizophrenia risk variant in TCF4 is associated with neurophysiologic traits thought to index attention and working memory abnormalities in psychotic disorders. 24413739_Among the few schizophrenia-risk genes that have been consistently replicated is TCF4. This review integrates the animal and the human perspective. [review] 24594265_TCF4 is an important regulator of neurodevelopment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 24846398_In human colorectal cancer cell lines and tissue samples, ITF2 appears to prevent activation of the beta-catenin-TCF4 complex and transcription of its gene targets. 24862328_These findings indicate that beta-catenin/TCF-4 is an important pathway for restricted HIV-1 replication in monocytes and plays a significant role in potentiating HIV-1 replication as monocytes differentiate into macrophages. 25150259_High TCF4 expression is associated with acute myeloid leukemia progression. 25168903_Complete sequencing of the TCF4 genomic region revealed no single causative variant for Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD). The intronic trinucleotide repeat expansion within TCF4 continues to be more strongly associated with FECD 25217366_This study showed that no effect of schizophrenia risk genes TGF4 on macroscopic brain structure. 25298419_Transethnic replication of the association between the CTG18.1 repeat expansion in the TCF4 gene and FECD suggests it is a common, causal variant shared in Eurasian populations conferring significant risk for the development of FECD. 25299301_TCF4 rs613872 is strongly associated with FCD in Caucasians. 25342617_TCF4 poses a major contributor to FECD manifestation globally, with a significant association of rs17089887 and CTG18.1 allele in the Indian population. 26010163_No significant association (P 103, whereas a biallelic expansion is sufficient to be causal for FCD at (CTG)n>40. 26218914_These findings show for the first time in a Japanese population the association of the TNR expansion in TCF4 with FECD. 26280645_expanded TGC allele with more than 50 TGC repeats in intron 2 and the described risk allele G of the polymorphism rs613872 in intron 3 of the TCF4 gene appear as an association to FECD. The chance to be affected by FECD is up to 30 times higher. With molecular genetics also donors with clinically unknown FECD may be detected. 26343600_Results suggested that the TCF4 rs2958182 variant may play an important role in the susceptibility to schizophrenia 26401622_The TCF4 triplet repeat expansion resulted in a more severe form of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy , with clinical and surgical therapeutic implications. 26451375_The data suggest that changes in the transcript level containing constitutive TCF4 exon encoding the amino-terminal part of the protein seem not to contribute to disease pathogenesis. 26622166_ZEB1 mutations and TCF4 rs613872 changes are associated with late onset Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy in patients from Northern India. 26884349_Studied promoter methylation of ITF2 and APC and associated microsatellite instability in two case-case studies nested in colorectal cancer. 27103199_We found that the genotype 'AG' of rs9320010 and 'GA' of rs7235757 decreased SCZ risk. In the genetic model analysis, we also observed that the allele 'A' of rs9320010 and 'G' of rs7235757 were inversely related with the risk of SCZ in the dominant model. Our study indicated that rs9320010, rs7235757, and rs1452787 were prominently associated with SCZ. 27121161_Analysis of SLC4A11, ZEB1, LOXHD1, COL8A2 and TCF4 gene sequences in a multi-generational family with late-onset Fuchs corneal dystrophy found no evidence for found polymorophisms causing the disease in this specific pedigree. 27132474_We suggest that screening for mutations in TCF4 could be considered in the investigation of non-syndromic intellectual disability. 27179618_Although validation in additional patients is required, the findings suggest that the dysmorphic features and severe intellectual disability characteristic of PTHS are partially rescued by overexpression of those short TCF4 transcripts encoding a nuclear localization signal, a transcription activation domain, and the basic helix-loop-helix domain. 27305091_Among the TCF4 variants, rs12966547 and rs8766 were significantly associated with earlier schizophrenia age of onset. 27374225_Results show that MLL-AF9 reduces Id2 and increases E2-2 expression to drive and sustain leukemia stem cell potential in MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Low expression of Id2 or of an Id2 gene signature is associated with poor prognosis in not only MLL-rearranged but also t(8;21) AML patients. 27440233_Altered DNA methylation in TCF4 involves in the etiology of Bipolar disorder and Major Depressive disorder . 27485769_Examination of X-ray structures of the closely related TCF3 and USF1 bound to DNA suggests TCF3 can undergo a conformational shift to preferentially bind to 5hmC while the USF1 basic region is bulkier and rigid precluding a conformation shift to bind 5hmC. These results greatly expand the regulatory DNA sequence landscape bound by TCF4. 27542264_TCF4 knockdown promoted HepG-2 cell differentiation and inhibited tumor formation, and TCF4 could be the potential downstream target for clopidogrel therapy 27689884_Expression of TCF4 in a neural progenitor cell line derived from the developing human cerebral cortex was reduced using RNA interference. Genes that were differentially expressed following TCF4 knockdown were highly enriched for involvement in the cell cycle. There was a nonsignificant trend for genetic association between the differentially expressed gene set and schizophrenia. 27755191_We demonstrate that expansion of the CTG18.1 trinucleotide repeat in TCF4 is associated with a higher risk of corneal transplantation at a younger age, assessed for the first time in a multiracial population sample with Fuchs corneal dystrophy from the United States. 27846392_Results identify TCF4 as a crucial transcriptional regulator required for maintenance of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm. 28051067_Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD4 directly associates with the Wnt pathway transcription factor TCF4 via their DNA-binding domains, forming a complex on target genes. VGLL4 binds to this TEAD4-TCF4 complex to inhibit transactivation of both TCF4 and TEAD4. 28118661_Corneal endothelium from FECD patients harbors a unique signature of mis-splicing events due to CTG TNR expansion in the TCF4 gene, consistent with the hypothesis that RNA toxicity contributes to the pathogenesis of FECD. 28341444_Expression of TCF4 at the mRNA and protein level may be significant in the etiology of recurrent depressive disorder and it is not dependent on sex and age. 28574827_Data show that silencing of immunoglobulin transcription factor 2 (ITF-2) by siRNA significantly enhanced susceptibility to the MEK inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) in resistant cells. 28608272_The CTG18.1 repeat expansion may reduce gene expression of TCF4 and ZEB1, suggesting that a mechanism triggering a loss of function may contribute to FECD. 28631899_Array-comparative genomic hybridization confirmed a de novo paternal deletion of the 15q11.2q13 region and exome sequencing identified a second mutational event in both girls, which was a novel variant c.145+1G>A affecting a TCF4 canonical splicing site inherited from the mosaic mother 28790108_we found that CypA binds beta-catenin and is recruited to Wnt target gene promoters. By increasing the interaction between beta-catenin and TCF4, CypA enhances transcriptional activity. Our results demonstrate that CypA enhances GIC stemness, self-renewal, and radioresistance through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling 28807867_A frameshift-causing partial TCF4 gene deletion was identified in an adult patient with mild ID and nonspecific facial dysmorphisms but without the typical features of Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. A nonsense variant within exon 8 was identified in a child presenting with a severe phenotype largely mimicking PTHS. 28832669_repeat expansion showed stronger association than the most significantly associated SNP, rs613872, in TCF4, with the disease in the Australian cohort 28886202_Our work suggests that DM1 patients are at risk for Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD). DMPK mutations contribute to the genetic burden of FECD but are uncommon. We establish a connection between two repeat expansion disorders converging upon RNA-MBNL1 foci and FECD. 28921696_In conclusion, this study provides genetic and some preliminary functional evidence to support the view that the TCF4 (NM_001243232) p.Pro29Thr mutation causes familial SAK. 29033371_The formation of the beta-catenin/TCF4 complex was disrupted by HI-B1 due to the direct interaction of HI-B1 with beta-catenin. Colon cancer patient-derived xenograft (PDX) studies showed that a tumor with higher levels of beta-catenin expression was more sensitive to HI-B1 treatment, compared to a tumor with lower expression levels of beta-catenin 29044056_rs613872, rs17595731, and CTG repeat expansions in intronic region of TCF4 are associated with increased risk of sporadic late-onset FECD in the Indian cohort studied 29105523_Our results showed that the mRNA level of TCF4 may be associated with schizophrenia, its psychopathology, IQ and cognitive impairments in an Iranian group of patients with schizophrenia. 29196769_Black patients with Fuchs' dystrophy were less likely than white patients to demonstrate CTG18.1 allele expansion. 29228394_TCF4 binding sites are found in a large number of neuronal genes that include many genetic risk factors for common neurodevelopmental disorders. 29666142_these results from tumor xenograft modeling depict a link between altered TCF4 expression and breast cancer chemoresistance. 29677349_Expanded CTG.CAG repeats in the context of the third intron of TCF4 are transcribed and translated via non-ATG initiation, providing evidence for RAN translation in corneal endothelium of patients with Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD). 29695756_these results highlight TCF4 as a frequent cause of moderate to profound intellectual disabilities (ID) and broaden the clinical spectrum associated to TCF4 mutations to nonspecific ID. 29901121_Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 enhances cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma through regulating miR-4695-5p/TCF4-beta-catenin signaling. 29905862_Thirteen genes within the 108 loci had both a TCF4 binding site +/-10kb and were differentially expressed in siRNA knockdown experiments of TCF4, suggesting direct TCF4 regulation. These findings confirm TCF4 as an important regulator of neural genes and point toward functional interactions with potential relevance for schizophrenia (SCZ). 29966009_Gene expression in the corneal endothelium of Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy patients with and without expansion of a trinucleotide repeat in TCF4 30098193_We observed instability of the TCF4 triplet repeat expansion in nearly a third of parent-child transmissions. Large mutant CTG18.1 alleles are prone to contraction, whereas intermediate mutant alleles tend to expand when unstably transmitted. Intergenerational instability of TCF4 repeat expansion has implications on FECD disease inheritance. 30288643_The rs8766 in TCF4 was selected for genotyping. rs8766 allele and genotype frequencies were not significantly different between case and control groups and a significant association cannot be suggested for the selected SNP for schizophrenia. 30315825_in cell fractions with erythroid lineage potential, TCF4 is expressed less in MDS patients than in healthy controls. This correlates with the low overall Hb levels seen in MDS patients compared with healthy individuals and is consistent with the positive impact of TCF4 on erythroid development while not having impact on white colonies. 30450687_Clinical and molecular characterization of carriers of TCF4 mosaic deletions and/or mutations contributes to our under-standing of the pathogenic mechanisms leading to Pitt Hopkins syndrome. 30527807_a serine determining the transcriptional activity of TCF-4 in lung carcinoma cells, was identified. 30593567_In contrast to HEB and E2A, which facilitate AML1-ETO-mediated leukemogenesis, E2-2 compromises the function of the AML1-ETO-containing transcription factor complex and negatively regulates leukemogenesis. 30682148_We found CTG repeat length to be a useful adjunct indicator which may be used to counsel a Fuchs' Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD) patient regarding his or her risk of significant clinical progression and keratoplasty over the next 10 years. There was more rapid clinical progression of FECD amongst patients who harbor an expanded TCF4 CTG18.1 allele (i.e. L40 group), during the first 5 years. 30705426_Findings provide new insight into the specific roles of Tcf4 molecular pathway in neocortical development and their relevance in the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric diseases. 30733599_in this study we demonstrate a custom application of an amplification-free long-read sequencing method to specifically study the TCF4 repeat element at a nucleotide level 30771755_rs1273263 is a potential regulator of TCF4 expression, and might be associated with schizophrenia. 30811544_Our findings showed that TCF4 mRNA is upregulated in the corneal endothelium of patients with Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy. 30973406_Our large German cohort demonstrated a significant association between the risk allele G in rs613872 and FECD, irrespective of TNR expansion, although this risk allele was more frequent in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy cases with TNR expansion than without. 31028223_We confirmed that rs613872 in the TCF4 gene is strongly and statistically associated with late-onset FECD in a Greek population. 31081034_Structural basis for preferential binding of human TCF4 to DNA containing 5-carboxylcytosine has been described. 31209209_Study identify TCF4 as a key regulator of neural stem cells (NSCs). TCF4 interacts with Mediator, colocalizes with Mediator at super enhancers and regulates neurogenic transcription factor genes with super enhancers and broad H3K4me3 domains. Data suggest that high binding-affinity for Mediator is an important organizing feature in the transcriptional network that determines NSC identity. 31261288_Coexpression of TCF4 and CD123 is a highly reliable feature of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms. 31276570_This first examination of the sequence structure of CAG repeats in CTG18.1 suggests that factors other than interruptions to the repeat structure account for the absence of disease in some elderly patients with repeat expansions in the TCF4 gene. 31288376_we observed that the beta-catenin/TCF4 complex mediates NRF3 expression by binding directly to the WRE site. 31535015_TCF4 may serve as a master regulator of a gene network dysregulated in schizophrenia at early stages of neurodevelopment. 31540772_these findings suggest that TINCR knockdown inhibits TCF4 by regulating miR-137 expression in colorectal cancer cells 31554942_Trinucleotide repeat expansion in the transcription factor 4 (TCF4) gene in Thai patients with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. 31666615_The subcellular localization of bHLH transcription factor TCF4 is mediated by multiple nuclear localization and nuclear export signals. 31678554_Knockdown of MFI2-AS1 increased cell viability but suppressed apoptosis, inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in LPS-treated chondrocytes by increasing miR-130a-3p and decreasing TCF4, indicating a novel target for the treatment of osteoarthritis 31933004_TCF4 promotes colorectal cancer drug resistance and stemness via regulating ZEB1/ZEB2 expression. 32023836_Regulation of Transcription Factor E2-2 in Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells by Monocyte-Derived TNFalpha. 32280673_Association between a TCF4 Polymorphism and Susceptibility to Schizophrenia. 32319632_Association between KCNQ2, TCF4 and RGS18 polymorphisms and silent brain infarction based on wholeexome sequencing. 32355234_Genetic variant rs613872 in transcription factor 4 (TCF4) is not associated with primary open-angle glaucoma. 32463444_Analyzing pre-symptomatic tissue to gain insights into the molecular and mechanistic origins of late-onset degenerative trinucleotide repeat disease. 32735996_TCF4-mediated Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: Insights into a common trinucleotide repeat-associated disease. 32802179_Super-enhancer-driven AJUBA is activated by TCF4 and involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33054062_Transcription factor 4 (TCF4) expression predicts clinical outcome in RUNX1 mutated and translocated acute myeloid leukemia. 33069932_Various haploinsufficiency mechanisms in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. 33116252_The Fuchs corneal dystrophy-associated CTG repeat expansion in the TCF4 gene affects transcription from its alternative promoters. 33122081_Causal links between major depressive disorder and insomnia: A Mendelian randomisation study. 33174523_Long Noncoding RNA PTPRG Antisense RNA 1 Reduces Radiosensitivity of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Cells Via Regulating MiR-200c-3p/TCF4. 33414364_Transcription factor 4 and its association with psychiatric disorders. 33462220_Survival control of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells requires the transcription factor 4 during olfactory bulb development. 33782268_Relationship of Body Mass Index With Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy Severity and TCF4 CTG18.1 Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion. 34021255_RBM24 exacerbates bladder cancer progression by forming a Runx1t1/TCF4/miR-625-5p feedback loop. 34134113_Molecular and Cellular Function of Transcription Factor 4 in Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome. 34240166_Increased miR-6875-5p inhibits plasmacytoid dendritic cell differentiation via the STAT3/E2-2 pathway in recurrent spontaneous abortion. 34518368_Isoform-Specific Reduction of the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor TCF4 Levels in Huntington's Disease. 34519126_Epilepsy, electroclinical features, and long-term outcomes in Pitt-Hopkins syndrome due to pathogenic variants in the TCF4 gene. 34644448_TCF4 trinucleotide repeat expansion in Swedish cases with Fuchs' endothelial corneal dystrophy. 34686186_Microarray profile analysis identifies ETS1 as potential biomarker regulated by miR-23b and modulates TCF4 in gastric cancer. 34748727_Functional consequences of TCF4 missense substitutions associated with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome, mild intellectual disability, and schizophrenia. 34779502_MicroRNA190b expression predicts a good prognosis and attenuates the malignant progression of pancreatic cancer by targeting MEF2C and TCF4. 34855896_Comparison of TCF4 repeat expansion length in corneal endothelium and leukocytes of patients with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. 34946954_Lower Fractions of TCF4 Transcripts Spanning over the CTG18.1 Trinucleotide Repeat in Human Corneal Endothelium. 35189377_Disruption and deletion of the proximal part of TCF4 are associated with mild intellectual disability: About three new patients. 35322736_Circ_0005526 contributes to interleukin-1beta-induced chondrocyte injury in osteoarthritis via upregulating transcription factor 4 by interacting with miR-142-5p. 35373860_An Osteoporosis Susceptibility Allele at 11p15 Regulates SOX6 Expression by Modulating TCF4 Chromatin Binding. 35501322_Transcription Factor 4 loss-of-function is associated with deficits in progenitor proliferation and cortical neuron content. 35900539_Transcription factor 4 expression and correlation with tumor progression in gallbladder cancer. 35908153_The recurrent TCF4 missense variant p.(Arg389Cys) causes a neurodevelopmental disorder overlapping with but not typical for Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. 36193501_Genetic Polymorphisms in miR-137 and Its Target Genes, TCF4 and CACNA1C, Contribute to the Risk of Bipolar Disorder: A Preliminary Case-Control Study and Bioinformatics Analysis. 36448207_TF and TCF4 gene polymorphisms are linked to autism spectrum disorder: a case-control study. |
ENSMUSG00000053477 |
Tcf4 |
520.314323 |
0.4314059564 |
-1.212882 |
0.095587676 |
160.484424 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000088676501668562885088067550381836032989169709919563098077346868458239027850455843922501191444168061606134756402752827852964401245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000013619824814026932286368372392717434746971022476718434211360972765767624915162559629817201883178467980428649752866476774215698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
280.1790669 |
128.9996614 |
654.5543802 |
215.2266816 |
| ENSG00000196639 |
3269 |
HRH1 |
protein_coding |
P35367 |
FUNCTION: In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Histamine is a ubiquitous messenger molecule released from mast cells, enterochromaffin-like cells, and neurons. Its various actions are mediated by histamine receptors H1, H2, H3 and H4. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. It mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, the increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, the release of catecholamine from adrenal medulla, and neurotransmission in the central nervous system. It has been associated with multiple processes, including memory and learning, circadian rhythm, and thermoregulation. It is also known to contribute to the pathophysiology of allergic diseases such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, anaphylaxis and allergic rhinitis. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:3269; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; G protein-coupled serotonin receptor activity [GO:0004993]; histamine receptor activity [GO:0004969]; neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0030594]; cellular response to histamine [GO:0071420]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; inositol phosphate-mediated signaling [GO:0048016]; memory [GO:0007613]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of inositol trisphosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0032962]; positive regulation of vasoconstriction [GO:0045907]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043114]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
11603849_could be detected at the feto-maternal interface of human 11898002_expressed on monocyte-derived dendritic cells 12218662_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12218662_genetic variant of this protein and body weight change during clozapine treatment in schizophrenia 12429384_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12680587_markedly different potency for activation of multiple signaling pathways by H1- and H2-HRs 12755404_there are three mechanisms for h1 receptor down regulation: phosphorylation of thr-140 or ser-398 or five sites 12757445_No significant differences in H1R or H2R mRNA levels between seasonal allergic rhinitic and nonrhinitic subjects in-season, despite observed differences in H reactivity. 15328002_Thr140 and Ser398 mainly contributed to downregulation, and Thr142 or Ser396 had a slight inhibitory effect on Thr140- or Ser398-mediated process, respectively 15542600_rapid termination of H1HR signaling is mediated by both the kinase activity and RGS function of GRK2 15820830_expression of the histamine (H) receptors 1 (H1) and 2 (H2) by germinal, interstitial, and peritubular cells in the testes of fertile and infertile patients 15928828_gene expression regulation of HRH1 gene by HRH1 15928843_expression in chondrocytes of osteoarthritic cartilage 15953854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16027157_analysis of agonist binding to histamine H(1) receptor 16408006_characterization of important steps in the activation of the human histamine H1 receptor 16484687_These data suggest the use of alternative promoters directing human H1 receptor gene expression, both within and between cell types. 16491014_The H1R-PKC-ERK pathway may play crucial roles in eliciting cytokine production from bronchial epithelial cells stimulated by histamine, leading to airway inflammation 16547808_results exclude the participation of histamine receptors other than the H1 subtype in the control of human intestinal motility by oxogenous histamine 16705383_histamine stimulates integrin alpha-V beta-3 expression in cultured trophoblast cells; the H1 receptor is implicated 16760260_Ascorbate enhancement of seven-transmembrane-spanning membrane receptor activity occurs in both adrenergic and histaminergic receptors. These receptors may play a significant role in maintaining extracellular ascorbate in a reduced state. 16888049_These data suggest postexercise skeletal muscle hyperemia exists in endurance trained men and women. 17122961_Histamine stimulates IL-6 release from SW982 cells by binding to the H1 receptor and this is coupled to the PI/PKC signal transduction pathway. 17243823_The data suggest a global functional analogy between H1 receptor activation and the meta I/meta II charge/discharge equilibrium in rhodopsin. 17517105_Cytokine-induced endothelial intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expressionwas inhibited by tecastemazole in a manner independent of H1 receptor antagonism. 17547532_roles of dermatopontin and histamine receptor H1 genes as downstream targets for the VDR were confirmed by gel electromotility shift and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays that showed the presence of VDR complex binding sequences 17627982_Histamine excites human enteric neurones and this effect involves histamine H1-4 receptors. 17637176_M3R was involved in the up-regulation of H1R by activating H1R gene transcription through a PKC-dependent process. 18258331_a dramatic alteration in the distribution of histamine receptors in colon cancer 18345497_Results describe the molecular interactions between histamine and the human H1 receptor that influence phospholipase C and cyclic AMP signaling. 18366640_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18366640_These results indicate that the polymorphisms analyzed are not a major risk factor for Parkinson disease, although the HRH1Leu449Ser amino acid substitution might be related to PD 18446005_Internalization-mediated changes in the binding properties of H1-receptor antagonists were well correlated with their sedative and non-sedative behaviors. 18498711_results indicate that the beta2AR is involved in the down-regulation of human H1R by inhibiting H1R gene transcription through a PKA-dependent process 18511496_Histamine stimulates phospholipase C-signaling in myometrial smooth muscle cells through H(1) histamine receptors and that GRK2 recruitment is a key mechanism in the regulation of H(1) histamine receptor signaling in human uterine smooth muscle. 18548114_Histamine upregulates keratinocyte MMP-9 production via the histamine H1 receptor 18682391_Histamine-induced Egr-1 expression is dependent on the activation of the H1 receptor, and rapidly and transiently activates PKCdelta, ERK1/2, p38 kinase, and JNK prior to Egr-1 induction. 18814859_anorexia nervosa patients may have higher expression of H1R in the limbic brain, particularly in the amygdala 19156168_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19193342_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19271144_Results compare the correlation between H1-receptor expression and SLPI levels within cultured amniotic epithelial cells derived from chorioamnionitis-complicated and normal pregnancies. 19443731_Human salivary gland cells express histamine H1 receptors and histamine-synthesizing enzymes, revealing the cellular mechanism of antihistamine-induced xerostomia. 19913013_Functional coupling of the H1R to Gq-PLC leads to the activation of RhoA and Rac small GTPases and suggest distinct roles for Rho GTPases in the control of cell proliferation by histamine. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602615_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21255012_Results demonstrate that LPS, through TLR4 activation, up-regulates the expression and function of H1R and amplifies histamine-induced inflammatory responses in HCAEC. 21433074_Measurement of H1R occupancy is a sensitive and absolute method to characterize the non-sedating property of drugs with H1 antagonistic activity. 21686228_H1 and PAR2 receptors enhance delivery of immune-competent cells and molecules by interrupting E-cadherin adhesion in lung epithelial cells. 21697825_crystal structure of the H(1)R complex with doxepin, a first-generation H(1)R antagonist 21730054_the PKCdelta/ERK/poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 signaling pathway is involved in histamine- or PMA-induced up-regulation of H1R gene expression in HeLa cells 21937795_The glu349asp polymorphism of histamine-1 receptor is not associated with antipsychotic induced weight gain. 22169095_evidence supports the involvement of histaminergic and gamma-aminobutyric acidergic mechanisms in the etiology of TS and show an overlap of rare CNVs in TS and autism spectrum disorder. 22860191_[review] The H1, H2, and H3 receptors are all involved in recovery of neurological function when extracellular histamine is gradually increasing, after cerebral ischemia. 23132961_Study revealed that epithelial cells and vascular endothelial cells showed intense immunoreactivity for histamine H1 receptor inperennial allergic rhinitis. 23225320_Histamine was able to synergistically augment bFGF-induced angiogenesis, and this action was linked to VEGF production through H1-receptor. 23414213_Our observations point to a close histamine-/HR-mediated activation of dermal macrophages, leading to modified cell differentiation and responsiveness via H1R, which might contribute to the aggravation of allergic skin inflammation in AD. 23609395_our study does not support the contribution of histamine H1HR gene variants to antipsychotic induced weight gain nor differences in distribution between healthy volunteers and patients with schizophrenia 23677734_In this review, we focus on the role of histamine and its receptors in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. 23900020_Histamine demonstrably inhibited ACh-induced sweating in both mice and humans via H1R-mediated signaling. 23962049_Overexpression of H1R further increases the oxidative output of Duox-expressing HEK-293 cells. 24236486_But carriers of one or three copies of HRH1 (5% of individuals), HRH2 (1.1%) and HRH4 genes (0.9%) were also identified. 24535227_The relationship between the expression of HRH1 and prognosis was found to vary in different types of cancers, even in the same cancer from different databases. 25293806_HRH1 transcript was significantly down-modulated in multiple sclerose compared with health control. 25582918_multiple signaling pathways contribute to histamine-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction via the H1 receptor. 25664905_Thus, the results in the initial study were due to the degradation of histamine in skeletal muscle by ascorbate, because the histaminergic vasodilatation was unaffected by N-acetylcysteine. 25682263_Study suggests that both MAPK p44/p42 and PKC pathways appear to be involved in histamine-upregulated matrix metalloproteinase-9 release via histamine H1 receptors in astrocytes. 25909280_HRH1-17 TT and HNMT-1639 TT genotypes were associated with the allergic asthma phenotype among African-American children and that the ABP 4107 GG genotype was associated with nonallergic asthma among white children. 26635083_Activation of the H1R by its full agonists resulted in a composite potentiating effect. Intriguingly, inactivation of the Gaq-PLC pathway by H1R inverse agonists resulted also in a potentiation of GR activity. 26752109_HRH1-mediated sensitization of TRPV1 is involved in IBS. Ebastine, an antagonist of HRH1, reduced visceral hypersensitivity, symptoms, and abdominal pain in patients with IBS. 27468652_Antihistamines displayed similar kinetic signatures on antagonizing histamine-induced beta-arrestin2 recruitment as compared to displacing radioligand binding from the H1R. 27871651_that histamine H1 receptor activation mediates MAPK activation through PLCbeta, Src, PKCdelta and MEK pathway, but does not lead to nuclear relocalization of phospho-ERK (pERK), classically associated with pro-proliferative changes. 28391980_H1R and H4R are useful biomarkers of allergic inflammation on the ocular surface. Most notably, H4R expressed on eosinophils is useful as a biomarker of eosinophilic inflammation of the ocular surface. 28400155_This study demonstrated that HRH1 gene polymorphisms associated with sedation in clozapine-treated patient with schizophrenia. 29063596_Human H1 receptors in Chinese hamster ovary cells are apparently down-regulated by a sustained increase in intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations with no process of endocytosis and lysosomal/proteasomal degradation of receptors. 29548821_Study identified HRH1 as a receptor frequently overexpressed in basal and HER2-targeted therapy-resistant breast cancer (BC) cells, demonstrating that HRH1 inhibition culminates in apoptotic death and hampers tumor growth. ERK activation was identified as the mechanism through which HRH1 blockade signals to promote death in basal BC cells. 30168182_HRH1 gene polymorphisms may correlate with oral H1-antihistamine efficacy for the treatment of patients with allergic rhinitis, which can be used as a biological indicator of the prediction of therapeutic efficacy of patients with allergic rhinitis. 31406237_Human H1 receptor (HRH1) gene polymorphism is associated with the severity of side effects after desloratadine treatment in Chinese patients with chronic spontaneous uticaria. 31740780_Upregulation of histamine receptor H1 promotes tumor progression and contributes to poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33080103_Histamine receptor 1 is expressed in leukaemic cells and affects differentiation sensitivity. 33918180_Analysis of Missense Variants in the Human Histamine Receptor Family Reveals Increased Constitutive Activity of E410(6.30x30)K Variant in the Histamine H1 Receptor. 34595742_Molecular Signaling and Transcriptional Regulation of Histamine H1 Receptor Gene. 34638832_P2X4 Receptors Mediate Ca(2+) Release from Lysosomes in Response to Stimulation of P2X7 and H1 Histamine Receptors. 35031480_Epigallocatechin gallate stimulated histamine production and downregulated histamine H1 receptor in oral cancer cell lines expressing histidine decarboxylase. |
ENSMUSG00000053004 |
Hrh1 |
114.819899 |
2.3018789750 |
1.202812 |
0.145040084 |
70.041451 |
0.00000000000000005807125644105914863156732579763039941788839285764789455157597330980934202671051025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000445032058707182286344844630164469593118864118065636237275839448557235300540924072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
160.1384730 |
13.9209828 |
70.0144586 |
4.8988218 |
| ENSG00000196689 |
7442 |
TRPV1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NER1 |
FUNCTION: Ligand-activated non-selective calcium permeant cation channel involved in detection of noxious chemical and thermal stimuli. Seems to mediate proton influx and may be involved in intracellular acidosis in nociceptive neurons. Involved in mediation of inflammatory pain and hyperalgesia. Sensitized by a phosphatidylinositol second messenger system activated by receptor tyrosine kinases, which involves PKC isozymes and PCL. Activation by vanilloids, like capsaicin, and temperatures higher than 42 degrees Celsius, exhibits a time- and Ca(2+)-dependent outward rectification, followed by a long-lasting refractory state. Mild extracellular acidic pH (6.5) potentiates channel activation by noxious heat and vanilloids, whereas acidic conditions (pH |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;ATP-binding;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Calmodulin-binding;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Capsaicin, the main pungent ingredient in hot chili peppers, elicits a sensation of burning pain by selectively activating sensory neurons that convey information about noxious stimuli to the central nervous system. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for capsaicin and is a non-selective cation channel that is structurally related to members of the TRP family of ion channels. This receptor is also activated by increases in temperature in the noxious range, suggesting that it functions as a transducer of painful thermal stimuli in vivo. Four transcript variants encoding the same protein, but with different 5' UTR sequence, have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7442; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic spine membrane [GO:0032591]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calcium channel activity [GO:0005262]; calcium-release channel activity [GO:0015278]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; chloride channel regulator activity [GO:0017081]; excitatory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005231]; extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005230]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ion channel activity [GO:0005216]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol binding [GO:0035091]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; temperature-gated ion channel activity [GO:0097603]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0005245]; behavioral response to pain [GO:0048266]; calcium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098703]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to acidic pH [GO:0071468]; cellular response to alkaloid [GO:0071312]; cellular response to ATP [GO:0071318]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to temperature stimulus [GO:0071502]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; chemosensory behavior [GO:0007635]; detection of chemical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050968]; detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050965]; detection of temperature stimulus involved in thermoception [GO:0050960]; diet induced thermogenesis [GO:0002024]; fever generation [GO:0001660]; glutamate secretion [GO:0014047]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; negative regulation of establishment of blood-brain barrier [GO:0090212]; negative regulation of heart rate [GO:0010459]; negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0010917]; negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003085]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; peptide secretion [GO:0002790]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of gastric acid secretion [GO:0060454]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; response to capsazepine [GO:1901594]; response to peptide hormone [GO:0043434]; sensory perception of mechanical stimulus [GO:0050954]; smooth muscle contraction involved in micturition [GO:0060083]; thermoception [GO:0050955] |
11884385_Direct phosphorylation of capsaicin receptor VR1 by protein kinase Cepsilon and identification of two target serine residues 12393854_ASICs are leading acid sensors in human nociceptors and VR1 participates in the nociception mainly under extremely acidic conditions. 12573376_In rectal hypersensitivity, nerve fibres immunoreactive to TRPV1 were increased in muscle, submucosal, and mucosal layers. 12808128_calmodulin binds to a 35-aa segment in the C terminus of TRPV1, and disruption of the calmodulin-binding segment prevents TRPV1 desensitization 12812762_Proposal that residue Y671 is critical for the high relative Ca(2+) permeability of TRPV1 and participates in the structural rearrangements of the channel protein leading to Ca(2+)-dependent desensitization. 14506258_Ser-116 and possibly Thr-370 are the most important residues involved in the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase pathway reduction of desensitization of capsaicin-activated currents. 14506258_Ser-116 and possibly Thr-370 of vanilloid receptor TRPV1 are the most important residues involved in the mechanism of PKA-dependent reduction of desensitization of capsaicin-activated currents 14520770_in fibers of human tooth pulp ... may play a role in perception of dental pain 14630912_vanilloid receptor 1 has a role in regulating vanilloid binding with Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II 14987252_VR1 is widely distributed in the skin, suggesting a major role for this receptor, e.g. in nociception and neurogenic inflammation. 15051629_Review notes that high expression of TRPV1 has been detected in inflammatory diseases of the colon and ileum, whereas neuropeptides released upon sensory nerve stimulation triggered by TRPV1 activation may play a role in intestinal motility disorders. 15190102_Our observations suggest that the homologous TRP domain in the TRP protein family may function as a general, evolutionary conserved AD involved in subunit multimerization 15306801_temperature sensing is tightly linked to voltage-dependent gating in the cold-sensitive channel TRPM8 and the heat-sensitive channel TRPV1 15574747_There is a minor role for transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor-1 as a mediator of cutaneous acid-induced pain. 15644492_TRPV1b receptors are expressed in trigeminal ganglion neurons and contribute to thermal nociception. 15685214_Piperine was agonistic to TRPV1 as measured by patch-clamp techniques. TRPV1 was antagonized by the competitive antagonist capsazepine and the non-competitive TRPV1 blocker ruthenium red. 15691846_Ca2+-dependent desensitization of TRPV1 might be in part regulated through channel dephosphorylation by calcineurin 15708075_Increased urothelial TRPV1 in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity may play a role in the pathophysiology, in concert with increased TRPV1 nerve fibers. 15738111_expression of vanilloid receptor subtype-1 and acid-sensing ion channel genes in the human trigeminal ganglion neurons 15793280_TRPV1 as a significant novel player in human hair growth control. 15992990_A progressive loss of TRPV1 expression in the urothelium as TCC stage increased and cell differentiation was lower. 16081411_several endogenous non-cannabinoid N-acylethanolamines activate TRPV(1) 16099171_Gadolinium activates and potentiates the TRPV1 by neutralizing two specific proton-sensitive sites on the extracellular side of the pore-forming loop. 16301147_may play a role in maintenance of the physiologic condition of the TMJ 16319926_NGF rapidly increases membrane expression of TRPV1 heat-gated ion channels 16406364_Results describe the modification of 12-phenylacetyl-ricinoleoyl-vanillamide and its activity at TRPV1 and CB2 receptors. 16777226_Both TRPV1 and TRPV2 are found in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. 16793902_PAR2 activates PKCepsilon and PKA in sensory neurons, and thereby sensitizes TRPV1 to cause thermal hyperalgesia 16842630_Opioid receptor agonist morphine acts via inhibition of adenylate cyclase to inhibit protein kinase A-potentiated TRPV1 responses. 16996476_TRPV1 antagonists, including TRPV1 siRNAs, have potential in the treatment of both, neuropathic and visceral pain 16996800_Here, we review the potential therapeutic indications and adverse effects of TRPV1 antagonists. 17016800_TRPV1 may play a role in urinary sensory urgency and premature first bladder sensation on filling. 17018028_data support the hypothesis that the TRPV1b splice variant is a naturally existing inhibitory modulator of TRPV1. 17074976_We propose a new model for nerve growth factor (NGF)-mediated hyperalgesia in which physical coupling of TRPV1 and PI3K in a signal transduction complex facilitates trafficking of TRPV1 to the plasma membrane. 17109831_These data do not rule out involvement of TRPV1 in the aetiology of burning dysaesthesia following lingual nerve injury but suggest that TRPV1 at the injury site does not play a primary role. 17176640_Gingerols and shogaols activated TRPV1 and increased adrenaline secretion. 17184838_we assigned a novel role to capsaicin-sensitive TRPV1 channels. They are important Ca2+ influx channels required for cell migration. 17217056_TRPV1 is a nonselective cation channel with significant permeability to calcium, protons, and large polyvalent cations--{REVIEW} 17347480_Capsaicin-induced calcium influx through TRPV1 channels prevents adipogenesis, prevents downregulation of TRPV1 expression and prevents obesity. 17385724_IGF-I and insulin enhance TRPV1 protein expression and activity, and impaired pain sensation might result from distorted TRPV1 regulation in the peripheral nervous system 17392452_Together, these results indicate that tonic TRPV1 activation regulates body temperature. TRPV1 function in thermoregulation is conserved from rodents to primates. 17428642_Recent studies indicate that primary sensory neurons of the pancreas express transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) channels whose activation induces pancreatic inflammation 17442041_TRPV1 gene and protein expression inversely correlated with glioma grading, with marked loss of TRPV1 expression in the majority of grade IV glioblastoma multiforme. 17442052_The advantage of SH-SY5Y(hTRPV1) is the ability of hTRPV1 to couple to neuronal biochemical machinery and produce large quantities of cells. 17508023_Heat-shock-induced MMP-1 expression is mediated by activation of TRPV1 and is dependent on a calcium-dependent signaling process in human epidermal keratinocytes. 17508360_TRPV1 activation induces inflammatory cytokine release in corneal epithelium through MAPK signaling. 17521436_accumulation of TRPV1 and TRPV3 in peripheral nerves after injury, in spared axons, matches our previously reported changes in avulsed DRG. 17560936_Here, we demonstrate the expression of TRPV1 in synovial fibroblasts (SF) from patients with symptomatic osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). 17567713_a novel group of compounds that activate TRPV1 and, consequently, provide a molecular mechanism that may account for off tastes of sweeteners and metallic tasting salts 17582772_TRPV1-positive fibres were overall significantly increased in tongue of Burning mouth syndrome. 17596456_We conclude that phosphoinositides have both inhibitory and activating effects on TRPV1, resulting in complex and distinct regulation at various stimulation levels. 17626206_Tonic activation of TRPV1 channels in the abdominal viscera by yet unidentified nonthermal factors inhibits skin vasoconstriction and thermogenesis, thus having a suppressive effect on body temperature. 17659837_These data provide the first clinical evidence that a TRPV1 antagonist may alleviate pain and hyperalgesia associated with inflammation and tissue injury. 17913835_Incorporation of multiple nonsynonymous polymorphisms, informed by the population-specific haplotype block structure of the TRPV1 gene 17927589_TRPV1 expression was significantly increased in distal small nerve fibre neuropathy compared with controls. 18076848_Increased expression within the pulps of hypomineralised teeth may be indicative of an underlying pulpal inflammation 18222434_Testicular hyperthermia in mice lacking transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor-1 results in a much more rapid and massive germ cell depletion from the seminiferous tubules than in wild-type animals. 18230619_several proton-sensitive sites on the extracellular side of the pore-forming loop of the TRPV1 channel may play an important role as a brake to suppress the excessive activity of this channel under physiological conditions. 18267041_TRPV1 may be involved in pain mechanisms associated with cervical ripening and labor. 18414789_Ara C treatment blocked insertion of TRPV1 in the cell membrane, resulting in accumulation of the receptors in the cytoplasm, loss of capsaicin sensitivity, and membrane-bound immunostaining, which was restored with a rebound on withdrawal of Ara C. 18482991_Increased translocation and multimerization of TRPV1 channels provide a cellular mechanism for fine-tuning of nociceptive responses that allow for rapid modulation of TRPV1 responses independent of transcriptional changes. 18499726_The results of this study support the hypothesis that 4-ONE is a relevant endogenous activator of vagal C-fibres via an interaction with TRPA1, and at less relevant concentrations, it may activate nerves via TRPV1. 18503554_TRPV1 mediates heat shock-induced MMP-1 expression via calcium-dependent PKCalpha signaling in HaCaT cells 18552442_expressed in airway C fibers and activated by neurogenic inflammation which leads to provocaion of cough reflex. 18559878_findings suggest that modification of I696, W697, & R701 to alanine altered channel function by affecting events downstream of initial stimuli-sensing step & imply that intersubunit interactions within the TRP box play an important role in TRPV1 gating. 18574245_PI(4,5)P(2), and not other phosphoinositides or other lipids, is the endogenous phosphoinositide regulating TRPV1 channels 18584893_TRPV1 regulates the expression and secretion of endothelial cell-derived CGRP. 18769453_TRPV1 signaling is a significant, previously unreported player in human sebocyte biology 18786439_Disease-free survival was significantly better in HCC patients with high versus those with low VR1 expression levels. 18787888_May be a mediator or part of a critical pathway in chronic hypoxia-induced proliferation of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 18791833_Full-length TRPV1 has been modeled by assembly of its major modules: the cytosolic N-terminal, C-terminal, and membrane-spanning region, by modeling of the vanilloid receptor in the closed and desensitized states. 18830626_Increased genetic expression may serve as a prognostic factor in prostate cancer. 18852901_Although keratinocytes express TRPV1 mRNA, neither responded to vanilloids with Ca(2+)-cytotoxicity 18983665_relative gene expression ofTRPV1-4 in leukocytes is: TRPV3 C, rs5981521 of pri-miR-325 and SCN10A is related to the development of functional dyspepsia. This involvement differed between Helicobater pylori-positive and -negative patients. 23074220_analysis of the functional interactions between MRGPR-X1 and TRPV1 23123284_These results indicate that CGRP may participate in trigeminal nociceptive system sensitization by induced increase in TRPV1 23139219_Capsaicin inhibits chloride secretion in part by causing NKCC1 internalization, but by a mechanism that appears to be independent of TRPV1. 23183769_an inward calcium current via the TRPV1 channels of endothelial cells correlates with a stronger adhesion between monocytes and endothelial cells 23264624_the direct anchoring of both PKA and AC to TRPV1 by AKAP79/150 facilitates the response to inflammatory mediators and may be critical in the pathogenesis of thermal hyperalgesia. 23279936_these results propose a novel mechanism by which cellular cholesterol depletion modulates the function of TRPV1. 23398938_This study demonstrated an increased activity of TRPV1 in DRG neurons as a new mechanism contributing to opioid withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia. 23453732_TRPV1 and TRPV2 are potential targets for potential therapeutic interventions in cardiovascular disease. 23458684_the activation of TRPM2 channel, which mediates ATP release, and TRPV1 channel plays significant roles in the cellular responses to DNA damage induced by gamma-irradiation and UVB irradiation. 23508958_Excitation and modulation of TRPA1, TRPV1, and TRPM8 channel-expressing sensory neurons by the pruritogen chloroquine. 23510405_This study evaluated the presence of TRPV1 in human and canine mammary cancer cells and the role of TRPV1 in regulating cell proliferation. 23616546_Disruption of the interaction of TRPV1 and an anchoring protein AKAP79 inhibits inflammatory hyperalgesia. 23689362_TRPV1 is a critical disease modifier in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and we identify a predictor of severe disease course and a novel target for MS therapy. 23699529_The results of this study suggested that antagonizing the TRPV1-AKAP79 interaction will be a useful strategy for inhibiting inflammatory hyperalgesia. 23709255_TRPV1 is expressed in cells that are particularly active in Ca(2) exchange as well as in cells with significant water transport activity in eyes of New Zealand White rabbits and humans 23820422_Data suggest that expression of neuronal markers VR1 (vanilloid receptor 1), PGP9.5 (ubiquitin C-terminal hydroxylase-L1, human), and NGFp75 (p75 neurotrophin receptor) in endometrium of women is independent of presence of endometriosis. 23902373_Evodiamine qualifies as structurally unique lead structure to develop new potent TRPV1 agonists/desensitizers. 24002057_Rhinovirus infection causes upregulation of neuronal TRPV1 expression mediated indirectly by virus-induced soluble factors. 24073800_The degradation of claudin-3 and claudin-4 induced by acidic stress could be attenuated by specific TRPV1 blockers. 24084605_In uveal melanoma cells, TRPV1, TRPA1 and TRPM8 gene expression were identified. 24098582_TRPV1 potentiates TGFbeta-induction of corneal myofibroblast development through an oxidative stress-mediated p38-SMAD2 signaling loop. 24139494_IR features an overexpression of TRPV1 in the nasal mucosa and increased SP levels in nasal secretions. Capsaicin exerts its therapeutic action by ablating the TRPV1-SP nociceptive signaling pathway in the nasal mucosa. 24152419_There is increased TRPV1 immunoreactivity in human osteoarthritis synovium, confirming the diseased joint as a potential therapeutic target for TRPV1-mediated analgesia. 24189713_TRPV1 mRNA or protein expression is not increased in the rectal mucosa of Irritable bowel syndrome patients,including visceral hypersensitivity. 24190005_In Burning mouth syndrome patients was increased TRPV1, decreased CB1 and increased CB2 expression in tongue epithelial cells also associated with a change in their distribution. 24275229_sensitization of TRPV1 via activation of TRPA1, which involves adenylyl cyclase, increased cAMP, subsequent translocation and activation of PKA, and phosphorylation of TRPV1 at PKA phosphorylation residues. 24296694_Laryngeal TRPV1 plays an important role in cough sensitivity. 24312564_intact 2-arachidonoylglycerol and 1-arachidonoylglycerol are endogenous TRPV1 activators 24340836_Our study demonstrates that TRPV1 may be a susceptible gene for type 1 diabetes in an Ashkenazi Jewish population 24458144_TRPV1-immunoreactive nerve fibers and NGF have a role in inflammation in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome 24564660_Comparison of the effects induced by mutations in homologous positions in different TRP receptors (or more generally in other distantly related ion channels) may elucidate the gating mechanisms conserved during evolution. [review] 24564662_There is now mounting evidence that TRPV1 receptors may be an important element in modulation of nociceptive information at the spinal cord level and represent an interesting target for analgesic therapy. [review] 24569998_furanocoumarins represent a novel group of TRPV1 modulators that may become important lead compounds in the drug discovery process aimed at developing new treatments for pain management. 24599956_the signaling lipid phosphoinositide 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) has opposite effects on the function of TRPV1 ion channels depending on which leaflet of the cell membrane it resides in. 24658385_Degradation of TRPV1 is mediated by autophagy, and that this pathway can be enhanced by cortisol. 24720453_genetic polymorphism of TRPV1 945G>C could be one of the pathophysiological factors of FD, especially in the case of H. pyloripositive patients in Korea. 24764033_TRPV1-, TRPV2-, P2X3-, and parvalbumin-immunoreactivity neurons in the human nodose ganglion innervate the pharynx and epiglottis through the pharyngeal branch and superior laryngeal nerve 24798548_TRPV1 channels are activated by intracellular long-chain acyl CoAs 24868547_sensory proteins P2X3 and TRPV1 are in correlation with urothelial differentiation, while P2X5 and TRPV4 have unique expression patterns 24871046_Demonstrated how and why these TRP channels TRPV1, TRPA1, and TRPM8 are important to start up a systemic response of energy expenditure, energy allocation, and water retention and how this is linked to a continuously activated immune system in chronic inflammatory diseases. [Review] 24889371_TRPV1 over-expression may be an effective way to induce necrosis and that this approach may not always be associated with enhancement of cancer cell proliferation. 24931369_airway epithelial cells TRPV1 activation potently induces allergic cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) release 25170901_The described L-carnitine osmoprotective effect is elicited through suppression of hypertonic-induced TRPV1 activation leading to increases in L-carnitine uptake through a described Na(+)-dependent L-carnitine transporter 25210497_TRPV1 may play a crucial role in 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid -induced calcium influx, nitric oxide production and angiogenesis. 25216685_High TRPV1 expression is associated with osteoporosis in thalassemia major. 25257701_Genetic variation in TRPV1 and TAS2Rs influence sensations from sampled EtOH and may potentially influence how individuals initially respond to alcoholic beverages. 25266715_fibroblast growth factor-17 and neuregulin 2 were significantly up-regulated in capsaicin-treat |
ENSMUSG00000005952 |
Trpv1 |
46.741829 |
0.2669732893 |
-1.905233 |
0.255363399 |
57.724655 |
0.00000000000003014998992183433340780820569080504943475446247291849033445032546296715736389160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000197520573123069134202150127504788487930705367934258731565932976081967353820800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.2725835 |
3.7722042 |
76.5159041 |
9.0428523 |
| ENSG00000196693 |
7582 |
ZNF33B |
protein_coding |
Q06732 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the zinc finger family of proteins. This gene shows decreased expression in cumulus cells derived from patients undergoing controlled ovarian stimulation. This gene is present in a gene cluster with several related zinc finger genes in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 10. Pseudogenes have been identified on chromosomes 7 and 10. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2015]. |
hsa:7582; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
88.745367 |
0.3625413219 |
-1.463783 |
0.532317685 |
6.737767 |
0.00943926949816967578166249097648687893524765968322753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018186087689986217552640113126471987925469875335693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.6645751 |
14.3466750 |
116.1642231 |
28.4974295 |
| ENSG00000196730 |
1612 |
DAPK1 |
protein_coding |
P53355 |
FUNCTION: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine kinase involved in multiple cellular signaling pathways that trigger cell survival, apoptosis, and autophagy. Regulates both type I apoptotic and type II autophagic cell deaths signal, depending on the cellular setting. The former is caspase-dependent, while the latter is caspase-independent and is characterized by the accumulation of autophagic vesicles. Phosphorylates PIN1 resulting in inhibition of its catalytic activity, nuclear localization, and cellular function. Phosphorylates TPM1, enhancing stress fiber formation in endothelial cells. Phosphorylates STX1A and significantly decreases its binding to STXBP1. Phosphorylates PRKD1 and regulates JNK signaling by binding and activating PRKD1 under oxidative stress. Phosphorylates BECN1, reducing its interaction with BCL2 and BCL2L1 and promoting the induction of autophagy. Phosphorylates TSC2, disrupting the TSC1-TSC2 complex and stimulating mTORC1 activity in a growth factor-dependent pathway. Phosphorylates RPS6, MYL9 and DAPK3. Acts as a signaling amplifier of NMDA receptors at extrasynaptic sites for mediating brain damage in stroke. Cerebral ischemia recruits DAPK1 into the NMDA receptor complex and it phosphorylates GRINB at Ser-1303 inducing injurious Ca(2+) influx through NMDA receptor channels, resulting in an irreversible neuronal death. Required together with DAPK3 for phosphorylation of RPL13A upon interferon-gamma activation which is causing RPL13A involvement in transcript-selective translation inhibition.; FUNCTION: Isoform 2 cannot induce apoptosis but can induce membrane blebbing. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;GTP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Translation regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Death-associated protein kinase 1 is a positive mediator of gamma-interferon induced programmed cell death. DAPK1 encodes a structurally unique 160-kD calmodulin dependent serine-threonine kinase that carries 8 ankyrin repeats and 2 putative P-loop consensus sites. It is a tumor suppressor candidate. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2013]. |
hsa:1612; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; DAPK1-calmodulin complex [GO:1990722]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity [GO:0004683]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097190]; cellular response to hydroperoxide [GO:0071447]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; defense response to tumor cell [GO:0002357]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of autophagic cell death [GO:1904094]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of NMDA receptor activity [GO:2000310]; regulation of response to tumor cell [GO:0002834] |
11809677_To determine the extent of promoter hypermethylation in early lung tumorigenesis, we analyzed promoter methylation status of the p16, death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) and glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) genes 12031912_upregulated significantly in acute myeloid leukemia patients whose white blood cell count was higher than 100 x 10(9)/L cells 12082610_promoter methylation studied in 80 patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) 12370243_Results indicate that DAP-kinase exerts apoptotic effects by suppressing integrin functions and integrin-mediated survival signals, thereby activating a p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. 12708480_Suppression of DAP kinase expression by DNA methylation might play a substantial role in the development of not only B-cell, but also T- and NK/T-cell lymphomas. 12730201_DAP kinase binds to syntaxin 1A in a signal transduction pathway 12792765_Frequent death-associated protein-kinase promoter hypermethylation is associated with brain metastases of solid tumors 12820391_Hepatoma cells may escape from apoptosis through the loss or reduction of DAP-kinase expression, while the block of IFN-gamma signal transduction as well as the methylation of promoter region may reduce the expression of DAP-kinase protein. 14504087_Loss of DAP-kinase function may be an early event in the transformation pathway to secondary leukemia via myelodysplasia. 14530257_cellular activities of DAPK are critical for antagonizing caspase-dependent apoptosis to promote cell survival under normal cell growth conditions. 14612952_DAPK promoter methylation and down-regulation is tightly associated with gastric atrophy, often contributes to the preneoplastic changes in gastric carcinogenesis. 14767518_DAPK downregulation and methylation of the DAPK promoter may be involved in carcinogenesis of human uterine and ovarian tissues 15018706_the expression of DAP kinase, p19ARF, p53, and p21WAF1 was significantly down-regulated in the chronically HIV-1SF2-infected HUT78 T cells 15048887_Expression and phosphorylation of DAP kinase in hippocampus of patients with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy is significantly increased compared with autopsy controls. 15492995_although DAP kinase alteration was relatively rare, DAP kinase alteration and/or p53 mutation may associate with tumor progression in soft-tissue LMSs 15634757_DAP kinase is involved in TRAIL-mediated cell apoptosis and a demethylating agent may have a role in enhancing TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in some NSCLC cells by reactivation of DAP kinase 15809761_DAP-kinase promoter methylation may be a potential prognostic marker for gastric cancer patients 16085644_DAPK has a role as a sensor of mitochondrial membrane potential 16142356_DAPK does not regulate radiation-induced cell death 16213824_RSK-mediated phosphorylation of DAPK is a unique mechanism for suppressing the proapoptotic function of this death kinase in healthy cells as well as Ras/Raf-transformed cells. 16847012_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847012_These data suggest that genetic variation in DAPK1 modulates susceptibility to LOAD. 16858683_Aberrant methylation and hence silencing of TIMP3, SLC5A8, DAPK and RARbeta2, in association with BRAF mutation, may be an important step in PTC tumorigenesis and progression. 16951219_The promoter hypermethylation of DAPK-1 is a marker of aggressive renal cell carcinoma and provides independent prognostic information on disease outcome. 17056602_the apoptosis regulatory activities mediated by DAPK are controlled both by phosphorylation status and protein stability 17209433_TIMP3, DAPK1 and AKR1B10 are important for squamous cell lung cancer tumorogenesis while AKR1B10 is potential oncogene whereas TIMP3 and DAPK1 are potential tumor suppressor genes. 17244621_data highlight a naturally occurring DAPK-1 mutation that alters the oligomeric structure of the death domain, de-stabilizes DAPK-1 binding to ERK, and prevents ERK:DAPK-1-dependent apoptosis 17319784_Aberrant hypermethylation on DAPK1 promoter is associated with the development of brain metastases from solid tumors 17324927_suggest that DAPK-1 forms a multiprotein survival complex with cathepsin B countering the rate of TNFR-1-dependent apoptosis 17324930_DAPK is found in two distinct immune complexes, one containing HSP90 and CHIP and a second complex containing only DIP1/Mib; strict modulation of DAPK activities by HSP90 heterocomplexes is critical for regulation of apoptosis and cellular homeostasis 17477876_results showed RASSF1A & DAPK genes' promoter methylation occurred frequently in lung tumors, although prevalence of this alteration in these genes was not associated with smoking status of the patients or occurrence of mutations in K-ras, p53 & EGFR 17523078_Promoter hypermethylation of DAPK was observed. 17540169_Study shows that loss or reduced expression of DAPK1 underlies cases of heritable predisposition to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and epigenetic silencing of DAPK1 by promoter methylation occurs in almost all sporadic CLL cases. 17592394_TIMP-3 promoter hypermethylation is elevated in HNSCC and is highly correlated with DAPK hypermethylation, implying a functional relationship between these genes. 17683884_Sodium arsenite caused DAPK promoter hypermethylation and gene silencing which may be involved in arsenic-induced carcinogenesis. 17690039_the DAPK gene epigenetically affected by methylation may be associated with the carcinogenesis of cholangiocarcinoma 17703233_these findings establish a major role for DAPk and its specific interaction with PKD in regulating the JNK signaling network under oxidative stress. 17868341_The promoter methylation of the DAPK gene is an important event during carcinogenesis and may have potential clinical application as a marker for the progression and prognosis of cancer. 17895359_study reports that DAP kinase 1 promotes in vitro & in vivo phosphorylation of tropomyosin-1 on Ser283 & that this phosphorylation is essential for the H2O2-induced organization of the assembly of actin stress fibers in endothelial cells 17953697_Exposure to arsenic may induce DAPK promoter hypermethylation and inactivate the function of DAPK in urothelial carcinoma. ...a key molecular event ...in the malignant phenotype of tumour arising in patients from arsenic-contaminated environments 18026971_Methylation of the DAPK gene is associated with cell transformation in HPV and EBV infection in cervical cells 18195017_a role for MAP1B in DAPK-1-dependent signaling in autophagy and membrane blebbing. 18292548_Expression of dominant-negative and constitutively active death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) selectively inhibits T cell receptor-activated NF-kappaB and T cell activation. 18336955_No association of DAPK1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism on chromosome 9 with Alzheimer's disease. 18336955_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18349282_Methylation of DAPK1 was present in 80% of NSCLC tissues but only 14% of noncancerous tissues. 18422656_These data highlight the existence of an alternative product of the DAPK-1 locus, and suggest that proteolytic removal of the C-terminal tail of s-DAPK-1 is required to stimulate maximally its membrane-blebbing function. 18425396_Promoter methylation of death-associated protein kinase has a role in irradiation response in cervical cancer, although it might not directly be responsible for the cellular radiosensitivity 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18583991_Results show that the serine/threonine kinase death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) is involved in the signal transduction of neogenin. 18799028_Promoter methylation may lead to inactivation of the DAPK gene, and may be related with tumorigenesis of cervical cancer. 18813964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18830724_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18974095_a novel interaction between DAPK and TSC2 proteins that has revealed a positive link between growth factor stimulation of DAPK and mTORC1 signaling that may ultimately affect autophagy, cell survival, or apoptosis. 18995835_DAPK-ZIPK-L13a axis forms a unique regulatory module that first represses, then repermits inflammatory gene expression. 19018866_results suggested that DAPK1 promoter methylation might play a significant role in the progression of chronic myeloid leukemia 19094228_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148529_of promoter hypermethylation of TIMP3, CDH1, DAPK, RASSF1A, p16INK4A and MGMT, only the epigenetic silencing of TIMP3 and CDH1 predicted a better outcome in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma 19180116_Data show that DAPK phosphorylates beclin 1 on Thr 119 located at a crucial position within its BH3 domain, and thus promotes the dissociation of beclin 1 from Bcl-XL and the induction of autophagy. 19196380_Aberrant methylation of DAPK1 gene promoter had no influence on the prognosis of MDS despite of its increasing occurrence during disease progression 19212339_the promoter of DAPK1 was typically methylated in NK and NK/T cell lines, but not in T-ALL cell lines 19237746_Nucleotide-induced changes are localized to the glycine-rich loop region of DAPK. 19259700_The Preoperative measurement of methylated Death-associated protein kinase promoter DNA in peripheral blood may contribute to better estimate postoperative survival chances of patients with esophageal carcinoma, especially adenocarcinoma. 19267229_identify a function of s-DAPK-1 in controlling the half-life of DAPK-1 protein itself and indicate that the degradation of each gene product is controlled by two distinct degradation pathways 19272801_Findings suggest that quantitative methylation analysis of BCL2 and hTERT, but not DAPK, in urine sediment may be a useful tool in the diagnosis of NMI UCB, deserving future applicability studies. 19395874_DAPk phosphorylates Beclin 1 on T119, a critical residue within its BH3 domain, and thus promotes Beclin 1 dissociation from Bcl-X(L) and autophagy induction. 19506903_p16INK4A, DAPK1, PTEN and MT1G genes were not frequently methylated in the stage I non-small cell lung cancer in China. 19521987_Loss of Med1 expression directly correlates with a loss of dapk1 expression in a number of human lung cancers and cancer cell lines. 19627511_DAPK1 was expressed in neurones of aged human frontal cortex, both in Alzheimer's disease and in control cases. 19695681_promoter hypermethylation of the p16, Runx3, MGMT, and DAPK genes may play an important role in the pathogenesis of gastric precancerous lesions and early gastric adenocarcinoma 19778817_5-aza-dc can inhibit the growth and induce apoptosis of bladder cancer cells through reversing unmethylation status of DAPK promoter. 19795445_Hypermethylation of DAPK was significantly associated with shorter time to recurrence of nonsmall cell lung cancer. 19878310_DAPK expression can be detected in some cancers, but its function is still repressed, suggesting that DAPK activity can be subverted at a post-translational level in cancer cells. Review. 19917631_death-associated protein kinase gene regulation leads to differentially silenced transcripts by methylation in cancer 19957692_No DAPK promoter hypermethylation was found in retinoblastoma tissues. 20005690_This review will summarize the functional and mechanistic studies that have linked DAP-kinase to the regulation of autophagy in general, and autophagic cell death, in particular. 20018188_Data demonstrate that c-mip interacts with Dip1 and upregulates DAPK, which blocks the nuclear translocation of ERK1/2. 20103772_Data show that the ability of DAPK to bind CaM correlated with its catalytic activity. 20220139_activation of DAPK by PP2A was found to be required for ceramide-induced anoikis. 20360646_Promoter hypermethylation of RASSF1A, p16, and DAPK genes was detected in lung cancer. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20413850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20471512_Epigenetic alterations by methylation of DAPK1 promoter sequences are associated with mammary carcinoma. 20514412_Endogenous DAPK mRNA may represent a potential candidate for molecularly targeted anticancer therapies. 20534741_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20574532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20630662_inactivation of DAPK by promoter hypermethylation mightcontribute to the initiation of the neoplastic process and development of ulcerative colitis -associated carcinoma. 20655775_Promoter methylation of DAPK1, E-cadherin and thrombospondin-1 in de novo and therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20682398_Investigated the methylation of the SFRP2, P16, DAPK1, HIC1, and MGMT genes, as well as the mutation of amino acid codons 12 and 13 of the KRAS gene in normal and tumor tissue DNA of patients diagnosed with sporadic colorectal cancer. 20682398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20704749_Combined effects of cigarette smoke and hypermethylations of DAPK are associated with non small cell lung cancer. 20811724_Demonstrate that DAPK regulates the survival of various kinds of human uterine cancer cell lines. 21115918_Highest frequencies of DNA methylation in DAPK gene were found in head and neck squamous cell tumours with aneuploidy. 21134130_TSC2 binds to the death domain of DAPK. This interaction is required for TSC2 to reduce DAPK protein levels and half-life. DAPK is regulated by the lysosome pathway. Lysosome inhibition blocks TSC2-mediated degradation of DAPK. 21152427_Studies show that the homodimerization of DAPK catalytic domain and the crucial role played by its basic loop structure that is part of the molecular fingerprint of death protein kinases. 21152877_The methylation of BNIP3 and DAPK can predict lower response to chemotherapy and poor prognosis in gastric cancer. 21159370_DAPK hypermethylation was neither specific for the tissue of origin nor for cancer. The high prevalence of leiomyoma compromises the utility of this gene as a serum marker for early ovarian cancer detection. 21167819_Variation in DAPK1 gene influences susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease in the northern Han Chinese population. 21172653_The recruitment of PP2A to UNC5H2/B allows the activation of DAPk via a PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation and that this mechanism is involved in angiogenesis regulation. 21176336_dapk gene promoter hypermethylation may be a common molecular event in AML. 21212658_we have demonstrated an aberrant methylation status in the CpG island of the promoter region of the DAPK1 gene in Chinese myelodysplastic syndrome patients 21287504_The p16, DAPK and RAR beta genes methylation are strongly associated with clinical data of non-small cell lung cancer, and methylation of p16 and DAPK genes are associated with tobacco smoking. 21302620_DAPK methylation in cancer tissues was significantly associated with the extent of differentiation and lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. 21311567_new roles of DAPK in modulating microtubules assembly and neuronal differentiation,tau phosphorylation (event associated with Alzheimer's disease pathology) 21353277_LMP1 of Epstein-Barr virus regulates DAPK1 in lymphoblastoid cell line. 21497122_Phosphorylation of Pin1 Ser71 by DAPK1 inhibits its catalytic activity and cellular function, providing strong evidence for an essential role of the Pin1 enzymatic activity for its cellular function. 21516484_DAPK hypermethylation is an early event in oral carcinogenesis. 21725354_Data show that pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) was a binding partner of death-associated protein kinase (DAPk). 21749573_DAPK1 intronic variants do not increase the risk of Parkinson's disease; further functional studies are required to elucidate the potential therapeutic implications of the dimerization of Dapk1 and Lrrk2 proteins. 21797120_DAPK negatively regulates Fas-mediated apoptosis in these human differentiated endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. 21918973_study concludes DAPK1 methylation in the 5' regulatory region is a very rare and most likely biologically not significant event in primary myeloblasts of acute myeloid leukemia and bone marrow cells of myelodysplastic syndrome patients 21922274_APAF-1, DAPK-1 and SPARC may have a role in progression and higher tumor stage of renal cell carcinoma in North Indian population 21965790_DAPK1 expression did not show any meaningful value in predicting outcome for patients with breast cancer. 21979297_DAPK mRNA and protein expression levels are association with DAPK promoter methylation in gastric cancer tissues of patients from central China. 22095288_DAPk is required for the induction of autophagy under oxidative stress.PKD, a known DAPk substrate, is a downstream mediator of DAPk-induced autophagy. 22096027_Flt3ITD promotes a noncanonical pathway via TAK1 and p52NF-kappaB to suppress DAPK1 in association with histone deacetylases, which explains DAPK1 repression in Flt3ITD(+) acute myeloid leukemia. 22116316_trend toward increasing methylation with severity of cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion cytology 22136354_Promoter hypermethylation of tumor suppressor DAPK1 is associated with prostate carcinoma. 22160140_Sodium butyrate induced DAPK1/2 expression in human gastric cancer cells and this expression prompted apoptosis by decreasing FAK levels. 22230750_Hypermethylation of DAPK is associated with cholangiocarcinoma. 22371043_There was no statistically significant difference in the percentage of methylation of the DAPK genes (Fisher test, p = .190) and p16 gene (Fisher test, p = .316) between the vulvar lichen sclerosus group (study) and the control group. 22420243_Stable angina patients had 5.1-times higher plasma level of DAPK1 nucleic acids (mRNA and DNA) than controls. 22465880_our data findings suggest that DAPk1 can mediate the pro-apoptotic activity of TNF-alpha and INF-gamma via the NF-kappaB signaling pathways. 22490852_Methylation of DAPK is involved in cervical carcinogenesis, and DAPK gene promoter methylation occurs in the early development of cervical cancer in Uyghur women in Xinjiang. 22490855_The expression of DAPK1 and CD147 is closely correlated with the clinicopathological characteristics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 22549447_The CpG islands of p16, DAPK and MGMT genes are hypermethylated in HL60 cells. Azacytidine inhibits proliferation of leukemic cells by hypomethylation of p16, DAPK and MGMT genes. 22552543_acquisition of fluorouracil-resistance may be accompanied by impairment of common apoptotic signals regulating both DAPK-dependent and DAPK-independent pathways. 22785394_We showed a positive association between rs4878104 and frontotemporal dementia , suggesting a possible implication of the DAPK1 genetic variant in the susceptibility to frontotemporal dementia 22827846_In the -197 A allele carrier with *1249 CC homozygote of IL17A, the methylation of DAPK and CDH1 increased gradually, but more rapidly, with age. 22988864_The GTP binding regulates DAPK catalytic activity in a novel manner by enhancing autophosphorylation on inhibitory Ser308, thereby promoting the kinase 'off' state. 23175185_The expression of kinase-dead DAPK or silencing DAPK (siDAPK) in CCN2 transfectants restored metastatic ability. 23245584_More aggressive managements should be considered in resected buccal cancer patients with both very close margin and DAPK promoter hypermethylation rather than post-operative observation or radiotherapy alone 23275143_Concurrent methylation of MGMT and DAPK genes could be the marker of tumor chemoresistance and disease recurrence. 23383130_Allele-specific methylation in DAPK1 is associated with allele-specific expression and potentially predisposing to chronic lymphocytic leukemia.. 23494221_Promoter methylation may therefore lead to the inactivation of the DAPK1 gene, and may be related to the progression of cervical oncogenesis. 23545262_Knockdown of DAPK1 attenuates curcumin-induced inhibition of STAT3 and NF-kappaB. Moreover, DAPK1 suppression diminishes curcumin-induced caspase-3 activation. 23702034_DAPK functions as a scaffold for the LIMK/cofilin complex and triggers a closer interaction of both proteins under TNF stimulation. 23800064_DAPK1 has a role in inducing autophagy in human dermal fibroblats treated with resveratrol 23804521_deregulation of p16-associated, and MLH1-associated pathways, because of promoter hypermethylation, is associated with increased cancer cell migration, tumor invasiveness, and, thus, aggressive phenotype 23806751_This review describes DAPK as a novel signaling pathway involved in mediating protective effects of shear stress on the vasculature. 23948915_DAPK1 is upregulated and accumulates in the brain of human tau transgenic mice. 24071855_An association between the T-allele of the rs16906252 SNP and MGMT methylation was observed (p-value=0.04), and DAPK1 methylation of the A-allele was associated with shorter overall survival (p-value=0.006). 24188325_In conclusion, hepatitis B virus x protein induces autophagy via activating DAPK in a pathway related to Beclin 1, but not JNK. 24314662_Methylation in the papillomavirus L2/L1 genes and in cellular DAPK1 is highly associated with the progression of cervical cancer. 24337450_The study identified a novel function of DAPK in regulating cellular VEGF/HIF-1alpha activity during tumorigenesis, which may act together with its anti-angiogenic function to inhibit tumor progression. 24531619_Viral infection induced DAPK1-IRF7 and DAPK1-IRF3 interactions and overexpression of DAPK1 enhanced virus-induced activation of the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) and IFN-beta promoters and the expression of the IFNB1 gene. 24559316_miR-34b/c, in addition to DAPK1 and miR-34a might be inactivated by DNA hypermethylation, in in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 24811488_Methylation of DAPK1, miR-34a and -34b/c is tumour-specific, and associated with gene/miRNAs silencing in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 24814955_The presence of aberrant DAPK1 methylation in bone marrow significantly reduced progression-free survival following immunochemotherapy, independent of Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index score. 24853415_Suggest that DAPK1 is a novel regulator of tau protein abundance, and that DAPK1 upregulation might contribute to tau-related pathologies in Alzheimer disease. 24877104_The results show that DAPK promoter hypermethylation and repressed expression of DAPK protein were more common in central neurocytoma than in oligodendroglioma. 25135476_Study shows that DAPK1 expression is regulated by ASK1, in response to IFN gamma and aids in the execution of autophagy. 25229255_DAPK1 methylation is associated with poor overall- and disease-specific survival in a large cohort of DLBCL patients uniformly treated with rituximab. 25268905_DAPK1 promoter methylation may be a biomarker during cervical carcinogenesis that might serve as an early indication of cervical cancer. [Meta-analysis] 25380824_These data define a novel link between DAPK and HSF1 and highlight a positive-feedback loop in DAPK regulation under mild inflammatory stress conditions in colorectal tumors. 25496179_Hypermethylation and down-regulation of DAPk1 were closely related to lymph node metastasis, advanced tumor stage, and low survival rates in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 25550789_DAPK1 gene over-expression can suppress the proliferation, migration, and invasion of carcinoma of pancreas BxPC-3 cell line 25848215_The frequency of DAPK methylation was significantly higher in lung cancer than in non-malignant lung tissues. 25963636_The authors discuss evidence suggesting potential contributions of DAPK in the regulation of gut inflammation and intestinal homeostasis. [review] 26075823_high DAPK1 expression causes increased cancer cell growth and enhanced signaling via the mTOR/S6K pathway; evaluation of breast cancer patient data sets revealed that high DAPK1 expression associates with worse outcomes in women with p53-mutant cancers 26100670_Besides mediating the anticancer effect, pDAPK(S308) may serve as a predictive biomarker for Raf inhibitors combination therapy, suggesting an ideal preclinical model that is worthy of clinical translation. 26165472_DAPK1 is highly expressed in the peritumoral region of glioblastoma multiforme brain neoplasms. 26191186_miR-191-DAPK1 axis may play an important role modulating the response of ovarian endometriosis and endometrioid carcinoma cells to TNF-alpha. 26213212_Results identified MGMT and DAPK1 as predictors of nodal metastasis in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma with a high predictive value and specificity and sensitivity. 26267895_A significant strong association between DAPK1 promoter methylation and CC was shown and confirmed independently by histological tumor type, method used to evaluate methylation and source of control samples. 26405175_DAPK seems to be a major player that influences the migratory capability of disseminating tumor cells and possibly affects the dynamic interface between pro- and anti-survival factors at the invasion front of colorectal cancer. 26406950_Our meta-analysis results reveal that DAPK promoter methylation might be associated with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in NSCLC patients, although no correlation with histological types and TNM stage in NSCLC patients were found. 26582930_downregulation of HOXC9 releases its transcriptional inhibition of DAPK1, resulting in the activation of the DAPK1-Beclin1 pathway, which induces autophagy in glioblastoma cells 26626260_Results show that CYP1B1 may promote renal cell carcinoma development by inducing CDC20 expression and inhibiting apoptosis through the down-regulation of DAPK1. 26810771_DAPK-1 and MLH1 methylation correlated inversely in tumors in the middle-third of the stomach 26823825_testing for DNA methylations of MGMT plus DAPK1 genes holds some promise for high grade cervical disease screening 27085326_Authors observed the cleavage of ATF6, the phosphorylation of MRLC, and the expression of death-associated protein kinase (DAPK1) by western blotting; the transcription of DAPK1 by RT-PCR; and the subcellular localization of ATF6 and mAtg9 by immunofluorescence. 27094130_in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains, elevated DAPK1 levels showed co-relation with the increase of APP phosphorylation. Combined together, these results suggest that DAPK1 promotes the phosphorylation and amyloidogenic processing of APP, and that may serve a potential therapeutic target for AD. 27286455_Data show that silencing DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) increased expression of tumor suppressor genes, RASSF1A and DAPK, in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells and ESCC xenograft in nude mice. 27452040_The sensitivity was found to be 62% and 83% for DAPK1 and SOX1, respectively, when analyzed separately in the singleplex assay, but increased to 90% in the multiplex assay when either or both of the SOX1 and the DAPK1 gene promoters showed methylation. 27590344_A transcription factor complex consisting of ATF6 (an endoplasmic reticulum-resident factor) and C/EBP-beta is required for the IFN-gamma-induced expression of DAPK1 IFN-gamma-induced proteolytic processing of ATF6 and phosphorylation of C/EBP-beta are obligatory for the formation of this transcriptional complex 27622827_The current study supports a relevant role for p15, p16, and DAPK hypermethylation in the genesis of the plasma cell neoplasm. DAPK hypermethylation also might be an important step in the progression from MGUS to MM. 27633052_the present study demonstrated that DAPK contributed to the Hcyinduced endothelial apoptosis via modulation of Bcl2/Bax expression levels and activation of caspase 3 27907054_The result suggests that DAPK promoter methylation is significantly increased in bladder cancer patients compared to normal controls. DAPK promoter methylation could serve as a biomarker for bladder cancer detection and management. 27930338_the DAPK-mTOR pathway is critical for anti-HCV effects of peg-IFN-alpha 28132841_Study provides evidence that DAPK1 is a negative-feedback regulator of the RIG-I pathway. RIG-I-mediated antiviral signaling activates DAPK1 kinase activity and DAPK1 inactivates RIG-I RNA sensing by direct phosphorylation of RIG-I. 28231808_Results show that DNA demethylation of distinct promoter regions is associated with re-expression of the tumor suppressor gene DAPK1. Its knockdown promotes tumor cell migration in breast cancer cell line. 28249042_Meta-analysis suggested that aberrant methylation of DAPK promoter was associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 28324774_findings evidence a positive correlation between SIRT1 and BCL6 expression increase in follicular lymphomas (FL) . SIRT1 methylation decreases in FL and diffuse large-B cell lymphomas (DLBCL)and this parallels the increase of KLF4, DAPK1 and SPG20 methylation 28339067_our study characterized DAPK1 as a novel transcriptional target of BRMS1. Transcriptional activation of DAPK1 might be another important mechanism accounting for the metastasis suppressive activity of BRMS1. 28361856_Down-regulation of mRNA expression was found in cases in which CASP8, TMS1 and DAPK were hypermethylated. 28388658_results suggest that DAPK1 is an important prognostic marker and therapeutic target for bladder cancer and have identified possible therapeutic agents for future testing in bladder cancer models with low DAPK1 expression 28412611_DNA hypermethylation of DAPK1 gene promoter is a promising biomarker for OSCC prediction/prognostics 28429084_rs4878104 T allele could significantly regulate increased DAPK1 expression in European population 28429233_A significant correlation between changes in the levels of expression and methylation was detected for the three apoptosis-regulatory genes (APAF1, DAPK1, and BCL2). The results suggest that methylation play an important role in the regulation of the apoptosis system genes in breast cancer. 28614711_Authors find that the LTP specificity of CaMKII synaptic accumulation is due to its LTD-specific suppression by calcineurin (CaN)-dependent DAPK1 activation, which in turn blocks CaMKII binding to GluN2B. 28858643_It is this DAPK1-NR2B interaction that arbitrates the pathological processes like apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy of neuronal cells observed in stroke injury, hence we aimed to inhibit this vital interaction to prevent neuronal damage. 28934284_DAPK1 methylation is associated with the risk of gastrointestinal cancer. 29317503_promoting ER stress-ATF6-DAPK1 signaling in transporting enterocytes counters the transcellular passage of bacteria evoked by dysfunctional mitochondria 29480000_High Promoter Methylation of DAPK1 gene is associated with Breast Cancer. 29578152_Our results showed that DAPK promoter methylation is tightly correlated with clinicopathological features of NSCLC and is associated with poor prognosis in patients. 29775889_LncRNA MIR22HG could act as a tumor suppressor and inhibited EC cells proliferation through regulating miR-141-3p/DAPK1 axis. 29807777_DAPK1 methylation level is associated with gliomas clinical features and outcomes 30460377_Silencing of DAPK1 in colorectal cancer cell lines promoted the metastasis and chemoresistance due to increased stemness of cancer stem cells and enhanced mesenchymal phenotype, an effect that was mediated via activation of the transcription factor, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1). 30664712_Results indicate that miR-483-5p inhibits the expression of death associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) by targeting the DAPK1 3'-UTR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells. 30718039_Study demonstrates that the loss of miR-26a caused by a reduction in the transcription factor C/EBPalpha in Parkinson's Disease (PD) mice and patients with PD leads to an elevation in DAPK1 expression posttranscriptionally. 30911150_Investigated the ability of death associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) to regulate neutrophil apoptosis and further explored whether 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine (Aza) can accelerate inflammatory resolution in acute respiratory distress syn |
ENSMUSG00000021559 |
Dapk1 |
372.890040 |
0.4468644793 |
-1.162091 |
0.164601615 |
49.013926 |
0.00000000000254151724270866935794693665112212042000647271855484632396837696433067321777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000014757196893147112348866498816430628971546612504539552901405841112136840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
224.3497151 |
34.6513318 |
504.5826093 |
55.7707716 |
| ENSG00000196754 |
6273 |
S100A2 |
protein_coding |
P29034 |
FUNCTION: May function as calcium sensor and modulator, contributing to cellular calcium signaling. May function by interacting with other proteins, such as TPR-containing proteins, and indirectly play a role in many physiological processes. May also play a role in suppressing tumor cell growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1372446, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22399290}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Direct protein sequencing;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may have a tumor suppressor function. Chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in breast cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6273; |
calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; transition metal ion binding [GO:0046914]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542] |
11260185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11813862_decrease in S100A2 staining from normal to cancer cases is more pronounced in glandular than in squamous epithelial tissue 11956617_Expression of S100A2 protein in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus 14519656_DeltaNp63 transactivated the S100A2 promoter, and significantly more fold changes were seen in DeltaNp63-introduced cells than in p53-introduced cells, suggesting that DeltaNp63 may be a novel stimulator of the S100A2 promoter. 15467767_Strong S100A2 expression was often associated with increasing levels of disorder in preinvasive bronchial lesions in non-small cell lung cancer. 15941720_in oral cancer cells the Ca(2+)- and cell cycle-dependent p53-S100A2 interaction might modulate proliferation 16015083_The five genes, and three of the encoded proteins, were shown differentially expressed between a group of keratoconus patients and a reference group using different techniques 16232198_abnormal transcription of TACSTD2 and S100A2 are thought to be unique molecular markers of the preinvasive stage of lung adenocarcinoma 16273244_S100A2 expression was demonstrated to be the only independent factor for late cervical metastasis. 16367903_Involvement of S100A2 and S100A4 in the progression of lung adenocarcinomas provides a list of targets regulated by S100A2 and S100A4. 16449968_S100A2 gene, whose transcript and protein are induced during keratinocyte differentiation, is a direct transcriptional target of p73beta and DeltaNp63alpha and is required for proper keratinocyte differentiation 17032501_results demonstrate frequent cytosolic overexpression of S100A2 and S100A4 in Barrett's adenocarcinoma 17067748_Increased S100 A2 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer 17077493_Preliminary analysis of the X-ray data indicates that there are two subunits per asymmetric unit. 17123307_S100A2 was down-regulated in lymph node metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma, head and neck neoplasms (SCCHN), suggesting that instead of being a putative tumor suppressor, S100A2 may play a role in the metastasis of SCCHN 17239974_Zn2+ might deactivate S100A2 by inhibiting response to intracellular Ca2+ signals 17874182_STMN1, but not SYK or S100A2, have roles in preventing progression of ER-positive primary breast cancer 18388131_Gene regulation is mediated by a novel transcriptional element in the S100A2 promoter which is bound by TAp63gamma but not by p53. 18656279_Analysis of S100A2 expression revealed that expression in adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas is significantly different, but not related to any of the found alterations. 18669640_S100A2 and S100A6 interact with another TPR protein Tom70 and regulate the Tom70-ligand interaction in vitro 18773213_Survival after UVA irradiation was greater in human keratinocytes compared to mouse skin with no S100A2 expression, showing a protective role for S100A2. A S100A2-dependent difference was observed in the induction of Cxcl13 transcripts in transgenic mice. 19118029_These findings identify S100A2 as a strong metastasis inducer in vivo. 19297317_S100A2 bound monomeric p53 as well as tetrameric, whereas S100A1 only bound monomeric p53. 19344608_Diminished expression of S100A2, a putative tumor suppressor, is an independent predictive factor of neck node relapse in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 19376121_S100A2 expression is a good predictor of response to pancreatectomy for Pancreatic Cancer and suggests that high S100A2 expression may be a marker of a metastatic phenotype. 19601998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19725154_S100A2 and p63 protein both play important roles in the carcinogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). An investigation into the combined expression of S100A2 and p63 may be helpful in early diagnosis. 20591429_S100A1, S100A2, S100A4, S100A6 and S100B interacted with MDM2 (2-125). 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20823519_Although the diffraction data of S100A2 were recorded at a wavelength of 0.90 A, which is usually not assumed to be suitable for calcium/sulfur SAD, the anomalous signal was satisfactory. 20949468_Loss of Reprimo and S100A2 expressions occurs frequently in gastric adenocarcinomas. The expressions of Reprimo and S100A2 may be potential biomarkers for gastric adenocarcinomas detection. 21029261_The coding sequence polymorphism S100A2_185G>A had no regulatory role in S100A2-mediated tumor suppression in oral cancer. 21443102_S100A2 is upregulated in gastric adenocarcinoma and is associated with tumor progression. 22747445_findings highlight an important link between the TGF-beta1-induced MAPK and p53 signalling pathways in the regulation of S100A2 expression and pro-tumorigenic actions 23337980_In conclusion, data from the present study demonstrated that loss of S100A2 expression contributes to gastric cancer development and progression 23344957_Data indicate S100A2 and S100P proteins as novel Ca2+-dependent regulators of the CHIP-proteasome pathway. 23621473_Expression of S100A2 in cholangiocarcinoma cells significantly correlated with the histological grade, lymph node metastasis, clinical stage, and a poor survival rate of the patients. Thus it is a strong tumor marker for the cancer. 23726265_Data indicate that S100A2 expression predicts longer disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients treated with adjuvant therapy and should be evaluated as a predictive biomarker. 23996929_S100A2 protumorigenic actions and its involvement in TGF-beta-mediated cancer cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 24318973_loss of S100A2 expression contributes to Ggastric cancer development and progression. 24556685_These data demonstrate the importance of S100A2 downstream of the BRCA1/DeltaNp63 signalling axis in modulating transcriptional responses and enforcing growth control mechanisms through destabilisation of mutant p53. 25591983_The potential of cytoplasmic S100A2 overexpression as a predictor of recurrence risk in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. 25874882_Our investigation complements the current understanding of laryngeal cancer progression. Furthermore, this study supports the concept that enhanced expression of S100A2 may be a promising strategy in developing novel cancer therapeutic drugs. 25999659_Data show higher expression level of S100A2 in high-invasive cholangiocarcinoma Cell Line suggesting it as potential marker of tumor progression and novel therapeutic target. 26361956_Our results indicate that serum levels of S100A2 and S100A6 are significantly elevated in early stage non-small cell lung cancer 26783118_S100A2 could have a role in poor prognosis in stage II and III colorectal cancer recurrence 27600583_These results indicate that oxidative stress impairs the ability of S100 proteins to bind and activate PP5, which in turn modulates the ASK1-mediated signaling cascades involved in apoptosis. 27876462_high S100A2 expression and NSCLC 28353163_S100A2 and S100P can be used as specific duct markers in eccrine sweat glands, and combined use of S100P or S100A2 with keratins enables easy to distinction between secretory coils and ducts. 29615682_p53-S100A2 positive feedback loop regulates wound repair process 32816365_S100A2 promotes glycolysis and proliferation via GLUT1 regulation in colorectal cancer. 33109571_Expression Profile of S100A2 and its Clinicopathological Significance in Renal Cell Carcinoma. 33306933_S100A2 Silencing Relieves Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. 33402562_S100A2: A potential biomarker to differentiate malignant from tuberculous pleural effusion. 33750880_High S100A2 expression in keratinocytes in patients with drug eruption. 35042454_High expression of S100A2 predicts poor prognosis in patients with endometrial carcinoma. 35107180_Transcriptional activation of S100A2 expression by HIF-1alpha via binding to the hypomethylated hypoxia response elements in HCC cells. |
ENSMUSG00000094018 |
S100a2 |
39.050245 |
12.3666272526 |
3.628380 |
0.416243021 |
77.822399 |
0.00000000000000000112734489799750309300748403794201263310421784236858193731234401013807655544951558113098144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000009411544510431644116268791484048132082065353182036802903720484891891828738152980804443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
62.1066031 |
15.1082621 |
4.9020248 |
1.0559555 |
| ENSG00000196782 |
55534 |
MAML3 |
protein_coding |
Q96JK9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional coactivator for NOTCH proteins. Has been shown to amplify NOTCH-induced transcription of HES1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12370315, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12386158}. |
Acetylation;Activator;Notch signaling pathway;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables transcription coactivator activity. Involved in Notch signaling pathway and positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nuclear speck. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55534; |
nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of transcription of Notch receptor target [GO:0007221] |
12386158_Identification of new human proteins defines a family that consists of positive regulators for notch signaling 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26655998_Suggest that hypoxia promotes SMO transcription through upregulation of MAML3 and RBPJ to induce proliferation, invasiveness and tumorigenesis in pancreatic cancer. 26752546_The present study further expands the genetic spectrum of small blue round cell tumors, with 2 novel fusions, BCOR-MAML3 and ZC3H7B-BCOR, identified 26785999_Results show that overexpression of MAML3 confers resistance to retinoic acid in multiple neuroblastoma cell lines. 27466498_These results suggest that PSK suppresses Hedgehog signaling through down-regulation of MAML3 and RBPJ transcription under hypoxia, inhibiting the induction of a malignant phenotype in pancreatic cancer. Our results may lead to development of new treatments for refractory pancreatic cancer using PSK as a Hedgehog inhibitor 27709636_PTTG1IP and MAML3 are associated with BHR severity in adult asthma. The relevance of these genes is supported by the eQTL analyses and co-expression of PTTG1lP with vimentin and E-cadherin1, and MAML3 with MAML2. 28512191_These findings indicate that the miR-2392-MAML3/WHSC1-Slug/Twist1 regulatory axis plays a critical role in GC metastasis. 30061220_RBPJ and MAML3 could be new therapeutic targets for SCLC. 33986121_Mastermind Like Transcriptional Coactivator 3 (MAML3) Drives Neuroendocrine Tumor Progression. |
ENSMUSG00000061143 |
Maml3 |
156.430735 |
0.3527034655 |
-1.503472 |
0.128111954 |
142.805547 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000648257063890930315675273234875355812703298424179522646797959787119186050349812892607676007017403208010364323854446411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000091126421552667916158319722722448104736203694038385520492274022438404560940123191100509236761695319728460162878036499023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
81.9175689 |
7.1611401 |
234.1649195 |
12.7949564 |
| ENSG00000196843 |
10865 |
ARID5A |
protein_coding |
Q03989 |
FUNCTION: Binds to AT-rich stretches in the modulator region upstream of the human cytomegalovirus major intermediate early gene enhancer. May act as repressor and down-regulate enhancer-dependent gene expressison (PubMed:8649988). May positively regulate chondrocyte-specific transcription such as of COL2A1 in collaboration with SOX9 and positively regulate histone H3 acetylation at chondrocyte-specific genes. May stimulate early-stage chondrocyte differentiation and inhibit later stage differention (By similarity). Can repress ESR1-mediated transcriptional activation; proposed to act as corepressor for selective nuclear hormone receptors (PubMed:15941852). As RNA-binding protein involved in the regulation of inflammatory response by stabilizing selective inflammation-related mRNAs, such as IL6, STAT3 and TBX21. Binds to stem loop structures located in the 3'UTRs of IL6, STAT3 and TBX21 mRNAs; at least for STAT3 prevents binding of ZC3H12A to the mRNA stem loop structure thus inhibiting its degradation activity. Contributes to elevated IL6 levels possibly implicated in autoimmunity processes. IL6-dependent stabilization of STAT3 mRNA may promote differentiation of naive CD4+ T-cells into T-helper Th17 cells. In CD4+ T-cells may also inhibit RORC-induced Th17 cell differentiation independently of IL6 signaling. Stabilization of TBX21 mRNA contributes to elevated interferon-gamma secretion in Th1 cells possibly implicated in the establishment of septic shock (By similarity). Stabilizes TNFRSF4/OX40 mRNA by binding to the conserved stem loop structure in its 3'UTR; thereby competing with the mRNA-destabilizing functions of RC3H1 and endoribonuclease ZC3H12A (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3U108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15941852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8649988}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repressor;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Members of the ARID protein family, including ARID5A, have diverse functions but all appear to play important roles in development, tissue-specific gene expression, and regulation of cell growth (Patsialou et al., 2005 [PubMed 15640446]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:10865; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; nuclear androgen receptor binding [GO:0050681]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; nuclear retinoid X receptor binding [GO:0046965]; nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding [GO:0046966]; RNA stem-loop binding [GO:0035613]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; transcription factor binding [GO:0008134]; cellular response to estrogen stimulus [GO:0071391]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of histone acetylation [GO:0035066]; positive regulation of interleukin-17 production [GO:0032740]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of T-helper 1 cell cytokine production [GO:2000556]; positive regulation of T-helper 17 type immune response [GO:2000318]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
24782182_AT-rich-interactive domain-containing protein 5A functions as a negative regulator of retinoic acid receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor gammat-induced Th17 cell differentiation. 29044508_Overexpression of ARID5A resulted in more number of cells in G0/G1 phase of cell cycle |
ENSMUSG00000037447 |
Arid5a |
241.607876 |
0.4875674217 |
-1.036326 |
0.107933993 |
93.167016 |
0.00000000000000000000048062464683825804901729043958136761624709323688775336358316829510339829312215442769229412078857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000004597550089003687406290818346661262395137521832931834923669130177348307597640086896717548370361328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
160.8011509 |
10.9679457 |
332.3729753 |
14.9505746 |
| ENSG00000196872 |
343990 |
CRACDL |
protein_coding |
Q6NV74 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:343990; |
|
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32005204_Stratified analyses of genome wide association study data reveal haplotypes for a candidate gene on chromosome 2 (KIAA1211L) is associated with opioid use in patients of Arabian descent. |
ENSMUSG00000026090 |
Cracdl |
9.342685 |
0.2837929246 |
-1.817089 |
0.574134701 |
10.362555 |
0.00128597097735253245061326499154574776184745132923126220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002945063091656071555674012429903996235225349664688110351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8397263 |
1.5038358 |
13.4920859 |
3.0888478 |
| ENSG00000196878 |
3914 |
LAMB3 |
protein_coding |
Q13751 |
FUNCTION: Binding to cells via a high affinity receptor, laminin is thought to mediate the attachment, migration and organization of cells into tissues during embryonic development by interacting with other extracellular matrix components. |
Amelogenesis imperfecta;Basement membrane;Cell adhesion;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Epidermolysis bullosa;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Laminin EGF-like domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
The product encoded by this gene is a laminin that belongs to a family of basement membrane proteins. This protein is a beta subunit laminin, which together with an alpha and a gamma subunit, forms laminin-5. Mutations in this gene cause epidermolysis bullosa junctional Herlitz type, and generalized atrophic benign epidermolysis bullosa, diseases that are characterized by blistering of the skin. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3914; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; laminin complex [GO:0043256]; laminin-5 complex [GO:0005610]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; basement membrane assembly [GO:0070831]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; endodermal cell differentiation [GO:0035987]; epidermis development [GO:0008544]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
11689492_Gene LAMB3 detected compound heterozygosity for the nonsense mutation R635X and a novel 2 bp deletion (1587delAG) resulting in a downstream premature termination codon. 12875969_Results identify the point during neoplastic progression in epithelia when the tumor suppressor p16 and laminin 5 are expressed and suggest that normal epithelia may use the same mechanism to generate non-dividing, motile cells for wound repair. 14612440_proteolytic processing of laminin-5 influences its interaction with alpha3beta1 integrin 15149852_co-cultures of epithelial cells and fibroblasts were studied to analyse the processing of laminin 5 alpha3, beta3, and gamma2 chains 15331737_Deletion analysis of laminin-beta3 indicated that the region comprising aa 726 to 875 of laminin-beta3 interacts with rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4. 15363037_In squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and colorectal carcinoma, laminin 5 beta3 chain is important in the invasiveness of cancer cells. 15370542_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15373767_homozygous frameshift mutation in LAMB3 was associated to illegitimate splicing leading to non-H junctional epidermolysis bullosa 15854126_the absolute mRNA levels generated from the laminin 5 genes do not determine the translated protein levels of the laminin 5 chains in keratinocytes; the expression of the laminin 5 genes may be controlled by common regulation mechanisms 16147969_DNA analysis revealed a compound heterozygote for mutations 2379delG and Q995X in the LAMB3 gene in Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa 16179086_The uncoordinated production of chains of ln-5 in allergic asthma could have a bearing on the poor epithelial cell anchorage in these patients. 16537560_tumor cell migration on laminin-5 is inhibited by HYD1, a biologically active integrin-targeting peptide 16870608_Ln-5 is an important regulator of ADPKD cell proliferation and cystogenesis; Ln-5 gamma(2) chain and Ln-5-alpha(6)beta(4) integrin interaction both contribute to these phenotypic changes 17137774_Laminin-5 alone stimulates global changes in gene/protein expression in mesenchymal stem cells that lead to commitment of these cells to the osteogenic phenotype, and this correlates with extracellular matrix production. 17476356_Multiple second-site mutations, all correcting the germline mutation LAMB3 (628G-->A;Glu210Lys), are present in 2 unrelated non-Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa patients with revertant mosaicism. 17482449_LM-332 is a crucial motility-promoting factor for B-CLL lymphocytes and is a potential constituent favoring the dissemination of B-CLL lymphocytes through vascular basement membranes and possibly lymph node compartments. 18284540_degradation [by Candida species] can exert functional disturbances on basement membrane integrity, possibly aiding Candida cell invasion into tissues 18331784_The expression of LAMB3 mrna was higher in malignant tissue and correlated with the depth of invasion and venous invasion in ESCC. 18387282_c.1945dupG mutation in Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa 18603785_the alpha3 chain can assemble with only beta3-gamma2 heterodimer to form a heterotrimer via disulfide bonds 19383890_Ln-332 gamma2 may be a therapeutic target against metastatic colon cancer because a lowered beta3:gamma2 ratio would reduce expression of heterotrimeric Ln-332 and increase monomeric gamma2 secretion. 19700013_Histopathology of anti-laminin 5 mucous membrane pemphigoid is characterized by subepidermal blistering and a sparse to moderate superficial lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with neutrophils and/or eosinophils 19701966_Results suggest that laminin (LN)gamma2 and LNbeta3, in conjunction with MMP7, play a key role in the progression of biliary tract cancer. 19940114_Bisecting GlcNAc residues on laminin-332 down-regulate galectin-3-dependent keratinocyte motility. 20163849_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20163849_The LAMB3 rs2566 variant CT/TT genotypes were associated with a significantly increased risk of cervical cancer, compared with the wild type CC genotype. 21034821_Cell surface COL17 can interact with laminin 332 and, together, participate in the adherence of a cell to the extracellular matrix. 21345334_These results suggest that epigenetic activation of LAMB3 and LAMC2 may play an important role in gastric carcinogenesis. 22563463_Data show laminin-332 (alpha3ss3gamma2)(Lm332) matrix supported adhesion of keratinocytes much more strongly and stably than purified Lm332. 22673183_invasive breast cancer cells confer an anoikis-resistant phenotype on myofibroblasts during tissue remodeling by inducing laminin-332 upregulation and integrin beta4 neoexpression 22898004_Laminin-5 is a useful biomarker in the evaluation of invasiveness in cervical adenocarcinoma. 23278291_we report a case of Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa with a novel heterozygous mutation in LAMB3,c.1597G>A (p.Ala533Thr). 23441154_osteopontin, LAMB3 and ITGB1 played important roles in the occurrence and metastasis of lung cancer, thus provided important clues to understanding the molecular mechanism of metastasis. 23632796_However, to our knowledge, this is the first report of dominant AI due to a LAMB3 mutation in the absence of JEB. 23769655_data further enhance the mutation spectrum of the LAMB3 and the COL7A1 genes, and also underscore the crucial roles of these genes in pathogenesis of epidermolysis bullosa 23958762_an 8-bp deletion (c.3446_3453del GACTGGAG) shifting the reading frame (p.Gly 1149Glufs*8) and a single nucleotide substitution (c.C3431A) generating an in-frame translation termination codon (p.Ser1144*)associated with amelogenesis imperfecta 24494736_Novel LAMB3 mutations cause non-syndromic amelogenesis imperfecta with variable expressivity. 24978847_Case Report: linear IgA/IgG bullous dermatosis with anti-laminin-332 autoantibodies. 25032755_LNbeta3 expression may play a key role in the progression and prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 25708563_Case Reports: Junctional epidermolysis bullosa with LAMB3 splice-site mutations. 25769099_Screening of ENAM and LAMB3 genes was performed by direct sequencing of genomic DNA from blood samples. 25867809_An algorithm combining CLDN10, HMGA2, and LAMB3 transcripts was able to discriminate tumors from BTL samples (94% sensitivity and 96% specificity in validation set). 27062385_The authors have identified a mutation in LAM3 causing lethal epidermolysis bullosa in a Balkan, Hungarian, population. Investigations into the genetic background of its unique carrier group, suggests that the estimated age of the mutation corresponds to the period of Roma migration in the Balkans. 27375110_Seventeen percent of the patients were compound heterozygous or homozygous for mutations in the gene LAMA3, 59% carried mutations in both alleles of LAMB3, and 12% were homozygous for mutations in LAMC2. In nine patients with severe generalized JEB, detection of two mutations in one of the genes LAMA3, LAMB3, or LAMC2 was not possible, so the molecular basis of disease could not be clarified completely 27431458_Whole-Exome Sequencing Suggests LAMB3 as a Susceptibility Gene for Morbid Obesity 27480391_Results show three specific LAMB3 mutations: c.823-1G>A, c.957ins77 and c.3228+1G>A are carried by 91% of all LAMB3 alleles and that at least one of these three mutations will be carried in junctional epidermolysis bullosa individuals in this Chilean population. 27698189_the tyrosine kinase FAK and the laminin subunit LAMB3 as functional targets of miR-1298. Silencing of FAK or LAMB3 recapitulated the synthetic lethal effects of miR-1298 expression in KRAS-driven cancer cells. 27863864_expression in preoperative biopsy material predictive of perineural invasion in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma 28653739_The expression of fascin-1 and lanminin-5 and the serum levels of fascin-1 and laminin-5 were related to the relapse of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. 29426928_High expression of LAMB3 is associated with papillary thyroid cancer invasion. 29555367_From these results, it was shown that laminin-332 is an essential niche component for the proper differentiation of Interfollicular epidermal stem cells. 29900604_Novel compound heterozygous and homozygous variants of LAMB3 gene underlie non-Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa in two paternal half-brothers from Saudi Arabia. 29946029_the gentamicin-induced laminin beta3 led to the restoration of laminin 332 assembly, secretion, and deposition within the dermal/epidermal junction, as well as proper polarization of alpha6beta4 integrin in basal keratinocytes 30120606_Mutations in LAMB3 and FAM20A were found in 3 Turkish families with Amelogenesis imperfecta 30122422_This study provides evidence for efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated in situ restoration of LAMB3 expression, paving the way for ex vivo clinical application of this strategy to laminin 332 deficiency. 30125583_LM332 expression in breast carcinoma is associated with tumor cell motility and decreased survival. 30414703_LAMB3 may be used as a prognostic biomarker in HNSCC and support that LAMB3 silencing could induce the sensitivity of anti-cancer drugs such as cisplatin. 30850586_results showed that LAMB3 could mediate cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells and alter the proliferative, invasive, and metastatic behaviors of PDAC by regulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 30887508_MiR-329 inhibits BDC progression through translational repression of LAMB3. 30905256_2 novel C-terminal variants in LAMB3 causing autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta in the absence of skin or mucous membrane abnormalities 31101337_The laminin-332 and type-XVII collagen were also localized to the intercellular site and critical for contact following. 32008745_Tissue substructure-specific deposition of the beta3-containing laminin-332 in the biliary epithelium of human and mouse livers. 32412777_LncRNA DDX11-AS1 Promotes Bladder Cancer Occurrence Via Protecting LAMB3 from Downregulation by Sponging miR-2355-5p. 32790894_Laminin-332 expression in oral lichen planus: Preliminary results of a cross-sectional study. 33179081_Laminin332 mediates proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, migration and epithelialtomesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 33715134_Endometrial laminin subunit beta-3 expression associates with reproductive outcome in patients with repeated implantation failure. 34007003_ITGA2, LAMB3, and LAMC2 may be the potential therapeutic targets in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: an integrated bioinformatics analysis. 34231856_Complexity of Transcriptional and Translational Interference of Laminin-332 Subunits in Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa with LAMB3 Mutations. |
ENSMUSG00000026639 |
Lamb3 |
77.158029 |
3.3773996176 |
1.755913 |
0.277510298 |
38.978866 |
0.00000000042841851797481161651681004257324718309529743009989033453166484832763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002108521949085768425120843995966557482546477331197820603847503662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
122.3527214 |
19.8625507 |
36.2107950 |
4.5788805 |
| ENSG00000196912 |
57730 |
ANKRD36B |
protein_coding |
Q8N2N9 |
|
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57730; |
identical protein binding [GO:0042802] |
|
|
|
33.482605 |
0.3135173868 |
-1.673383 |
0.343467413 |
23.467301 |
0.00000127054961110823834022299973905978376365055737551301717758178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004446019976282028847338733540395239174358721356838941574096679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2173367 |
3.0614281 |
42.6657188 |
6.6103964 |
| ENSG00000196924 |
2316 |
FLNA |
protein_coding |
P21333 |
FUNCTION: Promotes orthogonal branching of actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. Anchors various transmembrane proteins to the actin cytoskeleton and serves as a scaffold for a wide range of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Interaction with FLNB may allow neuroblast migration from the ventricular zone into the cortical plate. Tethers cell surface-localized furin, modulates its rate of internalization and directs its intracellular trafficking (By similarity). Involved in ciliogenesis. Plays a role in cell-cell contacts and adherens junctions during the development of blood vessels, heart and brain organs. Plays a role in platelets morphology through interaction with SYK that regulates ITAM- and ITAM-like-containing receptor signaling, resulting in by platelet cytoskeleton organization maintenance (By similarity). During the axon guidance process, required for growth cone collapse induced by SEMA3A-mediated stimulation of neurons (PubMed:25358863). {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BTM8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22121117, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25358863}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Deafness;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an actin-binding protein that crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins. The encoded protein is involved in remodeling the cytoskeleton to effect changes in cell shape and migration. This protein interacts with integrins, transmembrane receptor complexes, and second messengers. Defects in this gene are a cause of several syndromes, including periventricular nodular heterotopias (PVNH1, PVNH4), otopalatodigital syndromes (OPD1, OPD2), frontometaphyseal dysplasia (FMD), Melnick-Needles syndrome (MNS), and X-linked congenital idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction (CIIPX). Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:2316; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; actin filament bundle [GO:0032432]; axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; brush border [GO:0005903]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex [GO:1990779]; membrane [GO:0016020]; Myb complex [GO:0031523]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; Fc-gamma receptor I complex binding [GO:0034988]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; GTPase binding [GO:0051020]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; potassium channel regulator activity [GO:0015459]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting dopamine receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007195]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway [GO:0007597]; blood vessel remodeling [GO:0001974]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; cytoplasmic sequestering of protein [GO:0051220]; early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:0045022]; epithelial to mesenchymal transition [GO:0001837]; establishment of protein localization [GO:0045184]; heart morphogenesis [GO:0003007]; megakaryocyte development [GO:0035855]; mitotic spindle assembly [GO:0090307]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0043433]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; negative regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0042177]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I [GO:0016479]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; positive regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048680]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2001046]; positive regulation of platelet activation [GO:0010572]; positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901381]; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus [GO:0042307]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; protein localization to cell surface [GO:0034394]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; regulation of actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0032231]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:1905000]; regulation of membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:1905031]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway [GO:0071526]; synapse organization [GO:0050808]; tubulin deacetylation [GO:0090042]; wound healing, spreading of cells [GO:0044319] |
11909861_Cell death and mechanoprotection by filamin a in connective tissues after challenge by applied tensile forces 11914408_Two new pedigrees of bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia are reported with a mutation of FLN1 and a deletion in its C-terminus causing a distal protein truncation. 12198493_FLNa may be essential for Pak1-induced cytoskeletal reorganization 12324467_there is a mechanically coupled transcriptional circuit from p38 that induces filamin-A expression [filamin A] 12531889_an important role for filamin in the endocytic sorting and recycling of the internalized CTR 12589795_PH domain of ROCK binds to the carboxy-terminal region of filamin-A containing the last 24th repeat. ROCK co-localized with filamin-A at the protrusive cell membranes of HeLa cells. 12612583_filamin A has a role in signaling pathways that mediate organogenesis in multiple systems during embryonic development 12682292_FLNa interfered with androgen receptor (AR) interdomain interactions and competed with the coactivator transcriptional intermediary factor 2 to specifically down-regulate AR function. 12704190_Filamin A was identified as a direct binding partner of protein kinase Calpha; two binding sites were identified on filamin A; a Ca2+ and phospholipid-dependent association of the regulatory domain of protein kinase C with these sites was revealed. 12734206_Interaction of filamin A with the insulin receptor alters insulin-dependent activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. 12750292_Filamin A binding to PSMA reduces the internalization rate of PSMA and its N-acelylated-alpha linked-acidic dipeptidase activity. 12791664_shear-dependent VWF-induced platelet activation affects filamin A binding to GpIb-IX-V, and filamin A binding to the cytoplasmic tail of GpIbalpha regulates proaggregatory tyrosine kinase signaling. 12923176_filamin-A was found to have no effect on Kir2.1 channel behavior but, rather, increased the number of functional channels resident within the membrane 14660646_filamin-A has a role in the recovery from G2 arrest and subsequent mitotic cell death after DNA damage 14718723_A woman with complex partial seizures and periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) had an amino acid exchange, a transition of guanine to adenine at the first position of intron 13 (IVS13 + 1 G -> A) causing a splice site mutation (2022 + 1 G -> A) 14988809_Dual phenotype of periventricular nodular heterotopia and frontometaphyseal dysplasia in one patient is caused by two functionally different, aberrant filamin A proteins 15024089_Data provide substantial evidence that ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) phosphorylates filamin A, and suggest a novel role for RSK in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. 15128042_Filamin-A interacts with c-mip/Tc-mip in a new T-cell signaling pathway. 15194946_FLNA has diverse roles in embryonic, fetal and postnatal development [review] 15249610_Periventricular nodular heterotopia caused by FLN1 mutations in men has a wide clinical spectrum and is caused by different genetic mechanisms, including somatic mosaicism. 15459826_FLN1 mutations may have a role in periventricular heterotopia 15657061_Interaction with filamin A increases cellular CaR by preventing CaR degradation, thereby facilitating CaR signaling. 15668422_3 filamin A mutations were identified in periventricular heterotopia/Ehlers-Danlos patients: a 2762 delG, a C116 point mutation causing A39G, & a 4147 delG. 15687500_D3R, filamin A, and beta-arrestin form a signaling complex that is destabilized by agonist- or expression-mediated increases in GRK2/3 activity 15837785_G12, Rho, filamin-A, and the actin cytoskeleton are required for amino acid-stimulated Ca2+ oscillations produced by the Ca2+-sensing receptor 15994863_familial Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and periventricular nodular heterotopia is associated with an amino acid substition sssisns FLNA. 16030015_calmodulin and calcium regulate the binding of filamin A to actin filaments 16442073_A purified C-terminal region of filamin is a suitable substrate for calcineurin in vitro and in vivo 16611986_beta-arrestins and FLNA cooperate to regulate ERK activation and actin cytoskeleton reorganization. 16835913_Mutations in FLNA result in frontometaphyseal dysplasia and phenotypic diversity. 16849481_A novel role is revealed for filamin A in the T cell receptor/CD28 signaling pathway leading to transcription factor activation and interleukin-2 production via the inducible interaction with protein kinase C theta. 16949617_This suggests that the titin Z2-Zis1 domain can link filamins and alpha-actinin together in the periphery of the Z-line/dense bodies in a fashion that is conserved in smooth and striated muscles. 17060905_Data indicate that filamin A binding to CD28 is required to induce the T-cell cytoskeletal rearrangements leading to recruitment of lipid microdomains and signalling mediators into the immunological synapse. 17190868_filamin A is the first gene known to cause isolated nonsyndromic valvular heart disease. 17235394_In cells, filamin A tethered plasma membrane CFTR to the underlying actin network. This interaction stabilized CFTR at the cell surface and regulated the plasma membrane dynamics and confinement of the channel. 17357080_Filamin A is mutated in X-linked chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction with central nervous system involvement. 17389601_expression of FLNa regulates constitutive activation of the Ras/ERK pathway partly through a Ras-GRF1 mechanism to modulate the production of MMP-9. 17408621_Our results suggest a role for cyclin B1/Cdk1 in FLNa-dependent actin remodelling. 17420725_FlnA restored Casodex anticaner sensitivity in C4-2 prostatic cancer cells by decreasing Akt phosphorylation. 17431908_A novel mutation, 629G>T, in FLNA that had arisen de novo in the mother lead to Otopalatodigital syndrome type 2. 17536008_Essential for both the efficient signaling and sequestration of dopamine D3 receptor. 17572668_Filamin-A as an adaptor protein that links HIV-1 receptors to the actin cytoskeleton remodelling machinery, which may facilitate virus infection. 17690686_analysis of filamin a IgFLN domains suggests that auto-inhibition by adjacent IgFLN domains may be a general mechanism controlling filamin-ligand interactions. 17897634_in the absence of filamin A, chronic treatment with morphine, methadone or levorphanol leads to up-regulation of mu opioid receptor 18056414_A library of FLNa fragments was generated to examine their F-actin binding to define the structural properties of FLNa that enable its various functions. 18201775_Review explores the pathogenesis of persistent periventricular nodular heterotopia with respect to filamin-A (FLNa) mutations with mouse models. [review] 18322202_Filamin A plays a pivotal role in FcgammaRI surface expression via retention of FcgammaRI from a default lysosomal pathway. 18404377_mutant FLA lacking the actin binding domain is capable of restoring almost as well as full length FLA the down-regulation of the human mu opioid receptor. Some functions of FLA do not act via the actin cytoskeleton. 18427995_novel mutation, c.987G-->C mutation in exon 6 of the Filamin A (FLNA) gene in the genomic DNA in bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia 18556573_Characterize a novel cell surface protein ECSM2 that regulates endothelial chemotaxis and tube formation, and interacts with filamin A. 18598695_These data indicate that caveolin-1 specifies filamin A as a novel target for Akt-mediated filamin A Ser-2152 phosphorylation thus mediating the effects of caveolin-1 on IGF-I-induced cancer cell migration. 18644866_Datas suggest that filamin A links sphingosine kinase 1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 to locally influence the dynamics of actin cytoskeletal structures at lamellipodia to promote cell movement. 18799729_ASB2 may regulate hematopoietic cell differentiation by modulating cell spreading and actin remodeling through targeting of filamins A and B for degradation. 18829455_analysis of the migfilin-filamin interaction and competition with integrin beta 7 tails 19002047_role of filamin cleavage and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in shear-stress-induced platelet microparticle formation and of its suppression by the monoclonal antibody (mAb) Ib-23 directed against GPIbalpha 19018795_Our report also helps define the critical region with exclusion of FLNA in the X-linked mental retardation phenotype. 19137608_This study reports the structure of FLNa domain 24 (FLNa24), compare the structure with FLNc24, and discuss how dimerization is formed in FLNa24. 19144823_The interaction between FilGAP and FlnA plays a role in protecting cells against force-induced apoptosis. 19177143_Wnt5A activates calpain-1, leading to the cleavage of filamin A, which results in a remodeling of the cytoskeleton and an increase in melanoma cell motility 19213840_Filamin A modulates kinase activation and intracellular trafficking of epidermal growth factor receptors in human melanoma cells. 19292868_FLNA genes in cell cycle control and lipid metabolism with dynamically regulated binding sites for sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 and RNA polymerase II in HepG2 cells 19293932_Mutational analysis informed by structure can generate reagents for probing specific cellular interactions of filamin A (FLNa). Disease-related FLNa mutations have demonstrable effects on FLNa function 19458194_These findings support a role for FLNa-beta1 integrin as a mechanosensitive complex that bidirectionally senses the tension of the matrix and, in turn, regulates cellular contractility and response to this matrix tension. 19514078_Study performed all-atom discrete molecular dynamics (DMD) simulations to study thermally and force-induced unfolding of filamin A; DMD allows observation of force-induced unfolding of filamin A Ig domains under physiological forces. 19594548_High plasma filamin A is associated with high-grade astrocytoma and metastatic breast cancer. 19690385_propose that binding of pro-PrP to FLNa perturbs FLNa function, thus contributing to the aggressiveness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 19699211_Mechanical force applied to filamin can expose cryptic integrin binding sites. 19759182_Data suggest that filamin A association with caveolin-1 promotes caveolae-mediated transport by regulating vesicle internalization, clustering, and trafficking. 19773341_These data provide the first biochemical evidence for a gain-of-function mechanism for the otopalatodigital syndrome due to filamin A mutations. 19776392_Filamin A associates with vimentin and protein kinase C-epsilon, thereby enabling vimentin phosphorylation, which is important for beta1 integrin activation and cell spreading on collagen. 19808958_Loss of filamin-A is associated with decreased recombinational DNA double strand break repair in melanoma and breast cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917821_spectrum of mutations, including novel point and missense, associated with bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia 19923718_crystal structure of actin-binding domain of filamin A was solved at 3.2 A resolution. 20006946_We believe the results of this study implicate filamin-A as a tunable mechanosensor, where its sensitivity can be modulated by the degree of phosphorylation. 20156194_Filamin A is a scaffold protein whose function is to link MKK4 and MKK7 together and promote JNK1 activation. 20171211_the binding of filamin A to vimentin and protein kinase C epsilon is an essential regulatory step for the trafficking and activation of beta1 integrins and cell spreading on collagen 20186808_clinical manifestations and results of FLNA exon 22 mutation screening in two boys with the perinatally lethal form of Melnick-Needles syndrome and their affected mothers 20305393_Data report the identification of the actin-binding protein Filamin A (FLNA) as BRCA1 partner and demonstrate that FLNA is required for efficient regulation of early stages of DNA repair processes. 20351098_Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator interacts with multiple immunoglobulin domains of filamin A 20351101_analysis of the interaction between cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and immunoglobulin-like repeats of filamin 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20473907_High FLNA is associated with tumor cell migration. 20585650_data support a model in which R-Ras functionally associates with FLNa and thereby regulates integrin-dependent migration 20598277_TOD is caused by this single recurrent mutation in the FLNA gene. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20650901_Pro-prion binds filamin A, facilitating its interaction with integrin beta1, and contributes to melanomagenesis. 20730588_The cardiological phenotype typically consists of aortic or mitral regurgitation, coarctation of the aorta or other left-sided cardiac malformations. 20808917_FLNa as an important protein for controlling the internalization and spatial localization of the CCR2B receptor 20844545_FLNA p.V528M is neither associated with bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia nor with thrombocytopenia and giant platelets, and represents a functional polymorphism. 20847418_In transgenic mice with presenilin mutation Met146Leu, the hippocampus of the left hemisphere displays more pronounced upregulation of filamin than that of the right hemisphere. 20937704_FLNa down-regulation enhanced calpain activity through the mitogen-activated protein kinase-extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade and stimulated the cleavage of FA proteins. 21036706_Although our findings do not suggest that the expression of FLNA alone plays an independent prognostic role, the angiogenesis pathway mediated by FLNA appears to be responsible for controlling the growth of lung tumors. 21095189_Studies indicate that interactions of filamin A with intermediate filaments and protein kinase C enable tight regulation of beta1 integrin function and consequently early events in cell adhesion and migration on extracellular matrix proteins. 21156842_These outcomes suggest that the GPIbalpha-filamin A interaction not only regulates the architecture of the membrane skeleton, but also maintains the mechanical stability of the plasma membrane under conditions of high shear. 21169733_Filamin A mutations have been identified as the cause of the most common genetic heart valvular disorder, familiar cardiac valvular dystrophy. (Review) 21325883_Filamin A provides a platform for the assembly of the cyclin B1-cdk1- cdc25C complex resulting in cdk1 activation and mitotic progression. 21359179_The extra nuclear AR/FlnA/integrin beta 1 complex is the key by which androgen activates signaling leading to cell migration. Assembly of this ternary complex may control organ development and prostate cancer metastasis. 21412975_The presence of these clinical findings in a mutation-confirmed case of OPD2 supports the notion that corneal clouding, bifid tongue, and DWM are part of the constellation of abnormalities caused by mutations in FLNA. 21524097_filamin is mechanically stretched by integrin or migfilin via a multisite binding mechanism for regulating cytoskeleton and integrin-mediated cell adhesion 21566085_Adapter protein SH2B1beta binds filamin A to regulate prolactin-dependent cytoskeletal reorganization and cell motility 21660952_Maintaining endothelial barrier function is dependent upon active R-Ras and association between R-Ras and FLNa. 21705339_filamin A is involved in the distinct step of the Gag trafficking pathway. 21773876_Review: describe the genetic, echocardiographic and functional aspects of the filamin-A-related myxomatous mitral valve dystrophy. 21807941_regulates actin-linked caveolae dynamics following loss of cell adhesion 21815255_study reports on two brothers with X-linked cardiac valvular dystrophy and a hemizygous FLNA mutation and review previously described cases from the literature 21821884_crystal structure of FlnA-Ig10 determined at 2.44 A resolution provides insight into the perturbations caused by these mutations 21914078_Hepatitis C virus nonstructural (NS) 3 and NS5A proteins were associated with filamin A, while core protein partially with filamin A and vimentin. 21926999_Consistent with structural predictions, strain increases beta-integrin binding to FLNA, whereas it causes FilGAP to dissociate from FLNA, providing a direct and specific molecular basis for cellular mechanotransduction 21960593_mutations in FLNA may represent an unrecognized cause of macrothrombocytopenia with an altered platelet production and a modified platelet-vessel wall interaction 22076441_data highlight the critical role of FLNA in radial glia organization and function for neurogenesis and migration and also provide insight into the molecular pathogenesis of human periventricular nodular heterotopia 22174152_these data demonstrate that coordinated expression of GPIbalpha and filamin is required for efficient trafficking of either protein to the cell surface, and for production of normal-sized platelets. 22194892_Nephrin ligation resulted in abnormal morphology of actin tails in human podocytes when Ship2, Filamin or Lamellipodin were individually knocked down. 22238415_These results demonstrate that FLNA is prone to pathogenic rearrangements 22307607_findings reveal an additional role for FLNA as a regulator of rRNA gene expression and have important implications for our understanding of the role of FLNA in human disease 22334688_FLNa is involved in podosome stability and their organization as rosettes and three-dimensional podosomes in macrophages. 22366253_Novel FLNA mutations leading to bilateral periventricular nodular heterotopia in three unrelated patients 22676060_low-resolution structure of nine C-terminal domains of filamin A (peptide fragments as recombinant proteins); results suggest compact, but flexible, three-branched structure; studies include dimerization and binding of ligands (peptide fragments) 22740120_present a study of a mother-daughter pair who share bilateral widespread gray matter heterotopia caused by a novel mutation in FLNA and the same pattern of X-chromosome inactivation but who exhibit divergent reading and cognitive profiles 22771033_Here we show that BRCA2 is a component of the midbody that is recruited through an interaction with filamin A actin-binding protein. 22802962_study indicates that filamins are important regulators of polycystin-2 channel function, and further links actin cytoskeletal dynamics to the regulation of this channel protein 22870205_CCR2B receptor in Rab5-positive vesicles moves along filamin A-positive fibers. 23007402_EGF regulates alpha5beta1 integrin activation state in cancer cell lines through the p90RSK-dependent phosphorylation of filamin A. 23032111_Vascular and connective tissue anomalies associated with X-linked periventricular heterotopia due to mutations in Filamin A. 23037936_Our findings emphasize that congenital short bowel syndrome can be the presenting symptom in male patients with mutations in FLNA. 23041423_The combined interactions of calponin homology domains and the IgFLNa10 repeat provide the binding strength of the whole FLNa molecule to actin filaments. 23117662_FLNA mutation heterogeneity correlates with different platelet functional impacts and points to opposite regulatory roles of FLNA in spreading and flow adhesion under shear. 23161538_filamin reduces ENaC channel function through direct interaction on the cell surface 23340249_PAK1 phosphorylates serine (Ser) 2152 of the actin-binding protein filamin A to a greater extent when PAK1 is tyrosyl phosphorylated by JAK2. 23636454_These results suggest that a novel RACK1-FlnA interaction is an important regulator of CFTR surface localization. 23873601_This FLNA mutation, the most distal reported so far, causes in females classical XL-PNH, but in males an unusual, multi-organ phenotype, providing a unique insight into the FLNA-associated phenotypes. 24044920_Phosphorylation of serine 323 of ASB2 alpha by Erk kinases is critical for ASB2alpha-mediated degradation of FLNA. 24052262_data therefore reveal ubiquitin acceptor sites in FLNa and establish that ASB2alpha-mediated effects on cell spreading are due to loss of filamins. 24089360_Grb7 protein interacts with Filamin-a, an actin-crosslinking component of the cell cytoskeleton. 24120284_filamin A generates a scaffold for organizing a signaling complex that promotes E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion and keratinocyte differentiation 24200678_FlnA mutations alter the balance between RhoA and Rac1 GTPases activities in favor of RhoA. 24218340_FLNA may play important roles as a negative regulator to nasopharyngeal cancer CNE2 cell by promoting degradation of MMP-9. 24241900_FLNA expression decreased in gastric cancer and correlated significantly with lymph node metastasis, clinic stage, histological grade, and poor overall survival 24243761_TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 mutations do not play a major role in isolated myxomatous valve dystrophy. Screening for FLNA mutations is recommended in familial myxomatous valvular dystrophy, particularly if X-linked inheritance is suspected. 24390612_FLNA may play important roles as a negative regulator to prostate cancer PC-3 cell by promoting the degradation of MMP-9. 24403084_a major function of FLNa in modulating ion channel abundance and membrane trafficking in neurons, thereby shaping their biophysical properties and function. 24469451_Crystal Structures of FLNa Domains 3-5 and FLNc Domains 4-5 Show a Novel Domain-Domain Organization. 24706888_Proline isomerization toggles domain 20 between two conformations; a stable cis conformation with slow unfolding, and a less stable, uninhibited conformation promoted by the trans form. 24828612_FLNA is involved in SST2 stabilization and signaling in tumoral somatotrophs, playing both a structural and functional role. 24870795_FLNA expression was decreased in renal cell carcinoma tissue compared to normal kidney. FLNA may play important roles as a a tumor suppressor in RCC by promoting degradation of MMP-9. 24908328_Enhanced tumorigenesis occurs through increase in EGF-induced EGFR activation in FLNa-expressing melanoma cells. 25033545_Reviewed findings indicate that FLNA can be considered as a novel target in anti-cancer therapy. 25277454_Altered FLNA expression increases dendritic complexity and contributes to pathologic dendritic patterning in tuberous sclerosis. 25352621_Virus infection and RNase L activation disrupt its association with Filamin A and release RNase L to mediate its canonical nuclease-dependent antiviral activities. 25355818_this study proposes that FLNA interaction with ICL3(intracellular loop) is central for endocytosis and signaling of WT and WHIM-like CXCR4 receptors. 25445790_FLNa is phosphorylated by Cdk1/cyclin B1 in mitosis 25476896_The androgen-triggered AR/filamin A complex controls, through Rac 1, the decision of cells to halt cell cycle and migration. 25666618_Autoinhibited filamin is refractory to phosphorylation by PKA on a known Ser(2152) site despite its consensus motif being exposed and the corresponding isolated peptide being readily phosphorylated. 25686753_These observations imply that other interactions apart from those mediated by the canonical repeat 24 dimerisation interface contribute to FLNA homodimerization and that mutations affecting this region of the protein can have broad phenotypic effects. 25717257_FLNa showed low expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma, high correlation with the incidence and development of colorectal cancer, and was considered an indicator of prognosis. 25755106_Familial periventricular nodular heterotopia, epilepsy and Melnick-Needles Syndrome caused by a single FLNA mutation with combined gain-of-function and loss-of-function effects 25820619_FLNA analysis was performed by DHPLC followed by Sanger sequencing [Robertson et al., 2006]. Both sisters were heterozygous for a novel mutation, c.6611C>T in exon 41, that predicts the substitution p.Pro2204Leu within filamin repeat 20 25861040_FLNA anchors PC2 to the actin cytoskeleton through complex PC2-FLNA-actin to reduce degradation and increase stability, and possibly regulate PC2 function in a Ca-dependent manner. 25873011_Missense substitutions in FLNA were identified in four unrelated craniosynostosis patients. 25899317_Frontometaphyseal dysplasia and keloid formation without normally present in this condition FLNA mutations have been described in six unrelated children patients. 26059841_This study expands the diversity of the phenotypes associated with loss-of-function mutations in FLNA. 26134617_Our results support FLNA as a new downstream effector of mTORC2 controlling GBM cell motility. 26404489_FLNA gene mutation analysis was performed in a series of 10 fetuses and a neonatally deceased newborn displaying a multiple congenital anomalies syndrome suggestive of otopalatodigital spectrum disorders. 26446354_the actin-binding protein filamin-A has a critical role in incorporation of Tissue factor into extracellular vesicles and secretion of extracellular vesicles from ovarian cancer cells exposed to hypoxia 26460884_The data suggest a molecular mechanism for direct G protein-coupled receptors -cytoskeleton coupling via filamin A. 26546439_FLNA can function as a modulator of chemosensitivity to docetaxel in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells through regulation of the MAPK/ERK pathway both in vitro and in vivo. FLNA may serve as a novel therapeutic target for improvement of chemotherapy efficacy in TNBC. 26552704_Extracellular sphingosine-1-phosphate activates NF-kappaB only in melanoma cells that lack FLNA. 26554816_FLNA functions as a positive cellular transducer linking actin polymerization to MKL1-SRF activity, counteracting the known repressive complex of MKL1 and monomeric G-actin. 26572583_The function of different integrins is subjected to differential regulation by FLNa. 26686323_The findings in these cases are distinct from previously described FLNA related disorders by virtue of decreased joint mobility and spontaneous keloid scarring. They occur in association with a novel mutation and represent a novel genetic syndrome. 26707877_Our interpretation of these contradictions is that truncation and/or mutation of RhoGDI2 perturbs its conformation to expose a site that adventitiously binds FLNA and is not a bona-fide interaction. 26733502_Filamin-A is required to mediate SSTR2 effects in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours 26742839_studies suggest that Vpu hijacks the FLNa function in the modulation of tetherin to neutralize the antiviral factor tetherin. 26804200_The syndrome affecting the family shares phenotypic overlap with other syndromes caused by FLNA mutations, but appears to be a distinct phenotype, likely representing a unique genetic syndrome. 27059097_Results indicate that mTORC2 regulates filamin A-dependent focal adhesions and cell migration. 27188791_Lowering the FLNA level elevated RalA activity and resulted in selective interference with the normal intracellular trafficking and signaling of the D2R and D3R, through GRK2 and beta-arrestins, respectively. FLNA is a multi-functional protein that acts as a platform on which D2R and D3R can interact with various proteins causing selective regulation of these receptors occurs in combination with GRK2 and beta-arrestins. 27206800_Data show that AR-deficient and highly metastatic prostate cancer cell lines express higher levels of filamin A compared to normal prostate epithelial cells and AR-positive and less metastatic prostate cancer. Also, the results identified that Cao2+ via CaR-mediated signaling induces filamin A cleavage and promotes the migration in AR-deficient and highly metastatic prostate cancer cells. 27485544_Study identifies ANXA4 and FLNA as up-regulated in buccal squamous cell carcinoma arising from oral submucous fibrosis. 27738102_Mechanistic analysis revealed that FLNA suppresses pol III gene transcription by confining the recruitment of the RNA pol III transcription machinery at the promoters of the genes that are sensitive to the alteration of FLNA expression. 27739212_Our findings expand the male-specific phenotype of FLNA mutations that now includes classical-like EDS with lethal cardiac valvular dystrophy, and offer further insights for the genotype-phenotype correlations within this spectrum. 27779751_These results provide new insights into the regulation of SK2 channel trafficking by the cytoskeletal proteins FLNA and alpha-actinin2, involving distinct recycling pathways 27872158_FLNA is downregulated in parathyroid tumors and parallels the CASR expression levels. Loss of FLNA reduces CASR mRNA and protein expression levels and the CASR-induced ERK phosphorylation. FLNA is involved in receptor expression, membrane localization and ERK signaling activation of both 990R and 990G CASR variants. 27909248_CCR2B and beta2AR signals to FLNa to stimulate its endocytosis and recycling to the plasma membrane. 28175289_FlnA more strongly binds RhoA, although both filamins overlap with RhoA expression in the cell cytoplasm. FlnA promotes RhoA activation whereas FlnB indirectly inhibits this pathway. Moreover, FlnA loss leads to diminished expression of b1-integrin, whereas FlnB loss promotes integrin expression 28238652_The actin regulator FLNA interacts with the endoplasmic reticulum stress kinase PERK and this interaction is required for the efficient formation of ER-plasma membrane contact sites. 28348077_results reveal an unusual structural and thermodynamic basis for the P2204L-induced dysfunction of filamin and frontometaphyseal dysplasia disease. 28411558_The mutations of the FLNA gene were observed in 7 (30.4%) of the 23 patients who with Sporadic periventricular nodular heterotopia. 28428218_Case Report: Reduced binding of mutant FLNa to beta3 and the facilitated recruitment of talin by beta3 on platelet stimulation, explaining the increased alphaIIbbeta3 activation and the ensuing gain-of-platelet functions. 28432720_We report two brothers carrying a loss-of-function mutation of FNLA with gonadal differentiation disorder and hypospadias. Specific staining for AR shows almost an absolute absence of these receptors in the testicular tissue. 28457522_Respiratory failure secondary to progressive obstructive lung disease during infancy may be the presenting phenotype of FLNA-associated periventricular nodular heterotopia. 28727243_FLNA overexpression predicts early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. 28732005_In humans, mutations in the actin-binding protein Filamin-C result in myopathies, but the underlying molecular function is not well understood. Here we show using Drosophila indirect flight muscle that the filamin ortholog Cheerio in conjunction with the giant elastic protein titin plays a crucial role in keeping thin filaments stably anchored at the Z-disc 28778796_FLNA upregulation correlates with Snail-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal carcinoma. 29024177_these observations describe a new mechanism of tissue-specific regulation of FLNA that could reflect the differing mechanical requirements of these cell types during development. 29044292_The interaction between tissue factor and filamin A is dependent on the differential phosphorylation of Ser253 and Ser258. The interaction with filamin A may translocate cell surface TF to cholesterol-rich lipid rafts, increasing cell surface TF activity as well as TF incorporation and release into microvesicles. 29062687_This study also indicates that FLNA may affect white matter integrity in patients with periventricular nodular heterotopia related epilepsy. 29146485_The authors describe a family with a novel FLNA mutation with a male-expressed, apparently isolated, cardiac phenotype with no skewed X-inactivation pattern in female carriers. 29237676_Data indicate mutations in FLNA (Filamin A) associated with Ebstein anomaly. 29272322_Silencing filamin A (FLNa) expression in lung cancer cell line A549 cells promoted proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of A549 cells by enhancing the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor and ERK signaling pathway. 29284605_Filamin A modulates store-operated calcium entry and then the correct platelet function, by fine-tuning the distribution of STIM1 in the cytoskeleton and the interaction with Orai1 channels. 292 |
ENSMUSG00000031328 |
Flna |
230.223005 |
0.4858758195 |
-1.041340 |
0.102825737 |
104.528264 |
0.00000000000000000000000154967013369926244046369112760344388261457194143932052130350448041189864722966262888803612440824508666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000016373035915104591291436271846639455176384961027171199161235506762401836766684937174431979656219482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
151.2891220 |
10.9774122 |
313.3954002 |
14.8477376 |
| ENSG00000196950 |
57181 |
SLC39A10 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULF5 |
FUNCTION: May act as a zinc-influx transporter. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17359283}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Zinc;Zinc transport |
|
Zinc is an essential cofactor for hundreds of enzymes. It is involved in protein, nucleic acid, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism, as well as in the control of gene transcription, growth, development, and differentiation. SLC39A10 belongs to a subfamily of proteins that show structural characteristics of zinc transporters (Taylor and Nicholson, 2003 [PubMed 12659941]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:57181; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; zinc ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005385]; cellular zinc ion homeostasis [GO:0006882]; negative regulation of B cell apoptotic process [GO:0002903]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050861]; positive regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase activity [GO:1903615]; zinc ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0071578] |
19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24587242_Zinc and its transporters, ZIP6 and ZIP10, are required for the breast cancer cells motility stimulated with high glucose level, such as in diabetes. 25200496_A significant correlation between ZIP10 mRNA expressions with aggressiveness of RCC. 29180421_Slc39a10 plays a role in promoting the survival of macrophages through a Zn/p53-dependent axis in response to inflammatory stimuli. 30520657_ZIP10 is found in the proximal tubules collecting duct system and has a role in renal zinc transport. 31875492_Possible involvement of zinc transporter ZIP10 in atopic dermatitis. 32797246_The ZIP6/ZIP10 heteromer is essential for the zinc-mediated trigger of mitosis. 34706747_ZIP10 drives osteosarcoma proliferation and chemoresistance through ITGA10-mediated activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000025986 |
Slc39a10 |
492.068314 |
0.4951961364 |
-1.013928 |
0.101296986 |
99.536611 |
0.00000000000000000000001925704402646184863844419305205643823693297292829831044191742019273949626523290135082788765430450439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000194046271409105498483872135718079957501370100229555076910077822394118385318506625480949878692626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
326.1030095 |
24.4585793 |
664.1248879 |
34.8370624 |
| ENSG00000197008 |
7697 |
ZNF138 |
protein_coding |
P52744 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation as a repressor. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7697; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
74.455542 |
0.2093966954 |
-2.255689 |
0.706371879 |
8.590049 |
0.00338004880834042635909253426973464229376986622810363769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007156723628045430149469119385230442276224493980407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.3682752 |
14.3621822 |
85.7631839 |
51.9864805 |
| ENSG00000197013 |
353088 |
ZNF429 |
protein_coding |
Q86V71 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:353088; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
19207018_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000069184+ENSMUSG00000060314 |
Zfp72+Zfp941 |
93.407255 |
0.4373662933 |
-1.193086 |
0.158807161 |
57.347449 |
0.00000000000003652366533380906199263335740121620919234734364833272479700099211186170578002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000238218868902793519069918660671108993182824159484667347896902356296777725219726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.1815234 |
8.3445472 |
136.1114568 |
13.1956573 |
| ENSG00000197070 |
92714 |
ARRDC1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N5I2 |
FUNCTION: Functions as an adapter recruiting ubiquitin-protein ligases to their specific substrates (PubMed:23886940, PubMed:27462458). Through an ubiquitination-dependent mechanism plays for instance a role in the incorporation of SLC11A2 into extracellular vesicles (PubMed:27462458). More generally, plays a role in the extracellular transport of proteins between cells through the release in the extracellular space of microvesicles (PubMed:22315426). By participating in the ITCH-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of NOTCH1, negatively regulates the NOTCH signaling pathway (PubMed:23886940). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22315426, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23886940, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27462458}. |
Cell membrane;Membrane;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables several functions, including arrestin family protein binding activity; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity; and ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular protein metabolic process; extracellular vesicle biogenesis; and negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway. Located in cytoplasmic vesicle; extracellular vesicle; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92714; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular vesicle [GO:1903561]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arrestin family protein binding [GO:1990763]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ubiquitin ligase-substrate adaptor activity [GO:1990756]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; extracellular transport [GO:0006858]; extracellular vesicle biogenesis [GO:0140112]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0006511] |
21191027_The authors show that WWP1 changes the ubiquitination status of ARRDC1, suggesting that the arrestins may provide a platform for ubiquitination in PPXY-dependent budding. 34499929_PAX5-activated lncRNA ARRDC1-AS1 accelerates the autophagy and progression of DLBCL through sponging miR-2355-5p to regulate ATG5. 35300565_MicroRNA miR-124-3p suppresses proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via ARRDC1 (arrestin domain containing 1). |
ENSMUSG00000026972 |
Arrdc1 |
358.799962 |
0.3992489920 |
-1.324639 |
0.099211254 |
179.879391 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000005149371195945183006131077808200189262879048767015589540705881397215230322283264801686015957979753760061485817756121718957729171961545944213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000883775800606405765440717154363288805535365788922695237098727594522446960226946401826159174716154848369317753586926755815511569380760192871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
214.9830648 |
13.6489918 |
542.6444263 |
22.6059952 |
| ENSG00000197119 |
123096 |
SLC25A29 |
protein_coding |
Q8N8R3 |
FUNCTION: Mitochondrial transporter of arginine, lysine, homoarginine, methylarginine and, to a much lesser extent, ornithine and histidine (PubMed:19287344, PubMed:24652292). Does not transport carnitine nor acylcarnitines (PubMed:24652292). Functions by both counter-exchange and uniport mechanisms (PubMed:24652292). Plays a physiolocical role in the import of basic amino acids into mitochondria for mitochondrial protein synthesis and amino acid degradation (PubMed:19287344, PubMed:24652292). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19287344, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24652292}. |
Alternative splicing;Amino-acid transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial protein that is a member of the large family of solute carrier family 25 (SLC25) mitochondrial transporters. The members of this superfamily are involved in numerous metabolic pathways and cell functions. This gene product was previously reported to be a mitochondrial carnitine-acylcarnitine-like (CACL) translocase (PMID:128829710) or an ornithine transporter (designated ORNT3, PMID:19287344), however, a recent study characterized the main role of this protein as a mitochondrial transporter of basic amino acids, with a preference for arginine and lysine (PMID:24652292). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:123096; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; basic amino acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015174]; high-affinity L-arginine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005289]; high-affinity lysine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005292]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; acyl carnitine transport [GO:0006844]; amino acid transport [GO:0006865]; L-arginine transmembrane transport [GO:1903826]; L-histidine transmembrane transport [GO:0089709]; L-lysine transmembrane transport [GO:1903401]; mitochondrial L-ornithine transmembrane transport [GO:1990575]; ornithine transport [GO:0015822] |
19287344_The human and mouse SLC25A29 mitochondrial ornithine transporters (designated as ORNT3) rescue the deficient ornithine metabolism in fibroblasts of patients with the hyperornithinemia-hyperammonemia-homocitrullinuria (HHH) syndrome. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 23266187_Compares and contrasts all the known human SLC25A* genes and includes functional information. 24652292_The main physiological role of SLC25A29 is to import basic amino acids into mitochondria for mitochondrial protein synthesis and amino acid degradation. 29459713_Results provide evidence that aberrant elevated SLC25A29 in cancer functioned to transport more arginine into mitochondria, improved mitochondria-derived nitric oxide levels, thus modulated metabolic status to facilitate increased cancer progression. |
ENSMUSG00000021265 |
Slc25a29 |
343.216982 |
0.4959423494 |
-1.011756 |
0.106842484 |
90.075645 |
0.00000000000000000000229226098092955864297030431457963953116691490570981039640941281931851847275538602843880653381347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000021413779796531826986411998550943270077222423440413717375067209625072450762672815471887588500976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
235.7434281 |
16.4857077 |
478.5580702 |
22.3750495 |
| ENSG00000197122 |
6714 |
SRC |
protein_coding |
P12931 |
FUNCTION: Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase which is activated following engagement of many different classes of cellular receptors including immune response receptors, integrins and other adhesion receptors, receptor protein tyrosine kinases, G protein-coupled receptors as well as cytokine receptors. Participates in signaling pathways that control a diverse spectrum of biological activities including gene transcription, immune response, cell adhesion, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, migration, and transformation. Due to functional redundancy between members of the SRC kinase family, identification of the specific role of each SRC kinase is very difficult. SRC appears to be one of the primary kinases activated following engagement of receptors and plays a role in the activation of other protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) families. Receptor clustering or dimerization leads to recruitment of SRC to the receptor complexes where it phosphorylates the tyrosine residues within the receptor cytoplasmic domains. Plays an important role in the regulation of cytoskeletal organization through phosphorylation of specific substrates such as AFAP1. Phosphorylation of AFAP1 allows the SRC SH2 domain to bind AFAP1 and to localize to actin filaments. Cytoskeletal reorganization is also controlled through the phosphorylation of cortactin (CTTN) (Probable). When cells adhere via focal adhesions to the extracellular matrix, signals are transmitted by integrins into the cell resulting in tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of focal adhesion proteins, including PTK2/FAK1 and paxillin (PXN) (PubMed:21411625). In addition to phosphorylating focal adhesion proteins, SRC is also active at the sites of cell-cell contact adherens junctions and phosphorylates substrates such as beta-catenin (CTNNB1), delta-catenin (CTNND1), and plakoglobin (JUP). Another type of cell-cell junction, the gap junction, is also a target for SRC, which phosphorylates connexin-43 (GJA1). SRC is implicated in regulation of pre-mRNA-processing and phosphorylates RNA-binding proteins such as KHDRBS1 (Probable). Also plays a role in PDGF-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of both STAT1 and STAT3, leading to increased DNA binding activity of these transcription factors (By similarity). Involved in the RAS pathway through phosphorylation of RASA1 and RASGRF1 (PubMed:11389730). Plays a role in EGF-mediated calcium-activated chloride channel activation (PubMed:18586953). Required for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) internalization through phosphorylation of clathrin heavy chain (CLTC and CLTCL1) at 'Tyr-1477'. Involved in beta-arrestin (ARRB1 and ARRB2) desensitization through phosphorylation and activation of GRK2, leading to beta-arrestin phosphorylation and internalization. Has a critical role in the stimulation of the CDK20/MAPK3 mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by epidermal growth factor (Probable). Might be involved not only in mediating the transduction of mitogenic signals at the level of the plasma membrane but also in controlling progression through the cell cycle via interaction with regulatory proteins in the nucleus (PubMed:7853507). Plays an important role in osteoclastic bone resorption in conjunction with PTK2B/PYK2. Both the formation of a SRC-PTK2B/PYK2 complex and SRC kinase activity are necessary for this function. Recruited to activated integrins by PTK2B/PYK2, thereby phosphorylating CBL, which in turn induces the activation and recruitment of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to the cell membrane in a signaling pathway that is critical for osteoclast function (PubMed:8755529, PubMed:14585963). Promotes energy production in osteoclasts by activating mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase (PubMed:12615910). Phosphorylates DDR2 on tyrosine residues, thereby promoting its subsequent autophosphorylation (PubMed:16186108). Phosphorylates RUNX3 and COX2 on tyrosine residues, TNK2 on 'Tyr-284' and CBL on 'Tyr-731' (PubMed:20100835, PubMed:21309750). Enhances RIGI-elicited antiviral signaling (PubMed:19419966). Phosphorylates PDPK1 at 'Tyr-9', 'Tyr-373' and 'Tyr-376' (PubMed:14585963). Phosphorylates BCAR1 at 'Tyr-128' (PubMed:22710723). Phosphorylates CBLC at multiple tyrosine residues, phosphorylation at 'Tyr-341' activates CBLC E3 activity (PubMed:20525694). Phosphorylates synaptic vesicle protein synaptophysin (SYP) (By similarity). Involved in anchorage-independent cell growth (PubMed:19307596). Required for podosome formation (By similarity). Mediates IL6 signaling by activating YAP1-NOTCH pathway to induce inflammation-induced epithelial regeneration (PubMed:25731159). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P05480, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUD9, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11389730, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12615910, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14585963, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16186108, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18586953, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19307596, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19419966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20100835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20525694, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21309750, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21411625, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22710723, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25731159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7853507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8755529, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8759729, ECO:0000305|PubMed:11964124, ECO:0000305|PubMed:8672527, ECO:0000305|PubMed:9442882}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase which phosphorylates synaptophysin with high affinity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUD9}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 2]: Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase which shows higher basal kinase activity than isoform 1, possibly due to weakened intramolecular interactions which enhance autophosphorylation of Tyr-419 and subsequent activation (By similarity). The SH3 domain shows reduced affinity with the linker sequence between the SH2 and kinase domains which may account for the increased basal activity (By similarity). Displays altered substrate specificity compared to isoform 1, showing weak affinity for synaptophysin and for peptide substrates containing class I or class II SH3 domain-binding motifs (By similarity). Plays a role in L1CAM-mediated neurite elongation, possibly by acting downstream of L1CAM to drive cytoskeletal rearrangements involved in neurite outgrowth (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUD9}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase which shows higher basal kinase activity than isoform 1, possibly due to weakened intramolecular interactions which enhance autophosphorylation of Tyr-419 and subsequent activation (By similarity). The SH3 domain shows reduced affinity with the linker sequence between the SH2 and kinase domains which may account for the increased basal activity (By similarity). Displays altered substrate specificity compared to isoform 1, showing weak affinity for synaptophysin and for peptide substrates containing class I or class II SH3 domain-binding motifs (By similarity). Plays a role in neurite elongation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WUD9}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell adhesion;Cell cycle;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is highly similar to the v-src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. This proto-oncogene may play a role in the regulation of embryonic development and cell growth. The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine-protein kinase whose activity can be inhibited by phosphorylation by c-SRC kinase. Mutations in this gene could be involved in the malignant progression of colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6714; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic filopodium [GO:1902737]; dendritic growth cone [GO:0044294]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; podosome [GO:0002102]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic specialization, intracellular component [GO:0099091]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; synaptic membrane [GO:0097060]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATPase binding [GO:0051117]; BMP receptor binding [GO:0070700]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; connexin binding [GO:0071253]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; growth factor receptor binding [GO:0070851]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; nuclear estrogen receptor binding [GO:0030331]; phospholipase activator activity [GO:0016004]; phospholipase binding [GO:0043274]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; SH2 domain binding [GO:0042169]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; activation of protein kinase B activity [GO:0032148]; adherens junction organization [GO:0034332]; angiotensin-activated signaling pathway involved in heart process [GO:0086098]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; branching involved in mammary gland duct morphogenesis [GO:0060444]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cellular response to fatty acid [GO:0071398]; cellular response to fluid shear stress [GO:0071498]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus [GO:0071375]; cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus [GO:0036120]; cellular response to progesterone stimulus [GO:0071393]; cellular response to prolactin [GO:1990646]; DNA biosynthetic process [GO:0071897]; entry of bacterium into host cell [GO:0035635]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007173]; ERBB2 signaling pathway [GO:0038128]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; focal adhesion assembly [GO:0048041]; forebrain development [GO:0030900]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; interleukin-6-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070102]; intestinal epithelial cell development [GO:0060576]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; myoblast proliferation [GO:0051450]; negative regulation of anoikis [GO:2000811]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001237]; negative regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051895]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001243]; negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization [GO:0051902]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031333]; negative regulation of telomerase activity [GO:0051974]; negative regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase [GO:0032211]; neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048011]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; oogenesis [GO:0048477]; osteoclast development [GO:0036035]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:0038083]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045737]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of dephosphorylation [GO:0035306]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010634]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of glucose metabolic process [GO:0010907]; positive regulation of hippo signaling [GO:0035332]; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046628]; positive regulation of integrin activation [GO:0033625]; positive regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis [GO:2000394]; positive regulation of male germ cell proliferation [GO:2000256]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:1903997]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of ovarian follicle development [GO:2000386]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway [GO:2000588]; positive regulation of podosome assembly [GO:0071803]; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031954]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus [GO:1900182]; positive regulation of protein processing [GO:0010954]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902]; positive regulation of protein transport [GO:0051222]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; positive regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction [GO:0051057]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; primary ovarian follicle growth [GO:0001545]; progesterone receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050847]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein destabilization [GO:0031648]; regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045124]; regulation of caveolin-mediated endocytosis [GO:2001286]; regulation of cell projection assembly [GO:0060491]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion [GO:0022407]; regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport [GO:2000641]; regulation of epithelial cell migration [GO:0010632]; regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033146]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0098962]; regulation of protein binding [GO:0043393]; regulation of vascular permeability [GO:0043114]; response to acidic pH [GO:0010447]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to interleukin-1 [GO:0070555]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to mineralocorticoid [GO:0051385]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal complex assembly [GO:0007172]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; skeletal muscle cell proliferation [GO:0014856]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002223]; stress fiber assembly [GO:0043149]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; transcytosis [GO:0045056]; transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007179]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169]; uterus development [GO:0060065]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048010] |
11940607_Coordinate interactions of Csk, Src, and Syk kinases with [alpha]IIb[beta]3 initiate integrin signaling to the cytoskeleton. 11994743_v-Src's hold over actin and cell adhesions. 12014986_PLD1 is threonine-phosphorylated in human-airway epithelial cells by a PKCdelta and src dependent mechanism 12060669_The Src-cortactin pathway is required for clustering of E-selectin and ICAM-1 in endothelial cells 12063167_Activation of a Src-dependent Raf-MEK1/2-ERK signaling pathway is required for IL-1alpha-induced upregulation of beta-defensin 2 in human middle ear epithelial cells. 12162444_REVIEW: Arsenic carcinogenicity: relevance of c-Src activation 12216109_Functional involvement of src and focal adhesion kinase in a CD99 splice variant-induced motility of human breast cancer cells 12393736_The p85 subunit of PI 3-kinase activates Src independently of the enzymatic activity of PI 3- kinase. Ligand binding of GPIb, without receptor clustering, is sufficient to activate Src. 12416028_pp60c-src may be involved in stabilization of dynamic HT-29 cell adhesion to ECM components, and this kinase appears to be part of a mechanosensory protein complex during integrin-mediated cell adhesion 12420216_Src activation may contribute to colon tumor progression and metastasis in part by activating Akt-mediated survival pathways that decrease sensitivity of detached cells to anoikis. 12429742_mediation of synergism with epidermal growth factor receptor by STAT5b 12429837_Data report a novel positioning of Src, mediating signals from insulin to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and to beta(2)-adrenergic receptor trafficking. 12456372_Mutual interaction of c-Src with EGFR is required for many EGFR-mediated cellular functions including proliferation, migration, survival and EGFR endocytosis, as discussed in this review. 12462387_c-Src activation is associated with early stages of breast carcinomas with low aggressiveness. 12604776_src has a role in promoting destruction of c-Cbl and enabling EGFR to evade desensitization as part of an oncogenesis pathway 12618767_c-Src, lacking cysteine at position 520, is resistant to 1 microM N-(9-acridinyl) maleimide (NAM) but sensitive to 5 microM. Changing Phe520 to cysteine made it sensitive to 1 microM. Double mutation in clustered cysteines restored resistance to 5 microM. 12631284_Results demonstrate that c-Src and TRAF6 are key mediators of interleukin-1-induced AP-1 activation and provide evidence of cross talk between c-Src and TRAF6 molecules through PI3 kinase-Akt-JNK pathways. 12663375_c-Src regulates NAD(P)H oxidase-derived *O2- generation acutely by stimulating p47phox phosphorylation and translocation and chronically by increasing protein content of gp91phox, p22phox, and p47phox in Ang II-stimulated cells. 12829810_stimulated by HBX protein acting on the mitochondrial transition pore and effecting hepatitis B virus replication. 12842760_involvement of G(i), Src tyrosine kinase and PI3 Kinase, respectively, in TNFalpha production 12893822_v-SRC regulates the nucleo-cytoplasmic delocalization of the major isoform of TEL-ETV6 12907754_role of c-Src on PRL-stimulated proliferation of T47D and MCF7 breast cancer cells 12939401_FAK and Src are both important survival factors, playing a role in protecting colon cancer cell lines from Adenovirus-containing FAK-CD (Ad-FAK-CD)-induced apoptosis 12947321_Inhibition of Src signaling results in a marked reduction of pancreatic cancer cellular invasiveness. Src may represent a novel therapeutic target for this deadly cancer. 12975382_Src has an appreciable role in the organization of the Golgi apparatus, which may be linked to its involvement in protein transport from the Golgi apparatus to the endoplasmic reticulum 14504278_SRC tyrosine kinases are activated and have a role in tyrosine phosphorylation of ezrin and activation of p38 14523024_c-src activation of PLCgamma is mediated by GIT1 14562045_The data indicate an increase in the expression and total activity of endogenous p60(c-Src) in several GM-CSF-independent 1 cultured leukemia cell mutants. 14617636_focal adhesion kinase and src are stimulated by G alpha q and platelet activating factor receptor in vascular endothelium 14627343_role of IGF-1R and c-Src in human pancreatic carcinogenesis. Coexpression of both these molecules may play important role in transformation of pancreatic ductal cells. 14670955_data suggest that agonist-induced binding of Src kinase to the Src homology 3 binding sites in the P2Y(2) purinergic receptor facilitates Src activation and allows Src to efficiently phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor 14676843_A novel regulatory network RAFTK/Pyk2, Src and p38 appears to be critical for VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration. 14706618_v-Src and receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 activate beta-catenin-TCF-mediated transcription. 14766744_Ret tyrosine 981 constitutes the major binding site of the Src homology 2 domain of Src and therefore the primary residue responsible for Src activation upon Ret engagement 14963038_EGFR and c-Src-mediated Stat-3 activation is facilitated by Pyk2 15033452_src and protein kinase C have roles in inducing phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in epithelial cells after mechanical pressure 15060621_mechanisms of c-Src activation in human cancer (review) 15062576_both the androgen receptor interacting domains of the coactivator SRC1 and of the corepressor SMRT compete for interaction with the androgen receptor N-terminus 15075377_SH2 and SH3 domains of Src mediate peripheral accumulation of phospho-myosin, leading to integrin adhesion complex assembly, whereas loss of SH2 or SH3 function restores normal regulation of E-cadherin and inhibits vimentin expression 15094065_hTAF(II)68-mediated transactivation is linked to the cytoplasmic Src signal transduction pathway. The hTAF(II)68 protein can associate with the SH3 domains of several cell signaling proteins, including v-Src. 15117969_data suggest that colony-stimulating factor receptor-1R (CSF-1R) disrupts cell adhesion by uncoupling adherens junction complexes from the cytoskeleton and promoting cadherin internalization through a Src-dependent mechanism 15254245_Src kinase activity is suppressed by RAC1, which regulates G1/S progression 15271991_Src plays an obligatory role in the mechanism for receptor and diacylglycerol activation of TRPC3 15276210_Results provide important insight to the mechanism of SRC transcriptional activation in liver cancer cells. 15286700_A prolactin signalling cascade in W53 cells involves Src kinases that mediate stimulation of c-Myc expression. 15297464_colony stimulating factor 1 receptor phosphorylation was not markedly affected by Src-family kinases (SFK) inhibition, indicating that lack of SFK binding is not responsible for diminished Y559F phosphorylation. 15456896_Src inhibitors inhibited COX-2 induction in Helicobacter pylori infected gastric mucosa cells. 15467744_Fibronectin and type IV collagen activate ERalpha AF-1 by the c-Src pathway in breast cancer 15485865_G16-mediated activation of nuclear factor kappaB by the adenosine A1 receptor requires c-Src, protein kinase C, and ERK signaling 15494217_c-Src participates in regulating the endocytosis of PDGFbeta receptor-GPCR complexes in response to PDGF. 15498833_c-Src has a role in regulating the dissociation of AP-2 from agonist-occupied AT1R and beta-arrestin during the clathrin-mediated internalization of receptors 15522237_Data demonstrate that type I collagen synergistically enhances platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced smooth muscle cell proliferation through Src-dependent crosstalk between the alpha2beta1 integrin and the PDGF receptor beta. 15528270_src kinase potentiates tamoxifen agonist action through serine 167-dependent stabilization of estrogen receptor promoter interaction and through elevation of SRC-1 and cAMP response element binding protein-binding protein coactivation of ER 15532711_ERK activation mediated pure pressure-induced proliferative response of aortic smooth muscle cells. This activation was partly mediated by c-Src. 15564375_FRS2-dependent SRC activation is required for FGFR-induced phosphorylation of Sprouty and suppression of ERK activity 15583006_there is a complex interplay between PKCalpha, Syk, and Src involving physical interaction, phosphorylation, translocation within the cell, and functional activity regulation 15618223_PMA transactivates the EGFR and increases cell proliferation by activating the PKCdelta/c-Src pathway in glioblastoma cells 15623523_Csk achieves a low K(m) for the substrate Src, not by stabilizing protein-protein interactions but rather by facilitating a fast phosphoryl transfer step 15623525_Src phosphorylates ezrin at tyrosine 477 15637072_Involvement of c-Src and protein kinase C delta in the inhibition of Cl(-)/OH- exchange activity in Caco-2 cells by serotonin. 15647376_Src-dependent ezrin phosphorylation has a role in adhesion-mediated events in epithelial cells 15688032_SRC-1 is a novel Smad3/4 transcriptional partner, facilitating the functional link between Smad3 and p300/CBP. 15689620_Data show that ionizing radiation causes stress-induced activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor-Src-Mek-Erk-Egr-1 signaling that regulates the clusterin pro-survival cascade. 15735682_HIF-1alpha, STAT3, CBP/p300 and Ref-1/APE regulate Src-dependent hypoxia-induced expression of VEGF in pancreatic and prostate carcinomas 15746183_data demonstrate that Src tyrosine kinase modulates human airway smooth muscle (ASM) cell proliferation and migration 15774483_results indicated that Src kinase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of p47(phox) regulates hyperoxia-induced NADPH oxidase activation and reactive oxygen species production in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells 15777850_a specific cross-talk between TGF-beta1 and fibronectin-binding integrin signal pathways leads to the activation of c-Src/Rac1/actin-organization, leading to changes in cell cycle regulator levels in hepatoma cells 15818752_c-src codon 531 mutation in colorectal cancer is not the cause of c-src activation. 15853660_This review summarizes some of the latest evidence for the role of c-Src in tumorigenesis and particularly in human tumor progression. 15872086_calcium activates PLC-gamma1 via increased PIP3 formation mediated by c-src- and fyn-activated PI3K 15872089_dynamin, Cbl, and Src coordinately participate in signaling complexes that are important in the assembly and remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton, leading to changes in osteoclast adhesion, migration, and resorption 16002577_c-Src tyrosine kinase was identified as a binding partner of the BMPR-II C-terminus. 16055703_Semaphorin 4D/plexin-B1 induces endothelial cell migration through the activation of PYK2, Src, and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway 16158055_MUC1 is delivered to mitochondria by a mechanism involving activation of the ErbB receptor-->c-Src pathway and transport by the molecular chaperone HSP70/HSP90 complex 16158247_The Src, a proto-oncogene, has been strongly implicated in the growth, progression and metastasis of a number of human cancers. 16163059_Src activity contributes to constitutive and EGF-induced VEGF expression and angiogenic potential in pancreatic cancer cells 16168436_Data report three crystal structures of a dimeric active c-Src kinase domain, in an apo and two ligand complexed forms, with resolutions ranging from 2.9A to 1.95A. 16260653_FAK regulates integrin-dependent MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and release by T lymphoid cells through src kinase 16317091_rhMIF induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 up-regulation in 12 hours via Src, PI3K, and NFkappaB 16322069_LPC-induced Flk-1/KDR transactivation via c-Src may have important implications for the progression of atherosclerosis 16377083_Stat3 downregulation in vSrc transformed NIH3T3 cells or in breast cancer lines with activated Src induces apoptosis, but in normal cells Stat3 inhibition at post-confluence causes apoptosis while in sparsely growing cells it induces growth retardation 16400523_Cells with single Src family kinase knockdown show that Src, Fyn and Yes kinases are all required for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mitogenic signaling. 16407214_Epidermal growth factor receptor exposed to oxidative stress undergoes Src- and caveolin-1-dependent perinuclear trafficking 16412380_These studies also raise the possibility that fully active forms of c-Src and Fak in breast tumors. 16414009_IR-induced ERK1/2 activation involves EGFR through a Src-dependent pathway that is distinct from EGFR ligand activation 16440311_The results demonstrate that collagen-evoked ectodomain cleavage of DDR1 is mediated in part by Src-dependent activation 16441665_Data show that the interaction between Src and major vault protein (MVP) is critically dependent on Src activity and protein (MVP) tyrosyl phosphorylation, which are induced by epidermal growth factor stimulation. 16465417_Results suggest that c-Src may be involved in the formation of giant cells in cherubism, central giant cell granuloma and giant cell tumors. 16492668_arginine dimethylation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K by protein-arginine methyltransferase 1 inhibits its interaction with c-Src 16523241_These data suggest that FAK might differently regulate apoptosis and focal adhesion formation through site-specific, Src-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation in senescent cells. 16543952_nephrin phosphorylation results in Src kinase activation, recruitment of Nck, and assembly of actin filaments in an Nck-dependent fashion 16569657_Although a key factor in TRAF6-dependent activation of PI 3-kinase, ectopic expression of Src was insufficient for NF-kappaB activation and, in contrast to NF-kappaB, was not inhibited by IRAK2. 16619028_Src activation triggers Caspase-8 phosphorylation on Tyr380 and impairs Fas-induced apoptosis. 16636672_Study shows EGF-stimulation-induced Csk-binding protein (Cbp) tyrosine phosphorylation followed by Cbp-Csk association, in a SFK-dependent manner. 16690617_nNOS is a new p60(src) kinase substrate essential for SST5-mediated anti-proliferative action 16728403_the Src/Fak complex has a role in breast cancer tumorigenesis 16825188_Upon IGF-I stimulation, a complex assembles on SHPS-1 that contains SHP-2, c-Src, and Shc wherein Src phosphorylates Shc, a signaling step that is necessary for an optimal mitogenic response 16837460_v-Src-dependent down-regulation of the Ste20-like kinase SLK through casein kinase II. 16844778_Hsp90 inhibition transiently activates Src kinase and promotes Src-dependent p85 PI3K and Akt and Erk activation 16862215_Nicotine induces cell proliferation by beta-arrestin-mediated activation of the Src and Rb-Raf-1 pathways om ;img camcer. 16882656_extracellular matrix fragments produced by apoptotic EC initiate a state of resistance to apoptosis in fibroblasts via an alpha2beta1 integrin/SFK (Src and Fyn)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent pathway 16891307_A key coactivator for the proper function of HNF4 alpha in human liver and for an integrative control of multiple hepatic genes involved in metabolism and homeostasis. 16894533_Genetic alterations of SRC1 are rare in prostate cancer. The nuclear protein accumulation of SRC1 seems to be mildly increased in androgen ablation resistant prostate cancers. . 16951177_inhibition may be an attractive therapeutic approach for patients with ovarian carcinoma 16959222_Curcumin treatment inhibited v-src gene expression in K562 chronic leukaemia cells. 17018524_steps involving Src association, phosphorylation, and product release are fast, and a structural change in Csk participates in limiting the catalytic cycle 17030621_HSP90 binding to ErbB2 participates in regulation of src kinase activity as well as kinase stability 17038311_data delineate multiple PTH1R structural determinants for ERK1/2 activation and identify mechanism involving proline-rich motifs in receptor C terminus for reciprocal scaffolding of c-Src and beta-arrestin2 with a class II G-protein-coupled receptor 17046078_SHP1 activation, association with Src and dephosphorylation of specific proteins were dependent on extracellular calcium and maintenance of a higher cytosolic calcium plateau. 17056000_These results suggest that dimerization of Src plays an important role in the regulation of Src tyrosine kinase activity. 17062641_Serum-independent growth of 5637 cells involves the transmembrane signaling cascade via EGFR ligand(s) (but not HGF), EGFR, Src and p145(met) 17088251_Src and Rac1 have roles in focal adhesion kinase and ERK mitogenic signaling in epithelial cells 17135298_Stimulation of collagen type I secretion by TGF-beta requires a PKCdelta-Src-ERK1/2 signaling motif. 17215324_Src and focal adhesion kinase mediate cyclic mechanical strain-induced extracellular regulated kinase phosphorylation and proliferation of pulmonary epithelial cells. 17224200_P60-c-src suppresses apoptosis through inhibition of caspase 8 activation in hepatoma cells. 17307333_These lines of evidence suggested that a Gq-coupled receptor activates specifically p38 MAPK through lipid rafts and Src kinase activation, in which flotillins positively modulate the Gq signaling. 17317726_results delineate a novel force-activated inside-out Src/PI3K/FAK/Akt pathway by which cancer cells regulate their own adhesion. 17325034_study elucidated a nongenomic extranuclear signal mediated by the RAR-SRC interaction that is negatively regulated by CSK and is required for RA-induced neuronal differentiation 17369846_Src plays a crucial role in CUTL1-induced tumor cell migration 17443665_Fak/Src signaling to the PI3-K/Akt-1 and MEK/Erk pathways undergoes a differentiation state-specific uncoupling in enterocytes. 17471235_CD99 isoforms dictate opposite functions in tumour malignancy and metastases by activating or repressing c-Src kinase activity. 17510314_These data suggest that Src-induced u-PAR gene expression and invasion/intravasation in vivo is also mediated via AP-1 region -190/-171, especially bound with c-Jun phosphorylated at Ser(73/63). 17537434_The interplay between palladin, SPIN90 and Src and characterized the role of palladin and SPIN90 in platelet derived growth factor and Src-induced cytoskeletal remodeling, was analyzed. 17537435_These results suggest that palmitoylation of Src-family kinases (SFKs) is critical for SFK localization and trafficking and implicate that two distinct trafficking pathways for SFKs may be involved in SFKs' specific functions. 17553930_E-cadherin signaling is an important activator of c-Src at cell-cell contacts, providing a key input into a signaling pathway where quantitative changes in signal strength may result in qualitative differences in functional outcome. 17574549_These findings support a novel role for RACK1 as a key regulator of cell migration and adhesion dynamics through the regulation of Src activity, and the modulation of paxillin phosphorylation at early adhesions. 17593353_Indirect evidence for an impaired src kinase regulation of I (Ca,L) together with an increased phosphatase activity suggests that a complex alteration in the kinase/phosphatase balance leads to I (Ca,L) dysregulation in chronic AF. 17620427_Activated c-Src may play a role in survival, metastasis, and invasion of malignant pleural mesothelioma 17641225_c-Src controls functional association between integrin alphav-beta3 and VEGFR-2 via integrin beta3 phosphorylation. 17691821_These results demonstrate that the chimeric strategy is useful for detailed dissection of the mechanistic basis of substrate specificity and regulation of protein tyrosine kinases. 17716980_norepinephrine stimulation activates Src tyrosine kinase and this activation is required for increased IL-6 expression 17785844_Endothelial Src activity is required for ICAM-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin and for efficient neutrophil migration during passage of leukocytes across the vascular endothelial monolayer. 17803936_Src was identified as Death-associated protein kinase (DAPK) regulator through their reciprocal modification of DAPK Y491/492 residues and establishes a functional link of this DAPK-regulatory circuit to tumor progression. 17804738_Colorectal cancer cells may develop acquired resistance to cetuximab via altering EGFR levels through ubiquitination and degradation and using Src kinase-mediated cell signaling for cell growth and survival. 17849451_TAE226-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells with overexpressed SRC. 17855352_analysis of Src and C-terminal Src kinase interactions in integrin alphaIIbbeta3-mediated signaling to the cytoskeleton 17933561_These observations suggest that within in vivo-like conditions Src may have a leading role in the induction of sustained ERK1/2 activation through the Src/Ras/Raf pathway. 17934522_These results reveal a potentially important role for CHK in Src activation and tumorigenicity in colon cancer cells. 17967179_human breast cells are a uniquely permissive environment for HGF transactivation by Src/Stat3 which may allow for the inappropriate activation of HGF transcription during the early stages of breast transformation 17974954_This study suggests that (a) PTP1B can act as an important activator of Src in colon cancer cells via dephosphorylation at Y530 of Src and (b) elevated levels of PTP1B can increase tumorigenicity of colon cancer cells by activating Src. 17997837_Brk-mediated STAT5b phosphorylation leads to STAT5b transcriptional activity, and this activity is further increased by kinase active c-Src. 18024423_These data suggest that phosphorylation of PDK1 on Tyr(9), distinct from Tyr(373/376), is important for PDK1/Src complex formation, leading to PDK1 activation. 18057010_Silencing Cdc42 blocks activation of EGFR and Src induced by Ca2+ depletion, resulting in a reduction in E-cadherin degradation 18061419_Col-IV regulates the secretion of MMP-9 via a Src and FAK dependent pathway in MCF-7 cells 18063684_The SRC-STAT5 pathway is essential for decidualization of estrogen-primed human endometrial stromal cells. 18069897_novel mechanism of c-SRC regulation whereby in response to stress c-SRC activity is regulated, at least in part, through loss of the interaction with its inhibitor, PR55gamma 18070925_there is functional conservation between Qr domains of yeast Gal11p and mammalian SRC proteins as direct targets of activator proteins in yeast. 18080320_TNF activated ERK in an EGFR and Src dependent and an EGFR and Src independent modes 18086662_attenuation of the Erk1/2 signaling pathway is essential for andrographolide-mediated inhibition of v-Src transformation 18089800_Association of caspase-8 and Src may help reconcile why a potential tumor suppressor such as caspase-8 is rarely absent in cancers. 18095097_c-Src is a mediator of substance P-stimulated ERK1/2 phosphorylation in human U373 MG glioblastoma cells. 18156174_Src-dependent phosphorylation at Tyr-529 facilitates inactive ERK binding to RSK2, which might be a general requirement for RSK2 activation by EGF through the MEK/ERK pathway. 18180305_VE-cadherin has a role in modulating c-Src activation in VEGF signaling 18209475_This study analysed whether the serotonin transport mediated by the plasma-membrane transporter SERT is regulated by its Tyr-phosphorylation. 18211905_CD63 plays a role in the regulation of ROMK channels through its association with RPTPalpha, which in turn interacts with and activates Src family PTK, thus reducing ROMK activity. 18223692_Src, a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, is overexpressed in androgen-independent prostate carcinoma 18251740_These data provide direct evidence for increased activation of Src-family tyrosine kinases in the pathogenesis of hyperproliferative epidermal disorders. 18252715_a new signaling connection from ILK to cofilin for dynamic actin polymerization during cell adhesion, depending on the activity of ILK-associated c-Src. 18322799_Anoikis causes a down-activation of Fak, Src, Akt-1 and Erk1/2, a loss of Fak-Src association, and a sustained/enhanced activation of p38b, which is required as apoptosis/anoikis driver 18327819_results indicate that Src and E-cadherin may play an important role in epithelial-mesenchymal transformations, invasion, and aggressive clinicopathologic features of head and neck squamous carcinoma 18353785_results demonstrate that TGFbeta1 induces alphavbeta3 integrin expression via a beta3 integrin-, c-Src-, and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway 18388244_Role of Src kinase in the early action of TCDD through a nongenomic pathway in MCF10A cells is reported. 18397177_Rac1-dependent NADPH oxidases play a critical role in activating c-Src following hypoxia/reoxygenation injury 18403635_These findings suggest a novel MUC1-Src-CrkL-Rac1/Cdc42 signaling cascade following ICAM-1 ligation, through which MUC1 regulates cytoskeletal reorganization and directed cell motility during cell migration. 18434302_Within the endothelial cell, p11 is required for Src kinase-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of A2, which signals translocation of both proteins to the cell surface. 18441016_hnRNP K binds to the 3'-untranslated region of the c-Src mRNA and inhibits its translation by blocking 80 S ribosome formation 18445593_Csk serves to maintain the constancy of baseline excitatory synaptic transmission by inhibiting Src kinase-dependent synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus 18451158_A Met/c-Src-mediated signaling pathway is a mediator of EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation and cell growth in the presence of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 18457834_These results suggest that Src-family tyrosine kinases, including c-Src and Lyn, are involved in formation of the cortical actin cap, which may serve as a platform of tyrosine phosphorylation signaling. 18463161_c-Src is an important regulator of Nox1 activity 18467332_tau interactions with Src homology 3 domains of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, phospholipase Cgamma1, Grb2, and Src family kinases are regulated by phosphorylation 18474606_Src phosphorylation of Bif-1 suppresses the interaction between Bif-1 and Bax, resulting in the inhibition of Bax activation during anoikis. 18493848_Src kinase, in conjunction with antihormone therapies, effectively prevents antihormone resistance in breast cancer cells in vitro 18503159_a critical role for a EGF-R-connected p60c-src-kinase-mediated pathway involving STAT3 and contributing to cell survival and proliferation within colorectal carcinomatumours. 18509267_The effect of OGP(10-14) on differentiation of a cancer megakaryoblast cell line and its involvement on RhoA and Src family kinases signaling pathway, was evaluated. 18524994_pp60c-Src TK-activity was selectively induced by VEGF in MM tumor and ECs 18550772_These studies demonstrate positive cross talk between ER, c-Src, EGFR, and STAT5b in ER+ breast cancer cells. 18562041_the Src-specific sites are all required for overexpressed Focal adhesion kinase to inhibit invadopodia formation. 18566211_This study reveals for the first time that alpha-catenin is a key regulator of beta-catenin transcriptional activity and that the status of alpha-catenin expression in tumor tissues might have prognostic value for Src targeted therapy 18594011_expression and activation of c-Src as well as EGF receptor promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression 18594017_PLCgamma-1 and c-Src activation contribute to HNSCC invasion downstream of EGF receptor 18606683_study shows that TNFR1 associates with Jak2, c-Src, and PI3K in various cell types to engage signaling pathways, activate transcription factors, and modulate gene expression 18617000_Regulation of hERG channels by protein tyrosine kinases modifies the channel activity and thus likely alters electrophysiological properties including action potential duration and cell excitability in human heart and neurons. 18632638_analysis of PAFR activation and pleiotropic effects on tyrosine phospho-EGFR/Src/FAK/paxillin in ovarian cancer 18644869_This study demonstrates an important role of the dynamic raft reorganization induced by CD44 clustering in eliciting the matrix-derived survival signal through the CD44-SRC-integrin beta1 axis . 18662984_PI3K and Src-ELMO-Dock2 pathways work in parallel to activate Rac2 and modulate chemotaxis in response to a CXCL8 gradient in neutrophils. 18667434_In vascular smooth muscle cells shedding of membrane-bound epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor ligands and activation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinases Pyk2 and Src contributed to the thrombin-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. 18694941_The Diaphanous-related Formin FHOD1 associates with ROCK1 and promotes Src-dependent plasma membrane blebbing. 18802114_c-Src is involved in lipoteichoic acid-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression in human cultured tracheal smooth muscle cells. 18832467_data are compatible with a model wherein interaction of MDA-9/syntenin with c-Src promotes the formation of an active FAK/c-Src signaling complex, leading to enhanced tumor cell invasion and metastatic spread 18839319_Src overexpression downregulates alpha3 integrin total protein expression and localization to the cell surface of HCT116 colon cancer cells. This indicates that Src activity may enhance metastasis by altering alpha3 integrin expression. 18922903_Src and ADAM-17-mediated shedding of transforming growth factor-alpha is a mechanism of acute resistance to TRAIL. 18924149_Src and Src-associated signaling pathways are activated in relation to hypoxia in neoplasms 18948751_TCPTP is a negative regulator of SFK, JAK1 and STAT3 signalling during the cell cycle. 19035465_KV11 peptide (from human Apolipoprotein A) suppresses angiogenesis and tumor progression by targeting the c-Src/ERK signaling pathways in VEGF induced cells 19047046_as a mediator of SF- and Src-stimulated NF-kappaB activity. Finally, the Src/Rac1/MKK3/6/p38 and Src/TAK1/NF-kappaB-inducing kinase pathways exhibited cross-talk at the level of MKK3. 19048118_Src family kinases mediate betel quid-induced oral cancer cell motility 19066724_Data suggest that upon phosphorylation, Src is directly translocated from focal adhesions to membrane ruffles, thereby promoting formation of new adhesion complexes. 19074832_the c-Src-Rac1-p38 MAPK pathway is required for activation of Akt in response to radiation and plays a cytoprotective role against radiation in human cancer cells 19111446_Mechanical wounding induces significant ROS generation at the wound edge which, in turn, induced ligand-independent KGFR and FRS2 activation via c-Src kinase signaling. 19112177_HINT1 up-regulates cellular levels of p27(KIP1) by two mechanisms: 1) it inhibits its ubiquitylation by targeting the SCF(SKP2) ubiquitin ligase complex, and 2) it inhibits the phosphorylation of p27(KIP1) by Src via inhibiting Src expression. 19130504_Nef regulates the NADPH oxidase p47(phox)activity through the activation of the Src kinases and PI3K 19147496_S100B interacts with Src kinase, thereby stimulating the PI3K/Akt and PI3K/RhoA pathways. 19160018_Rho mediates various phenotypes of malignant transformation by Ras and Src through its effectors, ROCK and mDia [review] 19176482_Presenilin 1 affects focal adhesion site formation and cell force generation via c-Src transcriptional and posttranslational regulation 19199380_Increased PRL1 expression results in activation of Src and ERK1/2, which stimulates MMP2 and MMP9 production, leading to increased cell migration and invasion. 19223541_Sustained Src inhibition results in signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) activation and cancer cell survival via altered Janus-activated kinase-STAT3 binding. 19258394_These results suggest that SFK trafficking is specified by the palmitoylation state in the SH4 domain. 19262138_P-selectin cross-links PSGL-1 and enhances neutrophil adhesion to fibrinogen and ICAM-1 in a Src kinase-dependent, but GPCR-independent mechanism. 19262695_beta-arrestins and c-Src are implicated in the activation of Akt in response to ghrelin through the GHS-R1a 19265199_the signal transduction pathways mediated by c-Kit/D816V are markedly different from those activated by wild-type c-Kit and altered substrate specificity of c-Kit circumvents a need for Src family kinases in signaling of growth and survival 19302982_activated c-Src played a critical role in the HBx-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatoma cells. 19305428_mutant EGFR-Src interaction and cooperativity play critical roles in constitutive eng |
ENSMUSG00000027646 |
Src |
334.092883 |
27.6434062481 |
4.788863 |
0.311621453 |
198.896694 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000363580953151130429495002683127116430403372340131000592569236589479603330880718030142073618163645110525411344125075278899128505827320623211562633514404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000068889022702319441152337174932814635834149968667174851666662866730934719857952962003337674044999976349228289912180606124891824038058985024690628051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
651.9481131 |
94.2008012 |
22.7410597 |
2.9140680 |
| ENSG00000197140 |
203102 |
ADAM32 |
protein_coding |
Q8TC27 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in sperm development and fertilization This is a non-catalytic metalloprotease-like protein. {ECO:0000250}. |
Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the disintegrin family of membrane-anchored proteins that play a role in diverse biological processes such as brain development, fertilization, tumor development and inflammation. This gene is predominantly expressed in the testis. The encoded protein undergoes proteolytic processing to generate a mature polypeptide comprised of an metalloprotease, disintegrin and epidermal growth factor-like domains. This gene is located in a cluster of other disintegrin and metallopeptidase family genes on chromosome 8. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:203102; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; binding of sperm to zona pellucida [GO:0007339]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000037437 |
Adam32 |
21.253069 |
2.5368231369 |
1.343023 |
0.530368787 |
6.136627 |
0.01324096466381636041931280090011568972840905189514160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024741946884153626085023347513924818485975265502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.8724290 |
9.0070383 |
6.6113478 |
2.5192921 |
| ENSG00000197142 |
51703 |
ACSL5 |
protein_coding |
Q9ULC5 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of long-chain fatty acids to their active form acyl-CoAs for both synthesis of cellular lipids, and degradation via beta-oxidation (PubMed:17681178, PubMed:24269233, PubMed:22633490). ACSL5 may activate fatty acids from exogenous sources for the synthesis of triacylglycerol destined for intracellular storage (By similarity). Utilizes a wide range of saturated fatty acids with a preference for C16-C18 unsaturated fatty acids (By similarity). It was suggested that it may also stimulate fatty acid oxidation (By similarity). At the villus tip of the crypt-villus axis of the small intestine may sensitize epithelial cells to apoptosis specifically triggered by the death ligand TRAIL. May have a role in the survival of glioma cells. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17681178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18806831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19459852, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22633490, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24269233}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Fatty acid metabolism;Ligase;Lipid metabolism;Magnesium;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an isozyme of the long-chain fatty-acid-coenzyme A ligase family. Although differing in substrate specificity, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution, all isozymes of this family convert free long-chain fatty acids into fatty acyl-CoA esters, and thereby play a key role in lipid biosynthesis and fatty acid degradation. This isozyme is highly expressed in uterus and spleen, and in trace amounts in normal brain, but has markedly increased levels in malignant gliomas. This gene functions in mediating fatty acid-induced glioma cell growth. Three transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:51703; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; arachidonate-CoA ligase activity [GO:0047676]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; long-chain fatty acid-CoA ligase activity [GO:0004467]; lipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008610]; long-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0001676]; long-chain fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0035338]; positive regulation of long-chain fatty acid import across plasma membrane [GO:0010747]; regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001236] |
15736044_expression of ACS5 in the gastric body and the small intestine with metaplasia or heterotopia 15809837_ACS5 is a very suitable marker molecule for the detection of villus atrophy in the small intestine. 16198472_SREBP-1c-mediated insulin regulation of acyl-CoA synthestase 5 expression indicate that ACS-5 is involved in the anabolic fate of fatty acids. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17495181_Existence of a link between ACSL5 genotype and diet responsiveness. 17495181_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17681178_Suggest an ACSL5-dependent regulatory mechanism that contributes to the cellular renewal along the crypt-villus axis in human small intestine. 17761945_Oncostatin M directly lowers the plasma triglycerides in hyperlipidemia by stimulating the transcription of ACSL3/5 in the liver. 18228202_Expression of ACSL5 in human epidermis is reported. 18806831_These results indicate that ACSL5 is a critical factor for survival of glioma cells under acidic tumor microenvironment. 19218499_These results reveal a mechanism for elevated transcription of ACSL5 in skeletal muscle of carriers of the rs2419621(T) allele, associated with more rapid diet-induced weight loss. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20470896_Increased ACSL5 is associated with Fatty Liver. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22163040_High ACSL5 transcript levels associate with systemic lupus erythematosus and apoptosis in Jurkat T lymphocytes and peripheral blood cells 22171129_The data strongly indicate that human but not rat acyl-CoA synthetase 5 is sensitive to triacsin C and does not compensate for other triacsin C-sensitive ACSL isoforms. 23348389_Levels of acyl-coenzyme A synthetase 5 in urothelial cells and corresponding neoplasias reflect cellular differentiation. 24222123_Down-regulation of ACSL5 is associated with colorectal cancer. 24770931_Uncoupling of ACSL5 and mitochondrial mortalin by mutated TP53 could be important in colorectal carcinogenesis. 25356045_ACSL5 mediates antiproliferative activities via Wnt2B palmitoylation with diminished Wnt activity. The molecular pathway is probably relevant for intestinal homeostasis, overwhelmed by other pathways in carcinogenesis. 27189022_Functional variant (rs2256368:A>G) affecting ACSL5 exon 20 skipping was identified as a causal factor linked to the migraine-associated rs12355831:A>G, suggesting that the activation of long-chain fatty acids by the spliced ACSL5-Delta20 molecules is involved in migraine pathology. 28153554_colorectal adenocarcinomas with low (n=41; group 1) or high (n=31; group 2) ACSL5 levels were identified. In a one-year follow-up, tumour recurrence was significantly increased in group 1. 28498416_These results suggest that ACSL1, ACSL4 and ACSL5 expression is regulated by ER signaling pathways and ACSL5 is a potential novel biomarker for predicting prognosis of breast cancer patients. 28808653_our study has demonstrated that ACS5 expression was increased in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and CRC tissues and its upregulation closely correlated to poor tumor differentiation and excess muscular layer in patients with CRC 29605434_rs2419621 T allele carriers are more responsive to lifestyle interventions partly due to an increase in the short ACSL5 protein isoform, increasing cellular, tissue and whole-body fatty acid utilization. 30463708_downregulation of ACSL5 and Wnt2B could play an important role in the development of bronchial-alveolar structures in congenital pulmonary airway malformations (CPAMs). 30712446_Our findings reveal that LOX and ACSL5 are potential prognostic markers for the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients. 31053784_Our findings indicate that the variant rs2256368:A>G can predict a growth inhibitory activity, caused by the Spl isoform of ACSL5 protein, opposed to the activity of the NSpl. Deep understanding of its functioning might have application in metabolic diseases and cancer. 32012265_miR-497-5p mediates starvation-induced death in colon cancer cells by targeting acyl-CoA synthetase-5 and modulation of lipid metabolism. 32129880_ONECUT2 upregulation is associated with CpG hypomethylation at promoter-proximal DNA in gastric cancer and triggers ACSL5. 32347412_Roles of acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 5 and colony stimulating factor 2 in inhibition of palmitic or stearic acids in lung cancer cell proliferation and metabolism. 32686444_ACYL-CoA synthetase long-chain 5 polymorphism is associated with weight loss and metabolic changes in response to a partial meal-replacement hypocaloric diet.', trans 'El polimorfismo de la ACYL-CoA-sintetasa de cadena larga 5 se asocia a perdida de peso y cambios metabolicos en respuesta a una dieta hipocalorica parcial de reemplazo. 32968195_A multi-ethnic meta-analysis identifies novel genes, including ACSL5, associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 33191500_Deficiency of acyl-CoA synthetase 5 is associated with a severe and treatable failure to thrive of neonatal onset. 34859867_The gene variant rs2419621 of ACYL-CoA synthetase long-chain 5 gene is associated with weight loss and metabolic changes in response to a robotic sleeve gastrectomy in morbid obese subjects. |
ENSMUSG00000024981 |
Acsl5 |
205.627456 |
2.6724667919 |
1.418172 |
0.117752831 |
147.390580 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000064468736220467962125001407887459903334832490521508105111664142879479283076038868957933049633202138295473559992387890815734863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000009310748988396351682688974461599727939039449733213170385837163101983492614724000432544978589355366693780524656176567077636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
299.7309269 |
24.4624181 |
113.0204239 |
7.2533518 |
| ENSG00000197162 |
146540 |
ZNF785 |
protein_coding |
A8K8V0 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:146540; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
73.524544 |
0.4477279248 |
-1.159306 |
0.211195515 |
30.369618 |
0.00000003570772068141945863010847453389295935721747810021042823791503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000147425442589580777156413131899481694375708684674464166164398193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.4205388 |
7.2598068 |
104.5227710 |
11.1561433 |
| ENSG00000197168 |
341676 |
NEK5 |
protein_coding |
Q6P3R8 |
|
ATP-binding;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable ATP binding activity; metal ion binding activity; and protein kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein phosphorylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity and positive regulation of striated muscle cell differentiation. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:341676; |
ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
25725288_The hNek5 is mitochondrial localization and its role on cell death and cell respiration defects through COX11, MTX2 and BCLAF1. 25963817_Nek5 is required for the loss of centrosome linker proteins and enhanced microtubule nucleation that lead to timely centrosome separation and bipolar spindle formation in mitosis 30675923_Data show that up-regulated NEK5 was significantly associated with breast tumor progression and poor overall prognosis; and that silencing of NEK5 can significantly suppress the proliferation both in vivo and in vitro, inhibiting migration, and invasion. NEK5 can up-regulate Cyclin A2 by direct interaction. 31090963_NEK5 interacts with topoisomerase IIbeta and is involved in the DNA damage response induced by etoposide. 31906878_the NEK protein kinases emerge as important proteins in thyroid cancer development and may help to identify malignancy and aggressiveness features during diagnosis. 32196601_Knockdown of lncRNA XIST inhibits hypoxia-induced glycolysis, migration and invasion through regulating miR-381-3p/NEK5 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 33547867_NEK5 interacts with LonP1 and its kinase activity is essential for the regulation of mitochondrial functions and mtDNA maintenance. 33749548_Targeting Never-In-Mitosis-A Related Kinase 5 in Cancer: A Review. 34196902_NEK5 activity regulates the mesenchymal and migratory phenotype in breast cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000037738 |
Nek5 |
9.192133 |
0.4461940033 |
-1.164257 |
0.486833166 |
5.852344 |
0.01555632131947518037584643479931401088833808898925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028587064576127196868782220917637459933757781982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5445191 |
1.7941444 |
12.4645530 |
2.5819693 |
| ENSG00000197182 |
400931 |
MIRLET7BHG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
118.946783 |
0.0497890020 |
-4.328029 |
0.583105521 |
43.033916 |
0.00000000005379910150408201929353638575041058299264218334201359539292752742767333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000283193558559290499213499017869179880113605918268149252980947494506835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
15.1729841 |
5.8448552 |
306.4151910 |
81.8055237 |
| ENSG00000197191 |
375791 |
CYSRT1 |
protein_coding |
A8MQ03 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Located in extracellular exosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:375791; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802] |
|
ENSMUSG00000036731 |
Cysrt1 |
6.708141 |
0.1570337788 |
-2.670853 |
0.801332403 |
12.110731 |
0.00050132472720107717351067933009289845358580350875854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001230797234445758434051576557521912036463618278503417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8889241 |
0.9355269 |
12.2417773 |
2.9420971 |
| ENSG00000197249 |
5265 |
SERPINA1 |
protein_coding |
P01009 |
FUNCTION: Inhibitor of serine proteases. Its primary target is elastase, but it also has a moderate affinity for plasmin and thrombin. Irreversibly inhibits trypsin, chymotrypsin and plasminogen activator. The aberrant form inhibits insulin-induced NO synthesis in platelets, decreases coagulation time and has proteolytic activity against insulin and plasmin.; FUNCTION: [Short peptide from AAT]: Reversible chymotrypsin inhibitor. It also inhibits elastase, but not trypsin. Its major physiological function is the protection of the lower respiratory tract against proteolytic destruction by human leukocyte elastase (HLE). |
3D-structure;Acute phase;Alternative splicing;Blood coagulation;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hemostasis;Phosphoprotein;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease inhibitor;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a serine protease inhibitor belonging to the serpin superfamily whose targets include elastase, plasmin, thrombin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and plasminogen activator. This protein is produced in the liver, the bone marrow, by lymphocytic and monocytic cells in lymphoid tissue, and by the Paneth cells of the gut. Defects in this gene are associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, and chronic liver disease. Several transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:5265; |
collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; COPII-coated ER to Golgi transport vesicle [GO:0030134]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity [GO:0004867]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; negative regulation of endopeptidase activity [GO:0010951] |
11034936_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11131449_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11148177_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11199103_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11295654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11436564_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11562937_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11744816_Results show that nephropathy is not a direct and single expression of alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. 11754061_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11773044_have used reactive loop peptides to explore the differences between the pathogenic Z and normal M alpha(1)-antitrypsin 11785295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11834734_Concerted regulation of inhibitory activity of alpha 1-antitrypsin by the native strain distributed throughout the molecule. 11848724_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11862702_In vitro formation of triple-stranded dna structures in the human alpha1-Antitrypsin gene (alpha1-antitrypsin) 11936950_induction of expression by oncostatin M mediated by a 3' enhancer 11991955_reactivity and oxidation pathway of cysteine 232 residue 12009885_The oxidation kinetics of each of alpha 1-antitrypsin's methionines has been reported for recombinant alpha 1-AT(C232S) as well as for M351L and M358V mutants, with new insights into the protein's solution structure. 12023831_alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency and dementia 12023832_Gene regulation of the serine proteinase inhibitors alpha1-antitrypsin and alpha1-antichymotrypsin. 12083479_identified as a protective factor in plasma that neutralizes neutrophil degradation of scu-PA, tcu-PA, t-PA and plasmin 12223217_a protein identical to or highly homologous with serum A1AT was purified from follicular fluid; follicular fluid A1AT did not show a stimulatory effect on sperm motility 12324297_alpha(1)-antitrypsin and antichymotrypsin are produced by the mammary gland and are present in milk in relatively high amounts in early lactation 12368052_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12368052_the alpha 1 antitrypsin polymorphisms, especially Pi*Z, could help to predict asbestosis risk 12372062_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12452840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12460583_Acid denaturation of alpha1-antitrypsin: characterization of a novel mechanism of serpin polymerization. 12464659_deficiency involved in liver and mitochondrial injury (REVIEW) 12464660_Alpha1-antitrypsin polymerization and the serpinopathies(REVIEW) 12492914_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12498804_Data identify residues in alpha(1)-antitrypsin that appear to play a key role in inducing or preventing conformational change. 12514663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12528263_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12578879_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12608432_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12612303_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12649292_examination of novel mode of polymerization 12689922_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12786756_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815101_In the proposed stochastic model, the delayed onset of the glycan modification, relative to the duration of nonnative protein structure, coordinates preferential degradation of misfolded alpha 1-anatitrypsin monomer & spares the native molecule. 12815594_First comprehensive analysis of the genetic diversity of the AAT gene in a cohort from sub-Saharan Africa. 12815594_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12878320_alpha 1 antitrypsin simultaneously and differently inhibits processing of HIV-1 Env and Gag, intracellularly, at least in part, by blocking cellular furin. 12893950_Low plasma levels of A1AT may be a risk factor for spontaneous cervical artery dissections 12933574_Alpha1PI promotes copatching of human leukocyte elastase with canonical HIV receptors. HLE & its ligand alpha1PI can serve as HIV coreceptor and cofactor & potentially participate in the pathophysiology of HIV disease progression. 12934194_in community acquired pneumonia, both A1AT and SLPI were cleaved or complexed in infected lobes and A1AT was oxidized; conclude that mean elastase levels are increased and that mean anti-elastase capacity is decreased in pneumonic lobes 14523999_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14551891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14616761_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14639110_A new M-like-null variant of alpha-1-antitrypsin associated with panacinar emphysema was found in a 73 year-old woman non-smoker. 14766206_alpha1-antitrypsin has a role in neutrophil activation 14766207_HSP70 and alpha1AT have immunogenic roles in diabetes mellitus 14968215_No correlation between alpha-1-antitrypsin phenotype and lung, prostate, or breast cancer in Jordan 15079023_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15100318_A model cell system of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signals induced by variant Z alpha 1-antitrypsin (A1AT) demonstrates that both ER overload response and unfolded protein response are activated by the variant Z A1AT, but not wild-type A1AT. 15266208_Observational study of healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) 15271689_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15271889_identified as a new binding partner for E.coli EspB and EspD, suggesting a previously unappreciated role for AAT in host cell defense against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infections and potentially also against other bacterial pathogens. 15454649_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15474273_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15498560_C26, the C-terminal 26 residue peptide of serpin A1, significantly increased cell proliferation in cultures of hepatoma cells. 15532029_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15532029_screening the exonic regions, 5' and 3' flanking sequence of the AAT gene in order to generate a high density map of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) 15612581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15653097_This review characterizes the unique physiological properties of alpha 1-antitrypsin (AAT) and its role as a diagnostic tool in lung and liver disorders associated with AAT serum deficiency. 15659365_serpin/furin complex stability depends on pH and regulation at the deacylation step 15674733_Thirteen individuals showed biallelic expression of PI gene, and three individuals showed monoallelic expression. 15681822_polymeric alpha(1)-anti-trypsin co-localizes with neutrophils in the alveoli of individuals with Z alpha(1)-antitrypsin-related emphysema 15709777_Polymerizing alpha 1-antitrypsin study clearly shows existence of a kinetic lag phase during which short oligomers are formed prior to the formation of heterogeneous mixtures of longer polymers produced via condensation of shorter oligomers. 15775753_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15820772_The results revealed that the frequency of M1S, M2S, M1Z, and MV alpha 1-antitrypsin phenotypes were significantly higher in uveitis patients 15820782_The PIM3 allele of the alpha1AT gene is found to have an association with the pathogenesis of COPD in the Indian population. 15927063_We found acceptable variability in our study parameters, indicating the feasibility of their use in an evaluation of biochemical efficacy of alpha-1-antitrypsin augmentation therapy in Pi Z subjects. 15994391_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16011217_Point mutations in members of the serine proteinase inhibitor or serpin superfamily cause them to change shape, polymerise and be deposited in the tissues. 16029614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16044402_Genetic deficiency engender a cancer-prone state by surviving with intrinsic damage and by chronically stimulating in 'trans' adjacent relatively undamaged hepatocytes. (Review) 16099106_Taken together, these data suggest that aggrecanase-1 and alpha1-antitrypsin bind in vivo, although the physiological significance of the interaction between aggrecanase-1 and alpha1-antitrypsin remains unclear. 16137891_In individuals with advanced lung disease associated with alpha(1)-antitrypsin deficiency, cytotoxic concentrations of alpha-defensins might be present and unopposed, thus further aggravating lung disease in this population. 16172282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16175011_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16179568_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16183649_effect of mutant alpha1ATZ on several potential protective signaling pathways using cell lines with inducible expression of mutant alpha1AT 16204591_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16278826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16312203_AAT Deficiency affects at least 120.5 million carriers and deficient subjects worldwide for the two most prevalent deficiency alleles PIS. 16339299_The effects of heat shock on acute phase protein synthesis can be modified by preincubation with IL-6, whereas addition of this ligand after heat treatment has no effect on the suppressive effect of heat on the APPR. 16385367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16387939_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16501672_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16531799_AAT gene polymorphisms are not associated with renal arterial fibromuscular dysplasia. 16531799_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16540089_The structural and functional characteristics of 10 dysfunctional alpha1-antitrypsin variants (R39C, S53F, V55P, I92N, G115S, N158K, E264V, A336T, P369S, and P369L) were analyzed in detail. 16581345_Men with prostate cancer and those without prostate cancer but with PSA >2 ng/mL had significantly higher alpha 1-antitrypsin concentrations than those without these conditions. 16608528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16617455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16617455_Results suggest that the polymorphism (1237 G --> A) in the 3' enhancer region of the alpha-1-antitrypsin gene is a marker for a modifying effect on pulmonary phenotype in the Irish cystic fibrosis population by a mechanism that is yet to be explained. 16759229_mesotrypsin cannot activate pancreatic zymogens, but might activate certain proteinase-activated receptors because of its thrombin-like subsite specificity; alpha1AT Pittsburgh is an effective mesotrypsin inhibitor 16802007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16802007_The relatively high frequency of A1AT S allele carriers in Egyptian cases of HCV liver cirrhosis suggests the need to routinely screen for this risk genotype among affected families. 16819398_The PiMZ alpha1ATD heterozygous state may have a role in worsening liver disease due to hepatitis C virus or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 16859601_Genetic investigations for Wegener's granulomatosis (WG) have identified various candidate genes, with alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency being the most consistently reported genetic susceptibility factor to date. 16875754_Diabetes is associated with reduced alpha-1-antitrypsin activity of plasma. 16887359_In Alzheimer disease brain, alpha(1)-antitrypsin immunoreactivity was augmented and co-distributed with heme oxygenase-1 16900211_serpin A1 has an invasion-promoting effect in anaplastic large cell lymphoma 16954950_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16954950_study shows no association between cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) mutations and pancreatitis and the importance of alpha 1-antitrypsin(AAT) variants remains speculative 16979136_These data indicate that gp78 assumes multiple unique quality control roles over ATZ, including the facilitation of degradation and inhibition of aggregation of ATZ. 17003923_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17006922_AAT mutations are associated with hyperferritinemia and sinusoidal iron accumulation, but not with more severe liver damage in NAFLD. 17203708_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17204961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17237579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17240615_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17261591_Alpha1-antitrypsin has a role in anti-inflammatory activity in human monocytes by elevating cAMP 17573378_Serum level of sialic acid in patients with chronic alcohol abuse depends on the concentration of the most sialylated glycoproteins: alpha 1-antitrypsin, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein, and transferrin. 17635928_Regulator of G Signaling 16 has a role in the distinct endoplasmic reticulum stress state associated with aggregated mutant alpha1-antitrypsin Z in the classical form of alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency 17650587_analysis of the entire 1257 bp nucleotide sequence of protein coding region of the human AAT variant 17654345_AAT may be an anti-RGM host-defense factor, and anomalous AAT phenotypes or AAT deficiency may constitute risk factors for pulmonary disease due to rapidly growing mycobacteria 17659342_aat is associated with affective disorders, persons with 'intensive creative energy', white matter disease or multisystem disorders of memory 17660256_Local conformational change of A1AT was studied. 17688648_study found alpha1AT deficiency is not an important cause of neonatal cholestasis and childhood liver diseases in Malaysian children 17693072_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17727818_overexpression of Golgi alpha1,2-mannosidase IA, IB, and IC also accelerates ERAD of terminally misfolded human alpha1-antitrypsin variant null (Hong Kong) (NHK), and mannose trimming from the N-glycans on NHK in 293 cells 17855650_SERPINA1 was shown to be expressed in 85.7% of malignant versus 14.3% of nonmalignant insulinomas by immunohistochemistry; data are consistent to the possibility that SERPINA1 is a marker of malignancy in insulinomas 17906067_genetic heterogeneity is present in clinical 'P' phenotype variants and the deleterious P lowell variant appears to be relatively common 17972336_single nucleotide polymorphism confers a significant risk for liver disease in homozygous ZZ children 18028276_A1PI becomes a substrate for Basic carboxypeptidases 18031952_No significant difference in allele frequency between COPD patients and controls. 18031952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18060368_The lack of direct chemotactic effects of recombinant human alpha(1)-proteinase inhibitor 18089349_In enzyme deficient patients with portal hypertension, esophageal varices, or deterioration of hepatic function, liver transplantation should not be delayed. 18164971_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18164971_Prevalence of common HFE and SERPINA1 mutations in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a Moroccan population. 18258845_The persistence of HD5-chymotrypsinogen-trypsin complex in Crohn disease may be attributable to increased luminal levels of proteinase inhibitors such as alpha1-anti-trypsin. 18264947_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18283111_The results reveal ERGIC-53 to be an intracellular transport receptor of alpha1-AT and provide direct evidence for active receptor-mediated ER export of a soluble secretory protein in higher eukaryotes. 18294358_PI Z mutation age was 2902 years in Latvia (SD 1983) and 2362 years in Sweden (SD 1614) which correlates with previous studies based on microsatellite analysis. 18309698_Meta-analysis of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18340647_mutations in the AAT and SLC11A1 genes may change the balance between elastase produced by leukocytes during phagocytosis. 18353624_Serum levels of AAT are correlated with the severity of pulmonary phenotype. Subjects with Null mutations should be considered a subgroup at particularly high risk of emphysema within AAT deficiency 18433707_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18495745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18504338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18504338_Our results suggest that alpha(1)ATD carriers are at a 70% to 100% increased risk of lung cancer and may account for 11% to 12% of the patients with lung cancer in our study. 18515255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18515255_SERPINA1 gene variants associated with reduced serum alpha 1-antitrypsin concentrations. 18519826_Clinical trial and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18534053_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18534053_Report frequency of S and Z alleles for alpha-1-antitrypsin and tumor necrosis factor alpha -308 promoter polymorphism in northeastern Mexico. 18550704_Identification in human milk of complexes of matriptase with ATIII, A1AT, or A2AP, provides evidence that the proteolytic activity of matriptase, from cells that express no or low levels of HAI-1, may be controlled by secreted serpins. 18594986_The degradation or metabolization of acute-phase proteins, apolipoprotein A-I, and alpha1-antitrypsin, is a common response to gastric inflammation irrespective of Hp infection. 18609127_Antral alpha1-PI expression is specifically induced by H. pylori infection 18686007_analysis of human alpha1-antitrypsin (A1AT), a major therapeutic protein, expressed in genetically engineered tobacco plastids 18723439_Alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT), an endogenous inhibitor of serine proteases, inhibits the catalytic domain of human recombinant matriptase in vitro. 18725338_PiM2 allele can be considered as genetic risk factor for asthma. PiS and PiZ alleles are very rare in Tunisia in comparison with the European population, leading to a very small contribution in pulmonary diseases pathogenesis in Tunisia. 18766166_lung and prostate cancer patients have shown a significant elevation in alpha1-AT serum levels compared with healthy controls; breast cancer patients did not show a significant change in these levels 18931508_Age-of-onset for lower lung function and potentially lung function decline may be under genetic control in individuals with severe AAT deficiency. 19010440_Reports a distinct transcription initiation site for AAT expression in lung cells, which is located 9 bases upstream of the previously mapped full-length monocyte transcription start-site, and shows two Sp1 sites and a putative TATA box are functional. 19073710_The results showed that AAT in the amnion may function as a protective shield at inflammatory sites, and not as it loses it inhibitory activity in cases with PROM, possibly by oxidation, suggesting that its imbalance contributes to PROM. 19115690_In women with cervical cancer,serum alpha-1-antitrypsin activity was lower both before and after brachytherapy sessions as compared to controls; after the end of therapy, the activity reverted back to the values characteristic for healthy women 19129321_Assessment of myeloperoxidase and oxidative alpha1-antitrypsin in patients on hemodialysis. 19180336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19181511_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19197072_Cytokine production is increased in whole blood from alpha-1-Antitrypsin-deficient patients. 19251783_analysis of alpha1-proteinase inhibitor lung deposition in cystic fibrosis and alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency 19251947_Shed syndecan-1 restricts neutrophil elastase from alpha1-antitrypsin in neutrophilic airway inflammation. 19292870_the serine protease inhibitor alpha-1 antitrypsin binds preprohepcidin within the cell during maturation. Furthermore, alpha-1 antitrypsin binds prohepcidin significantly in the plasma 19306859_Haptoglobin and alpha-1-antitrypsin may constitute new and useful markers of breast cancer 19344972_The serum AAT level is significantly lower in gestational diabetes mellitus compared with normal pregnancies. 19368725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19368725_The pilot study demonstrated that alleles related to deficiency of Alpha 1 antitrypsin are not absent in the Tunisian population, and that rare AATD variants prevailed over commonest PI*Z variant. 19398551_Selenoprotein S/SEPS1 modifies endoplasmic reticulum stress in Z variant alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. 19417089_HDL-associated AAT was able to inhibit extracellular matrix degradation, cell detachment, and apoptosis induced by elastase in human vascular smooth muscle cells 19437508_we show that the P(brescia) mutant is retained in the endoplasmic reticulum as ordered polymers and is secreted more slowly than the normal M alpha(1)AT 19515129_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19515129_the presence of an S or Z allele is associated with higher attack frequency in cluster headadhe with alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency 19590686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19628210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657220_Genotype MS, SS and MZ were detected in 18.3, 3.8 and 1.3% of chronic pancreatitis patients, respectively 19657220_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19729499_PSA, but not PSA-ACT complexes in CSF do not seem to have a role in Alzheimer's disease 19738092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19738092_The SERPINA1 Z allele is a risk factor for liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Patients who carry the Z allele are at greater risk (OR, approximately 5) of developing severe liver disease with portal hypertension. 19747908_Data show that the SERPINA1 p.V213A polymorphism was found associated with disseminated bronchiectasis risk while the ADRB2 p.G16R is a risk factor for severe COPD in smokers. 19747908_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19751191_Based on charge differences over 90 genetic variants have been identified by isoelectric focusing 19763368_no consistent pattern among sites in the vagina in pelvic organ prolapse 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19794310_Sustained viral response (SVR) in A1AT wildtypes was not different from SVR in A1AT heterozygotes after hepatitis C combination therapy. 19815548_Results show that the phosphorylation of calnexin is linked to the efficiency of secretion of the cargo glycoprotein, in this case, alpha1-antitrypsin. 19853488_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19902353_an unidentified candidate breast cancer biomarker was identified as 41/42-aa C-terminal peptide of alpha1-antitrypsin in ductal fluid of breast cancer patients 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19944704_Kinetic instability of the serpin Z alpha1-antitrypsin promotes aggregation. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19956452_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19961268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19961268_Presence of Pi M homozygosity could be associated with liver disease via some mechanism different from Z allele-induced liver damage through accumulation of AAT polymers. 20049513_We found no effect of SERPINA1 over expression on tumor growth in SCID mice although cell migration and invasion were affected in in vitro assays. 20086110_gastric juice alpha1-antitrypsin concentration in gastric cancer patients markedly exceeds those in healthy subjects and patients with benign gastrointestinal diseases 20108056_Report the development of a simple PCR-based analysis designed for the detection of the PI*Mmalton (the most frequent Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency variant in regions of the Southern Mediterranean basin) deficiency alleles using two specific primers. 20109307_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20109307_gene polymorphism is associated with clinically severe chronic rhinosinusitis 20119870_Data describe polymorphisms in the HPC/ELAC-2 and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes that correlate with human diseases in an Indian population. 20119870_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20150872_Alpha1-AT and neopterin serum levels should be considered in the follow up as well as in the prognosis of cancer patients. 20170533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20170533_c.-1973T >C polymorphism was not a risk factor for liver disease of various aetiologies. 20226649_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20228200_The unfolded protein response is activated in unstimulated monocytes from alpha-1 antitrypsin-deficient individuals, affecting monocyte function and leading to an exaggerated inflammatory gene expression. 20298391_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20371432_Almost all of the acute-phase proteins were closely related to rheumatoid arthritis activity (based on DAS28) and their places in the downgrade scale were as follows: CRP, Tf, AGP, Hp and AAT. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20425789_Individuals with classic Williams syndrome deletions and SERPINA1 genotypes were more likely to have joint dislocation or scoliosis. 20425789_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20428906_No histological differences were found between skin samples from AAT deficiency and normal AAT phenotypes. 20435667_when data for the prevalence of AAT deficiency in individual cohorts are displayed as a function of ethnic subgroup, striking differences are found in the numbers in each of the five phenotypic classes of PI*S and PI*Z 20463814_a proteolytic fragment of alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), termed virus inhibitory peptide (VIRIP), was observed in plasma coincident with viremia in early HIV infection 20477988_Results identify the glycoprotein alpha1-antitrypsin as a cargo of VIP36. 20521180_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20521180_variants of AAT and neutrophil elastase genotypes with predicted intermediate or high activity could represent a risk factor for aggressive form of lung cancer 20558996_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561599_Findings for the first time highlight that the entry and cell association of SERPINA1 is dependent on lipid raft cholesterol and that SERPINA1 depletes lipid raft cholesterol. 20595457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634282_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20666480_Candidate biomarkers were in situ verified in tissue arrays, and relative concentrations were validated in 84 CRC patients and controls. Alpha1 antitrypsin (A1AT) and cathepsin D (CTSD)were further examined due to the possible importance in human cancers. 20667823_Loop-sheet mechanism of serpin polymerization tested by reactive center loop mutations. 20739079_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20811639_change in the glycosylation of A1AT with the progression from liver cirrhosis to cancer 20827781_Deficiency of alpha(1) -antitrypsin (alpha(1) AT) may be a determinant of susceptibility to Wegener's granulomatosis (WG). 20886426_Possible mechanisms for an eventual contribution of a heterozygosity of a heterozygous AAT-deficiency for a case of hepatocellular carcinoma are reviewed and discussed. 21060150_demonstrated that glycosylated AAT can bind to IL-8 (a ligand for CXCR1) and that AAT-IL-8 complex formation prevented IL-8 interaction with CXCR1 21067581_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21134340_HIV infection is associated with reduced serum alpha-1-antitrypsin concentrations. 21138453_a novel role of alpha1AT Z heterozygosity as a potential genetic susceptibility factor for cholangiocarcinoma formation and a contribution of aberrant alpha1AT function in biliary carcinogenesis 21138571_Patients with A1ATD related COPD have increased aortic stiffness. 21173712_Increased serum alpha 1-antitrypsin is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 21258324_The study structurally characterizes a sheet-opened state of the serpin alpha-1-antitrypsin and shows how local unfolding allows functionally essential strand insertion. 21263074_A unique mechanism of HIV inhibition applicable to human subjects occurs when AAT blocks the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB p50/p65 despite an unexpected elevation in associated phosphorylated and ubiquitinated IkappaBalpha. 21273701_AAT phenotypes were evaluated in patients with Klinefelter's syndrome. Patients with lowered AAT level and AAT deficiency, especially in men with lung diseases, may have risk of additional diseases. 21335450_The 11478G-->A genotype frequencies did not vary between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease cases and controls, or between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease frequent and infrequent exacerbators. 21470421_from meta analysis, identified 1 gene (SERPINA1) which identifies papillary thyroid carcinoma against benign nodules with 99% accuracy 21477074_examined the localization and production of A1AT in healthy donor neutrophils and found A1AT to be a constituent of all granule subtypes and to be released from neutrophils following stimulation 21505264_analysis of the effect of mutant alpha1-antitrypsin on alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency 21575917_relationship between C-reactive protein (CRP) and alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT) in the AAT deficiency diagnostic setting to verify whether variations in the CRP gene could influence CRP 21670848_Data sshow that that plasmid-derived circulating hAAT protects islet allografts from acute rejection. 21698349_Serum alpha 1 antitrypsin level and age were the independent predictors of aortic dilatation in patients with bicuspid aortic valves. 21702661_Review: The role of proteases, endoplasmic reticulum stress and SERPINA1 heterozygosity in lung disease and alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency. 21727732_results showed high prevalence of AAT deficiency allele in the Saudi population; of 158 subjects, 11.39% were carriers for S mutation, 2.53% were carriers for Z mutation; SZ genotype was present in 3.8%; SS genotype was present in 1.9% 21752289_alpha-1 Antitrypsin deficiency in Ireland is more prevalent than previously estimated with Z and S allele frequencies among the highest in the world 21763297_The SNP rs6609533 of TIMP-1 gene interacted with PIM3 of alpha(1)AT to make a possible risk combination for development of COPD. 21786332_Aim of this study is to determine the prevalence of AT deficiency in Turkish population and |
ENSMUSG00000072849+ENSMUSG00000079015+ENSMUSG00000066366+ENSMUSG00000071178+ENSMUSG00000071177 |
Serpina1e+Serpina1c+Serpina1a+Serpina1b+Serpina1d |
317.801451 |
2.7418899959 |
1.455171 |
0.091912210 |
256.643990 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000092483469095022698529912571528524232523897860255903754723244514852055481424964926823465993525664826763197107715016521497776710934162578454191257042171780966555161285214126110076904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000022788914922245993406657831778490099292505215259222367797371174030108367318379688050403140882491771046550006469657314775948110665245287275761099099469220163882710039615631103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
468.6623602 |
26.1955554 |
172.2621323 |
7.8436321 |
| ENSG00000197256 |
25959 |
KANK2 |
protein_coding |
Q63ZY3 |
FUNCTION: Involved in transcription regulation by sequestering in the cytoplasm nuclear receptor coactivators such as NCOA1, NCOA2 and NCOA3 (PubMed:17476305). Involved in regulation of caspase-independent apoptosis by sequestering the proapoptotic factor AIFM1 in mitochondria (PubMed:22371500). Pro-apoptotic stimuli can induce its proteasomal degradation allowing the translocation of AIFM1 to the nucleus to induce apoptosis (PubMed:22371500). Involved in the negative control of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway (PubMed:24671081). Involved in actin stress fibers formation through its interaction with ARHGDIA and the regulation of the Rho signaling pathway (PubMed:17996375, PubMed:25961457). May thereby play a role in cell adhesion and migration, regulating for instance podocytes migration during development of the kidney (PubMed:25961457). Through the Rho signaling pathway may also regulate cell proliferation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8BX02, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17476305, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17996375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22371500, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24671081, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25961457}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Apoptosis;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Methylation;Mitochondrion;Palmoplantar keratoderma;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the KN motif and ankyrin repeat domains (KANK) family of proteins, which play a role in cytoskeletal formation by regulating actin polymerization. The encoded protein functions in the sequestration of steroid receptor coactivators and possibly other proteins. Mutations in this gene are associated with impaired kidney podocyte function and nephrotic syndrome, and keratoderma and woolly hair. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]. |
hsa:25959; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; kidney epithelium development [GO:0072073]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:2000134]; negative regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway [GO:0033147]; negative regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043069]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway [GO:0070563]; podocyte cell migration [GO:0090521]; regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035023] |
17476305_SIP, a novel ankyrin repeat containing protein, sequesters steroid receptor coactivators in the cytoplasm. 24671081_Using whole-exome sequencing, authors identified a homozygous missense c.2009C>T mutation in KANK2 25961457_identified recessive mutations in kidney ankyrin repeat-containing protein 1 (KANK1), KANK2, and KANK4 in individuals with nephrotic syndrome. 26739330_liprin beta-1 is associated with expression of kank 1 and 2 proteins in melanoma 31114072_KANK2 protein is required for targeting microtubules to focal adhesions. |
ENSMUSG00000032194 |
Kank2 |
616.250066 |
0.2190417205 |
-2.190722 |
0.153052814 |
192.517301 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000008971747237920511085216506020365139925041815138309933934924190866158121554351643545611996453689968766157609905004255423932590929325670003890991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000001630824990538260464720056251344904052764999000855516728439932870987069121501871129754908983578907352339303462110398079687456629471853375434875488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
233.4904297 |
26.1423246 |
1073.2864099 |
84.1359848 |
| ENSG00000197283 |
8831 |
SYNGAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q96PV0 |
FUNCTION: Major constituent of the PSD essential for postsynaptic signaling. Inhibitory regulator of the Ras-cAMP pathway. Member of the NMDAR signaling complex in excitatory synapses, it may play a role in NMDAR-dependent control of AMPAR potentiation, AMPAR membrane trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Regulates AMPAR-mediated miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents. Exhibits dual GTPase-activating specificity for Ras and Rap. May be involved in certain forms of brain injury, leading to long-term learning and memory deficits (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Autism;Autism spectrum disorder;Disease variant;GTPase activation;Intellectual disability;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;SH3-binding |
|
This gene encodes a Ras GTPase activating protein that is a member of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex. The N-terminal domain of the protein contains a Ras-GAP domain, a pleckstrin homology domain, and a C2 domain that may be involved in binding of calcium and phospholipids. The C-terminal domain consists of a ten histidine repeat region, serine and tyrosine phosphorylation sites, and a T/SXV motif required for postsynaptic scaffold protein interaction. The encoded protein negatively regulates Ras, Rap and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor trafficking to the postsynaptic membrane to regulate synaptic plasticity and neuronal homeostasis. Allelic variants of this gene are associated with intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2016]. |
hsa:8831; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; axonogenesis [GO:0007409]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; maintenance of postsynaptic specialization structure [GO:0098880]; negative regulation of axonogenesis [GO:0050771]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046580]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; receptor clustering [GO:0043113]; regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043087]; regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048169]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; regulation of synapse structure or activity [GO:0050803]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
18323856_The C2 domain of SynGAP is essential for stimulation of the Rap GTPase reaction. 19196676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19196676_Results indicate that SYNGAP1 disruption is a cause of autosomal dominant nonsyndromic mental retardation. 19483657_These data suggest that NMDA receptor complex formation, localization, and downstream signaling may be abnormal in schizophrenia as PSD95, SynGAP and MUPP1 expression is altered. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20188038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20531469_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21237447_We provide evidence that truncating mutations in SYNGAP1 are common in nonsyndromic intellectual disability and can be also associated with autism. 21480541_SYNGAP1 is a brain-specific protein that interacts with key components of the proteins involved in experience-dependent changes in glutamate synapses involved in learning. 23161826_De novo missense mutations, p.R579X, and possibly all the other truncating mutations in SYNGAP1 result in a loss of its function, causing intellectual disability, autism, and a specific form of epilepsy. 23708187_De novo CHD2 and SYNGAP1 mutations are new causes of epileptic encephalopathies, accounting for 1.2% and 1% of cases, respectively. 24945774_Reduced cognition in mutant Syngap1 transgenic mice is caused by isolated damage to developing forebrain neurons. 25533468_Phosphorylation of synaptic GTPase-activating protein (synGAP) by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) alters the ratio of its GAP activity toward Ras and Rap GTPases. 26079862_De novo, heterozygous, loss-of-function mutations in SYNGAP1 cause a syndromic form of intellectual disability. 26110312_This is the first description of a special electroencephalogram phenomenon (normalization with eye opening) in association with SYNGAP1 mutations. 26558778_Syngap transgenic mice exhibited alterations in long-term depression and dendritic spine morphology. 29381230_our findings suggest that SYNGAP1 variants are causative for ID, which expands our knowledge of the disease spectrum and provides new information on the genotype-phenotype relationship. 29632532_Complement receptor 3 (Integrin alpha-M beta-2)-mediated phagocytosis of Francisella due to increased ras GTPase-activating protein (RasGAP) activity. 30541864_The SYNGAP1 mutations cause a generalized developmental and epileptic encephalopathy with a distinctive syndrome combining epilepsy with eyelid myoclonia with absences and myoclonic-atonic seizures. 30685520_This study demonstrated that eating induced seizures in association with SYNGAP1 mutations. 31025938_SynGAP protein retains biological functions throughout adulthood and that non-developmental functions may contribute to disease phenotypes. 31395010_A broad spectrum of neurologic and neurodevelopmental features are found with pathogenic variants of SYNGAP1. 31454529_Discussion on the clinical spectrum and molecular pathophysiology of SYNGAP1 mutations, aiming to understand how mutations in this protein affect neuronal development and function and how that translates into the clinical features observed in Mental retardation-type 5 patients (review). 32887745_SYNGAP1 Controls the Maturation of Dendrites, Synaptic Function, and Network Activity in Developing Human Neurons. 33189692_Distinct patterns of repetition suppression in Fragile X syndrome, down syndrome, tuberous sclerosis complex and mutations in SYNGAP1. 33308442_Multi-parametric analysis of 57 SYNGAP1 variants reveal impacts on GTPase signaling, localization, and protein stability. 33639450_SYNGAP1-DEE: A visual sensitive epilepsy. 34130248_Differential auditory brain response abnormalities in two intellectual disability conditions: SYNGAP1 mutations and Down syndrome. 35624196_Rho-Rho-Kinase Regulates Ras-ERK Signaling Through SynGAP1 for Dendritic Spine Morphology. 36183676_Generation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line (SDQLCHi044-A) from a patient with autosomal dominant mental retardation type 5 harboring heterozygous mutation in SYNGAP1 gene. 36261283_The SYNGAP1 3'UTR Variant in ALS Patients Causes Aberrant SYNGAP1 Splicing and Dendritic Spine Loss by Recruiting HNRNPK. |
ENSMUSG00000067629 |
Syngap1 |
71.341635 |
0.4583268142 |
-1.125551 |
0.453113430 |
5.927066 |
0.01491004905871913359394209663832953083328902721405029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027522801914293949093748281597981986124068498611450195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.0043341 |
36.8026722 |
94.2099561 |
52.2199342 |
| ENSG00000197296 |
128486 |
FITM2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N6M3 |
FUNCTION: Fatty acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) diphosphatase that hydrolyzes fatty acyl-CoA to yield acyl-4'-phosphopantetheine and adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate (PubMed:32915949) (By similarity). Preferentially hydrolyzes unsaturated long-chain acyl-CoA substrates such as oleoyl-CoA/(9Z)-octadecenoyl-CoA and arachidonoyl-CoA/(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenoyl-CoA in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen (PubMed:32915949) (By similarity). This catalytic activity is required for maintaining ER structure and for lipid droplets (LDs) biogenesis, which are lipid storage organelles involved in maintaining lipid and energy homeostasis (PubMed:18160536, PubMed:32915949) (By similarity). Directly binds to diacylglycerol (DAGs) and triacylglycerol, which is also important for LD biogenesis (By similarity). May support directional budding of nacent LDs from the ER into the cytosol by reducing DAG levels at sites of LD formation (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization (PubMed:21834987) (By similarity). {ECO:0000255|HAMAP-Rule:MF_03230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18160536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21834987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32915949}. |
Deafness;Disease variant;Dystonia;Endoplasmic reticulum;Hydrolase;Intellectual disability;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
FIT2 belongs to an evolutionarily conserved family of proteins involved in fat storage (Kadereit et al., 2008 [PubMed 18160536]).[supplied by OMIM, May 2008]. |
hsa:128486; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; acyl-coenzyme A diphosphatase activity [GO:0106399]; CoA pyrophosphatase activity [GO:0010945]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; triglyceride binding [GO:0017129]; cellular triglyceride homeostasis [GO:0035356]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; fatty-acyl-CoA catabolic process [GO:0036115]; lipid droplet formation [GO:0140042]; lipid droplet organization [GO:0034389]; lipid homeostasis [GO:0055088]; lipid storage [GO:0019915]; phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008654]; positive regulation of sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0010890]; regulation of cell morphogenesis [GO:0022604]; regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process [GO:0010866]; sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0030730] |
20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 28067622_In order to obtain independent evidence for the involvement of FITM2 in the human pathology, downregulation of the single Fitm ortholog, CG10671, in Drosophila melanogaster was pursued using RNA interference. 30020828_Low FIT2 expression is associated with type 2 diabetes. 32915949_FIT2 is an acyl-coenzyme A diphosphatase crucial for endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis. 33861319_FIT2 organizes lipid droplet biogenesis with ER tubule-forming proteins and septins. 34672358_High FITM2 expression promotes cell migration ability of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the formation of caveolae and indicates poor patient survival. |
ENSMUSG00000048486 |
Fitm2 |
58.850462 |
2.2771503803 |
1.187230 |
0.204734019 |
34.129992 |
0.00000000515505634414335886860178848750679847512401465792208909988403320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000023113193086134864995090682925245328949159784315270371735095977783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83.6205671 |
10.6518407 |
36.9976584 |
3.7432142 |
| ENSG00000197299 |
641 |
BLM |
protein_coding |
P54132 |
FUNCTION: ATP-dependent DNA helicase that unwinds single- and double-stranded DNA in a 3'-5' direction (PubMed:9388193, PubMed:24816114, PubMed:25901030). Participates in DNA replication and repair (PubMed:12019152, PubMed:21325134, PubMed:23509288). Involved in 5'-end resection of DNA during double-strand break (DSB) repair: unwinds DNA and recruits DNA2 which mediates the cleavage of 5'-ssDNA (PubMed:21325134). Negatively regulates sister chromatid exchange (SCE) (PubMed:25901030). Stimulates DNA 4-way junction branch migration and DNA Holliday junction dissolution (PubMed:25901030). Binds single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), forked duplex DNA and DNA Holliday junction (PubMed:20639533, PubMed:24257077, PubMed:25901030). Recruited by the KHDC3L-OOEP scaffold to DNA replication forks where it is retained by TRIM25 ubiquitination, it thereby promotes the restart of stalled replication forks (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O88700, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12019152, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20639533, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21325134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23509288, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24257077, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24816114, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25901030, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9388193}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;ATP-binding;Disease variant;DNA damage;DNA repair;DNA replication;DNA-binding;Dwarfism;Helicase;Hydrolase;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation;Zinc |
|
The Bloom syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by growth deficiency, microcephaly and immunodeficiency among others. It is caused by homozygous or compound heterozygous mutation in the gene encoding DNA helicase RecQ protein on chromosome 15q26. This Bloom-associated helicase unwinds a variety of DNA substrates including Holliday junction, and is involved in several pathways contributing to the maintenance of genome stability. Identification of pathogenic Bloom variants is required for heterozygote testing in at-risk families. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. |
hsa:641; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; lateral element [GO:0000800]; nuclear chromosome [GO:0000228]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; PML body [GO:0016605]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; RecQ family helicase-topoisomerase III complex [GO:0031422]; replication fork [GO:0005657]; 3'-5' DNA helicase activity [GO:0043138]; 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine DNA binding [GO:1905773]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA [GO:0008094]; bubble DNA binding [GO:0000405]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA helicase activity [GO:0003678]; DNA/DNA annealing activity [GO:1990814]; forked DNA-dependent helicase activity [GO:0061749]; four-way junction DNA binding [GO:0000400]; four-way junction helicase activity [GO:0009378]; G-quadruplex DNA binding [GO:0051880]; helicase activity [GO:0004386]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; molecular function activator activity [GO:0140677]; p53 binding [GO:0002039]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; single-stranded DNA binding [GO:0003697]; telomeric D-loop binding [GO:0061821]; telomeric G-quadruplex DNA binding [GO:0061849]; Y-form DNA binding [GO:0000403]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; cellular response to camptothecin [GO:0072757]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to hydroxyurea [GO:0072711]; cellular response to ionizing radiation [GO:0071479]; DNA double-strand break processing [GO:0000729]; DNA duplex unwinding [GO:0032508]; DNA recombination [GO:0006310]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; DNA replication [GO:0006260]; DNA unwinding involved in DNA replication [GO:0006268]; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination [GO:0000724]; G-quadruplex DNA unwinding [GO:0044806]; mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling [GO:0007095]; negative regulation of cell division [GO:0051782]; negative regulation of DNA recombination [GO:0045910]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; protein complex oligomerization [GO:0051259]; protein homooligomerization [GO:0051260]; regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0000079]; regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication [GO:0090329]; replication fork processing [GO:0031297]; replication fork protection [GO:0048478]; resolution of recombination intermediates [GO:0071139]; response to X-ray [GO:0010165]; t-circle formation [GO:0090656]; telomere maintenance [GO:0000723]; telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication [GO:0032201]; telomeric D-loop disassembly [GO:0061820] |
11472631_The C-terminal domain of the Bloom syndrome DNA helicase is essential for genomic stability as measured by the sister chromatid exchange assay. 11532193_Somatic frameshift mutations in the Bloom syndrome BLM gene are frequent in sporadic gastric carcinomas with microsatellite mutator phenotype 11691925_binds human mismatch repair protein MLH1; nuclear localization 11741924_mutation results in bloom syndrome 11781842_The Bloom syndrome protein interacts and cooperates with p53 in regulation of transcription and cell growth control 11876000_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11916980_is required for correct relocalization of RAD50/MRE11/NBS1 complex after replication fork arrest. 11919194_Colocalization, physical, and functional interaction between Werner and Bloom syndrome proteins 11960380_Bloom's syndrome protein response to ultraviolet-C radiation and hydroxyurea-mediated DNA synthesis inhibition. 12034743_ATM and BLM function together in recognizing abnormal DNA structures by direct interaction and that these phosphorylation sites in BLM are important for radiosensitivity status but not for SCE frequency. 12080066_recombinant p53 binds to BLM and WRN helicases and attenuates their ability to unwind synthetic Holliday junctions in vitro 12181313_binding by and stimulation of by telomere-binding proteing TRF2 12242432_data show that carriers of a BLM mutation have an increased risk for colorectal cancer 12433984_The Bloom's syndrome helicase stimulates the activity of topoisomerase IIIalpha 12444098_Immunofluorescence studies show that BLM helicase co-localizes with telomeric foci in approximately 70% of cells in asynchronous cultures of ALT human cell lines. 12606585_These results indicate that p53 and BLM functionally interact during resolution of stalled DNA replication forks and provide insight into the mechanism of genomic fidelity maintenance by these nuclear proteins. 12702560_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12818200_these data define a minimal helicase domain of BLM and demonstrate its ability to act as a suppressor of illegitimate recombination 12826610_Human BLM interacts with both scDna2 and scFEN1. It may participate in the same steps of DNA replication or repair as scFEN1 & scDna2, acting as a molecular matchmaker at a crossroad between replication & repair. 12974384_hMSH6, a component of the heterodimeric mismatch recognition complex hMSH2/hMSH6 (hMutS(alpha)), interacts with the BLM protein both in vivo and in vitro 12975363_BLM co-operates with RAD51 paralogs during the late stages of homologous recombination processes that serve to restore productive DNA replication at sites of damaged or stalled replication forks 14517203_BLM is essential for timely BRCA1/NBS1 function 14576316_NHEJ (non-homologous DNA end joining) activation mediates BLM dissociation from DNA, whereas, under conditions where homologous recombination is favored, e.g. at the replication fork, BLM exhibits an anti-recombinogenic role 14685245_BLM and hTOPO IIIalpha together effect the resolution of a recombination intermediate containing a double Holliday junction 14688284_the Bloom's syndrome protein has a role in stimulating flap endonuclease-1 15064730_hMSH2/6 formed a complex with BLM-p53-RAD51 in response to the damaged DNA forks during double-stranded break repair. 15229185_BLM functions in recombination-mediated telomere lengthening. 15257300_Fanconi anaemia core complex is necessary for BLM phosphorylation 15289897_Common mutations in the BLM gene were studied in 4 Japanese Bloom Syndrome kindreds. 15509577_interactions between BLM and DNA ligase IV play a role in DNA repair in human cells 15539948_Thus, optimal repair of damaged replication fork lesions likely requires both ATR and ATM. BLM recruits 53BP1 to these lesions independent of its helicase activity, and optimal activation of ATM requires both p53 and BLM helicase activities. 15579905_results suggest that BLM suppresses genome instability by aiding FEN1 cleavage of structure-containing flaps 15616572_SCE in the fancc/blm mutant was similar to that in blm cells, indicating functional linkage between FANCC and BLM 15726604_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15750625_BLM collaborates with RAD51 to facilitate recombination repair and promotes the resistance of BCR/ABL-positive leukemia cells to DNA-damaging agents. 15805243_Data suggest a new function of BLM in cooperating with Mus81 during processing and restoration of stalled replication forks. 15845538_WRN, BLM, and dmRecQ5b have a novel strand pairing capability that, when coordinated with the well established helicase activity, endows these RecQ helicases with a strand exchange function 15959913_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15965237_physical interaction between RPA and WRN or BLM helicases plays an important role in the mechanism for RPA stimulation of helicase-catalyzed DNA unwinding. 15990871_Dissolution is highly specific for BLM among human RecQ helicases and critically depends upon a functional HRDC domain in BLM. 16030011_POT1 and RecQ helicases WRN and BLM have cooperative roles in resolving DNA structures at telomeric ends, in a manner that protects the telomeric 3' tail as it is exposed during unwinding 16199871_BLM appears to dissociate from Top3alpha and PML following its phosphorylation and facilitates H2AX phosphorylation in response to replication double-strand breaks induced by Top1. 16412221_if a DNA oligomer complementary to one strand of the DNA substrate to be unwound is added during the helicase reaction, both WRN and BLM unwinding is enhanced, presumably by preventing protein-mediated re-annealing 16537486_a component of the BLM/TOPO IIIalpha complex, BLAP75/RMI1, promotes dissolution catalyzed by TOPO IIIalpha 16595695_BLM, Topo IIIalpha, and BLAP75 constitute a dissolvasome complex that processes HR intermediates to limit DNA crossover formation 16766518_data establish the existence of a eukaryotic protein that could promote replication fork regression in vivo and suggest a novel pathway through which BLM might suppress genetic exchanges 16864798_Results suggest that MPS1-dependent BLM phosphorylation is important for ensuring accurate chromosome segregation, and its deregulation may contribute to cancer. 16876111_both endogenous and overexpressed human BLM accumulates at sites of laser light-induced DNA double-strand breaks; its HRDC domain is sufficient for its recruitment to the damaged sites 16880735_BLM helicase is a new substrate for cdc2, which may have potential physiological implications for the role of BLM in mitosis. 17407155_The presence of widespread founder mutations in persons with Bloom syndrome points to population genetic processes that repeatedly and pervasively generate mutations that recur in unrelated persons. 17457718_BLM helicase deficiency results in genomic instability and cancer. 17591918_BLM helicase-dependent and -independent roles of 53BP1 during replication stress-mediated homologous recombination were studied. 17599064_BLM-defective cells display a higher frequency of anaphase bridges and lagging chromatin than do isogenic corrected derivatives that eptopically express the BLM protein. 17603497_BLM protein is required for two aspects of the cellular response to replicative stress: efficient replication-fork restart and suppression of new origin firing. 17634426_This is the first report of high ATM-Chk2 kinase activation and its linkage to replication defects in a Bloom syndrome model. 17728255_BLM is stably associated with TOP3A and RMI1 protein. 17855454_SNPs associated with prognosis of lung cancer was mapped to BLM. 17878217_Disease-causing BLM mutants had low ATPase and helicase activities but their ATP binding abilities were normal. 17943968_Loss of function suppresses mismatch repair mutator mechanism. 17961633_human SUV3 protein interacts with human BLM helicase. 17984114_BLM enhances the interaction and co-localization between 53BP1 and RAD51 during replication arrest 18003860_two novel activities of BLM: disruption of the Rad51-ssDNA (single-stranded DNA) filament, an active species that promotes homologous recombination, and stimulation of DNA repair synthesis 18054789_BLM helicase and Mus81 are required to induce transient double-stranded DNA breaks in response to DNA replication stress. 18264947_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18270339_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18278455_BLM protein expression may play an important role in the development of hematopoietic tumor cells 18390547_evolutionarily conserved N-terminal third of BLAP75 mediates complex formation with BLM and Topo IIIalpha and that the DNA binding activity resides in the C-terminal third of this novel protein. 18401830_BLM deficiency is associated with a relative excess of PRKAR1A in fibroblasts compared to other PKA subunits; PRKAR1A deficiency is associated with increased BLM protein in adrenal hyperplasias. 18448429_Human RecQ helicases, BLM and RECQ1, display distinct DNA substrate specificities 18471088_We report here four BLM gene mutations, three of which have not been described before. Three are frameshift mutations, and the fourth is a nonsense mutation. All introduce a stop codon, and may be considered to have deleterious biological effect. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18682526_The DNA polymerase delta enzyme, as well as the isolated p12 subunit, stimulates the DNA helicase activity of Bloom's syndrome helicase. 18708356_BLM, the RecQ DNA helicase mutated in Bloom syndrome, is preferentially modified by SUMO-2/3 both in vitro and in vivo 18971343_human BLM helicase, a member of the RecQ family, stimulates the nucleolytic activity of human exonuclease 1 (hExo1), a 5'-->3' double-stranded DNA exonuclease. 18974064_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18974064_results suggest a contribution of BLM and RAD51 to breast cancer development and provide support for the tumorigenic significance of the functional interaction between these two HR proteins 18978339_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19109166_Inability of Blm-deficient developing B cells to suppress replication errors manifests in delayed cell cycle progression in transgenic mice, likely accompanied by increased apoptosis rates and tumor development. 19165145_BLM helicase measures DNA unwound before switching strands and hRPA promotes unwinding reinitiation 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19205873_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19237606_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19329795_TEP1, TOPOIIalpha, and HSP90 interact directly with BLM in vitro and modulate its helicase activity on telomere-like DNA substrates but not on non-telomeric substrates. 19432957_Individuals carrying genetic variants of the BLM-TOP3A-RMI1 complex have an increased risk of acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplatic syndromes, malignant melanoma, bladder and breast cancer. 19432957_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19442250_Blm functions in multiple processes related to DNA recombination and repair. 19465921_Reuslts reveal new crosstalk between FANC and BLM proteins, extending their interaction beyond the S-phase rescue of damaged DNA to the safeguarding of chromosome stability during mitosis. 19500012_we suggest that when there are verified patients in whom no mutation is detected in the known BLM gene, especially if these patients are also men, the possibility of X-linked recessive inheritance should be taken into consideration. 19542097_BLM protein is a crucial suppressor of gene cluster instability. 19573080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19632996_Results demonstrate the important role of the RAD51 nucleoprotein filament conformation in stimulation of DNA pairing by BLM. 19661064_Results show that Blm promotes HR between diverged sequences through a novel ATPase-independent mechanism. 19671661_The N-terminal 1-212 amino acids of BLM of or an ATPase-dead mutant enhanced the ATPase and chromatin-remodeling activities of RAD54. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19714462_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19734539_WRN and BLM preferentially unwind telomeric D-loops containing 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine. 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917125_These results suggest an influence of BLM on susceptibility to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma 19935873_These results indicate that full-length BLM may require additional factors to unwind nucleosomal DNA in vivo, and that RPA is, on its own, unable to perform this auxiliary function. 19945966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19945966_We detected a significant association of BLM P868L with an increased rectal cancer risk (odds ratio = 1.29, 95% confidence interval 1.02-1.64 and P = 0.04), suggesting a potential cancer-site specificity. 19956565_In the absence of BLM SUMOylation, BLM perturbs RAD51 localization at damaged replication forks and inhibits fork repair by homologous recombination (HR). Conversely, BLM SUMOylation relieves its inhibitory effects on HR, and it promotes RAD51 function. 20154148_Data show that BLM-deficient mouse and human cells suppress homeologous recombination to a similar extent as wild-type cells. 20211839_a quantitative model for the translocation of a monomeric form of BLM along ssDNA is discussed. 20215422_Our results directly implicate BLM in limiting the lethality associated with RAD51 deficiency through the processing of anaphase bridges resulting from the RAD51 defect. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20445207_human topoisomerase IIIalpha functions as a decatenase with the assistance of BLM and RMI1 to facilitate the processing of homologous recombination intermediates without crossing over as a mechanism to preserve genome integrity 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20639533_Based on its surface charge separation and DNA-binding properties, the HRDC domain of BLM may be adapted for a unique function among RecQ helicases--that of bridging protein and DNA interactions. 20719863_Chk1-mediated phosphorylation on BLM at Ser(646) might be a determinant for regulating subnuclear localization and could act as a marker for the activation status of BLM in response to DNA damage. 20739603_Results show that Bloom syndrome protein C-terminal helicase-and-ribonuclease D-C-terminal is a compact, robust and acidic motif which may play a distinct role apart from DNA binding. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20813000_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21111748_Co-expressing sgs1 truncations of up to 900 residues, lacking all known functional domains of Sgs1, suppressed the hydroxyurea sensitivity of BLM-overexpressing cells, suggesting a functional relationship between Sgs1 and BLM. 21113733_RAD51 and ssDNA interact in overlapping regions; This suggests preferential binding for one partner that could regulate homologous recombination and helps to clarify the role of BLM in maintaining genomic stability. 21123383_These studies identify BLM as a new substrate for degradation by the adenovirus E1b55K/E4orf6 complex. 21129251_Abnormal expression of blm is correlated to the drug resistance of leukemia cells, and may play a significant role in repair of DNA damage. 21240188_FANCJ catalytic activity and its effect on BLM protein stability contribute to preservation of genomic stability and a normal response to replication stress. 21300576_BLM helicase influences double-strand break repair pathway choice in human chromosomes and suggests that BLM deficiency can engender genomic instability by provoking an increased frequency of homologous recombination events 21325134_BLM increases the affinity of EXO1 for ends, and MRN recruits and enhances the processivity of EXO1. 21567087_BLM deficiency causes the up-regulation of p53, double-strand break and apoptosis. 21712816_Pyrimidine pool imbalance induced by BLM helicase deficiency contributes to genetic instability in Bloom syndrome. 21736299_findings suggest that, subsequent to fork regression events, WRN and/or BLM could re-establish functional replication forks to help overcome fork blockage 21743438_PICH binds to BLM and enables BLM localization to anaphase centromeric threads. PICH and BLM unravel centromeric chromatin and keep anaphase DNA threads mostly free of nucleosomes. 21815139_This study demonstrates that BLM Q548X allele is recurrent in Slavic subjects and may be associated with breast cancer risk. 22106380_studies suggest that nucleolar BLM modulates rDNA structures in association with RNA polymerase I to facilitate RNA polymerase I-mediated rRNA transcription 22253018_The results show that the BLM core consisting of solely the two RecA domains and the ZnBD is capable of performing a multitude of mechanochemical activities utilized in DNA repair. 22272300_Data show that Bloom syndrome helicase (BLM) formed substantial complexes with only G4 quadruplex DNA while binding only marginally other DNA structures. 22356911_RAD54 that lacks helicase activity is more efficient in DNA heterology bypass than BLM or REQ1 helicases. 22544709_BLM and RECQL4 interact physically and functionally in vivo and in vitro. 22563370_Bloom syndrome protein was required for the correct recruitment to the centromere of active topoisomerase IIalpha, an enzyme specialized in the catenation/decatenation process. 22989712_Depleting BLM increased the mutation frequency at telomeres and at the MS32 minisatellite, which is a marker of Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres. 23028338_we identified faults in two genes, Fanconi C and Bloom helicase( FANCC and BLM), in six families. Faults in these genes appear to increase the risk of developing breast cancer 23129629_27 BLM alleles that are not currently known to be associated with Bloom syndrome, are identified. 23225144_Nonsense mutation p.Q548X in BLM protein is associated with breast cancer in Slavic populations. 23253856_BLM depletion compromises replication fork recovery and leads to extensive delay of cell division after hydroxyurea-induced stalling. 23261817_DNA topoisomerase I stimulates BLM helicase activity on a nucleolar-relevant RNA:DNA hybrid. 23268311_BLM helicase is major player in recombination-mediated telomere maintenance 23322570_Eighteen polymorphisms in four DNA repair genes were genotyped in 789 age related cataract patients and 531 normal controls from the Jiangsu Eye Study. 23404160_Case-control study to check an association between the genotypes of the c.-61 G>T and the g.38922 C>G polymorphisms of the RAD51 gene and the g.96267 A>C and the g.85394 A>G polymorphisms of the BLM gene and breast cancer occurrence. 23509288_Consistent with its role as a scaffolding protein for the assembly of BLM and RAD51 foci, cells depleted of SPIDR show increased rate of sister chromatid exchange and defects in homologous recombination repair. 23572515_FE65 interactions with BLM and MCM proteins may contribute to the neuronal cell cycle re-entry observed in brains affected by Alzheimer's disease. 23708797_an important biochemical link between the UbS-DDR and BLM-dependent pathways involved in maintaining genome stability. 24095737_Data highlight a dual role for BLM that influences the DSB repair pathway choice: protection against CtIP/MRE11 long-range deletions associated with A-EJ and promotion of DNA resection. 24096176_The BLM Q548X mutation does not predispose patients to prostate cancer or affect prostate cancer survival. 24108125_two proteins that interact with BLM, RMI1 and RMI2, are phosphorylated upon SAC activation, and, like BLM, RMI1, and RMI2, are phosphorylated in an MPS1-dependent manner. 24118499_Mutational analysis by direct DNA sequencing revealed a novel frameshift mutation (c.1980-1982delAA) in exon 8 of BLM gene, resulting in a truncated protein (p.Lys662fsX5). 24239288_BLM was ubiquitinated by E3 ligase MIB1 and degraded in G1 cells but was stabilized by TopBP1 in S phase cells. 24257077_The binding model of BLM RQC to a HJ offers the structural insights into the branch migration mechanism of BLM, in which DNA unwinding and annealing might be coordinated. 24816114_BLM protein crystal structure provides detailed information on the interactions of the protein with DNA and helps to explain the mechanism coupling ATP hydrolysis and DNA unwinding. 24858046_The data highlight the importance of Mus81 and Blm in DNA double-strand repair pathways, fertility, development and cancer. 24958861_identified mRNA and miRNA expression differences in Bloom syndrome patient and BLM-depleted cells 25015292_Chk1 phosphorylates BLM-S502 to inhibit cullin-3-mediated BLM degradation during interphase. 25084169_Results suggest that BRCA1 participates in ALT through its interactions with RAD50 and BLM. 25122754_WRN and BLM act epistatically with DNA2 to promote the long-range resection of double strand break ends in human cells. 25129257_A novel frameshift mutation in BLM gene associated with high sister chromatid exchanges (SCE) in heterozygous family members. 25182961_These findings indicate that the BLM p.Q548X mutation is not a strong risk factor for ovarian cancer. 25472581_this is the first genetic association study to show the significant association between BLM gene and Prostate cancer susceptibility in Chinese population. 25588990_RecQ-like helicase BLM subcellular localization is regulated by SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase RNF4 in response to DNA damage, presumably to prevent illegitimate recombination events. 25673821_BLM mRNA and BLM protein levels independently influenced BCSS. This is the first and the largest study to provide evidence that BLM is a promising biomarker in breast cancer. 25766002_Findings indicate that BLM functions in 2 distinct pathways. In one, BLM functions to suppress sister chromatid exchanges formation; in the second one, T99 and T122 phosphorylations are essential for suppression of chromosomal radial formation. 25794620_TopBP1 interacts with BLM to maintain genome stability but is dispensable for preventing BLM degradation.Crucial residues mediating BLM-TOP3A/RMI interactions identified. 26028025_evidence that BLM is a substrate for Fbw7alpha-dependent ubiquitylation and degradation during mitosis 26358404_these data indicate that carriers of deleterious BLM mutations are at increased risk to develop CRC, albeit with a moderate-to-low penetrance. 26778106_Israeli ATM, BLM, and FANCC heterozygous mutation carriers are not at an increased risk for developing cancer. 27083049_Mutations within the domain VI of BLM detected in human cancer samples demonstrate the functional importance of this domain, suggesting human tumorigenicity resulting from mtBLM may be at least partly attributed to mitigated FANCD2 activation. 27100209_BLM deficiency enables HeR in human cells 27169843_Aberrant BLM cytoplasmic expression associates with DNA damage stress and hypersensitivity to DNA-damaging agents in colorectal cancer. 27238185_In humans, mutations in BLM give rise to Bloom's syndrome features genomic instability and susceptibity to cancer. 27407146_Data show that helicases RHAU, BLM, and WRN exhibit distinct G-quadruplex (GQ) conformation specificity, but use a common mechanism of repetitive unfolding that leads to disrupting GQ structure multiple times in succession. 27427384_in Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres cells, FANCD2 promotes intramolecular resolution of stalled replication forks in telomeric DNA while BLM facilitates their resection and subsequent involvement in the intermolecular exchanges that drive Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres. 27601585_Results show that BLM-deficient human cells produce hemi-loss of heterozygosity by spontaneous deletion even though they exhibit a high spontaneous frequency of inter-allelic homologous recombination. 27612385_The authors show that the helicase of hDNA2 functionally integrates with BLM or WRN helicases to promote double-stranded DNA degradation by forming a heterodimeric molecular machine. This collectively suggests that the human DNA2 motor promotes the enzyme's capacity to degrade double-stranded DNA in conjunction with BLM or WRN and thus promote the repair of broken DNA. 28506294_Our data highlights that BLM helicase and hSSB1 function in a dynamic complex in cells and that this complex is likely required for BLM protein stability and function. 28673972_BLM is actively recruited to the alternative lengthening of telomeres that are experiencing replication stress and that the recruitment of BLM to these damaged telomeres is interdependent and is regulated by both ATR and Chk1. 28877996_The BLM-TOP3A-RMI (BTR) dissolvase complex is required for Alternative lengthening of telomeres-mediated telomere synthesis. BLM and SLX4 play opposing roles in recombination-dependent replication at human telomeres. 28912125_The anti-recombinase activity of BLM is of general importance for normal retention of RAD51 at DNA double strand break sites and regulation of homologous recombination. 29017749_These results showed that BLM enters the nucleus via the importin beta1, RanGDP and NTF2 dependent pathway, demonstrating for the first time the nuclear trafficking mechanism of a DNA helicase. 29042409_Sgs1 and BLM regulate R-loop-associated genome instability. 29348659_In the absence of BLM, sister chromatid exchange events do not occur randomly throughout the genome but are strikingly enriched at coding regions, specifically at sites of guanine quadruplex motifs in transcribed genes. 29385443_A tri-serine cluster within the topoisomerase IIalpha-interaction domain of the BLM helicase is required for regulating chromosome breakage in human cells. 29388204_Interaction of replication protein A with two acidic peptides from human Bloom syndrome protein 29523790_BLM utilizes its pro- and anti-DNA repair functions to maintain genome stability. 30044990_BS patient-derived BLM mutants cannot potentiate Fbw7alpha-dependent c-Jun degradation. The decrease in the levels of c-Jun in cells expressing BLM prevents effective c-Jun binding to 2,584 gene promoters. This causes decreases in the transcript and protein levels of c-Jun targets in BLM-expressing cells, resulting in attenuated c-Jun-dependent effects during neoplastic transformation. 30110632_RUNX1/RUNX3 poly(ADP-Ribosyl)ation and BLM interaction facilitate the Fanconi anemia pathway of DNA repair. 30279242_HERC2 is a master regulator of G-quadruplex, a DNA secondary structure that triggers genomic instability, through BLM, WRN, and RPA, and may serve as a potential molecular target in cancer therapy 30496191_BLM is required for suppression of chromosome fragile site (CFS) breakage upon oncogene expression. Both helicase activity and ATR-mediated phosphorylation of BLM are important for preventing genetic instability at CFS-AT sequences. 30936263_These results reveal that BLM limits interferon-stimulated gene induction, thus connecting DNA damage to cellular innate immune response, which may contribute to human pathogenesis. 31153714_RPA is phosphorylated during DNA resection as part of the DNA damage response (DDR); remarkably, pRPA inhibits DNA resection in cellular assays and in vitro via inhibition of BLM helicase. 31171703_BLM helicase is involved in the induction of the ALT pathway during G2 and M phases in ALT cancer cells 31210839_ROS act in concert with BLM to facilitate Prostate cancer (PC) oncogenesis, potentially via further enhancing AKT signaling and downregulating PTEN expression. Importantly, inhibiting the BLM-AKT-PRAS40 axis induced PC cell apoptosis. 31447390_SLX4IP antagonizes promiscuous BLM Activity during alternative lengthening of telomeres maintenance in osteosarcoma cells. 31544923_BLM can neither associate with nor translocate on ssDNA that is bound by the recombinase protein RAD51. Moreover, these data reveal that the presence of RAD51 also blocks BLM translocation on dsDNA substrates and potential regulator roles for BLM helicase during DNA replication and repair. 31816118_Truncating BLM germline mutations occur at a higher frequency in patients with advanced prostate cancer as compared to control populations. Though no biallelic loss of BLM was no noted in cancers, a surprising number of the BLM germline heterozygotes had pathogenic BRCA2 mutations in their tumor. 31918214_iPSC line derived from a Bloom syndrome patient retains an increased disease-specific sister-chromatid exchange activity. 31977077_Resolution of ROS-induced G-quadruplexes and R-loops at transcriptionally active sites is dependent on BLM helicase. 32704157_Investigating the pathogenic SNPs in BLM helicase and their biological consequences by computational approach. 33073370_Missing heritability in Bloom syndrome: First report of a deep intronic variant leading to pseudo-exon activation in the BLM gene. 33318203_Heterozygous germline BLM mutations increase susceptibility to asbestos and mesothelioma. 33432007_HERC2 inactivation abrogates nucleolar localization of RecQ helicases BLM and WRN. 33495511_Bloom syndrome DNA helicase deficiency is associated with oxidative stress and mitochondrial network changes. 33727188_Bloom helicase explicitly unwinds 3'-tailed G4DNA structure in prostate cancer cells. 33736941_Bloom syndrome and the underlying causes of genetic instability. 33832920_Bloom syndrome in a Mexican American family with rhabdomyosarcoma: evidence of a Mexican founder mutation. 34197737_EXO5-DNA structure and BLM interactions direct DNA resection critical for ATR-dependent replication restart. 34370039_A novel cell-cycle-regulated interaction of the Bloom syndrome helicase BLM with Mcm6 controls replication-linked processes. 34606619_USP37 regulates DNA damage response through stabilizing and deubiquitinating BLM. 35102151_Duplex DNA and BLM regulate gate opening by the human TopoIIIalpha-RMI1-RMI2 complex. 35218564_Phenotypic spectrum of BLM- and RMI1-related Bloom syndrome. 35922882_Bloom Syndrome Helicase Compresses Single-Stranded DNA into Phase-Separated Condensates. 36004459_Downregulation of BLM RecQ helicase inhibits proliferation, promotes the apoptosis and enhances the sensitivity of bladder cancer cells to cisplatin. |
ENSMUSG00000030528 |
Blm |
262.271864 |
0.1403517350 |
-2.832881 |
0.891180910 |
8.798177 |
0.00301531612543268516188343930650717084063217043876647949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006457641615117010354396587246128547121770679950714111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.2578086 |
40.7711032 |
546.8641755 |
207.9551092 |
| ENSG00000197301 |
100129940 |
HMGA2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
127.014150 |
0.2995588414 |
-1.739089 |
0.158240739 |
125.373535 |
0.00000000000000000000000000004216212699601985962834926901890418200167071622614896683457090481065928605866090228548870300073758698999881744384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000526937336546361667240699600242937046347033619647337065620350717871550513251785452517594876553630456328392028808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.8227500 |
6.7600061 |
204.5341937 |
14.1610851 |
| ENSG00000197312 |
84301 |
DDI2 |
protein_coding |
Q5TDH0 |
FUNCTION: Aspartic protease that mediates the cleavage of NFE2L1/NRF1 at 'Leu-104', thereby promoting release of NFE2L1/NRF1 from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane (PubMed:27676298, PubMed:27528193). Ubiquitination of NFE2L1/NRF1 is a prerequisite for cleavage, suggesting that DDI2 specifically recognizes and binds ubiquitinated NFE2L1/NRF1 (PubMed:27528193). Seems to act as a proteasomal shuttle which links the proteasome and replication fork proteins like RTF2 (Probable). Required, with DDI1, for cellular survival following replication stress. Together or redudantly with DDI1, removes RTF2 from stalled forks to allow cell cycle progression after replication stress and maintains genome integrity (PubMed:29290612). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:27528193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27676298, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29290612, ECO:0000305|PubMed:29290612}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aspartyl protease;Chromosome;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Phosphoprotein;Protease;Reference proteome |
|
Enables aspartic-type endopeptidase activity; identical protein binding activity; and ubiquitin binding activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to hydroxyurea; proteolysis; and regulation of DNA stability. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84301; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; aspartic-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004190]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; cellular response to hydroxyurea [GO:0072711]; proteasomal protein catabolic process [GO:0010498]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of DNA stability [GO:0097752]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 27461074_the 3D structures of the human Ddi2 UBL and RVP domains were solved and identified a new helical domain that extends on either side of the Rretroviral protease-like dimer. 27528193_Here the authors show that the aspartyl protease DNA-damage inducible 1 homolog 2 (DDI2) is required to cleave and activate Nrf1. 32521225_DDI2 Is a Ubiquitin-Directed Endoprotease Responsible for Cleavage of Transcription Factor NRF1. 34649278_Multiple myeloma cells depend on the DDI2/NRF1-mediated proteasome stress response for survival. 35589686_The aspartyl protease DDI2 drives adaptation to proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma. |
|
|
233.647395 |
2.4765905075 |
1.308355 |
0.155802251 |
69.958509 |
0.00000000000000006056509125138228140080855602910495066960028367813659300189499390398850664496421813964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000462941867876956240597114398737374356764096125678442650297483851318247616291046142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
330.1576730 |
30.6155014 |
134.4448280 |
9.5602573 |
| ENSG00000197405 |
728 |
C5AR1 |
protein_coding |
P21730 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the chemotactic and inflammatory peptide anaphylatoxin C5a (PubMed:1847994, PubMed:8182049, PubMed:7622471, PubMed:9553099, PubMed:10636859, PubMed:15153520, PubMed:29300009). The ligand interacts with at least two sites on the receptor: a high-affinity site on the extracellular N-terminus, and a second site in the transmembrane region which activates downstream signaling events (PubMed:8182049, PubMed:7622471, PubMed:9553099). Receptor activation stimulates chemotaxis, granule enzyme release, intracellular calcium release and superoxide anion production (PubMed:10636859, PubMed:15153520). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10636859, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15153520, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1847994, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29300009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7622471, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8182049, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9553099}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Chemotaxis;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sulfation;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables G protein-coupled receptor activity and complement component C5a receptor activity. Involved in several processes, including complement component C5a signaling pathway; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II; and positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. Located in apical part of cell and basolateral plasma membrane. Biomarker of Alzheimer's disease; asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; rhinitis; and severe acute respiratory syndrome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:728; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; secretory granule membrane [GO:0030667]; complement component C5a receptor activity [GO:0004878]; complement receptor activity [GO:0004875]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; amyloid-beta clearance [GO:0097242]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cognition [GO:0050890]; complement component C5a signaling pathway [GO:0038178]; complement receptor mediated signaling pathway [GO:0002430]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007200]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090023]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010575]; presynapse organization [GO:0099172]; regulation of tau-protein kinase activity [GO:1902947]; response to peptidoglycan [GO:0032494]; sensory perception of chemical stimulus [GO:0007606]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11705397_The C5a receptor residue Asp-282 near the extracellular face of transmembrane domain VII, is a component of the ligand-binding site responsible for C5a receptor activation. 12091343_C5a induced PAI-1 production in human mast cells and basophils and, in HMC-1 cells, was mediated by C5aR. 12453150_complement factor 5a receptor has multiple activated conformations 12464600_role of phosphorylation of key serine residues for internalization via a beta-arrestin, dynamin, and clathrin-dependent pathway 12651630_results indicated that the conversion of the RP S19 dimer from agonist to antagonist of C5a receptor is attributed to the IAGQVAAANKK moiety between Ile134 and Lys144 12759460_C5aR may mediate abnormal calcium signaling when expressed in hippocampal and cortical neurons of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia patients. 12794141_Within the C5a molecule three different discontinuous regions representing N-terminal, middle, and C-terminal regions of C5a exist and interact with the C5a receptor, as proposed by a three-site binding model. 14570896_A mutant of this protein is a potent antagonist for the human and mouse C5a receptor (CD88). 15039137_determination of whether the levels of complement factors C3a, C4a, and C5a are elevated at the site of inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and in asthma 15128829_A synthetic peptide complementary to amino acids 37-53 of C5a-anaphylatoxin binds to and inactivates C5a, inhibits induction of intracellular Ca2+ influx in neutrophils, and prevents C5a-mediated rapid lethal shock in a rat model. 15144465_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15158333_Human C5aR antagonist treatment reduced total hepatic reperfusion injury-induced mortality in rats. 15278436_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15485893_the C5a chemotactic cofactor function of vitamin D-binding protein requires its 20-amino-acid sequence (residues 130-149, 5'-EAFRKDPKEYANQFMWEYST-3') in domain I 15550394_analysis of binding mode for C5a to the C5aR 15944400_C5a receptor plays a role in glomerular physiology 16301808_the anaphylatoxin C5a potentiates cysLT production in human lung tissues and contributes to allergic inflammation in disorders such as asthma. 16511606_C5aR signaling at the dendritic cell/T cell interface during allergen priming provides protection against inflammatory responses to harmless antigens at the mucosal surface 16778800_C5aR is expressed on plasmacytoid dendritic cells. 16879222_C5a and its receptor have roles in PAI-1 production 17023413_analysis of the structural constraint for C5a docking with the complement factor 5a (C5a) receptor N terminus 17068344_C5L2 is a highly regulated scavenger receptor for C5a and C5a-des-Arg(74) 17090530_arboxyl-terminal tail acts together with the intracellular loops to generate a specificity filter for ths and other receptor-G protein interactions that functions primarily to restrict access of incorrect G proteins to the receptor. 17135254_Functional maps of the intracellular surface of thsi protein, and further, any G protein-coupled receptor to date. 17199736_The RP S19 dimer inhibits C5a-induced neutrophil migration and promotes apoptosis of neutrophils via the C5a receptor. 17234193_endothelial cells and subendothelial smooth muscle cells express both C3aR and C5aR 17724165_PLD control over expression of the Mac-1 activation epitope is critical for neutrophil migration to fMLP but not C5a. 17804836_A common genetic variant at the TRAF1-C5 locus on chromosome 9 is associated with an increased risk of anti-CCP-positive rheumatoid arthritis. 18187666_Our data establish a link between C5a and the gp130 receptor cytokine family with possible implications for the pathology of inflammatory diseases. 18538384_on the basis of the location of C3aR and C5aR, C5aR may play a role in activation of inflammatory cells, whereas C3aR may mediate mucus secretion and mucosal swelling in allergic nasal mucosa, especially severe persistent allergic nasal mucosa 18753257_C5aR plays an important role in mediating acute kidney allograft rejection 18772131_in the case of C5aR, the stimulation and phosphorylation of one monomer is enough to lead to dimer internalization. 19005416_Significantly more transcripts encoding alternative pathway components factor B, C3 and properdin, and C3a receptor and C5a receptor were detected in grade 3 versus grade 0 or 1 biopsies of human cardiac allografts. 19251703_the complex of CHIPS and a sulfated C5aR N-terminal peptide reveals the precise binding motif as well as the distinct roles of sulfated tyrosine residues sY11 and sY14. 19308263_C5a caused dysregulated induction of cytokines in Plasmodium falciparum infected monocytes; C5a levels were significantly elevated in women with placental malaria in Kenya. 19324972_C5a recapitulates impaired peripheral blood neutrophil phagocytosis and significantly down-regulates neutrophil CD88 (complement component 5a receptor) expression in vitro 19333232_in apoptosis-initiated cells, the ligand-dependent C5aR-mediated dual signal affects the fate of cells, either apoptosis execution or survival, through regulation of RGS3 gene expression and subsequent modulation of ERK signal. 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19464229_C5a has been found to be a significant pathogenic driver in a number of immuno-inflammatory diseases, making C5a inhibition an attractive therapeutic strategy. 19657723_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19657723_The aim of this study is to investigate C5a receptor (C5aR) gene polymorphism in patients with familial Mediterranean fever and its relation to the main features of the disease. 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19864971_expression profiles of CRegs and CD88 on leukocytes are specifically altered after polytrauma in humans, indicating a trauma-induced 'complementopathy 20044484_Data show that C5L2 is predominantly intracellular, while C5aR is expressed on the plasma membrane, and that internalized C5aR following ligand binding is co-localized with both C5L2 and beta-arrestin. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20473571_Data show that when a Gi/PI3K pathway is partially blocked, C5a receptors stimulate an alternative p38MAPK pathway. 20484595_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20500690_The elevated local and systemic C5a levels, and additional individual local C5a increase during the exacerbation support the importance of C5a in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 21292772_Among a cohort of 60 critically ill patients, C5a-mediated neutrophil dysfunction (as determined by reduced CD88 expression) was a strong predictor for subsequent acquisition of nosocomial infection 21613290_the monocyte C5aR selectively activates the classical pathway with the binding of C5a and the alternative pathway with the binding of C5a/RP S19. 21628869_C5a, a complement activation product, is a useful marker in predicting the severity of necrotizing enterocolitis. 22187344_The aim of this study was to investigate the genetic alterations and mRNA expression pattern of C5aR and C5L2 genes in neutrophils from attack-free familial Mediterranean fever patients. 22244896_Data show that incubation of C5 with cathepsin D resulted in generation of C5a, which was inhibited by the aspartate protease inhibitor pepstatin A. 22441801_Complement C5a upregulates prolabor mediators in human gestational tissues via CD88-mediated NFKB activation. 22496247_Intestinal epithelial cells express C5aR apically and directly respond to C5a through the ERK signaling pathway. 22608366_Analysis of the 3'UTR of the C5aR mRNA showed that it contained two AU-rich elements (AREs), however site directed mutagenesis showed that these had no effect on basal expression. 22960554_C5aR was expressed in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop and first part of the distal convoluted tubule. Under inflammatory conditions, C5aR was de novo expressed in proximal tubuli. 23041570_C5a receptor-dependent cell activation by physiological concentrations of desarginated C5a 23268185_C5aR-C5L2 homodimerization versus heterodimerization contribute to differential responses obtained following ASP vs C5a stimulation. 23287562_Data indicate that C5aR was aberrantly expressed in various cancers. 23346183_An RP S19 oligomer inhibitor and a C5aR inhibitor blocked the association of the K562 basophilic EB-like cells. 23394121_CD88 receptor expression is increased in brain from Alzheimer's disease patients compared to controls or vascular dementia patients. 23402022_the neutrophil C5aR acts as a dual pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptosis receptor during the initiation and the resolution phases of acute inflammation, respectively--{review} 23479227_C5aR is shed during sepsis, resulting in the appearance of a previously undetected circulating C5aR in the serum of patients that negatively correlates with survival. 23684309_The C5aR binding Panton-Valentine Leukocidin component, LukS-PV, is a potent inhibitor of C5a-induced immune cell activation. 23706417_High levels of CD88 are associated with poor prognosis of NSCLC. 24043889_C5aR is a regulatory switch that modulates TLR4 signaling via the Galphai/c-Raf/MEK/ERK signaling axis in human macrophages but not monocytes. 24134522_inhibition of TAFIa activity, however, was substrate-specific, because neither mAb inhibited the cleavage of thrombin-activated osteopontin and C5a by TAFIa, thus sparing the anti-inflammatory activity of TAFIa 24192237_The uPAR-C5aR axis, via the underlying NFkappaB transcriptional program, controls osteogenic differentiation with functional impact on vascular calcification in vivo. 24265019_complement can regulate Muller cells through C5aR, which may contribute to the pathogenesis of retinal diseases, including DR. 24327134_In patients with IgAN, urinary and renal C3a and C5a and renal expression of C3aR and C5aR are significantly correlated with the activity and severity of renal injury. 24446515_C5aR cleavage is induced by neutrophil serine protease. The consequent impairment of C5aR activity contributes to suboptimal local neutrophil priming and bacterial clearance. 24523571_C5aR and C5L2 may have roles in adiposity in women 24922578_Porphyromonas gingivalis induces C5aR-TLR2 coassociation in neutrophils. 25174320_These results illustrate the novel activity of the C5a-C5aR axis that promotes human NPC cell proliferation through PCAFmediated STAT3 acetylation. 25455139_C5AR1 SNP -1330T/G may serve as a useful pharmacodynamic predictor of nonsedating H1-antihistamine efficacy in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), and -1330T alleles may be taken as a risk factor for CSU. 25544179_Observed a positive correlation between the expression of anaphylatoxin-receptors C3aR and C5aR with platelet activation in patients with coronary artery disease. 25582053_). Low frequency of the C5aR 450 CT genotype, which apparently is a feature of certain kidney diseases, appears to be associated with good graft outcome in kidney transplantation. 25682807_96.7% of the metastatic RCCs had C5aR expression, vs. 50.5% of the non-metastatic ones. C5a triggered ERK- and PI3Kdependent invasion of the C5aR-expressing renal carcinoma cells. The C5a-C5aR axis plays a crucial role in renal carcinoma cell invasion. 25726869_C5AR and C5L2-mediated neutrophil dysfunction is associated with a poor outcome in sepsis. 25924896_that rs10853784 of C5aR1 gene are associated with coronary artery disease in Han population of China 26059553_C5a/C5aR1 signalling plays a key role in disrupting blood-brain barrier integrity through different cascades including NF-KappaB translocation leading to altered tight junction proteins, Claudin-5 and ZO-1, and actin reorganization in the lupus setting 26084468_The objective of the present study was to validate a receptor occupancy (RO) assay for a human anti-C5aR monoclonal antibody drug candidate, NNC0215-0384 (NN0384) 26176669_Inhibition of C5aR1 leads to a significant reduction of CD66b and CD11b expression indicating a lower neutrophil activation status and block of granule exocytosis. 26475622_that C5aR stimulates cell invasion and migration via ERK1/2-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells 26494574_Relation of C5aR expression to tumor development and poor prognosis of the breast cancer patients 26537334_These data thus suggest that C5aR1 acts as an enhancer of CCR5-mediated HIV entry into macrophages, the targeting of which may prove useful to reduce HIV infection by R5 strains. 27539194_the role of the active fragment complement C5a receptor (C5aR) in dental nerve regeneration in regards to local secretion of nerve growth factor (NGF) upon carious injury. 27606963_this study shows that downregulation of CD88 after stimulation with IL-8 is more pronounced in adults than in neonates, whereas fMLP induces changes in receptor expression that are of the same magnitude in neutrophils from neonates as from adults 27688239_C5aR expression in gastric cancer was associated with cancer progression, liver metastasis, and poor prognosis. 27721145_Serum containing active complement enhanced pneumococcal induced proinflammatory cytokine production through C5a release and C5aR crosstalk. 27756879_this study shows that C5a receptor (CD88) promotes motility and invasiveness of gastric cancer by activating RhoA 27821813_C5a-C5aR enriched clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients significantly had a poorer overall survival and recurrence free survival after nephrectomy. 28117704_Panton-Valentine leucotoxin LukS-PV/LukF-PV and the gamma-hemolysin HlgC/HlgB, bind the C5a complement-derived peptide receptor, inducing intracellular calcium release in neutrophils. 28228558_Reducing RPS19 in tumor cells or blocking the C5a receptor 1-RPS19 interaction decreases RPS19-mediated immunosuppression, impairs tumor growth, and delays the development of tumors in a transgenic model of breast cancer 28237029_C5aR plays a role in T helper cell polarization induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and this effect is strain- and donor-dependent. 28323848_Results showed that 7-oxygenated cholesterol derivatives have differential effects on monocyte/macrophage expression of IL-8 and C5a receptor and that C5a receptor is involved in 7alphaOHChol-induced IL-8 expression via PI3K and MEK. Study demonstrated expression of IL-8 and C5a receptor primarily by 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol in monocytes/macrophages. 28576324_Studies indicate that the complement response lie the active fragments, C3a and C5a, acting through their specific receptors, C3aR, C5aR1 and C5aR2 to direct the cellular response to inflammation. 28620195_In addition, an in vitro experiment revealed C5aR deficiency promoted the development of regulatory T cells whereas C5a activation abolished the differentiation of regulatory T cells. 28733463_TLR4 and C5aR crosstalk in dendritic cells induces a core regulatory network of RSK2, PI3Kbeta, SGK1, and FOXO transcription factors. 29031586_C5a/C5aR pathway promotes gastric cancer pathogenesis by suppressing p21/p-p21 expression via activation of PI3K/AKT signaling. 29138505_This study aimed to investigate the role of C3aR and C5aR in these two diseases...Our data indicates that increased C3aR expression may lead to over activation of the Th17 cell response and may therefore contribute to the pathogenesis of Behcet's disease (BD) and Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease (VKH). 29300009_X ray structure of a thermostabilized C5aR1 (known as C5aR1 StaR) in complex with NDT9513727 29551360_Low C5AR1 expression is associated with metastases of colon cancer. 29685955_Furthermore, Apigenin reduced the proliferation of human NPC cells triggered by C5a through negative regulation of C5aR/PCAF/STAT3 axis. These might provide a new insight into the function of Apigenin in cancer treatment, and also provide a potential strategy for treating human NPC through inhibition of C5aR expression on cancer cells 29765378_our results demonstrate that human renal tubular epithelial C5aR1 signaling has a role in facilitating UPEC adhesion to and invasion of the epithelial cells through upregulation of Man expression and suggest that upregulation of Man is through C5aR1-mediated ERK1/2/NF-kappaB activation and release of proinflammatory cytokines 30192927_Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-positive S. aureus colonization is associated with a variant of complement receptor 5a, the cellular target of the lukS PVL subunit. 30258440_Expression of C5aR1 and C5aR2 in whole blood was significantly attenuated by IL-6R-inhibition in non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients. 30612786_Our results show that there is a baseline intracellular expression of the complement C3, C5, C3aR and C5aR1 genes in normal CD4(+) T cells, but that expression is not increased during T-cell activation, but rather down regulated. 30953275_Study suggests that DF3016A is a novel C5aR antagonist promoting protective effects against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced damage that could be a new therapeutic approach to controlling CNS neuroinflammatory conditions. 31036565_uncover functional bias at C5aR1 and also provide a framework that can potentially be extended to chemokine receptors 31102985_CD14 blockade potentiated the effect of C5aR1 blockade, thus attenuating inflammation. 31270150_Monocyte tissue factor induction is dependent on complement C5aR1 32085887_Structural sequence evolution and computational modeling approaches of the complement system in leishmaniasis. 32669478_C5aR deficiency attenuates the breast cancer development via the p38/p21 axis. 33023856_The Complement C5a-C5aR1 GPCR Axis in COVID-19 Therapeutics. 33176600_Down-Regulation of C3aR/C5aR Inhibits Cell Proliferation and EMT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 33446393_Autoantibodies against C5aR1, C3aR1, CXCR3, and CXCR4 are decreased in primary Sjogren's syndrome. 33852936_C5aR inhibition of nonimmune cells suppresses inflammation and maintains epithelial integrity in SARS-CoV-2-infected primary human airway epithelia. 33936074_C5a-C5aR1 Axis Activation Drives Envenomation Immunopathology by the Snake Naja annulifera. 34030523_C5a complement receptor modulates odontogenic dental pulp stem cell differentiation under hypoxia. 34312368_C5aR1-positive neutrophils promote breast cancer glycolysis through WTAP-dependent m6A methylation of ENO1. 34971753_Complement C5a induces the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps by myeloid-derived suppressor cells to promote metastasis. 35132159_Complement C5aR/LPS-induced BDNF and NGF modulation in human dental pulp stem cells. 36323738_Differential expression of immune-regulatory proteins C5AR1, CLEC4A and NLRP3 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. 36466856_Differential expression of C5aR1 and C5aR2 in innate and adaptive immune cells located in early skin lesions of bullous pemphigoid patients. |
ENSMUSG00000049130 |
C5ar1 |
2219.634776 |
8.4185238263 |
3.073567 |
0.050639635 |
3889.239060 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4023.2120002 |
111.5478595 |
481.5043027 |
11.9943442 |
| ENSG00000197496 |
81031 |
SLC2A10 |
protein_coding |
O95528 |
FUNCTION: Facilitative glucose transporter required for the development of the cardiovascular system. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11592815, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16550171}. |
Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Sugar transport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the class III facilitative glucose transporter family. The encoded protein plays a role in regulation of glucose homeostasis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with arterial tortuosity syndrome.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2009]. |
hsa:81031; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate:proton symporter activity [GO:0005351]; D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0055056]; dehydroascorbic acid transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0033300]; glucose transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005355]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; artery development [GO:0060840]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; circulatory system development [GO:0072359]; dehydroascorbic acid transport [GO:0070837]; embryonic skeletal joint development [GO:0072498]; galactose transmembrane transport [GO:0015757]; glucose import across plasma membrane [GO:0098708]; glucose transmembrane transport [GO:1904659]; hexose transmembrane transport [GO:0008645]; negative regulation of connective tissue growth factor production [GO:0032683]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:2001045]; negative regulation of proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:1902729]; negative regulation of SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060392]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030512]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:1902730]; positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030511]; regulation of extracellular matrix organization [GO:1903053]; skin development [GO:0043588]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
12890477_expression in adipose tissue 12941788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12941788_variation in the coding region of SLC2A10 does not contribute substantially to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes 15936967_The SLC2A10 gene encodes a glucose transporter and is located on chromosome 20q13, where evidence has been found for linkage to type 2 diabetes (T2D) in multiple studies. 15975113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16051383_Complex regulatory mechanism of SLC2A10 expression through interaction of multiple transcription factors on basal promotor and prescence of distal repressor sequence suggests fine modulation of GLUT10 levels critical for glucose homeostasis. 16336637_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16550171_GLUT10 deficiency is associated with upregulation of the TGFbeta pathway in the arterial wall, a finding also observed in Loeys-Dietz syndrome, in which aortic aneurysms associate with arterial tortuosity 16586067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16586067_SLC2A10 genetic variations do not appear to be major determinants for type 2 diabetes susceptibility in the Taiwanese population. 18565096_the c.243C>G mutation in the Middle Eastern families may have a common origin and shared ances 18774132_analysis of a missense and a recurrent mutation in SLC2A10 gene of patients affected with arterial tortuosity syndrome 18818946_Patients of Kurdish origin who display arterial tortuosity associated with skin hyperextensibility, joint hypermobility, and characteristic facial features may carry a novel non-sense mutationin in the SLC2A10 gene. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20735855_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20735855_Our data demonstrate that genetic polymorphism of the SLC2A10 gene is an independent risk factor for PAD in type 2 diabetes. 22001912_Data show that homozygous and compound heterozygous changes found in PLOD1 and SLC2A10 may confer autosomal recessive effects, and three MYH11, ACTA2 and COL3A1 heterozygous variants were considered as putative pathogenic gene alterations. 25078964_Two SNPs replicated: the paternal rs2471083-C allele (located near the imprinted KCNK9 gene) and the paternal rs3091869-T allele (located near the SLC2A10 gene) increased BMI equally (beta = 0.11 (SD), P |
ENSMUSG00000027661 |
Slc2a10 |
19.470802 |
0.4245493808 |
-1.235996 |
0.346711939 |
13.081221 |
0.00029827097295238603211556260852432842511916533112525939941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000761674664494328321727445452182791996165178716182708740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7223390 |
2.4082774 |
25.4142532 |
3.6150956 |
| ENSG00000197497 |
79788 |
ZNF665 |
protein_coding |
Q9H7R5 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79788; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000067942 |
Zfp160 |
9.853213 |
0.4026905281 |
-1.312257 |
0.554165859 |
5.434417 |
0.01974367669193770324920222947184811346232891082763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.035447836999513503142278381119467667303979396820068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8571885 |
2.1809372 |
11.9444122 |
3.7163358 |
| ENSG00000197498 |
84154 |
RPF2 |
protein_coding |
Q9H7B2 |
FUNCTION: Involved in ribosomal large subunit assembly. May regulate the localization of the 5S RNP/5S ribonucleoprotein particle to the nucleolus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24120868}. |
Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis |
|
Enables 5S rRNA binding activity. Involved in protein localization to nucleolus; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator; and ribosomal large subunit biogenesis. Located in chromosome; nucleolus; and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84154; |
chromosome [GO:0005694]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; 5S rRNA binding [GO:0008097]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; rRNA binding [GO:0019843]; maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) [GO:0000463]; protein localization to nucleolus [GO:1902570]; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator [GO:1901796]; ribosomal large subunit assembly [GO:0000027]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273] |
19170763_BXDC1 and EBNA1BP2 function in a dynamic scaffold for ribosome biogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000038510 |
Rpf2 |
295.440076 |
2.6509087477 |
1.406487 |
0.158503138 |
76.535452 |
0.00000000000000000216294959635789699232734271592167129068850911533547585335890417468363011721521615982055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000017795505040268985375645185032888692229615493120000943583214336740638827905058860778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
426.4759531 |
41.1289063 |
162.0805372 |
11.7935233 |
| ENSG00000197506 |
64078 |
SLC28A3 |
protein_coding |
Q9HAS3 |
FUNCTION: Sodium-dependent, pyrimidine- and purine-selective (PubMed:11032837, PubMed:15861042, PubMed:16446384, PubMed:17140564, PubMed:21998139). Involved in the homeostasis of endogenous nucleosides (PubMed:11032837, PubMed:15861042). Exhibits the transport characteristics of the nucleoside transport system cib or N3 subtype (N3/cib) (with marked transport of both thymidine and inosine) (PubMed:11032837). Employs a 2:1 sodium/nucleoside ratio (PubMed:11032837). Also able to transport gemcitabine, 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT), ribavirin and 3-deazauridine (PubMed:11032837, PubMed:17140564). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11032837, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15861042, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16446384, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17140564, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21998139}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Nucleoside transporters, such as SLC28A3, regulate multiple cellular processes, including neurotransmission, vascular tone, adenosine concentration in the vicinity of cell surface receptors, and transport and metabolism of nucleoside drugs. SLC28A3 shows broad specificity for pyrimidine and purine nucleosides (Ritzel et al., 2001 [PubMed 11032837]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:64078; |
brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005337]; nucleoside:sodium symporter activity [GO:0005415]; purine nucleobase transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005345]; purine-specific nucleoside:sodium symporter activity [GO:0015390]; pyrimidine- and adenine-specific:sodium symporter activity [GO:0015389]; symporter activity [GO:0015293]; uridine transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015213]; nucleoside transmembrane transport [GO:1901642]; purine nucleobase transmembrane transport [GO:1904823]; purine nucleoside transmembrane transport [GO:0015860]; pyrimidine nucleoside transport [GO:0015864]; pyrimidine-containing compound transmembrane transport [GO:0072531]; uridine transport [GO:0015862]; xenobiotic transmembrane transport [GO:0006855] |
14504928_hCNT3 gene is evolutionarily conserved with hCNT1 and hCNT2. Physiologically, hCNT3 is a glycoprotein, which transports purine and pyrimidine nucleosides in a Na-dependent manner with high affinities. 15738947_genetic analysis and functional characterization of CNT3 variants suggest that this transporter does not tolerate nonsynonymous changes and is important for human fitness 15861042_examination of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the coding regions of the hCNT3 gene 15870078_hCNT3 possesses two Na+-binding sites, only one of which is shared by H+ 16271041_The effects of cysteine substitution mutants spanning transmembrane domains 11-13 on the transport activity of CNT3 expressed in S. cerevisiae are reported. 16446384_Minimal features required for human CNT3 transport are two hydrogen bond acceptors at 3'-OH and 5'-O and the hydrophobic center occupied by the base ring. 17409283_transcripts for CNT3 protein in human kidneys and in cultured proximal tubule cells suggest involvement of CNT3 in renal handling of nucleosides and nucleoside drugs 17412768_CNT3 was inserted into the apical membrane, thus generating, a transepithelial flux of both nucleosides and nucleoside-derived drugs. 17453413_hCNT2 shares common cation specificity and coupling characteristics with hCNT1, which differ markedly from those of hCNT3. 17696452_This study shows that adenosine elimination on human airway epithelia is mediated by ADA1, CNT2, and CNT3, which constitute important regulators of adenosine-mediated inflammation. 17926640_These data suggest that selected genes of the SLC28 and SLC29 families are not only targets of HIV-1 infection, but might also contribute to the development of adipose tissue alterations leading to lipodystrophy. 17993510_A polymorphic variant of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter, CNT3, is found that severely affects its functionality. 18199742_identified a C-terminal intramembranous cysteine residue of hCNT3 (Cys-561) that reversibly binds the hydrophilic thiol-reactive reagent p-chloromercuribenzene sulfonate (PCMBS) 18621735_a pivotal functional role for Cys-561 in Na+- as well as H+-coupled modes of hCNT3 nucleoside transport 18827020_The isolation and charcterization of an alternatively spliced SLC28A3-related mRNA is reported. 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19297449_This evidence suggested that apical CNT3 and basolateral ENT2 are involved in proximal tubular reabsorption of adenosine and some nucleoside drugs and that apical ENT1 is involved in proximal tubular secretion of 2'-deoxyadenosine. 19318496_Pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients with a high expression of hENT1 and hCNT3 immunostaining have a significantly longer survival after adjuvant gemcitabine-based chemoradiation 19380585_identified residues of functional importance and with a revised 15-TM membrane architecture, suggest a novel membrane-associated topology for a region of the protein (TM 11A) that includes the highly conserved CNT family motif (G/A)XKX(3)NEFVA(Y/M/F) 19380587_identified two conserved pore-lining glutamate residues (Glu-343 and Glu-519) with essential roles in CNT3 Na(+)/nucleoside and H(+)/nucleoside cotransport 20028759_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20172853_TGF-beta1 acts through activation of ERK1/2 and the small GTPase RhoA to promote plasma membrane trafficking of the hCNT3 protein. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20495821_H+ drives uridine and adenosine transport by hCNT3 with lower affinity but higher maximal transport rate than Na+. 20643903_Acidic and hydrophobic motifs in the N terminus tail of the hCNT3 control ER export and cell surface expression levels in nonpolarized cells, whereas a putative beta-turn domain contributes to hCNT3 polarized surface expression in epithelial cells. 21346688_A genetic variant in SCL28A3 coding for the concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 protects patients with chronic hepatitis C against hemolytic anemia without affecting sustained virological response in hepatitis C virus genotype 1. 21822668_Data show that ENT1, ENT2, ENT4 and CNT3 protein was detected on ovarian carcinoma cells in all effusions, with expression observed in 1-95% of tumor cells. 23195617_association between ribavirin (RBV) serum levels and SLC28A2 rs11854484 genotype, as well as the replicated association of ITPA and SLC28A3 genetic polymorphisms with RBV-induced anemia and treatment response 23441093_Validation of variants in SLC28A3 and UGT1A6 as genetic markers predictive of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in children. 24300978_The presence of homozygous major allele for SLC28A3 (CC genotype) were each associated with an almost two-fold increase in the formation clearance of dFdCTP. 24361227_Genetic polymorphisms in SLC28A3, SLC29A1 and RRM1 can influence the clinical outcome of metastatic breast cancer patients treated with paclitaxel-gemcitabine chemotherapy. 25955569_Results show that high CNT3 expression level is associated with overall favorable outcomes and is predictive of clinical outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia patients with t(8;21). 26188009_Genome-wide association analysis on normal hearing function identifies PCDH20 and SLC28A3 as good candidates for modulatory genes in the auditory system. [meta-analysis] 26481311_The co-expression of galectin-4 and CNT3 proteins is not impaired in inflamed colon from patients with Crohn's disease, thereby anticipating the integrity of this system for drug targeting. 27604902_CYR61 negatively regulates the nucleoside transporters hENT1 and hCNT3 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 28385889_results that validate the newly developed structural homology model of CNT membrane architecture for human CNTs, revealed extended conformationally mobile regions within transport-domain TMs, identified pore-lining residues of functional importance, and provided evidence of an emerging novel elevator-type mechanism of transporter function. 28661652_Data suggest that CNT3 forms a homotrimer in solution and membrane-bound inside cells; the quaternary structure creates an aqueous basin that significantly shortens the substrate translocation distance. 28774292_De novo structure prediction of three N-terminal transmembrane helices of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 (hCNT3) homotrimer belonging to the solute carrier 28 family of transporters (SLC28) using Rosetta program and its Broker protocol. 30096006_human CNT3 homology models generated validate previously published PCMBS SCAM data, and confirm an elevator-type mechanism of membrane transport 30778771_Association of SLC28A3 Gene Expression and CYP2B6*6 Allele with the Response to Fludarabine Plus Cyclophosphamide in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients. 32776918_Cryo-EM structure of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter CNT3. 33910126_Characterization of deoxyribonucleoside transport mediated by concentrative nucleoside transporters. 33974709_Gene-Gene Interactions of Gemcitabine Metabolizing-Enzyme Genes hCNT3 and WEE1 for Preventing Severe Gemcitabine-Induced Hematological Toxicity. 34751688_Allosteric and transport modulation of human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 at the atomic scale. |
ENSMUSG00000021553 |
Slc28a3 |
8.734063 |
3.7670622362 |
1.913440 |
0.599304713 |
10.550012 |
0.00116187325929344100090834235317061029491014778614044189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002677210186707842942688273524254327639937400817871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8515559 |
4.6359699 |
3.2776162 |
1.0476005 |
| ENSG00000197530 |
142678 |
MIB2 |
protein_coding |
Q96AX9 |
FUNCTION: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination of Delta receptors, which act as ligands of Notch proteins. Positively regulates the Delta-mediated Notch signaling by ubiquitinating the intracellular domain of Delta, leading to endocytosis of Delta receptors. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R516}. |
Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Metal-binding;Notch signaling pathway;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
The protein encoded by this gene is an E3 ubiquitin protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination of proteins in the Notch signaling pathway. The encoded protein may be a suppressor of melanoma invasion. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2017]. |
hsa:142678; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
15824097_Mib2 has functional similarities to Mib1, but might have distinct roles in Notch signaling as an E3 ubiquitin ligase 15869411_Skeletrophin, a novel RING molecule controlled by the chromatin remodeling complex, is down-regulated in melanoma. 15920166_skeletrophin is a novel ubiquitin ligase that targets the intracellular region of Jagged-2 and is aberrantly overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells. 16715130_skeletrophin might be a novel suppressor factor for melanoma invasion 17962190_Data identify Mind bomb-2 as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that interacts with and ubiquitinates the NR2B subunit of the NMDAR in mammalian cells. 21896478_identify MIB2 as a novel component of the activated BCL10 signaling complex and a missing link in the BCL10-dependent NF-kappaB signaling pathway. 25142606_The DLAIS motif in MAVS was found to be critical for MIB2 binding, the ligation of K63-linked ubiquitin to TANK-binding kinase 1, and phosphorylation-mediated IRF3/7 activation. 25565632_Here, we report a novel interaction between CYLD and MIB2 that supports the hypothesis that the CYLD/MIB2 interaction might play a pathogenic role in human cancer. 28013292_Missense p.V742G variant in MIB2 is associated with left ventricle hypertrabeculation/non-compaction and Menetrier-like gastropathy. 29642005_MIB2 represses the cytotoxic potential of RIPK1 by ubiquitylating lysine residues in the C-terminal portion of RIPK1. Disruption of MIB2-mediated ubiquitylation, either by mutation of MIB2's E3 activity or RIPK1's ubiquitin-acceptor lysines, sensitizes cells to RIPK1-mediated cell death. 31366726_Results suggest that MIB2 enhances NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation by promoting the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of CYLD. 33469115_MIND bomb 2 prevents RIPK1 kinase activity-dependent and -independent apoptosis through ubiquitylation of cFLIPL. 34971948_E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 2 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer through ubiquitination of Notch1. |
ENSMUSG00000029060 |
Mib2 |
232.285191 |
0.3534554594 |
-1.500400 |
0.220379377 |
44.965599 |
0.00000000002005264693362270198421756748897282858143387151983461080817505717277526855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000109136087293610285600217732716800834308346068723949429113417863845825195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
116.5978456 |
15.1449927 |
333.1016466 |
30.3472106 |
| ENSG00000197536 |
|
IRF1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.942603 |
0.2349271303 |
-2.089715 |
0.586721764 |
12.271017 |
0.00046004751523966624839750982900454800983425229787826538085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001137594458860357498133919484928355814190581440925598144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3353700 |
2.6683509 |
26.7281760 |
7.3287775 |
| ENSG00000197558 |
23145 |
SSPOP |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable peptidase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including cell adhesion; negative regulation of catalytic activity; and regulation of peptidase activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in extracellular matrix and extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
15053980_demonstrated SCO-spondin expression at relevant steps of gestation in the placenta 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
137.707844 |
0.0302093887 |
-5.048859 |
0.863029165 |
24.030639 |
0.00000094814866113520105976635249725448240099012764403596520423889160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003364482181102976957525830040141023857813706854358315467834472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
7.3308324 |
3.4986114 |
258.9351972 |
84.4861855 |
| ENSG00000197561 |
1991 |
ELANE |
protein_coding |
P08246 |
FUNCTION: Modifies the functions of natural killer cells, monocytes and granulocytes. Inhibits C5a-dependent neutrophil enzyme release and chemotaxis (PubMed:15140022). Capable of killing E.coli but not S.aureus in vitro; digests outer membrane protein A (ompA) in E.coli and K.pneumoniae (PubMed:10947984). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10947984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15140022}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Protease;Reference proteome;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
Elastases form a subfamily of serine proteases that hydrolyze many proteins in addition to elastin. Humans have six elastase genes which encode structurally similar proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the active protease. Following activation, this protease hydrolyzes proteins within specialized neutrophil lysosomes, called azurophil granules, as well as proteins of the extracellular matrix. The enzyme may play a role in degenerative and inflammatory diseases through proteolysis of collagen-IV and elastin. This protein also degrades the outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of E. coli as well as the virulence factors of such bacteria as Shigella, Salmonella and Yersinia. Mutations in this gene are associated with cyclic neutropenia and severe congenital neutropenia (SCN). This gene is present in a gene cluster on chromosome 19. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:1991; |
azurophil granule lumen [GO:0035578]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; secretory granule [GO:0030141]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; transcription repressor complex [GO:0017053]; cytokine binding [GO:0019955]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; acute inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002438]; biosynthetic process of antibacterial peptides active against Gram-negative bacteria [GO:0002812]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002523]; negative regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032682]; negative regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050922]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032717]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neutrophil-mediated killing of fungus [GO:0070947]; neutrophil-mediated killing of gram-negative bacterium [GO:0070945]; phagocytosis [GO:0006909]; positive regulation of immune response [GO:0050778]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:1903238]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; protein catabolic process [GO:0030163]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to UV [GO:0009411]; response to yeast [GO:0001878] |
11846296_Mutant neutrophil elastase induces accelerated apoptosis of promyelocytes, leading to maturation arrest in congenital and cyclic neutropenia. 11928814_UVA light stimulates the production of neutrophil elastase by dermal fibroblasts: a possible contribution to the remodeling of elastotic areas in sun-damaged skin. 11948122_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12020136_Elastase is mainly responsible for cartilage damage by stimulated human neutrophils, as demonstrated by the use of selective elastase inhibitors. 12042033_Neutrophil elastase-induced overexpression of mucin genes in cultured tumor cells is inhibited by a retinoic acid receptor alpha antagonist. 12083479_degraded scu-PA and also tcu-PA, t-PA and plasmin, resulting in loss of fibrinolytic activity 12091371_Precursor cells containing the ELA2 mutation are selectively lost during myelopoiesis or fail to develop into neutrophils, confirming the pathogenic nature of elastase mutations in humans. 12114510_HNE plays a role in neutrophil response to inflammation 12183836_plasma levels are increased during G-CSF induced hematopoietic stem cell mobilization 12223522_Treatment of human gingival fibroblasts with human leukocyte elastase down-regulated CD40 expression & binding to CD40 ligand. CD40 reduction by direct proteolysis by HLE was seen in skin & lung fibroblasts (not monocytes, macrophages, & dendritic cells). 12393522_Neutrophil elastase plays a role in providing negative feedback to granulopoiesis by direct antagonism of G-CSF. 12444202_Protease entry results in direct cleavage of p65 NF-kappaB in the N-terminal region by PR3 and in the C-terminal region by HNE. PR3 and HNE have specific, fundamental roles in endothelial responses during inflammation. 12483111_REVIEW: role of ela2 germline mutations in inherited neutropenia, gene feedback circuits, signalling genetics, and proposal that neutrophil elastase acts as an inhibitor of myelopoiesis 12700588_adherent PMNs induce a localized, sequential disassembly of endothelial adherens junctions, which is partially mediated by PMN-derived elastase 12745650_Review. Heterozygous mutations in the ELA2 gene have been described in cyclical & congenital neutropenia. A case of paternal mosaicism has provided genetic 'proof' of the pathogenicity of such mutations. 12771009_Fibrous and atheromatous plaques but not normal arteries contained NE; NE abounded in the macrophage-rich shoulders of atheromatous plaques with features of vulnerability. Neutrophil elastase and macrophages colocalized in such vulnerable plaques 12778173_Mutations in proto-oncogene GFI1 cause human neutropenia and target ELA2 12782302_Neutrophil elastase up-regulates interleukin-8 via toll-like receptor 4 12853121_Multimeric SFTPD was partially digested by ELA2 dose- and time-dependently with loss of its carbohydrate recognition domain. 12876407_in vitro challenge of neutrophils in asthmatic patients with allergens to which the patients were sensitive elicited a release of elastase by these cells. The in vitro activation of neutrophils was highly allergen specific. 12887060_the effect of kininogen degradation by human neutrophil elastase (HNE) on kinin generation 12893759_elastase overproduction by the leukemic clone can change the growth environment by digesting growth factors, thereby giving advantage to Ph+ hematopoiesis 12934194_NE levels in infected lobes were higher than those in uninvolved lobes, and NE levels were significantly elevated in both, compared with that in control lobes in community acquired pneumonia 14587040_NE-induced degradation of G-CSG and G-CSFR correlates with a reduction in the biologic activity of the cytokine and a decrease in the signaling function of the receptor because of decreased G-CSFR surface expression. 14636558_Since NE is maximally produced in promyelocytes, this protease may play a role in APL pathogenesis by facilitating the leukemogenic potential of PML-RARalpha 14688365_Serine proteinases neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G cooperate for the proteolytic regulation of CD87/urokinase receptor on monocytic cells. 14705961_An important part of the antimicrobial mechanism of neutrophil elastase may be a periplasmic bacteriostatic effect of protease that has translocated across the damaged outer membrane. 14730209_Results indicate that neutrophil elastase activates p38 MAP kinase which upregulates NF-kappaB and AP-1 activities, thus inducing interleukin-8 mRNA expression and protein synthesis. 14962902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14962902_the expression of neutropenia in cyclic and severe congenital neutropenia may be either homogeneous or variable according to the type of mutations, suggesting different pathogenetic mechanisms. 15010259_Results demonstrate that human neutrophil elastase is mitogenic for airway smooth muscle cells by increasing cyclin D1 activity through the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. 15059607_neutrophil elastase mutations play a role in human hereditary neutropenia, as shown in a dog model [review] 15131125_neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G are inhibited by PAI-1 mutants 15140022_Release of human leukocyte elastase from neutrophils specifically down-regulates the responsiveness of neutrophils to C5a, and this effect may play a role in the down-regulation of acute inflammation. 15161642_elastase released by polymorphonuclear leukocytes trapped within the mural thrombus impairs the spontaneous anchorage of mesenchymal cells to a fibrin matrix 15595387_secreted E coliO78 OmpA can play a role in protection of bacteria from NE by competitive inhibition 15601827_Neutrophil elastase has a role in PML-retinoic acid receptor alpha activities in early myeloid cells 15614130_Neutrophil elastase, MIP-2, and TLR-4 have roles in progression of human sepsis and murine peritonitis 15657182_data suggest mechanisms by which NE mutations cause neutropenia and suggest that abnormal protein trafficking and accelerated apoptosis of differentiating myeloid cells contribute to the severe congenital neutropenia phenotype of the G185R mutation. 15718918_elastase binds to the beta(2)-integrin CD11b and induces a conformational alteration of CD11b 15892999_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15941909_human AML cells constitutively secrete and express SDF-1-dependent cell-surface elastase, which regulates their migration and proliferation 16079102_Patients with cyclic neutropenia and agranulocytosis showed mutations in this enzyme. 16127146_HNE stimulation of mucin release by human airway epithelial cells involves intracellular activation of PKC, specifically the delta isoform. 16148149_HNE causes protein kinase C (PKC) activation and translocation from cytosol to plasma membrane, required for HNE-induced ROS generation and other responses 16244764_granulocyte-derived elastase is a potentially useful marker for the diagnosis of overt-disseminated intravascular coagulation and as a predictor of organ failure-related outcome 16282197_These data suggest that hypertonic saline upregulates polymorphonuclear neutrophil degranulation via ATP release and positive feedback through P2 and A3 receptors. 16321984_comparison of x-ray structures of alpha1PI complexes with trypsin, PPE, and human neutrophil elastase 16551967_cells expressing mutant HNE exhibited a significant increase in apoptosis associated with up-regulation of master ER chaperone BiP, indicating that disturbance of intracellular trafficking results in activation of the mammalian unfolded protein response 16624642_C-reactive protein degradation products generated by neutrophil elastase promote neutrophil apoptosis 16670064_The Leu92His mutation is near the glycosylation site Asn95. This AA substitution may alter the availability of this Asn residue resulting in abnormal glycosylation of the mutant protein. 16690986_Neutrophil derived elastase (NE) upregulates TGF-beta1 gene expression and release via My88/IRAK/NF-kappaB pathway, possibly through activation of TLR4, and shed light on a potential role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. 17023068_The identification of annexin 1 as a substrate for HLE supports the model in which annexin 1 participates in regulating leukocyte emigration into inflamed tissue. 17088257_analysis of human neutrophil protease 3 and elastase active site charge distribution 17395013_NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1has an important role as a mediator of neutrophil elastase-regulated oxidant stress and mucin 5AC mucin gene expression. 17397908_The activation of the neutrophil elastase-mediated fibrinolytic pathway may be insufficient to overcome the fibrinolytic shutdown by PAI-1 and may in part explain the poor prognosis of DIC patients associated with systemic inflammation. 17412886_The primary granule proteins elastase (ELA2) and proteinase 3 (PR3) both contain the nonapeptide PR1, which can induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against chronic myeloid leukemia. 17436313_An exceptional genetic phenomenon in which both a cyclic neutropenia patient and an SCN patient each possess two new ELA2 mutations; role in protein mistrafficking as disease mechanism. 17622939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17622939_The association of C4890A with myocardial infarction (MI) in Belfast exclusively, and the presumed absence of its functionality, provides little support for a substantial implication of common ELA2 gene variants in overall MI risk. 17690184_Data suggest that polymorphonuclear leukocytes decrease dendritic cell allostimulatory ability via production of elastase leading to a switch of immature DCs into TGF-beta1-secreting cells. 17761833_ELA2 mutations result in the production of misfolded NE protein, activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR), and ultimately apoptosis of granulocytic precursors 17785837_Induction of murine macrophage microbicidal activity by either neutrophils or purified human neutrophil elastase requires TLR4 expression by macrophages. 17853021_Leukocyte elastase is involved in renal injury occurring in the course of primary idiopathic glomerulonephritis, in particular in the proliferative types. 17998887_urinary trypsin inhibitor is insufficiently produced for neutrophil elastase release after cardiac arrest 18028488_study of severe congenital neutropenia patients; there was no significant difference in risk of myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukaemia in patients with mutant versus wild-type ELA2 18043239_Genetic evidence suggests that ELA2 mutations act in a dominant, cell-intrinsic fashion to disrupt granulopoiesis. Mutations of ELA2 may cause disease through induction of the unfolded protein response. Review. 18178964_Neutrophil elastase cleaves laminin-332 (laminin-5) generating peptides that are chemotactic for neutrophils. 18194283_PMN-elastase levels in serum and seminal plasma were not significantly correlated and there was no association with subsequent fertility. 18211966_Pre-eminent role for neutrophil elastase as the critical protease responsible for PSP-D depletion in inflammatory lung disease 18278188_In an in vitro atherosclerosis model neutrophil infiltration was mediated via IL-8-signalling and accompanied by release of elastase and induction of endothelial cell apoptosis. 18295791_Analysis of the NE proteolytic products of the Shigella virulence factor IpaB shows that NE has specific cleavage sites. 18399311_total amount and the percentage of free elastase activity were significantly higher in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus when compared with the controls 18403643_This result revealed a negative feedback loop whereby CUX1 shuts down the expression of the protease that cleaves it. 18476621_MBP and NE collaborated to cause the pathological effects of nasal polyps. 18485588_HLE may be a natural inactivator of MMP-7 which can counteract MMP-7-induced apoptosis resistance. 18669870_CD63 is involved in granule targeting of neutrophil elastase 18710383_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18799464_elafin is cleaved by its cognate enzyme NE present at excessive concentration in CF sputum, an effect which is promoted by P. aeruginosa infection 18980523_Non-surgical periodontal treatment was effective in reducing the levels of elastase in gingival crevicular fluid from diabetic patients with chronic periodontitis. 19132232_Modulation of endothelial cell tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor-1 by neutrophil elastase. 19180801_Report changes in plasma level of human leukocyte elastase during leukocytosis from physical effort. 19197381_The hypothesis that an imbalance between neutrophil elastase (HNE) and its inhibitors in blood is related to the development of ARDS, was tested. 19251947_Shed syndecan-1 restricts neutrophil elastase from alpha1-antitrypsin in neutrophilic airway inflammation. 19307610_leukocyte elastase-induced apoptosis of lung epithelial cells is mediated by a PAR-1-triggered pathway involving activation of NF-kappaB and p53, and a PUMA- and Bax-dependent increase in mitochondrial permeability leading to activation of distal caspases 19362143_elevated plasma levels in patients with acute myocardial infarction compared to patients with stable coronary artery disease 19415009_Three cases of familial congenital neutrophenia (P13L, R52P, and S97L), 2 of familial cyclic neutropenia (W212stop and P110L), and 1 of sporadic congenital neutropenia (V72M) were shown to have heterozygous mutations in the Ela2 gene 19506020_Data suggest that expression of PFAAP5 allows neutrophil elastase to potentiate the repression of Gfi1 target genes. 19542452_Neutrophil elastase inhibits interleukin (IL)-8/CXCL8 gene expression and protein release specifically in human airway smooth muscle cells by inducing NF-kappa B repressing factor (NRF). 19590686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19620298_Neutrophil elastase is one of the mediators responsible for complement-dependent opsonophagocytic killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae by human neutrophils. 19620402_Neutrophil elastase is severely down-regulated in severe congenital neutropenia independent of ELA2 or HAX1 mutations but dependent on LEF-1. 19763368_no consistent pattern among sites in the vagina in pelvic organ prolapse 19775295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20007580_Secretory leucoprotease inhibitor is cleaved and inactivated by neutrophil elastase present in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-positive secretions in the cystic fibrosis lung. 20033193_elevated in chronic compared to acute wounds 20111696_Sputum samples from cystic fibrosis patients had elevated human neutrophil elastase (HNE) levels which correlated with an increased MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio. 20179351_ELA2 as a major new epidermal protease involved in essential pathways for skin barrier function. 20346360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20354035_Sivelestat may attenuate neutrophil elastase or proinflammatory cytokines, and improve pulmonary dysfunction in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. 20376727_Neutrophil elastase inhibitor, Sivelestat, significantly reduced the postoperative decreases in AT III and platelet count in patients undergoing emergency surgery for acute aortic dissection. 20411049_NE digests ferritin increasing the extracellular iron pool available for cellular uptake 20423453_REVIEW: structural basis for the different ligand specificities and membrane binding mechanisms of human proteinase 3 and neutrophil elastase 20453419_In patients in preterm labor with a high elastase concentration in cervical secretions, treatment with urinary trypsin inhibitor reduced the risk of preterm delivery and improved neonatal outcomes. 20521180_variants of alpha-1-antitrypsin and ELA2 genotypes with predicted intermediate or high activity could represent a risk factor for aggressive form of lung cancer 20582973_coexistence of CN and SCN phenotypes in this kindred with a shared S97L ELANE paternal haplotype strongly suggests both a role for modifying genes in determination of congenital neutropenia disease phenotypes 20627279_Cluster analysis reveals two classes of thrombi according to neutrophil elastase -specific fibrin degradation products (NE-FDP),leukocyte and platelet content and also two according to NE-FDP, leukocyte and fibrin content. 20634941_Results describe the direct effects of the antibiotics colistin and tobramycin on neutrophil elastase activity in cystic fibrosis patients. 20646231_Findings of significantly elevated serum MMP-9, myeloperoxidase, and neutrophil elastase together with decreased TIMP-1 in smoker periodontitis patients provides support for the smoking associated risk of cardiovascular diseases in periodontitis patients 20803142_Results describe a multigenerational family with mutations in ELANE as unambiguous cause of severe congenital neutropenia. 20828556_The trafficking of precursor NE (proNE) and precursor PR3 (proPR3), was compared. 20883273_NE significantly promotes the proliferation of HaCaT cell. Meanwhile, it also up-regulates the expression levels of Ki67 and p53 in psoriasis lesion tissue, which plays an important role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis lesion. 20932306_Human neutrophil elastase treatment does not modify short-circuit current in control or nasal epithelial cells from cystic fibrosis patients. 20974816_The neutrophil elastase (NE) escapes from azurophilic granules and translocates to the nucleus, where it partially degrades specific histones, promoting chromatin decondensation. 21193404_NE is the predominant protease that cleaves hemoglobin in vivo in cystic fibrosis bronchoalveolar lavage fluid 21206270_The majority of patients with severe congenital neutropenia bear monoallelic mutations in the neutrophil elastase (ELANE) gene 21236472_The study shows that the alternative pathway for plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis by leukocyte elastase is activated, and contributes to the degradation of cross-linked fibrin in sepsis-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation. 21425445_Four novel heterozygous mutations in the ELANE gene in patients with congenital neutropenia 21448199_SCN with the identification of a mutation in the ELANE gene. 21475777_catalyses inactivation of factor VIII(a)via limited proteolysis 21477798_Immature dendritic cells treated with neutrophilic elastase or polymorphonuclear culture supernatant, promote the generation of CD4+FOXP3+ Tregs in vitro. 21488974_potential of HNE and CatG to be used as markers for early detection of infection. Significant differences in HNE and CatG levels in infected and non-infected wound fluids were observed. 21576245_a new mode of PAR regulation that involves biased PAR(2) signaling by neutrophil elastase and a disarming/silencing effect of cathepsin-G and proteinase-3. 21605276_Plasma neutrophil elastase may be involved in the pathogenesis of severe pneumonia. 21731773_heparin is able to accelerate the hydrolysis of TIMP-1 by HNE. 21796505_ELANE genetic polymorphism is associated with development of periodontitis in patients with severe congenital neutropenia 21843618_Tagetes erecta flower showed effective inhibition of leukocyte elastase. 22174830_In a process reminiscent of neutrophil extracellular traps formation, NE enhances sputum solubilization. 22407864_Chamomile infusion inhibited expression of neutrophil elastase and matrix metalloprotease-9 in adenocarcinoma gastric cells. 22500123_Report on development of pulmonary emphysema after intratracheal instillation of human neutrophil elastase. 22683569_High elastase expression is associated with defective alveolar septation and arrested lung growth. 22915586_NE and CG bind to the surface of cancer cells, presumably to a cell surface receptor, and subsequently undergo clathrin pit-mediated endocytosis. 22918834_Neutrophil extracellular traps-associated elastase digested amyloid fibrils into short species that were cytotoxic for BHK-21 and HepG2 cells. 22993338_Variations in SERPINA1 and ELA2 were not consistently or strongly associated with the risk of either COPD or NSCLC in either African Americans or caucasian. 22996420_Overexpression of G185R ELA2 mutant increases apoptosis through an unfolded protein response. 23001948_E-cadherin expression correlated negatively with PMN infiltration, compatible with the notion that E-cadherin is cleaved by PMN-derived elastase 23351986_A review discusses how ELANE mutations provide clues into the pathogenesis of cyclic and severe congenital neutropenia. 23392769_Neutrophil elastase can increase PAR2 expression and MUC5AC release. 23454784_4 ELANE mutations, 11 HAX1 mutations and 2 G6PC3 mutations have been identified in Iranian patients with severe congenital neutropenia. 23463630_Specific ELANE mutations have limited predictive value for leukemogenesis; the risk for leukemia was correlated with disease severity rather than with occurrence of an ELANE mutation. 23564510_Human neutrophil elastase induced goblet cell metaplasia in the wild-type mice and that HNE-induced goblet cell metaplasia was significantly attenuated in the Tace conditional deletion mice. 23692169_Neutrophil elastase activity in BAL fluid in early life was associated with early bronchiectasis in children with cystic fibrosis. 23741370_SPLUNC1 degradation by neutrophil elastase may increase airway susceptibility to bacterial infections. 23819644_neutrophil elastase reflects the severity and progression of acute pancreatitis. 23911525_It reports the synthesis and enzymatic studies on a new proteinase 3 intermolecular quenched substrate with enhanced selectivity over neutrophil elastase. 24023624_Polymorphonuclear cell proteases, especially neutrophil elastase, degrade decorin, and this degradation renders collagen fibrils more susceptible to MMP-1 cleavage. 24052258_Neutrophil elastase and proteinase-3 trigger G protein-biased signaling through proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1). 24184683_ELANE mutations disrupt translation initiation and are associated with neutropenia; they produce novel neutrophil elastase isoforms 24513040_The present findings highlight the peculiar activity of PMN elastase in disabling EMILIN1 suppressor function. 24616599_The leukocyte elastase gene is substituted at the 597th base (G to A) in intron 4 of severe congenital neutropenia. 24816969_Suggest a potential role of ELANE gene polymorphisms as therapy modulators in childhood bronchiectasis. 24848868_Human sex hormone-binding globulin mediates the targeted release of cortisol at sites of inflammation through cleavage of its reactive center loop by neutrophil elastase. 24877096_Elastase and cathepsin G are elevated in the plasma of HD patients, originating from primed PMNLs. In these patients, chronic elevation of these enzymes contributes to cleavage of VE-cadherin and possible disruption of endothelial integrity. 24914212_An interactive network of elastase, secretases, and PAR-2 protein regulates CXCR1 receptor surface expression on neutrophils 24929239_These in vivo data provide, for the first time, compelling evidence of the collateral involvement of cathepsin G, NE, and proteinase 3 in cigarette smoke-induced tissue damage and emphysema 25092677_Circulating protein levels and enzymatic activity of ELANE are markedly elevated in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, and are correlated with increased autoantibodies against beta-cell antigens. 25195861_The imbalance between Neutrophil elastase and its inhibitors, such as elafin, presents an important therapeutic target in breast cancer. 25248056_expression levels of ELANE and CTSG were determined by quantitative real-time PCR 25284053_Three proteins-matrix metalloproteinase-9, neutrophil elastase, and FAM49B-were significantly lower in abundance in samples from women with endometriosis. 25427142_Sequencing is useful for predicting outcomes of ELANE-associated neutropenia. 25465717_Neutrophil elastase mainly enhances tissue factor production by monocytes via the phospholipase C/conventional PKC/p38 MAPK pathway, although a novel PKC is also involved. 25652853_Over-expressed NE in K562 leukemia cells promotes cell proliferation, inhibits apoptosis and block cell cycle in S phase. 25666548_Sirtinol is a novel HNE inhibitor and may have the potential for clinical application in the treatment of inflammatory lung diseases. 25857284_Autoprocessing of neutrophil elastase near its active site reduces the efficiency of natural and synthetic elastase inhibitors. 25878251_PAR2 and TRPV4 are activated by neutrophil elastase to cause inflammation and pain 25893670_In patients with carotid plaques, both circulating and intraplaque polymorphonuclear neutrophils produce IL-8, VEGF and elastase, which are crucial for plaque development and progression. 25912133_mosaic mutations result in cyclic neutropenia 25956321_results suggest that elastase-like proteases in the microglial cells surrounding Abeta plaques are responsible for ApoE degradation in the brain. 26018813_Neutrophil elastase was increased in the saliva from COPD patients and additionally distinguished smoking status. 26174650_Paternal Somatic Mosaicism of a Novel Frameshift Mutation in ELANE Causing Severe Congenital Neutropenia. 26193632_Pathogenesis of ELANE-mutant severe neutropenia revealed by induced pluripotent stem cells. 26221769_Neutrophil elastase activity is deleterious for airway epithelial cell homeostasis. 26269588_analysis of the mechanistic link between neutrophil elastase expression in atherosclerotic plaques and concomitant pro-inflammatory bioactive IL-1beta secretion from endothelial cells 26372354_insights into the PPE and HNE inhibition 26444279_An increased NE: A1 AT ratio is closely associated with liver Inflammation in patients with NASH and could serve as a novel marker to predict NASH in humans 26567890_Different ELANE mutants show specific activation of different UPR pathways in congenital neutropenia. 26874351_Faecal biomarkers lactoferrin, calprotectin, and PMN-elastase were able to distinguish between ulcerative colitis patients with mucosal healing from clinical remission and mild disease, showed significant correlations with endoscopy, and were predictive of a flare. 26881964_The HNE-TACE signalling pathway has an important role in the process of MUC5AC overexpression in chronic rhinosinusitis. 26939803_The levels of both NE and PR3 correlated with absolute neutrophil counts and are reduced in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. 27035679_The results of the present study may indicate that NE activates the phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt signaling pathway in leukemia cells to inhibit apoptosis and enhance cell proliferation 27093231_Although circulating nucleosomes and elastase - alpha 1-antitrypsin complexes are at present the best characterized biomarkers for neutrophil extracellular traps formation and neutrophil activation, their lack of association with rs2288904 genotype does not exclude a role for SLC44A2 in neutrophil activation (and possibly NET formation) in Venous Thromboembolism. 27101808_Using different blood leukocyte and skin resident cell preparations, and recombinant proteins, the authors have identified that neutrophil elastase, but not other neutrophil derived proteases, cleaves IL-36Ra into its highly active antagonistic form. 27339896_In conclusion, site-specific CBG N-glycosylation regulates the bioavailability of cortisol in inflamed environments by fine-tuning the RCL proteolysis by endogenous and exogenous elastases. 27892542_PMN elastase is released by neutrophils in response to Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumolysin. 27935111_results suggest activation of elastase in tendinopathy of the long head of the biceps increases the degradation of elastin to increase the levels of elastase, becoming a vicious cycle to the progressive severity of tendinopathy 27942017_the impact of NE mutations that are typical of human congenital neutropenia in a murine model of in vitro and in vivo neutrophil differentiation 28004483_Our results suggest that associated serum levels of proMMP-9, NGAL, proMMP-9/NGAL and NE may reflect the state of systemic inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease related to cigarette smoking. 28073911_This study proposes that acquisition of CSF3R mutations may represent a mechanism by which myeloid precursor cells carrying the ELANE mutations evade the proapoptotic activity of the Neutrophil Elastase mutants in SCN patients. 28074935_Neutrophil elastase impaired the EMILIN1-alpha4beta1 integrin interaction by cleaving the gC1q domain in a region crucial for its proper structural conformation, paving the way to better understand NE effects on EMILIN1-cell interaction in pathological context. 28187039_Plasma Neutrophil Elastase and Elafin as Prognostic Biomarker for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. 28468826_Data suggest that neuropilin-1 (NRP1) functions as a receptor for neutrophil elastase (NE), mediates uptake/absorption of NE, and facilitates cross-presentation of PR1 (a peptide fragment of NE) in breast cancer cells. 28507169_The role of neutrophil elastase in the activation of unfolded protein response effector molecules via PERK and CHOP is reported. 28630087_Taken together, these observations support that the unusual HNE N-glycosylation, here reported for the first time, is involved in modulating multiple immune functions central to inflammation and infection. 28754797_Coincubation with the inhibitors, particularly MK0339, promoted cell survival and increased formation of mature neutrophils. These studies suggest that cell-permeable inhibitors of neutrophil elastase show promise as novel therapies for ELANE-associated neutropenia. 28888033_the effect of elastase on gammadelta T cells was mediated through the protease-activated receptor, PAR1, because the inhibition of this receptor with a specific antagonist, RWJ56110, abrogated the effect of neutrophils on gammadelta T-cell activation. 29046295_Suggest that free circulating elastase can serve as a new biomarker of inflammation and vascular complications in patients on chronic hemodialysis. 29624923_Neutrophil elastase correlates with increased sphingolipid content in cystic fibrosis sputum. These data suggest that NE may increase pro-inflammatory sphingolipid signaling, and the association is strengthened in female patients and patients with MRSA. 29767240_Munc134 mediates human neutrophil elastaseinduced airway mucin5AC hypersecretion by interacting with syntaxin2. 29976235_that NSPs play an important role in muscle inflammatory cell infiltration by increasing the permeability of vascular endothelial cells in IIM patients. 30056589_Results found that the neutrophil elastase is up-regulated in both overweight and obese subjects and associated with BMI and markers of cardiovascular disease. 30219097_High polymorphonuclear Elastase expression is associated with severe traumatic brain injury. 30343390_AGEs drive the effect of neutrophils on CD4(+) T cell differentiation into pro-inflammatory program through inducing MPO and NE productions in neutrophils, which is mediated by AGE-RAGE interaction. 30452386_Mass spectrometry confirmed the absence of neutrophil elastase (NE)-cleaved corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG) in plasma in which ELISA values were highly discordant. 30635825_Established the ELANE-mutated and non-mutated iPSCs. 30827416_the ability of an inflammatory protease, neutrophil elastase, to process the adherens junction protein E-cadherin to generate short peptide fragments with effects on epithelial function, is reported. 31009763_this study shows that two paternal mosaicism of mutation in ELANE causing severe congenital neutropenia exhibit normal neutrophil morphology and reactive oxygen species production 31362723_Neutrophil elastase is elevated in the sputum during exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 31466461_In HNE-induced CRS, miR-146a downregulates the expression of MUC5AC by inhibiting the activation of EGFR, and EGFR is a target gene of miR-146a. 31490025_A large-scale transcriptome analysis identified ELANE and PRTN3 as novel methylation prognostic signatures for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 31622584_alternative binding motif for human neutrophil elastase in EapH1 and EapH2 31626976_Evaluation of active neutrophil elastase in sputum of bronchiectasis and |
ENSMUSG00000020125 |
Elane |
21.157859 |
0.1421470667 |
-2.814544 |
0.453179840 |
42.402199 |
0.00000000007430644360568362446917652030682339796274771259732006001286208629608154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000387138407207868095238988798926366152741707082896027714014053344726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2219841 |
1.5048260 |
36.5955634 |
5.4589438 |
| ENSG00000197566 |
57547 |
ZNF624 |
protein_coding |
Q9P2J8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57547; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20453000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
21.773111 |
0.4461547167 |
-1.164384 |
0.361137715 |
10.403432 |
0.00125781308487641230869913400169934902805835008621215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002883709402419360780245316533410004922188818454742431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2932659 |
4.4108420 |
29.4306874 |
6.6456903 |
| ENSG00000197594 |
5167 |
ENPP1 |
protein_coding |
P22413 |
FUNCTION: Nucleotide pyrophosphatase that generates diphosphate (PPi) and functions in bone mineralization and soft tissue calcification by regulating pyrophosphate levels (By similarity). PPi inhibits bone mineralization and soft tissue calcification by binding to nascent hydroxyapatite crystals, thereby preventing further growth of these crystals (PubMed:11004006). Preferentially hydrolyzes ATP, but can also hydrolyze other nucleoside 5' triphosphates such as GTP, CTP and UTP to their corresponding monophosphates with release of pyrophosphate, as well as diadenosine polyphosphates, and also 3',5'-cAMP to AMP (PubMed:27467858, PubMed:8001561, PubMed:25344812, PubMed:28011303). May also be involved in the regulation of the availability of nucleotide sugars in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi, and the regulation of purinergic signaling (PubMed:27467858, PubMed:8001561). Inhibits ectopic joint calcification and maintains articular chondrocytes by repressing hedgehog signaling; it is however unclear whether hedgehog inhibition is direct or indirect (By similarity). Appears to modulate insulin sensitivity and function (PubMed:10615944). Also involved in melanogenesis (PubMed:28964717). Also able to hydrolyze 2',3'-cGAMP (cyclic GMP-AMP), a second messenger that activates TMEM173/STING and triggers type-I interferon production (PubMed:25344812). 2',3'-cGAMP degradation takes place in the lumen or extracellular space, and not in the cytosol where it is produced; the role of 2',3'-cGAMP hydrolysis is therefore unclear (PubMed:25344812). Not able to hydrolyze the 2',3'-cGAMP linkage isomer 3'-3'-cGAMP (PubMed:25344812). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P06802, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10615944, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25344812, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27467858, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28011303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28964717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8001561, ECO:0000305|PubMed:11004006}. |
3D-structure;Biomineralization;Calcium;Cell membrane;Diabetes mellitus;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Membrane;Metal-binding;Obesity;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Zinc |
|
This gene is a member of the ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (ENPP) family. The encoded protein is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein comprising two identical disulfide-bonded subunits. This protein has broad specificity and cleaves a variety of substrates, including phosphodiester bonds of nucleotides and nucleotide sugars and pyrophosphate bonds of nucleotides and nucleotide sugars. This protein may function to hydrolyze nucleoside 5' triphosphates to their corresponding monophosphates and may also hydrolyze diadenosine polyphosphates. Mutations in this gene have been associated with 'idiopathic' infantile arterial calcification, ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine (OPLL), and insulin resistance. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5167; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate binding [GO:0050656]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP diphosphatase activity [GO:0047693]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cyclic-GMP-AMP hydrolase activity [GO:0106177]; dinucleotide phosphatase activity [GO:0004551]; exonuclease activity [GO:0004527]; GTP diphosphatase activity [GO:0036219]; insulin receptor binding [GO:0005158]; nucleic acid binding [GO:0003676]; nucleoside triphosphate diphosphatase activity [GO:0047429]; phosphatase activity [GO:0016791]; phosphodiesterase I activity [GO:0004528]; polysaccharide binding [GO:0030247]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; UTP diphosphatase activity [GO:0036221]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate metabolic process [GO:0050427]; ATP metabolic process [GO:0046034]; biomineralization [GO:0110148]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; cellular phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0030643]; cellular response to insulin stimulus [GO:0032869]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; generation of precursor metabolites and energy [GO:0006091]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inorganic diphosphate transport [GO:0030505]; melanocyte differentiation [GO:0030318]; negative regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030502]; negative regulation of cell growth [GO:0030308]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of glucose import [GO:0046325]; negative regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045719]; negative regulation of hh target transcription factor activity [GO:1990787]; negative regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0046627]; negative regulation of protein autophosphorylation [GO:0031953]; nucleic acid phosphodiester bond hydrolysis [GO:0090305]; nucleoside triphosphate catabolic process [GO:0009143]; phosphate ion homeostasis [GO:0055062]; phosphate-containing compound metabolic process [GO:0006796]; regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030500]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; response to inorganic substance [GO:0010035]; sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0030730] |
11473061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11771660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11771660_The IVS15-14T --> C substitution in the human NPPS gene is associated not only with susceptibility to, but also with severity of OPLL. 11916943_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12126783_polymorphic in normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients 12147786_in type 1 diabetic patients, the ACE and the PC-1 genes interact in increasing the individual risk of having a faster diabetic nephropathy progression 12147787_Amino acid variant (K121Q) has no impact on progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients 12441313_Insulin modulates PC-1 processing and recruitment in cultured human cells.autophosphorylation. Insulin stimulates PC-1 posttranslational processing and translocation to the plasma membrane, which in turn impairs insulin receptor signaling. 12483464_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12483464_PC1 has a role in predisposition to early myocardial infarction 12547881_In healthy normoglycemic Finnish subjects, the K121Q polymorphism of the PC-1 gene is associated with insulin resistance but not with impaired insulin secretion or dyslipidemia. 12547881_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12715715_study suggests that both examined polymorphisms: the -308 G/A in the promoter region of TNF-alpha and K121Q amino acid variant of the PC-1 influence the development of insulin resistance as a prediabetic quantitative trait in a Polish population 12740448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12881724_Mutations in ENPP1 are associated with 'idiopathic' infantile arterial calcification. 14514598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14671192_PC-1 K121Q polymorphism associates with primary insulin resistance in migrant Asian Indians. High frequency of this polymorphism may be one factor contributing to insulin resistance susceptibility in Asian Indians. 15001634_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15001634_PC-1 Q121 allele is exceptionally prevalent in the Dominican Republic, contributing to both insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. 15045693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15126519_Interaction between the K121Q polymorphism of the PC-1 gene and birth length affects insulin sensitivity and increases susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and hypertension in adulthood 15374726_The K121Q polymorphism of the plasma cell membrane glycoprotein 1 gene is significantly associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) susceptibility. 15677494_Plays a role in insulin resistance and suggests that animals with overexpression of human PC-1 in liver may be interesting models to investigate insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. 15793263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793263_Our study supports the hypothesis that ENPP1 121Q predicts genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in both South Asians and Caucasians. 15802034_Increased lymphocyte PC-1 activity was associated with end-stage renal failure patients on haemodialysis 15834329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15834329_The IVS20-11delT variant of the NPPS gene and the A861G variant of the leptin receptor gene are associated with more extensive OPLL, but not with the frequency with which it occurs. 16025115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16186408_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16186408_ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1(ENPP1/PC-1) 121Q variant is associated with a progressive deterioration of the insulin resistance-atherogenic phenotype and earlier onset of type 2 diabetes and myocardial infarction 16207325_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16231022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16272817_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16272817_The K121Q polymorphism of the plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 (PC-1) gene is unlikely to be a major genetic factor predisposing to preeclampsia in Finnish women. 16278247_Overexpression of ENPP1 induces insulin resistance and hyperglycemia. 16527214_Analysis of the DNA variations of ENPP1 provides a first molecular basis for the physiopathologic association between severe insulin resistance and obesity, and further type 2 diabetes. 16527214_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16607460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16607460_the K121Q variant of the ENPP1 gene has very little, if any, impact on type 2 diabetes (T2D) susceptibility in Japanese, but may play a role in the inter-ethnic variability in insulin resistance and T2D 16609882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16865358_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16865358_the ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism does not seem to influence the risk of insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes in Danish white subjects; however, a meta-analysis of the present and published studies demonstrates evidence of association with type 2 diabetes 16936213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16936213_we found a new SNP, rs997509, in intron 1 that is strongly associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in obese individuals. 16941279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16968801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16968801_role of the K121Q polymorphism or derived ENPP1 haplotypes in increased susceptibility to obesity and early impairment of glucose and insulin metabolism in children. 17026496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17026496_a significant association of PC-1 K121Q with obesity 17043047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065358_No evidence that previously associated variants of ENPP1 are associated with type 2 diabetes or obesity in the U.K. population. 17065358_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17065359_No association with three variants and body mass index or type 2 diabetes. 17065359_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17129580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17129580_PC-1 (ENPP1) 121Q allele is associated with the genetic susceptibility for metabolic syndrome in patients with coronary heart disease 17143316_Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase 1 as a 'gatekeeper' of insulin receptors. 17192490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17228024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17287921_There is a lack of correlation between genetic expression of ENPP1 and body mass index. This may suggest that glucose metabolism is more complex than lipid metabolism. 17367703_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17491709_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17493546_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17493546_THE 121Q allele frequency may contribute to increased susceptibility to type 2 diabetes observed in US minority groups. 17563456_Overexpression of ENPP1 in insulin target tissues is an early, intrinsic defect observed in human insulin resistance 17606264_functional interactions between alkaline phosphatase and ENPP1(PC-1) may link insulin resistance to vascular calcification. 17704904_Nominal evidence of association between the K121Q polymorphism and both severe adult obesity at baseline and risk of hyperglycaemia or type 2 diabetes . 17704904_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17719609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17848394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986276_Our results suggest that the ENPP1121Q allele might contribute to the genetic susceptibility to abdominal obesity among subjects with MS. 18071025_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18071025_The ENPP1 Q121 variant increases risk of type 2 diabetes under a recessive model of inheritance in whites, an effect that appears to be modulated by body mass index. 18176722_K121Q polymorphism is more common among Afro-Brazilian descendants regardless of glycemic status or insulin sensitivity indices. Likewise, insulin sensitivity and DM chronic complications appear not to be related to the polymorphism in this sample. 18176722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18184924_Variants in the distal region of the ENPP1 gene may contribute to diabetes or diabetic nephropathy susceptibility in African Americans. 18222177_Results describe the activities of ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase and adenosine deaminase in patients with uterine cervix neoplasia. 18389334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18389334_Report association between K121Q polymorphism of ENPP1 and peripheral arterial disease. 18426862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426862_The Q allele of ENPP1 K121Q is associated with hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in whites. 18464750_ENPP1 is a genetic determinant of obesity-related phenotypes in a Mexican American population with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 18464750_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18498634_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18551113_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18551113_Results did not find association between the frequently studied ENPP1 K121Q variant, nor SNPs in the MCR or POMC genes and obesity or type 2 diabetes. 18583883_ENPP1 121Q genotype (KQ+QQ types) was not associated with type 2 diabetes (odds ratios [OR], 0.854; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.571-1.278) or obesity (OR, 0.933; 95% CI, 0.731-1.190) in South Korea 18583883_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18657335_ENPP1-121Q is involved in the genetic susceptibility of type 2 diabetes in the Tunisian population. 18664022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18664022_The prevalence of the PC-1 121Q allele was significantly higher in type 2 diabetic patients who suffered from CHD, compared to type 2 diabetic patients without CHD. 18690303_Ecto-nucleotide pyrophophastase/phosphodiesterase 1 polymorphism has no association with PCOS. 18690303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18719658_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18719658_Variants of ENPP1/PC-1 are associated with obesity in the male Turkish population; thus, these variants may contribute to the development of the obesity in these individuals. 18776139_Homozygous carriers of the ENPP1 Q121 variant are characterized by an altered glucose homeostasis 18776139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18823720_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18940878_ENPP1 rs997509T allele can predispose obese children to MS and IGT and that this variant might drive the association between the ENPP1 121Q allele and insulin resistance. 18940878_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18948963_ENPP1 single nucleotide polymorphism variant may protect against overweight and obesity in Italian chidren. 18948963_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18950909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18950909_Our data suggest that patients with type 2 diabetes carrying the ENPP1 Q121 variant are at increased risk of decreased GFR. 19017751_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19017751_ENPP1 K121Q is associated with increased diabetes incidence; the DPP lifestyle intervention eliminates this increased risk. 19046915_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19046915_There is an association of K11Q polymorphism in ENPP1 and type 2 diabetes and obesity in a Moroccan population. 19056482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19083193_Data suggest that HSP70, by affecting ENPP1 expression, may be a novel mediator of altered insulin signaling. 19086938_The investigators found evidence of an association between a polymorphism in the ENPP1 gene and the development of generalized arterial calcification of infancy that led to the death of the infant. 19107338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19107338_The K121Q variant of ENPP1 may be associated with hepatitis C viremia and core antigen levels in HCV carriers 19206175_Generalized arterial calcification of infancy is characterized by calcification of the major arteries and soft tissues and is aassociated with mutations in the ENPP1 gene. 19368707_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19374858_Inhibition of insulin signaling by PC-1 is somewhat specific and is dependent upon the enzymatic activity of the phosphodiesterase/pyrophosphatase. 19399648_K121Q, rs7566605, and rs894160 are not major contributing factors for obesity for ENPP1, INSIG2 and PLIN 19399648_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19403348_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19420105_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19506043_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19506043_epistatic effects of five candidate genes, including ADIPOQ, ENPP1, GHSR, PPAR and TCF7L2, are significantly associated with the risk of DN amongst Taiwanese T2D individuals. 19577557_Suppression of PC-1 expression improves insulin sensitivity in vitro and in an animal model of diabetes 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19643578_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19656007_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19656007_genetic variants of the ENPP1/PC-1 gene are associated with hypertriglyceridemia in male subjects, and may contribute to the development of the insulin resistance/metabolic syndrome in this population 19679831_ENPP1 Q121 variant is associated with increased pulse pressure in vivo and reduced insulin signaling and endothelial dysfunction in vitro 19679831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19876004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888898_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19888898_found evidence for association of bone geometry variation with an SNP in ENPP1, a gene in the mineralization pathway. The alteration of a binding site of the deregulator of extracellular matrix HOXA7 warrants further investigation 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19931660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20015201_NPP1 is down-regulated in calcified advanced plaques. NPP1 levels are higher in severely calcified lesions, most likely reflecting a counter-active mechanism. NPP1 serves as a novel player orchestrating plaque calcification. 20016754_ENPP1 coding region mutations are associated with generalized arterial calcification of infancy. 20091022_ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism determines individual susceptibility to the insulin-sensitising effect of lifestyle intervention 20091022_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20092902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20092902_Our study demonstrates that the ENPP1 K121Q and MMP3 -709A>G polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes, and that the ENPP1 Q allele is associated with increased aortic arch calcification in a Korean population. 20137772_The identification of an inactivating mutation in the ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1) gene causing autosomal-recessive hypophosphatemic rickets (ARHR) with phosphaturia, is demonstrated. 20137773_ENPP1 is the fourth gene-in addition to PHEX, FGF23, and DMP1-that, if mutated, causes hypophosphatemic rickets resulting from elevated FGF23 levels. 20176643_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20186155_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200332_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20231843_Associations were observed between ENPP1 polymorphisms and BMI (P=0.0037) and leptin (P=0.0068). 20231843_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20428609_No association was found between polymorphism K121A of ENPP1 gene and the presence of ischemic heart disease. 20428609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20446819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20446819_findings suggest that the upstream, promoter and 3' untranslated regions in the ENPP1 locus harbor genetic variants affecting different aspects of craniofacial morphology 20503258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20709678_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20709678_association of ENPP1 K121Q with type 2 diabetes in Hubei Han Chinese population is more evident in women. 20820885_ENPP1/PC-1 K121Q polymorphism is not associated with type 2 diabetes and related quantitative metabolic traits in North Indian Punjabi population. 20958205_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20958205_The specific role of ENPP1 K121Q on ethnic susceptibility to PTDM deserves further investigation in larger cohorts of transplanted patients. 20981035_K121Q of ENPP1 might not have a major role in the susceptibility to T2 diabetes mellitus or obesity in the Chinese Han population. 20981035_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21076580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21153685_The ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is not associated with type 2 diabetes and related metabolic traits in an Iranian population. 21162834_ENPP1 gene polymorphism rs1409181 was associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in older Chinese people in Guangzhou. 21195542_A correlation is found between the up-regulated expression of NPP1 and the grade of the astrocytic tumor 21198320_We confirmed the association between the rs1044498 SNP in ENPP1 and diabetic nephropathy, especially among obese diabetic patients, in the Taiwanese population. 21282363_The ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is an independent predictor of major cardiovascular events in high-risk individuals. In type 2 diabetes, this effect is exacerbated by obesity. 21452007_The ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is not associated with type 2 diabetes in the northern Chinese population. 21565692_The results from the present study have indicated that ENPP1/PC1 Q121 variant may increase the risk of obesity. 21573217_Data clearly indicate that ENPP1, especially when the Q121 variant is operating, affects insulin signaling and glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle- and liver-cells. 21602183_ESRD patients with left ventricular hypertrophy is consistently associated with genetic variability of ENPP1 gene in caucasian patients. 21647535_PC-1 2906C allele was significantly more frequent in patients who suffered from stroke before the age of 40 years. In these patients the risk for ischaemic stroke was increased four-fold. 21738662_Data identified two key mediators of vascular calcification and bone metabolism, ENPP1 and OPG, which offer a molecular explanation for the major phenotypic differences in vascular and bone disease in sporadic and hereditary HGPS. 21810932_In the presence of a high-fat diet, ENPP1 overexpression in adipocytes induces fatty liver, hyperlipidemia, and dysglycemia, thus recapitulating key manifestations of the metabolic syndrome. 22136912_In the Chinese population, the ENPP1 K121Q gene polymorphism was implied to be involved with type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility 22209248_ABCC6 mutations accounted for a significant subset of generalized arterial calcification of infancy patients, and ENPP1 mutations could also be associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum lesions in school-aged children. 22231969_K121Q polymorphism of the ENPP1 gene seems to be associated with insulin resistance and diabetic nephropathy development. 22327785_no association of PC-1 Gln121 gene found with obesity in Amerindians; PC-1 Gln121 gene is associated with higher levels of HDL-cholesterol than PC-1 Lys121 allele; Amerindians have intermediate frequency of PC-1 Gln121 gene compared with African Americans or Han Chinese 22366713_A genetic polymorphism in the intron 9 of the ENPP1 gene was associated with calcific aortic valve disease in a case-control cohort as well as with mRNA expression levels of ENPP1 in aortic valves. 22402064_Individuals carrying the ENPP1 Q121 variant are highly responsive to the effect of weight loss on fasting glucose so the Q121 variant interacts with adiposity in modulating glucose homeostasis. 22484154_Human phosphodiesterase 1 is regulated by a tandem of N-terminal calmodulin/Ca(2+)-binding domains. 22826605_Our results establish PCA-1/ALKBH3 as important gene in pancreatic cancer 22842219_NPP1 is known to play vital roles in calcium/phosphate regulation, and repression of soft tissue mineralisation, as well as maintaining skeletal structure and function. 22846899_The expression of ENTPD1 and ecto-adenosine deaminase in lymphocytes of Chagase disease patients are reported. 22899099_the ENPP-1 Q121 variant plays a role in modulating the risk of premature atherosclerotic events, particularly in obese individuals 23012391_Increased adipose tissue ENPP1 is associated with adipose tissue dysfunction, increased liver triglyceride deposition, and systemic insulin resistance in young normoglycemic men. 23111648_ENPP1 (and PLIN) genes contribute to the risk of type 2 diabetes in a Taiwanese population. 23122642_Mutations in the underlying disease genes ENPP1, ABCC6, NT5E, and SLC20A2, respectively, lead to arterial media calcification. 23422753_mutation in GOLGB1 (Y1212C) and another mutation in ENPP1 (K173Q) were confirmed as having significant associations with a decreased risk for stroke 23433854_Platelets and serum E-NPP1 activity increased in prostate cancer patients. 23451554_The findings suggest that ENPP1 polymorphisms may contribute to different metabolic characteristics, all of which are associated with insulin resistance in mixed ancestry children of South Africa. 23861746_these data suggest a potential role for Enpp1 in the development of breast cancer bone metastasis. 24075184_Biallelic mutations in ENPP1 were shown to underlie a number of recessive conditions characterized by ectopic calcification. 24222241_Specific genotypes of the NPP1 gene IVS20-11delT and A533C SNPs may predict ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament disease outcome after surgical intervention. 24242286_The mutant homozygous genotype of ENPP! K121Q, was more prevalent in diabetic hypertensive MI patients than it was among non-diabetic normotensive MI patients. 24338010_The combined studies expand our understanding of NPP1 and NPP4 substrate specificity and range and provide a rational mechanism by which polymorphisms in NPP1 confer stroke resistance. 24371178_The ENPP1 K121Q gene polymorphism is associated with insulin resistance in an obese North Indian population. 24531536_these results reveal that E-NPP1, by acting upstream of E2F1, is indispensable for the maintenance of glioblastoma stem-like cells in vitro and hence required to keep GSCs in an undifferentiated, proliferative state. 24947519_Both NPP1 and NPP3 ectoenzymes are expressed in N2a cells, their levels dramatically changing when cells differentiate into a neuronal-like phenotype 25025693_Polymorphisms in ALP, ENPP1 and ANKH are important genetic risk factors contributing to Pseudoxanthoma elasticum 25109753_findings show the Q allele of the ENPP1 K121Q gene may contribute to the susceptibility for type 2 diabetes in Caucasians and Asians 25222839_In pregnant women, association of both pre-gestational BMI and age with AA homozygous ENPP1 genotype increased significantly the risk of positive oral glucose tolerance test. 25231727_EphA3 was induced by PC-1 and contributed to the malignant progression of prostate cancer 25344812_ENPP1 2'3'-cGAMP-hydrolyzing activity is repsonsible for tumor progression in humans and mice. 25368487_the ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is associated with insulin resistance during web-based lifestyle intervention, and the K121 allele has a beneficial effect of weight loss on insulin resistance. 25504209_patterns were confirmed in human teeth, including widespread TNAP, and NPP1 restricted to cementoblasts lining acellular cementum 25594612_ENPP1 rs1805101 polymorphism is associated with Insulin resistance and advanced Diabetic nephropathy. 25615550_this study identified only 1 mutation in ENPP1 in the Chinese pseudoxanthoma elasticum population 25644539_Expression of NPP1 and 5'-nucleotidase by valve interstitial cells promotes the mineralization of the aortic valve through A2aR and a cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway. 25741938_Loss of function mutation in ENPP1 is associated with early onset hearing loss in autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets. 25794151_The present meta-analysis detected a significant association between the ENPP1K121Q polymorphism and increased susceptibility of diabetic kidney disease in European and Asian populations. 26065921_ENPP1 was also identified as a substrate of the 26S proteasome, the activity of which is downregulated in CSCs 26405014_we found that patients with severe asthma exacerbation had reduced activity of leukocyte ectonucleotidases and reduced expression of E-NPP1 in PMNs. 26617416_Results suggest that heterozygous mutations in the SMB domains of ENPP1 are necessary, but not always sufficient in themselves to cause Cole disease. 26868433_In this exploratory analysis, IRS1, ENNP1 and TRIB3, known to be associated with type 2 diabetes and harboring genes playing a prominent role in mediating insulin signaling, may modulate a number of cardiometabolic phenotypes in patients of Italian ancestry with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes. 26958016_Our findings demonstrate that ENPP1, TCF7L2, and FTO may predispose to T2DM in the mixed-ancestry population. 27029882_A rare type of idiopathic infantile arterial calcification resulting from a mutation in the gene encoding for the ENPP1 enzyme. 27029896_ENPP1 defines a subset of human B cells that differs significantly from mouse peritoneal B-1a and proposed human B-1 cells. 27219689_The K121Q polymorphism of ENPP1 shows no direct correlation with metabolic syndrome in Han Chinese. 27238374_The ENPP1 rs1044498 SNP is associated with T2D. 27467858_Results identified four mutants (p.Tyr471Cys, p.Ser504Arg, p.Tyr659Cys, p.His777Arg) in ENPP1 gene with residual NPP activity, inorganic pyrophosphate generation and plasma membrane localization. 27519661_We have identified TT genotype of SNP rs858339 (ENPP1 gene) as a protective factor against TMD in a population of patients with dentofacial deformities. 27835608_PC-1 works in conjunction with E3 ligase CHIP to regulate androgen receptor stability and activity. 28011303_study provides rational and meaningful explanations of the substrate promiscuity of NPP1 by combining biochemical and molecular docking data; biochemical data provide detailed information including all relevant kinetic parameters of NPP1 obtained for a broad range of natural nucleotides and an artificial substrate 28080219_Evidence of a causative link between ENPP1 and alterations in insulin signaling, glucose uptake, and lipid metabolism in subcutaneous abdominal Adipose tissue of gestational diabetes, which may mediate insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in Gestational diabetes. 28381371_This study identifies the genetic variant rs9373000 as a potentially causal variant for mandibular condyle geometry variation for patients presenting with dento-facial deformities. 28415752_these results show that ENPP1 polymorphism influences lower anterior face height, the distance from the upper lip to the nasal floor, and lip shape 28942038_Single nucleotide polymorphism in ENPP1 gene is associated with developing of bone disorders in type 2 diabetes. 28951309_Single nucleotide polymorphism in ENPP1 gene is associated with Gender differences in type 2 diabetes. 28964717_Study concludes that germline ENPP1 cysteine-specific mutations, primarily affecting the melanocyte lineage, cause a clinical spectrum of dyschromatosis, in which the p.Cys120Arg allele represents a recessive and more severe form of Cole disease. 29103441_We investigated whether ENPP1 gene which contribute to sagittal and vertical malocclusions also contribute to facial asymmetries and temporomandibular disorders before and after orthodontic and orthognathic surgery treatment 29194839_this study shows that ENPP1 is biomarker candidate for endometriosis 29244957_This study for the first time analyzed the effect of decreased PPi on dental development in individuals with generalized arterial calcification of infancy (GACI) due to loss-of-function mutations in the ENPP1 gene.These findings reveal a novel dental phenotype in GACI and identify ENPP1 genetic mutations associated with hypercementosis. 29783211_ENPP1 rs997509 polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus development in Ukrainian population. 29958952_ENPP1 gene variants may have a potential impact on the occurrence of T2 diabetes mellitus in Northern Iranians. 29979387_This meta-analysis revealed that the K121Q (rs1044498 C > A) in the ENPP1 gene is a risk factor for Coronary Heart Disease. 30099416_ENPP1 K121Q polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Ukrainian population. In carriers of the minor Q-allele the risk of T2DM is 1.4x higher than in homozygotes in the main K-allele. The risk increases in patients with BMI >/= 25 kg/m2 30188771_These studies demonstrate the cooperative metabolism between diadenosine triphosphate and ENPP1 function to provide a significant source of adenosine, subserving its role in inflammatory resolution. 30356045_Findings provide insights into how ENPP1 hydrolyzes both ATP and cGAMP to participate in the two distinct biological processes. 30799235_The ENPP1 is well known for its role in regulating skeletal and soft tissue mineralization. It primarily exerts its function through the generation of pyrophosphate, a key inhibitor of hydroxyapatite formation. 30985656_Pilot study examined 3 candidate genes, ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (ENPP1), ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 6 (ABCC6), and 5'-Nucleotidase Ecto (NT5E) involved in pyrophosphate (PPi) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) metabolism, which may predispose to coronary arterial or valvular calcification; report 4 new genetic variants potentially related to coronary calcification. 31250990_The first-ever report about the genotype of PC-1 gene in a Pakistani Punjabi population indicates that the PC-1 rs1044498 (K121Q) polymorphism was not found associated with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. 31318911_The aim of this study was t |
ENSMUSG00000037370 |
Enpp1 |
32.066341 |
5.0139880183 |
2.325959 |
0.402358391 |
35.416901 |
0.00000000266167284256644469716263423967293755278973321765079163014888763427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000012246350111060076497610361965368008796417598205152899026870727539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
63.1737403 |
15.0706333 |
12.6800785 |
2.6888237 |
| ENSG00000197599 |
645811 |
CCDC154 |
protein_coding |
A6NI56 |
|
Coiled coil;Endosome;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in bone mineralization involved in bone maturation. Predicted to act upstream of or within bone resorption; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth; and tooth eruption. Predicted to be located in early endosome. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:645811; |
early endosome [GO:0005769]; bone mineralization involved in bone maturation [GO:0035630]; bone resorption [GO:0045453]; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth [GO:0042475]; tooth eruption [GO:0044691] |
22895184_CCDC154 is a novel osteopetrosis-related gene involved in cell cycle regulation and tumor suppression growth. |
ENSMUSG00000059562 |
Ccdc154 |
13.021533 |
0.1894445400 |
-2.400153 |
0.554523614 |
19.550780 |
0.00000979607145701318260042327751291324489102407824248075485229492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000030705036038546311275617556324490919905656483024358749389648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3895551 |
1.6586201 |
23.5949633 |
4.9476368 |
| ENSG00000197635 |
1803 |
DPP4 |
protein_coding |
P27487 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface glycoprotein receptor involved in the costimulatory signal essential for T-cell receptor (TCR)-mediated T-cell activation (PubMed:10951221, PubMed:10900005, PubMed:11772392, PubMed:17287217). Acts as a positive regulator of T-cell coactivation, by binding at least ADA, CAV1, IGF2R, and PTPRC (PubMed:10951221, PubMed:10900005, PubMed:11772392, PubMed:14691230). Its binding to CAV1 and CARD11 induces T-cell proliferation and NF-kappa-B activation in a T-cell receptor/CD3-dependent manner (PubMed:17287217). Its interaction with ADA also regulates lymphocyte-epithelial cell adhesion (PubMed:11772392). In association with FAP is involved in the pericellular proteolysis of the extracellular matrix (ECM), the migration and invasion of endothelial cells into the ECM (PubMed:16651416, PubMed:10593948). May be involved in the promotion of lymphatic endothelial cells adhesion, migration and tube formation (PubMed:18708048). When overexpressed, enhanced cell proliferation, a process inhibited by GPC3 (PubMed:17549790). Acts also as a serine exopeptidase with a dipeptidyl peptidase activity that regulates various physiological processes by cleaving peptides in the circulation, including many chemokines, mitogenic growth factors, neuropeptides and peptide hormones such as brain natriuretic peptide 32 (PubMed:16254193, PubMed:10570924). Removes N-terminal dipeptides sequentially from polypeptides having unsubstituted N-termini provided that the penultimate residue is proline (PubMed:10593948). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10570924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10593948, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10900005, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10951221, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11772392, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14691230, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16254193, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16651416, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17287217, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17549790, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18708048}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human coronavirus MERS-CoV-2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23835475}. |
3D-structure;Aminopeptidase;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Membrane;Protease;Receptor;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The DPP4 gene encodes dipeptidyl peptidase 4, which is identical to adenosine deaminase complexing protein-2, and to the T-cell activation antigen CD26. It is an intrinsic type II transmembrane glycoprotein and a serine exopeptidase that cleaves X-proline dipeptides from the N-terminus of polypeptides. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is highly involved in glucose and insulin metabolism, as well as in immune regulation. This protein was shown to be a functional receptor for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and protein modeling suggests that it may play a similar role with SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2020]. |
hsa:1803; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; intercellular canaliculus [GO:0046581]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; aminopeptidase activity [GO:0004177]; chemorepellent activity [GO:0045499]; dipeptidyl-peptidase activity [GO:0008239]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; serine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008236]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; behavioral fear response [GO:0001662]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; endothelial cell migration [GO:0043542]; glucagon processing [GO:0120116]; locomotory exploration behavior [GO:0035641]; membrane fusion [GO:0061025]; negative regulation of extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0010716]; negative regulation of neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0090024]; peptide hormone processing [GO:0016486]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; psychomotor behavior [GO:0036343]; receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell [GO:0019065]; receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell [GO:0046813]; regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033632]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; T cell activation [GO:0042110]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] |
11739489_Soluble CD26 induces T cell proliferation in Antigen presenting cells 11773049_Intestinal dipeptidyl peptidase IV is efficiently sorted to the apical membrane through the concerted action of N- and O-glycans 11882590_DPPIV activity is depressed in individuals with hypertension during acute ACEI-associated angioedema. 11901152_Clustered charged amino acids of human adenosine deaminase comprise a functional epitope for binding the adenosine deaminase complexing protein CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV. 12023964_expression of the seprase-DPPIV complex is restricted to migratory cells involved in wound closure 12031601_Decrease of serum dipeptidylpeptidase activity in severe sepsis patients: relationship to procalcitonin. 12047913_chromogranin B(586-602) peptide can serve as a substrate for the lymphocyte surface glycoprotein CD26, also known as dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV), generating a new peptide ER-15 (CgB(588-602)) 12095981_DPIV mediated transcellular proteolysis 12112826_galectin-3 and CD26/DPPIV as preoperative diagnostic markers for thyroid nodules 12175726_CD26 interferes with transduction pathway(s) needed for the maturation of T cells and plays an important role in T lymphocyte homeostasis in peripheral blood. 12176563_examination of expression and enzymatic activity in recipients of kidney allografts 12213886_Involvement in extravillous trophoblast invasion and differentiation 12239451_Increased expression in human mesothelial cells by malignant ascites from ovarian carcinoma patients 12437097_REVIEW: expression and effects on immune cells 12471135_The process of CXCL12/SDF-1 alpha cleavage by CD26/DPPIV on a subpopulation of cord blood CD34+ cells represents a novel regulatory mechanism in hemopoietic stem and progenitor cells for the migration, homing, and mobilization of these cells. 12483204_The CD26 structure indicates how substrate specificity is achieved and reveals a new and unexpected opening to the active site. 12529175_catalytic properties and inhibition of this proline-specific enzyme 12579300_Review. CD26 has an essential role in human T-cell activation, as well as its ability to regulate the biological effects of selected chemokines through its DPPIV activity. 12595736_crystals of dipeptidylpeptidase IV belongs to the orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 118.04, b = 125.92, c = 136.84 A, and diffracts beyond 2.6 A resolution 12634639_Expressed in normal endometrial glandular cells, but expression in endometrial adenocarcinoma is down-regulated with increasing grade. Regulatory role in neoplastic transformation and progression of endometrial adenocarcinomas. 12646248_report the structure of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV especially focusing on a unique eight-bladed beta-propeller domain; discuss the way for the access of the substrate to this domain 12675218_an examination of the substrate specificity of this enzyme (REVIEW) 12675220_The active site of this enzyme is examined and compared with Porphyromonas gingivalis. 12675229_The kinetics of this enzyme are examined, after cloning in Pichia pastoris. 12675231_Protein-protein interactions dependent on this enzyme are investigated using surface plasmon resonance. 12675232_This protein acts synergistically with APN to regulate T cell function. 12675233_An increase in this enzyme is associated with graft rejection. Inhibition of this enzyme prevents kieney graft rejection. 12675238_plays a role in the digestion of an immunodominant epitope in celiac disease 12675243_This enzyme is expressed in cutaneous infiltrates from patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. 12675245_This enzyme is expressed in endometrial adenocarcinoma and is negatively correlated with tumor grade. 12675246_Adhesion to mesothelial is increased by overexpression of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. 12675247_This enzyme suppresses ovarian carcinoma in peritoneal dissemination in vitro and in vivo. 12675248_This enzyme is active in prostatic secretions and prostate cancer. 12675253_This enzyme is a marker of mood in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa patients. 12675254_Serum levels are decreased in patients with Crohn and inflammatory bowel disease who are clinically depressed. 12727530_elevated serum levels in chronic hepatitis C and other viral infections suggest that this activity originates not only from the liver, but also from other sources such as peripheral blood cells involved in the control of viral infections. 12767062_Increased adhesion of ovarian carcinoma cells to mesothelial cells by overexpression of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. 12820316_This enzyme is a marker in thyroid tumors. 12832764_structure of the binary complex with 1-[([2-[(5-iodopyridin-2-yl)amino]-ethyl]amino)-acetyl]-2-cyano-(S)-pyrrolidine has been solved, revealing the nature of the covalent interaction with the active-site serine 14525771_strong physical linkage of CD26 with CD45RA outside lipid rafts may be responsible for the attenuation of T-cell activation signaling through CD26 14691230_Glycosylation of DPPIV is not a prerequisite for catalysis, dimerization, or adenosine deaminase binding. 14718659_crystal structures of DPPIV in the free form and in complex with the first 10 residues of the physiological substrate, neuropeptide Y (residues 1-10; tNPY) 15002062_Plasma DPP-IV hyperactivity in the obese did not seem to be affected by the overweight degree. Selective DPP-IV inhibitors could represent an ideal approach to obesity management. 15016824_Adenosine deaminase binding is diminished by mutation of ADA residues known to interact with CD26. 15027119_DPPIV functions as a tumor suppressor, and its downregulation may contribute to the loss of growth control in NSCLC cells 15146553_CD26/DPPIV is likely to directly modulate various SDF-1alpha induced functions 15175333_the catalytic mechanism of dipeptidyl peptidase IV requires tyrosine 547 15213224_Crystal structure of CD26/dipeptidyl-peptidase IV in complex with adenosine deaminase 15215186_Adenosine down-regulates the surface expression of DPP4 on HT29 cells. 15292258_A mutant stromal cell derived factor-1 that does not interact with heparan sulsfate is readily cleaved by Dipepidtyl peptidase IV. 15323360_review of structure, function and tissue distribution of CD26 [review] 15353589_results suggest that CD26-caveolin-1 interaction plays a role in the up-regulation of CD86 on TT-loaded monocytes and subsequent engagement with CD28 on T cells, leading to antigen-specific T cell activation. 15375776_summarize key aspects of CD26/DPPIV involvement in tumor biology and its potential role in cancer development and behavior 15448155_identified the C-terminal loop as essential for dimer formation and optimal catalysis 15490304_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15540901_adult T-cell leukemia cells down-regulate CD26 antigens by means of epigenetic machinery; faintly detected transcripts of the gene were aberrantly methylated at the CpG islands within the promoter region in parallel with the advancement of ATL 15681827_decreased circulating CD26 levels in arthritis may influence CD26-mediated regulation of the chemotactic SDF-1/CXCR4 axis 15695814_HIV-1 Tat-derived nonapeptides Tat-(1-9) and Trp2-Tat-(1-9) bind to the active site of dipeptidyl-peptidase IV 15797249_analysis of substrate binding sites of human dipeptidyl peptidase-IV 15819895_comparison of the structure of X-PDAP from Lactococcus lactis (PepX) with its human counterpart DPP-IV 15864535_Chronic hyperglycaemia induces a significant increase in DPP-IV activity in type 1 and type 2 diabetes 15866709_The DAP IV from Pseudomonas sp. WO24 is expressed as 82 and 84-kDa isoforms, having two Met, Met-1 and Met-12, in its N-terminal sequence. 15911629_PLG has the potential to simultaneously regulate calcium signaling pathways and regulate pHi via an association with NHE3 linked to DPP IV, necessary for tumor cell proliferation and invasiveness 15985311_DPP-IV may play a role in converting endogenous beta-melanocortin MSH(5-22) to more potent peptides that regulate energy homeostasis in the hypothalamus. 16611738_Report shows that adenosine downregulation of DPPIV from the surface of colon cancer cells occurs independently of the classic receptors, and is mediated by a novel cell-surface mechanism that induces an increase in protein tyrosine phosphatase activity. 16621928_Results indicate that the adhesion mechanism by endometrial CD26 may be involved in human blastocyst implantation. 16700508_expression and function of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and related enzymes in cancer; upregulation is apparently accompanied by decreased proliferation or survival of glioma cells 16700520_Results describe dipeptidyl peptidase-IV activity in synovial fluid and plasma of patients with rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. 16700525_overexpression in HEK293 cells reduced cell adhesion, migration and invasion on ECM components, increased proliferation and promoted apoptosis, independently of enzyme activity 16704418_The dipeptidyl peptidase IV gene family contains the four peptidases dipeptidyl peptidase IV, fibroblast activation protein, dipeptidyl peptidase 8 and dipeptidyl peptidase 9. 16778789_Our data provide first evidence for a functional role of DP IV and APN in the sebaceous gland apparatus and for their inhibitors, used alone or in combination, as completely new substances possibly affecting acne pathogenesis in a therapeutic manner. 16781669_both wild HNF-1alpha and wild HNF-1beta have a stimulatory effect on DPP-IV gene expression, but that mutant hepatocyte nuclear factors (HNF)-1alpha and mutant HNF-1beta attenuate the stimulatory effect 16829852_The presence of dipeptidyl peptidase IV can be used to support diagnosis of deep penetrating nevi in doubtful cases. Loss of dipeptidyl peptidase IV may also be causally linked to the transition of invasive to metastatic phenotypes. 17071493_CD26 and cell surface adenosine deaminase are selectively expressed on ALK-positive, but not on ALK-negative, anaplastic large cell lymphoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma 17091451_DPP4 is increased in papillary thyroid cancer, however, its diagnostic usefulness as a single PTC marker is doubtfu 17244786_Levels in blood are suppresse after administration of vildagliptin to type 2 diabetics. 17270095_Significantly higher serum DPP IV and aminopeptidase N activities (P 10,000-fold selectivity for DPP-4. 18563594_degradation of CXCL12 by CD26/DPPIV may be involved in the metastatic cascades of Prostate cancer. 18595667_serum levels of soluble CD26 in patients with scleroderma; the DPPIV activity may be associated with fibrosis of the skin, lung, and other organs as a result of metabolic aberrations of collagen 18606664_findings demonstrate regulatory effects of DPPIV for the recruitment of eosinophils; furthermore, they illustrate that inhibitors of DPPIV have the potential to interfere with chemokine-mediated effects in vivo including but not limited to allergy 18682883_Genetic analysis does not support the notion that DPP4 polymorphisms could modulate the cardiovascular disease risk profile among obese patients. 18682883_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18708048_These results identify dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a novel lymphatic marker and mediator of lymphatic endothelial cell functions. 18820218_Increased plasma PAI-1 levels in CD36 deficiency may be due to abnormal fatty acids metabolism. 18940185_Effects on basal collagen metabolism following DPP4 inhibition in vivo are demonstrated and the amyloid peptide is identified as a novel DPP4 substrate. 18983807_Results indicate that the plasma levels of sCD26 and sCD30 are significantly higher in patients with non-healing form of CL than patients with healing form of CL or healthy control. 19024603_Differences of DPPIV level in esophageal carcinomas compared with normal epithelium showed that esophageal malignancies were associated with an increased amount of cell surface-bound DPPIV. 19061927_dipeptidyl peptidase IV serum level in diabetic patients serum level in diabetic patients 19153055_The ratio of ApoCI':ApoCI in plasma is determined by the activity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, DPP-IV (also known as the leucocyte antigen CD26), which was found to be elevated up to 3-fold in mucopolysacharidoses patients. 19247978_CD26 was absent in follicular and mantle cell lymphomas, high in multiple myelomas, hairy cell leukaemias, and variable in chronic lymphocytic leukaemias, in CD5(neg) B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative diseases and in diffuse large cell lymphomas. 19327104_REVIEW: clinical and preclinical studies 19358731_Selective inhibition of DPP-IV does not impair T dependent immune responses to antigenic challenge. 19459926_CD26 has a role in progression of B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia 19469710_results showed that the plasma DPPIV activity is significantly higher in leukemia patients 19632987_D6 cooperates with CD26 in the negative regulation of CCL14 by the selective degradation of its biologically active isoform. 19654580_CD26 expression on T cell lines increases SDF-1-alpha-mediated invasion. 19687096_CD26 is an endogenous inhibitor of T cell motility through inhibition of TSP-1 expression and chemokines stimulate cell polarity and migration through abrogation of the CD26-dependent inhibition 19734982_Report persistent expression of CD26/DPPIV after treatment with infliximab in psoriasis despite clinical improvement. (Letter) 19762327_Impaired recruitment of HHT-1 mononuclear cells to the ischaemic heart is due to an altered CXCR4/CD26 balance. 19811413_Decreased circulating number of iNKT cells and CD26 on iNKT cells can be important for the immunopathogenesis by exacerbating Th1-related inflammation in systemic lupus erythematosus 19817894_data suggest that FAP and DPP-IV are consistently expressed in bone and soft tissue tumour cells that are histogenetically related to activated fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts, irrespective of their malignancy. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19917055_DPPIV may be involved in the increased sensitivity to paclitaxel of epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC) cells regardless of the involvement of DPPIV activity. 20008019_Increased plasma DPP-4 activity in obesity is not associated with a generalized augmented incretin hormone metabolism. 20043068_DPP8 and DPP9 prevail over canonical DPP-IV/CD26 and FAPalpha in all examined meningioma patients 20075514_serum CD26 was related to non-inflammatory benign gastrointestinal tract pathologies (excluding rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, haemorrhoids, diverticula) and to inflammatory benign gastrointestinal tract pathologies. 20155839_central role for the serine protease activity of FAP and DPP-4/CD26 in protecting articular cartilage against invasion by synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis 20185737_Fasting DPP-IV levels do not appear to predict incident diabetes 20198559_The levels of both dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 and attractin in circulating monocytes were significantly higher in obese subjects as compared with levels in lean controls or in subjects with type 2 diabetes. 20361950_decreased presence of DPP-IV/CD26 in CD3+ fluid mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis 20455069_Hyperglycemia increased the DPP-4 activity only in microvascular endothelial cells but not in aortic endothelial cells. 20459800_Results support the pivotal role for DPP IV and neprilysin in the malignant transformation pathways of renal tumors and point to these peptidases as potential diagnostic markers. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20495958_The altered glycolipid composition in Fabry fibroblasts is associated with an intracellular accumulation and impaired trafficking of the Triton-X-100 DRM-associated membrane glycoprotein dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) in transfected Fabry cells 20520837_All three measurements of DPPIV/CD26 demonstrated potential as biomarkers for chronic fatigue syndrome . 20534982_The constitutive expression of DPIV mRNA and protein in chronic lymphocytic leukemia was demonstrated. 20569697_CD26-expression cells are responsible for tumor growth, metastasis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer 20572019_Results show unexpectedly that the DPPIV transmembrane domain dimerizes on its own and promotes dimer formation of the monomeric DPPIV in mammalian cells. 20584285_Low CD26 levels are associated with colorectal cancer and advanced adenomas. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20805868_serum DPP-4 activity should be considered as a novel liver disease biomarker 20828536_DPP-4 inhibition plays a pivotal role in endothelial growth and may have a potential role in the recovery of local circulation following diabetic vascular complications. 20841351_Core2 O-glycan structure is essential for expression of SI and DDP-IV during intestinal cell differentiation. 20847730_Higher DPP4 gene expression in VAT and its relationship with the plasma lipid profile may be explained by actually unknown DPP4 biological effect or, may also be a marker of VAT inflammation known to be associated with metabolic disturbances. 20878214_Loss of intracellular interleukin-16 in Sezary syndrome strongly corresponded to loss of surface CD26, which has been shown to occur with more advanced stage of CTCL. 20942971_The authors show for the first time that human-DPPIV and HIV1-Tat co-immunoprecipitate. 21108831_These results may suggest a novel role for CD26/DPPIV in protection against HIV infection in vivo. 21198750_effects of soluble human CD26 on human T-cell proliferation are mechanistically independent of both the enzyme activity and the adenosine deaminase-binding capability of soluble CD26 21281985_Increased frequency of breast cancer patients have been identified with higher serum DPPIV activity and decreased percentage of CD26+ white blood cells and decreased CD26 expression on lymphocytes. 21284881_Data show that CD26 mRNA and protein levels increase in a confluence-dependent manner in colon carcinoma cell lines, with c-Myc acting as a repressor and Cdx2 acting as an enhancer of CD26 expression. 21334743_Data suggest that the low serum activity of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV may be responsible for opioid-induced respiratory depression, induced by beta-casomorphin-7 in the general circulation. 21526345_the associated dynamics of DPP-IV and FAP gene expression in glioblastoma cells further argues in favor of their putative joint involvement in biological processes 21558160_DPPIV plays a significant role in modulating the actions of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in arterioles of young adult females; however, this role appears to diminish with age. 21593202_DPP4 is a novel adipokine that may impair insulin sensitivity in an autocrine and paracrine fashion. Furthermore, DPP4 release strongly correlates with adipocyte size, potentially representing an important source of DPP4 in obesity 21614532_CD26 expression may be associated in the regulation of DPP-IV in type 2 diabetes patients 21656024_Data suggest that high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a substrate of DPP4. (investigation of effects of proteolysis on function of HMGB1 in angiogenesis induction and antibody recognition of HMGB1 in plasma of subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus) 21672052_The up-regulation of CD26 in atopic dermatitis represents a new finding, which has also been seen in other inflammatory skin diseases; however, tissue expression of CD26/DPP4 in immunological skin response can either be beneficial or aggravating, depending on a possible Th1/Th2 shift 21674250_Investigated tumor-free neighboring stroma and tumor stroma in skin SCC as well as keratoacanthomas with respect to the presence of stromal CD34-positive fibrocytes, alpha-smooth muscle actin-positive myofibroblasts and expression of stromal CD26. 21785903_Higher serum DPP-4 activity and decreased CD26 lymphocyte expression on all lymphocyte subpopulations in T1DM. 21856036_[review] Recent studies clarify the interactions of DPPIV with adenosine deaminase (ADA) and transcription transactivator of the human immunodeficiency virus type (HIV) type-1 Tat. 21894438_Overexpression and localization of CD26 in mesothelioma tissue and mesothelioma cell lines 21917073_These findings hinted that CD26 may play a role in successful pregnancy and it is not an absolute surrogate marker for the Th1-type immunity as the dominant Th2-type immunity during pregnancy. 22001206_residues important for dimer formation and enzymatic activity 22062893_Because CD26 blood levels decrease rapidly after angioplasty, the enzyme could be considered an early marker of ischemia-reperfusion. 22086610_Concomitant CD26-positive and PTEN-negative status in cases of follicular adenoma suggests a state close to follicular carcinoma or further disease progression thus warranting careful follow-up. 22153807_A higher serum level of sCD26 is associated with a worse response to sitagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes controlled inadequately by metformin and/or sulfonylurea therapy. 22167343_Loss of DPP4 activity affects the anti-thrombogenic nature of the endothelium. 22179204_Hepatic DPP4 mRNA expression was significantly greater in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients than in control subjects. 22185679_Most lung tumor cells are deficient in DPP4 activity. 22261805_CD26 is a clinically significant biomarker for predicting response to chemotherapy for Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). 22369943_These results suggest that CD24 and CD26 differentially regulate the cancer stem cell potentials of malignant mesothelioma. 22382050_This study suggested that the involvement of the gene coding for DPPIV peptidase in predisposition to autism. 22388283_The urinary microvesicle-DPP IV level was positively correlated with urinary albumin/ creatinine ratio in type 2 diabetics. 22406180_an association between HbA1c and dipeptidyl peptidase IV activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus 22539793_Analysis of CD26 expression on different CD4+ T helper subsets shows that CD26 expression is highest on CD4+ T cells producing type 17 cytokines compared with T helper type (Th)1, Th2, and regulatory T cells. 22561447_DP4 is reduced in tissue and plasma in active Crohn's disease. 22648548_we report on up-regulation of dipeptidylpeptidase-IV in human brain gliomas 22674411_Higher plasma DPP4 was associated with better survival in all cancer types 22806538_decreased expression compromises T-cell recruitment in visceral leishmaniasis 22846168_suggests that clinical therapeutic benefit might be gained by using CD26 inhibitors as a strategy to improve engraftment of unfractionated mobilized peripheral blood cells as well as CB cells 22908963_lower serum activity and its expression on lymphocytes in patients with melanoma 22949266_Low expression of CD26 on human Treg cells makes it a specific negative selection marker for the positive identification of this type of cells. 22982114_Reduced CD26 expression is associated with improved cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction. 23035207_novel evidence shows the regulatory roles of DPP4 in chronic heart failure. 23063136_Elevated levels of serum DPP4 are identified in patients with severely decreased left ventricular ejection fractions, who received cardioverter/defibrillator implants. 23113658_CD26-mediated co-stimulation in human CD8(+) T cells provokes effector function via pro-inflammatory cytokine production. 23122333_A polymorphism in the DPP-IV gene in patients with known coronary artery disease may increase the risk of myocardial infarction 23160239_DPP4 cleaved within the N-termini of the colony-stimulating factor granulocyte-macrophage, G-CSF, interleukin-3 and erythropoietin and decreased their activity. 23184393_analysis of stem cell compartmentalization in humans led us to discover mechanisms of bone marrow unresponsiveness in diabetes determined by tissue-specific DPP-4 dysregulation. 23197976_DPP4 inhibition facilitated wound healing of chronic diabetic foot ulcers in type 2 diabetics. 23219738_Advanced glycation end products may up-regulate cellular DPP-4 expression and subsequently increase circulating levels of DPP-4 in humans. 23327927_We identified tissue-factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) as a biological inhibitor of CD26 in murine and human hematopoietic stem cells. 23382843_Our results demonstrate that combining a GPR119 agonist with a DPP-IV inhibitor may offer a novel therapeutic strategy for stimulating beta-cell regeneration and reversing diabetes. 23437290_Low baseline systemic concentrations of sCD26 predict favorable treatment outcome in chronic HCV infection and may be associated with higher blood counts of HCV-specific CD8(+) T cells. 23469960_immune disturbances that can occur in hematological malignancies might be related to the decrease in expression and activity of CD26/DPPIV that we observed. 23486063_identification of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4; also known as CD26) as a functional receptor for hCoV-EMC 23544270_DPP4 genetic variants influence baseline PSA levels, especially in men aged between 60 and 69. 23548652_Secondary benefits in addition to efficacy may make GLP-1 agonists and DPP-4 inhibitors a more favorable option than other second-line T2DM therapies. 23575259_Data suggest that hospital discharge with high DPP IV levels in plasma (highest quartile) after acute episode of heart failure is associated with approximately 3-fold higher risk of 6-month death due to heart failure. 23586735_Studies indicate that SDF-1a is rapidly inactivated by DPP-4-mediated cleavage, inhibition of this enzyme presents an alternative strategy of augmenting local SDF-1a bioactivity. 23603488_The V-shaped structure formed by the first two alpha-helices in the extended loop of the EMC human coronavirus S-receptor binding domain deeply inserts into the interface of DPP4 dimer. 23608773_DPP4 was found in endothelial cells of carotid atherosclerotic plaque. 23638030_interaction with nuclear CD26 and POLR2A gene 23654079_There is the association between high levels of soluble serum CD26 and CD30 and disease severity. 23677473_These results indicate that DPPIV functions as a chemorepellent of human and mouse neutrophils 23686701_Combined expression of CD10/CD26 had a better prognostic value than other features. 23805228_CUX-1 overexpression enhanced TNF- production on sCD26/LPS stimulation, while CUX-1 depletion had no effect. Neither CUX-1 overexpression nor CUX-1 depletion had an effect on IL-6 stimulation. These results are discussed in the context of a model that describes the mechanisms by which stimulation of monocytic cells by sCD26 and LPS leads to elevation of TNF- and IL-6 expression. 23880984_our results demonstrate major differences in DPP4 expression pattern in human and cynomolgus monkey skin. non-human primates studies aiming at understanding DPP4 function in skin biology are not readily translatable to human. 23894014_Circulating DPPIV activity is associated with poorer cardiovascular outcomes in heart failure. 23948634_DPP-IV enzymatic activity is significantly decreased in plasma from unipolar depression. 23984879_AGE-RAGE-induced oxidative stress stimulates the release of endothelial cell DPP-4, which could in turn act on ECs directly via the interaction with M6P/IGF-IIR, further potentiating the deleterious effects of AGEs. 24067970_The main regions of CD26 for binding to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus appear to be close to aa 358. 24099410_An excessive activity of circulating DPP4 is independently associated with subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in type 2 diabetics. 24130353_DPP4, a novel adipokine, has a higher release from VAT that is particularly pronounced in obese and insulin-resistant patients. 24180670_CD26 expression on T-anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) line Karpas 299 is associated with increased expression of versican and MT1-MMP and enhanced adhesion. 24257613_ADA acts as a natural antagonist for DPP4-mediated entry of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. 24342026_Review of the molecular basis of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor binding domain-receptor interaction and its complex with dipeptidyl peptidase 4. 24362726_Variation at the DPP4 locus is associated with ApoB in South Asians and displays heterogeneity related to BMI in other ethnicities. 24379520_DPPIV and other cytosolic peptidases may be involved in the development of thyroid cancer. 24412911_lower sDPP4 concentration and DPP activity might drive biased chemokine effects and highlight a novel role of this molecule in MS pathophysiology. 24466195_High CD26 expression is associated with enhancement of invasive potential of malignant mesothelioma. 24481594_The electrostatic and van der Waals interactions of the five inhibitors with DPP-4 are analyzed and discussed. The computed binding free energies using MM-PBSA method are in qualitatively agreement with experimental inhibitory potency of five inhibitors 24582858_The measurement of serum DPP-IV enzyme activity can be used complementary to the urinary GAG/Cre ratio for first-line mucopolysaccharidosis screening 24647445_DPP4 activity is an important predictor of the onset of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in apparently healthy Chinese men and women. 24743707_this study shows that CD26 is associated with SSTR4 in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells, and this interaction inhibits SSTR4-mediated cytostatic effects. 24747072_upregulation of periostin expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma cells results from the nuclear translocation of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor Twist1, a process that is mediated by CD26-associated activation of Src phosphorylation 24778155_Data indicate that dipeptidylpeptidase IV (CD26) is a biomarker and target of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cell. 24782177_DPP4, CDK5RAP2, and CCR6 are risk loci for rhe |
ENSMUSG00000035000 |
Dpp4 |
6.786582 |
0.1986657829 |
-2.331585 |
0.658308208 |
14.704907 |
0.00012571880477599519840802011483305022920831106603145599365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000341230150513734651913227979846965354226995259523391723632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6578930 |
1.2487013 |
13.4623695 |
3.1943769 |
| ENSG00000197646 |
80380 |
PDCD1LG2 |
protein_coding |
Q9BQ51 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the costimulatory signal, essential for T-cell proliferation and IFNG production in a PDCD1-independent manner. Interaction with PDCD1 inhibits T-cell proliferation by blocking cell cycle progression and cytokine production (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Involved in negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation; negative regulation of interferon-gamma production; and negative regulation of interleukin-10 production. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in external side of plasma membrane. Biomarker of pulmonary tuberculosis. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80380; |
endomembrane system [GO:0012505]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0046007]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042130]; negative regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032689]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295] |
12538684_Blockade of PD-L2 during T cell responses initiated by allogenic dendritic cells increases T cell proliferation and cytokine production, showing that PD-L2 functions to inhibit T cell activation. 12893276_Binding properties of B7-DC to programmed death-1. 14515261_regulatory role of PD-1 and the differential roles of B7-H1 and B7-DC in hapten-induced immune responses. 14724428_Administration of anti-PD-L2 mAb did not significantly affect the prolongation of graft survival. 15253154_Two novel splice variants of PD-L2 were cloned and identified. 15837746_Data suggest that PD-L2 status may be a new predictor of prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer. 16278812_Via its interaction with programmed death-1 (PD-1) on human T cells, PD-L2 acts only as a negative regulator of T cell activity, inhibiting proliferation, IL-2 production, and IFN-gamma production. 16598819_PD-L2 negatively regulates human T cell activation and thus might be a candidate molecule for immunotherapeutic approaches aimed to attenuate pathological immune responses. 17136123_data do not support an association between systemic lupus erythematosus and SNP's within the genes of the PDCD1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 17203303_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17311651_Modulation of PD-L2 system may play a role in the development of autoimmune liver diseases. 17343323_PD-L2 47103 T may be associated with susceptibility to SLE in Taiwan 17597384_Polymorphisms of PD-L2 are not associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan. 18203952_deficient cellular immunity observed in Hodgkin lymphoma patients can be explained by 'T-cell exhaustion,' which is led by the activation of PD-1-PD-L signaling pathway 18322304_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18378285_HRV-16 infection or exposure to dsRNA induces epithelial B7-H1 and B7-DC 18479731_Programmed death 1 is a marker of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma and B-cell small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 18566376_PD-1 has a key regulatory role during the immune response of the host to the pathogen 18992148_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19729380_Isolated decidual stromal cells constitutively express B7DC and B7H1; B7DC and B7H1 expression can be up-regulated (by IFN-gamma or TNF-alpha); B7DC and B7H1 appear to function in cell-to-cell communication. 19739236_All forms of chronic necroinflammatory liver disease examined correlate with increased B7-H1 and B7-DC expression on Kupffer cells, liver sinusoidal epithelial cells, and leukocytes. 20066438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20390427_Findings demonstrate that the pretreatment of tumor cells with IFN-gamma enhances B7-DC expression through ERK and JNK pathways. 20445553_the PD-1 pathway is active in immature Langerhans cells and inhibits iLC activities, but expression of receptor and ligands reverses upon maturation and PD-L1 and PD-L2 on mLC function to inhibit T-cell responses 20587542_PD-L1 and PD-L2 bound PD-1 with comparable affinities, but striking differences were observed at the level of the association and dissociation characteristics 20661763_Results suggest that over-expression of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 within liver may participate in local immune dysfunction, which could be one of the mechanisms involved in the chronicity of HBV infection and chronic inflammation seen in CHB patients. 20682852_PD-L1 and PD-L2 knockdown dendritic cells showed superior potential to expand minor histocompatibility antigen-specific CD8(+) effector and memory T cells from leukemia patients early after donor lymphocyte infusion and later during relapse. 20709947_Transgenic PD-L2 affects transition to memory when expressed on antigen (Ag)-presenting cells at the beginning of interaction with T cells; notably, interaction with PD-1 on T cells is required during the initial encounter with Ag. 20722638_REVIEW: role of PD-L1 and PD-L2 and ligands in allergic disease and asthma. 21457347_increased expression of PD-L2, as a costimulatory molecule, may have an important modulatory function on the local immune responses of OLP in vivo. 21752471_These observations indicate that PD-L2 is expressed following activation and is involved in the regulation of T cell function 21791547_Our results suggest that PD-1 G-536A, PD-L1 A8923C and PD-L2 C47103T polymorphisms are associated with the presence of ankylosing spondylitis. 21876620_Data suggest that PD-L1 may contribute to negative regulation of the immune response in chronic hepatitis B, and that PD-1 and PD-L1 and 2 may play a role in immune evasion of tumors. 22067141_Data suggest that brain endothelial cells contribute to control T cell transmigration into the CNS and immune responses via PD-L2 but not PD-L1 expression. 22322668_Data show that PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CCL17, and CCL22 mRNA was identified in papillomas. 22895698_expression of PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, in liver biopsies from HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) and chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients were analyzed; results showed all 3 molecules were observed in the HBV-ACLF samples and levels were significantly higher than in CHB 23388330_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expressed on hPMSCs could inhibit the hPMSCs-mediated up-regulation on the expression of IL-17 secreted by peripheral blood T cells 23533995_Macrophages from infected animals show increased expression of PDL2 and CD80 that was dependent from the sex of the host. 24270737_High Expression of PD-L2 is associated with myelodysplastic syndromes. 24406080_PD-1/PD-Ls pathways on PMCs inhibited proliferation and adhesion activity of CD4+ T cells, suggesting that Mycobacterium tuberculosis might exploit PD-1/PD-Ls pathways to evade host cell immune response in human. 24497532_Recurrent genomic rearrangement events in CD274 and PDCD1LG2 underlie an immune privilege phenotype in a subset of B-cell lymphomas. 24532425_Data indicate that the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) signaling pathway regulates PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MoDCs) during the maturation process. 25025450_conclude that PD-L2 protein is robustly expressed by the majority of primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphomas 25349132_Results show that human-derived chordoma cell lines demonstrate inducible expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, and that primary chordoma tissue shows variable expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in infiltrating immune cells 25662388_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma is associated with an increased number of CD8(+) tumor infiltrating lymphocytess and increased MET expression. 25675203_Suggest role for PD-L2 in recurrence of hepatitis C infection post orthotopic liver transplantation. 26081225_the inflammatory environment in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma may contribute to the expression of PD-L2. 26133691_We suggest that decreased expression of programmed death-ligand 1, 2 on psoriatic epidermis can contribute to its chronic unregulated inflammatory characteristics. 26317899_Genomic amplification of 9p24.1 targeting JAK2, PD-L1, and PD-L2 is enriched in high-risk triple negative breast cancer. 26329973_Data indicate that pulmonary pleomorphic carcinoma (PC) very frequently express CD274 antigen (PD-L1) and CD273 antigen (PD-L2). 26424759_PD-L2 expression was neither associated with VEGF-TKI responsiveness nor patients' outcome 26432559_PDL2 could promote the ability of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells to augment the secretion of IL-10. 26464193_High PD-L2 expression is associated with Renal Cell Carcinoma. 26541326_Report PD-L2 expression in breast neoplasms. 26599163_knocking down in dendritic cells results in activation of inflammatory T cells 26752545_PD-L1 and PD-L2 are useful new markers for identifying select histiocyte and dendritic cell disorders and reveal novel patient populations as rational candidates for immunotherapy 26913631_We observed cogain or coamplification of CD274 and PDCD1LG2 in 32 of 48 cervical and 10 of 23 vulvar squamous cell carcinomas 26980034_PDL2 was overexpressed in Epstein Barr virus-associated gastric adenocarcinoma. 27050074_PD-L2 copy number gains were not related to PD-L2 augmentation in non-small cell lung cancer. 27069084_PD-L1/PD-L2 copy number alterations are a defining feature of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 27268263_stable ectopic expression of wild-type PDCD1LG2 and the PDCD1LG2-IGHV7-81 fusion showed, in coculture, significantly reduced T-cell activation. 27447090_the binding affinities of the PD-1-PD-L1/PD-L2 co-inhibitory receptor system, was characterized. 27456947_Overexpression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma 27533014_this study shows that higher PD-L2 expression on blood dendritic cells, from Plasmodium falciparum-infected individuals, correlates with lower parasitemia 27564404_an IL-27/Stat3 axis induces expression of programmed cell death 1 ligands (PD-L1/2) on infiltrating macrophages in lymphoma 27609582_The expression levels of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 in CD3(+) T cells and CD19(+) B cells and serum IFN-gamma level in progressive hepatocellular carcinoma patients were significantly higher than controls. 27837027_in some tumor types, PD-L2 expression is more closely linked to Th1/IFNG expression and PD-1 and CD8 signaling than PD-L1 27921410_Downregulation of the immunosuppressive molecules, PD-1 and PD-L1, may imply that over-activation of immune cells in multiple sclerosis occurs through signaling dysfunction of these molecules and PD-L2 plays no important role in this context 28052400_higher expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 on CD1a(+) cells than that on CD83(+) cells in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma tumour tissues may contribute to negative regulation in anti-tumour immune responses 28369778_PDCD1LG2 (PD-L2) RNA in situ hybridization is a sensitive, specific, and practical marker of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 28488345_Low PD-L2 expression is associated with pediatric solid tumors. 28494868_PD-L2 is regulated by both interferon beta and gamma signaling. 28546465_The biopsy tumor key protein measurements demonstrate substantial between-tumor variation in expression ratios of these proteins and suggest that programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 PD-L2 is present in some tumors at levels sufficient to contribute to programmed cell death-1 PD-1-dependent T-cell regulation and possibly to affect responses to PD-1- and programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 PD-L1-blocking drugs. 28561677_PD-L2 expression has been reported in 52% of esophageal adenocarcinomas but little is known about the expression of other immune checkpoints 28619999_Clinical response to pembrolizumab in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)may be related partly to blockade of PD-1/PD-L2 interactions. Therapy targeting both PD-1 ligands may provide clinical benefit in these patients. 28754154_the positive rate of PD-L2 did not show any differences between primary tumors and metastatic lymph nodes. In multivariate analysis, PD-L1 expression, PD-L2 expression, a low density of CD8(+) T cells in primary tumors, and PD-1 expression on CD8(+) T cells in primary tumors were associated with poor prognosis. 29038297_Tumor PDCD1LG2 expression is inversely associated with Crohn-like lymphoid reaction to colorectal cancer, suggesting a possible role of PDCD1LG2-expressing tumor cells in inhibiting the development of tertiary lymphoid tissues during colorectal carcinogenesis. 29061851_Data suggest that hormonal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D is a direct transcriptional inducer of genes encoding PDL1 and PDL2 in myeloid cells/macrophages; this up-regulation of gene expression appears to be species- and cells-specific. 29112015_PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially expressed by macrophages or tumor cells in primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type. 29122656_Our results confirm and extend prior studies of PD-L1 and provide new data of PD-L2 expression in lymphomas 29676849_HOXC10 directly binds to the PD-L2 and TDO2 promoter regions thus stimulating proliferation, invasion and induction of immunosuppressive gene expression in glioma. 29890018_The high-affinity PD-1 mutant could compete with the binding of antibodies specific to PD-L1 or PD-L2 on cancer cells. 30036273_These results suggest the potential involvements of the EV beta2 integrin, as well as EV PD-L2 and soluble PD-L1, in the septic pathogenesis that occurs with the systemic immune activation leading to multiple organ dysfunctions. 30104397_soluble PD-1 ligands are elevated in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM) patients and, in addition to surface-bound ligands in WM BM, could regulate T-cell function. Given the capability of secreted forms to be bioactive at distant sites, soluble PD-1 ligands have the potential to promote disease progression in WM. 30236595_CD 274 antigen/CD273 antigen/Janus kinase 2 gene amplification was associated with durable response to immunotherapy for cutaneous melanoma and mucosal melanoma 30275216_High PD-L2 expression may be a target of immunotherapy in patients with PD-L1-negative Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 30348714_PD-L2-positive lung adenocarcinomas are less radiologically malignant and invasive than their PD-L1-positive counterparts 30555574_FISH technique and qPCR data coupled with immunofluorescence revealed that genetic alterations of 9p24.1 robustly contributed to PD-L1 and PD-L2 upregulation. In addition, increased expression of PD-L1 instead of PD-L2 also predicted poor survival by multivariate analyses. Meanwhile, high infiltration of PD-1(+) immune cells also indicated dismal survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. 30594267_The data indicate that a genetically determined individual difference in a non-synonymous missense SNP of PD-L2 might influence the susceptibility to chronic lymphatic filariasis in a South Indian population. 30633894_A subset of ocular invasive conjunctival squamous carcinomas express high levels of PD-L1 and CD8 and therefore may respond therapeutically to immune checkpoint inhibition. 30659749_Peripheral blood PD-L1 expression might be a prognostic marker for OSCC patients and a possible parameter to monitor immune dysfunction in malign diseases. In the peripheral blood, PD-L1 might be more relevant for immune tolerance than PD-L2. 30683910_High frequency of PD-L2 involving genetic aberrations was associated with EBV-positive lymphomas. 30761875_Studied expression levels of PDCD1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) and programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2) in patients with hematologic malignancies. 30815803_Low PD-L2 expression is associated with Lung Adenocarcinoma. 30864556_we noticed that chronic inflammation of colonic mucosa may lead to up-regulation of PD-L1 and -L2 expression in patients with UC, which may result in regulation of immune responses against this chronic inflammation and then prevent progressive and acute inflammation of the disease. 30886151_The study reveals a pro-metastatic functional mechanism for PD-L2 in osteosarcoma. 30992011_PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 were differentially expressed between primary and metastatic tumors. Histopathological examination of these immune check points in metastatic lesions of mRCC should be noticed, and its accurate diagnosis may be one of the effective ways to realize the individualized treatment. 31076547_Immune Suppression by PD-L2 against Spontaneous and Treatment-Related Antitumor Immunity. 31379843_TLR9 Mediated Tumor-Stroma Interactions in Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)-Positive Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Up-Regulate PD-L1 and PD-L2. 31394407_Strong PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 expression in Kaposi's sarcoma tissues from a cohort of HIV-co-infected patients indicates the effect of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus on immune escape. 31464648_High PD-L2 expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 31727844_Formation of a prominent pocket in the PD-1 protein upon binding PD-L2 was revealed by X-ray crystal structures of the PD-1/PD-L2 complex. 31825827_A Tumor-Specific Super-Enhancer Drives Immune Evasion by Guiding Synchronous Expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2. 31856276_EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p bound to PD-L1 and PD-L2 3'UTRs to reduce PD-L1/L2 surface protein expression. Results indicate a novel mechanism by which EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p plays a context-dependent counterregulatory role to fine-tune the expression of the LMP1-driven amplification of these inhibitory checkpoint ligands. 31882544_The structural features that distinguish PD-L2 from PD-L1 emerged in placental mammals. 32012401_Our findings indicate that cisplatin-upregulated PD-L2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) via STAT1/3 activation and the expression of PD-L2 are likely to be associated with malignancy in OSCC. The PD-L2 expression in cisplatin-resistant OSCC cells may be a critical factor in prognosis of advanced OSCC patients. 32089543_PD-L1/L2 protein levels rapidly increase on monocytes via trogocytosis from tumor cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 32210369_Prognostic and clinical impact of PD-L2 and PD-L1 expression in a cohort of 437 oesophageal cancers. 32248797_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in the tumor microenvironment including peritumoral tissue in primary central nervous system lymphoma. 32264742_Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death protein 1 and soluble programmed cell death protein ligand 2 are increased in systemic lupus erythematosus and associated with the disease activity. 32268011_Increased expression of immune checkpoint programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) on T cell subsets of bone marrow aspirates in patients with B-Lymphoblastic leukemia, especially in relapse and at diagnosis. 32401663_PD-L1 and PD-L2 Mutations in Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Do They Have Any Prognostic Significance? 32405745_Expression of PD-L1, PD-L2, and IDO1 on tumor cells and density of CD8-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma according to histological subtype. 32586358_Prognostic and predictive value of PD-L2 DNA methylation and mRNA expression in melanoma. 32596285_Profiles of PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2 in Gastric Cancer and Their Relation with Mutation, Immune Infiltration, and Survival. 32661872_Increasing the expression of programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2) but not 4-1BB ligand in colorectal cancer cells. 32684057_PD-1, CTLA4, PD-L1 and PD-L2 DNA methylation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. 32730911_High Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1 and Programmed Death Ligand 2 in Ophthalmic Sebaceous Carcinoma: The Case for a Clinical Trial of Checkpoint Inhibitors. 32820659_The influence of programmed cell death ligand 2 (PD-L2) expression on survival outcome and tumor microenvironment in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 32854650_DLBCL with amplification of JAK2/PD-L2 exhibits PMBCL-like CNA pattern and worse clinical outcome resembling those with MYD88 L265P mutation. 32915645_Lower PDL1, PDL2, and AXL Expression on Lung Myeloid Cells Suggests Inflammatory Bias in Smoking and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 33182023_Prognostic and clinicopathological utility of PD-L2 expression in patients with digestive system cancers: A meta-analysis. 33231797_AKT/mTOR Signal Cascade and Expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2 in Gastric Cancer. 33337915_Comprehensive assessment of PD-L1 and PD-L2 dysregulation in gastrointestinal cancers. 33339860_Prognostic relevance of programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PDCD1LG2/PD-L2) in patients with advanced stage colon carcinoma treated with chemotherapy. 33404124_ANO9 regulates PD-L2 expression and binding ability to PD-1 in gastric cancer. 33424844_PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression in Cervical Cancer: Regulation and Biomarker Potential. 33469839_PD-1 and PD-L2 expression predict relapse risk and poor survival in patients with stage III colorectal cancer. 33671892_High PD-L1/IDO-2 and PD-L2/IDO-1 Co-Expression Levels Are Associated with Worse Overall Survival in Resected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. 33721375_Soluble programmed cell death protein 1 (sPD-1) and the soluble programmed cell death ligands 1 and 2 (sPD-L1 and sPD-L2) in lymphoid malignancies. 33930105_The role of PD-1/PD-Ls in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. 33955303_Characterization of the Clinical Significance of PD-1/PD-Ls Expression and Methylation in Patients With Low-Grade Glioma. 34125179_Immune evasion in primary testicular and central nervous system lymphomas: HLA loss rather than 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 alterations. 34131208_Adipogenesis in triple-negative breast cancer is associated with unfavorable tumor immune microenvironment and with worse survival. 34167064_Phospho-beta-catenin expression in primary and metastatic melanomas and in tumor-free visceral tissues, and associations with expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2. 34347720_Molecular and Immune Correlates of PDCD1 (PD-1), PD-L1 (CD274), and PD-L2 (PDCD1LG2) DNA Methylation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. 34382413_DNA Methylation Patterns in the HLA-DPB1 and PDCD1LG2 Gene Regions in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis from Different Water Iodine Areas. 34563045_Regulation of Immunity in Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma: Role of PD-1, PD-L1, and PD-L2. 34697216_PD-L2 glycosylation promotes immune evasion and predicts anti-EGFR efficacy. 34768993_Clinical and Prognostic Value of Antigen-Presenting Cells with PD-L1/PD-L2 Expression in Ovarian Cancer Patients. 34899719_Inhibition of PI3Kdelta Differentially Regulates Poly I:C- and Human Metapneumovirus-Induced PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. 35037417_PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their correlation with immune infiltrates and DNA damage response molecules. 35169863_Differential expression of PDL1 and PDL2 is associated with the tumor microenvironment of TILs and M2 TAMs and tumor differentiation in nonsmall cell lung cancer. 35489160_Clinical relevance of PD-L2 expression in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma. 35613340_Exome sequencing identifies PD-L2 as a potential predisposition gene for lymphoma. 36138073_FAK promotes stromal PD-L2 expression associated with poor survival in pancreatic cancer. 36172747_Investigation of pd-l1 (cd274), pd-l2 (pdcd1lg2), and ctla-4 expressions in malignant pleural mesothelioma by immunohistochemistry and real-time polymerase chain reaction methods. |
ENSMUSG00000016498 |
Pdcd1lg2 |
9.139093 |
2.7803825509 |
1.475283 |
0.488323070 |
9.529007 |
0.00202249529001002426378819087915417185286059975624084472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004458854440709180029511760068317016703076660633087158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9877321 |
7.3936621 |
3.6199846 |
1.9372102 |
| ENSG00000197696 |
4828 |
NMB |
protein_coding |
P08949 |
FUNCTION: Stimulates smooth muscle contraction (By similarity). Induces sighing by acting directly on the pre-Botzinger complex, a cluster of several thousand neurons in the ventrolateral medulla responsible for inspiration during respiratory activity (By similarity). Contributes to the induction of sneezing following exposure to chemical irritants or allergens which causes release of NMB by nasal sensory neurons and activation of NMBR-expressing neurons in the sneeze-evoking region of the brainstem (By similarity). These in turn activate neurons of the caudal ventral respiratory group, giving rise to the sneezing response (By similarity). Contributes to induction of acute itch, possibly through activation of the NMBR receptor on dorsal root ganglion neurons (By similarity). Increases expression of NMBR and steroidogenic mediators STAR, CYP11A1 and HSD3B1 in Leydig cells, induces secretion of testosterone by Leydig cells and also promotes Leydig cell proliferation (By similarity). Plays a role in the innate immune response to influenza A virus infection by enhancing interferon alpha expression and reducing expression of IL6 (PubMed:31601264). Plays a role in CSF1-induced proliferation of osteoclast precursors by contributing to the positive regulation of the expression of the CSF1 receptor CSF1R (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P01297, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9CR53, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31601264}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Amidation;Cell projection;Cleavage on pair of basic residues;Immunity;Innate immunity;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the bombesin-like family of neuropeptides, which negatively regulate eating behavior. The encoded protein may regulate colonic smooth muscle contraction through binding to its cognate receptor, the neuromedin B receptor (NMBR). Polymorphisms of this gene may be associated with hunger, weight gain and obesity. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:4828; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; hormone activity [GO:0005179]; neuromedin B receptor binding [GO:0031710]; neuropeptide hormone activity [GO:0005184]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; arachidonic acid secretion [GO:0050482]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; Leydig cell proliferation [GO:0160024]; negative regulation of hormone secretion [GO:0046888]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; neuropeptide signaling pathway [GO:0007218]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of hormone secretion [GO:0046887]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of osteoclast proliferation [GO:0090290]; positive regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange [GO:1903942]; positive regulation of testosterone secretion [GO:2000845]; sensory perception of itch [GO:0160025]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; sneeze reflex [GO:0160023] |
11194934_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15158442_lysosomal degradation of neuromedin B is dependent on tripeptidyl peptidase-I 15528253_NMB and its receptor are coexpressed by proliferating cells in which they act in an autocrine fashion with similar and modest potency in both normal and malignant colonic epithelial cells. 15585758_Associated with eating behaviors 17299381_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17766645_REsults describe the expression of neuromedin B in adipose tissue and its regulation by changes in energy balance. 18271693_No significant differences in the genotype distribution were demonstrated between normal weight and overweight/obese subjects 18271693_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010906_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20010906_TT genotype of the NMB rs3809508 polymorphism was associated with a higher risk of obesity and moreover, the effects of this polymorphism on anthropometric values were influenced by the maternal educational level. 21527296_There was no association between eating behaviour traits, or anthropometric variables, and NMB p.P73T polymorphism. 23879873_Rs2292462 was associated with left ventricular hypertrophy in type 2 diabetic patients. 27634552_Genetic clues to the mechanism by which MC4R, FTO, and NMB influences changes in BMI and obesity. 30224376_GPNMB is exposed on the surface of dormant breast cancer cells and its activity contributes to the acquisition of stem cell-like properties |
ENSMUSG00000025723 |
Nmb |
129.492488 |
6.7603188233 |
2.757091 |
0.172042027 |
286.845273 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000024207806213504832046297664790423611346441656106309400341537634820200907551195333687245826121974061007989576516840570208985948321696975278487028916918527846264316133462202174086996819823980331420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006691146436541784902575850077710211033085046977622534773243121458233017131582219893292689284582154756235010789866597888542620764830126021474265189699523698283606387704480766842607408761978149414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
228.1708184 |
22.9810656 |
33.9864479 |
3.0886131 |
| ENSG00000197714 |
10794 |
ZNF460 |
protein_coding |
Q14592 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Zinc finger proteins, such as ZNF272, interact with nucleic acids and have diverse functions. The zinc finger domain is a conserved amino acid sequence motif containing 2 specifically positioned cysteines and 2 histidines that are involved in coordinating zinc. Kruppel-related proteins form 1 family of zinc finger proteins. See ZFP93 (MIM 604749) for additional information on zinc finger proteins.[supplied by OMIM, May 2004]. |
hsa:10794; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
15004467_Molecular cloning and tissue distribution of ZNF460. 34738503_Circular RNA mitochondrial translation optimization 1 homologue (CircMTO1) induced by zinc finger protein 460 (ZNF460) promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression through the microRNA miR-320a / alpha thalassemia/mental retardation, X-linked (ATRX) axis. |
|
|
14.555641 |
2.1182757703 |
1.082890 |
0.420816763 |
6.643793 |
0.00995018479499771950347319915408661472611129283905029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019078296645124233343882025337734376080334186553955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.7587495 |
4.6306909 |
8.8362192 |
1.7425571 |
| ENSG00000197747 |
6281 |
S100A10 |
protein_coding |
P60903 |
FUNCTION: Because S100A10 induces the dimerization of ANXA2/p36, it may function as a regulator of protein phosphorylation in that the ANXA2 monomer is the preferred target (in vitro) of tyrosine-specific kinase. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Isopeptide bond;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in exocytosis and endocytosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6281; |
AnxA2-p11 complex [GO:1990665]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nuclear matrix [GO:0016363]; plasma membrane protein complex [GO:0098797]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent protein binding [GO:0048306]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; membrane raft assembly [GO:0001765]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; positive regulation of binding [GO:0051099]; positive regulation of exocytosis [GO:0045921]; positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051894]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of plasma membrane repair [GO:1905686]; positive regulation of plasminogen activation [GO:0010756]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; vesicle budding from membrane [GO:0006900] |
12163506_These results suggest that epidermal growth factor treatment increased p11 bound to cPLA(2) may lead to the late suppression of AA release induced by EGF. 12198146_p11 interacts specifically with the TASK-1 K+ channel. 12235365_Calpactin light chain binds to bluetongue virus NS3 protein 12645529_IFN-gamma-stimulated p11 expression may serve a counterregulatory role in human epithelial cells 12730231_analysis of S100A10 interaction with tissue plasminogen activator, plasminogen, and plasmin 13679511_annexin 2/S100A10 complex functions in the intracellular positioning of recycling endosomes and that both subunits are required for this activity 15302870_Temperature stress-induced annexin 2 translocation is dependent on both expression of protein p11 tyrosine phosphorylation of annexin 2 15574370_S100A10 and annexin A2 play an important role in plasmin regulation and in cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis [review] 15849182_complex with annexin II is a substrate of thioredoxin 16230353_analysis of the structural determinant of the PtdIns(4,5)P2 selectivity of A2t (annexin II-p11 heterotetramer), which may be involved in the regulation of PtdIns(4,5)P2 clustering in the cell 16400147_results of the present study indicate that the dynamic modulation of 5-HT1B receptor function by p11 may be involved in molecular adaptations occurring in neuronal networks that are dysfunctional in depression-like states 16890384_It is proposed that p11 may act through the tPA/plasminogen/BDNF pathway to achieve its antidepressant effect. 16984913_that Annexin2 is required for strong binding of S100A10 to the C-terminal domain of the protein Ahnak. 17241856_p11 expression was increased in inflammatory bowel disease 17510952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17510952_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in S100A10 gene is not associated with major depressive disorder 17581860_The anx 2-S100A10/CFTR complex is important for CFTR function across epithelia. 17695432_S100A10 and annexin II contribute to the aggressive characteristics of anaplastic carcinoma, while playing a constitutive role in papillary carcinoma. 17824845_analysis of the pH-induced membrane binding of annexins A6 and A2-S100A10 17971878_p11/S100A10 light chain of annexin A2 is dispensable for annexin A2 association to endosomes and functions in endosomal transport 17999956_the annexin II-S100A10 complex, which regulates exocytosis, forms a ternary complex with TrpRS. 18288090_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18434302_Within the endothelial cell, p11 is required for Src kinase-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of A2, which signals translocation of both proteins to the cell surface. 18838110_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18838110_Our findings suggest that p11 genetic variants do not play a major role in the MDD susceptibility, antidepressant therapeutic response or the risk of suicide attempt in MDD. 19521263_Expression of S100A10 (but not other S100 proteins investigated) varied in melanoma cell lines (i.e., S100A10 was down-regulated in 3 cell lines compared with normal melanocytes). Expression of S100A10 correlated with proliferation marker, Ki67. 19601998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20093721_CFTR function by annexin A2-S100A10 complex has roles in health and disease [review] 20100475_First insights of S100A10 function as a regulator of the filamentous actin network. 20863517_The results of this study suggested that PBMC p11 mRNA levels may be a potential adjunctive biomarker for the assessment of suicide risk in mental disorders and warrants a larger translational study to determine its clinical utility. 21269277_The present study represents a first attempt to systematically understand the molecular basis for the calcium-insensitive open conformation of S100A10. 21310922_S100A10 plays a crucial role in the generation of plasmin leading to fibrinolysis, thus providing a link to the clinical hemorrhagic phenotype of acute promyelocytic leukemia 21367534_Understanding the chromatin remodeling involved in the glucocorticoid-mediated increase of p11 expression by stress may clarify stress-induced over-expression of p 21372205_DLC1 binding to S100A10 did not affect DLC1's RhoGAP activity, but it decreased the steady-state level of S100A10 expression. 21722919_This study demonstrates that PBMC p11 mRNA expression is associated with neural activation in the brain of BD patients and warrants a larger translational study to determine its clinical utility. 21849434_Both the annexin A2 and p11 subunits of calpactin I coimmunoprecipitate with human papillomavirus type 16 E5 in COS cells and in human epithelial cell lines, and an intact E5 C terminus is required for binding. 21928315_Interferon-gamma stimulates p11-dependent surface expression of annexin A2 in lung epithelial cells to enhance phagocytosis. 21938494_the overexpression of thioredoxin,S100-A10 and S100-A6 specifically distinguished metastatic from non-metastatic tumors. 22365974_COX7A2, TAGLN2 and S100-A10 as novel prognostic markers in Barrett's adenocarcinoma. 22797859_Human chondrocytes with downregulated S100A10 showed significantly decreased production of inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-10; hence, S100A10 might be considered a potential target for anti-inflammatory treatment 22830395_Annexin A2 anchors S100A10 to the cell surface and, in doing so, allows S100A10 to play a prominent role in the activation of plasminogen in angiogenesis and oncogenesis. 22927980_annexin A2 heterotetramer contributes to HPV16 internalization and infection of epithelial cells and this interaction is dependent on the presence of the L2 minor capsid protein 22940583_The AHNAK peptide adopts a coil conformation that arches across the heterotetramer contacting both annexin A2 and S100A10 protomers with tight affinity. 23091277_N-terminal acetylation of AnxA2 is required for S100A10 binding 23129259_results demonstrate the crucial role of S100A10 in actin dynamics promoting cell spreading via Rac1 activation 23275167_Binding of AHNAK to the surface of AnxA2 is governed by several hydrophobic interactions between side chains of AHNAK and pockets on S100A10. 23595865_Suggest annexin A10 as potential marker of sessile serrated adenoma/polyps. 23598417_Overexpression of miR-590-5P reduced the activity of luciferase expressed by a vector bearing the 3' untranslated region of S100A10 mRNA. Ectopic miR-590-5P overexpression mediated by lentiviral infection decreased expression of S100A10. 23637395_Annexin A2 and S100A10 regulate human papillomavirus type 16 entry and intracellular trafficking in human keratinocytes. 23696646_extracellular C-1-P, acting through the extracellular annexin a2-p11 heterotetrameric protein, can mediate vascular endothelial cell invasion. 23757730_complex formation of AnxA2 with S100A10 is a central regulatory mechanism in the acute release of VWF in response to cAMP-elevating agonists 23828264_Data suggest a role for S100A10 as a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. 23931152_Authors show here that AnxA2, p11 and AHNAK are required for type 3 secretion system-mediated Salmonella invasion of cultured epithelial cells. 23994525_an annexin A2-S100A10 molecular bridge participates in cell-cell interactions, revealing a hitherto unexplored function of this protein interaction 25303710_Annexin A2 complexes with S100 proteins: structure, function and pharmacological manipulation 25428414_TPH1 gene polymorphisms and S100A10 expression, which correlate with 5-HT signaling were associated with ramosetron effectiveness in IBS-D, and may possibly lead to prospective identification of the resistance to treatment. 26465153_These data show that disruption of ANX2/p11 interaction results in reduced ALL cell adhesion to osteoblasts, increased ALL cell sensitization to chemotherapy, and suppression of ALL cell homing and engraftment. 26760977_These findings identify S100A10 as a player in endometrial receptivity acquisition. 26821757_p11 might be a potential regulator on 5-HTR1b and 5-HTR4 as well as a predictor of or a therapeutic target for IFN-alpha-induced depression. 26925708_annexin A2 and S100A10 expressions are powerful predictors of serous ovarian cancer outcome. 27871932_Here, the authors demonstrate that S100A10 is required for ULK1 localization to autophagosome formation sites. Silencing of S100A10 reduces IFN-gamma-induced autophagosome formation. 28137881_Given that inflammation plays a role in both Parkinson's disease (PD)and depression, it is intriguing that peripheral p11 levels are altered in immune cells in both conditions. Our data provide insight into the pathological alterations occurring centrally and peripherally in PD. Moreover, if replicated in other cohorts, p11 could be an easily accessible biomarker 28382372_these studies define a new paradigm for plasminogen activation by the plasminogen receptor, S100A10 28418321_The S100A10 and S100B genes, which are located on different chromosomes, encode specialized calcium-binding proteins. These data support a role for calcium homeostasis in individuals with Cannabis Dependence and high risk sex behaviours. 28450451_Findings indicate that Munc13-4 supports acute WPB exocytosis by tethering WPBs to the plasma membrane via AnxA2-S100A10. 28687976_The overexpression of ANXA2 in U937 cells transfected with full-length ANXA2 cDNA was associated with increased S100A10 subunit, although S100A10 transcripts remained constitutive. PML/RARalpha fusion protein transactivated the ANXA2 promoter to upregulate ANXA2 and accumulate S100A10. 29028593_These findings provides evidence that gene-gene interactions between p11, tPA and BDNF are all associated with post stroke depression. 30009399_These findings delineate the clinical and functional contribution of S100A10 as a biomarker in pancreatic cancer. 30076379_the observed reduction in infection is less significant in the absence of S100A10 alone compared to full A2t, supporting an independent role for monomeric AnxA2. More broadly, we show that successful infection by multiple oncogenic HPV types is dependent on A2t. 30143909_study has localised AnxA2/S100A10 complexes to key anatomical locations in the placenta and suggests a role for this complex in amniotic epithelium, trophoblasts and syncytium, in addition to its well-known roles in endothelial cells 30206209_This study highlights the complex regulation of p11 by retinoid signaling and challenges the hypothesis that ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of p11 represents a universal mechanism of regulation of this protein. 30268496_The data show that S100A10 expression in lung squamous cell carcinoma is related to invasion of the lymphatic system, cancer stage progress, and a poorer prognosis. 30394687_S100A10 is overexpressed in gastric cancer.S100A10 is succinylated at lysine 47 in gastric cancer.A novel mechanism of S100A10 accumulation mediated by succinylation in gastric cancer, which promotes gastric cancer progression and is regulated by the succinyltransferase CPT1A and SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation. 31092442_High expression of Annexin A2 and S100A10 in stromal tissue from Epithelial Ovarian Cancer patients was associated with reduced overall survival; however, no independent prognostic value was found for any of the markers. 31585940_GAS6/AXL signaling activated the expression of S100A10 through SRC to promote plasmin production. 31728728_Membranous overexpression of S100A10 is associated with a high-grade cellular status of breast carcinoma. 31739800_The results of the present study reveal that S100A10 expression can be used as a predictive marker for the prognosis of ovarian cancer and chemosensitivity to carboplatin. 32427586_Chemotherapy-induced S100A10 recruits KDM6A to facilitate OCT4-mediated breast cancer stemness. 32442363_Annexin A2-S100A10 Represents the Regulatory Component of Maxi-Cl Channel Dependent on Protein Tyrosine Dephosphorylation and Intracellular Ca(2)(+). 32835655_Structural characterization of a dimeric complex between the short cytoplasmic domain of CEACAM1 and the pseudo tetramer of S100A10-Annexin A2 using NMR and molecular dynamics. 32976661_Upregulation of S100A10 in metastasized breast cancer stem cells. 34356598_Regulation of S100A10 Gene Expression. 34645932_The S100A10-AnxA2 complex is associated with the exocytosis of hepatitis B virus in intrauterine infection. 34944416_The ANXA2/S100A10 Complex-Regulation of the Oncogenic Plasminogen Receptor. 34944467_Mechanism of Zn(2+) and Ca(2+) Binding to Human S100A1. 34944495_The Annexin A2/S100A10 Complex: The Mutualistic Symbiosis of Two Distinct Proteins. 35217896_The prognostic value of S100A calcium binding protein family members in predicting severe forms of COVID-19. 35579448_S100 calcium-binding protein A10 contributes to malignant traits in osteosarcoma cells by regulating glycolytic metabolism via the AKT/mTOR pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000041959 |
S100a10 |
1081.550938 |
2.3990196423 |
1.262445 |
0.049278180 |
667.329530 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000380500462499249329940077266840080798573226534598600049545835212740827280177931895501787341156621974201892336747799409478236629649071074998912401530622706094189988737216554017816426295 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000243124970843676182532960412403868604870244717184476360988886823666094455220446659122995704483162500923151124579021829215833564846621304621365544059026807682506552957965493560567977092 |
Yes |
No |
1542.5906624 |
43.9441497 |
647.6615393 |
14.9069697 |
| ENSG00000197766 |
1675 |
CFD |
protein_coding |
P00746 |
FUNCTION: Factor D cleaves factor B when the latter is complexed with factor C3b, activating the C3bbb complex, which then becomes the C3 convertase of the alternate pathway. Its function is homologous to that of C1s in the classical pathway. |
3D-structure;Complement alternate pathway;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Hydrolase;Immunity;Innate immunity;Protease;Reference proteome;Secreted;Serine protease;Signal;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the S1, or chymotrypsin, family of serine peptidases. This protease catalyzes the cleavage of factor B, the rate-limiting step of the alternative pathway of complement activation. This protein also functions as an adipokine, a cell signaling protein secreted by adipocytes, which regulates insulin secretion in mice. Mutations in this gene underlie complement factor D deficiency, which is associated with recurrent bacterial meningitis infections in human patients. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. At least one of these variants encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]. |
hsa:1675; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; ficolin-1-rich granule lumen [GO:1904813]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; secretory granule lumen [GO:0034774]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; serine-type peptidase activity [GO:0008236]; complement activation [GO:0006956]; complement activation, alternative pathway [GO:0006957]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; response to bacterium [GO:0009617] |
19336475_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19344414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19538214_As adiponectin and adipsin levels in CSF did not correlate with their levels in plasma, it seems that there could be a secondary intrathecal synthesis of these adipocytokines in multiple sclerosis 19699327_increased serum levels in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21139680_CFD may not play a major role in the genetic susceptibility to age-related macular degeneration. 21205667_crystal structure of C3bB at 4 A and complex with factor D at 3.5 A; data show how factor B binding to C3b forms open 'activation' state of C3bB; Factor D binds open conformation of factor B through a site distant from the catalytic center 22003108_CFD regulates activation of the alternative complement pathway, which is implicated in age related macular degeneration pathogenesis. 22362762_Anti factor D Fab fragment inhibits FD proteolytic function by interfering with macromolecular substrate access rather than by inhibiting FD catalysis. 22930722_Increased activation of the alternative complement pathway in vitreous was controlled by disease stage and genetic variation in the complement pathway, supporting a role for complement activation in macular degeneration disease pathogenesis. 23956345_We demonstrate novel secretion of adipsin and ASP by placental Hofbauer cells. 24598742_Complement factor D (FD) is activated by its substrate through interactions outside the active site which lock the unbound native state into an ordered inactive conformation via the self-inhibitory loop in FD. 24958499_Data indicate that a urinary protein, adipsin, was significantly increased in patients with preeclampsia. 24995977_Study demonstrates that T2DM patients with beta cell failure are deficient in adipsin. 25840635_Overall adipsin levels among male asbestos industry workers were significantly higher than among control subjects. 26687459_our findings set up a novel mechanism for FABP4, adipsin and adiponectin through gut microbiota mediating expression in gut Paneth cells. 27535802_MASP-3 is the exclusive pro-factor D activator in resting blood: the lectin and the alternative complement pathways are fundamentally linked. 28189761_The strong association of PLIN1, CFD and ADIPOQ genes with adipogenesis prompted authors to study the influence the bone health status as evaluated by quantitative ultrasound (QUS) bone densitometer in a North Indian cohort. Overall, ADIPOQ (rs1501299 and rs3774261) and combined cluster of PLIN1 rs2304796 and rs2304795) and CFD (rs1683563) demonstrated correlation. 28219679_TZDs (pioglitazone, rosiglitazone, and ciglitazone) slow tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo with decreases in cell proliferation and increases in PPARg and adipsin 28864895_disturbance of reciprocal relationships between adipsin and leptin in obesity is associated with the development of insulin resistance 29138487_The results suggested that elevated IL-17A and IL-9 expressions and decreased levels of adipsin and CCL11 were positively associated with adult asthma. 30541001_increased circulating levels of adipsin and decreased circulating levels of visfatin and adiponectin were independently associated with the increased risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease 31026383_Senescent dermal fibroblasts negatively influence fibroblast extracellular matrix-related gene expression (such as MMP1) partly via secretion of complement factor D. 31651303_High plasma adipsin levels are associated with mild cognitive impairment. 31700183_these data suggest that adipsin/C3a and DUSP26-directed therapies may represent a novel approach to achieve beta cell health to treat and prevent type 2 diabetes. 32877502_Direct activation of the alternative complement pathway by SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins is blocked by factor D inhibition. 33881585_The function of adipsin and C9 protein in the complement system in HIV-associated preeclampsia. 34155972_Adipsin promotes bone marrow adiposity by priming mesenchymal stem cells. 34205507_Complement Factor D (adipsin) Levels Are Elevated in Acquired Partial Lipodystrophy (Barraquer-Simons syndrome). 34566967_Complement Factor D as a Strategic Target for Regulating the Alternative Complement Pathway. 35216336_Adipsin Serum Concentrations and Adipose Tissue Expression in People with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. 35436912_Plasma and aqueous levels of alarin and adipsin in patients with and without diabetic retinopathy. 35596679_Complement factor D as a predictor of Achilles tendon healing and long-term patient outcomes. 35909516_Elevated Adipsin and Reduced C5a Levels in the Maternal Serum and Follicular Fluid During Implantation Are Associated With Successful Pregnancy in Obese Women. |
ENSMUSG00000061780 |
Cfd |
393.142409 |
0.4060813958 |
-1.300159 |
0.081742085 |
258.742664 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000032254324130667147564384937261996147049093645767562725724764509256108712460287477307828237975840940064220607377664104972862447717977751577960994575772213366349205898586660623550415039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008055394655983875824112139120319410916106482178164518173358296856032928714882890552258439974598540012714510486094313405180723196754313771206961261595047574246564181521534919738769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
231.1829398 |
11.6192043 |
573.3398446 |
17.9721982 |
| ENSG00000197780 |
6884 |
TAF13 |
protein_coding |
Q15543 |
FUNCTION: The TFIID basal transcription factor complex plays a major role in the initiation of RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-dependent transcription (PubMed:33795473, PubMed:9695952). TFIID recognizes and binds promoters via its subunit TBP, a TATA-box-binding protein, and promotes assembly of the pre-initiation complex (PIC) (PubMed:33795473). The TFIID complex consists of TBP and TBP-associated factors (TAFs), including TAF1, TAF2, TAF3, TAF4, TAF5, TAF6, TAF7, TAF8, TAF9, TAF10, TAF11, TAF12 and TAF13 (PubMed:33795473). TAF13, together with TAF11 and TBP, play key roles during promoter binding by the TFIID and TFIIA transcription factor complexes (PubMed:33795473). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:33795473, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9695952}. |
3D-structure;Disease variant;Intellectual disability;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II requires the activities of more than 70 polypeptides. The protein that coordinates these activities is transcription factor IID (TFIID), which binds to the core promoter to position the polymerase properly, serves as the scaffold for assembly of the remainder of the transcription complex, and acts as a channel for regulatory signals. TFIID is composed of the TATA-binding protein (TBP) and a group of evolutionarily conserved proteins known as TBP-associated factors or TAFs. TAFs may participate in basal transcription, serve as coactivators, function in promoter recognition or modify general transcription factors (GTFs) to facilitate complex assembly and transcription initiation. This gene encodes a small subunit associated with a subset of TFIID complexes. This subunit interacts with TBP and with two other small subunits of TFIID, TAF10 and TAF11. There is a pseudogene located on chromosome 6. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:6884; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription factor TFIID complex [GO:0005669]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity [GO:0016251]; TBP-class protein binding [GO:0017025]; DNA-templated transcription initiation [GO:0006352]; mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0042789]; positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0060261]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex assembly [GO:0051123]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter [GO:0006367] |
28257693_two homozygous missense are associated with autosomal-recessive intellectual disability and microcephaly 29111974_In an integrative approach combining crystal coordinates, biochemical analyses and data from cross-linking mass-spectrometry (CLMS), the authors determine the architecture of the TAF11/TAF13/TBP complex, revealing TAF11/TAF13 interaction with the DNA binding surface of TBP. |
ENSMUSG00000048100 |
Taf13 |
474.833225 |
2.6149230958 |
1.386769 |
0.087898748 |
249.045536 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004192982852507425313522633989158087879386041564641604845603806682969607210317422984250176410397945183395048771502803567637540168437681239316239256709195615258067846298217773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000999813035589815780786661045932515165734014150177454132811784187469906974814459659664111272718954778834122004762795927405206433408964880171082567628104698087554425001144409179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
687.4519245 |
41.2430323 |
265.0277865 |
12.2140370 |
| ENSG00000197785 |
55210 |
ATAD3A |
protein_coding |
Q9NVI7 |
FUNCTION: Essential for mitochondrial network organization, mitochondrial metabolism and cell growth at organism and cellular level. May play an important role in mitochondrial protein synthesis. May also participate in mitochondrial DNA replication. May bind to mitochondrial DNA D-loops and contribute to nucleoid stability. Required for enhanced channeling of cholesterol for hormone-dependent steroidogenesis. Involved in mitochondrial-mediated antiviral innate immunity (PubMed:31522117). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17210950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22453275, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31522117}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Mitochondrion nucleoid;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a ubiquitously expressed mitochondrial membrane protein that contributes to mitochondrial dynamics, nucleoid organization, protein translation, cell growth, and cholesterol metabolism. This gene is a member of the ATPase family AAA-domain containing 3 gene family which, in humans, includes two other paralogs. Naturally occurring mutations in this gene are associated with distinct neurological syndromes including Harel-Yoon syndrome. High-level expression of this gene is associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients. A homozygous knockout of the orthologous gene in mice results in embryonic lethality at day 7.5 due to growth retardation and defective development of the trophoblast lineage. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
hsa:55210; |
mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; antiviral innate immune response [GO:0140374]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; regulation of cell growth [GO:0001558] |
17210950_Results suggest that mitochondrial DNA displacement loops serve to recruit ATAD3 protein for the purpose of forming or segregating mitochondrial nucleoids. 18639545_We also have shown that the loss of ATAD 3A/3B may be involved in the transformation pathway and the chemosensitivity of oligodendrogliomas. 20154147_Data show that the mitochondrial AAA(+) ATPase protein ATAD3A is involved in dynamic interactions between components of the outer and inner mitochondrial membranes which control a number of critical mitochondrial functions. 20332122_gene expression in lung adenocarcinoma correlates with drug resistance and poor prognosis 20349121_The N-terminal part of ATAD3A is outside the inner mitochondrial membrane and that the C-terminal part is inside the matrix. 20351179_Data show that ATAD3A is a calcium-dependent S100B target protein in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and suggest that S100B could assist the newly synthesized ATAD3A protein in proper folding and subcellular localization. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21584487_silencing of ATAD3A expression reduced PSA secretion and cisplatin resistance, suggesting that ATAD3A was associated with PSA secretion and drug resistance in PCa. 21743956_Results show that HPV infection correlates with increased ATAD3A expression and drug resistance in uterine cervical cancer. 22192748_ATAD3 may therefore be implicated in an unknown but essential and growth-linked mitochondrial function existing since pluri-cellular -organization and involved in tumorigenesis. 22318359_ATAD3 may be implicated in an unknown but essential and growth-linked mitochondrial function existing since pluri-cellular organization and involved in tumorigenesis. 22542587_Engineered a high copy strain expressing human ATAD3A-Myc-HIS at a relative high level (2.5mg/l of yeast culture)without significantly affecting yeast growth.Urea-denaturated ATAD3A-Myc-HIS bound to agarose-nickel beads and could be renatured and eluted. 22664726_ATAD3B is a negative regulator of ATAD3A and may function as an adaptor of mitochondrial homeostasis and metabolism in human pluripotent embryonic stem cells and cancer cells. 24057885_High ATAD3A expression correlates with radioresistance in glioblastoma. 24239551_exploring ATAD3 mRNA expression, we confirmed the existence of an alternative splicing in rodent and of several mRNA isoforms in human 25375035_These results demonstrate that ATAD3-mediated mitochondrial membrane formation participates in the optimal transfer of cholesterol from the endoplasmic reticulum into mitochondria. 25823022_stabilization of WASF3 function occurs through its interaction with ATAD3A and GRP78, which may provide a bridge between the ER and mitochondria, allowing communication between the two organelles 27640307_identification of a recurrent de novo ATAD3A c.1582C>T (p.Arg528Trp) variant by whole-exome sequencing in five unrelated individuals with a core phenotype of global developmental delay, hypotonia, optic atrophy, axonal neuropathy, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 28158749_Mutations in ATAD3A can thus be dominantly inherited and underlie variable neurological phenotypes, including hereditary spastic paraplegia with intrafamiliar variability. This finding extends the group of mitochondrial inner membrane AAA proteins associated with spasticity. 28549128_ATAD3A region deletions cause cerebellar dysfunction associated with altered mitochondrial DNA and cholesterol metabolism. 30914652_ATAD3A plays a key role in neurodegeneration by linking Drp1-induced mitochondrial fragmentation to defective mtDNA maintenance. 31727539_Our findings exclude the causative role of ATAD3B on this severe phenotype, expand the phenotypical spectrum of ATAD3A pathogenic variants and emphasize the vital role of ATAD3A in mitochondrial biogenesis. 32004445_Recurrent De Novo NAHR Reciprocal Duplications in the ATAD3 Gene Cluster Cause a Neurogenetic Trait with Perturbed Cholesterol and Mitochondrial Metabolism. 32219745_Using Genome-Editing Tools to Develop a Novel In Situ Coincidence Reporter Assay for Screening ATAD3A Transcriptional Inhibitors. 32933822_Mitochondrial dysfunction caused by novel ATAD3A mutations. 33113782_Emerging Links between Control of Mitochondrial Protein ATAD3A and Cancer. 33280610_Mitophagy promotes sorafenib resistance through hypoxia-inducible ATAD3A dependent Axis. 33580514_ATAD3A stabilizes GRP78 to suppress ER stress for acquired chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. 33845882_Functional interpretation of ATAD3A variants in neuro-mitochondrial phenotypes. 34387651_Enhanced cGAS-STING-dependent interferon signaling associated with mutations in ATAD3A. 34936866_ATAD3A has a scaffolding role regulating mitochondria inner membrane structure and protein assembly. 36289190_The oncoprotein MUC1 facilitates breast cancer progression by promoting Pink1-dependent mitophagy via ATAD3A destabilization. |
ENSMUSG00000029036 |
Atad3a |
201.885312 |
2.0600870178 |
1.042705 |
0.159074020 |
42.698342 |
0.00000000006386639630866971761676368510310072314217766376032159314490854740142822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000334516681872237388202739930248130056922306607702921610325574874877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
272.6275822 |
24.6134612 |
133.4075083 |
9.1298060 |
| ENSG00000197816 |
100499483 |
CCDC180 |
protein_coding |
A0A6E1Y6F7 |
|
Coiled coil;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains a coiled-coil domain. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in this gene has been associated with increased susceptibility to Behcet's Disease (PMID: 19442274). [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
Mouse_homologues |
|
30790560_High CCDC180 expression is associated with Liposarcoma . |
ENSMUSG00000035539 |
Ccdc180 |
20.076256 |
0.2259129786 |
-2.146161 |
0.715136805 |
7.952222 |
0.00480283683318909974252486350110302737448364496231079101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009858932943989170624710105528265557950362563133239746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9315987 |
6.6610308 |
45.4996652 |
20.6323150 |
| ENSG00000197822 |
100506658 |
OCLN |
protein_coding |
Q16625 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in the formation and regulation of the tight junction (TJ) paracellular permeability barrier. It is able to induce adhesion when expressed in cells lacking tight junctions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19114660}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a coreceptor for hepatitis C virus (HCV) in hepatocytes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19182773, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20375010}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes an integral membrane protein that is required for cytokine-induced regulation of the tight junction paracellular permeability barrier. Mutations in this gene are thought to be a cause of band-like calcification with simplified gyration and polymicrogyria (BLC-PMG), an autosomal recessive neurologic disorder that is also known as pseudo-TORCH syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene is present 1.5 Mb downstream on the q arm of chromosome 5. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]. |
hsa:100506658; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; apicolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016327]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endocytic vesicle [GO:0030139]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; tight junction [GO:0070160]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:0070830]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; positive regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability [GO:1905605]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glucose import [GO:0046326]; positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly [GO:0010592]; positive regulation of microtubule polymerization [GO:0031116]; positive regulation of wound healing [GO:0090303]; protein localization to cell leading edge [GO:1902463]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of glucose transmembrane transport [GO:0010827] |
12118072_The transmembrane domain TM4(-) isoform of Occludin may be translated at low levels in specific conditions and may contribute to regulation of Occludin function. 12169098_oxidative stress induces tyrosine phosphorylation and cellular redistribution of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes by a tyrosine-kinase-dependent mechanism. 12184633_a cyclic peptide with the sequence LYHY, in the second extracellular domain, inhibits endothelial cell barriers and prevents aggregation of fibroblasts transfected with cDNA encoding occludin. LYHY motif is an occludin cell adhesion recognition sequence. 12419305_different occludin variants were identified on the mRNA level 12667324_Occludin mRNA, being mainly located in epithelial cells and its expression correlated with tumor differentiation, may be involved in the development of multi-drug resistance in gastric cancer. 12668723_E-cadherin and claudins/occludin have roles in the regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium-mesenchyme transition, but are repressed by snail 14991532_Occludin expression decreased progressively in parallel with the increase in carcinoma grade, and the decreased occludin expression correlated with myometrial invasion and lymph node metastasis 15069537_MEK/ERK signaling pathway probably regulates the cell dissociation status of pancreatic cancer through influencing the intracellular localization and expression of occludin. 15472219_occludin 50-kDa form is an estrogen-specific-induced occludin isoform and that the mechanism of estrogen-abrogation of transcervical R(TJ) involves occludin modulation. 15500294_The occludin present in the tight junctions in HepG2 cells . 15622522_Activation of PKC by the phorbol ester TPA induced ZO-1 and occludin transcription, whereas PKC inhibition lead to decreased expression levels 15659655_distinct properties for these two extracellular segments of the occludin protein and provide an improved understanding of how specific domains of occludin may interact with proteins present at tight junction structures 15806147_Tight junction protein occludin has a potent inhibitory effect on the Raf1-mediated tumorigenesis 16081103_high-resolution crystal structure of its C-terminal distal cytoplasmic domain; identified a large positively charged surface that contains the binding site for ZO-1; this surface is required for proper localization of occludin to cell-cell junctions 16134968_ERK interacts with the C-terminal region of occludin and mediates the prevention of H2O2-induced disruption of TJs by EGF. 16207910_modulation of tight-junction function by H. pylori is ammonium-dependent and linked to the accumulation of a low-molecular-weight and detergent-soluble form of occludin. 16616143_CKI epsilon is a novel occludin kinase that may be important for the regulation of occludin 16924233_These findings support a role of Slug in mediating Raf 1-induced transcriptional repression of occludin and subsequent epithelial to mesenchymal transition. 16959951_Na-K-ATPase is required for controlling the tight junction gate function through phosphorylation of occlusion. 17038551_Estrogen modulates tight junctional resistance through estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated remodeling of occludin 17243118_OCLN accumulated at cell-to-cell junctions of the breast neoplasm cell line. 17283368_Expression of cytoplasmic occludin was decreased in acute acalculous cholecystitis. 17359339_Tight junction proteins contribute to the permeability barrier in epidermal keratinocytes 17553883_Rhesus monkey rotavirus infection of Caco-2 cells induced the disappearance of occludin. 17635647_Selected neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes expressed occludin, in all cases studied. 17855770_Complete/partial truncation of the COOH-terminal tail of occludin did not prevent targeting to epithelial cell tight junctions. TM4 deletions abolished tight junction targeting. 17962811_Occludin expression was determined in thyroid neoplasms. 18005733_B coxsackievirus entry depends on occludin and require the activity of Rab34, Ras, and Rab5, GTPases known to regulate macropinocytosis. 18276783_Heat stress-induced increase in occludin protein expression is mediated by HSF-1 activation and subsequent binding of HSF-1 to the occludin promoter. 18386163_Hepatocellular carcinomas and metastases are characterized by markedly different protein expression pattern of occludin and ZO-1, which phenomenon might be attributed to the different histogenesis of these tumors. 18397460_study of correlation between mutations & expression of E-cadherin, beta-catenin, occludin & claudin & complexity of colon carcinoma growth; perturbed expression & distribution of these proteins was found, but could not be linked to complexity of growth 18474622_These data demonstrate that the tight junction undergoes constant remodeling and suggest that this dynamic behavior may contribute to tight junction assembly and regulation. 18489585_Occludin mediates apoptosis and invasion by elevating the cytoplasmic calcium concentration and that exon 9 of occludin is an important region that mediates these effects. 18550469_neither occludin nor claudin-7 expression was associated with clinicopathologic findings in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. 18560860_Claudin-1 plays a crucial role in recruiting occludin to tight junctions, and occludin is involved in intercellular barrier function. 18782596_Glucocorticoids regulate the human occludin gene through a single imperfect palindromic glucocorticoid response element. 18802961_Hepatocyte tight junctions-associated proteins occludin, claudin-1, and Zonula Occludens protein-1 (ZO-1) disappeared from the borders of adjacent cells in hepatoma cells harboring genomic hepatitis c virus replicons. 19017651_a unique motif in the occludin sequence that is involved in the regulation of ZO-1 binding by reversible phosphorylation of specific Tyr residues. 19052094_The authors show that in addition to claudin-1 another tight junction protein, occludin, is also required for HCV entry. 19073886_VHL loss-of-function also has striking effects on the expression of the tight junction (TJ) components occludin and claudin 1 in vitro in VHL-defective clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) cells and in vivo in VHL-defective sporadic CCRCCs. 19114660_PKC eta directly interacts with the C-terminal domain of occludin and phosphorylates it on highly conserved T403 and T404, an important mechanism of epithelial TJ regulation by PKC eta. 19125584_Results suggest that Ser490 phosphorylation attenuates the interaction between occludin and ZO-1. 19174516_In cultures of brain microvascular endothelial cells, VEGF-A specifically down-regulated CLN-5 and OCLN protein and mRNA 19182773_human occludin (OCLN) is an essential HCV cell entry factor that is able to render murine cells infectable with HCVpp 19184677_ZO-1, occludin, and E-cadherin are downregulated in carcinomas arising from various compartments of the biliary tract 19332538_DEP-1 interacts with the tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 in a tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent manner. 19437620_Transcriptional control of OCLN expression in vascular endothelia: regulation by Sp3 and YY1 is reported. 19438816_JNK and p38MAPK inhibition prevented both Abeta 1-40-mediated down-regulation of occludin and the increase in paracellular permeability in hCMEC/D3 cells. 19515778_Occludin plays an essential role in HCV infection and probably affects late entry events. 19538290_Differential phosphorylation of occludin by casein kinase 1 (CK1) and casein kinase 2 19661441_is altered in early-stage psoriasis 19756380_The redox-dependent dimerization of occludin may play a regulatory role in the tight junction assembly under physiological and pathological conditions. 20003786_In lower neovaginal mucosa where squamous metaplasia occurred, the expression of occludin and ZO-1 was significant;y elevated. 20028514_MarvelD3 co-localises with occludin at tight junctions in intestinal and corneal epithelial cells. 20152177_Our data indicate that occludin is required for the leading-edge localization of polarity proteins aPKC-Par3 and PATJ and promotes cell protrusion by regulating membrane-localized activation of PI3K. 20164257_marvelD3, occludin, and tricellulin define the tight junction-associated MARVEL protein family 20463075_Data suggest that the natural splicing diversity of occludin might contribute to hepatitis C virus tissue tropism and possibly modify the outcome of HCV infection in humans. 20504882_Nedd4-2 interacts with occludin to inhibit tight junction assembly and the regulation of paracellular conductance in the collecting duct. 20663912_occludin is required for cells to transduce cytokine-mediated signals that either increase the electrical barrier or decrease the large solute barrier, possibly by coordinating the functions of caveolin-1. 20727516_The tight junction protein occludin (encoded by the OCLN gene) is involved in the pathogenesis of malformations of cortical development. 20822789_The authors conclude that the second extracellular loop of occludin dictates the Dynamin 2-dependent hepatitis C virus entry. 20844048_The second half of the second extracellular loop of OCLN is critical for modulating the HCV cell entry. 20878095_Loss of occludin leads to the progression of human breast cancer 20937238_The expression levels of occludin protein in the gastric adenocarcinomas is negative correlation with tumor genesis and development. 21415414_Suggest occludin plays a crucial role in the maintenance of tight junction barrier through the large-channel TJ pathway, the pathway responsible for the macromolecule flux. 21536752_occludin S408 dephosphorylation regulates paracellular permeability by remodeling tight junction protein dynamic behavior and intermolecular interactions between occludin, ZO-1, and select claudinszo 21551950_Expression of human factors CD81, claudin-1, scavenger receptor, and occludin in mouse hepatocytes does not confer susceptibility to hepatitis B virus entry into the liver. 21632765_show that murine OCLN can sustain HCVcc entry, albeit with about 5-fold reduced efficiency compared to that of human OCLN 21806988_PLSCR1 was required for the initial attachment of HCV onto hepatoma cells, where it specifically interacted with entry factor OCLN. We show that PLSCR1 is a novel attachment factor for HCV entry. 21821450_No correlation was found for p44 and occludin gene copy number and spinal muscular atrophy 21857898_Data suggest that the degradation of tight junction proteins ZO-1, claudin-5 and occludin by MMP-2 and -9 secreted by leukemic cells constitutes an important mechanism in the BBB breakdown which contributes to the invasion of leukemic cells to the CNS. 21956164_ClC-2 is closely associated with tight junction protein occludin during early cell-to-cell contacts and the modulation of the tight junction barrier. 22134947_Elevated occludin expression is associated with active ulcerative colitis. 22135309_IL-18 may potentiate inflammation in the context of inflammatory bowel disease by facilitating neutrophil transepithelial migration via MLCK-dependent disruption of tight junctional occludin. 22197032_Study found that Tat protein disrupts occludin by both inhibiting its expression and cleaving it via matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in brain endothelial cells; this finding may help us understand how HIV-1 factors act during neuroAIDS. 22711802_We define the interface between the ZO-1 PDZ3-SH3-U5-GuK (PSG) and occludin coiled-coil (CC) domains. 22761434_TTF-1 transcriptionally regulates occludin 22927233_Sinonasal epithelium in allergic fungal rhinosinusitis displays increased epithelial permeability and an altered expression of occludin. 23155001_HuR promotes occludin translation by blocking occludin mRNA translocation to P-bodies via the displacement of CUGBP1. 23220562_It is concluded that attenuated expression of the TJ proteins occludin and ZO-1 in human gastric epithelial cells could be involved in clopidogrel-induced gastric mucosal injury through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway 23390516_Loss of occludin is involved in adhesion, apoptosis, differentiation, Ca2+-homeostasis and neoplastic transformation in UV-exposed human keratinocytes and in skin neoplasms. 23428392_Data suggest components of diet supplements (here, glutamine/arginine) can improve permeability and tight junction protein expression (OCLN/zona occludens 1) in enterocytes exposed to deleterious effects of antineoplastic agents (here, methotrexate). 23555257_In HepG2 cells, both hepatitis C virus cell entry and tight junction formation were impaired by OCLN silencing and restored by expression of antibody regulatable OCLN mutant. 23792687_Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), an inflammatory atopic disease of the esophagus, causes massive eosinophil infiltration, basal cell hyperplasia, and sub-epithelial fibrosis. Western analysis of pinch biopsies from EoE and normal pediatric patients indicated reduced expression of intercellular junction proteins, E-cadherin and claudin-1 and increased expression of occludin and vimentin. 23793442_identification of a novel deletion/rearrangement of OCLN that results in band-like brain calcification, limited cognitive abilities, failure to thrive and renal dysfunction in early childhood 23924897_We conclude that OCEL-mediated occludin interactions are essential for limiting paracellular macromolecular flux. 24081143_actin cytoskeletal dynamics is detrimental to METH-induced BBB dysfunction by increasing internalization of occludin. 24318462_luciferase assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays showed that KLF4 up-regulated the promoter activities and interacted with 'CACCC' DNA sequence presented in the promoters of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5. 24739782_findings suggest that cerebral vascular cells express functional BACE1. Moreover, elevated vascular BACE1 may contribute to deficiency of occludin in caa. 24862212_LL-37 selectively increased the expression of several claudins and occludin, and enhanced their membrane distribution. 25201524_In conclusion, our present study indicated that miR-34c regulated the permeability of BTB via MAZ-mediated expression changes of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5. 25248927_Zonula occludens-1, occludin and E-cadherin expression and organization in salivary glands 25302477_Study uncovers a novel antiviral effect of miR-122 on human liver cells and shows that over-expression of miR-122 can decrease HCV entry into hepatocytes through down-regulation of OCLN. 25452107_miR-18a and RUNX1 could reversely regulate the permeability of blood-tumor barrier as well as the expressions and distributions of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-5. 25665057_TIMP1 downregulates MMP-2 activity and inhibits the degradation of occluding in Caco-2 intestinal cells 25972430_Glutamine increased claudin-1 expression in the colonic mucosa of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. In contrast, occludin expression was not significantly modified by glutamine. 26080028_Lipid raft-associated processes, such as PP2A and MMP-2 activation, participate in PCB153-induced disruption of occludin function in brain endothelial barrier. 26090670_Angiopoietin-1 Regulates Brain Endothelial Permeability through PTPN-2 Mediated Tyrosine Dephosphorylation of Occludin 26561856_Data show that claudin-6 (CLDN6) R209Q and occludin (OCLN) P24A mutations do not affect HCV pseudoparticles (HCVpp) entry. 26571379_resistance to HCV in HIV+ patients may be related to genetic variation in SCARB1 or OCLN 26662145_autotypic tight junctions molecular composition, like claudin-1 and occludin expression could influence the demyelinating process by altering the permeability of the blood-nerve barrier. 26689621_This is report of a family of Indian origin with two affected sibs and segregation of a homozygous novel OCLN mutation in the exon 3(NG_028291.1(OCLN_v001):c.252delC). 26731262_Data show that estrogen mediates control of hepatitis C virus through the G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor 30 (GPR30) pathway leading to cleavage of occludin by Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). 26731658_In hepatitis C virus -infected human livers, occludin and ADRP mRNA expression levels correlated with each other. Hepatitis C virus increases occludin expression via the upregulation of ADRP. 26863122_OCLN and ZO1 levels appear to be early prognostic markers in patients suffering from sepsis. 26887345_OCLN is essential for HCV infection of human hepatic cells. 26977027_Occludin expression has a clear relationship with bone metastasis in human cancer. 27151944_Intracellular zinc has an essential role in the maintenance of the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier through regulation of occludin proteolysis and claudin-3 transcription. 27185880_Study provides evidence that occludin contributes to the regulation of size-reductive proliferation and epithelial cell maturation in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. 27563375_These data suggest that the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway is involved in HIV-1 Tat-mediated changes in occludin, RAGE, and LRP1 in human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells cells. 27580405_STAT3 activation downregulates the ZO-1 and occludin levels and increases the endothelial permeability through the induction of VEGF production in retinal endothelial cells. 27616439_Report shows that silencing MARCH3 protects the endothelial barrier and upregulates OCLN in MARCH3-depleted cells. MARCH3 silencing results in the strengthening of cell-cell contacts and inactivates FoxO1. 27790907_The mechanism of transition from nondifferentiated to differentiated states in HepaRG cells was studed by proteomics. Two key factors (MMP-14 and OCLN) were validated by qRT-PCR and Western blot. 28153728_Data suggest that long noncoding RNA PlncRNA1 and microRNA miR-34c bound together to regulate the expressions of MAZ, ZO-1 and occludin. 28179633_Molecular studies of the OCLN gene (NM_001205254) identified six distinct candidate mutations in polymicrogyria. 28184927_Downregulation of OCLN is associated with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 28332063_decreased interaction between ZO-1 and occludin might contribute to the epiphora occurred in the transplanted submandibular glands 28386946_we describe a comprehensive molecular screening strategy taking into account the technical challenges associated with the genetic architecture of OCLN, which include the presence of a pseudo-gene and copy number variants. 28534944_Low occludin expression is associated with Renal cell carcinoma. 28642978_Viral infectivity was significantly reduced by miR-200c but enhanced by miR-122. 28681912_Suggest endothelial progenitor cell occluding regulates tube formation, sprouting, and proliferation. 28718701_pericytes share glucose and mitochondria with astrocytes, and that occludin levels modify the ability of pericytes to share those energetic resources 29136627_Endothelial cellsTLR4 strongly regulates retinal vessel permeability by reducing expression of occludin and zonula occludens 1. 29252987_integration of claudin-2, occludin and ZO-1 is necessary for maintaining the function of the proximal tubular epithelium. 29516973_Occludin protein may contribute to the development of cervical cancer. However, it was not correlated with the clinical features. 29750300_our findings for the first time identify the role of occludin as a tumor promoter and a prometastatic factor in lung cancer, demonstrating that occludin is a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in lung cancer 30851935_These results suggest that HO-1 protects the function of placental cells in oxidative stress via regulating ZO-1/occludin. 30868853_high expression affected the tight junction of spermatogenic cells through testis and led to a decrease in the sperm count 31182728_Progesterone decreases gut permeability through upregulating occludin expression in primary human gut tissues and Caco-2 cells. 31257482_in Basaloid squamous cell carcinomas , SOX2 and PCNA had diffuse staining patterns in almost all cancer cells. SOX2 overexpression had little effect on the expression levels of claudin4, occludin and PCNA 31328852_Eighteen residues in the c-terminus are essential for occludin trafficking and hepatitis C virus infection. 31375213_miR-424-5p could affect the expression of tight junction proteins, ZO-1 and occludin, via Endophilin-1, and thereby regulate blood brain barrier (BBB) permeability in an BBB model in vitro with Amyloid-beta incubated endothelial cells. 31794381_OCLN interacted with mitotic spindle regulators, NuMA and RAN, while full-length OCLN loss impaired spindle pole morphology, astral and mitotic microtubule integrity. 32240828_A homozygote frameshift mutation in OCLN gene result in Pseudo-TORCH syndrome type I: A case report extending the phenotype with central diabetes insipidus and renal dysfunction. 32884584_Peripheral Blood Occludin Level as a Biomarker for Perioperative Cerebral Edema in Patients with Brain Tumors. 33001231_Compromised barrier integrity of human feto-placental vessels from gestational diabetic pregnancies is related to downregulation of occludin expression. 33058236_Occludin, caveolin-1, and Alix form a multi-protein complex and regulate HIV-1 infection of brain pericytes. 33441633_Reduced occludin and claudin-7 expression is associated with urban locations and exposure to second-hand smoke in allergic rhinitis patients. 34400226_Application of quantitative immunofluorescence assays to analyze the expression of cell contact proteins during Zika virus infections. 34515239_MiR-224-5p Targeting OCLN Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. 34704946_OCLN gene variants identified in three patients with severe neurodevelopmental disorder associated with epilepsy, intellectual disability and malformation of cortical development. 35222802_Occludin Promotes Adhesion of CD8(+) T Cells and Melanocytes in Vitiligo via the HIF-1alpha Signaling Pathway. 35224833_Occludin facilitates tumour angiogenesis in bladder cancer by regulating IL8/STAT3 through STAT4. 35388524_Occludin stalls HCV particle dynamics apart from hepatocyte tight junctions, promoting virion internalization. |
ENSMUSG00000021638 |
Ocln |
25.553830 |
0.4302252962 |
-1.216836 |
0.305619734 |
16.251300 |
0.00005547150690192472984908766964196047410950995981693267822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000158520705105984335489544001518424920504912734031677246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.3547921 |
3.3373285 |
38.3299149 |
4.9681562 |
| ENSG00000197857 |
51710 |
ZNF44 |
protein_coding |
P15621 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:51710; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
54.767653 |
0.4469435605 |
-1.161835 |
0.255311288 |
20.720904 |
0.00000531327960600377559210582417703605528913612943142652511596679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017247417414694462926838536276363811339251697063446044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.0749636 |
6.2329436 |
74.4809406 |
9.6051210 |
| ENSG00000197860 |
54557 |
SGTB |
protein_coding |
Q96EQ0 |
FUNCTION: Co-chaperone that binds directly to HSC70 and HSP70 and regulates their ATPase activity. {ECO:0000250}. |
Acetylation;Chaperone;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;TPR repeat |
|
Predicted to enable molecular adaptor activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of chaperone-mediated protein folding; posttranslational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane; and ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway. Predicted to be part of TRC complex. Predicted to be active in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:54557; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; TRC complex [GO:0072380]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0006620]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
30943053_miR-365b promoted hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell motility and spreading. Furthermore, SGTB was found to be a downstream target of miR-365b, and knockdown of the SGTB gene could mimic the effect of miR-365b in hastening HCC cell migration and invasion. These results imply that miR-365b plays a tumor-promoting role in HCC by suppressing SGTB expression. |
ENSMUSG00000042743 |
Sgtb |
321.152208 |
3.5121805986 |
1.812367 |
0.107954037 |
285.885605 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000039180277729114129538571199164861319748378197450183586050854728477613381050933644009055859970929710963336075095315933239289323857743245013170364135394304271834547970243534109613392502069473266601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010769104269678297250516073850776287336120752881288439766290805021473206077099157351507907950946648107721591668037412411258234131762940273943923526529204228764646789073822219506837427616119384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
502.7453378 |
33.1618669 |
144.1199974 |
7.7578289 |
| ENSG00000197872 |
81553 |
CYRIA |
protein_coding |
Q9H0Q0 |
FUNCTION: May negatively regulate RAC1 signaling and RAC1-driven cytoskeletal remodeling (Probable). May regulate chemotaxis, cell migration and epithelial polarization by controlling the polarity, plasticity, duration and extent of protrusions (Probable). {ECO:0000305|PubMed:30250061}. |
Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable small GTPase binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of actin filament polymerization. Predicted to be located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:81553; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; regulation of actin filament polymerization [GO:0030833] |
29949196_confirmed that three genes (rs7922405 of MGMT, rs73039426 of RHPN2, and rs7552 of FAM49A) may contribute to nonsyndromic orofacial clefts in Chinese populations 34165494_CYRI-A limits invasive migration through macropinosome formation and integrin uptake regulation. |
ENSMUSG00000020589 |
Cyria |
205.452256 |
3.6117049565 |
1.852680 |
0.144419839 |
163.300718 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000021504315455750289257117593299824035021854045113297039637621057704288658300280581687160206597855989507639407065653358586132526397705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000003355218775125520627136096894617095711632464491765058943745538572976698391332081144987144362542771935942198524571722373366355895996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
303.5384239 |
45.4034587 |
84.2438472 |
9.4011905 |
| ENSG00000197930 |
30001 |
ERO1A |
protein_coding |
Q96HE7 |
FUNCTION: Oxidoreductase involved in disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Efficiently reoxidizes P4HB/PDI, the enzyme catalyzing protein disulfide formation, in order to allow P4HB to sustain additional rounds of disulfide formation. Following P4HB reoxidation, passes its electrons to molecular oxygen via FAD, leading to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the cell. Required for the proper folding of immunoglobulins (PubMed:29858230). Plays an important role in ER stress-induced, CHOP-dependent apoptosis by activating the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor IP3R1. Involved in the release of the unfolded cholera toxin from reduced P4HB/PDI in case of infection by V.cholerae, thereby playing a role in retrotranslocation of the toxin. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10671517, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10970843, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11707400, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12403808, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18833192, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18971943, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23027870, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29858230}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Electron transport;Endoplasmic reticulum;FAD;Flavoprotein;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transport |
|
Enables oxidoreductase activity. Involved in chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:30001; |
dendrite [GO:0030425]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; disulfide oxidoreductase activity [GO:0015036]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; protein-disulfide reductase activity [GO:0015035]; thiol oxidase activity [GO:0016972]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; chaperone cofactor-dependent protein refolding [GO:0051085]; endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response [GO:0030968]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; insulin processing [GO:0030070]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0070059]; peptidyl-proline hydroxylation to 4-hydroxy-L-proline [GO:0018401]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein folding in endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0034975]; protein maturation by protein folding [GO:0022417]; protein modification process [GO:0036211]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051209]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to temperature stimulus [GO:0009266] |
12752442_oxygen regulation of ERO1-Lalpha expression likely is to maintain the transfer rate of oxidizing equivalents to PDI in situations of an altered cellular redox state induced by changes of the cellular oxygen tension 15136577_two conserved cysteine triads in human Ero1alpha cooperate for efficient disulfide bond formation in the endoplasmic reticulum 15161913_glutathione limits Ero1-dependent oxidation in the endoplasmic reticulum 15592500_Hypoxic induction of Ero1-L alpha is key adaptive response in a previously unrecognized HIF-1-mediated pathway that operates to improve protein secretion under hypoxia and might be used for inhibiting tumor growth via inhibiting VEGF-driven angiogenesis. 16677073_Ero1alpha and Ero1beta are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum by interactions with PDI and ERp44 18833192_Results determine the redox-driven shutdown mechanism of Ero1alpha from the formation of a disulphide bond between the active-site Cys(94) and Cys(131). 18971943_Data suggest that partial regulatory disulfide reduction may be a mechanism for preventing excessive Ero1alpha activity and oxidation of PDI or that additional factors are required for Ero1alpha activation within the mammalian ER. 19766098_In this report, the structural model of human Ero1-L alpha was built at first. 20095866_proving that the activity of Ero1-Lalpha results in H(2)O(2) formation in the endoplasmic reticulum 20130085_an appropriate Ero1alpha-PDI ratio is critical for regulating the binding-release cycle of CTA1 by PDI during retro-translocation, and PDI's redox state has a role in targeting it to the retro-translocon 20186508_Results show that within the ER, Ero1alpha is almost exclusively found on the mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM). 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20562109_Ero1alpha is expressed on blood platelets in association with protein-disulfide isomerase and contributes to redox-controlled remodeling of alphaIIbbeta3. 20657012_The results demonstrate that the specificity of Ero1alpha toward the active sites of PDI requires the presence of the regulatory disulfides. 20802462_A dynamic equilibrium between Ero1- and glutathione disulphide-mediated oxidation of protein disulphide isomerases constitutes an important element of endoplasmic reticulum redox homeostasis. 20834232_Ero1alpha limits its oxidative activity using four regulatory cysteines properly positioned within a critical loop that transfers electrons from protein disulphide isomerase to the FAD-containing active site. 21398518_Molecular bases of cyclic and specific disulfide interchange between human ERO1alpha protein and protein-disulfide isomerase (PDI). 21757736_the intramolecular electron transfer from the a domain to the a' domain within PDI during its oxidation by ERO1alpha. 21854214_the levels, subcellular localization, and activity of Ero1alpha coordinately regulate Ca(2+) and redox homeostasis and signaling in the early secretory compartment. 23027870_hyperoxidation generated by Ero1alpha-C104A/C131A is addressed in the ER lumen and is unlikely to exert oxidative injury throughout the cell. 23335490_Report on the establishment of an engineered CHOS cell line that has been engineered to express both XBP-1S) and ERO1-Lalpha and has been named CHOS-XE. CHOS-XE cells produced increased antibody (MAb) yields (5.3- 6.2 fold) in comparison to CHOS cells. 23373818_The high expression of Ero1alpha in cancers of the esophagus and stomach demonstrates the importance of ER redox regulation in the gastro-intestinal (GI) tract in health and disease. 23530257_This paper reported the interactions of Ero1 with protein disulfide isomerase family proteins and chaperones, highlighting the effect that redox flux has on Ero1 partnerships. 23578220_The expression of hERO1-alpha in cancer cells is associated with poorer prognosis. 23919619_GPx7 promotes oxidative protein folding, directly utilizing Ero1alpha-generated hydrogen peroxide in the early secretory compartment. 23979138_Data indicate that protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and ERp44 dynamically localize Ero1alpha and peroxiredoxin 4 in early secretory compartment (ESC). 24022479_ER stress induced by misfolded proinsulin was limited by increased expression of Ero1alpha, suggesting that enhancing the oxidative folding of proinsulin may be a viable therapeutic strategy in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. 24758166_A simple feedback mechanism of regulation of Ero1alpha was identified involving its primary substrate. 25122773_These results indicate that BPA, a widely distributed and potentially harmful chemical, inhibits Ero1-PDI-mediated disulfide bond formation. 25258311_PDI has a role as a competent regulator and a specific substrate of Ero1alpha govern efficient and faithful oxidative protein folding and maintain the ER redox homeostasis 25387528_Data suggest that expression of ERO1alpha (oxidoreductin-1-L-alpha) and CHOP (c/EBP-homologous protein) is up-regulated in liver of patients with acute liver failure. 25595776_These results suggest that overexpression of ERO1-alpha in the tumor inhibits the T cell response by recruiting polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells 25870246_the cancer-associated ERO1-alpha regulates the expression of the MHC class I molecule via oxidative folding 26609561_Data indicate a new mechanism of Ero1alpha regulation in which thiol-disulfide exchange at Cys208-Cys241 affects the stability of the Cys94-Cys131 inhibitory disulfide through allosteric and/or inter-molecular communication. 26987398_High expression of ERO1L is associated with poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. These results indicate that ERO1L expression may be a clinically promising therapeutic target for prevention of gastric cancer. 27100727_Expression of ERO1-alpha in MDA-MB-231 cells promotes tumour growth via promoting angiogenesis. Knockdown of ERO1-alpha inhibits secretion of VEGF by inhibition of oxidative protein folding. In triple-negative breast cancer cases, the expression of ERO1-alpha was upregulated and related to the number of the blood vessels. ERO1-alpha was a poor prognosis factor in triple-negative breast cancer. 27161446_Study shows that ERO1L and NARS expression level are up-regulated in primary lung adenocarcinoma and identifies them with a potential to promote tumor metastasis and growth of cancer cells. 27703014_a mechanism of dual Ero1alpha regulation by dynamic redox interactions between PDI and the two Ero1alpha flexible loops that harbor the regulatory cysteines. 27855403_FBXO6 as a functional E3 ubiquitin ligase for Ero1L that plays a critical role in inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. 28160557_Authors investigated the influence of ERO1-alpha on expression of PD-L1 and immune escape and demonstrated that ERO1-alpha augmented the expression of PD-L1 via facilitation of oxidative protein folding within PD-L1. Authors showed that overexpression of ERO1-alpha increased HIF-1alpha protein expression, resulting in an increase of PD-L1 mRNA as well as protein. 28774960_ERO1alpha plays a crucial role in HSC proliferation via posttranslational modification of collagen and MT1-MMP 28839225_this study involving a gene-modification approach indicate that ERO1alpha is a major proliferation-enhancing factor in cancer cells and could be used as both a diagnostic biomarker of cancer exacerbation and a therapeutic target. 29858230_The authors show that endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1alpha (Ero1alpha), the pivotal sulfhydryl oxidase that catalyzes disulfide formation in the endoplasmic reticulum, is phosphorylated by Fam20C in the Golgi apparatus and retrograde-transported to the endoplasmic reticulum mediated by ERp44. 30076651_Mechanism analysis suggested that ERO1L promoted many tumor-associated signaling pathways, especially the Wnt/catenin pathway; it could activate the Wnt/catenin pathway and upregulate the targets of the Wnt/catenin pathway. 30377291_ERO1-Lalpha promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and angiogenesis through the S1PR1/STAT3/VEGF-A pathway. 30826359_Mutation of Val101 of Ero1 alpha results in a reduced Endoplasmic reticulum , retarded oxidative protein folding and decreased H2O2 levels in the Endoplasmic reticulum of cervical cancer cells and further impairs cell migration, invasion, and tumor growth. 31142270_Data found that ERO1alpha expression increased under chronic hypoxia. Our results show that ERO1alpha was hypoxia-induced in all the tested cancer cell lines. 32102847_Non-native proteins inhibit the ER oxidoreductin 1 (Ero1)-protein disulfide-isomerase relay when protein folding capacity is exceeded. 32724477_Endoplasmic Reticulum stress-dependent expression of ERO1L promotes aerobic glycolysis in Pancreatic Cancer. 32841447_ERO1L promotes NSCLC development by modulating cell cycle-related molecules. 33056994_ERO1L promotes IL6/sIL6R signaling and regulates MUC16 expression to promote CA125 secretion and the metastasis of lung cancer cells. 33531624_The ER stress response mediator ERO1 triggers cancer metastasis by favoring the angiogenic switch in hypoxic conditions. 33559868_ERO1alpha mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via microRNA-101/EZH2 axis in colon cancer RKO and HT-29 cells. 33681386_ERO1L Promotes Hepatic Metastasis through Activating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Pancreatic Cancer. 33751828_The NFIB-ERO1A axis promotes breast cancer metastatic colonization of disseminated tumour cells. 34074138_ERO1-PDI Redox Signaling in Health and Disease. 34354701_ERO1L Is a Novel and Potential Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Shapes the Immune-Suppressive Tumor Microenvironment. 35189109_Crosstalk between ERO1alpha and ryanodine receptor in arsenite-dependent mitochondrial ROS formation. 35785492_ERO1L promotes the proliferation and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma via the Wnt2/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 35853086_Endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1-alpha deficiency and activation of protein translation synergistically impair breast tumour resilience. 36063727_ERO1 alpha deficiency impairs angiogenesis by increasing N-glycosylation of a proangiogenic VEGFA. |
ENSMUSG00000021831 |
Ero1a |
476.708430 |
2.0178931854 |
1.012850 |
0.119004163 |
71.701213 |
0.00000000000000002503786457570290528745209380389457516952079380349264342564552521253062877804040908813476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000194915021696927670767791438829867779766238041513730372411572488999809138476848602294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
632.2294193 |
52.4423688 |
315.1469487 |
19.4538718 |
| ENSG00000197959 |
26052 |
DNM3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UQ16 |
FUNCTION: Microtubule-associated force-producing protein involved in producing microtubule bundles and able to bind and hydrolyze GTP. Most probably involved in vesicular trafficking processes, in particular endocytosis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Endocytosis;GTP-binding;Hydrolase;Microtubule;Motor protein;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins that associate with microtubules and are involved in vesicular transport. The encoded protein functions in the development of megakaryocytes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:26052; |
apical tubulobulbar complex [GO:0061828]; axon [GO:0030424]; basal tubulobulbar complex [GO:0061829]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; dendritic spine head [GO:0044327]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic endocytic zone membrane [GO:0098844]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; synapse [GO:0045202]; synaptic cleft [GO:0043083]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017]; nitric-oxide synthase binding [GO:0050998]; structural constituent of postsynapse [GO:0099186]; type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031798]; type 5 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0031802]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; filopodium assembly [GO:0046847]; negative regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061002]; positive regulation of filopodium assembly [GO:0051491]; positive regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling [GO:1903423]; postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization [GO:0098884]; receptor internalization [GO:0031623]; synapse assembly [GO:0007416]; synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0048488] |
17880892_dynamin-3 and the postsynaptic adaptor Homer positions the endocytic zones near the postsynaptic density 18033314_Upon comparison of PBMC and skin samples of Sezary syndrome versus mycosis fungoides, CDO1 and DNM3 were found upregulated only in Sezary syndrome. 19007685_Dynamin 3 participates in the growth and development of megakaryocytes. 19266077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20700106_Dynamin GTPase regulation is altered by PH domain mutations found in centronuclear myopathy patients. 20935629_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21671749_DNM3 not only participates in megakaryocyte progenitor amplification, but is also involved in cytoplasmic enlargement and the formation of the demarcation membrane system. 22972982_Data indicate that dynamin 3 (DNM3) harbors MEIS1 binding sites and is associated with differences in mean platelet volume (MPV). 24673776_Data show that the classical dynamin DNM1 and DNM3 genes reach their maximum expression levels (100% of maximal expression) in all normal central nervous system tissues studied. 26333682_Microdeletion of DNM3 harboring miR199 and miR214 is associated with skeletal abnormalities. 26784388_DNM3 attenuates the proliferation and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. 27023174_DNM3 may be involved in risk of obsessive-compulsive disorder. 27692902_Genetic variability in DNM3 modifies age of onset for LRRK2 Gly2019Ser parkinsonism. 27837435_In glioma, elevated miR-221 expression is a biomarker for glioma. DNM3 is a target of miR-221 and RELA regulates miR-221 expression. 30133089_DNM3 mutation was not associated with age of Parkinson's disease onset in LRRK2 risk variant carriers and non-carriers in Chinese samples 30340792_There is no evidence of an association between DNM3 variants and age at onset in idiopathic Parkinson's disease. 32573516_The Expression of Dynamin 1, 2, and 3 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Patient Prognosis. 32873436_Analysis of DNM3 and VAMP4 as genetic modifiers of LRRK2 Parkinson's disease. 33622874_TBX15 rs98422, DNM3 rs1011731, RAD51B rs8017304, and rs2588809 Gene Polymorphisms and Associations With Pituitary Adenoma. |
ENSMUSG00000040265 |
Dnm3 |
226.391561 |
2.2734039102 |
1.184854 |
0.105513966 |
127.354859 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001553568532457988619126148475790848628822637818892703387550759773200195776543747552822516411197284469380974769592285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000196829798618711703461215270139790612766705815413995025160836418317485321382177138049840436906379181891679763793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
307.4787700 |
19.9600484 |
136.1833731 |
6.8795915 |
| ENSG00000197965 |
9019 |
MPZL1 |
protein_coding |
O95297 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface receptor, which is involved in signal transduction processes. Recruits PTPN11/SHP-2 to the cell membrane and is a putative substrate of PTPN11/SHP-2. Is a major receptor for concanavalin-A (ConA) and is involved in cellular signaling induced by ConA, which probably includes Src family tyrosine-protein kinases. Isoform 3 seems to have a dominant negative role; it blocks tyrosine phosphorylation of MPZL1 induced by ConA. Isoform 1, but not isoform 2 and isoform 3, may be involved in regulation of integrin-mediated cell motility. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11751924, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12410637}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable structural molecule activity. Predicted to be involved in cell-cell signaling and transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Predicted to act upstream of or within positive regulation of cell migration. Located in cell surface and focal adhesion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:9019; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11751924_PZR is a major receptor of ConA and has an important role in cell signaling via c-Src. Considering the various biological activities of ConA, the study of PZR may have major therapeutic implications 12684038_Characterization of PZR1b, an alternative spliced isoform of PZR. 16702974_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16702974_the MPZL1/PZR gene may be important in the predisposition to schizophrenia among Han Chinese 18568953_Phosphorylation and localization of PZR in cultured endothelial cells is reported. 19064610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19629567_Clinico-electrophysiological features and MRI findings are described in leg musculature from three patients belonging to a CMT2J pedigree due to MPZ Thr124Met mutation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24296779_MPZL1 is a target gene within the 1q24.1-24.2 amplicon that plays a pivotal role in HCC cell migration and tumor metastasis, and a novel MPZL1/Src/cortactin signaling cascade. 28912526_These data demonstrate that the formation of this MPZL1-PTPN11-GRB2 complex is triggered by the attachment of HER2+ breast cancer cells to fibronectin. 30392906_dimerization of MPZL1 participates in control of its signal transmission in cell adhesion. 30877754_Data indicate that myelin protein zero-like 1 (PZR) may promote the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells through increasing the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and protooncogene SRC (Src). 31233194_High MPZL1 expression is associated with proliferation and metastasis of ovarian cancer. 31322261_The present study showed that the expression and protein levels of MPZL1 were significantly higher in gallbladder carcinoma tissues, especially in patients diagnosed with advanced tumor stages. 35637954_LncRNA TNFRSF10A-AS1 promotes gastric cancer by directly binding to oncogenic MPZL1 and is associated with patient outcome. 35727197_MPZL1 upregulation promotes tumor metastasis and correlates with unfavorable prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000026566 |
Mpzl1 |
183.210493 |
3.9021530775 |
1.964270 |
0.160660204 |
148.764332 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000032288997665544529045641669843561404050382662787680430398888950302725686639374237653932479992502369015028307330794632434844970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000004723345941956761588027543914850075959714534733662619804660840217126714351383418839618304890803912599039904307574033737182617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
290.3918057 |
26.3483118 |
74.9837999 |
5.4724034 |
| ENSG00000198039 |
10793 |
ZNF273 |
protein_coding |
Q14593 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene is a member of the krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family and encodes a protein with 13 C2H2-type zinc fingers and a KRAB domain. This nuclear protein is involved in transcriptional regulation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10793; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
|
ENSMUSG00000058246 |
Gm10037 |
82.369462 |
0.4312827905 |
-1.213294 |
0.226025705 |
28.405841 |
0.00000009836808557501514718299017803540551518892698368290439248085021972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000387907866153357457877345676119928974401318555464968085289001464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
53.9963677 |
8.4030832 |
126.0558743 |
13.4699212 |
| ENSG00000198053 |
140885 |
SIRPA |
protein_coding |
P78324 |
FUNCTION: Immunoglobulin-like cell surface receptor for CD47. Acts as docking protein and induces translocation of PTPN6, PTPN11 and other binding partners from the cytosol to the plasma membrane. Supports adhesion of cerebellar neurons, neurite outgrowth and glial cell attachment. May play a key role in intracellular signaling during synaptogenesis and in synaptic function (By similarity). Involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled cellular responses induced by cell adhesion, growth factors or insulin. Mediates negative regulation of phagocytosis, mast cell activation and dendritic cell activation. CD47 binding prevents maturation of immature dendritic cells and inhibits cytokine production by mature dendritic cells. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97797, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10469599, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11509594}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3-binding;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the signal-regulatory-protein (SIRP) family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP family members are receptor-type transmembrane glycoproteins known to be involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. This protein can be phosphorylated by tyrosine kinases. The phospho-tyrosine residues of this PTP have been shown to recruit SH2 domain containing tyrosine phosphatases (PTP), and serve as substrates of PTPs. This protein was found to participate in signal transduction mediated by various growth factor receptors. CD47 has been demonstrated to be a ligand for this receptor protein. This gene and its product share very high similarity with several other members of the SIRP family. These related genes are located in close proximity to each other on chromosome 20p13. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been determined for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:140885; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; cell-cell adhesion mediator activity [GO:0098632]; GTPase regulator activity [GO:0030695]; protein antigen binding [GO:1990405]; protein binding involved in heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0086080]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; protein tyrosine kinase binding [GO:1990782]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to interleukin-12 [GO:0071349]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; monocyte extravasation [GO:0035696]; negative regulation of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 production [GO:0071650]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900016]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of I-kappaB phosphorylation [GO:1903720]; negative regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050728]; negative regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032688]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046329]; negative regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha production [GO:0071641]; negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045019]; negative regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050765]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032675]; regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045428]; regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032680]; regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032649] |
11792697_Signal regulatory protein (SIRPalpha), a cellular ligand for CD47, regulates neutrophil transmigration 11907074_The interaction of SHPS-1 with CD47 may contribute to the recruitment of B lymphocytes via endothelial cells under steady state conditions. 12805067_MyD-1-coupling to this PI 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathway may therefore present a novel target for the development of therapeutic strategies for combating TNFalpha production and consequent inflammatory disease. 14729615_Expression of SIRPalpha1 on astrocytomas may be of considerable importance in brain tumor biology. 15359629_Review. The interaction between CD47 and SIRPalpha seems to be important to limit destruction of host cells in autoimmune diseases like autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), where macrophages destroy antibody or complement opsonized cells. 15374953_Down-modulation of EGFR signaling leads to transcriptional up-regulation of the inhibitory SIRPalpha1 gene. 15842360_SHPS-1 negatively regulates platelet function via CD47, especially alpha(IIb)beta(3)-mediated outside-in signaling 15888547_SHPS-1 functions as an anchor protein that recruits both Shc and SHP-2, whose recruitment is necessary for IGF-I-dependent Shc phosphorylation 16291597_SIRPalpha-CD47 interactions, which reportedly define self, exhibit cell type specificity and limited cross-species reactivity 16697668_highlight major species differences in CD47-SIRPalpha interactions and CD47 integration, suggesting that signaling by CD47 in man may be qualitatively different from mouse. 16825188_Upon IGF-I stimulation, a complex assembles on SHPS-1 that contains SHP-2, c-Src, and Shc wherein Src phosphorylates Shc, a signaling step that is necessary for an optimal mitogenic response 17070842_These results thus revealed the molecular basis by which SIRPalpha binds to CD47 and shed new light into the structural mechanisms of SIRP isoform mediated distinctive extracellular interactions and cellular responses. 17098740_analysis of species-specific CD47 interactions with signal regulatory protein alpha 17142753_the SIRP-alpha pathway might be part of the molecular machinery used by the DC to dampen or resolve an inflammatory response in an IL-10-independent manner 17178844_Relationship between ATM kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), a key mitogenic stimulator. 17360380_Genetic induction of human CD47 on porcine cells could provide inhibitory signaling to SIRPalpha on human macrophages, providing a novel approach to preventing macrophage-mediated xenograft rejection. 17632076_Forced expression of either SIRPalpha1 or SIRPalpha2 displayed distinct suppressive effect on the anchorage-independent growth of Hs578T breast carcinoma cells. 17954568_SIRPalpha may accomplish innate immune activation by seqeuestration of lipopolysaccharides and may modulate toll-like receptor signaling. 18051954_a specific functional role for SIRPalpha in chondrocyte mechano-transduction. 18647419_Data show that forced expression in muscle of the Shp2-activator SIRPalpha1 enhances the disassembly of AChR clusters, whereas the expression of a truncated SIRPalpha1 mutant that suppresses Shp2 signaling inhibites cluster disassembly. 18820737_SIRPalpha negatively regulates beta(2) integrin-mediated monocyte adhesion, transendothelial migration and phagocytosis 18855618_In this review, the CD47/thrombospondin-1/signal-regulatory protein (SIRP)-alpha inhibitory axis is proposed as an important sensor to maintain homeostasis and regulate innate and adaptive immune responses. 18954403_Expression levels of CD47, CD35, CD55, and CD59 on red blood cells and signal-regulatory protein-alpha,beta on monocytes from patients with warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19299420_Data emphasize the importance of formation of SHPS-1 signaling complex induced by IGF-I and provide novel insights into our knowledge of the role of this molecular scaffold in regulation of IGF-I-stimulated signal transduction and biological actions. 19628875_Data show show that the CD47-SIRPalpha interaction will span a distance of around 14 nm between interacting cells, comparable with that of an immunological synapse. 19748659_CD47/SIRP-alpha interactions are implicated in the pathogenesis of DC-driven allergic airway inflammation. 19874234_SIRP alpha gene expression is higher in monocytes from autoimmune hemolytic anemia patients, compared with basal expression. 20207740_Insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated insulin receptor substrate-1 negatively regulates Src homology 2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 function in vascular smooth muscle cells. 20299253_Inhibition of engulfment correlates with affinity of CD47 for SIRPA - but only at low levels of CD47. 20473329_SIRPalpha1 specifically affects the SHP-2/FAK/Grb2/Sos-1/MAPK activation loop to downmodulate EGFRvIII-mediated migration and transformation. 20643654_Findings reveal a novel mechanism for recruitment of PDK1 to the SHPS-1 signaling complex, which is required for IGF-I-stimulated AKT Thr(308) phosphorylation and inhibition of apoptosis. 20705613_Poor prognosis of breast cancer patients with high expression of CD47 is due to an active CD47/SIRPA signaling pathway in circulating cells. 20826546_The prolactin receptor (PRLr)-SIRPalpha-integrin complex provides a basis for integrin-PRLr cross-talk that contributes to the biology of breast cancer. 20826801_The role of cis dimerization of signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) in binding to CD47. 21169408_SHP-2 as an essential component of tumor suppression and anoikis mediated by SIRPalpha1 in human breast carcinoma cells as well as in v-Src-transformed cells. 21225905_Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in PTPNS1 is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 21369691_the relationships between SIRPalpha1 and beta-catenin in leukemia cells. 21788504_Sensing of cell surface CD47 expression by phagocyte SIRPalpha is a critical determinant of T- and natural killer-cell homeostasis under steady-state conditions in vivo. 21788509_hSIRPa-transgenic Rag2(-/-)gamma(c)(-/-) mice represent a unique mouse strain supporting high levels of human cell engraftment. 22409853_SIRPalpha1 in hepatic sinusoid Kupffer cells is associated with the extent of autoimmune hepatitis. 22451913_data, taken together with similar findings with other human neoplasms, show that CD47 is a commonly expressed molecule on all cancers, its function to block phagocytosis is known, and blockade of its function leads to tumor phagocytosis and elimination 22490440_SIRPalpha/CD172a and FHOD1 are unique markers of littoral cells, a recently evolved major cell population of red pulp of human spleen. 22511785_Surfactant protein D (Sp-D) binds to membrane-proximal domain (D3) of signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha), a site distant from binding domain of CD47, while also binding to analogous region on signal regulatory protein beta (SIRPbeta). 22738830_IFN-beta and IFN-gamma/TNF-alpha decrease erythrophagocytosis by human monocytes in vitro, and this effect does not apparently require an increase in SIRP-alpha or SHP-1 expression. 22747997_In the glomeruli of CNS patients carrying mutations in NPHS1, where SD formation is disrupted, the expression of SIRPalpha as well as Neph1 and nephrin was significantly decreased, indicating that SIRPalpha is closely associated with the nephrin complex 22815949_thymic Sirpalpha(+) cDCs crucially contribute to a process of intrathymic tumor immune tolerance that involves CCR2 and CCL2 23271705_neutrophils reduce their SIRPalpha expression during apoptosis, which may be part of the functional down-regulation seen in apoptotic neutrophils. 23314616_SHPS-1 negatively regulates the MyD88-dependent TLR signaling pathway through the inhibition of NF-kappaB activation 23320069_Expression of SIRPalpha on two low SIRPalpha acute myeloid leukemia (AML) expressing cell lines could be upregulated upon differentiation of the cells. 23504854_Signal regulatory protein alpha is associated with tumor-polarized macrophages phenotype switch and plays a pivotal role in tumor progression. 23669395_An avidity-improved CD47 fusion protein (CD47-Var1) suppresses the release of a wide array of inflammatory cytokines by CD172a(+) cells. 24026300_These results demonstrate a SIRPalpha-based mechanism that dynamically regulates polymorphonuclear leukocyte inflammatory responses. 24101669_SIRPA plays a protective role in cardiac hypertrophy through negative regulation of the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. 24143245_'clustering' SIRPalpha into plasma membrane microdomains is essential for activated monocytes and macrophages to effectively interact with CD47 and initiate intracellular signaling 24162948_The independent non-obstructive azoospermia risk alleles are driven by variants in the protein-coding sequence of the two genes, SIRPA and SIRPG. 24511121_These results suggest that thrombospondin-1 binding to SIRP-alpha on nonphagocytic cells activates NADPH oxidase, limits vasodilation, and promotes renal ischemia reperfusion injury. 24516072_negatively regulates neutrophil accumulation during inflammation 24550402_Polymorphisms in the human inhibitory signal-regulatory protein alpha do not affect binding to its ligand CD47. 24968096_Combinatorial expression of NKX2-5, SIRPA, VCAM1 and CD34 can be used to define discrete stages of cardiovascular cell lineage differentiation. 25837251_Velcro' engineering of high affinity CD47 ectodomain as signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) antagonists that enhance antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis 26085683_Loss of cell surface CD47 clustering formation and binding avidity to SIRPalpha facilitate apoptotic cell clearance by macrophages. 26116271_agents that block the CD47:SIRP-alpha engagement are attractive therapeutic targets as a monotherapy or in combination with additional immune-modulating agents for activating antitumor T cells in vivo 26492885_exploited by Hepatitis E virus to negative regulated IFN-beta of the host innate immune system to promote viral infection 26534964_the data suggest that combinatorial actions of ADAM10 and gamma-secretase on SIRPalpha cleavage promote inflammatory signaling. 26573233_Data suggest a reduction in the CD47 antigen/signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) pathway by programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade, which regulates Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and tumor associated macrophages (TAMs). 27728760_CD47, TSP1, and to a lesser extent SIRPalpha facilitate exosome-mediated myeloid-derived suppressor cells chemotaxis and migration. 27793032_SIRPalpha might play an important role in the progression of oral leukoplakia and oral cancer, and could be a pivotal therapeutic target in oral squamous cell carcinoma, regulating the phenotype of macrophages via targeting NF-kappaB signaling. 27856600_TTI-621 (SIRPalphaFc) is a fully human recombinant fusion protein that blocks the CD47-SIRPalpha axis by binding to human CD47 and enhancing phagocytosis of malignant cells..These data indicate that TTI-621 is active across a broad range of human tumors. 27900675_SIRP alpha protein is under-expressed in low and high-grades of astrocytoma from patients' brain samples. 28669759_Accumulation of SIRPalpha-inhibited macrophages in tumors favored tumor regression for 1-2 weeks, but donor macrophages quickly differentiated toward non-phagocytic, high-SIRPalpha TAMs. 29084248_data suggest that TTI-621 may be efficacious in triggering the destruction of cancer cells by a diverse population of TAMs found in vivo and support possible combination approaches to augment the activity of CD47 blockade 29158380_Anti-SIRPA antibody immunotherapy enhances neutrophil and macrophage antitumor activity. 30833751_QPCTL is critical for pyroglutamate formation on CD47 at the SIRPalpha binding site shortly after biosynthesis. 30863997_Collectively, the rs2477686 in PEX10 , rs6080550 in SIRPA-SIRPG, and rs10842262 in SOX5 gene may indeed be the genetic risk factors for nonobstructive azoospermia (NOA), which requires further investigation using larger independent sets of samples in different ethnic populations. 30888336_Signal regulatory protein alpha protects podocytes through promoting autophagic activity. 30910815_these results identify SIRPalpha as a counter-receptor for Mac-1 and suggest that the Mac-1-SIRPalpha interaction may be involved in macrophage fusion. 31089204_The enzymatic activity of isoQC is required for the sufficient binding of SIRPalpha to CD47. 31507080_Results show that SIRPalpha plays an important role as an anti-insulin mediator regulating pathways to cachexia. In muscle-specific SIRPalpha KO, changes in SIRPalpha serum levels seem to improve insulin signalling in muscle and white adipose tissue, suggesting crosstalk between muscle and adipose tissue. 31611550_Increased numbers of high SIRPalpha expressing CD14(+) monocyte /macrophages were associated with an inferior survival in Follicular Lymphoma. 32196807_TSP1-CD47-SIRPalpha signaling facilitates the development of endometriosis by mediating the survival of ectopic endometrium. 32240171_We also demonstrate the utility of the assay to characterize the activity of the first reported small molecule antagonists of the SIRPa-CD47 interaction. 32433947_The CD47-SIRPalpha Immune Checkpoint. 33799989_Expression and Prognostic Significance of CD47-SIRPA Macrophage Checkpoint Molecules in Colorectal Cancer. 34009732_Clinical significance of signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 34180101_Impact of SIRPalpha polymorphism on transplant outcomes in HLA-identical living donor kidney transplantation. 34512146_CD47/SIRPalpha pathway mediates cancer immune escape and immunotherapy. 34667145_XBP1 regulates the protumoral function of tumor-associated macrophages in human colorectal cancer. 34917090_Imaging of Glioblastoma Tumor-Associated Myeloid Cells Using Nanobodies Targeting Signal Regulatory Protein Alpha. 35222883_High SIRPA Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis and Correlates with Immune Infiltrates in Patients with Esophageal Carcinoma. 35795660_CD47-SIRPalpha Controls ADCC Killing of Primary T Cells by PMN Through a Combination of Trogocytosis and NADPH Oxidase Activation. 36202053_SIRPalpha maintains macrophage homeostasis by interacting with PTK2B kinase in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and through autophagy and necroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000095788+ENSMUSG00000095028+ENSMUSG00000074677+ENSMUSG00000037902+ENSMUSG00000078780+ENSMUSG00000078783 |
Sirpb1a+Sirpb1b+Sirpb1c+Sirpa+Gm5150+Gm9733 |
1497.055941 |
2.5715703102 |
1.362650 |
0.042691088 |
1037.927932 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001023887801939039425362736137469956780616500158682160852052727486174738524566001607028084812778349085518 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001103108318001476009947748868307649470313963137792396265226322944754396531800456294752591672188107389728 |
Yes |
No |
2173.8117661 |
55.0782756 |
851.0927862 |
17.4540103 |
| ENSG00000198108 |
337876 |
CHSY3 |
protein_coding |
Q70JA7 |
FUNCTION: Has both beta-1,3-glucuronic acid and beta-1,4-N-acetylgalactosamine transferase activity. Transfers glucuronic acid (GlcUA) from UDP-GlcUA and N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) from UDP-GalNAc to the non-reducing end of the elongating chondroitin polymer. Specific activity is much reduced compared to CHSY1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12907687}. |
Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
CSS3 is a glycosyltransferase that has both glucuronyltransferase and N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activities (Yada et al., 2003 [PubMed 12907687]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:337876; |
Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0008376]; glucuronosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase activity [GO:0047238]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase activity [GO:0050510]; chondroitin sulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0030206] |
12907687_The full-length open reading frame consists of 882 amino acids and encodes a typical type II membrane protein. This enzyme contains a beta 3-glycosyltransferase motif and a beta 4-glycosyltransferase motif similar to that found in CSS1. 17253960_results suggest that chondroitin polymerization is achieved by multiple combinations of chondroitin synthase-1, chondroitin synthase-2, and chondroitin-polymerizing factor 21468578_The present study focused on the expression of chondroitin-synthesizing enzymes in colorectal cancer. 33089528_Chondroitin synthase-3 regulates nucleus pulposus degeneration through actin-induced YAP signaling. 33390789_Reduction of pl-CSA through ChSy-2 knockout inhibits tumorigenesis and metastasis of choriocarcinoma in JEG3 cells. |
ENSMUSG00000058152 |
Chsy3 |
66.325196 |
0.2847031174 |
-1.812470 |
0.216893149 |
71.736948 |
0.00000000000000002458850600424695433402755018500685773901851670527034937618893195576674770563840866088867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000191517862070018489687798454923377346445934071459890613020604632765753194689750671386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.5331256 |
4.7979300 |
111.2906022 |
10.7365547 |
| ENSG00000198121 |
1902 |
LPAR1 |
protein_coding |
Q92633 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) (PubMed:9070858, PubMed:19306925, PubMed:25025571, PubMed:26091040). Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell migration, differentiation and proliferation, and thereby contributes to the responses to tissue damage and infectious agents. Activates downstream signaling cascades via the G(i)/G(o), G(12)/G(13), and G(q) families of heteromeric G proteins. Signaling inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity and decreases cellular cAMP levels (PubMed:26091040). Signaling triggers an increase of cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels (PubMed:19656035, PubMed:19733258, PubMed:26091040). Activates RALA; this leads to the activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (PubMed:19306925). Signaling mediates activation of down-stream MAP kinases (By similarity). Contributes to the regulation of cell shape. Promotes Rho-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in neuronal cells and neurite retraction (PubMed:26091040). Promotes the activation of Rho and the formation of actin stress fibers (PubMed:26091040). Promotes formation of lamellipodia at the leading edge of migrating cells via activation of RAC1 (By similarity). Through its function as lysophosphatidic acid receptor, plays a role in chemotaxis and cell migration, including responses to injury and wounding (PubMed:18066075, PubMed:19656035, PubMed:19733258). Plays a role in triggering inflammation in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via its interaction with CD14. Promotes cell proliferation in response to lysophosphatidic acid. Required for normal skeleton development. May play a role in osteoblast differentiation. Required for normal brain development. Required for normal proliferation, survival and maturation of newly formed neurons in the adult dentate gyrus. Plays a role in pain perception and in the initiation of neuropathic pain (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P61793, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18066075, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19306925, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19656035, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19733258, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25025571, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26091040, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9070858, ECO:0000305|PubMed:11093753, ECO:0000305|PubMed:9069262}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endosome;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The integral membrane protein encoded by this gene is a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor from a group known as EDG receptors. These receptors are members of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Utilized by LPA for cell signaling, EDG receptors mediate diverse biologic functions, including proliferation, platelet aggregation, smooth muscle contraction, inhibition of neuroblastoma cell differentiation, chemotaxis, and tumor cell invasion. Many transcript variants encoding a few different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2020]. |
hsa:1902; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; endosome [GO:0005768]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; G-protein alpha-subunit binding [GO:0001965]; lysophosphatidic acid binding [GO:0035727]; lysophosphatidic acid receptor activity [GO:0070915]; PDZ domain binding [GO:0030165]; activation of phospholipase C activity [GO:0007202]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; bleb assembly [GO:0032060]; cell chemotaxis [GO:0060326]; cellular response to 1-oleoyl-sn-glycerol 3-phosphate [GO:1904566]; cellular response to oxygen levels [GO:0071453]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; corpus callosum development [GO:0022038]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; myelination [GO:0042552]; negative regulation of cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0043951]; negative regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010977]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; optic nerve development [GO:0021554]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration involved in phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled signaling pathway [GO:0051482]; positive regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060999]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction [GO:0035025]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell chemotaxis [GO:0071673]; positive regulation of stress fiber assembly [GO:0051496]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization [GO:0099149]; regulation of synaptic vesicle cycle [GO:0098693] |
11948806_LP(A1) and myelin basic protein colocalized in brain, but oligodendrocyte soma showed stronger signals for LP(A1) than myelinated fibers, whereas the reverse was true for myelin basic protein so LP(A1) may be involved in myelin formation or maintenance. 12123830_demonstrate that two biological fluids, blood plasma and seminal plasma, differentially activate LPA receptors 12393875_Data suggest that LPA(1) receptors couple to a G(i)-phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Tiam1 pathway to activate Rac, with consequent suppression of RhoA activity, and thereby stimulate cell spreading and motility. 12668728_lysophosphatidic acid-coupled LPA1/EDG-2 receptors are endocytosed via a dynamin2- and Rab5-dependent pathway 12670925_LPA acts as a potent stimulator of colon cancer progression, although the binding to LPA1 and LPA2 induces slightly different responses. 14688263_LPA stimulation promotes the interaction of the LPA(2) receptor with a focal adhesion molecule, TRIP6 14696401_EDG-2 expression was increased in low-grade adenoma compared with that in normal mucosa (P |
ENSMUSG00000038668 |
Lpar1 |
133.733653 |
4.1958207819 |
2.068953 |
0.156262794 |
182.944391 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000001102981993581687597138285230116132657024087423551417680305247190246573833619040377642989200222285949253963471816675223635684233158826828002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000192891163806465753488722362338444624965554608220904798294411488833202520672736695382938378089768022716904427582562675524968653917312622070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
213.6958129 |
21.5650846 |
51.2463735 |
4.2844294 |
| ENSG00000198125 |
4151 |
MB |
protein_coding |
P02144 |
FUNCTION: Serves as a reserve supply of oxygen and facilitates the movement of oxygen within muscles. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Heme;Iron;Metal-binding;Muscle protein;Oxygen transport;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a member of the globin superfamily and is predominantly expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscles. The encoded protein forms a monomeric globular haemoprotein that is primarily responsible for the storage and facilitated transfer of oxygen from the cell membrane to the mitochondria. This protein also plays a role in regulating physiological levels of nitric oxide. Multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms exist for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. |
hsa:4151; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; oxygen binding [GO:0019825]; oxygen carrier activity [GO:0005344]; brown fat cell differentiation [GO:0050873]; enucleate erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0043353]; heart development [GO:0007507]; oxygen transport [GO:0015671]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666] |
12006163_Screening of exon 2 of the myoglobin gene in high altitude Tibetans does not show novel polymorphism or selection for specific myoglobin alleles as a function of altitude of residence or hypoxic challenge. 12030657_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12745799_myoglobin/carbonic anhydrase III ratio in the blood proved to be a more specific indicator for myocardial damage than myoglobin alone after myocardial infarction. 12760310_It was concluded that myoglobin levels on admission and TnT at 2 h had the greatest diagnostic rate for myocardial infarction. 14506721_Oxidative stress associated with myoglobin expression specifically in mitochondrial diseases. 15048578_determination of myoglobin concentration and succinate dehydrogenase activity in serial sections indicate that myoglobin can lead to a substantial reduction (18-60%) of the extracellular oxygen tension required to prevent an anoxic core in muscle cells 15226628_Quantitative test is useful for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarct and as an indicator of its severity. 15226631_Binding to blood fatty acid binding protein and may be a marker for cardiac damage in hemodialysis patients. 15485667_heme rotates about the alpha-gamma axis of human myoglobin without leaving the protein cage 15601759_energy analysis of myoglobin recognition of oxygen 15644316_S-nitroso oxymyoglobin stores vasoactive nitric oxide 17311997_iron mobilization and myoglobin down-modulation are elicited by enhanced erythropoiesis from elevated iron 17605115_Data show plasma MG may be considered as a novel marker of muscle mass indicating best the mass of MG-rich type 1 and 2a fibers as well as VO(2)max as an important functional readout. 17883274_analysis of covalent modification, unfolding, and aggregation of human holo-myoglobin induced by tyrosinase-generated quinones 17996904_In this study, we showed for the first time the connection of ROR2 in Dupuytren's disease. ROR2 and myoglobin may play an important role in the pathophysiology of this disease 19005161_Hypoxia reprograms calcium signaling and regulates myoglobin expression. 19523464_The Dimension Vista cTnI, CK-MB, MYO, NTproBNP, and hsCRP methods demonstrate acceptable performance characteristics for use as an aid in the diagnosis and risk assessment of patients presenting with suspected acute coronary syndromes. 19541931_myoglobin is expressed at high levels by human carcinoma cells 19650765_Exposure of vascular smooth muscle (either in cell culture or intact vessels) to pathological nitric oxide (*NO) promotes an up-regulation of the Mb gene and protein, suggesting a feedback relationship between *NO and Mb. 20124401_Using a cardiovascular model suggest that myoglobin oxygen storage/transport becomes significant during systolic reduction of coronary blood flow rather than during diastole. 20531416_71% of tumours displayed Mb protein expression in significant correlation with a positive hormone receptor status and better prognosis. 20668762_Water entry into the heme pockets of isolated hemoglobin subunits was detected by optical methods. 20873231_Kinetics of interaction between apomyoglobin and phospholipid membrane 21256983_These results show that glutathione reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced protein decomposition due to reduction of the C110-thiyl radical in WTwild type human Mb by electron transfer. 21601304_overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with histological subtype and hypoxia 21639835_Apomyoglobin mutants with point mutations at val10 forms amyloid structures at permissive temperature. 21640426_may have potential significance in the prognostication of lung adenocarcinomas 21782983_MD simulations supported NMR results indicating interesting structural/dynamical differences in the average volume and occurrence of the main cavities lining Mb prosthetic group. 21930697_The mitochondrion-impairing role of MB in hypoxic cancer cells is part of a novel tumor-suppressive function. 23247055_Our LFIA performance was additionally compared with electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLI) detection for simultaneous determination of hs-cTnI and myoglobin in patients with suggestive of acute myocardial infarction . 23297402_Hydrophobic effect drives oxygen uptake in myoglobin via histidine E7. 23839096_Misfolding and amyloid aggregation of apomyoglobin. 23931877_Blood myoglobin could serve as a valuable early predictor and marker of rhabdomyolysis and acute myoglobinuric kidney injury 24026678_the novel cancer-associated MB splice variants exhibited increased expression in tumor cells subjected to experimental hypoxia; the novel gene regulatory mechanisms unveiled in this study support the idea of a non-canonical role of MB during carcinogenesis 24076247_High myoglobin expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 24446190_Findings indicate that myoglobin (Mb) and neuroglobin (Ngb) can be expressed in nonmuscle and non-neural contexts. 25002394_A non-ischemic serum myoglobin release is rare, but could be associated in subgroups of patients. 25172328_Analogous to breast cancer, MB expression in prostate cancer is associated with steroid hormone signaling and markers of hypoxia 25452214_Data show that chimeric neuroglobin and myoglobin were generated by swapping a regulatory segment. 26271987_Data show that with the myoglobin (MYO) monoclonal antibody of high specificity and affinity, a one-step sandwich ELISA for detecting MYO has been established successfully, which provides a basis for the development of domestic ELISA kit. 26559958_analysis of myoglobin gene regulatory networks in breast and prostate cancer 26894983_In the absence of Mb, the Y-shape structure remains intact. So, a weak electrochemical signal is observed. Upon addition of target, the DApt leave the CS and bind to Mb, leading to disassembly of Y-shape structure and following the addition of Exo I, a strong electrochemical signal could be recorded. 27038680_Report morphology of myoglobin casts in renal biopsies with acute kidney injury. 27056440_Myoglobin is associated with larger hematoma volume and growth after adjusting potential confounding factors in intracerebral hemorrhage. 27323063_we found that the A79G polymorphism of the MB gene plays an important role in influencing the development of exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage. 27417724_Electroanalysis of myoglobin as a marker of acute myocardial infarction by means of screenprinted electrodes modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes and polymeric artificial antibodies is developed. Plastic antibodies to myoglobin (molecularly imprinted polymers, MIPs) based on o-phenylenediamine were produced by electropolymerization. Molecular imprinting technology in biosensor analysis was used. 29857573_The results showed that the MI-based bio-sensing system had high selectivity and sensitivity for detection of Cardiac biomarkers . Compared with the control region, ultrasensitive detections of CRP and Mb were accomplished with the detection limits of 1.0 pg/mL and 0.1 pg/mL, respectively. 30183107_Despite the structural similarity of myoglobin to alpha and beta subunits of hemoglobin, there is a functional difference between the two proteins, owing to the quaternary structure of hemoglobin. The effect of the quaternary structure of hemoglobin on the intrinsic dynamics of its subunits is explored by dynamical comparison of the two proteins. 30918256_Study identifies a recurrent c.292C>T (p.His98Tyr) substitution in MB in fourteen members of six European families suffering from an autosomal dominant progressive myopathy with highly characteristic sarcoplasmic inclusions in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Myoglobinopathy manifests in adulthood with proximal and axial weakness that progresses to involve distal muscles and causes respiratory and cardiac failure. 31894249_The role of myoglobin in epithelial cancers: Insights from transcriptomics. 32006209_Myoglobin for Detection of High-Risk Patients with Acute Myocarditis. 32260401_Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Kinetic Study of Fluoride Binding to V21C/V66C Myoglobin with a Cytoglobin-like Disulfide Bond. 32957872_Protective Potential of Uric Acid, Folic Acid, Glutathione and Ascorbic Acid Against the Formation of Toxic Met-Myoglobin. 34671319_Myoglobin Protects Breast Cancer Cells Due to Its ROS and NO Scavenging Properties. 34679218_Pseudoperoxidase activity, conformational stability, and aggregation propensity of the His98Tyr myoglobin variant: implications for the onset of myoglobinopathy. 34972240_GAPDH is involved in the heme-maturation of myoglobin and hemoglobin. |
ENSMUSG00000018893 |
Mb |
177.589507 |
0.4150841723 |
-1.268524 |
0.117926084 |
117.916054 |
0.00000000000000000000000000180883836479554096846651296662332112840667183559399624382667634888628466378890369270493465592153370380401611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000021273668736559509613882123438394484939403631790732042948281117407348102081587892797642780351452529430389404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
109.6985306 |
7.8107617 |
266.3252994 |
12.1362020 |
| ENSG00000198169 |
90987 |
ZNF251 |
protein_coding |
Q9BRH9 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to act upstream of or within hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90987; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis [GO:0061484]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000022526 |
Zfp251 |
117.940306 |
0.4922799694 |
-1.022449 |
0.160498082 |
40.992260 |
0.00000000015283331188663595962748260374494159441471907712184474803507328033447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000781913235163517145115759448767162737015112838889763224869966506958007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
80.4913744 |
10.0575640 |
164.6700668 |
14.0181422 |
| ENSG00000198185 |
55713 |
ZNF334 |
protein_coding |
Q9HCZ1 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a member of the C2H2 zinc finger family. The encoded protein contains a Krueppel-associated box, fourteen C2H2 zinc finger domains, and four C2H2-type/integrase DNA-binding domains. Decreased expression of this gene may be a marker for rheumatoid arthritis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2012]. |
hsa:55713; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
25738173_results obtained in vitro for helper lymphocytes of healthy individuals seem to mimic the regulatory effect of TNFalpha on the expression of ZNF334 in the cells of RA patients 35507080_Disruption of ZNF334 promotes triple-negative breast carcinoma malignancy through the SFRP1/ Wnt/beta-catenin signaling axis. 35534462_DNA hypermethylation modification promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma by depressing the tumor suppressor gene ZNF334. |
ENSMUSG00000017667 |
Zfp334 |
15.744821 |
0.2956343908 |
-1.758114 |
0.472519061 |
13.932160 |
0.00018952779720728606897145462895082346221897751092910766601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000498739576890629772616680970287461605039425194263458251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8281631 |
2.2589738 |
26.5065829 |
4.6182704 |
| ENSG00000198216 |
777 |
CACNA1E |
protein_coding |
Q15878 |
FUNCTION: Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells (PubMed:30343943). They are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1E gives rise to R-type calcium currents. R-type calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group and are blocked by nickel. They are however insensitive to dihydropyridines (DHP). Calcium channels containing alpha-1E subunit could be involved in the modulation of firing patterns of neurons which is important for information processing. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:30343943}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Calcium channel;Calcium transport;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Voltage-dependent calcium channels are multisubunit complexes consisting of alpha-1, alpha-2, beta, and delta subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. These channels mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells, and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. This gene encodes the alpha-1E subunit of the R-type calcium channels, which belong to the 'high-voltage activated' group that maybe involved in the modulation of firing patterns of neurons important for information processing. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]. |
hsa:777; |
neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; voltage-gated calcium channel complex [GO:0005891]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0008331]; voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:0005245]; voltage-gated cation channel activity [GO:0022843]; calcium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:0098703]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765] |
15845089_Review discusses the roles of Cav2.3-containing E-type Ca2+ channels which exhibit several subunit-specific features, trigger exocytosis and are also involved in long-term potentiation. 16855219_Full-length RGS3, RGS3T, and the core domain of RGS3 were equally effective in antagonizing inhibition of Ca(V)2.3 through M(2)R. 17050807_Neurokinin 1 receptorsmodulate CaV2.3 using three different signaling mechanisms: a fast inhibition mediated by Gbeta gamma, a slow inhibition mediated by Galpha(q/11), and a slow stimulation mediated by protein kinases C. 17189400_Amplification and overexpression of CACNA1E correlates with relapse in favorable histology Wilms' tumors. 17660294_analysis of a three-dimensional homology model of Ca(V)2.3 based upon Kv1.2 where hydrophobic residues at positions facing Val(1720) in IS6, IIS6, and IIIS6 play a critical role in stabilizing the closed state in Ca(V)2.3 17720895_A functional variant in CACNA1E contributes to type 2 diabetes susceptibility in Pima indians by affecting insulin action. 17720895_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17727731_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17934712_Genetic variation in the CACNA1E gene contributes to an increased risk of the development of type 2 diabetes by reducing insulin secretion. 17934712_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18037383_These findings strongly suggest that both H179 and H183 in the IS3-IS4 loop are essential structural determinants required for nickel sensitive inhibition of the Cav2.3. 18676988_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20026913_Swapping the I-II intracellular linker between L-type CaV1.2 and R-type CaV2.3 high-voltage gated calcium channels exchanges activation attributes. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21482359_Lack of high-voltage activated Cav2.3 channels results in a marked decrease in the sensitivity of transgenic animals to gamma-butyrolactone-induced absence epilepsy. 21691059_Ca(v)2.3 Ca2+ channel interacts with the G1-subunit of V-ATPase. 22178872_the II-III loop of the Ca(v)2.3 calcium channel binds APLP1 and that this binding promotes internalization of the channel 22427875_CACNA1E variants affect beta cell function in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. 22633975_The C-terminus of human Ca(v)2.3 voltage-gated calcium channel interacts with alternatively spliced calmodulin-2 expressed in two human cell lines 22846999_quartet of leucine residues in the guanylate kinase domain of CaVbeta determines the plasma membrane density of the CaV2.3 channel. 23940630_CACNA1E gene single nucleotide polymorphisms may be involved in fentanyl sensitivity. 25741585_Data suggest that, in vascular smooth muscle cells, increase in cytosolic endothelin-1 (EDN1) induces sustained increase in nuclear Ca2+ via stimulation of R-type calcium channel (CACNA1E) present at the nuclear membrane. 27480382_Carriers of the minor G allele of the rs3845446 SNP exhibited enhanced pain-related phenotypes after gastrointestinal surgery. The pain-related phenotypes of carriers of the minor allele of this SNP after gastrointestinal surgery were opposite to such phenotypes after orthognathic surgery. 28573794_This study identified a polymorphism in exon 20 of the CACNA1E gene (Asp859Glu - rs35737760) that is more prevalent in hemiplegic and brain stem aura migraine. 30343943_The variants in CACNA1E as a cause of DEEs. 32019549_F0F1 ATP synthase regulates extracellular calcium influx in human neutrophils by interacting with Cav2.3 and modulates neutrophil accumulation in the lipopolysaccharide-challenged lung. 32529299_Cav2.3 R-type calcium channels: from its discovery to pathogenic de novo CACNA1E variants: a historical perspective. 34702355_De novo variants in CACNA1E found in patients with intellectual disability, developmental regression and social cognition deficit but no seizures. 34837834_Direct inhibition of CaV2.3 by Gem is dynamin dependent and does not require a direct alfa/beta interaction. 35026540_Mutations and clinical significance of calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha 1E (CACNA1E) in non-small cell lung cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000004110 |
Cacna1e |
706.041217 |
15.0630591134 |
3.912943 |
0.631985795 |
28.572451 |
0.00000009025722708367804245422526482692249238937165500828996300697326660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000357636690404050414388833828080449528385997837176546454429626464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1345.2269133 |
479.4046584 |
89.9325290 |
23.2335254 |
| ENSG00000198270 |
89894 |
TMEM116 |
protein_coding |
Q8NCL8 |
|
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:89894; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189] |
34789718_TMEM116 is required for lung cancer cell motility and metastasis through PDK1 signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000029452 |
Tmem116 |
98.020777 |
2.6934139192 |
1.429436 |
0.601826953 |
5.387013 |
0.02028717316179768151429563260990107664838433265686035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036330826967742514688186616922394023276865482330322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
213.3249085 |
85.7760433 |
79.9561887 |
23.0307996 |
| ENSG00000198324 |
144717 |
PHETA1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N4B1 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in endocytic trafficking. Required for receptor recycling from endosomes, both to the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21233288}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a protein that localizes to the endosome and interacts with the enzyme, inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase OCRL-1. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
hsa:144717; |
clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; trans-Golgi network [GO:0005802]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; endosome organization [GO:0007032]; receptor recycling [GO:0001881]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147] |
20133602_Two closely related endocytic proteins, Ses1 and Ses2, which interact with OCRL, were identified. The interaction is mediated by a short amino acid motif similar to that used by the rab-5 effector APPL1. 21233288_Two novel OCRL1-binding proteins, termed inositol polyphosphate phosphatase interacting protein of 27 kDa (IPIP27)A and B (also known as Ses1 and 2), that also bind the related 5-phosphatase Inpp5b, were identified. 32152089_Deficiency in the endocytic adaptor proteins PHETA1/2 impairs renal and craniofacial development. |
ENSMUSG00000044134 |
Pheta1 |
334.008153 |
2.3620585429 |
1.240045 |
0.101938458 |
148.533398 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000036268892110624509181155127154524362455905658267920303355402647801158199829344863369099847758003640763035946292802691459655761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000005295043002500670355703834859373222233972201519281675394968826062026240650609872721572661535827108991725253872573375701904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
467.4077629 |
35.2489148 |
199.0516874 |
11.4694780 |
| ENSG00000198346 |
126017 |
ZNF813 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZN06 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:126017; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
66.518324 |
3.5617085827 |
1.832569 |
0.466239099 |
14.623980 |
0.00013123400102268756089660128871798860927810892462730407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000354634539563322670994993668358574723242782056331634521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
102.7287503 |
38.8030556 |
28.4968145 |
7.7759382 |
| ENSG00000198355 |
415116 |
PIM3 |
protein_coding |
Q86V86 |
FUNCTION: Proto-oncogene with serine/threonine kinase activity that can prevent apoptosis, promote cell survival and protein translation. May contribute to tumorigenesis through: the delivery of survival signaling through phosphorylation of BAD which induces release of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-X(L), the regulation of cell cycle progression, protein synthesis and by regulation of MYC transcriptional activity. Additionally to this role on tumorigenesis, can also negatively regulate insulin secretion by inhibiting the activation of MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2), through SOCS6. Involved also in the control of energy metabolism and regulation of AMPK activity in modulating MYC and PPARGC1A protein levels and cell growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15540201, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16818649, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17270021, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17876606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18593906}. |
Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and PIM subfamily. This gene is overexpressed in hematological and epithelial tumors and is associated with MYC coexpression. It plays a role in the regulation of signal transduction cascades, contributing to both cell proliferation and survival, and provides a selective advantage in tumorigenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2012]. |
hsa:415116; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0061179]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0007346] |
15540201_Aberrnntly expressed Pim-3 can cause autonomous cell proliferation or prevent apoptosis in hepatoma cell lines. 18593906_Pim kinases promote cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis by down-regulating p27(Kip1) expression at both transcriptional and posttranslational levels. 19154409_Ets-1 can induce aberrant Pim-3 expression and subsequently prevent apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. 19266083_expression of Pim-1 & Pim-3 is induced in response reactivation in KSHV-infected cells; they are required for KSHV reactivation under these conditions; data indicate Pim-1 & Pim-3 contribute to viral reactivation by phosphorylating the KSHV LANA 19624871_Ginsenoside Rg3 decreased both Pim-3 and pBad expressions in a dose-dependent manner in PANC-1 cells. 20101231_Pim-3 alone cannot cause, but can accelerate HCC development. 20939820_A cell-based test system useful for rapid and inexpensive pre-screening of compounds capable of preventing Pim-mediated phosphorylation is discussed. 21187426_Pim-3 has an important role in modulating c-Myc and PGC-1alpha protein levels and cell growth 21646687_Pim3 cooperates with other Pim kinases in supporting viability of Myc-induced B-cell lymphomas. 21870113_Pim protein kinase-3 is regulated by TNF-alpha and promotes endothelial cell sprouting. 22282239_Our study indicates that the expression of Pim kinases is physiologically related to DNA-PKcs and ATM in ECs. 23209281_PIM kinases promote the production of IFNgamma, the hallmark cytokine produced by Th1 cells. 23760491_Pim-1 and Pim-3 play overlapping but non-identical roles as it relates to gemcitabine sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells and Pim-3 is upregulated in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. 23845873_Pim-3 can promote pancreatic tumor growth and angiogenesis by stimulating the VEGF pathway. 24165482_observations indicate that TCTP enhances Pim-3 stability to simultaneously promote and prevent cell-cycle progression and apoptosis, respectively 24488669_the existence of different patterns of expression of Pim-3, c-Myc, and p-p27 and their clinicopathologic correlations in adenocarcinomas of the gastric cardia and the distal stomach. 24723452_we constructed a dual-function small hairpin RNA (shRNA) vector containing an shRNA targeting Pim-3 and a TLR7-stimulating ssRNA. 24789328_cancer development and in promoting tumor neovascularization and subsequent tumor growth. Targeting Pim-3 may play a dual role in halting tumor progression, by promoting tumor cell death and blocking angiogenesis 24799066_Blocking the activities of PIM kinases(PIM1, PIM2 and PIM3) could prevent pancreatic cancer development. PIM kinases(PIM1, PIM2 and PIM3) may be a novel target for cancer therapy 25238262_Data demonstrate the role of PIM kinases in driving myeloid leukemia, and as candidate molecules for therapy against human malignancies. 25817345_Knockdown of Pim-3 by specific shRNA slowed decreased proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase, and increased apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. 25921139_PIM3 expression is higher in ovarian cancer than in normal ovarian tissue. Upregulation of PIM3 promotes proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells. 26075720_Pim-3 kinase enhances growth and metastatic properties of prostate cancer xenografts. PC-3 prostate cancer cells overexpressing either Pim-1 or Pim-3 kinases form larger xenograft tumors than the parental PC-3 cells. 26238203_MicroRNA506 participates in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis by targeting PIM3 26551340_A high percentage of urothelial carcinomas express Pim kinases. Pim expression differs in NILG, NIHG, and IHG lesions. 26768612_Pim-3 expression showed a positive correlation with tumor cell differentiation. 27016481_Pim-3 has a role in human pancreatic cancer cell survival against radiation 27448973_show that PIM1 contributes to melanoma cell proliferation and tumor growth in vivo; however, the presence of PIM2 and PIM3 could also influence the outcome. 27525970_SSRP1/Ets-1/Pim-3 signalling is tightly associated with the proliferation, apoptosis, autophagy, invasion and clonogenicity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, and blockage of this signalling facilitates chemosensitivity of the cells to docetaxel. 27638830_Pim-3 expression was inversely correlated with that of miR-377. 27826135_The expression status of Pim-3 mRNA was significantly associated with pathological parameters such as pre-surgery prostate specific antigen, Gleason score, pathological stage, and lymphoid metastasis. 27826617_High PIM3 expression is associated with osteosarcoma. 28214201_Our study suggests that up-regulation of Pim-3 successfully accelerated Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease development, and aggravated lung damage 28698206_PIM kinases in classical Hodgkin lymphoma exhibit pleiotropic effects, orchestrating tumor immune escape and supporting Reed-Sternberg cell survival. 28729093_These results demonstrate the involvement of PIM kinases in LIF-induced regulation in different trophoblastic cell lines which may indicate similar functions in primary cells. 29170467_results demonstrate that PIM3 is induced upon mTORC1 inhibition, with potential implications for the effects of mTORC1 inhibitors in TSC, cancers, and the many other disease settings influenced by aberrant mTORC1 signaling. 31015445_Study identified that PIM1 and PIM3 phosphorylate HIV-2 Vpx at Ser13 and stabilize the interaction of Vpx with SAMHD1 thereby promoting ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of SAMHD1 and revealed a regulatory mechanism of virus-host interaction that governs viral escape from an intrinsic cellular immune defense via the post-translational modification of viral protein. 31882428_The down-regulation of Pim-3 was closely related to the activation status of the lung STAT3 signaling pathway, mediated cell proliferation inhibition and induced apoptosis. 31994402_Proto-Oncogene Serine/Threonine Kinase PIM3 Promotes Cell Migration via Modulating Rho GTPase Signaling. 32504181_High Expression of NEK2 and PIM1, but Not PIM3, Is Linked to an Aggressive Phenotype of Bronchopulmonary Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. 32707033_Kinase Interaction Network Expands Functional and Disease Roles of Human Kinases. 32800554_PIM 3 kinase, a proto-oncogene product, regulates phosphorylation of the measles virus nucleoprotein tail domain at Ser 479 and Ser 510. 33864024_CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of PIM3 suppresses tumorigenesis and cancer cell stemness in human hepatoblastoma cells. 33928496_Effects of PIM3 in prognosis of colon cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000035828 |
Pim3 |
578.882961 |
3.3047634352 |
1.724547 |
0.070104817 |
628.892639 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000087028708190047774667848672525836186049684305638924697754404921959569345175069223459051564958455983093899796821101216993565751409053268854015236935381053259477270757042052585446870007578057118 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000050572587908862406655016596442860135773058932727364993908270562671884896457941737743405737202803653774819423989528210375210689128268383755976304360876666502781535533327216204638534057073268411 |
Yes |
No |
894.9481084 |
36.3340745 |
272.8014266 |
9.3668645 |
| ENSG00000198363 |
444 |
ASPH |
protein_coding |
Q12797 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Specifically hydroxylates an Asp or Asn residue in certain epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) domains of a number of proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773073}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 8]: Membrane-bound Ca(2+)-sensing protein, which is a structural component of the ER-plasma membrane junctions. Isoform 8 regulates the activity of Ca(+2) released-activated Ca(+2) (CRAC) channels in T-cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22586105}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Dioxygenase;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Iron;Membrane;Metal-binding;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Sarcoplasmic reticulum;Signal-anchor;TPR repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene is thought to play an important role in calcium homeostasis. The gene is expressed from two promoters and undergoes extensive alternative splicing. The encoded set of proteins share varying amounts of overlap near their N-termini but have substantial variations in their C-terminal domains resulting in distinct functional properties. The longest isoforms (a and f) include a C-terminal Aspartyl/Asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase domain that hydroxylates aspartic acid or asparagine residues in the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains of some proteins, including protein C, coagulation factors VII, IX, and X, and the complement factors C1R and C1S. Other isoforms differ primarily in the C-terminal sequence and lack the hydroxylase domain, and some have been localized to the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Some of these isoforms are found in complexes with calsequestrin, triadin, and the ryanodine receptor, and have been shown to regulate calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Some isoforms have been implicated in metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:444; |
calcium channel complex [GO:0034704]; cortical endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0032541]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0014701]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0033018]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; electron transfer activity [GO:0009055]; peptidyl-aspartic acid 3-dioxygenase activity [GO:0062101]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; structural molecule activity [GO:0005198]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0097202]; activation of store-operated calcium channel activity [GO:0032237]; calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0055074]; calcium ion transmembrane transport [GO:0070588]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to calcium ion [GO:0071277]; detection of calcium ion [GO:0005513]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; limb morphogenesis [GO:0035108]; muscle contraction [GO:0006936]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389]; peptidyl-aspartic acid hydroxylation [GO:0042264]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol [GO:0010524]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of intracellular protein transport [GO:0090316]; positive regulation of proteolysis [GO:0045862]; positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060316]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling [GO:0010649]; regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0031585]; regulation of protein depolymerization [GO:1901879]; regulation of protein stability [GO:0031647]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0010880]; regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060314]; response to ATP [GO:0033198]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021] |
12118090_role of gene in neuroblastoma cell motility 12713872_AAH over-expression may contribute to the infiltrative growth pattern of cholangiocarcinoma cells by promoting motility. 15302852_junctate has a role in calcium homeostasis in eukaryotic cells 16154531_This review summarizes recent progress in elucidating the molecular mechanisms of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 activation, focusing on the role of oxygen-dependent prolyl hydroxylase in hypoxia signal transduction. 16341145_Overexpression of aspartyl beta-hydroxylase plays a role in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. 16564107_enhanced AAH gene activity is a common feature of human hepatocellular carcinoma and growth factor signaling through IRS-1 regulates AAH expression and increases cell motility and invasion 16673309_Human aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase (HAAH) mRNA is overexpressed in biliary cancer cell lines and possibly involved in the pathogenesis of bile duct cancer. 16949909_Abundant AAH expression in trophoblasts as well as in decidua and endometrial glands, with reduced expression in spontaneous abortion and small-for-gestational-age term deliveries, suggesting that AAH may serve as a biomarker of impaired implantation. 17020779_Study demonstrates that high levels of humbug immunoreactivity in colon carcinomas correlate with histologic grade and tumor behavior, suggesting that humbug can serve as a prognostic biomarker. 17156427_AAH and Humbug are over-expressed in SH-Sy5y neuroblastoma cells, and their mRNAs are regulated by insulin/IGF-1 signaling through Erk MAPK, PI3 kinase-Akt, and Cdk-5, which are known mediators of cell migration. 18288418_Expression analysis showed that the mRNA expression level of humbug was correlated with invasive potential in various human gastric cancer cell lines. 19087304_USF1 and USF2 positively regulate the core of P1 promoter od AAH. 19197126_Low expression of AAH in the endochylema and nucleus of trephocyte may play a role in patients with missed abortion. 19200576_High levels of aspartyl (asparaginyl)-beta-hydroxylase/humbug correlate with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, particularly squamous cell carcinoma subtype. 19663697_analysis of aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase monoclonal antibodies 21862239_Aspartyl-asparaginyl-beta-hydroxylase is an important, positive regulator of trophoblastic cell motility, and it's inhibition in vivo leads to impaired implantation and fetal growth, and alters Notch-signaling mechanisms. 22123818_Ca(2+) and JNT-dependent disassembly of the CSQ2 polymer 22586105_Data show that junctate (ASPH) is an interacting partner of Orai1-STIM1 complex. 24768550_this study provides evidence that ASPH is mutated in a distinct form of syndromic ectopia lentis. 25394783_Higher levels of HAAH/humbug mRNA were found in the hepatocellular carcinoma tissues relative to the adjacent cancerfree tissue. 29580991_the role of FTH1 in the FIH control of HIF-1 activity, is reported. 29733964_Expression of aspartate beta-hydroxylase (ASPH) promoted direct protein interaction between RB1, cyclin-dependent kinases, and cyclins. 29737090_The mRNA expression and promoter methylation rate of ASPH gene may play a role in the development and progression of breast cancer. 29764768_the hydroxylase activity of ASPH affected HCC metastasis through interacting with vimentin and regulating EMT. As such, ASPH might be a promising therapeutic target of HCC. 31012784_We report the 14th individual with Traboulsi syndrome and a novel homozygous deletion variant in exon 22 of ASPH gene associated with the phenotype. 31659163_An unexpected Cys3-4 disulfide bonding pattern is observed in the epidermal growth factor-like domains of AspH. 31694640_ASPH-Notch axis guides particularly selective exosomes to potentiate multifaceted metastasis. ASPH's pro-oncogenic/pro-metastatic properties are essential for breast cancer development/progression, revealing a potential target for therapy. 31888763_High ASPH expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasisthrough activation of SRC signaling pathway. 32107312_Kinetic parameters of human aspartate/asparagine-beta-hydroxylase suggest that it has a possible function in oxygen sensing. 32525968_Aspartate beta-hydroxylase targeting in castration-resistant prostate cancer modulates the NOTCH/HIF1alpha/GSK3beta crosstalk. 33125119_Diverse molecular functions of aspartate betahydroxylase in cancer (Review). 33251883_A novel mutation in the aspartate beta-hydroxylase (ASPH) gene is associated with a rare form of Traboulsi syndrome. 33380715_Characterization of the Relationship Between the Expression of Aspartate beta-Hydroxylase and the Pathological Characteristics of Breast Cancer. 33887099_Human Oxygenase Variants Employing a Single Protein Fe(II) Ligand Are Catalytically Active. 34018898_Expanding the clinical spectrum and management of Traboulsi syndrome: report on two siblings homozygous for a novel pathogenic variant in ASPH. 34433181_Overexpression of Human Aspartyl (Asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase in NSCLC: Its Diagnostic Value by Means of Exosomes of Bronchoalveolar Lavage. 35918038_Traboulsi syndrome caused by mutations in ASPH: An autosomal recessive disorder with overlapping features of Marfan syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000028207 |
Asph |
2147.600501 |
6.3489416205 |
2.666516 |
0.070569600 |
1344.735083 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000214677414216588981359953297545976977 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000301775107984462249066068547984645312 |
Yes |
No |
3706.7092615 |
159.7138781 |
587.6696127 |
19.8664067 |
| ENSG00000198380 |
2673 |
GFPT1 |
protein_coding |
Q06210 |
FUNCTION: Controls the flux of glucose into the hexosamine pathway. Most likely involved in regulating the availability of precursors for N- and O-linked glycosylation of proteins. Regulates the circadian expression of clock genes BMAL1 and CRY1 (By similarity). Has a role in fine tuning the metabolic fluctuations of cytosolic UDP-GlcNAc and its effects on hyaluronan synthesis that occur during tissue remodeling (PubMed:26887390). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P47856, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26887390}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Aminotransferase;Biological rhythms;Congenital myasthenic syndrome;Disease variant;Glutamine amidotransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Nucleotide-sugar biosynthesis; UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine biosynthesis; alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate from D-fructose 6-phosphate: step 1/1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P82808}. |
This gene encodes the first and rate-limiting enzyme of the hexosamine pathway and controls the flux of glucose into the hexosamine pathway. The product of this gene catalyzes the formation of glucosamine 6-phosphate. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:2673; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; carbohydrate derivative binding [GO:0097367]; glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing) activity [GO:0004360]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; energy reserve metabolic process [GO:0006112]; fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process [GO:0006002]; glutamine metabolic process [GO:0006541]; protein N-linked glycosylation [GO:0006487]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006048]; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process [GO:0006047] |
11587069_expression profiles of GFAT1 mRNA in various human tissues using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The identification and cDNA cloning of a novel GFAT1 splice variant expressed abundantly in skeletal muscle and heart is reported. 11679416_A novel variant of glutamine: fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase-1 (GFAT1) mRNA is selectively expressed in striated muscle. 12802498_An increased concentration of wild-type GFAT in mesangial cells is enhanced both TGF-beta1 and fibronectin 14988277_Genetic variation in GFPT1 is unlikely to have a major impact on susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. 14988277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308130_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308130_Variants in the GFPT1 gene show suggestive evidence of an association with diabetic nephropathy among African-American individuals, and increased GFPT1 gene expression may characterize Caucasian subjects with diabetic nephropathy. 15595739_On the basis of the docking results, a binding pocket of human GFAT1 dimer for UDP-GlcNAc is defined. 15613432_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15613432_two polymorphisms in the 5'-flanking region of GFAT, of which the -913 polymorphism seems to alter the risk for obesity and intramyocellular lipid accumulation in male subjects. 15878746_A novel single nucleotide polymorphism identified at position -1412 (G to C) had a functional effect on promoter activity and EMSA revealed specific binding of nuclear proteins to this region. 17024311_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17024311_Testing for association of an +36T>C polymorphism in the glutamine: fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 1 gene and type 2 diabetes in Japanese and Caucasians. 17941647_These findings suggest for the first time that hGfat1 may be regulated by kinases other than PKA. 19059404_The first structures of the isomerase domain of the human GFAT in the presence of cyclic glucose-6-phosphate and linear glucosamine-6-phosphate was reported. 19170765_The phosphorylation of GFAT1 at Ser243 by AMPK has an important role in the regulation of the GFAT1 enzymatic activity. 20845477_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21310273_Downregulation of the GFPT1 is associated with neuromuscular transmission defect. 21975507_This study demonstrated that Congenital myasthenic syndrome with tubular aggregates caused by GFPT1 mutations. 22987706_GFPT1 is the key enzyme in the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway. Mutations in GFPT1 cause defective glycosylation in the proteins of the neuromuscular junction. 23488891_Two GFPT1 untranslated mutations may cause limb-girdle myasthenia by reducing GFPT1 expression and ultimately impairing protein glycosylation. 23569079_Inhibition of GFPT1 enzymatic activity or siRNA silencing of GFPT1 expression resulted in reduced AChR expression. 23794683_The results found no correlation between end plate morphology and physiology or between genotype and phenotype in GFPT1-myasthenia. 24075873_Mapping of the regulatory site of glucosamine-6P synthase identified critical residues necessary for catalysis. 25765662_3'-UTR mutation creates a microRNA target site in the GFPT1 gene of patients with congenital myasthenic syndrome 26715276_Increased GFPT1 expression is associated with triple-negative breast cancer. 26887390_GNPDA1 siRNA induced GFAT2 which was hardly measurable in these cells under standard culture conditions, GNPDA2 siRNA increased GFAT1, and GFAT1 siRNA increased the expression of hyaluronan synthase 2 (HAS2). Silencing of GFAT1 stimulated GNPDA1 and GDPDA2, and inhibited cell migration. 27509259_Findings indicate that GFAT1 functions as a novel suppressor of EMT and tumor metastasis in gastric cancer. 27570073_mTORC2 responds to glutamine catabolite levels to modulate the hexosamine biosynthesis enzyme GFAT1, and is essential for proper expression and nuclear accumulation of the GFAT1 transcriptional regulator, Xbp1s. 27996048_high GFAT1 expression is identified as an independent predictor of adverse clinical outcome in our small number of pancreatic cancer patients, and the practical prognostic nomogram model may help clinicians in decision making and the design of clinical studies. 28008135_GFAT1 phosphorylation by AMPK promotes VEGF-induced angiogenesis. 28186970_High GFAT1 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. 28336748_The AMPK-GFAT1 signaling axis serves as an important communication point between two nutrient-sensitive signaling pathways and is likely to play a significant role in controlling physiological processes in many other tissues. 28712002_study reports nine new mutations of GFPT1 in limb-girdle congenital myasthenic syndrome (LG-CMS) 29753740_These results suggest that 2-deoxy-d-glucose reduces N-glycosylation of proteins following the increase of phosphorylation of GFAT1 and results in the inhibition of cell growth mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic cancer cells. 29905857_The Gfpt1tm1d/tm1d model allows for further investigation of pathophysiological consequences on genes and pathways downstream of GFPT1 likely to involve misglycosylation or hypoglycosylation of neuromuscular junction and muscle targets. 30305725_We also showed that IL-8 stimulation of colon and lung cancer cells-induced glucose uptake and expressions of glucose transporter 3 (GLUT3) and glucosamine fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase (GFAT), a regulator of glucose flux to the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway, resulting in enhancement of protein O-GlcNAcylation 30635494_GFPT1 variants and defects in other enzymes of this pathway have previously been associated with congenital myasthenia. These findings identify leukoencephalopathy as a previously unrecognized phenotype in GFPT1-related disease and suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction could contribute to this disorder. 30771196_MTOR2/C-MYC/GFAT1 axis is responsible for the modulation on the crosstalk between glycolysis and glutaminolysis in glioblastoma cells. 32019926_The longevity-associated G451E of GFAT1 variant shows drastically reduced sensitivity to UDP-GlcNAc inhibition. 32149084_GFAT1/HBP/O-GlcNAcylation Axis Regulates beta-Catenin Activity to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Aggressiveness. 32229685_LncRNA ELFN1-AS1 promotes esophageal cancer progression by up-regulating GFPT1 via sponging miR-183-3p. 33517899_High GFPT1 expression predicts unfavorable outcomes in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 34270713_Inhibition of GFAT1 in lung cancer cells destabilizes PD-L1 protein. 34735873_Cardiomyocyte protein O-GlcNAcylation is regulated by GFAT1 not GFAT2. 34978387_Diverse myopathological features in the congenital myasthenia syndrome with GFPT1 mutation. 35694932_GFPT1-Associated Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome Mimicking a Glycogen Storage Disease - Diagnostic Pitfalls in Myopathology Solved by Next-Generation-Sequencing. 36040914_GFPT1 promotes the proliferation of cervical cancer via regulating the ubiquitination and degradation of PTEN. |
ENSMUSG00000029992 |
Gfpt1 |
451.667742 |
2.3884272540 |
1.256061 |
0.093462048 |
180.099032 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000004611027216070042629956263131537719574952848913076645017775137015557303314851440871523464202527022021268696128082353880017763003706932067871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000792302231771755808866095555910137464974307651672082270223244531423517373118760323041134200696346306025050210131155381532153114676475524902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
627.0687137 |
33.9082278 |
264.6300276 |
11.0043523 |
| ENSG00000198382 |
7405 |
UVRAG |
protein_coding |
Q9P2Y5 |
FUNCTION: Versatile protein that is involved in regulation of different cellular pathways implicated in membrane trafficking. Involved in regulation of the COPI-dependent retrograde transport from Golgi and the endoplasmic reticulum by associating with the NRZ complex; the function is dependent on its binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) (PubMed:16799551, PubMed:18552835, PubMed:20643123, PubMed:24056303, PubMed:28306502). During autophagy acts as regulatory subunit of the alternative PI3K complex II (PI3KC3-C2) that mediates formation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and is believed to be involved in maturation of autophagosomes and endocytosis. Activates lipid kinase activity of PIK3C3 (PubMed:16799551, PubMed:20643123, PubMed:24056303, PubMed:28306502). Involved in the regulation of degradative endocytic trafficking and cytokinesis, and in regulation of ATG9A transport from the Golgi to the autophagosome; the functions seems to implicate its association with PI3KC3-C2 (PubMed:16799551, PubMed:20643123, PubMed:24056303). Involved in maturation of autophagosomes and degradative endocytic trafficking independently of BECN1 but depending on its association with a class C Vps complex (possibly the HOPS complex); the association is also proposed to promote autophagosome recruitment and activation of Rab7 and endosome-endosome fusion events (PubMed:18552835, PubMed:28306502). Enhances class C Vps complex (possibly HOPS complex) association with a SNARE complex and promotes fusogenic SNARE complex formation during late endocytic membrane fusion (PubMed:24550300). In case of negative-strand RNA virus infection is required for efficient virus entry, promotes endocytic transport of virions and is implicated in a VAMP8-specific fusogenic SNARE complex assembly (PubMed:24550300). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18552835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20643123, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24056303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28306502, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: Involved in maintaining chromosomal stability. Promotes DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair by association with DNA-dependent protein kinase complex DNA-PK and activating it in non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) (PubMed:22542840). Required for centrosome stability and proper chromosome segregation (PubMed:22542840). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22542840}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Centromere;Chromosome;Coiled coil;Cytoplasmic vesicle;DNA damage;DNA repair;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Lysosome;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene complements the ultraviolet sensitivity of xeroderma pigmentosum group C cells and encodes a protein with a C2 domain. The protein activates the Beclin1-PI(3)KC3 complex, promoting autophagy and suppressing the proliferation and tumorigenicity of human colon cancer cells. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with left-right axis malformation and mutations in this gene have been associated with colon cancer. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7405; |
autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000775]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane [GO:0033116]; endosome [GO:0005768]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; lytic vacuole [GO:0000323]; midbody [GO:0030496]; phagocytic vesicle [GO:0045335]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class III [GO:0035032]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; SNARE binding [GO:0000149]; autophagosome maturation [GO:0097352]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; centrosome cycle [GO:0007098]; chromosome segregation [GO:0007059]; DNA repair [GO:0006281]; double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining [GO:0097680]; maintenance of Golgi location [GO:0051684]; multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0071985]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate biosynthetic process [GO:0036092]; positive regulation of autophagosome maturation [GO:1901098]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; receptor catabolic process [GO:0032801]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506]; regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465]; regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071900]; retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0006890]; SNARE complex assembly [GO:0035493]; spindle organization [GO:0007051]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718] |
17106237_UVRAG: a new player in autophagy and tumor cell growth. 18495205_Frameshift mutations in the polyadenine tract in UVRAG gene are present in gastric carcinomas. 18552835_Data suggest that a Beclin1-binding autophagic tumour suppressor, UVRAG, interacts with the class C Vps complex, a key component of the endosomal fusion machinery. 18641390_Bcl-xL and UVRAG cause a monomer-dimer switch in Beclin1 18843052_These results suggest that mammalian cells have at least two distinct class III PI3-kinase complexes, and that beclin 1 interacts distinctly with mammalian Atg14 and UVRAG in two of these complexes. 20163458_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20163458_There is an association of UVRAG polymorphisms with susceptibility to non-segmental vitiligo in a Korean sample. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20643123_A specific sub-complex containing VPS15, VPS34, Beclin 1, UVRAG and BIF-1 regulates both receptor degradation and cytokinesis, whereas ATG14L, a PI3K-III subunit involved in autophagy, is not required. 20724836_Data indicate that mechanisms other than autophagy contribute to the tumorigenicity of microsatellite unstable colon carcinomas with monoallelic UVRAG mutation. 21597469_UVRAG has an essential role in the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis by regulating the localization of Bax. 21606679_UVRAG has cytoprotective functions in the cytosol that control the localization of Bax in tumor cells exposed to apoptotic stimuli 22314358_analysis of how the Beclin1 coiled-coil domain interface regulates homodimer and heterodimer formation with Atg14L and UVRAG 22493499_in Escherichia coli-containing phagosomes of mouse macrophages, Slamf1 interacts with the class III PI3K Vps34 in a complex with Beclin-1 and UVRAG 22542840_UVRAG promotes DNA double-strand-break repair by directly binding and activating DNA-PK in nonhomologous end joining. Disruption of UVRAG increases genetic instability and sensitivity of cells to irradiation. 23200933_Akt1 may inhibit autophagy by decreasing UVRAG expression, which also sensitizes cancer cells to UV irradiation. 24550300_UVRAG is required for virus entry through combinatorial interaction with the class C-Vps complex and SNAREs. 24882360_The reports that Grb2, when in excess, interacts with ultraviolet radiation resistance-associated gene protein (UVRAG) under excess conditions of AICD-Grb2 or Grb2. 24956373_Beclin 1 and UVRAG confer protection against radiation-induced DNA DNA double strand breaks and may maintain centrosome stability in established tumor cells. 25533187_Dephosphorylation of UVRAG facilitates the lysosomal degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), reduces EGFR signaling, and suppresses cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. 25807108_HCV, by differentially inducing the expression of Rubicon and UVRAG, temporally regulated the autophagic flux to enhance its replication. 26139536_tubulation requires mTOR activity, and we identified two direct mTOR phosphorylation sites on UVRAG (S550 and S571) that activate VPS34. 26234763_UVRAG frameshift is expressed as a truncated protein in colorectal cancer with microsatellite instability and promotes tumorigenesis. UVRAG(FS) expression renders cells more sensitive to standard chemotherapy regimen due to a DNA repair defect. 26717041_Under-expression of UVRAG is associated with colorectal cancer. 27203177_UVRAG is a regulator of CRL4(DDB2)-mediated nucleotide excision repair and its expression levels may influence melanoma predisposition. 27439570_UVRAG plays an essential role in protecting cells from UV-induced DNA damage by activating the nucleotide excision repair pathway 28982601_miR-216b enhances the efficacy of vemurafenib and reverses drug resistance by targeting Beclin-1, UVRAG and ATG5 in melanoma. 29277783_Our findings suggest that up-regulation of UVRAG by HDAC1 inhibition potentiates DNA-damage-mediated cell death in colorectal cancer cells 29710477_our study showed that the expression of miR-125b-5p is downregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients, accompanied by increased UVRAG expression and autophagy activation 29866835_To induce the redistribution of Beclin 1 among its self-associated form or Atg14L/UVRAG-containing complexes enhances both autophagy and endolysosomal trafficking. 30061422_results establish UVRAG as an important effector for melanocytes' response to alpha-MSH signaling as a direct target of MITF and reveal the molecular basis underlying the association between oncogenic BRAF and compromised UV protection in melanoma. 30221685_miR183 inhibits starvationinduced autophagy and apoptosis by targeting UVRAG in human gastric cancer cells. 30686098_UVRAG is ubiquitinated by SMURF1 at lysine residues 517 and 559, which decreases the association of UVRAG with RUBCN and promotes autophagosome maturation. 30894053_GORASP2/GRASP55 collaborates with the PtdIns3K UVRAG complex to facilitate autophagosome-lysosome fusion. 34646380_TNF-alpha-dependent neuronal necroptosis regulated in Alzheimer's disease by coordination of RIPK1-p62 complex with autophagic UVRAG. |
ENSMUSG00000035354 |
Uvrag |
299.472495 |
0.1727448108 |
-2.533286 |
0.880239060 |
5.662257 |
0.01733380271909521624928984806501830462366342544555664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031531541549648184341592127566400449723005294799804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
85.7332828 |
44.8002495 |
510.3222956 |
189.7530033 |
| ENSG00000198399 |
50618 |
ITSN2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NZM3 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein that may provide indirect link between the endocytic membrane traffic and the actin assembly machinery. May regulate the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles (CCPs). Seems to be involved in CCPs maturation including invagination or budding. Involved in endocytosis of integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) and transferrin receptor (TFR). Plays a role in dendrite formation by melanocytes (PubMed:23999003). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19458185, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22648170, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23999003}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Endocytosis;Host-virus interaction;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain |
|
This gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein which contains SH3 domains. This protein is a member of a family of proteins involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Intersectin 2 is thought to regulate the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles and also may function in the induction of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) endocytosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2017]. |
hsa:50618; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; presynapse [GO:0098793]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; clathrin-dependent synaptic vesicle endocytosis [GO:0150007]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; positive regulation of dendrite extension [GO:1903861] |
16394100_These results highlight a role of Numb for dendritic spine development and synaptic functions with intersectin and EphB2. 17390067_ITSN2C may be specifically expressed in neurons hinting to a physiologic role in neuronal cell function. 17696407_We show that the PPLP motif of K15 protein selectively binds the SH3-C domain of an endocytic adaptor protein, Intersectin 2 (ITSN2). 19622753_ITSN-2L, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Cdc42, regulates different steps of caveola endocytosis in ECs by controlling the temporal and spatial actin polymerization and remodeling sub-adjacent to the plasma membrane. 19911011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22449706_The ITSN2 interacts with Eps8 and stimulates the degradation of Eps8 proteins. 23274495_The sequence and structural alignment of ITSN-2L C2 domain with other members of C2 domain protein family indicate its vital cellular roles in membrane trafficking, the generation of lipid-second messengers and activation of GTPases. Moreover, our data show the possible roles of ITSN-2L C2 domain in regulating the activity of Cdc42. 23936226_ITSN1 and ITSN2 bind similar proline-rich ligands but are differentially recognized by SH2 domain-containing proteins. 26633357_ITSN2L interacts with RABEP1 and stimulates its degradation in regulation of endocytosis. 28161632_These findings provide the basis for further functional investigations of the ITSN/CR16 complex that may play an important role in actin remodeling and cellular invasion. |
ENSMUSG00000020640 |
Itsn2 |
818.656347 |
0.4471396465 |
-1.161203 |
0.324192858 |
11.978111 |
0.00053829133921938184578065422769554970727767795324325561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001313687196904443936149031735283188027096912264823913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
482.1156912 |
131.3171945 |
1060.8902840 |
208.5196517 |
| ENSG00000198400 |
4914 |
NTRK1 |
protein_coding |
P04629 |
FUNCTION: Receptor tyrosine kinase involved in the development and the maturation of the central and peripheral nervous systems through regulation of proliferation, differentiation and survival of sympathetic and nervous neurons. High affinity receptor for NGF which is its primary ligand (PubMed:1850821, PubMed:1849459, PubMed:1281417, PubMed:8325889, PubMed:15488758, PubMed:22649032, PubMed:17196528, PubMed:27445338). Can also bind and be activated by NTF3/neurotrophin-3. However, NTF3 only supports axonal extension through NTRK1 but has no effect on neuron survival (By similarity). Upon dimeric NGF ligand-binding, undergoes homodimerization, autophosphorylation and activation (PubMed:1281417). Recruits, phosphorylates and/or activates several downstream effectors including SHC1, FRS2, SH2B1, SH2B2 and PLCG1 that regulate distinct overlapping signaling cascades driving cell survival and differentiation. Through SHC1 and FRS2 activates a GRB2-Ras-MAPK cascade that regulates cell differentiation and survival. Through PLCG1 controls NF-Kappa-B activation and the transcription of genes involved in cell survival. Through SHC1 and SH2B1 controls a Ras-PI3 kinase-AKT1 signaling cascade that is also regulating survival. In absence of ligand and activation, may promote cell death, making the survival of neurons dependent on trophic factors. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P35739, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3UFB7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11244088, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1281417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15488758, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17196528, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1849459, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1850821, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22649032, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27445338, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27676246, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8155326, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8325889}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform TrkA-III]: Resistant to NGF, it constitutively activates AKT1 and NF-kappa-B and is unable to activate the Ras-MAPK signaling cascade. Antagonizes the anti-proliferative NGF-NTRK1 signaling that promotes neuronal precursors differentiation. Isoform TrkA-III promotes angiogenesis and has oncogenic activity when overexpressed. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15488758}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Chromosomal rearrangement;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Kinase;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor (NTKR) family. This kinase is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself and members of the MAPK pathway. The presence of this kinase leads to cell differentiation and may play a role in specifying sensory neuron subtypes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital insensitivity to pain, anhidrosis, self-mutilating behavior, cognitive disability and cancer. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been found, but only three have been characterized to date. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4914; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; GPI-linked ephrin receptor activity [GO:0005004]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase binding [GO:0019900]; nerve growth factor binding [GO:0048406]; nerve growth factor receptor activity [GO:0010465]; neurotrophin binding [GO:0043121]; neurotrophin p75 receptor binding [GO:0005166]; neurotrophin receptor activity [GO:0005030]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; aging [GO:0007568]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; axonogenesis involved in innervation [GO:0060385]; B cell differentiation [GO:0030183]; behavioral response to formalin induced pain [GO:0061368]; cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus [GO:1990090]; cellular response to nicotine [GO:0071316]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050966]; detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050965]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; mechanoreceptor differentiation [GO:0042490]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; nerve growth factor signaling pathway [GO:0038180]; neuron apoptotic process [GO:0051402]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048011]; olfactory nerve development [GO:0021553]; peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation [GO:0038083]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of kinase activity [GO:0033674]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043068]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0046579]; positive regulation of synapse assembly [GO:0051965]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; programmed cell death involved in cell development [GO:0010623]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051896]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to hydrostatic pressure [GO:0051599]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; Sertoli cell development [GO:0060009]; sympathetic nervous system development [GO:0048485]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11668614_congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA): novel mutations of the TRKA (NTRK1) gene, a putative uniparental disomy, and a linkage of the mutant TRKA and PKLR genes in a family with CIPA and pyruvate kinase deficiency 11705863_TrkA is expressed in pleural and peritoneal effusions and in advanced-stage ovarian carcinoma. 11850535_biologic effects of trkA neurotrophin receptor activation by nerve growth factor in a newly established Askin tumor cell line 11859925_Cys436 of the trkA is responsible for the rapid transfer of the transmembrane occupancy signal to the SHC adaptor protein for activation of the Ras-Erk pathway and DNA synthesis. 12102460_genetics of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IV: clinical, biological and molecular aspects of mutations (REVIEW) 12150951_role in tyrosine phosphorylation and processing of beta-APP 12208732_TrkA as a life and death receptor: receptor dose as a mediator of function. 12210794_No mutation in the TRKA (NTRK1) gene encoding a receptor tyrosine kinase for nerve growth factor in a patient with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type V. 12446789_These results suggest that Grit, a novel TrkA-interacting protein, regulates neurite outgrowth by modulating the Rho family of small GTPases. 12536040_Most of the GFAP-positive cells express TrkA, whereas a rare, novel subpopulation of astrocytes was found to be devoid of TrkA. Those results support the idea that astrocytes play an important neurotrophic role in the retina. 14642435_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14691455_Nerve growth factor decreases N-myc levels in TRKA-infected neuroblastoma cells and decreases cell proliferation via a MAPK path. 14988025_Constitutively activated Scr facilitates NGF-induced phosphorylation of TRKA. 15159601_CIPA patients had a branch site mutation in intron 7 (IVS7-33 T-->A) of the NTRK1 gene and a marked reduction of small myelinated and unmyelinated fibers and a relatively increased axon size. This is the first CIPA family encountered in Taiwan 15273715_genes are rearranged in papillary thyroid cancer. 15362372_a role for TrkA activation in a subset of melanomas as a predictor of an aggressive phenotype and poor outcome 15488758_a novel alternative TrkA splice variant, TrkAIII, that exhibits expression restricted to undifferentiated early neural progenitors, human neuroblastomas, and a subset of other neural crest-derived tumors 15523689_expression of NGF and its receptors, TrkA and p75NTR, in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC); NGF and its receptors are thought to have a role in cellular interactions involving HCC cells, hepatic stellate cells, arterial cells and nerve cells in HCC tissues 15637590_upregulation of proapoptotic genes and angiogenesis inhibitors 15870692_mechanism that regulates aberrant or increased TrkA expression in various cancer cell lines and in the course of pancreatic cancer progression. 15950763_These results strongly indicate that the expression level of PS1 protein has a cross talk with the Trk-dependent neuroprotective intracellular signaling pathway. 15961390_TrkA induces apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells through a p53-dependent mechanism 16091303_Data show that nerve growth factor activation of the TrkA receptor involves two distinct signalling pathways, and that both are necessary to induce airway smooth muscle cell proliferation. 16138253_Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis (CIPA) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase 1 (NTRK1) gene which encodes the receptor for nerve growth factor (NGF). 16181609_Phosphorylated TrkA is localized at the mitotic apparatus in a human glioma cell line. 16284401_Trk receptor signaling involves an inducible switch mechanism through an unconventional substrate that distinguishes neurotrophin action from other growth factor receptors 16373086_Novel frameshift and splice site mutations in the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1 gene (NTRK1) associated with hereditary sensory neuropathy type IV. 16483615_frequency of NTRK1 rearrangements in papillary thyroid carcinoma for the Polish population 16546643_Overexpression in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma may constitute a reason for perineural invasion 16586073_Some trkA immunoreactivity was observed in the outer membrane of cells in the basal and spinal layers of the epidermis in atopic dermatitis (AD). In the papillary dermis, a larger number of cells demonstrated strong trkA immunoreactivity. 16704535_Expression of TrkA in pancreatic cancer is a marker of tumor aggressiveness. 16786155_Light and electron microscopy immunohistochemistry showed that human tonsillar samples were positive for TrkA. 16860569_These results indicate that Fyn is activated by G-protein-coupled receptor stimulation and is responsible for transactivation of TrkA receptors on intracellular membranes. 16862449_Human lung adenocarcinomas express TrkA and TrkB, but not TrkC; A549 cells, express mRNA transcripts encoding nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), TrkA, TrkB, and p75, and high protein levels of TrkA and TrkB. 16919030_Findings report, for the first time, the expression pattern of NGF and TrkA proteins in human scalp skin and hair follicle. 16935282_These data strongly indicate that these anti-neutral glycosphingolipids antibodies have a functional impact on nerve growth factor (NGF)-Trk-mediated intracellular signal transduction pathway. 16996570_Data provide further evidence regarding the clinical role of p-TrkA in ovarian carcinoma. 17143529_CEP-701 could be used to reduce the metastasis formation in advanced prostatic cncer by inhibiting NTRK1. 17196528_We propose that TrkA and p75 likely communicate through convergence of downstream signaling pathways and/or shared adaptor molecules, rather than through direct extracellular interactions. 17447019_TrkA is located in carrier vesicles, including ring-like vesicles near the plasma membrane, and dense core vesicles around the nucleius in a glioma cell line. 17531524_trkA(NGFR) and p75(NTR) have roles with nerve growth factor in the healing process as a result of injury [review] 17617666_TrkA signaling appears to be proapoptotic in the absence of Ku70. 17619016_Data show that functional cooperation between TrkA and p75(NTR) accelerates neuronal differentiation by increased transcription of GAP-43 and p21(CIP/WAF) genes via ERK1/2 and AP-1 activities. 17635673_Our findings suggest that TrkA activation in human glioblastomas might be beneficial therapeutically, especially as several of the currently used chemotherapeutics also induce autophagic cell death. 17667845_NGF mRNA and its high-affinity tyrosine kinase receptor (trkA) expression were selectively increased in obstructive sleep apnea. 17671718_TrkA is a determinant of pancreatic adenocarcinoma chemoresistance and small interfering RNA induces better response to gemcitabine. 17673289_We show here high expression of TRKA in Hodgkin-Reed/Sternberg cell lines as compared to normal B cells and other B cell lymphomas, without major increases in TRKA gene dosage. 17850422_Differential expression throughout the epithelium suggests a role in epithelial differentiation 17971243_in astrocytomas, Trk receptors (TrkA, TrkB, TrkC) expression, but not p75NTR may promote tumor growth independently of grade 18005706_Diffusible TrkA and TrkA-blocking agents neutralize infection in cellular and animal models of acute Chagas' disease. 18072090_nuclear localization of the intracellular domain of Trk-A is observed constitutively in liver cells such as hepatocytes and activated stellate cells, while in other cell types it could be induced in response to soluble factors 18077166_missense, insertion and deletion mutation in NTRK1 associated with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis 18203754_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18221326_upregulation and activation in oral lichen planus is one of the pathways that can activate protein kinase B and thereby rescue epithelial cells from untimely cell death 18270328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18305571_Melanoma cells express the low-affinity (p75NTR) and the high-affinity tyrosine kinase NT receptors (Trk). 18319596_A potential role of all neurotrophins, through their different receptors, in pituitary functions. 18322713_Screening for mutations in the NTRK1 gene demonstrated one novel frameshift mutation, two novel nonsense mutations, and three unrelated kindreds with the same splice-site mutation. 18419753_TrkA receptor endolysosomal degradation is both ubiquitin and proteasome dependent 18427551_NGF/TrkA signaling contributes to aberrant signaling in chronic myelogenous leukemia. 18678285_The impact of Trk receptor expression on nonhomologous end joining-mediated DNA double-strand breaks repair, was analyzed. 18719857_findings showed Zhangfei activated the expression of trkA and Egr1 in medulloblastoma cells and caused these cells to display markers of apoptosis 18727839_Expression of Trk-A and Trk-B by cells of the nondegenerate and degenerate intervertebral disc suggests an autocrine role for neurotrophins in regulation of disc cell biology. 18780967_NTRK1 gene is associated with Alzheimer's disease in Italian population. 18780967_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19115484_Overexpression of TrkA caused massive cell death via both apoptosis and autophagy. 19120874_Expression of nerve growth factor and tyrosine kinase receptor A and correlation with perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer. 19169037_In glomerulonephritis, TrkA is overexpressed, whereas p75 did not show any difference versus controls. By contrast in hemodialysis, TrkA expression is associated with increased p75 levels. 19177265_Upregulation of NGF/TrkA in proinflammatory cytokine-activated fibroblast synovial cells suggest cross talk between NGF/NGFR and cells 19250380_We identified the same novel nonsense mutation in in the NTRK1 two unrelated families of Moroccan Jewish descent, each with two affected siblings 19330021_TRKA overexpression enhances growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells. 19386345_Expression pattern of TRKA in olfactory neuroblastoma is reported. 19399531_This study demonstrated the presence of NGF and TrkA in specimens collected from degenerative facet joints, suggesting that specific molecules could be used in order to modulate chronic pain in patients with degenerative lumbar spine. 19417027_Trk signaling pathways were found to be targeted therapy with Trk-selective inhibitors to treat neuroblastomas and other tumors with activated Trk expression. 19435634_From three independent cohorts Single Nucleotide polymorphism rs6336 in TRKA was nearly significantly (q = 0.12) associated with schizophrenia. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19564412_Results show that the TrkAIII oncogene promotes genetic instability by interacting with and exhibiting catalytic activity at the centrosome. 19598235_NTRK1 gene is associated with autistic traits, empathy, and Asperger syndrome. 19598235_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19635108_Both Trk A and Trk B revealed a pattern of immunoreactivity that was more prevalent in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary and endometriosis associated with the ovary, whereas reactivity was virtually absent in the eutopic endometrium and the ovary. 19651702_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19734938_Geldamycin-sensitive interactions with Hsp90 are critical for both TrkAI tumour suppressor and TrkAIII oncogenic function in neuroblastoma. 19749791_p53 repression of SHP-1 expression leads to trkA-Y674/Y675 phosphorylation and trkA-dependent suppression of breast-cancer cell proliferation. 19758420_Autocrine loop between NGF and its receptor TrkA is activated in pterygium and may be involved in angiogenic response taking place. 19816090_Data how that The differential expression of TrkA and TrkB with differentiation of retinoblastoma cells was mediated by extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation. 19883730_Molecular mechanisms underlying NTRK1 oncogenic rearrangements, are discussed. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19945432_the R100 mutation selectively disrupts binding of hNGF to p75NTR receptor, to an extent which depends on the substituting residue at position 100, while the affinity of hNGFR100 mutants for TrkA receptor is not affected. 19957796_beta-NGF and TrKA expression are higher in pancreatic adenocarcinoma than normal pancreas. 20003389_NTRK1 c.1810C>T polymorphism appears to be a new independent prognostic factor of poor outcome in neuroblastoma 20003389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20186105_High expression of TrkA is associated with lower-stage neuroblastomas. 20209132_STAT3 has a role in in vitro transformation triggered by TRK oncogenes 20219210_Data show taht one variant in NTRK1 was associated with a higher minBMI in eating disorders. 20219210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20542022_The levels of both NGF protein in seminal plasma and TrkA mRNA in spermatozoa are low in samples from oligoasthenozoospermic men. 20600627_A monovalent agonist of TrkA tyrosine kinase receptors can be converted into a bivalent antagonist. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20663926_TrkA is an hsp90 client protein, and inhibition of hsp90 depletes TrkA and its progrowth and prosurvival signaling in myeloid leukemia cells. 20680486_TrkA shares a functional connection with other mediators in the DNA damage response via JNK signaling. 20854189_levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system significantly reduced the expression of the NGF receptor, TrkA, in the endometrium and myometrium of patients with adenomyosis. 20943663_TrkA activity is neuroprotective, while p75NTR activity is neurotoxic through a paracrine mechanism in retinal neurodegeneration 20977883_caveolin-1 could suppress TrkA-mediated pleiotypic effects by altering TrkA modification via functional interaction. 21123453_By directly connecting MYCN to the repression of TRKA and p75NTR, findings establish a key pathway of clinical pathogenicity and aggressiveness in neuroblastoma. 21137076_Ku86 is upregulated in TrkA overexpressing breast cancer cells and is involved in TrkA-induced cell invasion 21139137_Studies indicate that insulin, IGF-1, TrkA, and TrkC receptors as trophic and as dependence receptors. 21150695_Data suggest that the effects of necdin deletion on the developing nervous system may depend on the relative expression of p75NTR and TrkA in the cells of particular regions of the nervous system. 21154590_Low TrkA is associated with neuroblastoma. 21184737_These all results suggest that cytoplasmic H2AX could play an important role in TrkA-mediated cell death by modulating TrkA upon DNA damage. 21236475_Results indicate that p-trkA may be considered as a new potential tumor marker in EOC. 21295543_These results suggest that TrkA, TrkB, TrkC may contribute to growth and metastasis of liver cancer. 21317683_Remarkably, although in five of the groups a higher frequency of the TRKA schizophrenia risk allele was indeed found in the patients compared with the controls, in the three other groups the SNP acted as a protective factor 21321391_TrkA moderately down-regulates expression of the beta-secretase beta-site amyloid beta precursor protein cleaving enzyme-1 and upregulates the expression of two enzymes with alpha-secretase activity. 21397006_The balance of nerve growth factor (NGF) expression and that of its receptors shifts toward cell death mechanisms during the progression of Alzheimer disease. 21419569_Coexpression of p75 also increased specificity of Trk-expressing cells to ligand. NT3-induced phosphorylation of TrkA and AKT was reduced in TrkA/p75 cells 21429417_The expressions of both NGF and TrkA in bronchiolar epithelial cells were significantly increased in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. 21503896_Dermal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts synthesize and secrete all neurotrophins (NTs)and express high-affinity NT receptors TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC. 21645891_Reduced neurotrophin receptor tropomyosin-related kinase A expression in human granulosa cells is associated with diminishing ovarian reserve. 21728718_The significant expression of Trk isoforms among advanced neuroblastoma cases support their role as possible risk assessment tools alongside N-Myc amplification status.. 21849536_The nerve growth factor/TrkA signaling pathway is involved in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis and can be used as a therapeutic target. 21990266_High NTRK1 gene expression is associated with neuroblastomas. 22128158_the existence of an autocrine loop stimulated by proNGF and mediated by TrkA and sortilin, with the activation of Akt and Src, for the stimulation of breast cancer cell invasion. 22138126_NGF receptors are localized in the mitochondrial compartment of undifferentiated human podocytes and in all tissues analyzed including rat central nervous system. 22272270_Data suggest that respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) upregulates the NGF-TrKA axis in airways by silencing miR-221 expression, and this favors viral replication by interfering with the apoptotic death of infected cells. 22343487_expression of neurotrophin receptors Pan-Trk, p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR) and ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor-alpha in ulveal melanoma does not show a role in growth. 22410777_Our findings highlight a fine-tuned regulatory system including S1P-dependent TRKA trafficking for executing TAM-like cell function in vitro as well as in vivo. 22445970_NGF can enhance the proliferation and invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells, and this effect is possibly mediated by Trk-A protein. 22454143_TrkA and p75NTR are expressed in all adenomyosis and control specimens in myometrial and endometrial tissue. 22539856_This study demonistrated that NTRK1-T is important for developing white matter microstructure. 22561027_TrkA inhibition resulted in radioprotection that correlated with enhanced repair of radiation-induced damage while TrkA stimulation by gambogic amide produced radiation sensitization 22653642_Two Chinese congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis cases were screened for mutations in the NTRK1 gene and their phenotype was examined. 22782892_Down-modulation of STK25, but not STK24, rescued medulloblastoma cells from NGF-induced TrkA-dependent cell death, suggesting that STK25 is part of the death-signaling pathway initiated by TrkA and CCM2. 22902478_study describes and analyzes the first high-resolution crystal structures of TrkA and TrkB in their apo-forms 22932111_The expressions of NGF, TrkA and P75NTR mRNA were suppressed by gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist in eutopic endometrial stromal cells. 22954667_In the absence of a functional nerve growth factor (NGF)/TrKA-mediated signaling pathway in AbetaPP-null mice, exogenous application of NGF can rescue long-term potentiation de fi cit. 22992069_TrkA autoinhibition closely resembles that seen for the insulin receptor, relying on projection of an activation loop tyrosine residue into the substrate-binding site and occlusion of the ATP-binding site by the activation loop. 23266087_There are only two established tyrosine TrkA sites (Y490 and Y785A) that are known to be directly involved in signal propagation. (Review) 23400852_provide evidence that TrkA expression in neuroblastoma leads to an increased immunogenicity that may contribute to a less malignant phenotype and/or spontaneous regression of neuroblastoma cells 23471969_the juxtamembrane region of p75(ICD) acts to cause a conformational change within the extracellular domain of TrkA. 23489213_The change in expression of neurotrophic factors in KC (keratoconus) may suggest that these factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of KC and serve as new markers for the progression of KC. 23569426_We conclude that pancreatic cancer cells with a high expression of NTRK1 are more sensitive to 2DG-induced apoptosis, through the p38-MAPK pathway 23589303_Dissecting the roles of tyrosines 490 and 785 of TrkA protein in the induction of downstream protein phosphorylation using chimeric receptors. 23746174_Significantly higher methylation was observed in genes NTKR1, GATA4 and WIF1 in the ovarian cancer group compared with the control group. 23841091_We propose that this novel role for TrkAIII contributes to MT involvement in the promotion and maintenance of an undifferentiated anaplastic NB cell morphology by restricting and augmenting MT nucleation and assembly at the centrosomal MTOC. 23869086_Patients with mastocytosis featured elevated serum levels of NGF, NT-3, and NT-4. TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC expression was also elevated. 23948750_results strongly suggest that expression of NTRK1-pY674/pY675 together with wild-type TP53 and low levels of PTPN6 expression are predictors of improved disease-free survival in breast cancer 24162815_Tumor samples from 3 of 91 patients with lung cancer (3.3%) without known oncogenic alterations assayed by next-generation sequencing or fluorescence in situ hybridization demonstrated evidence of NTRK1 gene fusions. 24369899_These data demonstrate that activating the Akt/mTOR cascade and inducing PLK-1 or Twist-1 by c-Src activity depends on the direct interaction between TrkA and c-Src. 24557415_NGFB and TrkA expression is elevated in salivary gland epithelial cells of primary Sjogren's syndrome. 24585880_Data indicate that nerve growth factor (NGF) binding to TrkA affects toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling, favoring pathways that mediate inhibition of inflammatory responses. 24603864_Data indicate how the neurotrophins function through tyrosine kinase receptors TrkC and TrkA. 24736663_TrkAIII oncoprotein inhibits mitochondrial free radical ROS-induced death of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells by augmenting SOD2 expression and activity at the mitochondria, within the context of a tumour stem cell-like phenotype 24801982_Co-expression of BDNF and TrkB had a significantly poor prognosis. 24825909_Increased NTRK1 expression is associated with spontaneous abortions. 24965840_Causative role for M379I and R577G NTRK1 mutations in melanoma development is highly unlikely. 25361003_Findings have implications for understanding the mature and less malignant neuroblastoma phenotype associated with NTRK1 expression, and could assist the development of new therapeutic strategies for neuroblastoma differentiation 25389033_IL-13 confers epithelial cell responsiveness to NGF by regulating NTRK1 levels by a transcriptional and epigenetic mechanism and that this process likely contributes to allergic inflammation. 25491371_NGF and its precursor proNGF are primarily considered as regulators of neuronal function that induce their responses via the tyrosine kinase receptor TrkA and the panneurotrophin receptor p75NTR. (Review) 25512530_approach identified 18 kinase and kinase-related genes whose overexpression can substitute for EGFR in EGFR-dependent PC9 cells, and these genes include seven of nine Src family kinase genes, FGFR1, FGFR2, ITK, NTRK1, NTRK2, MOS, MST1R, and RAF1. 25619719_the signaling endosome model has been used to describe the sustained NGF/TrkA retrograde signaling as a process of endocytosis and retrograde transport of NGF/TrkA-containing endosomes from the axon terminal 25840418_NGF-induced tyrosine kinase independent TrkA signaling through CD44 is sufficient to maintain tumor aggressiveness in breast cancer 25921289_findings suggest that Cbl-b limits NGF-TrkA signaling to control the length of neurites. 25948268_TrkA expression in neurons was found to be regulated at the gene promoter level by Bex3 protein. 26001971_Translocations in the NTRK1 gene are recurring events in colorectal cancer, although occurring at a low frequency (around 0.5%). 26408608_The percentage of p75NTR+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells increased in early stages of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (I-II), while TrKA+ peripheral blood mononuclear cells increased in late stages (III-IV). 26446845_This work identifies GGA3 as a key player in a novel DXXLL-mediated endosomal sorting machinery that targets TrkA to the plasma membrane, where it prolongs the activation of Akt signaling and survival responses. 26459250_Our results demonstrated that TrkA expression was associated with tumor progression and poor survival, and was an independent predictor of poor outcomes in gastric cancer patients 26472021_TrkA immunohistochemistry is an effective, initial screening method for NTRK1 rearrangement detection in the clinic. 26496938_TrkA as a candidate oncogene in malignant melanoma and support a model in which the NGF-TrkA-MAPK pathway may mediate a trade-off between neoplastic transformation and adaptive anti-proliferative response. 26546295_Data show that p.G595R and p.G667C TRKA mutations drive acquired resistance to entrectinib in colorectal cancers carrying NTRK1 rearrangements. 26564979_Two key biological processes for progressive hearing loss, TrkA signaling pathway and EGF receptor signaling pathway were significantly and differentially enriched by the two sets of allele-specific target genes of miR-96. 26569118_NGF has a role in modulating trkANGFR/p75NTR in alphaSMA-expressing conjunctival fibroblasts from human ocular cicatricial pemphigoid 26716414_High NTRK1 expression is associated with colon cancer. 26863915_Report novel variant of myo/haemangiopericytic sarcoma with recurrent NTRK1 gene fusions. 26962689_NGF FLIPs TrkA onto the death TRAIL in neuroblastoma cells 27184211_analysis of NTRK1 transcripts in peripheral blood cells of the patient revealed an influence of the variant on mRNA splicing. The C>A transversion generated a novel splice-site, which led to the incorporation of 10 intronic bases into the NTRK1 mRNA and consequently to a non-functional gene product. 27259011_Results suggest that NTRK1 oncogenic activation through gene fusion defines a novel and distinct subset of soft tissue tumors resembling lipofibromatosis (LPF), but displaying cytologic atypia and a neural immunophenotype, provisionally named LPF-like neural tumors. 27264679_Based on these current developments, the present review provides not only a broad overview of the biological effects of NGF-TrkA-p75NTR on cancer cells and their microenvironment, but also explains why NGF and its receptors are going to evoke major interest as promising therapeutic anti-cancer targets in the coming decade. 27445338_USP36 actions extend beyond TrkA because the presence of USP36 interferes with Nedd4-2-dependent Kv7.2/3 channel regulation. 27551041_TrkA misfolding and aggregation induced by some Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis mutations disrupt the autophagy homeostasis causing neurodegeneration. 27676246_we conclude that complete abolition of TRKA kinase activity is not the only pathogenic mechanism underlying HSAN IV. 27776007_NTRK1 gene fusion in spitzoid neoplasms results in tumors with Kamino bodies and were typically arranged in smaller nests with smaller predominantly spindle-shaped cells, occasionally forming rosettes. 27802234_This show evidence of variation in plasmatic monocytic TrkA expression during the progression of dementia. 27821809_Report a novel mechanism for the TRAIL-induced apoptosis of TrkAIII expressing NB cells that depends upon SHP/Src-mediated crosstalk between the TRAIL-receptor signaling pathway and TrkAIII. 27912827_This review highlights treatment options, including clinical trials for ROS1 rearrangement, RET fusions, NTRK1 fusions, MET exon skipping, BRAF mutations, and KRAS mutations. 28097808_NTRK fusions occur in a subset of young patients with mesenchymal or sarcoma-like tumors at a low frequency 28177573_This study identify four novel NTRK1 mutations (IVS14+3A>T, p.Ser235*, p.Asp596Asn, and p.Leu784Serfs*79) and demonstrate that they are pathologic mutations using an mRNA splicing assay and an NTRK autophosphorylation assay. 28192073_phenotypes, as well as both recurrent and novel mutations in NTRK1 in 2 Chinese patients with CIPA 28213521_ShcD binds to active Ret, TrkA, and TrkB neurotrophic factor receptors predominantly via its phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain. 28215291_Data suggest that kinase domains of neurotrophin receptor isoforms, TRKA, TRKB, and TRKC, exhibit a bulky phenylalanine gatekeeper, leading to a small and unattractive back pocket/binding site for antineoplastic kinase inhibitors. [REVIEW] 28328124_Nine patients have been reported from nine unrelated families with hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy IV due to various mutations in NTRK1, five of which are novel. 28345382_A novel nonsense mutation and a known splice-site mutation were detected in NTRK1 in two siblings and were shown to be associated with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis. 28356268_NT3 upregulates cellular proliferation, extracellular matrix protein production, and collagen deposition in human aortic valve interstitial cells through the Trk-Akt-cyclin D1 cascade. 28557340_TrkA plays an important role in the pathogenesis of NPM-ALK(+) T-cell lymphoma. 28591715_Results show frequent BRCA2, EGFR, and NTRK1/2/3 mutations in mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancers , sugggesting personalized medicine strategies to treat the patients with advanced disease who may have no remaining treatment options 28683589_6 patients with mesenchymal tumors composed of infiltrative fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumor cells were studied. Using next-generation DNA sequencing, TMP3-NTRK1 fusions were identified in 4 cases, an LMNA-NTRK1 fusion in one case, and a variant EML4-NTRK3 fusion in one case. 28719467_Pan-Trk immunohistochemistry is a time-efficient and tissue-efficient screen for NTRK fusions, particularly in driver-negative advanced malignancies and potential cases of secretory carcinoma and congenital fibrosarcoma. 28751539_We developed a comprehensive model of acquired resistance to NTRK inhibitors in cancer with NTRK1 rearrangement and identified cabozantinib as a therapeutic strategy to overcome the resistance 28981924_novel deletional mutation has enriched the spectrum of NTRK1 mutations 29037860_TrkA was detected in 20% of thyroid cancers, compared with none of the benign samples. TrkA expression was independent of histologic subtypes but associated with lymph node metastasis, suggesting the involvement of TrkA in tumor invasiveness. Nerves in the tumor microenvironment were positive for TrkA. 29054434_These results suggest that polymorphisms in NTRK1 play an important role in pain sensitivity in young Han Chinese women 29215016_Cleaved intracellular domain of CD271 controls proliferation, while the interaction of CD271 with the neurotrophin receptor Trk-A modulates cell adhesiveness through dynamic regulation of a set of cholesterol synthesis genes relevant for patient survival. 29370427_NTRK1 gene Rearrangement is associated with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. 29420916_The above results suggest that rutin preconditioning ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in OVX rats through ER-mediated BDNF-TrkB and NGF-TrkA signaling. 29463555_The G-allele of rs231775 in the CTLA-4 gene is associated with an improved OS in sunitinib-treated cc-mRCC patients and could potentially be used as a prognostic biomarker. 29507419_High expression of NTRK1 is closely associated with favorable risk factors and outcomes of patients with neuroblastoma (NB). The transcription of variants 1/2 is regulated by the NTRK1 P1 promoter region which is epigenetically regulated by EZH2- related histone modifications. Also, NTRK1 contributes to EZH2-regulated NB cell differentiation. 29553955_Report a novel subset of high-grade uterine sarcomas with features reminiscent of soft tissue fibrosarcoma and characterized by oncogenic activation of Trk through recurrent NTRK gene fusions. 29683819_NTRK1 gene fusion occurs in primary and metastatic melanomas. 29715200_We identified TrkA, a neurotrophin receptor tyrosine kinase, as a TRAF4-targeted ubiquitination substr |
ENSMUSG00000028072 |
Ntrk1 |
15.975492 |
0.1039273138 |
-3.266353 |
0.571957681 |
34.249254 |
0.00000000484861306321265354205163417770745037937984989184769801795482635498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000021783396350067107863680035233222564983179836417548358440399169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0366880 |
1.1392821 |
29.0610865 |
6.2007737 |
| ENSG00000198408 |
10724 |
OGA |
protein_coding |
O60502 |
FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Cleaves GlcNAc but not GalNAc from O-glycosylated proteins. Can use p-nitrophenyl-beta-GlcNAc and 4-methylumbelliferone-GlcNAc as substrates but not p-nitrophenyl-beta-GalNAc or p-nitrophenyl-alpha-GlcNAc (in vitro) (PubMed:11148210). Does not bind acetyl-CoA and does not have histone acetyltransferase activity (PubMed:24088714). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11148210, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11788610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20673219, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22365600, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24088714}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Cleaves GlcNAc but not GalNAc from O-glycosylated proteins. Can use p-nitrophenyl-beta-GlcNAc as substrate but not p-nitrophenyl-beta-GalNAc or p-nitrophenyl-alpha-GlcNAc (in vitro), but has about six times lower specific activity than isoform 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20673219}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Glycosidase;Host-virus interaction;Hydrolase;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The dynamic modification of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) addition and removal on serine and threonine residues is catalyzed by OGT (MIM 300255), which adds O-GlcNAc, and MGEA5, a glycosidase that removes O-GlcNAc modifications (Gao et al., 2001 [PubMed 11148210]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:10724; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; [protein]-3-O-(N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-serine O-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminase activity [GO:0102167]; [protein]-3-O-(N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-serine/L-threonine O-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminase activity [GO:0102571]; [protein]-3-O-(N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-threonine O-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminase activity [GO:0102166]; beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase activity [GO:0016231]; hyalurononglucosaminidase activity [GO:0004415]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; glycoprotein catabolic process [GO:0006516]; glycoprotein metabolic process [GO:0009100]; N-acetylglucosamine metabolic process [GO:0006044]; protein deglycosylation [GO:0006517]; protein O-linked glycosylation [GO:0006493] |
11148210_This protein is a cytosolic, neutral, O-GlcNAc specific hexosaminidase termed O-GlcNAcase. 12359146_Investigated this locus in Pima Indians who have the world's highest prevalence of NIDDM. Concluded that mutations in MGEA5 are unlikely to contribute to NIDDM in this population 12359146_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17546623_In type 2 Diabetes patients in Mexico City, the frequency of the T allele of MGEAT5 was higher (2.6%) in the cases than in controls (1.8%), but not a significant deviation from Hardy_Weinberg proportions. 17546623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18641620_review of modifications, phosphorylation and a specific form of glycosylation, O-linked -N-acetylglucosaminylation by O-GlcNAc, relevant to pathological tau phosphorylation 19423084_the short nuclear variant of O-GlcNAcase, which has the identical catalytic domain as the full-length enzyme, has similar trends in a pH-rate profile and Taft linear free energy analysis as the full-length enzyme 19715310_characterization of O-GlcNAcase transition states using several series of substrates to generate multiple simultaneous free-energy relationships 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198314_This study analyzes the activity of the enzyme involved in the removal of these sugar residues, i.e. beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase (O-GlcNAcase) as well as the level of N-acetylglucosamine in benign and malignant thyroid lesions. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20673219_N-terminal region of OGA contains the catalytic site and the C-terminal region stabilizes the protein structure and affects substrate affinity. 20863279_Results provide evidence that OGA may possess a substrate-recognition mechanism tinvolving interactions with O-GlcNAcylated proteins beyond the GlcNAc-binding site. 21178104_Direct evidence links muscle atrophy and the disruption of O-GlcNAcase activity in male bitransgenic mice. 21471514_Reducing ChREBP(OG) levels via OGA overexpression decreased lipogenic protein content (ACC, FAS), prevented hepatic steatosis, and improved the lipidic profile of OGA-treated db/db mice. 21567137_Decrease in MGEA5 and increase in O-GlcNAc transferease expression in higher grade tumors suggests that increased O-GlcNAc modification may be implicated in breast tumor progression and metastasis. 21717526_Chromosomal translocation t(1;10) is consistent with rearrangements of TGFBR3 and MGEA5 in both myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma and hemosiderotic fibrolipomatous tumor. 22311971_Data show that the interplay between O-GlcNAc and phosphorylation on proteins and indicate that these effects can be mediated by changes in hOGT and hOGA kinetic activity. 22730328_O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosaminylation (O-GlcNAcylation) in primary and metastatic colorectal cancer clones and effect of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase silencing on cell phenotype and transcriptome. 22783592_Analysis of urinary content of MGEA5 and OGT may be useful for bladder cancer diagnostics. 24365779_Estrogen replacement therapy and plyometric training influence muscle OGT and OGA gene expression, which may be one of the mechanisms by which HRT and PT prevent aging-related loss of muscle mass. 24705316_Report the presence of TGFBR3 and/or MGEA5 rearrangements in pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumors and the spectrum of related neoplasms. 25173736_Amino acid composition of splice variants, post-translational modifications, and stable associations with regulatory proteins influence subcellular distribution/substrate specificity of OGA and OGT (O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase). [REVIEW] 25183011_This work identifies the first target of miR-539 in the heart and the first miRNA that regulates OGA. 26269457_OGA overexpression in endothelial cells improves endothelial function and may have a beneficial effect on coronary vascular complications in diabetes. 26527687_E2F1 negatively regulates both Ogt and Mgea5 expression in an Rb1 protein-dependent manner. 26980036_TGFBR3 and/or MGEA5 rearrangements are much more common in hybrid hemosiderotic fibrolipomatous tumor-myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomas than in classical myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomas. 27231347_the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) processing enzymes, O-GlcNAc-transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA), interact with the (A)gamma-globin promoter at the -566 GATA repressor site 27601472_OGA is physically associated with the known RNA polymerase II (pol II) pausing/elongation factors SPT5 and TRIM28-KAP1-TIF1beta, and a purified OGA-SPT5-TIF1beta complex has elongation properties. 28319083_hOGA forms an unusual arm-in-arm homodimer in which the catalytic domain of one monomer is covered by the stalk domain of the sister monomer to create a substrate-binding cleft. 28627871_Data suggest that the substrate specificity of O-GlcNAcase/OGA does not extend to proteins/peptides modified with S-GlcNAc (an analog of O-GlcNAc); proteins modified with S-GlcNAc appear to be stable against O-GlcNAcase/OGA hydrolysis. 28742148_Tax interacts with the host OGT/OGA complex and inhibits the activity of OGT-bound OGA. 28939839_Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase substrate recognition and specificity 30052810_OGT promotes carcinogenesis and metastasis of cervical cancer cells. OGT's expression is significantly upregulated in cervical cancer, and low OGT level is correlated with improved prognosis 30920848_role of the tubular biomarkers NAG, kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients with chest pain before contrast media exposition 31501520_Study reports that OGA is upregulated in a wide range of human cancers and drives aerobic glycolysis and tumor growth by inhibiting pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). PKM2 is dynamically O-GlcNAcylated in response to changes in glucose availability. Under high glucose conditions, PKM2 is a target of OGA-associated acetyltransferase activity, which facilitates O-GlcNAcylation of PKM2 by O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT). 32365408_Pharmacological inhibition and knockdown of O-GlcNAcase reduces cellular internalization of alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils. 33086728_Involvement of NDPK-B in Glucose Metabolism-Mediated Endothelial Damage via Activation of the Hexosamine Biosynthesis Pathway and Suppression of O-GlcNAcase Activity. 33310751_Bacterial O-GlcNAcase genes abundance decreases in ulcerative colitis patients and its administration ameliorates colitis in mice. 33333092_Elucidating the protein substrate recognition of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) toward O-GlcNAcase (OGA) using a GlcNAc electrophilic probe. 34135314_OGA is associated with deglycosylation of NONO and the KU complex during DNA damage repair. |
ENSMUSG00000025220 |
Oga |
1015.354395 |
0.4037152599 |
-1.308590 |
0.076438486 |
289.177956 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007510575297549512101217857700689353927525480648678477536020966937345280700550995947697949406014121524130466679464507636265676604968178655403632743122699441938898076709385520643991185352206230163574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002095578287180166480752924770684921130708441187533072690392033436278172940959367363333126104527701910154599186422408285402687544139193879400250815313531531922444650639647534262621775269508361816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
589.2546947 |
33.4829167 |
1471.6244180 |
58.3607525 |
| ENSG00000198431 |
7296 |
TXNRD1 |
protein_coding |
Q16881 |
FUNCTION: Reduces disulfideprotein thioredoxin (Trx) to its dithiol-containing form (PubMed:8577704). Homodimeric flavoprotein involved in the regulation of cellular redox reactions, growth and differentiation. Contains a selenocysteine residue at the C-terminal active site that is essential for catalysis (Probable). Also has reductase activity on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (PubMed:10849437). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10849437, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8577704, ECO:0000305|PubMed:17512005}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 1]: Induces actin and tubulin polymerization, leading to formation of cell membrane protrusions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18042542, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8577704}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 4]: Enhances the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptors ESR1 and ESR2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15199063}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Enhances the transcriptional activity of the estrogen receptor ESR2 only (PubMed:15199063). Mediates cell death induced by a combination of interferon-beta and retinoic acid (PubMed:9774665). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15199063, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9774665}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Electron transport;FAD;Flavoprotein;NADP;Nucleus;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Redox-active center;Reference proteome;Selenocysteine;Transport;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase family, and is a member of the thioredoxin (Trx) system. Three thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) isozymes are found in mammals. TrxRs are selenocysteine-containing flavoenzymes, which reduce thioredoxins, as well as other substrates, and play a key role in redox homoeostasis. This gene encodes an ubiquitously expressed, cytosolic form of TrxR, which functions as a homodimer containing FAD, and selenocysteine (Sec) at the active site. Sec is encoded by UGA codon that normally signals translation termination. The 3' UTRs of selenoprotein mRNAs contain a conserved stem-loop structure, the Sec insertion sequence (SECIS) element, which is necessary for the recognition of UGA as a Sec codon rather than as a stop signal. Alternative splicing, primarily at the 5' end, results in transcript variants encoding same or different isoforms, including a glutaredoxin-containing isoform that is predominantly expressed in testis. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:7296; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; FAD binding [GO:0071949]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; NADPH peroxidase activity [GO:0050137]; thioredoxin-disulfide reductase activity [GO:0004791]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cell redox homeostasis [GO:0045454]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11782468_Methylseleninate is a substrate rather than an inhibitor of mammalian thioredoxin reductase. 11953436_Mutational analysis of human thioredoxin reductase 1. 12214272_identify a novel function of the TR enzyme as a signaling factor in the regulation of AP-1 activity via a cysteine motif located in the protein 12435734_selenoenzyme thioredoxin reductase is an important selenium-dependent ubiquinone reductase and may protect the cell from oxidative damage 12574159_Rapid induction of cell death by selenium-compromised thioredoxin reductase 1 but not by the fully active enzyme containing selenocysteine. 12668662_This protein is part of the host cytosolic translocation factor complex (CTF). ATP and the CTF are required for the cytoslic entry of the diphtheria toxin catalytic domain. 12949356_Thioredoxin reductase 1 is transcriptionally induced by elecrophiles via an antioxidant responsive element found in the promoter 13679440_Epithelial cells in normal, inflammatory, or neoplastic colonic mucosa do not expresss a relevant amount of TR1 mRNA and protein. 15123685_thioredoxin reductase is inhibited by 15-lipoxygenase-1 15183196_In a tumor cell line TrxR1 promoter fragments linked to a luciferase reporter gene allowed identification of a defined promoter region as specifically responding to the phospholipid component of oxodozed low density lipoproteins. 15199063_TrxR1b is an important modulator of estrogen signaling 15824742_TRR-Trx and APE/Ref-1 cooperate in the control of basal p53 activity, but not in its induction by DNA-damage. 15879598_modification of TrxR by curcumin shifts it from an antioxidant to a prooxidant 16424062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16481328_Motexafin gadolinium induces enzymatic generation of reactive oxygen species by thioredoxin reductase and inhibits ribonucleotide reductase 16750198_glutathione disu binding at the N-terminal active site of thioredoxin reductase is electrostatically disfavoured 16868544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16977661_showed 3D model of one of active site in thioredoxin reductase 1 with bound thioredoxin 17382897_Overexpression of TrxR1 markedly increased glucocorticoid receptor activity in outer root sheath cells cultured in vitro. In addition, TrxR1 protected GR activity against H(2)O(2). 17512005_Results report the first crystal structure of human thioredoxin reductase 1 (Sec-->Cys) in complex with FAD and NADP(+) at a resolution of 2.8 A. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17634480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18042542_the Grx domain of TXNRD1_v3 localizes first in the emerging cell membrane protrusion and is then followed into the protrusions by actin and subsequently by tubulin 18163424_FMRP negatively regulates TXNRD1 translation. 18187038_Subsequent analysis demonstrated that TRXR1 suppresses hydrogen peroxide and inhibits apoptosis of RA synovial cells. 18267104_Therefore, TrxR1 inhibition alone was not sufficient to oxidize Trx1, suggesting that Trx1-independent pathways should be considered when evaluating pharmacological and toxicological mechanisms involving TrxR1 inhibition. 18382651_thioredoxin reductase is a prooxidant killer of cells in a pathway involving SecTRAPs 18483336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18483336_Significant 80% reduction for advanced colorectal adenoma risk for carriers of the variant allele at TDXRD1 IVS1-181C>G. 18835810_TR-1 acts as a negative regulator of Tat-dependent transcription. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996185_Evidence for TXNRD1 as a modifier gene through association of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (FALS) with the intronic SNPs rs6539137 and rs4630362. 18996185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19020731_TrxR1 activity in tumor cell extracts is significantly inhibited by green tea extract and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate 19059456_Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase 1 by black tea and its constituents: implications for anticancer actions are reported. 19124506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19555664_This study suggests that TrxR1 enhances ROS generation, NF-kappaB activity and subsequent MCP-1 expression in endothelial cells, and may promote rather than prevent vascular endothelium from forming atherosclerotic plaque. 19595745_Observations underpin a likely critical antioxidant role for TrxR2 and TrxR1 in the endothelium. 19620238_Findings suggest that Trx and TrxR are multifunctional proteins that, in addition to modulating H(2)O(2) levels and transcription factor activity, aid ERalpha in regulating the expression of estrogen-responsive genes in target cells. 19654027_Using truncated versions of the protein we found that both the cytoplasmic filaments and the filopodia formation were exclusively dependent on the glutaredoxin domain of the protein. 19766715_High levels of expression in lung carcinoma cells modulate drug-specific cytotoxic efficacy 19820694_Caveolin 1 expression inhibits TrxR1-mediated cell transformation. 19896490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20160040_Results show the critical role of TxnRd1 in curcumin-mediated radiosensitization and suggest that TxnRd1 levels in tumors could have clinical value as a predictor of response to curcumin and radiotherapy. 20536427_TR1 and Trx1 interaction play key role in redox homoeostasis. 20584310_High expression of TXNRD1 is associated with breast cancer. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20920480_These results indicate the ability of TR1 to modulate the cytotoxic effects of selenium compounds in human lung cancer cells through mitochondrial dysfunction. 21172426_study reveals significant differences between TrxR1 and TrxR2 in substrate specificity and metal compound inhibition in vitro and in cells 21206984_Overexpression of TrxR1 could contribute to cancer progression and might be a potential molecular marker for therapy. 21593104_Our study suggests a novel interaction of up-regulated TXN-TXNRD1 system-mediated oxidative stress defense mechanisms and down-regulated angiogenesis pathways as an adaptive response in obese nondiabetic subjects. 22977247_Studies show that the glutaredoxin system with glutathione plays a backup role to keep oxidized thioredoxin 1 (Trx1) reduced in cells with loss of thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) activity. 23063346_Data suggest that dietary factor (selenium supplementation) up-regulates endogenous antioxidant systems and protects trophoblasts from oxidative stress; selenium upregulates GPX1 (glutathione peroxidase 1) and thioredoxin reductases (TXNRD1; TXNRD2). 23223577_By modifying Cys residues or regulating Cys redox states in TF extracellular domain, hTrx1/TrxR function as a safeguard against inappropriate TF activity. 23413027_v3 is an intricately regulated protein that expands TXNRD1-derived protein functions to the membrane raft compartment 23512591_These findings suggest that high levels of TrxR may be related to progression of glioblastoma multiforme 23603921_Increased sperm TR expression might be a defense mechanism against apoptosis in the spermatozoa of men with varicocele. 24407164_Targeting of TrxR1 by GA thus discloses a previously unrecognized mechanism underlying the biological action of GA and provides useful information for further development of GA as a potential agent in the treatment of cancer. 24583460_Targeting TrxR1 with shikonin thus discloses a previously unrecognized mechanism underlying the biological activity of shikonin and provides an in-depth insight into the action of shikonin in the treatment of cancer. 24624337_Data suggest TXNRD1 and TXRNRD2 function at the top of a redox pyramid that governs the oxidation state of peroxiredoxins and other protein factors, thereby dictating a hierarchy of phenotypic responses to oxidative insults. 24778250_The oxidoreductase activities of TRP14 thereby complement those of Trx1 and must therefore be considered for the full understanding of enzymatic control of cellular thiols and nitrosothiols. 24853413_Sec-containing TrxR1 is absolutely required for self-sufficient growth of MEFs under high-glucose conditions, owing to an essential importance of this enzyme for elimination of glucose-derived H2O2. 25179160_Thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) protein levels and activity were inducible up to 2.2-fold by selenium. 25343990_In gene-based analysis of Se metabolism and selenoprotein candidate genes, only thioredoxin reductase 1 (TXNRD1) was significantly associated with toenail Selenium levels. [meta-analysis] 25391969_Expression of TrxR1 correlated highly with both the astrocytoma grade and proliferative index 25495870_Thioredoxin reductase activity may be more important than GSH level in protecting human lens epithelial cells against UVA light. 25576832_Se/S-palmitoylation acts as an important modulator of TrxR1/hTrx1 activities 25592259_It seems to be involved in the malignant progression of meningiomas. 26064428_The association of TXNRD1 variability was found with physical performance, with three variants (rs4445711, rs1128446, and rs11111979) associated with physical functioning after 85 years of age. 26117319_TRX-1/PRX-1 levels are associated with NADPH oxidase-activity in vivo and in vitro in atherosclerosis. 26184858_Tissue microarrays containing human nevi and melanomas were used to evaluate levels of the antioxidant protein thioredoxin reductase 1 (TR1), which was found to increase as a function of disease progression. 26464515_TXNRD1_v1 and TXNRD1_v2 have distinct roles in differentiation, possibly by altering the expression of the genes associated with differentiation, and further emphasize the importance in distinguishing each unique action of different TrxR1 splice forms 26698667_Cardamonin exposure and selenium availability regulate expression of HO-1, GPX2 and TrxR1 in human intestinal cells. 26743692_Our findings demonstrate that elevated TrxR1 levels correlate with the acquisition of bortezomib resistance in MM. We propose considering TrxR1-inhibiting drugs, such as auranofin, either for single agent or combination therapy to circumvent bortezomib-resistance and improve survival outcomes of MM patients. 26760912_Analysis of 25 independent cohorts with 5910 patients showed that Trx1 and TrxR1 were both associated with a poor patient prognosis in terms of overall survival, distant metastasis free survival and disease free survival. 26871773_Rheumatoid arthritis patients with high disease activity had significantly elevated TrxR levels in plasma and synovial fluid than did those with low disease activity. 26898501_This study thus provides novel insights into the catalytic mechanisms of TrxR1. One-electron juglone reduction by TrxR1 producing superoxide should furthermore contribute to the well-known prooxidant cytotoxicity of juglone 26919094_Data show that small molecule B19 targets and inactivates thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) in gastric cancer cells. 27002142_Under the conditions of inhibition of TrxRs in cells, Parthenolide (PTL) does not cause significant alteration of cellular thiol homeostasis, supporting selective target of TrxRs by PTL. Importantly, overexpression of functional TrxR1 or Trx1 confers protection, whereas knockdown of the enzymes sensitizes cells to PTL treatment. 27233942_Mechanistic study uncovers for the first time that the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) is one of the targets by which PL-CL promotes the ROS generation 27346647_These results suggest that TrxR1 suppresses anabolic metabolism and adipogenesis by inhibition of intracellular signaling pathways downstream of insulin stimulation. 27377780_Endogenous TrxR1 is sensitive to nitrosylation-dependent inactivation. 27381867_Our results clearly demonstrate that DIMC can synergistically enhance the cancer cell killing when combined with radiation by targeting thioredoxin system. 27667125_It was observed that the combination of redox/protonation states of the N-terminal (FAD and Cys59/64) and C-terminal (Cys497/Selenocysteine498) redox centers defines the preferred relative positions and allows for the flexible arm to work as the desired electron 'shuttle.' 27706680_TXNRD1 variants may favor anti-tuberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity susceptibility in females and nonsmokers. 28093500_Here, the authors use a novel assay to demonstrate that the reduction in non-native disulfides requires NADPH as the ultimate electron donor, and a robust cytosolic thioredoxin system, driven by thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1 or TXNRD1). 28218611_Taken together, these findings indicate that auranofin inhibition of TrxR activity in Hep3B cells activates ROS- and caspase-dependent apoptotic signaling pathways and triggers cancer cell death. 28232204_Mutation of TXNRD1 was identified in a family with genetic generalized epilepsy. 28249720_thioredoxin reductase is inhibited by plumbagin, which leads to apoptosis in HL-60 cells 28471109_However, Ethaselen can induce a high level of ROS in K562/CDDP by TrxR activity inhibition and increased ratio of Bax to Bcl-2 in K562/CDDP by nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) suppression, which subsequently induces the release of cytochrome c in K562/CDDP. This response is partly responsible for the reversal of the cisplatin resistance in K562/CDDP cells. 28536696_Multivariate analysis found TXNRD1 was an independent prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)patients. In conclusion, our data suggested that TXNRD1 was a biomarker for the prognosis of patients with HCC. 28551108_Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase-1 by brevetoxin-2 is via the formation of a Michael adduct between selenocysteine and the alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehyde moiety of the toxin. 28653098_High TRXR1 expression is associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma. 28688915_In human colonic epithelial cells, significant upregulation of NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 (up to threefold) and thioredoxin reductase 1 (up to twofold) by 10muM sulforaphane (from broccoli), 5muM carnosol (rosemary), and 20muM cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon) was observed. 28774816_The reducing system of PTEN was comprised of NADPH, thioredoxin reductase (TrxR1), and thioredoxin (Trx). 29117711_The activity increase in acetylated TrxR1 (acTrxR1) is reversible and is reduced following deacetylation with histone deacetylase. 29305108_TrxR levels were decreased in asthenozoospermic males 29327078_Based on recent research, it has been reported that the modulation of the Trx/TrxR system may be considered as a new target in the management of the metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes, as well as in the treatment of hypertension and atherosclerosis. In this review evidence about a possible role of this system as a marker of the metabolic syndrome is reported. [review] 30225271_this study shows that miR-125a suppressed TrxR1 expression by targeting its 3'-UTR in endothelial cells 30561826_significant overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma 30880248_the cytotoxicity of cynaropicrin is enhanced through the genetic knockdown of TrxR, supporting the pharmacological effect of cynaropicrin is relevant to its inhibition of TrxR 31113439_We found that WZ35 significantly enhanced cisplatin-induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Further mechanism study showed that WZ35 synergized the anti-tumor effects of cisplatin by inhibiting TrxR1 activity. By inhibiting TrxR1 activity, WZ35 combined with cisplatin markedly induced the production of ROS, activated p38 and JNK signaling pathways, and eventually induced apoptosis 31176737_thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) is targeted by WZ26, which increases cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, resulting in the activation of JNK signaling pathway in human colon cancer cells 31359011_Menadione substantially increased reactive oxygen species generation via interaction with TXNRD1. 31367013_SLC27A5 deficiency activates NRF2/TXNRD1 pathway by increased lipid peroxidation in HCC. 31601260_DNA methylation levels of TXNRD1 were examined, and significantly hypermethylated sites were identified in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients. Significant correlations of hypermethylated sites with serum levels of folate, homocysteine (Hcy), and oxidative biomarkers were observed, and interactive effects of B vitamins and hypermethylated sites were significantly associated with cognitive performance. 31649256_ROS-mediated inactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in the antigastric cancer effects of thioredoxin reductase-1 inhibitor chaetocin. 31836775_Plasma activity of Thioredoxin Reductase as a Novel Biomarker in Gastric Cancer. 32142958_Accessing the transcriptional status of selenoproteins in skin cancer-derived cell lines. 32418115_Thioredoxin System Protein Expression Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome in Adult and Paediatric Gliomas and Medulloblastomas. 32596335_Licochalcone a Induces ROS-Mediated Apoptosis through TrxR1 Inactivation in Colorectal Cancer Cells. 33115246_Natural Molecules Targeting Thioredoxin System and Their Therapeutic Potential. 33167092_[Expression of thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) in gastric cancer and its effect on the growth of gastric cancer cells]. 33345387_DIAPH3 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by activating selenoprotein TrxR1-mediated antioxidant effects. 33455417_Patients with Osteoarthritis and Kashin-Beck Disease Display Distinct CpG Methylation Profiles in the DIO2, GPX3, and TXRND1 Promoter Regions. 34553295_Methionine restriction exposes a targetable redox vulnerability of triple-negative breast cancer cells by inducing thioredoxin reductase. 34673143_Thioredoxin reductase-1 levels are associated with NRF2 pathway activation and tumor recurrence in non-small cell lung cancer. 34688818_Association between genetic variants in oxidative stress-related genes and osteoporotic bone fracture. The Hortega follow-up study. 34999996_Correlation between TXNRD1/HO-1 expression and response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 36008942_Selenocysteine Machinery Primarily Supports TXNRD1 and GPX4 Functions and Together They Are Functionally Linked with SCD and PRDX6. 36319631_USF2-mediated upregulation of TXNRD1 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating Akt/mTOR signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000020250 |
Txnrd1 |
734.193319 |
2.1279835957 |
1.089487 |
0.069596463 |
245.451898 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000025468456302432834399247874132689518060593271568798086861454844278985461044968287978858520350531833326464770492556402579149605677347435403207881465803552600846160203218460083007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000006005022604215792573026537315454797905200481058560288103351602554050602422876003158004983256747834602378674946901126235688662848209132434640356024146967683918774127960205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1010.8856143 |
42.5203774 |
478.0991335 |
15.5848577 |
| ENSG00000198435 |
441478 |
NRARP |
protein_coding |
Q7Z6K4 |
FUNCTION: Downstream effector of Notch signaling. Involved in the regulation of liver cancer cells self-renewal (PubMed:25985737). Involved in angiogenesis acting downstream of Notch at branch points to regulate vascular density. Proposed to integrate endothelial Notch and Wnt signaling to control stalk cell proliferation and to stablilize new endothelial connections during angiogenesis (PubMed:19154719). During somitogenesis involved in maintenance of proper somite segmentation and proper numbers of somites and vertebrae. Required for proper anterior-posterior somite patterning. Proposed to function in a negative feedback loop to destabilize Notch 1 intracellular domain (NICD) and down-regulate the Notch signal, preventing expansion of the Notch signal into the anterior somite domain (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q91ZA8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19154719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25985737, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25985737}. |
3D-structure;ANK repeat;Developmental protein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Involved in Notch signaling pathway. Acts upstream of or within negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway and positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:441478; |
blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002043]; branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis [GO:0001569]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway involved in somitogenesis [GO:1902367]; negative regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045581]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:1905564]; somite rostral/caudal axis specification [GO:0032525]; T cell differentiation [GO:0030217]; vascular endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0101023] |
24778018_NRARP may stimulate cell proliferation in human breast cancer. 27364790_Downregulation of NRARP expression exerts significant antitumor activities against cell growth and invasion of thyroid cancer, that suggests a potential role of NRARP in thyroid cancer targeted therapy. 28207739_High NRARP expression is associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma progression. 31586130_NRARP displays either pro- or anti-tumoral roles in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia depending on Notch and Wnt signaling. 31690634_Extension of the Notch intracellular domain ankyrin repeat stack by NRARP promotes feedback inhibition of Notch signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000078202 |
Nrarp |
39.029402 |
2.4545325898 |
1.295448 |
0.277425109 |
22.032121 |
0.00000268125525111885189857808750590884017128701088950037956237792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009014880980982747010537767251570073767652502283453941345214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.4878933 |
9.2047683 |
23.5061499 |
3.0019741 |
| ENSG00000198496 |
10230 |
NBR2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene was identified by its close proximity on chromosome 17 to tumor suppressor gene BRCA1. Experimental evidence indicates that the two genes share a bi-directional promoter. Transcription for either gene is controlled individually by distinct transcriptional repressor factors. A short (112 amino acid) open reading frame is observed which includes a region derived from a LINE1 element. A strong Kozak signal is not observed for the putative ORF and the stop codon is more than 55 nucleotides upstream of the last splice site for the transcript, suggesting that the transcript is subject to nonsense-mediated decay. Therefore, this gene does not appear to encode a protein. Glucose starvation induces the expression of this gene and the long non-coding RNA transcribed by it functions with AMP-activated protein kinase in mediating the energy stress response. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
|
|
26999735_Data indicate that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) NBR2 (neighbour of BRCA1 gene 2) interacts with AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and promotes AMPK kinase activity during energy stress. 27792451_Data indicate that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) NBR2 (neighbour of BRCA1 gene 2) modulates cancer cell sensitivity to phenformin through NBR2 regulation of GLUT1 expression at transcriptional level. 27792451_NBR2-GLUT1 axis may serve as an adaptive response in cancer cells to survive in response to phenformin treatment. 28249151_High NBR2 expression is associated with breast cancer. 28586153_data suggested that miR-19a negatively controlled the autophagy of hepatocytes attenuated in D-GalN/LPS-stimulated hepatocytes via regulating NBR2 and AMPK/PPARalpha signaling. 31599420_LncRNA NBR2 inhibits EMT progression by regulating Notch1 pathway in NSCLC. 31888414_This study revealed a novel mechanism by which long noncoding RNA NBR2 mediates curcumin suppression of colorectal cancer proliferation by activating adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase and inactivating the mTOR signaling pathway. 33378941_LncRNA NBR2 inhibits tumorigenesis by regulating autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33651649_LncRNA NBR2 aggravates hepatoblastoma cell malignancy and promotes cell proliferation under glucose starvation through the miR-22/TCF7 axis. 34076984_NBR2 promotes the proliferation of glioma cells via inhibiting p15 expression. 34506209_Long non-coding RNA NBR2 suppresses the progress of colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo by regulating the polarization of TAM. 35951458_NBR2/miR-561-5p/DLC1 axis inhibited the development of multiple myeloma by activating the AMPK/mTOR pathway to repress glycolysis. |
|
|
48.179657 |
0.2977155047 |
-1.747994 |
0.240066128 |
56.065948 |
0.00000000000007008043046708836748695981150267321760827157056672476187486608978360891342163085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000449147700258021881728680614423842064949089075698296369409945327788591384887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.4922211 |
3.8504540 |
76.0639254 |
7.8990870 |
| ENSG00000198498 |
55319 |
TMA16 |
protein_coding |
Q96EY4 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the biogenesis of the 60S ribosomal subunit in the nucleus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:32669547}. |
3D-structure;ADP-ribosylation;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Ribosome biogenesis |
|
Located in nucleolus and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55319; |
nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; preribosome binding [GO:1990275]; ribosomal large subunit biogenesis [GO:0042273] |
|
ENSMUSG00000025591 |
Tma16 |
148.788758 |
2.0060246310 |
1.004339 |
0.156604119 |
40.902051 |
0.00000000016005310380510765371378404251298662938629568941450997954234480857849121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000816868538092458127564228958426796253777801837259175954386591911315917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
196.7112452 |
22.1955236 |
98.4140830 |
8.3752362 |
| ENSG00000198502 |
3127 |
HLA-DRB5 |
protein_coding |
Q30154 |
FUNCTION: Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;MHC II;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
HLA-DRB5 belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha (DRA) and a beta (DRB) chain, both anchored in the membrane. It plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells. The beta chain is approximately 26-28 kDa and its gene contains 6 exons. Exon one encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and exon 5 encodes the cytoplasmic tail. Within the DR molecule the beta chain contains all the polymorphisms specifying the peptide binding specificities. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. There are multiple pseudogenes of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2020]. |
hsa:3127; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; MHC class II protein complex [GO:0042613]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex [GO:0002503]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870] |
11034591_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11082515_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11082517_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11181188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11469465_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11555411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11704801_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11798795_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11934390_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11997714_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12133402_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12144077_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12144632_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12209103_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12296785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12392858_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12694574_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12956878_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14508706_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14617041_the identification of a new HLA-DRB5 allele found in two members of a British Caucasoid family. 14752708_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15902698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16405603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16426242_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16566202_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16916662_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17106278_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17153701_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17182961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17559577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17910142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18520346_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18569076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18713991_hMBP82-100-specific type B T cells escaped tolerance in HLA-DRB5*0101 Tg mice 18832704_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18832704_roles of HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DRB5 genes in multiple sclerosis 18846964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19223392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19235017_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19380721_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19663932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19811438_the gene frequency of HLADR5 was significantly decreased in the total group of patients with autoimmune liver disease 20193235_In our study, we found that the HLA-DR9 allele and HPV16E6 infection had a function of synergy in the process of malignant transformation of esophageal epithelial cells, and jointly promoting the occurrence and development of esophageal cancer. 20193583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20307907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20394989_DNA methylation of CpG dinucleotides across HLA-DRB1*1501 and HLA-DRB5 does not determine whether patients manifest benign or malignant multiple sclerosis. 20606439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20639878_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21299892_HLA-DRB5 was found to have bimodal expression in human skeletal muscle tissue. 22033527_Eighteen out of 19 individuals showed HLA-DRB5, and none of the HLA-DRB5*null individuals, carried the HLADRB1* 15 allele. The findings support a contribution for HLA-DRB5 in keloid pathogenesis. 22531795_There are no significant differences in the HLA-DRB3/B4/B5 homozygosity and heterozygosity rates between Korean males and females in both newborns and adults. 22723597_HLA-DRB5 was highly expressed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease. The HLA-DRB5*01:05 allele is a risk factor for interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis. 22862923_DRB5*01:01 is associated with Thai systemic lupus erythematosus; the association is stronger than that of DRB1*15:01; genetic contribution of DRB5*01:01 is due partially to linkage disequilibrium between DRB1*16:02 and DRB5*01:01 in northern Thai population 22888134_Transgenic mice expressing HLA-DRB5*01:01 genes are crossed with histocompatibility class (MHC) II knockout mice to replace mouse MHC class II genes with human MHC class II genes in a humanized model of autoimmunity. 24366815_findings indicated that copy number variants of HLA-DRB5 was associated with the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus, and copy number deletion appeared to be protective for SLE. 25365775_Brain DNA methylation in HLA-DRB5 was associated with pathological Alzheimer disease. 26740600_HLA-DRB5 affects type 1 diabetes risk and islet autoantibodies. 27088644_This study identified genetic overlap between Alzheimer disease and immune-mediated diseases, implicating the HLA locus and IPMK in the pathobiology of Alzheimer disease. 27713094_Variation at HLA-DRB5 being associated both with Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, ariation at HLA-DRB5 being associated both with Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. 28131168_Case-control study in Han Chinese from the southwest of the country suggests that risk of ALS is increased by the AA genotype at rs9268856 in the HLA-DRA/HLA-DRB5 gene, but not by the SNPs rs9268877 in HLA-DRA/HLA-DRB5, rs1980493 in BTNL2 or rs302668 in RAB38/CTSC 30679605_In this study, molecular dynamics simulation was performed on the complexes of Top1 peptide with various HLA-DR subtypes divided into ATASSc-associated alleles (HLA-DRB1*08:02, HLA-DRB1*11:01 and HLA-DRB1*11:04), suspected allele (HLA-DRB5*01:02), and non-associated allele (HLA-DRB1*01:01). 31624234_Chromatin profiling of cortical neurons identifies individual epigenetic signatures in schizophrenia. 31882398_Increased HLA-DR expression and cortical demyelination in MS links with HLA-DR15. |
ENSMUSG00000067341 |
H2-Eb2 |
100.659834 |
2.0898616163 |
1.063407 |
0.186996311 |
32.410865 |
0.00000001247868077751065942971377695572265942303147312486544251441955566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000053855359145046008033993079761048150544411328155547380447387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
138.9923521 |
15.4709715 |
67.0067526 |
5.7574703 |
| ENSG00000198673 |
338811 |
TAFA2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N3H0 |
FUNCTION: Has a role as neurotrophic factor involved in neuronal survival and neurobiological functions. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q7TPG7}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene is a member of the TAFA family which is composed of five highly homologous genes that encode small secreted proteins. These proteins contain conserved cysteine residues at fixed positions, and are distantly related to MIP-1alpha, a member of the CC-chemokine family. The TAFA proteins are predominantly expressed in specific regions of the brain, and are postulated to function as brain-specific chemokines or neurokines, that act as regulators of immune and nervous cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:338811; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; memory [GO:0007613]; visual learning [GO:0008542] |
19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 25112515_Variants of FAM19A2 (rs348644) are associated with forced expiratory volume in COPD. 27416945_Data identified two, BCL2 and FAM19A2, novel loci and replicated known variants associated with insulin sensitivity. Further studies are needed to clarify the causal variant and function at the BCL2 and FAM19A2 loci. 30485583_interleukin-1beta was found as an upstream regulator of TAFA2 expression. Our findings demonstrate that TAFA2 enhances hMSC migration and recruitment and thus is relevant for regenerative medicine applications. |
ENSMUSG00000044071 |
Tafa2 |
10.748999 |
0.1073891122 |
-3.219080 |
0.671100930 |
22.613782 |
0.00000198058711299603915342100630969657260038729873485863208770751953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006779560711461395527564679358567545364167017396539449691772460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5868509 |
0.7655867 |
14.8636474 |
4.3003102 |
| ENSG00000198682 |
9060 |
PAPSS2 |
protein_coding |
O95340 |
FUNCTION: Bifunctional enzyme with both ATP sulfurylase and APS kinase activity, which mediates two steps in the sulfate activation pathway. The first step is the transfer of a sulfate group to ATP to yield adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS), and the second step is the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to APS yielding 3'-phosphoadenylylsulfate/PAPS, the activated sulfate donor used by sulfotransferases (PubMed:19474428, PubMed:11773860, PubMed:23824674, PubMed:25594860). In mammals, PAPS is the sole source of sulfate while APS appears to only be an intermediate in the sulfate-activation pathway (PubMed:19474428, PubMed:11773860, PubMed:23824674, PubMed:25594860). Plays indirectly an important role in skeletogenesis during postnatal growth (PubMed:9771708). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19474428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23824674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25594860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9771708}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Disease variant;Dwarfism;Kinase;Multifunctional enzyme;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Reference proteome;Transferase |
PATHWAY: Sulfur metabolism; sulfate assimilation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11773860, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19474428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23824674, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25594860}. |
Sulfation is a common modification of endogenous (lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates) and exogenous (xenobiotics and drugs) compounds. In mammals, the sulfate source is 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS), created from ATP and inorganic sulfate. Two different tissue isoforms encoded by different genes synthesize PAPS. This gene encodes one of the two PAPS synthetases. Defects in this gene cause the Pakistani type of spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9060; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; adenylylsulfate kinase activity [GO:0004020]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; nucleotidyltransferase activity [GO:0016779]; sulfate adenylyltransferase (ATP) activity [GO:0004781]; 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate biosynthetic process [GO:0050428]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; bone development [GO:0060348]; hormone metabolic process [GO:0042445]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; sulfate assimilation [GO:0000103] |
11558903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11931653_Transcriptional regulation of human 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulphate synthase 2. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727025_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727025_Thirty-seven novel SNPs in the PAPSS2 gene and in two intergenic regions on chromosomes 2q33.1 and 18p11.32 were associated with exercise participation. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22242175_Unusual localisation signals of both PAPS synthase isoforms, are described. 22394585_Papss2 expression is reduced in articular cartilage following transforming growth factor-beta administration. 22791835_PAPSS2 is the disease gene for an autosomal recessive brachyolmia. 23824674_PAPSS2-brachyolmia includes phenotypes of the conventional clinical concept of brachyolmia, the Hobaek and Toledo types, and is associated with abnormal androgen metabolism. 25594860_Direct in vivo evidence for the significant functional impact of mutant PAPSS2 on DHEA sulfation and androgen activation. 25679447_Results suggest that the loss of the susceptible region on chromosome 10q, which implicates PTEN, FAS and PAPSS2 may serve as genetic predictors of PSA recurrence after radical prostatectomy. 26685716_Our results indicate that FGFR2 and PAPSS2 may play an important role in the regulation of magnesium homeostasis in children of European-American ancestry. 26896383_In an Amish population, using expression profiling of genes within regions identified by a meta-analysis GWAS of survival to age 90, we localized PAPSS2 as a candidate gene for extended life span. These results provide novel evidence for genetic loci implicated in longevity and incorporate gene expression results from a unique population to locate positional candidates. 27207664_Silencing of SULT1A1 and PAPSS2 led to a significant decrease in aristolactam-DNA levels in both cell lines following exposure to AA-I, indicating the critical role for sulfonation in the activation of AA-I in vivo Since HK-2 cells proved relatively resistant to knockdown with siRNAs 29743239_Energy-dependent scoring of docking solutions identified the interaction as specific for the PAPSS2 and SULT2A1 isoforms 29955124_Depletion of PAPSS2 in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells results in reduced cell migration, while overexpression of PAPSS2 promotes cell migration. 31313512_In all patients, exome and Sanger sequencing identified homozygous or compound heterozygous PAPSS2 variants, including c.809G>A, common to white European patients. 33819483_Intestinal Sulfation Is Essential to Protect Against Colitis and Colonic Carcinogenesis. 34818583_Structural basis for the substrate recognition mechanism of ATP-sulfurylase domain of human PAPS synthase 2. 35261200_Identification of variants in ACAN and PAPSS2 leading to spondyloepi(meta)physeal dysplasias in four Chinese families. |
ENSMUSG00000024899 |
Papss2 |
44.247916 |
2.9517099657 |
1.561551 |
0.248036079 |
40.841424 |
0.00000000016509619108057148445186380226600442872042506792240601498633623123168945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000841152840990415991388720045739309238985725869497400708496570587158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.4708456 |
10.0777105 |
23.0365321 |
2.8202428 |
| ENSG00000198691 |
24 |
ABCA4 |
protein_coding |
P78363 |
FUNCTION: Flippase that catalyzes in an ATP-dependent manner the transport of retinal-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugates like the 11-cis and all-trans isomers of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine from the lumen to the cytoplasmic leaflet of photoreceptor outer segment disk membranes, where N-cis-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (N-cis-R-PE) is then isomerized to its all-trans isomer (N-trans-R-PE) and reduced by RDH8 to produce all-trans-retinol (all-trans-rol) and therefore prevents the accumulation of excess of 11-cis-retinal and its schiff-base conjugate and the formation of toxic bisretinoid (PubMed:24097981, PubMed:22735453, PubMed:23144455, PubMed:20404325, PubMed:10075733, PubMed:29847635, PubMed:33375396). May display both ATPase and GTPase activity that is strongly influenced by the lipid environment and the presence of retinoid compounds (PubMed:22735453). Binds the unprotonated form of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine with high affinity in the absence of ATP, and ATP binding and hydrolysis induce a protein conformational change that causes the dissociation of N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1MWM0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10075733, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20404325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22735453, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23144455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24097981, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29847635, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33375396}. |
3D-structure;Age-related macular degeneration;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cone-rod dystrophy;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Retinitis pigmentosa;Sensory transduction;Stargardt disease;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Vision |
|
The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intracellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the ABC1 subfamily. Members of the ABC1 subfamily comprise the only major ABC subfamily found exclusively in multicellular eukaryotes. This protein is a retina-specific ABC transporter with N-retinylidene-PE as a substrate. It is expressed exclusively in retina photoreceptor cells, and the gene product mediates transport of an essental molecule, all-trans-retinal aldehyde (atRAL), across the photoreceptor cell membrane. Mutations in this gene are found in patients diagnosed with Stargardt disease, a form of juvenile-onset macular degeneration. Mutations in this gene are also associated with retinitis pigmentosa-19, cone-rod dystrophy type 3, early-onset severe retinal dystrophy, fundus flavimaculatus, and macular degeneration age-related 2. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2019]. |
hsa:24; |
cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; photoreceptor disc membrane [GO:0097381]; photoreceptor outer segment [GO:0001750]; rod photoreceptor disc membrane [GO:0120202]; 11-cis retinal binding [GO:0005502]; ABC-type transporter activity [GO:0140359]; all-trans retinal binding [GO:0005503]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0042626]; flippase activity [GO:0140327]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; lipid transporter activity [GO:0005319]; N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity [GO:0140347]; phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity [GO:0090555]; phospholipid transporter activity [GO:0005548]; retinoid binding [GO:0005501]; retinol transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0034632]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; phospholipid transfer to membrane [GO:0006649]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; photoreceptor cell maintenance [GO:0045494]; phototransduction, visible light [GO:0007603]; retinal metabolic process [GO:0042574]; retinoid metabolic process [GO:0001523]; transmembrane transport [GO:0055085]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11328725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11346402_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11444963_The nucleotide binding domain 1 (NBD1) of the retina-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter is a general ribonucleotidase capable of binding ATP, CTP, GTP and UTP. 11726554_Of the 21 missense ABCR mutations reported in patients with AMD, 16 (76%) show abnormalities in protein expression, ATP-binding or ATPase activity. 11919200_Biochemical defects in retina-specific human ATP binding cassette transporter nucleotide binding domain 1 mutants associated with macular degeneration 11973624_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11973624_The ABCA4 2588G>C Stargardt mutation 12202497_Three novel ABCA4 gene mutations were identified in Japanese patients with STGD and arRP. 12442277_Genotype-phenotype correlations highlighted the function of ABCA4 in retinitis pigmentosa (RP),cone-rod dystrophy (CRD) and Stargardt/Fundus Flavimaculatus disease (STGD/FFM). 12515255_The ABCA4 gene in autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophies 12592048_ABCA4 splicing mutations may be associated with a small proportion of AMD (Age-related macular degeneration) cases. 12592048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12754711_genomic deletion in patients with Stargardt disease: genomic alterations contribute to only a small fraction of retinopathy-associated alleles 12796258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12796258_Patients with autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy are likely to harbor a mutation in the ABCA4 gene as the cause of their disease. 12824224_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12824224_This study confirmed the very high degree of ABCA4 sequence polymorphism in the general population 12888572_nucleotide binding and ATPase activities of the N and C halves of ABCR individually and co-expressed 15017103_A homozygous nonsense mutation 2971G>T (G991X) was detected in a patient diagnosed with cone-rod dystrophy. 15223829_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15375613_a pilot study by analyzing 8 exudative ARMD patients for allelic variations in the GPX gene and three statistically significant mutations in the ABCR gene (R943Q, G1961E and D2177N) 15494742_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15947798_ABCA4 splicing mutations may be associated with a small proportion of AMD (Age-related macular degeneration) cases. 16303926_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16533065_These data indicate that changes in the oligomeric state of the nucleotide binding domains of ABCR are coupled to ATP hydrolysis and might represent a possible signal for the TMDs of ABCR to export the bound substrate. 16546111_Homozygous null mutations in ABCA4 produced a severe widespread retinal degeneration that showed marked central retinal involvement. 16604398_ABCA4 splicing mutations may be associated with a small proportion of AMD (Age-related macular degeneration) cases. 16681420_a new 6730-16del44 deletion is the first de novo mutation associated with cone-rod dystrophy and may contribute to a better understanding of the role of ABCA4 mutations in macular dystrophies [case report] 16917483_Major disease-associated allele, R1129L, which accounted for 24% of the mutated alleles detected, and a high frequency (12%) of complex alleles. 17325136_In the population studied, ABCA4 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of autosomal recessive cone-rod dystrophy . However, mutations in this gene are less frequently identified in other retinal dystrophies. 17325136_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17724221_Genotype-phenotype correlation of ABCA4, show that homozygosity for the novel c.4254-15del23 splicing mutation is associated with a severe progressive form of Stargardt-like disease. 17932850_Finding a high proportion of novel mutations merits the use of scanning methodologies to analyze the whole coding region of the ABCA4 gene. 17982420_ABCA4 mutation spectrum within relatively stable populations might be skewed due to founder effects. Patients either homozygous or compound heterozygous for N965S mutation show that this mutation has early and profound effect on retinal function. 17982420_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17997789_We report the unusual association of a retinal astrocytic hamartoma and Stargardt's disease in a patient with ABCR mutation. 18024811_Variations in the ABCA4 gene are common in bull's-eye maculopathy. 18214793_Stargardt's disease is caused by mutations in the ABCR (ABCA4) gene on chromosome 1. 18285826_Disease-associated ABCA4 alleles were identified in 20 of 64 patients with autosomal recessive cone (arCD) and cone rod dystrophy (arCRD). 18285826_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18334942_Two distinct retinal dystrophies with mutations affecting two different genes ABCA4 and CRB1 genes cosegregated in this family. 18506364_Data show that photoreceptor cell-specific ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA4) gene was found to be mutated in patients with Stargardt disease (STGD) and autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa (RP). 18523590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18523590_associations between clinical outcomes of congenital toxoplasmosis and polymorphisms at ABCA4 and COL2A1 provide novel insight into the molecular pathways that can be affected by congenital infection with this parasite 18649358_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18854780_Stargardt disease (STGD) can present with peripapillary atrophy. This relatively uncommon phenotype may arise from specific combinations of STGD ABCA4 mutations rather than single mutations. 18977788_Calculated prevalence of arSTGD based on the ABCA4 carrier frequency could be higher than previous estimation and this discrepancy between observed and estimated prevalence could be due to the existence of non-pathological or low penetrance alleles. 18977788_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19015224_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19028736_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19028736_a huge number of ABCA4 disease-associated alleles were identified, representing an increment of 4% of novel variants described in this gene, as 500 sequence changes have been described so far. 19056738_Role of the C terminus of the photoreceptor ABCA4 transporter in protein folding, function, and retinal degenerative diseases. 19074458_ABCA4 mutations lead to a wide spectrum of severity in retinal diseases. 19217903_the G1961E allele contributes to localized macular changes rather than generalized retinal dysfunction, and is a cause of bull's eye maculopathy in either the homozygosity or heterozygosity state 19265867_In STGD patients, 71 mutations were identified in 68 patients, 43 mutations had been reported in the literature, whereas 28 mutations had not been previously described and were not detected in 150 unaffected control individuals of Italian origin. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19352439_study identified 2 novel ABCA4 mutations, c.655A>T & c.5312+3A>T; in the compound heterozygous state, the mutations cause a phenotype of retinal dystrophy that initially manifests as Stargardt disease and slowly progresses to a severe cone-rod dystrophy 19365039_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19365039_Validated ABCR400 results provide an unequivocal molecular diagnosis, allowing family members to be offered diagnostic, predictive, carrier, and prenatal testing. 19365591_This study represents the first report of ABCA4 mutations in Portuguese Stargardt patients. 19430638_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19578016_In these patients with Stargardt disease and a Gly1961Glu mutation, most showed a clinical phenotype characterized by fundus changes localized to the foveal and parafoveal regions, normal ERG amplitudes. 19625466_This study shows that hepatitis delta virus p24 and p27 proteins inhibit HBV replication by trans-repressing its enhancers and by trans-activating the IFN-alpha-inducible MxA gene. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19959634_ABCA4 should be analyzed by an optimal screening technique, to perform further characterization of pathologic alleles. 20029649_ABCA4 microarray screening is usually requested in daily clinical practice to strengthen the diagnosis when the disease is atypical. 20128570_The presence of two severe mutations in the two alleles of ABCA4 gene was associated with a larger atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium in the macular area. 20163366_Genetic analysis with direct DNA sequencing of amplified products revealed four reported polymorphisms and one novel mutation, Met280Thr, in exon 7 of the ABCA4 gene 20335603_Families showing a variable macular dystrophy phenotype caused by mutations in PRPH2 should be tested for additional mutations in ABCA4 and ROM1, as they may alter the progression of the PRPH2 phenotype. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20404325_three macular degeneration-associated mutations lead to significant changes in the secondary structure of the ECD2 domain of ABCA4, as well as in its interaction with all-trans-retinal 20436469_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20436469_Replication studies from several populations showed confirming evidence, with families of European ancestry giving stronger evidence for markers in 8q24, whereas Asian families showed stronger evidence for association with MAFB and ABCA4. 20591486_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20647261_Multiple regression analysis was used to estimate the pathogenicity of specific alleles of ABCA4 in patients with retinal phenotypes ranging from Stargardt disease to retinitis pigmentosa. 20661590_Mutations found in diseased dogs are a basis for association studies of mutations in this protein in retinal diseases in humans 20696155_Loss of peripapillary sparing is likely associated with the more deleterious mutations of the ABCA4 gene. 20711710_The pathogenesis of diseases caused by mutations in ABCA4 is complex, comprising a loss-of-function component as well as photoreceptor stress caused by protein mislocalization and misfolding. Review. 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21330655_polymorphisms were identified that may act as risk factors (p.Asn1868Ile) and others that may act as protection factors (p.His423Arg and IVS10+5 delG). 21510770_ABCA4 mutations in diseases [Review] 21567910_An association of ABCA4 and MAFB with non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 21721517_Using human ABCA4 mutants heterologously expressed in mammalian cells, we showed that the Stargardt disease-associated alanine mutation in the phosphorylation site at position 901 led to protein misfolding and degradation 21786275_This case report reveals that ABCA4 gene mutation may be complicated by multiple and bilateral choroidal neovascularization. 21834038_none of any ABCA4 genotypes or alleles was associated with risk of nonsyndromic orofacial clefts or their subgroups. 21911583_The authors detected a total of 57 previously unknown, possibly pathogenic, variants: 29 missense, 4 nonsense, 9 small deletions and 15 splice-site-altering variants. 22060670_Mutations were detected in the ABCA4 gene by chip screening; SD-OCT revealed marked atrophy of the retina in the central macula, with focal defects in the RPE with disruptions in Bruch membrane and herniation of the retina 22220722_Progression of retinal degeneration in Abca4-deficient Rdh8-deficient mice is affected by differential vulnerability of rods and cones to light. 22229821_Scandinavian patients with ABCA4-related retinopathy appear to have a distinct mutation spectrum, which can be identified in patients of diverse clinical phenotypes. 22247458_Macular function in ABCA4-RD patients transitioned from lower sensitivity at the parafovea to higher sensitivity in the perifovea. RP patients had the inverse pattern. 22312191_The G1961E mutation in ABCA4, which has been considered 'mild,' yields a more severe phenotype in a family with Stargardt disease than the A1038V mutation, which has been considered 'severe.' 22395892_Mutations in ABCA4 that reduce or abolish this flippase activity result in the formation of toxic bisretinoids that can either injure the photoreceptors directly or accumulate in the underlying RPE 22427542_findings provide support for a complex role of ABCA4 in the etiology of a minor proportion of patients with age-related macular degeneration 22449572_Late-onset STGD1 is at the mild end of the spectrum of retinal dystrophies caused by ABCA4 mutations. The visual acuity is frequently preserved in late-onset STGD1 patients owing to foveal sparing. 22589445_A reduction in ABCA4 activity in the photoreceptors results in the increased production and accumulation of A2E and related bisretinoids within RPE cells. 22661473_Homozygous G1961E mutation in ABCA4 results in a range of retinal pathology. The phenotype usually is at the milder end of the disease spectrum, with severe phenotypes linked to the presence of additional ABCA4 variants. 22706241_FtMt mutation may determine a condition similar to haploinsufficiency resulting in a reduced protection from iron-dependent oxidative stress in mitochondria 22753311_ABCA4 gene has a functional role in the development of orofacial clefting in hispanic population. 22948568_Three novel heterozygous missense mutations in the ABCA4 gene were identified: c:2633C>A (p:Ser878X), c:5646G>A (p:Met1882Ile). 23096905_Four novel missense mutations in the ABCA4 gene are associated with autosomal recessive Stargardt disease. 23143460_A range of phenotypes can be associated with mutations in ABCA4 ; therefore, genetic testing is important in establishing a firm diagnosis. 23144455_The nucleotide binding domain 1 of ABCA4 is specific for 11-cis-retinal binding. 23167473_Study results support a potential role for ABCA4 in the etiology of cleft lip/palate in Caucasian individuals from Brazil, confirming previous findings in other population groups. 23419329_Our results expand the mutational spectrum of Stargardt disease by adding 12 novel ABCA4 pathogenic variants and support the occurrence of a founder effect for the p.A1773V mutation in the Mexican population. 23443024_Four patients with Leber congenital amaurosis were homozygous for a novel mutation in the CRB1 gene, while of two cases with Stargardt disease, one was homozygous for c.5461-10T>C in the ABCA4 gene and another was carrier of the same mutation. 23512105_All four of the genes originally identified as showing genome-wide significance (IRF6, ABCA4 and MAF, plus the 8q24 region) were confirmed in this independent sample of trios (who were primarily of European and Southeast Asian ancestry). 23755510_ABCR gene mutation is present in Stargardt disease. 23755871_Patients with classical arRP phenotypes, especially from the onset of the disease, should be screened first for mutations in known arRP genes and not ABCA4. 23769331_The common alleles identified, p.Gly1961Glu and p. Leu2027Phe, both have a mild structural and functional effect on the adult retina; the latter is associated with relatively retained photoreceptor architecture and function at the fovea. 23882696_Autosomal recessive STGD is caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene, which encodes a transporter protein located in the outer segment disc membranes of the photoreceptors. 23918662_mutations near rare alternate splice junctions in ABCA4 might cause disease by increasing the probability of mis-splicing at these sites 23940504_Data found pathogenic DNA variants in the genes RP1, USH2A, CNGB3, NMNAT1, CHM, and ABCA4, responsible for retinitis pigmentosa, Usher syndrome, achromatopsia, Leber congenital amaurosis, choroideremia, or recessive Stargardt/cone-rod dystrophy cases. 23949494_Analysis of the entire coding region of the ABCA4 gene revealed a (missense) mutation as well as a frameshift mutation in Stagartds disease. A splice sequence change was additionally found. 23953153_The presence of 2 distinct phenotypes of Stargardt disease (foveal sparing and foveal atrophy) suggests that there may be more than 1 disease mechanism in ABCA4 retinopathy. 23982839_Application of the NGS platform for ABCA4 screening enabled detection of the second disease-associated allele in approximately half of the patients in a British cohort where one mutation had been detected with the arrayed primer extension (APEX) array. 24011517_Three ABCA4 sequence variations were identified exclusively in 10 unrelated African American patients 24097981_structure-function relationships of ABCA1 and ABCA4 are broadly similar despite the fact that they transport different phospholipids in different directions. 24265018_ABCA4 variants were identified in 57 patients. There was a significant association between AF subtype and genotype. 24342785_To our knowledge, we reported for the first time the homozygous state of the c.2041C>T mutation. Among homozygous patients, the age at onset of Stargardt disease was early, the loss of visual acuity was important and the prognosis was severe. 24397708_Diagnosis of concurrent Stargardt disease and CSNB was made on the ophthalmic history; genetic testing revealed two previously reported mutations in the ABCA4 gene and two novel deletions in the GRM6 gene. 24428930_ABCA4 screening detected three variants; two variants p.L541V and p.A1038V commonly co-inherited in a complex allele and a third novel variant p.R881C. Patient 1 had all three variants and her sibling harboured the complex allele (p.L541V/p.A1038V). 24453473_This study confirms that ABCA4 mutations lead to a spectrum of retinal degenerations. 24457364_Select sequence variations in ABCA4 may confer a specific phenotype. The present data will help in assessing patients for emerging therapies. 24585425_In this family two sibs homozygous for the ABCA4 c.1937+1G>A splice-site variant have a less severe phenotype of Stargardt disease. 24632595_one novel ABCA4 mutation in Chinese patients with Stargardt disease 24664696_Mutations in CRB1 and ABCA4 were found in a Swedish family with Leber congenital amaurosis and Stargardt disease. 24713488_Most of the ABCA4 mutations were classified as 'severe' explaining the early onset, panretinal degeneration, and fast progression of the disease. 24763286_Seven disease-causing mutations in ABCA4 and two in PROM1 identified by capture next generation sequencing. 25082829_New mutations have been described in the ABCA4 genomic locus in Stargardt disease. 25139735_observed thickening of the ELM in STGD1 patients may be an early protective response of Muller cells to the stress elicited by ABCA4-deficiency. 25265374_The histopathology of the retina in this patient with Stargardt disease displayed a highly degenerated fovea. In all retinal locations studied, cones were more severely affected than rods. 25283059_The qAF method can differentiate between ABCA4-associated and non-ABCA4-associated BEM and may guide clinical diagnosis and genetic testing. 25301883_The optical gap phenotype in STGD1 can be structurally divided into three progressive stages spanning several years. This particular phenotype also appears to be highly associated with the p.G1961E mutation of ABCA4. 25312043_The relatively high proportion of deleterious ABCA4 variants supports the hypothesis that earlier onset disease is often owing to more severe variants in ABCA4 than those found in adult-onset disease. 25324290_The anatomy, metabolism, and biochemistry of the retina, as well as genetic variations in genes other than ABCA4, can influence the etiology of foveal sparing. 25346251_Study reveals high frequency of the deep intronic variant c.4539+2001G>A (V4)in ABCA4 gene that has founder effect and moderate-to-severe impact in the phenotype of Autosomal-recessive Stargardt disease Belgian patients. 25363634_Results show the presence of heterozygous deep-intronic and exonic variants and deletions in ABCA4 in patients with retinal dystrophies. 25444351_Thus, early-onset Stargardt lies at the severe end of the spectrum of ABCA4-associated retinal phenotypes. 25499508_Our study provides further evidence regarding the roles of genetic markers in ABCA4 in NSCL/P development in this northern Chinese Han population. G allele of rs560426 may be a risk factor for developing NSCL/P. 25640233_Two known disease-causing mutations in ABCA4 were identified in proband 1; c.4234C>T, p.(Gln1412*) in exon 28; and c.5882G>A, p.(Gly1961Glu) in exon 42. 25712131_The ABCA4 L541P;A1038V mutation causes severe retinal degenerations whereas the V mutation alone causes mild disease. 25884411_Our findings demonstrate that minor alleles of common genetic variants in ABCA4 significantly reduce susceptibility to develop toxic maculopathy under chloroquine treatment. 25921964_Significant evidence was found for a relationship between the G1961E and D2177N variants in ABCA4 with increased susceptibility to AMD, specifically for Americans 25922843_Identification of Novel Mutations in ABCA4 Gene: Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Indian Patients with Stargardt Disease. 26024099_high qAF levels of ABCA4-positive patients are a hallmark of ABCA4-related disease 26092729_Stargardt eye disease ABCA4 R1108C and R1129C are both temperature-sensitive processing mutants that engage the cellular quality control mechanism and show a strong interaction with the chaperone Hsp 27. 26261413_ABCA4 carriers demonstrated reduced macular function measured by mERG along with none to subtle and even extensive morphological retinal changes. The c.768 G>T, c.5461-10T>C, and c.319 C>T mutations were associated with the most deviant ERGs. 26261643_633C>A (CC+CA) genotype, 5646G>A and 6389T>A polymorphisms of ABCA4 gene and smoking are susceptible factors for age-related macular degeneration 26311262_A transient SD-OCT phenotype ascribed to patients with hydroxychloroquine retinopathy is associated with an early subtype of STGD1. 26527198_This family epitomizes the clinical and genetic complexity of ABCA4-associated diseases. It contained variants from all classes of mutations 26551331_With few exceptions, individuals heterozygous for ABCA4 mutations and between the ages of 9 and 60 years do not present with elevated qAF. 26593885_A combination of p.[(L541P; A1038V)] and/or a truncating ABCA4 mutation always resulted in an early disease onset. Identification of ABCA4 retinopathies provides a specific molecular diagnosis and justifies a prompt introduction of simple precautions that may slow disease progression. 26720470_This study indicates that carriers of monoallelic ABCA4 mutations are phenotypically normal. 26780318_The mutation spectrum of the ABCA4 gene in Chinese patients is quite different from that for Caucasian patients. The establishment of the mutation profile will facilitate ABCA4 screening and risk evaluation for Chinese patients with STGD1. 26806561_seven out of 27 families, displaying mutations in the ABCA4, RP1, RP2 and USH2A genes, could be genetically or clinically reclassified. These results demonstrate the potential of our panel-based NGS strategy in RP diagnosis 26976702_The ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T-->C is located on a founder haplotype lacking other disease-causing rare sequence variants. In vitro studies revealed that it leads to mRNA exon skipping and ABCA4 protein truncation. 27527345_Results identified nonsynonymous variants in MYH9 and ABCA4 to be the most frequent risk loci in nonsyndromic orofacial clefts in the Taiwanese population. 27583828_Nullizygosity for ABCA4 is associated with early onset cone-rod dysfunction with rapid progression shown by enlargement of central atrophy on FAF, decline of ERG amplitudes with age, and a high risk of reaching legal blindness by the fourth decade. 27739528_Two novel pathogenic ABCA4 mutations were identified in Chinese families with Stargardt disease. 27775217_This study describes the functional effect and the molecular mechanism of the pathogenic ABCA4 variant c.5461-10T>C. The variant is functionally important as it leads to splicing defects and a reduced level of ABCA4 protein. 27820952_study to determine the effect of 15 individual ABCA4 mutations on retinal disease severity; in the hemizygous state, 2/15 ABCA4 alleles retain preserved peripheral retinal function; 7/15 are associated with either preserved or only mildly abnormal retinal function, worse in older patients; 6/15 behave like null mutations 27939946_Ten novel ABCA4 variations are detected of which 8 belongs to non-Slavonian population. Most of the detected known variations are found in European and American Stargardt disease populations 28005406_Of the 225 genetic tests performed, 150 were for recessive IRD, and 75 were for dominant IRD. A positive molecular diagnosis was made in 70 (59%) of probands with recessive IRD and 19 (26%) probands with dominant IRD. Thirty-two novel variants were identified; among these, 17 sequence changes in four genes were predicted to be possibly or probably damaging including: ABCA4 (14), BEST1 (2), PRPH2 (1), and TIMP3 28044389_Studies indicate that variants in ABCA4 are associated with a wide variety of inherited retinal diseases. 28118664_Genetic risk score estimates suggest that defined common ABCA4 variants influence disease risk in carriers of a single pathogenic ABCA4 allele. 28290600_1268A>G missense variant of the ABCA4 gene has often been reported as causative of disease, and in other cases protective of disease, in our family case, the variant appears to reduce or delay the risk of onset of Stargardt disease. 28327576_Thirty six SNP including 9 previously not described, were identified in juvenile-onset blindness patients of south Asian decent. 28726568_We report an unusual phenotype in a child with a clinical diagnosis of recessive Stargardt disease (STGD1) and two pathogenic variants in the ABCA4 gene. 28885670_Our analyses allowed us to classify novel variants in ABCA4 as being clearly loss-of-function mutations, and thus pathogenic variants. 28947085_The ROC phenotype is a unique classification of ABCA4 disease, which is caused by deleterious null biallelic ABCA4 mutations and is characterized by the rapid deterioration of retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptor layers in the macula and significant choroidal thinning within the first 2 decades of life. 28980559_High prevalence of p.L541P, p.A1038V, and p.G1961E mutations of the ABCA4 gene has been established in patients with Stargardt disease by performing massive parallel sequencing of all coding regions of the ABCA4 gene. 29114839_Segregation analysis is important in order to confirm the molecular diagnosis of patients with Stargardt disease, given the frequency of complex alleles in the ABCA4 gene. The various pathogenic variation combinations observed in this study were associated with different phenotypes. 29162642_ABCA4 midigenes reveal the full splice spectrum of all reported noncanonical splice site variants in Stargardt disease. 29178665_In Stargardt patients with ABCA4 pathogenic mutations, the photopic negative response of the full-field photopic ERG is a very sensitive disease read-out. 29207047_These findings expand the mutation spectrums of ABCA4 and LRP5, and will be valuable for genetic counseling and development of therapeutic interventions for patients with Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. 29310964_In childhood-onset ABCA4-associated retinopathy, the earliest stages of macular atrophy involve the parafovea and spare the foveola. 29386879_Full-field electroretinography is a predictor of the natural course of ABCA4-associated retinal degeneration. 29422768_The results indicate that the p.Ala1773Val mutation in ABCA4 is associated with a severe retinal phenotype and thus, could be classified as null. 29461686_Two intronic variants c.4773+3A>G and c.5461-10T>C, both predicted to affect splicing, are indeed disease-causing mutations due to skipping of exons 33, 34, 39 and 40 of ABCA4 gene. The experimental proof that ABCA4 mutations in STGD patients affect protein function is crucial for their inclusion to future clinical trials. 29526278_neighboring deep-intronic ABCA4 variants (c.4539+2001G>A and c.4539+2028C>T) result in a retina-specific 345-nt pseudoexon insertion. 29847635_the expression and residual activity of ABCA4 mutants play a major role in determining the disease severity of STGD1 patients. 29847651_These studies corroborate RPE melanin as the major source of NIR-AF but also indicate that bisretinoid lipofuscin, when present at sufficient concentrations, contributes to the NIR-AF signal. Ocular melanin attenuates the SW-AF signal. 29902293_A clinically small best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) loss was observed during 2 years, and the change rate varied depending on baseline BCVA. Eyes without lesion in the fovea had better BCVA at baseline and showed minimal change of BCVA throughout 2 years. Eyes with no or modest acuity impairment but with a foveal lesion at baseline had the fastest loss rate. 29925512_There is a large spectrum of ABCA4 sequence variants, including 50 novel variants, in a well-characterised cohort thereby further adding to the unique allelic heterogeneity in STGD1. Approximately half of the cohort harbours missense variants only, indicating a relatively mild phenotype of the ProgStar cohort. 29971439_A significant fraction of genetically unexplained STGD1 cases carries p.Asn1868Ile as a second variant. Our findings suggest exceptional differences in disease expression or even nonpenetrance of this ABCA4 variant, pointing toward an important role for genetic or environmental modifiers in STGD1. 29975949_Novel ABCA4 gene mutations were found in Korean patients with STGD1. This study will facilitate better understanding of the relationships between ABCA4 gene mutations and clinical symptoms in Korean patients. 30060493_The study broadens the spectrum of ABCA4 mutations with 60 likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants, all associated with Stargardt disease. 30093795_Next-generation sequencing was effective for the molecular diagnosis of genetic diseases and specifically allowed a conclusive diagnosis in 80% (40/50) of the patients. As the ABCA4 gene does not show a preferential region for pathogenic variants, the diagnosis of Stargardt disease depends on broader analysis of the gene. The most common pathogenic variants in the ABCA4 gene described in the literature were also found. 30156925_Mutation in ABCA4 gene is associated with Stargardt disease as well as Stickler's Syndrome . 30166513_This article reviews the literature on incidence of IRD caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene and characteristics of the clinical progression of retinal diseases associated with various types of mutations, and presents analysis of clinical and genetic correlations in terms of the effect the mutation has on the structure or function of the protein [review] 30190494_Searching the second hit in patients with inherited retinal dystrophies and monoallelic variants in ABCA4, USH2A and CEP290 by whole-gene targeted sequencing. 30204727_CLINICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF STARGARDT DISEASE PATIENTS WITH THE p.N1868I ABCA4 MUTATION. 30347566_patients with hereditary retinal disease that carried ABCA4 gene mutations were featured with characteristics of early onset age, rapid progress and severe visual impairment 30563929_Identification of novel pathogenic ABCA4 variants in a Han Chinese family with Stargardt disease has been reported. 30643219_Sequencing of ABCA4 was performed in 8 STGD1 cases with one variant and p.Asn1868Ile in trans, 25 cases with one variant, and 3 cases with no ABCA4 variant...Our data demonstrate the importance of assessing noncoding variants in geneti |
ENSMUSG00000028125 |
Abca4 |
14.207750 |
33.5483826007 |
5.068171 |
0.904736527 |
39.446617 |
0.00000000033715124463292881435275468486264822259856899222540960181504487991333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001679497931414792268981887337058606091133583504415582865476608276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.5267286 |
9.8365366 |
0.4157757 |
0.2539236 |
| ENSG00000198711 |
619518 |
SSBP3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
7.252020 |
0.3309828685 |
-1.595172 |
0.565676174 |
8.417855 |
0.00371553950103331066812106797669912339188158512115478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007804377833392864630135399295340903336182236671447753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6001207 |
1.3935836 |
10.9181260 |
2.4940815 |
| ENSG00000198719 |
28514 |
DLL1 |
protein_coding |
O00548 |
FUNCTION: Transmembrane ligand protein of NOTCH1, NOTCH2 and NOTCH3 receptors that binds the extracellular domain (ECD) of Notch receptor in a cis and trans fashion manner (PubMed:11006133). Following transinteraction, ligand cells produce mechanical force that depends of a clathrin-mediated endocytosis, requiring ligand ubiquitination, EPN1 interaction, and actin polymerisation; these events promote Notch receptor extracellular domain (NECD) transendocytosis and triggers Notch signaling through induction of cleavage, hyperphosphorylation, and nuclear accumulation of the intracellular domain of Notch receptors (NICD) (By similarity). Is required for embryonic development and maintenance of adult stem cells in many different tissues and immune systeme; the DLL1-induced Notch signaling is mediated through an intercellular communication that regulates cell lineage, cell specification, cell patterning and morphogenesis through effects on differentiation and proliferation (PubMed:11581320). Plays a role in brain development at different level, namely by regulating neuronal differentiation of neural precursor cells via cell-cell interaction, most likely through the lateral inhibitory system in an endogenous level dependent-manner. During neocortex development, Dll1-Notch signaling transmission is mediated by dynamic interactions between intermediate neurogenic progenitors and radial glia; the cell-cell interactions are mediated via dynamic and transient elongation processes, likely to reactivate/maintain Notch activity in neighboring progenitors, and coordinate progenitor cell division and differentiation across radial and zonal boundaries. During cerebellar development, regulates Bergmann glial monolayer formation and its morphological maturation through a Notch signaling pathway. At the retina and spinal cord level, regulates neurogenesis by preventing the premature differentiation of neural progenitors and also by maintaining progenitors in spinal cord through Notch signaling pathway. Also controls neurogenesis of the neural tube in a progenitor domain-specific fashion along the dorsoventral axis. Maintains quiescence of neural stem cells and plays a role as a fate determinant that segregates asymmetrically to one daughter cell during neural stem cells mitosis, resulting in neuronal differentiation in Dll1-inheriting cell. Plays a role in immune systeme development, namely the development of all T-cells and marginal zone (MZ) B-cells (By similarity). Blocks the differentiation of progenitor cells into the B-cell lineage while promoting the emergence of a population of cells with the characteristics of a T-cell/NK-cell precursor (PubMed:11581320). Also plays a role during muscle development. During early development, inhibits myoblasts differentiation from the medial dermomyotomal lip and later regulates progenitor cell differentiation. Directly modulates cell adhesion and basal lamina formation in satellite cells through Notch signaling. Maintains myogenic progenitors pool by suppressing differentiation through down-regulation of MYOD1 and is required for satellite cell homing and PAX7 expression. During craniofacial and trunk myogenesis suppresses differentiation of cranial mesoderm-derived and somite-derived muscle via MYOD1 regulation but in cranial mesoderm-derived progenitors, is neither required for satellite cell homing nor for PAX7 expression. Also plays a role during pancreatic cell development. During type B pancreatic cell development, may be involved in the initiation of proximodistal patterning in the early pancreatic epithelium. Stimulates multipotent pancreatic progenitor cells proliferation and pancreatic growth by maintaining HES1 expression and PTF1A protein levels. During fetal stages of development, is required to maintain arterial identity and the responsiveness of arterial endothelial cells for VEGFA through regulation of KDR activation and NRP1 expression. Controls sprouting angiogenesis and subsequent vertical branch formation througth regulation on tip cell differentiation. Negatively regulates goblet cell differentiation in intestine and controls secretory fat commitment through lateral inhibition in small intestine. Plays a role during inner ear development; negatively regulates auditory hair cell differentiation. Plays a role during nephron development through Notch signaling pathway. Regulates growth, blood pressure and energy homeostasis (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P97677, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11006133, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11581320}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Autism spectrum disorder;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Epilepsy;Glycoprotein;Intellectual disability;Isopeptide bond;Membrane;Notch signaling pathway;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
DLL1 is a human homolog of the Notch Delta ligand and is a member of the delta/serrate/jagged family. It plays a role in mediating cell fate decisions during hematopoiesis. It may play a role in cell-to-cell communication. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:28514; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; Notch binding [GO:0005112]; receptor ligand activity [GO:0048018]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; Tat protein binding [GO:0030957]; astrocyte development [GO:0014002]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell fate determination [GO:0001709]; cerebellar molecular layer formation [GO:0021688]; cerebellar Purkinje cell layer structural organization [GO:0021693]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583]; compartment pattern specification [GO:0007386]; determination of left/right symmetry [GO:0007368]; endothelial tip cell fate specification [GO:0097102]; energy homeostasis [GO:0097009]; heart looping [GO:0001947]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; inhibition of neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0002085]; inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0042491]; lateral inhibition [GO:0046331]; left/right axis specification [GO:0070986]; loop of Henle development [GO:0072070]; marginal zone B cell differentiation [GO:0002315]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell differentiation [GO:2000726]; negative regulation of cell differentiation [GO:0045596]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epidermal cell differentiation [GO:0045605]; negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030857]; negative regulation of glial cell apoptotic process [GO:0034351]; negative regulation of hemocyte differentiation [GO:0045611]; negative regulation of inner ear auditory receptor cell differentiation [GO:0045608]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045638]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; nephron development [GO:0072006]; neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060563]; neuron fate specification [GO:0048665]; neuronal stem cell population maintenance [GO:0097150]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; Notch signaling pathway involved in arterial endothelial cell fate commitment [GO:0060853]; organ growth [GO:0035265]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of endocytosis [GO:0045807]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747]; positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048633]; positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis [GO:1903672]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; proximal tubule development [GO:0072014]; proximal/distal pattern formation [GO:0009954]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0030155]; regulation of cell division [GO:0051302]; regulation of growth [GO:0040008]; regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050767]; regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048631]; regulation of somitogenesis [GO:0014807]; regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway [GO:1900746]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0060042]; skeletal muscle tissue growth [GO:0048630]; skin epidermis development [GO:0098773]; somite specification [GO:0001757]; somitogenesis [GO:0001756]; spinal cord development [GO:0021510]; type B pancreatic cell development [GO:0003323] |
12393852_Delta-1 can enhance myeloid and lymphoid marrow-repopulating ability and promote the generation of thymus-repopulating T cell precursors. 12684674_suppresses the self-renewal capacity and long-term growth of two myeloblastic leukemia cell lines 12794186_Dll1 is a substrate for regulated intramembrane proteolysis, and its intracellular region possibly fulfills a specific function in the nucleus 12826675_Delta and Jagged undergo ADAM-mediated ectodomain processing followed by PS-mediated intramembrane proteolysis to release signaling fragments 14769803_induces a NIH 3T3 cell tranformed phenotype mediated by FGF signaling. 15254769_Delta-1 and Jagged-1 have roles in growth suppression in two myeloid leukemia cell lines 15492857_Notch ligand, Delta-1, reduced the TNF-alpha-induced growth suppression and apoptosis in U937 cells. 15781650_Down-regulation of Notch-1, Delta-like-1, or Jagged-1 by RNA interference induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in multiple glioma cell lines. 15851488_Density of the Notch ligand Delta1 determines generation of B and T cell precursors from hematopoietic stem cells. 15905513_When a dominant-negative form of kuzmanian in transgenic mice impairs Notch signaling in receiving T-cells, increasing Delta-1 on sending cells overcomes this defect. 15908431_Dll1 is presented on the surface of AJs formed at the apical termini of processes through interaction with MAGI1 to activate Notch on neighboring cells in the developing central nervous system 15976178_culture with increased amounts of Delta1(ext-IgG) induced apoptosis of CD34+ precursors resulting in decreased cell numbers, without affecting generation of CD7+ cells 16225865_The expression of the intracellular domain of Delta1 results in a non-proliferating senescent-like cell phenotype which is dependent on the expression of the cell cycle inhibitor, p21. 16307184_Data describe the immunohistochemical staining pattern of four Notch receptors (Notch1-4) and their ligands (Delta1 and Jagged1) in synovial tissues obtained from rheumatoid arthritis patients. 16317090_DL1-induced activation of the Notch1 pathway controls the lineage commitment of early thymic precursors by altering the levels between Spi-B and GATA-3. 17234965_Dll1 was expressed in arterial endothelial cells, not venous Ecs or capillaries. Notch signaling by induction of Dll1 is necessary & sufficient to regulate ephrin-B2 expression & EphB2- & EphB4-dependent branching morphogenesis in arterial EC. 17301032_with supervised resistance exercise training, expression of Notch1 and Hes6 genes were increased and Delta-like 1 and Numb expression were decreased. 17584735_Tbx18 interacts with Gata4 and Nkx2-5 and competes Tbx5-mediated activation of the cardiac Natriuretic peptide precursor type a-promoter. Tbx18 down-regulates Tbx6-activated Delta-like 1 expression in the somitic mesoderm in vivo 17939407_Notch ligand Delta-1 enhances the sIL-6R-mediated effects of IL-6 on the generation of erythroid cells. 18320325_Report the antitumor effects of COX2 inhibitors may be associated with effects on the Delta1/Notch1 pathway in colon tumor cells. 18676613_The intracellular region of Notch ligands Dll1 and Dll3 regulates their trafficking and signaling activity 19150223_Delta1 and Jagged1 are expressed in human umbilical cord epithelial cells at the mRNA and protein level. 19590514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19603167_DLL1 was found downregulated in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. 19680556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19724883_Findings suggest a positive feedback loop between Notch1 and DLL1 in the U251MG glioma cell line. 20170633_these results suggest a link between Dll1 expression and human goblet cell differentiation that might be mediated by a function that is distinct from its role as a Notch receptor ligand. 20418862_revealed a striking difference between the responses of Notch to trans- and cis-Delta: whereas the response to trans-Delta is graded, the response to cis-Delta is sharp and occurs at a fixed threshold, independent of trans-Delta 20554499_Delta1 protein is involved in the cytodifferentiation of squamous odontogenic tumors of the mandible. 20812035_Relapse-free survival and overall survival showed a significantly shorter survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients with higher Notch1 expression, higher Jagged1 expression, or higher Delta1 expression. 21196490_findings implicate DLL1 in early patterning of the forebrain and identify NOTCH as a new signaling pathway involved in Holoprosencephaly. 21238798_In this study, Delta 1 ligand was detected in the lining epithelium of human periapical cysts with limited inflammation, showing Notch pathway activation in those cells. 21372153_we have investigated their influence on early human hematopoiesis and show that Jagged2 affects hematopoietic lineage decisions very similarly as Delta-like-1 and -4, but very different from Jagged1 21392732_growth rate of Delta1-deficient dental pulp stem cells was significantly suppressed as compared with wild type cells 21602525_The stromal cell-mediated antiapoptotic effect on B- ALL cells is mediated by Notch-3 and -4 or Jagged-1/-2 and DLL-1 in a synergistic manner. 21602795_Notch1 and its ligand Delta-like 1(DLL1) are miR-449 bona fide targets 21643850_regulates Notch1 signaling through disruption of the Notch1-IC-RBP-Jk transcription activator complex 21726900_The receptors Notch2, -3, -4 and their ligands Jagged1, -2 and Delta1, -4 were detected at both the mRNA and protein level in early and late placenta 21742847_DLL1, which encodes Delta-like 1, the ligand for Notch3, is strongly implicated as the chromosome 6q27 Visceral leishmaniasis susceptibility gene. 21911304_as compared to MSC, OP9 cells were more efficient at inducing self-renewal and/or de novo generation of primitive (CD34(+) CD38(-) Lin(-)) cells, and suggest that such effects were due, at least in part, to the presence of Jagged-1 and DL1. 21931765_MiR-34a targeting of Notch ligand delta-like 1 impairs CD15+/CD133+ tumor-propagating cells and supports neural differentiation in medulloblastoma 21949024_An anti-delta1 Notch protein-blocking monoclonal antibody is able to prolong allograft survival in a fully histocompatibility-mismatched model of cardiac transplantation. 22080880_Notch1, Jagged1, and Delta1 expressions might be useful markers for clinical prognosis of ovarian carcinomas. 22094583_Dll1 and Notch interaction accelerates multiple myeloma disease development by promoting CD138+ MM-cell proliferation. 22561395_Twenty-one SNPs were genotyped in 941 visceral leishmaniasis cases and 992 controls. Gene expression profiling was done and DLL1 was the only gene to show differential expression that was higher (P |
ENSMUSG00000014773 |
Dll1 |
39.071276 |
4.3276852308 |
2.113596 |
0.427146008 |
23.377657 |
0.00000133115741741694716764835438455039096083964977879077196121215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004642694584374797126566196403540942583276773802936077117919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
60.0212259 |
15.4907497 |
14.0682675 |
2.8150809 |
| ENSG00000198720 |
124930 |
ANKRD13B |
protein_coding |
Q86YJ7 |
FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-binding protein that specifically recognizes and binds 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitin. Does not bind 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitin. Positively regulates the internalization of ligand-activated EGFR by binding to the Ub moiety of ubiquitinated EGFR at the cell membrane. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22298428}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;Cell membrane;Endosome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Enables ubiquitin-dependent protein binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of receptor internalization. Located in endosome; perinuclear region of cytoplasm; and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:124930; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; late endosome [GO:0005770]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ubiquitin-dependent protein binding [GO:0140036]; negative regulation of receptor internalization [GO:0002091] |
22298428_overexpression of wild-type as well as truncated-mutant Ankrd 13A, 13B and 13D proteins strongly inhibited rapid endocytosis of ubiquitinated EGFR from the surface in EGF-treated cells |
ENSMUSG00000037907 |
Ankrd13b |
19.231022 |
0.2731209051 |
-1.872388 |
0.431344496 |
19.068311 |
0.00001261218093954959703435671908300363952548650559037923812866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000039124798374895342219746685596959423492080532014369964599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.7983425 |
2.2718414 |
32.2708935 |
5.1326599 |
| ENSG00000198722 |
10497 |
UNC13B |
protein_coding |
O14795 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in vesicle maturation during exocytosis as a target of the diacylglycerol second messenger pathway. Is involved in neurotransmitter release by acting in synaptic vesicle priming prior to vesicle fusion and participates in the activity-depending refilling of readily releasable vesicle pool (RRP) (By similarity). Essential for synaptic vesicle maturation in a subset of excitatory/glutamatergic but not inhibitory/GABA-mediated synapses (By similarity). In collaboration with UNC13A, facilitates neuronal dense core vesicles fusion as well as controls the location and efficiency of their synaptic release (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z1N9}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Exocytosis;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene is expressed in the kidney cortical epithelial cells and is upregulated by hyperglycemia. The encoded protein shares a high level of similarity to the rat homolog, and contains 3 C2 domains and a diacylglycerol-binding C1 domain. Hyperglycemia increases the levels of diacylglycerol, which has been shown to induce apoptosis in cells transfected with this gene and thus contribute to the renal cell complications of hyperglycemia. Studies in other species also indicate a role for this protein in the priming step of synaptic vesicle exocytosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10497; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; presynaptic active zone [GO:0048786]; presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component [GO:0098831]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; synaptic vesicle membrane [GO:0030672]; terminal bouton [GO:0043195]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; diacylglycerol binding [GO:0019992]; GTP-dependent protein binding [GO:0030742]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; syntaxin-1 binding [GO:0017075]; acrosomal vesicle exocytosis [GO:0060478]; cellular response to glucose stimulus [GO:0071333]; chemical synaptic transmission [GO:0007268]; dense core granule priming [GO:0061789]; neuromuscular junction development [GO:0007528]; neuronal dense core vesicle exocytosis [GO:0099011]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential [GO:0097151]; positive regulation of protein secretion [GO:0050714]; positive regulation of synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0010808]; presynaptic dense core vesicle exocytosis [GO:0099525]; synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0035249]; synaptic vesicle docking [GO:0016081]; synaptic vesicle maturation [GO:0016188]; synaptic vesicle priming [GO:0016082] |
12871971_Munc13-1 regulates insulin exocytosis 16138900_Data suggest that diacylglycerol-activated hmunc13 serves as an effector of Rab34, mediating lysosome-Golgi trafficking. 18633107_Data identified a polymorphism in the UNC13B gene associated with nephropathy. UNC13B mediates apopotosis in glomerular cells in the presence of hyperglycemia, an event occurring early in the development of nephropathy. 18633107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19492809_In the bound state, the hydrophobic anchor residue of the calmodulin (CaM)-binding motif in Munc13 contacts two distinct methionine residues in the carboxyl-terminal domain of CaM. 19641095_mechanistic basis for high glucose-induced protein secretion is through interaction of munc13 and rab34, indicating a potentially critical role for this newly described pathway in the pathogenesis of DN. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24854537_The 1-5-8-26 CaM binding motif discovered in Munc13-1 cannot be induced in the classical CaM target skMLCK, indicating unique features of the Munc13 CaM binding motif. 26990377_A rare missense variation (V1525M) in UNC13B was identified by WES in the multiplex family; this variation was present in five of six affected individuals, but not in eight unaffected individuals or one individual of unknown disease status. Resequencing UNC13B coding regions identified five rare missense variations (T103M, M813T, P1349T, I1362T, and V1525M). 29485200_Assisted by NSF/alpha-SNAP, syntaxin-1 escapes tomosyn arrest and assembles into the Munc18-1/syntaxin-1 complex. Munc13-1 then catalyzes the transit of syntaxin-1 from the Munc18-1/syntaxin-1 complex to the SNARE complex 30117296_Abnormal splicing mutation in UNC13B was identified in the patient with bipolar disorder. 31713534_There were no significant differences in the distribution of allele or genotype frequencies in the five UNC13B SNP markers (rs13293564, rs17360668, rs10114937, rs661712, and rs2281999) between the Diabetic Kidney Disease group and control group of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus . 32134975_TRPC6 exocytosis by targeting to the C1 domain of Munc13-2. 33876820_UNC13B variants associated with partial epilepsy with favourable outcome. 35135883_Munc13 structural transitions and oligomers that may choreograph successive stages in vesicle priming for neurotransmitter release. |
ENSMUSG00000028456 |
Unc13b |
133.554343 |
0.4590724678 |
-1.123206 |
0.242090786 |
21.078485 |
0.00000440850313432191820932739070859618379927269415929913520812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000014443841567722866603483249103856422834724071435630321502685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.9595653 |
12.7437311 |
186.6950612 |
19.4651699 |
| ENSG00000198728 |
8861 |
LDB1 |
protein_coding |
Q86U70 |
FUNCTION: Binds to the LIM domain of a wide variety of LIM domain-containing transcription factors. May regulate the transcriptional activity of LIM-containing proteins by determining specific partner interactions. Plays a role in the development of interneurons and motor neurons in cooperation with LHX3 and ISL1. Acts synergistically with LHX1/LIM1 in axis formation and activation of gene expression. Acts with LMO2 in the regulation of red blood cell development, maintaining erythroid precursors in an immature state. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P70662}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Enables LIM domain binding activity; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding activity; and enzyme binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated and positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in chromatin. Part of beta-catenin-TCF complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8861; |
beta-catenin-TCF complex [GO:1990907]; cell leading edge [GO:0031252]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0140297]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; LIM domain binding [GO:0030274]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding [GO:0061629]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cellular component assembly [GO:0022607]; cerebellar Purkinje cell differentiation [GO:0021702]; epithelial structure maintenance [GO:0010669]; gastrulation with mouth forming second [GO:0001702]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; histone H3-K4 acetylation [GO:0043973]; mesendoderm development [GO:0048382]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045647]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of hemoglobin biosynthetic process [GO:0046985]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cell migration [GO:0030334]; regulation of focal adhesion assembly [GO:0051893]; regulation of kinase activity [GO:0043549]; regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II [GO:0034243]; somatic stem cell population maintenance [GO:0035019]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; transcription-dependent tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery [GO:0000972]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12153047_1H, 15N and 13C assignments of FLIN4, an intramolecular LMO4:ldb1 complex 12381786_Ssdp proteins interact with the LIM-domain-binding protein Ldb1 to regulate development 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17910069_characterize the assembly of a five-component complex containing TAL1, LMO2, Ldb1, E12, and DNA. The bHLH domains of TAL1 and E12 alone primarily formed helical homodimers, but together formed heterodimers, to which LMO2 bound with high affinity 18583962_Although the LIM interaction domain of Ldb1 (Ldb1(LID)) and Isl1(LBD) share low levels of sequence homology, X-ray and NMR structures reveal that they bind Lhx3 in an identical manner, that is, Isl1(LBD) mimics Ldb1(LID). 20423330_Expression of LDB1 (LIM-domain-binding 1) protein in which Lys134 is replaced with arginine leads to enhanced expression of the mutant protein compared with the wild-type protein. 20447379_These studies are consistent with a model in which TIF1gamma acts to ubiquitinate LDB1 leading to degradation of LDB1 and changes in transcription of LDB1-dependent promoters. 22010104_We investigated NLI (Ldb1 homolog) complex occupancy and chromatin conformation of the beta-globin locus in human erythroid cells. 23812588_In t(8;21) leukemia cells, LDB1 functions as a component of the stable AML1-ETO-containing transcription factor complex (AETFC). The AETFC components cooperatively regulate gene expression and contribute to leukemogenesis. 25079073_Clim2, in a complex with LMO4, supports mammary stem cells by directly targeting the Fgfr2 promoter in basal cells to increase its expression 26495868_SSBP3 Interacts With Islet-1 and Ldb1 to Impact Pancreatic beta-Cell Target Genes 26598604_Alanine scanning mutagenesis of the LIM interaction domain of LDB1 revealed a discrete motif, R(320)LITR, required for LMO2 binding. 27713177_Data indicate that LIM-domain-binding protein 1 (LDB1) has a strong role in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. 27941246_LDB1 maintains the terminally differentiated state of beta cells and is a component of active enhancers in both murine and human islets. 31892537_LDB1 dimerization supports long-range connections between enhancers and genes involved in erythropoiesis, including the beta-globin genes. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins (SSBPs) interact specifically with the LDB/Chip conserved domain (LCCD) of LDB proteins and stabilize LDBs by preventing their proteasomal degradation, thus promoting their functions in gene regulation. 32229578_LDB1 Enforces Stability on Direct and Indirect Oncoprotein Partners in Leukemia. 35881062_The Ldb1 transcriptional co-regulator is required for establishment and maintenance of the pancreatic endocrine lineage. |
ENSMUSG00000025223 |
Ldb1 |
396.164471 |
0.3708686672 |
-1.431020 |
0.131048901 |
117.590746 |
0.00000000000000000000000000213122636446313079708614793039901530397314254286368602294438643035800725125672450133151869522407650947570800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000024965794555139531784457839336499127667714214562439145288494747189464613434939366243270342238247394561767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
212.0674917 |
18.0966811 |
575.3482429 |
33.5585287 |
| ENSG00000198740 |
22834 |
ZNF652 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2D9 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a transcriptional repressor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16966434}. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:22834; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
18456661_CBFA2T3 interacts with ZNF652 to repress HEB expression, and in addition CBFA2T3 interacts with the HEB protein to inhibit its activator function. 19430483_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20204290_High levels of expression of both the androgen receptor and ZNF652 in clinically organ-defined prostate cancer are associated with a statistically increased risk of relapse 20414254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20542020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20542020_variation in FGF5 and ZNF652 gene upstream regions with altered susceptibility to hypertension in Han Chinese 20852445_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21045733_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21678463_De novo motif scanning of the ZNF652 binding sites identified a novel ZNF652 recognition motif that closely resembles the previously characterised in vitro binding site, being a 10 nucleotide core of that 13 nucleotide sequence. 25335771_Genetic association studies identify a novel variant in ZNF652 gene suggesting its role in prostate cancer. 34424826_Circular RNA circVRK1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by regulating zinc finger protein ZNF652 expression via microRNA miR-337-3p. 34926705_ZNF652-Induced circRHOT1 Promotes SMAD5 Expression to Modulate Tumorigenic Properties and Nature Killer Cell-Mediated Toxicity in Bladder Cancer via Targeting miR-3666. |
ENSMUSG00000075595 |
Zfp652 |
150.677664 |
0.4645717750 |
-1.106027 |
0.133949452 |
68.627690 |
0.00000000000000011892249587772538323362335145687175553371485437186699796185962441086303442716598510742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000893280427051005926053621928340076351400357644420846536803537674131803214550018310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
102.1347448 |
11.4555069 |
222.0618596 |
17.2238487 |
| ENSG00000198756 |
23127 |
COLGALT2 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYK4 |
FUNCTION: Beta-galactosyltransferase that transfers beta-galactose to hydroxylysine residues of collagen. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19075007}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Reference proteome;Signal;Transferase |
|
Predicted to enable procollagen galactosyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in collagen fibril organization. Predicted to be located in endoplasmic reticulum lumen. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23127; |
endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; procollagen galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0050211]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199] |
19075007_Two collagen beta(1-O)galactosyltransferases corresponding to the GLT25D1 and GLT25D2 proteins were identified. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 33760386_Genetic and Epigenetic Interplay Within a COLGALT2 Enhancer Associated With Osteoarthritis. 33783989_COLGALT2 is overexpressed in ovarian cancer and interacts with PLOD3. |
ENSMUSG00000032649 |
Colgalt2 |
18.680273 |
4.0192008039 |
2.006909 |
0.394862670 |
27.409744 |
0.00000016459979273690542069009132373352821687717550958041101694107055664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000634829616095302864054643419283729954827322217170149087905883789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.9053162 |
6.7155923 |
7.2740921 |
1.4663378 |
| ENSG00000198771 |
92241 |
RCSD1 |
protein_coding |
Q6JBY9 |
FUNCTION: Stress-induced phosphorylation of CAPZIP may regulate the ability of F-actin-capping protein to remodel actin filament assembly. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15850461}. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables actin filament binding activity. Involved in cellular hyperosmotic response. Predicted to be located in actin filament. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92241; |
actin filament [GO:0005884]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; cellular hyperosmotic response [GO:0071474]; skeletal muscle contraction [GO:0003009] |
15850461_The structure and function of CapZ-interacting protein are reported. 17541395_CapZIP is fused to ABL1 in a t(1;9)(q24;q34)-associated B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 19064610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000040723 |
Rcsd1 |
226.116330 |
0.2928639937 |
-1.771697 |
0.124943773 |
204.964091 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000017243315678728929838634749110771053183124849582250702771569238765803043803375360314513502147536187055122130965640562388907497393120138440281152725219726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003353245578630290368326530816921175489228962823632541609805816872012259752951482612978232155388830296501929135712322463391821258937852689996361732482910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.6605250 |
9.3843660 |
342.4728337 |
21.0102303 |
| ENSG00000198774 |
9182 |
RASSF9 |
protein_coding |
O75901 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in regulating vesicuar trafficking in cells. {ECO:0000250}. |
Coiled coil;Endosome;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene localizes to perinuclear endosomes. This protein associates with peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase, and may be involved with the trafficking of this enzyme through secretory or endosomal pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9182; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; endosome [GO:0005768]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; trans-Golgi network transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012510]; endosomal transport [GO:0016197]; intracellular transport [GO:0046907]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
27760139_Our analysis revealed 10 sun-exposure-dependent gene expression quantitative trait loci (se-eQTLs), including genes involved in skin pigmentation (SLC45A2) and epidermal differentiation (RASSF9). 30132526_RASSF9 is a direct target of miR-1254 in breast cancer. 33051258_RASSF effectors couple diverse RAS subfamily GTPases to the Hippo pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000044921 |
Rassf9 |
6.756862 |
4.0830825614 |
2.029659 |
0.605634007 |
12.280019 |
0.00045783360509310625516624093656048444245243445038795471191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001132689240894108138185680800802401790861040353775024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8083130 |
4.2397215 |
2.6561260 |
0.8965991 |
| ENSG00000198792 |
25829 |
TMEM184B |
protein_coding |
Q9Y519 |
FUNCTION: May activate the MAP kinase signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12761501}. |
Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25829; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
12761501_C22orf5 (FM08) represents a novel gene found during a screening of gene that activate the MAPK pathway. 25668004_Data shows that miR-26a and miR-26b were significantly downregulated and their direct target, TMEM184B significantly up-regulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. |
ENSMUSG00000009035 |
Tmem184b |
707.481070 |
2.0694955897 |
1.049279 |
0.069427156 |
229.040515 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000096514415522976119256252974688409160457335395326953968805815173554596695934497613493670572609249425128292822439050510902158511151137376682385138337849639356136322021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000021518924065243620672677223564854259929206792492621316286109537199084165548372886897443331418305125509903853849678120884664266152658251840534830989781767129898071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
969.3667511 |
37.8627273 |
471.5998139 |
14.4229132 |
| ENSG00000198795 |
25925 |
ZNF521 |
protein_coding |
Q96K83 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor that can both act as an activator or a repressor depending on the context. Involved in BMP signaling and in the regulation of the immature compartment of the hematopoietic system. Associates with SMADs in response to BMP2 leading to activate transcription of BMP target genes. Acts as a transcriptional repressor via its interaction with EBF1, a transcription factor involved specification of B-cell lineage; this interaction preventing EBF1 to bind DNA and activate target genes. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14630787}. |
Activator;Chromosomal rearrangement;Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables protein domain specific binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to act upstream of or within neuron fate commitment. Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25925; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; neuron fate commitment [GO:0048663]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
14630787_EHZF is likely to play a relevant role in the control of human hematopoiesis and might be implicated in the development of hematopoietic malignancies. 17543573_A review of possible roles for ZNF521 in development, stem cell regulation and oncogenesis. 19049973_ZNF521 modulates erythroid cell differentiation through direct binding with GATA-1. 19342626_Enhanced resistance of target cells to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity was induced by enforced expression of EHZF in the cervical carcinoma cell line HeLa and in the B lymphoblastoid cell line IM9 20392215_Zinc finger protein 521, a new player in bone formation. 21593590_Data show that ZNF521 can antagonize B-cell development and support the notion that it may contribute to conserve the multipotency of primitive lympho-myeloid progenitors by preventing or delaying their EBF1-driven commitment toward the B-cell lineage. 23907569_Data strongly support the notion that ZNF521, through the recruitment of the NuRD complex, contributes to the clonogenic growth, migration and tumorigenicity of medulloblastoma cells. 25774781_Newly discovered ZNF521-molecular partners of potentially relevant functional role, such as ZNF423, Spt16, Spt5, were discovered and validated by Western blotting. 26008984_Data show that zinc finger protein 521 (ZNF521) can function as a repressor of osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (bmMSCs). 26788497_two multi-zinc finger transcription cofactors named ZNF423 and ZNF521 have been characterised as potent inhibitors of EBF1 and are emerging as potentially relevant contributors to the development of B-cell leukaemias 27805002_Performance metrics were used to select SNPs in stage 1, which were then genotyped to another dataset (stage 2). Four SNPs (CPXM2 rs2362967, APOC1 rs4420638, ZNF521 rs7230380, and rs12965520) were identified for LOAD by both traditional P-values (without correcting for multiple tests) and performance metrics. 28412727_IHC based post-Ki67 levels may have distinct predictive power compared with the naive IHC Ki67. 28615219_knockdown of ZNF521 reduced proliferation in human leukemia cell lines possessing MLL-AF9 translocations 29938352_these results confirm a role for ZNF521 as a key negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. 30567301_Together with our previous findings, these results show that ZNF521 inhibits both adipocytic and osteoblastic maturation in Human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) and suggest that its expression may contribute to maintaining the immature properties of hADSCs 31227697_Examination of early adipogenic signals in subcutaneous adipose tissue identifies ZNF521 as a key regulator of maintaining human adipose stromal vascular fraction cells proliferative and uncommitted. Silencing ZNF521 increases BMP4 and nuclear import of the adipogenic marker and PPARgamma transcriptional activator ZNF423. 31526099_Zinc finger protein 521 can arrest the apoptosis and enhance the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells via regulating microRNA-204-5p. Our study may provide novel clues for the treatment of patients with gastric cancer. 31558698_The stem cell-associated transcription co-factor, ZNF521, interacts with GLI1 and GLI2 and enhances the activity of the Sonic hedgehog pathway. 34445164_Regulatory Role of microRNAs Targeting the Transcription Co-Factor ZNF521 in Normal Tissues and Cancers. 34639154_ZNF521 Enhances MLL-AF9-Dependent Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transformation in Acute Myeloid Leukemias by Altering the Gene Expression Landscape. 36191006_Enhanced ZNF521 expression induces an aggressive phenotype in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. |
ENSMUSG00000024420 |
Zfp521 |
152.610486 |
0.4656160228 |
-1.102787 |
0.200037461 |
30.163329 |
0.00000003971482083190958836530545100762523702542239334434270858764648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000162785547203272829983589889586703680635082491789944469928741455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
83.7230906 |
16.9500218 |
180.8518259 |
25.9535849 |
| ENSG00000198825 |
22876 |
INPP5F |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2H2 |
FUNCTION: Inositol 4-phosphatase which mainly acts on phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. May be functionally linked to OCRL, which converts phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to phosphatidylinositol, for a sequential dephosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate at the 5 and 4 position of inositol, thus playing an important role in the endocytic recycling (PubMed:25869669). Regulator of TF:TFRC and integrins recycling pathway, is also involved in cell migration mechanisms (PubMed:25869669). Modulates AKT/GSK3B pathway by decreasing AKT and GSK3B phosphorylation (PubMed:17322895). Negatively regulates STAT3 signaling pathway through inhibition of STAT3 phosphorylation and translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:25476455). Functionally important modulator of cardiac myocyte size and of the cardiac response to stress (By similarity). May play a role as negative regulator of axon regeneration after central nervous system injuries (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8CDA1, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17322895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25476455, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25869669}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coated pit;Endosome;Hydrolase;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) 5-phosphatase and contains a Sac domain. The activity of this protein is specific for phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]. |
hsa:22876; |
axon [GO:0030424]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle [GO:0045334]; clathrin-coated pit [GO:0005905]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; early endosome [GO:0005769]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; inositol monophosphate 1-phosphatase activity [GO:0008934]; inositol monophosphate 3-phosphatase activity [GO:0052832]; inositol monophosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0052833]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate 4-phosphatase activity [GO:0034596]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0034595]; phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate phosphatase activity [GO:0043812]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; adult locomotory behavior [GO:0008344]; cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress [GO:0014898]; clathrin-dependent endocytosis [GO:0072583]; negative regulation of axon regeneration [GO:0048681]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; negative regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042532]; phosphatidylinositol biosynthetic process [GO:0006661]; phosphatidylinositol catabolic process [GO:0031161]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856]; phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling [GO:0048015]; positive regulation of receptor recycling [GO:0001921]; regulation of cell motility [GO:2000145]; regulation of endocytic recycling [GO:2001135]; regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051896] |
16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19875726_Inpp5f is a polyphosphoinositide phosphatase that regulates cardiac hypertrophic responsiveness. 25476455_These findings suggest that INPP5F is a potential tumor suppressor in gliomas via inhibition of STAT3 pathway, and that deregulation of INPP5F may lead to contribution to gliomagenesis. 25869669_Sac2 colocalizes with early endosomal markers and is recruited to transferrin-containing vesicles during endocytic recycling. 26430724_we identified inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase F (INPP5F) as a prognostic factor for progression-free survival in Chronic lymphocytic leukemia 32693431_Imprinting aberrations of SNRPN, ZAC1 and INPP5F genes involved in the pathogenesis of congenital heart disease with extracardiac malformations. 35848021_Parkinson's Disease rs117896735 Variant Regulates INPP5F Expression in Brain Tissues and Increases Risk of Alzheimer's Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000042105 |
Inpp5f |
198.961560 |
0.0800862249 |
-3.642302 |
1.341379180 |
5.965344 |
0.01458975788602119225134678970334789482876658439636230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026985567217753483881814702272095018997788429260253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.3384581 |
19.8054622 |
241.1337187 |
168.5920231 |
| ENSG00000198829 |
56670 |
SUCNR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXA5 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for succinate. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15141213}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a G-protein-coupled receptor for succinate, an intermediate molecule of the citric acid cycle. It is involved in the promotion of hematopoietic progenitor cell development, and it has a potential role in renovascular hypertension which has known correlations to renal failure, diabetes and atherosclerosis. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]. |
hsa:56670; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; macrophage activation involved in immune response [GO:0002281]; positive regulation of chemotaxis [GO:0050921]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; regulation of angiotensin metabolic process [GO:0060177]; renin secretion into blood stream [GO:0002001]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592] |
15141213_GPR91 is a receptor for succinate and mediates succinate-induced hypertension. 15141213_This paper describes function in another species. 19204147_Succinate stimulates cell proliferation through GPR91 and requires activation of the Erk MAPK pathway. 22497252_A review of how neuron-derived factors, GPR91 and Semaphorin 3A, guide retinal vascularization and are major contributors to the pathogenesis of retinopathy of prematurity . 23770096_results show that GPR91 when expressed in HEK293s cells couples exclusively through the Galphai pathway and acts through Galphai not only to inhibit cAMP production but also to increase intracellular Ca(2+) 23833031_These findings suggest that deficiency in SUCNR1 is a possible contributing factor to the pathogenesis of dry age-related macular degeneration. 25539979_These results show for the first time that succinate plays an important role in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through GPR91 activation and extend our understanding of how ischemia can induce hypertrophic cardiomyopathy 26051274_results show that succinate plays an important role in HSC activation through GPR91 induction, and suggest that succinate and GPR91 may represent new therapeutic targets for modulating hepatic fibrosis 26759054_Through GPR91, succinate is involved in functions such as regulation of blood pressure, inhibition of lipolysis in white adipose tissue, development of retinal vascularization and cardiac hypertrophy. [review] 26808164_We give an exhaustive overview of the known and hypothetical signaling partners of SUCNR1 in different in vitro and in vivo systems and also discuss the link between SUCNR1 intracellular pathways and its pathophysiological roles. 26824665_The findings indicate that succinate-GPR91 signaling may be involved in right ventricular hypertrophy via PI3K/Akt signaling in vivo and in vitro. 27481132_Succinate is abundant in synovial fluids from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and these fluids elicit IL-1beta release from macrophages in a GPR91-dependent manner. 27527650_This study reports the expression of GPR91 on mouse and human mast cells and reveals a hyperactive behavior of mouse Sucnr1-/- mast cells in a mechanistic in vivo model of skin inflammation. 28061458_Data show that succinate upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression by activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 via its receptor G-protein coupled receptor 91 (GPR91). 28382382_activation of SUCNR1 in macrophages is important for both infiltration and inflammation of adipose tissue in obesity 28974722_succinate promotes DRP1-mediated mitochondrial fission via GPR91, consequently stimulating the hMSC migration through mtROS-induced F-actin formation. 29278707_This study shows that metformin can attenuate activation of HSCs by activating the AMPK pathway and inhibiting the succinate-GPR91 pathway. Metformin has therapeutic potential for treating steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. 31304868_Study demonstrates that the T allele of rs13079080 in SUCNR1 disrupts a binding site for miRNA-4470, potentially increasing SUCNR1 expression and consequently increasing the capacity of sensing and dealing with oxidative stress. Also, genotyping rs13079080 in an AMD case-control cohort revealed a protective effect of the TT genotype on age-related macular degeneration (AMD) compared to the CC genotype. 31735641_These effects are mediated by SUCNR1-triggered PI3K-hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) axis. 32377163_Inhibition of GPR91 Reduces Inflammatory Mediators Involved in Active Labor in Myometrium. 32946811_pH-Gated Succinate Secretion Regulates Muscle Remodeling in Response to Exercise. 32992522_GPR91 Receptor Mediates Protection against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity without Altering Its Anticancer Efficacy. An In Vitro Study on H9C2 Cardiomyoblasts and Breast Cancer-Derived MCF-7 Cells. 33127268_Associations of SUCNR1, GRK4, CAMK1D gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility of type 2 diabetes mellitus and essential hypertension in a northern Chinese Han population. 33776908_Succinate Mediates Tumorigenic Effects via Succinate Receptor 1: Potential for New Targeted Treatment Strategies in Succinate Dehydrogenase Deficient Paragangliomas. 34133934_Extracellular succinate hyperpolarizes M2 macrophages through SUCNR1/GPR91-mediated Gq signaling. 34769478_SUCNR1 Is Expressed in Human Placenta and Mediates Angiogenesis: Significance in Gestational Diabetes. 34813893_Succinate receptor 1 inhibits mitochondrial respiration in cancer cells addicted to glutamine. |
ENSMUSG00000027762 |
Sucnr1 |
124.791942 |
0.4989802389 |
-1.002945 |
0.134535737 |
56.553522 |
0.00000000000005468934725453550292789826593564749065577625802836436719189805444329977035522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000352803656239923089761890014499920078118021943280879781923431437462568283081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
82.9703640 |
7.8005765 |
167.3615760 |
10.3993646 |
| ENSG00000198842 |
92235 |
STYXL2 |
protein_coding |
Q5VZP5 |
FUNCTION: May be required for myofiber maturation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1QWM2}. |
Cytoplasm;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein dephosphorylation. Predicted to be located in sarcomere. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:92235; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; sarcomere [GO:0030017]; MAP kinase phosphatase activity [GO:0033549]; protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity [GO:0008138]; negative regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043409]; protein dephosphorylation [GO:0006470] |
19536175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20520587_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000026564 |
Dusp27 |
15.756131 |
0.0730771580 |
-3.774436 |
0.684485540 |
37.347951 |
0.00000000098824642022803275767320792943989790635406222918390994891524314880371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000004729739676577744598579017563976314986184945610148133710026741027832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2.4134653 |
1.1435282 |
33.3034075 |
6.3663891 |
| ENSG00000198848 |
1066 |
CES1 |
protein_coding |
P23141 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the detoxification of xenobiotics and in the activation of ester and amide prodrugs (PubMed:7980644, PubMed:9169443, PubMed:9490062, PubMed:18762277). Hydrolyzes aromatic and aliphatic esters, but has no catalytic activity toward amides or a fatty acyl-CoA ester (PubMed:7980644, PubMed:9169443, PubMed:9490062, PubMed:18762277). Hydrolyzes the methyl ester group of cocaine to form benzoylecgonine (PubMed:7980644). Catalyzes the transesterification of cocaine to form cocaethylene (PubMed:7980644). Displays fatty acid ethyl ester synthase activity, catalyzing the ethyl esterification of oleic acid to ethyloleate (PubMed:7980644). Converts monoacylglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol. Hydrolyzes of 2-arachidonoylglycerol and prostaglandins (PubMed:21049984). Hydrolyzes cellular cholesteryl esters to free cholesterols and promotes reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) by facilitating both the initial and final steps in the process (PubMed:18762277, PubMed:16024911, PubMed:11015575, PubMed:16971496). First of all, allows free cholesterol efflux from macrophages to extracellular cholesterol acceptors and secondly, releases free cholesterol from lipoprotein-delivered cholesteryl esters in the liver for bile acid synthesis or direct secretion into the bile (PubMed:18762277, PubMed:18599737, PubMed:16971496). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11015575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16024911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16971496, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18599737, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18762277, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21049984, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7980644, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9169443, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9490062}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid droplet;Lipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine esterase;Signal |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of the carboxylesterase large family. The family members are responsible for the hydrolysis or transesterification of various xenobiotics, such as cocaine and heroin, and endogenous substrates with ester, thioester, or amide bonds. They may participate in fatty acyl and cholesterol ester metabolism, and may play a role in the blood-brain barrier system. This enzyme is the major liver enzyme and functions in liver drug clearance. Mutations of this gene cause carboxylesterase 1 deficiency. Three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:1066; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; lipid droplet [GO:0005811]; carboxylic ester hydrolase activity [GO:0052689]; methylumbelliferyl-acetate deacetylase activity [GO:0047374]; sterol esterase activity [GO:0004771]; cellular response to cholesterol [GO:0071397]; cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus [GO:0071404]; cholesterol biosynthetic process [GO:0006695]; cholesterol ester hydrolysis involved in cholesterol transport [GO:0090122]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030855]; lipid catabolic process [GO:0016042]; medium-chain fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0051791]; negative regulation of cholesterol storage [GO:0010887]; positive regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010875]; positive regulation of cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0090205]; regulation of bile acid biosynthetic process [GO:0070857]; regulation of bile acid secretion [GO:0120188]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; reverse cholesterol transport [GO:0043691] |
12679808_crystal structure bound to analogs of cocaine and heroin 12773168_A serine esterase involved in both drug metabolism and activation. 12960109_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15475243_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15475733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15931389_Altered expression is associated with therapy failure and death in patients with multiple types of cancer. 16282638_Findings indicate that F417 but not L418, L420, or C390 participates in substrate hydrolysis by triacylglycerol hydrolase. 16419644_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16962139_Using multisite promiscuity, carboxylesterase 1 appears structurally capable of assembling several catalytic events, depending upon the physiological state of the cellular environment. 16971496_Cholesteryl ester hydrolase expression in human macrophages is potential target for attenuation of foam cell formation and regression of atherosclerotic plaques. 17537833_IL-6 alters the cellular responsiveness to clopidogrel, irinotecan, and oseltamivir by suppressing the expression of CES1. 17764701_comparative analysis of CES1 and CES2 in liver and small intestine of humans, monkeys, dogs, rabbits and rats 18305377_Carboxylesterase 1A1 mRNA expression level is much higher than the expression of carboxylesterase 1A2 mRNA in the liver and lung. 18328811_SNP haplotype in the CES1A2 promoter affects the Sp1 binding and transcriptional regulation; it well agreed with the efficacy of the medication of imidapril. 18485328_In vitro functional studies demonstrated the catalytic functions of both p.Gly143Glu and p.Asp260fs are substantially impaired, resulting in a complete loss of hydrolytic activity toward methylphenidate. 18485328_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18599737_hepatic CEH regulates the last step of RCT by promoting the flux of cholesterol entering the liver via SR-BI and increasing hepatic bile acid output [cholesteryl ester hydrolase] 18794728_pharmacogenomic characterization of human carboxylesterase 1A1, 1A2, and 1A3 genes 18983829_Carboxylesterases play critical roles in drug metabolism and insecticide detoxication; findings show large variability among different age groups or even within the same age group. 19185566_CES1 mutations Gly143Glu and Asp260fs are essentially dysfunctional enzymes with regard to the conversion of trandolapril to its more active metabolite trandolaprilat. 19332024_CES1 expression was linked to body fat and adipocyte fat content but not to lipolytic activity. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19508181_A comparison of the substrate specificity of CES1 versus CES2 reveals broad but distinct substrate preferences. 19658107_The high-resolution proteomic approach demonstrates that hCE1 is a good candidate for further validation as a serologic glycoprotein biomarker for HCC. 19715681_Luciferase assays revealed that the antioxidant response element (ARE) at -2025 in the CES1A1 gene was responsible for the transactivation by Nrf2 19733552_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19733552_We observed an association with the rare 143Glu-variant: 5 patients in the responder group carrying the Glu-allele required lower doses of MPH for symptom reduction. 19932971_Molecular dynamics results emphasize properties of the CES1 catalytic cavity, confirming that CES1 prefers substrates with relatively smaller and somewhat polar alkyl/aryl groups and larger hydrophobic acyl moieties. 20195289_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20529763_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20530478_The knockdown of CES1 with siRNA resulted in lower levels of HCV replication, and up-regulation of CES1 was observed to favor HCV propagation, implying an important role for this host cell protein. 20649590_Report CES1 mediated hydrolysis of heroin, cocaine and CPT-11. 20975297_Dysregulation of genes such as CES1 and APOE seems to be associated with some physiopathological markers of insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in obesity. 21081832_High mRNA levels of CES1 is associated with adiposity and lipolysis, thereby contributing to the development of obesity-associated phenotypes. 22237548_The comparison of the genotyping results between this novel assay and those previously reported methods highlighted the necessity of applying the discriminative genotyping assay in pharmacogenetic studies involving CES1 gene. 22525521_tested the hypothesis that an individual's CES phenotype can be characterized by reporter substrates/probes that interrogate native CES1 and CES2 activities in liver and immunoblotting methods 22588607_Genetic variability in Carboxylesterase 1 affects the pharmacokinetics of oseltamivir and indicate that CES1 plays an important role in the bioactivation of oseltamivir in humans. 22688218_An influence of carboxylesterase 1 -75 T>G polymorphism on the worsening of appetite reduction with MPH treatment in youths with ADHD. 22700792_This study provides the first evidence of functional compensation whereby increased expression of CES3 restores intracellular cholesteryl ester hydrolytic activity and free cholesterol efflux in CES1-deficient cells. 22943824_The CES1 SNP rs8192950 AC genotype and rs1968753 GG genotype might be the candidates for risk prediction of antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity. 23111421_Genetic variation in CES1 may be an important determinant of the efficacy of clopidogrel. 23275066_Deficient CES1 catalytic activity resulting from CES1 inhibition. 23468884_Carboxylesterase 1 gene duplication and mRNA expression in adipose tissue are linked to obesity and metabolic function. 23658012_carboxylesterase I controls RhoA methylation 23936796_PMPMEase overexpression in colorectal cancer and cancer cell death stemming from its inhibition is an indication of its possible role in cancer progression and a target for chemopreventive agents 24141856_CES1 plays a role in the metabolism of several drugs. 24170778_The conversion of 2-oxo-ticlopidine to M1 was further confirmed with recombinant paraoxonase 1 (PON1) and CES1. 24212379_After oral administration of dabigatran etexilate to humans, DABE is hydrolyzed by intestinal CES2 to the intermediate M2 metabolite followed by hydrolysis of M2 to DAB in the liver by CES1. 24350812_study found an association between two CES1 SNP markers and the occurrence of sadness as a side effect of short-acting methylphenidate 24563511_CEH is an important regulator in enhancing cholesterol elimination. 25704243_CES1 c.428G>A single nucleotide variation increases clopidogrel active metabolite concentrations and antiplatelet effects by reducing clopidogrel hydrolysis to inactive metabolites 26076923_some functional CES1 genetic variants (for example, G143E) may impair ACE inhibitor activation, and consequently affect therapeutic outcomes of ACEI prodrugs. 26340669_decreases of CES and CYP3A4 expression and enzymatic activities induced by Fluoxetine are through decreasing PXR and increasing DEC1 in HepG2 cells 26587656_Study found that CYP2C19*2, *3, and *8 were associated with lower odds of the primary and secondary endpoints in the symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic medical group compared with wild-type homozygotes; due to the low incidence of CES1 genetic variation, our study was unable to demonstrate any association between CES1 variations and the primary and secondary endpoints 26657071_The structure and activity of glycosylated and aglycosylated human CES1 has been determined. 26825642_These data suggest that infants younger than 3 weeks of age would exhibit significantly lower CES1- and CES2-dependent metabolic clearance compared with older individuals. 26871237_Study confirms previous reports of the CES1P1-CES1 translocation generating the CES1VAR allele with 11 SNPs in the 5'UTR, exon 1, and intron 1 derived from the CES1P1 sequence with decreased CES1 mRNA expression in the human liver by approximately 30% but normal protein expression. 26915813_We conclude that the -816A>C variant is not associated with interindividual variability in CES1 expression and activity or therapeutic response to ACEI prodrugs 27075303_HNF4alpha regulated CES1 expression by directly binding to the proximal promoter of CES1. 27130352_Suggest a primary metabolic role for CES1 in the capacity of skin/keratinocytes to mediated biotransformation of penta-ethyl ester prodrug of DTPA. 27228223_Data suggest oseltamivir activation is associated with an SNP in CES1 (rs71647871, G143E); in liver from donors with genotype 143G/E activation is 40% of that from donors with genotype 143G/G. Hepatic CES1 expression in females is 17.3% higher than in males; oseltamivir activation rate in females is 27.8% higher than in males. (Liver tissues used were obtained from tissue banks located in the United States.) 27450232_Our study identified CYP2C19*3 and CES1 rs8192950 as genetic polymorphisms related to recurrent ischemic events in patients with extracranial or intracranial occlusive disease, demonstrating the important roles of CYP2C19 and CES1 in patients treated with clopidogrel 27614009_These data suggest that CES1 genetic variants and gender are important contributing factors to variability in dabigatran etexilate activation in humans. 27638507_The intestinal transport of oseltamivir, a hCE1 substrate, could be evaluated in subclone #78 cell monolayers. 28139840_An association was identified with a genetic variation in CES1 and early-onset capecitabine-related toxicity. 28473326_Reduced CES1 expression/activity could promote development of METH-PAH. 28532270_Anordrin is predominantly catalyzed by CES1 and CES2 to generate the main active metabolite, anordiol. 28639420_none of the selected variations of CES1 had a clinically relevant impact on the metabolism of enalapril 28775293_The results showed that there was a significant association between CES1 S75N (rs2307240) and the outcome of clopidogrel therapy. Moreover, the frequency of the T allele of rs2307240 in acute coronary syndrome patients (MAF = 0.22) was more than four times higher than that in the general public 28786738_The frequencies of SNVs with a potential functional impact were below 0.02 suggesting limited pharmacogenetic potential for CES1 genotyping. 28838926_Study revealed that several nsSNPs significantly impaired CES1 activity on the metabolism of the CES1 substrates enalapril, clopidogrel, and sacubitril. 28990360_genetic association and pharmacogenomic studies in population in Finland: Data suggest that 2 SNPs in CES1 (rs12443580, rs8192935) are associated with variations in expression of CES1 (in whole blood samples but not in liver); these CES1 SNPs do not affect pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of clopidogrel, an inhibitor of platelet aggregation. A missense mutation in CES1 (rs71647871) impairs hydrolysis of clopidogrel. 29321244_These results are consistent with a model in which abrogation of CES1 function attenuates the CYP27A1-LXRalpha-ABCA1 signaling axis by depleting endogenous ligands for the nuclear receptors PPARgamma, RAR, and/or RXR that regulate cholesterol homeostasis. 29457755_Which selectively amplified CES1A1 and, if present, also CES1A2. 29631096_Study utilized humanized mouse model expressing WT (control), G143E and catalytically dead S221A variants of human CES1 in the liver in the absence of endogenous expression of the mouse orthologous gene shows that compared to wild-type CES1, expression of the CES1G143E confers resistance to development of high-fat diet induced hepatic steatosis and leads to improved metabolic profile. 29797594_Alterations in methylation of CpG sites of specific genes (HDAC4, RAX2, APOA5 and CES1 loci) may contribute to childhood obesity. 30833288_A potential for clinically significant inhibition of CES1 by THC and CBD. 30850966_The study has shown the CES1 gene SNP rs2244613 frequency heterogeneity in different ethnic groups in Russia. Based on these findings and the RE-LY conclusions about rs2244613 carriage association with dabigatran concentration and the risk of bleeding we can suppose that patients taking dabigatran in ethnic groups living in Russia have a lower risk of bleeding. 31128980_Studied role of CYP450 Enzymes, carboxylesterase 1(CES1), paraoxonase 1(PON1), ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1(ABCB1), and purinergic receptor P2Y12 (P2RY12) genetic polymorphisms in the response to clopidogrel treatment who had undergone neurointervention. 31698983_In the combined cohort, CES1 rs9921399T>C was associated with prolonged overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.40) whereas ABCC1 rs17501011G>A (HR = 2.08) and UGT1 rs1113193G>A (HR = 2.12) were associated with shorter OS (p = 0.005). 31717501_Provides important insights into the metabolism of hCES1 substrates and drug designing. 31871135_Carboxylesterase 1 and Precision Pharmacotherapy: Pharmacogenetics and Nongenetic Regulators. 33206527_Potential Regulatory Role of Human-Carboxylesterase-1 Glycosylation in Liver Cancer Cell Growth. 33791812_Clock gene Bmal1 controls diurnal rhythms in expression and activity of intestinal carboxylesterase 1. 33878036_Enhanced triacylglycerol catabolism by carboxylesterase 1 promotes aggressive colorectal carcinoma. 34185414_Melatonin inhibits lipid accumulation to repress prostate cancer progression by mediating the epigenetic modification of CES1. 34234263_Copy number variation in the CES1 gene and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver in a Chinese Han population. 34633041_Carboxylesterase-1 Assisted Targeting of HDAC Inhibitors to Mononuclear Myeloid Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. 34697082_Transcriptional Regulation of Carboxylesterase 1 in Human Liver: Role of the Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group H Member 3 and Its Splice Isoforms. 35459739_Adipose tissue-specific ablation of Ces1d causes metabolic dysregulation in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000057074+ENSMUSG00000074156+ENSMUSG00000057400+ENSMUSG00000078964+ENSMUSG00000056973 |
Ces1g+Ces1h+Ces1c+Ces1b+Ces1d |
130.797367 |
0.2747559352 |
-1.863777 |
0.171393142 |
120.996420 |
0.00000000000000000000000000038282218813651684895957904354536290545665212474272533433353241536434447293748423168935346438956912606954574584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000004616385209881526362498267145715660841549368965937074777148004988431558926267883613547837740043178200721740722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
57.5834792 |
9.8386550 |
210.5766298 |
24.5110085 |
| ENSG00000198873 |
2869 |
GRK5 |
protein_coding |
P34947 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates preferentially the activated forms of a variety of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Such receptor phosphorylation initiates beta-arrestin-mediated receptor desensitization, internalization, and signaling events leading to their down-regulation. Phosphorylates a variety of GPCRs, including adrenergic receptors, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (more specifically Gi-coupled M2/M4 subtypes), dopamine receptors and opioid receptors. In addition to GPCRs, also phosphorylates various substrates: Hsc70-interacting protein/ST13, TP53/p53, HDAC5, and arrestin-1/ARRB1. Phosphorylation of ARRB1 by GRK5 inhibits G-protein independent MAPK1/MAPK3 signaling downstream of 5HT4-receptors. Phosphorylation of HDAC5, a repressor of myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) leading to nuclear export of HDAC5 and allowing MEF2-mediated transcription. Phosphorylation of TP53/p53, a crucial tumor suppressor, inhibits TP53/p53-mediated apoptosis. Phosphorylation of ST13 regulates internalization of the chemokine receptor. Phosphorylates rhodopsin (RHO) (in vitro) and a non G-protein-coupled receptor, LRP6 during Wnt signaling (in vitro). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19661922, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19801552, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20038610, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20124405, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21728385}. |
3D-structure;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Kinase;Lipid-binding;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
This gene encodes a member of the guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. The protein phosphorylates the activated forms of G protein-coupled receptors thus initiating their deactivation. It has also been shown to play a role in regulating the motility of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2869; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; beta-adrenergic receptor kinase activity [GO:0047696]; G protein-coupled receptor kinase activity [GO:0004703]; phospholipid binding [GO:0005543]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007188]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0008277]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; tachykinin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007217]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12067742_Human substance P receptor undergoes agonist-dependent phosphorylation by G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 in vitro. 14691047_Data indicate that GRK5 does not regulate the sorting of human beta 2-adrenoceptors in the endocytic pathway. 14976207_a group of hydrophobic amino acids within the membrane binding motif is critical to mediating the PM localization of GRK5 15542828_GRK5 has a DNA-binding nuclear localization sequence 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16849637_High expression was detected in septic neutrophils and control cells treated with cytokines plus LPS. 18034461_Results show that GRK5 plays a distinctive role in the phosphorylation of the beta2AR. 18425130_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18622265_GRK5-Leu41 represents a gain-of-function polymorphism that evokes enhanced loss-of-function of beta2AR during persistent agonist exposure, and thus may contribute to beta-agonist variability in asthma treatment of African-Americans. 19008357_GRK5 overexpression causes nuclear accumulation of IkappaB alpha, leading to the inhibition of NFkappaB transcriptional activity. 19092051_Reciprocity of regulation between platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRbeta) and GRK5, or their activation/deactivation cycle, mirrors other reciprocal regulatory mechanisms affecting tyrosine kinases. 19487588_Data suggest that GRK2, but not GRK5, is correlated with increasing blood pressure in black Americans 19628119_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19661922_beta-arrestin1 phosphorylation by GRK5 regulates G protein-independent signalling 19801552_Results identify GRK5/6 as novel kinases for the single transmembrane receptor LRP6 during Wnt signaling. 19842931_GRK5 Gln41Leu polymorphism is not associated with sensitivity to beta(1)-adrenergic blockade in humans. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20023040_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20023040_it has been demonstrated that the GRK5 L41 variant causes a negative inotropic effect under conditions of acute catecholamine stimulationl8AAg 20038610_This study uncovered previously unrecognized functionally important sites in the regulator of G-protein signaling homology domain of GRK5 kinase. 20124405_GRK5 as a novel kinase of p53, as well as a negative regulator of p53-mediated signal transduction. 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20443868_This study shows for the first time that GRK5 negatively regulates VEGF signaling in human coronary artery endothelial cells. 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20730384_Studies seem to indicate that mild, soluble, Beta-amyloid accumulation can lead to a reduced membrane (functional) and an elevated cytosolic GRK2/5. 21127457_The GRK5 Leu41 allele protects from adverse cardiovascular outcomes in treated hypertensives. 21184589_GRK5 gene does not confer risk to sporadic Parkinson's disease in our sample from Southern Italy. 21575264_GRK5 mediates cell growth suppression by TIG1A. Thus, TIG1 may participate in the downregulation of G-protein coupled signaling by upregulating GRK5 expression. 21728385_Hip has been identified as a novel substrate of GRK5 in vitro and in cells, and phosphorylation of Hip by GRK5 plays a role in modulating CXCR4 internalization 21768220_GRK5 is a transcriptional modifier of a subset of Galphaq-downregulated genes, acting in opposition to the pathological effects of Galphaq and normalizing levels of these transcripts. 21784156_A reduced cortical concentration of GRK5 in schizophrenia (resembling that in aging) may result in altered G protein-dependent signaling, thus contributing to prefrontal deficits in schizophrenia. 22196842_Increased GRK5 expression in the failing myocardium suggests a relevant role in human heart failure. 22223642_GRK5 is localized in the centrosome and regulates microtubule nucleation and normal cell cycle progression. 22467873_GRK5 phosphorylates Ser-4 in nucleophosmin and regulates the sensitivity of cells to PLK1 inhibition. 22961080_A genome-wide association study identifies GRK5 and RASGRP1 as type 2 diabetes loci in Chinese Hans. 23139825_These data suggest cell type- and subcellular compartment-dependent differences in GRK/arrestin-mediated desensitization and signaling. 23658733_DNA-binding ability of GRK5 requires both the NLS and an N-terminal calmodulin (CaM)-binding site 23693024_we show, for the first time, that knocking down the expression of GRK5 decreased the proliferation rate of gliioblastoma stem cells in contrast to control. 23794609_In the largest genotyped TC cohort in the literature, we have found no association of genetic variants in the ERalpha, beta1AR, beta2AR, or COMT genes, or with the previously implicated GRK5, with occurrence of the syndrome. 24178511_genetic polymorophism is associated with plasma viscosity 24594703_GRK5 intronic (CA)n polymorphisms associated with type 2 diabetes in Chinese Hainan Island. 24613411_Low levels of GRK2/GRK5 causes a slow and not complete desensitization/down-regulation of GPR17. 24632620_Results demonstrate crosstalk among WIP1, CXCR4 and GRK5, which may be important for the aggressive phenotype of a subclass of medulloblastomas in children. 24755472_GRK5 regulates prostate cancer cell migration and invasion. GRK5 forms a complex with moesin, phosphorylates moesin principally on T66 residue, and regulates cellular distribution of moesin. 24807909_GRK5 dimerization is important for its plasma membrane localization and function. 25010510_A significant difference in the frequency of GRK5 polymorphism was found between Takotsubo cardiomyopathy patients and controls, supporting a genetic predisposition to this cardiac syndrome. 25049040_G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 gene polymorphisms may have a role in postoperative atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass grafting in patients receiving beta-blockers 25153362_These data suggest that increased GRK5 expression may contribute to the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. 25638254_This study sought to identify the distributed characteristics of these variant genotypes in Chinese population, and influence of GRK5 and ADRB1 polymorphisms on systolic heart failure morbidity. 26032409_GRK5 is found in a partially closed state with its kinase domain C-tail forming novel interactions with nucleotide and the N-lobe. 26066465_ADORA2A and GRK5 gene variants may influence the etiology of malaria infection. 26235218_The role of GRK5 single nucleotide polymorphisms in postoperative atrial fibrillation susceptibility following coronary artery bypass grafting among Chinese population 26248277_Suggest a common regulatory pattern for the beta(1)-AR/GRK5 which is independent of cellular type or pathology. 26515328_Specific patterns of altered heart GRK5 gene expression were found in models of cardiac hypertrophy. 26614013_We demonstrated that the SNPs and the related haplotypes of GRK5 could play a central role in predisposing Parkinson disease patients to cognitive impairment. 26820533_Thus, we provided new insight into the function of GRKs in agonist-unstimulated GPCR trafficking using a recombinant AM1 receptor and further determined the region of the CLR C-tail responsible for this GRK function. 26829117_Further, we will also present potential therapeutic strategies (i.e. small molecule inhibition, gene therapy) that may have potential in combating the deleterious effects of GRK5 in heart failure. 26860460_Candidate gene eQTL showed a trans-acting association between variants of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 gene, previously linked to altered BB response, and high expression of VOPP1. 27232975_demonstrate for the first time exosomal enrichment of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) 5 and GRK6, both of which regulate Src and IGF-IR signaling and have been implicated in cancer. 27618959_Data indicate two moderately frequent variants in G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5) and seven very rare polymorphisms in patients with laterality defects (heterotaxy) that were associated with a congenital heart defect (CHD). 28808053_Data suggest that perturbation of interface formed between large lobe of kinase domain of GRK5 and the RHD (regulator of G protein signaling homology domain) leads to higher phosphorylation activity/activation of kinase activity. 29463786_Depletion of GRK5 inhibited NSCLC cancerous cell proliferation, migration in vitro, and xenograft tumor formation in vivo. 29514624_There was no association of SNPs in ADRB1, GRK5 and BAG3 genes with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. 29628444_Loss of GRK5 expression is associated with cardiac hypertrophy. 29663513_T2DM patients with genotypes CC and CT at GRK5 rs10886471 had a significant reduction in terms of fasting plasma glucose compared with those with genotype TT (p |
ENSMUSG00000003228 |
Grk5 |
14.165976 |
0.3900615537 |
-1.358226 |
0.474646311 |
8.339191 |
0.00387988731963568363875216604697016009595245122909545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008110343696051932130264283671294833766296505928039550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2633605 |
7.1111770 |
13.3480110 |
11.8291190 |
| ENSG00000198892_ENSG00000223774 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33.884833 |
0.3016177689 |
-1.729207 |
0.363820933 |
22.550858 |
0.00000204653155666747501429227409919242575142561690881848335266113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006995554834741068116199524951070998213253915309906005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.2901687 |
4.3298942 |
50.9084457 |
9.6620148 |
| ENSG00000198910 |
3897 |
L1CAM |
protein_coding |
P32004 |
FUNCTION: Neural cell adhesion molecule involved in the dynamics of cell adhesion and in the generation of transmembrane signals at tyrosine kinase receptors. During brain development, critical in multiple processes, including neuronal migration, axonal growth and fasciculation, and synaptogenesis. In the mature brain, plays a role in the dynamics of neuronal structure and function, including synaptic plasticity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20621658, ECO:0000305}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hereditary spastic paraplegia;Hirschsprung disease;Immunoglobulin domain;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Neurodegeneration;Neurogenesis;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is an axonal glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin supergene family. The ectodomain, consisting of several immunoglobulin-like domains and fibronectin-like repeats (type III), is linked via a single transmembrane sequence to a conserved cytoplasmic domain. This cell adhesion molecule plays an important role in nervous system development, including neuronal migration and differentiation. Mutations in the gene cause X-linked neurological syndromes known as CRASH (corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, aphasia, spastic paraplegia and hydrocephalus). Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants, some of which include an alternate exon that is considered to be specific to neurons. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:3897; |
axon [GO:0030424]; axonal growth cone [GO:0044295]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; axon guidance receptor activity [GO:0008046]; protein domain specific binding [GO:0019904]; axon development [GO:0061564]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of axon extension [GO:0045773]; synapse organization [GO:0050808] |
11393533_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11425011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11438988_genetic and clinical aspects of X-linked hydrocephalus (L1 disease) 11857550_May be a modifier of a gene associated with Hirschsprung disease. 11897831_Hirschsprung disease and L1CAM: is the disturbed sex ratio caused by L1CAM mutations? 12435569_A novel missense mutation in the L1CAM gene is identified in a boy with X-linked hydrocephalus who had multiple small gyri, hypoplasia of the white matter, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and lack of cleavage of the thalami. 12490317_L1CAM might contribute to melanoma progression by promoting cell adhesion and migration. 12725590_X-linked hydrocephalus is a variable condition caused by mutations in the gene encoding for L1CAM. This gene is located at Xq28. 12957823_This review focuses on the L1CAM extracellular region and how recent work has clarified important aspects of its structure and function; new insights are provided for L1CAM binding to extracellular molecules, and how L1CAM initially folds. 14657231_Data show that L1-cell adhesion molecule interactions with ankyrinB (but not with ankyrinG) are involved in the initial formation of neurites. 14718570_L1-type CAMs are able to promote the adhesion-dependent activation of EGF receptor signaling in vitro and in vivo 15128735_This study provides a novel translational mechanism to account for the association between L1 expression and motile processes involved in metastasis and development. 15148591_L1CAM may be a modifying factor in the development of Hirschsprung's disease 15609076_The sixth Ig-like domain of L1 (L1Ig6) demonstrates angiogenic potential involving ligation and activation of alpha(v)beta3. 15716380_L1 expression conferred increased cell motility, growth in low serum, transformation and tumorigenesis. 15820228_Levels of CAM-L1 were increased in the prefrontal cortex of the major depression. 16000162_RanBPM is an adaptor protein that links L1 to the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/MAPK pathway. 16229685_The cleavage of the ectodomains of L1 and CD44 is initiated in an endosomal compartment that is subsequently released in the form of exosomes. 16400320_Data show that L1 is highly expressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors but not in leiomyoma and desmoid-type fibromatosis being important differential diagnoses. 16401420_L1CAM has a function in synapse formation by organizing microtubules in the synaptic terminal. 16506207_L1 cell adhesion molecule plays a critical role in melanoma invasion and progression and offers therapeutic potential in combination with conventional anticancer agents. 16650578_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17211730_High L1 expression is associated with colorectal cancer progression 17294222_A LiCAM mutation was presented in a boy with hydrocephalus and duplex kidneys. 17328266_L1CAM loss-of-function mutations cause a severe form of L1 syndrome. 17420921_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17699774_ADAM10 overexpression in colon cancer cells displaying endogenous L1-CAM enhanced L1-CAM cleavage and induced liver metastasis, and ADAM10 also enhanced metastasis in colon cancer cells stably transfected with L1-CAM. 17873897_a significant association of L1 expression and presence of disseminated tumor cells colorectal tumors 17952127_Expression of L1-CAM augments cell motility, invasiveness and tumor growth, causes sustained Erk kinase activation and augments transcriptional activity of proinvasive genes. 18059459_A soluble form of human L1 can be detected in the urine of patients with acute tubular necrosis and this may be a marker of distal nephron injury. 18090124_Alpha v beta 5, alpha v beta 5 and their ligands Del-1 and L1 play an important role in the process of tumor cells moving from the original place. 18332088_We propose that L1CAM could promote endometriosis development by increasing enervation and aggravation. L1CAM expression is higher in atypical endometriosis compared with normal endometriosis. 18386459_L1 (CAM) expression represents a novel diagnostic marker in serous ovarian neoplasms that show characteristics of tumor progressio; immunoreactivity correlated significantly with stage and grade 18483249_ALCAM coordinates tissue growth and cell migration in a process involvnig L1CAM 18555990_Importance of the RGD site in L1 for human tumors; nuclear signaling of L1 is dependent on integrins. 18676824_L1CAM is required for maintaining the growth and survival of CD133(+) glioma cells both in vitro and in vivo, and L1CAM may represent a cancer stem cell-specific therapeutic target for improving the treatment of malignant gliomas and other brain tumors 18701456_domains Ig1 to Ig4 are necessary and sufficient for L1 homophilic binding in trans, and that the rest of the molecule does not contribute to the affinity 18847309_L1-CAM has a role in metastasis in colon cancer cells [review] 18931829_a functional role of L1CAM expression on tumor endothelium that could favor metastasis and angiogenesis during tumor progression. 18972120_L1 expression indicates more mature stages of neuroblastoma and is associated with less aggressive tumor cell behavior.. 19018795_Our report also helps define the critical region with exclusion of L1CAM in the X-linked mental retardation phenotype. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19165527_Using shotgun mass spectrometry, we found this protein differentially expressed in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. 19260824_Results establish for the first time that regulated proteolytic processing by ADAM10 and PS/gamma-secretase is essential for the nuclear signalling of L1 in human carcinoma cell lines. 19273627_These results implicate L1 in the regulation of dendritic cells (DC) trafficking and shed light on novel mechanisms underlying transendothelial migration of DCs. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401151_These results indicate an important role of released L1 in tumor angiogenesis. 19414364_Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule L1 expression is associated with esophageal adenocarcinoma. 19435915_Mechanisms of tumoral L1CAM induction and how pancreatic myofibroblasts contribute to malignant transformation of pancreatic duct cells early in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis. 19565280_L1 cell adhesion molecule X-linked hydrocephalus in mice is affected by a modifier locus on chromosome 5 19617634_Pathogenic L1-CAM mutations reduce the activation of EGFR. 19639167_DNA hypomethylation at the L1CAM CpG islands might induce L1CAM aberrant expression and contribute to the acquisition of aggressive tumor behavior in colorectal cancer 19641926_Herein, we are describing a case of a patient with concurrent X-linked hydrocephalus and Hirschsprung's disease. Genetics testing showed hemizygous for R558X hemizygous mutation in the L1CAM gene. 19661372_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19661372_The AA genotype of a L1C G842A polymorphism is associated with ovarian cancer. 19720049_a model was proposed in which L1-CD folding reflects L1-CD phosphorylation state, with specific reference to the availability of T1172 19787228_High L1-CAM expression is associated with breast cancer. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19920102_L1 cell adhesion molecule may have a role in progression of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 20237819_overview of the pathological conditions caused by L1CAM malfunction [review] 20447653_Our findings support that L1CAM mutations are associated with widely heterogeneous L1 syndrome phenotypes 20501614_The L1 plays an important role in the tumor progression of Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma(ICC) by enhancing cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and survival. L1 may represent a novel therapeutic target for ICC . 20501702_Nuclear factor-kappaB signaling and ezrin are essential for L1CAM mediated metastasis of colon cancer cells. 20621658_L1 syndrome mutations affect neuronal L1 function at different levels, firstly by impairing endoplasmic reticulum export and secondly by interfering with polarized axonal targeting of L1. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20799950_Results suggest that the L1CAM gene has two functionally active promoter sites that are used in a cell-type specific manner. 20811670_The elevated expression of L1CAM already found in precursor lesions of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma points to a role of L1CAM quite early in tumorigenesis of this disease 20940017_L1's ubiquitination might be an additional mechanism to control its re-appearance at the cell surface 21094640_Data contribute to the design of high-affinity antibody for therapeutic purposes as well as to the understanding of neural cell remodeling and cancer progression mechanism mediated by L1CAM. 21097529_Increased L1-CAM expression is associated with renal cell carcinoma. 21123622_Results suggest that L1-mediated metastasis of CRC cells does not require changes in EMT and CSC markers. 21195422_strong L1 overexpression in tumors of neuroectodermal and neural crest origin 21195665_L1CAM downstream signaling that is fundamental for the development of anti-L1CAM antibody-mediated therapeutics in human tumor cells. 21271669_Novel L1CAM splice site mutation in a young male with L1 syndrome. 21318226_overexpression of cell adhesion molecule L1 is asociated with gallbladder carcinoma progression. 21367865_alcohol binding within a pocket bordered by Glu-33 and Tyr-418 inhibits L1 adhesion by disrupting the Ig1-Ig4 interaction. 21496863_L1 cell adhesion molecule expression could be used as a novel prognostic factor for patient survival and might be a potential therapeutic target in gallbladder carcinomas. 21541352_Metastasis formation upon up-regulation of full length-L1CAM correlated with increased invasive potential and elevated Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and -9 expression and activity. 21600041_These results suggest that high soluble L1 levels predict poor prognosis and may thus be a promising tumor marker that can contribute to individualise therapy. 21685041_Tumor regulation of L1CAM expression is associated with morphologic features at the invasive front in colorectal cancer. 21688291_Missense mutations of hL1CAM in the fibronectinIII domain cause the resultant pathogenesis because of a loss of expression on the cell surface resulting from misrouting to the degradative pathway. 21860410_inhibition of HIF-1 activity in BrCa cells inhibits primary tumor growth and metastasis of BrCa cells to the lungs by blocking expression of angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) and L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM);ANGPTL4 inhibits endothelial cell(EC)-EC interaction; L1CAM increases the adherence of BrCa cells to ECs 21884209_L1 might be involved functionally in growth and spread of adenoid cystic carcinoma and might thus present a molecular target for future therapeutic strategies. 21957033_L1CAM is essential for self-renewal and pluripotency. 21985405_L1CAM is a novel prognostic marker for non small cell lung cancer cells that is upregulated by epithelial mesenchymal transition induction and appears to be instrumental for enhanced cell invasion 22088438_L1CAM promoted cell proliferation by mainly activating ERK signaling. 22095073_H6c7 cells exhibiting elevated L1CAM expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated alterations show a decreased apoptosis sensitivity toward death ligands 22228447_L1CAM expression and shedding in the tumor microenvironment could contribute to enhanced invasion and tumor progression through increased IL-1beta production and NF-kappaB activation. 22246010_Two novel mutations in SPG11 gene identified that confirmed link between SPG11 and autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum. 22307136_Data suggest that targeted inhibition of L1CAM may be a novel therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). 22349829_data suggest a role for TGF-beta1 and anti-inflammatory macrophages in malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells, involving upregulation of L1CAM expression by which epithelial cells acquire an apoptosis-resistant and migratory phenotype 22472175_L1CAM plays an important role in determining tumor behavior and chemosensitivity in cell lines derived from ATCs. Therefore 22544341_Complex-type oligosaccharides in L1CAM enhance the invasiveness of metastatic melanoma cells. 22677742_L1 expression was demonstrated in benign as well as malignant neuro fi broma-associated tumors, including malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. 22764136_up-regulation of L1CAM augmented expression of IL-1beta and NF-kappaB activation. 22796939_The dualistic role of L1CAM as a cell adhesion and/or motility promoting cell surface molecule. [Review] 22815787_Binding of L1CAM to erbB enhances its response to neuregulins. 22846990_a novel mechanistic insight into how Rabex-5 regulates internalization and postendocytic trafficking of ubiquitinated L1 destined for lysosomal degradation. 22859744_Whole-urine TGFb and L1CAM have the best correlation with glomerular filtration rate in obstructive nephropathy. 22869145_Results suggest L1-mediated signaling by the L1-ezrin-NF-kappaB pathway, that induces IGFBP-2 expression, has an important role in colorectal cancer progression. 22888955_L1CAM expression in HCC was significantly correlated with the advanced tumor progression and was an independent poor prognostic factor for both overall survival and disease-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. 22948185_data show that TGF-beta1 dependent upregulation of L1CAM expression in GBM cells leads to the downregulation of caspase-8 and apoptosis resistance pointing to L1CAM as potential target for improved therapy of GBM patients 22973895_A new function is revealed for L1CAM: a positive, robust and dose-dependent modulation of neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor (Trk)A receptor activated spontaneously or by nerve growth factor (NGF). 22983139_Data indicate that L1-CAM expression on breast cancer cells can promote adherence to activated endothelial cells by binding to endothelial L1-CAM or ALCAM. This mechanism might lead to increased metastasis and poor prognosis in L1-CAM-positive cancer. 23048039_Interaction of Rabex-5 with Rab5 depends on interaction of the MIU domain with the ubiquitinated L1 to drive its internalization. 23212305_High L1CAM stimulates glioma cell motility and proliferation through the fibroblast growth factor receptor. 23267165_L1CAM appears to correlate with clinical prognostic parameters and might be useful biomarkers for therapy monitoring and, thus, could serve as attractive targets for therapy of ovarian cancer 23399902_our data suggest that Nrg1 regulates L1 expression in gliomas 23530769_L1CAM expression correlated with methylation of the L1CAM promoter in EC cell lines. In negative cell lines L1CAM expression is up-regulated by epigenetic mechanism. 23781004_Patients bearing L1CAM-positive type-I endometrial cancers had poorer disease-free and overall survival. L1CAM expression in type I cancers indicates the need for adjuvant treatment. 24002299_we investigated the role of L1CAM during metastasis formation 24046108_Overexpression of L1CAM is associated with tumor progression via ERK signaling in gastric cancer. 24140408_neuregulin 1-beta (Nrg1beta) increases L1 expression in neurons of the cerebral cortex, and decreases expression in neurons of the hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. 24155914_Human pathological H210Q, R184Q and Y1070C, but not the E309K and L120V L1CAM mutations affect outside-in signaling via the FIGQY Ankyrin binding domain which is required for synapse formation. 24166603_borderline tumors and carcinomas of the ovary present increased expression of CD24 and CD171 24422715_Expression of L1CAM and EPCAM in gastric cancer was significantly associated with lymph node and distant metastasis, and poor prognosis. 24497324_Data suggest that miR-34a can regulate L1CAM expression by targeting L1CAM mRNA for degradation. 24746181_The data show that L1CAM promotes the enrichment of immunosuppressive T cells in particular of a CD4(+)CD25(-)CD69(+)-phenotype in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma providing a novel mechanism of tumor immune escape which contributes to tumor progression. 24914828_This indicates that similar biofunctionalization approaches based on N-cadherin and L1 can be translated to 3-D 'transplantable' scaffolds with enhanced neurotrophic behaviors. 25126672_Data indicate that positive L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) expression was significantly correlated with risk of distant recurrence. 25149066_Findings shed new light on the complex regulation of L1CAM in cancers and advocate the use of L1CAM/miR-21-3p for diagnostic application. 25445362_a positive relationship between L1 and pPKD1 in both cultured cerebellar neurons and human cerebellar tissue, suggesting that L1 functions in the modulation of PKD1 phosphorylation. 25510351_L1CAM is expressed in triple-negative breast cancers and is inversely correlated with androgen receptor 25666757_This study identified predicted pathogenic, hemizygous variants on chromosome X in disease genes L1CAM. 25860483_Our findings establish Slug-induced L1CAM expression as a mediator of a chemoresistant and migratory phenotype in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. 25934484_novel missense variant in L1CAM was identified in two Caucasian families with mild-moderate intellectual disability without obvious L1 syndrome features 25948108_L1 syndrome should be considered in the differential diagnosis of intellectual disability or mental retardation in children, especially when other signs such as hydrocephalus or adducted thumbs are present. 26399194_Genes induced during L1-mediated colorectal cancer cell metastasis 26464672_Our results suggest that the overexpression of L1CAM may be related to several established markers of poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. 26478212_L1-CAM and N-CAM: From Adhesion Proteins to Pharmacological Targets 26743472_Report high frequency of L1CAM expression in high-risk endometrial cancers associated with mutant p53 expression. 26761817_the CE7-epitope of L1-CAM is a cell adhesion molecule aberrantly expressed in several cancers and may have a role in immunotherapy 26861585_L1CAM expression is an independent predictor of poor survival in endometrial cancer, and is associated with advanced stage, high-risk endometrial cancer. 26891472_Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM)-mediated cell-cell aggregation was severely impaired by L1CAM variants p.I37N, p.M172I and p.D202Y but was preserved by the variant p.T38M. 26933044_L1CAM is frequently expressed in testicular germ cell tumors but not in normal testis. 27028855_High L1CAM expression is associated with vulvar squamous cell carcinomas. 27165065_Involvement of L1CAM in the regulation of activity of the canonical Wnt pathway and expression of genes of class I melanoma-associated antigens in melanoma. 27174921_L1CAM mRNA expression appears to play a substantial role in the pathophysiology of ovarian cancer that is translated into poor clinical outcome. 27207492_Splicing variant c.1267+5delG was identified in fetal hydrocephalus. The same mutation and severe L1 syndrome was confirmed in the second pregnancy. 27233077_L1CAM may have a role in human endometrial cancer and miR-34a has an inverse role to L1CAMEXP 27267927_L1CAM is a neuronal cell adhesion molecule involved in the development of the nervous system and progression of malignancies. (Review) 27390347_Our preclinical assessment of the CE7 epitope on CD171 supports its utility and safety as a CAR T-cell target for neuroblastoma immunotherapy 27432152_High L1-CAM expression is associated with low radiosensitivity in neuroblastoma. 27488577_L1CAM failed to be a clinically relevant marker of poor prognosis in stage I endometrioid endometrial carcinoma 27505134_The expression of L1CAM was associated with advanced stage, nodal involvement, high tumour grade, non-endometrioid histology, lymphovascular space invasion, and distant recurrences in all cases, and with reduced survival in the endometrial carcinomas, but not in the non-endometrioid carcinomas. L1CAM may induce EMT-like changes, but seems to only play a role in metastasis, not in invasion. 27544757_This study revealed an unexpected role of L1CAM in the pathological crosstalk between the immune and nervous systems. 27641335_CD10 is a necessary component conferring the L1 effects in CRC cells. The identification of gene expression patterns of L1-domain-specific point mutations may provide novel markers and targets for interfering with L1-mediated CRC progression. 27695947_L1CAM was a significant independent prognosticator for disease-specific survival in endometrial carcinoma. 27749842_Mutations involving L1 cell adhesion molecule is associated with chemotherapy-resistant urothelial carcinoma. 27833079_this review and meta-analysis concludes that L1CAM might be an effective poor prognostic factor for patients with various tumor types 27867005_The differential expression timing of CD184 and CD171 permits identification and enrichment of RGCs from retinal organoids at differing maturation states from committed progenitors to differentiating neurons. 27876874_TWIST1, in part via GAS6 and L1CAM, led to higher expression and activation of Akt upon cisplatin treatment, and inhibition of Akt activation sensitized cells to cisplatin. 28026654_This study examined the spatiotemporal distribution of L1CAM in the early human fetal period by means of immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. In advanced differentiated epithelia such as those of the gastrointestinal system, L1CAM localization vanishes. In epithelia, however, which undergo further development such as those of the urogenital system, L1CAM is further needed for their fully establishment. 28061460_Data suggest that targeted therapy to neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1) might be effective in the treatment of retinoblastoma tumors. 28181176_High circulating levels of autoantibodies against L1-cell adhesion molecule is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 28535665_A functional role for L1CAM in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma carrying the activating KRAS mutation.L1CAM prmotes cell migration and invasion via JNK activation in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 28939985_L1CAM promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenicity by upregulating ezrin expression. 28941294_Our findings suggest that L1CAM is possibly involved in the pathogenesis of at least a subset of endometrial clear cell carcinomas 29050935_These results suggest that a deficiency in L1 may partially account for RTT phenotypes. 29432466_data make L1CAM a highly interesting therapeutic target to prevent further metastatic spread in melanoma patients 29483251_The directional force for laminin-induced growth cone haptotaxis is generated by the grip and slip of L1-CAM on the substrates, which occur asymmetrically under the growth cone. 29551399_L1 induces the expression of ASCL2 in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and the suppression of ASCL2 in cells transfected with L1 reduces their growth, motile, tumorigenic and metastatic abilities. 29980240_Our results demonstrate the expression of L1CAM and miR-34a in EC as prognostic factors that identify subgroup of patients at high risk of recurrence suggesting for them more aggressive schedules of treatment. 30050154_Study demonstrates that L1CAM expression correlates with high grade, high stage, and poor prognosis for overall survival and disease-free survival within the p53 wt subgroup of endometrial carcinomas. 30140948_In uterine carcinosarcoma, membranous L1CAM expression was positive in the epithelial component in 65.4% of cases. Remarkably, expression was negative in the mesenchymal component. In cases where both components were intermingled, expression limited to the epithelial component was confirmed by a double stain for L1CAM and keratin. Expression of L1CAM did not relate to overall or disease-free survival. 30171263_L1CAM is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and in adjacent Schwann cells in invaded nerves. L1CAM from these SC acts as a strong chemoattractant to cancer cells, via activation of MAP kinase signaling. L1CAM also upregulated expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 by PDAC cells, via STAT3 activation. There is a paracrine response between SCs and cancer cells in the neural niche, promoting invasion via L1CAM. 30251576_L1CAM immunopositive tumors constituted 26% of anaplastic supratentorial ependymomas cases and were predominantly seen in young children, in the frontoparietal location, and exhibited clear cell morphology with calcification. A consistent pattern of L1CAM immunopositivity was noted in paired primary and recurrent tumor samples. 30365056_the present study identified two novel pathogenic class II variants in L1CAM in two Chinese families with a history of hydrocephaly. 30591489_L1CAM is a promising independent prognostic marker associated with aggressive tumor behavior and recurrence risk, but not with overall survival 30829570_Here, the authors report that endothelial cells (ECs) express a novel isoform of the cell-surface adhesion molecule L1CAM, termed L1-DeltaTM. The splicing factor NOVA2, which binds directly to L1CAM pre-mRNA, is necessary and sufficient for the skipping of L1CAM transmembrane domain in ECs, leading to the release of soluble L1-DeltaTM. 30842511_L1cam-mediated developmental processes of the nervous system are differentially regulated by proteolytic processing. 31030434_A c.512G>A (p.Trp171Ter) hemizygous mutation of the L1CAM gene was detected in the fetal tissue 31421150_These results suggest that unlike for glioma cells, L1LE does not increase human neural progenitor cell motility, but rather decreases motility and influences the differentiation of normal brain progenitor cells. 31426278_These novel data show that CD171-decoratred exosomes stimulate motility, proliferation and invasion to influence glioblastoma cell behavior, which adds to the complexity of how CD171 stimulates cancer cells through not only soluble ectodomain but also through exosomes. 31504653_We report MAGEL2 and L1CAM mutations in four pedigrees with variable Congenital hypopituitarism and arthrogryposis. Human embryonic expression analysis revealed MAGEL2 transcripts in the developing hypothalamus and ventral diencephalon at Carnegie stages (CSs) 19, 20, and 23 and in the Rathke pouch at CS20 and CS23. L1CAM was expressed in the developing hypothalamus, ventral diencephalon, and hindbrain (CS19, CS20, CS23). 31510944_AMOG and L1 interdependently regulate their expression levels not only in U-87 MG cells but also in U251 and SHG44 human glioma cell lines. The capacity of AMOG to reduce L1 expression suggests that methods for increasing AMOG expression may provide a therapeutic choice for the management of glial tumors with high expression of L1. 31532272_Colorectal cancer patients displaying high expression of L1CAM in primary tumors exhibit high risk for metastasis. 31754264_L1CAM may serve as a feasible biomarker for identification of patients who have a high risk of recurrence of gastric cancer 31756056_A new frameshift mutation in L1CAM producing X-linked hydrocephalus. 32236821_Long Noncoding RNA POU3F3 and alpha-Synuclein in Plasma L1CAM Exosomes Combined with beta-Glucocerebrosidase Activity: Potential Predictors of Parkinson's Disease. 32291413_TGF-beta1 secreted by pancreatic stellate cells promotes stemness and tumourigenicity in pancreatic cancer cells through L1CAM downregulation. 32356487_The Diagnostic Value of Serum L1CAM in Patients With Colorectal Cancer. 32366597_L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) in stage IB cervical cancer: distinct expression in squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas. 32404617_Hemizygous mutations in L1CAM in two unrelated male probands with childhood onset psychosis. 32509846_L1CAM High Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in Glioma but Does Not Correlate with C11orf95-RELA Fusion. 32656539_L1CAM defines the regenerative origin of metastasis-initiating cells in colorectal cancer. 33167483_L1CAM as an E-selectin Ligand in Colon Cancer. 33196764_Exome Sequencing as a Potential Diagnostic Adjunct in Sporadic Congenital Hydrocephalus. 33754922_LncRNA CHRF promotes TGF-beta1 induced EMT in alveolar epithelial cells by inhibiting miR-146a up-regulating L1CAM expression. 33787629_High L1CAM expression predicts poor prognosis of patients with endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. 33818537_L1CAM Expression in Recurrent Estrogen Positive/HER2 Negative Breast Cancer: A Novel Biomarker Worth Considering. 33872388_High-risk endometrial cancer proteomic profiling reveals that FBXW7 mutation alters L1CAM and TGM2 protein levels. 33897875_Nodal-induced L1CAM/CXCR4 subpopulation sustains tumor growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer derived organoids. 34022682_Immunohistochemical analysis of L1 cell adhesion molecule and high endothelial venules in breast cancer brain metastasis. 34078883_An antibody against L1 cell adhesion molecule inhibits cardiotoxicity by regulating persistent DNA damage. 34092791_L1CAM is not associated with extracellular vesicles in human cerebrospinal fluid or plasma. 34228897_Role of L1CAM in retinoblastoma tumorigenesis: identification of novel therapeutic targets. 34510796_L1CAM variants cause two distinct imaging phenotypes on fetal MRI. 34645505_L1CAM promotes ovarian cancer stemness and tumor initiation via FGFR1/SRC/STAT3 signaling. 35048633_L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) and nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR, p75) expression patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas. 35525225_L1 cell adhesion molecule high expression is associated with poor prognosis in surgically resected brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma. 35776035_Interindividual variability in L1CAM expression in the human kidney during development: are there implications for fetal programming of kidney diseases presenting in adulthood? 35791503_Analysis of L1CAM gene mutation and imaging appearance in three Chinese families with L1 syndrome: Three case reports. 36111928_Expression of L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule (L1CAM) in extracellular vesicles in the human spinal cord during development. 36251972_p53, Pirh2, and L1CAM as Promising Prognostic Biomarkers of Endometrial Carcinoma: An Immunohistochemical and Genetic Study. |
ENSMUSG00000031391 |
L1cam |
252.398793 |
7.6439708938 |
2.934322 |
0.275915534 |
101.329799 |
0.00000000000000000000000778753652381517348328518603471086630605555088492089260022745698681251313999496233009267598390579223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000080044595467626709876280978212502072574165975224539769140874329728108094172966957557946443557739257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
418.4312882 |
78.0691323 |
55.0252551 |
7.7572359 |
| ENSG00000198929 |
9722 |
NOS1AP |
protein_coding |
O75052 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein involved in neuronal nitric-oxide (NO) synthesis regulation via its association with nNOS/NOS1. The complex formed with NOS1 and synapsins is necessary for specific NO and synapsin functions at a presynaptic level. Mediates an indirect interaction between NOS1 and RASD1 leading to enhance the ability of NOS1 to activate RASD1. Competes with DLG4 for interaction with NOS1, possibly affecting NOS1 activity by regulating the interaction between NOS1 and DLG4 (By similarity). In kidney podocytes, plays a role in podosomes and filopodia formation through CDC42 activation (PubMed:33523862). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54960, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33523862}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Disease variant;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a cytosolic protein that binds to the signaling molecule, neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). This protein has a C-terminal PDZ-binding domain that mediates interactions with nNOS and an N-terminal phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain that binds to the small monomeric G protein, Dexras1. Studies of the related mouse and rat proteins have shown that this protein functions as an adapter protein linking nNOS to specific targets, such as Dexras1 and the synapsins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009]. |
hsa:9722; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; caveola [GO:0005901]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; podosome [GO:0002102]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0033017]; T-tubule [GO:0030315]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; nitric-oxide synthase binding [GO:0050998]; positive regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity [GO:1902261]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction [GO:0010750]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; positive regulation of peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation [GO:2000170]; positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport [GO:1901381]; positive regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization [GO:1903762]; postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0098974]; regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel [GO:1902514]; regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098901]; regulation of heart rate by chemical signal [GO:0003062]; regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901841]; regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045428]; regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0050999]; regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization [GO:0060307] |
11867766_Characterization of the related mouse and rat proteins 15707951_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15707951_Our findings indicate that CAPON gene may be a candidate susceptibility gene for schizophrenia in Chinese Han population, and also provide further support for the importance of NMDAR-mediated glutamatergic transmission in the etiology of schizophrenia. 16146415_study adds support to a role of CAPON in schizophrenia, produces new evidence implicating this gene in the etiology of bipolar disorder, and suggests a possible mechanism of action of CAPON in psychiatric illness 16202394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16202394_The present finding weakens the evidence that mutations or variation in the CAPON gene are causing genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia in European populations. 16648850_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16648850_This genome-wide study identified NOS1AP (CAPON), a regulator of neuronal nitric oxide synthase, as a new target that modulates cardiac repolarization 17565224_NOS1AP variants influence QT interval 17565224_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17576865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17903306_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18077426_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18235038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18235038_Strong effects of NOS1AP variants in diabetic individuals suggest that this patient subset may be particularly susceptible to genetic variants that influence myocardial depolarization and repolarization as manifest in the QT interval. 18337493_provide a rationale for the association of CAPON gene variants with extremes of the QT interval in human populations 18430503_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18430503_Our results identified no single marker nor haplotype associated with schizophrenia, which did not suggest that CAPON was a susceptible site in the Chinese Han population. 18474209_Linkage and association studies from multiple samples drawn from different populations indicate that a schizophrenia susceptibility gene is located in the region of chromosome 1 containing NOS1AP. 18511491_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18551039_Common variation in the NOS1AP gene is associated with reduced glucose-lowering effect and with increased mortality in users of sulfonylurea. 18551039_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18766325_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18766325_Single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with incidence of diabetes mellitus in people who use calcium channel blockers. 18785031_Demonstrated that the common NOS1AP variant rs10494366 was associated with increased QT interval in healthy young adults. 18785031_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18927126_A common variant (rs10494366T > G) within NOS1AP gene was associated with QT-interval duration. 18927126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19019189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19076153_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19077434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19077434_study found significant association between eight SNPs in the NOS1AP gene region to schizophrenia (patients from a South American population isolate) and its clinical dimensions 19111066_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19111066_We failed to provide evidence of an association between NOS1AP rs7538490 and type 2 diabetes, overweight, obesity or related quantitative metabolic phenotypes in large-scale studies of Danes 19180230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180230_These data extend the association of genetic variants in NOS1AP with QT interval to a Black population...In addition, we identify a strong sex-interaction and the presence of a second independent site within NOS1AP associated with the QT interval. 19204306_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19204306_sequence variations in NOS1AP were associated with baseline QT interval and the risk of sudden cardiac death in white US adults. 19247217_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19247217_The minor alleles of both NOS1AP single nucleotide polymorphisms significantly potentiate the QTc prolonging effect of verapamil. 19255043_The A allele of rs12742393 appears to be a risk allele associated with schizophrenia that acts by enhancing transcription factor binding and increasing gene expression. 19305408_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19305409_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19339362_We do not know yet just how major a role NOS1AP will prove to play outside these Canadian families, but the replicated associations and the postmortem work suggest that the role may be more major than appreciated until now. 19553464_CPE mediates the effects of NOS1AP on dendrite morphology. 19587794_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19643915_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19643915_Study provided additional evidence for association between genetic variation within NOS1AP and SCD. 19800018_these findings support the hypothesis that NOS1 redistribution in injured myocardium requires the formation of a complex with the PDZ adaptor protein CAPON. 19822806_Association of NOS1AP genetic variants with risk for life-threatening arrhythmias suggests that this gene is a genetic modifier of the long-QT syndrome. 19822806_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937226_NOS1AP variants may not play a dominant role in susceptibility to type 2 diabetes, but a minor effect cannot be excluded. 19937226_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19943157_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19943157_the NOS1AP variant is associated with incidence of type 2 diabetes in calcium channel blocker users 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20031603_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20031603_The length of QT interval verify the importance of NOS1AP protein and to identify a SNP on chromosome 13 reaching genome-wide significance. 20215044_NOS1AP has a modest effect on ECG t-wave peak to t-wave end interval but is not related to T-wave morphology measures. 20215044_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20305679_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538168_NOS1AP tag SNP genotype may provide an additional clinical dimension, which helps assess risk and choice of therapeutic strategies in LQTS. 20538168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20541371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20602773_Two non-synonymous NOS1AP variations, V37I and D423N were identified in two families, one with two siblings with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and the other with two brothers with autism spectrum disorders. 20605702_Data show that NOS1AP protein levels are altered in BA46 and cerebellum of patients with schizophrenia. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20722683_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20722683_The genetic variant rs12143842 in NOS1AP is associated with QT interval duration in a Chinese population with Type 2 diabetes. 20921115_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20921969_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21685173_Common variations in or near CASQ2, GPD1L, and NOS1AP are associated with increased risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with coronary artery disease 21959512_relationship of nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein (NOS1AP) polymorphism with serum creatinine level and occurrence of delayed graft function in kidney transplant recipients 21996201_NOS1AP rs203462 polymorphisms did not correlate with an increased risk of QT interval prolongation among kidney recipients. 22019493_Decreased NOS1AP expression in rs10494366 TT and rs10918594 CC homozygotes may underlie shorter repolarization times.Myocardial tissue for gene expression analysis was obtained from extracted cardiac implantable electronic device. 22179838_NOS1AP colocalizes with both SCRIB and VANGL1 along cellular protrusions in metastatic breast cancer cells, but does not colocalize with either SCRIB or VANGL1 at cell junctions in normal breast cells 22682551_Common variations in the NOS1AP gene are associated with a significant increase in the risk of drug-induced long QT syndrome. 23146198_This is the first study reporting that a variant of the NOS1AP gene is associated with PTSD. Our data also suggest that a genetic variant in NOS1AP may increase the susceptibility to severe depression in patients with PTSD and increased risk for suicide. 23171141_rs10918859 of the NOS1AP gene is associated with CHD in Han Chinese. In addition, here we report a gender effect in the association between rs10918859 of the NOS1AP gene and CHD. 23347024_In atherosclerosis, NOS1AP variants were associated with QT in CAU, with weaker evidence for selected variants in HIS and CHN. Location of significant SNPs varied across ancestry. 24220657_This study suggested that NOS1 and NOS1AP were associated with schizophrenia. 24418727_The A allele of rs12567209 in NOS1AP may serve as an independent predictor of all-cause death and SCD in patients with CHF. 24504561_report of the association of common NOS1AP polymorphisms with sudden unexplained nocturnal death syndrome in the southern Chinese Han population. These findings suggest that the A allele of rs12567209 and haplotype GCTA may serve as a protective modifier. 24857694_We further localized NOS1AP to cardiomyocyte intercalated discs (IDs) and demonstrate that overexpression of NOS1AP in cardiomyocytes leads to altered cellular electrophysiology. 25639344_The study suggested that rs3751284 and rs348624 in the NOS1AP gene might be susceptibility loci for sudden unexplained death during daily activities. 26332198_SNPs in the NOS1AP gene influence QTc interval duration but we have not demonstrated a direct association with the risk of sudden cardiac death 26384012_Results suggest that NOS1AP variants are associated with various forms of depression in schizophrenia and are more prevalent in males. 26861996_results hint towards an involvement of NOS-I/NOS1AP interaction in the regulation of dendritic spine plasticity 27080431_gender modulated the interaction between NOS1AP promoter DNA methylation in intracranial aneurysm and brain arteriovenous malformation BAVM patients 27869735_Data indicate that overexpression of nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein short form (CAPON-S) led to the inactivation of the proto-oncogene protein Akt (Akt) signaling pathway. 27988371_Novel Hispanic/Latino-specific Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at NOS1AP implicate gene regulatory dysfunction in QT prolongation. 28416970_Results from genome-wide DNA methylation, functional network analysis and pyrosequencing, show selective CpG sites (NOS1AP, BID, and GABRB1) differentially methylated in smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients compared to nonsmokers. 28465168_Association between NOS1AP and PTSD severity, depression, anxiety, and stress was found. NOS1AP was associated with resilience. 28671047_If the expression of Capon is decreased, myeloma cells are adhered to fibronectin or bone marrow stromal cells (bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells). In addition, the sensitivity of the cell line to chemotherapeutic agents was reduced after silencing Capon in the myeloma cell line which was adhered to bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. 28720088_sex was identified as a moderator of the association between NOS1AP sequence variants and QTc prolongation in two long QT syndrome founder populations 28827735_Genetic variation rs12143842 in NOS1AP gene is associated with idiopathic ventricular tachycardia. 29100974_Findings showed that NOS1AP (rs348624, rs12742393 and rs1415263), DISC1 (rs821633 and rs1000731), DAOA (rs2391191) and GSK3B (rs6438552) SNPs had no association with development of early-onset schizophrenia; however, our finding suggested statistically significant role of the interaction of NOS1AP, DISC1, DAOA and GSK3B polymorphisms in schizophrenia susceptibility. 30307500_CAPON Is a Critical Protein in Synaptic Molecular Networks in the Prefrontal Cortex of Mood Disorder Patients and Contributes to Depression-Like Behavior in a Mouse Model. 31171914_The effects of CAPON-L overexpression on glioma cell proliferation are dependent on the AKT/mTOR/P53 activity. The overexpression of CAPON inhibits U251 cell proliferation through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, while overexpressing CAPON-L promoted U87 cell proliferation, possibly through down-regulating the P53 level. 31447468_the minor allele of rs10494366 may have an impact on the QT interval in women or diabetes mellitus patients and may have a potential role in sudden death in the Caucasian population(Meta-Analysis) 31747862_Effect of Sex and Underlying Disease on the Genetic Association of QT Interval and Sudden Cardiac Death. 32061134_NOS1AP polymorphisms reduce NOS1 activity and interact with prolonged repolarization in arrhythmogenesis. 32828023_Effects of interaction of NOS1AP gene polymorphisms and childhood abuse on paranoid personality disorder features among male violent offenders in China. 33523862_Recessive NOS1AP variants impair actin remodeling and cause glomerulopathy in humans and mice. 33805311_Differentiated PDGFRalpha-Positive Cells: A Novel In-Vitro Model for Functional Studies of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase. 34616002_A NOS1AP gene variant is associated with a paradoxical increase of the QT-interval shortening effect of digoxin. 34772419_PPARD rs2016520 (T/C) and NOS1AP rs12742393 (A/C) polymorphisms affect therapeutic efficacy of nateglinide in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 35353321_Evaluating Common NOS1AP Variants in Patients with Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators for Secondary Prevention : Evaluating SNPs in NOS1AP. 35732169_Influence of NOS1AP Risk Variants on the Corrected QT (QTc) Interval in the Pharmacotherapy of Schizophrenia. |
ENSMUSG00000038473 |
Nos1ap |
11.181160 |
2.1484816279 |
1.103317 |
0.451950501 |
5.988978 |
0.01439553637276199705985479937453419552184641361236572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026659738627599380983435040093354473356157541275024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.9914292 |
4.5687666 |
7.5420856 |
1.6583135 |
| ENSG00000198933 |
9755 |
TBKBP1 |
protein_coding |
A7MCY6 |
FUNCTION: Adapter protein which constitutively binds TBK1 and IKBKE playing a role in antiviral innate immunity. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21931631}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
TBKBP1 is an adaptor protein that binds to TBK1 (MIM 604834) and is part of the interaction network in the TNF (MIM 191160)/NFKB (see MIM 164011) pathway (Bouwmeester et al., 2004 [PubMed 14743216]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:9755; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; serine/threonine protein kinase complex [GO:1902554]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060337] |
17568778_results suggest that efficient signal transduction upon viral infection requires SINTBAD, TANK and NAP1 because they link TBK1 and IKKi to virus-activated signalling cascades 23286385_Studies show that three proteins expressed in HEK-293T cells (NAP1, TANK and TBKBP1) interact with TBK1. 23637848_TBKBP1 is associated with the severity of ankylosing spondylitis in the Chinese Han population 25494292_The two selected single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in TBKBP1 show no relationship with the clinical outcomes. None of the 12 SNPs is related to mSASSS. 30853402_we show that, essential for anti-bacterial autophagy, the cargo receptor NDP52 forms a trimeric complex with FIP200 and SINTBAD/NAP1, which are subunits of the autophagy-initiating ULK and the TBK1 kinase complex, respectively. FIP200 and SINTBAD/NAP1 are each recruited independently to bacteria via NDP52, as revealed by selective point mutations in their respective binding sites 31523044_Analysis of 47 Non-MHC Ankylosing Spondylitis Susceptibility Loci Regarding Associated Variants across Whites and Han Chinese. 31792381_The TBK1-TBKBP1 axis facilitates tumour-mediated immunosuppression. 35545683_A multi-step genomic approach prioritized TBKBP1 gene as relevant for multiple sclerosis susceptibility. |
ENSMUSG00000038517 |
Tbkbp1 |
268.387609 |
0.3641049971 |
-1.457574 |
0.107957035 |
186.019345 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000235109114254724983856777821666654337372284372033899014276717195591379015655918917401991140451774702293407824302273745331604004604741930961608886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000041709261134612274217894561619709636884504962598305335400021270049578684295437629713329464609410820083424363546864555019055842421948909759521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.8221696 |
10.2459254 |
397.9839114 |
18.1038611 |
| ENSG00000198947 |
1756 |
DMD |
protein_coding |
P11532 |
FUNCTION: Anchors the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton via F-actin. Ligand for dystroglycan. Component of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex which accumulates at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) and at a variety of synapses in the peripheral and central nervous systems and has a structural function in stabilizing the sarcolemma. Also implicated in signaling events and synaptic transmission. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P11531, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16710609}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative promoter usage;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cardiomyopathy;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Disease variant;Membrane;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Synapse;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene spans a genomic range of greater than 2 Mb and encodes a large protein containing an N-terminal actin-binding domain and multiple spectrin repeats. The encoded protein forms a component of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC), which bridges the inner cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. Deletions, duplications, and point mutations at this gene locus may cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), or cardiomyopathy. Alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing result in numerous distinct transcript variants and protein isoforms for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
hsa:1756; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell projection [GO:0042995]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cell-substrate junction [GO:0030055]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; costamere [GO:0043034]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex [GO:0016010]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection terminus [GO:0044306]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; synapse [GO:0045202]; syntrophin complex [GO:0016013]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; dystroglycan binding [GO:0002162]; myosin binding [GO:0017022]; nitric-oxide synthase binding [GO:0050998]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; vinculin binding [GO:0017166]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0086001]; cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0060048]; maintenance of blood-brain barrier [GO:0035633]; motile cilium assembly [GO:0044458]; muscle cell cellular homeostasis [GO:0046716]; muscle cell development [GO:0055001]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; negative regulation of peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation [GO:1902083]; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033137]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; peptide biosynthetic process [GO:0043043]; positive regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045666]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:2000651]; protein localization [GO:0008104]; protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0065003]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; regulation of cellular response to growth factor stimulus [GO:0090287]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of muscle system process [GO:0090257]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0010880]; regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060314]; regulation of skeletal muscle contraction [GO:0014819]; regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0014809]; regulation of voltage-gated calcium channel activity [GO:1901385]; response to muscle stretch [GO:0035994]; skeletal muscle tissue development [GO:0007519] |
11381192_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11726549_The absence of skeletal muscle degeneration associated with loss of dystrophin function was shown to be due to increased expression of brain (B) and cerebellar Purkinje (CP) isoforms of the gene exclusively in the skeletal muscle of XLDC patients. 11795488_SSCA and heteroduplex analysis showed a nucleotide change in exon 17 of patients with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. 11861579_Accumulation of repeated elements could account for intron expansion in the evolution of the gene. 11882782_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11917091_precise function of dystrophin is unknown, but the lack of protein causes membrane destabilization and the activation of multiple pathophysiological processes, many of which converge on alterations in intracellular calcium handling. 11922612_The MCK1350 promoter allows for sustained dystrophin expression after AdV-mediated gene transfer to skeletal muscle of newborn mdx mice, which may have implications for the use of muscle-specific promoters for gene therapy of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 12031623_Novel deletion at the M and P promoters of the human dystrophin gene associated with a Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 12062429_The dystrophin gene is alternatively spliced throughout its coding sequence. 12107815_3'-untranslated region is conserved and so may represent a significant target for pathogenic mutations 12140183_the dystrophin rod domain is not merely a spacer but likely contributes an important mechanical role to overall dystrophin function 12206800_We have identified antisense oligoribonucleotides with which the skipping of 11 other Duchenne muscular dystrophy exons could be induced in cultured human muscle cells. May restore the reading frame in a series of patients with different mutations. 12359139_missense mutations and other less severe mutations of the dystrophin gene predispose to the common form of sporadic dilated cardiomyopathy 12370193_Dp71Delta(110) is a component of the platelet membrane cytoskeleton, is involved in cytoskeletal reorganization and/or signaling, and plays a role in thrombin-mediated platelet adhesion 12376747_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12389738_tumor cells express Dp71f as part of lamellipodia and focal complex proteins, and possibly connected via distroglycan complexes to integrin complexes 12398834_Since Dp71 lacks the actin binding domain, it cannot form the essential linkage between the dystrophin associated proteins complex and the cytoskeleton. 12480947_The tryptophan residues of this protein interact with membrane phospholipids. 12522557_Two alternative exons can result from activation of the cryptic splice acceptor site deep within intron 2 of the dystrophin gene in a patient with as yet asymptomatic dystrophinopathy 12596052_No association with either sequence or structure elements involved in known illegitimate recombination mechanisms was identified. 12606026_Trans-acting factors may cause splicing misregulation in Becker muscular dystrophy skeletal muscles. 12632325_A method is provided for rapid direct sequence analysis of the dystrophin gene. 12754415_DNA mutational analysis in sporadic deletional Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cases 12754707_characterization of two deep intronic mutations in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene of two unrelated Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) patients, causing the aberrant inclusion of a pseudoexon in the mature transcripts 12757471_Patients with double deletion mutations within the dystrophin gene have a milder phenotype than patients harboring single deletions at either major or minor hot spots of the gene. 12833401_Parental attitudes regarding newborn screening of DMD were compiled and evaluated. 12920092_Intronic breakpoint regions in two patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy carrying the in frame isolated deletion of dystrophin exon 5, representing a known example of 'exception to the frame rule' dystrophin mutation. 14513410_86 haplotypes of dystrophin in 1,343 chromosomes from around the world 14514278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14556187_It was found that all of breakpoints were located in repeat sequences and the repeat sequences formed the single-strand hairpin which could make the introns instable and result in exon deletion. 14559354_Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) mRNA was significantly decreased by about 35% in neurons treated with brain-specific dystrophin antisense, whereas inducible NOS expression was not affected. 14636778_Review discusses current understanding of the genotype-phenotype relation for mutations in the dystrophin gene and their implications for gene functions. 14652441_deviation of more than 30% from the reading frame hypothesis in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients (47/147). 14659407_In 72 Duchenne and Becker Muscular Dystrophies (DMD/BMD) patients without gross gene defect, we encountered four unrelated cases with additional out-of-frame sequences precisely intercalated between two intact exons of the mature muscle dystrophin mRNA 15528988_predicted the translational reading frame for all the deletions in Egyptian dystrophin males, and the frameshift rule was confirmed positively ranging for 50 to 67% of the cases 15637982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15643612_Mutation rates of the dystrophin gene were studied in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. 15655674_Deletion of exons and rearrangements may apply to female carrier analysis in musscular dystsrophy. 15723292_Results indicate that 7% of dystrophinopathy patients do not have coding region mutations, suggesting that intronic mutations are not uncommon. 16133659_A novel cryptic exon was identified in the 3' region of intron 2 of the dystrophin gene. 16246949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16276108_Disruption of DMD and the absence of ACSL4 in a patient are responsible for neuromuscular disease and cognitive impairment. 16286242_These data reposition dystrophin as a signaling protein and connect an important cellular complex required for the structural integrity of muscle to the pathways that modulate muscle size. 16286249_similar to muscular dystrophy, DGC dysfunction plays a critical role in cancer-induced wasting 16295426_30 muscle biopsies of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) showed all or majority of muscle fibers deficient for dystrophin and positive for utrophin. 16331671_Dystrophin mutations were identified in 67% of Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. 16380627_No associations between dystrophin abnormalities and clinical variables in DMD/BMD carriers were found. 16439510_data demonstrate a time course for muscular adaptation to resistance training in which desmin increases shortly after strength gains and in conjunction with hypertrophy, but before changes in MHC isoforms, whereas dystrophin remains unchanged 16461336_First report of the molecular mechanism leading to exon 31 skipping in the dystrophin gene that results in a milder phenotype than that of the expected Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 16496225_These results demonstrate that mini-dystrophin is efficiently bound and incorporated into the dystrophin protein complex, via beta-dystroglycan in living cells, similarly to the full length dystrophin protein. 16524176_Dystrophin expression is disrupted in viral myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. 16569668_Our results suggest that mechanical destabilization, rather than signaling dysfunction, is the primary cause of myofiber necrosis in dystrophin-deficient muscle. 16710609_Review. The role of dystrophin in the assembly of the dystrophin glycoprotein complex in brain, blood-brain barrier & choroid plexus, retina, and kidney is discussed. 16716778_exon-skipping in dystrophin produces hybrid spectrin type repeats 16807118_dystrophin promoter can provide tissue-specific transgene expression and that the mini-dystrophin protein is expressed at the sarcolemma of skeletal muscles from mdx mice 16824516_The identification and characterization of a novel dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC) present in the nuclei of HeLa cells, which contains dystrophin Dp71 as a key component, is reported. 16883524_Five Duchenne muscular dystrophy -causing mutations in dystrophin gene, 697-698insGT, C616T, G1255T, C4279T, and C2302T, were identified in the new stop codons in downstream sites of mutations, respectively. 16883579_An unusual extended area of DNA association with the nuclear matrix in the human dystrophin gene, is characterised. 16891620_Deletions within the dystrophin gene account for >70% of mutations leading to Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. 16917894_Duplications of the DMD gene are associated with Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy. 16936400_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16936400_Out of seventy patients forty six (63%) showed large intragenic deletion in the dystrophin gene. About 79% of these deletions are located in the hot spot region i.e, between exon 42 to 53. 17145200_Using this new protocol of biplex exons DHPLC screening, new mutations were identified in four male patients affected by DMD who had tested negative for large DNA rearrangements. 17150596_The induction of exon skipping by the most effective 2'-O-Me RNA/ENA chimeras led to the expression of dystrophin in dystrophin-deficient myocytes by correcting the translational reading frames. 17166095_Stem cells from fetal blood differentiate into myotubes and express DMD in vitro only after exposure to in vivo muscle environment. 17285139_describe a panel of AOs designed to induce skipping of every exon within the human dystrophin gene transcript, with the exception of the first and last exons 17314512_Inactivation of dystrophin/DMD is involved in the pathogenesis of malignant melanoma. 17385798_rapid prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy-affected male with gene duplications in the absence of a known disease-causing variation in the pedigree 17428346_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17487735_lipoprotein lipase and dystrophin have roles in survival in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia 17487865_This study suggests that the aberrantly spliced dystrophin is responsible for the muscle wasting in type 1 myotonic dystrophy. 17503325_Red-green color vision impairment was shown in DMD patients who had the gene deletion downstream from exon 30. 17579806_Analysis of seven novel cryptic dystrophin exons completely homologous to intronic sequences (introns 1, 18, 29, 63, 67, and 77) indicates that a mutation deep within an intron that changed the splicing parameters could cause dystrophinopathy. 17680544_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 17767400_Comparative analysis of antisense oligonucleotide sequences for targeted skipping of exon 51 during dystrophin pre-mRNA splicing in human muscle was performed. 17826093_We found that dystrophin levels comprised between 29% and 57% were sufficient to avoid muscle weakness in these X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy families. 17981813_Mutant DMD platelets have a disorganized cytoskeleton and manifest Gs hyperactivity and reduced platelet collagen reactivity. 17993586_studies demonstrate that the accumulation of dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) is an integral feature for phenotype maturation of human airway smooth muscle cells 17997718_Adipose-derived stem cellshave the potential to interact with dystrophic muscle cells, restoring dystrophin expression of DMD cells in vitro. 18031759_Microsatellite analysis showed that though the deletion of dystrophnin was observed in the same locus in exon 45 it is a new independent mutation. 18039686_Splice pattern analysis showed that either a strong polypyrimidine tract (PPT) or a fully active dys-ESE19 (encodes exonic splicing enhancer) is sufficient for proper splicing. 18054699_This is the first report of a young female patient with exertional muscle pain as the only early presenting symptom of dystrophinopathy. 18059005_Both DMD and Becker muscular dystrophy can result from out-of-frame pseudoexons, with the difference in phenotype being due to variable efficiency of the newly generated splicing signal. 18083704_hDMD transgene rescued the lethal dystrophic phenotype of the mdx x Utrn-/- mice 18160999_Two tandem duplication events in the dystrophin gene should contribute to the understanding of the duplication mechanisms that contribute to the development of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 18253029_DMD gene and its immediately distal neighbor, the 1.8 Mb IL1RAPL1 gene are abundantly expressed in normal brain but were dramatically underexpressed in every brain tumor cell line and xenograft. 18261477_Data provide molecular evidence supporting the observations on the biological function of dystrophin. 18353051_The observed proportion of intragenic deletions in dystrophin gene in the Pakistani population is relatively low, comparable with most of the Asian data. 18445268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18570328_a rare dystrophin gene rearrangement; inversion of approximately 28 kb, flanked by a 10-bp duplication and an 11-kb deletion, which led to the omission of exons 49 and 50 from the mature mRNA and the variable inclusion of several pseudoexons 18583217_Most identified mutations either led to a predictable premature stop codon or resulted in splicing defects, which caused defective function of dystrophin. 18589007_produced various 2 STR fragments, chosen to have high and low alpha-helix content at their junctions with each other, and show that they exhibit markedly different stabilities 18639760_This study describe a case of female Becker muscular dystrophy with 45,X/46,X,r(X), carrying an out-of-frame deletion in a nonhot-spot region of the DMD gene. 18646563_We had a percentage of 61.1% deletion which is higher than data from previous Egyptian studies and most of the deletion was localized in the major hotspot region between exons 44 and 52 and we had 5% of the cases with duplication. 18652600_Study analyzed the splicing patterns of dystrophin mRNA in lymphocytes from 38 patients with dystrophinopathies due to nonsense mutations in the dystrophin gene; in 7 of the cases, partial skipping of the nonsense-encoding exon was observed. 18653336_Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification test proved to be a powerful tool in detecting deletions/duplications and in some cases point mutations/polymorphisms along the DMD 18752307_gene copy number variations, gene duplications, and small deletions identified in carriers and patients 18799475_Changes in transgenic dystrophin expression and the formation of rings are adaptations to myotendinous strain injury that help to prevent muscle necrosis and retain the function of necessary muscles during injury, aging and disease. 18853462_26 DMD gene duplications occurring in 33 unrelated patients and detected among a cohort of 194 mutation-positive Duchenne (DMD) and up to 5-19% of Becker (BMD) muscular dystrophies patients, is described. 18935728_Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is caused by deletion, duplication or point mutation of the dystrophin gene.Of the 7 exons most commonly deleted, 49,50 and 51 aooear to be the hot spots. 18957474_A mutation in the donor splice junction at the end of dystrophin exon 62 was associated with human Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. 18957722_Dystrophin gene mutations are associated with duchenne muscular dystrophy. 18957722_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18971620_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18974567_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18974567_This study demonistrated that thirty-two exons spanning different 'hot spot' regions using Multiplex PCR techniques were studied in 347 patients. Two hundred and twenty-two showed deletions in one or more of the 32 exons. 19001018_Studied dystrophin gene and found that exon 25 is spliced out in the +1G-->A mutation in intron 25, resulting in mild Becker muscular dystrophy, and that a cryptic splice site within exon 45 was activated in severe Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 19009915_The genomic basis of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is associated with contraction of the D4Z4 repeat region in the subtelomere of chromosome 4q 19012301_This study finding supports previous predictions that exons 45-55 are the optimal multiexon skipping target in antisense gene therapy to transform the severe Duchenne muscular dystrophy into the milder BMD. 19040728_identified three novel pure intronic rearrangements and defined all the mutation breakpoints both in the introns and in the 3' UTR region; and detected a novel polymorphic intron 2 deletion/duplication variation 19074751_DMD mutation was documented for 345 (73.4%) boys. Deletions were more common and point mutations were less common than that has been reported in specialty clinic or laboratory-based cohorts. 19074751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19084397_Using MLPA method, a large portion of the Hungarian DMD/BMD patients and their female relatives were exactly genotyped. For the first time, the incidence and prevalence of asymptomatic and symptomatic female carriers in Hungary was estimated. 19158079_A Two-amino Acid Mutation Encountered in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Decreases Stability of the Rod Domain 23 (R23) Spectrin-like Repeat of Dystrophin. 19158820_Deletion breakpoints in three patients with del45-55 in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, were characterized. 19173203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19173203_The frequency of deletions was 67.5% in 26 Mexican families with signs of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy. They were at the 5' end & in the central region, exons 44 to 52, of the gene. 19194174_Remodeling of dystrophin and sarcomeric Z-band occurs in pediatric cardiomyopathies: a unifying mechanism for force transmission defect. 19206170_Results directly demonstrate, for the first time, the use of alternate translational initiation codons within the DMD gene, and suggest that dystrophin protein lacking amino acids encoded by the first five exons retains significant function. 19230662_We highlight the importance of mRNA analysis for determination of pathogenicity in patients with ambiguous sequence variants in the DMD gene. 19379759_a new model of the dystrophin molecule lying along the membrane bilayer, in which the two sub-domains R1-3 and R4-19 interact with lipids and F-actin, while the distal sub-domain R20-24 does not exhibit any interaction was proposed. 19409785_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19409785_identified all previously found mutations in DMD by means of high resolution melting curve analysis, validating the method, and found 17 different pathogenic mutations in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy patients, of which 10 were novel. 19449031_regional genomic instability, aided by the presence of repetitive elements, a stem-loop structure, and possibly preexisting mutations, may elicit complex rearrangements of the DMD gene 19602481_Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients with mental retardation have mutations that significantly affect Dp71 expression. 19602481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19609279_Insertion of the IL1RAPL1 gene into the duplication junction of the dystrophin gene is associated with muscular dystrophy. 19687056_preimplantation genetic diagnosis in female carrier of de novo mutations in DMD gene; informative markers flanking the DMD gene were used 19783145_Present study illustrates the importance of NMD as a functional checkpoint in the multi-level process of dystrophin gene expression. 19793655_This study discovered that DMD Trp3X nonsense mutation associated with a founder effect in North American families with mild Becker muscular dystrophy. 19907931_About half the mothers of affected probands were not carriers of the dystrophin gene deletion, underscoring the need to use real time techniques for carrier detection. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19927354_Five of nine patients with Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy were found to have several hemizygous exon deletions in the dystrophin gene. 19937601_report of 1,111 mutations in the DMD gene, including 891 mutations with associated phenotypes 19959795_Study identified 121 mutations of 99 different typesin dystrophin- 56 patients show stop codons that represent the 46.3% of all cases. 20019182_Absence of members of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex constitutes a permissive environment for spontaneous development of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma associated with mutation of p53 and mutation or altered splicing of Mdm2. 20031633_Deletions of amino-terminal domain are associated with early-onset dilated cardiomyopathy, whereas deletions of the rod domain and hinge 3 have a later-onset dilated cardiomyopathy. 20098710_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20098710_correlation between FSIQ results with the location of the dystrophin gene mutation suggests that the risk of cognitive deficit is a result of the cumulative loss of central nervous system (CNS) expressed dystrophin isoforms 20373002_reduced expression of dystrophin and titin is associated with the pathophysiology of dilated cardiomyopathy, and TNF-alpha may modulate the expression of these proteins via NF-kappaB pathway. 20381484_Combination of traditional multiplex PCR of hotspot exons with real-time PCR quantification of only exons 4, 17, 47 and 52 positively diagnosed 59% of Syrian DMD/BMD patients. 20399196_adsorption behaviour of two sub-domains at the air/liquid interface and at the air/lipid interface in a Langmuir trough highlighted differences in interfacial properties 20434517_Distribution of dystrophin- and utrophin-associated protein complexes during activation of human neutrophils. 20485447_In this study there was described the complete mutation spectrum of 422 Japanese Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy cases. 20516809_Dystrophinopathy is an important cause of LGMD phenotype in girls and should be considered in the differential diagnosis. 20625423_The structural and functional properties of dystrophins and utrophins in brain, the consequences of dystrophins loss-of-function, are discussed. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20630757_We present the results of DMD mutation analysis in this manifesting carrier cohort, including the first example of a presumably compound heterozygous DMD mutation 20646909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20646909_Women heterozygous for dystrophinopathy demonstrate significant left ventricular systolic dysfunction, which is unmasked by exercise. 20696926_effect of four disease-causing mutations--L54R, A168D, A171P, and Y231N--on the structural and biophysical properties of isolated N-terminal actin binding domain 20847377_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 21109441_investigated the relationship between dystrophin mutations and cognition. duchenne muscular dystrophy patients who lack the dystrophin isoform Dp140 have significantly greater cognitive problems. 21151598_An evolutionarily-acquired cryptic intron was identified in the 5'-UTR of the human retinal dystrophin transcript. 21164104_SAP97 and dystrophin macromolecular complexes determine two pools of cardiac sodium channels Nav1.5 in cardiomyocytes. 21212803_dystrophin translation is repressed by miR-31 21305657_study introduces a new class of mutations in the DMD gene and emphasizes the potential role of underdetected intronic rearrangements in human diseases. 21396098_They are two frame-shifting mutations in the DMD gene 3'end in BMD and three novel splicing defects which creates pseudoexon retention within IVS65. 21399986_We revised the main aspects of the natural history of dystrophinopathies to define genotype-phenotype correlations in large patient cohorts with extended follow-up. 21402533_mutation-phenotype associations in a Chinese population 21507246_The exon skipping level, transcriptional expression of myostatin and its target genes, and combined myostatin and several dystrophin antisense oligonucleotides. 21515508_This study demonistrated that patients with dystrophinopathy had confirmed dystrophin mutations based on genetic test. 21523654_three microsatellite sites in the intron region of the dystrophin gene have a high degree of polymorphism 21624465_Dystrophin expression indirectly influences synaptic plasticity through modulation of GABA(A)-receptor clustering in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 21712383_Spectrin-like repeats 11-15 of human dystrophin show adaptations to a lipidic environment 21851881_Dystrophin defects in X-linked cardiomyopathies consisted of 21 in-frame deletions and 11 out-of-frame deletions as well as 1 stop and 1 splice-site mutation. 21854195_Exon skipping therapy for Duchenne's muscular dystrophy should be carefully monitored for their splicing outcomes. 21972111_a new model presented based on the combination of exon definition and intronic splicing regulatory elements for the selective association of BMD nonsense mutations with a subset of DMD exons prone to mutation-induced exon skipping. 22006698_An unusual DMD mutation leads to discrepant test results between polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) array-based diagnostic methods. 22090376_aberrant firing of replication origins to explain intragenic nonrecurrent rearrangements within genes, including the DMD gene. 22092019_A DMD nonsense mutation in somatic mosaicism causes isolated cardiomyopathy with genetic normalization in skeletal muscle. 22105192_This REVIEW discusses the experimental evidence supporting participation of dystrophin Dp71 in different cellular processes, including cell adhesion, water homeostasis, cell division, and nuclear architecture. 22234188_This study demonistrated that fail to find any mutation that are specific io DMD gene. 22234189_Combining the two techniques, mPCR followed by MLPA assay, has enabled more accurate detection and extent of deletions and duplications to identify Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 22275054_Examined the thermodynamic stability and aggregation of utrophin N-ABD and compared with that of dystrophin. Utrophin N-ABD has decreased denaturant and thermal stability, unfolds faster, and is correspondingly more susceptible to proteolysis. 22379338_Mutational tests in 29 DMD/BMD patients, their six female relatives, and two myopathic female patients in Korea. The overall mutation detection rate was 72.4% in DMD/BMD patients, identifying deletions in 58.6% 22425969_A literature-annotated disease nonsense mutation (c.10141C>T, NM_004006.1) in exon 70 that has been reported as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)-causing mutation was found in our two patients, the proband and his cousin. 22453924_identified 2 brothers with mild proximal weakness, recurrent abdominal pain, and moderately elevated serum creatine kinase; a novel mutation was found in exon 11 of the dystrophin gene (c.1280T>C); results suggest this missense mutation hinders dynamic properties of the dystrophin N-terminal region 22455600_The ventricular dilatation seen in 5'-XLDC patients appears to be functionally related to loss of the M isoform, the only isoform transcribed in human ventricles; in contrast, the B isoform is well expressed in heart but confined to the atria 22538063_Review of the role of DMD mutations in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and use in genetic diagnosis. 22616200_presents two related men with an unusually mild Becker muscular dystrophy associated with an exon 26 deletion. 22750404_identified differences in the stability, dystrophin structure and lipid binding properties of these end-product proteins produced by exon 51 skipping repair 22876130_A novel missense mutation in EDN3 and a deletion mutation in DMD has been found in the same Indian family members affected with Waardenburg syndrome and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 22894145_No relationship between X-inactivation pattern and transcriptional behaviour of DMD gene was observed in Duchenne muscular dystrophies. 22985905_Coexistence of two distinct intragenic dystrophin deletions is reported in two maternal cousins with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. 22987438_Both dystrophin and alpha-syntrophin exhibit lower densities in Muller cells (a class of retinal macroglia) compared with brain astrocytes of transgenic mice. 23028937_Findings reveal that DMD lncRNAs may contribute to the orchestration and homeostasis of the muscle dystrophin expression pattern by either selective targeting and down-modulating the dystrophin promoter transcriptional activity. 23199925_In solution, dystrophin N-terminal actin-binding domain binds to F-actin in a closed conformation. 23299919_Data indicate that the cognitive impairment in symptomatic Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) carriers is associated with mutations in the distal part of the dystrophin DMD gene. 23395799_The evidence obtained for multi-step splicing in a large intron of the human dystrophin pre-mRNA. 23438214_This study showeded for the first time comprehensive clinical and molecular genetic findings in Malaysian patients with DMD/BMD. 23588064_majority of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy patients have a deletion/duplication mutation in the dystrophin gene, with a hot deletion mutation region from exon 45 to 52 23650001_In the analyzed group of Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophies families, the frequency of combined occurrence of two mutations in one gene was 2 per 722 (0.3%). 23829870_Correction of the aberrant dystrophin expression is reported in induced pluripotent stem cells-derived cardiomyocytes, which has implications for the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene therapy. 23890933_In the absence of curative treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the exon skipping approach aims to convert the severe DMD into a milder BMD phenotype by modulating the pre-mRNA splicing of the dystrophin transcript. 23900271_A three base pair deletion in the dystrophin gene deletes Leu3238 of the brain-specific isoform of the protein. This results in elevation in serum creatine kinase, which is in line with impaired dystrophin function. 24014171_Ordered disorder of the astrocytic dystrophin-associated protein complex in the norm and pathology. 24063785_The A and B helices of dystrophin are not crucial by themselves for the interaction, but that the A-B loop is involved in the dystrophin-nNOS interaction. 24099565_37 patterns of deletion in the dystrophin gene were classified in Vietnamese Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients 24106963_This review briefly outlines the basic domain structure of Dp427 and the composition of the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex from skeletal muscle. [review] 24213305_MLPA analysis revealed the same dystrophin gene mutation of the carrier mother (i.e.deletion in exons 8-21) as that observed in her affected sons (the second and the third patients). 24225992_the carrier frequency of the mothers was significantly higher in BMD than in DMD. We also found that the carrier frequency of mothers in DMD tends to vary among types of mutation, and envisage that this is related to the nature of the mutation. 24236769_Germinal mosaicism and DMD gene deletion identified in families with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. 24505439_These data are consistent with the notion that altered N-glycolylneuraminic acid and cytotoxic T cell carbohydrate expression may modify severity of muscular dystrophy resulting from dystrophin deficiency in dogs and humans. 24770780_Novel mutations in the human dystrophin gene in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. 24793134_dystrophin is a tumor suppressor and likely anti-metastatic factor in myogenic tumors that progress to high-grade, lethal sarcomas 24928536_Results implicate a role for DMD UTRs in dystrophin expression and delineate the cis-acting elements required for the myotube-specific regulation of steady-state mRNA levels and translational enhancer activity found in the DMD 3' UTR 24996370_Exon 11-12 deletion in the dystrophin gene was found thatmight be a new ge |
ENSMUSG00000045103 |
Dmd |
64.877291 |
3.8534854773 |
1.946164 |
0.274494794 |
50.782861 |
0.00000000000103170670251574075440400948684409811900199172018943727380246855318546295166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006135371043163711845250215191245466350364323737665017688414081931114196777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
107.5376498 |
21.1210101 |
28.0426740 |
4.3931089 |
| ENSG00000198952_ENSG00000160781 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.689087 |
0.2177890851 |
-2.198996 |
0.776130794 |
7.272501 |
0.00700182431343436117304745991418712947051972150802612304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013877659039383802297429326699784724041819572448730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8144589 |
1.8635811 |
14.3616960 |
4.5655378 |
| ENSG00000198963 |
6096 |
RORB |
protein_coding |
Q92753 |
FUNCTION: Nuclear receptor that binds DNA as a monomer to ROR response elements (RORE) containing a single core motif half-site 5'-AGGTCA-3' preceded by a short A-T-rich sequence. Considered to have intrinsic transcriptional activity, have some natural ligands such as all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and other retinoids which act as inverse agonists repressing the transcriptional activity. Required for normal postnatal development of rod and cone photoreceptor cells. Modulates rod photoreceptors differentiation at least by inducing the transcription factor NRL-mediated pathway. In cone photoreceptor cells, regulates transcription of OPN1SW. Involved in the regulation of the period length and stability of the circadian rhythm. May control cytoarchitectural patterning of neocortical neurons during development. May act in a dose-dependent manner to regulate barrel formation upon innervation of layer IV neurons by thalamocortical axons. May play a role in the suppression of osteoblastic differentiation through the inhibition of RUNX2 transcriptional activity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P45446}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 1 is critical for hindlimb motor control and for the differentiation of amacrine and horizontal cells in the retina. Regulates the expression of PTF1A synergistically with FOXN4 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8R1B8}. |
Activator;Alternative promoter usage;Biological rhythms;Developmental protein;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Epilepsy;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Vision;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the NR1 subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors. It is a DNA-binding protein that can bind as a monomer or as a homodimer to hormone response elements upstream of several genes to enhance the expression of those genes. The encoded protein has been shown to interact with NM23-2, a nucleoside diphosphate kinase involved in organogenesis and differentiation, and to help regulate the expression of some genes involved in circadian rhythm. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:225998; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; melatonin receptor activity [GO:0008502]; nuclear receptor activity [GO:0004879]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; amacrine cell differentiation [GO:0035881]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; eye photoreceptor cell development [GO:0042462]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of circadian rhythm [GO:0042752]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; retina development in camera-type eye [GO:0060041]; retinal cone cell development [GO:0046549]; retinal rod cell development [GO:0046548]; rhythmic process [GO:0048511]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
11849752_In the suprachiasmatic nucleus, ROR beta mRNA signals showed a peak at early daytime and a trough at early nighttime. ROR beta is a transcription factor possibly related to the circadian pacemaking system. 19839995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19909500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 24125721_these data demonstrate that Rorbeta regulates known osteogenic pathways, and may represent a novel therapeutic target for age-associated bone loss. 25789810_associations between NR1D1, RORA and RORB genes and bipolar disorder.( 25816151_Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor RORbeta, circadian rhythm abnormalities and tumorigenesis 27352968_Nonsense variant in RORB was identified in four family members with epilepsy. Two de novo RORB deletions identified in patients with behavioral and cognitive impairment and epilepsy. 28137278_Results show that NRIP2 regulates the activity of the Wnt pathway via RORbeta. RORbeta inhibits tumorigenesis and the self-renewal of cancer initiating cells (CCICs) and targets HBP1 in regulating Wnt pathway to inhibit tumorigenesis and the self-renewal of CCICs. 32162308_Inherited RORB pathogenic variants: Overlap of photosensitive genetic generalized and occipital lobe epilepsy. 34278502_RORbeta suppresses the stemness of gastric cancer cells by downregulating the activity of the Wnt signaling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000036192 |
Rorb |
9.365788 |
3.9951315532 |
1.998243 |
0.541415344 |
14.664822 |
0.00012842076564908023583039264892136088747065514326095581054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000347796422198242988904626216140059113968163728713989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.2310861 |
5.1108412 |
3.8401088 |
1.1090907 |
| ENSG00000198964 |
259230 |
SGMS1 |
protein_coding |
Q86VZ5 |
FUNCTION: Major sphingomyelin synthase at the Golgi apparatus (PubMed:17449912, PubMed:14685263). Catalyzes the reversible transfer of phosphocholine moiety in sphingomyelin biosynthesis: in the forward reaction transfers phosphocholine head group of phosphatidylcholine (PC) on to ceramide (CER) to form ceramide phosphocholine (sphingomyelin, SM) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as by-product, and in the reverse reaction transfers phosphocholine from SM to DAG to form PC and CER. The direction of the reaction depends on the levels of CER and DAG in Golgi membranes (PubMed:14685263, PubMed:17449912, PubMed:14976195, PubMed:17982138, PubMed:19454763). Does not use free phosphorylcholine or CDP-choline as donor (PubMed:14976195, PubMed:14685263). Regulates receptor-mediated signal transduction via mitogenic DAG and proapoptotic CER, as well as via SM, a structural component of membrane rafts that serve as platforms for signal transduction and protein sorting (PubMed:14976195, PubMed:17449912, PubMed:17982138). Plays a role in secretory transport via regulation of DAG pool at the Golgi apparatus and its downstream effects on PRKD1 (PubMed:18370930, PubMed:21980337). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14685263, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14976195, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17449912, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17982138, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18370930, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19454763, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21980337}. |
Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;Golgi apparatus;Kinase;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Sphingolipid metabolism;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Sphingolipid metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17982138}. |
The protein encoded by this gene is predicted to be a five-pass transmembrane protein. This gene may be predominately expressed in brain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:259230; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi trans cisterna [GO:0000138]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ceramide cholinephosphotransferase activity [GO:0047493]; ceramide phosphoethanolamine synthase activity [GO:0002950]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; sphingomyelin synthase activity [GO:0033188]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; ceramide biosynthetic process [GO:0046513]; phosphorylation [GO:0016310]; regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001242]; sphingolipid biosynthetic process [GO:0030148]; sphingomyelin biosynthetic process [GO:0006686] |
11841947_The 1.6 kb Hmob33 clone obtained from the medulla oblongata cDNA library and mapped to the human chromosome 10 was examined to find the coding region(MOB) 14976195_SMS1 is responsible for SM synthase activity in mammalian cells and plays a critical role in cell growth of lymphoid cells. 15315829_MOB gene activity is believed to be controlled at least at the transcriptional and the posttranscriptional levels, strictly regulating the amount of the encoded protein product. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16508036_Adenovirus-mediated SMS1 overexpression increased lipoprotein atherogenic potential. 17449912_Data show that sphingomyelin synthases SMS1 and SMS2 are co-expressed in a variety of cell types and function as the key Golgi- and plasma membrane-associated SM synthases in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, respectively. 17467659_Overexpression of SMS1 is associated with suppressed ceramide response and apoptotic resistance after photodamage. 17616479_Results indicate that both synthase (SMS)1 and 2 contribute to sphingomyelin (SM) de novo synthesis and control SM levels in the cells and on the cell membrane including plasma membrane. 17982138_SMS1 and SMS2 are key factors in the control of sphingomyelin and diacylglycerol metabolism within the cell, and thus they influence apoptosis. 18370930_SMS1 regulates subcellular pools of diacylglycerol-binding proteins in the Golgi apparatus. 18694848_Both SMS1 and SMS2 contain two histidines and one aspartic acid which are conserved within the lipid phosphate phosphatase superfamily. Site-directed mutagenesis of these amino acids abolished SMS activity without altering cellular distribution. 18820264_Impaired TCR signaling through dysfunction of lipid rafts in SMS1-knockdown T cells 19506037_Results establish the sphingomyelin synthase (SMS1)-related enzyme SMSr as a key regulator of ceramide homeostasis that seems to operate as a sensor rather than a converter of ceramides in the endoplasmic reticulum. 19779494_Altogether, our data show that SMS1 is a novel caspase target that is functionally involved in the regulation of FasL-induced apoptosis. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21203393_sphingomyelin synthase has a role in controlling the antimicrobial activity of neutrophils against Cryptococcus neoformans 21418611_Cellular sphingomyelin levels are positively related to cellular cholesterol levels and sphingomyelin synthase overexpression-mediated cellular sphingomyelin content changes are related to cellular Apo A-I content and secretion 21549185_Our results indicate that the regulation of SMS1 expression is complex and occurs at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional and translational levels. 21856749_SMS1-mediated SM synthesis directs Tf-TfR to undergo clathrin-dependent endocytosis and recycling, promoting the proliferation of lymphoma cells. 21980337_SMS1 and SMS2 are capable of regulating TGN-mediated protein trafficking and secretion 22106271_Data indicate that the increased sphingomyelin mass was due to a rapid and highly specific activation of sphingomyelin synthases SMS1 and SMS2. 23160178_Findings indicate that Sms1 is a downstream target of Bcr-abl, involved in sustaining cell proliferation of Bcr-abl-positive cells. 23977395_SGMS activity impacts on amyloid precursor protein processing to produce amyloid-beta (Abeta) and it could be a contributing factor in Abeta pathology associated with Alzheimer's disease. 24062078_The amount of SMS1 transcripts varies considerably between different human tissues. 24960545_We found upregulation of specific sphingolipid enzymes, namely sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1), sphingomyelinase 3 (SMPD3), and glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) in the endometrium of endometriotic women. 25912551_A study of the expression of the full-length SMS1 protein and the sum of the alternative transcripts encoding this protein in human tissues. 26065260_The structural organization of 5'-UTR variants of SGMS1 transcripts, directed by alternative promoters, is substantially different; this can provide regulation of the gene functioning on post-transcriptional level. 27194473_Sphingomyelin synthase 1 positively regulates KCNQ1/KCNE1 channel density in a protein kinase D-dependent manner. 27394416_SMS regulates the expression and function of drug transporters P-gp and MRP2. 27927984_findings suggest that the C-terminal tails of SMSs are involved in homodimer formation, which is required for efficient transport from the ER. 28087695_HepG2 cells stably transfected with SMS1 (HepG2-SMS1) exhibit elevated enzyme activity in vitro and increased sphingomyelin content (mainly C22:0- and C24:0-sphingomyelin) but lower hexosylceramide (Hex-Cer) levels. 29128370_The inhibition of SMS 1 activity induced CD cells to lose their epithelial phenotype and to undergo an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. 29454087_the SGMS1 gene exhibits a complex regulation at the post-transcriptional level 29533737_An oncogene-Bcr-Abl-has been demonstrated to drive such a mechanism that up-regulates the expression of a functionally important target gene, SMS1. 30191692_PECULIARITIES OF THE STRUCTURE AND EXPRESSION OF HUMAN SPHINGOMYELIN SYNTHASE 1 GENE (SGMS1). 30242129_findings suggest that complex formation between SMS1 and GCS is part of a critical mechanism controlling the metabolic fate of Cer in the Golgi. 30535436_SMS1 could inhibit EMT and the migration and invasion of MDAMB231 cells via TGFbeta/Smad signaling pathway. 31164434_Differential lung tissue gene expression in males and females: implications for the susceptibility to develop COPD. 31262710_optively transferred wide-type B cells partially recovered B-cell activation and autoantibody production in SMS1 deficient bm12-induced lupus mice. Moreover, the SMS1 mRNA level in B cells of SLE patients was increased and positively correlated with the serum anti-dsDNA level, IgG and globulin titers. 31596951_Chlamydia trachomatis-infected human cells convert ceramide to sphingomyelin without sphingomyelin synthases 1 and 2. 31980461_Diacylglycerol kinase delta and sphingomyelin synthase-related protein functionally interact via their sterile alpha motif domains. 33037626_Regulation of human sphingomyelin synthase 1 translation through its 5'-untranslated region. 33226447_Overriding sorafenib resistance via blocking lipid metabolism and Ras by sphingomyelin synthase 1 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. 33500344_Sphingomyelin Biosynthesis Is Essential for Phagocytic Signaling during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Host Cell Entry. |
ENSMUSG00000040451 |
Sgms1 |
74.774485 |
2.2894334530 |
1.194991 |
0.528359929 |
4.881113 |
0.02715210286932326702591389278040878707543015480041503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.047182133076431764795444223636877723038196563720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
79.8397756 |
28.4064989 |
35.0447844 |
8.9913594 |
| ENSG00000203650 |
101928287 |
LINC01285 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.409163 |
0.2232032396 |
-2.163570 |
0.926270145 |
5.322945 |
0.02104641542721598368448354676729650236666202545166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.037526587545990322536404448783287080004811286926269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3606027 |
1.5513785 |
10.6374012 |
4.0494539 |
| ENSG00000203663 |
26246 |
OR2L2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NH16 |
FUNCTION: Odorant receptor. {ECO:0000305}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Olfaction;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose, to initiate a neuronal response that triggers the perception of a smell. The olfactory receptor proteins are members of a large family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) arising from single coding-exon genes. Olfactory receptors share a 7-transmembrane domain structure with many neurotransmitter and hormone receptors and are responsible for the recognition and G protein-mediated transduction of odorant signals. The olfactory receptor gene family is the largest in the genome. The nomenclature assigned to the olfactory receptor genes and proteins for this organism is independent of other organisms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:26246; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; olfactory receptor activity [GO:0004984] |
|
ENSMUSG00000045341 |
Olfr167 |
7.616401 |
0.2505094675 |
-1.997063 |
0.661452496 |
9.444838 |
0.00211744227857562023267790074498861940810456871986389160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004652195300949115049082838169169917819090187549591064453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5764950 |
1.1038808 |
9.7558543 |
2.5092356 |
| ENSG00000203709 |
|
MIR29B2CHG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.973841 |
0.0988547002 |
-3.338547 |
0.655857381 |
34.397052 |
0.00000000449403438687234237462793119124646046280702194053446874022483825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000020254029786331532049075001373703019957872584200231358408927917480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8417132 |
0.8201898 |
18.6884484 |
3.3577384 |
| ENSG00000203739 |
101928673 |
PRDX6-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36311744_PRDX6 AS1 gene polymorphisms and SLE susceptibility in Chinese populations. |
|
|
26.559081 |
0.3689555647 |
-1.438481 |
0.327276048 |
19.768608 |
0.00000874065269979902360636837138629928745103825349360704421997070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027596156973055313620189071821542370344104710966348648071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.3666140 |
3.3202607 |
38.9130142 |
5.6958110 |
| ENSG00000203799 |
221262 |
CCDC162P |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
This gene is the ortholog of the mouse coiled-coil domain containing 162 gene. This locus is transcribed, but is represented as a unitary pseudogene because there are multiple changes in the coding sequence, including multiple changes that result in premature stop codons, relative to the mouse coding sequence. Transcripts from this locus are expected to encode truncated proteins, and may be candidates for nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2018]. |
|
|
|
|
|
324.446129 |
0.1410904077 |
-2.825308 |
0.194144336 |
199.027881 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000340386666851784587758036958395489293950198153649642963128671869147380490259993819317128983875781027751278849137472892749656239175237715244293212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064660324359489576424206651654165446593775651176332075439694825322965560105236349214361593742828939082920246511198419936405912267218809574842453002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
78.6372318 |
10.2248754 |
561.5664725 |
47.8316836 |
| ENSG00000203865 |
84852 |
ATP1A1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
76.451837 |
0.4476859765 |
-1.159441 |
0.210625022 |
30.182448 |
0.00000003932523703216233321078347745861081286022908898303285241127014160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000161323095773962189472772133999600718823330680606886744499206542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.0699306 |
7.8794634 |
105.8998402 |
12.2035437 |
| ENSG00000203880 |
55251 |
PCMTD2 |
protein_coding |
Q9NV79 |
|
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Lipoprotein;Myristate;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein methylation. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55251; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase activity [GO:0004719] |
|
ENSMUSG00000027589 |
Pcmtd2 |
378.897351 |
0.3925849789 |
-1.348923 |
0.093947878 |
208.175537 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003434946706407241850878498005716899222641966230108932730429346212838925215654076184529405827440429206487577525228197851143302488097219793417025357484817504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000685132613332039073119579854498369380486322110511880067724485925304997979661084380129775682653927137292454635941507971527708598102890391601249575614929199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
223.8690006 |
21.0604299 |
574.1539096 |
37.5392012 |
| ENSG00000203896 |
54923 |
LIME1 |
protein_coding |
Q9H400 |
FUNCTION: Involved in BCR (B-cell antigen receptor)-mediated signaling in B-cells and TCR (T-cell antigen receptor)-mediated T-cell signaling in T-cells. In absence of TCR signaling, may be involved in CD4-mediated inhibition of T-cell activation. Couples activation of these receptors and their associated kinases with distal intracellular events such as calcium mobilization or MAPK activation through the recruitment of PLCG2, GRB2, GRAP2, and other signaling molecules. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:14610046}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Immunity;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane adaptor protein that links the T and B-cell receptor stimulation to downstream signaling pathways via its association with the Src family kinases Lck and Lyn, respectively. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. |
hsa:54923; |
B cell receptor complex [GO:0019815]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043405]; regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901222]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014066]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
22395814_these results establish LIME as a transmembrane adaptor protein linking TCR stimulation to IS formation and integrin activation through activation of Vav(Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor) 29484035_Results identified one differentially methylated region associated with cerebral palsy within the transcription start site of the LIME1 gene, which plays a key role in inflammatory pathways. |
ENSMUSG00000090077 |
Lime1 |
18.330657 |
0.0679411718 |
-3.879570 |
0.999642750 |
12.303154 |
0.00045219362799864341569480719051910000416683033108711242675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001119862072023486030888927977855473727686330676078796386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.4675330 |
2.0516685 |
39.6586973 |
20.5761321 |
| ENSG00000203930 |
286411 |
LINC00632 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32862599_LINC00632 inhibits the malignant development of non-small cell lung cancer by downregulating miR-1203. 34537772_Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome-Containing Linc00632 Regulates GATA Binding Protein-3 Expression in Allergic Rhinitis by Interacting with Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 to Inhibit T Helper Cell 2 Differentiation. 35617432_A brain-enriched lncRNA shields cancer cells from immune-mediated killing for metastatic colonization in the brain. |
|
|
9.905828 |
0.2607396100 |
-1.939318 |
0.630596103 |
9.157206 |
0.00247740473697593719878962126301757962210103869438171386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005381382475020578953772698582724842708557844161987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0495080 |
1.3652455 |
11.9124375 |
3.4542892 |
| ENSG00000204025 |
100329135 |
TRPC5OS |
protein_coding |
A6NMA1 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:100329135; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000072934 |
Trpc5os |
25.852792 |
0.2080424786 |
-2.265050 |
0.390435235 |
34.843136 |
0.00000000357367157686287175577466471664261210561264192620001267641782760620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000016205036090474957456117975477562220820715310765081085264682769775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1746910 |
2.3315587 |
44.2306555 |
6.5557843 |
| ENSG00000204044 |
109729184 |
SLC12A5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.607366 |
16.3721671617 |
4.033173 |
0.710501539 |
44.019979 |
0.00000000003250411718240177390621811420878145039436990515469005913473665714263916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000174078653705460881333902896698183349055710777975036762654781341552734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.4411080 |
10.5121972 |
1.4393082 |
0.6173014 |
| ENSG00000204084 |
3633 |
INPP5B |
protein_coding |
P32019 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtIns(4,5)P2) and the signaling molecule phosphatidylinositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (PtIns(1,4,5)P3), and thereby modulates cellular signaling events. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7721860}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Lipoprotein;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Methylation;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of a family of inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatases. These enzymes function in the regulation of calcium signaling by inactivating inositol phosphates. The encoded protein is localized to the cytosol and mitochondria, and associates with membranes through an isoprenyl modification near the C-terminus. Alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014]. |
hsa:3633; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment [GO:0005793]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; inositol-1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0052659]; inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0052658]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase activity [GO:0004439]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; inositol phosphate dephosphorylation [GO:0046855]; inositol phosphate metabolic process [GO:0043647]; phosphatidylinositol dephosphorylation [GO:0046856]; regulation of protein processing [GO:0070613]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
17956944_INPP5B is also localised to the early secretory pathway including the Golgi apparatus and ER-to-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). 19536138_The NH2-terminal region of OCRL, but not of INPP5B, binds clathrin heavy chain. 19700499_The homologous phosphatase Inpp5b was unable to complement the Ocrl1-dependent cell migration defect. 20808825_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20872266_study found mouse Inpp5b and human INPP5B differ in their transcription, splicing and amino acid sequence; observations form foundation for analyzing the functional basis for the difference in how Inpp5b and INPP5B compensate for loss of Ocrl function 24704254_The crystal structures of human INPP5B in complex with phosphoinositide substrate analogs revealed a membrane interaction patch likely to assist in sequestering substrates from the lipid bilayer. 25305077_OCRL-mutated fibroblasts from patients with Dent-2 disease exhibit INPP5B-independent phenotypic variability relatively to Lowe syndrome cells 35878408_The inositol 5-phosphatase INPP5B regulates B cell receptor clustering and signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000028894 |
Inpp5b |
216.121229 |
0.3982492844 |
-1.328256 |
0.132525576 |
100.335357 |
0.00000000000000000000001286593988141128093190977409013349294822871515431357540177955572392731742326077437610365450382232666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000130876135526967967666504784103269437911398646274724294120587542514244638880427373806014657020568847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
129.9211991 |
13.3420751 |
328.0991238 |
23.4707610 |
| ENSG00000204103 |
9935 |
MAFB |
protein_coding |
Q9Y5Q3 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a transcriptional activator or repressor (PubMed:27181683). Plays a pivotal role in regulating lineage-specific hematopoiesis by repressing ETS1-mediated transcription of erythroid-specific genes in myeloid cells. Required for monocytic, macrophage, osteoclast, podocyte and islet beta cell differentiation. Involved in renal tubule survival and F4/80 maturation. Activates the insulin and glucagon promoters. Together with PAX6, transactivates weakly the glucagon gene promoter through the G1 element. SUMO modification controls its transcriptional activity and ability to specify macrophage fate. Binds element G1 on the glucagon promoter (By similarity). Involved either as an oncogene or as a tumor suppressor, depending on the cell context. Required for the transcriptional activation of HOXB3 in the rhombomere r5 in the hindbrain (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P54841, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19143053, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27181683}. |
Activator;Disease variant;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that plays an important role in the regulation of lineage-specific hematopoiesis. The encoded nuclear protein represses ETS1-mediated transcription of erythroid-specific genes in myeloid cells. This gene contains no introns. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:9935; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; abducens nerve formation [GO:0021599]; brain segmentation [GO:0035284]; cornified envelope assembly [GO:1903575]; fat cell differentiation [GO:0045444]; inner ear morphogenesis [GO:0042472]; integrated stress response signaling [GO:0140467]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; negative regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045647]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; protein processing [GO:0016485]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355]; regulation of myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0045637]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; respiratory gaseous exchange by respiratory system [GO:0007585]; rhombomere 5 development [GO:0021571]; rhombomere 6 development [GO:0021572]; segment specification [GO:0007379]; sensory organ development [GO:0007423]; T cell differentiation in thymus [GO:0033077]; thymus development [GO:0048538] |
12542795_strong proliferative signals mediated by T-cell activation and interleukins (IL-4 and IL-12) downregulate the mafB messenger RNA transcript level when resting naive CD4+ T-helper cells enter the differentiation pathway in vitro. 12542796_Our data show that human monocytes, but not neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic or natural killer cells, downregulate the expression of Mac-1 after overnight exposure to surface-bound IgG. 15121870_novel role for MafB as a regulator of ERK-induced gene expression 15135046_Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein intracellular domain co-localizes with MafB to the nucleus and negatively regulates its transcriptional activity 15598817_high PU.1 activity favors dendritic cells at the expense of macrophage fate by inhibiting expression and activity of the macrophage factor MafB. 16456583_MafB is a key regulator of monocytopoiesis 16473681_Microarray analysis of Dupuytren's disease tissue has identified significant upregulated gene expression of MafB 18615156_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18830254_MafB may be a prognostic marker in the risk stratification of MM patients. 18832725_the vitamin D(3)/Hox-A10 pathway supports MafB function during the induction of monocyte differentiation. 19013005_Identification of primary MAFB target genes in multiple myeloma 19060906_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19332055_identified a Tfe3-binding site (EBox) in the MAFB promoter region 19395026_Both OH-2 and primary cells have a complex secondary translocation in which the IGK 3' enhancer is inserted between MYC and MAFB, resulting in dysregulation of both oncogenes 20436469_Expression studies support a role for MAFB in palatal development. 20436469_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20506502_These results suggest a suppressive effect of HBZ on Maf function, which may have a significant role in HTLV-1 related pathogenesis. 20581830_MafB acts as a metastable switch to control expression of IFN-beta. 20969674_MafB expression was higher in smokers with airflow limitation than in smokers without airflow limitation. 21129249_Abnormal expression of maf-b correlates with abnormal proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells. 21567910_An association of ABCA4 and MAFB with non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate. 21834038_findings confirmed the contribution of MAFB in the etiology of nonsyndromic orofacial clefts 21839147_The homozygous kreisler mutation eliminates most of rhombomere 5 and mis-specifies rhombomere 6, abolishes an early decrease in respiratory frequency within 10 min of hypoxia and an intrinsic hypoxic activation. 22387013_Identified previously unreported missense mutations clustering within a 51 base pair region of the single exon of MAFB, validated by Sanger sequencing. 22753311_MAFB gene suggest a role for the development of orofacial clefting in hispanic population. 22903061_the haematopoietic progenitor population can be the target for transformation in MafB-associated plasma cell neoplasias 23225151_miR-148a directly targeted MAFB mRNA by binding to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) and repressed MAFB protein expression 23863625_MAFA, MAFB, NKX6.1, and PDX1 activity provides a gauge of islet beta cell function, with loss of MAFA (and/or MAFB) representing an early indicator of beta cell inactivity 23956186_We identified MAFB mutations in all, including three novel missense mutations clustering within the hot spot mutation region 24327562_Mafb is responsible for executing one branch of the SGN differentiation program orchestrated by the Gata3 transcriptional network 24472656_data support the existence of a signaling cascade by which stimulation of macrophages with the IL-10 cytokine determines a sequential activation of STAT3 and MafB transcription factors 24972815_rs6065259 was the most important single nucleotide polymorphism in MAFB (OR6065259-AA=0.45; 95% CI: 0.28 to 0.71; p=0.0027), followed by rs13041247; no association was found between rs11696257 and NSCLP. 24989131_These findings indicate that only a few transactivation domain-specific mutations within MAFB cause multicentric carpotarsal osteolysis. 25721756_DNMT3A R882 mutation is associated with elevated expression of MAFB and M4/M5 immunophenotype of acute myeloid leukemia blasts. 25917456_Gata3 interacted with Gcm2 and MafB, two known transcriptional regulators of parathyroid development, and synergistically stimulated the PTH promoter. 26055874_MiR-223 negatively regulates the growth and migration of NPC cells via reducing MAFB expression, and this finding provides a novel insight into understanding miR-223 regulation mechanism in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis. 26115698_MAFB is a regulator and a marker of adipose tissue inflammation, a process that subsequently causes insulin resistance 26204962_The rs2902940A allele carriers in the MAFB conferred a decreased serum ApoAI level in controls and an increased risk of coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke. 26554594_MAFB represents a unique signature and likely important regulator of the primate islet beta-cell. 27097296_Epidermal differentiation gene regulatory networks are controlled by MAF and MAFB. 27181683_Loss of MAFB Function Causes Duane Syndrome, Aberrant Extraocular Muscle Innervation, and Inner-Ear Defects. 27448450_Results indicate a hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) regulatory pathway involving MafB transcription factor and cyclin D1, the dysfunction of which drives proliferative character in HCC. 27829226_Data suggest that SUMOylated MAFB promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis through cell cycle regulation. 28000885_The present study demonstrated that miR-152 was downregulated in NPC tissues and cell lines. In addition, miR-152 expression and MAFB knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and miR-152 suppressed the expression of MAFB at the mRNA and protein levels. 28093525_these results demonstrate that MAFB critically determines the acquisition of the anti-inflammatory transcriptional and functional profiles of human macrophages 28790455_MafB is strongly down-regulated upon elevated pro-inflammatory signaling or by pro-inflammatory and pro-atherogenic microRNAs, miR-155 and miR-33. 28933784_USP5 regulates c-Maf stability and multiple myeloma cell survival. 29138297_MAFB enhanced leukemogenesis by the naturally occurring Notch1 mutants, decreased disease latency, and increased disease penetrance. 29757260_These results suggest that MAFB and MAFF play critical roles in the antitumor effects of retinoids by regulating the expression of retinoid target genes such as TFPI2 and can be promising for developing therapies to combat HCC invasion. 29779709_Study in two unrelated families with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis associated with Duane Retraction Syndrome revealed that affected individuals harbor a rare heterozygous substitution (p.Leu239Pro) in MAFB, a leucine zipper transcription factor. 29980194_high levels of MAFb protein in MM cells with a translocation involving q20 or Iglambda insertion are associated with resistance to proteasome inhibitors. 30024657_This study further confirmed that the targeted single nucleotide polymorphisms at MAFB were associated with Non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate case-parent trios from Western Han Chinese population 30208859_Three cases of multicentric carpotarsal osteolysis syndrome caused by the MAFB loss of function mutation have been reported. 31679694_MAFB was expressed in tumor-associated macrophages in human lung cancer samples, and can be used to assess tumor malignancy. 31822558_The deubiquitinase USP7 stabilizes Maf proteins to promote myeloma cell survival. 32090104_miR-155 Knockdown Protects against Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury by Targeting MafB. 32213710_MicroRNA-148a facilitates inflammatory dendritic cell differentiation and autoimmunity by targeting MAFB. 32234710_MAFB Promotes Cancer Stemness and Tumorigenesis in Osteosarcoma through a Sox9-Mediated Positive Feedback Loop. 32278749_Identification of a novel mutation in the MAFB gene in a pediatric patient with multicentric carpotarsal osteolysis syndrome using next-generation sequencing. 32307629_Lymphatic MAFB regulates vascular patterning during developmental and pathological lymphangiogenesis. 32488111_Loss of the transcription factor MAFB limits beta-cell derivation from human PSCs. 32622525_Transcription factor MafB in podocytes protects against the development of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. 32646788_Association between MAFB rs17820943 and rs6072081 polymorphism and risk of nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate: a meta-analysis. 33268316_Expression of Mafb is down-regulated in the foreskin of children with hypospadias. 33312178_MAFB and MAF Transcription Factors as Macrophage Checkpoints for COVID-19 Severity. 34893889_Coordinated glucocorticoid receptor and MAFB action induces tolerogenesis and epigenome remodeling in dendritic cells. 34904217_GPBAR1 promotes proliferation and is related to poor prognosis of high-grade glioma via inducing MAFB expression. 34964110_Duane retraction syndrome characterized by inner ear agenesis and neurodevelopmental phenotype in an Italian family with a variant in MAFB. 35220623_Repression of Mafb promotes foreskin fibroblast proliferation through upregulation of CDK2, cyclin E and PCNA. 35430273_MAFB promotes the malignant phenotypes by IGFBP6 in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. 36153605_Circ_0051079 functions as an oncogenic regulator in osteosarcoma by leading to MAFB expression upregulation by competitively interacting with miR-1286. |
ENSMUSG00000074622 |
Mafb |
1778.186010 |
3.3556791589 |
1.746605 |
0.043751127 |
1625.127760 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2776.0614253 |
70.7285037 |
833.3250784 |
17.4643951 |
| ENSG00000204136 |
2681 |
GGTA1 |
protein_coding |
Q4G0N0 |
|
Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase (GGTA1) is an enzyme present in most mammals except man, apes, and Old World monkeys. This gene is thought to encode a truncated, non-enzymatic form of the GGTA1 protein that lacks the C-terminal catalytic domain. Aberrant expression of the GGTA1 protein in man can lead to autoimmune diseases and sometimes germ cell tumors. [provided by RefSeq, May 2020]. |
|
Golgi cisterna [GO:0031985]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; hexosyltransferase activity [GO:0016758]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; leukotriene D4 biosynthetic process [GO:1901750] |
11773054_Molecular basis of evolutionary loss of the alpha 1,3-galactosyltransferase gene 12499400_A transcription of the complete gene sequence for this enzyme 24033743_GGTA1/CMAH knockout pig samples had increased relative amounts of high-mannose, incomplete, and xylosylated N-linked glycans |
|
|
5.901285 |
0.1017573813 |
-3.296795 |
0.806960502 |
21.878783 |
0.00000290427340580385233502046932185791661140683572739362716674804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009727042312154495808107501630956903682090342044830322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3286452 |
0.7567474 |
13.1934675 |
3.2680311 |
| ENSG00000204172 |
642517 |
AGAP9 |
protein_coding |
Q5VTM2 |
FUNCTION: Putative GTPase-activating protein. {ECO:0000305}. |
Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;GTPase activation;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity and metal ion binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:642517; |
GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630] |
|
|
|
41.602835 |
0.4707832306 |
-1.086865 |
0.263242480 |
17.205914 |
0.00003353906663930751472441418870040763522410998120903968811035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000098632521138907933676287509427993427379988133907318115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.0521811 |
4.5759117 |
58.0231002 |
6.4328641 |
| ENSG00000204228 |
7923 |
HSD17B8 |
protein_coding |
Q92506 |
FUNCTION: Required for the solubility and assembly of the heterotetramer 3-ketoacyl-[acyl carrier protein] (ACP) reductase functional complex (KAR or KAR1) that forms part of the mitochondrial fatty acid synthase (mtFAS). Alpha-subunit of the KAR complex that acts as a scaffold protein required for the stability of carbonyl reductase type-4 (CBR4, beta-subunit of the KAR complex) and for its 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase activity, thereby participating in mitochondrial fatty acid biosynthesis. Catalyzes the NAD-dependent conversion of (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA into 3-ketoacyl-CoA (3-oxoacyl-CoA) with no chain length preference; this enzymatic activity is not needed for the KAR function (PubMed:19571038, PubMed:25203508, PubMed:30508570). Prefers (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA over (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA and displays enzymatic activity only in the presence of NAD(+) (PubMed:19571038). Cooperates with enoyl-CoA hydratase 1 in mitochondria, together they constitute an alternative route to the auxiliary enzyme pathways for the breakdown of Z-PUFA (cis polyunsaturated fatty acid) enoyl-esters (Probable) (PubMed:30508570). NAD-dependent 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase with highest activity towards estradiol (17beta-estradiol or E2). Has very low activity towards testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (17beta-hydroxy-5alpha-androstan-3-one). Primarily an oxidative enzyme, it can switch to a reductive mode determined in the appropriate physiologic milieu and catalyze the reduction of estrone (E1) to form biologically active 17beta-estradiol (PubMed:17978863). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17978863, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19571038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25203508, ECO:0000303|PubMed:30508570, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25203508}. |
3D-structure;Fatty acid biosynthesis;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Mitochondrion;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Steroid biosynthesis |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; estrogen biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17978863}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25203508}.; PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:25203508}. |
In mice, the Ke6 protein is a 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase that can regulate the concentration of biologically active estrogens and androgens. It is preferentially an oxidative enzyme and inactivates estradiol, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone. However, the enzyme has some reductive activity and can synthesize estradiol from estrone. The protein encoded by this gene is similar to Ke6 and is a member of the short-chain dehydrogenase superfamily. An alternatively spliced transcript of this gene has been detected, but the full-length nature of this variant has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7923; |
mitochondrial envelope [GO:0005740]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; oxidoreductase complex [GO:1990204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; (3R)-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (NAD) activity [GO:0106386]; 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0044594]; estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004303]; NADH binding [GO:0070404]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-OH group of donors, NAD or NADP as acceptor [GO:0016616]; quinone binding [GO:0048038]; testosterone dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0047035]; androgen metabolic process [GO:0008209]; estrogen biosynthetic process [GO:0006703]; fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0006633]; protein heterotetramerization [GO:0051290] |
16930994_The results indicate that aromatase, 17beta-HSD type 7 and 17beta-HSD type 12, but not 17beta-HSD type 1, are commonly expressed in human breast cancer. 17583490_transcription in liver is regulated by C/EBPbeta 17978863_Expression of the human Ke 6 gene, 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 8, in E. coli and the substrate specificity of the expressed protein were examined. The tissue distribution of mRNA expression of the human Ke 6 gene was also studied. 18794456_HSD17B8 mRNA is expressed in human skin, at lower levels in face vs arm or hip. HSD17B8 levels are not altered by topical 17-beta-estradiol treatment. 18852215_ERalpha is involved in the transcriptional regulation of HSD17B8 gene in response to E2 through its interaction with C/EBPbeta. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19571038_Hs17beta-HSD8 and HsCBR4 show a strong genetic interaction in vivo in yeast, where, only if they are expressed together, they rescue the respiratory deficiency and restore the lipoic acid content of oar1Delta cells. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20214802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 35184130_The Obesity-Related Metabolic Gene HSD17B8 Protects Against Breast Cancer: High RNA/Protein Expression Means a Better Prognosis. |
ENSMUSG00000073422 |
H2-Ke6 |
9.130281 |
0.2954532173 |
-1.758998 |
0.609120717 |
8.384877 |
0.00378355775607552152761670072322885971516370773315429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007928068211197430992243084801884833723306655883789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1974554 |
1.5931646 |
14.2813607 |
3.2388934 |
| ENSG00000204248 |
1302 |
COL11A2 |
protein_coding |
P13942 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in fibrillogenesis by controlling lateral growth of collagen II fibrils. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Collagen;Deafness;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Dwarfism;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Metal-binding;Non-syndromic deafness;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Stickler syndrome |
|
This gene encodes one of the two alpha chains of type XI collagen, a minor fibrillar collagen. It is located on chromosome 6 very close to but separate from the gene for retinoid X receptor beta. Type XI collagen is a heterotrimer but the third alpha chain is a post-translationally modified alpha 1 type II chain. Proteolytic processing of this type XI chain produces PARP, a proline/arginine-rich protein that is an amino terminal domain. Mutations in this gene are associated with type III Stickler syndrome, otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED syndrome), Weissenbacher-Zweymuller syndrome, autosomal dominant non-syndromic sensorineural type 13 deafness (DFNA13), and autosomal recessive non-syndromic sensorineural type 53 deafness (DFNB53). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene is located nearby on chromosome 6. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009]. |
hsa:1302; |
collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; collagen type XI trimer [GO:0005592]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-macromolecule adaptor activity [GO:0030674]; cartilage development [GO:0051216]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; roof of mouth development [GO:0060021]; sensory perception of sound [GO:0007605]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; soft palate development [GO:0060023] |
11289713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11341341_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12554743_differential regulation by EWS/ERG sarcoma fusion protein and wild-type ERG 12673280_sequence variations in these genes can play a role in the etiology of Robin sequence, cleft palate and micrognathia but are not common causes of these phenotypes. 15558753_Mutation in the COL11A2 gene was found in all affected individuals, which lends molecular support to the clinical notion that autosomal recessive Weissenbacher-Zweymuller syndrome (WZS) and otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED)are a single entity. 15922184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16033917_mutation type and location are critical determinants in defining the phenotype of COL11A2 associated diseases 16133074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16609882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16734381_COL11A2 transcription is regulated by Sp1 proteins and by binding to its proximal promoter 17471097_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18040076_This study is the first to show that collagen XI is present in the Golgi apparatus of normal human colon goblet cells and localizes collagen XI in both normal and malignant tissue. 18309376_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18381781_diagnosis ofOtospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia was diagnosed by identifying a mutation in the COL11A2 gene that encodes the pre-pro-alpha2(XI) chain of type XI collagen that is involved in type II collagen fibrillogenesis. 18469698_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18830248_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20618517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20618517_individuals carrying the C allele at the COL11A2 SNP site, rs2076311, had a lower risk of Kawasaki disease and had a lower probability of developing coronary artery lesions 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20672350_implication of IRF6, COL2A1, and WNT3 in occurrence of nonsyndromic cleft palate (NSCP); likely variation in cartilage collagen II and XI genes, IRF6, and Wnt and FGF signal pathway genes contributes susceptibility to NSCP in Northeast Europe populations 21204229_A novel homozygous COL11A2 deletion causes a C-terminal protein truncation with incomplete mRNA decay in a Turkish patient. 21293383_four loci showed the strongest associations with RA (P |
ENSMUSG00000024330 |
Col11a2 |
62.165796 |
0.2244994089 |
-2.155216 |
0.327029312 |
42.194464 |
0.00000000008263359744501640215971530591885759256531862604333582567051053047180175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000429613208273491417884914464518988919117248315160395577549934387207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.6147606 |
12.7260960 |
67.8589967 |
38.1790449 |
| ENSG00000204261 |
100507463 |
PSMB8-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 30669933_Our study suggests that lncRNA PSMB8-AS1 could be a new host factor target for developing antiviral therapy against influenza virus infection. 31812014_PSMB8-AS1 activated by ELK1 promotes cell proliferation in glioma via regulating miR-574-5p/RAB10. 32891166_LncRNA PSMB8-AS1 contributes to pancreatic cancer progression via modulating miR-382-3p/STAT1/PD-L1 axis. 33922041_Characterization of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Systemic Sclerosis Monocytes: A Potential Role for PSMB8-AS1 in Altered Cytokine Secretion. |
|
|
129.710246 |
0.3753301753 |
-1.413768 |
0.162212905 |
76.940928 |
0.00000000000000000176148607818859662320811558515659897061728539571930605978078432372058159671723842620849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000014573730108780090571446608891154392702028013537496504981039180393054266460239887237548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
74.2207030 |
9.2400976 |
199.1363067 |
16.5975172 |
| ENSG00000204262 |
1290 |
COL5A2 |
protein_coding |
P05997 |
FUNCTION: Type V collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen). It is a minor connective tissue component of nearly ubiquitous distribution. Type V collagen binds to DNA, heparan sulfate, thrombospondin, heparin, and insulin. Type V collagen is a key determinant in the assembly of tissue-specific matrices (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Collagen;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Ehlers-Danlos syndrome;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes an alpha chain for one of the low abundance fibrillar collagens. Fibrillar collagen molecules are trimers that can be composed of one or more types of alpha chains. Type V collagen is found in tissues containing type I collagen and appears to regulate the assembly of heterotypic fibers composed of both type I and type V collagen. This gene product is closely related to type XI collagen and it is possible that the collagen chains of types V and XI constitute a single collagen type with tissue-specific chain combinations. Mutations in this gene are associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, types I and II. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1290; |
collagen type V trimer [GO:0005588]; collagen type XI trimer [GO:0005592]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; eye morphogenesis [GO:0048592]; negative regulation of endodermal cell differentiation [GO:1903225]; ossification [GO:0001503]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; skin development [GO:0043588] |
11940702_Mutations in the COL5A2 gene have been identified by DNA sequence analysis in 10 patients with spontaneous vertebral artery dissections. 14557872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15136578_analysis of processing of the Pro-alpha1(V)Pro-alpha2(V)Pro-alpha3(V) procollagen heterotrimer 16431952_In the eye, COL5A1 and COL5A2 mutations manifest as abnormally thin and steep corneas with floppy eyelids. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19180518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20140262_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20625483_The formation of [alpha1(V)](3) homotrimers was considerably favored over the heterotrimer [alpha1(V)](2)alpha2(V). 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20648054_Physical and laboratory examinations revealed that true haploinsufficiency of COL3A1, COL5A2, and MSTN, but not that of SLC40A1, leads to a clinical phenotype. 20673868_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20847697_role of mutations in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (Review) 22132895_Before but not after developing bronchiolitis obliterans, lung transplantation patients had antibodies to Col-V, alpha2(V). Pep5-8 to alpha1,2(V) and pep9-14 to alpha2(V)were immunodominant. 22208904_This study suggests a fetal association of COL5A2 and a combined fetal-maternal association of COL5A1 with spontaneous preterm delivery. 22696272_study shows that over 90% of patients, which strictly satisfy all major Villefranche criteria for classic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)harbor a type V collagen defect which indicates that this is the major--if not only--cause of classic EDS 23574622_Col5a2 shows predictive potential in myocardial infarction , and in principle may represent a novel candidate marker for the identification and treatment of ischemic cardiovascular disease 23587214_data confirm that COL5A1 and COL5A2 are the major, if not the only, genes involved in classic Ehlers-danlos syndrome 25987251_COL5A2(+/-) humans, although unlikely to present with frank classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, are likely to have fragile connective tissues with increased susceptibility to trauma and certain chronic pathologic conditions. 28485813_Mutations affecting COL5A1 or COL5A2 are responsible for spectrum of mucocutaneous, ocular and facial features in 62 classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients. 29517678_Bladder cancer patients in COL5A2 low expression group were associated with better invasiveness (P |
ENSMUSG00000026042 |
Col5a2 |
16.995861 |
0.3945183160 |
-1.341836 |
0.480303962 |
7.545675 |
0.00601542791760768195269415414827562926802784204483032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012084893979024007026890075167102622799575328826904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.9733459 |
2.7478827 |
20.6570734 |
4.7864595 |
| ENSG00000204287 |
3122 |
HLA-DRA |
protein_coding |
P01903 |
FUNCTION: An alpha chain of antigen-presenting major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII) molecule. In complex with the beta chain HLA-DRB, displays antigenic peptides on professional antigen presenting cells (APCs) for recognition by alpha-beta T cell receptor (TCR) on HLA-DR-restricted CD4-positive T cells. This guides antigen-specific T-helper effector functions, both antibody-mediated immune response and macrophage activation, to ultimately eliminate the infectious agents and transformed cells (PubMed:29884618, PubMed:17334368, PubMed:8145819, PubMed:15322540, PubMed:22327072, PubMed:27591323, PubMed:31495665, PubMed:15265931, PubMed:9075930, PubMed:24190431). Typically presents extracellular peptide antigens of 10 to 30 amino acids that arise from proteolysis of endocytosed antigens in lysosomes (PubMed:8145819). In the tumor microenvironment, presents antigenic peptides that are primarily generated in tumor-resident APCs likely via phagocytosis of apoptotic tumor cells or macropinocytosis of secreted tumor proteins (PubMed:31495665). Presents peptides derived from intracellular proteins that are trapped in autolysosomes after macroautophagy, a mechanism especially relevant for T cell selection in the thymus and central immune tolerance (PubMed:17182262, PubMed:23783831). The selection of the immunodominant epitopes follows two processing modes: 'bind first, cut/trim later' for pathogen-derived antigenic peptides and 'cut first, bind later' for autoantigens/self-peptides (PubMed:25413013). The anchor residue at position 1 of the peptide N-terminus, usually a large hydrophobic residue, is essential for high affinity interaction with MHCII molecules (PubMed:8145819). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15265931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15322540, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182262, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17334368, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22327072, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23783831, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24190431, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25413013, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27591323, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29884618, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31495665, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8145819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9075930}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Isopeptide bond;Lysosome;Membrane;MHC II;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
HLA-DRA is one of the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha and a beta chain, both anchored in the membrane. This molecule is expressed on the surface of various antigen presenting cells such as B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and monocytes/macrophages, and plays a central role in the immune system and response by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins, in particular, pathogen-derived peptides to T cells. The alpha chain is approximately 33-35 kDa and its gene contains 5 exons. Exon 1 encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, and exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and the cytoplasmic tail. DRA does not have polymorphisms in the peptide binding part and acts as the sole alpha chain for DRB1, DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:3122; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; MHC class II protein complex [GO:0042613]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; MHC class II receptor activity [GO:0032395]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; polysaccharide binding [GO:0030247]; T cell receptor binding [GO:0042608]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0002491]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0002504]; cognition [GO:0050890]; immune response [GO:0006955]; myeloid dendritic cell antigen processing and presentation [GO:0002469]; peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex [GO:0002503]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:2000516]; positive regulation of CD4-positive, CD25-positive, alpha-beta regulatory T cell differentiation [GO:0032831]; positive regulation of memory T cell differentiation [GO:0043382]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; regulation of T-helper cell differentiation [GO:0045622] |
11181188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11239948_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11260509_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11294926_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11298540_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11320565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11361223_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11464148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11742191_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11854199_P. gingivalis membrane vesicles apparently inhibited IFN-gamma-induced MHC class II (HLA-DRalpha) by disrupting the IFN-gamma signaling transduction pathway. 12006557_IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DRA expression was inhibited by nitric oxide (NO) and antioxidants such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, and N-acetylcysteine 12073071_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12074713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12117677_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12370403_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12373032_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14736971_The donor TNFRSF6 polymorphism dierctly or indirectly influences acute kidney rejection episodes. 14976194_different regions of the cytoplasmic tails are involved in the association and the recruitment of HLA-DR(A & B1) into different compartments. HLA-DP and -DR interact differently with the cytoskeleton. 15105429_Data show that Oct-1 occupies the endogenous HLA-DRA promoter when the HLA-DRA promoter is inactive in retinoblastoma protein-defective cells. 15301866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15361126_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15467430_Overexpression of HLA-DRA is associated with ovarian and other cancers 15536412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15688398_Downregulation of HLA-DRA is associated with early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma 15836703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17660530_Alleles of IL2RA and IL7RA and those in the HLA locus are identified as heritable risk factors for multiple sclerosis. 17662350_frequency of HLA antigens was significantly increased suggesting that brain cavernoma susceptibility may be associated with HLA antigens 18270567_HLA-DR alpha 2 domain (sHLA-DRalpha2) induces negative signals by engaging TIRC7 on lymphocytes, inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells via activation of the intrinsic pathway 18371160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18846964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18931722_DNMT1 and HLA-DRalpha are prognostic factors for hepatocelluar carcinoma. 18932050_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18939942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19046302_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19047245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19117940_although lysine 219 is absolutely required for modification of DRalpha, other features of the DRalpha tail act to limit the extent of ubiquitination. 19120278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19143821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19188433_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19648278_T cell receptor view of HLA-DRA in pocket 9 shows that the arrangement of residues in this pocket promotes anchoring of either large aliphatic or aromatic amino acids at this position. 19660582_Findings show that Sug1 is crucial for regulating histone H3K4me3 and H3R17me2 at the cytokine inducible MHC-II and CIITA promoters. 19834503_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19834503_Studies indicate that five SNPs showed genome-wide significant association with MS: HLA-DRA, IL7R, IL2RA, CD58 and CLEC16A. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19861958_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20118277_Data show that pollen grains triggered the production of IL-8, TNF-alpha, IL-6 and strongly upregulated the membrane expression of CD80, CD86, CD83, HLA-DR and caused only a slight increase in the expression of CD40. 20202859_Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration is effective in removal of many plasma cytokines and in improvement of monocyte HLA-DR expression in septic patients. 20232575_predictive value of expression in diagnosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20362271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497195_Upregulation of HLA-DRA is associated with acute pancreas allograft rejection. 20546939_The skeletal muscles of myasthenia gravis up regulation of MHC class @@. 20584675_HLA-DR4, PAD4 and STAT4 are overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and may be involved in the pathogenesis of RA. 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20711177_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21072187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21282653_HLA-DR(+) endothelial cells regulate the local inflammatory allogeneic response, promoting either an IL-6/STAT-3-dependent Th17 response or a contact-CD54-dependent regulatory response according to the cytokine environment. 21482477_This study indicated that the association between rs3129882 and parkinson disease remains unclear and requires further study. 21791235_The rs3129882 noncoding variant in intron 1 of HLA-DRA is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson disease in a Chinese Han population. 21804607_small interfering RNA-mediated knock-down of AIM2 resulted in reduced expression of HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB and CIITA in IFN-gamma-treated cells 21898163_Molecular Dynamics simulations of the MuBetaRho 83-99 (Phe91) and MuBetaRho 83-99 (Tyr91) peptide analogues in complex with HLA-DR2 (DRA, DRB1*1501) and T-cell receptors were performed. 22096524_SNP1 is a Parkinson's disease-associated variant in HLA-DRA and is associated with HLA-DRA, DRB5 and DQA2 gene expression. 22243834_In this study observe no association between this single nucleotide polymorphism of HLA-DRA and Parkinson's disease in a Taiwanese population. 22391069_genetic polymorphism is associated with the presence of nasal polyposis in asthmatic patients 22889831_Data indicate that 25 +/- 1.3% of CD74 and 17 +/- 0.3% of HLA-DR are colocalized. 22890421_2 SNPs in the HLA-DRA gene were studied in Caucasian patients from 2 large studies of alcohol dependence. rs2239803 & rs4935356 were associated with AD in both cohorts. 23083294_The SNP rs3129882 in intron 1 of HLA-DRA has been shown to be most robustly associated with the Parkinson's disease. 23579001_The HLA-DRA variation rs3129882 is not associated with Parkinson's disease in Sweden.( 23878500_The expression of human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DR in epithelial cells and cluster of differentiation (CD8)-positive lymphocytes as possible markers of chronic ocular graft versus host disease, was investigated. 24039160_The effects of rs11248051 and rs1564282 variants of GAK, and the rs3129882 variant of HLA-DRA, were investigated in Parkinson's disease patients. 24214983_Data indicate five members of of DPbeta chains containing Lys-69 and GGPM 84-87, which assemble with DRalpha. 24384427_HLA-DOA, HLA-DRA, and HLA-DQA1 associated with spontaneous autoimmunity 24493819_suggest that binding of MAM to HLA-DR leads to a conformational change in MAM structure allowing its interaction with TLR2 and TLR4 and a better recognition by T cells. 24636145_Increased CD14+ monocytes with loss of HLA-DR expression were seen in patients with higher stage disease, more aggressive pathology, and in relapse or refractoriness to treatment. 24849299_This meta-analysis showed that the HLA-DRA rs3129882 A/G polymorphism was not a risk factor for Parkinson's disease in Chinese. 25224099_HLA-DRA variants predict penicillin allergy in genome-wide fine-mapping genotyping 25319953_The results suggest that rs3129882 polymorphism in HLA-DR may be a risk factor for Parkinson's disease in Iranian. 25695487_CD14+HLA-DR(-/low) cells were significantly increased in gastric cancer tissue and were shown to have a critical role in CD4+T-cell immunosuppression. 25720714_No significant association was found for HLA-DRA/PARK18 rs3129882 polymorphism and Parkinson's disease risk (meta-analysis). 25792471_The frequency of CD14(+)HLA-DR-/low MDSCs could be considered as a poor prognostic predictor in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and the elimination of MDSCs during medical interventions may improve the prognosis of SCLC patients. 27144640_In this prospective study we evaluated dynamic changes in monocyte HLA-DR expression during sepsis in relation to changes in HLA-DRA gene expression and Class II transactivator (CIITA), measured by quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR). 27356905_Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA not only downregulated HLA-DRalpha at the protein level through direct binding and degradation through the proteasome pathway but also indirectly downregulated the protein level of HLA-DRalpha by enhancing the expression of MARCH8, a member of the membrane-associated RING-CH (MARCH) proteins. 28131168_Case-control study in Han Chinese from the southwest of the country suggests that risk of ALS is increased by the AA genotype at rs9268856 in the HLA-DRA/HLA-DRB5 gene, but not by the SNPs rs9268877 in HLA-DRA/HLA-DRB5, rs1980493 in BTNL2 or rs302668 in RAB38/CTSC 28229240_This study demonstrated that only the non-suicidal depressed subgroup revealed significantly lower microglial reaction, i.e., a decreased density of HLA-DR positive microglia versus both depressed suicide victims and controls. 28771573_Low HLA-DRA expression is associated with sepsis. 29905830_Identified an intergenic variant between HLADRA and HLA-DRB that is associated with Ulcerative Colitis prognosis, but not with susceptibility, and confirmed its clinical impact on 30-year outcomes. 30962219_We report that risk for type 1 diabetes in HLA-DR3 homozygotes is increased significantly by a previously unreported haplotype of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the first intron of HLA-DRA1. 31082373_Cd64 is up-regulated in neutrophils, but HLA-DR antigens are down-regulated in monocytes in septic shock patients. 31237711_The 3A6-TCR/superagonist/HLA-DR2a complex shows similar interface and reduced flexibility compared to the complex with self-peptide. 31386235_The dynamic changes in HLA-DRA expression in peripheral blood can accurately reflect the immune status of sepsis patients, and the reduction in HLA-DRA may be an important reason for the abnormal T cell differentiation. 31617688_Insights into the polymorphism in HLA-DRA and its evolutionary relationship with HLA haplotypes. 32180339_Coronary artery bypass grafting is associated with immunoparalysis of monocytes and dendritic cells. 32253955_The rs3129882/rs4248166 in HLA-DRA and rs34372695 in SYT11 are not associated with sporadic Parkinson's disease in Central Chinese population. 32306077_Loss of HLA-DR expression is associated with colorectal cancer development. 33022050_Shared Signature of Recent Positive Selection on the TSBP1-BTNL2-HLA-DRA Genes in Five Native Populations from North Borneo. 34311991_Tri-SNP polymorphism in the intron of HLA-DRA1 affects type 1 diabetes susceptibility in the Finnish population. 34402606_Identification of three novel HLA-DRA alleles by next-generation sequencing. 34858413_Combination of HLA-DR on Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Specific Cells and Tuberculosis Antigen/Phytohemagglutinin Ratio for Discriminating Active Tuberculosis From Latent Tuberculosis Infection. 35543859_Expression of NOTCH1, NOTCH4, HLA-DMA and HLA-DRA is synergistically associated with T cell exclusion, immune checkpoint blockade efficacy and recurrence risk in ER-negative breast cancer. 35794593_HLA class II molecule HLA-DRA identifies immuno-hot tumors and predicts the therapeutic response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in NSCLC. 35895219_Genetic polymorphism of HLA-DRA and alcohol consumption affect hepatitis development in the Korean population. |
ENSMUSG00000036322 |
H2-Ea |
11.301030 |
2.5314319474 |
1.339954 |
0.449658448 |
9.123077 |
0.00252405054378496227635020332513704488519579172134399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005476258419265918331308995448125642724335193634033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.8996538 |
4.5243853 |
6.6949317 |
1.4631172 |
| ENSG00000204291 |
1306 |
COL15A1 |
protein_coding |
P39059 |
FUNCTION: Structural protein that stabilizes microvessels and muscle cells, both in heart and in skeletal muscle. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10049780}.; FUNCTION: Restin potently inhibits angiogenesis. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Angiogenesis;Cell adhesion;Collagen;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydroxylation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XV collagen, a member of the FACIT collagen family (fibril-associated collagens with interrupted helices). Type XV collagen has a wide tissue distribution but the strongest expression is localized to basement membrane zones so it may function to adhere basement membranes to underlying connective tissue stroma. The proteolytically produced C-terminal fragment of type XV collagen is restin, a potentially antiangiogenic protein that is closely related to endostatin. Mouse studies have shown that collagen XV deficiency is associated with muscle and microvessel deterioration. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]. |
hsa:1306; |
collagen type XV trimer [GO:0005582]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum lumen [GO:0005788]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength [GO:0030020]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; endothelial cell morphogenesis [GO:0001886]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11937714_type XV and XVIII collagens are expressed in specialized basement membranes. 17355226_Results show that the molecular structure of human tissue type XV presents a unique conformation among the collagens. 18171981_the primary determinant is the gene specifying collagen XV, a proteoglycan closely associated with the basement membrane 18203317_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18203317_Polymorphisms in COL15 (collagen XV) gene are not associated with systemic sclerosis 19365806_Data represent the first evidence of the expression of collagen type XV in human osteoblasts, a calcium-regulated protein which correlates to a specific functional state of these cells. 19834535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20932905_the crystal structure of the trimerization domain of human type XV collagen 22034088_Collagen type XV and osteocalcin expression are highly sensitive markers to extracellular calcium 23621901_These results suggest genetic variation in COL15A1 and COL18A1 can modify the age of onset of both early and late onset POAG. 23912340_COL15A1, provide evidence for concomitant epigenetic regulation and genetic susceptibility, and define a class of causal targets that sit at the intersection of genetic and epigenetic predisposition in the etiology of complex disease. 25134534_we identified an epithelial ovarian cancer susceptibility loci at 9q22.33 (rs1413299 in COL15A1, P(meta) = 1.88 x 10(-8)) 25509878_The obtained results indicate that the changes in gene expression in bone marrow progenitor cells can be involved into space flight-induced osteopenia. 26293333_COL15A1 mRNA was up-regulated in hepatocellular cancer (HCC) and collagen XV was expressed along the sinusoid-like endothelium of HCC but not in non-tumoral regions, which implies that collagen XV contributes to the capillarization of HCC. 26937007_This study demonstrated that novel role for collagen XV in motor axon pathfinding and neuromuscular development. 30537732_This study identified collagen XV as a new low O2 tension sensitive gene, and provided a novel mechanistic evidence that directly HIF-1alpha (hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha) mediates collagen XV expression in response to hypoxia, since it was found specifically in vivo recruited at collagen XV promoter, in hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells. 34404755_TGF-beta2 and collagen play pivotal roles in the spheroid formation and anti-aging of human dermal papilla cells. |
ENSMUSG00000028339 |
Col15a1 |
14.641771 |
0.3125555548 |
-1.677815 |
0.577967497 |
8.002399 |
0.00467154253884078177194716374742711195722222328186035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009605515445737134935799694801517034647986292839050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4675672 |
2.3274989 |
20.0746289 |
4.8657390 |
| ENSG00000204305 |
177 |
AGER |
protein_coding |
Q15109 |
FUNCTION: Mediates interactions of advanced glycosylation end products (AGE). These are nonenzymatically glycosylated proteins which accumulate in vascular tissue in aging and at an accelerated rate in diabetes. Acts as a mediator of both acute and chronic vascular inflammation in conditions such as atherosclerosis and in particular as a complication of diabetes. AGE/RAGE signaling plays an important role in regulating the production/expression of TNF-alpha, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Interaction with S100A12 on endothelium, mononuclear phagocytes, and lymphocytes triggers cellular activation, with generation of key pro-inflammatory mediators. Interaction with S100B after myocardial infarction may play a role in myocyte apoptosis by activating ERK1/2 and p53/TP53 signaling (By similarity). Receptor for amyloid beta peptide. Contributes to the translocation of amyloid-beta peptide (ABPP) across the cell membrane from the extracellular to the intracellular space in cortical neurons. ABPP-initiated RAGE signaling, especially stimulation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), has the capacity to drive a transport system delivering ABPP as a complex with RAGE to the intraneuronal space. Can also bind oligonucleotides. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19906677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20943659, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21559403, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21565706}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Inflammatory response;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The advanced glycosylation end product (AGE) receptor encoded by this gene is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell surface receptors. It is a multiligand receptor, and besides AGE, interacts with other molecules implicated in homeostasis, development, and inflammation, and certain diseases, such as diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Many alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms, as well as non-protein-coding variants, have been described for this gene (PMID:18089847). [provided by RefSeq, May 2011]. |
hsa:177; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; fibrillar center [GO:0001650]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; advanced glycation end-product receptor activity [GO:0050785]; amyloid-beta binding [GO:0001540]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; molecular adaptor activity [GO:0060090]; protein-containing complex binding [GO:0044877]; S100 protein binding [GO:0044548]; scavenger receptor activity [GO:0005044]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007166]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; glucose mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010255]; induction of positive chemotaxis [GO:0050930]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; learning or memory [GO:0007611]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; negative regulation of blood circulation [GO:1903523]; negative regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032693]; negative regulation of long-term synaptic depression [GO:1900453]; negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900272]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; positive regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902961]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of dendritic cell differentiation [GO:2001200]; positive regulation of endothelin production [GO:1904472]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034116]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production [GO:0071639]; positive regulation of monocyte extravasation [GO:2000439]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900745]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; protein localization to membrane [GO:0072657]; regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:2000514]; regulation of DNA binding [GO:0051101]; regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050727]; regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900271]; regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901222]; regulation of p38MAPK cascade [GO:1900744]; regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission [GO:0150003]; regulation of synaptic plasticity [GO:0048167]; regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001914]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to wounding [GO:0009611]; transcytosis [GO:0045056]; transport across blood-brain barrier [GO:0150104] |
11700025_mRNA and protein expression in Caco-2 cells 11739380_this study we have investigated a possible role of RAGE and amphoterin in the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. 11811511_susceptibility to the development of chronic periodontitis could be influenced by the 1704G/T polymorphism of the RAGE gene, independently of diabetes 11884895_Polymorphisms 1704G/T, 2184A/G, and 2245G/A in the rage gene are not associated with diabetic retinopathy in NIDDM 12029499_allele frequencies and genotype distribution combinations of four polymorphisms in the RAGE gene (6p21.3, G82S, 1704G/T, 2184A/G and 2245A/G) of 272 subjects (130 patients with plaque psoriasis and 142 healthy control). 12070776_increased prevalence of the 82S allele in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with control subjects 12477623_There is an association of Gly82Ser polymorphism in this gene with diabetic retinopathy in type II diabetic Asian Indian patients. 12495433_Data show that vascular endothelial cells and pericytes express three novel splice variants of receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) mRNA. 12579287_co-expression of RAGE and amphoterin is closely associated with invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer 12598893_These data reinforce the importance of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)-ligand interactions in modulating properties of CD4+ T cells that infiltrate the central nervous system 12606536_association between -374 T/A RAGE polymorphism and cardiovascular disease and albumin excretion in type 1 diabetics with poor metabolic control suggests gene-environment interaction in development of diabetic nephropathy and cardiovascular complications 12618340_The RAGE is expressed in dying neurons and suggest that RAGE may have a role in neuronal cell death mediated by ischemic stress. 12651613_Advanced glycation end products and receptor for advanced glycation end products are found in AA amyloidosis. 12837757_AGEs can augment inflammatory responses by up-regulating COX-2 via RAGE and multiple signaling pathways, thereby leading to monocyte activation and vascular cell dysfunction 12859967_Results suggest a possible role of S100 protein- and RAGE-mediated signal transduction in the development of specific cancers. 12935895_In vitro binding studies using a series of C-terminal deletion mutants of human RAGE revealed the importance of the membrane-proximal cytoplasmic region of RAGE for the direct ERK-RAGE interaction. 12941744_No association betwween -429T/C and -37T/A polymorphism in RAGE gene promoter with diabetic retinopathy in NIDDM in Chinese patients 14580673_identified three novel RAGE transcripts all encoding truncated soluble forms of RAGE. The relative expression ratios for the full-length RAGE transcript to the sum of its splice-variants encoding the soluble variants varied strongly among tissues. 14595542_Oleate, not ligands of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products, acts as an enhancer of human smooth muscle cell proliferation. 14704946_Our study failed to demonstrate an association between either - 429 T/C or - 374 T/A gene polymorphism of the RAGE gene and diabetic retinopathy in Caucasians with type 2 diabetes 14747204_RAGE G1704T polymorphisms may be useful in identifying the risk for developing diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. 15009731_AGE might be involved in the growth and invasion of melanoma through interactions with RAGE and represent promising candidates for assessing the future therapeutic potential of this therapy in treating patients with melanoma. 15019601_results suggest that the decrease in monocyte RAGE expression can be at least partly accounted for by the ligand engagement and may be a factor contributing to the development of diabetic vascular complications 15033494_AGER mediates S100A13 protein translocation in response to extracellular S100 15052533_Patients with type 2 diabetes and the 63bp deletion in the promoter of RAGE seem to be protected from diabetic nephropathy. 15053925_Only cells expressing RAGE at the cell surface showed hypersensitivity to Abeta. 15127201_Findings using advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs) with strong RAGE-binding properties indicate that AGEs may not uniformly play a role in cellular activation. 15155381_Review. RAGE is an amplification step in vascular inflammation and acceleration of atherosclerosis. 15170618_the RAGE pathway plays a critical proinflammatory role in vasculitic neuropathy. 15180953_Advanced glycation end products (AGE) by binding to AGE receptor (RAGE) per se could control mesangial cell growth. 15203887_Corellation of expression of tissue factor (TF) and the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGEs) and vascular complications in diabetic patients 15213278_RAGE expression is upregulated on monocytes from patients with chronic kidney disease 15239215_RAGE and MMP-9 are expressed concordant with the metastatic ability of the human pancreatic cancer cells. Could be key to regulating metastatic ability of pancreatic cancer. 15247020_AGER has a role as a pleiotropic antagonistic gene (review) 15289604_AGER1 suppressed AGE mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK/p44/p42 activities and suppressed AGE-mediated mesangial cell inflammatory injury through negative regulation of RAGE 15448098_Thiazolidinedione antidiabetics modulate vascular endothelial RAGE expression. 15539404_Down-regulation of RAGE may be considered as a critical step in tissue reorganization and the formation of lung tumours. 15547674_374T/A polymorphism of the RAGE gene may reduce susceptibility to coronary artery disease 15555779_RAGE may have multiple functions in the human brain, mediated by the individual or coordinated efforts of the different RAGE isoforms 15599399_data demonstrate that the RAGE-NF-kappaB axis operates in diabetic neuropathy, by mediating functional sensory deficits, and that its inhibition may provide new therapeutic approaches 15663911_RAGE, via its interaction with ligands, serves as a cofactor exacerbating diabetic vascular disease. (review) 15666359_DU145 cells, a hormone-independent prostate cancer cell line, showed the highest RAGE mRNA expression 15790669_The RAGE2 haplotype is associated with diabetic nephropathy (DN) in type 2 diabetics and with earlier DN onset and can be regarded as a marker for DN. 15798956_data suggest that G1704T and G82S polymorphisms of the advanced glycation end product receptor (RAGE) gene are not related to microalbuminuria in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients 15803111_82 Serine allele of the RAGE gene is a risk allele for developing advanced nephropathy in diabettes mellitus. 15893388_Reactive oxygen species generated by the TNF-alpha-stimulated umbilical vein endothelial cells induce RAGE expression. 15896660_results show that the -374A allele (-374T>A polymorphism) in the RAGE gene is related to the susceptibility of developing ischemic heart disease in African-Brazilians with type 2 diabetes 15911356_Antibodies against RAGE receptor blocked Abeta-induced activation of the p38, JNK pathways, and NF-kappaB in CTL cybrids and offered protection against the neurotoxic effects of Abeta. 15915542_results reveal HMGB1 and RAGE as the first known autocrine loop modulating the maturation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells 15926115_data suggest that activation of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) pathway may be one of the first steps in the pathogenesis of diabetic polyneuropathies 15930093_ACE inhibition reduces the accumulation of AGE in diabetes partly by increasing the production and secretion of sRAGE into plasma 15942078_polymorphisms G1704T and G82S of the RAGE gene are not related to DR in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. 15942086_polymorphisms G1704T and G82S of the RAGE gene are not related to DR in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. 15944249_Advanced glycosylation end-product receptor (RAGE) is required for the effect of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) on dendritic cells; HMGB1/RAGE interaction results in downstream activation of MAP kinases and NF-kappa B. 15986224_data suggests that the CML-RAGE-NF-kappaB pathway is an evident proinflammatory pathomechanism in mononuclear effector cells in polymyositis and dermatomyositis 16037279_RAGE, an endogenous decoy receptor, may be related to individual variations in resistance to the development of diabetic vascular complications, observed in transgenic mice. 16052547_The increase in RAGE noted in osteoarthritis(OA) cartilage and the ability of RAGE ligands to stimulate chondrocyte MAP kinase and NF-kappaB activity and to stimulate MMP-13 production suggests that chondrocyte RAGE signaling could play a role in OA. 16061848_S100P plays a major role in the aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer that is likely mediated by its ability to activate RAGE 16127291_These results suggest that RAGE expression appears to be closely associated with the invasiveness of oral squamous cell carcinoma and represents a promising candidate for assessing the future therapeutic potential in treating patients with oral carcinoma. 16159602_Analysis of specific manifestations of cardiovascular disease, including coronary heart disease (CHD), cardiovascular disease (CVD), myocardial infarction (MI) and ischemic disease (ISD) revealed no association with RAGE genotype. 16166741_Data suggest that re-expression of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products in lung cancer cells impairs the proliferative stimulus mediated by fibroblasts. 16271939_a cross-talk exists between the AGE-RAGE system and the angiotensin II receptor (renin-angiotensin system), and serum levels of sRAGE may reflect endothelial RAGE expression 16286548_Patients with Alzheimer disease have reduced levels of sRAGE in plasma compared with patients with vascular dementia and controls. 16374460_RAGE is mainly expressed in fibroblasts, dendrocytes, and keratinocytes and to a minor extent in endothelial and mononuclear cells. 16440015_study found a modest association with the -RAGE 374T/A polymorphism in the nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy subgroup 16493495_The existence of splice variants of RAGE in endothelial cells might explain the lack of interaction of extracellular AGEs with endothelial cells. 16644647_Association of level in serum with albuminuria may be a marker of microvascular damage in type 2 diabetes. 16728681_3 AGER genetic variants: -429T>C, -374T>A, and Gly82Ser were determined in cerebral ischemia and stroke patients. Specific haplotypes were associated with reduced risk of incident myocardial infarction & ischemic stroke, independent of diabetes status. 16728681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847147_CRP at concentrations known to predict future vascular events upregulates RAGE expression in human endothelial cells at both the protein and mRNA level. Silencing of the RAGE gene prevents CRP-induced macrophage chemoattractant protein 1 activation. 16899960_adhesion of red blood cells from type 2 diabetes patients was mediated by RAGE 16954185_AGER1 negatively regulates AGE-mediated oxidant stress-dependent signaling via the EGFR and Shc/Grb2/Ras pathway. 16954682_observation suggests that the RAGE gene polymorphism is not associated with in-stent restenosis after coronary artery stenting in non-diabetic patients in the Korean population 16969646_results show an association between the AGER -374 T/A polymorphism & type 1 diabetes; the polymorphism was associated with diabetic nephropathy in both type 1 & type 2 diabetes & with sight-threatening retinopathy in type 1 diabetic patients 16969649_Serum levels are associated with the severity of nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. 17004092_Telmisartan: it may work as an anti-inflammatory agent against AGE by suppressing RAGE expression via PPAR-gamma activation in the liver. 17024691_Serum levels are significantly higher in type 2 diabetic patients than in non-diabetics and are positively associated with the presence of coronary artery disease. 17035340_data suggest that the autocrine/paracrine release of HMGB1 and the integrity of the HMGB1/RAGE pathway are required for the migratory function of dendritic cells 17158877_Soluble RAGE forms tetramers that bind to hexamers of Ca2+-calgranulin C, creating a large platform for effectively transmitting RAGE-dependent signals from extracellular S100 proteins to the cytoplasmic signaling complexes. 17170388_association of RAGE and its ligands with sarcoidosis and suggest that an intrinsic genetic factor could be in part involved in its expression. In Italian patients, the -374 T/A polymorphism seems to be significantly associated with this disease. 17172923_The results of this large population study demonstrate that the AA/GA genotypes of the RAGE +557G>A polymorphism are associated with a significantly decreased risk of significant coronary artery disease. 17218539_study demonstrates that HOCl-modified albumin acts as a ligand for RAGE and promotes RAGE-mediated inflammatory complications 17224333_subjects with homozygosity for the minor S allele of the G82S polymorphism of RAGE had higher risk factors for cardiovascular disease 17237617_We demonstrated that after successful TX, PAPP-A and sRAGE decrease and early chronic vascular changes in the kidney TX are associated with elevation of their serum levels. 17343760_Soluble but not sescretory protein is associated with albuminuria in type 2 diabetic paaatients, whil neither is associated with markers of glucose control or macrovascular disease. 17345061_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17355942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17405935_evidence provided for activation of the NF-kappaB system in intervertebral discs in vivo which correlates with accumulated oxidative stress & increases in age & disc degeneration; oxidative stress may lead to RAGE activation & NF-kappaB translocation 17425804_the RAGE Ser82 allele does not predispose to cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis. 17434489_Accumulation of AGE may have a role in the development of osteoarthritis. 17497647_Expression of Endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation endproducts was significantly higher in chondrosarcomas 17508727_High level bacterial expression systems and purification protocols were generated for the extracellular region of RAGE (sRAGE) and the five permutations of single and tandem domain constructs. 17512509_The -429 T>C polymorphism in the RAGE promoter is associated with type 1 diabetes in a Brazilian population, with a 2-fold increase of C-allele frequency compared to non-diabetic subjects 17536039_Data show that soluble RAGE blocks scavenger receptor CD36-mediated uptake of hypochlorite-modified low-density lipoprotein. 17549666_it is concluded that CDK5RAP3, CCNB2, and RAGE genes may be used as a very reliable biomarkers of lung adenocarcinoma 17560613_Olmesartan may play a protective role against proliferative diabetic retinopathy by attenuating the deleterious effects of AGEs via down-regulation of RAGE. 17588956_RAGE was found throughout the testis, caput epididymis, particularly the principle cells apical region, and on sperm acrosomes in men with diabetes mellitus. 17592553_Serum levels of sRAGE are associated with inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes. 17593216_Multivariate analysis showed high-grade expression of RAGE to be an independent prognostic factor for disease-free survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17613396_Higher levels of plasma RAGE measured shortly after reperfusion predicted poor short-term outcomes from lung transplantation. Elevated plasma RAGE levels may have both pathogenetic and prognostic value in patients after lung transplantation. 17639302_Treating type 2 diabetic patients with thiazolidinedione can increase circulating levels of RAGE. 17640970_Data suggest that deregulation of RAGE expression in myoblasts might concur in rhabdomyosarcomagenesis and that increasing RAGE expression in rhabdomyosarcoma cells might reduce their tumor potential. 17660747_Structural and the binding data suggest that tetrameric S100B triggers RAGE activation by receptor dimerisation. 17661837_The receptor of advanced glycation end product (RAGE) -374 T/A single nucleotide polymorphism affected the dialysate-to-plasma ratio of creatinine at baseline, suggesting that the RAGE polymorphism may effect the basal peritoneal solute transport rate. 17700210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17714874_De-N-glycosylation or G82S mutation of RAGE increases affinity for AGE ligands, and may sensitize cells or conditions with it to AGE. 17924846_result confirms that the -374AA genotype of the RAGE gene promoter is a protective factor against the severity of coronary artery disease lesions in type 2 diabetic patients 18032526_Suggest key mechanisma by which AGER1 maintains cellular resistance against AGE-induced oxidative stress. 18046662_Plasma soluble RAGE and endogenous secretory RAGE are not associated with measures of diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes patients. 18050248_Calculating the S100A12:sRAGE ratio might help to detect patients with KD who are at risk of being unresponsive to IVIG therapy. 18058469_serum sRAGE levels were influenced by genetic polymorphisms (-429 T/C, Gly82Ser and 2184 A/G) of the RAGE gene in breast cancer. 18078623_HMGB-1 and BSA-AGE stimulated the invasiveness of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by activation of RAGE. 18079485_Single nucleotide polymorphisms may contribute to development of glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes. 18079965_endothelial RAGE and its ligands mediate vascular and inflammatory stresses that culminate in atherosclerosis in the vulnerable vessel wall 18080716_HCC during the early stage of tumorigenesis with less blood supply may acquire resistance to stringent hypoxic milieu by hypoxia-induced RAGE expression. 18089847_RAGE_v1 variant is the primary secreted soluble isoform of RAGE. identification of functional splice variants of RAGE underscores biological diversity of the RAGE gene & will aid in understanding of the gene in the normal & pathological state. 18179750_the -374AA genotype of the RAGE gene promoter could be associated with a reduced risk of in-stent restenosis after coronary stent implantation 18231794_This preliminary study supports the hypothesis that the RAGE system might participate in the disease pathway of primary Sjogren's syndrome (SS), and that sRAGE may be a potential biomarker to aid in the diagnosis of primary SS. 18245812_Loss of RAGE contributes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis. 18256374_Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease may be partly mediated by advanced glycation end product-induced inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through RAGE activation. 18279703_RAGE could also behave as a receptor for Mycobacterium tuberculosis 18279705_-374T/A RAGE polymorphism is an independent protective factor for cardiac events in nondiabetic patients with coronary artery disease 18302220_study identified advanced glycation end products as the ligand for RAGE on both invasive and non-invasive prostate cancer cells 18322992_The SAA-RAGE-stimulated NF-kappaB signaling pathway has an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. 18339893_S100A8/A9-promoted cell growth occurs through RAGE signaling and activation of NF-kappaB. 18355449_These findings reveal new aspects of RAGE regulation and signaling and also provide a new interaction between RAGE and human pathologies. 18421017_results indicate that RAGE serves a protective role in the lung, and that loss of the receptor is related to functional changes of pulmonary cell types, with the consequences of fibrotic disease 18427074_results show significant downregulation of the total RAGE mRNA transcripts in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with probable Alzheimer disease 18431028_low expression of endogenous secretory RAGE in the hippocampus would be associated with the development of Alzheimer's disease 18438937_shedding of RAGE might occur as reactive oxygen species accumulate in brain cells and be part of the process of neurodegeneration 18458846_AGEs induce ROS generation and intensify the proliferation and activation of HSCs, supporting the possibility that antioxidants may represent a promising treatment for prevention of the development of hepatic fibrosis in NASH. 18477569_the peritoneal membrane of the uraemic patients showed an increased submesothelial thickness and a marked induction of RAGE expression and NFkappaB-binding activity 18480271_Distinct regions of RAGE are involved in Abeta-induced cellular and neuronal toxicity with respect to the Abeta aggregation state, suggesing the blockage of particular sites of the receptor as a therapeutic strategy to attenuate neuronal death. 18519797_RAGE Gly82Ser polymorphism may confer not only an increased risk of gastric cancer but also with invasion of gastric cancer in the Chinese population. 18550199_Serum AGER levels are associated with the severity of renal dysfunction and duration of diabetes in type 2 diabetic patients/ 18575614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18575614_association between diabetic complications and LTA, TNF and AGER polymorphisms is complex, with partly different alleles conferring susceptibility in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients 18576917_Advanced oxidation protein products might be new ligands of endothelial RAGE. AOPPs-HSA activates vascular ECs via RAGE-mediated signals. 18595673_Circulating soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products is inversely associated with body mass index and waist/hip ratio in the general population. 18603587_The sheddase ADAM10 was identified as a membrane protease responsible for RAGE cleavage. 18606705_study defines RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation end products) as the hS100A7 receptor, whereas hS100A15 functions through a Gi protein-coupled receptor; hS100A7-RAGE binding, signaling, and chemotaxis are zinc-dependent in vitro 18615900_GFR is a principal determinant of sRAGE concentration and gradual sRAGE increase in subjects with advancing impairment of renal function is paralleled by AGE and its receptor 18615900_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18645306_Mediation of RAGE affects the balance of cellular proliferation and apoptosis 18657529_RAGE levels increase in conjunction with the onset of Alzheimer's disease, and continue to increase linearly as a function of pathologic severity 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18667420_Structural basis for pattern recognition by the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE). 18689872_RAGE, carboxylated glycans and S100A8/A9 play essential roles in tumor-stromal interactions, leading to inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis. 18698218_maternal esRAGE concentrations are significantly increased in patients with preeclampsia during pregnancy 18701333_association of low soluble isoform of RAGE (sRAGE) with high CML-protein levels in diabetic patients who developed severe diabetic complications supports the hypothesis that sRAGE protects vessels AGE-mediated diabetic microvascular damage 18775683_RAGE was markedly and diffusely expressed in blood vessels, neurons, and the choroid plexus in the brains of two patients who died as the result of brain edema that developed during the treatment of severe diabetic ketoacidosis 18777492_likely that circulating soluble RAGE and endogenous secretory RAGE are distinct markers and that circulating esRAGE levels are associated with the status of early-stage atherosclerosis. 18789567_Advanced glycation end products (AGE) and circulating receptor for AGE (RAGE) levels are independently associated with decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and seem to predict decreased GFR. 18796298_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18796298_We found no consistent association between prevalent type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin indices and AGER polymorphisms 18825489_elevated serum HMGB-1 and sRAGE levels are associated with the disease severity and immunological abnormalities in systemic sclerosis. 18854308_HNRNP K and microRNA-16 have roles in cyclooxygenase-2 RNA stability induced by S100b, a ligand of the receptor for advanced glycation end products 18922799_the interaction of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain with Dia-1 is required to transduce extracellular environmental cues evoked by binding of RAGE ligands to their cell surface receptor, resulting in Rac-1 and Cdc42 activation and cellular migration 18926539_Serum endogenous secretory RAGE level is an independent risk factor for the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in type 1 diabetes. 18948101_RAGE signaling contributes to neuroinflammation in infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 18952609_ADAM10 and MMP9 to be involved in RAGE shedding. 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18987644_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19005067_Thus, HMGB1-RAGE signaling links necrosis with macrophage activation and may provide a target for anti-inflammatory therapy in stroke. 19023628_Negative RAGE expression correlates with deeper tumor invasion and venous invasion in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19032093_new insight into AGE-RAGE interaction 19061941_A set of tumours, healthy tissues and various cancer cell lines were screened for RAGE splicing variants and analysed their structure. 19071026_These results indicate that RAGE signaling directly contributes to pathology in cerebral ischemia. 19087540_The increased expression of HMGB1 and RAGE in the placenta may play an important role in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. 19088375_Increased soluble RAGE is localized in ectopic endometrial cells of both adenomyosis and ovarian endometriomas; RAGE may contribute to the pathogenesis of endometriosis. 19103440_Our results provide support for a reduction of S100B levels during reconvalescence from acute paranoid schizophrenia that is regulated by its scavenger RAGE 19129693_Angiotensin II induced RAGE mRNA and protein expression through AT2 receptors. 19133252_No association of RAGE selected gene polymorphisms with 12-months outcome of renal transplants was shown in study. 19143681_several differences in the levels of advanced glycation end products, sRAGE, and proinflammatory cytokines between euglycemic and diabetic pregnancies 19143821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19167759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19183936_sRAGE is associated with greater prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes, which may be explained by endothelial and renal dysfunction. 19201044_treatment of THP-1 cells with 100 microg of CRP/ml/10(6) cells for 24 h, augmented the expression of RAGE and EN-RAGE genes 19204726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19217461_No significant correlation between serum levels off RAGE in hypertensive agents. 19217891_Plasma levels of sRAGE are significantly reduced in definite and borderline nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 19248116_IL-7 stimulates chondrocyte secretion of S100A4 via activation of JAK/STAT signaling, and then S100A4 acts in an autocrine manner to stimulate MMP-13 production via RAGE. 19252206_Elevated serum advanced glycation end products and their circulating receptors are associated with anaemia in older community-dwelling women. 19275767_a novel biological and genetic marker for vascular disease (Review) 19277685_The up-regulation of RAGE in the Alzheimer Disease optic nerves indicates that RAGE may play a role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer Disease optic neuropathy. 19284577_RAGE activity influences co-development of joint and vascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 19285601_G allele at RAGEG82S may be more associated with inflammatory markers under obese status than nonobese conditions. 19332646_the role of recombinant human RAGE in Abeta production was examined in the brain tissue of an AD animal model as well as in cultured cells 19376511_results suggest a possibility that RAGE-VEGF regulation may be related to reproductive dysfunction in aging women 19380603_AGE-2 and AGE-3 activate monocytes via the receptor for AGE (RAGE), leading to the up-regulation of adhesion molecule expression and cytokine production. 19380826_Amyloid beta protein-induced CC-type chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) up-regulation in human brain microvascular endothelial cells depends on RAGE. 19405075_Stimulation with advanced glycation end products up-regulated endothelial RAGE expression in saphenous vein endothelial cells cultured from diabetic patients. 19439163_This study demonstrated an association of decreased serum endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (esRAGE) level with coronary plaque progression in patients with diabetes. 19440065_Plasma levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products are associated with endothelial function and predict cardiovascular events in nondiabetic patients. 19448391_High circulating AGEs and RAGE predict cardiovascular disease mortality among older community-dwelling women 19451748_The plasma concentration of sRAGE was highest in patients with sepsis (2,210 +/- 252 pg/ml), while the levels of sRAGE correlated inversely with that of HMGB1 in patients with acute pancreatitis. 19501570_Proteolysis with thrombin or factor Xa revealed several protease sensitive sites in RAGE. 19530996_expression detected in synovial tissue and on the immune cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients; genetic polymorphism is associated with disease 19542745_G82S polymorphism in the RAGE gene is associated with diabetic retinopathy and G-A haplotype containing 1704G and 82S allele might be a genetic marker of diabetic retinopathy in Chinese T2DM patients. 19571577_Advanced glycation end products induce calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells through RAGE/p38 MAPK. 19576587_Report increased expression of RAGE and EN-RAGE in non-diabetic pre-mature coronary artery disease. 19578796_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19587357_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19591173_Extracellular domain of RAGE down-regulates RAGE expression and inhibits p65 and p52 activation in human-salivary gland-cell-lines. 19616266_advanced glycosylation end-product receptor may capture and eliminate circulating serum high mobility group box 1 in humans 19635564_Blockade of the renin angiotensin system by irbesartan may play a protective role against tubular injury in diabetes by attenuating the deleterious effects of AGEs via down-regulation of RAGE. 19659809_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19672558_Studies indicate that RAGE is subject to ectodomain shedding by ADAM10 and MMP9 and the derived sRAGE can sequester Abeta for systemic clearance and antagonize Abeta binding to cell surface RAGE. 19679874_may be important mediator of cellular injury in fetuses delivered in the setting of inflammation-induced preterm birth 19766904_G82S and -429 T/C polymorphisms of RAGE were associated with the circulating levels of esRAGE but not with coronary artery disease in Chinese patients with Diabetes Melitus, Type 2. 19786934_Data demonstrate that sRAGE level, but not HMGB1 level, is significantly higher in AP patients who develop organ failure than in AP patients without organ failure who recover. 19815443_findings show receptor engagement by distinct advanced glycation end-products differentially enhances expression of RAGE isoforms and adhesion of red blood cells from diabetic patients 19820033_Reduction of advenced glycation end products in normal diets may lower oxidant stress/inflammation and restore levels of AGER an antioxidant, in healthy and aging subjects. 19822091_Molecular study of receptor for advanced glycation endproduct gene promoter and identification of specific HLA haplotypes possibly involved in chronic fatigue syndrome. 19834494_Our data suggest that targeted inhibition of RAGE or its ligands may serve as novel targets to enhance current cancer therapies. 19851445_Observational study of gene-di |
ENSMUSG00000015452 |
Ager |
55.004768 |
0.4951470244 |
-1.014071 |
0.400162225 |
6.314042 |
0.01197854593000630997468025640273481258191168308258056640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022609122497045157362816070190092432312667369842529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.0756585 |
11.1112723 |
77.1117102 |
15.9822085 |
| ENSG00000204305_ENSG00000204304 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
197.250480 |
0.1180840264 |
-3.082114 |
0.438387561 |
40.362402 |
0.00000000021096206273945655985211057171748371893982287872404413064941763877868652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001066369878778896946922267383029130777272186492155015002936124801635742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.8136532 |
13.5036938 |
407.9577728 |
78.3754826 |
| ENSG00000204379 |
653220 |
XAGE1A |
protein_coding |
Q9HD64 |
|
Alternative splicing;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the XAGE subfamily, which belongs to the GAGE family. The GAGE genes are expressed in a variety of tumors and in some fetal and reproductive tissues. This gene is strongly expressed in Ewing's sarcoma, alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma and normal testis. The protein encoded by this gene contains a nuclear localization signal and shares a sequence similarity with other GAGE/PAGE proteins. Because of the expression pattern and the sequence similarity, this protein also belongs to a family of CT (cancer-testis) antigens. Alternative splicing of this gene, in addition to alternative transcription start sites, results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]. |
hsa:653067;hsa:653220; |
|
17332921_Recognition of XAGE-1b on OU-LU-6 tumor by the CD4-expressing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes was studied. 17704638_A 12-mer peptide XAGE-1b(37-48) as a new XAGE-1b epitope restricted to HLA-DRB1*0410 was identified. 18752338_The findings suggest that XAGE-1b and HLA class I expression elicited a CD8+ T-cell response against minimal residual disease after surgery and resulted in prolonged survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. 20178013_the XAGE-1b gene was expressed at the mRNA level in a proportion of human acute leukemia 23625514_Our results suggest that GAGE, XAGE1 and SSX4 might each have a role in melanoma progression 24008415_XAGE-1b gene was able to influence angiogenesis directly or indirectly, leading to tumorigenesis and metastasis of ACC. 24304136_Data indicate the involvement of immunoglobulin allotypes immunoglobulin gamma and kappa chains in immunity to a cancer-testis antigen, which has important implications for XAGE-1b-based immunotherapeutic interventions in lung adenocarcinoma. 26937656_Strong immune responses to the cancer testis antigen XAGE-1b have been found in non-small cell lung cancer Caucasian patients. 28631709_In patients with Colon cancer, the expression of XAGE-1 gene was related to a favorable prognosis. 29577858_High XAGE1 expression is associated with metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 34600138_Measurable Residual Disease Monitoring of SPAG6, ST18, PRAME, and XAGE1A Expression in Peripheral Blood May Detect Imminent Relapse in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia. |
|
|
241.389011 |
8.3564229302 |
3.062886 |
0.226133265 |
170.690455 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000522836584108452692187511367644204466702493021435404767926567663405925951073408038881286924745727296044706111644018164952285587787628173828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000085365796254875680837553654791937916316357075136249526122681657059670307685325120613767808027696169792530866970992065034806728363037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
363.1950873 |
62.5286545 |
43.6871027 |
5.7974740 |
| ENSG00000204394 |
7407 |
VARS1 |
protein_coding |
P26640 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the attachment of valine to tRNA(Val). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8428657}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Epilepsy;Intellectual disability;Ligase;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome |
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases catalyze the aminoacylation of tRNA by their cognate amino acid. Because of their central role in linking amino acids with nucleotide triplets contained in tRNAs, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are thought to be among the first proteins that appeared in evolution. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to class-I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase family and is located in the class III region of the major histocompatibility complex. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:7407; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; aminoacyl-tRNA editing activity [GO:0002161]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; valine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004832]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418]; valyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006438] |
16229838_The first three-dimensional structure of the the valyl-tRNA synthetase/elongation factor-1H complex as calculated from electron microscopic images of negatively stained samples of the human ValRS/EF-1H complex was obtained. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 29691655_Our study describes the phenotype associated with recessive VARS mutations and further functional delineation of the pathogenicity of novel variants identified, which widens the clinical and genetic spectrum of patients with progressive microcephaly 30755602_Variants map to the VARS tRNA binding domain and adjacent to the anticodon domain, and disrupt highly conserved residues. Patient primary cells show intact VARS protein but reduced enzymatic activity, suggesting partial loss of function. The implication of VARS in pediatric neurodegeneration broadens the spectrum of human diseases due to mutations in tRNA synthetase genes. 34382495_Effects of PPM1K rs1440581 and rs7678928 on serum branched-chain amino acid levels and risk of cardiovascular disease. |
ENSMUSG00000007029 |
Vars |
1213.397109 |
2.7023357375 |
1.434207 |
0.102089104 |
191.425746 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000015528423071354308312099297344972594176251512881454186503065663830301021703385913667245887831274036291788682214581873708425518998410552740097045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000002819182343581668016089828385403144867974222379787733721316575487516745216041490469364506131064197015095867818526564896330910414690151810646057128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1745.9280652 |
110.6293759 |
651.2113488 |
30.8186794 |
| ENSG00000204482 |
7940 |
LST1 |
protein_coding |
O00453 |
FUNCTION: Possible role in modulating immune responses. Induces morphological changes including production of filopodia and microspikes when overexpressed in a variety of cell types and may be involved in dendritic cell maturation. Isoform 1 and isoform 2 have an inhibitory effect on lymphocyte proliferation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10706707, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11478849}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell shape;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane protein that can inhibit the proliferation of lymphocytes. Expression of this gene is enhanced by lipopolysaccharide, interferon-gamma, and bacteria. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2011]. |
hsa:7940; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell morphogenesis [GO:0000902]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; immune response [GO:0006955]; negative regulation of lymphocyte proliferation [GO:0050672]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
11828009_Human dendritic cells activate resting natural killer (NK) cells and are recognized via the NKp30 receptor by activated NK cells. 12646700_Expression of this receptor, inhibited by TGF-beta1, affects NK-mediated killing of dendritic cells 16362817_The expression of LST1, specifically splice variants encoding soluble isoforms and NCR3, was increased in rheumatoid-arthritis-affected blood and synovium and was associated with more severe inflammation in the synovium. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19242354_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19663701_LST1 protein expression in human cell lines was found to be tightly regulated, allowing the expression of transmembrane isoforms but suppressing soluble isoforms 19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20173083_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20663564_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20668555_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20668555_Study found association between extended LTA, TNF, LST1 and HLA gene haplotypes and rubella vaccine-induced immunity. 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20854863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22589543_LST1 is expressed specifically in leukocytes of the myeloid lineage, where it localizes to the tetraspanin-enriched microdomains andit binds SHP-1 and SHP-2 phosphatases. 23239025_induces the formation of functional nanotubes 24682411_This is the first report demonstrating regulated LST1 expression in human intestinal epithelial and microvascular endothelial cells and in inflamed colonic tissue from IBD patients. 24803336_Psoriasis was associated with promoter variant, rs9267502 of LST1.Promoter activity was examined and it was larger than that of the other genetic variants, most probably due to changes in binding affinity to transcription factors. 24816991_Data indicate that the MHC class III gene LST1 5' untranslated regions (5'-UTR) contains several upstream open reading frames (uORFs). 27384923_Increased expression of LST1 in GC-responders before therapy warrants further investigation into their role as potential predictors for the response to GC, and in the inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis. 30055863_the present review describes LST1 promotor, gene organization, splice variants and expression in human tissues, cell lines and cancer with the focus on LST1 expression in inflammation, autoimmune diseases and cancer |
ENSMUSG00000073412 |
Lst1 |
429.257406 |
3.3093064148 |
1.726529 |
0.182896029 |
85.444186 |
0.00000000000000000002383348220451126859625664578967866461774222521043034296291465712336332671839045360684394836425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000213589676586876923667688520207915161051021599411128902134410223467853029433172196149826049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
655.9382045 |
79.5543004 |
199.6502810 |
17.9954479 |
| ENSG00000204577_ENSG00000131042 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.355610 |
2.5419283823 |
1.345923 |
0.386571412 |
12.412398 |
0.00042649278792291142733614228710337101801997050642967224121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001061736135898494253967938583116392692318186163902282714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.3722419 |
5.4186472 |
8.9074575 |
1.7281995 |
| ENSG00000204584 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.347773 |
0.3565693699 |
-1.487745 |
0.673453392 |
4.791556 |
0.02859957611331457108527764887639932567253708839416503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.049452875284972240554903777365325368009507656097412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5683118 |
2.0699439 |
13.0245133 |
3.8414958 |
| ENSG00000204634 |
11138 |
TBC1D8 |
protein_coding |
O95759 |
FUNCTION: May act as a GTPase-activating protein for Rab family protein(s). |
Alternative splicing;GTPase activation;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity. Predicted to be involved in activation of GTPase activity and intracellular protein transport. Predicted to be located in membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:11138; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630]; blood circulation [GO:0008015]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284] |
17686842_isolated a TBC Rab-GAP cellular binding partner interacting with the N terminus of HCV NS5A; depleting the expression of this partner severely impairs HCV RNA replication with no obvious effect on cell viability 20548944_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 30809301_TBC1D8 drives ovarian cancer tumorigenesis and metabolic reprogramming and serves as an independent prognosis factor for ovarian cancer patients |
ENSMUSG00000003134 |
Tbc1d8 |
299.552237 |
0.4163045454 |
-1.264289 |
0.128816311 |
95.171755 |
0.00000000000000000000017456326263064424894642047182077818462483215511779061218452396321565434078593170852400362491607666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001690652071147184463113025533599580088443201182287009491753311529738112994891707785427570343017578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
168.8061935 |
14.5893437 |
408.6045128 |
24.3643018 |
| ENSG00000204681 |
2550 |
GABBR1 |
protein_coding |
Q9UBS5 |
FUNCTION: Component of a heterodimeric G-protein coupled receptor for GABA, formed by GABBR1 and GABBR2 (PubMed:9872316, PubMed:9872744, PubMed:15617512, PubMed:18165688, PubMed:22660477, PubMed:24305054). Within the heterodimeric GABA receptor, only GABBR1 seems to bind agonists, while GABBR2 mediates coupling to G proteins (PubMed:18165688). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase (PubMed:10906333, PubMed:10773016, PubMed:10075644, PubMed:9872744, PubMed:24305054). Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase, stimulates phospholipase A2, activates potassium channels, inactivates voltage-dependent calcium-channels and modulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis (PubMed:10075644). Calcium is required for high affinity binding to GABA (By similarity). Plays a critical role in the fine-tuning of inhibitory synaptic transmission (PubMed:9844003). Pre-synaptic GABA receptor inhibits neurotransmitter release by down-regulating high-voltage activated calcium channels, whereas postsynaptic GABA receptor decreases neuronal excitability by activating a prominent inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) conductance that underlies the late inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (PubMed:9844003, PubMed:9872316, PubMed:10075644, PubMed:9872744, PubMed:22660477). Not only implicated in synaptic inhibition but also in hippocampal long-term potentiation, slow wave sleep, muscle relaxation and antinociception (Probable). Activated by (-)-baclofen, cgp27492 and blocked by phaclofen (PubMed:9844003, PubMed:9872316, PubMed:24305054). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9Z0U4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10075644, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10773016, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10906333, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15617512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18165688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22660477, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24305054, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9844003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9872316, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9872744, ECO:0000305}.; FUNCTION: Isoform 1E may regulate the formation of functional GABBR1/GABBR2 heterodimers by competing for GABBR2 binding. This could explain the observation that certain small molecule ligands exhibit differential affinity for central versus peripheral sites. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Sushi;Synapse;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a receptor for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. This receptor functions as a heterodimer with GABA(B) receptor 2. Defects in this gene may underlie brain disorders such as schizophrenia and epilepsy. Alternative splicing generates multiple transcript variants, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:2550; |
axolemma [GO:0030673]; dendritic shaft [GO:0043198]; dendritic spine [GO:0043197]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; G protein-coupled GABA receptor complex [GO:1902712]; G protein-coupled receptor heterodimeric complex [GO:0038039]; GABA-ergic synapse [GO:0098982]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial membrane [GO:0031966]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; presynaptic membrane [GO:0042734]; Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse [GO:0098685]; synaptic vesicle [GO:0008021]; extracellular matrix protein binding [GO:1990430]; G protein-coupled GABA receptor activity [GO:0004965]; G protein-coupled neurotransmitter receptor activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential [GO:0099579]; G protein-coupled neurotransmitter receptor activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential [GO:0150047]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathway [GO:0007214]; negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity [GO:0007194]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of dopamine secretion [GO:0033602]; negative regulation of epinephrine secretion [GO:0032811]; negative regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion [GO:0014053]; negative regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050805]; neuron-glial cell signaling [GO:0150099]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of glutamate secretion [GO:0014049]; positive regulation of growth hormone secretion [GO:0060124]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to nicotine [GO:0035094]; synaptic transmission, GABAergic [GO:0051932] |
11140838_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11844143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12115687_Alterations in inhibitory synaptic transmission through GABA(B)R1 appears to affect differentially certain hippocampal circuits in a population of epileptic patients and could contribute to the pathophysiology of temporal lobe epilepsy. 12130687_The intracellular loops of the GB2 subunit are crucial for G-protein coupling of the heteromeric gamma-aminobutyrate B receptor. 12555235_evidence that the translated polymorphism of exon 7 may be functionally meaningful and impact cortical EEG oscillations 12601092_The GABA(B[1]) polymorphism (G1465A) confers a highly increased susceptibility to temporal lobe epilepsy. Moreover, it seems to influence the severity of this common epileptic disorder 12645817_Post hoc analyses showed an association between EEG phenotype and exon 7 genotype in normal subjects only. 12770685_GABBR1 gene might not be a susceptibility gene for childhood absence epilepsy at least in the Chinese population 12770685_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12923192_GHB, administered in vivo, reduces MAP kinase phosphorylation via a direct activation of GABAB receptors by GHB, but was found ineffective on MAP kinase phosphorylation in brain slices 14625043_Increased expression of GABA(B) receptor subtype 1 indicates augmented presynaptic inhibition of glutamate release as a possible protective mechanism in temporal lobe epilepsy. 14643764_Altered GABA(B1a) receptor mRNA expression occurs in human temporal lobe epilepsy; possibly the observed changes may also serve to counteract ongoing hyperexcitability. 14707142_GABAB receptor cell surface stability is modulated by phosphorylation and chronic agonist treatment 14961561_GABA(B) receptor subunit GABA(B)R1 is found on the same neurons and follows the same distribution patterns in the basal ganglia as the GABABR2 receptor subunit. 14966130_Association of the GABA(B)R1 with the GABA(A) receptor gamma2S subunit robustly promotes cell surface expression of GABA(B)R1 in the absence of GABA(B)R2, that is usually required for efficient trafficking of GABA(B)R1 to the cell surface. 14978362_The GABA(B) receptor may be present as a heterodimer with subunits of GABA(B1) and GABA(B2) in the human colon. 15304491_Data show that the two CCP modules of the GABA(B) 1a receptor have strikingly different structural properties, reflecting their different functions. 15309313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15474078_The simultaneous blockade of GABAA and GABAB receptors suppressed acrosome reaction induced by follicular fluid(FF). GABA receptors may play role in sperm activation. This may shed further light on mechanism of FF action on human sperm acrosome reaction. 15482257_identification of the minimal functional domain which still binds a competitive radioligand and leads to a functional, GABA-responding receptor when co-expressed with GABA(B2) 15685626_The observed trends suggest that further investigations of the role of the GABBR1 gene in obsessive-compulsive disorder are warranted. 15759131_The changes in hippocampal GBR1 may reflect alterations in the balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitter systems, which likely contributes to dysfunction of hippocampal circuitry in Alzheimer disease. 15799783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15799783_Temporal lobe epilepsy preceded by febrile seizures is not associated with the polymorphisms or mutations in the GABBR1 gene. 15820424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15857448_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15863499_positive allosteric modulators bind a single subunit of (B) receptor (metabotropic glutamate receptor) dimers 15946333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16176975_COPI and 14-3-3 specifically bind to the GB1 RSR sequence and that COPI is involved in its intracellular retention 16499773_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16829628_Functional GABA(B) receptors are expressed in human airway smooth muscle cells 17264536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17264536_the Ala20Val polymorphism of the GABA(B)R1 gene may be associated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome(OSAS);Gly489Ser polymorphism does not seem to be involved in OSAS; C/C variant of the Phe658Phe polymorphism GABA(B)R1 gene seems associated with OSAS 17412563_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17591780_CaRs and GABA-B-R subunits can form heteromeric complexes in cells, and their interactions affect cell surface expression and signaling of CaR, which may contribute to extracellular Ca(2+)-dependent receptor activation in target tissues 17971048_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18098271_Data suggest the stimulation of GABA B R signaling as a novel target for the treatment and prevention of pancreatic cancer. 18255321_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18255321_The genotype distribution varied significantly between patients and controls. Heterozygous carriers of the A-allele had a 10-fold increase in risk for MTLE-HS (OR 10.01; 95% CI 3.98-25.18, p=3.788E-08). 18355961_no significant association between the GABBR1 c.1456G>A polymorphism and sporadic or familial temporal lobe epilepsy 18403780_GABA may modulate an uncharacterized signaling cascade via GABA(B) receptors coupled to G(i) protein in airway epithelium 18653317_No evidence of significant allelic, genotypic, or haplotypic associations were identified in the tag SNPs of the GABBR1 gene in patients with MTLE, and the polymorphism at G1465A was not observed in samples of this study. 19002745_Levels of GABBR1 are significantly decreased in brains of patients with autism compared with normal brains. 19052921_GABA-B(1A) receptors are able to activate the ERK1/2 pathway despite the absence of surface targetting partner GABA-B(2) 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19327013_Data show that GABA is a potent chemoattractant of HUCB stem/progenitor cells specifically through GABA(B)R activation. 19664746_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19763258_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19763258_variants of GABBR1 and GABBR2 are associated with nicotine dependence in European- and African-American populations 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20036641_GABAB1 subunits interact with DGCR6 in the endoplasmic reticulum prior to their recruitment into functional GABAB receptors. 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20398908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20468064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20538960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20557420_Significant reductions in GABA(B) receptor subunit 1 density are demonstrated in cingulate cortex and fusiform gyrus from patients with autism compared to controls. 20655478_This chapter summarizes current understanding of the molecular function of the GABA(B) receptor and recent developments in the identification of allosteric modulators. 20655479_This chapter focuses on the recently emerged mechanisms of GABA(B) receptor exocytosis, endocytosis, recycling, and degradation. 20655480_The role that this phosphorylation plays in determining GABA(B)R effector coupling and their trafficking within the endocytic pathway, is discussed. 20655481_The relationships between the GABA(B) receptor, its effectors and associated proteins that mediate GABA(B) receptor function within the brain, is described. 20655482_Current knowledge on a new role of GABA(B)R as an ambience-dependent regulator of synaptic signaling, is presented. 20655483_This chapter reviews data suggesting that neurogliaform cells produce electrophysiological effects onto other neurons in the cortical cell network via GABA(B)R-mediated volume transmission that is highly regulated by GAT1 activity. 20655490_The overexpression of one particular gene encoding for G-protein-activated inward rectifying potassium type 2 (GIRK2) channel subunit and its coupling to GABA(B) receptors may contribute to a range of mental and functional disabilities in Down syndrome. 21124972_Data suggest that the GABAB1 intron 4 containing N-terminal truncation is necessary for the inhibitory action of the new splice variants. 21303731_The results of this study provided evidence of Gabbr1 Deficit in schizophrenia and mood disorders. 21621395_The present meta-analysis suggests that GABBR1 G1465A polymorphism is associated with the risk of temporal lobe epilepsy. 21932037_We have discovered main triplets of amino acid residues in the GABAB1 receptor and several other neural receptors which seem to come from immunoglobulin chains and appear also as homologies in receptor heteromers. 22321358_This study does not support that GBR1 is involved in essential tremor. 22613715_Results show that GABA(B) receptors R1 and R2 must be activated for the modulation of N-type (Ca(v)2.2) calcium channels by analgesic alpha-conotoxins Vc1.1 and RgIA. 22660477_The GBR2 ectodomain directly interacts with the GBR1 ectodomain to increase agonist affinity by selectively stabilizing the agonist-bound conformation of GBR1. 22722631_Long interval intracortical inhibition is significantly reduced and the cortical silent period is significantly shortened in patients with succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) deficiency compared to heterozygous parents and control groups. 23007731_GABA may inhibit the growth of cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells through the GABAB receptor, and the anti-cancer effects may be partly mediated via the JAK/STAT3 pathway 23192081_Activation of GABA(B) receptors significantly inhibits Akt/GSK-3 signaling in a beta-arrestin-dependent pathway. 23391219_Authors suggest GABBR1, GABA receptor B1, is implicated in schizophrenia based on a Human endogenous retrovirus long terminal repeat (HERV-W LTR) in the regulatory region of GABBR1. 24006265_GABBR1 protein involved in phenylthiourea bitter taste detection. 24209778_Chronic alcohol altered exon/intron expression and splice junction levels. 24682435_GABBR1 receptors are expressed in aortic smooth muscle cells and regulate the [Ca(2+)]i via a Gi/o-coupled receptor pathway and a phospholipase C activation pathway. 24778228_The endoplasmic reticulum retention signal of GBR1 is not part of the core coiled-coil structure, suggesting that it is sterically shielded by GBR2 upon heterodimer formation. 25465316_the first report of abnormal levels of GABA+ and Glx in mood-related brain regions of women with PMDD, indicating that dysregulation of the amino acid neurotransmitter system may be an important neurobiological mechanism in the pathogenesis of PMDD. 25725285_GABA(B)R stimulation promotes chemotaxis in RBL cells which is dependent on signaling via PI3-K/Akt, Src kinases and on rearrangement of both microtubules and actin cytoskeleton. 26727527_Results show that GABBR1 minor genotypes/alleles were protective against risk for alcoholism in 3 ethnically diverse cohorts. 26817839_Cell surface ubiquitination precedes endocytosis, after which USP14 acts as an ubiquitin-binding protein that targets the ubiquitinated GABA B receptor to lysosomal degradation and promotes its deubiquitination. 27509181_Genotype and allele frequencies of rs29230 in GABR1 were significantly different between cases and controls, especially for male patients, for obstructive sleep apnea risk in Chinese Han population. 27812916_GABAB receptor modulation in Periodontal Ligament cells might become an important target in immunoinflammatory settings. 27922604_The combined analysis confirmed evidence of genome-wide significant associations in the Han Chinese population for three loci, at 2p16.1 (rs1051061, in an exon of VRK2, P=1.14 x 10-12, odds ratio (OR)=1.17), 6p22.1 (rs115070292 in an intron of GABBR1, P=4.96 x 10-10, OR=0.77) and 10q24.32 (rs10883795 in an intron of AS3MT, P=7.94 x 10-10, OR=0.87; rs10883765 at an intron of ARL3, P=3.06 x 10-9, OR=0.87). 28118741_There was no statistically significant association for the two SNPs of the GABBR1 gene (rs29230 and rs29267). However, a significant difference between AUD individuals and controls was observed at genotype level for rs2900512 of GABBR2 gene. 28213518_presynaptic gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor deficits contribute to altered neuronal excitability in fragile X syndrome 29026448_Results show that pregnancy anxiety is associated with differential DNA methylation patterns in newborns and, reveal a potential role for GABBR1 methylation in association with stress in newborns. 30143926_In a Chinese population, the C allele frequency of rs715044 of the GABBR1 gene was associated with methamphetamine use disorder. 30343129_GABA B receptor expression in myometrium 32555460_Structural basis of the activation of a metabotropic GABA receptor. 32580208_Structures of metabotropic GABAB receptor. 32581365_Structure of human GABAB receptor in an inactive state. 32881992_The neurotransmitter receptor Gabbr1 regulates proliferation and function of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. 33058878_Structural Basis for Activation of the Heterodimeric GABAB Receptor. 34448502_Adipose-derived stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit neuroblastoma growth by regulating GABBR1 activity through LINC00622-mediated transcription factor AR. 35909813_Phosphonate-Modified Cellulose Nanocrystals Potentiate the Th1 Polarising Capacity of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells via GABA-B Receptor. |
ENSMUSG00000024462 |
Gabbr1 |
7.001015 |
0.1696212033 |
-2.559612 |
0.854105036 |
9.725964 |
0.00181683046362312900119662106845908056129701435565948486328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004048983488310039027813225231966498540714383125305175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1290005 |
1.2384342 |
13.0151828 |
3.2478208 |
| ENSG00000204682 |
399726 |
MIR1915HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.036684 |
0.0343829100 |
-4.862165 |
1.028490997 |
32.966327 |
0.00000000937689764971112519208572689925762499996153565007261931896209716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000040947635890454493094485694578560375234133061894681304693222045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3996874 |
0.3077318 |
11.6651966 |
3.2210359 |
| ENSG00000204758 |
100268168 |
RPL26L1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.400816 |
0.3697914467 |
-1.435216 |
0.580083650 |
6.638987 |
0.00997706646884780230799538713881702278740704059600830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019127354342147493554415760286246950272470712661743164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6218928 |
1.9279581 |
12.6426180 |
2.9085017 |
| ENSG00000204779 |
653427 |
FOXD4L5 |
protein_coding |
Q5VV16 |
|
DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in anatomical structure morphogenesis; cell differentiation; and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. Predicted to be part of chromatin. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:653427; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
Mouse_homologues 27092474_We demonstrate that mouse and human homologs of Foxd4l1 have similar functional domains compared to the frog protein, as well as conserved transcriptional activities when expressed in Xenopus embryos and blastomere explants. |
ENSMUSG00000051490 |
Foxd4 |
17.414726 |
0.2819646003 |
-1.826414 |
0.403224310 |
21.665252 |
0.00000324618648698630447776156474071207469478395069018006324768066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010801107427393565136512602886664780044156941585242748260498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0204554 |
2.2367025 |
28.8079092 |
4.7747074 |
| ENSG00000204791 |
|
SMPD5 |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.641740 |
0.1950295283 |
-2.358236 |
0.460462015 |
29.671225 |
0.00000005118906818870661679961778082505186038275724058621563017368316650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000207056905032970597298799374924582750168156053405255079269409179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4572944 |
1.3291103 |
22.9890609 |
3.4475402 |
| ENSG00000204839 |
642475 |
MROH6 |
protein_coding |
A6NGR9 |
|
Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
|
hsa:642475; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737] |
|
ENSMUSG00000098678 |
Mroh6 |
198.345052 |
0.2223914776 |
-2.168827 |
0.223118974 |
90.642688 |
0.00000000000000000000172106857593945872046515813042093278822277291453644396264886784475578451747423969209194183349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000016159651514546063277608555729953616472620510885097356592286776955091909258044324815273284912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
71.9811214 |
16.0560507 |
326.9327538 |
51.3146769 |
| ENSG00000204977 |
10206 |
TRIM13 |
protein_coding |
O60858 |
FUNCTION: Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane anchored E3 ligase involved in the retrotranslocation and turnover of membrane and secretory proteins from the ER through a set of processes named ER-associated degradation (ERAD). This process acts on misfolded proteins as well as in the regulated degradation of correctly folded proteins. Enhances ionizing radiation-induced p53/TP53 stability and apoptosis via ubiquitinating MDM2 and AKT1 and decreasing AKT1 kinase activity through MDM2 and AKT1 proteasomal degradation. Regulates ER stress-induced autophagy, and may act as a tumor suppressor (PubMed:22178386). Also plays a role in innate immune response by stimulating NF-kappa-B activity in the TLR2 signaling pathway. Ubiquitinates TRAF6 via the 'Lys-29'-linked polyubiquitination chain resulting in NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:28087809). Participates as well in T-cell receptor-mediated NF-kappa-B activation (PubMed:25088585). In the presence of TNF, modulates the IKK complex by regulating IKBKG/NEMO ubiquitination leading to the repression of NF-kappa-B (PubMed:25152375). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17314412, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21333377, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22178386, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25088585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25152375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28087809}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Endoplasmic reticulum;Immunity;Innate immunity;Membrane;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation;Ubl conjugation pathway;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein ubiquitination. |
This gene encodes a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2, and a coiled-coil region. This gene is located on chromosome 13 within the minimal deletion region for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10206; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum quality control compartment [GO:0044322]; perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0097038]; transcription coactivator activity [GO:0003713]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; endoplasmic reticulum mannose trimming [GO:1904380]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of viral transcription [GO:0032897]; positive regulation of cell death [GO:0010942]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of macroautophagy [GO:0016239]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0043161]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; suppression of viral release by host [GO:0044790]; ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway [GO:0030433] |
16499869_TRIM13, also known as RFP2, promoter area contains multiple quadruplex forming GGGGA-repeats that possesses unusually hight activity, anomalously high electrostatic fields induced by sequence-dependent dipoles and very low nucleosome forming potential. 17314412_Rfp2 contains a C-terminal transmembrane domain indispensable for its localization to the ER 21333377_Data suggest that irradiation causes RFP2 overexpression, which enhances ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis by increasing p53 stability and decreasing AKT kinase activity through MDM2 and AKT degradation. 22178386_Results describe the role of TRIM13 in induction of autophagy, which may play an important role in regulation of ER stress and tumor suppression. 23647456_Shows important roles of TRIM13 in MM tumour survival and proliferation in multiple myeloma. 24021263_This study first time demonstrated the role of TRIM13 as novel regulator of caspase-8 activation and cell death during endoplasmic reticulum stress. 24565866_Results show that HRD1 and RFP2 contributes are required for the disposal of V247M alpha-sarcoglycan mutant. 25152375_TRIM13 mediated NF-kappaB repression is essential for negative regulation of clonogenic ability of the cells. 26288249_Results from a study on gene expression variability markers in early-stage human embryos shows that TRIM13 is a putative expression variability marker for the 3-day, 8-cell embryo stage. 30224829_The Trim13-mediated ubiquitination of Nur77 was optimal in the presence of the E2 enzyme UbcH5. Importantly, in addition to Trim13-mediated ubiquitination, the stability of Nur77 was also regulated by casein kinase 2alpha 30837324_Results from bioinformatics analysis suggest that Tripartite motif 13 (TRIM13) may be adopted as a promising predictive biomarker for prognosis of breast cancer. 31357025_results indicate that TRIM13 behaves as a tumor suppressor in non-small-cell lung carcinoma through regulating NF-kappaB pathway. 31901873_Altered DNA methylation of TRIM13 in diabetic nephropathy suppresses mesangial collagen synthesis by promoting ubiquitination of CHOP. 36180926_TRIM3 and TRIM16 as potential tumor suppressors in breast cancer patients. |
ENSMUSG00000035235 |
Trim13 |
1422.213518 |
2.1710716804 |
1.118407 |
0.051890520 |
464.216230 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000058126722853947979892379298260361012610285449058867572754929149372778631320244395793887512978629730066542365212320769685223365182910743855069100449168196604299413915241019148952073969491380908209604028050693440489212162004275873 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000025841880401333500170374745966361486881249032943832977894100405023683031569741061683114510196477922842526912989335748249924490881528526037476114188688506190728199434929402335966867796211757091955339439738343865914772532426600641 |
Yes |
No |
1956.2215124 |
57.5204615 |
907.1521087 |
20.7091104 |
| ENSG00000204991 |
84501 |
SPIRE2 |
protein_coding |
Q8WWL2 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an actin nucleation factor, remains associated with the slow-growing pointed end of the new filament (PubMed:21620703). Involved in intracellular vesicle transport along actin fibers, providing a novel link between actin cytoskeleton dynamics and intracellular transport (By similarity). Required for asymmetric spindle positioning and asymmetric cell division during meiosis (PubMed:21620703). Required for normal formation of the cleavage furrow and for polar body extrusion during female germ cell meiosis (PubMed:21620703). Also acts in the nucleus: together with SPIRE1 and SPIRE2, promotes assembly of nuclear actin filaments in response to DNA damage in order to facilitate movement of chromatin and repair factors after DNA damage (PubMed:26287480). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8K1S6, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21620703, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26287480}. |
3D-structure;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable actin binding activity. Involved in establishment of meiotic spindle localization; formin-nucleated actin cable assembly; and positive regulation of double-strand break repair. Predicted to be located in cytoskeleton; cytosol; and plasma membrane. Predicted to be active in cell cortex and cytoplasmic vesicle membrane. Predicted to colocalize with cleavage furrow. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84501; |
cell cortex [GO:0005938]; cleavage furrow [GO:0032154]; cytoplasmic vesicle membrane [GO:0030659]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030036]; actin filament network formation [GO:0051639]; actin filament polymerization [GO:0030041]; actin nucleation [GO:0045010]; cleavage furrow formation [GO:0036089]; establishment of meiotic spindle localization [GO:0051295]; formin-nucleated actin cable assembly [GO:0070649]; Golgi vesicle transport [GO:0048193]; intracellular transport [GO:0046907]; polar body extrusion after meiotic divisions [GO:0040038]; positive regulation of double-strand break repair [GO:2000781]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
19605360_both mammalian Spir proteins, Spir-1 and Spir-2, interact with mammalian Fmn subgroup proteins formin-1 and formin-2 25564607_We therefore characterized co-expressed Spir-2 and Fmn-2 fluorescent protein fusions . The data corroborate a model according to which Spir-2 exists in two different states, a cytosolic monomeric conformation and a membrane-bound state 26287480_This DNA damage-induced nuclear actin assembly requires two biologically and physically linked nucleation factors: Formin-2 and Spire-1/Spire-2. 27627128_influences intracellular replication of Salmonella typhimurium |
ENSMUSG00000010154 |
Spire2 |
18.632741 |
0.3779767209 |
-1.403631 |
0.377660654 |
14.372675 |
0.00014996278964423144356744865834940583226853050291538238525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000401205505736606095161522755887517632800154387950897216796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.9915403 |
2.4054880 |
23.7938511 |
3.8617757 |
| ENSG00000205084 |
79583 |
TMEM231 |
protein_coding |
Q9H6L2 |
FUNCTION: Transmembrane component of the tectonic-like complex, a complex localized at the transition zone of primary cilia and acting as a barrier that prevents diffusion of transmembrane proteins between the cilia and plasma membranes. Required for ciliogenesis and sonic hedgehog/SHH signaling (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Ciliopathy;Cilium;Cilium biogenesis/degradation;Disease variant;Glycoprotein;Joubert syndrome;Meckel syndrome;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a transmembrane protein, which is a component of the B9 complex involved in the formation of the diffusion barrier between the cilia and plasma membrane. Mutations in this gene cause Joubert syndrome (JBTS). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2013]. |
hsa:79583; |
ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; ciliary transition zone [GO:0035869]; MKS complex [GO:0036038]; camera-type eye development [GO:0043010]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; embryonic digit morphogenesis [GO:0042733]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701]; neuroepithelial cell differentiation [GO:0060563]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224]; vasculature development [GO:0001944] |
23012439_mutations in TMEM231 cause JBTS, reinforcing the relationship between this condition and the disruption of the barrier at the ciliary transition zone. 23349226_TMEM231 represents a novel MKS locus. The very recent identification of TMEM231 mutations in Joubert syndrome supports the growing appreciation of the overlap in the molecular pathogenesis between these two ciliopathies. 25869670_Tmem231 is critical for organizing the Meckel syndrome complex and controlling ciliary composition, defects in which cause OFD3 and MKS. 27449316_Results identified a rare gene conversion event in TMEM231, leading to loss of exon 4, which in combination with c.712G>A missense mutation caused Joubert syndrome and in combination with c.334T>G missense mutation caused Meckel-Gruber syndrome. 31663672_Long-read nanopore sequencing resolves a TMEM231 gene conversion event causing Meckel-Gruber syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000031951 |
Tmem231 |
34.076844 |
3.0571524992 |
1.612189 |
0.288353031 |
31.770754 |
0.00000001734855251661199692217675734102338980235913368233013898134231567382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000073793842981323656542727790555447064946292812237516045570373535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
48.0953783 |
8.5200052 |
15.8004391 |
2.2392555 |
| ENSG00000205085 |
346653 |
GARIN1A |
protein_coding |
Q6NXP2 |
FUNCTION: RAB2B effector protein required for accurate acrosome formation and normal male fertility. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B2RXB0}. |
Alternative splicing;Golgi apparatus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:346653; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; acrosome assembly [GO:0001675] |
17672918_validated occurrence of an unusual TG 3' splice site in intron 1 |
ENSMUSG00000079652 |
Garin1a |
17.401324 |
0.4311679846 |
-1.213678 |
0.386635563 |
10.125441 |
0.00146236655678489346418813532579861202975735068321228027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003318654732187119836550603935165781877003610134124755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
9.0881981 |
2.2859895 |
21.2210624 |
3.1661054 |
| ENSG00000205213 |
55366 |
LGR4 |
protein_coding |
Q9BXB1 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for R-spondins that potentiates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway and is involved in the formation of various organs. Upon binding to R-spondins (RSPO1, RSPO2, RSPO3 or RSPO4), associates with phosphorylated LRP6 and frizzled receptors that are activated by extracellular Wnt receptors, triggering the canonical Wnt signaling pathway to increase expression of target genes. In contrast to classical G-protein coupled receptors, does not activate heterotrimeric G-proteins to transduce the signal. Its function as activator of the Wnt signaling pathway is required for the development of various organs, including liver, kidney, intestine, bone, reproductive tract and eye. May also act as a receptor for norrin (NDP), such results however require additional confirmation in vivo. Required during spermatogenesis to activate the Wnt signaling pathway in peritubular myoid cells. Required for the maintenance of intestinal stem cells and Paneth cell differentiation in postnatal intestinal crypts. Acts as a regulator of bone formation and remodeling. Involved in kidney development; required for maintaining the ureteric bud in an undifferentiated state. Involved in the development of the anterior segment of the eye. Required during erythropoiesis. Also acts as a negative regulator of innate immunity by inhibiting TLR2/TLR4 associated pattern-recognition and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Plays an important role in regulating the circadian rhythms of plasma lipids, partially through regulating the rhythmic expression of MTTP (By similarity). Required for proper development of GnRH neurons (gonadotropin-releasing hormone expressing neurons) that control the release of reproductive hormones from the pituitary gland (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A2ARI4, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21693646, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21727895, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21909076, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22815884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23444378, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23756652}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Biological rhythms;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Differentiation;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Spermatogenesis;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Wnt signaling pathway |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a G-protein coupled receptor that binds R-spondins and activates the Wnt signaling pathway. This Wnt signaling pathway activation is necessary for proper development of many organs of the body. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2016]. |
hsa:55366; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; protein-hormone receptor activity [GO:0016500]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; bone mineralization [GO:0030282]; bone remodeling [GO:0046849]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in metanephric kidney development [GO:0061290]; cell differentiation involved in metanephros development [GO:0072202]; circadian regulation of gene expression [GO:0032922]; digestive tract development [GO:0048565]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in renal tubule morphogenesis [GO:2001013]; hair follicle development [GO:0001942]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intestinal stem cell homeostasis [GO:0036335]; male genitalia development [GO:0030539]; metanephric glomerulus development [GO:0072224]; metanephric nephron tubule morphogenesis [GO:0072282]; negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis [GO:0120163]; negative regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001818]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034122]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090190]; positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0090263]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283] |
17178856_GPR48 may play an important role in invasiveness and metastasis of carcinoma and might represent a potential prognostic marker or therapeutic target. 19301269_Testicular efferent ducts in the mutant mouse are dramatically shortened and less convoluted than in the wild-type animal, providing an explanation to the phenotype observed in LGR4KO. 19550120_Data show that GPR48 shRNA can inhibit in vitro invasion and in vivo metastasis of HeLa cells efficiently. 21693646_LGR4 and LGR5 bind the R-spondins with high affinity and mediate the potentiation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by enhancing Wnt-induced LRP6 phosphorylation. 22815884_R-Spondin potentiates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling through orphan receptors LGR4 and LGR5 23444378_Multi-functional norrin is a ligand for the LGR4 receptor. 23589304_Lgr4/Gpr48 plays a critical role in modulating the TLR2/4 signaling pathway and represents a useful therapeutic approach of targeting Lgr4/Gpr48 in TLR2/4-associated septic shock and autoimmune diseases. 23644456_the c.376C>T mutation is associated with low BMD and osteoporotic fractures, electrolyte imbalance, late onset of menarche, reduced testosterone levels, and an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and biliary tract cancer 23803691_Upregulation of GPR48 resulted in increased phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. 24083742_GPR48 overexpression promotes cancer cell proliferation via activation of Wnt signaling. 24083766_Lgr4 overexpression promoted glioma cell proliferation through activation of Wnt signaling. 24212090_A functional low-frequency human LGR4 variant (A750T) has been associated with body mass index in a Chinese obese-versus-control study. 24455684_our results suggest a previously unknown Stat3-LGR4 molecular network, which may control osteosarcoma development and progression 24519938_Lgr4, which regulates eye, kidney, testis, ovary, and uterine organ development as well as mental development through genetic and epigenetic surveillance, is a novel candidate gene for the pathogenesis of AGR syndrome 24639526_RSPO-LGR4 not only induces the clearance of RNF43/ZNRF3 to increase Wnt receptor levels but also recruits IQGAP1 into the Wnt signaling complex. 25480784_the LGR4-Rspo1 complex crystal structure shows divergent mechanisms of ligand recognition by leucine-rich repeat G-protein-coupled receptors 25531322_These findings suggest that aberrant RSPO3-LGR4 signaling potentially acts as a driving mechanism in the aggressiveness of Keap1-deficient lung ADs. 25636507_LGR4 promotes tumorigenesis of prostate cancer via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 26986507_miR-218 directly targets LGR4 and modulated the PI3K/Akt and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways in the LNCaP-IL-6+ cells. 27064449_LGR4 is another receptor for RANKL. LGR4 competes with RANK to bind RANKL and suppresses canonical RANK signaling during osteoclast differentiation. 27178473_A mechanistic understanding of RANKL-LGR4 interaction has provided new insight into LGR4 mediated RANKL signaling in osteoporosis and other diseases 27693558_Lgr4 is a critical positive factor for skin tumorigenesis by mediating the activation of MEK1/ERK1/2 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways. 27743893_Lgr4 activates Jmjd2a/AR signaling pathway to promote interaction AR with PSA promoter, causing reduction of prostate cancer apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. 27925416_The LGR4 A750T variant is correlated with central obesity-related characteristics in young subjects. 27977785_miR-34a gene expression upregulation inhibits ARPE-19 cell proliferation, migration and adhesion partly by suppressing LGR4 expression. 28220828_Loss of LGR4 abrogated RSPO3-regulated osteogenesis and RSPO3-induced ERK1/2 signalling inhibition. 28768769_Data (including data from studies using transgenic/knockout mice) suggest that LGR4 is key protein necessary for prostate cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis; LGR4 expression is elevated in human prostate cancer cell lines with metastatic potential; LGR4 silencing in prostate cancer cell line impairs cell migration and invasion without affecting cell proliferation. 28777797_High LGR4 expression is associated with osteoarthritis. 28842478_the host protein leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 4 (Lgr4) is essential for VSV and VSV-G pseudotyped lentivirus (VSVG-LV) to infect susceptible cells. 29269400_findings support a crucial role of the Wnt signaling component LGR4 in breast cancer initiation, metastasis, and breast cancer stem cell. 29786747_Luciferase reporter assay was performed to confirm that LGR4 is a direct target gene of miR-137 with a potential binding site in the 3'UTR of LGR4. 30100064_The miR-193a-3p regulates osteoblast differentiation by modulating LGR4/ATF4 signaling and suggests that the miR-193a-3p/LGR4/ATF4 regulation axis may play an important role in regulating bone remodeling. 30803215_High expression of LGR4 is associated with Primary intestinal-type carcinomas than diffuse tumours. 31097406_our studies demonstrate that Rspo2-LGR4 is crucial for the growth, migration and invasion, EMT and stem-like properties of TSCC cells. These actions occur through the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 31661551_MicroRNA-34a negatively controls LGR4, thereby inhibiting the migration and invasion of uveal melanoma cells. Ultimately, both miR-34a and LGR4 impact the aggressiveness of uveal melanoma with alterations in the markers of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 32176632_LGR4 overexpression is associated with clinical parameters and poor prognosis of serous ovarian cancer. 32375050_LGR4, Not LGR5, Enhances hPSC Hematopoiesis by Facilitating Mesoderm Induction via TGF-Beta Signaling Activation. 32399675_Association between LGR4 polymorphisms and peak bone mineral density and body composition. 32493844_LGR4 deficiency results in delayed puberty through impaired Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. 32559496_Targeting RSPO3-LGR4 Signaling for Leukemia Stem Cell Eradication in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. 32626928_MicroRNA137 regulates hypoxiamediated migration and epithelialmesenchymal transition in prostate cancer by targeting LGR4 via the EGFR/ERK signaling pathway. 32980127_LGR4 maintains HGSOC cell epithelial phenotype and stem-like traits. 33171177_Ablation of LGR4 signaling enhances radiation sensitivity of prostate cancer cells. 33946652_The Role of LGR4 (GPR48) in Normal and Cancer Processes. 34707566_LGR4 Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated With Bone and Obesity Phenotypes in Chinese Female Nuclear Families. 34847079_RSPO2 and RANKL signal through LGR4 to regulate osteoclastic premetastatic niche formation and bone metastasis. 35008827_Clinical Significance of Stem Cell Biomarkers EpCAM, LGR5 and LGR4 mRNA Levels in Lymph Nodes of Colon Cancer Patients. 36008975_Bioinformatics Analysis of LGR4 in Colon Adenocarcinoma as Potential Diagnostic Biomarker, Therapeutic Target and Promoting Immune Cell Infiltration. |
ENSMUSG00000050199 |
Lgr4 |
100.047112 |
0.3240186468 |
-1.625851 |
0.195569322 |
69.106139 |
0.00000000000000009330449126316598984535111874489066404894216491582373262936300761793972924351692199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000705519616313693659139625708533887608746709696732474226266162986576091498136520385742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.3181769 |
6.5317618 |
162.2289009 |
13.1001161 |
| ENSG00000205220_ENSG00000141086 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.686367 |
0.3382082936 |
-1.564016 |
0.246505500 |
41.050881 |
0.00000000014831726475245762223274972045513860410825834890147234546020627021789550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000759862140835221966161001848588489593350203676891396753489971160888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.7081520 |
4.2962412 |
82.4935158 |
8.0306913 |
| ENSG00000205238 |
441273 |
SPDYE2 |
protein_coding |
A6NHP3 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Promotes progression through the cell cycle via binding and activation of CDK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15611625}.; + ;NA |
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to enable protein kinase binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100310812; |
protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045737] |
Mouse_homologues 36272447_Murine fertility and spermatogenesis are independent of the testis-specific Spdye4a gene.; + ;NA |
ENSMUSG00000039296+ENSMUSG00000029586 |
Spdye4a+Spdye4b |
19.948664 |
0.2947769841 |
-1.762304 |
0.737864659 |
5.314972 |
0.02114293139728881665284632163093192502856254577636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.037680471797148389068166096649292740039527416229248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.0973235 |
6.9846790 |
35.1787772 |
16.5896120 |
| ENSG00000205268 |
5150 |
PDE7A |
protein_coding |
Q13946 |
FUNCTION: Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes (PubMed:8389765, PubMed:9195912, PubMed:19350606). May have a role in muscle signal transduction (PubMed:9195912). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19350606, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8389765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9195912}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;cAMP;Cytoplasm;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
PATHWAY: Purine metabolism; 3',5'-cyclic AMP degradation; AMP from 3',5'-cyclic AMP: step 1/1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8389765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9195912}. |
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) family, and PDE7 subfamily. This PDE hydrolyzes the second messenger, cAMP, which is a regulator and mediator of a number of cellular responses to extracellular signals. Thus, by regulating the cellular concentration of cAMP, this protein plays a key role in many important physiological processes. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:5150; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004115]; 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity [GO:0004114]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; cAMP catabolic process [GO:0006198]; cAMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019933]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12067300_PDE7 has the potential to regulate human T cell function including cytokine production, proliferation and expression of activation markers. 12388353_Ubiquitous expression of phosphodiesterase 7A in human proinflammatory and immune cells; PDE7A was expressed in neutrophils and alveolar macrophages 15994308_crystal structure of PDE7A1 catalytic domain complexed with the inhibitor 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine & kinetic analysis on mutant PDE7A1 and PDE4D2; results show several residues must work together to switch inhibitor selectivity between PDE4 & PDE7 18420479_results show that specific gene silencing with the RNAi method is a useful tool for inhibiting the gene expression of specific PDEs and that PDE7 silencing upregulates several osteogenic genes and increases mineralization 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 23661015_PDE7 has roles in regulating oligodendrocyte precursor survival and differentiation during brain development and in adulthood 25128584_PDE7A is a high-speed and low-affinity phosphodiesterase for cCMP. 28356347_Low PDE7A expression is associated with sepsis. 28867658_Here we describe a compound, BC54, that is a selective inhibitor of enzymes from the cAMP-specific PDE4 and PDE7 families. Consistent with the biological effect of other PDE4 and PDE7 inhibitors, BC54 displays potent anti-inflammatory properties and is superior to a combination of rolipram (a PDE4 inhibitor) and BRL50481 (a PDE7A inhibitor) for inducing apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells 31473904_Phosphodiesterase 7 Regulation in Cellular and Rodent Models of Parkinson's Disease. 33370523_Long non-coding RNA TUSC7 suppressed colorectal cancer progression via regulation of miR-23b/PDE7A Axis. 34077501_Circ_0091702 relieves lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced cell injury by regulating the miR-182/PDE7A axis in sepsis. |
ENSMUSG00000069094 |
Pde7a |
493.503179 |
0.4619114133 |
-1.114312 |
0.074468882 |
226.701762 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000312360070267692260014243463401024880926115345484499563645242592177224503354516661432439815033655660972847693094995240499579304029043047563618529238738119602203369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000068709905173638413191785748862653620407973575187530004187632157031999731678957617696454694770475173765243191083196669858339992835449816510617893072776496410369873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
311.3754399 |
14.0654104 |
679.0557749 |
19.8735477 |
| ENSG00000205307 |
100316904 |
SAP25 |
protein_coding |
Q8TEE9 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the transcriptional repression mediated by the mSIN3A but not the N-CoR corepressor complex. {ECO:0000250}. |
Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100316904; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
|
ENSMUSG00000079165 |
Sap25 |
29.329491 |
0.0203668215 |
-5.617635 |
1.079909170 |
23.845177 |
0.00000104403138063951685206764887631214477892171998973935842514038085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003683935734697410322834986579065841283409099560230970382690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0611218 |
1.0487907 |
50.3252168 |
28.1955729 |
| ENSG00000205307_ENSG00000077454 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85.873877 |
0.1376051662 |
-2.861393 |
0.553870611 |
23.974932 |
0.00000097598193092341048534459676394581251201998384203761816024780273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003454554748304445761921755223000651824349915841594338417053222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.7263944 |
13.8328356 |
127.8285593 |
68.8027161 |
| ENSG00000205339 |
10527 |
IPO7 |
protein_coding |
O95373 |
FUNCTION: Functions in nuclear protein import, either by acting as autonomous nuclear transport receptor or as an adapter-like protein in association with the importin-beta subunit KPNB1. Acting autonomously, is thought to serve itself as receptor for nuclear localization signals (NLS) and to promote translocation of import substrates through the nuclear pore complex (NPC) by an energy requiring, Ran-dependent mechanism. At the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC, Ran binds to importin, the importin/substrate complex dissociates and importin is re-exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where GTP hydrolysis releases Ran. The directionality of nuclear import is thought to be conferred by an asymmetric distribution of the GTP- and GDP-bound forms of Ran between the cytoplasm and nucleus. Mediates autonomously the nuclear import of ribosomal proteins RPL23A, RPS7 and RPL5 (PubMed:11682607). In association with KPNB1 mediates the nuclear import of H1 histone and the Ran-binding site of IPO7 is not required but synergizes with that of KPNB1 in importin/substrate complex dissociation. In vitro, mediates nuclear import of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 histones. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10228156, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11682607, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9687515}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Mediates the nuclear import of HIV-1 reverse transcription complex (RTC) integrase. Binds and mediates the nuclear import of HIV-1 Rev. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12853482, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16704975}. |
Acetylation;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Host-virus interaction;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
The importin-alpha/beta complex and the GTPase Ran mediate nuclear import of proteins with a classical nuclear localization signal. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of a class of approximately 20 potential Ran targets that share a sequence motif related to the Ran-binding site of importin-beta. Similar to importin-beta, this protein prevents the activation of Ran's GTPase by RanGAP1 and inhibits nucleotide exchange on RanGTP, and also binds directly to nuclear pore complexes where it competes for binding sites with importin-beta and transportin. This protein has a Ran-dependent transport cycle and it can cross the nuclear envelope rapidly and in both directions. At least four importin beta-like transport receptors, namely importin beta itself, transportin, RanBP5 and RanBP7, directly bind and import ribosomal proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10527; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear pore [GO:0005643]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; GTPase regulator activity [GO:0030695]; histone binding [GO:0042393]; SMAD binding [GO:0046332]; small GTPase binding [GO:0031267]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045736]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606] |
12080050_role of IMP7 in nuclear transport of H1 histones 12853482_Nuclear import of HIV-1 intracellular reverse transcription is mediated by IPO7. 17848547_These results identify EZI as a novel cargo protein for importin-7 and demonstrate a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling mechanism that is mediated by importin-7-dependent nuclear localization and CRM1-independent nuclear export. 18003734_When the import assay was performed with a low concentration of each importin- subtype, NPI2/importin-7 elicited more efficient transport activity of the human herpesvirus 6 U69 protein 18519565_TGF-beta-induced and basal state spontaneous nuclear import of Smad4 require importin 7 and 8. 19193229_Although imp7 may not be essential for HIV-1 infection, our results suggest that imp7 facilitates nuclear trafficking of DNA and that HIV-1 exploits imp7 to maximize nuclear import of its DNA genome. 19435463_Data show that ARHI could compete for Ran-importin binding and induce disruption of importin-binding to cargo proteins, including STAT3. 19609347_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19788888_importins 4 and 7 accomplish nuclear import of HIF-1alpha more efficiently than the classical importin alpha/beta NLS receptor 21419860_essential for Egr-1 nuclear translocation 22284678_Importin 7 (IPO7)is regulated positively by c-Myc and negatively by p53. 23067392_imp7 is a part of an intrinsic pathway that promotes nuclear import of exogenous and endogenous DNA in mammalian cells. 24100013_Importin 7 contributes to the regulation of androgen receptor import by restraining import until androgen is detected in the cytoplasm. 24586428_Importin 7 as a soluble nuclear transport factor that is required for efficient import of the protein component of human telomerase. 26085085_Depletion of IPO7 by IPO7 siRNA reduced nuclear accumulation of GLI1. In addition, FOXM1 induced nuclear import of GLI1 by promoting IPO7 expression. 27381982_AKT and 14-3-3 proteins down-regulate the activity of several BCR-associated components, including BTK, BLNK and SYK and also inhibit SYK's interaction with Importin 7 27528606_Importins, Impbeta, Kapbeta2, Imp4, Imp5, Imp7, Imp9, and Impalpha, show the H3 tail binding more tightly than the H4 tail. The H3 tail binds Kapbeta2 and Imp5 with KD values of 77 and 57 nm, respectively, and binds the other five Importins more weakly. 31505435_Pediatric ependymoma: GNAO1, ASAH1, IMMT and IPO7 protein expression and 5-year prognosis correlation. 33482249_The sequence [EKRKI(E/R)(K/L/R/S/T)] is a nuclear localization signal for importin 7 binding (NLS7). 35588577_IPO7 promotes pancreatic cancer progression via regulating ERBB pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000066232 |
Ipo7 |
1222.518436 |
2.2705123670 |
1.183018 |
0.063190887 |
348.049230 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001127069735305939826359700563260864808444029509252213727890020282662668731691997064926134923094864111605259544293755586337430520265923240627786168032341613493082072246658612988674342298854504779148655302378756459802389144897460937500000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000366421790597261466500307925797091086824720530646025134609200975641344480615405625531146033974460486109990046017830830028902737126871875829666182736476387583997042129576194781343062049851384831544720555029925890266895294189453125000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1714.5199043 |
60.8674421 |
760.4721918 |
20.7894729 |
| ENSG00000205356 |
25851 |
TECPR1 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z6L1 |
FUNCTION: Tethering factor involved in autophagy. Involved in autophagosome maturation by promoting the autophagosome fusion with lysosomes: acts by associating with both the ATG5-ATG12 conjugate and phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PtdIns(3)P) present at the surface of autophagosomes. Also involved in selective autophagy against bacterial pathogens, by being required for phagophore/preautophagosomal structure biogenesis and maturation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21575909, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22342342}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Autophagy;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Lipid-binding;Lysosome;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes a tethering factor involved in autophagy. The encoded protein is found at autolysosomes, and is involved in targeting protein aggregates, damaged mitochondria, and bacterial pathogens for autophagy [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2012]. |
hsa:25851; |
autophagosome membrane [GO:0000421]; cytoplasmic vesicle [GO:0031410]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate binding [GO:0032266]; autophagosome maturation [GO:0097352]; autophagy [GO:0006914]; macroautophagy [GO:0016236]; regulation of autophagosome maturation [GO:1901096] |
22342342_The concerted interactions among TECPR1, Atg12-Atg5, and PtdIns(3)P provide the fusion specificity between autophagosomes and lysosomes and that the assembly of this complex initiates the autophagosome maturation process. 32532970_TECPR1 promotes aggrephagy by direct recruitment of LC3C autophagosomes to lysosomes. 36197771_TECPR1 Induces Apoptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma via ATG5 Upregulation-Induced Autophagy Promotion. |
ENSMUSG00000066621 |
Tecpr1 |
246.530825 |
0.3702198144 |
-1.433546 |
0.154182054 |
85.352605 |
0.00000000000000000002496329523834114352025967600542658907851515500987631910332145701580941477004671469330787658691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000223308022859342588786610539976102259567855919689073271316992475021834252402186393737792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
130.1480242 |
17.4681235 |
353.5751220 |
33.4225038 |
| ENSG00000205476 |
317762 |
CCDC85C |
protein_coding |
A6NKD9 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in cell-cell adhesion and epithelium development through its interaction with proteins of the beta-catenin family (Probable). May play an important role in cortical development, especially in the maintenance of radial glia (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q6B2, ECO:0000305|PubMed:25009281}. |
Acetylation;Cell junction;Coiled coil;Developmental protein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Tight junction |
|
Predicted to be involved in cerebral cortex development. Located in adherens junction. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:317762; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical junction complex [GO:0043296]; bicellular tight junction [GO:0005923]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987] |
25649651_Genome-wide SNP analysis identified multiple suggestive novel loci and two of them were also significant in gene-based analysis (CCDC85C and NARS2) that survived after controlling for false-discovery rate at 0.05. |
ENSMUSG00000084883 |
Ccdc85c |
48.903988 |
0.4738424584 |
-1.077521 |
0.428000941 |
6.165291 |
0.01302809515579203894497517524087015772238373756408691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024390497780249934672847089700553624425083398818969726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.4888680 |
9.7579856 |
75.5142966 |
14.4521955 |
| ENSG00000205482 |
100505767 |
SPDYE18 |
protein_coding |
P0DV79 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Promotes progression through the cell cycle via binding and activation of CDK1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15611625}.; + ;NA |
Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
|
Mouse_homologues mmu:74673;;NA |
protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; positive regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0045737] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000039296+ENSMUSG00000029586 |
Spdye4a+Spdye4b |
6.802985 |
0.0779226552 |
-3.681813 |
0.860871238 |
26.038492 |
0.00000033467777051838626842478023604154913073216448538005352020263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001246805626666173990170320695636263508276897482573986053466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0644983 |
0.6536794 |
13.5528393 |
3.2038841 |
| ENSG00000205559 |
100144603 |
CHKB-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.295243 |
0.4663667570 |
-1.100463 |
0.405805649 |
7.303863 |
0.00688065054618444693623757757450221106410026550292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013657665688768482609161125651553447823971509933471679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4704419 |
3.5286776 |
29.1657825 |
4.9828077 |
| ENSG00000205560 |
1375 |
CPT1B |
protein_coding |
Q92523 |
|
Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Fatty acid metabolism;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion outer membrane;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; fatty acid beta-oxidation. |
The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the carnitine/choline acetyltransferase family, is the rate-controlling enzyme of the long-chain fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway in muscle mitochondria. This enzyme is required for the net transport of long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene, and read-through transcripts are expressed from the upstream locus that include exons from this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
hsa:1375; |
mitochondrial outer membrane [GO:0005741]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; carnitine O-palmitoyltransferase activity [GO:0004095]; carnitine metabolic process [GO:0009437]; carnitine shuttle [GO:0006853]; fatty acid beta-oxidation [GO:0006635]; fatty acid metabolic process [GO:0006631]; long-chain fatty acid transport [GO:0015909]; response to blue light [GO:0009637] |
12015320_Genetic analysis, comparison, and tissue distribution of CPT1b 12565845_Leucine-764 near the extreme C-terminal end of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I is important for enzyme activity. 15356291_Transcriptional activation of the CPT1B promotor by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-alpha and myocyte-specific enhancer-binding-factor 2C. 15579906_muscle carnitine palmitoyltransferase I has a single cysteine residue (Cys-305) important for catalysis 15647998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17089095_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17987377_Three replacements of nucleotides resulting in missense mutations of I66V, S427C, and E531K were observed in the M-CPTI gene of patients showing abnormal fatty acid metabolism 18660489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18820697_A single nucleotide polymorphism located between CPT1B and CHKB, was associated with narcolepsy in Japanese (rs5770917[C], odds ratio (OR) = 1.79, combined P = 4.4 x 10(-7)) and other ancestry groups (OR = 1.40, P = 0.02). 18820697_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19074885_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19404393_Japanese CNS hypersomnias (essential hypersomnia: EHS) other than narcolepsy with cataplexy was significantly associated with SNP rs5770917 (located between CPT1B and CHKB) and HLA-DRB1*1501-DQB1*0602 haplotype 19404393_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19553926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19553926_There is a novel association between common nonsynonymous coding variants in CPT1B and ectopic skeletal muscle fat among middle-aged and older African ancestry men. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19937377_C305 was replaceable with aspartic acid but that substitution with other amino acids caused both loss of function and reduced expression. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22177342_The study extends on the observation of a strong multiethnic association of polymorphisms in the TCRA and P2RY11 with narcolepsy, but does not confirm the association of CPT1B/CHKB (rs5770917) in the Chinese population. 22538307_Genetic mutations causative for McArdle disease, carnitine palmitoyl transferase deficiency 2, myoadenylate deaminase deficiency, and malignant hyperthermia have all been associated with Exertional rhabdomyolysis. 22809552_present results confirm the association of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1B coding polymorphisms with the metabolic syndrome 23566841_CPT1B heterozygous variants of G320D and S427C among control subjects showed significantly higher levels of total and free carnitine in the blood compared to acute myocardial infarction patients. 24571861_study identified a novel haplotype consisting of the indel variation, which had not been detected in previous studies in Japanese and Korean populations, and observed four single-nucleotide polymorphisms in CHKB/CPT1B 24905907_E531K substitution in CPT1B decreases the mitochondrial beta-oxidation pathway, which increases the non-protein respiratory quotient value during recovery from exercise. 26041663_CPT1 is active on the outer surface of mitochondria and serves as a regulatory site for fatty acid oxidation due to its sensitivity for malonyl-CoA. CPT1b is the muscle isoform. 26058865_Differential DNA methylation may underlie the depressed expression of CPT1B in response to lipid, contributing to the metabolic inflexibility associated with severe obesity. 26080315_In subjects with PTSD, significant over-expression of CPT1B was also observed in the two common dysregulated pathways: fatty acid metabolism and PPAR. 29657112_CPT1b overexpression could be helping to maintain metabolic health with increasing age. Thus, it is suggested that targeting CPT1b expression might be an interesting strategy to counteract frailty at an early stage. In addition, future studies should examine the role of sirtuin in CPT1b expression regulation. 30846479_Low expression of CPT1B in high-grade urinary bladder cancer was associated with low fatty acid oxidation and low acyl carnitine levels. 32648618_Targeting CPT1B as a potential therapeutic strategy in castration-resistant and enzalutamide-resistant prostate cancer. 33675111_Resting skeletal muscle PNPLA2 (ATGL) and CPT1B are associated with peak fat oxidation rates in men and women but do not explain observed sex differences. 34176754_The impact of CPT1B rs470117, LEPR rs1137101 and BDNF rs6265 polymorphisms on the risk of developing obesity in an Italian population. 35810398_Low carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 activity is a risk factor for narcolepsy type 1 and other hypersomnia. |
ENSMUSG00000078937 |
Cpt1b |
69.688791 |
0.2040046406 |
-2.293326 |
0.314210593 |
52.823676 |
0.00000000000036487631758708286369822968266610134870954473829129938167170621454715728759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002239324094630080119967939148184238751931873778744375158566981554031372070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.7334872 |
5.3402036 |
122.1388968 |
17.1839279 |
| ENSG00000205659 |
91750 |
LIN52 |
protein_coding |
Q52LA3 |
|
3D-structure;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleoplasm. Predicted to be part of DRM complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:91750; |
DRM complex [GO:0070176]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000085793 |
Lin52 |
86.538117 |
2.0673265931 |
1.047766 |
0.425786502 |
5.887344 |
0.01525008528695105843031587511404723045416176319122314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028104789466275141573969875707916799001395702362060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.6700161 |
75.2150829 |
40.1170406 |
24.1288384 |
| ENSG00000205702 |
|
CYP2D7 |
protein_coding |
A0A087X1C5 |
FUNCTION: May be responsible for the metabolism of many drugs and environmental chemicals that it oxidizes. It may be involved in the metabolism of codeine to morphine (PubMed:15051713). However, another study could not confirm it (PubMed:18838503). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15051713, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18838503}. |
Cytoplasm;Glycoprotein;Heme;Iron;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Monooxygenase;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
|
hsa:1564; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; aromatase activity [GO:0070330]; heme binding [GO:0020037]; iron ion binding [GO:0005506]; oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen [GO:0016712]; steroid hydroxylase activity [GO:0008395]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; organic acid metabolic process [GO:0006082]; xenobiotic catabolic process [GO:0042178]; xenobiotic metabolic process [GO:0006805] |
|
|
|
30.513364 |
0.2655543154 |
-1.912921 |
0.369510330 |
26.469294 |
0.00000026776069383301093491714351367549706850468282937072217464447021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001007943851307126157523927009740383198277413612231612205505371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.2923527 |
4.0767961 |
53.7759690 |
10.1524998 |
| ENSG00000205744 |
79958 |
DENND1C |
protein_coding |
Q8IV53 |
FUNCTION: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) which may activate RAB8A, RAB13 and RAB35. Promotes the exchange of GDP to GTP, converting inactive GDP-bound Rab proteins into their active GTP-bound form. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154091, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20937701}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the early endosomal small GTPase RAB35, which regulates endosomal membrane trafficking and is involved in actin polymerization. The encoded protein activates RAB35 by promoting the exchange of RAB35-bound GDP for GTP. This gene may play a role in linking RAB35 activation with the clathrin machinery. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
hsa:79958; |
centrosome [GO:0005813]; clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; phosphatidylinositol phosphate binding [GO:1901981]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; endocytosis [GO:0006897] |
22072793_whereas connecdenn 1 and 2 activate Rab35 for endosomal trafficking, connecdenn 3 uniquely activates Rab35 for its role in actin regulation |
ENSMUSG00000002668 |
Dennd1c |
291.604782 |
0.4292851393 |
-1.219992 |
0.114660119 |
113.435301 |
0.00000000000000000000000001732429634759451967292701346179398292353538441695646811727415905333873728799698454849931295029819011688232421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000195345006944610466228767773381622398193328527680080719290836723279493856997302003719596541486680507659912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
175.1536587 |
12.4130859 |
411.0123880 |
19.5685201 |
| ENSG00000205795 |
192668 |
CYS1 |
protein_coding |
Q717R9 |
|
Cell membrane;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable chromatin binding activity and transcription corepressor activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within animal organ development and regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in cytoskeleton; membrane raft; and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:192668; |
ciliary membrane [GO:0060170]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; cytosol [GO:0005829] |
12733055_genomic region comprises three coding exons, which span 22 kb and the transcript harbors an open reading frame of 477 nucleotides encoding a protein with 158 amino acid residues, which is called cystin 34521872_Cystin genetic variants cause autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease associated with altered Myc expression. |
ENSMUSG00000062563 |
Cys1 |
6.903617 |
6.1097542001 |
2.611114 |
0.794211370 |
11.158860 |
0.00083631295558255066766029095504109136527404189109802246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001977251197244665661262308375967222673352807760238647460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1714413 |
5.4839389 |
2.0320912 |
0.8032482 |
| ENSG00000205856 |
150297 |
C22orf42 |
protein_coding |
Q6IC83 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:150297; |
|
|
|
|
13.754108 |
39.6796906137 |
5.310329 |
0.917500800 |
64.046226 |
0.00000000000000121533874839491888761625269525399518045984288694416619591720518656075000762939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000008661709283587158223463519823343986622418960025227008259207650553435087203979492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.8718667 |
16.0392681 |
0.6192588 |
0.3973945 |
| ENSG00000205885 |
283314 |
C1RL-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.189338 |
0.2368337229 |
-2.078054 |
0.566623373 |
13.155261 |
0.00028671308374286449439927171312092468724586069583892822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000733810493505233202814197479568747439770959317684173583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5810904 |
1.9115718 |
18.9902932 |
5.0924638 |
| ENSG00000205913 |
100128788 |
SRRM2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31742692_Silencing of long noncoding RNA SRRM2-AS exerts suppressive effects on angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating MYLK-mediated cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. |
|
|
19.973691 |
0.4309465537 |
-1.214419 |
0.369376652 |
11.083784 |
0.00087085929855058733309314256132438458735123276710510253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002051697246066507343553730891017039539292454719543457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.6161153 |
2.8241727 |
24.8313069 |
4.2036987 |
| ENSG00000205923 |
752014 |
CEMP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6PRD7 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in development of the periodontium which surrounds and supports the teeth by promoting the differentiation of multi-potent cells from the periodontal ligament into cementoblasts to form the cementum (PubMed:21929512, PubMed:17509525, PubMed:21465469). Binds hydroxyapatite and may promote the biomineralization of the cementum (PubMed:19393626). Also promotes cell proliferation (PubMed:17509525, PubMed:21929512, PubMed:26011628). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17509525, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19393626, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21465469, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21929512, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26011628}. |
Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Enables hydroxyapatite binding activity. Involved in several processes, including biomineral tissue development; cell population proliferation; and odontogenesis. Located in cytoplasm and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:752014; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; hydroxyapatite binding [GO:0046848]; biomineral tissue development [GO:0031214]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476] |
17509525_CEMP1 might participate in differentiation and mineralization of nonosteogenic cells, and it might have a potential function in cementum and bone formation 19393626_CEMP1 plays a role during the biomineralization process by promoting octacalcium phosphate crystal nucleation. 21465469_These data demonstrate for the first time that the CEMP1 is not only a marker protein for cementoblast-related cells, but it also regulates cementoblast commitment in periodontal ligament cells 22349547_human primary cementoblasts subjected to compression and IL-1beta stimulation impeded BSP and CEMP-1 expression, proteins that are associated with cementogenesis. 24117017_when HIF-1 was activated by gene introduction or chemically, CEMP1 expression and mineralization increased. 26011628_CEMP1 exerts modulation of a number of cellular genes. 26652387_The synthesis of hydroxyapatite with different crystallinities by controlling the concentration of recombinant CEMP1 for biological application. 30113883_data demonstrate that CEMP-1-p1 is an effective bioactive peptide for bone tissue regeneration. The application of this bioactive peptide may lead to implementing new strategies for the regeneration of bone and other mineralized tissues 30804111_On day 14, mineralization nodules appeared, as seen by positive von Kossa staining; the nodules increased in number and size by day 21. The expression of CEMP1 was detected on day 5, and its expression level increased gradually by day 7, reached a peak on day 14, and decreased by day 21 31410920_Cementum protein 1-derived peptide (CEMP 1-p1) modulates hydroxyapatite crystal formation in vitro. 32075221_Carboxy-Terminal Cementum Protein 1-Derived Peptide 4 (cemp1-p4) Promotes Mineralization through wnt/beta-catenin Signaling in Human Oral Mucosa Stem Cells. 35442377_Protease-activated receptor type 1 (PAR1) increases CEMP1 gene expression through MAPK/ERK pathway. |
|
|
27.185973 |
0.0292993980 |
-5.092985 |
0.961181225 |
24.465811 |
0.00000075640219800646985213684637960884771246128366328775882720947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002709829233634829101566533424150229336646589217707514762878417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8505909 |
1.4096145 |
48.9745167 |
48.2211750 |
| ENSG00000205927 |
10215 |
OLIG2 |
protein_coding |
Q13516 |
FUNCTION: Required for oligodendrocyte and motor neuron specification in the spinal cord, as well as for the development of somatic motor neurons in the hindbrain. Functions together with ZNF488 to promote oligodendrocyte differentiation. Cooperates with OLIG1 to establish the pMN domain of the embryonic neural tube. Antagonist of V2 interneuron and of NKX2-2-induced V3 interneuron development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EQW6}. |
Chromosomal rearrangement;Cytoplasm;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor which is expressed in oligodendroglial tumors of the brain. The protein is an essential regulator of ventral neuroectodermal progenitor cell fate. The gene is involved in a chromosomal translocation t(14;21)(q11.2;q22) associated with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Its chromosomal location is within a region of chromosome 21 which has been suggested to play a role in learning deficits associated with Down syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:10215; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; HMG box domain binding [GO:0071837]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; myelination [GO:0042552]; negative regulation of neuron differentiation [GO:0045665]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; neuron fate commitment [GO:0048663]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation [GO:0048714]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; spinal cord motor neuron differentiation [GO:0021522]; spinal cord oligodendrocyte cell fate specification [GO:0021530]; thalamus development [GO:0021794] |
15198128_Analysis of 180 primary, metastatic, and non-neural human tumors shows OLIG2 is highly expressed in all diffuse gliomas. Immunohistochemistry and microarray analyses demonstrate higher OLIG2 in anaplastic oligodendrogliomas versus glioblastomas. 16103065_Overexpression of OLIG2 was not only found in oligodendroglioma samples and normal neural tissue but also in a wide spectrum of malignant cell lines including leukemia, non-small cell lung carcinoma, melanoma, and breast cancer cell lines. 16267213_Olig1 and Olig2 transcription factors in the human central nervous system are important not only for differentiation of the oligodendrocyte lineage, but they may also have a role in neural cell specification. 16469306_Transcriptional regulation of transgenic Olig2 is involved in segregation of motoneuron precursor neuroblasts in the developing mouse spinal cord. 16554441_A novel function of OLIG2 is to suppress glial tumor cell growth via cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. 16682644_Findings show a general requirement for Olig2 function in glial cell development and highlight further roles for Olig transcription factors in neural progenitor cells. 16891421_Data provide strong convergent evidence that variation in OLIG2 confers susceptibility to schizophrenia alone and as part of a network of genes implicated in oligodendrocyte function. 16891421_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17010574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17171653_Mutations in OLIG1 and OLIG2 are not likely to be associated with this subgroup of hypomyelinating disorders. 17283288_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17431671_OLIG2 expression was predominant over ID2 expression in oligodendroglial tumors, while ID2 expression was predominant over OLIG2 expression in astrocytic tumors. 17690840_No significan correlation was found between proliferation index in pilocytic astrocytomas and Olig-2 expression. 17917751_IL-13Ralpha2 and Olig2 have been identified and confirmed to be interesting candidate genes whose differential expression likely plays a role in malignant progression of astrocytomas 17918228_absence of OLIG2 mutation in three PMLD patients presenting with a phenotype characterized by severe hypomyelination and motor neuron dysfunction 17934761_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17934761_The SNP rs762178 in OLIG2 seems to be a potential candidate in altering risk for schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population. 17951409_OLIG2 suppresses the motile phenotype of glioblastoma cells by activating RhoA. 17964117_We found that genetic polymorphisms in CNP (rs2070106) and OLIG2 (rs1059004 and 18312545_analysis of Olig2 immunohistochemistry in microcystic areas might therefore be useful for the differential diagnosis of pilocytic astrocytoma and diffuse astrocytomas . 18552083_Olig2-immunohistochemistry is useful and potentially more reliable than the epithelial membrane antigen-immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of ependymoma 19093005_Olig2-induced neural stem cell differentiation involves downregulation of Wnt pathway. 19477230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19477230_Significant evidence for association of psychotic symptoms within cases was identified for two SNPs, rs762237 and rs2834072. 19772605_transplantation of human neural stem cells genetically modified to express Olig2 transcription factor improved locomotor recovery and enhanced myelination in a rat contusive spinal cord injury model. 20081802_1p19q whole loss was also significantly associated with Olig2 overexpression, but was never observed in tumors overexpressing p53 protein in oligodendroglial tumors 21193945_suggesting that OLIG2 function in pediatric gliomas is cell lineage dependent 21206754_analysis of conserved and non-conserved functional elements at the Olig1 and Olig2 locus 21446039_Olig2 expression is restricted to isolation and during membrane production of regenerating oligodendrocyte cultures isolated from white matter of medically intractable epilepsy patients. 21624811_The Olig2 can induce desired neuronal lineages from most expressing neural progenitor cells by a mechanism resembling developmental binary cell-fate switching. 21835431_Nogo-A is more useful and specific than Olig-2 in differentiating oligodendrogliomas from other gliomas. 22343408_OLIG2 over-expression inhibits neural progenitor proliferation through changes in potassium channel activity, thereby contributing to the reduced neuronal numbers and brain size in DS. 22505278_We found that the risk allele OLIG2 (A) was associated with reduced white matter integrity in the corona radiata bilaterally 23025580_Olig2-positive cells in glioneuronal tumors, and some of them also exhibited neuronal features 23041832_Report role of OLIG2 immunostaining pattern in diagnosing rare and glioblastoma variants. 23165259_This study review OLIG2 have developmental functions in patterning, neuron subtype specification and the formation of oligodendrocytes and play the role in the postnatal brain during repair processes and in neurological disease states. 23793848_LGR5 expression may be functionally correlated with the neurogenic competence, and be regulated by OLIG2 in stem-like cells in glioblastoma. 24395742_Authors investigated the role of Pten in these two critical cellular compartments in adult and developing brains using methods for activation or suppression of PI3K signaling in glial and neuronal progenitors expressing Olig2. 24821492_Our study suggests that CGT expression is controlled by balanced expression of the negative modulator OLIG2 and positive regulator Nkx2.2, providing new insights into how expression of GalCer is tightly regulated in cell-type- and stage-specific manners. 25085214_High Olig2 expression is associated with oligodendrogliomas. 25384509_OLIG2 is the most specific GSC marker. 25966902_The results demonstrate that the expression of Olig2 in dental pulp stem cells reduces the expression of stem cell markers and induces the development of oligodendrocyte progenitors. 26271930_The present study is the first to verify the associations of SNPs rs762178, rs1059004, and rs9653711 of the OLIG2 gene with OCD in a Chinese Han population. Thus, OLIG2 might serve as a potential target for OCD treatment 26287936_Olig2 was positive in 5 out of 44 ependymomas (11%) and 50 out of 54 (93%) non-ependymal tumors 27154355_Olig2 was expressed in cord blood eosinophils on d 24, when cord blood eosinophils are considered fully differentiated, but no earlier. It was also expressed in human peripheral-blood eosinophils but not neutrophils, monocytes, lymphocytes, or cord blood mast cells. Many genes, including eosinophil surface molecules, were up-regulated along with OLIG2. OLIG2 shRNA or siRNA downregulated SIGLEC-8 mRNA and protein. 27179219_Olig2 expressions were successfully detected in 12 (15.58%) of 77 SVZ type II Glioblastomas (GBs) and 16 (21.3%) of 75 SVZ type III GBs. 27396340_Ectopic expression of phosphomimetic Olig2 is sufficient to block TGF-beta2-mediated invasion. 27447975_Data suggest positive feedback loops including oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 (OLIG2): loops of epigenetic regulation. 27785726_Data indicate that transcription factors Sox10 and Olig2 play key roles in oligodendrocytes (OLs) specification. 27905023_OLIG2 immunoreactivity was observed in GABAergic cells of the proliferative zones of the MGE and septum, but not necessarily co-expressed with NKX2.1, and OLIG2 expression was also extensively seen in the LGE, CGE, and cortex 28339768_indicate Olig2 as an onco-requisite factor in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma 28355568_phosphorylation of the motif itself serves as a template to prime phosphorylation of additional serines and creates a highly charged 'acid blob' in the amino terminus of Olig2. 28760688_Data show that oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 (OLIG2) is epigenetically regulated via DNA methylation and expressed in a subset of AML patients. 29681511_Results show that Olig2(+) oligodendrocyte precursor-like glioma cells invade by single-cell vessel co-option and preserve the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Conversely, Olig2-negative glioma cells form dense perivascular collections and promote angiogenesis and BBB breakdown, leading to innate immune cell activation. Olig2 was found to regulate Wnt7b expression in a p53-dependent manner. 30178266_Variants of the OLIG2 Gene are Associated with Cerebral Palsy in Chinese Han Infants with Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. 31130512_altered OLIG2 expression may underlie neurodevelopmental abnormalities and cognitive defects in Down syndrome patients 31299267_Our findings identify OLIG2 expression as a unique manifestation of a neurodevelopmental gene expression signature driven by the oncogenic fusion protein characteristic of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma 31431405_The OLIG2 gene may be involved in obsessive-compulsive disorder 31493794_Positive reaction with OLIG2 (6 tumours) was always associated with the presence of PAX3/7-FOXO1 rearrangement 31568682_Prognostic impact of glioblastoma stem cell markers OLIG2 and CCND2. 31785364_Association of rs1059004 polymorphism in the OLIG2 locus with whole-brain functional connectivity in first-episode schizophrenia. 32285113_Ethnicity-Dependent Effects of Schizophrenia Risk Variants of the OLIG2 Gene on OLIG2 Transcription and White Matter Integrity. 32483381_Olig2 SUMOylation protects against genotoxic damage response by antagonizing p53 gene targeting. 32563948_Association of rs1059004 polymorphism in the OLIG2 locus with functional brain network in first-episode negative schizophrenia. 32716131_Rapid induction of gliogenesis in OLIG2 and NKX2.2-expressing progenitors-derived spheroids. 32790583_Pediatric Soft Tissue Tumors With BCOR ITD Express EGFR but Not OLIG2. 33539525_OLIG2 maintenance is not essential for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma cell line growth but regulates tumor phenotypes. 33770499_One-step Reprogramming of Human Fibroblasts into Oligodendrocyte-like Cells by SOX10, OLIG2, and NKX6.2. 33833342_Olig2 regulates p53-mediated apoptosis, migration and invasion of melanoma cells. 34565408_Gene clusters based on OLIG2 and CD276 could distinguish molecular profiling in glioblastoma. 34948016_Profiling Glioblastoma Cases with an Expression of DCX, OLIG2 and NES. 35114775_Can oligodendrocyte transcriptional factor-2 (Olig2) be used as an alternative for 1p/19q co-deletions to distinguish oligodendrogliomas from other glial neoplasms? 35132566_The Epigenetic Regulation of OLIG2 by Histone Demethylase KDM6B in Glioma Cells. 35736214_OLIG2 Is a Determinant for the Relapse of MYC-Amplified Medulloblastoma. 35856894_Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Mutations Are Associated with Different Expression and DNA Methylation Patterns of OLIG2 in Adult Gliomas. 35967956_Investigation of OLIG2 as a candidate gene for schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder. |
ENSMUSG00000039830 |
Olig2 |
40.907498 |
3.0184138874 |
1.593791 |
0.253757391 |
40.708374 |
0.00000000017672822823093065951397169572109754551170190950415417319163680076599121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000896790850572483454941071856839074349920792883494868874549865722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.7795529 |
9.2378408 |
20.6084725 |
2.5564333 |
| ENSG00000205930 |
|
C21orf62-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.904459 |
0.2567063118 |
-1.961809 |
0.564585626 |
13.043017 |
0.00030441736157108337246235407747008139267563819885253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000776564164671481298868327414197665348183363676071166992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6278223 |
2.3361575 |
21.4203149 |
5.0802188 |
| ENSG00000206052 |
220164 |
DOK6 |
protein_coding |
Q6PKX4 |
FUNCTION: DOK proteins are enzymatically inert adaptor or scaffolding proteins. They provide a docking platform for the assembly of multimolecular signaling complexes. DOK6 promotes Ret-mediated neurite growth. May have a role in brain development and/or maintenance. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15286081}. |
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
DOK6 is a member of the DOK (see DOK1; MIM 602919) family of intracellular adaptors that play a role in the RET (MIM 164761) signaling cascade (Crowder et al., 2004 [PubMed 15286081]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:220164; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
15286081_Dok-6 binds to the phosphorylated Ret Tyr(1062) residue resulting in phosphorylation of tyrosine residue(s) located within the unique C terminus of Dok-6 predominantly through a Src-dependent mechanism 20210798_DOK-6 is involved in RET signaling with less influence when compared with DOK-1, DOK-4, and SHC. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 34545688_Association between ABHD1 and DOK6 polymorphisms and susceptibility to Hirschsprung disease in Southern Chinese children. |
ENSMUSG00000073514 |
Dok6 |
25.080296 |
17.8232182287 |
4.155686 |
0.884853711 |
15.883377 |
0.00006736782913208848788330640466881504835328087210655212402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000190395087049015560888565179453735254355706274509429931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.3974277 |
28.7245607 |
2.4878108 |
1.2740799 |
| ENSG00000206190 |
57194 |
ATP10A |
protein_coding |
O60312 |
FUNCTION: Catalytic component of P4-ATPase flippase complex, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled to the transport of phosphatidylcholine (PC) from the outer to the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane (PubMed:25947375, PubMed:29599178, PubMed:30530492). Initiates inward plasma membrane bending and recruitment of Bin/amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain-containing proteins involved in membrane tubulation and cell trafficking (PubMed:29599178). Facilitates ITGB1/beta1 integrin endocytosis, delaying cell adhesion and cell spreading on extracellular matrix (PubMed:29599178, PubMed:25947375). Has low flippase activity toward glucosylceramide (GlcCer) (PubMed:30530492). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25947375, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29599178, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30530492}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Endoplasmic reticulum;Lipid transport;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Translocase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of aminophospholipid-transporting ATPases. The aminophospholipid translocases transport phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from one side of a bilayer to another. This gene is maternally expressed. It maps within the most common interval of deletion responsible for Angelman syndrome, also known as 'happy puppet syndrome'. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:57194; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex [GO:1990531]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; ATP hydrolysis activity [GO:0016887]; ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity [GO:0140326]; glycosylceramide flippase activity [GO:0140351]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; phosphatidylcholine flippase activity [GO:0140345]; phosphatidylcholine floppase activity [GO:0090554]; ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034220]; phospholipid translocation [GO:0045332]; positive regulation of membrane tubulation [GO:1903527]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360] |
11353404_ATP10A gene is imprinted, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in human brain. 12105293_report the generation of the complete genomic structure 18186074_In the analysis of a four-marker haplotype located in ATP10C, a statistically significant difference was observed in the frequency of one haplotype between male autism patients and controls 18186074_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18726118_monoallelic expression of human ATP10A is variable in the population and is influenced by both gender and common genetic variation 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20198315_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20609483_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21209057_has been proven that hypocaloric diets induce changes in the DNA methylation pattern in PBMCs (CpG18 of ATP10A and CpG 21 of WT1) and that some of these markers could be used as early indicators of response to metabolic effects of weight-loss programs 25947375_results suggest that enhanced PC flipping activity due to exogenous ATP10A expression alters the lipid composition at the plasma membrane |
ENSMUSG00000025324 |
Atp10a |
328.776147 |
4.4375401108 |
2.149760 |
0.149888786 |
198.241276 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000505397473077541357399984610452140114523878922122240164143188216892913217804673975966778871751122639364061362690812295728193248578463681042194366455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000095148809982455487552794574301322211531196430947735339055256435182620024744988677443916730823550559082323180011379892828671245297300629317760467529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
517.7042017 |
47.5115786 |
117.4918211 |
8.3584652 |
| ENSG00000206262 |
401089 |
FOXL2NB |
protein_coding |
Q6ZUU3 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Located in fibrillar center. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:401089; |
fibrillar center [GO:0001650] |
31221094_This study presents a new upstream regulator of FOXL2 and demonstrats that this new STAT3-FOXL2 pathway has an important function in HeLaHeLa cell apoptosis, providing new insights regarding the targeting of FOXL2 for cancer prevention and treatment. |
|
|
9.572133 |
0.2296297673 |
-2.122618 |
0.530973599 |
17.381275 |
0.00003058240792306373551090459272927546408027410507202148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000090605447800967629768363609255032997680245898663997650146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5946411 |
1.2547756 |
15.7939849 |
3.0495612 |
| ENSG00000206337 |
10866 |
HCP5 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18684101_HCP5 single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping can serve as a simple screening tool for prediction of hypersensitivity reactions to abacavir. 18684101_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18982067_Data demonstrate that the influence of ZNRD1 alleles on disease progression rates are attributable to HLA-A10, help clarify the relationship between the HCP5, HLA-C and HLA-B*57 alleles, and reaffirm a critical role of HLA-B*57 alleles in HIV disease. 18982067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19050382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19115949_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19935381_No significant HIV-1 restriction was observed in the cells throughout HIV-1 life cycle, suggesting that the association of HCP5 variant with viral control is likely due to HLA-B*5701-related effect or other functional variants in the haplotype or both 20534626_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20559009_HLA-B44 allele is prevalent in Polish patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria 21084992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21510768_Haplotype analysis revealed that HLA-B*5701 and the HCP5 rs2395029(G) allele are in complete LD (r(2) = 1) in this Mexican Mestizos sample. 21860345_assessed whether increases in viral load set points are associated with genetic markers in CCR5, HCP5, and HLA-C genes 23665287_confirms the MICA/HCP5 region as a susceptibility locus for HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma and identifies rs2244546 in HCP5 as a novel tagging SNP 24322967_We confirmed the association of HCP5 with the Stevens Johnsons Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis susceptibility in a population from Mozambique treated with nevirapine 25264125_The aim of this study was to investigate whether the HCP5, TNIP1, TNFAIP3, SPATA2 and COG6 genes were genetic risk factors for psoriasis in Chinese population. 25297839_Genome-wide association analyses in 22,981 participants (2280 shingles cases) from the electronic Medical Records and Genomics Network identified a genomic region in the combined and European ancestry groups that has an age of onset effect reaching genome-wide significance region tags the non-coding gene HCP5 (HLA Complex P5). 25369137_Evidence of a higher risk to develop pericarditis with STAT4 genotypes, and an association between HCP5 rs3099844 and anti-Ro/SSA antibodies in Italian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. 27083073_The minor alleles of rs2395029, rs9264942, and rs3689068 in the HCP5 and HLA-C, and ZNRD1 genes associate with lower viral loads (VL) among antiretroviral-naive individuals and with shorter time to first VL less 51 copies/ml during anti-HIV therapy. 28855716_Six single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in three loci were associated significantly with Kawasaki disease (KD) susceptibility, including the previously reported BLK locus. The other two loci were newly identified: NMNAT2 on chromosome 1q25.3 and the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) region on chromosome 6p21.3 (HLA-C, HLA-B, MICA and HCP5). 28928439_This study showed that polymorphisms in MICA, but not in DEPDC5, HCP5 or PNPLA3, are associated with with chronic hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma development in Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. 29193002_The results of this study confirms the minor allele HCP5 is positively associated with allopurinol-induced drug hypersensitivity. 30554864_we confirmed that SP1-induced upregulation of long non-coding RNA HCP5 promotes the development of osteosarcoma. 30882006_We confirmed the association of Sjogren's syndrome with the STAT4 and IL10 genes and we describe a novel association with HCP5. 31002129_HCP5 promotes colon cancer development by activating AP1G1 via PI3K/AKT pathway. 31131047_HCP5 is a SMAD3-responsive long non-coding RNA that promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via miR-203/SNAI axis. 31137555_HCP5 is a unique human-specific gene within the MHC class I genomic region that encodes a hybrid HLA class I endogenous retroviral lncRNA with peptide coding potential. 31215169_Results observed that long noncoding RNA HCP5 was upregulated in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines and specimens. HCP5 promotes TNBC progression as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate BIRC3 by sponging miR-219a. 31622249_High HCP5 expression is associated with childhood obesity. 31746434_HCP5 was found to be highly expressed in prostate cancer. Mechanistically, HCP5 was found to promote the proliferation of prostate cancer cells via sponging miR4656 to upregulate the expression of CEMIP. These results provide novel insight into clarifying the critical function of HCP5 in regulating the progression of prostate cancer. 31836918_LncRNA HCP5 promotes LAML progression via PSMB8-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway activation. 31891769_LncRNA HCP5 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis via miR-27a-3p/IGF-1 axis in human granulosa-like tumor cell line KGN. 32112110_Decreased expression of HCP5 in biochemical premature ovarian insufficiency (bPOI) contributed to dysfunctional granulosa cells by regulating MSH5 transcription and DNA damage repair via the interaction with YB1, providing a novel epigenetic mechanism for POI pathogenesis. 32165090_Gene expression of indoleamine and tryptophan dioxygenases and three long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. 32271414_Long non-coding RNA HCP5 promotes proliferation and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via targeting miR-140-5p/IGF1R pathway. 32300102_MSC-induced lncRNA HCP5 drove fatty acid oxidation through miR-3619-5p/AMPK/PGC1alpha/CEBPB axis to promote stemness and chemo-resistance of gastric cancer. 32357145_The Effect of Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) HCP5 on Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)-Related Markers in Gastric Carcinoma Is Partially Reversed by miR-27b-3p. 32407143_LncRNA HCP5 Regulates Pancreatic Cancer Progression by miR-140-5p/CDK8 Axis. 32501499_An Intronic HCP5 Variant Is Associated With Age of Onset and Susceptibility to Graves Disease in UK and Polish Cohorts. 32657103_Knockdown of lncRNA HCP5 protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating miR-652-3p. 33044391_HCP5 rs2395029 is a rapid and inexpensive alternative to HLA-B*57:01 genotyping to predict abacavir hypersensitivity reaction in Spain. 33245911_Long non-coding RNA HCP5 in cancer. 33371778_Silencing of long non-coding RNA HCP5 inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration, and promotes apoptosis via regulation of miR-299-3p/SMAD5 axis in gastric cancer cells. 33371788_T Cell Factor 4 Is Involved in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma via Regulating Long Non-Coding RNA HCP5. 33439936_Down-regulation of HCP5 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating EPHA7 by competitively binding miR-101 in osteosarcoma. 33613117_MEF2A-mediated lncRNA HCP5 Inhibits Gastric Cancer Progression via MiR-106b-5p/p21 Axis. 33693951_Knockdown of long noncoding RNA HCP5 suppresses the malignant behavior of retinoblastoma by sponging miR36195p to target HDAC9. 33993846_HCP5 contributes to cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer through miR-128/HMGA2 axis. 34187448_LncRNA HCP5 knockdown inhibits high glucose-induced excessive proliferation, fibrosis and inflammation of human glomerular mesangial cells by regulating the miR-93-5p/HMGA2 axis. 34187569_HCP5, as the sponge of miR-1291, facilitates AML cell proliferation and restrains apoptosis via increasing PIK3R5 expression. 34190001_LncRNA HCP5 promotes malignant cell behaviors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. 34195851_lncRNA HCP5 acts as a ceRNA to regulate EZH2 by sponging miR1385p in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. 34969363_Knockdown long non-coding RNA HCP5 enhances the radiosensitivity of esophageal carcinoma by modulating AKT signaling activation. 35122570_LncRNA HCP5 Participates in the Tregs Functions in Allergic Rhinitis and Drives Airway Mucosal Inflammatory Response in the Nasal Epithelial Cells. 35389828_HLA complex P5 upregulation is correlated with poor prognosis and tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 35545536_Overexpression of lncRNA HCP5 in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promoted the proliferation and inhibited the apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells via the musashi RNA-binding protein 2/oestrogen receptor alpha 1 axis. 35769676_Silencing of Long Noncoding RNA HLA Complex P5 (HCP5) Suppresses Glioma Progression through the HCP5-miR-205-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Feedback Loop. 35899856_Long noncoding RNA HCP5 promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via the miR-29b-3p-LOXL2 axis. 35931662_Dexmedetomidine Mitigates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Mitochondrial Apoptosis through Targeting lncRNA HCP5. |
|
|
14.844617 |
0.3170720625 |
-1.657117 |
0.451369815 |
13.741715 |
0.00020974391122613420825569752192762962295091710984706878662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000547351508079515700067041450438409810885787010192871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.0740697 |
1.7659920 |
19.5222096 |
3.3564043 |
| ENSG00000206503 |
3105 |
HLA-A |
protein_coding |
P04439 |
FUNCTION: Antigen-presenting major histocompatibility complex class I (MHCI) molecule. In complex with B2M/beta 2 microglobulin displays primarily viral and tumor-derived peptides on antigen-presenting cells for recognition by alpha-beta T cell receptor (TCR) on HLA-A-restricted CD8-positive T cells, guiding antigen-specific T cell immune response to eliminate infected or transformed cells (PubMed:2456340, PubMed:2784196, PubMed:1402688, PubMed:7504010, PubMed:9862734, PubMed:10449296, PubMed:12138174, PubMed:12393434, PubMed:15893615, PubMed:17189421, PubMed:19543285, PubMed:21498667, PubMed:24192765, PubMed:7694806, PubMed:24395804, PubMed:28250417). May also present self-peptides derived from the signal sequence of secreted or membrane proteins, although T cells specific for these peptides are usually inactivated to prevent autoreactivity (PubMed:25880248, PubMed:7506728, PubMed:7679507). Both the peptide and the MHC molecule are recognized by TCR, the peptide is responsible for the fine specificity of antigen recognition and MHC residues account for the MHC restriction of T cells (PubMed:12796775, PubMed:18275829, PubMed:19542454, PubMed:28250417). Typically presents intracellular peptide antigens of 8 to 13 amino acids that arise from cytosolic proteolysis via IFNG-induced immunoproteasome or via endopeptidase IDE/insulin-degrading enzyme (PubMed:17189421, PubMed:20364150, PubMed:17079320, PubMed:26929325, PubMed:27049119). Can bind different peptides containing allele-specific binding motifs, which are mainly defined by anchor residues at position 2 and 9 (PubMed:7504010, PubMed:9862734). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12138174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12393434, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12796775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1402688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15893615, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17079320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17189421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18275829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19542454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19543285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20364150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21498667, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24192765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24395804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2456340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25880248, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26929325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27049119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2784196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28250417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7504010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7506728, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7679507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7694806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9862734}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*01:01: Presents a restricted peptide repertoire including viral epitopes derived from IAV NP/nucleoprotein (CTELKLSDY), IAV PB1/polymerase basic protein 1 (VSDGGPNLY), HAdV-11 capsid L3/hexon protein (LTDLGQNLLY), SARS-CoV-2 3a/ORF3a (FTSDYYQLY) as well as tumor peptide antigens including MAGE1 (EADPTGHSY), MAGEA3 (EVDPIGHLY) and WT1 (TSEKRPFMCAY), all having in common a canonical motif with a negatively charged Asp or Glu residue at position 3 and a Tyr anchor residue at the C-terminus (PubMed:1402688, PubMed:7504010, PubMed:17189421, PubMed:20364150, PubMed:25880248, PubMed:30530481, PubMed:19177349, PubMed:24395804, PubMed:26758806, PubMed:32887977). A number of HLA-A*01:01-restricted peptides carry a post-translational modification with oxidation and N-terminal acetylation being the most frequent (PubMed:25880248). Fails to present highly immunogenic peptides from the EBV latent antigens (PubMed:18779413). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1402688, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17189421, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18779413, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19177349, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20364150, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24395804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25880248, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26758806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30530481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7504010}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*02:01: A major allele in human populations, presents immunodominant viral epitopes derived from IAV M/matrix protein 1 (GILGFVFTL), HIV-1 env (TLTSCNTSV), HIV-1 gag-pol (ILKEPVHGV), HTLV-1 Tax (LLFGYPVYV), HBV C/core antigen (FLPSDFFPS), HCMV UL83/pp65 (NLVPMVATV) as well as tumor peptide antigens including MAGEA4 (GVYDGREHTV), WT1 (RMFPNAPYL) and CTAG1A/NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC), all having in common hydrophobic amino acids at position 2 and at the C-terminal anchors. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11502003, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12138174, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12796775, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17079320, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18275829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19542454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20619457, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22245737, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26929325, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2784196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28250417, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7694806, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7935798, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8630735, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8805302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8906788, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9177355}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*03:01: Presents viral epitopes derived from IAV NP (ILRGSVAHK), HIV-1 nef (QVPLRPMTYK), HIV-1 gag-pol (AIFQSSMTK), SARS-CoV-2 N/nucleoprotein (KTFPPTEPK) as well as tumor peptide antigens including PMEL (LIYRRRLMK), NODAL (HAYIQSLLK), TRP-2 (RMYNMVPFF), all having in common hydrophobic amino acids at position 2 and Lys or Arg anchor residues at the C-terminus (PubMed:7504010, PubMed:7679507, PubMed:9862734, PubMed:19543285, PubMed:21943705, PubMed:2456340, PubMed:32887977). May also display spliced peptides resulting from the ligation of two separate proteasomal cleavage products that are not contiguous in the parental protein (PubMed:27049119). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19543285, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21943705, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2456340, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27049119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7504010, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7679507, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9862734}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*11:01: Presents several immunodominant epitopes derived from HIV-1 gag-pol and HHV-4 EBNA4, containing the peptide motif with Val, Ile, Thr, Leu, Tyr or Phe at position 2 and Lys anchor residue at the C-terminus. Important in the control of HIV-1, EBV and HBV infections (PubMed:10449296). Presents an immunodominant epitope derived from SARS-CoV-2 N/nucleoprotein (KTFPPTEPK) (PubMed:32887977). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449296, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32887977}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*23:01: Interacts with natural killer (NK) cell receptor KIR3DL1 and may contribute to functional maturation of NK cells and self-nonself discrimination during innate immune response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182537}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*24:02: Presents viral epitopes derived from HIV-1 nef (RYPLTFGWCF), EBV lytic- and latent-cycle antigens BRLF1 (TYPVLEEMF), BMLF1 (DYNFVKQLF) and LMP2 (IYVLVMLVL), SARS-CoV nucleocapsid/N (QFKDNVILL), as well as tumor peptide antigens including PRAME (LYVDSLFFL), all sharing a common signature motif, namely an aromatic residue Tyr or Phe at position 2 and a nonhydrophobic anchor residue Phe, Leu or Iso at the C-terminus (PubMed:9047241, PubMed:12393434, PubMed:24192765, PubMed:20844028). Interacts with natural killer (NK) cell receptor KIR3DL1 and may contribute to functional maturation of NK cells and self-nonself discrimination during innate immune response (PubMed:17182537, PubMed:18502829). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12393434, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182537, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18502829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20844028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24192765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9047241}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*26:01: Presents several epitopes derived from HIV-1 gag-pol (EVIPMFSAL, ETKLGKAGY) and env (LVSDGGPNLY), carrying as anchor residues preferentially Glu at position 1, Val or Thr at position 2 and Tyr at the C-terminus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15893615}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*29:02: Presents peptides having a common motif, namely a Glu residue at position 2 and Tyr or Leu anchor residues at the C-terminus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8622959}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*32:01: Interacts with natural killer (NK) cell receptor KIR3DL1 and may contribute to functional maturation of NK cells and self-nonself discrimination during innate immune response. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17182537}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*68:01: Presents viral epitopes derived from IAV NP (KTGGPIYKR) and HIV-1 tat (ITKGLGISYGR), having a common signature motif namely, Val or Thr at position 2 and positively charged residues Arg or Lys at the C-terminal anchor. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1448153, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1448154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:2784196}.; FUNCTION: Allele A*74:01: Presents immunodominant HIV-1 epitopes derived from gag-pol (GQMVHQAISPR, QIYPGIKVR) and rev (RQIHSISER), carrying an aliphatic residue at position 2 and Arg anchor residue at the C-terminus. May contribute to viral load control in chronic HIV-1 infection. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21498667}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Glycoprotein;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;MHC I;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Sulfation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
HLA-A belongs to the HLA class I heavy chain paralogues. This class I molecule is a heterodimer consisting of a heavy chain and a light chain (beta-2 microglobulin). The heavy chain is anchored in the membrane. Class I molecules play a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from the endoplasmic reticulum lumen so that they can be recognized by cytotoxic T cells. They are expressed in nearly all cells. The heavy chain is approximately 45 kDa and its gene contains 8 exons. Exon 1 encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the alpha1 and alpha2 domains, which both bind the peptide, exon 4 encodes the alpha3 domain, exon 5 encodes the transmembrane region, and exons 6 and 7 encode the cytoplasmic tail. Polymorphisms within exon 2 and exon 3 are responsible for the peptide binding specificity of each class one molecule. Typing for these polymorphisms is routinely done for bone marrow and kidney transplantation. More than 6000 HLA-A alleles have been described. The HLA system plays an important role in the occurrence and outcome of infectious diseases, including those caused by the malaria parasite, the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV). The structural spike and the nucleocapsid proteins of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), are reported to contain multiple Class I epitopes with predicted HLA restrictions. Individual HLA genetic variation may help explain different immune responses to a virus across a population.[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:3105; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum exit site [GO:0070971]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi medial cisterna [GO:0005797]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; MHC class I peptide loading complex [GO:0042824]; MHC class I protein complex [GO:0042612]; phagocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030670]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; recycling endosome membrane [GO:0055038]; beta-2-microglobulin binding [GO:0030881]; CD8 receptor binding [GO:0042610]; peptide antigen binding [GO:0042605]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; T cell receptor binding [GO:0042608]; TAP binding [GO:0046977]; TAP complex binding [GO:0062061]; antibacterial humoral response [GO:0019731]; antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I [GO:0019885]; antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-dependent [GO:0002485]; antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-independent [GO:0002486]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I [GO:0042590]; CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:0036037]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; detection of bacterium [GO:0016045]; immune response [GO:0006955]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell activation [GO:2001187]; positive regulation of CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell proliferation [GO:2000566]; positive regulation of memory T cell activation [GO:2000568]; positive regulation of T cell cytokine production [GO:0002726]; positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001916]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; protection from natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042270]; T cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0001913]; T cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target [GO:0002419]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
10954160_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11010837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11053636_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11064107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11082518_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11098929_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11118029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11119299_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11120862_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11133384_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11144289_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11169240_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11169242_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11169245_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11180452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11181188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11182228_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11182232_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11208333_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11260506_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11260507_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11266078_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11285127_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11285128_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11294566_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11374682_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423179_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11464148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11480844_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11485622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11507979_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11543892_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11543893_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11543903_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11556970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11556980_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11600222_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11678832_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11752149_magnitude and specificity of influenza A virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in humans is related to HLA-A and -B phenotype 11840200_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11840504_Proposed association of A24 and A26 with schizophrenia in Japan was not confirmed. 11841366_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11861287_Soluble HLA class I molecules induce natural killer cell apoptosis through the engagement of CD8. HLA-A2, -Cw4, and -Bw46 alleles, or HLA-G1 leads to NK cell apoptosis. 11862383_Disparate binding of chaperone proteins by HLA-A subtypes 11887210_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11903375_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11904677_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11914421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11927505_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11929590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11953475_HLA-A*3303 restricts an HIV-1 Vpu epitope associated with non-progression. 11956863_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11979305_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11984513_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12010826_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12028541_Eight new HLA-A alleles associated with antigens in the A2 CREG. 12028542_two new HLA-A alleles, A*2419 and A* 3011, that were initially recognized by an aberrant serological pattern. 12029127_Polymorphisms in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase were most evident at sites of least functional or structural constraint and frequently were associated with particular host HLA-A and HLA-B alleles 12043563_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12047355_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12077441_a soluble recombinant HLA-A*1101 molecule has been expressed and used to assemble a complex with beta2-microglobulin and a Nef decapeptide. 12100571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12100686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12115193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12121673_The HLA class I A locus affects susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. 12144620_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12145797_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12168074_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12174215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12186703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12296785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12351949_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12366787_The nucleotide sequences of HLA-A*1112 exons 2 and 3 are identical to HLA-A*11011 except for a single nucleotide substitution in codon 90 (GAC-->GCC). 12366788_HLA-A*6818 N displays a sequence identical to that of the HLA-A*6802 allele. This duplication creates a shift of the reading frame, which leads to a premature non-sense codon at position 59 of the null allele. 12366789_The new allele HLA-B*4431 only displayed B44 seroreactivity, which demonstrates that epitopes crucial for B60(40) specificity must be located in the alpha1 domain. 12366790_The allelic product of HLA-B*3531 is composed of B35 in its alpha1 domain and of B61(40) in its alpha2 domain. Both specificities are only weakly detectable with available sera. 12370085_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12370503_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12372094_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12392856_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12414957_Nef binds directly to the HLA-A2 cytoplasmic tail 12437654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12443029_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12445315_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12445318_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12445319_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12458337_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12459502_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12464650_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12472657_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12472660_HLA-A allele associations with secondary dengue virus infections correlate with disease severity and the infecting viral serotype in ethnic Thais. 12486530_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12486606_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12507820_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12507823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12507825_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12507828_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12516093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12574360_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12578601_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12584329_results indicate that the most prominent effect of Nef on HLA-A2 in T cells was to inhibit transport to the cell surface 12590984_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12648281_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12651075_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12665835_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12691707_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12694583_HLA-A, -B, and -DRB1 alleles in a total of 236 Taiwanese adults with Graves' disease and 533 racially matched normal control subjects were examined 12694583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12714268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12717621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12753657_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12753666_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12753667_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12768083_Familial predisposition to IgA nephropathy is associated with HLA antigens and particular candidate genes. 12774051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12803653_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12811505_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12825172_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12826374_identified 21 critical polymorphic functional residue positions (CPFRP) that significantly reduced functional pocket variability to just 189 among 212 HLA-A alleles 12826378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12850493_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12859593_A computational method was used to predict the serologic specificity of HLA molecules encoded by HLA-A. 12859597_A Gambian TNF haplotype matches the European HLA-A1, B8, DR3 and Chinese HLA-A33, B58, DR3 haplotypes. 12866921_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12917841_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12941076_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12956877_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12956878_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12974801_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12975536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14501786_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14504973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14510801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14522093_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14527201_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14527733_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14551034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14581545_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14601650_a novel HLA-A0201-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-epitope (28-SLYKFSPFPL; FSP06) derived from a mutant O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase 14617036_we examine the contribution of the HLA region to the clinical phenotype of UC. 14617038_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14648147_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14651518_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14656748_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14673570_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14674935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14686115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14693734_HLA alleles plays an important role in the development of central nervous system meningiomas. 14693734_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14700596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14700597_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 14700598_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14700599_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14705987_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14727382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14748996_The frequency of haplotypes HLA-A in systemic lupus erythematosus group was significantly higher than that of control. 14871250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14969772_HLA-A*2402 together with microsatellite D6S248-15 allele could be B27-independent markers of additional susceptibility gene/s localised in the region telomeric to HLA-A in Basque ankylosing spondylitis patients. 14969772_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14989713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15000695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15009803_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15009808_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15034213_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15046556_In patients with autoimmune thyroiditis the HLA-A24 frequency of was higher than control values while in patients with polyglandular activation of autoimmunity, the HLA-A3 frequency was found to be higher. 15057902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15061705_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15070694_selective down-regulation of HLA-A and HLA-Bw6 allospecificities associated with HLA-Bw4 preservation in leukemic cells 15072129_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15072129_Significant increase in frequency of HLA-A were observed in leprosy patients when compared with controls. 15086350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15100263_Novel conditions are required for priming and antigen-specific expansion of cytotoxic T cells reactive to the HIV-1 p17 Gag(77-85) epitope on circulating naive CD8+ precursor cells derived from HLA-A*0201 HIV-seronegative healthy donors. 15113995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15122136_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15124939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15128805_The apparent association of HLA-A*1101 with resistance to HIV-1 infection may reflect, at least in part, an interplay of functional advantages that particular structural features of the peptide-binding groove may confer to HLA-A*1101. 15128924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131131_Results indicate that mutations at both position 65 and position 66 influence peptide binding by the human class I major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-A2 to various extents. 15140031_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15140038_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15144462_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15191527_identification of a new variant of the A*2607 allele, named A*260702 15191952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15202948_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15211110_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15220037_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15228651_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15236755_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15239092_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15243926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15245373_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15245377_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15245541_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15251317_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15275783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15275783_These results suggest that the HLA-A*3303-B*4403-DRB1*1302 haplotype plays an important role in the development of PHN after herpes zoster, but not in the onset of herpes zoster. 15280452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15301865_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15301866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15304010_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15307871_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15314693_Prevalent expression of the immunostimulatory MHC class I chain-related molecule is counteracted by shedding in prostate cancer. 15321756_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15323271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15361126_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15361135_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15362660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15385740_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15455355_Coordinated downregulation of the antigen presentation machinery and HLA class I/beta2-microglobulin complex is responsible for HLA-ABC loss in bladder cancer 15459953_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15471368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15480178_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15483462_HTLV-1 Tax protein epitopes were tested for protective efficacy in a preclinical model of infection using HTLV-1 Tax recombinant vaccinia virus and HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice. 15491536_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15496200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15496201_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15498100_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15534563_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15546341_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15554365_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15555263_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15567775_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15596859_transport of HLA-A2 to cell surface disrupted by Nef 15607698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15613143_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15621102_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15629059_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15631661_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15640334_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15640334_The genetic susceptibility of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension is controlled by HLA polymorphism. 15662734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15666025_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15681828_the T cell epitope HCV core 35-44 stabilizes HLA-A2 and HLA-E and inhibits cytolysis mediated by natural killer cells 15683420_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15701833_Loss of HLA class I gene is associated with pancreatic carcinoma progression 15726104_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15740492_Additional risk of hereditary hemochromatosis given by class I HLA antigens may be secondary to the HFE gene linkage disequilibrium with certain class I alleles or to the existence of other neighboring genetic pathogenetic factors in our Spanish sample. 15740492_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15743917_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15772003_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15784468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793795_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15793795_The distribution of HLA-A, -B allele polymorphism in the Luoba nationality is distinctive, but some of the gene distribution in the Luoba group is nearer to that in the Tibetan group. 15807454_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15809757_ABCE1 and its peptides could be target molecules in specific immunotherapy for HLA-A2(+) colon cancer patients. 15836703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15847654_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15853898_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15853903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15853904_A new alleles, HLA-A*6824, differs from A*680102 by a single nucleotide change at position 275 in exon 2, which results in a conservative amino acid substitution from lysine to arginine in the peptide-binding groove at codon 68. 15853906_A new allele, HLA-A* 0261, differs from HLA-A* 020601 by a single-nucleotide substitution at codon 57 (CCG-->GCG) resulting in an amino acid change from Pro to Ala. 15854278_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15858601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15896205_analysis of novel allele HLA-A*0278 15896206_analysis of novel allele HLA-A*2442 15935891_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15940053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15952133_The HLA-DRB1 loci are highly polymorphic in Monba population of Xizang Autonomous Region. Compared with other ethnic groups in China, the Monba ethnic group is close to Tibetan ethnic group. 15968843_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15975271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15982254_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15982258_new HLA class I alleles found in Caucasian population: A*3012, B*270505, B*3541 and Cw*0716 15982259_analysis of HLA-A*2451, a new allele found in a Chinese donor 15983206_Identification of HLA-A2-restricted, naturally processed epitopes derived from proinsulin, an autoantigen likely to play an important role in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. 16019679_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16029431_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16041067_the first high-resolution X-ray structure of HLA-A*1101 in complex with a peptide derived from SARS coronavirus (CoV) nucleocapsid protein is described 16053028_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16086294_In a northwest Chinese Han population, fifteen alleles for the locus HLA-A, 28 alleles for the HLA-B locus and 13 alleles for the HLA-DRB1 were detected. The results showed that the most frequent HLA alleles found were A02, B13, and DRB1*15. 16086295_Guangdong Han population in China has twelve HLA-A, 23 B, 11 Cw and 13 DRB1 alleles and a total of 9 HLA-A-B, 20 Cw-B, 7 A-Cw, and 8 A-DRB1, 9 B-DRB1, 10 Cw-DRB1 haplotypes. 16086925_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16095491_anti-HLA class I Abs play an important role in the pathogenesis of obliterative airway disease by inducing growth factor production, apoptosis and chemotaxis of inflammatory cells 16101833_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16101834_HLA-A *0101 is mutated in a colorectal tumor cell line 16103458_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16113298_suballeles of the HLA-A2 supertype can effectively present antigenic epitopes in response to preerythrocytic malarial antigens derived from Malian children 16120569_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16129034_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16143070_HLA-A01 alleles in Han population, Gansu province seem to contribute to the genetic susceptibility, while HLA-A11 and -DR03 alleles to the genetic resistance, to leukemia. 16143070_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16156661_A fluorescence polarization competitive peptide-binding assay was tested on a panel of 15 well-defined HLA-A0201 ligands from various sources covering a broad range of binding affinities. 16173256_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16174649_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16185325_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16185329_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16185849_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16185849_The HLA-A*02 and -A*03 were observed increased frequencies in patients less than 50% hair loss, and HLA-B*27 equally in patients of 50-99% hair loss, alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis. 16215732_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16215957_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16215957_The HLA-A,-B,-DRB1 distribution in Shanxi Han population shares some genetic characteristics with other Han populations in northern part of China, but it exhibits its own characteristics. 16216678_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16235173_HLA-A polymorphism is one of the host genetic factors that alter the risk for the development of cervical cancer in Chinese women. 16235173_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16267409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16305683_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16307312_EBV isolates from nasopharyngeal carcinoma of southern China and Taiwan is dominated by an HLA A2-restricted 'epitope-loss variants' of LMP-1 16310048_HLA-A2 mutants with substitutions at known TCR contact sites were compared for recognition by hapten-cross-reactive CTL. Similar AA contacts are made by the TCR during recognition of immunizing or cross-reacting complexes. 16322289_HLA class I antigen loss was significantly correlated with glioblastoma multiforme 16331510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16331567_HLA-A allele frequency distributions were consistent with the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a group of indigenous Hans in Shenyang, China. 16343061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16361713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16365741_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16386646_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16386651_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16405603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16441486_Gene frequencies and haplotypic associations within HLA-A loci were determined at a high-resolution allelic level and should provide useful information in anthropology, bone marrow donor registry, legal medicine, and disease association studies. 16441486_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16441487_The HLA-A*1115-bearing haplotype was B*350101; Cw*040101; DRB1*140101; DRB3*020201; DQA1*010401; DQB1*0503; DPA1*0103/07; DPB1*030101. Extensive serological typing indicated that this allele essentially encodes a 'normal' HLA-A11 specificity. 16441491_HLA-A*2313 is closest to A*2301 but is likely to stimulate T cells when mismatched 16441492_Identification of a novel HLA-A*02 allele, A*0287 16441493_Identification of a new allele, HLA-A*3308 16441494_A novel HLA-A*680104 variant 16441495_Identification of two new HLA-A variants, HLA-A*2911 and HLA-A*6827 16451198_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16451199_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16451204_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16456797_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16456803_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16459714_Intrathecal production and fluctuations in CSF and serum concentrations of sHLA-I were reciprocal in multiple sclerosis. 16463424_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16473309_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16481299_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16481299_The susceptibility to PBC in Chinese individuals is associated with DRB1*0701 allele. 16493087_Transgenic expression in NOD mice of HLA-A*0201, in the absence of murine class I MHC molecules, is sufficient to mediate autoreactive CD8+ T cell responses contributing to development of type 1 diabetes 16532100_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16533342_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16538176_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16583211_A novel HLA-A allele, HLA-A*0279, was identified. 16604503_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16608404_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16609350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16611249_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16671946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16675560_In hepatocellular carcinoma patients, HLA-A could induce cytotoxic T lymphocytes for glypican 3-based immunotherapy (HLA-A2 AND HLA-A24) 16698425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16704965_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16720216_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16720216_The association and linkage of the class I HLA-A2 allele with autism suggests its involvement in the etiology of autism. 16731854_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16767661_A novel allele of HLA-A has been identified and officially named HLA-A*3308 by standard of the WHO Nomenclature Committee. 16786814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16857416_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16866883_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16866885_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16878186_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16883565_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16922942_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16926287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17021767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17026471_Observational study of ge |
ENSMUSG00000037130+ENSMUSG00000048231+ENSMUSG00000037334+ENSMUSG00000073411+ENSMUSG00000079507+ENSMUSG00000054128+ENSMUSG00000091705+ENSMUSG00000035929+ENSMUSG00000073402+ENSMUSG00000060550+ENSMUSG00000037537+ENSMUSG00000067235+ENSMUSG00000024448+ENSMUSG00000079492+ENSMUSG00000067201+ENSMUSG00000067212+ENSMUSG00000024459+ENSMUSG00000016206+ENSMUSG00000058124+ENSMUSG00000023083+ENSMUSG00000073409+ENSMUSG00000056116+ENSMUSG00000037246+ENSMUSG00000092243+ENSMUSG00000079491+ENSMUSG00000016283+ENSMUSG00000064308+ENSMUSG00000061232 |
H2-M10.6+H2-M10.4+H2-M1+H2-D1+H2-Q1+H2-T3+H2-Q2+H2-Q4+Gm8909+H2-Q7+H2-M11+H2-Q10+H2-M10.1+Gm11127+H2-M9+H2-T23+H2-M5+H2-M3+H2-M10.3+H2-M10.2+H2-Q6+H2-T22+H2-M10.5+Gm7030+H2-T10+H2-M2+2410137M14Rik+H2-K1 |
166.287004 |
0.1389585825 |
-2.847273 |
0.372681853 |
52.402206 |
0.00000000000045221578740470066238541187304603305511770464097942578973743366077542304992675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002758142571112967705574634857009134569598429731485111915390007197856903076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
42.2760229 |
10.5409675 |
307.2513343 |
52.8850192 |
| ENSG00000206530 |
55779 |
CFAP44 |
protein_coding |
Q96MT7 |
FUNCTION: Flagellar protein involved in sperm flagellum axoneme organization and function. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:E9Q5M6}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cilium;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Flagellum;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Enables peptidase activity. Involved in sperm axoneme assembly. Acts upstream of or within microtubule cytoskeleton organization. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm; cytoskeleton; and motile cilium. Implicated in spermatogenic failure 20. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:55779; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; motile cilium [GO:0031514]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; cilium-dependent cell motility [GO:0060285]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; sperm axoneme assembly [GO:0007288] |
25602530_Results show that the rs13064411 polymorphism in the WDR52 gene was associated with a modified effect of statin therapy on serum LDL and total cholesterol levels. 28552195_biallelic mutations in either CFAP43 or CFAP44 can cause sperm flagellar abnormalities and impair sperm motility. 29277146_Study demonstrated that biallelic mutations in CFAP44 and CFAP43 cause multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella (MMAF). These results provide researchers with a new insight to understand the genetic etiology of MMAF and to identify new loci for genetic counselling of MMAF. 29449551_demonstrate that CFAP43 and CFAP44 have a similar structure with a unique axonemal localization and are necessary to produce functional flagella in species ranging from Trypanosoma to human 30904354_important cause of multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagellum in the Chinese population |
ENSMUSG00000071550 |
Cfap44 |
53.874152 |
0.4699259193 |
-1.089495 |
0.366421552 |
8.682197 |
0.00321333405020652555089677449018381594214588403701782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006832153641752854514312964795408333884552121162414550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.8267604 |
7.5663579 |
68.3102332 |
11.3397082 |
| ENSG00000206561 |
8292 |
COLQ |
protein_coding |
Q9Y215 |
FUNCTION: Anchors the catalytic subunits of asymmetric AChE to the synaptic basal lamina. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Collagen;Congenital myasthenic syndrome;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Neurotransmitter degradation;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse |
|
This gene encodes the subunit of a collagen-like molecule associated with acetylcholinesterase in skeletal muscle. Each molecule is composed of three identical subunits. Each subunit contains a proline-rich attachment domain (PRAD) that binds an acetylcholinesterase tetramer to anchor the catalytic subunit of the enzyme to the basal lamina. Mutations in this gene are associated with endplate acetylcholinesterase deficiency. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8292; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; cell junction [GO:0030054]; collagen trimer [GO:0005581]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; neuromuscular junction [GO:0031594]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synaptic cleft [GO:0043083]; extracellular matrix structural constituent [GO:0005201]; heparin binding [GO:0008201]; acetylcholine catabolic process in synaptic cleft [GO:0001507]; establishment of protein localization to membrane [GO:0090150]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; regulation of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction [GO:0008582]; skeletal muscle acetylcholine-gated channel clustering [GO:0071340] |
11865139_Three novel colq protein mutations in eight kinships. 12609505_Both patients presented a novel splicing mutation (IVS1-1G-->A) affecting the exon encoding the proline-rich attachment domain (PRAD), which interacts with acetylcholinesterase. 16256971_muscle fiber type-specific expression pattern of ColQ transcripts was regulated by a slow upsteam regulatory element (SURE) and a fast intronic regulatory element (FIRE) 17300939_we found familial occurrence of congenital ptosis in heterozygous carriers of 950delC. 18180250_Twenty different mutations of the COLQ gene have been identified in our patients: The mutations are missense (6), splice-site (3), in-frame deletion (1), non-sense (4) and frameshift (6). The majority of the mutations are protein truncating. 20370815_two siblings have identical novel heterozygous mutations but different phenotypic expressions. 22088788_Long-term follow-up of patients with COLQ mutations showed no genotype-phenotype correlation, 80% of patients were ambulant and 87% of patients had no respiratory trouble in spite of severe relapses. 22490774_This study presented that four cases illustrate the clinical spectrum of the recurrent homozygous W148X mutation in the COLQ gene. 23553736_We proved that the missense mutations in ColQ-CTD cause endplate AChE deficiency by compromising ColQ-MuSK interaction at the NMJ. 24281389_findings suggest that the impaired attachment of COOH-terminal mutants causing EP AChE deficiency is in part independent of MuSK, and that the COOH-terminus of ColQ may interact with other proteins at the BL 24938146_study identified the molecular cause underlying congenital myasthenic syndrome in two patients in a Syrian family, a novel missense mutation, homozygous single nucleotide substitution (c.1010T>C) in the COLQ gene 26282582_Global splicing analysis with RNA-seq revealed that exons carrying the hnRNP H-binding GGGGG motif are predisposed to be skipped compared to those carrying the SRSF1-binding GGAGG motif in both human and mouse brains. 28024842_Mutations in RAPSN and COLQ are the most common causes of congenital myasthenic syndrome in Israel. 28585551_COLQ rs7609897-T association with diverticular disease in Iceland and Denmark population. 29630557_To study cholinesterase distribution in patients with COLQ gene mutation, immunohistochemical staining and indirect immunofluorescence method was used to detect cholinesterase lack of disease in patients with resectable pancreatic or lung tissue samples, confirmed cholinesterase distribution in nerve fibers surrounding the vessels. Expression of cholinesterase in mutant patients was significantly higher than wildtype. 30124556_This data highlight COLQ (R410W) as a variant to initially test for in patients who have isolated limb-girdle myasthenia and are not responsive to acetylcholine receptor inhibitors, especially those from southern India. 33353066_The First Case of Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome Caused by a Large Homozygous Deletion in the C-Terminal Region of COLQ (Collagen Like Tail Subunit of Asymmetric Acetylcholinesterase) Protein. 34225052_COLQ and ARHGAP15 are Associated with Diverticular Disease and are Expressed in the Colon. |
ENSMUSG00000057606 |
Colq |
32.120505 |
0.0937053588 |
-3.415725 |
0.565042005 |
32.378493 |
0.00000001268830462289698008443996301002759663489882768772076815366744995117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000054712058496628518643409988400985732859282961726421490311622619628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5288148 |
2.5397306 |
70.8008300 |
18.4863339 |
| ENSG00000211455 |
23012 |
STK38L |
protein_coding |
Q9Y2H1 |
FUNCTION: Involved in the regulation of structural processes in differentiating and mature neuronal cells. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15037617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15067004}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Actin-binding;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Kinase;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
Enables ATP binding activity; magnesium ion binding activity; and protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Involved in intracellular signal transduction. Acts upstream of or within protein phosphorylation. Located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:23012; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; actin binding [GO:0003779]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0018105]; postsynapse organization [GO:0099173]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cellular component organization [GO:0051128] |
15067004_NDR1 and NDR2 serine-threonine kinases are regulated by mob proteins 15582665_The NDR1 and NDR2 kinases were incorporated into HIV-1 particles and were cleaved by the HIV-1 protease. 16314523_Activation of NDR2 is a multistep process involving phosphorylation of the hydrophobic motif site Thr444/2 by MST3, autophosphorylation of Ser281/2, and binding of MOB1A. 16488889_NDR2 is an upstream kinase of ARK5 that plays an essential role in tumor progression through ARK5 19062280_findings identify NDR1/2 as novel proapoptotic kinases and key members of the RASSF1A/MST1 signaling cascade 19240061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21262772_These findings establish a novel MST3-NDR-p21 axis as an important regulator of G(1)/S progression of mammalian cells. 23435566_NDR2-mediated Rabin8 phosphorylation is crucial for ciliogenesis by triggering the switch in binding specificity of Rabin8 from PS to Sec15. 23897809_cyclin D1 has a role in promoting cell cycle progression by enhancing NDR1/2 kinase activity independent of Cdk4 28556638_It was found that STK38L*I/D genotype had positive association with longevity in the ethnically homogeneous group of Tatars from the Republic of Bashkortostan, Russia. 29108249_This study shows that STK38L is co-amplified with oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer cell lines, where it regulates LATS2 gene expression. 30504095_These results suggest that NDR2 may play important roles in IL-17-associated inflammation by promoting Smurf1-mediated MEKK2 ubiquitination and degradation. 30714141_Study identified rs10842893 as a novel independent SNP in the gene STK38L that was significantly associated with glioma risk in Chinese population, and furthermore confirmed previously reported associations of rs498872 and rs6010620 with glioma risk in European descent population and Chinese Han population. 30775439_NDR2 positively regulated an antiviral innate immune response in a kinase activity-independent manner. NDR2 interacts with RIG-I and promotes TRIM25-mediated RIG-I ubiquitination, which is required for downstream signaling activation and type I IFN production. 31427083_The results demonstrate that NDR2 is a reversible acetylated kinase regulated by SIRT1 and p300/CBP. 35670107_TRIM27 cooperates with STK38L to inhibit ULK1-mediated autophagy and promote tumorigenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000001630 |
Stk38l |
1047.276946 |
2.7582234658 |
1.463739 |
0.109660491 |
172.841471 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000177251642886782774779639646172151189718950099713063243964911941140772653772667130922419606288213781179405326149378652189625427126884460449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000029199042957688765624864749801578062098286480302431258304627510059349868146023518975508951934811231049282653771115292329341173171997070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1449.2609633 |
99.6778962 |
529.1776725 |
26.9997195 |
| ENSG00000212694 |
338799 |
LINC01089 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27485121_Interestingly, EGF rapidly downregulates LINC01089 (here renamed LncRNA Inhibiting Metastasis; LIMT) expression by enhancing histone deacetylation at the respective promoter. 30868865_Glioma tissues exhibit loss of LINC01089 (LncRNA001089) expression, which is associated with poor prognosis in glioma patients. 33025678_LINC01089 inhibits the progression of cervical cancer via inhibiting miR-27a-3p and increasing BTG2. 33892399_LncRNA-LINC01089 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via sponging miR-543. 34281560_LINC01089 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and migration via miR-301b-3p/STARD13 axis. 36399257_The crosstalk between LINC01089 and hippo pathway inhibits osteosarcoma progression. |
|
|
37.303615 |
0.2398772391 |
-2.059632 |
0.291305401 |
52.954591 |
0.00000000000034134916203032476381774111287884577211736852886403426055039744824171066284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002098423003568343641227860923264878054324278355835531328921206295490264892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.8559165 |
2.6850142 |
62.2979905 |
6.2845547 |
| ENSG00000212864 |
727800 |
RNF208 |
protein_coding |
Q9H0X6 |
|
Metal-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables ubiquitin-protein transferase activity. Involved in protein autoubiquitination. Located in cytosol and nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:727800; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; ubiquitin-protein transferase activity [GO:0004842]; protein autoubiquitination [GO:0051865]; protein ubiquitination [GO:0016567] |
31862882_RING finger protein 208 (RNF208) decreases the stability of soluble Vimentin protein through a polyubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation pathway, thereby suppressing metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. RNF208 was significantly lower in TNBC than the luminal type, and low expression of RNF208 was strongly associated with poor clinical outcomes. |
ENSMUSG00000044628 |
Rnf208 |
9.947458 |
0.1814676976 |
-2.462215 |
0.586094551 |
19.684954 |
0.00000913175287934067773942554274713145900932431686669588088989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000028738736140526311584920959862898826031596399843692779541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9281721 |
1.1306461 |
16.3954955 |
3.2356187 |
| ENSG00000212978 |
339803 |
C2orf74-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73.046447 |
0.4887914388 |
-1.032709 |
0.216374226 |
22.849518 |
0.00000175193277419444085580917634670239380056955269537866115570068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006028781672558267762591140831451852477584907319396734237670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.7627488 |
6.4206916 |
98.9335219 |
8.8704562 |
| ENSG00000213121 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57.883509 |
0.3345145747 |
-1.579859 |
0.235566850 |
45.510249 |
0.00000000001518422458022824626901369974549304078803579898249154211953282356262207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000083222857335376501297361832196029666000591795693708263570442795753479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.0448823 |
4.4473799 |
87.2118951 |
8.4156349 |
| ENSG00000213139 |
1427 |
CRYGS |
protein_coding |
P22914 |
FUNCTION: Crystallins are the dominant structural components of the vertebrate eye lens. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cataract;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Eye lens protein;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Crystallins are separated into two classes: taxon-specific, or enzyme, and ubiquitous. The latter class constitutes the major proteins of vertebrate eye lens and maintains the transparency and refractive index of the lens. Since lens central fiber cells lose their nuclei during development, these crystallins are made and then retained throughout life, making them extremely stable proteins. Mammalian lens crystallins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma families; beta and gamma crystallins are also considered as a superfamily. Alpha and beta families are further divided into acidic and basic groups. Seven protein regions exist in crystallins: four homologous motifs, a connecting peptide, and N- and C-terminal extensions. Gamma-crystallins are a homogeneous group of highly symmetrical, monomeric proteins typically lacking connecting peptides and terminal extensions. They are differentially regulated after early development. This gene encodes a protein initially considered to be a beta-crystallin but the encoded protein is monomeric and has greater sequence similarity to other gamma-crystallins. This gene encodes the most significant gamma-crystallin in adult eye lens tissue. Whether due to aging or mutations in specific genes, gamma-crystallins have been involved in cataract formation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1427; |
structural constituent of eye lens [GO:0005212]; lens development in camera-type eye [GO:0002088]; morphogenesis of an epithelium [GO:0002009]; visual perception [GO:0007601] |
12093281_Deamidation in cataractous lenses is influenced by surface exposure. 12475213_A lens gamma S-crystallin has been identified with an in vivo modification, S-methylation of cysteine residues, that may block intermolecular disulfide bondng and serve as a form of protection against cataract. 14763903_when glutathione becomes bound to gammaS-crystallin, it causes it to bind in turn to the beta-crystallin polypeptides to form a dimer 17905830_analysis of folding and stability of the isolated Greek key domains of the long-lived human lens proteins gammaD-crystallin and gammaS-crystallin 19262743_report a novel missense mutation, p.V42M, in CRYGS associated with bilateral congenital cataract in a family of Indian origin 19358562_Fast charge transfer quenching is an evolved property of the gamma S-crystallin fold, probably protecting it from ultraviolet-induced photodamage. 19558189_Results confirm the high stability of wild-type HgammaS-crystallin and demonstrates that the G18V mutation destabilizes the protein toward heat and GuHCl-induced unfolding. 20621668_Partially folded aggregation intermediates of human gammaD-, gammaC-, and gammaS-crystallin are recognized and bound by human alphaB-crystallin. 21244846_Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, circular dichroism (CD), and dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements were used to investigate the aggregation propensity of the eye-lens protein gammaS-crystallin. 21447408_The presence of significant amounts of small peptides derived from gammaS- and betaB1-crystallins in the water-insoluble fraction of the lens indicates that these interact tightly with cytoskeletal or membrane components. 21866213_Novel mutations in the crystalline genes have been identified in Chinese families with congenital cataracts. 22593035_The degree of deamidation for Gln92 and Gln170 was found to increase from birth to teen-age years and then to remain constant for four decades. 22995907_age-dependent cleavage of gammaS-crystallin generates a peptide that binds to cell membranes 23284690_replacement of valine in position 42 by the longer and bulkier methionine in human gammaS-crystallin perturbs the compact beta-sheet core packing topology in the N-terminal domain of the molecule 23761725_The cataract-associated mutant D26G of human gammaS-crystallin is remarkably close to the wild type molecule in structural features, with only a microenvironmental change in the packing around the mutation site. 24287181_The effects of the V41M mutation on the structural changes of gamma S-crystallin were studied. 24328668_novel mutation (G57W) in CRYGS in this Chinese family is associated with autosomal dominant pulverulent cataract. 26158710_The data suggest that enhanced attractive protein-protein interactions, arising from the deamidation of HGS, promote protein aggregation, thereby leading to increased light scattering and opacity over time. 27052457_Cataract-related G18V point mutation affects CRYGS stability and hydration. 29857103_aberrant modifications in gammaS-crystallin structure might contribute to the lower stability and higher aggregatory potency of the mutated protein, which subsequently resulted in cataracts in the patients 29964096_The Tyr67Asn substitution was predicted to decrease the local hydrophobicity and affect the three-dimensional structure of gammaS-crystallin, and resulted in a portion of mutant protein translocation from the cytoplasm to cell membrane. This observations expand the mutation spectrum of CRYGS and provide further evidence for the genetic basis and molecular mechanism of congenital cataract. 30391002_These results highlight the vital role of conserved Tyr corners in stabilizing Greek key motifs in gammaS crystallin and provide useful structural and functional insights into the mechanism of cataract formation in humans. 30769148_Molecular structure of G57W mutant of human CRYGS and its involvement in cataract formation has been reported. 30827504_This study reports conformational dynamics in CRYGS for the first time with crucial consequence of cataract formation. 31084934_These results establish a direct conformational link between the structure, dynamics, design and function in human gamma S-crystallin such that the G57W cataract variant promotes enhanced structural excursions concomitant with increased instability, elucidating very crucial molecular details of cataract formation affecting infants across the globe. 31092325_This work highlights functional aspects of structural malleability in human crystallin gamma S. Chemical shift curvatures indicate structural ruggedness in crystallin gamma S-G57W variant causing cataracts. 31266635_Kinetic Stability of Long-Lived Human Lens gamma-Crystallins and Their Isolated Double Greek Key Domains. 31371024_It has been proposed that domain interface acts as an intrinsic stabilizer for the otherwise floppy N-terminal domain in CRYGS G57W than in the wild-type protein where it serves an extrinsic role. 31647219_Zn2+-driven aggregation of gamma S crystallin proceeds through cysteine coordination, whereas Cu2+-driven aggregation results from methionine oxidation. 31812542_Human alphaB-crystallin distinguishes between highly similar variants of a structural crystallin, binding the cataract-related gammaS-G18V variant, but not the function-preserving gammaS-G18A variant, which is monomeric at physiological temperature. 32234236_The cataract-related S39C variant increases gammaS-crystallin sensitivity to environmental stress by destroying the intermolecular disulfide cross-links. 32307080_ATP antagonizes the crowding-induced destabilization of the human eye-lens protein gammaS-crystallin. 32697405_Cumulative deamidations of the major lens protein gammaS-crystallin increase its aggregation during unfolding and oxidation. 32753316_Cataract-causing G18V eliminates the antagonization by ATP against the crowding-induced destabilization of human gammaS-crystallin. 33004175_ATP differentially antagonizes the crowding-induced destabilization of human gammaS-crystallin and its four cataract-causing mutants. 33454329_A novel F30S mutation in gammaS-crystallin causes autosomal dominant congenital nuclear cataract by increasing susceptibility to stresses. 35021623_Human gammaS-Crystallin Resists Unfolding Despite Extensive Chemical Modification from Exposure to Ionizing Radiation. |
ENSMUSG00000033501 |
Crygs |
11.655758 |
0.4797230136 |
-1.059726 |
0.484543211 |
4.834441 |
0.02789668986279205190048635643051966326311230659484863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.048339415634516401387710260451058275066316127777099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.3441067 |
2.2750908 |
15.4145585 |
3.1351897 |
| ENSG00000213203 |
170575 |
GIMAP1 |
protein_coding |
Q8WWP7 |
FUNCTION: May regulate lymphocyte survival. Required for normal levels of mature T-lymphocytes and mature B-cells (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Endoplasmic reticulum;Golgi apparatus;GTP-binding;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein belonging to the GTP-binding superfamily and to the immuno-associated nucleotide (IAN) subfamily of nucleotide-binding proteins. In humans, the IAN subfamily genes are located in a cluster at 7q36.1. This gene is thought to be involved in the differentiation of T helper (Th) cells of the Th1 lineage, and the related mouse gene has been shown to be critical for the development of mature B and T lymphocytes. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the downstream GIMAP5 (GTPase, IMAP family member 5) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:170575; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; GTP binding [GO:0005525] |
11814688_The himap1 gene belongs to a gene family clustered on chromosome 7q32-36 within a region highly syntenic to the mouse imap38 locus on chromosome 6B. 18701445_GIMAP1 and GIMAP4 genes are up-regulated by IL-12 and other Th1 differentiation-inducing cytokines in cells induced to differentiate toward Th1 lineage and down-regulated by IL-4 in cells induced to Th2. 20194894_Shows a critical role for the related mouse gene in mature lymphocyte development and survival. 24626161_GIMAP1 and SERHL variants may be important for appendicular lean mass |
ENSMUSG00000090019 |
Gimap1 |
18.906568 |
0.4944333592 |
-1.016152 |
0.400972890 |
6.421254 |
0.01127625147133986920067183490345996688120067119598388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021406748773887648157332463938473665621131658554077148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.1357011 |
3.4474531 |
26.6648689 |
4.7770302 |
| ENSG00000213213 |
84960 |
CCDC183 |
protein_coding |
Q5T5S1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:84960; |
|
21048031_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
19.126507 |
0.4013032069 |
-1.317235 |
0.455730401 |
8.218374 |
0.00414683424015061929263081808016977447550743818283081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008619528712100145775854009855265758233144879341125488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8764191 |
3.0406631 |
27.2075373 |
5.0923252 |
| ENSG00000213300 |
|
HNRNPA3P6 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75.439054 |
8.1950003893 |
3.034744 |
1.006264507 |
7.900981 |
0.00494079831024617308760094047670463623944669961929321289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010113185835422758979129653766904084477573633193969726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
135.4337500 |
60.9866516 |
16.6682858 |
5.5401137 |
| ENSG00000213316 |
4056 |
LTC4S |
protein_coding |
Q16873 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conjugation of leukotriene A4 with reduced glutathione (GSH) to form leukotriene C4 with high specificity (PubMed:7937884, PubMed:27791009, PubMed:27365393, PubMed:9153254, PubMed:23409838). Can also catalyze the transfer of a glutathionyl group from glutathione (GSH) to 13(S),14(S)-epoxy-docosahexaenoic acid to form maresin conjugate in tissue regeneration 1 (MCTR1), a bioactive lipid mediator that possess potent anti-inflammatory and proresolving actions (PubMed:27791009). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23409838, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27365393, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27791009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7937884, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9153254}. |
3D-structure;Direct protein sequencing;Endoplasmic reticulum;Leukotriene biosynthesis;Lipid biosynthesis;Lipid metabolism;Lyase;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Lipid metabolism; leukotriene C4 biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305}. |
The MAPEG (Membrane Associated Proteins in Eicosanoid and Glutathione metabolism) family includes a number of human proteins, several of which are involved the production of leukotrienes. This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the biosynthesis of cysteinyl leukotrienes, potent biological compounds derived from arachidonic acid. Leukotrienes have been implicated as mediators of anaphylaxis and inflammatory conditions such as human bronchial asthma. This protein localizes to the nuclear envelope and adjacent endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4056; |
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nuclear outer membrane [GO:0005640]; enzyme activator activity [GO:0008047]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; glutathione transferase activity [GO:0004364]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; leukotriene-C4 synthase activity [GO:0004464]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; leukotriene biosynthetic process [GO:0019370]; leukotriene metabolic process [GO:0006691]; long-chain fatty acid biosynthetic process [GO:0042759] |
11770699_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11934880_Distinct roles of receptor phosphorylation, G protein usage, and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation on platelet activating factor-induced leukotriene C(4) generation 12063521_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12063521_no relationship between the polymorphism and LTC4S activity in eosinophils, although LTC4S activities were significantly higher in patients with aspirin induced asthma than in patients with aspirin tolerant asthma 12360108_A(-444)C polymorphism of this gene and clinical response to pranlukast in Japanses patients with moderate asthma 12360108_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12589355_C-to-A promoter polymorphism was associated with the increased presence of chronic hyperplastic eosinophilic sinusitis and the expression of cysteinyl leukotrienes 12591277_expression of LTC(4)S during normal and leukemic myelopoiesis and correlation with the activity of the disease-specific tyrosine kinase p210 BCR-ABL in CML myeloid cells. 12664565_Gene expression in mononuclear phagocytes is regulated by SP1 and SP3. 12728163_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12816731_Data show that mucosal mast cells, and not eosinophils, were the dominating leukotriene C4 synthase-containing cells in both untreated and treated aspirin-tolerant asthma. 12968987_Clinical trial and meta-analysis of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14520724_We further conclude that the A(-444)C polymorphism in the LTC(4) synthase gene probably contributes to asthma interpatient variability in montelukast-evoked changes in FE(NO)* and warrants further study. 14749922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131571_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131571_independent of transcriptional activity, the C(-444) allele in the LTC(4) synthase gene is weakly associated with the asthma phenotype, but it is not related to disease severity or aspirin intolerance 15530365_calculated a projection map of recombinant human LTC(4) synthase at a resolution of 4.5 A by electron crystallography 16024972_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16024972_leukotriene C4 synthase gene promoter polymorphism is associated with asthma and/or atopy 16211251_Glu 4 Lys amino acid substitution in the LTC4S might be associated with allergic diseases. 16211251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16293801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16340173_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16675353_The C allele of the leukotriene C4 synthase (A-444C) polymorphism is associated with asthma phenotype or severity. 16730545_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17063752_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17110605_LTC4S plays a key role in the process of inflammation as the rate limiting enzyme in the conversion of arachidonic acid to cysteinyl-leukotrienes, important mediators of inflammatory responses. 17110605_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17153879_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17153879_The combination of 927T CYSLTR1 and -444A LTC4S was less common in male patients with asthma than in controls and the combination of 927C CYSLTR1 and -444A LTC4S was slightly more frequent in patients with asthma 17291864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17460547_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17483957_The results of a case-control study aimed at investigating the association of MGST1 gene locus polymorphisms with colorectal cancer risk among Han Chinese are presented. 17632546_crystal structure of the human LTC4 synthase in its apo and GSH-complexed forms to 2.00 and 2.15 A resolution, respectively 17632548_atomic structure of human LTC4S in a complex with glutathione at 3.3 A resolution by X-ray crystallography 17883728_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17924829_Observational study of gene-gene interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18276912_Leukotriene C(4) synthase -1072 AA genotype predict increased risk, whereas -444 CC genotype predict decreased risk of ischemic cerebrovascular disease. 18276912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18323512_Genetic variation in leukotriene pathway members and their receptors confer an increased risk of ischemic stroke in 2 independent populations 18366797_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18974840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19028820_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19080532_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19080532_In a Southwest Chinese Han population LTC(4)S A(-444)C polymorphism might be a determinant factor in the clinical response of asthma to leukotriene receptor antagonists. 19080797_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19080797_The combined study of polymorphisms in genes of the leukotriene pathway could explain the differences observed in the studies reported on polymorphism -444A |
|
|
19.240789 |
0.2473864122 |
-2.015162 |
0.418826501 |
24.033962 |
0.00000094651385994828900532566595335537407152060040971264243125915527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003359919329686567141896253244071068877474317559972405433654785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5971140 |
2.1091743 |
31.1542868 |
5.0716085 |
| ENSG00000213347 |
83463 |
MXD3 |
protein_coding |
Q9BW11 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional repressor. Binds with MAX to form a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein complex which recognizes the core sequence 5'-CAC[GA]TG-3'. Antagonizes MYC transcriptional activity by competing for MAX and suppresses MYC dependent cell transformation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repressor;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the Myc superfamily of basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcriptional regulators. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with the cofactor MAX which binds specific E-box DNA motifs in the promoters of target genes and regulates their transcription. Disruption of the MAX-MXD3 complex is associated with uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Transcript variants of this gene encoding different isoforms have been described.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2008]. |
hsa:83463; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex [GO:0090575]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
22808009_Increased level and/or duration of MXD3 expression ultimately reduces cell numbers via increased cell death and cell cycle arrest in medulloblastoma cells. 25053245_Acute MXD3 activation results in a transient increase in DAOY cell proliferation while persistent activation of MXD3 results in an overall decrease in cell number, suggesting that the time course of MXD3 expression dictates the cellular outcome. 25554682_The results suggest that MXD3 is important for survival of Reh preB ALL cells, possibly as an anti-apoptotic factor. 28419087_results indicate that MXD3 is a potential new target and that the use of MXD3 siRNA nanocomplexes is a novel therapeutic approach for neuroblastoma 34943942_MXD3 Promotes Obesity and the Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathway in Gender-Disparity Hepatocarcinogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000021485 |
Mxd3 |
83.930855 |
0.4135136764 |
-1.273993 |
0.170940460 |
57.185736 |
0.00000000000003965367503141447452510613792425408049213339523042520795570453628897666931152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000258063599410792616797081018314487401267912081159749959624605253338813781738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.3409549 |
5.7285144 |
122.5278995 |
8.7296785 |
| ENSG00000213366 |
2946 |
GSTM2 |
protein_coding |
P28161 |
FUNCTION: Conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles. Participates in the formation of novel hepoxilin regioisomers (PubMed:21046276). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16549767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21046276}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Lipid metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase |
|
Cytosolic and membrane-bound forms of glutathione S-transferase are encoded by two distinct supergene families. At present, eight distinct classes of the soluble cytoplasmic mammalian glutathione S-transferases have been identified: alpha, kappa, mu, omega, pi, sigma, theta and zeta. This gene encodes a glutathione S-transferase that belongs to the mu class. The mu class of enzymes functions in the detoxification of electrophilic compounds, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress, by conjugation with glutathione. The genes encoding the mu class of enzymes are organized in a gene cluster on chromosome 1p13.3 and are known to be highly polymorphic. These genetic variations can change an individual's susceptibility to carcinogens and toxins as well as affect the toxicity and efficacy of certain drugs. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:2946; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0016529]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; fatty acid binding [GO:0005504]; glutathione binding [GO:0043295]; glutathione peroxidase activity [GO:0004602]; glutathione transferase activity [GO:0004364]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; cellular detoxification of nitrogen compound [GO:0070458]; cellular response to caffeine [GO:0071313]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; hepoxilin biosynthetic process [GO:0051122]; linoleic acid metabolic process [GO:0043651]; negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060315]; nitrobenzene metabolic process [GO:0018916]; positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060316]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0010881]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0010880]; regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion [GO:0014809]; relaxation of cardiac muscle [GO:0055119]; xenobiotic catabolic process [GO:0042178] |
12486119_identification of residues capable of driving functional diversification in evolution 12871945_dinitrosyl-diglutathionyl-iron complex, a natural carrier of nitric oxide, binds with extraordinary affinity to GSTA1-1, which is explained by molecular modeling and related to molecular evolution 14634838_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15725629_GST-M2 may play an important future role in lowering the incidence of benzo[a]pyrene-diolepoxide-induced DNA damage. 16002077_CVD risk was higher in smokers compared to non-smokers with GSTT1-1. No significant associations were observed by GSTM1. 17197702_dinitrosyl-diglutathionyl-iron complex bound to Alpha class glutathione S-transferases with extraordinary high affinity in hepatocytes 18007994_A significant association was found between oxidative stress GSTM1 deletion and the HMOX-1 long repeat and heart rate variation in response to particulate air pollution. 18065725_Meta-analysis and HuGE review of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18308613_hGSTM2-2 modifies both cardiac & skeletal ryanodine receptor (RyR) activity when it binds to luminal domain of RyR channel complex. GSTM2-2 can interact with specific luminal sites on RyR complex & interaction is likely to be within pore of RyR channel. 18510611_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18551009_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19151192_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19151192_children with variants in GSTM2 (glutathione S-transferase mu 2) were more susceptible to effects of in utero tobacco smoke exposure on lung function 19168034_The active center of GSTM2-2 for inhibition of cardiac ryanodine receptors involves the helix6 sequence and is essential for its efficacy. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19696791_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19856098_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19859803_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19859803_it is unlikely that glutathione S-transferases GSTA2, GSTM2, GSTO1, GSTO2, and GSTZ1 participate in breast cancer susceptibility. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20200426_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20417188_The structure of helix 6 in the carboxyl-terminal fold is critical to GSTM2-2's inhibitory action on the cardiac ryanodine receptor. 20485444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21246532_GST-M2 exhibited high frequency of promoter hypermethylation in lung cancer cells, CpG hypermethylation abated Sp1 binding to the GST-M2 promoter in lung cancer 21268265_High GSTM2 is associated with mesenchymal stem-like cells derived from ovarian teratoma. 21454564_analysis of active-site residues and modulation of catalytic functions in GST-M2 21455499_it was noted that the alpha-6 helix of GST-C plays a stabilising role in the fold of this domain. By destabilising the conformation of GST-C, an increase in cell translocation efficiency of up to approximately 2-fold was observed. 23675469_High expression of GSTM1 and GSTM4, along with increased endogenous reduced glutathione levels, help to maintain a more reduced state of cytochrome c which decreases apoptosis thus contributing to methotrexate resistance in human MCF7 breast cancer cells. 24048194_the absence of GSTM1 activity can be compensated for by the overexpression of GSTM2. 24399650_demonstrated that the GSTM1 and GSTT1 null genotype may be associated with an increased risk of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and that individuals having the combination of both defective GST genotypes may be more susceptible to developing HCC 24852519_The absence of GSTM1 and GSTT1 genes increases the risk of lung cancer because of radon exposure. 27566576_the methylation status of CpG sites in GFRA1 and GSTM2 may have a role and could be used as potential biomarkers for the screening of rectal cancer 32574561_Small Extracellular Vesicles Have GST Activity and Ameliorate Senescence-Related Tissue Damage. 33555546_Cellular Trafficking of Glutathione Transferase M2-2 Between U373MG and SHSY-S7 Cells is Mediated by Exosomes. 36038661_GSTM2 is a key molecular determinant of resistance to SG-ARIs. |
ENSMUSG00000004035 |
Gstm7 |
23.397246 |
0.1254328335 |
-2.995013 |
0.537637600 |
32.545118 |
0.00000001164573133249009529364825104875286188033101097971666604280471801757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000050407916266144809689668304436213630559393550356617197394371032714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8169079 |
1.8447944 |
38.7402905 |
8.6620175 |
| ENSG00000213366_ENSG00000168765 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.991082 |
0.0197999236 |
-5.658361 |
1.447481707 |
13.099294 |
0.00029540704307093784740725905813008012046338990330696105957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000754622353016102826589461827211380295921117067337036132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7566746 |
0.7652808 |
32.8636744 |
17.3876854 |
| ENSG00000213373 |
388387 |
LINC00671 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33168412_Long noncoding RNA LINC00671 exacerbates osteoarthritis by promoting ONECUT2-mediated Smurf2 expression and extracellular matrix degradation. 34404767_STAT3/LINC00671 axis regulates papillary thyroid tumor growth and metastasis via LDHA-mediated glycolysis. |
|
|
11.376232 |
0.0218077154 |
-5.519018 |
1.006141781 |
59.684078 |
0.00000000000001113739562758443443460240964214041521099468699113055336624711344484239816665649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000074620045148954268436426564171210690210619791151724911060227896086871623992919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.4396302 |
0.3334744 |
20.3126232 |
4.5940363 |
| ENSG00000213398 |
3931 |
LCAT |
protein_coding |
P04180 |
FUNCTION: Central enzyme in the extracellular metabolism of plasma lipoproteins. Synthesized mainly in the liver and secreted into plasma where it converts cholesterol and phosphatidylcholines (lecithins) to cholesteryl esters and lysophosphatidylcholines on the surface of high and low density lipoproteins (HDLs and LDLs) (PubMed:10329423, PubMed:19065001, PubMed:26195816). The cholesterol ester is then transported back to the liver. Has a preference for plasma 16:0-18:2 or 18:O-18:2 phosphatidylcholines (PubMed:8820107). Also produced in the brain by primary astrocytes, and esterifies free cholesterol on nascent APOE-containing lipoproteins secreted from glia and influences cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) APOE- and APOA1 levels. Together with APOE and the cholesterol transporter ABCA1, plays a key role in the maturation of glial-derived, nascent lipoproteins. Required for remodeling high-density lipoprotein particles into their spherical forms (PubMed:10722751). Catalyzes the hydrolysis of 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet-activating factor or PAF) to 1-O-alkyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (lyso-PAF) (PubMed:8016111). Also catalyzes the transfer of the acetate group from PAF to 1-hexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine forming lyso-PAF (PubMed:8016111). Catalyzes the esterification of (24S)-hydroxycholesterol (24(S)OH-C), also known as cerebrosterol to produce 24(S)OH-C monoesters (PubMed:24620755). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10329423, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10722751, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12354767, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14636062, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19065001, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24620755, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26195816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8016111, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8820107}. |
3D-structure;Acyltransferase;Cholesterol metabolism;Corneal dystrophy;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Steroid metabolism;Sterol metabolism;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes the extracellular cholesterol esterifying enzyme, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. The esterification of cholesterol is required for cholesterol transport. Mutations in this gene have been found to cause fish-eye disease as well as LCAT deficiency. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3931; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; high-density lipoprotein particle [GO:0034364]; 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase activity [GO:0003847]; apolipoprotein A-I binding [GO:0034186]; phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase activity [GO:0004607]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; platelet-activating factor acetyltransferase activity [GO:0047179]; sterol esterase activity [GO:0004771]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; cholesterol metabolic process [GO:0008203]; cholesterol transport [GO:0030301]; high-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034375]; lipid metabolic process [GO:0006629]; lipoprotein biosynthetic process [GO:0042158]; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:0006656]; phosphatidylcholine metabolic process [GO:0046470]; phospholipid metabolic process [GO:0006644]; regulation of high-density lipoprotein particle assembly [GO:0090107]; response to copper ion [GO:0046688]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; reverse cholesterol transport [GO:0043691]; very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling [GO:0034372] |
11882335_The lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activity in cord blood was extremely low. 11966470_Results suggest that LCAT may take part in the detoxification of oxidants even after the loss of its cholesterol esterification function. 12032172_IL-6 induced activation of full-length LCAT promoter activity. A minimal IL-6 response element mapped within the distal promoter and was sufficient to mediate the IL-6 response 12048121_In conclusion, 12% of Hypoalphalipoproteinemia subjects were found to carry mutations in apo A-I, LCAT, or GBA genes 12048121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12051518_The results suggest that as follicle maturation progresses, Toc and Asc concentrations increase in follicular fluid, thus protecting LCAT from oxidative damage and loss of activity 12139471_Endotoxin-lipoprotein complex formation as a factor in atherogenesis: associations with hyperlipidemia and with lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity 12174215_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12573451_comparison of 5 natural point mutations of apo A-I illustrates that a specific sequence between amino acids 110 and 162 is required for LCAT activation 12673583_608T polymorphism of LCAT gene was associated with higher plasma HDL-C level in Coronary Arteriosclerosis patients. 12673583_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12957688_Familial lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) deficiency, arising from mutation, is associated with complete absence of Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) activity. 15102891_Postprandial chylomicrons may play an important role in promoting reverse cholesterol transport in vivo by serving as the preferred ultimate vehicle for transporting cholesterol released from cell membranes to the liver via LCAT and CETP. 15110745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15115696_T13M mutation of LCAT gene causes fish-eye disease. 15297675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15297675_tested whether rare sequence variants of ABCA1, APOA1, and LCAT collectively contribute to variation in plasma levels of high density lipoprotein cholesterol; nonsynonymous sequence variants were significantly more common in individuals with low HDL-C 15472210_role of LCAT in estradiol-2 esterification and its involvement in antioxidant protection of HDL 15544352_Selective LCAT-mediated reactivity with pre-beta 1-high density lipoprotein represents a novel mechanism increasing the efficiency of reverse cholesterol transport. 15936482_Deficiency is manifested by fish eye disease. 15994445_the inheritance of a mutated LCAT genotype causes a gene-dose-dependent alteration in the plasma lipid/lipoprotein profile, which is remarkably similar between subjects classified as LCAT deficiency or fish eye disease 16051254_a novel G-->A mutation in exon 6 of LCAT gene, which resulted in an amino acid substitution of valine for methionine in familial LCAT deficiency 16061733_Mutation underlies increased carotid artery intima-media thickness, which suggests that LCAT protects against atherosclerosis. 16115486_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16216249_analysis of mutations in the LCAT gene that result in an intermediate phenotype between LCAT-deficiency and fish-eye disease (case report) 16542392_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16543491_Decreased LDL in LCAT-deficiency is attributable to increased catabolism caused by rapid catabolism of abnormal LDL and upregulation of LDL receptor pathway. Decreased catabolism of LpX contributes to its accumulation in LCAT-deficiency. (Lipoprotein X) 16770077_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16780378_Redistribution of charged residues in mutant LCAT may be a major factor responsible for the dramatically reduced activity of the enzyme with HDL and reconstituted high density lipoprotein (rHDL). 16883530_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16883530_The LCAT 608C/T polymorphism is possibly a predisposing factor in atherosclerotic cerebral infarction happening of Chinese Han population. 17113061_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17206937_HDL particles generated by this pathway may account at least for some of the atheroprotective functions of apolipoprotein E 17216278_Apolipoprotein A=I activation affects the kinetics of the LCAT reaction 17272829_decreased cholesterol-total cholesterol ratio in the plasma of human apolipoprotein A-I transgenic Scavenger Receptors, Class B, Type I-/- mice is attributed to a reduction in LCAT reactivity with sphingomyelin-enriched HDL particles 17357073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17526537_analysis of mutations in LCAT in two patients with severe LCAT deficiency [case report] 17711302_The study establishes that apoA-I(Leu141Arg)Pisa and apoA-I(Leu159Arg)FIN inhibit an early step in the biogenesis of HDL due to inefficient esterification of the cholesterol of the prebeta1-HDL particles by the endogenous LCAT. 17855807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18178167_Multiple linear regression analysis confirmed the independent association of cellular cholesterol efflux to plasma with cholesteryl ester transfer protein genotype 18397721_Analysis of the LCAT gene showed two novel point mutations in exon 2 and exon 3, leading to amino acid substitution. As far, these mutations have not been reported in FLD or FED patients. 18485513_HbA1c provides an easy-to-assess, accurate measure of LCAT activity in type 2 diabetes. 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18719109_oxidation of a single Met in apoA-I results in impaired LCAT activation 18782872_Plasma LCAT activity is elevated in metabolic syndrome and may be a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis 18823627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18922527_Functional LCAT is not required for macrophage cholesterol efflux to human serum. 18996102_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19060906_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19306528_Recent research findings from animal and human studies have revealed a potential beneficial role of LCAT in reducing atherosclerosis--REVIEW 19336370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19515369_Suggest that a LCAT-/- genotype associated with an APOE epsilon2 allele could be a novel mechanism leading to dysbetalipoproteinemia in familial LCAT deficient patients. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19671930_Low LCAT plasma levels are not associated with increased atherosclerosis in the general population. 19687369_Genetically determined low LCAT activity in Italian families is not associated with enhanced preclinical atherosclerosis despite low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19698944_lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase activity is not responsible for low incidence of cardiovascular events 19800416_Plasma lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase activity modifies the inverse relationship of C-reactive protein with HDL cholesterol in nondiabetic men. 19878569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20031551_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20160193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20167577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20571754_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20634891_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20679960_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20714348_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20855565_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20884842_Novel N-terminal mutation of human apolipoprotein A-I reduces self-association and impairs LCAT activation 20890173_LCAT activity is significantly decreased in type 2 diabetes. The lower LCAT activity in type 2 diabetes might be through ox-LDL mechanism. Ox-LDL may adversely affect high-density lipoprotein -cholesterol metabolism by reducing LCAT activity. 20972250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21315357_Case Report: familial LCAT deficienty can cause nephropathy at a very early age. 21597230_analysis of a mutation that causes a complete loss of catalytic activity of LCAT, which is also defective in secretion [case report] 21600519_LCAT activity and enzyme levels were significantly lower among subjects with low HDL-C compared with subjects with high HDL-C. 21798542_Continuous and intermittent walking alters HDL(2)-C and LCATa 21822774_AAV8-mediated overexpression of human LCAT in hCETP/Ldlr(+/-) mice resulted in profound changes in plasma lipid profiles. 21875686_mutations in ABCA1, APOA1, and LCAT are sufficient to explain more tha 40 percent of familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia 21901787_functional mutations in LCAT were found in 29% of patients with low HDL-c, thus constituting a common cause of low HDL-c in referred patients in The Netherlands (LCAT) 22090275_Low plasma HDL cholesterol levels robustly associated with increased risk of MI but genetically decreased HDL cholesterol did not. 22133847_Carriers of LCAT gene mutations exhibit increased carotid atherosclerosis 22189200_This review focuses on mutations in the LCAT gene as cause of familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia, and on their impact on plasma HDL-C, HDL profile and coronary heart disease. 22326749_Studies suggest that absence of lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) may protect against insulin resistance, diabetes and obesity. 22418575_Studies indicate the direct effects of HDL and its major modulators, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1), apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), and lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) on the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). 23023370_carriers of LCAT mutations present with significant reductions in LCAT activity, HDL cholesterol, apoA-I, platelet-activating factor-acetylhydrolase activity and antioxidative potential of HDL, but this is not associated with parameters of increased lipid peroxidation 23078883_Pulse wave velocity is increased in LCAT mutation carriers with low HDL-c and is associated with carotid wall thickening. 23132909_a novel function of apoA-IV in the biogenesis of discrete HDL-A-IV particles with the participation of ABCA1 and LCAT 23142243_while LCAT activity is decreased in patients with T2DM, LCAT levels is increased. Patients with NIDDM exhibit opposing effects on LCAT activity and LCAT production which is more severe in women 23152129_Male soccer players had significantly higher lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activity than sedentary controls. 24140107_Results show that recombinant lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase rhLCAt efficiently reduces the amount of unesterified cholesterol and promotes the production of plasma cholesteryl esters in LCAT deficient plasma. 24383078_The present study provides an important insight into the potential interactions between LCAT and lipoproteins and also suggests that peptides, initially present in a disordered conformation, are able to sense the lipid environment provided by lipoproteins of plasma and following a disorder-to-order transition, change their conformation to an ordered alpha-helix. 24423117_Activity of LCAT in HDL was increased in type 2 diabetes following increased fruit and vegetable intake. 24620755_The enzyme lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase esterifies cerebrosterol and limits its toxic effect on cultured neurons. 24789697_A synonymous H287H mutation in the coding region of exon 6 of the lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase gene was observed in an individual with HDLC levels of 75 mg/dl. 24842300_Cosyntropin testing in an unselected subgroup of 8 ABCA1 mutation carriers and 3 LCAT mutation carriers did not reveal differences between carriers and controls. 25110219_genetic polymorphism is associated with coronary artery disease in Egyptians 25589508_A robust all-atom model for LCAT generated by homology modeling 25894629_Increased LCAT activity may be associated with increased formation of triglyceride rich lipoproteins, leading to a reduction in LDL particle size and atherosclerosis. 25948084_This study investigated how the natural LCAT[T147I] and LCAT[P274S] mutations affect the pathway of biogenesis of high-density lipoproteins. 25964513_increased cholesterol esterification by LCAT is atheroprotective 26073399_The data indicate that this novel apoA-I missense is associated with markedly decreased levels of HDL cholesterol and very large alpha-1 HDL, as well as decreased serum cellular cholesterol efflux and LCAT activity 26117245_rs5923 polymorphism is not associated with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(HDL-C)levels in Iranian population 26195816_Mapping the naturally occurring mutations onto the structure provides insight into how they may affect LCAT enzymatic activity. 26232163_Report slightly reduction in LCAT that would probably reflect a delay in reverse cholesterol transport occurring in MetS. 29030428_data suggests a model wherein the active site of LCAT is shielded from soluble substrates by a dynamic lid until it interacts with HDL to allow transesterification to proceed 29208698_data suggest that Arg123 of apoA-I on discoidal HDL participates in lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT)-mediated cholesterol esterification 29570220_The CETP rs708272 polymorphism is associated with a heightened risk of developing ACS. In addition, we report the association of the rs708272 and rs2292318 polymorphisms with HDL-C levels and HDL subclasses. 29758034_Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in LCAT gene is associated with dyslipidemia. 29773713_APOA1 may use a reciprocating thumbwheel-like mechanism to activate HDL-remodeling proteins 29947103_Plasma LCAT activity was higher in patients with NAFLD. 30055622_It has been found a significant association between LCAT serum activity and risk of diabetes mellitus in men but not in women. 30059844_Plasma LCAT mass concentration is upregulated in CAD patients and inversely related to plaque volume, suggesting atheroprotective effects. 30479275_the crystal structure of human LCAT in complex with a potent piperidinylpyrazolopyridine activator and an acyl intermediate-like inhibitor, revealing LCAT in an active conformation, is reported. 30500525_results demonstrated increased CETP and decreased LCAT and PON-1 activities in colorectal cancer (CRC)patients. In preliminary analysis CETP mass was identified as potential significant predictor of CRC development, suggesting that alterations in HDL-C levels, alongside with changes in HDL structure might have a role in carcinogenesis. 30518338_Increased LCAT activity may be associated with increased formation of TRLs, leading to a reduction in the LDL-particle size in patients at a high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 31039173_7 putative enhancers harboring associated single nucleotide polymorphisms were identified, 3 of which lie within the introns of LCAT and ABCA1, genes that play crucial roles in cholesterol biogenesis and lipoprotein metabolism. 31103331_The P274S LCAT mutation was found to cause familial LCAT deficiency with renal involvement. 31164121_Genetic, biochemical, in vitro and in silico analyses indicate that the rare mutations p.M404 V and p.V333 M in LCAT gene lead to suppression of LCAT enzyme activity and cause clinical features of familial LCAT deficiency. 31779197_LCAT, ApoD, and ApoA1 Expression and Review of Cholesterol Deposition in the Cornea. 32450892_ApoE and apoC-III-defined HDL subtypes: a descriptive study of their lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein content and activity. 32561542_Esterification of 4beta-hydroxycholesterol and other oxysterols in human plasma occurs independently of LCAT. 32618730_Genetic, biochemical, and clinical features of LCAT deficiency: update for 2020. 33173066_Single nucleotide polymorphisms in LCAT may contribute to dyslipidaemia in HIV-infected individuals on HAART in a Ghanaian population. 33298249_Common plasma protein marker LCAT in aggressive human breast cancer and canine mammary tumor. 34256778_LCAT deficiency: a systematic review with the clinical and genetic description of Mexican kindred. 34634315_Altered HDL proteome predicts incident CVD in chronic kidney disease patients. 35598637_Plasma FA composition in familial LCAT deficiency indicates SOAT2-derived cholesteryl ester formation in humans. |
ENSMUSG00000035237 |
Lcat |
20.244619 |
0.4239996943 |
-1.237865 |
0.478030187 |
6.466224 |
0.01099438750351252984394090361774942721240222454071044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020917396178376505833096388187186676077544689178466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8763844 |
4.6589097 |
33.1307204 |
7.3207515 |
| ENSG00000213420 |
221914 |
GPC2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N158 |
FUNCTION: Cell surface proteoglycan that bears heparan sulfate. May fulfill a function related to the motile behaviors of developing neurons (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Heparan sulfate;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Proteoglycan;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to be involved in several processes, including positive regulation of neuron projection development; regulation of protein localization to membrane; and smoothened signaling pathway. Located in endoplasmic reticulum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:221914; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; Golgi lumen [GO:0005796]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; synapse [GO:0045202]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of protein localization to membrane [GO:1905475]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966]; smoothened signaling pathway [GO:0007224] |
28440309_Gpc2 is enriched in neurogenic regions of the adult brain. Its expression is increased by physiological stimuli that increase hippocampal neurogenesis and decreased in transgenic models in which neurogenesis is selectively ablated. Changes in neurogenesis also result in changes in Gpc2 protein level in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). 28898695_these findings validate GPC2 as a non-mutated neuroblastoma oncoprotein and candidate immunotherapeutic target. 34195677_CAR T cells targeting tumor-associated exons of glypican 2 regress neuroblastoma in mice. 35345673_GPC2 Is a Potential Diagnostic, Immunological, and Prognostic Biomarker in Pan-Cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000029510 |
Gpc2 |
18.495659 |
0.2219476104 |
-2.171709 |
0.414369253 |
28.096331 |
0.00000011542444801737574170724567445417418909414664085488766431808471679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000452620842916170551953130522099266741520295909140259027481079101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.2620818 |
1.8980882 |
28.3715795 |
5.5653235 |
| ENSG00000213533 |
375346 |
STIMATE |
protein_coding |
Q86TL2 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a regulator of store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) at junctional sites that connect the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and plasma membrane (PM), called ER-plasma membrane (ER-PM) junction or cortical ER (PubMed:26322679, PubMed:26644574). SOCE is a Ca(2+) influx following depletion of intracellular Ca(2+) stores (PubMed:26322679). Acts by interacting with STIM1, promoting STIM1 conformational switch (PubMed:26322679). Involved in STIM1 relocalization to ER-PM junctions (PubMed:26644574). Contributes to the maintenance and reorganization of store-dependent ER-PM junctions (PubMed:26644574). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26322679, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26644574}. |
Endoplasmic reticulum;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables calcium channel regulator activity. Involved in activation of store-operated calcium channel activity; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source; and positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade. Located in cortical endoplasmic reticulum; endoplasmic reticulum membrane; and endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact site. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:375346; |
cortical endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0032541]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact site [GO:0140268]; membrane [GO:0016020]; calcium channel regulator activity [GO:0005246]; activation of store-operated calcium channel activity [GO:0032237]; calcium-mediated signaling using intracellular calcium source [GO:0035584]; positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070886] |
26322679_Data show that transmembrane protein 110 STIMATE is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident protein that co-localizes with membrane protein STIM1. 26644574_Research on calcium signaling has centered on STIM1, ORAI1, and proteins that modulate their function. TMEM110 regulates the maintenance of ER-plasma membrane junctions and the short-term remodeling of junctions during store-dependent calcium signaling. |
ENSMUSG00000006526 |
Stimate |
236.832722 |
2.2059044404 |
1.141370 |
0.211513964 |
28.535688 |
0.00000009198727258580627482414108402400398922793556266697123646736145019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000364017014503311709646614325805447087702759745297953486442565917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
315.9776499 |
45.8331723 |
144.3578444 |
15.4127457 |
| ENSG00000213599 |
100526830 |
SLX1A-SULT1A3 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring SLX1A (SLX1 structure-specific endonuclease subunit homolog A) and SULT1A3 (sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 3) genes on the short arm of chromosome 16. A duplicate read-through locus also exists between the SLX1B and SULT1A4 genes located approximately 730 kb upstream on the same chromosome. The read-through transcript is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), and is thus unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
|
|
|
|
|
93.738882 |
0.4077828610 |
-1.294127 |
0.233838280 |
30.497665 |
0.00000003342685297185014537677523005325397331688463964383117854595184326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000138318446018207513919585135292456001820937672164291143417358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.9261996 |
8.4332236 |
138.0484018 |
14.0873217 |
| ENSG00000213648 |
445329 |
SULT1A4 |
protein_coding |
P0DMN0 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the sulfate conjugation of phenolic monoamines (neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin) and phenolic and catechol drugs. |
Catecholamine metabolism;Cytoplasm;Lipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Transferase |
|
Sulfotransferase enzymes catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs, and xenobiotic compounds. These cytosolic enzymes are different in their tissue distributions and substrate specificities. The gene structure (number and length of exons) is similar among family members. This gene encodes a phenol sulfotransferase with thermolabile enzyme activity. Four sulfotransferase genes are located on the p arm of chromosome 16, this gene and SULT1A3 arose from a segmental duplication. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the upstream SLX1B (SLX1 structure-specific endonuclease subunit homolog B) gene that encodes a protein containing GIY-YIG domains. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:445329;hsa:6818; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; aryl sulfotransferase activity [GO:0004062]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; catecholamine metabolic process [GO:0006584]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; sulfation [GO:0051923] |
29705271_Effects of human SULT1A3/SULT1A4 genetic polymorphisms on the sulfation of acetaminophen and opioid drugs by the cytosolic sulfotransferase SULT1A3 31145702_The results obtained showed clearly the differential enzymatic characteristics of SULT1A3 allozymes in mediating the sulfation of phenylephrine and salbutamol. This information may contribute toward a better understanding of the pharmacokinetics of these two drugs in individuals with distinct SULT1A3 and/or SULT1A4 genotypes. |
ENSMUSG00000000739 |
Sult5a1 |
33.920638 |
0.0777715773 |
-3.684613 |
0.611034570 |
32.257931 |
0.00000001350049276028798693116297040131904005910712385229999199509620666503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000057960230698618578548142081042007789370984482957283034920692443847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5354320 |
3.9124573 |
77.3816747 |
35.8029508 |
| ENSG00000213658 |
27040 |
LAT |
protein_coding |
O43561 |
FUNCTION: Required for TCR (T-cell antigen receptor)- and pre-TCR-mediated signaling, both in mature T-cells and during their development (PubMed:25907557, PubMed:23514740). Involved in FCGR3 (low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III)-mediated signaling in natural killer cells and FCER1 (high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor)-mediated signaling in mast cells. Couples activation of these receptors and their associated kinases with distal intracellular events such as mobilization of intracellular calcium stores, PKC activation, MAPK activation or cytoskeletal reorganization through the recruitment of PLCG1, GRB2, GRAP2, and other signaling molecules. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10072481, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23514740, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25907557}. |
Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Immunity;Lipoprotein;Mast cell degranulation;Membrane;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is phosphorylated by ZAP-70/Syk protein tyrosine kinases following activation of the T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) signal transduction pathway. This transmembrane protein localizes to lipid rafts and acts as a docking site for SH2 domain-containing proteins. Upon phosphorylation, this protein recruits multiple adaptor proteins and downstream signaling molecules into multimolecular signaling complexes located near the site of TCR engagement. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27040; |
cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; COP9 signalosome [GO:0008180]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; immunological synapse [GO:0001772]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; signaling receptor complex adaptor activity [GO:0030159]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; lymphocyte homeostasis [GO:0002260]; mast cell degranulation [GO:0043303]; positive regulation of protein kinase activity [GO:0045860]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050863]; T cell activation [GO:0042110] |
9846483_LAT is required for T cell activation. 12029091_LAT displacement from lipid rafts is a molecular mechanism by which PUFAs inhibit T cell signaling 12186560_Phosphorylation of the linker for activation of T-cells by Itk promotes recruitment of Vav. 12515827_LAT has a role in signal transduction for T cell activation and is stably associated with plasma membrane rafts 12570875_interaction with open-active form of Lck in lipid rafts reveals a new mechanism for the regulation of Lck in T cells 12646565_examination of synergistic assembly in T cell plasma membrane domains 12847255_The T cell adapter molecule LAT is required for correct orientation of the microtubule-organizing center, as it moves toward the interface of the T cell and antigen-presenting cell. 15029250_Results reveal the basis for preferential recognition of specific LAT sites by Gads. 15100278_CD3/T cell receptor complex signaling to beta 1 integrins is defective in LAT-deficient Jurkat T cells, and can be restored with expression of wild-type LAT. 15153499_LAB resembled a LAT molecule unable to bind phospholipase C-gamma1. 15449076_A variable reduction in LAT expression was observed in almost all the inflammatory and neoplastic skin conditions investigated, irrespective of the particular disease. 15699071_Data show that the adaptor molecules LAT and SLP-76 are specifically targeted by Yersinia to inhibit T cell activation. 15745852_The loss LAT in mast cells is associated with a defective effector response. 16236370_identify a novel post-translational modification of LAT by ubiquitination that is likely to influence LAT protein stability, intracellular localisation and/or recycling 16460687_human LAT mutant lacking palmitoylation became unstable when the extracellular portion was swapped for that from mouse, indicating that both palmitoylation and the extracellular portion regulate the stability of LAT. 16464244_mapped the transcriptional start sites for the LAT gene and localized the 5' and 3' boundaries of the proximal promoter 16906159_In T cells, the SH2 domain of GRB2 binds phosphorylated tyrosines on the adaptor protein LAT and the GRB2 SH3 domains associate with the proline-rich regions of SOS1 and CBL. 17492476_LAT, ZAP-70, and DNMT1 protein levels in CD4(+) T cells can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. 17938199_These data indicate that following the rapid formation of signaling complexes upon T cell receptor stimulation, c-Cbl activity is involved in the internalization and possible downregulation of a subset of activated signaling molecules. 18579528_PLSCR1 is a novel amplifier of FcepsilonRI signaling that acts selectively on the Lyn-initiated LAT/phospholipase Cgamma1/calcium axis, resulting in potentiation of a selected set of mast cell responses 18645037_These data show that natural killer cell immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs preferentially use a signaling cassette regulated by interplay between LAT and LAB. 18683785_A significant decrease of mRNA expression of LAT gene in T cells of asthmatic patients may be due to the up-regulation of its upstream regulatory factors Lck and ZAP-70. 19018007_while Vav-1 and LAT preferentially bound to Syk, phospholipase C-gamma1 bound to both Syk and ZAP-70 19068093_Elevated expression of LAT1 is associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. 19343046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19380807_In addition to its essential role in pre-T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated signaling, LAT plays an important role in TCR signaling in double-positive (DP)thymocytes and is required during thymocyte differentiation from DP to single-positive. 19427038_the formation of LAT-mediated complexes do not appear to depend on PI3K activity, whereas the optimal downstream function of these complexes requires the catalytic function of PI3K. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20723025_PECAM-1-mediated inhibition of GPVI-dependent platelet responses result from recruitment of SHP-2-p85 complexes to tyrosine-phosphorylated PECAM-1, which diminishes the association of PI3K with activatory signaling molecules Gab1 and LAT 20875087_Studies indicate that LAT is present in membrane rafts and involved in signalling through a number of receptors other than the T cell receptor. 20940326_The adaptor LAT contains several conserved serine-based motifs, which are essential for proper signal transduction through the TCR. 21152094_Results indicate for the first time that LAT promotes TCR signal initiation and suggest that this adaptor may contribute to maintain active Lck in proximity of their substrates. 21251717_These results reveal a novel role of HSP90 as a positive regulator for expression of LAT gene in activated T cells. 21282515_LAT recruits Src homology 2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa (SLP-76) following T-cell receptor ligation and Akt kinase phosphorylation in Jurkat cells, activating the phosphoinositide 3-hydroxykinase (PI3K) signaling cascade. 21282648_LAT ubiquitylation is a molecular checkpoint for attenuation of T-cell signaling. 21508261_Data show that MAL regulates membrane order and the distribution of microtubule and transport vesicle docking machinery at the IS and, by doing so, ensures correct protein sorting of Lck and LAT to the cSMAC. 21642986_Activation of T cell antigen receptors resulted in the recruitment and phosphorylation of linker for activation of T cells (Lat) from subsynaptic vesicles. Studies of Lat mutants confirmed that recruitment preceded Lat phosphorylation. 21966541_Basal LAT-diacylglycerol-RasGRP1 signals in T cells maintain TCRalpha gene expression. 22034845_the segment comprising residues 112-126 of human LAT is required for its interaction with Lck. 22396725_Modeling and simulation of aggregation of membrane protein LAT with molecular variability in the number of binding sites for cytosolic Grb2-SOS1-Grb2 22802418_Nef employs a dual mechanism to disturb early TCR signaling by limiting the communication between LAT and SLP-76 22984075_Expression of constitutively active Raf transgene enhances lymphoproliferation, indicating a role for the Ras-MAPK pathway in LAT-mediated autoimmune hyperproliferation. 22998346_LAT is required to maintain calcium homeostasis in T cells. 23240581_LAT cleavage may act as a regulator of TCR-mediated activation of T-cells and not only as a transducer of cell death promoting stimuli. 23360572_Histone hypoacetylation on LAT promoter could inhibit LAT expression and enhanced Th2 differentiation, while trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, promoted LAT expression and inhibited Th2 cytokine production 23487428_LAT located at the cell surface can be recruited efficiently to activation-induced microclusters within seconds of T cell receptor (TCR) engagement. 23514740_A novel function and mechanism of TRAF6 action in the T cell receptor(TCR)-LAT signaling pathway indicates that LAT also plays an adapter role in TCR/CD28-induced activation of TRAF6. 24038088_findings show that L-type amino acid transporter 1 is a major transporter for essential amino acids into activated human T cells 24200054_mutation of palmitoylation site of LAT-EGFP attenuated the signal transduction of CD59 in T cells 24204825_LAT is a modulator of CD3zeta and ZAP-70 tyrosine phosphorylation. 24673455_Patients with severe aplastic anemia had increased levels of LAT and disturbed Th1-Th2 balance. 25907557_HSV-1-encoded Us3 protein interrupted TCR signaling and interleukin-2 production by inactivation of the linker for activation of T cells. 26271970_Data show that the palmitoylation mutation of linker for activation of T cells (LAT)attenuated the signal transduction induced by glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored CD59 antigen in T cells. 26715756_IFT20 is required for the delivery of the intracellular pool of LAT to the immune synapse in naive primary T lymphocytes. 26936531_High expression of LAT1 and ASCT2 correlates with metastasis and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 27221712_LAT and phospholipase C-gamma dephosphorylation by SHP-1 inhibits natural killer cell cytototoxicity 27242165_This is the first report of a LAT-related disease in humans, manifesting by a progressive combined immune deficiency with severe autoimmune disease. 27370798_Here we report that phosphotyrosine-mediated assembly of adaptor protein LAT networks yields two distinct kinetic species of the Ras activator SOS 27486861_Data show that LAT1 plays an important role in regulating the uptake of essential amino acids such as leucine into endometrial cancer cells. Increased ability of BCH compared to LAT1 shRNA at inhibiting Ishikawa spheroid area suggests that other LAT family members may also contribute to cell growth. 27522155_this study shows that inherited LAT deficiency should be considered in patients with combined immunodeficiency with T-cell abnormalities 27875277_LAT and SLP-76 are randomly dispersed throughout the clusters that form upon T cell receptor engagement. 27896837_Data indicate that the T cell-specific adaptor protein (TSAd) SH2 domain interacts with CD6 antigen and linker for activation of T cells protein (LAT) phosphotyrosine (pTyr) peptides. 28538176_Nur77 suppresses CD4(+) T cell proliferation and uncover a suppressive role for Irf4 in TH2 polarization; halving Irf4 gene-dosage leads to increases in GATA3(+) and IL-4(+) cells. 28815339_LAT1 overexpression represents a negative prognostic marker that has been linked to tumor grade, proliferating potential and angiogenesis and mediates intracellular transport of anticancer agents. 28951535_The dimerization-dependent, cooperative binding of the growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 family to LAT may increase antigen receptor sensitivity by reducing signalosome formation at incompletely phosphorylated linker of activated T cells LAT molecules, thereby prioritizing the formation of complete signalosomes. 28965845_Overexpression of LAT is associated with microcephaly. 29045874_Study examined molecular mobility within LAT:Grb2:SOS assemblies on supported membranes by single-molecule tracking. Trajectory analysis reveals a discrete temporal transition to subdiffusive motion below a characteristic timescale, indicating that the LAT:Grb2:SOS assembly has the dynamical structure of a loosely entangled polymer. 29440364_LAT, once internalized, transits through the Golgi-trans-Golgi network (TGN), where it is repolarized to the immune synapse. 29789604_Plasma membrane LAT activation precedes vesicular recruitment defining two phases of early T-cell activation. 29915297_Discovery of a conserved proline-rich motif in LAT that mediates efficient LAT phosphorylation. 30637450_that LAT1 is not only associated with poor prognosis of ovarian carcinoma, but also associated with chemoresistance in ovarian carcinoma 32727906_LRCH1 deficiency enhances LAT signalosome formation and CD8(+) T cell responses against tumors and pathogens. 32979494_The membrane proximal proline-rich region and correct order of C-terminal tyrosines on the adaptor protein LAT are required for TCR-mediated signaling and downstream functions. 33458942_The role of prolines and glycine in the transmembrane domain of LAT. 33562083_A Novel, LAT/Lck Double Deficient T Cell Subline J.CaM1.7 for Combined Analysis of Early TCR Signaling. 33572370_Retrograde and Anterograde Transport of Lat-Vesicles during the Immunological Synapse Formation: Defining the Finely-Tuned Mechanism. 34924127_L-type amino acid transporter 1 as a target for inflammatory disease and cancer immunotherapy. 36205741_Identification of LAT/ZAP70 characterized immune subtypes of prostate cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000030742 |
Lat |
432.133736 |
6.8618448572 |
2.778597 |
0.150992586 |
323.033843 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000316281730400966921086900282168298310202790207137600413296244701248544743507676022470032715662931194108215349084145264024534276561037198191555950206882290572324422692314874278811213936801749468941125087440013885498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000096452858279303135314263514765418113019609480972393524590178243154322247697607986290458015417000412822708476706134516405866172506232954400627791046799436245035921585179802687295969043645982310408726334571838378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
772.7813283 |
66.3980259 |
113.3643936 |
7.9041818 |
| ENSG00000213672 |
51517 |
NCKIPSD |
protein_coding |
Q9NZQ3 |
FUNCTION: Has an important role in stress fiber formation induced by active diaphanous protein homolog 1 (DRF1). Induces microspike formation, in vivo (By similarity). In vitro, stimulates N-WASP-induced ARP2/3 complex activation in the absence of CDC42 (By similarity). May play an important role in the maintenance of sarcomeres and/or in the assembly of myofibrils into sarcomeres. Implicated in regulation of actin polymerization and cell adhesion. Plays a role in angiogenesis. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22419821}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;SH3-binding |
|
The protein encoded by this gene contains a nuclear localization signal. It plays a role in signal transduction, and may function in the maintenance of sarcomeres and in the assembly of myofibrils into sarcomeres. It also plays an important role in stress fiber formation This protein is involved in the formation and maintenance of dendritic spines, and modulates synaptic activity in neurons. The gene is involved in therapy-related leukemia by a chromosomal translocation t(3;11)(p21;q23) that involves this gene and the myeloid/lymphoid leukemia gene. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2019]. |
hsa:51517; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; intermediate filament [GO:0005882]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; Arp2/3 complex binding [GO:0071933]; cytoskeletal protein binding [GO:0008092]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976] |
14559906_the interaction of the betaPIX.WASP.SPIN90 complex with Nck is crucial for stable cell adhesion and can be dynamically modulated by SPIN90 phosphorylation that is dependent on cell adhesion and ERK activation 16253999_SPIN90 participates in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton and in actin-based cell motility 17398099_DIP binds to and inhibits actin assembly by the FH2 domain of the formin mDia2 17398099_These observations point to a pivotal role for DIP in the control of nonbranched and branched actin-filament assembly that is mediated by Diaphanous-related formins and activators of Arp2/3, respectively. 17537434_The interplay between palladin, SPIN90 and Src and characterized the role of palladin and SPIN90 in platelet derived growth factor and Src-induced cytoskeletal remodeling, was analyzed. 19460367_SPIN90 and IRSp53 positively cooperated to mediate Rac activation, and co-expression of SPIN90 and IRSp53 in COS-7 cells led to the complex formation of SPIN90-IRSp53 in the leading edge of cells 23024796_Dia2 and DIP co-tether to nascent blebs and this linkage is required for bleb formation. 23342115_Findings show that SPIN90 modulates synaptic activity in neurons as a result of its phosphorylation. 23765104_SPIN90 dephosphorylation is a prerequisite step for releasing cofilin so that cofilin can adequately sever actin filaments into monomeric form. 24340049_findings suggest that SPIN90 contributes to the formation and movement of endosomal vesicles, and modulates the stability of EGFR protein, which affects cell cycle progression 28652253_Low SPIN90 expression is associated with Breast Cancer. 30322896_Structure of the nucleation-promoting factor SPIN90 bound to the actin filament nucleator Arp2/3 complex. 31358736_The findings suggest that SPIN90, as an adaptor protein, simultaneously binds inactive Rab5 and Gapex5, thereby altering their spatial proximity and facilitating Rab5 activation. |
ENSMUSG00000032598 |
Nckipsd |
259.410610 |
0.4033643327 |
-1.309845 |
0.104813415 |
158.153385 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000286500774800990610118701136584971352700779371891393038225100426389953468793307597371102878166995026054664208459143992513418197631835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000043505673210520796376106142130423387318827020057132663941730035860187829501594278602282276323387488758953622891567647457122802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
166.7870134 |
12.1230558 |
416.0942952 |
20.0965079 |
| ENSG00000213694 |
1903 |
S1PR3 |
protein_coding |
Q99500 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the lysosphingolipid sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). S1P is a bioactive lysophospholipid that elicits diverse physiological effect on most types of cells and tissues. When expressed in rat HTC4 hepatoma cells, is capable of mediating S1P-induced cell proliferation and suppression of apoptosis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10617617}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the EDG family of receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors. This protein has been identified as a functional receptor for sphingosine 1-phosphate and likely contributes to the regulation of angiogenesis and vascular endothelial cell function. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1903; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor activity [GO:0038036]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007193]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903141]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032651]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222] |
11915348_activates Rho family G proteins and cell motility 12763936_a 9-amino acid peptide (KRX-725), derived from the second intracellular loop of S1P3 (EDG3) mimics sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) by triggering a Gi-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signal. 15894172_S1P(3) function is not subject to conventional regulation by GRK phosphorylation 16527273_Expression of the sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor in primary endothelial cells is both sufficient and necessary for the expression of Akt3. 17331465_Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced inflammatory response genes expression is mediated through S1P(1) and S1P(3) 17395891_Reults describe the role of mu opioid receptors and S1P3 transactivation in the attenuation of vascular permeability by methylnaltrexone. 18502815_Cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha activation induced by S1P is mediated by the S1P3 receptor in lung epithelial cells.( 18612546_Results suggest that S1PR3 is involved in COX2 dependent effects of high-density lipoprotein on vascular smooth muscle. 18658144_Plays essential roles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by modulating fibroblast-like synoviocyte migration, cytokine/chemokine production, and cell survival. 19309361_Report different response patterns of several ligands at the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor subtype 3 (S1P(3)). 19633297_IGFBP-3 in MCF-10A cells requires SphK1 activity and S1P1/S1P3, suggesting that S1P, the product of SphK activity and ligand for S1P1 and S1P3 19748727_amplification of SHC3 and EDG3 genes suggests that the two proteins co-operate and are important for ependymomas in vivo. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20648639_this study demonstrated that reactive astrocytes in MS lesions and cultured under proinflammatory conditions strongly enhance expression of S1P receptors 1 and 3. 20889557_These results support a model in which the interaction between sphingosine kinase 1, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1 and/or 3, and ERK-1/2 might drive breast cancer progression 20979115_These results suggest a potential role for HDL and S1P receptors in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. 20980685_The follicular fluid-HDL-associated S1P promotes granulosa lutein cell migration via S1PR3 and RAC1 activation. This may represent a novel mechanism contributing to the development of the corpus luteum. 21145832_SphK/S1P/S1PRs signaling axis plays an important role in liver fibrosis and is involved in the directed migration of hepatic myofibroblasts into the damaged areas. 21652634_S1P regulates MMP-9 induction and invasiveness through coupling of S1P3 and G(alphaq) in MCF10A cells, thus providing a molecular basis for the crucial role of S1P in promoting breast cell invasion. 21660960_These data have identified an additional function regulated by S1P/S1PR1,3 axis involving migration and fibrogenic activation of hepatic stellate cells. 22308044_S1PR3 was higher in iliac-femoral arteries compared with carotid arteries. 22344462_Suggest that the enhanced S1P3-EGFR signaling axis may contribute to the tumorigenesis or progression of lung adenocarcinomas. 22547907_abdominal aortic aneurysms have down-regulation of the S1P2 protein with simultaneous up-regulation of the S1P3 protein, but not S1P1 22595806_However, growing evidence strongly suggests that the assessment of Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1/3 (S1P1/3) own advantages over present measurements in predicting the risk of developing diabetic cardiovascular diseases. 22771388_S1PR3 is nitrated on specific tyrosine residues and released as endothelial cell microparticles during acute lung injury. 22889737_S1P receptors S1P1,2,3 are expressed in human anaplastic thyroid cancer C643 and THJ-16T cells at both mRNA and protein levels 23142484_Inhibition of S1P3 receptors prevented E2-induced activation of Cdc42, supporting the important role of the S1P receptor in E2 signaling. 23392686_S1P3 receptors are detected in virtually all neurons in dorsal root ganglion and mediate pain behavior. 23466305_key role of Sphk1, S1PR1 and S1PR3 in angiogenesis underlying the liver fibrosis process 23589284_S1PR agonists are pro-fibrotic via S1P2R and S1P3R stimulation using Smad-independent pathways. 23911438_associations were found for 2 promoter SNPs across 2 European descent samples supporting association of alleles -1899G and -1785C with decreased risk for sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); alleles reduced transcription factor binding to S1PR3 promoter and S1PR3 promoter activity; associated with lower plasma S1PR3 protein in ARDS patients 23918395_Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 regulates recruitment of anti-inflammatory monocytes to microvessels during implant arteriogenesis. 24038457_we provide evidences that S1PR1/3, but not S1PR2, negatively regulate the expression of collagen in hMSCs using cellular and molecular approaches in vitro 24064218_a novel signaling axis, i.e., ROCK-JNK-ETS-1-CD44 pathway, which plays an essential role in the S1P3-regulated chemotactic response. 24851274_Data indicate that sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) induced transloaction of integrin beta4, S1P receptors S1PR2 and S1PR3 to endothelial cell membrane caveolin-enriched microdomains (CEMs). 24903384_Data show that sphingosine kinase SphK1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors S1P1, S1P2, S1P3, and S1P5 were expressed from primary, up to recurrent and secondary glioblastomas, with sphingosine kinase SphK2 levels were highest in primary tumors. 25254944_Stimulation with sphingosine-1-phosphate enhances cancer stem cells via S1PR3 and subsequent Notch1 activation. 25832730_S1pr3 promotes leukocyte rolling by mobilization of endothelial P-selectin. 25971967_TRPC1 functions as a major regulator of S1P3 and VEGFR2 expression. 27282481_The S1P1,3 activation results in Akt phosphorylation and subsequent activation of eNOS via phosphorylation at serine(1177) and dephosphorylation at threonine(495). 27616330_in breast cancer cells overexpression of S1P3 and its activation by S1P has pro-inflammatory and pro-metastatic potential by inducing COX-2 expression and PGE2 signaling via EP2 and EP4. 27856637_High S1PR3 expression is associated with increased lung adenocarcinoma. 28179022_HDL-associated ApoM is anti-apoptotic by delivering sphingosine 1-phosphate to S1P1 and S1P3 receptors on vascular endothelium. 28240350_The study shows that S1P receptor 3 (S1PR3) mRNA is overexpressed in EBV-positive NPC patient-derived xenografts and a subset of primary NPC tissues, and that knockdown of S1PR3 suppressed the activation of AKT and the S1P-induced migration of NPC cells. 28850247_Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 (S1PR3) mediates multiple aspects of the inflammatory response during sepsis. 28982858_S1PR1/3 silencing alters proliferation, adhesion, viability and lateral motility in estrogen receptor-negative MCF-7 and estrogen receptor-positive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. 29450744_these findings argue that HDL promotes angiogenesis via S1P3-dependent up-regulation and activation of VEGFR2 and also suggest that the S1P-S1P3-VEGFR2 signaling cascades as a novel target for HDL-modulating therapy implicated in vascular remodeling 29605826_Authors found that elevated levels of pSphK1 were positive correlation with high expression of S1P, which in turn promoted metastasis of TNBC through S1P/S1PR3/Notch signaling pathway. 30006619_Reactive astrocytic S1P3 signaling modulates the blood-tumor barrier in brain metastases. 30192865_S1P induced the expression of some asthma-related genes, such as ADRB2, PTGER4, and CCL20, in bronchial epithelial cells. The knock-down of SIPR3 suppressed the expression of S1P-inducing CCL20. 30712233_High expression of S1PR3 is associated with bladder transitional cell carcinoma. 30972941_Hyperglycemia-Triggered Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 3 Signaling Worsens Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Regulating M1/M2 Polarization. 31415870_This study demonstrated that S1P significantly promotes angiogenesis, inflammation, and barrier integrity, which was attenuated by inhibition of S1P2 or S1P3, suggesting that regulation of S1P2 and S1P3 is a novel therapeutic target for CNV. 31489649_S1PR3 deficiency alleviates radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis through the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting miR-495-3p. 32185202_Overexpression of Sphingosine Kinase-1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor-3 in Severe Plasmodium falciparum Malaria with Pulmonary Edema. 33458693_Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 potentiates inflammatory programs in normal and leukemia stem cells to promote differentiation. 33645008_Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 is implicated in BBB injury via the CCL2-CCR2 axis following acute intracerebral hemorrhage. 33919234_Divergence of Intracellular Trafficking of Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 3 in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells and MCF-7-Derived Stem Cell-Enriched Mammospheres. 34326314_EGR2-mediated regulation of m(6)A reader IGF2BP proteins drive RCC tumorigenesis and metastasis via enhancing S1PR3 mRNA stabilization. 34473432_Intracellular Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 3 Contributes to Lung Tumor Cell Proliferation. 34992498_The lncRNA H19/miR-766-3p/S1PR3 Axis Contributes to the Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes and Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis via the AKT/mTOR Pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000067586 |
S1pr3 |
96.853591 |
3.0735646189 |
1.619913 |
0.173355741 |
89.117575 |
0.00000000000000000000372031133930950542283150455181356999960805677090781046103921958501103972594137303531169891357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000034427457911102377754124866408857832096740488850299024680551296384578563447576016187667846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
146.0420888 |
14.6067623 |
47.8829577 |
3.9324961 |
| ENSG00000213719 |
1192 |
CLIC1 |
protein_coding |
O00299 |
FUNCTION: Can insert into membranes and form chloride ion channels. Channel activity depends on the pH. Membrane insertion seems to be redox-regulated and may occur only under oxydizing conditions. Involved in regulation of the cell cycle. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10834939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11195932, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11551966, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11940526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11978800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14613939, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9139710}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Cell membrane;Chloride;Chloride channel;Cytoplasm;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glutathionylation;Ion channel;Ion transport;Membrane;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport;Voltage-gated channel |
|
Chloride channels are a diverse group of proteins that regulate fundamental cellular processes including stabilization of cell membrane potential, transepithelial transport, maintenance of intracellular pH, and regulation of cell volume. Chloride intracellular channel 1 is a member of the p64 family; the protein localizes principally to the cell nucleus and exhibits both nuclear and plasma membrane chloride ion channel activity. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1192; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; brush border [GO:0005903]; chloride channel complex [GO:0034707]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; nuclear envelope [GO:0005635]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; vesicle [GO:0031982]; cadherin binding [GO:0045296]; chloride channel activity [GO:0005254]; voltage-gated ion channel activity [GO:0005244]; chloride transport [GO:0006821]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045669]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of ion transmembrane transport [GO:0034765]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
9139710_NCC27 (CLIC1) is a 27 kDa intracellular ion channel localized to the nucleus and cytoplasm that exists in both a soluble and integral membrane form 10834939_By selectively tagging either N- or C-termini of NCC27 (CLIC1) and varying the side of the membrane from which channel activity is recorded, NCC27 can be seen to be a TM protein forming part of an ion channel. 11195932_NCC27 (CLIC1) is broadly expressed and highly conserved. NCC27 blockers led to arrest of CHO-K1 cells in the G2/M stage of the cell cycle, the same stage at which this ion channel is selectively expressed on the plasma membrane 11551966_The soluble form of CLIC1 has been determined at 1.4-A resolution. The protein is monomeric and structurally homologous to the glutathione S-transferase superfamily, and it has a redox-active site resembling glutaredoxin. 11978800_Soluble E. coli-derived recombinant CLIC1 moves from solution into artificial bilayers and forms chloride-selective ion channels with essentially identical properties to those observed in CLIC1-transfected CHO cells. 14613939_The structure of oxidized CLIC1 has been determined. The oxidized CLIC1 dimer maintains its ability to form chloride ion channels in artificial bilayers and vesicles, whereas a reducing environment prevents the formation of ion channels by CLIC1 14613939_on oxidation CLIC1 undergoes a reversible transition from a monomeric to a non-covalent dimeric state due to the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond (Cys-24-Cys-59) 15190104_Amyloid-b stimulation of neonatal rat microglia increases CLIC1 protein and functional expression of CLIC1 chloride conductance. Blocking CLIC1 or reducing it by siRNA in amyloid-b treated microglia cocultured with neurons inhibits neurotoxicity 15827065_insulin induces the proteasome-dependent degradation of SRp20 as well as the subnuclear relocalization of CLIC1 17326840_In certain polarized columnar epithelia, CLIC1 may play a role in apical membrane recycling. 17347778_CFTR confers cAMP regulation to CLIC1 activity in the plasma membrane 18028448_Data showed that CLIC1 and CLIC5, but not CLIC4, were strongly and reversibly inhibited (or inactivated) by F-actin. 18710659_CLIC1 and TPD52 were significantly (P |
ENSMUSG00000007041 |
Clic1 |
2840.669018 |
2.3221097540 |
1.215436 |
0.030771385 |
1581.892667 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4036.5810628 |
72.7310056 |
1750.7275821 |
25.2872826 |
| ENSG00000213753 |
65996 |
CENPBD2P |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
215.628763 |
2.0284928156 |
1.020408 |
0.110253705 |
86.650759 |
0.00000000000000000001294808551317443487713599490987615325996698076811641404666557153557704396007466129958629608154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000117104008685327615901003552759549605621687463034643630031828021031969910836778581142425537109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
293.7400134 |
19.6528619 |
145.8484684 |
7.7080945 |
| ENSG00000213801 |
399669 |
ZNF321P |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.712576 |
0.4315286903 |
-1.212472 |
0.520475073 |
5.076048 |
0.02425859807705093434959664477901242207735776901245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.042671541844508616148079482854882371611893177032470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9549439 |
3.1007967 |
22.9056342 |
4.8795212 |
| ENSG00000213903_ENSG00000213906 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
137.117964 |
0.1394599180 |
-2.842078 |
1.054169255 |
6.230376 |
0.01255770538112359509252957678882012260146439075469970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.023599660227321652555820818975007568951696157455444335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.5997899 |
18.6288937 |
215.4497742 |
91.8901319 |
| ENSG00000213930 |
2592 |
GALT |
protein_coding |
P07902 |
FUNCTION: Plays an important role in galactose metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22461411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27005423}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Carbohydrate metabolism;Cataract;Disease variant;Galactose metabolism;Metal-binding;Nucleotidyltransferase;Reference proteome;Transferase;Zinc |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate metabolism; galactose metabolism. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22461411, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27005423}. |
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT) catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, namely the conversion of UDP-glucose + galactose-1-phosphate to glucose-1-phosphate + UDP-galactose. The absence of this enzyme results in classic galactosemia in humans and can be fatal in the newborn period if lactose is not removed from the diet. The pathophysiology of galactosemia has not been clearly defined. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
hsa:2592; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; UDP-glucose:hexose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase activity [GO:0008108]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; galactose catabolic process [GO:0019388]; galactose catabolic process via UDP-galactose [GO:0033499]; galactose metabolic process [GO:0006012]; UDP-glucose catabolic process [GO:0006258]; UDP-glucose metabolic process [GO:0006011] |
11511927_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11678552_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11704127_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11919338_Observational study of genotype prevalence and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 11936817_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11936817_no effect seen of N314D GALT genotype on risk of borderline or invasive ovarian cancer 12370157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12521227_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12606594_Data found no association between congenital absence of the uterus and vagina (CAUV) and the N314D allele of the galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT) gene. 12606594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12851678_Increased expression of Galactosyltransferase is associated with ovarian cancer 12869412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14614623_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14707519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14707519_association of decreased galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase activity with idiopathic presenile cataract 15308134_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15506833_children and adolescents with galactosemia function generally within the low average IQ range and have less well-developed executive functions. 15749517_No statistically significant differences were observed in the allele frequencies between the infertile women and control groups for GALT 15749517_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15841485_Nine novel mutations in the GALT gene associated with Classical galctosemia are described. 16009197_No association of GALT mutations is found in 86 patients with idiopathic premature ovarian failure. 16009197_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16125333_We postulate that molecular link between defective GALT enzyme, which result in classic galactosemia and the cerebroside galactosyl transferase, responsible for galactosylation of cerebrosides, is dependent on concentrations of UDP-galactose. 16274605_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16274605_no relationship was found between ovarian failure and GALT polymorphisms in Indian women 16416427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16507021_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16595241_no significant differences between women carrying at least one N314D or Q188R GALT allele and controls in IVF outcomes measured: numbers of follicles and oocytes obtained; fertilization rates and percentage of Grade A embryos; and pregnancy rates. 17041746_analysis of classical galactosaemia mutations in GALT1 in Spain and Portugal 17143577_analysis of a patient with galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase mutations p.Q188R and p.R333W and galactose metabolite levels during breast-feeding [case report] 17303100_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17876724_Identified novel mutations in GALT gene using DNA testing. 17876724_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18089596_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18210213_The R204X mutation severely compromises both expression and function of human GALT;T268N is one of a very small number of naturally occurring rare but neutral missense polymorphisms in human GALT. 18454942_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18454942_Synergistic effect of GALT and lactase mutations on cataract formation. 18956253_Results suggest that classical galactosaemia shows low allelic heterogeneity in Mexican patients. 19224951_4 bp 5' deletion in GALT is a causal mutation in Duarte galactosemia. 19646668_Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase deficiency is not associated with Mullerian aplasia in Dutch patients 20008339_The simulated point mutations have a direct effect on the active site, or on the dimer assembly and stability, or on the monomer stability. 20151200_live birth incidence of classical galactosemia in Estonia is 1:19.700 20222886_Congenital eye abnormalities and galactosemia were found in a family with Q188R and G1391A mutations. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20547145_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20734064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21059483_GALT deletion mutation carrier frequency was 1 in 127 (0.79%). 21059483_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 21188552_3 different GALT mutations viz. Q188R, N314D and S307X were found to be present in the family of a neonate diagnosed with galactosemia and having the heterozygote genotype Q188R/S307X. S307X is a novel GALT mutation linked to galactosemia. 22749219_Duarte1 (D1) and D2 genotypes of GALT do not appear to play a role in the association between galactose intake, possible ovarian dysfunction, and the link with ovarian cancer 22798028_The study determined the frequency of the two most common GALT mutations and their variants in Indian galactosemia patients. 22944367_Forty four novel variations in the GALT gene were identified, among them 27 nucleotide substitutions, in the French cohort of galactosemic patients. 22963887_Mutations of the galactose-1-phosphate uridyltranseferase gene is associated with galactosemia. 23022339_The novel GALT gene mutations included 6 missense mutations viz. Y89H, Q103R, P166A, S181F, K285R, R333L; one nonsense mutation, S307X and 3 silent mutations--Q103Q, K210K and H319H. 23583749_HGALT requires a level of flexibility to function optimally and that altered folding is the underlying reason of impairment in all the variants tested here. 23690308_Data suggest that in classic galactosemia residual GALT activity (predicted from activity of recombinant GALT matching patient's mutation) correlates with reduced ovarian reserve (as indicted by biological marker, circulating anti-Mullerian hormone). 23924834_In this report, we present GALT gene mutations in 56 cases of galactosemia from Turkey identified using DNA microarray resequencing. 24045215_suggests that GALT mutations are ethnic-specific and that galactosemia is a heterogeneous disorder at the molecular level 25052314_Mutation activates a cryptic donor splice site, inducing an aberrant splicing of the GALT pre-mRNA, which in turn leads to a frameshift with inclusion of a premature stop codon. 25124065_In Korean population, novel GALT mutations were identified in the galactosemia patients different from those of other populations. 25268296_GALT activity in red blood cells of patients with galactosaemia 25592817_Novel missense mutations identified in Italian galactosemic patients. 25920691_A novel noncoding homozygous GALT variant associated with asymptomatic galactosemia has been described in an infant of consanguineous heterozygous parents. 27005423_we present the 1.9 A resolution crystal structure of human GALT (hGALT) ternary complex, revealing a homodimer arrangement that contains a covalent uridylylated intermediate and glucose-1-phosphate in the active site, as well as a structural zinc-binding site, per monomer 27308838_17 VUS (37%; 7 in ACADM, 9 in GALT, and 1 in PAH) were reclassified from uncertain (6 to benign or likely benign and 11 to pathogenic or likely pathogenic). We identified common types of missing information that would have helped make a definitive classification and categorized this information by ease and cost to obtain 28374897_This review summarizes the current knowledge of galactosemia, in particular the putative mechanisms of neonatal and long-term complications and the molecular genetics of GALT deficiency. 28450132_novel splicing mutation in GALT gene causing Galactosemia in Ecuadorian family 28644047_The mutational spectrum of the GALT gene in Greek galactosemia patients is presented for the first time. 28816213_Study found no statistically significant difference in the occurrence of the GALT gene mutation between Indian patients with idiopathic presenile cataract and controls. 29252199_GALT mutation is associated with galactosemia. 30172461_Although all individuals in this study showed markedly reduced RBC GALT activity, we observed significant differences in RBC GAL1P concentrations among galactosemia genotypes. 31194682_Biallelic pathogenic variants in the GALT gene are associated with galactosemia. 31194895_Heterogeneity of disease-causing variants in the Swedish galactosemia population: Identification of 16 novel GALT variants. 31774565_Galactose 1-phosphate accumulates to high levels in galactose-treated cells due to low GALT activity and absence of product inhibition of GALK. 32748411_A founder noncoding GALT variant interfering with splicing causes galactosemia. 34641485_Analysis of the Structure-Function-Dynamics Relationships of GALT Enzyme and of Its Pathogenic Mutant p.Q188R: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study in Different Experimental Conditions. 36093991_A multinational study of acute and long-term outcomes of Type 1 galactosemia patients who carry the S135L (c.404C > T) variant of GALT. |
ENSMUSG00000036073 |
Galt |
174.042719 |
0.2879551976 |
-1.796084 |
0.172222654 |
108.027076 |
0.00000000000000000000000026513131252258308745103929597992713388596335806869462462602755220032746397151868222863413393497467041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000002879571871106200682732707189796582076277073102539409342825481633552919813467951826169155538082122802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
80.7197623 |
13.2440916 |
282.3397288 |
32.1846408 |
| ENSG00000213949 |
3672 |
ITGA1 |
protein_coding |
P56199 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-1/beta-1 is a receptor for laminin and collagen. It recognizes the proline-hydroxylated sequence G-F-P-G-E-R in collagen. Involved in anchorage-dependent, negative regulation of EGF-stimulated cell growth. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15592458}. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Cell adhesion;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Integrin;Magnesium;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes the alpha 1 subunit of integrin receptors. This protein heterodimerizes with the beta 1 subunit to form a cell-surface receptor for collagen and laminin. The heterodimeric receptor is involved in cell-cell adhesion and may play a role in inflammation and fibrosis. The alpha 1 subunit contains an inserted (I) von Willebrand factor type I domain which is thought to be involved in collagen binding. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3672; |
acrosomal vesicle [GO:0001669]; basal part of cell [GO:0045178]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; integrin alpha1-beta1 complex [GO:0034665]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; perikaryon [GO:0043204]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; collagen binding involved in cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0098639]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein phosphatase binding [GO:0019903]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cellular extravasation [GO:0045123]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0042059]; neuron projection morphogenesis [GO:0048812]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032516]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11454259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11877061_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11937138_results suggest that the inadequate trophoblastic invasion, induced by antiphospholipid antibodies, can be the result of decreased alpha1 integrin and VE-cadherin and increased alpha5 integrin and E-cadherin expression in the trophoblast 12078857_role of VLA1 in migration of multiple sclerosis derived antigen-reactive T-cell migration 12662928_determination of crystal structure in complex with an antibody Fab fragment 12694973_endometrial integrin alpha1 and alpha4 expression is more consistently present in the early luteal phase in stimulated cycles than in natural cycles 15109703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15132990_VEGF-A induced alpha1 & alpha2 integrins, promoting lymphatic endothelial tube formation & haptotactic migration. Lineage-specific integrin receptor expression contribute to the distinct dynamics of wound-associated angiogenesis & lymphangiogenesis. 15485856_alpha(1)beta(1) and Col-IV contribute to beta-cell functions known to be important for islet morphogenesis and glucose homeostasis 15679046_Enhanced expression of Integrin alpha1 is associated with liver metastases from gastrointestinal tumours 16043429_analysis of binding between collagen type III and integrins alpha1beta1 and alpha2beta1 16412752_No statistical difference was observed on the expression of alpha1 integrin subunit expression in endometrium in tubal phimosis or hydrosalpinx 16472776_identified integrin alpha1 as a protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA-interacting protein for the first time, and verified this physical association with pull-down and co-immunoprecipitation assays 17312461_alpha1beta1 integrin is a type IV collagen receptor in pancreatic cancer cells 17603494_results define a crucial role for alpha1beta1 in controlling the accumulation of epidermal type 1 polarized effector memory T cells in a common human immunopathology and provide the basis for new strategies in psoriasis treatment 17669516_thrombopoietin-induced in vitro differentiation of primary human cord blood mononuclear cells into megakaryocytes, we observed rapid, progressive CpG methylation of ITGA1, but not PELO or ITGA2. 17891451_A significant subset of VLA-1-positive effector T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients persists in vivo and in vitro during monoclonal antibody therapy and contributes to residual and recurring inflammation. 17931993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17931993_are suggestive of the association of ITGA1 with osteoporosis and related risk in postmenopausal women 17982677_Activation of the FAK-src molecular scaffolds and p130Cas-JNK signaling cascades by alpha1-integrins during colon cancer cell invasion. 18048918_Group B streptococci ACP binds alpha(1)beta(1)-integrin via the D1 domain that promotes GBS internalization within epithelial cells. 18081024_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18269595_Expression of VLA-1 was found significantly higher in lesional dermal blood vessels of psoriatic patients compared with atopic patients. 18377961_progesterone has an impact on alpha(1)-integrin distribution in the endometrium of patients with unexplained infertility 18454440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18587047_These results indicate that NSP4 interaction with integrin alpha1 and alpha2 is an important component of enterotoxin function and rotavirus pathogenesis, further distinguishing this viral virulence factor from other microbial enterotoxins. 18647959_distinct amino acids distal to the GFFKR motif of the alpha1 integrin cytoplasmic tail mediate activation of selective downstream signaling pathways and specific endothelial cell functions 18813796_MYCN may limit cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix and promote cell migration by downregulating integrin alpha1 19397781_alpha(1)beta(1) integrin is of importance not only for the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into myofibroblasts but also for the neovascularization and connective tissue organization 19730683_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19780039_ERbeta affects integrin expression and clustering and consequently modulates adhesion and migration of breast cancer cells. 19850917_Results show that plumieribetin, a fish lectin from the scorpionfish (Scorpaena plumieri), inhibits alpha1beta1 integrin binding to basement membrane collagen IV. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20232313_Pancreatic beta cell mesenchymal transition and decline in insulin gene expression are induced by elements of the ECM, by b1-integrin ligation, and by signaling via Src, JNK, and ERK. 20436081_Androgens increased INT alpha1 and alpha2 subunits in tubuloepithelial cells and in healthy labial salivary glands. 20531279_Prostate tissue-derived CD133+ cells exhibited a moderate level of expression of alpha1 integrin 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21521694_Streptococcus pyogenes M49 plasminogen/plasmin binding facilitates keratinocyte invasion via integrin-integrin-linked kinase (ILK) pathways and protects from macrophage killing 21647271_Integrin alpha2beta1 might play a more crucial role in maintaining the mechanical creep properties of the collagen matrix than does integrin alpha1beta1. 21965670_the C-linker has a role as a spring-like element that allows relaxation of the alphaI domain in the resting state and controlled tension of the alphaI domain during activation, exerted by the beta chain 22002573_There was no evidence for differences in integrin alpha1, alpha4, beta1 and beta3 protein levels between the follicular and mid-luteal staged samples. 22030389_study characterized the collagen binding properties of an activated variant of the alpha1I domain, harboring a gain-of-function mutation E317A; the activated alpha(1)I domain represents a novel conformation of the alphaI domain, mimicking the structural state where the Arg(287)-Glu(317) ion pair has just broken during the integrin activation 22298882_study identified integrin alpha1/beta1 and alpha2/beta1 heterodimer as a new candidate IgA1 receptor in human mesangial cells 22698912_we have identified a new locus candidate, ITGA1, influencing both fasting glucose and BMD, that may begin to explain the genetic contribution to the epidemiological observations linking type 2 diabetes and osteoporosis 22847004_Dynamic structural changes are observed upon collagen and metal ion binding to the integrin alpha1 I domain. 22919661_CagL is a versatile surface protein equipped with at least two motifs to promote binding to integrins, thereby causing aberrant signaling within host cells and facilitating translocation of CagA into host cells. 23070086_Collagen receptors alpha(1)beta(1) and alpha(2)beta(1) integrins are involved in transmigration of peripheral blood eosinophils, but not mononuclear cells through human microvascular endothelial cells monolayer 23284937_Discoidin domain receptors promote alpha1beta1- and alpha2beta1-integrin mediated cell adhesion to collagen by enhancing integrin activation. 23448258_Pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha strongly promotes pericyte proliferation and migration, and concomitantly induces a switch in pericyte integrins, from alpha1 to alpha2 integrin. 23819010_17-beta-estradiol modulates connexins and integrins as well as ER-beta expression induced by high frequency electromagnetic fields. 24018042_miR-101:DNMT-3B interaction modulates integrin alpha-1 epigenetically. 24124332_ITGA1 gene SNPs rs1862610, rs24321 43, and rs2447867 and the ITGA1 haplotype block that includes SNPs rs1862610 and rs2432143 were significantly associated with gastric cancer. 24164540_CD49a promoted Con A-induced hepatitis through enhancing inflammatory cytokine production (IFN-gamma and IL-17A) by CD4(+) T and invariant natural killer T cells. 24187131_small angle x-ray scattering data suggest that at low collagen peptide concentrations the complex exists in equilibrium between a 1:1 and 2:1 alpha1I-peptide complex. 25550552_Integrin alpha1 and beta4 are downregulated, following Dendrofalconerol A treatment, in H460 cells. 25672754_Data indicate that CD49a(+) NK cells retain their phenotype after expansion in long-term in vitro cultures. 26096932_MYC is a key regulating factor for the control of ITGA1 expression in colorectal cancer. 27294728_favors adhesive over migratory fibroblast phenotype 27342747_a comparative study between the wild type integrin alpha1 I and a gain-of-function E317A mutant. NMR HDX results suggest a relationship between regions exhibiting a reduced local stability in the unbound I domain and those that undergo significant conformational changes upon binding. 27929375_A range of affinities from almost no interaction to the relatively high avidity that characterizes alphaIIbbeta3 is seen between various alpha subunits and beta1 transmembrane and cytosolic domains. 28318877_Studies suggest there are two nonoverlapping NK cell populations that are potentially liver resident in humans: CD49a+ NK cells and Eomes hi. 28809852_Results suggest that genetic variants in ITGA1 may be involved in the etiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the single-nucleotide polymorphisms -set based analysis is a promising strategy for the detection of underlying genetic risk factors. 28855593_ITGA1 promotes therapy resistance and metastatic potential in pancreatic cancer. 28952190_IL-12 and IL-15 induce the expression of CXCR6 and CD49a on peripheral natural killer cells. 29079572_Data suggest that the residue volume at phenylalanine (Phe) in alpha1-helix is critical for alpha(L)/beta(2) integrin (CD49a/CD18) activation and binding with soluble/immobilized ICAM1 (intercellular cell adhesion molecule 1). 29504106_It was found that the levels of integrin alpha1 and VE-cadherin mRNA increased during co-culturing of activated endothelium cells with mesenchymal stromal cells. 29761640_These data indicate that integrin alpha2 signaling may have an increased osteogenic effect relative to integrin alpha1 . 29937357_VLA1-collagen recognition is regulated by magnesium. 32753478_An interspecies translation model implicates integrin signaling in infliximab-resistant inflammatory bowel disease. 32986180_Alginate oligosaccharide protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress injury via integrin-alpha/FAK/PI3K signaling. 34566986_CD49a Identifies Polyfunctional Memory CD8 T Cell Subsets that Persist in the Lungs After Influenza Infection. 34906278_Nanofluorescence Probes to Detect miR-192/Integrin Alpha 1 and Their Correlations with Retinoblastoma. 35013194_The catalytic activity of TCPTP is auto-regulated by its intrinsically disordered tail and activated by Integrin alpha-1. 35060996_Erianin Controls Collagen-Mediated Retinal Angiogenesis via the RhoA/ROCK1 Signaling Pathway Induced by the alpha2/beta1 Integrin-Collagen Interaction. 36301458_Hsa_circ_0043949 reinforces temozolomide resistance via upregulating oncogene ITGA1 axis in glioblastoma. |
ENSMUSG00000042284 |
Itga1 |
1198.573035 |
9.8250650828 |
3.296467 |
0.066785058 |
2745.626555 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2219.7810183 |
85.4589937 |
227.6069777 |
8.0428554 |
| ENSG00000213983 |
8906 |
AP1G2 |
protein_coding |
O75843 |
FUNCTION: May function in protein sorting in late endosomes or multivesucular bodies (MVBs). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9733768}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Involved in MVB-assisted maturation of hepatitis B virus (HBV). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16867982, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17553870}. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Membrane;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Adaptins are important components of clathrin-coated vesicles transporting ligand-receptor complexes from the plasma membrane or from the trans-Golgi network to lysosomes. The adaptin family of proteins is composed of four classes of molecules named alpha, beta-, beta prime- and gamma- adaptins. Adaptins, together with medium and small subunits, form a heterotetrameric complex called an adaptor, whose role is to promote the formation of clathrin-coated pits and vesicles. The protein encoded by this gene is a gamma-adaptin protein and it belongs to the adaptor complexes large subunits family. This protein along with the complex is thought to function at some trafficking step in the complex pathways between the trans-Golgi network and the cell surface. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:8906; |
AP-1 adaptor complex [GO:0030121]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; Golgi-associated vesicle [GO:0005798]; membrane [GO:0016020]; transport vesicle [GO:0030133]; cargo adaptor activity [GO:0140312]; clathrin adaptor activity [GO:0035615]; Golgi to vacuole transport [GO:0006896]; intracellular protein transport [GO:0006886]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
17553870_These results demonstrate that HBV exploits the multivesicular bodies machinery with the aid of gamma 2-adaptin. 18772139_gamma2-adaptin's ubiquitin-interacting motif mediates a specific physical interaction with the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4 and promotes ubiquitination of gamma2-adaptin 20708039_Data show that gamma2-adaptin in MVB sorting specifically interacts with the ESCRT subunits Vps28 and CHMP2A. 27909244_Depletion of the gamma2 or mu1A (AP1M1) subunits of AP-1, but not of gamma1 (AP1G1), precludes Nef-mediated lysosomal degradation of CD4. |
ENSMUSG00000040701 |
Ap1g2 |
409.309432 |
0.2812494511 |
-1.830078 |
0.227903423 |
61.279381 |
0.00000000000000495239592636818192785163262039971884072211277816322194667009171098470687866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000033888439440516626386508726248361536306189390616028234148870978970080614089965820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
179.8408925 |
33.0304208 |
642.0757029 |
84.2844207 |
| ENSG00000213999 |
4207 |
MEF2B |
protein_coding |
Q02080 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional activator which binds specifically to the MEF2 element, 5'-YTA[AT](4)TAR-3', found in numerous muscle-specific genes. Activates transcription via this element. May be involved in muscle-specific and/or growth factor-related transcription. |
3D-structure;Activator;Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The product of this gene is a member of the MADS/MEF2 family of DNA binding proteins. The protein is thought to regulate gene expression, including expression of the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain gene. This region undergoes considerable alternative splicing, with transcripts supporting two non-overlapping loci (GeneID 729991 and 100271849) as well as numerous read-through transcripts that span both loci (annotated as GeneID 4207). Several isoforms of this protein are expressed from either this locus or from some of the read-through transcripts annotated on GeneID 4207. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:100271849;hsa:4207; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; muscle organ development [GO:0007517]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12700764_Crystal structure of the MADS-box/MEF2S domain of human MEF2B bound to a motif of the transcriptional co-repressor Cabin1 and DNA at 2.2 A resolution 15084602_myogenin and myocyte enhancer factor-2 expression are triggered by membrane hyperpolarization during human myoblast differentiation 15567413_The crystal structure of a histone deacetylase 9 (HDAC9)/myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2)/DNA complex reveals that HDAC9 binds to a hydrophobic groove of the MEF2 dimer. 16504037_Study demonstrates that human intestinal cell BCMO1 expression is dependent on the functional cooperation between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and myocyte enhancer factor 2 isoforms. 19093215_MEF2 proteins are an important component in Galpha13-mediated angiogenesis. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21796119_32% of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and 89% of follicular lymphoma cases had somatic mutations in MLL2, and 11.4% and 13.4% of DLBCL and FL cases, respectively, had mutations in MEF2B 21951798_The phylogenetic tree result shows that MEF2B may be original because of its difference of sequences and evolutional relation. 22302709_MEF2B has a role in myogenic transformation of the epithelial to a myofibroblast phenotype 23974956_MEF2B mutations lead to deregulated expression of the oncogene BCL6 in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. 26089142_We conclude that MEF2B is a valuable marker of normal germinal center B cells, potentially useful in differential diagnosis of small B cell lymphomas. 26245647_K4E, Y69H and D83V mutations decrease the capacity of MEF2B to activate transcription and decrease its effects on cell migration. 26468528_Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA1 bound to host genes of high significance for B-cell growth and function, including MEF2B, IL6R, and EBF1. 28851661_Expression of J chain immunoglobulin and MEF2B are useful in differentiating classical Hodgkin lymphoma from nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. 29309299_MEF2B shows superior sensitivity and specificity than LMO2 and HGAL in the differential diagnosis of follicular lymphoma versus marginal zone lymphoma and is particularly useful in FL with plasmacytoid differentiation, which may have morphologic and immunophenotypic overlap with MZL. 29477338_Although the mechanisms by which the D83V mutation in MEF2B promote oncogenesis in lymphoma cells remain to be elucidated, the observation that a mutation hotspot coincides with a conformation switch site on MEF2B reflects a remarkable convergence of tumor growth selection pressure and the physical/ chemical forces behind protein folding. 29944822_The Apo structure of MEF2B reveals a largely preformed DNA binding interface that may be important for recognizing the shape of DNA from the minor groove side. 30205047_Mef2b deletion reduces germinal center (GC) formation in mice and identify MEF2B transcriptional targets in GC, with roles in cell proliferation, apoptosis, GC confinement, and differentiation. The most common lymphoma-associated MEF2B mutant (MEF2BD83V) is hypomorphic yet escapes binding and negative regulation by components of the HUCA complex and class IIa HDACs. 30446717_Studied expression of myocyte enhancer factor 2B (MEF2B) as part of the diffuse large (DLBCL) B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) transcription complex in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma tissue samples and cell lines. Findings indicate MEF2B to be an essential component of the BCL6 gene transcriptional complex for the regulation of DLBCL growth thru promotion of BCL6 expression. 31241765_Convergent Evidence From Humans and Drosophila melanogaster Implicates the Transcription Factor MEF2B/Mef2 in Alcohol Sensitivity. 31914533_expression of MEF2B in mantle cell lymphomas is related to the pathological subtypes 32681840_Crystal Structures of Ternary Complexes of MEF2 and NKX2-5 Bound to DNA Reveal a Disease Related Protein-Protein Interaction Interface. 32738045_Landscape of DNA binding signatures of myocyte enhancer factor-2B reveals a unique interplay of base and shape readout. 34418874_Systematic transition modeling analysis in the MEF2B-DNA binding interface due to Y69H and K4E variants. |
ENSMUSG00000079033 |
Mef2b |
12.605065 |
0.1493350617 |
-2.743375 |
0.981053970 |
6.619240 |
0.01008828497778873137247224178736360045149922370910644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019323006264230686152005844746781804133206605911254882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.7389011 |
2.4806774 |
17.3671681 |
10.1993566 |
| ENSG00000214021 |
26140 |
TTLL3 |
protein_coding |
Q9Y4R7 |
FUNCTION: Monoglycylase which modifies alpha- and beta-tubulin, adding a single glycine on the gamma-carboxyl groups of specific glutamate residues to generate monoglycine side chains within the C-terminal tail of tubulin. Not involved in elongation step of the polyglycylation reaction (By similarity). Preferentially glycylates a beta-tail peptide over the alpha-tail, although shifts its preference toward alpha-tail as beta-tail glutamylation increases (By similarity). Competes with polyglutamylases for modification site on beta-tubulin substrate, thereby creating an anticorrelation between glycylation and glutamylation reactions (By similarity). Together with TTLL8, mediates microtubule glycylation of primary and motile cilia, which is essential for their stability and maintenance (By similarity). Involved in microtubule glycylation of primary cilia in colon which controls cell proliferation of epithelial cells and plays an essential role in colon cancer development (PubMed:25180231). Together with TTLL8, glycylates sperm flagella which regulates axonemal dynein motor activity, thereby controlling flagellar beat, directional sperm swimming and male fertility (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A4Q9E5, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B2GUB3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25180231}. |
Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell projection;Cilium;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Flagellum;Ligase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome |
|
Enables protein-glycine ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in axoneme assembly and flagellated sperm motility. Predicted to be located in axoneme; microtubule cytoskeleton; and sperm flagellum. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:26140; |
axoneme [GO:0005930]; cilium [GO:0005929]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; sperm flagellum [GO:0036126]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein-glycine ligase activity [GO:0070735]; protein-glycine ligase activity, initiating [GO:0070736]; axoneme assembly [GO:0035082]; cilium assembly [GO:0060271]; cilium movement [GO:0003341]; flagellated sperm motility [GO:0030317]; protein polyglycylation [GO:0018094] |
11054573_Characterization of another human tubulin tyrosine ligase-like gene family member |
ENSMUSG00000030276 |
Ttll3 |
409.942805 |
0.4294757418 |
-1.219351 |
0.195544719 |
38.001748 |
0.00000000070681280563153393831431894276653635222906757462624227628111839294433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003421632342119200315809712936178897668693110745152807794511318206787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
248.7695488 |
32.2121418 |
583.0498471 |
53.8084948 |
| ENSG00000214110 |
|
LDHAP4 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.611204 |
3.5561517228 |
1.830317 |
0.320438043 |
34.158695 |
0.00000000507957723982713172017114028659011404354117757975473068654537200927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000022788620078981297071762791134862113917591841527610085904598236083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.2400233 |
9.3888303 |
11.9082323 |
2.1621099 |
| ENSG00000214176_ENSG00000215769_ENSG00000266820 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
183.210051 |
0.3649860657 |
-1.454087 |
0.226512019 |
39.875242 |
0.00000000027071300750440969580726428221064891466163260247412836179137229919433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001355401625089920937304071359716731159927860517200315371155738830566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
98.9782877 |
28.1298672 |
274.1522450 |
55.6467991 |
| ENSG00000214193 |
79729 |
SH3D21 |
protein_coding |
A4FU49 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Located in nucleoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79729; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; cell migration [GO:0016477] |
|
ENSMUSG00000073758 |
Sh3d21 |
28.115353 |
0.3666063525 |
-1.447696 |
0.345106133 |
17.722627 |
0.00002555685674916050826124304384823204827625886537134647369384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000076357421764580631637700514069422297325218096375465393066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2348903 |
2.8881922 |
36.5515246 |
5.1307867 |
| ENSG00000214293 |
100505854 |
APTR |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24748121_APTR associates with the promoter of CDKN1A/p21 and this association requires a complementary-Alu sequence encoded in APTR. A different module of APTR associates with and recruits the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) to repress the p21 promote 29274906_Results show that portal venous levels of APTR was significantly decreased after TIPS treatment and its aberrant expression levels were positively correlated with Model for End Stage Liver Disease (MELD), portal hepatic venous pressure gradient (PHPG) in patients. Higher APTR expression in portal vein was associated with poor prognosis. 30317613_APTR contributed to osteosarcoma progression through repression of miR-132-3p and upregulation of YAP1 expression. 30539519_Down-Regulation of APTR and it's Diagnostic Value in Papillary and Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. |
|
|
41.061594 |
0.3072504856 |
-1.702513 |
0.249999779 |
48.147165 |
0.00000000000395400161537573140249040165772312816101774490817888363380916416645050048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000022585551022811841729566806845782526037141879626801710401196032762527465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.6510033 |
3.0779340 |
64.4759429 |
6.2082629 |
| ENSG00000214455 |
|
RCN1P2 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.443086 |
3.1361758081 |
1.649006 |
0.665264059 |
5.983095 |
0.01444363178419815624264899156514729838818311691284179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026739099341366302092781737087534565944224596023559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.5960015 |
10.9617037 |
9.5199440 |
2.6848036 |
| ENSG00000214595 |
400954 |
EML6 |
protein_coding |
Q6ZMW3 |
FUNCTION: May modify the assembly dynamics of microtubules, such that microtubules are slightly longer, but more dynamic. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Microtubule;Reference proteome;Repeat;WD repeat |
|
Predicted to enable microtubule binding activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm and microtubule. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:400954; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule binding [GO:0008017] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000044072 |
Eml6 |
29.961812 |
0.0566077787 |
-4.142856 |
0.761675749 |
24.731952 |
0.00000065882842802199018549696215435451662756349833216518163681030273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002381657506148561332499045961608175048240809701383113861083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9279984 |
1.5316734 |
53.3482340 |
17.1656639 |
| ENSG00000214706 |
7866 |
IFRD2 |
protein_coding |
Q12894 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:7866; |
nucleus [GO:0005634] |
9722946_Identification of a new family of IFRD (interferon developmental regulator) genes, of which SkMC15 is part, being named IFDR2 9722946_Identification of the IFRD gene family, comprising the two genes PC4 / Tis7 / IFRD1 and SKMc15 / IFRD2, and in situ-hybridization analysis of their expression during developments 9722946_This publication discusses both IFRD1 and IFRD2. 20689807_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000010048 |
Ifrd2 |
231.456152 |
2.4590644970 |
1.298110 |
0.181233281 |
50.514763 |
0.00000000000118271732222279410857322059174051874291463959387726845307042822241783142089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007007991841031088390150799805284541040342749518288201215909793972969055175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
330.5414133 |
36.4488887 |
135.3293123 |
11.2780003 |
| ENSG00000214756 |
751071 |
CSKMT |
protein_coding |
A8MUP2 |
FUNCTION: Protein-lysine methyltransferase that selectively trimethylates citrate synthase (CS) in mitochondria (PubMed:28391595, PubMed:28887308). Seems to conduct trimethylation in a highly distributive manner rather than in a processive manner, and thus introduces a single methyl group per binding event (PubMed:28887308). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28391595, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28887308}. |
Methyltransferase;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase;Transit peptide |
|
Enables protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity. Involved in peptidyl-lysine dimethylation; peptidyl-lysine monomethylation; and peptidyl-lysine trimethylation. Predicted to be located in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:751071; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016278]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279]; peptidyl-lysine dimethylation [GO:0018027]; peptidyl-lysine monomethylation [GO:0018026]; peptidyl-lysine trimethylation [GO:0018023]; protein methylation [GO:0006479] |
28391595_Data suggest that METTL12, localized in mitochondrial matrix, modifies/methylates Lys368 of citrate synthase in external surface region close to its catalytic site; addition/removal of methylation has no effect on citrate synthase activity; Lys368 occurs in highly conserved sequence of amino acid residues of citrate synthase. |
|
|
24.262331 |
0.2546486047 |
-1.973420 |
0.798203812 |
5.000309 |
0.02534278831958747951746957483010191936045885086059570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044372336925661393092212847477640025317668914794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4315749 |
4.0463699 |
29.8499978 |
11.5871131 |
| ENSG00000214783 |
84820 |
POLR2J4 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.501577 |
0.2843095350 |
-1.814466 |
0.382503688 |
22.537554 |
0.00000206075337724155515655593585988558658073088736273348331451416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007040907372241980224111899261396629867704177740961313247680664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3239073 |
4.1467250 |
48.3483555 |
9.9885685 |
| ENSG00000214787 |
643680 |
MS4A4E |
protein_coding |
Q96PG1 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: May be involved in signal transduction as a component of a multimeric receptor complex.; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Alternative splicing;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
Most MS4A genes, including MS4A4E, encode proteins with at least 4 potential transmembrane domains and N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic domains encoded by distinct exons.[supplied by OMIM, Apr 2004]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:66607;;mmu:666907;;; |
Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21460840_ABCA7 and the MS4A6A/MS4A4E gene cluster are new Alzheimer's disease susceptibility loci. 26449541_We replicated the rs11136000 (CLU)- rs670139 (MS4A4E) interaction, demonstrated an association in APOE epsilon4 negative subjects, and reported evidence of a possible dominant effect for MS4A4E. 27781389_Addition of the minor allele for rs670139 (MS4A4E), rs9331896 (CLU), and rs12155159 (NME8) was nominally associated with change on the DWRT, DSST, and WFT, respectively, in whites. For rs670139 and rs9331896 the association was only significant in individuals bearing at least one APOE 4 allele in stratified analyses. |
ENSMUSG00000024678+ENSMUSG00000101389+ENSMUSG00000024675+ENSMUSG00000056290 |
Ms4a4d+Ms4a4a+Ms4a4c+Ms4a4b |
12.929231 |
0.4320764467 |
-1.210642 |
0.505834252 |
5.706005 |
0.01690697296665196261433727897838252829387784004211425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.030831099701974670063142625053842493798583745956420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4291475 |
2.4781257 |
17.2454759 |
3.9110704 |
| ENSG00000214827 |
4515 |
MTCP1 |
protein_coding |
P56278 |
FUNCTION: Enhances the phosphorylation and activation of AKT1 and AKT2. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10983986}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Chromosomal rearrangement;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome |
|
This gene was identified by involvement in some t(X;14) translocations associated with mature T-cell proliferations. This region has a complex gene structure, with a common promoter and 5' exon spliced to two different sets of 3' exons that encode two different proteins. This gene represents the upstream 13 kDa protein that is a member of the TCL1 family. This protein may be involved in leukemogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009]. |
hsa:4515; |
protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity [GO:0043539]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0071902] |
17136114_Transgenic mice overexpressing MTCP1 develop leukemias with a CD8 central memory phenotype in most cases. 19064571_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 34732719_Rare t(X;14)(q28;q32) translocation reveals link between MTCP1 and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. |
ENSMUSG00000031200 |
Mtcp1 |
10.082661 |
0.4298834339 |
-1.217983 |
0.554057090 |
4.874459 |
0.02725698536744176544988071952957398025318980216979980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.047336522417159715425682975364907179027795791625976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9623231 |
2.0353889 |
13.8294840 |
2.9085143 |
| ENSG00000214900 |
196913 |
LINC01588 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
123.765899 |
4.3309426719 |
2.114681 |
0.219295950 |
90.967673 |
0.00000000000000000000146038655711457661613982679500602870807006029238294759209902153040960826047012233175337314605712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000013738244476106534187816992373614042353154465424855306733033233346219503800966776907444000244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
199.8850713 |
22.1992907 |
46.1642255 |
4.2045935 |
| ENSG00000214967 |
101059938 |
NPIPA7 |
protein_coding |
P0DM63 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:101059938;hsa:101059953; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
90.289548 |
0.2350647921 |
-2.088870 |
0.595653224 |
10.809944 |
0.00100956363305087191972742033385657123290002346038818359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002346639247847381263417654295722059032414108514785766601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.0236587 |
10.6929701 |
114.2689841 |
33.0004769 |
| ENSG00000215014 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.123376 |
2.1142993951 |
1.080180 |
0.464373337 |
5.489229 |
0.01913398360380200863284372303496638778597116470336914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034470596605897428632570012041469453833997249603271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7190239 |
4.4571368 |
7.4694411 |
1.6681135 |
| ENSG00000215039 |
678655 |
CD27-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34006845_LncRNA CD27-AS1 promotes acute myeloid leukemia progression through the miR-224-5p/PBX3 signaling circuit. |
|
|
95.082124 |
0.2072996785 |
-2.270210 |
0.208856894 |
121.138981 |
0.00000000000000000000000000035627772957560105439994819502623450238115493711606311492271157844327065568074824897237817822315264493227005004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000004303321840045721231158101126424664999879468018495914112226894526600949261729844863566540880128741264343261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
36.3030219 |
8.3429037 |
175.2976678 |
27.6793724 |
| ENSG00000215068 |
153684 |
ANXA2R-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85.008476 |
0.1295827646 |
-2.948054 |
0.585799788 |
21.416374 |
0.00000369601254390331800204279495691839230175901320762932300567626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000012215213871028430216354211668150497871465631760656833648681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.8266804 |
10.2567263 |
162.5612753 |
52.1006269 |
| ENSG00000215105 |
|
TTC3P1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.392486 |
0.4818510643 |
-1.053341 |
0.273638242 |
15.151565 |
0.00009921601957937516960608220761841380408441182225942611694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000272959636345121642916206061713069175311829894781112670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.3885431 |
3.4243597 |
40.5277606 |
4.5640354 |
| ENSG00000215252 |
440270 |
GOLGA8B |
protein_coding |
A8MQT2 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in maintaining Golgi structure. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization and spindle assembly. Located in Golgi apparatus and cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440270; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030]; spindle assembly [GO:0051225] |
35593117_Silencing GOLGA8B inhibits cell invasion and metastasis by suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway in lung squamous cell carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
521.309083 |
0.2414804611 |
-2.050022 |
0.183728573 |
118.181301 |
0.00000000000000000000000000158242106954575118413248470951350533637231322306539128209113560646858728016977968522382980154361575841903686523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000018685227989196229442702839521737103096546215461339471728880555332117470099251299586740060476586222648620605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
207.3969904 |
25.4053724 |
865.2963198 |
73.7129893 |
| ENSG00000215375 |
4636 |
MYL5 |
protein_coding |
Q02045 |
|
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Metal-binding;Motor protein;Muscle protein;Myosin;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
This gene encodes one of the myosin light chains, a component of the hexameric ATPase cellular motor protein myosin. Myosin is composed of two heavy chains, two nonphosphorylatable alkali light chains, and two phosphorylatable regulatory light chains. This gene product, one of the regulatory light chains, is expressed in fetal muscle and in adult retina, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4636; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; muscle myosin complex [GO:0005859]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; structural constituent of muscle [GO:0008307]; regulation of muscle contraction [GO:0006937] |
20201926_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
137.148997 |
0.2921589713 |
-1.775175 |
0.402143919 |
18.456300 |
0.00001738452176282540069421171657904068297284538857638835906982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000052971829318600932373032469380191855634620878845453262329101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
65.5550000 |
16.5391962 |
225.0978683 |
40.4225632 |
| ENSG00000215386 |
388815 |
MIR99AHG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 25027842_This study reveals an unprecedented function of long non-coding RNAs MONC and MIR100HG as regulators of hematopoiesis and oncogenes in the development of myeloid leukemia. 33931593_MIR99AHG is a noncoding tumor suppressor gene in lung adenocarcinoma. 35895506_Host-Directed Targeting of LincRNA-MIR99AHG Suppresses Intracellular Growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
|
|
18.037221 |
0.4831867517 |
-1.049347 |
0.403119500 |
6.815374 |
0.00903763601332273000532602225121081573888659477233886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017462430626606035427572649609828658867627382278442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.1783264 |
3.0744754 |
23.2956444 |
4.3266112 |
| ENSG00000215417 |
407975 |
MIR17HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene is the host gene for the MIR17-92 cluster, a group of at least six microRNAs (miRNAs) that may be involved in cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenesis. Amplification of this gene has been found in several lymphomas and solid tumors. Two non-protein coding transcript variants have been found for this host gene, but only the longest is a polycistronic transcript containing the MIR17-92 cluster. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012]. |
|
|
19597473_miR-17-92 overexpression may serve as a fine-tuning influence to counterbalance the generation of DNA damage in RB-inactivated SCLC cells. 19696742_p53-mediated repression of miR-17-92 expression likely has an important function in hypoxia-induced apoptosis 20167088_The type-2-skewing tumor microenvironment induces the down-regulation of miR-17-92 expression in T cells, thereby diminishing the persistence of tumor-specific T cells and tumor control. 20300951_Auroroa kinase A induces miR-17-92 cluster through regulation of E2F1 transcription factor. 20305691_miR-17-92 and its target CTGF mediate effects of differentiation-promoting treatment on glioblastoma cells through multiple regulatory pathways. 21664042_the Myc-inducible miR-17-92 cluster miRNAs contribute to tumorigenesis and poor prognosis in multiple myeloma 21796614_study demonstrates that the MYCN-induced downregulation of Dickkopf-3 (DKK3) results from direct upregulation of miR-17-92 components effecting both DKK3 mRNA stability 21892160_We demonstrate that haploinsufficiency of miR-17 approximately 92 is responsible for skeletal and growth developmental abnormalities. 21897363_Upon macrophage differentiation PU.1 represses the miR-17-92 cluster promoter by an Egr-2/Jarid1b-mediated H3K4 demethylation mechanism whose deregulation may contribute to leukaemic states. 22022595_The network involving miR-17-92 exhibits high noise sensitivity due to a positive feedback loop and also maintains resistance to noise from a negative feedback loop. 22024720_members of the oncomir miR-17-92 cluster were upregulated, but themiR-125b/miR-99a/let-7c, miR-106b/miR-93/miR-25 and miR-212/miR-132 clusters are also coordinately regulated either by stromal cell contact alone or by CD154 22116552_inhibition of miR-17 approximately 92 expression suppressed the PI3K/AKT pathway and inhibited tumor growth in a xenograft MCL mouse model 22343732_High miR-17-92 is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 22383169_Upreg'n of miR-17-92 cluster was seen in MYC-amplified AS compared to AS lacking MYC amplification and controls. Moreover, MYC-amplified ASs were associated with a significantly lower expression of THBS1 than AS without MYC amplification or controls. 22451425_Imbalanced miR-17-92 expression, also mediated by p53, directly transforms the hematopoietic compartment. 22665768_results reveal a temporal expression pattern of miR-17-92 by antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells during viral infection, the precise control of which is critical to the effector expansion and memory differentiation of CD8(+) T cells 22731656_Overexpression of miR-17-92 cluster accelerates cell proliferation. 22969266_Oncogenic microRNA 17-92 cluster is regulated by epithelial cell adhesion molecule and could be a potential therapeutic target in retinoblastoma. 22995834_MiR-17-92 cluster microRNAs regulate the mRNA expression of their target genes in a dose-dependent manner. 23288173_HDAC9 promotes angiogenesis and transcriptionally represses the endothelial cell miR-17-92 cluster. 23438603_c-Myc-regulated members of the miR-17~92 and miR-106a~363 clusters inhibit trophoblast differentiation by repressing GCM1 and CYP19A1. 23532756_c-Myc-mediated overexpression of miR-17-92 suppresses replication of hepatitis B virus in human hepatoma cells. 23546593_The combined detection of PTEN and miR-92 may provide critical clinical evidence for the early diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 23550645_The structural complexity of mir-17-92 as a polycistronic miRNA oncogene, along with the complex mode of interactions among its components, constitutes the molecular basis for its unique functional complexity during normal and tumor development.[Review] 23759744_miR-17~92 miRNA cluster is up-regulated in transgenic mouse models of polycystic kidney disease. 23825564_the upregulation of miR-17-92 may play a role in the biology of adenoid cystic carcinoma 23858035_The miR-17-92 cluster was specifically required for the accumulation of activated Ag-specific Treg and for differentiation into IL-10-producing effector Treg. 23921550_miR-17~92 is a powerful cancer driver that coordinates the activation of multiple oncogenic pathways in lymphomagenesis 24068957_our data indicate that miR-17-92 modulates expression of critical T-box transcriptional regulators during midface development and is itself a target of Bmp-signaling and the craniofacial pioneer factor AP-2alpha 24145352_miR-17-92 cluster family is involved in medulloblastoma progression. 24169826_The Myc-miR-17-92-BCR axis, frequently affected by genomic rearrangements, constitutes a novel lymphomagenic feed-forward loop. 24280866_data demonstrate the role of miR-17~92 in regulation of apoptosis, and identify BCL2 as a therapeutic target of particular relevance in BCR-ABL-positive ALL. 24305714_High miR-17-92 expression is associated with pediatric high-grade glioma. 24378993_BMPR2 downregulation is mediated by miR-17-92. 24469837_Study describes a novel mechanism, involving c-Myc and miR-17-92, which integrates cell proliferation and apoptosis resistance. 24583285_The promoter of the miR-17-92 gene cluster is transactivated through the promoter binding of STAT3 while BIM expression is decreasesed during Toxoplasma gondii infection. 24625819_miR-17-92, particularly miR-19 as a key component, can induce proliferation of cardiomyocytes and help protect the heart from ischemic injury caused by Myocardial infarction. 24645838_Upregulation of microRNA-17-92 cluster associates with tumor progression in osteosarcoma. 25140305_the high sensitivity of leukemia cells to HQ17(3) may be associated with the reduction of topo IIalpha and c-Myc activities, as well as with the downregulation of the miR-17-92 cluster expression. 25239565_A novel IL-6/Stat3-miR-17-92 cluster-PTEN signaling axis is crucial for cholangiocarcinogenesis and tumor progression. 25359779_STAT3 activation is related to the up-regulation of miR-17-92 clusters in retinoblastoma cells via positive feedback loop between them 25415674_The current results of our study support a relationship between the miR-17-92 family and lipid metabolism 25634356_The oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster is involved in cutaneous B-cell lymphoma progression. 25732734_WEE1 is a valid target of the miR-17-92 cluster in leukemia. 25870038_Functional interactions among members of the miR-17-92 cluster in lymphocyte development, differentiation and malignant transformation 25887381_Our findings identify the miR-17-92 cluster as a functionally determining family of miRNAs in pancreatic cancer stem cells, and highlight the putative potential of developing modulators of this cluster to overcome drug resistance in pancreatic CSCs. 26233958_Our findings demonstrate an important role of the miR-17-92 cluster in hepatocarcinogenesis and suggest the possibility of targeting this pivotal miRNA cluster for potential therapy. 26360630_Germline heterozygous deletions of MIR17HG is associated with feingold syndrome-2. 26545119_vFLIP and vCyclin induce the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster in endothelial cells 26804174_these findings indicate that SLU7 is co-opted by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and other tumor cell types to maintain survival, and identify this splicing regulator as a new determinant for the expression of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster. This novel mechanism may be exploited for the development of antitumoral strategies in cancers displaying such SLU7-miR-17-92 crosstalk. 26837962_MIR17HG gene expression is dysregulated in gastric cancer. 26891588_Findings establish a key tumor-promoting role of the miR-17-92 cluster in the carcinogenesis of prostate cancer. It plays a crucial role in cell growth of prostate cancer cells and cisplatin-resistance. 27044389_Expression of miR-17-92 was found to be a prognostic factor in diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma. 27080303_miR-17~92 suppressed tumor progression by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis in a genetically engineered mouse model, indicating the presence of cellular context-dependent pro- and anti-cancer effects of miR-17~92. 27229531_MCM3AP antisense RNA 1 (MCM3AP-AS) and miR-17-92 (MIR17HG) acted synergistically to regulate mRNAs in a network module of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competitive endogenous RNA network (LMCN). 27498867_The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster is a global regulator of tumor metabolism. 27501757_Autophagy-related gene ATG7 was validated as a target of miR-17 seed family. 27650539_Our data demonstrate a tumor suppressor effect of miR-17-92a cluster miRNAs in prostate cancer cells and restoration of expression of these miRNAs has a therapeutic benefit for both androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer cells. 27720936_we demonstrate that miR-17-92 exercises broader control over the BCR pathway by targeting its additional regulators at multiple levels. 27869313_This review presented that the role of the miR-17-92 cluster in adult CNS regeneration through modulating neurogenesis and angiogenesis. 28030800_Data show that mutation of micrRNA hsa-miR-17-92 seed sequences in putative target 3' untranslated regions (3'UTRs) results in up-regulation of reporter activity. 28187958_miR-17-92 cluster may have a role in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and miR-143-145 cluster may have a role in basal cell carcinoma 28222938_Data show the potential of microRNA miR-17-92 for oncogenesis regulation in stem cells. 28461114_The miR-17-92 is a critical contributor to CML leukemogenesis via targeting A20 and activation of NF-kappaB signaling. 28827775_In summary, this meta-analysis towards high-expression of miR-17-92 cluster has indicated poor prognosis of various cancers. 29255972_In Antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis, expression of the miR-17-92 cluster is reduced in both serum and granulocytes, though this alteration does not correlate with bone marrow characteristics or thyroid function. 29333091_Expressions of miRNA-20a and miRNA-92a in gastric cancer samples were negatively correlated with the prognosis of patients. miRNA-19b/20a/92a facilitated the self-renewal of gastric cancer stem cells. 29752469_findings demonstrate that cytokine-induced overexpression of miR-17-92 cluster can promote the proliferation and the immune function of keratinocytes, and thus may contribute to the development of inflammatory skin diseases like psoriasis. 30055570_theses findings indicate that the miR-17-92 cluster contributes to antibody production, and miR-18a and miR-17 are involved in follicular helper T cells differentiation after hepatitis B vaccination. 30170406_The results suggest that the miR-17-92 plasma level is associated with the progression of advanced GC and effectiveness of XELOX chemotherapy. 30226589_Study identified that TRAF3 was a direct and functional target of the miR-17-92 cluster in MGC-803 gastric cancer cells. The loss-of-function of TRAF3 led to the acquirement of phenotypes, like what had been observed in the MGC-803 cells overexpressing the miR-17-92 cluster. Survival analyses revealed that TRAF3 served as an important prognostic indicator in patients with gastric cancer. 30431147_Unilesional mycosis fungoides (MF) exhibits a microRNA profile distinct from that of conventional early MF , with a higher level of miR-17~92 members along with Th1 skewing. These findings suggest a robust reactive T-cell immune response in unilesional MF and might account for the localized nature of this disease. 30854399_Here we review the role of the miR-17-92 cluster that has received little attention in relation to neurological diseases, cardiac diseases, and the development of bone and tumors. 30941921_Overall analysis found that rs7336610 and rs1428 and haplotype CTAGA were significantly associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer. However, we found rs7318578 was associated with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer in the dominant model. Stratification analysis showed that rs7336610, rs7318578, and rs1428 were also associated with rectal cancer risk. 31186404_MIR17HG-derived miR-18a and miR-19a coordinately mediate gastric cancer cell metastasis by directly inhibiting SMAD2 expression and upregulating Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. 31238254_we proposed a model for a SOX4/miR-17-92/RB1 axis which gives insight into how RB1 protein is reduced (besides RB1 loss). Mechanically, SOX4 downregulates RB1 protein expression by upregulating the miR-17-92 cluster expression. 31290724_A positive feedback loop of SIRT1 and miR17HG promotes the repair of DNA double-stranded breaks. 31409641_These findings provide mechanistic insight into the role of the lncRNA MIR17HG and its miRNA members in regulating colorectal cancer carcinogenesis and progression. 31703587_The study suggested that GA and GG genotypes of rs9301654 polymorphism n the promoter of miR-17-92 cluster were associated with significant decreased risk of ischemic stroke. 31706574_Mechanistically, MIR17HG targeted the miR-130a-3p/SP1 axis, moreover, transcription factor SP1 bind with the MIR17HG promoter region to promote its expression. MIR17HG displays the tumor-promotive role in the progression of osteosarcoma through SP1/MIR17HG/miR-130a-3p/SP1 feedback loop. 31802000_show that miR-17-92 R-loop-associated chromosomal instability can be induced by the loss of DICER1 function 32046383_A Functional Polymorphism in the Promoter of miR-17-92 is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma. 32068173_The Expression of MIR17HG Protein as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Meningioma. 32466856_The MiR-17-92 Gene Cluster is a Blood-Based Marker for Cancer Detection in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. 32478334_Repression of LKB1 by miR-17 approximately 92 Sensitizes MYC-Dependent Lymphoma to Biguanide Treatment. 32558936_SMARCB1 loss induces druggable cyclin D1 deficiency via upregulation of MIR17HG in atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors. 32748943_MIR17HG polymorphism (rs7318578) is associated with liver cancer risk in the Chinese Han population. 32843613_JMJD3 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma pathogenesis through epigenetic regulation of MYC. 32933626_[Role of microRNA-17-5p in the pathogenesis of pediatric nephrotic syndrome and related mechanisms]. 33036577_Genetic variants in MIR17HG affect the susceptibility and prognosis of glioma in a Chinese Han population. 33293632_The transcription factor TAL1 and miR-17-92 create a regulatory loop in hematopoiesis. 33299861_The Genetic Polymorphisms in the MIR17HG Gene Are Associated with the Risk of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Chinese Han Population. 33430425_mRNA and miRNA Expression Analyses of the MYC/E2F/miR-17-92 Network in the Most Common Pediatric Brain Tumors. 33803955_Prognostic Value of microRNA-221/2 and 17-92 Families in Primary Glioblastoma Patients Treated with Postoperative Radiotherapy. 33818875_Feingold syndrome type 2 in a patient from China. 34274472_MIR17HG genetic variations affect the susceptibility of IgA nephropathy in Chinese Han people. 34598688_miR-17-5p drives G2/M-phase accumulation by directly targeting CCNG2 and is related to recurrence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 34781979_Association of MIR17HG and MIR155HG gene variants with steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in the population of northern China. 35051418_KHDRBS3 promotes paclitaxel resistance and induces glycolysis through modulated MIR17HG/CLDN6 signaling in epithelial ovarian cancer. 35063745_Hypermethylation of miRNA-17-92 cluster in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in diabetic retinopathy. 35137671_LncRNA miR-17-92a-1 cluster host gene (MIR17HG) promotes neuronal damage and microglial activation by targeting the microRNA-153-3p/alpha-synuclein axis in Parkinson's disease. 35232666_The Interaction of NTN4 and miR-17-92 Polymorphisms on Breast Cancer Susceptibility in a Chinese Population. 35253975_LncRNA MIR17HG promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of retinoblastoma cells by up-regulating HIF-1alpha expression via sponging miR-155-5p. 35272588_MIR17HG: A Cancerogenic Long-Noncoding RNA in Different Cancers. 35288592_MIR17HG polymorphisms contribute to high-altitude pulmonary edema susceptibility in the Chinese population. 35328059_MicroRNA-17-92a-1 Host Gene (MIR17HG) Expression Signature and rs4284505 Variant Association with Alopecia Areata: A Case-Control Study. 35872559_Overexpression of the miR-17-92 cluster in colorectal adenoma organoids causes a carcinoma-like gene expression signature. |
|
|
26.795795 |
0.4067098550 |
-1.297928 |
0.359948842 |
13.102762 |
0.00029486076906128360231723606332820963871199637651443481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000753487699332504507788998981965278289862908422946929931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.9422516 |
3.3244972 |
37.0402652 |
5.2722881 |
| ENSG00000215424 |
114044 |
MCM3AP-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27229531_MCM3AP antisense RNA 1 (MCM3AP-AS) and miR-17-92 (MIR17HG) acted synergistically to regulate mRNAs in a network module of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competitive endogenous RNA network (LMCN). 30782188_Circular RNA MCM3AP-AS1 directly bound to miR-194-5p and acted as competing endogenous RNA while subsequently facilitating miR-194-5p target gene FOXA1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 31030335_promotes papillary thyroid cancer by regulating the MCM3AP-AS1/miR-211-5p/SPARC axis 31237446_MCM3AP-AS1 regulates EGFR expression.MiR-455 directly targets and regulates LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 in the hepatocellular carcinoma.MCM3AP-AS1 was significantly upregulated in the hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. 31830901_Investigated the role between MCM3AP antisense RNA 1 (MCM3AP-AS1) and miR-138-5p, and between microRNA 138-5p and forkhead box K1 (FOXK1), in pancreatic cancer. 31836002_up-regulated in osteoarthritis; may regulate miR-142-3p/HMGB1 to promote LPS-induced chondrocyte apoptosis 31985002_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation in cervical squamous cell carcinoma by down-regulating miRNA-93. 32485570_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes breast cancer progression via modulating miR-28-5p/CENPF axis. 32678686_Overexpression of long non-coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 in breast cancer tissues compared to adjacent non-tumour tissues. 32690597_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating miR-204-5p/FOXC1. 33450091_lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-19a-3p/FOXF2 axis. 33596783_Identification of HCG18 and MCM3AP-AS1 That Associate With Bone Metastasis, Poor Prognosis and Increased Abundance of M2 Macrophage Infiltration in Prostate Cancer. 33686713_Long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 enhances cell proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating miR-193a-5p/SENP1. 33942704_Long non-coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1beta-induced inflammation via regulating miR-138-5p/SIRT1. 34256796_The MCM3AP-AS1/miR-126/VEGF axis regulates cancer cell invasion and migration in endometrioid carcinoma. 34271873_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 sponges miR-148a to enhance cell invasion and migration in small cell lung cancer. 34346845_Long non-coding RNA MCM3AP antisense RNA 1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through targeting microRNA-195-5p. 34587438_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 Downregulates LncRNA MEG3 in Triple Negative Breast Cancer to Inhibit the Proliferation of Cancer Cells. 34822133_Overexpression of long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via miR-143-3p/IGFBP5 axis. 35156580_MCM3AP-AS1: A LncRNA Participating in the Tumorigenesis of Cancer Through Multiple Pathways. 35202986_SOX4-activated lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 aggravates osteoarthritis progression by modulating miR-149-5p/Notch1 signaling. 35695665_LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 Regulates miR-21/PTEN Axis to Affect Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis. 35783356_Long Non-Coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1: A Crucial Role in Human Malignancies. 36172487_Prognostic Analysis of LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 in Colorectal Cancer and the Mechanism of Its Effect on Tumor Cell Activity. |
|
|
45.073501 |
0.4689230886 |
-1.092577 |
0.262305129 |
17.473434 |
0.00002913505504676035069906193941680072612143703736364841461181640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000086473640154872860358499508937057953517069108784198760986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
28.6019438 |
4.7098065 |
61.4187809 |
6.7351503 |
| ENSG00000215440 |
79716 |
NPEPL1 |
protein_coding |
Q8NDH3 |
FUNCTION: Probably catalyzes the removal of unsubstituted N-terminal amino acids from various peptides. |
Alternative splicing;Aminopeptidase;Hydrolase;Manganese;Metal-binding;Protease;Reference proteome;Zinc |
|
Predicted to enable manganese ion binding activity and metalloaminopeptidase activity. Predicted to be involved in proteolysis. Located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79716; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; metalloaminopeptidase activity [GO:0070006]; peptidase activity [GO:0008233]; proteolysis [GO:0006508] |
|
ENSMUSG00000039263 |
Npepl1 |
293.161688 |
0.3013534116 |
-1.730472 |
0.102450911 |
294.324573 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000567929740608568625653834172714101854649905718220837798726643764189845141162851910133395914032628538927609480468000584589797461923842610566513252096379296904180488878011168196735525270923972129821777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000161827084389623039823260336626396738238580290868350469307398722830202835668095974887884687674692973582838517279640140151161213829624665784370073579822792733630063000127563554997323080897331237792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
139.7154831 |
10.0285074 |
467.1470854 |
21.2730447 |
| ENSG00000215769 |
109286553 |
ARHGAP27P1-BPTFP1-KPNA2P3 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This locus represents naturally-occurring readthrough transcription between multiple unprocessed pseudogene loci. Readthrough transcripts likely do not encode functional proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]. |
|
|
|
|
|
121.904175 |
0.2087173336 |
-2.260378 |
0.163901356 |
207.803969 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004139895179242492644485020534434489744389273855542072277796977404764352982907250607476640294057354564538411201784731023936569904719817714067175984382629394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000822407171542654098762803533006596799223810392414708077915031443521427199083652890039541616034636413387282388419712193805555244807692361064255237579345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.6525868 |
5.8962547 |
214.8922435 |
17.5176330 |
| ENSG00000215769_ENSG00000266820_ENSG00000291117 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
108.398115 |
0.2324617369 |
-2.104935 |
0.491683695 |
16.122795 |
0.00005936518903278922338782527812206524231442017480731010437011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000169189069342338087439600591288524356059497222304344177246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.6721017 |
12.8320042 |
174.5517337 |
38.8061433 |
| ENSG00000215883 |
606495 |
CYB5RL |
protein_coding |
Q6IPT4 |
FUNCTION: NADH-cytochrome b5 reductases are involved in desaturation and elongation of fatty acids, cholesterol biosynthesis, drug metabolism, and, in erythrocyte, methemoglobin reduction. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;FAD;Flavoprotein;NAD;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable cytochrome-b5 reductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H. Predicted to be involved in bicarbonate transport. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:606495; |
endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; cytochrome-b5 reductase activity, acting on NAD(P)H [GO:0004128]; bicarbonate transport [GO:0015701] |
|
ENSMUSG00000028621 |
Cyb5rl |
115.591607 |
0.4399990666 |
-1.184428 |
0.158212326 |
56.508672 |
0.00000000000005595106368879520131272950773209907505083672910051184601343265967443585395812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000360627816614243339017130116301635080384730552838234984847076702862977981567382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.4267921 |
7.0981055 |
168.0753778 |
10.6203110 |
| ENSG00000215914 |
8511 |
MMP23A |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
This locus represents the partially duplicated copy of the MMP23B gene, and therefore considered a pseudogene. This pseudogene is part of a duplicated region of chromosome 1p36.3. It belongs to the more centromeric copy of the duplicated region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
11328856_Compares rat and mouse proteins, describes unique type II topology, and suggests a role in reproductive processes. 19965868_analysis of potassium channel modulation by a toxin domain in matrix metalloprotease 23 |
|
|
35.532046 |
0.4511126783 |
-1.148440 |
0.274437987 |
17.690332 |
0.00002599444397137186868115832361070260958513244986534118652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000077573391228760377180684315590042388066649436950683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6758640 |
3.9202397 |
48.2126056 |
5.6915570 |
| ENSG00000216775 |
|
|
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.962699 |
0.0048123988 |
-7.699028 |
1.082347912 |
96.254353 |
0.00000000000000000000010103280288518643293880942865615842590742150606115062770960614808163358091519512527156621217727661132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000987578920917451508555293937993962618844850137687139908287611844706077590672066435217857360839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2025190 |
0.2261746 |
44.3387764 |
22.5063030 |
| ENSG00000216895 |
100506302 |
RBM33-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37.096775 |
0.3164195760 |
-1.660089 |
0.557826171 |
7.803504 |
0.00521450046486348316177039663443792960606515407562255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010616478700414015354236418886557657970115542411804199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.0435360 |
4.9288088 |
44.5896401 |
10.9327913 |
| ENSG00000217236_ENSG00000231453 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
157.789373 |
0.4073561041 |
-1.295638 |
0.384009731 |
11.002106 |
0.00091008438832177677556972694716819205495994538068771362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002134908704963354216660453843701361620333045721054077148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
91.8706045 |
64.2099529 |
224.8794691 |
110.2433733 |
| ENSG00000217684 |
100271253 |
RPS3AP24 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.732882 |
0.3856342148 |
-1.374695 |
0.502797081 |
7.700898 |
0.00551933454152638003353814610818517394363880157470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011179549585965330507630888234871235908940434455871582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8069047 |
1.9279139 |
15.2759149 |
3.0484519 |
| ENSG00000217801 |
|
|
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.526335 |
4.1890059810 |
2.066608 |
0.701644007 |
8.189270 |
0.00421388750701834520484556634301043231971561908721923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008750278503600278021123948235526768257841467857360839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
24.0245405 |
15.8387428 |
5.4574303 |
2.6388069 |
| ENSG00000218336 |
55714 |
TENM3 |
protein_coding |
Q9P273 |
FUNCTION: Involved in neural development by regulating the establishment of proper connectivity within the nervous system. Acts in both pre- and postsynaptic neurons in the hippocampus to control the assembly of a precise topographic projection: required in both CA1 and subicular neurons for the precise targeting of proximal CA1 axons to distal subiculum, probably by promoting homophilic cell adhesion. Required for proper dendrite morphogenesis and axon targeting in the vertebrate visual system, thereby playing a key role in the development of the visual pathway. Regulates the formation in ipsilateral retinal mapping to both the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) and the superior colliculus (SC). May also be involved in the differentiation of the fibroblast-like cells in the superficial layer of mandibular condylar cartilage into chondrocytes. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WTS6}. |
Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Differentiation;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Microphthalmia;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a large transmembrane protein that may be involved in the regulation of neuronal development. Mutation in this gene causes microphthalmia. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]. |
hsa:55714; |
axon [GO:0030424]; membrane [GO:0016020]; neuron projection [GO:0043005]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; heterophilic cell-cell adhesion via plasma membrane cell adhesion molecules [GO:0007157]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; regulation of homophilic cell adhesion [GO:1903385]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22766609_Null mutation in ODZ3 causes autosomal recessive microphthalmia in humans. 27103084_This report supports the association of TENM3 mutations with colobomatous microphthalmia and expands the phenotypic spectrum associated with mutations in this gene 29753094_TENM3 missense mutation was identified in a patient with eye abnormalities and intellectual disability. 30273960_novel A to C transversion at position 183721398 on chromosome four found to co-segregate with the affected phenotype of developmental dysplasia of the hip 32799327_Exome sequencing in patients with microphthalmia, anophthalmia, and coloboma (MAC) from a consanguineous population. 32960451_Ten-m/Odz3 regulates migration and differentiation of chondrogenic ATDC5 cells via RhoA-mediated actin reorganization. 34174923_Replicative verification of susceptibility genes previously identified from families with segregating developmental dysplasia of the hip. |
ENSMUSG00000031561 |
Tenm3 |
56.145471 |
7.4681480676 |
2.900751 |
0.266926073 |
127.905654 |
0.00000000000000000000000000001177074323660198674521369442319541551880678191587609834759075023945022772615476638891074401271907845512032508850097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000149514776396080322573026037109636391566003052857645907518551379720835807062701006131533176812808960676193237304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
95.3459344 |
17.6188057 |
12.7980102 |
1.9904823 |
| ENSG00000219607 |
648791 |
PPP1R3G |
protein_coding |
B7ZBB8 |
FUNCTION: Glycogen-targeting subunit for protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). Involved in the regulation of hepatic glycogenesis in a manner coupled to the fasting-feeding cycle and distinct from other glycogen-targeting subunits (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable glycogen binding activity and protein phosphatase 1 binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process. Predicted to act upstream of or within glucose homeostasis; positive regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity; and positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be part of protein phosphatase type 1 complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:648791; |
protein phosphatase type 1 complex [GO:0000164]; glycogen binding [GO:2001069]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; glucose homeostasis [GO:0042593]; glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005978]; positive regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity [GO:2000467]; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045725]; regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005979] |
34592886_Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3G (PPP1R3G) correlates with poor prognosis and immune infiltration in lung adenocarcinoma. 34862394_RIPK1 dephosphorylation and kinase activation by PPP1R3G/PP1gamma promote apoptosis and necroptosis. |
ENSMUSG00000050423 |
Ppp1r3g |
102.308407 |
0.4248125925 |
-1.235102 |
0.155572520 |
64.591042 |
0.00000000000000092173466590177218301515799919346973295415474669578514976819860748946666717529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000006617122406960193221562038435745745221817904185152015017479243397247046232223510742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.4750417 |
6.6860085 |
145.7257298 |
10.2835549 |
| ENSG00000220008 |
645191 |
LINGO3 |
protein_coding |
P0C6S8 |
|
Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Leucine-rich repeat;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in extracellular matrix and extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:645191; |
extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020] |
33941035_LINGO3 regulates mucosal tissue regeneration and promotes TFF2 dependent recovery from colitis. |
ENSMUSG00000051067 |
Lingo3 |
69.058029 |
0.2884201558 |
-1.793756 |
0.227409483 |
63.456968 |
0.00000000000000163908589397463004191887059329476596094457942816985385192651847319211810827255249023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000011614454054280143205454787677749379879051355030084025088399357628077268600463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.2968460 |
4.5122351 |
109.4868792 |
9.6923151 |
| ENSG00000221817 |
101929145 |
PPP3CB-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48.546644 |
0.3210746017 |
-1.639020 |
0.292524861 |
31.631264 |
0.00000001864043585878325615606083617836752353014162508770823478698730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000078947728343082032300911683037059063394735858310014009475708007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.1208881 |
5.3402471 |
66.2573169 |
11.3234818 |
| ENSG00000221821 |
441150 |
C6orf226 |
protein_coding |
Q5I0X4 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:441150; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000062619 |
2310039H08Rik |
17.532366 |
0.2829682925 |
-1.821288 |
0.415727133 |
20.066981 |
0.00000747765843534092365939595567492226280137401772662997245788574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000023827771698107089095187288707577977220353204756975173950195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6385915 |
2.3649532 |
27.2608936 |
5.2790189 |
| ENSG00000221886 |
63920 |
ZBED8 |
protein_coding |
Q8IZ13 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:63920; |
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
21.714468 |
0.4278352775 |
-1.224873 |
0.367678801 |
11.262863 |
0.00079073171989625537590257176034924668783787637948989868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001876398743676644395930730446764300722861662507057189941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.5910592 |
3.4590441 |
32.0475273 |
5.3592024 |
| ENSG00000221890 |
23467 |
NPTXR |
protein_coding |
O95502 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in mediating uptake of synaptic material during synapse remodeling or in mediating the synaptic clustering of AMPA glutamate receptors at a subset of excitatory synapses. {ECO:0000250}. |
Calcium;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Metal-binding;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a protein similar to the rat neuronal pentraxin receptor. The rat pentraxin receptor is an integral membrane protein that is thought to mediate neuronal uptake of the snake venom toxin, taipoxin, and its transport into the synapses. Studies in rat indicate that translation of this mRNA initiates at a non-AUG (CUG) codon. This may also be true for mouse and human, based on strong sequence conservation amongst these species. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23467; |
glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; membrane [GO:0016020]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor activity [GO:0098962] |
9261167_non-AUG translation initiation site. Comparison of rat determined N-terminal amino acid sequence with cDNA sequence indicates that a CUG codon is used as an initiator codon and codes for a methionine. The CTG is present in cDNAs of mouse, rat, and human. 16115696_The purpose of the present study was to assess the toxic effect of taipoxin in SCLC-cell lines and to determine if toxicity correlates to NPR and NP1 and NP2 expression levels. 19368810_study suggests that NCAM-120, alpha-dystroglycan, and NPR are candidate biomarkers in CSF for neurodegenerative diseases, and that the changes in the CSF level of NPR may be specific for Alzheimer's disease 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 32450185_Decreased cerebrospinal fluid neuronal pentraxin receptor is associated with PET-Abeta load and cerebrospinal fluid Abeta in a pilot study of Alzheimer's disease. |
ENSMUSG00000022421 |
Nptxr |
224.322089 |
0.2501667584 |
-1.999038 |
0.126024916 |
261.112003 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000009820374868283387382584784946237660562004155495775504647606477375823154399840182839331676487028173278507303230599175599098408503620590312527838272073366088221746394992806017398834228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002465114507752768915678375057288110881556789143641175561792603198855075830826566102717915542292290827929210900127343434330265505136786885263366474879687118004767398815602064132690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.5274340 |
7.3966070 |
364.6911359 |
17.9635901 |
| ENSG00000221923 |
400713 |
ZNF880 |
protein_coding |
Q6PDB4 |
|
Alternative splicing;Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:400713; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
|
|
16.075286 |
0.3733357013 |
-1.421455 |
0.401585944 |
12.650095 |
0.00037554655403872850899169022476087320683291181921958923339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000943340220832476631165897096309436165029183030128479003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.9463185 |
2.3446770 |
24.2165171 |
4.0547684 |
| ENSG00000221955 |
84561 |
SLC12A8 |
protein_coding |
A0AV02 |
FUNCTION: Cation/chloride cotransporter that may play a role in the control of keratinocyte proliferation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11863360}. |
Alternative splicing;Chloride;Glycoprotein;Ion transport;Membrane;Potassium;Potassium transport;Reference proteome;Symport;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene is thought to be a candidate for psoriasis susceptibility. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:84561; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; potassium:chloride symporter activity [GO:0015379]; cell volume homeostasis [GO:0006884]; chloride ion homeostasis [GO:0055064]; chloride transmembrane transport [GO:1902476]; potassium ion homeostasis [GO:0055075]; potassium ion import across plasma membrane [GO:1990573] |
11863360_Maps to 3q21. Associated with suseptibility to psoriasis 16297188_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16297188_SLC12A8 is a susceptibility locus for psoriasis vulgaris. 19472210_Molecular characterization of a human cation-Cl- cotransporter (SLC12A8A, CCC9A) that promotes polyamine and amino acid transport. 23325410_Review summarizes three human disorders that have been linked to the mutation/dysfunction of Na-Cl, Na-K-2Cl, and K-Cl cotransporters (Bartter's, Gitleman's, and Andermann's syndromes). 34365894_Solute carrier family 12 member 8 (SLC12A8) is a potential biomarker and related to tumor immune cell infiltration in bladder cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000035506 |
Slc12a8 |
146.741471 |
5.5979331752 |
2.484894 |
0.218755297 |
125.084277 |
0.00000000000000000000000000004877844328269003498374113656511939741439181241247252564856200183506902523348797845459401401058130431920289993286132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000606545764829405983726492134701725099933296055853844176307850542856634271354082654781336714222561568021774291992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
246.6004802 |
30.7638208 |
44.2386421 |
4.4451450 |
| ENSG00000221988 |
9374 |
PPT2 |
protein_coding |
Q9UMR5 |
FUNCTION: Removes thioester-linked fatty acyl groups from various substrates including S-palmitoyl-CoA. Has the highest S-thioesterase activity for the acyl groups palmitic and myristic acid followed by other short- and long-chain acyl substrates. However, because of structural constraints, is unable to remove palmitate from peptides or proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10417332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12855696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9341199}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a member of the palmitoyl-protein thioesterase family. The encoded glycosylated lysosomal protein has palmitoyl-CoA hydrolase activity in vitro, but does not hydrolyze palmitate from cysteine residues in proteins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the downstream EGFL8 (EGF-like-domain, multiple 8) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:9374; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; palmitoyl hydrolase activity [GO:0098599]; palmitoyl-(protein) hydrolase activity [GO:0008474]; thiolester hydrolase activity [GO:0016790]; fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0046949] |
12855696_The crystal structure of palmitoyl protein thioesterase-2 (PPT2) reveals the basis for divergent substrate specificities of the two lysosomal thioesterases, PPT1 and PPT2. 19143821_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20010835_Meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 24387323_We identified that PPT2 on chromosome 6p21 is associated with loss of lung function in the Korean population. |
ENSMUSG00000015474 |
Ppt2 |
12.959338 |
0.3281641359 |
-1.607511 |
0.490260605 |
10.954327 |
0.00093385268153294009874088033029693178832530975341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002184762336253953749626299796204875747207552194595336914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
6.8166913 |
2.1430717 |
20.8810061 |
4.1682156 |
| ENSG00000222009 |
149478 |
BTBD19 |
protein_coding |
C9JJ37 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:149478; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000073771 |
Btbd19 |
109.859651 |
0.4022586722 |
-1.313805 |
0.146261209 |
83.633629 |
0.00000000000000000005955137452171049473320043289700470204541890423984143226529552883619089698186144232749938964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000527281516460975963902257370068302187522282210713073713134746434150201821466907858848571777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
62.2160025 |
5.9697713 |
155.8547475 |
9.2392973 |
| ENSG00000223501 |
6293 |
VPS52 |
protein_coding |
Q8N1B4 |
FUNCTION: Acts as component of the GARP complex that is involved in retrograde transport from early and late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network (TGN). The GARP complex is required for the maintenance of the cycling of mannose 6-phosphate receptors between the TGN and endosomes, this cycling is necessary for proper lysosomal sorting of acid hydrolases such as CTSD (PubMed:15878329, PubMed:18367545). Acts as component of the EARP complex that is involved in endocytic recycling. The EARP complex associates with Rab4-positive endosomes and promotes recycling of internalized transferrin receptor (TFRC) to the plasma membrane (PubMed:25799061). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15878329, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18367545, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25799061}. |
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Endosome;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is similar to the yeast suppressor of actin mutations 2 gene. The yeast protein forms a subunit of the tetrameric Golgi-associated retrograde protein complex that is involved in vesicle trafficking from from both early and late endosomes, back to the trans-Golgi network. This gene is located on chromosome 6 in a head-to-head orientation with the gene encoding ribosomal protein S18. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]. |
hsa:6293; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; EARP complex [GO:1990745]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; GARP complex [GO:0000938]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; membrane [GO:0016020]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; syntaxin binding [GO:0019905]; ectodermal cell differentiation [GO:0010668]; embryonic ectodermal digestive tract development [GO:0048611]; endocytic recycling [GO:0032456]; Golgi to vacuole transport [GO:0006896]; lysosomal transport [GO:0007041]; protein targeting [GO:0006605]; retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi [GO:0042147]; vesicle-mediated cholesterol transport [GO:0090119] |
12210484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12366783_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15878329_Golgi associated retrograde protein complex, consisting of the Vps52, Vps53, and Vps54 proteins, shows significant conservation between various species but diversification and specialization result in important differences in human cells. 18367545_Missorting of cathepsin D in GARP-depleted cells results from accumulation of recycling MPRs in a population of light, small vesicles downstream of endosomes. 19620288_Golgi-associated retrograde protein orchestrates retrograde transport from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network by promoting vesicle tethering and assembly of SNARE complexes in consecutive, independent steps.[Golgi associated retrograde protein] 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 25269472_our data indicate that cisplatin resistance in HOCCs is partially attributable to their high expression of p62, which plays an important role in preventing ROS stress-induced apoptosis by regulating the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. 27889639_These data demonstrate that the beneficial properties of SFN extend beyond activation of the KEAP1-Nrf2-ARE system and warrant further interrogation given the current use of this agent in multiple clinical trials 28791438_Loss of heterozygosity and stop-gain mutation of VPS52 were found in gastric cancer. 31533953_The Sac2 operates upstream of granule docking, since loss of Sac2 prevented granule tethering to the plasma membrane and resulted in both reduced granule density and number of exocytic events. |
ENSMUSG00000024319 |
Vps52 |
556.917744 |
0.4808410616 |
-1.056368 |
0.131987058 |
62.856587 |
0.00000000000000222318881188044753660855662127310489918703326726878710672963279648683965206146240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000015573928269271668133278634021100050427557958190871723047621344448998570442199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
374.0415656 |
31.8850680 |
783.3763054 |
47.6666414 |
| ENSG00000223509 |
|
WHAMMP1 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.970106 |
0.3330115529 |
-1.586356 |
0.525962181 |
8.355360 |
0.00384551228860165661069259179782875435194000601768493652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008047605469978794806573674236460647080093622207641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
23.1795630 |
8.3567064 |
70.0882035 |
17.1769665 |
| ENSG00000223653 |
|
BCL10-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.110441 |
0.4647748800 |
-1.105396 |
0.372294463 |
8.632063 |
0.00330297380470566566412760067805720609612762928009033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007007602897435047210883407586834437097422778606414794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.5669661 |
4.3257241 |
39.9723398 |
6.2534359 |
| ENSG00000223745 |
|
CCDC18-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
404.463649 |
0.3836887748 |
-1.381992 |
0.147065967 |
86.045011 |
0.00000000000000000001758863068984536440559795436318397138362093219391290470961924929937936212809290736913681030273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000158201212054916274574457114150125371783744577054181708591212851544582917995285242795944213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
229.8710192 |
23.2837565 |
604.3226474 |
42.8852385 |
| ENSG00000223749 |
|
MIR503HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
540.209002 |
0.1172604689 |
-3.092211 |
0.111067299 |
794.128678 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000101999486744103877997710058243207754468752772507477628665899611027909257680756235599881876315112187719636906842096931860276044973791955059577225584645183878 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000078412105434529860783730633045598063387872592604357932237829643817295252638043611063587809561974172244651364186187962731369518215382262144661108601640841455 |
Yes |
No |
113.6678502 |
9.1443084 |
974.2890971 |
48.0741211 |
| ENSG00000223764 |
100130417 |
LINC02593 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.679751 |
0.0373286052 |
-4.743575 |
0.940486900 |
30.174923 |
0.00000003947812231280598223697180133850981320620121550746262073516845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000161905275170051748511506283477456857866627615294419229030609130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
1.0807491 |
0.7930149 |
29.2984750 |
10.0215165 |
| ENSG00000223891 |
100505783 |
OSER1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31635804_OSER1-AS1 acted as a ceRNA to sponge miR-372-3p, thereby positively regulating the Rab23 expression and ultimately acting as a tumor suppressor gene in hepatocellular carcinoma progression 32627026_Long noncoding RNA OSER1AS1 promotes the malignant properties of nonsmall cell lung cancer by sponging microRNA4333p and thereby increasing Smad2 expression. 33113263_Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs4142441 and MYC co-modulated long non-coding RNA OSER1-AS1 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer by sequestering ELAVL1. 34525476_Expression and Clinical Significance of lncRNA OSER1-AS1 in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. |
|
|
28.004344 |
0.3102484589 |
-1.688504 |
0.435538998 |
14.551333 |
0.00013639213745781248463342927301766849268460646271705627441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000367496887345256009055338708435556327458471059799194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
11.9274810 |
3.4185403 |
38.4565548 |
7.3252420 |
| ENSG00000224032 |
|
EPB41L4A-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
162.584269 |
0.3280312684 |
-1.608095 |
0.661272091 |
5.577677 |
0.01819083279681305703734395251558453310281038284301757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032916107892725351979912318256538128480315208435058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.5606388 |
28.7518351 |
259.4451467 |
62.4652367 |
| ENSG00000224086 |
|
PPM1F-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75.334809 |
0.4272457929 |
-1.226862 |
0.178106179 |
48.783472 |
0.00000000000285838522070932487219308608222112901356415370912600337760522961616516113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000016538520524370693261283459825910114194408295773541794915217906236648559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.1085265 |
5.3851646 |
108.5469709 |
8.0176924 |
| ENSG00000224126 |
|
UBE2SP2 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.622385 |
3.0578971270 |
1.612540 |
0.356997756 |
20.970687 |
0.00000466364504443298041533316755646865203743800520896911621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000015242559976933301609772382356755571208850597031414508819580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.6338117 |
7.3771812 |
11.3880462 |
1.9934676 |
| ENSG00000224186 |
100996485 |
PITX1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34431063_Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes block malignant behaviors of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through a lncRNA C5orf66-AS1/microRNA-127-3p/DUSP1/ERK axis. |
|
|
32.142510 |
0.2504196347 |
-1.997580 |
0.356019054 |
32.230747 |
0.00000001369069802712054706347488984346724705254416676325490698218345642089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000058725574798110808176635812011961990108943609811831265687942504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.3986636 |
2.9709816 |
49.9704089 |
7.4317149 |
| ENSG00000224259 |
100505633 |
LINC01133 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25908174_LINC01133 is upregulated in lung squamous cell cancer. 26840083_Authors found that there was negative correlation between LINC01133 and KLF2, P21 or E-cadherin in NSCLC. 27443606_LINC01133 inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transformation and metastasis in colorectal neoplasms by directly binding to SRSF6 as a target mimic. 28537675_Our results indicated that reduced LINC01133 expression contributed to colorectal cancer metastasis and poor prognosis 28887321_study identifies a group of differentially expressed lncRNAs in human gallbladder cancer (GBC) tissues, including prognosis-associated gallbladder cancer lncRNA (lncRNA-PAGBC), which was found to be an independent prognostic marker in GBC. Functional analysis indicates lncRNA-PAGBC promotes tumour growth and metastasis of GBC cells 29458145_our findings revealed that the C/EBPbeta-LINC01133 axis performs an oncogenic function in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by activating CCNG1 30134915_Findings suggest that reduced expression of LINC01133 is associated with aggressive tumor phenotypes and poor patient outcomes in gastric cancer (GC). LINC01133 inhibits GC progression and metastasis by acting as a ceRNA for miR-106a to regulate APC expression and the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, suggesting that LINC01133 may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker. 30332510_Data indicate that LINC01133 inhibited OSCC metastasis via a feedback regulation loop of reciprocal inhibition with GDF15. 30518158_tissue-specific down-regulation of PCAT18 and LINC01133 in gastric and other gastrointestinal cancers imply that these long noncoding RNAs may have a tumor suppressive function in the development of these tumor entities. 30548306_The knockdown of LINC01133 dramatically repressed hepatocellular carcinoma tumor progression through targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo. 30580676_Study clarified the distinct effect of LINC01133 on pancreatic cancer. In summary, by inducing the methylation of DKK1 promoter, LINC01133 silencing suppresses the development of pancreatic cancer cells through the Wnt signaling pathway. 31283068_Authors establish that LINC01133 is sufficient, on its own, in promoting phenotypic and growth characteristics of cancer stem cell-like cells, and that it is a direct mediator of the MSC-triggered miR-199a-FOXP2 pathway in TNBC models. 31390932_we unveiled that LINC01133 may function as a ceRNA for miR-4784 to advance AHDC1 expression, intensifying CC cell malignant phenotypes and EMT process, which may demonstrate the implied value of LINC01133 as a therapeutic target for CC patients. 31640854_Because of its role as an miR-205 sponge, LINC01133 repressed the development of ovarian cancer by up-regulating LRRK2. 32661199_Hydrostatic pressure induces osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells through increasing lncRNA-PAGBC. 32792860_MiR-216a-5p inhibits tumorigenesis in Pancreatic Cancer by targeting TPT1/mTORC1 and is mediated by LINC01133. 33036757_LINC01133 contribute to epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis by regulating miR-495-3p/TPD52 axis. 33078907_LINC01133 promotes the progression of cervical cancer via regulating miR-30a-5p/FOXD1. 33175096_Sevoflurane protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reperfusion injury via LINC01133/miR-30a-5p axis. 33728699_Exosomes-mediated transfer of long noncoding RNA LINC01133 represses bladder cancer progression via regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. 34047479_LINC01133 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-199a-5p and activating annexin A2. 34318683_LINC01133 hampers the development of gastric cancer through increasing somatostatin via binding to microRNA-576-5p. 34445100_LINC01133 Inhibits Invasion and Promotes Proliferation in an Endometriosis Epithelial Cell Line. 35017464_Linc01133 contributes to gastric cancer growth by enhancing YES1-dependent YAP1 nuclear translocation via sponging miR-145-5p. 35195032_Clinical potential of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 as a promising biomarker and therapeutic target in cancers. 35446199_Linc01133 promotes proliferation and metastasis of human renal cell carcinoma through sponging miR-760. 35481341_Role of LINC01133 in Osteogenic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells by Targeting miR-199b-5p. |
|
|
11.605258 |
0.1187434684 |
-3.074080 |
0.610652752 |
30.462333 |
0.00000003404123574910779150589677593229109842098978333524428308010101318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000140781350422199781619505957498683645923165386193431913852691650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6843737 |
1.2325150 |
22.7842006 |
5.3641544 |
| ENSG00000224307 |
|
LINC02975 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.415993 |
0.2381275650 |
-2.070193 |
0.791703703 |
6.279288 |
0.01221571605963844668607531929183096508495509624481201171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.023000889021592484801059796950539748650044202804565429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3271200 |
2.8361334 |
17.3046067 |
7.3535827 |
| ENSG00000224505 |
|
HEXIM2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.370532 |
0.3099717541 |
-1.689791 |
0.371486972 |
21.463580 |
0.00000360613123216450595542501532386747697955797775648534297943115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011928842892592582752776982080167300637185689993202686309814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.0671824 |
2.7139311 |
32.8489497 |
5.5728645 |
| ENSG00000224596 |
283050 |
ZMIZ1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.754921 |
3.5071148435 |
1.810285 |
0.325589959 |
31.545271 |
0.00000001948442859996955837203382456805644817876554952817969024181365966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000082451309098495026794814596795418770724950263684149831533432006835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.8990867 |
8.1506623 |
13.3498841 |
1.9784188 |
| ENSG00000224616 |
|
RTCA-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
138.523420 |
0.3742701587 |
-1.417848 |
0.148558742 |
93.203305 |
0.00000000000000000000047189259656457986776803382651304863242288400564006363889708092068664413432088622357696294784545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000004519879769820375792680458256326878324178406609075682326685970136015413345376146025955677032470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.4889156 |
7.1603504 |
200.5107966 |
12.1471055 |
| ENSG00000224660 |
100505696 |
SH3BP5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93.068959 |
0.3522046383 |
-1.505514 |
0.201668929 |
55.521238 |
0.00000000000009245474471234349666128139599343024429252760332254013064812170341610908508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000586686170229660424175314292167116223789165296853553854816709645092487335205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.9814951 |
6.0176672 |
142.2582432 |
10.9216110 |
| ENSG00000224699 |
101410535 |
LAMTOR5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34374893_LAMTOR5 expression level is a biomarker for colorectal cancer and lncRNA LAMTOR5-AS1 predicting miRNA sponging effect. 34588094_Long Noncoding RNA LAMTOR5-AS1 Interference Affects MicroRNA-506-3p/E2F6-Mediated Behavior of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. 36173004_LncRNA LAMTOR5-AS1 sponges miR-210-3p and regulates cervical cancer progression. |
|
|
37.373780 |
0.0452092615 |
-4.467238 |
0.716255870 |
31.411590 |
0.00000002087311972292404456551356806658092946094029684900306165218353271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000088050084912934795197019584994668761623870523180812597274780273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4513034 |
2.3046616 |
80.9159067 |
36.3714144 |
| ENSG00000224892 |
220433 |
RPS4XP16 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.233715 |
0.4792259798 |
-1.061222 |
0.455805132 |
5.541493 |
0.01857073062938622426409907006927824113517999649047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.033566493275745859503622625652496935799717903137207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
7.9087546 |
2.3300987 |
16.6919410 |
2.9709114 |
| ENSG00000224975 |
8552 |
INE1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
X chromosome inactivation provides dosage compensation for the expression level of X-linked genes from the single X in males and the two in females. This X chromosome gene is intronless and was identified because its transcription escapes X inactivation in females. This gene does not make a protein.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010]. |
|
|
|
|
|
9.317159 |
0.2719055494 |
-1.878822 |
0.652402139 |
8.345418 |
0.00386661155634053250312875960048586421180516481399536132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008087173950912039666061303933020099066197872161865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9110669 |
1.6657344 |
14.2068497 |
3.7394020 |
| ENSG00000224985 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.868211 |
2.2869412878 |
1.193419 |
0.339186197 |
12.612234 |
0.00038323027267815574581702464662669171957531943917274475097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000961168874210633554337757100682892996701411902904510498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.8363856 |
5.8912933 |
12.2362885 |
2.0736860 |
| ENSG00000225032 |
102723566 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.606577 |
0.3968604922 |
-1.333296 |
0.402307473 |
10.958739 |
0.00093163186528978311502086073758732709393370896577835083007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002180021939565335992172734336236317176371812820434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2593553 |
2.7511697 |
28.3511487 |
4.4304378 |
| ENSG00000225138 |
|
SLC9A3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
239.103529 |
0.3488397767 |
-1.519364 |
0.145897155 |
107.262219 |
0.00000000000000000000000038999873911643588098966036073220499131764081453762572638323773613192903264579314281945698894560337066650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000004214042012707608609512690397275682508825942498246876205708993348882096530161334158037789165973663330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
122.6049237 |
11.0660942 |
353.6696083 |
21.1228143 |
| ENSG00000225377 |
100507459 |
NRSN2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34791059_Long non-coding RNA NRSN2-AS1 facilitates tumorigenesis and progression of ovarian cancer via miR-744-5p/PRKX axis. 35715622_Long non-coding RNA NRSN2-AS1, transcribed by SOX2, promotes progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the ubiquitin-degradation of PGK1. |
|
|
48.552414 |
0.3976068111 |
-1.330586 |
0.308276032 |
18.227224 |
0.00001960563893453372895999027580860030184339848347008228302001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000059469632279843366660498221731856460792187135666608810424804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.1893631 |
5.1173087 |
66.6484159 |
8.4714058 |
| ENSG00000225422 |
|
RBMS1P1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.296893 |
0.3043482044 |
-1.716205 |
0.466992396 |
14.430484 |
0.00014542904510358108691008005575184824920143000781536102294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000390065910544949430265038170517755133914761245250701904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6943489 |
1.5372978 |
15.3924789 |
3.0528326 |
| ENSG00000225434 |
100507540 |
LINC01504 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40.149800 |
0.4612594314 |
-1.116350 |
0.305850275 |
13.289154 |
0.00026694590949070858823186092045887107815360650420188903808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000686312772005375111572522683900388074107468128204345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.7998014 |
8.0836244 |
36.9987187 |
12.6052846 |
| ENSG00000225614 |
84627 |
ZNF469 |
protein_coding |
Q96JG9 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a zinc-finger protein. Low-percent homology to certain collagens suggests that it may function as a transcription factor or extra-nuclear regulator factor for the synthesis or organization of collagen fibers. Mutations in this gene cause brittle cornea syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of extracellular matrix organization [GO:1903053] |
18452888_30% homology to a number of collagens suggests that ZNF469 could act as a transcription factor involved in the synthesis and/or organization of collagen fibers. 19661234_The results confirm that BCS (brittle cornea syndrome) is associated with mutations in ZNF469. 20485516_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20719862_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20938016_ZNF469 mutation may predispose to childhood blue sclera without BCS only in certain individuals, depending on other genetic and/or environmental conditions 21664999_ZNF469 and PRDM5, two genes that when mutated cause brittle cornea syndrome, participate in the same regulatory pathway. 22486320_We document a novel homozygous ZNF469 mutation in an adult with corneal fragility but lacking clinical evidence for extraocular manifestations. 22814818_Mutations in COL5A1 gene is associated with central corneal thickness in glaucoma. 23010198_A novel homozygous 14 bp duplication in exon 2 of ZNF469 (c.8817_8830dup) was uncovered by direct sequencing 23680354_ZNF469 frequently mutated in the brittle cornea syndrome (BCS) is a single exon gene possibly regulating the expression of several extracellular matrix components. 24895405_Results show that enrichment of rare potentially pathogenic alleles in ZNF469 in 12.5% of keratoconus patients represents a significant mutational load and highlights ZNF469 as the most significant genetic factor responsible for keratoconus identified. 25097247_Rare missense mutations in ZNF469, predicted to be pathogenic, occurred heterozygously, at a frequency of 23% in a keratoconus population. 25564447_The presence of heterozygous loss-of-function alleles in the ZNF469 gene did not cause keratoconus in the individuals examined. 26806788_we have not found a significant enrichment of sequence variants in ZNF469 in Polish patients with keratoconus (KTCN). High prevalence of ZNF469 variants identified in our KTCN group is typical for a common genetic variation observed in general population. 28484309_ZNF469 has a pathogenic role in Chinese patients with keratoconus. 28622062_New detected ZNF 469 P873T and Q2188H heterozygote coding variants in isolated advance keratoconus patients may be associated with the disease pathogenesis. 29187250_genotype frequencies did not differ between the sporadic or familial keratoconus cases 29228253_Rare variants in ZNF469 do not contribute to keratoconus susceptibility and do not account for the association at rs9938149. 29755127_Linc-ZNF469-3 promotes lung metastasis of TNBC through miR-574-5p-ZEB1 signaling axis. 30865045_This is the first report of a ZNF469 homozygous mutation causing a Brittle cornea syndrome phenotype in a consanguineous Pakistani family. 31107761_CXL may be associated with the development of corneal perforation in particular at-risk individuals with keratoconus. Identifying clinical and genetic risk factors, including screening of ZNF469 and PRDM5, may be useful in the prevention of significant complications after CXL. 33739556_More than meets the eye: Expanding and reviewing the clinical and mutational spectrum of brittle cornea syndrome. |
ENSMUSG00000043903 |
Zfp469 |
157.624547 |
0.4215549823 |
-1.246207 |
0.127039951 |
98.227463 |
0.00000000000000000000003729812784663371433963945708311425933144982687570005938246865987914513418388651189161464571952819824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000370970597719887899644369987958865296075287762531557597068458502487242611778128775767982006072998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.5531343 |
7.9367992 |
225.9483837 |
12.1258920 |
| ENSG00000225684 |
100128385 |
FAM225B |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33299501_FAM225B Is a Prognostic lncRNA for Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. 33495826_Knockdown of FAM225B inhibits the progression of the hypertrophic scar following glaucoma surgery by inhibiting autophagy. 34255617_Long noncoding RNA FAM225B facilitates proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by regulating miR-613/CCND2 axis. |
|
|
46.960662 |
3.9259439282 |
1.973040 |
0.323206070 |
36.710448 |
0.00000000137043022184436889237733606447663600724773402816936140879988670349121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006464541410809487598362117511145361059554659277637256309390068054199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
77.1395530 |
15.4057395 |
19.7221030 |
3.1803793 |
| ENSG00000225774 |
|
SIRPAP1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.233314 |
3.2037848374 |
1.679777 |
0.441793547 |
15.021618 |
0.00010628667131255958313261478220823619267321191728115081787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000291434380191970925089162136600862140767276287078857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.5003425 |
5.9435574 |
7.1091096 |
1.5542748 |
| ENSG00000225791 |
401264 |
TRAM2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.755974 |
0.2828778968 |
-1.821749 |
0.238720727 |
61.098394 |
0.00000000000000542923995651625125578160814973020872485545001984164059649629052728414535522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000037014125523408712373006081727299945458649517437965670296762255020439624786376953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.5084973 |
3.2424487 |
72.8238566 |
6.9012929 |
| ENSG00000225828_ENSG00000160058 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
87.963508 |
0.2849173325 |
-1.811385 |
0.231969905 |
61.342220 |
0.00000000000000479682933895940530528480675633794565168235976213018112446206941967830061912536621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000032884905268481571934962732477233188675897531533243167700675257947295904159545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.7193802 |
20.8917073 |
143.3805053 |
51.8921371 |
| ENSG00000225889 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.469623 |
0.1838420332 |
-2.443461 |
0.716048192 |
11.302232 |
0.00077413978293252086720216409432282489433418959379196166992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001839688165526325632631587936316464038100093603134155273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0747769 |
1.6566541 |
16.6681570 |
5.4842770 |
| ENSG00000225914 |
414764 |
TSBP1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.232858 |
0.4175542589 |
-1.259964 |
0.515187920 |
5.909970 |
0.01505543139452069842376680242068687221035361289978027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027763389228276549869356415456422837451100349426269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.5729499 |
4.1183593 |
30.0443835 |
6.7148670 |
| ENSG00000226009 |
|
KCNIP2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.465552 |
0.0553193905 |
-4.176071 |
0.836065387 |
38.134287 |
0.00000000066039428704038107682742532117208499042870784023762098513543605804443359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003202174663835750644268112876191824389682238916066125966608524322509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0525728 |
0.6377310 |
18.5666438 |
4.2582374 |
| ENSG00000226179 |
|
LINC00685 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.117557 |
0.2615084824 |
-1.935070 |
0.512519155 |
14.442500 |
0.00014450417545899683002472158044326988601824268698692321777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000388008300850426238962770364437915304733905941247940063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4431578 |
2.1880793 |
20.6506329 |
5.2681115 |
| ENSG00000226200 |
|
SGMS1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.616467 |
0.1096701491 |
-3.188757 |
0.365172106 |
89.014057 |
0.00000000000000000000392016936226220155940155580552250892707831863025299778372119441360865721435402520000934600830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000036140974257957586608549574122069656162187936534874979806197803355871656094677746295928955078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3941237 |
1.5632009 |
58.7879587 |
7.3457667 |
| ENSG00000226268 |
|
|
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.369003 |
2.4396268794 |
1.286661 |
0.312153461 |
17.269336 |
0.00003243795869818586868329676753397450283955549821257591247558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000095737706535737530618226931444780802848981693387031555175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.6005496 |
8.4803952 |
15.9716157 |
2.7451677 |
| ENSG00000226445 |
|
THBS2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
142.175190 |
0.3017079628 |
-1.728775 |
0.164818163 |
111.501473 |
0.00000000000000000000000004594638403741034776876798887454264282530653063436952221266778981283119762113464901176485000178217887878417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000509518128018164319382382433172459196789260659553674585715814582330233928342266835898044519126415252685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.0306188 |
6.5946572 |
217.0638681 |
13.7526628 |
| ENSG00000226648 |
101927117 |
PLCG1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.010882 |
0.2761118425 |
-1.856675 |
0.601920251 |
10.399593 |
0.00126043099251047256356694781231908564222976565361022949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002889262532917312355923433742077577335294336080551147460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0468440 |
1.2470669 |
11.0207283 |
2.4275089 |
| ENSG00000226696 |
104355426 |
LENG8-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.334166 |
0.2726781314 |
-1.874729 |
0.362368926 |
27.120820 |
0.00000019112844390647116310689860099736314680285431677475571632385253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000732361327118254029056010866172155004960586666129529476165771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.3217284 |
2.6338812 |
45.8585146 |
5.8608994 |
| ENSG00000226711 |
440078 |
FAM66C |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28005267_FAM66C expression is significantly downregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing 32430927_Long non-coding RNA FAM66C is associated with clinical progression and promotes cell proliferation by inhibiting proteasome pathway in prostate cancer. 35874989_LncRNA-FAM66C Was Identified as a Key Regulator for Modulating Tumor Microenvironment and Hypoxia-Related Pathways in Glioblastoma. |
|
|
9.067535 |
0.3638482726 |
-1.458591 |
0.560227073 |
6.849638 |
0.00886592575727079314218403993663741857744753360748291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017155357128646683134709505225146131124347448348999023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9132548 |
1.9082537 |
13.6020059 |
3.4252687 |
| ENSG00000226742 |
440498 |
HSBP1L1 |
protein_coding |
C9JCN9 |
|
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable transcription corepressor activity. Predicted to be involved in cellular heat acclimation. Predicted to be active in cytosol and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440498; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription corepressor activity [GO:0003714]; cellular heat acclimation [GO:0070370] |
|
ENSMUSG00000078963 |
Hsbp1l1 |
9.757479 |
0.1797135923 |
-2.476229 |
0.587688636 |
19.944313 |
0.00000797307405776647859648679356192602085684484336525201797485351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000025329869369916748519499377634289771776820998638868331909179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8156543 |
1.1871672 |
15.7838558 |
3.6503785 |
| ENSG00000226752 |
253039 |
CUTALP |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
61.629103 |
0.4413084329 |
-1.180141 |
0.199151305 |
35.864020 |
0.00000000211580006816382507110735904543464408478214977549214381724596023559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000009835971340503325831072221647078529516150524614204186946153640747070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.8390636 |
5.1330986 |
86.3545756 |
7.6334966 |
| ENSG00000226758 |
104472714 |
DISC1-IT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
152.380488 |
0.2697460919 |
-1.890326 |
0.234928612 |
63.129362 |
0.00000000000000193567002673567794493451802134501818925129508139337808358959591714665293693542480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000013604995045056478593944693617729151777256046615405260524767072638496756553649902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.0739680 |
13.2214661 |
217.2501035 |
34.6858698 |
| ENSG00000226791 |
101927070 |
LINC02611 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.764809 |
0.1978315255 |
-2.337656 |
0.542551558 |
17.346746 |
0.00003114311149962179452567803683571412420860724523663520812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000092174117853302111333727020259232176613295450806617736816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2681794 |
2.8359382 |
41.2939122 |
9.0583427 |
| ENSG00000226800 |
404665 |
CACTIN-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.511132 |
0.3786334129 |
-1.401126 |
0.456055781 |
9.575880 |
0.00197150300186935308055513615954623674042522907257080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004359458323234704710258391457955440273508429527282714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.1480904 |
2.2882437 |
21.6679780 |
3.8567254 |
| ENSG00000226849 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.113051 |
0.4412068545 |
-1.180473 |
0.466338879 |
6.580401 |
0.01031076596081922751302339946732899989001452922821044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019703120867645234487453009819546423386782407760620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3978123 |
2.1980934 |
14.7685864 |
3.2374408 |
| ENSG00000226981 |
|
ABHD17AP6 |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.226013 |
0.1164619712 |
-3.102069 |
0.725622410 |
21.554833 |
0.00000343854995703994908369028650485521581003922619856894016265869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011405167947395426707407443955855086414885590784251689910888671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4983729 |
0.7543301 |
12.9638840 |
3.3324896 |
| ENSG00000227028 |
100128590 |
SLC8A1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34855149_Association of Circulating Biomarkers of lnc-IGSF3-1:1, SCOC-AS1, and SLC8A1-AS1 with Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in Chinese Population. 35599603_SLC8A1 antisense RNA 1 suppresses papillary thyroid cancer malignant progression via the FUS RNA binding protein (FUS)/NUMB like endocytic adaptor protein (Numbl) axis. |
|
|
10.747347 |
0.1403944921 |
-2.832442 |
0.719081028 |
16.028675 |
0.00006239035547334527561594980094028528583294246345758438110351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000177228954346916140957790553045470005599781870841979980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1316147 |
1.1345461 |
15.3758204 |
4.7643949 |
| ENSG00000227039 |
100505746 |
ITGB2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29941860_LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 could promote the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by up-regulating ITGB2. 30260245_study suggested that ITGB2-AS1 played critical roles in the development and progression of osteosarcoma via Wnt/beta-catenin signalling, indicating that ITGB2-AS1 might be a valuable diagnostic biomarker and potential anticancer therapeutic target for osteosarcoma. 32165090_Gene expression of indoleamine and tryptophan dioxygenases and three long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer. 34170494_LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 promotes the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by modulating miR-328-5p/HMGA1 axis. 34627422_[Overexpression of LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 Predicts Adverse Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia]. |
|
|
506.141955 |
0.3091656610 |
-1.693548 |
0.079473702 |
465.248390 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000034654919855350116891643671868772646286063840245429858424107156048789762399828220293324771449572616156318947801318216842428589887396029441130600272520450695138501689527004981058864999523712625250086284353464627862116828288016816 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000015453372116766397148767229465506889588353435911386498034101885827459261204530123910733752559217148215302933594976772520591018586101890070208587032083107730588819812653414856433189709693521416427569308833930161993125891328621568 |
Yes |
No |
244.8309976 |
11.6458001 |
797.7325094 |
23.1289461 |
| ENSG00000227082 |
107985194 |
LINC02798 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.062316 |
0.4841226013 |
-1.046556 |
0.421034190 |
6.169076 |
0.01300024891758316814005524975073058158159255981445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024347630252953628843259892278183542657643556594848632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3788586 |
3.4581892 |
27.5243420 |
4.7435972 |
| ENSG00000227124 |
100131827 |
ZNF717 |
protein_coding |
Q9BY31 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
This gene encodes a Kruppel-associated box (KRAB) zinc-finger protein, which belongs to a large group of transcriptional regulators in mammals. These proteins bind nucleic acids and play important roles in various cellular functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, and in regulating viral replication and transcription. A pseudogene of this gene was identified on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, May 2016]. |
hsa:100131827; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
29327728_ZNF717 gene exhibited a high frequency of mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma at both single-cell and population levels. |
|
|
21.629823 |
0.4676585753 |
-1.096472 |
0.348545802 |
9.964051 |
0.00159626475219033802689649892414536225260235369205474853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003598727316683884326631304162447122507728636264801025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8641446 |
3.0196730 |
29.8277454 |
4.4092662 |
| ENSG00000227155 |
124902108 |
DOCK8-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.779973 |
0.2166606836 |
-2.206491 |
0.769524165 |
7.445302 |
0.00636022493874953409598305142935714684426784515380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012715281064058394158711173815845540957525372505187988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9914781 |
3.0557074 |
26.9560753 |
9.1836951 |
| ENSG00000227232 |
|
WASH7P |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
378.199034 |
0.4027939200 |
-1.311886 |
0.091661415 |
208.087874 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003589603487512888407558697980837922949290201650806567605381266512367829223539003646468664827480736820852658432367311171478502229703622106171678751707077026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000715014135974227107107831328082980929889399994063865191652816002078278038102010938936266576392039580506383267679908991715231891816983988974243402481079101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
217.0987600 |
12.3970469 |
543.3046848 |
19.6834436 |
| ENSG00000227345 |
8505 |
PARG |
protein_coding |
Q86W56 |
FUNCTION: Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase that degrades poly(ADP-ribose) by hydrolyzing the ribose-ribose bonds present in poly(ADP-ribose) (PubMed:15450800, PubMed:21892188, PubMed:23102699, PubMed:23474714, PubMed:33186521, PubMed:34321462, PubMed:34019811). PARG acts both as an endo- and exoglycosidase, releasing poly(ADP-ribose) of different length as well as ADP-ribose monomers (PubMed:23102699, PubMed:23481255). It is however unable to cleave the ester bond between the terminal ADP-ribose and ADP-ribosylated residues, leaving proteins that are mono-ADP-ribosylated (PubMed:21892188, PubMed:23474714, PubMed:33186521). Poly(ADP-ribose) is synthesized after DNA damage is only present transiently and is rapidly degraded by PARG (PubMed:23102699, PubMed:34019811). Required to prevent detrimental accumulation of poly(ADP-ribose) upon prolonged replicative stress, while it is not required for recovery from transient replicative stress (PubMed:24906880). Responsible for the prevalence of mono-ADP-ribosylated proteins in cells, thanks to its ability to degrade poly(ADP-ribose) without cleaving the terminal protein-ribose bond (PubMed:33186521). Required for retinoid acid-dependent gene transactivation, probably by removing poly(ADP-ribose) from histone demethylase KDM4D, allowing chromatin derepression at RAR-dependent gene promoters (PubMed:23102699). Involved in the synthesis of ATP in the nucleus, together with PARP1, NMNAT1 and NUDT5 (PubMed:27257257). Nuclear ATP generation is required for extensive chromatin remodeling events that are energy-consuming (PubMed:27257257). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15450800, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21892188, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23102699, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23474714, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23481255, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24906880, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27257257, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33186521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34019811, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34321462}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA damage;Hydrolase;Mitochondrion;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) is the major enzyme responsible for the catabolism of poly(ADP-ribose), a reversible covalent-modifier of chromosomal proteins. The protein is found in many tissues and may be subject to proteolysis generating smaller, active products. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]. |
hsa:8505; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase activity [GO:0004649]; ATP generation from poly-ADP-D-ribose [GO:1990966]; base-excision repair, gap-filling [GO:0006287]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975]; nucleotide-sugar metabolic process [GO:0009225]; regulation of DNA repair [GO:0006282]; regulation of histone modification [GO:0031056] |
12878198_Subcellular localization of human poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase in mammalian cells. 15212953_PARG is expressed in alternatiuve splice variants yielding isoforms that localize to different cell compartments. 15868399_PARG in modulating chromatin structure, participares in transcription, DNA repair and apoptosis [review]. 16117724_PARG is resident in FMRP (Fragile-X mental retardation protein)-associated messenger ribonucleoparticles complexes. 16526943_results suggest that PARG may play an autonomous role in the cellular response to oxidative DNA damage 17509564_hPARG55, that can be expressed through alternative translation initiation from hPARG60 transcripts is strictly targeted to the mitochondria. 17548475_PARG is identified as a novel and critical component of single-strand break repair that accelerates this process in concert with PARP-1. 18407589_PPAR gamma ligands inhibit growth and induce apoptosis of liver cancer cell 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19076642_suggest that PU.1-binding motifs are essential for PARG promoter activity and that PU.1 modulates PARG gene expression during differentiation of HL-60 cells. 19389396_The identification of a PARG isoform as a component of the mitochondrial matrix raises several interesting possibilities concerning mechanisms of nuclear-mitochondrial cross talk involved in regulation of cell death pathways. 19454480_PARG could be a novel potential therapeutic target for radiotherapy. 19571039_These data indicate that PARG is a survival factor at mild oxidative damage but contributes to the apoptosis-necrosis switch in severely damaged cells. 19812418_PARP-1 and PARG, nuclear enzymes with opposing enzymatic activities, localize to target promoters and act in a similar, rather than antagonistic, manner to regulate gene expression 22333589_inhibition of PARG leads to an accumulation of PAR polymers, the collapse of replication forks and the induction of homologous recombination in wild-type cells. 22508044_PARG knockdown, concomitant with inhibition of PARP, suppressed the metastatic potency of colon carcinoma cells by activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 22839996_Silencing of Apoptosis-Inducing factor and poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase reveals novel roles in breast cancer cell death after chemotherapy. 22918473_PARG silencing could inhibit the ability of HUVEC migration and proliferation by downregulating the activity of NF-kappaB in LoVo cells that in turn decreases angiogenic factors such as VEGF, b-FGF, ICAM-1, MMP-9, as well as phosphorylation of p38 and ERK. 23102699_Results define PARG as a coactivator regulating chromatin remodeling during retinoic acid receptor-dependent gene expression. 23254695_Therefore, strategies that target PAR metabolism for the improved treatment of cancer may be required to target PARP-1 and PARG individually in order to optimize cancer cell death. 23467693_The amount of poly(ADP-ribose) in a cell is regulated under the control of PARP1/PARG gene expression balance. 23744356_PARG knockdown enhances sensitivity to MMS in MIAPaCa2 and RKO tumor cell lines. 23776710_poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase is crucial for Trypanosoma cruzi infection cycle. 24211580_Radiation-induced G2/M arrest was largely suppressed by PARG siRNA in PC-14 and A427 cells, which exhibited significantly enhanced radiosensitivity in response to PARG knockdown. 25133494_Nuclear Smad function is negatively regulated by PARP-1 that is assisted by PARP-2 and positively regulated by PARG during the course of TGFB signaling. 25535335_Poly(ADP-ribosyl) glycohydrolase (PARG) is involved in cell proliferation and DNA synthesis, with depletion leading to replication-coupled H2AX phosphorylation. In addition, PARG depletion or inhibition slows down individual replication forks similarly to mild chemotherapeutic treatment. 26091342_Studies indicate that poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) and terminal ADP-ribose glycohydrolase 1 (TARG1) are key enzymes in poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs)-mediated ADP-ribosylation. 27129221_Data show that poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) opposes the function of poly-(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase (PARG) during regulation of bone morphogenetic protein target gene expression. 28254358_PARG inhibition leads to stalled replication forks and increased homologous recombination (HRR). The lack of HRR proteins at PARG inhibitor-induced replication stalling that induces cell death. 28934471_PARG is acetylated at multiple sites.PARG interacts with PCNA via a non-canonical PIP-box. 30459355_Oncogenic activity of poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase 31067465_PARG, an enzyme family that hydrolyzes poly(ADP-ribose), is sufficient to dissociate damaged DNA-rich compartments in vitro and initiates the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of FUS in cells. 31273064_PARG role in the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 32343702_DNA methylation-mediated repression of exosomal miR-652-5p expression promotes oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma aggressiveness by targeting PARG and VEGF pathways 32439163_PARG has a robust endo-glycohydrolase activity that releases protein-free poly(ADP-ribose) chains. 33046907_Regulation of ALT-associated homology-directed repair by polyADP-ribosylation. 33649309_PARG overexpression partially but significantly inhibited ASK3 dephosphorylation under hyperosmotic stress, while the glycohydrolase-inactive PARG mutant did not. 34019811_Unrestrained poly-ADP-ribosylation provides insights into chromatin regulation and human disease. 36076593_Upregulation of PARG in prostate cancer cells suppresses their malignant behavior and downregulates tumor-promoting genes. |
ENSMUSG00000021911 |
Parg |
138.916095 |
0.2048643051 |
-2.287259 |
0.784513121 |
7.711816 |
0.00548605489977185747235699508905781840439885854721069335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011119770711429910817202859618646471062675118446350097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.1164345 |
23.7797714 |
285.9310295 |
82.5791105 |
| ENSG00000227354 |
100505538 |
RBM26-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.792157 |
0.4893088325 |
-1.031183 |
0.393502046 |
6.780270 |
0.00921709626342379073626887020509457215666770935058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017785898921183835447168419818808615673333406448364257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.1875106 |
6.2587564 |
37.0919415 |
8.8609516 |
| ENSG00000227398 |
|
KIF9-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.715422 |
0.2738013527 |
-1.868799 |
0.506436868 |
14.042909 |
0.00017868630863222278201511705741921787193859927356243133544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000472460791368094006840300247418440449109766632318496704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4970408 |
1.8627591 |
20.2884578 |
4.0874225 |
| ENSG00000227502 |
285758 |
MROCKI |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.914579 |
0.2557218542 |
-1.967353 |
0.468177846 |
17.150402 |
0.00003453362738195815532550592141802781043224968016147613525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000101355406672838017933559184857728041606605984270572662353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.4142377 |
7.5143172 |
39.0897530 |
19.2854342 |
| ENSG00000227507 |
4050 |
LTB |
protein_coding |
Q06643 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to LTBR/TNFRSF3. May play a specific role in immune response regulation. Provides the membrane anchor for the attachment of the heterotrimeric complex to the cell surface. Isoform 2 is probably non-functional. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Lymphotoxin beta is a type II membrane protein of the TNF family. It anchors lymphotoxin-alpha to the cell surface through heterotrimer formation. The predominant form on the lymphocyte surface is the lymphotoxin-alpha 1/beta 2 complex (e.g. 1 molecule alpha/2 molecules beta) and this complex is the primary ligand for the lymphotoxin-beta receptor. The minor complex is lymphotoxin-alpha 2/beta 1. LTB is an inducer of the inflammatory response system and involved in normal development of lymphoid tissue. Lymphotoxin-beta isoform b is unable to complex with lymphotoxin-alpha suggesting a function for lymphotoxin-beta which is independent of lympyhotoxin-alpha. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4050; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; immune response [GO:0006955]; lymph node development [GO:0048535]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; skin development [GO:0043588] |
15077289_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15248211_Heterotypic interaction between LTbeta-producing lymphocytes and responding fibroblast-like synoviocytes contributes to establishment of complex lymphoid microstructures. May be one element in susceptibility of synovial membrane to lymphoid organogenesis. 15910501_The identification of IL-6 and IL-1beta as activators of LT-beta supports their involvement in LT-beta signaling in liver regeneration associated with chronic liver damage. 15969671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17981284_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18292573_Lymphotoxin (LT) beta receptor ligands LTalpha1 and -beta2 activate both the classical and noncanonical NF-kappa B pathways in human vascular endothelial cells and dermal microvascular endothelial cells in vitro. 18379788_LT-Beta may play a role in rheumatoid arthritis disease pathogenesis by contributing to a more intense inflammatory reaction in the synovium 19222863_blocking the lymphotoxin-beta receptor pathway results in ablation of the lymphoid organization in the NOD salivary glands and thus an improvement in salivary gland function. 19729601_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19735075_Overexpression of human TNF, lymphotoxin-alpha, and lymphotoxin-beta in mice (transgenic mice) resulted in thymic atropy. Chronic infections may promote thymic atrophy by upregulating lymphotoxin and TNF production. 19800575_Sustained LT signaling represents a pathway involved in hepatitis-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20356761_Soluble LTalphabeta in synovial fluid is associated with a proinflammatory cytokine milieu that contributes to synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21029472_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21211989_Data show differential expression of interferon-gamma, TNFSF3, TNFSF10, TNFSF12 and PDGFbeta in CD8+, CD14+ and CD4+ cells. 21248773_Findings provide evidence of additional complexity in the transcriptional regulation of LTB with implications for coordinate expression of genes in this important genomic locus. 22294627_A strong association was found between several single nucleotide polymorphisms in the LTA/LTB/TNFalpha locus and Sjogren syndrome. 22652080_The multifaceted character of lymphotoxin beta may be involved in inflammatory myopathies and muscular dystrophies. 22742857_TNF is able to upregulate LT-beta expression in hepatic cells at the transcriptional level by the binding of NF-kappaB p50/p65 heterodimers and Ets1 to their respective sites in the LT-beta promoter. 28196873_Combination of an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor and a NF-kappaB inhibitor effectively suppressed cetuximab-resistant HNSCC and interfering with the EGFR-LTbeta interaction reverses resistance. |
ENSMUSG00000024399 |
Ltb |
34.452066 |
4.3971449934 |
2.136567 |
0.307800253 |
50.522008 |
0.00000000000117835940879744052610565649790180678489065480007980113441590219736099243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000006984973844919767752962713554068472916573628861414135826635174453258514404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.8186484 |
10.5474344 |
12.9775012 |
2.0473822 |
| ENSG00000227543 |
|
SPAG5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.445369 |
0.4139052927 |
-1.272627 |
0.360004158 |
12.759416 |
0.00035422147526392608286524565919251017476199194788932800292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000894492553446629441032955654122815758455544710159301757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.6931087 |
2.8038753 |
30.8591275 |
4.2559379 |
| ENSG00000227704 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.660355 |
0.2109931049 |
-2.244732 |
0.545497388 |
18.900500 |
0.00001377165863325567941063791443934150038330699317157268524169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000042525037955408750988978844320698158298910129815340042114257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3278574 |
1.2375131 |
15.8448366 |
3.1711920 |
| ENSG00000227706 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1259.857731 |
0.1703305266 |
-2.553591 |
0.063611647 |
1704.151378 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
381.6698064 |
17.3559723 |
2257.2811010 |
61.0426303 |
| ENSG00000227775 |
|
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.083672 |
0.4921490742 |
-1.022833 |
0.305888723 |
11.275935 |
0.00078518309948288152102374715113342062977608293294906616210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001864131019521848104877892460251587181119248270988464355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.1199682 |
5.1191180 |
45.2340165 |
7.1236879 |
| ENSG00000227825 |
121456 |
SLC9A7P1 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.957416 |
3.1286916331 |
1.645559 |
0.479422463 |
12.113969 |
0.00050045511435170542385159064835420394956599920988082885742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001229275667803490183077608222106391622219234704971313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.9750367 |
5.4508622 |
6.4457819 |
1.4588436 |
| ENSG00000227827 |
283955 |
PKD1P2 |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64.782318 |
0.4846779685 |
-1.044902 |
0.265363791 |
15.450394 |
0.00008469927766988256685048996885711858340073376893997192382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000235258061424062223576311736472632674121996387839317321777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
43.5981760 |
9.6455959 |
90.6497606 |
14.2083649 |
| ENSG00000227917 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
233.629568 |
0.2987243707 |
-1.743113 |
0.117572967 |
224.788445 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000816491007571266126135322900042660642251948223805716900395293993358792337977087358660147091437070408090810495117639303136909949710348088913747233164031058549880981445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000178539366988916869077158353235793874579001614500807249774070120167734224184103093256027061305717221602309493370470727712298608658159082551719620823860168457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
111.3393484 |
8.3224727 |
375.4340360 |
17.4413821 |
| ENSG00000227917_ENSG00000231808 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.447758 |
0.3793610321 |
-1.398357 |
0.478989110 |
8.268602 |
0.00403365594473036742639848739599983673542737960815429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008406772344566538351928741690244351048022508621215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.4848175 |
4.3189169 |
40.9070078 |
7.6505081 |
| ENSG00000227946 |
|
INO80D-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.465189 |
0.4941132619 |
-1.017086 |
0.356775703 |
8.228684 |
0.00412334239177003774451391038269321143161505460739135742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008575529618504404080758796169448032742366194725036621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.7616918 |
3.3197662 |
25.9742376 |
4.4904593 |
| ENSG00000227953 |
|
LINC01341 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.721604 |
0.0796147278 |
-3.650821 |
0.602298525 |
47.985646 |
0.00000000000429350979070998607198704788110632708537234281109817857213784009218215942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000024486941464791111674625420977168238200610828059211598883848637342453002929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3726003 |
1.0115206 |
30.4793501 |
5.5977456 |
| ENSG00000228049 |
246721 |
POLR2J2 |
protein_coding |
Q9GZM3 |
FUNCTION: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB11 is part of the core element with the central large cleft (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-directed RNA polymerase;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription |
|
This gene is a member of the RNA polymerase II subunit 11 gene family, which includes three genes in a cluster on chromosome 7q22.1 and a pseudogene on chromosome 7p13. The founding member of this family, DNA directed RNA polymerase II polypeptide J, has been shown to encode a subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for synthesizing messenger RNA in eukaryotes. This locus produces multiple, alternatively spliced transcripts that potentially express isoforms with distinct C-termini compared to DNA directed RNA polymerase II polypeptide J. Most or all variants are spliced to include additional non-coding exons at the 3' end which makes them candidates for nonsense-mediated decay (NMD). Consequently, it is not known if this locus expresses a protein or proteins in vivo. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:246721;hsa:548644; |
RNA polymerase II, core complex [GO:0005665]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II activity [GO:0001055] |
|
ENSMUSG00000039771 |
Polr2j |
83.612104 |
0.3042043953 |
-1.716887 |
0.475424250 |
12.070964 |
0.00051213212785078843659186675907335484225768595933914184570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001255034070575732465038787388778018794255331158638000488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.6016728 |
24.2915897 |
141.5152496 |
55.5354584 |
| ENSG00000228109 |
100507057 |
MELTF-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27513470_results indicated lncRNA MFI2 could promote proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells by regulating FOXP4 expression, which suggested critical roles of lncRNA MFI2 and FOXP4 in occurrence and development of human osteosarcoma 28819235_Long non-coding RNA MFI2-AS1 expression was associated with dramatically increased risk of relapse compared to patients with undetectable MFI2-AS1 who had favorable outcomes. 31210294_Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA MFI2 functions as an oncogenic role in cervical cancer progression. 31298339_MFI2-AS1 regulates the aggressive phenotypes in glioma by modulating MMP14 via a positive feedback loop. 31678554_Knockdown of MFI2-AS1 increased cell viability but suppressed apoptosis, inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in LPS-treated chondrocytes by increasing miR-130a-3p and decreasing TCF4, indicating a novel target for the treatment of osteoarthritis 32106369_LncRNA MFI2-AS1 promotes HCC progression and metastasis by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-134 to upregulate FOXM1 expression. 35441579_Long non-coding MELTF Antisense RNA 1 promotes and prognosis the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-1299. 35508543_Copy number amplification and SP1-activated lncRNA MELTF-AS1 regulates tumorigenesis by driving phase separation of YBX1 to activate ANXA8 in non-small cell lung cancer. |
|
|
13.471791 |
0.3050705588 |
-1.712785 |
0.550879730 |
9.481785 |
0.00207521952286382699651157146547575393924489617347717285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004565544814051287689227187627238890854641795158386230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6329850 |
1.6516814 |
15.2600076 |
3.5490459 |
| ENSG00000228172 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.097020 |
0.1990821093 |
-2.328565 |
0.664614775 |
12.930594 |
0.00032325523012192546989246322297617552976589649915695190429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000820930350412873294230209353372629266232252120971679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6852257 |
1.1500182 |
13.7541481 |
3.2305380 |
| ENSG00000228288 |
100506696 |
PCAT6 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27458097_PCAT6 is a novel potential oncogenic lncRNA in lung cancer. Combined with the results that high PCAT6 expression positively correlated with metastasis and showed poor overall survival in lung cancer patients, our studies suggest that PCAT6 may be a potential molecular therapeutic target or a prognostic marker for patients with lung cancer. 30314898_mechanistic investigation demonstrated that the oncogenic activity of PCAT6 is partially attributable to its repression of LATS2 via association with the epigenetic repressor EZH2 (Enhancer of zeste homolog 2). 30569799_Our data highlighted that PCAT6 acts as a key activator of ARC expression by forming a complex with EZH2, inhibiting cell apoptosis and contributing to colon cancer progression. These findings elucidated that PCAT6 may be a novel prognostic predictor and therapeutic target of colon cancer 30915737_Long noncoding RNA PCAT6 regulates cell growth and metastasis via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and is a prognosis marker in cervical cancer. 30938104_we demonstrate that the abnormal PCAT6 overexpression inhibits miR-204 expression in CRC, thereby promoting HMGA2/PI3K signaling activity, ultimately enhancing the chemoresistance of CRC cells to 5-FU; PCAT6 represents a promising target for dealing with CRC chemoresistance. 31646553_LncRNA PCAT6 promotes occurrence and development of ovarian cancer by inhibiting PTEN. 31676070_PCAT6, acting as a competitive endogenous RNA, upregulated expression of TGFBR1 and TGFBR2 to activate TGF-beta pathway via sponging miR-185-5p. 32039820_Silencing of long non-coding RNA PCAT6 restrains gastric cancer cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting microRNA-15a. 32064636_LncRNA PCAT6 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes proliferation through the regulation of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. 32339330_PCAT6 mediates cellular biological functions in gastrointestinal stromal tumor via upregulation of PRDX5 and activation of Wnt pathway. 32908134_M2 macrophage-induced lncRNA PCAT6 facilitates tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer through modulation of VEGFR2. 32990800_LncRNA PCAT6 Regulated by YY1 Accelerates the Progression of Glioblastoma via miR-513/IGF2BP1. 33090394_LncRNA PCAT6 aggravates the progression of bladder cancer cells by targeting miR-513a-5p. 33125146_Long noncoding RNA PCAT6 promotes the development of osteosarcoma by increasing MDM2 expression. 33142195_LncRNA PCAT6: A potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of bladder cancer. 33761616_Promising role of long non-coding RNA PCAT6 in malignancies. 34185427_m(6) A modification of lncRNA PCAT6 promotes bone metastasis in prostate cancer through IGF2BP2-mediated IGF1R mRNA stabilization. 35081872_Long non-coding RNA prostate cancer-associated transcript 6 inhibited gefitinib sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer by serving as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-326 to up-regulate interferon-alpha receptor 2. 35609331_Knockdown of lncRNA PCAT6 suppresses the growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting macrophages M2 polarization via miR-326/KLF1 axis. |
|
|
10.267369 |
0.2557870040 |
-1.966985 |
0.575573865 |
12.047865 |
0.00051851730743047519736621531194487033644691109657287597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001269206543561163247346712523722089827060699462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8200851 |
1.5950961 |
15.3674019 |
4.0137079 |
| ENSG00000228315 |
91316 |
GUSBP11 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This transcribed pseudogene is similar to two functional genes. The 5' portion of the pseudogene is related to glucuronidase, beta, and the 3' portion is related to immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
|
|
|
|
|
377.986649 |
0.1035147469 |
-3.272092 |
0.785233933 |
13.081539 |
0.00029822034452215887652057335621691436244873329997062683105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000761674664494328321727445452182791996165178716182708740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
66.5391300 |
30.7560253 |
653.3357488 |
214.4984039 |
| ENSG00000228340 |
284757 |
MIR646HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33150676_MiR-646 regulates proliferation and migration of laryngeal carcinoma through the PI3K/AKT pathway via targeting GPX1. |
|
|
35.825146 |
2.3693476920 |
1.244490 |
0.334415529 |
13.757104 |
0.00020803257623167492780524856499368979712016880512237548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000543444859730857275474658063529886931064538657665252685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.6359154 |
10.3194303 |
22.2600917 |
3.3314642 |
| ENSG00000228451 |
157489 |
SDAD1P1 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.780612 |
0.3906469628 |
-1.356063 |
0.504777258 |
7.429126 |
0.00641764970316754772283740493321602116338908672332763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012817930936231800367886002334216755116358399391174316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9593432 |
2.3903285 |
12.6232525 |
3.9920415 |
| ENSG00000228463 |
728481 |
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.145146 |
6.9399575364 |
2.794927 |
0.747298402 |
12.570451 |
0.00039189408041419705568120246397256778436712920665740966796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000981064556803519114899780895200365193886682391166687011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.3181867 |
16.5029502 |
4.1995009 |
1.7227127 |
| ENSG00000228492 |
|
RAB11FIP1P1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.669842 |
0.1859394498 |
-2.427095 |
0.410298909 |
38.962543 |
0.00000000043201553344173264300219192122240290110379845600618864409625530242919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002125516424533324566347656687527976904217297260402119718492031097412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.0207834 |
1.6430592 |
32.5363222 |
4.7696231 |
| ENSG00000228536 |
|
LYPLAL1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.081665 |
2.7750099231 |
1.472493 |
0.564407501 |
6.656971 |
0.00987686599213563436172602649776308680884540081024169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018957417691017160871203017791231104638427495956420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.5924928 |
6.5482986 |
6.4715416 |
1.8395682 |
| ENSG00000228544 |
100131193 |
CCDC183-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33541391_Long non-coding RNA CCDC183-AS1 acts AS a miR-589-5p sponge to promote the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating SKP1 expression. |
|
|
33.229418 |
0.2945792275 |
-1.763272 |
0.408775468 |
18.105092 |
0.00002090416560469447284959128297021635489727486856281757354736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000063213580070741744827353403302083734160987660288810729980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.2608138 |
4.4496341 |
55.7916486 |
10.1606433 |
| ENSG00000228638 |
|
FCF1P2 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.758937 |
0.2438457870 |
-2.035959 |
0.778329789 |
6.529504 |
0.01060995358535176541492361934615473728626966476440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020252023382900788406324465995567152276635169982910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2032358 |
3.4880095 |
21.8742729 |
14.3026805 |
| ENSG00000228727 |
401251 |
SAPCD1 |
protein_coding |
Q5SSQ6 |
|
Alternative splicing;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:401251; |
|
19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000036185 |
Sapcd1 |
18.265397 |
0.3668799822 |
-1.446620 |
0.381450929 |
14.865288 |
0.00011546835682868693208520671777961297266301698982715606689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000315030119554790977859370926239535037893801927566528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5654351 |
2.5102980 |
28.9206004 |
4.1344327 |
| ENSG00000228748 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.024063 |
0.0285954245 |
-5.128072 |
1.095523847 |
29.288268 |
0.00000006237217618618992603883984188542499715879330324241891503334045410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000250438879354777812275207379139052576988433429505676031112670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.6064477 |
0.6912655 |
20.7219692 |
12.2836469 |
| ENSG00000228824 |
642345 |
MIR4500HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.502339 |
0.0970485649 |
-3.365149 |
0.425344155 |
74.449493 |
0.00000000000000000622096617102816955609061634996398020450326474961458625423382784447312587872147560119628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000050203094961386434230126675125634726123150859038515858578932693490060046315193176269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7323490 |
1.3632746 |
48.9606150 |
6.8531234 |
| ENSG00000228834 |
|
ATP5MFP2 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.244945 |
0.3066805589 |
-1.705191 |
0.501306307 |
11.945520 |
0.00054778949720289140355722334874144507921300828456878662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001334660445479478058788957994806878559757024049758911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6192872 |
2.5025250 |
21.6768280 |
5.3505278 |
| ENSG00000228956 |
|
SATB1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
61.638708 |
0.1276598492 |
-2.969623 |
0.384477854 |
57.384113 |
0.00000000000003584913822166336736597385949862948614693400686825874856822338188067078590393066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000234026218554511838044936912787754513718373183817078597712679766118526458740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8145545 |
3.9991912 |
107.6954799 |
19.9573085 |
| ENSG00000228960 |
|
OR2A9P |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.958946 |
0.0162316560 |
-5.945046 |
1.110118931 |
24.162990 |
0.00000088517081910820955506247762270555234920266229892149567604064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003149739944560553005556803943254529087880655424669384956359863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8374139 |
1.6137347 |
100.8824601 |
109.1953695 |
| ENSG00000229043 |
101927021 |
ZFAND2A-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66.236075 |
0.4950984139 |
-1.014213 |
0.195543022 |
27.379162 |
0.00000016722350782994074956638158851313091801671362190973013639450073242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000644443596754549747921358114621792623211149475537240505218505859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.3280883 |
5.5620740 |
88.1075816 |
7.3113960 |
| ENSG00000229186 |
|
ADAM1A |
unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.894587 |
0.1731212247 |
-2.530145 |
0.953592577 |
6.543960 |
0.01052408268782127273577309267693635774776339530944824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020095143657469855674735370598682493437081575393676757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8310283 |
2.4886237 |
16.1491309 |
9.2230045 |
| ENSG00000229191 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.555058 |
2.4038871971 |
1.265369 |
0.447707893 |
8.184791 |
0.00422430380418057499491979456252011004835367202758789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008766390410646945907657823227054905146360397338867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.7887099 |
4.8243997 |
6.9980704 |
1.6038703 |
| ENSG00000229236 |
246119 |
TTTY10 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34.852956 |
0.3446246606 |
-1.536902 |
0.305527556 |
25.505199 |
0.00000044119248441885171071449650223583738295474176993593573570251464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001627186674168478459275044047116498546756702126003801822662353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.4170498 |
3.7039736 |
56.0602088 |
6.7292144 |
| ENSG00000229271 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.739927 |
7.7575946231 |
2.955609 |
0.488605274 |
37.790386 |
0.00000000078769004944792064614144663981703045618765202107169898226857185363769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003798204877442440056624004245805492629983746155630797147750854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
42.0752610 |
10.8169900 |
5.4694022 |
1.2671086 |
| ENSG00000229299 |
|
ZBTB46-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.770460 |
0.1105057195 |
-3.177807 |
1.364410284 |
4.949179 |
0.02610306604888535525477166743257839698344469070434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.045514619596166309978269026714770006947219371795654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2381712 |
1.3998480 |
10.3704549 |
7.2739008 |
| ENSG00000229314 |
5004 |
ORM1 |
protein_coding |
P02763 |
FUNCTION: Functions as transport protein in the blood stream. Binds various ligands in the interior of its beta-barrel domain. Also binds synthetic drugs and influences their distribution and availability in the body. Appears to function in modulating the activity of the immune system during the acute-phase reaction. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17008009, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17321687}. |
3D-structure;Acute phase;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transport |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a key acute phase plasma protein. Because of its increase due to acute inflammation, this protein is classified as an acute-phase reactant. The specific function of this protein has not yet been determined; however, it may be involved in aspects of immunosuppression. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:5004; |
blood microparticle [GO:0072562]; collagen-containing extracellular matrix [GO:0062023]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; platelet alpha granule lumen [GO:0031093]; specific granule lumen [GO:0035580]; tertiary granule lumen [GO:1904724]; acute-phase response [GO:0006953]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 production [GO:0032732]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; regulation of immune system process [GO:0002682] |
11814462_Different ORM1 phenotypes may affect the disposition of quinidine 11911961_demonstrate that orosomucoid and/or its glycoforms affects thyroid cell function in vitro and that it does so by influencing the second messenger cAMP probably by interacting directly with the TSH receptor 11925509_The effect of alpha2,6-linked sialic acid on anti-IgM antibody-induced apoptosis in Ramos cells. 12480518_folds as a highly symmetrical all-beta protein dominated by a single eight-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet 12576428_exerts significant effects on the pharmacokinetics, plasma concentrations, and intracellular distribution of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients 15013397_tertiary structure analysis 15111541_Urinary levels are increaed in normoalbuminuric type 2 diabetic patients. 16261636_the N-linked glycosylation pattern of AGP was explored 16290938_The binding of coumarin enantiomers to ORM1 is studied. 17048007_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17321687_The drug binding site of AGP was gained from circular dichroism and electronic absorption spectra. 17675532_Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 may be an endogenous ligand for Siglec-5 as a signaling molecule that participates directly in the regulation of neutrophil responses. 17944232_Different ORM1 genotypes affect the protein binding percentage and the concentration of serum free nortriptyline. 17944232_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17987628_A different distribution of the area percentage of AGP forms is observed when comparing samples from diseased and healthy individuals, the most acidic AGP forms being present in a higher proportion in the samples from cancer patients. 18273814_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18273814_Polymorphisms of the human ORM1 gene in Mexico have been evaluated. 18510947_Bile pigment biliverdin and is the endogenous ligand of AAG. 18680736_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18823996_The crystal structure of the recombinant unglycosylated human AGP at 1.8 A resolution, which was solved using the new method of UV-radiation-damage-induced phasing, is reported. 18981009_Clinical trial of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19018521_The ORM1 variant is predominantly responsible for the acute-phase property of alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. 19141860_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19198000_A site-directed mutagenesis study of drug-binding selectivity in genetic variants of AGP1 is reported. 19395425_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19395425_ORM1*S/*S genotype predicted failure to complete a 6-week trial of antidepressants, whereas elevated plasma concentration of orosomucoid predicted failure to respond to antidepressant therapy at 6 weeks. 19459043_The present study investigated enhanced fucosylation of AGP in the sera of chronic hepatitis B (HBV-CH) and hepatitis B cirrhosis (HBV-LC) patients. 19616527_Results describe modifications in alpha-1-acid glycoprotein fucosylation in relation to different stages of human pregnancy. 19794411_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 19958090_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20371432_Almost all of the acute-phase proteins were closely related to rheumatoid arthritis activity (based on DAS28) and their places in the downgrade scale were as follows: CRP, Tf, AGP, Hp and AAT. 20442402_ORM integrates inflammatory and metabolic signals to modulate immune responses to protect adipose tissue from excessive inflammation and thereby from metabolic dysfunction. 20617306_Characterized are more than 150 human Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein isoforms, differing both in the amino acid sequence and in the glycosylation. 20959405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21300760_Data suggest that GDC-0449 pharmacokinetics are mediated by AAG binding. 21349832_analysis of differences in drug-binding selectivity between two forms of human alpha1-acid glycoprotein genetic variants, the A and F1*S forms 21621584_Importance of pH and disulfide bridges on the structural and binding properties of human alpha-acid glycoprotein. 21638284_Identify ORM genetic variations/haplotype structure associated with serum alpha-1-acid glycoprotein level and the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel in Japanese cancer patients. 21726491_The distribution of the AGP phenotypes did not differ significantly among the disease groups studied 22048274_Leukocytospermia was associated with the alterations of terminal monosaccharide expression in human seminal fibronectin and alpha{1}-acid glycoprotein 22147846_Urinary MCP1 and AGP are biomarkers of lupus nephritis in patients with juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus, providing insight into its pathophysiology 22216449_In this study, the potential of CZE-UV and CZE-ESI-MS analysis of intact AGP isoforms to study the correlation of this protein with bladder cancer is shown. 22574522_Characterization of 6-mercaptopurine binding site on human alpha1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid) using molecular docking. 22587817_The binding properties of the polymyxin class of antibiotics for human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AGP) have been characterized. 22633841_AGP has a direct effect in brain microvasculature and may play an important role in altering blood brain barrier integrity in inflammatory-related diseases. 22708402_change of the maintenance of three acute phase proteins: ceruloplasmin, alpha1-antitripsin and orosomucoid in an oral fluid and blood plasma at paradontitis and myocardial infarction 22807450_alpha(1)-Acid glycoprotein up-regulates CD163 via TLR4/CD14 protein pathway: possible protection against hemolysis-induced oxidative stress. 22908695_Analyses of Nicaraguan population surveillance data suggest that preschool children with elevated AGP1 levels have higher prevalence of anemia than children with normal AGP1 levels. 23192962_Drug-binding energetics of human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. 23526947_A cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between periodontitis and the common systemic inflammatory markers in 32 morbidly obese patients. The severity of periodontitis was associated with the plasma level of orosomucoid. 23936770_analysing the glycosylation of AGP in patients receiving methadone may aid in determining whether the therapy is likely to be effective. 23940561_The ORM1 A113G polymorphism was associated with the PKs variability after taking telmsiartan, as well as ABCC2 C3972T. The heterozygotes of ORM1 113AG showed a larger AUC and a notable BP change(%) from the baseline compared with the wild-type. 23973664_The ORM1 may be considered as a signaling molecule involved in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and remodeling. 24357727_Identified is the ORM1 gene, coding for orosomucoid, as a novel locus associated with lag time variability, reflecting the initiation process of thrombin generation. 24359035_Data suggest that human serum albumin (HSA) might serve as a carrier in delivering chitooligomers to target tissues than alpha-1-glycoprotein (AGP) which has pharmacological importance 24389491_These findings suggest that the ORM distal promoter region differentially regulates expression of ORM genes at basal level and in acute phase responses. 25408356_Data indicate that the band intensity of sialic acid content in alpha-1 Acid glycoprotein (AGP) of alcoholic liver cirrhosis was found to be lower than that in pooled control group. 25689617_ORM1 stimulates quiescent monocytes to polarize to M2b monocytes. 26193215_The results of this study suggest that the expression of VEGF-A and ORM-1 may be associated with two mechanisms (angiogenesis and tumor structural viscosity) that may influence tumor growth in odontogenic myxoma. 26563422_Glycosylated Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 is ostensibly expressed in lung cancer patients and is a potential lung cancer serum biomarker. 26563517_Altogether, these results indicate that alpha1-3 fucosylated glycoforms of AGP are increased in PDAC and could be potentially regarded as a PDAC biomarker. 27021626_Results indicate that advanced extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma (ENKL) patients with unfavourable treatment outcomes displayed higher levels of S100A9 and ORM1. 27754964_Data suggest that serum haptoglobin, fetuin-A, platelet factor-4, hs-CRP (high sensitive-C-reactive protein), SAP (serum amyloid P), AGP (alpha1-acid glycoprotein) levels of adolescents with metabolic syndrome are significantly higher than those of controls subjects. 28554261_Studies suggest plasma alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) as a potential predictive biomarker of docetaxel non-haematological AEs namely oral mucositis and rash. 28927749_Data provide evidence that Orm1 is induced in response to hepatic injury and executes liver regeneration by activating cell cycle progression in hepatocytes. 31399619_Evaluation of AGP Fucosylation as a Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma of Three Different Etiologies. 31482685_Dramatically changed immune-related molecules as early diagnostic biomarkers of non-small cell lung cancer. 31601857_Fucosylated alpha1-acid glycoprotein as a biomarker to predict prognosis following tumor immunotherapy of patients with lung cancer. 31736338_Taken together, AFP and ORM1 in the urine may be used as a diagnostic or screening biomarker of Hepatocellular carcinoma 31930291_Orosomucoid 1 is involved in the development of chronic allograft rejection after kidney transplantation. 33070381_Different glycoforms of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein contribute to its functional alterations in platelets and neutrophils. 33459949_miR-362-3p Targets Orosomucoid 1 to Promote Cell Proliferation, Restrain Cell Apoptosis and Thereby Mitigate Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Cardiomyocytes Injury. 33580265_Proteomic Profile of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles Identifies AGP1 as a Potential Biomarker of Primary Aldosteronism. 33640788_Acute phase alpha1-acid glycoprotein as a siderophore-capturing component of the human plasma: A molecular modeling study. 33813392_Serum Proteomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed IGHG3 and A1AG1 as Potential Predictors of Chemotherapeutic Response in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. 34210751_alpha1-Acid Glycoprotein Enhances the Immunosuppressive and Protumor Functions of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. 34265865_The connection of alpha-1 acid glycoprotein inflammatory marker with anthropometric, hormonal, and metabolic characteristic of women with polycystic ovary syndrome. 34654351_Orosomucoid 1 promotes epirubicin resistance in breast cancer by upregulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. 34758357_The structural basis for high affinity binding of alpha1-acid glycoprotein to the potent antitumor compound UCN-01. 34963738_Orosomucoid in liver diseases. 35188865_Characterization of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein as a potential biomarker for breast cancer. 35272364_Integrated GWAS and Gene Expression Suggest ORM1 as a Potential Regulator of Plasma Levels of Cell-Free DNA and Thrombosis Risk. 35765957_ORM 1 as a biomarker of increased vascular invasion and decreased sorafenib sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma. |
ENSMUSG00000061540+ENSMUSG00000028359+ENSMUSG00000039196 |
Orm2+Orm3+Orm1 |
11.898532 |
5.0177967680 |
2.327054 |
0.626703197 |
13.931438 |
0.00018960066106809723637804943052742601139470934867858886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000498842380991999117569035693264822839410044252872467041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.5384735 |
7.4246150 |
3.9193710 |
1.2247244 |
| ENSG00000229334 |
|
TMEM44-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.961325 |
0.2919467379 |
-1.776223 |
0.552962347 |
10.863347 |
0.00098086280959559270231640226711533614434301853179931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002284243463179385941891341715859198302496224641799926757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9014959 |
1.4459541 |
13.3052943 |
2.9236459 |
| ENSG00000229474 |
197135 |
PATL2 |
protein_coding |
C9JE40 |
FUNCTION: RNA-binding protein that acts as a translational repressor. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q4V7K4}. |
Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Nucleus;Reference proteome;RNA-binding |
|
Predicted to enable RNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in P-body assembly and deadenylation-dependent decapping of nuclear-transcribed mRNA. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA processing body assembly. Located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:197135; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; P-body [GO:0000932]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; deadenylation-dependent decapping of nuclear-transcribed mRNA [GO:0000290]; negative regulation of cytoplasmic mRNA processing body assembly [GO:0010607]; negative regulation of translation [GO:0017148]; P-body assembly [GO:0033962] |
28965844_Mutation in PATL2 gene is associated with Female Infertility. 28965849_Nonsense mutation in PATL2 gene is associated with Female Infertility. 29661911_Data indicate PAT1 homolog 2 protein (PATL2) mutation as a major cause of oocyte meiotic deficiency. 29697801_this study confirms previous findings that PATL2 is required for human oocyte maturation and female fertility, and also indicates the potential prognostic value of testing for PATL2 mutations in infertile women with oocyte germinal vesicle arrest. 30765866_This work further indicates the critical role of PATL2 in oocyte maturation and early embryo development and will provide a basis for pursuing the determination of genetic variation in PALT2 as an additional criterion for evaluating the quality of oocytes and embryos for assisted reproduction techniques. 32048119_Novel homozygous mutations in PATL2 lead to female infertility with oocyte maturation arrest. 34008465_PATL2 regulated the apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells in patients with PCOS. 35091966_Novel mutations in NLRP5 and PATL2 cause female infertility characterized by primarily oocyte maturation abnormality and consequent early embryonic arrest. |
ENSMUSG00000027233 |
Patl2 |
97.282808 |
0.1392873669 |
-2.843864 |
0.209756653 |
210.556977 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001038365059050964311045799730938380416826869611631156471210323100430209594923634954210185432425833215367871886478367618998099042304517070078873075544834136962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000209375249611915752808788966315052696963689267536478692495452167849233177520539209799009151080322414924397557422036078751681476006751836393959820270538330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.0549502 |
3.5880952 |
166.4753640 |
14.4387405 |
| ENSG00000229484 |
|
LINC02766 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.290810 |
0.3055241021 |
-1.710642 |
0.421733136 |
17.211668 |
0.00003343764065656488619930272743197008367133093997836112976074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000098393057434389497376003852480153000215068459510803222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.1635891 |
1.9614039 |
23.6726007 |
3.7354311 |
| ENSG00000229619 |
401093 |
MBNL1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31113460_the present study suggests an inhibitory role of lncRNA MBNL1-AS1 in CSC drug resistance of Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by upregulating miR-301b-3p-targeted TGFBR2. 31769229_LncRNA MBNL1-AS1 represses cell proliferation and enhances cell apoptosis via targeting miR-135a-5p/PHLPP2/FOXO1 axis in bladder cancer. 33648424_Muscleblind-like 1 antisense RNA 1 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of prostate cancer by sponging miR-181a-5p and regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. 34459372_The Regulatory Role of Both MBNL1 and MBNL1-AS1 in Several Common Cancers. 35094653_Up-regulation of long noncoding RNA MBNL1-AS1 suppresses breast cancer progression by modulating miR-423-5p/CREBZF axis. 35112997_Tumour-suppressing functions of the lncRNA MBNL1-AS1/miR-889-3p/KLF9 axis in human breast cancer cells. 35311623_LncRNA MBNL1-AS1 represses gastric cancer progression via the TGF-beta pathway by modulating miR-424-5p/Smad7 axis. |
|
|
255.584998 |
0.3960912364 |
-1.336095 |
0.197879493 |
44.404122 |
0.00000000002671240260693187838705788720469161585946427095450417255051434040069580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000143948544168789529630669065639596727185223201672670256812125444412231445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
141.1217751 |
25.8697800 |
360.1373939 |
47.1714144 |
| ENSG00000229644 |
646309 |
NAMPTP1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42.167081 |
7.4994718294 |
2.906789 |
0.309275000 |
100.074979 |
0.00000000000000000000001467355823740970116359061174867533830541517606988469397718879961255156185728765194653533399105072021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000148547132773777221801225248668353734446022342586764269623228040123619209111893724184483289718627929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.9531436 |
15.1363820 |
10.0328410 |
1.7826073 |
| ENSG00000229739 |
102724919 |
PDC-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.998010 |
0.3681589709 |
-1.441599 |
0.543083945 |
7.207196 |
0.00726118339107942063065381788078411773312836885452270507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014339719942779268618826549186451302375644445419311523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3547502 |
1.8896968 |
14.5595621 |
3.0749535 |
| ENSG00000229809 |
146542 |
ZNF688 |
protein_coding |
P0C7X2 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
Alternative splicing;DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:146542; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001227]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
Mouse_homologues 17971504_Zfp688 is most abundantly expressed in tissues rich in highly ciliated cells, such as olfactory sensory neurons, and is predicted to be important to cilia. |
ENSMUSG00000045251 |
Zfp688 |
47.147747 |
0.4060755134 |
-1.300180 |
0.254514686 |
26.439351 |
0.00000027194358248095526887997547271780263145046774297952651977539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001023167799495003704450166691353185655088964267633855342864990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.4572082 |
5.3788026 |
65.7550000 |
9.0287664 |
| ENSG00000229855 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.560339 |
4.1229659571 |
2.043683 |
0.565482252 |
13.418910 |
0.00024910041906527909767385398076555702573386952280998229980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000642895993251183656136404920289351139217615127563476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.2757807 |
6.6744140 |
4.6791426 |
1.3513208 |
| ENSG00000229921 |
100505879 |
KIF25-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.435159 |
0.4310891322 |
-1.213942 |
0.340572699 |
13.008054 |
0.00031015412662706098130202536644617339334217831492424011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000790106128583952351321362250757829315261915326118469238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.6075019 |
2.7581077 |
29.4567265 |
4.0251723 |
| ENSG00000229956 |
|
ZRANB2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.441453 |
0.3100751712 |
-1.689310 |
0.581682106 |
8.285145 |
0.00399707091512725449372611663534371473360806703567504882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008336409030278123244439569816677249036729335784912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1037397 |
2.1537670 |
16.6014945 |
4.6320564 |
| ENSG00000230021 |
101928626 |
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.309535 |
0.3986132723 |
-1.326938 |
0.374612589 |
12.998359 |
0.00031176406791196865659482329036222836293745785951614379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000793796384747396527314933223351545166224241256713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7131044 |
3.7639010 |
24.5909606 |
6.4289608 |
| ENSG00000230084 |
|
ZBTB47-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.092561 |
0.3548522456 |
-1.494710 |
0.528912960 |
7.759139 |
0.00534414346217821842333073334430082468315958976745605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010857475223916104520305303537952568149194121360778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7111715 |
2.6537715 |
22.2836607 |
4.8606955 |
| ENSG00000230487 |
114796 |
PSMG3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31661146_Results demonstrated that PSMG3AS1 expression was increased in breast cancer tumor tissues and cell lines. Its knockdown increased the level of miR143 expression, which led to the mitigation of proliferation and migration capacity in breast carcinoma cells. Additionally, its knockdown was demonstrated to reduce the mRNA and protein expression levels of COL1A1. 32471413_MiR-449b-5p targets lncRNA PSMG3-AS1 to suppress cancer cell proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma. 32529538_Overexpression of LncRNA PSMG3-AS1 Distinguishes Glioblastomas from Sarcoidosis. 33849377_LncRNA PSMG3AS1 promotes proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-613 to upregulate SphK1. 34751795_LncRNAs PSMG3-AS1 and MEG3 negatively regulate each other to participate in endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation. |
|
|
189.604623 |
0.4887444785 |
-1.032848 |
0.142543859 |
52.191235 |
0.00000000000050350379830708157394557933217729301929137253335255763886380009353160858154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000003054548320185994210897853391971774840094044911609216796932741999626159667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
120.2968916 |
12.2986208 |
248.4774879 |
17.3873546 |
| ENSG00000230513 |
439931 |
THAP7-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34608273_lncRNA THAP7-AS1, transcriptionally activated by SP1 and post-transcriptionally stabilized by METTL3-mediated m6A modification, exerts oncogenic properties by improving CUL4B entry into the nucleus. |
|
|
11.231952 |
0.4593145790 |
-1.122446 |
0.431629547 |
6.944642 |
0.00840706652524094745493332681007814244367182254791259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016348919883077257103609625232820690143853425979614257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7935330 |
1.9267130 |
14.9163529 |
2.6850217 |
| ENSG00000230606 |
|
LINC02969 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
156.964008 |
0.4428727848 |
-1.175036 |
0.212847119 |
30.059716 |
0.00000004189441570015009651590482211459820494070527274743653833866119384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000171101708836252168675998728067377818717886839294806122779846191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.1974065 |
13.1365323 |
214.1761005 |
20.9284937 |
| ENSG00000230638 |
100418723 |
|
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.997198 |
2.1713868069 |
1.118617 |
0.480760626 |
5.502391 |
0.01899049579057163553152953738845098996534943580627441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034220451455113827521348213167584617622196674346923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.5928958 |
4.2353396 |
6.2956347 |
1.5486303 |
| ENSG00000230724 |
|
LINC01001 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.161265 |
0.0654533391 |
-3.933389 |
0.868654531 |
20.151424 |
0.00000715469719955323700880112092193030548514798283576965332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000022857863780390860433027258591387465003208490088582038879394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4565055 |
0.8933374 |
19.3784149 |
6.7951174 |
| ENSG00000230733 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.397522 |
0.1992033466 |
-2.327686 |
0.791597394 |
7.364025 |
0.00665416584607322978556220860468783939722925424575805664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013250875322185762944515730055172753054648637771606445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5894912 |
6.7464954 |
38.6181153 |
22.5532324 |
| ENSG00000230735 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
448.249374 |
0.0005881194 |
-10.731603 |
2.041389443 |
7.433654 |
0.00640152154047934560110455493031622609123587608337402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012792642558553363185680495917040389031171798706054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.2085576 |
6.4072321 |
8358.7134748 |
13280.7240372 |
| ENSG00000230813 |
|
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.919227 |
0.1124661291 |
-3.152438 |
0.351142536 |
95.634189 |
0.00000000000000000000013819899884512791459605407955871023378059757274869870124331850021193179856027200003154575824737548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001343753111300453278277815772168024662006566204417169493412573949564503550391236785799264907836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.9173498 |
1.8922166 |
70.6319421 |
8.4305298 |
| ENSG00000230910 |
|
ADGRB3-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.149214 |
0.2059158027 |
-2.279874 |
0.660879178 |
13.298600 |
0.00026560440682964642786570430565973310876870527863502502441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000683101767695692800586027004783318261615931987762451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8945214 |
1.4562081 |
13.8232778 |
3.5372694 |
| ENSG00000230943 |
101927686 |
LINC02541 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.615232 |
0.4831504606 |
-1.049456 |
0.458519352 |
5.282300 |
0.02154327216687833973507437690386723261326551437377929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.038333779045584603917262711547664366662502288818359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7751877 |
2.5832894 |
15.9801555 |
3.5246943 |
| ENSG00000231064 |
105371450 |
THBS3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.421113 |
0.1241098464 |
-3.010311 |
0.633039174 |
26.977081 |
0.00000020588222406977530069057281264521819252877321559935808181762695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000785577539892460797041004189750212916010241315234452486038208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.2170122 |
1.0149552 |
18.0829315 |
4.2167053 |
| ENSG00000231106 |
|
LINC01436 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.212737 |
0.2658359366 |
-1.911392 |
0.314781425 |
37.838103 |
0.00000000076865704170896616595656265154040860665407564056295086629688739776611328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003708851891344995273787916024825495053818258384126238524913787841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.9278695 |
3.0598760 |
56.6784739 |
7.0774504 |
| ENSG00000231113 |
|
LINC02976 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
134.714479 |
0.2391394613 |
-2.064076 |
0.194628885 |
111.129050 |
0.00000000000000000000000005544163040096091823454858226648072513095671151747863015090203501984483444586793154940096428617835044860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000613432132472401165306948663135774869815430428452251675203195454449175277877870371412427630275487899780273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.6795611 |
6.8019434 |
225.8211305 |
18.4114122 |
| ENSG00000231131 |
101928687 |
LNCAROD |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29691407_A-ROD enhances DKK1 transcription via its nascent spliced released form. 32216017_LNCAROD is stabilized by m6A methylation and promotes cancer progression via forming a ternary complex with HSPA1A and YBX1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 33393726_Genetic Association of a Gain-of-Function IFNGR1 Polymorphism and the Intergenic Region LNCAROD/DKK1 With Behcet's Disease. 34551796_LNCAROD enhances hepatocellular carcinoma malignancy by activating glycolysis through induction of pyruvate kinase isoform PKM2. 35351056_Analysis of lncRNA sequences: FAM3D-AS1, LINC01230, LINC01315 and LINC01468 in endometrial cancer. |
|
|
32.759974 |
2.8760961676 |
1.524112 |
0.446970580 |
11.196905 |
0.00081933857766485266010264565395004865422379225492477416992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001940538736574650780300488328578012442449107766151428222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
50.7748714 |
15.9441671 |
17.7487583 |
4.0612349 |
| ENSG00000231160 |
|
KLF3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90.892207 |
0.0210323074 |
-5.571249 |
1.578183557 |
7.822303 |
0.00516053889004426322162366602697147754952311515808105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010522051870614994306674105928323115222156047821044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0107857 |
4.2799092 |
183.2873490 |
130.9359470 |
| ENSG00000231305 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.519556 |
0.3081188499 |
-1.698441 |
0.469212842 |
13.513403 |
0.00023686567549384177316755539788317719285259954631328582763671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000613034783498001760275453175808024752768687903881072998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3230086 |
1.6799271 |
17.4524300 |
3.2979706 |
| ENSG00000231346 |
|
LINC01160 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
234.989347 |
0.3875866869 |
-1.367409 |
0.226180780 |
35.483928 |
0.00000000257163713604698212622729114231866914819235603317792993038892745971679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011860807726784306139083233926946603364882548703462816774845123291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
130.0999447 |
18.7219076 |
338.1484974 |
33.9837559 |
| ENSG00000231426 |
100132735 |
FILNC1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene produces a long non-coding RNA that is induced by forkhead box O proteins and plays a role in stress-induced apoptosis. Knock down of transcripts at this locus results in increased renal tumor growth and alteration in genes involved in glucose metabolism. This RNA interacts with heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D and prevents it from binding to Myc mRNA, therefore suppressing Myc activity. Alternative splicing and transcriptional start site usage results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2017]. |
|
|
28978906_FOXO induced long non-coding RNA 1 (FILNC1) is induced upon energy stress through FoxO transcription factors, and inhibits c-Myc-mediated energy metabolism and renal tumor development. 28978906_Upon energy stress FoxOs induce the expression of the long non-coding RNA FILNC1, which inhibits survival of RCC by downregulating c-Myc and c-Myc-dependent metabolic rewiring. |
|
|
20.137368 |
0.2341227544 |
-2.094663 |
0.404343064 |
28.337520 |
0.00000010190162264740260772857789522624627487346060661366209387779235839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000401084786740176656396386070321802286287038441514596343040466308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5156871 |
2.0365837 |
32.1860453 |
5.1283830 |
| ENSG00000231443 |
|
|
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.145308 |
0.0761216405 |
-3.715550 |
0.821748979 |
26.816742 |
0.00000022369104387367238313136046622131569705516085377894341945648193359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000849634536174833855731388949222848694375898048747330904006958007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9217026 |
0.5977659 |
13.4274571 |
4.1481108 |
| ENSG00000231453 |
285084 |
LINC01305 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32549529_Silencing LncRNA LINC01305 inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells by regulating TNXB-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 33638945_LncRNA LINC01305 promotes cervical cancer progression through KHSRP and exosome-mediated transfer. 34022433_linc01305 promotes metastasis and proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through interacting with IGF2BP2 and IGF2BP3 to stabilize HTR3A mRNA. |
|
|
284.314984 |
0.1760169017 |
-2.506214 |
0.165491653 |
220.945263 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005625999419770806767026939373019585339750809278375898293343895297192529219575263279089738639213246243975133243201837844614293573236585288555033912416547536849975585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001198264811483652337554581300759767919931117871830145298335836833473807827375807775725387762286193218983737873821858782363630399614429222765465965494513511657714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.0815645 |
11.1638986 |
528.4089783 |
42.3372083 |
| ENSG00000231528 |
286333 |
FAM225A |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31331909_High FAM225A expression is associated with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. 32343052_FAM225A facilitates colorectal cancer progression by sponging miR-613 to regulate NOTCH3. 33006432_Exosomal lncRNA FAM225A accelerates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression and angiogenesis via sponging miR-206 to upregulate NETO2 and FOXP1 expression. 35809496_LncRNA FAM225A activates the cGAS-STING signaling pathway by combining FUS to promote CENP-N expression and regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. |
|
|
180.803260 |
9.6828215492 |
3.275428 |
0.217207629 |
224.227254 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001082307250961507514392759719954543760667446469608628610186564219133294914636845337269904796841933632875665649381056896834413065533464504142102668993175029754638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000235965362248033225839705569374554605801232641856505624066628776392441068667106745186571264489796610226477818740467626918084261683494773365055152680724859237670898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
329.6793502 |
34.4708958 |
34.2730311 |
3.2162203 |
| ENSG00000231609 |
100132215 |
EHBP1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.689668 |
0.1266043708 |
-2.981601 |
0.336284331 |
89.756231 |
0.00000000000000000000269388544550402848988998633986200073025321971689867476217310898745083136418543290346860885620117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000025070459757654136824902740621432735261117194709213155652625243385855924316274467855691909790039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.2088078 |
2.4408373 |
73.8961918 |
11.3278794 |
| ENSG00000231652 |
101928489 |
CD109-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.835969 |
0.2491034511 |
-2.005183 |
0.338018694 |
36.968448 |
0.00000000120056389221894052851181446117667661610539653338491916656494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005705190936623168607404973137319642573217493008996825665235519409179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1799970 |
2.3495300 |
41.2191098 |
5.7696061 |
| ENSG00000231683_ENSG00000001084 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
406.589165 |
3.9926370504 |
1.997342 |
0.285163530 |
45.544098 |
0.00000000001492406665719979168939011069732424302064499599396185658406466245651245117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000081857756915744681579653710264642390431744090051324747037142515182495117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
661.8728286 |
957.6884896 |
170.5448909 |
162.1906107 |
| ENSG00000231711 |
|
LINC00899 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64.489182 |
0.0762488252 |
-3.713141 |
0.324448711 |
140.448929 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000002123461645894733913787489583886553921141991622456846024631524735713659283702959513161732940655923584927222691476345062255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000293467171286575559699008069860196885722736583680554817777757188829703623409842795904250989380557257391046732664108276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3343915 |
2.1939216 |
137.5457892 |
15.4363198 |
| ENSG00000231770 |
|
TMEM44-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40.447906 |
0.4402707829 |
-1.183537 |
0.240330441 |
24.885605 |
0.00000060834983921527068683647934688174530037940712645649909973144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002207287027241247347457853839047814403784286696463823318481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.1630431 |
3.8134445 |
57.5702074 |
5.4798884 |
| ENSG00000231808 |
|
LINC01388 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.459259 |
0.3390288058 |
-1.560520 |
0.288826331 |
28.864309 |
0.00000007763025671046684741689446890289261204998183529824018478393554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000309514475701375100865513946557516788971042842604219913482666015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.6570613 |
6.2706796 |
105.8908581 |
12.4460955 |
| ENSG00000231877 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
125.616384 |
0.0376522249 |
-4.731121 |
0.817677744 |
25.791131 |
0.00000038043264846501309047041225475105363784678047522902488708496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001410850726468239492829639947224507068312959745526313781738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.0100601 |
3.8850415 |
222.1429314 |
61.8920273 |
| ENSG00000231877_ENSG00000234464 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
309.058524 |
0.0929424921 |
-3.427518 |
0.149261351 |
568.802350 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001022911959505159821347251854083972253900496103357369682856248885037830935858026866106439378060512968034335087029878115381796174789870831790869164158643852324171831283487379490252788919626821138492954341326 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000549024746265314898867145435184615092511089136089284676204753853509058488387322491923246876093193901352456979482026425972026703098166898749152117866342505907434202872282518931014559318741947025390761893337 |
Yes |
Yes |
54.1754445 |
5.9838782 |
586.9456297 |
38.0372292 |
| ENSG00000232053 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.655555 |
13.1185951527 |
3.713541 |
0.646265013 |
41.010753 |
0.00000000015139396428445355167515867933497467415215886887835949892178177833557128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000774817930942626385049674149084388691255398384782893117517232894897460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.1118865 |
10.5586842 |
1.9990017 |
0.7543780 |
| ENSG00000232098 |
|
ZNF584-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51.201952 |
0.3413773454 |
-1.550561 |
0.324546813 |
22.195008 |
0.00000246313446000941756348912026197695013252086937427520751953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008332767506243182043098802203040520453214412555098533630371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.8667327 |
7.1621310 |
81.7704533 |
14.3939810 |
| ENSG00000232160 |
101928578 |
RAP2C-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.165211 |
0.3597542266 |
-1.474916 |
0.425878760 |
12.470887 |
0.00041334372862807935641860090925092663383111357688903808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001031263258037601630509594308193754841340705752372741699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.0943800 |
1.9464322 |
19.8771428 |
3.2444589 |
| ENSG00000232164 |
729348 |
LINC01873 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.666231 |
0.3536445915 |
-1.499628 |
0.537003071 |
7.767109 |
0.00532061262330511212242933893890040053520351648330688476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010817113267215352004346762271325133042410016059875488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7982016 |
2.8567555 |
21.5718948 |
5.1089947 |
| ENSG00000232300 |
|
FAM215B |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.762424 |
0.4925742519 |
-1.021587 |
0.286954548 |
12.882210 |
0.00033172033476343531751065474288964196603046730160713195800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000841270127338196709726458877298682637047022581100463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.9590823 |
4.2434497 |
40.8544411 |
5.7942092 |
| ENSG00000232354 |
|
VIPR1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.388337 |
0.0983633732 |
-3.345735 |
0.787864854 |
20.764735 |
0.00000519304617541248765983643784216461369851458584889769554138183593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000016879401354126473194447455306033134547760710120201110839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2342558 |
0.7097176 |
12.8497836 |
3.4363108 |
| ENSG00000232434 |
389813 |
AJM1 |
protein_coding |
C9J069 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in the control of adherens junction integrity. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:A0A1C3NSL9}. |
Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Membrane;Methylation;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in cell-cell junction organization. Predicted to be located in adherens junction; apical plasma membrane; and cilium. Predicted to be active in apical junction complex and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:389813; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; apical junction complex [GO:0043296]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cilium [GO:0005929]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cell-cell junction organization [GO:0045216] |
|
ENSMUSG00000029419 |
Ajm1 |
32.718586 |
0.3616583833 |
-1.467301 |
0.319525123 |
21.367806 |
0.00000379083557521018462668944970506146319166873581707477569580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000012508994654617107853355160995700856574330828152596950531005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.9408919 |
3.5096140 |
46.9596225 |
6.2569825 |
| ENSG00000232611 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.099410 |
0.3099208346 |
-1.690028 |
0.649904250 |
6.905188 |
0.00859459926918064616441217395959029090590775012969970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016682413264458070129014899407593475189059972763061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9735843 |
1.6166574 |
12.8736935 |
3.1517079 |
| ENSG00000232653 |
643699 |
GOLGA8N |
protein_coding |
F8WBI6 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be located in Golgi apparatus. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:643699; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
307.865939 |
0.1745448705 |
-2.518330 |
0.167169504 |
215.873422 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000071867661917580576932138231597663016951269205542719437870504451632083989832534543556680108028844531893183677402044586470940441824684086213892442174255847930908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014898408566060242852361848343970448212100783183729431693664955187530411245556066046232107004252459842457622061695016657187351505342576274415478110313415527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.7355640 |
10.0948078 |
535.8624970 |
38.6720419 |
| ENSG00000232725 |
|
PLXNB3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.521940 |
0.1799224972 |
-2.474553 |
0.876589566 |
6.528318 |
0.01061702820500776828227529335890721995383501052856445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020259513420286319462793045431681093759834766387939453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4635386 |
2.8026074 |
25.8336701 |
10.9113780 |
| ENSG00000232810 |
7124 |
TNF |
protein_coding |
P01375 |
FUNCTION: Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. It is mainly secreted by macrophages and can induce cell death of certain tumor cell lines. It is potent pyrogen causing fever by direct action or by stimulation of interleukin-1 secretion and is implicated in the induction of cachexia, Under certain conditions it can stimulate cell proliferation and induce cell differentiation. Impairs regulatory T-cells (Treg) function in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis via FOXP3 dephosphorylation. Up-regulates the expression of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), which dephosphorylates the key 'Ser-418' residue of FOXP3, thereby inactivating FOXP3 and rendering Treg cells functionally defective (PubMed:23396208). Key mediator of cell death in the anticancer action of BCG-stimulated neutrophils in combination with DIABLO/SMAC mimetic in the RT4v6 bladder cancer cell line (PubMed:22517918, PubMed:16829952, PubMed:23396208). Induces insulin resistance in adipocytes via inhibition of insulin-induced IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation and insulin-induced glucose uptake. Induces GKAP42 protein degradation in adipocytes which is partially responsible for TNF-induced insulin resistance (By similarity). Plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing VEGF production synergistically with IL1B and IL6 (PubMed:12794819). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P06804, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12794819, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16829952, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22517918, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23396208}.; FUNCTION: The TNF intracellular domain (ICD) form induces IL12 production in dendritic cells. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16829952}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a multifunctional proinflammatory cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. This cytokine is mainly secreted by macrophages. It can bind to, and thus functions through its receptors TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. This cytokine is involved in the regulation of a wide spectrum of biological processes including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, lipid metabolism, and coagulation. This cytokine has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including autoimmune diseases, insulin resistance, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis ankylosing spondylitis, tuberculosis, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, and cancer. Mutations in this gene affect susceptibility to cerebral malaria, septic shock, and Alzheimer disease. Knockout studies in mice also suggested the neuroprotective function of this cytokine. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2020]. |
hsa:7124; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; phagocytic cup [GO:0001891]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; recycling endosome [GO:0055037]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; transcription cis-regulatory region binding [GO:0000976]; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding [GO:0005164]; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0006919]; acute inflammatory response [GO:0002526]; astrocyte activation [GO:0048143]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cellular response to amino acid stimulus [GO:0071230]; cellular response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904646]; cellular response to nicotine [GO:0071316]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cellular response to toxic substance [GO:0097237]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chronic inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002439]; circadian rhythm [GO:0007623]; cognition [GO:0050890]; cortical actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0030866]; defense response to Gram-positive bacterium [GO:0050830]; detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain [GO:0050966]; embryonic digestive tract development [GO:0048566]; endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:0072577]; epithelial cell proliferation involved in salivary gland morphogenesis [GO:0060664]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097191]; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors [GO:0008625]; glucose metabolic process [GO:0006006]; humoral immune response [GO:0006959]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; JNK cascade [GO:0007254]; leukocyte migration involved in inflammatory response [GO:0002523]; leukocyte tethering or rolling [GO:0050901]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; liver regeneration [GO:0097421]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; necroptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097527]; negative regulation of alkaline phosphatase activity [GO:0010693]; negative regulation of amyloid-beta clearance [GO:1900222]; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001234]; negative regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly [GO:1903347]; negative regulation of bile acid secretion [GO:0120190]; negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration [GO:0043537]; negative regulation of branching involved in lung morphogenesis [GO:0061048]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of cytokine production involved in immune response [GO:0002719]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001937]; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand [GO:2001240]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of glucose import [GO:0046325]; negative regulation of heart rate [GO:0010459]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of L-glutamate import across plasma membrane [GO:0002037]; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process [GO:0050995]; negative regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010888]; negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0045930]; negative regulation of myelination [GO:0031642]; negative regulation of myoblast differentiation [GO:0045662]; negative regulation of myosin-light-chain-phosphatase activity [GO:0035509]; negative regulation of neurogenesis [GO:0050768]; negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation [GO:0045668]; negative regulation of oxidative phosphorylation [GO:0090324]; negative regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0043242]; negative regulation of signaling receptor activity [GO:2000272]; negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003085]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of vascular wound healing [GO:0061044]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; osteoclast differentiation [GO:0030316]; positive regulation of action potential [GO:0045760]; positive regulation of amyloid-beta formation [GO:1902004]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; positive regulation of blood microparticle formation [GO:2000334]; positive regulation of calcidiol 1-monooxygenase activity [GO:0060559]; positive regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade [GO:0070886]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production [GO:2000343]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of chronic inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002876]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043280]; positive regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in execution phase of apoptosis [GO:2001272]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response [GO:1900017]; positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process [GO:2000573]; positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0051091]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:2001238]; positive regulation of fever generation [GO:0031622]; positive regulation of fractalkine production [GO:0032724]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of hair follicle development [GO:0051798]; positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation [GO:2000347]; positive regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034116]; positive regulation of humoral immune response mediated by circulating immunoglobulin [GO:0002925]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of I-kappaB phosphorylation [GO:1903721]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-18 production [GO:0032741]; positive regulation of interleukin-33 production [GO:0150129]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to arterial endothelial cell [GO:1904999]; positive regulation of leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cell [GO:1904996]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis [GO:0051044]; positive regulation of miRNA transcription [GO:1902895]; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division [GO:0045840]; positive regulation of mononuclear cell migration [GO:0071677]; positive regulation of neuroinflammatory response [GO:0150078]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of neutrophil activation [GO:1902565]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity [GO:0051000]; positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process [GO:0051173]; positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045672]; positive regulation of oxidative stress-induced neuron death [GO:1903223]; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation [GO:0033138]; positive regulation of phagocytosis [GO:0050766]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of podosome assembly [GO:0071803]; positive regulation of programmed cell death [GO:0043068]; positive regulation of protein catabolic process [GO:0045732]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface [GO:2000010]; positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:1903078]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of protein transport [GO:0051222]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly [GO:0031334]; positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly [GO:0043243]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of superoxide dismutase activity [GO:1901671]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission [GO:0050806]; positive regulation of synoviocyte proliferation [GO:1901647]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of translational initiation by iron [GO:0045994]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904707]; positive regulation of vitamin D biosynthetic process [GO:0060557]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; protein localization to plasma membrane [GO:0072659]; regulation of branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis [GO:0060693]; regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process [GO:2000351]; regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903140]; regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045598]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002637]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process [GO:2000377]; regulation of synapse organization [GO:0050807]; regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051966]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; response to 3,3',5-triiodo-L-thyronine [GO:1905242]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to ethanol [GO:0045471]; response to fructose [GO:0009750]; response to glucocorticoid [GO:0051384]; response to gold nanoparticle [GO:1990268]; response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0140460]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor [GO:0036005]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; response to paracetamol [GO:1901554]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; response to salt stress [GO:0009651]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; sequestering of triglyceride [GO:0030730]; skeletal muscle contraction [GO:0003009]; toll-like receptor 3 signaling pathway [GO:0034138]; tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0033209]; vascular endothelial growth factor production [GO:0010573]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11023480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11023482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11023485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11035665_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11037831_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11045789_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11072751_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11083263_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11092520_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11097747_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11106199_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11113269_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11118029_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11120931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11121160_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11138328_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11144293_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11145126_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11153913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11157631_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11163081_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11163083_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11165717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11167813_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11176446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11179110_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11179116_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11192323_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11196671_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11196686_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11199329_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11211945_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11223972_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11230752_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11233912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11241233_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11243953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11244489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11246532_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11250044_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11257271_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11258696_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11264025_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11266856_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11266927_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11266928_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11267084_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11273064_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11285131_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11294926_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11298547_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11316066_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11316069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11319038_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11319647_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11319665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11324946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11325850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11328953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11334675_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11349201_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11354638_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11371414_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11379335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11389006_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11391238_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11401868_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11401880_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11404167_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11409121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11411907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11423177_A high in vivo and in vitro production of TNF-alpha found in carriers of the common Caucasoid haplotype HLA-B8,DR3 is associated with multiple autoimmune diseases and immune response dysregulation in healthy subjects. 11427627_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11453117_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11506397_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11506478_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11508580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11528523_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11533078_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11544427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544434_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11570978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11571703_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11576577_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11585553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11600224_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11602932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11607791_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11640949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11640992_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11668577_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11689215_Observational study of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11697432_Elevated tumour necrosis factor-alpha levels may play a role in the development of necrotizing enterocolitis. The A(-308) and A(-238) variants of the promoter region of the TNF-alpha gene are reportedly associated with altered TNF-alpha production. 11697432_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11704803_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11715861_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11716174_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11722460_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11724772_-A significantly reduced PGN-elicited tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) secretion by U937 cells and rat alveolar macrophages. 11725485_Anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases 11735091_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737072_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11737221_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11743056_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11744409_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11744409_affects susceptibility to acute rejection after cardiac transplantation 11748357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11752507_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11756988_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11759867_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11774563_Interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon gamma serum levels in patients with anorexia nervosa. 11774822_Postburn plasma TNF alpha level increased in all patients, especially obvious in those with sepsis. 11775944_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11776328_PAI-1 gene activation by TNF-alpha apparently is yet to be defined for the location of the response element and/or the signaling pathway, while TGF-beta is the most important cytokine for PAI-1 transcriptional activation through its 5' proximal promoter. 11781187_effect on cell proliferation and apoptosis in conjunction with interferon-gamma 11781708_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11792123_CD40 ligation induces macrophage IL-10 and TNF-alpha production: differential use of the PI3K and p42/44 MAPK-pathways. 11796554_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11798757_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11798770_Damage of the ehdothelial cells of placental blood vessels is associated with the abnormal increase in the maternal blood TNFalpha. 11799112_role of PTEN in blocking induction of NF-kapp B-dependent transcription by inhibiting the transactivation potential of the p65 subunt 11800584_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11801679_TNF-alpha potentiates adhesion of C5a-stimulated eosinophils to human bronchial epithelial cells (HBEC) by a mechanism in which eosinophil contact with HBEC is essential for priming. 11808761_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11816715_The phagocytosis of platelets opsonised by anti-beta2GPI antibodies determined the release of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta by dendritic cells and macrophages. 11820636_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11824966_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11826759_The role of TNF/TNFR in organ-specific and systemic autoimmunity is reviewed: implications for the design of optimized 'anti-TNF' therapies. 11828995_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11830340_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11830425_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11830590_Critical role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and NF-kappa B in interferon-gamma -induced CD40 expression in microglia/macrophages. 11831440_Transient exposure of human bronchial epithelial cells to TNFA leads to persistent increased expression of ICAM-1. 11831864_Incubation of endothelial cells with conditioned media derived from stimulated macrophages modulates ICAM1 mRNA expression. Results suggest TNF-alpha and activation of the NF-kB pathway are involved. 11832442_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11838837_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11838837_The A1 allele of TNF-alpha associates with rheumatoid arthritis.Genotypes A1A2 of TNF-alpha is associated with more severe disease. 11841482_Breast cancer is not associated with SNPs in the TNFA promoters; TNFB*A allele induces some function(s) leading to the inhibition of tumorigenesis in breast cancer 11841482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11841484_Genetic variation in TNFalpha production is unlikely to play a major role in risk of cutaneous malignant melanoma. 11841484_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11841486_association of TNF alleles with HLA-DR, -DQ and -B alleles in 216 healthy individuals from the north of England 11846846_Genetic polymorphisms in the TNF-alpha gene at positions -376, -308, -238 and +489 could not be identified as susceptibility or severity factors in periodontitis 11846846_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11847479_TNF-deficient mice are protected from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. 11849390_TNF-alpha--accelerated apoptosis abrogates ANCA-mediated neutrophil respiratory burst by a caspase-dependent mechanism. 11849463_Carriage of ILbeta2 and IL1RN*2, together with non-carriage of TNF2is associated with increased susceptibility, but not with a prognosis of IgAN. 11851889_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11852287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11857057_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11857057_Polymorphisms in or near tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-gene do not determine levels of endotoxin-induced TNF production. 11858187_In dengue shock syndrome pts, TNF-alpha was significantly associated with D-dimer, an activation marker of fibrinolysis (p |
ENSMUSG00000024401 |
Tnf |
438.895752 |
18.8412599534 |
4.235824 |
0.125576419 |
1607.646308 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
836.5610124 |
66.0420690 |
44.7189314 |
3.3705773 |
| ENSG00000232815 |
|
DUX4L50 |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.884628 |
0.4337304365 |
-1.205129 |
0.376499833 |
10.463232 |
0.00121774063542890559862230670518101760535500943660736083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002797051319472556099587912115111976163461804389953613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3521632 |
2.4133184 |
24.0057259 |
3.5409457 |
| ENSG00000232859 |
201229 |
LYRM9 |
protein_coding |
A8MSI8 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:201229; |
|
24315451_3 SNPs associated with the fraction of exhaled nitric oxide in childhood asthma are rs3751972 in LYRM9; rs944722 in NOS2; and rs8069176 near GSDMB; all at 17q12-q21. |
ENSMUSG00000072640 |
Lyrm9 |
36.524468 |
0.2364023744 |
-2.080684 |
0.337000079 |
38.303787 |
0.00000000060545025637742271893450395550272287448212438221162301488220691680908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002947376577879538088010333271907735530614758090450777672231197357177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.9709364 |
2.8878651 |
59.4937620 |
7.7247720 |
| ENSG00000232884 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.370295 |
0.2251438013 |
-2.151081 |
0.523061736 |
18.499851 |
0.00001699175564473804280894893292686020913606625981628894805908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000051828541706206556285724956767424487225071061402559280395507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5043691 |
1.2241427 |
15.7000131 |
3.0027452 |
| ENSG00000232956 |
285958 |
SNHG15 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene represents a snoRNA host gene that produces a short-lived long non-coding RNA. This non-coding RNA is upregulated in tumor cells and may contribute to cell proliferation by acting as a sponge for microRNAs. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]. |
|
|
26662309_Our findings present that elevated lncRNA SNHG15 could be identified as a poor prognostic biomarker in GC and regulate cell invasion. 29048682_SNHG15 and miR-153 are new potential therapeutic targets for anti-angiogenesis treatment of glioma 29217194_Long noncoding RNA SNHG15 was highly expressed in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. SNHG15 knockdown significantly inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. In mechanism, we found that SNHG15 acted as a competing endogenous RNA to sponge miR-211-3p, which was downregulated in breast cancers and inhibited cell proliferation and migration. 29604394_Results show that enhanced expression of lncRNA SNHG15 promoted colon cancer cell progression and was correlated with poor prognosis in colon cancer patients. Mechanistically, SNHG15 maintains Slug stability in living cells by impeding its ubiquitination and degradation through interaction with the zinc finger domain of Slug. 29630731_the ectopic overexpression of SNHG15 contribute to the non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis by regulating CDK14 protein via sponging miR-486. 29750422_the present study suggested that SNHG15 may be involved in the nuclear factorkappaB signaling pathway, induce the epithelialmesenchymal transition process, and promote renal cell carcinoma invasion and migration. 29771418_The expression of SNHG15 is up-regulated on non-small lung cancer cells, promoting promotes cell proliferation and invasion. 30280769_SNHG15 levels were significantly up-regulated in both sera and tumors tissues from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients. Clinicopathologic analysis revealed that high SNHG15 expression was associated with tumor differentiation, lymph node metastasis, tumor stage and shorter overall survival. Cox multivariate analyses confirmed that SNHG15 expression was an independent prognostic factor in PDAC. 30317592_Lnc-SNHG15 overexpression was significantly associated with colorectal liver metastasis and poor survival. 30402848_SNHG15 is highly expressed in lung cancer (LC) tissues, which promotes the occurrence and progression of LC via regulating proliferation and migration of LC cells by targeting microRNA-211-3p. 30840276_Overexpression of lncSNHG15 remarkably promoted the proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells. lncSNHG15 could bind to miR-211-3p. 30945457_SNHG15 served as a ceRNA and reversed the activity of miR-338-3p, thus facilitating CRC tumorigenesis by enhancing the expression of FOS and RAB14. 30981837_Results show that SNHG15 is upregulated in prostate cancer (PCa) cells and promoted cell proliferation. Its downregulation inhibited PCa cell migration and invasion. SNHG15 was located in the cytoplasm of PCa cells and acted as a molecular sponge of miR-338 resulting in post-transcriptional regulated FKBP1A. These study suggested that SNHG15 functions as an oncogene by modulating miR-338/FKBP1A axis in prostate cancer. 31014355_Several of these genes are functionally related to AIF, a protein that we found to specifically interact with SNHG15, suggesting that the SNHG15 acts, at least in part, by regulating the activity of AIF. 31310393_LncRNA SNHG15 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-141-3p. 31636472_Up-regulation of SNHG15 was found in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and was related to aggressive behaviors in HCC patients. Knockdown of SNHG15 restrained HCC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. SNHG15 served as a molecular sponge for miR-490-3p which directly targets HDAC2. HDAC2 was involved in HCC progression by interacting with the SNHG15/miR-490-3p axis. 31696491_Elevated expression of lncRNA SNHG15 in spinal tuberculosis: preliminary results. 31774607_LncRNA SNHG15 may serve as a prospective and novel biomarker for molecular diagnosis and therapeutics in patients with cancer. 32141559_Up-regulation of SNHG15 facilitates cell proliferation, migration, invasion and suppresses cell apoptosis in breast cancer by regulating miR-411-5p/VASP axis. 32247266_Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 is a competing endogenous RNA of miR-141-3p that prevents osteoarthritis progression by upregulating BCL2L13 expression. 32633324_High lncSNHG15 expression may predict poor cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis based on the PRISMA and the bio-informatics analysis. 32633365_LncRNA SNHG15 promotes the proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via sponging miR-141-3p to upregulate KLF9. 32643707_Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 15 (SNHG15) Alleviates Osteoarthritis Progression by Regulation of Extracellular Matrix Homeostasis. 32655137_LncRNA SNHG15 regulates EGFR-TKI acquired resistance in lung adenocarcinoma through sponging miR-451 to upregulate MDR-1. 33372376_Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 deteriorates liver cancer via microRNA-18b-5p/LIM-only 4 axis. 33572758_The Expression of the Cancer-Associated lncRNA Snhg15 Is Modulated by EphrinA5-Induced Signaling. 33899079_LncRNA SNHG15 modulates gastric cancer tumorigenesis by impairing miR-506-5p expression. 34016097_Down-regulation LncRNA-SNHG15 contributes to proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer cells. 34551140_Increased serum exosomal long non-coding RNA SNHG15 expression predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. 34734088_lncRNA SNHG15 Promotes Ovarian Cancer Progression through Regulated CDK6 via Sponging miR-370-3p. 34868528_LncRNA SNHG15 Promotes Oxidative Stress Damage to Regulate the Occurrence and Development of Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Targeting the miR-141/SIRT1 Axis. 35650158_LncRNA SNHG15 Modulates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Human AC16 Cardiomyocytes Depending on the Regulation of the miR-335-3p/TLR4/NF-kappaB Pathway. |
|
|
116.145054 |
2.8128374106 |
1.492026 |
0.152997919 |
96.748226 |
0.00000000000000000000007872810656075497756635878501268504436609719954537132004907754728728619397770671639591455459594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000773138291973881224702886708633326237637031909840264215792770066681960372534376801922917366027832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
179.1825203 |
17.0197783 |
64.1363252 |
4.8470975 |
| ENSG00000233024 |
100288332 |
NPIPA9 |
protein_coding |
A0A0B4J1W7 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
313.987663 |
0.1897979906 |
-2.397463 |
0.364136633 |
37.958294 |
0.00000000072273161214641114443134184753040304138860250304787768982350826263427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003495255109856169128969159882753398038701675432093907147645950317382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.9210017 |
28.7593996 |
511.8532708 |
111.2324545 |
| ENSG00000233030 |
124904411 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.812898 |
0.2952908475 |
-1.759791 |
0.548387503 |
9.773344 |
0.00177060142424264395540067784651228066650219261646270751953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003952522235605175973671698841371835442259907722473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8135607 |
2.6910621 |
25.8096984 |
5.7517840 |
| ENSG00000233070 |
107987337 |
ZFY-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.414680 |
0.1054897460 |
-3.244825 |
0.743933904 |
24.506577 |
0.00000074056631360679845473021397014856681551009387476369738578796386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002656966161603389530115968547585580949998984578996896743774414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5135532 |
0.8247328 |
14.4320488 |
3.6682428 |
| ENSG00000233086 |
102723932 |
LNCARSR |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27117758_Data suggest that lncARSR (long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) activated in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with sunitinib resistance) may serve as a predictor and a potential therapeutic target for sunitinib resistance. 27886176_lncARSR interacts with Yes-associated protein (YAP) to block its phosphorylation by LATS1, facilitating YAP nuclear translocation. 30391438_High lncARSR expression is associated with liver cancer. 31038847_Genetic variants in a long noncoding RNA related to Sunitinib Resistance predict risk and survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma. 32558022_Long noncoding RNA ARSR is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. 32798250_lncARSR sponges miR-34a-5p to promote colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis via hexokinase-1-mediated glycolysis. 35637970_Renal cell carcinoma-derived exosomes deliver lncARSR to induce macrophage polarization and promote tumor progression via STAT3 pathway. |
|
|
11.489189 |
0.1756419756 |
-2.509290 |
0.669909458 |
14.683202 |
0.00012717466876637430910935988581655919915647245943546295166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000344737945085708873214219716274442362191621214151382446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7422780 |
1.7472446 |
21.4002802 |
5.8031219 |
| ENSG00000233098 |
339260 |
CCDC144NL-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31358062_CCDC144NL-AS1-knockdown human PSCs reveal naive-like pluripotency features, such as elevated expression of naive pluripotency-associated genes, increased developmental capacity, analogous transcriptional profiles to human naive PSCs, and global reduction of repressive chromatin modification marks. 32647147_Long non-coding RNA CCDC144NL-AS1 sponges miR-143-3p and regulates MAP3K7 by acting as a competing endogenous RNA in gastric cancer. 34115289_LncRNA CCDC144NL-AS1 Serves as a Prognosis Biomarker for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Promotes Cellular Function by Targeting miR-490-3p. 34704289_Identification of lncRNA-associated competing endogenous RNA networks for occurrence and prognosis of gastric carcinoma. |
|
|
522.510549 |
0.4346827779 |
-1.201965 |
0.116506198 |
104.538381 |
0.00000000000000000000000154177718956428147393271204578208967288383505340404207740360339432168779172371841923450119793415069580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000016301311832355870385222539235151542427220827400253358402547787693592784563634268124587833881378173828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
326.6713617 |
22.2531426 |
757.3280812 |
35.8491925 |
| ENSG00000233198 |
643596 |
RNF224 |
protein_coding |
P0DH78 |
|
Metal-binding;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable metal ion binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:643596; |
metal ion binding [GO:0046872] |
|
ENSMUSG00000089953 |
Rnf224 |
9.147924 |
0.1611513735 |
-2.633512 |
0.599709420 |
22.613981 |
0.00000198038261118898686544012935351055659793928498402237892150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006779560711461395527564679358567545364167017396539449691772460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6433359 |
1.0869525 |
16.3242972 |
3.3412091 |
| ENSG00000233355 |
100506915 |
CHRM3-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40.409805 |
0.0660894531 |
-3.919436 |
0.469864016 |
78.209470 |
0.00000000000000000092673159041782050998682360407233895249023557164470919073062660231698828283697366714477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000007754284736149110656957577540874750434727481509221153760380573771726631093770265579223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1802721 |
2.3711463 |
74.9111790 |
20.9437813 |
| ENSG00000233448_ENSG00000265479 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.896389 |
0.0700953490 |
-3.834537 |
1.084617837 |
11.072213 |
0.00087631017397145751033488147996308725851122289896011352539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002063880352292757607707285316678280651103705167770385742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9033772 |
1.2940692 |
14.2310794 |
12.1896632 |
| ENSG00000233452 |
729178 |
STXBP5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30659475_we found a significant SNP-based heritability for self-rated Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The top hit of the genome-wide meta-analysis (SNP rs12661753; p-value = 3.02 x 10(-7)) was present in the long non-coding RNA gene STXBP5-AS1. This association was also observed in a meta-analysis of childhood ADHD symptom scores in eight population-based pediatric cohorts 33160411_LncRNA STXBP5-AS1 suppresses stem cell-like properties of pancreatic cancer by epigenetically inhibiting neighboring androglobin gene expression. 33965377_Aberrant hypermethylation induced downregulation of antisense lncRNA STXBP5-AS1 and its sense gene STXBP5 correlate with tumorigenesis of glioma. |
|
|
92.821499 |
2.1013553391 |
1.071320 |
0.199278422 |
28.934091 |
0.00000007488332331450708208586019469857331110063114465447142720222473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000298966148802305782085836144065793540391950955381616950035095214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
129.6337058 |
16.8726812 |
62.1159093 |
6.1682471 |
| ENSG00000233539 |
730338 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49.685416 |
33.4092646129 |
5.062176 |
0.528127722 |
109.907584 |
0.00000000000000000000000010266734788029429622357222245276307782200296921915576753783608027117274508199784577300306409597396850585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000001128347025102861962433576495149372946395762416150084870730563126376387594884675991124822758138179779052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
93.5809607 |
29.8796621 |
2.8524448 |
0.8546920 |
| ENSG00000233695 |
|
GAS6-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
179.917043 |
0.1260360373 |
-2.988092 |
0.196441238 |
226.552505 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000336672726407546868817549615656816207074031910238657255701936143764178073488899475859375348971931429019930299473869506030646411203280377044677607045741751790046691894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000073837881750005823209017098986687988446576185009939786986799437006353390711432647095178790822490443124762287084523227788566642794398919846798889921046793460845947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.7867360 |
5.8647496 |
310.6286046 |
30.8249315 |
| ENSG00000233705 |
|
SLC26A4-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.646396 |
0.4585519152 |
-1.124843 |
0.341063239 |
10.915670 |
0.00095354229380377984737204855036907247267663478851318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002226591402712196042512626803500097594223916530609130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.1085602 |
3.7528111 |
37.5262435 |
5.4168370 |
| ENSG00000233828 |
|
MIR4280HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
83.554842 |
0.1942298320 |
-2.364163 |
0.210687074 |
133.423709 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000073036033462196082503147645364923694544046729321328853181865449392800206905008943061158310783298475143965333700180053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000009642324274615512148936100367146819821452542797750408005504316581784992319870348023713724217031995067372918128967285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.1202245 |
4.2786484 |
145.2647841 |
13.4323444 |
| ENSG00000233928 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.830083 |
0.4680640411 |
-1.095222 |
0.483535529 |
5.234204 |
0.02214693802928386842654440158639772562310099601745605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.039294242734971736308313694507887703366577625274658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3284319 |
1.9231294 |
13.5122370 |
2.6689004 |
| ENSG00000233954 |
440567 |
UQCRHL |
protein_coding |
A0A096LP55 |
FUNCTION: May be a component of the ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase complex (complex III or cytochrome b-c1 complex), which is part of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. This protein may mediate formation of the complex between cytochromes c and c1. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P00127}. |
Acetylation;Disulfide bond;Electron transport;Membrane;Mitochondrion;Mitochondrion inner membrane;Reference proteome;Respiratory chain;Transit peptide;Transport |
|
This gene has characteristics of a pseudogene derived from the UQCRH gene. However, there is still an open reading frame that could produce a protein of the same or nearly the same size as that of the UQCRH gene, so this gene is being called protein-coding for now. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:440567; |
mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III [GO:0005750]; mitochondrial electron transport, ubiquinol to cytochrome c [GO:0006122] |
Mouse_homologues 34750991_Characterising a homozygous two-exon deletion in UQCRH: comparing human and mouse phenotypes. |
ENSMUSG00000063882 |
Uqcrh |
26.909215 |
0.4873126294 |
-1.037080 |
0.346503857 |
9.039232 |
0.00264246566361100608186229798945987568004056811332702636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005717208032087136432286555987047904636710882186889648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.7103656 |
3.7774028 |
36.6363225 |
5.1656292 |
| ENSG00000234072 |
|
GTF3C2-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
146.621902 |
0.4055272029 |
-1.302129 |
0.131633867 |
100.551585 |
0.00000000000000000000001153531943407115502666778372742088883710123304334562730085771337963651550495569608756341040134429931640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000117746414140311362132998362269042492039385644780597968867301081341558699477900518104434013366699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
89.3258543 |
7.5351258 |
221.7948348 |
11.6851802 |
| ENSG00000234147 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
410.572989 |
0.3545722357 |
-1.495849 |
0.207731375 |
50.144587 |
0.00000000000142824584936892634658823134739062655183816641368821365176700055599212646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000008392081503457544661876333565688536883855896952866260107839480042457580566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
227.1722892 |
42.4974960 |
643.7933668 |
86.2196770 |
| ENSG00000234191 |
|
LINC01283 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
83.479769 |
26.7802254465 |
4.743096 |
0.626374102 |
46.257311 |
0.00000000001036988551910405833467483179741085923090959663994681250187568366527557373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000057400480666827013459218957818698167959448053210280704661272466182708740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
133.3826929 |
69.0019429 |
4.9418307 |
1.9149602 |
| ENSG00000234362 |
101929723 |
LINC01914 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.428872 |
0.1983914322 |
-2.333578 |
0.572282392 |
16.912299 |
0.00003914712277796242160567141699090143447392620146274566650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000114169439281313050277288922984553209971636533737182617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9183789 |
2.0309981 |
25.0250039 |
6.4151926 |
| ENSG00000234409 |
388849 |
CCDC188 |
protein_coding |
H7C350 |
|
Coiled coil;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000090777 |
Ccdc188 |
22.337787 |
0.1516646504 |
-2.721043 |
0.396639515 |
52.497479 |
0.00000000000043080097452150438884402418678405669483395812324744156285305507481098175048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002632969931237020775626153574849594234900257427867131809762213379144668579101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
5.3421806 |
1.3647252 |
35.3119709 |
4.8740257 |
| ENSG00000234420 |
100129482 |
ZNF37BP |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
87.334242 |
0.4431537741 |
-1.174121 |
0.171756346 |
47.519720 |
0.00000000000544533875517894346830168097609949139168566967228457542660180479288101196289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000030800493025280946449310833854646173024516286886864691041409969329833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.5372592 |
5.7636475 |
114.8594693 |
8.5409538 |
| ENSG00000234464 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
210.244517 |
0.1336374252 |
-2.903604 |
0.830441440 |
9.315675 |
0.00227201696321267148162559301738383510382845997810363769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004964466377056850864002424117416012450121343135833740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.3174900 |
40.0329324 |
554.4298149 |
205.0217097 |
| ENSG00000234465 |
390940 |
PINLYP |
protein_coding |
A6NC86 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable phospholipase inhibitor activity. Predicted to be involved in negative regulation of catalytic activity. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:390940; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; phospholipase inhibitor activity [GO:0004859] |
Mouse_homologues 34969857_Phospholipase A2 inhibitor and LY6/PLAUR domain-containing protein PINLYP regulates type I interferon innate immunity. |
ENSMUSG00000011632 |
Pinlyp |
2464.090409 |
3.0479045949 |
1.607818 |
0.034547913 |
2209.437285 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3702.4774894 |
75.7212585 |
1223.4076540 |
20.3675111 |
| ENSG00000234678 |
|
ELF3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34.464541 |
0.3135978699 |
-1.673012 |
0.546429966 |
8.713026 |
0.00315944371094632444132987991736172261880710721015930175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006731147398032296183534306521778489695861935615539550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.6104023 |
6.8995041 |
56.6181755 |
15.3396434 |
| ENSG00000234684 |
100507495 |
SDCBP2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34218800_Long non-coding RNA SDCBP2-AS1 delays the progression of ovarian cancer via microRNA-100-5p-targeted EPDR1. 36209503_SDCBP-AS1 destabilizes beta-catenin by regulating ubiquitination and SUMOylation of hnRNP K to suppress gastric tumorigenicity and metastasis. |
|
|
13.597091 |
0.2393648824 |
-2.062717 |
0.447622980 |
21.757796 |
0.00000309330373054506768291591067843171458662254735827445983886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010325002954058162951277329011379180201402050442993640899658203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9708678 |
1.4643381 |
20.8697718 |
3.8859058 |
| ENSG00000234719 |
729978 |
NPIPB2 |
protein_coding |
A6NJ64 |
|
Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
15789617_sPLA2-X induces potent arachidonic acid release without activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha. |
|
|
74.119486 |
0.3532433414 |
-1.501266 |
0.419259175 |
11.864198 |
0.00057223419065118225675797836160541010031010955572128295898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001391004060278565714406373565736885211663320660591125488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.1066131 |
14.5418132 |
105.4035382 |
30.1465298 |
| ENSG00000234769 |
|
WASH4P |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40.251188 |
0.3476605964 |
-1.524249 |
0.503607635 |
8.831205 |
0.00296122759154907912171328376871315413154661655426025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006350097232495193096124541654035056126303970813751220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.7666281 |
7.6835395 |
63.1491080 |
15.3746748 |
| ENSG00000234771 |
|
SLC25A25-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90.274168 |
0.4218962019 |
-1.245040 |
0.255118922 |
23.495322 |
0.00000125217837736087507395502712442825199445906036999076604843139648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004384852396167619186678234000087428512415499426424503326416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.4841149 |
8.6278076 |
128.0199061 |
14.1607715 |
| ENSG00000234997 |
|
LINC02966 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.403923 |
0.2404263135 |
-2.056333 |
0.539522701 |
15.604314 |
0.00007807627421508965678484393002634078584378585219383239746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000218300020347551301325497719041379696136573329567909240722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7042064 |
1.5168855 |
15.3239284 |
3.7754682 |
| ENSG00000235016 |
100129060 |
SEMA3F-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.336157 |
0.4475863455 |
-1.159762 |
0.522456296 |
4.869864 |
0.02732965399858154273426968927651614649221301078796386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.047451557818969952728949124320934060961008071899414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5396855 |
2.2494189 |
14.5493193 |
3.3086314 |
| ENSG00000235092 |
|
ID2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66.237904 |
0.3694753625 |
-1.436450 |
0.415613411 |
11.056964 |
0.00088354693870559505332329397475632504210807383060455322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002079928678675371962747409071425863658078014850616455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.2907996 |
29.2265277 |
79.6559093 |
54.1933293 |
| ENSG00000235162 |
387882 |
C12orf75 |
protein_coding |
Q8TAD7 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:387882; |
|
27986894_Study identified three novel transcripts of the OCC-1 gene; two of them, including a novel miRNA, are shown to be associated with the Wnt signaling pathway. Also, OCC-1 was found to affect the transcription level of its neighboring gene APPL2. 30218350_OCC-1D overexpression resulted in increased sub-G1 cell population in MCF7 cells, detected by flow cytometry. Results suggest that OCC1-D variant have an inhibitory effect on APPL2 expression and may regulate the cell cycle status. 34074799_Pan-cancer analysis of the prognostic value of C12orf75 based on data mining. 35397713_OCC-1D regulates Wnt signaling pathway: potential role of long noncoding RNA in colorectal cancer. 35576683_Downregulation of C12orf75 gene inhibits migration and invasion of liver cancer cell via suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in vitro. |
ENSMUSG00000087651 |
1500009L16Rik |
37.997512 |
2.3813223319 |
1.251763 |
0.257701005 |
24.084708 |
0.00000092189496372683098703742533841509754211074323393404483795166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003276467533014212532284327103471177622395771322771906852722167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
55.0613761 |
8.6844034 |
23.2804770 |
2.9474878 |
| ENSG00000235194 |
90673 |
PPP1R3E |
protein_coding |
Q9H7J1 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a glycogen-targeting subunit for PP1. PP1 is involved in glycogen metabolism and contributes to the activation of glycogen synthase leading to an increase in glycogen synthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15752363}. |
Carbohydrate metabolism;Glycogen metabolism;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable [phosphorylase] phosphatase activity; glycogen binding activity; and protein phosphatase 1 binding activity. Predicted to be involved in positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process. Predicted to be located in glycogen granule. Predicted to be part of protein phosphatase type 1 complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:90673; |
glycogen granule [GO:0042587]; protein phosphatase type 1 complex [GO:0000164]; [phosphorylase] phosphatase activity [GO:0050196]; glycogen binding [GO:2001069]; protein phosphatase 1 binding [GO:0008157]; glycogen metabolic process [GO:0005977]; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0045725]; regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process [GO:0005979] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000072494 |
Ppp1r3e |
61.465302 |
0.3860771328 |
-1.373039 |
0.246913941 |
31.044765 |
0.00000002521454516817417472386162120064762026672156025597359985113143920898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000105639138995813445508298940474223304164524961379356682300567626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.1532455 |
5.7024830 |
94.0966524 |
9.7411658 |
| ENSG00000235244 |
642776 |
DANT2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.324413 |
0.3050361661 |
-1.712948 |
0.444056003 |
15.685687 |
0.00007478796806843616452875611599893090897239744663238525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000209861294427779020849156310646321799140423536300659179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1911808 |
1.7601779 |
20.3684341 |
3.3764714 |
| ENSG00000235257 |
101928153 |
ITGA9-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.682724 |
0.2926466999 |
-1.772768 |
0.530783705 |
11.865103 |
0.00057195616520819996843327803759393646032549440860748291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001390742808022376588925062002033428143477067351341247558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0643718 |
1.4267978 |
13.7494491 |
2.9240100 |
| ENSG00000235314 |
|
LINC00957 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.891531 |
0.3955780938 |
-1.337966 |
0.535744912 |
6.398910 |
0.01141904452863731246614609204925727681256830692291259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021636084370049643577083031686925096437335014343261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3057608 |
1.7085585 |
13.4402848 |
2.5724540 |
| ENSG00000235374 |
728039 |
SSR4P1 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.273920 |
0.3894127764 |
-1.360628 |
0.552364998 |
6.054110 |
0.01387397015954305520835099230225750943645834922790527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025781165750328023655857379026201670058071613311767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1737216 |
2.6516012 |
16.0295826 |
4.7049541 |
| ENSG00000235531 |
100132891 |
MSC-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30915884_we demonstrated that MSC-AS1/miR-29b-3p axis modulates the cell proliferation and GEM-induced cell apoptosis in PDAC cell lines through CDK14. We provided a novel experimental basis for PDAC treatment from the perspective of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. 31551149_MSC-AS1 might promote the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs through sponging microRNA-140-5p to up-regulate BMP2, thus alleviating the progression of osteoporosis 31916281_lncRNA MSC-AS1 activates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway to modulate cell proliferation and migration in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma via miR-3924/WNT5A. 32155139_Downregulated Long Non-Coding RNA MSC-AS1 Inhibits Osteosarcoma Progression and Increases Sensitivity to Cisplatin by Binding to MicroRNA-142. 33106913_MSC-AS1 knockdown inhibits cell growth and temozolomide resistance by regulating miR-373-3p/CPEB4 axis in glioma through PI3K/Akt pathway. 33390824_Long non-coding RNA MSC-AS1 facilitates the proliferation and glycolysis of gastric cancer cells by regulating PFKFB3 expression. 33625998_Expression of lncRNA MSC-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and its effect on proliferation, apoptosis, and migration. 33819916_MSC-AS1 induced cell growth and inflammatory mediators secretion through sponging miR-142-5p/DDX5 in gastric carcinoma. 33821667_LncRNA MSC-AS1 facilitates lung adenocarcinoma through sponging miR-33b-5p to up-regulate GPAM. 34617815_Role of hypermethylated-lncRNAs in the prognosis of bladder cancer patients. 35126911_lncRNA MSC-AS1 Aggravates Diabetic Nephropathy by Regulating the miR-325/CCNG1 Axis. 36206100_LncRNA MSC-AS1, as an oncogene in melanoma, promotes the proliferation and glutaminolysis by regulating the miR-330-3p/ YAP1 axis. |
|
|
148.449437 |
3.1494717019 |
1.655110 |
0.691650320 |
5.039006 |
0.02478270477417971254241457756961608538404107093811035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043505319037451542496519607539084972813725471496582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
252.7441157 |
85.9803910 |
79.8710546 |
19.7422382 |
| ENSG00000235703 |
100272228 |
EOLA2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42.504604 |
0.0640942701 |
-3.963661 |
0.760740917 |
21.292547 |
0.00000394261321228099325021535306867725978463568026199936866760253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000012998206614533719670560515946355906180542660877108573913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.2198734 |
2.1550667 |
65.7382874 |
22.1686478 |
| ENSG00000235706 |
400242 |
DICER1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30536305_DICER1-AS1 is up-regulated in osteosarcoma and may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for osteosarcoma |
|
|
16.977531 |
0.2403996163 |
-2.056494 |
0.444202804 |
22.665788 |
0.00000192769715585550596302806536375129553562146611511707305908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006612319316855047116325734546382619782889378257095813751220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4039008 |
1.9556107 |
26.7978562 |
4.8549339 |
| ENSG00000235847 |
|
LDHAP7 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.436916 |
3.3436119732 |
1.741407 |
0.528227909 |
11.202374 |
0.00081692745393675337325228857920933478453662246465682983398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001935449313018696793423090163344113534549251198768615722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.1566087 |
5.1804916 |
4.9028617 |
1.3005717 |
| ENSG00000235859 |
|
|
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.642197 |
0.3970927901 |
-1.332452 |
0.322458900 |
17.582040 |
0.00002751749965685978586244983534747632347716717049479484558105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000081886753011139196286281849435084723154432140290737152099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.5295232 |
3.2717959 |
34.2865363 |
5.3740169 |
| ENSG00000235863 |
8705 |
B3GALT4 |
protein_coding |
O96024 |
FUNCTION: Involved in GM1/GD1B/GA1 ganglioside biosynthesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9582303}. |
Glycoprotein;Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Protein modification; protein glycosylation. |
This gene is a member of the beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase (beta3GalT) gene family. This family encodes type II membrane-bound glycoproteins with diverse enzymatic functions using different donor substrates (UDP-galactose and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine) and different acceptor sugars (N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, N-acetylgalactosamine). The beta3GalT genes are distantly related to the Drosophila Brainiac gene and have the protein coding sequence contained in a single exon. The beta3GalT proteins also contain conserved sequences not found in the beta4GalT or alpha3GalT proteins. The carbohydrate chains synthesized by these enzymes are designated as type 1, whereas beta4GalT enzymes synthesize type 2 carbohydrate chains. The ratio of type 1:type 2 chains changes during embryogenesis. By sequence similarity, the beta3GalT genes fall into at least two groups: beta3GalT4 and 4 other beta3GalT genes (beta3GalT1-3, beta3GalT5). This gene is oriented telomere to centromere in close proximity to the ribosomal protein S18 gene. The functionality of the encoded protein is limited to ganglioseries glycolipid biosynthesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8705; |
cytosolic small ribosomal subunit [GO:0022627]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; ganglioside galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0047915]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; UDP-galactose:beta-N-acetylglucosamine beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase activity [GO:0008499]; ganglioside biosynthetic process [GO:0001574]; oligosaccharide biosynthetic process [GO:0009312]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
19225246_We found beta3Gal-T4 and T5 enzymatic activity in ovarian cancer tissues, indicating that these enzymes are expressed at least in ovarian cancer 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20594196_Data showed that GM1/GD1b/GA1 synthase transfectant cells had definite reduction in cell growth and invasion. 21519903_Induction of GM1a/GD1b synthase triggers complex ganglioside expression and alters neuroblastoma cell behavior; a new tumor cell model of ganglioside function 30131660_Colorectal cancer (CRC) patients expressing both high B7-H3 and high B3GALT4 contributed to a significant decrease in overall survival. The expression of B3GALT4 in CRC is positively correlated with B7-H3 expression in vitro. B7-H3/B3GLAT4 may be used as dual prognostic biomarkers for CRC. 30372681_In patients with late-onset Alzheimer disease, a number of differentially methylated postitions were hypomethylated in B3GALT4 compared with controls. 30611881_B3GALT4 knockdown decreases GM1 ganglioside level and enhances vulnerability for neurodegeneration. |
ENSMUSG00000067370 |
B3galt4 |
37.077771 |
0.1835611428 |
-2.445667 |
0.353069632 |
49.154804 |
0.00000000000236538361103507669553688834623955244409673759342638277303194627165794372558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000013756131638643707662981016590194644931208212135231860884232446551322937011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.1237087 |
2.8454389 |
60.9697503 |
9.5580483 |
| ENSG00000235890 |
54082 |
TSPEAR-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35477008_LncRNA TSPEAR-AS1 predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes metastasis via miR-1915-5p. |
|
|
13.128601 |
0.1717897679 |
-2.541284 |
0.512396836 |
27.964814 |
0.00000012354154847129819470020182549385712178491303347982466220855712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000482911349427002488268832053330825715420360211282968521118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4384977 |
1.2017322 |
20.3955671 |
3.6870765 |
| ENSG00000235897 |
100874214 |
TM4SF19-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35987447_TM4SF19-AS1 facilitates the proliferation of lung squamous cell carcinoma by recruiting WDR5 to mediate TM4SF19. |
|
|
76.939450 |
8.6054393777 |
3.105249 |
0.247955451 |
166.621456 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000004046846583374400575397800542276718999428898868261762441770867142347194451380277667199516059488341186006765681781871535349637269973754882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000647846589702886642039309965464324659238389303035930545218210750922176060277555164487568494034296778805170902160170953720808029174804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
136.8293413 |
20.2093771 |
16.0493670 |
2.0475127 |
| ENSG00000235903 |
100509894 |
CPB2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.841218 |
0.4281839764 |
-1.223697 |
0.381699721 |
10.596764 |
0.00113285745089788383518913938985406275605782866477966308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002618380202826928442733089852367811545263975858688354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.2672643 |
2.2149135 |
21.7429268 |
3.1831479 |
| ENSG00000235989 |
150291 |
MORC2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.781315 |
0.2300017270 |
-2.120283 |
0.677622506 |
9.583151 |
0.00196371139571651287178410960621022240957245230674743652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004345484287972373529940206537958147237077355384826660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4288045 |
1.7363680 |
14.5086465 |
4.6570953 |
| ENSG00000235994 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.558174 |
0.1250186588 |
-2.999785 |
0.872863249 |
12.707434 |
0.00036420473867808790622430104022555497067514806985855102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000917505025241265991658989875645602296572178602218627929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4925481 |
1.0826036 |
12.3977018 |
5.1422136 |
| ENSG00000236008 |
101929567 |
LINC01814 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.388320 |
0.4310185425 |
-1.214178 |
0.443260538 |
7.389750 |
0.00655966151210913769875610057624726323410868644714355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013075030914075741819702081158993678400292992591857910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.8706127 |
3.9213025 |
35.0494644 |
6.4033829 |
| ENSG00000236017 |
|
ASMTL-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56.142850 |
0.1939694816 |
-2.366098 |
0.405704938 |
32.558783 |
0.00000001156413419708998682759633753981340364980212598311481997370719909667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000050084102332467201213357508486970215422218188905389979481697082519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.7714915 |
6.9578051 |
101.5964534 |
24.2267330 |
| ENSG00000236017_ENSG00000236871 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
299.162704 |
0.1824453000 |
-2.454464 |
0.111963313 |
517.769771 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000129348022860301291546986264152880682416440757251562272111912072523227811393447180816861515862131960654811209406718119523177114669599520193666426668155396108929028798330465575990545711562582949674995271346644411097242 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000064282047724513371274562644682705538274702789978545523368600205562533526533465385285432405438751015481638994141265632307350342059973962628506486326658695174570741360941589633440707586941484512051530009688950850506838 |
Yes |
No |
93.0128473 |
6.8638062 |
513.3055746 |
21.4725274 |
| ENSG00000236088 |
100874058 |
COX10-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34323174_Regulating COX10-AS1 / miR-142-5p / PAICS axis inhibits the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer. |
|
|
87.046398 |
4.9151266385 |
2.297229 |
0.378490550 |
33.245696 |
0.00000000812193363154123903695655398984540318529923297319328412413597106933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000035667878727030255554898875583816342249576791800791397690773010253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.0161914 |
44.1334878 |
22.5909796 |
6.7550796 |
| ENSG00000236090 |
|
LDHAP3 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.528633 |
2.2103857193 |
1.144298 |
0.454240465 |
6.424418 |
0.01125617634711541942271750826876086648553609848022460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021376886629364846154066626127132622059434652328491210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.9291204 |
4.8568385 |
8.2034841 |
1.7545642 |
| ENSG00000236144 |
100506469 |
TMEM147-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36181243_The long non-sacoding RNA TMEM147-AS1/miR-133b/ZNF587 axis regulates the Warburg effect and promotes prostatic carcinoma invasion and proliferation. |
|
|
54.181292 |
0.4354452368 |
-1.199437 |
0.237573175 |
25.545293 |
0.00000043211899385538970231208097741437690331167686963453888893127441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001595316745699237628074791846277680207322191563434898853302001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.0326420 |
6.5485506 |
80.9607854 |
10.3120324 |
| ENSG00000236200 |
|
KDM4A-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93.992020 |
0.2176034211 |
-2.200227 |
0.330901962 |
41.762961 |
0.00000000010303696560017420555556542511365454746485870174410592881031334400177001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000532688480650988142856428112203439825811379648712318157777190208435058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
33.3144597 |
10.4150379 |
150.1950548 |
33.1150932 |
| ENSG00000236204 |
400945 |
LINC01376 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.501608 |
0.2573375594 |
-1.958266 |
0.676465486 |
8.403254 |
0.00374549886220195381303366133352028555236756801605224609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007861712628853930601158239710457564797252416610717773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2058520 |
1.5175153 |
12.7630231 |
3.5840950 |
| ENSG00000236333 |
|
TRHDE-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.841443 |
0.2876692620 |
-1.797517 |
0.315005264 |
31.946224 |
0.00000001585001708651761128367041052845270998616911128920037299394607543945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000067634071175773327289005209996680667572377387841697782278060913085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.6276859 |
4.7912368 |
82.5955650 |
10.7731418 |
| ENSG00000236393 |
101927476 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.922990 |
4.2096039966 |
2.073685 |
0.532430101 |
15.543266 |
0.00008063837088352085815962794201894325851753819733858108520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000224739870513740170850439104022200353938387706875801086425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.0386372 |
6.9158749 |
4.5314167 |
1.3486775 |
| ENSG00000236453 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
120.302178 |
56.0592283044 |
5.808880 |
0.379383152 |
477.977734 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000058855374816091979840946648626585360093449662957522805045655217626047991532188690915247745112052613912057347704171736426196864271291109118000007966021706880097440386692793310749667669912692919654682973555630523740234826914288 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000026729394839554390325403715254531931135791272240632975934413656694023368075865877594555175133728547957036519102428084900061651062073679737643838488678637036715446287176468993424763159132953833191986551235810923756494115012065 |
Yes |
No |
252.0272046 |
65.6156426 |
4.5174591 |
1.1384543 |
| ENSG00000236548 |
7955 |
RNF217-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
77.948648 |
0.0341141994 |
-4.873484 |
0.975232669 |
15.387702 |
0.00008755628898568305321006149943841023741697426885366439819335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000242645667560773930756037874978403579007135704159736633300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
5.6181823 |
3.2370156 |
174.3550657 |
67.6609994 |
| ENSG00000236618 |
100306951 |
PITPNA-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31700026_PITPNA-AS1 abrogates the inhibition of miR-876-5p on WNT5A to facilitate hepatocellular carcinoma progression. 32460193_Long noncoding RNA PITPNA-AS1 promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating the cell cycle and apoptosis by targeting the miR-876-5p/c-MET axis. 32871048_LncRNA PITPNA-AS1 boosts the proliferation and migration of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells by recruiting TAF15 to stabilize HMGB3 mRNA. 33495838_Long noncoding RNA PITPNAAS1 silencing suppresses proliferation, metastasis and epithelialmesenchymal transition in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by targeting microRNA325p. 34470587_LncRNA PITPNA-AS1 stimulates cell proliferation and suppresses cell apoptosis in glioblastoma via targeting miR-223-3p/EGFR axis and activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 35588441_LncRNA PITPNA-AS1/miR-223-3p/PTN axis regulates malignant progression and stemness in lung squamous cell carcinoma. |
|
|
10.196291 |
0.2972764096 |
-1.750123 |
0.649031864 |
7.022004 |
0.00805140516874757426746267441330928704701364040374755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015744401204387147713559258477289404254406690597534179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9518913 |
2.8207133 |
16.4778800 |
6.2060548 |
| ENSG00000236671 |
|
PRKG1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95.000596 |
0.4934502225 |
-1.019024 |
0.217631330 |
21.821005 |
0.00000299305430395798719169181238697330371678617666475474834442138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010008491510289960435510156488980726408044574782252311706542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
62.2461425 |
8.9499130 |
127.1489124 |
12.5851285 |
| ENSG00000236682 |
|
MAP3K2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.208920 |
0.2929891020 |
-1.771081 |
0.380070844 |
21.906453 |
0.00000286269637813824077461491782181646215121872955933213233947753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009596502053445477576341417214056406237432383932173252105712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.5215325 |
2.5940437 |
33.0357625 |
5.7182885 |
| ENSG00000236700 |
154092 |
LINC01010 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34830378_HBV HBx-Downregulated lncRNA LINC01010 Attenuates Cell Proliferation by Interacting with Vimentin. |
|
|
107.254581 |
6.2654876910 |
2.647427 |
0.308820587 |
69.208191 |
0.00000000000000008859932731446225486266465780423558035109923825510536143923445706604979932308197021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000671317284990484095406281570746947433010986790516416711227520863758400082588195800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
188.8313319 |
34.5503061 |
30.2771326 |
4.4703217 |
| ENSG00000236810 |
100506963 |
ELOA-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.938847 |
0.3205189766 |
-1.641518 |
0.470300615 |
12.167943 |
0.00048617895086133100382777549874901978910202160477638244628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001196399018791804817751778244883098523132503032684326171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.1946502 |
2.7442737 |
28.8245579 |
5.5451851 |
| ENSG00000236824 |
618 |
BCYRN1 |
scRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene, which encodes a neural small non-messenger RNA, is a member of the family of interspersed repetitive DNA, and its product represents an example of a primate tissue-specific RNA polymerase III transcript. The RNA sequence is divided into three domains: a 5' portion homologous to the Alu Lm, a central adenosine-rich region, and the terminal 43-nt nonrepetitive domain. It is believed that this gene was retropositionally generated and recruited into a function regulating dendritic protein biosynthesis. At least two pseudogenes of this gene have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
15240511_potential of BC200 expression to serve as a molecular tool in the diagnosis and/or prognosis of breast cancer. 16054886_We further showed that the promoter can be active in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells and reduced expression of targeted protein, although the BC1 RNA gene is a rodent-specific gene. 17553964_Dendritic BC200 was studied in aging and in Alzheimer disease. 24244371_Protein interaction analysis of senataxin and the ALS4 L389S mutant yields insights into senataxin post-translational modification and uncovers mutant-specific binding with a brain cytoplasmic RNA-encoded peptide. 26740632_BCYRN1 has direct affinity for RHAU in vitro. 27277684_BC200 knockout suppresses tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo by expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-xS isoform. 28027391_BC200 RNA interacts with hnRNP E1 and E2 mainly through its unique 3' C-rich domain. 28277927_Results suggest that BC200 RNA up-regulates S100A11 expression by stabilizing the S100A11 mRNA at the post-transcriptional level, and this upregulation of S100A11 contributes to the ability of BC200 RNA to increase cancer cell motility. 28651607_BC200 expression is elevated in proliferating cultured cells regardless of origin.BC200 expression is largely restricted to the cytoplasm.BC200 role in cancer cell survival and proliferation. 28761139_Data show that increases in both RNA stability and transcription contribute to the upregulation of BC200 RNA in cancer cells. Since BC200 RNA role in promoting metastasis, its biosynthetic regulation should be related to cancer pathogenesis. Results provide a molecular basis for the regulation of BC200 RNA biosynthesis and improve the understanding of BC200 RNA-mediated regulatory networks in cancer. 29967012_This work establishes the potential of BC200 RNA detection in blood to serve as a molecular indicator of invasive breast malignancy. 29979260_Findings confirmed that inhibition of BC200 significantly suppressed BACE1 expression. BC200 may act as a basic regulating factor to induce cell apoptosis in the process of Alzheimer's disease through mediating BACE1. 30072491_The presented combination of experimental and bioinformatic approaches not only enabled the determination of the most reliable secondary and tertiary structures of human BC200 RNA (largely in agreement with the previous phylogenetic model), but also verified the compatibility and potential disadvantages of utilizing in silico structure prediction programs. 30114690_BCYRN1 knockdown significantly inhibited the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and NPR3 was identified to be a target of BCYRN1 and was downregulated by BCYRN1 knockdown. 30247708_CSDE1 binds directly to BC200 RNA.CSDE1 and BC200 expression levels are mutually dependent. 30400024_Mechanistically, BC200 directly interacted with cyclin E2 and promoted CDK2-cyclin E2 complex formation. Upregulation of cell cycle-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma samples was positively correlated with BC200 expression. Our collective findings support the utility of a potential therapeutic strategy involving targeting of BC200 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. 30486938_Long Non-Coding RNA Brain Cytoplasmic RNA 1 Acts as an Oncogene and Regulates Cell Proliferation and Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. 30779077_BC200 is highly expressed in NSCLC, which is positively correlated with tumor stage and metastasis of NSCLC patients. 30898877_findings provide the first evidence for impaired Pol III transcription in cellular models of POLR3-HLD and identify several candidate effectors, including BC200 RNA, having a potential role in oligodendrocyte biology and involvement in the disease 31152845_Esophageal cancer related gene-4 inhibits the migration and proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma through BC200 lncRNA/MMP-9 and -13 signaling pathway. 31234958_Analysis of BC200 RNA was performed to identify functional RNA motifs responsible for its translationalinhibition activity. Various RNA variants were assayed for their ability to inhibit translation of luciferase mRNA in vitro. We found that the 111-200-nucleotide region consisting of part of the Alu domain as well as the A/C-rich domain is most effective for translation inhibition. 31250622_BC200 RNA sequences are highly heterogeneous in cancer cells by virtue of multiple adenine nucleotide insertions in the internal A-rich region. 31339046_High BCYRN1 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. 31646972_Long non-coding RNA BC200 (BC200) is upregulated in nulliparous women, and breast cancer cells and tissue. When overexpressed in luminal and triple negative breast cancer cell lines, BC200 shows increased proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro. In vivo, overexpression of BC200 increases tumor size. 31652309_BCYRN1 is correlated with progression and prognosis in gastric cancer. 31773686_Clinical significance of lncRNA BCYRN1 in colorectal cancer and its role in cell metastasis. 31894342_Effect of lncRNABC200 on proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. 32705287_Long noncoding RNA BCYRN1 promotes prostate cancer progression via elevation of HDAC11. 32784466_Targeting BC200/miR218-5p Signaling Axis for Overcoming Temozolomide Resistance and Suppressing Glioma Stemness. 32978519_LncRNA BCYRN1 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by competitively binding with miR-619-5p to regulate CUEDC2 expression and the PTEN/AKT/p21 pathway. 33391513_LncRNA BCYRN1-induced autophagy enhances asparaginase resistance in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. 33410401_The noncoding RNA BC200 associates with polysomes to positively regulate mRNA translation in tumor cells. 34323412_Tumor-derived exosomal BCYRN1 activates WNT5A/VEGF-C/VEGFR3 feedforward loop to drive lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer. 34654723_The HNF4alpha-BC200-FMR1-Positive Feedback Loop Promotes Growth and Metastasis in Invasive Mucinous Lung Adenocarcinoma. 35136029_LncRNA BC200/miR-150-5p/MYB positive feedback loop promotes the malignant proliferation of myelodysplastic syndrome. 35225646_LncRNA BCYRN1 promotes cell migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer via the miR-30b-3p/ROCK1 axis. 35586620_The Long Non-Coding BC200 Is a Novel Circulating Biomarker of Parathyroid Carcinoma. 35705019_Long Noncoding RNA Brain Cytoplasmic RNA 1 Induces Cisplatin-Resistance of Cervical Cancer Cells by Sponging MicroRNA-330-5p and Upregulating High-Mobility Group Box 3. 35730016_Long Noncoding RNA BCYRN1 Recruits BATF to Promote TM4SF1 Upregulation and Enhance HCC Cell Proliferation and Invasion. |
|
|
30.262520 |
2.3719909483 |
1.246099 |
0.366228207 |
11.539382 |
0.00068137271773444964013261015978173418261576443910598754882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001636891489869869188711337670838474878109991550445556640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.2831345 |
8.3334367 |
17.9365263 |
2.7828260 |
| ENSG00000236901 |
81571 |
MIR600HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32270866_MIR600HG suppresses metastasis and enhances oxaliplatin chemosensitivity by targeting ALDH1A3 in colorectal cancer. 35378445_lncRNA MIR600HG induces the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via regulating miR-144-3p/KIF3A. |
|
|
80.175812 |
0.1679218569 |
-2.574138 |
0.214222377 |
160.518805 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000087155923542729486093263661298290168142036443989173977058933340980093804429616771664753716421583651374760393082397058606147766113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000013400223244694657985695904782325429700487515672432646694961586155992791563190298863381138714731544148150987894041463732719421386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1397725 |
3.3477027 |
138.9175084 |
11.0014784 |
| ENSG00000237036 |
220930 |
ZEB1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This locus produces long non-coding RNA that is transcribed from a shared bi-directional promoter with zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1). This transcript binds lysine methyltransferase 2A and promotes histone modifications that are thought to promote expression of ZEB1. Expression of this gene is correlated with tumor progression. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
|
|
26617942_lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 was associated with tumor progression and could be an independent prognostic factor for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. 27589728_Glioma patients with high ZEB1-AS1 levels had poor prognoses. ZEB1-AS1 functioned as an important regulator of migration and invasion via activating epithelial to mesenchymal transition. 28075045_study revealed a novel regulatory mechanism between ZEB1-AS1, miR-200s, and ZEB1. The interplay between ZEB1-AS1 and miR-200s contributes to osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration, and targeting this interplay could be a promising strategy for osteosarcoma treatment. 28445936_these findings indicated that ZEB1-AS1 plays regulatory roles in bladder cancer and it may become a novel molecular biomarker of prognosis and therapy in bladder cancer. 28618933_Upregulation of ZEB1-AS1 colorectal cancer promotes cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis. In addition, cell cycle inhibitory protein p15 participates in the oncogenic function of ZEB1-AS1. Collectively, ZEB1-AS1 has asignificant effect on colorectal cancer pathological process and serves as a valuable prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. 28830551_Studied role of lncRNA ZEB1 antisense 1 in prostate cancer epigenetic processes and ZEB1 expression. 28861713_Studied the role of ZEB1-AS1, and it's association with IL-11, in promoting STAT3 activation in B-lymphoblastic leukemia. 28967064_colorectal cancer (CRC) patients of the high ZEB1-AS1 expression group had a poorer prognosis and a significantly lower survival rate than those of the low expression group, and Cox regression analysis indicated that ZEB1-AS1 expression and metastasis were independent predictors of poor prognosis. 29113674_High Levels of ZEB1-AS1 expression is associated with gastric cancer 29771411_LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 is highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues and cells, promoting cell migration and neoplasm metastasis. 29771414_Extracellular vesicles deliver lncZEB1 to esophageal cancer cells, promoting esophageal cancer cell proliferation by upregulating the expression of downstream ZEB1. 29778540_High expression of ZEB1-AS1 was associated with advanced clinicopathological characteristics, and ZEB1-AS1expression may be a potential prognostic biomarker in human cancer. 29885321_High expression of lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 was an unfavorable predictor of cancer prognosis in terms of OS, DFS, RFS, tumor differentiation, depth of invasion, clinical stage, organ metastasis and lymph node metastasis and the expression of lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 might be used as a promising prognostic biomarker for cancer. 29886791_miR-181a-5p targets not only protein-coding genes but also the lncRNA ZEB1-AS1. 30626729_ZEB1-AS1 can promote cell proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung carcinoma cells by silencing ID1 expression. 30823924_we found that ZEB1-AS1 is a downstream target of TGF-beta1 and is involved in its regulatory mechanism on cell migration and invasion by affecting miR-200b/FSCN1 axis in bladder cancer cells 31072267_the present findings suggest that ZEB1 antisense RNA 1 is an independent prognostic factor for patients with advanced gastric cancer receiving chemotherapy. 31115480_the data from the present study demonstrated that ZEB1AS1 induced bladder cancer metastasis via an AUF1mediated translation activation of ZEB1 mRNA mechanism. 31383874_Whole transcriptome analysis reveals correlation of long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 with invasive profile in melanoma. 31638344_LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 down-regulation suppresses the proliferation and invasion by inhibiting ZEB1 expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 31828845_ZEB1-AS1 promotes PAK2 expression by sponging miR-455-3p, thus facilitating colon adenocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis. 31922280_ZEB1 induced-upregulation of long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 facilitates the progression of triple negative breast cancer by binding with ELAVL1 to maintain the stability of ZEB1 mRNA. 31962131_LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 facilitates ox-LDL-induced damage of HCtAEC cells 32236578_Long noncoding RNA ZEB1AS1 predicts a poor prognosis and promotes cancer progression through the miR200a/ZEB1 signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 32275162_Downregulation of lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Represses Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Through Mediating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling by miR-342-3p/CUL4B Axis in Prostate Cancer. 32513531_LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by regulating miR-505-3p/TRIB2 axis. 32756112_Clinical value of long noncoding RNA ZEB1 anti-sense1 in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. 33151424_Long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 affects paclitaxel and cisplatin resistance by regulating MMP19 in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. 33788950_Long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting miR-299-3p/E2F1 axis. 33818551_Exosomes-Mediated LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Facilitates Cell Injuries by miR-590-5p/ETS1 Axis Through the TGF-beta/Smad Pathway in Oxidized Low-density Lipoprotein-induced Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. 33865414_LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting miR-23c. |
|
|
18.448911 |
0.3969118917 |
-1.333109 |
0.487019187 |
6.995195 |
0.00817288186013083971237502822759779519401490688323974609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015943924961079988106282812054814712610095739364624023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.7245288 |
3.9092249 |
29.9380271 |
6.3655890 |
| ENSG00000237037 |
100132273 |
NDUFA6-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.166697 |
0.3024636345 |
-1.725166 |
0.336893080 |
27.274534 |
0.00000017652103533715306458554996065640763092119414068292826414108276367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000679033224283653766319688617481009629273103200830519199371337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.8156111 |
2.7531362 |
32.6745565 |
6.0501021 |
| ENSG00000237172 |
84752 |
B3GNT9 |
protein_coding |
Q6UX72 |
|
Glycosyltransferase;Golgi apparatus;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable UDP-glycosyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in Golgi membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:84752; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0016757]; hexosyltransferase activity [GO:0016758]; UDP-glycosyltransferase activity [GO:0008194]; poly-N-acetyllactosamine biosynthetic process [GO:0030311]; protein glycosylation [GO:0006486] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000069920 |
B3gnt9 |
24.589118 |
0.4899158643 |
-1.029394 |
0.305704319 |
11.492696 |
0.00069870210306684503616392323266381936264224350452423095703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001673619448436649247147212093977941549383103847503662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.5978020 |
3.2259990 |
34.0001490 |
4.2243014 |
| ENSG00000237181 |
101926963 |
PRKAR1B-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
450.334103 |
2.5990281781 |
1.377972 |
0.108211029 |
160.163509 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000104213435469352241596632195572059602686109798969338372466446542985278957900473561651079938775990227362022721990797435864806175231933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000015972900389695109839533565626720492734208626804364137687818076865335555763560609238470240677301714704583446291508153080940246582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
648.4557190 |
45.8191154 |
251.3663205 |
13.3880099 |
| ENSG00000237361 |
400128 |
TUSC8 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24667250_Results suggested that XLOC_010588 plays a pivotal role in cervical cancer cell proliferation via decreasing c-Myc expression. 31033083_These results demonstrated that overexpression of TUSC8 could inhibit the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells by upregulating PTEN via miR-641. 32945345_TUSC8 inhibits the development of osteosarcoma by sponging miR1973p and targeting EHD2. 34076977_TUSC8 enhances cisplatin sensitivity of NSCLC cells through regulating VEGFA. |
|
|
11.890972 |
0.1467451720 |
-2.768615 |
0.581913496 |
25.191132 |
0.00000051920380937108194819846855583289624291865038685500621795654296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001901128312160052058981231717926796420670143561437726020812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8085017 |
1.1265120 |
19.2160158 |
4.2099228 |
| ENSG00000237441 |
5863 |
RGL2 |
protein_coding |
O15211 |
FUNCTION: Probable guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Putative effector of Ras and/or Rap. Associates with the GTP-bound form of Rap 1A and H-Ras in vitro (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Guanine-nucleotide releasing factor;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of catalytic activity and small GTPase mediated signal transduction. Predicted to act upstream of or within negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling; and regulation of Ral protein signal transduction. Predicted to be located in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:5863; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity [GO:0005085]; negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:0010667]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; Ras protein signal transduction [GO:0007265]; regulation of Ral protein signal transduction [GO:0032485] |
18540861_RGL2 is phosphorylated by PKA and phosphorylation reduces the ability of RGL2 to bind H-Ras. results of the present study indicate that Ras may distinguish between the different RalGDS family members by their phosphorylation by PKA. 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20801877_Rgl2 and RalB both localized to the leading edge, and this localization of RalB was dependent on endogenous Rgl2 expression. 21160498_SAMD9, an IFN-gamma-responsive protein, interacts with RGL2 to diminish the expression of EGR1, a protein of direct relevance to the pathogenesis of ectopic calcification and inflammation. |
ENSMUSG00000041354 |
Rgl2 |
770.099156 |
0.3205739008 |
-1.641271 |
0.085132980 |
367.926286 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000052930893656716931505790098971672368269500987336479085143015819209753556961611925801634353091711406577068155017020370278005306204285857251155092470226596435891799929713832270876009241979254117880485282221503240407400880940258502960205078125000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000018211188586786524581143416324414306796928184983265775981176948398450967763863002077532753054233582693947698704278009724895726819792448349031255033506438914623197867089066120002862023614178166899509395126877109305496560409665107727050781250000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
369.7347533 |
20.1337572 |
1162.3282776 |
42.0393340 |
| ENSG00000237489 |
387723 |
C10orf143 |
protein_coding |
A0A1B0GUT2 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
Mouse_homologues mmu:77252; |
|
|
ENSMUSG00000040139 |
9430038I01Rik |
6.440419 |
0.2647599512 |
-1.917243 |
0.662667531 |
9.040620 |
0.00264046029513579716754834159075926436344161629676818847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005713706781440311584241431575037495349533855915069580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2203764 |
1.4640304 |
12.2823119 |
3.1770675 |
| ENSG00000237499 |
100130476 |
WAKMAR2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 27189370_aberrant methylation of LOC100130476 in peripheral white blood cells andgastric cardia adenocarcinoma ( GCA) tissues may be used as a potential valuable biomarker in GCA diagnosis and prognosis 30594489_Study data suggest that WAKMAR2 is an important regulator of skin wound healing through production of inflammatory chemokines by keratinocytes, and cell migration enhancing and its deficiency may contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic wounds. |
|
|
167.270580 |
0.4250643545 |
-1.234247 |
0.122221449 |
104.304190 |
0.00000000000000000000000173521689123933260886741164911515503239661002789728210610387175395416536893833381327567622065544128417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000018281085877724874116239269073687229647390533758089826930373861333528617834076612780336290597915649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
104.8268103 |
11.0588971 |
248.7596085 |
17.7475911 |
| ENSG00000237541 |
3117 |
HLA-DQA2 |
protein_coding |
P01906 |
FUNCTION: Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22407913}. |
Adaptive immunity;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Immunity;Lysosome;Membrane;MHC II;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the HLA class II alpha chain family. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with a class II beta chain. It is located in intracellular vesicles and plays a central role in the peptide loading of MHC class II molecules by helping to release the CLIP molecule from the peptide binding site. Class II molecules are expressed in antigen presenting cells (B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages) and are used to present antigenic peptides on the cell surface to be recognized by CD4 T-cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010]. |
hsa:3118; |
clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030669]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; ER to Golgi transport vesicle membrane [GO:0012507]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; MHC class II protein complex [GO:0042613]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; trans-Golgi network membrane [GO:0032588]; transport vesicle membrane [GO:0030658]; MHC class II protein complex binding [GO:0023026]; MHC class II receptor activity [GO:0032395]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II [GO:0019886]; immune response [GO:0006955]; peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex [GO:0002503]; positive regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050870] |
18065200_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19116923_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20159242_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20159242_a significant single nucleotide polymorphism , rs3998159, between HLA-DQB1 and HLA-DQA2 was identified in patients with asthma 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20711174_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22096524_Parkinson's disease-associated SNP4 is correlated (r2=0.95) with variants that are associated with HLA-DQA2 expression. 22125590_Results indicate that two SNPs rs9468925 in HLA-C/HLA-B and rs2858881 in HLA-DQA2 were repeatedly selected in all models, suggesting that multiple loci outside PSOR1 locus were associated with psoriasis. 22407913_HLA-DQA2 and HLA-DQB2 genes are expressed in human Langerhans cells and encode a new HLA class II molecule. 23257407_HLA-DQB1/HLA-DQA2 rs9275328 may play a part in influencing the systemic lupus erythematosis susceptibility in Malays and Chinese in Malaysia. 31605414_Association of GWAS-supported noncoding area loci rs404860, rs3117098, and rs7775228 with asthma in Chinese Zhuang population. |
|
|
48.973399 |
75.2760988353 |
6.234120 |
0.676857221 |
233.203031 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011935356933094631788513288817535851044045365773207358826048510084887883853495475682916577005933361378992704364517260144014683742662123744349145226806285791099071502685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002689555241717202687470810732123658133538573473765618248942979585125112867793393482735667018119299881314253404153334310408646960592615737795085806283168494701385498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.6121804 |
47.0554681 |
1.3324752 |
0.6212841 |
| ENSG00000237651 |
339804 |
C2orf74 |
protein_coding |
A8MZ97 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:339804; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
33571247_Frameshift variant in MITF gene in a large family with Waardenburg syndrome type II and a co-segregation of a C2orf74 variant. |
ENSMUSG00000020286 |
1700093K21Rik |
72.883528 |
0.4015434877 |
-1.316372 |
0.213595976 |
38.179334 |
0.00000000064532264122970600779416068594495671517652368720519007183611392974853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003131151276972537778808229754715780623897103396302554756402969360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
42.6676163 |
5.6738601 |
106.5947221 |
9.2415622 |
| ENSG00000237886 |
|
NALT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.736001 |
0.3094996947 |
-1.691990 |
0.437759988 |
15.432137 |
0.00008552147227971119861165277820092001093144062906503677368164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000237407735724757808183291163395267631130991503596305847167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5444086 |
1.8318687 |
21.2693803 |
3.6443854 |
| ENSG00000238045 |
|
MVP-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.088984 |
0.2713294490 |
-1.881882 |
0.513600375 |
12.358407 |
0.00043900510876457966109517871977629965840606018900871276855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001090494009654189785929467859659780515357851982116699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.9279966 |
4.6300191 |
51.0128250 |
11.7084799 |
| ENSG00000238113 |
103352539 |
LINC01410 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29483646_Results show that increased expression of LINC01410 suppresses miR-532 expression, which leads to the up-regulation of NCF2 and NF-kappaB signaling, thereby promoting a series of oncogenic effects in gastric cancer (GC) cells. Activated NF-kappaB could then in turn up-regulate LINC01410 expression, which forms a positive feedback loop. 31137129_Down-regulation of LINC01410 expression inhibits the proliferation and migration of pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells 31644316_The expression of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1410 (LINC01410) is elevated in papillary thyroid carcinoma (TC) cells. LINC01410 knockdown suppresses proliferation and facilitated apoptosis in TC. LINC01410 positively regulates forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) expression through targeting miR-3619-5p, and that FOXM1 in turn transcriptionally activates LINC01410. 31951299_LINC01410 promotes cell proliferation and migration of cholangiocarcinoma through modulating miR-124-3p/SMAD5 axis. 32314193_LINC01410/miR-23c/CHD7 functions as a ceRNA network to affect the prognosis of patients with endometrial cancer and strengthen the malignant properties of endometrial cancer cells. 32886453_Long noncoding RNA LINC01410 promotes the tumorigenesis of neuroblastoma cells by sponging microRNA-506-3p and modulating WEE1. 33401246_LINC01410 accelerated the invasion and proliferation of osteosarcoma by sponging miR-3128. 33583123_The LINC01410/miR-122-5p/NDRG3 axis is involved in the proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma cells. 33712887_LncRNA LINC01410 Induced by MYC Accelerates Glioma Progression via Sponging miR-506-3p and Modulating NOTCH2 Expression to Motivate Notch Signaling Pathway. 33978387_High Expression of Long Noncoding RNA 01410 Serves as a Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. 34435542_Silencing lncRNA LINC01410 suppresses cell viability yet promotes apoptosis and sensitivity to temozolomide in glioblastoma cells by inactivating PTEN/AKT pathway via targeting miR-370-3p. 34605103_Long noncoding RNA LINC01410 promotes tumorigenesis of osteosarcoma cells via miR-497-5p/HMGA2 axis. |
|
|
115.294084 |
0.3546475296 |
-1.495542 |
0.246971948 |
35.927968 |
0.00000000204748474093611871437328015525120017414906214980874210596084594726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000009536407313416571048759139660189187992500592372380197048187255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.3589547 |
8.8188771 |
166.6118276 |
16.7733334 |
| ENSG00000238197 |
100506215 |
PAXBP1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.651604 |
0.3579203445 |
-1.482290 |
0.274969440 |
29.776689 |
0.00000004847861312090909527228456648954846297527865317533724009990692138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000196740261112075423116765703415720345503814314724877476692199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.1647176 |
3.3675270 |
57.0441664 |
5.9517413 |
| ENSG00000238243 |
343171 |
OR2W3 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z3T1 |
FUNCTION: Odorant receptor. {ECO:0000305}. |
Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Olfaction;Receptor;Reference proteome;Sensory transduction;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose, to initiate a neuronal response that triggers the perception of a smell. The olfactory receptor proteins are members of a large family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) arising from single coding-exon genes. Olfactory receptors share a 7-transmembrane domain structure with many neurotransmitter and hormone receptors and are responsible for the recognition and G protein-mediated transduction of odorant signals. The olfactory receptor gene family is the largest in the genome. The nomenclature assigned to the olfactory receptor genes and proteins for this organism is independent of other organisms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:343171; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; olfactory receptor activity [GO:0004984] |
25374392_Our results provided a new insight into susceptibility of USF1 variant with male infertility. rs11204546 of OR2W3 and rs11677854 of GTF2A1L might be additional valuable molecular predictive markers 25783483_A novel missense mutation, c. 424 C > T transition (p.R142W) in OR2W3 gene, was identified as a potentially causative mutation for autosomal dominant Retinitis pigmentosa. 25847845_OR2W3 is associated with genetic susceptibility to Japanese male infertility. 26891008_We therefore conclude that this sequence variant, and hence the OR2W3 gene, do not cause RP. Prompted by these findings and based on simple principles of population genetics, we suggest that WES studies should consider DNA variants as the possible cause of dominant RP only if they are present in less than 1:100,000 individuals from the general population. 27916748_This outstanding specificity of extremely narrowly tuned human OR2M3 can explain both odor qualities and odor threshold trend within a homologous series of 3-mercapto-2-methylalkan-1-ols and suggests a modern human-specific, food-related function of OR2M3 in detecting a single onion key food odorant. 28262088_A signal in a nearby olfactory receptor on chromosome 1, olfactory receptor family 2 subfamily L member 13 (OR2L13), tagged by rs151319968, was nominally associated with PTSD in the AI sample. Although no variants were significantly associated after correction for multiple testing in a meta-analysis of the two cohorts, pathway analysis of the top hits showed an enrichment cluster of terms related to sensory transduction. 33097666_The odorant receptor OR2W3 on airway smooth muscle evokes bronchodilation via a cooperative chemosensory tradeoff between TMEM16A and CFTR. |
ENSMUSG00000060030+ENSMUSG00000063549 |
Olfr317+Olfr322 |
8.346200 |
0.0118209164 |
-6.402514 |
1.162970229 |
39.056799 |
0.00000000041165298357863604279405989561319099273584143361404130700975656509399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002031426960087150909005243525052263053876089315963326953351497650146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.1683367 |
0.2263426 |
14.1358024 |
9.6102176 |
| ENSG00000239213 |
|
NCK1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
112.421093 |
0.4707043572 |
-1.087107 |
0.328340776 |
10.552809 |
0.00116011622132282474911812997220295073930174112319946289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002675100051042789486843709312324790516868233680725097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.0224094 |
19.6262530 |
161.9029512 |
29.7376064 |
| ENSG00000239593 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.424662 |
0.0348090939 |
-4.844392 |
1.636009326 |
5.821274 |
0.01583346874768838327685038791514671174809336662292480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029024093233467530839053694080575951375067234039306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7324952 |
2.9795165 |
28.7517421 |
59.5911450 |
| ENSG00000239636 |
105378645 |
TFAP2E-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.497998 |
0.1626175231 |
-2.620445 |
0.314494822 |
69.400345 |
0.00000000000000008037459080651636351506191577858923089518015388894520145690592016762821003794670104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000609937768793923690863971711727647256197705515675527854213555656315293163061141967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.2520899 |
3.7251071 |
73.1215975 |
14.9706410 |
| ENSG00000239642 |
728637 |
MEIKIN |
protein_coding |
A0A087WXM9 |
FUNCTION: Key regulator of kinetochore function during meiosis I: required both for mono-orientation of kinetochores on sister chromosomes and protection of centromeric cohesin from separase-mediated cleavage. Acts by facilitating kinetochore mono-orientation during meiosis I, when kinetochores on sister chromosomes face the same direction and are thus captured and pulled by spindle fibers from the same pole. Also required to prevent cleavage of cohesin at centromeres during meiosis I, possibly by acting as a regulator of the shugoshin-dependent protection pathway. Acts in collaboration with PLK1: required for PLK1 enrichment to kinetochores. Not required during meiosis II or mitosis. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q5F2C3}. |
Centromere;Chromosome;Chromosome partition;Kinetochore;Meiosis;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in meiotic chromosome segregation. Predicted to be located in kinetochore. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:728637; |
condensed chromosome, centromeric region [GO:0000779]; kinetochore [GO:0000776]; female meiosis chromosome segregation [GO:0016321]; homologous chromosome segregation [GO:0045143]; male meiosis chromosome segregation [GO:0007060]; meiotic sister chromatid cohesion involved in meiosis I [GO:0010789]; meiotic sister chromatid cohesion, centromeric [GO:0051754] |
18718982_Single marker analysis indicated that SNP5 (rs1355095) in LOC728637 is associated with schizophrenia in Han Chinese. |
ENSMUSG00000020332 |
Meikin |
52.699687 |
4.4054761934 |
2.139298 |
0.392915012 |
27.885495 |
0.00000012871105370796924909079848690918179698883250239305198192596435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000501922101117470587517809671451729514046746771782636642456054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
89.7458228 |
20.8609488 |
20.3528840 |
3.7219490 |
| ENSG00000239672 |
4830 |
NME1 |
protein_coding |
P15531 |
FUNCTION: Major role in the synthesis of nucleoside triphosphates other than ATP. The ATP gamma phosphate is transferred to the NDP beta phosphate via a ping-pong mechanism, using a phosphorylated active-site intermediate. Possesses nucleoside-diphosphate kinase, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, geranyl and farnesyl pyrophosphate kinase, histidine protein kinase and 3'-5' exonuclease activities. Involved in cell proliferation, differentiation and development, signal transduction, G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis, and gene expression. Required for neural development including neural patterning and cell fate determination. During GZMA-mediated cell death, works in concert with TREX1. NME1 nicks one strand of DNA and TREX1 removes bases from the free 3' end to enhance DNA damage and prevent DNA end reannealing and rapid repair. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12628186, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16818237, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8810265}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cytoplasm;Differentiation;Direct protein sequencing;Endocytosis;Isopeptide bond;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleotide metabolism;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transferase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene (NME1) was identified because of its reduced mRNA transcript levels in highly metastatic cells. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDK) exists as a hexamer composed of 'A' (encoded by this gene) and 'B' (encoded by NME2) isoforms. Mutations in this gene have been identified in aggressive neuroblastomas. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Co-transcription of this gene and the neighboring downstream gene (NME2) generates naturally-occurring transcripts (NME1-NME2), which encodes a fusion protein comprised of sequence sharing identity with each individual gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4830; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; deoxyribonuclease activity [GO:0004536]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; magnesium ion binding [GO:0000287]; nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity [GO:0004550]; ribosomal small subunit binding [GO:0043024]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; CTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006241]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; GTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006183]; lactation [GO:0007595]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; nucleoside diphosphate phosphorylation [GO:0006165]; positive regulation of DNA binding [GO:0043388]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation [GO:0050679]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981]; UTP biosynthetic process [GO:0006228] |
11319942_There is an inverse correlation between nm23-H1 gene product expression and lymphatic vessel invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 11726210_Identification of structural domains affecting transactivation potential 11776896_There was a significant difference of nm23-H1 protein expression level between 3-year survival and 7-year survival group (P 5' exonuclease. NDK1 excised nucleotides from single-strand break produced by APE1 or Nth1. When human cells were treated with various DNA-damaging agents, human NDK1 translocated from cytoplasm to nucleus 16317582_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16415009_Nm23-H1 and EBNA3C can modulate expression of COX-2 in the context of EBV infection and transformation. 16466905_The data provide novel insight into the subunit composition of the epithelial CFTR/AMPK/NDPK complex, such that: CFTR interacts specifically with AMPK alpha1, gamma2 and NDPK-A and not NDPK-B or AMPK gamma1. 16531762_These data imply that nm-23 may be tumor suppressor gene involved in neck squamous cell carcinomas but that it may not function as a tumor metastasis suppressor in high-stage laryngeal carcinoma. 16631833_The effects of the EBV nuclear antigen 3C on the activities of Nm23-H1 via GATA-1 and Sp1 are reported. 16739125_Nm23-H1 has a role in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 16739379_Expression of nm23 protein was significantly higher in the group without lymph node metastasis than those with lymph node metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 16759016_The low level expression of nm23-H1 protein and the high level expression of VEGF protein may be associated with the development and poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 16848180_The expressions of CD44 and nm23-H1 in the metastatic lymph node tumor had no difference compared with that in primary tumor of supraglottic or hypopharyngeal cancer. 16862176_Novel roles of NM23 proteins in skin homeostasis, repair and disease. 16891807_Results suggest that the expression of nm23-H1 protein can be used as a poor prognostic marker in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, and the mutational change of gene may operate in the lymphomagenesis. 16944571_Data show that the nm23H1 gene have the effect of suppressing gastric cancer occurring and lymph metastasizing. 16957985_Overexpression of wild type nm23-H1 mutant in INS cells markedly potentiated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. 17008916_Cleavage of SET by GzmK abrogates its nucleosome assembly activity.After GzmK loading, SET and DNase NM23H1 rapidly translocate into the nucleus and SET is cleaved, where the nuclease activity of NM23H1 is activated to nick chromosomal DNA. 17103045_Impairment of the multifunctional role of Nm23-H1 is an important feature consistent with the complex strategy carried out by HPV-16 E7 to promote cell transformation and tumor progression. 17155928_The double mutant H118N/S120G was expressed in inclusion bodies in E. coli. Its renaturation stops at a folding intermediate and cannot be reactivated by ATP in vitro. 17197349_Reduced expression seems to be related to increased metastatic potential in most carcinoma types. May play tissue-specific role. 17283532_The expressions of KAI1, nm23, ETS-1 and VEGF proteins were highly related to microvascular density, cervical lymph node metastasis, and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 17314099_the direct interaction of NM23-H1 and STRAP is important for the regulation of TGF-beta-dependent biological activity as well as NM23-H1 activity 17348207_There was negative correlation between the positive expression of nm23H1mRNA and bone metastasizing, TNM staging, MVD in prostate cancer. 17359290_Results reveal a significantly positive relationship between expression of hTERT and nm23-H1 in normal and neoplastic tissues of uterine cervix. 17578003_Studies show that the productivity of rhNDPK-A was 1.15 g per 100 g wet cells, and high yield provides material for the translation researches of NDPK. 17591363_In advanced breast cancer, nm23-H1, as detected by reverse transcripted-polymerase chain reaction, seems to be a predictor of bad prognosis. 17655525_C-terminal domain mediated h-Prune homodimerization, as well as its interaction with NM23-H1 17688968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17688968_The polymorphisms of NME1 gene and the susceptibility to and severity of lung cancer was demonstrated. 17695492_The intensity of nm23 staining in the gastric tumor cells was not significantly correlated with depth of tumor infiltration (T-stage), lymph node metastasis (N-stage), distant metastasis (M-stage), UICC-stage, or prognosis. 17885583_Reduced nm23-H1 expression is correlated with uveal melanoma 17918157_Nm23-H1 may have a role in progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma 17975005_The complementary abilities of ER alpha and NM23-H1 together to influence gene expression, cell migration, and apoptosis could be key factors in helping to determine tumor cell fate 18058029_Nm23-H1 homologs -H2, -H4 and -H5 may suppress metastasis. Motility suppression appears to be cell context dependent, but sequence disparities between -H1/H2 and the other family members may reveal regions critical for this inhibitory phenotype. 18089805_Nm23-H1 down-regulation of EDG2 is functionally important to suppression of tumor metastasis in breast neoplasms. 18154714_NM23 gene is a metastasis suppressor gene, which exhibits a reduced expression in metastatic tumor cells. 18219290_Downregulated NM23-H1 expression is associated with intracranial invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 18239814_Expression of nm23 in the cytoplasm was detected almost 3-fold more often than in the nuclei; cytoplasmic expression more strictly correlated with patient's age, tumor location, and its histological structure than nuclear expression. 18301251_nm23-H1 expression in B-cell NHL was not significantly increased in clinically aggressive versus indolent neoplasms 18307927_The high expressions of VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 and inactivation of nm23-H(1) may play an important role in lymphatic metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 18330957_nm23-H1 immunoreactivity showed no difference in primary and metastatic gastric cancer. 18408655_Nm23 may have a biological function that leads to poor clinical outcomes in ovarian carcinoma. 18440302_The knockdown of nm23-H1 expression may change the lung cancer cells to a more invasive phenotype through alteration in the expression of a set of genes. 18470881_Nm23-H1 can negatively regulate cell migration and tumor metastasis by modulating the activity of Cdc42 through direct interaction with Dbl-1. 18476632_CD44 and nm23-H1 proteins play an important coordinated regulation role in the carcinogenesis, development and metastasis of laryngeal carcinoma. 18635542_NM23-H4 binds the inner mitochondrial membrane with high affinity to cardiolipin and couples nucleotide transfer with respiration 18668641_High nm23-H1 expression is predictive of worse overall survival for cervical cancer patients. 18676749_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676749_promoter polymorphisms in the NME1 gene may alter its expression and influence breast cancer survival 18700747_Human metastasis regulator protein H-prune is a short-chain exopolyphosphatase 18728402_Nm23-H1 can negatively regulate cell migration and tumor metastasis by modulating the activity of Cdc42 and possibly other Rho family members through interaction with Dbl-1 18810774_Report relationship between nm23H1 genetic instability and clinical pathological characteristics in Chinese digestive system cancer patients. 18815136_direct interaction between NM23-H1 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is critical for alleviation of MIF-mediated suppression of p53 activity 18996649_nm23 cannot be considered as a useful marker for the evaluation of invasion in differentiated thyroid carcinomas or in distinctions between follicular adenoma and carcinoma. 19024519_The expressions of nm23 and KAI1 proteins are negatively correlated with clinical stage, but positively with histopathological grade in gallbladder adenocarcinoma. 19026164_Results suggest that nm23-H1 may act as a cellular protector against oxidative stress, possibly triggering increased expression of GPX1 and the p53-related antioxidative pathway. 19170058_IFI16 and NM23/NDPK are simultaneously bound in vivo to the promoters of the oncogene cMYC and of P53 19183483_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19186179_Rescue of the neuroblastoma mutant of the human NME1 by the natural osmolyte trimethyloxamine is reported. 19263457_Data contribute to the overall knowledge about nm23-H1 and its role in cell adhesion, migration, and invasion, especially in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 19332021_Nm23-H1 was modified with SUMO-2 after X-ray irradiation. 19513384_The data confirm the role of the studied proteins in invasion and metastases of malignant tumors and suggest a relationship between changes in the expression of nm23 protein and mechanisms of stomach cancer progress. 19619546_Data suggest that transglutaminase 2 is overexpressed in cystic fibrosis and affects nucleoside diphosphate kinase function 19624895_nm23-H1 gene could inhibit proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells. 19655221_important role of extracellular NM23-H1 in the malignant progression of leukemia 19664043_These findings suggest an important role for extracellular NM23-H1 in the malignant progression of leukemia 19664078_downregulation of nm23-H1 proteins was significantly associated with proliferation, invasion depth and lymph node metastasis of ESCC. statistically significant correlations between expression of beta-catenin and nm23-H1. 19724852_nm23 was not related to lymph node metastases 19951590_The results indicated that those patients who died within 5 years after surgery had a lower expression of nm23 than those who survived. 19956735_key enzymatic and metastasis suppressor functions of Nm23-H1 are regulated by oxido-reduction of its Cys109 20099494_There was no significant correlation between cyclooxygenase-2 and nm23 (non-metastatic cells protein1) expression or microvessel density in ovarian serous carcinoma 20101217_Plakoglobin has a role in regulating the metastasis suppressor activity of Nm23. 20113651_A higher expression of nm23-H(1) in children with T-ALL may be contributed to a low remission rate and a poor prognosis. 20145075_The expression of NME1 in either villi or decidua is higher significantly in miscarriage than that of the normal early pregnancy. 20209495_Data demonstrated that the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of NM23-H1 is necessary for metastasis suppressor function. 20304626_Defining the mechanism by which Nm23-H1 transcriptionally downregulates LAP1 remains a lingering question and an area of ongoing study that will need to be addressed. 20403806_formation of disulfide bonds in NDPK-A is involved in the regulation of the oligomerization and bioactivity of this multiple function protein, and that C145 is a key residue in the regulation of NDPK-A. 20448457_These results suggest that Nm23-H1 may have a role in the regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis in human B-cells. 20508983_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20559153_Upregulation of NM23-H1 is associated with pemetrexed responsiveness in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 20560137_High NM23-H1 is associated with recurrence in colorectal cancer patients undergoing 5-fluorouracil adjuvant chemotherapy 20570897_Translocation of small amount of NM23H1 into the nucleus induced by the overexpressions of SEI1/SET could increase the frequency of sister chromatid exchangein esophageal cancers. 20599259_Heterozygous genotypes TC in rs16949649 and CT in rs2302254 of nm23-H1 promoter are potential susceptibility factors for endometrial cancer in Taiwan women. 20599259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20671611_The prognostic significance of the genes casein kinase 2 alpha subunit (CSNK2A1), anti-apoptosis clone-11 (AAC-11), and tumor metastasis suppressor NME1 in completely resected non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, was analysed. 20713695_Data show that the loss of Nm23-H1, an event suspected to promote metastasis, may additionally function at an earlier stage of tumor development to drive the acquisition of chromosomal instability. 20841469_NM23-H1 is critical for control of cell-cell adhesion and cell migration at early stages of the invasive program in epithelial cancers, orchestrating a barrier against conversion of in situ carcinoma into invasive malignancy. 20872186_nm23-H1 (and estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor status) are independent predictive factors of pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant docetaxel plus epirubicin combination chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20955383_nm23 does not appear to be a more useful biomarker than p16 in identifying cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 or high-risk human papillomavirus infection. 20959063_After nm23-H1 gene is transfected into L9981, proteome in L9981 is remarkably changed. 21045303_preliminary electron-density map shows a large conformational change of the C-terminal domain of NDPK-A induced by a novel disulfide bond that is formed under oxidative conditions 21080107_Basal-like status and nm23-H1 status were significant for pathological complete response in breast cancer patients. 21085602_Studies indicate that most of the proteins known to interact with human NME proteins were also found in starlet sea anemone. 21121676_Using pH titration of LC buffers and MS/MS i.d., recombinant NM23-H1 subjected to autophosphorylation was shown to contain phosphorylated histidine at residue 118 at pH 5 and 6, with each level giving over 75% peptide coverage for identification. 21169412_Nm23-H1 expression was significantly associated with IL1beta and IL6 expression in primary uncultured AML samples. These findings have implications for the role of Nm23-H1 in AML and its use as a prognostic marker. 21176535_There is a significant relationship between polymorphism of Nme1-1465 T>C and the prognosis of carcinoma of stomach. 21221850_EGFR and nm23 can serve as reliable biomarkers for prognosis prediction in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma who may benefit from alternate treatment strategy and targeted treatment. 21265090_NM23-H1 gene may be the upstream regulator of metastasis-associated genes in lung cancer. 21270158_The authors found that Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus increases expression and nuclear translocation of Nm23-H1 and that nuclear translocation of Nm23-H1 is regulated by the virus-encoded latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA). 21273640_This study found that the overexpression of lipocalin 2 or knockdown of nm23-H1 genes increased the proliferation of uterine cervical cancer cells. 21350102_In early pheochromocytoma, evaluation of nm-23, galectin-3, and COX-2 expression could predict the outcome. 21442621_Cervical cancer patients with positive nm23-H1 and negative lipocalin 2 expression had the worst recurrence probability and overall survival. 21448569_NM23-H1 opposes not only the motile and invasive characteristics of metastatic cells but also the acquisition of mutations that drive malignant progression to the metastatic phenotype itself.[review] 21469425_NM23 acts like an oncogene in ovarian carcinomas. 21478336_Expression of nm23-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. 21484438_The aggregation process is triggered by the reduced stability of the S120G variant of the NM23-H1 gene. 21553004_Our findings suggest a correlation between high levels of NM23-H1 protein in the cytoplasm of the cells and progression of prostate cancer to metastasis, thus definitively identifying NM23-H1 as a new negative prognostic marker in prostate cancer. 21769563_Nm23-H1 protects cells against oxidative stress through the engagement of DNA BER enzyme APE1 21846466_Functional modulation of the metastatic suppressor Nm23-H1 by oncogenic viruses. 21913743_results indicated that expression patterns of ER, NM23-H1, and HER2 in primary breast cancer lesions warn that cells might have metastatic potential 22035418_correlated five single nucleotide polymorphisms within the NME1 promoter with drug-induced toxicity, disease-free survival and overall survival (OS) in 360 Caucasian patients suffering from acute myeloid leukemia 22290468_Sodium valproate at concentrations of 0.8-3.2 mM inhibits migration of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells and modulates Nm23H1 gene expression in a concentration-dependent manner. 22328561_Studies identified three genes, CHD5, PAFAH1B1, and NME1, strongly associated with patient outcome. 22349375_nm23-H1 behaves as a metastasis suppressor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and nm23-H1 downregulation in the is a biomarker for poor NPC prognosis. 22364921_Data suggest that TSLP might downregulate NME1 expression via STAT3 signaling pathway, affecting TIMP1 expression in influencing trophoblast invasion. 22421058_NME mRNA and high NME2 mRNA are strong indicator of increased event-free survival independent of FLT3-internal tandem duplication in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia 22429576_Downregulation of nm23-H1 gene expression enhanced the invasiveness compared with the controls. 22451184_ROC curve showed that NM23HI expression was a strongly correlated (r=0.816) sensitive and specific metastasis marker. NM23HI expression did not show asignificant relationship with histologic degree of invasive ductal carcinoma. 22531683_the present findings do not support a significant role of Nm23-H1 in metastasis suppression of LLSCC 22683585_Our studies suggest that rs16949649 and rs2302254 polymorphisms in the nm23 gene promoter may influence the prognosis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. 22718351_These results indicate a novel function of Nm23-H1 to control contact inhibition of locomotion, and its negative regulation by ephrin-B1. 22869372_NDPK-A exists in a functional cellular complex with AMPK and CFTR in airway epithelia, and NDPK-A catalytic function is required for the AMPK-dependent regulation of CFTR 22903495_Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the promoter regions of non-metastatic cells 1 gene is associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. 22920000_higher expression of nm23 gene correlated with an early stage of tumor and its good differentiation 23137649_nm23-H1 is a negative regulator of TGF-beta1-dependent induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer 23158994_Expressions of TIMP-1 and nm-23, tumor size and lymph node involvement were independent prognostic factors in HER-2-positive breast cancer. 23448979_Data indicate that the D388A and D422A mutant h-Prune proteins interact weakly with Nm23-H1. 23464856_High NM23-H1 expression is associated with radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 23479363_High serum NM23A is associated with kidney cancer. 23519676_The crystal structure of oxidized Nm23-H1 is presented. It reveals the formation of an intramolecular disulfide bond between Cys4 and Cys145 that triggers a large conformational change that destabilizes the hexameric state. 23553196_Positive expression of Nm23 protein was found in ovarian tissue in 77.7 % cases in BRCA1 mutation carriers and in 90.9 % in the control group. 23583378_STAT3 directly bound to the STAT3 binding site on the nm23-H1 promoter and activated its expression 23679306_High NM23 expression is associated with sporadic colorectal cancer. 23694823_NM23 demonstrated no discriminatory value in the interpretation of lymph node nevus rests. 23725501_NM23 suppressor protein may have a role in gastric carcinoma pathogenes 23734265_Data indicate that the activation of MAPK and PI3K pathways resulted in TGF-beta1 signaling by down-regulating Nm23-H1 expression and up-regulating the expression of TbetaRI and TbetaRII, favoring further activation of multiple signaling pathways. 23768014_In laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma patients, the disease recurrence rate correlates inversely with nuclear nm23-H1 expression. 23818346_Reduced nm23 immunohistochemical expression is an independent negative prognostic factor for overall survival and progression-free survival in invasive breast cancer. 23856325_Abnormally low expression of NME1 in endometrial stromal cells (ESCs) may be involved in the pathogenesis of endometriosis by up-regulating growth, adhesion and invasion of ESCs. 24096484_Data shows that c-Abl and Arg induce NM23-H1 degradation by increasing expression and activation of cathepsin L and B, which directly cleave NM23-H1 in the lysosome. 24133580_abnormal lower expression of NME1 in endometriotic stromal cells leads to more secretion of IL-8 and VEGF, up-regulates the level of CD62E and CD105, and leads to angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells, which promotes development of endometriosis. 24811176_NME1L is a potent antimetastatic protein and may be a useful weapon in the fight against cancers. 24858271_NM23H1 gene suppresses hyperplasia and metastasis of prostate cancer, thereby improving the survival rate. 24915993_Interaction between Nm23 and the tumor suppressor VHL 24970086_findings show NDPKs (NM23-H1/H2/H4) interact with and provide GTP to dynamins, allowing these motor proteins to work with high thermodynamic efficiency for membrane remodeling 25010650_NDPK-A was not able to bind to model membranes mimicking the inner leaflet of plasma membrane, suggesting that its in vivo membrane association is mediated by a non-lipidic partner or other partners than the studied phospholipids. 25017017_Dual functions of NME1 in suppression of cell motility and enhancement of genomic stability in melanoma 25048347_The metastasis suppressor NME1 regulates expression of genes linked to metastasis and patient outcome in melanoma and breast carcinoma. 25119778_The case for extracellular Nm23-H1 as a driver of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression 25199839_Regulation of the metastasis suppressor Nm23-H1 by tumor viruses 25277180_NM23-H1 may participate in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell responses to cisplatin and be considered a potential therapeutic target. 25321081_Nm23 loss could be associated with a more favorable environment for the development and dissemination of breast cancer 25373728_Using the described method for detecting histidine and aspartic acid phosphorylations and our prostate cancer progression cell system, the potential function of NM23-H1 in suppressing metastasis with a two-component regulation system is discussed 25501107_nm23-H1 protein may be an important prognostic factor in peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified;the nm23-H1-positive group had significantly shorter overall survival (Review). 25748386_Overexpression of Nm23H1 did not affect tumorigenesis in nude mice assays, while overexpression of Nm23H2 enhanced tumor growth with elevated expression of the c-Myc proto-oncogene. 25808322_Fibronectin is an important effector of the motility-suppressing function of NME1 in melanoma cells. 26565392_Results confirmed that NME1L, but not NME1, is likely responsible for regulating breast cancer cell growth by inhibiting IGF1-stimulated ERK phosphorylation through N-terminal 25 amino acid-mediated interaction with KSR1. 26634527_CRC patients with NM23-positive tumors had a better prognosis, and thus NM23 expression maybe used as a key prognostic indicator for CRC. 26825905_NM23 expression is reduced in CRC tissues and low NM23 levels tightly correlate with higher Dukes stages, poorer differentiation grade, and positive lymph node metastases. 27094059_Study reveals that NME1L may perform potent biological roles on the cellular behaviors through the extra N-terminal region as well as hexameric conformation. Because the N-terminal region itself has no effect on NF-kappaB signaling, the dimerization of NME1L is likely a pivotal process to confer the IKKbeta binding ability and subsequent regulation of NF-kappaB signaling on the region. 27222072_elevated NDKA was associated with severe characteristics of adenomas (>/=3 lesions, size >/= 1 cm or villous component). Setting specificity to 85%, NDKA showed a sensitivity of 30.19% and 29.82% for advanced adenomas and advanced neoplasia, respectively. 27449069_Down-regulation of Dyn1 activity enhances extracellular Nme1 in human colon tumor cell lines. 27509166_A strong association between NME1 heterozygous genotype and breast cancer risk in Kashmiri population 27518571_High NME1 expression is associated with well tumor differentiation in Digestive System Neoplasms 27592483_nm23-H1 and MMP-2 may be as an indicator for esophageal cancer metastasis and prognosis 27604954_Results demonstrate that nm23 plays a vital role in decidualization in mice and humans and that nm23 gene expression is hormonally regulated. 27888614_This study suggested that EGFR was an important predictive factor for the prognosis of the post-operative patients with colorectal carcinoma TNM stage I-II, and nm23 is important for predicting the prognosis of the patients with stage III-IV; it is better that EGFR and nm23 are as predictor of combination. 28161101_NM23 might be an indicator of good progno |
ENSMUSG00000037601 |
Nme1 |
322.135991 |
3.8193392350 |
1.933323 |
0.120207234 |
257.973384 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000047454405606112732463703528702016347131747534804387540850487936860661128793958986254615100248971328197480029958524031535736726060277415653678746969984514336715619720052927732467651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011791700786973465456818291744938421953962224164736013700677508840490487967394517929663150923007881454995391279811113318165785334115253440924638017595071914911386556923389434814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
513.5550933 |
34.2066961 |
135.4209722 |
7.3738979 |
| ENSG00000239732 |
54106 |
TLR9 |
protein_coding |
Q9NR96 |
FUNCTION: Key component of innate and adaptive immunity. TLRs (Toll-like receptors) control host immune response against pathogens through recognition of molecular patterns specific to microorganisms. TLR9 is a nucleotide-sensing TLR which is activated by unmethylated cytidine-phosphate-guanosine (CpG) dinucleotides. Acts via MYD88 and TRAF6, leading to NF-kappa-B activation, cytokine secretion and the inflammatory response (PubMed:11564765, PubMed:17932028). Controls lymphocyte response to Helicobacter infection (By similarity). Upon CpG stimulation, induces B-cell proliferation, activation, survival and antibody production (PubMed:23857366). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EQU3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11564765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17932028, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23857366}. |
Alternative splicing;Cytoplasmic vesicle;Disulfide bond;Endoplasmic reticulum;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Leucine-rich repeat;Lysosome;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family, which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. Studies in mice and human indicate that this receptor mediates cellular response to unmethylated CpG dinucleotides in bacterial DNA to mount an innate immune response. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]. |
hsa:54106; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; early phagosome [GO:0032009]; endolysosome [GO:0036019]; endolysosome membrane [GO:0036020]; endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; endoplasmic reticulum membrane [GO:0005789]; endosome [GO:0005768]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; interleukin-1 receptor binding [GO:0005149]; pattern recognition receptor activity [GO:0038187]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; siRNA binding [GO:0035197]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; unmethylated CpG binding [GO:0045322]; cellular response to chloroquine [GO:1902350]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to metal ion [GO:0071248]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; defense response to virus [GO:0051607]; I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0007249]; I-kappaB phosphorylation [GO:0007252]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; maintenance of gastrointestinal epithelium [GO:0030277]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; microglial cell activation [GO:0001774]; MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002755]; negative regulation of ATPase-coupled calcium transmembrane transporter activity [GO:1901895]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032715]; negative regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032717]; negative regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0032088]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034122]; positive regulation of autophagy [GO:0010508]; positive regulation of B cell activation [GO:0050871]; positive regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030890]; positive regulation of chemokine production [GO:0032722]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043123]; positive regulation of immunoglobulin production [GO:0002639]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of interferon-beta production [GO:0032728]; positive regulation of interleukin-10 production [GO:0032733]; positive regulation of interleukin-12 production [GO:0032735]; positive regulation of interleukin-18 production [GO:0032741]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; positive regulation of JUN kinase activity [GO:0043507]; positive regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043410]; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity [GO:0051092]; positive regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901224]; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase biosynthetic process [GO:0051770]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034165]; positive regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0034123]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; positive regulation of type II interferon production [GO:0032729]; regulation of B cell differentiation [GO:0045577]; regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production [GO:0002730]; regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034163]; response to molecule of bacterial origin [GO:0002237]; toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway [GO:0034162]; toll-like receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002224] |
11867692_TLR9 acts at the cell surface and engages an intracellular signaling pathway that includes MyD88, IRAK, and TRAF6 11976718_Toll-like receptor 9 functions in the activation of RF expressing B-cells. 12560217_In naive B cells, the expression of TLR9 and TLR10 is rapidly induced following B-cell-receptor (BCR) triggering. In contrast, memory B cells express several TLRs at constitutively high levels. 12573264_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12600829_All nine patients expressed all of the TLRs studied, whereas only five out of the nine patients had any granulomas positive for IL-4.The associations between TLRs 1, 5, and 9 were different in IL-4-negative compared with IL-4-positive patients. 12689944_normal and neoplastic human B lymphocytes express a distinct TLR repertoire including TLR9 and TLR10 and expression is increased upon engagement of the antigen receptor complex or TLR9 itself 12734363_Costimulation with TLR9 (or TLR2) and TLR4 induces synergistic release of Th1 cytokines, IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, and additive HIV-LTR trans-activation and HIV replication, as measured by p24 antigen release from HIV-1 transgenic mouse spleen cells. 12778475_A synergistic role is played by the TLR9/CD40 system in the orchestration of CpG-ODN-induced responses in B lymphocytes. 14694183_peptidoglycan signaling through TLR2 and bacterial CpG DNA signaling through TLR9 are functionally equivalent at synergizing with IFN-gamma in regulating Tap-1 expression in macrophages 14716310_mechanism of cellular activation involving the recruitment of TLR9 from the ER to sites of CpG DNA uptake, where signal transduction is initiated 14987294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15153500_TLR signals that activate NF-kappaB are diverse among different TLRs, and TLR9 signaling uniquely depends on IRF-8 in DCs. 15294971_mechanism of TLR9 gene regulation 15307186_Toll-like receptor 9 binds single-stranded CpG-DNA in a sequence- and pH-dependent manner. 15585868_TLR9 expression may function as a proinflammatory activation marker during the transition from monocyte to dendritic cells. 15607737_Moreover, the TLR9 transfectant demonstrated its usefulness for evaluation of immunostimulation by bacterial DNA through the detection of T(H)-1, T(H)-2 type cytokine induction via TLR9 signaling. 15631627_The expression of functionally active TLR9 in human malignant tumors might affect treatment approaches using CpG-ODN and shows that malignant cells can be regarded as active players in tumor-immunology. 15730519_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15730519_TLR9 gene polymorphisms were not significantly associated with the susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in Korean patients. 15790341_The TLR9 was analyzed by ICS as it was reported to be expressed in an intracellular compartment. 15860583_a CpR dinucleotide is recognized by TLR9 and leads immune-cell activation and cytokine secretion in vitro and in vivo 15878652_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16002719_Diminished expression and function of TLR9 is a likely consequence of chronic filarial antigen stimulation and could serve as a novel mechanism underlying the dysfunctional immune response in lymphatic filariasis 16024265_results demonstrated that TLR9 expression is correlated with immune activation and differs between individuals with non-activated or chronically immune activated background 16125159_Data indicate that the two TLR-9 promotor polymorphisms are not involved in atherogenesis. 16125159_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16164440_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16230478_TLR9 may have a critical role in the promotion of lupus through the induction of IFN-alpha by predendritic cells. 16237063_TLR9- and FcepsilonRI-mediated responses oppose one another in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by down-regulating receptor expression. 16371473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16394009_Activation of TLR-9 induces IL-8 secretion through peroxynitrite signaling in neutrophils. 16424230_Broad TLR9 activation defects in common variable immune deficiency prevent CpG-DNA-initiated innate immune responses; these defects may lead to impaired responses of plasmacytoid dendritic cells and loss of B cell function. 16428738_Bacterial DNA preparations from different species differ in their capacity to activate TLR-9, which is dependent on the individual [CG] content. Moreover, increased intracellular delivery results in a marked enhancement of immunostimulation. 16437636_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16437636_significant increase of the combined carriership of the CD14 -260T and TLR9 -1237C alleles in the chronic relapsing pouchitis group suggests that these markers identify a subgroup of patients with a risk of developing chronic or refractory pouchitis 16575840_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16608528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16731773_we here demonstrate that S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, and N. meningitidis each activate several TLRs in species-specific patterns and show that infection with live pathogens may lead to activation of PRR not targeted by inactivated bacteria. 16779724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16779724_TLR4 and TLR9 polymorphisms increased the risk of low birth weight in infants; polymorphisms of TLR4 increased the risk of maternal anemia. 16847112_findings demonstrate that TLR-3 and TLR-9 mediate the activation of corneal cells by Herpes simplex virus 1, HSV-1 DNA and HSV-1-antibody complexes 16849519_Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) recognizes microbial DNA. We show here that TLR9 protein is expressed in human breast cancer cells and clinical breast cancer samples. 16864658_This establishes that the primary determinant of TLR9 signaling is not valency but endosomal location and demonstrates a strict compartmentalization of the biological response to TLR9 activation in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs). 16920494_Plays a role of in the recognition of M. bovis BCG by dendritic cells. 16951309_TLR2 and TLR9 cooperate in the control of parasite replication during Trypanosoma cruzi infection; TLR9 has a primary role in the MyD88-dependent induction of IL-12/IFN-gamma synthesis during infection with T. cruzi. 16971956_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16990271_The results of this study suggest a model where modification of the cytoplasmic tail of TLR9 results in trafficking to early endosomes where it encounters CpG DNA. 17000223_reviews experience with two distinct therapeutic strategies: TLR9-based immunomodulation and TLR9-based vaccination 17040905_TLR8 inhibits TLR7 and TLR9, and TLR9 inhibits TLR7 but not vice versa in HEK293 cells transfected with TLRs in a pairwise combination. 17075805_In patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus, the proportion of peripheral blood memory B cells and plasma cells expressing TLR-9 is increased 17142771_HMGB1 suppresses PDC cytokine secretion and maturation in response to TLR9 agonists including the hypomethylated oligodeoxynucleotide CpG- and DNA-containing viruses 17145922_immune cells use several mechanisms to discriminate between stimulatory and nonstimulatory DNA; however, it appears that TLR9 itself binds rather indiscriminately to a broad range of DNAs 17229603_Development of skin lesions in mycosis fungoides appears associated with an increase of TLR9 expression by keratinocytes in cutaneous lesions. 17258734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17292969_expression levels of TLR2, TLR3, TLR4 & TLR9 in endometrium varied in a similar pattern during the menstrual cycle; levels were high in perimenstrual period & low in periovulatory period 17295441_Human peripheral blood B cells express TLR9 and that its expression is increased in patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. 17301562_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17301562_Rapid progression of HIV-1 infection was associated with TLR9 polymorphisms 17325049_These results demonstrate that intestinal epithelial cells recognize pathogenic bacterial DNA and respond by increasing surface localization and expression of TLR9. 17328813_The widespread expression of TLR9 in the nasal mucosa along with its rich representation in leukocytes in different compartments. 17344245_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17344245_The presence of the G allele at position +1174 of TLR9 predisposes humans to an increased risk of SLE. 17373717_TLR9-mediated invasion may represent a novel mechanism through which infections promote prostate cancer. 17440926_TLR9 expression, which was mainly observed as cytoplasmic staining, gradually increased in accordance with the histopathological grade 17469139_These findings suggest that tubular TLR-9 activation has a pathogenetic role in tubulointerstitial inflammation and damage in experimental and human lupus nephritis. 17473064_TLR-9 may play a role in the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis during conditions in which bacterial DNA is present. 17482427_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17516623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17516623_Our results do not indicate a major influence of these putative functional TLR5 and TLR9 single nucleotide polymorphisms on the susceptibility to (or protection from) systemic lupus erythematosus. 17534115_TLR 9 play a distinct role in the inflammatory response that clears viruses from the retina. 17573724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17573724_the TLR9 promoter polymorphism C-1237T might affect atopic eczema susceptibility in particular in patients with the intrinsic variant of AE 17636117_synthetic agonists of TLR9 interfere with growth and angiogenesis also by epidermal growth factor receptor- and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity-independent mechanisms affecting endothelial cell functions 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17768129_Overexpression of TLR9 is associated with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia 17854429_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17854429_SNPs in the TLR9 gene were not significantly associated with susceptibility to Behcet's disease 17854755_Patients with severe and mild malaria showed increased surface expression of TLR2 and TLR4 on CD14(+)monocytes and myeloid dendritic cells and decreased intracellular expression of TLR9 on plasmacytoid dendritic cells compared to healthy controls. 17878374_suggest the existence of an IRAK-4-independent TLR9-induced transduction pathway leading to PI3K activation 17893430_direct CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides and TLR-9 interactions in HT-29 cells could provide new approaches in malignant tumor therapeutic strategies 17894360_polymorphism of TLR9 gene is significantly associated patients with mold infections, suggesting a possible role for this genetic variant as a risk factor for mold infections in pediatric patients receiving chemotherapy for hematological diseases 17914947_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17914947_TLR9 variants were not major risk factors for Crohn's disease in New Zealand population, but may associations with disease worldwide. 17932028_Btk as a key signaling molecule that interacts with and acts downstream of TLR8 and TLR9. 17964520_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17984204_an NF-kappaB luciferase reporter assay in human embryonic kidney cells transfected with human TLR9 demonstrated that Entamoeba histolytica DNA signaled through Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) in a manner similar to that seen with CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides. 17986857_Functional expression of TLR9 is associated to the metastatic potential of human lung cancer cell. 18036648_Autocrine TNF-alpha secretion resulting from IgE/FcepsilonRI-dependent activation plays a critical role in suppressing TLR9-dependent responses in plasmacytoid dendritic cells that normally promote T(H)1 activity 18092352_Benign prostate epithelial cells express both TLR 4 (LPS-specific) and TLR 9 (CpG-specific) when exposured to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and CpG DNA. 18160420_abnormality of innate immunity plays a crucial role in the pathology of sysemic lupus erythematosus: blockade of CpG-TLR9 interaction may be a new therapeutic approach. 18208876_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18208876_no significant association with multiple sclerosis and no protective effect of T-1237C concerning age of onset, disease severity or disease subtype in patients 18215354_There is downregulation of TLR9 expression mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of hepatitis B virus-infected patients, but an increased TLR9 expression at the protein level 18253698_expression of TLR9 within human glioblastomas strengthens the rationale for the utilization of oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs in this disease 18262306_This review will focus on the roles of TLR9 in immune responses, and its signaling pathways--REVIEW 18275280_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18275280_Susceptibility to allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis was associated with allele C on T-1237C (Toll like receptor 9) 18312481_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18312481_it was concluded that TLR9 and CD14 gene polymorphisms may contribute to an inherited predisposition to asthma in Tunisian children. 18318750_Impaired TLR9-dependent immune responses in Human plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are associated with allergic status and inversely correlated with Fc epsilon RI alpha expression. 18332208_these data demonstrate that TLR9 detects A. fumigatus DNA, resulting in the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, which may contribute to the immune response to the pathogen. 18406377_TLR7-9 recognize single-stranded RNA, nucleoside analogs and single-stranded CpG-DNA, respectively, and their activation initiates the immune response against viruses and bacteria [review] 18437017_TLR3 and 9 as well as IFN-beta and TNF-alpha are expressed in verruca and molluscum contagiosum skin lesions and may play a pivotal role in cutaneous innate immune responses 18524824_B cells from HIV-infected persons express reduced levels of TLR9 mRNA, and this defect is especially pronounced among memory B cells 18535206_CD300a and CD300c play an important role in the cross-regulation of TNF-alpha and IFN-alpha secretion from pDCs; CD300a/c RNA and surface expression were downregulated after stimulation of pDCs with TLR7 and TLR9 ligands 18539711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18568766_Targeting toll-like receptor 9 with CpG oligodeoxynucleotides enhances anti-tumor responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from human lung cancer patients. 18595521_TLR9 is expressed by nasal epithelial cells 18606688_study demonstrated that infection with Trypanosoma cruzi parasites promotes recruitment of TLR9 to the endo-lysosome compartment 18633634_TLR9 is expressed in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and its activation promotes in vitro myofibroblast differentiation. 18686608_Human epidermal keratinocytes constitutively express all TLR 1-10 mRNA, which may enable human keratinocytes to respond to a wide range of pathogenic micro-organisms. 18763053_both mRNA and protein levels of TLR4 and TLR9 were strongly expressed in lung cancer tissue; the expression level of TLR4 correlated with malignancy of lung cancer 18769358_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18776126_activation of the TLR9/MyD88 pathway by common antigens may affect the severity of IgAN 18776592_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18806803_Divergent TLR7 and TLR9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and nonpathogenic AIDS virus infections. 18818748_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18832675_Activation of human plasmacytoid dendritic cells by TLR9 impairs Fc gammaRII-mediated uptake of immune complexes and presentation by MHC class II 18841790_The expression of TLR-9 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps patients was lower than in controls. 18922969_TLR9 expression is increased in breast cancer and CpG oligonucleotide-induced cellular invasion is mediated via TLR9 and TRAF6, independent of MyD88. 18946062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19019335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19033535_Toll-like receptor 2, 4, and 9 overexpression is associated with neutrophil dysfunction in alcoholic hepatitis. 19034349_TLR9 activation induces a Th1-like pattern of cytokine release which led to interest in the use of synthetic CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODN) for the prevention and treatment of Th2-associated atopic disorders such as asthma 19050243_TLR9-mediated B cell stimulation induces zeta-chain associated protein kinase 70kDa (ZAP70) expression; ZAP70 expression in human B cells represents an exclusive hallmark of TLR9-mediated B cell activation. 19079358_TLR9 bound to CpG DNA had glycan modifications indicative of Golgi processing confirming that TLR9 travels through the Golgi complex to access CpG DNA in endolysosomes 19096003_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19120473_inappropriate activation of TLR9 predisposes to systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases; nucleotides with antagonistic effect on TLR9 reported for the treatment 19129482_activation via TLR7 and TLR9 affects several eosinophil functions 19130296_Among 77 patients with SLE, the CC, CT and TT genetype frequencies of the SNP of TLR-9(rs352140) were 20.8, 61.0 and 18.2%, respectively. 19130296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19201477_Human microsatellite DNA mimicking oligodeoxynucleotides down-regulate TLR9-dependent and -independent activation of human immune cells. 19211891_Stimulation of innate immunity via toll-like receptor 9 is highly effective at reducing the parenchymal and vascular amyloid burden in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. 19247692_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19254290_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19264973_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19275920_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19284650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19284650_no association of TLR9 genetic variants with severe malaria was found; report also shows that TLR9 expression is potentially modulated through cis-regulatory variants, which may lead to differential inflammatory responses to infection between individuals. 19289178_The authors conclude that HBV infection results in reduced frequency of circulating pDCs and their functional impairment via inhibiting the expression of TLR9. 19297619_TLR9 and MyD88 are essential to initiate IL12 and IFNgamma responses and favor host hyperresponsiveness to TLR agonists resulting in overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines and the sepsis-like symptoms of acute malaria. 19299739_bacterial DNA predominantly signals through TLR9 in HUVECs 19317913_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 19317913_Similar frequencies of TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, and MAL genetic polymorphisms in populations with different histories of malaria exposure suggest that these innate immune pathways have not been under strong selective pressure by malaria. 19319670_TLR9 signaling could promote the tumor progression of human tumor cells, which might provide novel insight into the implications for CpG based anti-tumor therapies. 19337058_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19337058_The CD14-159C/T and the TLR9-1237T/C promoter polymorphisms increase the risk of precancerous outcomes, but they do not seem to increase the risk of gastric cancer itself. 19362685_increased expression in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 19367581_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19390575_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19401392_IFN-alpha amplifies the inductive effect of CpG ODN on naive B activation and on Ig production through a mechanism involving TLR-9/MyD88-dependent signaling. 19406482_expressed on Fallopian tube and uterus 19423540_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19459480_Two-fold, 4.4-fold, and 3-fold rise in expression of TLR9, NF-kappaB, and TNFalpha genes respectively was revealed in pregnant women with herpesvirus infection compared to women with physiologically occurring pregnancy. 19505919_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19513613_TLR9 mRNA and protein are down-regulated in PBMC of HBV-infected or HCV-infected patients. 19527514_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19539691_A significant association was observed between the presence of the T-1237C polymorphism (TLR9) and susceptibility to viral pneumonia (p=0.04; odds ratio [OR]: 1.73). 19539691_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19564354_Data show that BST2 directly binds to purified ILT7, initiates signaling via the ILT7-FcepsilonRIgamma complex, and regulates TLR7/9 responses in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. 19578108_Activation of TLR-9 expressing glomerular cells by endogenous nucleic acids (nucleosomes) may amplify the inflammatory response. There is an up-regulation of TLR-9 within the glomerulus of patients with lupus nephritis. 19601804_Studies indicate the role of Toll-like receptors including TLR9 in modulating the immune response to respiratory viral disease, including the role of maturation of the TLR system in early life. 19618291_TLR9 up-regulates COX-2 expression in prostate cancer cells, at least partially through the activation of NF-kappaB, which may be implicated in tumor invasion and metastasis. 19620253_Higher activation of TLR9 in dendritic cells by microbial DNA compared with self-DNA based on CpG-specific recognition of phosphodiester DNA is reported. 19627277_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19639721_lower expression in nonatopic children in foster care than in nonatopic children living with their parents 19714766_TLR9 signaling mediates the anti-inflammatory effects of natural commensal-origin DNA on the gut because TLR9 silencing abolished the inhibitory effect of natural commensal-origin DNA on TNF-alpha-induced IL-8 secretion in polarized intestinal epithelium 19723394_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19724876_TLR9 signal pathway, by activating NF-kappaB, negatively regulates ERalpha-mediated transactivation of breast cancer 19740627_Cultured human melanocytes express functional toll-like receptors 2-4, 7 and 9. 19745833_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19745833_Study showed that TLR9 polymorphisms, and TLR9 and MYD88 haplotypes are related to the development of HL. 19771452_Findings in three independent population samples indicate that variations in TLR2 and TLR9 might play important roles in determining susceptibility to TB. 19771452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19794067_These results reveal a TLR7/9-dependent signaling pathway used by human PBMCs to initiate a type I IFN response to the extracellular bacterium B. burgdorferi. 19796535_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19796535_only the distribution of TLR9 (toll-like receptor 9)1486 T/C genotype and allele frequencies was different between Behcets disease patients and healthy controls, but did not reach statistical significance 19809335_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19810822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19840968_TLR9 mediates cigarette smoke-induced release of CXCL8 and this may contribute to the accumulation of neutrophils and inflammation within the airways of smokers 19844589_NGF is able to induce TLR4/TLR9 overexpression in vernal keratoconjunctivitis-endothelial cells. 19854217_agonist CpG ODNs stimulates lung cancer cells proliferation via CDK2 upregulation 19855253_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19855253_Results suggest a potentially new role for TLR4 polymorphisms in HIV-1 peak viral load and confirms a role for TLR9 polymorphisms in disease progression. 19903791_a toll-like receptor 9 agonist cooperates with trastuzumab in trastuzumab-resistant breast tumors through multiple mechanisms of action 19906293_Data show that the CD40 mAb CP-870,893 activates both memory and naive B cells and triggers their T cell stimulatory capacity, and that simultaneous TLR9 ligation augments the effect of CP-870,893 alone. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19914718_These findings reveal a novel mechanistic insight into an interrelationship between SR-A1 and TLR-3/-9 signaling in human cytomegalovirus-exposed monocytes. 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 19953283_TLR2, TLR4, and TLR9 were expressed by infiltrating cells of perimysium in dermatomyositis, whereas they were expressed by infiltrating cells of endomysium in polymyositis 20026892_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20026892_results indicate that the major genetic variations in TLR9 is rare and may not be associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease in Korea 20038537_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20041977_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20041977_TLR9 haplotypes may be associated with susceptibility to chronic periodontitis; haplotype T(-1486)/T(-1237)/A(2848) was significantly more frequent and the haplotype T(-1486)/T(-1237)/G (2848) of the TLR9 gene was less frequent. 20044998_The TLR9, IL6, and CDH1 variants all persisted as independent risk factors for post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome (PI-IBS) when controlling for previously identified clinical risk factors. 20054821_Expression of TLR9 is increased in prostate cancer specimens, especially in the most poorly differentiated forms. 20085599_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20085599_Significant associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms with wheeze in the past year were detected in only four genes (IL4R, TLR4, MS4A2, TLR9). Variants in IL4R and TLR4 were also related to allergen-specific IgE, but not for MS4A2 and TLR9. 20100933_Studies show substantial decreases in older compared with young individuals in cytokine production in response to TLR1/2, TLR6, TLR3, TLR5, and TLR8, TLR7 and TLR9 in DCs. 20130217_Data show that Sigirr overexpression depresses NF-B-mediated diverse TLR responses. 20132814_Expression of TLR9 shows significant correlation in bone marrow cells from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes which convert to overt leukemia. 20137629_The polymorphism of rs187084 and rs352139 in TLR-9 is not associated with SLE in Han Chinese. 20181802_TLR9 is involved in the etiology of lupus nephritis and it may play some role in podocyte injury. 20194452_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20197609_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20197609_TLR3c.1377 and TLR9 2848 polymorphisms might be related to multiple sclerosis in Han people in south China. 20207250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227302_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20227302_Polymorphisms in TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 that recognize bacterial and viral pathogens are associated with bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation. 20227772_TLR9-mediated IL-10 production by B cells was significantly decreased in multiple sclerosis, and this decrease is likely due to decreased TLR9 expression in memory B cells, suggesting a role of TLR9 in immunoregulation in multiple sclerosis 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20307689_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20348497_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20348497_This study presents the first human data that toll-like receptor single nucleotide polymorphisms are associated with altered cytokine production in parasitic infection. 20363151_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 20364327_SIGIRR can inhibit TLR4, 5, and 9-mediated immune responses in human airway epithelial cells. 20375564_TLR9 activation contributes to the insufficient host response against virulent mycobacteria. 20375566_High-grade breast cancers had significantly increased TLR9 expression as compared with lower-grade tumors. TLR9 expression was highest in the mucinous and the lowest in tubular breast cancers. 20399690_In individuals affected by primary Sjogren's syndrome, TLR9 mRNA levels are up-regulated in the mononuclear blood cells and TLR9-positive cells exist in the epithelial islands, lymphocytes, and ductal epithelial cells of the parotid glands. 20406964_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20422193_A single nucleotide polymorphism (rs187084) in TLR9 gene may be a susceptibility factor for rheumatoid arthritis in this Turkish population. 20422193_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20438785_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20442853_The first year of life represents a critical period during which adult-like levels of TLR responses are reached for most but not all cytokine responses 20452482_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497632_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20497632_TLR9 gene have a role in establishing an autoimmune background and pathogenesis in human lupus nephritis 20500814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20500814_These results demonstrate a significant correlation between specific genetic variants of the TLR9 gene and risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20514021_TLR9 triggering resulting in histone modifications to negatively affect the activation of the promoter of EBV's master regulatory lytic gene BZLF1 20559388_a new role for self nucleic acid recognition by toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR9 on B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20592251_Human plasmacytoid predendritic cells were highly sensitive to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis but they were protected by microbial stimulation through TLR7 and TLR9. 20595247_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20604744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20622911_5-year OS in acute myeloid leukemia patients with the CC gene variant of TLR9 was 70.2% compared with 44.8% (P |
ENSMUSG00000045322 |
Tlr9 |
13.772823 |
0.0069018242 |
-7.178807 |
1.132320510 |
58.062512 |
0.00000000000002539193051858383603092030126843751177968507362625594225846725748851895332336425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000166719259098886765231592430447346550917951668591143743469729088246822357177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2047465 |
0.2842379 |
30.9119563 |
21.7137974 |
| ENSG00000239775_ENSG00000136279 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
389.210868 |
0.2939616895 |
-1.766300 |
0.245354869 |
48.637745 |
0.00000000000307886192118513305356927791294842421208205474059127482178155332803726196289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000017758500178465246600908625537386549813473335390767715580295771360397338867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
183.7276343 |
146.5084255 |
642.7884197 |
356.9266063 |
| ENSG00000239998 |
11027 |
LILRA2 |
protein_coding |
Q8N149 |
FUNCTION: Part of the innate immune responses against microbial infection (PubMed:12529506, PubMed:27572839). Specifically recognizes a set of N-terminally truncated immunoglobulins that are produced via cleavage by proteases from a range of pathogenic bacteria and fungi, including L.pneumophila, M.hyorhinis, S.pneumoniae, S.aureus and C.albicans (PubMed:27572839). Recognizes epitopes that are in part in the variable region of the immunoglobulin light chains, but requires also the constant region for signaling (PubMed:27572839). Binds to a subset of cleaved IgM, IgG3 and IgG4 molecules, but does not bind cleaved IgA1 (PubMed:27572839). Binding of N-terminally truncated immunoglobulins mediates activation of neutrophils (PubMed:27572839). In monocytes, activation leads to the release of CSF2, CF3, IL6, CXCL8 and CCL3 and down-regulates responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), possibly via down-regulation of TLR4 expression and reduced signaling via TLR4 (PubMed:22479404). In eosinophils, activation by ligand binding leads to the release of RNASE2, IL4 and leukotriene C4 (PubMed:12529506). Does not bind class I MHC antigens (PubMed:19230061). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12529506, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19230061, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22479404, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27572839}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunity;Immunoglobulin domain;Innate immunity;Membrane;Nitration;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA; + ;NA |
This gene encodes a member of a family of immunoreceptors that are expressed predominantly on monocytes and B cells, and at lower levels on dendritic cells and natural killer cells. The encoded protein is an activating receptor that inhibits dendritic cell differentiation and antigen presentation and suppresses innate immune response. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found. This gene is located in a cluster of related genes on chromosome 19 and there is a pseudogene for this gene on chromosome 3. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:11027; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; antigen binding [GO:0003823]; IgM binding [GO:0001791]; inhibitory MHC class I receptor activity [GO:0032396]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0019221]; defense response [GO:0006952]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; innate immune response activating cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002220]; negative regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031665]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034144]; neutrophil activation involved in immune response [GO:0002283]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of cell activation [GO:0050867]; positive regulation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0071657]; positive regulation of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor production [GO:0032725]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of interleukin-6 production [GO:0032755]; positive regulation of interleukin-8 production [GO:0032757]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
12529506_LIR7 is an activating receptor for eosinophils that elicited the release of cytotoxic granule proteins, de novo lipid mediator generation, and cytokine release through vesicular transport 15242876_Cross-linking of basophil LIR7 resulted in the concentration-dependent net release of histamine and cysteinyl leukotrienes that were maximal at 30 minutes, and of IL-4 that was maximal at 4 hours 17998301_Progenitor mast cells expressed cell surface activating LILRA2. Mature cord-blood-derived mast cells had detectable mRNA encoding multiple LILRs, none were expressed on the cell surface. 18056355_LILRA2 activation, by altering GM-CSF-induced monocyte differentiation into immature DC, provides a mechanism for down-regulating the ability of the innate immune system to activate the adaptive T cell response while promoting an inflammatory response. 18273033_LILRA2 Delta 419-421 isoform encoded by the splice site SNP may play a role in systemic lupus erythematosus and microscopic polyangiitis. 18273033_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19230061_The authors report the LILRA2 extracellular D1D2 domain crystal structure, which reveals structural shifts of the corresponding MHC-binding amino acid residues in comparison with LILR B1/B2, explaining its non-binding to MHC molecules. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20331378_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22479404_LILRA2-mediated activation of monocytes is significantly different to LPS and that LILRA2 selectively modulates LPS-mediated monocyte activation and FcgammaRI-dependent phagocytosis. 27572839_LILRA2 recognizes microbially cleaved antibodies and activates innate immunity, suggesting that LILRA2 detects dangerous immunological situations in which antibodies are destroyed by pathogens. 27572839_findings demonstrate that LILRA2 is a type of innate immune receptor in the host immune system that detects immunoglobulin abnormalities caused by microbial pathogens. 32424043_Molecular mechanism of the recognition of bacterially cleaved immunoglobulin by the immune regulatory receptor LILRA2. |
ENSMUSG00000081665+ENSMUSG00000030427+ENSMUSG00000074417+ENSMUSG00000089942+ENSMUSG00000074419+ENSMUSG00000070873+ENSMUSG00000058818 |
Pira1+Lilra6+Pira12+Pira2+Pira13+Lilra5+Pirb |
196.266209 |
0.3258136109 |
-1.617881 |
0.122653318 |
179.556010 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000006058455254015332140337279356201644733858387907587970013099895632235045219470406488767604068732188654384379633555113287002313882112503051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000001035577286453130829791037194981189204898876439032876815900858851599696884543217233233056194241319573423956712510118904901901260018348693847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
101.8903213 |
8.4970234 |
314.9726032 |
16.4416124 |
| ENSG00000240038 |
280 |
AMY2B |
protein_coding |
P19961 |
|
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Carbohydrate metabolism;Chloride;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
Amylases are secreted proteins that hydrolyze 1,4-alpha-glucoside bonds in oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, and thus catalyze the first step in digestion of dietary starch and glycogen. The human genome has a cluster of several amylase genes that are expressed at high levels in either salivary gland or pancreas. This gene encodes an amylase isoenzyme produced by the pancreas. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
hsa:280; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; alpha-amylase activity [GO:0004556]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975] |
16152770_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 28659346_It was concluded that the genetic variant determining starch metabolism influences the response to weight-loss dietary intervention. Overweight and obese individuals carrying the AMY1-AMY2 rs11185098 genotype associated with higher amylase activity may have greater loss of adiposity during low-calorie diet interventions. 30938472_A significant link between serum amylase activity and ABO blood type in Chinese subjects. 31478242_alpha-Amylase expressed in human small intestinal epithelial cells is essential for cell proliferation and differentiation. |
|
|
62.030498 |
0.1556691248 |
-2.683445 |
0.497093038 |
27.307116 |
0.00000017357143008970392348895193327523722715000076277647167444229125976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000668209261378202902909538823256196948818796954583376646041870117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.8508199 |
11.3372027 |
113.8947625 |
52.6091511 |
| ENSG00000240053 |
58496 |
LY6G5B |
protein_coding |
Q8NDX9 |
|
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
LY6G5B belongs to a cluster of leukocyte antigen-6 (LY6) genes located in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. Members of the LY6 superfamily typically contain 70 to 80 amino acids, including 8 to 10 cysteines. Most LY6 proteins are attached to the cell surface by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor that is directly involved in signal transduction (Mallya et al., 2002 [PubMed 12079290]).[supplied by OMIM, Mar 2008]. |
hsa:58496; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802] |
17975119_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19023099_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19143814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) |
ENSMUSG00000043807 |
Ly6g5b |
107.290761 |
0.3058368788 |
-1.709166 |
0.256613509 |
43.291608 |
0.00000000004716018586779820374866634014365048433586879994550145056564360857009887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000249313876579047810703943963242827305815119132148538483306765556335449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.6507009 |
8.0589917 |
163.1680020 |
17.9746081 |
| ENSG00000240344 |
53938 |
PPIL3 |
protein_coding |
Q9H2H8 |
FUNCTION: PPIases accelerate the folding of proteins. It catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides. May be involved in pre-mRNA splicing. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Isomerase;Methylation;mRNA processing;mRNA splicing;Reference proteome;Rotamase;Spliceosome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the cyclophilin family. Cyclophilins catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of peptidylprolyl imide bonds in oligopeptides. They have been proposed to act either as catalysts or as molecular chaperones in protein-folding events. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2008]. |
hsa:53938; |
catalytic step 2 spliceosome [GO:0071013]; peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity [GO:0003755]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization [GO:0000413] |
15989758_The novel full-length gene of human PPIL3 may be correlated with the formation of human glioma. 16510998_Human cyclophilin J, a new member of the cyclophilin family, has been expressed and crystallized. 18474220_Human peptidyl-prolyl isomerase-like 3 (Ppil3) is one of the Apoptin-associated proteins. 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 26020957_Suppression of CYPJ could repress the growth of HCC, which makes CYPJ a potential target for the development of new strategies to treat this malignancy. 26977013_CYPJ structurally resembles CYPA. It is sensitive to inhibition by CsA and plays a role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis. 28739742_Cyclophilin J expression was up-regulated in gastric carcinoma compared to normal gastric tissues. |
ENSMUSG00000026035 |
Ppil3 |
117.390667 |
0.3923450933 |
-1.349805 |
0.285712695 |
21.721242 |
0.00000315280803847372631331475931193430994881055084988474845886230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010509360128245755507093127378848151920465170405805110931396484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
66.6201294 |
18.6151328 |
172.0549434 |
34.6830846 |
| ENSG00000240356 |
|
RPL23AP7 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.120684 |
2.6883775655 |
1.426736 |
0.426925362 |
10.757590 |
0.00103852534575662753396629867097544774878770112991333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002409783698061283233743390397307848616037517786026000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.0714496 |
19.4152337 |
27.8151742 |
5.4293563 |
| ENSG00000240583 |
358 |
AQP1 |
protein_coding |
P29972 |
FUNCTION: Forms a water-specific channel that provides the plasma membranes of red cells and kidney proximal tubules with high permeability to water, thereby permitting water to move in the direction of an osmotic gradient. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1373524}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Blood group antigen;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
This gene encodes a small integral membrane protein with six bilayer spanning domains that functions as a water channel protein. This protein permits passive transport of water along an osmotic gradient. This gene is a possible candidate for disorders involving imbalance in ocular fluid movement. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]. |
hsa:358; |
apical part of cell [GO:0045177]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; axon [GO:0030424]; basal plasma membrane [GO:0009925]; basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; brush border [GO:0005903]; brush border membrane [GO:0031526]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nuclear membrane [GO:0031965]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; sarcolemma [GO:0042383]; ammonium transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0008519]; carbon dioxide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0035379]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; glycerol transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015168]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; intracellular cGMP-activated cation channel activity [GO:0005223]; nitric oxide transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0030184]; potassium channel activity [GO:0005267]; potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0015079]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; water channel activity [GO:0015250]; water transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0005372]; ammonium transmembrane transport [GO:0072488]; camera-type eye morphogenesis [GO:0048593]; carbon dioxide transmembrane transport [GO:0035378]; carbon dioxide transport [GO:0015670]; cell volume homeostasis [GO:0006884]; cellular homeostasis [GO:0019725]; cellular hyperosmotic response [GO:0071474]; cellular response to cAMP [GO:0071320]; cellular response to copper ion [GO:0071280]; cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus [GO:0071549]; cellular response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0070301]; cellular response to hypoxia [GO:0071456]; cellular response to inorganic substance [GO:0071241]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to mercury ion [GO:0071288]; cellular response to nitric oxide [GO:0071732]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; cellular response to salt stress [GO:0071472]; cellular response to UV [GO:0034644]; cellular water homeostasis [GO:0009992]; cerebrospinal fluid secretion [GO:0033326]; cGMP-mediated signaling [GO:0019934]; corticotropin secretion [GO:0051458]; defense response to Gram-negative bacterium [GO:0050829]; establishment of localization in cell [GO:0051649]; establishment or maintenance of actin cytoskeleton polarity [GO:0030950]; fibroblast migration [GO:0010761]; glomerular filtration [GO:0003094]; glycerol transmembrane transport [GO:0015793]; hyperosmotic response [GO:0006972]; lateral ventricle development [GO:0021670]; lipid digestion [GO:0044241]; metanephric descending thin limb development [GO:0072220]; metanephric glomerulus vasculature development [GO:0072239]; metanephric proximal convoluted tubule segment 2 development [GO:0072232]; metanephric proximal straight tubule development [GO:0072230]; multicellular organismal water homeostasis [GO:0050891]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; nitric oxide transport [GO:0030185]; odontogenesis [GO:0042476]; pancreatic juice secretion [GO:0030157]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of saliva secretion [GO:0046878]; potassium ion transport [GO:0006813]; renal water absorption [GO:0070295]; renal water homeostasis [GO:0003091]; renal water transport [GO:0003097]; secretory granule organization [GO:0033363]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; transepithelial water transport [GO:0035377]; water transport [GO:0006833]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11884383_transmembrane biogenesis is cotranslational in intact mammalian cells 11909995_A novel role for aquaporin-1 as a gated ion channel reshapes our current views of this ancient family of transmembrane channel proteins. 11922632_These data suggest that the transcription of the AQP1 by hypertonicity in renal cells is upregulated by the interaction with putative DNA binding proteins to a novel HRE located at -54 to -46 in the AQP1 gene. 12002613_This study showed the distinct localization of AQP1 in the mesangial cells of human glomeruli, suggesting its role in water movement through these cells. 12027013_visualization of the water-selective pathway at 3.7A resolution in a three-dimenional density map (REVIEW) 12237771_In astrocytomas, aquaporin 1 expressed in microvessel endothelia and neoplastic astrocytes. In metastatic carcinomas, aquaporin 1 present in microvessel endothelia and reactive astrocytes. Aquaporin 1 may participate in formation of brain tumour oedema. 12399631_Data suggest that variations found in plasma osmolarity during hemodialysis may induce aquaporin 1 expression on the membrane of intact red blood cells. 12498798_Data present a detailed comparison between the cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography model structures of the human and bovine water channel aquaporin-1 (AQP1). 12781664_Transmembrane helices at the periphery of the hAQP1 tetramer exhibited smaller extraction forces than helices at the interface between hAQP1 monomers. 14514735_substantial and striking upregulation of AQP-1 in the glomeruli of most diseased kidneys. 14592814_presence of AQP-1 in endothelia and water-transporting epithelia and new locations: mammary epithelium, articular chondrocytes, synoviocytes, and synovial microvessels where it may be involved in milk, chondrocyte volume, synovial fluid, and homeostasis. 14701836_lack of significant cyclic guanine nucleotide ion channel activity rules out a secondary role of aquaporin 1 water channels in cellular signal transduction 14753493_Increased expression. Over-expression occurred on astrocytic processes. Induction of AQP1 and AQP4 on reactive astrocytes in subarachnoid hemorrhage. May be involved in brain edema formation or resolution. 14753494_Intense upregulation of AQP1 expression was found in all glioblastomas. Expression of aquaporins in glioblastomas suggests pathologic role. Selective AQP inhibition might be new therapeutic option for tumor-associated cerebral edema. 15024704_AQP1 has a role in the movement of extracellular matrix and metabolic water across the membranes of chondrocytes and synoviocytes 15135660_AQP1 co-localizes with t-tubular and caveolar proteins 15502805_Aquaporin-1 is a reliable marker for clear cell renal cell carcinomas of lower grades but not for higher grades. 15563082_The expression of AQP-1 mRNA was positively correlated with Bcl-2 mRNA expression in nasal polyps. AQP-1 contributes to the survival of eosinophils in nasal polyps. 15667881_AQP-1 may be a possible critical reabsorption factor, acting to reduce abnormal fluid retention in endotubular cells and the extracellular matrix and, to a lesser extent, in Leydig cells. 15783300_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15809704_increased AQP1 expression in some human adenocarcinomas may be a consequence of angiogenesis and important for the formation or clearance of tumor edema 15847654_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 16300893_AQP1 expression heavely in cystic hemangioblastomas. 16481371_Aquaporin (AQP) 1 is predominantly situated in the apical plasma membrane domain of the human choroid plexus, although distinct basolateral and endothelial immunoreactivity is also observed. 16515633_high AQP1 expression may play an important role in ovarian carcinogenesis, disease progression, and ascites formation. 16534779_AQPs are differentially expressed in the peripheral versus central nervous system and that channel-mediated water transport mechanisms may be involved in peripheral neuronal activity by regulating water homeostasis in nerve plexuses and bundles. 16574458_Review. In Colton (null) RBC ghosts, lack of AQP1 resulted in about 30% reduction of the alkalinization rates. 16698771_aquaporin-1-mediated CO(2) permeation is to be expected only in membranes with a low intrinsic CO(2) permeability 16814974_These results in human fetal brain lend morphological support to the previous findings that aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 play different roles in the regulation of the water homeostasis of the brain. 16871401_Significant increased expression levels of AQP1 and AQP4 were seen in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, but not in advanced Alzheimer's disease and diffuse Lewy body disease. 17012249_AQP1 is responsible for 60% of the high P(CO2) of red cells and that another, so far unidentified, CO2 pathway is present in this membrane that may account for at least 30% of total P(CO2). 17077939_In hemangioblastomas, expression of AQP1 was predominantly localized on membranes of stromal cells. The expression level of AQP1 in cystic group of hemangioblastomas is much higher than that of solid group. 17219999_Inhibiting AQP-1 with acetazolamide may significantly induce apoptosis of Hep-2 cells. 17273788_The deregulation of aquaporin-1 in menorrhagia may be involved in abnormal endometrial vascular growth and permeability. 17408468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17409744_AQP1 is expressed at the endomysial capillary endothelial cell and further AQP1 may be expressed at the human skeletal myofiber plasma membrane. 17511167_AQP1 mRNA and protein expression level in laryngeal tumor tissues is remarkably stronger than that in normal tissues. 17545093_Data show that AQP-1, 3, 8, 9 mRNA expression was detected in both amnion and chorion and can be associated with intramembranous transport and volume regulation of amniotic fluid. 17549682_Only the presence of AQP1, but not AQP4, enhanced cell growth and migration, typical properties of gliomas, while AQP4 enhanced cell adhesion suggesting differential biological roles for AQP1 and AQP4 in glioma cell biology. 17632520_In AQP1, Asn49 and Lys51 interact with Asp185 at the C terminus of TM5 to form a polar, quaternary structural motif that influences multiple stages of folding. 17854859_AQP-1 is up-regulated in biliary dysplasia...and down-regulation of AQP-1 is associated with mucin production and aggressive progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 17890385_These results establish the nature and determinants of AQP1 diffusion in cell plasma membranes and demonstrate long-range nonanomalous diffusion of AQP1. 17894331_a detailed mechanism for ion exclusion in aquaporin-1 (AQP1) at an atomistic level is investigated by calculating the free energy for transport of ions in AQP1 17898873_Increased AQP1 expression may relieve intracellular acidosis and edema in highly glycolytic glioma cells. 18052958_Aquaporin 1 may be involved in the pathophysiology of migraine. 18067501_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18080132_These data illustrate the potential of the peritoneal membrane as an experimental model in the investigation of the role of AQP1--REVIEW 18202181_For small solutes permeating through AQP1, a remarkable anticorrelation between permeability and solute hydrophobicity is observed, rendering AQP1 a selective filter for small polar solutes. 18247144_The aim of this study was to use immunohistochemsitry to investigate the expression of aquaporins 1, 2 and 3 within the human intervertebral disc. 18275976_AQP1 is involved in hypoxia-inducible angiogenesis in retinal vascular endothelial cells through a mechanism that is independent of the VEGF signaling pathway. 18280225_AQP1 is not expressed in human airway epithelial cells from the A549 adeoncarcinoma cell line. 18282122_The genomic, structural and functional aspects of AQP1 are briefly described. Its role in human tumors and, in particular, those of the kidney is discussed. Review. 18313673_AQP1 may be involved in the tumorigenesis and progression of endometrioid adenocarcinoma by promoting angiogenesis, and AQP1 level may be both a tumor indicator and a new therapeutic target. 18392839_Our study shows that AQP4 downregulation can occur in muscular dystrophies with either normal or disrupted expression of dystrophin-associated proteins, and that this might be associated with upregulation of AQP1. 18509662_These observations suggest the possible association of astrocytic AQP1 with Abeta deposition in Alzheimer disease brains. 18510579_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 18538351_Modulation of AQP1 expression by maternal hormones may regulate invasion and fetal-placental-amnion water homeostasis during gestation. 18544259_We show high expression of AQP1 water channels in intractable epilepsy and suggest two mechanisms to explain this finding. Increased AQP1 expression of astrocytes may be a cause or a consequence of IE. 18563339_AQP1 and HIF1 interact each other and regulate the oncogenesis of breast cancer 18575775_The objective of this study was to evaluate the AQP1 expression in endometrial blood vessels during normal cycle and after mifepristone treatment. 18841368_AQP1 expression in invasive breast carcinomas is associated with a basal-like phenotype and poor prognosis. 19080511_The expression level of AQP1 of patients with preeclampsia increases in placenta and peritoneum and decreases in embryolemma. 19253825_Hypoxia regulates the expression of AQP1 in vascular endothelial cells. 19306058_AQP1 expression is a new characteristic feature of a particularly aggressive subgroup of basal-like breast carcinomas. 19424603_AQP1-specific siRNA knockdown impaired water permeability of ARPE-19 cells. 19472194_These results provide evidence that NPA motifs are important for water permeation but not essential for the expression, intracellular processing and the basic structure of human aquaporin 1. 19522191_The expression of AQP1 in tumor cells and micro-angiogenesis of primary laryngeal carcinoma are higher than normal. 19545896_Alteration of aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 3 expression in fetal membranes and placenta may be important in the pathophysiology of isolated oligohydramnios. 19619954_AQP-1 was overexpressed in hepatitis B virus associated cirrhotic liver tissues. AQP-1, similar to CK19, might be a more specific and more sensitive marker than CK7 for the identification of HPCs. 19670620_The expression of AQP1 and VEGF in laryngeal carcinoma was significantly higher than that in vocal cord polyps and normal controls. 19726340_The expression of AQP1 mRNA was significantly lower in oligohydramnios placenta than in normal pregnancy placenta at term. 19772916_TXA(2) receptor mediates water influx through aquaporins in astrocytoma cells via TXA(2) receptor-mediated activation of G alpha(12/13), Rho A, Rho kinase and Na(+)/H(+)-exchanger. 19787701_AQP1 activity of cell membrane affects HT20 colon cancer cell migration. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20063900_An increase in the level of water transport in response to changing osmotic conditions in the cellular environment may be due to a protein kinase C-dependent increase in AQP1 membrane localization. 20101282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20101282_There was no association between common sequence variants in the AQP1 or SLC4A10 genes and primary open-angle glaucoma in the Caucasian population. 20137115_Inhibiting AQP1 expression with siRNA can inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of K562 cells. 20149606_Potential role for synovial AQP1 and other aquaporins in joint swelling and vasogenic edema. 20360993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20409716_Aquaporin 1 is localized in the dura mater following chronic subdural hematoma; the outer membrane might be the source of increased fluid accumulation responsible for chronic hematoma enlargement. 20424473_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20431033_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20461409_Expression of AQP1, AQP4, or AQP6 mRNA did not differ in vestibular endorgans from patients with Meniere's disease. 20578142_AQP-1 enhances osmotic water permeability and FGF-induced dynamic membrane blebbing in liver endothelial cell and thereby drives invasion and pathological angiogenesis during cirrhosis. 20628061_Data identify miR-320a as a potential modulator of aquaporin 1 and 4 and explore the possibility of using miR-320a to alter the expression of aquaporin 1 and 4 in normal and ischemic conditions. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20739606_Compared with human AQP1, zebrafish Aqp1a has about twice the selectivity for CO(2) over NH(3). 20795314_The physiology and molecular basis of the Colton blood group antigen AQP1 is discussed. Review. 20806077_The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of down-regulation of Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) and Aquaporin 5 (AQP5) on cell proliferation and migration in human corneal endothelial (HCEC) and human corneal epithelial (CEPI17) cell lines, respectively. 20828513_The expression level of aquaporin-1 in nasopharyngeal cancer tissue could be involved in tumour migration. 20965731_Expression of AQP1 in pediatric brain tumors. Increased in ependymomas in posterior fossa and in pilocytic astrocytomas. Not expressed in medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor, germinoma. 20969805_This review outlines newly emerging evidence indicating that AQP-1 plays an important role in pain signal transduction and migraine. 21063116_After sequencing analysis of the coding regions and exon-intron boundaries one single variation, no significant mutation in AQP 1 was found. 21063116_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21107133_No difference is found between aquaporin 1 expression in Alzheimer's disease brain and its expression in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. 21237499_Expression patterns of aquaporin 1, 3, and 5 in lung cancer cells are mostly associated with cellular differentiation. 21244858_AQP1 and AQP5 might play an important role in the development of lung edema and lung injury 21252246_The late rise of AQP1 suggests a role in corpus luteum formation. 21271497_The researchers found an association between carriers of the AQP1 single nucleotide polymorphism and greater fluid loss in long-distance running. 21360438_An important role of AQP1 in tumor angiogenesis is sustained by the abundant expression of this protein in the endothelia of tumor capillaries. 21373963_Water flux through human aquaporin 1 was studied under osmotic challenges and the inhibition by intracellular furosemide. 21395179_AQP1 and VEGF had a higher expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues than in non-tumor tissues. 21538271_AQP-1 expression is increased in colorectal carcinoma while the expression of AQP-3 is not. There is no correlation between the expression of AQP-1 and AQP-3 in CRC. 21551254_AQP1 is a promising oncogene candidate for ACC and is transcriptionally regulated by promoter hypomethylation. 21612401_hypoxia-induced expression of AQP1 requires transcriptional activation, and the HIF-1 binding site of the 5'-promoter is necessary for transcriptional activation 21760919_Negative stain transmission electron microscopy and single particle analysis of KCC4 and the aquaporin-1 AQP1 water channel, revealed the expected quaternary structures within homogeneous preparations, and thus correct protein folding and assembly. 21784068_REVIEW: summarizes literature data concerning the involvement of AQP-1 and -4 in human brain tumor growth and edema formation 21793635_our results suggest, for the first time, that the rs1049305 (C/G, UTR3) AQP1 polymorphism could be involved in the genetic susceptibility to develop water retention in patients with liver cirrhosis. 21839760_This study demonistrated that AQP1 in inner ear plays an important role in the development of motion sickmness, and might be a potential target for the prevention or management of motion sickness. 21896312_The mean concentration of AQP1 in CSF was significantly elevated in patients with BM (BM: 3.8+/-3.4ng/ml, controls 22006723_Phosphorylation of tyrosine Tyr253 in the carboxyl terminal domain, acts as a master switch regulating responsiveness of AQP1 ion channels to cGMP, and the tetrameric central pore is the ion permeation pathway. 22093331_Aberrant expressions of AQP1 in periportal sinusoidal regions in human cirrhotic liver indicate the proliferation of arterial capillaries directly connected to the sinusoids, contributing to microvascular resistance in cirrhosis. 22269467_AQP1 is normally expressed in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disc with a role in the maintenance of TMJ homeostasis 22310126_regulates microvessel permeability and barrier function and contributes to blood vessel formation 22334691_novel pathway in mammalian cells whereby a hypotonic stimulus directly induces intracellular calcium elevations through transient receptor potential channels, which trigger AQP1 translocation 22348807_A new AQP1 null allele identified in a Gypsy woman who developed an anti-CO3 during her first pregnancy. 22372348_We found AQP1 and AQP4 in lung cancer cell extravasation and spread, which may provide a functional explanation for the expression of AQP1 and AQP4 in lung cancer tissues and lung cancer cell lines. 22472942_expression of aquaporin 1 and 5 was higher in uterine leiomyomata than in unaffected uteri 22901156_AQP1 expression significantly increased in advanced stage of cervical cancer, deeper infiltration, metastatic lymph nodes and larger tumor volume. 22901921_Exosomal AQP1 is downregulated after the release of ureteropelvic junction obstruction. This may be due to locally increased TGF-beta-1 in the postobstructed kidney. 22964306_Data indicate reconstitution of AQP-1 into cholesterol-containing vesicles leads to drastic increases in P(CO2). 23029502_Selective expression of AQP1 in the trigeminal neurons innervating the oral mucosa indicates an involvement of AQP1 in oral sensory transduction. 23219802_Stomatin interacts with GLUT1/SLC2A1, band 3/SLC4A1, and aquaporin-1 in human erythrocyte membrane domains 23220481_This study demonstrated that laminar shear stress stimulates the endothelial expression of AQP1 that plays a role in wound healing. 23268390_K562 cells show a significant increase of AQP1 expression after retinoic acid-induced erythroid differentiation. 23276695_AQP1(+) cells immediately beneath the epithelial basement membrane may be stromal niche-like cells that directly interact with N-cad(+) limbal basal epithelial progenitor cells. 23313295_High AQP1 expression is associated with malignant pleural mesothelioma. 23317544_These findings suggest that NKCC1 and AQP1 participate in meningioma biology and invasion 23332061_hAQP1 is a constitutively open channel that closes mediated by membrane-tension increments. 23361277_AQP1-immunoexpression had a good correlation with high-grade tumors. 23393355_AQP1 expression correlates with the grade of malignancy in astrocytoma and is associated with angiogenesis, as well as with invasion of grade IV tumour in areas of tumour infiltration 23450058_Estrogen induces AQP1 expression by activating ERE in the promoter of the Aqp1 gene, resulting in tubulogenesis of vascular endothelial cells. 23549977_AQP-1 appears to be involved in the arterial capillary proliferation in the cirrhotic liver. [Review] 23928039_AQP1 and 4 gene expression levels did not differ between mesial temporal sclerosis patients and control groups 23949237_Aquaporin-1 is associated with arterial capillary proliferation and hepatic sinusoidal transformation contributing to portal hypertension in primary biliary cirrhosis. 23974882_The data suggest that the increased expression of AQP1 and AQP3 in pterygial tissues may be involved in the pathogenesis of pterygia 24014128_Cox-regression analyses revealed the AQP1 -783G/C genotype status as an independent prognostic-factor when jointly considering other predictors of survivalin glioblastoma multiforme. 24028651_Aquaporin-1 is induced in leukocytes of patients with sepsis and exhibits higher expression in septic shock. 24086369_Anti-AQP1 autoantibodies are present in a subgroup of patients with chronic demyelination in the central nervous sytem and similarities with anti-AQP4-seronegative neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. 24169407_Over expression of aquaporin 1 causes increased intracranial pressure, and downregulation reduces pressure and alleviates the symptomatology and complications of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. 24252214_Report is the first to establish astrocytic water channel loss in a subset of human central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) cases and suggests AQP1 and AQP4 may be involved in the pathogenesis of CPM 24333057_the prevalence of this AQP1 c.601delG allele in the ethnic minority of Romani 24493792_AQP1 promoter hypomethylation is common in ACC, and AQP1 tends to be overexpressed in these tumors. Increased AQP1 methylation is associated with improved prognosis. 24688444_the expression of AQP1, at both the mRNA and protein levels, in membranes from PVR and ERM. 24777974_Results show that in AQP1, helix 3 inverts its orientation in the membrane after the initial insertion, whereas this does not occur in the homologous AQP4. 24803718_Freshly obtained urine samples from renal cell carcinoma patients are positive for AQP1 whereas archived samples and fresh healthy control samples are negative. 24918928_Aquaporin 1 and 3 were upregulated in cervical cancer compared to mild cervicitis and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2-3 (P |
ENSMUSG00000004655 |
Aqp1 |
9.027217 |
33.7274621315 |
5.075852 |
1.073726182 |
38.398269 |
0.00000000057683543561807853345613993453116011278503094672487350180745124816894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002811786997926961454046499667091228713555750573505065403878688812255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.5095730 |
12.6620734 |
0.4971578 |
0.3684836 |
| ENSG00000240859 |
100507642 |
LINC03014 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.808656 |
0.4196554241 |
-1.252723 |
0.248147538 |
26.022163 |
0.00000033752047052812581526382127057595017305402507190592586994171142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001256761388747511966928658254383233128237407072447240352630615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.7930145 |
4.1163532 |
61.8799033 |
6.1120565 |
| ENSG00000240875 |
730091 |
LINC00886 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32111441_Aberrant DNA hypermethylation-silenced LINC00886 gene accelerates malignant progression of laryngeal carcinoma. 35616822_Downregulation of LINC00886 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through SIRT7/ELF3/miR-144 pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. |
|
|
21.972935 |
0.2302948024 |
-2.118446 |
0.429771862 |
24.343992 |
0.00000080577683437887064705693052069079840293852612376213073730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002878331576822877915891899999745184857147251022979617118835449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6357656 |
3.3264686 |
28.5922067 |
9.8528501 |
| ENSG00000240990 |
221883 |
HOXA11-AS |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene produces a long non-coding RNA in antisense to transcription of the homeobox A11 gene. This transcript may associate with chromatin factors such as Polycomb repressive complex and act as a sponge for microRNAs, thereby participating in the regulation of expression of target genes. High levels of this transcript may be associated with tumor progression. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]. |
|
|
26430965_These findings demonstrate for the first time a role for HOXA11-AS in epithelial ovarian cancer with effects that could be modified by germline variants 27651312_a model in which the EZH2/HOXA11-AS/LSD1 complex and HOXA11-AS/miR-1297/EZH2 cross-talk serve as critical effectors in gastric cancer tumorigenesis. 27737536_These findings highlight the clinical significance of HOXA11as to predicting the prognosis of SOC patients and suggest its potential in promoting tumor aggressiveness via regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), MMP-9, and EMT-related mechanisms. 27792998_HOXA11-AS overexpression correlated with poor survival in patients with cervical cancer. 28441948_Findings show that HOXA11-AS not only could promote gastric cancer (GC) cells migration and invasion in vitro, but also promotes GC cells metastasis in vivo, at least in part, by regulating beta-catenin and KLF2. 28717185_HOXA11-AS plays a significant role in non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, invasion, migration, apoptosis and cell cycle. 28791375_our data suggested that the transcript level of HOXA11AS was highly upregulated in breast cancer both in vivo and in vitro. Knockdown of HOXA11AS in MDAMB231 and MDAMB436 cells inhibited colony formation and cell proliferative rate, and caused cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase. 28942241_increased expression of HOXA11-AS is a risk factor for poor clinical outcomes in numerous tumors 28946213_HOXA11-AS acted as an oncogenic long non-coding RNA that promoted cell growth and metastasis of glioma through regulating miR-214-3p/EZH2 axis. 29017417_study findings suggest that homeobox (HOX)A11-AS1 (HOXA11-AS1) lncRNA may play a role in the development of peritoneal endometriosis, but HOXA11-AS1 may not influence endometrial receptivity in endometriosis-associated infertility. 29164588_HOXA11-AS suppressed cell proliferation and promoted cell apoptosis via targeting mir-124-3p and knockdown inhibited cell apoptosis. 29953617_HOXA11-AS could promote renal cancer cells growth and invasion by modulating miR-146b-5p-MMP16 axis. 30064227_Glioma patients with high LncRNA HOXA11-AS expression had shorter overall survival time than those with low expression. Silencing HOXA11-AS significantly increased miR-124-3p expression. 30099826_lncRNA HOXA11-AS acted as a ceRNA to promote cisplatin resistance of human LUAD cells via the miR-454-3p/Stat3 axis. 30657566_lncRNA HOXA11-AS was overexpressed in glioma and overexpression was correlated with advanced stages of glioma and poor prognosis. Downregulating HOXA11-AS expression significantly suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cells and increased their apoptosis. HOXA11-AS exerted its oncogenic effects by binding to miR-130a-5p, thereby neutralizing the suppressive effect of miR-130a-5p on HMGB2. 31013434_Propofol promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via alleviating the suppression of lncRNA HOXA11-AS on miRNA let-7i. 31099097_HOXA11-AS regulates JAK-STAT pathway by miR-15a-3p/STAT3 axis to promote the growth and metastasis in liver cancer. 31144606_Data found that HOXA11-AS was upregulated in cisplatin resistant lung adenocarcinoma tumors and cell lines. Functional analysis showed that the knockdown of HOXA11-AS expression in A549 cells inhibits cell proliferation, induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. 31235999_Up-regulation of HOXA11-AS was found in gastric cancer (GC) tissues, cell lines, and serum samples. Decreased serum HOXA11-AS levels were negatively related with tumor size, TNM stage, and lymph node metastasis and were associated with a better overall survival rate. HOXA11-AS promoted GC cell proliferation and invasion. SRSF1 may be the target regulated by HOXA11-AS in GC cells. 31275988_The findings highlight the importance of HOXA11-AS/miR-214-3p/PIM1 axis in the drug resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. 31680444_LncRNA HOXA11-AS regulates calcium oxalate crystal-induced renal inflammation via miR-124-3p/MCP-1. 31731187_LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes OSCC progression by sponging miR-98-5p to upregulate YBX2 expression. 31878829_Long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS accelerates the progression of keloid formation via miR-124-3p/TGFbetaR1 axis. 31971633_CTCF was validated to activate HOXA11-AS transcription in PCa cells. 32009419_LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes migration and invasion through modulating miR-148a/WNT1/beta-catenin pathway in gastric cancer. 32236611_Recent advances in unraveling the molecular mechanisms and functions of HOXA11AS in human cancers and other diseases (Review). 33115978_Long Noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS Modulates the Resistance of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells to Cisplatin via miR-454-3p/c-Met. 33261854_LncRNA HOXA11-AS Aggravates Keloid Progression by the Regulation of HOXA11-AS-miR-205-5p-FOXM1 Pathway. 33514011_Long Noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS and Transcription Factor HOXB13 Modulate the Expression of Bone Metastasis-Related Genes in Prostate Cancer. 33839699_Inhibition of long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS against neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model via targeting miR-124-3p mediated FSTL1/NF-kappaB axis. 34050851_Long noncoding HOXA11-AS knockdown suppresses the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-3619-5p/SALL4 axis. 34337714_LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes cell growth by sponging miR-24-3p to regulate JPT1 in prostate cancer. 34655977_LncRNA HOXA11-AS aggravates the keloid formation by targeting miR-148b-3p/IGFBP5 axis. 34974809_Long non-coding RNA HOXA11 antisense RNA upregulates spermatogenesis-associated serine-rich 2-like to enhance cisplatin resistance in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing microRNA-518a. 35114391_Increased expression of HOXA11-AS attenuates endometrial decidualization in recurrent implantation failure patients. 35320748_Uterine HOXA11 antisense long non-coding RNA prevents decidualization: A new pathway-regulating pregnancy. 35700456_The minor allele of rs17427875 in long non-coding RNA-HOXA11-AS influences the prognosis of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) via modulating miR-15a and STAT3 expression. 35706412_Long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS knockout inhibits proliferation and overcomes drug resistance in ovarian cancer. 36142607_An Axis between the Long Non-Coding RNA HOXA11-AS and NQOs Enhances Metastatic Ability in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. |
|
|
129.663941 |
0.1014538554 |
-3.301104 |
0.969873660 |
9.724178 |
0.00181859617094693847699771183101802307646721601486206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004051695016328575767172726074250022065825760364532470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.9172772 |
16.4568286 |
270.7483787 |
114.8049641 |
| ENSG00000241015_ENSG00000160336 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75.374949 |
2.2973634624 |
1.199979 |
0.477292798 |
6.146003 |
0.01317094776710173512079826707577012712135910987854003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024627274040876310362557788380399870220571756362915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
108.0140932 |
50.7793749 |
46.7050667 |
15.7907052 |
| ENSG00000241316 |
101927111 |
SUCLG2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
109.283057 |
0.0130954325 |
-6.254792 |
1.443686020 |
12.021101 |
0.00052601624429630619312475703353015887842047959566116333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001286495404442995716884357015885598229942843317985534667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3431077 |
3.1710073 |
253.3670610 |
162.3707525 |
| ENSG00000241404 |
80864 |
EGFL8 |
protein_coding |
Q99944 |
|
Calcium;Coiled coil;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable signaling receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in anatomical structure development. Predicted to act upstream of or within in utero embryonic development. Predicted to be active in cell surface and extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80864; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; anatomical structure development [GO:0048856] |
19143814_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19851445_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20587610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21737648_Reduced expression of EGFL8 is closely related to metastastic potential and poor prognosis of CRC, suggesting the down-regulation of EGFL8 as a novel prognostic biomarker for CRC patients. 21965749_The down-regulation of EGFL8 might be a novel biomarker for advanced gastric cancer. 33712610_Schwann cell plasticity regulates neuroblastic tumor cell differentiation via epidermal growth factor-like protein 8. 34130659_Down-regulation of EGFL8 regulates migration, invasion and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through activating Notch signaling pathway. 34626176_Whole-exome sequencing reveals a role of HTRA1 and EGFL8 in brain white matter hyperintensities. |
ENSMUSG00000015467 |
Egfl8 |
9.933422 |
0.1161561525 |
-3.105863 |
0.774435061 |
17.177305 |
0.00003404799011908717684248698587268222581769805401563644409179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000100049439410258156216496083779077252984279766678810119628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.4035303 |
1.4782071 |
23.7960910 |
7.4399875 |
| ENSG00000241472 |
100506994 |
PTPRG-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32844927_Overexpression of long noncoding RNA PTPRG-AS1 is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. 33174523_Long Noncoding RNA PTPRG Antisense RNA 1 Reduces Radiosensitivity of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Cells Via Regulating MiR-200c-3p/TCF4. 35300558_Long non-coding RNA PTPRG-AS1/microRNA-124-3p regulates radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the LIM Homeobox 2-dependent Notch pathway through competitive endogenous RNA mechanism. |
|
|
13.150341 |
0.4071788188 |
-1.296266 |
0.562422579 |
5.165572 |
0.02303886741958477077374389807573606958612799644470214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.040729869818310122930871131075036828406155109405517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9385402 |
2.5078068 |
16.9396801 |
4.3284632 |
| ENSG00000241489 |
|
|
protein_coding |
B3KWA1 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
sulfuric ester hydrolase activity [GO:0008484] |
|
|
|
279.455191 |
0.1966930518 |
-2.345982 |
0.298306866 |
55.444928 |
0.00000000000009611436791981265763170642327470868709806545160390101045777555555105209350585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000609123259122556833194207925351338291683304937418341751254047267138957977294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
87.3360292 |
24.9811899 |
455.4486121 |
93.0255490 |
| ENSG00000241743 |
|
XACT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
432.341370 |
0.1671537692 |
-2.580752 |
0.456317166 |
27.572124 |
0.00000015134430665016875920252667833687532095154892886057496070861816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000586002614416707955780202685125424011403083568438887596130371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
131.8856878 |
29.9998772 |
793.9371295 |
129.1361049 |
| ENSG00000241769 |
100131434 |
EOLA1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.858625 |
0.2022235493 |
-2.305977 |
0.443040297 |
27.050473 |
0.00000019821169618498369481569669221104890155515931837726384401321411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000757732358376161429242413684892465397524574655108153820037841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
9.3721563 |
3.3673705 |
46.2156942 |
10.7237096 |
| ENSG00000241860 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
93.994360 |
0.2705914062 |
-1.885812 |
0.502553742 |
13.183499 |
0.00028242486522920759450805405776918632909655570983886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000723462514887730670336274396703402089769951999187469482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.7498185 |
16.4504245 |
138.9164918 |
42.9750859 |
| ENSG00000241956 |
102546299 |
LINC03000 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44.061240 |
0.4852128881 |
-1.043310 |
0.229911739 |
21.035811 |
0.00000450778641881998287410963574539657372497458709403872489929199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000014756027398931680669029453678575691810692660510540008544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.1042291 |
4.5845389 |
60.5501270 |
6.1893199 |
| ENSG00000242028 |
25764 |
HYPK |
protein_coding |
Q9NX55 |
FUNCTION: Component of several N-terminal acetyltransferase complexes (PubMed:20154145, PubMed:29754825, PubMed:32042062). Inhibits the N-terminal acetylation activity of the N-terminal acetyltransferase NAA10-NAA15 complex (also called the NatA complex) (PubMed:29754825, PubMed:32042062). Has chaperone-like activity preventing polyglutamine (polyQ) aggregation of HTT in neuronal cells probably while associated with the NatA complex (PubMed:17947297, PubMed:20154145). May play a role in the NatA complex-mediated N-terminal acetylation of PCNP (PubMed:20154145). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:17947297, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20154145, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29754825, ECO:0000269|PubMed:32042062}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Enables protein N-terminus binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of apoptotic process and protein stabilization. Located in cytoplasm; microtubule cytoskeleton; and nucleoplasm. Part of protein-containing complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25764; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; protein folding chaperone [GO:0044183]; protein N-terminus binding [GO:0047485]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; protein stabilization [GO:0050821] |
17947297_The present study, has confirmed, by confocal microscopy and immunoprecipitation, that HYPK interacts with the N-terminal of Htt. 23272104_HYPK has roles in regulating cell growth, cell cycle, unfolded protein response and cell death 24361604_maintenance of HYPK expression by HSF1 is necessary for the survival of cells under thermal stress conditions 24465598_Chaperone-like protein HYPK is induced by cellular stress and is under transcriptional regulation by HSF1. 25116620_By virtue of its flexibility and nascent peptide binding activity, HYPK may play an important role in assisting protein (re)folding. 25446099_specific interaction of HYPK with HTT-N17 is crucial for the chaperone activity of HYPK 27017930_HYPK can act as negative regulator of heat shock response by repressing transcriptional activity of HSF1. 27067261_Results show that HYPK, possibly with its interacting partners, induces autophagy. results further confirm that HYPK could also be involved in clearing mutant HTT aggregates by augmenting autophagy pathway. 28585574_In combination with acetylation assays, the HypK N-terminal region is identified as a negative regulator of the NatA acetylation activity 29381348_study provides evidence of the existence of disordered nanostructure in HYPK protein that mechanistically plays a decisive role in preventing both self and non-self protein aggregation. 29754825_Results find that HYPK harbors intrinsic hNatA-specific inhibitory activity through a bipartite structure: a ubiquitin-associated domain that binds a hNaa15 metazoan-specific region and an N-terminal loop-helix region that distorts the hNaa10 active site. 30251673_this studu identified the metastable states in the seeds of the Ubiquitin associated (UBA) domain of Huntingtin Interacting Protein K (HYPK). 31397627_Results find the novel mode of internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation initiation of HYPK mRNA, along with the determination of mechanism of the nuclear localization process of HYPK. 32042062_Huntingtin interacting protein K (HYPK) forms a tetrameric complex with the human N-terminal acetyltransferase E (NatE). HYPK exhibits negative cooperative binding to NAA15 auxiliary subunit by inducing NAA15 shifts in opposing directions. HYPK inhibits NAA10 and NAA50 catalytic activities through structural alteration of the NAA10 and the NatE substrate-binding sites, respectively. 34836490_HYPK coordinates degradation of polyneddylated proteins by autophagy. 35857868_Phosphorylation of Arl4A/D promotes their binding by the HYPK chaperone for their stable recruitment to the plasma membrane. |
ENSMUSG00000027245 |
Hypk |
67.039463 |
2.2349739626 |
1.160258 |
0.223526070 |
26.782012 |
0.00000022774741599888295682362494409128883532389409083407372236251831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000863930059147651696189161314026749849404041015077382326126098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
84.3624055 |
11.3618609 |
38.0051508 |
3.7427381 |
| ENSG00000242193 |
730102 |
CRYZL2P |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
67.898973 |
0.4691006439 |
-1.092031 |
0.228368419 |
22.907408 |
0.00000169995424911037938451956446489488072870699397753924131393432617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005856985228027357667866369811404680945088330190628767013549804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.7272395 |
6.5021700 |
94.0805791 |
9.4526669 |
| ENSG00000242258 |
285972 |
LINC00996 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51.115701 |
12.9352883948 |
3.693240 |
0.383954678 |
91.924754 |
0.00000000000000000000090035711918260956870053354696081510973673968301374144135372327990562979493915918283164501190185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000008524227760830865081408834499031887555803671722828154864830263459651860102894715964794158935546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.3070297 |
31.0097791 |
7.8545832 |
1.9224539 |
| ENSG00000242282 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.960591 |
0.0224782214 |
-5.475328 |
1.061773564 |
49.039909 |
0.00000000000250807161945989359164094690552565796587414226337386935483664274215698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000014568727706898085458947609567960726484336930752760963514447212219238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5270086 |
0.4322036 |
23.6939362 |
6.3597413 |
| ENSG00000242352 |
|
FAM91A3P |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.246100 |
0.3982791004 |
-1.328148 |
0.597994996 |
5.019932 |
0.02505714721058036054124329439218854531645774841308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043924405324010228068853933791615418158471584320068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6060296 |
2.1437847 |
13.9645685 |
3.3812292 |
| ENSG00000242498 |
348110 |
ARPIN |
protein_coding |
Q7Z6K5 |
FUNCTION: Regulates actin polymerization by inhibiting the actin-nucleating activity of the Arp2/3 complex; the function is competitive with nucleation promoting factors. Participates in an incoherent feedforward loop at the lamellipodium tip where it inhibits the ARP2/2 complex in response to Rac signaling and where Rac also stimulates actin polymerization through the WAVE complex. Involved in steering cell migration by controlling its directional persistence. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24132237}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Reference proteome |
|
Involved in directional locomotion; negative regulation of cell migration; and negative regulation of cellular component organization. Predicted to be located in lamellipodium. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:348110; |
lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; directional locomotion [GO:0033058]; negative regulation of actin nucleation [GO:0051126]; negative regulation of cell migration [GO:0030336]; negative regulation of lamellipodium morphogenesis [GO:2000393] |
25892881_Arpin protein affects the expression of tight junction proteins and may have an impact on bacterial translocation in severe acute pancreatitis. 26648569_Arpin downregulation may contribute to the initiation and development of breast cancer metastasis. 26774128_Data reveal that Arpin is comprised of an elongated globular core from which the C-terminal tail extends as a linear peptide, thus forming a primary epitope that is readily available to tether Arpin to interacting proteins. 28293092_Low Arpin levels are associated with clinicopathological variables and a poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients 28531800_ARPIN is down-regulated in breast cancer cells and predicts poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Data suggest that restoration of ARPIN in breast cancer cells suppresses cell proliferation, colony formation, cell cycle distribution, invasion in vitro, and tumorigenesis in vivo (xenograft experiments in nude mice); Arpin acts as tumor suppressor in breast cancer and is associated with inhibition of Akt signaling. 31721415_Arpin is critical for phagocytosis in macrophages and is targeted by human rhinovirus. 33923443_Arpin Regulates Migration Persistence by Interacting with Both Tankyrases and the Arp2/3 Complex. |
ENSMUSG00000039043 |
Arpin |
48.237410 |
0.3706201609 |
-1.431987 |
0.239905939 |
36.603190 |
0.00000000144794560748332204844166134339146848053481164697586791589856147766113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000006825831097557914813484703398394765061496514135797042399644851684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.0355534 |
3.9350611 |
70.7145824 |
6.6480190 |
| ENSG00000242539 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.118653 |
0.3659839385 |
-1.450148 |
0.617283481 |
5.480125 |
0.01923388316128525621362399533609277568757534027099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034637886220176959672922833988195634447038173675537109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3280942 |
6.9478604 |
23.7590527 |
13.5289870 |
| ENSG00000242588 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
861.234983 |
0.3545634756 |
-1.495884 |
0.057628057 |
691.910002 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001717678838381897732535302278465255231029908317504778505930220374589857004679531889245215097466968519557563619765483648987292155600106018886757873503007808666128854632975174827216 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001179206495558921263140403514225531394585663619186138391023811993185281847424047674536370777583175679755116951857556878158214072775825773545234052699438774225449601154931514727325 |
Yes |
No |
453.6304395 |
16.6241502 |
1288.2353824 |
29.4758189 |
| ENSG00000242732 |
340526 |
RTL5 |
protein_coding |
Q5HYW3 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:340526; |
|
Mouse_homologues 28919299_The results introduce Rgag4 to the repertoire of effectors serving to couple the chromatin remodeler Ikaros with the hormonal stress response. |
ENSMUSG00000049191 |
Rtl5 |
9.928182 |
0.2958708494 |
-1.756961 |
0.521124316 |
12.098761 |
0.00050455335287506980056909666743081288586836308240890502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001237694447139110797209693437537225690903142094612121582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5102071 |
1.5657178 |
15.3330611 |
3.0629124 |
| ENSG00000242948 |
|
EPS15P1 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
71.243455 |
52.6448719584 |
5.718221 |
0.460771575 |
287.862608 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014530495456615946462058558560744769013956806333883762758452876602907623263215884920063099947933132438038081570155664552935759241240424825393424417563164877451173037647969010777160292491316795349121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004038985177771212239198313458806184900009379181897456822666350542067829121317557278142696374076547368892022754106905122172118695326297553053478116425087341648941796634630918561015278100967407226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
140.4768623 |
42.8611827 |
2.6910763 |
0.8007085 |
| ENSG00000243056 |
8637 |
EIF4EBP3 |
protein_coding |
O60516 |
FUNCTION: Repressor of translation initiation that regulates EIF4E activity by preventing its assembly into the eIF4F complex: hypophosphorylated form competes with EIF4G1/EIF4G3 and strongly binds to EIF4E, leading to repress translation. In contrast, hyperphosphorylated form dissociates from EIF4E, allowing interaction between EIF4G1/EIF4G3 and EIF4E, leading to initiation of translation. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q13541}. |
Phosphoprotein;Protein synthesis inhibitor;Reference proteome;Translation regulation |
|
This gene encodes a member of the EIF4EBP family, which consists of proteins that bind to eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E and regulate its assembly into EIF4F, the multi-subunit translation initiation factor that recognizes the mRNA cap structure. Read-through transcription from the neighboring upstream gene (MASK or ANKHD1) generates a transcript (MASK-BP3) that encodes a protein comprised of the MASK protein sequence for the majority of the protein and a different C-terminus due to an alternate reading frame for the EIF4EBP3 segments. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:8637; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F complex [GO:0016281]; membrane [GO:0016020]; eukaryotic initiation factor 4E binding [GO:0008190]; translation repressor activity [GO:0030371]; negative regulation of translational initiation [GO:0045947] |
12482586_4E-BP3 is associated with eIF4E in the cell nucleus and cytoplasm 14507920_PHAS-II, but not PHAS-III, contributes to the control of protein synthesis by insulin 14557257_there are overlapping reading frames in the mouse and human genes for 4E-BP3 and MASK 20621385_potential prognostic factor for survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma 21088106_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 22684010_4E-BP3 regulates eIF4E-mediated nuclear mRNA export and interacts with replication protein A2 27319316_The data reveal that 4E-BP3 expression is controlled by the transcription factor TFE3 through a cis-regulatory element in the EIF4EBP3 gene promoter. 29333098_Role of the eIF4EBP3 gene in miR-22-3p-mediated cervical squamous carcinoma cell growth 31853750_eIF4EBP3 was downregulated by methylation and acted as a tumor suppressor by targeting eIF4E/beta-catenin in gastric cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000090264 |
Eif4ebp3 |
9.122542 |
0.0815354008 |
-3.616430 |
0.781188108 |
26.953343 |
0.00000020842634374204749146713326959923229253490717383101582527160644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000794723025996543765115624063932742160432098899036645889282226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1408557 |
0.6675954 |
14.5316433 |
4.0870777 |
| ENSG00000243323 |
148713 |
PTPRVP |
unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17693256_Transgenic mice lacking protein tyrosine phosphatase OST-PTP are hypoglycemic and are protected from obesity and glucose intolerance because of an increase in islet beta-cell proliferation, insulin secretion, and insulin sensitivity. |
|
|
14.051847 |
0.0494526026 |
-4.337810 |
0.818439522 |
31.315109 |
0.00000002193657340660284300803591886388360654436269214784260839223861694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000092385834092176094915038048454442032308975285559426993131637573242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6182043 |
0.9746191 |
33.2837902 |
10.4407013 |
| ENSG00000243422 |
653236 |
RPL23AP49 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.241225 |
0.2416656257 |
-2.048916 |
0.521153123 |
15.840252 |
0.00006892064984256137847532658335936162075086031109094619750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000194518053709891159102490787446981812536250799894332885742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8584777 |
1.3797505 |
16.1364414 |
3.5489039 |
| ENSG00000243477 |
24142 |
NAA80 |
protein_coding |
Q93015 |
FUNCTION: N-alpha-acetyltransferase that specifically mediates the acetylation of the acidic amino terminus of processed forms of beta- and gamma-actin (ACTB and ACTG, respectively) (PubMed:30028079, PubMed:29581253). N-terminal acetylation of processed beta- and gamma-actin regulates actin filament depolymerization and elongation (PubMed:29581253). In vivo, preferentially displays N-terminal acetyltransferase activity towards acid N-terminal sequences starting with Asp-Asp-Asp and Glu-Glu-Glu (PubMed:30028079, PubMed:29581253). In vitro, shows high activity towards Met-Asp-Glu-Leu and Met-Asp-Asp-Asp (PubMed:10644992, PubMed:29581307). May act as a tumor suppressor (PubMed:10644992). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10644992, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29581253, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29581307, ECO:0000269|PubMed:30028079}. |
3D-structure;Acyltransferase;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;Transferase;Tumor suppressor |
|
This gene encodes a member of the N-acetyltransferase family. N-acetyltransferases modify proteins by transferring acetyl groups from acetyl CoA to the N-termini of protein substrates. The encoded protein is a cytoplasmic N-acetyltransferase with a substrate specificity for proteins with an N-terminal methionine. This gene is located in the tumor suppressor gene region on chromosome 3p21.3 and the encoded protein may play a role in cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed. This gene overlaps and is on the same strand as hyaluronoglucosaminidase 3, and some transcripts of each gene share a portion of the first exon. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]. |
hsa:24142; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; acetyl-CoA binding [GO:1905502]; N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0008080]; peptide alpha-N-acetyltransferase activity [GO:0004596]; actin modification [GO:0030047]; N-terminal peptidyl-aspartic acid acetylation [GO:0017190]; N-terminal peptidyl-glutamic acid acetylation [GO:0018002]; protein acetylation [GO:0006473]; regulation of actin polymerization or depolymerization [GO:0008064] |
11929860_Characterization of the murine hyaluronidase gene region reveals complex organization and cotranscription of Hyal1 with downstream genes, Fus2 and Hyal3. 15036368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15036368_newly identified polymorphism leads to a non-conservative amino acid change (R222W) located between the acetyltransferase and the proline-rich domains; analysis suggests no likely association between nasopharyngeal cancer and the FUS2 gene polymorphism 19789190_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29581253_NAT6/FUS-2 is the N-alpha acetyltransferase 80 (NAA80/NatH) acting post-translationally and specifically on processed animal actins. This NAA80 mediated actin N-terminal acetylation is crucial for actin polymerization and depolymerization, and regulates the actin cytoskeleton and cell motility. 29581253_the results demonstrate NAA80's role as actin's NAT and reveal a crucial role for actin Nt-acetylation in the control of cytoskeleton structure and dynamics. 29581307_NAA80/NatH is dedicated to the post-translational N-terminal acetylation of processed actins. The structure of NAA80 reveals features like a positively charged catalytic groove perfectly suited to bind the acidic actin N-terminus. A cellular factor restricting NAA80 to processed actins is NatB, which co-translationally acetylates all cellular Met-starting N-termini with acidic amino acids at the second position. 29581307_this study reveals the molecular and cellular basis of NAA80 Nt acetylation and provides a scaffold for development of inhibitors for the regulation of cytoskeletal properties. 30028079_findings reveal that NAT6 plays a critical role in the maturation of actins by carrying out the acetylation of their N-terminal acidic residue 32209306_N-terminal acetylation of actin by NAA80 is essential for structural integrity of the Golgi apparatus. 32978259_PFN2 and NAA80 cooperate to efficiently acetylate the N-terminus of actin. 34896361_The Final Maturation State of beta-actin Involves N-terminal Acetylation by NAA80, not N-terminal Arginylation by ATE1. |
ENSMUSG00000079334 |
Naa80 |
43.486759 |
0.4082525192 |
-1.292466 |
0.298591107 |
18.504243 |
0.00001695264785702157262848102647900816464243689551949501037597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000051730635180822491004954538640348005174018908292055130004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.1274369 |
4.8628604 |
64.7579055 |
7.9441724 |
| ENSG00000243655 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.742781 |
0.4818633794 |
-1.053304 |
0.354738555 |
8.906161 |
0.00284210140690853733588805418719402950955554842948913574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006114184049842590930323726894357605488039553165435791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.2485065 |
3.0835050 |
27.6131354 |
4.2105981 |
| ENSG00000243696 |
|
|
protein_coding |
D6R8Y8 |
|
Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
nucleus [GO:0005634]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; chondrocyte proliferation [GO:0035988]; tissue regeneration [GO:0042246] |
|
|
|
35.140430 |
0.2196583455 |
-2.186667 |
0.294957960 |
58.457754 |
0.00000000000002077033756880798406736561657062215806182712413141544516292924527078866958618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000137106521697498137587506563760303015901947237820124314566783141344785690307617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.7773936 |
3.7661541 |
67.0040065 |
10.9058739 |
| ENSG00000243708 |
100137049 |
PLA2G4B |
protein_coding |
P0C869 |
FUNCTION: Calcium-dependent phospholipase A1 and A2 and lysophospholipase that may play a role in membrane phospholipid remodeling. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10085124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10358058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 3]: Calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipase. Cleaves the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached to the sn-2 position of phosphatidylethanolamines, producing lysophospholipids that may be used in deacylation-reacylation cycles. Hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholines with low efficiency but is inefficient toward phosphatidylcholines. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059}.; FUNCTION: [Isoform 5]: Calcium-dependent phospholipase A1 and A2 and lysophospholipase. Cleaves the ester bond of the fatty acyl group attached to the sn-1 or sn-2 position of diacyl phospholipids (phospholipase A1 and A2 activity, respectively), producing lysophospholipids that may be used in deacylation-reacylation cycles. Can further hydrolyze lysophospholipids enabling complete deacylation. Has no activity toward alkylacyl phospholipids. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10085124, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10358058, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16617059}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cytoplasm;Endosome;Hydrolase;Lipid degradation;Lipid metabolism;Membrane;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a member of the cytosolic phospholipase A2 protein family. Phospholipase A2 enzymes hydrolyze the sn-2 bond of phospholipids, releasing lysophospholipids and fatty acids. This enzyme may be associated with mitochondria and early endosomes. Most tissues also express read-through transcripts from the upstream gene into this gene, some of which may encode fusion proteins combining the N-terminus of the upstream gene including its JmjC domain with the almost complete coding region of this gene, including the C2 and cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 domains. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:100137049;hsa:8681; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; early endosome membrane [GO:0031901]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0047498]; calcium-dependent phospholipid binding [GO:0005544]; lysophospholipase activity [GO:0004622]; phosphatidyl phospholipase B activity [GO:0102545]; phospholipase A1 activity [GO:0008970]; phospholipase A2 activity [GO:0004623]; arachidonic acid metabolic process [GO:0019369]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; glycerophospholipid catabolic process [GO:0046475]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; parturition [GO:0007567]; phosphatidylcholine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036151]; phosphatidylethanolamine acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036152]; phosphatidylglycerol acyl-chain remodeling [GO:0036148] |
19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20167866_TLR2 cooperates with MyD88, PI3K, and Rac1 in lipoteichoic acid-induced cPLA2/COX-2-dependent airway inflammatory responses 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 28030848_JMJD7-PLA2G4B may serve as an important therapeutic target and prognostic marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma development and progression. |
ENSMUSG00000098488 |
Pla2g4b |
49.248359 |
0.1042727949 |
-3.261565 |
0.640510711 |
20.039342 |
0.00000758651880630150047543159078089480829021340468898415565490722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024143384558216937890023912061110422655474394559860229492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3013339 |
7.4450659 |
89.0511601 |
43.4998955 |
| ENSG00000243716 |
100132247 |
NPIPB5 |
protein_coding |
A8MRT5 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100132247; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
404.577467 |
0.3879736589 |
-1.365969 |
0.229950851 |
34.261120 |
0.00000000481914023623028586654120698253012111678117435076273977756500244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000021659716774287155955472540655101787443470584548776969313621520996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
224.9405745 |
37.6980995 |
584.5223920 |
70.3680953 |
| ENSG00000243742 |
113157 |
RPLP0P2 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27460542_Our study ascertained that low expression of RPLP0P2 in LAD is associated with poor prognosis and decreased proliferation and adhesion ability of tumor cells 33649783_Downregulation of lncRNA RPLP0P2 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes apoptosis in colorectal cancer. |
|
|
13.534280 |
6.3222265734 |
2.660433 |
0.469066895 |
34.871289 |
0.00000000352237009556350708988711518964993124614082375956058967858552932739257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015986052651315944516288144799584514110790678387274965643882751464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.1701406 |
6.7767433 |
3.5264730 |
0.9098580 |
| ENSG00000243766 |
|
HOTTIP |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.872400 |
0.0144786993 |
-6.109924 |
1.142226077 |
38.383080 |
0.00000000058134256180287303551875421599257759419643321052717510610818862915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002831886538683302299351051043948580832054773281925008632242679595947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2441133 |
0.2170462 |
17.1182640 |
5.9889715 |
| ENSG00000244040 |
101928376 |
IL12A-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26097239_CCR1, KLRC4, IL12A-AS1, STAT4, and ERAP1 are bona fide susceptibility genes for Behcet's disease. |
|
|
316.215661 |
0.3036891222 |
-1.719333 |
0.099768554 |
306.498201 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001264974877094831658145953950562716635920365586356524924785143160327480664611566116184880606720414044553463600312084429794777119759762329315520496286417598895447266302673530735667384305997984483838081359863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000374920264777504310272805507796243365624436569306964061183918050206699546851382273181507340758873200408058783602984001349950710041135431481529805086713004663912960842675481387686886591836810111999511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
153.2930605 |
9.7030660 |
508.3601373 |
19.6366321 |
| ENSG00000244055 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
76.990964 |
0.3761447699 |
-1.410640 |
0.214976421 |
43.449960 |
0.00000000004349405337242865855161109979252337647687154387199370830785483121871948242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000230510674246695530312591783663150706018551971965280245058238506317138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.2337331 |
5.4904774 |
110.2976682 |
9.5155570 |
| ENSG00000244119 |
|
PDCL3P4 |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73.959874 |
0.3625534472 |
-1.463734 |
0.296547704 |
24.064505 |
0.00000093161850287518767968079945809845021642559004249051213264465332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003309431793607164705569786966599110655806725844740867614746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.1336758 |
8.0733652 |
114.3519645 |
15.0852974 |
| ENSG00000244198 |
|
ARHGEF35-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
158.164016 |
0.3628673738 |
-1.462486 |
0.197623261 |
53.652491 |
0.00000000000023928016285994363402694827236845946948117294650337782968563260510563850402832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001485187217751374356768379245816963742966854145066690762178041040897369384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
89.5542542 |
16.2408343 |
246.7237165 |
31.1393335 |
| ENSG00000244227 |
646168 |
LRRC77P |
transcribed_unitary_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.891050 |
0.3689174314 |
-1.438630 |
0.513199724 |
7.625830 |
0.00575381769589776437268113795653334818780422210693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011608303607360717646379555390012683346867561340332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.8872213 |
3.2715818 |
27.1037881 |
6.2201412 |
| ENSG00000244242 |
402778 |
IFITM10 |
protein_coding |
A6NMD0 |
|
Cell membrane;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. Predicted to be active in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:402778; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886] |
|
ENSMUSG00000045777 |
Ifitm10 |
18.310226 |
7.1904793446 |
2.846088 |
0.874350771 |
9.592643 |
0.00195358485064238982312212478120727610075846314430236816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004325669426264877430454713902463481645099818706512451171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.1118856 |
12.9470559 |
3.9048404 |
1.3680949 |
| ENSG00000244270 |
729215 |
RPL32P29 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.684711 |
0.4902562140 |
-1.028392 |
0.447034189 |
5.243509 |
0.02202880223181409233279559600759966997429728507995605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.039112849866663780551423457154669449664652347564697265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2884134 |
3.2891636 |
22.9249708 |
4.4594594 |
| ENSG00000244300 |
|
GATA2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.733198 |
0.3418495185 |
-1.548567 |
0.367037224 |
18.187957 |
0.00002001403692044465950565339251721042046483489684760570526123046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000060671017651625220028655666171246707563113886862993240356445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.9963034 |
3.1053115 |
35.5509038 |
5.8506292 |
| ENSG00000244480 |
|
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.614959 |
0.2002065534 |
-2.320439 |
0.540427714 |
20.041891 |
0.00000757641327577329955683454673631693765400996198877692222595214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000024126830625763515916944179640069023662363179028034210205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9728778 |
1.4872361 |
19.9538016 |
4.1940024 |
| ENSG00000244480_ENSG00000196295 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
81.563015 |
0.2499786341 |
-2.000123 |
0.477671203 |
16.608378 |
0.00004594761108576316037356221388954224948975024744868278503417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000132977792083502788927917848127435718197375535964965820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.8147540 |
17.3350538 |
140.4298331 |
49.1634935 |
| ENSG00000244879 |
|
GABPB1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
263.251515 |
0.4904165177 |
-1.027921 |
0.263777327 |
14.786808 |
0.00012037467796887873334142626813303422750323079526424407958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000327628664359330679361342886224406356632243841886520385742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
177.3817950 |
31.0074548 |
363.6793912 |
45.4489400 |
| ENSG00000245025 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.799050 |
0.3725630297 |
-1.424444 |
0.297210132 |
22.576822 |
0.00000201905869385246057460051027909742060728603973984718322753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000006906444106897408717203774852766429148687166161835193634033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.2625024 |
3.9156896 |
57.3115868 |
7.0314229 |
| ENSG00000245060 |
729678 |
LINC00847 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33426857_LncRNA LINC00847 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma progression by acting as a sponge of miR-99a to induce E2F2 expression. 35356750_Expression of LINC00847 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Children with Asthma and Its Prediction between Asthma Exacerbation and Remission. 35435130_Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 847 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the microRNA-181a-5p/zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 axis. |
|
|
88.708189 |
0.4719359689 |
-1.083337 |
0.183546431 |
34.999582 |
0.00000000329776131888447713117795801027361257684589190830592997372150421142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015027773098714074384960832160736121654309727091458626091480255126953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.1838870 |
6.6216221 |
126.1814829 |
9.2669383 |
| ENSG00000245112 |
100128055 |
SMARCA5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.034482 |
4.0701983460 |
2.025099 |
0.578062833 |
13.231780 |
0.00027524231754731204530398103180743873963365331292152404785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000705921217549665652550572314538612772594206035137176513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4004109 |
4.9717310 |
3.3291876 |
1.0474962 |
| ENSG00000245156 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.261426 |
0.4100996731 |
-1.285954 |
0.551754369 |
5.576881 |
0.01819910984013068180886740776713850209489464759826660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032925006274385194837694967873176210559904575347900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3785956 |
1.5403131 |
10.6346392 |
2.3504616 |
| ENSG00000245275 |
386627 |
SAP30L-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30599235_Results show that SAP30L-AS1 is increased in prostate cancer tissues and cell lines. Moreover, increased expression of SAP30LAS1 indicates greater Gleason score, advanced pathological T stage, and poor overall survival. Functional experiments revealed that ectopic expression of SAP30L-AS1 promotes prostate cancer proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in vitro. |
|
|
18.448080 |
0.4977771760 |
-1.006428 |
0.397181114 |
6.372439 |
0.01159061909200973135292134230667215888388454914093017578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021935829952309734980353539413044927641749382019042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.6868084 |
3.0882350 |
25.5386826 |
4.1567479 |
| ENSG00000245532 |
283131 |
NEAT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene produces a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) transcribed from the multiple endocrine neoplasia locus. This lncRNA is retained in the nucleus where it forms the core structural component of the paraspeckle sub-organelles. It may act as a transcriptional regulator for numerous genes, including some genes involved in cancer progression. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. |
|
|
19716791_Results assign a biological function to a large noncoding nuclear RNA, NEAT1, in the regulation of mRNA export. 20881053_Data from high-resolution in situ hybridization of NEAT1 transcripts revealed a highly ordered organization of IGAZ/PSPs. 21170033_Data shsow that FRAP analyses supported a critical structural role for Men varepsilon/beta (also known as Neat1) ncRNAs in paraspeckle organization. 21532345_genes that were significantly downregulated were the lncRNA NEAT-1 22960638_HNRNPK affects production of the essential NEAT1_2 isoform by negatively regulating its 3'-end polyadenylation by arresting CFIm complex binding near NEAT1_1's alternative polyadenylation site. 23129630_Formation of triple-helical structures by the 3'-end sequences of MALAT1 and MENbeta noncoding RNAs, is reported. 23362321_Based on the findings from NEAT1 knockdown, authors have identified the nuclear paraspeckle body as another important subcellular organelle for HIV-1 replication. 23835137_NEAT1_2 long coding RNA may act as a scaffold of RNAs and RNA binding proteins in the nuclei of amyotrophic lateral scleoris motor neurons. 24173718_NEAT1 controls target gene transcription by protein sequestration into paraspeckles. 24280234_we demonstrate that NEAT1 mRNA expression is increased in the villous trophoblasts of IUGR term placentas compared to CTRL term placentas, probably concomitantly with an increase inparaspeckle number. 24507715_NEAT1 plays an important role in the innate immune response through the transcriptional regulation of antiviral genes by the stimulus-responsive cooperative action of NEAT1 and SFPQ. 25245097_Our results indicate that reduced expression of the nuclear long noncoding RNA NEAT1 may play a role in the myeloid differentiation of APL cells. 25415230_NEAT1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer, and drives oncogenic growth by altering the epigenetic landscape of target gene promoters to favour transcription. 25417700_Induction of NEAT1 in hypoxia also leads to accelerated cellular proliferation, improved clonogenic survival and reduced apoptosis 25553361_Paraspeckle formation proceeds in conjunction with NEAT1 lncRNA biogenesis and involves the cooperation of multiple paraspeckle-localized RNA-binding proteins. {review] 25818739_High NEAT1 expression is associated with metastasis in lung cancer. 25831520_subunits of SWItch/Sucrose NonFermentable (SWI/SNF) chromatin-remodeling complexes were identified as paraspeckle components that interact with PSPs and NEAT1 lncRNA 25854373_NEAT1 expression was positively correlated with patient age. 25917923_Long non-coding RNA is an important regulator in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases. 25971364_Loss of NEAT1 expression is associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 26139386_Study indicates that NEAT1 and MALAT1 may interact with HIV-1 in vivo. The correlation between plasma levels of NEAT1 and CD4 T-cell counts indicates that NEAT1 levels in plasma could be a potential biomarker for HIV-1 infection. 26191242_Our study demonstrates that NEAT1 acts as a pivotal player in tumorigenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. 26242266_NEAT1 functions a molecular sponge for miR-449b-5p and leads to the upregulation of c-Met. This regulation menchaism promotes glioma pathogenesis and may provide a potential target for the prognosis and treatment of glioma. 26314847_expression of NEAT1 in colorectal cancer may play an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer differentiation, invasion and metastasis 26459763_demonstrated that reexpression of NEAT1 in miR-140 knockout adipocyte-derived stem cells is sufficient to restore their ability to undergo differentiation 26552600_Whole blood NEAT1 expression is a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of overall survival in colorectal cancer. 26582084_This study supports NEAT1 as a potential prognostic predictor with its high expression in cancer tissues and its association with carcinogenesis and progression in glioma. 26822763_Results show that NEAT1 regulated CDK6 expression in laryngeal squamous cell cancer (LSCC) cells which was mediated by miR-107; NEAT1 plays an oncogenic role in the tumorigenesis of LSCC. 26911892_Increased expression of NEAT1 lncRNA promotes growth of gastric adenocarcinomas. 27020592_NEAT1 regulated mesenchymal transition (EMT)phenotype and radioresistance by modulating the miR-204/ZEB1 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). 27075229_our research demonstrated that NEAT1 acts as a key regulator in human ovarian carcinogenesis and revealed two regulatory factors (HuR and miR-124-3p) of NEAT1 expression. 27095450_LncRNA NEAT1 plays an important role on gastric cancer tumorigenesis and progression and may act as a potential biomarker for therapeutic strategy and prognostic prediction 27154519_Its oncogenic activity is partially due to its repression of p21. and it may be a potential target for HCC therapy. 27270317_Study showed that NEAT1 could function as a competing endogenous lncRNA in lung cancer, mediating CTR1 by sponging hsa-mir-98-5p. 27351135_NEAT1 modulated the expression of E2F3 and MiR377 and promoted non small cell lung cancer progression. 27376578_NEAT1 is engaged in a negative feedback loop with p53 and thereby modulates cancer formation in mice by dampening oncogene-dependent activation of p53. Consistent with this finding, NEAT1 targeting sensitized established human cancer cells to both chemotherapy and p53 reactivation therapy. 27481557_Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 expression is increased in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. 27556696_NEAT1 promoted oncogenesis by downregulating let-7e expression in glioma stem cells. 27664948_Suggest role for NEAT1 in endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration at least partly via cell cycle regulation and modulation of several metastasis-related genes. 27783096_herpes simplex virus-1 infection increases NEAT1 expression and paraspeckle formation in a STAT3-dependent manner. 27878295_Targeting NEAT1 may provide a novel therapeutic opportunity for developing a relapse-free treatment of glioma patients. 27888106_Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay revealed that NEAT1 directly bound to the miR-506-3p, which has been reported to act as a tumor suppressor in diverse cancers. the tumor-promoting effects of NEAT1 in pancreatic cancer cells is at least partly through negative modulation of miR-506-3p. 27926523_The meta-analysis results from present study suggested that increased expression level of NEAT1 was associated with unfavorable prognosis and may serve as a predictive factor for clinicopathological features in various cancers. 28000845_Results suggest that high expression of NEAT1 promoted the onset of thyroid carcinoma. In addition, NEAT1 promoted the malignant progression of thyroid cancer through regulating miRNA214 expression. 28013491_NEAT1 knockdown signally inhibited growth and facilitated apoptosis. 28034643_NNEAT1 interacted with miR-101 modulates breast cancer growth by targeting EZH2 28054653_These results indicate a role for NEAT1 in modulating human neuronal activity and suggest a novel mechanistic link between an activity-dependent long non-coding RNA and epilepsy. 28118609_Our study suggests that NEAT1 may play different roles in the initiation and progression of digestive system cancers 28122578_NEAT-1 is a downstream effector of gemcitabine sensitivity in CCA. The expression of BAP1 is a determinant of sensitivity to therapeutic drugs that can be exploited to enhance responses through combination strategies. 28185956_Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates permeability of the blood-tumor barrier via miR-181d-5p-mediated expression changes in ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5. 28202761_NEAT1 modulates the innate immune response against Hantaan virus infection, providing another layer of information about the role of lncRNAs in controlling viral infections. 28269753_NEAT1 may be an important mediator in the regulation of Clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression and predicts the poor prognosis in patients with Clear cell renal cell carcinoma 28288210_results suggest that NEAT1 depletion rescues CX5461-induced nucleolar stress through facilitating c-Myc translation by relocating P54nrb/PSF from nuclear paraspeckles to c-Myc mRNAs 28295289_Results indicate that the induction of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 expression contributes to the tumor-suppressor function of p53 and suggest that p53 and NEAT1 constitute a transcriptional network contributing to various biological functions and tumor suppression. 28358873_we scrutinize noncoding mutations, discovering potentially impactful ones associated with MET. We also notice an elevation of mutations in the long noncoding RNA NEAT1, and these mutations are associated with increased expression and and unfavorable outcome 28379604_In Osteoarthritis tissues, OPN mRNA, and NEAT1 expression was upregulated, whereas miR-181c expression was downregulated, indicating that targeting NEAT1 to rescue miR-181c expression so as to inhibit OPN expression and synoviocyte proliferation 28401449_High NEAT1 expression is associated with Chemotherapy Resistance in Gastric Cancer. 28507281_This meta-analysis showed that NEAT1 expression may be a useful biomarker for predicting a poor prognosis in patients with cancer. 28526689_The results provide strong evidence that upregulated NEAT1 promotes the proliferation of cancer cells in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and this regulatory mechanism depends on the microRNA (miR)-129-5p-valosin-containing protein-IkappaB axis. 28615056_NEAT1 expression is controlled by Oct4 transcriptional regulation in lung cancer. 28643459_NEAT1 was potentially communicated with mTOR signaling target protein mLST8 via the association with miR-181b in type 2 diabetes mellitus. 28698299_identify Neat1 as a p53-regulated large intergenic ncRNA (lincRNA) with a key role in suppressing transformation and cancer initiation. 28712728_Identify a HEXIM1-containing ribonuclear protein complex composed also of DNA-PK, paraspeckle subunits, and the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) NEAT1, which acts as a key nuclear regulator of DNA-mediated activation of innate immune response through the cGAS-STING pathway. 28720546_NEAT1 facilitates cell growth and invasion via the miR-211/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer 28762332_our study suggested that lncRNA NEAT1 plays an oncogenic role in NSCLC progression and provides potential mechanisms by which lncRNA NEAT1 contributes to this disease. 28783584_NEAT1 was notably upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and cells; higher NEAT1 expression associated with larger tumor size and vascular invasion of HCC patients 28805661_the FOXN3-NEAT1-SIN3A complex promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro as well as dissemination and metastasis of breast cancer in vivo 28810932_High NEAT1 expression is associated with Growth and Metastasis of Cholangiocarcinoma. 28846091_Mechanistic dissection reveals that NEAT1 broadly interacts with the NONO-PSF heterodimer as well as many other RNA-binding proteins and that multiple RNA segments in NEAT1, including a 'pseudo pri-miRNA' near its 3' end, help attract the Drosha-DGCR8 Microprocessor. 28911096_Star-PAP-specific polyadenylation sites usage regulates the expression of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor EIF4A1, the tumor suppressor gene PTEN and the long non-coding RNA NEAT1. 28946559_NEAT1 expression was significantly up-regulated in breast cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues, and higher NEAT1 was positively associated with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. miR-218 was shown to be a direct target of NEAT1 in breast cancer cells. In addition, NEAT1 promoted cell invasion and proliferation by negatively regulating miR-218 in breast cancer. 29031635_NEAT1 and the coding gene IFI27 were highly co-expressed and negatively correlated with dengue severity. Monitoring NEAT1and IFI27 expression in PBMC may be useful in understanding dengue virus-induced disease progression. 29047232_Knockdown of NEAT1 suppressed proliferation and invasion and induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting miR-194 expression. 29091312_Data show that NEAT1 was high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). NEAT1 promotes tumor cell EMT, migration and invasion capacities by stimulating the activation of HIF-2alpha in HCC. 29095526_NEAT1/hsa-mir-98-5p/MAPK6 is involved in the development and progress in non-small-cell lung cancer. 29111326_C/EBPbeta contributes to all-trans retinoic acid-induced activation of NEAT1 during acute promyelocytic leukemia cell differentiation. 29138341_our current work revealed that the glioblastoma-associated lncRNA NEAT1 was an oncogenic factor that was regulated by EGFR pathway, promoting tumorigenesis by serving as a scaffold and recruiting the chromosome modification enzyme EZH2 to silence target-specific genes (Axin2, ICAT and GSK3B) to promote beta-catenin nuclear transport. 29147064_LncRNA NEAT1 regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell viability and invasion via the miR-129/CTBP2 axis. 29205703_Data suggest that NEAT1 is highly expressed in dexamethasone-(DEX-)-resistant multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines; up-regulation of NEAT1 is tightly linked to poor prognosis in MM patients. During development of DEX resistance in MM cells, MIRN193a levels are down-regulated resulting in up-regulation of expression of target gene myeloid cell leukemia-1 (MCL1). (NEAT1 = nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1) 29207151_NEAT1 acts a sponge of miR-101 in cervical cancer, and NEAT1 level is upregulated in cervical cancer, where it correlates with unfavorable clinicopathologic factors and poor prognosis. NEAT1 plays a crucial role in cervical cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion targeting miR-101. 29219178_NEAT1 can act as a competing endogenous lncRNA (ceRNA) to regulated STAT3 by sponging miR-485 in HCC. 29225160_Data suggest that NEAT1, SRC3, and IGF1R are highly expressed in prostate cancer cells; NEAT1 appears to interact with SRC3 and promote cell proliferation via up-regulation of SRC3/IGF1R/AKT signaling pathway. (NEAT1 = nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript-1; SRC3 = steroid receptor coactivator protein-3; IGF1R = insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) 29257236_Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced neat1_2mediated paraspeckle formation in macrophages. 29319165_KLK7 accelerated the deterioration of PTC in vitro experiments which could be reversed by sh-lnc RNA NEAT1 and miR-129-5p mimics. In vivo experiments, silence of lncRNA NEAT1 restrain tumor growth in weight and volume. 29323713_we uncovered that NEAT1 participated in breast cancer progression by regulating miR-448 and ZEB1. NEAT1 can be provided as a vital biomarker in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment therapy. 29363783_NEAT1 is upregulated in gastric cancer cells. NEAT1 downregulation could dramatically inhibit gastric cancer progression, while overexpression of NEAT1 induced gastric cancer development. NEAT1/miR-506/STAT3 might play a vital role in gastric cancer progression. 29388017_we found three common lncRNAs across the four subtype-related ceRNA networks, NEAT1, OPI5-AS1 and AC008124.1, which played specific roles in each subtype through competing with diverse mRNAs. 29394378_We propose a secondary structural model of the shorter (3,735 nt) isoform hNEAT1_S, in which the RNA folds into four separate domains. The secondary structures of mouse and human NEAT1 are largely different, with the exception of several short regions that have high structural similarity. 29463949_Study found upregulated NEAT1 expression in patients with sepsis indicating an association between NEAT1 and immune dysfunction in patients with sepsis. NEAT1 is a potential molecular marker for sepsis diagnosis. 29484420_NEAT1 silencing also inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Collectively, we revealed that the NEAT1/miR365/RGS20 axis may be a novel mechanism or therapeutic strategy for OSCC treatment. 29534600_lncRNA NEAT1 plays a role in the occurrence and development of IDD. 29544562_upregulation of NEAT1 may promote proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via targeting miR-335-5p/ROCK1 axis 29654165_Suppression of miR-34c could up-regulate the expressions of its target genes BCL-2 and CCND1 to antagonize the effects of NEAT1 knockdown. Furthermore, overexpressed NEAT1 reduced the sensitivity of cisplatin (DDP) and inhibited DDP-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via miR-34c 29662142_This study determined that Hepatitis Delta Virus replication induces the delocalization of PSP1 to cytoplasmic foci containing PABP and increases NEAT1 level causing an enlargement of NEAT1 foci. 29764424_Results revealed that the NEAT1 modulates ATGL expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and disrupts the lipolysis of hepatoma cells via ATGL. NEAT1-regulated abnormal lipolysis facilitates HCC cell growth in vivo. 29788922_Study confirmed that galectin-3 as a ligand of TLR4 induced TLR4 signaling activation in lung adenocarcinoma cells, thereby activating downstream p65 nucleus translocation, promoting NEAT1 expression, and finally affecting lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and migration. 29790629_NEAT1 promoted ovarian cancer cells metastasis through regulating the miR-382-3p/ROCK1 axis 29797561_we speculated that NEAT1 can modulate TGF-b1 expression by sponging hsa-mir-139-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) . These data indicates that targeting the NEAT1/hsa-mir-139-5p/TGF-b1 axis could be a new strategy for HCC. 29864936_NEAT1 regulates lung cancer cell progression by competing endogenous RNA network of NEAT1/let-7a/IGF2. 29871935_One target of CDC5L, ARGN, mediated the strong phenotypic consequences of NEAT1 reduction. 29932899_Authors demonstrate that the enrichment of NONO dimers on the redundant NEAT1_2 subdomains initiates construction of phase-separated paraspeckles, providing mechanistic insights into lncRNA-based nuclear body formation. 29972301_The discovery of MALAT1, NEAT1, and NORAD lncRNA-binding proteins has been reported. 29997370_Study demonstrated that NEAT1 and HOTAIR negatively regulate CDK5R1 mRNA levels, while MALAT1 has a positive effect. 30024596_LncRNA NEAT1 regulates cervical carcinoma proliferation and invasion by targeting AKT/PI3K 30024601_NEAT1 was up-regulated in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. 30036787_HIV-1 replication was higher in the knock-out cell lines lines than parental Jurkat cells, demonstrating an anti-HIV function of NEAT1 long noncoding RNA. 30036873_NEAT1 may function as a ceRNA to sponge miR-193a-3p and relieve the inhibitory effect of miR-193a-3p on the USF1 gene. 30053878_lncRNA NEAT1 was proved to be up-regulated in glioma and targeted miR-132. As a target gene of miR-132, SOX2 was over-expressed in glioma. NEAT1 knockdown could inhibit the growth and invasiveness of glioma cells through indirectly down-regulating SOX2 by targeting miR-132. 30096244_these results indicated that NEAT1 plays an important role in the regulation cervical cancer cell growth by targeting miR-9-5p. 30097212_data indicate that NEAT1 promoter mutations may not be common in common cancers 30114626_The NEAT1 expression was inversely correlated with age at onset and disease duration in female patients. 30123061_LncRNA NEAT1 was up-regulated in osteosarcoma tissue, promoting proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. These findings indicate the role of this substance, as a growth regulator in osteosarcoma 30132508_The downregulation of NEAT1 suppressed the inflammatory response by modulating the intestinal epithelial barrier and through exosomemediated polarization of macrophages in IBD. 30139920_Data suggest that NEAT1 is a therapeutic target for treating occlusive vascular diseases. 30153828_Data showed that NEAT1 is an essential mediator of the apoptosis induced by imatinib in BCR-ABL-expressing cells. Moreover, NEAT1 is a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc, c-Myc represses NEAT1 expression by binding to the NEAT1 promoter, and SFPQ is required for NEAT1-mediated apoptosis in K562 cells. 30154460_NEAT1, stabilized by LIN28B, promoted HGSOC progression by sponging miR-506. 30175971_Our results showed that NEAT1_1 plays an oncogenic role in DLBCL. NEAT1_1 expression may serve as a predictive marker for DLBCL patients. 30180948_analysis of NEAT1 upregulation using guide RNAs in the NEAT1 promoter region for CRISPR activation 30185232_Findings indicated that NEAT1 activated Wnt signaling to promote colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. 30203547_LncRNA NEAT1 could impede miR-339-5p expression to maintain the expression of TGF-beta1, which led to the development of osteosarcoma. 30239724_the genes dysregulated in HD human brain samples overlap with pathways affected by a reduction in NEAT1, confirming the correlation of NEAT1L and HD-induced perturbations. Cumulatively, the role of NEAT1L in polyQ disease model systems and human tissues suggests that it may play a protective role in CAG-repeat expansion diseases 30246348_NEAT1 repressed the expression of miR-23a-3p, and therefore promoted SMC1A, which in turn suppressed myeloid leukemia cell proliferation and enhanced apoptosis 30250064_Data indicate long noncoding RNA NEAT1 (nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1) and paraspeckle regulation, and reveal a cross-regulation between paraspeckles and mitochondria. 30291867_it was exhibited that Wnt signal pathway was inactivated by knockdown of NEAT1 whereas activated by NEAT1 overexpression in A549/CDDP cells; it was indicated that NEAT1 could exert a novel biological role in non-small cell lung cancer chemo-resistance 30305397_NEAT1 is upregulated during the heat shock response. The NEAT1 promoter contains a heat shock element that binds HSF1 to promote paraspeckle formation. 30312725_Up-regulated NEAT1 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer both in vitro and in vivo. 30338809_NEAT1 is highly expressed in multiple myeloma, enhancing cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis to promote tumor formation by activating SOX13/PI3K/AKT pathway. 30362505_RELA, NEAT1, and miR-302a-3p form a feedback loop in pancreatic ductal carcinoma to modulate tumor cell proliferation and migration. 30383193_Data indicate a long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1)/miR-196a-5p/glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) regulatory pathway in colorectal cancer (CRC). 30407674_The author's findings demonstrate that lncRNA NEAT1 acts as an oncogenic role in colorectal cancer cells by sponging miR-193a and may represent a potential marker for colorectal cancer patients. 30452118_Progesterone exerted suppressive influence on endometrial cancer progression via regulation of lncRNA NEAT1/miR-146b-5p-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 30479013_NEAT1 promotes the development of retinoblastoma (RB) via miR-204/CXCR4 axis. 30480816_our findings indicated that NEAT1/miR-107/CDK14 axis participated in glioma development. NEAT1 could act as a significant prognostic biomarker in glioma progression. 30485482_High NEAT1 expression is associated with cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma. 30515782_LncRNA NEAT1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of glioma through regulating miR-139-5p/CDK6 pathway. 30534569_the expression of NEAT1 increased during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, and it might be associated with the outcome of tuberculosis. 30575330_Our findings on colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues, cell lines, and xenograft models overall support that NEAT1 serves as an oncogene, with knockdown attenuating CRC cell development. 30618186_NEAT1 is a potential prognostic biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), but more studies are needed to further verify the prognostic value of NEAT1 in patients with NPC. 30622287_Report renal cell carcinomas with NEAT1-TFE3 and KAT6A-TFE3 gene fusions. 30638953_NEAT1 promotes osteogenic differentiation in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating miR-29b-3p/BMP1 axis. 30639603_NEAT1 is up-regulated in the childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia samples and correlated with dysregulation of miR-335-3p.NEAT1 indirectly regulates multidrug resistant genes including ABCA3. 30717168_NEAT1's function in non-cancerous diseases predominantly focuses on paraspeckle-mediated effects on gene expression. (Review) 30782035_NEAT1 mediates paclitaxel-resistance of non-small cell of lung cancer through activation of Akt/mTOR signalling pathway. 30803129_findings describe a relationship of the plasma levels of H19/miR-675 and NEAT1/miR-204 in the different breast cancer subtypes; in addition, they reveal an interplay between these lncRNAs and miRNAs in the regulatory network in MCF-7 cells. 30845377_NEAT1 up-regulation induced by HIF-2alpha over-expression could promote the progression of non-small cell lung cancer under hypoxic condition. 30883005_High NEAT1 expression is associated with sepsis. 30894512_NEAT1 conferred oncogenic role by regulating apoptosis and cell cycle progression in triple-negative breast cancer cells (TNBC). The knockdown of NEAT1 sensitized cells to chemotherapy, indicating the involvement in chemoresistance. shNEAT1 reduced stem cell populations such as CD44+/CD24-, ALDH+, and SOX2+, implicating that NEAT1 was closely related to cancer stemness in TNBC. 30924864_NEAT1 is a novel lncRNA-type immunoregulator affecting T cell and monocyte/macrophage lineage differentiation and functions in myocardial infarction. 30924966_NEAT1 expression was abnormally decreased in chronic hepatitis B patients in the active phase. 30928097_NEAT1 promotes the proliferation and migration, whereas inhibits the apoptosis of the hemangioma endothelial cells via regulating miR-361-5p/VEGFA axis. 30932200_NEAT1 knockdown inhibited cervical cancer development through repressing cell proliferation, colony formation, capacity of migration, and invasion and also inducing the apoptosis. 31038819_NEAT1 promotes retinoblastoma progression via modulating miR-124. 31044561_Overexpression of NEAT1 accelerated proliferation and reduced apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. NEAT1 positively regulates the expression of HOXA13 by competing with miR-34a-5p. 31062612_NEAT1 played an important role in the activation of ERalpha to regulate AQP7-mediated hepatic steatosis 31090110_LncRNA NEAT1 promotes hypoxia-induced renal tubular epithelial apoptosis through downregulating miR-27a-3p. 31173352_we suggest that NEAT1 exerts an oncogenic effect on melanoma development via inhibition of miR-495-3p and induction of E2F3. NEAT1 might serve as a crucial prognostic biomarker of melanoma. 31173354_it was indicated that NEAT1 promoted colon cancer development through modulating miR-495-3p and CDK6 in vivo. Taken these together, we reported that NEAT1 could sponge miR-495-3p to contribute to colon cancer progression through activating CDK6. 31173767_Trimethylamine N-oxide caused increased expression of lncRNA-NEAT1. NEAT1 showed a circadian rhythmic expression in HUVECs, and its overexpression reduced cell proliferation. NEAT1 regulation of Clock-Bmal1 via MAPK pathways was involved in TMAO-repressed HUVECs proliferation 31190421_Relative NEAT1 expression level was significantly increased in serum of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients 4.7 (1.31-6.82) (p |
|
|
2846.739962 |
0.2692726857 |
-1.892860 |
0.082202869 |
504.683286 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000090989475124419218807867736445616071041264100781929820184587118427253745696175827430994661881099779701298723803475571571409649464610442261200497308016982996860207039494273883756655446520886874376875182485268050887227751 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000043604047170013885084179891525273217095725379978713464629359054454906153903108144921824100767878582722554700559819011854215760619093432970978018888422935437622352252578806608462029389751370122063393233394951594102252640 |
Yes |
No |
1223.5885528 |
98.1168514 |
4579.7046695 |
262.8226770 |
| ENSG00000245556 |
728769 |
SCAMP1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31207033_Knockdown of LncRNA SCAMP1 suppressed malignant biological behaviours of glioma cells via modulating miR-499a-5p/LMX1A/NLRC5 pathway. |
|
|
28.965373 |
0.4085255157 |
-1.291502 |
0.337283317 |
14.769129 |
0.00012150854710000030226187128779002932787989266216754913330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000330531912126060564531548902067470407928340137004852294921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.9753743 |
6.0351197 |
46.7218866 |
10.2019910 |
| ENSG00000245648 |
101928100 |
KLRK1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.398810 |
0.3215853289 |
-1.636727 |
0.439866906 |
14.411272 |
0.00014692022563659036765541798796874672916601411998271942138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000393707794189555838285793365471931792853865772485733032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.8394806 |
1.9718268 |
21.5007384 |
3.7142424 |
| ENSG00000245685 |
728339 |
FRG1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.481526 |
0.3833846027 |
-1.383136 |
0.566366876 |
6.058934 |
0.01383611390815307935764355562469063443131744861602783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025720534166793380947968472582942922599613666534423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1161140 |
1.8149881 |
13.4096517 |
3.0962150 |
| ENSG00000245849 |
100505648 |
RAD51-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26230935_results identify TPIP as a novel E2F1 co-activator, suggest a similar role for other TPTEs, and indicate that the TODRA lncRNA affects RAD51 dysregulation and RAD51-dependent DSB repair in malignancy 28667302_Overexpression of RAD51-AS1 promoted EOC cell proliferation, while silencing of RAD51-AS1 inhibited EOC cell proliferation, delayed cell cycle progression and promoted apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. 29749376_Corylin increases the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy through long noncoding RNA RAD51-AS1-mediated inhibition of DNA repair. 33314669_LncRNA RAD51-AS1/miR-29b/c-3p/NDRG2 crosstalk repressed proliferation, invasion and glycolysis of colorectal cancer. |
|
|
46.831197 |
0.1788349434 |
-2.483299 |
0.311078891 |
66.912861 |
0.00000000000000028377746774724578158823582620068863709677223954377933701209713035495951771736145019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002089055074288951317264695641161845095220504211694367846519071463262662291526794433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.8621772 |
2.7617100 |
78.2961750 |
8.7891102 |
| ENSG00000245904 |
|
BTG1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
114.768135 |
0.3149818870 |
-1.666659 |
0.178052854 |
90.131328 |
0.00000000000000000000222864762640693299791944609131473042375524751087673740261021690378662185594293987378478050231933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000020832703588199070602724142144276179078537712513033779116681382115316978342889342457056045532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.6574175 |
6.6985207 |
168.4634912 |
13.6429351 |
| ENSG00000246090 |
100507053 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.152877 |
0.2244953564 |
-2.155242 |
0.708081422 |
8.148253 |
0.00431026699946383904521463037440298649016767740249633789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008932819560809639874987553298524289857596158981323242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3385732 |
2.6254151 |
24.3763439 |
7.7305727 |
| ENSG00000246263 |
|
UBR5-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.115319 |
0.1373241752 |
-2.864342 |
0.372849006 |
70.413199 |
0.00000000000000004809703524694955272519325508785222932666641537744617318494988467136863619089126586914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000369938634833233672024060603471358321272807956813996610456740654626628383994102478027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1915844 |
1.8715028 |
45.6447884 |
7.8757681 |
| ENSG00000246273 |
283104 |
SBF2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27154193_Study identified a novel lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that is upregulated and correlated with advanced TNM stage. SBF2-AS1 could promote proliferation of NSCLC cells in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that it might be an oncogenic lncRNA in NSCLC. 30115383_Long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 modulated TGFBR1 through sponging miR-140-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. 30338801_LncRNA SBF2-AS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by regulating epithelial mesenchymal transformation. 30856345_LncRNA SBF2-AS1 expression is increased in cervical cancer (CC). High SBF2-AS1 expression was associated with advanced FIGO stage and lymph node metastasis of CC patients. Function assays shows that SBF2-AS1 inhibition significantly reduces CC cells proliferation both in vitro and in vivo. SBF2-AS1 upregulation restrain the activity of miR-361-5p and leads to overexpression of Forkhead Box Protein M1 in CC cells. 30912164_downregulation of miR-619-5p or HDAC3 overexpression reversed SBF2-AS1-silencing-caused suppression on proliferation and metastasis. 30992025_Transcription factor ZEB1 was found to directly bind to the SBF2-AS1 promoter region to regulate SBF2-AS1 level and affected TMZ resistance in GBM cells. SBF2-AS1 functions as a ceRNA for miR-151a-3p, leading to the disinhibition of its endogenous target, X-ray repair cross complementing 4 (XRCC4), which enhances DSB repair in GBM cells. 31050364_SBF2-AS1: An oncogenic lncRNA in small-cell lung cancer. 31062614_SBF2-AS1 could act as a miRNA sponge in AML progression 31432728_Silencing of long noncoding RNA SBF2-AS1 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion and contributes to apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by upregulating microRNA-30a to suppress FOXA1 expression. 31928130_LncRNA SBF2-AS1 affects the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer via modulating microRNA-302a/MBNL3 axis. 32301277_Down-regulated lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in M2 macrophage-derived exosomes elevates miR-122-5p to restrict XIAP, thereby limiting pancreatic cancer development. 32364763_E2F1-induced overexpression of SBF2-AS1 promotes the expression of GRB2 by targeting miR-362-3p to facilitate the metastasis of NSCLC 32626753_Long Noncoding RNASBF2-AS1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression via Regulating miR-545/EMS1 Axis. 33436941_The molecular mechanisms of the long noncoding RNA SBF2-AS1 in regulating the proliferation of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 33906548_The Clinical Prognostic Value of lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. 34341185_Downregulation of lncRNA SBF2-AS1 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and migration by regulating the miR-361-5p/TGF-beta1 signaling pathway. 34644425_Low expression of lncRNA SBF2-AS1 regulates the miR-302b-3p/TGFBR2 axis, promoting metastasis in laryngeal cancer. 34850542_Silencing of SBF2-AS1 inhibits cell growth and invasion by sponging microRNA-338-3p in serous ovarian carcinoma. 35440300_LncRNA SBF2-AS1: A Budding Star in Various Cancers. 35444785_LncRNA SBF2-AS1 Facilitates Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Progression by Targeting miR-520a-3p. 35968497_Long Noncoding RNA SBF2-AS1 Promotes Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation through the miRNA-520f-3p/SMARCD1 Axis. |
|
|
22.445264 |
0.3614220264 |
-1.468244 |
0.352177832 |
17.814790 |
0.00002434832444512175075716255145952260363628738559782505035400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000072896809089248887922676822803680352080846205353736877441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.1205014 |
2.4959587 |
30.9523712 |
4.2574130 |
| ENSG00000246308 |
101928053 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.710499 |
0.1795474139 |
-2.477563 |
0.793372257 |
8.432330 |
0.00368607739557168852945201464876845420803874731063842773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007746903368736740222444403514145960798487067222595214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.4131985 |
1.2498476 |
12.9990604 |
4.4169664 |
| ENSG00000246366 |
286190 |
LACTB2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.673283 |
0.3071046190 |
-1.703198 |
0.690955857 |
6.251243 |
0.01241061807081444284817095535800035577267408370971679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.023335123914040915155121425073048158083111047744750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6401112 |
2.2285682 |
11.6691326 |
4.4739240 |
| ENSG00000246451 |
|
KLC1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41.183007 |
0.4820937495 |
-1.052614 |
0.464728284 |
5.000882 |
0.02533440677610192259816557225349242798984050750732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044363013882461076187180282204280956648290157318115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.7491424 |
7.7221926 |
55.4855149 |
11.2092859 |
| ENSG00000246695 |
|
RASSF8-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
58.011452 |
0.4510632994 |
-1.148598 |
0.345007287 |
10.760731 |
0.00103676447640912300363069675768201705068349838256835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002406076049024946043181083510376083722803741693496704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.4014661 |
9.8109878 |
80.5455405 |
15.2504586 |
| ENSG00000246705 |
55766 |
H2AJ |
protein_coding |
Q9BTM1 |
FUNCTION: Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Chromosome;DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Methylation;Nucleosome core;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is located on chromosome 12 and encodes a replication-independent histone that is a variant H2A histone. The protein is divergent at the C-terminus compared to the consensus H2A histone family member. This gene also encodes an antimicrobial peptide with antibacterial and antifungal activity.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2015]. |
hsa:55766; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; nucleosome [GO:0000786]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; protein heterodimerization activity [GO:0046982]; structural constituent of chromatin [GO:0030527] |
11331621_In this paper, the authors identified and cloned the H2AFJ gene on chr 12 and used it as a control for studying two macroH2A genes. 21178486_The antimicrobial protein buforin I results from proteolytic cleavage of the histone protein H2A in the stomach. 28489069_Histone variant H2A.J (H2A.J) accumulates in senescent fibroblasts with DNA damage. 33266246_Histone Variant H2A.J Marks Persistent DNA Damage and Triggers the Secretory Phenotype in Radiation-Induced Senescence. 34828271_Histone Variant H2A.J Is Enriched in Luminal Epithelial Gland Cells. |
ENSMUSG00000060032 |
H2aj |
48.738121 |
0.4386398594 |
-1.188891 |
0.217236954 |
31.109018 |
0.00000002439354733233404963367027063272929332526928192237392067909240722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000102286579154900729496708200634558227903880833764560520648956298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.2061870 |
4.1101080 |
67.0332909 |
5.6619721 |
| ENSG00000246763 |
503569 |
RGMB-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29288973_lncRNA RGMB-AS1 serves an anti-oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma. 29687852_E2F1 promotes the transcription of lncRNA RGMB-AS1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). 31351424_lncRNA RGMB-AS1 could exert as an oncogenic factor through modulating miR-22/NLRP3 pathway. 32064882_RGMB-AS1/miR-22-3p/NFIB axis contributes to the progression of gastric cancer. 34468207_LncRNA RGMB-AS1 facilitates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration but inhibits cell apoptosis via miR-574-3p/PIM3 axis. 34583851_LncRNA RGMB-AS1 up-regulates ANKRD1 Through Competitively Sponging miR-3614-5p to Promote OSA Cell Proliferation and Invasion. 35184697_Long non-coding RNA RGMB-AS1 represses nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression via binding to forkhead box A1. |
|
|
27.017513 |
0.1992090031 |
-2.327645 |
0.436135375 |
27.566584 |
0.00000015177842852158628083662187009672539517168843303807079792022705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000587529400728721093940414878231681683473652810789644718170166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5169347 |
2.9671179 |
37.2157461 |
10.0639366 |
| ENSG00000246859 |
100505678 |
STARD4-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
380.576633 |
0.1417902545 |
-2.818170 |
0.117320458 |
607.362124 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004192708047358756647773497661520609734112364839142902038772194000085524954669895763764523477199410853927320330873994640605144833898635017555064124748722692293106613094565138969171850186935571001071 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002335259274679820477233617437462362620315148391960238342251617823986904401266850416644897048723179018952418217741014032415534495148291913840873703345881889225694153533122135583649748949533889690337 |
Yes |
No |
93.2069918 |
7.1482270 |
661.8591255 |
29.1929644 |
| ENSG00000246898 |
|
LINC00920 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.304622 |
0.3574240082 |
-1.484292 |
0.366711987 |
16.891445 |
0.00003957956847518208387017024652010377394617535173892974853515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000115362249347094686586015499507595905015477910637855529785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2115597 |
2.7445480 |
31.6792790 |
4.7892018 |
| ENSG00000246922 |
390595 |
UBAP1L |
protein_coding |
F5GYI3 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable ubiquitin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway. Predicted to be part of ESCRT I complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:390595; |
ESCRT I complex [GO:0000813]; ubiquitin binding [GO:0043130]; ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway [GO:0043162] |
|
ENSMUSG00000086228 |
Ubap1l |
19.341446 |
0.2773996176 |
-1.849962 |
0.478166255 |
14.863049 |
0.00011560550037565002815496961741104087195708416402339935302734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000315345996219662614429291025430757144931703805923461914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6519553 |
2.5913371 |
31.6850495 |
6.0043588 |
| ENSG00000247081 |
105369147 |
BAALC-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.106759 |
0.3586438545 |
-1.479376 |
0.356988964 |
17.047114 |
0.00003646374337977483724151581134798050243261968716979026794433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000106744318184346810422270801499422532288008369505405426025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.0119069 |
4.4210742 |
42.6326575 |
8.6426207 |
| ENSG00000247151 |
338739 |
CSTF3-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.254889 |
0.0239774139 |
-5.382180 |
0.513315911 |
102.481401 |
0.00000000000000000000000435436605359622519270955723789934187649677152251462805136195675145133199279712243878748267889022827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000045197217265176010263748133442719447780545601105745988842320593880524937091536230582278221845626831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
0.7019439 |
0.2497254 |
29.4376327 |
6.8570232 |
| ENSG00000247199 |
102546294 |
FBXO38-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
161.782879 |
0.4775424863 |
-1.066299 |
0.130448689 |
67.541359 |
0.00000000000000020631351310593786874959832575313720535937201641836502563620570072089321911334991455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001531014305401530020492490616870319778652142291182347566547150563565082848072052001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
104.2697420 |
8.8593322 |
219.9636963 |
12.4708675 |
| ENSG00000247373 |
|
TMED2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33.528629 |
0.4206941717 |
-1.249156 |
0.271493964 |
21.700638 |
0.00000318685290056184475270743654273797318410288426093757152557373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010615650826516097161400335735503830392190138809382915496826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.4171318 |
3.6772505 |
49.0771931 |
5.5892922 |
| ENSG00000247400 |
100289274 |
DNAJC3-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33629299_LncRNA DNAJC3-AS1 functions as oncogene in renal cell carcinoma via regulation of the miR-27a-3p/PRDM14 axis. 34895046_miRNA-144 targeting DNAJC3-AS1 reverses the resistance of the breast cancer cell line Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 to doxorubicin. |
|
|
24.445368 |
0.3017063689 |
-1.728783 |
0.400184574 |
18.831972 |
0.00001427540224172733249695648599653097221562347840517759323120117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000043979323124169362199762517429135755264724139124155044555664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7808220 |
3.0624871 |
35.6590726 |
6.5133321 |
| ENSG00000247626 |
92935 |
MARS2 |
protein_coding |
Q96GW9 |
|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase;ATP-binding;Deafness;Disease variant;Ligase;Mitochondrion;Neurodegeneration;Nucleotide-binding;Primary mitochondrial disease;Protein biosynthesis;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
This gene produces a mitochondrial methionyl-tRNA synthetase protein that is encoded by the nuclear genome and imported to the mitochondrion. This protein likely functions as a monomer and is predicted to localize to the mitochondrial matrix. Mutations in this gene are associated with the autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease spastic ataxia-3 (SPAX3). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:92935; |
mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; methionine-tRNA ligase activity [GO:0004825]; methionyl-tRNA aminoacylation [GO:0006431]; tRNA aminoacylation for protein translation [GO:0006418] |
15274629_Sequence analysis of mitochondrial MetRS indicates that this protein contains consensus motifs characteristic of class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase but lacks Zn2+ binding motif and C-terminal dimerization region found in MetRSs from various organisms. 20877624_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 22448145_MARS2 is mutated in Autosomal Recessive Spastic Ataxia with Leukoencephalopathy patients. 25754315_Novel, compound heterozygous, single-nucleotide variants in MARS2 associated with developmental delay, poor growth, and sensorineural hearing loss 34273914_Increased Mars2 expression upon microRNA-4661-5p-mediated KDM5D downregulation is correlated with malignant degree of gastric cancer cells. |
ENSMUSG00000046994 |
Mars2 |
98.505784 |
2.5472623190 |
1.348948 |
0.166053099 |
67.068480 |
0.00000000000000026223787271427511828626307095674320048601214179148644056738248764304444193840026855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001937252753384735086740117139833279352822921265050992722933642653515562415122985839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.9856398 |
13.7999187 |
56.8777303 |
4.4235519 |
| ENSG00000247679 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.500766 |
0.3306418813 |
-1.596659 |
0.295191228 |
30.118880 |
0.00000004063557436483809141347168288754820864028260984923690557479858398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000166374778814149852320704303654252953492687083780765533447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.4833169 |
3.5009729 |
53.2573171 |
6.6949361 |
| ENSG00000247774 |
100233209 |
PCED1B-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31680313_LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 activates the proliferation and restricts the apoptosis of glioma through cooperating with miR-194-5p/PCED1B axis. 34036383_Long noncoding RNA PCED1BAS1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression by regulating the miR4113p/HIF1alpha axis. 34516330_Long non-coding RNA PCED1B antisense RNA 1 promotes gastric cancer progression via modulating microRNA-215-3p / C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 axis. 35997114_LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 Upregulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Regulation of the miR-10a/BCL6 Axis to Promote Cell Proliferation. 36274134_LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 knockdown inhibits osteosarcoma via methylation-mediated miR-10a downregulation. 36418980_Upregulation of PCED1B-AS1 in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and its involvement in retinal vascular endothelial cell proliferation. |
|
|
95.924335 |
0.4913789235 |
-1.025092 |
0.168932829 |
37.013526 |
0.00000000117312595197544566157614239230782757217319556275469949468970298767089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005576598728231103918543910206561536879732443594548385590314865112304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.5140849 |
8.9226704 |
126.9064269 |
12.7309203 |
| ENSG00000247796 |
257396 |
MOCS2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.079878 |
0.4833988375 |
-1.048714 |
0.480476523 |
4.835653 |
0.02787708723834316643097608334755932446569204330444335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.048316792817983227059652762136465753428637981414794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4830632 |
2.0510234 |
13.4890689 |
2.7779867 |
| ENSG00000247903 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.982272 |
0.2471638648 |
-2.016460 |
0.753233129 |
7.362286 |
0.00666060402332542978581786385916529980022460222244262695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013260118071794353006298550212704867590218782424926757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9392488 |
1.4703115 |
12.1650655 |
3.5739740 |
| ENSG00000247934 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.982885 |
0.3456938617 |
-1.532433 |
0.335045420 |
21.553365 |
0.00000344118415944930778591114364783898338373546721413731575012207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011408777671489618010520865343249141687920200638473033905029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1028395 |
2.6922495 |
35.3558172 |
4.8931967 |
| ENSG00000247993 |
|
FOXD1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42.052991 |
0.3637700813 |
-1.458901 |
0.276612534 |
28.158520 |
0.00000011177452275816134366468899627444777422624611062929034233093261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000438774456359165284735981971131479895120719447731971740722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6736731 |
4.9617727 |
59.9719873 |
9.2431935 |
| ENSG00000248015 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.805157 |
0.2370841021 |
-2.076529 |
0.729960037 |
7.793452 |
0.00524359140006882065709881146631232695654034614562988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010670813327590761288021781183488201349973678588867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3.7366097 |
1.5657834 |
15.4443162 |
4.1404356 |
| ENSG00000248019 |
285512 |
FAM13A-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.597510 |
0.3273805156 |
-1.610960 |
0.323325236 |
25.623227 |
0.00000041501367793196748794137557886374523263839364517480134963989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001534085120529887374702261021441884736304928082972764968872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.1230071 |
3.5032259 |
46.4378423 |
6.7386151 |
| ENSG00000248079 |
|
DPH6-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.780341 |
0.3350456506 |
-1.577570 |
0.417187586 |
14.687485 |
0.00012688601627946729426613114988242614344926550984382629394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000344018662800319103330787262606804688402917236089706420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9682745 |
2.3232268 |
21.0437140 |
4.5604585 |
| ENSG00000248187 |
124900778 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.907773 |
12.2771617904 |
3.617905 |
0.388772169 |
106.008973 |
0.00000000000000000000000073402070601213592230307381803016189858472223844635275563530863016017263822377003634755965322256088256835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000007845145272077570624056152771706186904076958965323142987268842016811143391663563306792639195919036865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.5708195 |
16.7367579 |
5.7178952 |
1.2733631 |
| ENSG00000248318 |
101927543 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.145844 |
0.0637381912 |
-3.971698 |
0.705219768 |
43.663423 |
0.00000000003899931077411104720751972721772807186496612175119480525609105825424194335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000207359447775893029170199619151465295074920902607118478044867515563964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3950707 |
0.6937517 |
21.9322589 |
4.5259322 |
| ENSG00000248323 |
100505994 |
LUCAT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23672216_these results identify a novel and intriguing new noncoding RNA that may act downstream of NRF2 to regulate gene expression and mediate oxidative stress protection in airway epithelial cells. 28423699_lncRNA LUCAT1 expression is significantly up-regulated in NSCLC tissues and cell lines. Its abnormal expression can predict a poor prognosis of NSCLC patients, and it may be an independent prognostic marker. 29089067_lncRNA LUCAT1 could act as an oncogenic lncRNA that promotes glioma tumorigenesis via regulating miR-375. 29170124_Rescue experiments confirmed the combined role of LUCAT1, miR-200c and ABCB1 on osteosarcoma proliferation, invasion and methotrexate resistance. Overall, results indicate the vital role of LUCAT1 in the methotrexate resistance regulation through miR-200c/ABCB1 pathway, providing a novel insight and treatment strategy for osteosarcoma drug resistance. 29247823_Data show that long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 activated DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), a major DNA methylation protein, to repress the expression of tumor-suppressor genes, leading to the development and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). 29932248_Results indicate that highly expressed LUCAT1 acts as an oncogenic lncRNA that promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) through the miR-495-3p-SATB1 axis, indicating that LUCAT1 could be a useful marker for ccRCC. 30032137_LUCAT1 promoted proliferation and invasion in ccRCC cells partly through inducing the phosphorylation of AKT and suppressing the phosphorylation of GSK-3beta. 30479162_it was found that LUCAT1 was activated by STAT3 and promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in HB through modulation of the miR-301b/STAT3 axis. 30588744_LUCAT1 inhibited the phosphorylation of Annexin A2 (ANXA2) to reduce the degradation of ANXA2-S100A10 heterotetramer (AIIt). 30690837_our findings indicate that suppression of LUCAT1 induces CRC cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding UBA52 and activating the RPL40-MDM2-p53 pathway. These results implicate LUCAT1 as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for CRC. 30831032_SP1-induced up-regulation of lncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer by sponging miR-181a 31300015_LUCAT1 might be a significant biomarker to evaluate prognosis in breast cancer survivors. LUCAT1 increased BCCs stem-like properties and BCSCs stemness by competitively binding miR-5582-3p with TCF7L2 and enhancing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. 31399501_LncRNA LUCAT1 facilitates tumorigenesis and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through modulating miR-5702. 31577719_Up-regulation of LUCAT1 was significantly related to worse overall survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 31591432_LncRNA LUCAT1 as a novel prognostic biomarker for patients with papillary thyroid cancer. 31635802_the expression of lnc-LUCAT1 was highly up-regulated in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Over-expression of lnc-LUCAT1 enhanced cell proliferation, migration and invasion in breast cancer cell lines. 31646588_Knockdown of long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 reverses high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte injury via targeting CYP11B2. 31769911_LUCAT1 contributes to MYRF-dependent smooth muscle cell apoptosis and may facilitate aneurysm formation via the sequestration of miR-199a-5p. 31789465_LncRNA LUCAT1 contributes to cell proliferation and migration in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via sponging miR-539. 31957853_Downregulated long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of cardiomyocyte via miR-612/HOXA13 pathway in chronic heart failure. 31964396_Hypoxia induced LUCAT1/PTBP1 axis modulates cancer cell viability and chemotherapy response. 31968402_ELF1-mediated LUCAT1 promotes choroidal melanoma by modulating RBX1 expression. 32141534_LncRNA LUCAT1 promotes proliferation of ovarian cancer cells by regulating miR-199a-5p expression. 32812490_Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Promotes Multiple Myeloma Cell Growth by Regulating the TGF-beta Signaling Pathway. 32844284_Serum LUCAT1 implicates the pathogenesis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer via targeting miR-199a-5p and miR-199b-5p. 32945379_Long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 contributes to cisplatin resistance by regulating the miR514a3p/ULK1 axis in human nonsmall cell lung cancer. 32998707_LncRNA LUCAT1/miR-181a-5p axis promotes proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via targeting KLF6 and KLF15. 33097685_The long noncoding RNA LUCAT1 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation by antagonizing Nucleolin to regulate MYC expression. 33215214_Lung cancerassociated transcript 1 facilitates tumorigenesis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through the targeted inhibition of miR493. 33282949_Downregulation of Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Suppresses the Migration and Invasion of Bladder Cancer by Targeting miR-181c-5p. 33311506_The long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 is a negative feedback regulator of interferon responses in humans. 33426083_Knockdown of the Long Noncoding RNA LUCAT1 Inhibits High-Glucose-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through the miR-199a-5p-ZEB1 Axis in Human Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. 33541136_MiR-133b inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis via lncRNA-LUCAT1. 33577028_The progression of pancreatic cancer cells is promoted by a long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 by activating AKT phosphorylation. 33787082_LUCAT1 as an oncogene in tongue squamous cell carcinoma by targeting miR-375 expression. 34125980_Expression of long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its potential functions in regulating cigarette smoke extract-induced 16HBE cell proliferation and apoptosis. 34272987_Knockdown of lncRNA LUCAT1 attenuates sepsisinduced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-642a. 34383427_IncRNA LUCAT1 acts as a Potential Biomarker and Demonstrates Malignant Biological Behaviors in Gastric Cancer. 34414854_Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 inhibits myocardial oxidative stress and apoptosis after myocardial infarction via targeting microRNA-181a-5p. 34526564_Concomitant and decoupled effects of cigarette smoke and SCAL1 upregulation on oncogenic phenotypes and ROS detoxification in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 35441392_LncRNA PVT1 is increased in renal cell carcinoma and affects viability and migration in vitro. 35711895_lncRNA LUCAT1/ELAVL1/LIN28B/SOX2 Positive Feedback Loop Promotes Cell Stemness in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. |
|
|
335.328147 |
3.1539349720 |
1.657153 |
0.206609167 |
61.880502 |
0.00000000000000364945369814958740735135494581934488810557107307808166751783574000000953674316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000025194544707524745494081489038850180955009423755530661992452223785221576690673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
493.0942742 |
68.7609546 |
157.3583598 |
16.2343195 |
| ENSG00000248458 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.191655 |
0.2428618810 |
-2.041792 |
0.476722912 |
19.209386 |
0.00001171360656725671680169001409588247497595148161053657531738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000036452210190324505585321435141565871163038536906242370605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8164449 |
1.9215924 |
24.1383067 |
4.8105904 |
| ENSG00000248473 |
102577426 |
LINC01962 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.654270 |
0.0454894910 |
-4.458323 |
0.946703449 |
29.378547 |
0.00000005953303665461631671316025411072603290563165501225739717483520507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000239429869488320656766770604118033105578433605842292308807373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9879641 |
0.6712565 |
20.4429691 |
5.9652512 |
| ENSG00000248485 |
654790 |
PCP4L1 |
protein_coding |
A6NKN8 |
|
Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:654790; |
|
15053978_Cloning and expression analysis of the mouse Pcp4l1 gene, and sequence comparison to human PCP4L1. |
ENSMUSG00000038370 |
Pcp4l1 |
6.447899 |
0.1019792712 |
-3.293652 |
0.814516378 |
21.165623 |
0.00000421253211583243225465652062600163674233044730499386787414550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013826322888522725305287044972324395075702341273427009582519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3147671 |
0.7453387 |
12.7826376 |
3.0337908 |
| ENSG00000248489 |
100289230 |
CHD1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.580446 |
0.4838210842 |
-1.047454 |
0.383199200 |
7.512839 |
0.00612607459499231975230681968014323501847684383392333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012285443073653076750950674522755434736609458923339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.2322174 |
2.5626196 |
21.2046188 |
3.5216470 |
| ENSG00000248592 |
100526772 |
STIMATE-MUSTN1 |
protein_coding |
A8MSY1 |
|
Membrane;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring TMEM110 (transmembrane protein 110) and MUSTN1 (musculoskeletal, embryonic nuclear protein 1) genes. The read-through transcript encodes a fusion protein that shares sequence identity with each individual gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:100526772; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; chondrocyte proliferation [GO:0035988]; tissue regeneration [GO:0042246] |
|
|
|
54.811301 |
0.1854757848 |
-2.430697 |
0.386404440 |
37.853019 |
0.00000000076280250864321059607448319894230405469048861277769901789724826812744140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003684216304834354913484251674684125110736943042866187170147895812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.7831433 |
5.2095821 |
66.8041473 |
18.5723017 |
| ENSG00000248643 |
100526737 |
RBM14-RBM4 |
protein_coding |
Q96PK6 |
FUNCTION: Isoform 1 may function as a nuclear receptor coactivator, enhancing transcription through other coactivators such as NCOA6 and CITED1. Isoform 2, functions as a transcriptional repressor, modulating transcriptional activities of coactivators including isoform 1, NCOA6 and CITED1 (PubMed:11443112). Regulates centriole biogenesis by suppressing the formation of aberrant centriolar protein complexes in the cytoplasm and thus preserving mitotic spindle integrity. Prevents the formation of the STIL-CENPJ complex (which can induce the formation of aberrant centriolar protein complexes) by interfering with the interaction of STIL with CENPJ (PubMed:25385835). Plays a role in the regulation of DNA virus-mediated innate immune response by assembling into the HDP-RNP complex, a complex that serves as a platform for IRF3 phosphorylation and subsequent innate immune response activation through the cGAS-STING pathway (PubMed:28712728). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11443112, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25385835, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28712728}. |
3D-structure;Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;Immunity;Innate immunity;Isopeptide bond;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Repressor;RNA-binding;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring RBM14 (RNA binding motif protein 14) and RBM4 (RNA binding motif protein 4) genes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, one of which encodes a fusion protein that shares sequence identity with each individual gene product. This fusion protein contains RRM and zinc finger domains, and it functions to stimulate transcription in a hormone and receptor-dependent manner. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:100526737;hsa:10432; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; nucleolus [GO:0005730]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ribonucleoprotein complex [GO:1990904]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; mRNA binding [GO:0003729]; nuclear receptor coactivator activity [GO:0030374]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; activation of innate immune response [GO:0002218]; centriole assembly [GO:0098534]; histone deacetylation [GO:0016575]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; mRNA splicing, via spliceosome [GO:0000398]; negative regulation of centriole replication [GO:0046600]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; SMAD protein signal transduction [GO:0060395] |
|
|
|
66.896167 |
2.0737145395 |
1.052217 |
0.420792327 |
5.909643 |
0.01505822231897654267518404935799480881541967391967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027765067011629451787513289673370309174060821533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
78.8980460 |
22.8668323 |
39.0535205 |
8.3362208 |
| ENSG00000248671 |
285407 |
ALG1L9P |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.234515 |
0.4881645117 |
-1.034561 |
0.451041121 |
5.297296 |
0.02135856149708053805524876622712326934561133384704589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.038032617649524515235359700682238326407968997955322265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4914344 |
2.5203547 |
17.5382753 |
3.4021339 |
| ENSG00000248672 |
100526664 |
LY75-CD302 |
protein_coding |
O60449 |
FUNCTION: Acts as an endocytic receptor to direct captured antigens from the extracellular space to a specialized antigen-processing compartment (By similarity). Causes reduced proliferation of B-lymphocytes. {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Glycoprotein;Lectin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring lymphocyte antigen 75 (LY75) and CD302 molecule (CD302) genes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding fusion products that share sequence identity with each individual gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:100526664;hsa:4065; |
external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; endocytosis [GO:0006897]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954] |
|
|
|
11.552716 |
124.1959841690 |
6.956475 |
1.147366703 |
50.262574 |
0.00000000000134490156169058311927859044971811231634038763527172477552085183560848236083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007924449920380442839281560835755117500403543751019697083393111824989318847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.0956828 |
36.6617786 |
0.2040201 |
0.2333429 |
| ENSG00000248727 |
102467147 |
LINC01948 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.716923 |
0.1825435231 |
-2.453688 |
0.730157108 |
11.864854 |
0.00057203249237830955300360136206450079043861478567123413085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001390742808022376588925062002033428143477067351341247558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4614306 |
0.7811898 |
7.8631327 |
2.2120483 |
| ENSG00000249001 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
103.799939 |
3.2912338388 |
1.718629 |
0.189036080 |
83.790336 |
0.00000000000000000005501308522236984347561235766032302158788127957512014277845213694462245257454924285411834716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000488857999929066215807219544201307506918267586819504743819719827513381460448727011680603027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
161.6701852 |
19.4165608 |
49.4139870 |
4.7872572 |
| ENSG00000249087 |
148898 |
ZNF436-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.947027 |
0.3349922936 |
-1.577800 |
0.592190239 |
7.032799 |
0.00800301600259387298230695506617848877795040607452392578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015655999496127975811887722557003144174814224243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9440661 |
1.6618773 |
11.9476318 |
3.0536971 |
| ENSG00000249307 |
100505875 |
LINC01088 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29440672_LINC01088 might function as a tumor suppressor, inhibiting the tumorigenesis of ovarian epithelial cells through LINC01088/ miR-24-1-5p/ PAK4 axis 30280763_Low LINC01088 expression was associated with the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer. 31811854_High LINC01088 expression is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. 35357586_Upregulated LINC01088 facilitates malignant phenotypes and immune escape of colorectal cancer by regulating microRNAs/G3BP1/PD-L1 axis. |
|
|
9.898753 |
0.2628139904 |
-1.927886 |
0.521029568 |
14.615701 |
0.00013181174397094934228925888763939155978732742369174957275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000355870009330750357821882001729818512103520333766937255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4583128 |
1.7363936 |
17.0503418 |
4.0393546 |
| ENSG00000249437 |
4671 |
NAIP |
protein_coding |
Q13075 |
FUNCTION: Anti-apoptotic protein which acts by inhibiting the activities of CASP3, CASP7 and CASP9. Can inhibit the autocleavage of pro-CASP9 and cleavage of pro-CASP3 by CASP9. Capable of inhibiting CASP9 autoproteolysis at 'Asp-315' and decreasing the rate of auto proteolysis at 'Asp-330'. Acts as a mediator of neuronal survival in pathological conditions. Prevents motor-neuron apoptosis induced by a variety of signals. Possible role in the prevention of spinal muscular atrophy that seems to be caused by inappropriate persistence of motor-neuron apoptosis: mutated or deleted forms of NAIP have been found in individuals with severe spinal muscular atrophy.; FUNCTION: Acts as a sensor component of the NLRC4 inflammasome that specifically recognizes and binds needle protein CprI from pathogenic bacteria C.violaceum. Association of pathogenic bacteria proteins drives in turn drive assembly and activation of the NLRC4 inflammasome, promoting caspase-1 activation, cytokine production and macrophage pyroptosis. The NLRC4 inflammasome is activated as part of the innate immune response to a range of intracellular bacteria such as C.violaceum and L.pneumophila. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Apoptosis;ATP-binding;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Protease inhibitor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Thiol protease inhibitor;Zinc |
|
This gene is part of a 500 kb inverted duplication on chromosome 5q13. This duplicated region contains at least four genes and repetitive elements which make it prone to rearrangements and deletions. The repetitiveness and complexity of the sequence have also caused difficulty in determining the organization of this genomic region. This copy of the gene is full length; additional copies with truncations and internal deletions are also present in this region of chromosome 5q13. It is thought that this gene is a modifier of spinal muscular atrophy caused by mutations in a neighboring gene, SMN1. The protein encoded by this gene contains regions of homology to two baculovirus inhibitor of apoptosis proteins, and it is able to suppress apoptosis induced by various signals. Alternative splicing and the use of alternative promoters results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2016]. |
hsa:4671; |
basolateral plasma membrane [GO:0016323]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; inflammasome complex [GO:0061702]; IPAF inflammasome complex [GO:0072557]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043027]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein serine/threonine kinase binding [GO:0120283]; defense response to bacterium [GO:0042742]; detection of bacterium [GO:0016045]; icosanoid biosynthetic process [GO:0046456]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process [GO:0043154]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0010804]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002221]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of JNK cascade [GO:0046330]; pyroptosis [GO:0070269]; regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0042981] |
11912351_NAIP gene deletion was higher in type I spinal muscular atrophy than in type U or V. In type I patients lacking the NAIP gene, deterioration in their respiratory function is more rapid than in those type I patients retaining the NAIP gene. 12127562_NAIP-deltaEx10-11: a novel splice variant of the apoptosis inhibitor NAIP is differently expressed in drug-sensitive and multidrug-resistant HL60 leukemia cells. NAIP transcripts might be involved in tumor resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. 12445469_NAIP:Structural requirements for binding hippocalcin and effects on survival of sympathetic neurons. 15280366_NAIP does not interact with Smac and requires ATP to bind caspase-9 15340105_Alterations in C/CAAT enhancer binding protein alpha and neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein expression occurred in human adipose stromal-vascular cells after weight loss 17222062_Multiple, domesticated long terminal repeats (LTRs) of endogenous retroviral elements provide NAIP promoter function in human, mouse, and rat. 17510375_a role for NAIP in increasing the survival of cells undergoing terminal differentiation as well as the possibility that the protein serves as an intestinal pathogen recognition protein was suggested 17903057_80% neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein gene deletion in 5q-spinal muscular atrophy patients (91% spinal muscular atrophy-I, 50% spinal muscular atrophy-II and -III), and in 5% (two of forty) of spinal muscular atrophy parents, was found. 17923748_While there was no evidence of NAIP expression in the normal breast tissue, NAIP was expressed in all breast cancer samples. 17932457_May be a modifying factor for disease severity of spinal muscular atrophy. 18071605_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18071605_The present study is the first one giving detailed information on SMN and NAIP deletion rates in Iranian SMA patients. 18339188_Data show elevated expression of NAIP in peripheral mononuclear cells from children with Fabry disease. 18453601_hNAIP and hIpaf mediate innate intracellular defense against flagellated Legionella in human cells. 18533950_The presence of one NAIP copy, that is, heterozygous NAIP deletion, was common in Vietnamese SMA, regardless of clinical phenotype. 18566024_HIAP-1 and HIAP-2 mRNA levels were elevated in resting T cells while NAIP mRNA was increased in whole blood in multiple sclerosis 18759060_in glioma & glioblastoma multiforme, selective upregulation of miRNA-221 & down-regulation of a miRNA-221 mRNA target encoding BIRC1 were observed; expression of BIRC5 & caspase-3 were found to be significantly up-regulated, particularly in stage IV GBM 18842367_Data show that NAIP deletion predicts disease severity in spinal muscular atrophy. 18842367_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18974562_Among the SMA Type I patients, 43% showed deletions of SMN1 and NAIP. 19198020_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19198020_findings of homozygous deletions of exon 7 and/or exon 8 of SMN1 gene confirmed the diagnosis of SMA, and suggested that the deletion of SMN1 exon 7 is a major cause of SMA in southern Chinese children. 19287802_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19287802_higher number of SMN2 copies makes the clinical symptoms more benign, and the NAIP gene deletion is associated with a more severe phenotype 19488400_a novel NAIP isoform derives from intragenic Alu SINE promoters 19923725_Results provide the first structures of BIR domains from human NAIP and cIAP2. 20044205_Expression of NAIP may be associated with enhanced survival of prostate cancer in response to castration 20171302_an inhibitor of procaspase-9 preventing apoptosis at the initiation stage 21371431_NOD domain is essential for effective inhibition of procaspase-9 and procaspase-3 cleavage by the NAIP protein in apoptosis. 21821450_There is a close relationship between SMN2, NAIP and H4F5 gene copy number and spinal muscular atrophy disease severity 22067212_NAIPFull gene duplication might have been evolutionary maintained, or even selected for, because it may confer an advantage to the host against flagellated bacteria 23012363_the NAIP5-NLRC4 inflammasome is induced by direct interactions with conserved N- and C-terminal regions of flagellin 23940371_/NAIP1 and NAIP2/5 formed a large oligomeric complex with NLRC4 in the presence of corresponding bacterial ligands, and could support reconstitution of the NLRC4 inflammasome in a ligand-specific manner. 23994529_identified an intronic region of the NAIP gene responding to TEAD1/YAP activity, suggesting that regulation of NAIP by TEAD1/YAP is at the transcriptional level 24711022_Copy number variations of SMN2 and NAIP genes in patients are related to spinal muscular atrophy clinical types (P |
|
|
75.774518 |
0.4374729091 |
-1.192734 |
0.204720520 |
34.277961 |
0.00000000477761509847155673574265957606957422321158901468152180314064025878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000021486166622011026088867060267195707723431041813455522060394287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.0472249 |
7.4240214 |
108.5452551 |
11.5252799 |
| ENSG00000249572 |
|
TARS1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.671422 |
0.3795830574 |
-1.397512 |
0.442618417 |
10.321100 |
0.00131517878324453624944156970855146937537938356399536132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003004494480837231491082706114070788316894322633743286132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.1015498 |
2.0963742 |
18.8532155 |
3.4352776 |
| ENSG00000249626 |
|
|
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.251485 |
0.1730673118 |
-2.530595 |
0.625300016 |
17.278788 |
0.00003227699028563626965993363371332236511079827323555946350097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000095319803244496063517922357366529695354984141886234283447265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1547245 |
2.0278670 |
20.1910597 |
8.0972081 |
| ENSG00000249709 |
163050 |
ZNF564 |
protein_coding |
Q8TBZ8 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Isopeptide bond;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:163050; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
34414857_Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 alleviates bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity by regulating the miR-421/zinc finger protein564 (ZNF564) axis. |
|
|
58.476682 |
0.4970434799 |
-1.008556 |
0.259513856 |
15.014751 |
0.00010667406713730170171247624288923816493479534983634948730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000292279419147312613438266515331065420468803495168685913085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.3045694 |
8.3755879 |
83.7642103 |
11.8284089 |
| ENSG00000249859 |
5820 |
PVT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene represents a long non-coding RNA locus that has been identified as a candidate oncogene. Increased copy number and overexpression of this gene are associated with many types of cancers including breast and ovarian cancers, acute myeloid leukemia and Hodgkin lymphoma. Allelic variants of this gene are also associated with end-stage renal disease attributed to type 1 diabetes. Consistent with its association with various types of cancer, transcription of this gene is regulated by the tumor suppressor p53 through a canonical p53-binding site, and it has been implicated in regulating levels of the proto-oncogene MYC to promote tumorigenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
|
|
17395743_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17395743_PVT1 may be a candidate gene which contribute to end stage renal disease susceptibility in diabetes. 17503467_Data indicate that PVT-1 expression is restricted to a low number of normal tissues compared to c-Myc mRNA, whereas the gene is highly expressed in many transformed cell types including neuroblastoma cells that do not express c-Myc. 17881614_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17881614_Role for PVT1 in mediating susceptibility to end-stage renal disease attributable to diabetes. 17908964_MYC and PVT1 contribute independently to ovarian and breast pathogenesis when overexpressed because of genomic abnormalities 19549893_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21037568_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21316338_these results identified PVT1 as a regulator of Gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells. 21526116_that PVT1 may mediate the development and progression of diabetic nephropathy through mechanisms involving extracellular matrix accumulation. 21814516_we identified a new functional prostate cancer risk variant at the 8q24 locus that is associated with increased expression of PVT1 located 0.5 Mb downstream. 22110125_p53-Dependent induction of PVT1 and miR-1204. 22869583_Data indicate that the PVT1-NBEA and the PVT1-WWOX chimeric genes were associated with the expression of abnormal NBEA and WWOX. 23547836_Deletion or methylation of CDKN2A/2B and PVT1 rearrangement occur frequently in highly aggressive B-cell lymphomas harboring 8q24 abnormality. 24196785_PVT-1, which maps to 8q24, generates antiapoptotic activity in CRC, and abnormal expression of PVT-1 was a prognostic indicator for CRC patients. 24204837_miR-1207-5p, a PVT1-derived microRNA, is abundantly expressed in kidney cells, and is upregulated by glucose and TGF-beta1. 24780616_the GG genotype of SNP rs13281615 plays a role in breast cancer likely by influencing PVT1 expression, and that during oncogenesis, 'protective' mutations could occur. 24821155_Report frequency of PVT1 SNPs in diabetic nephropathy. 24926545_Our in vitro findings suggest that C-MYC and PVT1 copy number gains may promote a malignant malignant pleural mesothelioma phenotype. 25043044_Gain of PVT1 long non-coding RNA expression was required for high MYC protein levels in 8q24-amplified human cancer cells 25043274_Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2. 25245984_our study identified novel PVT1-NSMCE2 and CCDC26-NSMCE2 fusion genes that may play functional roles in leukemia. 25400777_lncRNA PVT1 is significantly upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer. 25883951_PVT1 has a role in competing endogenous RNA activity and regulation of protein stability of important oncogenes, primarily of the MYC oncogene [review] 25890171_LncRNA PVT1 may serve as a candidate prognostic biomarker. 25956062_PVT-1 was highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues of cisplatin-resistant patients and cisplatin-resistant cells. 26097562_we have identified a potential mechanism by which PVT1 regulated by carboplatin plus docetaxel contributes to the carboplatin-docetaxel-induced anticancer action in ovarian cancer. 26427660_lncRNA PVT1 may contribute to tumorigenesis of thyroid cancer through recruiting EZH2 and regulating TSHR expression. 26490983_PVT1 knockdown increased the number of lung cancer cells in the G0/G1 phase and reduced the number of cells in the S phase, while overexpression of PVT1 could promote cell cycle progression. 26517688_Data show that long non-coding RNA PVT1 was upregulated in bladder cancer tissues and cell lines. 26545364_Findings sugggest that the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) PVT1 may play an important role in the proliferation of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cells and may be useful for future therapeutic management. 26850852_Studies on the association between PVT1 and cancer have shown that PVT1 is a potential oncogene in a variety of cancer types. [review] 26908628_we found that PVT1 functioned as an oncogene and may be a crucial prognostic factor for NSCLC patients. PVT1 contributed to lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, partly though EZH2-medicated suppression of the LATS2/MDM2/P53 pathway. 26925791_PVT1 expression was remarkably increased in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines compared with that in the normal control, and its up-regulation was significantly correlated to invasion depth, advanced TNM stage and regional lymph nodes metastasis in gastric cancer. 27028998_our findings indicate that salivary HOTAIR and PVT1 show potential as novel non-invasive biomarkers for detecting pancreatic cancer 27232880_PVT1 expression is significantly increased in ICC tissue versus normal cervix and that higher expression of PVT1 correlates with poorer overall survival 27272214_PVT1 binds to EZH2, recruits EZH2 to the miR-200b promoter, increases histone H3K27 trimethylation level on the miR-200b promoter, and inhibits miR-200b expression. 27366943_Study discloses the role of PVT1 as a novel prognostic factor and as a molecular target for novel therapeutic interventions in renal carcinoma. 27484035_PVT1 regulates both IL-6 release and proliferation in airway smooth muscle cells from patients with severe asthma. 27588491_PVT1 epigenetically down-regulates PTCH1 expression via competitively binding miR-152, contributing to EMT process in liver fibrosis 27756785_Our study suggests that PVT1 promotes tumor progression by interacting with FOXM1 27794184_Our study suggested a regulatory relationship between lncRNA PVT1 and miR-146a during the process of the prostate cancer tumorigenesis. PVT1 regulated prostate cancer cell viability and apoptosis depending on miR-146a. 27813492_lncRNA PVT1 is overexpressed in osteosarcoma and decreased the survival rate of osteosarcoma patients. Silencing PVT1 by siRNA inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion and promoted apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in osteosarcoma cells via miR-195. 27928058_Identification of CircPVT1, generated by circularization of an exon of the PVT1 gene, as a circular RNA with a function in cell senescence. 27986464_Findings suggest that circPVT1 is a novel proliferative factor and prognostic marker in GC. 28235236_PVT1-derived miR-1207-5p promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells by targeting STAT6. 28258379_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 in gastric cancer might act as a ''sponge'' to inhibit miR-152, and increase the expression of CD151 and FGF2. 28265576_results indicate that PVT1 functions as an oncogene in melanoma and could be a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for melanoma. 28276314_Results reveal a tumor-promoting role for PVT1, acting as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) or a molecular sponge in negatively modulating miR-424. 28296507_infer that PVT1 could decrease miR-195 expression via enhancing histone H3K27me3 in the miR-195 promoter region and also via direct sponging of miR-195 28351322_PVT1 overexpression increased the expression of Atg7 and Beclin1 by targeting miR-186, which induced protective autophagy, thus promoting glioma vascular endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. Therefore, PVT1 and miR-186 can provide new therapeutic targets for future anti-angiogenic treatment of glioma 28381186_PVT1 may be a new oncogene co-amplified with c-Myc in colorectal cancer tissues and extracellular vesicles and functionally correlated with the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. 28404954_Results indicate that PVT1 is up-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and predict overall prognosis. Knockdown of PVT1 inhibits proliferation and migration of ESCC in vitro and suppressed tumor growth in vivo. Meanwhile, PVT1 acts as the molecular sponge to regulate expression of miR-203 and LASP1. These data provided evidence that PVT1 promoted ESCC progression via activation of the miR-203/LASP1 axis. 28409552_our study demonstrates that PVT1 modulates melanoma tumorigenesis by acting as an endogenous sponge of miR-26b 28520497_LncRNA PVT1 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by acting as a sponge for miR-488-3p. 28534994_PVT1 played a pivotal part on the regulation of p21 expression in breast cancer cell lines. 28602700_findings suggested that PVT1 contributes to osteosarcoma (OS) cell glucose metabolism, cell proliferation, and motility through the miR-497/HK2 pathway, and revealed a novel relation between lncRNA and the alteration of glycolysis in OS cells 28656879_it was identified that plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 regulated the expression of the miR-186-5p target gene, yes-associated protein 1. Taken together, plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 served as an endogenous sponge for miR-186-5p to reduce its inhibiting effect on yes-associated protein 1 and thus promoted the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma 28657147_we revealed that PVT1 functions as an endogenous 'sponge' by competing for miR-448 binding to regulate the miRNA target SERBP1 and, therefore, promotes the proliferation and migration of PC cells. 28731781_LncRNA-PVT1 is a novel critical regulator in non-small cell lung cancer invasion.LncRNA-PVT1 regulates MMP9 expression. 28800314_PVT1 has a higher expression levels in HCC tissues than that in the adjacent normal tissues, and functions as an oncogene by promoting HCC cell proliferation, invasion. Furthermore, we found that PVT1 interacted with EZH2 repressed miR-214 expression in HCC cells 28848163_PVT1 directly interacted with miR-195 and regulated its expression. PVT1 knockdown enhanced the sensitivity of NSCLC cells to ionizing radiation by suppressing cell survival and inducing cell apoptosis. 28866116_Elevated PVT1 expression was related to poor prognosis 28882595_These data suggest that elevated expression of SOX2 can activate lncRNA PVT1 expression promoted breast cancer tumorigenesis and progression. PVT1 may be a prognostic predictive biomarker for breast cancer, and the interaction of PVT1-SOX2 could be a therapeutic target in breast cancer. 28972861_High PVT1 expression is associated with Lung Cancer Progression. 29035442_high expression correlated with poor prognosis [meta-analysis] 29046366_These data inferred that long non-coding RNA PVT1 could be served as an indicator of glioma prognosis, and PVT1-EZH2 regulatory pathway may be a novel therapeutic target for treating glioma. 29050519_PVT1 played an oncogenic role in prostate cancer 29081406_Data suggest that long noncoding RNA PVT1 may be an oncogene as well as may promote metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and could serve as a potential biomarker to predict the prognosis of ccRCC patients. 29115513_we first report that PVT1 promotes expression of HIF-1alpha, a critical endogenous hypoxia marker, in NSCLC. With this finding, we demonstrated that PVT1 modulated HIF-1alpha by competing for miR-199a-5p as a ceRNA to regulate cell proliferation. 29193797_the action of PVT1 is moderately attributable to its repression of ANGPTL4 via association with the epigenetic repressor Ezh2. 29244840_Based on these findings, we infer that PVT1 expression is modulated by both DNA amplification and methylation and its expression might serve as a valuable and specific prognostic biomarker in terms of OS in uveal melanoma 29262850_We found that circPVT1 behaves as an oncogene in HNSCC and that the mut-p53/YAP/TEAD complex transcriptionally regulates its expression. 29277611_Thus, our results indicated that lncRNA-PVT1-5 may function as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-126 to promote cell proliferation by regulating the miR-126/SLC7A5 pathway, suggesting that lncRNA-PVT1-5 plays a crucial role in lung cancer progression and lncRNA-PVT1-5/miR-126/SLC7A5 regulatory network may shed light on tumorigenesis in lung cancer. 29280051_results indicate that ROR, PVT1, and HOTAIR have important regulatory roles during the development of papillary thyroid carcinomas 29286144_long noncoding RNA PVT1 may contribute to the tumorigenesis and metastasis of melanoma. 29445147_Long non-coding RNA PVT1 predicts poor prognosis and induces radioresistance by regulating DNA repair and cell apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 29452232_PVT1 promotes prostate cancer invasion and metastasis by modulating endothelial-mesenchymal transition. Furthermore, PVT1 can promote EMT by up-regulation of Twist1, a transcription factor associated with EMT. We then confirmed that PVT1 acts as a sponge for miRNA-186-5p and positively regulates Twist1 by a sponge effect. 29501773_PVT1-miR-190a-5p/miR-488-3p-MEF2C-JAGGED1 axis is involved in proliferation and progression of glioma. Thus, PVT1 may become a novel target in glioma therapy. 29505758_Combining the results of replication study with the previous GWAS data by meta-analysis, overall significance of PVT1 rs10087240 increased to a P-value of 5.11 x 10-11 and odds ratio of 1.17. These results confirm PVT1 as a vitiligo susceptibility locus in the European population. 29510227_High PVT1 expression is associated with hematologic malignancies. 29512788_The results of the present study suggest that PVT1 may serve a critical role in CRC progression and metastasis and may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. 29552759_results indicate that PVT1 could promote metastasis and proliferation of colon cancer via suppressing miR-30d-5p/RUNX2 axis, which may offer a new way for interpreting the mechanism of colon cancer development 29620147_PVT1 was able to bind and degrade miR26b to promote connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and angiopoietin 2 (ANGPT2) expression. 29693171_PVT1 knockdown reverses drug resistance in 5-FU resistant CRC cell lines, and that PVT1 overexpression promotes the development of MDR in CRC primarily by inhibiting apoptosis and upregulating the expression of MRP1, P-gp, mTOR and Bcl-2. 29693417_circPVT1 is upregulated in ALL. Silencing circPVT1 results in cell growth arrest and apoptosis of the cells. Our results also suggested a therapeutic potential of targeting circPVT1 in ALL. 29706652_The mechanism of PVT1-mediated angiogenesis via evoking the STAT3/VEGFA signalling axis. 29715456_PVT1 interacts with STAT1 to inhibit IFN-alpha signaling and tumor cells proliferation. 29731168_the PVT1 promoter mutation promotes cancer cell growth 29739059_Studies indicate that lncRNA PVT1 might serve as a potential therapeutic target for various cancers. 29749550_The results therefore provide significant information on the differentially expressed miRNAs associated with PVT1 in HCC, and we hypothesized that PVT1 may play vital roles in HCC by regulating different miRNAs or target gene expression (particularly MAPK8) via the MAPK or Wnt signaling pathways. Thus, further investigation of the molecular mechanism of PVT1 in HCC is needed 29760406_PVT1, KLF5, and beta-catenin were also revealed to be co-expressed in clinical TNBC samples. 29803929_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 enhances the expression of IGF1R through competitive binding to miR-30a. 29845201_Knockdown of PVT1 inhibited the TGFbeta/Smad signaling. 29948619_High expression of PVT1 is associated with Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. 29957467_PVT1 regulates ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating miR-133a expression. 29975928_PVT1 could affect the biological function of HCC cells via targeting miR-424-5p and regulating INCENP. Focusing on the new insight of the PVT1/miR-424-5p/INCENP axis, this study provides a novel perspective for HCC therapeutic strategies. 30076414_PVT1-214 modulates the derepression of Lin28 by interacting with miR-128 30076714_PVT1 can regulate VEGFC expression by competitively binding miR-128 in bladder cancer cells. 30083911_PVT1 could serve as a novel biomarker for metastasis, clinical stage and poor prognosis in various tumors. 30141114_High expression of PVT1 is associated with Nasopharyngeal Cancer. 30205391_PVT1 knockdown could inhibit the expression of HIG2 through up-regulating miR-150 expression. 30222365_No differences were found between the combined AML patient populations and the healthy controls with respect to the expression levels of PVT1, CCDC26, and CCAT1, however the AML-M3 patients had higher PVT1 expression (p = 0.017). 30252166_PVT1 acts as competing RNA to microRNAs to protect mRNAs from miRNAs repression[review and meta-analysis] 30295989_this study shows that PVT1 regulates trophoblast viability, proliferation, and migration and is downregulated in spontaneous abortion 30304557_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma development by acting as a molecular sponge to regulate miR-519d-3p. 30317572_LncRNA PVT1 was overexpressed in bladder cancer cells, and it downregulated miR-31 ezpression and enhanced CDK1 expression to facilitate bladder cancer cells proliferation, migration, and invasion. 30347597_Down-regulation of PVT1 could enhance chemosensitivity of paclitaxel, induce apoptosis of glioma cells and noteworthy inhibit glioma cells proliferation. Our findings of PVT1 could contribute to attenuate paclitaxel resistance in clinical medicine. 30371726_Results indicate that long non-coding RNA PVT1 (PVT1) affected the role of mature adipogenic medium in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells via modulating cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A protein (p21) expression. 30504754_Results suggest that PVT1 could promote metastasis and proliferation of colon cancer via endogenous sponging and inhibiting the expression of miR-26b, which may highlight the significance of lncRNA PVT1 in colon cancer tumorigenesis. 30590312_Knockdown of circular PVT1 inhibited non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation. 30649422_We demonstrated that the lncRNA Pvt1, activated early during muscle atrophy, impacts mitochondrial respiration and morphology and affects mito/autophagy, apoptosis and myofiber size in vivo. 30661902_We showed that lncRNA PVT1 played a contributory role in chemoresistance of osteosarcoma cells through c-MET/PI3K/AKT pathway activation, which was largely dependent on miR-152 30679629_PVT1 has a high expression level in the gastric cancer tissues of both Han and Uygur patients. The level of PVT1 in tissues can help to assess the risk of lymphatic metastasis in gastric cancer patients. PVT1 can be a potential biomarker to predict the tendency for metastasis in both Han and Uygur gastric cancer patients. 30794914_Authors confirmed that the effect of PVT1 promoting autophagy was dependent on regulating ATG3 expression. Further investigations revealed that PVT1 could upregulate autophagy-related gene 3 (ATG3) expression by acting as an endogenous sponge of miR-365, which was an inhibitor gene on ATG3 protein by targeting 3'UTR of ATG3 mRNA. 30820968_The presence of rs13281615 G > A polymorphism on PVT1 and the rs2910164 C > G polymorphism on miR-146a contributes to a favorable prognosis in colon cancer patients via modulating the activity of the PVT1/miR-146a/COX2 signaling pathway. 30825877_Long non-coding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor progression by regulating the miR-143/HK2 axis in gallbladder cancer. 30832754_PVT1 knockdown could negatively regulate miR-424 to inhibit cellular activity, migration, and invasiveness in human gliomas, which explained the oncogenic mechanism of PVT1 in human gliomas. It also suggested that PVT1 might be a novel therapeutic target for human gliomas. 30909189_PVT1 is highly expressed in gliomas and its level is positively related to WHO glioma grade and prognosis of gliomas. Therefore, it may be explored as a new molecular marker for predicting malignancy and prognosis of gliomas. 30914434_Interactions of PVT1 and CASC11 on Prostate Cancer Risk in African Americans. 30943439_Results provide evidence that high expression level of PVT1 is associated with poor prognosis while being poor prognostic biomarker in t(8;21) associated acute myeloid leukemia. 30993787_Investigating the diagnostic performance of HOTTIP, PVT1, and UCA1 long noncoding RNAs as a predictive panel for the screening of colorectal cancer patients with lymph node metastasis. 31002139_LncRNA PVT1 knockdown affects proliferation and apoptosis of uveal melanoma cells by inhibiting EZH2. 31028131_Potential natural source of anti-gastric cancer drugs via epigenetic mechanism to inhibit LncRNA-PVT1-STAT3 axis. 31221783_Microhomology-mediated end joining drives complex rearrangements and overexpression of MYC and PVT1 in multiple myeloma. 31222482_PVT1 long-non-coding RNA (PVT1) is amplified in ovarian cancer patients and is correlated with poor survival outcomes. Knockdown of PVT1 causes decreased cell viability, metabolic activity, and smaller proportion of S-phase cells. PVT1 directly bound to miR-140 and acted as a microRNA sponge, while transcription of PVT1 is regulated by the transcription factor FOXO4. 31277104_A meta-analysis showed that high expression of PVT1 was significantly associated with tumor size, TNM stage, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, and overall survival time , especially in breast cancer, liver cancer and lung cancer. 31297833_Long noncoding RNA PVT1: A highly dysregulated gene in malignancy. 31309249_Summary of the coamplification of PVT1 and MYC in cancer, the positive feedback mechanism, and the latest promoter competition mechanism of PVT1 and MYC, as well as how PVT1 participates in the downstream signaling pathway of c-Myc by regulating key molecules. [review] 31320749_The lncRNA PVT1 regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation via activating the KAT2A acetyltransferase and stabilizing HIF-1alpha. 31322217_LncRNA PVT1 inhibits the effect of miR16, promoting the cell cycle and inhibiting cellular apoptosis of cervical cancer cells, potentially via the NFkappaB pathway. 31326971_Results showed that higher PVT1 was expressed in NSCLC and the elevated PVT1 was closely related to angiogenesis and poor prognosis in NSCLC. 31369196_research reveals that down-regulation of lncRNA PVT1 could potentially promote expression of miR-145 to repress cell migration and invasion, and promote cell apoptosis through the inhibition of FSCN1. 31371698_The silencing of PVT1 or the overexpression of FOXA1 relieved the damage and inhibited the apoptosis of podocytes in Diabetic nephropathy. 31485648_CircPVT1 functioned as competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to increase the STAT3 level and cell proliferation through sponging miR125b. 31509024_The PVT1 gene rs1252200336 locus polymorphisms are associated with the risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC) in the Han Chinese population. The rs1252200336 locus deletion mutation (D) may impact the binding of hsa-miR-455-5p to the lncRNA PVT1 and its role in the development and progression of CRC. 31577086_LncRNA PVT1 participates in the development of oral squamous cell carcinomas through accelerating EMT and serves as a diagnostic biomarker. 31577719_The overexpression of PVT1 was significantly associated with poor overall survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 31601234_Our results provide strong evidence that PVT1 confers an aggressive phenotype to EAC and is a poor prognosticator. 31604907_PVT1 exerts an oncogenic role through activating Wnt/ss-catenin signaling in pituitary adenoma cells. 31626590_LncRNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and invasion through enhancing Smad3 expression by sponging miR-140-5p in cervical cancer. 31627090_This study provided the evidence that PVT1 played a vital role in trophoblast cells, and it is important for maintaining the normal physiological function of trophoblast cells. 31677796_Silencing of PVT1 by ectopic miR-214 or siRNAs markedly inhibited viability and invasion of HCC cells. 31696483_LncRNA PVT1 aggravates the progression of glioma via downregulating UPF1. 31699956_Long non-coding RNA PVT1 encapsulated in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by stabilizing ERG and sponging miR-183-5p. 31707347_XJD inhibits NSCLC cell growth via reciprocal interaction of PVT1 and miR181a-5p followed by reducing SP1 expression. 31755246_SP1-mediated lncRNA PVT1 modulates the proliferation and apoptosis of lens epithelial cells in diabetic cataract via miR-214-3p/MMP2 axis. 31850702_Long noncoding RNAs (IncRNA) PVT1 was overexpressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) tissues compared to paired-adjacent normal tissues. 31877167_The results indicate that the assay can be used to quantify both low and high copy numbers of PVT1-derived transcripts. This is the first report of a copy number-based quantification assay for non-invasive detection of PVT1 derived transcripts. 31894346_lncRNA PVT1 promotes hepatitis B viruspositive liver cancer progression by disturbing histone methylation on the cMyc promoter. 31932969_The expression of MYC is strongly dependent on the circular PVT1 expression in pure Gleason pattern 4 of prostatic cancer. 31957871_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 acts as an oncogenic driver in human pan-cancer. 31986409_CircPVT1 contributes to chemotherapy resistance of lung adenocarcinoma through miR-145-5p/ABCC1 axis. 32003019_YY1-PVT1 affects trophoblast invasion and adhesion by regulating mTOR pathway-mediated autophagy. 32171788_LncRNA PVT1 induces chondrocyte apoptosis through upregulation of TNF-alpha in synoviocytes by sponging miR-211-3p. 32196583_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes metastasis via miR-484 sponging in osteosarcoma cells. 32202906_The long non-coding RNA PVT1/miR-145-5p/ITGB8 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 32249539_Circular RNA PVT1 promotes metastasis via regulating of miR-526b/FOXC2 signals in OS cells. 32293498_Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating miR-543-dependent SCUBE2 in rheumatoid arthritis. 32342557_Long non-coding RNA PVT1, a novel biomarker for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease progression surveillance and acute exacerbation prediction potentially through interaction with microRNA-146a. 32358016_Population Differentiation at the PVT1 Gene Locus: Implications for Prostate Cancer. 32385030_[Effects of Long Non-coding RNA Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 Gene on Inflammatory Response and Cell Migration in Helicobacter Pylori Infected Gastric Epithelial Cell Line]. 32407172_Long Noncoding RNA Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 Regulates Cisplatin Resistance via miR-3619-5p/TBL1XR1 Axis in Gastric Cancer. 32428696_High PVT1 expression is associated with Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. 32441301_Long non-coding RNA PVT1-mediated miR-543/SERPINI1 axis plays a key role in the regulatory mechanism of ovarian cancer. 32499447_LncRNA PVT1 promotes exosome secretion through YKT6, RAB7, and VAMP3 in pancreatic cancer. 32557622_lncRNA PVT1 promotes the migration of gastric cancer by functioning as ceRNA of miR-30a and regulating Snail. 32562719_Lowly expressed lncRNA PVT1 suppresses proliferation and advances apoptosis of glioma cells through up-regulating microRNA-128-1-5p and inhibiting PTBP1. 32572930_Expression level of lncRNA PVT1 in serum of patients with coronary atherosclerosis disease and its clinical significance. 32602581_Nonsense-mediated decay factor SMG7 sensitizes cells to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis via CYLD tumor suppressor and the noncoding oncogene Pvt1. 32614682_Serum long noncoding RNAs FAS-AS1 & PVT1 are novel biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematous. 32689767_LncRNA PVT1 regulates gallbladder cancer progression through miR-30d-5p. 32725807_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor growth and predicts poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 32727463_LncRNA PVT1 promotes gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic cancer via activating Wnt/beta-catenin and autophagy pathway through modulating the miR-619-5p/Pygo2 and miR-619-5p/ATG14 axes. 32729021_LncRNA PVT1 induces aggressive vasculogenic mimicry formation through activating the STAT3/Slug axis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. 32734834_Clinical significance of circPVT1 in patients with non-small cell lung cancer who received cisplatin combined with gemcitabine chemotherapy. 32781203_Tissue-based long non-coding RNAs ''PVT1, TUG1 and MEG3'' signature predicts Cisplatin resistance in ovarian Cancer. 32812642_SOX2 knockdown slows cholangiocarcinoma progression through inhibition of transcriptional activation of lncRNA PVT1. 32827544_LncRNA PVT1 regulates ferroptosis through miR-214-mediated TFR1 and p53. 32830409_LncRNA PVT1 exacerbates the inflammation and cell-barrier injury during asthma by regulating miR-149. 32866660_PVT1 induces NSCLC cell migration and invasion by regulating IL-6 via sponging miR-760. 32918701_Long non-coding RNA PVT1 can regulate the proliferation and inflammatory responses of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting microRNA-145-5p. 32921988_LncRNA PVT1 Suppresses the Progression of Renal Fibrosis via Inactivation of TGF-beta Signaling Pathway. 32945498_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes tumor cell proliferation, invasion, migration and inhibits apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR1505p/GLUT1. 32945521_Propofol suppresses gastric cancer tumorigenesis by modulating the circular RNAPVT1/miR1955p/E26 oncogene homolog 1 axis. 32960438_The lncRNA PVT1 promotes invasive growth of lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting miR-378c to regulate SLC2A1 expression. 32960485_Long noncoding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation gene 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma. 32992461_Long Noncoding RNA PVT1 Is Regulated by Bromodomain Protein BRD4 in Multiple Myeloma and Is Associated with Disease Progression. 33049089_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 facilitates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte death through the miR-23a-3p/CASP10 axis. 33067424_Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promoted gallbladder cancer proliferation by epigenetically suppressing miR-18b-5p via DNA methylation. 33106979_Downregulating long non-coding RNA PVT1 expression inhibited the viability, migration and phenotypic switch of PDGF-BB-treated human aortic smooth muscle cells via targeting miR-27b-3p. 33148262_The PVT1 lncRNA is a novel epigenetic enhancer of MYC, and a promising risk-stratification biomarker in colorectal cancer. 33167678_Amplified LncRNA PVT1 promotes lung cancer proliferation and metastasis by facilitating VEGFC expression. 33174011_Knockdown of exosomemediated lncPVT1 alleviates lipopolysaccharideinduced osteoarthritis progression by mediating the HMGB1/TLR4/NFkappaB pathway via miR935p. 33188158_LncRNA PVT1 accelerates malignant phenotypes of bladder cancer cells by modulating miR-194-5p/BCLAF1 axis as a ceRNA. 33275233_Long non-coding RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) promotes glioblastoma multiforme progression via regulating miR-1301-3p/TMBIM6 axis. 33327894_Long Non-Coding RNA PVT1 Regulates the Resistance of the Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 to Doxorubicin via Nrf2. 33369809_circPVT1 promotes osteosarcoma glycolysis and metastasis by sponging miR-423-5p to activate Wnt5a/Ror2 signaling. 33408314_Knockdown of plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) inhibits high glucose-induced proliferation and renal fibrosis in HRMCs by regulating miR-23b-3p/early growth response factor 1 (EGR1). 33430890_PVT1 signals an androgen-dependent transcriptional repression program in prostate cancer cells and a set of the repressed genes predicts high-risk tumors. 33443959_Role of PVT1 polymorphisms in the glioma susceptibility and prognosis. 33453148_CircPVT1 promotes progression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by sponging miR-145-5p and regulating TBX15 expression. 33558065_LncRNA PVT1 promotes the malignant progression of acute myeloid leukaemia via sponging miR-29 family to increase WAVE1 expression. 33600954_PVT1: A long non-coding RNA recurrently involved in neoplasia-associated fusion transcripts. 33670447_Serum Long Non-Coding RNAs PVT1, HOTAIR, and NEAT1 as Potential Biomarkers in Egyptian Women with Breast Cancer. 33712566_JAK2 activation promotes tumorigenesis in ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma via regulating oncogenic STAT1-PVT1 lncRNA axis. 33728345_Elevated Circular RNA PVT1 Promotes Eutopic Endometrial Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Adenomyosis via miR-145/Talin1 Axis. 33733809_Long noncoding plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 faci |
|
|
74.270733 |
2.3011075813 |
1.202328 |
0.282657426 |
17.825225 |
0.00002421516799903965840717878776899851800408214330673217773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000072527572984136637638738487332545901153935119509696960449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
108.6728515 |
19.8727851 |
47.5456005 |
6.5714570 |
| ENSG00000249931 |
653125 |
GOLGA8K |
protein_coding |
D6RF30 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues ;mmu:99412; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
11.231380 |
0.0836886219 |
-3.578825 |
0.883976415 |
15.036113 |
0.00010547343211421234346076430954397551431611645966768264770507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000289258241918575640608951582422037063224706798791885375976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4107836 |
0.9538389 |
18.4805430 |
7.3403999 |
| ENSG00000249992 |
25907 |
TMEM158 |
protein_coding |
Q8WZ71 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for brain injury-derived neurotrophic peptide (BINP), a synthetic 13-mer peptide. {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Constitutive activation of the Ras pathway triggers an irreversible proliferation arrest reminiscent of replicative senescence. Transcription of this gene is upregulated in response to activation of the Ras pathway, but not under other conditions that induce senescence. The encoded protein is similar to a rat cell surface receptor proposed to function in a neuronal survival pathway. An allelic polymorphism in this gene results in both functional and non-functional (frameshifted) alleles; the reference genome represents the functional allele. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2015]. |
hsa:25907; |
membrane [GO:0016020]; peptide binding [GO:0042277] |
16280139_Suggested role of Ris-1 as tumor suppressor gene is not evident, at least in breast cancer. 16737913_RIS1 exhibits frameshift mutations in high-frequency microsatellite instability tumors, and its alteration is correlated with mutations in two target genes BAX and TGFBR2, linking it to the mutator pathway in colorectal carcinogenesis. 31389251_Silencing of TMEM158 Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Multidrug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. 31531884_TMEM158 promotes pancreatic cancer aggressiveness by activation of TGFbeta1 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 33428142_TMEM158 May Serve as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: An Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis. 34992215_TMEM158 promotes the proliferation and migration of glioma cells via STAT3 signaling in glioblastomas. |
ENSMUSG00000054871 |
Tmem158 |
414.849909 |
2.3789740971 |
1.250340 |
0.095601461 |
171.372487 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000371029547497635685582522571765657653877549368174978091283918273257889697983104320778321974113841182768558368820777104701846837997436523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000060781310999612689253909168281569108944813393437150304110439274957644676205568063474194490738999625129013182345261157024651765823364257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
592.1393156 |
31.7196594 |
250.6733385 |
10.5576024 |
| ENSG00000250041 |
124902629 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.164100 |
2.7486719807 |
1.458735 |
0.445896729 |
10.919397 |
0.00095162580936252372156708423389659401436801999807357788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002223171406487946949459555412431654985994100570678710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.9777466 |
4.8640122 |
6.2545149 |
1.4392154 |
| ENSG00000250067 |
374887 |
YJEFN3 |
protein_coding |
A6XGL0 |
FUNCTION: May accelerate cholesterol efflux from endothelial cells to high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and thereby regulates angiogenesis. May orchestrate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell emergence from the hemogenic endothelium, a type of specialized endothelium manifesting hematopoietic potential. YJEFN3-mediated cholesterol efflux activates endothelial SREBF2, the master transcription factor for cholesterol biosynthesis, which in turn transactivates NOTCH and promotes hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell emergence (By similarity). May play a role in spermiogenesis and oogenesis (PubMed:17533573). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q1LVI2, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17533573}. |
Alternative splicing;Lipid transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable NADHX epimerase activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including hematopoietic stem cell proliferation; membrane raft distribution; and negative regulation of angiogenesis. Predicted to be active in mitochondrion. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:374887; |
mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; NADHX epimerase activity [GO:0052856]; hematopoietic stem cell proliferation [GO:0071425]; lipid transport [GO:0006869]; membrane raft distribution [GO:0031580]; negative regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0016525]; regulation of cholesterol efflux [GO:0010874]; regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0008593]; sprouting angiogenesis [GO:0002040] |
|
ENSMUSG00000048967 |
Yjefn3 |
47.082955 |
0.2756652443 |
-1.859011 |
0.394232016 |
21.631204 |
0.00000330432113391139153468593903095751329601625911891460418701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010982161661007011966054679186211018304675235413014888763427734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.8171626 |
4.9883773 |
65.8890101 |
12.0354836 |
| ENSG00000250138 |
728488 |
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.302407 |
0.1188463490 |
-3.072831 |
0.762485833 |
19.492346 |
0.00001010035916649139027881365571204241859959438443183898925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000031618515651625221153132871965141248438158072531223297119140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5581902 |
0.8039272 |
13.1941390 |
3.1145209 |
| ENSG00000250155 |
107986412 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.747756 |
0.1380874206 |
-2.856346 |
0.671672534 |
20.507151 |
0.00000594088846294043444447394858309863252543436829000711441040039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000019145745352183585609277816086404300222056917846202850341796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5784971 |
0.7731263 |
11.4720846 |
3.0008266 |
| ENSG00000250290 |
|
NCAPGP1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.736627 |
0.1188559345 |
-3.072714 |
0.631524102 |
29.803585 |
0.00000004781071128810516865872038035079061302212721784599125385284423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000194083085426961590419633798404452917907292430754750967025756835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0504596 |
0.8973171 |
17.3749497 |
3.4731997 |
| ENSG00000250397 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.256094 |
0.2901264470 |
-1.785246 |
0.627177742 |
8.748070 |
0.00309929924067833427112073074738418654305860400199890136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006613511174268065992420950749419716885313391685485839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3748029 |
0.9868348 |
8.3373933 |
1.9919798 |
| ENSG00000250471 |
728564 |
GMPSP1 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.746558 |
3.7258254984 |
1.897560 |
0.703687223 |
6.933706 |
0.00845862588344275904972402457815405796281993389129638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016440521206164751544243074476980837062001228332519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.1195769 |
8.8763991 |
6.0775262 |
1.8985239 |
| ENSG00000250506 |
1018 |
CDK3 |
protein_coding |
Q00526 |
FUNCTION: Serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays a critical role in the control of the eukaryotic cell cycle; involved in G0-G1 and G1-S cell cycle transitions. Interacts with CCNC/cyclin-C during interphase. Phosphorylates histone H1, ATF1, RB1 and CABLES1. ATF1 phosphorylation triggers ATF1 transactivation and transcriptional activities, and promotes cell proliferation and transformation. CDK3/cyclin-C mediated RB1 phosphorylation is required for G0-G1 transition. Promotes G1-S transition probably by contributing to the activation of E2F1, E2F2 and E2F3 in a RB1-independent manner. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15084261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18794154, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8846921}. |
ATP-binding;Cell cycle;Cell division;Kinase;Mitosis;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase family. The protein promotes entry into S phase, in part by activating members of the E2F family of transcription factors. The protein also associates with cyclin C and phosphorylates the retinoblastoma 1 protein to promote exit from G0. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:1018; |
cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex [GO:0000307]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004693]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; cell division [GO:0051301]; cell population proliferation [GO:0008283]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; G0 to G1 transition [GO:0045023]; G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000082]; negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045746]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468] |
15084261_A non-cdk8-associated cellular pool of cyclin C combines with cdk3 to stimulate pRb phosphorylation at S807/811 during the G0/G1 transition, and this phosphorylation is required for cells to exit G0 efficiently. 18794154_Expression level of cdk3 is higher in human cancer cell lines and glioblastoma tissue compared with normal brain tissue. cdk3 phosphorylates activating transcription factor 1 (ATF1)and enhances the transactivation and transcriptional activities of ATF1. 21067790_The Walleye dermal sarcoma virus cyclin functions as a structural ortholog of cyclin C in spite of its limited amino acid sequence identity with C cyclins or with any known cyclins and activates Cdk8 and Cdk3. 24691537_CDK3 is associated with the progression of NPC, and may be a potential biomarker for prediction of the prognosis of patients with NPC. 25531331_Mir-873 inhibits ESR1 activity and cell growth via targeting CDK3. 26498144_Data indicate that microRNA miR-214 has tumor-suppressive activity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through inhibition of E2F2 transcription factor (E2F2), cyclin-dependent kinases CDK3 and CDK6. 26755651_High Cdk3-promoted epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activating AP-1 is involved in colorectal cancer metastasis. 27893713_These results provided evidence supporting the oncogenic potential of NFAT3 and suggested that CDK3-mediated phosphorylation of NFAT3 has an important role in skin tumorigenesis. 28108217_The analysis of tumor and matched normal lung tissues indicates that miR-150 downregulation in lung tumors correlates with higher CDK3 levels. In addition, miR-150 transfection experiments with cancer-derived cell lines reveal that miR-150-mediated CDK3 suppression directly induces growth inhibition. 28501005_ectopic expression of HuR promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and survival by directly binding to and stabilizing CDK3 mRNA. 28939591_These results suggest that miR-125a-3p can function as a novel tumor suppressor in ER(+) breast cancer by targeting CDK3, which may be a potential therapeutic approach for TamR breast cancer therapy 29344850_HuR facilitated lung cancer stemness dependent on CDK3 expression. miR-873 or miR-125a-3p level was negatively correlated with HuR and CDK3 expression levels in lung cancer tissues. HuR facilitates lung cancer stemness via regulating miR-873/CDK3 and miR-125a-3p/CDK3 axis. 33504681_circRNA_141539 can serve as an oncogenic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-4469 and activating CDK3 gene. |
ENSMUSG00000092300 |
Cdk3 |
51.441748 |
0.3110735865 |
-1.684672 |
0.428431093 |
14.443203 |
0.00014445024333686762459637298317005615899688564240932464599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000387934059616478572538045277440232894150540232658386230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.1130996 |
6.6052221 |
84.3899975 |
14.5338108 |
| ENSG00000250510 |
27239 |
GPR162 |
protein_coding |
Q16538 |
FUNCTION: Orphan receptor. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene was identified upon genomic analysis of a gene-dense region at human chromosome 12p13. It appears to be mainly expressed in the brain; however, its function is not known. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:27239; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930] |
19773279_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 26827797_Data show certain SNPs variants in GPR162 gene associated with impairments in glucose homeostasis in obese patients. |
ENSMUSG00000038390 |
Gpr162 |
45.684824 |
0.3632817811 |
-1.460839 |
0.290873298 |
25.033436 |
0.00000056344693750515296572591895929438265966382459737360477447509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002049908010247980857655670725026020306813734350726008415222167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
25.4938903 |
4.9899376 |
70.7294652 |
9.3872558 |
| ENSG00000250571 |
2738 |
GLI4 |
protein_coding |
P10075 |
|
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription, DNA-templated. Predicted to be located in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:2738; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006355] |
|
|
|
135.529920 |
0.4587439754 |
-1.124239 |
0.193166706 |
33.382518 |
0.00000000757013979823940977754709850565048578907578757934970781207084655761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000033353809976720504883767112877177019036878391489153727889060974121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
81.3687922 |
10.8146029 |
179.3755014 |
16.2073801 |
| ENSG00000250657 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
106.193731 |
2.3751633053 |
1.248027 |
0.182828749 |
46.612874 |
0.00000000000864901540441768650660835484168139611522996279546759978984482586383819580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000048227981627958086704378263186190315021939500894632146810181438922882080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
147.9851522 |
18.9512809 |
62.6767932 |
6.1936273 |
| ENSG00000250673 |
345051 |
REELD1 |
protein_coding |
A0A1B0GV85 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
|
|
11.057782 |
0.3725545246 |
-1.424477 |
0.467633634 |
9.605200 |
0.00194027194551313689196980760698352241888642311096191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004299416591468833460931708856378463678993284702301025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9467496 |
1.9363258 |
16.1136420 |
3.2590116 |
| ENSG00000250722 |
6414 |
SELENOP |
protein_coding |
P49908 |
FUNCTION: Might be responsible for some of the extracellular antioxidant defense properties of selenium or might be involved in the transport of selenium. May supply selenium to tissues such as brain and testis. |
Direct protein sequencing;Glycoprotein;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Secreted;Selenium;Selenocysteine;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a selenoprotein that is predominantly expressed in the liver and secreted into the plasma. This selenoprotein is unique in that it contains multiple selenocysteine (Sec) residues per polypeptide (10 in human), and accounts for most of the selenium in plasma. It has been implicated as an extracellular antioxidant, and in the transport of selenium to extra-hepatic tissues via apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (apoER2). Mice lacking this gene exhibit neurological dysfunction, suggesting its importance in normal brain function. Sec is encoded by the UGA codon, which normally signals translation termination. The 3' UTRs of selenoprotein mRNAs contain a conserved stem-loop structure, designated the Sec insertion sequence (SECIS) element, that is necessary for the recognition of UGA as a Sec codon, rather than as a stop signal. The mRNA for this selenoprotein contains two SECIS elements. The use of alternative polyadenylation sites, one located in between the two SECIS elements, results in two populations of mRNAs containing either both (predominant) or just the upstream SECIS element (PMID:27881738). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have also been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2018]. |
hsa:6414; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; platelet dense granule lumen [GO:0031089]; selenium binding [GO:0008430]; brain development [GO:0007420]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; regulation of growth [GO:0040008]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; selenium compound metabolic process [GO:0001887]; sexual reproduction [GO:0019953] |
11280803_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12173025_A DNA-repeat structure within the promoter contains a functionally relevant polymorphism and is genetically unstable under conditions of mismatch repair deficiency 12423375_selenoprotein P functions as a Se-supply protein, delivering Se to the cells 17245539_SePP-like immunoreactivity localizes to neurons and ependymal cells and thus appears strategically situated for maintenance and control of selenium-dependent anti-oxidative defense systems. 17511039_SePmRNA expression in the tissues of normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is significantly different, suggesting that SeP might play a role in the occurrence and development of HCC. 17536041_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17536041_Results reveal two common functional nucleotide polymorphisms within the human selenoprotein P gene that may predict behavior of biomarkers of selenium status and response to supplementation and thus susceptibility to disease. 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17937618_Both non-glycosylated and partially glycosylated SeP is utilised as selenium donor by target cells. 17961124_local Sepp expression is required to maintain selenium content in selenium-privileged tissues such as brain and testis during dietary selenium restriction 17986007_selenoprotein P reduces lipid hydroperoxides and maintains the viability of myofibroblasts. a novel pathophysiologic function of myofibroblasts as a generator of lipid hydroperoxides, and a self-defense mechanism against self-generated oxidative stress. 18483336_Four variants in SEPP1 were significantly associated with advanced colorectal adenoma risk. 18483336_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18977241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19074884_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19170196_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19215687_selenoprotein P expression was low in gastric adenocarcinoma tissues compared with control tissues 19453253_Data conclude that functional polymorphisms in the SEPP-1 gene influence the proportion of SePP isoforms in plasma. 19513589_The glucocorticoid receptor inhibits selenoprotein P transactivation via response elements; the finding provides insight into a potential mechanism of selenium redistribution during development. 19625176_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19692168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19747622_In a study of 817 randomly selected adult Danes, the median selenoprotein P level in serum was 2.72 (2.18-3.49) mg/L. Serum selenoprotein P increased with age and was higher in men than in women. 19779296_Early decrease in Sel-P plasma concentrations was specifically observed in septic shock and was similar in SIRS patients whereas GPx activity remained unchanged. 20178852_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20360971_tear SeP is a key molecule to protect the ocular surface cells against environmental oxidative stress 20378690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20521393_Our findings demonstrate that Selenoprotein P protects neuronal cells from amyloid beta-induced toxicity, suggesting a neuroprotective role for SelP in preventing neurodegenerative disorders. 20542496_Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa causes a decline in locally produced selenoprotein P in the colon that eventually may contribute to the emergence of inflammatory bowel disease-related colorectal cancer. 20565998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20565998_The present results show no significant difference in genotype and allele distribution of SNP r25191g/a between individuals with Kashin-Beck disease and controls. 20800603_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20852007_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20875901_These findings suggest an association between the individual selenoprotein concentration and the presence of diabetes. 21035759_Using serial analysis of gene expression and DNA chip methods, the study found that hepatic SeP mRNA levels correlated with insulin resistance in humans. 21052528_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21456065_Selenoprotein P levels in prostate cells determine basal reactive-oxygen-species levels and H2O2-induced cytotoxicity. Deregulation of selenoprotein P during prostate carcinogenesis may increase free radicals, thus promoting tumor development. 21677040_Circulating SeP concentrations were elevated in patients with glucose metabolism dysregulation and were related to various cardiometabolic parameters including insulin resistance, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. 22496878_Circulating selenoprotein P levels were positively correlated with fasting plasma glucose and negatively associated with both total and high-molecular adiponectin in type 2 diabetics. 22715394_Selenium, selenoenzymes, oxidative stress and risk of neoplastic progression from Barrett's esophagus: results from biomarkers and genetic variants. 22932905_hepatocellular SAM-dependent protein methylation is required for both SEPP1 and gluconeogenic enzyme expression and that inhibition of protein arginine methylation might provide a route to therapeutic interventions in type II diabetes. 23056383_Higher tumor grade and tumor stage at diagnosis correlated to lower SePP and Se concentrations. 23129481_SEPP1 genetic variation was associated with prostate cancer incidence; replication of these results in an independent dataset is necessary. 23268326_This study demonistrated that Sepp1 in midbrain was expressed in neurons of the substantia nigra (SN), and expression was concentrated within the centers of Lewy bodies, the pathological hallmark of Parkinson disease 23760059_We speculate that there could be a feedback regulation between hepatic Sepp1 and pancreatic insulin and that increased circulating Sepp1 might be the result rather than the cause of abnormal glucose metabolism.[Review] 23770201_These results demonstrate that SEPP1 represents a previously unrecognized regulator of Polychlorinated biphenyl-induced biological effects. 24039907_The data provide evidence that single nucleotide polymorphisms in SEPP1 and GPX1 modulate risk of breast cancer. 24055274_AMPK activators ameliorated carrageenan-induced insulin resistance via SeP inhibition. 24157689_Sepp1 secreted from epithelial cells may support the intestinal immune system by providing immune cells (including plasma cells) with selenium 24161883_Genetic variants in selenoprotein P plasma 1 gene (SEPP1) are associated with fasting insulin and first phase insulin response in Hispanics 24257750_metformin decreases binding of FoxO3a, a direct target of AMPK, to the SEPP1 promoter. 24278290_data suggest that SEPP1 alters breast cancer risk among women with higher levels of NA ancestry 24361887_SePP is not only involved in Selenium transport to testes supporting GPX4 biosynthesis but it also becomes secreted into seminal plasma. 24437729_The histidine-rich domain of selenoprotein P is capable of binding Cu ions in both oxidation states of Cu(+) and Cu(2+) with high affinity and of modulating Cu(+) and Cu(2+)-mediated ABETA aggregation, reactive oxygen species production, neurotoxicity. 24563517_SEPP1 rs7579 was found to be associated with lower risk of advanced prostate cancer. 24638201_Elevated SeP concentrations are independently associated with a reduced risk of MetS in children 24708917_Data suggest that plasma SEPP1 level can be up-regulated by dietary factors; here, significantly higher plasma SEPP1 is observed in women at risk of pre-eclampsia treated with dietary supplement of selenium-enriched yeast started in first trimester. 24914767_These results demonstrated that SelP interacts with tubulin, alpha 1a (TUBA1A). 25395084_this study provide preliminary genetic evidence that the SEPP1 functional variants contribute to the AAA risk. 26348725_Impaired renal function is positively correlated with serum concentrations of SePP. 26399395_Studied gene-specific regulation of hepatic selenoprotein expression by interleukin-6; by testing human hepatocytes in culture, found IL-6 reduced the concentrations of SePP mRNA and secreted SePP in a dose-dependent manner. 26514640_Selenoprotein P concentrations are not elevated in women with gestational diabetes mellitus but are associated with BMI and HDL cholesterol. 26658762_GPX1 and SEPP1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism were not associated with any changes in the expression of related genes. GPX1 was shown to modulate the expression of unrelated target, SEP15, upon Se supplementation, both alone and in combination with SEPP1. 26675765_women who carry the SEPP1 rs3877899 A allele are better able to maintain selenium status during pregnancy, and their GPx3 activity increases more with supplementation, which suggests better protection from low selenium status. 26944060_preliminary result indicated the beneficial effect of serine on the expression of SelP and GPx, which suggested that it might be a candidate for combined selenium supplement. 27371843_Data show that the cell proliferative ability was inhibited in the cells overexpressing selenoprotein P, plasma 1 (SEPP1), and the colony forming ability of The cell evidently decreased. 27524654_SeP was higher in individuals who were overweight/obese, and associated with insulin resistance by HOMA-IR and by clamp, but not independently of BMI. 27881738_Study suggests the 3' UTR structural elements (SECIS) in Sepp1 functions with site specificity and further illustrates how mRNA processing may produce transcripts with altered coding potential to produce diversity in selenoprotein isoforms. 27908419_The selenium levels in the tissues were correlated to the genotype of the SELENOP selenium carrier protein, but not to other proteins whose levels have been reported to be responsive to selenium availability, including GPX1, SELENOF and SBP1. 28064116_Biomarkers of Se status in clinical research need to be measured by validated assays in order to avoid erroneous data and incorrect interpretations, especially when analyzing young women. The Se content of circulating SELENOP differs between individuals and may provide some important diagnostic information on Se metabolism and status 28190280_We have demonstrated a significant decrease in circulating SeP levels according to MetS status in patients with documented cardiovascular disease. 28263310_Increased amounts of circulating SeP predicted the ineffectiveness of training on endurance capacity in humans. 28459371_erum microRNA-7 and selenoprotein P appear to be potential non-invasive diagnostic markers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Moreover, the results suggest that selenium could be used as an anticancer therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma by affecting both microRNA-7 and selenoprotein P 28598259_The study suggests the possible importance of SEPP1 rs3877899 and SEP15 rs5859 polymorphisms in susceptibility to breast cancer. 28696394_Genetic variations in selenoprotein genes modulated both GPX1 and SELENOP selenoprotein gene expression and global gene expression in response to Brazil nut supplementation. 28700468_Results indicate that the 2 genetic variants of rs7579 and rs230813 in SEPP1 may not play a role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia in Chinese Han Women. 29069514_Results indicate a diversity of RNA elements conducting multiple occurrences of UGA redefinition to control the synthesis of full-length and truncated selenoprotein P (SELENOP) isoforms. 29314169_Results indicate an interaction between selenium status and selenoprotein genotypes that may contribute to the disparity in prostate cancer incidence and outcome experienced by African Americans 29609868_Although the regulation of selenoproteins expression is mainly during translation, the mRNA expression of selenoproteins, such as SELENOF (Selenoprotein 15), SELENOK and SEPHS1 can be altered by Se status. 29636330_Selenoprotein P promotes the development of pulmonary hypertension by stimulating excessive proliferation and apoptosis resistance of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. 29648467_When rs13154178 gene polymorphism was compared with AA homozygous individuals, fasting blood glucose levels were significantly higher in carriers of either polymorphism than in those with no polymorphism. We suggest rs13154178 gene polymorphism may lead to gestational diabetes mellitus in the Turkish society. 29932230_Selenium supplementation was not found to influence the expression of SEPP1 in mRNA and protein levels in subjects with and without metabolic syndrome suffering from coronary artery disease. 30084959_This study of adult men living in selenium non-deficient areas in China provides little support for the inverse association between pre-diagnostic plasma SELENOP concentration and lung cancer risk. 30243837_Data identify core coding region sequence determinants within the SELENOP mRNA that govern SELENOP synthesis. The N-terminal coding sequence (upstream of the second UGA) and C-terminal coding sequence context are two independent determinants for efficient synthesis of full-length SELENOP. In addition, the distance between the first UGA and the consensus signal peptide is also critical for efficiency. 30425271_elevation of circulating SELENOP, but not of circulating selenium, was positively and independently associated with future onset of glucose intolerance in a general Japanese population 30448992_Higher serum SELENOP levels were associated with an overall healthy metabolomics profile 30582190_NKX3.1 and SELENOP genotypes were associated with a more aggressive prostate tumor grade at the time of prostatectomy, but there were no significant interactions of NKX3.1 genotype with either selenium status or SELENOP genotype. 30974086_The authors show that hepatitis C infection increases the levels of hepatic selenoprotein P (SeP) mRNA (SEPP1 mRNA) and serum SeP, a hepatokine linked to insulin resistance. SEPP1 mRNA inhibits type I interferon responses by limiting the function of retinoic-acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I), a sensor of viral RNA. 31158358_Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) revealed HMGB1 had 32% sensitivity and 100% specificity in differentiating HCV from HCV+HCC patients, both SEPP1 and HMGB1 had high sensitivity (92%,60%) and 93% specificity in differentiating healthy from HCV+HCC group 31542866_Studied association of selenoprotein S (SEPS1) and selenoprotein P (SEPP1) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with expression of SEPS1 and SEPP1 in patients with metabolic syndrome and history of cardiovascular disease. 32377302_Diverse Associations of Plasma Selenium Concentrations and SELENOP Gene Polymorphism with Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components. 32605214_Higher Serum Selenoprotein P Level as a Novel Inductor of Metabolic Complications in Psoriasis. 32735635_Selenoprotein P inhibits cell proliferation and ROX production in HCC cells. 32838475_Toenail selenium, plasma selenoprotein P and risk of advanced prostate cancer: A nested case-control study. 33094480_SeP is elevated in NAFLD and participates in NAFLD pathogenesis through AMPK/ACC pathway. 33266488_Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Derangements in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of Selenoprotein P. 33388316_Colonic Epithelial-Derived Selenoprotein P Is the Source for Antioxidant-Mediated Protection in Colitis-Associated Cancer. 33938349_Elevated circulating Selenoprotein P levels in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. 34563873_Serum selenium, selenoprotein P and glutathione peroxidase 3 as predictors of mortality and recurrence following breast cancer diagnosis: A multicentre cohort study. 34616844_Lack of Association between Common Polymorphisms in Selenoprotein P Gene and Susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer, Breast Cancer, and Prostate Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. 34884891_Natural Autoimmunity to Selenoprotein P Impairs Selenium Transport in Hashimoto's Thyroiditis. 35205233_An Assessment of GPX1 (rs1050450), DIO2 (rs225014) and SEPP1 (rs7579) Gene Polymorphisms in Women with Endometrial Cancer. 35636018_Autoimmunity to selenoprotein P predicts breast cancer recurrence. 35840466_Elevated Selenoprotein P Levels in Thalassemia Major Patients. 35905604_The role of selenoprotein P in the determining the sensitivity of cervical cancer patients to concurrent chemoradiotherapy: A metabonomics-based analysis. |
ENSMUSG00000064373 |
Selenop |
21.381567 |
0.0707014457 |
-3.822116 |
0.661484240 |
35.531000 |
0.00000000251023694917645698458750939746023794763019054698816034942865371704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011585708996199030836713622129308109975909246713854372501373291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6210202 |
1.2128086 |
36.9636089 |
8.4815116 |
| ENSG00000250802 |
728723 |
ZBED3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33712067_Lnc13728 facilitates human mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic differentiation via positive regulation of ZBED3 and downregulation of the WNT/beta-catenin pathway. |
|
|
30.036194 |
0.3445653270 |
-1.537151 |
0.326811683 |
22.502759 |
0.00000209841964538257566750775219566182983044200227595865726470947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007159656487713087025877463365208797085870173759758472442626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0215966 |
3.3027498 |
46.9103269 |
6.1708060 |
| ENSG00000250903 |
100508120 |
GMDS-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31860169_LncRNA GMDS-AS1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma development by regulating miR-96-5p/CYLD signaling. 34981821_lncRNA GMDSAS1 upregulates IL6, TNFalpha and IL1beta, and induces apoptosis in human monocytic THP1 cells via miR965p/caspase 2 signaling. |
|
|
16.983484 |
0.2633077987 |
-1.925178 |
0.477221897 |
16.511099 |
0.00004836612403905093948708326934138312935829162597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000139539482176777150266785976207017938577337190508842468261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5811893 |
2.2825532 |
25.1123320 |
5.5142359 |
| ENSG00000250929 |
|
LINC01181 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.270639 |
2.4664349630 |
1.302427 |
0.485552625 |
7.117921 |
0.00763171448814154405881904352781930356286466121673583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014993650905787489144294077902941353386268019676208496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.5324296 |
8.0631763 |
12.0477782 |
2.6245080 |
| ENSG00000251002 |
105370401 |
TRD-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
113.125472 |
0.0324399385 |
-4.946085 |
0.285964284 |
435.369664 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000110204117202566283466710630944641677591772174001563613826418257324713709755419667721255356597484296664953821618214204286837785101492424486820629909456519168639383413470462552157655354369349928559995484985897660896320893225427029428671 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000044687164008513138279161785886845699892611333785922944692230714203171959669241010139745871508742762460382966542195662967383849252475851185179536301570105835150607469729149967763922423633252596975355794641978629165360472620817012157253 |
Yes |
Yes |
8.5766364 |
1.7031300 |
266.1965893 |
22.5127903 |
| ENSG00000251209 |
91948 |
LINC00923 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.717789 |
0.3653732204 |
-1.452557 |
0.395395509 |
13.428061 |
0.00024788824745121743053921647970128105953335762023925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000640103312172842745138290343476228372310288250446319580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.2191235 |
4.5775258 |
47.4318408 |
8.4095782 |
| ENSG00000251247 |
25850 |
ZNF345 |
protein_coding |
Q14585 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in transcriptional regulation. |
DNA-binding;Metal-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
Enables sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:25850; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006359]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; transcription by RNA polymerase III [GO:0006383] |
|
ENSMUSG00000051034 |
Zfp11 |
26.098500 |
0.4951430151 |
-1.014083 |
0.432780740 |
5.358001 |
0.02062741023407662493971415074156539048999547958374023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036864096749602975888748801480687689036130905151367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.8450136 |
4.8029650 |
36.0736510 |
6.6714358 |
| ENSG00000251322 |
85358 |
SHANK3 |
protein_coding |
A0A0U1RQS4 |
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Major scaffold postsynaptic density protein which interacts with multiple proteins and complexes to orchestrate the dendritic spine and synapse formation, maturation and maintenance. Interconnects receptors of the postsynaptic membrane including NMDA-type and metabotropic glutamate receptors via complexes with GKAP/PSD-95 and HOMER, respectively, and the actin-based cytoskeleton. Plays a role in the structural and functional organization of the dendritic spine and synaptic junction through the interaction with Arp2/3 and WAVE1 complex as well as the promotion of the F-actin clusters. By way of this control of actin dynamics, participates in the regulation of developing neurons growth cone motility and the NMDA receptor-signaling. Also modulates GRIA1 exocytosis and GRM5/MGLUR5 expression and signaling to control the AMPA and metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated synaptic transmission and plasticity. May be required at an early stage of synapse formation and be inhibited by IGF1 to promote synapse maturation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21423165, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21558424, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23739967, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24153177}. |
ANK repeat;Phosphoprotein;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;SH3 domain;Synapse |
|
This gene is a member of the Shank gene family. Shank proteins are multidomain scaffold proteins of the postsynaptic density that connect neurotransmitter receptors, ion channels, and other membrane proteins to the actin cytoskeleton and G-protein-coupled signaling pathways. Shank proteins also play a role in synapse formation and dendritic spine maturation. Mutations in this gene are a cause of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), which is characterized by impairments in social interaction and communication, and restricted behavioral patterns and interests. Mutations in this gene also cause schizophrenia type 15, and are a major causative factor in the neurological symptoms of 22q13.3 deletion syndrome, which is also known as Phelan-McDermid syndrome. Additional isoforms have been described for this gene but they have not yet been experimentally verified. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2012]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:58234; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; neuron spine [GO:0044309]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; ionotropic glutamate receptor binding [GO:0035255]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; structural constituent of postsynaptic density [GO:0098919]; AMPA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:0097113]; associative learning [GO:0008306]; brain morphogenesis [GO:0048854]; dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0060997]; embryonic epithelial tube formation [GO:0001838]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; glial cell proliferation [GO:0014009]; guanylate kinase-associated protein clustering [GO:0097117]; locomotion [GO:0040011]; locomotory exploration behavior [GO:0035641]; long-term synaptic depression [GO:0060292]; long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:0060291]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; memory [GO:0007613]; negative regulation of actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0032232]; negative regulation of cell volume [GO:0045794]; neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:0061351]; neuromuscular process controlling balance [GO:0050885]; NMDA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:0097114]; positive regulation of AMPA receptor activity [GO:2000969]; positive regulation of dendritic spine development [GO:0060999]; positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:2000463]; positive regulation of glutamate receptor signaling pathway [GO:1900451]; positive regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity [GO:0048170]; positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation [GO:1900273]; positive regulation of synapse structural plasticity [GO:0051835]; positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic [GO:0051968]; postsynaptic density assembly [GO:0097107]; regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor clustering [GO:1904717]; regulation of behavioral fear response [GO:2000822]; regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis [GO:0061001]; regulation of grooming behavior [GO:2000821]; regulation of long-term synaptic depression [GO:1900452]; response to interleukin-17 [GO:0097396]; social behavior [GO:0035176]; striatal medium spiny neuron differentiation [GO:0021773]; vocalization behavior [GO:0071625] |
12920066_Haploinsufficiency of the gene SHANK3, which codes for a structural protein of the postsynaptic density, may be a major causative factor in the neurological symptoms of 22q13 deletion syndrome. 16284256_Common breakpoint within SHANK3 responsible for mental retardation and developmental delays. 17173049_Mutation of a single copy of SHANK3 on chromosome 22q13 can result in language and/or social communication disorders. 17999366_Haploinsufficiency of SHANK3 can cause a monogenic form of autism in sufficient frequency to warrant consideration in clinical diagnostic testing. 18615476_Novel de novo SHANK3 mutation in autistic patients is reported. 18615476_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19077115_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19371741_Shank3 is one of a number of host synaptic proteins likely to play key roles in bacteria-host interactions. 19384346_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19384346_SHANK3 deletions may be limited to lower functioning individuals with autism 19454329_Chromosome 22q13.3 deletion syndrome with a de novo interstitial 22q13.3 cryptic deletion disrupting SHANK3 is reported. 19566951_We suggest that SHANK3 might not represent a major susceptibility gene for autism in Chinese Han population 19736351_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20080650_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20385823_De novo mutations in the gene encoding the synaptic scaffolding protein SHANK3 in patients ascertained for schizophrenia. 20442744_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21062623_[review] The presumptive exon containing the variant in the neurodevelopmentally disabled autism case highlighted in this review is not likely to be present in most or all SHANK3 transcripts. 21271662_A translocation between Xq21.33 and 22q13.33 causes an intragenic SHANK3 deletion in a woman with Phelan-McDermid syndrome and hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. 21378602_The SHANK3 gene was analyzed in 128 autistic patients with manifestations similar to those seen in the 22q13.3 deletion syndrome. 21606927_the data of this study provided new insights into the synaptic alterations caused by SHANK3 mutations in humans and provide a robust cellular readout for the development of knowledge-based therapies. 21984749_Deletion size in the SHANK3 gene and adjacent regions determine the severity of phenotypes in Phelan-McDermid syndrome (22q13 deletion syndrome). 22093425_SHANK3 microdeletion is an important genetic component for autism, which may explain 2% typical autism cases. 22509352_These findings suggest that 22q13 deletions may be a more frequent cause for Chinese ID patients than previously thought, and the SHANK3 gene is involved in the neurite development 22749736_n this article we review recent findings in regard to higher brain functions of SHANK3, epigenetic regulation of SHANK3 expression, and SHANK3-related autism spectrum disorder--REVIEW 22892527_SHANK3 variants were detected in patients affected with any autism spectrum disorders subtypes. SNP rs76224556 may have a genotype-phenotype correlation in autism spectrum disorders. 22966748_This study demonistrated that rare variants within the re-sequenced structural domains of ANK3 exon 48 do not contribute to BPD-I. 23100419_This study revealed that alterations in transsynaptic signaling caused by ProSAP2/Shank3 gain or loss of function were also exhibited by neurons expressing ProSAP2/Shank3 carrying the autism-associated mutations R87C, R375C, Q396R, or InsG. 23225497_Mutation or deletion of SHANK3 has been associated with autism. 23300510_Copy number variation in the SHANK3 is associated with variation in fluid intelligence. 23468870_Lack of association between NLGN3, NLGN4, SHANK2 and SHANK3 gene variants and autism spectrum disorder in a Chinese population. 23897824_analysis of SHANK3 mutations associated wtih autism and their effect on ligand binding to the ankyrin repeat region 24132240_We show that Phelan-McDermid syndrome neurons have reduced SHANK3 expression and major defects in excitatory, but not inhibitory, synaptic transmission 24136618_This study is the first to identify specific chromosome 22q13.2q13.32 genomic regions, in addition to the terminal 22q13.33 genomic region encompassing SHANK3, associated with key phenotypes in Phelan-McDermid syndrome. 24153177_findings indicate that SHANK3 overexpression causes a hyperkinetic neuropsychiatric disorder 24186872_The ability to alter the epigenetic modification and expression of SHANK3 by environmental factors suggests that SHANK3 may be a valuable biomarker for dissecting the role of gene and environment interaction in the etiology of ASD. 24382453_This study demonistrated that the uncoupling of ProSAP2/Shank3 nuclear shuttling from synaptic activity may represent a molecular mechanism that contributes to the pathology of SCZ in patients with mutations in ProSAP2/Shank3. 24398551_our results suggested that this commonly genetic variant in SHANK3 gene strikingly decreased the risk of ism spectrum disorder in China. 24700646_because the deletions in our patients do not involve the SHANK3 gene, we posit the existence of a new contiguous gene syndrome proximal to the smallest terminal deletions in the 22q13 region. 25048004_This study identified and confirmed SHANK3 protein changes within the postsynaptic density in schizophrenia 25646853_a mutation in SHANK3 that underscores its relevance in Autism Spectrum Disorder. 25882257_miR-7 binds to 3-prime untranslated regions of SHANK3 mRNA and causes the alteration of neuronal morphology and function, potentially playing a crucial role in the pathophysiological process of schizophrenia 25931020_De novo SHANK3 mutation causes Rett syndrome-like phenotype in a female patient. 26572867_post-transcriptional regulation of SHANK3 expression by three microRNAs (miRNAs), miR-7, miR-34a, and miR-504, is reported. 26966193_these data suggest that SHANK3 mutations predispose to autism, at least partially, by inducing an Ih channelopathy that may be amenable to pharmacological intervention. 27271042_The association of SHANK3 gene polymorphism and autism. 27512916_This study does not provide evidence for a major role of SHANK3 in the pathogenesis of bipolar disorder. 27519580_Haploinsufficiency of SHANK3 is a predisposing factor in adults with catatonia. 27554343_No specific EEG abnormality is present in epilepsy due to to SHANK3 loss-of-function mutations. 27592227_SHANK3 expression was increased in the neocortex of temporal lobe epilepsy patients and rats. 27790361_SHANK3, CHD8, and ADNP had distinctly higher scores than all other genes in the dataset describing the genes associated with autism spectrum disorders. 27876814_GWA study identified maternal genetic effects not previously identified in ASD at a locus in SHANK3. 27916453_Partial knockdown of SHANK3 expression in human dorsal root ganglion neurons abrogates TRPV1 function. 28263956_SHANK1 and SHANK3 act as integrin activation inhibitors by sequestering active Rap1 and R-Ras via the SPN domain and thus limiting their bioavailability at the plasma membrane. 28345660_Results showed decreased expression of Zn uptake transporters ZIP2 and ZIP4 on mRNA and protein level correlating with SHANK3 expression levels, and found reduced levels of ZIP4 protein co-localizing with SHANK3 at the plasma membrane. ZIP4 exists in a complex with SHANK3. Further results confirmed a link between enterocytic SHANK3, ZIP2 and ZIP4. 28371232_Missense mutation in SHANK3 gene is associated with schizophrenia. 28754298_We report a family with four affected individuals including the 37 year-old mother, her 12 year-old male monozygotic twins and 8 year-old daughter harboring a novel SHANK3 interstitial microdeletion 28906292_SHANK3 expression correlated with ZO-1 and PKCepsilon in colonic tissue of patients with Crohn's disease. The expression level of SHANK3 affects ZO-1 expression and the barrier function in intestinal epithelial cells. 28948968_Authors suggest that SHANK3 has a critical role in neuronal morphogenesis in placodal neurons and that early defects are associated with ASD-associated mutations. 29408620_the present study did not provide evidences to support the fact that SHANK3 variants could influence the susceptibility to Autism spectrum disorder in the Northeastern Han Chinese population 29719671_SHANK3 haploinsufficiency due to point mutations alone is sufficient to cause a broad range of phenotypic features associated with Phelan-McDermid syndrome. 29735556_we identify USP8 as a key enzyme that regulates SHANK3 protein levels in neurons 29939863_Our report details a 10-year-old boy with a de novo heterozygous c.1231del, p.Arg411Val frameshift variant in SHANK3, a high-risk candidate autism gene. We report significant speech delay and seizures as an association with this phenotype. 30329048_We have used clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeat/CRISPR-associated nuclease 9 to generate a cynomolgus monkey model by disrupting SHANK3 at exons 6 and 12. Analysis of the live mutant monkey revealed the core behavioral abnormalities of ASD, including impaired social interaction and repetitive behaviors, and reduced brain network activities detected by positron-emission computed tomography 30610205_An autism-linked missense mutation in SHANK3 reveals the modularity of Shank3 function. 30696942_A kinome-wide RNAi screen identifies ERK2 as a druggable regulator of Shank3 stability. 31788990_Severe white matter damage in SHANK3 deficiency: a human and translational study. 31879129_Shank3 Binds to and Stabilizes the Active Form of Rap1 and HRas GTPases via Its NTD-ANK Tandem with Distinct Mechanisms. 32202324_Truncating mutations in SHANK3 associated with global developmental delay interfere with nuclear beta-catenin signaling. 32522805_Autism-associated SHANK3 mutations impair maturation of neuromuscular junctions and striated muscles. 32564287_Dynamic Change of Shanks Gene mRNA Expression and DNA Methylation in Epileptic Rat Model and Human Patients. 32769989_A chimeric mouse model to study human iPSC-derived neurons: the case of a truncating SHANK3 mutation. 33023580_Fraternal twins with Phelan-McDermid syndrome not involving the SHANK3 gene: case report and literature review. 33234429_Rare variations in the SHANK3 gene confers susceptibility to schizophrenia in Uygur Chinese population. 33256793_A 29 Mainland Chinese cohort of patients with Phelan-McDermid syndrome: genotype-phenotype correlations and the role of SHANK3 haploinsufficiency in the important phenotypes. 33388374_Altered striatum centered brain structures in SHANK3 deficient Chinese children with genotype and phenotype profiling. 33568460_CaMKII Phosphorylation Regulates Synaptic Enrichment of Shank3. 34206779_Sensory Reactivity Phenotype in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome Is Distinct from Idiopathic ASD. 34369668_Neurocognitive follow-up in adult siblings with Phelan-McDermid syndrome due to a novel SHANK3 splicing site mutation. 34788607_Homer1a regulates Shank3 expression and underlies behavioral vulnerability to stress in a model of Phelan-McDermid syndrome. 35819558_SHANK3 genetic polymorphism and susceptibility to ASD: evidence from molecular, in silico, and meta-analysis approaches. 36202854_Modeling human telencephalic development and autism-associated SHANK3 deficiency using organoids generated from single neural rosettes. |
ENSMUSG00000022623 |
Shank3 |
30.832769 |
0.3619653675 |
-1.466076 |
0.321938349 |
20.904525 |
0.00000482752957056423263318065131066703088436042889952659606933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000015743335497465327731635154062672654617927037179470062255859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.7185301 |
4.0539006 |
46.5476297 |
7.7222298 |
| ENSG00000251349 |
100526694 |
MSANTD3-TMEFF1 |
protein_coding |
Q8IYR6 |
FUNCTION: May inhibit NODAL and BMP signaling during neural patterning (By similarity). May be a tumor suppressor in brain cancers. {ECO:0000250, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12743596}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Developmental protein;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription from the neighboring MSANTD3 (Myb/SANT-like DNA-binding domain containing 3) and TMEFF1 (transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 1) genes. The read-through transcript encodes a fusion protein that shares sequence identity with the products of each individual gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013]. |
hsa:100526694;hsa:8577; |
basement membrane [GO:0005604]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; dendrite development [GO:0016358]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; tissue development [GO:0009888] |
|
|
|
23.256704 |
4.2946043901 |
2.102525 |
0.407649552 |
26.976714 |
0.00000020592137546368094148909659666518701115478506835643202066421508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000785577539892460797041004189750212916010241315234452486038208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.7969345 |
8.5807487 |
8.9933580 |
1.7313984 |
| ENSG00000251364 |
100506258 |
SYT9-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.398948 |
0.1517145117 |
-2.720569 |
0.619861852 |
18.038452 |
0.00002164877644533048868568173017656874890235485509037971496582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000065393782150740579974142197006159449301776476204395294189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2028371 |
2.2361022 |
34.7528613 |
9.2516808 |
| ENSG00000251493 |
2297 |
FOXD1 |
protein_coding |
Q16676 |
FUNCTION: Transcription factor involved in regulation of gene expression in a variety of processes, including formation of positional identity in the developing retina, regionalization of the optic chiasm, morphogenesis of the kidney, and neuralization of ectodermal cells (By similarity). Involved in transcriptional activation of PGF and C3 genes (PubMed:27805902). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q61345, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27805902}. |
DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
This gene belongs to the forkhead family of transcription factors which are characterized by a distinct forkhead domain. Studies of the orthologous mouse protein indicate that it functions in kidney development by promoting nephron progenitor differentiation, and it also functions in the development of the retina and optic chiasm. It may also regulate inflammatory reactions and prevent autoimmunity. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:2297; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA binding, bending [GO:0008301]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; canonical Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0060070]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; dichotomous subdivision of terminal units involved in ureteric bud branching [GO:0060678]; luteinizing hormone secretion [GO:0032275]; metanephric capsule development [GO:0072213]; metanephric capsule specification [GO:0072267]; metanephric nephron development [GO:0072210]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; nephrogenic mesenchyme development [GO:0072076]; positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030513]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of kidney development [GO:0090184]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
15716278_the level of Smad6s can alter the level of TGF-beta and the subsequent induction of PAI-1 via a FoxD1 transcription site 24099863_In this review, we focus on the role of four specific FOX factors (FOXD1, FOXL2, FOXO1 and FOXP3) in gonadotropin hormone production 25462566_FOXD1 promotes breast cancer proliferation and chemotherapeutic drug resistance by targeting p27 25550559_Lung cancer patients with high FOXD1 expression survive for a significantly shorter time than those with low FOXD1 expression. 27569208_our findings define a FOXD1-ALDH1A3 pathway in controling the clonogenic and tumorigenic potential of mesenchymal glioma stem-like cells in glioblastoma tumors 27805902_Results showed that FOXD1 is a major actor in mammalian reproduction as sequence variants generated recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) and embryonic resorption (ER). Data propose that the FOXD1-p.429AlaAla mutation might be used as an RSA molecular marker while FOXD1 p.Ala88Gly variant might have a protective effect. 28075458_The role of FOXD1 in glioma tumorigenesis, migration and progression.High FOXD1 expression in glioma. 29864920_FOXD1 promoted the expression of Plk2 mRNA and protein in colorectal cancer cells. 29936179_FOXD1 is overexpressed in osteosarcoma while MiR-30a-5p is lowexpressed. MiR-30a-5p directly regulates FOXD1 by binding its 3'-UTR. 30110134_FOXD1 may influence invasion and migration via indirect regulation of MMP9 and RAC1B alternative splicing in melanoma cells. 30158529_FOXD1-dependent MICU1 expression regulates mitochondrial activity and cell differentiation 30225541_as well as stemness abilities but stronger senescence and higher apoptosis rate. CONCLUSION: We found that overexpression of miR-338-5p suppresses glioma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and accelerates its senescence and apoptosis by decreasing FOXD1 expression via inhibition of activation of MAPK-signaling pathway. 30562753_Mechanistic analyses revealed that FOXD1 expressed its oncogenic characteristics through activating Vimentin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. 30635407_Suppression of miR-92a-1-5p and restoration of FOXD1 may be a preventive approach for gastric IM in patients with bile regurgitation. 30933975_YAP cooperated with TEA domain transcriptional factor (TEAD) to activate the expression of forkhead box D1 (FOXD1), a geroprotective protein. YAP deficiency led to the down-regulation of FOXD1. 31252264_long noncoding RNA POU3 F3, induced by transcription factor SP1, acts as an oncogene in the cervical cancer tumorigenesis via regulating miR-127-5p/FOXD1 axis. 31395028_Investigated forkhead box D1 (FOXD1) gene mutations in patients affected by repeated implantation failure (RIF), intra-uterine growth restriction(IUGR), and preeclampsia )PE) by direct sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. Results argue in favour of FOXD1 mutations' central role in recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), RIF, IUGR and PE. 32294305_miR-30a inhibits androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer via targeting MYBL2, FOXD1, and SOX4. 32351986_miR-30a-5p Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Targeting FOXD1. 32460412_FOXD1-AS1 regulates FOXD1 translation and promotes gastric cancer progression and chemoresistance by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. 32568181_FOXD1, negatively regulated by miR-186, promotes the proliferation, metastasis and radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 33352248_Forkhead box D1 promotes EMT and chemoresistance by upregulating lncRNA CYTOR in oral squamous cell carcinoma. 33761914_FOXD1 regulates cell division in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. 33837564_FOXD1 promotes dedifferentiation and targeted therapy resistance in melanoma by regulating the expression of connective tissue growth factor. 34028536_FOXD1 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with macrophages infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. 34184566_Investigation of Candidate Genes and Pathways in Basal/TNBC Patients by Integrated Analysis. 34269372_FOXD1 expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma: a study based on TCGA, GEO and meta-analysis. 34767742_LINC00641 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell malignancy through FOXD1 upregulation at the post-transcriptional level. 34772357_Aberrant overexpression of transcription factor Forkhead box D1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cancer progression in HNSCC. 35112956_Foxhead box D1 promotes the partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells via transcriptionally activating the expression of zinc finger protein 532. 35126932_FOXD1 Regulates the Sensitivity of Cetuximab by Regulating the Expression of EGFR in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer. 35435161_Correlations between forkhead box D1 expression and clinicopathological characteristics of patients with bladder cancer and influence on biological behaviors of bladder cancer cells.', trans 'Correlacion entre la expresion de Forkhead Box D1 y caracteristicas clinico-patologicas de pacientes con cancer de vejiga y su influencia en el comportamiento biologico de las celulas tumorales. 35579380_Combination of FOXD1 and Plk2: A novel biomarker for predicting unfavourable prognosis of colorectal cancer. 35607308_The Expression and Survival Significance of FOXD1 in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis, Immunohistochemistry Validation, and Bioinformatics Analysis. 35974001_USP21 promotes self-renewal and tumorigenicity of mesenchymal glioblastoma stem cells by deubiquitinating and stabilizing FOXD1. 36057597_FOXD1 facilitates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by regulating GLUT1-mediated aerobic glycolysis. |
ENSMUSG00000078302 |
Foxd1 |
401.654995 |
0.3925209578 |
-1.349158 |
0.082302497 |
275.311169 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007895943193646635065053018913083862706396111433012998795869264501928574576642636124263722867138269055116920596868921603016859118836242400604465034549318564610631554501196660567075014114379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002081145027468291827402318055947742016766787452794246901444405612780850855988000622953961098785477538438881634600537875822230200773410643704802222141592854542935242534440476447343826293945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
230.7295072 |
12.8080785 |
592.1323891 |
21.0667571 |
| ENSG00000251562 |
378938 |
MALAT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene produces a precursor transcript from which a long non-coding RNA is derived by RNase P cleavage of a tRNA-like small ncRNA (known as mascRNA) from its 3' end. The resultant mature transcript lacks a canonical poly(A) tail but is instead stabilized by a 3' triple helical structure. This transcript is retained in the nucleus where it is thought to form molecular scaffolds for ribonucleoprotein complexes. It may act as a transcriptional regulator for numerous genes, including some genes involved in cancer metastasis and cell migration, and it is involved in cell cycle regulation. Its upregulation in multiple cancerous tissues has been associated with the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2015]. |
|
|
16441420_Upregulation of MALAT-1 is associated with endometrial stromal sarcoma of the uterus 19041754_Study identified a highly conserved small RNA of 61 nucleotides originating from the MALAT1 locus that is broadly expressed in human tissues; although the long MALAT1 transcript localizes to nuclear speckles, the small RNA is found only in the cytoplasm. 19690017_Results suggest that MALAT-1 in placenta previa I/P is increased and its down-regulation inhibits trophoblast-like cell invasion. MALAT-1 might be involved in regulating trophoblast invasion during the development of advanced invasive placentation. 20149803_expression of the tumor marker MALAT1 noncoding RNA is sensitive to cell surface receptor activation by oxytocin in a neuroblastoma cell line 20213048_Our data demonstrated that MALAT1 was involved in cervical cancer cell growth, cell cycle progression, and invasion through the regulation of gene expression. 20711585_The expression of the long ncRNA MALAT1 correlates with tumor development, progression or survival in lung, liver and breast cancer. 20797886_MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating the levels of active serine/arginine (SR) splicing factors. 21503572_mutations were found on the long non-coding RNA MALAT-1 in CRC colorectal cancer 21678027_Our data suggest that MALAT1 plays an important role in tumor progression and could be a novel biomarker for predicting tumor recurrence after liver transplantation 21941126_Studies indicate the correlation of differential expression of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript1 (MALAT1) with tumor development, progression or survival in several cancerous conditions. 22078878_Pc2, methylation controls the protein's interaction with two distinct ncRNAs, TUG1 and NEAT2, which results in the exclusive subnuclear localization of methylated and unmethylated Pc2 in Polycomb bodies and interchromatin granules, respectively. 22088988_Our results suggest that MALAT-1 transcript induces migration in Non-small cell lung cancers and stimulates tumor growth and invasion in vivo. 22560368_MALAT-1 is upregulated in specific regions of the human alcoholic brain. 22722759_Study verified that MALAT-1 levels were upregulated in bladder cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues, and MALAT-1 expression was remarkably increased in primary tumors that subsequently metastasized 22858678_The quantitative loss of MALAT1 did neither affect proliferation nor cell cycle progression nor nuclear architecture in human lung or liver cancer cells. 23129630_Formation of triple-helical structures by the 3'-end sequences of MALAT1 and MENbeta noncoding RNAs, is reported. 23153939_MALAT1 is upregulated in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, and high MALAT1 expression levels were associated with high-grade and high-stage carcinoma. 23243023_The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. 23555285_These findings provide mechanistic insights on the role of MALAT1 in regulating cellular proliferation 23726266_MALAT-1 miniRNA can be used as a novel plasma-based biomarker for prostate cancer detection and can improve diagnostic accuracy by predicting prostate biopsy outcomes. 23898077_The levels of plasma lncRNAs, H19, HOX antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR), and metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript-1 (MALAT1), were analyzed in patients with gastric cancer (GC) and healthy controls. 23973260_down-regulation of MALAT-1 expression compromised the cytoplasmic translocation of hnRNP C in the G2/M phase and resulted in G2/M arrest 23985560_microRNA-9 targets the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for degradation in the nucleus. 24120702_Genetic translocations involving MALAT1 gene is associated with mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver. 24244343_resveratrol down-regulates MALAT1, resulting in decreased nuclear localization of beta-catenin thus attenuated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, which leads to the inhibition of CRC invasion and metastasis. 24449823_malat1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by associating with suz12. 24468535_Malat1 is a critical regulator of maintaining the transformative phenotype in liver cancer. 24602777_MALAT1 regulates endothelial cell proliferation/migration and vessel growth. 24658096_MALAT1 might serve as an oncogenic lncRNA that promotes proliferation and metastasis of gallbladder cancer and activates the ERK/MAPK pathway. 24815433_MALAT1 might be considered as a potential prognostic indicator and may be a target for diagnosis and gene therapy for pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma. 24857172_These results suggest that MALAT1 may function as a promoter of gastric cancer cell proliferation partly by regulating SF2/ASF. 24892958_Knockdown of UCA1 or Malat-1 lncRNA could attenuate the migrational ability of melanoma cells in in-vitro studies. Increased expression of UCA1 and Malat-1 lncRNAs might have a correlation with melanoma metastasis. 25025966_MALAT1 binds to SFPQ releasing PTBP2 from the SFPQ/PTBP2 complex, the increased SFPQ-detached PTBP2 promotes cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer. 25031737_The expression of MALAT1 is upregulated in colorectal cancer 25036876_An interaction of Bcl-2 with MALAT-1 lncRNA expression was revealed, which merits further investigation for risk prediction in resectable NSCLC patients. 25085246_Findings establish a novel PCDH10-Wnt/beta-catenin-MALAT1 regulatory axis that contributes to EEC development. 25187517_the mechanism of transcriptional activation of LTBP3 promoter depends on MALAT1 initiated from neighboring gene LTBP3 and involves both the direct interaction of the Sp1 and promoter-specific activation 25217850_Results showed that the high level of MALAT1 is associated with lung cancer brain metastasis and survival and demonstrated the potential role of MALAT1 in identification of non-small cell lung cancer patients at high risk of brain metastasis 25269958_MALAT-1 may serve as an oncogenic lncRNA that is involved in malignancy phenotypes of pancreatic cancer. 25280565_High MALAT1 expression drives gastric cancer development and promotes peritoneal metastasis. 25369863_MALAT1 was overexpressed in patients with myeloma and may play a role in its pathogenesis. In addition, MALAT1 may serve as a molecular predictor of early progression. 25431257_MALAT1 might suppress the tumor growth and metastasis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. 25446987_data indicate that MALAT1 may promote CRC tumor development via its target protein AKAP-9 25480417_Our data suggested that lncRNA MALAT1 was a novel molecule involved in ccRCC progression, which provided a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. 25481511_overexpression of lncRNA MALAT1 serves as an unfavorable prognostic biomarker in pancreatic cancer patients. 25538231_High MALAT1 expression is associated with proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 25546229_tumor-associated dendritic cell-derived CCL5 increases human colon cancer cell migration, invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in a MALAT-1dependent manner 25600645_MALAT1 expression was higher in human renal cell carcinoma tissues, where it was associated with reduced patient survival. 25613066_lncRNA MALAT1 plays an important role on glioma progression and prognosis. 25613496_MALAT1 serves as an oncogene in ESCC, and it regulates ESCC growth by modifying the ATM-CHK2 pathway. 25772239_Loss of WIF1 enhances the migratory potential of glioblastoma through WNT5A that activates the WNT/Ca(2+) pathway and MALAT1. 25773124_The data suggest that upregulation of MALAT1 was mediated by the transcription factor Sp1 in A549 lung cancer cells 25787249_Studies indicate that long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates glucose-induced up-regulation of inflammatory mediators tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) through activation of serum amyloid antigen 3 (SAA3). 25811929_Results found the potential effects of MALAT-1 on the stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells, suggesting a novel role of MALAT-1 in tumor stemness. 26139386_Study indicates that NEAT1 and MALAT1 may interact with HIV-1 in vivo. The correlation between plasma levels of NEAT1 and CD4 T-cell counts indicates that NEAT1 levels in plasma could be a potential biomarker for HIV-1 infection. 26159858_A poorer OS in patients with high MALAT-1 expression. 26191181_MALAT1 is a novel regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in breast cancer. 26241674_MALAT1 is a potential prognostic indicator and a target for the diagnosis and gene therapy for PVR diseases. 26242259_MALAT1 can promote HR-HPV (+) cancer cell growth and invasion at least partially through MALAT1-miR-124-RBG2 axis. 26254614_high tissue MALAT1 level was associated with an inferior clinical outcome in various cancers, suggesting that MALAT1 might serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for various cancers [meta-analysis] 26265046_MALAT1 expression by regulation of TDP-43 controls cellular growth, migration, and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro. 26275461_Hsa-miR-1 suppresses breast cancer development by down-regulating K-ras and long non-coding RNA MALAT1 26282005_high expression of MALAT1 might be a novel prognostic biomarker in different types of cancers 26311052_MALAT1 and miR-145 had some level of synergic effect in reducing cancer cell colony formation, cell cycle regulation, and inducing apoptosis in cervical cancer 26335021_Malat1 plays a critical role in maintaining the proliferation potential of early-stage hematopoietic cells. 26352013_Human SP1 and SP3 transcription factors regulate MALAT1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. 26364720_Data show that long ncRNAs MALAT1 silencing downregulated the expression of the microRNA miR-22-3p target gene CXCR2 and AKT pathway. 26406400_High MALAT1 expression was associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 26415832_Posttranscriptional silencing of MALAT1 by miR-217 provides a link, through EZH2, between ncRNAs and the EMT and establishes a mechanism for cigarette smoke extract-induced lung carcinogenesis. 26423854_MALAT1 may potentially be used as a new prognostic marker to predict poorer survival of patients with cancer. 26434412_In this review, we document the molecular characteristics and functions of MALAT1 and shed light on the implication in the molecular pathology of various cancers. 26461224_High MALAT1 expression is associated with clear cell kidney carcinoma. 26482776_MALAT1 regulates cancer stem cell activity and radioresistance by modulating the miR-1/slug axis. 26493997_MALAT-1 knockdown induced a decrease in proliferation-enhanced apoptosis, inhibited migration/invasion, and reduced colony formation and led to cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. These data indicates that MALAT-1 could be exploited for therapeutic benefit 26516927_Data show that long non-coding RNA MALAT1 may be a crucial RNA cofactor of Polycomb protein enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and that may provide a new avenue for development new strategies for treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). 26522444_MALAT1 is an important prognostic factor and therapeutic target for OSCC. 26575981_oncogenic role in osteosarcoma 26614531_MALAT1 level is associated with liver damage, and has clinical utility for predicting development of hepatocellular carcinoma 26619802_there was reciprocal repression between MALAT1 and miR-140, and miR-140 mediated the effects that MALAT1 knockdown exerted 26634309_Using drugs that specifically inhibit or activate the PERK or IRE1alpha sensors, we demonstrate that signalling through the PERK axis activates this expression, through a transcriptional mechanism 26676637_MALAT1 was upregulated in triple-negative breast cancer. MALAT1 knockdown inhibited proliferation, motility, and increased apoptosis in vitro. In vivo, MALAT1 knockdown inhibited tumor growth and metastasis. Patients with high MALAT1 expression had poorer overall survival. MALAT1 overexpression increased expression of miR-1, while miR-1overexpression decreased MALAT1 expression. MALAT1 acts through the miR-slug axis. 26722461_MALAT-1 may play an important role in the regulation of proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, migration and invasion of trophoblast cells, and under-expression of MALAT-1 during early placentation may be involved in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. 26735578_High MALAT1 expression is associated with liver neoplasms. 26782531_An elevated MALAT1 expression correlates with large tumor size, advanced tumor stage, and poor prognosis, and might therefore be utilized to evaluate clinical pathological features and prognostic outcome for cancer patients. (Meta-analysis) 26798987_These results suggest that MALAT1 functions to promote cervical cancer invasion and metastasis via induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 26821178_The overexpression of MALAT-1 may be a potential prognostic indicator for various human cancers. 26826711_Natural antisense RNA promotes 3' end processing and maturation of MALAT1 lncRNA. 26848616_Up-regulation of MALAT1 expression is associated with neuroblastoma. 26848980_EZH2 is recruited to the E-cadherin promoter by the long non-coding RNA, MALAT-1 (metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1), where it represses E-cadherin expression 26871474_we found that long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) MALAT1 binds EZH2, suppresses the tumor suppressor PCDH10, and promotes gastric cellular migration and invasion 26884862_MALAT1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells is regulated by DNA methylation. 26887056_Findings suggest MALAT1 increases AKAP-9 expression by promoting SRPK1-catalyzed SRSF1 phosphorylation in CRC cells. These results reveal a novel molecular mechanism by which MALAT1 regulates AKAP-9 expression in CRC cells. 26895470_High MALAT1 expression is associated with multiple myeloma. 26909935_Meta-analysis: Poor overall survival and shortened disease-free, recurrence-free, disease-specific, or progression-free survival can be predicted by high MALAT-1 expression for various cancers. 26917489_Hsa-miR-448 disrupting KDM5B-MALAT1 signalling axis and associated activities in TNBC cells, projects it as a putative therapeutic factor for selective eradication of TNBC cells. 26918449_our data highlight the pivotal role of MALAT1 in breast cancer tumorigenesis 26926567_miR-1 bound both MALAT1 and cdc42 3'UTR directly. Further study showed that MALAT1 induced migration and invasion of breast cancer cells while reduced the level of cdc42. 26935028_observations suggest that MALAT1 promotes hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by increasing nuclear SREBP-1c protein stability. 26938295_Overexpression of Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) caused significant reduction in cell proliferation and invasion in vitro, and tumorigenicity in both subcutaneous and intracranial human glioma xenograft models. 26964565_MALAT1 knockdown reduces reactive gliosis, Muller cell activation, and RGC survival in vivo and in vitro MALAT1-CREB binding maintains CREB phosphorylation by inhibiting PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation, which leads to continuous CREB signaling activation. 26989678_This study demonstrated that the incidence of lymph node metastasis in patients detected with high MALAT-1 expression was higher than that in patients with low MALAT-1 expression in China. 27015363_MALAT1 promotes the initiation and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 27101025_Overexpression of GLI1 through a recurrent MALAT1-GLI1 translocation or GLI1 up-regulation delineates a pathogenically distinct subgroup of plexiform fibromyxomas with activation of the Sonic Hedgehog signalling pathway. 27134488_The knockdown ofmetastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcription 1 increased apoptosis rate of the two cell line and the expression levels of some tumor markers were reduced such as CCND1 and MYC. 27172249_Results reveal a complex expression pattern of various MALAT1 transcript variants in breast tumours. 27191262_Malat1 is overexpressed in gallbladder cancer (GBC) tissue and cells 27191888_In 26 pairs of estrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer samples, MALAT1 expression was significantly up-regulated compared with adjacent normal tissues (P = 0.012). Furthermore, of 204 breast cancer patients, high MALAT1 expression was associated with positive ER (P = 0.023) and progesterone receptor (PR) (P = 0.024) status. 27197265_we show that a ribonucleoprotein complex including the long noncoding RNA MALAT1 and the RNA-binding protein HuR (ELAVL1) binds the CD133 promoter region to regulate its expression 27215451_MALAT1 regulated 153 miRNAs in lung cancer. 27227769_The present study found that MALAT-1 is highly expressed in ovarian tumors. MALAT-1 promotes the growth and migration of ovarian cancer cells, suggesting that MALAT-1 may be an important contributor to ovarian cancer development. 27250026_long non-coding RNA MALAT1 is a metastasis driver in ER negative lymph node negative breast cancer 27259812_Up-regulated MALAT1 promoted the invasion and metastasis of GC, and the increase of EGFL7 expression was a potential mechanism via altering its H3 histone acetylation level 27287256_MALAT1, acting through HIF-1alpha stabilization, is a mediator that enhances glycolysis induced by arsenite. These results provide a link between the induction of lncRNAs and the glycolysis in cells exposed to arsenite, and thus establish a previously unknown mechanism for arsenite-induced hepatotoxicity. 27348442_lncRNA MALAT1 may serve as a potential novel prognostic biomarker in digestive system cancers 27362960_The findings propose that functional polymorphism rs619586A > G in MALAT1 gene plays an important role in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) pathogenesis and may serve as a potential indicator for PAH susceptibility. 27371730_MALAT1 could facilitate the advanced progression of tumors in vivo Our study highlights the new roles of MALAT1 on protumorigenic functioning and anticancer therapy via activating autophagy in pancreatic cancer. 27420766_These data demonstrated that the MALAT1/miR-363-3p/MCL-1 regulatory pathway controls the progression of gallbladder cancer. 27431200_the present study found that MALAT1 was significantly highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues with bone metastasis and in NSCLC cell lines with high bone metastatic ability 27434861_MALAT1 suppressed LPS-induced mRNA accumulation of TNFa and IL-6 without suppressing IL-1beta mRNA production. abnormal expression of MALAT1 was found to be NF-kappaB-dependent 27458156_Results suggest a long non-coding RNA MALAT1/MIR376A/transforming growth factor alpha (TGFA) axis mediates osteosarcoma (OS) cell proliferation and tumor progression. 27466303_MALAT1 upregulation plays an important role in breast cancer (BC) development, and serum MALAT1 level may be a potential tumor marker for BC diagnosis. 27470543_MALAT1 promoted the proliferation and invasion of thyroid cancer cells via regulating the expression of IQGAP1. 27470544_MALAT1 could be a predictor for prognosis of esophageal cancer patients. 27486823_Data suggest that MALAT1 could function as an oncogene in gastric cancer, and high MALAT1 level could serve as a potential biomarker for the distant metastasis of gastric cancer. 27524242_there is a HIF-2alpha-MALAT1-miR-216b axis regulating multi-drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via modulating autophagy. 27564100_MALAT1 acts as a competing endogenous RNA to promote malignant melanoma growth and metastasis by sponging miR-22 27565324_Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed SK-OV-3 cell viability, proliferation, migration and invasion (P |
|
|
11742.213662 |
0.3908942558 |
-1.355150 |
0.023334659 |
3322.912109 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6485.3908933 |
98.4340335 |
16712.8697468 |
175.2159473 |
| ENSG00000251602 |
100507437 |
MTA1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.523730 |
0.3870444616 |
-1.369429 |
0.499630739 |
7.866026 |
0.00503722342448459457081577639314673433545976877212524414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010289152746387020959106806117233645636588335037231445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5336557 |
1.7669637 |
14.4866974 |
2.7121175 |
| ENSG00000251867 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.855308 |
0.3880788070 |
-1.365578 |
0.546293694 |
6.178311 |
0.01293257032288532004660197571865865029394626617431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024251650103644686179427125694019196089357137680053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7257051 |
2.5228855 |
17.6581836 |
4.3434868 |
| ENSG00000253123 |
100507403 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
58.370966 |
2.7102262202 |
1.438413 |
0.284477033 |
25.047841 |
0.00000055925330821322743270917381488982478288107813568785786628723144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002035654458502401094126786629256997684933594428002834320068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
90.0590655 |
14.3285825 |
32.8123544 |
4.1738447 |
| ENSG00000253140 |
105375822 |
LINC02947 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.160614 |
6.9508015739 |
2.797179 |
0.997044659 |
6.875771 |
0.00873720445445765568626139696561949676834046840667724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016930699454876591697471965858312614727765321731567382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1013875 |
6.8049627 |
1.9912632 |
0.9201842 |
| ENSG00000253177 |
101926956 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.868144 |
0.1204332824 |
-3.053694 |
0.387320966 |
76.601750 |
0.00000000000000000209154281168012430271934822422059454752350750139742053407276856091812078375369310379028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000017227216462276023562691951874677639081353410459426442336017260004155104979872703552246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5148449 |
1.4704711 |
46.1760825 |
5.9764656 |
| ENSG00000253187 |
100874323 |
HOXA10-AS |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29729275_HOXA10-AS is upregulated by the transcription factor ELK1. 30132568_Study addressed HOXA10-AS as a regulator of cell proliferation and apoptosis in glioma, and identified HOXA10 as a target of HOXA10-AS. Additionally, the oncogene HOXA10 had an important role in promoting the tumorigenesis of glioma. 34686327_Pan-cancer analysis of non-coding transcripts reveals the prognostic onco-lncRNA HOXA10-AS in gliomas. 35222681_+HOXA10-AS Promotes Malignant Phenotypes of Gastric Cancer via Upregulating HOXA10. 35521747_LncRNA HOXA10-AS functions as an oncogene by binding miR-6509-5p to upregulate Y-box binding protein 1 in gastric cancer. 35858923_Modular scaffolding by lncRNA HOXA10-AS promotes oral cancer progression. |
|
|
33.185705 |
0.2874749268 |
-1.798492 |
0.438525716 |
16.442794 |
0.00005014040610448066868573557819388497591717168688774108886718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000144291751628413864559641321960725690587423741817474365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.4109333 |
3.7781890 |
50.4781673 |
8.6762914 |
| ENSG00000253230 |
157627 |
MIR124-1HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including gene silencing by miRNA; long-term synaptic potentiation; and sensory perception of sound. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
27253412_RNCR3 has an atheroprotective role in atherosclerosis. 31761491_Long Non-coding RNA LINC-PINT and LINC00599 Polymorphisms are Associated With High-altitude Pulmonary Edema in Chinese. 34245766_Association between LINC-PINT and LINC00599 gene polymorphism and the risk of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in the population of northern China. |
|
|
229.736457 |
0.2693846920 |
-1.892260 |
0.377999414 |
23.457823 |
0.00000127682430636271207831280560113240696296088572125881910324096679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004465859422254414249503235573302006855556101072579622268676757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
109.7396789 |
28.2048362 |
411.0201658 |
75.3584325 |
| ENSG00000253293 |
3206 |
HOXA10 |
protein_coding |
P31260 |
FUNCTION: Sequence-specific transcription factor which is part of a developmental regulatory system that provides cells with specific positional identities on the anterior-posterior axis. Binds to the DNA sequence 5'-AA[AT]TTTTATTAC-3'. |
Alternative splicing;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Homeobox;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
In vertebrates, the genes encoding the class of transcription factors called homeobox genes are found in clusters named A, B, C, and D on four separate chromosomes. Expression of these proteins is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. This gene is part of the A cluster on chromosome 7 and encodes a DNA-binding transcription factor that may regulate gene expression, morphogenesis, and differentiation. More specifically, it may function in fertility, embryo viability, and regulation of hematopoietic lineage commitment. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Read-through transcription also exists between this gene and the downstream homeobox A9 (HOXA9) gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]. |
hsa:3206; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; histone deacetylase binding [GO:0042826]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; embryonic limb morphogenesis [GO:0030326]; male gonad development [GO:0008584]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; proximal/distal pattern formation [GO:0009954]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; single fertilization [GO:0007338]; skeletal system development [GO:0001501]; spermatogenesis [GO:0007283]; uterus development [GO:0060065] |
11830466_regulates hematopoietic lineage commitment, enhancing the monocytic differentiation pathway 11875117_beta3-Integrin expression was directly up-regulated by HOXA10 in the endometrium 12145285_SHP1 has a role in myeloid differentiation and is regulated by HoxA10 12215336_its expression is diminished by hydrosalpinx fluid in the endometrium 12482956_In these studies we identify and characterize the regulation of EMX2 by HOXA10. 12493691_FKHR and HOXA10 interact directly and can function cooperatively to stimulate IGFBP-1 promoter activity in endometrial cells 12519859_HOXA10 expression was repressed by testosterone in vitro; endometrium of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome demonstrated decreased HOXA10 mRNA 14512427_HoxA10 represses gene transcription in undifferentiated myeloid cells by interacting with histone deacetylase 2 14607569_Cell-free media that had contained human embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage contain a soluble molecule that induces HOXA10 expression in an endometrial epithelial cell line. 14960020_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14966272_Data report novel nucleoporin 98 fusions with homeobox (HOX)A10, HOXB3 and HOXB4, and describe the results of coexpression of these proteins with the Hox cofactor Meis1 in leukemic induction. 15213244_Results show for the first time that SIRT2 interacts with the homeobox transcription factor, HOXA10. 15236964_HOXA10 estrogen response element(ERE)1 therefore demonstrated ligand specificity distinct from the consensus ERE 15674412_The HOXA10 gene cluster is in T-cell malignancies resulting in deregulated HOXA gene expression. 15731295_HOXA10 and HOXA11 expression increases during the menstrual cycle, increasing drastically in the midluteal phase, at the time of implantation. 15749785_HOXA10 is down-regulated in the process of decidualization 15905361_A direct role of vitamin D in the regulation of HOXA10 in primary human endometrium and myelomonocytic cells was identified. 16098858_The aberrant methylation at HOXA10 may be responsible for the aberrant gene expression in the endometrium of women with endometriosis. 16210632_Cytokine-stimulated pathways regulate HoxA10-mediated repression of the CYBB and NCF2 genes in differentiating myeloid cells and in mature phagocytes during the inflammatory response. 16424022_findings reveal a novel role for HOXA10 deregulation in the progression of endometrial carcinoma by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition 16597639_The expression of HOXA10 is restricted to primordial and early primary follicles. 16647375_However, the diminished expression of HOXA10 in ectopic endometrium might not allow for normal endometrial development and might contribute to the pathogenesis of endometriosis by creating P resistance. 16861351_synergism between NUP98-HOX and wt-Flt3 is the result of the ability of Flt3 to increase proliferation of myeloid progenitors blocked in differentiation by NUP98-HOX fusions, revealing a direct role for wt-Flt3 in the pathobiology of AML. 17173899_HOXA10 is necessary for implantation. 17439948_HoxA10 is a bifunctional protein that is involved in dynamic regulation of multiple aspects of phagocyte phenotype and function 17482600_No DNA sequence differences were found in either patients with congenital absence of uterus and vagina or normal controls in either of the two protein-coding exons of the HOXA10 gene. 17482600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17688409_We sought to understand the role of HOXA10 in megakaryopoiesis better, by investigating its transcriptional regulation by 5' region GATA-1 and Ets-1 sites. 17709569_HOXA10 is differentially expressed in the functionalis and basialis zones of the luteal phase monkey endometrium and is suppressed upon antiprogestin treatment but induced by embryonic stimuli 17828513_Both estrogen and progestin can up-regulate the expression of HOXA10 gene in Ishikawa cells, but RU486 can inhibit the effect and HB-EGF can elevate the expression level of HOXA10 gene. 18190961_Reduction of HOXA10 expression is associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia 18339267_Endometriosis patients with HOXA10 polymorphism were associated with a lower serum cancer antigen-125, a lower American Fertility Society score and less severe obliterated cul-de-sac. 18339267_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18456676_HOXA10 is actively involved in promoting cell proliferation through the regulation of hundreds of genes. 18829447_Calpain5 expression is regulated by HOXA10. Calpain5 expression was decreased in endometriosis likely as a result of decreased HOXA10 expression. 18832725_the vitamin D(3)/Hox-A10 pathway supports MafB function during the induction of monocyte differentiation. 18930214_The dramatic decrease of endometrial HOXA10 in response to copper intrauterine device use may contribute to contraceptive efficacy 19017365_Gynaecologic epithelial histologic type is regulated by WT1 expression through its selective repression of HOX genes. 19022774_constitutive SHP2 activation synergizes with HoxA10 overexpression to accelerate progression to acute myeloid leukemia 19084499_These results indicate that p/CAF is a novel HOXA10 target gene, and HOXA10 promotes human endometrial development, at least in part, through the regulation of p/CAF gene. 19131054_In the endometrium HOXA10 gene expression is increased in response to increasing human chorionic gonadotropin concentration. 19453261_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19727442_HoxA-11 is required for prolactin expression in decidualized embryonic stem cells and turns into an activator when combined with FOXO1A; HOXA-10 is unable to upregulate PRL expression when co-expressed with FOXO1A 19736237_findings suggest that altered expression of HOXA-10 in endometrial stromal cells during the window of implantation may be one of the potential molecular mechanisms of infertility in infertile patients 19778996_Data suggest HOXA10 regulates expression of 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) in endometrium. 19849868_Hoxa10 is expressed in the developing uterus. 19854516_role in embryo implantation and decidualization (Review) 19938081_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19956865_HOXA10 expression could contribute to oral squamous cell carcinoma progression 20009888_HOXA10 is overexpressed in human ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma. 20036708_Induction of HOXA10 in ovarian surface epithelium cells promotes homophilic cell adhesion and prevents anoikis. 20151152_Promoter hypomethylation is an important mechanism for high expression of HOXA10 in human ovarian cancer and may be a potential prognostic factor in ovarian cancer. 20371740_HOXA10 is an essential mediator that regulates expression of endothelin type A receptor in endometrium and decidua in a manner similar to the process seen in vascular smooth muscle cells. 20400074_When endometrial stromal cells from both groups of women were differentiated to decidual phenotype, PROK1 mRNA was up-regulated and PR and HOXA10 mRNA were down-regulated to the same extent. 20457539_No subject with female genital tract anomalies showed a plausible causative mutation in HOX A10 or HOX A11. 20457539_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20463357_homeobox A10(HOXA10) directly and selectively repressed Kruppel-like factor 9 expression in endometrial epithelial cells 20478621_transient knock-down predecidual cells does not influence its ability to subsequently decidualize 20821045_Abnormal endometrial HOXA10 expression is associated with infertility in endometriosis patients. 20935218_Data show an in vitro link between phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated HOXA9/HOXA10 expression, and a drug-resistant, progenitor cell phenotype in MGMT-independent pediatric glioblastoma. 20971605_DNA hypermethylation can be one of the potential molecular mechanisms silencing HOXA10 expression in the midluteal endometrium associated with infertility in women with endometriosis. 21067721_HOXA10 gene expression is decreased in the secretory phase endometrium of women with adenomyosis 21087928_autocrine stimulation of myeloid progenitors by Tgfbeta2 as one mechanism by which HoxA10 expands this population. 21328509_Ectopic expression of NA10 (Nup98-HoxA10) augments erythroid differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. 21454682_HoxA10 influences protein ubiquitination by activating transcription of ARIH2, the gene encoding Triad1 21471217_positive feedback relationship between HoxA10 and Cdx4, which potentially amplified the contribution of either transcription factor to the pathogenesis of AML. 21518888_Several targets of MLL fusions, MEIS1, HOXA7, HOXA9, and HOXA10 are functionally related and have been implicated in leukemias. Each of the four genes was knocked down separately in the precursor B-cell leukemic line RS4;11 expressing MLL-AF4. 21526497_The result suggest that HOXA-10 gene expression in the endometrium during the implantation window may not be altered in patients with idiopathic infertility. 21576276_results indicate that the coding regions of INHBA, SFRP4 and HOXA10 do not harbour mutations responsible for linkage to endometriosis in the families studied 21670700_The expression of HOXA10 was deregulated in endometrial carcinomas and up-regulated by sex hormones. 21757506_Spastin was identified as a novel component of the HOXA10 transcriptional complex in Ishikawa nuclear extracts. 21900391_mutation of HOXA10 gene may contribute to the development of Mullerian duct anomalies; it is an important transcription factor in reproductive tract development 21956427_HOXA10 was aberrantly regulated in the endometrium of women with endometriosis by both miR135a and miR135b. 22279148_regulates FKBP4 during decidualization 22411957_HOXA10 expression was associated with GC with the intestinal mucin phenotype. 22493287_found that increased Fgf2 production by HoxA10-overexpressing myeloid progenitor cells induced a phosphoinositol 3-kinase-dependent increase in beta-catenin protein 22915150_The level of HOXA10 decreases in the eutopic endometrium of patients with endometriosis. 23038246_a molecular mechanisms through which increased expression of HoxA10 increases Cdx4 expression by direct CDX4 activation and by Fgf2-induced beta-catenin activity. This results in Cdx4-induced HoxA10-expression, creating a positive feedback mechanism 23051705_HOXA10 has been found to be methylated in all hereditary breast cancer patients analyzed but never in healthy subjects. 23092574_Compared with the negative control and untreated groups, mRNA level of HOXA10 decreased by (92.3+/-1.3)%, protein levels decreased by 91.1%, and the inhibition rate of U937 cells [(43.9+/-0.7)%] increased in the interference group 23108137_We found that MLL directly activates the Homeobox gene HOXA10 in human glioblastoma 23376215_Rare DNA sequence variations in the HOXA10 gene could contribute to the misdevelopment of female internal genitalia. 23412855_There are complex etiopathogenic mechanisms for endometriosis between INFG and HOXA10. 23815210_Endometrial cancer tissue displays significantly higher methylation status in HOXA10 gene promoter than normal tissue. 23888944_this study demonstrated that an increased HOXA10 expression in human ovarian cancer is a result of the co-activation of HOXA10 gene promoter's hypomethylation and the binding of transcription factor WT1. 23979130_Lower expression of HOXA10 is associated with endometriosis-associated infertility. 24032603_This study documented significantly higher HOXA10 promoter methylation levels in women with ovarian endometriomas than in healthy controls during the mid-luteal phase. 24037888_HOXA10-PCAF association impairs embryo implantation by inhibiting ITGB3 protein expression in endometrial epithelial cells. 24222951_Co-activation of miR-196b and HOXA10 characterized a poor-prognosis subgroup of patients with gastric cancer. 24464212_HOXA10 promotes cell invasion and MMP-3 expression of pancreatic cancer cells via TGFbeta2-p38 MAPK pathway. 24565841_These results demonstrate that the HOXA10-mediated expression of MMP-26 promotes embryo adhesion during the process of embryonic implantation. 24607788_Inhibition of HOXA10 expression with miR-135a mimics and HOXA10 siRNA resulted in cell apoptosis with concomitant enhancement of caspase-3, increase of p53 expression and reduction of Bcl-2 expression, and also suppressed cell growth and adhesion. 24903309_these results suggested that the miR-135a-VLDLR-p38 axis may contribute to gallbladder cancer cell proliferation 24943991_Expression of HOXA10 and p21 gene decreased in endometrial cancer, and the expression level of HOXA10 was correlated with cancer grade. 24951955_regulatory mechanism of HoxA10 in prostate cancer 24963168_The HOXA10 gene is more methylated in the eutopic endometrium of patients with endometriosis. 25120782_The regulatory mechanism of miR-218 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells was acting through PTEN/AKT/PI3K pathway and possibly associated with HoxA10. 25217304_HOXA10 is expressed in rectosigmoid endometriosis, where it likely imparts the de novo identity of endometriotic lesions. 25307539_Data show that recruitment of MLL1 (mixed lineage leukaemia histone methylase 1) to the homeobox-containing gene HOXA10 EREs (estrogen response elements) is mediated via ERalpha (estrogen receptor alpha). 25500095_miR-494 repressed the expression of HOXA10 and also reduced the proliferation of oral cancer cells. These data give more evidence of the role of miR-494 as a tumor suppressor miRNA in oral cancer. 25622821_the CpG island of the HOXA10 alternative promoter appears to escape hypermethylation in the HOX-high glioblastoma. 25757424_The results showed overexpression of HOXA10 mRNA and protein in Ishikawa cell. 26056923_Peri-implantation HOXA-10 mRNA expression is increased following laparoscopic endometrioma resection. 26097543_HOXA10 is overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and its expression is functionally associated with several important biological processes related to oral tumorigenesis, such as proliferation, migration and invasion. 26151663_confirmed that HOXA10 promoted epithelialmesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells 26478432_Promoter activity of HOXA10 lies in 5.3-6.1 kb upstream of protein coding region.CTCF negatively regulates HOXA10 expression in breast cancer cells.CTCF flanks important promoter element of HOXA10. 26552644_The combinatory expression of HOXA10 and CD44 was correlated with poor gastric cancer prognosis. 26552702_Regulated HOXA10 and HOXA11 expression is necessary for endometrial receptivity; decreased HOXA10 or HOXA11 expression leads to decreased implantation rates. Alternation of HOXA10 and HOXA11 expression has been identified as a mechanism of the decreased implantation associated with endometriosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome, leiomyoma, polyps, adenomyosis, and hydrosalpinx. 26840046_Reduced expression of HOXA10 is associated with Hydrosalpinx. 26865543_The HOXA10 gene in women with endometriosis was hypomethylated compared to controls. 27035504_HOXA10 was expressed at a high level in the K562/ADM cells, and knockdown of HOXA10 enhances the sensitivity of the K562/ADM cells to cytotoxic killing by the therapeutic drug, ADR, as a result of the increased intracellular accumulation of ADR. 27108669_The results demonstrated that mutation in HOXA10 gene contributes to the pathogenesis of cryptorchidism, but may not be a common cause. 27793380_Endometrial expression of HOXA10 and E-cadherin are reduced in women with recurrent implantation failure and recurrent miscarriage. 28074437_To summarize, significant differential methylation of HOXA10 and COMT promoter regions was found between the ectopic and eutopic endometrial tissues. This is the first study investigating the methylation of HOXA10 and COMT genes and their linkage to endometriosis in Chinese patients. 28372536_We conclude that the expression patterns of HoxA10, HoxA11, and HoxA13 and their actions in regulating CAP genes in the uterus create regionalized myometrium phenotypes in women that may be important to control regionalized myometrium contractility for maintaining pregnancy. 28384324_using both knockdown and knockout approaches we show that Hottip expression is required for activation of the 5' Hoxa genes (Hoxa13 and Hoxa10/11) and for retaining Mll1 at the 5' end of Hoxa. Moreover, we demonstrate that artificially inducing Hottip expression is sufficient to activate the 5' Hoxa genes and that Hottip RNA binds to the 5' end of Hoxa 28520923_These results suggest that downregulation of HOXA10 in the decidual cells promotes the expression of a cascade in the trophoblast cells, leading to an increase in matrix metalloproteinases to facilitate invasion. 28674422_Our data suggest that loss of DLX5, TLX1 and HOXA10 expression in late gestation is required for proper placental differentiation and function. 28748001_Results show that a combination of HOXA9 and HOXA10 promoter methylation markers is significantly associated with the prognosis of breast cancer patients a subtype-independent manner. 29039487_Results show that the inhibition of HOXA10 in DAOY cell line led to increased in vitro cell migration while in vitro cell proliferation or in vivo tumorigenic potential were unaffected. This suggests that HOXA10 plays a role in migration events. 29453320_Results demonstrated that HOXA10 is upregulated in gastric cancer and may play a vital role in human gastric carcinogenesis, patients' prognosis, and clinical outcome. HOXA10 promoter hypomethylation mediates HOXA10 overexpression in gastric cancer. 29592776_Study shows that the HOXA10 gene, as a homeodomain transcription factor, is dynamically expressed in the endometrium, and peak expression occurs in the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle. Study focused on the epigenetic role of the HOXA10 gene related to clinical pathophysiology of endometriosis. 29658437_HOXA10 protein and mRNA were decreased in ovarian endometriomas compared with eutopic endometria of women with endometriosis and normal endometria. Moreover, HOXA10 was found to have a significant negative correlation with autophagy. 29845297_the present study demonstrated that miR135a serves as a tumor suppressor in AML by targeting HOXA10, and miR135a may be a promising prognostic biomarker for AML patients. 29870276_Significant HOXA10 overexpression in CRC may be a potential biomarker indicating poor prognosis and 5-FU resistance 30132568_Study addressed HOXA10-AS as a regulator of cell proliferation and apoptosis in glioma, and identified HOXA10 as a target of HOXA10-AS. Additionally, the oncogene HOXA10 had an important role in promoting the tumorigenesis of glioma. 30309386_Methylation analysis of HOXA10 regulatory elements of patients with endometriosis showed no difference from control subjects. 30545354_HOXA10 was the most highly expressed HOX transcription factor in liver cancer and liver TICs. LncHOXA10 drove the transcriptional activation of HOXA10. This work revealed the important role of HOX transcription factor in liver TIC self-renewal and added a new layer for liver TIC regulation. 30562617_HOXA-10 gene expression in women with endometriosis is significantly lower than in those without. Decreased expression HOXA-10 may be related with endometriosis-associated infertility. Severe endometriosis cases express significantly lower levels of HOXA-10 gene than moderate cases. 30614022_IHC profiling of HOXA10 revealed inverse correlations between HOXA10 expression and Gleason pattern, Gleason score, and pathological stage (P |
ENSMUSG00000000938 |
Hoxa10 |
127.449969 |
0.3069312505 |
-1.704013 |
0.167380556 |
104.732011 |
0.00000000000000000000000139823754374684288637213565804320458861673323492986537469731936290853052673455181320605333894491195678710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000014804868110260690119800699760857741065813981780808005545225825060409730049570953269721940159797668457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.5015317 |
6.5525719 |
208.5826158 |
13.6415025 |
| ENSG00000253320 |
|
MAILR |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56.696565 |
0.4911762931 |
-1.025687 |
0.279337011 |
13.214951 |
0.00027772479920005262599841389103971778240520507097244262695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000712040652456622630804561335793323451071046292781829833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.5673212 |
7.9743174 |
84.9614729 |
11.7422539 |
| ENSG00000253368 |
388610 |
TRNP1 |
protein_coding |
Q6NT89 |
FUNCTION: DNA-binding factor that regulates the expression of a subset of genes and plays a key role in tangential, radial, and lateral expansion of the brain neocortex. Regulates neural stem cells proliferation and the production of intermediate neural progenitors and basal radial glial cells affecting the process of cerebral cortex gyrification. May control the proliferation rate of cells by regulating their progression through key cell-cycle transition points (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Cell cycle;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable DNA binding activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including cerebellar cortex morphogenesis; neural precursor cell proliferation; and regulation of cell population proliferation. Predicted to be active in nucleus. Predicted to colocalize with euchromatin. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388610; |
euchromatin [GO:0000791]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cerebellar cortex morphogenesis [GO:0021696]; neural precursor cell proliferation [GO:0061351]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127] |
23622239_TRNP1 expression levels exhibit regional differences in the cerebral cortex of human fetuses, anticipating radial or tangential expansion. |
ENSMUSG00000056596 |
Trnp1 |
14.660718 |
0.1231504682 |
-3.021506 |
0.526012422 |
42.719387 |
0.00000000006318299144114224140833190558464555440509879957744487910531461238861083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000331143198606669930118201181822512255137347381150902947410941123962402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9797020 |
1.0856512 |
24.3434089 |
3.9237441 |
| ENSG00000253522 |
107075116 |
MIR3142HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31513017_Polymorphisms in MIR3142HG are associated with susceptibility to Glioma. 34338955_MIR3142HG promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating miR-450b-5p/HMGB1 axis. |
|
|
250.796269 |
5.9788459723 |
2.579867 |
0.750423563 |
10.341449 |
0.00130075893354055210221487115518357313703745603561401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002974775621174240766014795767091527523007243871688842773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
397.1896933 |
180.8627791 |
67.4873618 |
22.0726589 |
| ENSG00000253549 |
|
CA3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.336775 |
0.1757109692 |
-2.508724 |
0.328212125 |
59.677712 |
0.00000000000001117348053767902072089143141835205922346538776751545540832921687979251146316528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000074827846069030104570121943372349235715072258978697306019967072643339633941650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
11.0168557 |
2.3433280 |
63.3223825 |
8.2113780 |
| ENSG00000253671 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.910061 |
0.0499320308 |
-4.323891 |
0.535919205 |
95.271042 |
0.00000000000000000000016602403147626872781956070100127632231074800988852887687061208980832116566261902335099875926971435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000001610062223777744091369402174672781267924226977661508355521135377186325854381721001118421554565429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5478782 |
0.9815754 |
51.4779617 |
8.2319606 |
| ENSG00000253831 |
440695 |
ETV3L |
protein_coding |
Q6ZN32 |
FUNCTION: Transcriptional regulator. {ECO:0000250}. |
DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Predicted to enable DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific. Predicted to be involved in cell differentiation and regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Predicted to be active in nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440695; |
nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
|
ENSMUSG00000118505 |
Etv3l |
40.409055 |
28.3191806085 |
4.823708 |
0.487169321 |
168.524213 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000001554178971399424591324032280512090610372761042649658461230293582044960315429983392446933881687193279574898951977957040071487426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000250981199320082171235111917934911474682587929390413372197074044396884012991207323238908349344170913008955636769314878620207309722900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
80.0853162 |
26.5101824 |
2.8523256 |
0.9038818 |
| ENSG00000253858 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.954057 |
0.2728256032 |
-1.873949 |
0.579065322 |
10.907259 |
0.00095788178715321256519871218060302453523036092519760131835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002236052859957087402681397136916530143935233354568481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5229108 |
1.4044771 |
13.0512246 |
3.0304338 |
| ENSG00000253968 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.264471 |
0.1961471514 |
-2.349992 |
0.847103312 |
6.651796 |
0.00990559273131604196838129183788623777218163013458251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019005140870170904310310078244583564810454845428466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7976920 |
4.4028019 |
39.8959974 |
15.7058554 |
| ENSG00000254054 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.245989 |
0.2541952948 |
-1.975991 |
0.371221345 |
29.861758 |
0.00000004639745360199921694627578166135462023333957404247485101222991943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000188605457219914188534543291603240433573773771058768033981323242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7109981 |
2.4577395 |
38.4920206 |
5.7544728 |
| ENSG00000254087 |
4067 |
LYN |
protein_coding |
P07948 |
FUNCTION: Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase that transmits signals from cell surface receptors and plays an important role in the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses, hematopoiesis, responses to growth factors and cytokines, integrin signaling, but also responses to DNA damage and genotoxic agents. Functions primarily as negative regulator, but can also function as activator, depending on the context. Required for the initiation of the B-cell response, but also for its down-regulation and termination. Plays an important role in the regulation of B-cell differentiation, proliferation, survival and apoptosis, and is important for immune self-tolerance. Acts downstream of several immune receptors, including the B-cell receptor, CD79A, CD79B, CD5, CD19, CD22, FCER1, FCGR2, FCGR1A, TLR2 and TLR4. Plays a role in the inflammatory response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Mediates the responses to cytokines and growth factors in hematopoietic progenitors, platelets, erythrocytes, and in mature myeloid cells, such as dendritic cells, neutrophils and eosinophils. Acts downstream of EPOR, KIT, MPL, the chemokine receptor CXCR4, as well as the receptors for IL3, IL5 and CSF2. Plays an important role in integrin signaling. Regulates cell proliferation, survival, differentiation, migration, adhesion, degranulation, and cytokine release. Down-regulates signaling pathways by phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIM), that then serve as binding sites for phosphatases, such as PTPN6/SHP-1, PTPN11/SHP-2 and INPP5D/SHIP-1, that modulate signaling by dephosphorylation of kinases and their substrates. Phosphorylates LIME1 in response to CD22 activation. Phosphorylates BTK, CBL, CD5, CD19, CD72, CD79A, CD79B, CSF2RB, DOK1, HCLS1, LILRB3/PIR-B, MS4A2/FCER1B, SYK and TEC. Promotes phosphorylation of SIRPA, PTPN6/SHP-1, PTPN11/SHP-2 and INPP5D/SHIP-1. Mediates phosphorylation of the BCR-ABL fusion protein. Required for rapid phosphorylation of FER in response to FCER1 activation. Mediates KIT phosphorylation. Acts as an effector of EPOR (erythropoietin receptor) in controlling KIT expression and may play a role in erythroid differentiation during the switch between proliferation and maturation. Depending on the context, activates or inhibits several signaling cascades. Regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and AKT1 activation. Regulates activation of the MAP kinase signaling cascade, including activation of MAP2K1/MEK1, MAPK1/ERK2, MAPK3/ERK1, MAPK8/JNK1 and MAPK9/JNK2. Mediates activation of STAT5A and/or STAT5B. Phosphorylates LPXN on 'Tyr-72'. Kinase activity facilitates TLR4-TLR6 heterodimerization and signal initiation. Phosphorylates SCIMP on 'Tyr-107'; this enhances binding of SCIMP to TLR4, promoting the phosphorylation of TLR4, and a selective cytokine response to lipopolysaccharide in macrophages (By similarity). Phosphorylates CLNK (By similarity). Phosphorylates BCAR1/CAS and NEDD9/HEF1 (PubMed:9020138). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P25911, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10574931, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10748115, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10891478, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11435302, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11517336, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11825908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14726379, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15795233, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16467205, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17640867, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17977829, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18056483, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18070987, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18235045, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18577747, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18802065, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19290919, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20037584, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7687428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9020138}. |
3D-structure;Adaptive immunity;Alternative splicing;ATP-binding;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Golgi apparatus;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Inflammatory response;Innate immunity;Kinase;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Palmitate;Phosphoprotein;Proto-oncogene;Reference proteome;SH2 domain;SH3 domain;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a tyrosine protein kinase, which maybe involved in the regulation of mast cell degranulation, and erythroid differentiation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]. |
hsa:4067; |
adherens junction [GO:0005912]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; endocytic vesicle membrane [GO:0030666]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; Golgi apparatus [GO:0005794]; integrin alpha2-beta1 complex [GO:0034666]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; mitochondrial crista [GO:0030061]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; perinuclear region of cytoplasm [GO:0048471]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynaptic density [GO:0014069]; postsynaptic specialization, intracellular component [GO:0099091]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; ephrin receptor binding [GO:0046875]; gamma-tubulin binding [GO:0043015]; glycosphingolipid binding [GO:0043208]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004715]; phosphoprotein binding [GO:0051219]; phosphorylation-dependent protein binding [GO:0140031]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004713]; scaffold protein binding [GO:0097110]; SH3 domain binding [GO:0017124]; signaling receptor binding [GO:0005102]; transmembrane transporter binding [GO:0044325]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; adaptive immune response [GO:0002250]; B cell homeostasis [GO:0001782]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; C-X-C chemokine receptor CXCR4 signaling pathway [GO:0038159]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus [GO:0006974]; cellular response to extracellular stimulus [GO:0031668]; cellular response to heat [GO:0034605]; cellular response to retinoic acid [GO:0071300]; dendritic cell differentiation [GO:0097028]; ephrin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048013]; erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0030218]; Fc receptor mediated inhibitory signaling pathway [GO:0002774]; Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway [GO:0002431]; Fc-epsilon receptor signaling pathway [GO:0038095]; Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis [GO:0038096]; growth hormone receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0060397]; hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation [GO:0002244]; histamine secretion by mast cell [GO:0002553]; immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002768]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; leukocyte migration [GO:0050900]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; negative regulation of B cell proliferation [GO:0030889]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070373]; negative regulation of immune response [GO:0050777]; negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus [GO:0002862]; negative regulation of intracellular signal transduction [GO:1902532]; negative regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043407]; negative regulation of mast cell proliferation [GO:0070667]; negative regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation [GO:0002762]; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001933]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway [GO:0034136]; negative regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034144]; neuron projection development [GO:0031175]; oligodendrocyte development [GO:0014003]; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0018108]; platelet degranulation [GO:0002576]; positive regulation of aspartic-type endopeptidase activity involved in amyloid precursor protein catabolic process [GO:1902961]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of dendritic cell apoptotic process [GO:2000670]; positive regulation of Fc receptor mediated stimulatory signaling pathway [GO:0060369]; positive regulation of glial cell proliferation [GO:0060252]; positive regulation of mast cell proliferation [GO:0070668]; positive regulation of neuron projection development [GO:0010976]; positive regulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation [GO:0070447]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity [GO:0043552]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of stress-activated protein kinase signaling cascade [GO:0070304]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of B cell apoptotic process [GO:0002902]; regulation of B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050855]; regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033628]; regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001817]; regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070372]; regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045646]; regulation of mast cell activation [GO:0033003]; regulation of mast cell degranulation [GO:0043304]; regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090025]; regulation of platelet aggregation [GO:0090330]; regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001932]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; response to amino acid [GO:0043200]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; response to carbohydrate [GO:0009743]; response to hormone [GO:0009725]; response to insulin [GO:0032868]; response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0014070]; response to sterol depletion [GO:0006991]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; signal transduction [GO:0007165]; stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002223]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; tolerance induction to self antigen [GO:0002513]; toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway [GO:0034142]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
11826756_The Lyn/CD22/SHP-1 pathway is important in autoimmunity. Naive and tolerant B-cells differ in their calcium signaling in response to antigenic stimulation. 11877294_Activation of Lyn kinase is necessary for proliferation of CD45+ myeloma cells by IL-6. 11943772_Association of Fyn and Lyn with the proline-rich domain of glycoprotein VI regulates intracellular signaling 12393728_CD45 tyrosine phosphatase inhibits erythroid differentiation of umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells associated with selective inactivation of Lyn. 12495897_role in transduction of the TPO proliferative signal in a megakaryocyte cell line 12509383_STI571 resistance is acquired through selection of BCR-ABL independent cells that overexpress src-related kinase LYN 12642697_Lyn tyrosine kinase inhibits nuclear export of the p53 tumor suppressor in breast neoplasms 12882960_SHIP-1 and Lyn have roles in the negative regulation of M-CSF-R-induced Akt activation 14662334_Two Src kinases are selectively activated by TPO signaling in primary megakaryocytes, Fyn and Lyn, but only Fyn expression is significantly upregulated during MK differentiation, suggesting variable gene regulation. 14969582_SRC kinases LYN & HCK let engaged b2 integrins form focal-adhesion-like structures needed for stable shear-resistant PMN adhesion. SRC-dependent outside-in signalling is needed for integrin adhesiveness triggered by a classical chemoattractant like IL-8. 15166241_SHIP1 and Lyn have roles as negative regulators of integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) adhesive and signaling function 15173188_The kinase domain of Lyn plays a role in Lyn trafficking besides catalysis of substrate phosphorylation. 15190072_LYN and FYN are downregulated by CBL in osteoblast differentiation induced by constitutive FGFR2 activation 15262430_LYN amplification is associated with malignant mixed tumor of salivary gland 15501776_role in the regulation of lipopolysaccharide priming in neutrophils 15665117_Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K1 protein-mediated constitutive Lyn kinase activation in K1 lymphoma cells is crucial for the production of VEGF and NF-kappaB activation 15744341_The LYN is present in the majority of mediastinal B cell lymphomas. 15795233_HS1 Tyr phosphorylation catalyzed by Syk and Lyn plays a crucial role in the translocation of the protein to the membrane and is involved in the cytoskeleton rearrangement triggered by thrombin in human platelets 16320343_altered Lyn expression in B cells from a majority of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus 16467205_in hematopoietic cells stimulated via CXCR4, Lyn kinase is a positive regulator of cell movement while negatively regulating adhesion to stromal cells by inhibiting the ICAM-1-binding activity of beta(2) integrins 16568084_LYN can short-circuit conventional B cell receptor signaling in SLP65-deficient B cell lymphoma cells and thereby promote activation of survival and proliferation-related molecules 16597828_A key result is that the conformational transition involves a switch in an electrostatic network of six polar residues between the active and the down-regulated conformations. The exchange between interactions links the three main motions of the CD. 16687414_lysophosphatidic acid-induced IL-8 secretion is partly dependent on EGFR transactivation regulated by PKCdelta-dependent activation of Lyn kinase and MMPs and proHB-EGF 16791881_Activation of Lyn and its interaction with rafts and toll-like receptor 2 play an important role in the initial stages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa interaction with host lung cells. 17230226_FLT3/ITD (internal tandem duplication)specifically associates with Lyn, phosphorylating Lyn in vivo. FLT3/ITD receptors bind Lyn with a higher affinity than wild-type in vitro. This is relative to the intensity of tyrosyl phosphorylation of the receptor. 17233630_Hic-5 and paxillin function as negative feedback regulators of Src family kinases in aggregated platelets 17692281_Thus, these results suggest that endogenous c-Src, c-Yes, and Lyn are differentially activated through Cdc2 activation during M phase. 17701175_Lyn is weakly phosphorylated in normal B cells, but strongly phosphorylated in myeloma B cells. 18070987_role in control of proliferation and survival in most B-non-Hodgkin lymphomas 18086677_Thus the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of caspase-8, mediated by Lyn and SHP-1, respectively, represents a novel, dynamic post-translational mechanism for the regulation of neutrophil apoptosis 18174230_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18235045_Lyn activation is BCR-ABL independent, it is complexed with the Gab2 and c-Cbl adapter/scaffold proteins, and it mediates persistent Gab2 and BCR-ABL tyrosine phosphorylation in the presence or absence of imatinib. 18272395_A crystal of the mono-phosphorylated sample was diffracted to 3.2A 18363812_P-selectin-PSGL-1-induces TF and IL8 expression through Lyn phosphorylation, and part of the inhibitory effect of IL10 depends on reduced phosphorylation 18457834_These results suggest that Src-family tyrosine kinases, including c-Src and Lyn, are involved in formation of the cortical actin cap, which may serve as a platform of tyrosine phosphorylation signaling. 18577747_LYN activation was independent of BCR-ABL in cells from imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia patients (CML); LYN kinase may be involved in imatinib resistance in CML patients with mutation-negative BCR-ABL 18579528_PLSCR1 is a novel amplifier of FcepsilonRI signaling that acts selectively on the Lyn-initiated LAT/phospholipase Cgamma1/calcium axis, resulting in potentiation of a selected set of mast cell responses 18768392_Geldanamycin-induced Lyn dissociation from aberrant Hsp90-stabilized cytosolic complex is an early event in apoptotic mechanisms in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 18802065_Lyn is an important part of a regulatory network that couples SDF-1/CXCR4-induced monocyte chemotactic signals with down-regulation of beta2 integrin/LFA-1-dependent adhesion to activated brain microvascular endothelial cells. 18817770_These results suggest that Lyn being imported into and rapidly exported from the nucleus preferentially accumulates in the nucleus by inhibition of the kinase activity and lipid modification. 19086053_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19234487_Lyn is downstream of Jak2, and Jak2 maintains activated Lyn kinase in CML through the SET-PP2A-Shp1 pathway. 19258394_These results suggest that SFK trafficking is specified by the palmitoylation state in the SH4 domain. 19290526_B-CLL & CML overexpressed Lyn versus de novo ALL, de novo AML & Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms. AML secondary to myelodysplastic syndromes lacked Lyn. Lyn overexpression in B-CLL was associated with microRNA-337-5p down-regulation. 19340007_The caspase-cleaved form of Lyn exerts a negative feedback on imatinib-mediated CML cell apoptosis that is entirely dependent on its kinase activity and likely on the BCR-ABL pathway. 19369946_Combined European-derived population, consisting of 2463 independent cases and 3131 unrelated controls, shows significant association with rs6983130 in a female-only analysis with 2254 cases and 2228 controls. 19369946_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19492092_These results highlight a new role for Lyn as an effector of EpoR in controlling Kit expression. 19590497_Analysis of Lyn expression in human skin biopsies of psoriatic patients led to the detection of Lyn cleavage product whose expression correlates with the activation of caspase 1. 19619611_Results provide a novel role of the Lyn catalytic domain in the Golgi targeting of newly synthesized Lyn in a manner independent of its kinase activity. 19641380_Four genes, PCSK1, (P=0.008), EGFR,(P=0.003), PAX4,(P=0.008), and LYN,(P=0.002) consistently yielded statistical evidence for association with longevity. 19710703_Identification of a novel TEL-Lyn fusion gene in primary myelofibrosis. 19893451_Study identified the previously reported pathogenic mutation of NTRK3 in a KRAS/BRAF wild-type tumor and 2 somatic mutations in the Src family of kinases (YES1 and LYN) that would be expected to cause structural changes. 19965664_Data show that RTX treatment results in a time-dependent inhibition of the BCR-signaling cascade involving Lyn, Syk, PLC gamma 2, Akt, and ERK, and calcium mobilization. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20079716_the activation of the Lyn-phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase-Akt cascade suppressed the expression of a tumor-suppressor and pro-apoptotic protein, p53, and supported the survival and proliferation of myeloma cells. 20189992_Lyn stimulates platelet secretion by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-nitric oxide (NO)-cyclic GMP pathway and also provide an explanation why Lyn can both stimulate and inhibit platelet activation 20215510_Findings define a prognostically relevant EMT signature in breast cancer and identify LYN as a mediator of invasion/ 20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20546612_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20561033_In the membrane environment of ALK+ lymphoma rafts, where the glycosphingolipid to signaling protein ratio is higher than in B-NHL rafts, the Lyn activity is suboptimal and does not allow the formation of an efficient Lyn-Cbp/PAG signalosome 20605918_Results suggest that initiation of Golgi export of Lyn involves association of ACSL3 with the Lyn C-lobe, which is exposed to the molecular surface in an open conformation. 20679348_ADAM17-mediated activation of Lyn/Akt maintains the viability of U937 cells and that suppression of the pathway is responsible for PILP-1-induced apoptosis. 20693279_Lyn-dependent regulation of miR181 is a novel mechanism of regulating Mcl-1 expression and cell survival. 20962850_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21106848_Lyn contributes to the upregulation of the Ras-ERK-MAP kinase 1/2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt cascades, as well as the increased leukotriene C4 release observed in response to formylated tripeptide F-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLP) in primed eosinophils. 21345943_Lyn coimmunoprecipitates with the interleukin-2 beta receptor and JAK3 proteins in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected T-cells. 21513978_PTPIP51 is phosphorylated by Lyn and c-Src kinases lacking dephosphorylation by PTP1B in acute myeloid leukemia. 21628423_describe a Lyn-dependent mechanism for promoting localized integrin activation and establishing adhesion sites at the leading edge to allow neutrophils to move forward in the chemoattractant gradient. 21730355_an oncogenic signaling mediated by Lyn and Syk can bypass the need of Bcr-Abl in CML cells 21749309_Data show that a higher percentage of classical Hodgkin lymphoma cases expressing Lyn, Fyn and Syk compared with previous reports. 21918188_Lyn is a likely candidate to be the kinase required for myeloid differentiation factor-2 tyrosine phosphorylation following exposure to lipopolysaccharide 21951684_In chorea acanthocytosis red blood cells, band 3 Tyr phosphorylation by Lyn was independent of the canonical Syk-mediated pathway. 21978158_Lyn kinase blockage down-regulates TLR9-induced cytokines, but up-regulates non-canonical TLR3-induced cytokines in THP1 cells exposed to cytomegalovirus. 22246800_The role of the Src family kinase Lyn in the immunomodulatory activities of cathelicidin peptide LL-37 on monocytic cells 22393415_the activation of Hck, Lyn and c-Src by Nef is highly conserved among all major clades of HIV-1 22430206_our findings demonstrate that Yes and Lyn phosphorylate EGFR at Y1101, which influences EGFR nuclear translocation in this model of cetuximab resistance. 22490227_findings show that Lyn mediates tumor progression of EGFRvIII-expressing head and neck squamous cell carcinomas 22731636_Lyn is involved in CD24-induced ERK1/2 activation in colorectal cancer. 22845063_The interaction between Lyn and FcepsilonRIbeta is indispensable for FcepsilonRI-mediated human mast cell activation. 22895079_Oridonin inhibiting activations of LYN (one of SRC family kinases) and ABL and their downstream Akt/mTOR, Raf/MEK/ERK and STAT5 pathways. 23039362_Associations between treatment response and Lyn, Syk, PLCgamma2 and ERK were not found. 23223229_The Dok-3/Grb2 protein signal module attenuates Lyn kinase-dependent activation of Syk kinase in B cell antigen receptor microclusters 23378338_results define a novel signaling pathway in basal breast cancer involving Lyn and SgK269 that offers clinical opportunities for therapeutic intervention 23396948_The E613R allele of CD45 produces neither a pure hypomorphic nor a hypermorphic variant of the phosphatase; rather, it appears to alter CD45 substrate selectivity for specific Src-family kinases. 23450709_These results reveal that elevated expression of miR-30a is responsible for the reduction in levels of Lyn in B cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, suggesting that miR-30a plays an important role in B cell hyperactivity. 23583449_these data suggest a novel role for Lyn in erythroid cell survival. 23696637_CBL linker region and RING finger mutations lead to enhanced granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) signaling via elevated levels of JAK2 and LYN. 23866081_Lyn, a Src family kinase, regulates activation of epidermal growth factor receptors in lung adenocarcinoma cells. 23896410_Data indicate that combined treatment using SFK (LYN, HCK, or FGR) and c-KIT inhibitor dasatinib dasatinib and chemotherapy provides a novel approach to increasing p53 activity and enhancing targeting of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) stem cells. 23918783_These data demonstrate a mechanism whereby Fyn and Lyn, redundantly mediate anticryptococcal killing by inducing the polarization of perforin-containing granules to the NK cell-cryptococcal synapse. 23949219_MBNL142-43 bind the Src-homology 3 domain of Src family kinases (SFKs) via their proline-rich motifs. 23975833_Lyn gene expression levels increase with primary glioma tumor grade and inversely correlate with patient survival. TWEAK protein promotes glioblastoma cell chemotaxis via Lyn activation. 24091144_Our data suggest that the LYN/PTEN expression ratio may be a sensitive monitor of disease progression in unmutated CML patients under imatinib or nilotinib treatment. 24108461_in contrast to c-Src and Yes, which increase vascular permeability in response to stimuli, Lyn stabilizes endothelial junctions through phosphorylation of FAK. 24217950_An EphA4-Lyn pathway was identified that is essential for the metabolism of amyloid precursor protein. 24407241_PSTPIP2 dysregulation contributes to aberrant terminal differentiation in GATA-1-deficient megakaryocytes by activating LYN. 24469048_molecular or pharmacologic inhibition of the Lyn-PI3K/AKT pathway, markedly increased the sensitivity of the otherwise chemoresistant Cbl mutant-JMML cells to chemotherapeutic agents currently used in the treatment of JMML patients 24686085_Lyn kinase activity is important for CD38-associated signaling that may drive all-trans retinoic acid-induced differentiation. 25104351_Cell detachment-induced Lyn activation through the change in the membrane distribution of Lyn plays an important role in survival of suspension cells. 25173936_Lyn tyrosine kinase promotes silencing of ATM-dependent checkpoint signaling during recovery from DNA double-strand breaks. 25401474_These results suggest that LYN mutations mediate escape from antiestrogens in a subset of ER(+) breast cancers. 25418321_interaction between LacCer and Lyn in the lipid rafts of neutrophil-like cells 25817574_Suggest an interrelated kinase module involving c-Raf/PI3K/Lyn and perhaps Fgr functions in a nontraditional way during retinoic acid-induced maturation or during rescue of RA induction therapy using inhibitor co-treatment in RA-resistant leukemia cells. 25823815_Diminished Lyn levels impair Claudin-2 expression in breast cancer cells. The Lyn-selective kinase inhibitor, Bafetinib (INNO-406), reduces Claudin-2 expression and suppresses breast cancer liver metastasis. 25965880_Demonstrate role for CBL in the control of AXL/SYK/LYN network mediating resistance to nilotinib treatment in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. 25967238_Fyn, but not Lyn, was required for complete Pyk2 phosphorylation by thrombin. 26055819_positively regulates NF-kappaB transactivation through the phosphorylation of the p110 subunit of PI 3-kinase 26308013_This study showed an interdependence between ROS generation and lipid rafts and Lyn relocation leading the cells to undergo the successive acrosome reaction. 26457672_LPS tolerance interferes with TLR4 signaling by inhibiting Lyn and c-Src phosphorylation and their recruitment to TLR4, while increasing the phosphatase activity and expression of PP2A, PTPN22, PTP1B and MKP1. 26460485_SRC, LYN and CKB expression or DNA methylation could be useful markers for predicting tumor progression. 26517678_Inhibition of Lyn activity using dasatinib in mantle cell lymphoma overcomes bortezomib resistance. 26708841_Authors discovered in this study that LYN was a critical gene. It was found to be the key nodule of several significant biological networks. 26742467_SYK, LYN and PTPN6 were markedly elevated in atherosclerotic plaques of carotid atherosclerosis patients. 26984511_Our data suggests that nuclear Lyn is a potential therapeutic target for clear cell renal cell carcinoma and dasatinib affects cellular functions associated with cancer progression via a Src kinase independent mechanism. 27690342_overexpression LYN promoted tumor growth, meanwhile knockdown LYN inhibited tumor growth. These results indicate that LYN tyrosine kinase is an oncogenic gene and can serve as a novel target for cervical cancer research and therapy. 27728807_Authors demonstrate that LYN kinase is essential for CLL progression. Lyn deficiency results in a significantly reduced CLL burden in vivo. 27756880_LYN is a useful prognostic marker and a selective target of dasatinib therapy in the lung adenocarcinoma subpopulation, especially in female non-smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. 28024734_Our studies indicate not only a concept of mucus hypersecretion in asthma that involves Lyn kinase but also an important therapeutic candidate for asthma. 28205598_these findings demonstrated that Lyn overexpression ameliorated airway mucus hypersecretion by down-regulating STAT6 and its binding to the MUC5AC promoter. 28288135_A novel pancancer mechanism of Lyn-dependent control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and role of this kinase in tumor progression. 28368000_Fyn and Lyn as important factors that promote Plasmacytoid dendritic cell responses. 28811476_SHP-1 tyrosine 536 phosphorylation by Lyn activates the phosphatase promoting inhibitory signaling through the immunoreceptor. 29031599_We demonstrate a novel role for DJ-1 in the early activation of Lyn by FcepsilonRI, which is essential for human mast cell responses 29391601_The molecular mechanism through which the oncogenic tyrosine kinase Lyn negatively regulates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, which may contribute to the transformation and/or the chemotherapeutic resistance of cancer cells, involves Bim. 30537294_Hematopoietic cell-specific Lyn substrate, HCLS1, is a versatile actin-binding protein in leukocytes. (Review) 30579930_The inhibitory action of estrogen on osteoclast was severely restrained in LYN knockdown condition, demonstrating the importance of LYN as a key mediator of the effect of estrogen on osteoclastogenesis. 30590041_dual mechanisms-uncoupling from upstream signals and splice isoform ratios-drive the activity of LYN in aggressive breast cancers. 30840855_Upon BCR activation, Lyn, Syk and ZAP-70 recruitment into lipid rafts (LR) increased significantly in B cells of healthy controls and patients with inactive Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). In active SLE patients there was a great heterogeneity in the recruitment of signaling molecules and the recruitment of ZAP-70 was mainly observed in patients with decreased Syk recruitment into LR of activated B cells. 31477108_Lyn expression was up-regulated in COPD-smoker patients. 31828293_LYN is a direct target of miR-122-5p in gastric cancer cells. Silencing LYN expression by its siRNA inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Overexpression of LYN restored miR-122-5p-mediated inhibition of the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells. 31881245_Lyn regulates creatine uptake in an imatinib-resistant CML cell line. 32543003_Erlotinib is effective against FLT3-ITD mutant AML and helps to overcome intratumoral heterogeneity via targeting FLT3 and Lyn. 33199837_Leukemic cells expressing NCOR1-LYN are sensitive to dasatinib in vivo in a patient-derived xenograft mouse model. 33512474_CBL mutations drive PI3K/AKT signaling via increased interaction with LYN and PIK3R1. 35103068_Three Potential Tumor Markers Promote Metastasis and Recurrence of Colorectal Cancer by Regulating the Inflammatory Response: ADAM8, LYN, and S100A9. 36058999_Fyn and Lyn gene polymorphisms impact the risk of thyroid cancer. |
ENSMUSG00000042228 |
Lyn |
1730.173944 |
3.7647167999 |
1.912541 |
0.107848030 |
297.587263 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000110517836348449664000197168368755594098763585844072147762601030615220857007709698650752455066928694435277196679225618812897255632470433326497224053442933492321197780881847361200698287575505673885345458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000031798114317799554687084713584858293997148575933509003799950695241202866857322309854050634804065292192422596631212355722734189506664081877337147982365892983109699650168256113147435826249420642852783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
2734.1352180 |
258.6355609 |
732.9065598 |
50.7938709 |
| ENSG00000254102 |
401463 |
BHLHE22-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
82.120740 |
0.2283046897 |
-2.130968 |
0.211867673 |
106.493316 |
0.00000000000000000000000057486071319424864227442505098728186252437012221273237639744680793196102142061931772332172840833663940429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000006166383813042957436386209172289797303698533376000858978561152822384788807497102425259072333574295043945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.6716265 |
4.5507318 |
135.5316906 |
12.1010559 |
| ENSG00000254154 |
89866 |
CRYZL2P-SEC16B |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.525363 |
0.1219885014 |
-3.035183 |
0.847429082 |
13.056755 |
0.00030219250883735230845533736854235939972568303346633911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000771155157406521341717509088198312383610755205154418945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.4083537 |
1.6280266 |
21.5831398 |
8.2665318 |
| ENSG00000254162 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.993158 |
0.2921792740 |
-1.775074 |
0.681565986 |
6.825914 |
0.00898445534464777095795540162725956179201602935791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017364221669111050416756114600502769462764263153076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1088074 |
1.3741464 |
10.3130411 |
2.8437261 |
| ENSG00000254398 |
100419574 |
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.488936 |
0.2103441796 |
-2.249176 |
0.414730350 |
29.047412 |
0.00000007062839032047891331080784541041062141175643773749470710754394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000282284062044481116266815036441872877048808732070028781890869140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7464315 |
3.6469038 |
50.9511861 |
11.3677345 |
| ENSG00000254413 |
386593 |
CHKB-CPT1B |
protein_coding |
H3BT56 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
The genes CHKB and CPT1B are adjacent on chromosome 22 and read-through transcripts are expressed that include exons from both loci. The read-through transcripts are candidates for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and are unlikely to express proteins. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009]. |
|
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; choline kinase activity [GO:0004103]; ethanolamine kinase activity [GO:0004305]; CDP-choline pathway [GO:0006657]; phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process [GO:0006656]; phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthetic process [GO:0006646] |
|
|
|
349.656143 |
0.3254385643 |
-1.619543 |
0.171796113 |
86.020724 |
0.00000000000000000001780597885067553408511779499052079523478621462033163818598074934484998266270849853754043579101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000160058616221663140289636935873788947606286071101613498624677278669992119830567389726638793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
167.0928776 |
21.9462430 |
517.8911579 |
47.9578190 |
| ENSG00000254473 |
105376114 |
UBQLN1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.331104 |
0.3819105078 |
-1.388693 |
0.531579462 |
6.951014 |
0.00837717245050075345891293920885800616815686225891113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016303674231196087218709322996801347471773624420166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3960549 |
1.9818239 |
14.2311269 |
3.3665828 |
| ENSG00000254614 |
728975 |
CAPN1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.524585 |
0.1656742591 |
-2.593579 |
0.574493078 |
22.966205 |
0.00000164874463842825998538923256558907937119329289998859167098999023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005695172212310113703790694084094781146632158197462558746337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9115326 |
1.1263114 |
17.6780142 |
3.6356362 |
| ENSG00000254703 |
100507392 |
SENCR |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26898221_Data showed that SENCR contributes to the regulation of endothelial differentiation from pluripotent cells and controls the angiogenic capacity of human umbilical endothelial cells. 29845247_Long non-coding RNA SENCR alleviates the inhibitory effects of rapamycin on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. 30584103_These findings support SENCR as a flow-responsive lncRNA that promotes EC adherens junction integrity through physical association with CKAP4, thereby stabilizing cell membrane-bound CDH5. 32401347_Preliminary study on the mechanism of long noncoding RNA SENCR regulating the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. 35351345_LncRNA SENCR overexpression attenuated the proliferation, migration and phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells in aortic dissection via the miR-206/myocardin axis. 35500152_Super enhancer-LncRNA SENCR promoted cisplatin resistance and growth of NSCLC through upregulating FLI1. |
|
|
13.505526 |
0.2226590663 |
-2.167092 |
0.562263439 |
15.431420 |
0.00008555394417986611271462193961667708208551630377769470214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000237408576065956724307839942333941962715471163392066955566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3498525 |
1.8629042 |
19.7766056 |
5.2853646 |
| ENSG00000254815 |
692247 |
LMNTD2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.486256 |
0.0666602512 |
-3.907029 |
0.451754446 |
89.830274 |
0.00000000000000000000259493034518078780231215682272105785120204168132470704156858701261434418938733870163559913635253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000024180032761911885912274424639978036170296647586072705498737994700420017579745035618543624877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5264301 |
1.3740386 |
69.0230707 |
9.7998434 |
| ENSG00000254837 |
100287896 |
LIPT2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.246482 |
0.4974834648 |
-1.007280 |
0.354046372 |
8.089936 |
0.00445117430532329487469223039397547836415469646453857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009196435154895273023090140895874355919659137725830078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.1266037 |
3.5286715 |
30.6302171 |
4.8373269 |
| ENSG00000254851 |
|
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.341007 |
3.7251000729 |
1.897279 |
0.810178265 |
5.274326 |
0.02164215990451980042852397900787764228880405426025390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.038495815882226107340624565722464467398822307586669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.7237096 |
9.7682245 |
5.2226831 |
2.0592930 |
| ENSG00000254852 |
642799 |
NPIPA2 |
protein_coding |
E9PIF3 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be involved in mRNA transport and protein transport. Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
89.260892 |
0.3851281555 |
-1.376589 |
0.175066485 |
63.442645 |
0.00000000000000165104729132188590835586162237343445285719977302929528661934455158188939094543457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000011687989457990904718778943759739496785179024493372956783332483610138297080993652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.7124896 |
5.7864284 |
130.0668230 |
9.6293259 |
| ENSG00000254870 |
100532737 |
ATP6V1G2-DDX39B |
protein_coding |
F2Z307 |
FUNCTION: Subunit of the V1 complex of vacuolar(H+)-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme composed of a peripheral complex (V1) that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane integral complex (V0) that translocates protons. V-ATPase is responsible for acidifying and maintaining the pH of intracellular compartments and in some cell types, is targeted to the plasma membrane, where it is responsible for acidifying the extracellular environment. {ECO:0000256|RuleBase:RU364019}. |
Hydrogen ion transport;Ion transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring ATP6V1G2 (ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 13kDa, V1 subunit G2) and DDX39B (DEAD box polypeptide 39B) genes located in the major histocompatibility complex class III region of chromosome 6. The read-through transcript and is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), and is thus unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
|
vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex [GO:0016471]; proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism [GO:0046961] |
|
|
|
84.297062 |
138.4922324465 |
7.113661 |
1.474259792 |
14.304557 |
0.00015548799119193286292529843084508911488228477537631988525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000415084599383781674246385318127749997074715793132781982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
166.1456603 |
87.1524827 |
1.7559095 |
0.8055065 |
| ENSG00000254912 |
|
MPHOSPH10P2 |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.633570 |
0.0249766842 |
-5.323274 |
1.081674951 |
50.272867 |
0.00000000000133786618061642190861995710549584178133269984911635219759773463010787963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007886144099799675377415482480890622941221979047554668795783072710037231445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5156411 |
0.4246615 |
20.7922142 |
4.7558216 |
| ENSG00000255031 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.853404 |
0.2646467380 |
-1.917860 |
0.418431611 |
21.833641 |
0.00000297340783989619510086725023834119951970933470875024795532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009945048655533161993322344152090863644843921065330505371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6210774 |
2.1449657 |
32.7029429 |
4.6181903 |
| ENSG00000255045 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.942533 |
0.0454576806 |
-4.459332 |
1.135518277 |
26.022543 |
0.00000033745389078548856239220341685092208194873819593340158462524414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001256761388747511966928658254383233128237407072447240352630615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5248575 |
0.4591392 |
11.6468481 |
3.4683469 |
| ENSG00000255145 |
|
STX17-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.325545 |
0.4498692516 |
-1.152422 |
0.426473125 |
7.124187 |
0.00760508914618759305353856703391102200839668512344360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014944896258518022141847936268277408089488744735717773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0592326 |
4.7171597 |
35.8991224 |
7.2125136 |
| ENSG00000255182 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44.983360 |
0.2436128853 |
-2.037338 |
0.337575955 |
35.637538 |
0.00000000237663383635071450697918082287790619844258799275849014520645141601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000010993141781427935852078088801303534793873950548004359006881713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.7231389 |
5.0545592 |
72.1716189 |
13.9767971 |
| ENSG00000255284 |
171391 |
GATD1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.112696 |
0.3149990699 |
-1.666581 |
0.372684903 |
20.811090 |
0.00000506886007405728196461083823187721009162487462162971496582031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000016493909764789567705964637434057351583760464563965797424316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3532297 |
2.1618565 |
26.4516136 |
4.2365053 |
| ENSG00000255299 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41.894139 |
4.4076904584 |
2.140023 |
0.335431787 |
40.675850 |
0.00000000017969425625088184077494699145859840053174316665263177128508687019348144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000911438907994163541133245482947760479630616714530333410948514938354492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
68.0890646 |
13.9143580 |
15.6169005 |
2.5544350 |
| ENSG00000255330 |
387104 |
|
protein_coding |
Q5TF21 |
|
Coiled coil;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
|
|
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020]; regulation of autophagy [GO:0010506] |
|
|
|
19.178840 |
3.0735948600 |
1.619927 |
0.630116555 |
6.309758 |
0.01200752225520179163054113047337523312307894229888916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022655123160779552099475253612581582274287939071655273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.3954302 |
10.2354254 |
8.4841917 |
2.4348190 |
| ENSG00000255366 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.489698 |
0.2463105743 |
-2.021450 |
0.477594898 |
19.273925 |
0.00001132423516333982422405173701163150212778418790549039840698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000035300044564075144814564721773564315299154259264469146728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8703447 |
1.8221654 |
19.8869473 |
4.5299694 |
| ENSG00000255398 |
8843 |
HCAR3 |
protein_coding |
P49019 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for 3-OH-octanoid acid mediates a negative feedback regulation of adipocyte lipolysis to counteract prolipolytic influences under conditions of physiological or pathological increases in beta-oxidation rates. Acts as a low affinity receptor for nicotinic acid. This pharmacological effect requires nicotinic acid doses that are much higher than those provided by a normal diet. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12522134, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19561068}. |
Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;G-protein coupled receptor;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity and purinergic nucleotide receptor activity. Predicted to be involved in G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway. Located in cell junction. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:8843; |
cell junction [GO:0030054]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; nicotinic acid receptor activity [GO:0070553]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186] |
12563315_HM74 is highly expressed in adipose tissue and is a nicotinic acid receptor 19237584_These results suggest that aromatic D-amino acids elicit a chemotactic response in human neutrophils via activation of GPR109B. 19502010_An A allele in HM74 was significantly associated with schizophrenia and with schizophrenia plus bipolar disorder combined. 19502010_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19561068_the ligand receptor pair 3-OH-octanoic acid/GPR109B mediates a negative feedback regulation of adipocyte lipolysis in human but not in mouse 19633298_Data show that the coordinated PPARgamma-mediated regulation of the GPR81, GPR109A and GPR109B presents a novel mechanism by which TZDs may reduce circulating free fatty acid levels and perhaps ameliorate insulin resistance in obese patients. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20380810_these results demonstrate that GPR109A and GPR109B dimerization is a constitutive process occurring early during biosynthesis. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21655214_In contrast, in a squamous cell carcinoma derived cell line, both GPR109A and GPR109B show a more diffuse cellular localization and the receptors are nearly non-functional. 22289163_Activated HCAR3 signals to MAP kinase cascades via the PLC-dependent PKC and MMP-mediated EGFR pathways 25839160_HCA1/3 are necessary for breast cancer cells to balance lipid/fatty acid metabolism. 26656756_new insights into the G protein coupling profiles of the HCA receptors and the function of the receptor's C terminus 32102673_Natural biased signaling of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 and G protein-coupled receptor 84. 34852802_Rare and potentially pathogenic variants in hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor genes identified in breast cancer cases. 34948292_Alterations in Kynurenine and NAD(+) Salvage Pathways during the Successful Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Suggest HCAR3 and NNMT as Potential Drug Targets. 34968686_Hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 and GPR84 - Two metabolite-sensing G protein-coupled receptors with opposing functions in innate immune cells. |
ENSMUSG00000045502 |
Hcar2 |
24.891268 |
9.2296673255 |
3.206279 |
0.433906850 |
63.799135 |
0.00000000000000137774074567098856277738415671287206628101542141284774345422192709520459175109863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000009790781611027342844100970676569332795584972746472107729687195387668907642364501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.3889972 |
12.3380899 |
5.0787159 |
1.2277016 |
| ENSG00000255455_ENSG00000120451 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
161.235395 |
0.3808568626 |
-1.392679 |
0.156590563 |
79.461160 |
0.00000000000000000049179886623750921497412699909109124588394180790804294592377665651383722433820366859436035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000004169414856786695253275318951189833498184800273620191288226344283884827746078372001647949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
92.4196160 |
8.9899455 |
244.2008139 |
15.4783383 |
| ENSG00000255587 |
401258 |
RAB44 |
protein_coding |
Q7Z6P3 |
|
Cell membrane;Coiled coil;GTP-binding;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Prenylation;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable GTP binding activity; GTPase activity; and calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be located in azurophil granule membrane; plasma membrane; and specific granule membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:401258; |
azurophil granule membrane [GO:0035577]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; histamine secretion by mast cell [GO:0002553]; histamine secretion mediated by IgE immunoglobulin [GO:0097279]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
33641252_Rab44 isoforms similarly promote lysosomal exocytosis, but exhibit differential localization in mast cells. |
ENSMUSG00000064147 |
Rab44 |
68.167568 |
0.1789920747 |
-2.482032 |
0.215013951 |
152.362493 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000005279599816563793396388376146950727566843710740251649761036087516440088795414581732229580661452938983302374253980815410614013671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000780830594113041953291549715080979864466254094935097247948577604022748101798349067175679730223869512428791495040059089660644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.3744872 |
2.8901608 |
114.6636757 |
8.3961798 |
| ENSG00000255639 |
|
|
protein_coding |
H3BRM9 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.414935 |
2.3160580210 |
1.211671 |
0.429362877 |
7.837944 |
0.00511607529454999668261372391953045735135674476623535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010438706848870443408272556951033038785681128501892089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.8658838 |
10.8385221 |
13.7828678 |
3.5114806 |
| ENSG00000255666 |
|
LINC02700 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.386300 |
0.3674004142 |
-1.444575 |
0.305071421 |
22.890416 |
0.00000171504867622662393940476382309112679536156065296381711959838867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005906233891998359301596984577420457185326085891574621200561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.4168639 |
3.0373397 |
39.5284956 |
5.3044517 |
| ENSG00000255819 |
8302 |
KLRC4-KLRK1 |
protein_coding |
K7EPB6 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90.016062 |
0.1303383697 |
-2.939666 |
0.295959047 |
94.125638 |
0.00000000000000000000029611884997557759223100626029194948372065394018449721222195234957008658227550768060609698295593261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000002851085600547635665108511033988923565273587391211633813316826679962190382866538129746913909912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.6914891 |
8.6599597 |
190.3937680 |
48.0358377 |
| ENSG00000255872 |
|
|
protein_coding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.038196 |
2.8119565808 |
1.491574 |
0.292850720 |
26.296301 |
0.00000029284906575489124895726668514062129844433002290315926074981689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001096808092801486026588342510834639398353829164989292621612548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
52.4367568 |
8.5288971 |
18.8155389 |
2.5119469 |
| ENSG00000255921 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56.168746 |
34.3465916592 |
5.102095 |
0.566766216 |
75.112521 |
0.00000000000000000444637505882905814622229150040967301836516495849513375127060044178506359457969665527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000036158950891634649685215737822859130014187103508479376179352016151824500411748886108398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
110.0478549 |
35.8606424 |
3.1674110 |
0.9105014 |
| ENSG00000256073 |
84996 |
URB1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.228731 |
0.3416558047 |
-1.549384 |
0.395675429 |
16.027399 |
0.00006243240881938829636363386121900020953034982085227966308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000177314287891893650412136751448599625291535630822181701660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.5323811 |
2.1919645 |
25.2632665 |
3.8624068 |
| ENSG00000256092 |
112268105 |
SBNO1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.156541 |
0.3250955660 |
-1.621064 |
0.563173271 |
8.762539 |
0.00307480637767545235058963548624433315126225352287292480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006567893217726436701220382730070923571474850177764892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1057200 |
1.2259561 |
9.6287289 |
2.2708729 |
| ENSG00000256268 |
|
LINC02454 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.617007 |
2.2365867966 |
1.161299 |
0.359469675 |
10.237529 |
0.00137611802881545215379577307146519160596653819084167480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003134491065635196596628198051348590524867177009582519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.0565050 |
8.5621737 |
17.3523442 |
2.9268671 |
| ENSG00000256594 |
|
|
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55.297934 |
12.6083301505 |
3.656305 |
1.448038604 |
4.990396 |
0.02548837966178545133555388702006894163787364959716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044590314544026704579593456401198636740446090698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
113.1711889 |
81.4749709 |
9.3090842 |
4.8304958 |
| ENSG00000256673 |
|
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
40.734287 |
0.0138665041 |
-6.172252 |
1.431342905 |
12.528970 |
0.00040069059880934980314229343356657864205772057175636291503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001001726497023374589170896520329279155703261494636535644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1152881 |
0.9433969 |
72.7194689 |
37.7297777 |
| ENSG00000257108 |
283948 |
NHLRC4 |
protein_coding |
P0CG21 |
|
Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to enable ubiquitin protein ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in protein K48-linked ubiquitination. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:283948; |
ubiquitin protein ligase activity [GO:0061630]; protein K48-linked ubiquitination [GO:0070936] |
|
ENSMUSG00000090113 |
Nhlrc4 |
7.409479 |
0.0685058042 |
-3.867630 |
0.958557709 |
19.959849 |
0.00000790855379283081995388585139217241248843492940068244934082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000025135713605121211126382230194309386206441558897495269775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8888329 |
0.5623137 |
12.5979938 |
3.2984730 |
| ENSG00000257135 |
|
ODC1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.883356 |
0.3951552850 |
-1.339508 |
0.469978805 |
8.284101 |
0.00399937007800608545354803524674025538843125104904174804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008340025763120912857817579322272649733349680900573730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.3075448 |
2.3066672 |
18.7375764 |
3.6736289 |
| ENSG00000257176 |
100506606 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.591110 |
0.3647848925 |
-1.454882 |
0.407460587 |
12.176167 |
0.00048404018362381529775456678876821570156607776880264282226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001191731961682654427139849140360183810116723179817199707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.2982301 |
4.5952888 |
51.1001768 |
8.4788949 |
| ENSG00000257258 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
279.813061 |
0.1962277606 |
-2.349399 |
0.160973061 |
210.782622 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000927089012081561806154220893298109648346749313509346991601948527443373428776131720934078131293010806840504046985346293051864774437120786387822590768337249755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000187193349087877617601607966851395856676820979339709813394682492343700316197913685956512809024974633017192353066676831219172782994064618833363056182861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.1029095 |
12.8551670 |
544.4145806 |
42.8484663 |
| ENSG00000257303 |
|
CNPY2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.832804 |
0.3374422655 |
-1.567287 |
0.551531458 |
7.567384 |
0.00594339708945468021134006519901049614418298006057739257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011953200850299916177532644212533341487869620323181152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.5406757 |
2.4116168 |
21.7666465 |
4.3718651 |
| ENSG00000257335 |
8972 |
MGAM |
protein_coding |
O43451 |
FUNCTION: Alpha-(1,4) exo-glucosidase involved in breakdown of dietary starch oligosaccharides in small intestine. Cleaves the non-reducing alpha-(1,4)-linked glucose residue in linear dextrins with retention of anomeric center stereochemistry (PubMed:12547908, PubMed:18356321, PubMed:27480812, PubMed:18036614, PubMed:22058037). Mainly hydrolyzes short length oligomaltoses having two to seven glucose residues (PubMed:12547908, PubMed:18356321, PubMed:27480812, PubMed:18036614, PubMed:22058037). Can cleave alpha-(1,2), alpha-(1,3) and alpha-(1,6) glycosidic linkages with lower efficiency, whereas beta glycosidic linkages are usually not hydrolyzed (PubMed:27480812). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12547908, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18036614, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18356321, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22058037, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27480812}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Membrane;Multifunctional enzyme;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal-anchor;Sulfation;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
PATHWAY: Carbohydrate degradation. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:18036614, ECO:0000305|PubMed:22058037, ECO:0000305|PubMed:27480812}. |
This gene encodes maltase-glucoamylase, which is a brush border membrane enzyme that plays a role in the final steps of digestion of starch. The protein has two catalytic sites identical to those of sucrase-isomaltase, but the proteins are only 59% homologous. Both are members of glycosyl hydrolase family 31, which has a variety of substrate specificities. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:8972; |
apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; ficolin-1-rich granule membrane [GO:0101003]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; alpha-1,4-glucosidase activity [GO:0004558]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; catalytic activity [GO:0003824]; glucan 1,4-alpha-glucosidase activity [GO:0004339]; hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds [GO:0004553]; maltose alpha-glucosidase activity [GO:0032450]; dextrin catabolic process [GO:1901027]; maltose catabolic process [GO:0000025]; starch catabolic process [GO:0005983] |
12547908_genetic analysis of MGAM, exon boundaries, and chromosome mapping 17485087_Raw starch granule degradation with recombinanat human MGAM indicates that pancreatic alpha-amylase hydrolysis is not a requirement for native starch digestion in the human small intestine. 18036614_Intestinal maltase-glycoamylase: crystal structure of the N-terminal catalytic subunit and basis of inhibition and substrate specificity. 18377903_Acarbose has been found to improve insulin levels and thus glucose/insulin ratios more effectively in overweight patients compared with nonoverweight patients with PCOS. 19472353_This study reported the first diagnosed Finnish patient with a phenotype compatible with the late-onset form of Pompe disease. Molecular genetic analysis of the GAA gene revealed a novel missense mutation (Y575X),combined with (P545L) mutation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20356844_analysis of substrate selectivity of human maltase-glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase N-terminal domains 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 22036121_These results suggest that the N-terminal and C-terminal catalytic domains of maltase-glucoamylase differ in their substrate specificities and inhibitor tolerance despite their structural relationship 22058037_we report crystal structures of C-terminal maltase-glucoamylase alone at a resolution of 3.1 angstroms, and in complex with its inhibitor acarbose 22563462_Findings suggest that C-terminal subunits of recombinant maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) assists alpha-amylase in digesting starch molecules and potentially may compensate for developmental or pathological amylase deficiencies. 23405089_The over-expression of MGAM was confirmed with a 6.6 fold increase in expression at the mRNA level whereas the fold change in ADAM9 demonstrated a 1.6 fold increase. 25037326_Starch internal structure modulates its susceptibility to MGAM. The internal branch amounts negatively affect the glucose release rate. 25776870_MGAM, or nearby regulatory elements, may be involved in the etiology of oral clefts. 29548257_Mechanistic Pathway on Human alpha-Glucosidase Maltase-Glucoamylase Unveiled by QM/MM Calculations |
ENSMUSG00000068587 |
Mgam |
23.037364 |
13.8966421413 |
3.796664 |
0.634616659 |
32.193325 |
0.00000001395694188777135077970986454286642097777360049803974106907844543457031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000059815465233305791419272598192363732394483122334349900484085083007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
41.5147865 |
19.8989922 |
2.9856738 |
1.1822179 |
| ENSG00000257337 |
283335 |
TNS2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.782338 |
0.4304219271 |
-1.216177 |
0.514793377 |
5.419003 |
0.01991873259699359841046195640501537127420306205749511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.035727365795555417193885006099662859924137592315673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6821347 |
3.1538529 |
22.9901075 |
4.9154109 |
| ENSG00000257354 |
120766144 |
MIRLET7IHG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.284850 |
0.2857642967 |
-1.807102 |
0.307305677 |
36.116624 |
0.00000000185854516640238508151172964094925352251941319536854280158877372741699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000008694810350586119701354923612526132137290346690861042588949203491210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.1942255 |
2.7973000 |
49.9808828 |
5.8056778 |
| ENSG00000257390 |
|
|
protein_coding |
H0YHG0 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule [GO:0036464]; nuclear speck [GO:0016607]; dopamine receptor binding [GO:0050780] |
|
|
|
94.572467 |
2.4657160431 |
1.302007 |
0.247193448 |
27.459402 |
0.00000016042703276869406761244538518057511922165758733171969652175903320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000619221496774561849668898523557647450843433034606277942657470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
134.1507710 |
22.2521752 |
54.7322196 |
6.8543416 |
| ENSG00000257551 |
100873924 |
HLX-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.627202 |
0.3780892568 |
-1.403201 |
0.574997858 |
6.074443 |
0.01371515085857688553971911460394039750099182128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025511736190623166692370560326708073262125253677368164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6451232 |
1.8635481 |
12.5290353 |
3.0960978 |
| ENSG00000257576 |
|
HSPD1P4 |
processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.830661 |
0.3773090031 |
-1.406182 |
0.381807631 |
13.920374 |
0.00019071986265456548534889813506509881335659883916378021240234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000501429492836014687254242438996243436122313141822814941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.8312112 |
3.0351777 |
26.3484847 |
5.3801393 |
| ENSG00000257698 |
100506844 |
GIHCG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29364470_Knockdown of GIHCG significantly represses proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma cells. Serum GIHCG level is positively correlated with GIHCG expression in RCC tissues. 30556850_GIHCG is highly expressed in ovarian cancer, which promotes tumor development by stimulating cell cycle progression and cell proliferation by regulating microRNA-429. |
|
|
18.248148 |
0.3717907637 |
-1.427437 |
0.421906763 |
11.564172 |
0.00067234828586759524168131596510988856607582420110702514648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001616000765250888513563376491788403654936701059341430664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5458270 |
2.8040752 |
28.6292745 |
4.8082653 |
| ENSG00000257702 |
151534 |
LBX2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30824187_LncRNA LBX2-AS1 promoted cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. LBX2-AS1 interacting with HNRNPC to promote ZEB1/2 mRNA stability. 31512745_LBX2-AS1 might be associated with periodontitis 31539129_Novel long non-coding RNA LBX2-AS1 indicates poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis through Notch signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. 31673844_LBX2-AS1/miR-219a-2-3p/FUS/LBX2 positive feedback loop contributes to the proliferation of gastric cancer. 32559617_LncRNA LBX2-AS1 facilitates abdominal aortic aneurysm through miR-4685-5p/LBX2 feedback loop. 33099720_ELK1 activated-long noncoding RNA LBX2-AS1 aggravates the progression of ovarian cancer through targeting miR-4784/KDM5C axis. 33342041_LBX2-AS1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by facilitating E2F2 gene expression via miR-455-5p and miR-491-5p sponging. 33637977_Silencing of lncRNA LBX2-AS1 suppresses glioma cell proliferation and metastasis through the Akt/GSK3beta pathway in vitro. 33733923_Overexpression of Long Noncoding RNA LBX2-AS1 Promotes the Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer. 35253306_Long noncoding RNA LBX2-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer progression via binding with PTBP1 and stabilizing KAT2A expression. 35816228_Long non-coding RNA LBX2-AS1 predicts poor survival of colon cancer patients and promotes its progression via regulating miR-627-5p/RAC1/PI3K/AKT pathway. |
|
|
63.441349 |
0.4290097087 |
-1.220918 |
0.203022821 |
36.499793 |
0.00000000152682484228724616829786026516932451180252883204957470297813415527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007179335671283769514248621301756234092117381351272342726588249206542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.6390454 |
5.2677600 |
92.9990784 |
8.1324745 |
| ENSG00000257815 |
101928062 |
PRANCR |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.790502 |
0.3787598461 |
-1.400645 |
0.365162124 |
14.753943 |
0.00012249108165240273808985205228339054883690550923347473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000332959183276144499771115325970072262862231582403182983398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.4668797 |
2.9507107 |
30.3250967 |
5.1363785 |
| ENSG00000257839 |
|
PHLDA1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.188206 |
0.2509432435 |
-1.994567 |
0.554865317 |
13.830783 |
0.00020003202551488696815315537769208731333492323756217956542968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000524045562051780552427493464762164876447059214115142822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4822818 |
1.3462206 |
13.9916527 |
3.1287182 |
| ENSG00000257894 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.822717 |
0.3545149646 |
-1.496082 |
0.465687157 |
10.804831 |
0.00101235548777243804761949430570666663697920739650726318359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002352758148247706578015669975911805522628128528594970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5850428 |
1.6519124 |
15.8338762 |
2.7618547 |
| ENSG00000257900 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.395945 |
0.2376310910 |
-2.073204 |
0.527831722 |
15.462400 |
0.00008416294957233928244154375075680718509829603135585784912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000233900420954194672440440427862995420582592487335205078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3384434 |
2.3056670 |
26.4028877 |
6.0505433 |
| ENSG00000257921 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A494C1I5 |
|
Methyltransferase;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
|
|
methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; methylation [GO:0032259] |
|
|
|
15.477247 |
8.7647549495 |
3.131714 |
0.875453646 |
11.787725 |
0.00059622553998513367918415939428200545080471783876419067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001444864561199251480269611924711625761119648814201354980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.0779404 |
16.2255662 |
2.2580353 |
1.4394565 |
| ENSG00000257932 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66.005313 |
10.1155597745 |
3.338504 |
0.279348145 |
165.488613 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000007154422076120124980131811690740844219754918051095035101866725629095175236728340350726260103036459325753781968160183168947696685791015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001136698276033724952613732685520000933524092929306839094190892485669809709723557553877560547612914770843062228777853306382894515991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
122.2381582 |
20.0890455 |
12.1712046 |
1.8439670 |
| ENSG00000258077 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.927942 |
0.3337786285 |
-1.583037 |
0.317116920 |
25.949983 |
0.00000035037844682486203762118780018208763493703372660093009471893310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001303651594437853209921618705124934933792246738448739051818847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.5512089 |
2.7804683 |
37.9229580 |
5.1737106 |
| ENSG00000258082_ENSG00000238005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.735591 |
0.1190762683 |
-3.070042 |
0.781219466 |
18.132757 |
0.00002060265367340175714119636374288546676325495354831218719482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000062365703080272756522045574101298370806034654378890991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1092720 |
0.5921680 |
9.4186146 |
2.5600076 |
| ENSG00000258088_ENSG00000258077 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.622909 |
0.1337668018 |
-2.902208 |
0.649197495 |
23.567592 |
0.00000120601701521702696073823617844977817981089174281805753707885742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004229225741174463569841106974633859749701514374464750289916992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8667486 |
0.8742866 |
14.1591153 |
3.4945297 |
| ENSG00000258183 |
105369893 |
LINC02392 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
172.046930 |
12.1945479510 |
3.608164 |
0.216982888 |
283.628756 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000121575242102923379216646486251391609384880011240838354720518638196112250214356567492259894731427082361343411343722664229635810328824493075035098936500165770629999784091523906681686639785766601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000032986223776454947384023566594331848018847279513190645468508412699054899050180647561873137286265682747315832274620663785905434155817962554530951340635405765258636456849217211129143834114074707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
312.5036640 |
40.6866407 |
25.6318214 |
2.9086010 |
| ENSG00000258227 |
23601 |
CLEC5A |
protein_coding |
Q9NY25 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a positive regulator of osteoclastogenesis (By similarity). Cell surface receptor that signals via TYROBP (PubMed:10449773). Regulates inflammatory responses (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10449773}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Critical macrophage receptor for dengue virus serotypes 1-4 (PubMed:18496526, PubMed:21566123). The binding of dengue virus to CLEC5A triggers signaling through the phosphorylation of TYROBP (PubMed:18496526). This interaction does not result in viral entry, but stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokine release (PubMed:18496526). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18496526, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21566123}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Immunity;Innate immunity;Lectin;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. Members of this family share a common protein fold and have diverse functions, such as cell adhesion, cell-cell signalling, glycoprotein turnover, and roles in inflammation and immune response. The encoded type II transmembrane protein interacts with dnax-activation protein 12 and may play a role in cell activation. Alternative splice variants have been described but their full-length sequence has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:23601; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; specific granule membrane [GO:0035579]; tertiary granule membrane [GO:0070821]; carbohydrate binding [GO:0030246]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; cellular defense response [GO:0006968]; innate immune response [GO:0045087]; myeloid cell differentiation [GO:0030099]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of myeloid cell apoptotic process [GO:0033033]; osteoblast development [GO:0002076]; positive regulation of cytokine production [GO:0001819]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
18496526_blockade of CLEC5A-mediated signalling attenuates the production of proinflammatory cytokines by macrophages infected with Dengue virus (either alone or complexed with an enhancing antibody) 20057064_The crystal volume per unit weight (VM) was calculated to be 2.34 A3 Da-1, with nine molecules per asymmetric unit and a solvent content of 47.38%. CLEC5A plays an important role in the pathophysiology of dengue-virus-induced disease. 20237496_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21094529_CLEC5A expression in monocyte/macrophage and granulocytes is regulated by PU.1. 21566123_CLEC5A is homodimeric at the cell surface and binds to dengue virus serotypes 1-4. 22536019_No significant associations were noted between the genotypes and allele frequency of the 4 CLEC5A tSNPs between controls and Kawasaki disease patients. 23152543_Blockade of CLEC5A inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyrotopsis in dengue-virus-infected inflammatory macrophages. Thus, DV can activate NLRP3 inflammasome via CLEC5A. 24465901_Concordant overexpression of MDL-1 and DAP12 were correlated with increased production of proinflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients. 27033255_CLEC5A is critical for dengue virus-induced osteoclast activation and bone homeostasis 27795434_The results suggest that CLEC5A-mediated enhancement of the inflammatory response in myeloid cells contributes to influenza pathogenicity in vivo and may be considered a therapeutic target in combination with effective antivirals. 27832191_Mannose Receptor and CLEC5A on Macrophage first attracts the Dengue Virus with high avidity, and the virus concurrently interacts with CLEC5A in close proximity to form a multivalent hetero-complex and facilitate CLEC5A-mediated signal transduction. Dengue Virus Infection Is through a Cooperative Interaction between a Mannose Receptor and CLEC5A on Macrophage as a Multivalent Hetero-Complex. 28764923_this study shows association of rs1285933 single nucleotide polymorphism in CLEC5A gene with dengue severity 29126450_MDL-1 is mainly expressed in atherosclerotic lesional macrophages and increased macrophage MDL-1 expression is associated with early plaque progression and promotes macrophage survival. 30834619_CLEC5A was highly upregulated in glioblastoma compared to normal brain tissues, which had an opposite relation with the overall patient survival. Downregulation of CLEC5A could inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion via promoting apoptosis and G1 arrest. 31364785_CEBPB can inhibit the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells via regulating the expression of CLEC5A. 31591460_CLEC5A expressed on myeloid cells as a M2 biomarker relates to immunosuppression and decreased survival in patients with glioma. 31867016_CLEC2 and CLEC5A: Pathogenic Host Factors in Acute Viral Infections. 32033754_CLEC5A promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. 32152943_REVIEW: CLEC5A, a Promiscuous Pattern Recognition Receptor to Microbes and Beyond 32476786_Genetic association analysis of CLEC5A and CLEC7A gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms and Crohn's disease. 35252461_Activation of the Innate Immune Checkpoint CLEC5A on Myeloid Cells in the Absence of Danger Signals Modulates Macrophages' Function but Does Not Trigger the Adaptive T Cell Immune Response. 35820906_CLEC5A and TLR2 are critical in SARS-CoV-2-induced NET formation and lung inflammation. |
ENSMUSG00000029915 |
Clec5a |
159.979656 |
13.2414549596 |
3.726990 |
0.382671839 |
80.833724 |
0.00000000000000000024553178759700560370206782985177602790020229167203345398834413160216172400396317243576049804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000002108231055806749442219301501496361475401390302549181968161384759241627762094140052795410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
310.2984240 |
65.4356255 |
23.1404870 |
3.9304289 |
| ENSG00000258232 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
317.519693 |
2.3226929447 |
1.215798 |
0.096206461 |
161.172558 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000062728400836508997483301284847330393775420830106535101333296612777205883319286841273898054302266685811062529865012038499116897583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000009705148808667429295007989336342505048171436516203189486435158938162287992429758053622219535986476168787362439616117626428604125976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
446.8655429 |
24.7478696 |
193.7953600 |
8.5540096 |
| ENSG00000258388 |
100532746 |
PPT2-EGFL8 |
protein_coding |
Q9UMR5 |
FUNCTION: Removes thioester-linked fatty acyl groups from various substrates including S-palmitoyl-CoA. Has the highest S-thioesterase activity for the acyl groups palmitic and myristic acid followed by other short- and long-chain acyl substrates. However, because of structural constraints, is unable to remove palmitate from peptides or proteins. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10417332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12855696, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9341199}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Lysosome;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring PPT2 (palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 2) and EGFL8 (EGF-like-domain, multiple 8) genes located in the major histocompatibility complex class III region of chromosome 6. The read-through transcript is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), and is thus unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:9374; |
extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; lysosomal lumen [GO:0043202]; lysosome [GO:0005764]; palmitoyl hydrolase activity [GO:0098599]; palmitoyl-(protein) hydrolase activity [GO:0008474]; thiolester hydrolase activity [GO:0016790]; fatty-acyl-CoA biosynthetic process [GO:0046949] |
|
|
|
11.280759 |
0.2702808127 |
-1.887469 |
0.706853812 |
6.119051 |
0.01337326011653832899539473544336942723020911216735839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024954401936802244471591549768163531553000211715698242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5378943 |
2.7099011 |
20.8879823 |
6.7424389 |
| ENSG00000258461 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A1W2PQD3 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
alpha-1,4-glucosidase activity [GO:0004558]; alpha-glucosidase activity [GO:0090599]; hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds [GO:0004553]; N-glycan processing [GO:0006491] |
|
|
|
89.340168 |
0.2361180038 |
-2.082420 |
0.463499539 |
18.742574 |
0.00001496048289811137780582709494447968268104887101799249649047851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000045926940011673033986087238966788959260156843811273574829101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.1096074 |
16.9056651 |
161.4424436 |
51.7777006 |
| ENSG00000258559 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.278015 |
0.2419095748 |
-2.047460 |
0.736654841 |
7.496705 |
0.00618119653023818313442028227200353285297751426696777343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012385889327493290051895868941755907144397497177124023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1405591 |
2.0198138 |
17.2259361 |
5.3896116 |
| ENSG00000258634 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37.139331 |
0.4466453742 |
-1.162798 |
0.244739437 |
23.213472 |
0.00000144978121048415270142857656093804408214964496437460184097290039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005036189848610518238658691203557538074164767749607563018798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.4545528 |
3.6241964 |
52.8275988 |
5.0756392 |
| ENSG00000258727_ENSG00000259431 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
162.480470 |
0.3614758595 |
-1.468029 |
0.356878819 |
16.273655 |
0.00005482087735621589023394042983206020380748668685555458068847656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000156813207321268718256318530634985108918044716119766235351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
89.9849336 |
27.5373497 |
247.2947484 |
54.0008120 |
| ENSG00000258744 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.311392 |
0.3248935068 |
-1.621961 |
0.450876473 |
13.156797 |
0.00028647811411692392221869929436195434391265735030174255371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000733336275471001925937986065662244072882458567619323730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0171838 |
2.2618535 |
24.8356367 |
4.2980500 |
| ENSG00000258839 |
4157 |
MC1R |
protein_coding |
Q01726 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for MSH (alpha, beta and gamma) and ACTH (PubMed:1325670, PubMed:8463333, PubMed:1516719, PubMed:11442765, PubMed:11707265). The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylate cyclase (PubMed:1325670, PubMed:11707265, PubMed:16463023, PubMed:19737927). Mediates melanogenesis, the production of eumelanin (black/brown) and phaeomelanin (red/yellow), via regulation of cAMP signaling in melanocytes (PubMed:31097585). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11442765, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11707265, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1325670, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1516719, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16463023, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19737927, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31097585, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8463333}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Disease variant;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This intronless gene encodes the receptor protein for melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). The encoded protein, a seven pass transmembrane G protein coupled receptor, controls melanogenesis. Two types of melanin exist: red pheomelanin and black eumelanin. Gene mutations that lead to a loss in function are associated with increased pheomelanin production, which leads to lighter skin and hair color. Eumelanin is photoprotective but pheomelanin may contribute to UV-induced skin damage by generating free radicals upon UV radiation. Binding of MSH to its receptor activates the receptor and stimulates eumelanin synthesis. This receptor is a major determining factor in sun sensitivity and is a genetic risk factor for melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. Over 30 variant alleles have been identified which correlate with skin and hair color, providing evidence that this gene is an important component in determining normal human pigment variation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4157; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; hormone binding [GO:0042562]; melanocortin receptor activity [GO:0004977]; melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor activity [GO:0004980]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger [GO:0007187]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556]; melanin biosynthetic process [GO:0042438]; negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032720]; pigmentation [GO:0043473]; positive regulation of feeding behavior [GO:2000253]; positive regulation of protein kinase A signaling [GO:0010739]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of protein kinase C signaling [GO:0090037]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222]; sensory perception of pain [GO:0019233]; UV protection [GO:0009650]; UV-damage excision repair [GO:0070914] |
11179997_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11254446_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11305330_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11487574_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11487744_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11500805_MC1R genotype modifies genetic susceptibility to melanoma in families with CDKN2A mutations. 11500805_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11500806_mutations modify risk in Dutch families for melanoma 11511307_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11532853_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11689486_The human receptor efficiently rescued mouse Mc1r deficiency and appeared to be completely resistant to the effect of agouti, suggesting agouti protein may play a role in human pigmentary variation. 11710950_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11720436_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11933208_Four novel variants in MC1R in red-haired South African individuals of European descent: S83P, Y152X, A171D, P256S. 12006619_Loss-of-function mutations in the MC1R gene sensitize human melanocytes to the DNA damaging effects of UV radiation, which may increase skin cancer risk. 12177778_Immunohistochemistry revealed a strong expression of melanocortin 1 receptor in all tested primary and metastatic melanomas, but also demonstrated low levels of expression in adrenal medulla, cerebellum, liver and keratinocytes. 12204775_MC1R expression is regulated by microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) 12244039_the function of the MC1 and MC4 receptors can be positively modulated by metal ions acting both as partial agonists and as potentiators for other agonists 12439754_suggests an alternative non-pigmentary mechanism whereby MC1R variants could modify melanoma susceptibility or progression 12453185_Melanocortin 1 receptor is regulated by paracrine factors, including its own ligands, by specific endocrine sex hormones, and by UVR. 12473109_MC1R second transmembrane fragment is critical for agonist binding and maintenance of a resting conformation, whereas the second intracellular loop is essential for coupling to the cAMP system 12579416_The MC1R gene probably does not play as significant role as other genes in the pigmentation variation between African and European populations. 12653999_Structural requirements that allow an active conformation without binding to a ligand, as a consequence of the E/K mutation, are not conserved within MC receptors; results are discussed in relationship to feather colour in chicken, structure and evolution 12663858_women with two variant MC1R alleles displayed significantly greater analgesia from the kappa-opioid, pentazocine, than all other groups 12753400_melanocortin-1 receptor has a role in skin cancer risk phenotypes through a polymorphism 12817591_A candidate gene for pigmentation. 12839583_Red hair in black Jamaicans is due to a mutation in MC1R. 12851329_data show considerable gene sequence variation with the detection of eight synonymous and three nonsynonymous mutations in normally pigmented African individuals 12859622_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12876664_mutations in the MC1R gene were responsible for the red (rather than yellow/blond) hair in the six of eight who continued to have red hair after birth; the first demonstration of a gene modifying the oculocutaneous albinism phenotype in humans 12883368_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12883368_There were no significant differences in the frequency of any of the five most common variants of MC1R between 62 ocular melanoma cases and ethnicity-matched population controls. 12930311_In a study of 20 persons, 10 of whom were homozygous for MC1R mutations, we measured erythema over a 21-day period in response to a range of ultraviolet B doses. We detected no consistent differences in UV B-induced erythema between the groups studied. 12950734_MC1R appears the limiting factor controlling the output of the cAMP signalling pathway 14757863_Strong association between functional MC1R variant alleles and malignant melanoma in the French population. 15009725_MC1R genotype was predictive of hair melanin expressed as the ratio of the loge of eumelanin to pheomelanin ratio, with a dosage effect evident 15009732_ultraviolet irradiation affects the expression of both alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and the melanocortin-1 receptor in human epidermis in vivo 15105175_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15159314_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15210908_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15221796_Eight novel MC1R missense mutations found Italians Melanoma patients. 15221796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15305821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15358786_UV-induced expression of POMC and MC1R is dependent on the p-38-activated upstream stimulating factor-1 15470082_Outlining the ligand recognition sites in the melanocortin receptors. 15482480_Asp84Glu, Val92Met, Arg163Gln, and Asp294His variants of the human MC1 receptors differ in ability to bind alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) peptides and increase intracellular cAMP 15582585_melanocortin receptors (MC1R and MC3R) exist as constitutively pre-formed dimers 15650023_Melanocortin 1 receptor signaling is regulated by GRK2 and GRK6, which may be important determinants of skin pigmentation. 15726415_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15889046_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15957185_analysis of the highly polymorphic locus MC1R 15972726_Altered cell surface expression of human MC1R variant receptor alleles associated with red hair and skin cancer risk. 15979202_review of polymorphism and selection at the MC1R coding and promoter regions in human populations, the pattern of MC1R evolution in nonhuman primates, and the interaction of MC1R with other genes [review] 15993512_The MC1R C-terminal pentapeptide is essential for proper receptor expression on the plasma membrane. 15994880_C57BL/6-Mc1r(e/e) mutant mice and human redheads--both with non-functional MC1Rs--display reduced sensitivity to noxious stimuli and increased analgesic responsiveness to the mu-opioid selective morphine metabolite, M6G. 15998953_MC1R was associated with melanoma risk and progression in a Mediterranean population, particularly in the absence of other strong risk factors, such as freckling or many nevi. 16081629_Dermal papilla cells expressed both MC1R and MC4R in vitro, and immunoreactivity for these receptors was also present in cells of the human dermal papilla in situ. 16417234_Cells expressing epitope-tagged MC1R revealed dimeric and oligomeric species in detergent-solubilized extracts. 16420249_Results describe the relative expression levels of both melanocortin-1 receptor mRNA and protein in a subset of different cell types. 16463023_Novel functional variants of the melanocortin 1 receptor gene originated from Asians. 16567973_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16601669_MC1R polymorphisms are a predisposing factor of melanoma in a southern European population with a relatively low incidence of the disease. 16601669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16645598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16645598_Our data show that MC1R and PTCH variants are associated with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) risk in the French population. 16721784_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16721784_effects of the MC1R variants on skin cancer risk were independent from self-reported phenotypic pigmentation 16809487_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16809487_findings show that MC1R variants are strongly associated with BRAF mutations in non-chronic sun-induced damage melanomas; in this subtype, risk for melanoma associated with MC1R is due to increase in risk of developing melanomas with BRAF mutations 16864968_Disruption of the endogenous anti-inflammatory circuit based on MC1R could contribute to tissue damage during brain death. 16877522_MC1R isosform is a negative regulator of skin pigmentation and MC1R isoform-specific expression is closely related to skin pigmentation and photoprotection. 16914085_Variant amino acids in different domains of the human melanocortin 1 receptor compromise normal MC1R processing and impair cell surface expression. 16982779_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16988943_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17072629_Melanoma risk increased with the number of variant MC1R alleles carried by an individual 17072629_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17130136_Desensitization and internalization of three variant MC1R forms associated with red hair and increased skin cancer risk. 17222061_These findings offer insights into the transcriptional nature of the response to ultraviolet rays (UV) in the skin and provide a molecular framework for the mechanisms by which melanocytes and the Mc1r independently afford protection against UV radiation. 17279550_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17316231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17317724_examined POMC processing in human skin and the effect of POMC on the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC-1R) and melanocyte regulation 17371441_Based on these in vitro studies, we believe that the result we observed for Val92Met could be attributed to impaired MC1R function, while, for Arg163Gln, other factors, e.g. effect of other loci, need to be considered. 17371441_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17397031_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17397031_study of cutaneous phenotype & MC1R variants as modifying factors for development of melanoma in CDKN2A G101W mutation carriers; suggests these factors differentially contribute to development of melanoma 17434924_Both red hair color and non-red hair color variants, and possibly other rare non-synonymous variants of MC1R are implicated in the development of malignant melanoma in the Spanish population. 17434924_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17487313_Cell surface-enforced expression of melanocortin 1 receptor on HaCaT keratinocytes and alpha-MSH stimulation do not affect the formation of UVB-induced DNA photoproducts and their subsequent repair. 17496785_analysis of the Y152X MC1R gene mutation in ethnically diverse Jewish malignant melanoma patients 17570052_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17616515_direct correlations between variant MC1R biochemical properties and pigmentation phenotype. 17916200_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17952075_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17960121_Pink-eye-dilution gene mutations underlie oculocutaneous albinism in this family. Two known mutations in MC1R caused red hair color in one family member. No modifier effect of MC1R on P mutations could be deduced. 17960564_Fundamental differences in physiology of melanocytes expressing red hair color MC1R receptors and those of wild-type genotype, which are likely to contribute to increased skin cancer risk for individuals that carry these variants. 18006116_confirmed p38 signaling as an MC1R-regulated pathway and identified a large synergistic interaction between UV irradiation and MC1R stimulation for the activation of p38 18067130_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18067130_Our data confirmed the status of the nonsynonymous MC1R variants as independent genetic risk factors for BCC (Basal Cell Carcinoma). 18079748_MC1R polymorphisms may have a role in development of freckles and solar lentigines 18094732_R151C variant is associated with red hair and weak cAMP accumulation failing to stimulate tyrosinase activity 18222116_quadruple Cys35-267-273-275Ala mutant migrating as a monomer in SDS-PAGE in the absence of reducing agents was able to dimerize with WT. 18282185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18292087_These data identify the NR4A receptor family as potential mediators of an MC1R-coordinated DNA damage response to ultraviolet rays exposure in melanocytic cells. 18368129_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18368129_This study confirms that the known MC1R-melanoma risk association is confined to subjects whose melanomas harbor BRAF mutations. 18402696_This study further quantifies the degree of population-specific genetic variation and suggests that positive selection may be present in European populations in MC1R 18483556_Genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18484624_red hair and fair skin is found in the absence of MC1R function [case report] 18510673_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18637131_MC1R R mutations had a 3.7-fold increase in melanoma risk and a 3.3-fold increase in basal cell carcinoma risk. 18637131_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18657399_the association of D84E variant of the alpha-MSH receptor 1 gene as an independent risk factor for an earlier onset of cutaneous malignant melanoma. 18683857_MC1R and SLC45A2 variants had additive effects on melanoma risk, and after adjusting for pigmentation characteristics, the risk was persistent 18683857_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18711112_Interplay of red hair color variant genotype, red hair/fair skin phenotype, and multiple sclerosis (MS) is complex. Modification of past sun exposure by MC1R genotype suggests ultraviolet radiation or vitamin D may be causally related to reduced MS risk. 18711112_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18717860_A significant proportion of the population showed risk factors for skin cancer. The inhabitants of the Canary Islands are phenotypically and genotypically close to Mediterranean populations. MC1R gene polymorphisms. 18717860_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18761657_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18761657_Results indicate that the melanocortin 1 receptor gene is not a frequent target of somatic alterations in melanoma. 18795926_dermoscopic features of early melanoma in CDKN2A mutation-positive Spanish individuals; mean +/- SD ABCD total dermoscopy score (TDS) was significantly higher in noncarriers of red hair MC1R polymorphisms than in carriers of 2 MC1R gene red hair variants 18803811_The effect of discovered MC1R variants on the individual's pigmentation characteristics, or risk of skin cancer, remains to be elucidated 18839200_Eighteen SNPs in the MC1R gene and P genes were genotyped in 52 individuals by the direct sequencing method, and 4 SNPs (MC1R gene: R163Q and P gene: IVS5 + 1001, IVS13 + 113, and H615R) were selected on the basis of differences in frequencies. 18839200_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18946769_MC1-R-effector coupling in (differentiated) human adipocytes is too weak to induce a regulatory effect on lipolysis or inflammation; by contrast, MC1-R stimulation in undifferentiated MSCs induces an inhibitory signal on cell proliferation. 18983535_MC1R variant is associated with multiple primary melanoma. 18983535_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19016241_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19017395_transcriptional regulation of the melanocyte-specific MC1R gene requires an internal promoter located in the 150 base pairs upstream the initiation codon. 19077144_MC1R and CDKN2A variation in relation to phenotype, clinical factors and cutaneous malignant melanoma risk in the Swedish population, was investigated. 19077144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19194882_In the case-control study, participants with Cys/Cys genotype, which was associated with red hair, had a greater PD risk, relative to the Arg/Arg genotype (adjusted RR, 3.15; 95% confidence interval, 1.1-9.4). 19194882_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19208107_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19208107_Using various approaches study showed that there is an interaction between MC1R and HERC2 in determination of skin and hair colour in the studied population sample. 19269164_22 MC1R variants were identified in Israeli Jewish individuals, two of which (i.e. M73I and 496_497insG) are novel. 19269164_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19320745_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19338054_The functional characterization of six MC1R alleles found in Spanish melanoma patients. 19339902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19340012_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19452503_Aberrant trafficking of human melanocortin 1 receptor variants associated with red hair and skin cancer: Steady-state retention of mutant forms in the proximal golgi. 19484507_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19484507_the factors modifying significantly the melanoma risk associated with CDKN2A mutations (stepwise procedure) were: MC1R and dysplastic nevi (increasing the risk) and GSTT1 (decreasing the risk). 19493000_MC1R is expressed in normal & neoplastic thyroid epithelial cells, but at lower levels than in melanocytes. The strong association between BRAF mutations and MC1R variants previously found in melanoma does not extend to thyroid cancer. 19493000_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19558415_Results demonstrate activation of the melanocortin 1 receptor by tripeptide melanocortin analogs. 19571053_Participants with MC1R gene variants reported significantly more dental care-related anxiety and fear of dental pain than did participants with no MC1R gene variants. They were more than twice as likely to avoid dental care. 19571821_We observed no association between germline MC1R status and somatic BRAF mutations in melanomas 19578364_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19585506_Melanocortin receptor 1 variants are associated with melanoma. 19585506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19656326_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19679055_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19710684_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19755124_the melanoma-associated MC1R mutations impact differently on cAMP and ERK signalling, suggesting that cAMP is not responsible for functional coupling of MC1R to the ERK cascade. 19790046_The pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)-derived neuropeptide alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) mediates its effects via melanocortin (MC) receptors in human articular chondrocytes. 19924138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19924138_genetic variations of MC1R are important determinants for severe photoaging 19932942_In this cohort of cancer patients, deoxyribonucleic acid sequence variants of the MC1R gene, especially the R160W variant, have been associated with unexpectedly severe acute reactions to radiation therapy. 19932942_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20043015_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20043015_no support for MC1R variants with BRAF mutation for melanoma risk 20129839_MC1R homozygote variant alleles at R151C, R160W, D294H and D84E are related fair skin, red hair and to spending less time outdoors. DLBCL and FL risk were not related to genetic variation in MC1R, pigmentation or time spent outdoors. 20189796_MC1R variants significantly increase penetrance of CDKN2A mutations in melanoma-prone families, especially with respect to multiple MC1R variants and to red hair color variants. 20189796_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20301115_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20301115_These data indicate that MC1R genotypes provide information about melanoma risk in those individuals who would not be identified as high risk based on their phenotypes or exposures alone. 20374726_The association of MC1R variant alleles with skin cancer risk remains after correction for pigmentation phenotype, indicating regulation of nonpigmentary pathways. 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20519635_findings highlight the molecular mechanisms by which the melanocortin 1 receptor genotype controls genomic stability of and the mutagenic effect of ultraviolet radiation on human melanocytes 20539244_relevance of loss of function MC1R variants in the risk of melanoma in multiple primary melanoma cases with family history from areas with low melanoma incidence rate. 20585627_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20588308_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20629734_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20629734_variants R160W and D294H individually associated with malignant melanoma risk 20670983_Multiple sclerosis outcome is influenced by interactions between host response to ultraviolet radiation and MC1R single nucleotide polymorphisms. 20670983_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20720566_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20720566_association between MC1 receptor germline variation and BRAF/NRAS mutations in melanoma 20721616_MC1R and pigmentary phenotype may modify the effects of sun exposure on melanoma risk on more continuously sun-exposed skin. 20721616_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20797666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20802377_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20831872_Further analysis of binding and functional data suggests that the ASIP C-terminal loop (a six-amino-acid segment closed by the final disulfide bond) is essential for high-affinity MC1R binding and inverse agonism. 20876876_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20876876_Results show that MC1R variants, hair color, and number of nevi were jointly associated with melanoma risk in CDKN2A mutation carriers. 20970119_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21052032_MC1R gene might be associated with major depressive disorder and with treatment response to desipramine 21052032_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 21071418_The human melanocortin 1 receptor gene, has a highly complex and inefficient poly(A) site which is instrumental in allowing intergenic splicing between this locus and its immediate downstream neighbour tubulin-beta-III (TUBB3). 21084381_MC1R signaling activated the ERK pathway in normal human melanocytes and melanoma cells through cKIT. 21097776_This small study of XP patients suggests that defective DNA repair has a greater influence on skin cancer risk than variants of MC1R. 21128237_the nine most common MC1R variants make a sizeable contribution to the burden of melanoma (Meta-analysis) 21197618_Data show that Mc1R, HERC2, IRF4, TYR and EXOC2 are ranked highest in hair color prediction analysis. 21199646_complex functions of the melanocortin MC(1) receptor and the molecular mechanisms underlying the association between melanocortin MC(1) receptor variant alleles and the red hair colour phenotype 21378282_Spatiotemporal localization of MC1R and alpha-MSH in cutaneous wounds warrants future investigation into the role of MC1R/alpha-MSH signaling in the inflammatory and fibroproliferative responses to cutaneous injury. 21541274_TYR gene mutations have a more severe effect on pigmentation than mutations in OCA2 and the GPR143 gene. Nevertheless, mutations in these genes affect the development of visual function either directly or by interaction with other genes like MC1R. 21570562_The presence of two major diminished function variants was found to be a risk factor for facial photoaging in French middle-aged women. 21602033_Data suggest that antagonists of MC1R and MC5R could be effective inhibitors of sebaceous gland differentiation and the production of sebum-specific lipids. 21733131_These results demonstrate that UBE3A plays a role in MC1R transcriptional regulation. 21737053_higher frequency of superficial spreading melanomas and melanomas associated with melanocytic nevi in patients carrying certain mutations in MC1R 21749400_Melanocortin 1 receptor remains the best characterized genetic determinant of human skin and hair pigmentation as well as the more firmly validated low penetrance skin cancer susceptibility gene. (Review) 21898403_Suggest that constitutive activity of MC1R in keratinocytes may reduce UVA-induced oxidative stress via EGFR and cAMP-dependent mechanisms. 21931793_Results suggest that in MC1R, which lacks an extracellular loop 2, the first extracellular loop may play a more prominent role during receptor activation than in general. 22095472_study found that MC1R variants are associated with increased risk of early-onset melanoma 22158557_MC1R, number of moles, skin reaction to first summer sun for 1 hour, and hair and skin color were independently associated with basal cell carcinoma. 22325793_A survival benefit for inherited MC1R variants in melanoma patients. 22336944_work supports the hypothesis that MC1R is required to mediate the nuclear excision repair process through p38 activation and the postulation that persons with red hair color skin phenotype are compromised in their ability to activate p38 and so mediate DDB2 degradation 22364200_Beta-defensin 3 may be a novel melanocortin-1 receptor agonist involved in regulating melanocyte responses in humans. 22447455_By using a population-based material of high-risk melanoma cases, we demonstrate a significant effect of both MC1R red hair color (RHC) variants and an ASIP haplotype, but could not replicate an association with postulated risk SNPs of TYR and TYRP1. 22464347_In South European populations, MC1R red hair color and SCL45A2 p.Phe374Leu variants are strong melanoma risk predictors. 22464597_At least 1 of the following was present in 58% of cutaneous melanoma patients: V60L, V92M, I155T, R163Q and especially R160W & D294H. Carriers had a history of sunburn.Carriers of R160W also had melanomas associated with melanocytic nevi. 22493442_MC1R regulates melanoma cell migration via inhibition of syndecan-2 expression. 22512251_The results indicate that polymorphism at MC1R constitutes a pigmentation-independent risk factor in the development of basal cell carcinoma. 22512708_The results indicated that melanogenesis is dramatically enhanced in skin autografts by the melanocortin-1 receptor, and suggest that overexpression of melanocortin-1 receptor may play an important role in the hyperpigmentation process of skin autografts. 22547573_Further assessment of MC1R variants in A549 cells, an in vitro model of inflammation, revealed an enhanced inflammatory response resulting from expression of the F196L variant (versus the wild-type MC1R). 22572817_results identify HBD3 as an antagonist of the MC1R that is expressed in human melanocytes and shed new light on the regulation of MC1R expression and activity by its agonist and antagonists. 22572819_Germline melanocortin-1-receptor genotype is associated with severity of cutaneous phenotype in congenital melanocytic nevi and MC1R has a role in human fetal development 22622028_Results show that p53 is an important target of the downstream melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R) signaling that reduces oxidative stress and possibly malignant transformation of melanocytes. 22804906_multivariate logistic analysis confirmed the role of MC1R as independent risk factor for CDKN2A- melanoma cases only. 22854540_Association of melanocortin 1 receptor gene polymorphisms with skin reflectance and freckles in Japanese 22961816_Description of an association of two SNPs, rs3212345:C>T and rs3212346:G>A, located approximately 2.5 kb upstream of the melanocortin-1 receptor (MC1R) translation initiation codon, with pigmentation phenotype variation in a Southeast Brazilian miscegenated population. 22965007_Report MC1R polymorphisms and dermatoscopic features in atypical naevi and melanomas from high risk melanoma patients. 22978401_two high-risk MC1R variants in our identical twins 23000456_The cAMP pathway is more frequently impaired in melanoma than could be predicted by the MC1R or NRAS genotype. 23096702_We observed a nonsignificant association between germline MC1R status and somatic BRAF mutations in melanomas from trunk sites whereas we observed a significant inverse association between MC1R and BRAF for melanomas of the head and neck. 23146638_Red hair and the MC1R gene were significantly linked to higher levels of dental anxiety but were unrelated to success rates of the inferior alveolar nerve block in women with healthy pulps. 23165166_We examined the association between 12 variants of four pigmentation-related genes (TYR, OCA2, SLC45A2, MC1R) and variations in the 23224873_NCKX5, a natural regulator of human skin colour variation, regulates the expression of key pigment genes MC1R and alpha-MSH and alters cholesterol homeostasis in normal human melanocytes. 23312576_On mutation screening of MC1R, a novel c.917G>A mutation was found to be solely associated with oculocutaneous albinism in a Pakistani family. 23360207_the MC1R gene was directly sequenced and their associations with cutaneous melanoma (CM) risk was assessed in a hospital-based study of 1106 patients with CM and control subjects in Texas; 61 MC1R variants were identified 23392000_melanocortin 1 receptor mutation is associated with melanoma. 23452314_Our results suggest that genetic variations of MC1R are important determinants of the development of sleep lines 23489693_The novel melanoma cell lines were compared to metastatic cell lines (HBL, LND1), wild type (wt) for MC1R and BRAF genes. 23522749_Results suGGEST the contribution of melanocortin 1 receptor gene (MC1R) variants to a genetic predisposition to melanoma in Latvia. 23647022_Results suggest that certain MC1R variants could increase the risk of melanoma due to their impact on pathways other than pigmentation, and may therefore be linked to specific melanoma subtypes. 23711066_CDKN2A mutation and MC1R variants may have a role in the development of dysplastic melanocytic lesions 23744330_No association between the selected SNPs of MC1R gene has been found with development of freckles for the selected Chinese Han population from Chengdu. 23749232_Melanocyte stem cells migrate to th |
ENSMUSG00000074037 |
Mc1r |
12.196265 |
0.2739815628 |
-1.867849 |
0.777994256 |
5.595530 |
0.01800636115704186412944665107715991325676441192626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032628942661111839940168977136636385694146156311035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1416861 |
2.5446386 |
19.0217740 |
6.1554992 |
| ENSG00000258859 |
|
LINC02296 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.204217 |
0.2817229061 |
-1.827651 |
0.350380344 |
28.870413 |
0.00000007738601427960336572936327721380922461946738621918484568595886230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000308624039656024218977931929119851162113263853825628757476806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.4090685 |
2.3926345 |
36.9270268 |
4.8983099 |
| ENSG00000258875 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60.228421 |
2.3619602315 |
1.239985 |
0.270079791 |
20.871382 |
0.00000491178450809059213372437593947417155959556112065911293029785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000016000428015761894093293982166414934908971190452575683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
85.7516960 |
12.3272242 |
36.3281156 |
4.0595027 |
| ENSG00000258920 |
400236 |
FOXN3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.944506 |
0.4977156398 |
-1.006606 |
0.402973285 |
6.324400 |
0.01190877696934145371643332111943891504779458045959472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022494695171164560271170884675484558101743459701538085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5668275 |
2.6562353 |
21.3693125 |
3.4860955 |
| ENSG00000258947 |
10381 |
TUBB3 |
protein_coding |
Q13509 |
FUNCTION: Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a cylinder consisting of laterally associated linear protofilaments composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin heterodimers (PubMed:34996871). Microtubules grow by the addition of GTP-tubulin dimers to the microtubule end, where a stabilizing cap forms (PubMed:34996871). Below the cap, tubulin dimers are in GDP-bound state, owing to GTPase activity of alpha-tubulin (PubMed:34996871). TUBB3 plays a critical role in proper axon guidance and maintenance (PubMed:20074521). Binding of NTN1/Netrin-1 to its receptor UNC5C might cause dissociation of UNC5C from polymerized TUBB3 in microtubules and thereby lead to increased microtubule dynamics and axon repulsion (PubMed:28483977). Plays a role in dorsal root ganglion axon projection towards the spinal cord (PubMed:28483977). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:20074521, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28483977, ECO:0000269|PubMed:34996871}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell projection;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;GTP-binding;Isopeptide bond;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Microtubule;Nucleotide-binding;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
This gene encodes a class III member of the beta tubulin protein family. Beta tubulins are one of two core protein families (alpha and beta tubulins) that heterodimerize and assemble to form microtubules. This protein is primarily expressed in neurons and may be involved in neurogenesis and axon guidance and maintenance. Mutations in this gene are the cause of congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles type 3. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 6. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2010]. |
hsa:10381; |
axon [GO:0030424]; cell periphery [GO:0071944]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; dendrite [GO:0030425]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium [GO:0030175]; growth cone [GO:0030426]; intercellular bridge [GO:0045171]; lamellipodium [GO:0030027]; microtubule [GO:0005874]; microtubule cytoskeleton [GO:0015630]; mitotic spindle [GO:0072686]; neuronal cell body [GO:0043025]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; GTP binding [GO:0005525]; GTPase activity [GO:0003924]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; netrin receptor binding [GO:1990890]; peptide binding [GO:0042277]; structural constituent of cytoskeleton [GO:0005200]; axon guidance [GO:0007411]; dorsal root ganglion development [GO:1990791]; microtubule cytoskeleton organization [GO:0000226]; mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000278] |
12789263_Patients with low beta-tubulin III levels had better response in the paclitaxel/carboplatin 12905530_Human brain and testis specific betaIII-tubulin diminishes microtubule assembly, and is able to confer weak resistance to paclitaxel when expressed at moderate levels in mammalian cells. 15671559_class III beta-tubulin has a role in paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer 16061864_high level of expression of class III beta-tubulin in tumor cells is associated with resistance to vinorelbine and a poor prognosis in patients with NSCLC receiving vinorelbine-based chemotherapy 16675570_useful to identify poor prognosis ovarian cancer patients candidates to more aggressive and/or targeted therapy. 16816122_Deleterious post-translational modifications of beta 3 tubulin accumulate in a pathological protein fraction in Alzheimer dissease. 17289895_bTubIII has a role in progression of non-small cell lung cancer 17406983_Data suggest that aberrant expression and interactions of betaIII-tubulin and gamma-tubulin may be linked to malignant changes in glial cells. 17543088_study concludes that class III beta-tubulin is expressed in some cases of major primary brain tumour types except pilocytic astrocytoma; extent of class III beta-tubulin expression is variable 17714470_TUBB3 is expressed in most pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Up-regulation of TUBB3 in PanIN lesions suggests that microtubule dysfunction is an early feature of this disease. 18178340_Methylation analysis of 3' enhancer showed that it was free of methylation in 70% cells in A2780, while in less than 16% in both TC1 and HeLa cells, thereby suggesting that TUBB3 increase upon hypoxia is abolished through methylation of the 3' enhancer. 18379434_In the midgestational human brain, betaIII-tubulin is not neuron specific because it is constitutively expressed in GFAP+/nestin+ presumptive fetal astrocytes 18435451_roles of cys124 & ser239 in function of betaIII tubulin; results indicate roles of these residues in colchicine binding & microtubule integrity are complex & residues at which betaIII differs from other isotypes keep betaIII in functional conformation 18497984_Epigenetic modification involved in aberrant expression of TUBB3 is associated with ovarian cancer 18645017_TUBB3 was analyzed in a panel of drug-sensitive and drug-resistant cell lines. 18946987_Study of expression of beta-III tubulin in human eye tissues during prenatal development 18977553_the level of tubulin beta 3 expression may predict survival in NSCLC patients receiving carboplatin and paclitaxel 19074767_Roles of tubulin beta 1,3 residues Ala428 and Thr429 in microtubule formation in vivo. 19122647_loss of TUBB3 protein may be induced by histone deacetylation in a subset of malignant melanomas, and may be associated with chemosensitivity to taxane 19360438_This is the first report documenting a preferential localization of beta(III)-tubulin in the invading epithelium of colorectal cancer. 19405953_This protein has been found differentially expressed in the Wernicke's Area from patients with schizophrenia. 19690549_betaIII-tubulin expression is augmented in prostate cancer by androgen ablation and that the expression of this beta-tubulin isoform is associated with the progression of prostate cancer to the castration-resistant state. 19724850_Class III beta-tubulin a potential candidate to distinguish small basal cell carcinoma non-neoplastic hair buds 19828208_This paper reviews the evidence base for betaIII tubulin expression as a prognostic and predictive biomarker inN on-small cell lung cancer 19899405_The immunostaining pattern of tubulin did not correlate with age, clinical stage, histological grade, depth of invasion of endometrial cancer. 20021611_determination of the expression of excision repair cross-complementation group 1 and class IIIbeta tubulin is useful to predict the effects of platinum-based anticancer drugs. 20074521_Work to define the TUBB3 syndromes establishes the requirement for a neuronal beta-tubulin isotype in axon guidance and normal brain development. 20087230_Over-expression of class III beta-tubulin is associated with resected non-small cell lung cancer. 20220512_A variety of neoplastic and non-neoplastic lymphoproliferative disorders exhibited characteristic TUBB3 expression patterns. 20393110_congenital fibrosis of extraocular muscle type 3 caused by TUBB3 R262C and D417N amino acid substitutions features abnormalities: subarachnoid CN3 hypoplasia, occasional abducens nerve hypoplasia, and subclinical optic nerve hypoplasia 20403547_betaIII tubulin expression is emerging as a valuable biomarker for taxane resistance in advanced disease, as well as offering prognostic information for outcomes among patients with earlier stage disease. 20534991_HER2 and TUBB3 status might be a good biomarker for determining the most appropriate therapeutic modality in extramammary Paget disease. 20587520_HuR gene silencing revealed that TUBB3 translation is HuR dependent in hypoglycemia because HuR silencing inhibited the entry of TUBB3 mRNA into cytoskeletal and free polysomes. 20829227_Mutations in the neuronal beta-tubulin subunit TUBB3 result in malformation of cortical development and neuronal migration defects. 20868593_In postoperative NSCLC patients who are receiving adjuvant chemotherapy, patients with high expression of beta-tubulin 3 tend to be resistant to taxane drugs. 21045157_Findings suggest a role for betaIII-tubulin as candidate theranostic biomarker to predict the response to docetaxel-based chemotherapy as well as to target for treatment of docetaxel-resistant CRPC. 21071418_The human melanocortin 1 receptor gene, has a highly complex and inefficient poly(A) site which is instrumental in allowing intergenic splicing between this locus and its immediate downstream neighbour tubulin-beta-III (TUBB3). 21163067_The expression of III beta-tubulin and MDR1 may play an important role in the development and progression of human non-small cell lung cancer. 21289518_High TUBB3 is associated with thymic epithelial tumors. 21315408_class III beta-tubulin expression in prechemotherapy effusions is associated with poor chemoresponse and shorter survival in serous ovarian carcinoma. 21520077_Class IIIbeta-tubulin behaves as a gateway for prosurvival signals, such as those of proto-oncogene protein PIM1 in ovarian cancer cells, which are capable of moving into the cytoskeleton under hypoxic conditions. 21586171_In Chinese advanced gastric cancer, Thymidine Phosphorylase positive & beta-tubulin III negative might predict response and prognosis to capecitabine plus paclitaxel chemotherapy. 21781528_The expression level of BRCA1 and class IIIbeta-tubulin in tumor tissue is probably a predictor for the efficacy of chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. 21820201_betaIII-Tubulin is required for interphase microtubule dynamics in untransformed human mammary epithelial cells 22159867_TUBB3 expression occurs in a cell cycle-dependent manner. 22180309_Data suggest that the increased betaII- and betaIII-tubulin contributed significantly to the resistance phenotype. 22209775_Higher levels of TUBB3 were detected in uterine carcinosarcoma (CS) cell lines and fresh frozen tissues when compared to ovarian CS and were associated with sensitivity to patupilone. 22358390_TUBB3 expression may be a predictive marker for chemoresistance to docetaxel in NSCLC with postoperative recurrent disease 22438565_in colorectal cancer patients, there was a link between poor survival, the expression of TUBB3/TUBB6, and androgen receptor only in females 22502701_High beta III-tubulin expression is associated with drug resistance to docetaxel in patients with advanced breast cancer. 22684772_negative REST and positive TUBB3 protein expression was detected as independent prognostic factors. 22740207_Overexpression of betaIII-tubulin is associated with drug resistance to docetaxel-based chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. 22766748_low levels of TUBB3 in serum could predict better response and survival for advanced gastric cancer patients receiving paclitaxel plus capecitabine. 23218766_High expression levels of tubulin beta 3 class III is associated with response to therapy in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. 23378218_A novel syndrome caused by E410K amino acid substitution in TUBB3 is linked to Kallmann syndrome, cyclic vomiting and Moebius syndrome. 23454725_GLI3, fascin and TUBB3 are the most sensitive markers in Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. 23532817_Gastric cancer tumors with low TUBB3 expression demonstrate improved response to cytotoxic therapy. 23585021_Tubulin-beta-III overexpression in Uterine serous carcinoma discriminates poor prognosis, serves as a marker for sensitivity to epothilones, and may contribute to paclitaxel resistance 23810210_High tubulin beta 3 expression is associated with malignant pleural mesothelioma. 23817083_human melanocytes express TUBB3 and that this protein should be recognized as a wider marker for multiple neural crest-derived cells. 23853246_Higher response rates were observed among betaIII-tubulin-positive patients. 23869586_results suggest that in aggressive breast cancers, as modeled by MDA-MB-231 cells, beta-tubulin class III is a biomarker for cell survival mediated through ZEB1-induced tumor progression pathways. 23941826_Results indicate that Yg-3-46a has the potential to evade drug resistance mediated by P-gp and beta-III tubulin overexpression. 24053422_TUBB3 was a strong predictive marker in recurrent and metastatic gastric cancer patients receiving taxane-based first-line palliative chemotherapy. 24113009_Mutation of EGFR E21 is negatively correlated with TUBB3 gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer. 24232867_Our data support the use of TUBB3 staining in differentiating follicular lymphoma, including BCL2-negative cases, from follicular hyperplasia 24612975_Patients with exotropia, vertical gaze limitation, and ptosis do not have classic Moebius syndrome and may have TUBB3 mutations associated with CFEOM3. 24661907_Sox9 allows the survival of ovarian cells upon hypoxic condition, through the activation of betaIII-tubulin expression. 24705847_The expression level of TUBB3 may be a useful biomarker to predict the clinical outcomes of the taxane/vinorebine-based chemotherapy in patients with NSCLC. 24722794_The sensitivity of gastric cancer patients to paclitaxel treatment was inversely correlated with the mRNA and protein expression of class III beta-tubulin. 24762590_ERCC1 mRNA levels were higher in metastatic adenocarcinoma NSCLC; TUBB3 mRNA levels were significantly higher in poorly differentiated tumors and in advanced stage NSCLC, which indicates the poor prognosis. 24894670_Data indicate that ABCB1 protein, beta tubulin I and III (betaI, and betaIII tubulin) might contribute to the multidrug resistance (MDR) of MCF7/DOC and be potential therapeutic targets for overcoming MDR of breast cancer. 25039376_This study revealed that TUBB3 is a moderately sensitive and highly specific tissue marker for discriminating peripheral intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas from other primary liver tumours. 25130963_betaIII-tubulin down-regulated significantly sensitized NSCLC A549/Taxol cells to Paclitaxel 25244496_evidence for a direct linkage between HIF-2alpha and increased expression of betaIII-t by hypoxia 25414139_Findings revealed how betaIII-tubulin influences tumor growth in NSCLC, defining new biologic functions and mechanism of action of betaIII-tubulin in tumorigenesis. 25416788_Results show that cabazitaxel resistance mechanisms involve alterations in microtubule dynamicity, as manifested by higher expression of TUBB3 and decreased BRCA1. 25482575_These results therefore suggested that certain TUBB3 mutations may predominantly be associated with axonal peripheral neuropathy. 25544769_Data suggest that silencing of beta III-tubulin expression may be a potential therapeutic strategy to increase the long-term survival of pancreatic cancer patients. 25559402_First report of an autosomal-dominant inheritance of the TUBB3 c.1228G>A mutation in a family provides new insights into the spectrum and variability of endocrine phenotypes associated with the TUBB3 E410K syndrome. 25661915_This review discusses the confirmation that Gli1 overexpression is associated with decreased response to tumor chemotherapy, it was possible to sensitize cells to epothilones after addition a suitable inhibitor. 25724666_Results show an overexpression of TUBB3 in breast cancer brain metastases and its expression was significantly associated with distant metastases. These findings suggest a novel role of TUBB3 in regulation of metastases and integrin-Src signaling. 25894372_High level of stathmin exhibited poor response to chemotherapy . Similar effects were not observed for b-III-tubulin. 25964544_High TUBB3 expression in NSCLC appeared to correlate with lower PTX sensitivity 26165688_In advanced cervical squamous cell cancer, TUBB3 was highly expressed in 20.%% of cases. It had no impact on survival in patients treated with antimicrotubule agents. 26198101_Findings suggest that overexpression of Class III beta-tubulin, Sox2, and nuclear Survivin might be predictive of taxane resistance and poor progression-free survival in patients with stage III ovarian epithelial cancer. 26252353_TUBB3, TOP2A, CYP19A1 and CYP2D6 gene expression, but not protein expression, was associated with patient survival in breast cancer . 26406408_High TUBB3 mRNA expression was associated with breast cancer. 26416565_Depletion of betaIII-tubulin from MCF7 breast cancer cells increased mitotic arrest by ixabepilon. Increased betaIII-tubulin may be an important contributor to the development of resistance to ixabepilone. 26426765_The decreased expression of TUBB3 could be a significant marker for predicting unfavourable prognosis in patients with cutaneous malignant melanoma. 26586574_It findings reveal that expression of relatively low levels of TUBB3 in mitotic cells can be detrimental for their cytokinesis and underscore the importance of CIT-K in counteracting this event. 26591579_blocking of the beta-III tubulin expression in colorectal cancer cells does not affect their viability, but reduces the cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix 26639658_TUBB3 mutations cause both Congenital Fibrosis of the Extraocular Muscles type 3 and malformations of cortical development. 26657157_Functional characterization of MC1R-TUBB3 intergenic splice variants of the human melanocortin 1 receptor has been undertaken in response to ultraviolet irradiation. 27046833_mutations proximal to the TUBB3 kinesin-binding site alter polymerization dynamics. 27129203_Epitaxial growth of alpha1A/betaIII microtubules from heterogeneous brain seeds is inefficient but can be fully rescued by incorporating as little as 5% of brain tubulin into the homogeneous alpha1A/betaIII lattice. 27188792_a positive correlation was observed between Snail presence and TUBB3 upregulation in tested adenocarcinoma cell lines. 27207668_This elucidates a hitherto unknown role for this microtubule protein and provides insight into correlations between high betaIII-tubulin expression and poor patient outcome in this disease 27284014_The authors found that transient TUBB3 activation, through ABCB1, in response to the stimulation of FOXO3a expression, significantly contributes to the cross-resistance of the paclitaxel-resistant cell population and consequently limits the efficacy of both agents where cancer cells have developed multiple resistance. 27428177_By linkage and sequencing analyses, we identified the mutation c.784C>T (p.R262C) in TUBB3 gene in six members of a Turkish family with congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles. 27586205_This is the first study that relates concurrent expression of Tubbeta3, ZEB1, and beta-catenin to abnormal epithelial and myofibroblast differentiation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, providing indirect but robust evidence of miR-200 deregulation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition activation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. 28024114_High TUBB3 expression is associated with Melanoma. 28025079_TUBB3 overexpression is linked to an aggressive subtype of urinary bladder cancers, which is characterized by increased genetic instability, p53 alterations, and rapid cell proliferation. 28056823_The expressions of TYMS, TUBB3 and STMN1 were significantly associated with the clinicopathological characteristics of age, gender and family history of gastric cancer, but not with differentiation, growth patterns, metastasis and TNM staging in patients with gastric cancer. 28075472_TUBB3 involvement in breast cancer cells apoptosis 28275089_The miR-34a/STMN1/betaIII-tubulin axis maintains the microtubule cytoskeleton in osteosarcoma, and combining miR-34a with microtubule inhibitors can be investigated as a novel therapeutic strategy. 28397704_The central findings of our study are that TSA and VPA affect the expression of neuronal lineage genes in an rMSCs culture. After exposure to TSA or VPA, the expression of early neuronal gene decreases but equally the expression of mature neuron genes increases 28640948_The remarkable high prevalence of TUBB3 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas emphasizes its putative relevance as a target for future drugs targeting TUBB3 28648944_TUBB3 and TUBB4 are necessary for the transport and proper localization of N-cadherin within the plasma membrane. 29022485_these results identify a broad spectrum of cancers that can at least sporadically express TUBB3. Testing of TUBB3 in cancer types eligible for taxane-based therapies could be helpful to identify patients who might best benefit from this treatment. 29339176_Our data indicate that an absence of TUBB3 expression in specimens obtained by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration may be a favorable predictive marker of the response to nab-P + Gem in patients with unresectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. 29382549_Results demonstrated that TUBB3 mutations impair the interaction of DCC with polymerized TUBB3 in MTs and inhibit netrin-1-induced neurite outgrowth, branching and attraction. These results suggest a disease mechanism underlying TUBB3 mutation-associated axon guidance defects: mutations in TUBB3 disrupt engagement of netrin/DCC signaling with MT dynamics, resulting in specific defects of netrin-1-mediated axon projection. 29491095_Tubulin beta 3 (TUBB3) expression was identified as a useful predictive factor for survival. 30570863_The expression levels of TUBB3, ERCC1 and P-gp in ovarian cancer tissues were significantly higher than those in adjacent normal tissues (p |
ENSMUSG00000062380 |
Tubb3 |
88.010147 |
2.8712556190 |
1.521682 |
0.192750073 |
62.630020 |
0.00000000000000249422521188422698864629980482058138165421664819709768323718890314921736717224121093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000017414741782124497007176974062607720318313249407982112870740820653736591339111328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
128.4550551 |
14.4776194 |
45.1365972 |
4.0525073 |
| ENSG00000259024 |
100533496 |
TVP23C-CDRT4 |
protein_coding |
Q96ET8 |
|
Acetylation;Alternative splicing;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring readthrough transcription between the neighboring TVP23C (trans-golgi network vesicle protein 23 homolog) and CDRT4 (CMT1A duplicated region transcript 4) genes on chromosome 17. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, one of which encodes a protein that shares sequence identity with the upstream gene product, but its C-terminus is distinct due to frameshifts relative to the downstream gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:100533496;hsa:201158; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; protein secretion [GO:0009306]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
|
|
|
9.109878 |
0.0926342929 |
-3.432310 |
0.643353314 |
33.574351 |
0.00000000685912633995431512780726349349028070356837361032376065850257873535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000030347933086848230290623166811175837054292969696689397096633911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0218836 |
0.4417983 |
11.1546652 |
2.9459306 |
| ENSG00000259030 |
100526835 |
FPGT-TNNI3K |
protein_coding |
Q59H18 |
FUNCTION: May play a role in cardiac physiology. {ECO:0000303|PubMed:12721663}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;ANK repeat;ATP-binding;Cardiomyopathy;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Disease variant;Kinase;Magnesium;Metal-binding;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Serine/threonine-protein kinase;Transferase |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription from the neighboring fucose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase (FPGT) and TNNI3 interacting kinase (TNNI3K) genes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that are composed of in-frame exons from each individual gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:100526835;hsa:51086; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; protein C-terminus binding [GO:0008022]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein serine kinase activity [GO:0106310]; protein serine/threonine kinase activity [GO:0004674]; troponin I binding [GO:0031013]; bundle of His cell to Purkinje myocyte communication [GO:0086069]; protein phosphorylation [GO:0006468]; regulation of cardiac conduction [GO:1903779]; regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0055117]; regulation of heart rate [GO:0002027]; regulation of postsynapse organization [GO:0099175] |
|
|
|
73.767750 |
0.3389687994 |
-1.560776 |
0.388953026 |
15.388207 |
0.00008753290126159005873126423002972273934574332088232040405273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000242626408003956647082416386851377865241374820470809936523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.8841820 |
14.5088696 |
108.2700819 |
30.9463361 |
| ENSG00000259049 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.864337 |
0.0120717249 |
-6.372224 |
1.161896388 |
38.592345 |
0.00000000052223334810101220383699303204572302050667786943449755199253559112548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002556605047419880565603731928251210470115495354548329487442970275878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.1931557 |
0.1802152 |
16.1159489 |
5.6879406 |
| ENSG00000259172 |
|
SNRPA1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.871136 |
0.1298067316 |
-2.945563 |
0.979116589 |
8.191485 |
0.00420874608226264913801717426622417406179010868072509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008740831880427282415957357386560033774003386497497558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1056049 |
3.5539118 |
39.8599644 |
18.3260025 |
| ENSG00000259207 |
3690 |
ITGB3 |
protein_coding |
P05106 |
FUNCTION: Integrin alpha-V/beta-3 (ITGAV:ITGB3) is a receptor for cytotactin, fibronectin, laminin, matrix metalloproteinase-2, osteopontin, osteomodulin, prothrombin, thrombospondin, vitronectin and von Willebrand factor. Integrin alpha-IIb/beta-3 (ITGA2B:ITGB3) is a receptor for fibronectin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, prothrombin, thrombospondin and vitronectin. Integrins alpha-IIb/beta-3 and alpha-V/beta-3 recognize the sequence R-G-D in a wide array of ligands. Integrin alpha-IIb/beta-3 recognizes the sequence H-H-L-G-G-G-A-K-Q-A-G-D-V in fibrinogen gamma chain. Following activation integrin alpha-IIb/beta-3 brings about platelet/platelet interaction through binding of soluble fibrinogen. This step leads to rapid platelet aggregation which physically plugs ruptured endothelial surface. Fibrinogen binding enhances SELP expression in activated platelets (By similarity). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to fractalkine (CX3CL1) and acts as its coreceptor in CX3CR1-dependent fractalkine signaling (PubMed:23125415, PubMed:24789099). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to NRG1 (via EGF domain) and this binding is essential for NRG1-ERBB signaling (PubMed:20682778). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to FGF1 and this binding is essential for FGF1 signaling (PubMed:18441324). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to FGF2 and this binding is essential for FGF2 signaling (PubMed:28302677). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to IGF1 and this binding is essential for IGF1 signaling (PubMed:19578119). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to IGF2 and this binding is essential for IGF2 signaling (PubMed:28873464). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to IL1B and this binding is essential for IL1B signaling (PubMed:29030430). ITGAV:ITGB3 binds to PLA2G2A via a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and this induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1 (PubMed:18635536, PubMed:25398877). ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for fibrillin-1 (FBN1) and mediates R-G-D-dependent cell adhesion to FBN1 (PubMed:12807887). In brain, plays a role in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Involved in the regulation of the serotonin neurotransmission, is required to localize to specific compartments within the synapse the serotonin receptor SLC6A4 and for an appropriate reuptake of serotonin. Controls excitatory synaptic strength by regulating GRIA2-containing AMPAR endocytosis, which affects AMPAR abundance and composition (By similarity). ITGAV:ITGB3 act as a receptor for CD40LG (PubMed:31331973). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O54890, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12807887, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18441324, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18635536, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19578119, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20682778, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23125415, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24789099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25398877, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28302677, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28873464, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29030430, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31331973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9195946, ECO:0000303|PubMed:16322781, ECO:0000303|PubMed:17635696}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for Herpes virus 8/HHV-8. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18045938}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for Coxsackievirus A9. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:7519807}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Hantaan virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9618541}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for Cytomegalovirus/HHV-5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15834425}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGA5:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for Human metapneumovirus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:24478423}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts aP05556s a receptor for Human parechovirus 1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11160695}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Integrin ITGAV:ITGB3 acts as a receptor for West nile virus. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:23658209}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10397733}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell adhesion;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Cell projection;Direct protein sequencing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Integrin;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Postsynaptic cell membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Synapse;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The ITGB3 protein product is the integrin beta chain beta 3. Integrins are integral cell-surface proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. A given chain may combine with multiple partners resulting in different integrins. Integrin beta 3 is found along with the alpha IIb chain in platelets. Integrins are known to participate in cell adhesion as well as cell-surface mediated signalling. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:3690; |
alpha9-beta1 integrin-ADAM8 complex [GO:0071133]; alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex [GO:0035868]; alphav-beta3 integrin-IGF-1-IGF1R complex [GO:0035867]; alphav-beta3 integrin-PKCalpha complex [GO:0035866]; alphav-beta3 integrin-vitronectin complex [GO:0071062]; apical plasma membrane [GO:0016324]; cell surface [GO:0009986]; cell-cell junction [GO:0005911]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; filopodium membrane [GO:0031527]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; glutamatergic synapse [GO:0098978]; glycinergic synapse [GO:0098690]; integrin alphav-beta3 complex [GO:0034683]; integrin complex [GO:0008305]; lamellipodium membrane [GO:0031258]; melanosome [GO:0042470]; microvillus membrane [GO:0031528]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; platelet alpha granule membrane [GO:0031092]; postsynaptic membrane [GO:0045211]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; receptor complex [GO:0043235]; ruffle membrane [GO:0032587]; synapse [GO:0045202]; cell adhesion molecule binding [GO:0050839]; coreceptor activity [GO:0015026]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; extracellular matrix binding [GO:0050840]; fibrinogen binding [GO:0070051]; fibronectin binding [GO:0001968]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding [GO:0005161]; protease binding [GO:0002020]; protein disulfide isomerase activity [GO:0003756]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding [GO:0043184]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; activation of protein kinase activity [GO:0032147]; angiogenesis involved in wound healing [GO:0060055]; apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038027]; apoptotic cell clearance [GO:0043277]; blood coagulation [GO:0007596]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033627]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0007160]; cell-substrate adhesion [GO:0031589]; cell-substrate junction assembly [GO:0007044]; cellular response to insulin-like growth factor stimulus [GO:1990314]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus [GO:0036120]; cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0071466]; embryo implantation [GO:0007566]; heterotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034113]; integrin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0007229]; maintenance of postsynaptic specialization structure [GO:0098880]; mesodermal cell differentiation [GO:0048333]; negative chemotaxis [GO:0050919]; negative regulation of cell death [GO:0060548]; negative regulation of lipid storage [GO:0010888]; negative regulation of lipid transport [GO:0032369]; negative regulation of lipoprotein metabolic process [GO:0050748]; negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor activity [GO:1905598]; negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation [GO:0010745]; platelet activation [GO:0030168]; platelet aggregation [GO:0070527]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of adenylate cyclase-inhibiting opioid receptor signaling pathway [GO:1900731]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045780]; positive regulation of cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033630]; positive regulation of cell-matrix adhesion [GO:0001954]; positive regulation of endothelial cell migration [GO:0010595]; positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation [GO:0001938]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of fibroblast migration [GO:0010763]; positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048146]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of glomerular mesangial cell proliferation [GO:0072126]; positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation [GO:0033690]; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation [GO:0050731]; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation [GO:0001934]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:1900026]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0030949]; regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization [GO:0032956]; regulation of bone resorption [GO:0045124]; regulation of extracellular matrix organization [GO:1903053]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping [GO:0150054]; regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization [GO:0099149]; regulation of protein localization [GO:0032880]; regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0061097]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; regulation of serotonin uptake [GO:0051611]; regulation of trophoblast cell migration [GO:1901163]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to radiation [GO:0009314]; smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014909]; substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading [GO:0034446]; tube development [GO:0035295]; viral entry into host cell [GO:0046718]; wound healing [GO:0042060] |
11028489_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11053714_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11151063_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 11235724_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11257275_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11279932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11341749_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 11397354_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11447076_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11454259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11533523_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11545752_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11568114_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11583324_Distinct domains of alphaIIbbeta3 support different aspects of outside-in signal transduction and platelet activation induced by LSARLAF. 11686325_Both the high affinity thrombin receptor (GPIb-IX-V) and GPIIb/IIIa are implicated in expression of thrombin-induced platelet procoagulant activity. 11704375_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11714857_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11739968_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11776310_A naturally occurring point mutation in the beta3 integrin MIDAS-like domain affects differently alphavbeta3 and alphaIIIbbeta3 receptor function. 11812069_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11812775_Lateral clustering of platelet GP Ib-IX complexes leads to up-regulation of the adhesive function of integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 11858476_Review. Alpha(v)beta3 integrins are involved in vascular repair processes. The challenge is to develop a therapeutic agent that will prove effective in reducing restenosis in humans following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). 11858493_GPIIb-IIIa complexes are not in an activated conformational state after dissociation of abciximab unless there is an additional source of activation. 11875117_beta3-Integrin expression was directly up-regulated by HOXA10 in the endometrium 11891802_location was observed on or near the cell surface suggesting it might participate in surface membrane transport of iron 11897046_A novel 196Leu to Pro substitution in the beta3 subunit of the alphaIIbbeta3 integrin in a patient with a variant form of Glanzmann thrombasthenia prevents GPIIbIIIa from binding fibrinogen when platelets are activated. 11934894_Unique ability of integrin alpha(v)beta 3 to support tumor cell arrest under dynamic flow conditions (Integrin alpha-v beta-3) 11940607_Coordinate interactions of Csk, Src, and Syk kinases with [alpha]IIb[beta]3 initiate integrin signaling to the cytoskeleton 11959660_Del1 mediates vascular smooth muscle cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation through interaction with integrin alpha(v)beta(3). 11962738_Immunohistochemical analysis of human tumor sections from several organs showed a heterogeneus distribution of CD61 in metastatic cases from colon and breast carcinoma. However, no staining was found in metastasis from melanoma. 11994301_Relationships between Rap1b, affinity modulation of integrin alpha IIbbeta 3, and the actin cytoskeleton (integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3)) 12008962_Site-directed mutagenesis of residues on the top surface of the integrin beta3 I-domain that contains a putative ligand binding site identified D158 and N215 as novel residues critical for ligand binding. 12031826_Factor XIII mediates adhesion of platelets to endothelial cells through alpha(v)beta(3) and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa integrins. 12036875_A new platelet polymorphism Duv(a+), localized within the RGD binding domain of glycoprotein IIIa, is associated with neonatal thrombocytopenia 12049640_collagen receptor glycoprotein VI and alphaIIbbeta3 trigger distinct patterns of receptor signalling in platelets, leading to tyrosine phosphorylation of PLCgamma2 (integrin alphaiibbeta3) 12071877_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12073410_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082590_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12082592_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12140290_Integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 has agonist-specific activation states and causes intrasubunit and intersubunit allosteric effects 12152649_Two different beta3 cysteine substitutions alter alphaIIb beta3 maturation and result in Glanzmann thrombasthenia. 12152651_Integrin-linked kinase transiently associates with and phosphorylates beta3, regulating platelet integrin alphaIIb beta3 in a PI3-kinase dependent manner 12161360_Alpha(v)beta(3) integrin engagement enhances cell invasiveness in human multiple myeloma. 12168086_integrin alphaVbeta3 expression is reduced when ROR alpha is activated in prostate cancer cells 12198771_Integrin alphavbeta3. Expression of integrin alpha v beta 3 promotes the metastatic phenotype in human melanoma by supporting specific adhesive, invasive and migratory properties of the tumor cells 12200372_Disruption of the long-range GPIIIa Cys(5)-Cys(435) disulfide bond results in the production of constitutively active GPIIb-IIIa (alpha(IIb)beta(3)) integrin complexes. 12209993_Role for beta3 integrins in human melanoma growth and survival. 12210725_alpha v beta 3 integrin signaling through Shc recruitment in response to mechanical stimulation in human osteoblasts 12218055_regulation of integrin function by CD47 ligands: differential effects on integrin-mediated adhesion 12237112_phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2alpha was found to be differentially regulated by alpha(v)beta(3) engagement 12237321_promotion of integrin alpha Vbeta 3-dependent endothelial cell adhesion by PGE2 12297512_co-stimulation of G(12/13) and G(i) pathways is sufficient to activate GPIIb/IIIa in human platelets in a mechanism that involves intracellular calcium 12358597_Data show clearly that integrin alpha(v)beta(3) interacts with the latency-associated peptide (LAPbeta1 and 3) RGD motif. 12362250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12364323_role in mediating pro-angiogenic activity of CYR61 12370491_An autocrine loop of the integrin alpha(V)beta(3)/CD47 receptor complex and thrombospondin-1 is identified as the molecular coupling device between mechanical loading and apoptosis. 12372469_in patients with endometriosis a significant negative correlation was observed between luminal expression of eNOS and alpha(v)beta(3) integrin and between glandular expression of eNOS and luminal expression of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin 12372811_thrombin interacts with alphavbeta3 as demonstrated by direct binding of alphavbeta3 protein to immobilized thrombin. 12393510_a 17-amino acid sequence is identified as a common epitope for antibodies associated with quinine-induced immune thrombocytopenia 12399420_activation state of alphaVbeta3 integrin is an important regulator of the duration of insulin-like growth factor I receptor phosphorylation and this regulation is mediated through changes in the subcellular localization of SHP-2 12426312_Ligand binding promotes the entropy-driven oligomerization of this protein 12427871_Data show a novel mechanism by which ECM regulates membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) association with beta1 or alphavbeta3 integrins, thus modulating its internalization, activity, and function on human endothelial cells. 12460991_role of Pro33 polymorphism in enhanced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and myosin light chain kinase 12486108_integrin alpha5beta1-mediated control of the levels of integrin alphaVbeta3 is important for the distribution of focal contacts 12499711_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12511588_Integrin alphaiibbeta3 plays a role in signal transduction that leads to a defect in leukocyte adhesion 12514663_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12518110_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12553378_has a role in the early phase of liver metastasis 12578602_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 12586134_possible association between the GPIIb/IIIa PIA1/A2 polymorphism and the occurrence of cryptogenic stroke in young patients 12609844_data suggest that despite partial disruption of calf-1 or calf-2 domain by mutation in Glanzmann thrombasthenia, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex is formed but its transport from the endoplasmic reticulum is impaired 12637342_Review. A signal is initiated at the cytoplasmic tail to transform the extracellular domain of alphaIIbbeta3 into a functional receptor for fibrinogen or von Willebrand factor to support platelet aggregation & thrombus formation. 12639965_thymidine phosphorylase and 2-deoxyribose-induced focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation was blocked by the antibodies to integrins alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3, directly linking their migration and signaling components 12645863_decreased expression of endometrial integrin alphavbeta3 suggests that functional, but not morphological, endometrial defect may be one of the causes for the patients with unexplained infertility and recurrent IVF-ET failures 12660257_Alphavbeta3 integrin expression and pinopode formation in human endometrium are processes closely related to endometrial maturation; unlikely as targets for contraceptive approaches or fertility-promoting strategies 12668663_Intercellular calcium communication is primarily mediated by a signaling mechanism operating between this protein, ITGA2B and the adenosine diphosphate purinergic receptor P2Y12. 12682293_tumstatin binds to alpha v beta 3 integrin in a vitronectin/fibronectin/RGD cyclic peptide independent manner 12690117_in megakaryocytes turbulence induces Rap1 activation that controls alphaIIbbeta3-mediated cell adhesion 12690916_role of polymorphisms in cardiovascular thrombotic disease [review] 12691260_Data suggest that this alphavbeta3 binding to alpha5-laminins is involved in the regulation of cellular responses to growth factors known to be involved in epithelial and endothelial development. 12694355_This study revealed detailed topography of integrins in malignant tumours derived from intercalated acinar segment of salivary gland which might be useful their diagnosis , especially of fine-needle aspiration products or from incisional biopsy. 12714203_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12716314_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12719784_binding of thrombin to GPIbalpha induces fibrin binding to resting alphaIIbbeta3 leading to fibrin-dependent platelet aggregation and clot retraction, that can be selectively inhibited by alphaIIbbeta3 antagonists 12720308_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12730600_results suggest that homomeric associations involving transmembrane domains provide a driving force for integrin activation; results also suggest a structural basis for the coincidence of integrin activation and clustering 12736272_the extracellular Ig domain of IAP(CD47), when bound to thrombospondin, interacts with integrin alphaIIbbeta3 and can change alphaIIbbeta3 in a high affinity state without the requirement of intracellular signaling 12738509_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12750158_signaling through JAM-1 and alphavbeta3 is necessary for bFGF-induced angiogenesis. 12765524_Data provide the first evidence that alphavbeta3 integrin can generate apoptosis-stimulating signals. 12771130_alphavbeta3 expression in LNCaP (beta3-LNCaP) prostate cancer cells causes increased cdc2 mRNA levels as evaluated by gene expression analysis, and increased cdc2 protein and kinase activity levels 12791034_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12799374_identification of binding site in gamma C-domain of fibrinogen 12807887_alpha 5 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 are both important but cell-specific fibrillin-1 receptors 12818249_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12818251_Low concentrations of agonists resulted in enhanced platelet aggregation in subjects with the GNB3 CC-genotype compared to carriers of a 825T-allele. 12818251_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12826159_relationships between the expression levels of CD61, CD63, and PAC-1 on the platelet surface and the incidences of acute rejection and tubular necrosis as well as the recovery of graft function after renal transplantation 12827240_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12855229_analyzed the possible cooperation effect between the PlA2 allele (GPIIIa) and LL genotype (SLC6A4) in the development of myocardial infarction 12871468_high prevalence of the HPA-1b allele of beta3 in Glanzmann thrombasthenia 12871600_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12874388_integrin alphavbeta3 cooperates with metalloproteinase MMP-9 in regulating migration of metastatic breast cancer cells 12899665_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12902444_Individuals homozygous for the Leu33Pro polymorphism of the beta3 integrin subunit have an increased cancer risk. 12902444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12911597_Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa has a role in platelet-activating factor-induced platelet activation with protein kinase C activity 12932598_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12941045_the 749EATSTFT756N and 755TNITYRG762T regions of beta3 contribute to the regulation of alphaIIbbeta3 anchorage to the cytoskeleton and platelet spreading to an adhesive surface 12952967_beta3 integrin has a role in causing structural rearrangements of the 10-23 DNAzyme 12957761_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 13678940_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14499914_predictions of hydrophilicity, surface accessibility and antigenicity and the three dimensional structure of the beta(3) integrin correlate with autoantibody binding to a recombinant GPIIIa peptide 'B' containing residues 468-691. 14517343_increased expression of the alpha(v)beta(3) integrin during breast cancer progression can make tumor cells more responsive to malignancy-promoting ligands such as OPN and result in increased tumor cell aggressiveness. 14521607_the E749ATSTFTN756 region of the beta3-tail stabilizes the binding of soluble and surface-bound ligand to integrin alphaIIbbeta3 via a mechanism that involves the phosphorylation of FAK 14524530_integrin alpha(v)beta3 has an important role in bone metabolism and angiogenesis, and in controlling growth of metastatic prostate cancer cells in the bone 14525764_proteins regulated by CBFA2 are required for inside-out signal transduction-dependent activation of GPIIb-IIIa 14557872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14593208_results invoke a model whereby Src is primed for activation by direct interaction with an integrin beta tail, and integrin clustering stabilizes activated Src by inducing intermolecular autophosphorylation 14614355_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14629479_The mutation at the position 29 107 of intron 10, G-->T, in the beta3 genomic DNA was found to induce an aberrant splicing and to be responsible for Glanzmann's thrombasthenia in this patient 14634961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14669168_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14675395_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 14681220_activation of the beta subunit I-like domain of integrin beta3 is analogous to that of the alpha subunit I domain 14690453_Cysteine residues in the epidermal growth factor domains of the beta3 subunit are important for the ligand binding activity of the integrin alphaIIbbeta3 complex. 14691438_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14691579_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14746139_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 14963283_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14966135_CD47-alpha(v)beta(3) interactions that lead to integrin clustering are detergent resistant and do not require cholesterol or the transmembrane region of CD47 14987913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14992889_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15044441_alphavbeta3 integrin has a role in regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells 15045135_in the absence of GPIbalpha or following inhibition of thrombin binding to GPIbalpha, there is a reduction in the thrombin-induced calcium flux, beta3 cleavage and micro -calpain activation. 15056669_analysis of the three-dimensional model of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 15076187_APOC3, LPL and GpIIIa genes were found to be associated with BP levels. The contributions of these genes, although modest, are consistent with the polygenic nature of blood pressure levels. 15076187_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15131115_integrin alpha(IIb)beta3 adhesive function is regulated by platelet FXIII and calpain 15134555_This review discusses the major role played by glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GPIIb/IIIa) in the regulation of platelet adhesion and aggregation during hemostasis. 15147527_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166241_alpha IIb beta 3 signaling in platelets is regulated by SHIP1 and Lyn kinase 15166939_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166949_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15178823_GpIIIa gene polymorphism as a risk factor for stroke caused by large vessel disease in males. 15178823_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15187087_results indicate a new interaction partner for the alpha(v)beta(3) integrin, the TGFbetaIIR, in which TGFbeta1-induced responses are potentiated in the presence alpha(v)beta(3) ligands 15219201_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15226180_CD151 is essential for normal platelet function and that disruption of CD151 induced a moderate outside-in integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) signaling defect 15227729_For HPA-1 gene polymorphism, only the HPA-1a/a (PlA1/A1) genotype was observed in Korean population cardiac patients 15227729_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15299032_secondary structure analysis of integrin alphaVbeta3 15331787_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15331787_The HPA-1b (PlA2) allele significantly protected against subarachnoid hemorrhage. 15344881_analysis of F11R dimerization, phosphorylation and complex formation with the integrin GPIIIa in human platelets 15355503_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15355504_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15456946_Data suggest that modulating the expression of integrin subunits beta3/5 in human neurons may enhance adenoviral infectivity via the coxsackie-adenovirus receptor. 15468167_beta3 integrins play important roles during transendothelial migration of PC3 cells while interacting with the matrix underneath the endothelium. These interactions are independent of the ability to cluster beta3 integrins into focal adhesions. 15509546_CEACAM1 and alpha(v)beta(3) integrin are functionally interconnected with respect to the invasive growth of melanomas 15546585_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15564935_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15565371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15565371_PlA1/A2 polymorphism of platelet glycoprotein IIIa (GPIIIa) has is not implicated in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. 15575508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15590407_A novel 465T-->C (S123P) mutation in exon 3 interfered with the platelet aggregation in a manner similar to Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. 15609125_Inheritance of the integrin beta3 Leu33Pro polymorphism may increase the breast cancer risk by age 45 in the German population. 15609125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15627799_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15634267_a novel missense mutation of Ile304 to Asn in addition to the missense mutation His280 to Pro in the integrin beta3 gene as a cause of the absence of platelet alphaIIbbeta3 in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia 15638730_The Integrin beta3 receptor is expressed on almost all cells originating from the mesenchyme and seem to mediate several biological processes, including adhesion of osteoblasts to the bone matrix. 15663601_Mu-calpain is activated in human endometrial cells during hypoxia and that subsequent cleavage of the integrin beta3 cytoplasmic domain may give some adverse effects to the function of human endometrium 15676177_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15695828_Pyk2 is a phosphorylated beta(3) binding partner, providing a potential structural and signaling platform to achieve alpha(V)beta(3) -mediated remodeling of the actin cytoskele 15699036_there is a phosphorylation-dependent association between beta(3) integrin and Vav1 which is essential for cell progression to a Rho-dominant phenotype during cell adhesion 15701653_integrin alphaIIbbeta3 has a role in mechanotransduction for shear activation of platelets 15701721_alphaIIb-mediated outside-in signaling resulting in TxA(2) production and granule secretion is negatively regulated by a sequence of residues in the membrane distal beta3 cytoplasmic domain sequence RKEFAKFEEER. 15705408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15705408_association between early fetal loss and the presence of the PLA2 polymorphism of the ITGB3 gene 15730528_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15748237_Of the 22 Glanzmann thrombasthenia patients studied, mutations were detected in 12 individuals. Of these, 11 were novel mutations. 15795319_We conclude that the ectodomain of alphaVbeta3 manifests a bent conformation that is capable of stably binding a physiological ligand in solution. 15817799_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15817799_This study provides evidence that ITGB3 plays a role in the pathogenesis of asthma and sensitization to mold allergens. 15826939_dephosphorylation events play a role via serine/threonine phosphatases during the integrin outside-in signaling mechanism, and the Leu(33) --> Pro polymorphism regulates this process 15834425_Epidermal growth factor receptor and alphavbeta3 work together as coreceptors for Human cytomegalovirus entry and signaling. 15834589_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15834589_variation in ITGB3 in addition to Leu33Pro could contribute to susceptibility to cardiovacular disease and serotonin in a sex-specific manner 15840736_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15840736_Results support the hypothesis that carriers of the GP IIIa PlA2 allele might have an increased risk for acute coronary syndrome in Hungarian population. 15842360_SHPS-1 negatively regulates platelet function via CD47, especially alpha(IIb)beta(3)-mediated outside-in signaling 15847651_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 15863506_TPO integrates G(i), but not G(q), stimulation, supports integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) activation platelet aggregation independently of phospholipase C but requires PI3-kinase and Rap1B 15886806_an apparently silent beta3 mutation results in aberrant splicing and reduced beta3 mRNA and may play a causative role in Type I Glanzmann thrombasthenia 15890274_electron tomography analysis of the three-dimensional structure of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in the active state 15917997_PI3-K and calcium oscillation are synergistically operated and form a positive-feedback regulation in integrin alpha(IIb)beta3-mediated outside-in signaling 15921657_Gal3ST-2 is involved in tumor metastasis process by regulation of adhesion ability to selectins and expression of integrin alphaV but not beta3 15968394_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15970922_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15976180_reactive oxygen species produced in platelets significantly affected alphaIIbbeta3 integrin activation 15978110_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15978110_platelet membrane integrins alpha IIb(beta)3 (HPA-1b/Pl) and alpha2(beta)1 (alpha807TT) polymorphisms may have a role in premature myocardial infarction 15990752_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15998788_melanoma cells cross-present, in an alpha v beta3-dependent manner, an antigen derived from secreted matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) to human leukocyte antigen A*0201-restricted T cells 16005200_integrin alphavbeta6, alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, alpha5beta1 and alpha9beta1 binding to osteopontin is controlled by specific structural motifs that are recognized by extracellular proteases 16035619_Highest expression of alphavbeta3 integrin is associated with metastatic potential of osteosarcoma cells by enhancing the ability of the cells to migrate specifically to the lung 16051597_the engagement of alphaIIb beta3 by the C-terminal sequence of the fibrinogen gamma-chain initiates signals that suppress subsequent fibronectin assembly by spread platelets 16091654_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16100725_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16102042_GPVI and integrin alphaIIb beta3 have roles in signaling during platelet adhesion and platelet aggregation [review] 16105876_Data show that alpha(v)beta3/Tat interaction triggers the activation of NF-kappaB in endothelial cells in a focal adhesion kinase-, RhoA- and pp60src-dependent manner, and this activation is required for motogenic activity of Tat in endothelial cells. 16113799_ITGbeta3 subunit cytoplasmic domains require membrane anchorage and the NPXY motif to recruit to adhesion complexes 16115959_Data show that protein-tyrosine phosphatase (PTP)-1B is an essential positive regulator of the initiation of outside-in alphaIIbbeta3 integrin signaling in platelets. 16133898_Glycoprotein IIIa allele has been found in many studies to associate with risk of thrombosis. 16133898_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16150802_alphavbeta3 integrin is transiently up-regulated (and activated) in graft arteriopathy 16153930_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16157382_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16158739_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16195248_The 177-184 sequence of beta3 is necessary for vitronectin binding to alphaVbeta3. 16213489_Cells overexpressing beta3 integrin can bind human ADAM12 via beta3 integrin. 16228296_PI3K and granular released ADP in coordinating the feedback regulations in integrin alpha(IIb)beta3-mediated platelet activation 16248996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16307159_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16317099_beta3 knockout mice transfused with wild-type platelets generated specific anti-beta3 antibodies which were able to induce thrombocytopenia in wild-type mice. 16317580_ITGB3 gene polymorphisms is associated with breast cancer 16317580_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16322334_Integrin beta(3) Leu33Pro homozygotes have an increased risk of ovarian cancer. 16322334_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16322781_analysis of platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3 structure and function (review) 16340127_the beta3 integrin gene is the direct target of NFAT1 in osteoclast formation 16353042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16357324_Outside-in signaling through integrin alpha2beta1 triggered inside-out activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 and promoted fibrinogen binding. (alpha2beta1 AND integrin alphaIIbbeta3 16359515_three beta-propeller mutations do not affect the production of pro-alpha(IIb), its ability to complex with beta3, or its stability, but do cause variable defects in transport of pro-alpha(IIb)beta3 complexes from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi 16380674_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16380674_Our results did not show the causative relationship between the existence of platelets GP IIIa mutations and venous system thrombosis in the women in labor. 16385340_Expression of integrins alphavbeta1, alphavbeta3, and alphavbeta5 in cerebral arteriovenous malformations and cavernous malformations. (Integrins alphavbeta1, alphavbeta3, and alphavbeta5) 16400188_the signal interaction between IGF-1R and alpha(v)beta3 integrin plays an important role in promoting the development and progression of cervical cancer 16407244_cardiotoxin A5 binds to alpha(v)beta3 integrin and inhibits bone resorption 16412752_The endometrial expression of beta3 integrin subunit is reduced in the presence of tubal phimosis or hydrosalpinx, during the window of implantation. 16444441_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16469512_Inhibition of alphaIIbbeta3 activation by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitors and superoxide scavengers was independent of NO/cGMP signaling demonstrating a direct role of platelet NAD(P)H oxidase-generated ROS for integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation. 16504741_T cells from kidney allograft recipients can express significant amounts of alpha-beta 3 integrin (CD41/CD61. 16513293_These results establish the beta3 gene as a direct target of NFATc1 in RANKL-dependent osteoclast formation. 16567932_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16573563_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16582881_Increase in the affinity of alphaIIb beta3-mediated cell adhesion through binding to calcium- and integrin-binding protein following agonist stimulation is impaired in patients because of mutations. 16634766_the Pro33 isoform of purified integrin alphaIIbbeta3 has increased fibrinogen and prothrombin binding 16635210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16636497_P-selectin expression, but not activated GPIIb/IIIa, is enhanced in ADP-activated platelets in the inflammatory stage of Takayasu's arteritis. SELP may play a significant role in the inflammatory and thrombotic responses associated with intractable TA 16675000_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16676352_Results describe the multifunctional behavior of integrins, including integrin beta 3, based on their modification potential at hydroxyl groups of amino acids as a source of interplay. 16702043_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16716076_while the C-terminal region of the alpha(IIb) tail minimally influences alpha(IIb)beta(3) activation, the C-terminal region of the beta(3) tail is critically involved 16721604_Data showed that ITGB3 and SLC6A4 expression levels are correlated. 16721604_Observational study of gene-disease association. |
ENSMUSG00000020689 |
Itgb3 |
63.419067 |
4.2709335753 |
2.094551 |
0.233074165 |
84.673008 |
0.00000000000000000003520235908733063780280568616450275211410580115542763687992711130192446944420225918292999267578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000314329594754386074868864856570805189862656101222748044644872411623737207264639437198638916015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
109.5909503 |
14.4791731 |
25.8226466 |
2.9554072 |
| ENSG00000259248 |
100130855 |
USP3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.032083 |
0.3683875675 |
-1.440704 |
0.380310230 |
14.299225 |
0.00015592903480042782948279678212344379062415100634098052978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000416036253372074297119526109511866707180161029100418090820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.9429099 |
3.1094539 |
32.2907319 |
5.4647273 |
| ENSG00000259250 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.129879 |
0.3423508807 |
-1.546452 |
0.443883687 |
12.553823 |
0.00039539646359775323805965663304107238218421116471290588378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000989161322492006526638230745618329819990321993827819824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4162144 |
2.0994284 |
21.8498377 |
3.7306141 |
| ENSG00000259291 |
109729181 |
ZNF710-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
84.873264 |
0.3691698815 |
-1.437643 |
0.243277186 |
34.563618 |
0.00000000412545189651276353917984404218004257369756260231952182948589324951171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000018649822356057702062263146795297041879990729285054840147495269775390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.1387469 |
7.2000954 |
123.2075433 |
13.3514708 |
| ENSG00000259319 |
|
JDP2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.502946 |
0.2911466949 |
-1.780182 |
0.571285362 |
9.705985 |
0.00183668889788995742980148850875821153749711811542510986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004086452838838674703203501792359020328149199485778808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.2083148 |
2.6012470 |
25.0105049 |
5.5563029 |
| ENSG00000259448 |
|
LINC02352 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.442246 |
0.0703321576 |
-3.829672 |
1.108030087 |
14.965520 |
0.00010949374043661659139728414835701642005005851387977600097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000299782528073541285843633952268305620236787945032119750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.6334810 |
0.5325974 |
8.9843408 |
3.4542481 |
| ENSG00000259456 |
101927631 |
ADNP-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.013155 |
0.4384855408 |
-1.189399 |
0.515891047 |
5.328065 |
0.02098466606463435940588269090767425950616598129272460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.037425528167472590923559039310930529609322547912597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3978843 |
1.7836038 |
12.3624443 |
2.5668511 |
| ENSG00000259471 |
102723165 |
LINC01169 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.149112 |
3.7306408977 |
1.899423 |
0.613457956 |
8.690797 |
0.00319820832322286656770882196099137217970564961433410644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006802933398295072861539090069982194108888506889343261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.9630999 |
15.9991913 |
7.6441354 |
2.9859479 |
| ENSG00000259515 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.976405 |
0.4909169704 |
-1.026449 |
0.463060701 |
4.941810 |
0.02621457269427720365717604522615147288888692855834960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.045698251206747551866893530814195401035249233245849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4167421 |
2.4080568 |
15.2099170 |
3.2789142 |
| ENSG00000259661 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.661218 |
0.2768722712 |
-1.852708 |
0.353936951 |
27.517755 |
0.00000015565893974856313853505536144022913802587027021218091249465942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000601761642401464590079165819375139889757519995328038930892944335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.9264648 |
4.6724735 |
62.2704563 |
11.3385978 |
| ENSG00000259803 |
146429 |
SLC22A31 |
protein_coding |
A6NKX4 |
FUNCTION: Organic anion transporter that mediates the uptake of ions. {ECO:0000305}. |
Ion transport;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
Predicted to enable transmembrane transporter activity. Predicted to be involved in ion transport and transmembrane transport. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020]; transmembrane transporter activity [GO:0022857]; ion transport [GO:0006811] |
|
|
|
62.395055 |
0.3552571418 |
-1.493064 |
0.339210719 |
18.762912 |
0.00001480177841247165963800037913333795813741744495928287506103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000045496511738459326191445081244424386568425688892602920532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.9468741 |
9.1241625 |
98.3223838 |
18.0431453 |
| ENSG00000259807 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.005834 |
0.2601221048 |
-1.942739 |
0.542292732 |
14.270849 |
0.00015829757764046321834479347234747592665371485054492950439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000422203152506909454473593701351319396053440868854522705078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8042954 |
1.3787089 |
14.5975294 |
2.8610762 |
| ENSG00000259877 |
|
ZNF778-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53.960125 |
0.3490814546 |
-1.518364 |
0.235708063 |
42.522185 |
0.00000000006988506007079807388446043780544586834779785533555696019902825355529785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000364746636013076230056452275247666494628617783746449276804924011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.0085470 |
4.4512575 |
80.7532693 |
8.1580286 |
| ENSG00000259891 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.072395 |
0.4250533803 |
-1.234284 |
0.328578010 |
14.396855 |
0.00014804933799294258539580582123562635388225317001342773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000396589515204325362713461133878922737494576722383499145507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.3094194 |
2.7619288 |
31.4584400 |
4.0615348 |
| ENSG00000259943 |
|
ZMPSTE24-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
483.820677 |
0.4273541202 |
-1.226496 |
0.077485449 |
253.902256 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000366217028842070794828441133116595527533725675729973471926833296230493511771134748851013770114663285432337447524296481529276020478173963604523553222458431832819769624620676040649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000089197414945692500506616537775379094011980727161746447818308551308021047436170360763603555640414759620483601859339840697212341943008517071607432757929245781269855797290802001953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
293.7459931 |
14.4591693 |
691.9892931 |
22.0334672 |
| ENSG00000259972 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.567187 |
0.3891085821 |
-1.361755 |
0.340015072 |
15.624495 |
0.00007724741442958280165324153054839939613884780555963516235351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000216300086500402705732420960416106936463620513677597045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.9006671 |
8.0894704 |
92.8408925 |
14.4945776 |
| ENSG00000260000 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.036740 |
0.3219955361 |
-1.634887 |
0.454066689 |
13.731516 |
0.00021088585327103315973998332033545466401847079396247863769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000549845467988067438704080647227101508178748190402984619140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1795721 |
1.9760138 |
19.4237632 |
3.7068195 |
| ENSG00000260005 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.088738 |
0.4719765308 |
-1.083213 |
0.489290571 |
4.998408 |
0.02537064898624931397197457272341125644743442535400390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.044410671138168864024997617434564745053648948669433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6687710 |
2.0365125 |
14.3050165 |
2.7760458 |
| ENSG00000260051 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.467419 |
0.1570433063 |
-2.670766 |
0.761013964 |
13.870853 |
0.00019581180525011306244043129964893523720093071460723876953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000513810176976296751304162935269914669333957135677337646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8613457 |
0.9737898 |
12.0241155 |
3.1703892 |
| ENSG00000260077 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.777867 |
0.2309477960 |
-2.114361 |
0.199610539 |
122.750532 |
0.00000000000000000000000000015813216110992238224011749237643507975464767625636511051220593747237129646611777933351561387098627164959907531738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001930546483029325330633027358747583677405674658969670154473398862805656284007127521107349821249954402446746826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.1473691 |
3.7202791 |
118.3344834 |
9.2212461 |
| ENSG00000260121 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
131.412444 |
0.1262411265 |
-2.985746 |
0.183300445 |
304.605684 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003268684678426727823677970655427053508315618737480320755637095392404609692988365848164703121637969844134840146123328734174862198550082334599339085841785449538095634122421631606592029584135161712765693664550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000959160752556232685308819830912288240582816400943641589162307121744117909431661626250374583259274970179457949067255355033966144712718216983343141101366066390441280113329791667808876809431239962577819824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.6459957 |
4.5999092 |
236.0152687 |
22.1544978 |
| ENSG00000260135 |
|
MMP2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.398059 |
7.9381004350 |
2.988794 |
0.704305431 |
19.495218 |
0.00001008518512407832286228038382036586995127436239272356033325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000031577711589180320261513457147373173938831314444541931152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.1670345 |
6.1163248 |
1.7506267 |
0.6734477 |
| ENSG00000260139 |
100302666 |
CSPG4P13 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
160.646493 |
2.9553469764 |
1.563328 |
0.178902096 |
75.554062 |
0.00000000000000000355537823576940975620052013637516960105118215377541755761736652630133903585374355316162109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000029009056252048911499044516431062053402962056962216194633263910418463638052344322204589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
240.4478883 |
25.3319114 |
81.8955864 |
6.7420871 |
| ENSG00000260188 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33.507669 |
0.2077297235 |
-2.267220 |
0.301997109 |
62.540973 |
0.00000000000000260958691896604990312847460011075864387862033658138649627744598546996712684631347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000018160067385166851725186395577494589025964065107099365548037894768640398979187011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.0361311 |
2.3809286 |
58.4891397 |
6.1779316 |
| ENSG00000260197 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.071935 |
0.2099532851 |
-2.251860 |
0.583404283 |
16.847529 |
0.00004050603173648584340738737497034094303671736270189285278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000117969421552985615398063956593688317298074252903461456298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9088614 |
1.2606662 |
13.8824727 |
3.3207182 |
| ENSG00000260219 |
101928707 |
CD2BP2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.706994 |
0.4615803532 |
-1.115346 |
0.489950415 |
5.103707 |
0.02387476502521127322276051074823044473305344581604003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.042081625480310289044716398620948893949389457702636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4006943 |
3.0188552 |
18.2915104 |
4.5571448 |
| ENSG00000260273 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.196864 |
0.3568143891 |
-1.486754 |
0.480727684 |
9.854759 |
0.00169392952355478442968972352389300795039162039756774902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003796871642774277653964443146605844958685338497161865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.0929540 |
2.1240314 |
17.2866229 |
3.7691993 |
| ENSG00000260274 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.474294 |
0.3260036702 |
-1.617040 |
0.636285258 |
6.104007 |
0.01348756774350338798196258238704103860072791576385498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025135834534746083479550549100167700089514255523681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.9732529 |
6.8200190 |
52.9435716 |
14.6148080 |
| ENSG00000260279 |
105371414 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.268544 |
0.2207597905 |
-2.179451 |
0.350399522 |
42.654129 |
0.00000000006532640436957651772247016195983133034219658696883925586007535457611083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000341436872696511785906596873942380095112714144534038496203720569610595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.5416677 |
1.9510813 |
38.9460759 |
4.7839526 |
| ENSG00000260280 |
100526831 |
SLX1B-SULT1A4 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring SLX1B (SLX1 structure-specific endonuclease subunit homolog B) and SULT1A4 (sulfotransferase family, cytosolic, 1A, phenol-preferring, member 4) genes on the short arm of chromosome 16. A duplicate read-through locus also exists between the SLX1A and SULT1A3 genes located approximately 730 kb downstream on the same chromosome. The read-through transcript is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), and is thus unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2017]. |
|
|
|
|
|
170.389858 |
0.4303674827 |
-1.216359 |
0.199959658 |
36.369813 |
0.00000000163211622709351821719753771643612524910871286465408047661185264587402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007659788716025541665634276445890488149714769861020613461732864379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
104.8988916 |
13.4580107 |
245.8481740 |
21.8324340 |
| ENSG00000260285 |
|
TRMT61A-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.732756 |
0.2345685382 |
-2.091919 |
0.543200646 |
15.281290 |
0.00009262944669516594731629305359277282150287646800279617309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000256175872816310525037497569655897677876055240631103515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9662823 |
1.7893312 |
20.9889657 |
4.5019680 |
| ENSG00000260303 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.559601 |
0.1614282207 |
-2.631035 |
0.281575667 |
100.249867 |
0.00000000000000000000001343343255908858721169844068231315545565292160468389855471787498741864652629374177195131778717041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000136460746436440147044703571208051329942768584030264492143057122180982432269047421868890523910522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.4462024 |
2.4781924 |
78.0221762 |
8.3853358 |
| ENSG00000260306 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.558148 |
0.3886737566 |
-1.363368 |
0.427039811 |
10.564268 |
0.00115294702945895792892128106643667706521227955818176269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002661063042191433476724160556159404222853481769561767578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7896911 |
1.9287225 |
17.6191362 |
3.0819255 |
| ENSG00000260314 |
4360 |
MRC1 |
protein_coding |
P22897 |
FUNCTION: Mediates the endocytosis of glycoproteins by macrophages. Binds both sulfated and non-sulfated polysaccharide chains.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as phagocytic receptor for bacteria, fungi and other pathogens.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Dengue virus envelope protein E. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:18266465}.; FUNCTION: (Microbial infection) Interacts with Hepatitis B virus envelope protein. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19683778}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Calcium;Cell membrane;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Endocytosis;Endosome;Glycoprotein;Host cell receptor for virus entry;Host-virus interaction;Lectin;Membrane;Receptor;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
The recognition of complex carbohydrate structures on glycoproteins is an important part of several biological processes, including cell-cell recognition, serum glycoprotein turnover, and neutralization of pathogens. The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane receptor that mediates the endocytosis of glycoproteins by macrophages. The protein has been shown to bind high-mannose structures on the surface of potentially pathogenic viruses, bacteria, and fungi so that they can be neutralized by phagocytic engulfment.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:4360; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; endosome membrane [GO:0010008]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; cargo receptor activity [GO:0038024]; mannose binding [GO:0005537]; signaling receptor activity [GO:0038023]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; virus receptor activity [GO:0001618]; cellular response to interleukin-4 [GO:0071353]; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0071222]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; receptor-mediated endocytosis [GO:0006898] |
12368450_reduced expression in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected human macrophages exhibiting enhanced cellular adhesion 14568928_Engagement of the endocytic C-type 1 mannose receptor elicits a secretory program in dendritic cells characterized by a repertoire of anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and the ability to inhibit the generation of Th1-polarized immune responses. 15042510_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15155616_alveolar macrophage mannose receptor mediates Pneumocystis mediated NF-kB nuclear translocation and may represent an important mechanism of the host cell response to Pneumocystis infection 15190005_Endocytosis of glycosylated protein by the mannose receptor does not enhance presentation of antigen. The postulated role of the mannose receptor in presentation of glycoprotein-derived antigen is reevaluated in light of these results. 15767290_MR is a binding receptor, which requires a partner to trigger phagocytosis in some specialized cells such as macrophages. 16000387_The mannose receptors on human AM may suppress select proinflammatory cytokine release and may serve to regulate the innate inflammatory responses to infectious challenge in the lungs. 16203868_Engagement of the Mannose Receptor by mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan during the phagocytic process directs Mycobacterium tuberculosis to its initial phagosomal niche, thereby enhancing survival in human macrophages. 16385451_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17020928_Pc-mediated IL-8 release by human AM requires the coexpression of MR and TLR2 and further supports the concept that combinatorial interactions of macrophage innate receptors provide specificity of host defense cell responses to infectious challenge. 17360361_Mannose receptor (MR) may serve as a binding and an entry site, but the MR-mediated pathway does not lead to productive HIV-1 infection. 17502612_demonstrate that entry of FVIII into human dendritic cells (DC) leading to T cell activation, is mediated by mannose-terminating glycans on FVIII 18279703_RAGE could also behave as a receptor for Mycobacterium tuberculosis 18353434_The expressions of CD105, DC-SIGN and MMR were the strongest in decidua basalis of mid pregnancy and indicate the importance of decidual macrophages in tissue homeostasis at the uteroplacental interface. 19196802_The mannose receptor and hCG were colocalized on the surface of uterine natural killer cells. 19197942_The studies provide the first demonstration of a significant role for mannose receptor, synergistic with TLR2, in activating a proinflammatory response to P. aeruginosa infection. 19224860_macrophage mannose receptor oligomerization enhances gp120-mediated binding of HIV-1 19403625_Expansion of small sputum macrophages in cystic fibrosis shows a failure to express MARCO and CD206. 19683778_These data suggest that in hepatitis B virus infected patients, mannose receptor-mediated interaction between HBsAg and dendritic cells and subsequent impairment of dendritic cells predominantly occurs at the main site of infection, the liver. 19772890_Data show that macrophages cocultured with MSCs consistently showed high-level expression of CD206, a marker of alternatively activated macrophages. 19902202_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19902202_Results suggest that sequence variations in the MRC1 gene are associated with the development of asthma in two independent and ethnically diverse populations. 20035344_A significant association of exon 7 encoded amino acid haplotypes with leprosy per se (P = 0.012) and multibacillary leprosy (P = 0.004). 20035344_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20554962_Data identify a new molecular pathway that links engagement of the mannose receptor, an important pattern recognition receptor for M. tuberculosis, with PPARgamma activation, which regulates the macrophage inflammatory response. 20610655_MR plays a key role in the T helper type (Th)2 cell polarization observed after dust mite glycoallergen Der p 1 exposure through regulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity. 21029423_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21029423_This is the first study to imply that genetic variants in MRC1, a major member of the C-type lectin, contribute to the development of sarcoidosis. 21331365_Studies show that tumoral mucin-mediated ligation of the MR on infiltrating TAM may contribute to their immune suppressive phenotype. 21416197_MMR distribution in liver, spleen, lung, kidney, heart, diaphragm, quadriceps, and triceps in these animal models and compared them with MMR distribution in wild-type mice. 22132194_hMR expressed by vaginal epithelial cells has high affinity for HIV gp120 and this binding induces production of matrix metalloproteinases. 22289891_Sugar moieties on ADAMTS13 interact with MR, thereby promoting its endocytosis by antigen presenting cells. 22314623_elderly subjects had twofold higher CD68 and CD206 gene expression (both P G polymorphism. Infections occurred more frequently among the heterozygous genotype (AG) and homozygous genotype (GG) patients. 29225077_Structural Insights into the pH-dependent conformational change and collagen recognition of the human mannose receptor have been reported. 29732570_Galectin-9 binds to CD206 on M2 macrophages, which appear to drive angiogenesis and the production of chemokines that support melanoma growth. 30177769_The expression of macrophage mannose receptor, CD206, predicts prognosis in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. 30521839_We suggest that sMR has potential as a new biomarker for the prediction of disease severity in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. 31143953_Levels of serum sCD206 are increased in patients with dermatomyositis/clinically amyopathic DM with anti-MDA5 antibody. 31242338_These data indicate that CD163 and CD206 are shed from the macrophages by very different mechanisms potentially involving distinctive inflammatory processes. 31491467_The binding pocket of 4-SO4-GalNAc of the mannose receptor has pH-dependent conformational change. 31822747_Macrophage Mannose Receptor CD206 Predicts Prognosis in Community-acquired Pneumonia. 31825135_High CD206 levels in Hodgkin lymphoma-educated macrophages are linked to matrix-remodeling and lymphoma dissemination. 31982413_Peritoneal Level of CD206 Associates With Mortality and an Inflammatory Macrophage Phenotype in Patients With Decompensated Cirrhosis and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. 32690608_Ozone-derived oxysterols impair lung macrophage phagocytosis via adduction of some phagocytosis receptors. 33192174_Increased Levels of Soluble CD206 Associated with Rapidly Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Dermatomyositis. 33545173_Structural analysis of carbohydrate binding by the macrophage mannose receptor CD206. 34267749_CD206 Expression in Induced Microglia-Like Cells From Peripheral Blood as a Surrogate Biomarker for the Specific Immune Microenvironment of Neurosurgical Diseases Including Glioma. 34486997_The myeloid cell biomarker EMR1 is ectopically expressed in colon cancer. 34608184_The mannose receptor (CD206) identifies a population of colonic macrophages in health and inflammatory bowel disease. 34990410_Human CD206+ macrophages associate with diabetes and adipose tissue lymphoid clusters. 36376784_CD206[+]CD68[+] mono-macrophages and serum soluble CD206 level are increased in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies associated glomerulonephritis. |
ENSMUSG00000026712 |
Mrc1 |
17.707991 |
0.0542467842 |
-4.204319 |
0.631608316 |
66.269594 |
0.00000000000000039327870084196844145022023863089557069229823212976049351397023201570846140384674072265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000002872238309959155755980488292425699401473734775208646041733118181582540273666381835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6861042 |
0.7639324 |
31.4531402 |
5.7607148 |
| ENSG00000260317 |
|
LINC02986 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.609362 |
0.3882147110 |
-1.365073 |
0.569479581 |
5.822924 |
0.01581862725423769863719591910466988338157534599304199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029000489165637612087866870069774449802935123443603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6014899 |
2.2604949 |
14.6170467 |
3.7892356 |
| ENSG00000260428 |
642658 |
SCX |
protein_coding |
Q7RTU7 |
FUNCTION: Plays an early essential role in mesoderm formation, as well as a later role in formation of somite-derived chondrogenic lineages. {ECO:0000250}. |
Activator;Developmental protein;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
Enables DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific and bHLH transcription factor binding activity. Contributes to E-box binding activity. Involved in positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Located in nucleus. Part of transcription regulator complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:642658; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; bHLH transcription factor binding [GO:0043425]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; E-box binding [GO:0070888]; protein dimerization activity [GO:0046983]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; BMP signaling pathway [GO:0030509]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; cellular response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0071260]; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus [GO:0071560]; chondrocyte differentiation [GO:0002062]; collagen fibril organization [GO:0030199]; deltoid tuberosity development [GO:0035993]; developmental process [GO:0032502]; DNA-templated transcription [GO:0006351]; embryonic skeletal system development [GO:0048706]; endochondral ossification [GO:0001958]; face morphogenesis [GO:0060325]; heart valve formation [GO:0003188]; heart valve morphogenesis [GO:0003179]; mesoderm formation [GO:0001707]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; positive regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061036]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of collagen biosynthetic process [GO:0032967]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of gastrulation [GO:2000543]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of cartilage development [GO:0061035]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; sclerotome development [GO:0061056]; Sertoli cell differentiation [GO:0060008]; skeletal muscle cell differentiation [GO:0035914]; tendon cell differentiation [GO:0035990]; tendon development [GO:0035989]; tendon formation [GO:0035992]; tissue homeostasis [GO:0001894] |
17129431_Scleraxis was expressed in periodontal ligament cells, bone marrow cells, and gingival fibroblasts, and may play an important role in differentiation of periodontal ligament cells. 19087640_High glucose inhibited osteogenetic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells and up-regulated Scleraxis expression. 19828133_Scx and E47 might modulate the primary chondrogenesis by associating with the Sox9-related transcriptional complex, and by binding to the conserved E-box on Col2a1 promoter. 21988170_collagen type I and several T/L-related proteoglycans were upregulated in hMSC-Scx cells 22796342_Scleraxis thus appears to play a key role in the transcriptional regulation of type I collagen synthesis. 24157418_These studies identify an important role for Scx in regulating proteoglycans in embryonic and mature valve cells. 26851078_Abnormal upregulation of HIF-2alpha served as a key switch to direct TSPCs differentiation into osteochondral-lineage rather than teno-lineage. Notably, Scleraxis (Scx), an essential tendon specific transcription factor, was suppressed on constitutive activation of HIF-2alpha and mediated the effect of HIF-2alpha on TSPCs fate decision. 29750994_The transcription factor scleraxis is an important inducer of extracellular matrix gene expression in the heart that also control MMP2 expression. The scleraxis can exert control over both extracellular matrix synthesis and breakdown, and thus may contribute to matrix remodeling in wound healing and disease. 29906225_Scleraxis regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition via direct transactivation of the Twist1 and Snai1 genes. 32027517_Scleraxis as a prognostic marker of myocardial fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (SPARC) study. 32183051_Tenogenic Contribution to Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: The Secretome of Scleraxis Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhances Myogenic Differentiation In Vitro. 32708589_The Transcription Factor SCX is a Potential Serum Biomarker of Fibrotic Diseases. 32795590_The transcription factor scleraxis differentially regulates gene expression in tenocytes isolated at different developmental stages. 35563778_Regulation of Cardiac Fibroblast GLS1 Expression by Scleraxis. |
ENSMUSG00000034161 |
Scx |
19.372797 |
0.2759581635 |
-1.857479 |
0.379719874 |
25.203800 |
0.00000051580454943993989714602892843187120774928189348429441452026367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001889150161224196704422219512953251552289657411165535449981689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.7291704 |
2.1082007 |
31.6451564 |
4.3367317 |
| ENSG00000260482 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.861003 |
0.3904563134 |
-1.356767 |
0.342455204 |
15.595283 |
0.00007845005044573988002391817797587236782419495284557342529296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000219262023211346435049712289000467535515781491994857788085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.8489252 |
4.6900805 |
53.4616096 |
7.9920378 |
| ENSG00000260563 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.538348 |
0.3094969563 |
-1.692003 |
0.361392155 |
22.393664 |
0.00000222105509348257314447831929637988679360205424018204212188720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007558322019964276341347491489086607430181175004690885543823242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8627852 |
2.6421807 |
38.4543411 |
5.2925370 |
| ENSG00000260565 |
|
ERVK13-1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
149.386608 |
0.3659657373 |
-1.450220 |
0.231378702 |
37.720417 |
0.00000000081645554304810449117561677682681879619774889533800887875258922576904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003926648359527540506124493579478626492651471835415577515959739685058593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
84.7614376 |
12.2330853 |
233.7360473 |
22.9979179 |
| ENSG00000260588 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.251409 |
0.4850751416 |
-1.043720 |
0.444299448 |
5.675952 |
0.01719900495607274565346145323019300121814012527465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.031324939924930121637469682127630221657454967498779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.8417428 |
1.9701004 |
14.1680490 |
2.5500945 |
| ENSG00000260643 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A1W2PPE4 |
FUNCTION: The H protein shuttles the methylamine group of glycine from the P protein to the T protein. {ECO:0000256|RuleBase:RU364055}.; FUNCTION: The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The H protein (GCSH) shuttles the methylamine group of glycine from the P protein (GLDC) to the T protein (GCST). {ECO:0000256|ARBA:ARBA00025432}. |
Lipoyl;Mitochondrion;Reference proteome;Transit peptide |
|
|
|
glycine cleavage complex [GO:0005960]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; glycine decarboxylation via glycine cleavage system [GO:0019464] |
|
|
|
7.793519 |
4.4909781354 |
2.167030 |
0.633659931 |
12.097357 |
0.00050493358471095082552759780725182281457819044589996337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001238421354325961116008003592980912799248471856117248535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.0863605 |
6.2675476 |
2.4462090 |
1.0651054 |
| ENSG00000260693_ENSG00000178115 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.404720 |
0.0597982379 |
-4.063753 |
0.523865784 |
63.315936 |
0.00000000000000176074028246707278736065271722447743307256437170216223364604957168921828269958496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000012422813847616632399064457707844562946858379959280682669486850500106811523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0550635 |
1.8455940 |
70.8735771 |
19.5705977 |
| ENSG00000260729 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A087WUJ7 |
|
Glycosidase;Hydrolase;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
|
|
lysosome [GO:0005764]; beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase activity [GO:0004563]; N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminidase activity [GO:0102148]; carbohydrate derivative metabolic process [GO:1901135]; carbohydrate metabolic process [GO:0005975] |
|
|
|
17.601701 |
0.3614219730 |
-1.468244 |
0.547146390 |
6.974526 |
0.00826781246473194154911201536606313311494886875152587890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016107828930760750840711637010826962068676948547363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.1137763 |
3.9433587 |
24.1607436 |
8.0326408 |
| ENSG00000260735 |
100505915 |
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
76.293967 |
0.3254251894 |
-1.619602 |
0.181513665 |
83.702195 |
0.00000000000000000005752132017058717663234605754356022733140626134990699394773649988366059915279038250446319580078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000510531981790659472130267606451139301465208695760564314852780753994920814875513315200805664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.9817248 |
5.1050923 |
117.5805315 |
9.9118018 |
| ENSG00000260793 |
101926967 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.169394 |
0.0427415443 |
-4.548217 |
0.926689235 |
40.936293 |
0.00000000015727323578628984690027771366547084189169147805387183325365185737609863281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000803236318410255389310597167872463747473332773552101571112871170043945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8540792 |
0.5719744 |
20.2793989 |
4.1724642 |
| ENSG00000260853 |
|
NFATC2IP-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.770551 |
0.3668922914 |
-1.446572 |
0.354324943 |
16.304210 |
0.00005394397344859830166876116241958527552924351766705513000488281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000154634501476269347686534616492792792996624484658241271972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.9205865 |
4.5161378 |
57.4366366 |
8.5782724 |
| ENSG00000260861 |
|
|
protein_coding |
H3BUA5 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.900487 |
21.0348107525 |
4.394707 |
0.918923594 |
23.713658 |
0.00000111786397384639152315186517300249491313479666132479906082153320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003935990518600366578738213724220074141157965641468763351440429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.5340743 |
13.1825008 |
1.5102835 |
0.6747823 |
| ENSG00000260876 |
101928248 |
LINC01229 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.553090 |
0.1732926986 |
-2.528717 |
0.538678696 |
24.017851 |
0.00000095446656029283322450289511057475166921904019545763731002807617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003384893423816006500934533765545531025509262690320611000061035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0617613 |
1.5426075 |
23.5261132 |
4.9801894 |
| ENSG00000260892 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.320347 |
143.2374012596 |
7.162264 |
1.111267931 |
65.113142 |
0.00000000000000070718860064110746993721217929908959755973241710635956991382045089267194271087646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000005096730344464231929439265347869904835797203769554020169607611023820936679840087890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.0572127 |
23.4441752 |
0.1860596 |
0.1520282 |
| ENSG00000260911_ENSG00000103496 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
72.142171 |
0.4406343851 |
-1.182346 |
0.195809864 |
36.938657 |
0.00000000121904811980559057792509128093647388646481033447344088926911354064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000005787439771093765241050690907240183769033592398045584559440612792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.8915809 |
5.3185022 |
102.6965432 |
7.7281307 |
| ENSG00000260917 |
103344931 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.471623 |
0.4812954716 |
-1.055005 |
0.347731412 |
9.273507 |
0.00232492157960422765258790001041688810801133513450622558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005072556173681950532350359850397580885328352451324462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.9761002 |
3.1706425 |
31.1156338 |
4.2420398 |
| ENSG00000260941 |
644242 |
LINC00622 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.940363 |
4.7195000238 |
2.238634 |
0.341457935 |
46.209813 |
0.00000000001062435081394431240630697293704309087589154891873022279469296336174011230468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000058754371679961799230929619025426066669659519448032369837164878845214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.9071048 |
8.9305753 |
9.3583818 |
1.6602511 |
| ENSG00000260942 |
101752400 |
CAPN10-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.794125 |
0.4630813944 |
-1.110662 |
0.438569836 |
6.525486 |
0.01063395100631356858522647002018857165239751338958740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020286560275712586798313452618458541110157966613769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.4963743 |
3.0936181 |
22.8044095 |
4.3931146 |
| ENSG00000261036 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.393928 |
14.7484676589 |
3.882493 |
0.838312095 |
26.257511 |
0.00000029879050701046469855080346157694126674186918535269796848297119140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001117908208738772866150217033531788501932169310748577117919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.1278165 |
8.9298998 |
1.0338000 |
0.5502649 |
| ENSG00000261052 |
6818 |
SULT1A3 |
protein_coding |
P0DMN0 |
FUNCTION: Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the sulfate conjugation of phenolic monoamines (neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin) and phenolic and catechol drugs. |
Catecholamine metabolism;Cytoplasm;Lipid metabolism;Reference proteome;Steroid metabolism;Transferase |
|
Sulfotransferase enzymes catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs, and xenobiotic compounds. These cytosolic enzymes are different in their tissue distributions and substrate specificities. The gene structure (number and length of exons) is similar among family members. This gene encodes a phenol sulfotransferase with thermolabile enzyme activity. Four sulfotransferase genes are located on the p arm of chromosome 16; this gene and SULT1A4 arose from a segmental duplication. This gene is the most centromeric of the four sulfotransferase genes. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the upstream SLX1A (SLX1 structure-specific endonuclease subunit homolog A) gene that encodes a protein containing GIY-YIG domains. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]. |
hsa:445329;hsa:6818; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; aryl sulfotransferase activity [GO:0004062]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; catecholamine metabolic process [GO:0006584]; steroid metabolic process [GO:0008202]; sulfation [GO:0051923] |
12228221_M-PST is involved in protective and detoxification mechanisms that may operate in neurodegenerative processes in the brain 12424257_structure-function relationships in the stereospecific and manganese-dependent 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine/tyrosine-sulfating activity of human monoamine-form phenol sulfotransferase, SULT1A3 12761191_the differential substrate specificity of the two enzymes M-PST and P-PST for the thirteen drug compounds tested 14622112_Eight single nucleotide polymorphisms were observed in African American[AA] and five in Caucasian-American subjects, including one (Lys234Asn) that was observed only in AA subjects with an allele frequency of 4.2% 14871892_For SULT1A3, substrate inhibition is found for dopamine but not with pNP. Based on modeling and kinetic studies, it is proposed that substrate inhibition by dopamine in SULT1A3 is caused by binding of two dopamine molecules in the active site. 15358107_2 SULT1A3 genes were present on chromosome 16 in all DNA samples studied. 16083857_X-ray crystallographic analysis of SULT1A3 complexed with dopamine and 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate 17002600_Of the 11 human cytosol sulfotransferase enzymes tested, only SULT1A3 displayed sulfating activity toward nitrotyrosine. The pH-dependence and kinetic constants of SULT1A3 with nitrotyrosine or dopamine as substrate were determined. 17963788_data from this study shows that the human SULT1A3 gene is inducible by glucocorticoids through a glucocorticoid receptor-mediated mechanism and the glucocorticoid response element at position (-1211 to -1193) is necessary for this induction. 19447296_Concerted action of cytosolic sulfotransferase, SULT1A3, and catechol-O-methyltransferase in the metabolism of dopamine in SK-N-MC human neuroblastoma cells. SULT1A3 is the major enzyme responsible for the sulfation of both dopamine and 3-methyldopamine. 21168432_SULT1A3 has a role in the inactivation of excess chlorotyrosine and nitrotyrosine during inflammation in lung endothelial and epithelial cells. 22352375_Studies indicate that SULT1A3 is the main isoform responsible for flavonoid sulfonation in the Caco-2 cells. 22949271_The expression of ALDOA and/or SULT1A3 is significantly higher. 24039991_Data indicate that protein-ligand interaction energy by using docking Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships(QSAR) models showed accuracy of 67.28%, 78.00% and 75.46%, for the isoforms SULT1A1, SULT1A3 and SULT1E1, respectively. 24136195_Taken together, these results show that dopamine can induce its own metabolism and protect neuron-like cells from damage, suggesting that SULT1A3 activity may be a risk factor for dopamine-dependent neurodegenerative diseases. 24692077_The common SULT1A3 single-nucleotide polymorphism 105A>G is not an important determinant of salbutamol enantiomer pharmacokinetics under normal clinical use and does not place some individuals at greater risk of accumulation in the body. 25941087_Genetic polymorphism of SULT1A3,a major ritodrine-sulfating SULT, appeared to exert a dramatic effect on the sulfating activity of SULT1A3 allozymes. 26067475_A systematic analysis showed that three of the twelve human SULTs, SULT1A1, SULT1A3 and SULT1C4, displayed the strongest sulphating activity towards acetaminophen. 26291395_This study aimed to establish SULT1A3 stably transfected HEK293 cells, and to determine the contributions of BCRP and MRP transporters to excretion of chrysin and apigenin sulfates. 26611713_Sulfate metabolites R-6-S and R-4'-S were generated from raloxifene in SULT293 expression HEK293 cells. Cellular excretion of the raloxifene sulfates was mainly mediated by BCRP and MRP4. 27582324_The present study revealed SULT1A3 as the major human SULT enzyme capable of sulfating dextrorphan 28374858_In Alzheimer's disease patients, there was a significantly lower copy number in SULT1A3 genes compared to controls. 28630292_analysis of the catechin-binding site of SULT1A3 29025375_Our results implied that SULT1A3/4 exhibited bidirectional effect on tumor and normal hepatocytes and may thus provide a novel strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma clinical targeting. In addition, SULT1A3/4 re-expression could serve as a biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. 29705271_Effects of human SULT1A3/SULT1A4 genetic polymorphisms on the sulfation of acetaminophen and opioid drugs by the cytosolic sulfotransferase SULT1A3 31145702_The results obtained showed clearly the differential enzymatic characteristics of SULT1A3 allozymes in mediating the sulfation of phenylephrine and salbutamol. This information may contribute toward a better understanding of the pharmacokinetics of these two drugs in individuals with distinct SULT1A3 and/or SULT1A4 genotypes. 32152050_Interaction of the Brain-Selective Sulfotransferase SULT4A1 with Other Cytosolic Sulfotransferases: Effects on Protein Expression and Function. |
ENSMUSG00000000739 |
Sult5a1 |
23.685507 |
0.2849982839 |
-1.810975 |
0.730444009 |
5.133894 |
0.02346303343478267633415157433773856610059738159179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.041420209723405369828252986508232424966990947723388671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.3789825 |
5.1342304 |
32.1964922 |
12.1801092 |
| ENSG00000261064 |
|
LINC02256 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.293588 |
0.0166009677 |
-5.912589 |
1.214672181 |
27.323152 |
0.00000017213792304130700547597969483210045282817191036883741617202758789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000663036467664324428726075645601500951897833147086203098297119140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2018856 |
0.2050506 |
12.5871442 |
5.4126639 |
| ENSG00000261064_ENSG00000232653 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
187.896058 |
0.2315699674 |
-2.110480 |
0.392093679 |
26.197809 |
0.00000030817198504805486593909036839578075017698211013339459896087646484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001152132345316436120755783020785933956631197361275553703308105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
67.6536905 |
25.4714348 |
286.1389850 |
76.4611420 |
| ENSG00000261067 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
71.444842 |
0.3968138849 |
-1.333466 |
0.228151892 |
33.862343 |
0.00000000591526158976301725500066772947191373610564824048196896910667419433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000026369453658985844242379256827275846308822337960009463131427764892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
43.5621896 |
9.3351434 |
109.4298615 |
16.3190623 |
| ENSG00000261094 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.568664 |
0.2725286371 |
-1.875520 |
0.510548112 |
13.938258 |
0.00018891399433555925552706555858861747765331529080867767333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000497213009342520394044651066423057272913865745067596435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6969603 |
1.7072530 |
17.3727913 |
3.9625197 |
| ENSG00000261159 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.070256 |
0.1472431532 |
-2.763728 |
0.676037922 |
20.577686 |
0.00000572596550561221298797452000650665127068350557237863540649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000018485400451189034162378585501862460205302340909838676452636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8066072 |
0.8362205 |
12.3677504 |
2.6066123 |
| ENSG00000261220 |
|
ST3GAL1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.616508 |
0.2171128143 |
-2.203483 |
0.486165741 |
23.052690 |
0.00000157621860668424209626144617130139025107382622081786394119262695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005457421213853955132796254984262063203459547366946935653686523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9979749 |
1.2819792 |
18.5560537 |
3.1276012 |
| ENSG00000261247 |
653075 |
GOLGA8T |
protein_coding |
H3BQL2 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues ;mmu:99412; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
101.892891 |
0.0503103884 |
-4.313000 |
0.927573628 |
16.616894 |
0.00004574175405909947810705398762998186157346935942769050598144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000132459935238828384372958280046361778659047558903694152832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.6455116 |
9.8571710 |
246.9036932 |
141.3965538 |
| ENSG00000261324 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.004554 |
0.3747091604 |
-1.416157 |
0.544056477 |
6.987851 |
0.00820648380264409928186442044761861325241625308990478515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016002877541638264174972405839980638120323419570922851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4730083 |
1.5775855 |
11.9843642 |
2.5274839 |
| ENSG00000261326 |
|
LINC01355 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.233145 |
0.4567092856 |
-1.130652 |
0.390635258 |
8.437294 |
0.00367602882545124470467512445281954569509252905845642089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007727985395764188497613744743830466177314519882202148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.7303682 |
2.7787385 |
25.8229015 |
3.9498191 |
| ENSG00000261377 |
|
PDCD6IPP2 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.275283 |
0.2367169708 |
-2.078765 |
0.711247271 |
8.032968 |
0.00459335190866418108246449492071405984461307525634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009461048586642940502744458797224069712683558464050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7001566 |
4.9191032 |
27.0180266 |
13.3427952 |
| ENSG00000261377_ENSG00000290880 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
123.838347 |
0.0408064512 |
-4.615059 |
0.293010286 |
321.686336 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000621703926357909075462895516238332353562483922972867908097564909646304805576113749220191123450912685600056449448737346428109451538009724095856517372165987536577623939134607726313130893203151572379283607006072998046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000188426077064532618349676091875275777950581346368084305126926848575866352912223393449794807719203196744617034272159842049284392913797609500424121537269654903181315330059703494133827028633731970330700278282165527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.0959224 |
2.1244865 |
248.0186646 |
25.0399151 |
| ENSG00000261455 |
100128822 |
LINC01003 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44.588682 |
0.3987403573 |
-1.326478 |
0.237892231 |
31.882249 |
0.00000001638072875821113900972526454188904487807576515479013323783874511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000069757517735486559613866978327850754126870924665126949548721313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.0679124 |
4.0621543 |
65.6106056 |
6.4160748 |
| ENSG00000261480 |
653720 |
GOLGA8M |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
68.146482 |
0.0255805840 |
-5.288807 |
0.441167472 |
258.005889 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000046686469476438961474240521305979340436820679171943857485606156077175124059856461755563532804744185707627560250997050143111925039913836798704052395009300724382228509057313203811645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000011620443330054620397566415072892225898494766083432071116331146382883862672099336438147073535520939941875031429718610867096526917187189410947401047025095977005548775196075439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
3.5774336 |
1.0987632 |
141.1628141 |
13.7339618 |
| ENSG00000261480_ENSG00000188626 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
136.068946 |
0.0091275762 |
-6.775552 |
1.193741983 |
17.889421 |
0.00002341189045446373840383795517094966953663970343768596649169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000070221398721374673839411284514966382630518637597560882568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4071000 |
6.5757630 |
417.4290851 |
391.3565311 |
| ENSG00000261485 |
|
PAN3-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57.001185 |
0.1841195802 |
-2.441285 |
0.250207567 |
103.083691 |
0.00000000000000000000000321285057306017351750910660249485376025060242308576863201038646840855539377201921524829231202602386474609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000033608557376589766659794401541439144437216446895042805867635468154708267007890754030086100101470947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.0110532 |
2.9136326 |
98.4142434 |
8.7232665 |
| ENSG00000261487 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.242057 |
0.1898189402 |
-2.397304 |
0.874903091 |
7.170151 |
0.00741265407370282798649174793581551057286560535430908203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014593940793364510929985833342925616307184100151062011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8867427 |
6.6177340 |
24.8742423 |
21.7101835 |
| ENSG00000261505 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.104595 |
0.2995442070 |
-1.739159 |
0.590466719 |
8.475726 |
0.00359916639159487284499450154839905735570937395095825195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007583682503917247783031818642029975308105349540710449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4737060 |
4.7526057 |
26.1330742 |
9.9028710 |
| ENSG00000261584 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.224598 |
0.3480530900 |
-1.522621 |
0.526195927 |
8.725760 |
0.00313745323495537211527794951848591153975576162338256835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006688158542452526944543933495879173278808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0868115 |
2.0052742 |
14.8668353 |
3.6199678 |
| ENSG00000261732 |
|
|
protein_coding |
J3QT63 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
nucleus [GO:0005634]; chromatin binding [GO:0003682]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389] |
|
|
|
19.808928 |
0.0927128138 |
-3.431087 |
0.457613862 |
59.132229 |
0.00000000000001474247637796626092369417519232804953343250742303638389785191975533962249755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000097885268258561398393219939642576570056216843374041758352177566848695278167724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.4147091 |
0.8622937 |
26.0035445 |
5.9084277 |
| ENSG00000261739 |
653061 |
GOLGA8S |
protein_coding |
H3BPF8 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
Mouse_homologues ;mmu:99412; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
26.925488 |
0.1769310390 |
-2.498741 |
0.351249146 |
57.426770 |
0.00000000000003508001020887316289325358236135982949123381796630027906758186873048543930053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000229208034830884424613779022288739033934128197511626012783381156623363494873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2809066 |
1.9314453 |
47.0822848 |
5.6955657 |
| ENSG00000261794 |
728498 |
GOLGA8H |
protein_coding |
P0CJ92 |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;FUNCTION: Peripheral membrane component of the cis-Golgi stack that acts as a membrane skeleton that maintains the structure of the Golgi apparatus, and as a vesicle thether that facilitates vesicle fusion to the Golgi membrane (PubMed:28028212). Required for normal protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and the cell membrane (PubMed:28028212). Together with p115/USO1 and STX5, involved in vesicle tethering and fusion at the cis-Golgi membrane to maintain the stacked and inter-connected structure of the Golgi apparatus. Plays a central role in mitotic Golgi disassembly: phosphorylation at Ser-37 by CDK1 at the onset of mitosis inhibits the interaction with p115/USO1, preventing tethering of COPI vesicles and thereby inhibiting transport through the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. Also plays a key role in spindle pole assembly and centrosome organization (By similarity). Promotes the mitotic spindle pole assembly by activating the spindle assembly factor TPX2 to nucleate microtubules around the Golgi and capture them to couple mitotic membranes to the spindle: upon phosphorylation at the onset of mitosis, GOLGA2 interacts with importin-alpha via the nuclear localization signal region, leading to recruit importin-alpha to the Golgi membranes and liberate the spindle assembly factor TPX2 from importin-alpha. TPX2 then activates AURKA kinase and stimulates local microtubule nucleation. Upon filament assembly, nascent microtubules are further captured by GOLGA2, thus linking Golgi membranes to the spindle (By similarity). Regulates the meiotic spindle pole assembly, probably via the same mechanism (PubMed:21552007). Also regulates the centrosome organization (By similarity). Also required for the Golgi ribbon formation and glycosylation of membrane and secretory proteins (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q08379, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q62839, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21552007, ECO:0000269|PubMed:28028212}. |
Coiled coil;Reference proteome |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;NA |
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:728498; |
cis-Golgi network [GO:0005801]; Golgi cis cisterna [GO:0000137]; Golgi cisterna membrane [GO:0032580]; Golgi organization [GO:0007030] |
Mouse_homologues NA; + ;21552007_GM130 regulates microtubule organization and might cooperate with the MAPK pathway to play roles in spindle organization, migration and asymmetric division during mouse oocyte maturation 26083584_In oocyte meiosis, GM130 localization and expression patterns are regulated by FMNL1. 28028212_Deletion of GM130 in neurons causes fragmentation. 28055014_the GM130-deficient mouse provides a valuable model for investigating the etiology of human globozoospermia. 29128360_Therefore, we confirmed the associations among Golgi function, fibrosis, and autophagy. Moreover, GOLGA2 knockout mice may be a potentially valuable animal model for studying autophagy-induced fibrosis. 30630895_knockdown of GM130 (also known as GOLGA2) or p115 (also known as USO1), two regulators of the early secretory pathway, impairs GC and ERES reorganisation. This in turn results in inhibition of myotube fusion and M-cadherin (also known as CDH15) transport to the sarcolemma. 32873390_Loss of GM130 does not impair oocyte meiosis and embryo development in mice. |
ENSMUSG00000075425+ENSMUSG00000002546 |
Gm13547+Golga2 |
11.150900 |
0.0335037236 |
-4.899535 |
1.020499950 |
32.751435 |
0.00000001047289360024940293685060023346281021794368371047312393784523010253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000045518230135359595440833365125737897116664498753380030393600463867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7787852 |
0.6703120 |
23.8137360 |
9.2181393 |
| ENSG00000261795 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.394645 |
0.2994628162 |
-1.739551 |
0.470493653 |
14.348788 |
0.00015187746528400804138340951521257693457300774753093719482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000405960048459246404355116322193453015643171966075897216796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4907512 |
1.6881862 |
18.4706205 |
3.3605199 |
| ENSG00000261798_ENSG00000284719 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.692568 |
0.2955733172 |
-1.758412 |
0.746699047 |
5.367280 |
0.02051794401870872877613471985114301787689328193664550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036695123435858581495416785855923080816864967346191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.6961718 |
5.0958950 |
23.3468889 |
12.0804571 |
| ENSG00000261971 |
|
MMP25-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
84.204554 |
0.1868654873 |
-2.419928 |
0.350112421 |
44.474474 |
0.00000000002576952811251624197868714792224246719690161633309344324516132473945617675781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000138969029938158486231645107118639996535147673739629681222140789031982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.3327068 |
6.0854336 |
140.9537667 |
21.7734438 |
| ENSG00000262155 |
283887 |
LINC02175 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.209801 |
0.3049669819 |
-1.713275 |
0.533105109 |
10.311251 |
0.00132221631099460807702572484600977986701764166355133056640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003018235810436191435268682425885344855487346649169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3741463 |
1.8976539 |
17.7514237 |
3.8926728 |
| ENSG00000262370 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
126.130172 |
0.2866771843 |
-1.802501 |
0.186972027 |
93.289563 |
0.00000000000000000000045176802748042838908171540218323055244460190948015945138340008352395571478155034128576517105102539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000004329932523124105758844974356065170070509149675563974397798742976828378914433415047824382781982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.3592862 |
7.5830392 |
205.3059974 |
17.2819044 |
| ENSG00000262406 |
4321 |
MMP12 |
protein_coding |
P39900 |
FUNCTION: May be involved in tissue injury and remodeling. Has significant elastolytic activity. Can accept large and small amino acids at the P1' site, but has a preference for leucine. Aromatic or hydrophobic residues are preferred at the P1 site, with small hydrophobic residues (preferably alanine) occupying P3. |
3D-structure;Calcium;Disulfide bond;Extracellular matrix;Glycoprotein;Hydrolase;Metal-binding;Metalloprotease;Protease;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Signal;Zinc;Zymogen |
|
This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Proteins in this family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This protease degrades soluble and insoluble elastin. This gene may play a role in aneurysm formation and mutations in this gene are associated with lung function and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). This gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes on chromosome 11. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]. |
hsa:4321; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular matrix [GO:0031012]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; collagen binding [GO:0005518]; core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0001046]; endopeptidase activity [GO:0004175]; metalloendopeptidase activity [GO:0004222]; sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0043565]; serine-type endopeptidase activity [GO:0004252]; zinc ion binding [GO:0008270]; bronchiole development [GO:0060435]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; collagen catabolic process [GO:0030574]; elastin catabolic process [GO:0060309]; extracellular matrix disassembly [GO:0022617]; extracellular matrix organization [GO:0030198]; lung alveolus development [GO:0048286]; negative regulation of endothelial cell-matrix adhesion via fibronectin [GO:1904905]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; negative regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060339]; positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation involved in wound healing [GO:0060054]; positive regulation of interferon-alpha production [GO:0032727]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0060340]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; proteolysis [GO:0006508]; regulation of defense response to virus by host [GO:0050691]; response to amyloid-beta [GO:1904645]; wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells [GO:0035313] |
11546917_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11575928_substrate specificity based on x ray crystallography 11575929_crystal structure in complex with hydroxamic acid inhibitor 11875051_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11875051_These data suggest that polymorphisms in the MMP1 and MMP12 genes, but not MMP9, are either causative factors in smoking-related lung injury or are in linkage disequilibrium with causative polymorphisms. 12103254_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12742660_The presence of MMP-12 has been demonstrated in multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions, particularly in foamy macrophages in actively demyelinating lesions, suggesting a role for MMP-12 during demyelination in MS. 12858542_Migration of monocytes/macrophages in vitro and in vivo is accompanied by MMP12-dependent tunnel formation and by neovascularization. 15474460_MMP-12 is expressed in and secreted by human bronchial epithelial cells 15654955_abnormal production of tropoelastin and fibrillin by heat in human skin and that their degradation by various MMP, such as MMP-12, may contribute to the accumulation of elastotic material in photoaged skin. 15709175_MMP-12 might be not only a prognostic marker, but also a valuable therapeutic target. 15723202_Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients produce greater quantities of MMP-12 than controls 15781250_findings provide novel evidence of a direct relationship between cigarette smoke exposure and MMP-12 in human airway epithelia and suggest several targets for modulation of this potentially pathogenic pathway 15802269_By regulating the proliferation of corneal epithelial cells, Wnt-7a and MMP-12 appear to contribute to corneal wound healing 15944607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15983040_NADPH oxidase restrains the MMP-12 activity of macrophages 15987457_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15989693_cathepsin F, matrix metalloproteinases 11 and 12 are upregulated in cervical cancer 16082623_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16166618_Matrix metalloproteinase 12, a proteinase that plays a critical role in mouse models, was the third most highly induced gene in smokers (ninefold, p G, MMP9 R279Q, and MMP12 -82A>G polymorphisms on atherosclerotic plaque presence may be site- and sex-dependent 24146820_Early elevation of serum MMP-3 and MMP-12 predicts protection from World Trade Center-lung injury in New York City Firefighters. 24398311_role of matrix metalloproteinase 12 in non-small cell lung cancer 24424266_Thrombin-activated microglia expression of tumor necrosis factor-a, interleukin-1b and MMP-12 was significantly reduced through contact-dependent and paracrine mechanisms when the HAESCs were co-cultured with microglia cells 24432723_In acute aortic dissection patients, macrophage activation is strongly related to the clinical outcome of atherosclerotic disease and the role of MMP-12 as a specific marker. 24784232_These findings suggest that inhibiting extracellular MMP-12 could be a new avenue for the development of antiviral treatments 24834994_findings showed that there was an important joint effect of the MMP-12 polymorphisms and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the risk of Ischemic Stroke and therefore it can be considered as a potential marker of cerebrovascular disorders in diabetic patients. 24885469_HnRNP K can induce MMP12 expression and enzyme activity through activating MMP12 promoter, which promotes cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. 24914938_Macrophage MMP12 regulates adipose tissue expansion, insulin sensitivity, and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. 25006744_MMP12 is located in genes previously associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease susceptibility. 25078452_We identified a novel association with an MMP12 locus in large artery atherosclerosis (rs660599; p = 2.5x10), with independent replication in a second population 25435370_fluid shear stress induces the synthesis of Insulin growth factor-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) B and D, which in turn transactivate MMP-12. 26040769_These results proved that MMP-12 expression was increased in cutaneous melanoma and associated with tumor progression. It also provided the first evidence that MMP-12 level could be an independent prognostic marker for patients with cutaneous melanoma 26120586_Patients with Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma are characterized by an increased mRNA expression of MMP1, MMP9, MMP12, TIMP1 and IL-1b genes as compared to the control group . 26608672_MMP12 causes arterial stiffening in mice and suggest that it functions similarly in humans. 26887942_Productive complex between MMP-12 and synthetic triple-helical collagen V, are revealed through paramagnetic NMR. 27329669_The results of this study demonstrate that the gene expression of MMP9, MMP12, TIMP1 and TIMP2 was influenced by the addition of TGF-beta1. These results may be translated to chronic venous insufficiency framework and suggest involvement of TGF-beta1 in the vein wall pathology. 27345464_This study demonstrated that the MMP-12 levels was significantly higher in patients with atheromatous plaques than in those without plaques. 27377745_To conclude, Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection induced the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system appeared to be a key player in MMP-12 and MMP-13 expression, which is further controlled by NF-kappaB signaling. 27391467_Matrix metalloprotease (MMP) regulation was the top pathway involved in gingival aging. MMP3, MMP9, MMP12, and MMP13 were upregulated in old gingival tissues, concomitantly with interleukin-1 beta (IL1B) expression. 27746079_Study evaluated MMP-12 and TIMP-1, TIMP-2, TIMP-3, and TIMP-4 levels in 40 patients with asymptomatic and symptomatic critical carotid artery stenosis (CAS) with neurologic symptoms onset within the preceding 12 hours; results suggest that MMP-12 is related to critical CAS independently on symptoms, moreover, TIMP-3 and TIMP-4 seem to be specifically related to stroke 27807143_In the present report, hypoxia is shown to activate a HIF-KDM3A-MMP12 signaling cascade that promotes trophoblast invasion and trophoblast-directed uterine spiral artery remodeling. 27987113_There were no statistically significant differences in the distribution of MMP7 -181 A/G and MMP12 -82 A/G genotype, allele, or haplotype frequencies between IRSA patients and controls, as well as patients' primary and secondary idiopathic recurrent spontaneous abortion 28098914_High MMP12 expression is associated with gastric cancer. 28122331_Data indicate that MMP1, MMP12 and PPARG and hsa-miR-31-5p, hsa-miR-224-5p, and hsa-miR-223-3p were able to distinguish tumors from NPT with high sensitivity and specificity. 28343758_M4 macrophages are a possible source for HDAC9 and MMP12 expression in advanced human carotid plaques. 28385529_We also found that MMP12 facilitated type I collagen induced platelet aggregation, adhesion and alpha granule secretion. Similarly, one short peptide, WYKG, facilitated type I collagen induced platelet alpha granule secretion. We conclude that platelet express MMP12 may facilitate platelet activation through shedding of CEACAM1. 28551623_Increased levels of MMP1 and MMP12 on tumor-associated macrophages in the peripheral areas of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberance might contribute to local invasion 28655442_The current results suggest that MMP12 rs652438 but not MMP12 rs2276109 may affect the risk for Parkinson Disease 28692348_G allele of MMP12 -82 A > G promoter polymorphism as a protective factor for COPD in Bulgarian population 28958661_Review/Meta-analysis: MMP-1 -1607 1G/2G and MMP-12 -82 A/G gene polymorphisms are associated with ischemic stroke risk. 28990117_The MMP12 down regulation by increasing oxygen concentration enables temporal expression control of MMP12 and involves several mechanisms including HIF-1alpha. These findings suggest MMP12 involved in trophoblast invasion during the first trimester. 29033183_that MMP-12 might act as a potential target for the development of novel therapeutics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma 29101312_MMP12 levels were increased in gingival tissue of periodontitis patients. MMP12-producing monocyte-derived cells also had reduced CD200R surface levels. MMP12 production by these cells was induced by CSF2, and treatment with a CD200R ligand reduced CSF2-induced MMP12 production. This novel association of the CD200/CD200R pathway with MMP12 production by monocyte-derived cells may play a key role in PD progression. 29317790_MMP-12 (-82A/G) polymorphisms associate with obesity risk and its severity. 29390099_Studied association of matrix metallopeptidase 12 (MMP12) -82 A>G promoter single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) with bronchial asthma in a Bulgarian population. Results suggest the variant G allele of the MMP12 -82 A>G promoter polymorphism might considered protective for development of bronchial asthma. 29429629_Tumor cell-derived matrix metalloproteinase 12 promotes tumor propagation in the lung. 29458338_rs3025058 in MMP3 and rs2276109 in MMP12 might not contribute to the risk of developing rheumatic heart disease in a Han population in Southern China. 29906531_Significant association observed for MMP-12 (-1082 A/G) (OR 2.55; 95% CI 1.75 to 3.71) gene polymorphism and risk of ischemic stroke. [meta-analysis] 29925830_In active human systemic lupus erythematosus, MMP12 levels were lower and IFN-gamma higher compared to treated patients or healthy individuals. Hence, macrophage proteolytic truncation of IFN-gamma attenuates classical activation of macrophages as a prelude for resolving inflammation. 30658596_Results confirm that patients with COPD exhibited more MMP-12 protein, and the -82G allele of SNP rs2276109 was more frequent in controls than in COPD patients group. On the other hand, no relationship between the mentioned genetic polymorphism and MMP-12 level was found. Nevertheless, the data, together with other findings, suggest that MMP-12 affects COPD development. 30691826_MMP-12 induces pro-osteogenic responses in aortic valve interstitial cells ( AVICs) by activation of p38 MAPK-mediated LRP-6 and beta-catenin signaling pathways. 30789935_Finding show that increase serum levels of MMP-12 in a multivariate regression model were independent predictors of concomitant COPD and carotid plaque. 31304819_Role of Matrix Metallopeptidase 12 in the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 31499120_Results detected that MMP12 expression is increased in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patients tissues, and its knockdown attenuates CRPC cell line invasion. Also, endogenous estrogen produced by aromatase upregulates MMP12 expression via ERalpha. These data suggest that upregulating MMP12 expression may be a crucial mechanism by which aromatase promotes CRPC metastasis. 31862687_MMP-12 as a potential biomarker to forecast ischemic stroke in obese patients. 32650441_Matrix Metalloproteinase Genes (MMP1, MMP10, MMP12) on Chromosome 11q22 and the Risk of Non-Contact Anterior Cruciate Ligament Ruptures. 32702535_The association between plasma proteomics and incident cardiovascular disease identifies MMP-12 as a promising cardiovascular risk marker in patients with chronic kidney disease. 33065600_Revisiting matrix metalloproteinase 12: its role in pathophysiology of asthma and related pulmonary diseases. 33404658_Imbalanced MMP-3 and MMP-12 serum levels in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with Jaccoud's arthropathy and a distinctive MRI pattern. 33892690_Estimation of salivary matrix metalloproteinases- 12 (MMP- 12) levels among patients presenting with oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma. 33902302_Causal Effect of MMP-1 (Matrix Metalloproteinase-1), MMP-8, and MMP-12 Levels on Ischemic Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. 33958583_MTA2 silencing attenuates the metastatic potential of cervical cancer cells by inhibiting AP1-mediated MMP12 expression via the ASK1/MEK3/p38/YB1 axis. 34319576_Blocking MMP-12-modulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition by repurposing penfluridol restrains lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via uPA/uPAR/TGF-beta/Akt pathway. 34384863_Increased MMP12 mRNA expression in induced sputum was correlated with airway eosinophilic inflammation in asthma patients: Evidence from bioinformatic analysis and experiment verification. 34459757_THE ROLE OF POLYMORPHISMS OF MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES' POLYMORPHISMS 1 AND 12 IN THE FORMATION OF WHEEZING SYNDROME AMONG CHILDREN WITH RECURRENT BRONCHITIS. 34812434_Evaluation of MMP-12 expression in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. 34894337_Matrix metalloproteinase 12 is an independent prognostic factor predicting postoperative relapse of conventional renal cell carcinoma - a short report. 35313071_DRP1 contributes to head and neck cancer progression and induces glycolysis through modulated FOXM1/MMP12 axis. 35442508_Matrix metalloproteinase 12 (MMP12) as an adverse prognostic biomarker of vascular invasion in hepatic cell carcinoma. 35576280_Analytical Study Of Salivary Mmp-12 Expression In Oral Submucous Fibrosis. 35733520_Circulating MMP-12 as Potential Biomarker in Evaluating Disease Severity and Efficacy of Sublingual Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis. 36208531_Matrix metalloproteinase -12: A marker of preeclampsia? |
ENSMUSG00000049723 |
Mmp12 |
441.948130 |
11.8654883155 |
3.568700 |
0.110403578 |
1276.663473 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000133232918913668591291616384071501817478352252524284 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000172501568698749882636514895726771055333208784678395 |
Yes |
No |
824.7926494 |
56.1833412 |
70.0123244 |
4.4126597 |
| ENSG00000262728 |
|
ARHGAP11A-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.792615 |
0.1445613677 |
-2.790246 |
0.633701326 |
18.747938 |
0.00001491845521024701463029538128779449834837578237056732177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000045807447244278325104455823479909781781316269189119338989257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7235816 |
2.2410259 |
33.3904357 |
9.9083207 |
| ENSG00000262766_ENSG00000278133 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
82.087276 |
0.4345896045 |
-1.202274 |
0.240342399 |
24.832083 |
0.00000062547714802942845636180404025883383667405723826959729194641113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002264976129763092018662993046285158982300345087423920631408691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.1235725 |
9.4603787 |
116.6717086 |
15.2778903 |
| ENSG00000262877 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.310018 |
0.0571909024 |
-4.128071 |
0.913606466 |
32.572830 |
0.00000001148085518555873232812386086458544820487759352545253932476043701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000049767231288941813646107853886385585795437691558618098497390747070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9906300 |
0.6544092 |
17.4344399 |
3.7063192 |
| ENSG00000262879 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
183.206825 |
0.4882073741 |
-1.034434 |
0.218080595 |
21.940055 |
0.00000281300809179179858851224671489887896314030513167381286621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000009436363507919759888013279403029542891090386547148227691650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
109.0606245 |
16.1713704 |
225.4950966 |
23.7806608 |
| ENSG00000262903 |
|
CTNS-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.826473 |
0.3092233820 |
-1.693279 |
0.519982239 |
11.236862 |
0.00080188599513146758320653040286174473294522613286972045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001901644808505858043681802094226895860629156231880187988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8441217 |
1.7500792 |
15.7985667 |
3.3843164 |
| ENSG00000263126 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.610206 |
0.1591021013 |
-2.651975 |
0.434067266 |
41.798366 |
0.00000000010118792282083428013989532787106936755072705835800661589019000530242919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000523679432270516833699101803356688172863542263257841113954782485961914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9037049 |
1.7542641 |
37.4104650 |
5.9810787 |
| ENSG00000263142_ENSG00000108433 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.681811 |
0.2485721771 |
-2.008263 |
0.334961413 |
37.734780 |
0.00000000081046578267937036661484653110717676915975005158543353900313377380371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003901655235599317498367996062593604511548051050340291112661361694335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1846874 |
2.6867614 |
48.6894037 |
6.2610193 |
| ENSG00000263155 |
100820829 |
MYZAP |
protein_coding |
P0CAP1 |
FUNCTION: Plays a role in cellular signaling via Rho-related GTP-binding proteins and subsequent activation of transcription factor SRF (By similarity). Targets TJP1 to cell junctions. In cortical neurons, may play a role in glutaminergic signal transduction through interaction with the NMDA receptor subunit GRIN1 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell junction;Cell membrane;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a protein that is abundantly expressed in cardiac tissue. The encoded protein localizes to intercalated discs in cardiomyocytes and functions as an activator of Rho-dependent serum-response factor signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Readthrough transcription also exists between this gene and the neighboring downstream gene POLR2M (polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide M) and is represented with GeneID: 145781. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014]. |
hsa:100820829;hsa:145781; |
anchoring junction [GO:0070161]; cortical actin cytoskeleton [GO:0030864]; extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane [GO:0031234]; I band [GO:0031674]; Z disc [GO:0030018]; intracellular signal transduction [GO:0035556] |
Mouse_homologues 20093627_Reveal myozap as a previously unrecognized component of a Rho-dependent signaling pathway that links the intercalated disc to cardiac gene regulation. 24698889_Cardiac overexpression of Myozap results in cardiomyopathy with hypertrophy and left ventricular dilation. |
ENSMUSG00000041361 |
Myzap |
19.881967 |
0.2009461333 |
-2.315119 |
0.478770037 |
25.408143 |
0.00000046395563615695910143231820398079801037738434388302266597747802734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001706025209187024579255385903220343379871337674558162689208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
6.2808340 |
2.1922553 |
31.3656438 |
6.1881838 |
| ENSG00000263276 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.420306 |
0.2523981950 |
-1.986227 |
0.633181941 |
8.806958 |
0.00300083974965050393618470891965444025117903947830200195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006431002252293450786868600488332958775572478771209716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3286127 |
3.4607370 |
33.1150997 |
9.0082803 |
| ENSG00000263327 |
202020 |
TAPT1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.812190 |
0.3266474353 |
-1.614194 |
0.325615146 |
25.762588 |
0.00000038610045790437206156199990286781442705432709772139787673950195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001431150868575723661310335546592575894919718848541378974914550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.6507386 |
2.5321152 |
35.6652688 |
4.6616444 |
| ENSG00000263590 |
|
LINC02591 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.338473 |
0.0983448781 |
-3.346006 |
1.074710665 |
8.678006 |
0.00322073225983508272529665106276297592557966709136962890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006844925580297455021405728103900401038117706775665283203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0578245 |
1.0674743 |
10.7879065 |
6.5463215 |
| ENSG00000263843 |
100287042 |
MIF4GD-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.717622 |
0.4140294339 |
-1.272195 |
0.484832446 |
6.890322 |
0.00866636467675758678796960055024101166054606437683105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016806901370059808276113955116670695133507251739501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.6602261 |
4.5908696 |
33.0541229 |
7.5739392 |
| ENSG00000263874 |
100505576 |
LINC00672 |
protein_coding |
A0A1B0GWH6 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020] |
28232485_These findings indicate that LINC00672 can influence LASP1 expression as a locus-restricted cofactor for p53-mediated gene suppression, thus impacting endometrial cancer and chemosensitivity to paclitaxel. |
|
|
19.997485 |
0.4470392952 |
-1.161526 |
0.374708974 |
9.655675 |
0.00188767505511310690335946560480806510895490646362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004189787039619466933737523817171677364967763423919677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.6482708 |
2.8354686 |
28.5187359 |
4.0417092 |
| ENSG00000263956 |
200030 |
NBPF11 |
protein_coding |
Q86T75 |
|
Alternative splicing;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;Repeat |
|
Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:200030; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737] |
|
|
|
219.302375 |
0.4760529171 |
-1.070806 |
0.126037828 |
72.361435 |
0.00000000000000001791815621681674407124603794336423382057087168143811456433311946057074237614870071411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000140601799978849089284908708244985026257527693446802707910592289408668875694274902343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
138.9466495 |
10.1908432 |
293.9993204 |
14.2359037 |
| ENSG00000263961 |
440712 |
RHEX |
protein_coding |
Q6ZWK4 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a signaling transduction factor of the EPO-EPOR signaling pathway promoting erythroid cell differentiation (PubMed:25092874). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:25092874}. |
Cell membrane;Differentiation;Erythrocyte maturation;Membrane;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Enables erythropoietin receptor binding activity. Involved in erythropoietin-mediated signaling pathway and positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation. Located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440712; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; erythropoietin receptor binding [GO:0005128]; cellular response to erythropoietin [GO:0036018]; erythrocyte maturation [GO:0043249]; erythropoietin-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0038162]; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation [GO:0045648] |
25092874_RHEX(C1orf186) comprises a new EPO/EPOR target and regulator of erythroid cell expansion that additionally acts to support late-stage erythroblast development |
|
|
12.807183 |
0.1999274934 |
-2.322451 |
0.531769372 |
20.447636 |
0.00000612852031493563307928745462205277760858734836801886558532714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000019728889825179920754823909012642957350180950015783309936523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
4.3813721 |
1.5380502 |
22.0633514 |
4.2642327 |
| ENSG00000264207 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.905565 |
0.2984010207 |
-1.744676 |
0.466123959 |
14.776557 |
0.00012103081735408008703935855976396851474419236183166503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000329293062515432642840818022733628822606988251209259033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3599780 |
1.7934378 |
18.0767023 |
3.6625781 |
| ENSG00000264343 |
388677 |
NOTCH2NLA |
protein_coding |
P0DPK4 |
FUNCTION: Human-specific protein that promotes neural progenitor proliferation and evolutionary expansion of the brain neocortex by regulating the Notch signaling pathway (PubMed:29856954, PubMed:29856955, PubMed:29561261). Able to promote neural progenitor self-renewal, possibly by down-regulating neuronal differentiation genes, thereby delaying the differentiation of neuronal progenitors and leading to an overall final increase in neuronal production (PubMed:29856954). Acts by enhancing the Notch signaling pathway via two different mechanisms that probably work in parallel to reach the same effect (PubMed:29856954). Enhances Notch signaling pathway in a non-cell-autonomous manner via direct interaction with NOTCH2 (PubMed:29856954). Also promotes Notch signaling pathway in a cell-autonomous manner through inhibition of cis DLL1-NOTCH2 interactions, which promotes neuronal differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P0DPK3, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29561261, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29856954, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29856955}. |
Alternative splicing;Calcium;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Glycoprotein;Neurodegeneration;Notch signaling pathway;Reference proteome;Repeat;Secreted;Triplet repeat expansion |
|
Enables Notch binding activity. Involved in cerebral cortex development and positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway. Located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:388677; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; cerebral cortex development [GO:0021987]; Notch signaling pathway [GO:0007219]; positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway [GO:0045747] |
29856954_the emergence of human-specific NOTCH2NL genes may have contributed to the rapid evolution of the larger human neocortex, accompanied by loss of genomic stability at the 1q21.1 locus and resulting recurrent neurodevelopmental disorders 32330268_Evolution of Human Brain Size-Associated NOTCH2NL Genes Proceeds toward Reduced Protein Levels. |
|
|
83.007286 |
2.9471613848 |
1.559326 |
0.286419536 |
28.808329 |
0.00000007990675584855713020333254107893661277728369896067306399345397949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000318161239904155187618021603454532275634392135543748736381530761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
106.9916758 |
25.2324340 |
36.4515516 |
6.2639443 |
| ENSG00000264772 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
251.661900 |
5.0295546983 |
2.330431 |
0.730412818 |
9.226489 |
0.00238538644432052760954721115638221817789599299430847167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005194497479812774758112237094564989092759788036346435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
214.9556512 |
199.8314482 |
42.4659365 |
27.2272289 |
| ENSG00000265206 |
|
MIR142HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52.828283 |
0.3951176993 |
-1.339646 |
0.219279573 |
38.401001 |
0.00000000057602842337166750140834924190152629974726039563392987474799156188964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002808780815647774138032425218086673979200895701069384813308715820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.6233981 |
4.3716605 |
78.1908891 |
6.9720161 |
| ENSG00000265298 |
|
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
80.373624 |
0.3412873556 |
-1.550941 |
0.194235528 |
65.222434 |
0.00000000000000066903548224788591770201252217585153546816861651336250105259750853292644023895263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004838296775099851191452543572048315041518476518206393066634518618229776620864868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.9311570 |
5.1150704 |
120.6720242 |
9.4283018 |
| ENSG00000265303 |
|
|
protein_coding |
J3QRE1 |
|
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay [GO:0000184] |
|
|
|
6.413234 |
0.0149766363 |
-6.061143 |
1.186338522 |
31.606871 |
0.00000001887605630870792833093718470979793799813251098385080695152282714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000079922716900897594669475718261175689605124716763384640216827392578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2001801 |
0.2730537 |
13.9884919 |
9.6682968 |
| ENSG00000265531 |
100132417 |
FCGR1CP |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
The gene represents one of three related immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor genes located on chromosome 1. This family member lacks the transmembrane and coiled-coiled domains found in other family members and is thought to be a pseudogene of Fc-gamma-receptor 1A. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009]. |
|
|
|
|
|
28.664920 |
0.0723608554 |
-3.788647 |
0.445085601 |
99.621830 |
0.00000000000000000000001844600202184291042857533410033977251956521258196421674143799769932106080716494034277275204658508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000186099104471907970322890747901151613395849016973388291848126455466094775204055622452870011329650878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8790422 |
1.2938323 |
54.0352867 |
8.6587178 |
| ENSG00000265690 |
|
|
protein_coding |
J3QRK9 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
cytosol [GO:0005829]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; SCF ubiquitin ligase complex [GO:0019005]; entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod [GO:0043153]; G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle [GO:0000086]; regulation of cell cycle [GO:0051726]; SCF-dependent proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process [GO:0031146] |
|
|
|
26.752337 |
0.1981797847 |
-2.335118 |
0.479325779 |
23.373412 |
0.00000133409844798293222980578934255824208321428159251809120178222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000004650754154990099285783486382506168865802465006709098815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6771388 |
2.8367361 |
44.1504399 |
9.2879049 |
| ENSG00000265728 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.577757 |
0.1923487022 |
-2.378204 |
0.543224688 |
19.647435 |
0.00000931282259034729198476140060725114722117723431438207626342773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000029271137443255119102176325940334322694980073720216751098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9143631 |
1.6386958 |
19.7836306 |
4.8308365 |
| ENSG00000265972 |
10628 |
TXNIP |
protein_coding |
Q9H3M7 |
FUNCTION: May act as an oxidative stress mediator by inhibiting thioredoxin activity or by limiting its bioavailability. Interacts with COPS5 and restores COPS5-induced suppression of CDKN1B stability, blocking the COPS5-mediated translocation of CDKN1B from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Functions as a transcriptional repressor, possibly by acting as a bridge molecule between transcription factors and corepressor complexes, and over-expression will induce G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Required for the maturation of natural killer cells. Acts as a suppressor of tumor cell growth. Inhibits the proteasomal degradation of DDIT4, and thereby contributes to the inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12821938, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17603038, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18541147, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21460850}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Cell cycle;Cytoplasm;Disulfide bond;Isopeptide bond;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Tumor suppressor;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene encodes a thioredoxin-binding protein that is a member of the alpha arrestin protein family. Thioredoxin is a thiol-oxidoreductase that is a major regulator of cellular redox signaling which protects cells from oxidative stress. This protein inhibits the antioxidative function of thioredoxin resulting in the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and cellular stress. This protein also functions as a regulator of cellular metabolism and of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. This protein may also function as a tumor suppressor. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]. |
hsa:10628; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; mitochondrial intermembrane space [GO:0005758]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; enzyme inhibitor activity [GO:0004857]; ubiquitin protein ligase binding [GO:0031625]; cell cycle [GO:0007049]; cellular response to tumor cell [GO:0071228]; keratinocyte differentiation [GO:0030216]; negative regulation of cell division [GO:0051782]; negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0000122]; platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway [GO:0048008]; positive regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043065]; protein import into nucleus [GO:0006606]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; response to calcium ion [GO:0051592]; response to estradiol [GO:0032355]; response to glucose [GO:0009749]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to mechanical stimulus [GO:0009612]; response to progesterone [GO:0032570]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410] |
12054598_overexpression of mRNA sensitized HeLa cells to paraquat 12189205_association of induction with decreased mRNA levels in prostate cancer cells [thioredoxin-binding protein 2] 12821938_VDUP1 is a novel antitumor gene which forms a transcriptional repressor complex 14632196_VDUP1 could have a unique role in epidermis regulating the conversion of postmitotic cells to differentiating ones. 14766217_VDUP1 is upregulated by heat shock factor during stresses such as high density and serum deprivation cultures 15128745_reduced thioredoxin activity through interaction with Txnip is an important mechanism for vascular oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus 15136067_TXNIP gene does not ply a major role in familial combined hyperlipidemia, or related traits. 15234975_interaction of TBP-2 was specific to Rch1 among other importin alpha subfamilies 15537450_thioredoxin binding protein-2 and redox-sensitive signaling regulate human osteoclast differentiation 15696199_Data suggest that thioredoxin-interacting protein and thioredoxin are key components of biomechanical signal transduction and establish them as potentially novel regulators of tumor necrosis factor signaling and inflammation in endothelial cells. 15705778_thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP)is a novel proapoptotic beta-cell gene elevated in insulin resistance/diabetes and up-regulated by glucose through a unique carbohydrate response element 16301999_findings indicate that txnip is a novel glucocorticoid-induced primary target gene involved in mediating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis 16723126_By Northern blot, we confirm hypoxia-induced expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (igfbp3), thioredoxin-interacting protein (txnip), neuritin (nrn1). 16766796_Txnip cysteines 63 and 247 are important for formation of a disulfide-linked complex with thioredoxin that inhibits thioredoxin's reducing activity 16766796_identified two Txnip cysteines that are important for thioredoxin binding and showed that this interaction is consistent with a disulfide exchange reaction between oxidized Txnip and reduced thioredoxin 17381501_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17381501_first report to implicate TXNIP in Type 2 diabetes; effect of TXNIP on triglycerides is influenced by plasma glucose concentration, suggesting biological relevance of TXNIP variations may be particularly relevant in recurrent episodes of hyperglycaemia 17472435_TXNIP regulates both insulin-dependent and insulin-independent pathways of glucose uptake in human skeletal muscle. Data suggests that TXNIP might play a key role in defective glucose homeostasis preceding overt type 2 diabetes mellitus. 17555594_In response to glucose, increased level of TXNIP RNA is followed by increased level of protein that is associated with increasing levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduced thioredoxin activity in a metastatic breast cancer-derived cell line. 17579352_Enhanced VDUP1 gene expression by PPARgamma agonist induces apoptosis in human macrophages. 17671698_downregulation of TXNIP may be partly involved in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis, including inflammation and colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis. 17675577_Results suggest that high glucose induces Txnip through a TGF-beta1-independent pathway. 18202760_D-allose, a simple monosaccharide, may act to cause TXNIP induction and p27kip1 protein stabilization in tumor cells 18301748_TXNIP is directly repressed by FOXO1a, modulating the cellular response to oxidative stress and affecting life span 18376310_TXNIP is induced in response to hypoxia in a HIF-1alpha-dependent manner in pancreatic cancer cells, resulting in increased apoptosis and increased sensitivity to platinum anticancer therapy. 18458340_These studies suggest a key role for MondoA:Mlx complexes in the adaptive transcriptional response to changes in extracellular glucose concentration and peripheral glucose uptake. 18541147_These studies indicate that hnRNP G promotes the expression of Txnip and mediates its tumor-suppressive effect. 18793170_Results show that inhibition of TXNIP protects against glucotoxic beta-cell apoptosis and therefore may represent a novel therapeutic approach to halt diabetes progression. 18835792_The expressions of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor-A, thioredoxin, and thioredoxin interacting protein were related to macrophage infiltration rather than neovascularization in carotid atherosclerotic plaques 18848838_stimulation of PPARalpha in human macrophages might reduce arterial inflammation through differential regulation of the Trx-1 and VDUP-1 gene expression 18974842_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19018770_TXNIP is involved in the antitumor activity of CD437. 19052253_TXNIP is transcription induced in carcinoma cells in an increased glucose metabolism-dependent or -independent response, and a putative glucose regulatory system including ChREBP and ChoRE is needed for glucose-induced TXNIP gene in prostate carcinoma 19214472_Repression of TXNIP by insulin is probably an important compensatory mechanism protecting beta cells from oxidative damage and apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. 19246513_The transcription of the Txnip gene is induced by adenosine-containing molecules, of which an intact adenosine moiety is necessary and sufficient. 19254690_upregulation of Txnip and subsequent impairment of thioredoxin antioxidative system through p38 MAPK and FOXO1 may represent a novel mechanism for glucose-induced increase in intracellular ROS. 19327827_TXNIP expression contributes to mouse leukemia virus-induced murine leukemia as well as human acute myelocytic leukemia. 19605364_Txnip regulates cellular metabolism independent of its binding to thioredoxin and the arrestin domains are crucial structural elements in metabolic functions of alpha-arrestin proteins 19619006_Data suggest that thioredoxin binding protein 2 modulates lipid metabolism as well as natural killer T cell activity. 19773351_p21(WAF1) can induce thioredoxin secretion and angiogenesis in cancer cells, by direct transcriptional repression of the thioredoxin-binding protein 2 promoter 19808645_Data suggest that Txnip expression and promoter activity are mediated via divergent effects of KLF6 and PPAR-gamma transcriptional regulation. 19847012_Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) is a feedback regulator of S-nitrosylation. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20027290_These findings suggest a synergy between the tandem CCAAT and carbohydrate response element motifs and associated NF-Y and Mondo/MLX transcription factors in enhancing transcription from the Txnip promoter. 20068034_itch regulates apoptosis by targeting thioredoxin-interacting protein for ubiquitin-dependent degradation 20172870_TBP-2 mRNA levels in the endometrium were lower, and the TRX to TBP-2 ratio was higher in patients with endometriosis than in the control group. 20398702_TBP-2 is directly involved in the switching of glucocorticoid (GC) sensitivity and GC resistance in HTLV-I infected T cell lines. 20558747_Findings suggest that the Txnip expression is tightly correlated with glycolytic flux, which is regulated by oxidative phosphorylation status 20584310_Low expression of TXNIP is associated with breast cancer. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20656682_VDUP1 expression was regulated by FOXO3A at the transcriptional level and by miR-17-5p at the post-transcriptional levels during the senescence process. 20680488_HDAC10 is involved in transcriptional downregulation of TXNIP, leading to altered reactive oxygen species signaling in human gastric cancer cells. 20826751_VDUP1 negatively regulates hepatocarcinogenesis by suppressing TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation. 20844768_Induction of TXNIP under lactic acidosis is caused by the activation of the glucose-sensing helix-loop-helix transcriptional complex MondoA:Mlx, which is usually triggered upon glucose exposure. 21151022_transfection experiment showed that TBP-2 expression induced apoptosis in IL-2-independent adult T-cell leukemia cells 21192937_Data indicate that down-regulation of Txnip via reduced mRNA transcription may be an important cellular compensatory mechanism in response to hypoxia; cancer cells may regulate metabolism in low oxygen concentrations through such a mechanism. 21271679_Breast cancer cell line studies showed that microRNA, miR-373, was capable of promoting breast cancer invasion and metastasis via translational inhibition of TXNIP and RABEP1 that were the direct target genes of miR-373. 21439723_TXNIP expression is increased by the combination of radiation and D-allose in human head and neck cancer cells 21448924_This study investigated the effect of glucose on GSK3beta and beta-catenin expression and the involvement of the Wnt pathway in response to conditions resembling normoglycemia and hyperglycemia. 21460850_these results collectively demonstrate that TXNIP stabilizes Redd1 protein induced by ATF4 in response to 2-DG, resulting in potentiation of mTOR suppression. 21510938_knockdown of TXNIP prevented high glucose-induced cell apoptosis and activation of ASK1 may be via reduction of oxidative stress in mesangial cells. 21543874_N-terminal domain of TXNIP has been crystallized. The crystals belonged to a monoclinic space group and diffracted to 3 A resolution using synchrotron radiation 21636804_role for the TXNIP-TRX1 complex to enable inflammation by promoting endothelial cell survival and vascular endothelial growth factor signaling under conditions of physiological oxidative stress 21705327_thioredoxin regulates the intrinsic function of Txnip as an inhibitor of adipogenesis through protein stabilization. 21771725_Loss of TXNIP is associated with bladder carcinogenesis. 21908621_the MondoA-TXNIP regulatory circuit has a role in the hexose transport curb, although other redundant pathways also contribute 21916829_Chronic lymphocytic leukemia samples had an average of 57% higher TXNIP RNA levels, which correlated positively with reactive oxygen species levels. This was also seen in a transgenic mouse model. 21929372_The TXNIP transcription and protein stability are highly regulated by multiple tissue-specific stimuli, it appears that TXNIP should be a good therapeutic target for metabolic diseases. 22113441_Findings indicated that the TXNIP G allele may contribute to increased arterial stiffness in the Brazilian general population and suggest a possible interaction with diabetes. 22236479_Suggest that genetic variation in the TXNIP gene may act as a 'common ground' modulator of diabetes and hypertension. 22267843_Thioredoxin interacting protein promotes endothelial cell inflammation in response to disturbed flow by increasing leukocyte adhesion and repressing Kruppel-like factor 2. 22450549_Data indicate that TXNIP may mediate some of the detrimental effects of glucocorticoids on osteoblast (OB) function as well as modulate OB-mediated osteoclastogenesis by regulating the OPG/RANKL ratio. 22750447_an overview of TXNIP protein and function 22760822_A thioredoxin interacting protein mutant with all but one cysteine changed to serine (Cys247) showed an enhanced capacity to form complexes with TRX. 22768160_TBP-2 deficiency enhances TGF-beta signaling and promotes TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. 23112551_TXNIP is underexpressed in 85% of gastric cancer cells 23152583_insulin stimulates Txnip degradation by a PI3 kinase-dependent mechanism, which activates the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway and likely serves to mitigate insulin resistance 23291592_high cellular levels of TBP-2 can potentially suppress Thioredoxin bioavailability and increase oxidation sensitivity. Overexpression of TBP-2 also causes slow growth by mitotic arrest and apoptosis by activating the ASK death pathway. 23387972_The results for the first time demonstrate FAK-regulated TXNIP expression which is important for apoptotic, survival and oxidative stress signaling pathways in cancer cells. 23393387_TXNIP is essential for VEGFR2 internalization in Rab5 positive endosomes, which is required for endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis. 23453806_Glucose influx through GLUT1 restores ATP-to-ADP ratios in the short run and ultimately induces TXNIP protein production. 23454121_Using a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, we have found that TXNIP mRNA expression is regulated in a biphasic manner in hypoxia whereby TXNIP expression showed an initial rapid decrease, followed by an increase under prolonged hypoxia. 23461678_Serum TXNIP is elevated in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and may be a contributing factor for insulin resistance. 23519408_The crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of TXNIP is reported, providing the first structural information on any of the alpha-arrestins. 23520550_Suppression of Txnip by lipopolysaccharide is accompanied by a decrease of the glucose sensing transcription factor MondoA in the nuclei. 23691179_Thioredoxin interacting protein is a potential regulator of glucose and energy homeostasis in endogenous Cushing's syndrome. 23803610_FOXO1 inhibits beta cell TXNIP transcription and suggest that FOXO1 confers this inhibition by interfering with ChREBP DNA binding at target gene promoters. 23880345_TXNIP has a role in the pathway involving hEcd to increase p53 stability and activity 24041652_Knockdown of TXNIP inhibits high glucose-induced activation of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 and ameliorates high glucose-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. 24198286_These data implicate a critical role for TXNIP in diabetes-related impairment of ischemia-mediated angiogenesis and identify TXNIP as a potential therapeutic target for the vascular complications of diabetes. 24283717_TXNIP is a promising new target for the development of new therapies for the treatment of retinal neurodegenerative diseases. 24376827_Over-expression of TXNIP abolishes nuclear migration of TRX-1 under nitrosative/oxidative stress conditions. 24389582_The inhibition of TRX by TXNIP is mediated by an intermolecular disulphide interaction resulting from a novel disulphide bond-switching mechanism. This bond dissociates in the presence of high concentrations of reactive oxygen species. 24492284_Hyperglycemia leads to dysfunction of autophagy in renal tubular cells and decreases autophagic clearance. HG-induced overexpression of TXNIP may contribute to the dysfunction of tubular autophagy in diabetes. 24628418_TXNIP stimulates its own expression by promoting dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation of its transcription factor, carbohydrate response element-binding protein. 24645981_Our findings indicate that TXNIP functions as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cells, and its downregulation is likely important in the transition from differentiated to advanced thyroid cancer 24720336_Data suggest that hyperglycemia, as exhibited in 85% of pancreatic cancer patients, up-regulates expression of TXNIP and modulates activity of TRX (thioredoxin) and production of reactive oxygen species in pancreatic cancer cells. 24843047_Txnip is located in the endoplasmic reticulum and interacts with endogenous PDIA6. Txnip increases PDI activity. 24878528_Our data suggest that glucose-induced BCL-6 overexpression could abrogate the etoposide chemotherapy effect on tumor cell death. 24911120_TXNIP has been discovered to control pancreatic B-cell microRNA expression, B-cell function, and insulin production. [Review] 24925443_diabetes was associated with a >30-fold increase in TxnIP gene expression and a 17 % increase in TxnIP protein expression. 25332233_regulatory relationship between mTOR and the MondoA-TXNIP axis that we propose contributes to glucose homeostasis 25341426_Data identify the metastasis suppressor TXNIP as new target of miR-224/miR-452 that induces feedback inhibition of E2F1 and show that miR-224/452-mediated downregulation of TXNIP is essential for E2F1-induced EMT and invasion 25605021_Suggest that TXNIP plays a critical role in anti-Her-1/Her-2 treatment and may be a potential prognostic marker in breast cancer. 25726203_The expression of TXNIP was significantly higher in normal-weight type- 2 diabetic patients than in obese ones. 25754218_Foam cell-released 4-hydroxnonenal activates PPARdelta in Vascular endothelial cells, leading to increased TXNIP expression and consequently to senescence. 25812606_our data support the hypothesis that TXNIP is an effective target for the treatment of breast cancer. 25834832_HG-induced NADPH oxidase activation is driven by TXNIP which subsequently triggers NALP3 inflammasome activation in podocytes and ultimately led to podocyte injury 25854388_Expression of TXNIP was up-regulated in all three NSCLC cell lines. 25870263_data suggest that loss of the p53 tumor suppressor cooperates with Mychigh/TXNIPlow-driven metabolic dysregulation to drive the aggressive clinical behavior of TNBC. 26122224_The protein expression level of TXNIP was negatively correlated with the level of miR-373 in MCF-7 cells and in breast cancer tissue of various migration and invasion abilities. TXNIP was regulated by miR-373. 26147751_Metformin down-regulates high-glucose-induced TXNIP transcription by inactivating ChREBP and FOXO1 in endothelial cells, partially through AMP-activated protein kinase activation 26196741_Activation of the miR-373-TXNIP-HIF1alpha-TWIST signaling axis is correlated with a worse outcome in patients with breast cancer. 26643952_An association has been found between the TXNIP gene methylation pattern and type 2 diabetes mellitus in ischemic stroke patients through epigenetic mechanisms, related to sustained hyperglycemia levels with HbA1c >/= 7%. 26763822_No evidence that SNPS in TXNIP has effect, but the rs4485648 polymorphism of the TrxR2 gene might exert an independent effect on the development of Diabetic retinopathy. 26806835_Glucose exerts strong stimulatory effects on activation histone marks while having inhibitory effects on repression marks in the promoter of the TXNIP gene, and this was associated with a marked increase in expression of the proinflammatory gene in kidney. 26858253_These findings thereby provide new mechanistic insight into the regulation of TXNIP and beta-cell biology and reveal novel links between proinflammatory cytokines, carbohydrate response element binding protein-mediated transcription, and microRNA signaling. 26919541_The crystal structure of the complex between a phosphorylated PPxY motif of TXNIP and the SH2 domain of Vav2 reveals a conserved recognition mechanism. 27274779_Heme oxygenase rs2071749 polymorphism was positively associated with obesity in Mexicans. 27381856_TXNIP contributes to the dysregulation of tubular autophagy and mitophagy in diabetic nephropathy through activation of the mTOR signaling pathway. 27437069_These data identify novel Txnip protein interactions. 27470124_TXNIP Single nucleotide polymorphisms may individually and cumulatively affect CAD risk through a possible mechanism for regulating TXNIP expression and gene-environment interactions. 27497988_thioredoxin-interacting protein deficiency alleviates diabetic renal lipid accumulation through regulation of Akt/mTOR pathway 27510506_This finding suggested statistically significant role of interaction of TXNIP and AF1q polymorphisms (TXNIP-rs2236566, TXNIP-rs7211, and AF1q-rs2769605) in schizophrenia susceptibility. 27567705_results suggest that TXNIP is required early in the apoptotic-inducing pathway resulting from r-Moj-DM binding to the alphav integrin subunit 27762463_Hypoxia suppresses thioredoxin binding protein-2 gene expression, which may ultimately alter placental development. 27833015_Taken together, our results firstly reveal that TMAO induces inflammation and endothelial dysfunction via activating ROS-TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome, suggest a likely mechanism for TMAO-dependent enhancement in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risks. 27989964_histone acetylation serves as a key regulator of glucose-induced increase in TXNIP gene expression 28029659_Study showed that the expression of TXNIP was significantly increased in RNF2 knockdown prostate tumor cells and that TXNIP is an important downstream target of RNF2. 28064010_the association of TXNIP (thioredoxin-interacting protein) with NLRP3 induced by ROS promoted NLRP3 inflammasome activation in senescent HUVEC endothelial cells 28137209_summarize the current state of our understanding of TXNIP biology, highlight its role in metabolic regulation and raise critical questions that could help future research to exploit TXNIP as a therapeutic target 28243945_High expression of TXNIP indicates a lower pathological grade of meningnioma, and is also associated with longer recurrence-free time. 28322443_All-trans retinoic acid plays a key role in inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation via suppressing TXNIP expression, which reduces oxidative stress levels. 28326454_intracellular TXNIP protein is a critical regulator of activation of the fructose-induced NLRP3 inflammasome 28440491_This study provides insight into the molecular mechanisms of TXNIP overexpression in liver cancer cell survival and apoptosis and indicated that TXNIP may be a novel promising agent for liver cancer treatment. 28651973_Depletion of glycolytic intermediates led to a consistent decrease in TXNIP expression in response to 1,25(OH)2D3, an effect that coincided with the activation of AMPK signaling and a reduction in c-MYC expression. 28694028_This study thus characterizes ERK-mediated suppression of TXNIP as a presently unreported mechanism by which ap junctions regulate cell behaviors. 28755477_The data of this study suggested that TXNIP blocked autophagic flux and induced alpha-synuclein accumulation through inhibition of ATP13A2. 28844667_Study shows that TXNIP expression is down-regulated in new Multiple Sclerosis (MS) patients compared to controls and might be implicated in pathogenesis of the disease. 29077742_We found no evidence of decreased TXNIP DNA methylation or increased gene expression in metabolic target tissues of offspring exposed to maternal diabetes. Further studies are needed to confirm and understand the paradoxical SAT TXNIP DNA methylation and gene expression changes in O-GDM subjects 29203232_Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) is highly induced in retinal vascular endothelial cells under diabetic conditions. Data (including data from studies using knockout mice) suggest that TXNIP in retinal vascular endothelial cells plays role in diabetic retinal angiogenesis via VEGF/VEGFR2 and Akt/mTOR signaling. (VEGFR2 = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2) 29339473_Consistent with its enhanced expression in Laron syndrome, we provide evidence that TXNIP gene expression is negatively regulated by IGF1. 29378331_Results indicate an internal ribosome entry sites (IRESes) within the thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) protein; 5' untranslated region (5'UTR), and regulatory IRES trans-acting factors. 29524408_Compared with normal tissues, TXNIP expression was significantly decreased in human breast cancer tissues and canine mammary tumors, along with tumor progression. 29653364_miR-20a could negatively regulate TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling to protect human aortic endothelial cells from inflammatory injuries. 29852169_Using oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R) to create a cell model of hepatic I/R injury, we found that the mRNA and protein expression levels of TXNIP were upregulated in HL7702cells exposed to OGD/R. 29856480_Thus, CSE inhibits insulin production by upregulating TXNIP via MALAT1-mediated downregulation of miR-17, which provides an understanding of the processes involved in the reduced beta-cells function caused by cigarette smoke 29897613_Age-dependent upregulation of TXNIP results in decreased stress resistance to oxidative challenge in primary human cells. 29934340_Data show that thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) is a tumor suppressor that is downregulated in esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC). 29955142_TXNIP functions as a tumor suppressor gene with loss of its expression associated with ductal carcinoma in situ recurrence 29980378_vitamin D and TXNIP were associated with different beta-cell dysfunction markers, indicating their potential abilities to predict the beta-cell status in people with diabetes 29999276_Results found the mRNA level of TRX-1 was significantly decreased (p |
ENSMUSG00000038393 |
Txnip |
4204.223234 |
0.4103277042 |
-1.285152 |
0.030518486 |
1777.757134 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2453.4246815 |
58.9633662 |
6022.1717317 |
99.6018231 |
| ENSG00000266074 |
57597 |
BAHCC1 |
protein_coding |
Q9P281 |
|
Acetylation;Coiled coil;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to enable chromatin binding activity. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:57597; |
chromatin binding [GO:0003682] |
27928163_variants. We identified two candidate homozygous missense variants, R942Q in the tubulin-folding cofactor D (TBCD) gene and H250Q in the bromo-adjacent homology domain and coiled-coil containing 1 (BAHCC1) gene, located on chromosome 17q25.3 with an interval of 1.4 Mbp. 33139953_BAHCC1 binds H3K27me3 via a conserved BAH module to mediate gene silencing and oncogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000039741 |
Bahcc1 |
462.811327 |
0.2222824060 |
-2.169534 |
0.442772650 |
22.117767 |
0.00000256425478856241341932124290503569596921806805767118930816650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008649086078423497435168840197228234956128289923071861267089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
161.4532034 |
99.7960385 |
731.5087525 |
319.4411791 |
| ENSG00000266256 |
284276 |
LINC00683 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30963639_Downregulation of long noncoding RNA LINC00683 associated with unfavorable prognosis in prostate cancer based on TCGA. 34617815_Role of hypermethylated-lncRNAs in the prognosis of bladder cancer patients. |
|
|
6.649994 |
0.1832868121 |
-2.447825 |
0.728484261 |
12.016540 |
0.00052730505331966210161298569403243163833394646644592285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001289433828197185513339539930655064381426200270652770996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.7715808 |
0.9489793 |
9.6966498 |
2.8653298 |
| ENSG00000266369 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.415438 |
0.1973083364 |
-2.341476 |
0.673889199 |
12.348490 |
0.00044134325776236816435416088211241003591567277908325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001095564494546342939468308586015155015047639608383178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1368148 |
1.4048671 |
15.9945832 |
4.1484762 |
| ENSG00000266490 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.626515 |
0.3006138769 |
-1.734016 |
0.615876578 |
8.422612 |
0.00370582937459999631549245613371112995082512497901916503906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007786198088127536769131875615812532487325370311737060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0357863 |
1.2921054 |
10.0489688 |
2.5091466 |
| ENSG00000266709 |
84815 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.679601 |
13.5387295906 |
3.759020 |
0.721293396 |
35.913911 |
0.00000000206231010629862066117182718889312698085092279143282212316989898681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000009599399927142112550998563245355926776269939182384405285120010375976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.5343102 |
9.6216619 |
1.5301137 |
0.6700774 |
| ENSG00000266714 |
80022 |
MYO15B |
protein_coding |
Q96JP2 |
FUNCTION: Unknown, due to the absence of a functional motor domain. |
3D-structure;Cytoplasm;Reference proteome;SH3 domain |
|
Predicted to enable ATP binding activity; actin binding activity; and cytoskeletal motor activity. Predicted to be located in brush border; cytoplasm; and cytoskeleton. Predicted to be part of myosin complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:80022; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; myosin complex [GO:0016459]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; cytoskeletal motor activity [GO:0003774] |
11964073_myosin XVBP is a transcribed pseudogene (myosin XVBP=MYO15BP) |
ENSMUSG00000034427 |
Myo15b |
982.053637 |
0.2407862588 |
-2.054175 |
0.110629965 |
329.732738 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000010989992549378351285455675933463756266800282578135153897489483062462237863966609773113445822728190307808971835506184313848048741918711985335763276562269637992340739825700809915038627315175823184745240723714232444763183593750000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003429435307163307810915225723842030297395767800454521203502718148722224769919319247179663654905178452836025756777085395881759288857555571994021824755166675793567692598324026811117126722905368296778760850429534912109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
367.2591277 |
39.7100125 |
1535.2256842 |
117.8919675 |
| ENSG00000266820 |
|
KPNA2P3 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
42.650060 |
0.3393372710 |
-1.559208 |
0.343068105 |
20.685961 |
0.00000541112874841811097354924917079976864897616906091570854187011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000017534195461394362581999256667231179562804754823446273803710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
19.2608985 |
4.3862119 |
57.0485366 |
8.5295986 |
| ENSG00000266896 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.591876 |
0.4988667493 |
-1.003274 |
0.429385665 |
5.556235 |
0.01841497786840694608767599049770069541409611701965332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.033297203642984996019293930658022873103618621826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.3011119 |
2.6621442 |
18.7937226 |
3.5039338 |
| ENSG00000266918 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.932581 |
0.3712165013 |
-1.429667 |
0.454036055 |
10.287871 |
0.00133907506791509445590038218654171942034736275672912597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003054829675800122684714565934882557485252618789672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5251751 |
1.8562804 |
17.7116119 |
3.0122646 |
| ENSG00000266947 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.461302 |
0.2983435869 |
-1.744953 |
0.483454419 |
13.460215 |
0.00024367586511838429277725104338259143332834355533123016357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000629997507295034517640908156010937091195955872535705566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6040808 |
1.9626404 |
18.9373111 |
4.1565978 |
| ENSG00000267080 |
339201 |
ASB16-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29763751_Our findings support that ASB16-AS1 and SYN2 may represent two novel functional genes underlying bone mineral density variation 30949502_the present study revealed that lncRNA ASB16-AS1 improves the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells. 33219221_Long noncoding RNA ASB16-AS1 inhibits adrenocortical carcinoma cell growth by promoting ubiquitination of RNA-binding protein HuR. 34289570_[LncRNA ASB16-AS1 regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells by targeting miR-1258]. 34870557_LncRNA ASB16-AS1 drives proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through regulating miR-185-5p/TEAD1 axis. |
|
|
87.538126 |
0.4004463271 |
-1.320319 |
0.197167684 |
44.989136 |
0.00000000001981305910318125815667356154102854686599455291684535040985792875289916992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000107911716739097923798682311962891192808067231112545414362102746963500976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
51.0730614 |
6.1643109 |
128.7917341 |
10.1763776 |
| ENSG00000267100 |
147727 |
ILF3-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28935763_Long noncoding RNA ILF3-AS1 promotes EZH2-mediated cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via negatively regulating miR-200b/a/429 in melanoma. 30819403_The expression levels of lncRNA ILF3-AS1 was up-regulated in osteosarcoma tissues and cell lines, and was modulated by SP1. LncRNA ILF3-AS1 promoted osteosarcoma cells proliferation and metastasis via modulation of miR-212-SOX5 pathway. 32404536_LncRNA ILF3-AS1 mediated the occurrence of epilepsy through suppressing hippocampal miR-212 expression. 32962500_Up-regulated long non-coding RNA ILF3-AS1 indicates poor prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and promoted cell metastasis. 34080029_Mechanism underlying long noncoding RNA ILF3AS1mediated inhibition of cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotion of apoptosis. |
|
|
84.423795 |
0.3707487038 |
-1.431486 |
0.202721551 |
50.435782 |
0.00000000000123128599442787169147433354741681698664435007373185726464726030826568603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007287001314256369699459440221688498722646398775282250426243990659713745117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
45.6031393 |
5.6386183 |
123.7668382 |
9.7799249 |
| ENSG00000267169 |
100507373 |
ADGRL1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52.093831 |
0.3097361985 |
-1.690888 |
0.258310734 |
43.140893 |
0.00000000005093642714005095073945907631991682901206885958345083054155111312866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000268603667233709192280136909608198592103178725665202364325523376464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
22.2435035 |
4.1246972 |
72.2070272 |
8.9060835 |
| ENSG00000267202 |
105372068 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.097323 |
0.0319990470 |
-4.965827 |
1.155571251 |
25.207059 |
0.00000051493384873819143862769178582317053383121674414724111557006835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001886429289495087051868214486627373105420701904222369194030761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3275031 |
0.2995693 |
10.3048385 |
3.5115922 |
| ENSG00000267221 |
110806298 |
C17orf113 |
protein_coding |
A0A1B0GUU1 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
12.080061 |
0.4248947036 |
-1.234823 |
0.448885215 |
7.753481 |
0.00536091142973510285940630382128802011720836162567138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010888544475421787008362350945844809757545590400695800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4171577 |
2.0843202 |
17.6304803 |
3.0481946 |
| ENSG00000267244 |
100288123 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.329488 |
0.1994860136 |
-2.325640 |
0.584023785 |
15.588627 |
0.00007872670890898948541352514451929778260819148272275924682617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000219743990827663568474875654956690596009138971567153930664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7126160 |
2.0889202 |
29.4129796 |
6.4155964 |
| ENSG00000267265 |
|
GP6-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.559216 |
0.3193448581 |
-1.646813 |
0.522594014 |
10.159113 |
0.00143589719148849910036747079544738880940712988376617431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003262598914157981318251433577870557201094925403594970703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0447458 |
1.6231797 |
16.0686740 |
3.0507209 |
| ENSG00000267270 |
100130522 |
PARD6G-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 29545821_Maternal 5mCpG imprints at the PARD6G-AS1 gametic (primary) differentially methylated region (iDMR) are decoupled from parent-of-origin expression effects in multiple human tissues. Despite the constitutive methylation asymmetry observed between the parental alleles at the iDMR, PARD6G-AS1 was expressed biallelically in six tissues: brain amygdala, brain putamen, heart atrial appendage, pituitary, testis, and thyroid. |
|
|
8.052680 |
2.7524727409 |
1.460728 |
0.577205329 |
6.597150 |
0.01021421544426232008717647659068461507558822631835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019533793723414336063193275094818091019988059997558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.6690629 |
4.3959713 |
4.6783570 |
1.3265570 |
| ENSG00000267278 |
|
MAP3K14-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75.586651 |
0.4303691163 |
-1.216354 |
0.198595539 |
38.017101 |
0.00000000070127259877185051366067501088497580796765618060817359946668148040771484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003397040878855436264105416052758341927120255832051043398678302764892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
46.9010561 |
6.0964549 |
109.7054284 |
9.3834242 |
| ENSG00000267283 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.079771 |
0.0531223328 |
-4.234538 |
0.933672603 |
23.957208 |
0.00000098500822050637011860474683694333108974205970298498868942260742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003485668025575167438905553607408904781550518237054347991943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.6365889 |
0.5076227 |
14.1033299 |
5.3714003 |
| ENSG00000267296 |
80054 |
CEBPA-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29281558_Study results clarify that CEBPA-AS1 up-regulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), correlated with poor differentiation, lymph node metastasis and high clinical stage, could be a prognostic biomarker of OSCC patients. 34790046_Long noncoding RNA CEBPA-DT promotes cisplatin chemo-resistance through CEBPA/BCL2 mediated apoptosis in oral squamous cellular cancer. 35088289_LncRNA CEBPA-AS1 knockdown prevents neuronal apoptosis against oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation by regulating the miR-455/GPER1 axis. |
|
|
19.751161 |
0.2824842891 |
-1.823757 |
0.378862237 |
24.518751 |
0.00000073590163123245263382919689743033586637466214597225189208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002642800018732603653303986010469905920672317733988165855407714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.9840327 |
1.9392069 |
28.3376061 |
4.0508998 |
| ENSG00000267348 |
105372419 |
GEMIN7-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.607204 |
0.2341528561 |
-2.094477 |
0.382065153 |
33.031385 |
0.00000000906831203602151775809001228202677058476410820730961859226226806640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000039682266721517219208702762552748444235817260050680488348007202148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0320259 |
1.9927240 |
34.6802610 |
4.5784017 |
| ENSG00000267365 |
400617 |
KCNJ2-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.741253 |
0.4274843679 |
-1.226056 |
0.317578612 |
15.180486 |
0.00009770791498352512222374394168511457792192231863737106323242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000269111555356751409352755732840023483731783926486968994140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.2050790 |
3.4883347 |
38.1946353 |
5.3272942 |
| ENSG00000267368 |
100134938 |
UPK3BL1 |
protein_coding |
E5RIL1 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100134938; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000006143 |
Upk3bl |
267.458857 |
0.2251864868 |
-2.150808 |
0.390240001 |
26.317432 |
0.00000028966238884226245233534944092945728755239542806521058082580566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001085958054181303960878529624167754263908136636018753051757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
112.3806751 |
36.5417018 |
492.2219841 |
114.1728531 |
| ENSG00000267432 |
|
DNAH17-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.211958 |
0.1695481044 |
-2.560233 |
0.790376777 |
9.346625 |
0.00223396444024732791777676510491801309399306774139404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004886383393309210940169684533884719712659716606140136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
8.6229933 |
4.5808387 |
51.4116042 |
19.1670182 |
| ENSG00000267519 |
|
MIR23AHG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
558.071493 |
12.3436385434 |
3.625696 |
1.198795545 |
7.440327 |
0.00637783179585550263207549548383212822955101728439331054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012747027394289399057636380518943042261525988578796386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1297.3394099 |
961.9040620 |
106.0436359 |
55.0306609 |
| ENSG00000267523 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.136447 |
0.4796986806 |
-1.059800 |
0.293142367 |
13.207950 |
0.00027876413742570051515490270332975342171266674995422363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000714581220632744002624336943085836537647992372512817382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.9732602 |
3.4694556 |
39.8173409 |
4.6822942 |
| ENSG00000267534 |
9294 |
S1PR2 |
protein_coding |
O95136 |
FUNCTION: Receptor for the lysosphingolipid sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) (PubMed:10617617). S1P is a bioactive lysophospholipid that elicits diverse physiological effects on most types of cells and tissues (PubMed:10617617). When expressed in rat HTC4 hepatoma cells, is capable of mediating S1P-induced cell proliferation and suppression of apoptosis (PubMed:10617617). Receptor for the chemokine-like protein FAM19A5 (PubMed:29453251). Mediates the inhibitory effect of FAM19A5 on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P47752, ECO:0000269|PubMed:10617617, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29453251}. |
3D-structure;Cell membrane;Deafness;Disease variant;G-protein coupled receptor;Glycoprotein;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Non-syndromic deafness;Palmitate;Receptor;Reference proteome;Transducer;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a member of the G protein-coupled receptors, as well as the EDG family of proteins. The encoded protein is a receptor for sphingosine 1-phosphate, which participates in cell proliferation, survival, and transcriptional activation. Defects in this gene have been associated with congenital profound deafness. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]. |
hsa:9294; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; postsynapse [GO:0098794]; G protein-coupled peptide receptor activity [GO:0008528]; G protein-coupled receptor activity [GO:0004930]; G protein-coupled receptor binding [GO:0001664]; integrin binding [GO:0005178]; lipid binding [GO:0008289]; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor activity [GO:0038036]; actin cytoskeleton reorganization [GO:0031532]; adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007189]; excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0060079]; filopodium assembly [GO:0046847]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; negative regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential [GO:0090394]; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014912]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904706]; positive regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008284]; positive regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier [GO:1903142]; positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation [GO:0010800]; regulation of metabolic process [GO:0019222]; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway [GO:0003376] |
11915348_suppress rac protein, a Rho family G protein and cell motility 15208267_Amyloid beta-protein stimulated in monocytes the gene expression for sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 5, which is amyloid beta-protein-induced migration. 15764699_S1P2R receptor actively regulates the PTEN phosphatase by a Rho GTPase-dependent pathway to inhibit cell migration. 17431187_S1P2R activation in endothelial cells increases vascular permeability. The balance of S1P1 and S1P2 receptors in the endothelium may determine the regulation of vascular permeability by S1P. 17710232_antagonism of the S1P2R may be a novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and/or treatment of pathologic ocular neovascularization 18088600_These results suggest that S1P(2) receptors/G(12/13)-proteins/Rho signaling pathways mediate S1P-induced inhibition of glioma cell migration. 18612546_Results suggest that S1PR2 is involved in COX2 dependent effects of high-density lipoprotein on vascular smooth muscle. 18658144_Plays essential roles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis by modulating fibroblast-like synoviocytes migration, cytokine/chemokine production, and cell survival. 18765664_impairment of function in senescent ECs in culture is mediated by an increase in S1P signaling through S1P(2)-mediated activation of the lipid phosphatase PTEN 18922980_These data suggest that CTGF protein induced by S1P2 might act as a growth inhibitor in Wilms' tumor. 19139947_the S1P(2) receptor is involved in S1P-induced platelet aggregation and Rho kinase activation. 19903857_S1P(2) signaling may play a critical role in suppressing diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 19948975_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 20194630_S1PR2 receptors play a critical role in regulating human mast cell functions, including degranulation and cytokine and chemokine release 21145832_SphK/S1P/S1PRs signaling axis plays an important role in liver fibrosis and is involved in the directed migration of hepatic myofibroblasts into the damaged areas. 21289286_S1P2, and not S1P1 or S1P3, receptor activation increases conventional outflow resistance in whole-eye perfusions. 22244964_Inflammatory mediators lipopolysaccharide and TNF-alpha induce S1PR2 expression in endothelium, suggesting that S1PR2 up-regulation may be involved in LPS and TNF-alpha elicited endothelial barrier dysfunction. 22547907_abdominal aortic aneurysms have down-regulation of the S1P2 protein with simultaneous up-regulation of the S1P3 protein, but not S1P1 22889737_S1P receptors S1P1,2,3 are expressed in human anaplastic thyroid cancer C643 and THJ-16T cells at both mRNA and protein levels 23106337_identify the S1PR2 as the specific and necessary receptor to induce phosphorylation of ERM proteins and subsequent filopodia formation 23300082_Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors 1 and 2 coordinately induce mesenchymal cell migration through S1P activation of complementary kinase pathways 23589284_S1PR agonists are pro-fibrotic via S1P2R and S1P3R stimulation using Smad-independent pathways. 23629860_Data indicate that EGF-induced cellular invasion required sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)-mediated activation of sphingosine-1-phosphate 2 receptor (S1PR2) and ezrin phosphorylation. 23666803_Activation of the S1P2 receptor counteracts the detrimental phosphorylation of p38 MAPK by IL-1beta. 23723450_S1PR2 is a key regulator of the proinflammatory phenotype of the endothelium. 23770055_TNFalpha treatment activates autocrine S1P/S1P2 signaling, which subsequently activates NFkappaB and leads to the proinflammatory responses in endothelial cell 23993968_The S1P2R specifically activates RhoC via G12/13 proteins and LARG. 24038457_we provide evidences that S1PR1/3, but not S1PR2, negatively regulate the expression of collagen in hMSCs using cellular and molecular approaches 24064301_extracellular S1P induces COX-2 expression via activation of S1P2 and subsequent Gi and p42/p44 MAPK-dependent signaling in renal mesangial cells leading to enhanced PGE2 formation and cell migration that essentially requires COX-2. 24614064_Sphingosylphosphorylcholine stimulates alpha-SMA protein expression and human lung fibroblast mediated collagen gel contraction via S1P2 receptor. 24700501_Conjugated bile acids promote cholangiocarcinoma growth through S1PR2. 24812668_S1PR2 expression was increased in disease-susceptible regions of the CNS of female patients with multiple sclerosis compared with their male counterparts. 24851274_Data indicate that sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) induced transloaction of integrin beta4, S1P receptors S1PR2 and S1PR3 to endothelial cell membrane caveolin-enriched microdomains (CEMs). 24903384_Data show that sphingosine kinase SphK1 and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors S1P1, S1P2, S1P3, and S1P5 were expressed from primary, up to recurrent and secondary glioblastomas, with sphingosine kinase SphK2 levels were highest in primary tumors. 25557733_Activation of S1PR2-calcium influx-RhoA/ROCK dominates the high-dose S1P-induced endothelial monolayer hyperpermeability response. 25673082_both S1PR1 and S1PR2 play a pivotal role in hyperglycemia-induced EC dysfunction and endothelial injury by reducing and enhancing the production of oxidative stress. 26105954_AB1 displayed potency at least equivalent to JTE-013 in affecting signaling molecules downstream of S1P2. 26243335_be detected in the human cerebrovascular endothelium 26321412_Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced IL-8 gene expression is mainly regulated via S1PR(1), and its secretion is regulated through S1PR(2) receptor subtype. 26518876_S1PR2 plays a critical role in TCA-induced COX-2 expression and CCA growth and may represent a novel therapeutic target for CCA. 26631556_S1PR2 mediates Rho activation in normal cells neighboring RasV12-transformed cells. 26669941_LXR-alpha might downregulate S1PR2 expression via miR-130a-3p in quiescent HUVECs. Stimulation of TNF-alpha attenuates the activity of LXR-alpha and results in enhanced S1PR2 expression. 26729899_S1PR2 is repressed by FOXP1 in activated B-cell and germinal center B-cell DLBCL cell lines with aberrantly high FOXP1 levels; S1PR2 expression is further inversely correlated with FOXP1 expression in 3 DLBCL patient cohorts. 27160553_Data show that sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) was significantly upregulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues and low levels of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase 1 (SGPL1) mRNA correlated with a worse overall survival, and that sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2) is over-expressed in a subset of tumours, which in part mediates sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)-induced migration of OSCC cells. 27383011_SNPs within 0.1 Mb of the S1PR2 gene as well as within the gene itself were interrogated as a candidate gene association for hearing loss. For 1 kHz thresholds, the adjacent SNP rs74930654 showed the most significant association. For 4 kHz, the most significant association was with rs201930568. These findings suggest that variants affecting the S1PR2 gene do contribute to auditory thresholds in the UK population. 27562371_Butyrate and bioactive proteolytic form of Wnt-5a regulate colonic epithelial proliferation and spatial development 28181168_Data suggest that activation of SR-BI by APOAI down-regulates sphingosine 1-phosphate/S1PR2-mediated inflammation in vascular endothelial cells by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway; oxidized-LDL does the opposite. (APOA1 = apolipoprotein A-I; SR-BI/SCARB1 = scavenger receptor class B type I; S1PR2 = sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2; PI3K = phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt = proto-oncogene c-akt) 28206609_High S1PR2 expression is associated with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. 28302479_CONCLUSION: MiR-126 down-regulated S1PR2 and then prevented the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which ultimately could damage intestinal mucosal barrier function. 29208234_Although extravillous trophoblasts express three S1P receptor isoforms, S1P predominantly signals through S1PR2/Galpha12/13 to activate Rho, and thereby acts as potent inhibitor of extravillous trophoblast migration. 29453251_Novel adipokine, FAM19A5, was capable of inhibiting postinjury neointima formation via sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2-G12/13-RhoA signaling. 29458005_14-3-3zeta promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invasion by repressing S1PR2 protein expression through NF-kappaB signaling 29475983_The migration and homing of the Muse cells was confirmed pharmacologically (S1PR2 [sphingosine monophosphate receptor 2]-specific antagonist JTE-013 coinjection) and genetically (S1PR2-siRNA [small interfering ribonucleic acid]-introduced Muse cells) to be mediated through the S1P (sphingosine monophosphate)-S1PR2 axis 29776397_Study describes a novel variant in S1PR2 that causes an amino acid exchange (p.Arg108Gln) in the same amino acid residue as one of the previously reported Pakistani families (p.Arg108Pro) with hearing loss. This finding emphasizes the importance of the p.Arg108 amino acid in normal hearing and confirms and consolidates the role of S1PR2 in autosomal recessive hearing loss. 29903770_Here it is demonstrated that S1P activates YAP and that the S1P receptor 2 (S1PR2/S1P2) mediates S1P-induced YAP activation in both human and mouse hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. S1P promotes YAP-mediated upregulation of cysteine-rich protein 61 and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and stimulates HCC cell proliferation 29963993_High S1PR2 expression is associated with Invasive Growth of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. 30226616_both SphK1 overexpression and S1P addition increased mTOR phosphorylation as shown by ELISA, while S1PR2 inhibition had the inverse effect. These data suggest that CerS6 and SphK1 regulate mTOR signaling in breast cancer cell proliferation. Moreover, mTOR activity can be regulated by the balance between S1P and C16ceramide, which is generated by CerS6. 30512203_these data point to an important role of EDG5 in the maintenance and acquisition of pluripotency. 30664326_Bile acids increase steroidogenesis in cholemic mice and induce cortisol secretion in adrenocortical H295R cells via S1PR2, ERK and SF-1. 30666658_EBV oncogene LMP1 regulates expression of S1PR2 in aggressive ABC-subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. 30712233_High expression of S1PR2 is associated with bladder transitional cell carcinoma. 30877143_T cell S1PR1 and S1PR4, and lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) S1PR2, were required for migration across LECs and into lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. S1PR1 and S1PR4 differentially regulated T cell motility and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) binding. S1PR2 regulated LEC layer structure, permeability, and expression of the junction molecules VE-cadherin, occludin, and zonulin-1 through the ERK pathway. 31415870_This study demonstrated that S1P significantly promotes angiogenesis, inflammation, and barrier integrity, which was attenuated by inhibition of S1P2 or S1P3, suggesting that regulation of S1P2 and S1P3 is a novel therapeutic target for CNV. 31431671_S1P2 contributes to microglial activation and M1 polarization following cerebral ischemia through ERK1/2 and JNK. 31477835_The specific antagonism of beta3-AR by SR59230A inhibits Neuroblastoma growth and tumor progression, by switching from stemness to cell differentiation both in vivo and in vitro through the specific blockade of SK2/S1P2 signaling. 32647340_Increased S1P induces S1PR2 internalization to blunt the sensitivity of colorectal cancer to 5-fluorouracil via promoting intracellular uracil generation. 33197483_Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 2 Is Central to Maintaining Epidermal Barrier Homeostasis. 33225975_Unveiling role of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 as a brake of epithelial stem cell proliferation and a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. 35013382_The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2/4 antagonist JTE-013 elicits off-target effects on sphingolipid metabolism. 35905868_Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 promotes erythrocyte clearance by vascular smooth muscle cells in intraplaque hemorrhage through MFG-E8 production. |
ENSMUSG00000043895 |
S1pr2 |
187.760447 |
7.1998594847 |
2.847969 |
0.142169158 |
459.362262 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000661719939438741890693267251485610552678351236207207528322591156424924918103714263158631587883361725624948854262569751742026083422056769797641707674631671420152701083740090720549521855796772078672832884802314182326302128411545633 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000289821552110262031045086815557516885388837234928732290603575139536859014229796444878119306263201487730167765192393628437503189895722765393955653682847564949981979752765389520754906530475477286639680964879393670842392430572621740 |
Yes |
No |
335.3485197 |
29.2001507 |
46.9191343 |
3.6769928 |
| ENSG00000267561 |
|
|
protein_coding |
Q7LGA3 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the transfer of sulfate to the C2-position of selected hexuronic acid residues within the maturing heparan sulfate (HS). 2-O-sulfation within HS, particularly of iduronate residues, is essential for HS to participate in a variety of high-affinity ligand-binding interactions and signaling processes. Mediates 2-O-sulfation of both L-iduronyl and D-glucuronyl residues (By similarity). {ECO:0000250}. |
Alternative splicing;Disease variant;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Golgi apparatus;Intellectual disability;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal-anchor;Transferase;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
|
hsa:9653; |
Golgi membrane [GO:0000139]; membrane [GO:0016020]; heparan sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase activity [GO:0004394]; sulfotransferase activity [GO:0008146]; gene expression [GO:0010467]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process [GO:0015012]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process, enzymatic modification [GO:0015015]; heparan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthetic process, polysaccharide chain biosynthetic process [GO:0015014]; heparin metabolic process [GO:0030202]; ureteric bud formation [GO:0060676] |
|
|
|
6.262183 |
5.2806770232 |
2.400723 |
0.787305308 |
9.577966 |
0.00196926466032662852989609802989434683695435523986816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004355813934725166237937887814268833608366549015045166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.9632142 |
6.6778174 |
2.1667856 |
1.0520202 |
| ENSG00000267571 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.787718 |
0.1713524050 |
-2.544962 |
0.613923168 |
19.688710 |
0.00000911382181631440955983051305233644256986735854297876358032226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000028688421840221940499991715167737993397167883813381195068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6466020 |
1.1055564 |
15.5213643 |
3.3006872 |
| ENSG00000267580 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46.212065 |
0.3349988690 |
-1.577772 |
0.376297574 |
17.071683 |
0.00003599501833634926781756158131742040495737455785274505615234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000105434901894128831446179050956857281562406569719314575195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1957804 |
12.3874344 |
70.4797724 |
26.3988270 |
| ENSG00000267607 |
|
ICAM4-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.525854 |
4.3178800094 |
2.110323 |
0.651167486 |
10.406236 |
0.00125590498025445309118741654685891262488439679145812988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002880677157506717628310255463475186843425035476684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.6445314 |
8.1009756 |
5.3065593 |
1.5367612 |
| ENSG00000267733 |
|
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.042364 |
0.0158979525 |
-5.975015 |
1.150541989 |
35.491699 |
0.00000000256139878746208585786584004020515620281273072578187566250562667846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011818145077505592793080119585862053366298596301930956542491912841796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2162352 |
0.1934439 |
13.7037618 |
4.3229058 |
| ENSG00000267858 |
100131691 |
MZF1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.106210 |
0.4808706831 |
-1.056279 |
0.358753656 |
8.582263 |
0.00339453325565125920218467747702106862561777234077453613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007184300380472122792008260461216195835731923580169677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.4770508 |
5.1227601 |
37.0887587 |
7.4209808 |
| ENSG00000268027 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.302255 |
0.2598343107 |
-1.944336 |
0.445545349 |
19.905505 |
0.00000813657096110061667335478646778668121442024130374193191528320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000025821498040388111034097382012753030267049325630068778991699218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4870742 |
1.9596017 |
25.2338993 |
4.3874301 |
| ENSG00000268204 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.850822 |
0.1533701937 |
-2.704910 |
0.761537118 |
14.907580 |
0.00011290839590164810464154032665362592524616047739982604980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000308730626807766992802245509253111777070444077253341674804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5365551 |
0.8907805 |
10.0938259 |
3.0630386 |
| ENSG00000268218 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.442629 |
0.4666906820 |
-1.099461 |
0.405784702 |
7.422765 |
0.00644037711815905866002962554262012417893856763839721679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012861583853880085778764730264356330735608935356140136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.5046461 |
2.4097514 |
20.3994667 |
3.2530142 |
| ENSG00000268471 |
54553 |
MIR4453HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.559224 |
0.4437709675 |
-1.172113 |
0.419614535 |
7.956114 |
0.00479252104217389382490033256090100621804594993591308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009841069919655907882738432590485899709165096282958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2512055 |
2.4391213 |
18.8553616 |
3.5950142 |
| ENSG00000268531 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.178618 |
0.0723302899 |
-3.789256 |
0.638010927 |
45.678997 |
0.00000000001393084679435097511394938834850969243753238124838844669284299015998840332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000076523743462828574893737580308770377529592465748464746866375207901000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1420513 |
0.9551695 |
29.8752081 |
5.8946554 |
| ENSG00000268575 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.848516 |
0.3362311554 |
-1.572475 |
0.455066452 |
11.425111 |
0.00072458104932504846084490024438196087430696934461593627929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001729713130848733017644325293815654731588438153266906738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.9876846 |
3.6271855 |
37.3240619 |
6.9817818 |
| ENSG00000268583 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.859871 |
0.2553629395 |
-1.969379 |
0.628696776 |
10.498713 |
0.00119457698190621598548222248581396343070082366466522216796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002747266477553092500762943473091581836342811584472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8992084 |
1.2834809 |
11.3662262 |
2.8576384 |
| ENSG00000268686 |
101928295 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.766055 |
0.4298830897 |
-1.217984 |
0.277229316 |
19.621142 |
0.00000944185901344736600655956071381780247975257225334644317626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000029632540726872874409670438611286158447910565882921218872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.3628141 |
4.4342722 |
50.0599307 |
6.9401757 |
| ENSG00000269044 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.693920 |
0.4674073091 |
-1.097248 |
0.370513873 |
8.817122 |
0.00298417011780278181726222541669812926556915044784545898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006397436592413806646928442489752342225983738899230957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.8732011 |
3.2105378 |
31.9984128 |
4.5373427 |
| ENSG00000269220 |
200298 |
LINC00528 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31833800_LINC00528 regulates myocardial infarction by targeting the miR-143-3p/COX-2 axis. |
|
|
15.346439 |
0.3095860596 |
-1.691588 |
0.425237965 |
16.484218 |
0.00004905673575296767841003031662694411352276802062988281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000141379500298552710727678638491511264874134212732315063476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.3117261 |
1.9741612 |
23.8587224 |
3.7809689 |
| ENSG00000269352 |
|
PTOV1-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
51.028110 |
0.4948620439 |
-1.014902 |
0.235754180 |
18.646994 |
0.00001572950650989839673139260300960273752934881485998630523681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000048177529795829077249782329550598092282598372548818588256835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.7658455 |
5.0674372 |
72.7405345 |
6.5869868 |
| ENSG00000269386 |
100507567 |
RAB11B-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31900259_HIF2-Induced Long Noncoding RNA RAB11B-AS1 Promotes Hypoxia-Mediated Angiogenesis and Breast Cancer Metastasis. 35596159_METTL16 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through downregulating RAB11B-AS1 in an m(6)A-dependent manner. |
|
|
10.826914 |
0.3918044982 |
-1.351794 |
0.491584374 |
7.722555 |
0.00545351722367049766143631828185789345297962427139282226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011059894781722525922140754062183987116441130638122558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7630997 |
1.8690053 |
14.8122303 |
3.0263183 |
| ENSG00000269404 |
6689 |
SPIB |
protein_coding |
Q01892 |
FUNCTION: Sequence specific transcriptional activator which binds to the PU-box, a purine-rich DNA sequence (5'-GAGGAA-3') that can act as a lymphoid-specific enhancer. Promotes development of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), also known as type 2 DC precursors (pre-DC2) or natural interferon (IFN)-producing cells. These cells have the capacity to produce large amounts of interferon and block viral replication. May be required for B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, which is necessary for normal B-cell development and antigenic stimulation. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10196196, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12393575, ECO:0000269|PubMed:1406622, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15583020}. |
Activator;Alternative splicing;Cytoplasm;DNA-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transcription;Transcription regulation |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional activator that binds to the PU-box (5'-GAGGAA-3') and acts as a lymphoid-specific enhancer. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011]. |
hsa:6689; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0001228]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000978]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; cell differentiation [GO:0030154]; positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0045944]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357] |
12393575_Spi-B is expressed in plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors and inhibits T-, B-, and NK-cell development 15583020_Spi-B is a key regulator of human pDC development. 16263717_c-Myb and c-Ets family members (Ets-1/2, PU.1, and Spi-B) control hGR 1A promoter regulation in T- and B-lymphoblast cells 16317090_DL1-induced activation of the Notch1 pathway controls the lineage commitment of early thymic precursors by altering the levels between Spi-B and GATA-3. 18552212_By chromatin immunoprecipitation and assays using an inducible Spi-B construct BLIMP1 and XBP-1 were identified as direct target genes of Spi-B mediated repression. 18792017_findings suggest that the concurrent action of Spi-B and E2-2 controls the development of progenitor cells into the plasmacytoid dendritic cell lineage 20826618_These results suggest that Spi-B could regulate JC virus gene expression in susceptible cells, and may play an important role in JC virus activity in the immune and nervous systems. 22071512_The effect of mutating Spi-B-binding sites within the JC virus promoter/enhancer on early viral gene expression strongly suggests a role for Spi-B binding to the viral promoter/enhancer in the activation of early viral gene expression. 22257840_Fine mapping identified 26 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across the CLEC16A-SOCS1 and 11 SNPs across the SPIB locus with significant association to primary biliary cirrhosis. 22510878_The transcription factor Spi-B regulates human plasmacytoid dendritic cell survival through direct induction of the antiapoptotic gene BCL2-A1. 22698399_Data show that in a cereblon-dependent fashion, lenalidomide downregulates IRF4 and SPIB, transcription factors that together prevent IFNbeta production. 23165482_Our data indicate that the CBFbeta-SMMHC's C-terminus is essential to induce embryonic hematopoietic defects and leukemogenesis. 23439650_The SRC family tyrosine kinase HCK and the ETS family transcription factors SPIB and EHF regulate transcytosis across a human follicle-associated epithelium model. 24801987_Findings establish a molecular hierarchy among POU2F2, SPIB and ID2 during B-cell differentiation, and suggest that aberrant expression of these transcription factors plays an important role in arresting plasmacytic differentiation in WM. 27348272_our data indicate that SPIB expression is a clinically novel poor prognostic factor in DLBCL that contributes to treatment resistance, at least in part, through an anti-apoptotic mechanism. 28754672_High SPIB expression is associated with Lung Cancer metastasis. 28893618_These results show that the mechanism of action of lenalidomide in ABC-DLBCL cells involves downregulation of SPIB transcription by cereblon-induced degradation of IKAROS. 29554889_Results provide evidence that SPIB is a specific transcription factor that participates in pH-mediated regulation of AQP1 gene expression. 30986496_Taken together, this study identifies SPIB as an important target of ETV6-RUNX1 in regulation of B-cell gene expression in t(12;21) leukemia. 32129936_SPIB promotes anoikis resistance via elevated autolysosomal process in lung cancer cells. 34530056_SPIB acts as a tumor suppressor by activating the NFkB and JNK signaling pathways through MAP4K1 in colorectal cancer cells. 35770729_SPI1-related protein inhibits cervical cancer cell progression and prevents macrophage cell migration. 35831411_Integrated transcriptomic and regulatory network analyses uncovers the role of let-7b-5p, SPIB, and HLA-DPB1 in sepsis. 35969172_Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis reveals the prognostic value and immunological role of SPIB. |
ENSMUSG00000008193 |
Spib |
18.141511 |
0.2551703886 |
-1.970467 |
0.778234370 |
5.207738 |
0.02248657513740520003109324420620396267622709274291992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.039829815075975126548168958606765954755246639251708984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8356769 |
5.8302034 |
47.7882607 |
14.3103031 |
| ENSG00000269486 |
|
ERVK9-11 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.747495 |
0.3604575738 |
-1.472099 |
0.544461442 |
7.657925 |
0.00565234783040094099226813284531090175732970237731933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011430148510305231449035723301221878500655293464660644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9636656 |
1.3967498 |
11.0171193 |
2.3072499 |
| ENSG00000269583_ENSG00000234465 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73.328120 |
2.5059207533 |
1.325341 |
0.289852146 |
20.428824 |
0.00000618905780318077725679062547903264146498258924111723899841308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000019910743935254633809163807289799308364308672025799751281738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
103.8313127 |
17.9637829 |
41.7668758 |
5.5066841 |
| ENSG00000269737 |
|
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.507358 |
0.0846333906 |
-3.562629 |
0.573779937 |
48.994899 |
0.00000000000256628993027917968022526603507070156557842710576267108990577980875968933105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000014889323652091466703989614624930942158448354817323888710234314203262329101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.8707267 |
0.7320653 |
22.4183207 |
4.1955664 |
| ENSG00000269821 |
10984 |
KCNQ1OT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Human chromosomal region 11p15.5 contains two clusters of epigenetically-regulated genes that are expressed from only one chromosome in a parent-of-origin manner. Each cluster, or imprinted domain, is regulated by a functionally independent imprinting control region (ICR). The human CDKN1C/KCNQ1OT1 domain is regulated by an ICR located in an intron of KCNQ1, and contains at least eight genes that are expressed exclusively or preferentially from the maternally-inherited allele. The DNA of the ICR is specifically methylated on the maternally-inherited chromosome, and unmethylated on the paternally-inherited chromosome. The ICR contains the promoter of the KCNQ1OT1 gene that is exclusively expressed from the paternal allele. The KCNQ1OT1 transcript is the antisense to the KCNQ1 gene and is a unspliced long non-coding RNA. It interacts with chromatin and regulates transcription of multiple target genes through epigenetic modifications. The transcript is abnormally expressed from both chromosomes in most patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, and the transcript also plays an important role in colorectal carcinogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]. |
|
|
10369866_KCNQ1OT1 gene encodes a non-protein coding, antisense RNA that is preferentially expressed from the paternal allele. 11813134_epigenetic alterations of H19 and LIT1 distinguish patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome with cancer and birth defects 12136243_Hypomethylation of kcnq10t1 causes Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome 12439823_Association of in vitro fertilization with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and epigenetic alterations of LIT1 and H19 12772698_In vitro fertilization may increase the risk of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome related to the abnormal imprinting of the KCN1OT gene 14627666_An epimutation at KvDMR1, the absence of maternal methylation, causes the aberrant silencing of CDKN1C, some 180 kb away on the maternal chromosome. 15007390_Loss of CpG methylation was associated with loss of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methylation at DMR-LIT1. DMR-LIT1 epigenetically regulates CDKN1C expression not through histone modifications at CDKN1C promoter, but through that of DMR-LIT1. 15233993_promotor analysis for gene regulation 15340049_Deletion of the elements necessary for Kcnq1ot1 promoter function resulted in the loss of silencing activity. 15851119_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15888726_KCNQ1OT1 is part of an imprinted gene network that may play a role in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. 15952111_LIT1, imprinted genes related to BWS, was expressed only in stages of 8-cell and blastocyst. 16575194_Recent advances in epigenetic control of the CDKN1C/KCNQ1OT1 imprinted domain in both humans and mice, causing Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and cancer. (review) 16950814_Maternal methylation imprints were already established at the germinal vesicle stageshowing that the KvDMR1 carries a germline methylation imprint. 16965397_Loss of imprinting of LIT1 and epigenetic status at the KvDMR1 is associated with colorectal cancers 18079696_KCNQ1OT1 can silence cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C (Cdkn1c) in transgenic mice by a mechanism independent of Kcnq1ot1 transcription. 18249379_We described a simplified and high-performance test (E-Q-PCR) for rapid assessment of the DNA methylation status at LIT1, a major genetic locus of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS). 18299392_A domain at the 5' end of the Kcnq1ot1 RNA that carries out transcriptional silencing of linked genes using an episomal vector system was characterized. 18762571_Results suggests that hyperstimulation likely recruits young follicles that are unable to acquire imprint at KvDMR1 during the course of the maturing process. 19178079_Epimutations of the KCNQ1OT1 imprinting center of chromosome 11 in early human embryo lethality 19494037_Hypomethylation at KvDMR1 was observed in 3/18 clinically normal children conceived by ARTs 19711451_Data found biallelic expression of KCNQ10T1 gene in one induced pluripotent stem cell line. 20618351_exclusive correlation of the observed Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome symptoms to locally restricted epimutations at the KvDMR1 of the maternal chromosome 21420679_Vitrification at the germinal vesicle stage does not affect the methylation profile of H19 and KCNQ1OT1 imprinting centers in human oocytes. 21920939_KCNQ1OT1 RNA interacts with chromatin through its most 5' 20 kb sequence in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome patients. 22300968_Hypermethylation of KvDMR1 was associated with developmental delay. 22610651_findings show that hypomethylation of the KCNQ1OT1 gene contributes to the occurrence of adrenocortical carcinoma and adenoma in patients without clear phenotypic features of the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome 23040914_Human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells contain a unique epigenetic signature during in vitro cell culture. H19 and KCNQ1OT1 possessed a substantial degree of hypermethylation status, and variable DNA methylation patterns of SNRPN was observed. 23153226_Based on these findings we conclude that the imprinted gene expression of KCNQ1OT1, CDKN1C, H19, and PLAGL1 are conserved between human and bovine 23984860_a tetranucleotide repeat polymorphism within KCNQ1OT1 contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma, possibly by affecting KCNQ1OT1 expression through a structure-dependent mechanism 24468603_In patients with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome due to hypomethylation of KvDMR1, the clinical presentation of Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia is quite heterogeneous with no correlation with the degree of KvDMR1 hypomethylation. 24934635_No evidence for copy number and methylation variation in H19 and KCNQ10T1 imprinting control regions in children born small for gestational age. 26106604_the cases with partial loss of methylation in KCNQ1OT1 and SNRPN present clinical features different to those associated with the corresponding imprinting syndromes 26323944_HOTAIR, H19 and KCNQ101T are confirmed as potential breast tumour markers demonstrable by in situ hybridization. 26868975_beta-catenin signaling may contribute to development of colorectal cancer by functioning as a novel Long noncoding RNAs regulatory factor via direct targeting of KCNQ1OT1. 27436784_The mean Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS)score was 5.6 for 19 subjects with 'IC2 hypomethylation'(KCNQ1OT1-associated ), compared with 3.8 for 2 subjects with pUPD. The BWS score of one subject with CDKN1C mutation and one with IC1( H19-associated imprinting center) hypermethylation was 6 and 7, respectively 27611768_Analysis of the chromatin status of Cdkn1c promoter and KvDMR1 in unresponsive compared to responsive cell types showed that their differential responsiveness to the MyoD-dependent induction of the gene does not involve just their methylation status but, rather, the differential H3 lysine 9 dimethylation at KvDMR1. 28535504_Knockdown of KCNQ1OT1 expression significantly suppressed H2O2-induced SRA01/04 cell pyroptosis in vitro, which is the critical step in cataract formation. 28600629_lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 was highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma (LAD) and functioned as a potential oncogene to inhibit malignancy and chemoresistance of LAD cells 28749187_Differential methylation/imprinting of KCNQ1OT1 is associated with the risk for symptomatic prolonged QTc. 28803575_findings showed that pathogenesis of selective intrauterine growth restriction may be related to the co-effect of the up-regulated protein expression of CDKN1C and down-regulated mRNA expression of KCNQ1OT1 in the placenta. 29047350_Findings suggest that KCNQ1OT1: Transcription Star Site-Differentially Methylated Region (KCNQ1OT1:TSS-DMR) could be a susceptibility locus for the isolated omphalocele. 29504267_Our preliminary data showed that KCNQ1OT1 is overexpressed in early stage Lung cancer (LC) and is correlated with better prognosis in Lung cancer (LC) patients, possibly by suppressing cell proliferation. 29667930_KCNQ1OT1 may act as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate MET expression in an mir-153-dependent manner 29749509_a constructed SMAD4 RNA interference experiment confirmed that the function of KCNQ1OT1 was to act on lens epithelial cell proliferation and EMT, and this was achieved via the SMAD4 signaling pathway. The findings of the present study may provide a novel target for molecular therapy of cataracts disease. 29966655_KCNQ1OT1 was significantly up-regulated in oxaliplatin-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells. KCNQ1OT1 modulated oxaliplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-7-5p/ ABCC1 axis. 30157476_Knockdown of KCNQ1OT1 inhibited viability and promoted apoptosis of MCF7 and SK-BR-3 cells and induced tumors with the smallest volume and weight in nude mice. 30250027_Kcnq1ot1 was significantly elevated in the serum of diabetic patients. Kcnq1ot1 regulates the expression of miR-214-3p, which is decreased in serum of diabetic patients. 30471108_The data revealed a role for KCNQ1OT1 as an oncogene through miR-27b-3p/HSP90AA1 axis during non-small-cell lung cancer progression. 30703347_KCNQ1OT1 positively regulated osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by acting as a ceRNA to regulate BMP2 expression through sponging miR-214. 30784065_that KCNQ1OT1 could sponge miR-1470 and further regulate EGFR in diabetic retinopathy 30794031_our research findings revealed that ZEB1-induced upregulation of KCNQ1OT1 improved the proliferation, migration and EMT formation of CRC cells via regulation of miR-217/ZEB1 axis. 30922639_Heterogeneity in DNA methylation of the KvDMR1 region exists during first trimester and a consistent hypomethylation in the amnion in this period of gestation. 30932685_High KCNQ1OT1 expression is associated with colon adenocarcinoma. 30941792_KCNQ1OT1, HIF1A-AS2 and APOA1-AS are promising novel biomarkers for diagnosis of coronary artery disease 30973654_By a transcriptomic approach and validates PNN and KCNQ1OT1 as molecular biomarkers. 30997746_KCNQ1OT1 enhanced the methotrexate resistance of colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-760-mediated PPP1R1B expression via the cAMP signalling pathway. 31210283_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 delayed fracture healing through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 31392505_the results of rescue experiments suggested that the oncogenic role of KCNQ1OT1 was performed through sponging miR-4458 and upregulating CCND2 during osteosarcoma development, providing a novel perspective of intervention in osteosarcoma management. 31486494_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and its expression level is related to clinicopathology. 31653278_Long Noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 Accelerates the Progression of Ovarian Cancer via MicroRNA-212-3/LCN2 Axis. 31693400_KCNQ1OT1 mediated pyroptosis induced by high glucose via targeting miR-214. 31696465_Effects of LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 on proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells by Wnt/beta-catenin. 31709597_Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-204/EphA7 axis. 31755091_The KCNQ1OT1 promoted oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tumorigenesis via the modulation of miR-185-5p/Rab14 axis, which may serve as a therapeutic target for the treatment of OSCC. 31837329_High KCNQ1OT1 expression is associated with progression and chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia. 31909901_KCNQ1OT1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via modulating MIR-142-5p/CAPN10 axis. 31957833_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 contributes to the cisplatin resistance of tongue cancer through the KCNQ1OT1/miR-124-3p/TRIM14 axis. 32102564_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury via regulating miR-192-5p/XIAP axis. 32252801_MicroRNA-1202 plays a vital role in osteoarthritis via KCNQ1OT1 has-miR-1202-ETS1 regulatory pathway. 32271402_KCNQ1OT1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of hBMSC by miR-320a/Smad5 axis. 32379482_Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 is correlated with human breast cancer cell development through inverse regulation of hsa-miR-107. 32390393_Diagnostic Value of Serum Long-Chain Noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 in Airway Remodeling in Children with Bronchial Asthma. 32447323_Paternal 132 bp deletion affecting KCNQ1OT1 in 11p15.5 is associated with growth retardation but does not affect imprinting. 32495890_Significance of LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 expression in diagnosis and prognosis judgment of myelodysplastic syndrome. 32519270_KCNQ1OT1 Exacerbates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Targeted Inhibition of miR-140-3P. 32538770_Effect of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 on autophagy and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting miR-338-3p. 32564010_Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by enhancing aerobic glycolysis via hexokinase-2. 32608222_Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes cell motility in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-506-3p/FOXQ1. 32757174_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 is a key factor in the reversal effect of curcumin on cisplatin resistance in the colorectal cancer cells. 32779042_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 ameliorates the liver injury induced by acetaminophen through the regulation of miR-122-5p/CES2 axis. 32820233_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 facilitates the progression of bladder cancer by targeting MiR-218-5p/HS3ST3B1. 32854478_[Regulatory relationship between lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 and miR-146a-3p in preeclampsia]. 32897512_Long Noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 Confers Gliomas Resistance to Temozolomide and Enhances Cell Growth by Retrieving PIM1 From miR-761. 32936716_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 inhibits the radiosensitivity and promotes the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-146a-5p/ACER3 axis. 32950535_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 knockdown inhibits viability, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human lens epithelial cells via miR-26a-5p/ITGAV/TGF-beta/Smad3 axis. 32953888_Knockdown of KCNQ1OT1 Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Drug Resistance by Regulating miR-129-5p-Mediated LARP1 in Osteosarcoma. 32989627_KCNQ1OT1/miR-18b/HMGA2 axis regulates high glucose-induced proliferation, oxidative stress, and extracellular matrix accumulation in mesangial cells. 33000204_KCNQ1OT1 contributes to sorafenib resistance and programmed deathligand1mediated immune escape via sponging miR506 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 33051357_lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of retinoblastoma cells by upregulating HIF-1alpha via sponging miR-153-3p. 33082306_Upregulation of KCNQ1OT1 promotes resistance to stereotactic body radiotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma by inducing ATG5/ATG12-mediated autophagy via miR-372-3p. 33293505_LncRNA kcnq1ot1 promotes lipid accumulation and accelerates atherosclerosis via functioning as a ceRNA through the miR-452-3p/HDAC3/ABCA1 axis. 33345272_KCNQ1OT1 regulates the retinoblastoma cell proliferation, migration and SIRT1/JNK signaling pathway by targeting miR-124/SP1 axis. 33349156_Long Non-Coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 Promotes Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by miR-148a-3p/IGF1R Axis. 33394291_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 acts as miR-216b-5p sponge to promote colorectal cancer progression via up-regulating ZNF146. 33682985_Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via the miR-145-5p/ARF6 axis. 33705625_Inhibition of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Improves Apoptosis and Chemotherapy Drug Response in Small Cell Lung Cancer by TGF-beta1 Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. 33744257_Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes hydrogen peroxide-induced lens epithelial cell apoptosis and oxidative stress by regulating miR-223-3p/BCL2L2 axis. 33783609_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates osteoarthritic chondrocyte dysfunction via the miR-218-5p/PIK3C2A axis. 33818859_Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting miR-134 in retinoblastoma. 34089766_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 as a miR-26a-5p sponge regulates ATG12-mediated cardiomyocyte autophagy and aggravates myocardial infarction. 34108052_Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes cell viability and migration as well as inhibiting degradation of CHON-001 cells by regulating miR-126-5p/TRPS1 axis. 34301223_Silencing of long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 alleviates LPS-induced lung injury by regulating the miR-370-3p/FOXM1 axis in childhood pneumonia. 34404765_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 activated by c-Myc promotes cell proliferation via interacting with FUS to stabilize MAP3K1 in acute promyelocytic leukemia. 34464666_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 depletion inhibits the malignant development of atherosclerosis by miR-145-5p. 34476933_KCNQ1OT1 promotes the proliferation and migration of psoriatic keratinocytes by regulating miR-183-3p/GAB1. 34636202_Long non-coding RNA potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1 overlapping transcript 1 regulates the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by targeting miR-24-3p. 34698362_lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 may function as a competitive endogenous RNA in atrial fibrillation by sponging miR2233p. 34704601_Long non-coding RNA-KCNQ1OT1 mediates miR-423-5p/microfibril-associated protein 2 axis in colon adenocarcinoma. 34704918_Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 facilitates the progression of cervical cancer and tumor growth through modulating miR-296-5p/HYOU1 axis. 34761437_Potential of long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 as a biomarker reflecting systemic inflammation, multiple organ dysfunction, and mortality risk in sepsis patients. 34783627_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 (potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1) aggravates acute kidney injury by activating p38/NF-kappaB pathway via miR-212-3p/MAPK1 (mitogen-activated protein kinase 1) axis in sepsis. 34850551_ALKBH5-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 triggers the development of LSCC via upregulation of HOXA9. 34911869_lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulated high glucose-induced proliferation, oxidative stress, extracellular matrix accumulation, and inflammation by miR-147a/SOX6 in diabetic nephropathy (DN). 34993814_KCNQ1OT1 affects cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through a miR-34a / Notch3 axis in breast cancer. 35163809_Long Non-Coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 Regulates Protein Kinase CK2 Via miR-760 in Senescence and Calorie Restriction. 35193115_KCNQ1OT1 polymorphism rs35622507 and methylation status of KCNQ1OT1 promoter influence the drug resistance to L-OHP. 35218109_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1-mediated cervical cancer progression by sponging miR-1270 as a ceRNA of LOXL2 through PI3k/Akt pathway. 35226820_Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 overexpression promotes osteogenic differentiation of staphylococcus aureus-infected human bone mesenchymal stem cells by sponging microRNA miR-29b-3p. 35266286_LncRNA-miRNA network analysis across the Th17 cell line reveals biomarker potency of lncRNA NEAT1 and KCNQ1OT1 in multiple sclerosis. 35341776_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes osteogenic differentiation via miR-205-5p/RICTOR axis. 35347427_Downregulation of Kcnq1ot1 attenuates beta-cell proliferation and insulin secretion via the miR-15b-5p/Ccnd1 and Ccnd2 axis. 35443864_Silencing of LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 confers an inhibitory effect on renal fibrosis through repressing miR-124-3p activity. 35817112_The effects of endosulfan on cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells via the KCNQ1OT1/miR-137-3p/PTP4A3 axis. 35989482_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 contributes to hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress of cardiomyocytes via miR-130a-3p/ZNF791 axis. 36100884_LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the metastasis of ovarian cancer by increasing the methylation of EIF2B5 promoter. 36235643_SNPs in lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Modulate Its Expression and Confer Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Chinese Han Population. 36359902_LncKCNQ1OT1 Promotes the Odontoblastic Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells via Regulating hsa-miR-153-3p/RUNX2 Axis. |
|
|
185.066856 |
0.4098286397 |
-1.286907 |
0.118179569 |
121.485058 |
0.00000000000000000000000000029924671491097962044163671113957831582254836244505213797839201550662700096732543597610742835968267172574996948242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000003632303875070772399881019599020135007584262512417486350523424016021104259593910157377649738918989896774291992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
107.6023338 |
8.1773423 |
264.4590175 |
12.7376625 |
| ENSG00000269896 |
100129534 |
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.967748 |
0.4122787280 |
-1.278308 |
0.447704514 |
8.451280 |
0.00364786654260829991403003447203445830382406711578369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007678623811879422070281187018281343625858426094055175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7077984 |
2.2880869 |
16.5141292 |
3.5729824 |
| ENSG00000269910_ENSG00000246451 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.904008 |
0.4411066474 |
-1.180801 |
0.413320845 |
7.877254 |
0.00500604402005543243359131366787551087327301502227783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010232545317271593554586672780715161934494972229003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.1243547 |
8.0900278 |
63.9142005 |
12.8073095 |
| ENSG00000269918 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.649824 |
0.4905201295 |
-1.027616 |
0.267375027 |
14.946299 |
0.00011061480481133715713000509328622911198181100189685821533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000302627343654371914766915141470349226437974721193313598632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.6241191 |
3.8331075 |
48.5074339 |
5.0256420 |
| ENSG00000269929 |
112903833 |
MIRLET7A1HG |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.879084 |
0.2372451397 |
-2.075550 |
0.526433531 |
14.512420 |
0.00013923851881297819878778587732170990420854650437831878662109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000374550854324687135590843389820747688645496964454650878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5027557 |
4.7133637 |
43.2384382 |
13.5410313 |
| ENSG00000269930 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.936694 |
0.2532010834 |
-1.981645 |
0.618070212 |
10.727654 |
0.00105546182206523266912390202065807898179627954959869384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002446775010787315043220280230684693378861993551254272460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5186942 |
2.3057595 |
13.9946340 |
6.0024448 |
| ENSG00000269934 |
124904535 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.073081 |
0.1579654026 |
-2.662319 |
0.378998165 |
57.098299 |
0.00000000000004145640061560708802511704406525713300166050348516399992604419821873307228088378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000269202143900730573405563717636135366399752211208351582172326743602752685546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.1412809 |
1.8748246 |
45.6322416 |
6.2195380 |
| ENSG00000269983 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.685191 |
0.1869592921 |
-2.419204 |
0.542572458 |
19.740288 |
0.00000887113588989330522130948020187446445561363361775875091552734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027978197806586576181289705012034119135932996869087219238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9826123 |
2.2417547 |
36.5306318 |
6.8516863 |
| ENSG00000269987 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.866298 |
0.2084034295 |
-2.262549 |
0.885885403 |
5.410517 |
0.02001579208751862529180876038026326568797230720520019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.035883349995955104994038720178650692105293273925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0180177 |
13.6627561 |
40.3401167 |
43.2264824 |
| ENSG00000270012 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.499770 |
0.3062529885 |
-1.707204 |
0.452906951 |
14.739781 |
0.00012341461500465475452717467597096856479765847325325012207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000335222620071531863996522337956207593379076570272445678710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.9900481 |
1.7783669 |
19.7948358 |
3.5067225 |
| ENSG00000270049 |
101927837 |
ATP6V0D1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.058881 |
0.1353468079 |
-2.885267 |
0.615056115 |
21.177211 |
0.00000418713697519732996665592014706724910411139717325568199157714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013749086040914925571383015112658654288679827004671096801757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6132866 |
1.4131443 |
26.9803052 |
6.2467276 |
| ENSG00000270055 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37.215227 |
0.2309480155 |
-2.114360 |
0.282109332 |
60.991606 |
0.00000000000000573186659719418703944401233249268461034315377128356416847054788377135992050170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000039005233275512311479433317657513773315137040748057373207302589435130357742309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.9936357 |
2.5754343 |
60.9999422 |
6.2600239 |
| ENSG00000270112 |
105372097 |
ST8SIA5-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.842643 |
0.3514641558 |
-1.508551 |
0.605858718 |
5.962316 |
0.01461483157032817357945386760320616303943097591400146484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.027018401049354188320217318164395692292600870132446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.4109664 |
8.2505769 |
36.7192486 |
15.4953409 |
| ENSG00000270164 |
101927931 |
LINC01480 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.674002 |
0.0896406124 |
-3.479704 |
0.744224967 |
26.845221 |
0.00000022041870769574942761575653358413484639299895206931978464126586914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000838283979796253951400155941114933355606808618176728487014770507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0658340 |
0.8259267 |
15.1913242 |
6.5520036 |
| ENSG00000270344 |
|
POC1B-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.747914 |
0.2422745149 |
-2.045285 |
0.529912554 |
16.302850 |
0.00005398268929202595603098965848509749321237904950976371765136718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000154685399718560090886673719090538270393153652548789978027343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0314089 |
1.3907346 |
16.6732576 |
3.0839888 |
| ENSG00000270605 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.728171 |
0.4706650442 |
-1.087227 |
0.424378793 |
6.733565 |
0.00946153071238202761361613113422208698466420173645019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018224219406858768732782039023732068017125129699707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.3990246 |
2.0507320 |
15.8139102 |
2.7707262 |
| ENSG00000270641 |
9383 |
TSIX |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
In mammals, dosage compensation of genes on the X chromosome occurs by X inactivation, which is regulated in cis by the X-inactivation center (XIC) and expression of the XIST non-coding RNA. This gene expresses a non-coding antisense transcript across the 3' end of the XIST locus, and is coexpressed with XIST only from the inactive X chromosome. The mouse ortholog of this locus is required for imprinted X inactivation in extraembryonic tissues and silences Xist through modification of the chromatin structure in the Xist promoter region. In contrast, imprinted X inactivation does not occur in human extraembryonic tissues and transcripts from this locus do not repress XIST expression or affect random X chromosome inactivation in embryonic cells. This transcript is thought to be unspliced and extend over more than 30 kb, but its exact nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
11555794_comparison with mouse counterpart; gene expression 11743158_It's proposed that Tsix and CTCF together establish a regulatable epigenetic switch for X-inactivation 25981039_Tsix is not required at the onset of random X-inactivation; instead, it protects the active-X from ectopic silencing once X-inactivation has commenced. 26566700_TSIX is overexpressed in systemic sclerosis dermal fibroblasts in vivo and in vitro, and is higher in SSc sera. TSIX is a new regulator of collagen expression and stabilizes its mRNA. TSIX upregulation may result from activated endogenous TGF-beta signaling. 31004302_Authors selected an HCC-specific RNA-based biomarker panel that depended on the integration of suppressor of glucose autophagy-associated (SOGA1) gene expression with the chosen panel of epigenetic regulators of this gene [long non-coding RNA antisense for X-inactive-specific transcript (lncRNA-TSIX) and microRNA-548-a-3p (miR-548-a-3p)]. 32535070_Dysregulation in the expression of (lncRNA-TSIX, TP53INP2 mRNA, miRNA-1283) in spinal cord injury. |
|
|
8.486533 |
0.3458579762 |
-1.531748 |
0.527575272 |
8.766463 |
0.00306819932143754994097184507495512661989778280258178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006556626897990189446752129498463546042330563068389892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4924167 |
1.5977906 |
13.1397649 |
2.7666393 |
| ENSG00000270800 |
100529239 |
RPS10-NUDT3 |
protein_coding |
A0A1W2PQS6 |
|
Hydrolase;Reference proteome;Ribonucleoprotein |
|
This locus represents naturally occurring read-through transcription between the neighboring RPS10 (ribosomal protein S10) and NUDT3 (nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 3) genes on chromosome 6. The read-through transcript produces a fusion protein that shares sequence identity with each individual gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]. |
hsa:100529239; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; hydrolase activity [GO:0016787] |
|
|
|
270.452676 |
2.0224243467 |
1.016086 |
0.167699753 |
36.372525 |
0.00000000162984617266304719561795682933281678717030160896683810278773307800292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000007651567909830336025251786328475051002229179175628814846277236938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
374.1709849 |
38.7408031 |
186.5200257 |
14.2642395 |
| ENSG00000270820 |
|
USP34-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.073857 |
0.1797814055 |
-2.475684 |
0.534361920 |
22.195679 |
0.00000246227306747035183028004569349977970205145538784563541412353515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008331763061866663937497963499101416573466849513351917266845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8407655 |
1.7345207 |
26.8636250 |
5.6802959 |
| ENSG00000271216 |
|
LINC01050 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53.438433 |
10.2010010852 |
3.350639 |
0.353807266 |
94.359331 |
0.00000000000000000000026314347086287086728769370671202707616615951874155965536949443317471519776518107391893863677978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000002535246494736275686518142493673985653269255455475177197057802536139803351034061051905155181884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
99.1655111 |
20.8896935 |
9.7725886 |
1.8166304 |
| ENSG00000271503 |
6352 |
CCL5 |
protein_coding |
P13501 |
FUNCTION: Chemoattractant for blood monocytes, memory T-helper cells and eosinophils. Causes the release of histamine from basophils and activates eosinophils. May activate several chemokine receptors including CCR1, CCR3, CCR4 and CCR5. One of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T-cells. Recombinant RANTES protein induces a dose-dependent inhibition of different strains of HIV-1, HIV-2, and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). The processed form RANTES(3-68) acts as a natural chemotaxis inhibitor and is a more potent inhibitor of HIV-1-infection. The second processed form RANTES(4-68) exhibits reduced chemotactic and HIV-suppressive activity compared with RANTES(1-68) and RANTES(3-68) (PubMed:16791620, PubMed:1380064, PubMed:8525373, PubMed:9516414, PubMed:15923218). May also be an agonist of the G protein-coupled receptor GPR75, stimulating inositol trisphosphate production and calcium mobilization through its activation. Together with GPR75, may play a role in neuron survival through activation of a downstream signaling pathway involving the PI3, Akt and MAP kinases. By activating GPR75 may also play a role in insulin secretion by islet cells (PubMed:23979485). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1380064, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15923218, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16791620, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17001303, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23979485, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8525373, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9516414}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Inflammatory response;Oxidation;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is one of several chemokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines form a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CC subfamily, functions as a chemoattractant for blood monocytes, memory T helper cells and eosinophils. It causes the release of histamine from basophils and activates eosinophils. This cytokine is one of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ cells. It functions as one of the natural ligands for the chemokine receptor chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5), and it suppresses in vitro replication of the R5 strains of HIV-1, which use CCR5 as a coreceptor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
hsa:6352; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; CCR1 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031726]; CCR4 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031729]; CCR5 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031730]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; chemokine receptor antagonist activity [GO:0046817]; chemokine receptor binding [GO:0042379]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity [GO:0004435]; phospholipase activator activity [GO:0016004]; protein homodimerization activity [GO:0042803]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; protein self-association [GO:0043621]; receptor signaling protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030298]; activation of phospholipase D activity [GO:0031584]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; cellular response to virus [GO:0098586]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; dendritic cell chemotaxis [GO:0002407]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; leukocyte cell-cell adhesion [GO:0007159]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation by host of viral transcription [GO:0043922]; negative regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0045744]; negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070233]; negative regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045071]; neutrophil activation [GO:0042119]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of activation of Janus kinase activity [GO:0010536]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of cell adhesion [GO:0045785]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin [GO:0033634]; positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process [GO:0031328]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of homotypic cell-cell adhesion [GO:0034112]; positive regulation of innate immune response [GO:0045089]; positive regulation of macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0010759]; positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0090026]; positive regulation of natural killer cell chemotaxis [GO:2000503]; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014068]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration [GO:0014911]; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:0048661]; positive regulation of T cell apoptotic process [GO:0070234]; positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010820]; positive regulation of T cell migration [GO:2000406]; positive regulation of T cell proliferation [GO:0042102]; positive regulation of translational initiation [GO:0045948]; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT protein [GO:0042531]; positive regulation of viral genome replication [GO:0045070]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of chronic inflammatory response [GO:0002676]; regulation of insulin secretion [GO:0050796]; regulation of neuron death [GO:1901214]; regulation of T cell activation [GO:0050863]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; response to virus [GO:0009615] |
11125885_Observational study of gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 11197694_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11500196_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11544456_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11750041_Differential production of RANTES and MCP-1 in synovial fluid from the inflamed human knee. 11816717_RANTES levels in blood, quantities released from platelets ex vivo, and quantities released from SFFLRN stimulated platelets ex vivo were compared for preeclamptic and normal pregnancies. 11844139_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11897701_synthesis was detected in human Leydig cells exposed to the Sendai virus, but not in human total germ cells 11907119_The prototypic inflammatory chemokine RANTES activates a defined transcriptional profile in fresh human monocytes consisting of stimulation of at least 42 genes of 5600 examined. 11920567_We determined that human serum contains a molecule that suppresses RANTES (CCL5) binding to endothelial cells, PBMC and CHO cells. 11929421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12093895_A translational rheostat for RFLAT-1 regulates RANTES expression in T lymphocytes. 12114533_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12114533_modulating influence on HIV/AIDS by interacting with variants 12139952_in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis, the proportion of RANTES relative to IL-8 was significantly increased 12154092_CCR5 protein has a role as a HIV-1 receptor favoring the recruitment of fusiogenic proteins and the formation of a fusion pore. 12165487_TNF-alpha potently induced RANTES secretion, but IL-17 dose-dependently inhibited the TNF-alpha-induced RANTES secretion in human colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts. This was also observed at the mRNA level. 12200463_functional AhR are present in endometrial and endometriotic stromal cells and that TCDD up-regulates the expression of RANTES, providing a possible mechanistic link between dioxin exposure and chemokine expression in endometriosis. 12204866_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12218153_Expression of RANTES is induced by stimulation of monocytic cells through Fc gamma receptors and involves activation of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta sites. 12270118_results demonstrate that both CCR1 and CCR4 are functional receptors on human mast cells with capacity to mediate migration towards CCL5 12359436_role of viral accessory protein Vpr and Nef in RANTES/CCL5 expression 12377943_role of IL-12 and IFN-gamma on inducing inflammatory chemokine (CCL5) secretion and down-regulating CCR5 expression in human T cells 12462338_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12475226_The RANTES(9-68)-heparin interaction has been characterized by a complex binding model that involves heparin-induced dimerization of the chemokine through a mechanism of positive cooperativity. 12509457_RANTES expression is regulated by CFTR in airway epithelial cells 12557141_Associations of RANTES polymorphisms with clinical outcomes and treatment responses of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatitis C virus-seropositive whites with the RANTES -403-A allele were less likely to have severe hepatic inflammation. 12557141_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12610055_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12610055_RANTES promoter -28G genotype and CCR5 promoter 59029A genotype may be independent risk factors for diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and may have an additive effect on nephropathy. 12660426_mast cells may regulate lymphocytic infiltration in basal cell carcinoma through the production of RANTES 12663241_TNF-alpha-induced expression of RANTES plays important roles in cell-mediated liver injury in alcoholic liver diseases. 12668159_RANTES is not upregulated by leptin in human monocytic cells 12763925_Efficient leukocyte arrest in flow but not transmigration may thus require the presentation of RANTES oligomers to bridge surface-bound RANTES and CCR1. 12789231_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12789231_The RANTES promoter polymorphism is a genetic risk factor for near-fatal asthma in Chinese children. 12803993_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12803993_case-control study was performed to evaluate the role of -403G --> A and -28C --> G as susceptibility factors for HIV-1 infection in the Spanish population; data consistent with lack of association between these SNPs and HIV-1 infection in this population 12819030_Data suggest that in oral lichen planus, the presence of CCL5 and CXCL10 in the cytolytic granules of tissue-infiltrating CD8(+)T cells expressing CCR5 and CXCR3 reveals a potential self-recruiting mechanism involving activated effector cytotoxic T cells 12837926_Data are consistent with the lack of association between RANTES polymorphisms and endometriosis, but do not exclude a possible role of other variants within the RANTES gene in this pathology. 12837926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12842758_A putative signal transduction pathway leading to RANTES production from fibroblasts when the DR molecules were ligated was detected 12858455_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12960233_dichotomous effects of RANTES on HIV-1 entry at the moment of infection, and on production and spread of virus progeny in primary macrophages 14647058_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14651522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14687494_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14687494_Two single nucleotide polymorphisms in RANTES promoter region and intron I were found to be associated with the genetic susceptibility to HIV-1 infection among Chinese and the In1.1C allele displayed a stronger association with HIV-1 infection in males. 14687706_RANTES expression and production increase in nasal mucosa (septal and turbinate portions) of allergic patients compared to the same mucosa in non-allergic patients 15001640_peritoneal macrophage stimulation of RANTES production by endometrium stromal cells could lead to a self-propagating recruitment of inflammatory cells that contribute to the development and progression of endometriotic lesions. 15021309_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15064621_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15064621_The study results indicated that the -403 and -28 alleles in the RANTES promoter region belong to the predictor gene set for allergic rhinitis and could be used in genomic analysis. 15122808_prior or simultaneous treatment of HEp-2 cells with recombinant human CCL5 provides dose-dependent inhibition of infection with RSV. 15140220_TWEAK acts on human keratinocytes as an inducer of RANTES via Fn14. 15192276_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15228586_Our results demonstrate that IFNbeta plays a positive regulatory role in the expression of RANTES/CCL5 in human astrocytes through several distinct mechanisms 15239133_CCL% expression frequent in ATL and HTLV-I-infected cell lines; aberrant expression may impact pathophysiology of HTLV-I-associated diseases 15256089_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15265023_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15265023_SNP -403G may be associated with increased susceptibility to HIV infection, while -28G may be associated with advanced disease 15280531_A strong upregulation of MCP-1 and RANTES was observed in all the cases, mainly in tubular cells, and there was a strong correlation between the expression of these chemokines and NF-kappaB activation in the same cells. 15302103_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15319853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15368437_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15368437_RANTES haplotypes might contribute to polygenic interaction between hepatitis C virus and host immune system and could help to risk stratify patients prior to antiviral therapy. 15459010_Stimulation of monocytes with supernatants of activated platelets triggered arrest involving RANTES and PF4. 15468376_Data show that RANTES -28 promoter, but not monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulatory polymorphisms are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese children. 15468376_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15471370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15471370_There is a significant but complex association of the RANTES gene with multiple sclerosis 15482330_Increased gene expression and protein production in synovial fibroblasts, in response to interleukin-1beta, may play an important role in recruitment of inflammatory cells into synovium and progression of synovitis in temporomandibular joint disorders 15488313_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15500552_secretion induced by binding of HCV E2 to CD81 with subsequent intracellular accumulation of CCR5. 15537425_However, In the presence of TNF-alpha, melatonin promoted RANTES melatonin, respectively) expression in a dose dependent manner in A549 cells). 15588341_produced by neonatal natural killer cells and contributes to suppession of HIV replication 15592421_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15602730_Role in the development of bronchiolitis associated with influenza and RSV infections in infants and children. 15611878_Observational study of genotype prevalence and gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15645140_RANTES, MIP-1beta and IL-18 are expressed in LGL leukemia 15715189_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15740484_Even though H. pylori itself induces expression of RANTES, at the transcriptional level, genetic variations leading to higher transcriptional activity do not modify the degree of inflammation. 15742444_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15781227_PI3K-Akt activation and subsequent inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK3beta are required for HGF-induced suppression of RANTES in human kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells 15793370_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15793370_Treatment to enhance RANTES expression may assist in delaying the progression of AIDS by decreasing the initial viral load. 15794069_RANTES appears to play an important role in mobilization of eosinophils into the local inflamed tissue. 15848524_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15850807_Sphingosine 1-phosphate attenuates cell migration by inhibiting a Rac1-dependent signaling pathway and decreases RANTES production by stimulating a Galpha(q)-dependent mechanism both possibly through the S1P(2) receptors 15851378_RANTES itself could inhibit the replication of SARS-CoV in THP-1 cells when it was added into the culture before or at the same time with the virus; No inhibition effect was shown when RANTES were added into the culture after SARS-CoV infected the cells 15863470_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15890969_Platelet microparticles may serve as transcellular delivery system for RANTES, triggering monocyte arrest; introducing a novel mechanism for platelet-dependent monocyte recruitment in inflammation and atherosclerosis. 15899487_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15899487_Patients carrying the RANTES -403A or In1.1C allele had a significantly higher all-cause mortality risk, mainly due to cardiac events. The other SNPs studied showed no effect on survival. 15971427_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15971427_Polymorphism in the promoter region of RANTES gene is associated with the susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in the Chinese population 15978191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16024972_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16029496_Cigarette smoke may directly cause the release of IL-8 from HASMC, an effect enhanced by TNF-alpha which is overexpressed in COPD 16032408_It is reported that 2 polymorphisms in the RANTES promoter do not correlate with SLE individually; interaction of the polymorphisms probably exerts a risk effect against SLE; and polymorphism at the 403 locus is probably related with renal damage. 16032408_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16046258_No differences in mRNA levels between atopic dermatitis patienets and controls with the -401A genotype 16078996_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16161154_expression of CCL5 & CCR5 in prostate cancer (PCa) cell lines, primary cultures, & tissues; study suggests CCL5 may function as an autocrine factor that binds to PCa cell-surface receptors, activating cellular responses important in cancer progression 16239564_The mucosal inflammatory response to H. pylori infection involves different signaling pathways for activation of the RANTES promoter, with both OipA and the cag PAI being required for full activation of the RANTES promoter 16246299_Neither the biotinylated ovalbumin nor the unlabeled HSP70 cross-linked with a biotinylated protein stimulated RANTES production which was induced by biotinylated HSP70 itself. 16254204_role of inflammation also in the early stages of atherogenesis possibly involving monocyte-derived RANTES as an important mediator 16314800_In heart transplantation, outcomes of early and late rejection episodes may be influenced by genetic variant interactions such as 'CX3CR1 249I*CCR5 No-E' and 'CCR5 E*RANTES -403A.' 16314800_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16323127_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16340468_HIV-1-infected long-term nonprogressors of more than 16 years is not associated with SNPs in the RANTES gene promoter in white Spanish HIV-1-infected subjects. 16340468_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16379602_Higher amounts of MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and RANTES were detected in plasma of HIV-1-positive individuals, particularly those with concomitant pulmonary tuberculosis, although the increase was not found to be statistically significant. 16437690_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16441357_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16441357_functional mutation at -403 in the promoter does not seem to influence acute rejection development and allograft survival in liver recipients 16442182_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16468043_the production of RANTES was enhanced by the interaction with chondrocyte-T cel and that chondrocyte-T cell contact was possible in vivo. 16489254_Data show that RANTES is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and is a potential mediator influencing intensity and composition of cellular infiltration in joints affected with inflammatory arthritis. 16507178_High levels of CCL5 are present in synovial fluid of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Present in synovial biopsies, in particular on endothelium of small and medium sized vessels. 16511411_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16517749_mast cell beta-tryptase selectively cleaves asthmatic airway smooth muscle (ASM)-derived eotaxin and RANTES and abrogates their chemotactic activities, thus providing an explanation for the eosinophil paucity in asthmatic ASM bundles 16564576_elevated TGF-beta1 in rheumatoid synovial tissue may suppress joint inflammation by inhibiting RANTES secretion from synovial fibroblasts, thus blocking the infiltration of immune cells 16614115_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16635746_The platelet-derived chemokine RANTES exhibited particular changes after stem cell transplantation (SCT); results suggest that RANTES plays a role in GVDH after allo-SCT 16719905_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16791620_Studying 95 African samples from Cameroon, there was found a naturally occurring variant of CCL5/RANTES containing a missense mutation located in the first amino acid of the secreted form (S24F). 16799229_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16807236_CCL5-GAG binding and CCL5 aggregation are important for CCL5 activity in T cells, specifically in the context of CCR5-mediated apoptosis 16855620_RANTES SNPs are significantly associated with RANTES serum concentration and development of type 1 diabetes. 16864713_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16864989_15d-PGJ2 significantly decreased CD40 and RANTES expression in HK-2 cells, which were partially mediated by PPAR-gamma-dependent pathways. 16865553_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16897666_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16897666_The effect of RANTES polymorphisms on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) disease progression in an urban population of Uganda, which protection from death. 16911685_Data suggest that RANTES and IL-10 are secreted from mesenteric adipose tissue and creeping fat, and that the elevated RANTES secretion from creeping fat in Crohn's disease is caused by steroid treatment. 16988194_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16995340_C-reactive protein (CRP) activates the MAP-K pathway of renal distal tubular cells (DTC). CRP upregulated RANTES expression of DTC in a significant and dose-dependent manner. 16997300_Women with endometriosis-associated infertility have a poor IVF outcome. 17005260_findings show that CCL3, CCL4 and CCL5 bind on the Leishmania promastigotes 17015691_RANTES down-regulates TLR4 ligation-induced IL-6 and TNF-alpha secretion by enhancing IL-10 production in PB monocytes. 17016617_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17018392_Thrombocytopenia may be a source of reduced RANTES which may contribute, at least in part, to suppression of erythropoiesis in children with malarial anemia. 17027916_Adenylyl cyclase activator forskolin reproduced the effects of ISO. Isoproterenol was found to inhibit the release of RANTES from the human bronchial epithelial cells 17038526_under shear stress, T cells encountering apically presented CXCL12 were primed to undergo robust LFA-1-dependent transendothelial migration toward subendothelial CCL5 17063508_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17074812_KLF13 is a key regulator of late RANTES expression in T lymphocytes 17075265_Through RANTES production in response to specific allergen, mononuclear cells play a crucial role in asthma pathogenesis, particularly in eosinophil and T lymphocyte recruitment into the inflamed focus of asthma. 17076674_Progesterone significantly increased intracellular RANTES expression in CD4+ and CD8+ endometrial T cells 17101151_RANTES is regulated by extracellular parts of the CCR5 receptor 17112859_The increased expressions of RANTES and CCR5 mRNAs in renal transplant recipients with hyperlipidemia might be involved in chronic allograft nephropathy due to hyperlipidemia. 17117952_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17117952_Promoter polymorphisms have a role in susceptibility to atopic dermatitis in a Japanese population. 17202846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17207890_the differential regulation of expression by PKCalpha/beta in lung adenocarcinoma cells 17305874_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17305874_polymorphisms investigated are not associated with chronic periodontitis 17328045_Antiviral gene expression in RA, especially due to TLR ligands and TNFalpha, is dependent on IKKepsilon and IRF-3, and this pathway plays a key role in the production of type I IFNs and chemokines such as RANTES. 17413295_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17416433_the lung epithelial cell is a possible target of dengue viruses and IL-6 and RANTES may play pivotal roles in lung related immuno-pathogenesis 17417600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17426779_In this review we focus on the known polymorphisms of two chemokines: CCL2, CCL5 and their corresponding receptors (CCR2, CCR5) and we also discuss their associations with susceptibility and progression to selected immune-mediated diseases [REVIEW] 17488389_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17488389_Our study suggests that patients with the RANTES -403GG genotype have a lower incidence of recurrent acute rejection episodes in kidney transplantation 17494888_renal compartments differ in their capacity to present chemokines, which may help explain the differential recruitment of leukocytes during allograft injury 17504241_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17504241_results of the present study demonstrate that the RANTES -403A allele is associated with lower serum RANTES concentrations and consequently with reduced coronary artery disease risk 17519498_first report of an association between a functional promotor polymorphism in the RANTES gene, with an odds ratio of 4.16 for the development of primary sclerosing cholangitis in patients with Crohn's disease 17530998_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17530998_results suggest that RANTES -28G was associated with delayed AIDS progression, while DC-SIGN -139C was associated with accelerated AIDS progression in HIV-1-infected Japanese hemophiliacs. 17540042_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17540042_it is concluded that RANTES -28 G allele plays a role in the pathogenesis of SARS 17541284_The Th1 cytokine IFN stimulated the expression of RANTES. 17560067_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17560067_The RANTES -403 G/A polymorphism was significantly associated with non-determined leukoencephalopathy 17565659_HCV core protein have opposite effects on the expression of RANTES in different cell types in vitro, possibly reflecting a similar scenario in different microenvironments in vivo. 17585540_in lupus nephritis RANTES may participate in interstitial lesions via CCR5+ cells 17596666_RANTES, MCP-1, CCR2, CCR5, CXCR1 and CXCR4 gene polymorphisms do not have a role in progression of hepatitis B virus infection 17599774_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17620002_A significant correlation exists between bronchoalveolar lavage concentration of CCL5 and eosinophils in veterans with sulfur mustard gas-induced pulmonary fibrosis. 17625600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17625600_findings support the association between RANTES functional polymorphisms and tuberculosis 17653092_RANTES signaling is required for invasion in TGFbetaRII-deficient neoplastic cells. 17674321_The levels of intralesional expression of mRNA of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interferon, interleukin-10, RANTES, and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase in Mediterranean spotted fever are reported; levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase are also reported. 17678722_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17678722_Our data suggest that -28 C/G and -403 G/A polymorphisms within the RANTES promoter region play an important role in asthma predisposition and in the severity of airway obstruction. 17678915_Women with endometriosis had increased peritoneal mRNA expression of RANTES and VCAM-1 during menstrual compared with luteal phase. 17700210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17711627_RANTES may have an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B. The elevation of hepatic RANTES may be caused by hepatitis B virus and TNFa. 17728497_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17728497_Results showed there were no associations of MCP-1 and RANTES promoter SNPs with diabetic ESRD in Korean population. 17884183_In summary, our multifaceted study supports the notion that polymorphisms in CCL5 and CCR5 modify the course of MS. 17884183_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17909104_CCL18 and CCL5 are transiently raised during episodes of UAP, and peak levels of both chemokines are indicative of refractory symptoms. 17922439_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17984846_CCL5 has a role in leukocyte trafficking and may be involved with the development of cGVHD 17984846_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17986095_The PD group presented with significantly increased RANTES levels as compared to the control group. A strong and significant correlation between RANTES levels and UPDRS III score was observed in PD patients. 17989610_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17990036_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17990036_The polymorphisms within the RANTES promoter may have a disease-modifying effect in Korean children with asthma. 18060801_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18060801_The frequency of the RANTES-403G allele was significantly higher in patients with stenosis >70% (OR, 2.45; 95% CI 1.12-5.71; p=0.015). 18162936_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18162936_This observation supports the previously reported results indicating RANTES as an important mediator of Respiratory Syncytial Virus infection. 18186796_Human CCL5/RANTES gene promoter polymorphisms are not associated with the different types of bronchial asthma in Spanish population 18186796_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18191726_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18191726_data suggest that SDF-1 G801A and RANTES-28 polymorphisms are not associated with the genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus 18195571_We show that the level of CCL5 production is a main factor determining CD4+ T cell surface CCR5 density. 18217191_Genetic variation of CCL5 might be an important risk factor for albuminuria in the non-diabetic Japanese general population. 18217191_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18218038_RANTES-28G and CCR5 59353C mutations might be associated with HIV infection or pathogenesis in the Korean population. 18306985_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18306985_Our data indicate that women who inherit A allele at RANTES -403 may be at reduced risk for gastric cancer. 18336625_chemokine CCL5 may induce migration of leukocytes to the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis 18337562_mechanism by which CCL5 influences translation of rapamycin-sensitive 18361934_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18385174_CC chemokine ligand 5 gene may be part of a common pathway in the pathogenesis of late-onset asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with milder emphysema 18385174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18415893_CCL5 was significantly increased in Graves' disease patients compared with Hashimoto's thyroiditis or nontoxic nodular thyroid disease subjects. 18426815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18426815_RANTES/CCL5 gene variants and serum levels are not causally related with type 2 diabetes and that elevated RANTES levels in patients with type 2 diabetes may be a consequence of hyperglycemia 18439751_The overall current information suggests that CCL2 and CCL5 are inflammatory mediators with pro-malignancy activities in breast cancer. 18447907_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18461620_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18461620_results implicate that RANTES In1.1 T allele and haplotype II (ACT) may be a risk factor for HIV-1 transmission while RANTES In1.1 C allele may be risk factor for disease progression among North Indians 18559339_analysis of binding of CC-chemokine receptor 1 (CCR1) to CC-chemokine 3 and 5 (CCL3 and CCL5) 18636124_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18676680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18678243_Data show that basal level of RANTES is higher in Parkinson's disease patients than in healthy control subjects. 18696265_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18696265_the RANTES G-403A allele increased the relative risk for cerebral infarction in the subjects without the IL-4 VNTR allele 3 18716401_findings suggest that platelet activation, resulting in elevated RANTES release, could be one of the factors responsible for the increase of airway inflammation observed in consequence of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatics 18790652_observations support a major tumor-promoting role for co-expression of the chemokines in breast malignancy, and agree with the significant association of joint RANTES and MCP-1 expression with advanced stages of breast cancer. 18800033_Among three possible YB-1 binding sites in the CCL5 promoter, a critical element was mapped at -28/-10 bps. This site allowed up-regulation of CCL5 transcription in human monocytes; however, it repressed transcription in differentiated macrophages 18824472_RANTES promotes an adequate pro-implantatory microenvironment that influences trophoblast cell survival and modulates the balance of maternal Treg/T effector lymphocytes in favor of maternal tolerance. 18936436_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 18953865_Endometrial stromal cells, peritoneal mesothelial cells and monocytes of patients with endometriosis promote the secretion of RANTES in autocrine and paracrine manners. 18956302_Human adipocytes express the chemokine RANTES. but lipopolysaccharides and interferon gamma V do not seem to play a significant role for its expression. 18958622_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18958622_Polymorphism of the RANTES promoter is not associated with susceptibility to peptic ulcers, but the -28 G carrier is associated with a reduced risk of more severe intestinal metaplasia in female subjects and those older than 60 yr. 18986692_Cigarette smoke extract plus dsRNA induces exaggerated epithelial RANTES expression in patients with CRS. 19017985_Because the phenotypic consequence of -403A is reported to be higher levels of RANTES, we propose a model in which excess RANTES in combination with low CCR5 favors recovery from an HBV infection 19017985_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19064579_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19073147_results suggest that CCL5 acts through PI3K/Akt, which in turn activates IKKalpha/beta and NF-kappaB, resulting in the activation of alphavbeta3 integrin and contributing to the migration of human lung cancer cells 19080516_RANTES accounts for the majority of chemotactic activity in IL-1beta-induced monocytes. 19099590_A alleles in TNF-A and RANTES influenced prostate cancer susceptibility and acted independently of each other in these subjects. No epistatic effect was found for the combination of different polymorphisms studied. 19099590_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19099677_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19099677_The RANTES gene promoter -28C/G polymorphism is associated with the susceptibility to r |
|
|
2235.019474 |
13.3129684287 |
3.734760 |
0.061725406 |
3826.681981 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4141.1302616 |
156.1456660 |
312.9820410 |
10.3438790 |
| ENSG00000271533 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45.297307 |
0.4737072496 |
-1.077932 |
0.264091316 |
16.835364 |
0.00004076650630362045732348746929218918921833392232656478881835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000118681189949001580094881114213478667807066813111305236816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.9669383 |
4.8219979 |
63.7193020 |
6.7057067 |
| ENSG00000271614 |
338758 |
ATP2B1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32155320_Silencing of ATP2B1-AS1 contributes to protection against myocardial infarction in mouse via blocking NFKBIA-mediated NF-kappaB signalling pathway. 33756228_Elevated linc00936 or silenced microRNA-425-3p inhibits immune escape of gastric cancer cells via elevation of ZC3H12A. 34935307_Long non-coding ribonucleic acid ATP2B1-AS1 modulates endothelial permeability through regulating the miR-4729-IQGAP2 axis in diabetic retinopathy. |
|
|
44.712900 |
2.3828565450 |
1.252692 |
0.228956779 |
30.520000 |
0.00000003304422783012768256541451987809421275699151010485365986824035644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000136849832427801491462911577870475987595000333385542035102844238281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
64.1116439 |
9.1481306 |
27.0855405 |
3.1035067 |
| ENSG00000271643 |
105377023 |
PDCD6IP-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
53.002237 |
0.4844449782 |
-1.045595 |
0.225850965 |
21.622594 |
0.00000331918744608357283443753928120489860020825290121138095855712890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011021643802968174679604747290273536464155768044292926788330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
35.7281494 |
4.9315806 |
74.0930598 |
6.6035361 |
| ENSG00000271646 |
|
IRF2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55.234530 |
0.4276514668 |
-1.225493 |
0.234093839 |
27.781673 |
0.00000013580651008619342655134158183438675138177131884731352329254150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000528613947487398418874902407404992032979862415231764316558837890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.3358482 |
4.9194331 |
78.5116622 |
7.5072562 |
| ENSG00000271723 |
100527960 |
MROH7-TTC4 |
protein_coding |
Q68CQ1 |
|
Alternative splicing;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
|
hsa:374977; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
|
|
28.329720 |
0.4170599247 |
-1.261673 |
0.478955607 |
6.750583 |
0.00937170635934391968446810494697274407371878623962402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018062991102626831108057814390122075565159320831298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.0762724 |
8.9610031 |
41.1410575 |
15.0888719 |
| ENSG00000271730 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.456141 |
0.2788763654 |
-1.842302 |
0.622065071 |
9.169468 |
0.00246086033086956529683519967477423051605001091957092285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005347018766912230158805385826781275682151317596435546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2030903 |
1.5691329 |
11.1340902 |
3.4882593 |
| ENSG00000271797 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.836095 |
0.4365705206 |
-1.195713 |
0.485393624 |
6.151780 |
0.01312798756920222596755731814255341305397450923919677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024555708594782014314583662439872568938881158828735351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.3994958 |
2.2096211 |
17.0601867 |
3.2093934 |
| ENSG00000271853 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.449675 |
0.2475653925 |
-2.014118 |
0.232988685 |
75.883032 |
0.00000000000000000300975294970628910975989485828168363120523131037627531658706914186041103675961494445800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000024638909338693746648799278629616819401075495575515958424084317357483087107539176940917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.9954108 |
4.8330564 |
122.6778753 |
12.5997486 |
| ENSG00000271856 |
101929623 |
LINC01215 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.389022 |
40.8538884317 |
5.352401 |
0.819367525 |
51.409540 |
0.00000000000074973316789197933232531602683765091640552546969900049589341506361961364746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000004494744743332906699486970494098942211468050711431487798108719289302825927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.4101804 |
22.7907661 |
0.9308602 |
0.4967276 |
| ENSG00000271857 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.111220 |
0.0788670621 |
-3.664433 |
0.466935153 |
78.596291 |
0.00000000000000000076192328645930828933756740194435092757529368126003226774356491546313918661326169967651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000006407970204068028749072770284677695587483842527056496565784904362317320192232728004455566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9406364 |
1.2248702 |
49.7321958 |
6.6663573 |
| ENSG00000271913 |
105378083 |
TAGAP-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.814500 |
0.2675403249 |
-1.902172 |
0.532083936 |
12.807333 |
0.00034526331593561534723593742235436820919858291745185852050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000872767005173776867256452138832401033141650259494781494140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1056804 |
1.8159782 |
19.1563402 |
4.2719349 |
| ENSG00000271976 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.080220 |
0.4284346313 |
-1.222853 |
0.416908494 |
8.909784 |
0.00283646793516703719234550717942511255387216806411743164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006102954332808377055363813212807144736871123313903808593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.2643173 |
1.9670646 |
17.0925261 |
2.8345343 |
| ENSG00000272030 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.063404 |
0.4467638645 |
-1.162416 |
0.417301918 |
7.957137 |
0.00478981103876985423589696111434932390693575143814086914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009836873651348691446894001444434252334758639335632324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5839069 |
3.2679678 |
23.7428611 |
4.7935049 |
| ENSG00000272054 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.343994 |
0.4518852629 |
-1.145972 |
0.430467933 |
7.202546 |
0.00728002447869455400486504714763213996775448322296142578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014371159730577988400401778790183016099035739898681640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8026984 |
2.3905434 |
17.0800638 |
3.3871886 |
| ENSG00000272068 |
|
BCAN-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
72.970018 |
0.3222166585 |
-1.633897 |
0.185549866 |
81.683438 |
0.00000000000000000015972643707088049422303570241239842212482459212308201013455488670444992749253287911415100097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001382734434701581236401853061689963239321644318718452278810238098571971931960433721542358398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.4783217 |
4.5272218 |
114.1101440 |
8.5044612 |
| ENSG00000272144 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.432248 |
0.0118969995 |
-6.393258 |
1.076466085 |
74.945686 |
0.00000000000000000483843350880651594683581990789407568780328631663956336084186915513782878406345844268798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000039217615919815584527387049379594296879112867942971526469264631487021688371896743774414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3081542 |
0.2512627 |
26.0889083 |
5.1251421 |
| ENSG00000272145_ENSG00000237899 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
304.835269 |
0.4761060820 |
-1.070645 |
0.092953660 |
134.557713 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000041255320559848038839601934188260581944599892645055147400333246531994586831405965546976100100096118694636970758438110351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000005490789282807547921396864411336904931398837527144662090811670458290047571578884784415652831057741423137485980987548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
199.2503675 |
11.6353208 |
421.7967913 |
15.9853040 |
| ENSG00000272288 |
101929243 |
ILRUN-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.852982 |
0.1916345391 |
-2.383570 |
0.610764260 |
14.675350 |
0.00012770551519324525435034045628412968653719872236251831054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000345986307682140240872536995908603785210289061069488525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4923818 |
1.9950513 |
23.6146390 |
6.8271707 |
| ENSG00000272316 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.569908 |
0.3751469395 |
-1.414472 |
0.271219243 |
28.030180 |
0.00000011943814168871465019594059996099755238674333668313920497894287109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000467614581253429224546680573887380560904603044036775827407836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.5889370 |
3.4258204 |
52.6659839 |
5.7068328 |
| ENSG00000272374 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.063355 |
0.4546619168 |
-1.137134 |
0.423465745 |
7.297623 |
0.00690458789161718395482880694657978892792016267776489257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013703337001515348073099609393921127775683999061584472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.9055001 |
2.3984327 |
19.7801402 |
3.3830222 |
| ENSG00000272382 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.075291 |
0.0919239564 |
-3.443415 |
0.865132739 |
21.365387 |
0.00000379562154984331474131815757633301444684548187069594860076904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000012521987947180895884517065619334630355297122150659561157226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0316561 |
0.6447474 |
11.2036028 |
2.9581980 |
| ENSG00000272398 |
100133941 |
CD24 |
protein_coding |
P25063 |
FUNCTION: May have a pivotal role in cell differentiation of different cell types. Signaling could be triggered by the binding of a lectin-like ligand to the CD24 carbohydrates, and transduced by the release of second messengers derived from the GPI-anchor. Modulates B-cell activation responses. Promotes AG-dependent proliferation of B-cells, and prevents their terminal differentiation into antibody-forming cells (PubMed:11313396). In association with SIGLEC10 may be involved in the selective suppression of the immune response to danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) such as HMGB1, HSP70 and HSP90. Plays a role in the control of autoimmunity (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P24807, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11313396}. |
Alternative splicing;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;GPI-anchor;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal |
|
This gene encodes a sialoglycoprotein that is expressed on mature granulocytes and B cells and modulates growth and differentiation signals to these cells. The precursor protein is cleaved to a short 32 amino acid mature peptide which is anchored via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) link to the cell surface. This gene was missing from previous genome assemblies, but is properly located on chromosome 6. Non-transcribed pseudogenes have been designated on chromosomes 1, 15, 20, and Y. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:100133941; |
cell surface [GO:0009986]; external side of plasma membrane [GO:0009897]; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle [GO:0043231]; membrane [GO:0016020]; membrane raft [GO:0045121]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; protein tyrosine kinase activator activity [GO:0030296]; B cell receptor transport into membrane raft [GO:0032597]; cell activation [GO:0001775]; cell migration [GO:0016477]; cell-cell adhesion [GO:0098609]; chemokine receptor transport out of membrane raft [GO:0032600]; cholesterol homeostasis [GO:0042632]; glomerular parietal epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0072139]; immune response-regulating cell surface receptor signaling pathway [GO:0002768]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:0097193]; negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta3 production [GO:0032913]; podocyte differentiation [GO:0072112]; positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation [GO:0042104]; positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration [GO:0007204]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation [GO:2000768]; regulation of cytokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0001959]; regulation of epithelial cell differentiation [GO:0030856]; regulation of MAPK cascade [GO:0043408]; regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042325]; respiratory burst [GO:0045730]; response to estrogen [GO:0043627]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to molecule of bacterial origin [GO:0002237]; T cell costimulation [GO:0031295]; Wnt signaling pathway [GO:0016055] |
12218294_The correlation between CD24 expression and invasiveness was calculated to be highly significant 12368195_is expressed in ovarian cancer and is a new independent prognostic marker of patient survival 12447971_assessment of expression on bone marrow neutrophilic granulocytes: a marker for myelocytic leukemia staging 12496407_CD24 mediates apoptosis in precursor-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines in the pro-B and pre-B stages accompanying activation of multiple caspases. 12610508_high level of CD24 expression is associated with nonsmall cell lung cancer 12829373_N-glycans of the mouse glycoprotein HSA and its human analogue CD24 from lymphoblastoma, neuroblastoma and astrocytoma cell lines as well as from mouse brain homogenate were analysed and compared to each other 14657362_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15616015_Deficiency in function of the CD4(+)CD25(+) T-cell population may influence the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. 16125303_Overexpression of CD24 is associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma 16164042_CD24 constitutes an important molecular marker for various epithelial neoplasms 16166435_CD24 is commonly up-regulated in colorectal cancer and is a new independent prognostic marker. 16288985_CD24 expression was upregulated in chordoma, while it was absent in chondrosarcoma 16621031_CD80-CD24 molecule spontaneously incorporated onto cell membrane through its glycolipid anchor suggesting that this hybrid costimulatory molecule can be used in protein transfer to develop effective cancer vaccines 16631259_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16681720_Over-expression of CD24 is associated with primary and relapsed ovarian cancer 16890615_CD24 is overexpressed in the colonic mucosa, already at an early stage of carcinogenesis. It may be a useful target for early detection and in CRC therapy. 16892043_The study documented that cytoplasmic-membranous expression of CD24 represented an extremely strong unfavourable prognostic factor in breast cancer. 16900767_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16900767_association between the V/V genotype at aa 57 of this gene and multiple sclerosis in Basque natives 16930538_CD24 regulates E-cadherin and TGF-beta3 expression in cultured oral epithelial cells 17411341_A destabilizing dinucleotide deletion in the 3' UTR of CD24 mRNA conveys significant protection against both multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. 17411341_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17475624_CD24 is modulated by IGFBP-2 and contributes to IGFBP-2-enhanced invasiveness of glioblastoma cells 17540049_CD24 deficient breast cancer cells are successful in overcoming an engraftment incompatibility that exists when injecting human cells into mouse adipose tissue. 17700640_CD24 is not essential for exosome formation or release but may be a convenient exosome marker. Our studies suggest that exosomal secretion from the embryonic kidney could play a biological role at the fetal-maternal interphase. 17763438_Observational study and meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17763438_findings suggest that the CD24 A57V polymorphism plays a role in susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in a Spanish population 17900673_Study identifies CD24 and EpCAM as cargo proteins of exosomes of cultured ovarian cancer cell lines and malignant ascites. 17944116_A decrease in CD4+CD25+ T cell numbers in mitral stenosis patients might suggest a role for cellular autoimmunity in a smoldering rheumatic process. 17950993_High CD24 is associated with neoplasm invasiveness in breast cancer 17980703_CD24 acts as a gate-keeper for lipid rafts, thereby regulating the activity of integrins and other proteins 18381780_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18381780_There is a potential role for the CD24 gene in the susceptibility to giant cell arteritis in our population in Spain. 18384848_CD24 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma may be associated with high nuclear grade, large tumor size, and shortened progression-free survival 18404683_CD24 is repressed by estrogen and this repression is a direct transcriptional effect depending on ER alpha and histone deacetylases. 18413748_As a putative new oncogene that is overexpressed in gastrointestinal malignancies early in the carcinogenesis process, CD24 my be a potential target for early intervention in the prevention and treatment of cancer. 18417991_low expression of CD24 may cause the enhanced immune reaction and could play a role in the abnormal development of placenta in pre-eclampsia 18495204_In breast tissue, CD44(+)/CD24(-/low) tumor cells seem to be associated with lack of lymph node metastasis and a tendency toward an increase of the relapse-free survival of the patients. 18559090_analysis of CD44 and CD24 expression in breast tumors 18566397_MOG specific T cells (2D2) will escape clonal deletion and can result in spontaneous EAE. CD24 deficient MOG specific T cells (2D2CD24KO) are depleted from the thymic compartment, and the T cells in the periphery are CD4 negative. 18632604_CD44 but not CD24 may be involved in the breast cancer pathway and is a target for oncolytic virotherapy 18752058_Overexpression of CD24 is associated with prostate cancer. 19043399_Expression of CD24, P-cadherin and S100A4 in tumors of the ampulla of Vater. 19050962_Overexpression of CD24 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 19072375_CD24 appears to be highly expressed in a large variety of human cancers and to contribute to the acceleration of tumor growth and metastases shedding by binding to platelet (P)-selectin 19130400_Enhanced CD24 expression in endometrial carcinoma and its expression pattern in normal and hyperplastic endometrium are reported. 19243896_The results of our study showed that overall cytoplasmic and nuclear BAG-1 expression and overall and cytoplasmic CD24 expression, correlates with adverse prognostic parameters for breast carcinoma. 19610054_dinucleotide deletion at position 1527-1528 (P1527(del)), which reduces CD24 expression, is associated with a significantly reduced risk of chronic HBV infection 19706825_Overexpression of CD24 in hepatocellular carcinoma was associated with invasiveness and metastatic potential, high tumor proliferation status, and activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. 19725119_Dynamic changes in surface expression of the identified antigens CD15, CD24, and CD29 in combination can be exploited for the experimental separation of key neural cell populations. 19786366_gene polymorphisms are associated with risk and progression of several autoimmune diseases 19787233_CD24 overexpression is associated with cancer development and progression. 19794958_Data show that tumor cells containing the stem cell-like CD44(+)/CD24(-) signature had a lower expression of the M-phase cell cycle genes than the CD44(-)/CD24(+) cells, and in the CD44(+)/CD24(-) cocultures, these genes were induced. 19860845_The linkage of CD24 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway may unravel a novel mechanism in the regulation of colorectal cancer proliferation. 19896210_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19896210_The data of this study revealed that the susceptibility and the progression of MS in individuals with the CD24V/V genotype were greater than in those with the CD24A/V and CD24A/A genotypes. 19906290_Data demonstrate that the invasive, mesenchymal CD44posCD24neg phenotype is under dynamic control in breast cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. 19946098_upregulation of CD24 is an early and common event during the development of colorectal cancer (CRC) and it may be expressed in any cellular compartment, including the nucleus; CD24 is not, however, a good prognostic marker in CRC 19998456_Upregulation of CD24 is associated with inflammatory bowel disease. 20019840_Transcriptional down-regulation of CD24 by TWIST1 is implicated in breast cancer stem cells. 20019840_ata demonstrate that the overexpression of Twist in breast cells can promote the generation of a cancer stem cell phenotype characterized by the high expression of CD44, little or no expression of CD24, and increased aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 activity. 20177845_The relationship between expression and staining intensity of CD24 and galectin-1 and clinicopathologic variables in gastric adenocarcinoma were assessed. 20199686_EGFR genome modulation in the CD44+/CD24-/low subpopulation of the breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468 leads to different coexisting subclones 20230526_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20336055_cell-specific expression of CD24 in the developing human kidney and its dysregulation during fetal urinary tract obstruction 20354454_High CD24 is associated with non-small cell lung carcinoma. 20378664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20405247_Lack of CD44 expression was associated with lymph node involvement, regardless of CD24 status, whereas the lack of both CD44 and CD24 was connected with high histologic grade and unfavorable prognosis which, notably, was the worse among all phenotypes 20491779_Combined anticancer agents formestane and herceptin are active on a subpopulation of CD44high/CD24low breast cancer cells. 20567952_CD24 is an important marker of malignancy and poor prognosis in gallbladder carcinoma 20619441_CD24 is involved in the progression of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas and in the malignant behavior of pancreatic cancers. 20621328_P-cadherin and CD24 are expressed in carcinomas of the biliary tract with high frequency and at an early stage of carcinogenesis. 20628624_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21041728_Based on the combined analyses of healthy donors and CVID patients, new subsets of human naive B cells are identified that are defined by immunoglobulin M and CD24. expression. 21086907_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21086907_There was no relationship between a CD24 exon 2 SNP and disease susceptibility or clinical findings in Japanese sarcoidosis patients. 21147107_Anti-CD24 SWA11 mAb can deliver a PE exotoxin derivative to colorectal cancer cells and cause them to undergo apoptosis, without toxicity to normal tissues. 21266361_CD24 may play a role in the inhibition of cell invasion and metastasis, and that intracellular CD24 inhibits invasiveness and metastasis through its influence on the posttranscriptional regulation of BART mRNA levels via G3BP RNase activity. 21299347_Results indicate that the CD44(+)/CD24(-) cells are transit progenitors and have no association with the molecular subtypes and clinicopathological parameters in invasive ductal carcinomas. 21308865_CD24-positive cells could differentiate into insulin-producing cells but CD24-negative cells could not 21359202_Regions of aberrant DNA methylation which were consistent with alteration of TGM-2, MMP-2, and CD24 transcript and protein expression. 21536545_FUS-CREB3L2/L1-positive sarcomas show a specific gene expression profile with upregulation of CD24 and FOXL1. 21633165_Data show that the IL-6/JAK2/Stat3 pathway was preferentially active in CD44+CD24- breast cancer cells compared with other tumor cell types, and inhibition of JAK2 decreased their number and blocked growth of xenografts. 21641619_A strong association is shown between the presence of the 1626 polymorphism (A/G) of the CD24 gene and the risk of disease progression in Argentinean patients with multiple sclerosis. 21666711_found for the first time that tGLI1, but not GLI1, binds to and enhances the human vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) gene promoter, leading to its upregulation 21676268_Our findings indicate that NDRG2 and CD24 regulate HCC adhesion, migration and invasion. 21684315_CD24 rs3838464 genetic variant is a risk factor for Crohn's disease specifically for age of diagnosis between 17 and 40 years and the ileocolonic location. 21697762_Transforming growth factor beta1 may contribute to the invasiveness of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by suppressing the conversion from CD24-positive cells to CD24-negative cells at the tumor site. 21710320_CD24 is induced c-src signaling that increases the formation of focal adhesion complexes, integrin-dependent adhesion and cell spreading, and tumor cell invasion. 21726833_CD24 was found to be a functional liver tumor-initiating cells (T-IC) marker that drives T-IC genesis through STAT3-mediated NANOG regulation. 21802218_CD24 and VEGF may play important roles in breast tumorigenesis and progression 21806966_Ligation of CD24 expressed by oral epithelial cells with an anti-CD24 antibody induced formation of tight junctions and live-cell imaging confirmed that paracellular diffusion of fluorochrome-labeled dextran was reduced. 21813394_Expression patterns of the pancreatic cancer stem cell surface markers CD44, CD24 and ESA were diverse in different pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines and changed with their local microenvironment. 21815873_The CD24 single nucleotide polymorphism genotype influences both relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis disease risk and severity in Iranian patients. 21824412_Hypoxia, as indicated by HFI-1alpha expression, might be related to the worse prognosis found in CD44+CD24-/low positive breast tumors. 21828044_CD24 enhances cell invasion through increased generation or transmission of contractile forces 21835433_These findings suggest that CD44(+)/CD24(-/low) breast cancer stem-like cells play an important role in the clinical behavior of triple-negative breast cancer. 21849440_LMP1 induces the CD44(high) CD24(low) cancer stem cells/cancer progenitor cells-like phenotype as well as self-renewal abilities in LMP1-expressing epithelial cell lines. 21935375_CD44+/CD24(-or low) phenotypic radiation resistance of breast cancer cells is mediated through the enhanced activation of ATM signaling 21956537_CD24+ (P=0.07) and claudin-7 positivity (P=0.05) were associated with reduced time of recurrence, suggesting a contribution of these markers to aggressiveness of breast cancer. 21961844_Results obtained through a large cohort of European caucasian patients with systemic sclerosis do not support the contribution of CD19, CD20, CD22, CD24 variants to the genetic susceptibility. 21984372_inverse expression of CD24 and TFPI-2 was observed by immunohistochemical analysis of primary breast cancers (N = 1,174). TFPI-2 expression was highest in CD24 negative samples and lowered with increasing CD24 expression 22014860_study demonstrated that invasive micropapillary carcinoma represents a distinct entity of breast carcinoma with high expression of CD24 with a typical inverted apical membrane pattern, compared to invasive ductal carcinomas 22119938_CD24 and CD44 expression can individually yield prognostic data in breast cancer, but importantly, when both markers are considered; the CD44(+)/CD24(-) phenotype had the best prognosis, while the CD44(-)/CD24(+) phenotype had the worst prognosis. 22135002_Our data suggest that NDRG2 down-regulation or CD24 up-regulation is an important feature of primary gallbladder carcinoma 22237177_Regarding the correlation of CD44/CD24 status with tumor characteristics, the tumors of group A were significantly associated with axillary lymph node metastasis compared with those of group B (p = 0.033). 22262195_We could not show any relationship between the CD24V/V genotype, oligoclonal band status and IgG index in multiple sclerosis patients. CD24V/V allele may exert its effects on the disease course independently of CSF IgG synthesis. 22322379_The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) correlated with CD24+CD44+ and CD133+ cells in pancreatic cancer. 22335271_Analysis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma tissue microarrays showed that CD24 was significantly associated with late-stage pancreatic adenocarcinomas, and RPN2 was exclusively coexpressed with CD24 in a small population of CD24-positive cells. 22354323_Overexpression of CD24 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with invasiveness, metastatic potential and high tumor proliferation status. 22369943_These results suggest that CD24 and CD26 differentially regulate the cancer stem cell potentials of malignant mesothelioma. 22480875_Pretreatment of tumor cells with STAT3 specific inhibitors or knocking down of STAT3 by SiRNA makes the tumor cell more susceptible to apoptosis and dendritic cell mediated inhibition of both CD24 and HER-2/neu 22500096_Investigate the expression of CD24 in 151 glioma specimens and 10 nonneoplastic brain tissues. Results show CD24 was overexpressed in gliomas. 22528516_Our results suggest that the decreased expression of NDRG2 or the increased expression of CD24 is an important feature of lung adenocarcinoma. 22529013_human embryonic stem cells expressed CD24 in the pluripotent state, during the whole process of endoderm formation and upon further differentiation towards pancreatic endoderm. 22610780_the CD44+/CD24- phenotype in ovarian cancer cells demonstrate cancer stem cell-like properties of enhanced differentiation, invasion, and resistance to chemotherapy. 22731636_The expression of CD24 is associated with activation of Lyn and ERK1/2, which might be a novel mechanism related to CD24-mediated regulation of CRC development. 22745528_Explored the expression profile of CD24 in the retinoblastoma tumor samples. High-risk tumors showed significantly increased expression of CD24 compared to tumors with low-risk (P T polymorphism in CD24 increases the risk of multiple sclerosis (MS), while the 1527-1528 TG>del seems to have a protective role against MS. 26040280_CD24(+) cells account for heterogeneity in mammary tumors. CD24 expression at early stages of the cancer process is an indication of a highly invasive tumor. 26059947_CD24-bearing plasma membrane-derived extracellular microvesicles were released in response to CD24 engagement. 26072079_Results showed higher expression levels of CD24 mRNA and protein in ovarian cell line with high metastatic potential suggesting that CD24 may play an important role in the development of anoikis resistance in ovarian cancer. 26076835_CD24 is a conserved marker for tracking divergent states in both reprogramming and standard pluripotent culture. 26097606_Suggest CD24 expression as independent prognostic factor in colorectal carcinoma. 26187149_CD24 A1626 G is more frequent in OLP patients, contributes to disease risk, and could play a role in OLP susceptibility. 26191160_TROP-1/Ep-CAM and CD24 may play key roles in the progression of ovarian cancer through promoting migration, proliferation, inhibiting cell apoptosis and adhesion, and disturbing cell cycle. 26227486_The CD24-positive phenotype is associated with cisplatin resistance in endometrial cancer tumor xenografts and is accompanied by high expression of ABC transporters. 26245161_Studied the relationship between two CD24 polymorphisms, rs8734/rs52812045 and rs3838646, and autoimmune disease. 26298632_Basal like tumors are enriched for cancer stem cells (CSC) with CD44(+)/CD24(-/low) phenotype. CD133 can detect a different population of CSC in breast carcinoma 26351781_Increased expression of CD24 may be associated with tumor progression and prognosis in patients with uterine cervical cancer. 26444008_CD24 gene expression was associated with histone acetylation. 26608371_These results reveal the underlying link between the HCC processes mediated by CD24. Moreover, as a clear tumor promoter, CD24 is considered a potential new target for HCC treatment. 26617852_CD44(+)/CD24(-) phenotype may be an important factor for malignant relapse following surgical resection and chemotherapy in patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. 26647656_we present evidence that CD44v3 immunoexpression and CD44v3+/CD24- immunophenotypes could give prognostic information associated with unfavorable clinical outcomes. 26707501_our results suggest that CD24 is upregulated in cervical cancer tissues and plays its functions by affecting the MAPK signaling pathway in cervical cancer. 26712693_Silencing of CD24 enhanced restoration of PRIMA-1-induced mutant p53 in endogenous TP53(P223L/V274F) DU145 cells. 26718436_The functional CD24 A57V and TG/del polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. (Meta-analysis) 26830684_CD24 regulates EGFR signaling by inhibiting EGFR internalization and degradation in a RhoA-dependent manner in gastric cancer cells. 26852663_The frequencies of CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B-regulatory lymphocyte were significantly increased in children with beta-thalassemia. 26900300_The P-534 site in CD24 gene affects the overall survival of gastric cancer and may serve as a prognostic marker for gastric cancer. 26910849_notochord-specific marker during early intervertebral disc development 27157614_Expression of CDH1 and CD24 was transcriptionally upregulated by direct binding of HOXA5 to their promoter sequences as demonstrated by luciferase and ChIP analyses 27179633_CD24 cell surface expression may serve as a valuable biomarker in order to identify mammary tumors that will positively respond to targeted IGF1R therapies. 27276062_CD24 expression level directly affects cisplatin sensitivity and affects the expression of critical apoptotic, stem and drug resistance genes. 27287269_Of the 66 apocrine lesions, 62 (94 %) did not express C-KIT compared to 4/63 (6 %) of the normal glands 27332878_co-expression of CD90 and CD24 may have an important role in the development and progression of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. 27377469_These data suggest a significant association of CD24 genetic variants with prostate cancer onset and progression, which provides new insight into molecular genetics of prostate cancer. 27470135_High CD24 expression is associated with breast neoplasms. 27494878_CD24 induced colorectal cancer angiogenesis in Hsp90-dependent manner and activated STAT3-mediated transcription of VEGF. 27521216_CD44 and CD24 collaboratively drive the reprogramming of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through STAT3-mediated stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition activation 27589896_CD24 is a highly sensitive and specific marker of ovarian carcinoma in the differential diagnosis from malignant mesothelioma and reactive mesothelium in effusions. 27613575_The early stage of root development demonstrated higher CD24 expressing cells than later stage. In conclusion, quantity of CD24 expressing cells influenced SCAPs self-renewal and multi-lineage differentiation but did not influence on cell proliferation. 27659530_CD133+CD24lo phenotype defines 5-FU-resistant human colon cancer stem cell-like cells. 27768764_CD44+/24- and ALDH1-positive rates in primary tumors differed according to intrinsic subtype. ER-positive patients with CD44+/24- tumors had significantly longer disease-free-survival than all other ER-positive patients 27798870_In this work, we analyzed the expression of CD133, FOXP3, ABCG2 and CD24 in women affected by vulvar cancer, correlating these with common clinical prognostic factors 27837613_CD44+/CD24- cells were present in all tumor tissues. The percentage of CD44+/CD24- cells was higher in early-stage disease, but without statistical si |
ENSMUSG00000047139 |
Cd24a |
20.861485 |
0.1328156074 |
-2.912503 |
0.516094895 |
32.614451 |
0.00000001123760662288189174302467708641689592141688081028405576944351196289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000048755753601921432204496049608866137248242011992260813713073730468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.8918679 |
1.3927526 |
29.2595006 |
6.1470661 |
| ENSG00000272462 |
|
LINC02980 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.994126 |
0.4177530010 |
-1.259278 |
0.546194849 |
5.381543 |
0.02035087325460126911336189436951826792210340499877929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036436061285530653430786429680665605701506137847900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5072895 |
1.9548097 |
13.0575835 |
3.0050907 |
| ENSG00000272476 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.445951 |
0.3889932855 |
-1.362183 |
0.252519762 |
30.097457 |
0.00000004108696075682391494928298548636180775872617232380434870719909667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000167943378778931318120635433205345421470155997667461633682250976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.5192170 |
3.3375879 |
52.9833906 |
5.2814791 |
| ENSG00000272501 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.448174 |
0.2451251572 |
-2.028410 |
0.645392037 |
10.261763 |
0.00135815821313907663520081925412341661285609006881713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003095971463464520546937652767383042373694479465484619140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2823492 |
1.4018932 |
13.4515695 |
3.3756194 |
| ENSG00000272502 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.951734 |
0.1797552103 |
-2.475895 |
0.329796421 |
59.749507 |
0.00000000000001077321687038866006254168942530429212351469198116760139782854821532964706420898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000072245652433864897775680597735171721793267542166550043702955008484423160552978515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.0952582 |
2.6262021 |
67.7442945 |
8.4505738 |
| ENSG00000272505 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.497006 |
0.2142663632 |
-2.222523 |
0.351892333 |
42.619973 |
0.00000000006647712437886325443445547346907201560761713210467860335484147071838378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000347205362997884512289543535709440344461107486040418734773993492126464843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3817808 |
2.3332045 |
48.8399111 |
6.1500557 |
| ENSG00000272625 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.644093 |
5.4183849422 |
2.437863 |
0.426522744 |
34.248854 |
0.00000000484960978362605169990411386874741561658908040044480003416538238525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000021783396350067107863680035233222564983179836417548358440399169921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
40.5012089 |
9.7931660 |
7.5859927 |
1.5995191 |
| ENSG00000272638 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.316241 |
0.1633736423 |
-2.613753 |
0.813346615 |
10.686492 |
0.00107920687398004771020976200190943927736952900886535644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002498681327050275308848670263728308782447129487991333007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1340745 |
2.0017531 |
12.9233378 |
7.6714273 |
| ENSG00000272668 |
107985216 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
107.220407 |
0.0486958861 |
-4.360056 |
0.925749050 |
14.182957 |
0.00016586611453203451891323660927213268223567865788936614990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000441193701656664128644275146839959234057459980249404907226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.2477478 |
4.8990717 |
100.8648685 |
53.8973370 |
| ENSG00000272669 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.106855 |
0.2317510838 |
-2.109352 |
0.646945505 |
11.390750 |
0.00073810717700244048156132947724472614936530590057373046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001759725720005818599273039737340695864986628293991088867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8587222 |
1.3809204 |
13.0296109 |
3.5449572 |
| ENSG00000272720 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.716456 |
0.0659483501 |
-3.922520 |
0.406838864 |
124.273965 |
0.00000000000000000000000000007337943488287790685595956979738668834005462357541713938165880387935895742650138640073009810294024646282196044921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000907102561868742014623959467245527727124763954862537647717579180472804458411351102853359407163225114345550537109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0444523 |
1.4501375 |
77.1119120 |
10.0046898 |
| ENSG00000272734 |
|
ADIRF-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104.171300 |
0.1538837314 |
-2.700087 |
0.258035693 |
107.086599 |
0.00000000000000000000000042613572890749749163635506983896355067625327342253775190416016497609030810878039119415916502475738525390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000004597780232949315060673409155208019690992741522819579655720306332177677033357099389832001179456710815429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.5476852 |
5.0679070 |
185.6066004 |
20.9141064 |
| ENSG00000272752 |
101752399 |
STAG3L5P-PVRIG2P-PILRB |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This locus represents naturally occurring readthrough transcription among the neighboring LOC101735302 (stromal antigen 3 pseudogene), LOC101752334 (poliovirus receptor related immunoglobulin domain containing pseudogene) and PILRB (paired immunoglobin-like type 2 receptor beta) genes on chromosome 7. The readthrough transcript is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), and is unlikely to produce a protein product. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2013]. |
|
|
|
|
|
175.135872 |
0.4863992030 |
-1.039787 |
0.193144676 |
28.659937 |
0.00000008627016840492671253927208473155641144103356054984033107757568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000342481895012565441384306879832322145773559896042570471763610839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
123.3194791 |
15.5075088 |
253.9620245 |
21.6367917 |
| ENSG00000272767 |
84989 |
JMJD1C-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.373673 |
0.2236825858 |
-2.160475 |
0.355383663 |
40.360793 |
0.00000000021113580854578316851431569038010293767881897508686961373314261436462402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001066882757321383034635402136986077892277791079322923906147480010986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6218790 |
2.4033551 |
38.8952750 |
6.5601442 |
| ENSG00000272779 |
|
BMS1P20 |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.067848 |
7.6356367362 |
2.932748 |
0.363433544 |
71.131780 |
0.00000000000000003341442823485685081922738016825902989907129861488384314771593608384137041866779327392578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000258760210255239840601412982576317716653628716542284715629307356721255928277969360351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.3421455 |
21.5252369 |
7.5486861 |
2.1613235 |
| ENSG00000272831 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.618688 |
0.3464385267 |
-1.529329 |
0.309413317 |
24.768571 |
0.00000064642958412686036131589249059681279163669387344270944595336914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002338554083753053716108203166634815772795263910666108131408691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.1839706 |
3.9192890 |
55.8383919 |
7.3253595 |
| ENSG00000272841 |
117981787 |
MAP3K4-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.204297 |
4.4087466266 |
2.140369 |
0.345956128 |
39.780946 |
0.00000000028410328468620121149220519626951882152798845027064089663326740264892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001421479485412993307092940975316312096632387351746729109436273574829101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.4057988 |
9.3140339 |
10.8671317 |
1.8350649 |
| ENSG00000272849 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.953846 |
0.1999893790 |
-2.322005 |
0.490644413 |
24.744625 |
0.00000065451084137668993380014840696712319356720399810001254081726074218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002366629107966669310199282413864629859290289459750056266784667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4856072 |
1.4255485 |
22.3476500 |
3.7040067 |
| ENSG00000272871 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.492676 |
0.4272944356 |
-1.226698 |
0.488042159 |
6.513863 |
0.01070367581436783288584280171562568284571170806884765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020409024030495957757747049754470936022698879241943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.7365437 |
2.0593112 |
13.5242417 |
3.1057097 |
| ENSG00000272872 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.061185 |
0.1182402004 |
-3.080207 |
0.597736772 |
31.500803 |
0.00000001993578458260430715052319294855465159344021230936050415039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000084249266988823034278383147712560008457671756332274526357650756835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6345948 |
1.1218755 |
22.2775325 |
4.7720685 |
| ENSG00000272896 |
|
|
protein_coding |
V9GYN2 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.348076 |
0.3314385100 |
-1.593187 |
0.505575361 |
9.938292 |
0.00161875670442371668092396141958033695118501782417297363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003640827203778125575883706233071279712021350860595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0935341 |
2.6189594 |
24.5439296 |
5.1729065 |
| ENSG00000272902 |
100506286 |
TBC1D8-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.200006 |
0.3043679949 |
-1.716111 |
0.556206986 |
9.543084 |
0.00200704208160635243218816725629949360154569149017333984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004430742016827663928846270380290661705657839775085449218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9988458 |
1.9866804 |
16.6427730 |
4.0993445 |
| ENSG00000272931 |
|
LRRC8D-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.467167 |
0.1572993349 |
-2.668416 |
0.535182666 |
29.469549 |
0.00000005680217982687867392754704786751729361782281557680107653141021728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000228758574145901564507609338323945724624763897736556828022003173828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9295395 |
1.0762945 |
18.8035363 |
3.4597110 |
| ENSG00000272977 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.632871 |
0.4024026891 |
-1.313288 |
0.565221400 |
5.540954 |
0.01857645632286420919743186175310256658121943473815917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.033572731152868337534123099885619012638926506042480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3705939 |
1.7466727 |
10.8094719 |
2.7356450 |
| ENSG00000273002 |
107985209 |
ARHGEF2-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.554840 |
0.2536314197 |
-1.979195 |
0.544849027 |
14.089809 |
0.00017428553351861176537104802797273350734030827879905700683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000461841018803359041906136939203975089185405522584915161132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.9442957 |
1.3429744 |
15.6884409 |
2.8734227 |
| ENSG00000273018 |
80039 |
FAM106A |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95.290038 |
0.4063217640 |
-1.299305 |
0.225701235 |
32.892396 |
0.00000000974035328043183988107179649244826702414457031409256160259246826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000042471968809209446508354495863207800354643950413446873426437377929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.0598613 |
7.1113949 |
121.7196907 |
11.8053207 |
| ENSG00000273033 |
100129550 |
LINC02035 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.213162 |
0.3159445511 |
-1.662257 |
0.500207489 |
11.088723 |
0.00086854260360605948284445920748453318083193153142929077148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002046565905048760951323583157090979511849582195281982421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7743867 |
2.3106172 |
24.8153010 |
4.5865832 |
| ENSG00000273066 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.154352 |
0.3735077955 |
-1.420790 |
0.519788203 |
7.395599 |
0.00653836585825641296298993410118782776407897472381591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.013039553251445993101165221617065981263294816017150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.1702208 |
3.1579816 |
22.2709367 |
5.6696842 |
| ENSG00000273136 |
101060684 |
NBPF26 |
protein_coding |
A0A494C0A2 |
|
Coiled coil;Disulfide bond;EGF-like domain;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal |
|
Predicted to enable calcium ion binding activity. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
calcium ion binding [GO:0005509] |
|
|
|
392.900864 |
4.9132791850 |
2.296686 |
0.792703747 |
7.100947 |
0.00770432181619956028134632575188334158156067132949829101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015121780586051264405611505026172380894422531127929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
349.9283306 |
185.2874763 |
75.2220693 |
28.3970829 |
| ENSG00000273142 |
|
LINC02604 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
69.092834 |
0.3031737084 |
-1.721783 |
0.217159006 |
64.364247 |
0.00000000000000103417844141609886294757436944420005754221897516231809532882834901101887226104736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000007406343423241930129039066671940862722934174194877599006758828181773424148559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.7218496 |
4.5633912 |
108.2414186 |
9.2933332 |
| ENSG00000273151 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66.596092 |
0.1532143522 |
-2.706377 |
0.241685683 |
140.702670 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000001868782081496513681801676456289933798442309705597096425541828315209533873616050552736965462141682792207575403153896331787109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000258997403970784437252661660934126993058514754116468736636047248116231451503684284770612222814634151291102170944213867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.5554495 |
3.2599920 |
115.7704305 |
12.5785640 |
| ENSG00000273154 |
84619 |
|
protein_coding |
A0A0J9YYD9 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
|
|
B cell receptor complex [GO:0019815]; protein kinase binding [GO:0019901]; B cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050853]; regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:0043122]; regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043405]; regulation of NIK/NF-kappaB signaling [GO:1901222]; regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling [GO:0014066]; regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol [GO:0051279]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; T cell receptor signaling pathway [GO:0050852] |
|
|
|
104.917446 |
0.3125289222 |
-1.677938 |
0.176504897 |
92.896426 |
0.00000000000000000000055103922905548762725364586303134992575606587988304130808474984304368149423680733889341354370117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000005260891992793658674954191254916148559102037598409632712377452523622167745998012833297252655029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
47.7067419 |
13.2354712 |
151.3993878 |
29.6213983 |
| ENSG00000273203 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.231239 |
0.3564032776 |
-1.488417 |
0.391421116 |
15.019644 |
0.00010639788098959841635814810301141619675036054104566574096679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000291685126932851514647976332028633805748540908098220825195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6086873 |
2.1641482 |
24.3311672 |
3.6789493 |
| ENSG00000273218 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.913234 |
0.4465914771 |
-1.162972 |
0.383846178 |
9.431971 |
0.00213235016063552992177099199011536256875842809677124023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004684251878401610516555741980937455082312226295471191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1408241 |
2.4166158 |
22.9505344 |
3.3769245 |
| ENSG00000273230 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.046601 |
0.4586451327 |
-1.124550 |
0.369256369 |
9.519974 |
0.00203247478811300610543333355906270298874005675315856933593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004480186360894260373666231345168853295035660266876220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1482688 |
2.3572908 |
22.3020577 |
3.2245606 |
| ENSG00000273247 |
|
RAB33B-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.386454 |
0.1852472630 |
-2.432476 |
0.411708452 |
35.614395 |
0.00000000240503720422536609587400529652705116756550296486238949000835418701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011117553753324898681680292684970101646513285231776535511016845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.5240336 |
2.1502913 |
46.1624951 |
7.0604053 |
| ENSG00000273270 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65.133121 |
0.3884146768 |
-1.364330 |
0.200724142 |
47.485687 |
0.00000000000554070188730167242960283015496378733900223467756518402893561869859695434570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000031297650155596128993852955639979143177831222288887147442437708377838134765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
36.1601033 |
4.6426195 |
93.7338939 |
7.5472271 |
| ENSG00000273314 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.403511 |
0.4221672647 |
-1.244113 |
0.368278424 |
11.812064 |
0.00058848146448934907527111848324352649797219783067703247070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001427676925684219716786160780941372649976983666419982910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3648010 |
2.6613595 |
24.4653240 |
3.9295434 |
| ENSG00000273333 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
112.300510 |
0.3937894187 |
-1.344504 |
0.234672644 |
32.259618 |
0.00000001348877254826404932696796409906728198002667795663001015782356262207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000057926762529059455676464087748103737318672301626065745949745178222656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
63.0438562 |
11.1009461 |
161.5215996 |
19.7909827 |
| ENSG00000273344 |
202781 |
PAXIP1-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31823805_LncRNA PAXIP1-AS1 was highly expressed in glioma and associated with poor prognosis. Highly expressed lncRNA PAXIP1-AS1 promoted glioma cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis by recruiting transcription factor ETS1 to upregulate KIF14 expression. However, its silencing inhibited migration, invasion and angiogenesis of glioma cells. 34108034_H3K27ac-induced lncRNA PAXIP1-AS1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, EMT and apoptosis in ovarian cancer by targeting miR-6744-5p/PCBP2 axis. 34245091_LncRNA PAXIP1-AS1 fosters the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension via ETS1/WIPF1/RhoA axis. |
|
|
22.447662 |
0.4391341128 |
-1.187266 |
0.329333240 |
13.322872 |
0.00026218826624644232369670815430140464741270989179611206054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000674668551219924860461174542791695785126648843288421630859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.0886956 |
2.9603112 |
32.3775196 |
4.2710019 |
| ENSG00000273373 |
|
SLC16A4-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50.668388 |
0.4294327154 |
-1.219496 |
0.243082178 |
25.273790 |
0.00000049742228864718256898136850702174527327770192641764879226684570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001825448279570466136647872816556326114323383080773055553436279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.1546287 |
4.5396979 |
70.8810342 |
6.8840421 |
| ENSG00000273443 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.966024 |
2.5283913884 |
1.338220 |
0.530697534 |
6.420435 |
0.01128145349330238363105838317324014496989548206329345703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021412576543710655496699502009505522437393665313720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.1628769 |
4.9677120 |
6.0455237 |
1.5518997 |
| ENSG00000273448 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.484995 |
0.1652893850 |
-2.596934 |
0.628926623 |
18.038193 |
0.00002165172177308056960577144212098943398814299143850803375244140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000065393782150740579974142197006159449301776476204395294189453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.7494572 |
1.1997058 |
16.8996635 |
4.0934718 |
| ENSG00000273486 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49.560216 |
0.3373588178 |
-1.567644 |
0.277918833 |
32.082760 |
0.00000001477425920062686597367111225468164215079980294831329956650733947753906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000063171513847408035694395100033415868523434255621396005153656005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.0824798 |
8.3262877 |
69.7820418 |
17.6186194 |
| ENSG00000273487 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.815314 |
0.1035511808 |
-3.271584 |
0.781946739 |
23.020715 |
0.00000160265225753295509160726260711182789009399130009114742279052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000005545041566147777249587511733119882251230592373758554458618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2385376 |
0.6798757 |
12.0068351 |
2.8247079 |
| ENSG00000273576 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.204658 |
0.1981417810 |
-2.335395 |
0.812727190 |
7.995943 |
0.00468822859581849004512177359060842718463391065597534179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009637639843214612644928251938836183398962020874023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0360584 |
2.1171564 |
15.7747277 |
6.8621269 |
| ENSG00000273576_ENSG00000167258 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
68.140222 |
0.4531935969 |
-1.141801 |
0.334054526 |
11.257327 |
0.00079309347407746644265102986537385731935501098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001881700639347919047292267968884971196530386805534362792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.0425116 |
10.7731094 |
97.6270726 |
16.6720096 |
| ENSG00000273669 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.569613 |
0.2937466539 |
-1.767356 |
0.557097682 |
10.294775 |
0.00133407397863090555235887624263568795868195593357086181640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003044361769417465272968836842437667655758559703826904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4433693 |
1.6785033 |
15.0679450 |
3.4312343 |
| ENSG00000273702 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.492517 |
0.2403943853 |
-2.056525 |
0.637794532 |
11.424268 |
0.00072490988556429098669392496745444987027440220117568969726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001730218290900539064233742969634022301761433482170104980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.3700273 |
1.0313942 |
9.8572209 |
2.3712933 |
| ENSG00000273706 |
3975 |
LHX1 |
protein_coding |
P48742 |
FUNCTION: Potential transcription factor. May play a role in early mesoderm formation and later in lateral mesoderm differentiation and neurogenesis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:9212161}. |
Developmental protein;Differentiation;DNA-binding;Homeobox;LIM domain;Metal-binding;Neurogenesis;Nucleus;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;Repeat;Transcription;Transcription regulation;Zinc |
|
This gene encodes a member of a large protein family which contains the LIM domain, a unique cysteine-rich zinc-binding domain. The encoded protein is a transcription factor important for the development of the renal and urogenital systems. This gene is a candidate for Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome, a disorder characterized by anomalies in the female genital tract. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]. |
hsa:3975; |
chromatin [GO:0000785]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; protein-containing complex [GO:0032991]; transcription regulator complex [GO:0005667]; cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000987]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity [GO:0003700]; DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific [GO:0000981]; metal ion binding [GO:0046872]; RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding [GO:0000977]; sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding [GO:1990837]; anatomical structure formation involved in morphogenesis [GO:0048646]; anatomical structure morphogenesis [GO:0009653]; animal organ morphogenesis [GO:0009887]; anterior/posterior axis specification [GO:0009948]; anterior/posterior pattern specification [GO:0009952]; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0001658]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus [GO:0044344]; cerebellar Purkinje cell differentiation [GO:0021702]; cerebellar Purkinje cell-granule cell precursor cell signaling involved in regulation of granule cell precursor cell proliferation [GO:0021937]; cerebellum development [GO:0021549]; cervix development [GO:0060067]; comma-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072049]; dorsal spinal cord interneuron posterior axon guidance [GO:0097379]; dorsal/ventral pattern formation [GO:0009953]; ectoderm formation [GO:0001705]; embryonic pattern specification [GO:0009880]; embryonic retina morphogenesis in camera-type eye [GO:0060059]; embryonic viscerocranium morphogenesis [GO:0048703]; endoderm formation [GO:0001706]; epithelium development [GO:0060429]; forebrain regionalization [GO:0021871]; gastrulation with mouth forming second [GO:0001702]; head development [GO:0060322]; kidney development [GO:0001822]; lateral motor column neuron migration [GO:0097477]; mesendoderm development [GO:0048382]; mesonephric duct development [GO:0072177]; metanephric comma-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072278]; metanephric glomerulus development [GO:0072224]; metanephric part of ureteric bud development [GO:0035502]; metanephric renal vesicle morphogenesis [GO:0072283]; metanephric S-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072284]; motor neuron axon guidance [GO:0008045]; negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045892]; nephric duct elongation [GO:0035849]; nephric duct morphogenesis [GO:0072178]; nervous system development [GO:0007399]; neuron differentiation [GO:0030182]; oviduct development [GO:0060066]; oviduct epithelium development [GO:0035846]; paramesonephric duct development [GO:0061205]; pattern specification process [GO:0007389]; positive regulation of anterior head development [GO:2000744]; positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis [GO:0090190]; positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription [GO:0045893]; positive regulation of embryonic development [GO:0040019]; positive regulation of gastrulation [GO:2000543]; positive regulation of nephron tubule epithelial cell differentiation [GO:2000768]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; primitive streak formation [GO:0090009]; pronephros development [GO:0048793]; regulation of gene expression [GO:0010468]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; renal vesicle morphogenesis [GO:0072077]; retina layer formation [GO:0010842]; S-shaped body morphogenesis [GO:0072050]; somite rostral/caudal axis specification [GO:0032525]; spinal cord association neuron differentiation [GO:0021527]; telencephalon development [GO:0021537]; transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006366]; ureter morphogenesis [GO:0072197]; ureteric bud development [GO:0001657]; urogenital system development [GO:0001655]; uterine epithelium development [GO:0035847]; uterus development [GO:0060065]; vagina development [GO:0060068]; ventral spinal cord development [GO:0021517] |
19849868_Lim1 (also known as Lhx1) gene consists of a DNA-binding homeodomain and 2 cysteine-rich LIM domains, which may participate in protein to protein interactions, and encodes a transcription factor. 21132009_findings establish that the developmental marker Lim1 acts as an oncogene in cancer cells and targeting Lim1 may constitute an innovative therapeutic intervention in human lear cell carcinoma 21778788_Eleven dysplastic kidneys showed no expression of LIM1. In contrast, 12 of 32 nephroblastomas showed nuclear positivity. 22217964_Mutations in the coding regions of LHX1 may not be a common genetic etiologic factor involved in Han Chinese patients with mullerian duct abnormalities. 22231913_Lim1/LIM1 expression in neonatal, adult mouse and human endometrium suggesting Lim1/LIM1 may have a role in endometrial development and remodelling 22740494_study concludes that heterozygous mutations of LHX1 might be one cause of the Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome in a subgroup of patients 22875024_Data indicate that expression of ERAS, LHX1, and CCRK is increased in aggressive subgroups of medulloblastomas. 23954021_Data have identified TBX6 as a new gene associated with Mullerian aplasia. The results also support the relevance of LHX1 and CNVs in the development of this congenital malformation. 28061432_Report novel missense mutation in LHX1 in congenital absence of the uterus and vagina which could change the transcriptional activity of LHX1 and its effect on the regulation of the downstream target gene GSC. 28600106_Our MRKH families included 43 quads, 26 trios, and 30 duos. Of our MRKH probands, 87/147 (59%) had MRKH type 1 and 60/147 (41%) had type 2 with additional anomalies. CONCLUSION(S): Although the prevalence of WNT4, HNF1B, and LHX1 point mutations is low in people with MRKH, the prevalence of CNVs was approximately 19%. 30076415_The potential pro-metastatic role of Lim1 in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo in a nude mouse model. Lim1 was found constitutively expressed in all metastatic tissues. Lim1 silencing decreased pulmonary metastasis in the in vivo model. Lim1 is involved in the expression of various proteins regulating cell movements and EMT, and induced clonogenicity in CCC cells. |
ENSMUSG00000018698 |
Lhx1 |
19.575283 |
0.1119864563 |
-3.158604 |
0.591472932 |
27.678990 |
0.00000014320970063405246198102234878729577260969563212711364030838012695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000556403048528195371000770134278790024495719990227371454238891601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1192377 |
1.2192026 |
28.4389127 |
6.4586183 |
| ENSG00000273759 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.377685 |
0.2897208956 |
-1.787264 |
0.609134151 |
9.299852 |
0.00229172383877369791743694449337453988846391439437866210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005004563376283441104852567349325909162871539592742919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8120105 |
1.1992340 |
9.8158829 |
2.3913583 |
| ENSG00000273783 |
|
GTF2A1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.890532 |
0.2854262530 |
-1.808810 |
0.531650441 |
12.111190 |
0.00050120134674917554348794190843818796565756201744079589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001230699031445322069733272485336783574894070625305175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9773788 |
1.8013401 |
17.5224249 |
3.8496064 |
| ENSG00000273812 |
|
LINC02970 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.586954 |
7.1758702105 |
2.843154 |
0.379939419 |
61.992801 |
0.00000000000000344715235093443570497917985180698910367721294299714340780838028877042233943939208984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000023820210065445818992423902328581765512887247898676790214267384726554155349731445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.7910148 |
10.8112330 |
6.3035692 |
1.3363041 |
| ENSG00000274070 |
729438 |
CASTOR2 |
protein_coding |
A6NHX0 |
FUNCTION: Functions as a negative regulator of the TORC1 signaling pathway through the GATOR complex. As part of homodimers or heterodimers with CASTOR1, directly binds and inhibits the GATOR subcomplex GATOR2 and thereby mTORC1. Does not directly bind arginine, but binding of arginine to CASTOR1 disrupts the interaction of CASTOR2-containing heterodimers with GATOR2 which can in turn activate mTORC1 and the TORC1 signaling pathway. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26972053}. |
Cytoplasm;Reference proteome |
|
Enables identical protein binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of TORC1 signaling. Located in cytosol. Colocalizes with GATOR2 complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:729438; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cellular response to L-arginine [GO:1903577]; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling [GO:1904262]; regulation of intracellular signal transduction [GO:1902531] |
26972053_Study establishes the CASTOR1 homodimer and CASTOR1-CASTOR2 heterodimer as arginine sensors for the mTORC1 pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000015944 |
Castor2 |
138.933907 |
0.3704638710 |
-1.432595 |
0.137189317 |
112.435148 |
0.00000000000000000000000002868974021536368355743589477975786376798613142331848046634277704018765181581684942102583590894937515258789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000321046675950544358137799410291498550432114790182563127214473712754206138897394851028366247192025184631347656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.6803607 |
6.9452178 |
203.0384865 |
11.9492849 |
| ENSG00000274180 |
256302 |
NATD1 |
protein_coding |
Q8N6N6 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:256302; |
|
33435607_Development of A Continuous Fluorescence-Based Assay for N-Terminal Acetyltransferase D. |
ENSMUSG00000018931 |
Natd1 |
32.368138 |
0.4975409882 |
-1.007113 |
0.309163796 |
10.625561 |
0.00111535102426549032755831447616401419509202241897583007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002579937489133151112125075243852734274696558713912963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.6600217 |
4.2648390 |
43.9607117 |
5.7565083 |
| ENSG00000274253 |
283683 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.908309 |
0.2847555907 |
-1.812204 |
0.723838327 |
6.076270 |
0.01370097990642845861564147469380259281024336814880371093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025492803488584941246086756905242509674280881881713867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0461003 |
1.6246322 |
10.5852125 |
3.6439587 |
| ENSG00000274270 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.740662 |
0.4143148122 |
-1.271201 |
0.527478434 |
5.888036 |
0.01524408990678074657387774948347214376553893089294433593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028097248629381097601021011200828070286661386489868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2521407 |
1.8179510 |
12.6046439 |
2.8024526 |
| ENSG00000274272 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
174.300745 |
0.2495003688 |
-2.002886 |
0.218025144 |
80.955538 |
0.00000000000000000023085364851403765609343449880328576438319519547318807786706607032556348713114857673645019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000001985664249456407698021768536190631640007799809221201818576485464973302441649138927459716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.1441444 |
9.8158823 |
293.9710314 |
26.3403829 |
| ENSG00000274386 |
100129924 |
TMEM269 |
protein_coding |
A0A1B0GVZ9 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
|
|
13.054252 |
0.4202148096 |
-1.250801 |
0.445635780 |
8.046747 |
0.00455854327835293355458690101045249321032315492630004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009393284767344590655002711798715608892962336540222167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.8789771 |
2.4052458 |
16.4722299 |
3.8087250 |
| ENSG00000274422 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.442391 |
0.2796869431 |
-1.838115 |
0.276145055 |
47.177982 |
0.00000000000648245567899665132028785335146715731579475372470255933876615017652511596679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000036449922217901171849409475189988331239598906563514901790767908096313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7443833 |
2.7604395 |
56.7210425 |
5.6516420 |
| ENSG00000274471 |
|
|
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33.852693 |
0.4660141217 |
-1.101554 |
0.486038216 |
5.070930 |
0.02433033073193169998349461025100026745349168777465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.042790449296019668345980591084298794157803058624267578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.4420818 |
8.7010536 |
48.4281959 |
13.1228873 |
| ENSG00000274512 |
729873 |
TBC1D3L |
protein_coding |
B9A6J9 |
FUNCTION: Acts as a GTPase activating protein for RAB5. Does not act on RAB4 or RAB11 (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8IZP1}. |
Cell membrane;GTPase activation;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Palmitate;Reference proteome;Ubl conjugation |
|
Predicted to enable GTPase activator activity. Predicted to be involved in activation of GTPase activity and intracellular protein transport. Predicted to be located in plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:101060376; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; GTPase activator activity [GO:0005096]; activation of GTPase activity [GO:0090630] |
|
|
|
70.128662 |
0.4209665504 |
-1.248222 |
0.563768160 |
4.770627 |
0.02894928315185572170742389630504476372152566909790039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.049987297534088731554291484826535452157258987426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.4749322 |
17.4026720 |
104.1273438 |
29.5544121 |
| ENSG00000274565 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.575694 |
0.1728974477 |
-2.532012 |
0.477663986 |
30.294484 |
0.00000003711800501835264319789518512940351691042906168149784207344055175781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000152905876101279656402264070166885367996201239293441176414489746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.1357961 |
1.6432796 |
29.9190319 |
5.3412805 |
| ENSG00000274600 |
440804 |
RIMBP3B |
protein_coding |
A6NNM3 |
FUNCTION: Probable component of the manchette, a microtubule-based structure which plays a key role in sperm head morphogenesis during late stages of sperm development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3V0F0}. |
Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Differentiation;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;Spermatogenesis |
|
Predicted to enable benzodiazepine receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in fertilization and spermatid development. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in nucleus. Predicted to colocalize with manchette. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:440804; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; benzodiazepine receptor binding [GO:0030156]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; spermatid development [GO:0007286] |
Mouse_homologues 19091768_RIM-BP3 plays an essential role in manchette development and function through its interaction with Hook1. |
ENSMUSG00000071636 |
Rimbp3 |
28.012520 |
0.2192403061 |
-2.189415 |
0.358776334 |
39.178054 |
0.00000000038686435200447528046735330203235569274111682602779183071106672286987304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001913578363132056169554394428416153883798500601187697611749172210693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1378373 |
5.0122931 |
46.3096263 |
15.6232196 |
| ENSG00000274615_ENSG00000278599 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46.165518 |
0.3978494450 |
-1.329706 |
0.264290534 |
25.623327 |
0.00000041499210338906292312746129820333340632032559369690716266632080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001534085120529887374702261021441884736304928082972764968872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.3917717 |
4.5598022 |
64.2439224 |
7.5211586 |
| ENSG00000274925 |
112577464 |
ZKSCAN2-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.898721 |
0.3897374854 |
-1.359425 |
0.473985095 |
8.298307 |
0.00396820600299542351752091207117700832895934581756591796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008280993309365089483087274402350885793566703796386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.0842476 |
2.4590878 |
20.6182842 |
4.0562079 |
| ENSG00000275278 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.479777 |
0.1406046735 |
-2.830284 |
0.583590343 |
28.291674 |
0.00000010434383815194428308507793110720962559412328118924051523208618164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000410369051724672936622514323248833711943461821647360920906066894531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.5972196 |
1.0619716 |
18.6208419 |
3.7576432 |
| ENSG00000275302 |
6351 |
CCL4 |
protein_coding |
P13236 |
FUNCTION: Monokine with inflammatory and chemokinetic properties. Binds to CCR5. One of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T-cells. Recombinant MIP-1-beta induces a dose-dependent inhibition of different strains of HIV-1, HIV-2, and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). The processed form MIP-1-beta(3-69) retains the abilities to induce down-modulation of surface expression of the chemokine receptor CCR5 and to inhibit the CCR5-mediated entry of HIV-1 in T-cells. MIP-1-beta(3-69) is also a ligand for CCR1 and CCR2 isoform B. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10540332, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12070155, ECO:0000269|PubMed:8525373}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a mitogen-inducible monokine and is one of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T-cells. The encoded protein is secreted and has chemokinetic and inflammatory functions. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2012]. |
hsa:388372;hsa:6351; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; CCR1 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031726]; CCR5 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031730]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; cytokine activity [GO:0005125]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; establishment or maintenance of cell polarity [GO:0007163]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation by host of viral transcription [GO:0043922]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050850]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of natural killer cell chemotaxis [GO:2000503]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; response to virus [GO:0009615]; signal transduction [GO:0007165] |
11129109_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12036855_Cholesterol is essential for macrophage inflammatory protein 1 beta binding and signaling and conformational integrity of CC chemokine receptor 5. (Is MIP-1 beta the entry SCYA4 or LD78? If so, please add the term to SCYA4 or LD78.) 12070155_results demonstrate that NH(2)-terminally truncated MIP-1 beta functions as a chemokine agonist with expanded receptor reactivity; may represent an important mechanism for regulation of immune cell recruitment during inflammatory and antiviral responses 12200385_role in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma 12218153_Expression of MIP-1 beta is induced by stimulation of monocytic cells through Fc gamma receptors and involves activation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta sites. 12377943_role of IL-12 and IFN-gamma on inducing inflammatory chemokine (MIP-1beta) secretion and down-regulating CCR5 expression in human T cells 12393595_After stimulation via high-affinity FcepsilonRI, the transcriptional levels of I-309 (CCL1), MIP-1alpha (CCL3) and MIP-1beta (CCL4) were found among the 10 most increased human and mouse transcripts from approximately 12 000 genes 12393716_Lymphotactin, (MIP)-1alpha, and MIP-1beta chemokines were all rapidly induced by engagement of CD28 and were calcineurin sensitive. 12401480_MIP-1alpha and MIP-1beta show diverging signaling capacities [review] 12411442_binding surface and affinity of monomeric and dimeric forms for various glycosaminoglycan disaccharides 12603824_IL-1beta-induced MIP-1alpha and -1beta expression in NT2-N cells 12651610_Cathepsin D specifically cleaves this protein that is expressed in human breast cancer. 12679478_results suggest that endometrial macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta may be involved in the recruitment of NK cells from circulating peripheral blood 14582706_MIP-1beta may be related to the scattering and invasion step of gastric carcinoma cells with undifferentiated phenotype 14673550_Monocytes and B cells utilize different mechanisms to regulate expression of the 2 CCL4 genes (ACT-2 and LAG-1) & suggest that the 2 genes may not have identical activities. 14746807_Results suggest that interleukin-1beta-mediated up-regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta production in hepatic cells may contribute to continuous recruitment of inflammatory cells to the liver and maintenance of inflammation. 14761932_Activated T cells from GRK2+/- mice, which have a 50% reduction in GRK2 protein levels, showed a significant 40% increase in chemotaxis toward the CCR5 ligand CCL4 15529362_MCP-1, MIP-1beta, and IL-8 elevated in relapsing polychondritis(RP) are proinflammatory chemokines, characteristic of activation of monocytes and macrophages and, in the case of IL-8, also of neutrophils. Role for cell-mediated immune response in RP. 15585099_lymphocytes of HIV patients display a disrupted capacity to secrete the beta-chemokines MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta, which may constitute a mechanism of immune dysfunction in progressive HIV infection 15588341_produced by neonatal natural killer cells and contributes to suppession of HIV replication 15645140_RANTES, MIP-1beta and IL-18 are expressed in LGL leukemia 15831560_Normal human vaginal epithelial cells constitutively secrete the chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein CCL20, known to recruit Langerhans cell precursors selectively via its cognate CC chemokine receptor CCR6. 15897346_upregulation of MIP-1beta and downregulation of VE-cadherin may strongly participate in human acute heart rejection. 16379602_Higher amounts of MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and RANTES were detected in plasma of HIV-1-positive individuals, particularly those with concomitant pulmonary tuberculosis, although the increase was not found to be statistically significant. 16773571_variation in the CCL18-CCL3-CCL4 chemokine gene cluster influences HIV Type 1 transmission and AIDS disease progression 16963564_Results describe the structure of an orthopoxvirus vCCI in complex with a human CC chemokine, MIP-1beta (macrophage inflammatory protein 1beta). 17005260_findings show that CCL3, CCL4 and CCL5 bind on the Leishmania promastigotes 17330138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17644519_the CC chemokine MIP-1beta dimer is not able to bind or activate its receptor and implicates the CC chemokine monomer as the sole receptor-interacting unit 17703412_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18076643_The strong upregulation of CCL3 and CCL4 implicates these chemokines in the etiology and pathogenesis of TLE. 18203956_PC-PLC activation through CCR5 is specifically induced by gp120, since triggering CCR5 through its natural ligand CCL4 (MIP-1beta) does not affect PC-PLC cellular distribution and enzymatic activity, as well as CCL2 secretion 18346864_Data show that MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta bind to the HIV co-receptor CCR5 and blok HIV entry into CD4(+) lymphocytes. 18368065_Population structure in copy number variation and SNPs in the CCL4 chemokine gene are reported. 18623207_MCP-1, MIP-1beta, and IL-8 play important roles in the pathophysiology of Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). In addition, the serum concentrations of these chemokines may be sensitive markers for assessing disease activity in patients with HLH. 18802359_CysLTs induce MIP-1alpha and MIP-1beta production mediated by ERK via binding to the CysLT(1) receptor in human monocytes/macrophages. 19047106_CX3CL1, IL-15, and CCL4 can serve as independent predictors of biochemical recurrence. 19057841_Data suggest that increased MIP-1alpha/beta production enhances multiple myeloma cell binding to stromal cells by VLA-4-VCAM-1 adhesion, forming a 'vicious cycle' between MM cell adhesion to stromal cells and MIP-1 production via VLA-4-VCAM-1 interaction. 19074730_A novel mechanism of cross talk between chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and their microenvironment, namely, the secretion of 2 T-cell chemokines in response to nurselike cells coculture and BCR stimulation. 19103522_observed that CCL4, CXCL1 and CXCL8 secretion, following PROK1 induction 19258923_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19328808_Serum MIP-1beta level might be a useful predictor for cerebro-cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients. 19358850_ELISpot analysis of LPS-stimulated leukocytes: human granulocytes selectively secrete IL-8, MIP-1beta and TNF-alpha. 19565503_There is a unique role of osteopontin in leukocyte migration, in the context of perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis through the induction of MCP-1 and MIP-1beta. 19620252_An arrestin-dependent multi-kinase signaling complex mediates MIP-1beta/CCL4 signaling and chemotaxis of primary human macrophages. 19841187_Late memory CD8(+) T cells produced abundant amounts of CC chemokines (MIP-1beta, MIP-1alpha, and RANTES) but not IL-2. 19846870_chronic hepatitis C virus infection is associated with an expansion of CD56(-) NK cells functionally skewed toward MIP-1beta production only 19917679_CCL3, CCL4, and CCL5 did not induce chemotaxis, but at relatively high concentrations they transiently enhanced CXCL12-mediated chemotaxis of CD34(+) cord blood cells. 20056178_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20200978_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20482449_Data show that pre-CPB, plasma levels of EGF and MIP-1beta, 2 h following CPB, sVCAM-1, fractalkine and MIP-1ALPHA, and at later time points, sVCAM-1 and IL-6 were associated with AKI. 20503287_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20575639_eleveted tear levels in cystic fibrosis patients 20702408_CCAAT/Enhancer-binding protein {beta} and NF-{kappa}B mediate high level expression of chemokine genes CCL3 and CCL4 by human chondrocytes in response to IL-1{beta}. 20952681_ET-1-mediated MIP-1beta gene expression is regulated via hypoxia-response elements, AP-1, and NF-kappaB cis-binding elements in its promoter and negatively regulated by microRNA-195, which targets the 3' untranslated region of MIP-1beta RNA 20959807_Crystal structures reveal that MIP-1 aggregation is a polymerization process and human MIP-1-alpha and MIP-1-beta form rod-shaped, double-helical polymers. 21030011_In CD8+ T-lymphocyte transwell culture, MIP-1beta and MIP-1alpha strongly correlate with the magnitude of soluble noncytolytic suppression of CXCR4-tropic virus. 21082024_Data show that the ex vivo NKT cell response is predominantly comprised of the chemokines MIP1-alpha, and MIP1-beta as well as the Th1 cytokines IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. 21464938_LPA5 is a bona fide LPA receptor on human mast cells responsible for the majority of LPA induced MIP-1beta release. 21890375_The effect of adiponectin on CCL2, -3, -4, and -5 and their corresponding receptors CCR1, CCR2, and CCR5 has been analyzed. 21914058_study of the involvement of host factors in the rapid progression to fulminant hepatic failure during an outbreak of hepatitis B; NKT cells and CCL4 might be playing a pivotal role in limiting HBV infection among the patients investigated 21978000_Data show that HLA-B*5701+LTNP displayed a higher expansion ability of Gag and Nef-specific MIP(+) TNF(-) IL-2(+) T cells than HLA-B*5701-LTNP. 22085486_Data indicate that IFN2b treatment upregulates the expression of CCR5, RANTES, MIP-1alpha and MIP-1beta on monocytes/macrophages. 22156348_IL-27 priming results in enhanced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced MIP-1beta expression in human primary monocytes 23152559_Tumor-infiltrating monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells produce high levels of transgenic CCR5 ligands CCL3, CCL4, and CCL5 and directly attract regulatory T cells (Tregs) in a CCR5-dependent manner. 23509148_These findings indicate that dipterinyl calcium pentahydrate (DCP) induced mycobacterial killing via MIP-1beta- and nitric oxide-dependent effects. 23760235_Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)-mediated Jun N-terminal protein kinase activation was responsible for upregulation of CCL3 and CCL4 in B cells. 23996681_CCL2 genetic polymorphism is associated with drug-resistant epilepsy in Chinese paediatric patients 23998687_The allele and genotype frequencies of CCL2, CCL3 and CCL4 were not different between HCs and patients with PTB. 24116893_the role of Tax2-mediated activation of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) signalling pathway on the production of the anti-viral CC-chemokines MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta and RANTES. 24370436_Transcription of CCL3 and CCL4 by THP-1 monocytic cells up-regulated in the presence of 27-Hydroxycholesterol and 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol. 24489105_BRAF inhibition causes decreased CXCL8 secretion from melanoma cells and induce an immune response against the tumor associated with increased IFN-gamma, CCL4, and TNF-alpha. 24500432_Report CCL4 expression following resistance exercise. 24797975_MIP-1beta in the ascitic fluid was significantly higher in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. 25004830_suggest possible role of CD8+ cells and CD4+ cells in recruiting T cells to the site of inflammation in sarcoidosis through the release of CCL4. 25063291_Studied expression level of MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta and MCP-1 in psoriasis vulgaris, and explored their roles in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. 25449536_identified 13 ADCC-activated genes. Six gene expression assays including 8 of the 13 genes (CCL3, CCL4/CCL4L1/CCL4L2, CD160, IFNG, NR4A3 and XCL1/XCL2) were analyzed in 127 kidney biopsies 25548252_the secretion of IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-12b, and CCL4 occurs during gelatinase degranulation, a process controlled by STX3. 25620312_Findings demonstrated that miR-125b is a negative regulator of CCL4 and its reduction is partially responsible for the age-related increase of CCL4. 25744730_we found that Brachyury expression was inversely correlated with CCL2 and CCL4 expression in human lung tumors 25889297_CXCL13 and CCL4 could act as circulating biomarkers in autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), and higher plasma soluble TNFRII might favor the diagnosis of SLE-related instead of primary AIHA. 26074318_MIP-1beta, TNF-alpha and fractalkine are expressed in plasma, which reflects the levels of several pro-atherogenic cytokines in plaque tissue 26115437_Elevated pre-treatment levels of CCL4 identified long-term immunological nonresponse patients who started treatment at CD4 counts |
ENSMUSG00000018930 |
Ccl4 |
141.566054 |
47.7454064866 |
5.577290 |
0.314100745 |
637.375481 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001243759817954071625859265002822614192812634007334514027475863400813326549407982147037676100210182521750744257194979589100639821645105440986069269417101445782503092305539654201928488935259393 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000734315796520083940115695176067918622473336326170833943457050494043036254671100992054992665054919895394863642250910572935598973490122962532064393330433812213392979504335204681187405413608615 |
Yes |
No |
280.4630252 |
58.3270160 |
5.9141589 |
1.2050334 |
| ENSG00000275793 |
85376 |
RIMBP3 |
protein_coding |
Q9UFD9 |
FUNCTION: Probable component of the manchette, a microtubule-based structure which plays a key role in sperm head morphogenesis during late stages of sperm development. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q3V0F0}. |
3D-structure;Coiled coil;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Differentiation;Reference proteome;Repeat;SH3 domain;Spermatogenesis |
|
Predicted to enable benzodiazepine receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in fertilization and spermatid development. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in nucleus. Predicted to colocalize with manchette. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:85376; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytoskeleton [GO:0005856]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; benzodiazepine receptor binding [GO:0030156]; fertilization [GO:0009566]; spermatid development [GO:0007286] |
35931115_Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase HIPK4 regulates phosphorylation of manchette protein RIMBP3 during spermiogenesis. |
ENSMUSG00000071636 |
Rimbp3 |
45.700645 |
0.3257352017 |
-1.618228 |
0.326029927 |
24.418774 |
0.00000077509658127513904964691867152670745610976155148819088935852050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002775455007186087519154135336285627033703349297866225242614746093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.6955225 |
5.6538836 |
70.1528617 |
11.8298498 |
| ENSG00000275888 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.727780 |
0.1909605205 |
-2.388654 |
0.588773287 |
17.232017 |
0.00003308140372161550243510982904915351809904677793383598327636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000097480838277309812475723838076646643457934260368347167968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6956451 |
1.3451673 |
19.1592270 |
3.8504311 |
| ENSG00000275964 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.516359 |
0.4242678224 |
-1.236953 |
0.398823067 |
9.814714 |
0.00173121230518021159902608552272340602939948439598083496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003873968105588223697494099084792651410680264234542846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.3629654 |
2.3997216 |
22.2375618 |
3.6396509 |
| ENSG00000276070 |
9560 |
CCL4L2 |
protein_coding |
Q8NHW4 |
FUNCTION: Chemokine that induces chemotaxis of cells expressing CCR5 or CCR1. Inhibits HIV replication in peripheral blood monocytes that express CCR5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:15240137}. |
Alternative splicing;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is one of several cytokine genes that are clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins that function in inflammatory and immunoregulatory processes. The protein encoded by this family member is similar to the chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 4 product, which inhibits HIV entry by binding to the cellular receptor CCR5. The copy number of this gene varies among individuals, where most individuals have one to five copies. This gene copy contains a non-consensus splice acceptor site at the 3' terminal exon found in other highly similar gene copies, and it thus uses other alternative splice sites for the 3' terminal exon, resulting in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:388372;hsa:9560; |
extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547] |
17330138_Neither CCL3L1 nor CCL4L1 gene copy number variation showed appreciable impact on susceptibility to or control of HIV-1 infection. 17330138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18368065_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18464913_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19148142_A combined analysis of CCL4L copy number variation and the rs4796195 CCL4L single nucleotide polymorphism demonstrated that the effect of CCL4L copy number in acute rejection is mainly because of the number of copies of the CCL4L1 allelic variant. 19148142_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19279442_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19898927_higher level of expression at systemic level is associated with protection from HIV-1 infection in women from Benin 20659124_Studies indicate that complete phenotypic impact requires dissecting the combinatorial genomic complexity posed by various proportions of distinct CCL3L and CCL4L genes among individuals. 21614014_CCL4L1 allele frequency is higher in severe psoriasis, whereas CCL4L2 is more frequent in patients with a milder disease. 24727646_PCR results show that lower copy numbers of CCL4L2 are observed in the Caucasian population nd higher copy numbers are observed in the Black population of South Africa. 25449536_identified 13 ADCC-activated genes. Six gene expression assays including 8 of the 13 genes (CCL3, CCL4/CCL4L1/CCL4L2, CD160, IFNG, NR4A3 and XCL1/XCL2) were analyzed in 127 kidney biopsies |
ENSMUSG00000018930 |
Ccl4 |
44.667824 |
21.1168983015 |
4.400326 |
0.432844867 |
132.234368 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000132958283396188379380411689182072369991194713980157691168931594344119671735507219600957995453427429310977458953857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000017320955542168937194984483415346351915094976979478119286504600145695347995528513146412663559203792829066514968872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.4858531 |
23.2493156 |
3.9077248 |
1.0002945 |
| ENSG00000276085 |
6349 |
CCL3L3 |
protein_coding |
P16619 |
FUNCTION: Chemotactic for lymphocytes and monocytes. Is a ligand for CCR1, CCR3 and CCR5. Is an inhibitor of HIV-1-infection. The processed form LD78-beta(3-70) shows a 20-fold to 30-fold higher chemotactic activity and is a very potent inhibitor of HIV-1-infection. LD78-beta(3-70) is also a ligand for CCR1, CCR3 and CCR5. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:10961862, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11449371}. |
Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This gene is one of several cytokine genes that are clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins that function in inflammatory and immunoregulatory processes. The protein encoded by this gene binds to several chemokine receptors, including chemokine binding protein 2 and chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5). CCR5 is a co-receptor for HIV, and binding of this protein to CCR5 inhibits HIV entry. The copy number of this gene varies among individuals, where most individuals have one to six copies, and a minority of individuals have zero or more than six copies. There are conflicting reports about copy number variation of this gene and its correlation to disease susceptibility.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]. |
hsa:414062;hsa:6349; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547] |
15728180_severe periodontal tissue destruction in Papillon-Lefevre syndrome may be related to excess accumulation of LD78beta and LD78alpha and dysregulation of the microbial-induced inflammatory response in the periodontium |
ENSMUSG00000000982 |
Ccl3 |
352.717240 |
10.3229469297 |
3.367783 |
0.156115406 |
459.780851 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000536514951514907734205932456855006590674609223995284735762949821432761962517582761580381279164368661727385746692111571880496246729106953467435456236360053064938376111216025938548209963714319308424282267356302517732663804060053923 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000235683353701191621839028034727152728213809283710567218473111358993095387647738964448421408490196030107836304414611035653098186447561013595707509070180530596209202392353018108354499833462406938125457283032392574996148974886161765 |
Yes |
No |
649.2670018 |
49.9899070 |
63.4322736 |
4.3585620 |
| ENSG00000276231 |
146850 |
PIK3R6 |
protein_coding |
Q5UE93 |
FUNCTION: Regulatory subunit of the PI3K gamma complex. Acts as an adapter to drive activation of PIK3CG by beta-gamma G protein dimers. The PIK3CG:PIK3R6 heterodimer is much less sensitive to beta-gamma G protein dimers than PIK3CG:PIK3R5 and its membrane recruitment and beta-gamma G protein dimer-dependent activation requires HRAS bound to PIK3CG. Recruits of the PI3K gamma complex to a PDE3B:RAPGEF3 signaling complex involved in angiogenesis; signaling seems to involve RRAS. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:21393242}. |
Angiogenesis;Cell membrane;Cytoplasm;Membrane;Reference proteome |
|
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma is a lipid kinase that produces the lipid second messenger phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. The kinase is composed of a catalytic subunit and one of several regulatory subunits, and is chiefly activated by G protein-coupled receptors. This gene encodes a regulatory subunit, and is distantly related to the phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 5 gene which is located adjacent to this gene on chromosome 7. The orthologous protein in the mouse binds to both the catalytic subunit and to G(beta/gamma), and mediates activation of the kinase subunit downstream of G protein-coupled receptors. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2014]. |
hsa:146850; |
cytosol [GO:0005829]; membrane [GO:0016020]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex [GO:0005942]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IA [GO:0005943]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex, class IB [GO:0005944]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase regulator activity [GO:0046935]; phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase activity [GO:0046934]; angiogenesis [GO:0001525]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; immune response [GO:0006955]; positive regulation of angiogenesis [GO:0045766]; positive regulation of MAP kinase activity [GO:0043406]; positive regulation of T cell differentiation [GO:0045582]; regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity [GO:0042269] |
16476736_p87PIKAP is a novel regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma that is highly expressed in heart and interacts with PDE3B [p87PIKAP] 18323525_ablation of PI3Kgamma reduced SDF1alpha-induced integrin activation in human EPCs and in murine Lin(-) BM-derived progenitor cells 18596232_RACK1 regulates directional cell migration by acting on G betagamma at the interface with its effectors PLC beta and PI3K gamma 21996737_knockdown of p84 in MDA-MB-231 cells enhanced Akt phosphorylation and lung colonization 22728827_GPCR activation of Ras and PI3Kc in neutrophils depends on PLCb2/b3 and the RasGEF RasGRP4. 24014027_expression and activities of PI3Kgamma are modified differently by p87 and p101 in vitro and in living cells, arguing for specific regulatory roles of the non-catalytic subunits in the differentiation of PI3Kgamma signaling pathways. 25753393_Our findings suggest that p84 binding to p110gamma may represent a novel negative feedback signal that terminates PI3Kgamma activity. 33155192_RBBP6 aggravates the progression of ovarian cancer by targeting PIK3R6. |
ENSMUSG00000046207 |
Pik3r6 |
17.898703 |
19.6244469489 |
4.294580 |
0.691892379 |
37.920819 |
0.00000000073674846022537241958402860056757087414691653748377575539052486419677734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003561875949206189569298645642564382640671283297706395387649536132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.4076164 |
13.6743215 |
1.0271752 |
0.5273961 |
| ENSG00000276570 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.450898 |
0.1115015687 |
-3.164864 |
0.647947006 |
25.040215 |
0.00000056146975581208333127902288320343338057227811077609658241271972656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002043218342156397879542592543877788102690828964114189147949218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9722676 |
2.0677162 |
27.3740470 |
12.1605663 |
| ENSG00000276724 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.220478 |
0.1531790858 |
-2.706709 |
0.467371752 |
38.993670 |
0.00000000042518191791818000595614705561025789548601494516333332285284996032714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000002093290563199578789639876600747574186822674846553127281367778778076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5367472 |
1.4581939 |
29.8879252 |
4.8860336 |
| ENSG00000276728 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.571696 |
0.2256429419 |
-2.147886 |
0.615238378 |
12.553025 |
0.00039556537818191033276105095239927322836592793464660644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000989416197587696328100137499461652623722329735755920410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4176225 |
1.3300289 |
14.8149507 |
3.1419077 |
| ENSG00000276842 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.659371 |
0.0240617057 |
-5.377117 |
1.123640048 |
34.887391 |
0.00000000349335791136671786971189128704565890481958945201768074184656143188476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000015865219314391618056974425795234429070745818535215221345424652099609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.3168697 |
0.2762821 |
13.2915832 |
3.8271762 |
| ENSG00000277007 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.324886 |
0.2577718483 |
-1.955833 |
0.588408051 |
11.705665 |
0.00062310098976400428352068194826074432057794183492660522460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001505200682636874702155505012513003748608753085136413574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3109957 |
1.3601297 |
12.9976046 |
3.1087039 |
| ENSG00000277247 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.779050 |
0.0468969454 |
-4.414362 |
1.173383875 |
12.368159 |
0.00043671795118933089954391113529652557190274819731712341308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001085177939318943476920686919129366287961602210998535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.3710529 |
1.0079615 |
21.3966959 |
7.7967271 |
| ENSG00000277443 |
4082 |
MARCKS |
protein_coding |
P29966 |
FUNCTION: MARCKS is the most prominent cellular substrate for protein kinase C. This protein binds calmodulin, actin, and synapsin. MARCKS is a filamentous (F) actin cross-linking protein. |
Actin-binding;Calmodulin-binding;Cytoplasm;Cytoskeleton;Lipoprotein;Membrane;Myristate;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is a substrate for protein kinase C. It is localized to the plasma membrane and is an actin filament crosslinking protein. Phosphorylation by protein kinase C or binding to calcium-calmodulin inhibits its association with actin and with the plasma membrane, leading to its presence in the cytoplasm. The protein is thought to be involved in cell motility, phagocytosis, membrane trafficking and mitogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:4082; |
actin cytoskeleton [GO:0015629]; actin filament bundle [GO:0032432]; cell cortex [GO:0005938]; centrosome [GO:0005813]; cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; extracellular exosome [GO:0070062]; focal adhesion [GO:0005925]; germinal vesicle [GO:0042585]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; actin filament binding [GO:0051015]; calmodulin binding [GO:0005516]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; protein kinase C binding [GO:0005080]; actin crosslink formation [GO:0051764]; actin filament bundle assembly [GO:0051017]; actin filament organization [GO:0007015]; apoptotic process [GO:0006915]; central nervous system development [GO:0007417]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; neural tube development [GO:0021915]; neurogenesis [GO:0022008]; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress [GO:0034976] |
11825894_Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) sequesters spin-labeled phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in lipid bilayers. 14506265_role in interaction with calmodulin 15239673_MARCKS proteolysis is necessary for the fusion of myoblasts. 15623535_MARCKS-mediated neurotensin release occurs via protein kinase C-delta downstream of the Rho/ROK pathwaymediated neurotensin release occurs via protein kinase C-delta downstream of the Rho/ROK pathway 15889447_elevations in MARCKS expression are detrimental to specific aspects of hippocampal function 16677610_These findings suggest that some PDBu-induced MARCKS phosphorylation includes the RhoA/ROCK pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. 16941482_Results suggest that unphosphorylated MARCKS is involved in neurite initiation, and highlight the important role played by MARCKS in organization of the actin cytoskeleton. 17292354_We suggest that the downregulation of MRP by beta3 is not required for increased cell spreading but instead that MRP downregulation is a secondary effect of increased cell spreading. 18055557_PKC delta plays an important role in mucin secretion by airway epithelium via regulation of MARCKS phosphorylation. 18314541_First evidence that cysteine string protein and HSP70, and their interactions with MARCKS, are involved in mucin secretion from airway epithelium. 18329017_The present study indicates that MARCKS play a major key role in PDGF-BB-induced chemotaxis in activated human hepatic stellate cells. 18940893_identify MARCKS as a pathogenic contributor to intimal hyperplasia 19302977_These data suggested that miR-21 could promote apoptosis resistance, motility, and invasion in prostate cancer cells and these effects of miR-21 may be partly due to its regulation of PDCD4, TPM1, and MARCKS. 19475567_MARCKS regulates lamellipodia formation induced by IGF-I via association with PIP2 and beta-actin at membrane microdomains. 19574534_MARCKS, via its myristoylated aminoterminus, is a key regulator of neutrophil migration and adhesion. 19773446_Myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS), previously implicated in cell adhesion and motility, contributes to EGFR-mediated invasion of human GBM cells. 19924305_reducing MRP expression promotes formation of adherens junctions in EpRas cells, allowing collective cell migration, but interferes with oncogenic beta-catenin signaling and tumorigenesis 20047593_role for MARCKS as one of the key players in the migration of CCA cells and suggest that cycling between MARCKS and pMARCKS can regulate the metastasis of biliary cancer cells. 20203291_MARCKS and related chaperones bind to unconventional myosin V isoforms in airway epithelial cells 21448919_BK promotes neurite outgrowth through transient MARCKS phosphorylation involving the PKC-dependent RhoA/ROCK pathway and PP2A in a neuroblastoma cell line. 21763456_Relative mRNA expression of MARCKS in white blood cells of O. viverrini-infected patients was higher than in healthy subjects; thus, MARCKS is expressed in macrophages and plays a role in inflammation-related cholangiocarcinoma induced by O. viverrini. 22555845_These findings implicate that MARCKS is essential for proper cytokinesis and that MARCKS and its partner actin are key mitotic regulators during cell cycle in human hepatic stellate cells. 22710197_Cleavage ofMARCKS by Calpain may have an important role in regulation of the PKC/MARCKS pathway regulating airway mucin secretion 22773836_a critical role for H(2)O(2) in angiotensin-II signaling to the endothelial cytoskeleton in a novel pathway that is critically dependent on MARCKS, Rac1, and c-Abl. 23376641_MARCKS plays an articulated role in the progression of colorectal cancer 23377348_heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) and cysteine string protein (CSP), associate with MARCKS in the secretory mechanism in bronchial epithelial cells 23704996_MARCKS is a negative modulator of the acrosomal exocytosis. 23876235_High MARCKS expression is associated with therapeutic responsiveness in breast cancer. 24240590_MARCKS may represent a potential biomarker for the prognosis of primary lung SCC. 24568864_decreased MARCKS and pMARCKS in the frontal cortex in schizophrenia was found; results suggest a mechanism other than myristoylation was responsible for decreased MARCKS expression in schizophrenia 24662837_Finding that MARCKS acts as a mediator of apoptosis in microsatellite stable colorectal cancer cells adds a novel tumor-suppressing function to the established roles of MARCKS in cell motility and proliferation. 24735036_Phospho-MARCKS, a post-translational modification, is associated with cell motility, and has a role in the regulation of cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis. 25179733_MARCKS overexpression was observed in several drug-resistant human myeloma cell lines and in drug-resistant primary multiple myeloma samples. 25318062_results suggest a key role for MARCKS PSD in cancer disease and provide a unique strategy for inhibiting the activity of MARCKS PSD as a treatment for lung cancer. 25515270_isotype delta-PKC is responsible for myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) phosphorylation in human neutrophils following f-Met-Leu-Phe stimulation and MARCKS phosphorylation is essential for neutrophil migration and adhesion. 25524703_A key role of the effector domain of MARCKS in terms of cellular response, particularly to radiation: the importance of MARCKS phosphorylation status for its subcellular localization in lung cancer. 25757715_MARCKS and PPP1R9A might contribute to spine loss in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder through their interactions. 26015406_unresponsiveness of breast cancer to paclitaxel treatment is, at least in part, mediated by phospho-MARCKS 26450120_MARCKS upregulation increases vascular smooth muscle cell motility by activation of Rac1 and Cdc42, promoting neointima formation. 26470026_A novel role for MARCKS in regulating nuclear functions such as gene expression. 26528715_MARCKS knockdown arrested VSMC cell cycle by decreasing KIS expression. Decreased KIS expression resulted in nuclear trapping of p27kip1 in VSMCs. 26722462_Knockdown of MARCKS in HepG2 cells reduced cell migration and invasion, but not cell proliferation. 26818658_Findings suggest that MIR429 modulates mucin secretion in human colorectal cells and mouse colitis tissues by up-regulating of MARCKS expression. 27050372_Data indicate MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate) as a target of miR-21. 27081703_Authors determined that myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) was highly expressed in ovarian stroma, and was required for the differentiation and tumor promoting function of CAFs. 27119641_Ca(2+)-PKC-MARCKS-PIP2-PI3K-PIP3 system functions as an activation module in vitro 27542283_we propose a role for MARCKS in a novel mechanism of BTZ resistance via exocytosis of ubiquitinated proteins in BTZ-resistant cells leading to quenching of proteolytic stress. 27557632_Study identifies MARCKS phosphorylation at Ser46 is a hallmark of neurite degeneration, the classical hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology. MARCKS phosphorylation is induced by HMGB1 via TLR4. 27933776_Findings show that calmodulin (CaM) stimulates phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) lipid kinase activity by binding MARCKS and displacing it from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) headgroups, thereby releasing free PIP2 that recruits active PI3K to the membrane and serves as the substrate for the generation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3). 28009981_MARCKS overexpression might in part explain the poor prognosis of inflammatory breast cancer. 28075441_These data suggested that miR34c3p acts as a tumor suppressor via regulation of MARCKS expression in OS progression 28166200_data suggest a major contribution of MARCKS to kidney cancer growth and provide an alternative therapeutic strategy of improving the efficacy of multikinase inhibitors. 28866462_Raman spectra show vibrational bands of Phenylalanine and Lysine residues specific for the protein effector domain, and evidence the presence of alpha helix structure in both configurations. 29295532_tromal MARCKS overexpression in tumors might contribute to cancer-associated fibroblasts activation and to the poor prognosis of Epithelial ovarian cancer. 29588366_High MARCKS expression is associated with liver tumor. 30209404_MARCKS is a putative target for drug design. 30816497_Study found that the expression of MARCKS was significantly upregulated in glioblastoma (GBM) and was associated with a poor clinical outcome in patients with GBM. Knockdown of MARCKS suppressed the migration and invasion of GBM cells in vitro and reduced the expression of phosphorylated phosphoinositide 3kinase and protein kinase B, as well as SNAI1 expression. 30942445_Study, using a tetracyclineinducible system in PTENnull U87 cells, demonstrated that MARCKS overexpression suppresses growth and enhances radiation sensitivity in vivo. The overexpression of the nonphosphorylatable effector domain (ED) mutant exerted growthsuppressive and radiationsensitizing effects, while the pseudophosphorylated ED mutant exhibited an enhanced colony formation and clonogenic survival ability. 31373006_Morphine at 10(-6) mol/l could benefit miR-543 expression to inhibit MARCKS expression. 31771045_MARCKS was overexpressed in epithelial tumor cells in 66% of the MBC samples versus 26% of normal samples (p= 1.40 x 10-7). Such positive MARCKS expression in epithelial tumor cells was associated with positive HER2 status (p= 4.0 x 10-3). 32056006_Cells devoid of MARCKS function showed incomplete ABCB1 internalization, leading to higher ABCB1 activity enhancing chemoresistance. 32182160_Multiplexed Phosphoproteomic Study of Brain in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease and Age-Matched Cognitively Healthy Controls. 32220540_MARCKS inhibition cooperates with autophagy antagonists to potentiate the effect of standard therapy against drug-resistant multiple myeloma. 33735912_MARCKS affects cell motility and response to BTK inhibitors in CLL. 33754052_MARCKS cooperates with NKAP to activate NF-kB signaling in smoke-related lung cancer. 34279157_MARCKS on Tumor-Associated Macrophages is Correlated with Immune Infiltrates and Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. 34509657_The myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrates (MARCKS): A membrane-anchored mediator of the cell function. |
ENSMUSG00000069662 |
Marcks |
592.640333 |
2.0160704008 |
1.011546 |
0.070087607 |
209.487662 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001776822189496462863274048355267925994623932573368609887164896804828199275157427909008356468384558055513108228658816057461342086121192096470622345805168151855468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000355846614884230525542563274499934325200676070285405947864002209701354721075784183359745884692989221427983151854463998720046191692745196633040904998779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
802.4244847 |
34.2440390 |
401.0608153 |
13.2976497 |
| ENSG00000277476 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.656525 |
0.2689463444 |
-1.894610 |
0.391356945 |
24.992849 |
0.00000057543348235325449827531419169646120792549481848254799842834472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002089910974294792338006813287032414905297628138214349746704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6898044 |
2.3123457 |
29.1183538 |
5.3348558 |
| ENSG00000277496 |
|
SLCO4A1-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.198763 |
0.4523920919 |
-1.144354 |
0.421331666 |
7.545322 |
0.00601660666766383467329859513483825139701366424560546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012085617095089574990485203898060717619955539703369140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.4269413 |
2.2542633 |
18.6897519 |
3.1318088 |
| ENSG00000277561 |
|
GOLGA8IP |
transcribed_unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.458886 |
0.0333065619 |
-4.908050 |
0.868840663 |
34.310321 |
0.00000000469883355209796856178512648120199068912938855646643787622451782226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000021151199520880150624391427441155222322066720153088681399822235107421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2888538 |
1.0443992 |
44.5779995 |
19.7575902 |
| ENSG00000277632 |
6348 |
CCL3 |
protein_coding |
P10147 |
FUNCTION: Monokine with inflammatory and chemokinetic properties. Binds to CCR1, CCR4 and CCR5. One of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ T-cells. Recombinant MIP-1-alpha induces a dose-dependent inhibition of different strains of HIV-1, HIV-2, and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:8525373}. |
3D-structure;Chemotaxis;Cytokine;Direct protein sequencing;Disulfide bond;Inflammatory response;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal |
|
This locus represents a small inducible cytokine. The encoded protein, also known as macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha, plays a role in inflammatory responses through binding to the receptors CCR1, CCR4 and CCR5. Polymorphisms at this locus may be associated with both resistance and susceptibility to infection by human immunodeficiency virus type 1.[provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]. |
hsa:6348; |
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; cytosol [GO:0005829]; extracellular region [GO:0005576]; extracellular space [GO:0005615]; calcium-dependent protein kinase C activity [GO:0004698]; CCR chemokine receptor binding [GO:0048020]; CCR1 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031726]; CCR5 chemokine receptor binding [GO:0031730]; chemoattractant activity [GO:0042056]; chemokine activity [GO:0008009]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; kinase activity [GO:0016301]; phospholipase activator activity [GO:0016004]; protein kinase activity [GO:0004672]; astrocyte cell migration [GO:0043615]; calcium ion transport [GO:0006816]; calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0019722]; cell activation [GO:0001775]; cell-cell signaling [GO:0007267]; cellular calcium ion homeostasis [GO:0006874]; cellular response to interleukin-1 [GO:0071347]; cellular response to organic cyclic compound [GO:0071407]; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor [GO:0071356]; cellular response to type II interferon [GO:0071346]; chemokine-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0070098]; chemotaxis [GO:0006935]; cytoskeleton organization [GO:0007010]; eosinophil chemotaxis [GO:0048245]; eosinophil degranulation [GO:0043308]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway [GO:0007186]; granulocyte chemotaxis [GO:0071621]; inflammatory response [GO:0006954]; lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway [GO:0031663]; lymphocyte chemotaxis [GO:0048247]; macrophage chemotaxis [GO:0048246]; MAPK cascade [GO:0000165]; monocyte chemotaxis [GO:0002548]; negative regulation by host of viral transcription [GO:0043922]; negative regulation of bone mineralization [GO:0030502]; negative regulation of gene expression [GO:0010629]; negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation [GO:0045671]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593]; osteoblast differentiation [GO:0001649]; positive regulation of calcium ion import [GO:0090280]; positive regulation of calcium ion transport [GO:0051928]; positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050850]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade [GO:0070374]; positive regulation of gene expression [GO:0010628]; positive regulation of GTPase activity [GO:0043547]; positive regulation of inflammatory response [GO:0050729]; positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production [GO:0032731]; positive regulation of microglial cell activation [GO:1903980]; positive regulation of microglial cell migration [GO:1904141]; positive regulation of natural killer cell chemotaxis [GO:2000503]; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043525]; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling [GO:0051897]; positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production [GO:0032760]; protein kinase B signaling [GO:0043491]; regulation of behavior [GO:0050795]; regulation of cell shape [GO:0008360]; regulation of sensory perception of pain [GO:0051930]; release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0014808]; response to cholesterol [GO:0070723]; response to toxic substance [GO:0009636]; signaling [GO:0023052]; T cell chemotaxis [GO:0010818] |
11861262_Inhibition of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha production by Epstein-Barr virus. 12186702_enhances the migration of bone marrow stromal cells 12200385_role in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma 12218153_Expression of MIP-1 alpha is induced by stimulation of monocytic cells through Fc gamma receptors and involves activation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta sites. 12370381_Burned patients seem to be more susceptible to infectious complications when the production of MIP-1 alpha is impaired. 12377943_role of IL-12 and IFN-gamma on inducing inflammatory chemokine (MIP-1alpha) secretion and down-regulating CCR5 expression in human T cells 12393595_After stimulation via high-affinity FcepsilonRI, the transcriptional levels of I-309 (CCL1), MIP-1alpha (CCL3) and MIP-1beta (CCL4) were found among the 10 most increased human and mouse transcripts from approximately 12 000 genes 12393716_Lymphotactin, (MIP)-1alpha, and MIP-1beta chemokines were all rapidly induced by engagement of CD28 and were calcineurin sensitive. 12401480_MIP-1alpha and MIP-1beta show diverging signaling capacities [review] 12408680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12413001_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12413001_The polymorphisms of the MCP-1 and MIP-1A genes do not play a substantial role in genetic predisposition for sarcoidosis or in clinical manifestations of sarcoidosis in this Japanese population. 12447751_may not only mark a subset of patients with a greater risk of having more severe disease but also may play a relevant pathophysiological role in human schistosomiasis mansoni 12506012_Besides its role in development of osteolytic bone destruction, MIP-1 alpha also directly affects cell signaling pathways mediating growth, survival, and migration in MM cells and might play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of MM. 12560229_AML-1A and AML-1B regulate the expression of this protein in multiple myeloma cells. 12603824_IL-1beta-induced MIP-1alpha and -1beta expression in NT2-N cells 12651610_Cathepsin D specifically cleaves this protein that is expressed in human breast cancer. 12651617_Potential interaction between CCR1 and its ligand, this protein is enduced by endogenously produced interleukin-1 in human hepatomas. 12771199_Transcriptional activation of the MIP-1alpha promoter by RUNX1 and MOZ. 14680814_Therefore, soluble factors such as prostaglandin E(2) released from lung fibroblasts are responsible for the co-culture-induced inhibition of macrophage-derived MIP-1alpha production. 14733721_MIP-1-alpha is substantially regulated upon monocyte contact with various cell wall components from Gran-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. 15077296_Collagen II-reactive T cells in rheumatoid arthritis joints can increase the production of chemokines such as IL-8, MCP-1, and MIP-1 alpha through interaction with synoviocytes. 15585099_lymphocytes of HIV patients display a disrupted capacity to secrete the beta-chemokines MIP-1 alpha and MIP-1 beta, which may constitute a mechanism of immune dysfunction in progressive HIV infection 15588341_produced by neonatal natural killer cells and contributes to suppession of HIV replication 15602730_Role in the development of bronchiolitis associated with influenza and RSV infections in infants and children. 15728180_severe periodontal tissue destruction in Papillon-Lefevre syndrome may be related to excess accumulation of LD78beta and LD78alpha and dysregulation of the microbial-induced inflammatory response in the periodontium 16234357_Involvement of the 3 10 helical-turn motif in chemokine function identifies a novel, functionally essential motif within chemokines. 16379602_Higher amounts of MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta, and RANTES were detected in plasma of HIV-1-positive individuals, particularly those with concomitant pulmonary tuberculosis, although the increase was not found to be statistically significant. 16427155_HIV p17 was able to reduce MIP-1alpha secretion in IL-15 stimulated monocytes 16439481_Levels of MIP-1alpha are low in plasma and follicular fluid of both menstrual and in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles. 16507178_High levels of CCL3 are present in synovial fluid of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 16712957_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16849642_MIP-1 alpha promoter function, gene expression, and protein secretion were each down-regulated following inhibition of FGFR3 signaling. 17005260_findings show that CCL3, CCL4 and CCL5 bind on the Leishmania promastigotes 17270460_MIP-1alpha and other chemokines may constitute a link between the innate immune system and familial Mediterranean fever 17330138_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17357337_CCL3 concentration was much lower in CSF than in serum of the tickborne encephalitis patients, which argues against its significant role as chemoattractant in this condition. 17572013_found a negative correlation between the tear levels of MIP-1alpha and clinical severity in Cystic fibrosis (CF) patients and a positive correlation between the tear levels of MIP-1alpha and the presence of dry eye findings in CF patients 17625600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17656823_brain Alzheimer's disease-derived microvessels express high levels of MIP-1alpha mRNA and release high levels of MIP-1alpha protein 17914560_Significantly higher expression of CCL3 is associated with tumor metastasis and local host defense in oral squamous cell carcinoma 18070228_CCL2 and CCL3 induce both immediate and delayed skin reactions in atopics and nonatopics, and evoke a similar profile of local T cell/macrophage and granulocyte recruitment 18076643_The strong upregulation of CCL3 and CCL4 implicates these chemokines in the etiology and pathogenesis of TLE. 18164590_TNF-alpha unveils a previously unknown capacity of neutrophils to migrate to CCL3 through the intervention of Mac-1. 18196935_Plasma soluble CD40 ligand and stimulated MIP-1alpha production were both reduced (p |
ENSMUSG00000000982 |
Ccl3 |
628.124442 |
20.6243255225 |
4.366275 |
0.116718396 |
1792.760321 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1220.1855134 |
87.7553687 |
59.6015942 |
4.0346067 |
| ENSG00000277701 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
61.729374 |
0.4607020748 |
-1.118094 |
0.217210969 |
26.595620 |
0.00000025081166008814340688122773541379739725698527763597667217254638671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000948253100128328991917702004560419837275730969849973917007446289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
38.8555234 |
9.6131574 |
84.1303584 |
14.7267375 |
| ENSG00000277782 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.534768 |
0.2609498012 |
-1.938156 |
0.507598075 |
15.660588 |
0.00007578707433607634129900387787159843355766497552394866943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000212382232238558354281421358678016986232250928878784179687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4853004 |
1.4850982 |
17.2828409 |
3.1730194 |
| ENSG00000277938 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.363940 |
0.3517609102 |
-1.507333 |
0.519364273 |
8.805182 |
0.00300376169890686616631425565060453664045780897140502929687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006434598532799789237512921857842229655943810939788818359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4612196 |
1.5097206 |
12.6603326 |
2.5010680 |
| ENSG00000277954 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.268155 |
0.2077264448 |
-2.267243 |
0.452928777 |
26.934873 |
0.00000021042763374889351513928094101341104149582861282397061586380004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000801939549221189841010366643192508462334444629959762096405029296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8384471 |
1.7946645 |
28.3901990 |
4.8992414 |
| ENSG00000277978 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.158633 |
0.4293778227 |
-1.219680 |
0.372572245 |
11.012549 |
0.00090497089319147830301787172047056628798600286245346069335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002125277706206240256603390292866606614552438259124755859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1466409 |
2.4622158 |
23.9870412 |
3.5771609 |
| ENSG00000278133 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.007897 |
0.4880244589 |
-1.034975 |
0.465878962 |
4.927184 |
0.02643736190529949112160146285077644279226660728454589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.046053990525459748139880389317113440483808517456054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.1157168 |
2.3018572 |
16.7975985 |
3.2591746 |
| ENSG00000278535 |
79154 |
DHRS11 |
protein_coding |
Q6UWP2 |
FUNCTION: Catalyzes the conversion of the 17-keto group of estrone, 4- and 5-androstenes and 5-alpha-androstanes into their 17-beta-hydroxyl metabolites and the conversion of the 3-keto group of 3-, 3,17- and 3,20- diketosteroids into their 3-hydroxyl metabolites. Exhibits reductive 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity toward 5-beta-androstanes, 5-beta-pregnanes, 4-pregnenes and bile acids. May also reduce endogenous and exogenous alpha-dicarbonyl compounds and xenobiotic alicyclic ketones. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26920053}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Lipid metabolism;NADP;Nucleotide-binding;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Steroid metabolism |
PATHWAY: Steroid biosynthesis; estrogen biosynthesis. {ECO:0000305|PubMed:26920053}. |
Enables 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity; 17-beta-ketosteroid reductase activity; and 3-keto sterol reductase activity. Involved in steroid biosynthetic process. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:79154; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD+) activity [GO:0044594]; 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity [GO:0072582]; 17-beta-ketosteroid reductase activity [GO:0072555]; 3-keto sterol reductase activity [GO:0000253]; cycloeucalenone reductase activity [GO:0102176]; estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase activity [GO:0004303]; nucleotide binding [GO:0000166]; estrogen biosynthetic process [GO:0006703]; steroid biosynthetic process [GO:0006694] |
26920053_The recombinant protein (DHRS11) efficiently catalyzed the conversion of the 17-keto group of estrone, 4- and 5-androstenes and 5alpha-androstanes into their 17beta-hydroxyl metabolites with NADPH as a coenzyme. 31926269_Human dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family member 11 (DHRS11) and aldo-keto reductase 1C isoforms in comparison: Substrate and reaction specificity in the reduction of 11-keto-C19-steroids. |
ENSMUSG00000034449 |
Dhrs11 |
33.398307 |
0.4148899529 |
-1.269199 |
0.327855967 |
15.147699 |
0.00009941940664987520908345286496654580332688055932521820068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000273468215086127095642121176410910265985876321792602539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
20.4176932 |
4.2900921 |
49.5825425 |
6.7492295 |
| ENSG00000278704 |
|
|
protein_coding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.573366 |
0.3214118968 |
-1.637505 |
0.434997516 |
14.477929 |
0.00014181138102421783435923285932034332290641032159328460693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000381193950813595928191895856329551861563231796026229858398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2453743 |
2.4198698 |
25.8419205 |
4.7923114 |
| ENSG00000278727 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.034403 |
2.7930707992 |
1.481852 |
0.367818362 |
16.706936 |
0.00004362122855058422112852975494057261585112428292632102966308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000126766948888880310675544849097207134036580100655555725097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.9033405 |
6.8383532 |
10.3783303 |
1.9816437 |
| ENSG00000278784 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.205428 |
0.4471779153 |
-1.161079 |
0.314151929 |
14.042668 |
0.00017870925462114286793625927973749867305741645395755767822265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000472460791368094006840300247418440449109766632318496704101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.1528341 |
2.6582828 |
29.6276094 |
3.7768889 |
| ENSG00000278864 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.444896 |
0.1884073178 |
-2.408073 |
0.389317553 |
41.819934 |
0.00000000010007787083491965292982302733717689911807635638751889928244054317474365234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000518116230629047408711678647253709092956874826541024958714842796325683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.9547732 |
1.7629528 |
37.0311907 |
5.1621002 |
| ENSG00000278895 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.154219 |
0.4618408141 |
-1.114532 |
0.380714167 |
8.585769 |
0.00338800237920771490918170343320525716990232467651367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007172535157358845420150217364607669878751039505004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1726483 |
2.8556760 |
26.3114444 |
3.9020718 |
| ENSG00000278931 |
|
|
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.581091 |
0.3624948300 |
-1.463968 |
0.470287952 |
10.120398 |
0.00146637322377343812945804657488224620465189218521118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003326724374868728593968025819549438892863690853118896484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8653101 |
1.7869650 |
16.3746785 |
2.9365937 |
| ENSG00000278949 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.852254 |
0.4232531151 |
-1.240407 |
0.531551438 |
5.512336 |
0.01888281535186070447807082928193267434835433959960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.034047196994070855202707548414764460176229476928710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5128938 |
2.3067110 |
15.4584552 |
3.5452679 |
| ENSG00000279019 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
75.761073 |
0.0673624597 |
-3.891911 |
0.318139151 |
175.576612 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000044801308699913783081464481054263695979865704106496969886242969138932821278695917915450675121324694929504650620089023504988290369510650634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000007463513729240717149262245985756911023390253793322600326060860322343452960862492192017632686814774482103596042747994943056255578994750976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6235357 |
2.0682374 |
143.9013462 |
15.3209989 |
| ENSG00000279080 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.426606 |
0.4960922191 |
-1.011320 |
0.318994007 |
10.050730 |
0.00152287579166789869417053537858919298741966485977172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003445906283154712233113281527607796306256204843521118164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.9672788 |
3.2309055 |
34.5247464 |
4.2637183 |
| ENSG00000279088 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.059906 |
0.1820777320 |
-2.457374 |
0.664950411 |
11.655065 |
0.00064027958033136109141508773845430368965025991201400756835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001544150068515238180891224750723722536349669098854064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7793938 |
5.4096140 |
59.9120948 |
20.7270464 |
| ENSG00000279089 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.604533 |
0.4069007286 |
-1.297251 |
0.506844874 |
6.675489 |
0.00977477075385401253382333663921599509194493293762207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018776108319480115660393693133300985209643840789794921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3352860 |
2.0928975 |
15.5680065 |
3.2339835 |
| ENSG00000279108 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.445709 |
0.1613467925 |
-2.631763 |
0.689525714 |
16.646990 |
0.00004502170030173593414475272100894187587982742115855216979980468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000130554085747273550168617850530949908716138452291488647460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.1141855 |
0.9752008 |
13.2110119 |
3.0200693 |
| ENSG00000279159 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.438446 |
0.4020306194 |
-1.314623 |
0.239474774 |
30.733881 |
0.00000002959521303284276918761909968245971125355708863935433328151702880859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000123194815512263824198809403394350159288705981452949345111846923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.2582997 |
3.9489568 |
68.3456109 |
6.1508427 |
| ENSG00000279198 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.749935 |
0.4643752326 |
-1.106637 |
0.503272892 |
4.921863 |
0.02651889952156081392553588216287607792764902114868164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.046190577878007739454080393670665216632187366485595703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1855476 |
2.0012888 |
13.3773443 |
2.7597193 |
| ENSG00000279217 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.178680 |
0.4836382272 |
-1.048000 |
0.416076507 |
6.407935 |
0.01136114996373076800606494174417093745432794094085693359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021540214960136947613955626934512110892683267593383789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.4992874 |
2.3997119 |
19.8310490 |
3.2289578 |
| ENSG00000279254 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.781170 |
0.0248382209 |
-5.331294 |
1.125623959 |
35.585696 |
0.00000000244073196118826454563120764186534561446251245797611773014068603515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011270692429052158091070206494439809308261146725271828472614288330078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2825639 |
0.2370201 |
11.3591742 |
2.9881254 |
| ENSG00000279267 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.665394 |
2.8107869159 |
1.490974 |
0.320120697 |
22.199065 |
0.00000245793523776163892925620060858626914068736368790268898010253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008318991999395044923781665502371396314629237167537212371826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.2195328 |
7.5914458 |
14.0514896 |
2.2198136 |
| ENSG00000279278 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.180369 |
0.4917950088 |
-1.023871 |
0.346938679 |
8.750862 |
0.00309455724938655822933708527955332101555541157722473144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006605302241640722583915223964368124143220484256744384765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.5459889 |
3.9187986 |
35.8498643 |
5.3253223 |
| ENSG00000279289 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.853001 |
0.3359596744 |
-1.573640 |
0.553506397 |
8.251875 |
0.00407099245401792465826051881094826967455446720123291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008476209426055094156571279029321885900571942329406738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.3495141 |
1.5974292 |
13.0198651 |
2.9033652 |
| ENSG00000279322 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.219664 |
15.5035979721 |
3.954531 |
0.961437912 |
16.866010 |
0.00004011353007724480722838433788268730495474301278591156005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000116872424780918557937585411377057198478723876178264617919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.7579412 |
13.6310137 |
1.5440336 |
0.7694293 |
| ENSG00000279382 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.596859 |
0.2842990972 |
-1.814519 |
0.319411989 |
33.749952 |
0.00000000626706042405422546751796522568334069092088611796498298645019531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000027828463254825621849296762898642865202702978422166779637336730957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.1353621 |
2.8226461 |
42.8936790 |
6.1539494 |
| ENSG00000279425 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.328318 |
0.3533514064 |
-1.500824 |
0.504672499 |
9.170785 |
0.00245909037353322749985817807782950694672763347625732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005344672816490985030324356586106659960933029651641845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5393094 |
1.8023206 |
15.7280773 |
3.0833949 |
| ENSG00000279457 |
|
WASH9P |
unprocessed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
161.838645 |
0.3164146440 |
-1.660112 |
0.237283984 |
47.147211 |
0.00000000000658502837201574008785704655313110553616767761653250090603251010179519653320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000036984405925019911299707965080527712758984293373032414820045232772827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
73.3056053 |
12.2640445 |
232.3613677 |
26.9093447 |
| ENSG00000279605 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.537893 |
0.3114344448 |
-1.683000 |
0.453816500 |
13.382441 |
0.00025399096308390429208370897562474510777974501252174377441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000654716488843595442737033351932041114196181297302246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.7370021 |
3.4373058 |
32.5217102 |
7.5284984 |
| ENSG00000279631 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.809661 |
0.3666555906 |
-1.447503 |
0.361190970 |
16.505939 |
0.00004849792854252634951867789725454827021167147904634475708007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000139892402831285711604231147831001180747989565134048461914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5722654 |
2.5543946 |
28.9648698 |
4.3618516 |
| ENSG00000279649 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.291655 |
0.4723415073 |
-1.082098 |
0.370932703 |
8.673737 |
0.00322828533187059091291715162697073537856340408325195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006859990137980120222804814034134324174374341964721679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8189816 |
2.6422187 |
23.0411283 |
3.6403015 |
| ENSG00000279713 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.043474 |
0.1926435087 |
-2.375995 |
0.424927443 |
33.818024 |
0.00000000605155912348360409221075838291474535690639413587632589042186737060546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000026936372938063329865486446616437699042023723450256511569023132324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.0182596 |
1.7412560 |
31.4549642 |
5.1953631 |
| ENSG00000279780 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.055810 |
0.1007852597 |
-3.310643 |
0.768375398 |
25.091373 |
0.00000054676920967493153018907335594089857977451174519956111907958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001994147154633552955911275986200514864776778267696499824523925781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1749331 |
0.6504160 |
11.8071260 |
2.8467840 |
| ENSG00000279801 |
112268198 |
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.494956 |
0.2975114670 |
-1.748983 |
0.459369892 |
15.229253 |
0.00009521700883722966082204491877760688112175557762384414672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000262692158960282245473705220462079523713327944278717041015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3126914 |
1.9459189 |
21.3297278 |
3.9314758 |
| ENSG00000279821 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.112574 |
0.4771545379 |
-1.067472 |
0.340803491 |
9.950389 |
0.00160815422458764198040959136903893522685393691062927246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003621106995410159484771739357711339835077524185180664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.0438438 |
3.0022623 |
29.7690987 |
4.0466427 |
| ENSG00000279833 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.985522 |
0.0775328487 |
-3.689049 |
0.763475581 |
32.566612 |
0.00000001151764413576951150405743582241790967657379951560869812965393066406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000049897395786309946291148649738858567026511536823818460106849670410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.2688325 |
0.6752638 |
16.4517748 |
3.4368536 |
| ENSG00000279846 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
113.701430 |
0.1571555534 |
-2.669735 |
0.190777157 |
213.789916 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000204666998694066438486163774826141100029188791359433705649075682867283676512961519681498983563193125111066828405444841177578466084874264652171405032277107238769531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000042073605859671594688039972011522661837644713191276753023638090070932486507643065841110191094962347815101388197440258421080927497825996397295966744422912597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.7391357 |
3.9807470 |
196.5259864 |
14.2581819 |
| ENSG00000279907 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.482747 |
0.0864703839 |
-3.531650 |
0.732767569 |
30.222180 |
0.00000003852782177158580207418299727259447529092994955135509371757507324218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000158315882335358126632365990613116046858976915245875716209411621093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.4477877 |
0.7765901 |
16.6865960 |
4.1825311 |
| ENSG00000279930 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.829091 |
0.2241868262 |
-2.157227 |
0.579828690 |
15.540467 |
0.00008075784934339199023015098966027380811283364892005920410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000225030367435995046947530551229021966719301417469978332519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.7925993 |
1.1325986 |
12.5680882 |
2.7481215 |
| ENSG00000279933 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.266959 |
0.4255174402 |
-1.232710 |
0.396002783 |
9.818218 |
0.00172791680640565635702909919046987852198071777820587158203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003867179994321074364138635104382046847604215145111083984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.5702063 |
2.6192499 |
25.1237470 |
3.9161195 |
| ENSG00000279970 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41.921221 |
0.1739161393 |
-2.523536 |
0.639292926 |
13.955842 |
0.00018715519096589676158008674899946299774455837905406951904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000493111499224676208194551030317143158754333853721618652343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.4332315 |
6.1222338 |
66.4752559 |
24.5450261 |
| ENSG00000280007 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.450695 |
0.1777639805 |
-2.491965 |
0.312018781 |
69.124136 |
0.00000000000000009245694630317750577802193433391112215642533919560466793008401964470976963639259338378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000699469260602204029475801495514502235231732766261580902522609903826378285884857177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.8313845 |
2.5084845 |
67.0197254 |
8.0692286 |
| ENSG00000280061 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.780253 |
0.2243944366 |
-2.155891 |
0.360836714 |
39.464797 |
0.00000000033402708313022313287707168403812933721308553458584356121718883514404296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001665059016211446428731522820037777576906989907001843675971031188964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2519804 |
1.9080973 |
37.1880467 |
4.5071549 |
| ENSG00000280077 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.920906 |
0.4193148997 |
-1.253894 |
0.275591922 |
21.270131 |
0.00000398898834733100398459385710348001907732395920902490615844726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000013139359073109935577218683466771409484863397665321826934814453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
19.2688323 |
3.4152894 |
46.4043707 |
5.1369439 |
| ENSG00000280143 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.937425 |
0.2900863231 |
-1.785446 |
0.727106832 |
5.789320 |
0.01612382088262763468744509509633644483983516693115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029516010942277549899959154799944371916353702545166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.1332938 |
5.1406013 |
25.3813351 |
12.4753675 |
| ENSG00000280163 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.974679 |
0.1491448267 |
-2.745214 |
0.735797125 |
17.039630 |
0.00003660775292010767979376459346774197456397814676165580749511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000107080941954179422229663509735786419696523807942867279052734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.5531343 |
0.7986684 |
10.4821027 |
2.5178519 |
| ENSG00000280165 |
64881 |
PCDH20 |
protein_coding |
Q8N6Y1 |
FUNCTION: Potential calcium-dependent cell-adhesion protein. |
Calcium;Cell adhesion;Cell membrane;Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Repeat;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the protocadherin gene family, a subfamily of the cadherin superfamily. This gene encodes a protein which contains 6 extracellular cadherin domains, a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic tail differing from those of the classical cadherins. Although its specific function is undetermined, the cadherin-related neuronal receptor is thought to play a role in the establishment and function of specific cell-cell connections in the brain. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
hsa:64881; |
plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; calcium ion binding [GO:0005509]; RNA binding [GO:0003723]; cell adhesion [GO:0007155]; homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules [GO:0007156] |
24910204_In conclusion, these data here strongly suggested that PCDH20 may act as a candidate tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. 25736877_Study shows that PCDH20 expression is downregulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells (NPC) and identified it as a functional tumor suppressor and an important antagonist of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and EMT, with frequent epigenetic inactivation in NPC. 26188009_Genome-wide association analysis on normal hearing function identifies PCDH20 and SLC28A3 as good candidates for modulatory genes in the auditory system. [meta-analysis] 27935871_low expression of PCDH20 was found to be associated with poor OS in HCC patients; hence, this protein represents a promising potential prognostic biomarker 31450490_Low PCDH20 expression is associated with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma through the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. |
ENSMUSG00000050505 |
Pcdh20 |
132.997546 |
4.8760575047 |
2.285715 |
0.165865726 |
199.751015 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000236682567259323979692603946349021105950731541225683080049220679212825009579685946401567577010766381812727158221376297375648789511615177616477012634277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000045134815151778061822591010965268369706331508213281353924758563823949618859485842317480220177437630130235860230654421076934568191063590347766876220703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
224.0335888 |
21.7554932 |
46.2724225 |
3.8623588 |
| ENSG00000280195 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.821295 |
0.4952391920 |
-1.013803 |
0.386777372 |
7.009066 |
0.00810979806723426122072595489953528158366680145263671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015841797177392494266889855225599603727459907531738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.8167265 |
2.3151519 |
19.9440263 |
2.9623283 |
| ENSG00000280211 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.880473 |
0.1399230988 |
-2.837294 |
0.928654486 |
8.706017 |
0.00317161486454675504986777667681963066570460796356201171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006751230949049624903424149380271046538837254047393798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7548222 |
3.1777643 |
27.0540218 |
14.9766058 |
| ENSG00000280213 |
100113386 |
UCKL1-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.230309 |
0.4511410106 |
-1.148350 |
0.480575028 |
5.819023 |
0.01585374733805173380618569467515044379979372024536132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029057656861994733688003833549373666755855083465576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.0169942 |
2.2646740 |
15.6647132 |
3.2588364 |
| ENSG00000280239 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.641290 |
0.3064392704 |
-1.706327 |
0.451451970 |
15.096632 |
0.00010214539163370043694644556664385959265928249806165695190429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000280548191386940514065184704151079131406731903553009033203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8104694 |
1.6819557 |
19.0573792 |
3.2028543 |
| ENSG00000280244 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.466830 |
0.2980731669 |
-1.746262 |
0.533518424 |
11.495475 |
0.00069765844313296248788147657649005850544199347496032714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001671662113740669851694176095691091177286580204963684082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6397436 |
1.2946065 |
12.3028917 |
2.5198976 |
| ENSG00000280254 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.586533 |
0.3088530129 |
-1.695008 |
0.534823650 |
10.380259 |
0.00127369818582426935771323428525647614151239395141601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002917862055372686270332538427396684710402041673660278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9635220 |
1.7126775 |
15.9519301 |
3.1722682 |
| ENSG00000280303 |
|
ERICD |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50.181422 |
6.2325465505 |
2.639822 |
0.321697177 |
68.018160 |
0.00000000000000016199663656483215256027915855815775690665166597521917868363061643321998417377471923828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000001208221503636646075306209337906936189519611240562879661553097321302630007266998291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.8936873 |
15.9277141 |
14.1563305 |
2.2199900 |
| ENSG00000280332 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.621144 |
0.2603880332 |
-1.941265 |
0.461730446 |
19.017874 |
0.00001294996802445096345871022869289390655467286705970764160156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000040088407726698032263346754833222007619042415171861648559570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0553631 |
1.6165542 |
19.5654621 |
3.6187053 |
| ENSG00000280378 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.000673 |
0.3688548735 |
-1.438875 |
0.536046374 |
7.549634 |
0.00600222513468740524744671205326085328124463558197021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012063295613832529865061538032477983506396412849426269531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5566943 |
1.6057144 |
12.4863474 |
2.5835353 |
| ENSG00000280383 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.801800 |
0.3649196852 |
-1.454349 |
0.370362295 |
15.850802 |
0.00006853748432995644169780230514632535232522059231996536254882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000193499095009593940737782635785890761326299980282783508300781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.7204354 |
2.4710084 |
29.5946173 |
4.1507643 |
| ENSG00000280407 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.783058 |
0.3630482188 |
-1.461767 |
0.574592915 |
6.481502 |
0.01090028484342697723263881925959140062332153320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020751735365533624522171862736286129802465438842773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7606279 |
2.6140112 |
21.4774452 |
4.6127948 |
| ENSG00000280414 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.632973 |
0.2878804830 |
-1.796458 |
0.441046409 |
17.535422 |
0.00002820046137174424315339354984999431508185807615518569946289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000083817722482268429504831397380826274456921964883804321289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5994139 |
1.9293246 |
22.7706857 |
3.8137283 |
| ENSG00000280434 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.097620 |
0.4724321060 |
-1.081821 |
0.415102323 |
6.958227 |
0.00834346635990606579069694959116532118059694766998291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016242358674784164451754264746341505087912082672119140625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.7983266 |
2.0464375 |
16.6261635 |
2.7136293 |
| ENSG00000280486 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.470366 |
0.2349529048 |
-2.089556 |
0.674293400 |
9.952457 |
0.00160634875554060258494304402887564720003865659236907958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003617593474485702575299539418551830749493092298507690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.1190866 |
1.5179601 |
12.8629884 |
3.7093678 |
| ENSG00000280543 |
100507117 |
ASAP1-IT2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.858150 |
0.3831719155 |
-1.383936 |
0.527287230 |
7.136781 |
0.00755186175650871850673073737425511353649199008941650390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014850183789777336718085365419028676114976406097412109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0382606 |
1.6757222 |
13.2746780 |
2.6444773 |
| ENSG00000280721 |
|
LINC01943 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.056320 |
0.3744910279 |
-1.416997 |
0.437015352 |
10.778558 |
0.00102682624375757922292884405379709278349764645099639892578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002384511541513824415400302214607108908239752054214477539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6276677 |
2.2527432 |
20.5650113 |
3.7952310 |
| ENSG00000280832 |
|
GSEC |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
55.346525 |
0.3257893729 |
-1.617989 |
0.247955734 |
42.913233 |
0.00000000005722227701018319422535462869012113252403795016221010882873088121414184570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000300676685179887492860715426590202843659671572140723583288490772247314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.6557297 |
4.9343751 |
85.4513542 |
10.0817774 |
| ENSG00000280927 |
285463 |
CTBP1-AS |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25552498_CTBP1-AS, a novel androgen receptor regulator, is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in Chinese women. 31165609_Overexpressed LncRNA CTBP1-AS promoted breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion as well as migration, inhibited cell apoptosis and accelerated breast cancer development by sponging microRNA-940. 34611799_Androgen receptor coregulator long noncoding RNA CTBP1-AS is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome in Kashmiri women. 35656892_CTBP1AS upregulation is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome and can be effectively downregulated by cryptotanshinone. |
|
|
23.789384 |
0.2777965549 |
-1.847899 |
0.357061474 |
27.888775 |
0.00000012849302147962878792025601722842642615773911529686301946640014648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000501336768976822895891773922139034169731530710123479366302490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.4833213 |
2.7735049 |
38.1238499 |
6.2789662 |
| ENSG00000281005 |
283876 |
LINC00921 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.767089 |
0.3912258852 |
-1.353926 |
0.356607271 |
14.561569 |
0.00013565314567669955504725098904827973456121981143951416015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000365639231224997387787595259922568402544129639863967895507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.6626059 |
3.1047404 |
35.0839035 |
5.0661909 |
| ENSG00000281026 |
116828 |
N4BP2L2-IT2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.108499 |
0.4527554918 |
-1.143196 |
0.434839507 |
7.131788 |
0.00757291696246090162425446123961592093110084533691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014887620453639173814797125316999881761148571968078613281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.2809754 |
2.2864439 |
16.3882605 |
3.2470163 |
| ENSG00000281103 |
100506776 |
TRG-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31196742_TRG-AS1 promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation by acting as a ceRNA of miR-877-5p to regulate SUZ12 expression 32615889_TRG-AS1 is a potent driver of oncogenicity of tongue squamous cell carcinoma through microRNA-543/Yes-associated protein 1 axis regulation. |
|
|
54.574414 |
0.3133421471 |
-1.674189 |
0.304526211 |
29.680720 |
0.00000005093894824063057278658436452523083914911694591864943504333496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000206158178237375156143499797464779810240997903747484087944030761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
26.2635156 |
5.3218737 |
84.6079632 |
11.4535993 |
| ENSG00000281181 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
251.950424 |
2.0454644974 |
1.032428 |
0.137217478 |
56.407571 |
0.00000000000005890313165708819568706175770627242737091308621977248094481183215975761413574218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000379489403430214692108993718323133590483026145179223931336309760808944702148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
349.8541293 |
33.3268500 |
171.9985651 |
12.2826086 |
| ENSG00000281332 |
|
LINC00997 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.714458 |
0.3846733300 |
-1.378294 |
0.421306957 |
10.680153 |
0.00108291113258350037151789280187585973180830478668212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002506471431226668655778411221035639755427837371826171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.3978891 |
2.9294281 |
27.3164582 |
4.9908127 |
| ENSG00000281344 |
|
HELLPAR |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
139.859186 |
0.4942091860 |
-1.016806 |
0.132100292 |
60.187023 |
0.00000000000000862590403889183429869060273298906653837347848629013569166090746875852346420288085937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000058083185955311797456174020708774519581251392918996856451485655270516872406005859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
93.6806880 |
7.4656566 |
190.9715817 |
9.7396516 |
| ENSG00000281392 |
100846978 |
LINC00506 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
50.324030 |
0.4353787885 |
-1.199657 |
0.259313264 |
21.520452 |
0.00000350075201434459227689999401278431179207473178394138813018798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000011590610254050088200831331031182003243884537369012832641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.6476325 |
5.7415525 |
73.2224517 |
8.9975244 |
| ENSG00000281404 |
100506516 |
LINC01176 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.865949 |
0.3918856038 |
-1.351496 |
0.480648795 |
7.650345 |
0.00567614724674097605172651270777350873686373233795166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011475131264470184860870816123679105658084154129028320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.2354859 |
3.6511037 |
26.8997749 |
6.4515625 |
| ENSG00000281571 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22.165497 |
0.3223271377 |
-1.633402 |
0.628868734 |
6.117590 |
0.01338431824809769438155981902127678040415048599243164062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024968723122083161247708460450667189434170722961425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.5868668 |
4.2922383 |
29.7172154 |
9.1855981 |
| ENSG00000281691 |
100775107 |
RBM5-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This gene produces a non-coding RNA in antisense to the RNA binding motif protein 5 (RBM5) gene. This transcript interacts with beta catenin and may regulate expression of WNT target genes. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
|
|
31869662_Long non-coding RNA RBM5-AS1 promotes the aggressive behaviors of oral squamous cell carcinoma by regulation of miR-1285-3p/YAP1 axis. 33816613_LncRNA RBM5-AS1 Promotes Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. 34019714_lncRNA RBM5-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by epigenetically silencing miR-132/212 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. 34225779_RBM5-AS1 promotes radioresistance in medulloblastoma through stabilization of SIRT6 protein. 35110544_Hypoxia-induced lncRNA RBM5-AS1 promotes tumorigenesis via activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in breast cancer. |
|
|
5.993032 |
0.2115193168 |
-2.241139 |
0.861469865 |
6.946100 |
0.00840021551253139660275781608334000338800251483917236328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016339902604765869226222108068213856313377618789672851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.7230567 |
1.0892162 |
8.2980584 |
3.1607570 |
| ENSG00000282278 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A0B4J203 |
|
ATP-binding;Kinase;Nucleotide-binding;Nucleus;Reference proteome;Transferase;Tyrosine-protein kinase |
|
|
|
nucleoplasm [GO:0005654]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity [GO:0004714]; positive regulation of phosphorylation [GO:0042327]; positive regulation of response to stimulus [GO:0048584]; protein autophosphorylation [GO:0046777]; regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0042127]; transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway [GO:0007169] |
|
|
|
183.819237 |
2.8009767451 |
1.485930 |
0.168246268 |
76.878886 |
0.00000000000000000181770072027886188212913639255419429853094301968090100440900158673684927634894847869873046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000015013577297882486374975714600087796674771363261680599821001891314153908751904964447021484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
271.1278221 |
27.2059711 |
97.6743985 |
7.6043662 |
| ENSG00000282508 |
|
LINC01002 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.911643 |
0.4669264399 |
-1.098733 |
0.232902508 |
22.403159 |
0.00000221010217172605606016566257010502738467039307579398155212402343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007523318278292571166900645079911313928278104867786169052124023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
35.1407222 |
4.8149748 |
75.8909529 |
6.8096456 |
| ENSG00000282798 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.327695 |
0.4959229253 |
-1.011812 |
0.230688941 |
19.475655 |
0.00001018900342412215984805052421124926809170574415475130081176757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000031882486864541674065169629681548713051597587764263153076171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
31.2824867 |
4.7051225 |
63.6508588 |
6.2780790 |
| ENSG00000283149 |
|
|
protein_coding |
H7C2Y5 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
endoplasmic reticulum [GO:0005783]; misfolded protein binding [GO:0051787]; unfolded protein binding [GO:0051082]; protein folding [GO:0006457]; protein maturation [GO:0051604] |
|
|
|
64.526372 |
2.0305437230 |
1.021866 |
0.327332538 |
9.488072 |
0.00206812016514596255789548706616187701001763343811035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.004551961472942797973240125486427132273092865943908691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
86.3498090 |
18.3104788 |
43.0960862 |
6.8000017 |
| ENSG00000283183 |
105374338 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.625284 |
0.1393817543 |
-2.842886 |
0.870246257 |
11.802800 |
0.00059141695661465174069931771683172883058432489633560180664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001434091388143955746528601657985291240038350224494934082031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6419743 |
0.9988267 |
12.0319901 |
3.5593681 |
| ENSG00000283189 |
84276 |
|
protein_coding |
Q9BSH3 |
|
Alternative splicing;Microtubule;Nucleus;Reference proteome |
|
|
hsa:84276; |
microtubule [GO:0005874]; nucleoplasm [GO:0005654] |
|
|
|
75.386430 |
0.1826695078 |
-2.452692 |
0.234023588 |
116.553330 |
0.00000000000000000000000000359578927028366610554650816442173478322590674554254677706309982500017339429598806077592598740011453628540039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000041757552816197414504974500905221968532054638283702745266396521365675478451584545780406187986955046653747558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.5748733 |
4.4923093 |
130.2601388 |
15.6016656 |
| ENSG00000283228 |
785 |
|
protein_coding |
A0A1B0GUR1 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
125.822499 |
2.0538393204 |
1.038323 |
0.364421776 |
7.883612 |
0.00498847498171156936153103345077397534623742103576660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010202284984074097215489551615519303595647215843200683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
152.5936879 |
35.4735758 |
74.7105887 |
12.5220474 |
| ENSG00000283580 |
|
|
protein_coding |
B4DSR2 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.718172 |
0.2028157811 |
-2.301758 |
0.973313754 |
5.854872 |
0.01553398404224066824130812136672830092720687389373779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028560239718917818790844265208761498797684907913208007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9306768 |
0.8381140 |
4.4667710 |
2.6070622 |
| ENSG00000283632 |
90332 |
EXOC3L2 |
protein_coding |
A0A1C7CYX0 |
|
Proteomics identification;Reference proteome |
|
The protein encoded by this gene is upregulated by vascular endothelial growth factor A and interacts with exocyst complex component 4. The encoded protein may be part of an exocyst complex that plays a role in cell membrane dynamics. Mutations in this gene may be associated with Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, May 2017]. |
|
exocyst [GO:0000145]; exocytosis [GO:0006887]; in utero embryonic development [GO:0001701] |
20460622_Observational study, meta-analysis, and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 21566143_exoc3l2 silencing inhibits VEGF receptor 2 phosphorylation and VEGFA-directed migration of cultured endothelial cells. 22381399_This study suggests that the rs597668 polymorphism near EXOC3L2 may not play a major role in the susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease in the Northern Han Chinese population. 23663385_This meta-analysis assesses an association between rs597668 polymorphism in EXOC3L2 and Alzheimer's disease. 28423615_EXOC3L2 rs597668 variant is associated with Alzheimer's disease susceptibility. 30327448_We propose that biallelic EXOC3L2 mutations lead to a novel syndrome that affects hindbrain development, kidney and possibly the bone marrow. |
ENSMUSG00000011263 |
Exoc3l2 |
16.595400 |
0.0238196917 |
-5.391701 |
0.893681006 |
79.068183 |
0.00000000000000000060002921524392467580328725267151163602182718448331717742139090887576458044350147247314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000005063711387650273528906180928456739087892067045299426472637627227868506452068686485290527343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7926817 |
0.5195791 |
33.4841503 |
5.9329879 |
| ENSG00000283674 |
729732 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.677843 |
0.4506509875 |
-1.149918 |
0.260952831 |
19.777246 |
0.00000870123920255349317344137349827803973312256857752799987792968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027501132897149797152227049257255941938637988641858100891113281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.9628633 |
4.0101856 |
48.9651871 |
5.9041897 |
| ENSG00000283737 |
|
|
TEC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.745034 |
0.4286797138 |
-1.222028 |
0.289812332 |
17.507751 |
0.00002861387526573373648848888639584231441403971984982490539550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000085012238108339352308552572257127621924155391752719879150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.4322608 |
9.2291468 |
65.7600718 |
15.0119485 |
| ENSG00000284428 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.920878 |
0.2986657440 |
-1.743396 |
0.561742556 |
10.166660 |
0.00143003064452017171134801110099488141713663935661315917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003250269835712616805362129568379714328330010175704956054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.3225888 |
1.2424944 |
11.2722613 |
2.4981645 |
| ENSG00000284624 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.119937 |
0.4974832612 |
-1.007280 |
0.430310205 |
5.576775 |
0.01820021180167403704319717405724077252671122550964355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.032925006274385194837694967873176210559904575347900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.3916294 |
2.5527434 |
18.9111613 |
3.2452560 |
| ENSG00000284690 |
100130520 |
CD300H |
protein_coding |
A0A0K2S4Q6 |
FUNCTION: May play an important role in innate immunity by mediating a signal for the production of a neutrophil chemoattractant. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:26221034}. |
Alternative splicing;Disulfide bond;Glycoprotein;Immunoglobulin domain;Membrane;Reference proteome;Secreted;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene belongs to the CD300 gene family, which in turn, belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. This gene is located within a CD300 cluster on chromosome 17. The encoded protein may be involved in innate immunity as well as autoimmune response. A G>A mutation, represented by the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs905709, at the splice donor site of the 5' terminal exon may be associated with lack of expression of this gene in homozygous (AA) individuals. The human reference assembly (GRCh38.p2) represents the 'A' allele at this SNP. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
hsa:100130520; |
extracellular region [GO:0005576]; plasma membrane [GO:0005886]; transmembrane signaling receptor activity [GO:0004888]; neutrophil chemotaxis [GO:0030593] |
26221034_Results suggest that CD300H may play an important role in innate immunity. |
|
|
8.062407 |
83.9035426955 |
6.390660 |
1.134743003 |
43.523443 |
0.00000000004189108426889625698221722019046068044567654453658178681507706642150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000222254638320959296654883627014707807301174824488043668679893016815185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.4052994 |
12.5322573 |
0.1846157 |
0.1451247 |
| ENSG00000284691 |
728743 |
|
protein_coding |
A0A286YF50 |
|
Metal-binding;Proteomics identification;Reference proteome;Zinc;Zinc-finger |
|
|
|
|
|
ENSMUSG00000053297 |
AI854703 |
54.442569 |
2.3670464194 |
1.243088 |
0.208772664 |
36.254049 |
0.00000000173199751541977742019288849642305247455986716431652894243597984313964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000008120247855617313738662351330771516089157557871658354997634887695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
78.3742011 |
9.6769479 |
33.3481157 |
3.3483022 |
| ENSG00000284707_ENSG00000243554_ENSG00000284627 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.807837 |
0.2994047560 |
-1.739831 |
0.677520226 |
6.668016 |
0.00981584068503880101397296442655715509317815303802490234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.018847639978037296348833962156277266331017017364501953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.6319580 |
2.1250794 |
15.3601778 |
4.3258279 |
| ENSG00000284719 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
317.917349 |
0.1693684644 |
-2.561763 |
0.135563209 |
362.680814 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000734260723303751933495660741369675503084200334347277039561889224167867436572359496963753406986942754465904912076771082408233821004623152828301009726420746802001853617079827498130924795697773814891163787765826498343813000246882438659667968750000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000249142259217548906862107980925807812957265595141744910981978199481191892425706586585925827067130038055818524025570908294312844575486371580361019590937338812961174293280586658521538329479399820126292453004168692132225260138511657714843750000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
91.8458286 |
9.1839746 |
545.8055235 |
34.5554700 |
| ENSG00000284738 |
101928059 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.990532 |
0.2063582000 |
-2.276777 |
0.593849024 |
16.086878 |
0.00006050181558167489078402245805676784584647975862026214599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000172195680290304924033722988596650793624576181173324584960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.9560344 |
1.1618908 |
14.4239442 |
3.0806052 |
| ENSG00000284753 |
110599564 |
EEF1AKMT4 |
protein_coding |
P0DPD7 |
FUNCTION: Protein-lysine methyltransferase that efficiently catalyzes three successive methylations on 'Lys-36' in eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha (EEF1A1 or EEF1A2). {ECO:0000269|PubMed:28520920}. |
3D-structure;Alternative splicing;Methyltransferase;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome;S-adenosyl-L-methionine;Transferase |
|
This gene encodes a member of the lysine-specific methyltransferase (KMT) family. The encoded enzyme catalyzes the methylation of lysine-36 of the eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha. Methylation by this enzyme may affect endoplasmic reticulum-related processes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2017]. |
hsa:110599564; |
methyltransferase activity [GO:0008168]; protein-lysine N-methyltransferase activity [GO:0016279] |
28520920_Methylation of lysine (K36) in eukaryotic elongation factor alpha (eEF1A) proteins is dependent on EEF1A lysine methyltransferase 4 (eEF1A-KMT4) in vivo. |
ENSMUSG00000115219 |
Eef1akmt4 |
24.385601 |
3.0372358740 |
1.602759 |
0.344952482 |
22.191275 |
0.00000246792765290777373616399291422762729553141980431973934173583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008347069696819143819633418646120048833836335688829421997070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
37.0880560 |
8.4560549 |
12.3111129 |
2.2554162 |
| ENSG00000284820 |
|
|
protein_coding |
H7C152 |
|
Autophagy;Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix;Transport |
|
|
|
autophagosome [GO:0005776]; phagophore assembly site [GO:0000407]; phagophore assembly site membrane [GO:0034045]; autophagy of mitochondrion [GO:0000422]; late nucleophagy [GO:0044805]; protein localization to phagophore assembly site [GO:0034497] |
|
|
|
24.384844 |
0.1312116005 |
-2.930033 |
0.473042420 |
40.235501 |
0.00000000022511988035225171245940810227939782653394651390499348053708672523498535156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001135213335838481471192856642345690720841133725116378627717494964599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4586840 |
1.9946411 |
42.3582984 |
9.4589197 |
| ENSG00000284829 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.966662 |
0.2472354216 |
-2.016043 |
0.827688739 |
5.167353 |
0.02301525708037577971909470875289116520434617996215820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.040697878819497601554644461430143564939498901367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2566551 |
1.9963553 |
13.8424646 |
5.5074678 |
| ENSG00000284842 |
|
FAM91A2P |
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.740352 |
0.3081880648 |
-1.698117 |
0.682249213 |
6.084939 |
0.01363390452524336840522956038057600380852818489074707031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.025383000856785079696331663967612257692962884902954101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.4179291 |
2.8070502 |
20.9625935 |
6.0573426 |
| ENSG00000284906 |
89839 |
|
protein_coding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.292721 |
0.4144114240 |
-1.270864 |
0.512980610 |
6.329590 |
0.01187397861234862524171251862981080194003880023956298828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.022434706133930584076585645902923715766519308090209960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6676118 |
2.0971260 |
13.7049531 |
3.4461629 |
| ENSG00000284930 |
101928143 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26.749607 |
2.4168372708 |
1.273120 |
0.466549640 |
7.189102 |
0.00733476839555961910438464101957833918277174234390258789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.014461819599046216167081979619979392737150192260742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
39.8287864 |
11.9288946 |
16.6246676 |
3.8253700 |
| ENSG00000284946 |
26276 |
|
protein_coding |
A0A2R8YDQ0 |
|
Protein transport;Reference proteome;Transport |
|
|
|
clathrin-coated vesicle [GO:0030136]; late endosome membrane [GO:0031902]; lysosomal membrane [GO:0005765]; protein transport [GO:0015031]; vesicle-mediated transport [GO:0016192] |
|
|
|
80.760836 |
0.4281733783 |
-1.223733 |
0.327498654 |
13.602001 |
0.00022594452579977568470667725897271793655818328261375427246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000586621143501264642912407243358074993011541664600372314453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
50.3207796 |
11.3286617 |
117.7106622 |
18.5648002 |
| ENSG00000284968 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.767350 |
0.2616041750 |
-1.934543 |
0.365597637 |
28.352324 |
0.00000010112530906734568032749604785461294831350187450880184769630432128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000398347894804916510903066047266651850122798350639641284942626953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.4736236 |
3.3387777 |
48.4131629 |
8.2690544 |
| ENSG00000284981 |
107983993 |
UPK3BL2 |
protein_coding |
E5RIL1 |
|
Glycoprotein;Membrane;Reference proteome;Signal;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
hsa:100134938; |
membrane [GO:0016020] |
|
ENSMUSG00000006143 |
Upk3bl |
27.338435 |
0.0034598638 |
-8.175069 |
1.070220216 |
126.839974 |
0.00000000000000000000000000002013736825574323500209142550179091068646745426193414773857508944655107587130967936039915855417348211631178855895996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000254257960183721249044820832113552714842398145283230624925457574586742720210152945981008087983354926109313964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.1991832 |
0.4196747 |
58.2101857 |
65.0654104 |
| ENSG00000285006 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.888702 |
4.4346442041 |
2.148818 |
0.535626861 |
16.407997 |
0.00005106931066879858360178096043924256264290306717157363891601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000146707478682652208302333862732780289661604911088943481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.4002974 |
16.9893122 |
4.7133581 |
2.7069321 |
| ENSG00000285184 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57.499242 |
0.3368887311 |
-1.569656 |
0.349087419 |
19.748729 |
0.00000883204164577369055949291470897222211533517111092805862426757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000027866809468067482892386990678268432475306326523423194885253906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.3785367 |
7.3615500 |
90.8046721 |
15.0997899 |
| ENSG00000285314 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.626829 |
0.0551141418 |
-4.181434 |
1.306120448 |
8.140932 |
0.00432770365513015543845742882922422722913324832916259765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008965179782416995979410501149686751887202262878417968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.1456423 |
3.2438984 |
20.4453002 |
32.6582844 |
| ENSG00000285331 |
145783 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
191.254999 |
0.4381424689 |
-1.190528 |
0.131185760 |
82.943658 |
0.00000000000000000008442577330439038071208054334789229042659281405825775069888539103857283407705835998058319091796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000741299472916598514111596029557045616154884214027962797965987107318142079748213291168212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
120.6358731 |
10.4247794 |
277.2161015 |
16.1018575 |
| ENSG00000285410 |
55056 |
GABPB1-IT1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
118.553226 |
0.4410471603 |
-1.180995 |
0.147727340 |
65.004308 |
0.00000000000000074734525763798761988349362645924165730490181577122532630141904519405215978622436523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000005375641326869735712117816009701057157281998966080749369211844168603420257568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
74.3972276 |
6.8434602 |
169.8256881 |
9.9131056 |
| ENSG00000285446 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A2R8Y6J1 |
|
Isomerase;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
chondroitin-glucuronate 5-epimerase activity [GO:0047757]; chondroitin sulfate metabolic process [GO:0030204]; dermatan sulfate metabolic process [GO:0030205] |
|
|
|
12.563795 |
8.4194659930 |
3.073729 |
1.206481885 |
5.865712 |
0.01543861672637417310760543642800257657654583454132080078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.028401997631950212652718334993551252409815788269042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.0365333 |
15.5327982 |
2.7653523 |
1.4345551 |
| ENSG00000285508 |
8195 |
MKKS |
protein_coding |
V9GZ13 |
|
Membrane;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
This gene encodes a protein which shares sequence similarity with other members of the type II chaperonin family. The encoded protein is a centrosome-shuttling protein and plays an important role in cytokinesis. This protein also interacts with other type II chaperonin members to form a complex known as the BBSome, which involves ciliary membrane biogenesis. This protein is encoded by a downstream open reading frame (dORF). Several upstream open reading frames (uORFs) have been identified, which repress the translation of the dORF, and two of which can encode small mitochondrial membrane proteins. Mutations in this gene have been observed in patients with Bardet-Biedl syndrome type 6, also known as McKusick-Kaufman syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2013]. |
|
membrane [GO:0016020] |
11567139_Unaffected individuals in 2 pedigrees had 2 but not all 3 mutations that affecteds had which suggests that Bardet-Biedle syndrome might not be a single-gene recessive disease but a complex trait requiring three mutant alleles to manifest the phenotype. 12837689_The presence of three mutant alleles in the BBS family correlates with a more severe Bardet-Biedl phenotype. 15483080_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15731008_MKKS/BBS6 is a novel centrosomal component required for cytokinesis 17003356_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18094050_These results indicate that the MKKS mutants have an abnormal conformation and that chaperone-dependent degradation mediated by CHIP is a key feature of McKusick-Kaufman syndrome/Bardet-Biedl syndrome diseases. 18813213_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18813213_results suggest that genetic variation in the MKKS gene may play a role in the development of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. 19077438_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 19247371_genetic variations at MKKS gene influence the risk of metabolic syndrome 19876004_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20472660_Using sequence analysis, the role of BBS6, 10 and 12 was assessed in a Bardet-Biedl syndrome patient population comprising 93 cases from 74 families. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20801516_Observational study of genetic testing. (HuGE Navigator) 23432027_Novel mutation (c.1272+1G>A) in BBS6 found in Tunisian families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. 23671934_Three uORFs (uMKKS0, uMKKS1 and uMKKS2) are reported, and they can repress the translation of the downstream MKKS ORF. uMKKS1 and uMKKS2 are highly conserved in mammals and they encode two different mitochondrial membrane proteins respectively. 23716571_Findings indicate that Bbs proteins play a central role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and control the cilia length through alteration of RhoA levels. 24400638_we report here, for the first time, in Indian population, a novel, different profile of mutations in BBS genes (BBS3, BBS9, BBS10 and BBS2) compared to worldwide (BBS1 and 10) reports. 26900326_We identified a novel H395R substitution in MKKS/BBS6 that results in a unique phenotype of only retinitis pigmentosa and polydactyly. 28624958_found compound heterozygous variants (c.1192C>T, p.Q398* and c.1175C>T, p.T392M) in MKKS in both the siblings, and these were likely to be pathogenic variants 28761321_Two novel mutations and three previously reported variants, identified in the present study, further extend the body of evidence implicating BBS6, BBS7, BBS8, and BBS10 in causing Bardet-Biedl Syndrome. 29232001_Novel sequence variants in the MKKS gene cause Bardet-Biedl syndrome in two consanguineous families with intra- and inter-familial variable phenotypes. 31989739_Novel mutation in MKKS/BBS6 linked with arRP and polydactyly in a family of North Indian origin. 33741323_Apparent but unconfirmed digenism in an Iranian consanguineous family with syndromic Retinal Disease. |
ENSMUSG00000115423 |
Gm56450 |
9.055828 |
4.2091450459 |
2.073527 |
0.851738015 |
5.770387 |
0.01629844487957416571122237769486673641949892044067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.029813489456254144149838225530402269214391708374023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.5055198 |
19.0907290 |
3.7162849 |
2.9808145 |
| ENSG00000285533 |
105369347 |
RELA-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.841423 |
0.2880568238 |
-1.795575 |
0.506222832 |
12.043336 |
0.00051977860266106767992561055180544826725963503122329711914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001272082934053616254041485511550035880645737051963806152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.4335014 |
2.8251479 |
34.1301077 |
6.5698201 |
| ENSG00000285589 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A3B3IU31 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
peptidyl-lysine modification to peptidyl-hypusine [GO:0008612] |
|
|
|
40.081510 |
0.4304875269 |
-1.215957 |
0.329637947 |
13.557699 |
0.00023134050474699565541104873123146035140962339937686920166015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000599365604715754933355664757499425832065753638744354248046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.7608195 |
5.0937691 |
55.5614170 |
8.0436625 |
| ENSG00000285596 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.557842 |
0.1769375631 |
-2.498688 |
0.900607225 |
6.942761 |
0.00841590875584292616440329481974913505837321281433105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.016363959061552049017995713597883877810090780258178710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4747812 |
3.9417628 |
22.4005932 |
16.5858122 |
| ENSG00000285684 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
184.225355 |
0.0153519022 |
-6.025439 |
1.607696646 |
8.528197 |
0.00349685950198709268391117355179176229285076260566711425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007384983008918226746186697084795014234259724617004394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5460174 |
7.0523369 |
415.6481715 |
301.8596942 |
| ENSG00000285722 |
124905143 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.835984 |
0.4374958492 |
-1.192659 |
0.470509549 |
6.490301 |
0.01084646154390969848002601594316729460842907428741455078125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.020659926750304185433249060110938444267958402633666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.2605645 |
2.4670540 |
18.9552632 |
3.5911837 |
| ENSG00000285730 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.372050 |
0.3255358968 |
-1.619111 |
0.601257631 |
7.570616 |
0.00593275147811273863285297380798510857857763767242431640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.011933416709858821538881024082456860924139618873596191406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.6283521 |
1.5613234 |
11.2273386 |
2.9587169 |
| ENSG00000285733 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A3B3IS69 |
|
Reference proteome;Signal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.128156 |
0.0363866347 |
-4.780448 |
0.945491315 |
31.166273 |
0.00000002368455642676411779913860328021513179663770642946474254131317138671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000099398365896797947700799802112775482854090114415157586336135864257812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9839549 |
0.8930308 |
29.3997502 |
13.4072989 |
| ENSG00000285752 |
|
CDC42-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.662821 |
0.3393308061 |
-1.559236 |
0.464142057 |
11.569738 |
0.00067033851976728545032230277556095643376465886831283569335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001611695154221393262716777172727233846671879291534423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5809051 |
2.6560021 |
19.6622116 |
5.1793917 |
| ENSG00000285793 |
285074 |
ANAPC1P2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
78.195365 |
0.2324899028 |
-2.104760 |
0.197138325 |
122.728911 |
0.00000000000000000000000000015986479535615404595445810153192641529939489143313020305940915652365674466759554173123092368768993765115737915039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000001950086264013911948931245123905112005268477635491378373173770857857724225770112980171688832342624664306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.6661538 |
3.9806742 |
128.6258623 |
10.0128133 |
| ENSG00000285796 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.970466 |
0.2633329970 |
-1.925040 |
0.278444223 |
50.131847 |
0.00000000000143754870421559626573324955642024832315299665008723195569473318755626678466796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000008443381963478791184153722426639245143484280298196154035395011305809020996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.5399275 |
3.0332225 |
63.3835801 |
6.8232999 |
| ENSG00000285851 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.830496 |
0.2345033189 |
-2.092320 |
0.591245065 |
11.817364 |
0.00058680892209595663430027334683813933224882930517196655273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001424555870088210557042329718058226717403158545494079589843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8430320 |
3.1323077 |
33.0784101 |
8.6610626 |
| ENSG00000285864 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.751868 |
6.4124617790 |
2.680878 |
0.801750039 |
10.984700 |
0.00091867135951848749066128707596590174944140017032623291015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002153341157137188700138041852483183902222663164138793945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.4558643 |
9.3909405 |
2.8604273 |
1.1768680 |
| ENSG00000285886 |
124901671 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.615856 |
0.2990835382 |
-1.741380 |
0.600846427 |
8.875866 |
0.00288965091635787858434514241423585190204903483390808105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006207429417179782457636427750458096852526068687438964843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7366807 |
1.4595901 |
12.4942518 |
2.7881853 |
| ENSG00000285967 |
646719 |
NIPBL-DT |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
148.369883 |
0.4873387734 |
-1.037003 |
0.145603622 |
51.134014 |
0.00000000000086270398892327383029615790199892692749050054912274276830430608242750167846679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000005155267561339077365577087008576061093190201489733226480893790721893310546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
98.0721347 |
10.3595825 |
202.9959653 |
14.4867129 |
| ENSG00000285979 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.601812 |
0.4174398918 |
-1.260360 |
0.311863600 |
16.674699 |
0.00004436881592553226316775344395537672426144126802682876586914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000128762037566035444837581058763475994055625051259994506835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.1764450 |
3.0949556 |
39.0029286 |
4.6901608 |
| ENSG00000286018 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.383579 |
0.4426275033 |
-1.175835 |
0.530045215 |
5.035872 |
0.02482757921601102049646847547137440415099263191223144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.043568549426741487451408829656429588794708251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3128118 |
1.7650895 |
12.1560208 |
2.4780929 |
| ENSG00000286067 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.317710 |
0.3778759960 |
-1.404015 |
0.360439745 |
15.592724 |
0.00007855629345028011898278280655816274702374357730150222778320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000219475845414751939092129484620841139985714107751846313476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2241714 |
2.7439496 |
29.9902314 |
4.6137209 |
| ENSG00000286071 |
105373170 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.065167 |
0.0868722910 |
-3.524960 |
0.514524122 |
52.326476 |
0.00000000000046999507740035707061434736601069271329841198214793962506519164890050888061523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000002863032332822645738671348072583802430585153686593002930749207735061645507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.7100352 |
1.2467767 |
21.3426852 |
10.3509095 |
| ENSG00000286195 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.237064 |
0.3058506809 |
-1.709101 |
0.642422378 |
6.997603 |
0.00816189426393998211650693264118672232143580913543701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015926700070829472727362841055764874909073114395141601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1632686 |
2.4072618 |
14.3413725 |
5.3081542 |
| ENSG00000286196 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.730736 |
0.4330799443 |
-1.207295 |
0.461770909 |
7.018498 |
0.00806718711207159676346289955972679308615624904632568359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015768995070080355641595204474469937849789857864379882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.3577276 |
1.9225289 |
14.7844433 |
2.8056558 |
| ENSG00000286207 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.254994 |
0.2250155225 |
-2.151904 |
0.420487162 |
27.042380 |
0.00000019904329167547572900889602150187318585494722356088459491729736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000760714392835324077518535483555250920062462682835757732391357421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.2565743 |
2.6349127 |
41.7827960 |
7.1184051 |
| ENSG00000286215 |
|
|
transcribed_processed_pseudogene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.971479 |
0.3251939945 |
-1.620627 |
0.608585950 |
7.450520 |
0.00634181395100115539303908818169475125614553689956665039062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012681909486082786758798235382528218906372785568237304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8113191 |
1.1403817 |
8.6167382 |
2.0660121 |
| ENSG00000286235 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A494C100 |
|
ATP-binding;Chromosome;DNA-binding;Membrane;Nucleotide-binding;Reference proteome;Transmembrane;Transmembrane helix |
|
|
|
chromosome [GO:0005694]; membrane [GO:0016020]; nucleus [GO:0005634]; ATP binding [GO:0005524]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; phosphotransferase activity, for other substituted phosphate groups [GO:0016780]; DNA duplex unwinding [GO:0032508]; DNA-templated DNA replication [GO:0006261]; phospholipid biosynthetic process [GO:0008654] |
|
|
|
36.480964 |
3.5935157524 |
1.845396 |
0.733707810 |
5.379438 |
0.02037544304622594670828306107068783603608608245849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036471202930183722890067343769260332919657230377197265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
53.8671409 |
26.9535917 |
15.0404261 |
5.4978784 |
| ENSG00000286293 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49.733420 |
0.3807370641 |
-1.393133 |
0.225013448 |
39.527032 |
0.00000000032354946751128573200479867167983407533204953665517678018659353256225585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001613920290796410109284175092212148400205862230905040632933378219604492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.6630832 |
5.4716355 |
73.2837574 |
9.6898099 |
| ENSG00000286473 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.312466 |
0.3893717172 |
-1.360780 |
0.246826604 |
31.485685 |
0.00000002009160592095841807335873294669548183577489908202551305294036865234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000084874671835531267197023854061133096848834611591883003711700439453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.1798783 |
3.5078924 |
57.3142224 |
5.5218485 |
| ENSG00000286482 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.829720 |
0.2488297191 |
-2.006769 |
0.779198179 |
6.600730 |
0.01019369893001655959230422610062305466271936893463134765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.019502138199228049447730981569293362554162740707397460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7192859 |
1.7515424 |
15.0593061 |
4.3166245 |
| ENSG00000286535 |
124902026 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.818420 |
0.2349695641 |
-2.089454 |
0.569841806 |
14.692853 |
0.00012652526656383353254563262080267804776667617261409759521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000343229725139162491695521417511827166890725493431091308593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0898814 |
1.1364059 |
13.2054264 |
2.6401144 |
| ENSG00000286646 |
|
MAP3K5-AS2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
415.509413 |
0.3899508129 |
-1.358636 |
0.085861073 |
254.169653 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000320219043596891708353331894993812243241793245686989853906570548905135144591703508475719797564061746643363310633608444415969865161088475787824064733300133411830756813287734985351562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000078122860884134241799647890716508053909298301531762940738591373537991768901611010248014482478261471943228754427991698987779237499553432183671194954932559539884096011519432067871093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
238.3594209 |
13.3976768 |
615.5794463 |
22.3329643 |
| ENSG00000286656 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.475546 |
0.0944110171 |
-3.404901 |
0.505095987 |
56.306087 |
0.00000000000006202312800597017712628701912229779248978637357092580373318924102932214736938476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000398373093719808429269025761331235026903481444282562051739660091698169708251953125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0424761 |
1.0722444 |
32.3323812 |
5.4785519 |
| ENSG00000286680 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.446783 |
0.2117452239 |
-2.239599 |
0.516917870 |
19.856772 |
0.00000834665005650722381354625345473152719932841137051582336425781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000026448380170469433883030652143730776515440084040164947509765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.0793518 |
1.7575883 |
24.0636134 |
4.7549152 |
| ENSG00000286681 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.634882 |
0.3093778055 |
-1.692558 |
0.435227233 |
15.894412 |
0.00006697616617941516247835415098776934428315144032239913940429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000189441258442868496608690875859792868141084909439086914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.5565618 |
1.7986164 |
21.3025773 |
3.3480512 |
| ENSG00000286808 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.636608 |
0.2705591925 |
-1.885984 |
0.659510740 |
7.932524 |
0.00485540202523001944434621890422931755892932415008544921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009960491159471172514794368169077642960473895072937011718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.4969201 |
2.2738376 |
20.2367233 |
5.3366532 |
| ENSG00000286834 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
256.088498 |
0.3892700320 |
-1.361157 |
0.115764330 |
139.020362 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000004359564492560227893411968949400505673912443398026051516083788404720784991848785106752922624551160879491362720727920532226562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000596912540910843749058507140456116766716894477596283741043449609065137686131734804685644579791414798819459974765777587890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
143.9521455 |
10.6076446 |
372.7116975 |
17.8694943 |
| ENSG00000286931 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38.125800 |
0.4453212179 |
-1.167082 |
0.309643371 |
14.232028 |
0.00016159665780336897452848510248202273942297324538230895996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000430613227871046405463573147898159731994383037090301513671875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
22.4544118 |
5.3806883 |
50.9051950 |
8.3565344 |
| ENSG00000286986 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95.193706 |
0.4752473043 |
-1.073250 |
0.161434288 |
44.895813 |
0.00000000002078017263157321678804701602354137622216678771280840010149404406547546386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000112970662262254400956540771645565104583375237723430473124608397483825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
61.9460175 |
6.1736732 |
131.3340163 |
8.3989916 |
| ENSG00000286989 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.822831 |
0.2947129460 |
-1.762618 |
0.543220875 |
11.050367 |
0.00088669638071595764314269949579738749889656901359558105468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002087009819704597948092361647809411806520074605941772460937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7174945 |
1.3303869 |
12.7378935 |
2.5662068 |
| ENSG00000287047 |
105378473 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.454299 |
43.1789552529 |
5.432256 |
1.122585819 |
36.236175 |
0.00000000174795579893928059110719965511945503400248469461075728759169578552246093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000008190421457886914415253473004119300071579345967620611190795898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.9079319 |
10.5090457 |
0.3019445 |
0.2367852 |
| ENSG00000287097 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.086383 |
27.8132844019 |
4.797702 |
0.796685724 |
65.016808 |
0.00000000000000074261933189307699167433158602047787235612920277855186768078965542372316122055053710937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000005344252237319267241643088856713779085526219280594117932992048736196011304855346679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.6276730 |
14.9688418 |
0.9983883 |
0.5264450 |
| ENSG00000287104 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.058799 |
0.4636429964 |
-1.108914 |
0.390067291 |
8.267332 |
0.00403647870890077534872242281949183961842209100723266601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008411467703427282296968492403266282053664326667785644531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6511487 |
2.4232566 |
20.8910706 |
3.3220190 |
| ENSG00000287110_ENSG00000231305 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.688622 |
0.1568530764 |
-2.672514 |
0.667096170 |
18.707688 |
0.00001523669117959569077830426359065896235733816865831613540649414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000046726275048999038391403515468880414118757471442222595214843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.9587585 |
0.8828668 |
12.6103603 |
2.7902454 |
| ENSG00000287151 |
29798 |
C2orf27A |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.303215 |
2.1407925102 |
1.098145 |
0.264059829 |
17.281761 |
0.00003222653501345540595244762438476016086497111245989799499511718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000095189845266880482375741745482145006462815217673778533935546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.5147969 |
8.0454980 |
23.3248165 |
2.8408434 |
| ENSG00000287156 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.726092 |
0.0293349271 |
-5.091237 |
1.025863281 |
42.916493 |
0.00000000005712699979273764574875852940080158369473561918994164443574845790863037109375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000300282947628492757602988729538412079889120320785877993330359458923339843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5438718 |
0.4240646 |
18.6259691 |
4.5328927 |
| ENSG00000287168 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.582949 |
0.4876922790 |
-1.035957 |
0.282503561 |
13.595437 |
0.00022673602313225113872273419612923817112459801137447357177734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000588469087644105290878238090357399414642713963985443115234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
21.5608621 |
3.8188941 |
44.4786201 |
4.9006777 |
| ENSG00000287170 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.585478 |
0.1928965043 |
-2.374101 |
0.422069837 |
35.602991 |
0.00000000241915854571123034271643225344688293843020687745593022555112838745117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000011177410465474425797049900827180579643282953838934190571308135986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8828549 |
1.6594434 |
30.7181591 |
4.5604115 |
| ENSG00000287255 |
101929667 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
188.327419 |
0.1346344246 |
-2.892881 |
0.662378393 |
15.785298 |
0.00007095171854670331737340027711269385690684430301189422607421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000199818234258603499246126355970432086905930191278457641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.3785112 |
25.3075211 |
518.9351715 |
133.7186084 |
| ENSG00000287263 |
643977 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
129.901207 |
0.2926869880 |
-1.772569 |
0.177116155 |
100.198927 |
0.00000000000000000000001378341438408465907940142327634586317602441709232059973443522697851559843940094651770778000354766845703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000139919667337750733029948772372359130437600025480931974785107300279785036423163546714931726455688476562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
58.5033680 |
7.2848098 |
201.7948529 |
16.4498473 |
| ENSG00000287301 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.281763 |
0.0346621750 |
-4.850494 |
0.906686565 |
55.610045 |
0.00000000000008837090833528243861590762347033849126031086751442700233383220620453357696533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000561737556859934822418446210263288611479540191062653775588842108845710754394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8027020 |
0.5361101 |
23.2091429 |
4.6419775 |
| ENSG00000287306 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.868215 |
0.4874903150 |
-1.036555 |
0.366614144 |
8.077472 |
0.00448189273587828226202978143533073307480663061141967773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009253425203743663451927403684749151580035686492919921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.7833972 |
3.0158441 |
28.4119873 |
4.0154657 |
| ENSG00000287315 |
101927401 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.331923 |
0.0424826022 |
-4.556984 |
0.938757249 |
39.534659 |
0.00000000032228828577483713200168128022911080005075135090919502545148134231567382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001608716637820965895476507720571104215201430065462773200124502182006835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8001070 |
0.5477037 |
19.2940831 |
4.2288716 |
| ENSG00000287431 |
|
RENO1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.215894 |
0.1872378405 |
-2.417056 |
0.437143620 |
34.043337 |
0.00000000538981672770447331544124911482419870711879639202379621565341949462890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000024114487693518651147668469003106095360777771929861046373844146728515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3709556 |
1.5769762 |
28.8517392 |
4.5657332 |
| ENSG00000287480 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.149988 |
0.1434632473 |
-2.801247 |
0.419797571 |
50.484207 |
0.00000000000120127593977038559302840641477949822015121317253516508571919985115528106689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007115101473118334437897864932850994093907481818916949123376980423927307128906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7415496 |
2.1828548 |
47.2117997 |
8.6770006 |
| ENSG00000287557 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.642111 |
0.1931979236 |
-2.371849 |
0.493820915 |
24.558661 |
0.00000072081612390307231303374947695150609661141061224043369293212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002591777341975480597523282672023370309943857137113809585571289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.9905660 |
1.7449678 |
25.9780653 |
5.3035326 |
| ENSG00000287562 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.902175 |
0.3722441870 |
-1.425679 |
0.345512951 |
17.623760 |
0.00002692039072650401787555919652650260331938625313341617584228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000080223090475105849131431945409076433861628174781799316406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.2619596 |
2.8045660 |
33.2175992 |
4.6985639 |
| ENSG00000287576 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.850118 |
0.3804182264 |
-1.394342 |
0.501462966 |
8.002240 |
0.00467195090683922027025021250778991088736802339553833007812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009605515445737134935799694801517034647986292839050292968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5109278 |
1.8031042 |
14.5953161 |
2.9144147 |
| ENSG00000287721 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15.472882 |
0.2921874623 |
-1.775034 |
0.454302618 |
15.840139 |
0.00006892475751373514905508826933200339226459618657827377319335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000194518053709891159102490787446981812536250799894332885742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.4418117 |
2.0324719 |
25.3280469 |
3.9878180 |
| ENSG00000287769 |
124902204 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.402690 |
0.4686229292 |
-1.093501 |
0.445877443 |
6.161004 |
0.01305970889740492094088786245720257284119725227355957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.024446582539720561333407289339447743259370326995849609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.1890580 |
2.1436336 |
15.4561971 |
2.8831070 |
| ENSG00000287778 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.112951 |
6.8104798913 |
2.767756 |
0.752253812 |
15.079407 |
0.00010308168767956831684325796905099537070782389491796493530273437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000282909206052515515682904689853671698074322193861007690429687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2286899 |
5.4638658 |
1.6731324 |
0.7228269 |
| ENSG00000287823 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.690836 |
2.3663947612 |
1.242691 |
0.445470106 |
7.885873 |
0.00498224111761657543345771514964326343033462762832641601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010192360207348670486648956057251780293881893157958984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7720046 |
4.0490826 |
6.7689041 |
1.3970973 |
| ENSG00000287825 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.104139 |
0.1513232745 |
-2.724294 |
0.228143688 |
164.501569 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000011754171849622189932234857720494311422486703326630243426687904049362204407184088148282719550412854514487293045021942816674709320068359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000001853542483978883983328805911389664825458378090432496284690951992030223197133325613410834113302556869218307156188529916107654571533203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.0440384 |
3.1641680 |
120.0754161 |
12.1001950 |
| ENSG00000287920 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.783404 |
0.2533311127 |
-1.980904 |
0.522766280 |
15.244394 |
0.00009445670287614967627204398681328711973037570714950561523437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000260692022148834934638927940397934435168281197547912597656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4906870 |
1.5773856 |
17.8606417 |
3.5914550 |
| ENSG00000288046 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.188376 |
0.1321305744 |
-2.919964 |
0.561979445 |
32.145550 |
0.00000001430439426568077950679690630306564735896301954198861494660377502441406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000061251192155917700948232376516322528203772890265099704265594482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8712953 |
1.1048495 |
21.8923543 |
4.0919475 |
| ENSG00000288156 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
149.223201 |
0.3028125030 |
-1.723503 |
0.132578850 |
178.114305 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000012507074618754021585579571643241170663906065209020310143978499963341017208754832511967738490537831066821972125779893758590333163738250732421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000002124331661367196463726261545811883276104589165469303774909521943473891336707434656976363963761894560963727762725739012239500880241394042968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
69.0397472 |
5.9804418 |
229.6167375 |
11.7896769 |
| ENSG00000288520 |
|
|
protein_coding |
G9CGD6 |
FUNCTION: Required for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-dependent activation of Arf6 and HGF-stimulated cell migration. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:22085542}. |
Alternative splicing;Phosphoprotein;Reference proteome |
|
|
|
cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; membrane [GO:0016020]; positive regulation of cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus [GO:2001114]; regulation of signal transduction [GO:0009966] |
|
|
|
8.279460 |
0.0355205593 |
-4.815202 |
1.389920300 |
10.907229 |
0.00095789717029191488121414588263746736629400402307510375976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002236052859957087402681397136916530143935233354568481445312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.7194136 |
1.1006999 |
22.6461220 |
19.6681845 |
| ENSG00000288596 |
56260 |
C8orf44 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Located in nucleoplasm. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
27.281573 |
0.2714919675 |
-1.881019 |
0.600597211 |
9.150789 |
0.00248610870200377271493907826993563503492623567581176757812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005397905919619841799694803796683117980137467384338378906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
11.5582876 |
4.9050235 |
42.9283857 |
12.4392581 |
| ENSG00000288663 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19.652252 |
0.1765073812 |
-2.502200 |
0.809102556 |
8.776978 |
0.00305056102397389342778533105615679232869297266006469726562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.006524214672277131067679167841788512305356562137603759765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.7922964 |
5.0104181 |
39.0289753 |
19.2928853 |
| ENSG00000288669 |
|
|
protein_coding |
A0A7I2V366 |
|
Reference proteome |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.478855 |
0.1101193742 |
-3.182860 |
0.800433521 |
18.174284 |
0.00002015825116516460006454297682054743745538871735334396362304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000061083101457160636602213010792894465339486487209796905517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.9898261 |
0.6547009 |
8.9338983 |
3.1316694 |
| ENSG00000288674 |
5664 |
|
protein_coding |
|
|
|
|
Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients with an inherited form of the disease carry mutations in the presenilin proteins (PSEN1 or PSEN2) or the amyloid precursor protein (APP). These disease-linked mutations result in increased production of the longer form of amyloid-beta (main component of amyloid deposits found in AD brains). Presenilins are postulated to regulate APP processing through their effects on gamma-secretase, an enzyme that cleaves APP. Also, it is thought that the presenilins are involved in the cleavage of the Notch receptor such that, they either directly regulate gamma-secretase activity, or themselves act are protease enzymes. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms of PSEN2 have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
11436125_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11568920_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11799129_enhancement of amyloid beta protein by Herp, and endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducible protein 11847232_interaction with CALP/KChIP4 11876645_inhibition of endoproteolysis by gamma-secretase inhibitors 11891288_Notch receptor cleavage depends on but is not directly executed by presenilins 11904448_Wild-type and mutated presenilins 2 trigger p53-dependent apoptosis and down-regulate presenilin 1 expression in HEK293 human cells and in murine neurons 11987239_PS2 mRNA is present only in lymphocytes, in contrast to PS1 mrna, which is found in both myeloid and lymphoid cells. 12048259_regulation by nicastrin and role in determining amyloid beta-peptide production via complex formation 12058025_interaction with GFAP epsilon 12173418_mutant presenilin 2 induces apoptosis accompanied by increased caspase-3-like activity and decreased bcl-2 expression in neuronal cells 12198112_PS2/gamma-secretase contains PEN-2 and requires it for presenilin expression 12210343_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12210343_There is no evidence to suggest that variations in the PSEN2 gene pose as major risk factors for sporadic early-onset Alzheimer disease 12232783_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12232783_in oxygen stress conditions relatively minor variations in PSEN2 promoter DNA sequence structure can enhance PSEN2 gene expression and that may play a role in the induction and/or proliferation of an inflammatory response in AD brain. 12403846_Transcriptional synergism on the pS2 gene promoter between a p160 coactivator and estrogen receptor-alpha depends on the coactivator subtype, the type of estrogen response element, and the promoter context. 12471034_presenilin binds to APH-1, which plays a role in the maturation of presenilin-nicastrin complexes 12556443_C-terminal fragment-PS2 could exhibit some of its functions in the absence of the presenilin 2 N-terminal fragment (NTF-PS2) counterpart derived from the presenilinase cleavage. 12605888_Overexpression of either wild type or mutant presenilin 2 in various cell lines does not directly induce apoptosis or increase the susceptibility to apoptosis. 12770698_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12770698_the current study does not support the notion that the polymorphism in the PS2 gene constitutes a risk factor for either late-onset or early-onset AD 12817569_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12846562_In vitro characterization of the presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase complex using a novel affinity ligand 12885769_presenilins are multifunctional proteins with catalytic activity as well as roles in the generation, stabilization, and transport of the gamma-secretase complex 12925374_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 12925374_a novel mutation in the PSEN2 gene in a family with early-onset Alzheimer disease. The variation in the age at onset confirms that PSEN2 mutations are associated with variable clinical expression. 14577603_identification of two novel spliced presenilin 2 transcripts in lymphocytes and brain under oxidant stress 14741365_IMP1 is a bi-aspartic polytopic protease capable of cleaving transmembrane proteins such as presenilin 2. 14769392_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15004330_HeLa cells overexpressing both PS2 and ubiquilin-1 had PS2 mRNA levels lower than HeLa cells overexpressing PS2 alone, indicating that ubiquilin-1 overexpression, in fact, decreases PS2 transcription. 15006697_Ca(2+) release from intracellular stores was significantly reduced in fibroblasts from familial Alzheimer patients with presenilin 2 mutations. 15537629_results suggest that the proximal two-thirds of the PEN-2 TMD1 is functionally important for endoproteolysis of PS1 holoproteins and the generation of PS1 fragments, essential components of the gamma-secretase complex 15591316_dimeric (NCSTN/APH-1) and trimeric (NCSTN/APH-1/PS1) intermediates of gamma-secretase complex assembly are retained within the ER and incorporation of the fourth binding partner (PEN-2) also occurs on immature NCSTN. 15629423_knock down of anterior pharynx defective 1 homolog A (APH-1A), but not APH-1b, resulted in impaired maturation of nicastrin and reduced expression of presenilin 1, presenilin 2, and PEN-2 proteins 15663477_Four verified PS2 familial Alzheimer disease(FAD) mutations cause substantial changes in the Abeta 42/40 ratio, like PS1 mutations that cause very-early-onset FAD and may represent partial loss of function mutations 15755689_In fibroblasts from familial Alzheimer's disease the presenilin 2 mutation Thr122Arg reduces both Ca2+ release from and capacitative Ca2+ entry to intracellular stores, revealing a modulatory role in disease pathogenesis. 15776278_Of the nine pathogenic mutations found in 12 cases, three were in APP, one in PSEN2, and five in PSEN1, including two novel Greek mutations (L113Q and N135S) in Alzheimer disease 15951428_Wild-type PS2 transgenes expressed in the mouse CNS support little Abeta40 or Abeta42 production. 15975068_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 16014629_Presenilin (PS)1 mutations interfere with PS2-mediated activity by reducing PS2 fragments 16135086_endoproteolysis, N and C terminal fragment interactions, and the assembly and activity of gamma-secretase complexes are very conserved between PS1 and PS2 16233903_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16258850_identification of genes whose expression is modulated by overexpression of mutant presenilin-2 in transgenic mice 16375654_mechanisms by which presenilin 2 affects the programmed cell death include the role of the proteolytically derived presenilin fragments generated by both presenilinase- and caspases 16423463_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16474849_in breast cancer cases two germline alterations, R62H and R71W, in presenilin-2 (PS-2) 16620965_Familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD)-linked Presenilin mutants lower the Ca(2+) content of intracellular stores. 17268504_reduced presenilin proteolytic function leads to increased Abeta42/Abeta40 in Alzheimer disease (Review) 17268505_mutations in Alzheimer disease (Review) 17345043_Presenilin 2 Ser130Leu mutation in a case of late-onset 'sporadic' Alzheimer's disease. 17401156_Exogenous cholesterol and compartmentalization in neuroblastoma cells play a relevant role in regulating the transcription of presenilin 2. 17401676_presenilin 2 overexpression may facilitate assembly into the more active gamma-secretase complex 17412506_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17560791_all known gamma-secretase complexes are active in APP processing and that all combinations of APH-1 variants with either familial Alzheimer mutant PS1 or PS2 support pathogenic Abeta(42) production 17614368_We found that the mutant polypeptides were unable to bind ubiquilin, suggesting that loss of ubiquilin interaction leads to destabilization of presenilin polypeptides. 17727891_It is concluded that in the Northern Han Chinese population, the +A/-A polymorphism of the PSEN2 promoter is a moderate genetic risk factor for developing SAD, independent of the APOE epsilon4 allele. 17727891_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17903177_HMGA1a is a sequence-specific RNA-binding factor causing sporadic Alzheimer's disease-linked exon skipping of presenilin-2 pre-mRNA 18087668_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18087668_We examined association between AD and PSEN2 polymorphisms located in two 5'UTR regions 18283638_Most signet ring cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of the urinary bladder expressed ps2 peptide. 18293935_Mature integrin beta1 with increased expression level is delivered to the cell surface, which results in an increased cell surface expression level of mature integrin beta 1 in presenilin (PS)1 and PS2 double-deficient fibroblasts. 18350357_We reort a late onset familial Alzheimer's disease: novel presenilin 2 mutation and PS1 E318G polymorphism. 18427071_description of an Italian family with hereditary dementia associated with a novel mutation in the presenilin 2 gene (A85V mutation) 18591429_SERCA activity is diminished in fibroblasts lacking both PS1 and PS2 genes, despite elevated SERCA2b steady-state levels. 18667258_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18727676_In vitro expression of a new PSEN2 missense mutation (V393M) cDNA from a patient with early-onset dementia did not result in detectable increase of the secreted Abeta42/40 peptide ratio. 18842294_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 19036728_equilibrium of PS1- and PS2-containing active complexes is dynamic and altered by overexpression of Pen2 or PS1 mutants and that formation of PS2 complexes is positively correlated with increased Abeta42:Abeta40 ratios 19073399_Three-year follow-up of a patient with early onset Alzheimer disease with PSEN2 mutation- case report and review of the literature. 19276543_In PSEN2, T122P and M239V mutations presented with severe behavioral disturbances 19382908_Presenilin-2 dampens intracellular Ca2+ stores by increasing Ca2+ leakage and reducing Ca2+ uptake 19573580_The PSEN2 regulatory region includes two separate promoters modulated by Egr-1, a transcription factor involved in learning and memory. Differential Psen2 regulation in human and mouse has implications for Alzheimer disease mouse models. 19768372_a novel Arg62His Presenilin2 mutation in patient with frontotemporal dementia 19834068_Data show that presenilins 1 and 2 are highly enriched in a subcompartment of the endoplasmic reticulum associated with mitochondria that forms a physical bridge between the two organelles. 19889971_Transactivation of the Pen2 promoter by presenilin 1/2 is p53-dependent. 19913121_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20008660_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20009122_Mutations of the genes for amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin 1 (PSEN1), and presenilin 2 (PSEN2) are responsible for development of the disease in 50 percent of patients with FAD. 20164579_this study demonistreated that an Italian pedigree linked to a novel mutation (S175C) at the third transmembrane domain of PSEN2 in atypical alzeheimer disease. 20333730_A genome scan within nine families for loci influencing age-at-onset, while simultaneously controlling for variation in the primary PSEN2 mutation (N141I) and APOE, was performed. 20375137_Mutations in presenilin 2 are rarely associated with Alzheimer's disease. The best studied Asn141Iso mutation produces an Alzheimer's disease phenotype with a wide range of onset ages. 20457965_A family with the N141I mutation in PSEN2 that presently lives in Germany has been connected to the haplotype that carries the same mutation in pedigrees descended from the Volga Germans. 20468060_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 20594621_The PSEN2 and PSEN1 genes have a very similar genetic structure and encode two proteins expressed in a multiplicity of tissues including the brain. 20628086_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 20677014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20701429_familial Alzheimer disease presenilin 2 protein interactions with InsP(3) receptor causes exaggerated calcium signaling that may contribute to the disease pathology by enhanced generation or reactive oxygen species 20850903_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 20850903_One distinct haploblock in PSEN2 was detected and the frequent haplotypes were analyzed using 4 tagging single nucleotide polymorphisms 21234330_The PS2 mutation causes early cerebral amyloid accumulation and memory dysfunction. 21285369_Presenilin 2 modulates endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interactions and Ca2+ cross-talk. 21409510_PSEN2 Arg62His mutation may lead to a phenotypic heterogeneity presenting either as Alzheimer's disease or Lewy body dementia. 21545304_[review] The role of presenilin 2 in general physiology and Alzheimer's disease pathology due to its mutation are discussed. 21914807_Polar transmembrane-based amino acids in presenilin 1 are involved in endoplasmic reticulum localization, Pen2 protein binding, and gamma-secretase complex stabilization 21959359_the PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP genes exhibited no pathogenic mutations in our cohort of early-onset Alzheimer disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration patients 22027014_The results of this study demonistrated that common variants at AbetaPP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 and MAPT are unlikely to make strong contributions to susceptibility for late onset Alzheimer's disease. 22045484_The results of this study demonstrated that upregulation of PSEN2 and the upregulation of BACE1 is an ancient, conserved, and thus selectively advantageous response to hypoxia/oxidative stress. 22074918_the PS1 complex is only marginally less active than the PS2 complex in Abeta production. 22249458_The results of this study suggested that oxidative stress-mediated ERK activation contributes to increases in beta-secretase and, thus, an increase of Abeta generation in neuronal cells expressing mutant PS2. 22302987_results indicate that PS2 modulates the degradation of RBP-Jk through phosphorylation by p38 MAPK. 22312439_Rare coding variants in APP, PSEN1 and PSEN2, increase risk for or cause late onset Alzheimer's disease 22503161_Here we report a frequency of 11.2% of mutations and variants in the known Alzheimer disease genes in the dementia cohort studied and 24% in the early onset subgroup of patients 22580083_analysis supports the hypothesis that the PSEN2 rs8383 polymorphism is associated with an enlarged risk of sporadic Alzheimer's disease 22753229_we found that the protein expression of presenilin 2 (PS2) was significantly increased in glioma tissues 22755192_Current findings established the involvement of APP, PS1, and PS2 in familial case of Alzheimer disease, while APO polymorphism suggests the existence of other unknown genetic factors or risk factors in the cause of this disease. 22872014_For the Abeta40 region on chromosome 1, association of several SNPs was observed at the presenilin 2 gene (PSEN2) in 125 subjects with severe hypertension. 23546527_Alzheimer's disease pathology induced by overexpression of human mutant presenilin 2 (PS2) protein induced changes in glucose metabolism, were investigated. 23589300_Interactome analyses of mature gamma-secretase complexes reveal distinct molecular environments of presenilin (PS) paralogs and preferential binding of signal peptide peptidase to PS2. 23884042_Functional disruption of the DMN occurs early in the course of autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease, beginning before clinically evident symptoms, and worsening with increased impairment. 24145027_At the transcriptional level, PSEN1/2 removal induced cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB)/CREB-binding protein binding. 24594196_A review, representing the first attempt to systematically organize the available evidence concerning the phenotypic characteristics of familial Alzheimer's disease due to PSEN2 mutations 24650794_Its mutation is the major causes of eraly-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. 24704512_evaluation of contribution of mutations in PS1 and PS2 genes to familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD) cases and sporadic late-onset AD; identified 1 novel frameshift mutation in PS1 gene and 2 novel frameshift mutations in PS2 gene; mutational analysis reports a correlation between clinical symptoms and PS1 and PS2 genetic factors in EOAD 24838186_Mutation in PSEN2 causes of early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. 24844686_study describes a previously unrecognized sequence change (c.376G>A) in PSEN2 in an early onset Alzheimer's disease patient and her likewise affected mother 24858037_The loss of PS2 could have a critical role in lung tumor development through the upregulation of iPLA2 activity by reducing gamma-secretase. 24885952_the structures of presenilin 2 protein with native Val 214 residue and Leu 214 mutation revealed significant structural changes in the region 24927704_The results of this study showed that PSEN2 was significantly downregulated in the auditory cortex of Alzheimer's disease patients when compared to controls. 25323700_PSEN2 mutations are common in the Chinese Han population with a history of AD and FTD 25429133_Levels of presenilin 2 are higher in the cerebral cortex of presenilin 1 knockout mice, suggesting a compensatory upregulation. 25614624_Mutation of on PS1 and PS2 AXXXAXXXG motifs strongly impacts gamma-secretase activity. 25814654_Both human PS2V and zebrafish PS1IV can stimulate gamma-secretase activity despite extreme structural divergence. 25998117_Mutations in PSEN2 are relatively rare cause of the autosomal-dominant cases of Early onset familial Alzheimer Disease. 26159191_This study identified variants in PSEN2 across a range of phenotypes (Alzheimer's Disease , Alzheimer's Disease and cerebrovascular disease,frontotemporal dementia and progressive supranuclear palsy. 26166204_Its mutations of PSEN2 account for pathogenicity of early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease. 26203236_PSEN2 mutations appeared not only in Alzheimer's Disease patients but also in patients with other disorders, including frontotemporal dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, breast cancer, dilated cardiomyopathy, and Parkinson's disease with dementia 26312828_The search for the genetic factors contributing to Alzheimer disease (AD) has evolved tremendously throughout the years. It started from the discovery of fully penetrant mutations in Amyloid precursor protein, Presenilin 1, and Presenilin 2 as a cause of autosomal dominant AD 26337232_Familial Alzheimer's disease Patients with PSEN2 mutations have a delayed AOO with longest disease duration and presented more frequently with disorientation. [review] 26422362_Its mutation is pathogenic to early onset familial AD associated with atypical symptom presentation. 26522186_German early-onset Alzheimer's disease cohort reveals a substantial frequency of PSEN2 variants. 27059953_Data show that presenilin 1 (PS1)-containing gamma-secretase complexes were targeted to the plasma membrane, whereas presenilin 2 (PS2)-containing ones were addressed to the trans-Golgi network, to recycling endosomes. 27135718_This review reveled that Mutations in APP and PS-1 and PS-2 genes that are associated with early-onset, autosomal, dominantly inherited AD. 27239030_Presenilin 2 (PS2), mutations in which underlie familial Alzheimer's disease (FAD), promotes endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria coupling only in the presence of mitofusin 2 (Mfn2). 27293189_Study identified a unique motif in PSEN2 that directs gamma-secretase to late endosomes/lysosomes via a phosphorylation-dependent interaction with the AP-1 adaptor complex. PSEN2 selectively cleaves late endosomal/lysosomal localized substrates and generates the prominent pool of intracellular Abeta that contains longer Abeta; familial Alzheimer's disease-associated mutations in PSEN2 increased the levels of longer Ab... 27608597_Data show that presenilin 1 (PS1)/anterior-pharynx-defective protein 1 (Aph1b), presenilin 2 (PS2)/Aph1aL, PS2/Aph1aS and PS2/anterior pharynx defective 1 homolog B (Aph1b) gamma-secretase produced amyloid beta peptide (Abeta) with a higher Abeta42+Abeta43-to-Abeta40 (Abeta42(43)/Abeta40) ratio than the other gamma-secretases. 27799753_Most of the early-onset Alzheimer's disease -associated mutations have been detected in PSEN1, and several novel PSEN1 mutations were recently identified in patients from various parts of the world, including Asia. Until 2014, no PSEN2 mutations were found in Asian patients; however, emerging studies from Korea and the People's Republic of China discovered probably pathogenic PSEN2 mutations. [review] 28106563_Whole-exome sequencing of 238 African American subjects identified 6 rare missense variants within the early-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) genes, which were observed in AD cases but never among controls. These variants were analyzed in an independent cohort of 300 African American subjects, which indicated that a PSEN2 and PSEN1 novel rare variants, may contribute to AD risk in this population. 28502043_Young healthy adults carrying APOE epsilon4 and APP/presenilin-1/2 displayed different hippocampus functional connectivity patterns 28987665_The results show that in cognitively normal young adults carrying Presenelin 2 mutations had different spontaneous brain activity patterns without cerebral structural differences. 28994238_PS1- and PS2-dependent substrate processing in murine cells lacking presenilins (PSs) or stably re-expressing human PS1 or PS2 in an endogenous PS-null (PSdKO) background, were studied. 29078389_Dominant negative effect of the loss-of-function gamma-secretase mutants on the wild-type enzyme through heterooligomerization has been demonstrated. 29109765_The present data suggest that PS2 mutations suppress lung tumor development by inhibiting the iPLA2 activity of PRDX6 via a gamma-secretase cleavage mechanism and may explain the inverse relationship between lung cancer and Alzheimer's disease incidence. 30104866_Determined whether a pathogenic mutation in the PSEN2 gene in a Korean patient was associated with early onset Alzheimer's disease. Findings revealed that the p.His169Asn might be an important residue in PSEN2, which may alter the functions of PSEN2, suggesting its potential involvement with AD phenotype. 30119059_Results showed a novel PSEN2 mutation with adenosine replacing cysteine at nucleotide position 665, codon 222. 30560948_Results provide evidence that, unlike their significant role in neurogenesis during embryonic development, PSEN1 and PSEN2 are not required for cell-intrinsic regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. 30822634_Thirteen of 148 (8.8%) individuals had possible pathogenic APP, PSEN1, or PSEN2 variants, including 2 (15.4%) APP variants, 8 (61.5%) PSEN1 variants, and 3 (23.1%) PSEN2 variants 30892128_Mutated PSEN2 impairs autophagy by causing a block in the degradative flux at the level of the autophagosome-lysosome fusion step. 31020001_PSEN2 splice isoforms associated with sporadic Alzheimer disease 31167792_results obtained with HEK293T cells suggest that selective presenilin 1 or presenilin 2 inhibition by a given GSI does not explain the previously observed differences in functional and pharmacological properties among various gamma-secretase inhibitors 31182772_Genetic analyses of early-onset Alzheimer's disease using next generation sequencing. 31914229_PSEN1, PSEN2, and APP mutations in 404 Chinese pedigrees with familial Alzheimer's disease. 31991578_Intracellular Calcium Dysregulation by the Alzheimer's Disease-Linked Protein Presenilin 2. 32087291_Systematic validation of variants of unknown significance in APP, PSEN1 and PSEN2. 32420742_Identification of Structural Calcium Binding Sites in Membrane-Bound Presenilin 1 and 2. 32556937_Exploring the Role of PSEN Mutations in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. 32917274_Amyloid-beta1-43 cerebrospinal fluid levels and the interpretation of APP, PSEN1 and PSEN2 mutations. 32957903_Exploring the Role of Aggregated Proteomes in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease. 32992716_Presenilin-2 and Calcium Handling: Molecules, Organelles, Cells and Brain Networks. 33413468_Presence of a mutation in PSEN1 or PSEN2 gene is associated with an impaired brain endothelial cell phenotype in vitro. 33720885_Relevance of a Truncated PRESENILIN 2 Transcript to Alzheimer's Disease and Neurodegeneration. 33769986_Evaluation of the Clinical Features Accompanied by the Gene Mutations: The 2 Novel PSEN1 Variants in a Turkish Early-onset Alzheimer Disease Cohort. 33973882_Novel PSEN1 and PSEN2 Mutations Identified in Sporadic Early-onset Alzheimer Disease and Posterior Cortical Atrophy. 34002480_Plasma amyloid beta levels are driven by genetic variants near APOE, BACE1, APP, PSEN2: A genome-wide association study in over 12,000 non-demented participants. 34009547_A Rare Variation in the 3' Untranslated Region of the Presenilin 2 Gene Is Linked to Alzheimer's Disease. 34067945_Alzheimer's Disease Associated Presenilin 1 and 2 Genes Dysregulation in Neonatal Lymphocytes Following Perinatal Asphyxia. 34102969_Clinical Phenotype and Mutation Spectrum of Alzheimer's Disease with Causative Genetic Mutation in a Chinese Cohort. 34948396_Conformational Models of APP Processing by Gamma Secretase Based on Analysis of Pathogenic Mutations. 34987110_Presenilin Is Essential for ApoE Secretion, a Novel Role of Presenilin Involved in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis. 35491795_PSEN2 Mutation Spectrum and Novel Functionally Validated Mutations in Alzheimer's Disease: Data from PUMCH Dementia Cohort. |
|
|
41.974810 |
0.3860128362 |
-1.373279 |
0.465904109 |
8.544289 |
0.00346607966596641347417628864491234708111733198165893554687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.007327318228253261109261806893755419878289103507995605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.5883712 |
8.7660342 |
66.9684166 |
15.9447923 |
| ENSG00000288714 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.738058 |
0.1532200083 |
-2.706323 |
0.664175879 |
19.519448 |
0.00000995806730443529486982226495150882783491397276520729064941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000031186308808288764195075504215282080622273497283458709716796875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.0035244 |
0.9077350 |
13.1648746 |
2.9236730 |
| ENSG00000288741 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.611310 |
0.3678316410 |
-1.442883 |
0.593672086 |
6.031228 |
0.01405495482381469846133725809522729832679033279418945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026101048464960360101505543184430280234664678573608398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7556637 |
1.9027801 |
12.9983309 |
3.2701805 |
| ENSG00000288852 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.115942 |
0.4417193933 |
-1.178798 |
0.457261514 |
6.860114 |
0.00881409232700863798370960466854739934206008911132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.017068486322047691366998733997206727508455514907836914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1538876 |
1.9317923 |
14.0234089 |
2.7729043 |
| ENSG00000288856 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
17.676007 |
2.4509306906 |
1.293330 |
0.389333496 |
11.198746 |
0.00081852646286662553761631633264528318250086158514022827148437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001938926431056233563518520490731589234201237559318542480468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.6759750 |
5.8172606 |
10.5663385 |
1.9371775 |
| ENSG00000288871 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.415195 |
0.2967756165 |
-1.752556 |
0.538325099 |
10.597686 |
0.00113229265353892959156123509956159978173673152923583984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002617894668896397422641619812111457576975226402282714843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.1801489 |
2.5237573 |
20.7383850 |
5.3898759 |
| ENSG00000288924 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35.521409 |
0.3325274928 |
-1.588454 |
0.263549918 |
38.099705 |
0.00000000067220294489542514166774011299650484763112956443364964798092842102050781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003258363043236937858667883093012791750897605425052461214363574981689453125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.1466455 |
3.1204845 |
54.7297428 |
5.6052888 |
| ENSG00000288927 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
29.314719 |
0.4017526163 |
-1.315621 |
0.286592445 |
21.747488 |
0.00000310996877596487492163217052076884527878064545802772045135498046875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000010371246979946125812738384752709208669330109842121601104736328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.0719625 |
3.5191477 |
42.8429348 |
5.6589691 |
| ENSG00000288966 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.702511 |
0.2402806518 |
-2.057208 |
0.309479385 |
47.080113 |
0.00000000000681436155078089741580458327845593263869666822429849162290338426828384399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000038257883792136186497754457052074641455752246343990918830968439579010009765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8734067 |
2.9459016 |
54.0306543 |
7.5344738 |
| ENSG00000288979 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.810824 |
0.3130463312 |
-1.675552 |
0.506101353 |
11.427672 |
0.00072358293471548422448602622125690686516463756561279296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001727609853833799412325955557889756164513528347015380859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.2726706 |
1.7467175 |
16.9702650 |
3.3356233 |
| ENSG00000288990 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.091773 |
0.2348377447 |
-2.090264 |
0.331505916 |
43.547020 |
0.00000000004138940465311566865168883933798768884337881956980709219351410865783691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000219671921136277327207857148398759822294223909011634532362222671508789062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.6775264 |
2.1293645 |
41.4419628 |
5.0248730 |
| ENSG00000289007 |
101928092 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.044681 |
0.1894434233 |
-2.400161 |
0.575413431 |
19.262000 |
0.00001139519029612016700313010392209278620612167287617921829223632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000035513726514090719339582225000384596569347195327281951904296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5050447 |
1.3300568 |
18.3921796 |
3.6041073 |
| ENSG00000289056 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.076052 |
0.4572931087 |
-1.128809 |
0.447497843 |
6.434020 |
0.01119548877229580713388301660415891092270612716674804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.021272581652817472430694323293209890834987163543701171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.6707976 |
2.4491861 |
19.1297541 |
3.4932960 |
| ENSG00000289135 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.320011 |
0.3115383701 |
-1.682518 |
0.517832681 |
11.022837 |
0.00089996247045696464543496073673622959177009761333465576171875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002115535286501799266262180410080873116385191679000854492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7664506 |
1.7558539 |
15.4865775 |
3.5108028 |
| ENSG00000289161 |
100310756 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
45.287070 |
0.4513086864 |
-1.147814 |
0.244752813 |
22.353925 |
0.00000226749132711108273961373923977014044339739484712481498718261718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000007706233476435545931776741057639412701973924413323402404785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.4903736 |
4.2799476 |
63.5599003 |
6.1059993 |
| ENSG00000289206 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.304845 |
0.0420943446 |
-4.570230 |
1.104103473 |
24.548258 |
0.00000072471847132186130278777916324806085413001710548996925354003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002605174046933919191585283386958238338593218941241502761840820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.5457562 |
0.4651065 |
12.9150532 |
4.0068603 |
| ENSG00000289209 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.666769 |
0.3377493208 |
-1.565975 |
0.482620799 |
10.815304 |
0.00100664490645200124796510010583006078377366065979003906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002340223471291784027026317005493183387443423271179199218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.2420137 |
1.8973946 |
18.4950158 |
3.4367555 |
| ENSG00000289295 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.227325 |
0.1756667877 |
-2.509087 |
0.641692484 |
15.973385 |
0.00006423928367342790707664179628011424938449636101722717285156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000182235600042244074749098192711471710936166346073150634765625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.2169267 |
1.3158864 |
18.4281938 |
4.2424123 |
| ENSG00000289365 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.680393 |
3.2185770504 |
1.686423 |
0.472821294 |
12.398853 |
0.00042959759280398031539363601361003475176403298974037170410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001069104783305808428414684918550392467295750975608825683593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
28.6006181 |
7.4720299 |
8.9977815 |
1.9005324 |
| ENSG00000289397 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
102.090503 |
0.0112245298 |
-6.477201 |
1.554685157 |
10.353357 |
0.00129239473196514505735910116612785714096389710903167724609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002957480037799308566354161698086500109639018774032592773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.4610553 |
0.5367727 |
43.9282552 |
30.3240445 |
| ENSG00000289443 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.631583 |
0.3000743403 |
-1.736608 |
0.513183834 |
11.634385 |
0.00064743760439933434758935648645206129003781825304031372070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001560192496479049020785545565104257548227906227111816406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8804293 |
1.8950616 |
19.7975515 |
3.9179494 |
| ENSG00000289444 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.649575 |
0.0938967784 |
-3.412781 |
1.301397513 |
5.350115 |
0.02072090331602454219006581581652426393702626228332519531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.037004299206838744962233533897233428433537483215332031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3998828 |
6.7995057 |
60.4649046 |
50.8523061 |
| ENSG00000289470 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
399.580000 |
15.7392549944 |
3.976295 |
0.135007429 |
994.511560 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002800646294768230314427350672029954125605021268382250668503633010747940325596563229038077215322834564081348315051 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002931740376650998456257610043950328198678068761678168449731285587319435193987842386404045240969228411101561830260 |
Yes |
No |
726.9943461 |
59.2188962 |
46.5252357 |
3.4624205 |
| ENSG00000289483 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.866941 |
0.2921080928 |
-1.775426 |
0.417178445 |
18.804368 |
0.00001448350190191698465757511732343587596005818340927362442016601562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000044592508984625513440789440489098183206806425005197525024414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.6430863 |
2.2416431 |
26.3356369 |
4.7257190 |
| ENSG00000289537 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.572011 |
0.3432390445 |
-1.542714 |
0.479729227 |
10.884479 |
0.00096973463336035687319680587137327165692113339900970458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002260467970372530971401303645507141482084989547729492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.5595107 |
1.9425161 |
16.2515187 |
3.5041633 |
| ENSG00000289626 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.169838 |
0.0154435337 |
-6.016853 |
1.147259807 |
35.776452 |
0.00000000221306635130914625202892724120749129435026247847417835146188735961914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000010275199542410506318507995419421485738808996757143177092075347900390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.1911880 |
0.1738587 |
12.4716840 |
4.1417041 |
| ENSG00000289688 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18.191164 |
0.3332970613 |
-1.585119 |
0.402764081 |
15.903626 |
0.00006665089587537168349176686099610833480255678296089172363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000188588926791696668335690523221614967042114585638046264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.0038106 |
2.2655238 |
27.2273626 |
4.1559528 |
| ENSG00000289913 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.040700 |
0.1267619435 |
-2.979806 |
0.675825274 |
24.394800 |
0.00000078480233899821223197322767398120824111629190156236290931701660156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000002806804585319508844209373046862943112955690594390034675598144531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6597557 |
0.7840553 |
13.2222016 |
2.9093855 |
| ENSG00000289932 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.017042 |
0.0445690027 |
-4.487816 |
0.839056072 |
44.645313 |
0.00000000002361623092302081161388715901405674574622950423474776471266523003578186035156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000127964599274518047543077946566069010014832230126557988114655017852783203125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.8884919 |
0.5525946 |
20.5000126 |
4.8754629 |
| ENSG00000290034 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.686242 |
0.3171481512 |
-1.656771 |
0.475547365 |
12.904527 |
0.00032778831953054029168734273547158863948425278067588806152343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000831869944338166095870734650929989584255963563919067382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.3117585 |
1.6969361 |
16.8717627 |
3.1401008 |
| ENSG00000290085 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.998534 |
0.3160851484 |
-1.661615 |
0.601617516 |
8.043472 |
0.00456679328357028485596558198267302941530942916870117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.009408971086752846574308151161858404520899057388305664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.4220961 |
1.4464400 |
10.9309695 |
2.7475937 |
| ENSG00000290395_ENSG00000290450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65.530938 |
0.0014367780 |
-9.442947 |
1.073586672 |
177.012789 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000021761020210261219620530834145844534425686309913923213857277754102022296821162516595542231714996008964816201491920821808889741078019142150878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000003666582857345383697219059921122619380043871648499646538387595399594422531965880848344948063406186075305348559538742847507819533348083496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.1803364 |
0.3366324 |
127.7748356 |
126.1126282 |
| ENSG00000290399 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.978442 |
0.0739089528 |
-3.758107 |
0.642200652 |
33.242483 |
0.00000000813536160080085725538090625627227203686686607397859916090965270996093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000035716221662052546630431256900403691467715816543204709887504577636718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.0748422 |
1.5694647 |
42.4574326 |
13.3512663 |
| ENSG00000290418 |
387590 |
TPTEP1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31072375_our findings suggest a tumor suppressing role of TPTEP1 in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression and provide a novel understanding of TPTEP1 during the chemotherapy for Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 32323798_lncRNA TPTEP1 competitively sponges miR3285p to inhibit the proliferation of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. 33173989_lncRNA TPTEP1 inhibits stemness and radioresistance of glioma through miR106a5pmediated P38 MAPK signaling. 33576890_TPTEP1 suppresses high glucose-induced dysfunction in retinal vascular endothelial cells by interacting with STAT3 and targeting VEGFA. 35985238_LncRNA TPTEP1 inhibits the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through miR-548d-3p/KLF9/PER1 axis. |
|
|
27.160470 |
0.4950019724 |
-1.014494 |
0.317491581 |
10.355519 |
0.00129088201323080309541879717727397292037494480609893798828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002954476432824725429943102383845143776852637529373168945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
18.4920349 |
3.9962897 |
37.4330116 |
5.4949979 |
| ENSG00000290425 |
728233 |
PI4KAP1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable 1-phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase activity. Predicted to be involved in phosphatidylinositol phosphate biosynthetic process and phosphatidylinositol-mediated signaling. Predicted to be active in cytoplasm and plasma membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
160.608631 |
0.2425000821 |
-2.043943 |
0.281140127 |
50.246137 |
0.00000000000135621425237070787871684401408821013588872073096780468404176644980907440185546875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007984731697244374429062835804555799861306764064750041143270209431648254394531250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
62.6928599 |
13.5766895 |
260.8661121 |
39.4172164 |
| ENSG00000290427 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.606172 |
2.0867536144 |
1.061260 |
0.399888386 |
7.011128 |
0.00810046475689225019267691862978608696721494197845458984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.015827754806953878152775416765507543459534645080566406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
32.2978798 |
7.4440407 |
15.6435445 |
2.7895821 |
| ENSG00000290474 |
387036 |
GUSBP2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.218730 |
0.2618037376 |
-1.933442 |
0.616266088 |
10.240658 |
0.00137378594705947639463550213889675433165393769741058349609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003129662074177785510697979987071448704227805137634277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.0239773 |
1.6939192 |
15.5782156 |
3.9105229 |
| ENSG00000290535 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.755862 |
0.3209686283 |
-1.639496 |
0.391326120 |
18.018235 |
0.00002187991042481572158146657658406297741748858243227005004882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000066055937383980377450472254441393715751473791897296905517578125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.1954154 |
2.4567879 |
32.0385407 |
4.6743419 |
| ENSG00000290537 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.505843 |
0.4914356896 |
-1.024925 |
0.444679056 |
5.372920 |
0.02045171337445258336051878700345696415752172470092773437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.036598846921304578616584990413684863597154617309570312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
7.8429482 |
2.2719767 |
16.2400384 |
2.9668642 |
| ENSG00000290560 |
653188 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable beta-glucuronidase activity; carbohydrate binding activity; and signaling receptor binding activity. Predicted to be involved in glucuronoside catabolic process. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
12.398558 |
0.2924081354 |
-1.773945 |
0.523469890 |
11.702730 |
0.00062408454096666969058981866425028783851303160190582275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001506868611920177472573989518878079252317547798156738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.8421559 |
2.1660067 |
20.3276344 |
4.6870826 |
| ENSG00000290571 |
55592 |
GOLGA2P5 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization and spindle assembly. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
7.955435 |
0.3684749013 |
-1.440362 |
0.537018320 |
7.542685 |
0.00602541764452875147628496677043585805222392082214355468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.012101668857428816636345736412749829469248652458190917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.4504880 |
1.5608933 |
12.1079837 |
2.4714858 |
| ENSG00000290600 |
155060 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
43.403888 |
0.1803623421 |
-2.471030 |
0.425815570 |
32.337851 |
0.00000001295647358946842488654190635611468396248824319627601653337478637695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000055819483415222985634635054306290635750542605819646269083023071289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
12.8196945 |
5.2138102 |
71.7186150 |
20.0037355 |
| ENSG00000290659 |
220594 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.899593 |
0.1899025788 |
-2.396669 |
0.733500287 |
10.685397 |
0.00107984552680357175254155510657483318937011063098907470703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002499767875724704952605792485087476961780339479446411132812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.8161214 |
1.5990022 |
15.6321247 |
5.2831147 |
| ENSG00000290718 |
100133036 |
FAM95B1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.315878 |
0.0876899976 |
-3.511444 |
1.049105870 |
9.010760 |
0.00268394738589315716772998321459908765973523259162902832031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005801005039651925543342514401956577785313129425048828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.6189358 |
1.2234212 |
18.3181687 |
7.9979697 |
| ENSG00000290735 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.066444 |
0.1135047031 |
-3.139176 |
0.561322768 |
32.084181 |
0.00000001476345307523618785459509303867667306953137540403986349701881408691406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000063143601098373263023949737444279195486274147697258740663528442382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.5072015 |
2.0825562 |
32.3587311 |
12.4769774 |
| ENSG00000290758 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7.364614 |
0.0607588432 |
-4.040762 |
1.379682614 |
7.916683 |
0.00489809960701771771734991389735114353243261575698852539062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010036922143493198431030144490705424686893820762634277343750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
1.0002225 |
1.4843133 |
18.4645929 |
15.8597908 |
| ENSG00000290762 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
39.597584 |
0.1791282696 |
-2.480935 |
0.515291999 |
21.010324 |
0.00000456815161566575527206162873894434994781477143988013267517089843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000014937066426058163707744040615832403773310943506658077239990234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.0783251 |
4.3360315 |
73.6024946 |
16.5066992 |
| ENSG00000290796 |
91355 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable coreceptor activity. Predicted to be involved in several processes, including animal organ development; cholesterol homeostasis; and osteoblast development. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
32789677_The novel mutation P36R in LRP5L contributes to congenital membranous cataract via inhibition of laminin gamma1 and c-MAF. |
|
|
8.546347 |
0.3227205895 |
-1.631642 |
0.534627741 |
9.792081 |
0.00175264972753280440405376783274959962000139057636260986328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.003917188064564535408818013451082151732407510280609130859375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.8713457 |
1.7196440 |
15.1796903 |
3.0595125 |
| ENSG00000290842 |
114819 |
CROCCP3 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in centrosome cycle. Predicted to be located in ciliary rootlet. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
70.892013 |
0.0554113625 |
-4.173674 |
0.751431853 |
24.030423 |
0.00000094825514047346780141842887898451230910268350271508097648620605468750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003364482181102976957525830040141023857813706854358315467834472656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
6.8471139 |
4.7929697 |
134.1199500 |
64.4338952 |
| ENSG00000290851 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
44.425012 |
0.2555201124 |
-1.968491 |
0.292779817 |
47.020154 |
0.00000000000702604940829770196034928693259904563389595111289054329972714185714721679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000039401401696988628665158285143191568139497960032713308464735746383666992187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.3079943 |
3.2833219 |
68.6992428 |
7.6375870 |
| ENSG00000290854 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.403222 |
0.3373245714 |
-1.567791 |
0.329893742 |
22.184030 |
0.00000247725788631047092377686184849761019677316653542220592498779296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000008373365199147347122821810616599691456940490752458572387695312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.7331562 |
5.7038451 |
82.6943841 |
11.2083555 |
| ENSG00000290860 |
643180 |
CCT6P3 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
100.862252 |
0.2351967183 |
-2.088060 |
0.303828091 |
45.241301 |
0.00000000001741925751745583818307198053101876372358858269251413730671629309654235839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000095154789399573712344545455249744366280073570862896303879097104072570800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
29.8343424 |
18.5024231 |
129.6684456 |
56.5611476 |
| ENSG00000290879 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.472333 |
0.0885516749 |
-3.497337 |
0.437733717 |
74.918443 |
0.00000000000000000490565818613750424859218680303179575168377686339091225953268349257996305823326110839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000039718878128024991787342948231331320812359435230625911983359799251047661527991294860839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.5240596 |
1.3676757 |
51.5206663 |
7.8686615 |
| ENSG00000290912 |
100132101 |
HERC2P7 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.184495 |
0.1585973354 |
-2.656560 |
1.021094691 |
6.019708 |
0.01414699002189612545010710675796872237697243690490722656250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.026248846351123421294371240719556226395070552825927734375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
5.6592200 |
7.5966658 |
35.0952506 |
30.6568916 |
| ENSG00000290926 |
441242 |
LINC03006 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46.407329 |
0.2963274336 |
-1.754736 |
0.296190767 |
35.015777 |
0.00000000327044692085495562413376178058973392515085265586094465106725692749023437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000014926344017260094182247720409444091682615862737293355166912078857421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
17.9310722 |
4.5677436 |
60.7699023 |
10.4531702 |
| ENSG00000290951 |
54441 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable chromatin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in sister chromatid cohesion. Predicted to be part of cohesin complex. Predicted to be active in chromatin and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
55.212302 |
0.4073021476 |
-1.295829 |
0.362241316 |
12.661690 |
0.00037322477559499124283998172657561553933192044496536254882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000938146745194494272902796527802138371043838560581207275390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.8294591 |
7.8708532 |
83.9418939 |
12.9620227 |
| ENSG00000290962 |
7221 |
TRPC2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable several functions, including calmodulin binding activity; diacylglycerol binding activity; and inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate binding activity. Predicted to act upstream of or within several processes, including inter-male aggressive behavior; mating behavior; and territorial aggressive behavior. Predicted to be located in several cellular components, including Golgi membrane; dendrite membrane; and nuclear envelope. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
12601176_human TRPC2 gene is compared to mouse isoforms of TRPC2: it may never have been an active gene because of incomplete ancestral duplication or loss of chromosomal sequences 12631698_Relaxed selective pressure in primate evolution. 17217050_the mammalian genome codes for seven TRPCs of which TRPC2 is the largest with the most restricted pattern of expression and has several alternatively spliced variants--{REVIEW} |
|
|
24.690687 |
0.0807258042 |
-3.630826 |
0.467839980 |
70.640940 |
0.00000000000000004285311961848001558529430399641466082528755028309246088991102396903443150222301483154296875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000330811739314207645015302313662108678702347328275806814801285327121149748563766479492187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
3.7142368 |
1.1753373 |
46.3985322 |
7.2702895 |
| ENSG00000290993 |
132241 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
122.671868 |
0.4531120388 |
-1.142060 |
0.145404337 |
62.768698 |
0.00000000000000232464110771599922825054816245782789990381397328411683389504105434753000736236572265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000016269181009904292677546962750156044233515884728236144951551978010684251785278320312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
76.0636400 |
9.9026973 |
169.5505362 |
15.0092006 |
| ENSG00000291003 |
400322 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30809632_Cell colony formation, Transwell and cell scratch tests were performed to evaluate the role of HERC2P2 in glioblastoma growth. Furthermore, we overexpressed HERC2P2 in U87 cells and established a mouse intracranial glioma model to examine the function of HERC2P2 in vivo |
|
|
2199.899629 |
0.4168003317 |
-1.262572 |
0.049150827 |
655.140196 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000170304671164292723642220998491788838295626477274824770158339088968733496148477890928092184311533595191019207143169014339956050734946330141431847622838988405128730056075268187713167530920 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000105175604451253581344387743067809423602821388951349497482084079512899985839746585741375279068282460075438275595791782886298714214819596453495213455549826378960474855966939153013785598757 |
Yes |
No |
1312.6536996 |
45.2164007 |
3172.7711308 |
75.5426211 |
| ENSG00000291004 |
283796 |
GOLGA8IP |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in Golgi organization. Predicted to be active in Golgi cis cisterna; Golgi cisterna membrane; and cis-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
7.742664 |
0.0142198925 |
-6.135946 |
1.174906507 |
32.733088 |
0.00000001057221237012080212353726433888861935272984737821388989686965942382812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000045936371675885497642642652221106613907863902568351477384567260742187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
0.2249410 |
0.2208990 |
16.0121458 |
6.4614245 |
| ENSG00000291006 |
730101 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28943432_Overexpression of LOC730101 prompted the proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer both in vitro and in vivo while Silencing observed opposite phenomenon. 29253564_Taken together, our findings enlarged the knowledge about the roles of LOC730101 in osteosarcoma progression. 30024599_LOC730101 was significantly upregulated in human osteosarcoma tissues compared with corresponding adjacent normal tissues; elevated LOC730101 expression was correlated with advanced clinical stage and distant metastasis |
|
|
126.501172 |
0.2458726557 |
-2.024017 |
0.182496558 |
125.303317 |
0.00000000000000000000000000004368072487939327118533803418190842946837897206027476970375740946128536854097066527424786386291089002043008804321289062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000545454737072626638862016006350244415938789295661683506534119454749047381210760865322129120613681152462959289550781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
49.4025156 |
6.6297892 |
202.3488907 |
17.5860136 |
| ENSG00000291010 |
100887750 |
MRPS31P5 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32992457_Transcriptome and Gene Fusion Analysis of Synchronous Lesions Reveals lncMRPS31P5 as a Novel Transcript Involved in Colorectal Cancer. |
|
|
41.769160 |
0.3166833325 |
-1.658887 |
0.358963399 |
20.263298 |
0.00000674827847669616504830457717756253543939237715676426887512207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000021629661306413766082420643832584516985662048682570457458496093750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
16.0105979 |
4.4566203 |
52.0158423 |
10.0898551 |
| ENSG00000291026 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.400888 |
0.2483917774 |
-2.009311 |
0.669250593 |
9.077294 |
0.00258802748568277146690164158826519269496202468872070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.005609293052669266956000715396157829673029482364654541015625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1223061 |
2.4462259 |
16.8488328 |
6.5478971 |
| ENSG00000291038 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
85.383619 |
0.4745452269 |
-1.075383 |
0.171261467 |
40.149196 |
0.00000000023528827429683003540095539322192421533008754863658396061509847640991210937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000001184466210307370820319479648788374426260361360618844628334045410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
56.9008150 |
5.9334640 |
120.8939092 |
8.0478413 |
| ENSG00000291040 |
401577 |
CD99P1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.314000 |
0.2693369162 |
-1.892516 |
0.487916667 |
15.737857 |
0.00007275344537108805831413654852113381821254733949899673461914062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000204346499272551820761481544685977951303357258439064025878906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.7155133 |
1.7475331 |
17.5636669 |
4.0145709 |
| ENSG00000291055 |
728609 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.832320 |
0.3404591967 |
-1.554446 |
0.238550436 |
43.194901 |
0.00000000004954963878022391233421233061754243316016088627407043532002717256546020507812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000261477536072972824231876504247318836193780811072429060004651546478271484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
25.5343308 |
5.5360737 |
75.6345931 |
11.2131170 |
| ENSG00000291058 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.817505 |
0.1583895371 |
-2.658451 |
0.664248503 |
17.457004 |
0.00002938795620150699700588205198759084169068955816328525543212890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000087206721659477935432863704434680585109163075685501098632812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6884460 |
1.3106179 |
17.1070755 |
4.7103578 |
| ENSG00000291063 |
107984974 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19291764_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
47.176853 |
0.4879494200 |
-1.035196 |
0.462586979 |
4.833295 |
0.02791522753947701940280268217975390143692493438720703125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.048365859664594529343517592678836081176996231079101562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.7025332 |
10.4884835 |
71.2594906 |
15.2729709 |
| ENSG00000291064 |
118433 |
RPL23AP7 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
71.879879 |
2.1782348492 |
1.123160 |
0.285385948 |
15.173121 |
0.00009808979332699039276315805535588765451393555849790573120117187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000269961840295800537935927421173687434929888695478439331054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.2995696 |
15.8020628 |
46.0754239 |
5.6113776 |
| ENSG00000291068 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
214.964067 |
0.2591262434 |
-1.948273 |
0.117751094 |
291.544625 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000002290865352310783048880622713081878843035972148866893745044573384676322270304655331474742858025145244979251639239238473531652476841516481555612564883150097816573963205311059709856635890901088714599609375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000649005232247738152672724461793009360424747354464216248029122383201758212770601426872988832263082933639387188782285674286452927915792270536751909986752557299265198320625813721562735736370086669921875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
94.3290411 |
9.1301417 |
365.6748056 |
22.6020243 |
| ENSG00000291069 |
399761 |
BMS1P1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34.794308 |
0.4757421220 |
-1.071748 |
0.273383471 |
15.624226 |
0.00007725840488008964442295106733737952708906959742307662963867187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000216300086500402705732420960416106936463620513677597045898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.1531364 |
3.9189372 |
49.0719646 |
5.3216165 |
| ENSG00000291072 |
84809 |
CROCCP2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in centrosome cycle. Predicted to be located in ciliary rootlet. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
233.740537 |
0.4712868408 |
-1.085323 |
0.120958921 |
80.771147 |
0.00000000000000000025343138366387306510968529845784156188123916780562973598972531519279982603620737791061401367187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000002173531216082955604801698160355319023281648286251743935892921655295140226371586322784423828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
136.6913380 |
25.9771297 |
292.6311956 |
39.7432343 |
| ENSG00000291074 |
339184 |
CCDC144NL |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30496345_CCDC144NL-AS1 might be involved in the pathogenesis of Endometriosis and provide a novel target for ovarian Endometriosis. |
|
|
29.595622 |
0.2109144249 |
-2.245270 |
0.519148157 |
17.600197 |
0.00002725601564040452387191471039784573804354295134544372558593750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000081190472422274626474077152682440328135271556675434112548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
8.3350781 |
3.3136568 |
38.8566540 |
10.5072816 |
| ENSG00000291082 |
440248 |
HERC2P9 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
127.669102 |
0.2926513019 |
-1.772745 |
0.333282604 |
26.843697 |
0.00000022059258304164357229168501664529067340936308028176426887512207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000838729141085692789073008281824916920754731108900159597396850585937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
59.8541539 |
17.0512085 |
204.5323275 |
41.3103327 |
| ENSG00000291085 |
84222 |
TMEM191A |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
9.149499 |
0.2094083746 |
-2.255609 |
0.779273328 |
8.151747 |
0.00430196884862301797552985860306762333493679761886596679687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.008918126433381424675306270444252731977030634880065917968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
2.6285395 |
1.2485346 |
13.1898704 |
3.7548342 |
| ENSG00000291090 |
284047 |
CCDC144BP |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47.355210 |
0.3921938458 |
-1.350361 |
0.405323439 |
10.735681 |
0.00105089332236745934198718366303637594683095812797546386718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.002437332721267080736654575545685474935453385114669799804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
26.6196741 |
8.1721371 |
68.3487689 |
14.8199532 |
| ENSG00000291092 |
5387 |
PMS2P3 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in mismatch repair. Predicted to be part of mismatch repair complex. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
20819778_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
24.439007 |
0.2829555423 |
-1.821353 |
0.404751450 |
20.260369 |
0.00000675861609708048784595901120608729684136051218956708908081054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000021653391272608640355729417437125050582835683599114418029785156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
10.5321135 |
3.2447831 |
37.3580100 |
7.6976267 |
| ENSG00000291093 |
102724316 |
SVIL-AS1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
35068325_N6-methyladenosine-induced SVIL antisense RNA 1 restrains lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation by destabilizing E2F1. |
|
|
134.450044 |
0.1751184682 |
-2.513597 |
0.990223111 |
5.713241 |
0.01683742139180233188255897402996197342872619628906250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.030723246352206998871503529358051309827715158462524414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
36.6582644 |
31.2455396 |
209.1061213 |
123.8062412 |
| ENSG00000291114 |
284367 |
SIGLEC17P |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70.381984 |
12.5061786489 |
3.644569 |
0.264007778 |
248.865110 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000004590480244064991757972607132513597960720618679354848778844617503749109569447800355620185865568169074727518800584021760470744542219606842666304591382697708468185737729072570800781250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001091070666705302304856755746726479584782344930046851888930895076122274718928556467731162381099957962206248972095141640886821004962315090434238351591034188459161669015884399414062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
130.1136350 |
22.0943293 |
10.4990683 |
1.6549337 |
| ENSG00000291118 |
79970 |
ZNF767P |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20379614_Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) |
|
|
72.263335 |
0.4564035192 |
-1.131618 |
0.283013471 |
15.591260 |
0.00007861714239232779697762881765399356481793802231550216674804687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000219521192151108258255876037878806528169661760330200195312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
44.4598885 |
7.7176455 |
98.9075027 |
11.7268646 |
| ENSG00000291122 |
352954 |
CASTOR3 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in cellular response to L-arginine and negative regulation of TORC1 signaling. Predicted to be active in cytosol. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
31381506_Study demonstrated for the first time that downregulation of GATS by shRNA could decrease the cell autophagy in MDA-MB-231 cells by the the PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway. And the molecular experiments showed that GATS could promote the proliferation and metastasis of MDA-MB-231 cells, this may provide an effective method for developing targeted drug to treat TNBC. |
|
|
70.103727 |
0.3327922812 |
-1.587306 |
0.226374770 |
50.279832 |
0.00000000000133312610333719794659168638655868312117673546435270282017881982028484344482421875000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000007864484926161887498197238510202426026163280425862467382103204727172851562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
30.0890104 |
5.7573437 |
91.0489774 |
11.6190944 |
| ENSG00000291129 |
728448 |
PPIEL |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This transcribed pseudogene is related to PPIE (Gene ID: 10450). Expression of this pseudogene may be downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Differential DNA methylation of this locus may be associated with intellectual disability and bipolar disorder in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]. |
|
|
|
|
|
102.501064 |
0.4874684111 |
-1.036619 |
0.230651676 |
19.937585 |
0.00000800118095684970755663602270946199723766767419874668121337890625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000025413692903615600328587689760162504626350710168480873107910156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
66.4562082 |
9.0231960 |
137.8146457 |
12.7685029 |
| ENSG00000291135 |
2210 |
FCGR1BP |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Three distinct, but closely related classes of receptors that bind the Fc portion of IgG have been identified (Fcgamma RI, II and III). The FcgammaRI family consists of three closely related genes termed A, B, and C. This gene likely encodes a non-functional protein that is not detectable at the cell surface and binds ligand with low affinity. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2019]. |
|
|
11802953_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17124586_Fcgamma receptor I Ab and Fcgamma receptor I play an important role in the regulation of alopecia areata (AA), are useful for a marker of the disease prognosis and are worth intense research for the reasonable and specific therapy of AA. 19330030_Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 21135020_The increased CD64 expression during pregnancy in patients with multiple sclerosis is indicative of enhanced innate immune functions. 32073518_Up-regulation of CD64 Expression on Monocytes in Patients With Active Adult-Onset Still Disease: A Possible Biomarker of Disease Activity. 35381635_[Diagnostic value of FCGR1B gene transcription level in active tuberculosis]. |
|
|
40.162983 |
0.2313341736 |
-2.111950 |
0.372070840 |
31.500601 |
0.00000001993785159837119727085496135449149690543890756089240312576293945312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000084249266988823034278383147712560008457671756332274526357650756835937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.5428650 |
3.9975740 |
68.3770987 |
11.4193280 |
| ENSG00000291137 |
2630 |
GBAP1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28983119_Using skin-derived induced pluripotent stem cells of PD patients with GBA mutations and controls, we observed a significant GBA up-regulation during dopaminergic differentiation, paralleled by down-regulation of miR-22-3p. Our results describe the first microRNA controlling GBA and suggest that the GBAP1 non-coding RNA functions as a GBA ceRNA 30951202_Pseudogene GBAP1 contributes to the development and progression of gastric cancer by sequestering the miR-212-3p from binding to GBA. 31670439_Parkinson's Disease: Glucocerebrosidase 1 Mutation Severity Is Associated with CSF Alpha-Synuclein Profiles. |
|
|
131.084568 |
0.3208850895 |
-1.639871 |
0.237488369 |
46.285173 |
0.00000000001022346742568893359433109851645257769650609880329739098669961094856262207031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000056658436779063939571499781226105916208390933519467580481432378292083740234375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
65.2041377 |
11.9834040 |
202.6180112 |
25.5564748 |
| ENSG00000291139 |
349152 |
DPY19L2P2 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable glycosyltransferase activity. Predicted to be involved in spermatid development. Predicted to be integral component of membrane. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
20.046638 |
0.3141332888 |
-1.670551 |
0.458596198 |
12.956847 |
0.00031875360372473254865280378744785139133455231785774230957031250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000810474279238079645983072740733632599585689604282379150390625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
9.9292548 |
2.9983453 |
32.1669149 |
6.3100117 |
| ENSG00000291143 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.730599 |
0.4018081857 |
-1.315421 |
0.462789190 |
7.797318 |
0.00523238450331744899685082472728936409112066030502319335937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.010650944044816651121165840265803126385435461997985839843750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
15.7403520 |
4.7536509 |
39.6065192 |
8.7024886 |
| ENSG00000291151 |
155400 |
NSUN5P1 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
This locus represents a transcribed pseudogene of a nearby locus on chromosome 7, which encodes a putative methyltransferase. There is also a third closely related pseudogene locus in this region. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013]. |
|
|
|
|
|
222.677753 |
0.4636929260 |
-1.108758 |
0.136878222 |
65.456970 |
0.00000000000000059396804419508283967616067464703565708133601534074452743539040966425091028213500976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000004310210586194406579847866835484898598491489141171228993698605336248874664306640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
144.0800308 |
12.5333313 |
313.1958653 |
18.1872776 |
| ENSG00000291153 |
64940 |
STAG3L4 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to enable chromatin binding activity. Predicted to be involved in sister chromatid cohesion. Predicted to be part of cohesin complex. Predicted to be active in chromatin and nucleus. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
27.914269 |
0.3657035970 |
-1.451253 |
0.363459487 |
15.945200 |
0.00006520289806480153731085142032597445904684718698263168334960937500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000184791623547709410717992950523580475419294089078903198242187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
14.6281733 |
3.5061873 |
40.1494060 |
6.4506720 |
| ENSG00000291156 |
100288175 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
324.425995 |
5.3601789430 |
2.422281 |
0.131146846 |
338.076716 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000167390599151216450392125721959815858608810553639255989584008935748561618305571636217312425285779812278958567348935516373176172043139041051652322196506024456289349233401755851846984257669248563615838065743446350097656250000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000053594039988545657043867932837988033789015248966722864210654637866611607084159145321453016482477129662999311080540274127723313579111647136527772996400563024132302388986744704316053352147197763599706377135589718818664550781250000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
557.4404108 |
43.9496381 |
104.6929442 |
6.6833712 |
| ENSG00000291158 |
57234 |
LINC00869 |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Predicted to be involved in intracellular protein transport and vesicle tethering to Golgi. Predicted to be active in cytoplasmic vesicle and trans-Golgi network. [provided by Alliance of Genome Resources, Apr 2022] |
|
|
|
|
|
153.762857 |
13.5057682438 |
3.755504 |
0.987522234 |
11.388655 |
0.00073894023813266560083562461969108881021384149789810180664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.001761142889526585465775898597939885803498327732086181640625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
233.3328055 |
232.3388488 |
15.5998101 |
10.6361148 |
| ENSG00000291171 |
347918 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
65.222834 |
0.4772624012 |
-1.067145 |
0.277216798 |
14.814626 |
0.00011861200354434746871701289450129479519091546535491943359375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000323129046200547906473460324505708740616682916879653930664062500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
44.1524849 |
9.5260978 |
93.3280679 |
13.7878272 |
| ENSG00000291175 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66.324854 |
0.3092408615 |
-1.693197 |
0.271852057 |
37.780614 |
0.00000000079164556613583245344363832138984658770564095675581484101712703704833984375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000003814785685982659472130559678067912576793219159299042075872421264648437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
33.5256268 |
5.7625326 |
108.3651799 |
12.2587248 |
| ENSG00000291176 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.841579 |
0.3041155558 |
-1.717308 |
0.334969846 |
26.840754 |
0.00000022092885323828696660946224912536184348255119402892887592315673828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000839575147733551949099956458050231233869453717488795518875122070312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
13.7312846 |
3.0988257 |
45.2533933 |
6.4513798 |
| ENSG00000291194 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.630555 |
0.3103556907 |
-1.688005 |
0.371302576 |
21.075280 |
0.00000441588169594989125599790794063359555821079993620514869689941406250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000014464805555308565541733530068757573872062494046986103057861328125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
11.2609015 |
3.0026457 |
36.5645632 |
6.3455199 |
| ENSG00000291202 |
101926918 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
91.610168 |
0.4786941561 |
-1.062824 |
0.187713548 |
32.469341 |
0.00000001210878154843277244142421046353003122320046713866759091615676879882812500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000052350795446651359672394289738669992395614372071577236056327819824218750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
62.2275099 |
8.2242768 |
130.8893301 |
11.4019367 |
| ENSG00000291207 |
641977 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
Septins, such as SEPT13, are conserved GTP-binding proteins that function as dynamic, regulatable scaffolds for the recruitment of other proteins. They are involved in membrane dynamics, vesicle trafficking, apoptosis, and cytoskeleton remodeling, as well as infection, neurodegeneration, and neoplasia (Hall et al., 2005 [PubMed 15915442]).[supplied by OMIM, Jul 2008]. |
|
|
|
|
|
71.533975 |
0.4170855995 |
-1.261585 |
0.345925824 |
12.933092 |
0.00032282416157968960804952596177486157102975994348526000976562500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000819976703651044370665945670850760507164523005485534667968750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
43.6960967 |
9.6271276 |
105.4253065 |
16.2309341 |
| ENSG00000291208 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64.678948 |
0.2554415560 |
-1.968935 |
0.267419382 |
54.354850 |
0.00000000000016736444337171004159777602864050715500876705121857668245866079814732074737548828125000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000001047180663063348938587755217992087390264585589072510174446506425738334655761718750000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
23.8317304 |
6.4991081 |
94.0982363 |
17.6758634 |
| ENSG00000291215 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
179.962233 |
0.3822704917 |
-1.387334 |
0.134963087 |
106.083854 |
0.00000000000000000000000070680176339573926465270971818857367083784832633848516115421474118431580113686152344598667696118354797363281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000000000000000000007559705817189210858145477502577632343488756838673787153323724817555184785078381537459790706634521484375000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
100.3257569 |
9.5304285 |
264.7375521 |
17.0728389 |
| ENSG00000291230 |
256236 |
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14.469446 |
0.1506723598 |
-2.730513 |
0.571935715 |
23.705310 |
0.00000112272325423358366443076210988705199156356684397906064987182617187500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000003952157222153039453150288190519390241206565406173467636108398437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
4.1485693 |
1.5330057 |
28.0268888 |
5.4610554 |
| ENSG00000291237 |
6648 |
SOD2 |
protein_coding |
|
Mouse_homologues FUNCTION: Destroys superoxide anion radicals which are normally produced within the cells and which are toxic to biological systems. |
Mouse_homologues Acetylation;Direct protein sequencing;Manganese;Metal-binding;Mitochondrion;Nitration;Oxidoreductase;Reference proteome;Transit peptide;Ubl conjugation |
|
This gene is a member of the iron/manganese superoxide dismutase family. It encodes a mitochondrial protein that forms a homotetramer and binds one manganese ion per subunit. This protein binds to the superoxide byproducts of oxidative phosphorylation and converts them to hydrogen peroxide and diatomic oxygen. Mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic cardiomyopathy (IDC), premature aging, sporadic motor neuron disease, and cancer. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 1. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016]. |
Mouse_homologues mmu:20656; |
Mouse_homologues cytoplasm [GO:0005737]; mitochondrial inner membrane [GO:0005743]; mitochondrial matrix [GO:0005759]; mitochondrial nucleoid [GO:0042645]; mitochondrion [GO:0005739]; myelin sheath [GO:0043209]; DNA binding [GO:0003677]; enzyme binding [GO:0019899]; identical protein binding [GO:0042802]; manganese ion binding [GO:0030145]; oxidoreductase activity [GO:0016491]; oxygen binding [GO:0019825]; superoxide dismutase activity [GO:0004784]; acetylcholine-mediated vasodilation involved in regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure [GO:0003069]; aging [GO:0007568]; apoptotic mitochondrial changes [GO:0008637]; cellular response to ethanol [GO:0071361]; cellular response to oxidative stress [GO:0034599]; detection of oxygen [GO:0003032]; erythrophore differentiation [GO:0048773]; glutathione metabolic process [GO:0006749]; heart development [GO:0007507]; hemopoiesis [GO:0030097]; hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process [GO:0050665]; hydrogen peroxide metabolic process [GO:0042743]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage [GO:0008630]; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to oxidative stress [GO:0008631]; iron ion homeostasis [GO:0055072]; liver development [GO:0001889]; locomotory behavior [GO:0007626]; mitochondrion organization [GO:0007005]; negative regulation of apoptotic process [GO:0043066]; negative regulation of cell population proliferation [GO:0008285]; negative regulation of fat cell differentiation [GO:0045599]; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation [GO:0048147]; negative regulation of membrane hyperpolarization [GO:1902631]; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process [GO:0043524]; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway [GO:1902176]; negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation [GO:1904706]; neuron development [GO:0048666]; oxygen homeostasis [GO:0032364]; positive regulation of cell migration [GO:0030335]; positive regulation of hydrogen peroxide biosynthetic process [GO:0010729]; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process [GO:0045429]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell apoptotic process [GO:1905461]; positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation involved in phenotypic switching [GO:1905932]; post-embryonic development [GO:0009791]; protein homotetramerization [GO:0051289]; regulation of blood pressure [GO:0008217]; regulation of catalytic activity [GO:0050790]; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential [GO:0051881]; regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II [GO:0006357]; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria [GO:0001836]; removal of superoxide radicals [GO:0019430]; respiratory electron transport chain [GO:0022904]; response to activity [GO:0014823]; response to axon injury [GO:0048678]; response to cadmium ion [GO:0046686]; response to cold [GO:0009409]; response to electrical stimulus [GO:0051602]; response to gamma radiation [GO:0010332]; response to hydrogen peroxide [GO:0042542]; response to hyperoxia [GO:0055093]; response to hypoxia [GO:0001666]; response to immobilization stress [GO:0035902]; response to isolation stress [GO:0035900]; response to L-ascorbic acid [GO:0033591]; response to lipopolysaccharide [GO:0032496]; response to magnetism [GO:0071000]; response to manganese ion [GO:0010042]; response to nutrient levels [GO:0031667]; response to oxidative stress [GO:0006979]; response to reactive oxygen species [GO:0000302]; response to selenium ion [GO:0010269]; response to silicon dioxide [GO:0034021]; response to superoxide [GO:0000303]; response to xenobiotic stimulus [GO:0009410]; response to zinc ion [GO:0010043]; superoxide anion generation [GO:0042554]; superoxide metabolic process [GO:0006801]; vasodilation [GO:0042311] |
11124296_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11299047_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11323405_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11350569_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11481695_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11719088_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11721640_Review: Contribution of proteomics to the molecular analysis of renal cell carcinoma with an emphasis on manganese superoxide dismutase. 11756571_Cu,Zn-SOD and Mn-SOD are differently regulated by estrogen and progesterone in human endometrial stromal cells 11836586_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11836586_Polymorphism in MnSOD is associated with age among hispanics with colorectal carcinoma 11837748_Increased expression of manganese superoxide dismutase is associated with that of nitrotyrosine in myopathies with rimmed vacuoles. 11849743_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 11853549_AP-2 down-regulates transcription of the human SOD2 gene via its interaction with Sp1 within the promoter region. 11912921_Transcription regulation of human manganese superoxide dismutase gene. 11912930_Catalytic pathway of manganese superoxide dismutase by direct observation of superoxide. 11977425_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12032830_NF-kappaB-dependent MnSOD expression protects adenocarcinoma cells from TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis 12063011_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12078513_Manganese superoxide dismutase transgenic mice: characteristics and implications 12127599_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12161520_Nuclear factor-kappa B is required for tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced manganese superoxide dismutase expression in human endometrial stromal cells. 12239572_PKB-regulated Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a (also known as FKHR-L1) protects quiescent cells from oxidative stress by directly increasing their quantities of manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) messenger RNA and protein 12447859_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12447859_Val-Ala polymorphism in Mn-SOD influences neither susceptibility to alcohol-induced liver fibrosis nor alcohol-induced oxidative stress. 12469139_Manganese superoxide dismutase expression within tumor cells is closely related to mode of invasion in human gastric carcinoma 12517793_a new thiol-sensitive mutant form of the human mitochondrial enzyme 12540612_Gene transfer of this enzyme extends islet graft function in a mouse model of autoimmune diabetes. 12551919_This isoform, when expressed in PC-12 cells affects t-butylhydroperoxide-induced apoptosis differentially from its isoenzyme. 12590982_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12592389_In prostate cancer cells, one of the downstream mediators of the senescence-associated tumor suppression effect of mac25/IGFBP-rP1 is SOD-2. 12624725_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12627943_Replacement of His-30 with Val in human MnSOD results in a mutant with much decreased catalytic activity and highly susceptible to product inhibition compared to wild-type. 12644569_protein whose expression is deregulated in the epidermis of the elderly 12673575_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12683635_It is indicated that polymorphic mutations of Mn-SOD exist in human normal cells and that the deletions might be obtained in the course of malignant transformation of OSC although decrease in Mn-SOD activity is not involved in the transformation. 12684509_data suggest communication between the proximal promoter region and the TNF-responsive element which involves chromatin remodeling and histone acetylation during the induction process of Mn-SOD in response to TNF. 12700280_MnSOD may be a tumor suppressor gene in human pancreatic cancer 12711112_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 12732398_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12815947_Higher frequencies of SOD2 allele Val and genotype Val/Val and of SOD3 allele Arg and genotype Arg/Arg were established for group DPN+. On this evidence, SOD2 and SOD3 were associated with DPN in DM type 1. 12815947_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12829021_Overexpression of the human MnSOD transgene in 32D cl 3 cells results in stabilization of the mitochondria and reduction in radiation-, TNF-alpha-, or IL-3 withdrawal-induced damage. 12880680_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12880680_no significant differences in the genotype, allele, and phenotype frequencies of MnSOD gene polymorphisms between patients with ankylosing spondylitis and controls 12946273_Elevated expression of MnSOD in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. 12948282_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 12960753_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 12960753_the influence of a functional polymorphism of the dopamine D3 receptor, and its interaction with a Mn superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) polymorphism, in contributing to tardive dyskinesia in a chronic inpatient population with schizophrenia 12963120_No association of the Ala-9Val MnSOD polymorphism to the development of breast cancer 12963120_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14503839_Results suggest that the failure of manganese-superoxide dismutase mRNA induction by oxidative stress in peripheral lymphocytes may be involved in the development of gastric cancer. 14515147_Regulation of MnSOD by IL-1 in retinoic acid-differentiated neuroblastoma cells was mediated by the nuclear factor kappaB. 14578853_Cu/Zn-SOD in cytosol and Mn-SOD in mitochondria each are capable of protecting HepG2 cells expressing CYP2E1 against cytotoxicity induced by pro-oxidants. 14611903_The role of manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn SOD) genes polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). 14638684_His30 and Tyr166 in wild-type Mn-SOD have roles in prolonging the lifetime of the inhibited complex 14643949_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14687717_CYP1A1 4887A may be a risk factor for the development of reactive arthritis, especially in the presence of Mn SOD 1183T/T 14687717_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14688256_an active site mutant of human manganese-superoxide dismutase has anti-proliferative functions and demonstrates the signaling role of MnSOD 14704872_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 14729580_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 14744747_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15075214_Increase in hydroxyl radical concentration in the extracellular space of muscles from wild-type mice after the contraction protocol most likely results from degradation of hydrogen peroxide generated by MnSOD activity. 15087454_human SOD2 gene is induced by nucleophosmin and NF-kappaB 15088300_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15094225_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15094225_functional polymorphisms in MTP and MnSOD may be involved in determining susceptibility of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis 15131792_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15166009_Review. Blood vessels express 3 isoforms of superoxide dismutase, 1 of which is manganese SOD in mitochondria. This review will focus mainly on the role of individual SODs in relation to endothelium under normal conditions and in disease states. 15168344_Neoplastic cells in breast carcinomas retain their capability to produce MNSOD, thus are protected from possible cellular damage by reactive oxygen species. MNSOD content varies according to the degree of differentiation of breast carcinoma. 15184255_MnSOD Ala allele polymorphism increases risk of breast cancer in cigarette smokers. 15184255_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 15196853_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15213518_Finds homozygous variant MnSOD genotype is associated with increased lung cancer risk among individuals with zero or 'low' asbestos exposure score and no association among the 'high' AES group. 15213518_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15217492_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15247771_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15266664_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15308628_Vascular endothelial growth factor is coupled to Mn-SOD expression through growth factor-specific reactive oxygen species. 15330761_results indicate that the PKC pathway leading to SOD2 induction proceeds at least in part through NF-kappaB 15331175_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15337840_Although (MnSOD) in DEV cells was significantly increased in acute infection with viral and nutritional stress, in persistent infection and nutritional stress, the expression of the MnSOD was drastically downregulated. 15338334_Cu, Zn- and MnSOD levels were significantly increased in frontal cortex and substantia innominata of the index group in schizophrenia 15345661_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15386537_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15455371_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15512788_Iindoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, manganese superoxide dismutase, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein transferred to isolated NOD mouse donor islets protect islet grafts from diabetogenic T cells. 15512801_Overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase promotes the survival of prostate cancer cells exposed to hyperthermia 15534883_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15535847_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15581626_Data show that TNF-alpha increased the level of two antioxidant enzymes, thioredoxin and manganese superoxide dismutase, by an NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism in Ewing sarcoma cells. 15589819_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15591282_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15591282_the functional A16V MnSOD polymorphism affects the risk of cardiomyopathy related to iron overload and possibly to other known and unknown risk factors, and may represent an iron toxicity modifier 15598343_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 15610954_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15621215_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15673194_Reduced the oriental medicine-induced cytotoxicity and decreased the number of the oriental medicine-induced apoptotic cells. 15701646_Sod2 can serve as an alternative physiological source of the potent signaling molecule, H2O2 via PTEN oxidation 15705913_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15706661_HIV-1 Tat regulates the SOD2 basal promoter by altering Sp1/Sp3 binding activity 15734083_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15734485_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15734485_The association of the manganese superoxide dismutase polymorphisms at -102 C>T and the -9 T>C were not found to be associated with gastric cancer in a Polish case-control study. 15743756_MnSOD protects the redox-sensitive checkpoint which regulates the progression of fibroblasts from G0/G1 to S-phase. 15765450_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15767364_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15774926_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15781667_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 15809720_hydrogen peroxide overload on p53-independent pathway due to MnSOD overexpression plus buthionine sulfoximine might increase apoptosis frequency without acceleration of apoptotic process of each cell 15817612_Mitochondria-localized MnSOD dramatically reduced the release of cytochrome c to cytosol by proline oxidase in colorectal cells. 15838728_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15869407_Study findings suggest a novel mechanism by which Tat modulates the repression of the MNSOD gene and establishes a link between HIV infection and liver cancer. 15878096_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15883815_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15883815_Polymorphism in the manganese superoxide dismutase gene is associated with breast cancer 15887859_Altered nuclear expression of Mn-SOD parallels, together with changes in other elements of the antioxidant protective system, the loss of differentiation occurring during the progression of thyroid tumors. 15894290_The data show that MnSOD affects sensitivity of cells to Pc 4-PDT-initiated apoptosis, and partly ceramide accumulation, suggesting that the processes are superoxide-mediated. 15908783_Epigenetic silencing of SOD2 in multiple myeloma increases cell proliferation. 15923250_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15933380_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 15951095_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16006997_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16047490_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16076760_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16084535_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16107721_uncoupling of the electrochemical gradient by increased MnSOD activity gives rise to p53 up-regulation 16148556_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16157826_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16166634_Protein kinase D-mediated MnSOD expression promotes increased survival of cells upon release of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species 16170370_HIF-1alpha accumulation and VEGF expression could be modulated by the antioxidant enzyme MnSOD. 16179351_the increase in Mn-SOD expression in ovarian cancer is a cellular response to intrinsic ROS stress 16215873_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16281056_Endogenously generated matrix superoxide does not regulate UCP activity and in vivo energy expenditure; transgenic Sod2 demonstrates absence of effect on any UCP activities, and transgenic mice display normal resting metabolic rates 16324912_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16369462_Data show that manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase levels are much higher in the hippocampi of Alzheimer's diseased brains than in non-diseased control brains. 16423340_Ala-9Val polymorphism does not seem to be a significant predisposing factor for bronchial asthma in the Czech population 16423340_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16424062_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16458347_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16458347_We did not observe an association between the C47T polymorphism in the MnSOD gene and survival 16467073_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16475114_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16485861_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16485861_the Ala-9Val polymorphism in the MnSOD gene is not associated with genetic susceptibility in Alzheimer's disease patients 16510607_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16538174_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16540901_SODs might be important in the pathogenesis of NP; however, the roles these SOD isoforms play in both normal nasal mucosa and NP require further clarification. 16543247_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16626843_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16630148_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16740634_presence of p53 in a transcription complex of NPM and Sp1 or NF-kappaB at the promoter of the MnSOD gene was verified. p53 interacts with Sp1 to suppress expression of the MnSOD gene. 16769586_May be a genetic factor regulating the cellular redox state in determining the outcome of leukemia chemotherapy 16769586_Observational study of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 16780268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16780879_that the localization of Cu/Zn- and Mn-SODs in adrenal tissues reflects the specificity of the adrenal cells that produce the tissue-specific hormones 16807759_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16807759_The results suggest that Ala/Val polymorphism of the SOD2 gene could be associated with the risk of developing methamphetamine psychosis. 16819819_These studies show that residues at the dimeric interface, such as Tyr169, have significantly less conformational freedom or mobility than do residues at the tetrameric interface, such as Tyr45. 16847469_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16847469_determination of MnSOD polymorphism and different genotypes of MnSOD associated with its antioxidant enzyme activity in chronic pelvic pain syndrome patients 16859522_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16868544_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16933053_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16933053_The MnSOD Ala-9Val polymorphism may contribute to an increase in breast cancer risk in the context of high alcohol consumption, however the polymorphism is not an overall risk factor for breast cancer in this primarily premenopausal population. 16945136_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16945136_Polymorphisms in the GPX-1 and MnSOD genes may have a role in development of breast cancer 16956821_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16956909_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16966185_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 16966488_Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 led to an activation of NFkB, and increased mRNA levels of the antioxidant enzyme manganese-superoxide dismutase (MnSOD). 16969494_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 16969494_the MnSOD Val16Ala variant allele may have a role in preventing development of breast cancer in women who never breast fed 17005595_Mean relative levels of SOD2 & its mRNA were significantly decreased in women > or =38 years, which may account for granulosa-cell changes associated with reproductive aging. 17018785_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17055157_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17085785_Binding of NF-kappaB members to the MnSOD gene leads to the induction of MnSOD mRNA and protein levels, leading to subsequent protection against oxidative stress-induced neuronal injury. 17142144_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17145829_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17149600_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17171548_Systemic activity of the enzymatic antioxidants (CuZn/SOD, MnSOD, GSH-Px, and CAT) as well as level of lipid peroxidation determined by MDA may not be increased in the course of immune-inflammatory processes associated with chronic idiopathic urticaria. 17186424_No significant association between MnSOD gene polymorphism and the risk of skin cancer. 17186424_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17188257_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17192491_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17192491_Smoking and homozygosity for the MnSOD Val allele is associated with an increased risk of diabetic nephropathy. 17211829_Activation of pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system results in strong upregulation of SOD2 gene expression suggesting that SOD2 protects macrophages from oxidative stress during microbial infection. 17217237_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17277236_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17277236_SNPs involving the GSTP1, MnSOD and GPX2 genes were not associated with Barrett's esophagus or esophageal adenocarcinoma 17290392_An increased risk of pleural mesothelioma was found in those with the Ala/Ala genotypes at codon 16 within MnSOD. 17290392_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17291655_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17293864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17296902_Extracellular SOD, endothelial NOS, and inducible NOS gene polymorphisms do not constitute a risk factor for developing BD (Behcet disease) in Japan. 17296902_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17299255_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17299970_Gene polymorphisms of PON1 55 Met/Leu, PON2 148 Ala/Gly and MnSOD 9 Ala/Val seemed to involve in the morbidity of CHD by influencing the plasma activities of PON and MnSOD. 17299970_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17331249_10T/9T polymorphism in the SOD2 intron 3 results in alternative splicing of exon 4; over-representation of 9T alleles indicates that this polymorphism may be involved in the altered susceptibilities to disorders that are more common in African-Americans 17331249_Observational study of genotype prevalence. (HuGE Navigator) 17336594_Ala-encoding MnSOD allele is represented equally in controls and patients with HCV-related cirrhosis, and it does not significantly influence the risks of liver iron overload, HCC, or death. 17336594_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17340208_No association between SOD polymorphism and bladder cancer incidence. 17340208_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17376152_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17376152_Under a dominant model, family-based association tests showed significant evidence for association of Alzheimer's disease with the first three loci of superoxide dismutase 2 in two candidate gene sets of families. 17400324_Observational study of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17400324_study of the relationship between genetic polymorphisms of MnSOD, NQO1, GSTM1 and GSTT1 and the susceptibility to drug-induced liver injury (DILI); MnSOD mutant C allele may increase the susceptibility to DILI 17409931_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17409931_The common Val16Ala MnSOD polymorphism does not confer increased or reduced risk of lung cancer in Chinese in Hong Kong 17449559_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17453961_No major modifying role for the Mn-SOD gene polymorphism in patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome. 17453961_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17459574_UDN glycoprotein regulated SOD2 activity and is a potential modulator of inflammatory signal pathways in a lipopolysaccharide-treated colonic cancer cell line. 17465268_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17465268_mutation of the MnSOD gene may be an important risk factor for prostate cancer 17473980_MnSOD plays a role in regulating tumor cell growth and invasive properties of estrogen-independent metastatic breast cancer cells via hydrogen peroxide. 17491681_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17548672_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17548864_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17548864_Polymorphisms of MnSOD and GSTP1 are not associated with chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. 17567676_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17567676_analysis of superoxide dismutase and catalase polymorphisms in smokers with COPD 17575500_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17577737_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17577737_Significant difference in the genotype frequency between healthy subjects and patients with sepsis. 17582511_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17582511_The distribution of the MnSOD genotypes and alleles was not significantly different between patients and controls. Logistic regression analysis also failed to reveal any association between MnSOD genotypes and TD. 17588204_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17601350_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17616699_that an O(2)(*-) signaling pathway regulates NAC-induced G(1) arrest by decreasing cyclin D1 protein levels and increasing MnSOD activity 17617122_During neoplastic transformation of cirrhotic liver, an increase in MnSOD activity may occur already during the precancerous phase, making this enzyme a probable malignancy-associated parameter. 17628794_Manganese superoxide dismutase gene polymorphisms is associated with urolithiasis 17628794_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17634480_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17646272_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17646272_These results suggest that the Ala variant of SOD2 is associated with moderately increased risk of prostate cancer. 17652337_p50 shows a negative effect on MnSOD induction upon repeated applications of TPA and provide an insight into a cause for the reduction of MnSOD expression during early stages of skin carcinogenesis. 17653087_Overexpression of MnSOD at moderate levels is able to protect cells from TRAIL-induced apoptosis. 17693525_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17719580_Data suggest that MnSOD may be useful in treating HER2/neu-mediated human breast tumor malignancy. 17822322_Increased activity of superoxide dismutase in advanced stages of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with locoregional metastases 17879532_Clinical trial of gene-environment interaction and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17922231_Observational study of gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 17922231_the combined genotype group of SOD2-01 and GSTP1-01 was an independent predictor of progression free survival and breast cancer specific survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer 17936883_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 17936883_study concludes that the Val9Ala MnSOD polymorphism does not influence ovarian cancer risk or survival 17965603_Epigenetic silencing of SOD2 constitutes one mechanism leading to the decreased expression of MnSOD observed in many breast cancers. 17967822_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 17974967_These findings suggest that the association between increased Sod2 activity and poor prognosis in cancer can be attributed to alterations in their migratory and invasive capacity. 18023606_Findings provide further evidence of an association between the Ala-9Val MnSOD polymorphism and HCC occurrence in hepatitis C virus-infected Moroccan patients. 18023606_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18044968_emphasize the role of residue 66 in catalysis and inhibition and provide a structural explanation for differences in catalytic properties between human and certain bacterial forms of MnSOD 18057537_concludes that the VV genotype of the V16A polymorphism of the manganese superoxide dismutase(Mn-SOD) gene was associated with diabetic retinopathy in Caucasians with type 2 diabetes 18095014_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18095014_in systemic lupus erythematosus patients, MnSOD2 (superoxide dismutase 2)Val/Val genotype was associated with Raynaud's phenomenon and contributed to immunologic manifestations and autoantibody production 18167182_MnSOD was overexpressed in ESCC and its up-regulation in esophageal cancer cells was associated with apoptosis resistance. 18167310_Thus, long-term exposure of human cells to RES results in a highly specific upregulation of MnSOD, and this may be an important mechanism by which it elicits its effects in human cells. 18180754_Meta-analysis of gene-disease association and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) 18180754_Meta-analysis shows a protective effect against antipsychotic-induced tardive dyskinesia for Ala9Val and Val carriers. 18205184_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18205184_Polymorphisms of the inflammatory pathway genes MPO -G463A and SOD2 Ala16Val are associated with elevated pancreatic cancer risk 18247479_Kinetic mechanism of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase. 18258609_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18291700_Manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) activity has been used as an index of mitochondrial antioxidant defence in type 2 diabeates. 18296681_MnSOD is not associated with risk of prostate cancer, but MnSOD T to C (Val-9Ala, rs4880) polymorphism modifies associations between risk of clinically aggressive prostate cancer and dietary iron intake 18296681_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18305395_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18327668_Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-gene interaction. (HuGE Navigator) 18373354_Glu162 at the tetrameric interface in human MnSOD supports stability and efficient catalysis and has a significant role in regulating product inhibition 18387669_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18387669_Polymorphisms of CuZn-SOD, MnSOD, GSTM1 and GSTT1 in the placental tissue were not associated with preeclampsia. 18396798_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18413745_Overexpression of MnSOD in breast epithelial cells alters stabilization of HIF-1 alpha under hypoxic conditions. 18423055_Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) 18423055_genotype distribution of the SOD2 in patients with diabetes mellitus can differ from nondiabetic individuals 18434620_Shear stress influences spatial variations in vascul |
ENSMUSG00000006818 |
Sod2 |
2047.251330 |
6.4812905843 |
2.696281 |
0.079618037 |
1063.229231 |
0.00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003242836254046943787335379752836032091316113335212297337436514592799028957883799147861843186345007 |
0.000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003598816775167886401160827300593537407473078262809540345911350040568526397644257567163836147588490 |
Yes |
No |
3394.6144726 |
151.5938944 |
527.2765597 |
18.2517217 |
| ENSG00000291258 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
64.062820 |
0.4896009280 |
-1.030322 |
0.205229617 |
25.419626 |
0.00000046120209632888844783669642958534584664676003740169107913970947265625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000001696745498956728237673454232070646696683979826048016548156738281250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
Yes |
37.2298630 |
5.1104082 |
76.6103802 |
7.0383755 |
| ENSG00000291259 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
41.482439 |
0.4815287719 |
-1.054306 |
0.285867710 |
13.654349 |
0.00021973181335834557370047248614497448215843178331851959228515625000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000571194358078404513037740208858394908020272850990295410156250000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
27.3448856 |
6.3856697 |
57.4647662 |
9.2594301 |
| ENSG00000291272 |
|
|
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.507952 |
0.4418700158 |
-1.178306 |
0.299055581 |
15.295585 |
0.00009193112358989108596259848260601188485452439635992050170898437500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000254339903315237570845946946107574149209540337324142456054687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
34.1524118 |
6.0213484 |
77.6812443 |
9.2041339 |
| ENSG00000291300 |
124221 |
PRSS30P |
lncRNA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.890362 |
0.2435697083 |
-2.037593 |
0.395060853 |
26.826226 |
0.00000022259590174822679390182692937133479560429805133026093244552612304687500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
0.000000845692537916043092934795678133896856820683751720935106277465820312500000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 |
Yes |
No |
10.8074498 |
3.7800490 |
42.9403253 |
9.8507618 |